Patents
Literature
222 results about "Magnetic marker" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
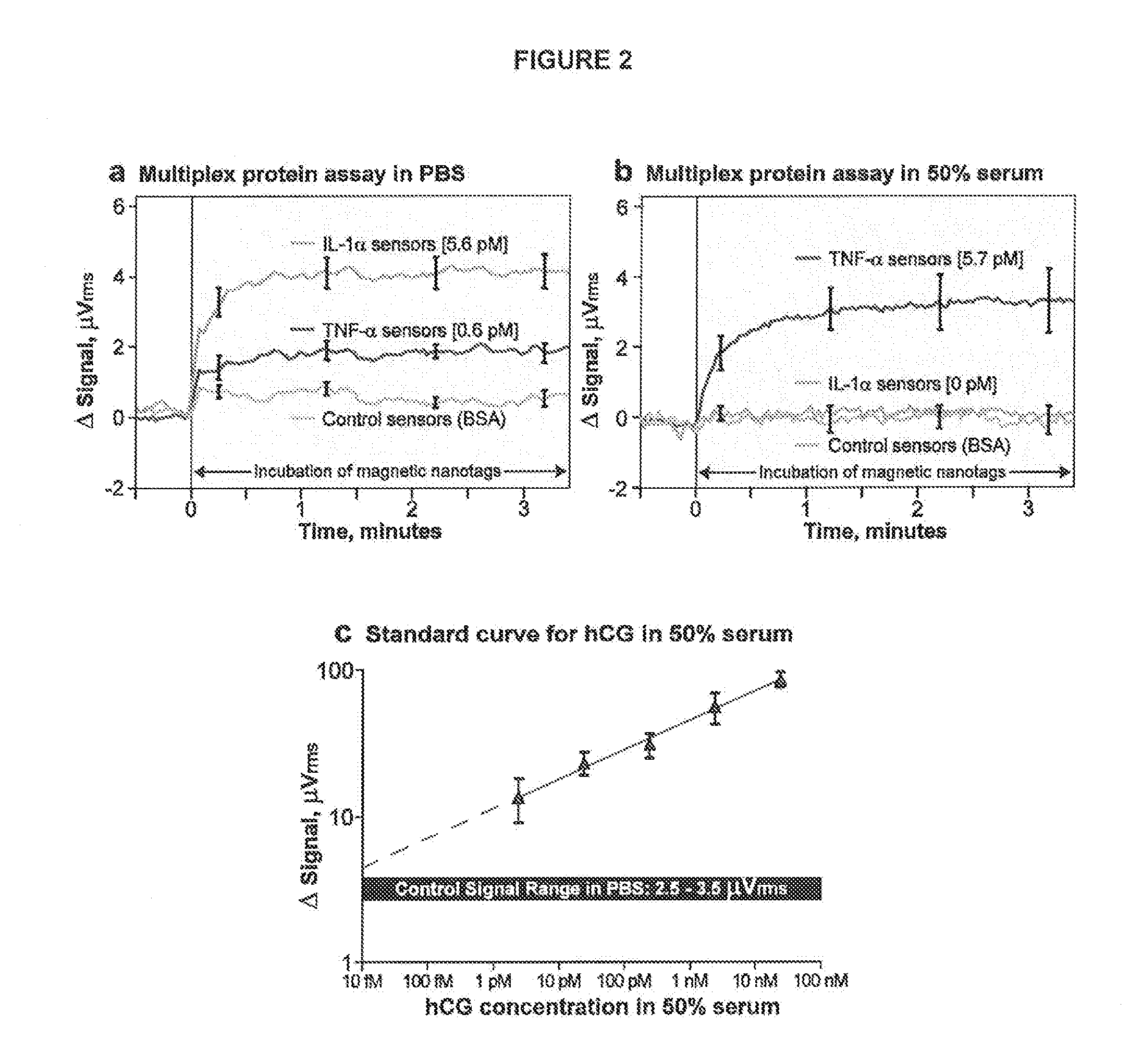
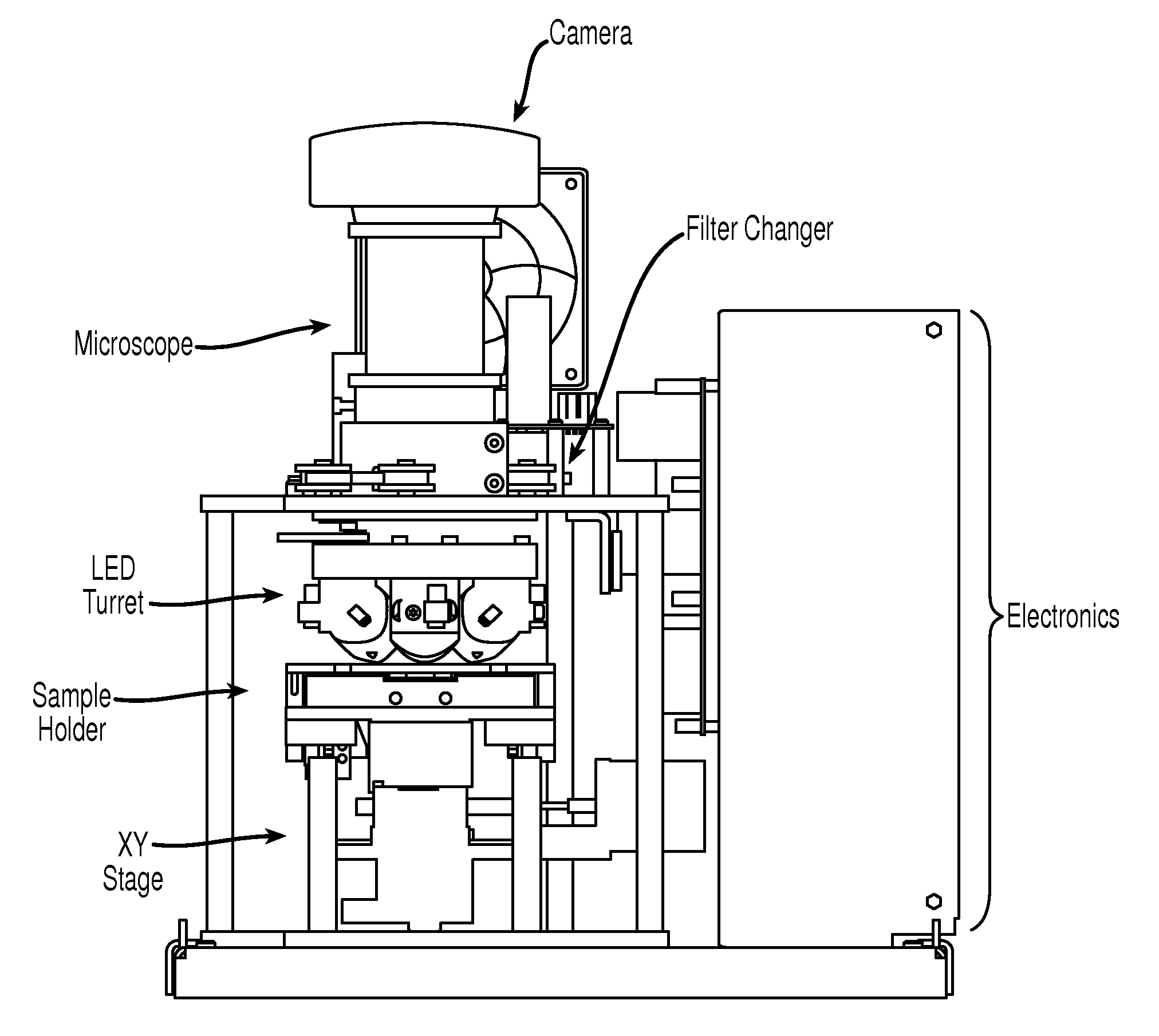
Methods and algorithms for cell enumeration in low-cost cytometer
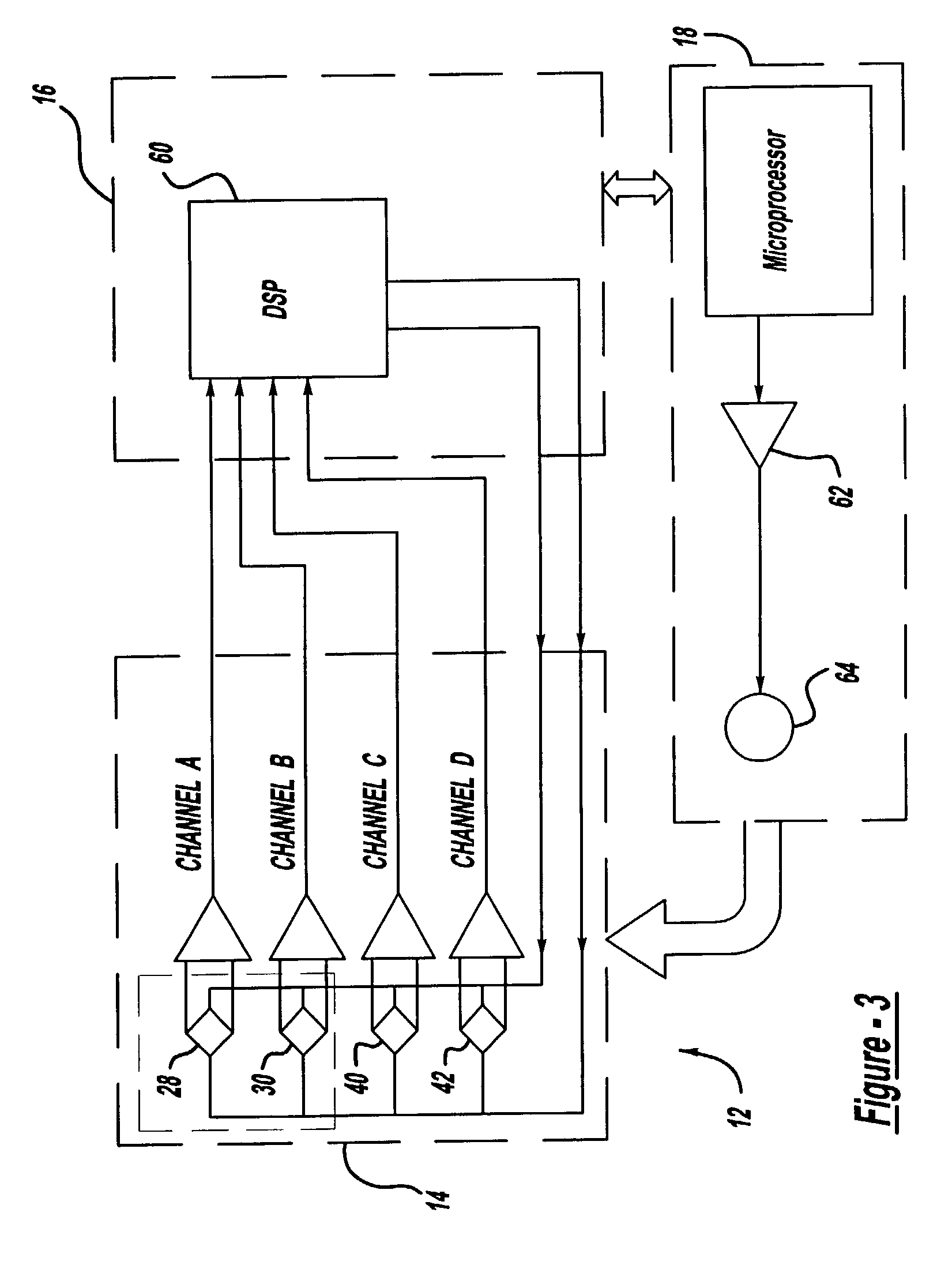
InactiveUS20060024756A1Simple designReduce operating costsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWhite blood cellCcd camera
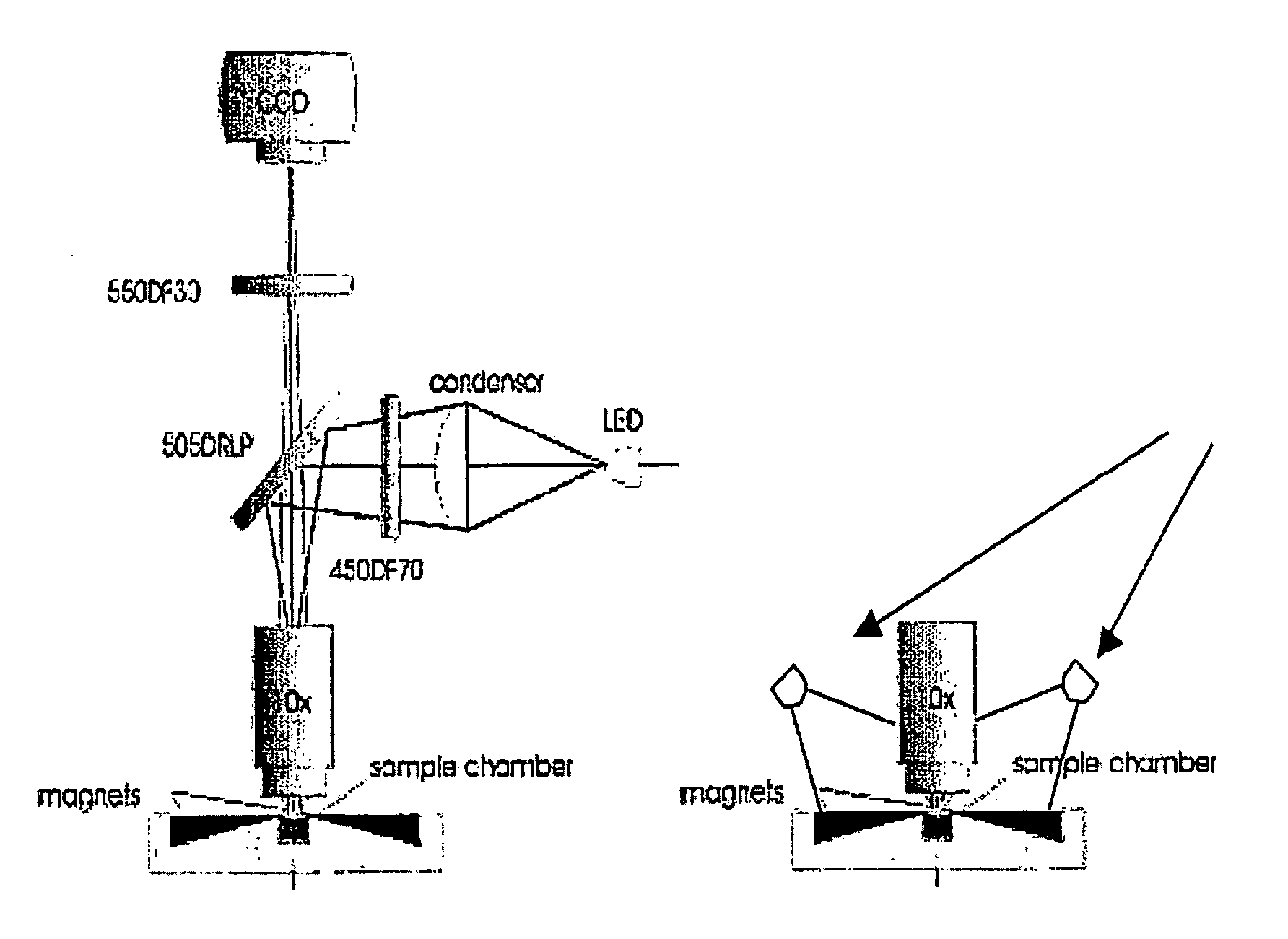
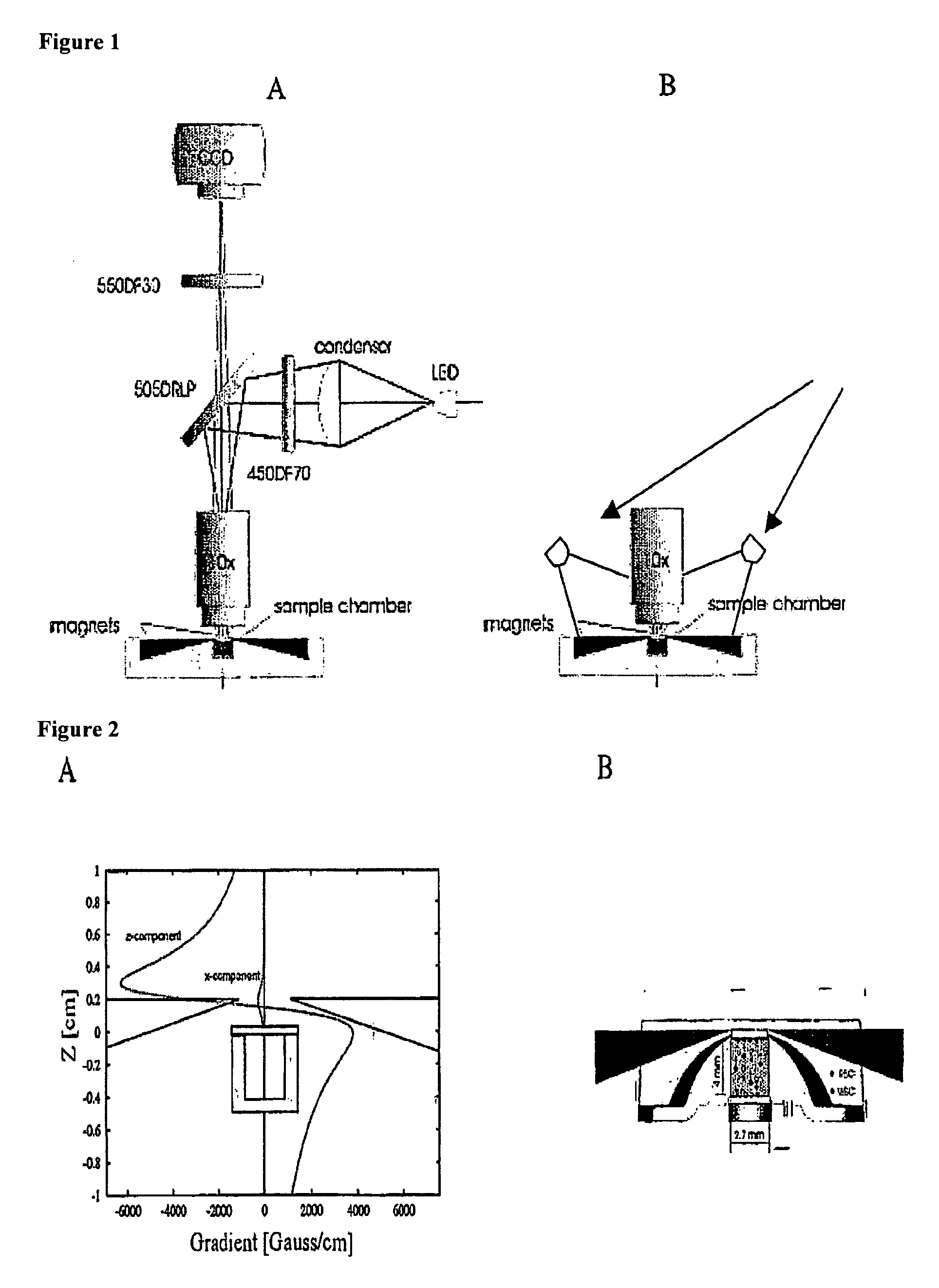
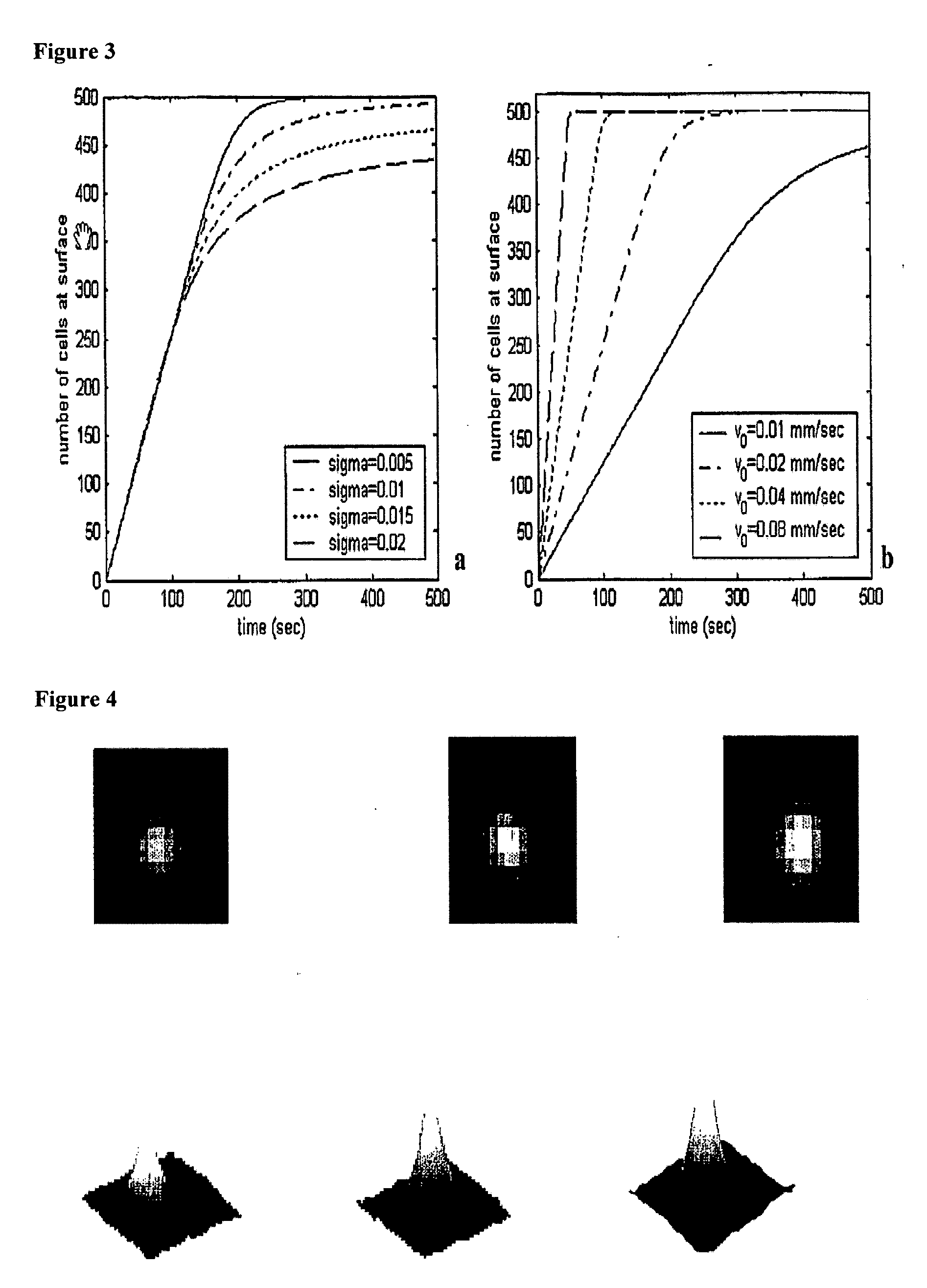
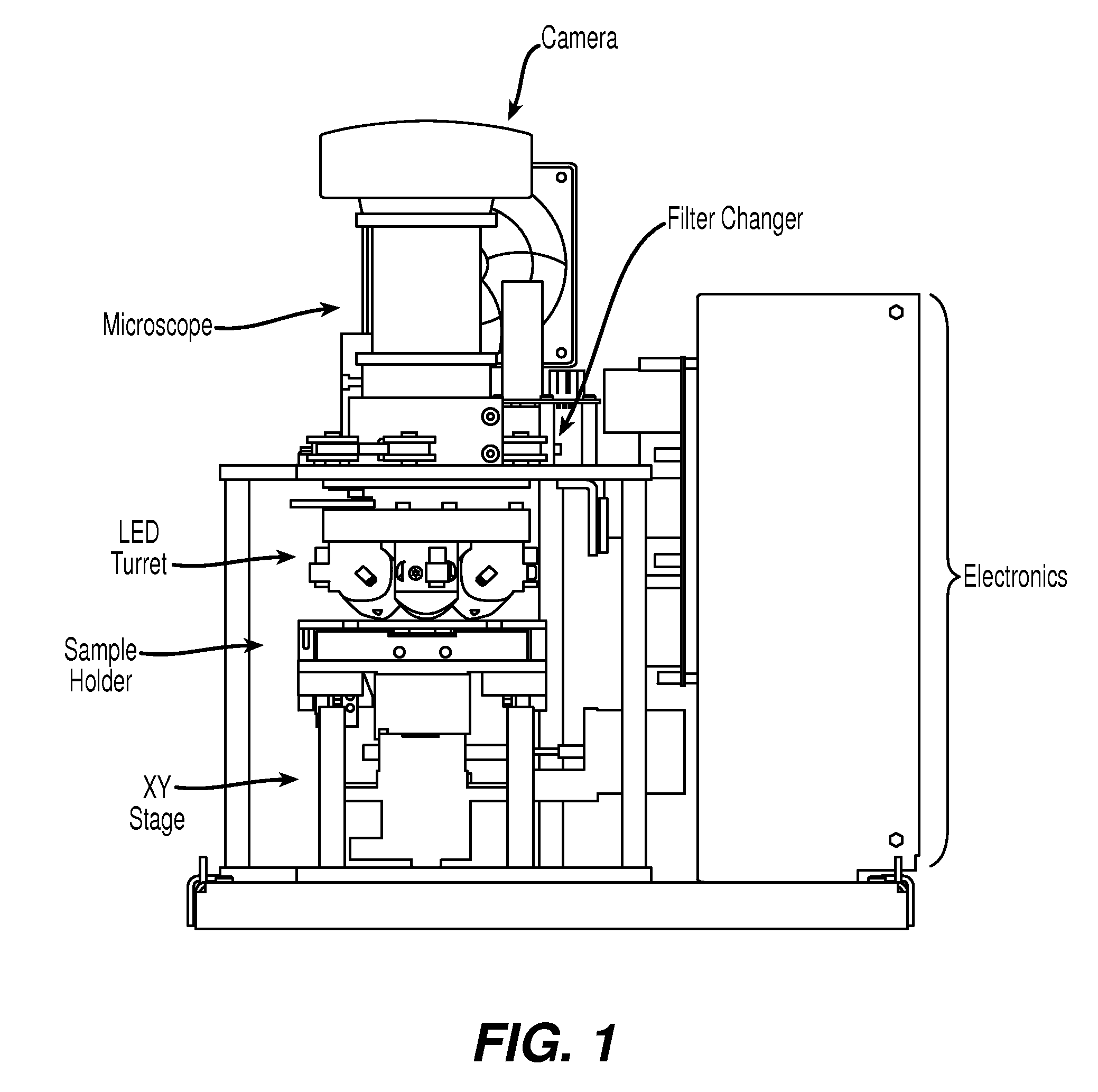
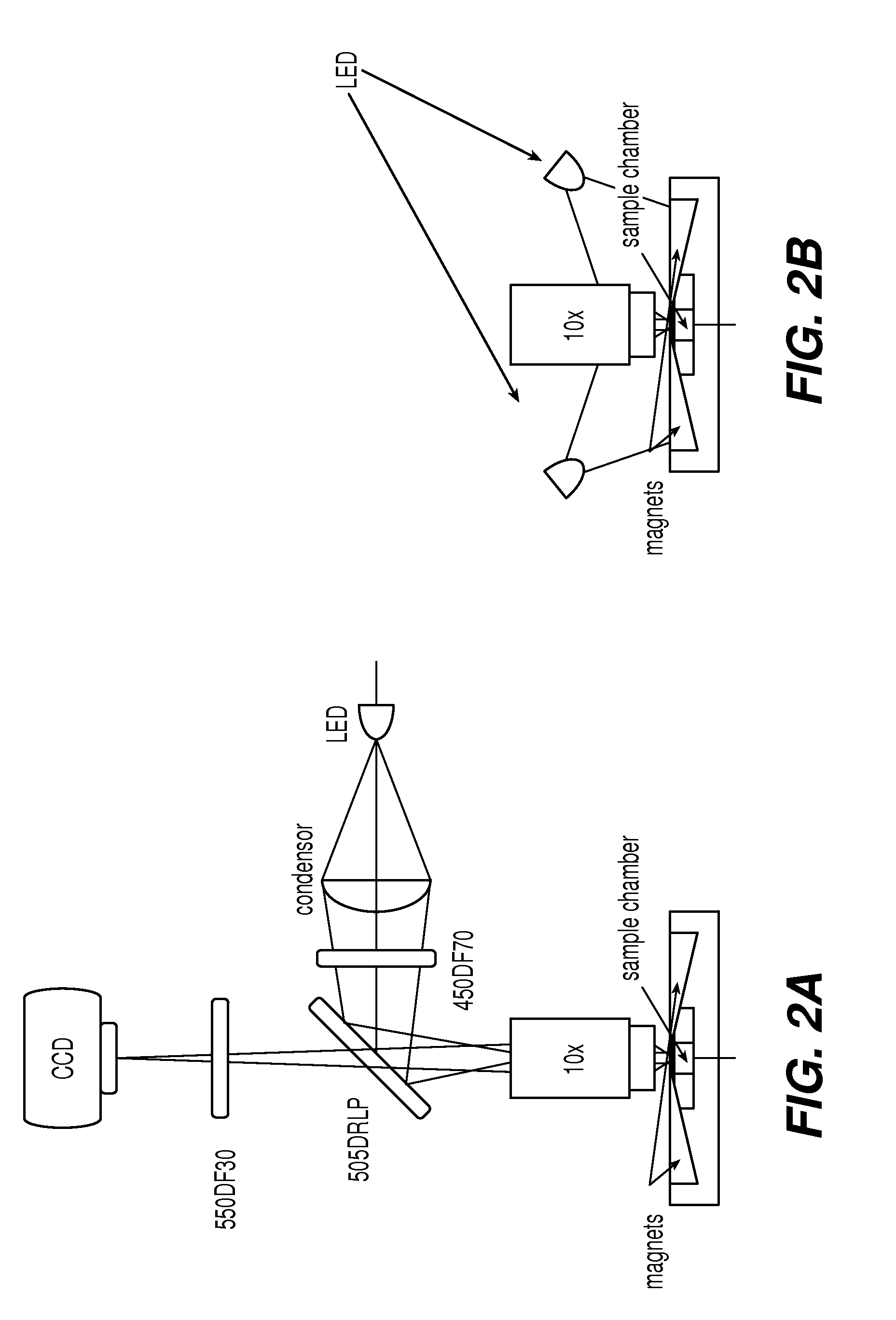
The enumeration of cells in fluids by flow cytometry is widely used across many disciplines such as assessment of leukocyte subsets in different bodily fluids or of bacterial contamination in environmental samples, food products and bodily fluids. For many applications the cost, size and complexity of the instruments prevents wider use, for example, CD4 analysis in HIV monitoring in resource-poor countries. The novel device, methods and algorithms disclosed herein largely overcome these limitations. Briefly, all cells in a biological sample are fluorescently labeled, but only the target cells are also magnetically labeled. The labeled sample, in a chamber or cuvet, is placed between two wedge-shaped magnets to selectively move the magnetically labeled cells to the observation surface of the cuvet. An LED illuminates the cells and a CCD camera captures the images of the fluorescent light emitted by the target cells. Image analysis performed with a novel algorithm provides a count of the cells on the surface that can be related to the target cell concentration of the original sample. The compact cytometer system provides a rugged, affordable and easy-to-use technique, which can be used in remote locations.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TWENTE
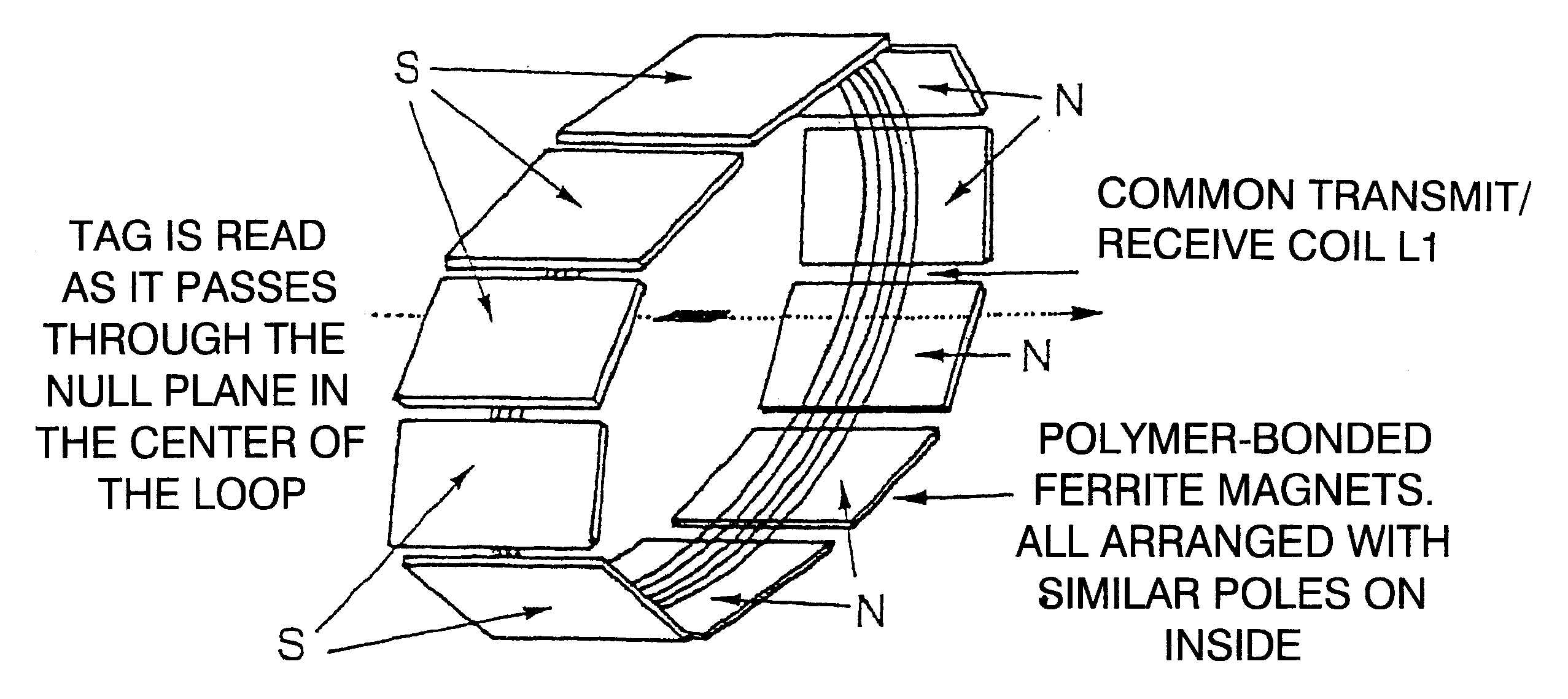
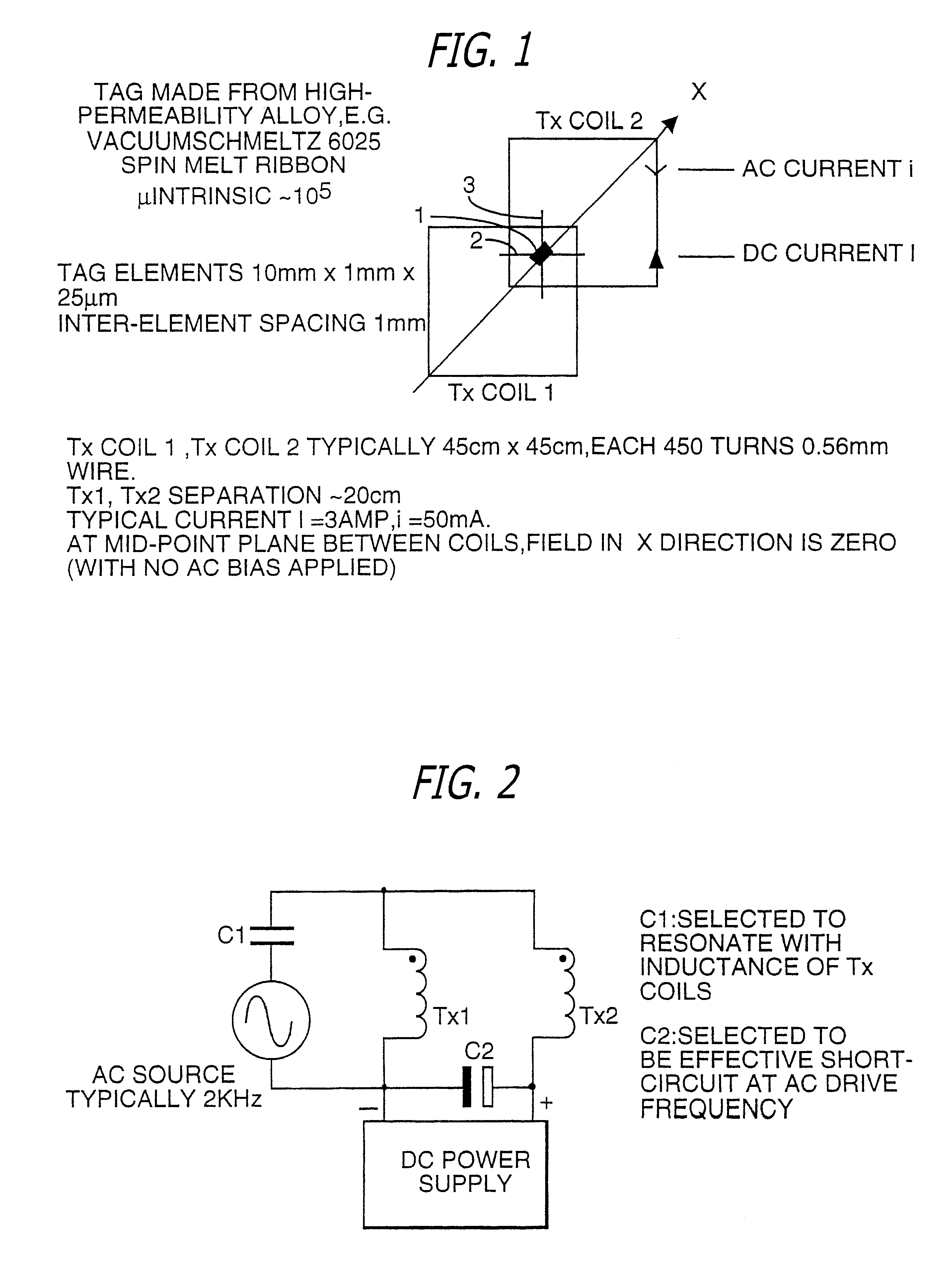
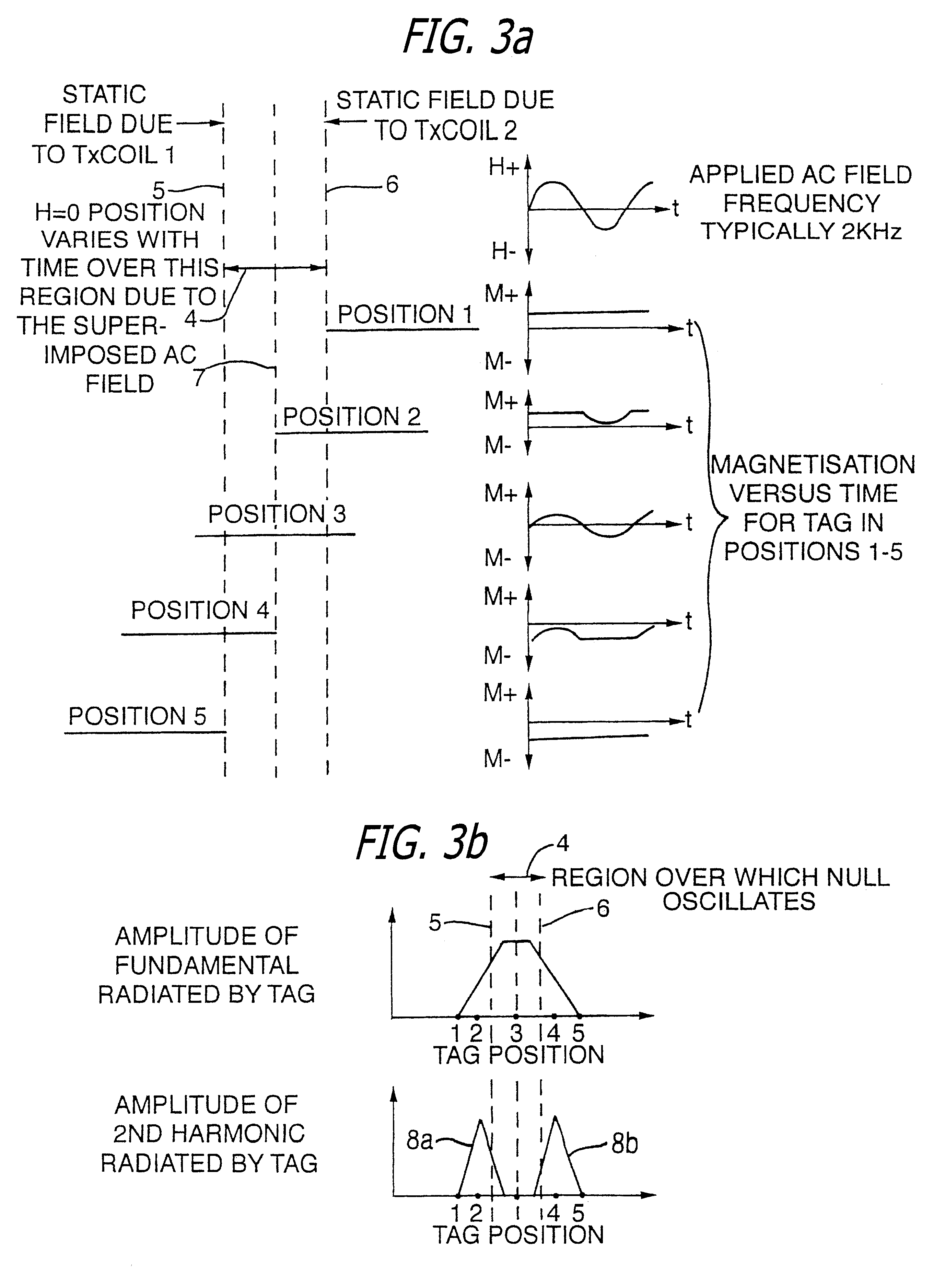
Spatial magnetic interrogation
InactiveUS6144300AAvoid the needThe location information is accurateDigitally marking record carriersDiagnosticsMagnetic markerEngineering
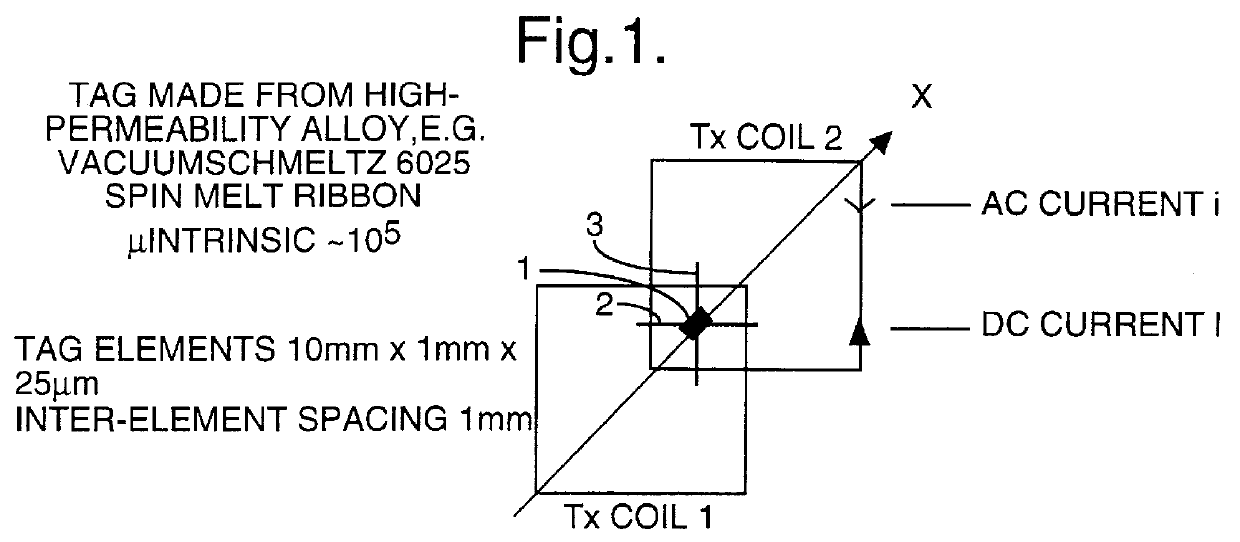
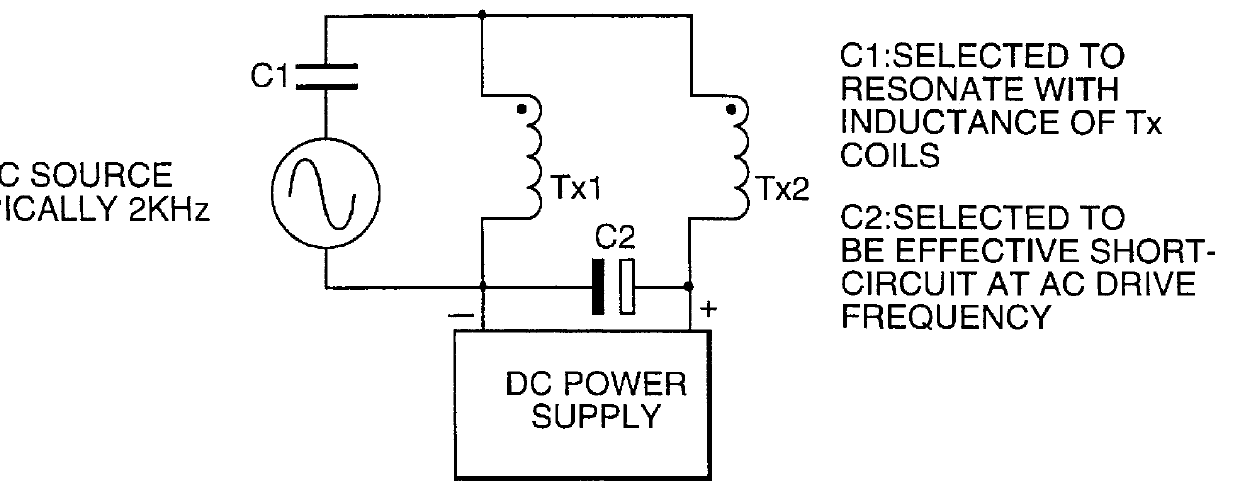
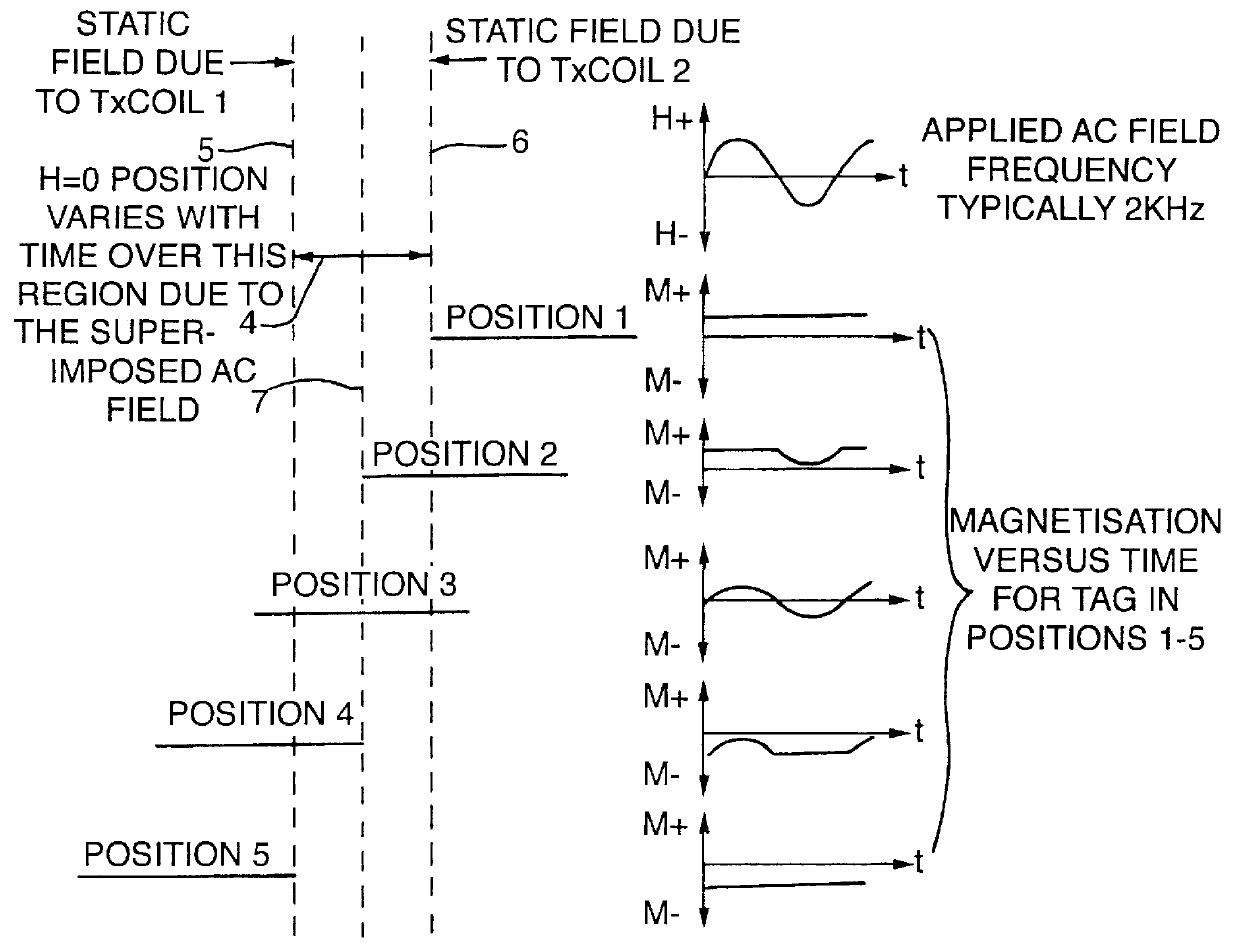
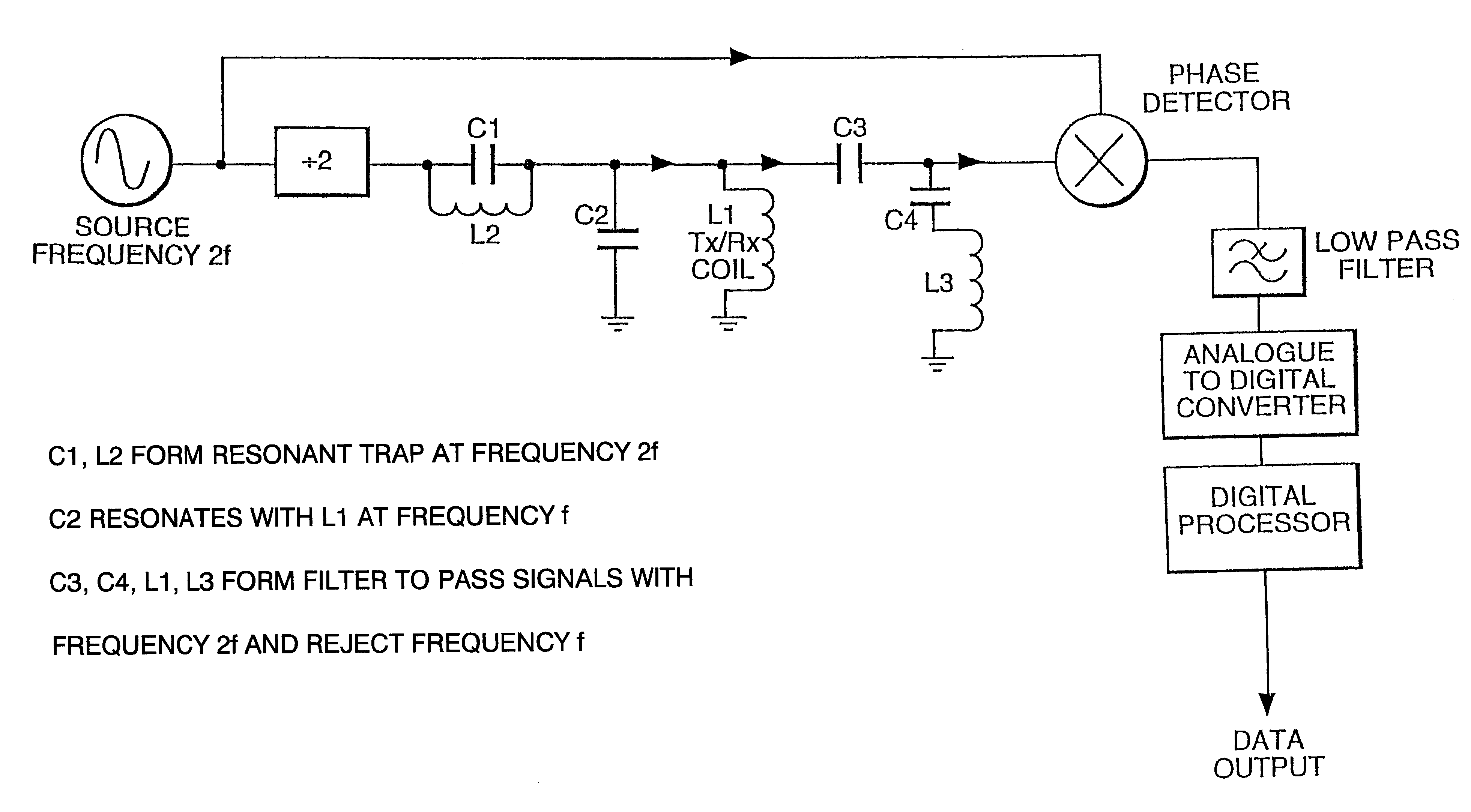
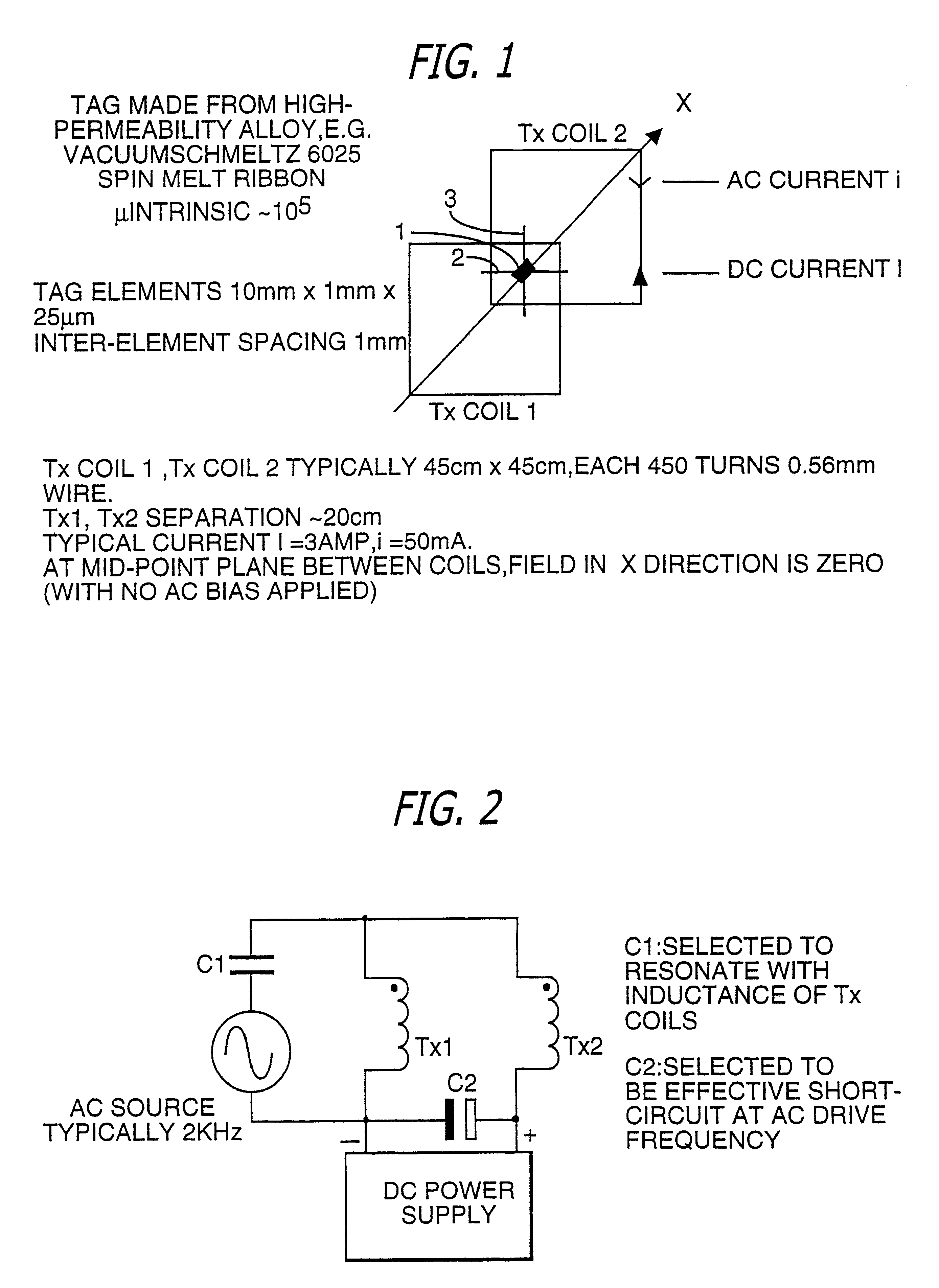
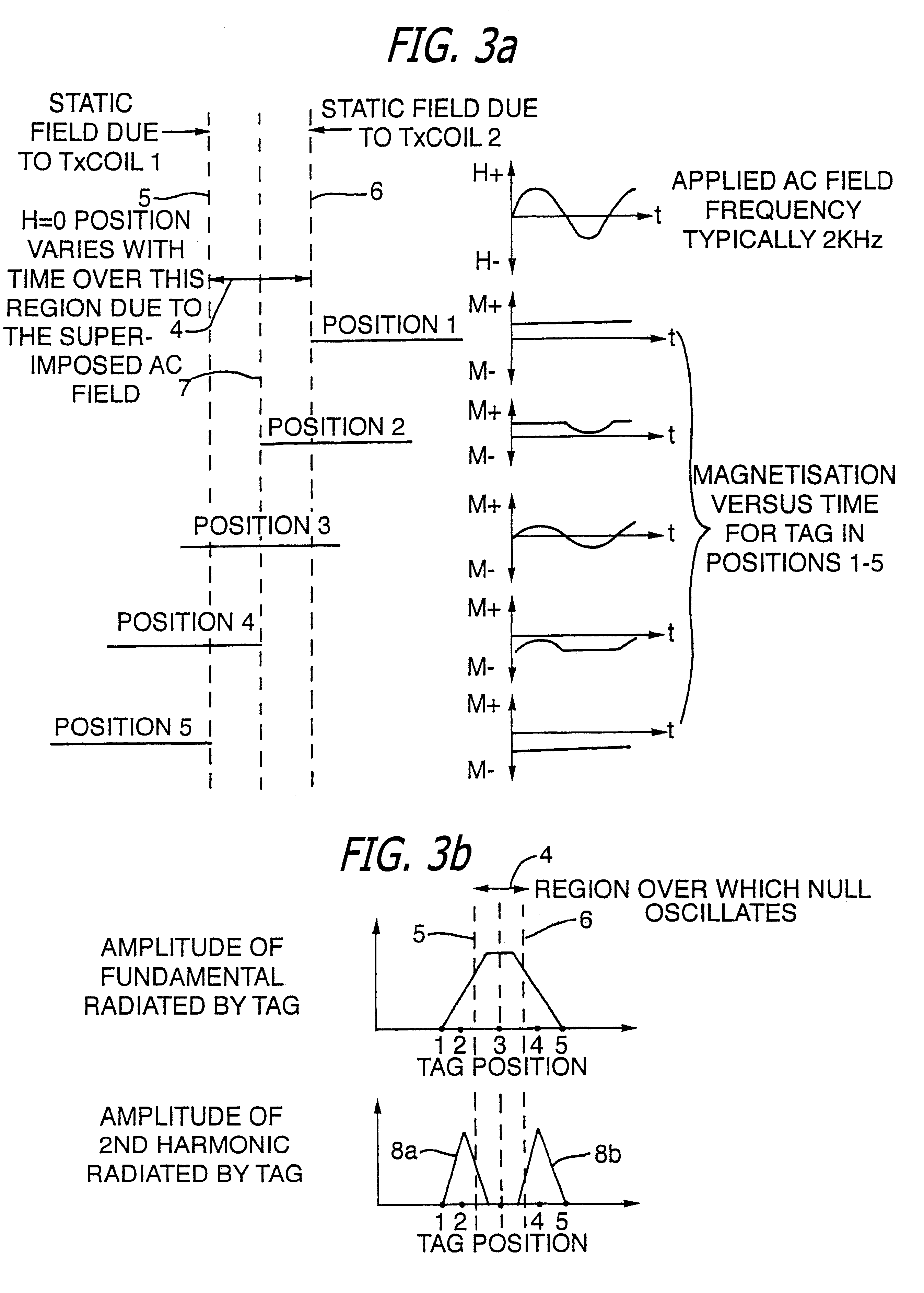
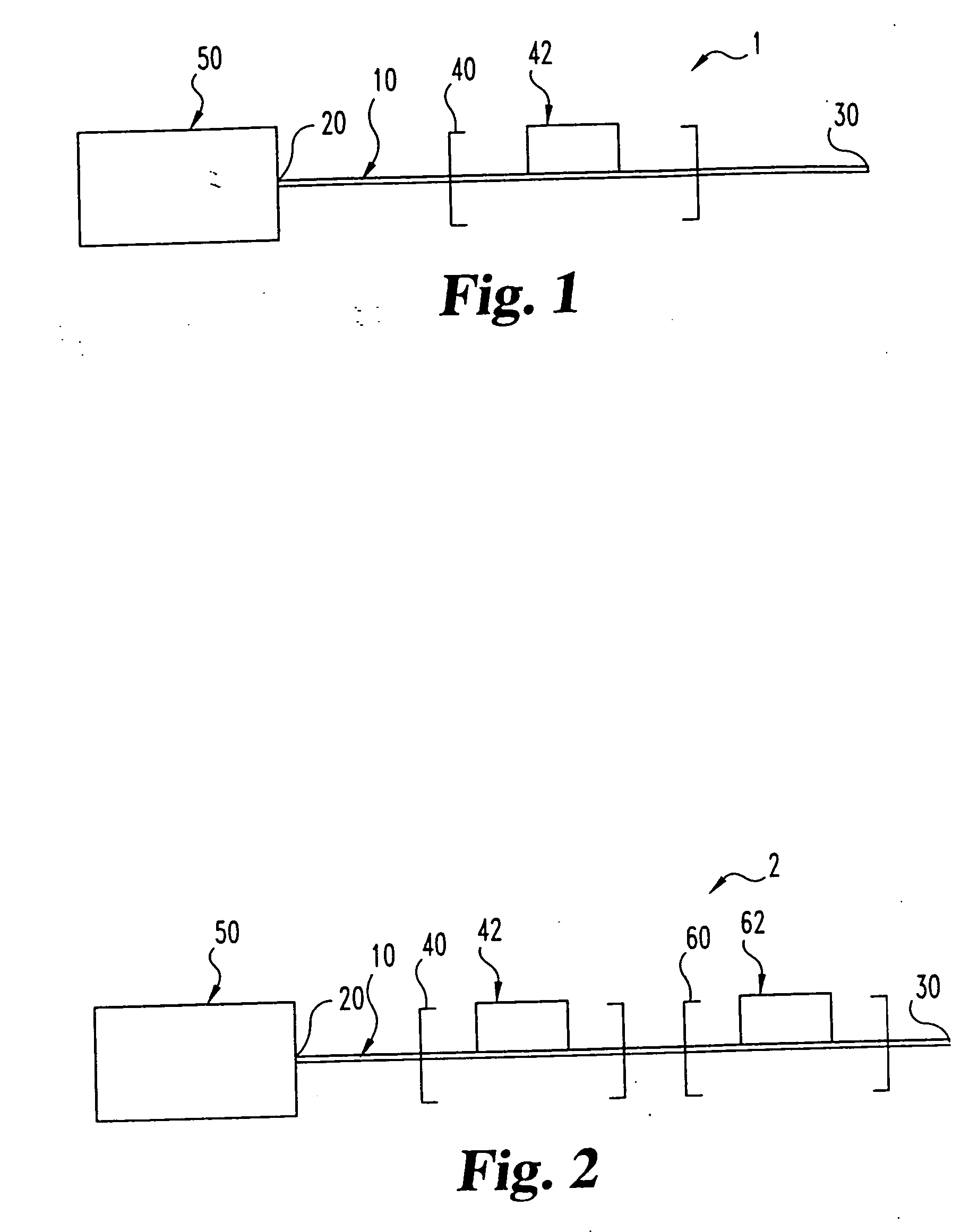
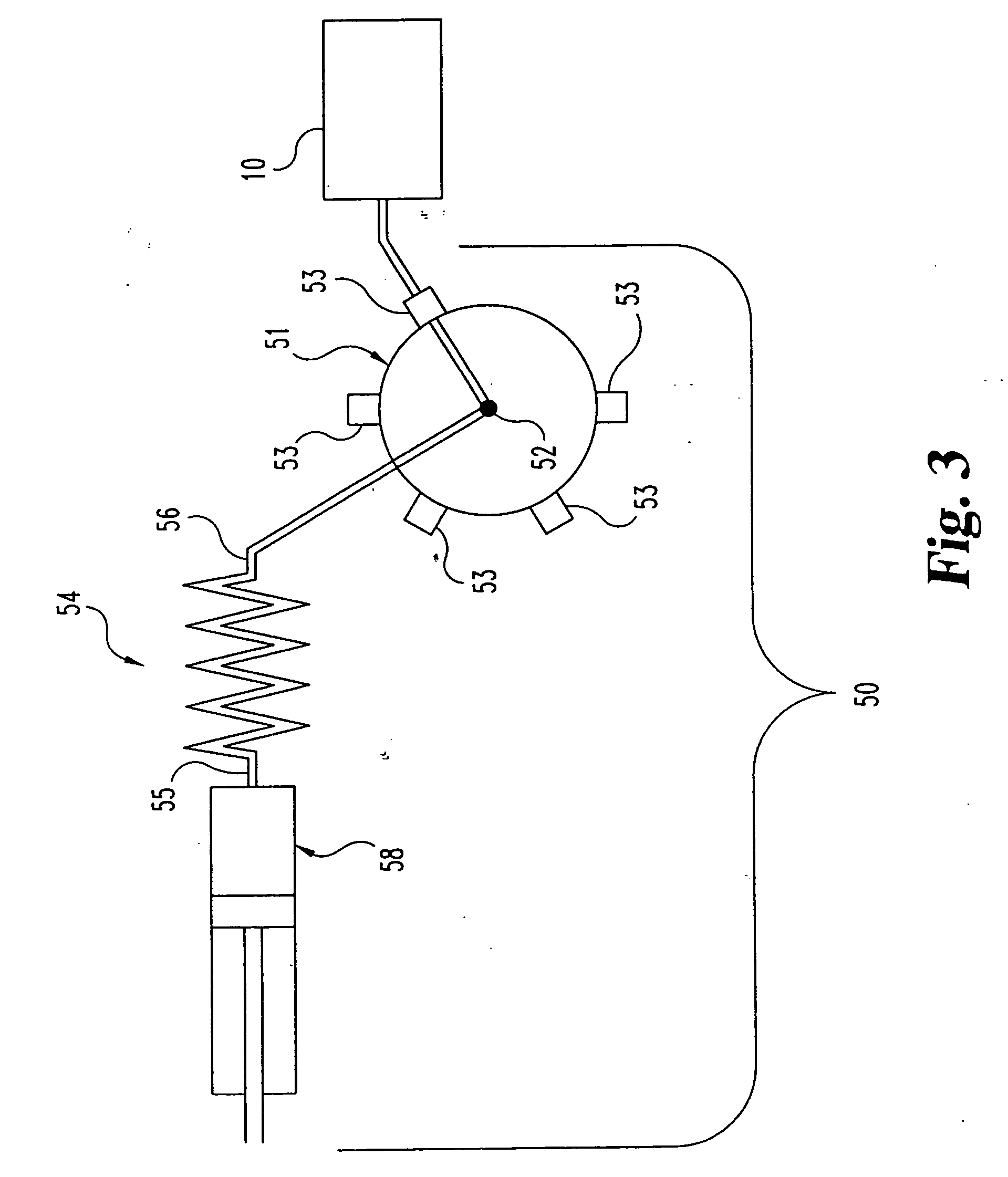
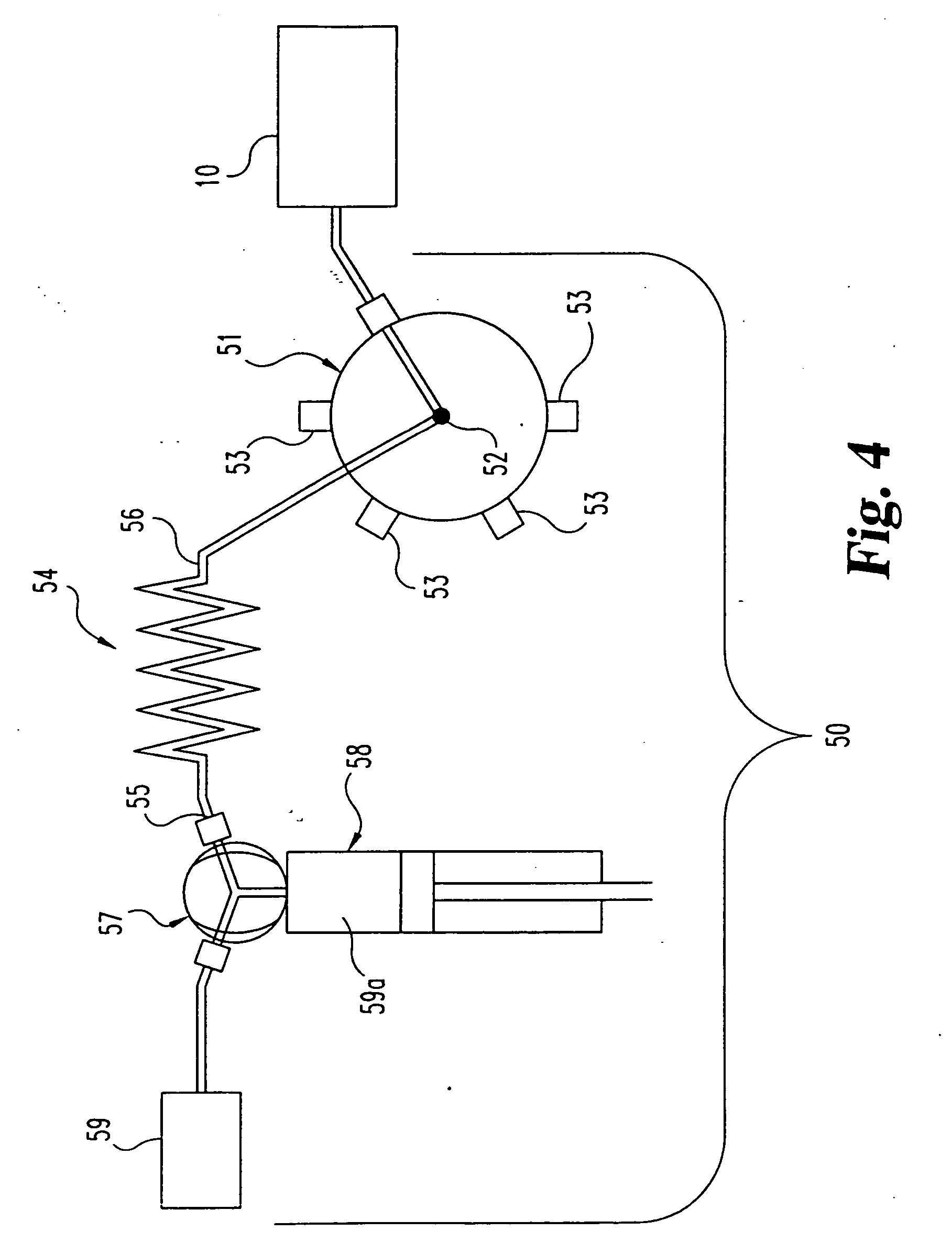
PCT No. PCT / GB96 / 00823 Sec. 371 Date Jan. 12, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jan. 12, 1998 PCT Filed Apr. 3, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 31790 PCT Pub. Date Oct. 10, 1996Magnetic tags or markers are disclosed, together with a variety of techniques by means of which such tags may be interrogated. In one aspect, the magnetic marker or tag which is characterized by carrying a plurality of discrete magnetically active regions in a linear array. In another aspect, the invention provides a method of interrogating a magnetic tag or marker within a predetermined interrogation zone, the tag comprising a high permeability magnetic material, for example to read data stored magnetically in the tag or to use the response of the tag to detect its presence and / or to determine its position within the interrogation zone, characterized in that the interrogation process includes the step of subjecting the tag sequentially to: (1) a magnetic field sufficient in field strength to sacurate the high permeability magnetic material, and (2) a magnetic null as herein defined. Applications of such techniques are describer, inter alia, in relation to (a) identifying articles to which tags are attached; (b) accurate determination of position, as in the location of surgical probes; and (c) totalisation of purchases, where cash item carries a tag coded with data representing its nature and its price.
Owner:DIGITAL MAGNETIC TECH L L C
Analyte detection with magnetic sensors
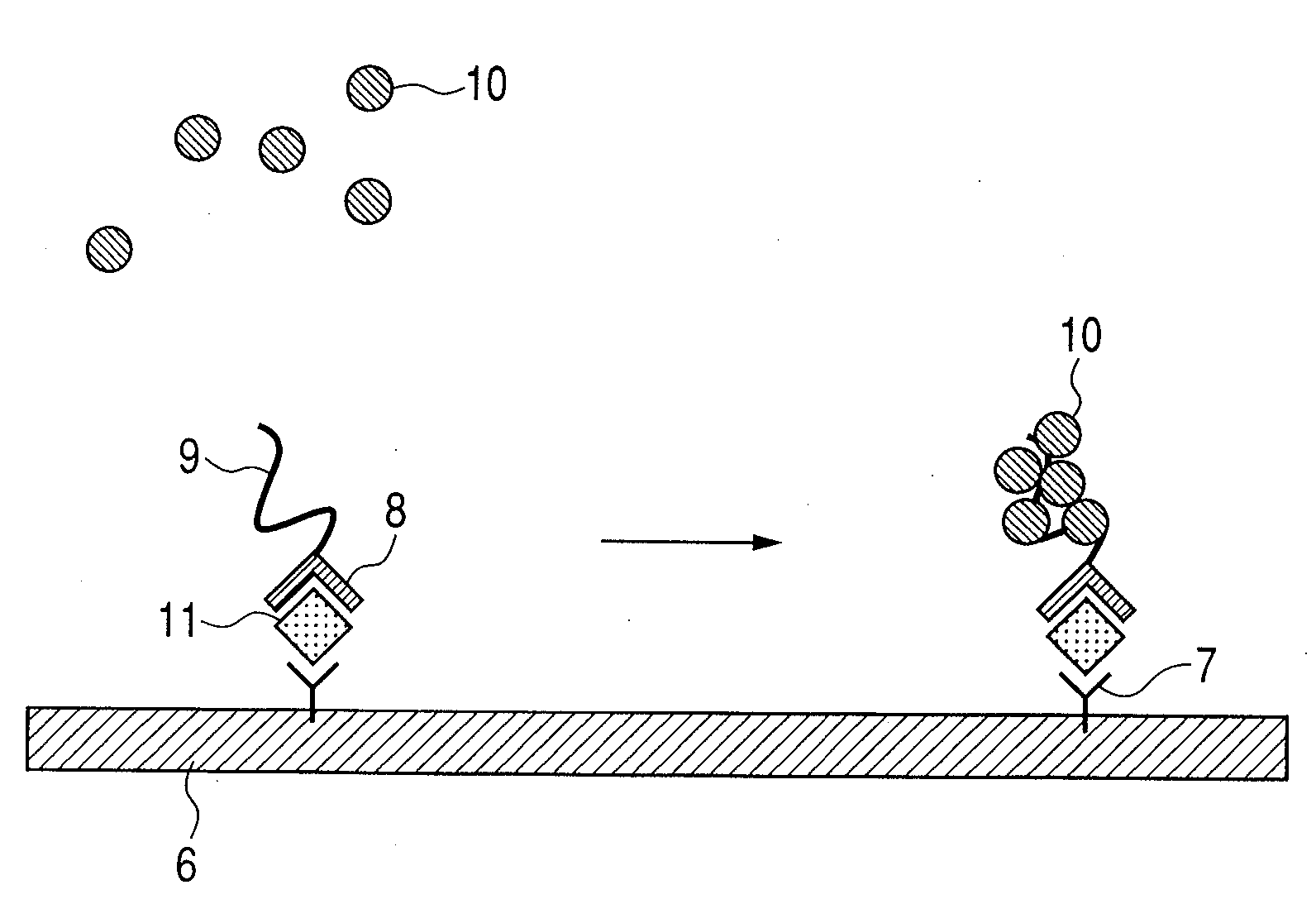
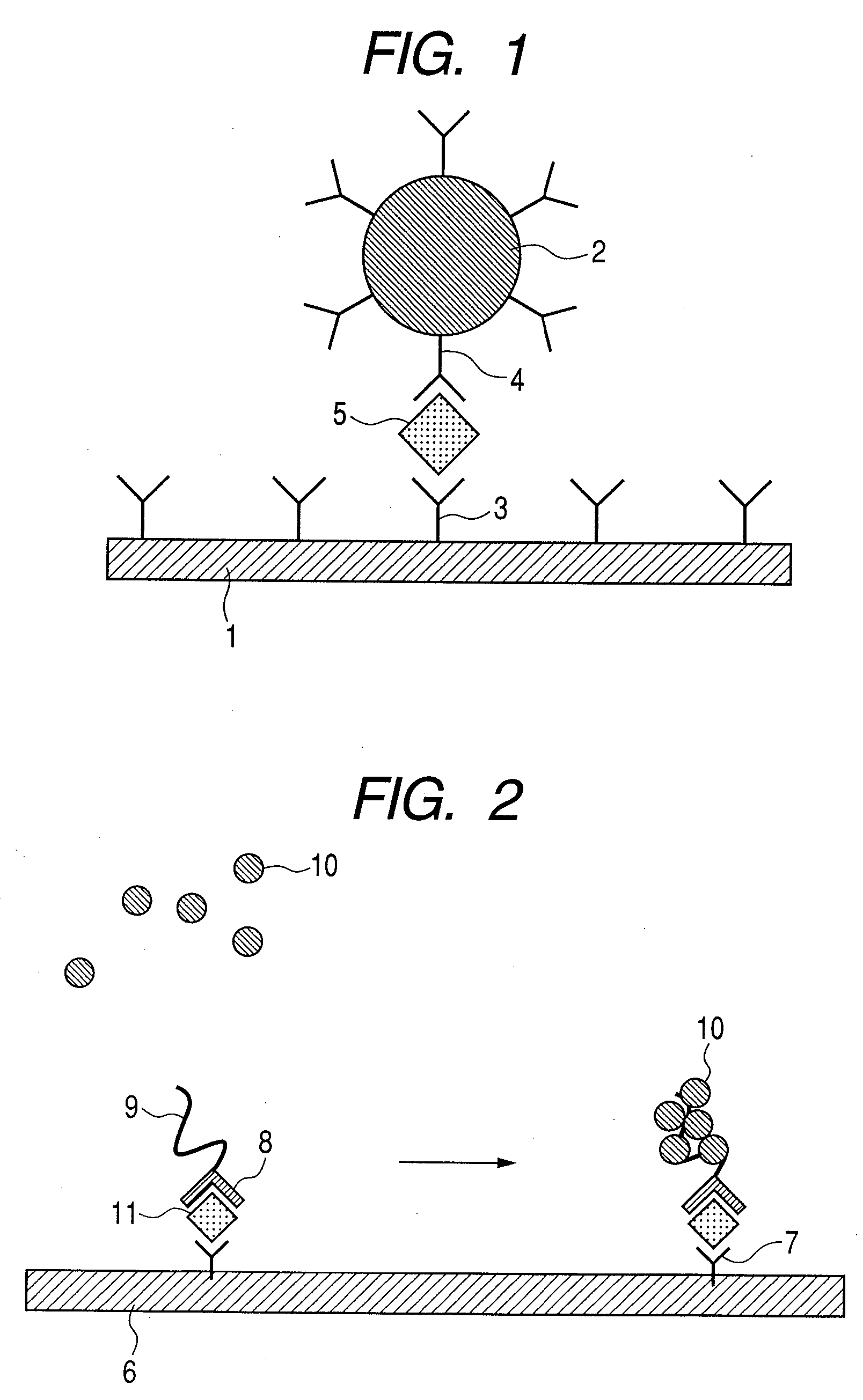
ActiveUS20090104707A1Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiological testingDisease markersAnalyte
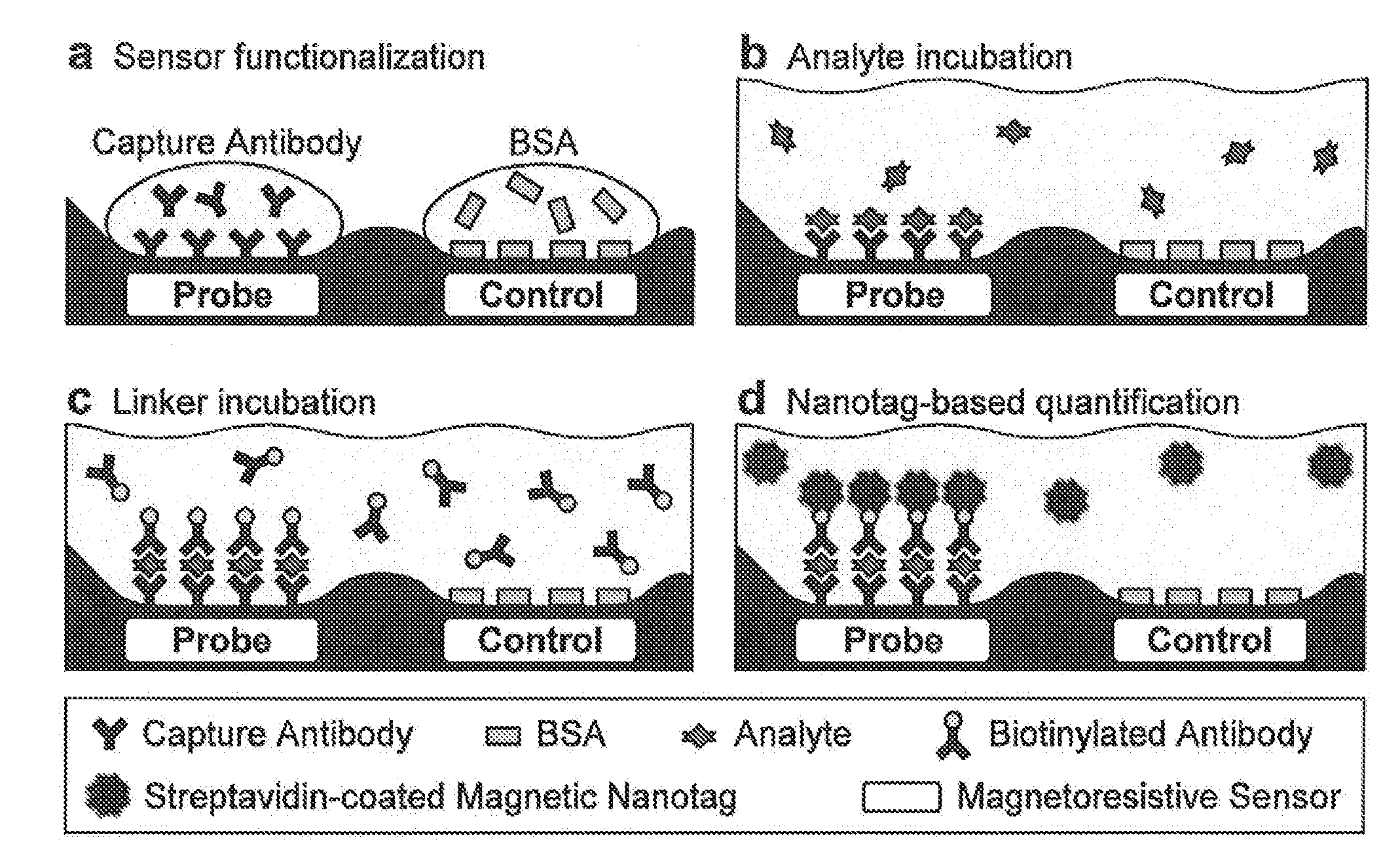
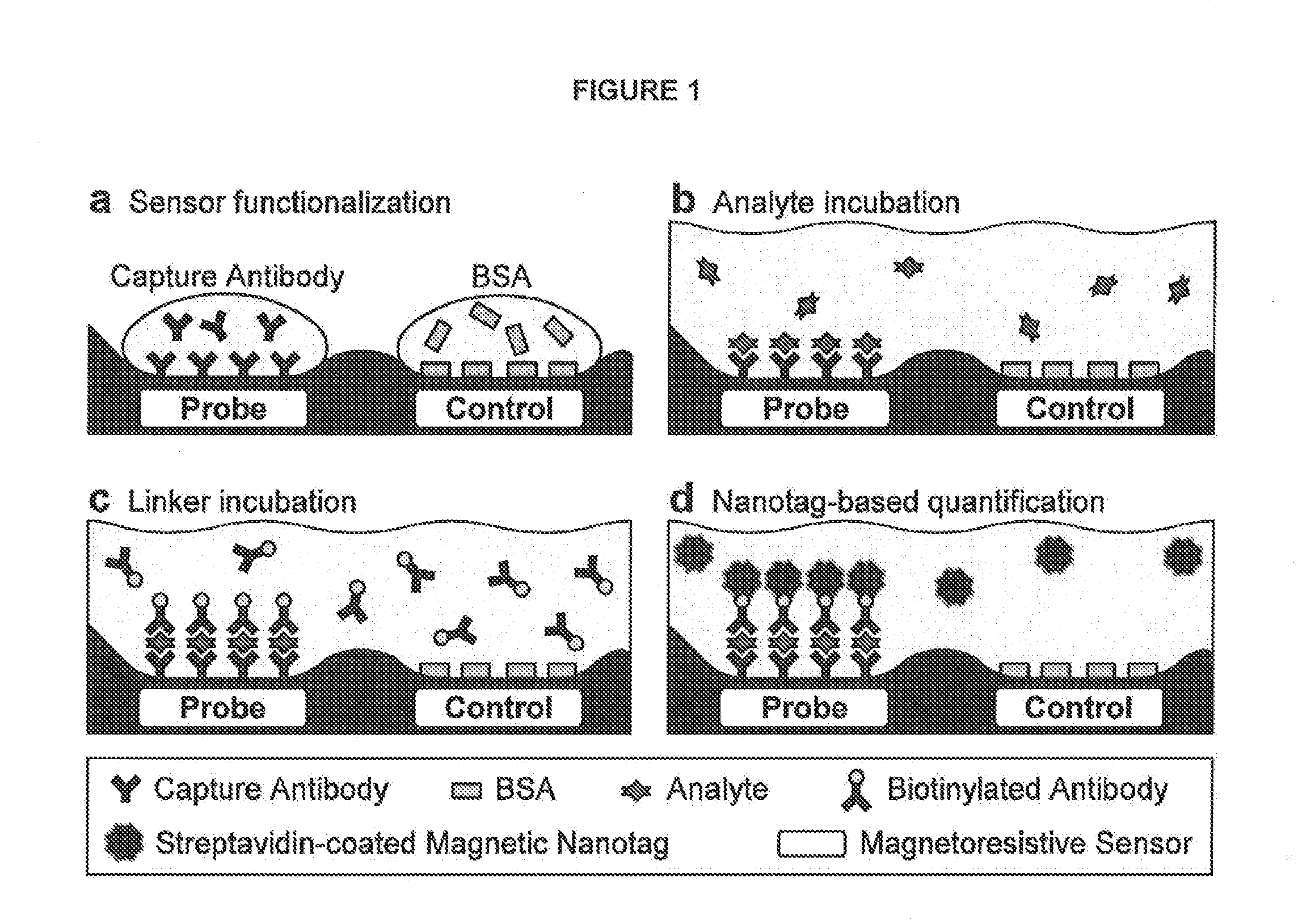
Methods for analyte detection with magnetic sensors are provided. Aspects of the methods include producing a magnetic sensor device having a magnetically labeled analyte from a sample, such as a serum sample, bound to a surface of a magnetic sensor thereof; and obtaining a signal, e.g., a real-time signal, from the magnetic sensor to determine whether the analyte is present in the sample. Also provided are devices, systems and kits that find use in practicing the methods of the invention. The methods, devices, systems and kits of the invention find use in a variety of different applications, including detection of biomarkers, such as disease markers.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Apparatus for interrogating a magnetically coded tag
InactiveUS6323770B1Improve accuracyDigitally marking record carriersDiagnosticsMagnetic markerMagnetic tension force
Magnetic tags or markers are disclosed, together with a variety of techniques by means of which such tags may be interrogated. In one aspect, the magnetic marker or tag which is characterized by carrying a plurality of discrete magnetically active regions in a linear array. In another aspect, the invention provides a method of interrogating a magnetic tag or marker within a predetermined interrogation zone, the tag comprising a high permeability magnetic material, for example to read data stored magnetically in the tag or to use the response of the tag to detect its presence and / or to determine its position within the interrogation zone, characterized in that the interrogation process includes the step of subjecting the tag sequentially to: (1) a magnetic field sufficient in field strength to saturate the high permeability magnetic material, and (2) a magnetic mill as herein defined. Applications of such techniques are described, inter alia, in relation to (a) identifying articles to which tags are attached; (b) accurate determination of position, as in location of surgical probes, and (c) totalization of purchases, where each item carries a tag coded with data representing its nature and its price.
Owner:DIGITAL MAGNETIC TECH L L C
Apparatus for interrogating a magnetically coded tag
InactiveUS6323769B1Improve accuracyDigitally marking record carriersDiagnosticsMagnetic markerEngineering
Magnetic tags or markers are disclosed, together with a variety of techniques by means of which such tags may be interrogated. In one aspect, the magnetic marker or tag which is characterized by carrying a plurality of discrete magnetically active regions in a linear array. In another aspect, the invention provides a method of interrogating a magnetic tag or marker within a predetermined interrogation zone, the tag comprising a high permeability magnetic material, for example to read data stored of the tag to detect its presence and / or to determine its position within the interrogation zone, characterized in that the interrogation process includes the step of subjecting the tag sequentially to: (1) a magnetic field sufficient in field strength to saturate the high permeability magnetic material, and (2) a magnetic null as herein defined. Applications of such techniques are described, inter alia, in relation to (a) identifying articles to which tags are attached; (b) accurate determination of position, as in the location of surgical probes; and (c) totalization of purchases, where each item carries a tag coded with data representing its nature and its place.
Owner:DIGITAL MAGNETIC TECH L L C
Medical surgical sponge and instrument detection system and method
A magnetic detector locates magnetically tagged items, such as surgical sponges or instruments, introduced to and remaining in the body cavity of a surgical patient. The magnetic detector is a wand or probe that is manually handleable, and spatially manipulable and moveable, by an operator, such as a medical professional. The detector is moved about at a spatial location of an ambient magnetic field at the patient and operating table. A characteristic of the ambient magnetic field at the spatial location is saved by the detector. The detector is subsequently moved about at the same spatial location. If any magnetically tagged item is present in the vicinity of the detector during this subsequent movement at the spatial location, an anomalous magnetic effect is detected by comparison of the prior detection reading absent the tagged item to the detection reading in presence of the tagged item in the patient. The anomalous magnetic effect, and thus the tagged item, is locatable spatially in the patient, by three-dimensional sensor(s), arrays of sensors, and pluralities of arrays of sensors of the detector. The different detection readings with and without presence of the anomalous magnetic effect caused by presence of the tagged item in the patient are calculable as scalar, vector array, and / or gradient array determinations, according to the particular number and configuration of sensors in the detector.
Owner:MED SURG SOLUTIONS
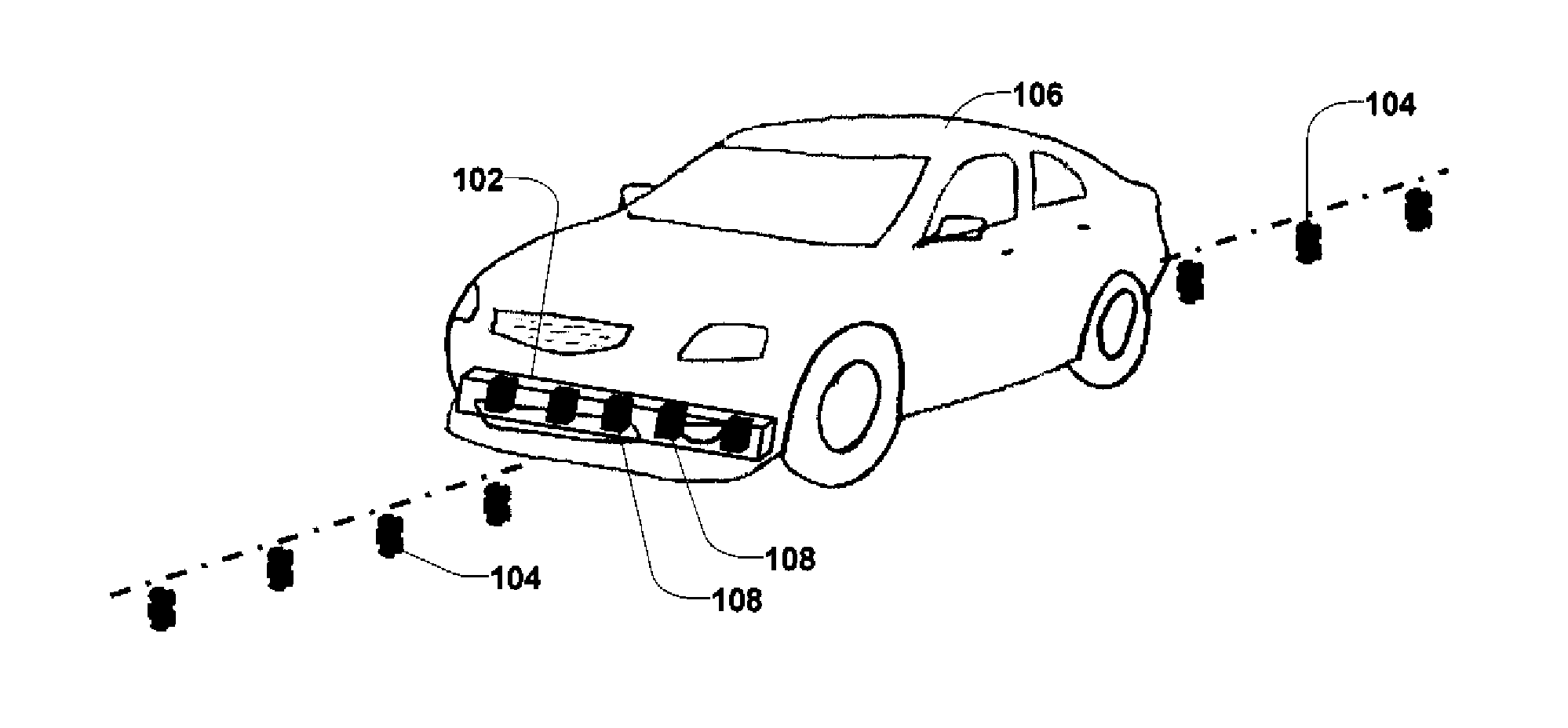
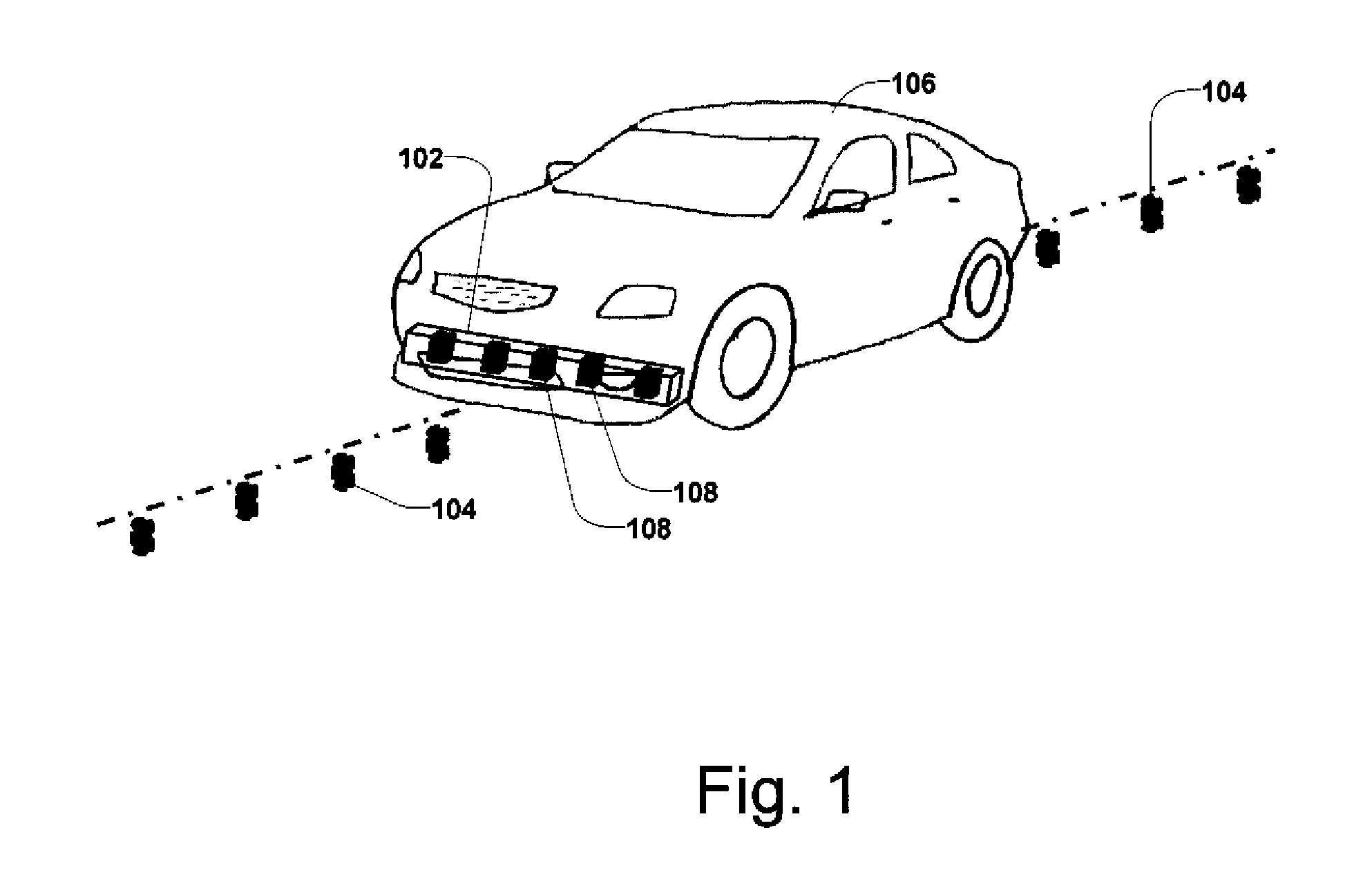
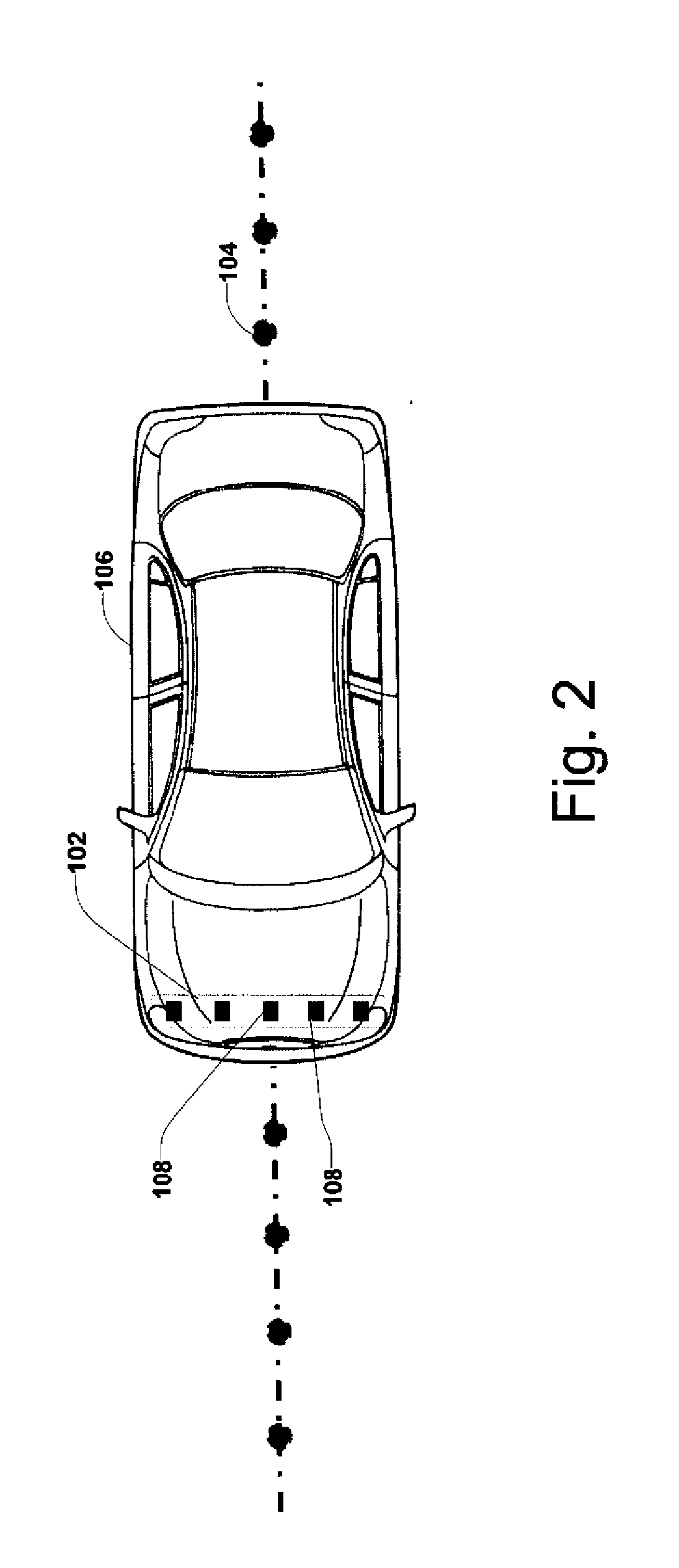
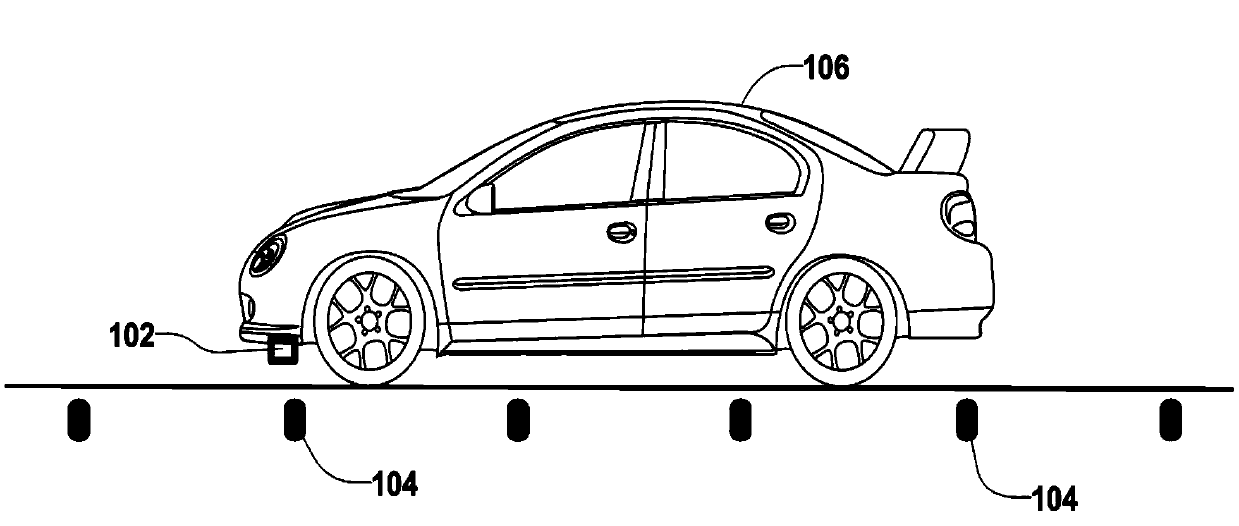
Driverless vehicle guidance system and method
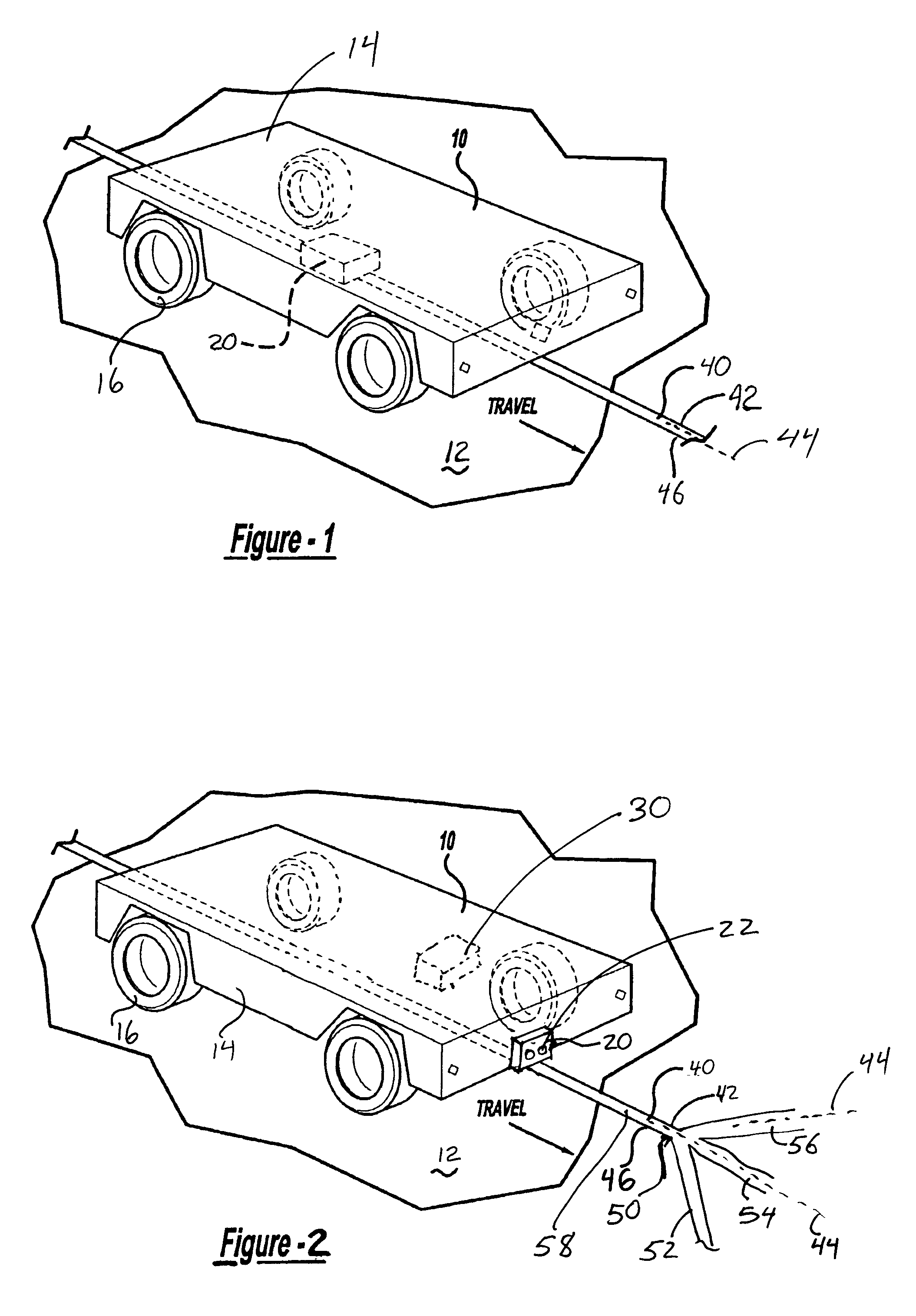
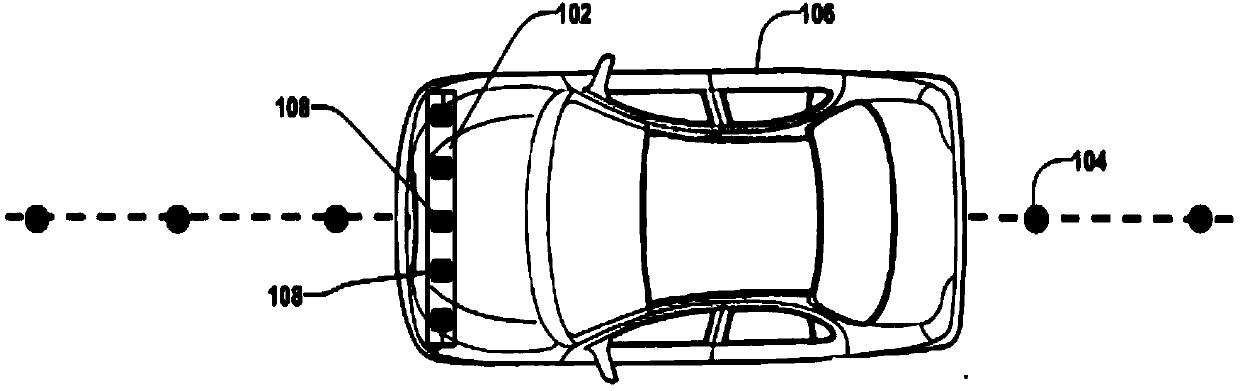
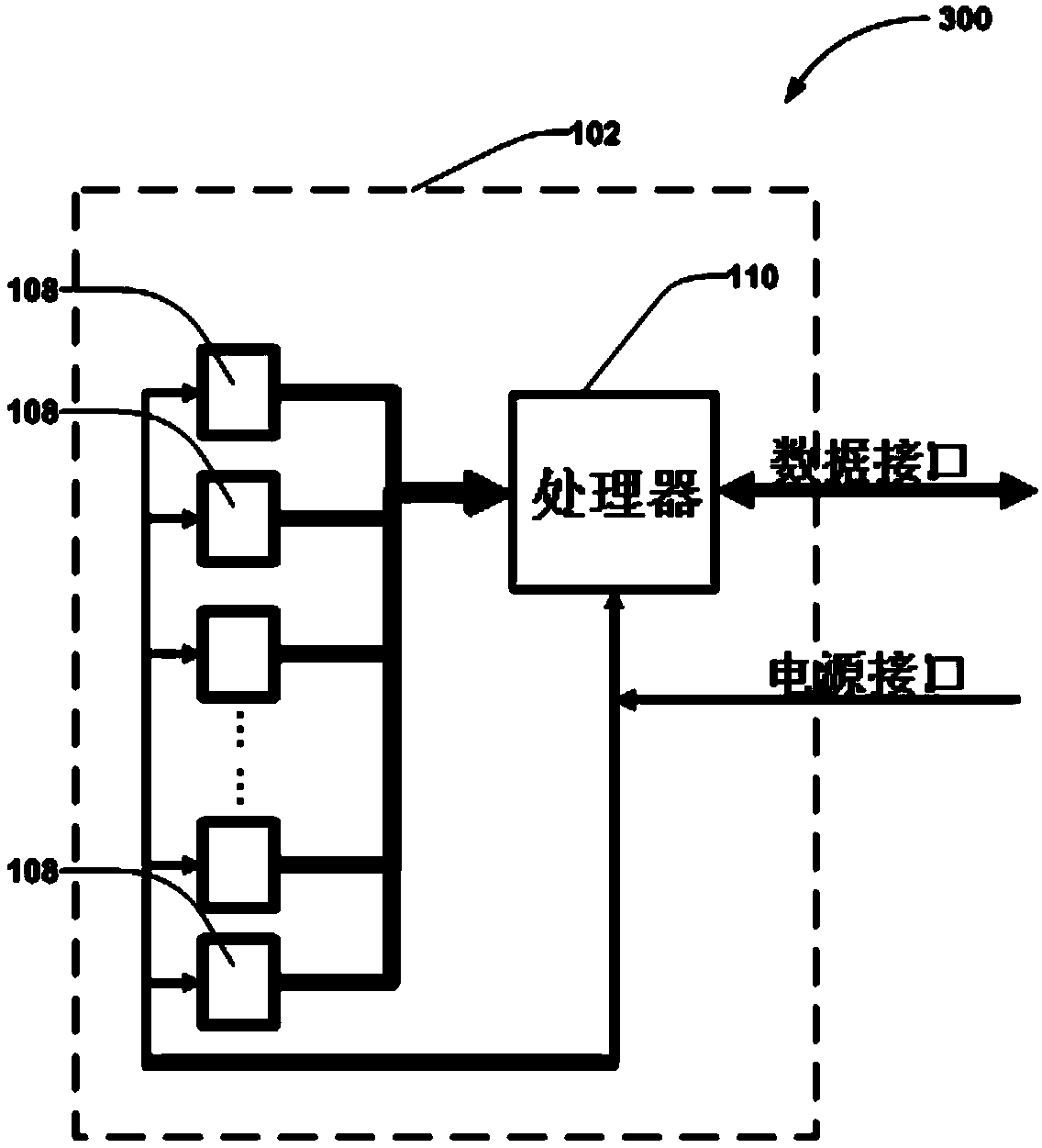
InactiveUS6971464B2Prevent false detectionAutomatic initiationsNon-mechanical steering controlMagnetic markerEngineering
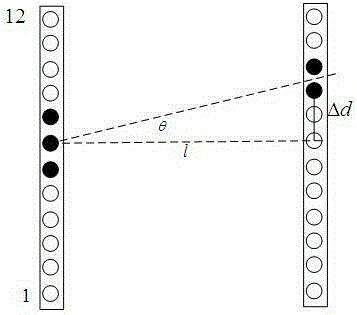
A vehicle guidance system for guiding a vehicle along a magnetic marker including a first magnetic sensor having a sensing axis, the first sensor measuring a first magnetic field. A second magnetic sensor has a sensing axis, the second sensor measuring a second magnetic field. The sensing axis of the second magnetic sensor crosses the sensing axis of the first magnetic sensor at a vehicle guide point. A processor is configured to receive data representative of the magnetic field measured by the first and second sensors and to calculate a lateral offset between the guide point and the magnetic marker based upon the measured magnetic fields. A method for guiding a vehicle in response to a marker having magnetic field is also disclosed. The steps of the method include measuring magnetic field strength proximate the marker, measuring ambient magnetic field strength remote from the marker, nulling the ambient magnetic field by removing the remote magnetic field strength from the proximate magnetic field strength, calculating a lateral displacement between the vehicle and the marker using the nulled magnetic field strength, and guiding the vehicle in response to the lateral displacement between the vehicle and the marker.
Owner:JERVIS B WEBB INT CO
Methods and algorithms for cell enumeration in a low-cost cytometer
InactiveUS20070117158A1Simple designReduce operating costsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsImage analysisWhite blood cellCcd camera
The enumeration of cells in fluids by flow cytometry is widely used across many disciplines such as assessment of leukocyte subsets in different bodily fluids or of bacterial contamination in environmental samples, food products and bodily fluids. For many applications the cost, size and complexity of the instruments prevents wider use, for example, CD4 analysis in HIV monitoring in resource-poor countries. The novel device, methods and algorithms disclosed herein largely overcome these limitations. Briefly, all cells in a biological sample are fluorescently labeled, but only the target cells are also magnetically labeled. In addition, non-magnetically labeled cells are imaged for viability in a modified slide configuration. The labeled sample, in a chamber or cuvet, is placed between two wedge-shaped magnets to selectively move the magnetically labeled cells to the observation surface of the cuvet. An LED illuminates the cells and a CCD camera captures the images of the fluorescent light emitted by the target cells. Image analysis performed with a novel algorithm provides a count of the cells on the surface that can be related to the target cell concentration of the original sample. The compact cytometer system provides a rugged, affordable and easy-to-use technique, which can be used in remote locations.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TWENTE
Flow-controlled magnetic particle manipulation
InactiveUS20070105163A1Increase flow rateIncrease concentrationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMagnetic markerChemical physics
Inventive methods and apparatus are useful for collecting magnetic materials in one or more magnetic fields and resuspending the particles into a dispersion medium, and optionally repeating collection / resuspension one or more times in the same or a different medium, by controlling the direction and rate of fluid flow through a fluid flow path. The methods provide for contacting derivatized particles with test samples and reagents, removal of excess reagent, washing of magnetic material, and resuspension for analysis, among other uses. The methods are applicable to a wide variety of chemical and biological materials that are susceptible to magnetic labeling, including, for example, cells, viruses, oligonucleotides, proteins, hormones, receptor-ligand complexes, environmental contaminants and the like.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
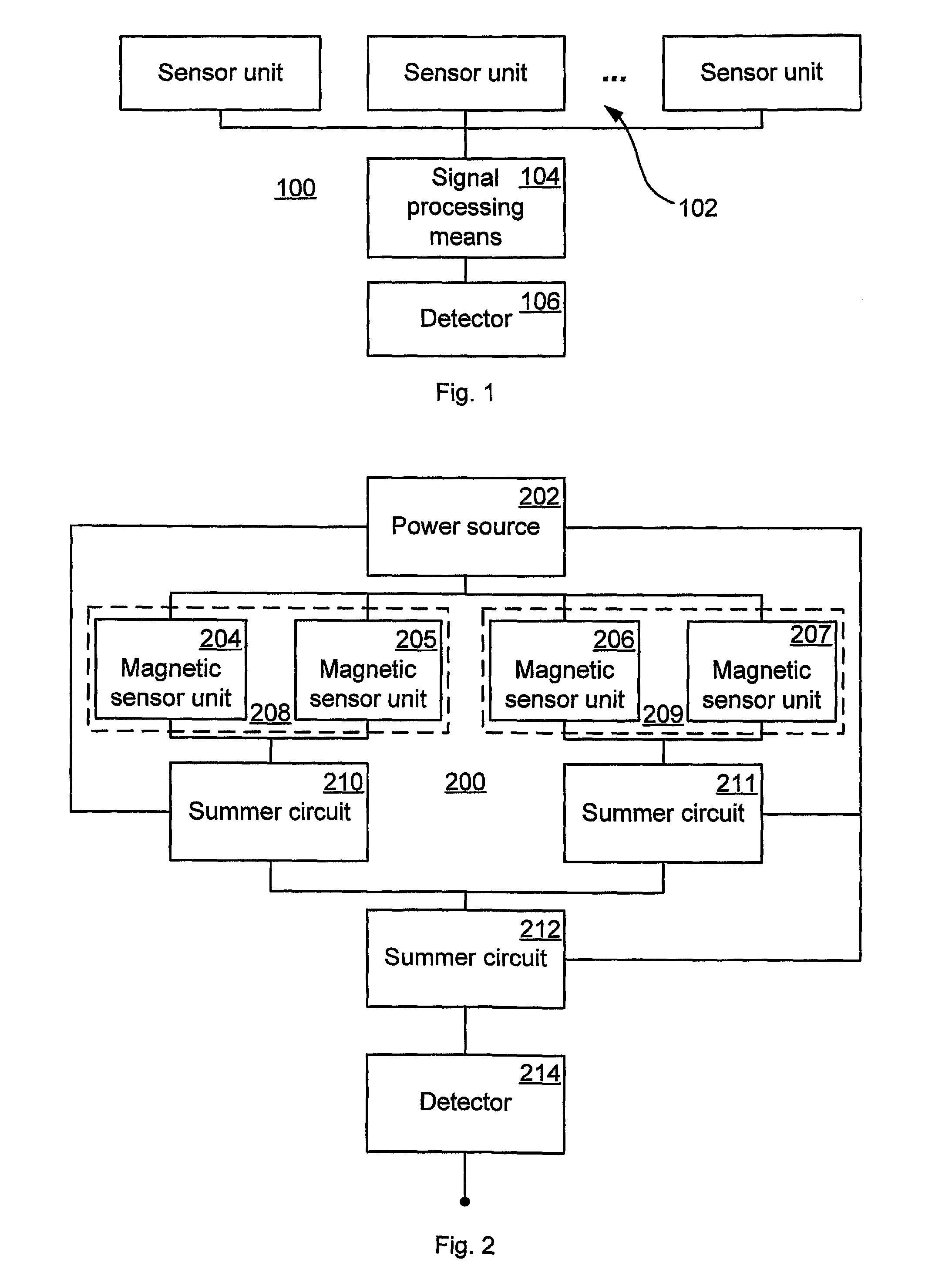
Position Detector and Method for Detecting a Position of a Packaging Material with Magnetic Marking
InactiveUS20080309327A1Robust positioningSimple signal processingMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsElectric/magnetic position measurementsMagnetic markerPack material
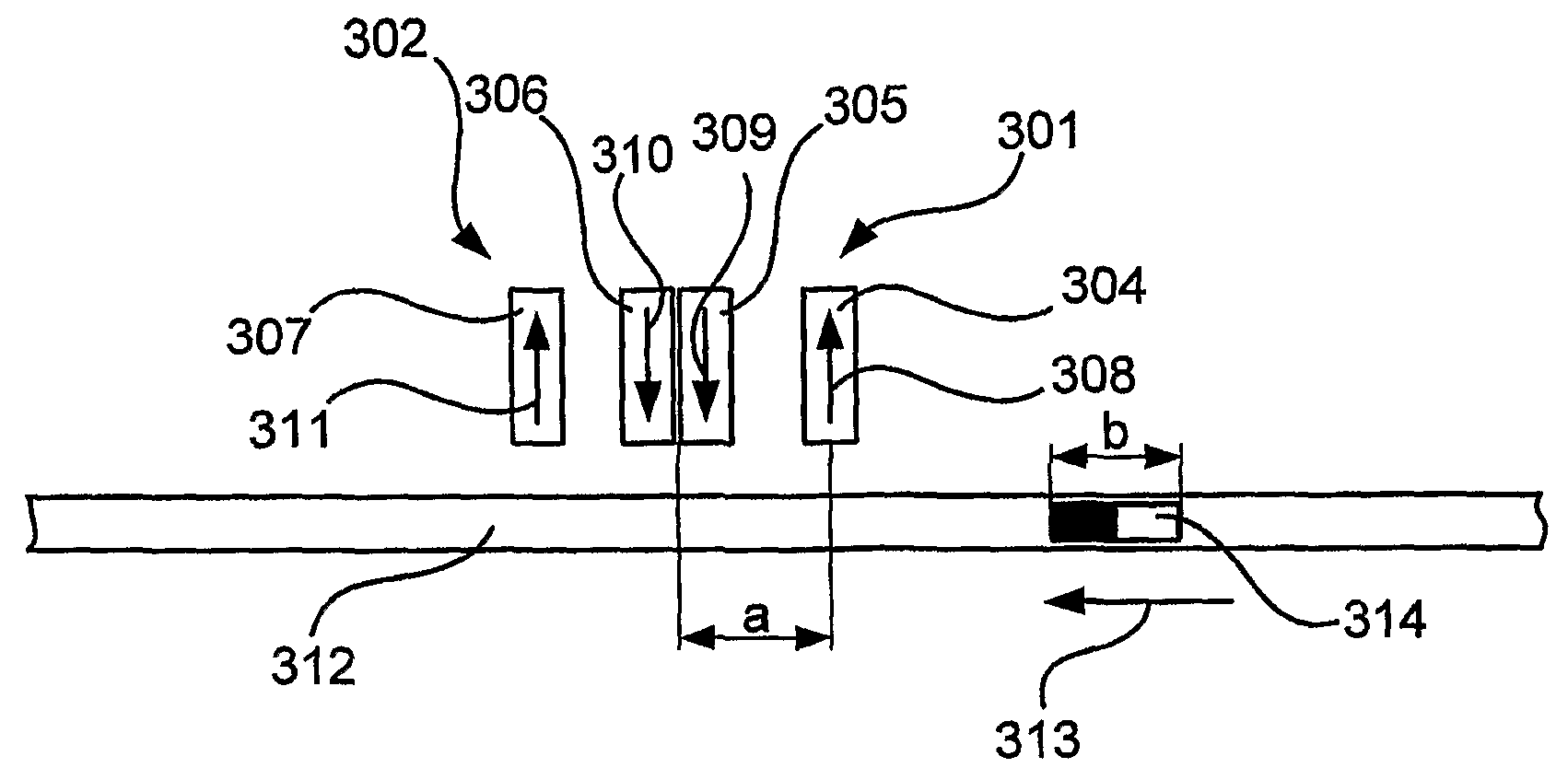
A position detector arrangement for detecting a position of a packaging material with magnetic marking comprises a sensor assembly comprising a plurality of magnetic sensor units each comprising an output providing an output signal. The magnetic sensor units are arranged in at least two sensor unit pairs, with the sensor units of each pair arranged with opposite sensitivity directions, and with the sensor units arranged to sense magnetic markings of the packaging material. A signal processing assembly is connected to the outputs of the magnetic sensors and comprises a combiner arranged to aggregate the output signals of the sensors to an aggregated signal; and a detector arranged to determine the position of the packaging material from the aggregated signal. Further, a method for detecting a position of a packaging material with magnetic markings is disclosed.
Owner:TETRA LAVAL HLDG & FINANCE SA
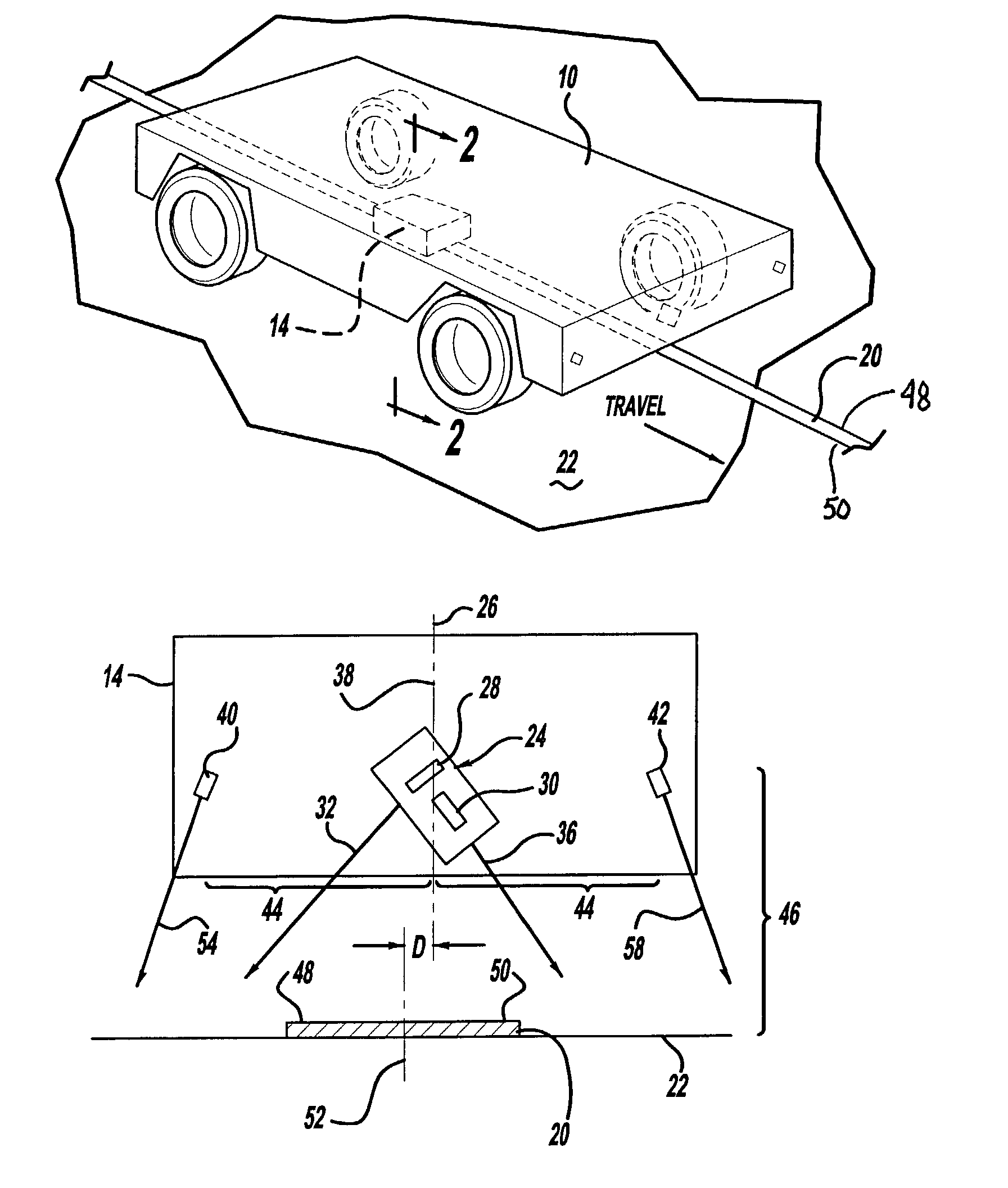
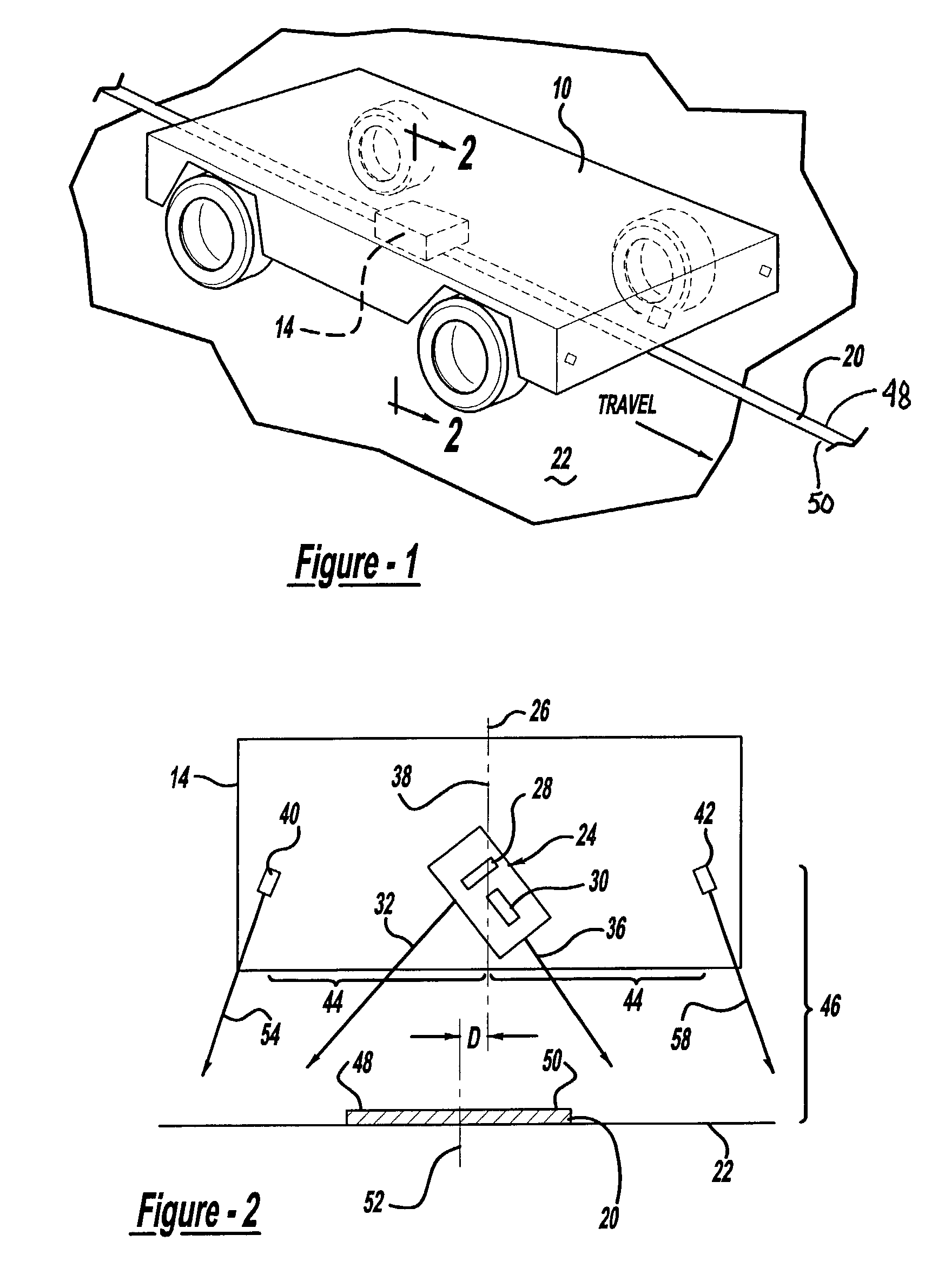
Magnetic apparatus for detecting position of vehicle
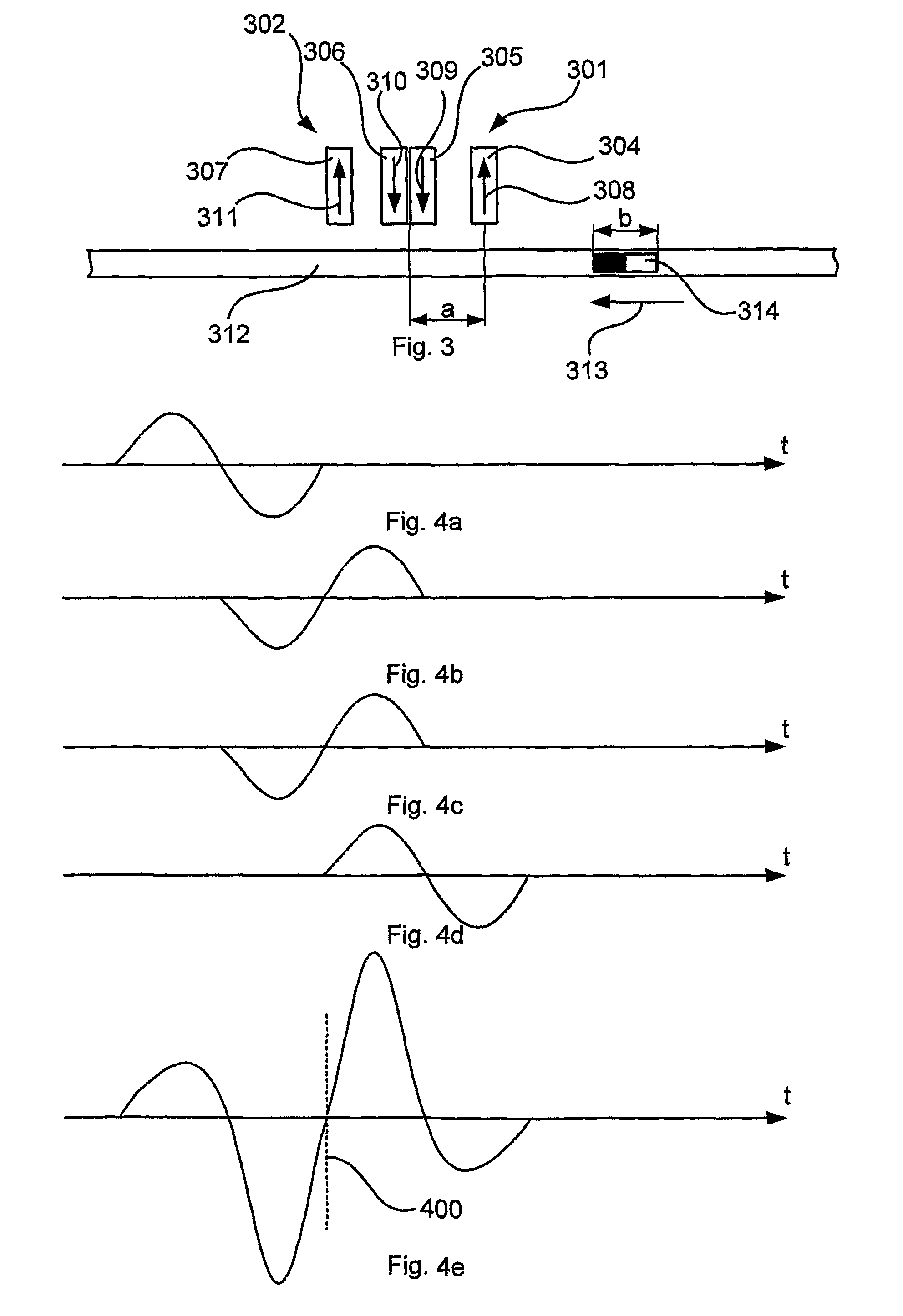
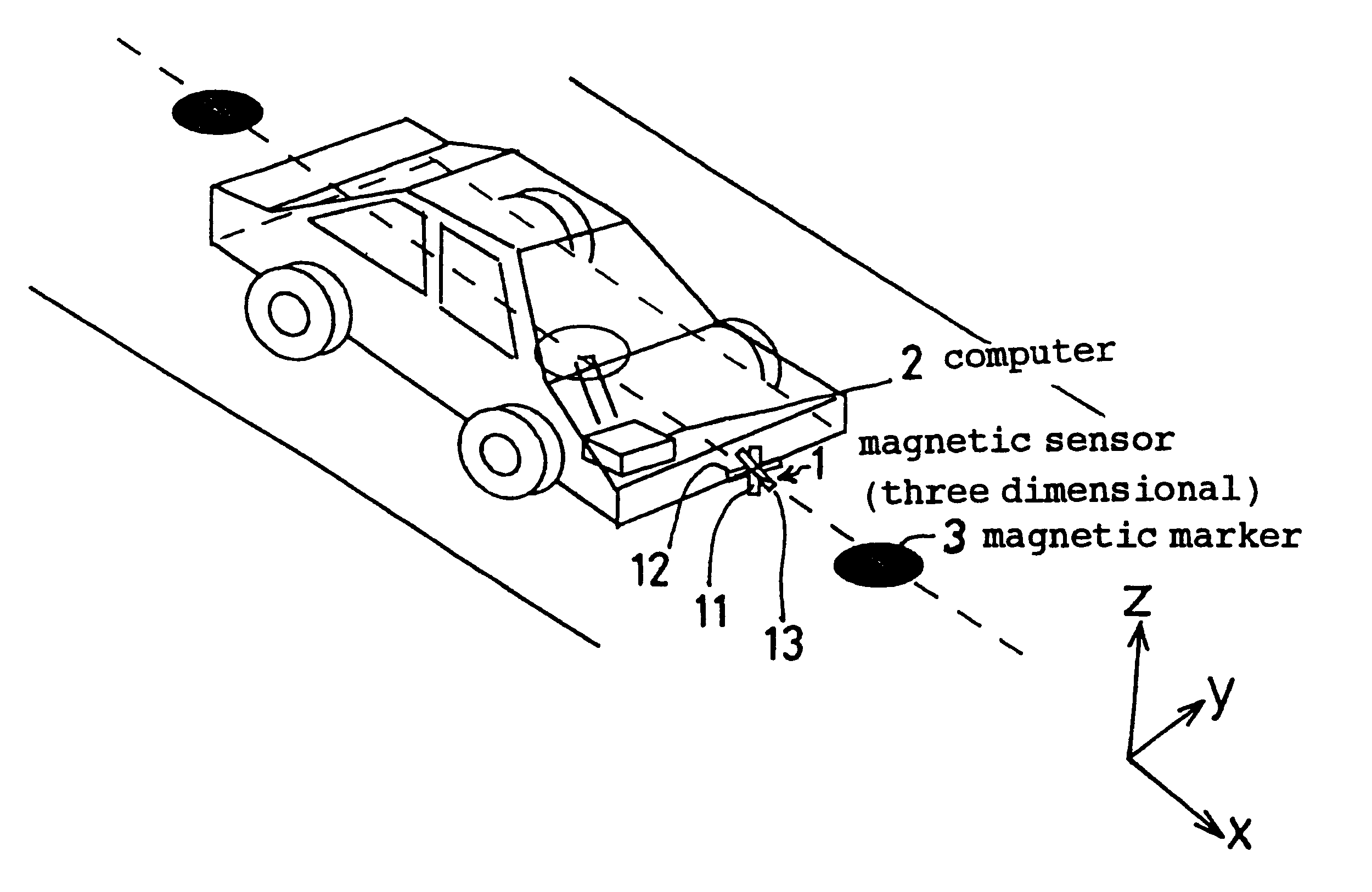
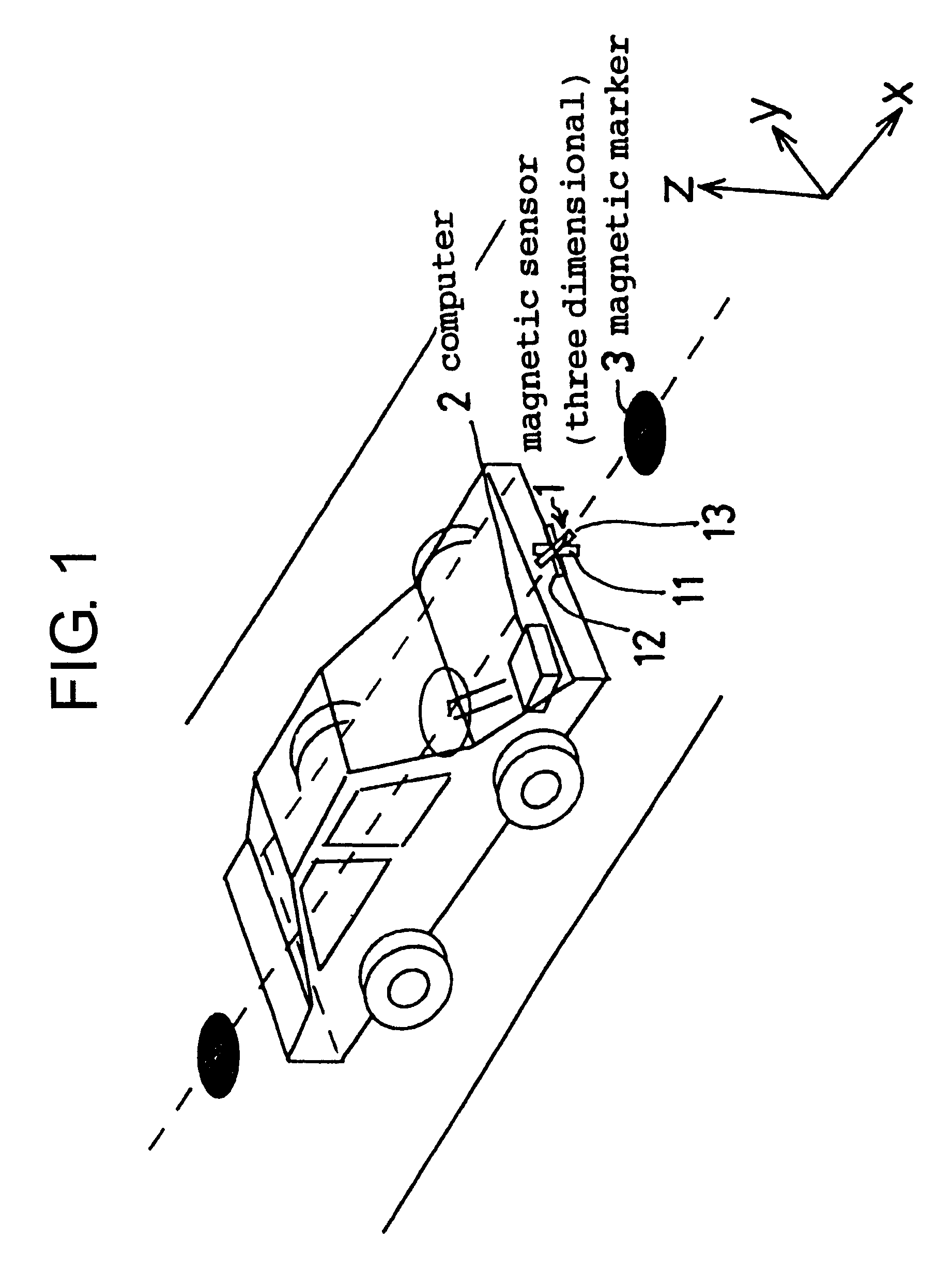
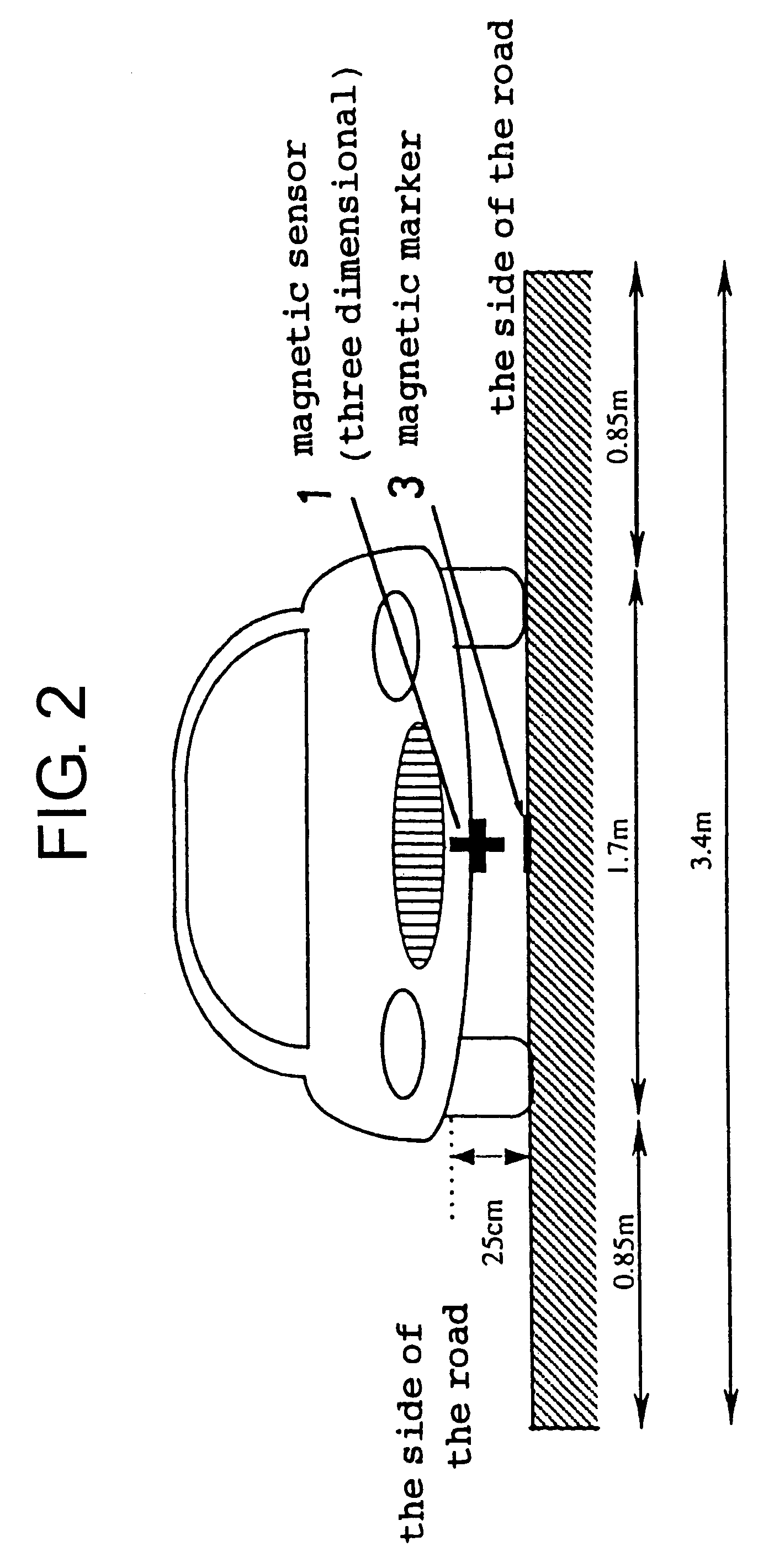
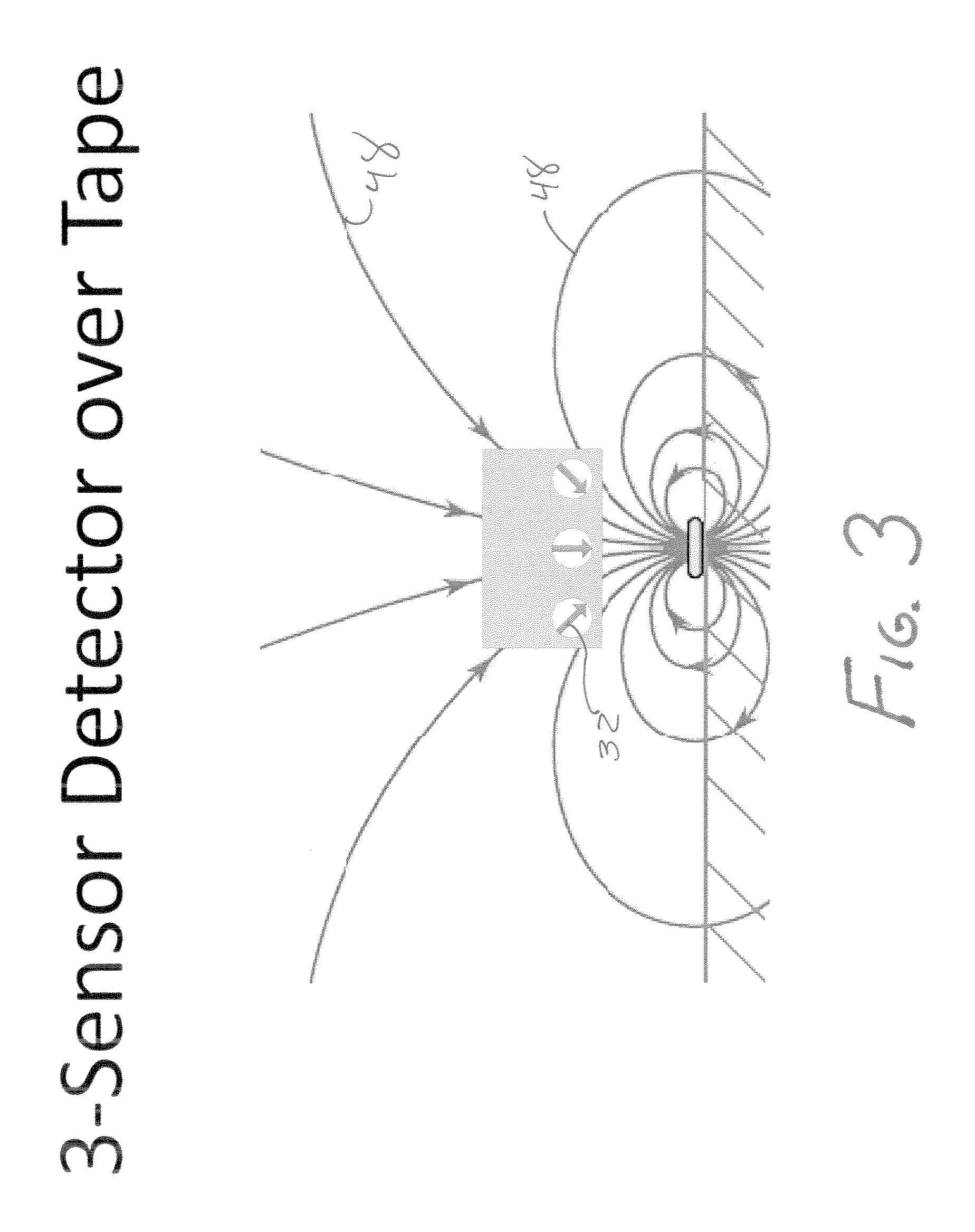
InactiveUS6336064B1Improve abilitiesExpand the scope of detectionInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlMagnetic markerDistance detection
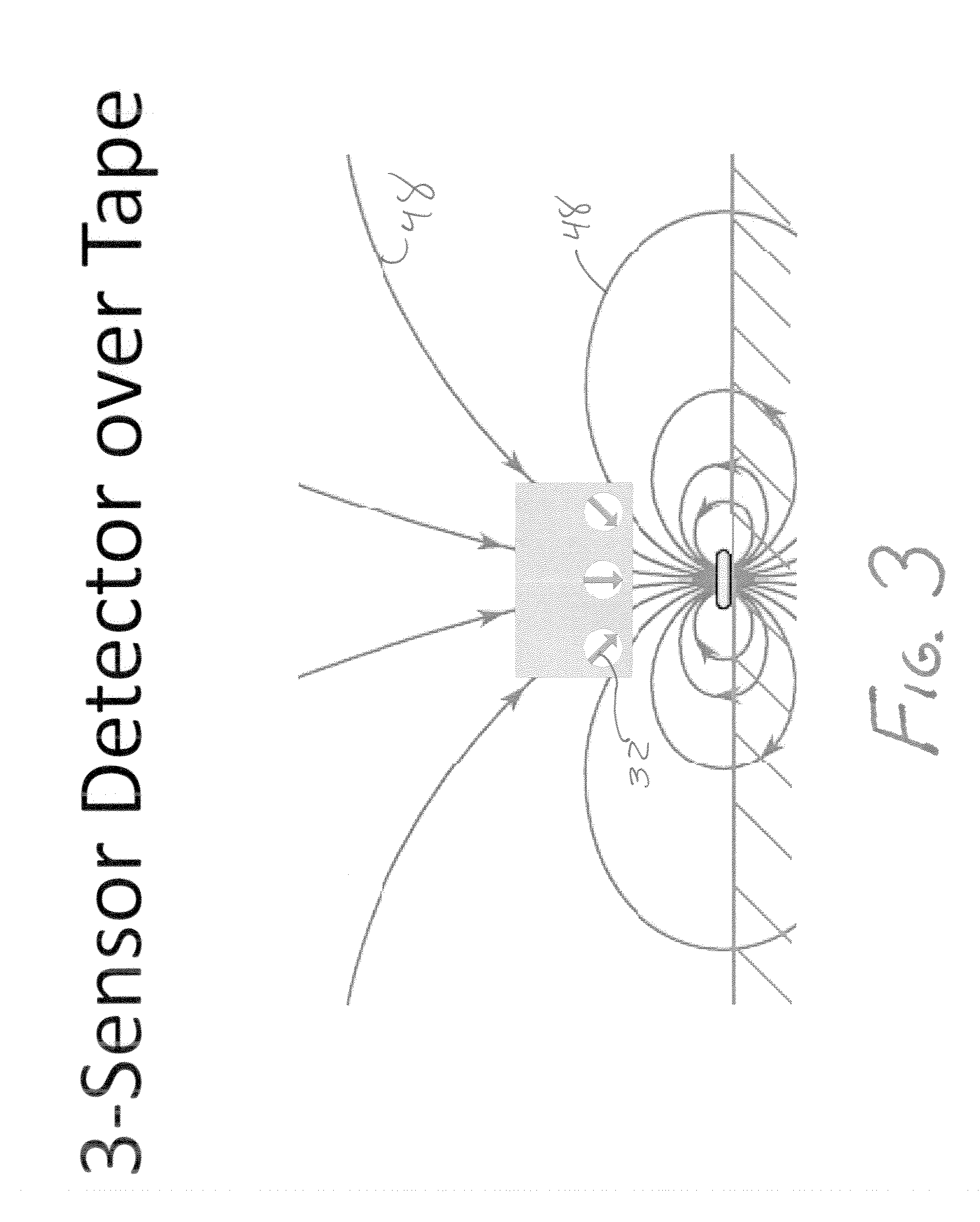
A magnetic apparatus for detecting a position of a vehicle, capable of detecting a lateral deviating distance of a vehicle over a lateral deviation width with a high accuracy and at a high speed, wherein a magnetic field component in the direction of advance of the vehicle is detected; or more preferably a three dimensional magnetic sensor (1), which comprises a magnetic sensor element for the direction of advance of the vehicle, and magnetic sensor elements for two directions crossing the first-mentioned direction and provided additionally, is used, whereby it becomes possible to heighten a center retaining capability of the vehicle, widen a lateral deviating distance detecting range around four times from around 25 cm to around 1 m, and detect a magnetic marker (3) reliably even when disturbance magnetic field exerts influence upon this detection operation to thereby start center side guidance reliably.
Owner:AICHI STEEL
Microfluidic platform of arrayed switchable spin-valve elements for high-throughput sorting and manipulation of magnetic particles and biomolecules
InactiveUS20050170418A1Impaired mobilitySolve the lack of spaceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMagnetic markerMedical diagnosis
Arrays of spin-valve elements that can be selectively activated to trap, hold, manipulate and release magnetically tagged biological and chemical particles, including molecules and polymers. The spin-valve elements that can be selectively activated and deactivated by applying a momentary applied magnetic field thereto. The spin valve element array can be used for selectively sorting and transporting magnetic particles one particle at a time within the array. As the magnetically tagged particles are held by the spin-valve elements, application of an auxiliary magnetic field can be used to apply tension or torsion to the held particles or to move, e.g. rotate, the trapped particles. The arrays of spin-valve elements can be used in a variety of applications including drug screening, nucleic acid sequencing, structural control and analysis of RNA / DNA and protiens, medical diagnosis, and magnetic particle susceptibility and size homogenization for other medical applications.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF COMMERCE THE THE NAT INST OF STANDARDS & TECH
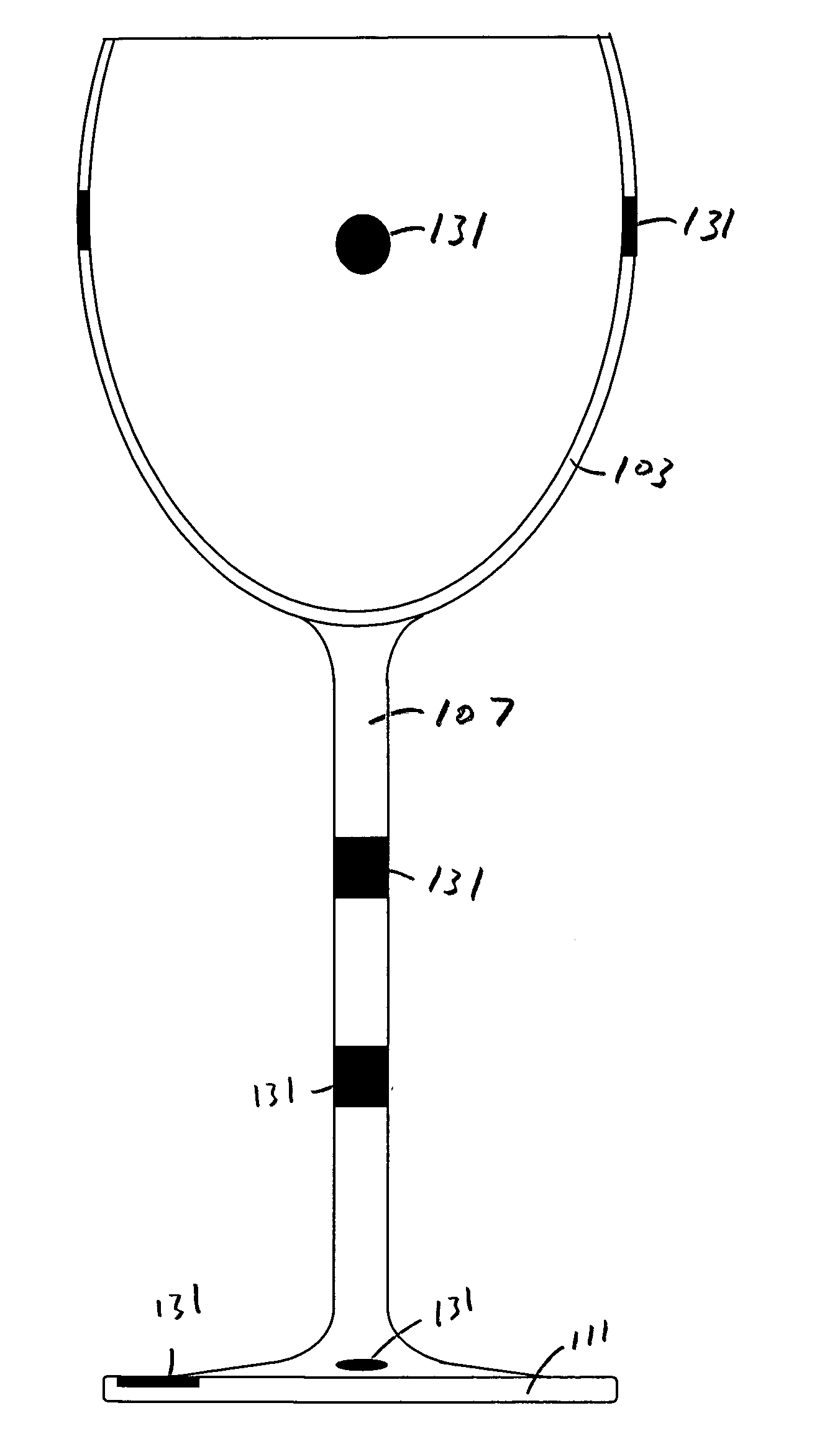
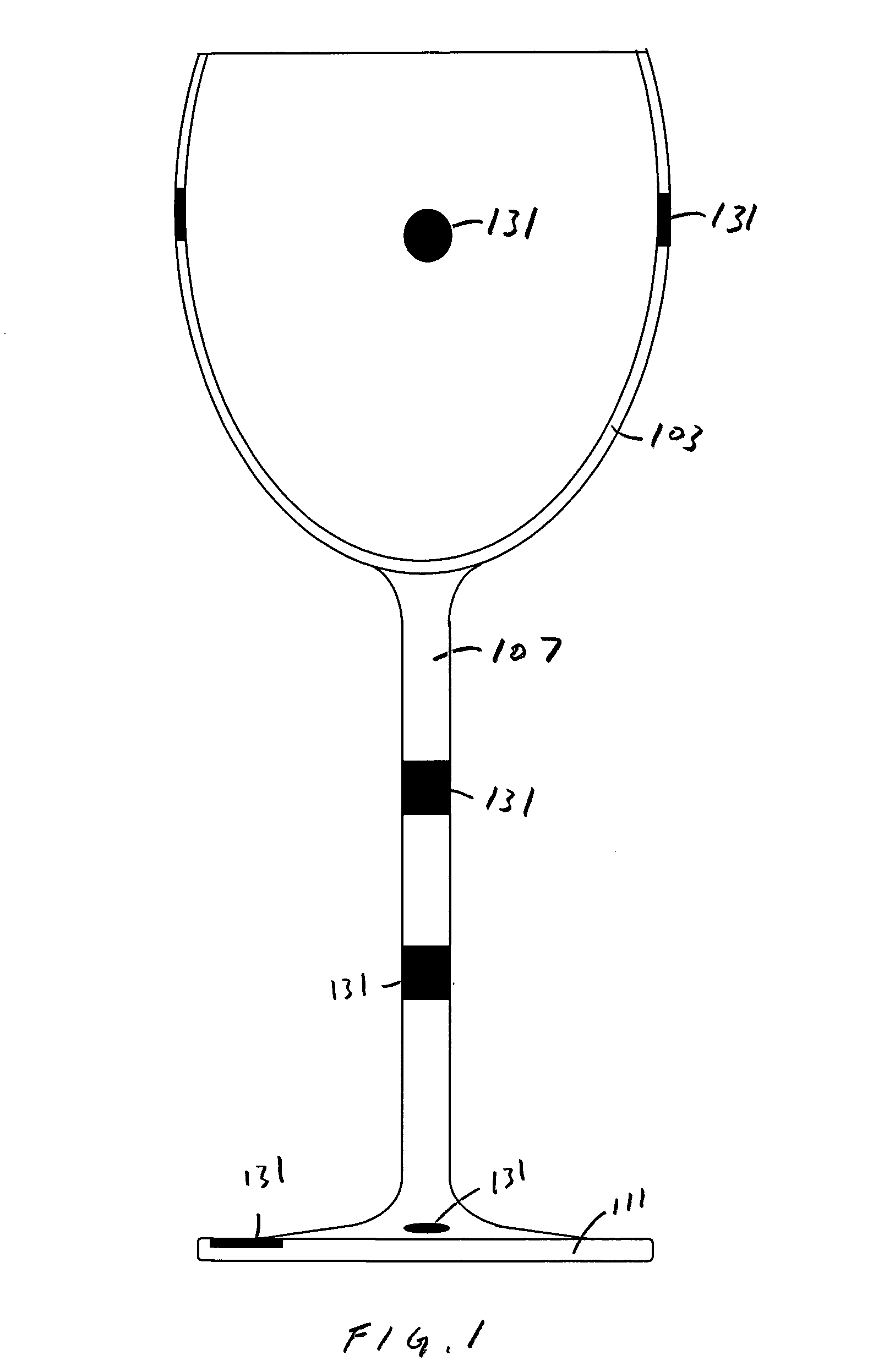
Drinking glass with a removable magnetic marker
InactiveUS20080128429A1Avoid accidental removalImprove adhesionDwelling equipmentArticle advertisingMagnetic markerEngineering
Drinking glasses are used to drink water and wine. A glass has a cup and a base. A wine glass has a cup portion, a stem and a circular base. A magnet that is attached to the drinking glass. A marker has a magnet and an ornamental side. The marker is held in place against an outer surface of the glass by the magnetic attraction of the cup magnet and the marker magnet.
Owner:FORMATION
Methods and Algorithms For Cell Enumeration in a Low-Cost Cytometer
InactiveUS20110052037A1Functional simplicity in designReduce operating costsCharacter and pattern recognitionMaterial analysisWhite blood cellFluorescence
The enumeration of cells in fluids by flow cytometry is widely used across many disciplines such as assessment of leukocyte subsets in different bodily fluids or of bacterial contamination in environmental samples, food products and bodily fluids. For many applications the cost, size and complexity of the instruments prevents wider use, for example, CD4 analysis in HIV monitoring in resource-poor countries. The novel device, methods and algorithms disclosed herein largely overcome these limitations. Briefly, all cells in a biological sample are fluorescently labeled, but only the target cells are also magnetically labeled. In addition, non-magnetically labeled cells are imaged for viability in a modified slide configuration. The labeled sample, in a chamber or cuvet, is placed between two wedge-shaped magnets to selectively move the magnetically labeled cells to the observation surface of the cuvet. An LED illuminates the cells and a CCD camera captures the images of the fluorescent light emitted by the target cells. Image analysis performed with a novel algorithm provides a count of the cells on the surface that can be related to the target cell concentration of the original sample. The compact cytometer system provides a rugged, affordable and easy-to-use technique, which can be used in remote locations.
Owner:VERIDEX LCC
Method and apparatus for imaging target components in a biological sample using permanent magnets
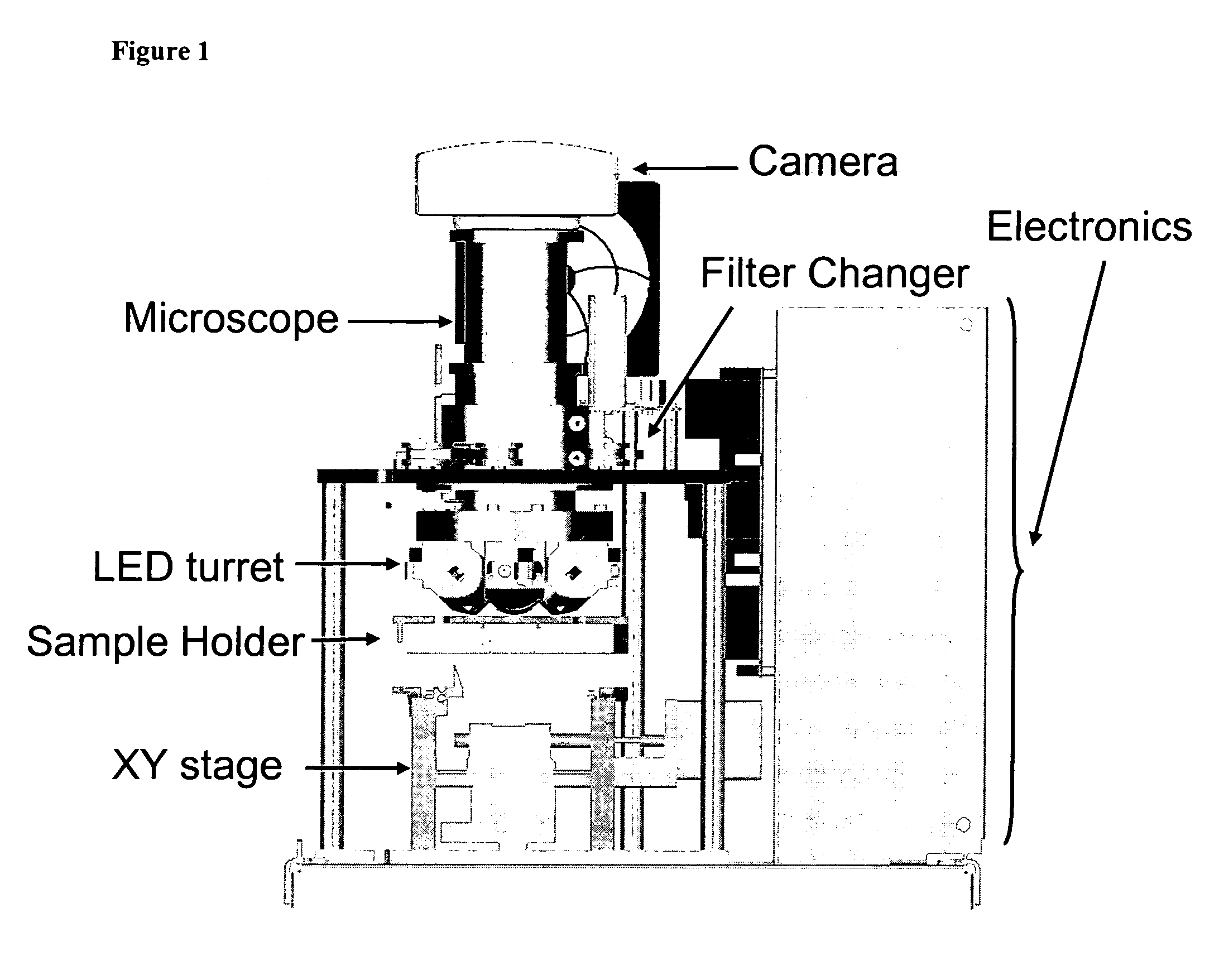
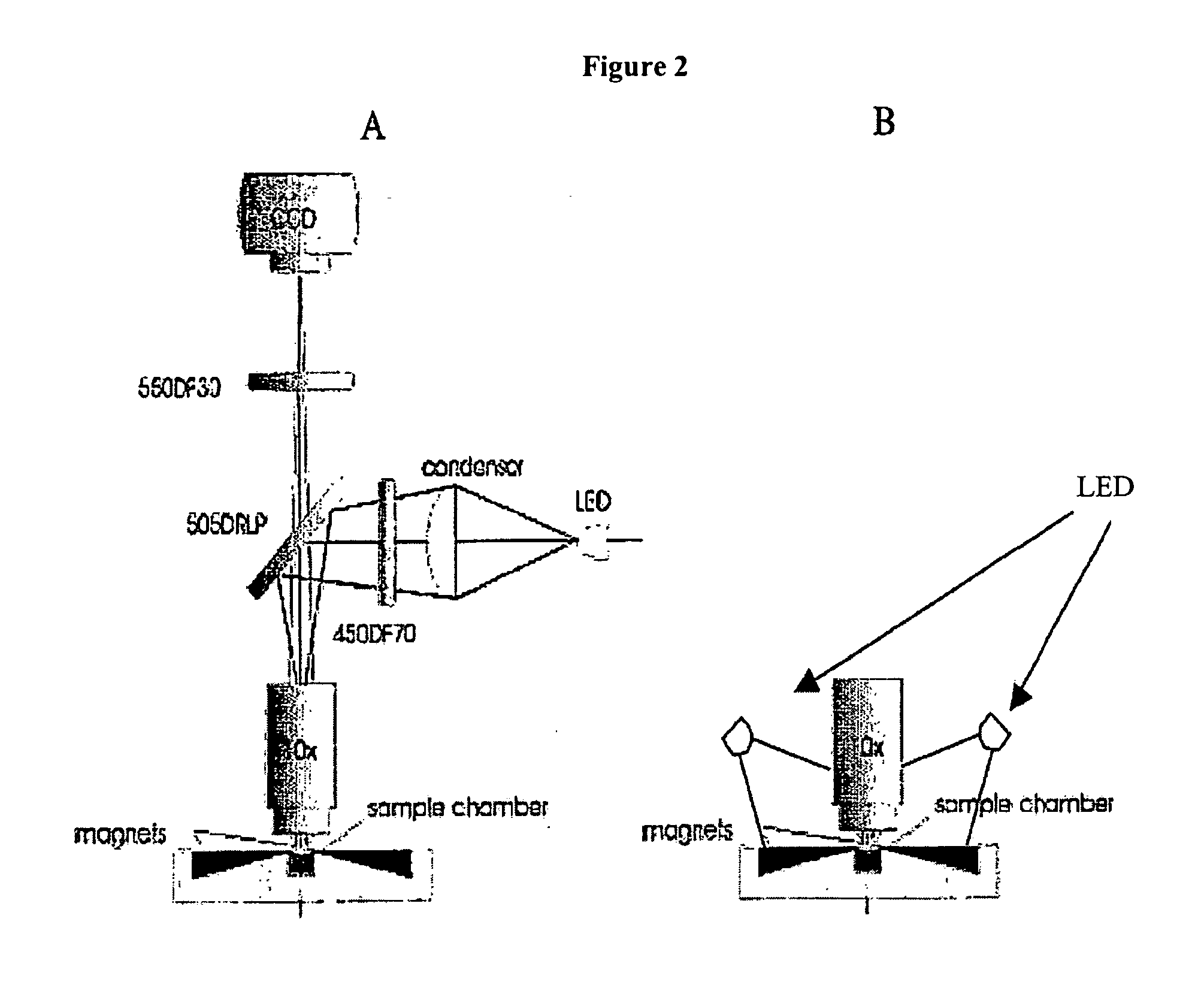
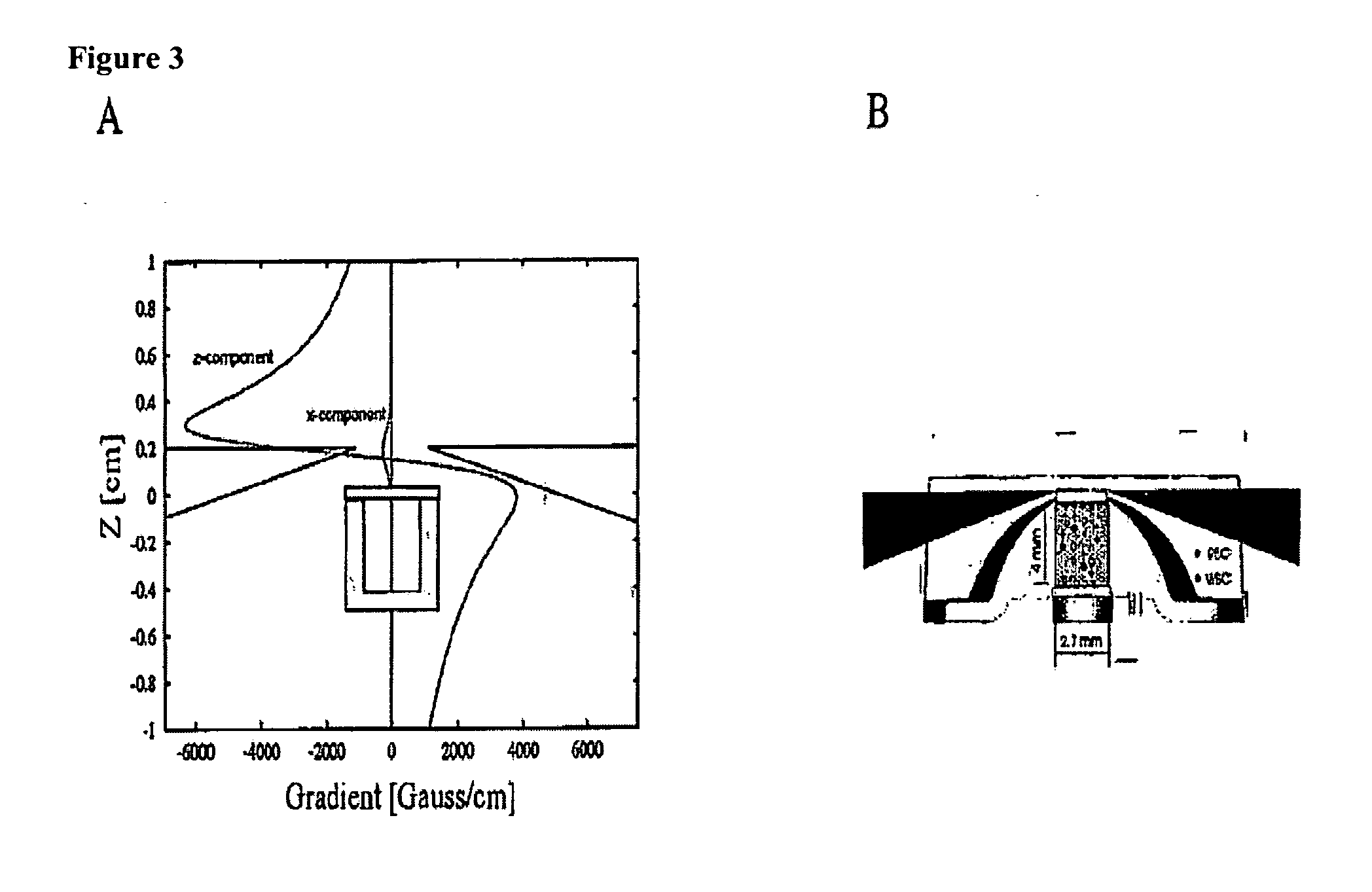
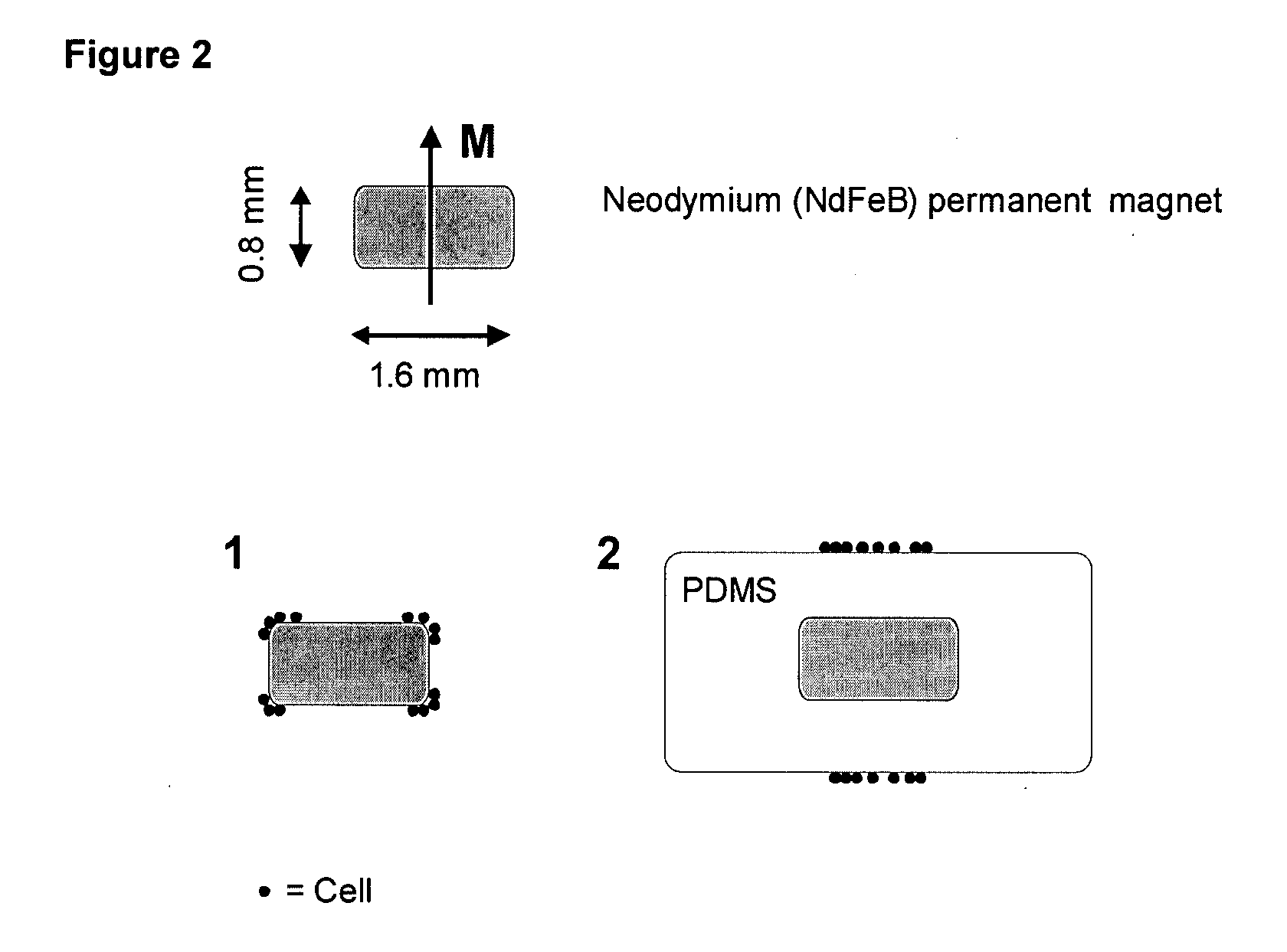
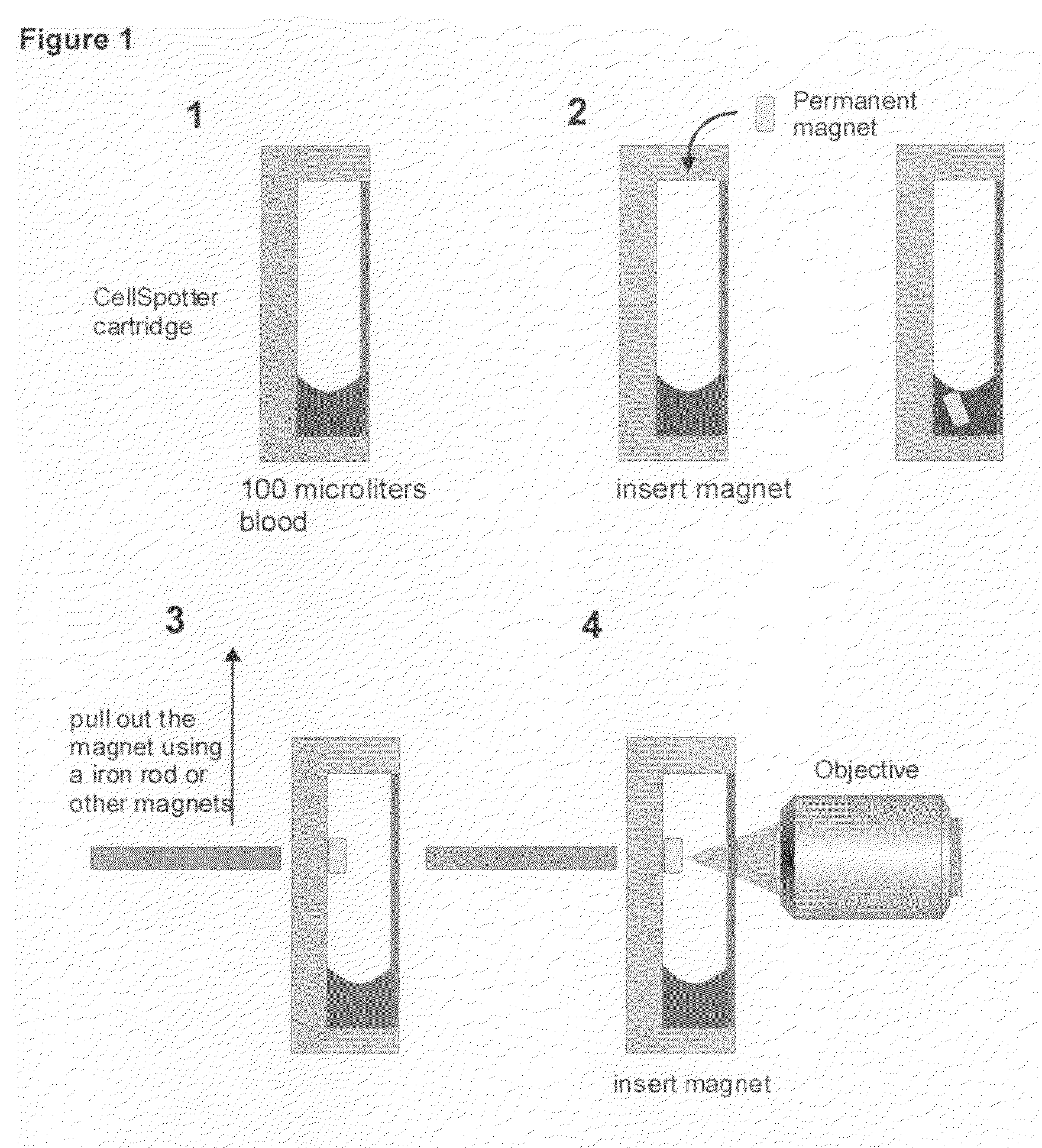
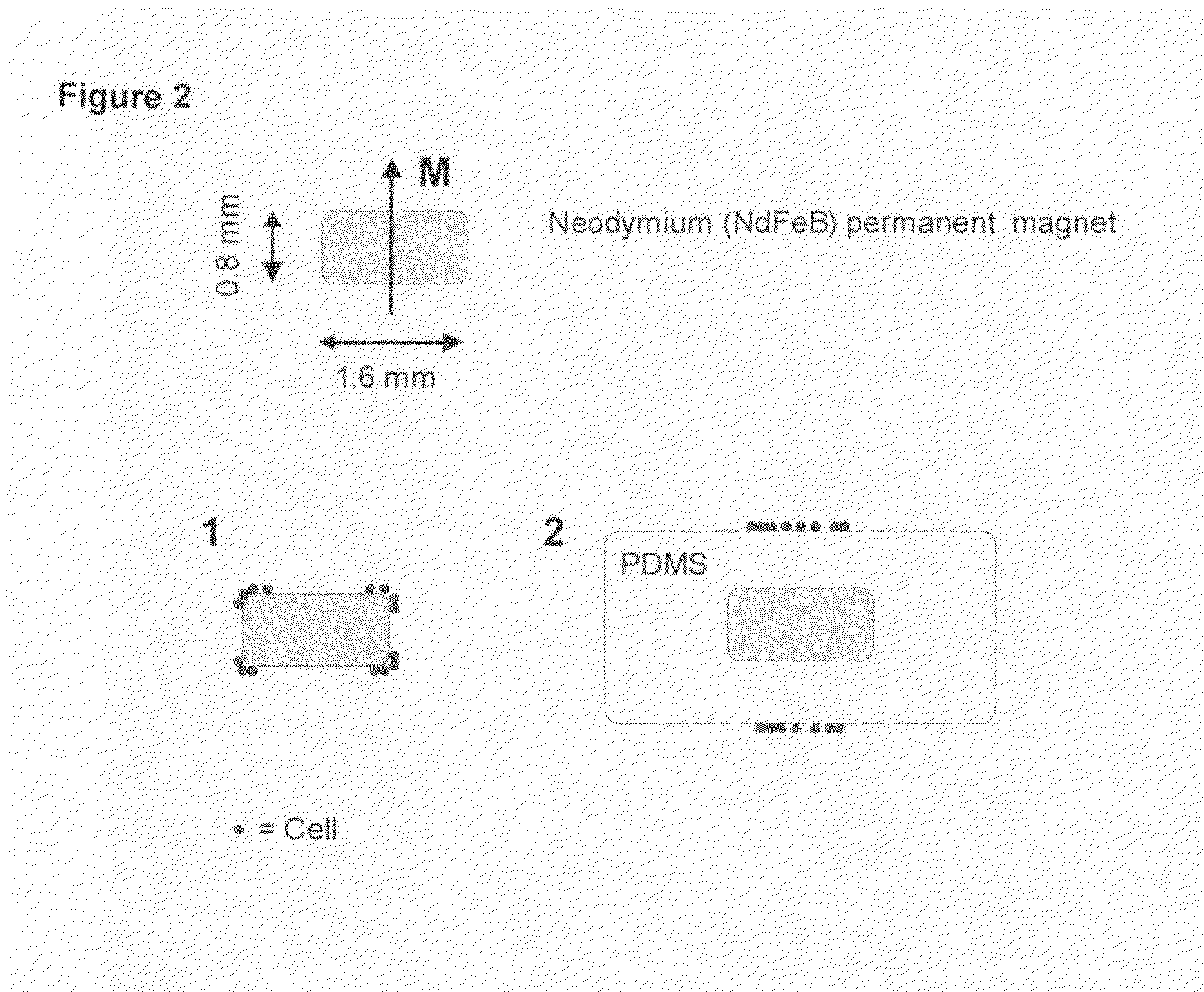
ActiveUS20090061476A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMagnetic markerWhite blood cell
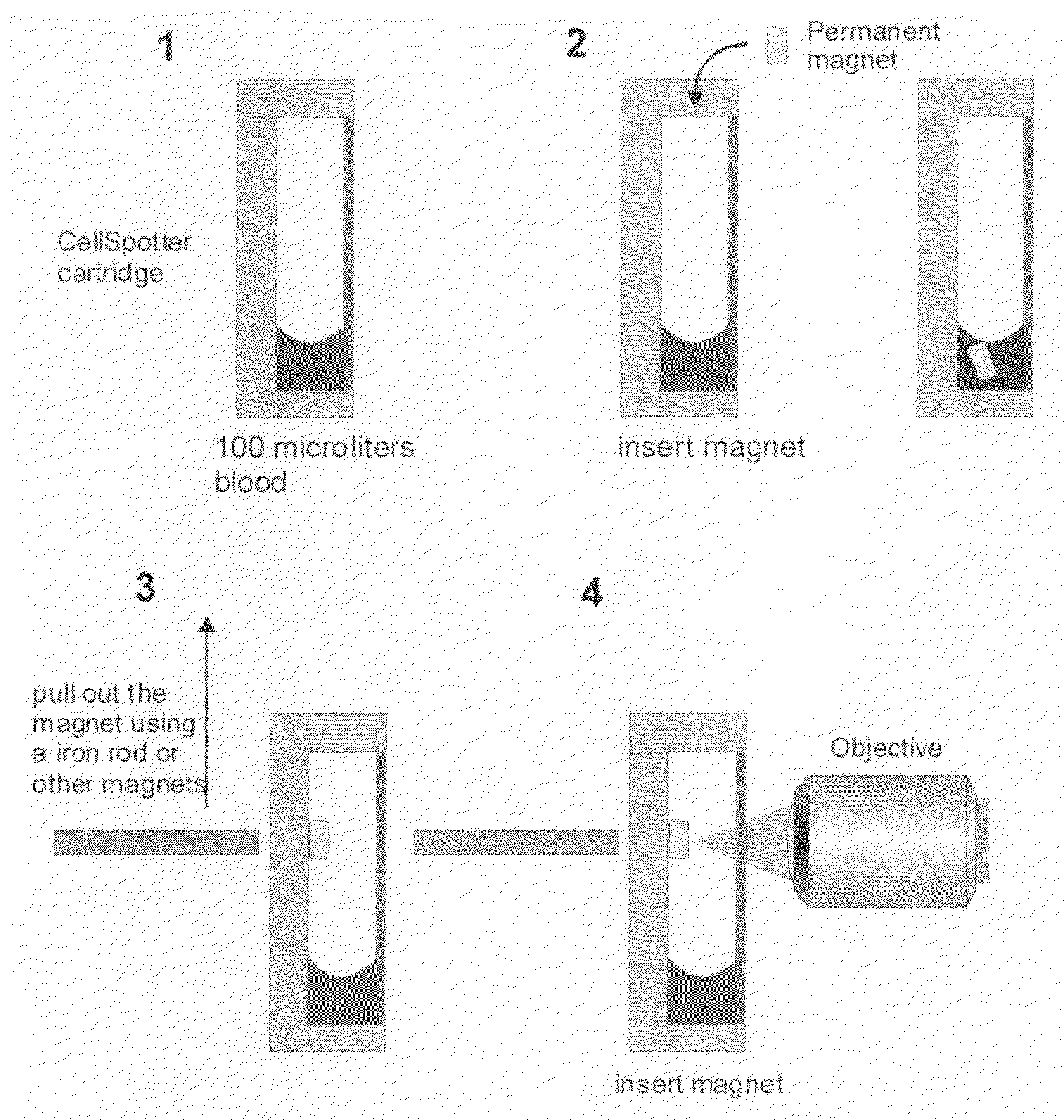
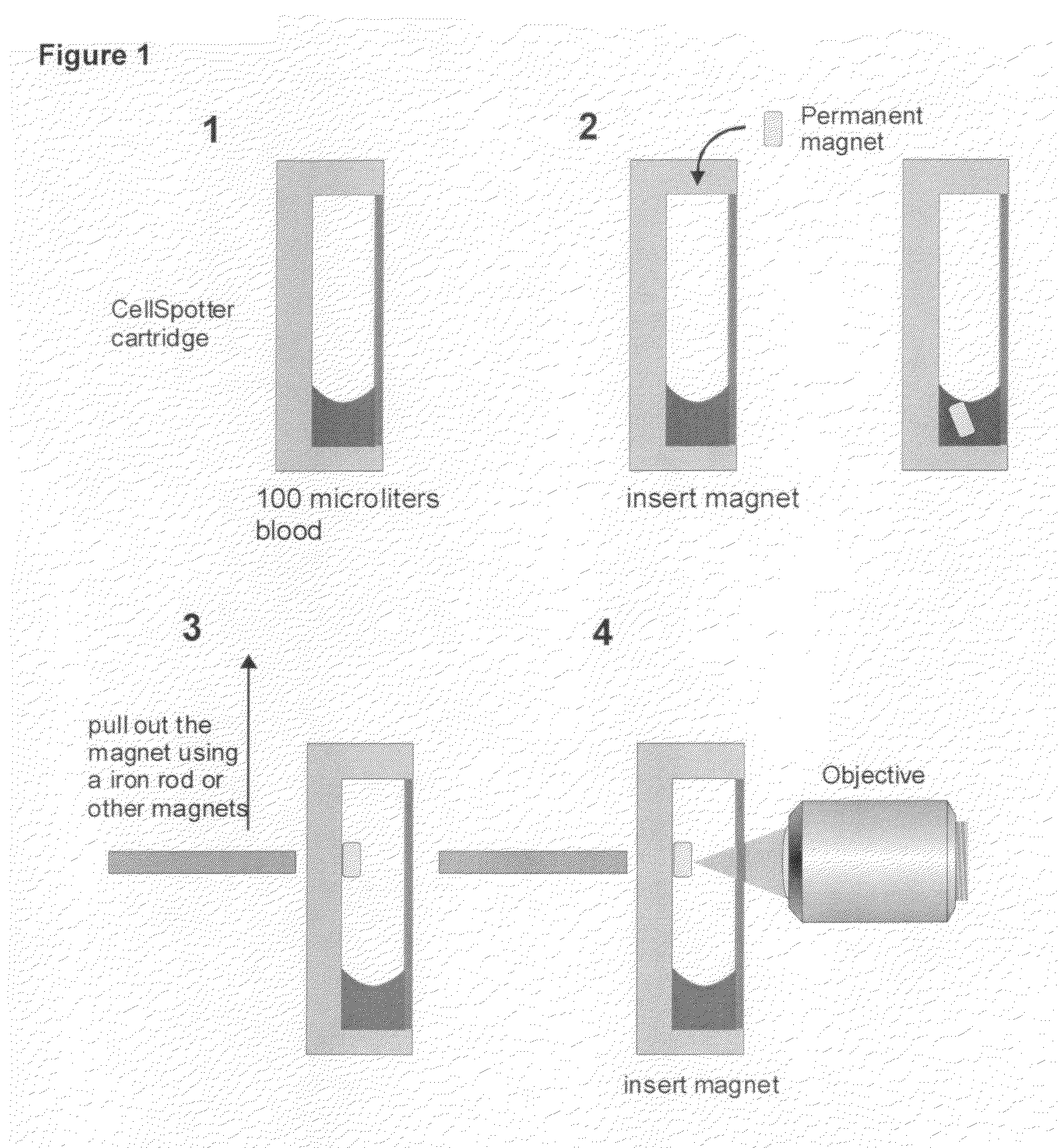
A system for enumeration of cells in fluids by image cytometry is described for assessment of target populations such as leukocyte subsets in different bodily fluids or bacterial contamination in environmental samples, food products and bodily fluids. Briefly, all cells in a biological sample are fluorescently labeled, but only the target cells are also magnetically labeled. A small, permanent magnet is inserted directly into the chamber containing the labeled sample. The magnets are coated with PDMS silicone rubber to provide a smooth and even surface which allows imaging on a single focal plane. The cells are illuminated and the images of the fluorescent light emitted by the target cells are captured by a CCD camera. Image analysis performed with a novel algorithm provides a count of the cells on the surface that can be related to the target cell concentration of the original sample.
Owner:MENARINI SILICON BIOSYSTEMS SPA
Method and apparatus of obtaining security tag operation using local magnetic marker
InactiveUS6744366B2Electric signalling detailsBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalElectromagnetic launchMagnetic marker
Disclosed is a method and an apparatus implying nearly 100% security with a tag system showing low cost and compact volume. Like a conventional tag, the disclosed tag system will respond properly to an interrogation signal. In addition, the disclosed tag system is able to monitor the environment local to a merchandise. Whenever the merchandise package is opened and / or impaired, alarm will be generated on the spot. It is almost impossible to disarm the tag system, unless a password is attained. The disclosed tag system shows a high sensitivity, and it does not need an electronic searching machine, or an interrogation gate, to operate. When combined with an electromagnetic transmitter, a smart tag system results, allowing merchandise to be traced on the computer screen, capable of performing discriminative tasks according to the imposed regulation rules on the merchandise IDs.
Owner:HOW HOTON
Material for improving sensitivity of magnetic sensor and method thereof
InactiveUS20080241964A1High detection sensitivityMaintaining dispersibilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMagnetic markerHall element
The present invention relates to a capture agent member being used in a magnetic sensor to detect the presence or concentration of a target substance in a test solution by detecting the presence or number of the magnetic marker, wherein the capture agent member contains a capture agent for capturing the target substance and a labeling agent serving as a nucleus for the magnetic marker to agglutinate, and wherein the capture agent is labeled with the labeling agent. The present invention relates to a material which improves detection sensitivity of a biosensor using a magnetic sensor while maintaining reactivity and dispersibility. In particular, according to the present invention, there can be provided a material which enables realization of high sensitivity by using a simple magnetic biosensor such as a semiconductor Hall element and a magnetoresistance effect element.
Owner:CANON KK
Position sensing system for intelligent vehicle guidance
InactiveUS20150247719A1Situation is exacerbatedDigital data processing detailsAutomatic steering controlMagnetic markerControl system
A method for determining a position deviation of an object with respect to a magnetic marker. The method senses at least two axial field strength components of the magnetic field emitted from the magnetic marker with each of at least two magnetic field sensors mounted on the object. For each axial direction, the method computes a difference in the axial field strength components sensed by the two sensors. The method then determines the position deviation of the object from the magnetic marker as a function of the two differences (i.e., one difference for each axial direction). The method can be used by an intelligent lateral control system to provide lateral deviation of a mobile object, such as a vehicle, from a desired path, and the intelligent lateral control determines and applies the desired steering control to the mobile object so as to guide it along a desired path automatically.
Owner:TOMORROWS TRANSPORTATION TODAY
Automatic guided vehicle system and method
ActiveUS20140067184A1Accurately and precisely following weak magnetic fieldDistance measurementPosition/course control in two dimensionsMagnetic markerEngineering
An apparatus and method for guiding an automatic guided vehicle along a magnetic pathway and more specifically to an apparatus and a method capable of accurately and precisely following a weak magnetic field emitted by a substantially continuous passive magnetic marker having route junctions.
Owner:JERVIS B WEBB INT CO
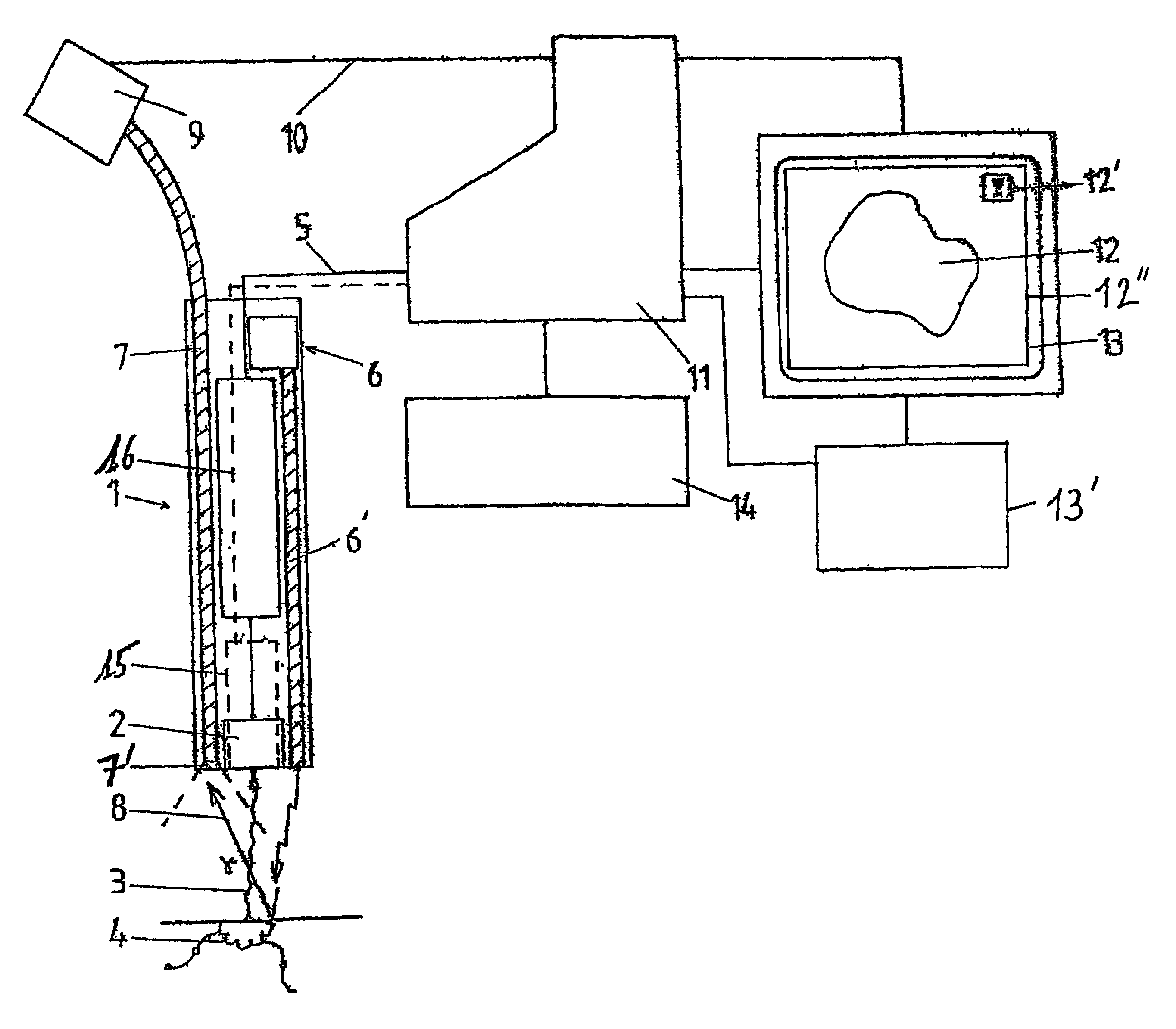
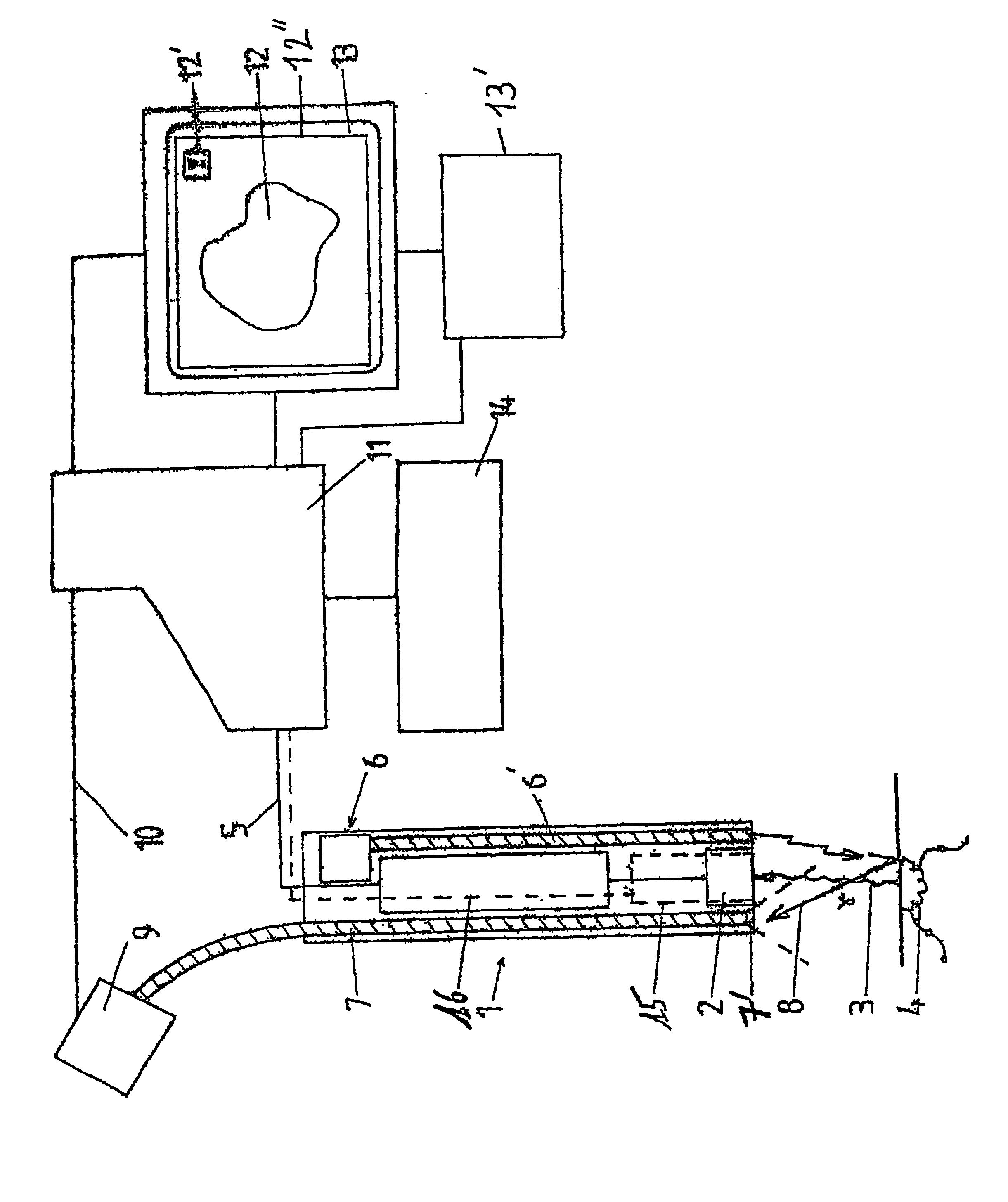
Pre-operative device for localizing marked tissues and process using such a device
InactiveUS6920346B2Accurate contourMaterial analysis by optical meansHandling using diaphragms/collimetersMagnetic markerElectrical connection
A pre-operative device includes at least one elongated probe (1) integrating at least one element for detecting radioactive radiation (3) emitted by tissues (4) marked by radioactive isotopes or radioactive colloids, generating a first representative electrical signal (5), at least one element (6) for emitting luminous radiation toward the tissues (4) and at least one element (7) for receiving and transmitting reflected luminous radiation (8) reflected by the tissues (4) marked by vital colorants or magnetic markers, toward at least one element (9) for converting the reflected luminous radiation (8) into a second representative electrical signal (10), electrical connection elements for conveying the first and second electrical signals (5, 10) and, at least one electronic means (11) for processing electronic signals.
Owner:EURORAD 2 6
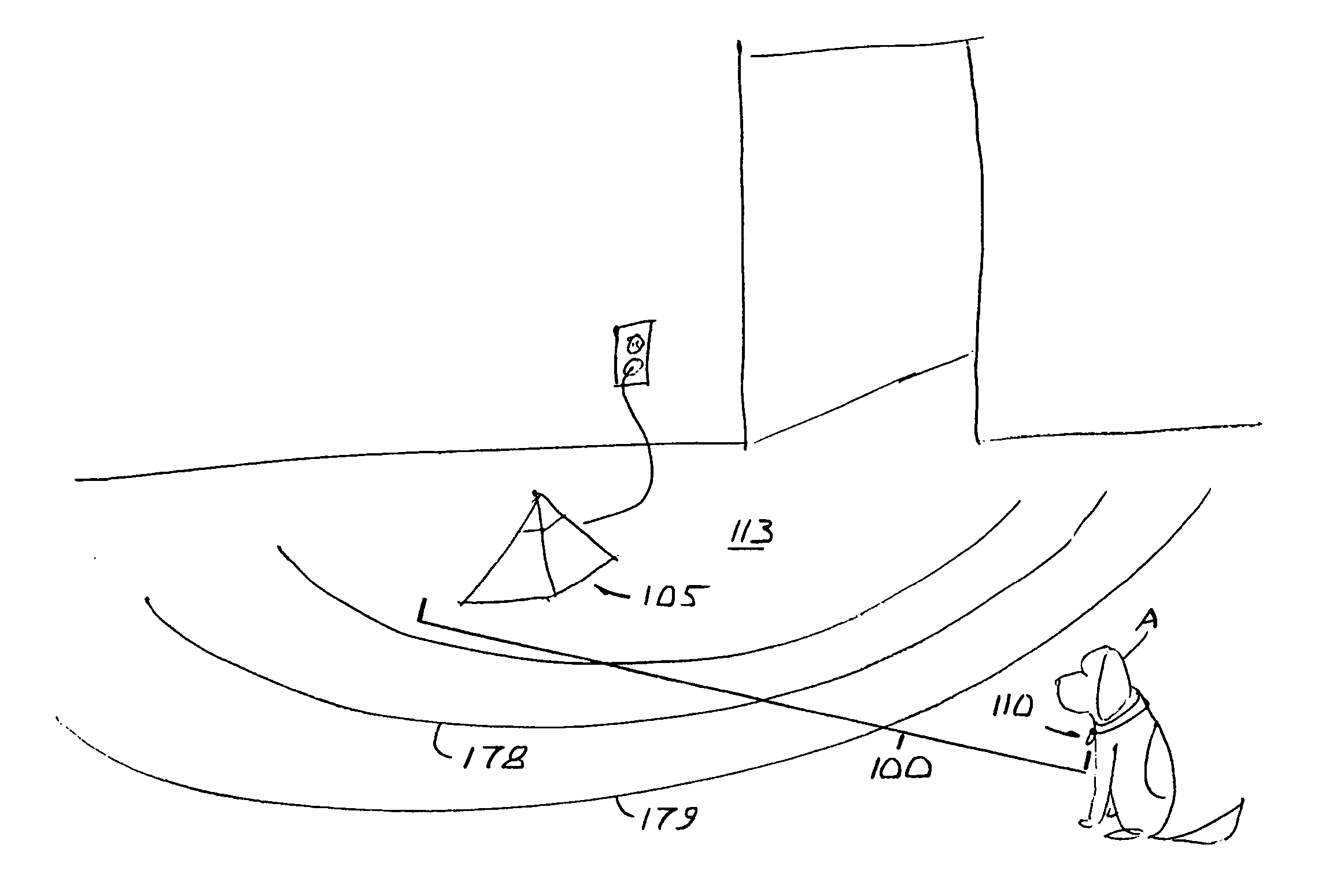
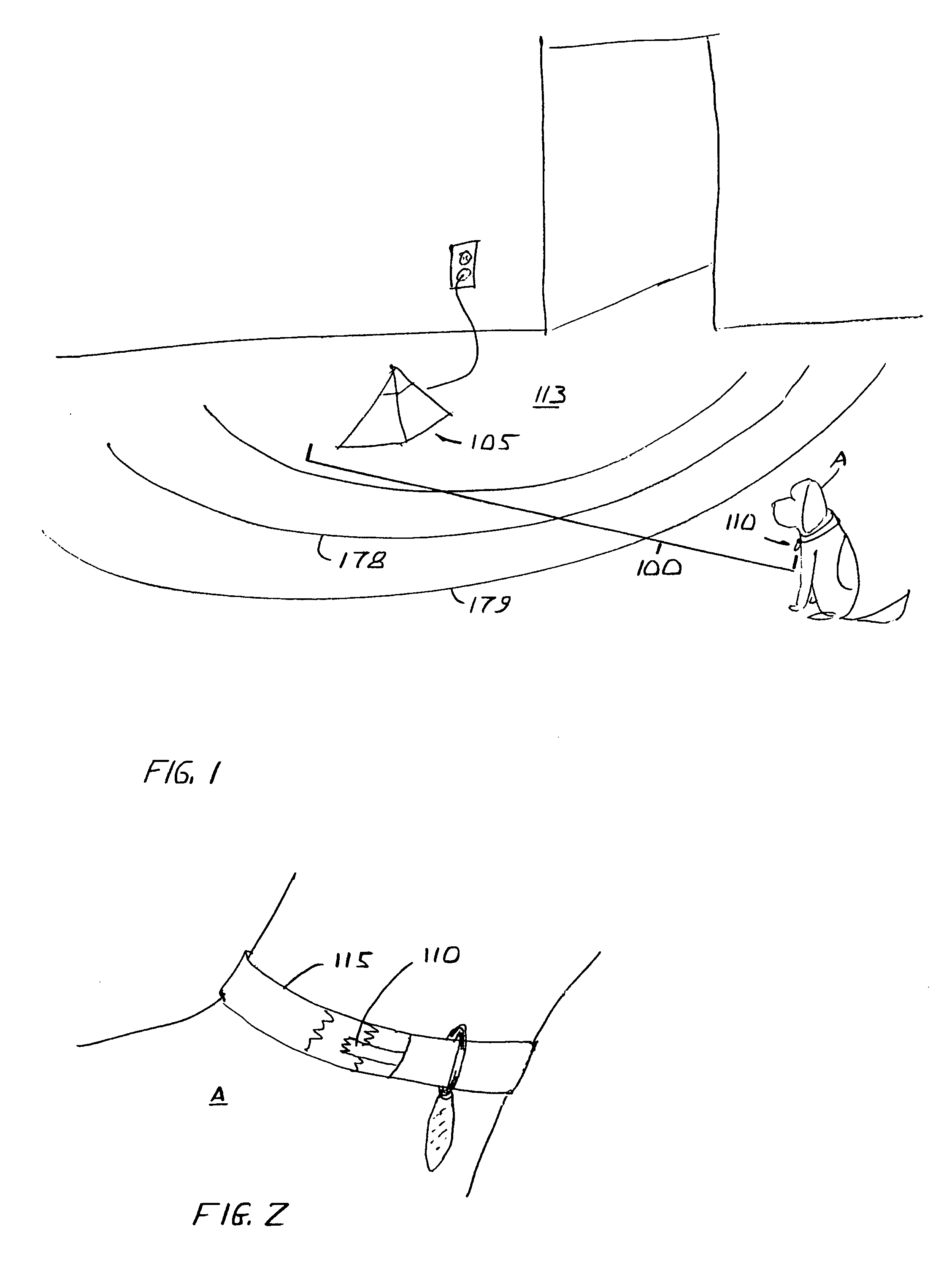
Pet containment apparatus and method
An electronic containment apparatus for and method of controlling the movement of an animal relative to a protected area employs magnetic fields for designating exclusion or containment areas within a household. The animal is provided with a collar, which includes a magnetic marker designed to perturb a magnetic field produced by an exclusion unit's magnetic field generator. The exclusion unit produces stimuli to which the animal responds, but to which humans do not respond.
Owner:VIGGIANO GREGORY R
Inertial navigation method applicable to AGV storage
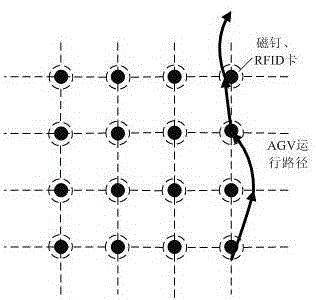
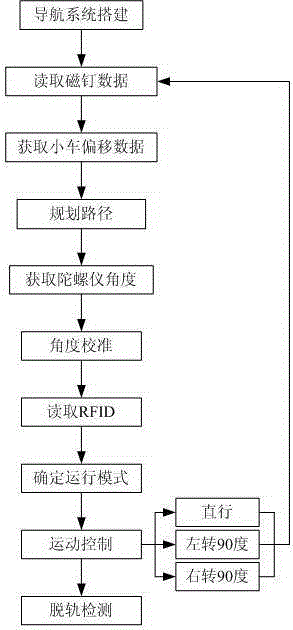
InactiveCN105180932ALow costSolve defects that are more affected by dusty environmentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsPosition/course control in two dimensionsMagnetic markerGyroscope
The invention discloses an inertial navigation method applicable to AGV storage, which comprises the following steps of S1, building a navigation system; S2, reading magnetic marker data; S3, acquiring trolley offset data; S4, programming a route; S5, acquiring gyroscope angle; S6, correcting the angle; S7, reading RFID; S8, determining an operational mode; S9, controlling movement; and S10, repeating the steps S2-S9. According to the invention, the magnetic marker is adopted to replace a magnetic stripe and a two-dimension code, so that the cost is saved, and the defect that the two-dimension code is influenced seriously by dirty environment at the same time, and the trackless navigation can be realized; the system is accurate in measurement position, the positional accuracy can be + / -5mm, the angle accuracy is + / -0.1 degree, the navigation accuracy is high and can be + / -10mm and the navigation speed is 1m / s, and the resource is saved effectively.
Owner:CHENGDU SIWI HIGH TECH IND GARDEN
Method and apparatus for imaging target components in a biological sample using permanent magnets
ActiveUS8110101B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMagnetic markerWhite blood cell
A system for enumeration of cells in fluids by image cytometry is described for assessment of target populations such as leukocyte subsets in different bodily fluids or bacterial contamination in environmental samples, food products and bodily fluids. Briefly, all cells in a biological sample are fluorescently labeled, but only the target cells are also magnetically labeled. A small, permanent magnet is inserted directly into the chamber containing the labeled sample. The magnets are coated with PDMS silicone rubber to provide a smooth and even surface which allows imaging on a single focal plane. The cells are illuminated and the images of the fluorescent light emitted by the target cells are captured by a CCD camera. Image analysis performed with a novel algorithm provides a count of the cells on the surface that can be related to the target cell concentration of the original sample.
Owner:MENARINI SILICON BIOSYSTEMS SPA
Automatic guided vehicle system and method
ActiveUS8676426B1Accurately and precisely following weak magnetic fieldActuated automaticallyAutomatic initiationsMagnetic markerAutomated guided vehicle
An apparatus and method for guiding an automatic guided vehicle along a magnetic pathway and more specifically to an apparatus and a method capable of accurately and precisely following a weak magnetic field emitted by a substantially continuous passive magnetic marker having route junctions.
Owner:JERVIS B WEBB INT CO
Flow Cytometric Systems for Sterile Separation of Magnetically Labeled Sample Components
ActiveUS20150010939A1Maximize amount of timeIncrease separationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSubject specificFlow Cytofluorometry
Systems for sterile separation of magnetically labeled sample components and methods for using the same are provided. Embodiments of the systems include a magnetic separation device and a pliant sample container, where a portion of the pliant sample container is operatively coupled under pressure to the magnetic separation device. Also provided are methods of using the systems, as well as pliant sample containers configured for use with the subject systems and methods.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
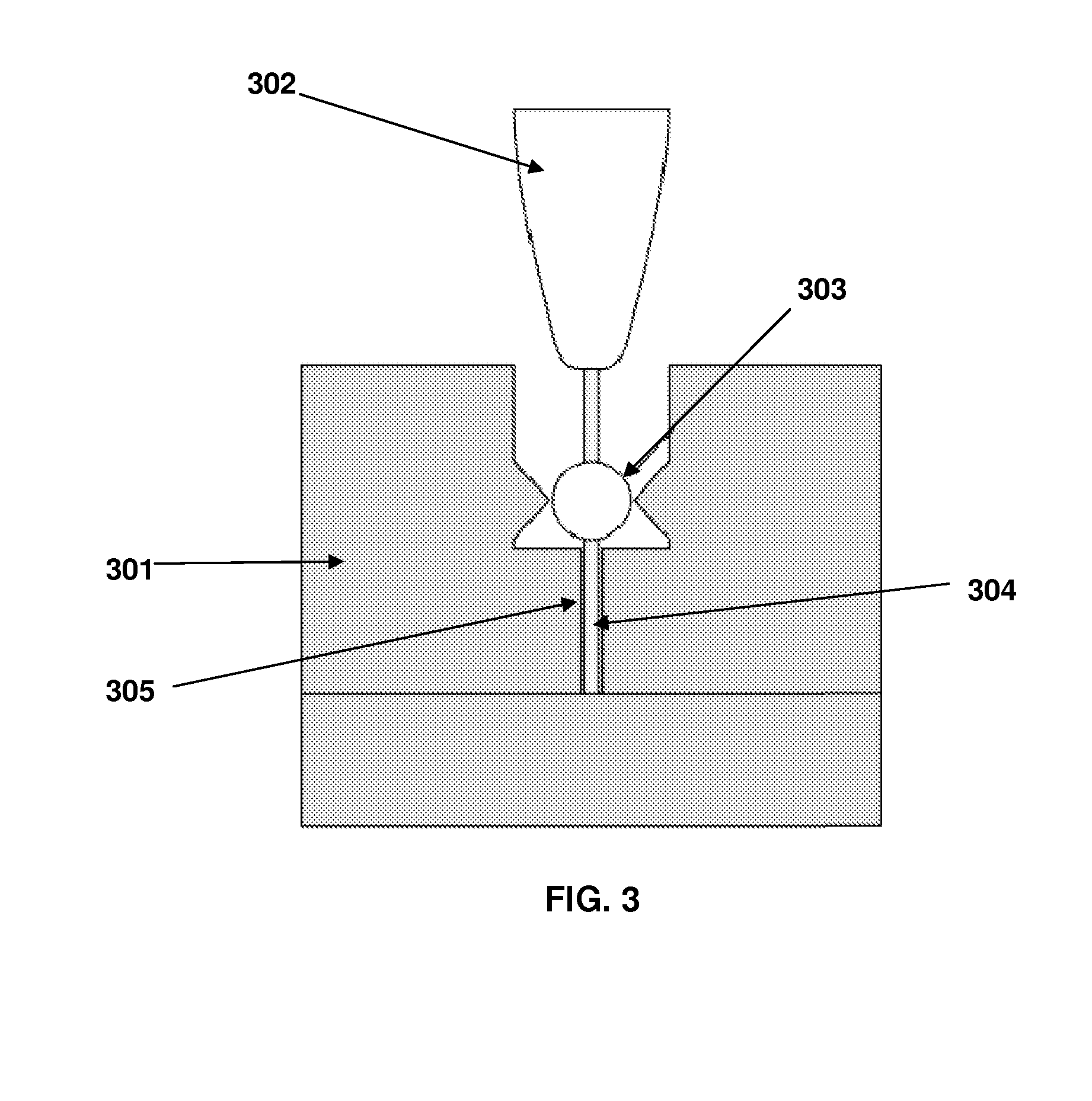
Subterranean formation deformation monitoring systems
ActiveUS20120138291A1Great deformation detailImprove accuracyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyMagnetic markerEnvironment effect
Method, devices and systems are provided for measuring deformation in subterranean formations. Such methods include introduction of spaced-apart depth magnetic markers along the longitudinal length of a well bore and measuring the position of each depth marker over time so as to determine deformation of the subterranean formation. In certain embodiments, depth markers comprise rare earth magnets. In further embodiments, orientation of each magnetic bullet is determined over time to determine the change in orientation of each magnetic bullet. Advantages of the methods and devices herein include, but are not limited to, improved accuracy and reliability of deformation measurements and reduced environmental impact due to the avoidance of radioactive markers used by the present invention.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO +1
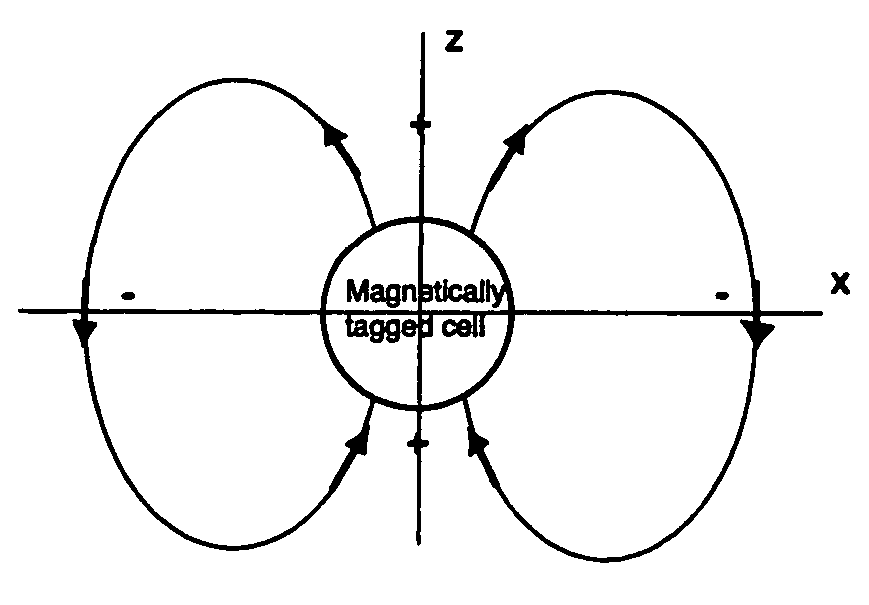
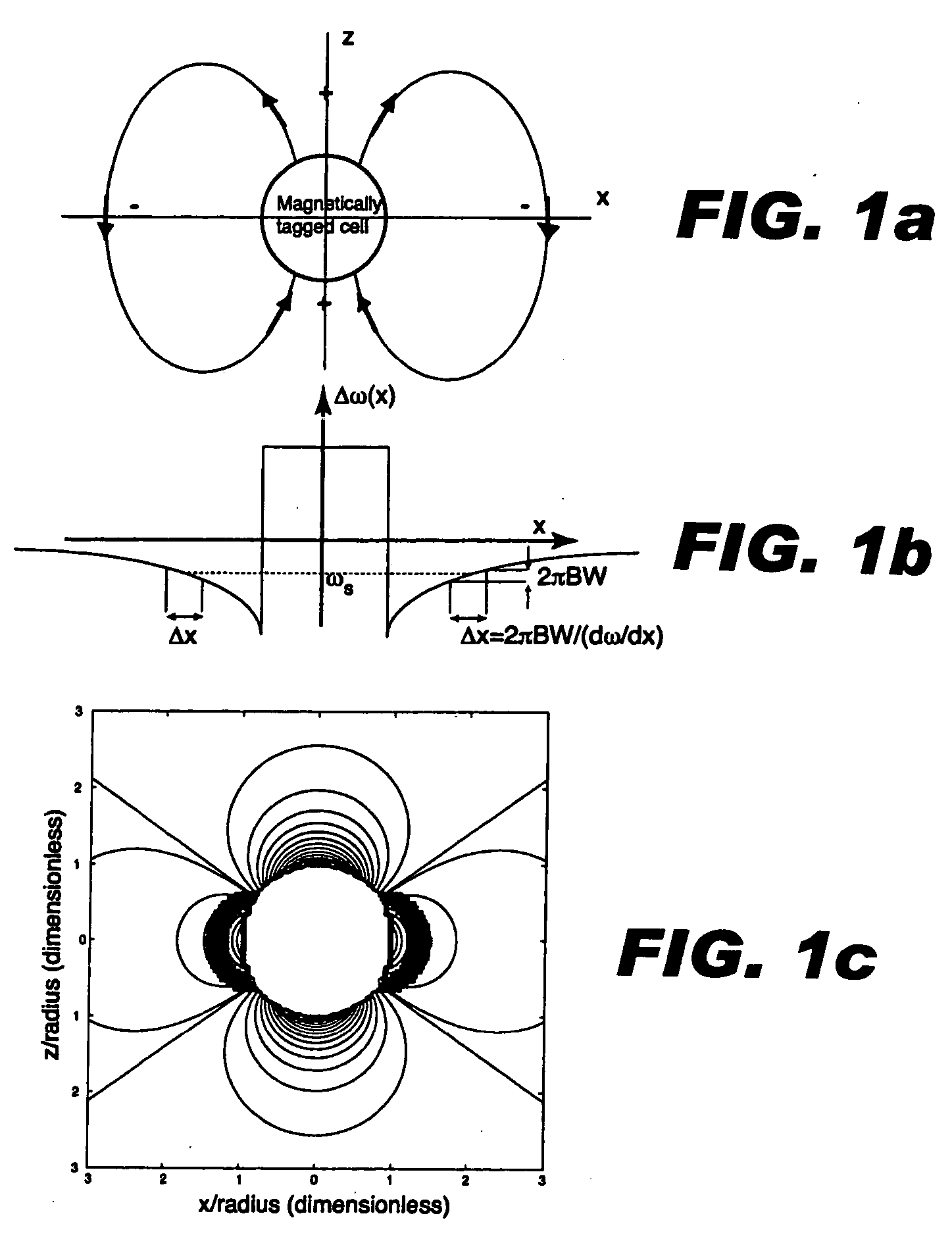
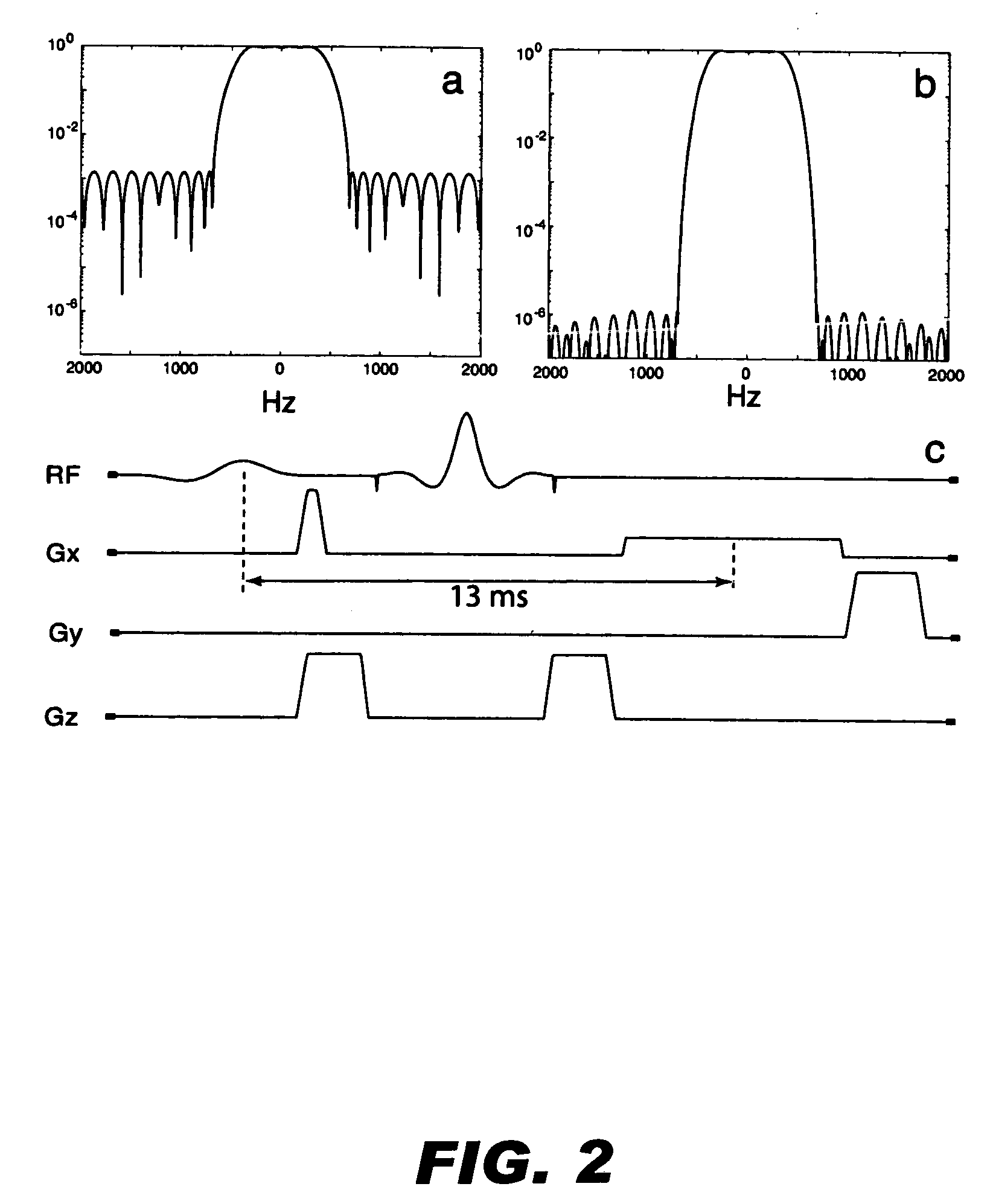
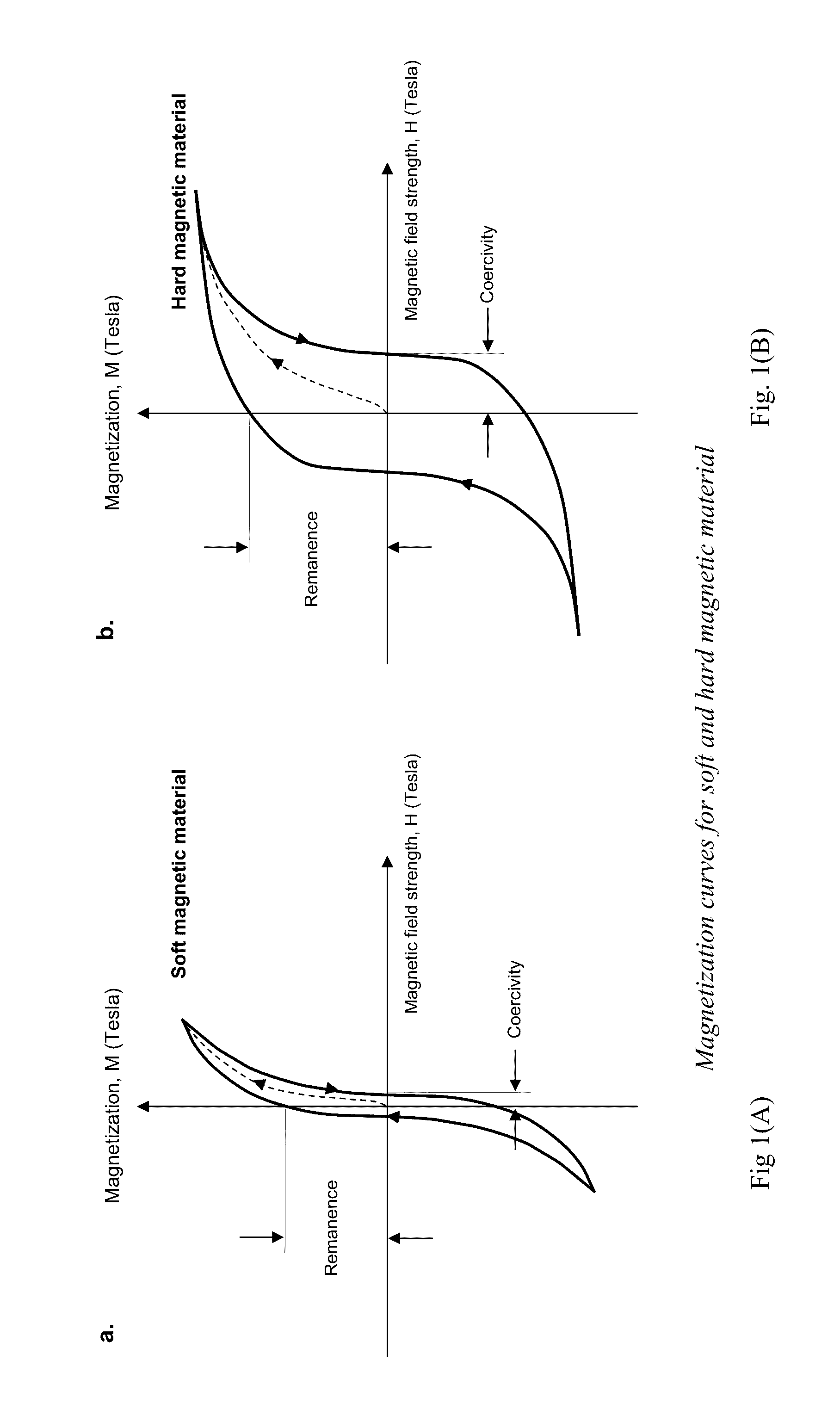
Positive contrast MRI of magnetically tagged cells, objects, tissues
ActiveUS20050261575A1Positive contrastReadily apparentDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsNegative Contrast AgentMagnetic marker
Contrast agents incorporating super-paramagnetic iron-oxide (SPIO) nanoparticles have shown promise as a means to visualize labeled cells using MRI. Labeled cells cause significant signal dephasing due to the magnetic field inhomogeneity induced in water molecules near the cell. With the resulting signal void as the means for detection, the particles are behaving as a negative contrast agent, which can suffer from partial-volume effects. Disclosed is a new method for imaging labeled cells with positive contrast. Spectrally-selective RF pulses are used to excite and refocus the off-resonance water surrounding the labeled cells so that only the fluid and tissue immediately adjacent to the labeled cells are visible in the image. Phantom, in vitro, and in vivo experiments show the feasibility of the new method. A significant linear correlation (r=0.87, p<0.005) between the estimated number of cells and the signal has been observed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Position sensing system of intelligent vehicle navigation
InactiveCN104197944AFrequent updatesInstruments for road network navigationNon-mechanical steering controlMagnetic markerSteering control
Owner:TOMORROWS TRANSPORTATION TODAY
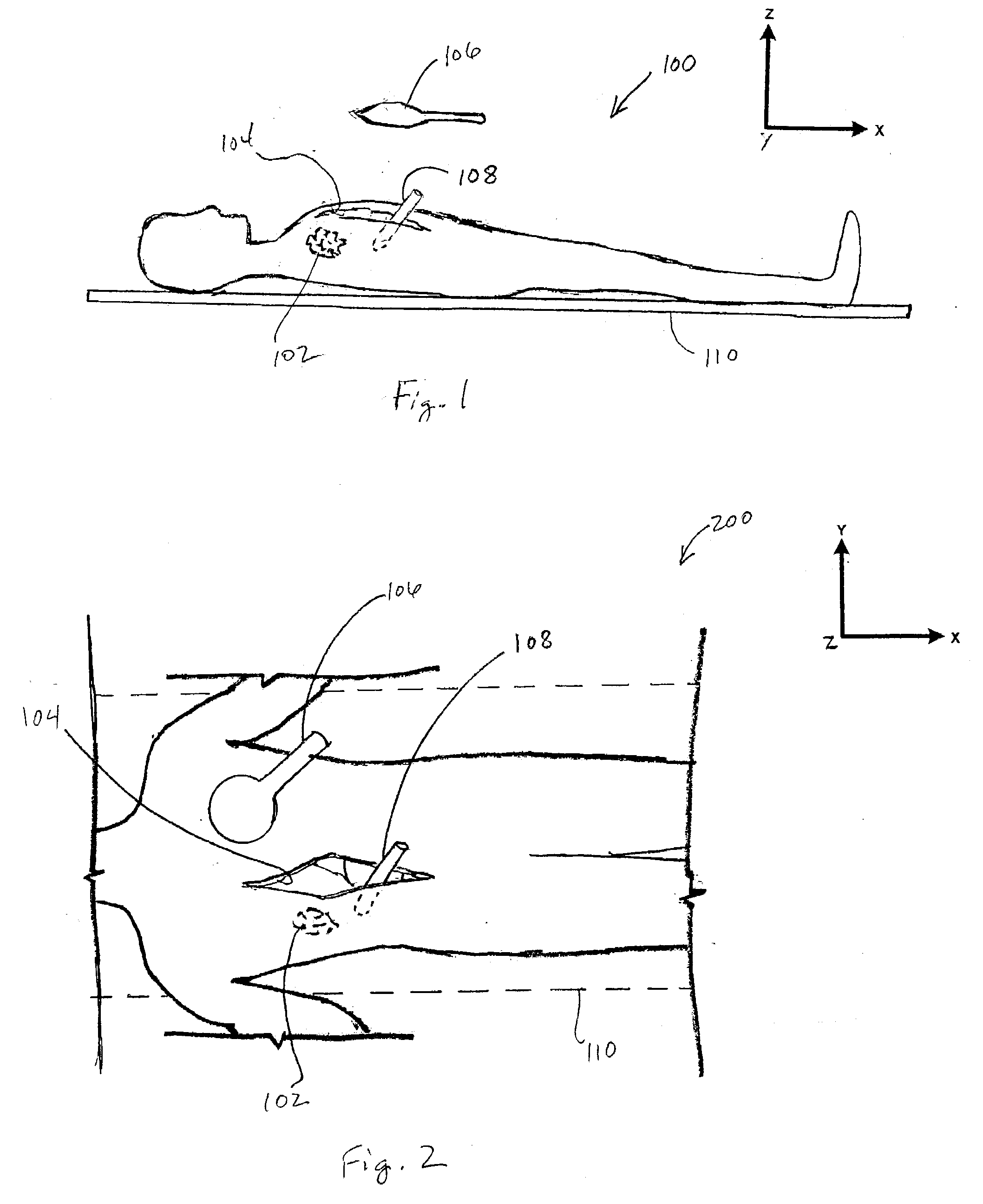
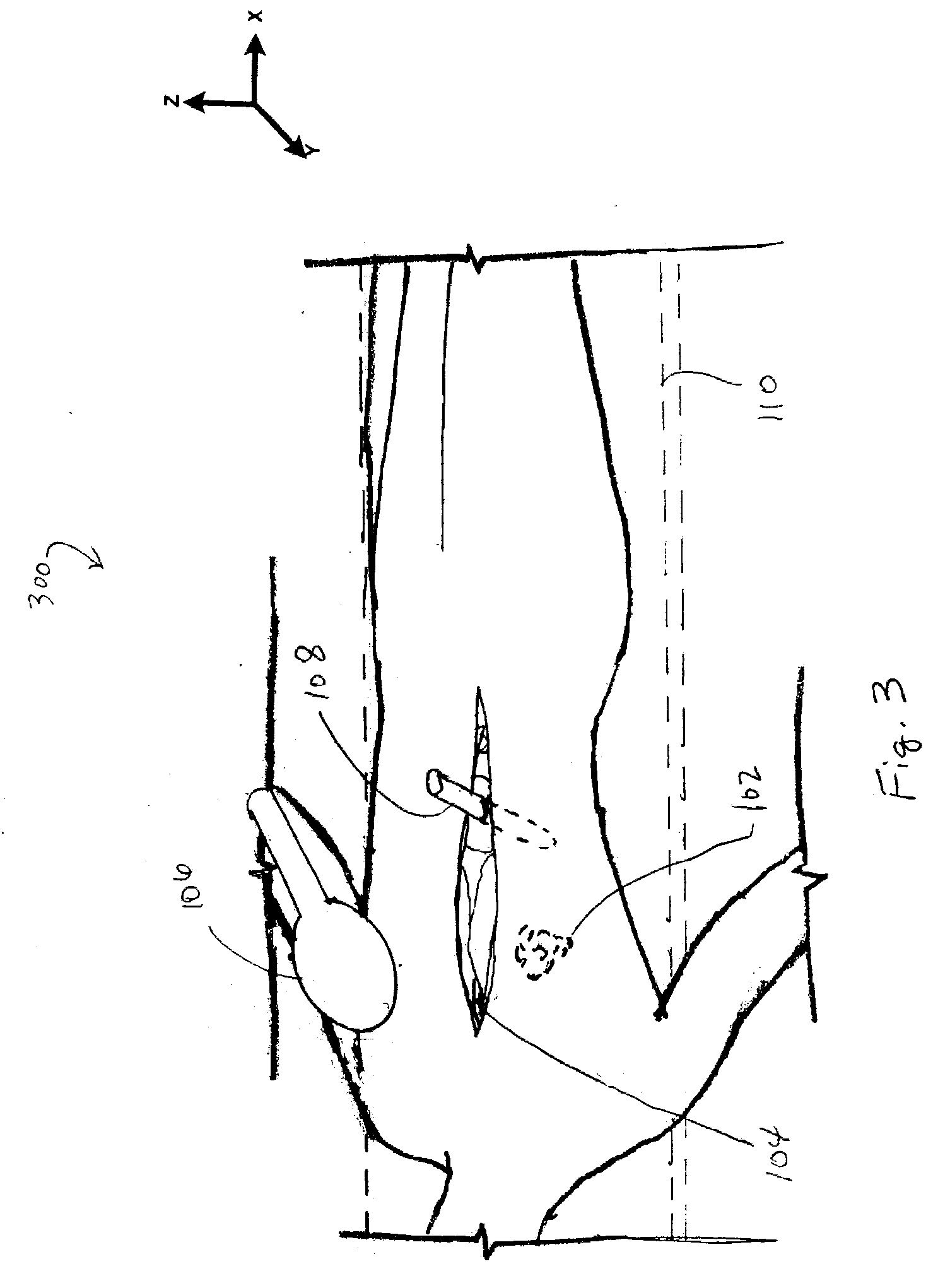
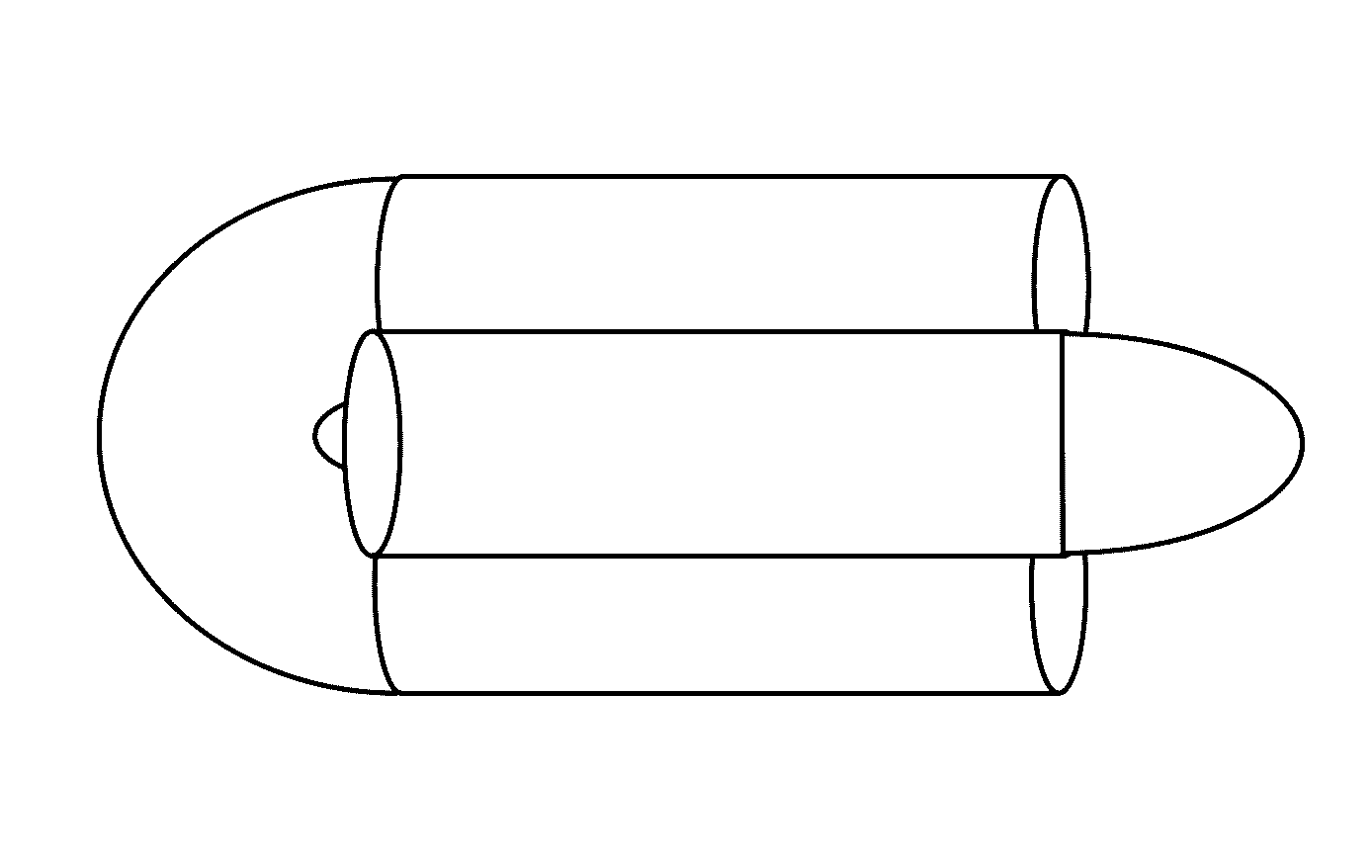
Marker Materials and Forms for Magnetic Marker Localization (MML)
ActiveUS20160354178A1Uniform magnetic responseSurgeryInorganic material magnetismMagnetic markerBiology
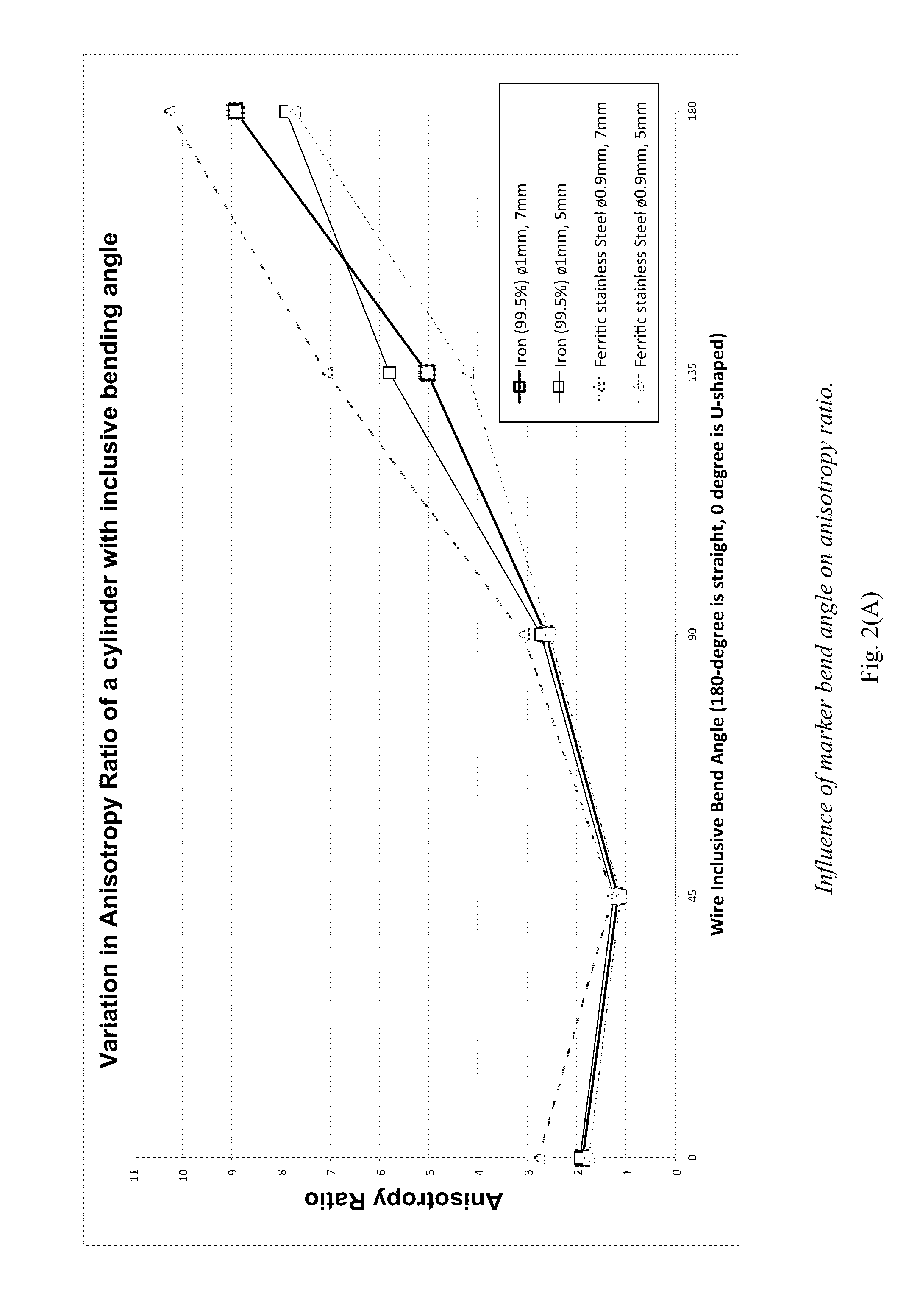
A magnetic marker for marking a site in tissue in the body. In one embodiment, the marker comprises a magnetic metallic glass. In another embodiment, the marker is in a non-spherical configuration having an anisotropy ratio less than 9. In yet another embodiment, the marker is in a non-spherical configuration having an anisotropy ratio less than 6. In yet another embodiment, the marker is in a non-spherical configuration having an anisotropy ratio less than 3.
Owner:ENDOMAGNETICS LTD
Method of identifying and documenting hail damage
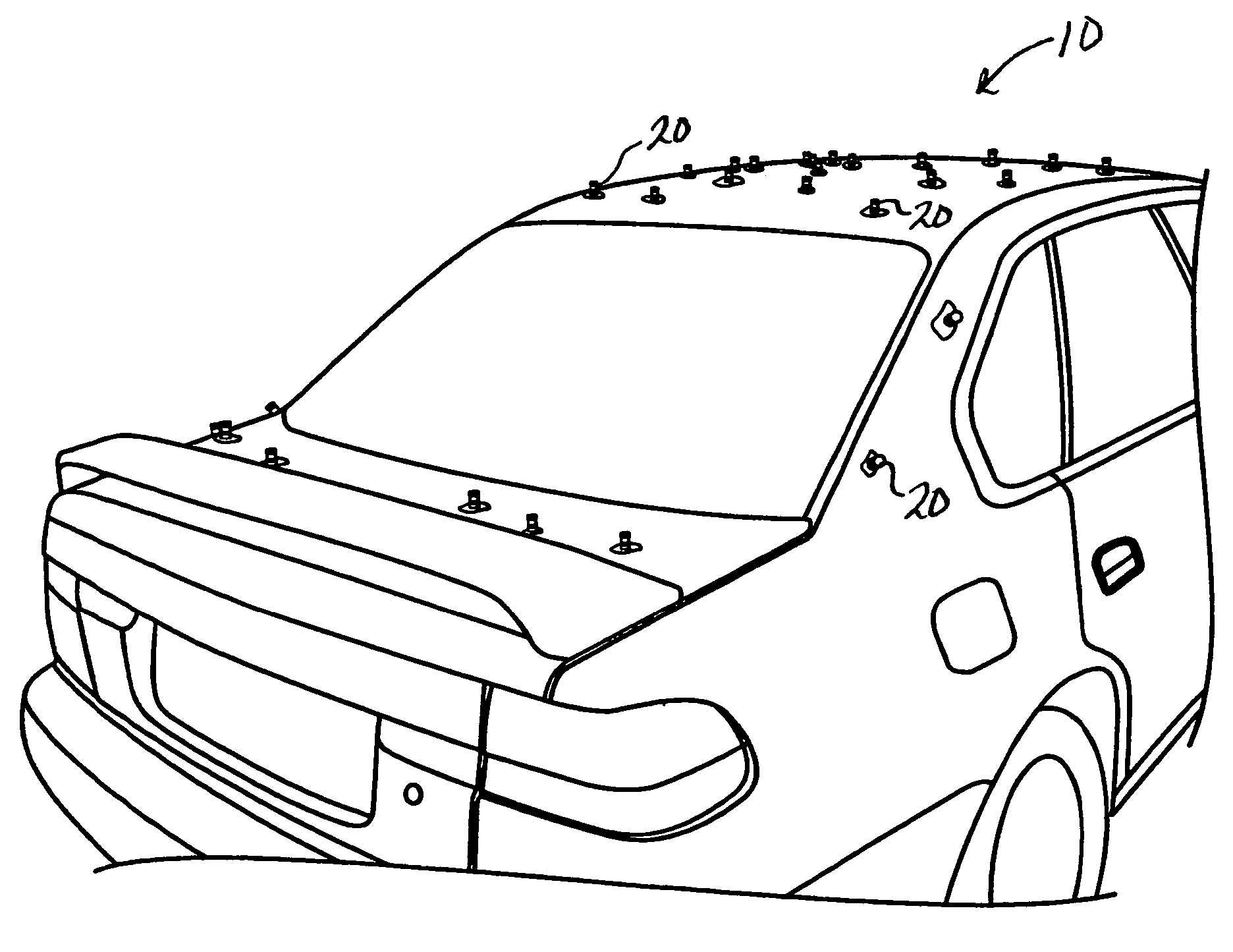
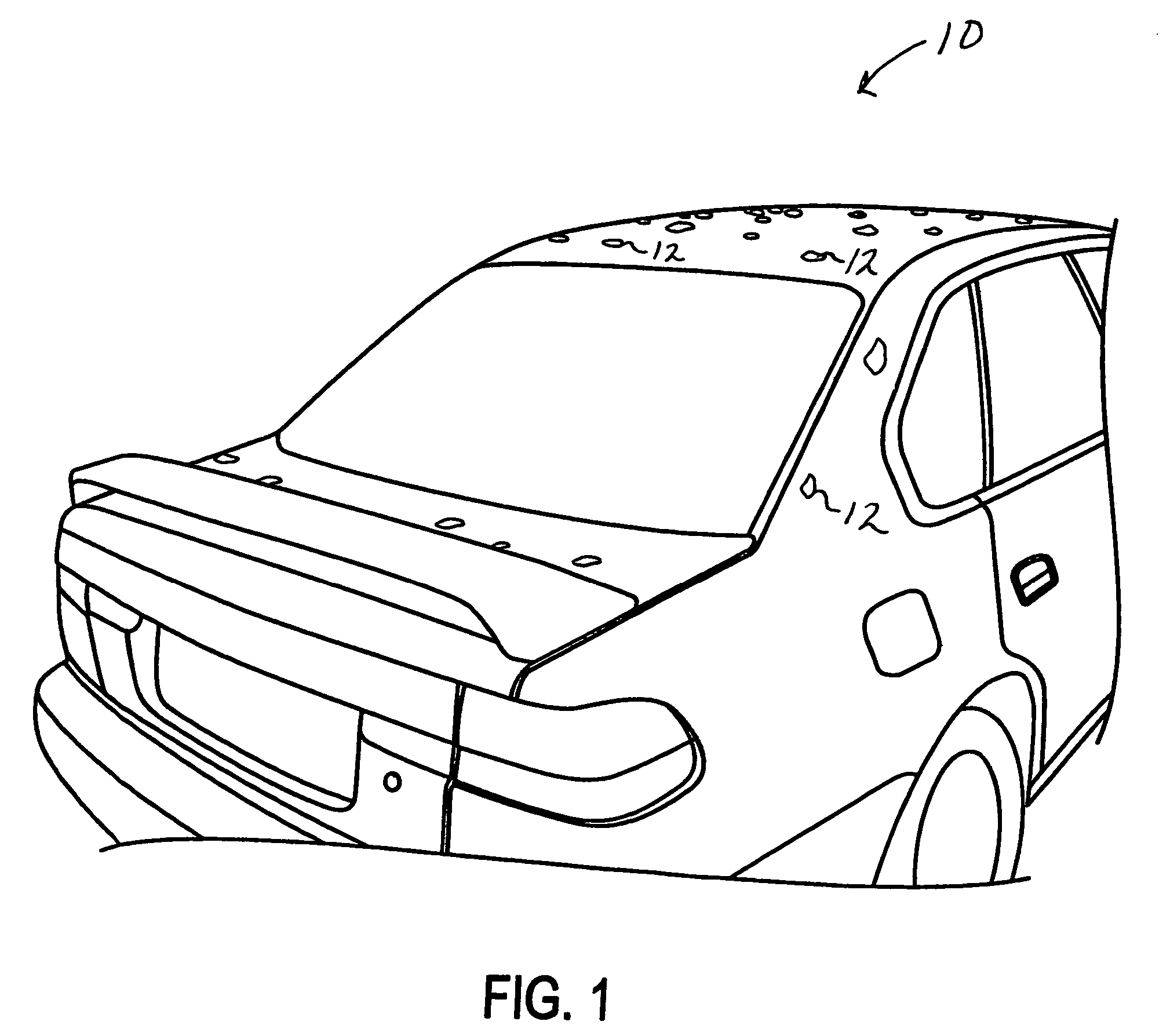
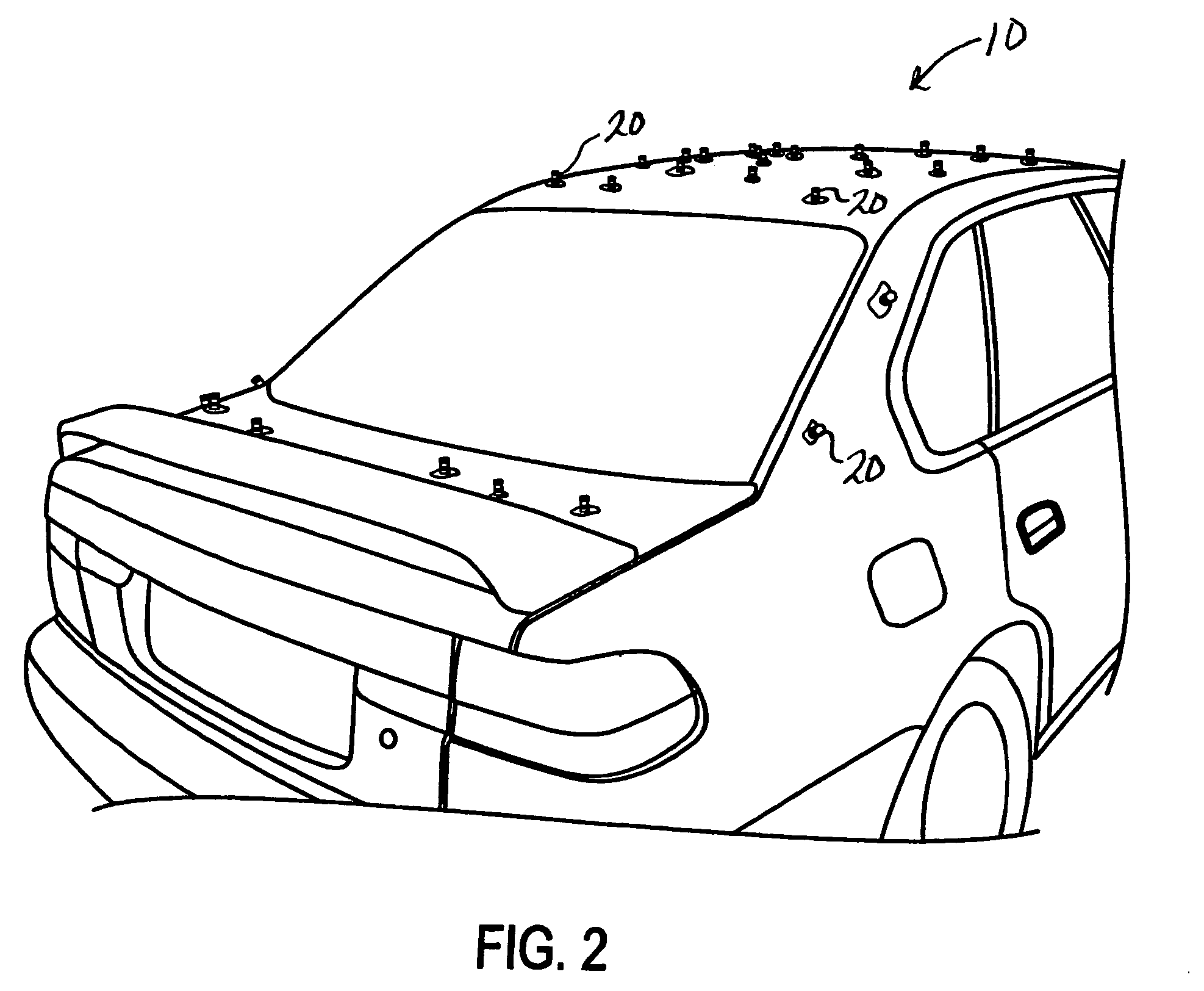
A consistent and effective method of identifying and documenting vehicle dent damage includes the steps of identifying dents on a damaged vehicle, applying an easily visible magnetic marker over each dent on the damaged vehicle, counting the markers on the damaged vehicle, photographing the markers on the damaged vehicle and removing the markers from the damaged vehicle.
Owner:BAUERNFEIND JASON
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com