Patents
Literature
98 results about "Magnetic tracking" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
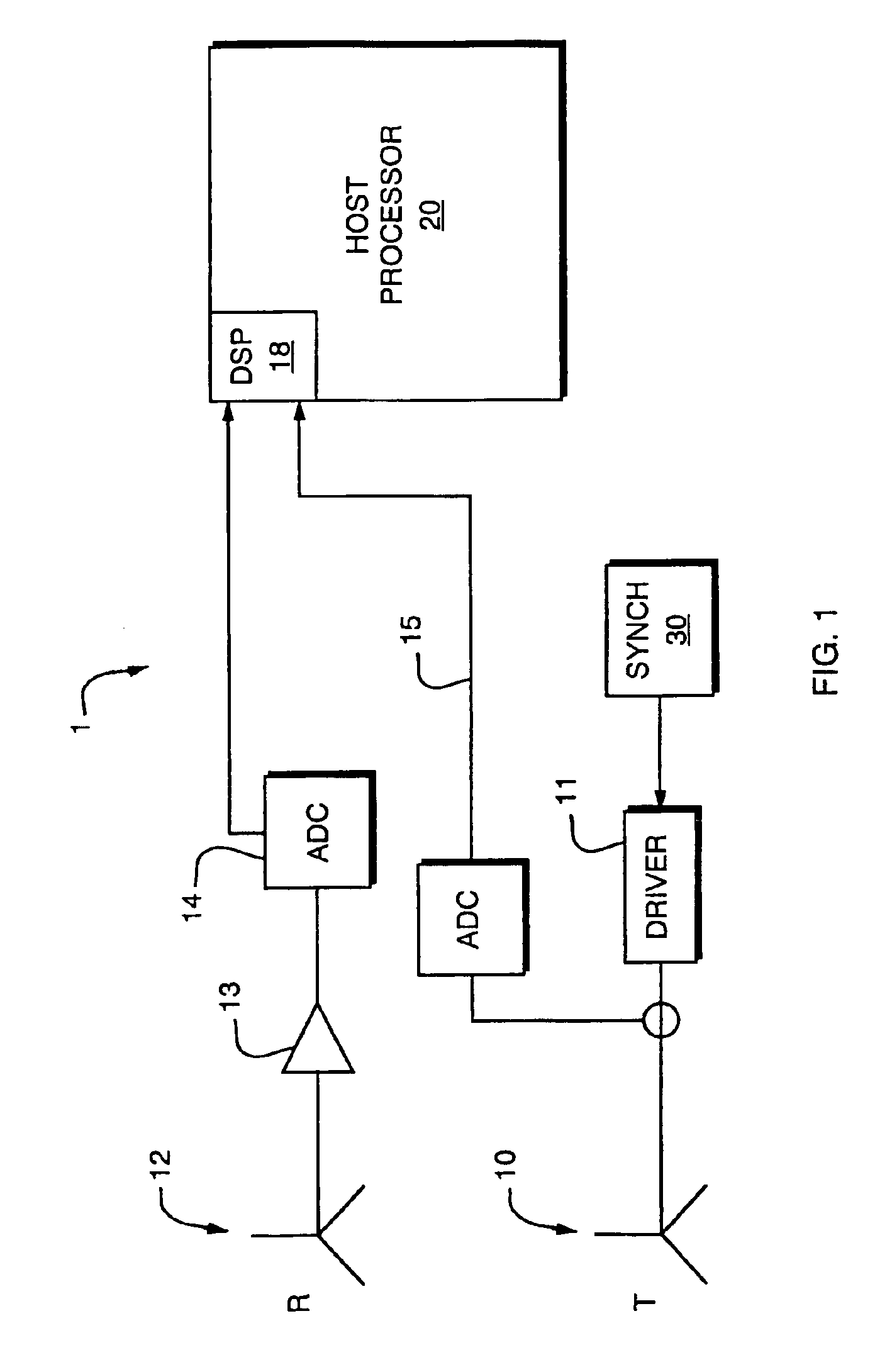
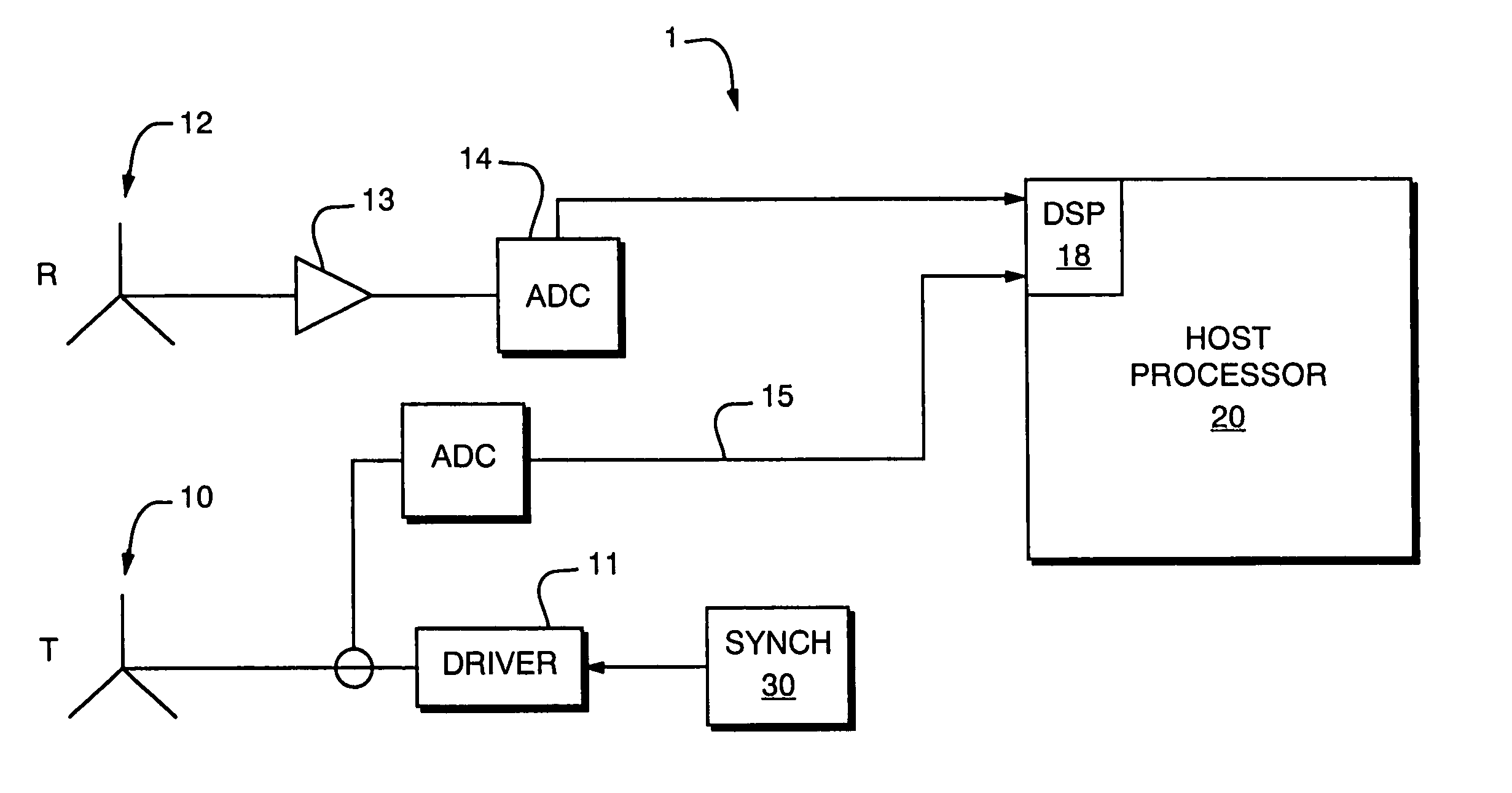
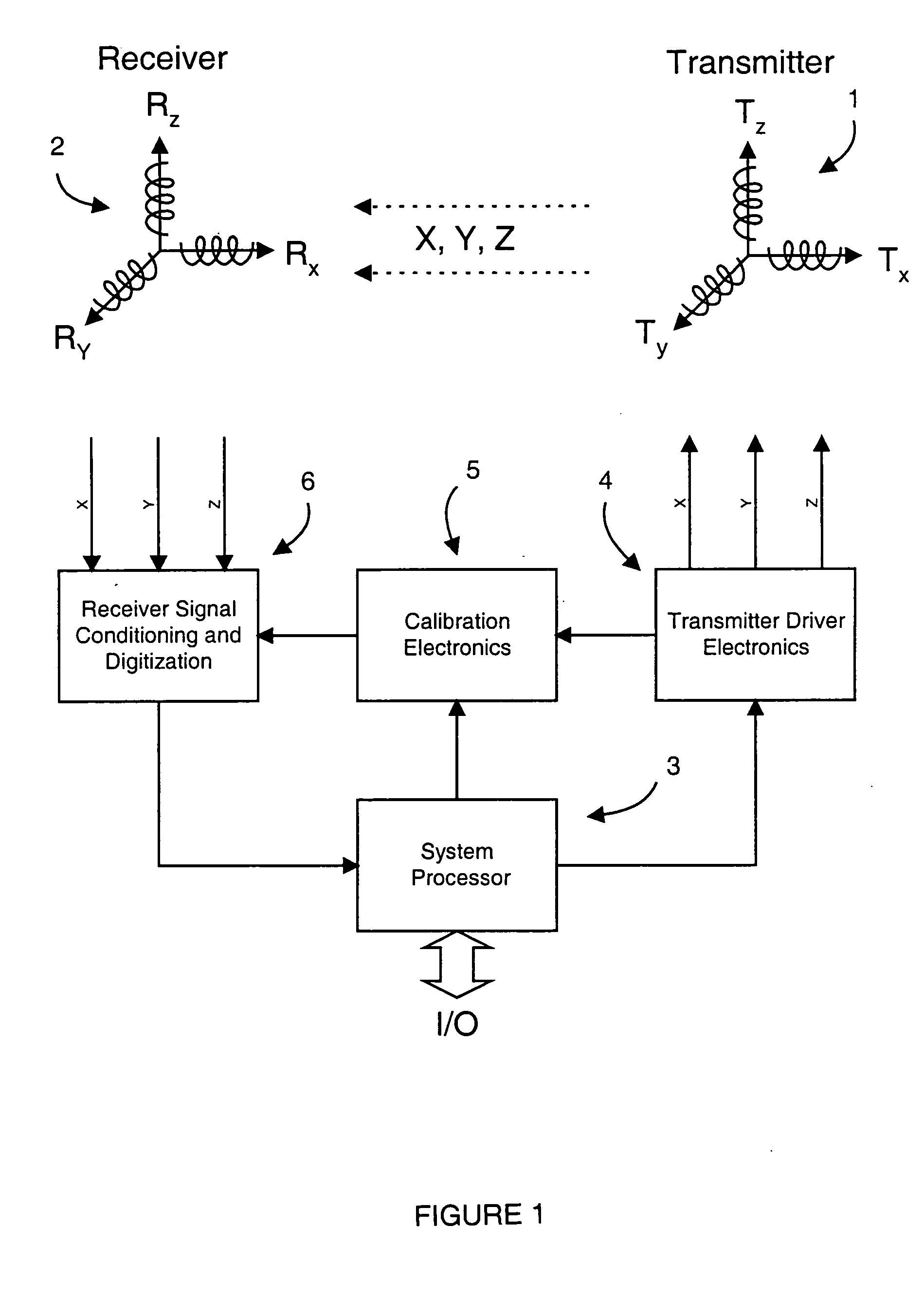
Measuring position and orientation using magnetic fields
InactiveUS6073043APrecise positioningMinimize timeMagnetic measurementsSurgeryMagnetic trackingMagnetic field coupling
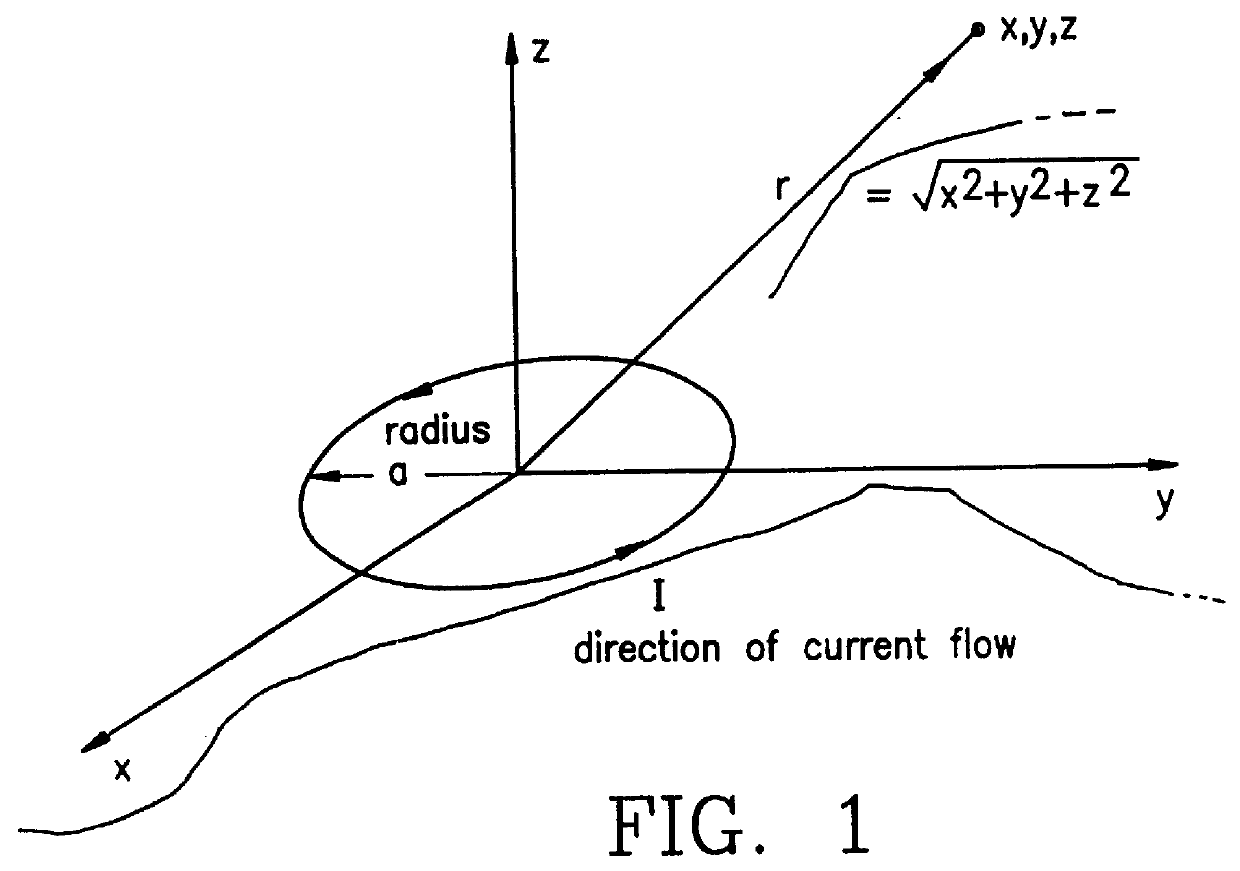
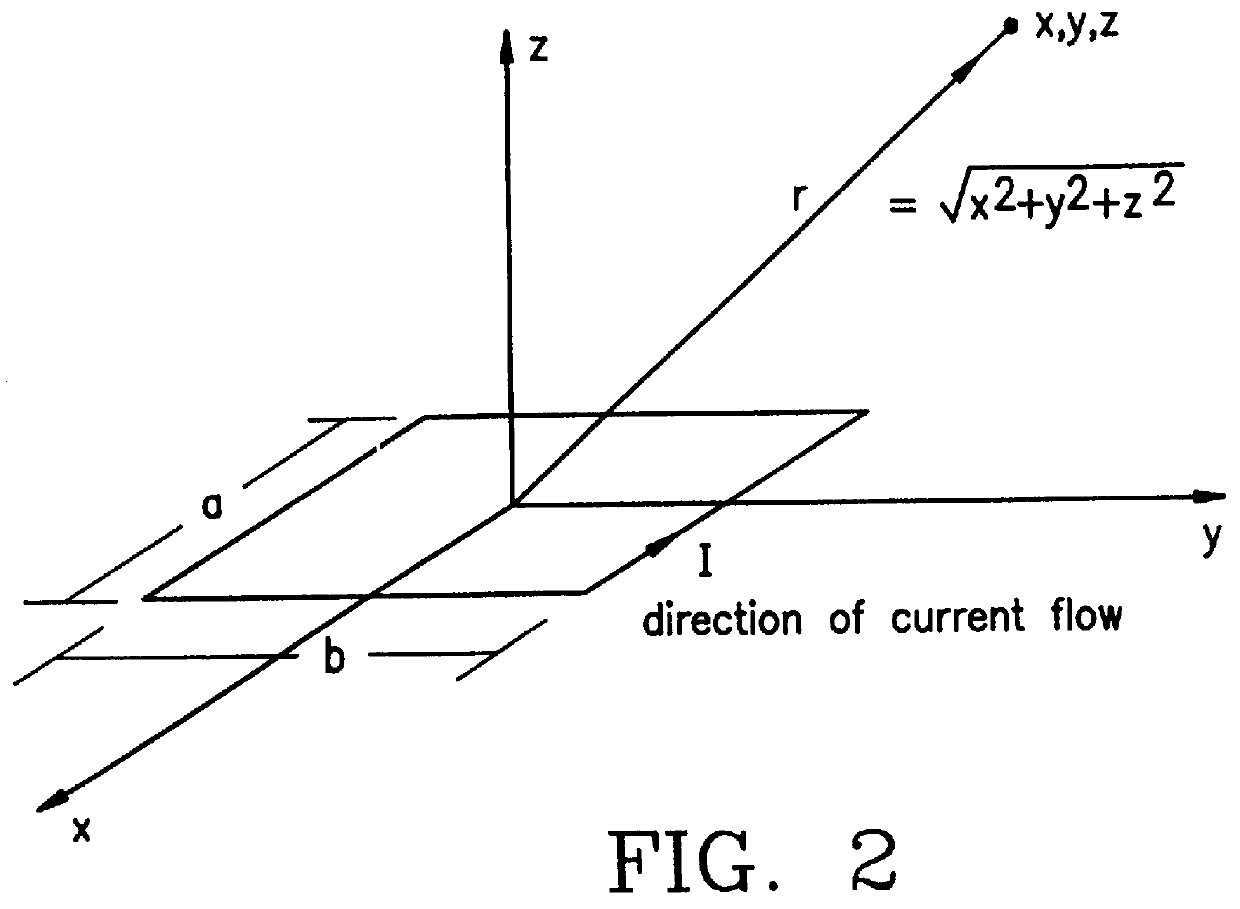
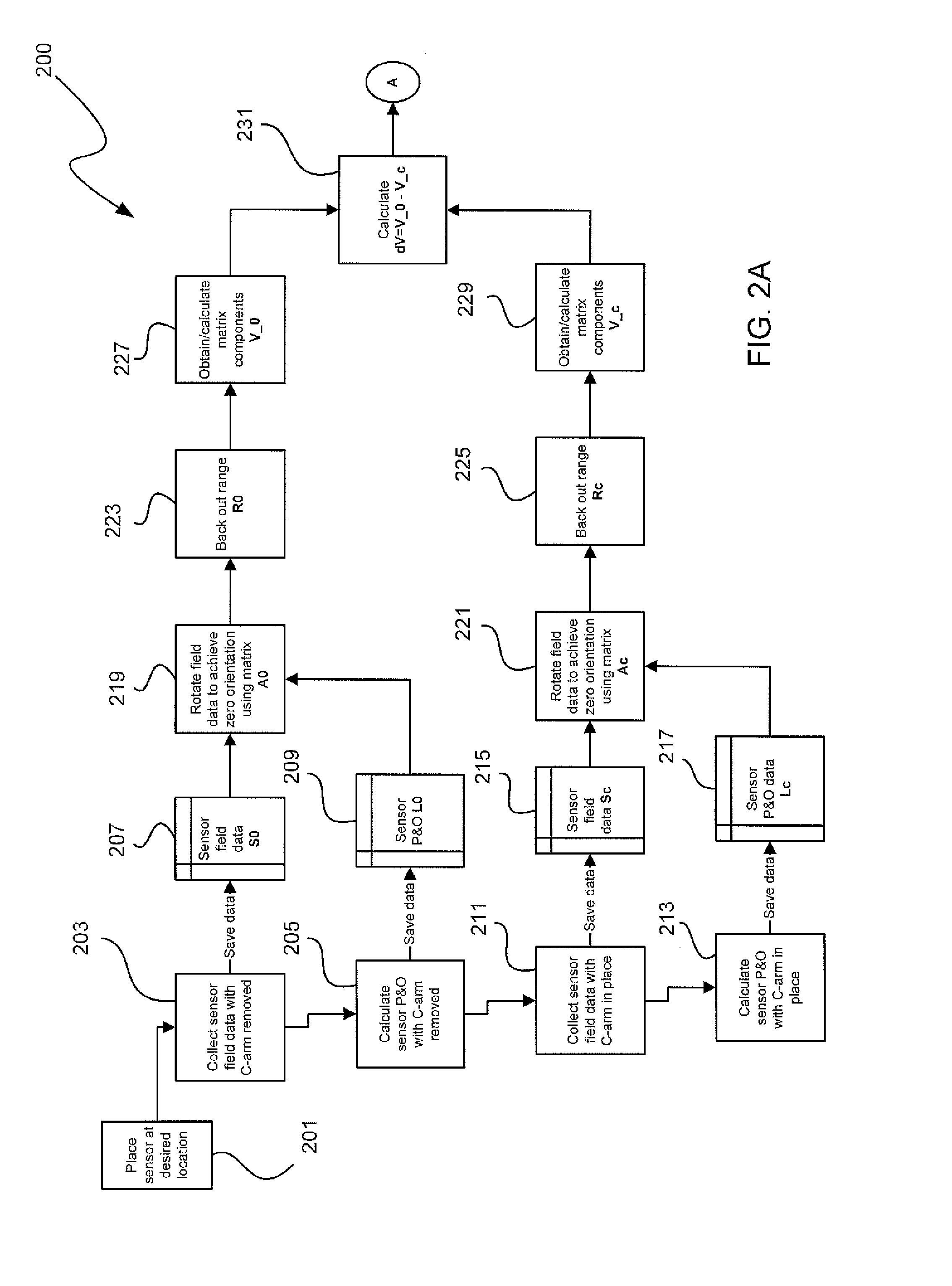
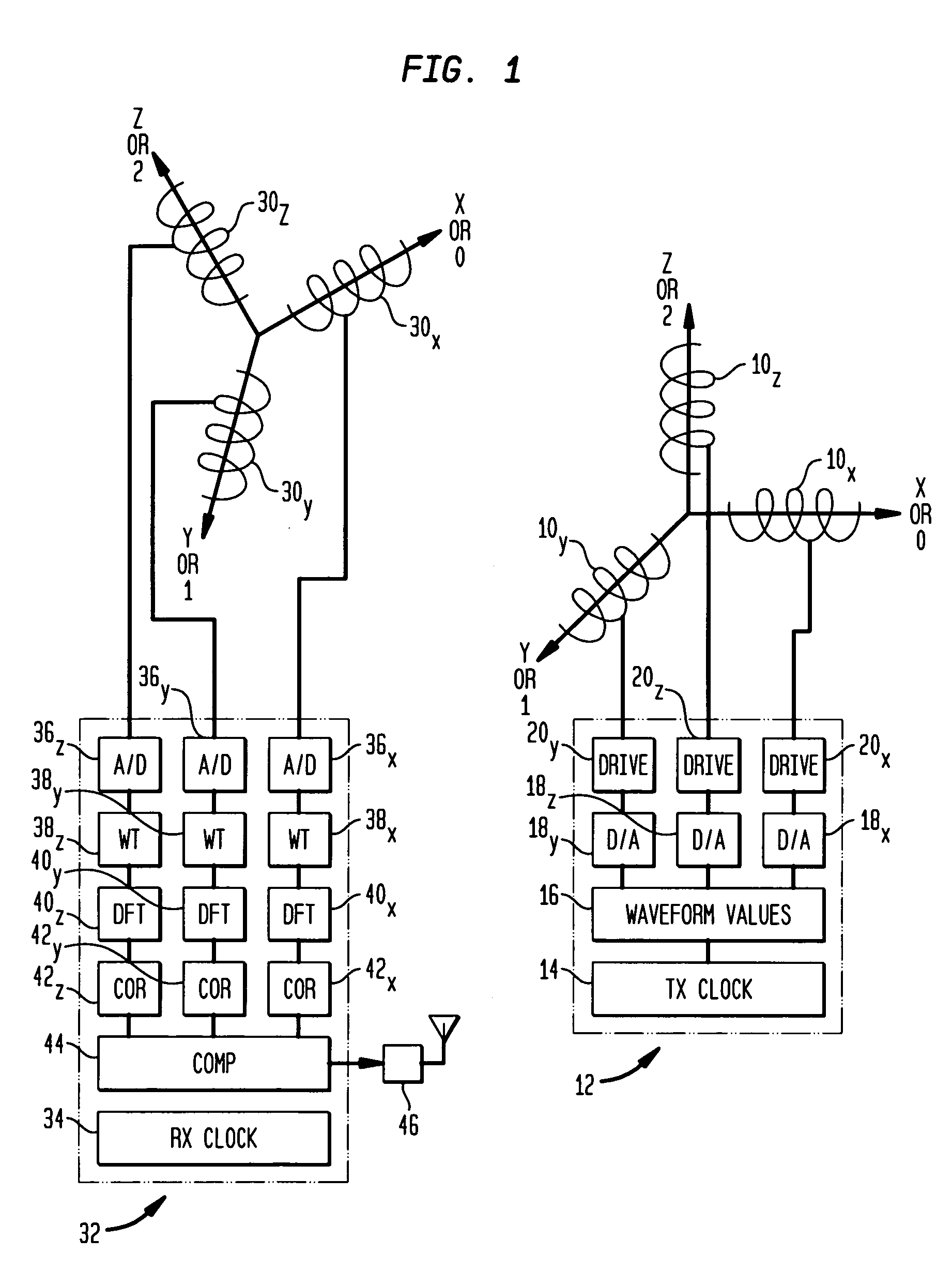
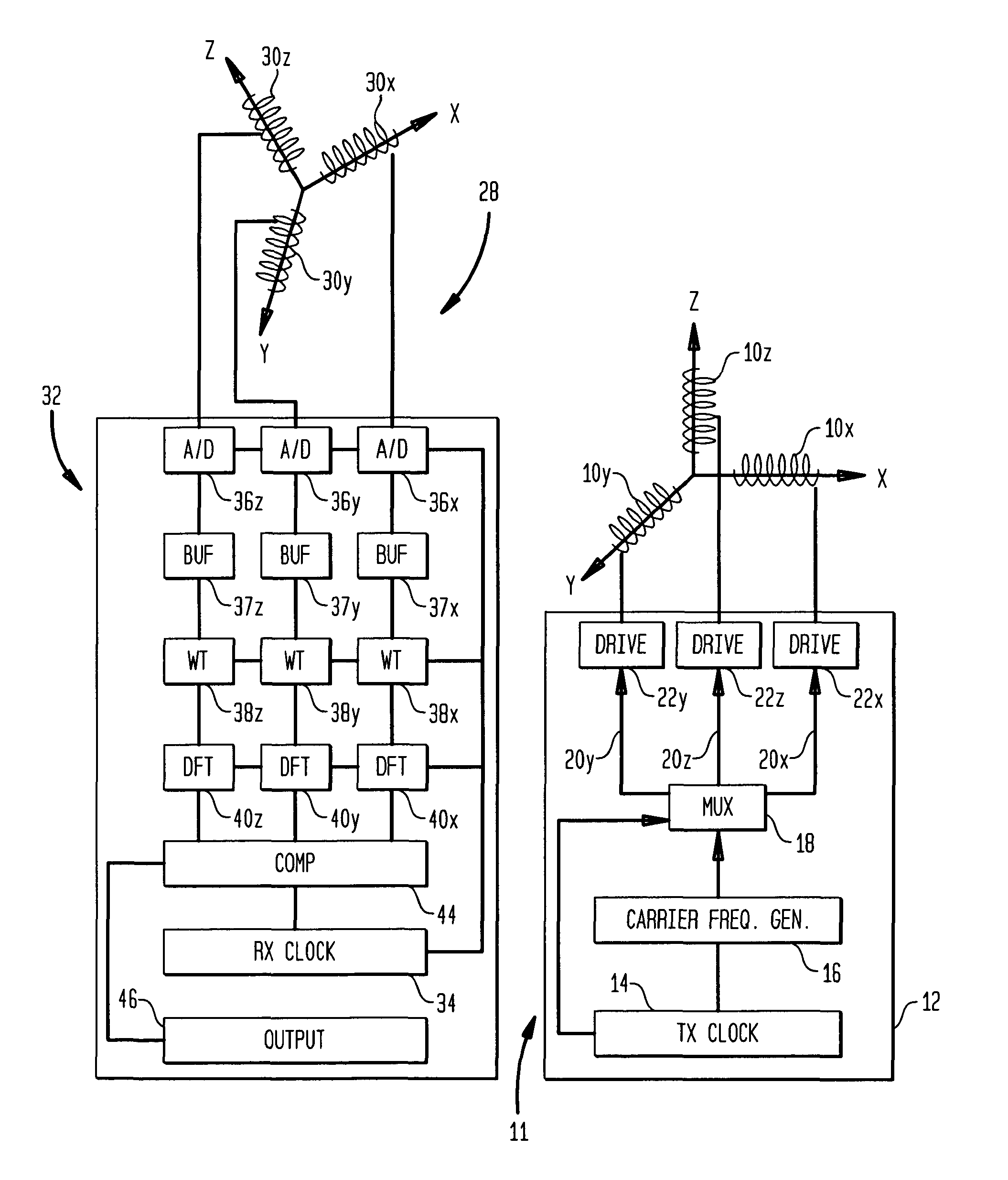
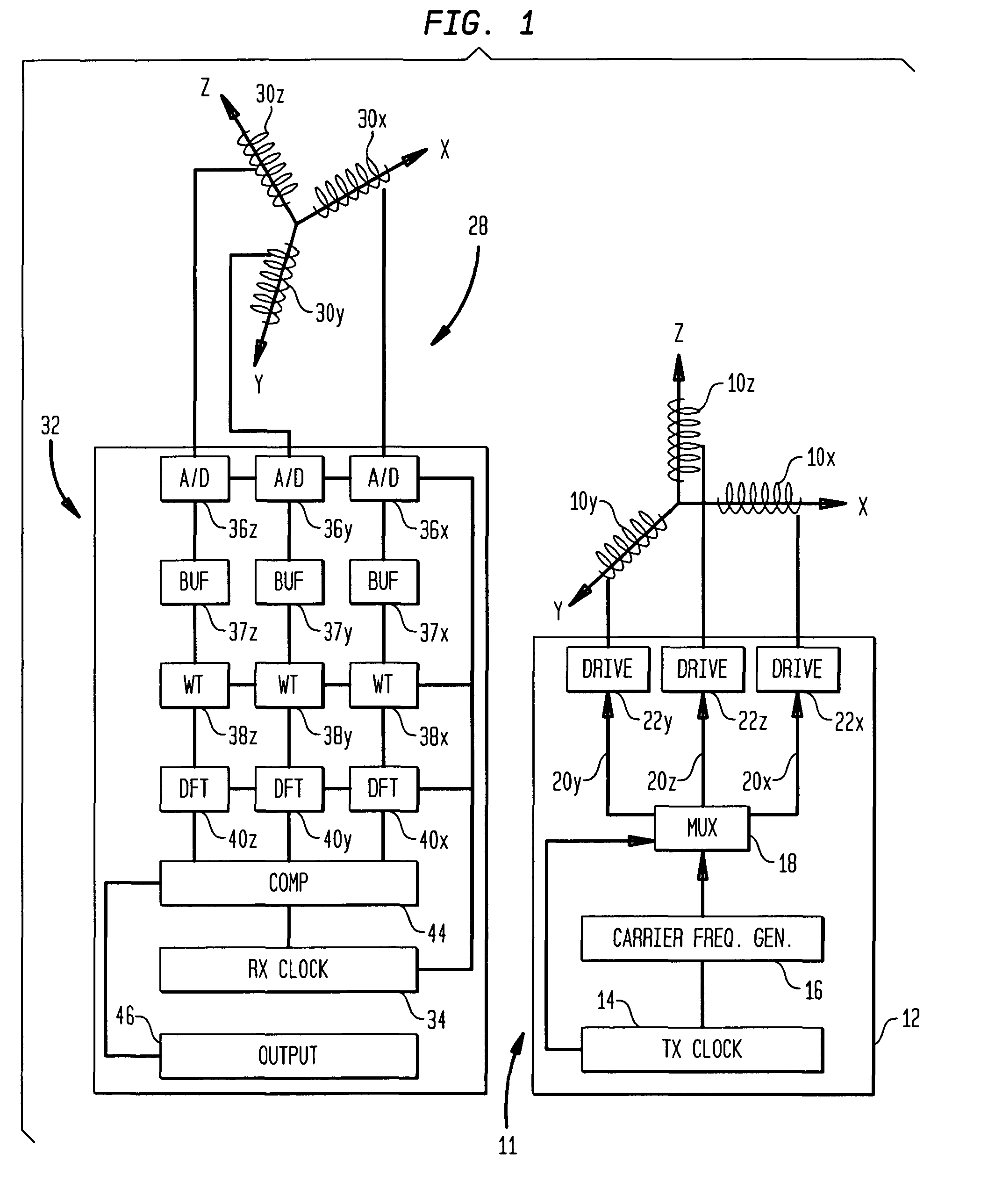
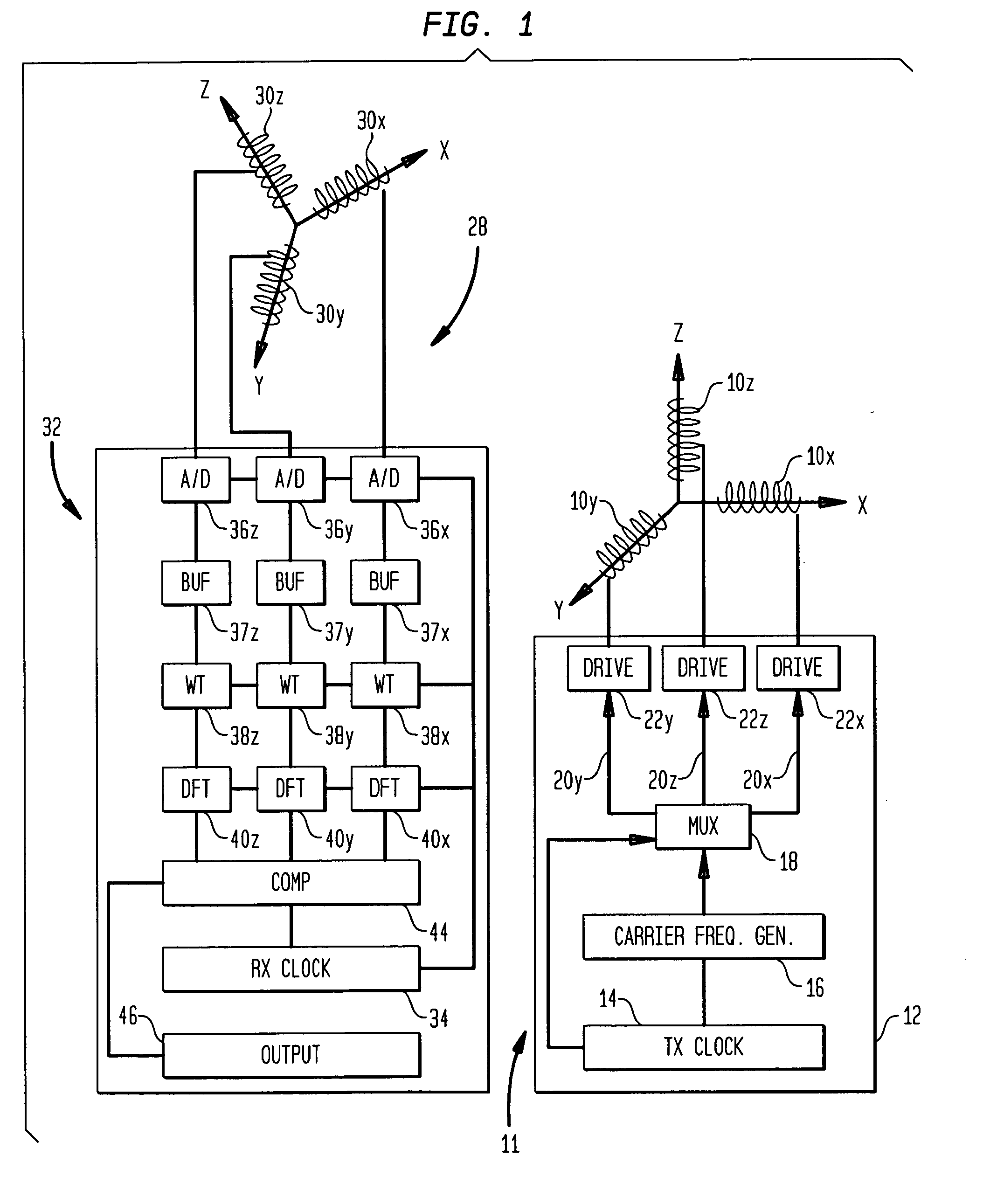
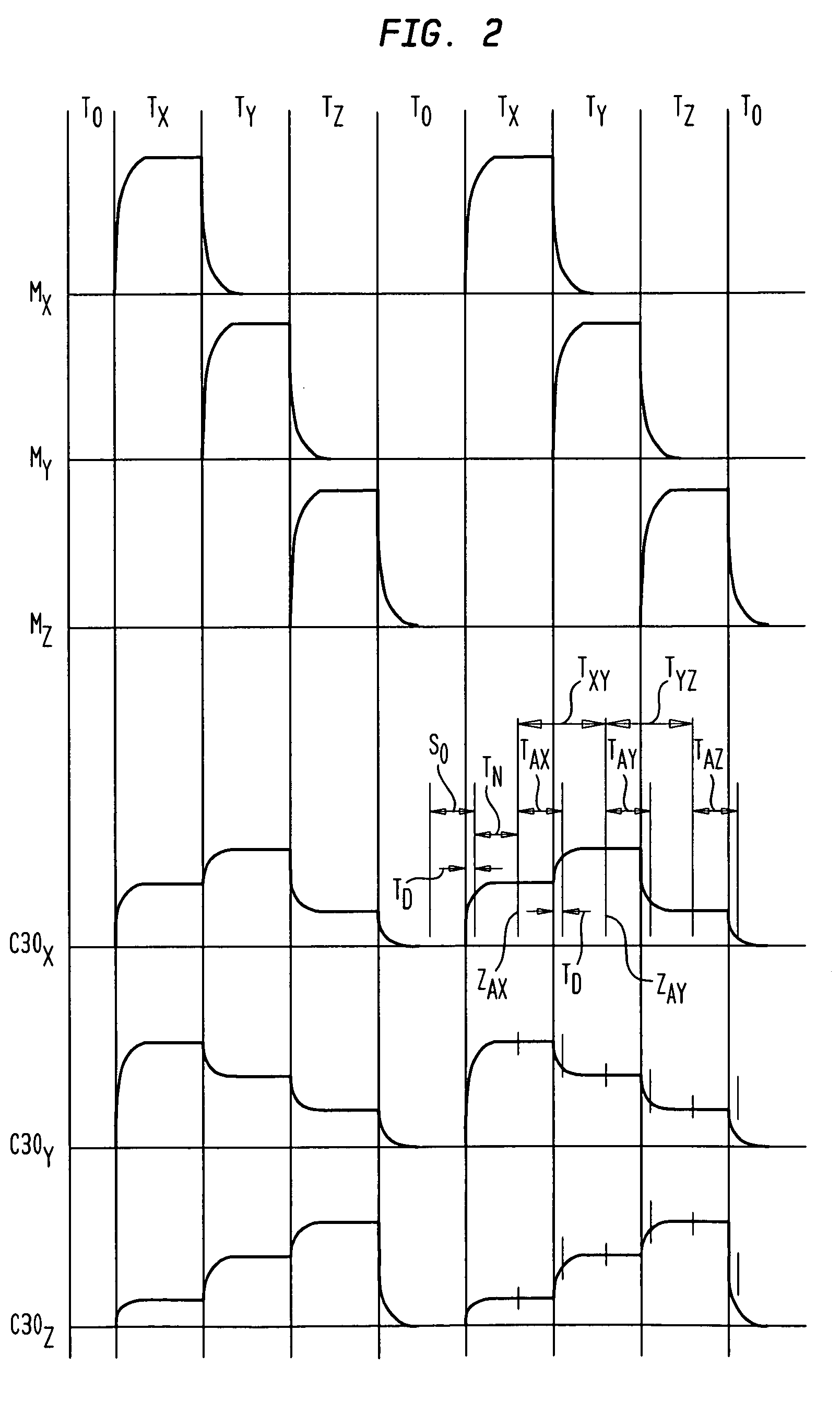
A method and apparatus for determining the position and orientation of a remote object relative to a reference coordinate frame includes a plurality of field-generating elements for generating electromagnetic fields, a drive for applying, to the generating elements, signals that generate a plurality of electromagnetic fields that are distinguishable from one another, a remote sensor having one or more field-sensing elements for sensing the fields generated and a processor for processing the outputs of the sensing element(s) into remote object position and orientation relative to the generating element reference coordinate frame. The position and orientation solution is based on the exact formulation of the magnetic field coupling as opposed to approximations used elsewhere. The system can be used for locating the end of a catheter or endoscope, digitizing objects for computer databases, virtual reality and motion tracking. The methods presented here can also be applied to other magnetic tracking technologies as a final "polishing" stage to improve the accuracy of their P&O solution.
Owner:CORMEDICA
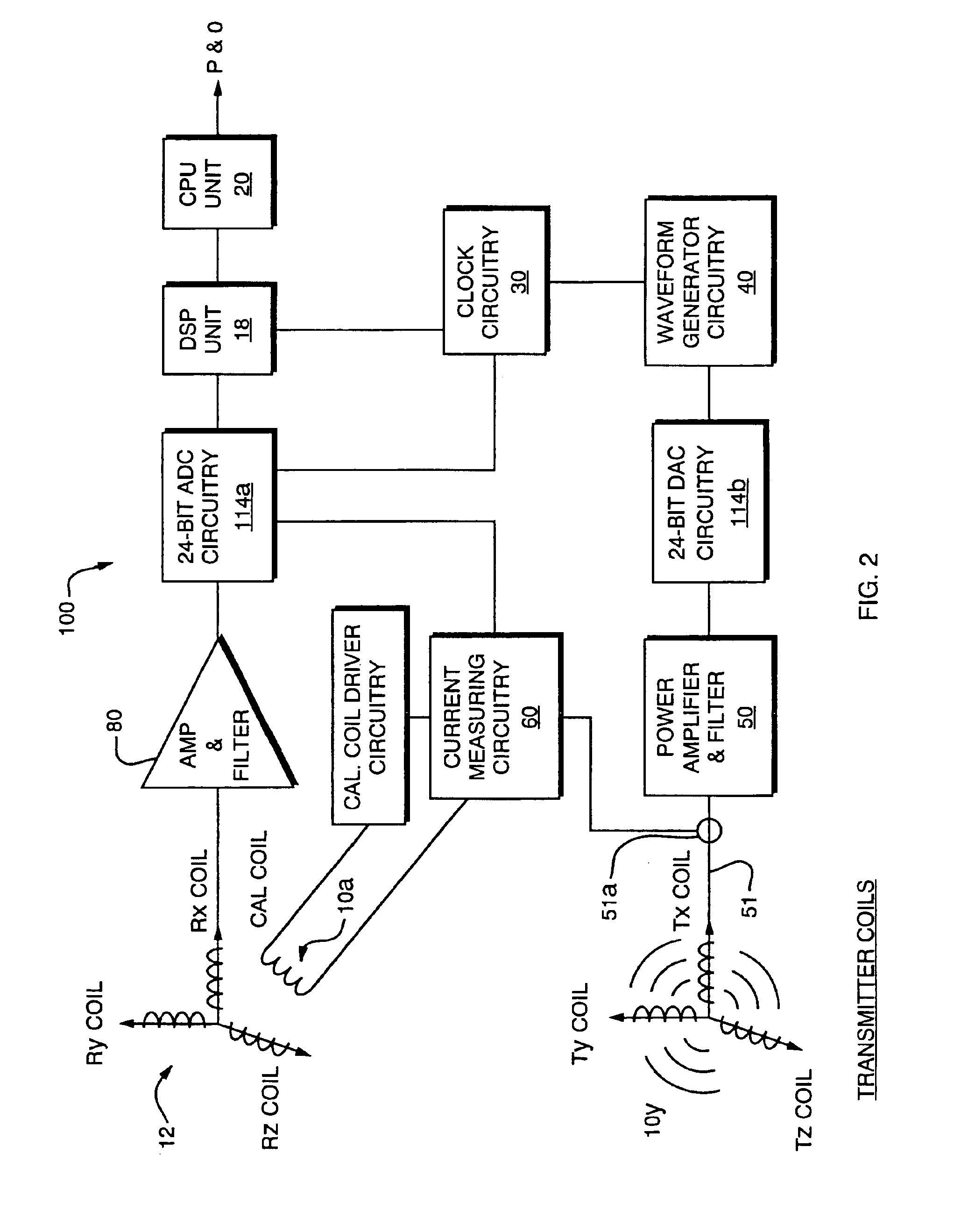
Magnetic tracking system
InactiveUS6980921B2Improve accuracyEliminates patchingSurgical navigation systemsDigital computer detailsMagnetic trackingSignal conditioning
The present invention provides an electromagnetic tracking system that includes a field generator and a field sensor arranged to generate and detect, respectively, an electromagnetic field. Both the transmitter and receiver coils are connected to signal conditioning and processing circuitry to provide outputs indicative of the coil signals. A processor operates on the signals to determine the coordinates of the sensing assembly relative to the generator assembly. The signal processor produces ratiometric outputs, and applies a mutual inductance model to solve for position / orientation coordinates. In some embodiments, a disturber in the form of a conductive ring or a sheath is disposed about an interfering piece of equipment to moderate and standardize disturbances due to eddy currents.
Owner:NORTHERN DIGITAL
Detection of metal disturbance in a magnetic tracking system
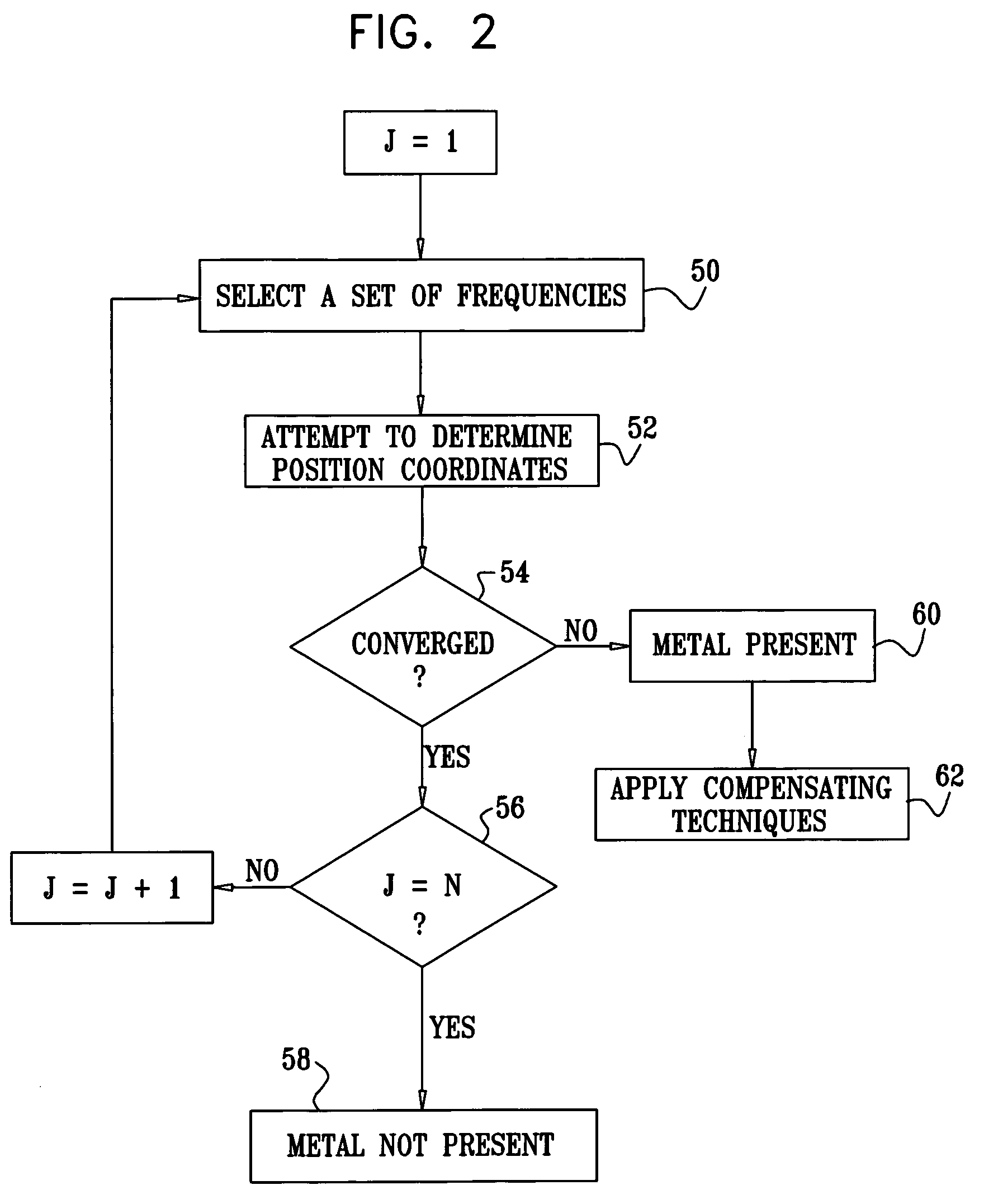
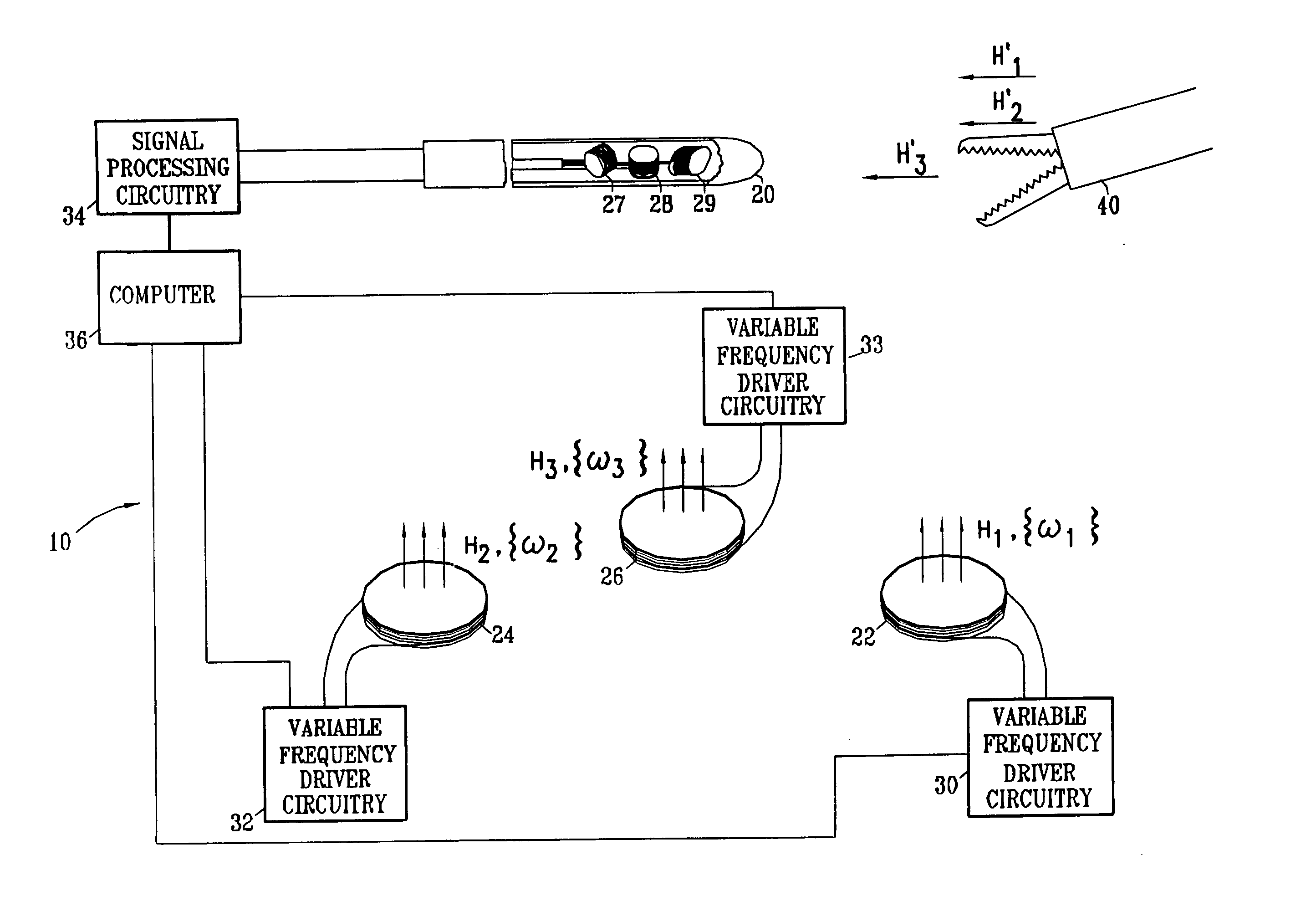
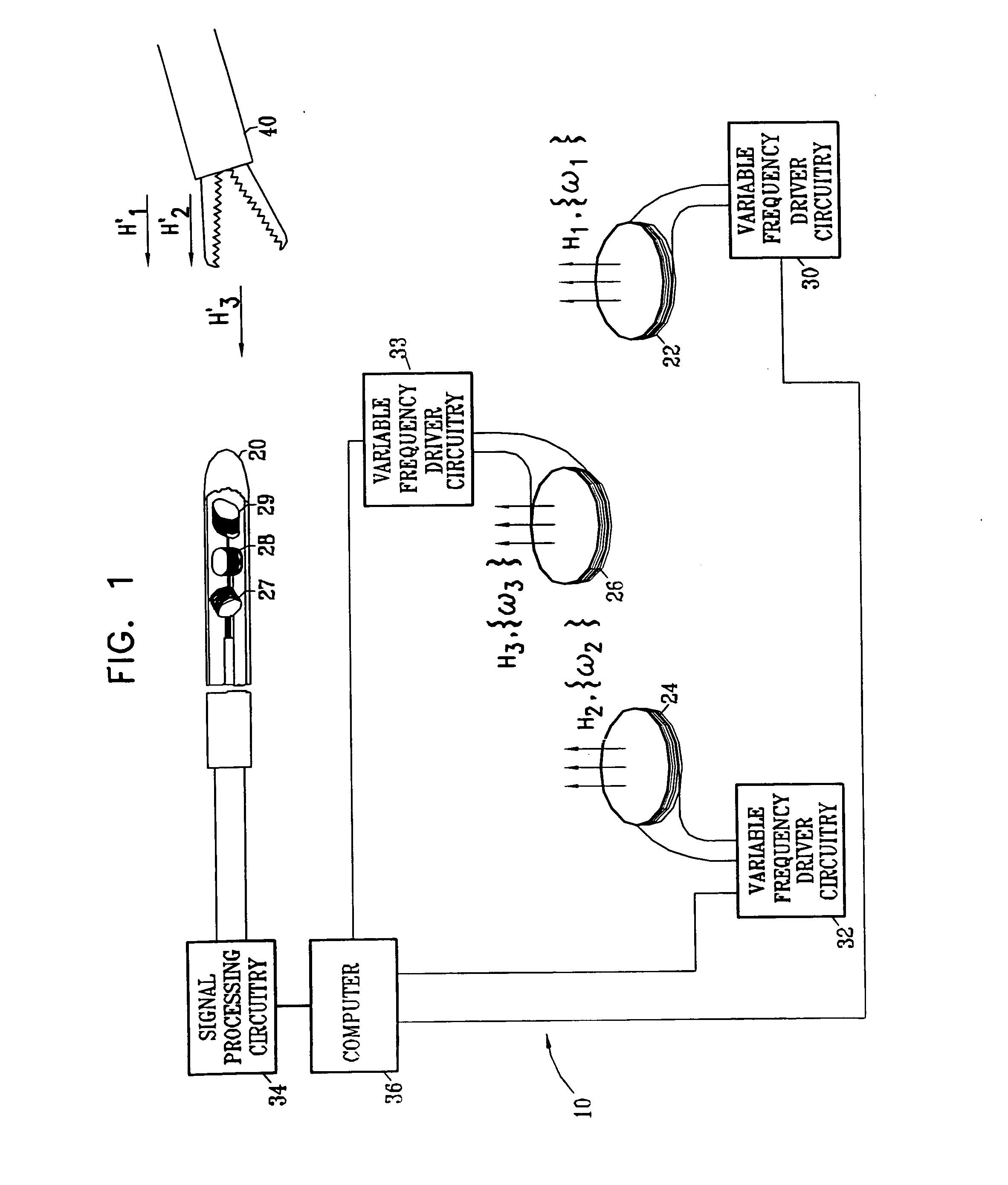
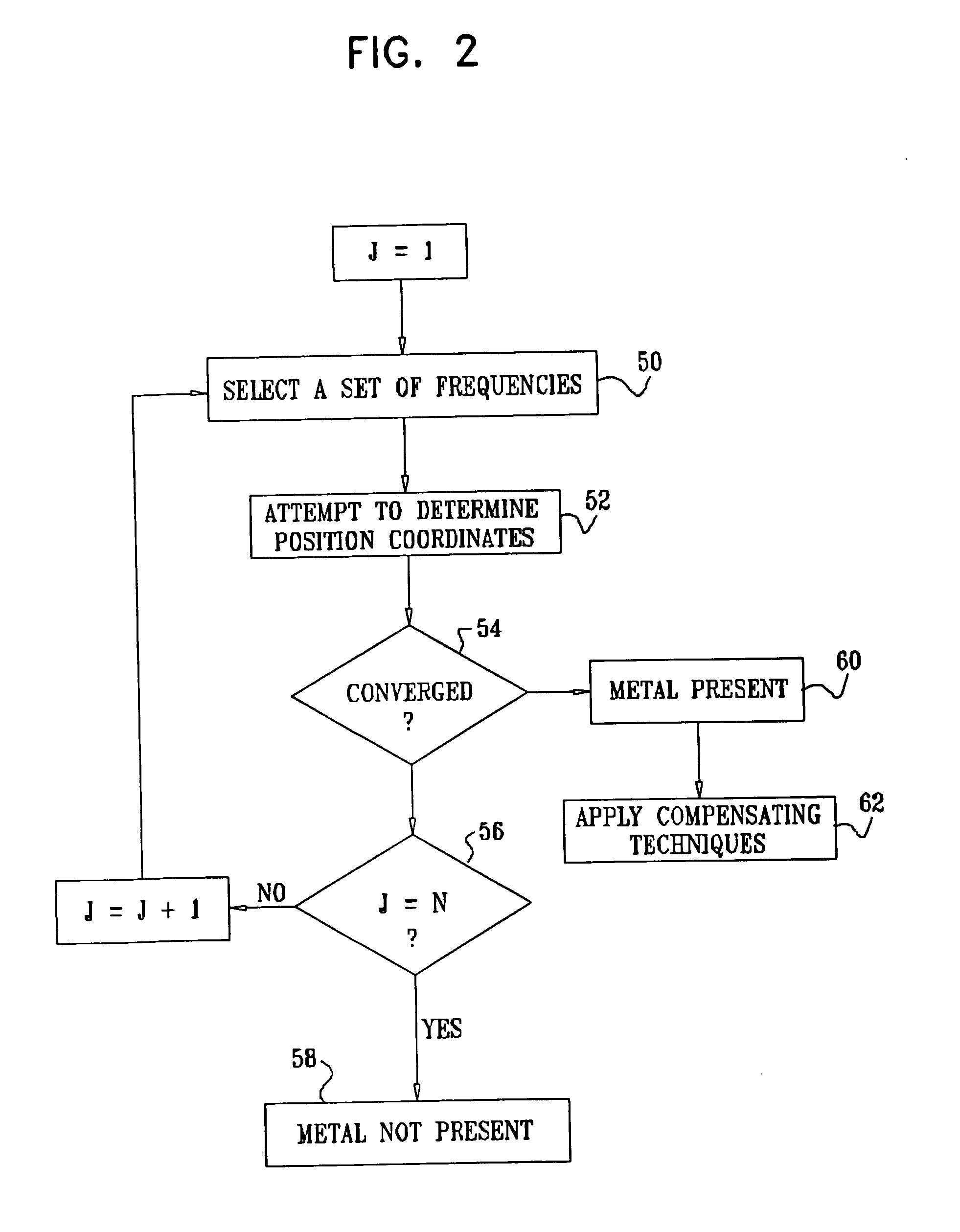
InactiveUS7321228B2Improve accuracyPosition fixationDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic trackingComputational physics
A method for tracking an object includes producing energy fields at a plurality of different frequencies in a vicinity of the object, and receiving signals that are generated at a location of the object at the different frequencies in response to the energy fields. Multiple computations are made of spatial coordinates of the object based on the signals received at the different frequencies. Convergence of the computations is tested in order to ascertain whether the energy fields have been perturbed by an article in the vicinity of the object.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
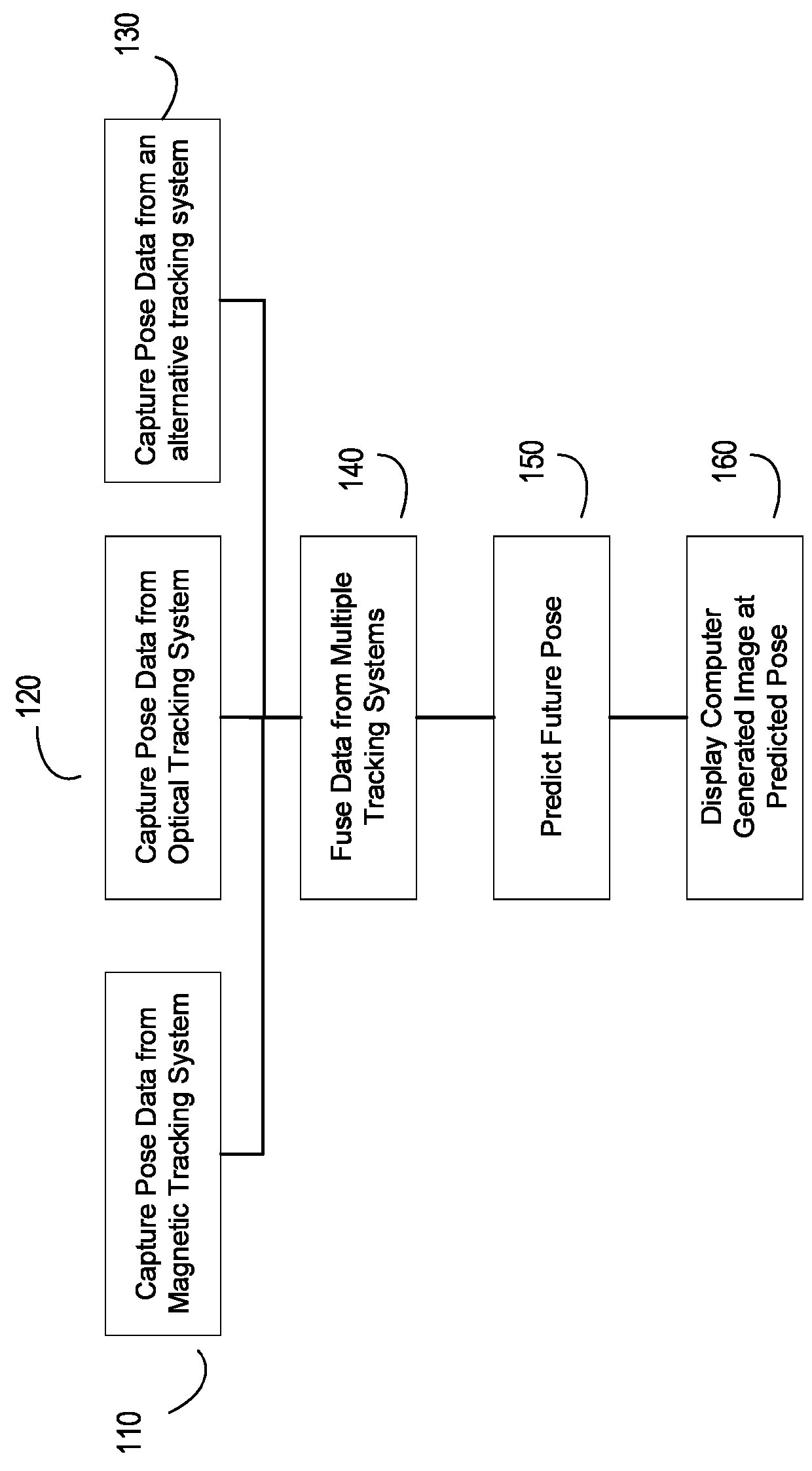
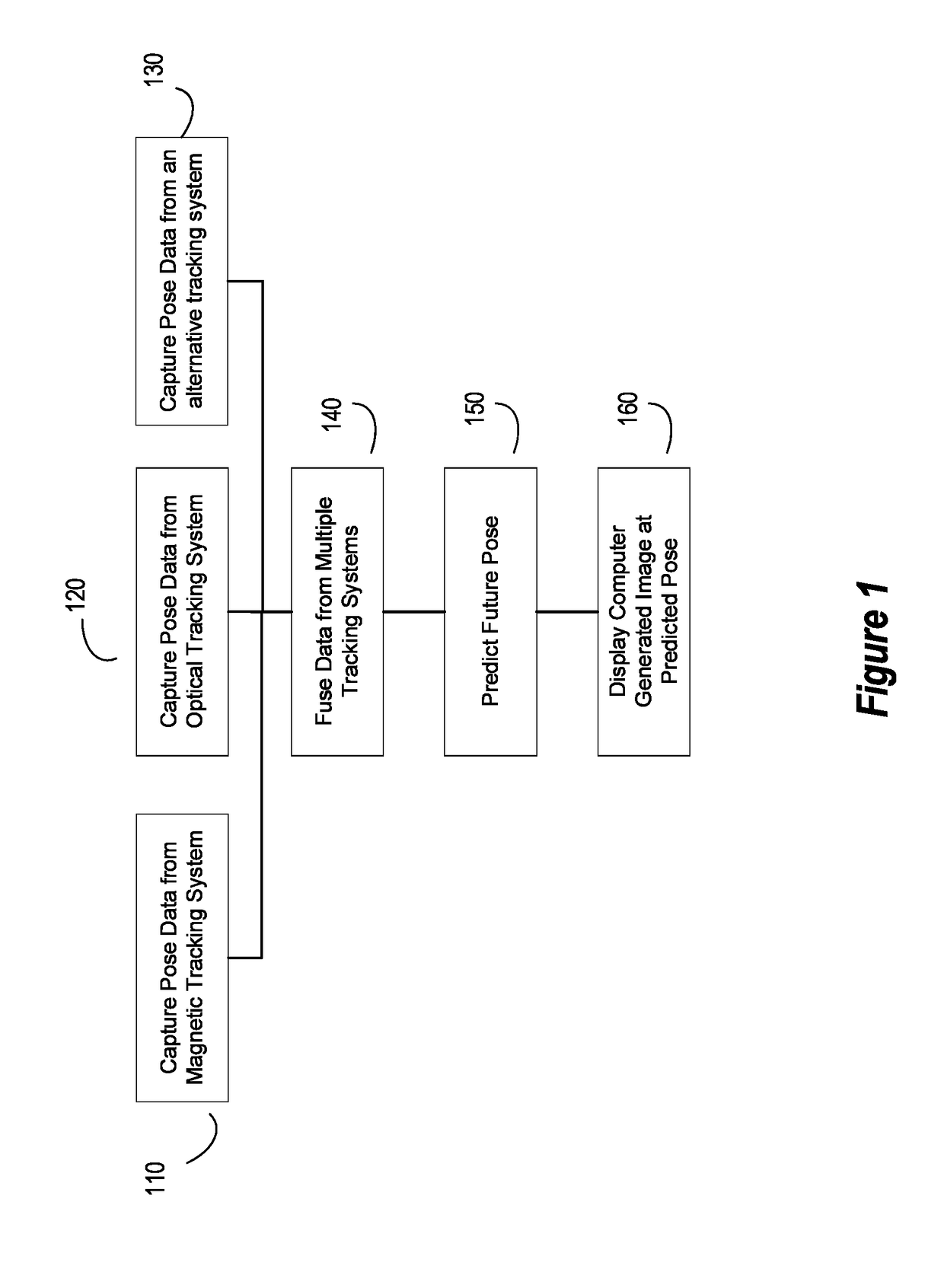
Generating and Displaying a Computer Generated Image on a Future Pose of a Real World Object
Methods and systems for displaying a computer generated image corresponding to the pose of a real-world object in a mixed reality system. The system may include of a head-mounted display (HMD) device, a magnetic track system and an optical system. Pose data detected by the two tracking systems can be synchronized by a timestamp that is embedded in an electromagnetic field transmitted by the magnetic tracking system. A processor may also be configured to calculate a future pose of the real world object based on a time offset based on the time needed by the HMD to calculate, buffer and generate display output and on data from the two tracking systems, such that the relative location of the computer generated image (CGI) corresponds with the actual location of the real-world object relative to the real world environment at the time the CGI actually appears in the display.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Surgical training simulator having multiple tracking systems
A surgical training device, includes a body form, at least two cameras configured to obtain image data of at least one implement located within the body form, and a magnetic tracking system operative to transmit signals, the signals corresponding to position and alignment information of the at least one implement. The surgical training device also includes a computer configured to receive the image data from the at least two cameras, receive the signals from the magnetic tracking system, and generate position and alignment data of the at least one implement from the image data and the signals. A display is operatively coupled to the computer and operative to display at least one image of the at least one implement and a virtual background, the virtual background depicting a portion of a body cavity.
Owner:CAE HEALTHCARE
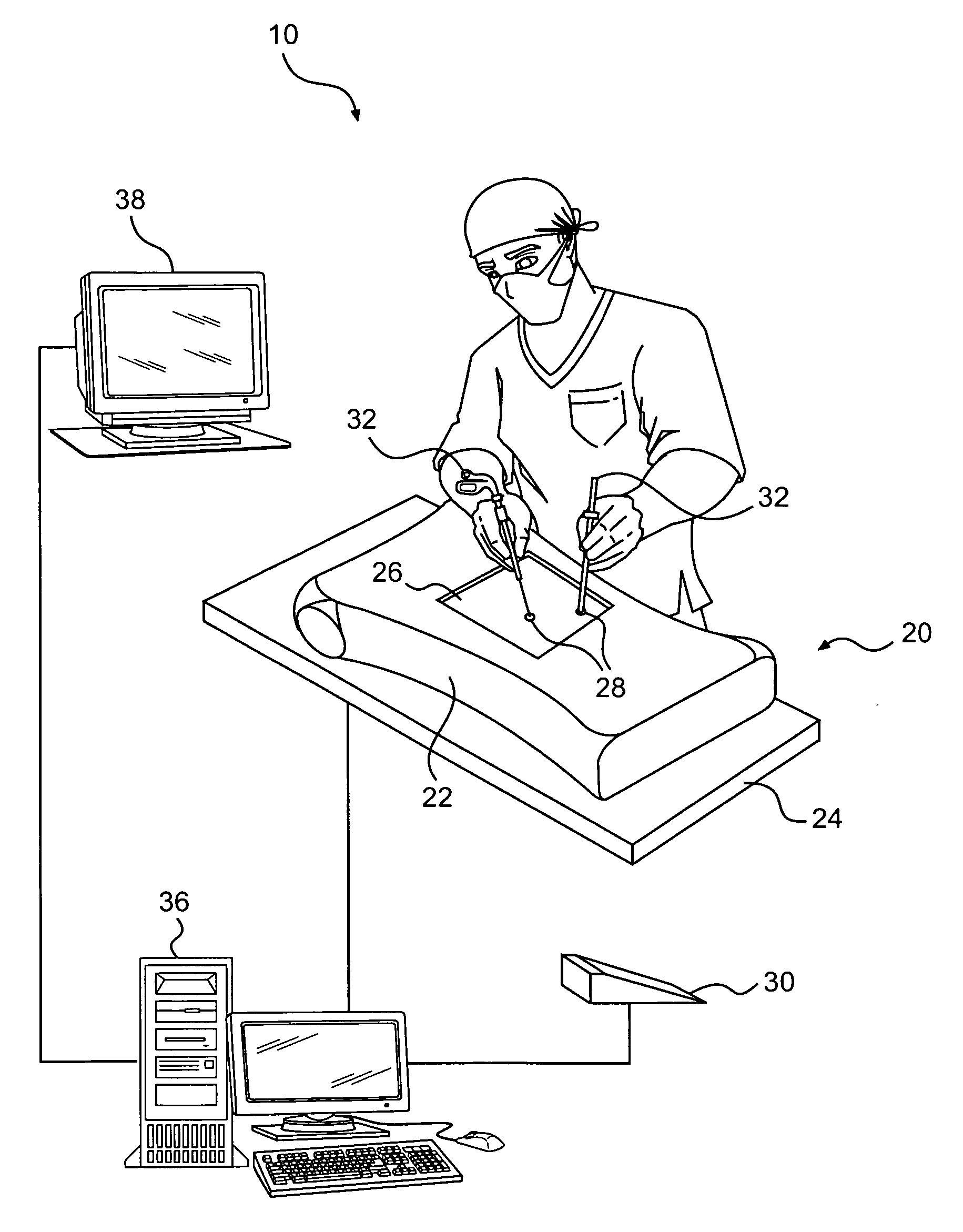
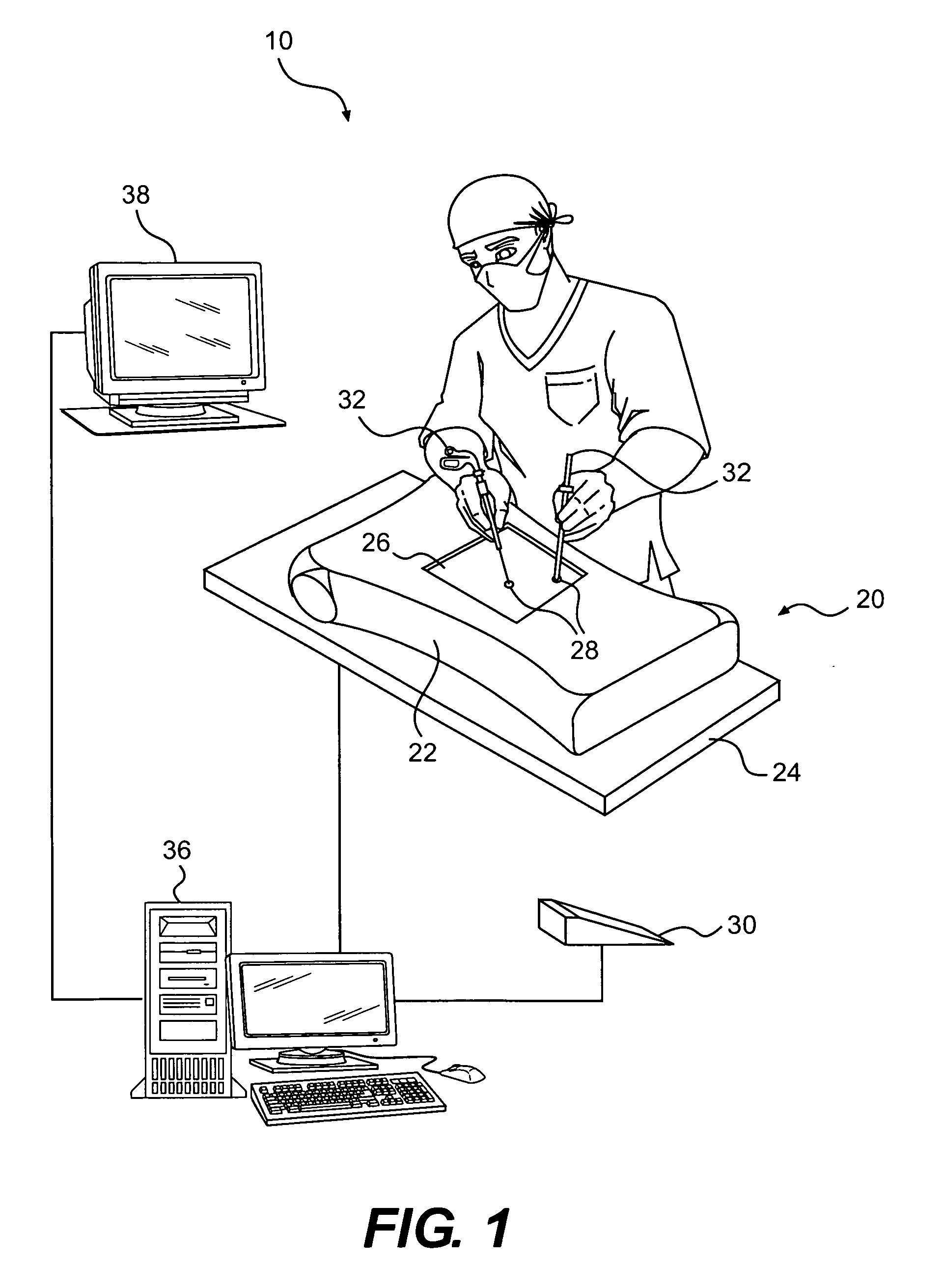
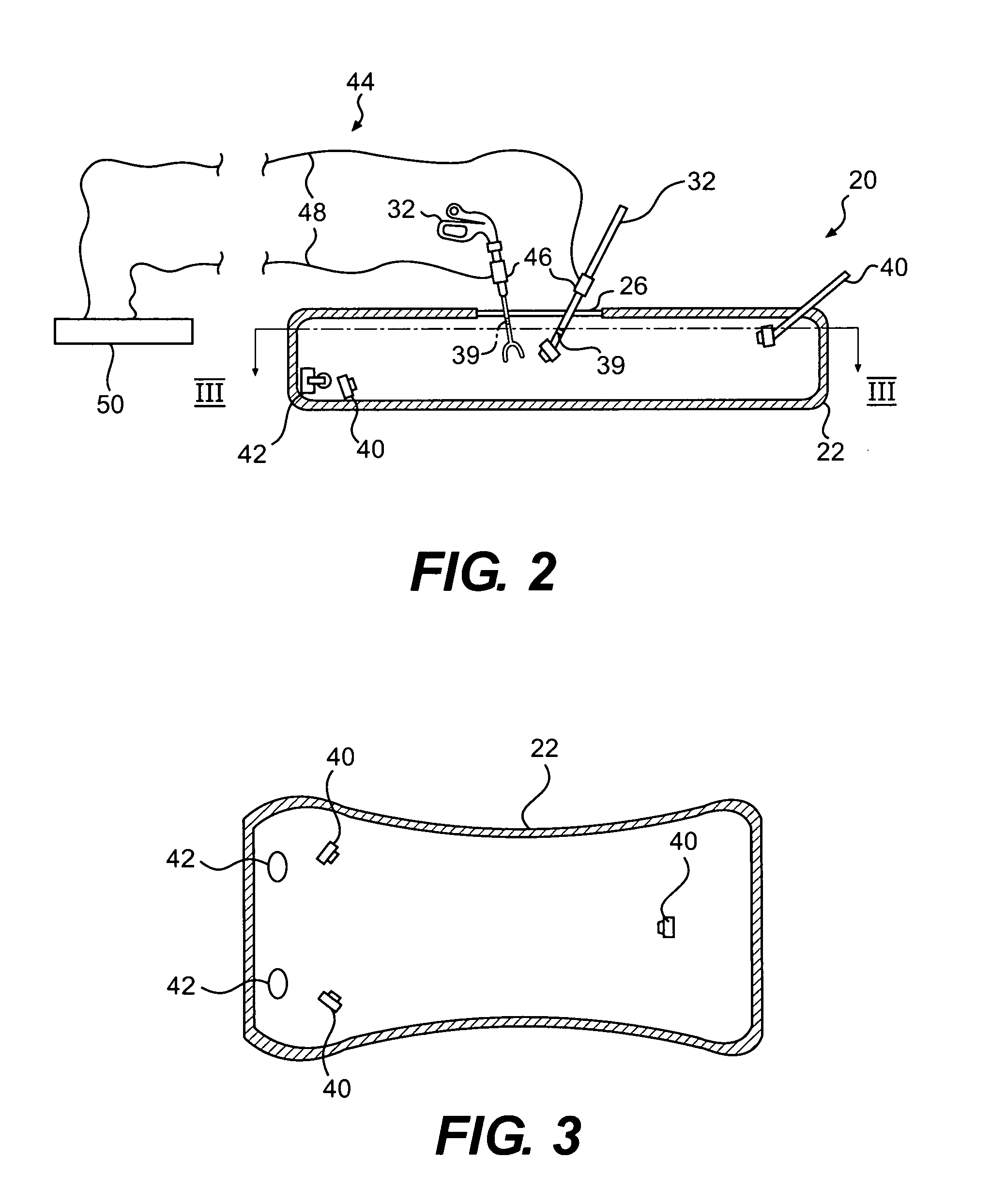
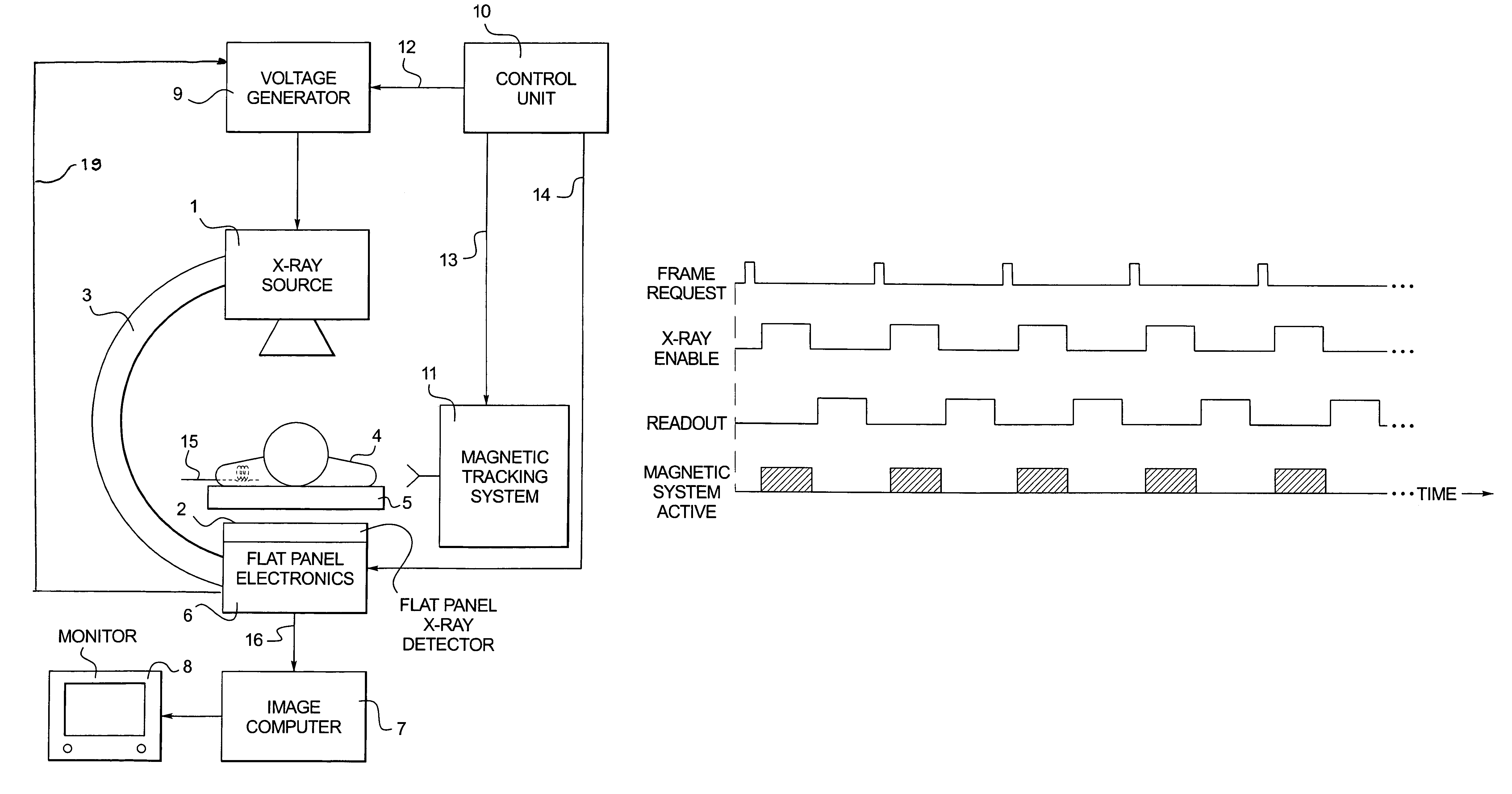
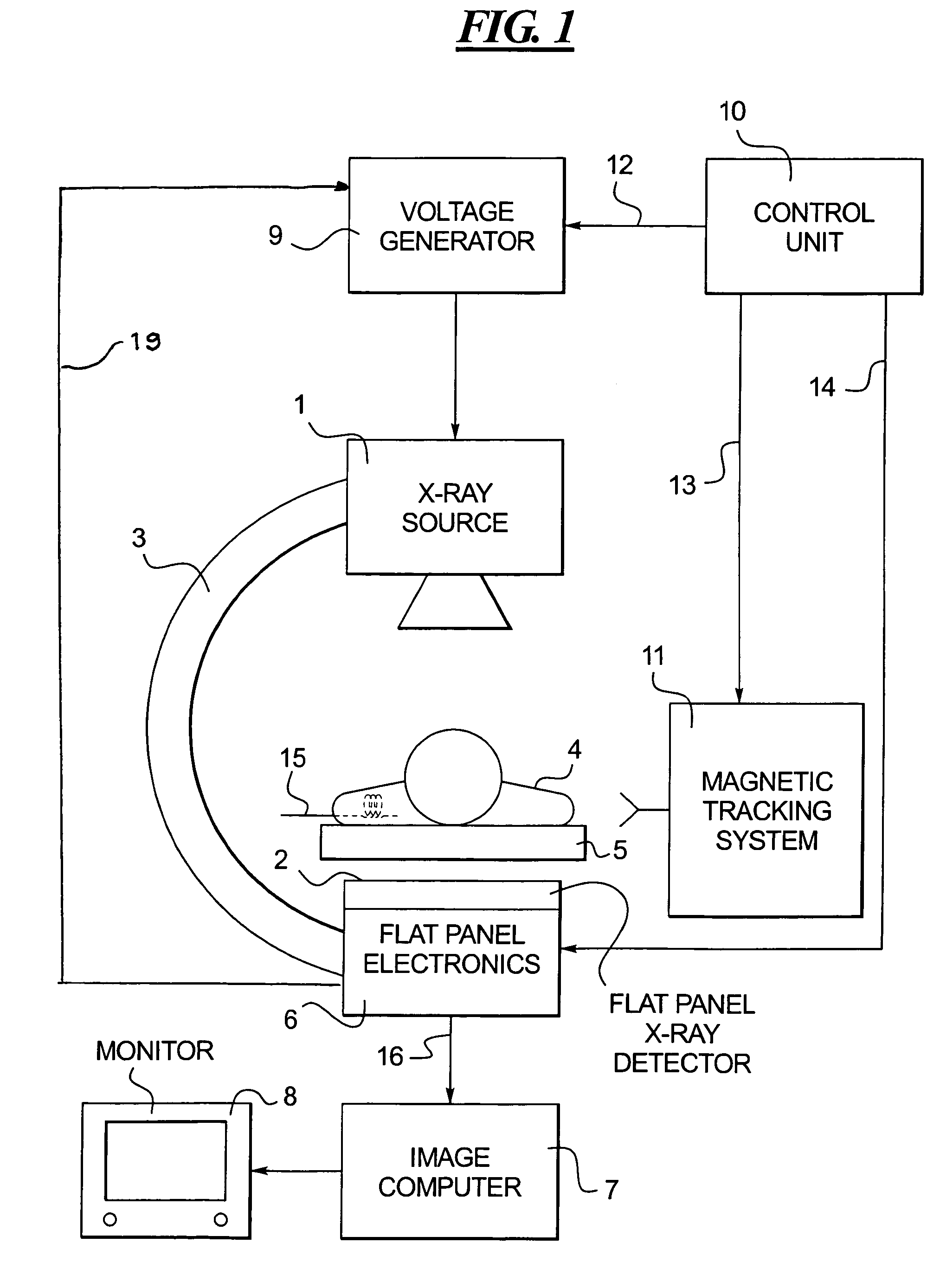
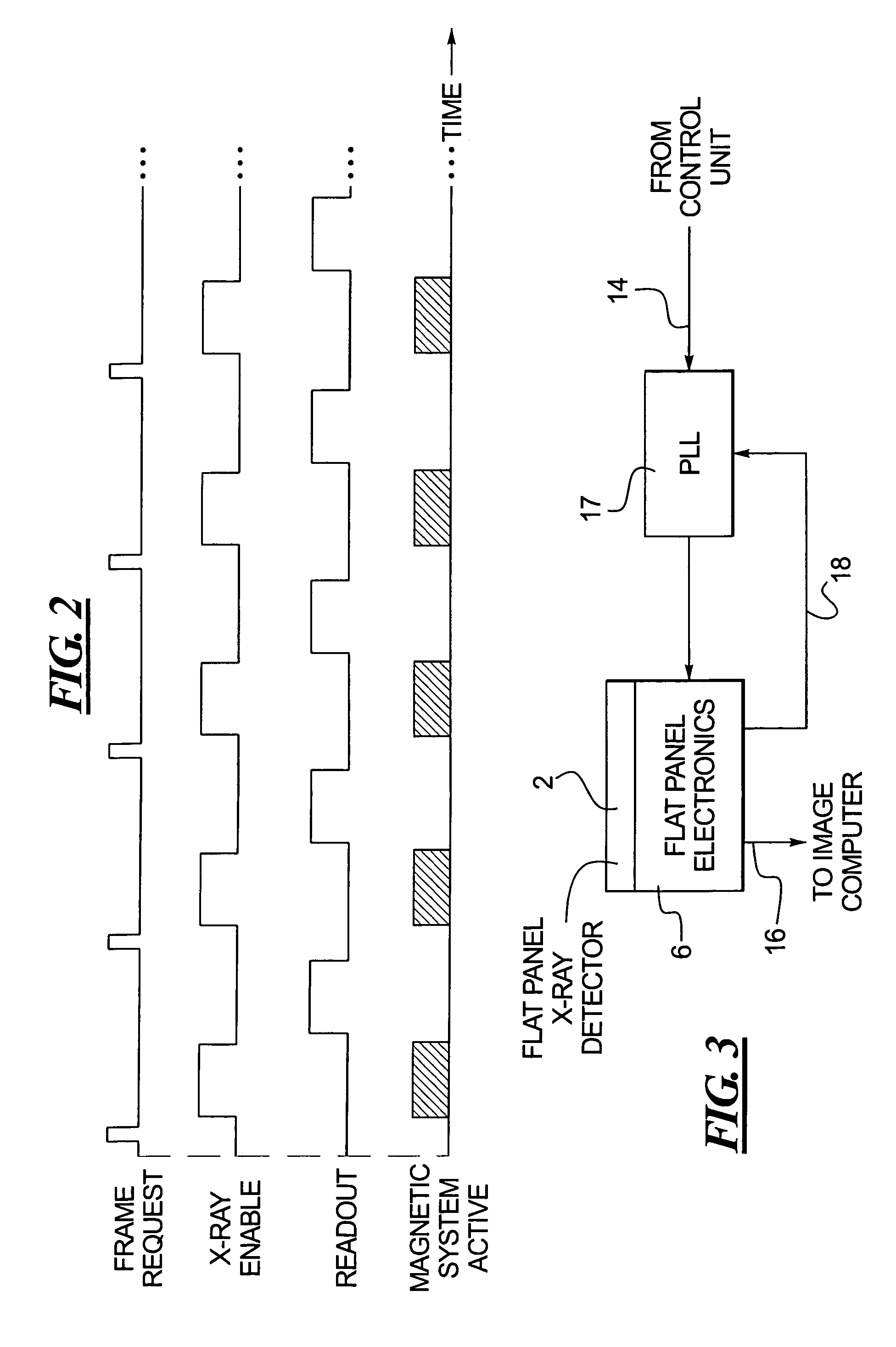
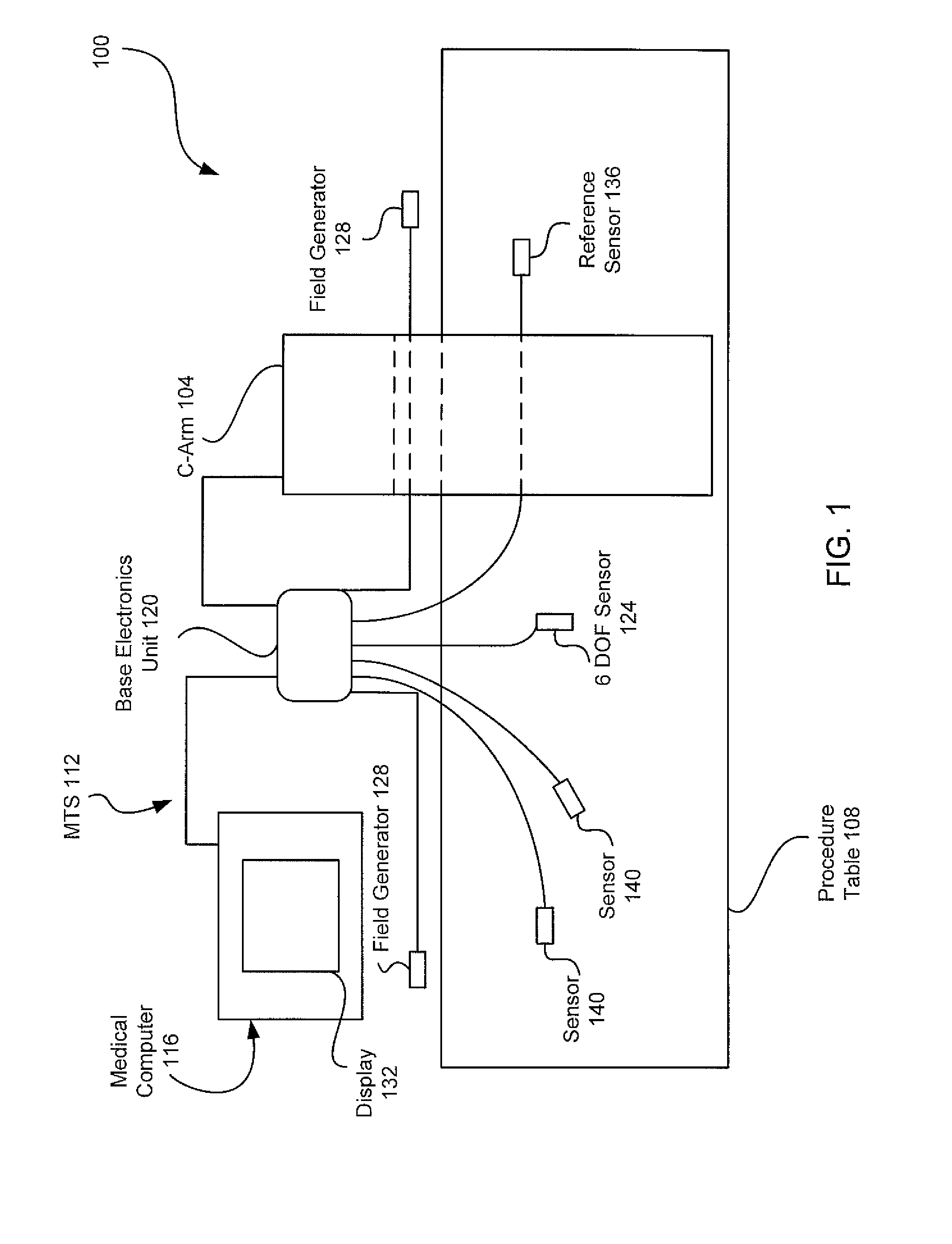
Method and apparatus for synchronizing operation of an x-ray system and a magnetic system
ActiveUS7236567B2Operating disturbanceSurgical navigation systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic trackingLocalization system
An x-ray apparatus has a flat panel x-ray detector, the operation of which is susceptible to interference by strong magnetic fields. In order to allow the x-ray system to be operated concurrently with a magnetic system, such as a magnetic tracking system or a magnetic localization system, that emits a magnetic field of sufficient field strength to interfere with the operation of the flat panel x-ray detector, a control unit is provided that operates both the flat panel x-ray detector and the magnetic system. The control unit synchronizes operation of the magnetic system with the operation of the flat panel x-ray detector so that the magnetic system emits the magnetic field only at times that do not interfere with the operation of the flat panel x-ray detector.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Chip Referee
This invention is an RFID system and method to determine the physical outer edges or perimeters of athletic objects of play in relationship to the outside edges or perimeters and relevant scoring or rules of play zones contained on an athletic field of play. It contemplates the electro magnetic tracking of objects of play and the adjudication of the rules of play as they relate to professional athletic competitions. This invention is designed as a replacement for, or adjunct to, a video referee or instant replay judge. This invention contemplates embedding an RFID transponder into an object of play and tracking it from interrogator controlled antennas embedded into the boundaries of play. A back end computer host system calibrates the electro magnetic digital data regarding the physical location of the object of play in relationship to its physical location on the field of play which electro magnetic data is interpreted and then displayed on the scoreboard at the field of play. The calibration is made through algorithms programmed into the middleware. This invention contemplates sensors encompassing the objects of play and laser guided interrogation beams to assist in precise measurements of the boundaries of play and relevant scoring or rules of play areas.
Owner:RODGERS JAMES NEIL
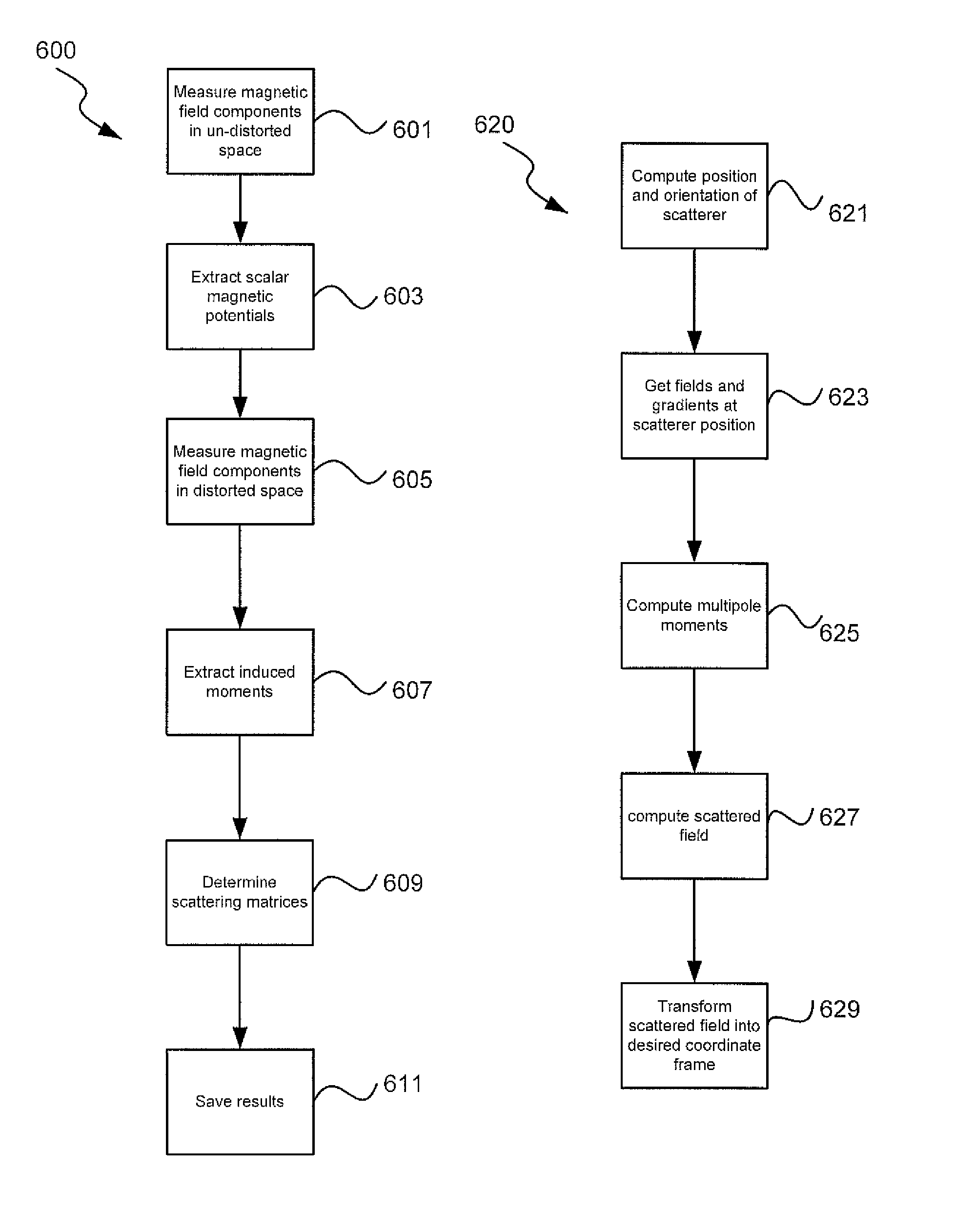
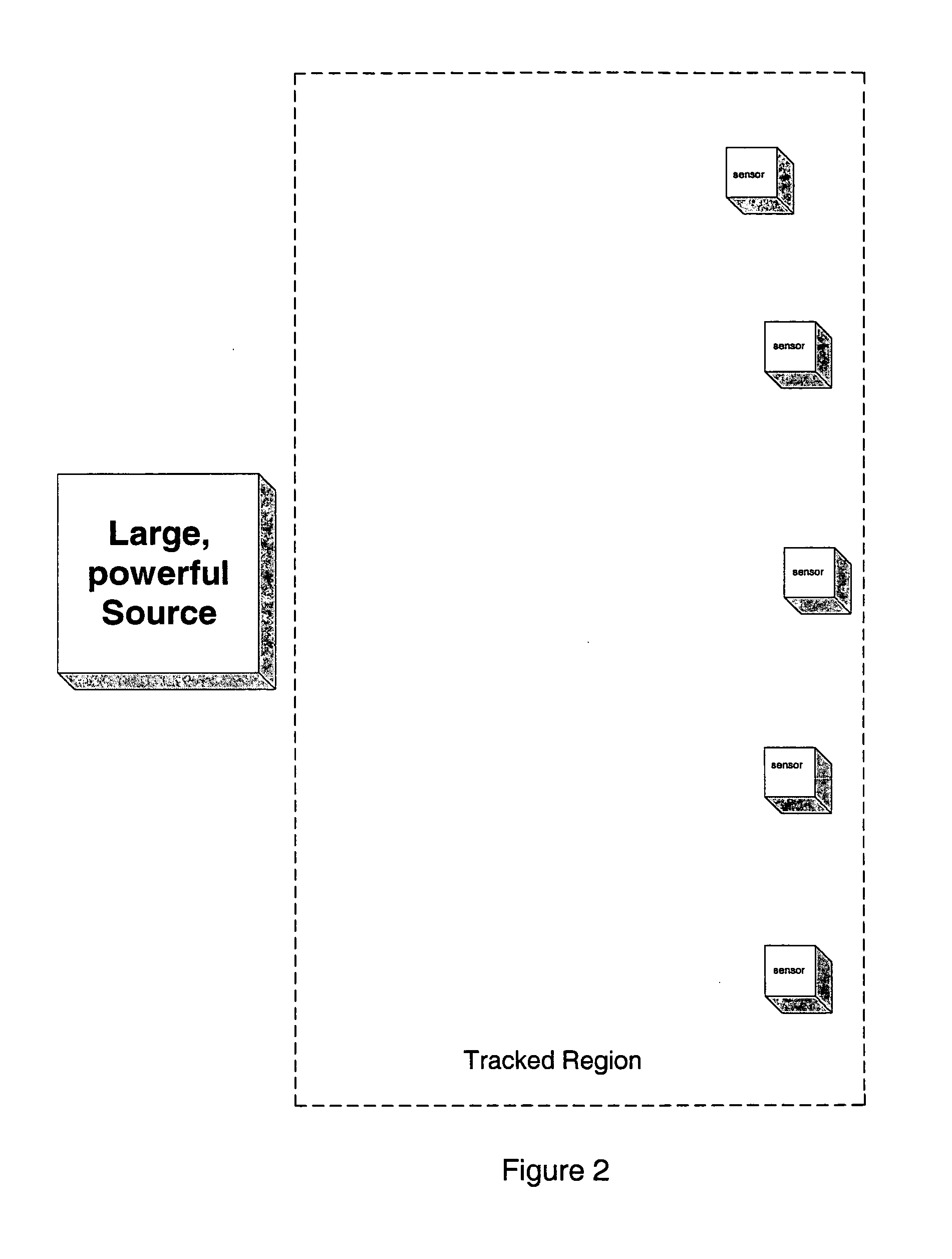
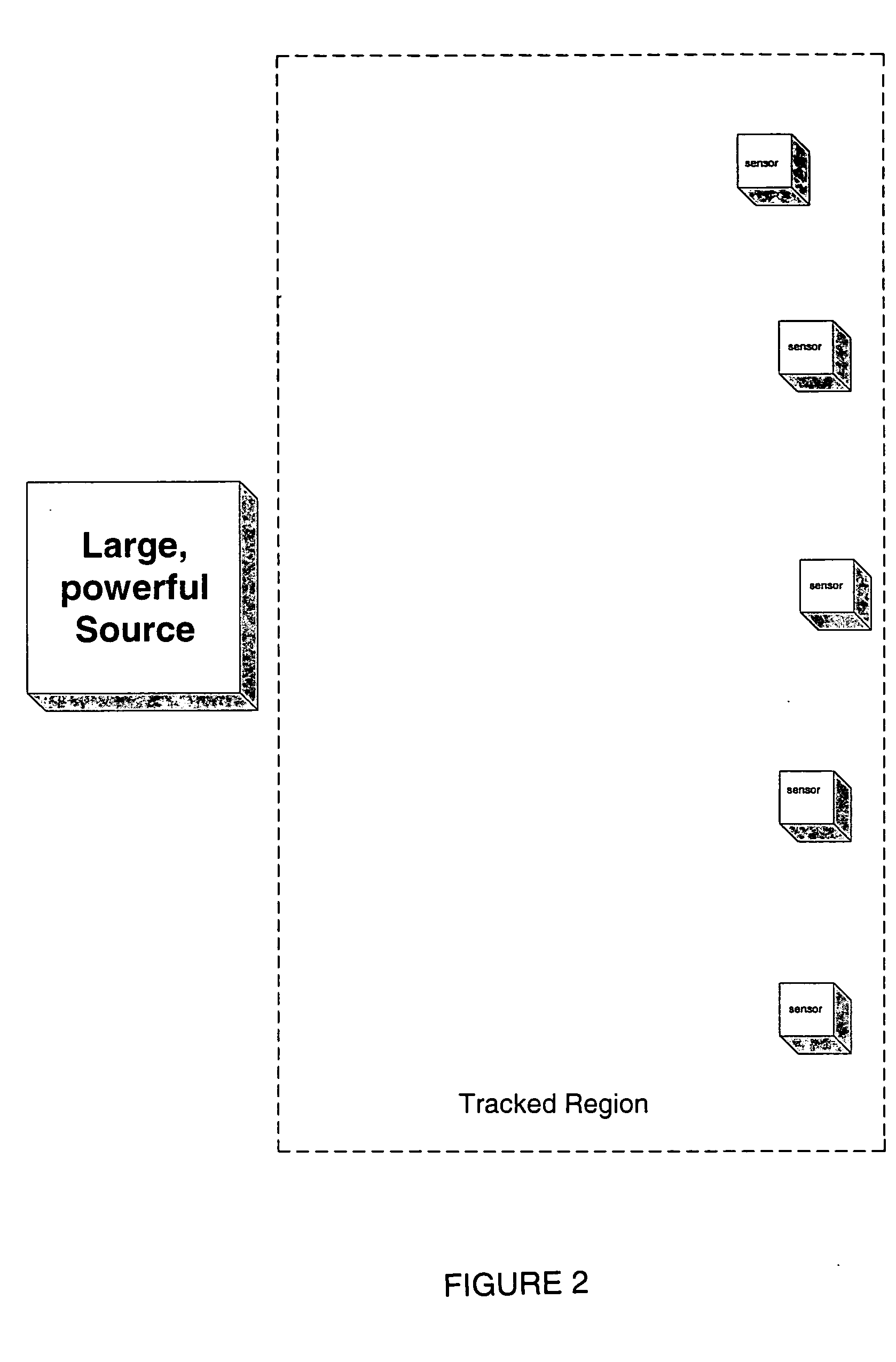
Systems and methods for compensating for large moving objects in magnetic-tracking environments
ActiveUS8228028B2Batteries circuit arrangementsDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic trackingDistortion
Methods for accurately tracking position and orientation of a magnetic-field sensor in a tracking volume when a large magnetic-field distorter is present in the tracking volume. In some of the methods, magnetic field data is collected from within the tracking volume both with and without the large magnetic-field distorter present in the tracking volume. This data is used to obtain correction information that is subsequently used during real-time operation of the magnetic-field sensor to correct the position and orientation solutions for the sensor for magnetic-field distortions caused by the presence of the large magnetic-field distorter in the tracking volume. Others of the methods involve modeling the large magnetic-field distorter using dipole and multipole modeling. Magnetic tracking systems for implementing the methods include hardware and software for carrying out the methods.
Owner:ASCENSION TECH
Method And Apparatus For Self-Relative Body Tracking For Virtual Reality Systems Using Magnetic Tracking
ActiveUS20160033768A1Character and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsMagnetic trackingField of view
A method and apparatus for self-relative body tracking in virtual reality systems using magnetic tracking is disclosed, which allows more accurate tracking of a user's body relative to the user's field of vision. A head-mounted magnetic tracking (HMMT) system is used, in which other parts of a user's body are tracked relative to the HMD on the user's head, rather than relative to a base station. This results in less distortion of the magnetic field used for tracking and thus allows for more accurate determination of the position and orientation of a user's body parts relative to the user's field of vision, so that a more accurate avatar may be presented on the HMD to the user. This allows the avatar of the user's body part to be shown in a location that corresponds closely to its physical position. In an alternative embodiment, multiple portions of the user's body may be tracked.
Owner:PENUMBRA
Detection of metal disturbance in a magnetic tracking system
ActiveUS20050024043A1Improve accuracyPosition fixationDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic trackingObject based
A method for tracking an object includes producing energy fields at a plurality of different frequencies in a vicinity of the object, and receiving signals that are generated at a location of the object at the different frequencies in response to the energy fields. Multiple computations are made of spatial coordinates of the object based on the signals received at the different frequencies. Convergence of the computations is tested in order to ascertain whether the energy fields have been perturbed by an article in the vicinity of the object.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
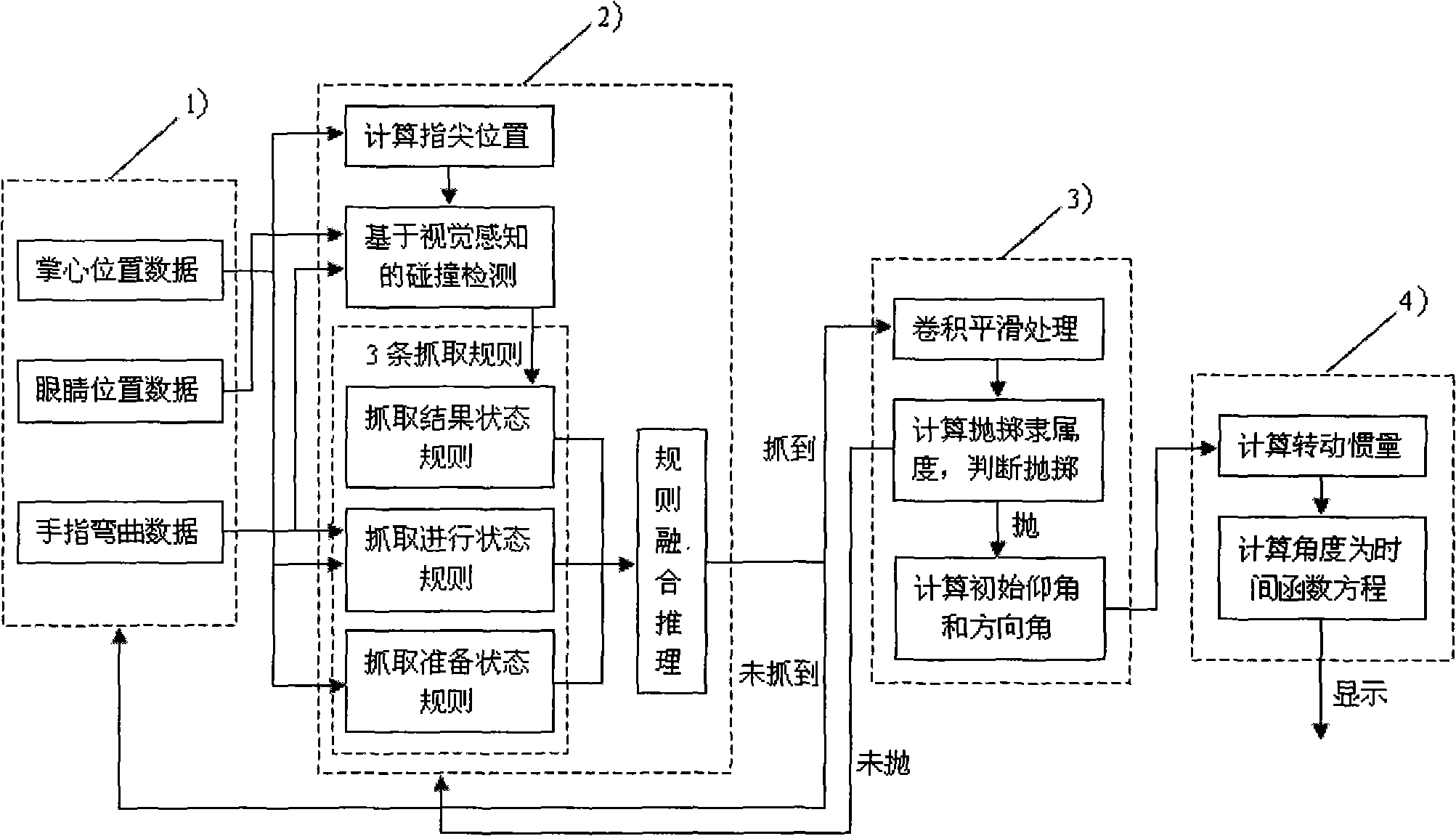
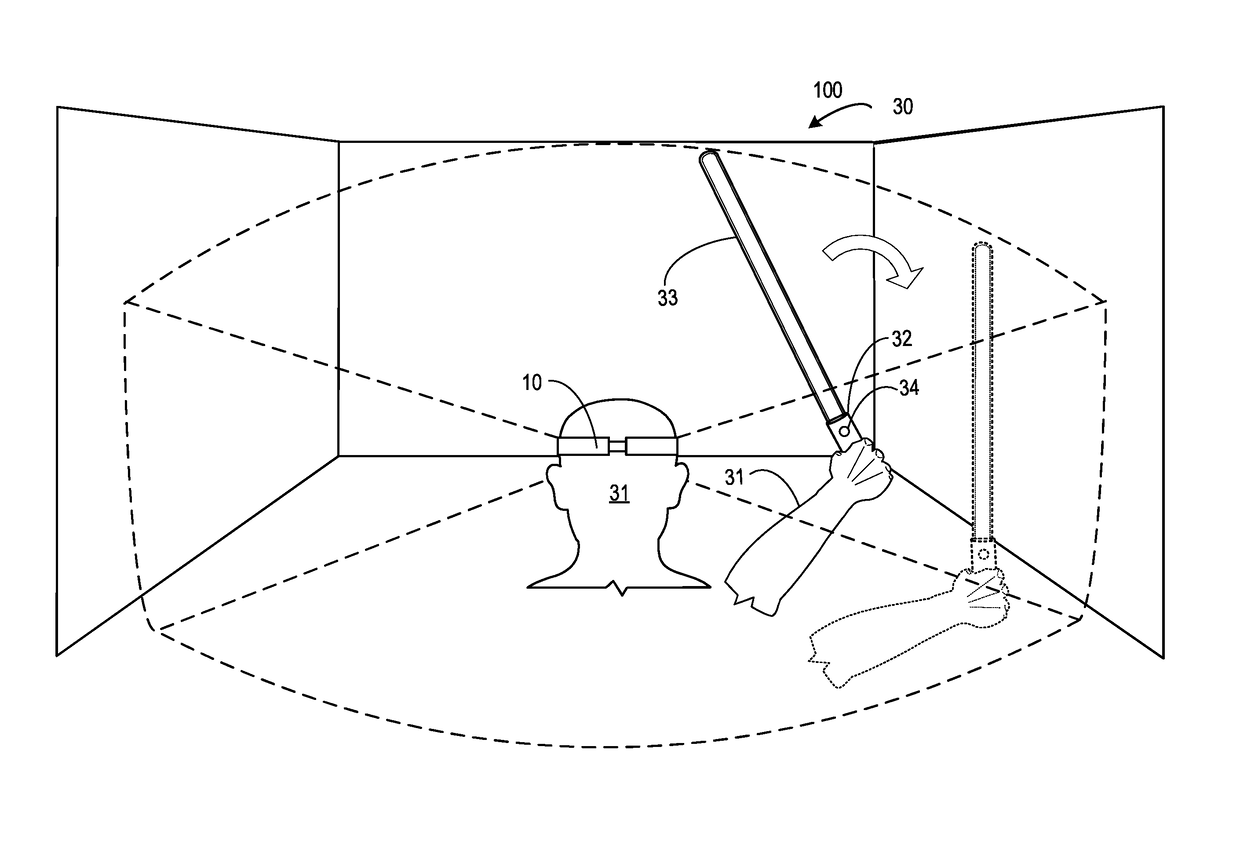
Human-computer interaction method for grapping and throwing dummy object and system thereof
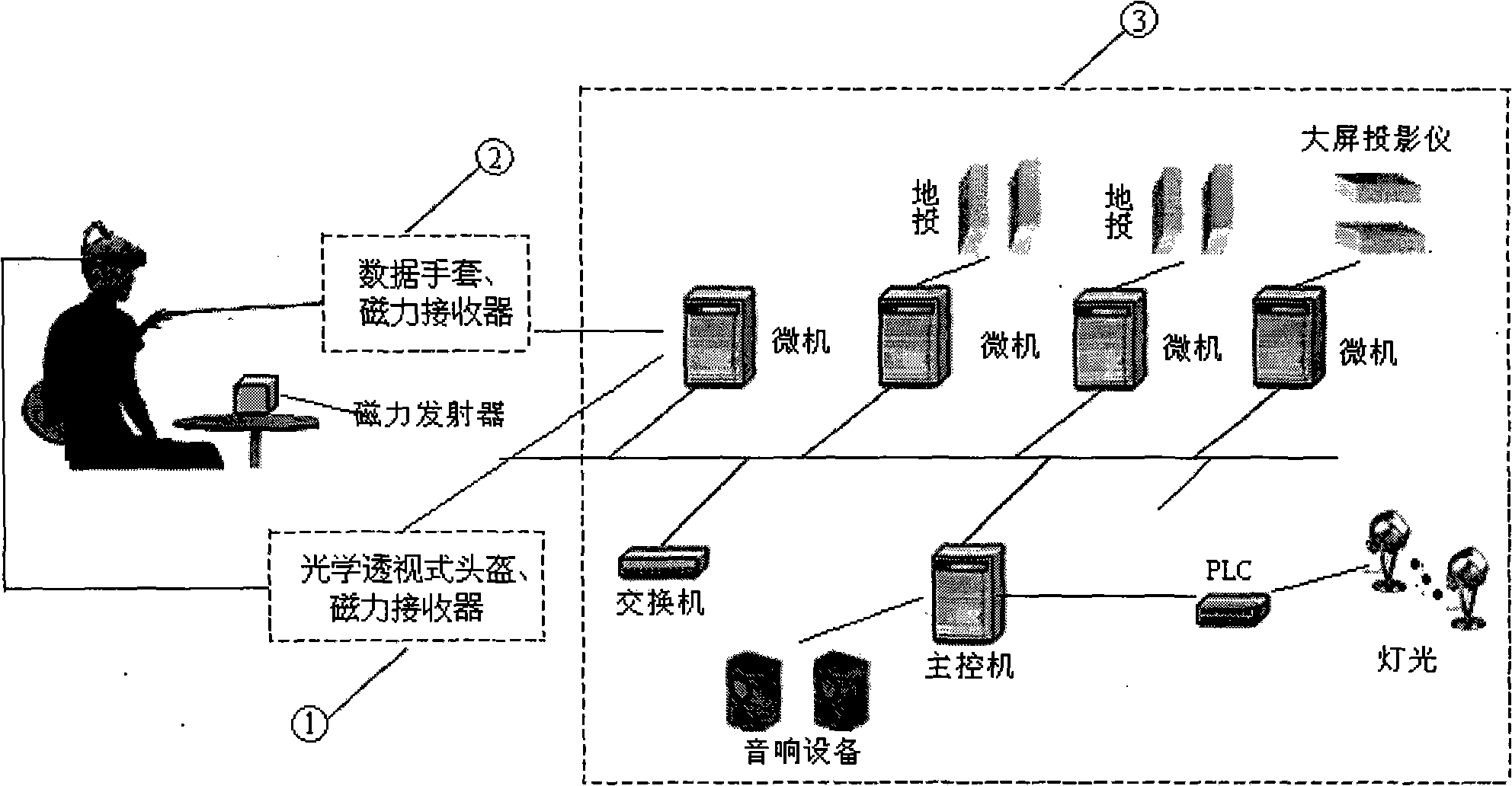
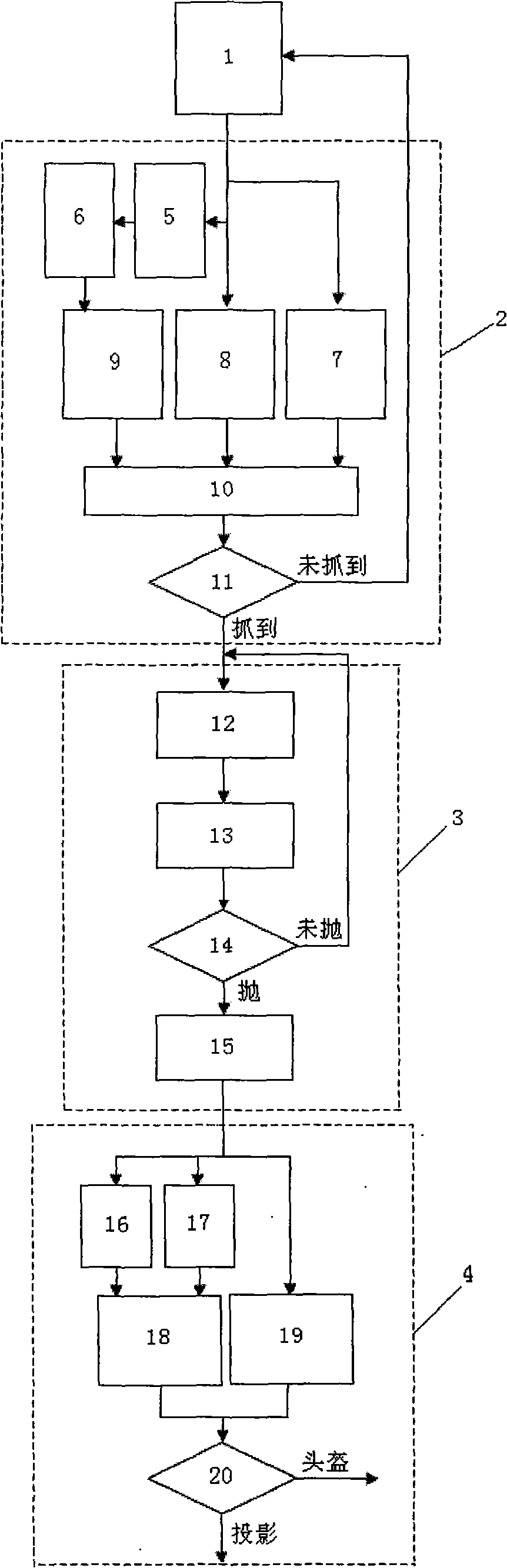
InactiveCN101515198AStrong real-timeOperate naturallyInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingMagnetic trackingVision based
The invention relates to a human-computer interaction method for grapping and throwing a dummy object and a system thereof. The method provided by the invention has work steps: (1) gaining data of a head and a hand, (2) realizing grapping recognition based on visual perception, (3) realizing throwing recognition based on magnetic tracking, (4) realizing the real rotation of a projectile. The system provided by the invention comprises a grapping recognition subsystem based on the visual perception, a throwing recognition subsystem based on the magnetic tracking and a path display subsystem with the real rotation. The invention can combine the consistency movement of snatching and throwing as an interactive method and uses the augmented-reality technique for taking the dummy object as a target to be snatched and thrown. The realization of the functions only needs an optical see-through helm and a magnetic tracker to be worn (a camera is not used); thereby a user can directly perceive the shocking effect of the scene. The invention has the advantages of natural operation, high real-time, and being economical and practical.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
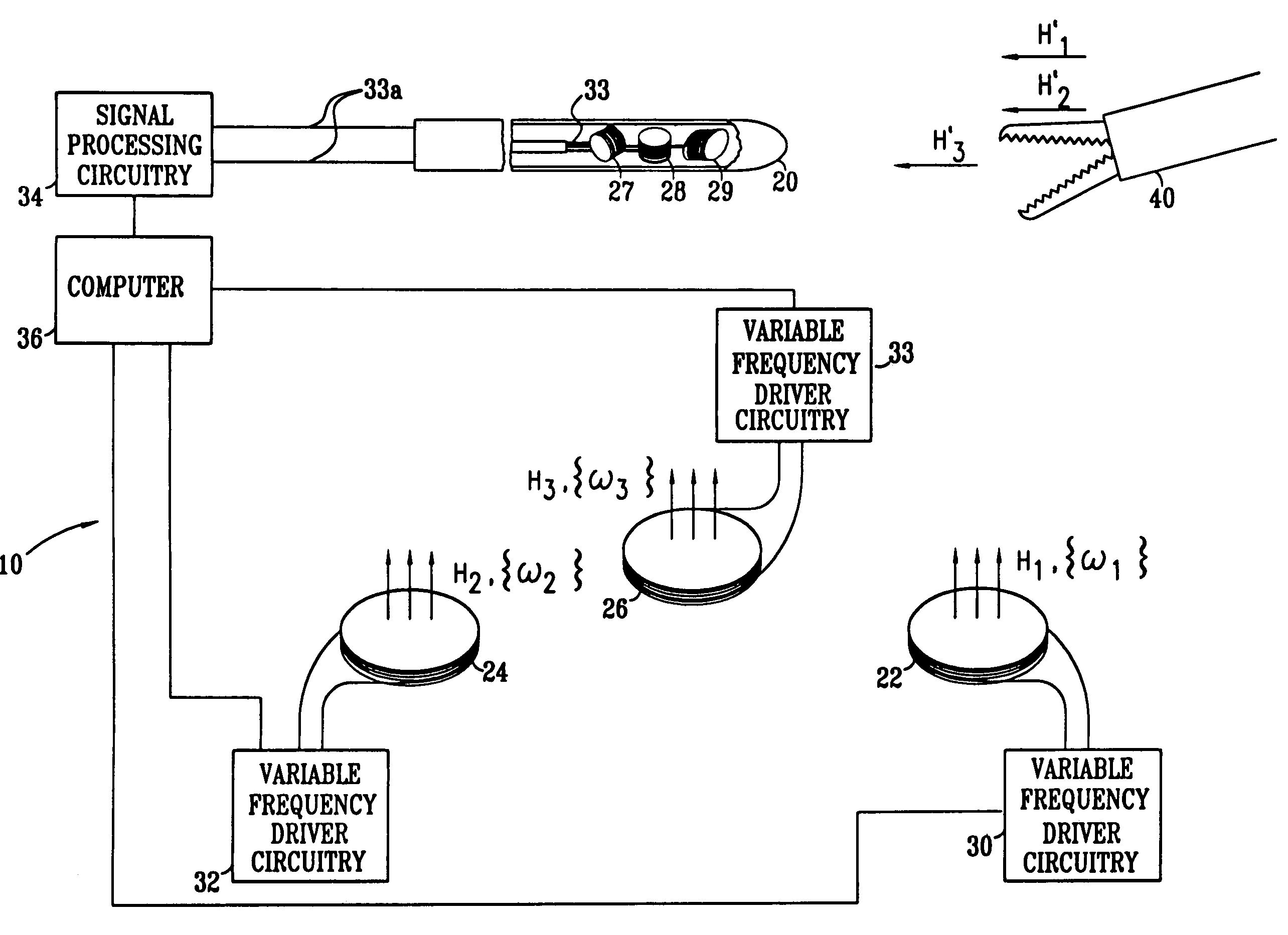
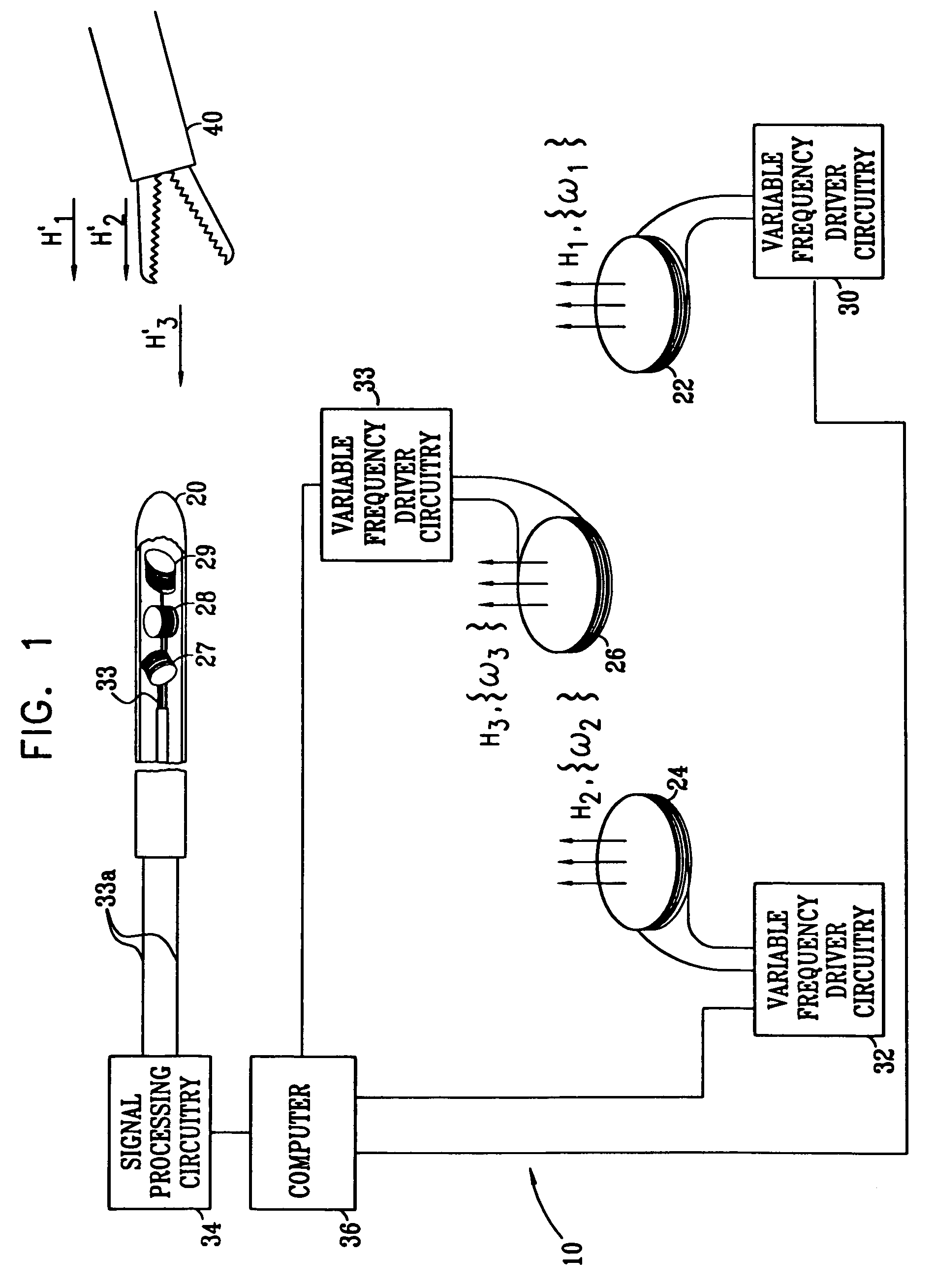
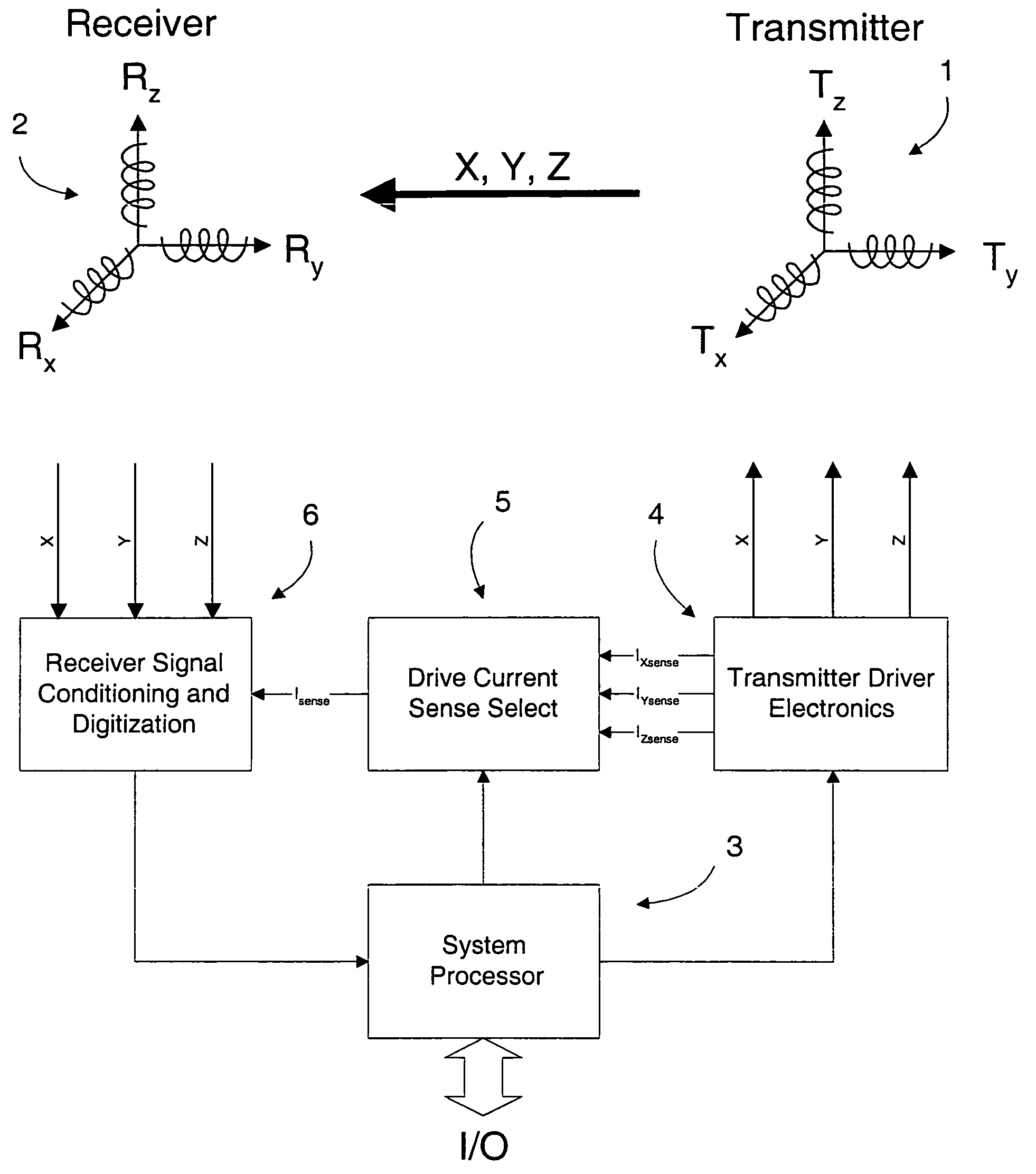
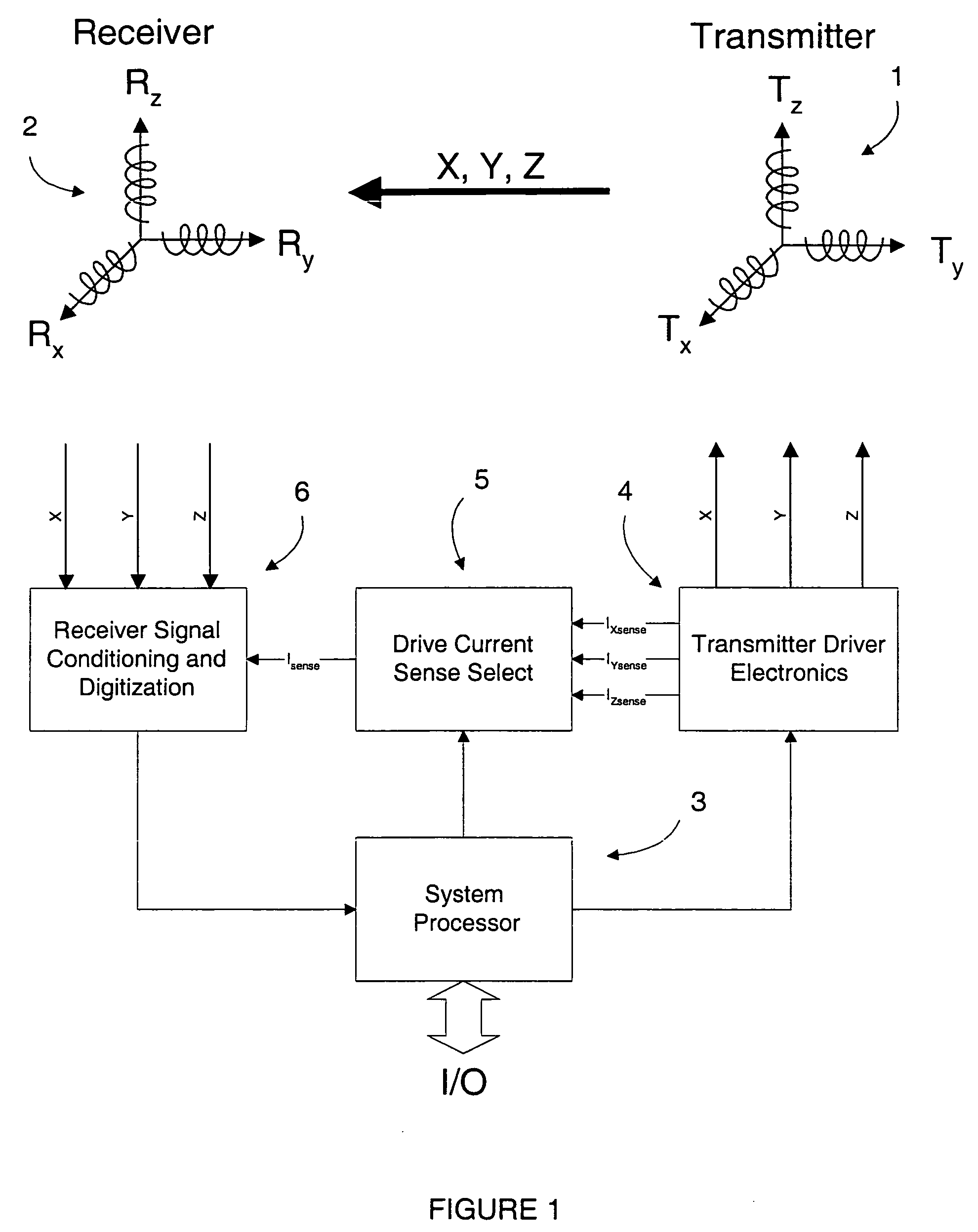
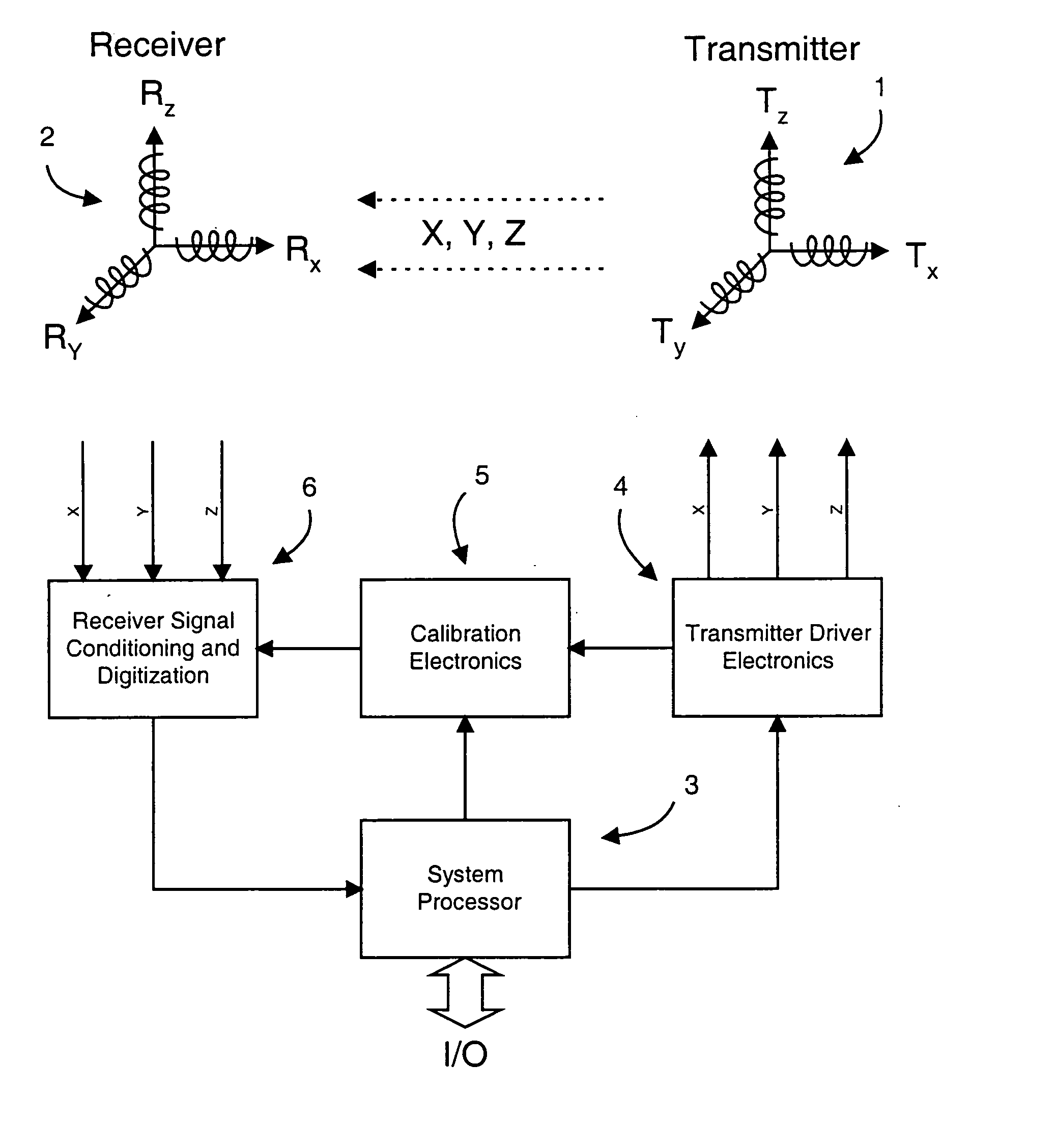
Electromagnetic position and orientation sensing system
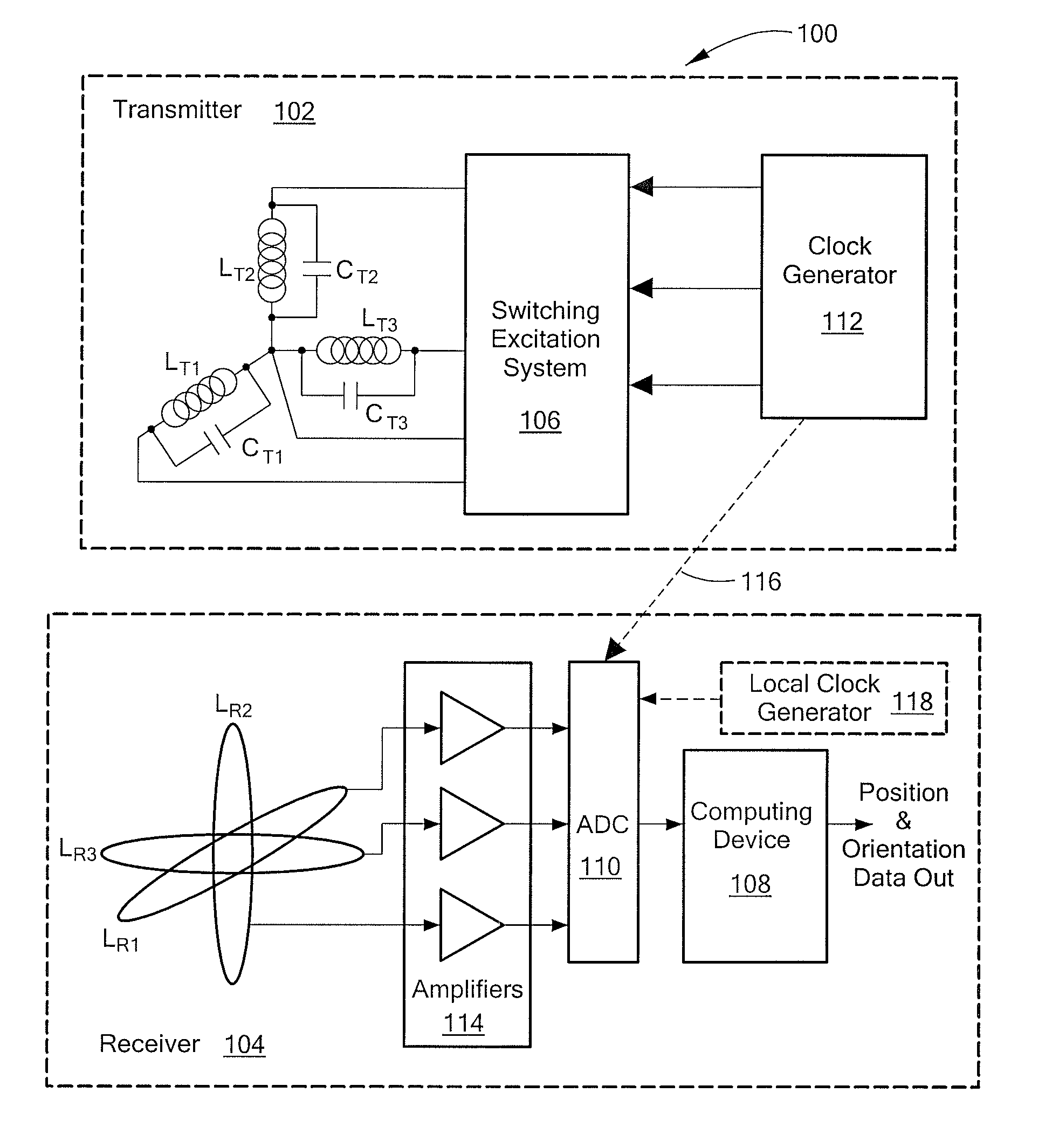
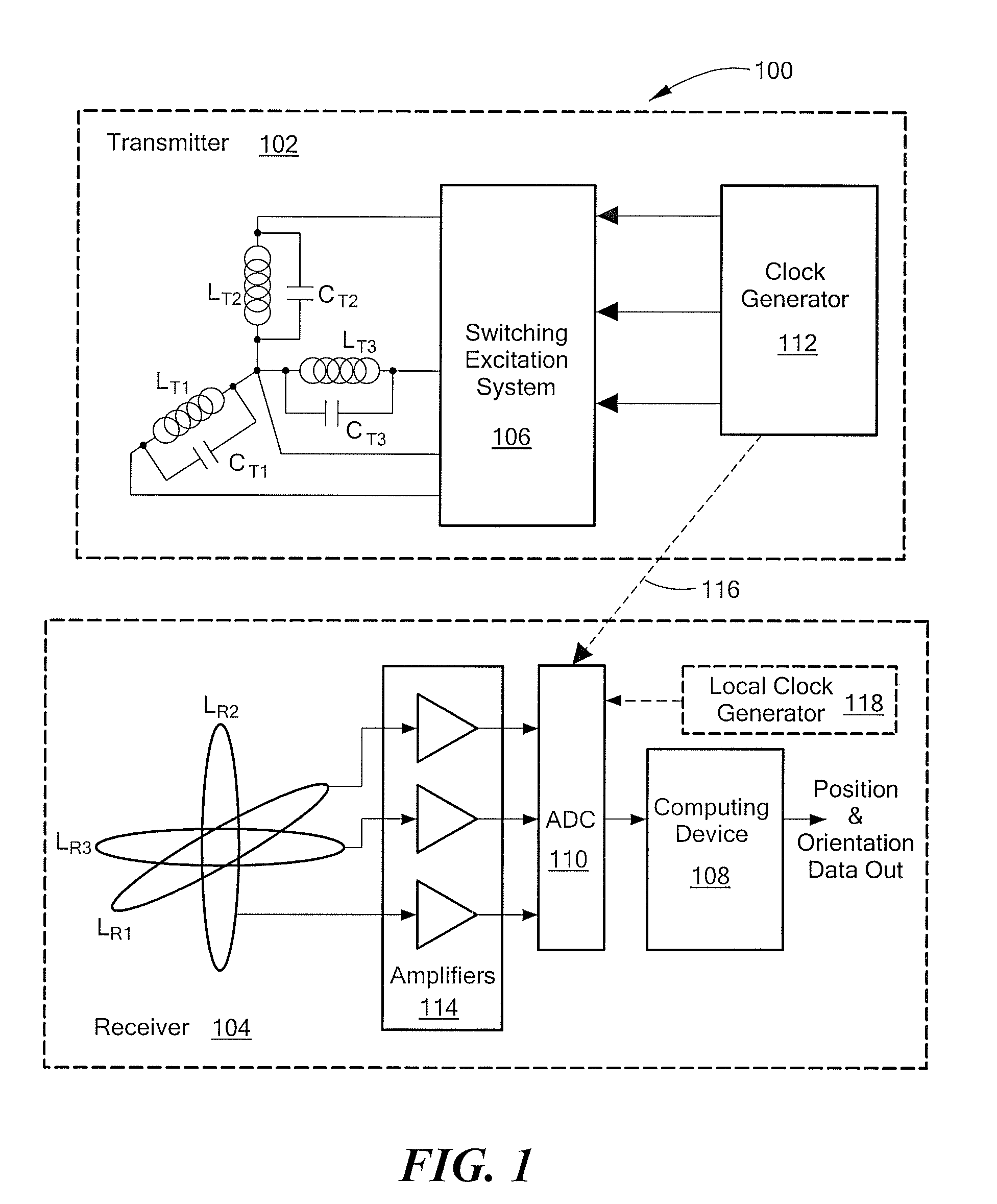
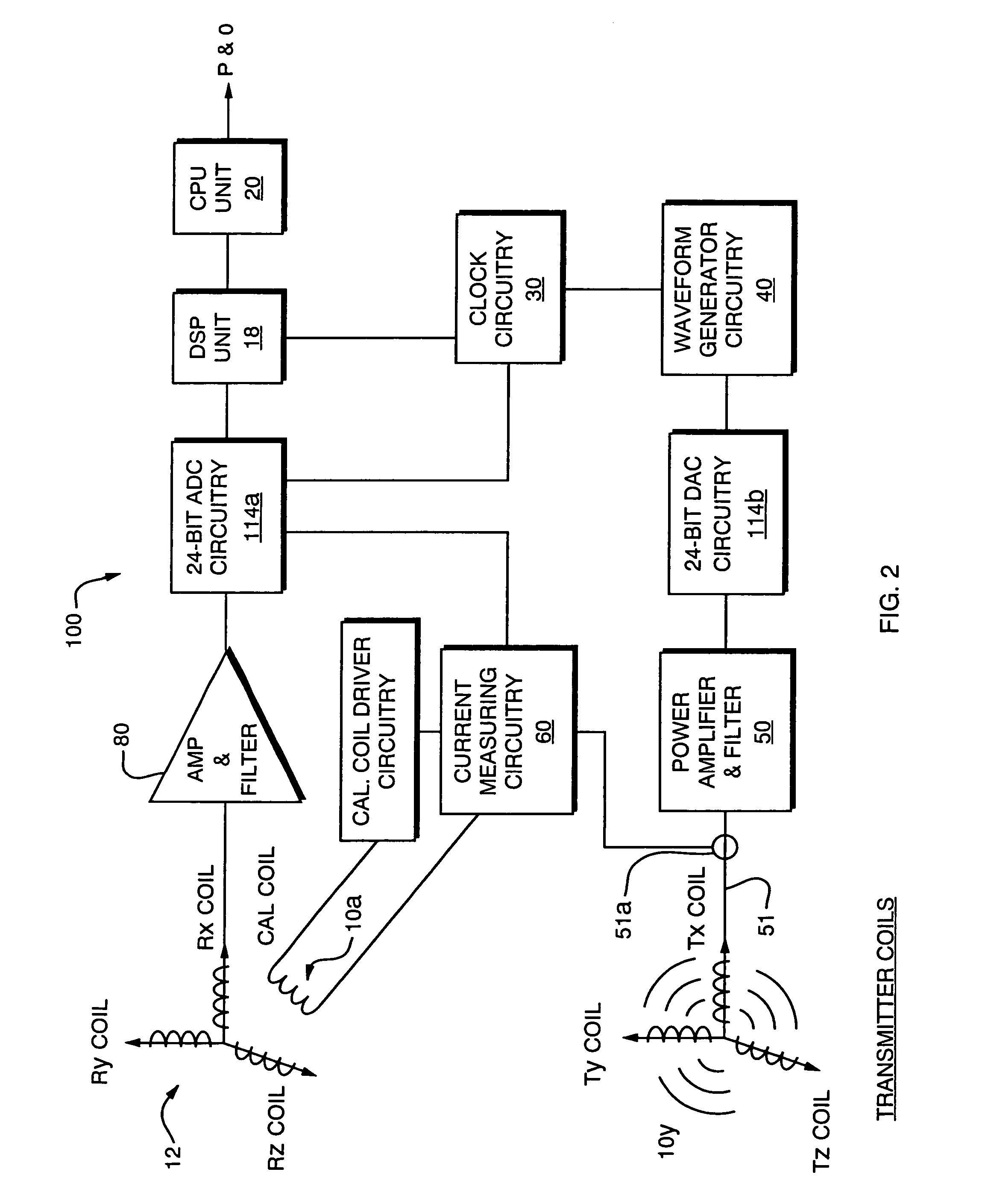
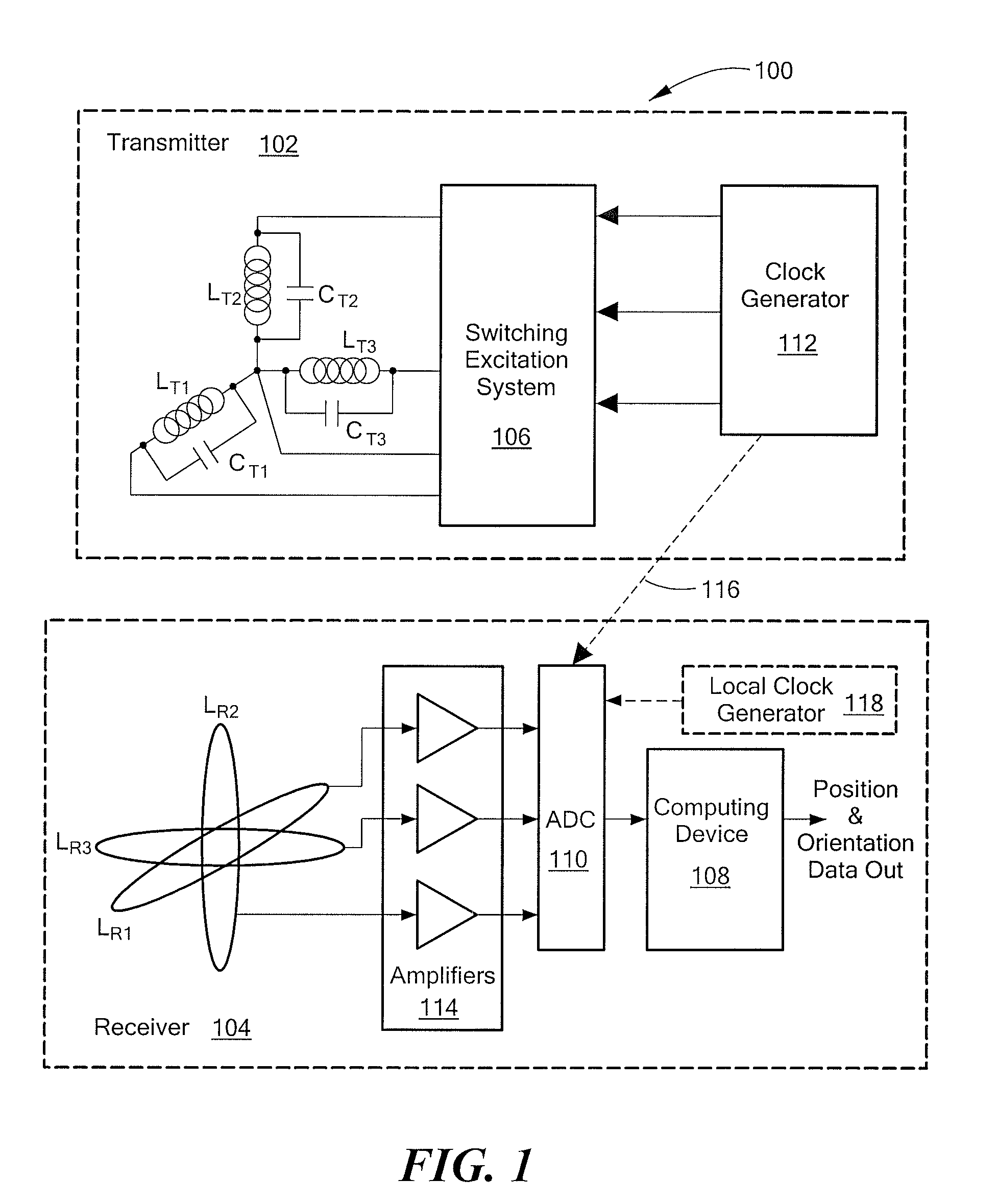
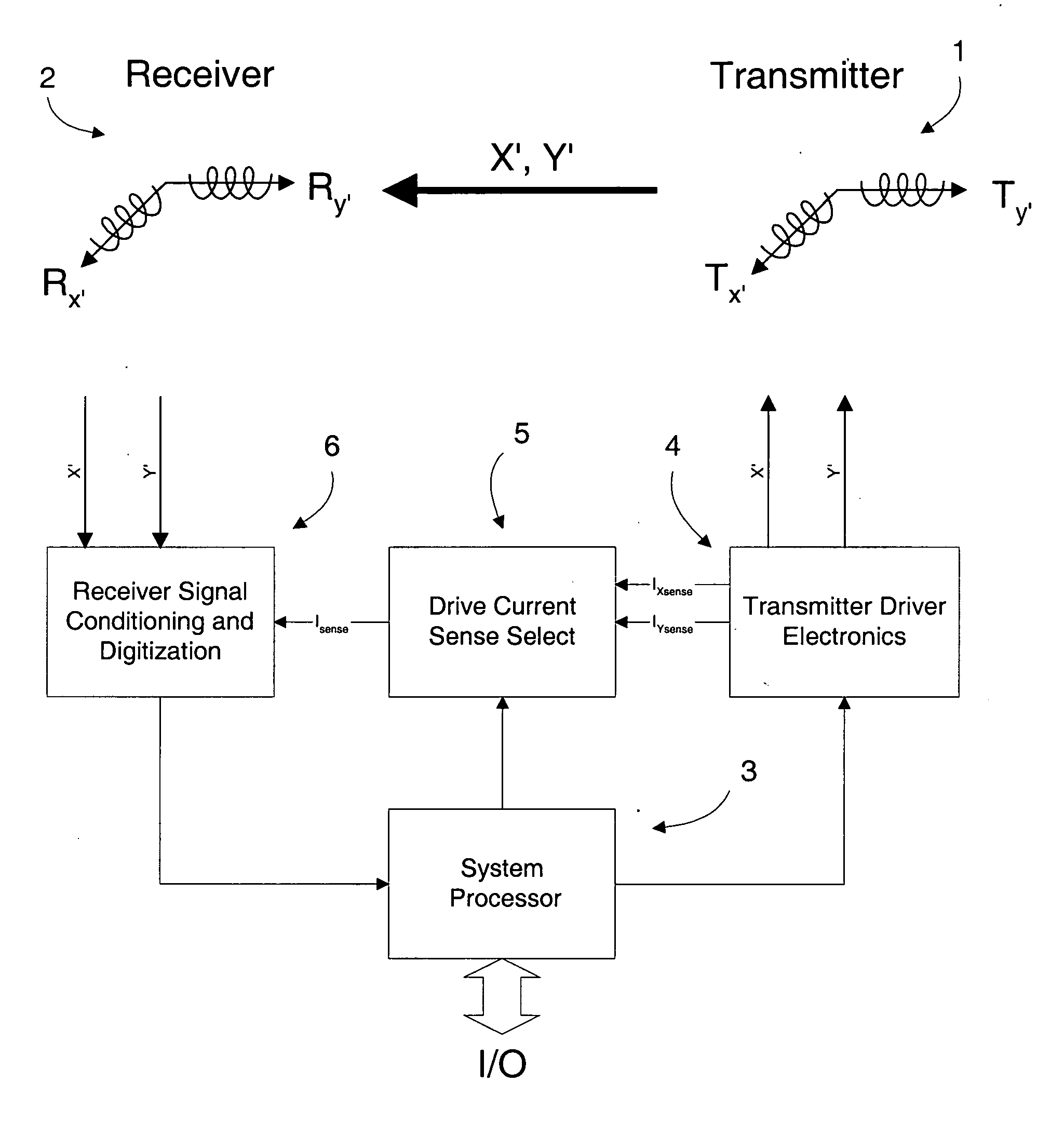
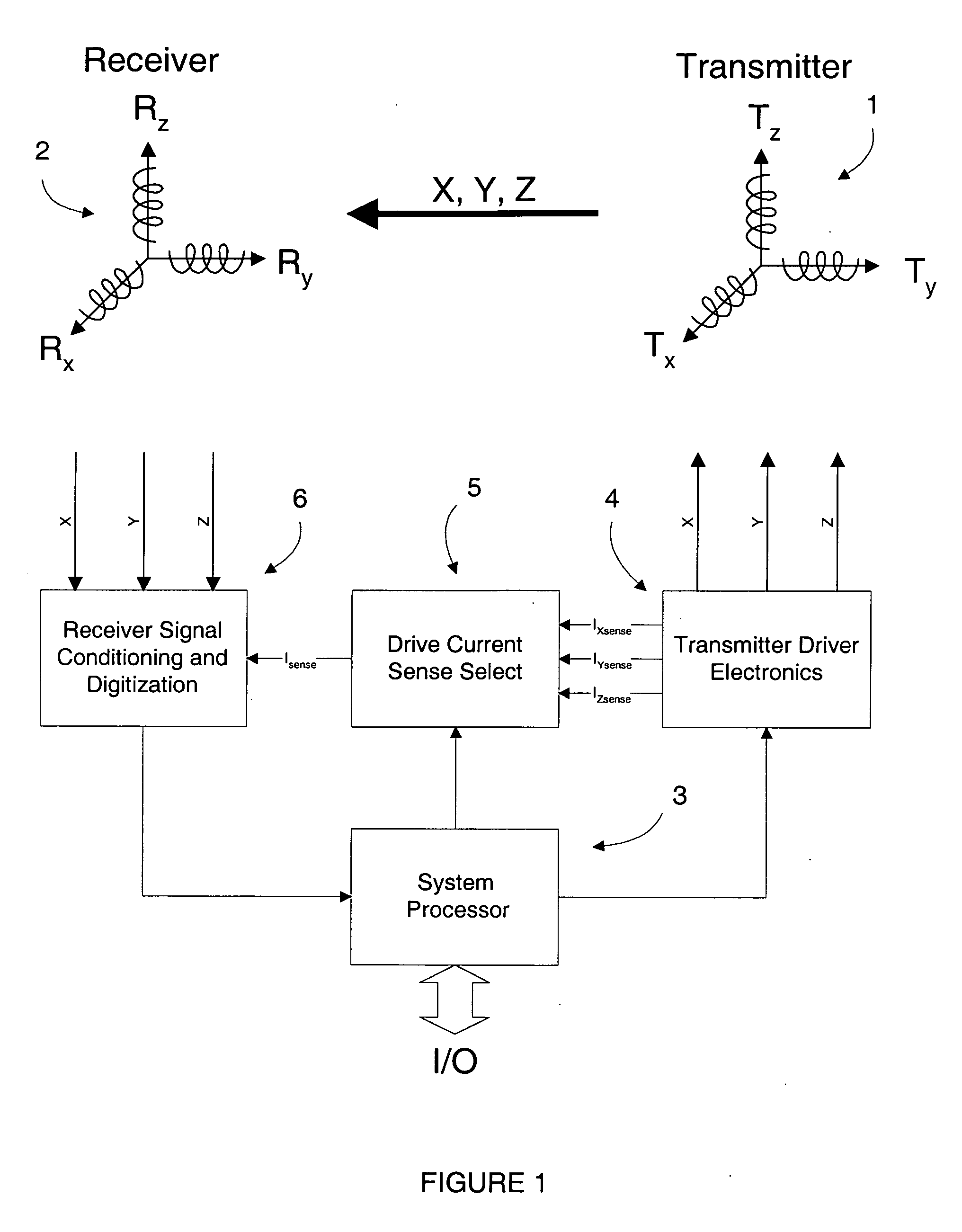
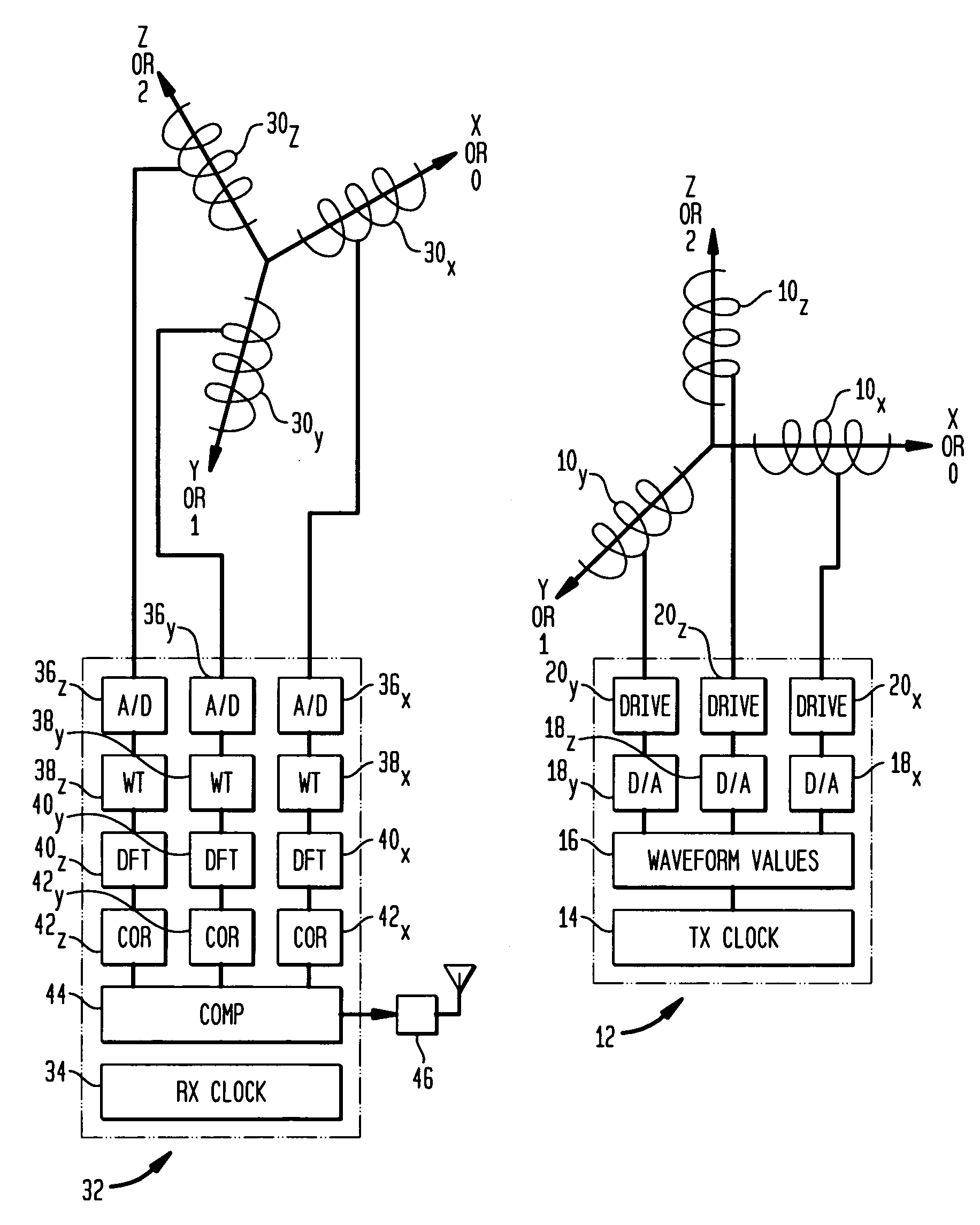
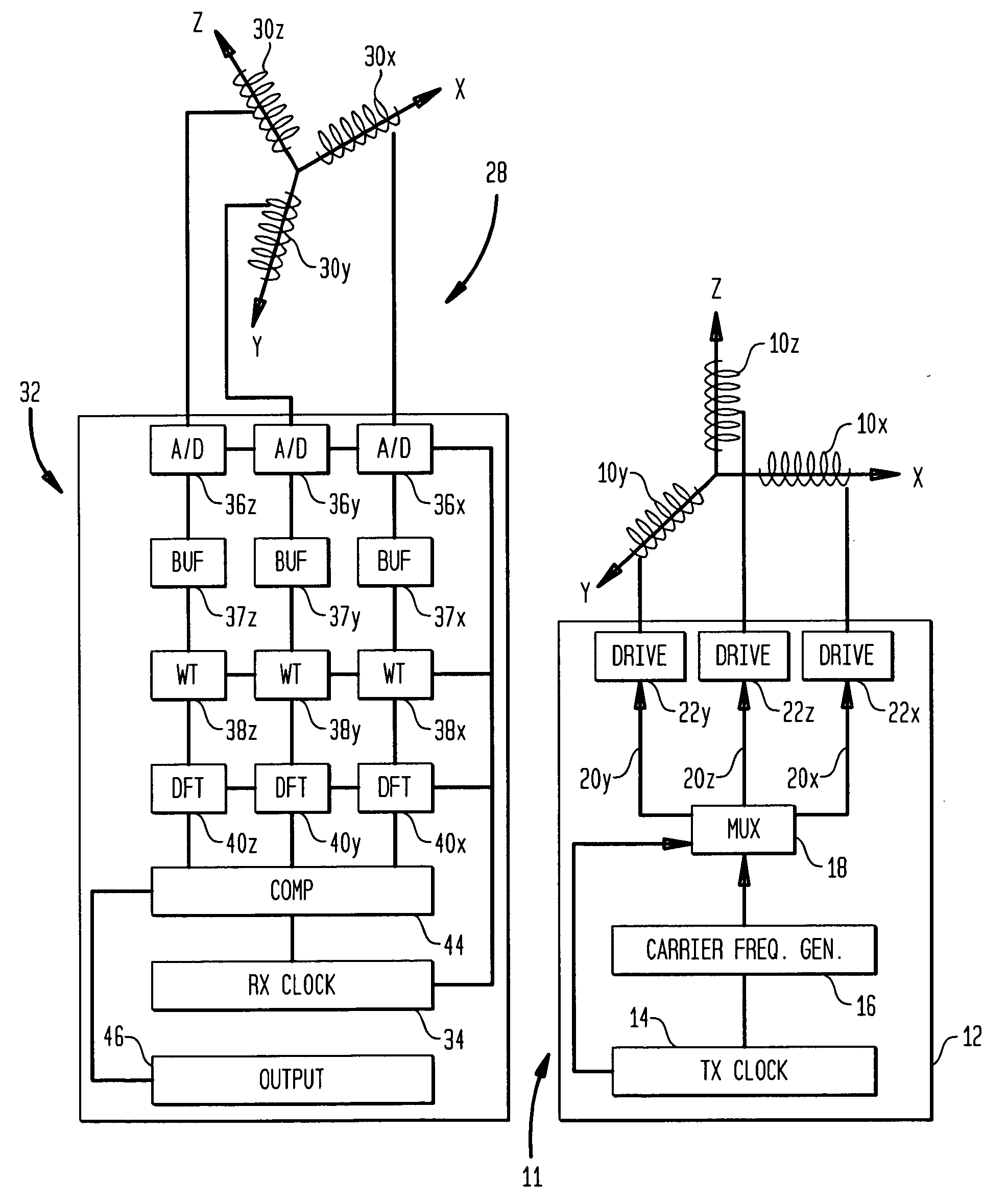
InactiveUS20100271012A1Easy to embedRaise the possibilityMagnetic measurementsBeacon systems using radio wavesTransmitter coilMagnetic tracking
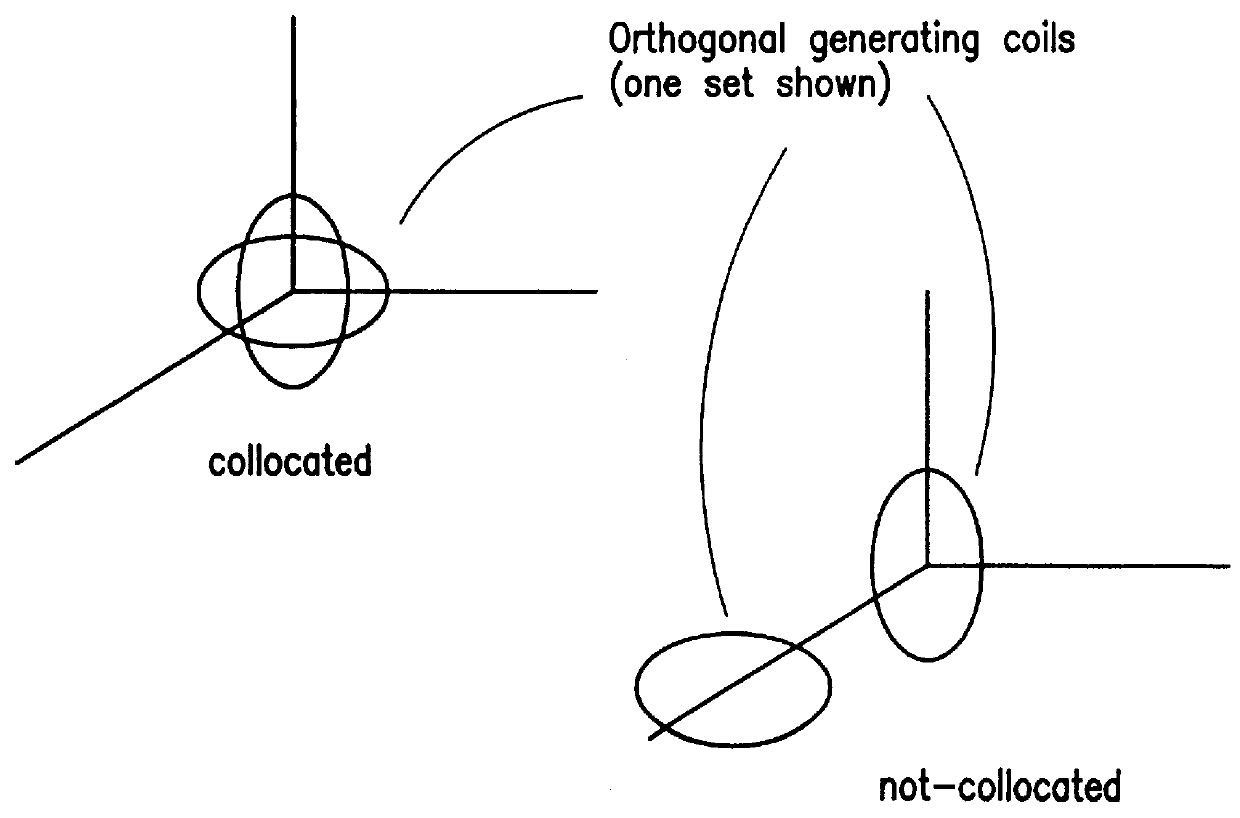
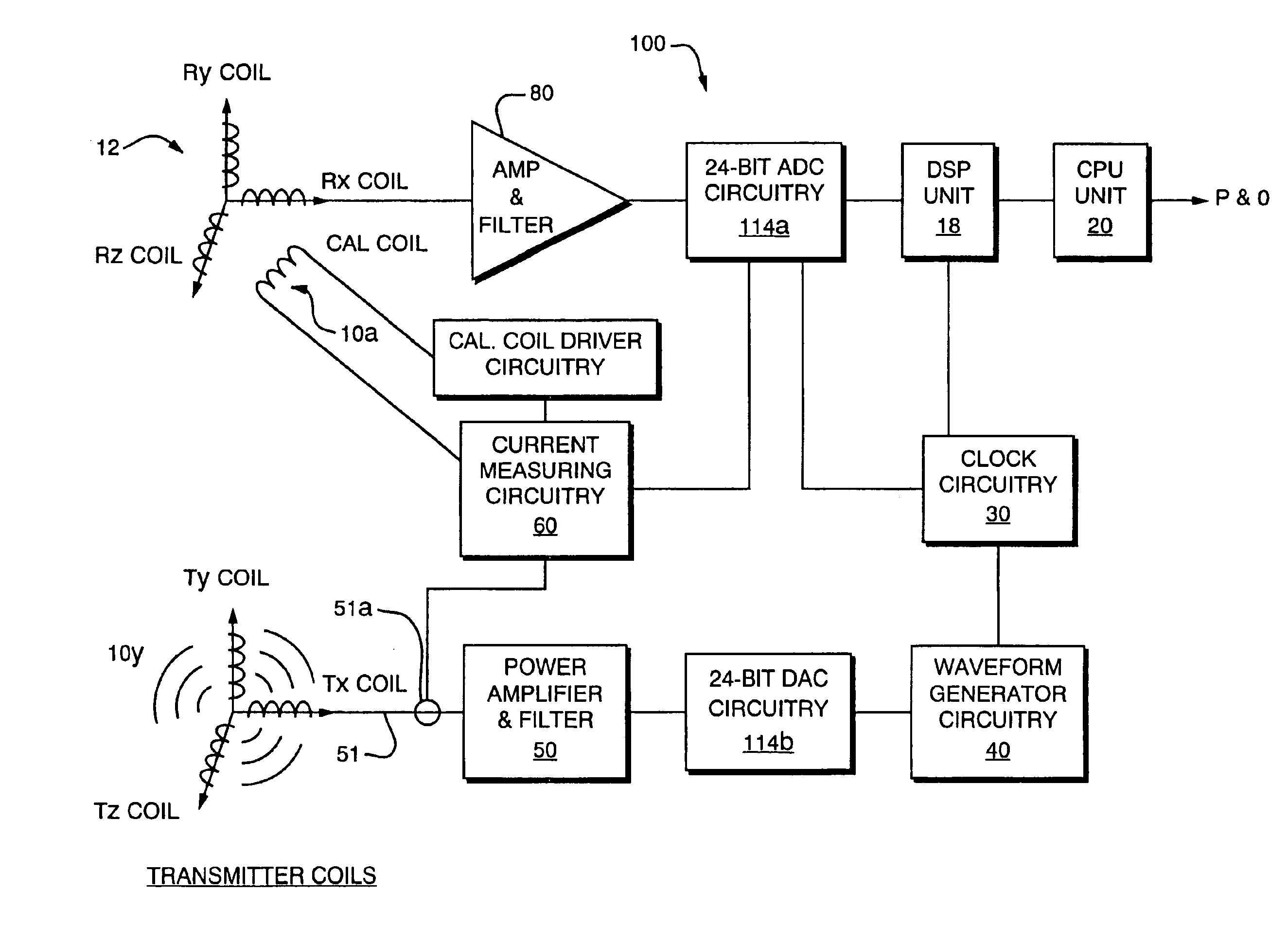
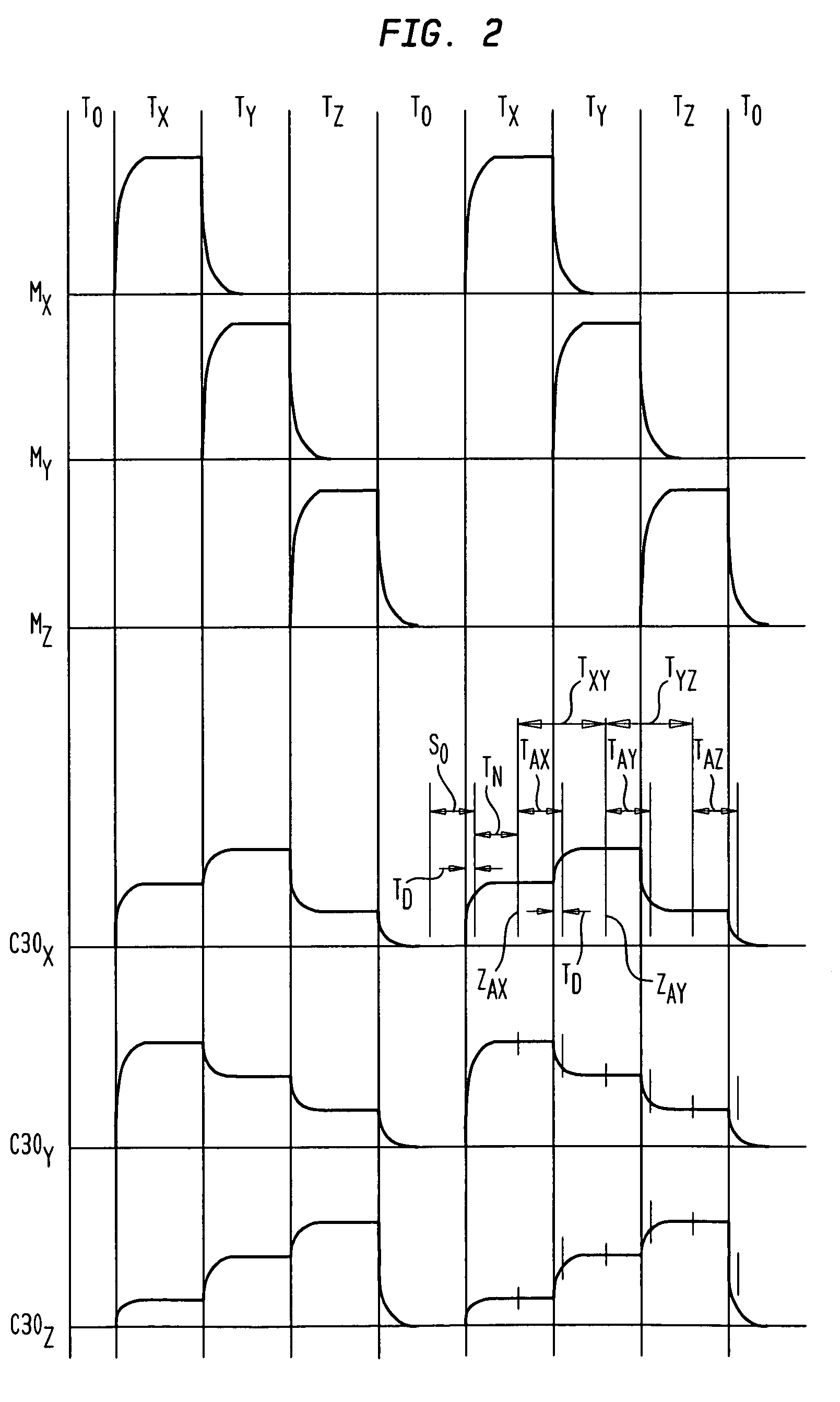
Magnetic tracking systems and methods for determining the position and orientation of a remote object. A magnetic tracking system includes a stationary transmitter for establishing a reference coordinate system, and at least one receiver. The remote object is attached to, mounted on, or otherwise coupled to the receiver. The transmitter can include a set of three mutually perpendicular coils having a common center point, or a set of three coplanar coils with separate centers. The receiver can include a set of three orthogonal coils. The position and orientation of the receiver and the remote object coupled thereto is determined by measuring the nine mutual inductances between the three transmitter coils and the three receiver coils. The magnetic tracking system provides reduced power consumption, increased efficiency, digital compensation for component variation, automatic self-calibration, automatic synchronization with no connections between transmitter and receiver, and rapid low-cost implementation.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
Systems and Methods for Compensating for Large Moving Objects in Magnetic-Tracking Environments
ActiveUS20100082280A1Batteries circuit arrangementsDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic trackingDistortion
Methods for accurately tracking position and orientation of a magnetic-field sensor in a tracking volume when a large magnetic-field distorter is present in the tracking volume. In some of the methods, magnetic field data is collected from within the tracking volume both with and without the large magnetic-field distorter present in the tracking volume. This data is used to obtain correction information that is subsequently used during real-time operation of the magnetic-field sensor to correct the position and orientation solutions for the sensor for magnetic-field distortions caused by the presence of the large magnetic-field distorter in the tracking volume. Others of the methods involve modeling the large magnetic-field distorter using dipole and multipole modeling. Magnetic tracking systems for implementing the methods include hardware and software for carrying out the methods.
Owner:ASCENSION TECH
Magnetic tracking system
InactiveUS20050165297A1Improve tracking accuracyImprove accuracySurgical navigation systemsDigital computer detailsMagnetic trackingSignal conditioning
The present invention provides an electromagnetic tracking system that includes a field generator and a field sensor arranged to generate and detect, respectively, an electromagnetic field. Both the transmitter and receiver coils are connected to signal conditioning and processing circuitry to provide outputs indicative of the coil signals. A processor operates on the signals to determine the coordinates of the sensing assembly relative to the generator assembly. The signal processor produces ratiometric outputs, and applies a mutual inductance model to solve for position / orientation coordinates. In some embodiments, a disturber in the form of a conductive ring or a sheath is disposed about an interfering piece of equipment to moderate and standardize disturbances due to eddy currents.
Owner:NORTHERN DIGITAL
Electromagnetic position and orientation sensing system
InactiveUS8450997B2Reduce power consumptionCompensation changesMagnetic measurementsBeacon systems using radio wavesTransmitter coilMagnetic tracking
Magnetic tracking systems and methods for determining the position and orientation of a remote object. A magnetic tracking system includes a stationary transmitter for establishing a reference coordinate system, and at least one receiver. The remote object is attached to, mounted on, or otherwise coupled to the receiver. The transmitter can include a set of three mutually perpendicular coils having a common center point, or a set of three coplanar coils with separate centers. The receiver can include a set of three orthogonal coils. The position and orientation of the receiver and the remote object coupled thereto is determined by measuring the nine mutual inductances between the three transmitter coils and the three receiver coils. The magnetic tracking system provides reduced power consumption, increased efficiency, digital compensation for component variation, automatic self-calibration, automatic synchronization with no connections between transmitter and receiver, and rapid low-cost implementation.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
Method and apparatus for collection of cardiac geometry based on optical or magnetic tracking
ActiveUS8409098B2Organ movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsMagnetic trackingControl system
A cardiac imaging system including an imaging module including an ultrasound emitter and one or more position markers. A tracking and control system may include a position sensing system for sensing a location and orientation of the position marker relative to a predetermined reference. The tracking and control system may be operable with the imaging module to produce at least a three dimensional image of a patient's anatomy. A method of cardiac imaging may include operatively attaching one or more position markers to an imaging module including an ultrasound emitter. The method may further include sensing a location and orientation of the position marker relative to a predetermined reference, and producing at least a three dimensional image of a patient's anatomy by evaluating one or more images obtained by the imaging module and aligning the image(s) obtained by the imaging module relative to the location and orientation of the position marker.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
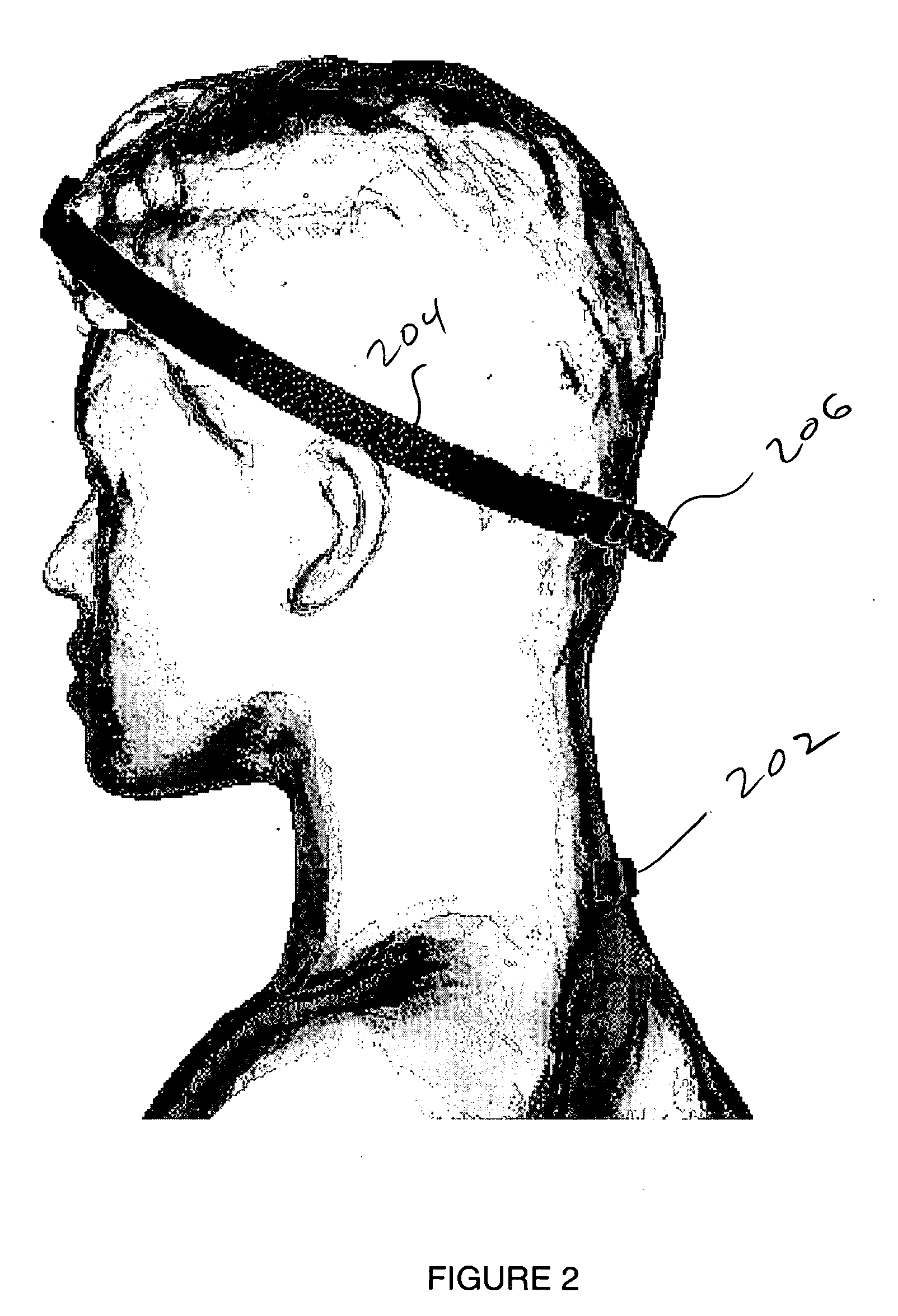
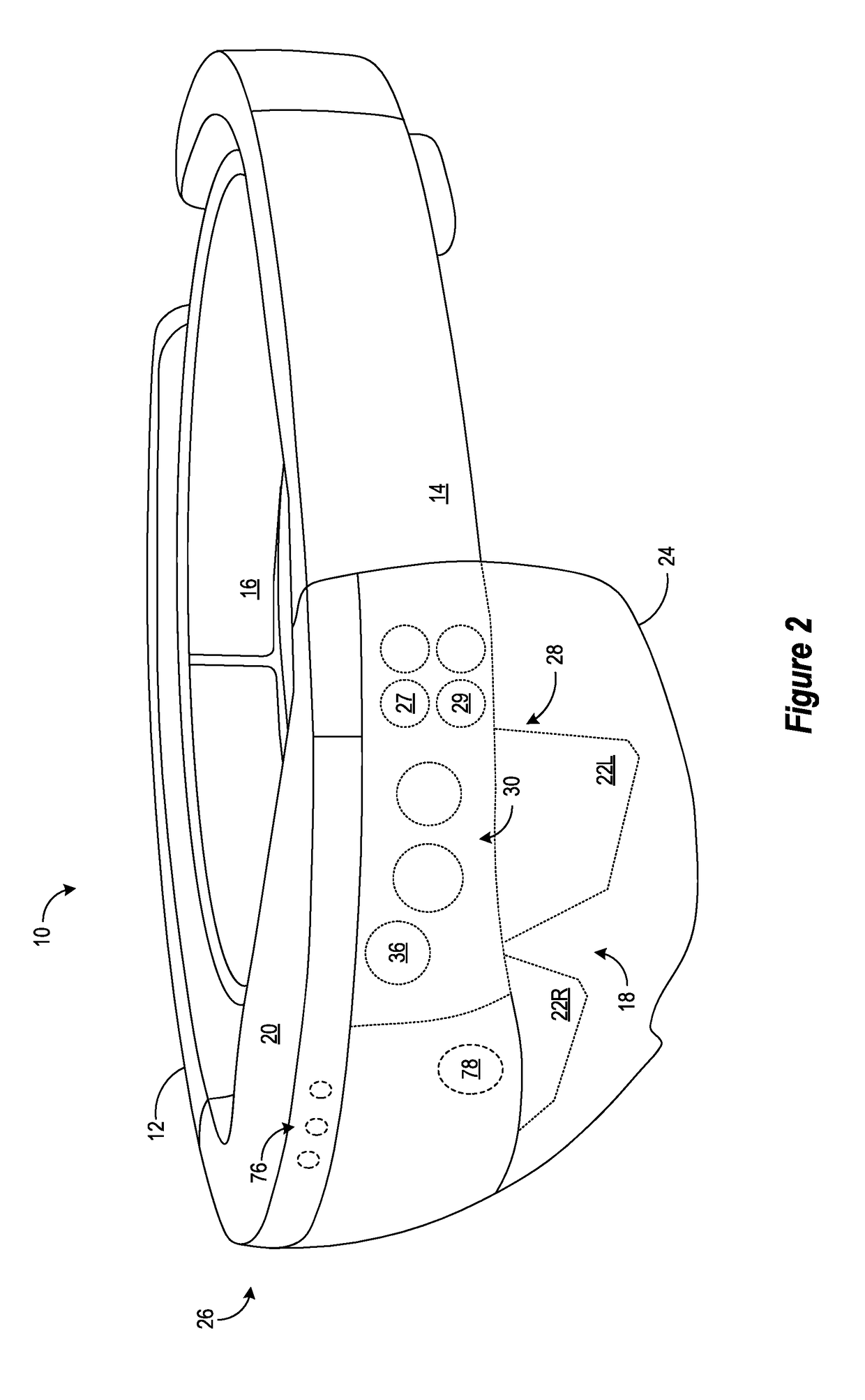
Head-mounted pointing and control device
ActiveUS20060012571A1Avoid collectingEliminate shortcomingsCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingHead movementsJoystick
A magnetic tracker system for use on an operator's head makes “mouse” / cursor movements on a screen similar to that of the classic computer “mouse” / track ball / touchpad / joystick. Only head movements are used as opposed to lifting a hand from the keyboard for making such moves. The new “mouse” avoids interrupting the hands from their position on the keyboard and has no moving mechanical parts that become clogged and that need a special surface (mouse pad) or special surface measurements (optical mouse).
Owner:ALKEN INC DBA POLHEMUS
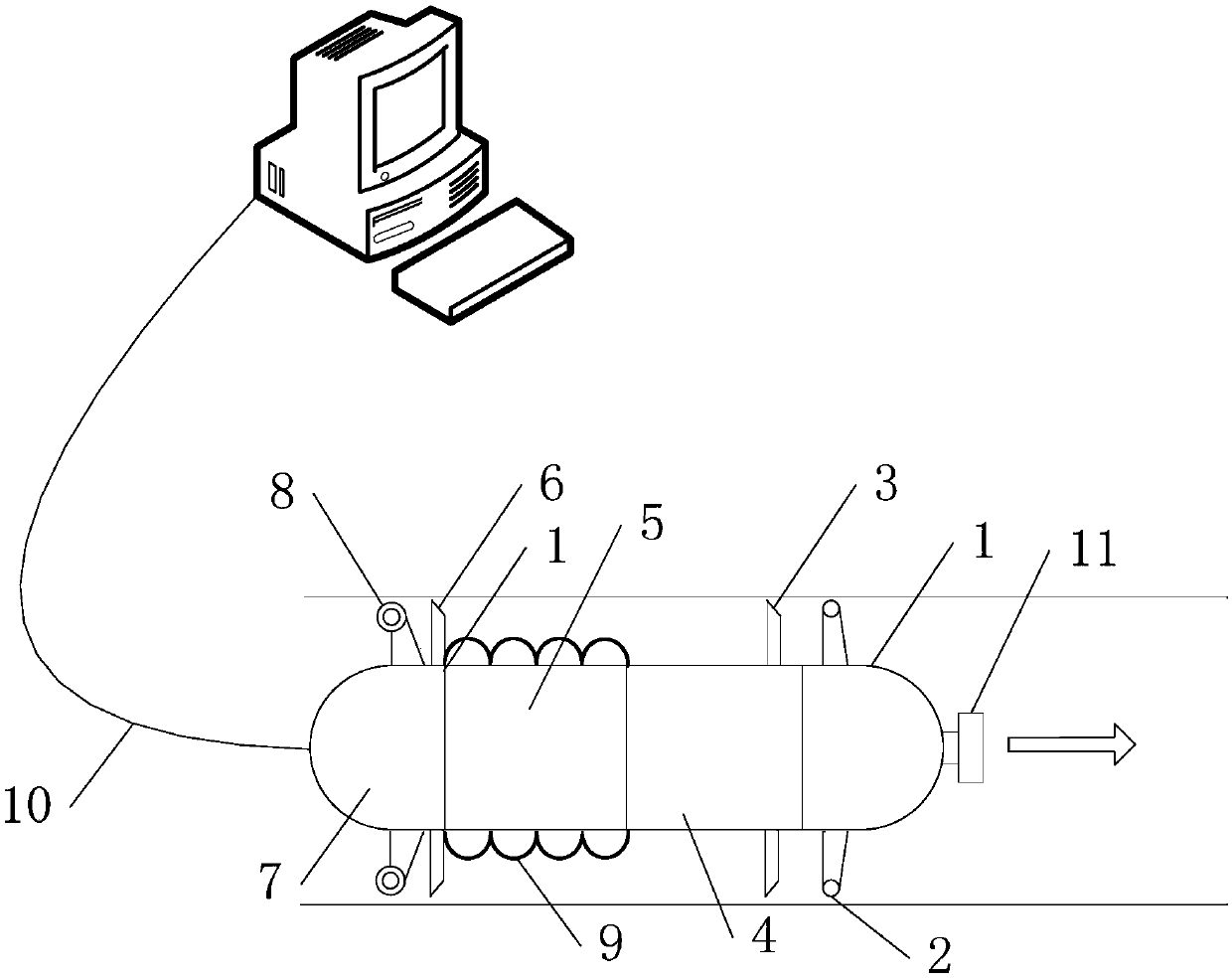
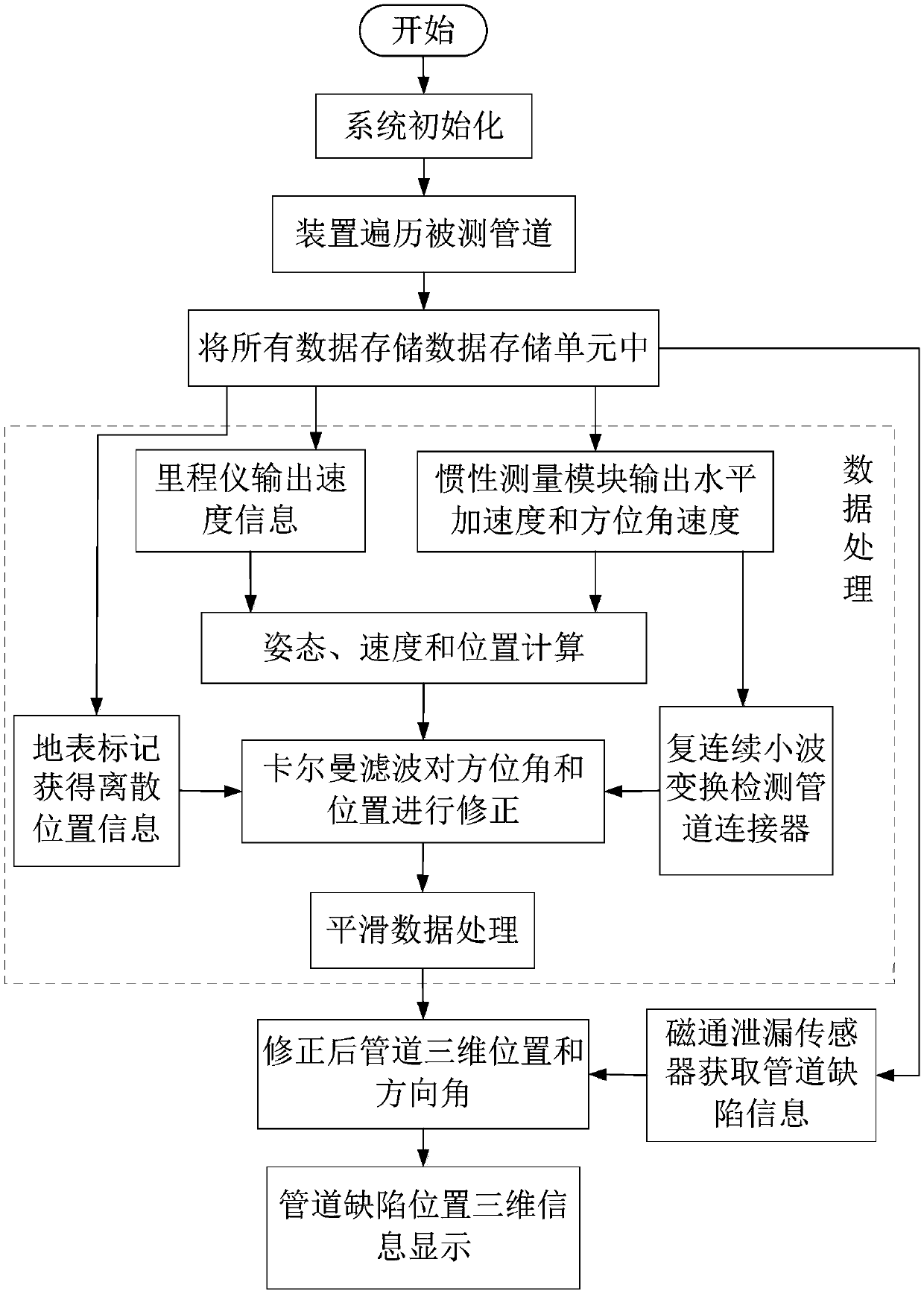
Positioning device and method for pipeline detection
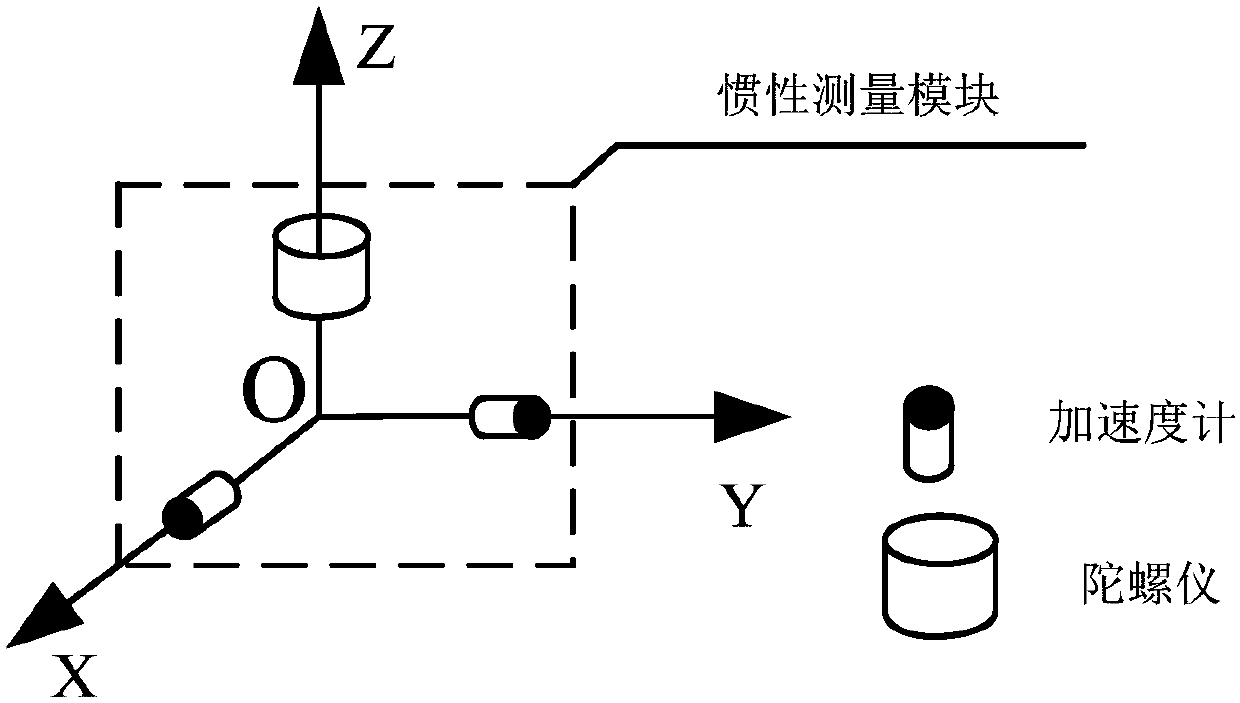
InactiveCN107664266ARealize detection and positioningAvoid error accumulationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsPipeline systemsMagnetic trackingGyroscope
The invention relates to the technical field of pipeline geographic information measurement, in particular to a positioning device and method for pipeline detection. The problems that in the prior art, the precision is low, and remote measurement cannot be achieved are solved. The positioning device comprises a power supply module, two supporting rollers, a first plastic sealing ring, an inertia measuring module, a data processing unit, a second plastic sealing ring, a data storage unit, a mileage instrument, a flux leakage sensor, a communication cable and a magnetic tracking module. The inertia measuring module is composed of a gyroscope and two accelerometers; on the basis of the mileage instrument, and three-dimensional attitude angle, speed and position coordinate measurement inside the pipeline can be achieved. According to the positioning method, a complex continuous wavelet transform method is adopted for analyzing operating data of the inertia measuring module inside the pipeline, a pipeline connector is detected, and the method is used for correcting azimuth angle errors of the positioning device for pipeline detection. The device and method are applicable to detection ofland and underwater oil and gas pipelines.
Owner:哈尔滨航士科技发展有限公司 +3
AC magnetic tracking system with phase locking
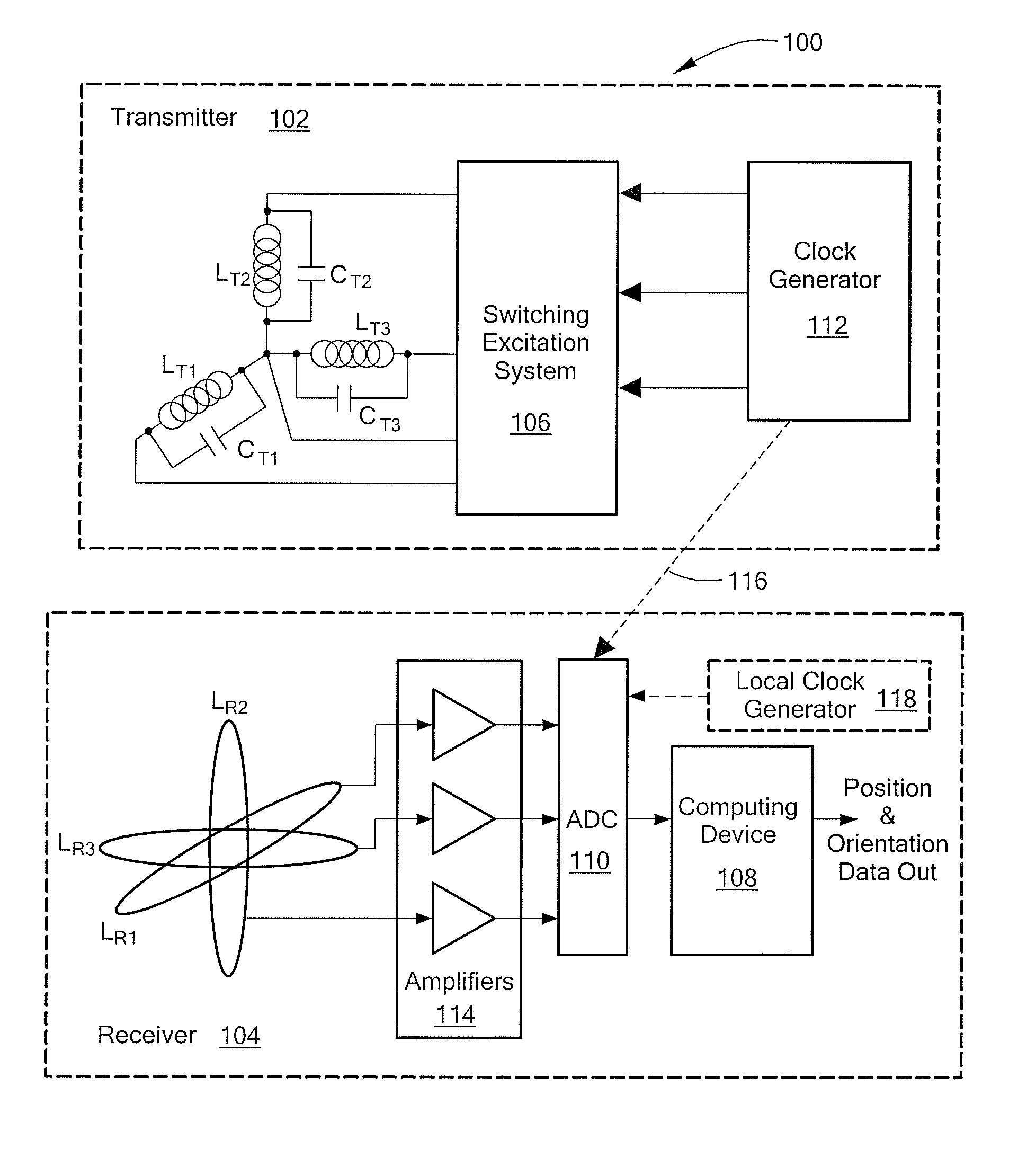
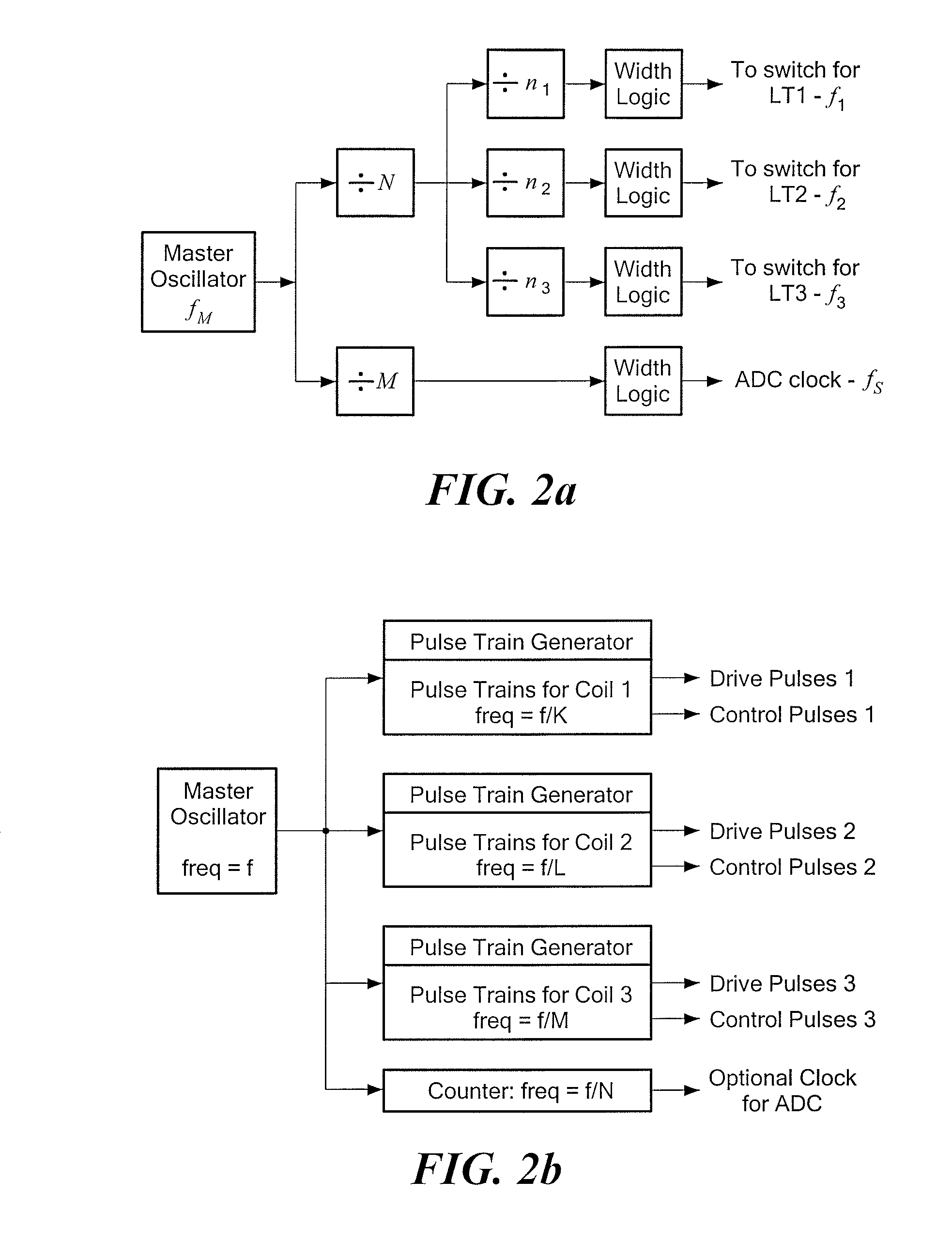
ActiveUS20090030646A1Improve efficiencyInterfere with accurateDiagnosticsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesTransmitter coilMagnetic tracking
Plural transmitter coils of a magnetic locating system are driven with widely-separated main frequencies. One of the transmitter coils is also driven with a marker frequency close to the main frequency applied to that coil. The receiver determines a phase relationship with the transmitter based on the main and marker frequencies, so that the receiver does not suffer from phase ambiguity. The main and marker frequencies may interfere with one another, and the receiver may correct for such interference based on known characteristics of the signals at the main and marker frequencies.
Owner:ALKEN INC DBA POLHEMUS
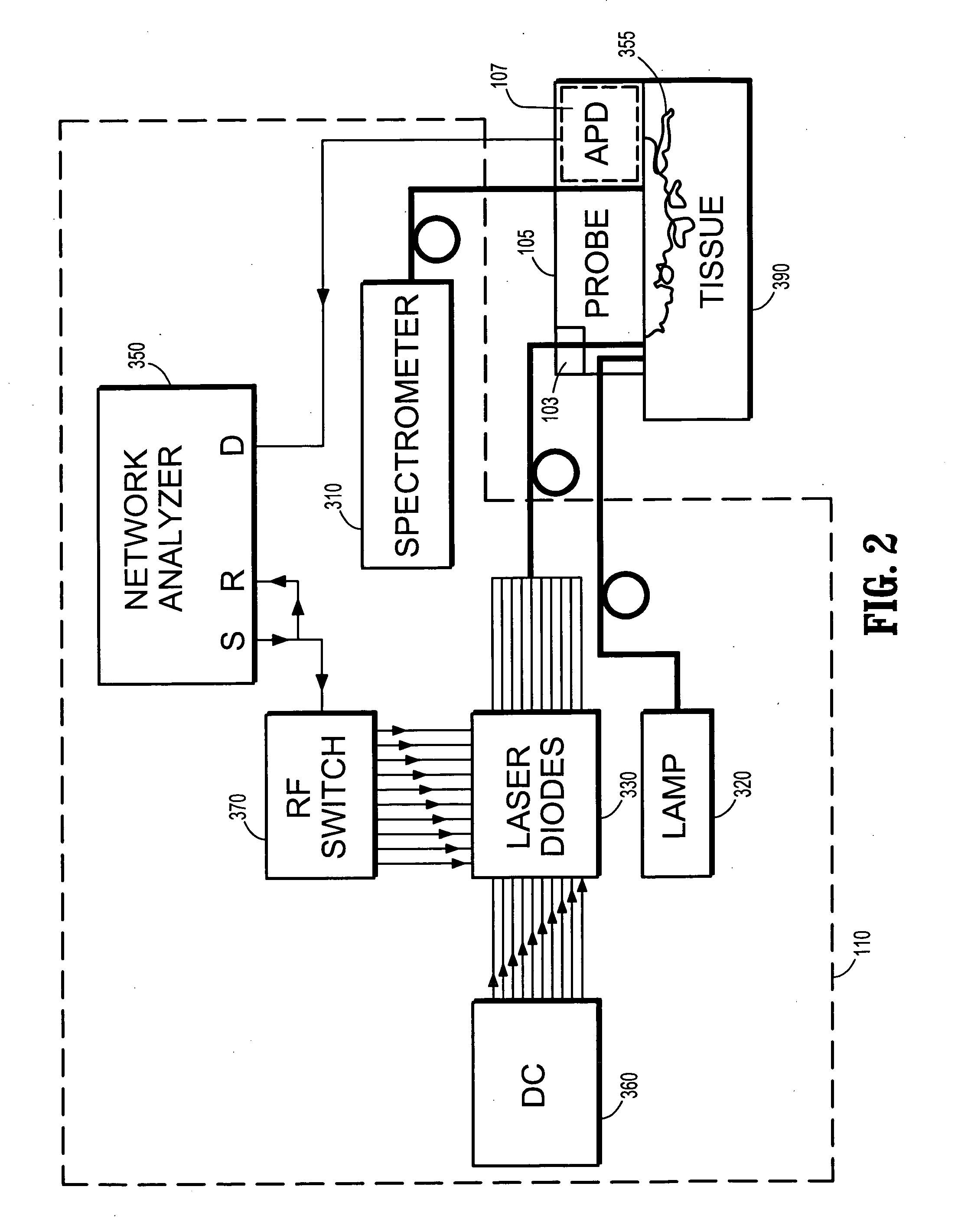
Three-dimensional breast anatomy imaging system
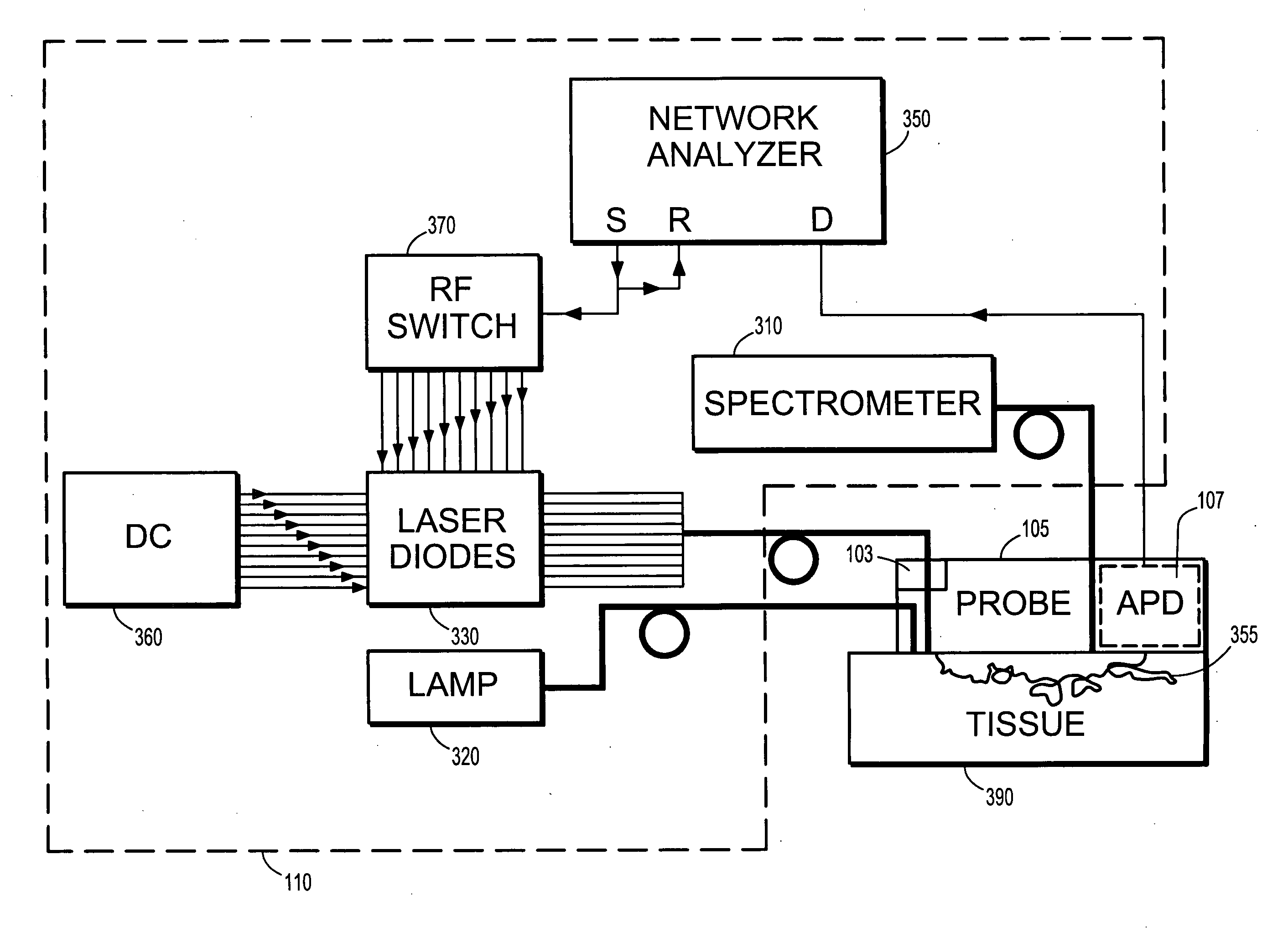
InactiveUS20070219450A1High measurement sensitivityMinimize uncertaintySurgical navigation systemsMaterial analysis by optical meansMagnetic trackingBreast anatomy
A diffuse optical spectroscopy system comprises a laser breast scanner, a handheld probe connected to the laser breast scanner for scanning a breast, and a tracking device coupled to the handheld probe, wherein the tracking device determines locations of the handheld probe relative to the breast. The tracking device comprises a magnetic tracking device, an optical tracking device or a laser tracking device.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Generating and displaying a computer generated image on a future pose of a real world object
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
AC magnetic tracking with phase disambiguation
ActiveUS8121812B2Digital computer detailsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsMagnetic trackingAmbiguity
A method and system for magnetic locating resolves phase ambiguity. The system uses time-division multiplexed magnetic fields emitted from plural transmit coils. The magnetic fields are alternating fields at a carrier frequency, and the fields emitted from different coils in different transmit intervals have known phase relationship with one another as, for example where the alternating fields are coherent with one another. A receiver uses a plurality of sensor coils and derives plural components using the common phase reference or plural phase reference times having a known relationship. If the determinant of a matrix of the components has a first value, the phase information in the components is correct, and position and orientation are derived from the components. If the determinant has a second value, the phase information in the components is incorrect. In this case, corrected components are formed by shifting the phases of the components π radians; the position and orientation are derived from the corrected components.
Owner:ALKEN INC DBA POLHEMUS
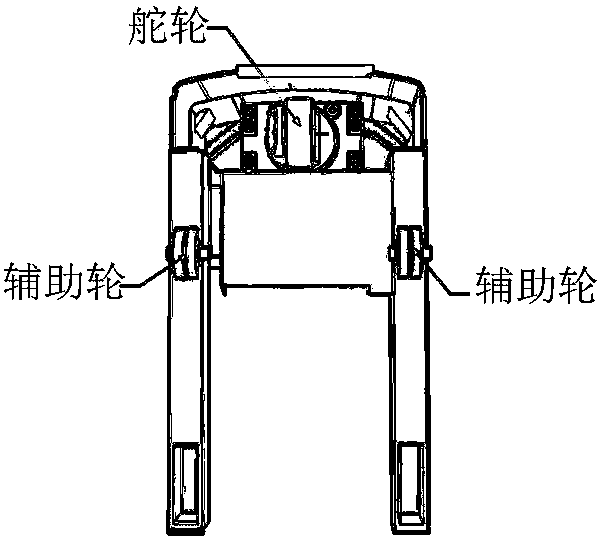
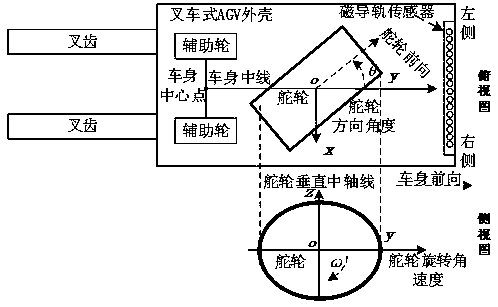
Magnetic guide rail tracking control system and method for forklift-type AGV
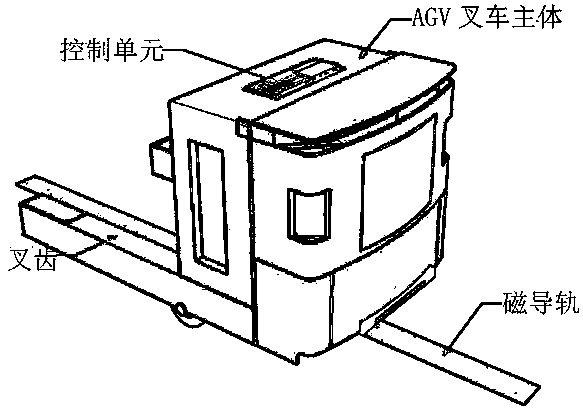
ActiveCN109279543AReduce oscillationAchieve integrated trackingLifting devicesMagnetic trackingSteering wheel
The invention discloses a magnetic guide rail tracking control system and method for a forklift-type AGV. The magnetic guide rail tracking control system comprises a magnetic guide rail sensing sub-system, a speed and angle detection sub-system, a steering wheel control sub-system and a tracking control sub-system. The magnetic guide rail tracking control method comprises the basic steps that thetracking control sub-system acquires sensor information from the magnetic guide rail sensing sub-system to determine the posture and relative position of a vehicle body, the current operating state ofthe forklift-type AGV is determined in combination with the rotation speed and direction angle, acquired from the speed and angle detection sub-system, of a steering wheel, and magnetic tracking guide rails in different modes are used according to the operating state. According to the magnetic guide rail tracking control system and method for the forklift-type AGV, positioning of the vehicle bodyand recognition of the operating state can be achieved only through magnetic guide rail sensor detection, and the rotation speed and direction angle of the steering wheel of the forklift-type AGV areautomatically adjusted, so that smooth control over the speed of the forklift-type AGV and stable tracking of linear and curved magnetic guide rails are integrally achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
AC magnetic tracking system employing wireless field source
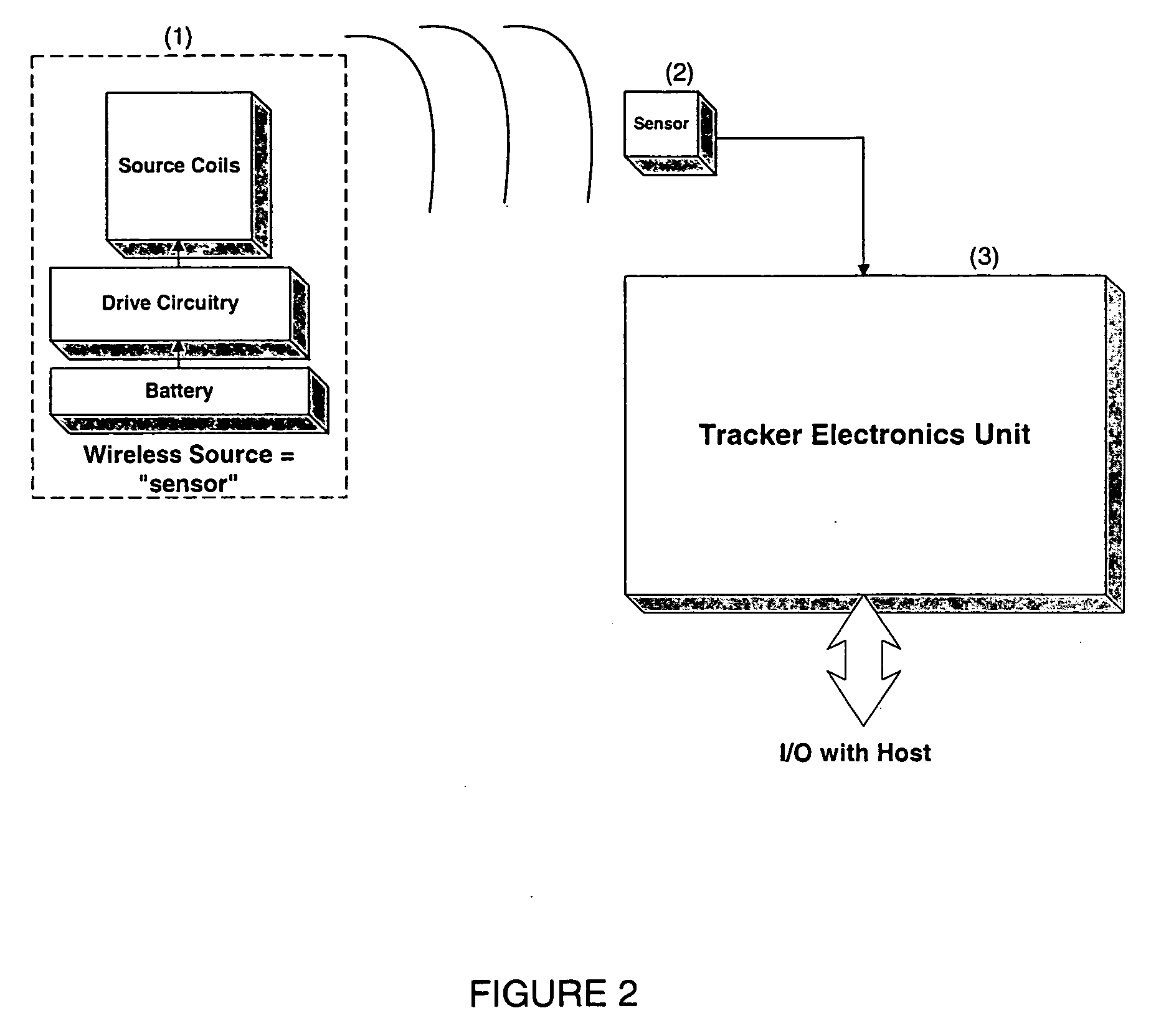
InactiveUS20050285591A1Less power consumptionFreedom of movementElectromagnets without armaturesUsing electrical meansMagnetic trackingEngineering
A small, lightweight field source acts as a “pseudo-sensor” in an AC magnetic tracking system, facilitating wireless operation. Upon activation, the source sends out three continuous low-power magnetic signals, a separate frequency from each of three resonant orthogonal coils, without the need for switching to a receive mode or detecting a synchronizing signal to start the three signals simultaneously. This simple structure allows the source to be kept small and consume little power so that it can operate for over one hour before needing to be re-charged. This design approach thus allows a user or object being tracked to move about freely with no restricting cabling to a base station or even to a body-mounted electronics module and bulky battery. A family of frequencies can be used for each of several such pseudo-sensor sources in order for the base station sensors and electronics to track multiple sources.
Owner:AIKEN INC D B A POLHEMUS
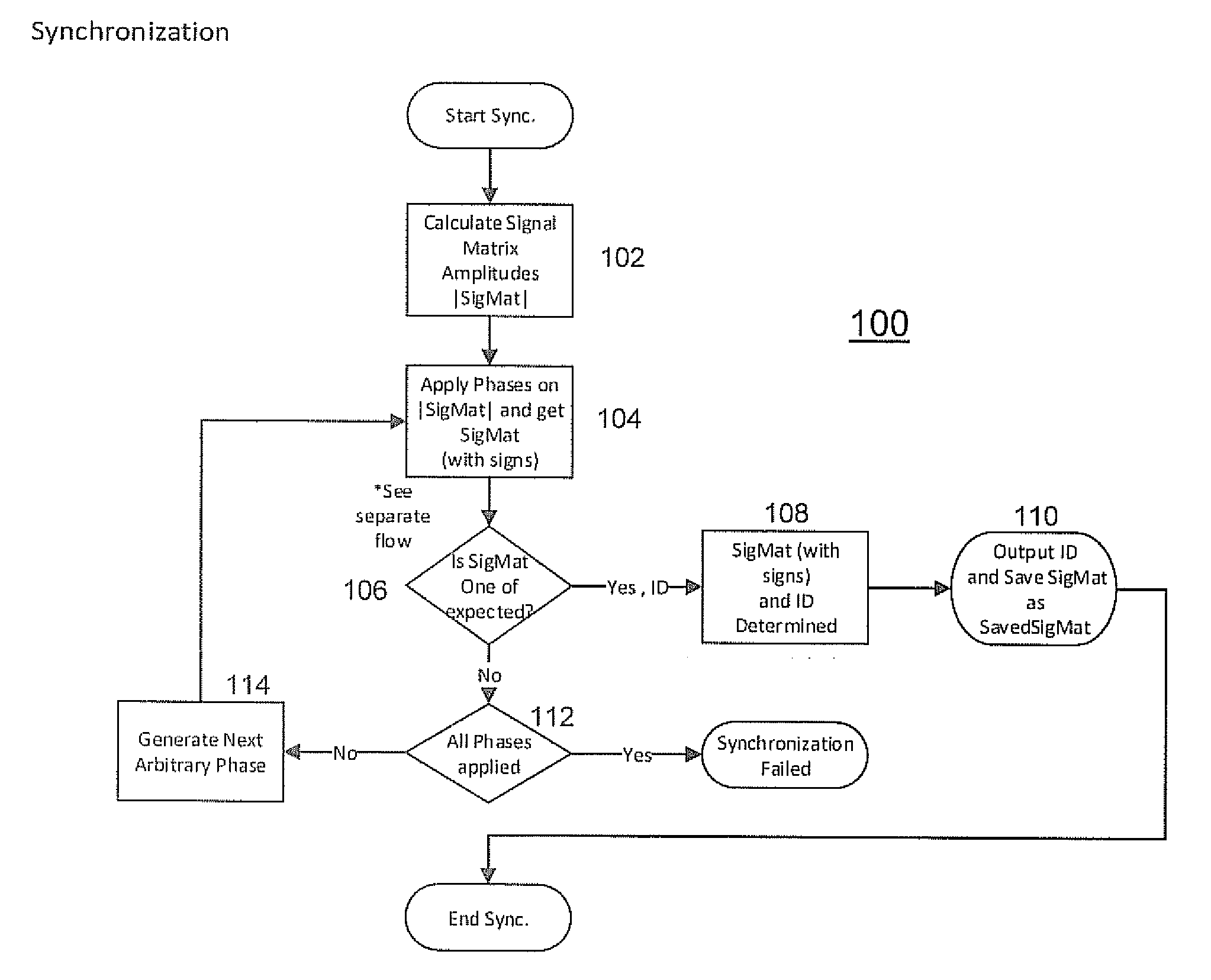
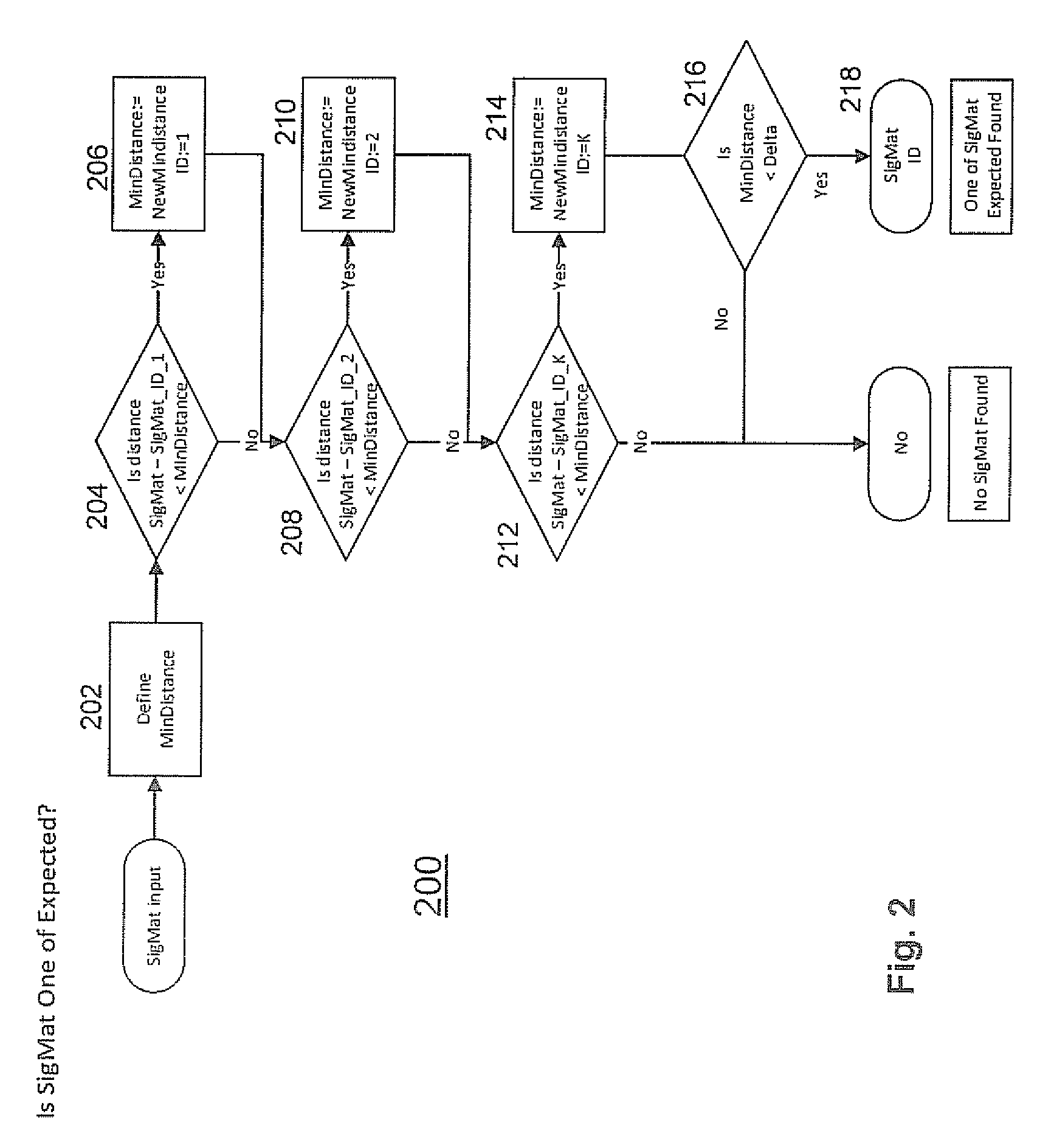
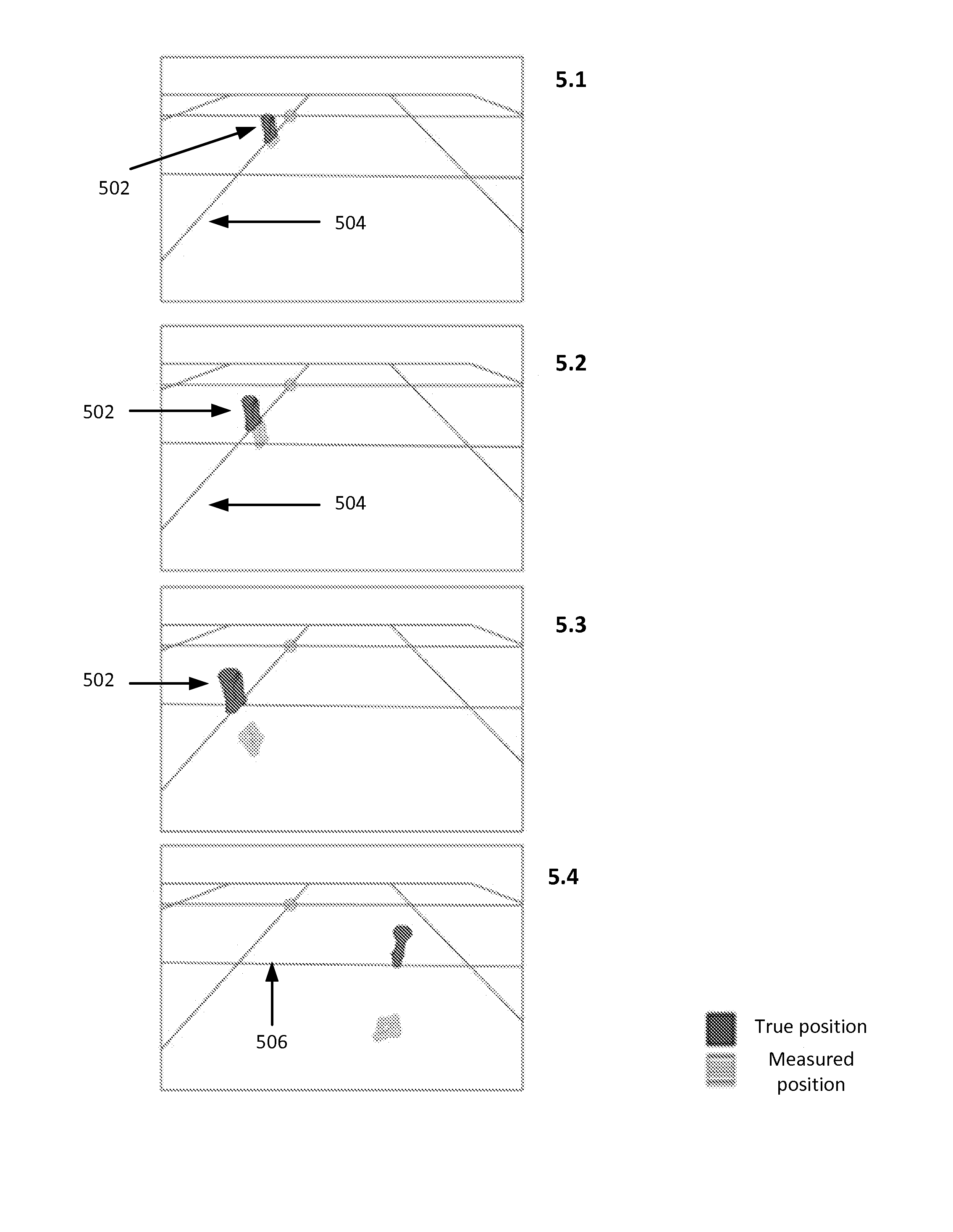
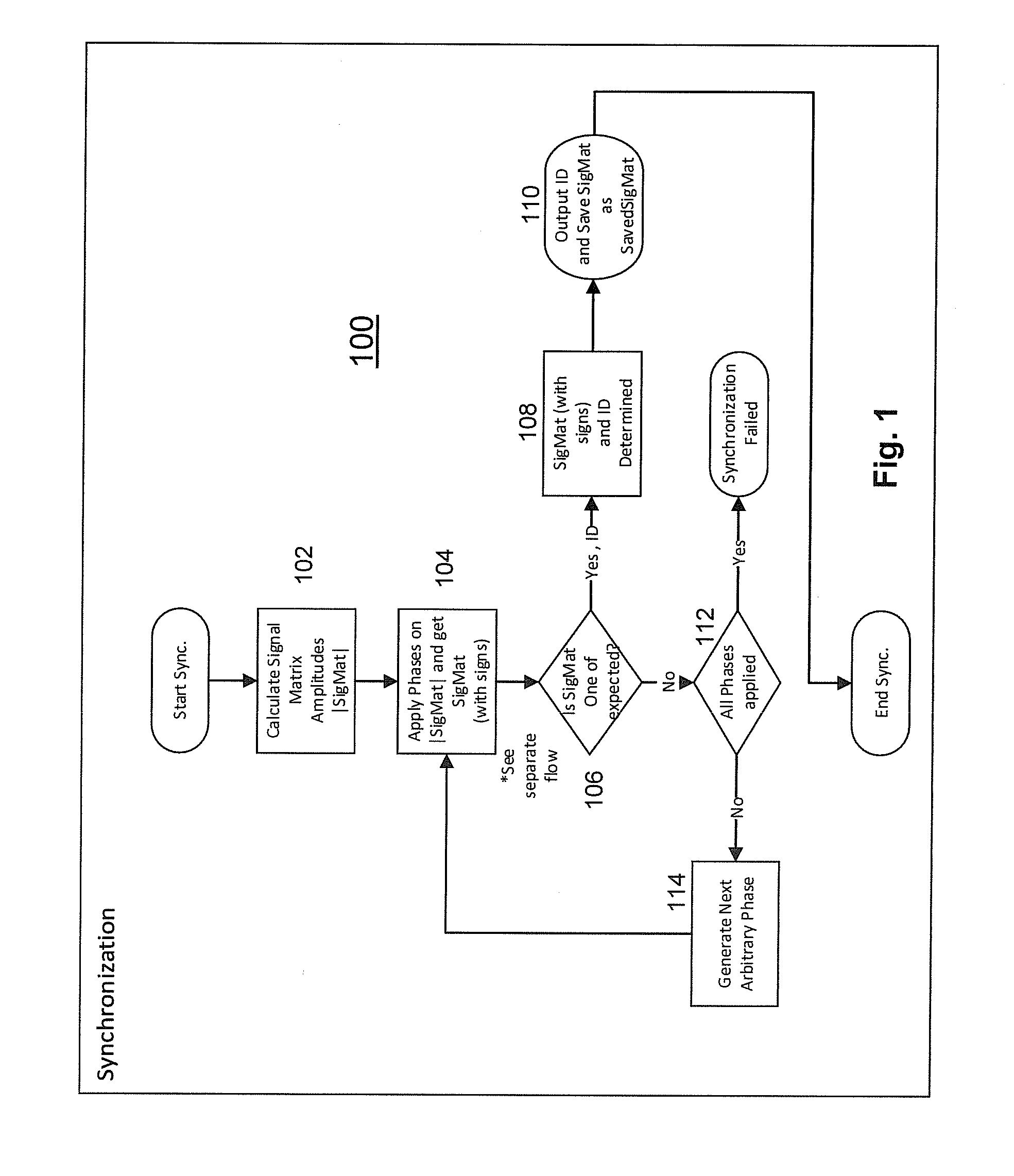
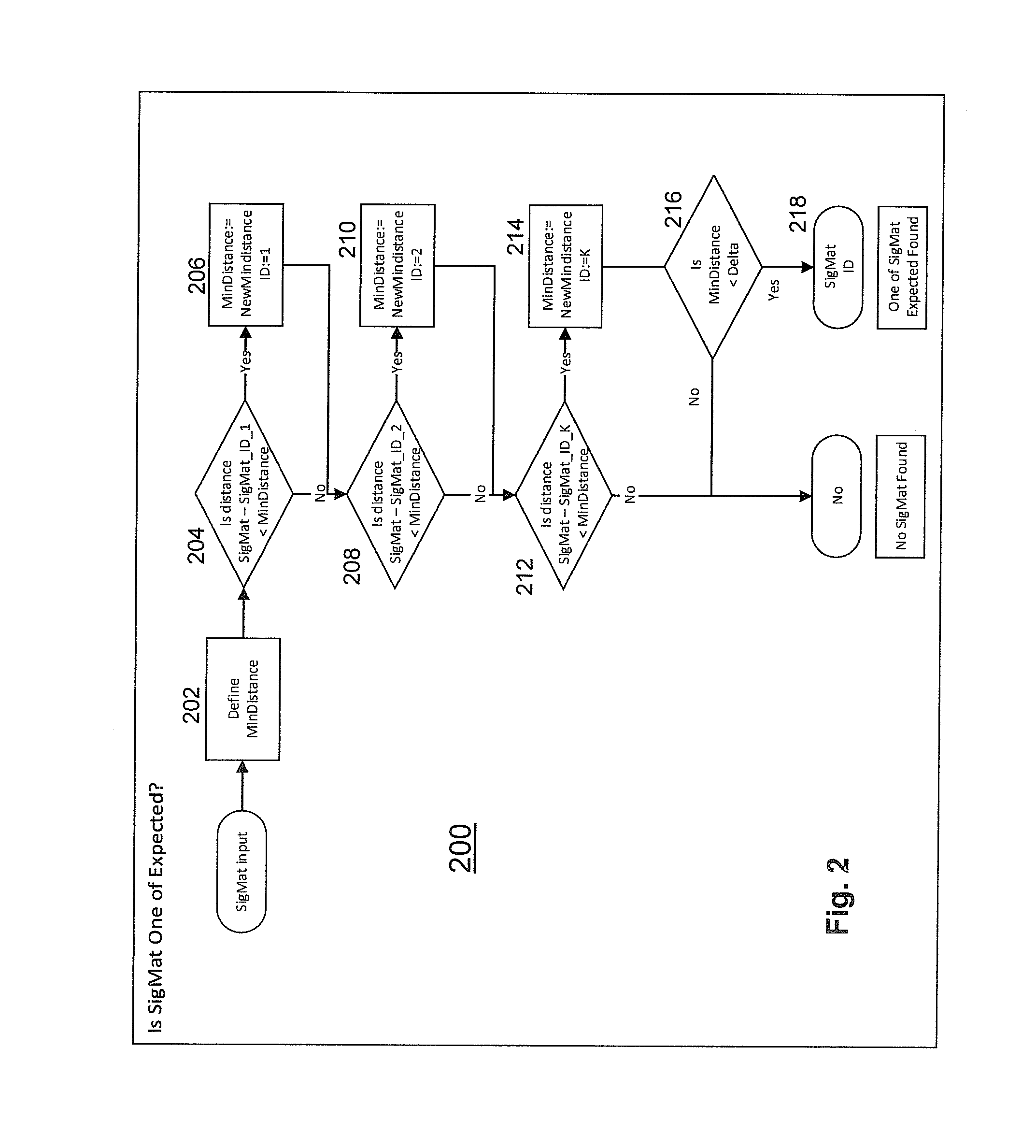
Method And Apparatus For Synchronizing a Transmitter and Receiver in a Magnetic Tracking System
A method and apparatus is disclosed for synchronizing a magnetic field transmitter and receiver to resolve phase ambiguity so that phase information for the position and orientation of the receiver may be derived and maintained. A synchronization process allows for the phase information to be initially derived based upon known information from other sources, and then tracked from one measurement to the next. In another embodiment, information from an inertial measurement unit (IMU) is used to determine the phase information or to correct for errors in the determination from receiver data of the position and orientation of a receiver, and prevent such errors from accumulating as the receiver moves away from a transmitter.
Owner:PENUMBRA
Method And Apparatus For Correcting Magnetic Tracking Error With Inertial Measurement
A method and apparatus is disclosed for synchronizing a magnetic field transmitter and receiver to resolve phase ambiguity so that phase information for the position and orientation of the receiver may be derived and maintained. A synchronization process allows for the phase information to be initially derived based upon known information from other sources, and then tracked from one measurement to the next. In another embodiment, information from an inertial measurement unit (IMU) is used to determine the phase information or to correct for errors in the determination from receiver data of the position and orientation of a receiver, and prevent such errors from accumulating as the receiver moves away from a transmitter.
Owner:PENUMBRA
AC magnetic tracking with phase disambiguation
A method and system for magnetic locating resolves phase ambiguity. The system uses time-division multiplexed magnetic fields emitted from plural transmit coils. The magnetic fields are alternating fields at a carrier frequency, and the fields emitted from different coils in different transmit intervals have known phase relationship with one another as, for example where the alternating fields are coherent with one another. A receiver uses a plurality of sensor coils and derives plural components using the common phase reference or plural phase reference times having a known relationship. If the determinant of a matrix of the components has a first value, the phase information in the components is correct, and position and orientation are derived from the components. If the determinant has a second value, the phase information in the components is incorrect. In this case, corrected components are formed by shifting the phases of the components π radians; the position and orientation are derived from the corrected components.
Owner:ALKEN INC DBA POLHEMUS
Self-training AC magnetic tracking systems to cover large areas
InactiveUS20060038555A1Avoid distortionExact referenceUsing electrical meansDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic markerMetrology
Self-calibrating AC magnetic tracking systems and combination “outside-in” and “inside-out” architectures offer unique motion tracking capabilities. More area is covered with minimal distortion using the tracking system itself to determine overall P&O based on the P&O of an initial, reference marker. The output as anticipated and needed by the user is output without confusion and without costly and time-consuming metrology while covering a large region when distance from the reference may be great. A method according to the invention includes the steps of positioning a plurality of stationary AC magnetic “markers” in a tracking volume and moving a mobile AC magnetic marker proximate to a first one of the stationary markers designated as a reference marker. The position and orientation (P&O) of the mobile marker is determined relative to the reference marker, then moved so as to be proximate to a second one of the stationary markers. The P&O of the second marker is determined relative to the reference marker, allowing the P&O of the mobile marker to be determined relative to the reference marker based upon the P&O of the second marker relative to the reference marker. The stationary markers may be AC magnetic sensors, with the mobile marker being an AC source, or vice-versa.
Owner:ALKEN INC DBA POLHEMUS
Drawing system and drawing method for three-dimensional model
InactiveCN104866121ADraw intuitivelySimple structureInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingGraphicsMagnetic tension force
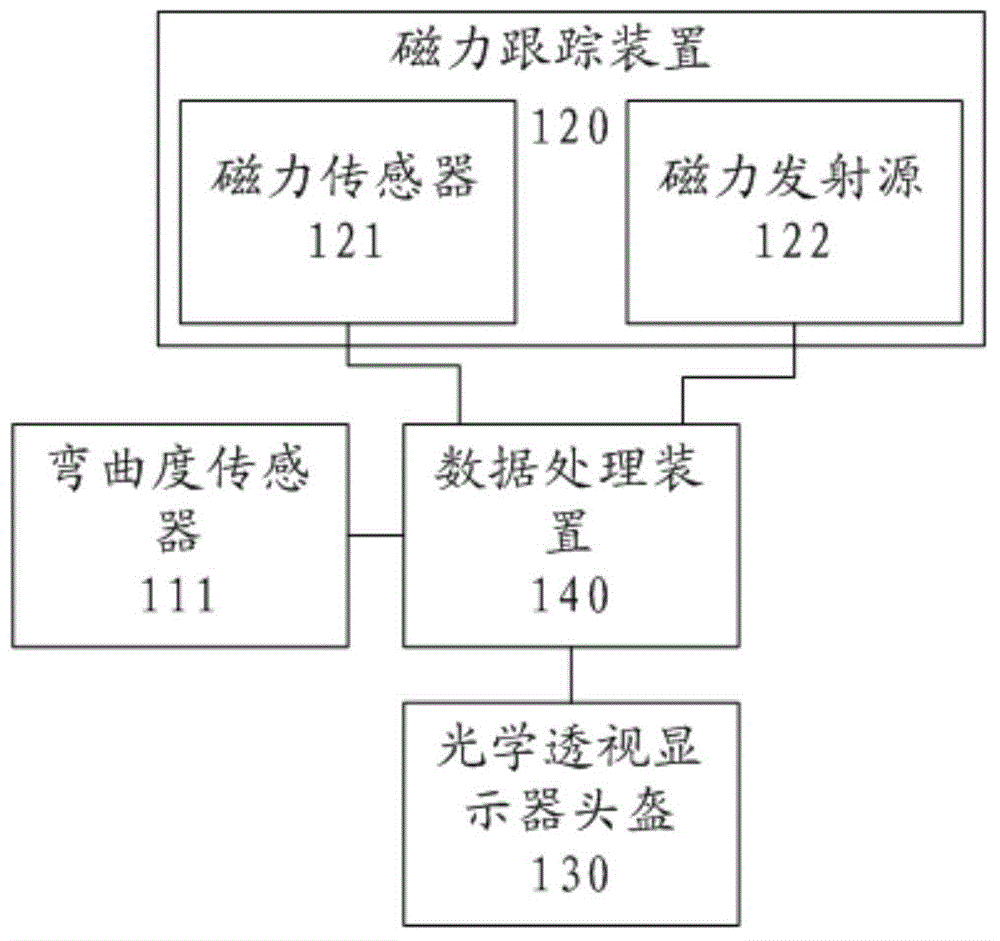
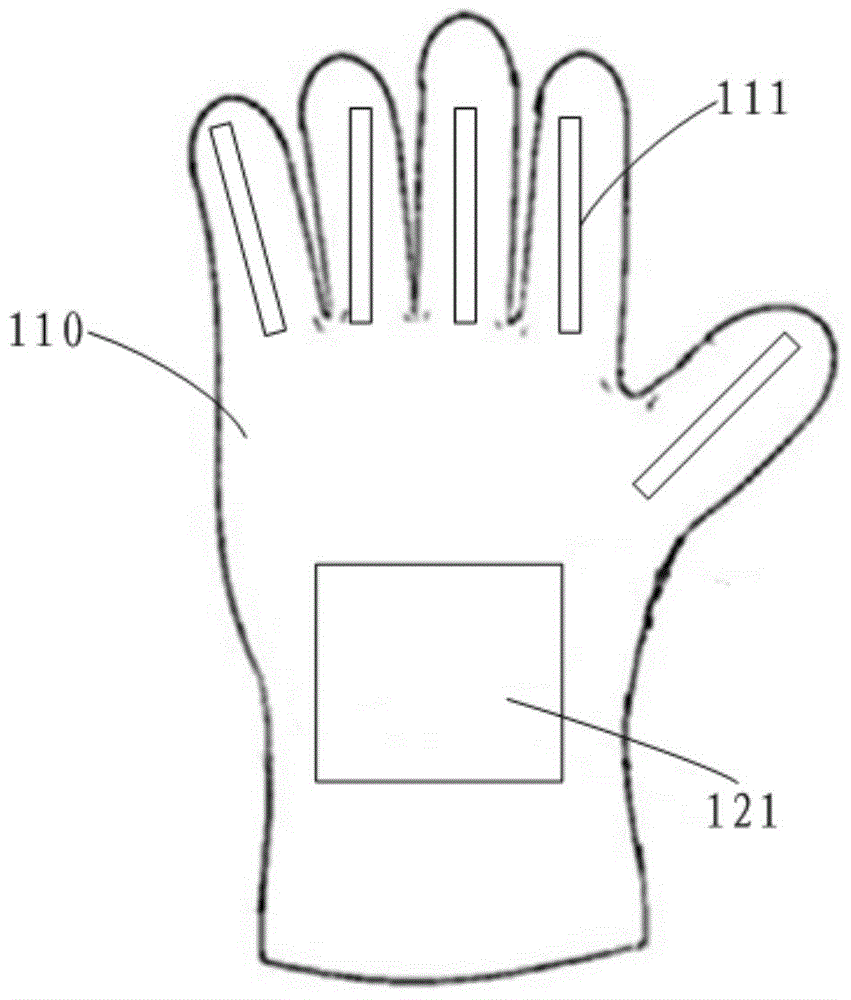
The invention discloses a drawing system for a three-dimensional model. The drawing system comprises a sensing glove, a magnetic tracking device, an optical perspective display helmet and a data processing device, wherein each of five finger parts of the sensing glove is provided with a curvature sensor; the magnetic tracking device comprises a magnetic sensor and a magnetic emission source; the magnetic sensor is arranged on the sensing glove; and the curvature sensors, the magnetic sensor, the magnetic emission source and the optical perspective display helmet are all connected to the data processing device. The drawing system is simple in structure and convenient to operate; a user can directly draw a model which the user wants to create in a three-dimensional virtual space by utilizing two flexible hands; in comparison with the existing manner, the drawing system is more efficient and convenient, and breaks a restriction that the three-dimensional model is only created on a two-dimensional plane, so that the user can draw a graph in a space more directly.
Owner:SHANGHAI QIBAO HIGH SCHOOL
AC magnetic tracking system with non-coherency between sources and sensors
InactiveUS20050285590A1Photometry using reference valueMagnetic measurementsMagnetic trackingThree-dimensional space
In an AC magnetic tracker one or more multi-axis field sources, each operating at a different frequency, or frequency set, are detected and tracked in three-dimensional space, even when wireless or otherwise not physically connected to the tracking system. Multiple sources can be tracked simultaneously as they each operate with their own unique detectable set of parameters. The invention not only provides the ability to uniquely identify one or more sources by their frequencies, but also to synchronize with these frequencies in order to measure signals that then allow tracking the position and orientation (P&O) of the source(s). Further, these sources need not be present at the time of system start-up but can come and go while being detected, discriminated and tracked. It also should be noted that application of such systems in multiples with more sensors not synchronized to a source or sources also could be employed to give the reverse appearance of a known source phase and incoherency with the sensors.
Owner:ALKEN INC DBA POLHEMUS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com