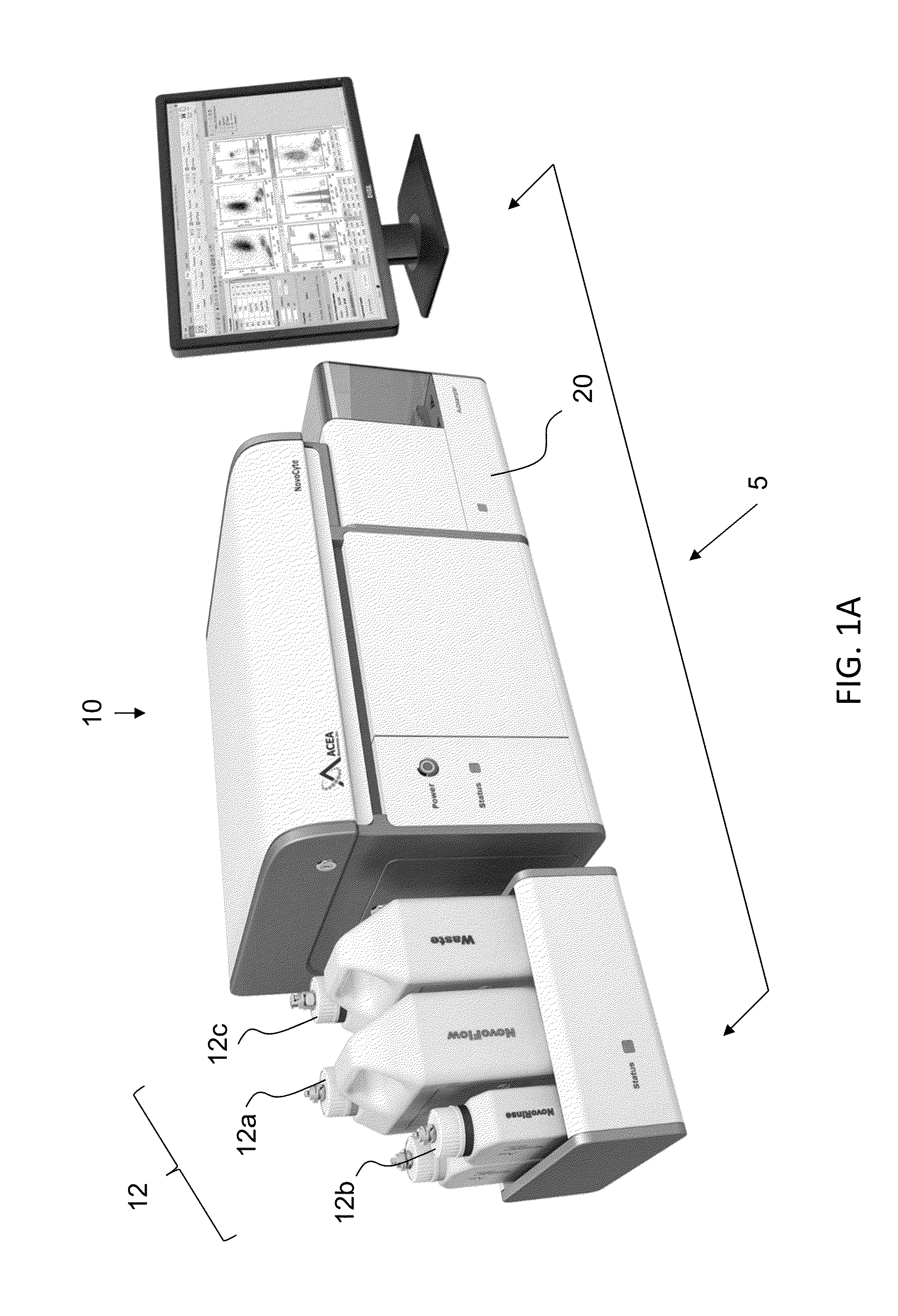
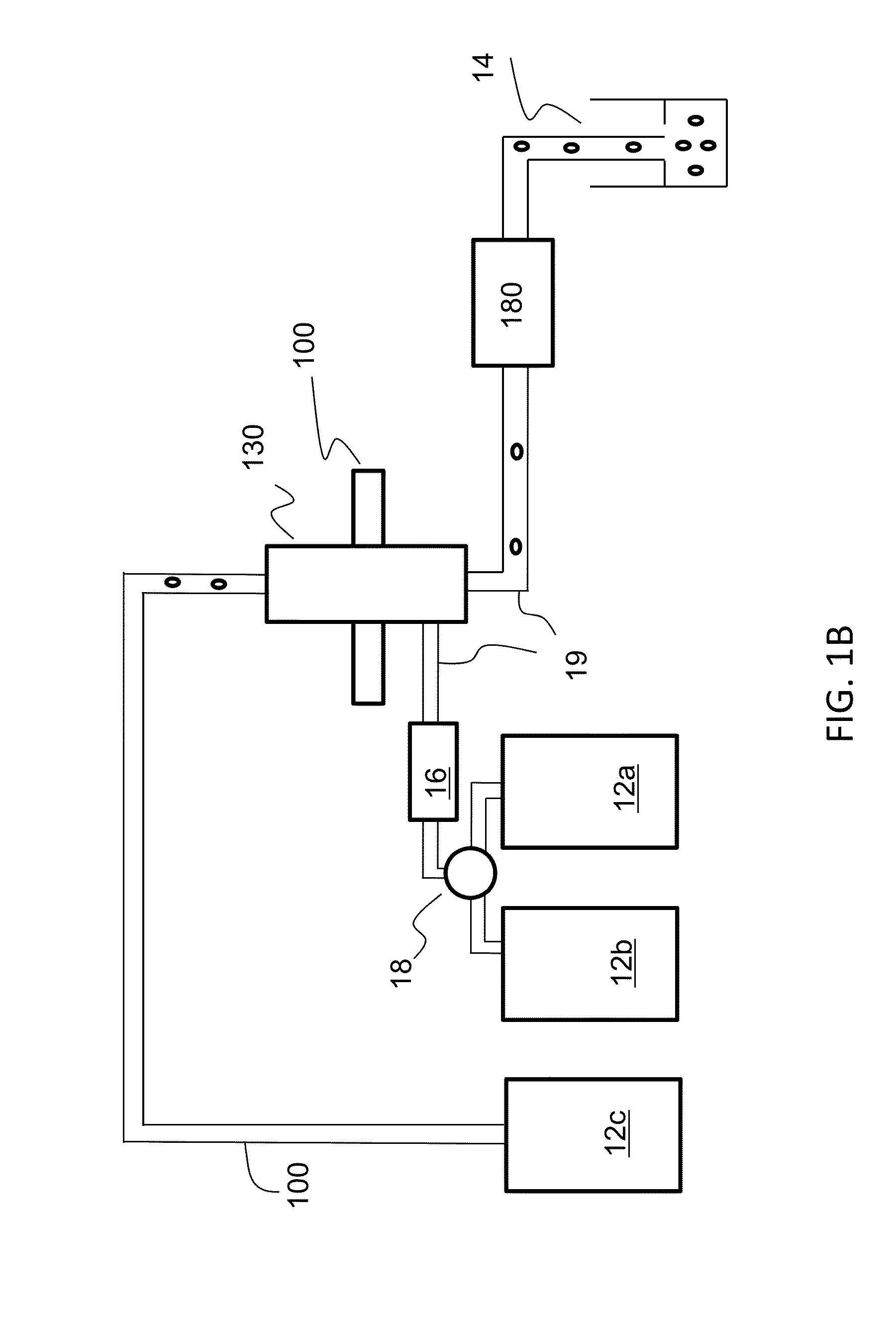
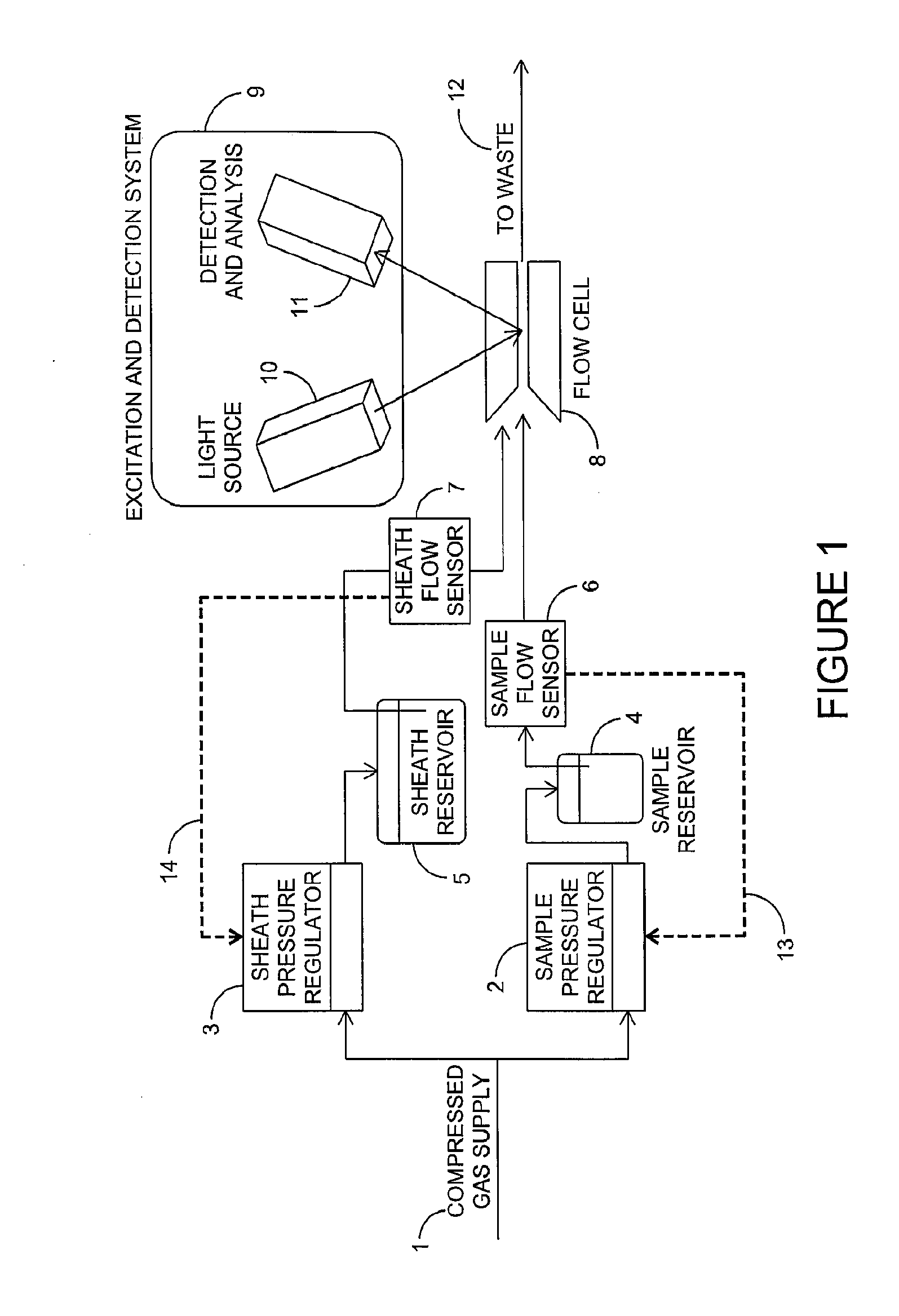
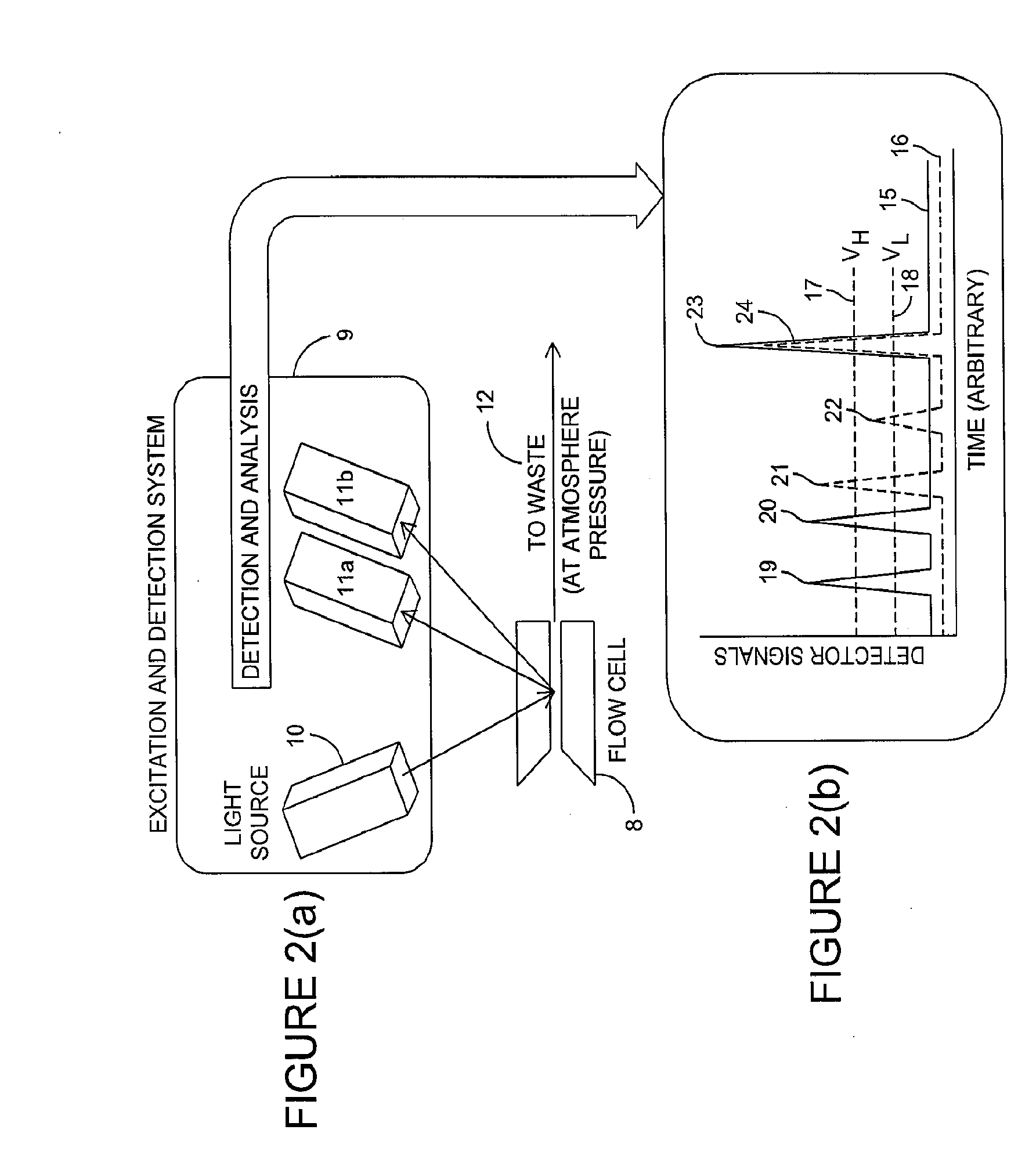
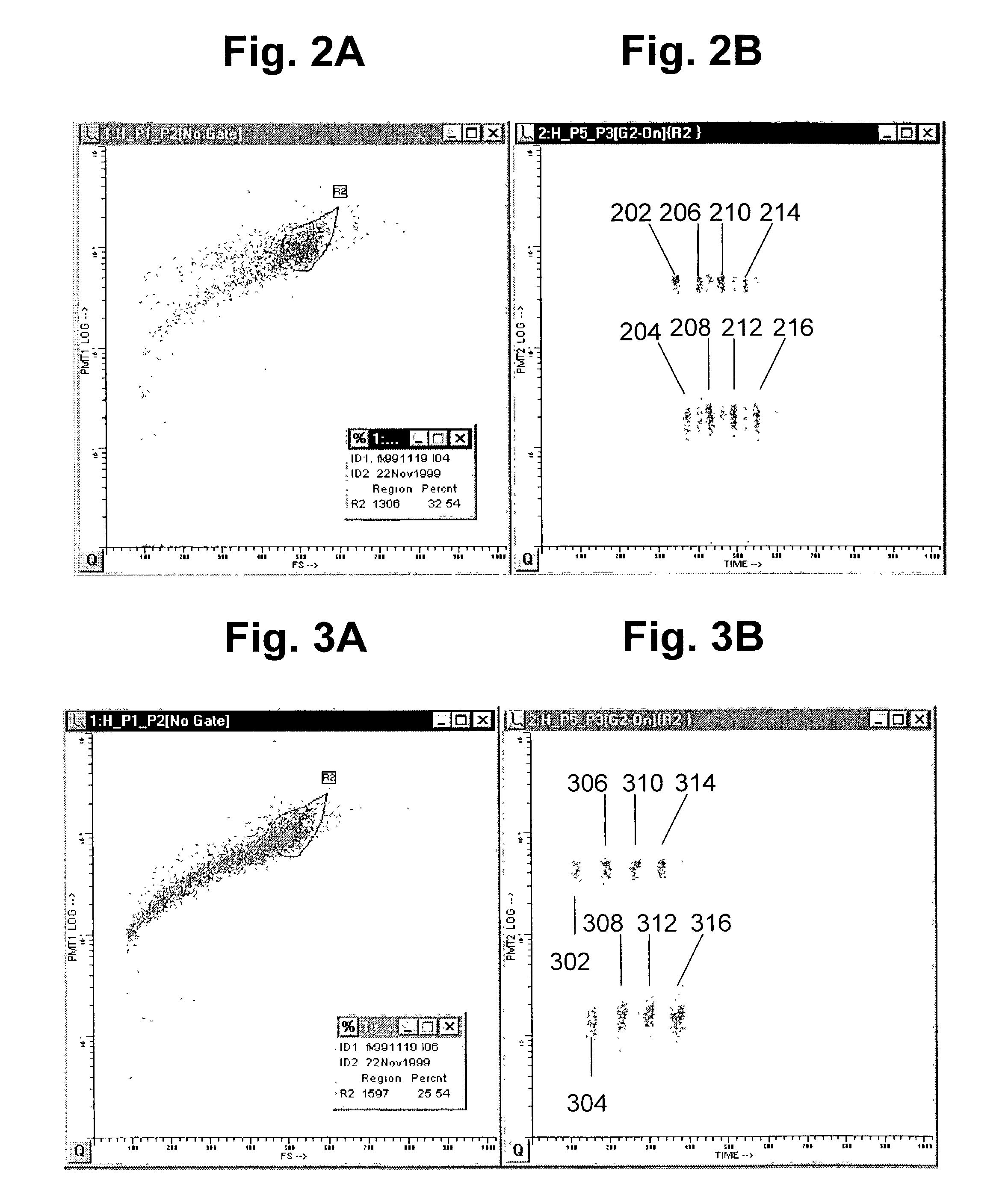
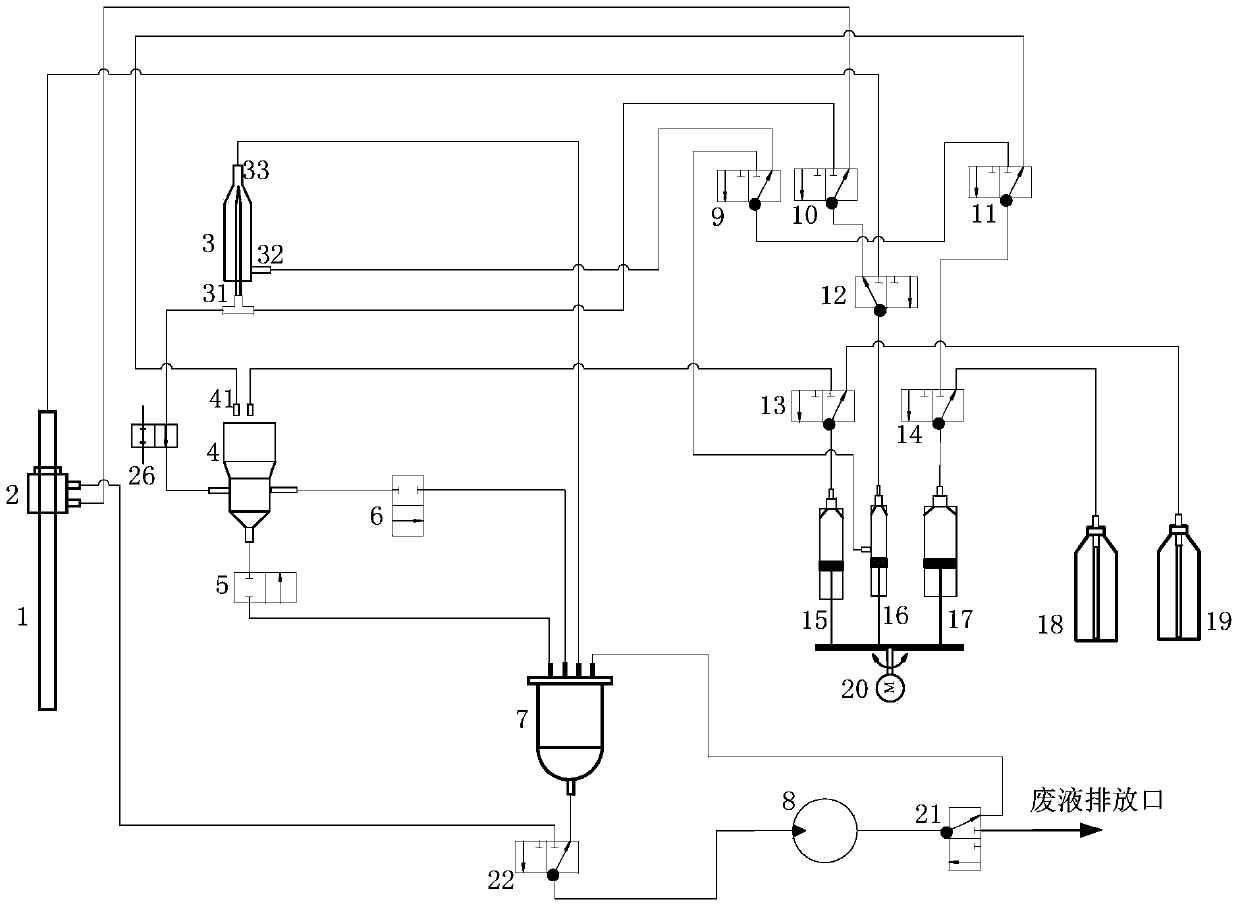
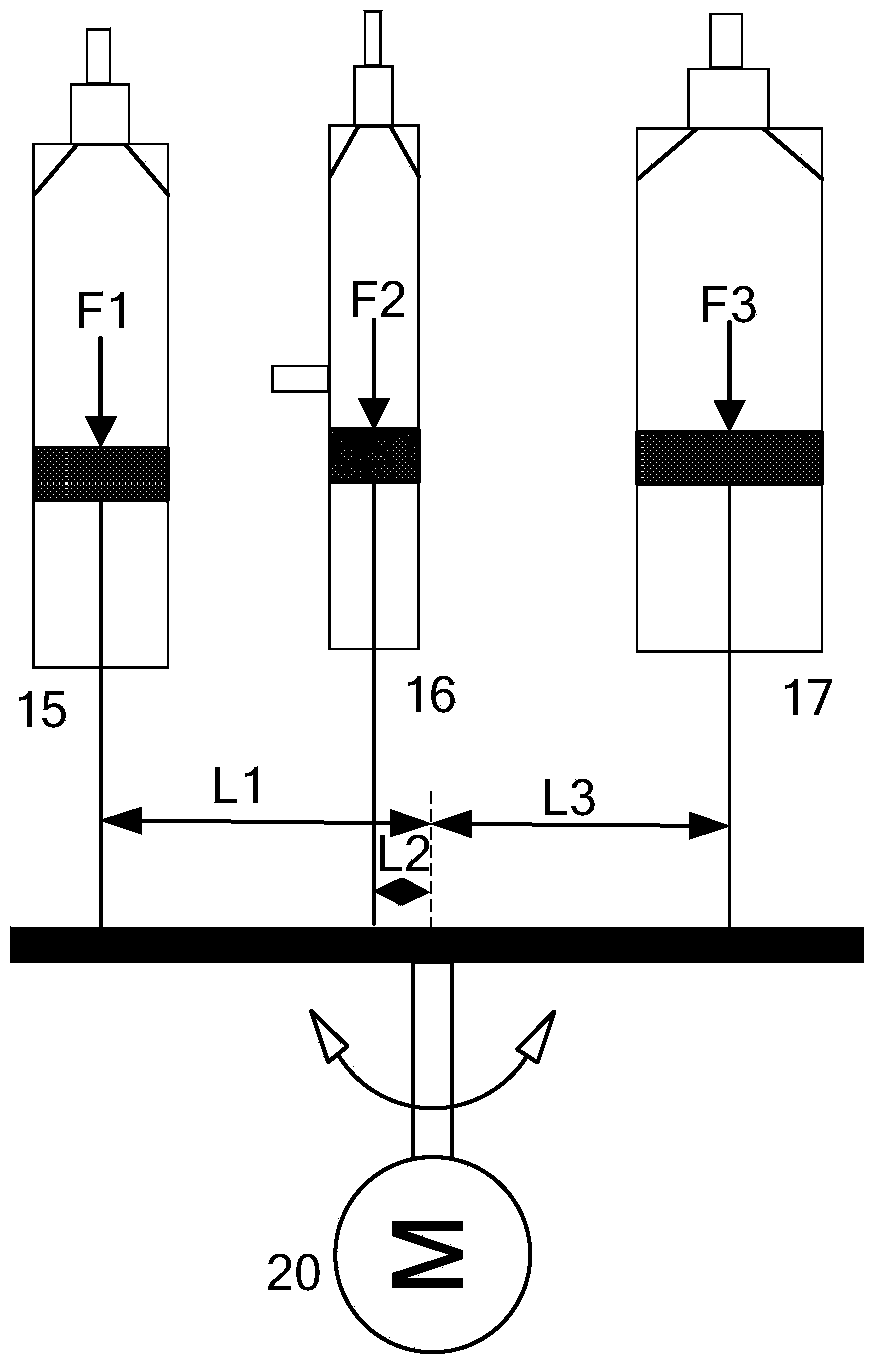
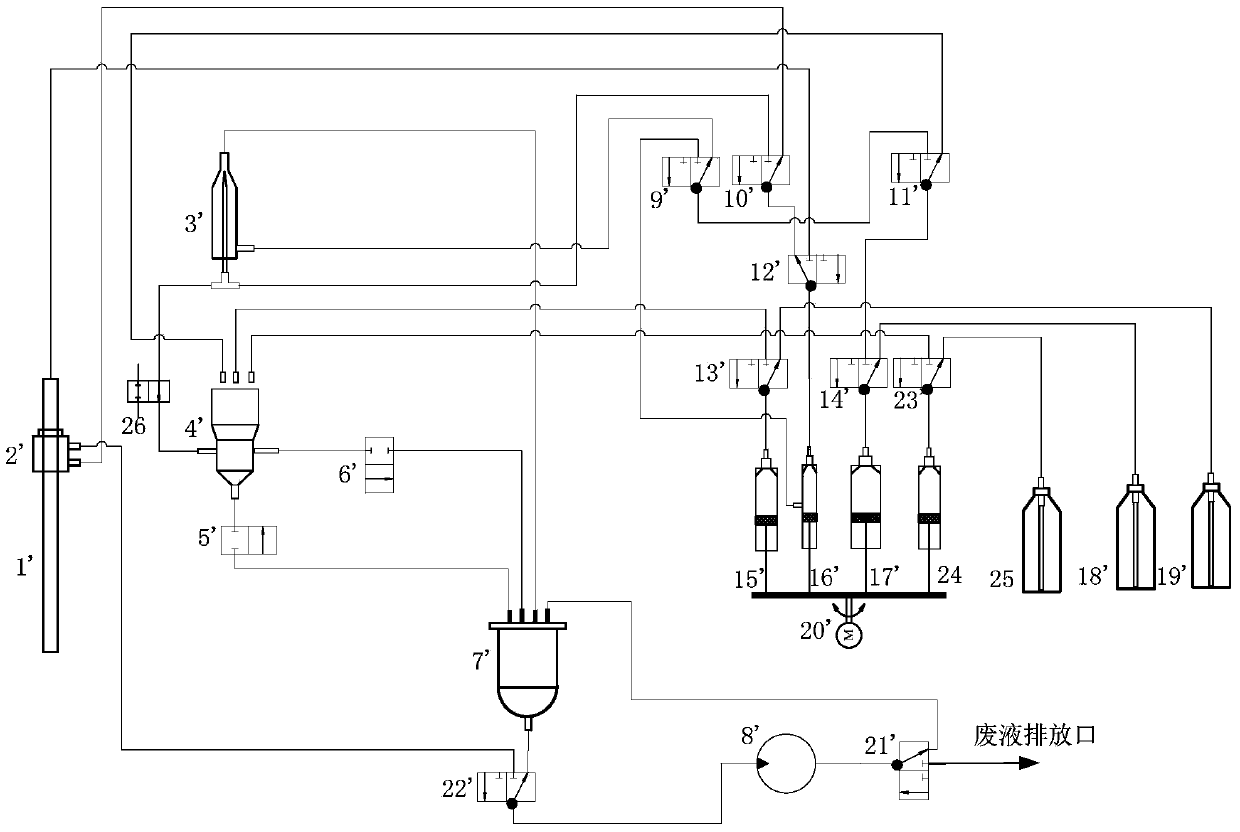
Patents
Literature
230 results about "Flow Cytofluorometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cytofluorometry, Flow (n.) 1.(MeSH)Technique using an instrument system for making, processing, and displaying one or more measurements on individual cells obtained from a cell suspension.
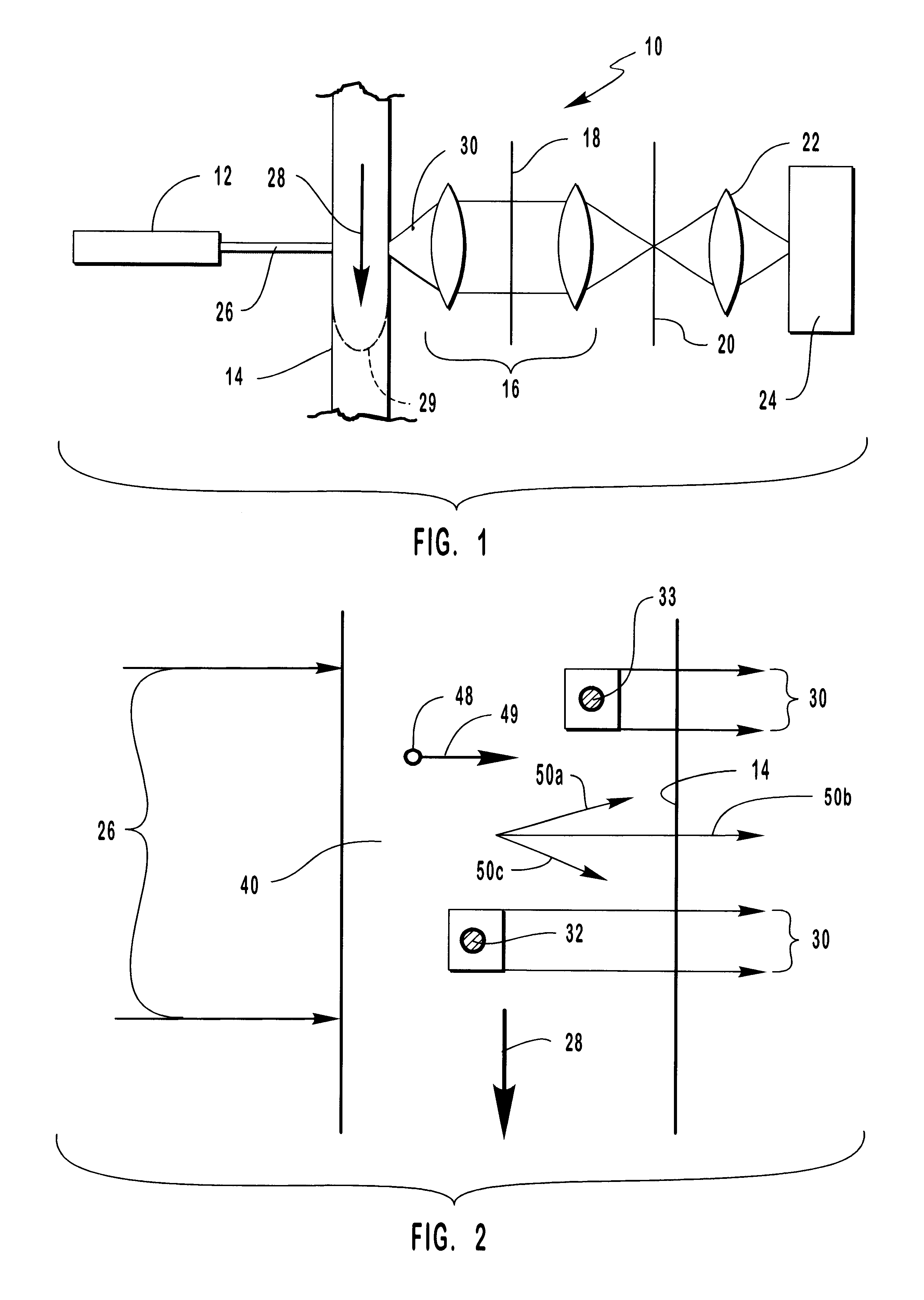
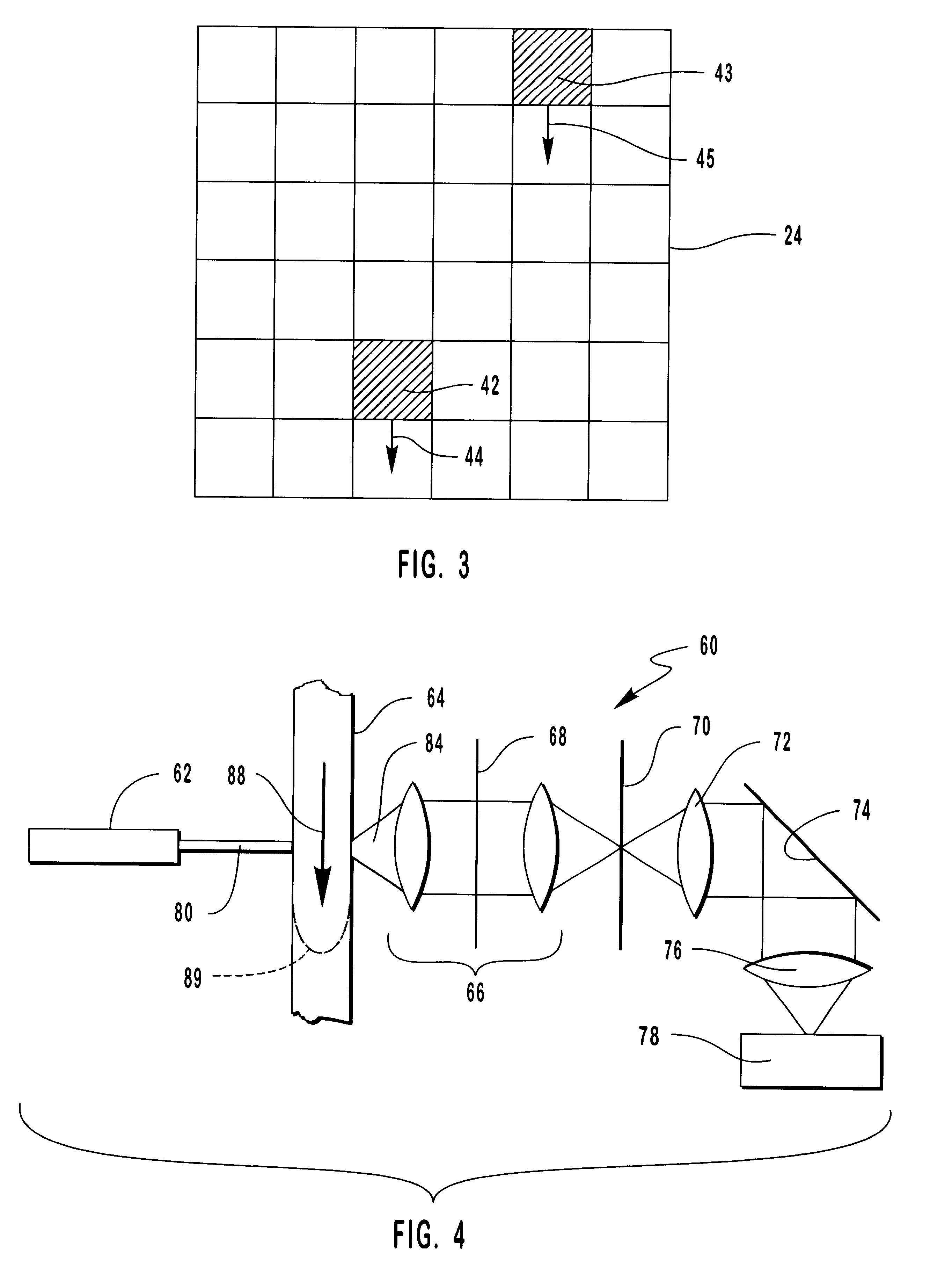
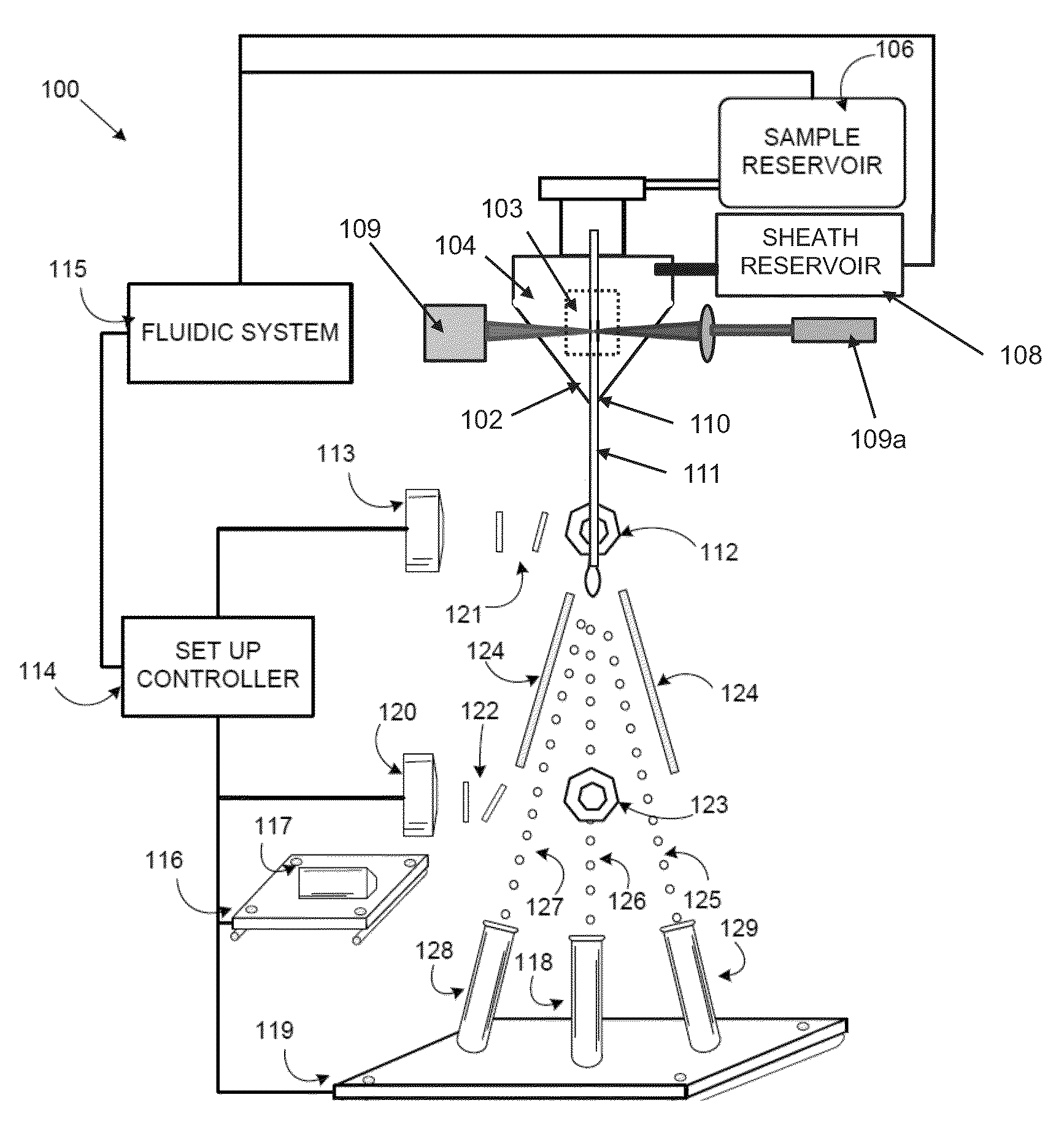
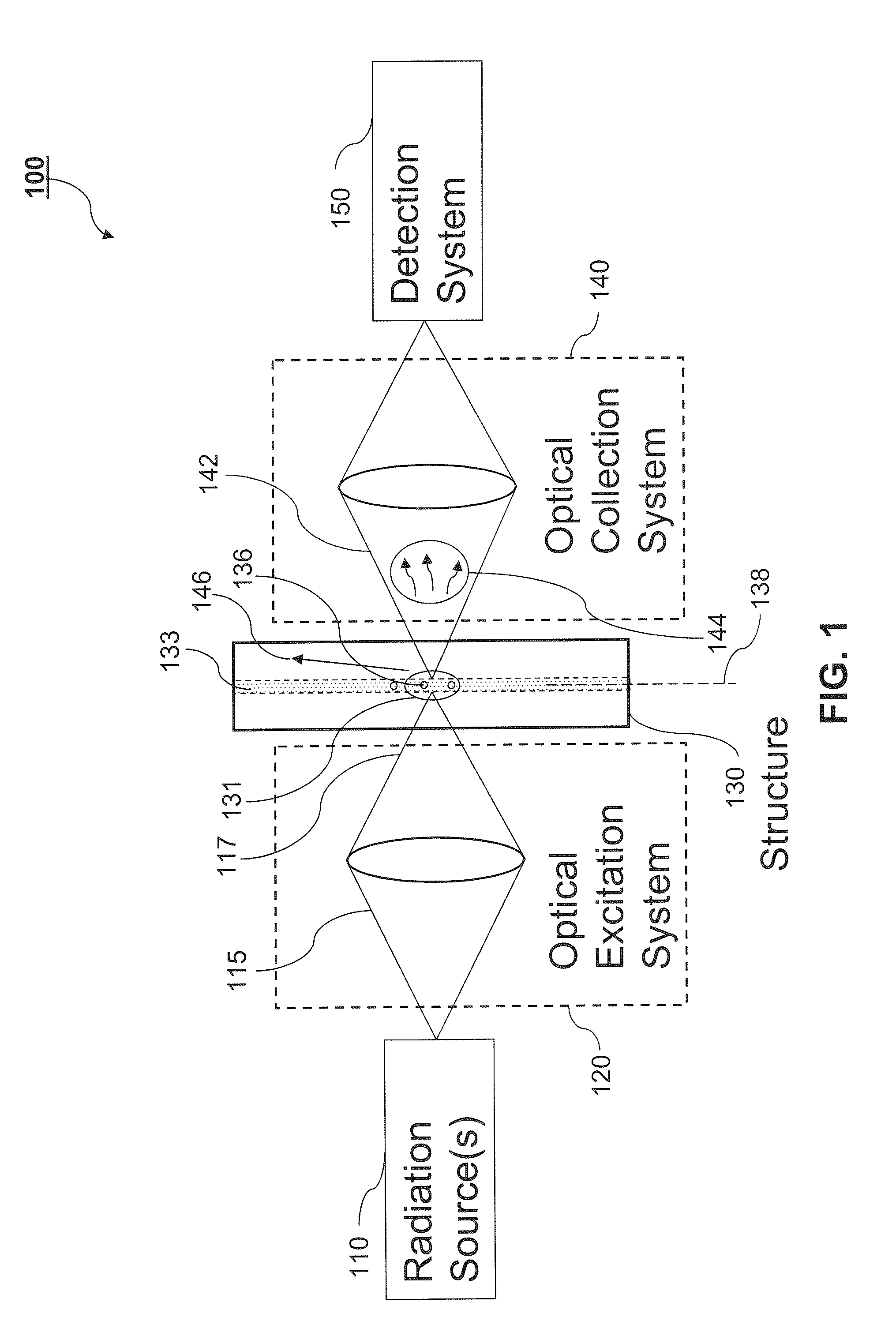
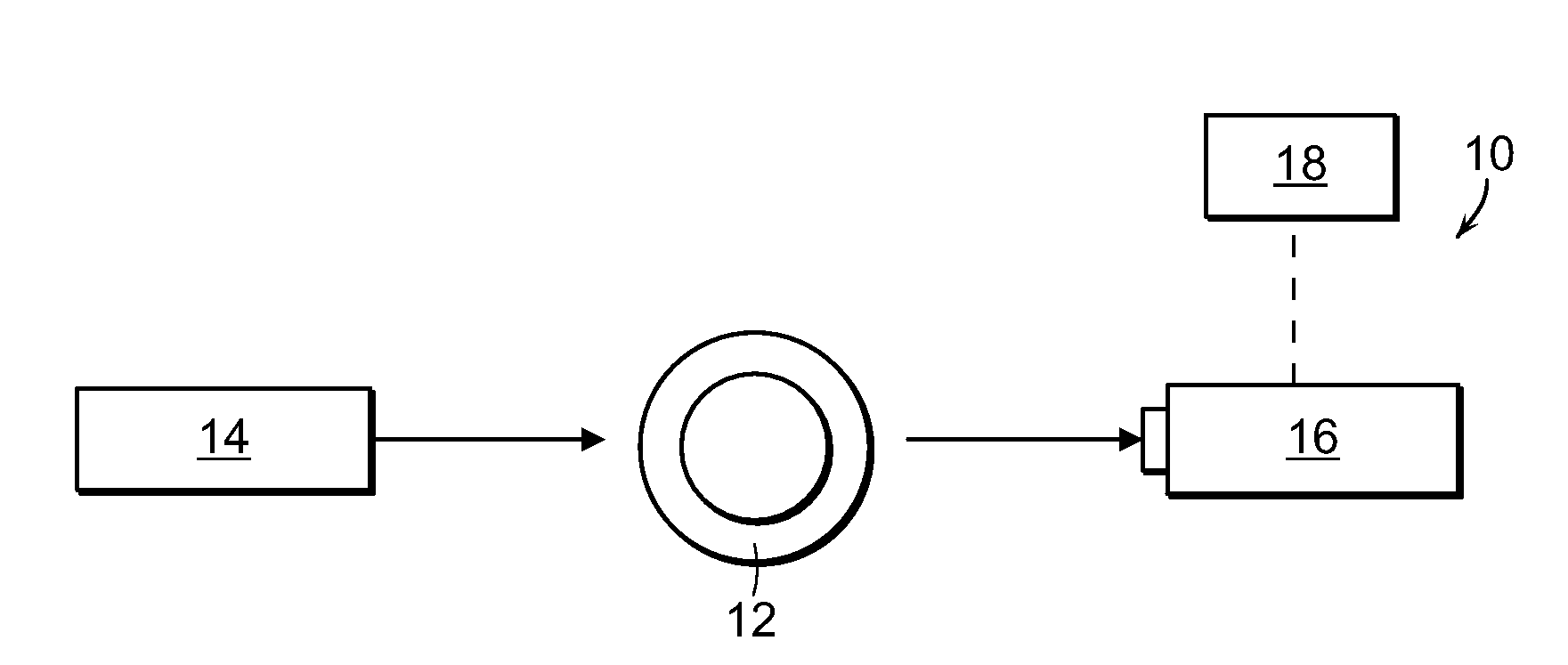
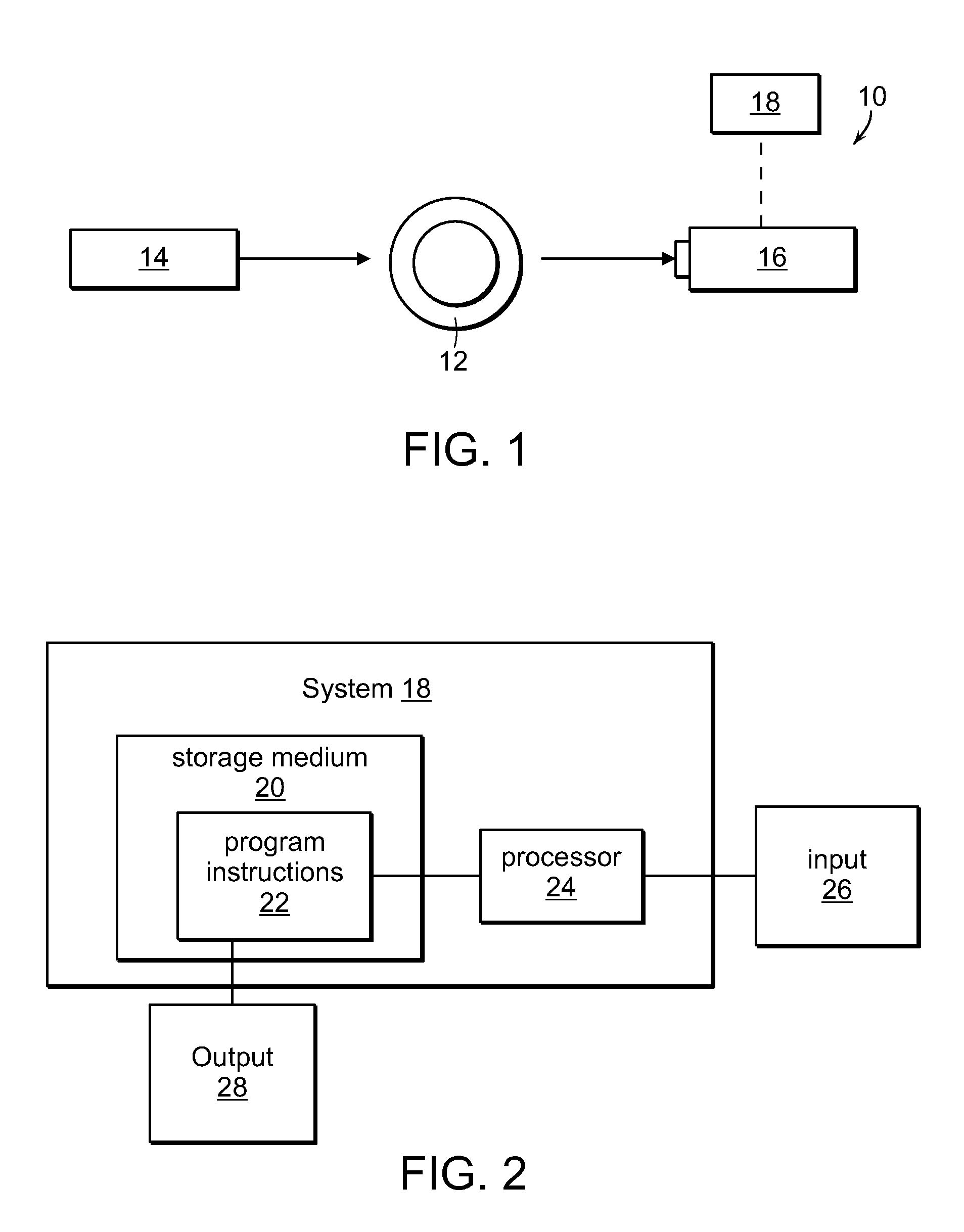
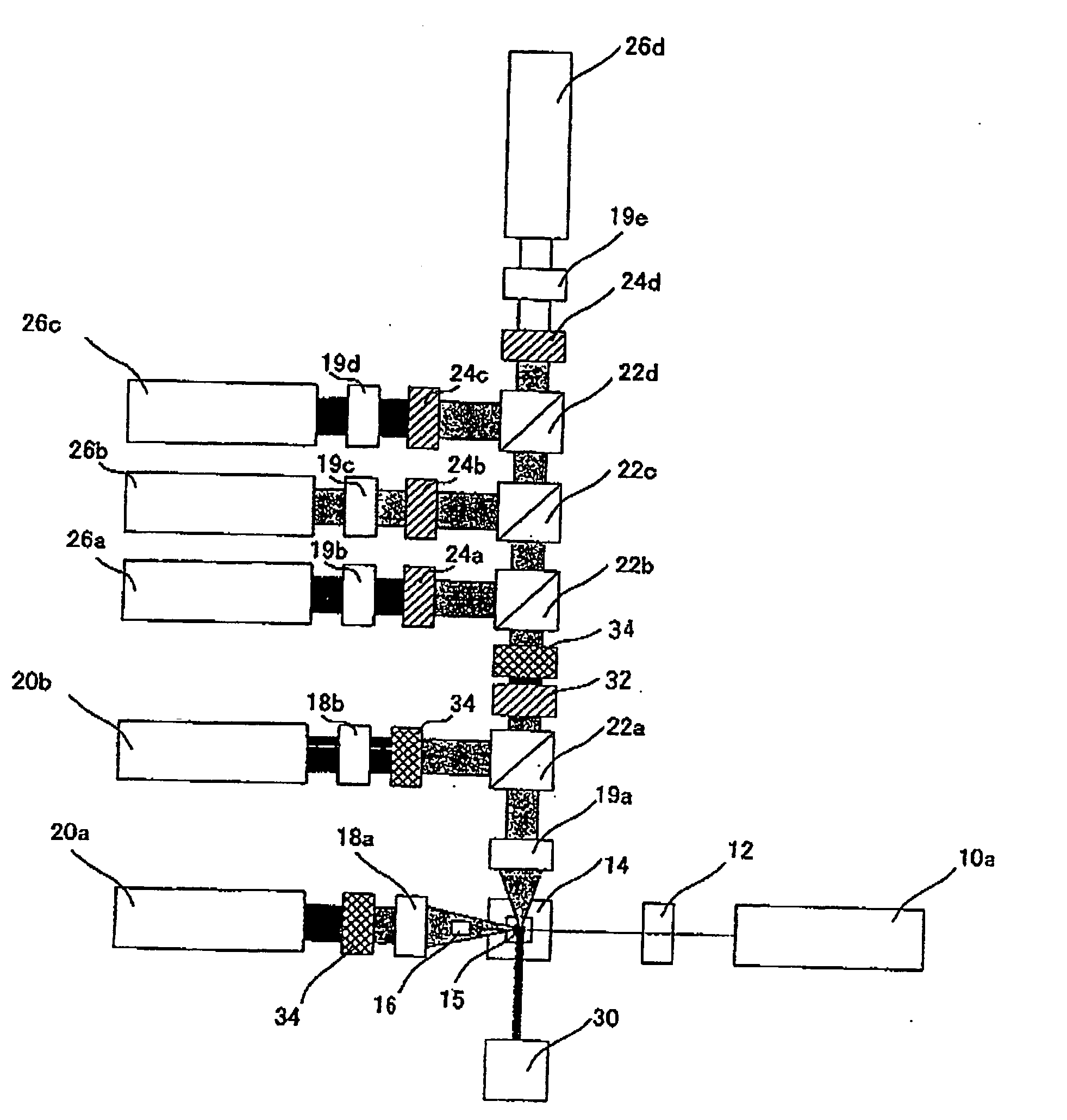
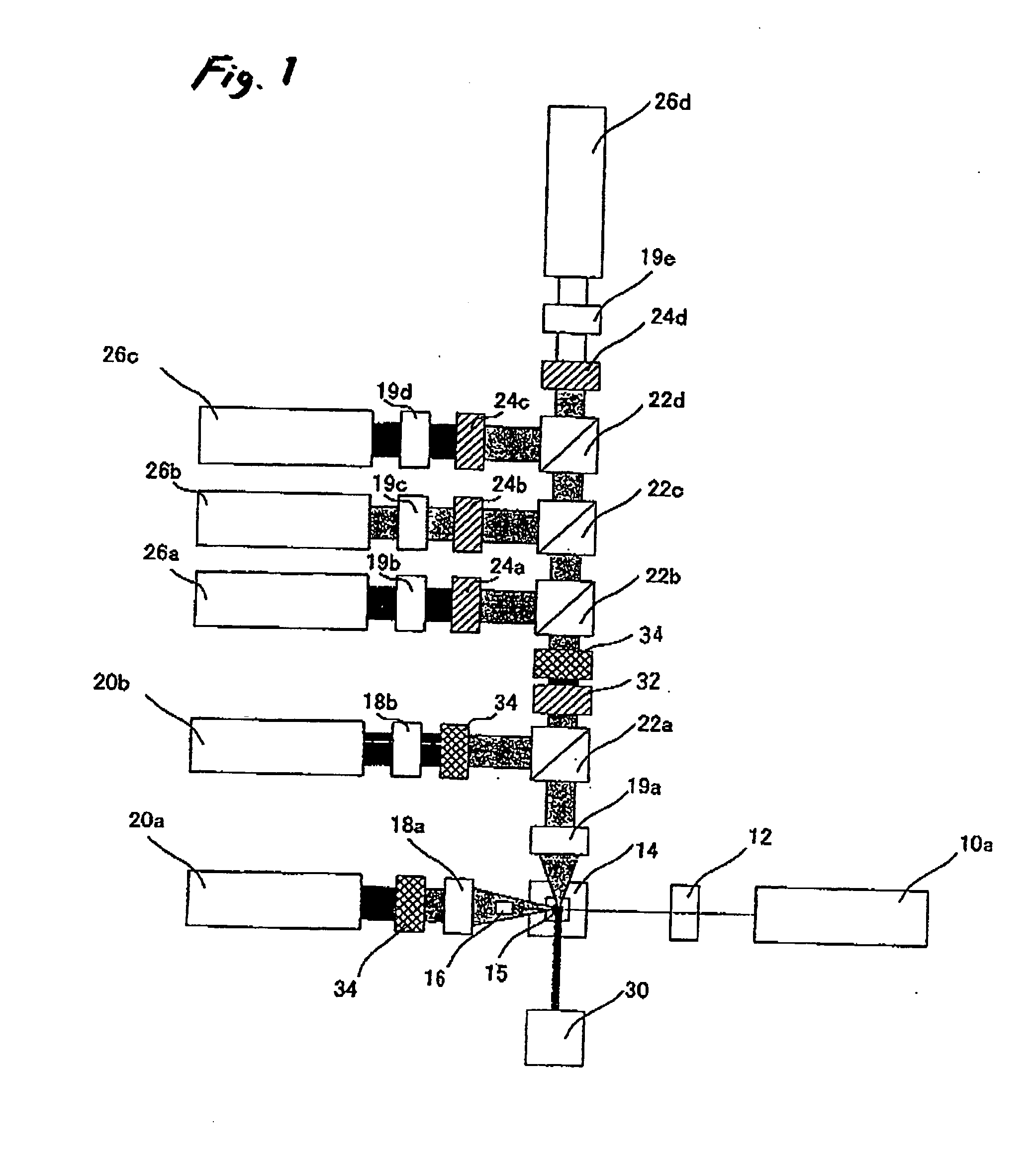
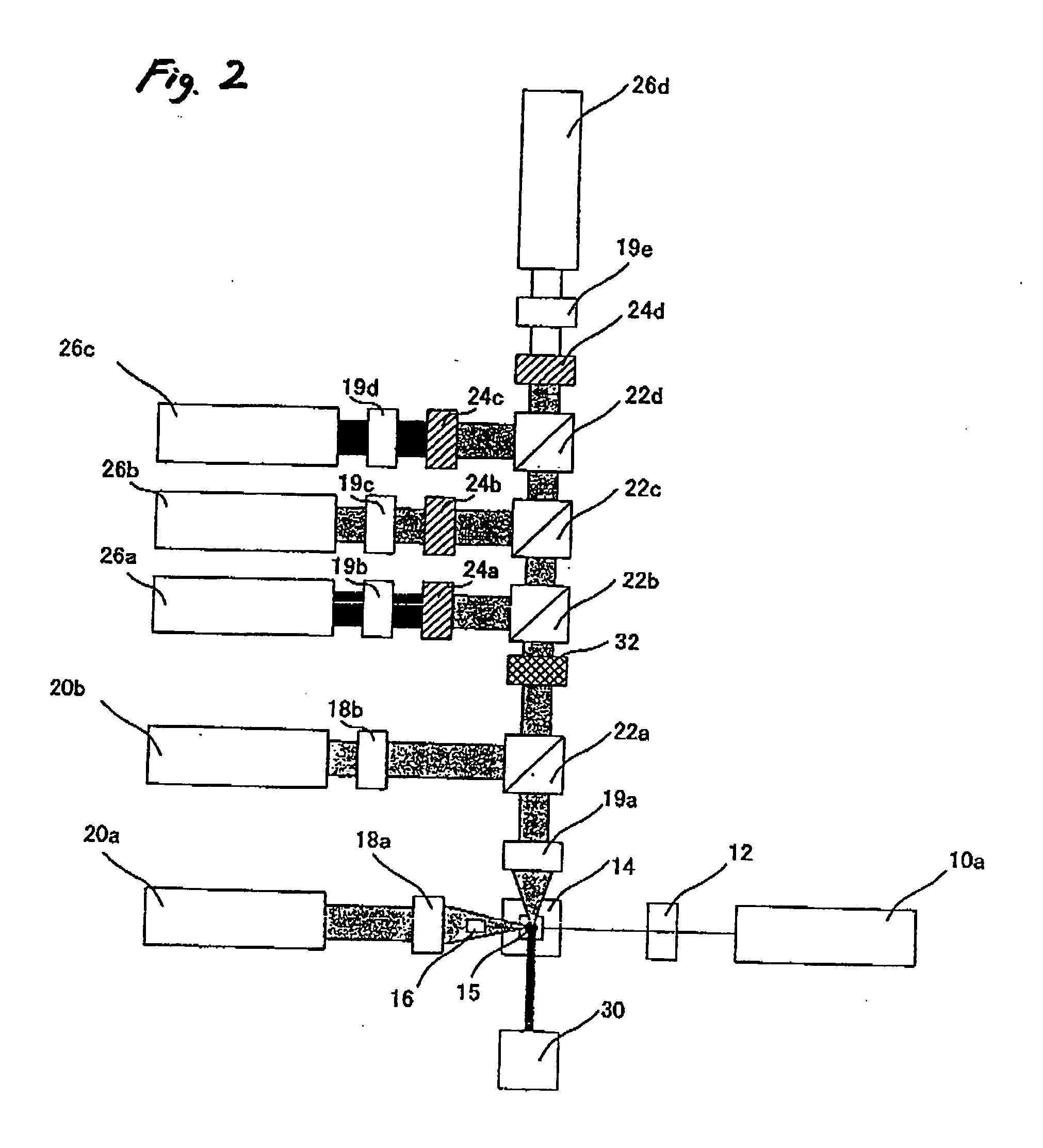
Method and apparatus for flow cytometry
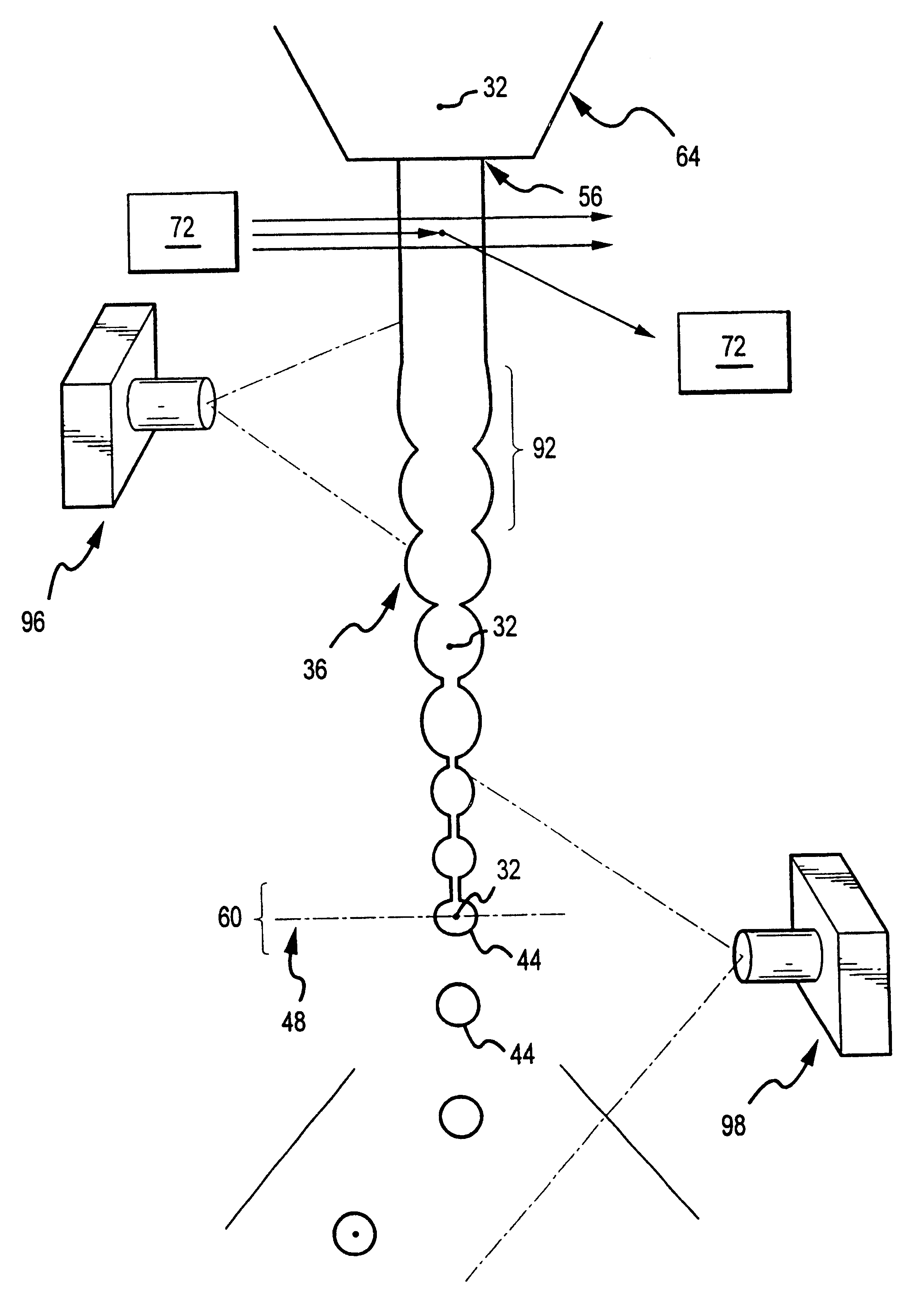
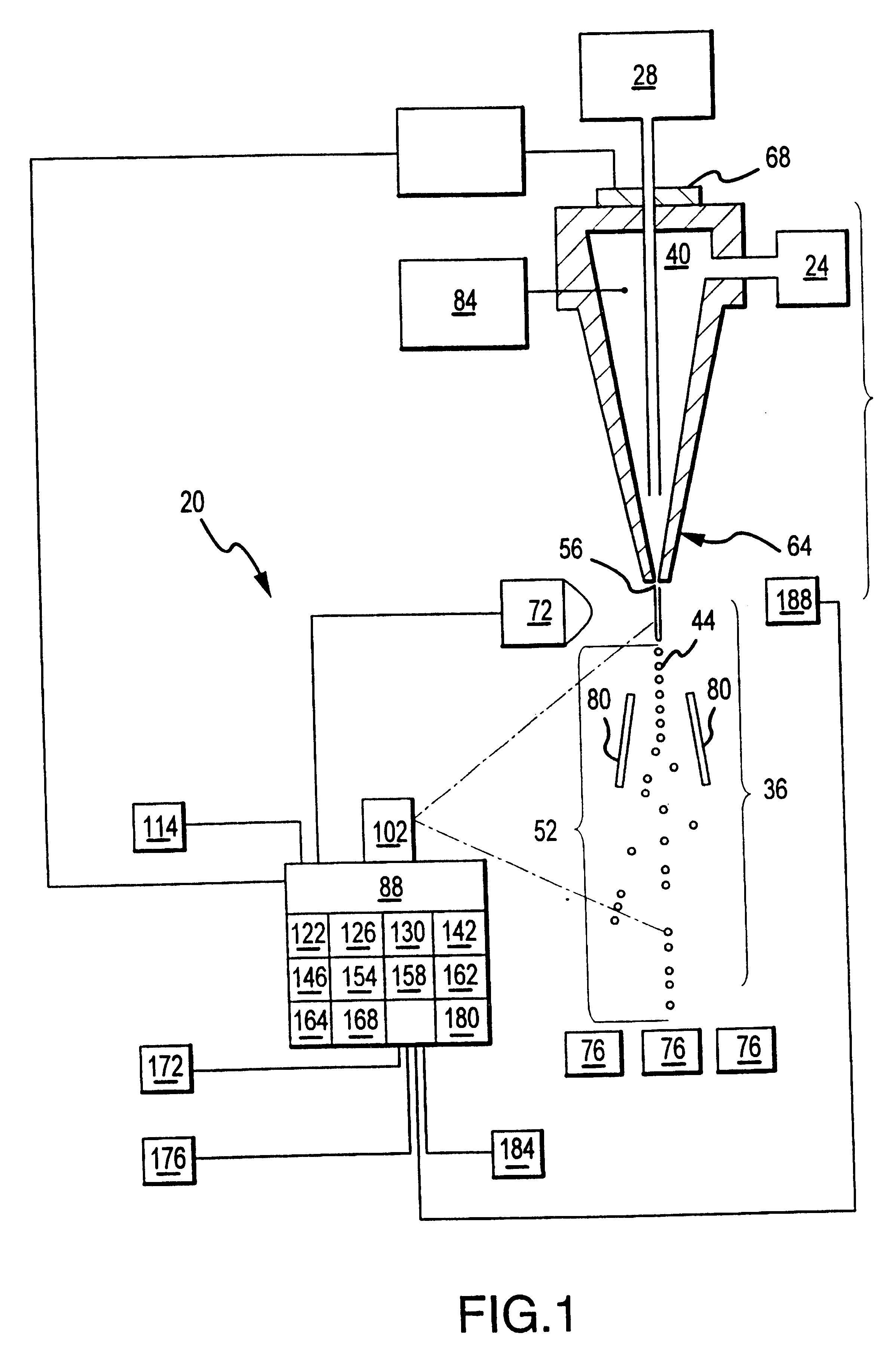
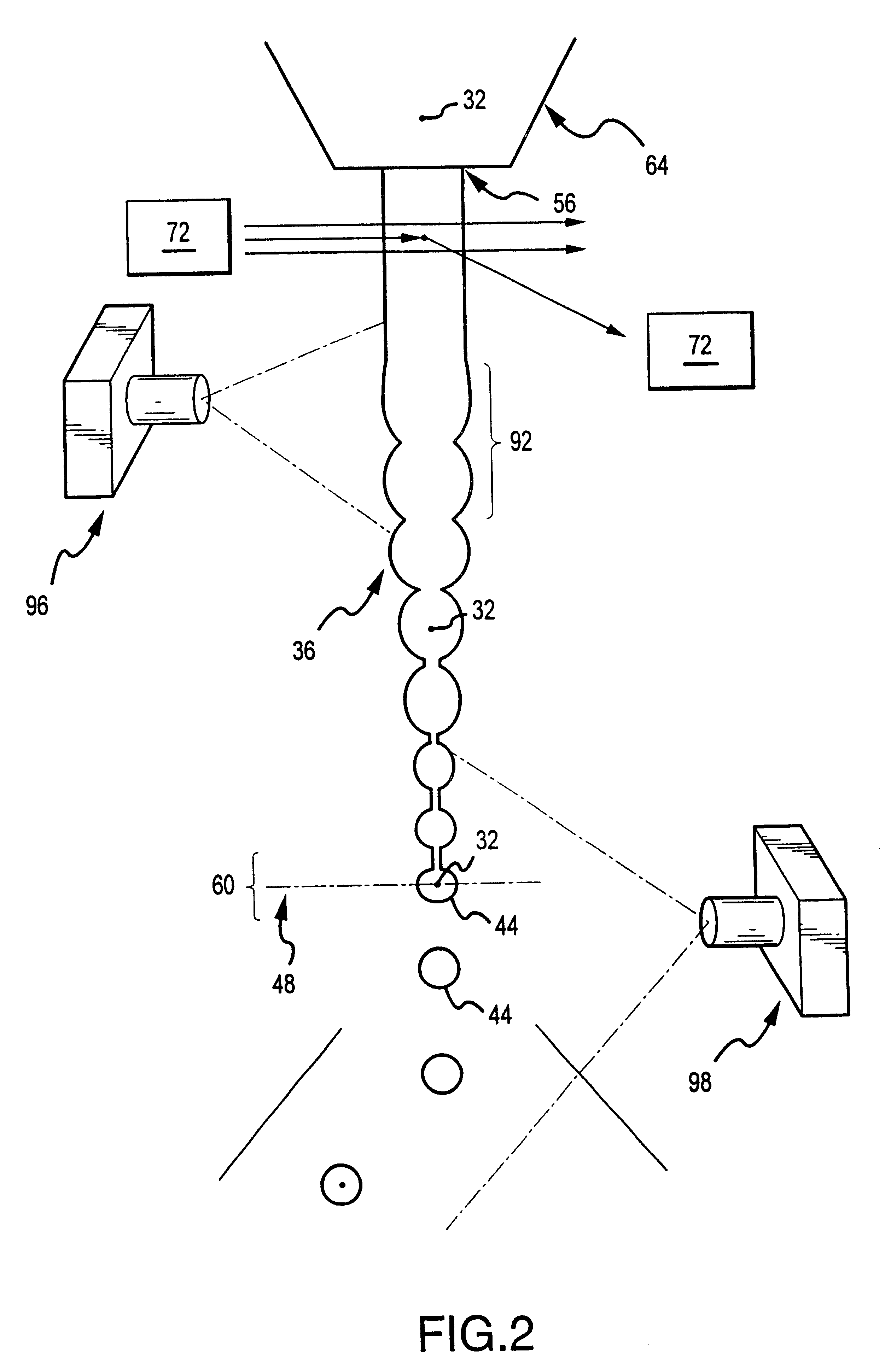
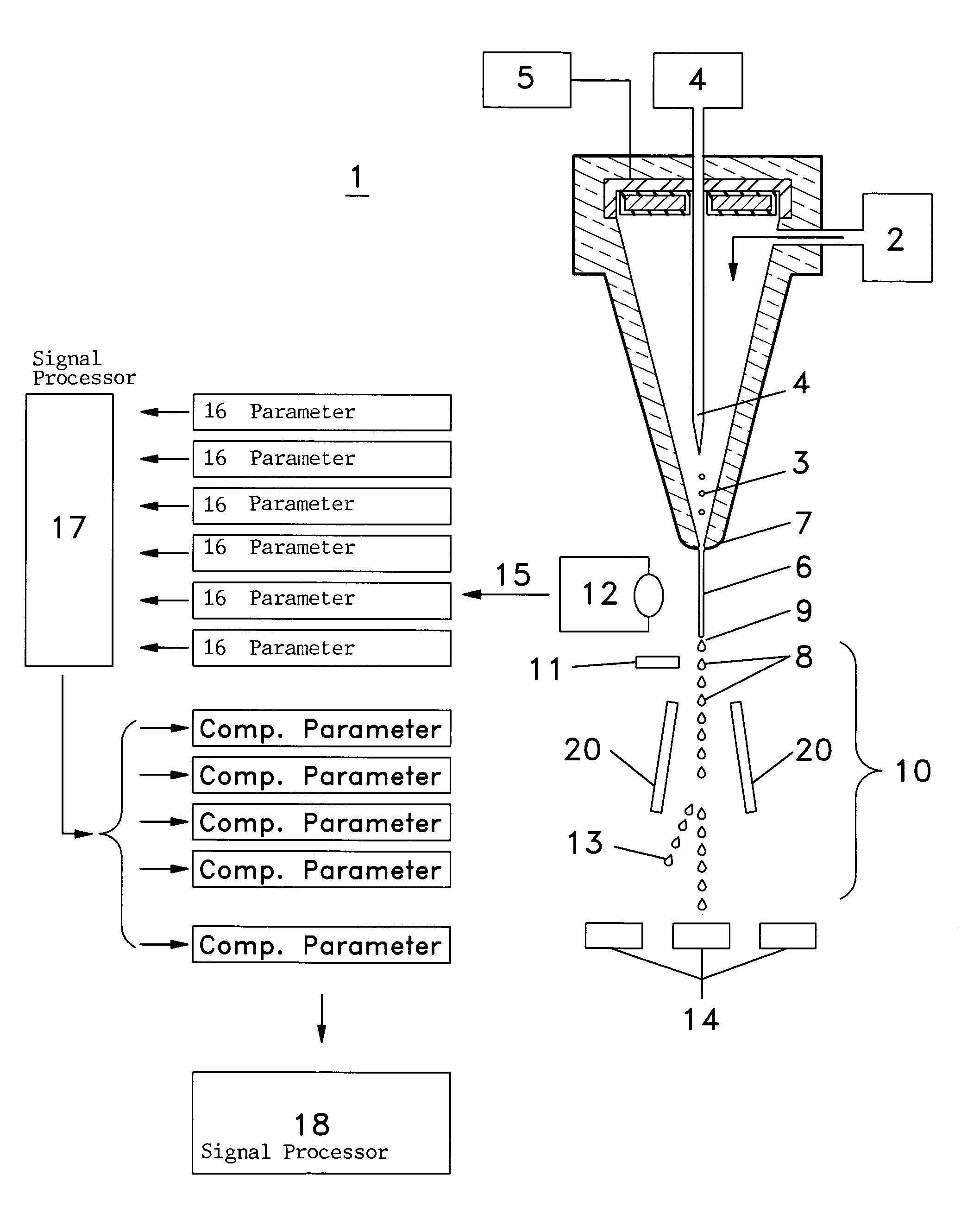
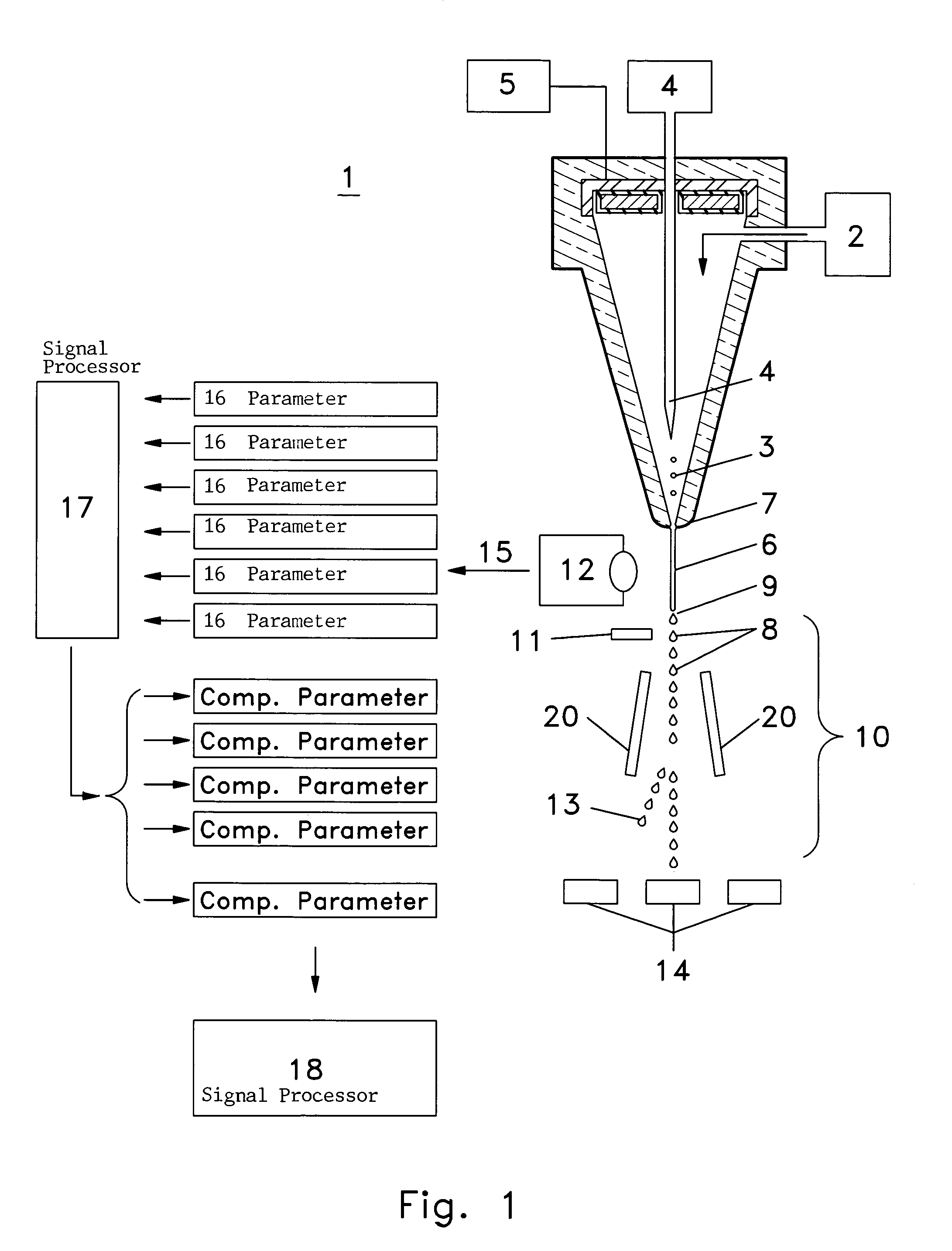
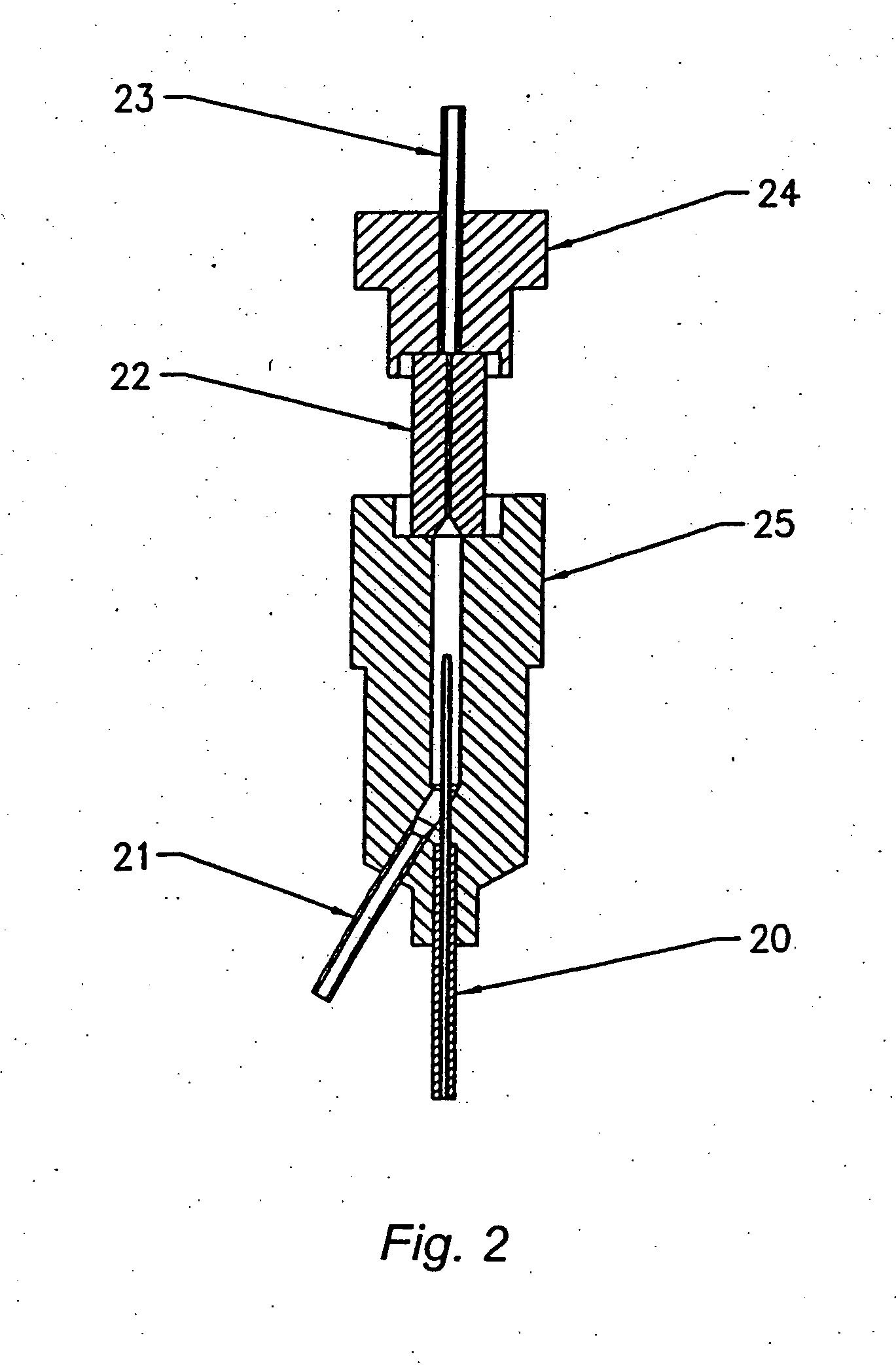
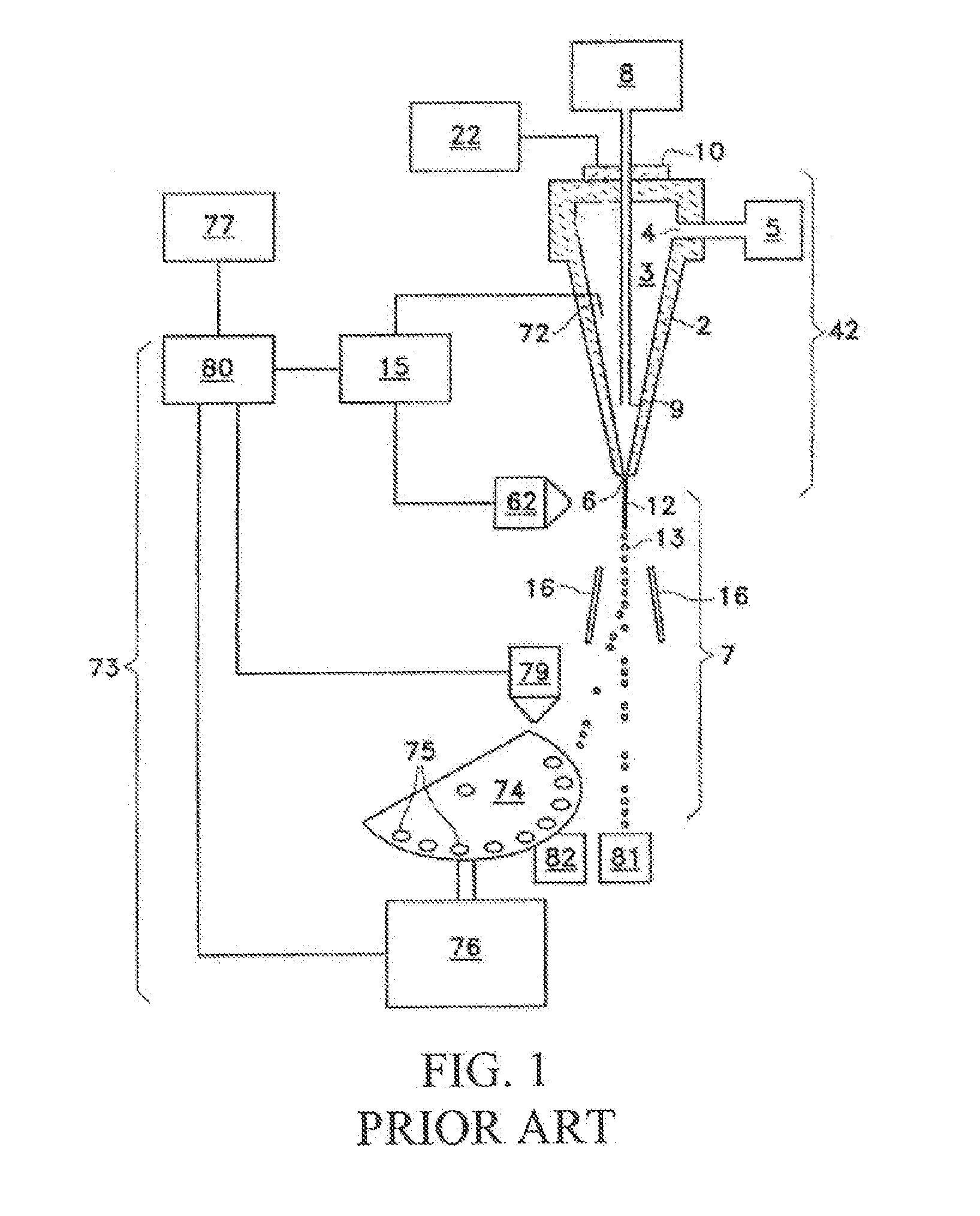
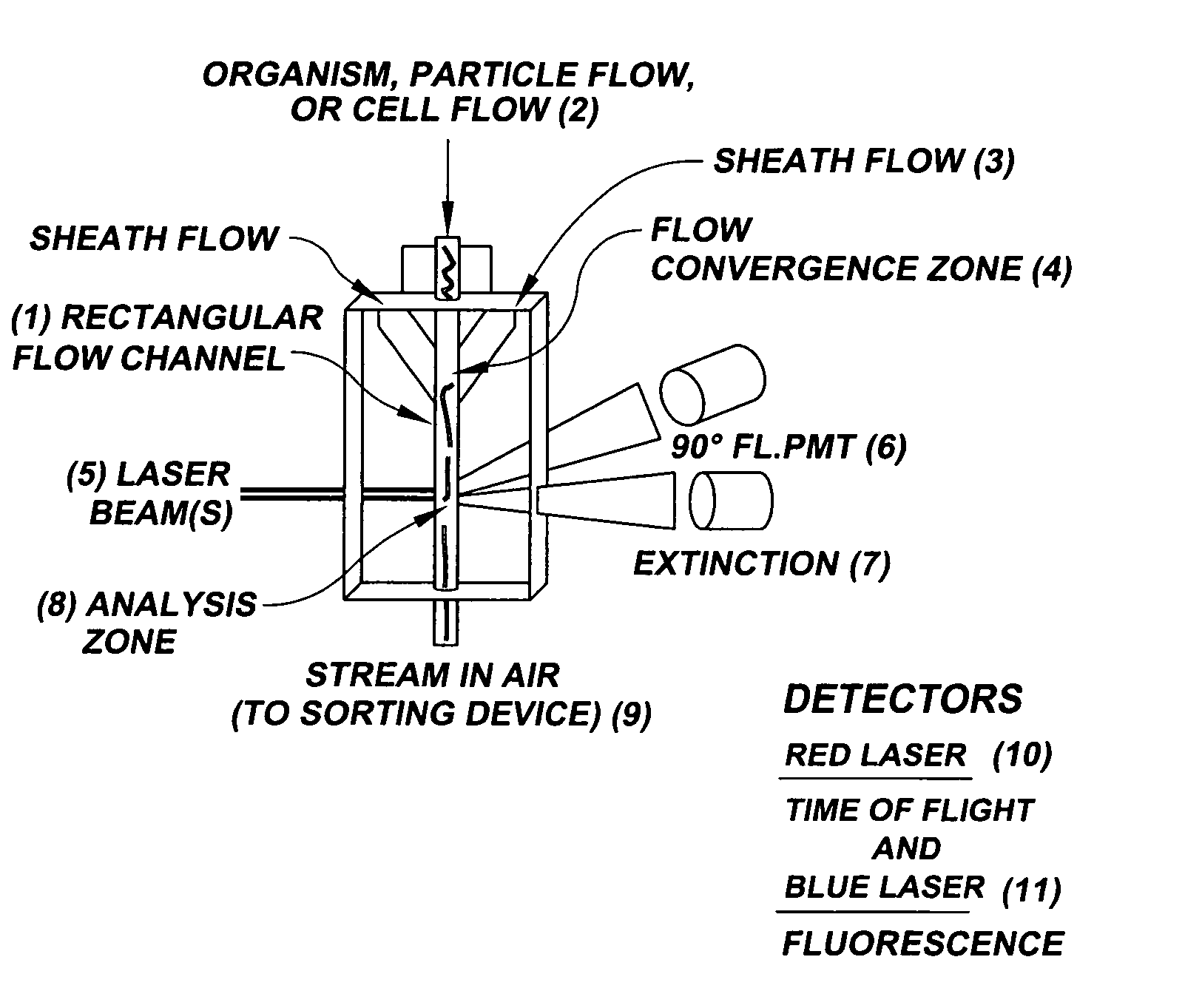
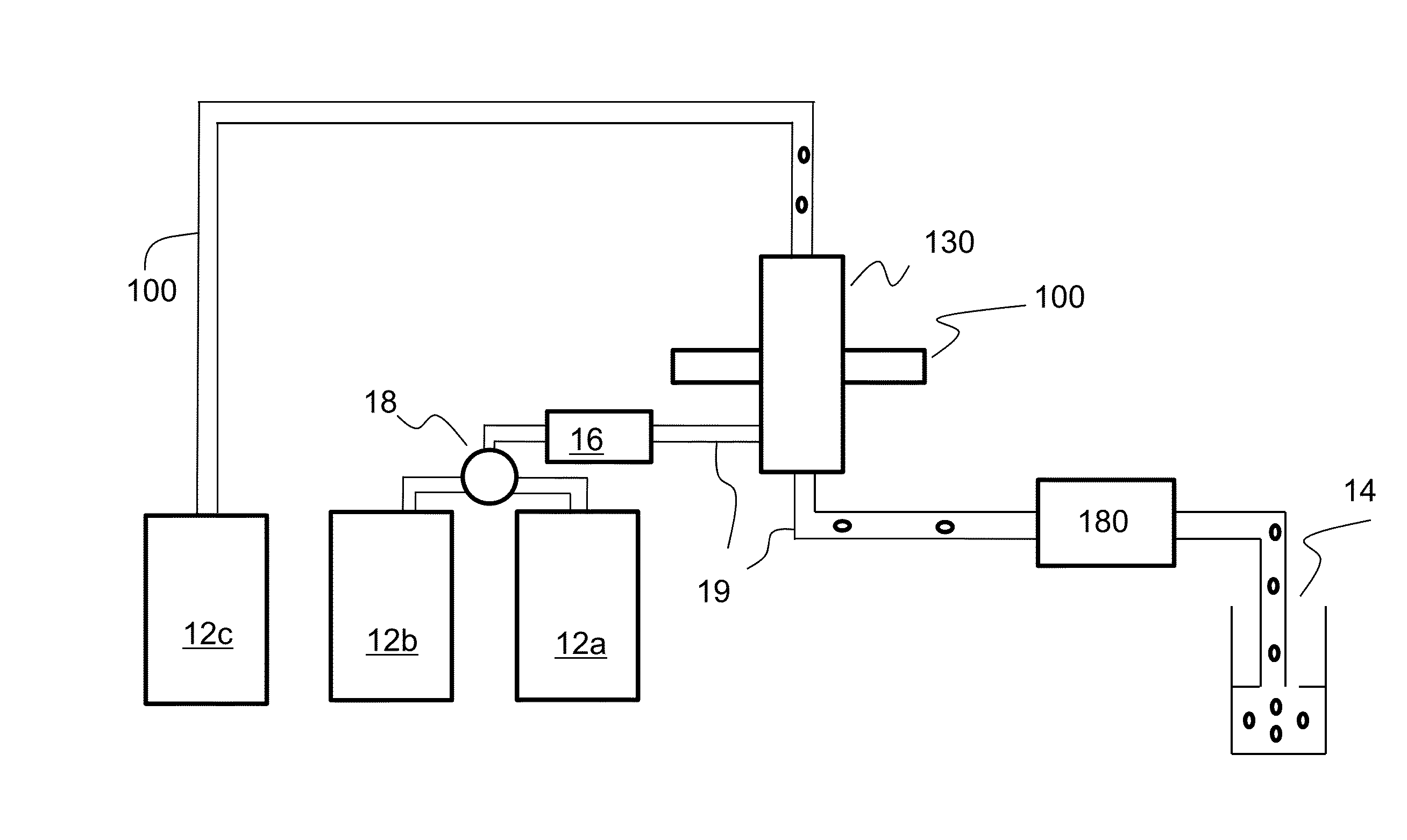
InactiveUS6589792B1Accurately determining a drop delay timeAccurate chargesElectrostatic separationCharacter and pattern recognitionDelayed timeLength wave
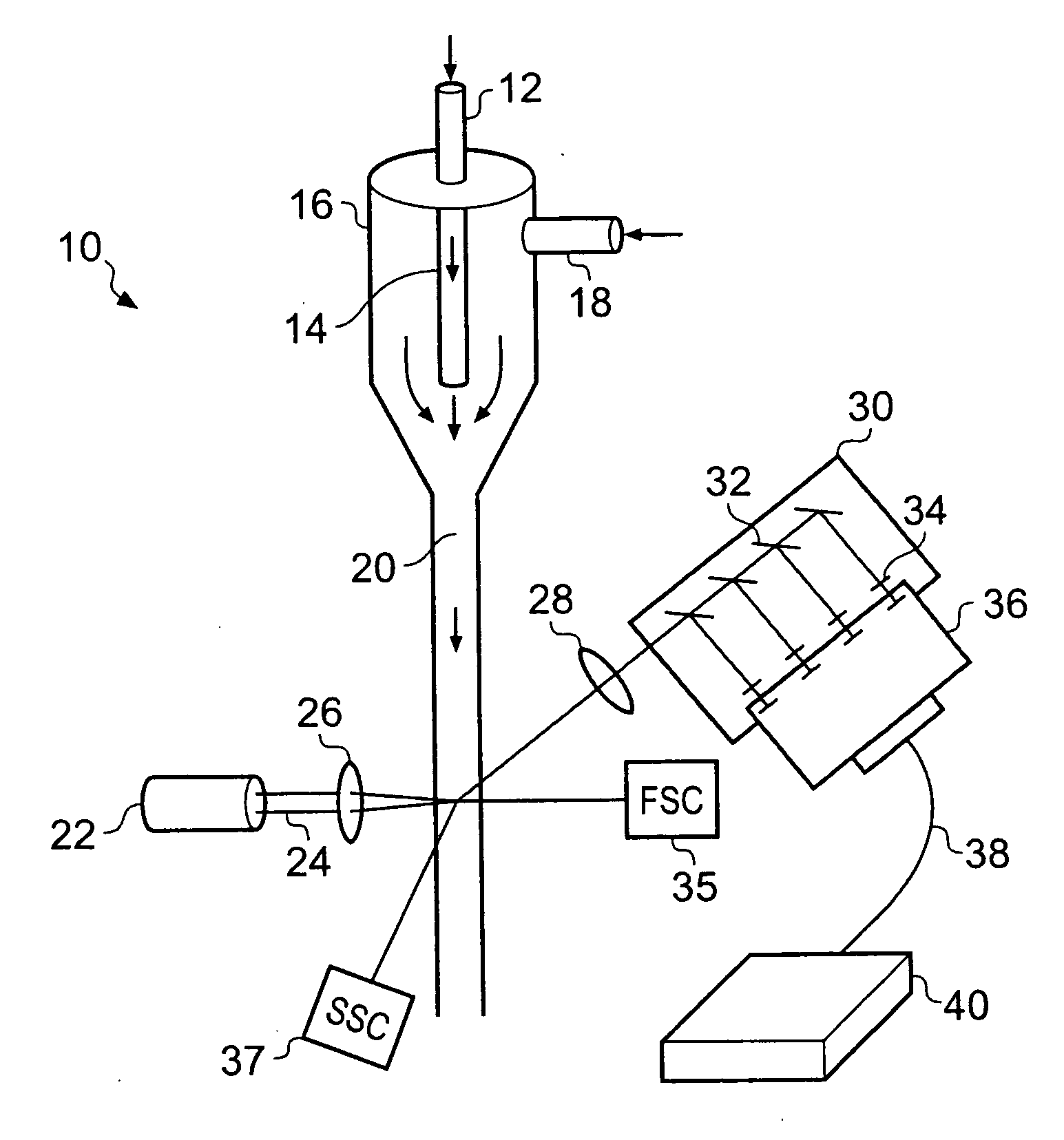
A flow cytometer (20) capable of utilizing an imaging system including a sensor (88) to determine various properties of the flow cytometer (20). Importantly, the imaging allows for determination of a drop delay time (154). Other characteristics that can be determined include at least the width of the stream, pressure of the stream, effect of charged droplets on other droplets (44), trajectory of the stream, resonant frequency, wavelengths, change in position of droplet break-off point (150), and others. An automatic warning system (180) can be used to alert an operator of an anomaly during setup or during normal operation. Furthermore, a mechanical interrupter can be used to shield a sort result from contamination by an incorrectly functioning stream. The cytometer (20) also allows for the disablement of the sort, particularly the charging and deflection systems. In addition, a more accurate system for detecting the speed of the stream can be used. The imaging system including a sensor (88) can allow for the removal of background noise and the monitoring of a change in a stream characteristic.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
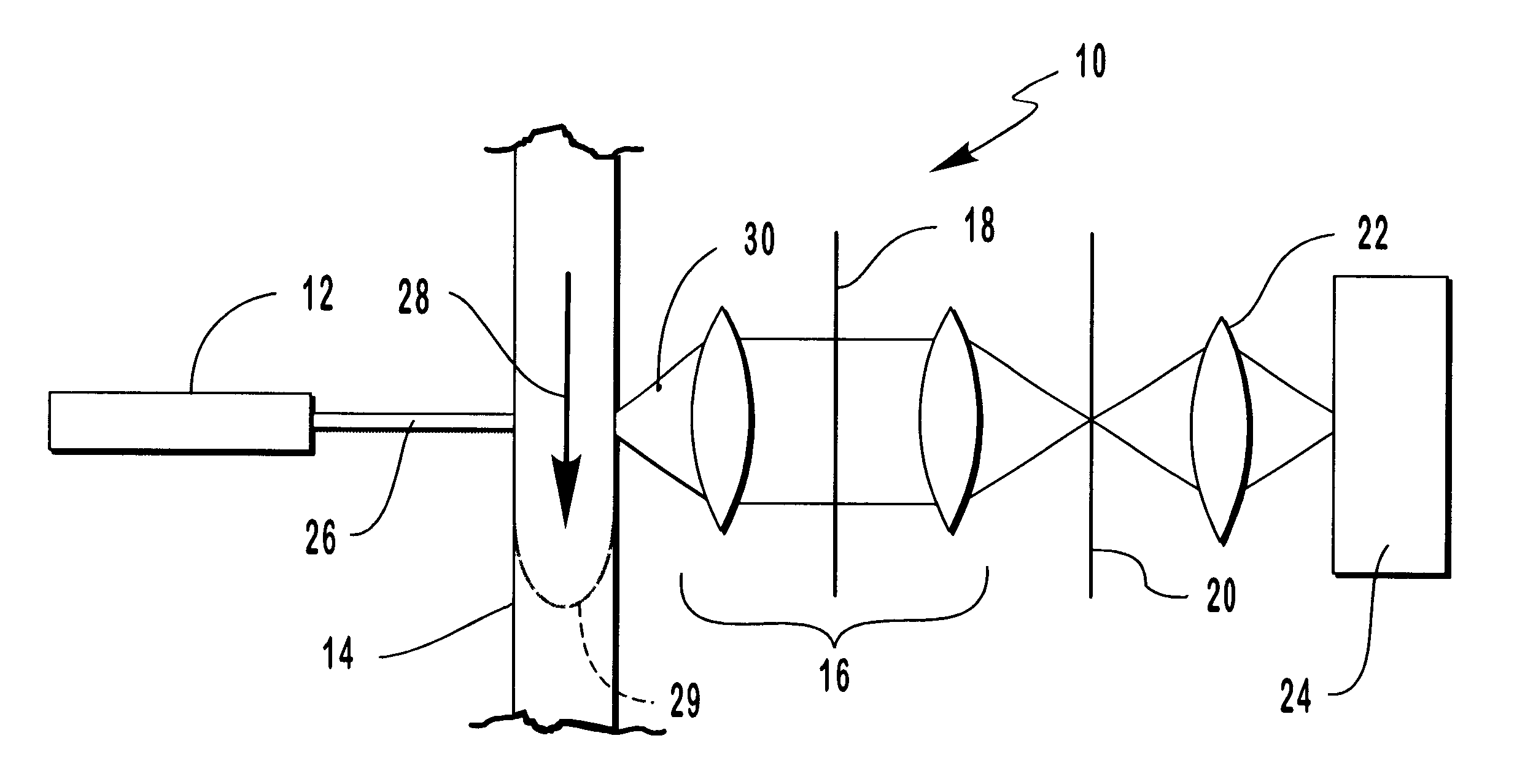
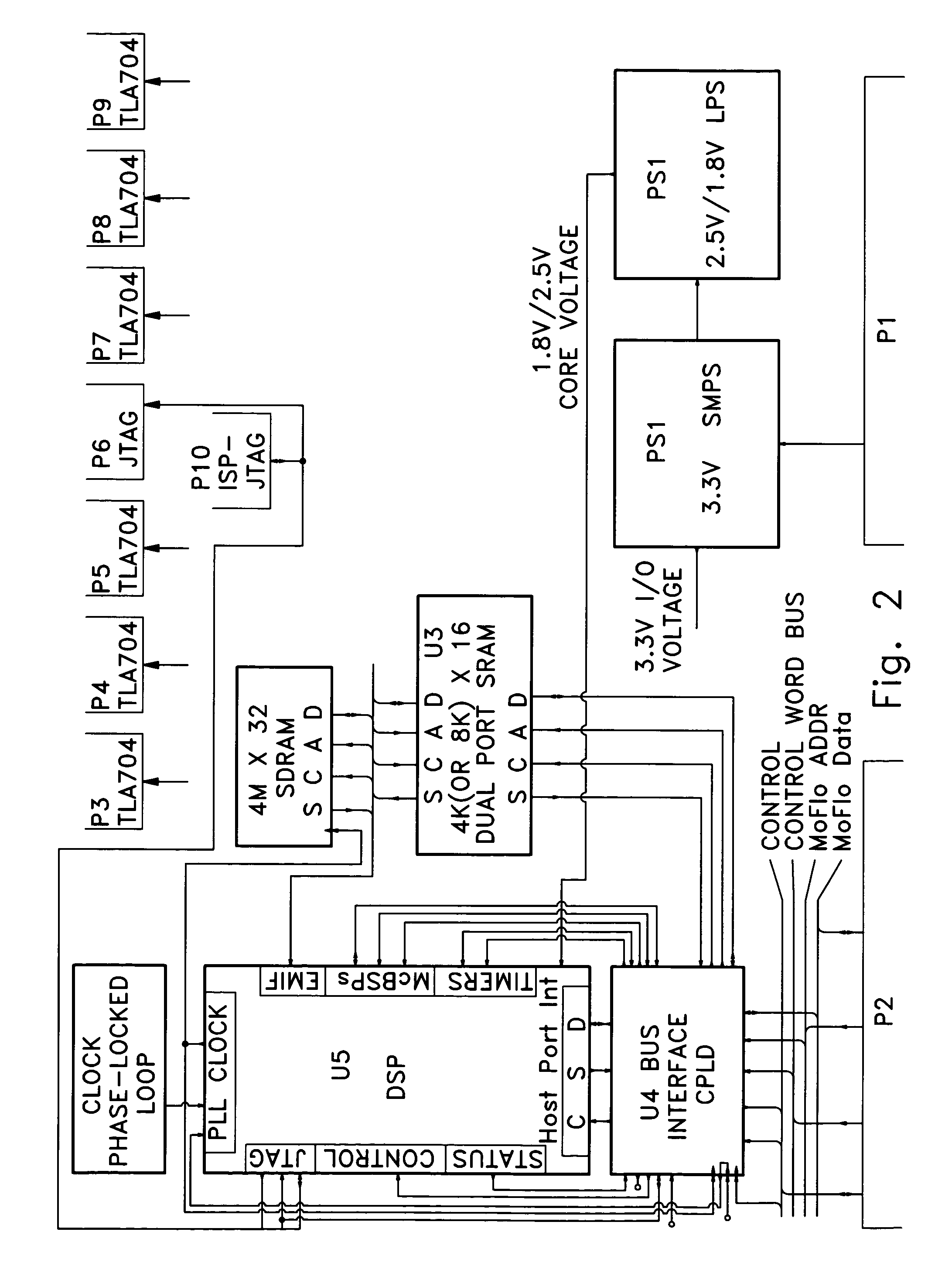
Flow cytometry apparatus and method
InactiveUS6256096B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce contributionParticle size analysisIndividual particle analysisBiological cellStatistical analysis
A flow cytometer for detecting target particles such as microorganisms including biological cells and viruses as well as molecular species. The flow cytometer includes a detection system involving a CCD having a time delay integration capability to thereby increase the signal from the target particle and decrease the noise detected by the CCD. Calibration particles can be included in the sample stream of the flow cytometer for coordinating the readout of the CCD with the rate of flow of the sample stream to improve the detection capability of the CCD. Statistical analysis techniques can also be used to determine the rate of flow of target particles in the sample stream to thereby coordinate the readout rate of the CCD with the rate of flow of the target particles.
Owner:SOFTRAY
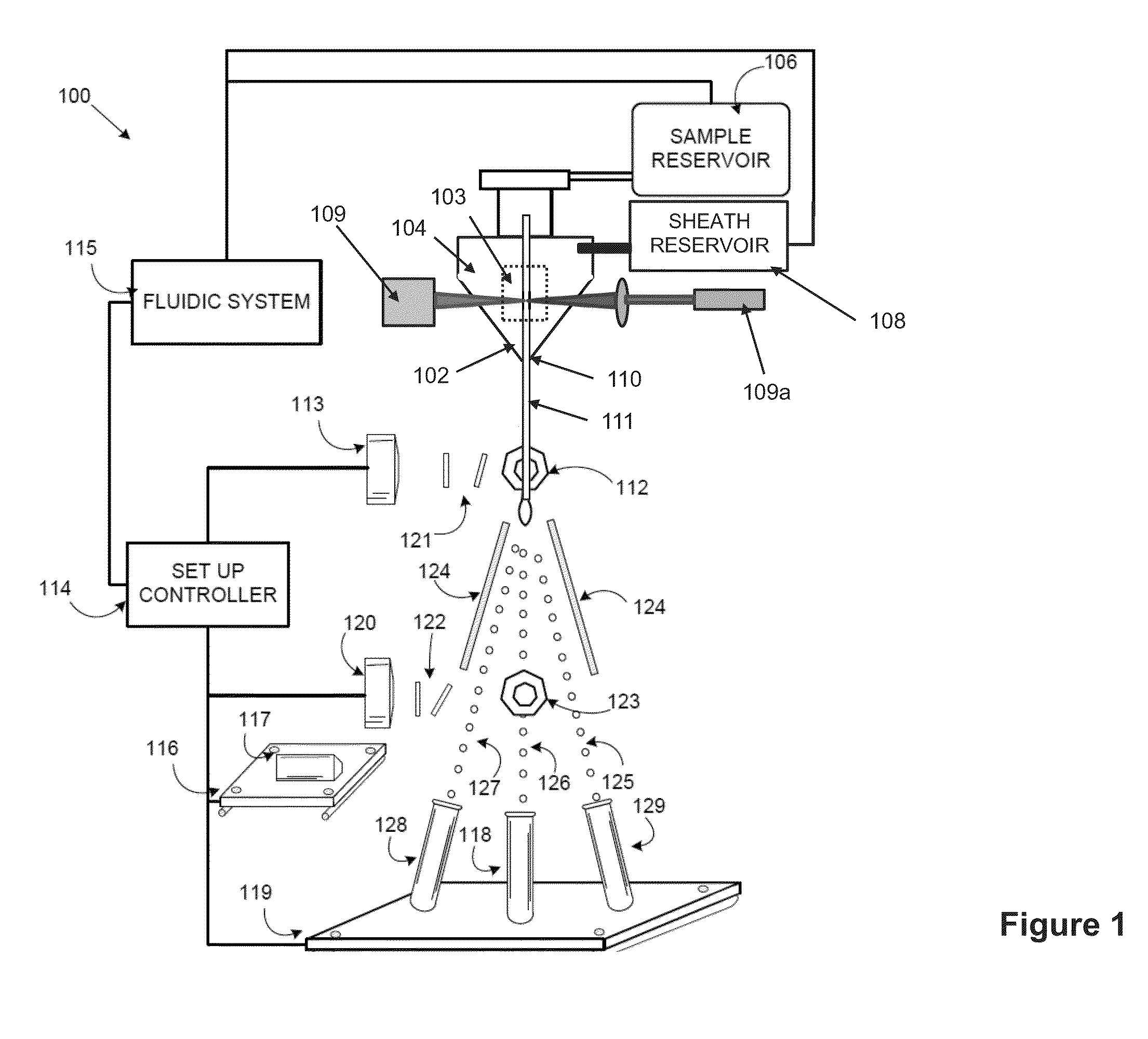
Automated set-up for cell sorting
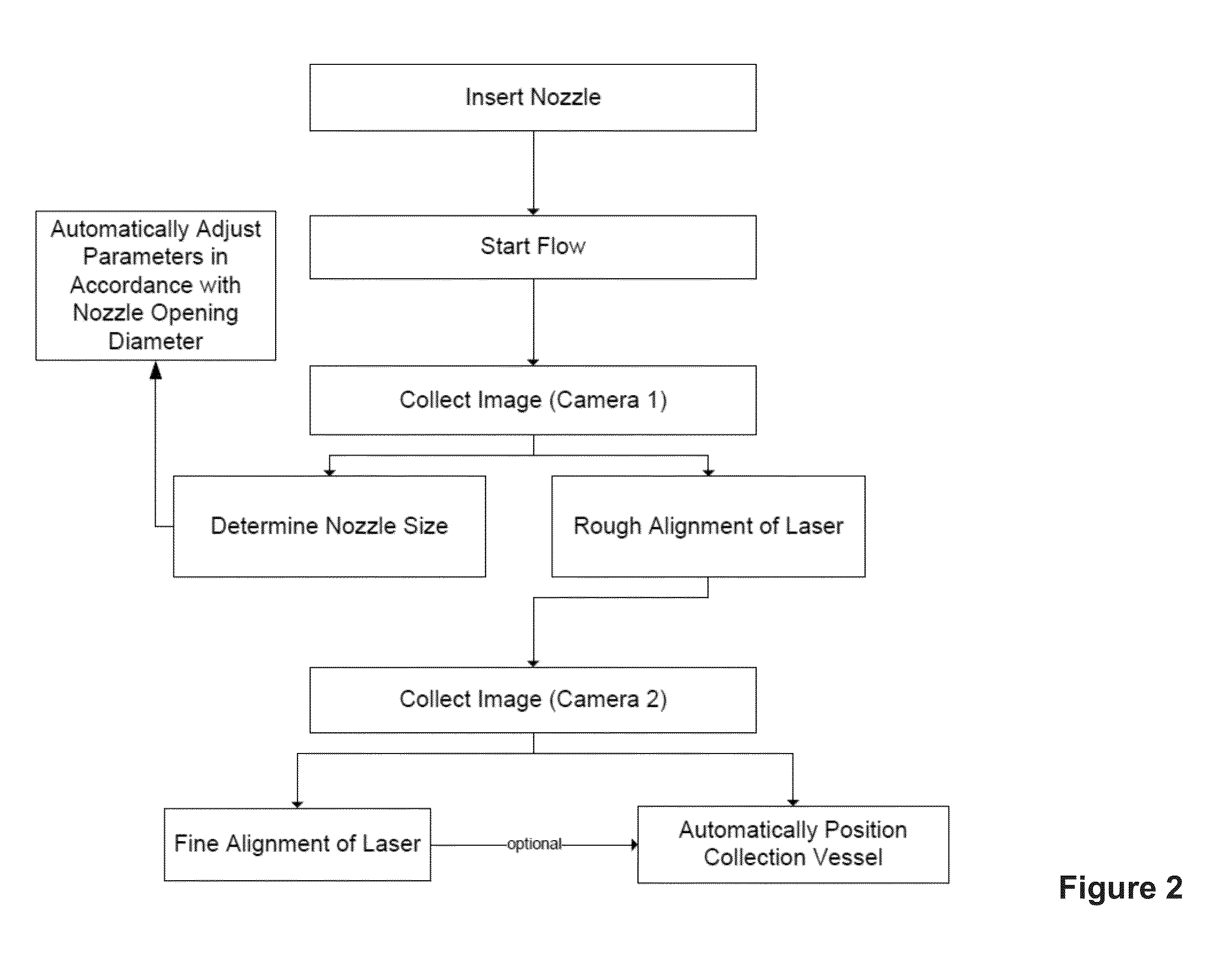
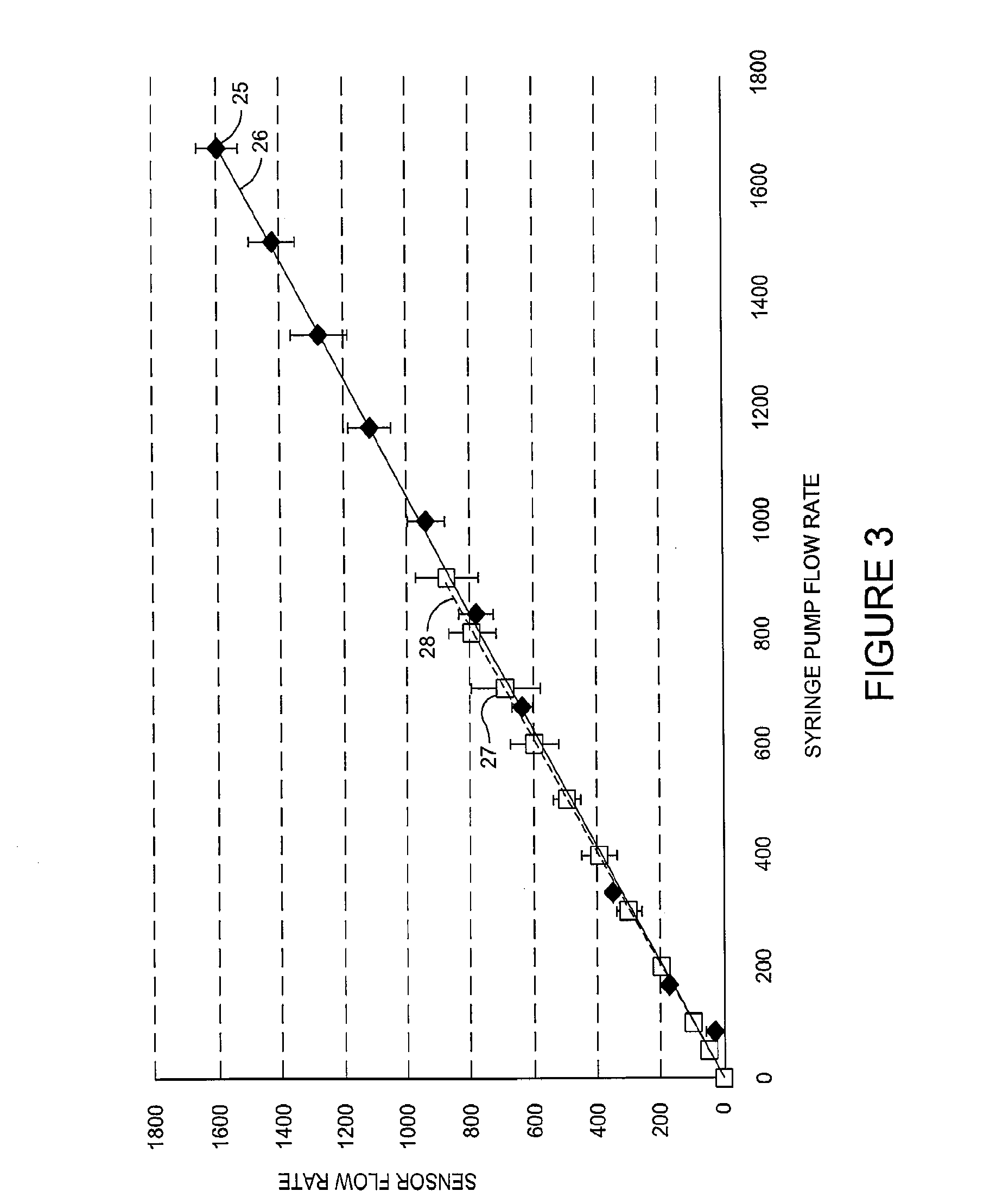
ActiveUS8975595B2Guaranteed uniform velocityReduce needImage analysisVolume/mass flow measurementComputer scienceFlow Cytofluorometry
Apparatus and methods are described for automatically performing set-up steps for flow cytometry operations. The invention provides for the spatial determination of a flow stream and the subsequent automatic alignment of analysis devices and / or collection vessels. The automatic determination of flow stream properties provides for the automatic configuration flow cytometer parameters.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Efficient haploid cell sorting flow cytometer systems
InactiveUS20060263829A1Increase ratingsHigh resolutionMicrobiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsImage resolutionManipulator
A flow cytometry system (1) for sorting haploid cells, specifically irradiatable sperm cells, with an intermittingly punctuated radiation emitter (56). Embodiments include a beam manipulator (21) and even split radiation beams directed to multiple nozzles (5). Differentiation of sperm characteristics with increased resolution may efficiently allow differentiated sperm cells to be separated higher speeds and even into subpopulations having higher purity.
Owner:XY
Transiently dynamic flow cytometer analysis system
InactiveUS7024316B1Good compensationShort transition timeFlow propertiesVolume/mass flow measurementHigh rateComputer science
A flow cytometry apparatus and methods to process information incident to particles or cells entrained in a sheath fluid stream allowing assessment, differentiation, assignment, and separation of such particles or cells even at high rates of speed. A first signal processor individually or in combination with at least one additional signal processor for applying compensation transformation on data from a signal. Compensation transformation can involve complex operations on data from at least one signal to compensate for one or numerous operating parameters. Compensated parameters can be returned to the first signal processor for provide information upon which to define and differentiate particles from one another.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Chip-Based Flow Cytometer Type Systems for Analyzing Fluorescently Tagged Particles
ActiveUS20070269345A1Individual particle analysisFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicrofluidic AnalysisTagged particle
Portable systems for processing and analyzing biological or environmental samples as well as different configurations of chip-based flow cytometers are provided. The portable systems include an automated assay preparation module configured to process a sample into a fluid assay with fluorescently tagged particles and a microfluidic analysis module coupled to the fluid assay module, wherein the microfluidic analysis module includes a chip-based flow cytometer.
Owner:LUMINEX
Flow-cytometry-based hematology system
InactiveUS20060203226A1Reduce wasteLow costWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationMedicine.hematologyFlow cell
Owner:IDEXX LABORATORIES
Flow cytometer
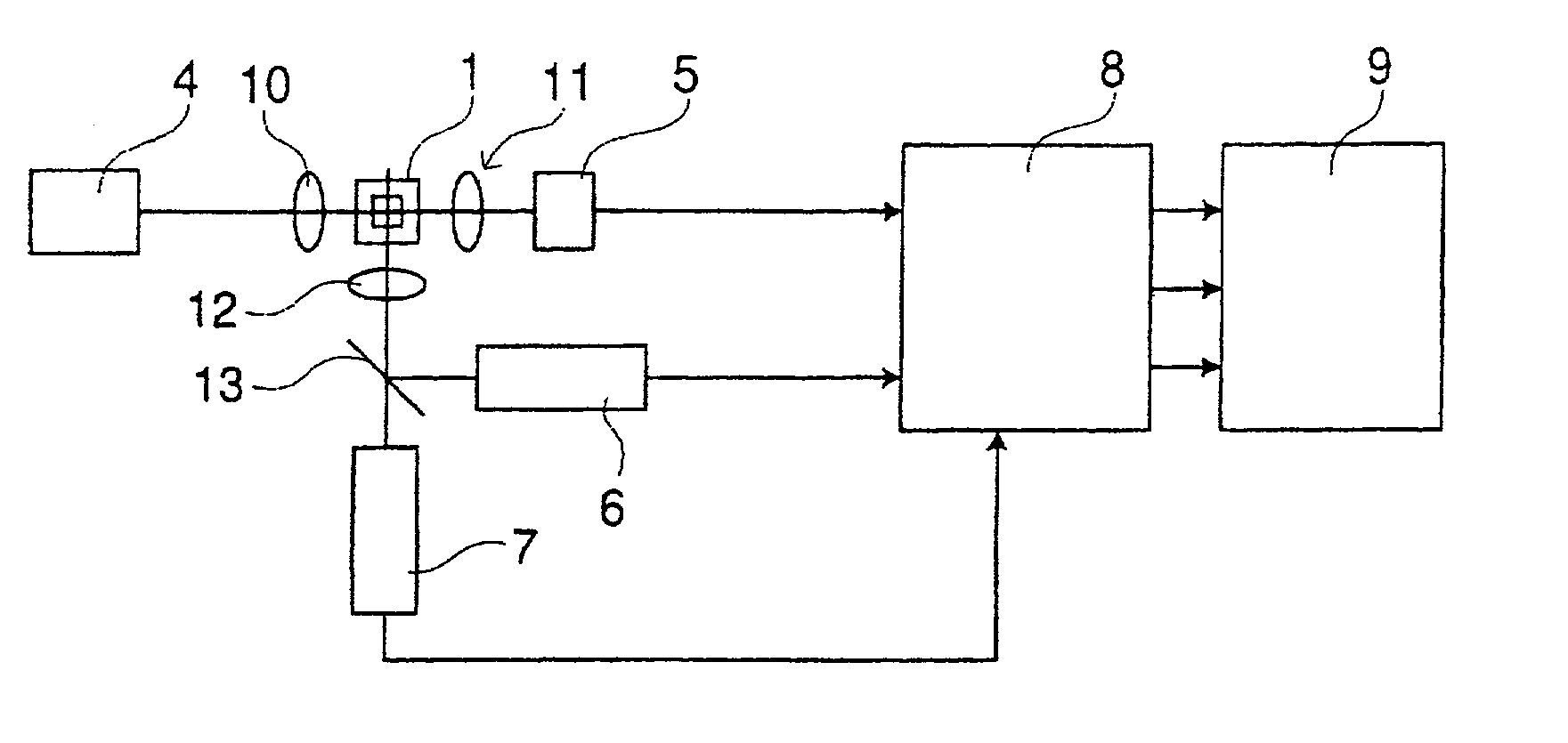
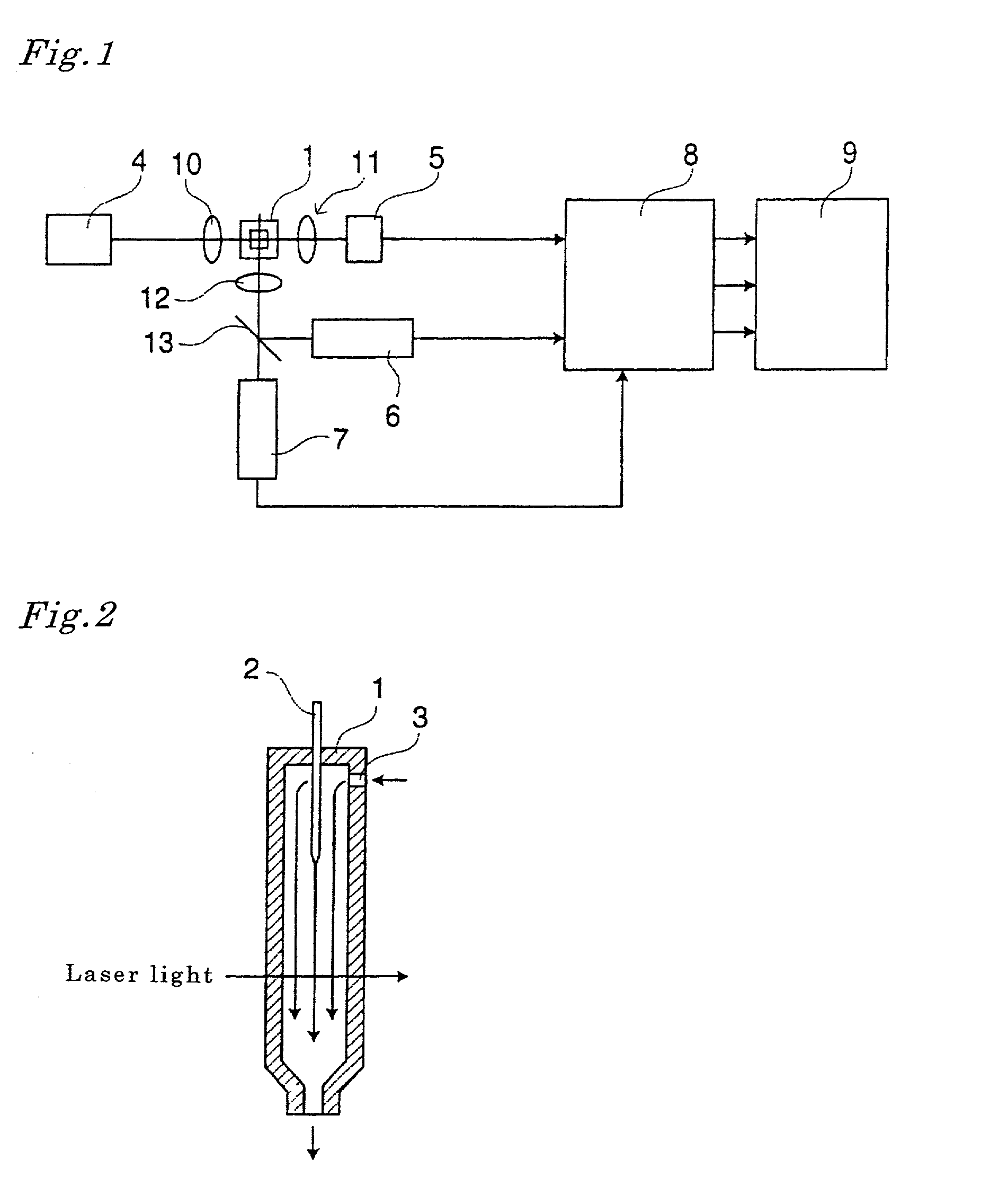
ActiveUS7477363B2Analyzing especially fluorescence of a target particle more appropriately and efficientlyEliminate scatterRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationFlow cellFluorescence
A laser light source emits a first light beam irradiating a solution including target particles and being flowed in a flow cell to generate forward scattered light and orthogonal scattered light therefrom. A light emitting diode emits a second light beam irradiating the solution in the flow cell to generate at least one wavelength of fluorescence therefrom. A first detector is adapted to detect the forward scattered light. A second detector is adapted to detect the orthogonal scattered light. At least one third detector is adapted to detect the at least one fluorescence. A first filter is disposed between the flow cell and the third detector and adapted to eliminate scattered light generated from the target particles by the irradiation of the first light beam.
Owner:NIHON KOHDEN CORP
Methods for controlling one or more parameters of a flow cytometer type measurement system
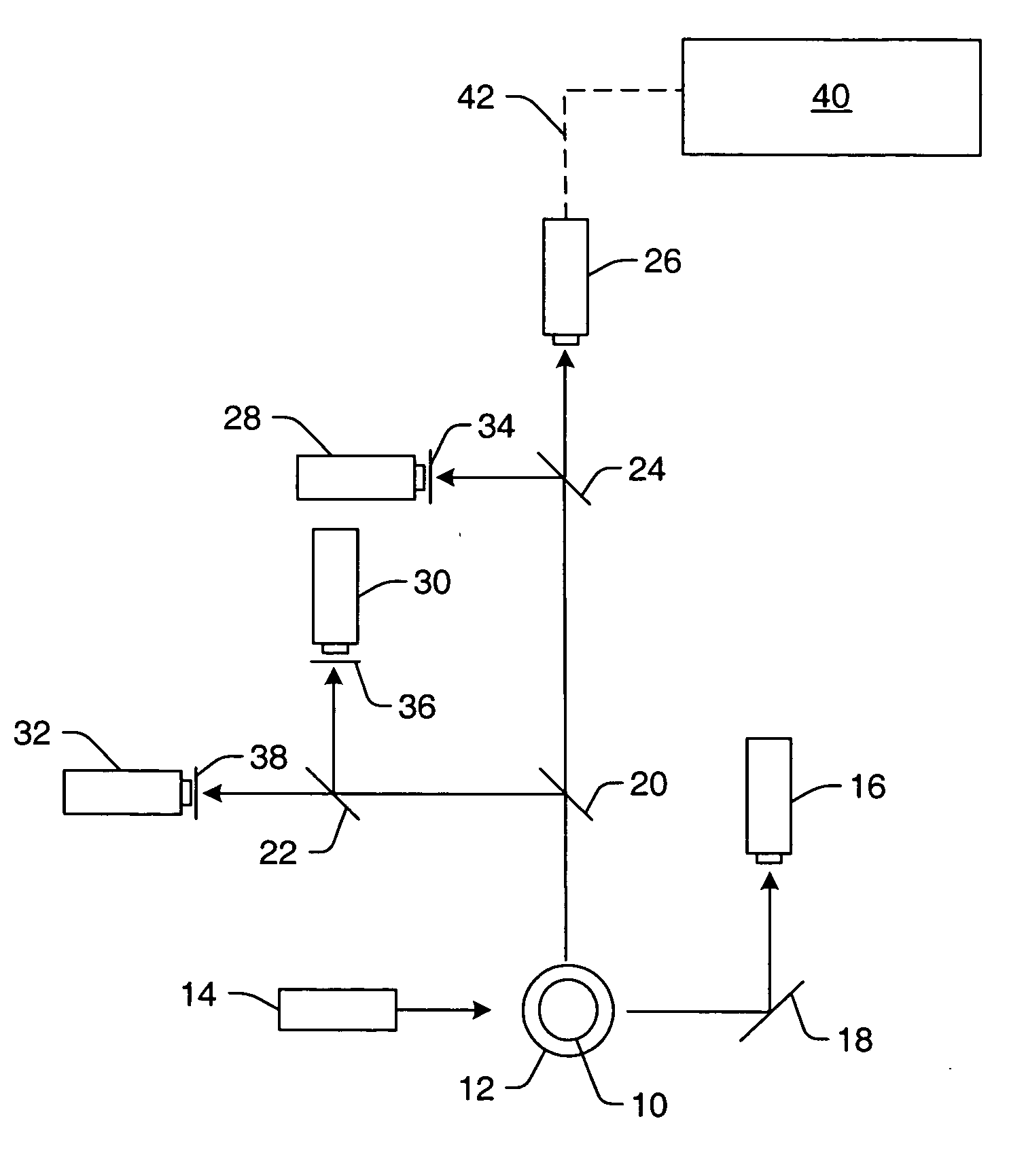
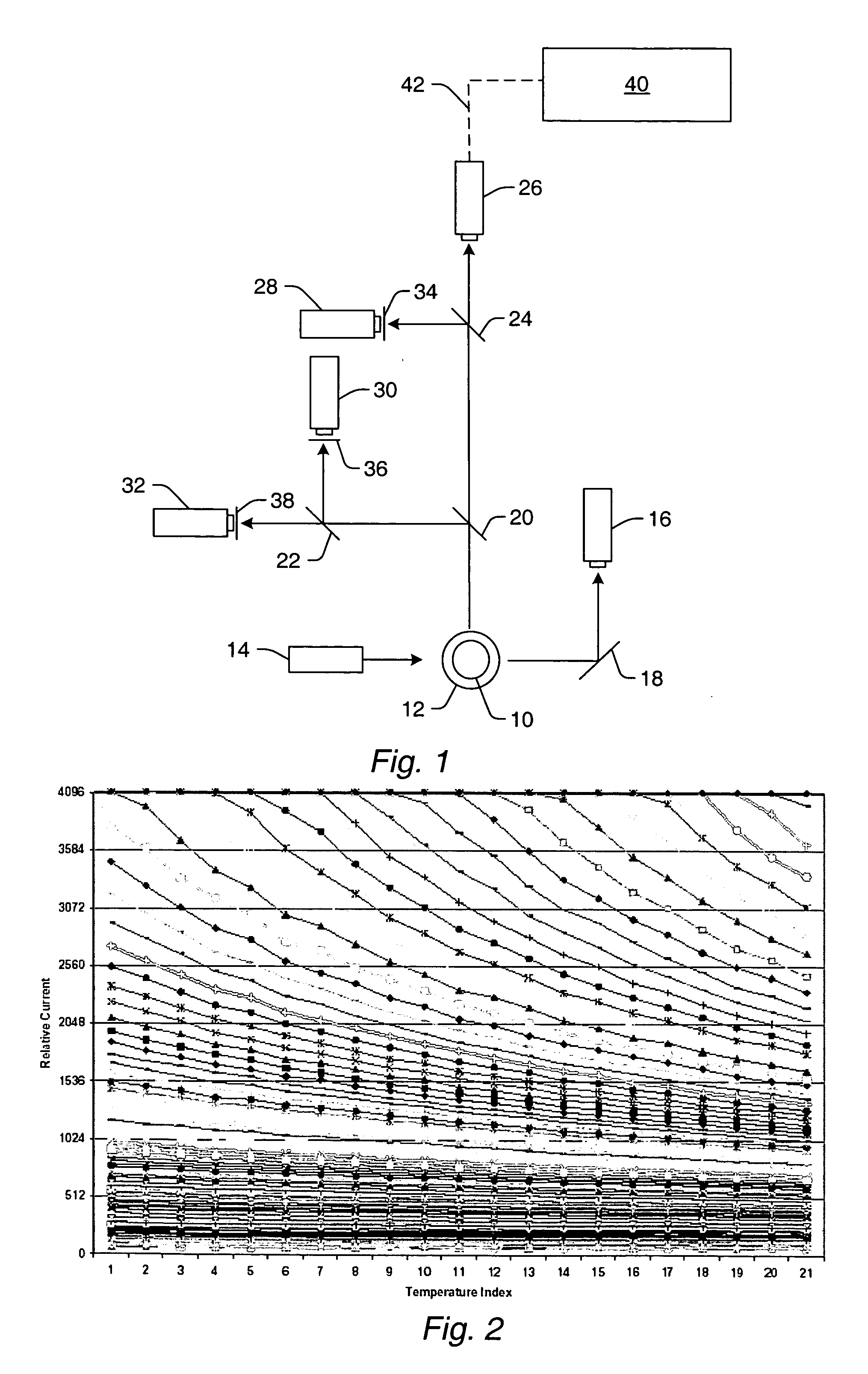
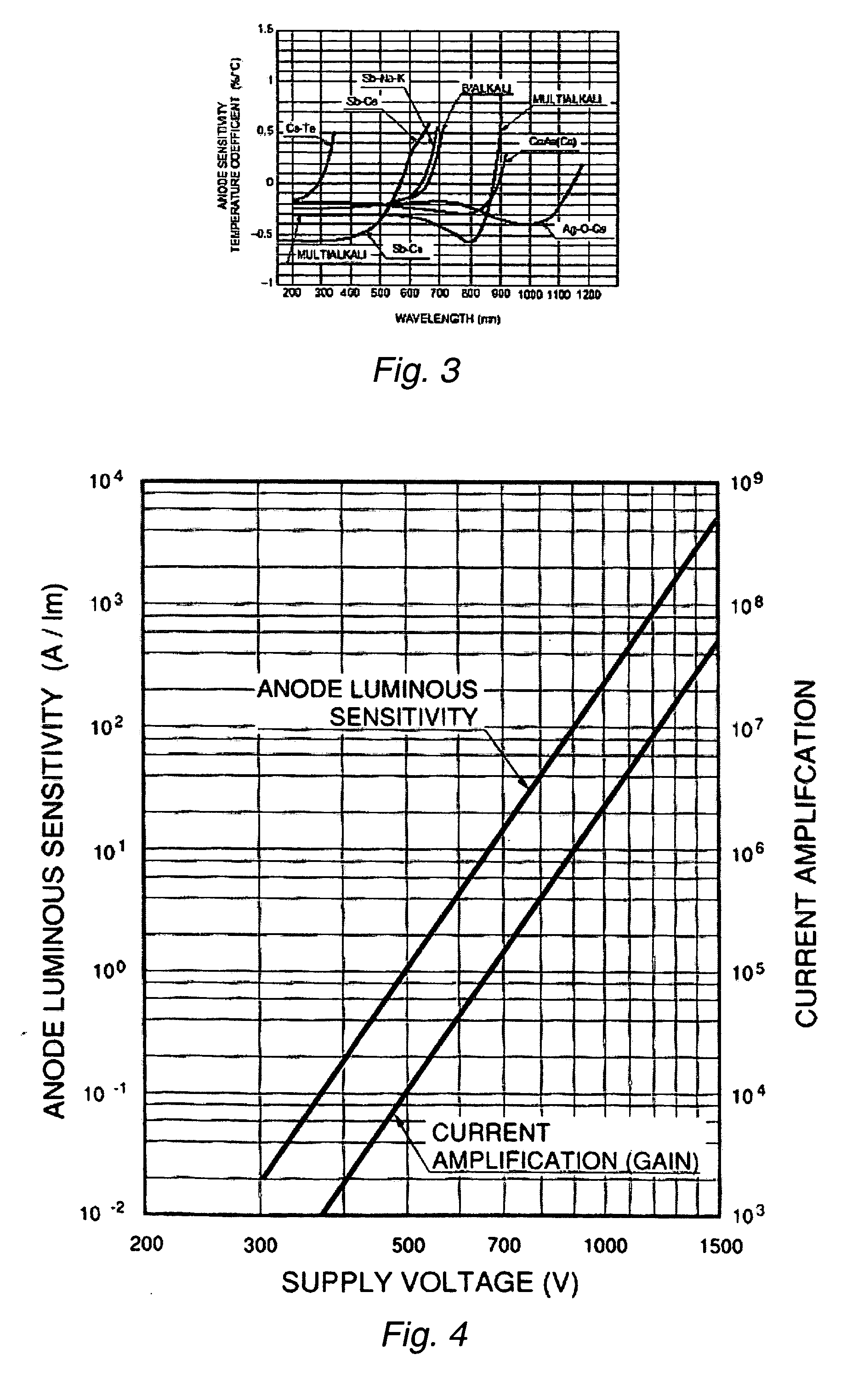
ActiveUS20050073686A1Increase calibration rangeMaterial analysis by optical meansIndividual particle analysisFlow CytofluorometryEngineering
Various methods for controlling one or more parameters of a flow cytometer type measurement system are provided. One embodiment includes monitoring parameter(s) of the measurement system during measurements of sample microspheres. The method also includes altering the parameter(s) in real time based on the monitoring. Another method includes monitoring a temperature proximate to the measurement system. One such method includes altering a bias voltage of an avalanche photo diode in response to the temperature using empirically derived data. A different such method includes altering output signals of a photomultiplier tube in response to the temperature using a characteristic curve. Some methods include monitoring a temperature of a fluid, in which sample microspheres are disposed, that will flow through the flow cytometer type measurement system. This method also includes determining a velocity of the sample microspheres in the measurement system from a viscosity of the fluid at the temperature.
Owner:LUMINEX
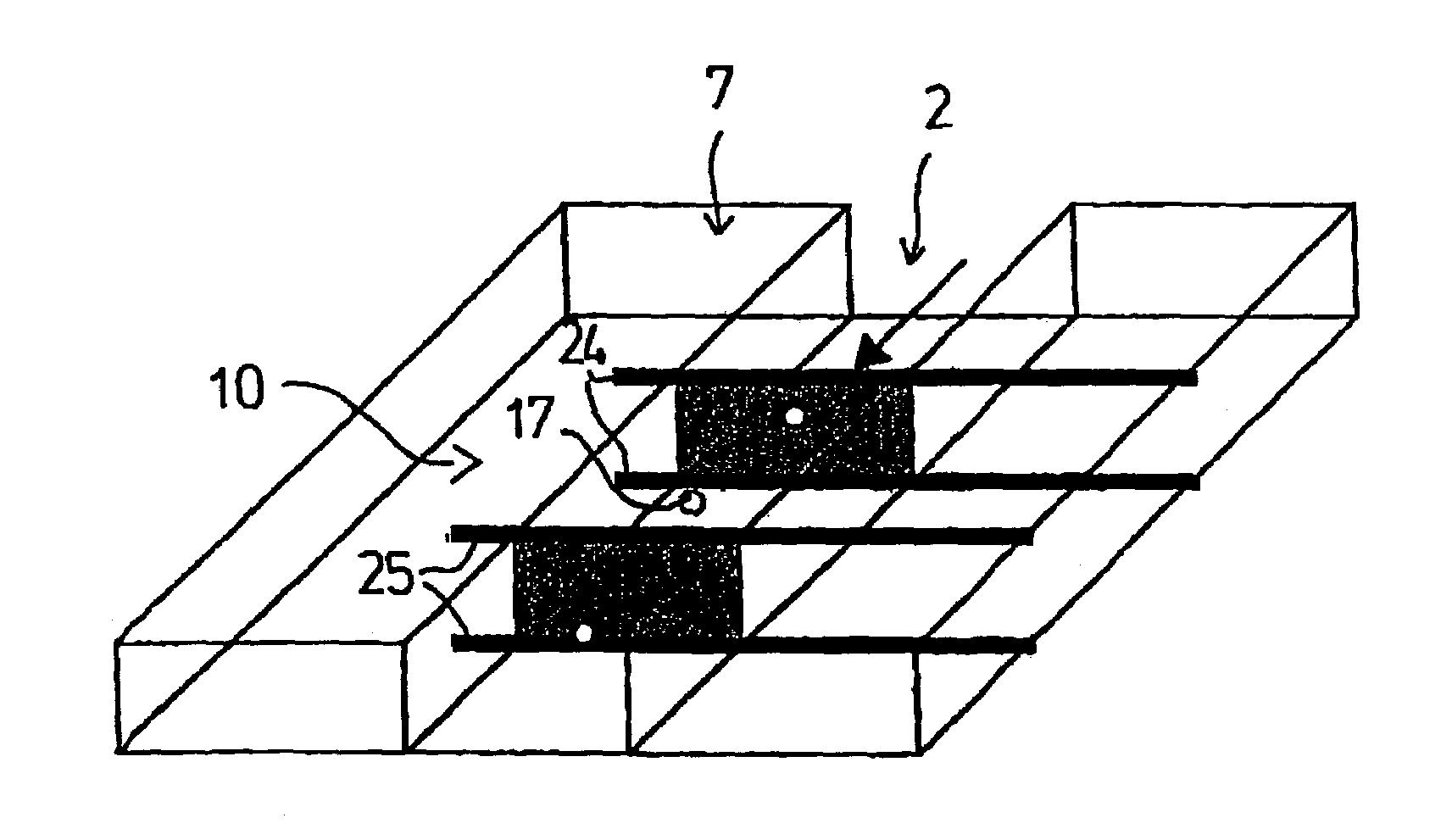
Micro-fluidic chip structure for flow cytometer, and preparation method of micro-fluidic chip
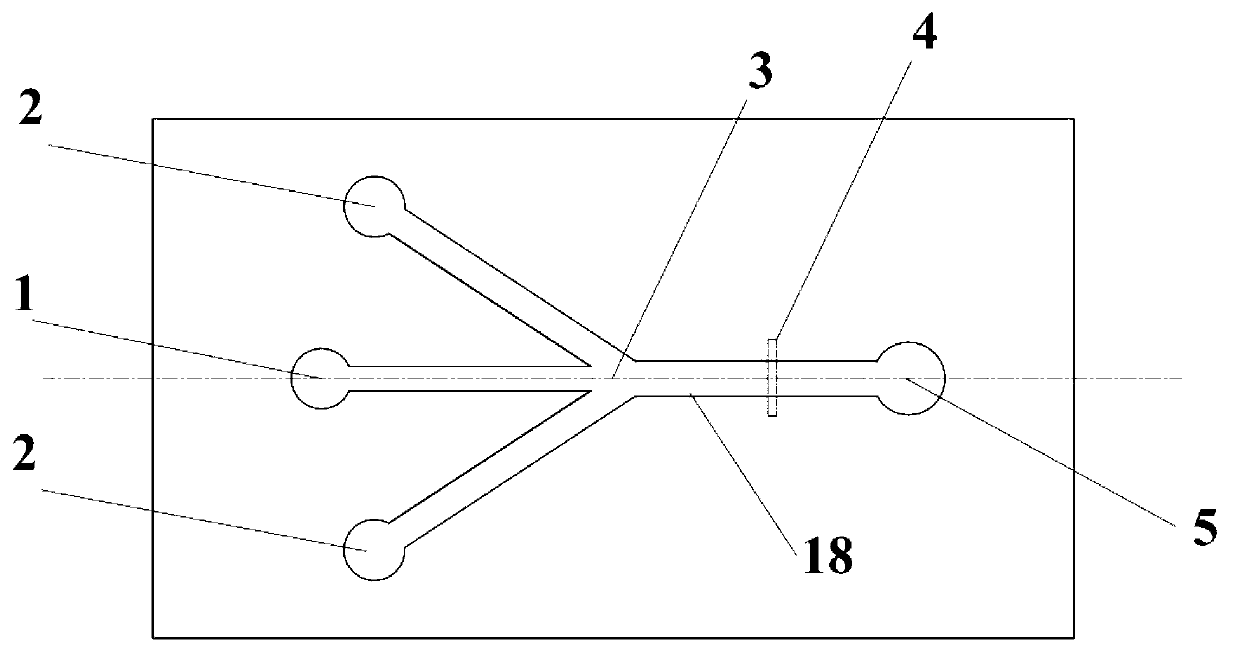
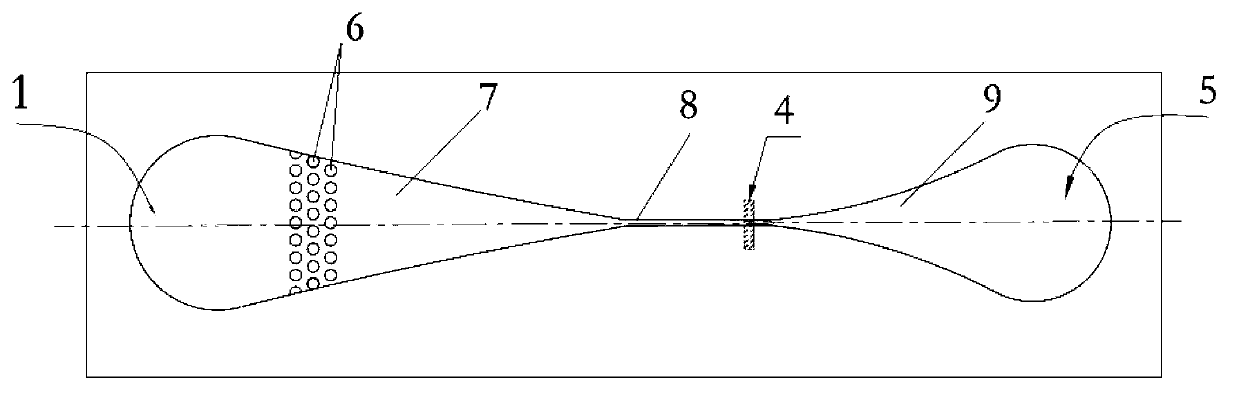
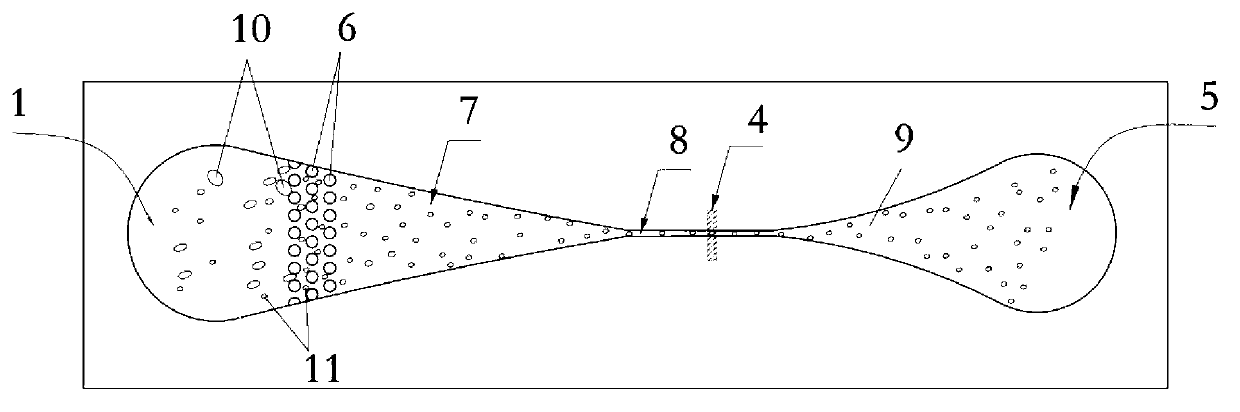
InactiveCN103341372ASimple processing methodEasy to processLaboratory glasswaresIndividual particle analysisBiocompatibility TestingImpurity
The invention discloses a micro-fluidic chip structure for a flow cytometer, and a preparation method a micro-fluidic chip. The chip comprises a sample liquid inlet 1, a column array structure 6, a conical focusing structure 7, a micro-channel 8, a detection zone 4, a flow expanding channel 9 and a waste liquid outlet end 5, wherein the column array structure 6 can play a role of filtering agglomerate protein impurities and other large biological solids inside sample liquid; and the conical focusing structure 7 has a focusing effect which is similar to that of the traditional sheath liquid system, so that cell granules flow inside the micro-channel 8 one by one; and the micro-channel 8 restricts the cells through the channel, so that the cells pass through the detection zone 4 one by one. By adopting the chip structure disclosed by the invention, the focusing effect without sheath flow liquid can be achieved; and blockage is not generated, so as to reduce use of the sheath flow liquid; and meanwhile, the situation that the cell granules pass through the detection zone one by one is ensured. The processing method of the micro-fluidic chip is convenient; the used bonding method is a common bonding method, and is simple and convenient to operate; and the used material PDMS (polydimethylsiloxane) is easy to process and has good biocompatibility.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
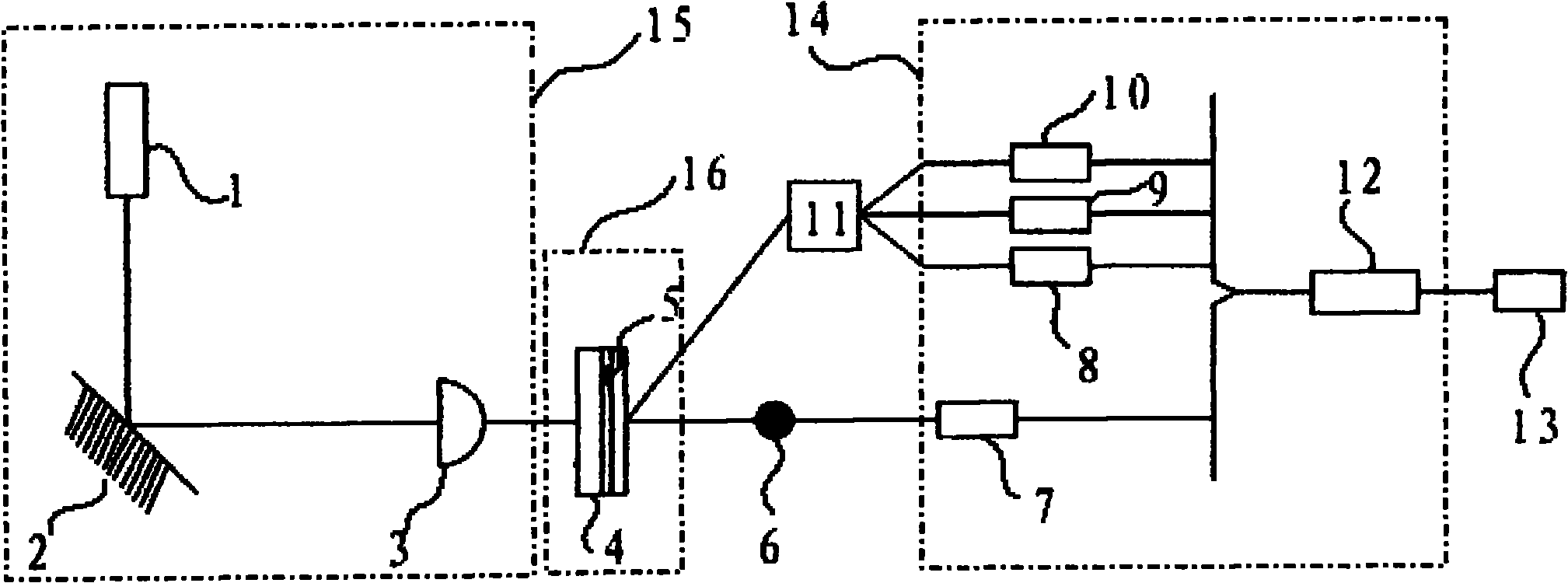
Method and apparatus for syringe-based sample introduction within a flow cytometer
InactiveUS20070025879A1Less componentsLess spaceAnalysis using chemical indicatorsAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionEngineeringPlunger
An apparatus for introducing a specimen into a flow cytometer comprises: a syringe having a hollow barrel containing the specimen, a plunger partially within the barrel and a needle that extends into a volume of a nozzle of the flow cytometer; a one-way port in the nozzle forming a seal against the needle; a mounting platform coupled to both the syringe and to the flow cytometer; and a syringe pump coupled to the plunger, the syringe pump comprising a motor, a drive mechanism coupled to the motor; and a clamping mechanism coupled to the drive mechanism, wherein the motor operates the drive mechanism so as to cause the clamping mechanism to depress the plunger into the barrel.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
System and method for measuring particles in a sample stream of a flow cytometer or the like
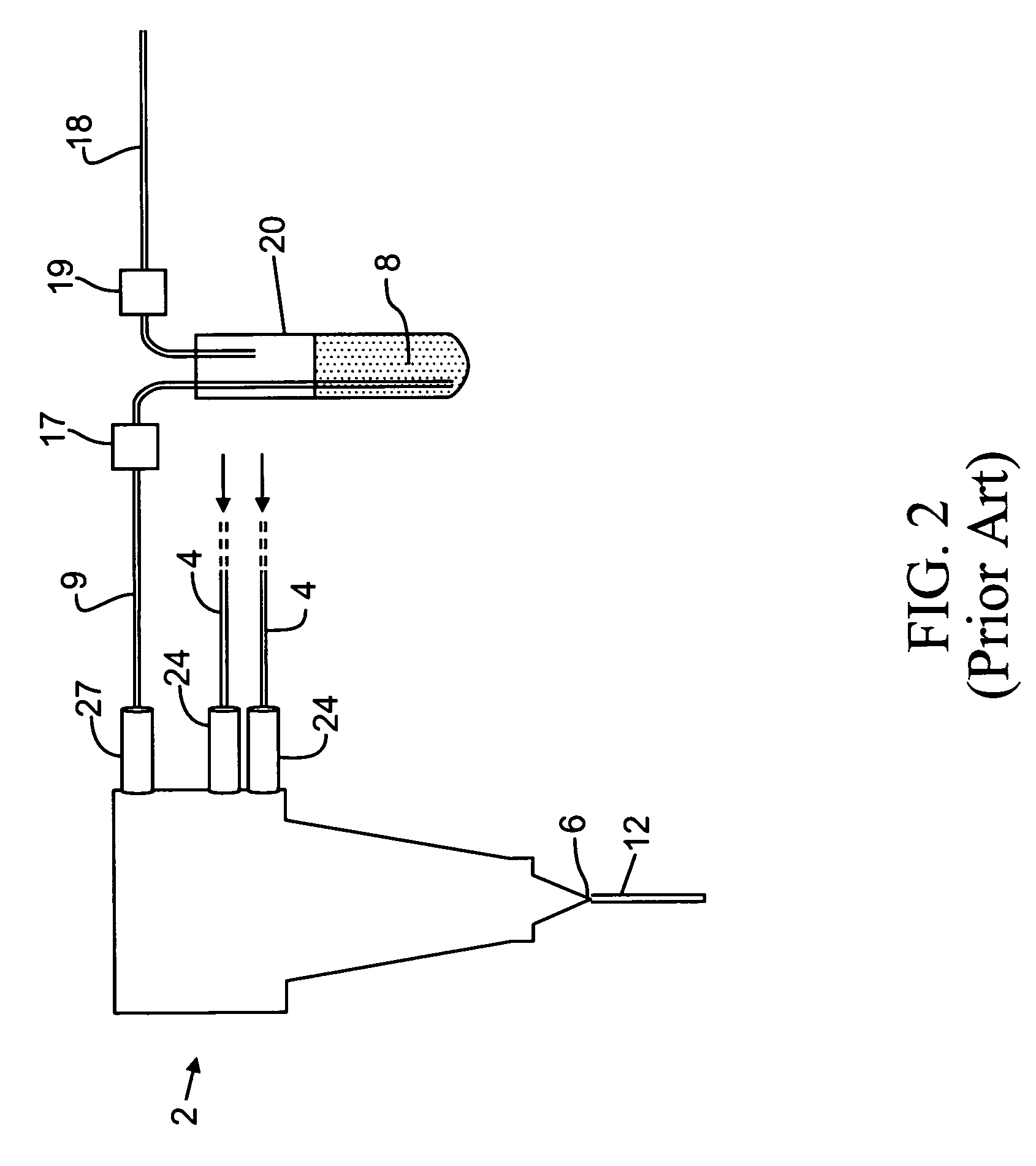
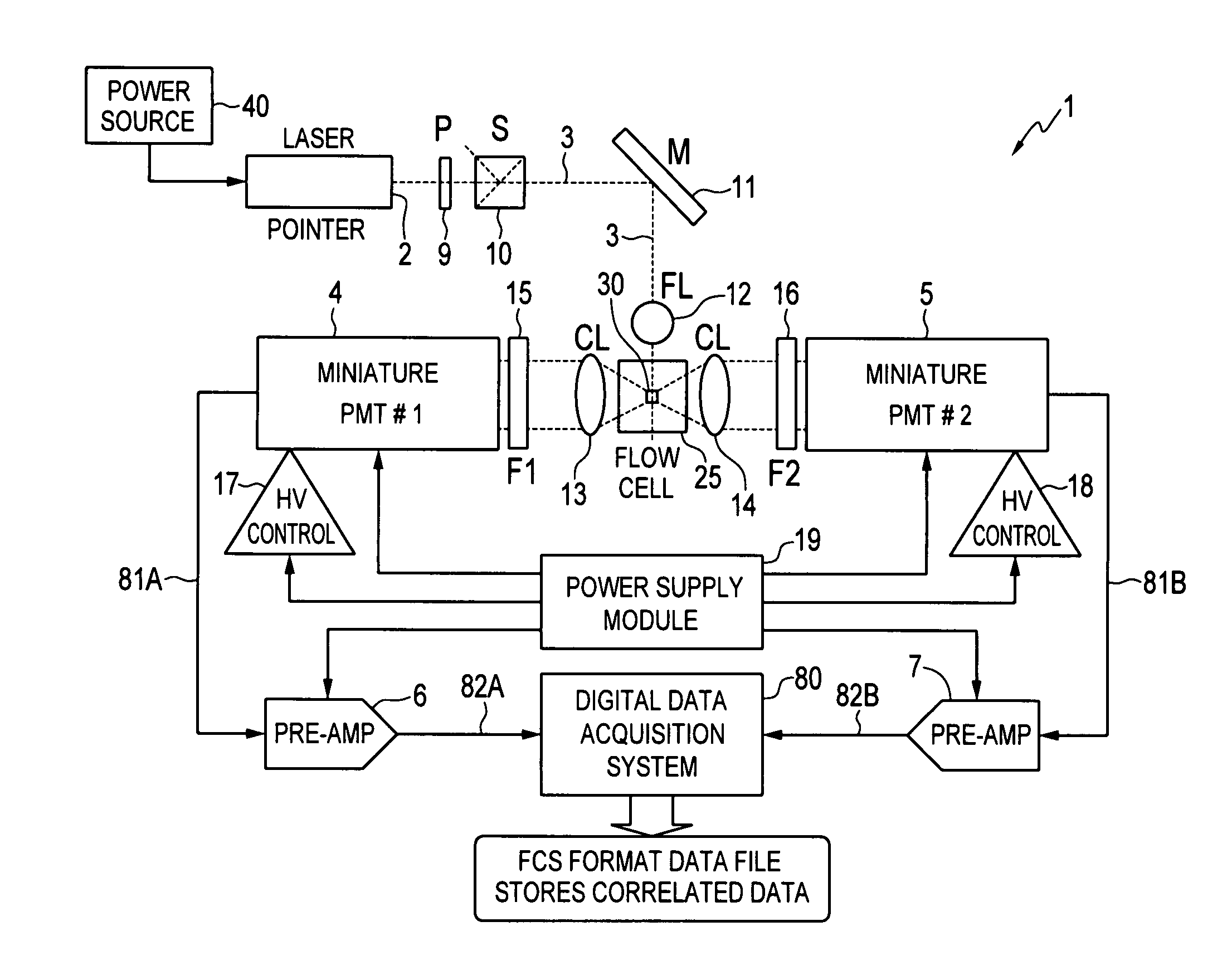
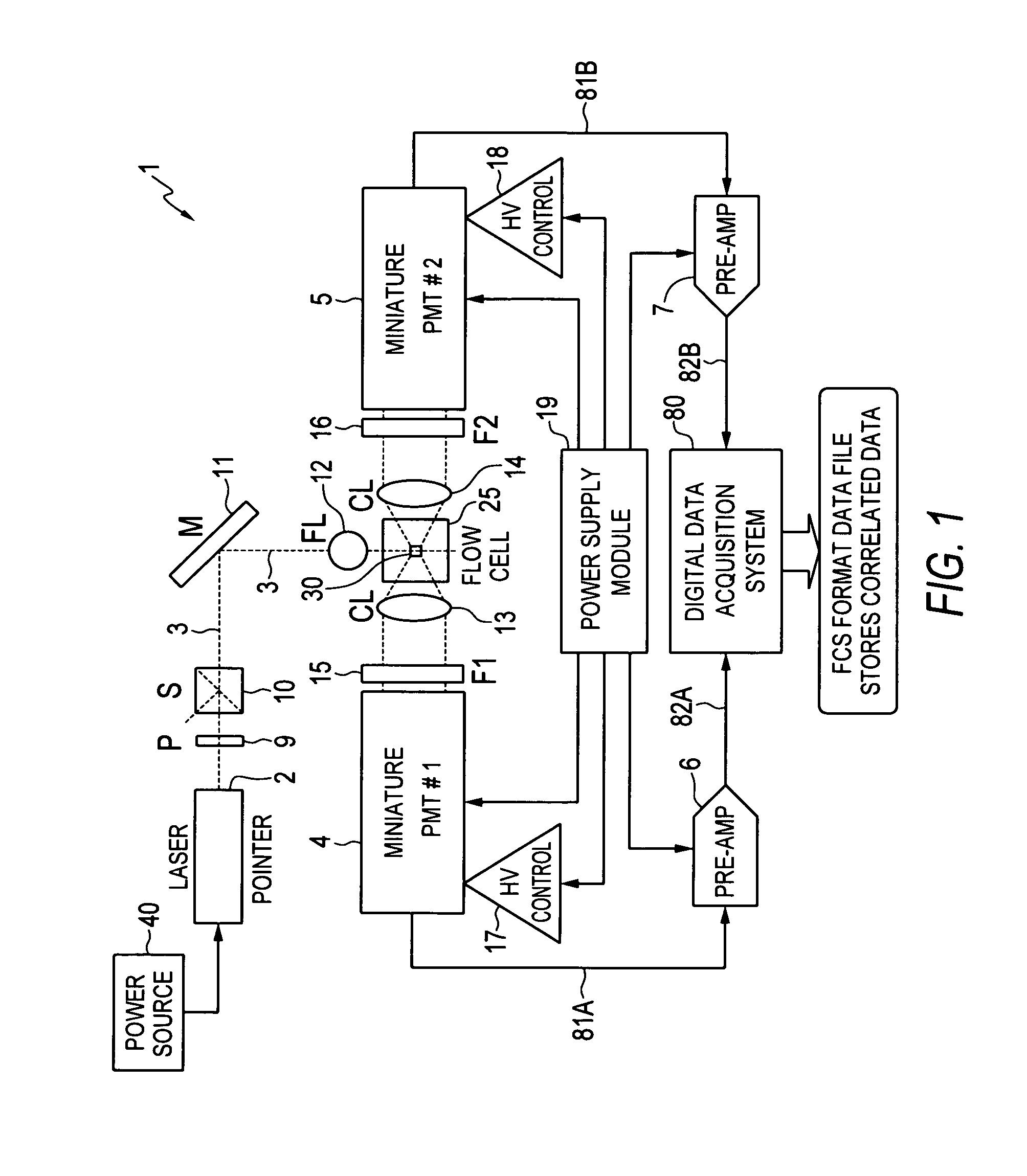
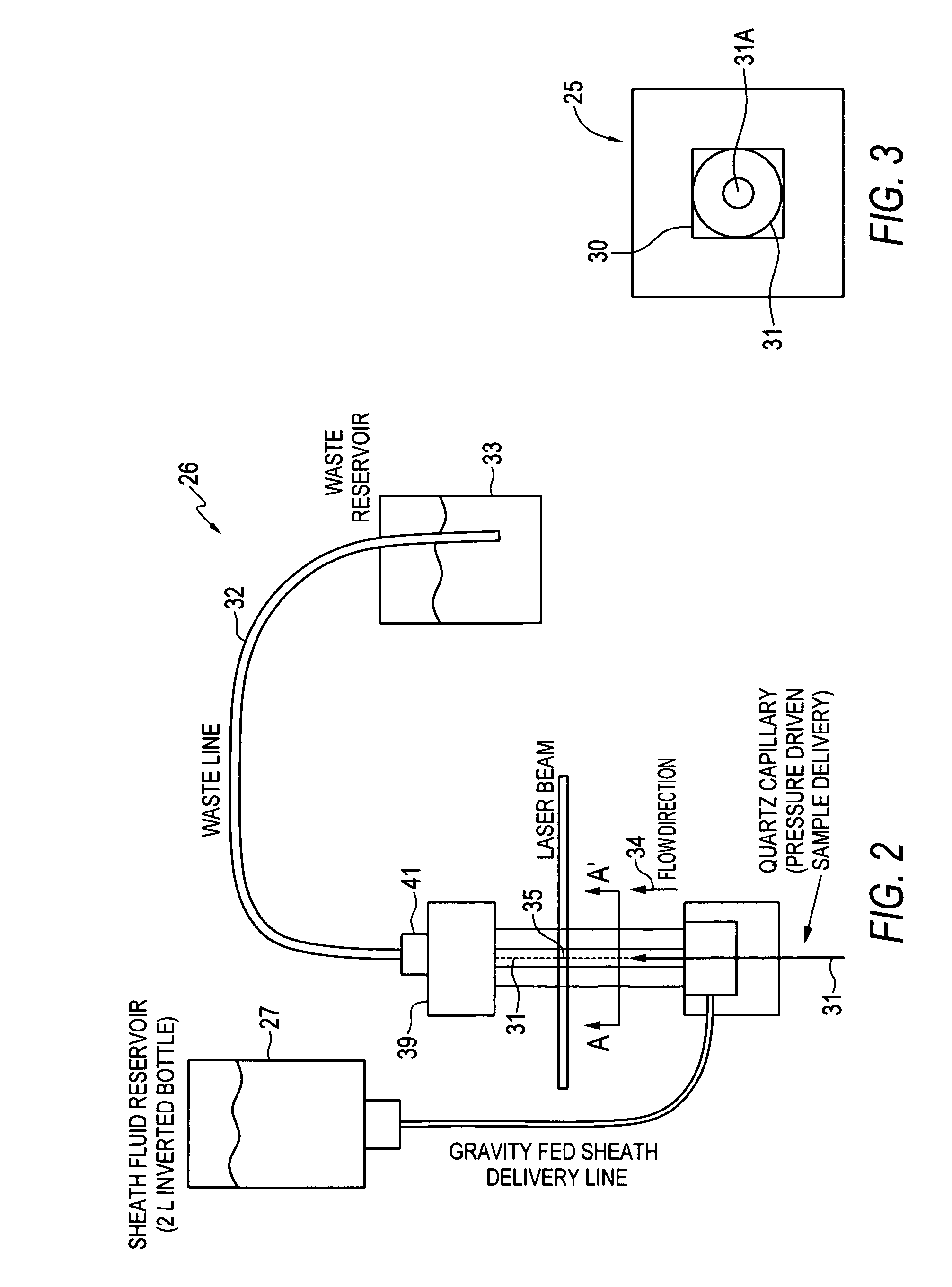
ActiveUS20080106736A1Low costExtended shipping timeScattering properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluidicsSignal conditioning
A system and method for analyzing a particle in a sample stream of a flow cytometer or the like. The system has a light source, such as a laser pointer module, for generating a low powered light beam and a fluidics apparatus which is configured to transport particles in the sample stream at substantially low velocity through the light beam for interrogation. Detectors, such as photomultiplier tubes, are configured to detect optical signals generated in response to the light beam impinging the particles. Signal conditioning circuitry is connected to each of the detectors to condition each detector output into electronic signals for processing and is designed to have a limited frequency response to filter high frequency noise from the detector output signals.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
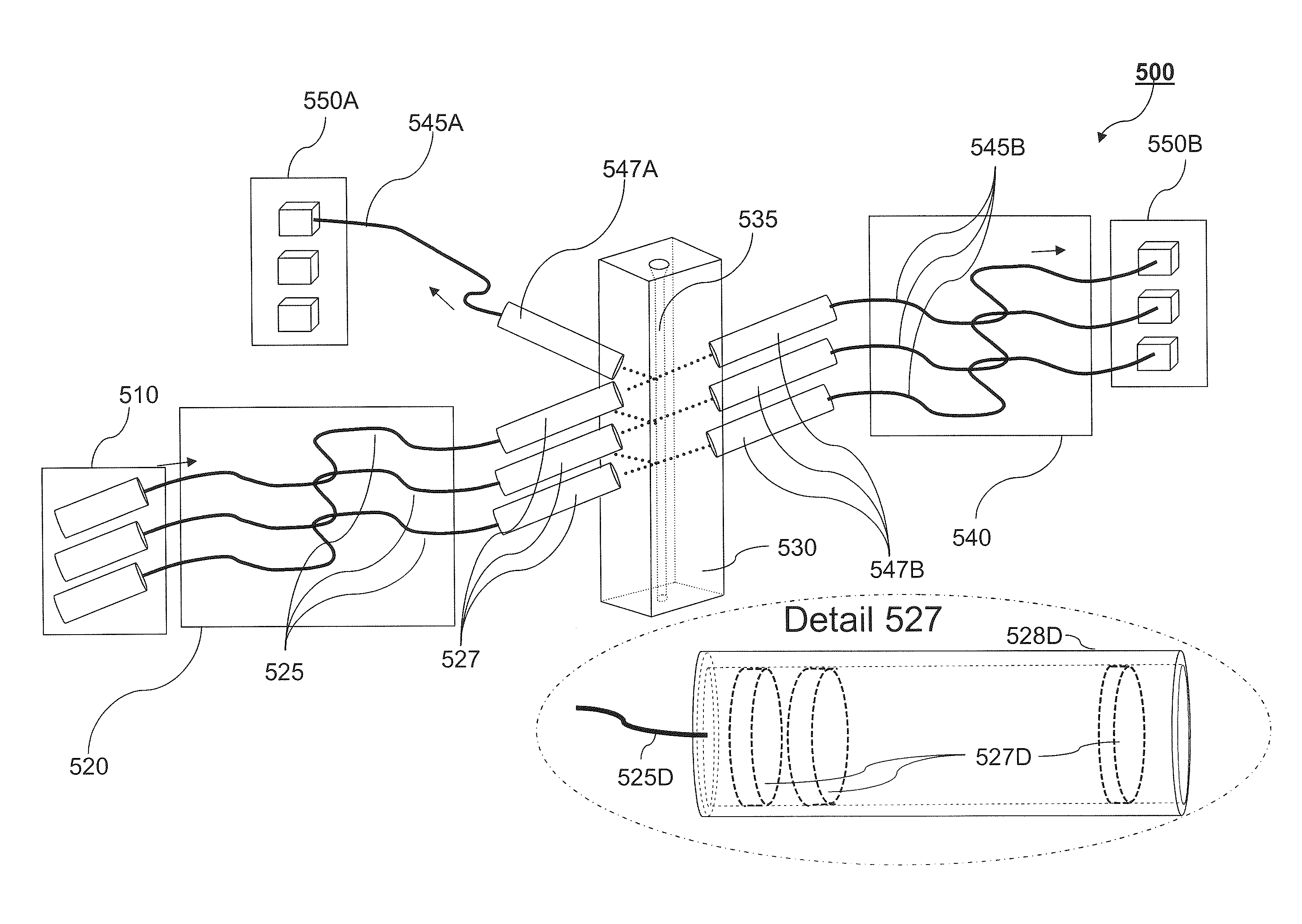
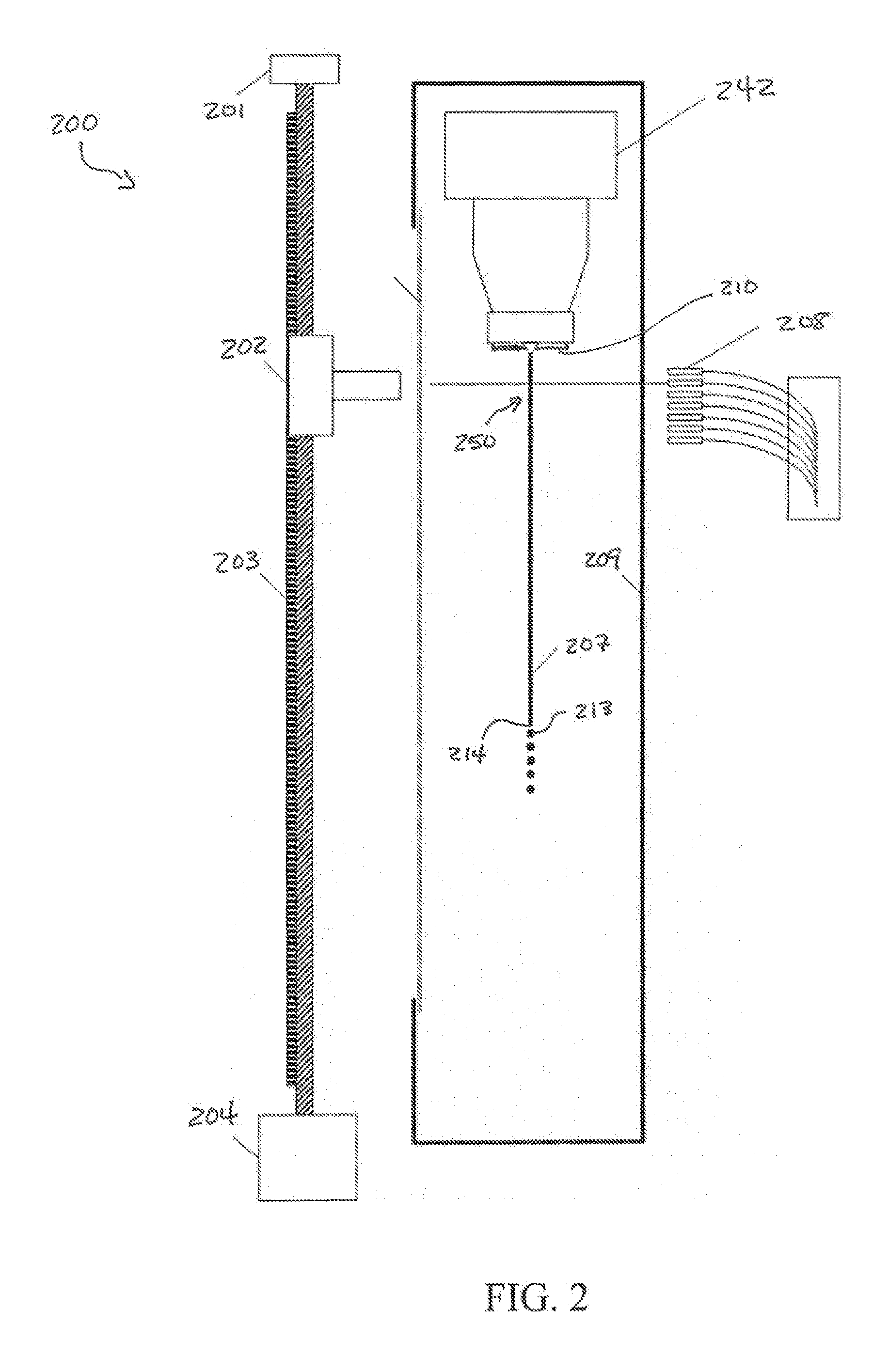
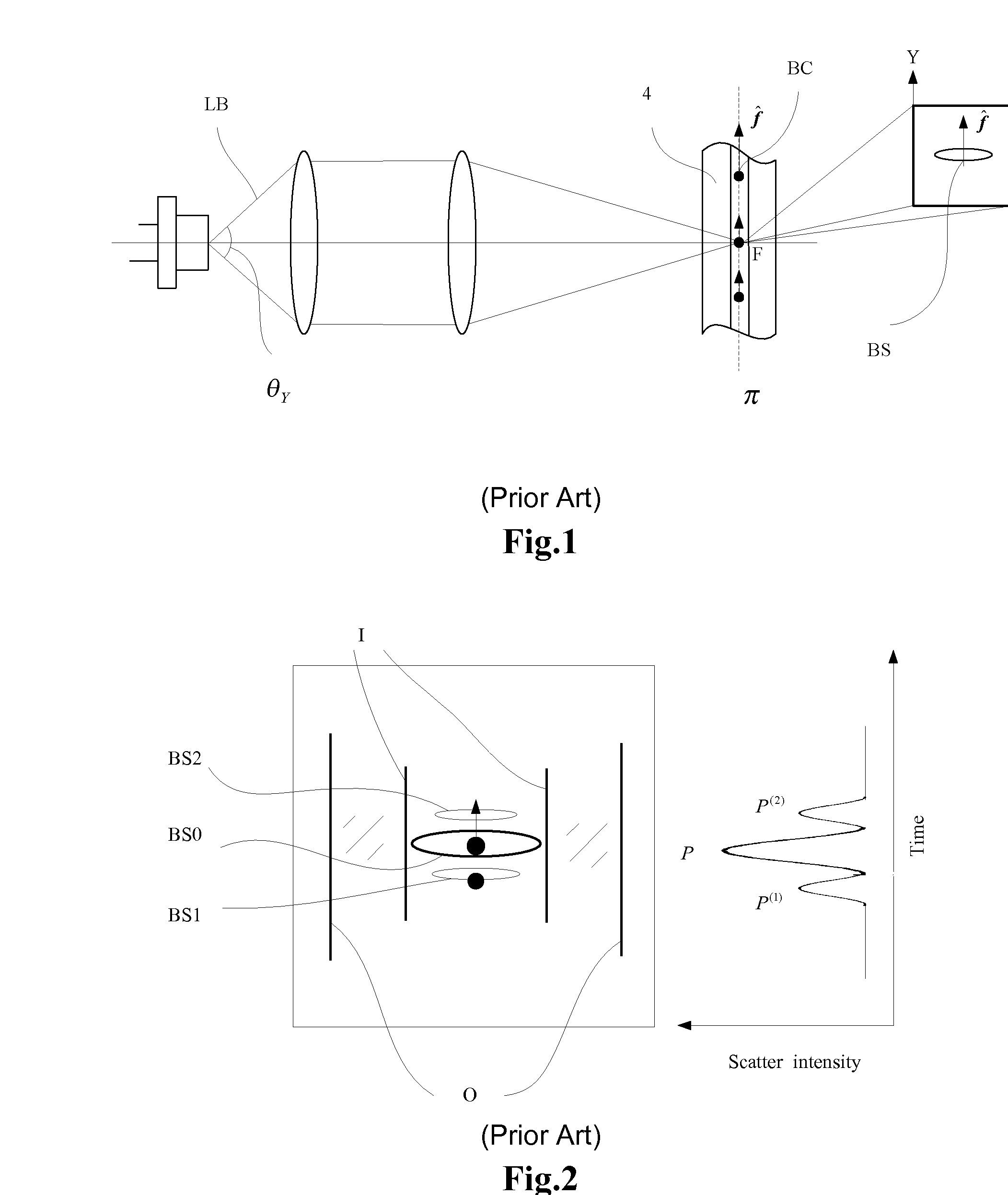
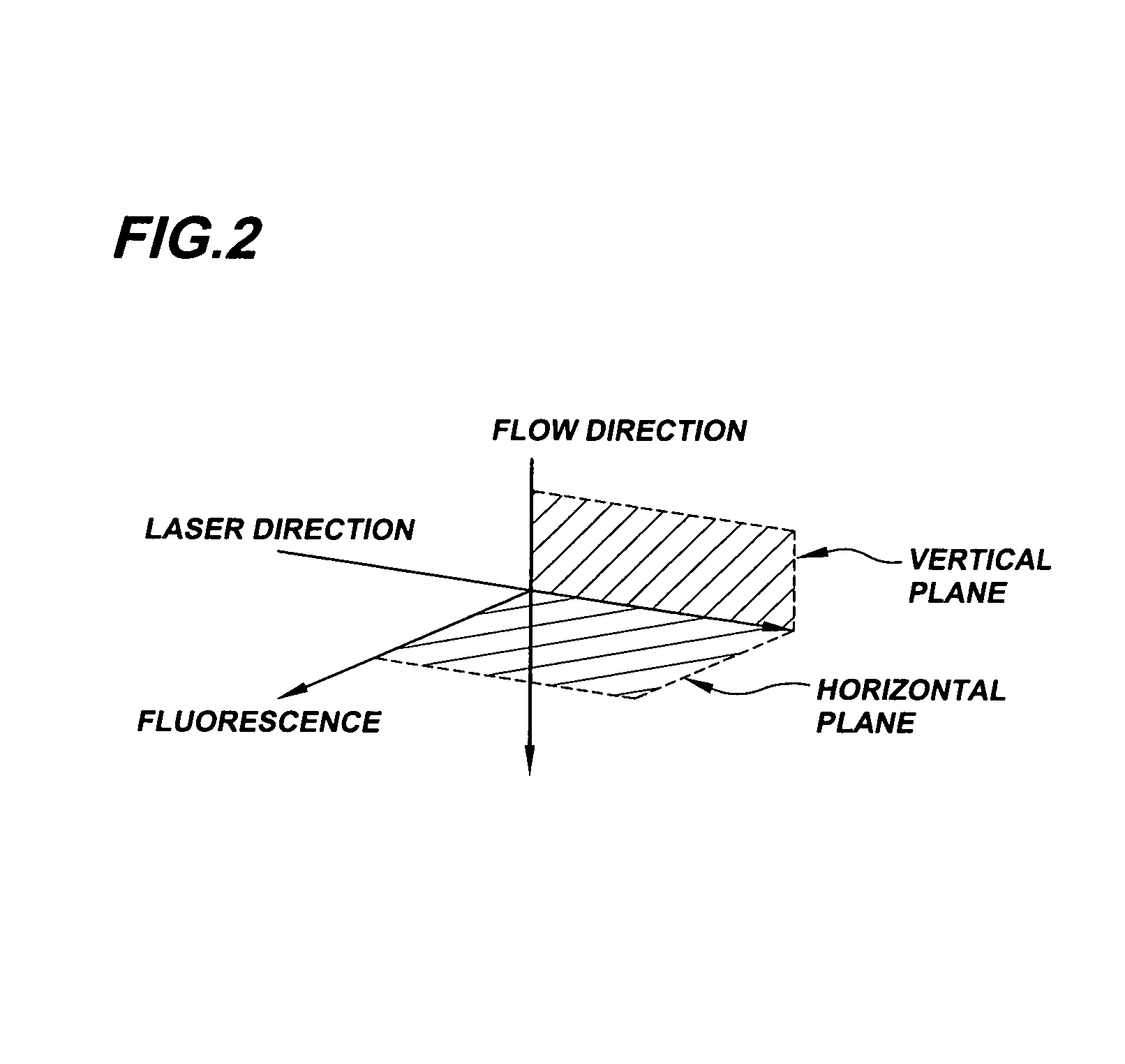
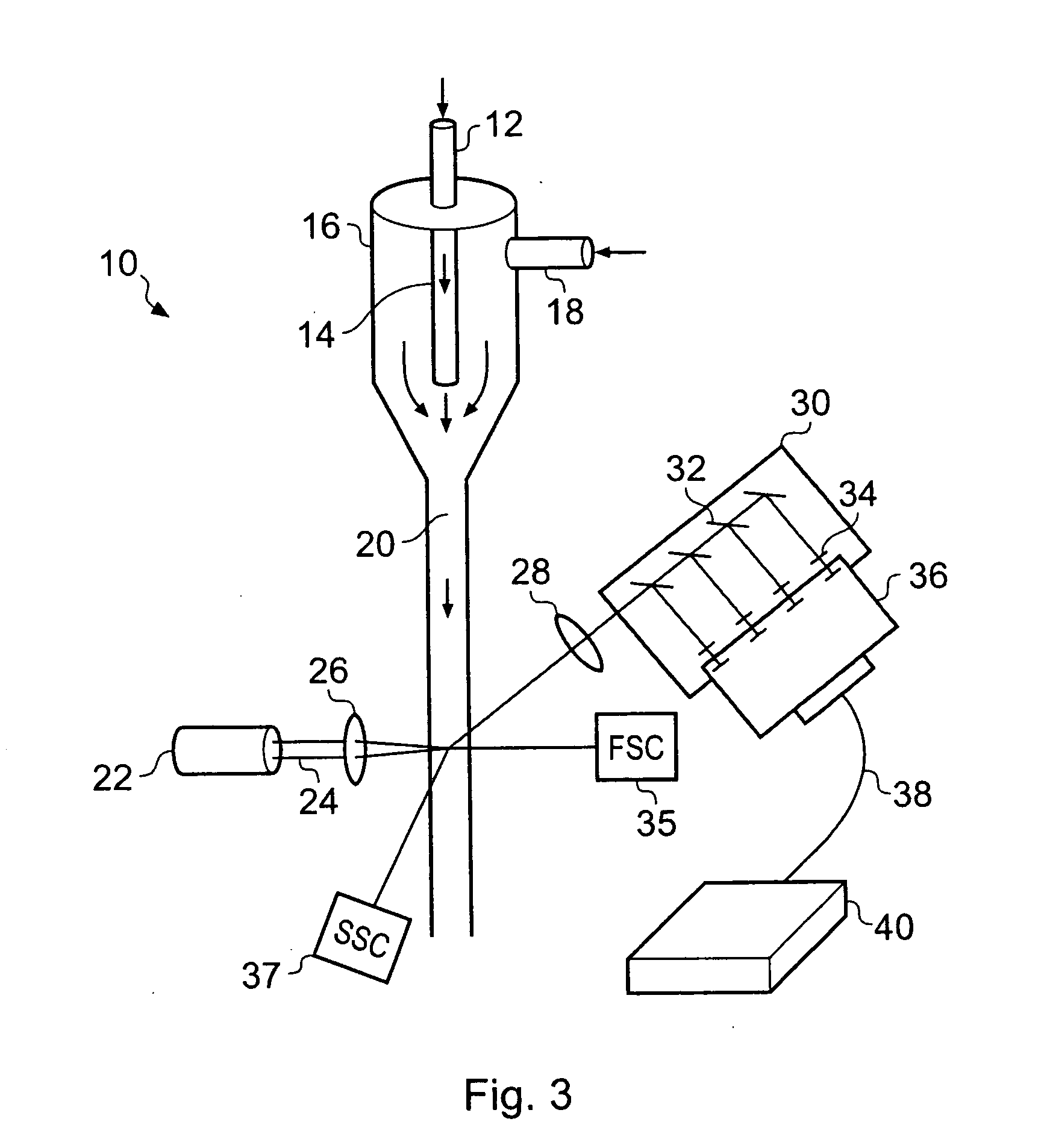
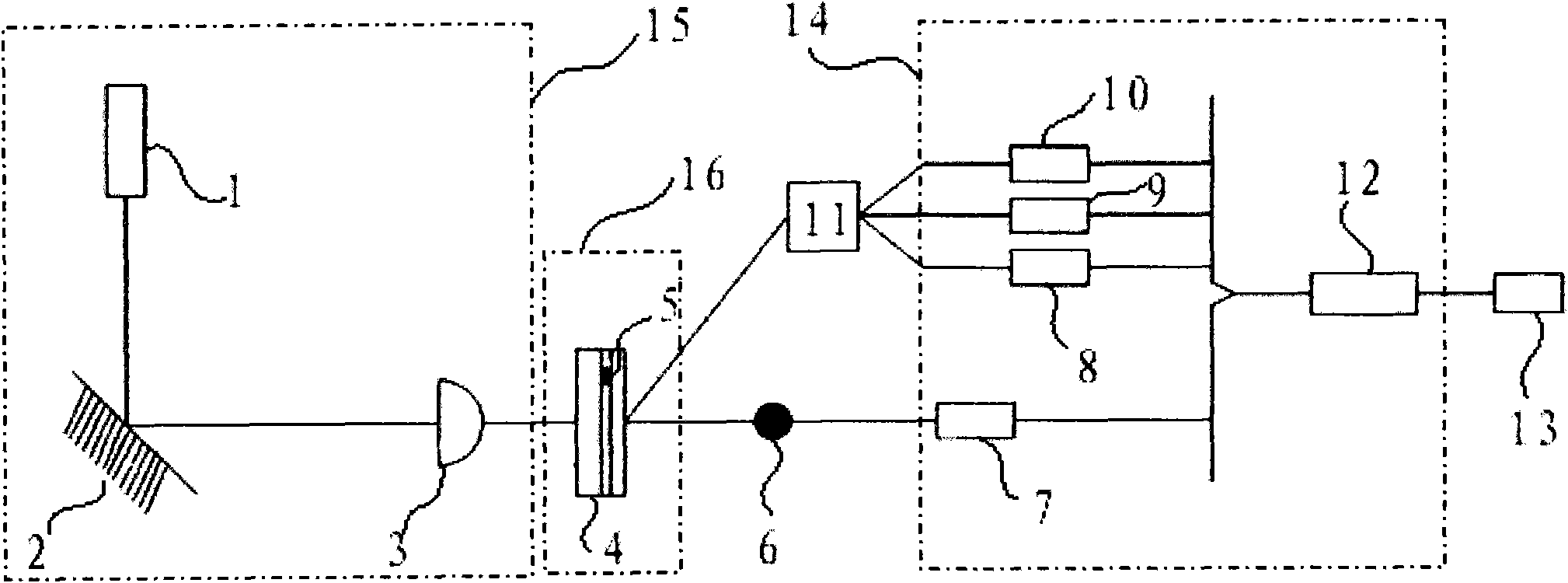
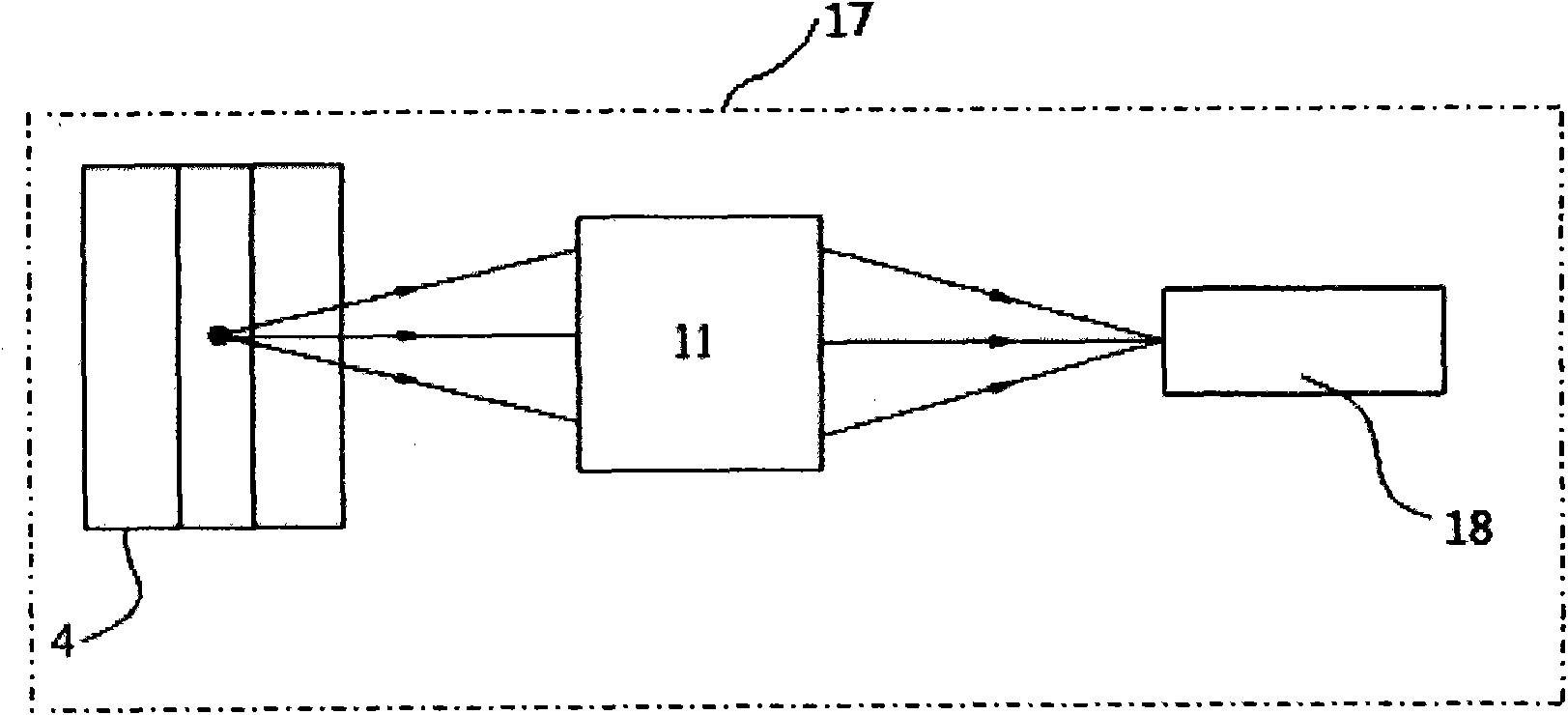
Stabilized Optical System for Flow Cytometry
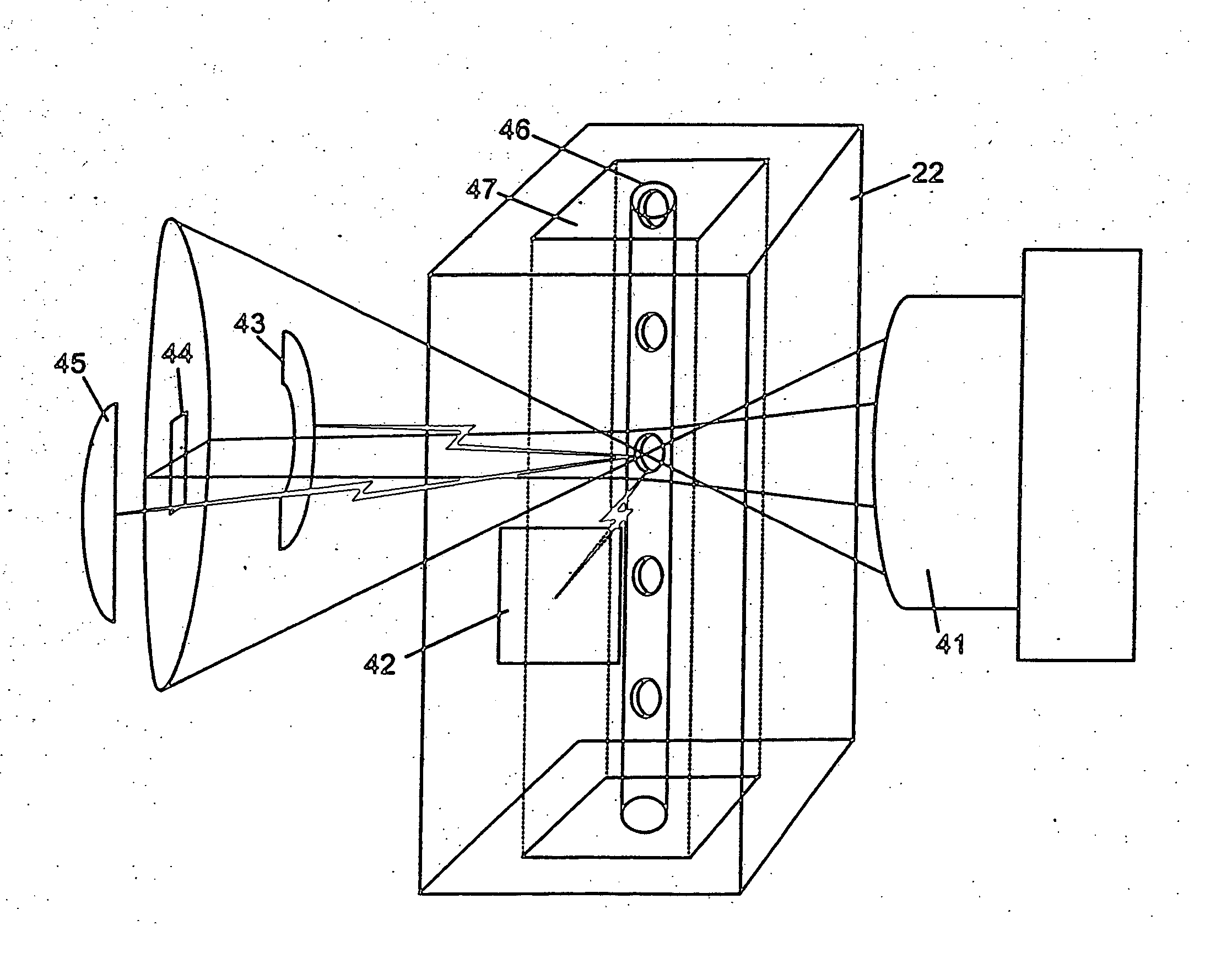
A particle analyzer that includes optical waveguides, a support, and a detector. The optical waveguides direct spatially separated beams from a source of radiation to produce measuring beams in a sample flow measuring area. The support maintains each of the optical waveguides in a fixed relative position with respect to each other and maintains the positioning of the measuring beams within the measuring area. The detector senses light produced from the measuring beams interacting with a particle flowing through the measuring area. At least one of the support and the detector can be coupled to the core stream sample system. The coupling can use an optical waveguide device configured to convey optical radiation arising from sample interaction to the detector. In another example, a particle analyzer comprises an optical system configured to be fixedly coupled to a sample system and configured to direct beams along independent beam paths from a source of radiation to produce measuring beam spots in a sample flow measuring area of the sample system and a detection system configured to sense radiation delivered from the sample flow measuring area.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
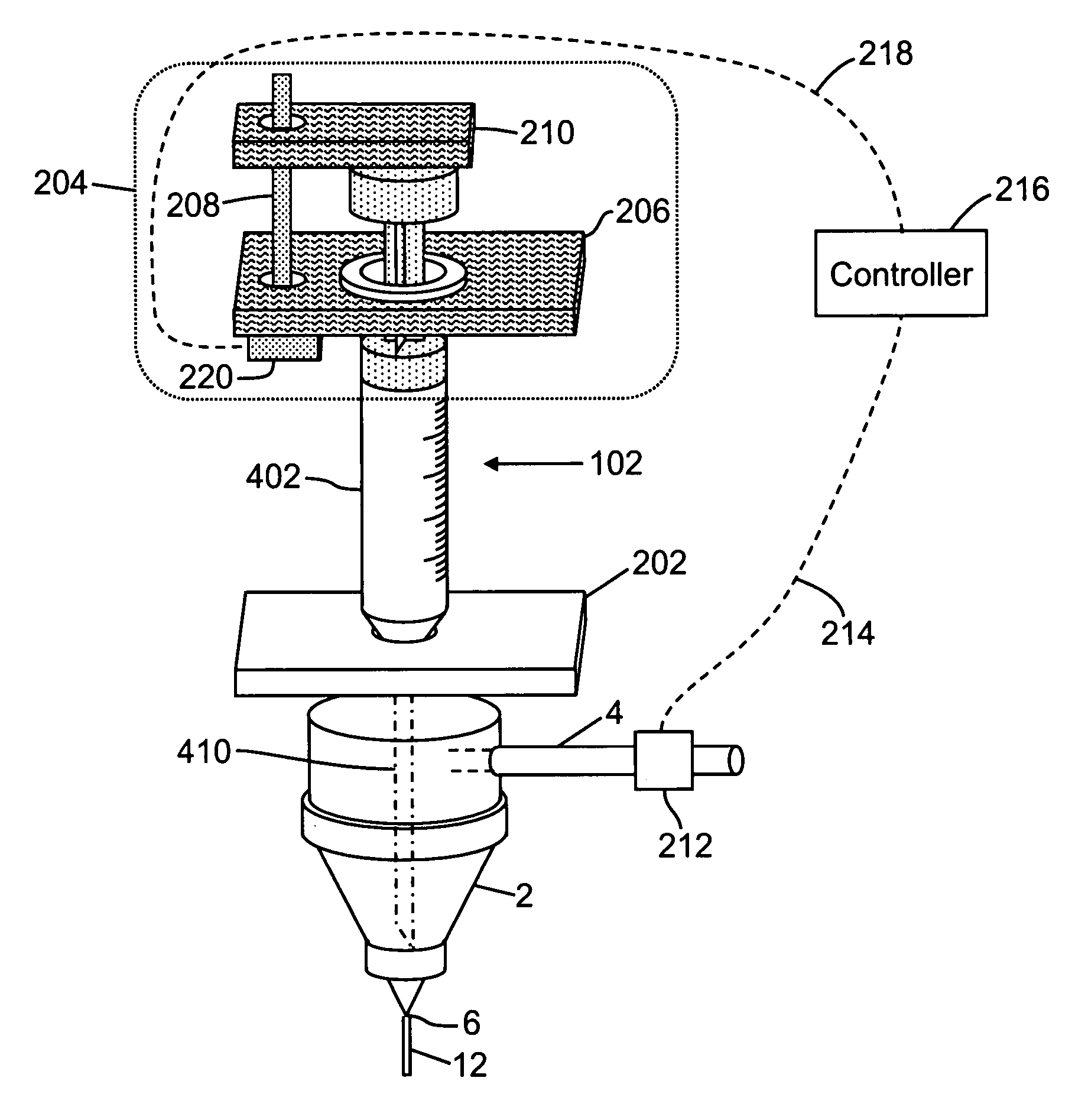
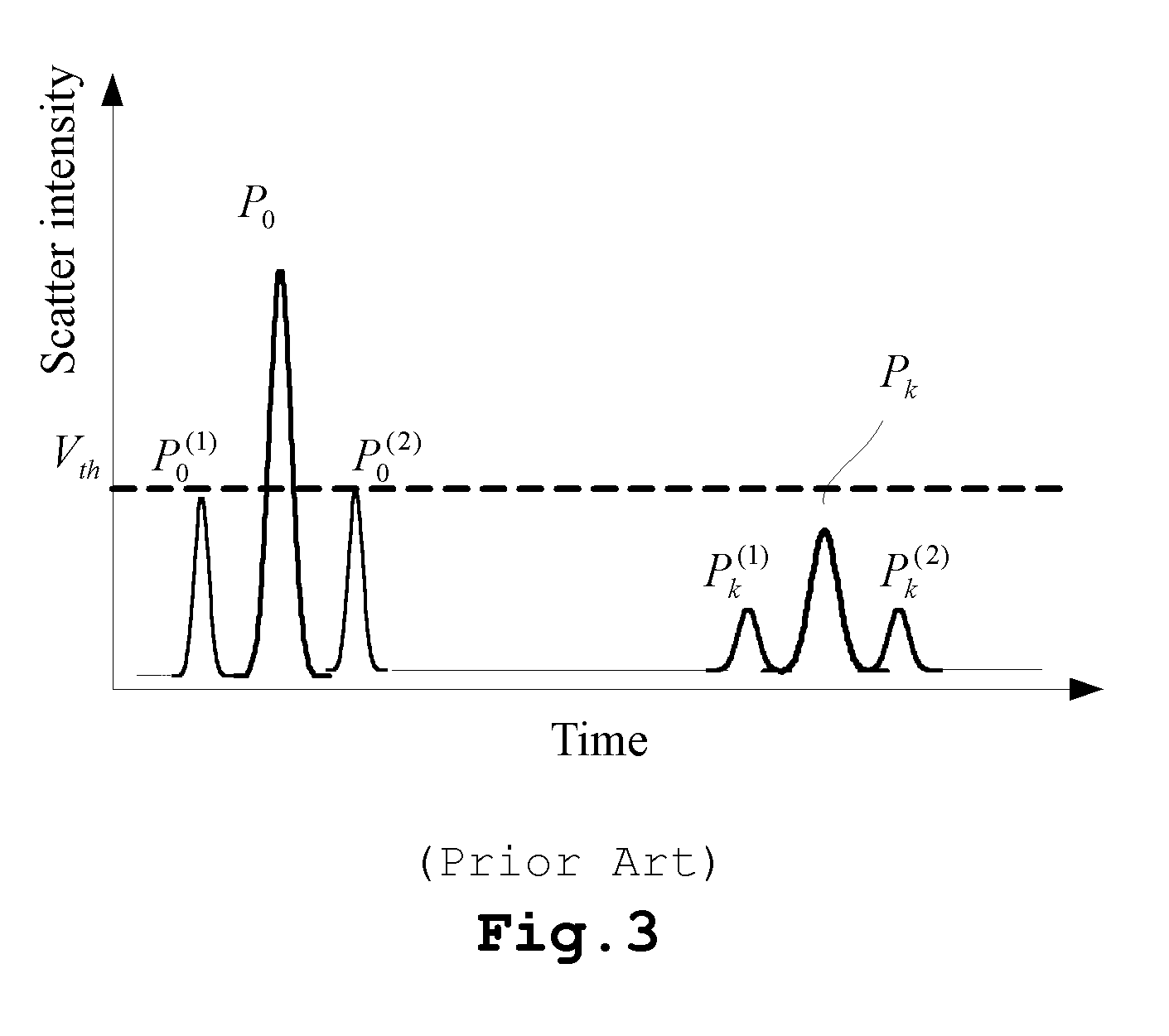
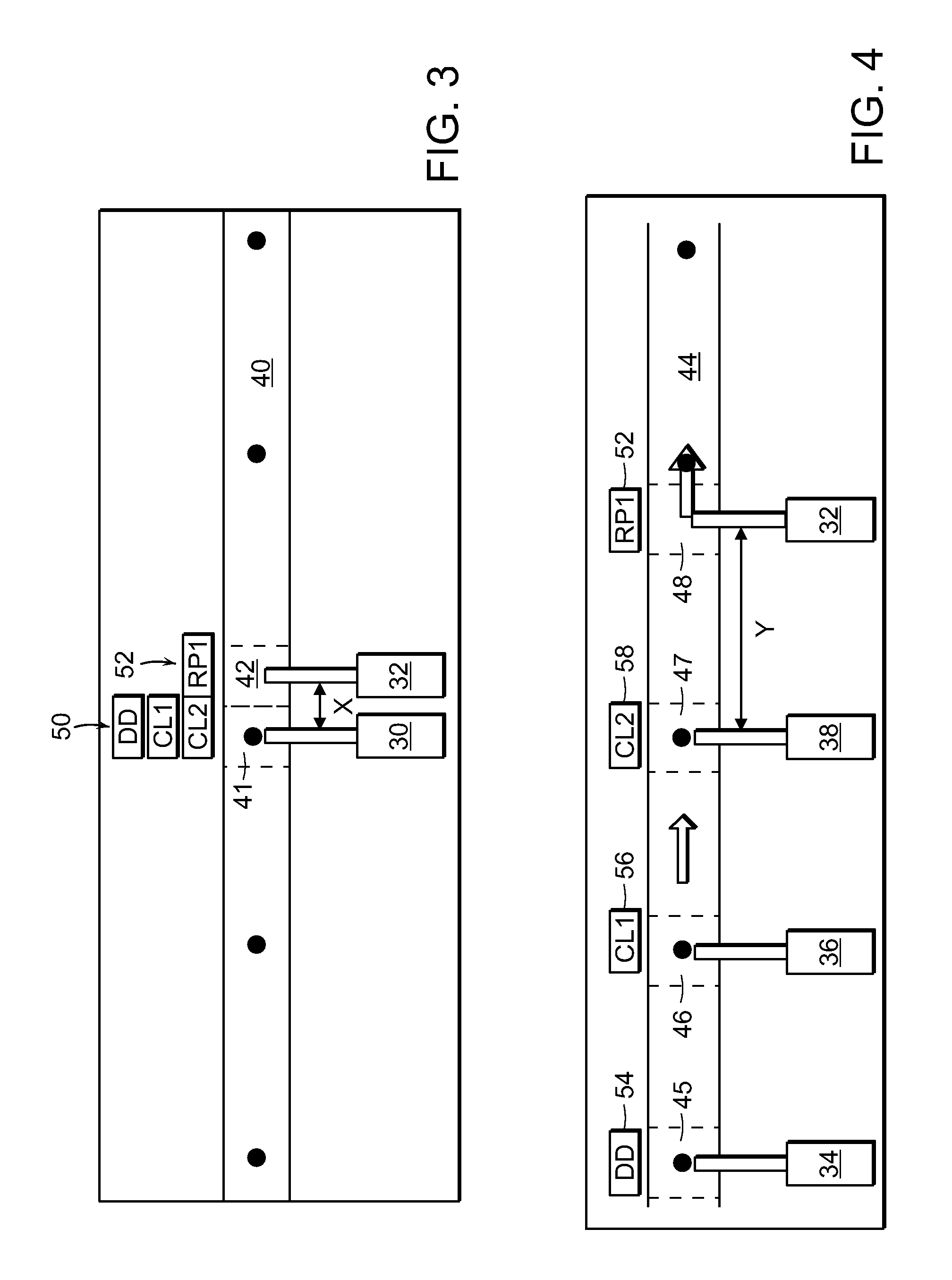
Calculate Drop Delay for Flow Cytometry Systems and Methods
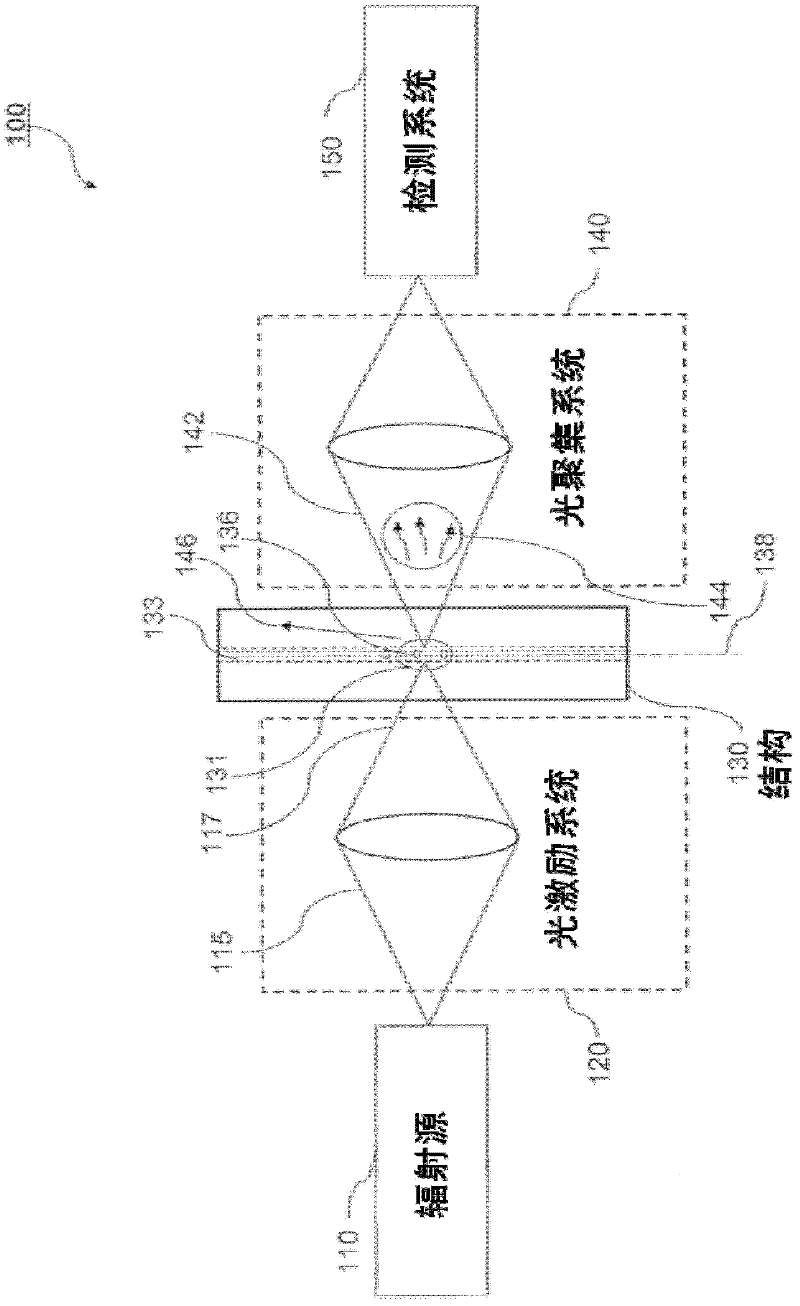
ActiveUS20110221892A1Material analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionParallel computingFlow Cytofluorometry
A method of calculating a drop delay in a stream of a flow cytometer. In one embodiment the method includes the steps of determining a widths plot by measuring the width of a stream based on an image of the stream and setting drop delay based on the widths plot. In another aspect the invention relates to a flow cytometer system for automatically calculating drop delay. In one embodiment the flow cytometer system includes means for determining a widths plot based on an image of the stream; and means for calculating drop delay based on the widths plot.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Flow cytometer
ActiveUS7561267B2Improve stabilityNarrow distributionMaterial analysis by optical meansParticle size analysisInstabilityLight beam
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Flow cytometry for high throughput screening
InactiveUS6878556B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsEngineering
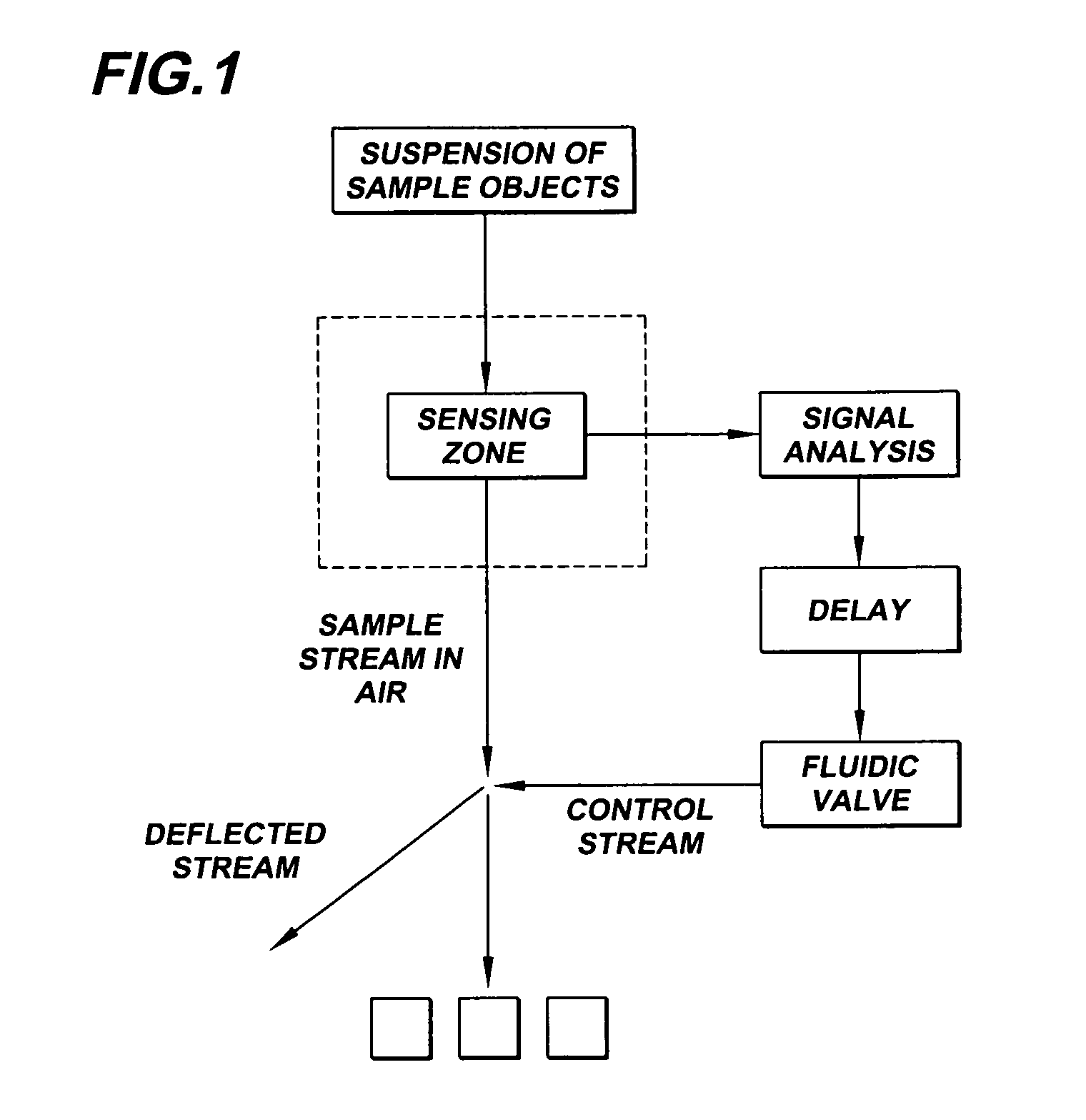
The present invention, provides a flow cytometry apparatus for the detection of particles from a plurality of samples comprising: means for moving a plurality of samples comprising particles from a plurality of respective source wells into a fluid flow stream; means for introducing a separation gas between each of the plurality of samples in the fluid flow stream; and means for selectively analyzing each of the plurality of samples for the particles. The present invention also provides a flow cytometry method employing such an apparatus.
Owner:STC UNM
System for axial pattern analysis of multicellular organisms
A method of using elongate multicellular organisms in conjunction with a specialized flow cytometer for drug discovery and compound screening. A stable, optically detectable linear marker pattern on each organism is used to construct a longitudinal map of each organism as it passes through the analysis region of the flow cytometer. This pattern is used to limit complex data analysis to particular regions of each organism thereby simplifying and speeding analysis. The longitudinal marker pattern can be used to alter signal detection modes at known regions of the organism to enhance sensitivity and overall detection effectiveness. A repeating pattern can also be used to add a synchronous element to data analysis. The marker patterns are established using known methods of molecular biology to express various indicator molecules. Inherent features of the organism can be rendered detectable to serve as marker patterns.
Owner:UNION BIOMETRICA
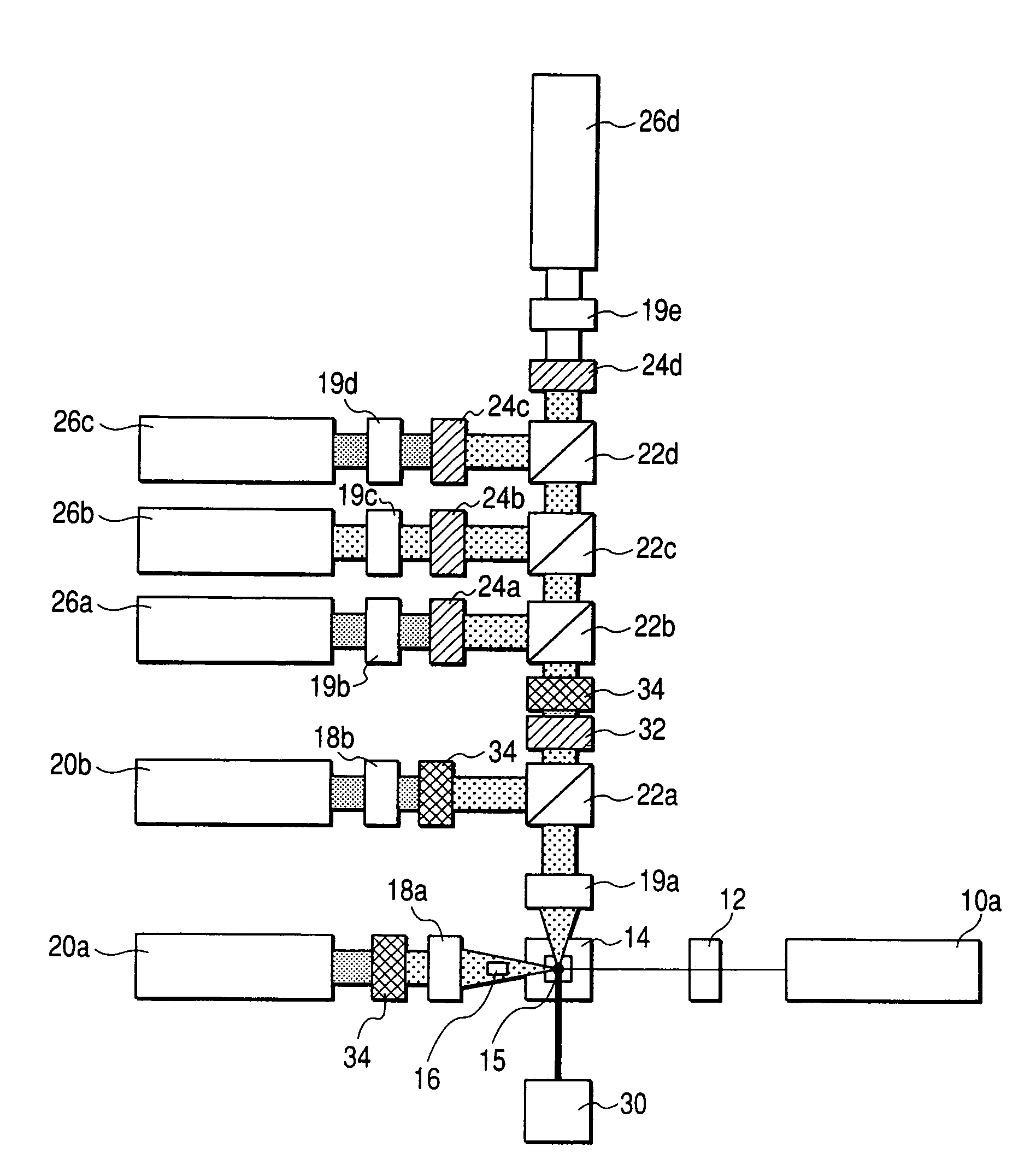
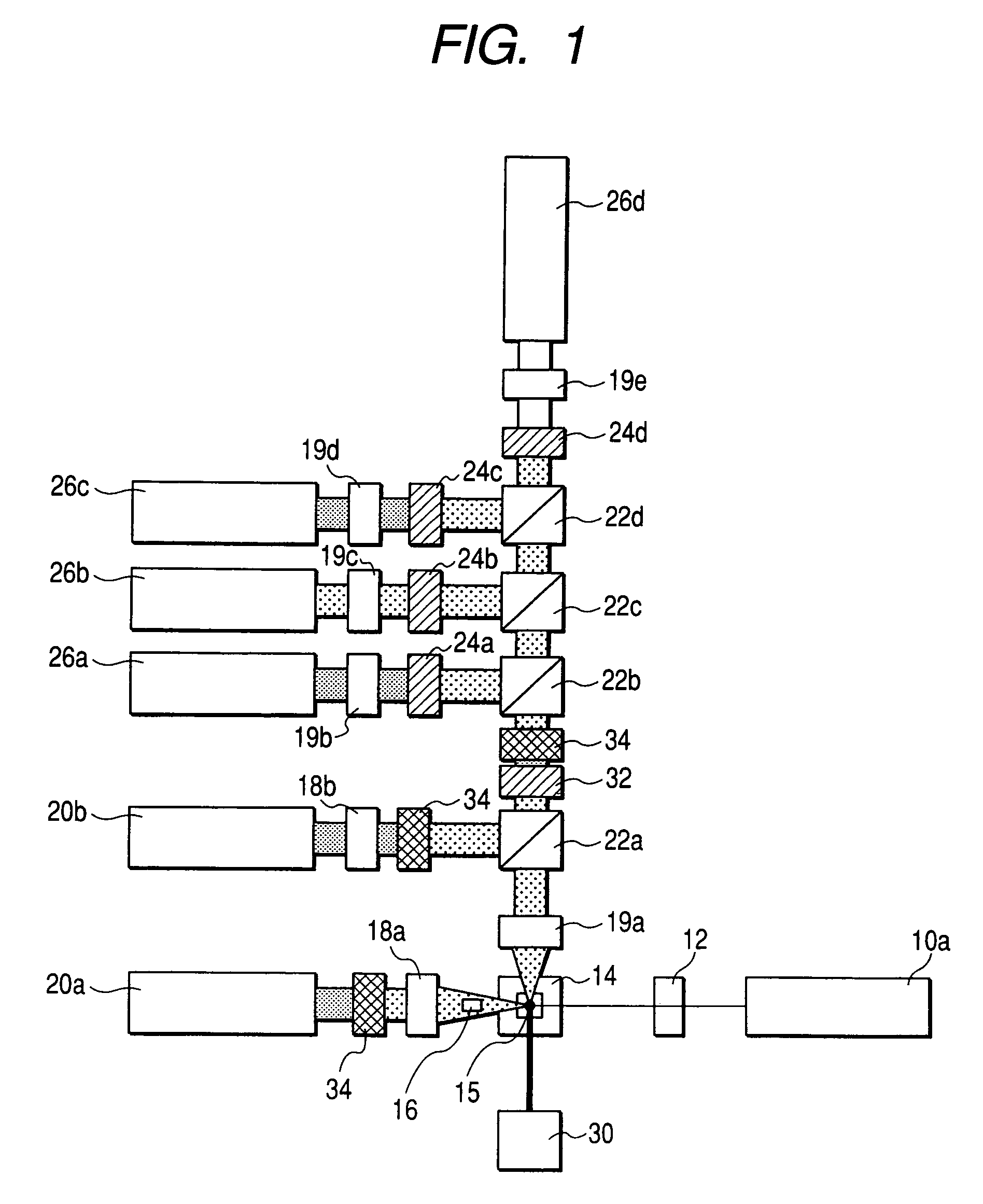
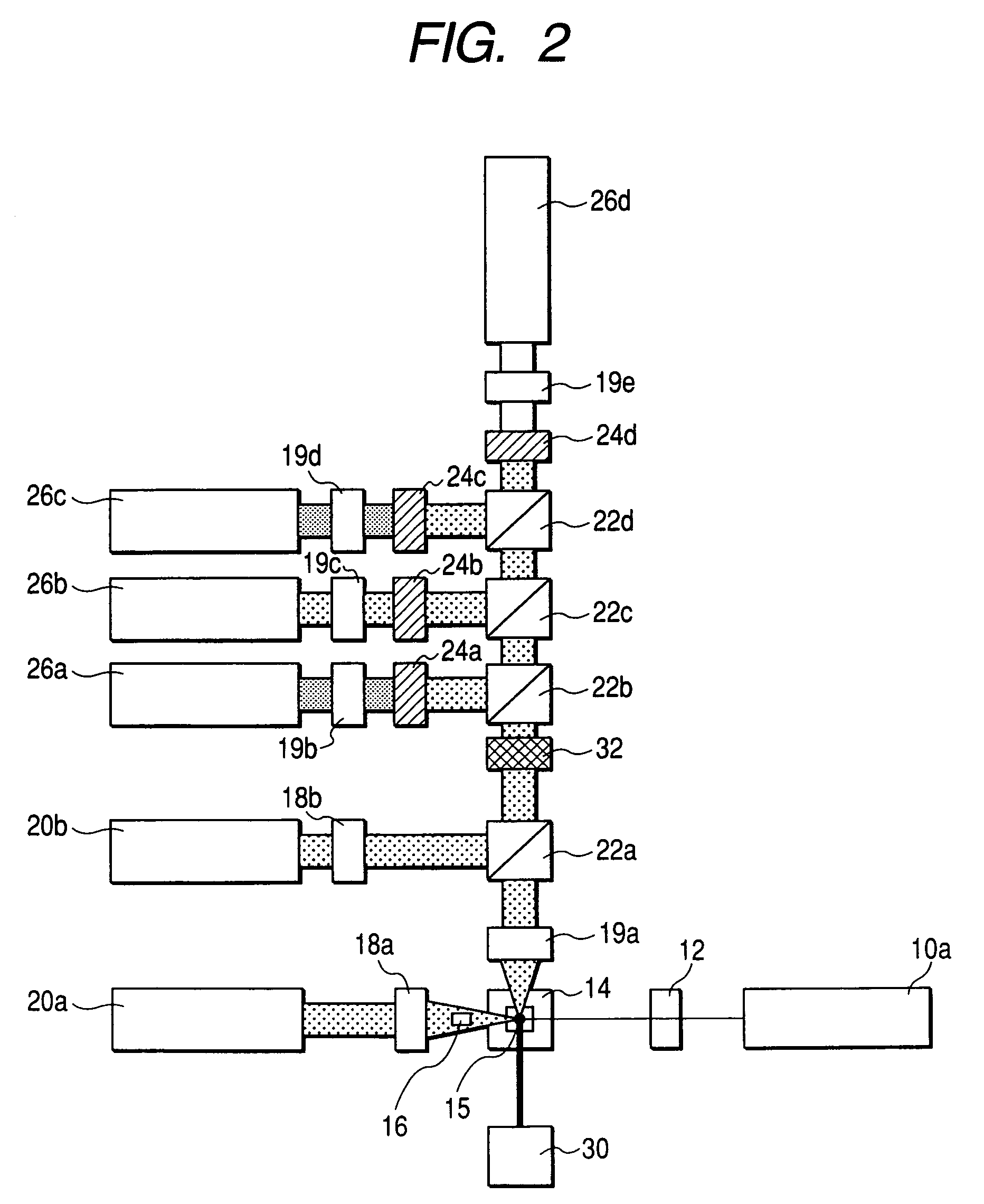
Optical engine for flow cytometer, flow cytometer system and methods of use
ActiveUS20150140577A1Improve accuracyIncrease speedOptical radiation measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectricityFlow cell
An optical engine for use in a bench top flow cytometer, the optical engine comprising a set of lasers; a different set of beam shaping optics for each laser, wherein each set comprises two lenses to adjustably focus light horizontally along an x-axis to a same horizontal position and vertically along a y-axis to a different vertical position along a same plane; collection optics for collecting fluorescence from the flow cell; filtration optics that filter the collected fluorescence from the flow cell into different detection channels according to wavelength ranges; and a detector for each detection channel that converts the filtered fluorescence to electrical signals, wherein electrical signals are processed so that the fluorescence from each laser at the different vertical positions is distinguished at the same detector.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Flow Measurement and Control for Improved Quantification of Particles in Flow Cytometry
ActiveUS20120070818A1Accurate and rapid enumerationImprove accuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical physicsBiological particles
The present invention relates to methods that enable improved accuracy for quantitative particle counting in a flowing liquid stream. The methods of the present invention utilize the real-time measurement of flow rates and flow rate control through feedback mechanisms to improve quantification, and this improved quantification translates to more accurate particle counting. In certain embodiments, particles being counted are biological particles in a liquid sample, such as viruses.
Owner:SARTORIUS BIOANALYTICAL INSTR INC
Flow cytometer
InactiveUS20020080341A1Analysis by electrical excitationIndividual particle analysisElectricityFlow cell
A flow cytometer includes a sheath flow cell for forming a sample solution flow by surrounding sample solution containing particles with sheath liquid, a light source for radiating light to the sample solution flow, a detecting part for detecting optical information from particles contained in the sample solution flow and converting it to electric signals, and a signal processing part for extracting fluctuation signals from the electric signals which the detecting part outputs.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Flow cytometry based on microfluidic chip
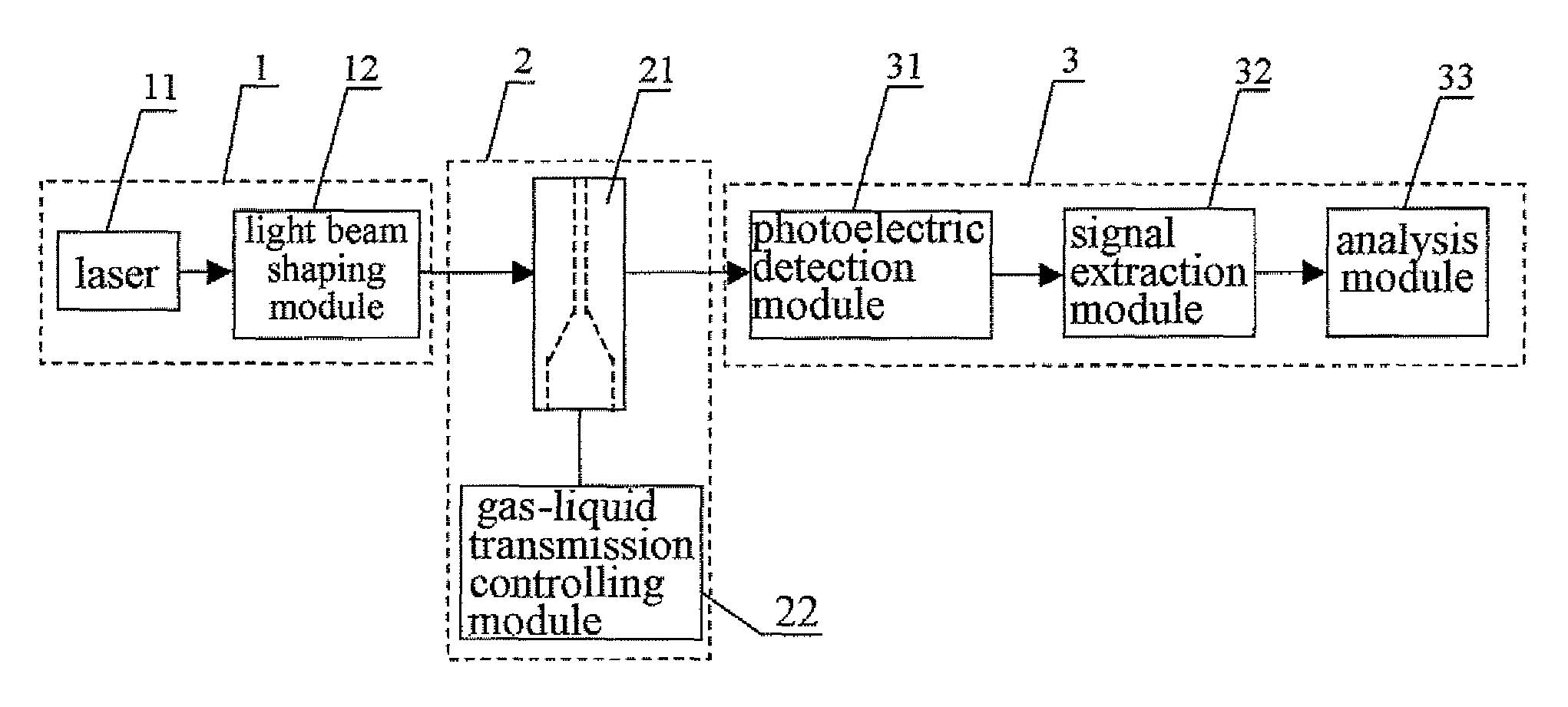
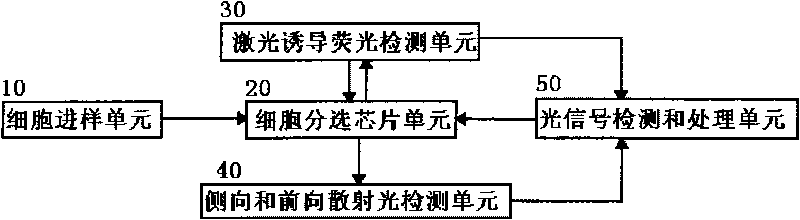
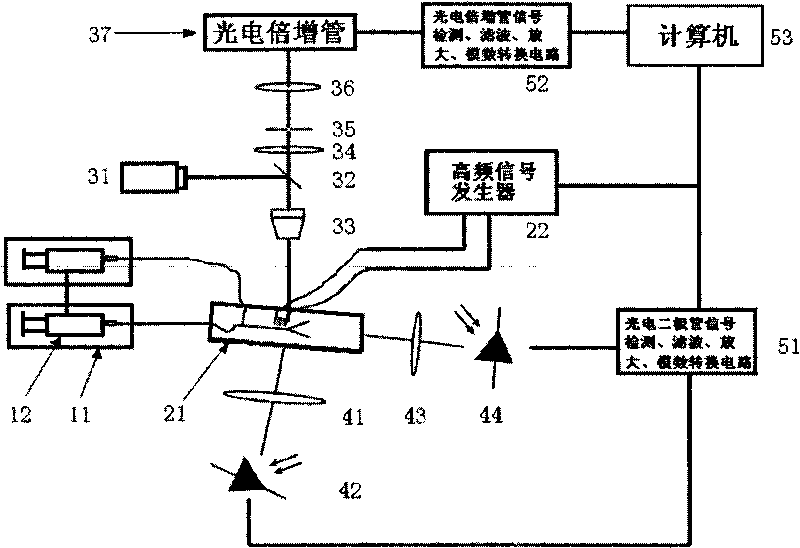
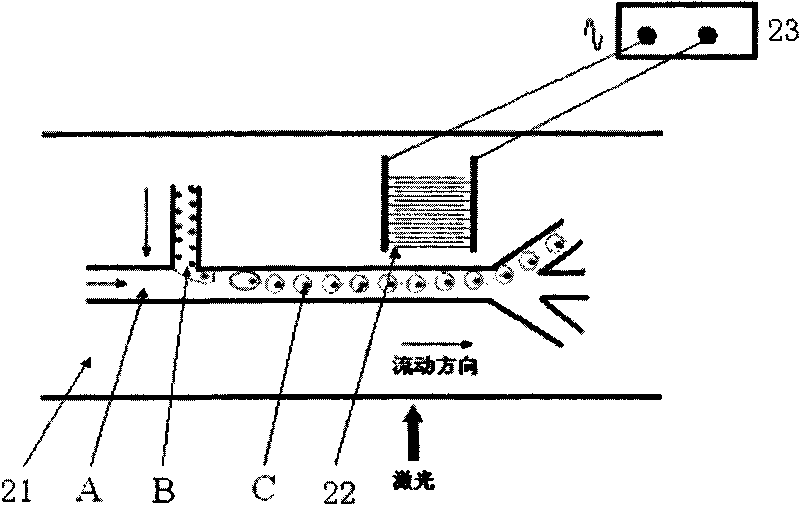
InactiveCN101726585AHighly integratedImprove throughputBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMiniaturizationTreatment unit
The invention discloses a flow cytometry based on a microfluidic chip, relating to a flow cytometry for biomedical inspection. The structure of the flow cytometry is as follows: a cell sample introduction unit (10), a laser induce fluorescence (LIF) inspection unit (30) and an optical signal inspection and processing unit (50) are respectively connected with a cell sorting chip unit (20); the cell sorting chip unit (20) is connected with lateral and front scattered light inspection units (40); and the LIF inspection unit (30) and the lateral and the front scattered light inspection units (40) are respectively connected with the optical signal inspection and processing unit (50). Compared with the commercial flow cytometry, the flow cytometry has the following advantages and beneficial effects of high integration degree, convenient operation, small volume, high pass, sensitivity and speed, miniaturization, customization and multiple sorting force, and is suitable for individual flow cytometric analysis.
Owner:宁波基内生物技术有限公司
Method and apparatus for measuring hematological sample
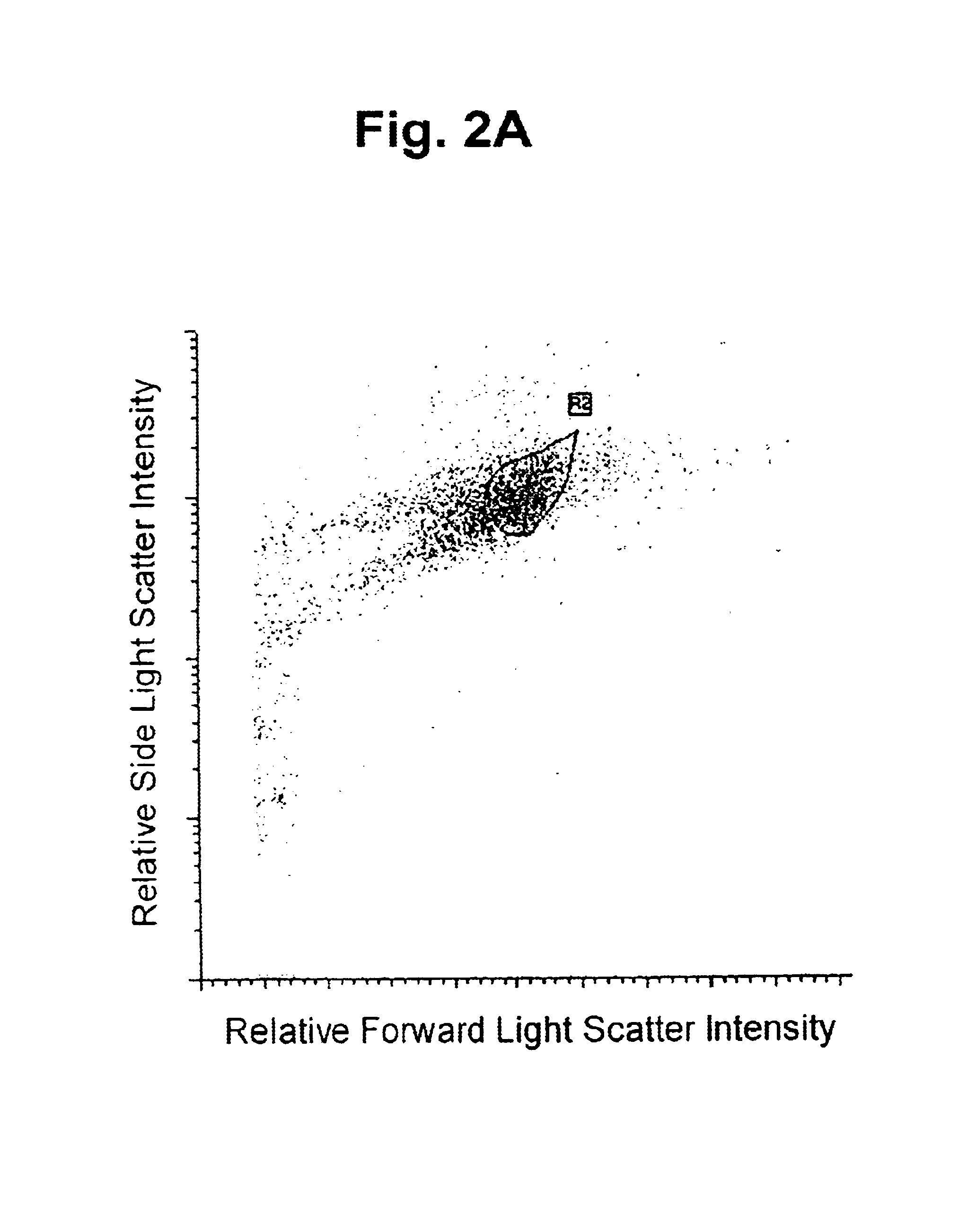
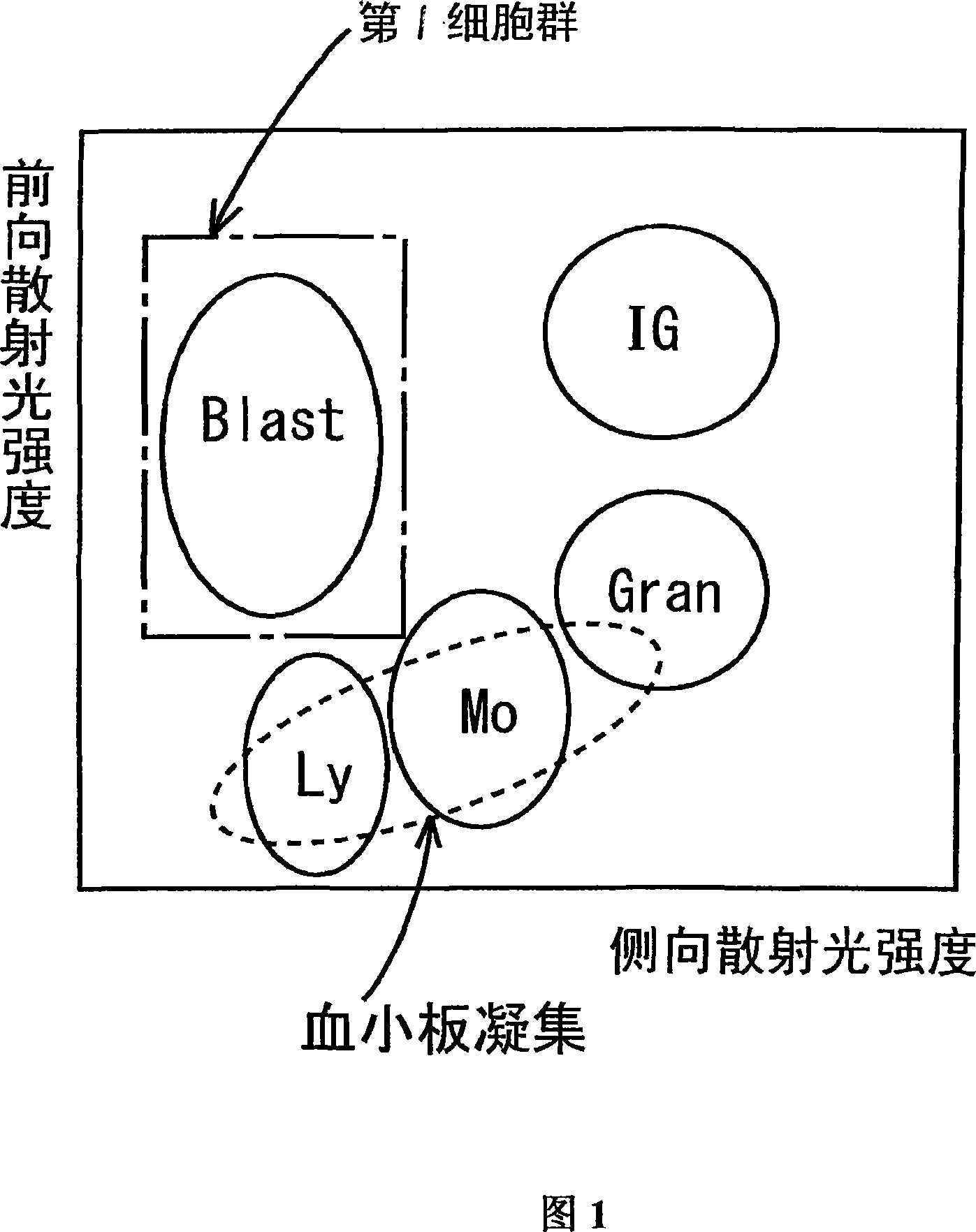
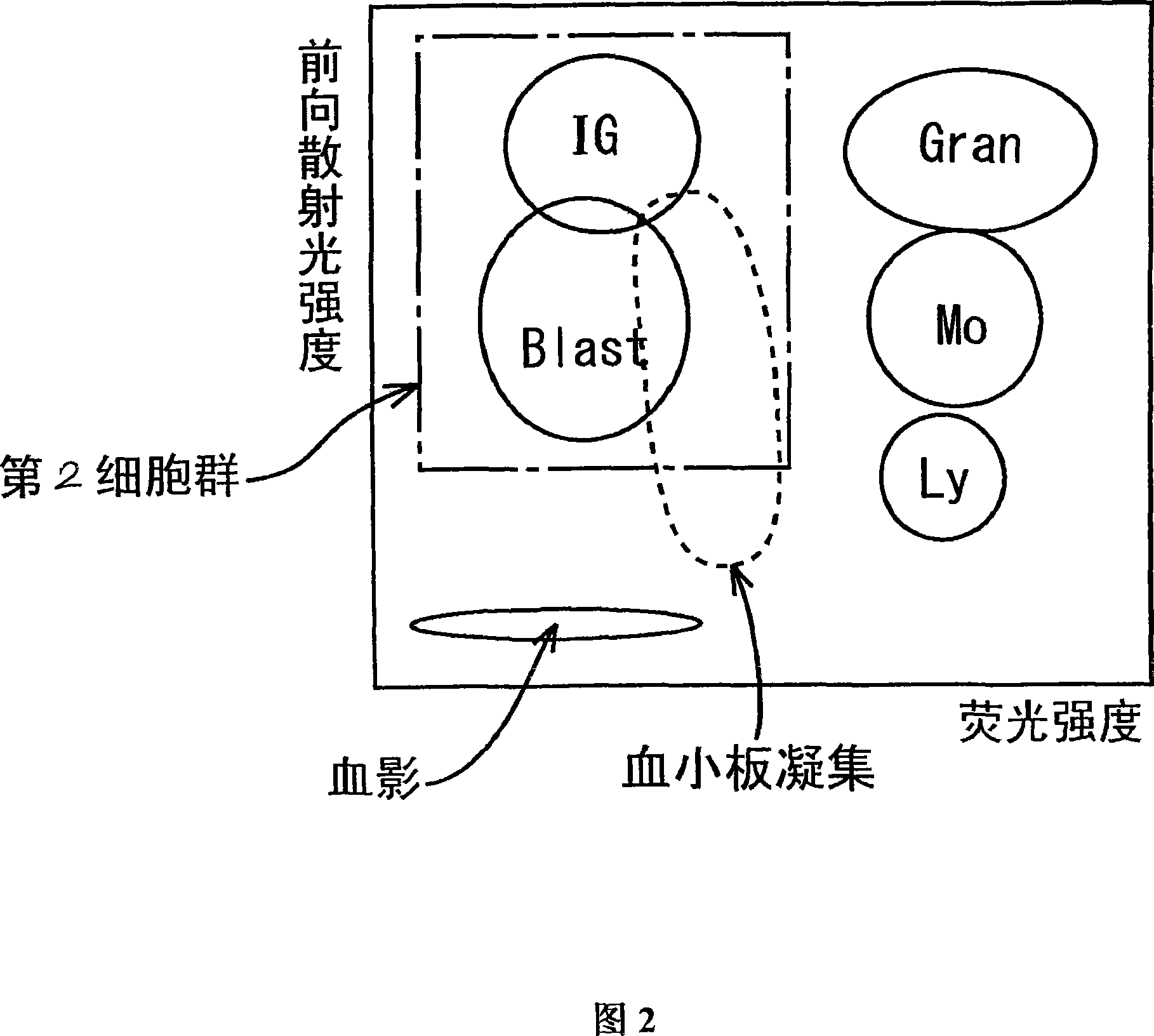
ActiveCN101046439AExclude the effect of agglutinationAccurately classify and countIndividual particle analysisBiological testingRed blood cellFluorescence
The invention provides a measuring method which can classify and count myeloblast more precisely without influence of other component in a sample including platelet aggregation in measurement of a blood sample with a flowcytometry, wherein damage is given to a cell membrane of erythrocyte and mature leukocyte contained in a hematological sample, a hemocyte in which a cell membrane is damaged is constricted, and this is dyeing-treated with a fluorescent dye which can stain a nucleic acid to obtain a sample, the sample is measured with a flowcytometer, and a cell contained in a first cell group containing myeloblast, which is specified based on forward scattered light information and side scattered light information, and contained in a second cell group containing myeloblast, which is specified based on forward scattered light information and fluorescent information, is counted as myeloblast. The invention further provides a measuring device comprising following systems: a sample treating system, an information acquisition system, a first specific system, a second specific system and a counting system.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Flow cytometers
ActiveUS20080108146A1Reliably comparedWithdrawing sample devicesChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceFlow cellData value
A calibration method for a flow cytometer with a multichannel detector module. During calibration, the fluorescence intensity data values for the different detector channels are used to calculate normalization factors needed to adjust subsequent data collected by each of the channels. By using a multichannel detector module, the results from the different flow cells can be reliably compared, so that multiple stages of flow cells can be arranged in series along a common flow path, for example to measure the same sample at defined time intervals.
Owner:GENETIX LTD
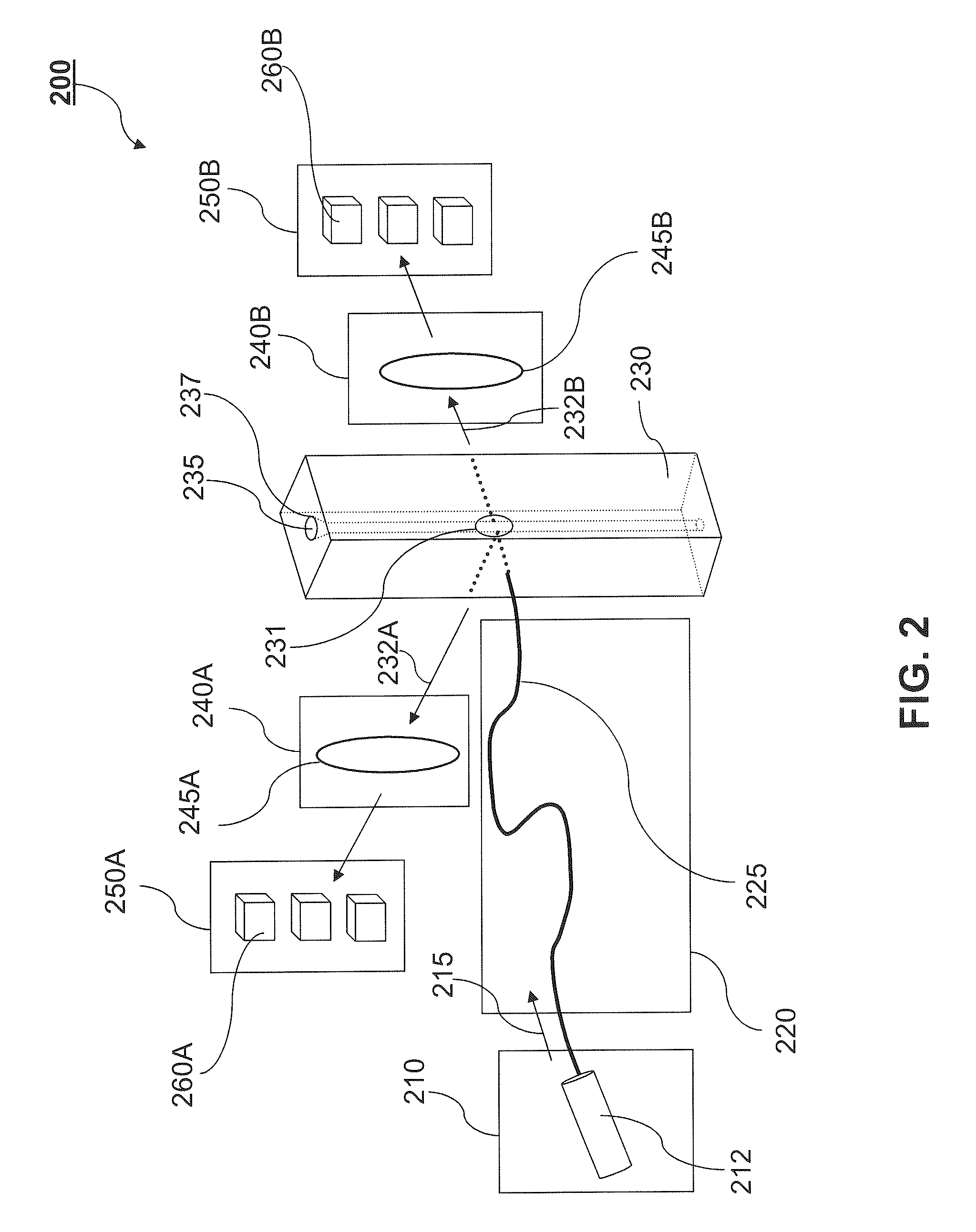
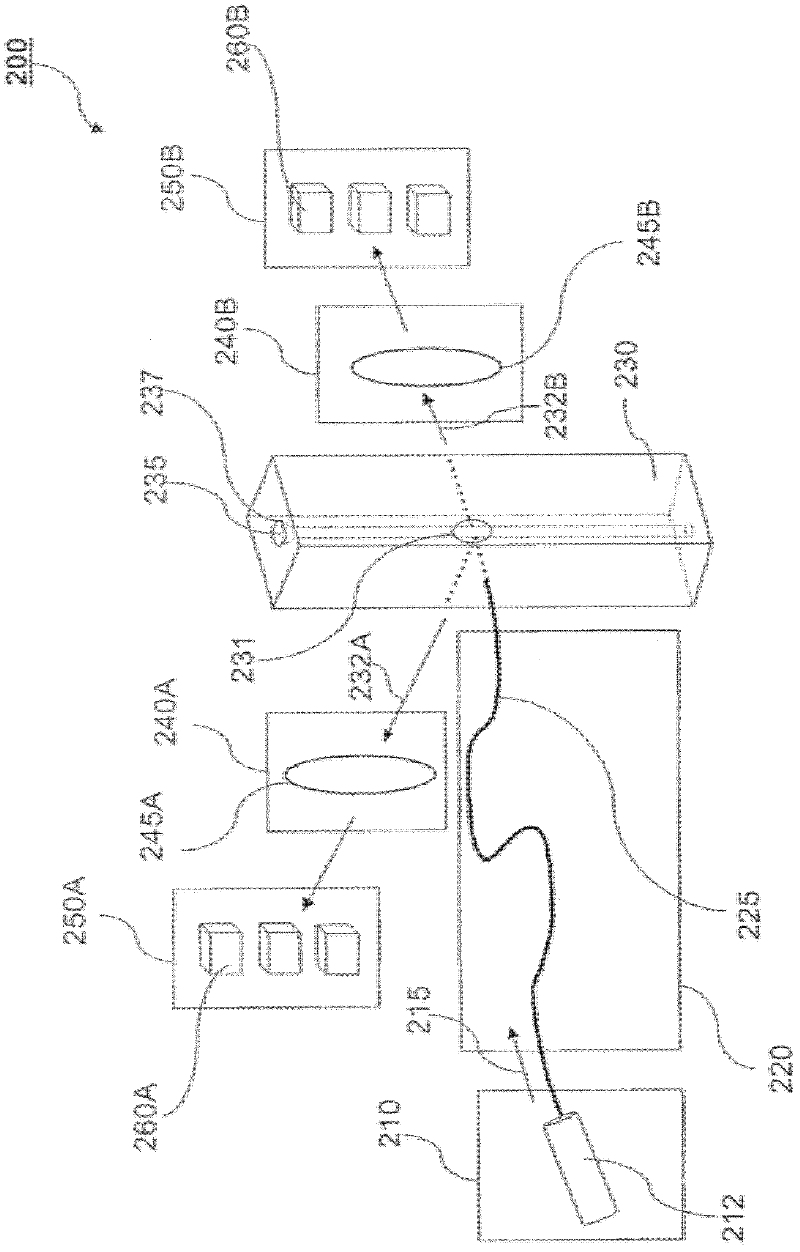
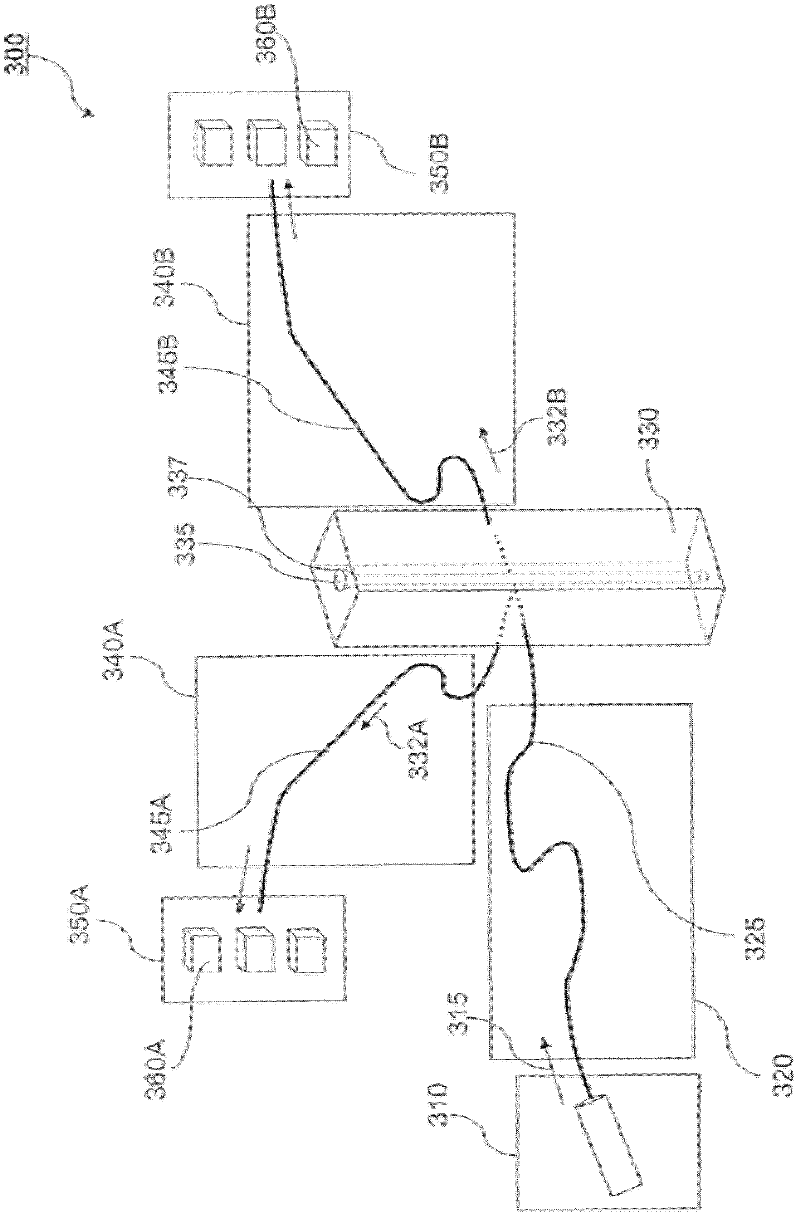
Stabilized optical system for flow cytometry
A particle analyzer that includes optical waveguides, a support, and a detector. The optical waveguides direct spatially separated beams from a source of radiation to produce measuring beams in a sample flow measuring area. The support maintains each of the optical waveguides in a fixed relative position with respect to each other and maintains the positioning of the measuring beams within the measuring area. The detector senses light produced from the measuring beams interacting with a particle flowing through the measuring area. At least one of the support and the detector can be coupled to the core stream sample system. The coupling can use an optical waveguide device configured to convey optical radiation arising from sample interaction to the detector. In another example, a particle analyzer comprises an optical system configured to be fixedly coupled to a sample system and configured to direct beams along independent beam paths from a source of radiation to produce measuring beam spots in a sample flow measuring area of the sample system and a detection system configured to sense radiation delivered from the sample flow measuring area.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
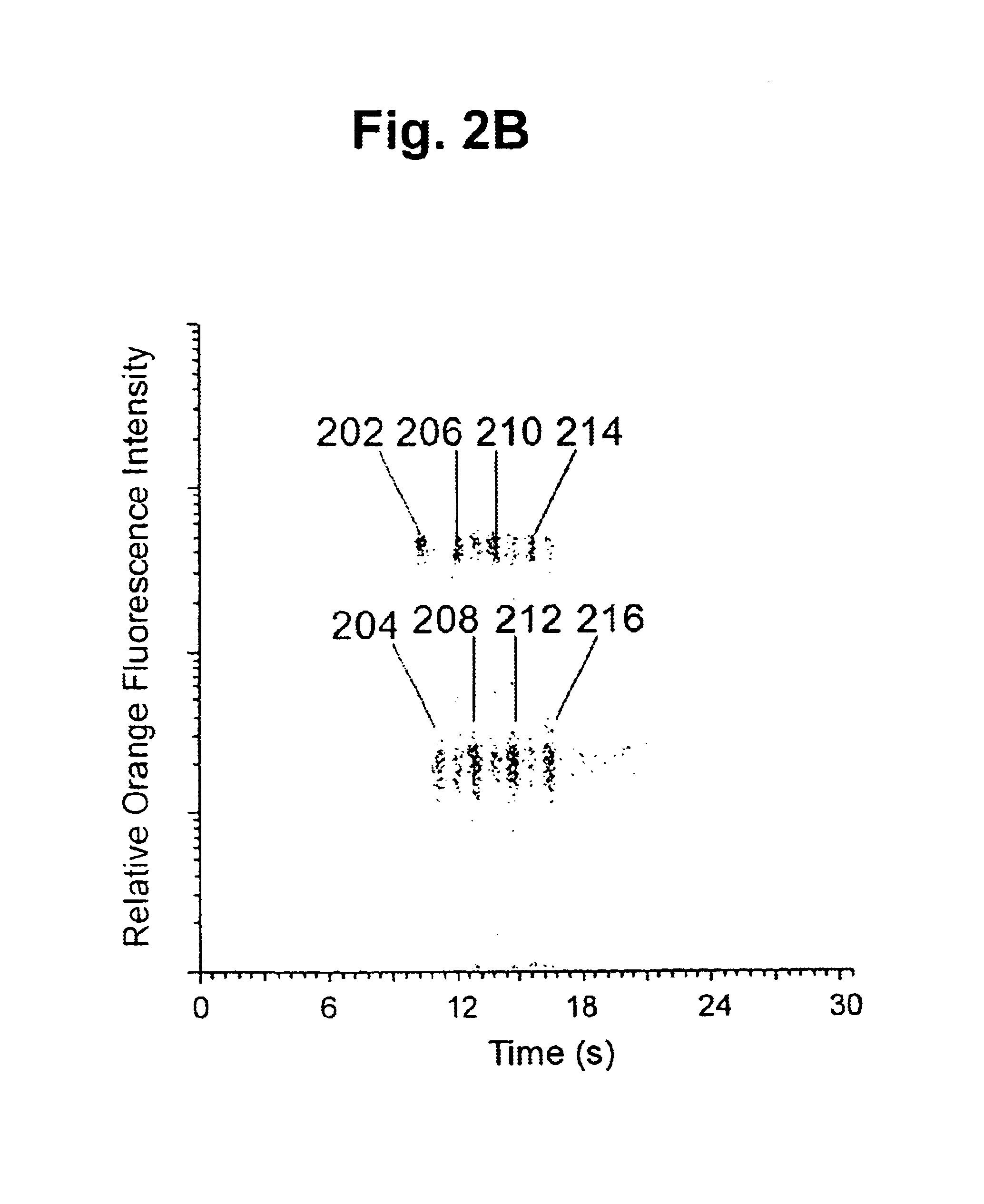
Systems, Storage Mediums, and Methods for Identifying Particles in Flow
ActiveUS20090071225A1Scattering properties measurementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansParticle flowComputational physics
Methods, storage mediums, and systems for correlating pulses generated from multiple interrogation regions in a flow cytometer to particular particles flowing through the flow cytometer are provided. Embodiments of the methods, storage mediums, and systems include configurations for calibrating a flow cytometer using a calibration particle having a unique signature to determine a time-of-flight for particles flowing through the flow cytometer. Based on the calculated time-of-flight and relative positions of interrogation regions corresponding to collectors of the flow cytometer, the methods, storage mediums, and systems may further include configurations for associating other signal pulses to particles of one or more different particle sets.
Owner:LUMINEX
Flow cytometry
InactiveCN102087198AGood photon counting performanceImprove time resolutionIndividual particle analysisFlow cellNear infrared fluorescence
The invention discloses a flow cytometry. The flow cytometry comprises a light source irradiation system, a liquid flow system, a light split system, a signal detection, analysis and processing system, and a personal computer (PC) display control system; the liquid flow system comprises a flowing chamber; linearly flowing cells are accommodated in the flowing chamber; a solid laser is used as an excitation light source of the light source irradiation system, and laser passes through a reflecting mirror and a plano-convex lens to be converged and irradiated on the flowing chamber, is integrated and then is further converged on the optical part of the flowing chamber to be irradiated on the linearly flowing cells; the signal detection, analysis and processing system comprises a lateral scattering detector, a yellow fluorescence channel detector, a near-infrared fluorescence channel detector, a forward scattering detector and a signal processing module; and all detectors are multi-pixel photon counters (MPPC). The flow cytometry has the characteristics of large dynamic detection range, high sensitivity, small size and compactness and convenience in maintenance.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH
Flow cytometry for high throughput screening
InactiveUS20020170365A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsEngineering
The present invention, provides a flow cytometry apparatus for the detection of particles from a plurality of samples comprising: means for moving a plurality of samples comprising particles from a plurality of respective source wells into a fluid flow stream; means for introducing a separation gas between each of the plurality of samples in the fluid flow stream; and means for selectively analyzing each of the plurality of samples for the particles. The present invention also provides a flow cytometry method employing such an apparatus.
Owner:STC UNM
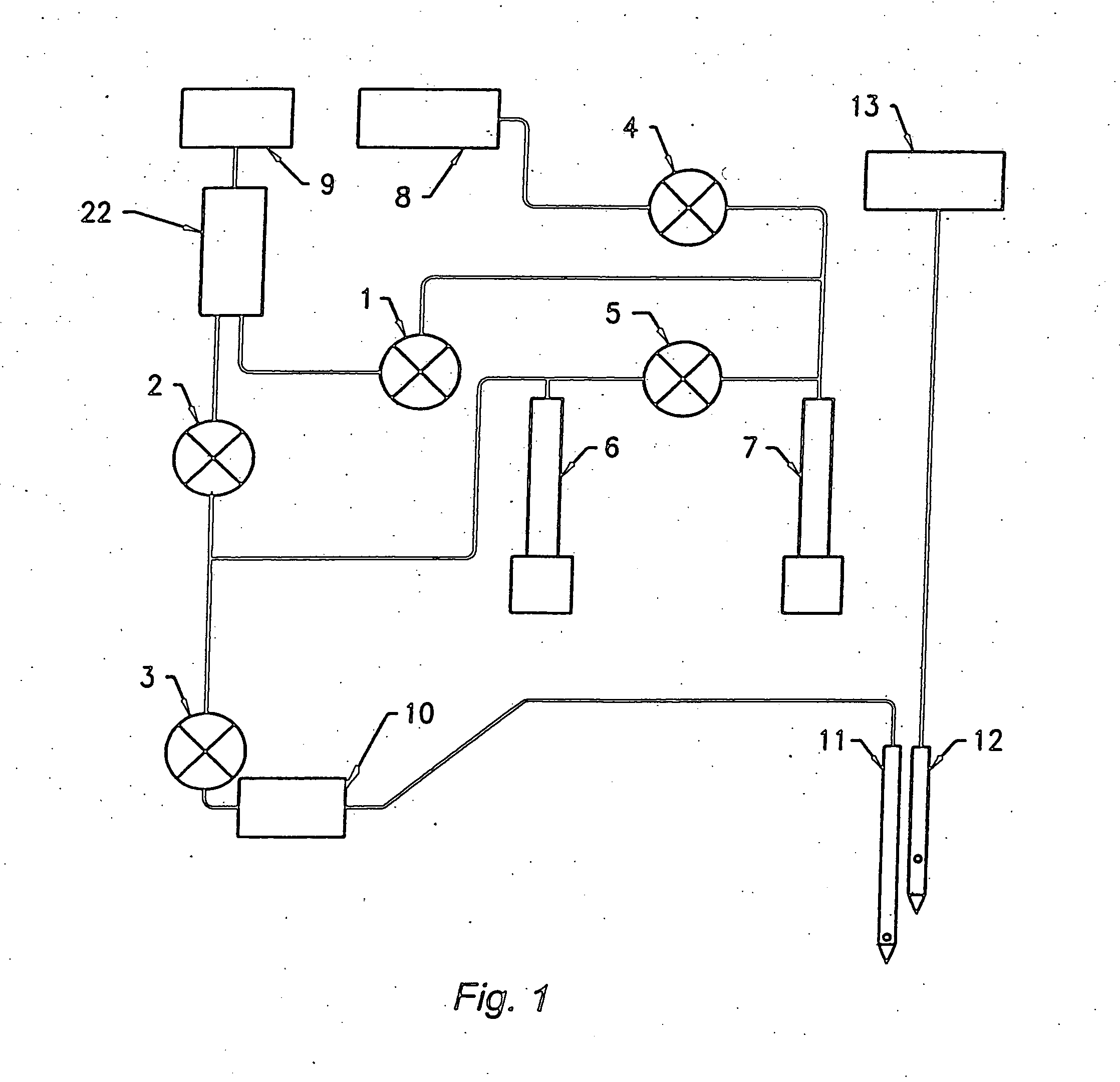
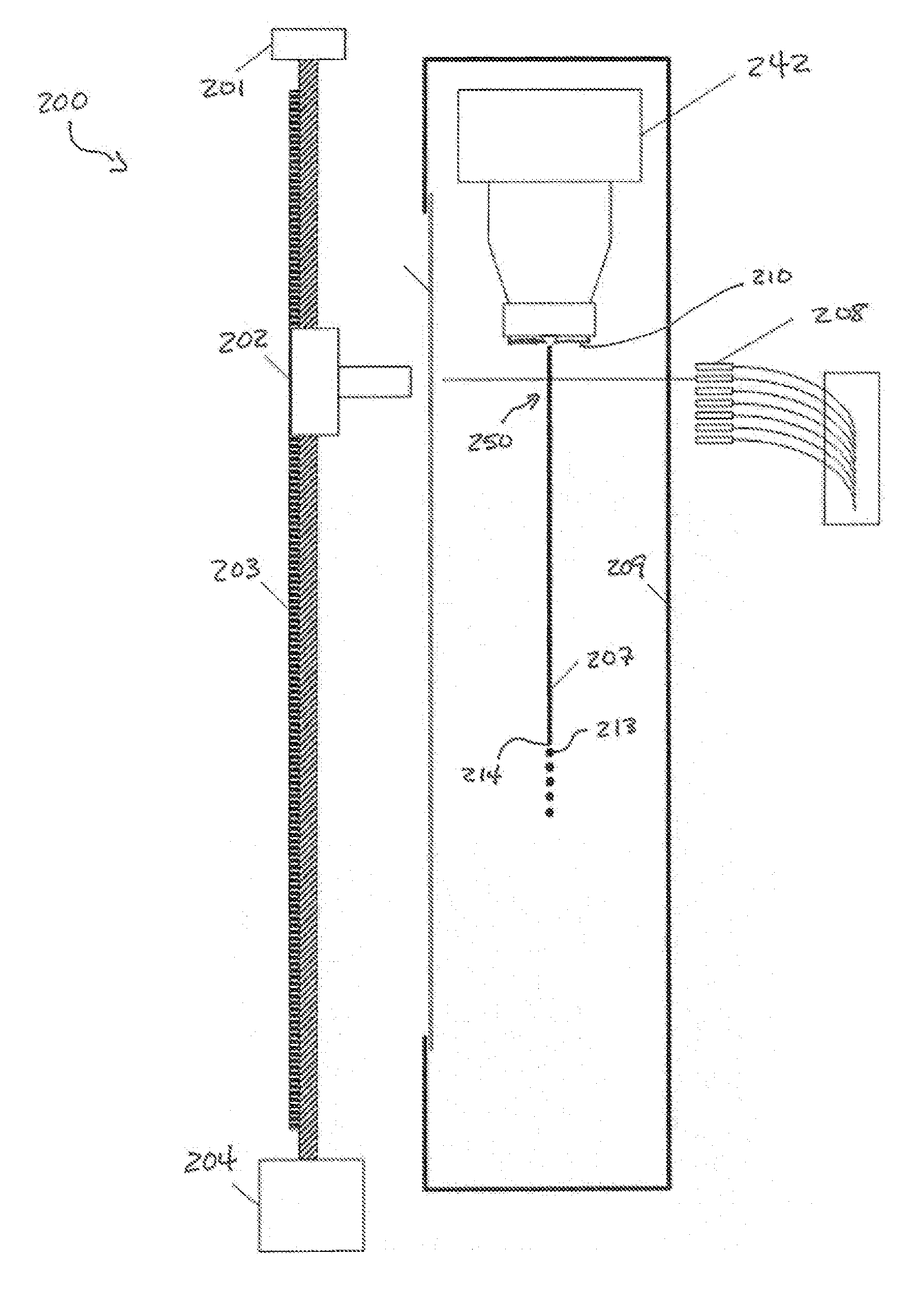
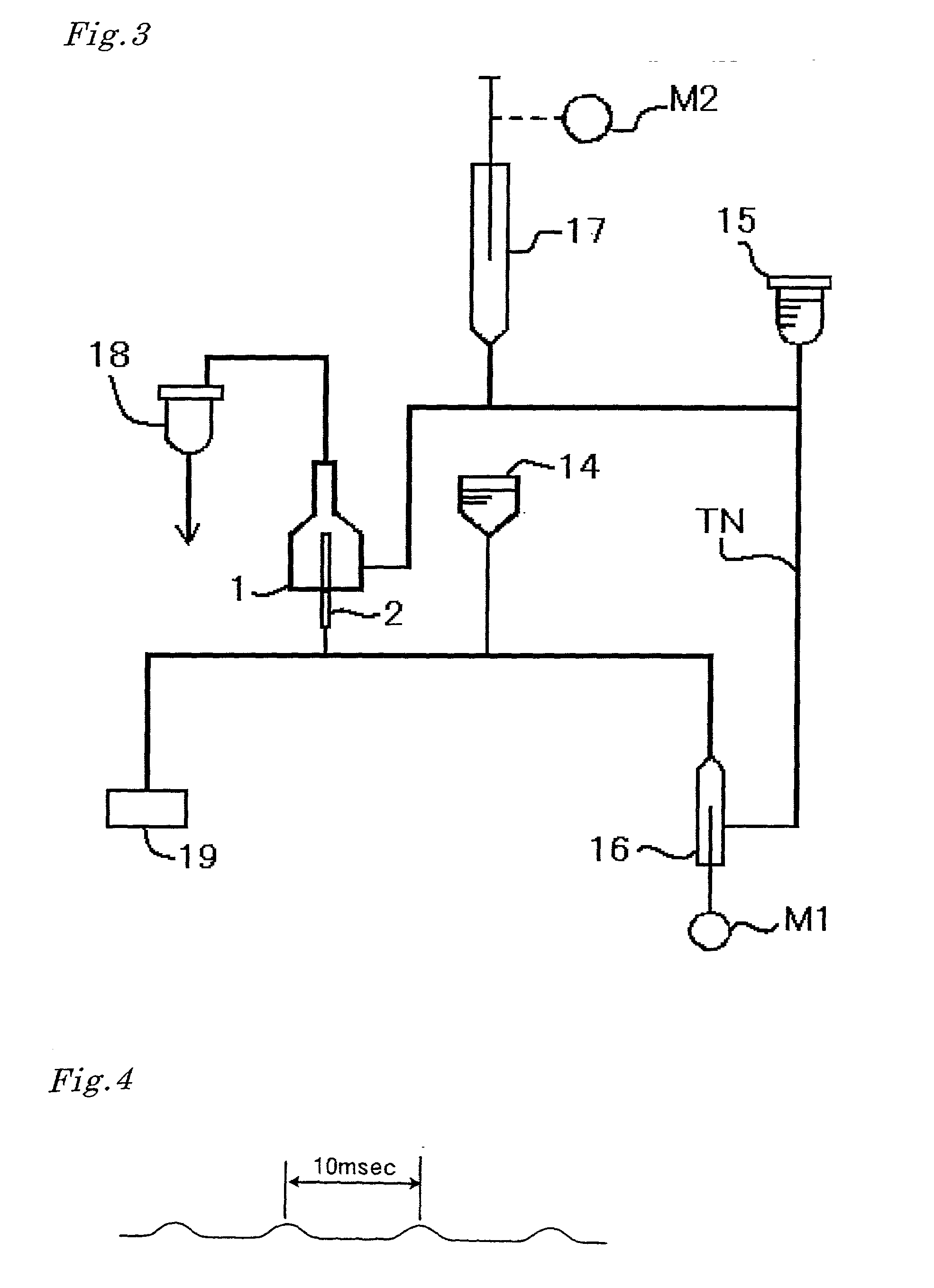
Fluid system of flow cytometer and flow cytometric detection method
The invention discloses a fluid system of a flow cytometer and a flow cytometric detection method. The fluid system comprises a sampling needle, a sampling needle cleaning device, a flowing chamber, a reaction tank, a hemolytic agent syringe, a sample syringe, a diluent syringe, a diluent bottle, a hemolytic agent bottle and a motor, wherein the sample syringe is respectively communicated with the sampling needle, the reaction tank, the flowing chamber, the sampling needle cleaning device and the diluent syringe, the diluent syringe is respectively communicated with the diluent bottle, the flowing chamber and the reaction tank, the hemolytic agent syringe is respectively communicated with the hemolytic agent bottle and the reaction tank, and the hemolytic agent syringe, the sample syringe and the diluent syringe are all driven and controlled by the motor. According to the invention, driving motors for a plurality of syringes are integrated into one, arrangement of the syringes satisfies moment balance, integral rigidity and inertia are improved, gap instability of the driving motor can be buffered, a more stationary sample flow can be obtained, and thus, detection precision of the flow cytometer is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN DYMIND BIOTECH
Flow cytometer
ActiveUS20050225745A1Analyzing especially fluorescence of a target particle more appropriately and efficientlyEliminate scatterRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationFlow cellFluorescence
A laser light source emits a first light beam irradiating a solution including target particles and being flowed in a flow cell to generate forward scattered light and orthogonal scattered light therefrom. A light emitting diode emits a second light beam irradiating the solution in the flow cell to generate at least one wavelength of fluorescence therefrom. A first detector is adapted to detect the forward scattered light. A second detector is adapted to detect the orthogonal scattered light. At least one third detector is adapted to detect the at least one fluorescence. A first filter is disposed between the flow cell and the third detector and adapted to eliminate scattered light generated from the target particles by the irradiation of the first light beam.
Owner:NIHON KOHDEN CORP
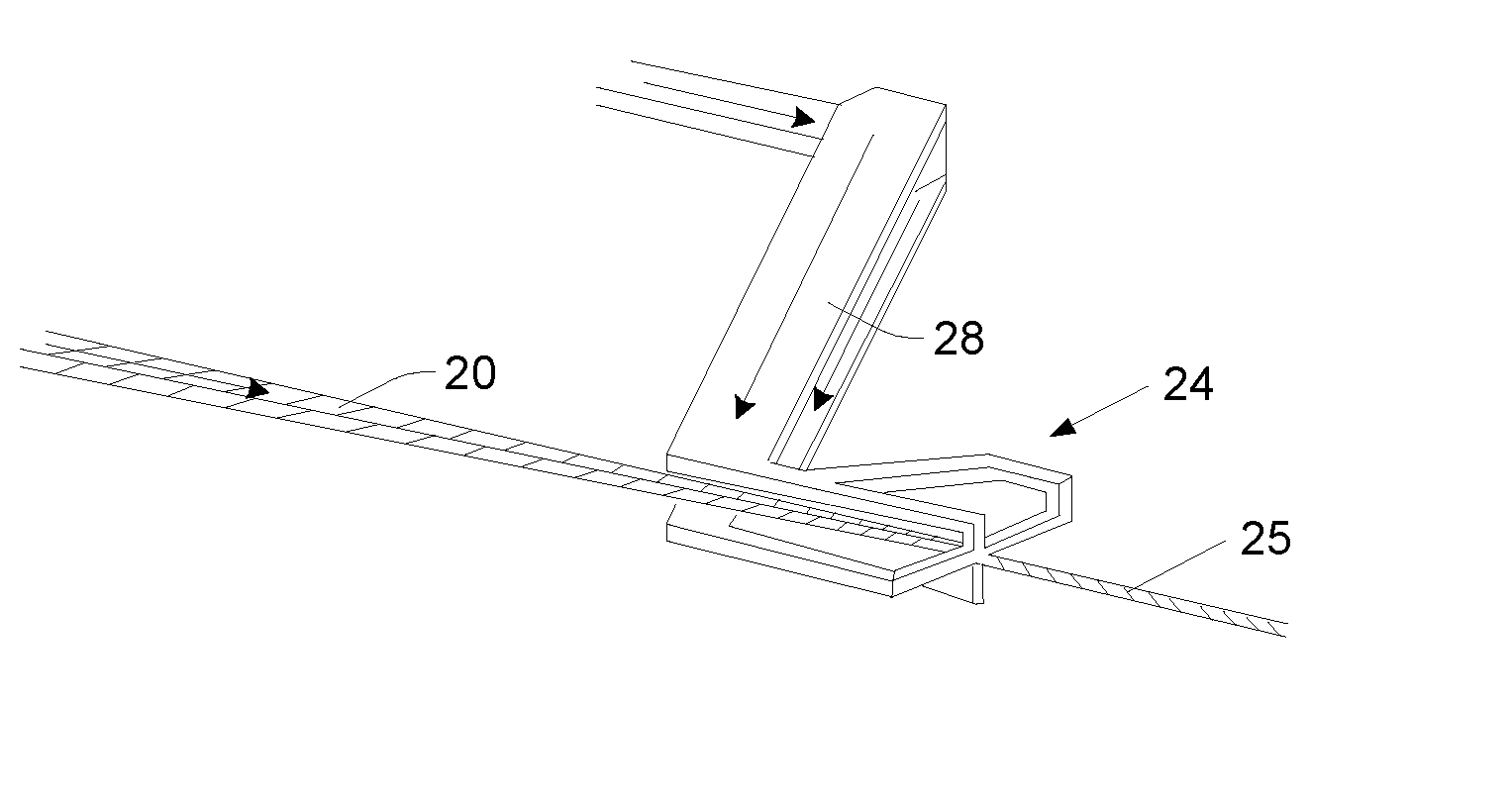
Microfluidic component and method for sorting particles in a fluid
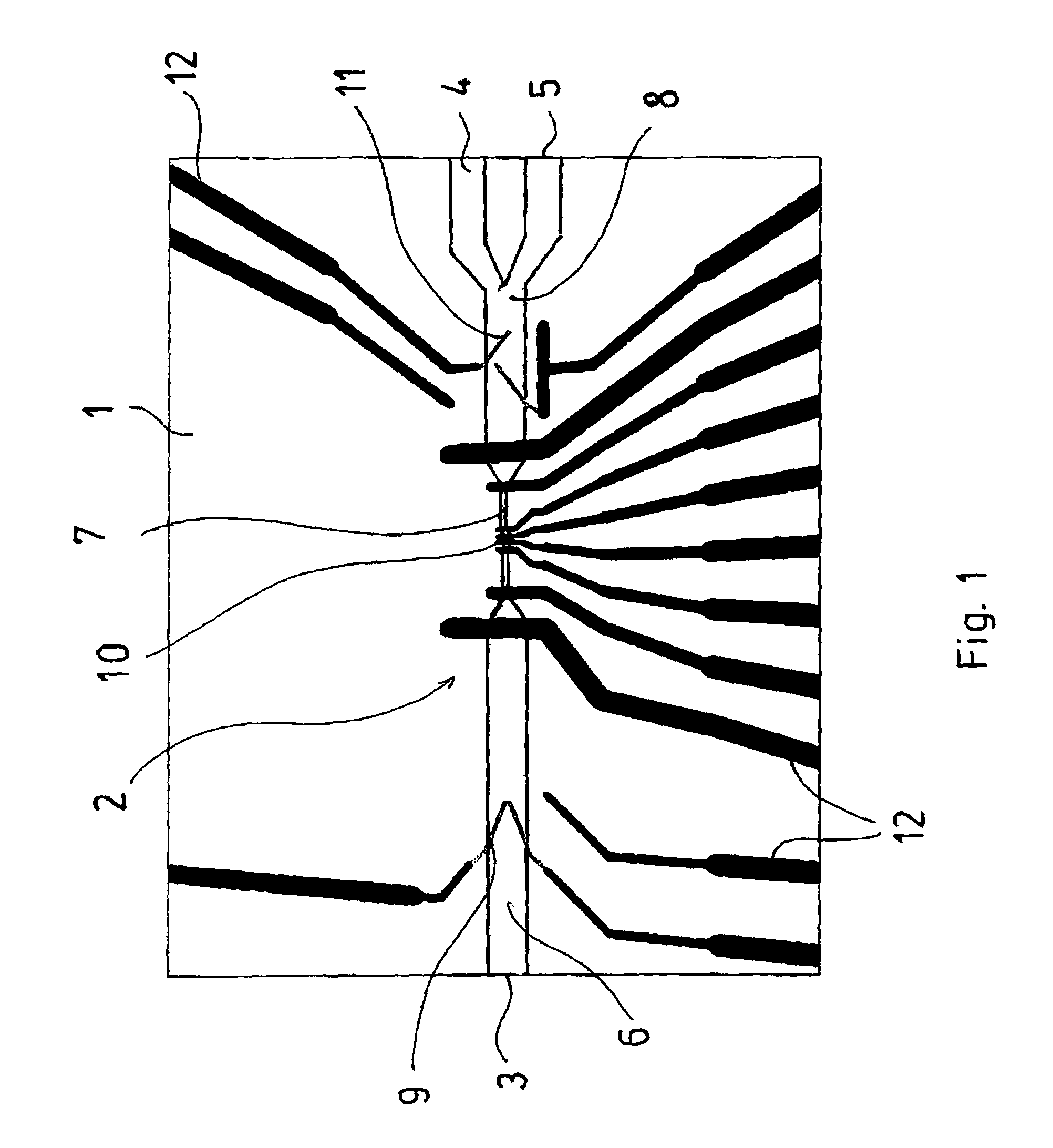
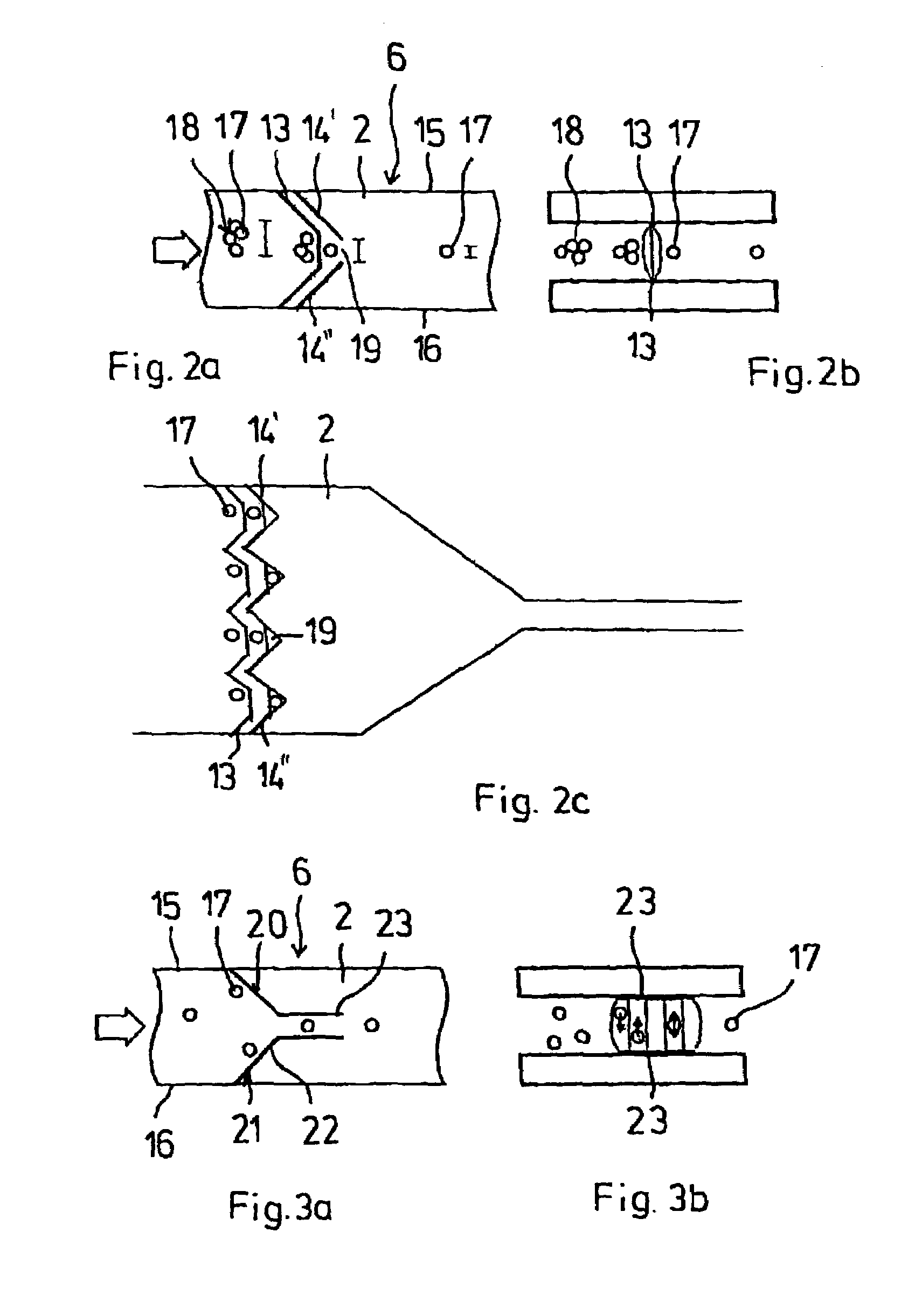
InactiveUS7294249B2Reduce riskAccurately determineElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentBiological cellDielectrophoresis
Microtechnologically prepared component as a flow cytometer. The component contains a preparation area to specifically influence and separate the particles, preferably by dielectrophoresis, a measuring channel area for characterizing the particles, and a sorting area for sorting the particles identified in the measuring channel area by dielectrophoresis. The sorting includes switching elements which permit active guidance of the particles into two or more subchannels corresponding to the criteria which have been registered in the measuring channel area. With a component configured in this way for the use of a flow cytometer, quick and precise sorting of particles, in particular biological cells in a suspension, can be implemented.
Owner:AMPHASYS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com