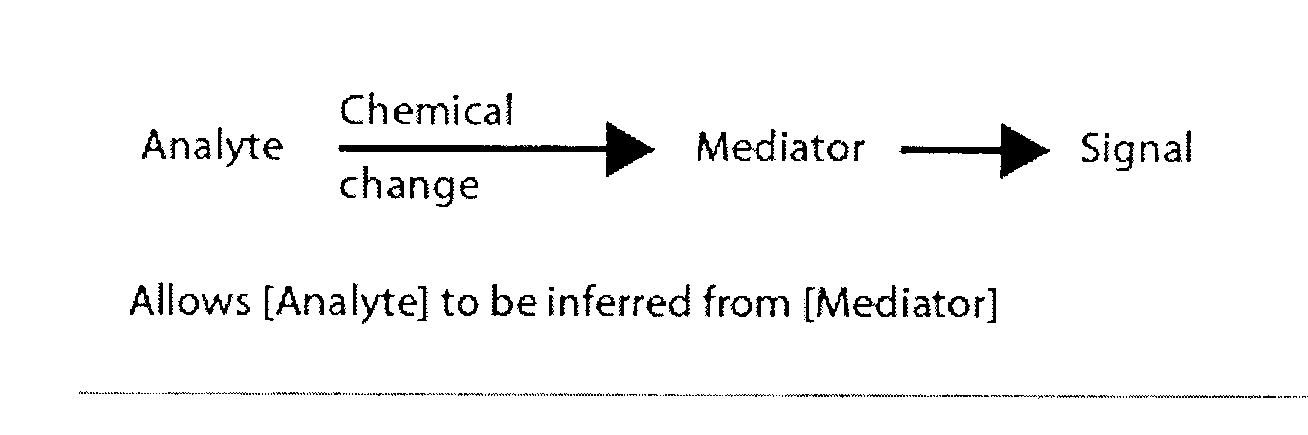
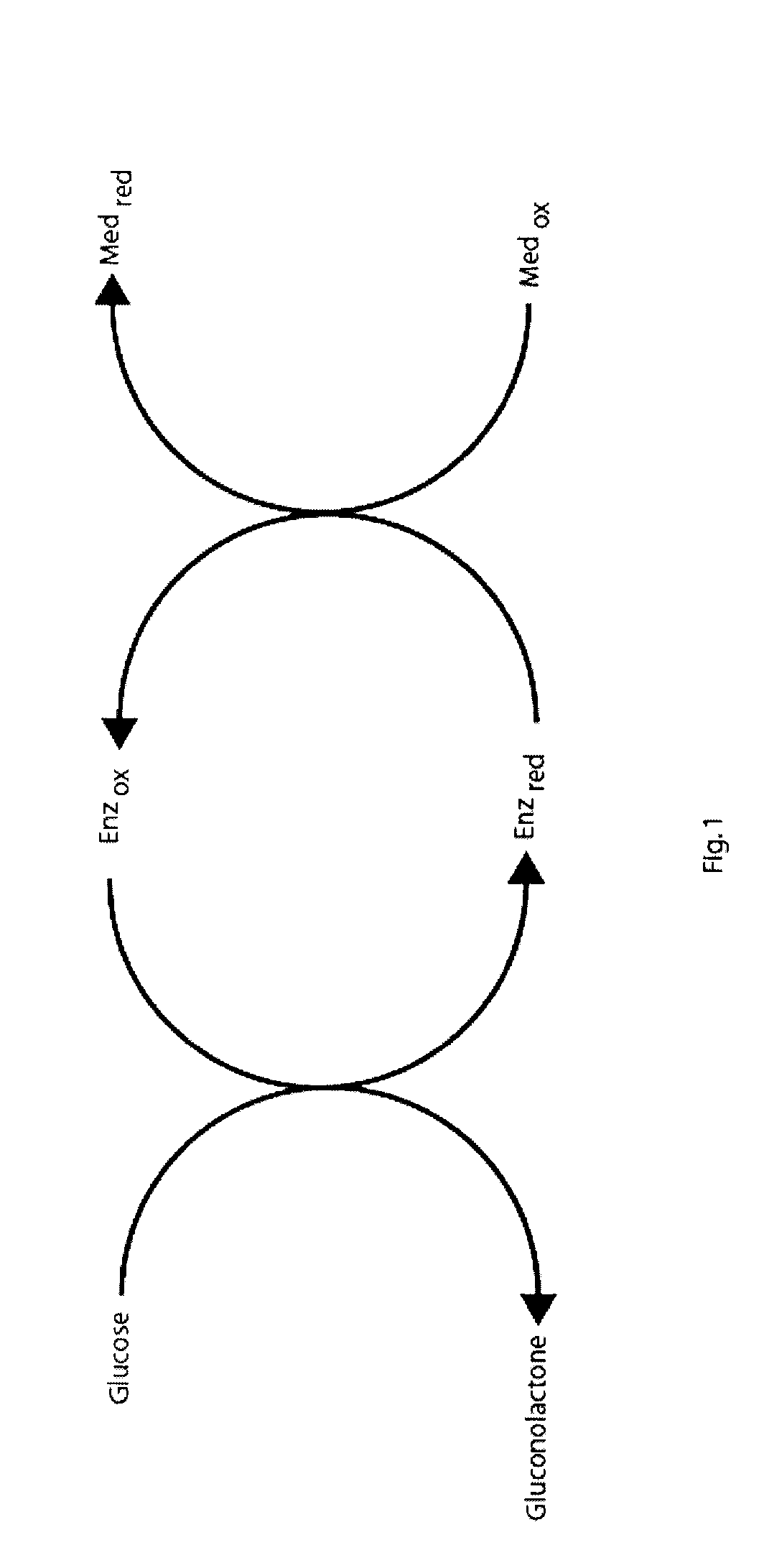
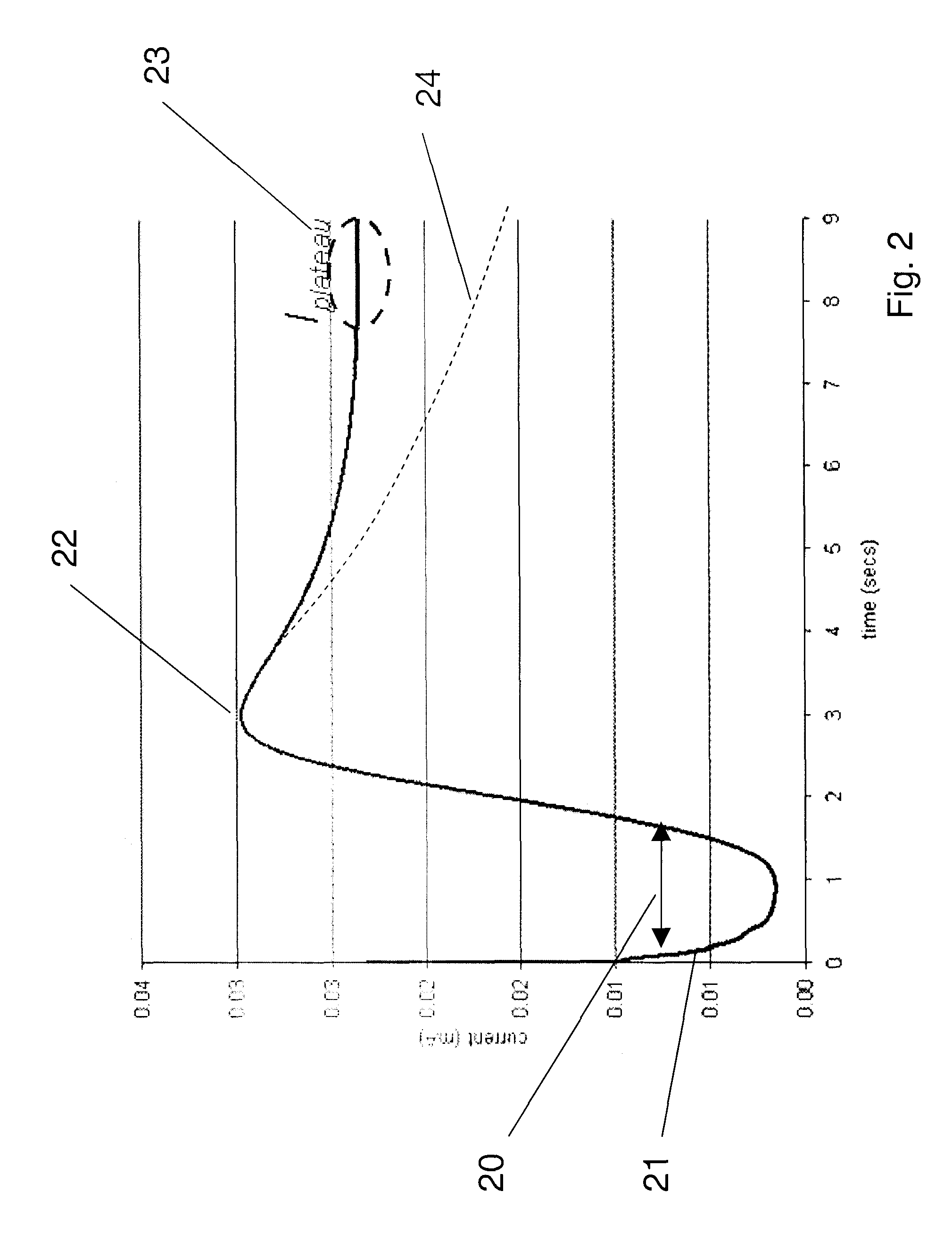
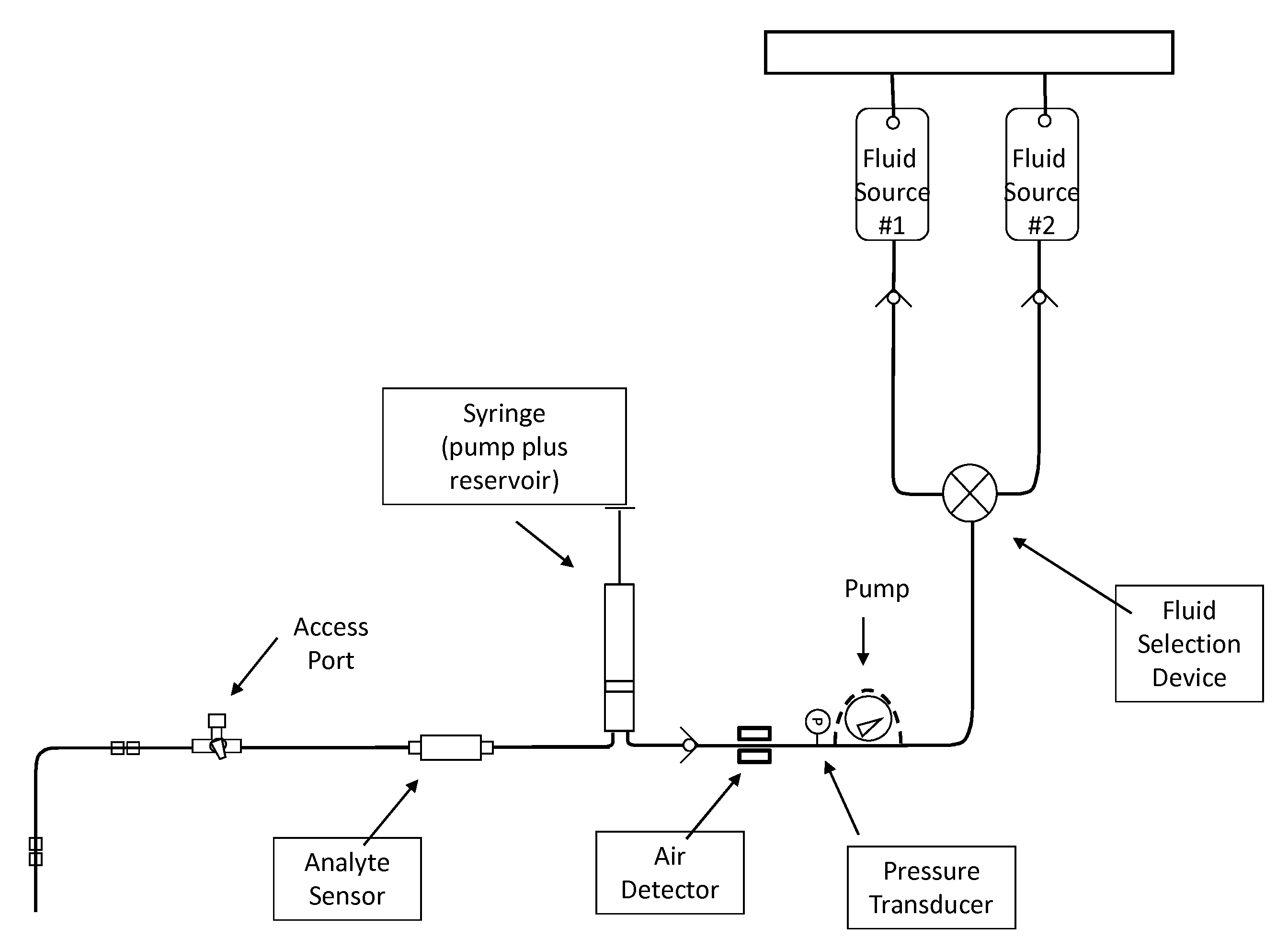
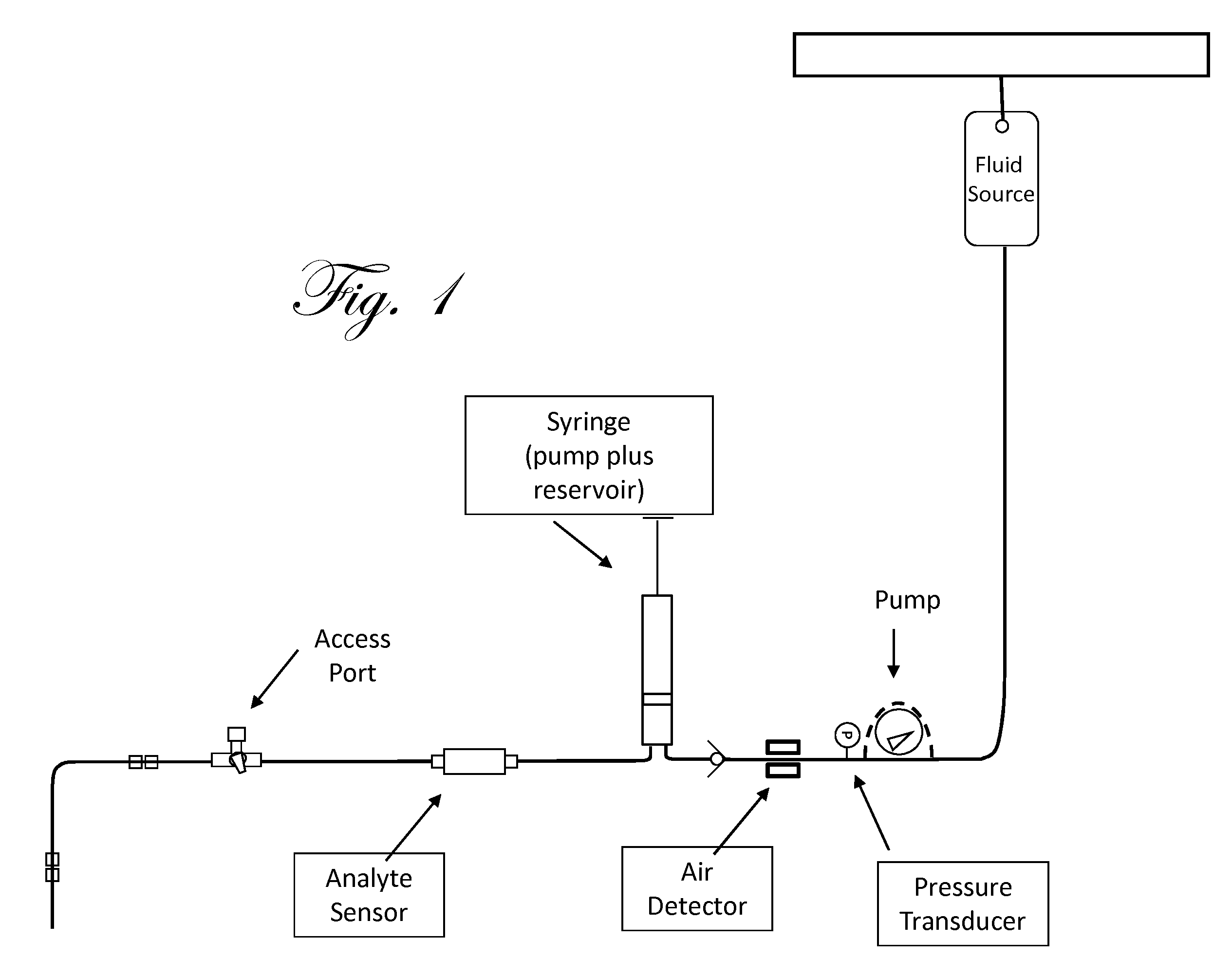
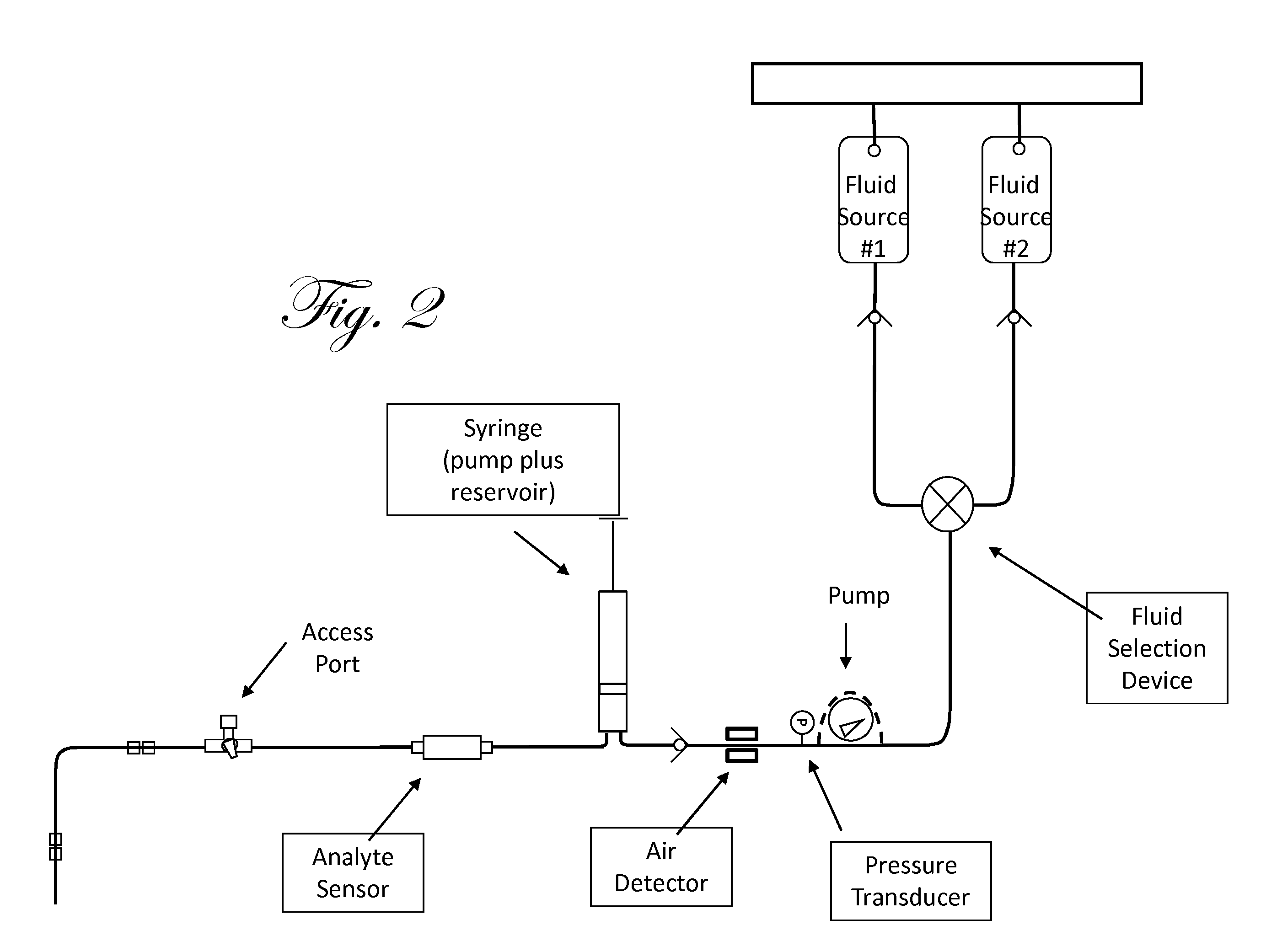
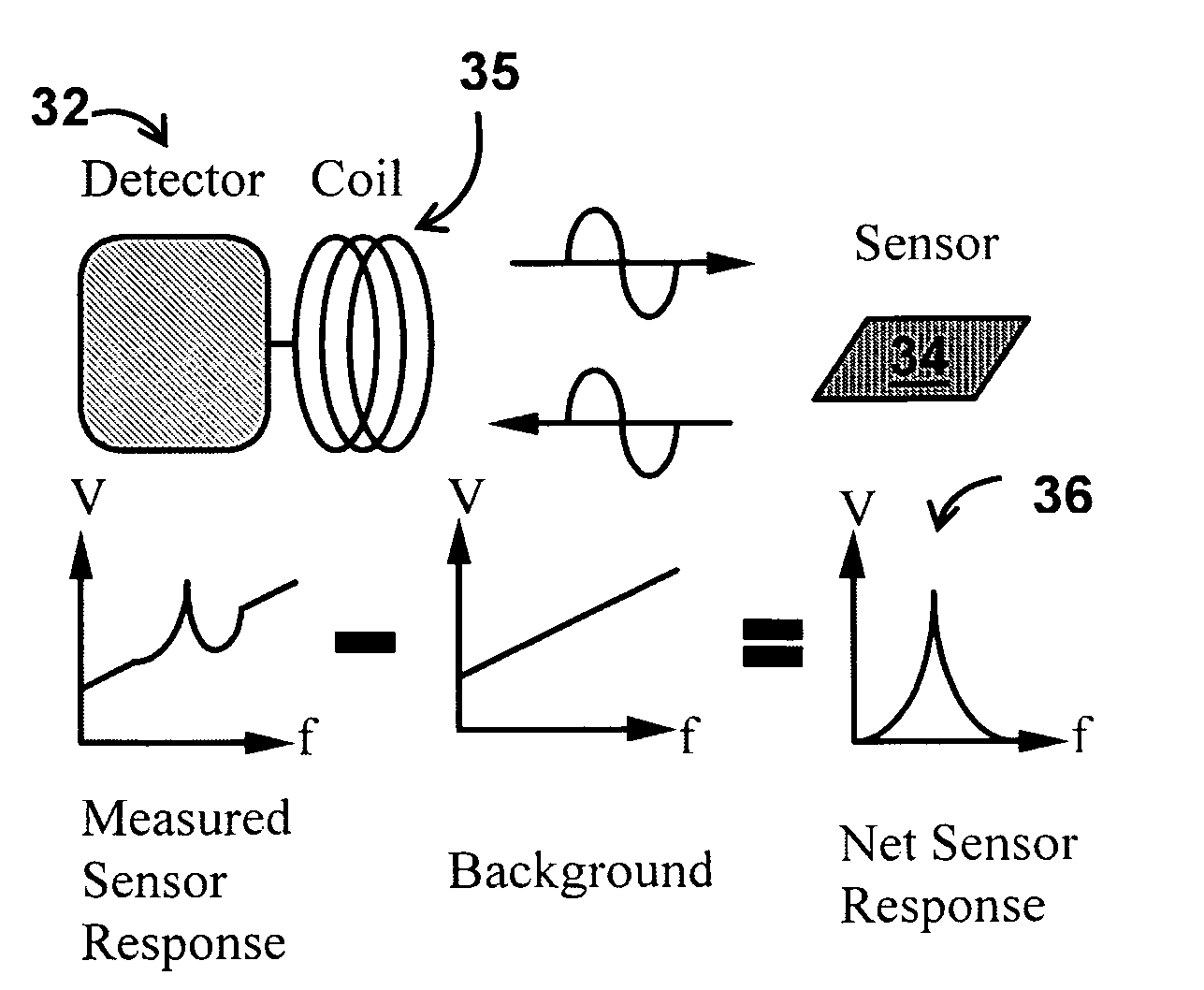
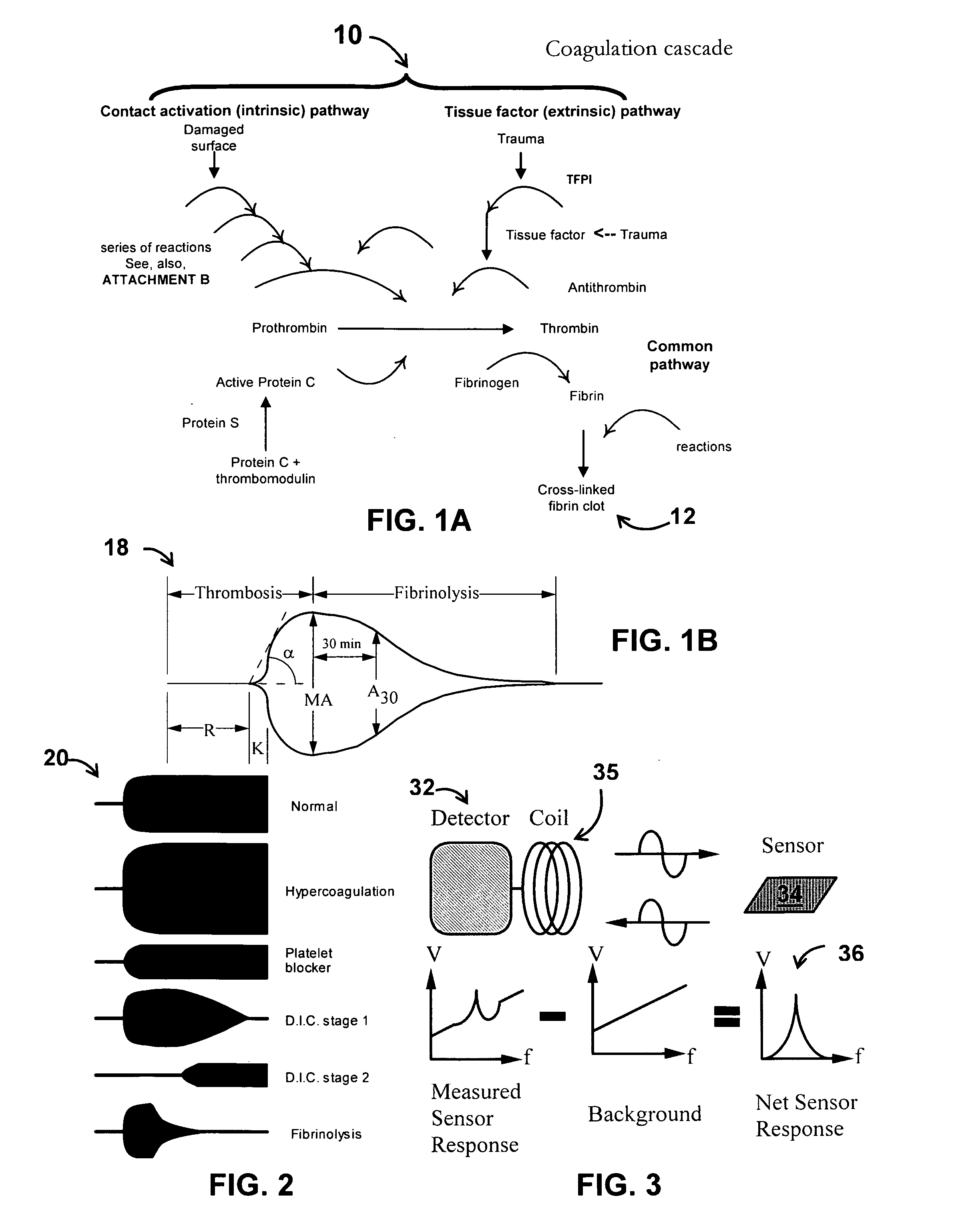
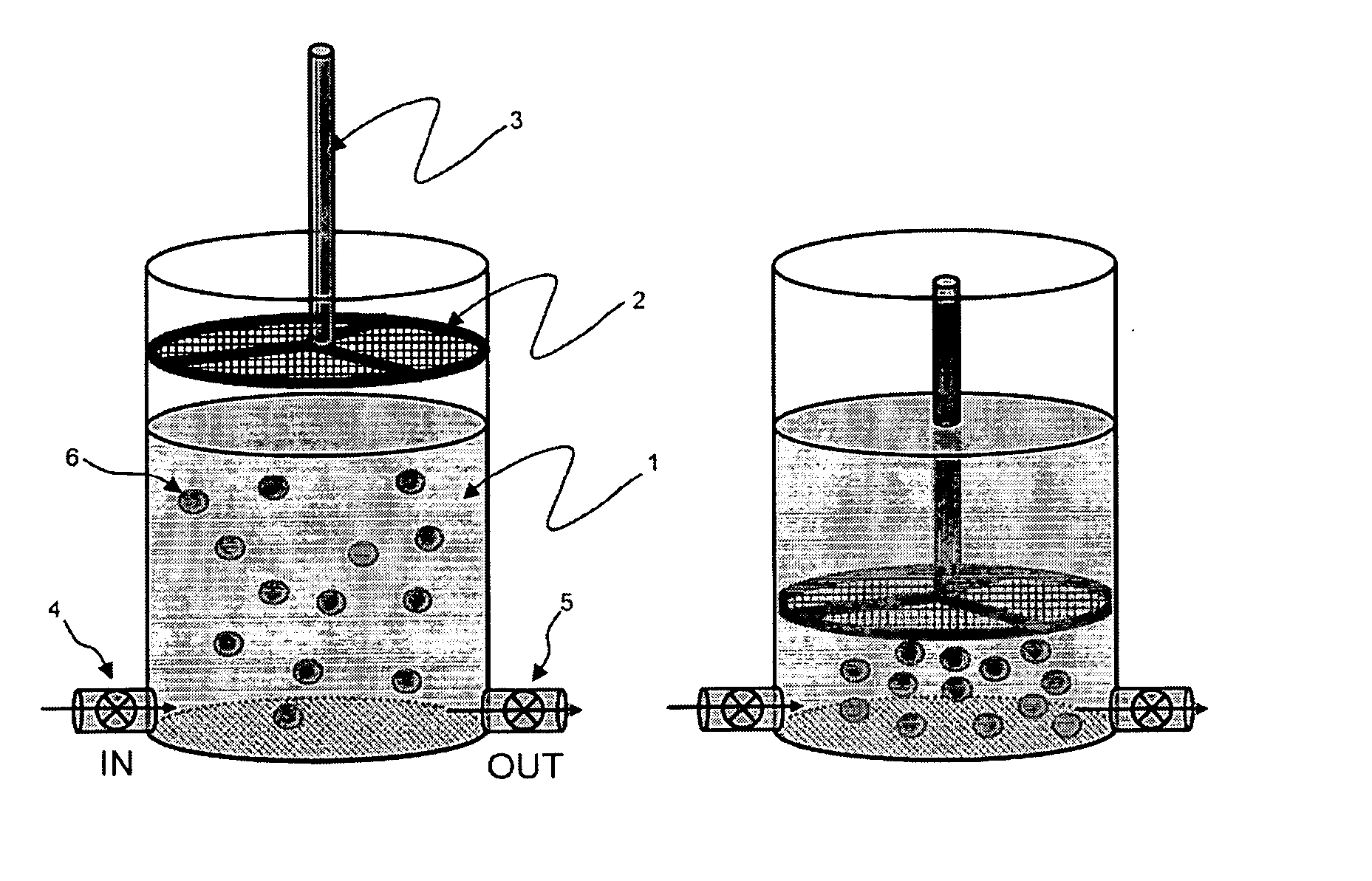
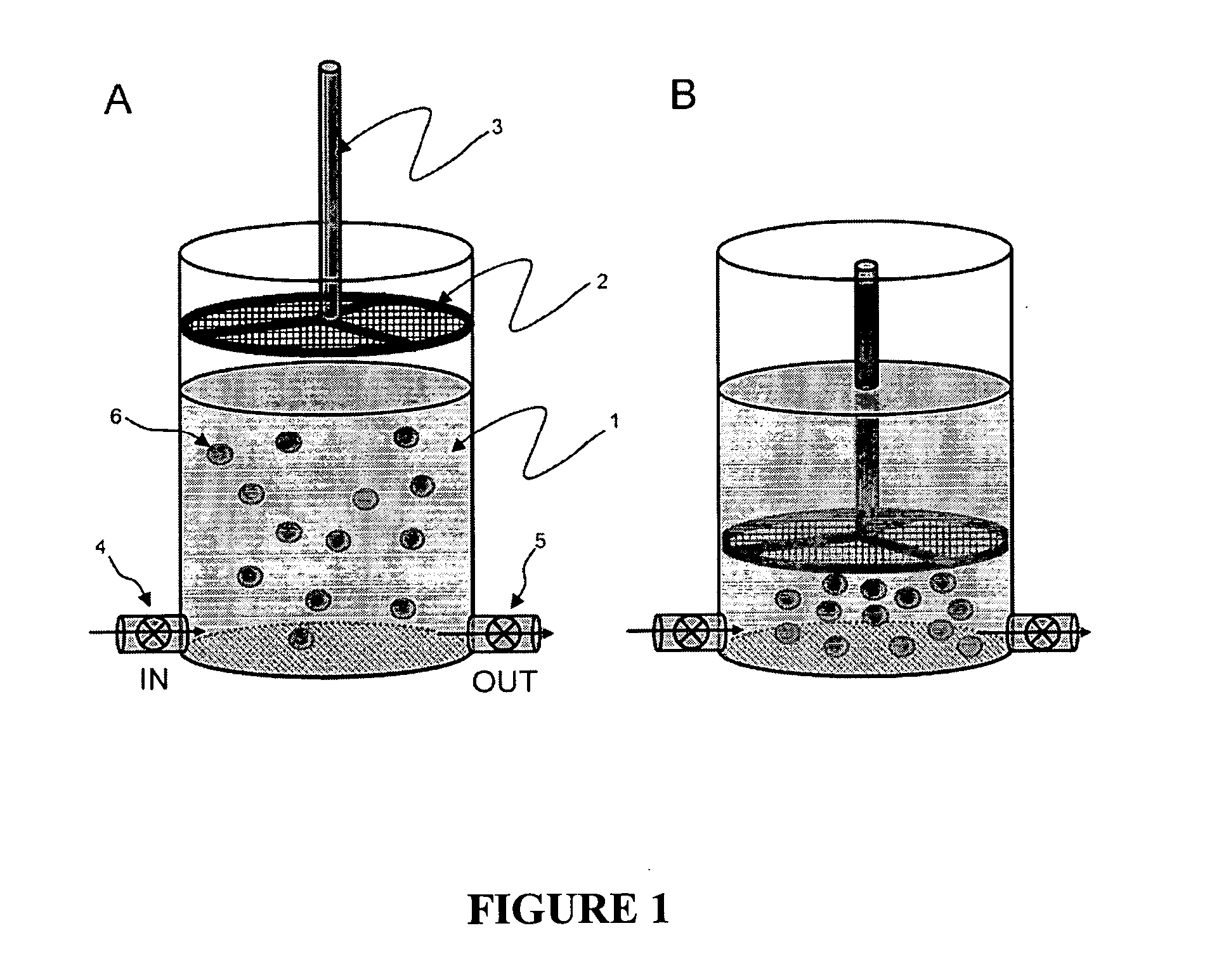
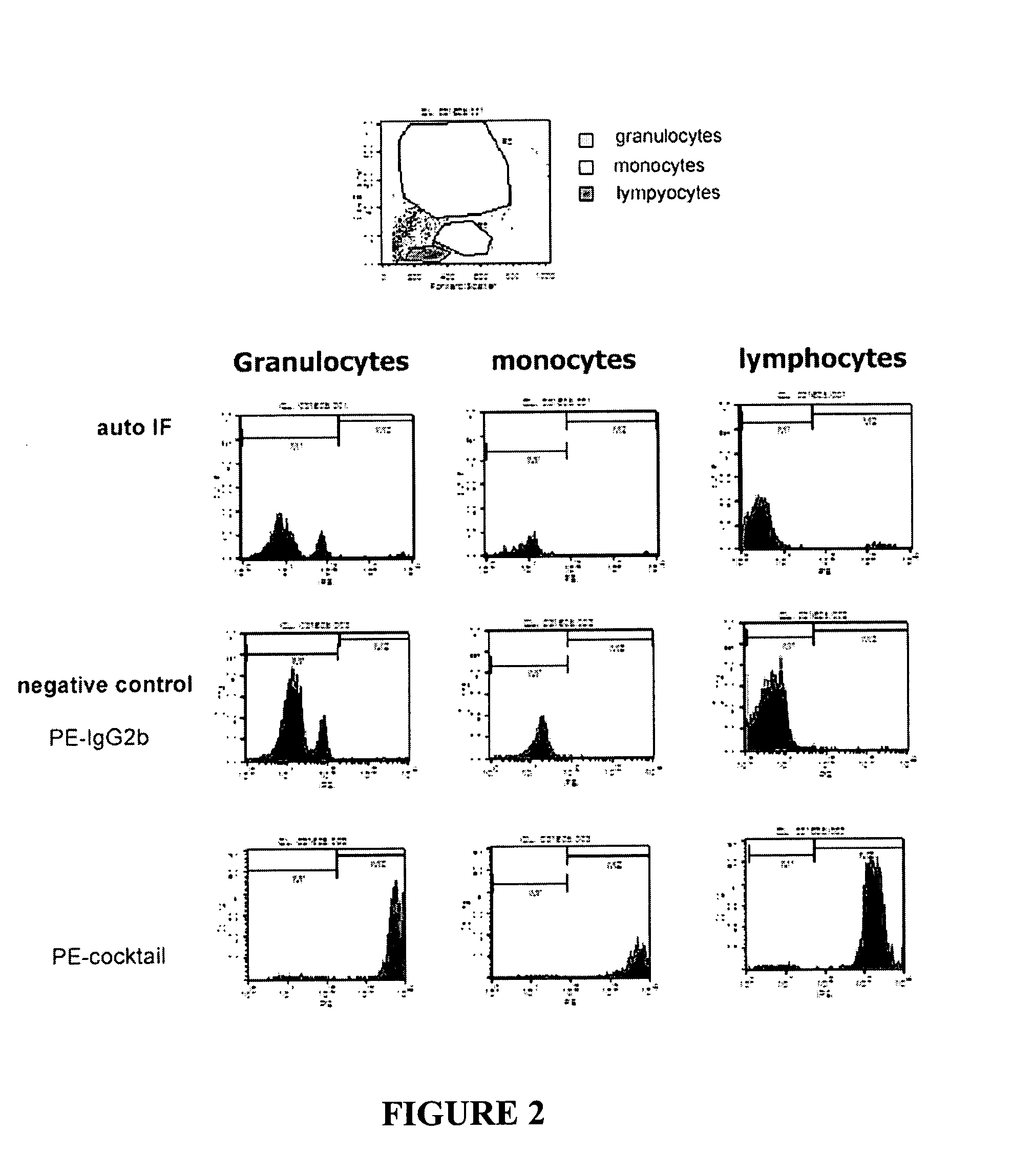
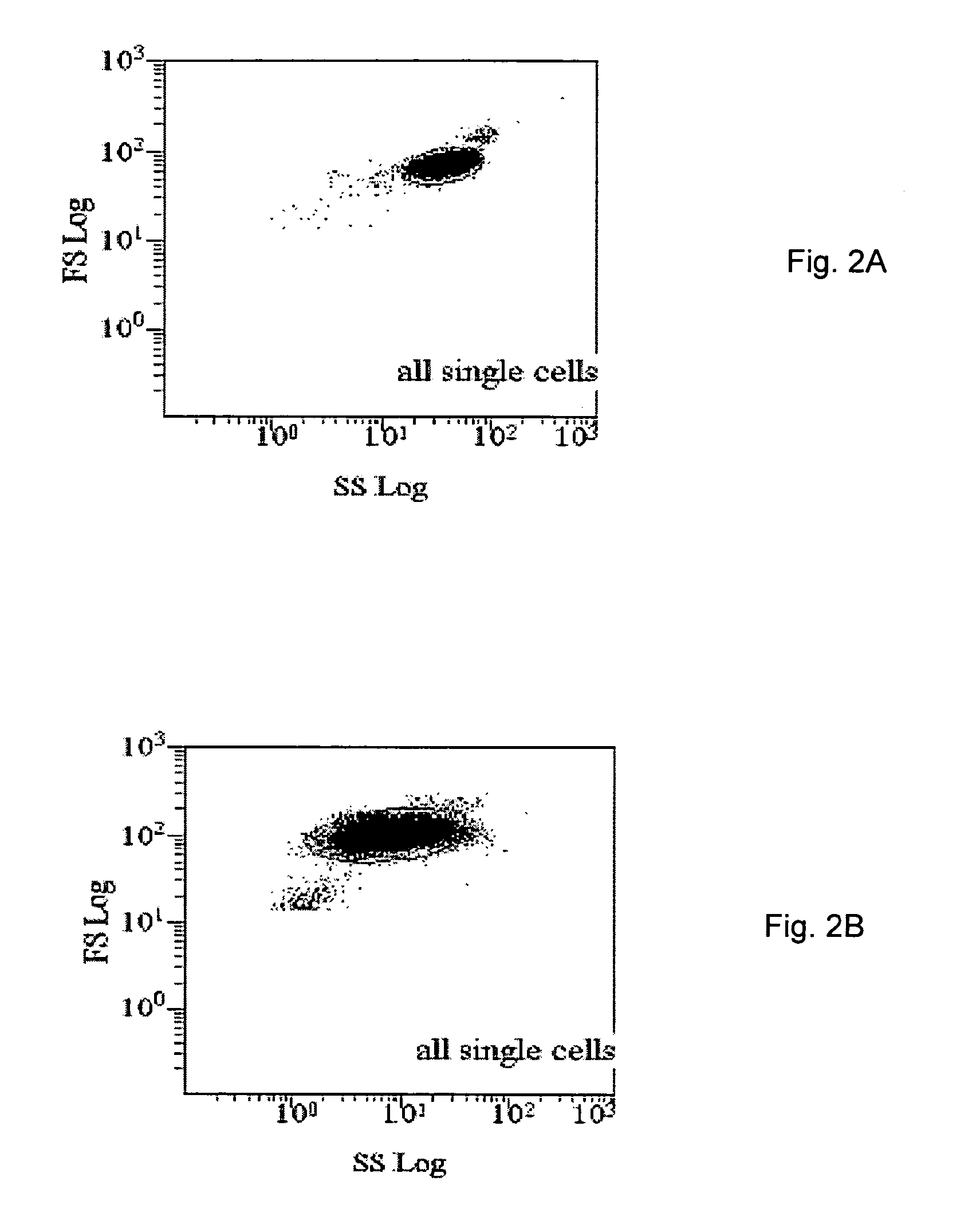
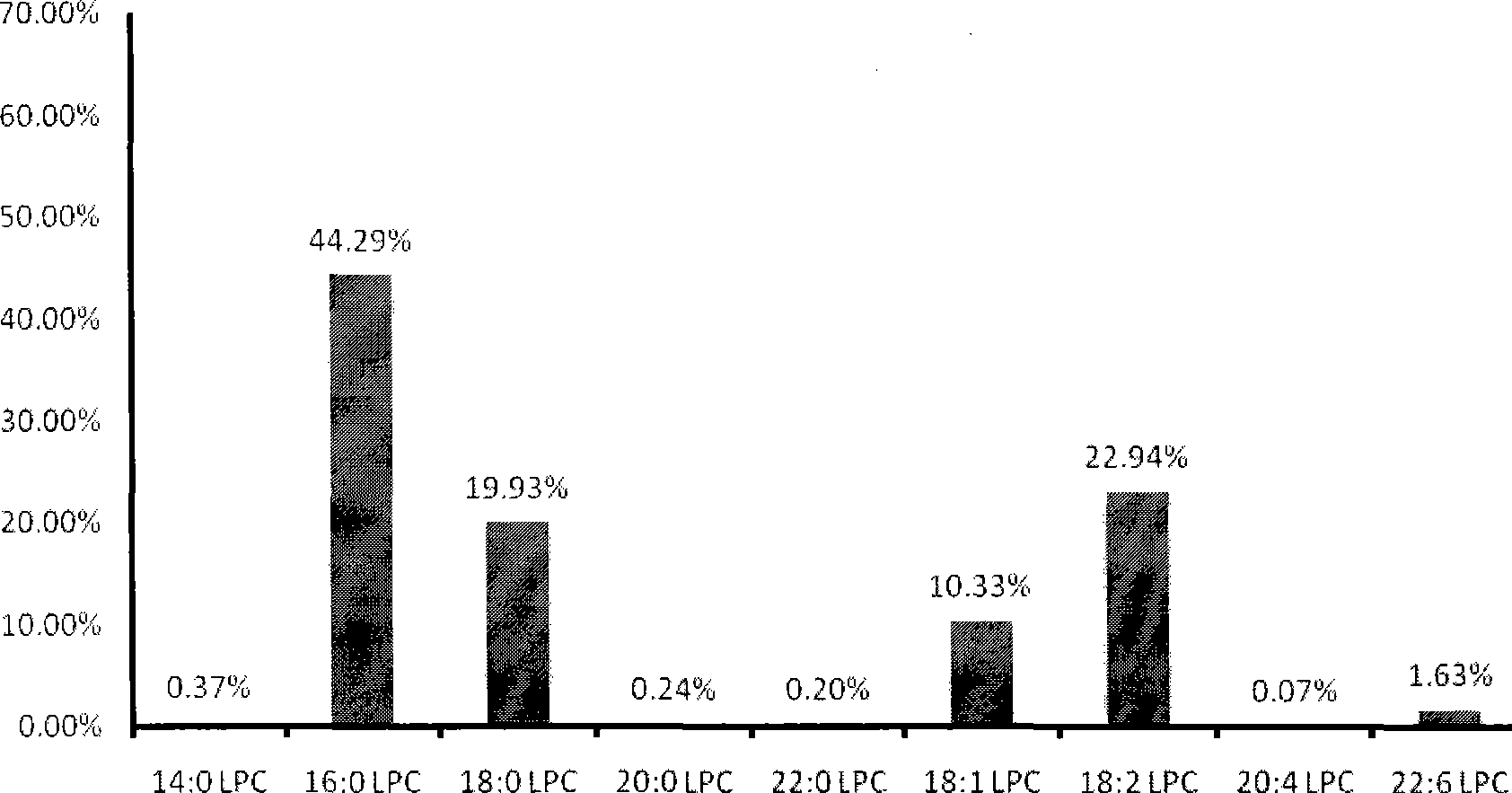
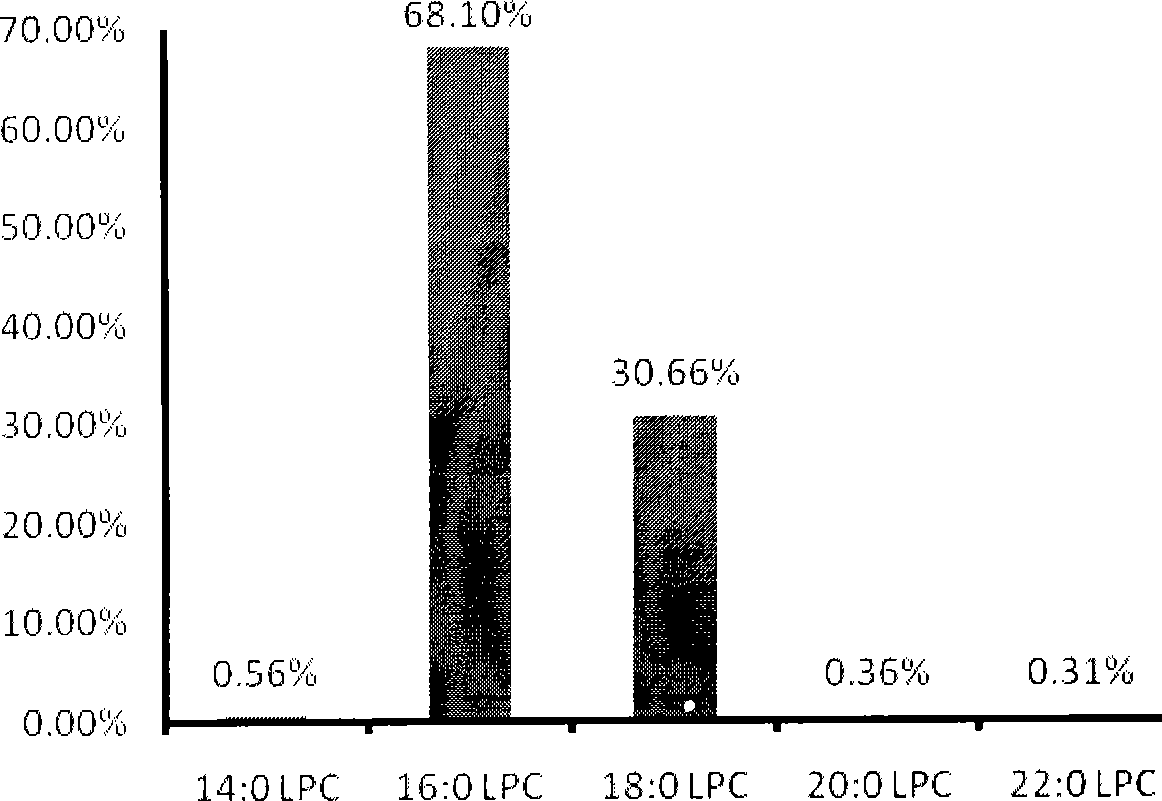
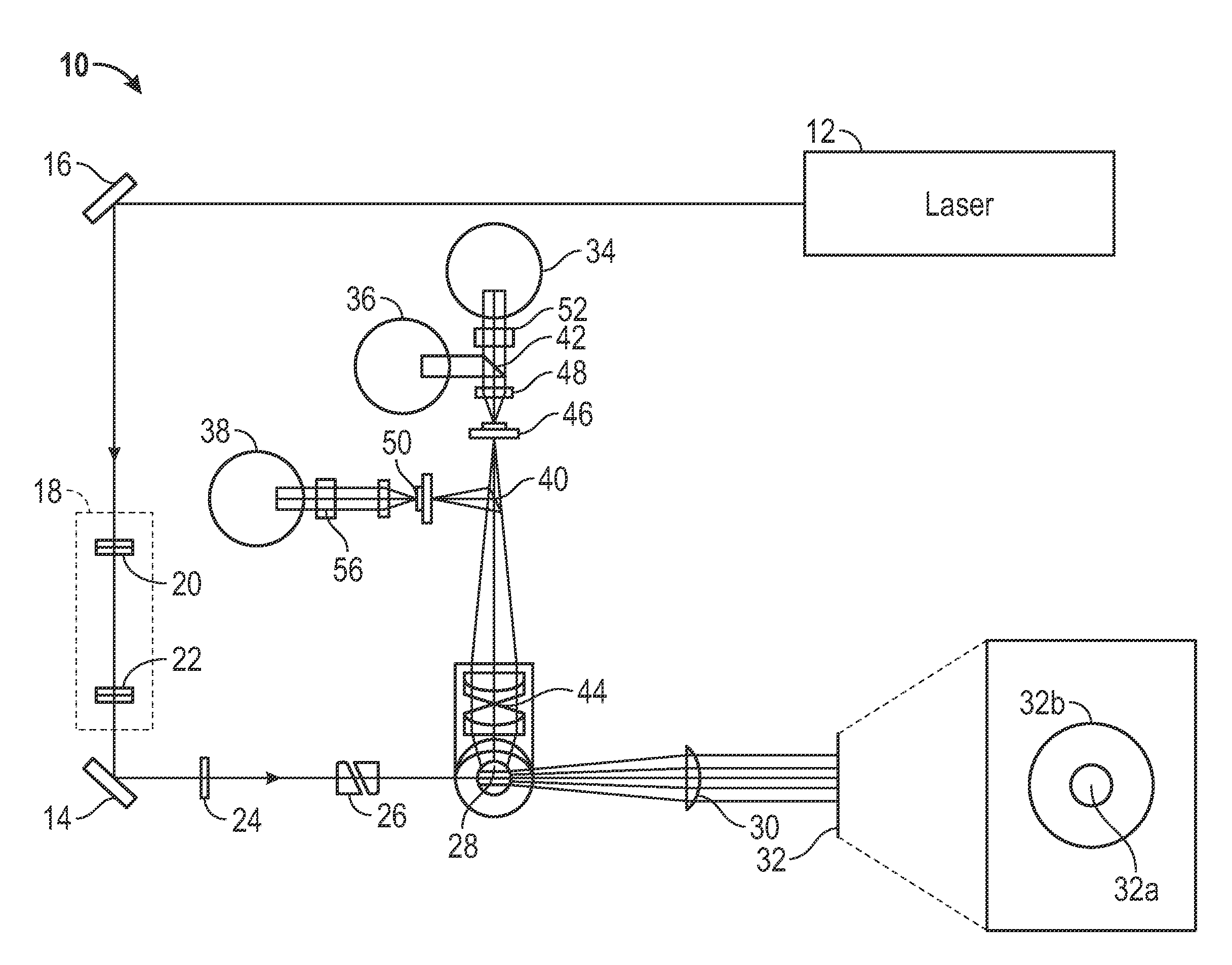
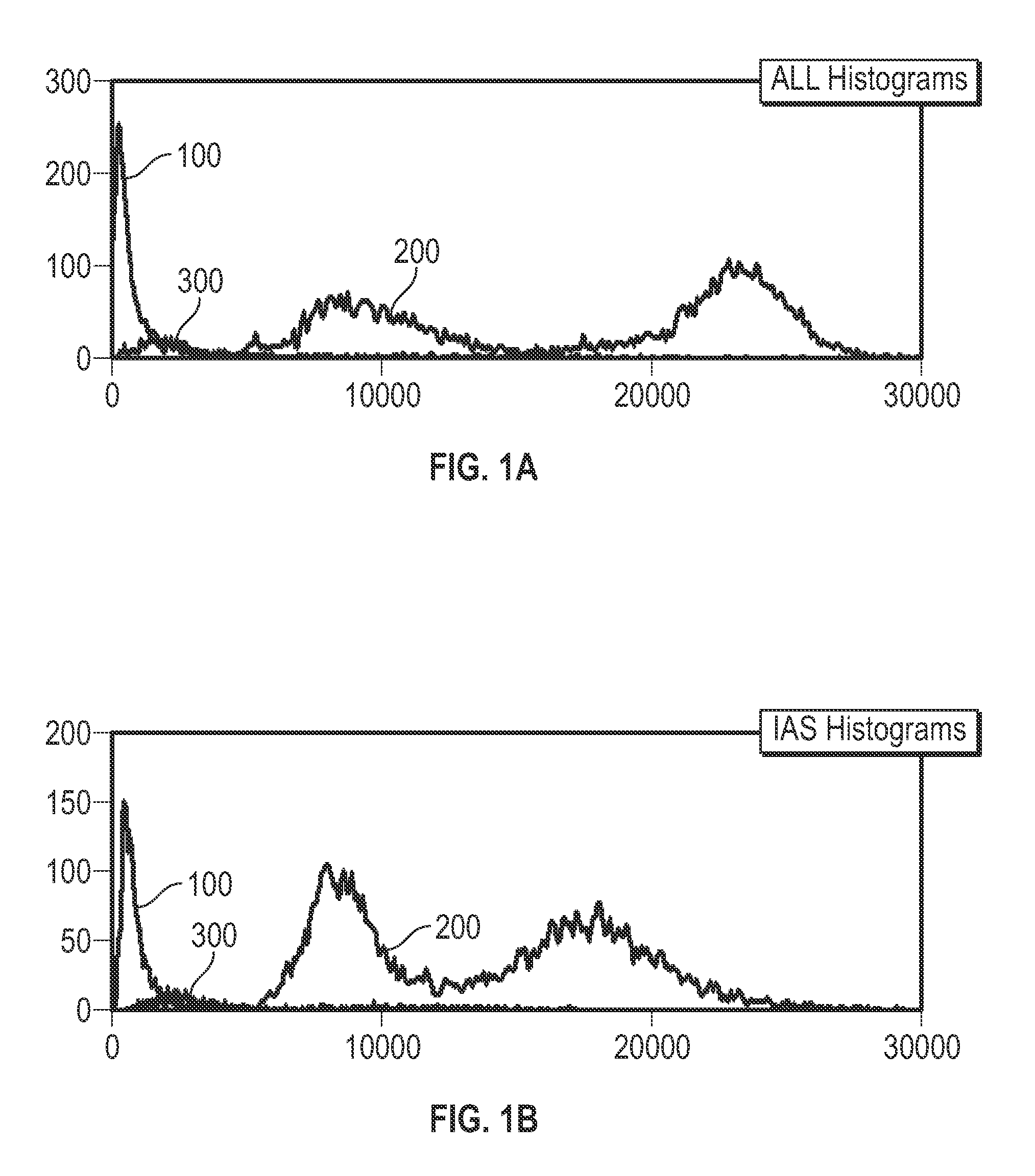
Patents
Literature
249 results about "Hematological sample" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
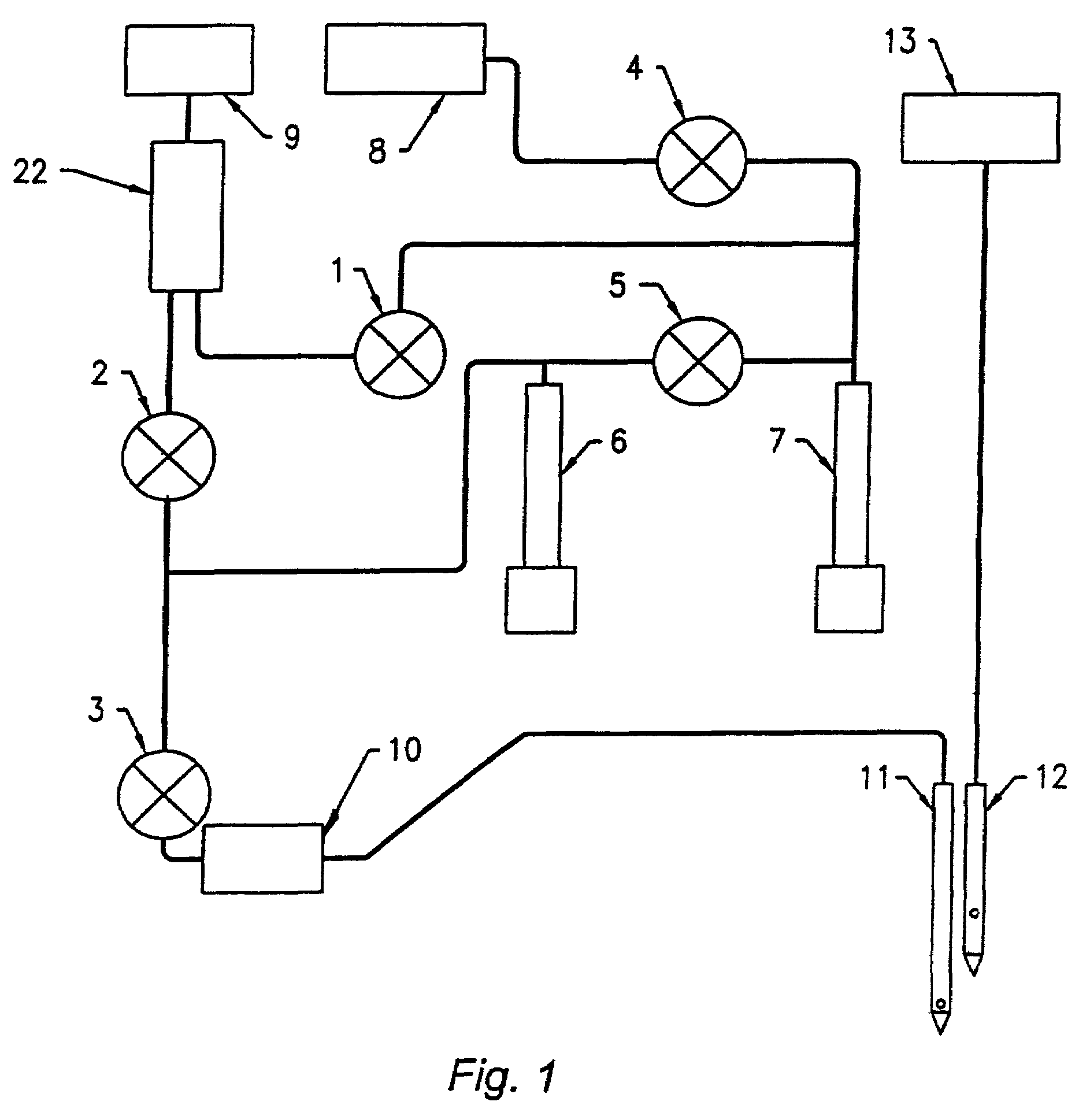
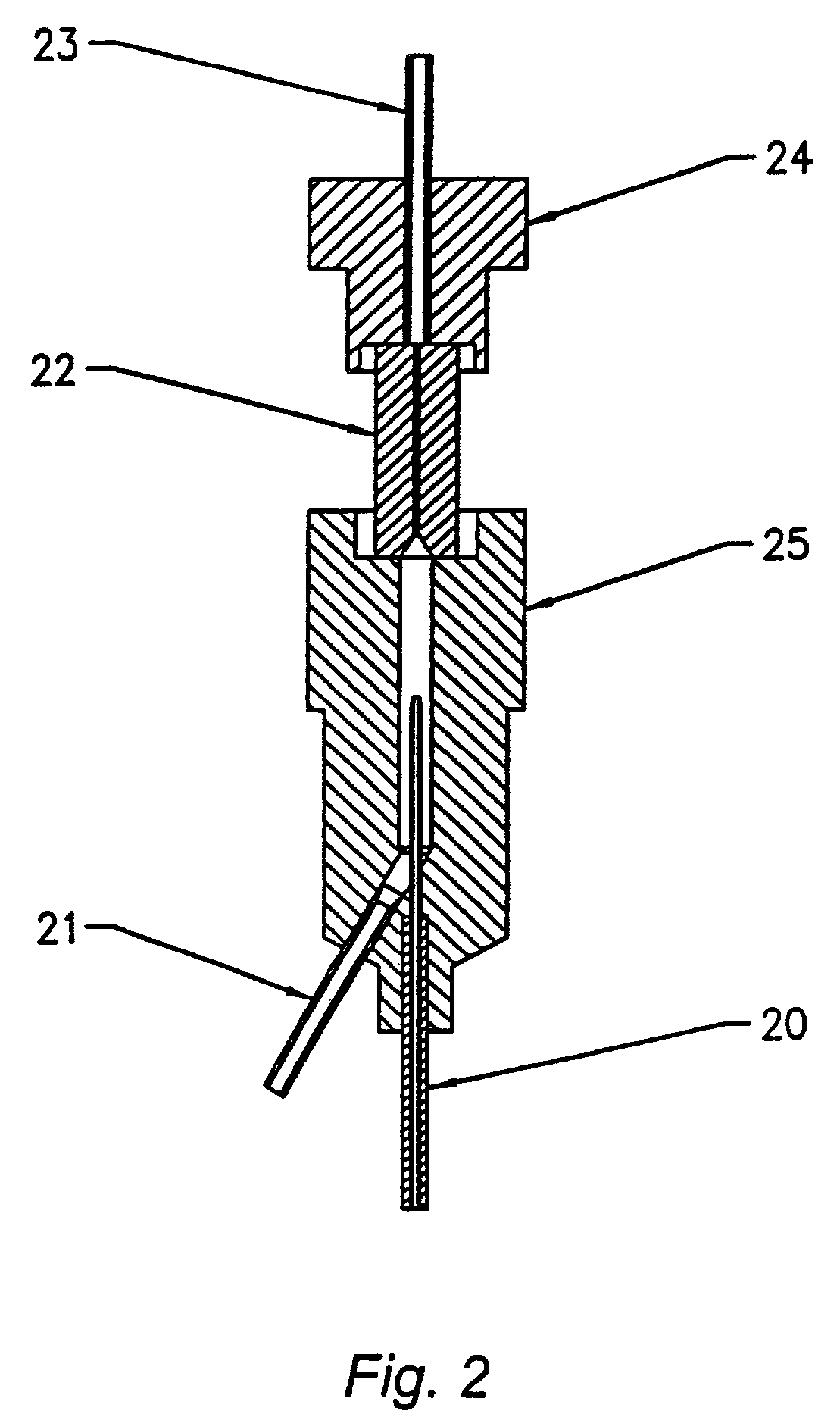
Analyte determination method and analyte meter
The presence of oxygen or red blood cells in a sample applied to an electrochemical test strip that makes use of a reduced mediator is corrected for by an additive correction factor that is determined as a function of the temperature of the sample and a measurement that reflects the oxygen carrying capacity of the sample. The measured oxygen carrying capacity can also be used to determine hematocrit and to distinguish between blood samples and control solutions applied to a test strip.
Owner:AGAMATRIX INC
Methods and apparatuses related to blood analyte measurement system
InactiveUS20100168535A1Accurate measurementEfficient implementationMedical devicesCatheterOperational systemPotassium
The present invention relates to a blood analyte measurement system for the procurement of blood samples for measurement of blood properties such as analyte concentration or analyte presence. A blood access system can be coupled with a measurement system such as an electrochemical sensor, and can also be used with other measurement modalities. Embodiments of the present invention can facilitate accurate measurement of blood glucose by the clinician in a sterile manner. Embodiments of the present invention can also enable the calibration of the sensor at one or more calibration points. One desired analyte of measurement is glucose for the effective implementation of glycemic control protocols. Embodiments of the present invention can also be used for the measurement of other analytes such as arterial blood gases, lactate, hemoglobin, potassium and urea. Additionally, embodiments of the present invention can function effectively on a variety of blood access points and specifically enables glucose monitoring in an existing arterial line that is already in place for hemodynamic monitoring. The present invention does not consume a significant amount of blood. Some embodiments of the present invention can re-infuse the blood into the patient, which can facilitate operation of the system in a sterile manner.
Owner:ROBINSON MARK RIES +4
System/unit and method employing a plurality of magnetoelastic sensor elements for automatically quantifying parameters of whole blood and platelet-rich plasma
InactiveUS20080261261A1Quantifying platelet-fibrin clot strengthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsClot formationBlood plasma
A system / analyzer-unit and method / platform—using information obtained from at least one, adapted for a plurality of, magnetoelastic sensor elements in contact with one or more samples comprising blood from a patient—for automatically quantifying one or more parameters of the patient's blood. Information obtained from emissions measured from each of the sensor elements is uniquely processed to determine a quantification about the patient's blood, such as, quantifying platelet aggregation to determine platelet contribution toward clot formation; quantifying fibrin network contribution toward clot formation; quantifying platelet-fibrin clot interactions; quantifying kinetics of thrombin clot generation; quantifying platelet-fibrin clot strength; and so on. Structural aspects of the analyzer-unit include: a cartridge having at least one bay within which a sensor element is positioned; each bay in fluid communication with both (a) an entry port for injecting a first blood sample composed of blood taken from the patient (human or other mammal), and (b) a gas vent through which air displaced by injecting the first blood sample into the bay.
Owner:KMG2 SENSORS CORP
Device for performing a blood, cell, and/or pathogen count and methods for use thereof
ActiveUS20130273524A1Rapid and accurate and affordable laboratory-quality blood testingEliminate replacementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPoint of careBlood test
Devices and methods for performing a point of care blood, cell, and / or pathogen count or a similar blood test. Disclosed herein are systems that can be used to provide rapid, accurate, affordable laboratory-quality testing at the point of care. The systems described herein are capable of imaging and counting individual cells in a prepared cell sample (e.g., a peripheral blood smear or a blood sample prepared in a microfluidic device) or another prepared cell-containing sample without the need for a microscope or other expensive and cumbersome optics. The systems described herein are designed to eliminate or replace expensive, centralized clinical testing equipment and technical personnel. Such systems may include automated data reporting and decision support.
Owner:I CALQ
Methods and compositions for detecting rare cells from a biological sample
InactiveUS20080057505A1Strong specificityEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiomass after-treatmentHematopoietic cellWhite blood cell
The present invention provides methods and compositions for isolating and detecting rare cells from a biological sample containing other types of cells. In particular, the present invention includes a debulking step that uses a microfabricated filters for filtering fluid samples and the enriched rare cells can be used in a downstream process such as identifies, characterizes or even grown in culture or used in other ways. The invention also include a method of determining the aggressiveness of the tumor or of the number or proportion of cancer cells in the enriched sample by detecting the presence or amount of telomerase activity or telomerase nucleic acid or telomerase expression after enrichment of rare cells. This invention further provides an efficient and rapid method to specifically remove red blood cells as well as white blood cells from a biological sample containing at least one of each of red blood cells and white blood cells, resulting in the enrichment of rare target cells including circulating tumor cells (CTC), stromal cells, mesenchymal cells, endothelial cells, fetal cells, stem cells, non-hematopoietic cells etc from a blood sample. The method is based upon combination of immuno-microparticles (antibody coated microparticles) and density-based separation. The final enriched target cells can be subjected to a variety of analysis and manipulations, such as flowcytometry, PCR, immunofluorescence, immunocytochemistry, image analysis, enzymatic assays, gene expression profiling analysis, efficacy tests of therapeutics, culturing of enriched rare cells, and therapeutic use of enriched rare cells. In addition, depleted plasma protein and white blood cells can be optionally recovered, and subjected to other analysis such as inflammation studies, gene expression profiling, etc.
Owner:AVIVA BIOSCI
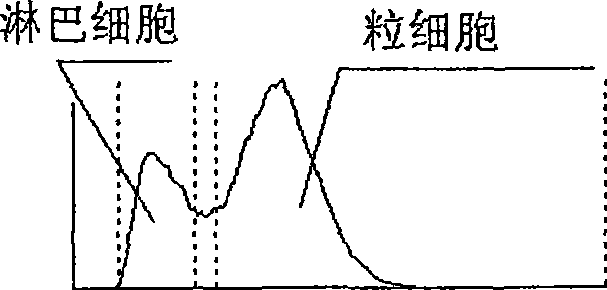
Method of classifying counting leucocytes
ActiveUS20050202400A1Low costAccurate classificationMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceStainingRed blood cell
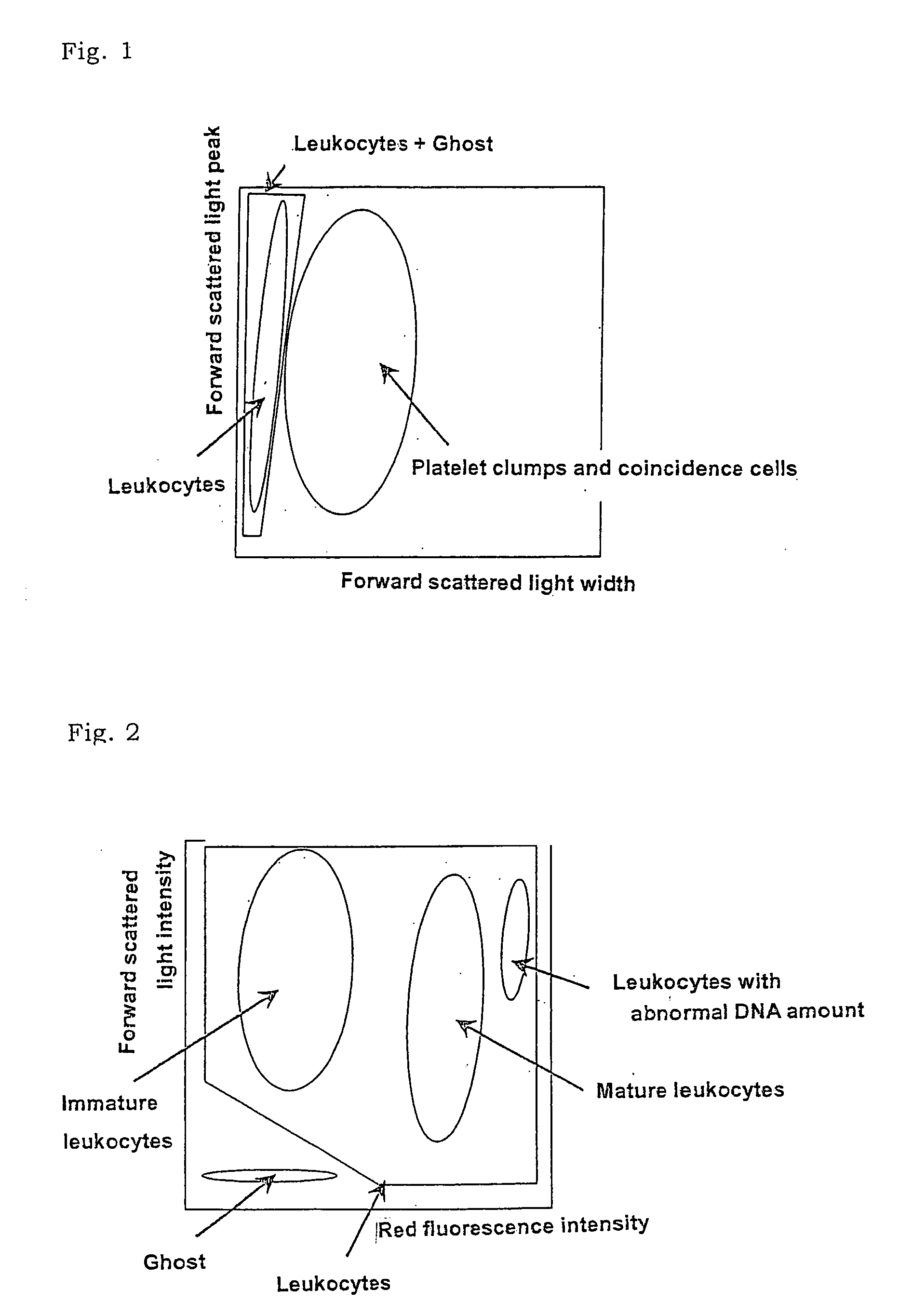
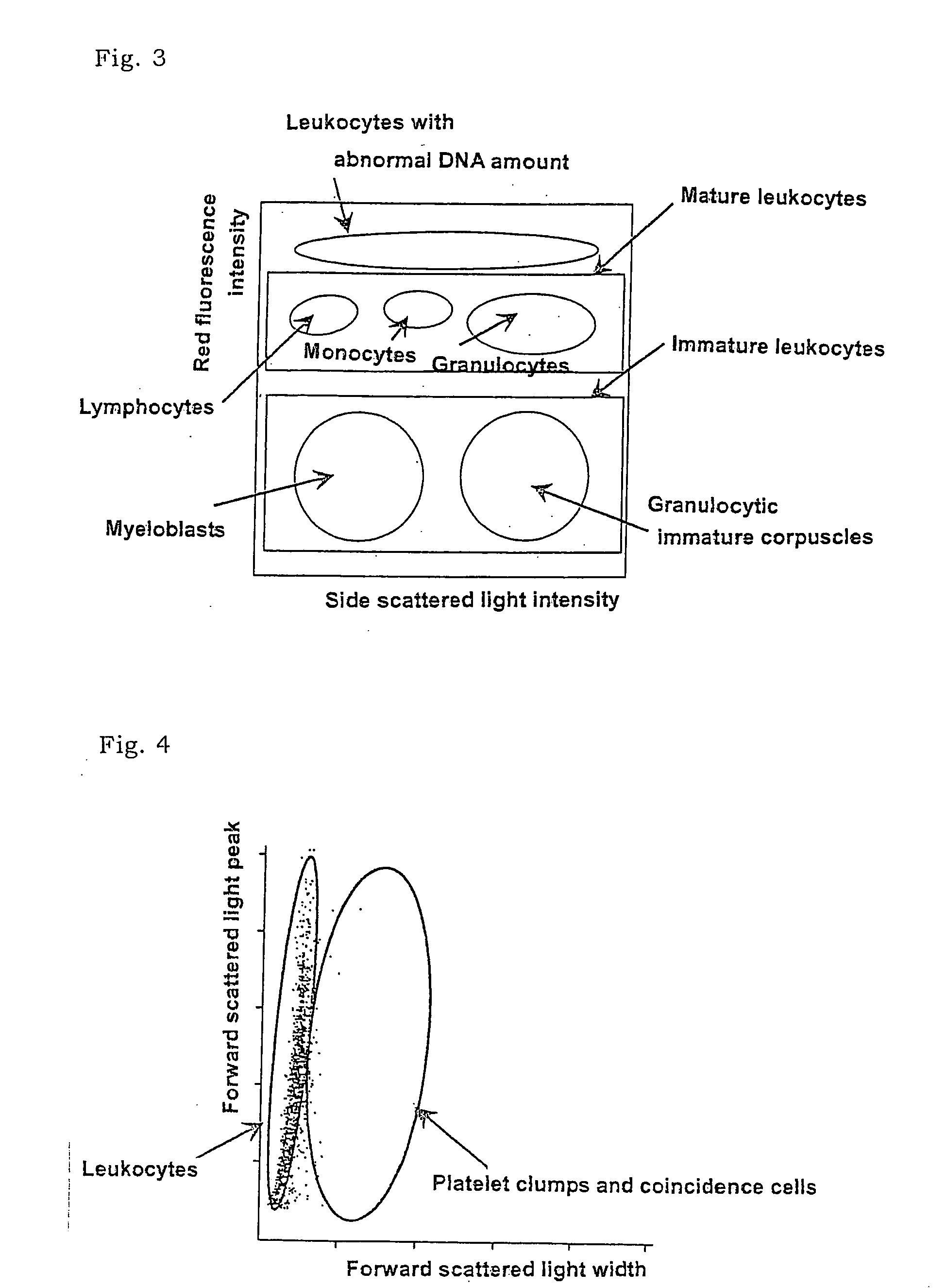
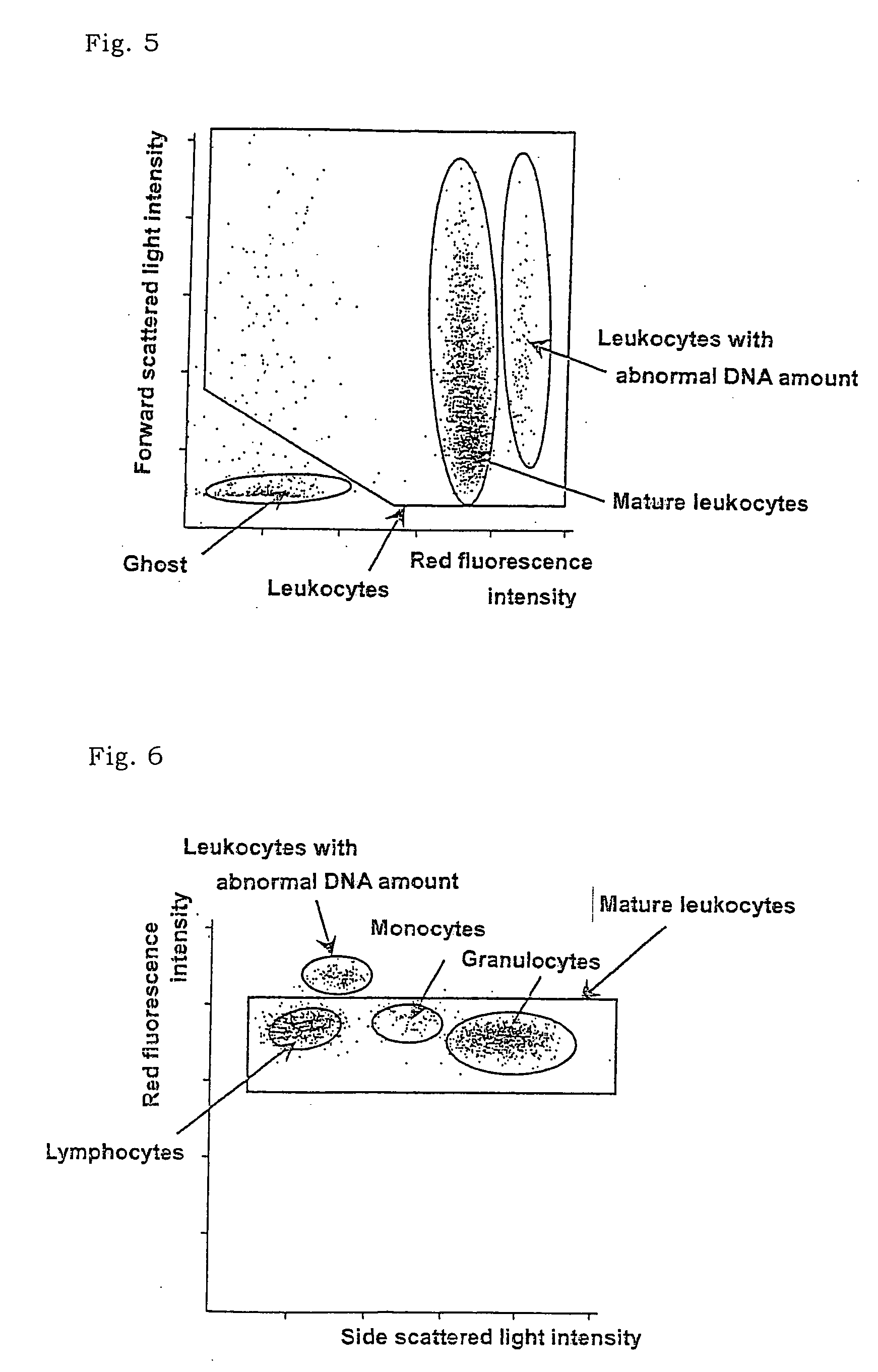
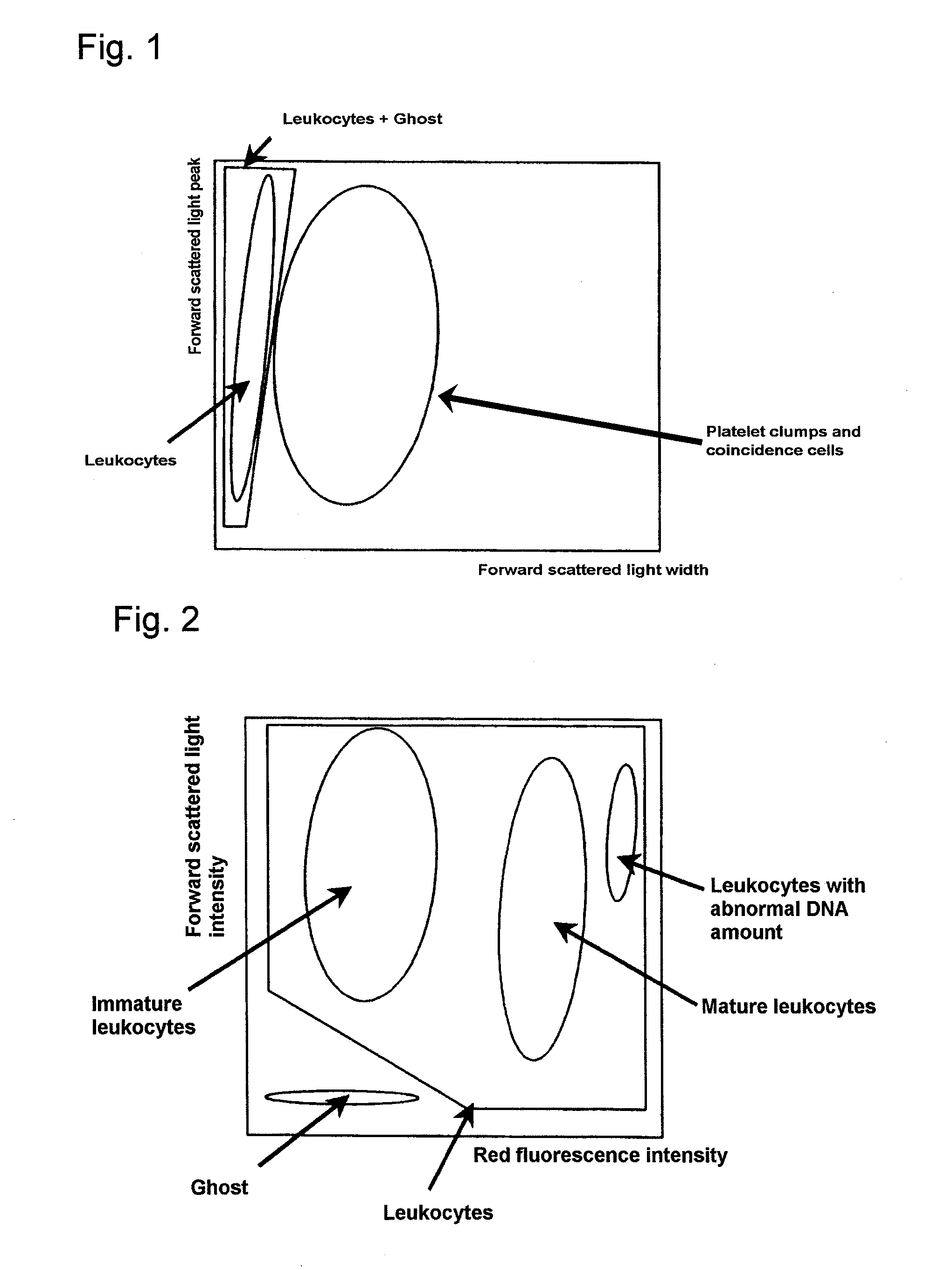
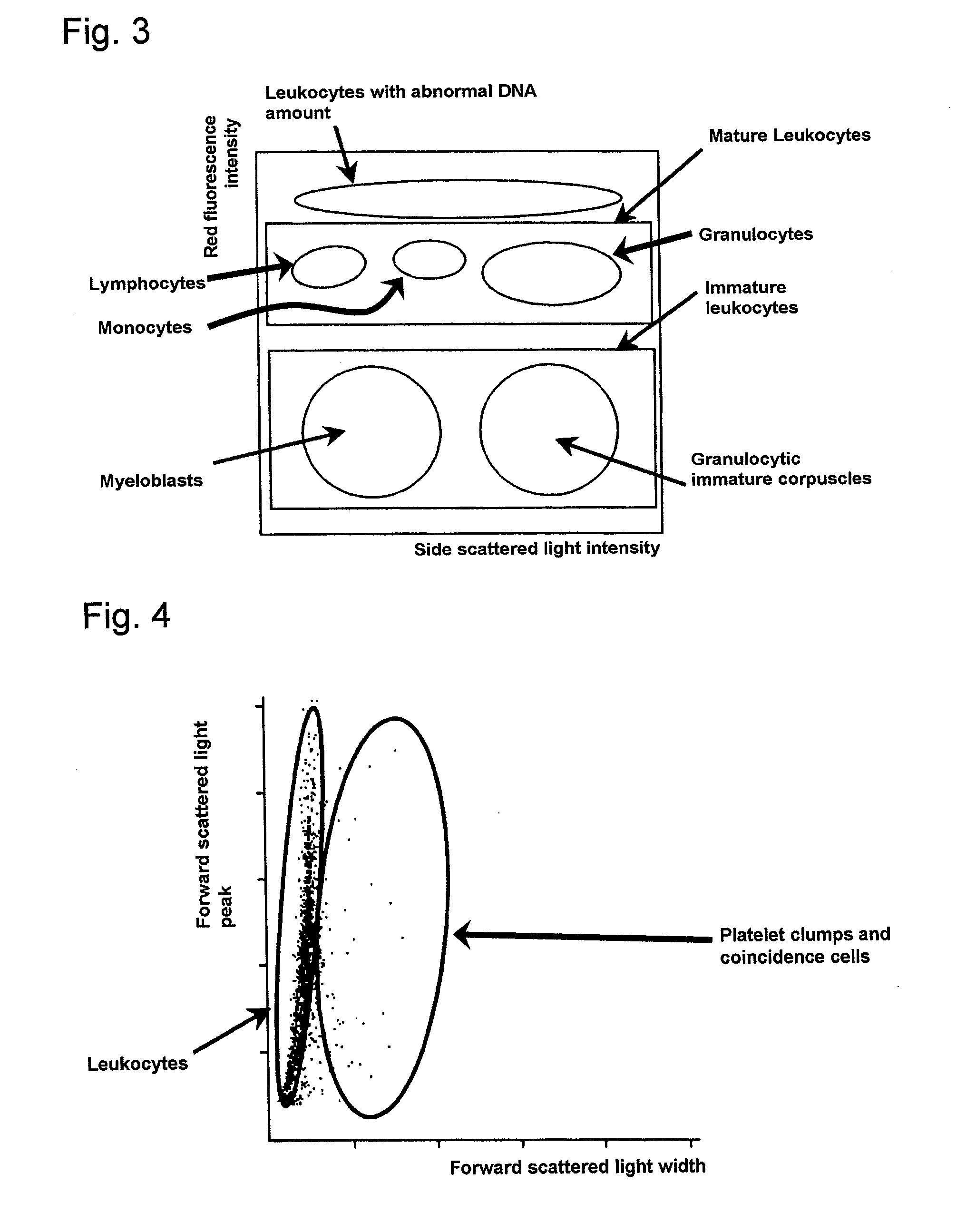
There is provided a method for classifying and counting leukocytes with abnormal DNA amount, which comprises: (1) a step of staining cells in a sample obtained from a hematological sample by treatment with a hemolytic agent to lyse erythrocytes, with a fluorescent dye which can make a difference in the fluorescence intensity at least among mature leukocytes, leukocytes with abnormal DNA amount and immature leukocytes; (2) a step of introducing the sample containing the stained cells into a flow cytometer to measure scattered light and fluorescence of the respective cells; (3) a step of classifying leukocytes and coincidence cells / platelet clumps utilizing a difference in the intensity of a scattered light peak and a difference in the scattered light width; (4) a step of classifying and counting mature leukocytes, leukocytes with abnormal DNA amount and immature leukocytes, utilizing a difference in the scattered light intensity and a difference in the fluorescence intensity of leukocytes classified in the step (3).
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
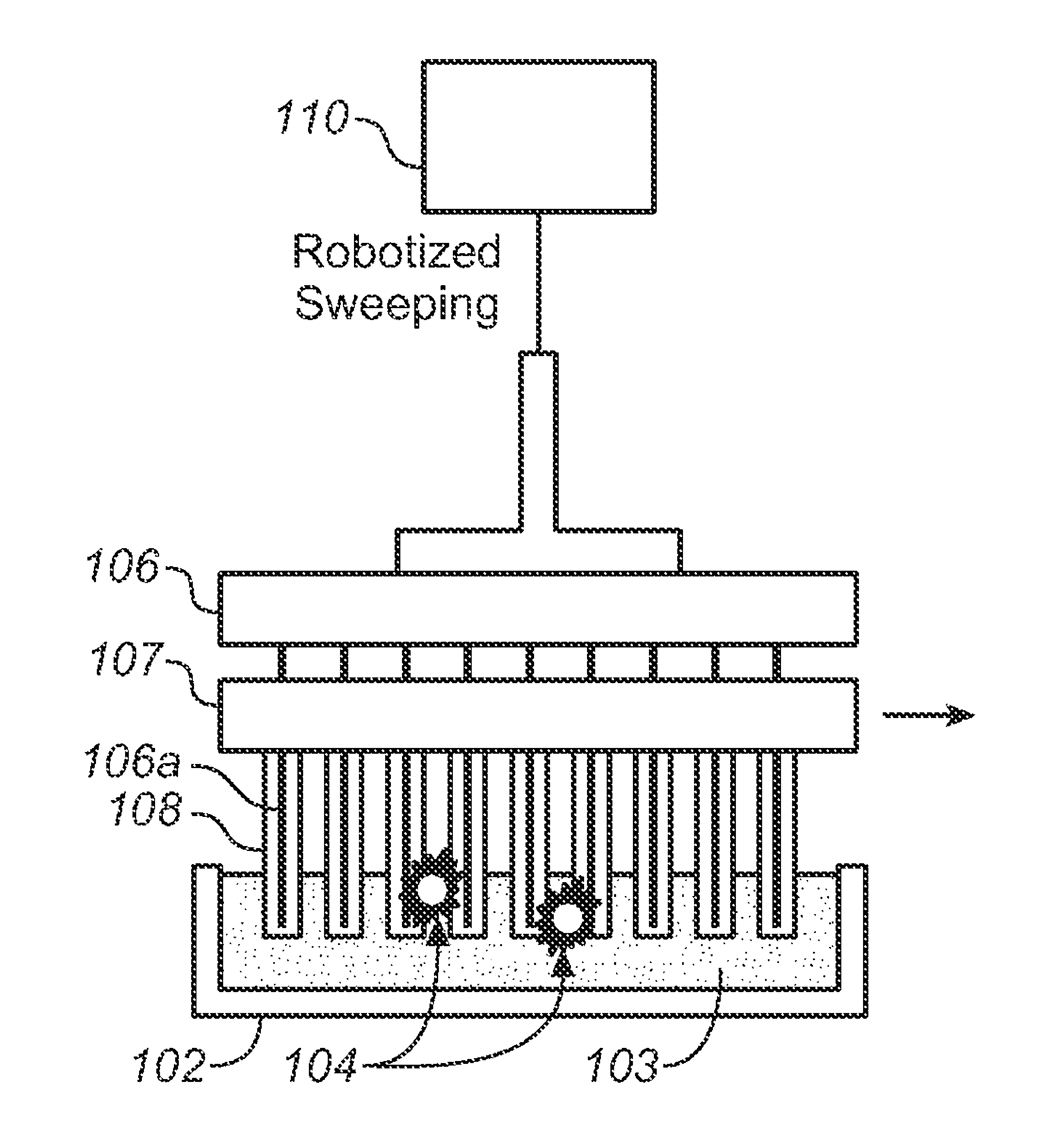
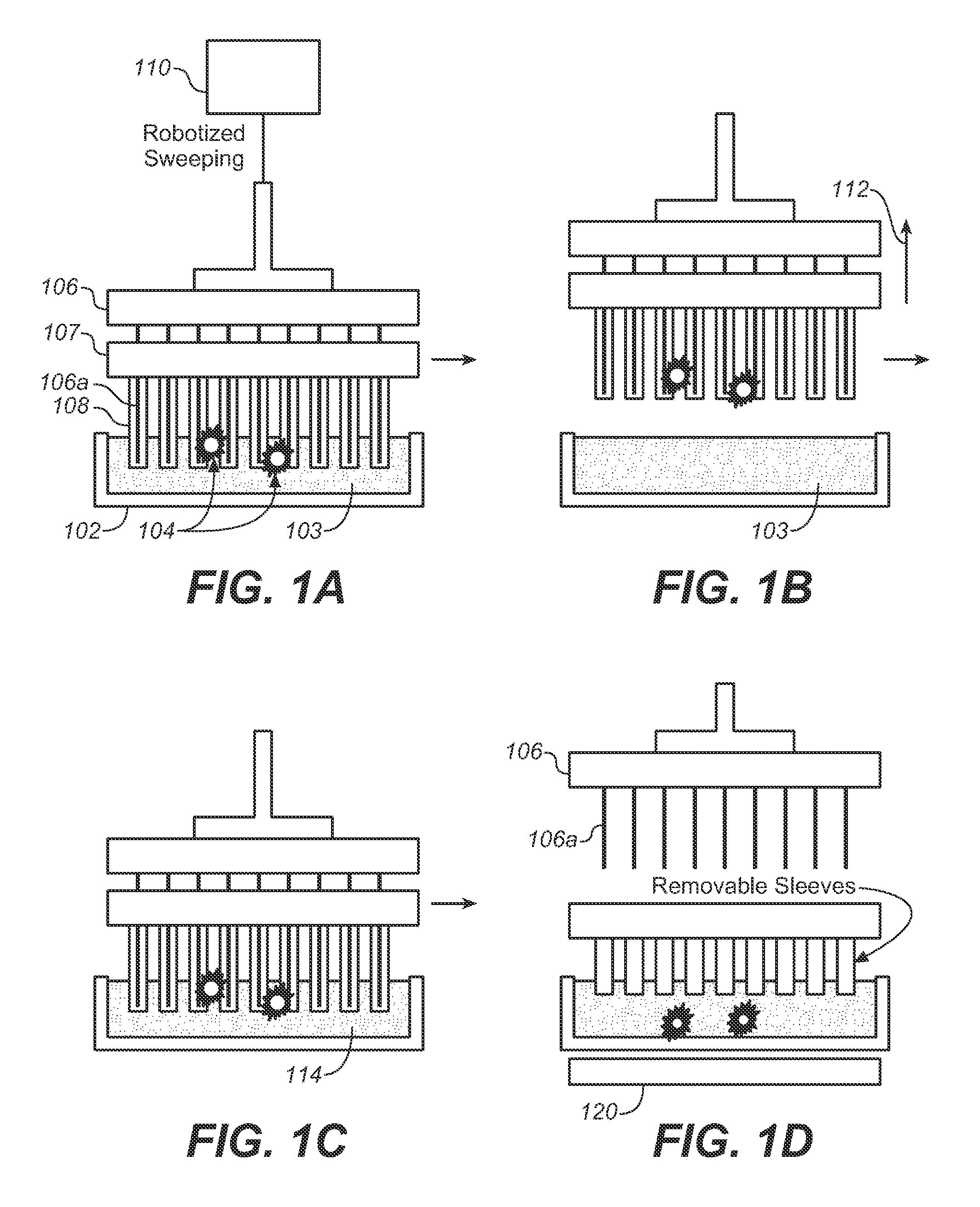
Methods and Apparatus for Magnetic Separation of Cells
ActiveUS20090220979A1Increase the magnetic field strengthStir wellBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSuperparamagnetic beadsTumor cells
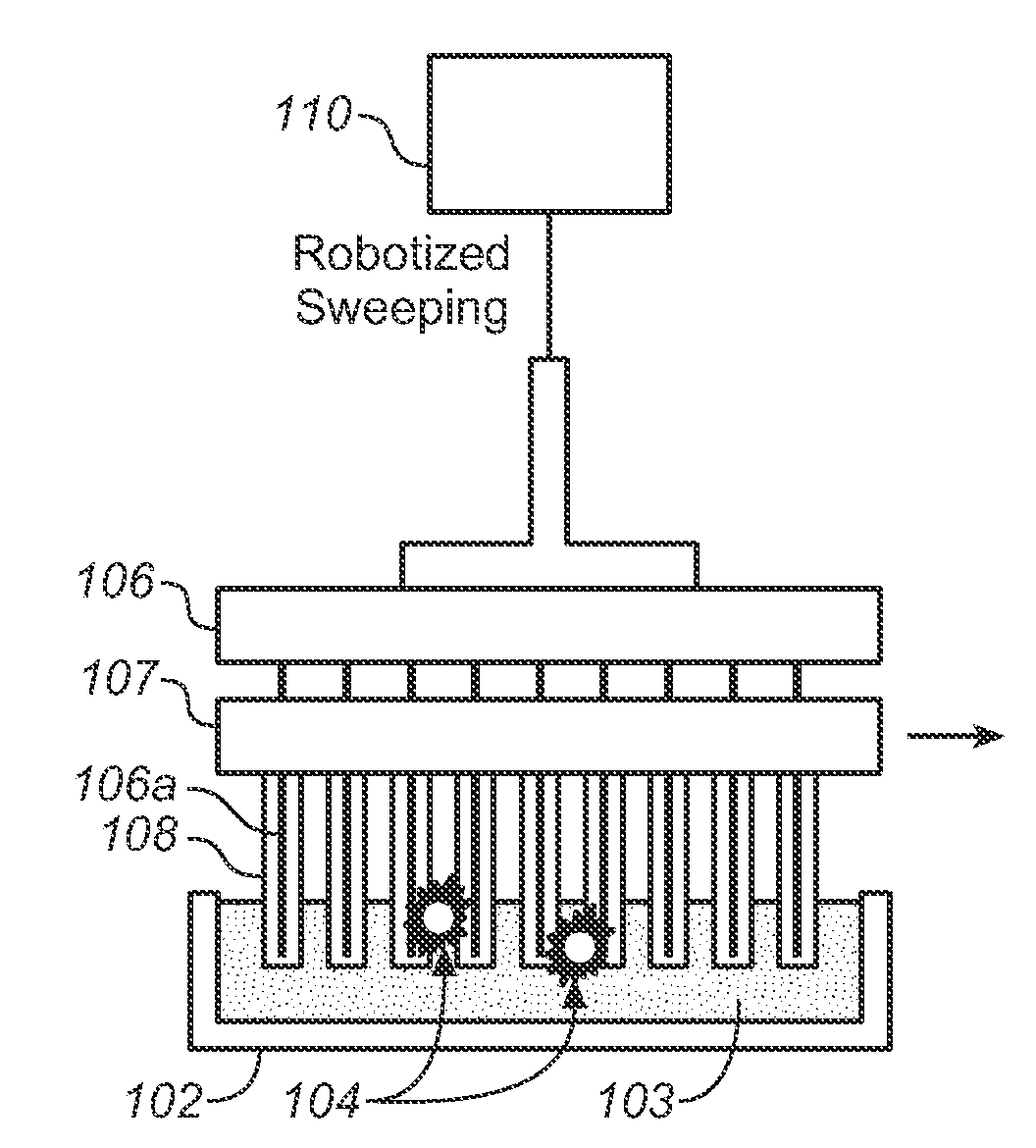
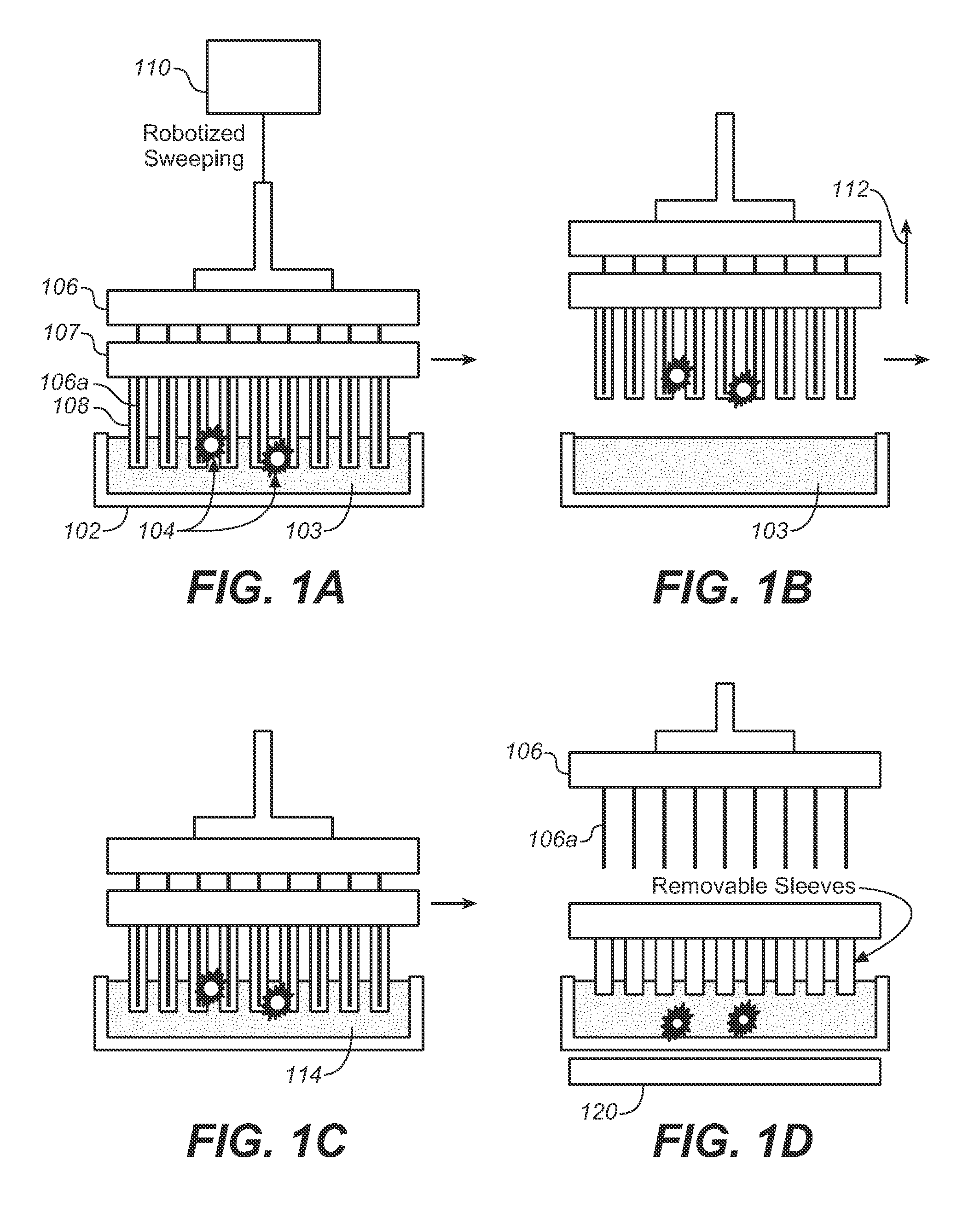
Described here is an automated robotic device that isolates circulating tumor cells (CTCs) or other biological structures with extremely high purity. The device uses powerful magnetic rods covered in removable plastic sleeves. These rods sweep through blood samples, capturing, e.g., cancer cells labeled with antibodies linked to magnetically responsive particles such as superparamagnetic beads. Upon completion of the capturing protocol, the magnetic rods undergo several rounds of washing, thereby removing all contaminating blood cells. The captured target cells are released into a final capture solution by removing the magnetic rods from the sleeves. Additionally, cells captured by this device show no reduced viability when cultured after capture. Cells are captured in a state suitable for genetic analysis. Also disclosed are methods for single cell analysis. Being robotic allows the device to be operated with high throughput.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Apparatus for differentiating blood cells using back-scatter
InactiveUS6869569B2Material thermal conductivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPhotodetectorRed blood cell
Blood cells of interest are readily distinguishable from other blood cells and look-a-like particles found in a blood sample by their back-scatter signature. A preferred method for differentiating platelets in a blood sample is to irradiate the cells and particles, one at a time, with a beam of radiation, and to detect back-scattered (reflected) radiation using a plurality of optical fibers to transmit the back-scattered radiation to a high-gain photodetector, e.g. a photomultiplier tube. Preferably, the back-scatter signal so obtained is combined with a second signal representing, for example, either the level of forward-scatter within a prescribed, relatively narrow angular range, or the level of side-scattered radiation, or the level of attenuation of the cell-irradiating beam caused by the presence of the irradiated cell or particle in the beam, or the electrical impedance of the irradiated cell or particle, to differentiate the cells of interest. The method and apparatus of the invention are particularly useful in differentiating platelets and basophils in a blood sample.
Owner:COULTER INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
Test strip for determining concentration of multiple analytes in a single fluid sample
InactiveUS20050003523A1Produced economically and reliablyAvoid needBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemistryKetone
A multilayer test strip that measures concentrations of multiple analytes from a single whole blood sample. The test strip includes a test matrix of several layers held together in constant contact by a test strip holder. The invention is characterized in that it has no moving parts, which is made possible by the novel use of an elongate disbursement layer that spreads blood throughout its entire length, despite having layers with known wicking properties adjacent to and in contact with it. Since the invention relies primarily on a vertical flow format, the test strip is advantageously quite compact. With a single 35 microliter sample of blood applied thereto, the novel test strip can provide readings of total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol and triglycerides. From these, LDL can be calculated, thereby providing a full “lipid panel.” Other analytes such as glucose and ketones may be included in the test strip in addition to or in lieu of one or more of the other analytes.
Owner:POLYMER TECH SYST
Consumable tube for use with a flow cytometry-based hematology system
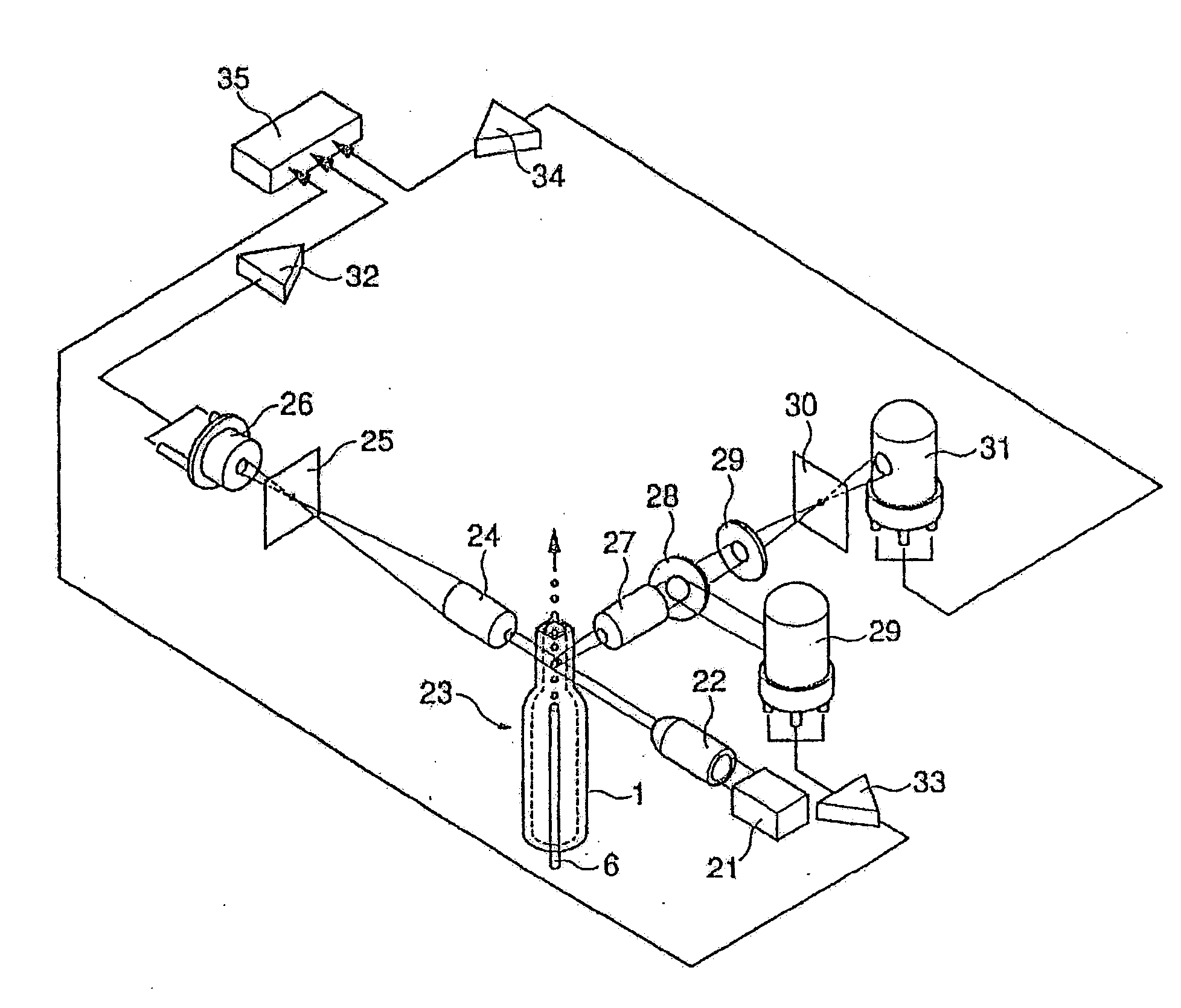
InactiveUS7064823B2Minimizes reagent wasteReduces systemWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationMedicine.hematologyFlow cell
The present invention is a flow cytometry-based hematology system useful in the analysis of biological samples, particularly whole blood or blood-derived samples. The system is capable of determining at least a complete blood count (CBC), a five-part white blood cell differential, and a reticulocyte count from a whole blood sample. The system preferably uses a laser diode that emits a thin beam to illuminate cells in a flow cell and a lensless optical detection system to measure one or more of axial light loss, low-angle forward scattered light, high-angle forward scattered light, right angle scattered light, and time-of-flight measurements produced by the cells. The lensless optical detection system contains no optical components, other than photoreactive elements, and does not include any moving parts. Finally, the system uses a unique system of consumable reagent tubes that act as reaction chambers, mixing chambers, and waste chambers for the blood sample analyses. The consumable tubes incorporate reference particles, which act as internal standards to ensure that the dilutions made during processing of the samples have been carried out correctly, and to ensure that the instrument is working properly. The present invention also relates to methods for using the system.
Owner:IDEXX LABORATORIES
Methods and apparatus for magnetic separation of cells
ActiveUS8071395B2Removing the magnetic fieldIncrease the magnetic field strengthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSuperparamagnetic beadsCancer cell
Described here is an automated robotic device that isolates circulating tumor cells (CTCs) or other biological structures with extremely high purity. The device uses powerful magnetic rods covered in removable plastic sleeves. These rods sweep through blood samples, capturing, e.g., cancer cells labeled with antibodies linked to magnetically responsive particles such as superparamagnetic beads. Upon completion of the capturing protocol, the magnetic rods undergo several rounds of washing, thereby removing all contaminating blood cells. The captured target cells are released into a final capture solution by removing the magnetic rods from the sleeves. Additionally, cells captured by this device show no reduced viability when cultured after capture. Cells are captured in a state suitable for genetic analysis. Also disclosed are methods for single cell analysis. Being robotic allows the device to be operated with high throughput.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
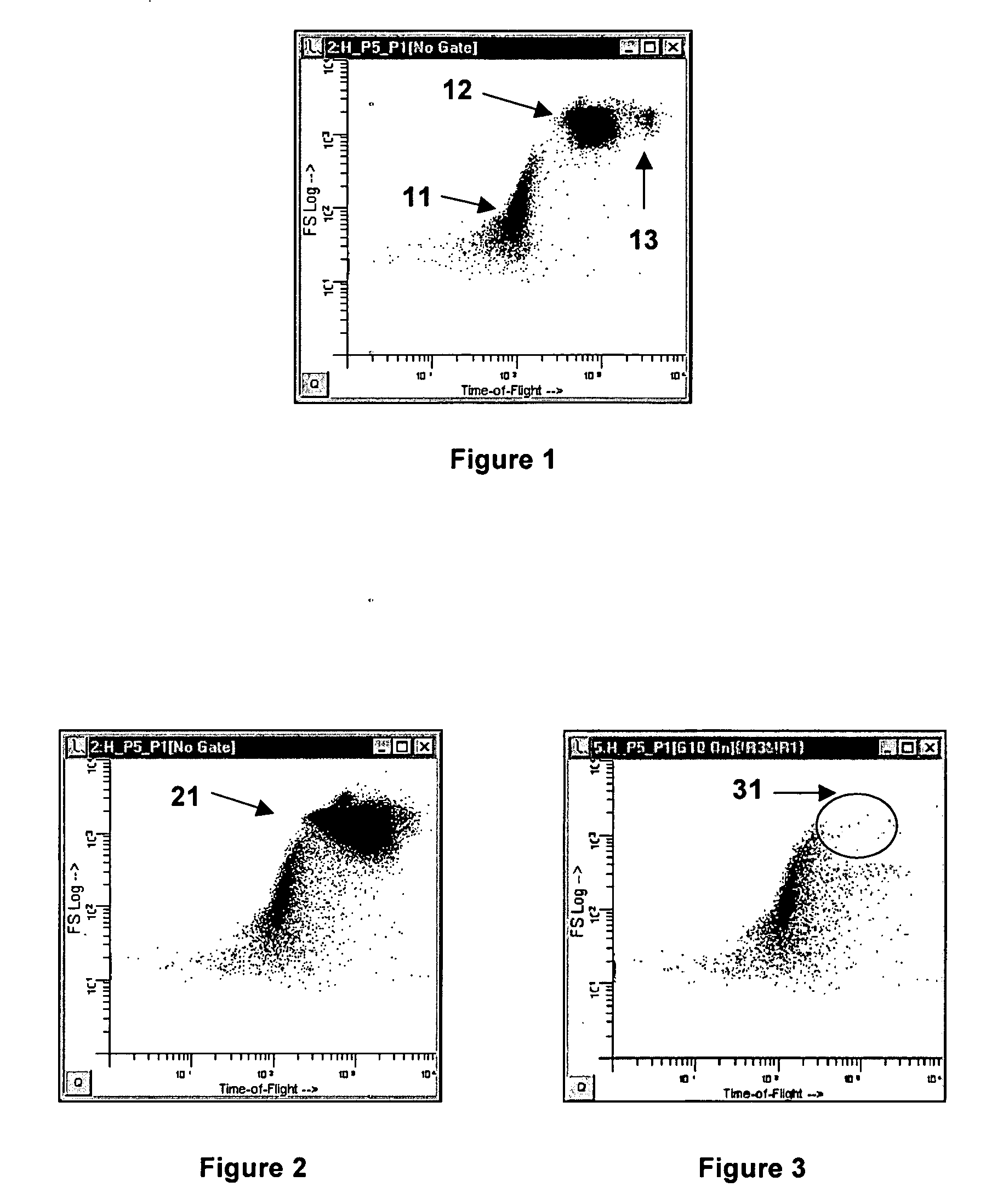
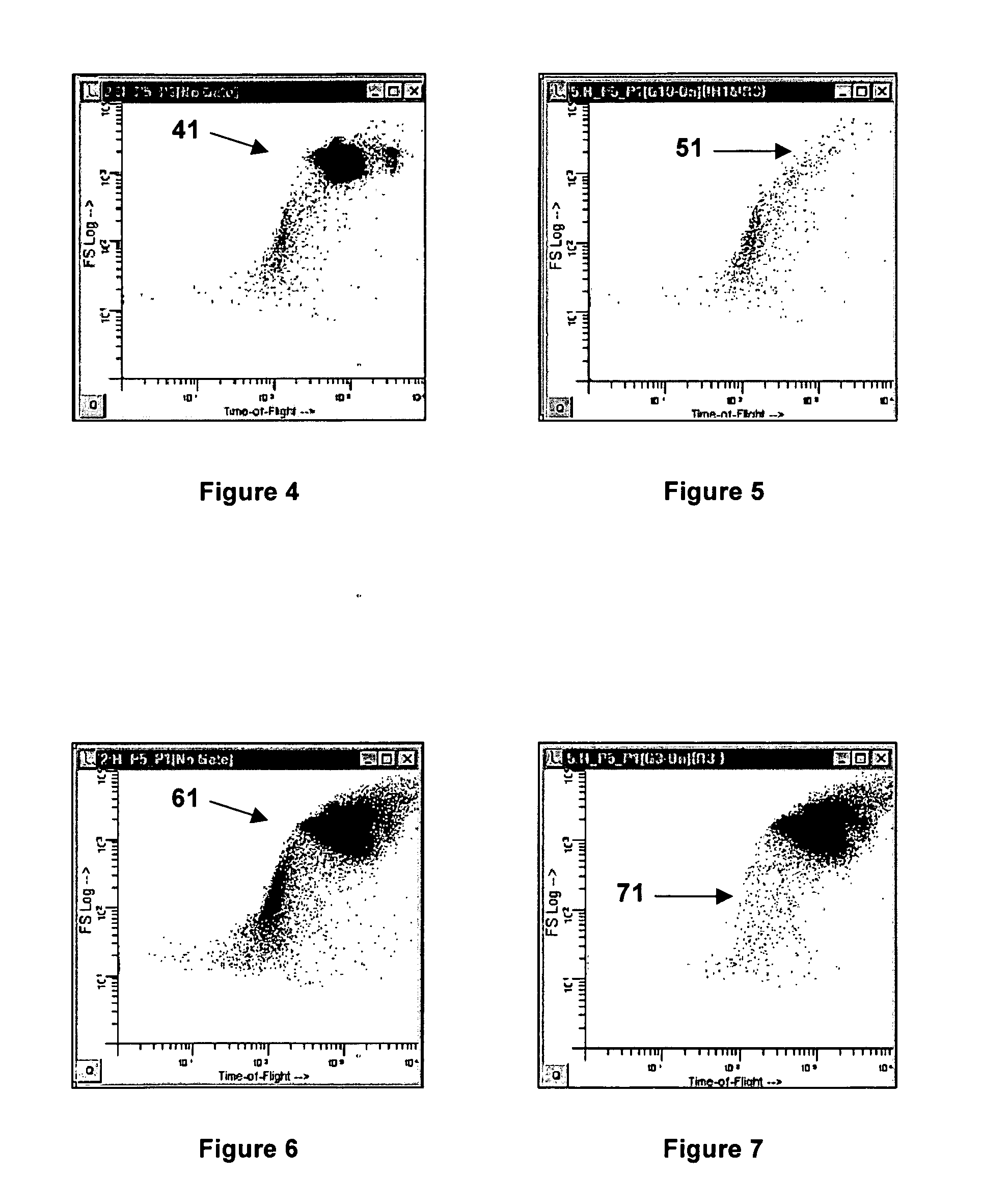
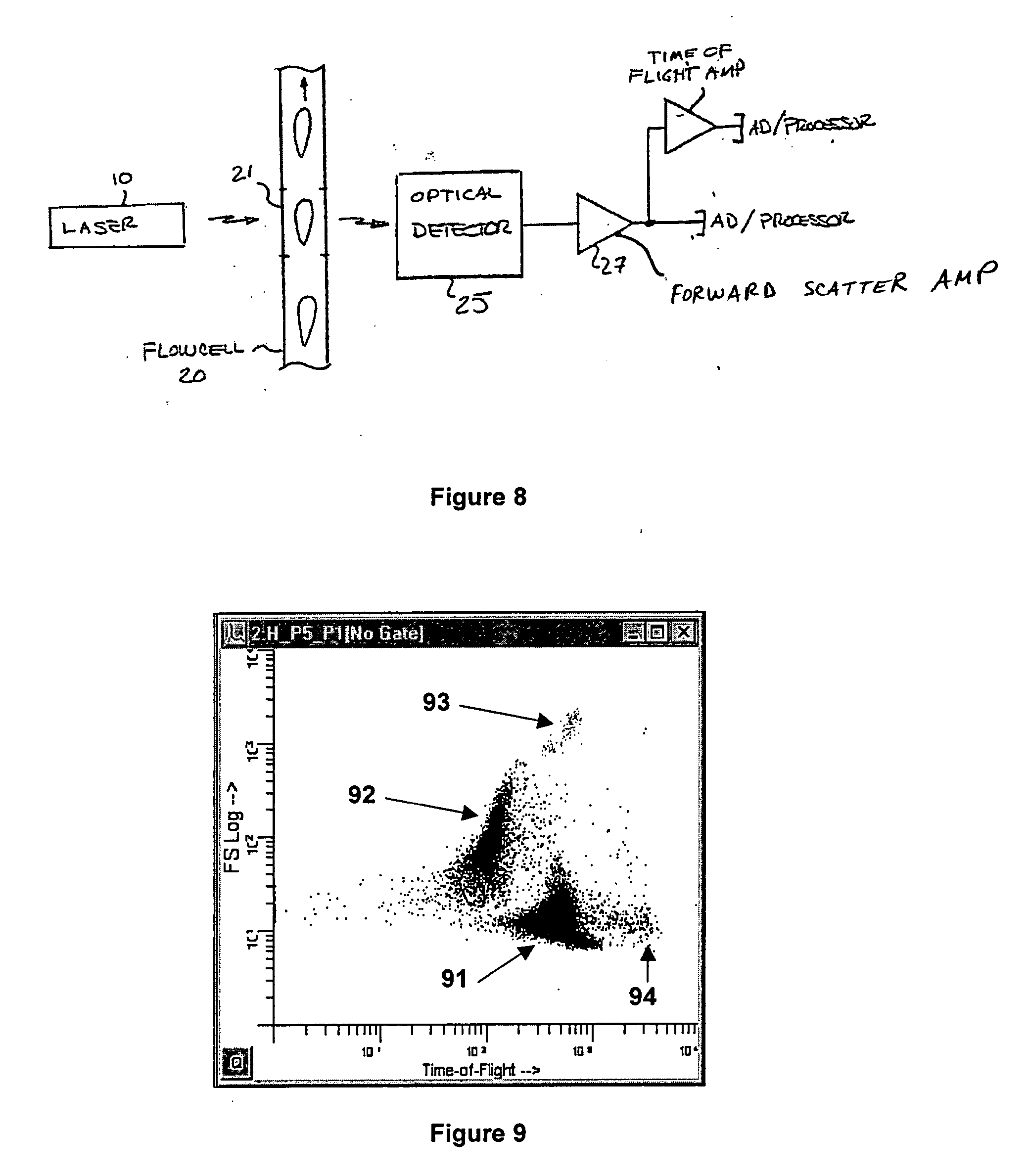
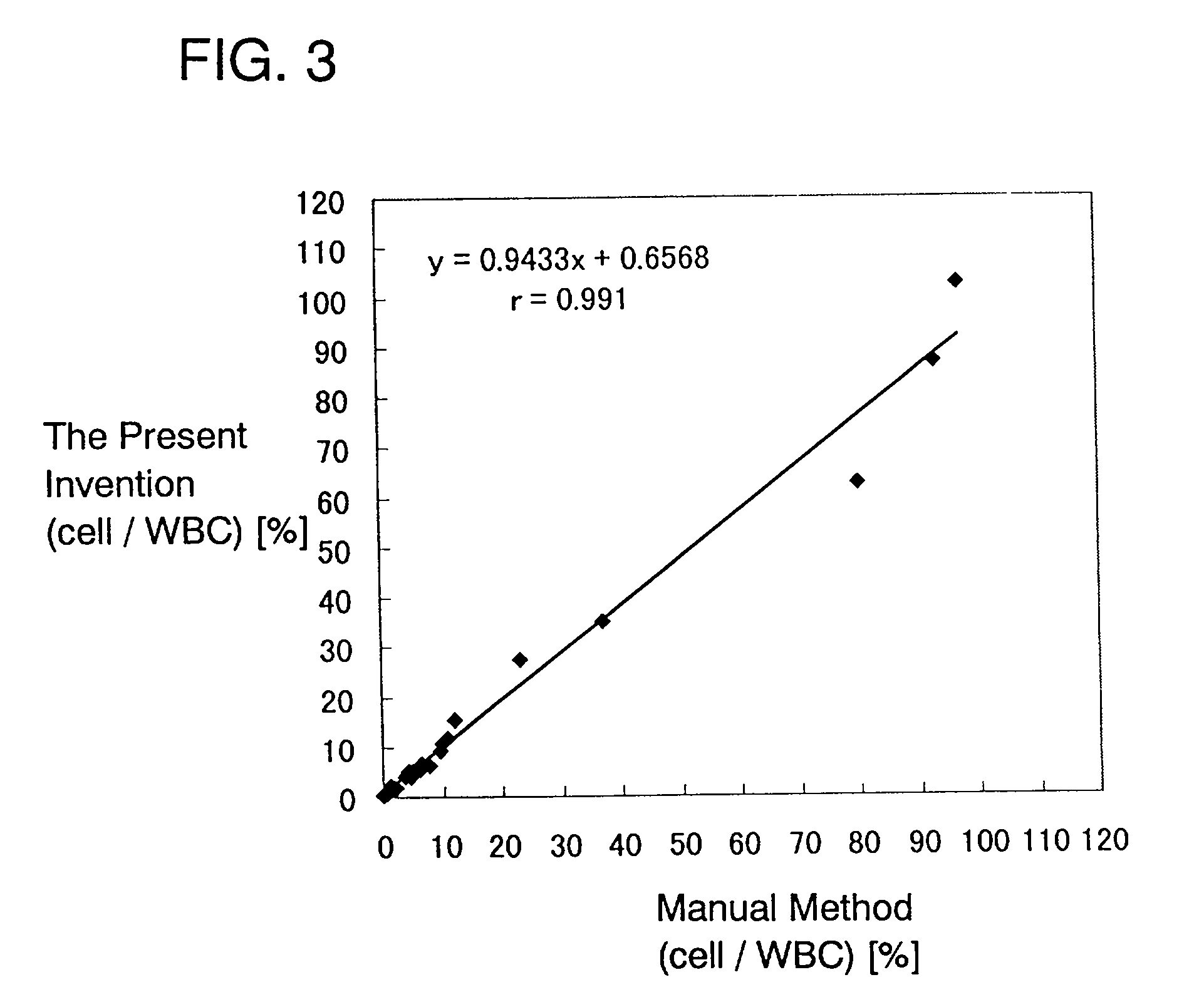
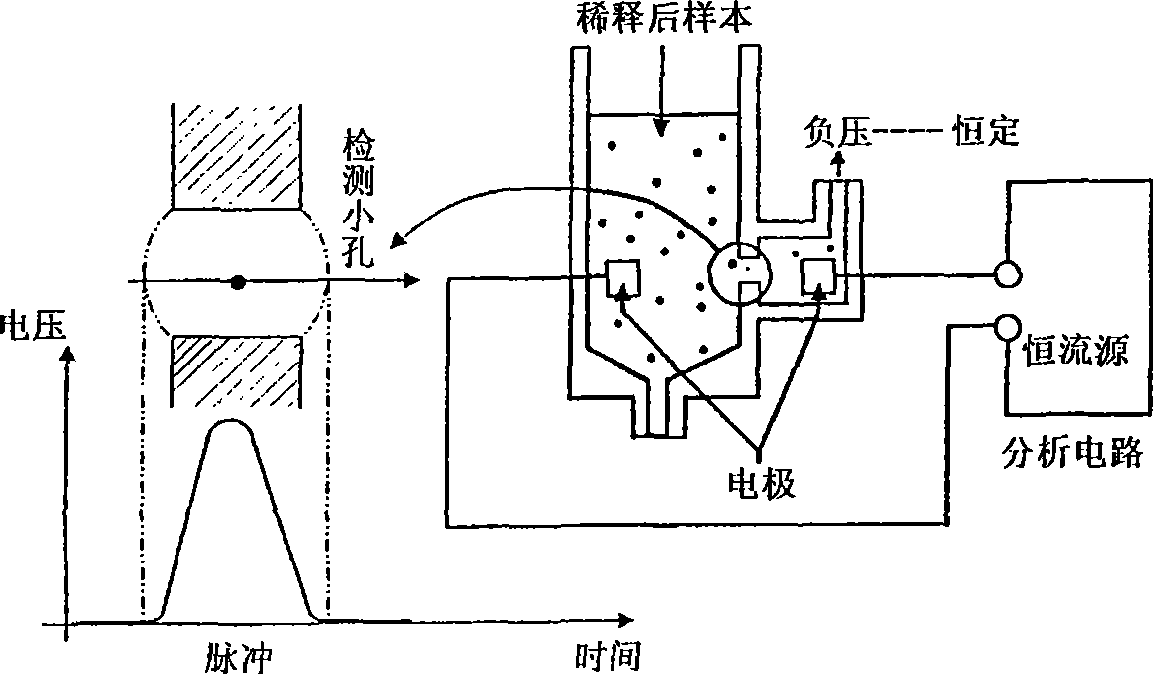
Method and apparatus for measuring hematological sample
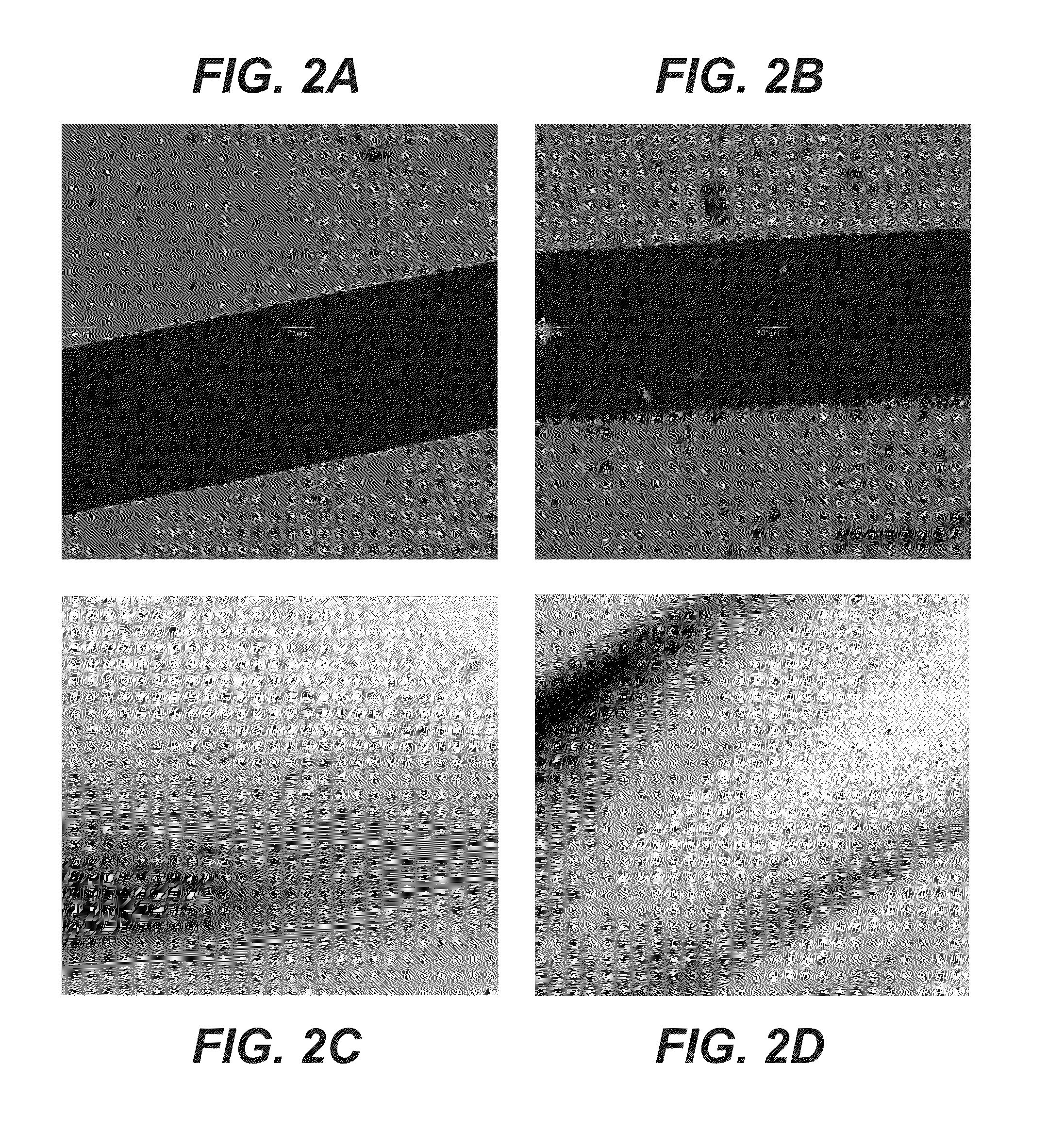
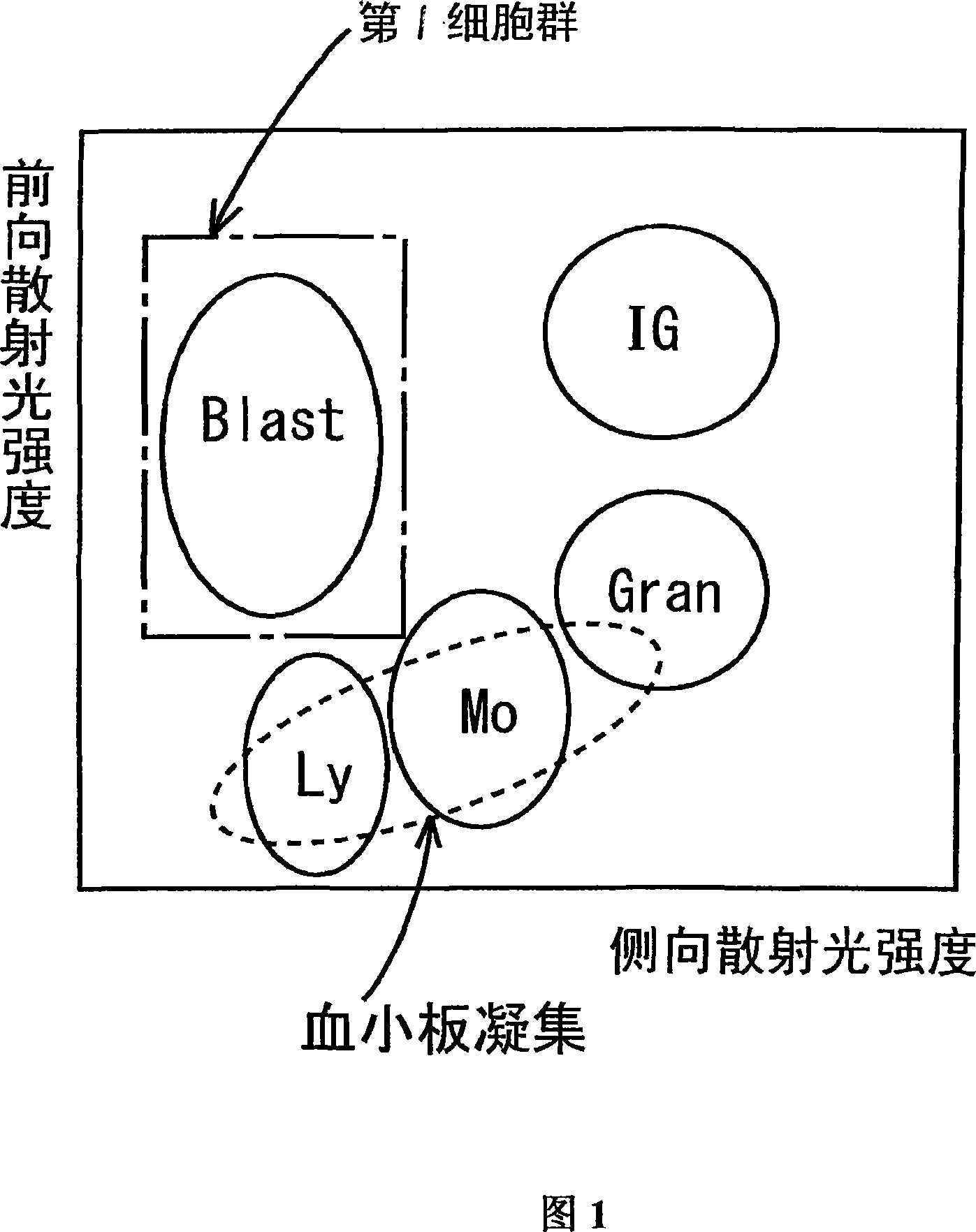
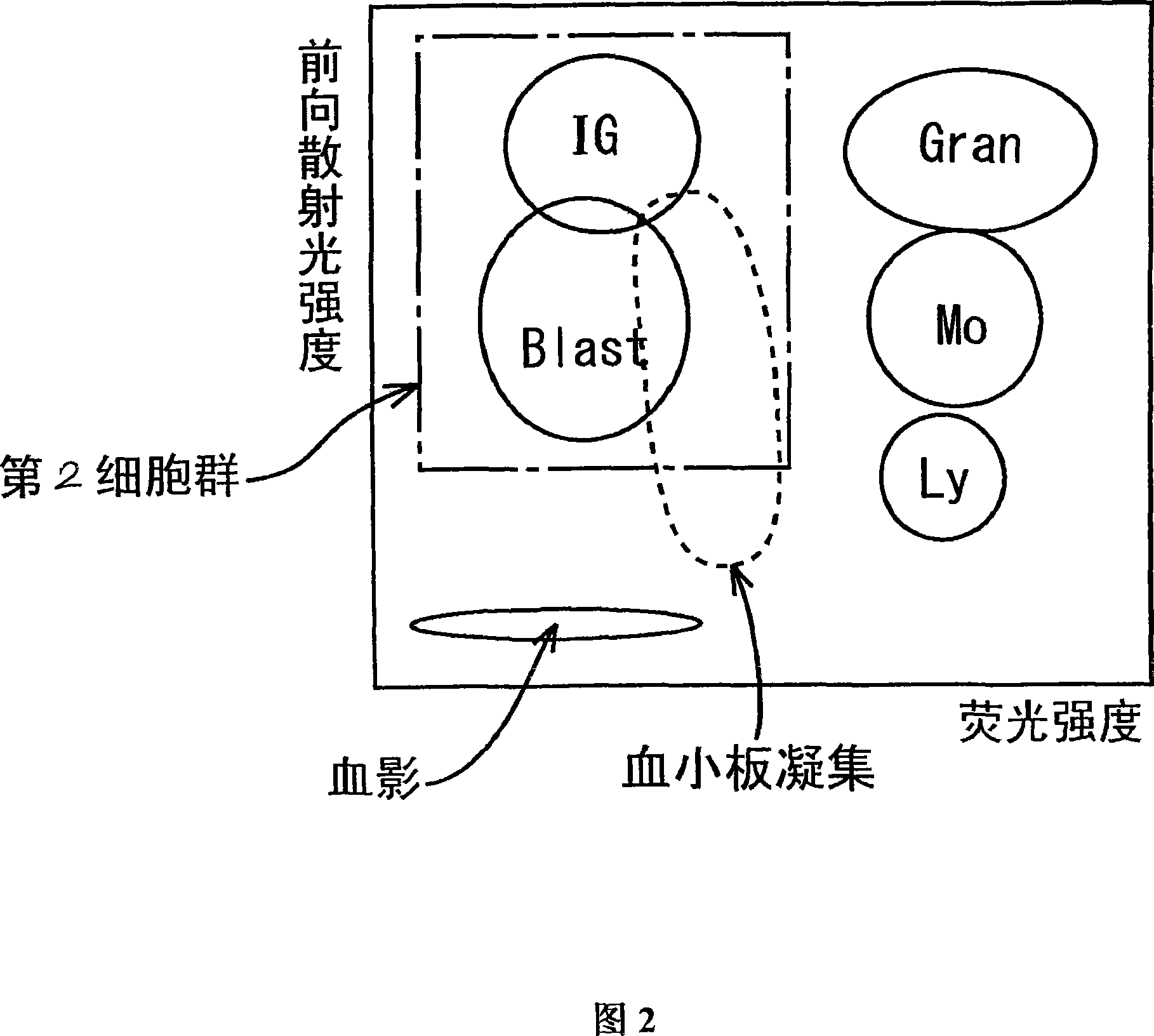
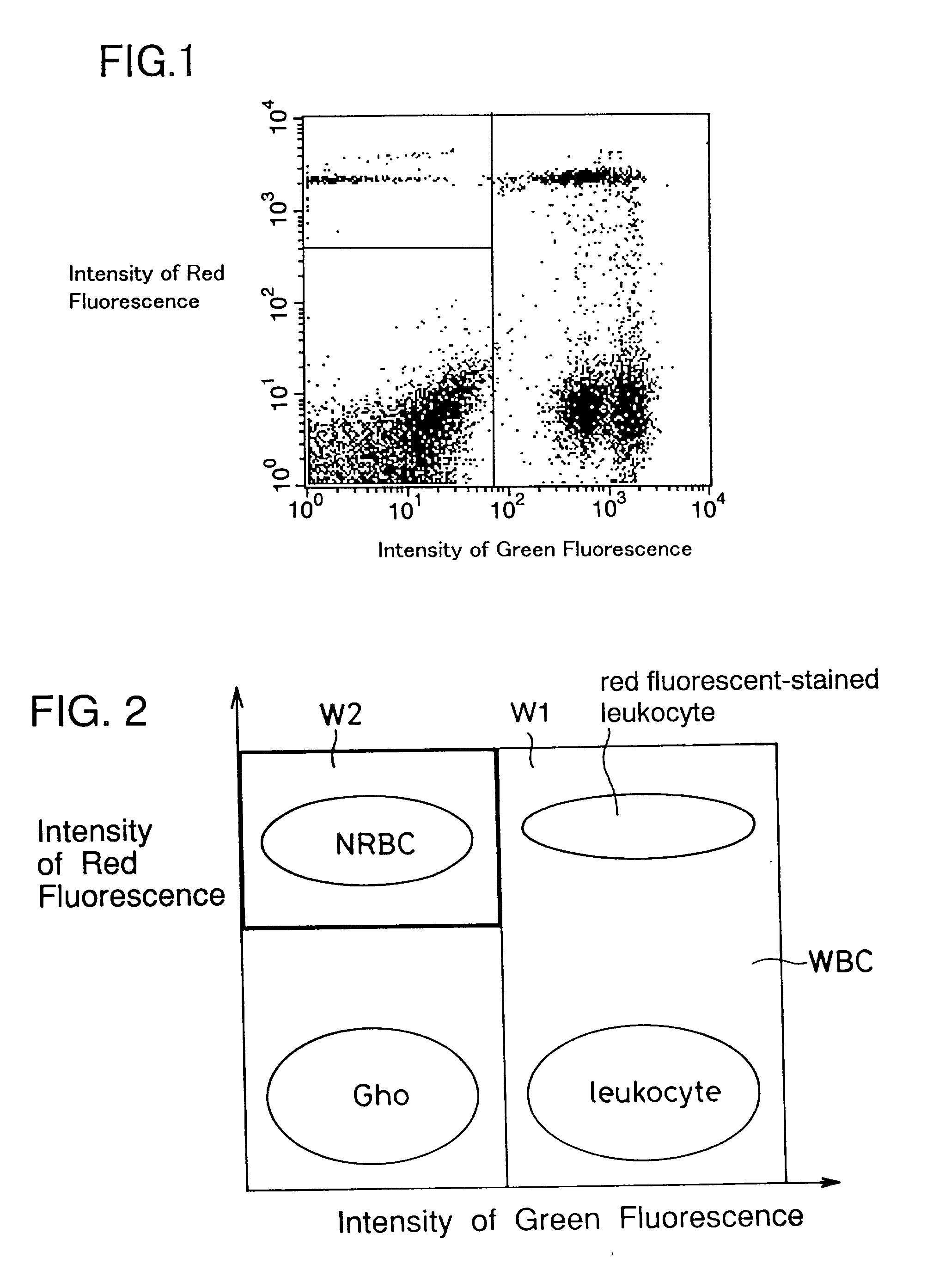
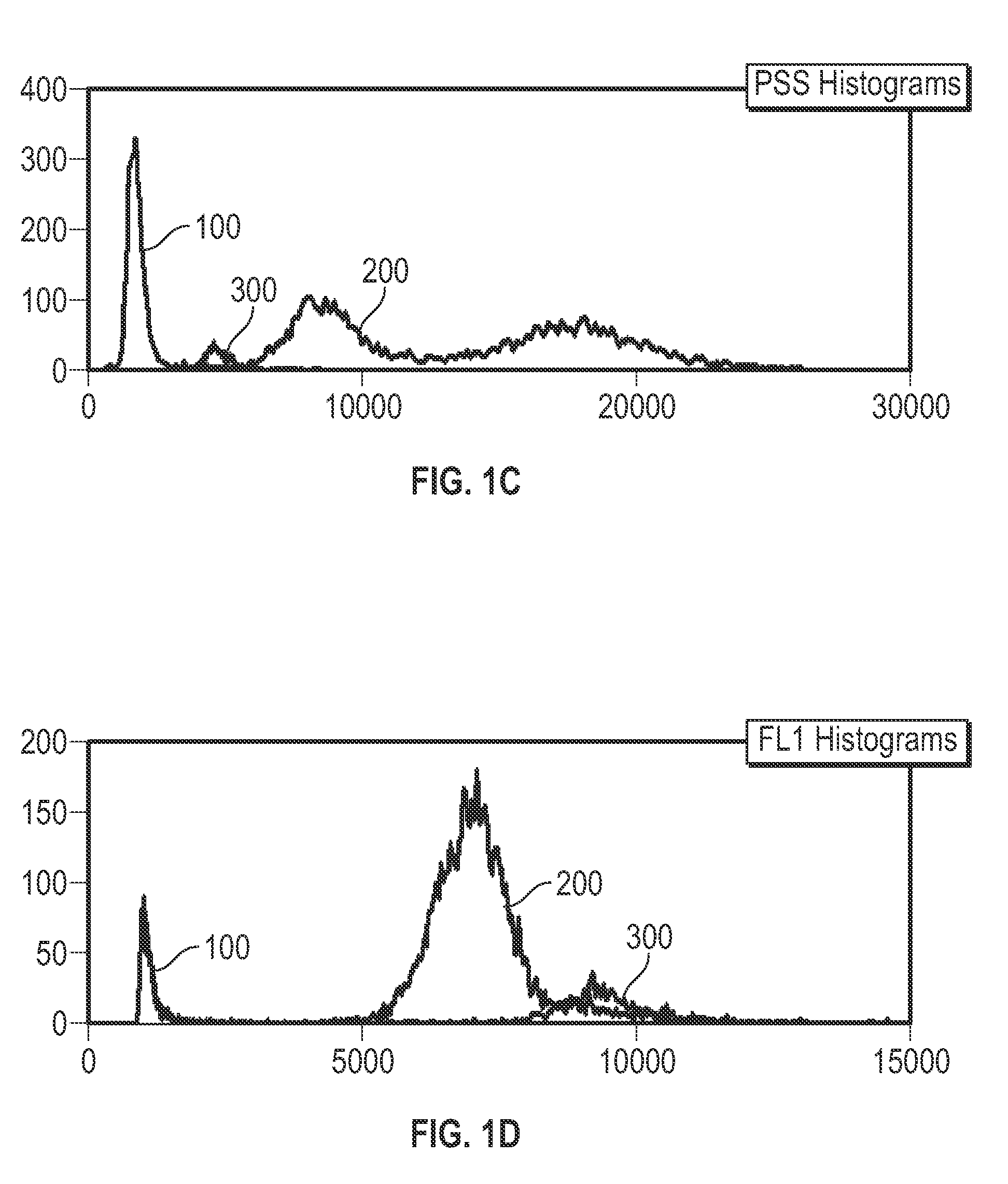
ActiveCN101046439AExclude the effect of agglutinationAccurately classify and countIndividual particle analysisBiological testingRed blood cellFluorescence
The invention provides a measuring method which can classify and count myeloblast more precisely without influence of other component in a sample including platelet aggregation in measurement of a blood sample with a flowcytometry, wherein damage is given to a cell membrane of erythrocyte and mature leukocyte contained in a hematological sample, a hemocyte in which a cell membrane is damaged is constricted, and this is dyeing-treated with a fluorescent dye which can stain a nucleic acid to obtain a sample, the sample is measured with a flowcytometer, and a cell contained in a first cell group containing myeloblast, which is specified based on forward scattered light information and side scattered light information, and contained in a second cell group containing myeloblast, which is specified based on forward scattered light information and fluorescent information, is counted as myeloblast. The invention further provides a measuring device comprising following systems: a sample treating system, an information acquisition system, a first specific system, a second specific system and a counting system.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Blood separation system and method for a dry test strip
InactiveUS20120282634A1Less brittleImprove hydrophilicityBiological material analysisEnzymology/microbiology apparatusGlass fiberAnimal science
A dry test strip layer for filtering red blood cells includes a Borosilicate Glass Fiber layer and lectin, impregnated in the borosilicate layer, such that the dry test strip is configured to filter red blood cells from a blood sample.
Owner:POLYMER TECH SYST
Method for classifying and counting leukocytes
InactiveUS6900023B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWhite blood cellRed Cell
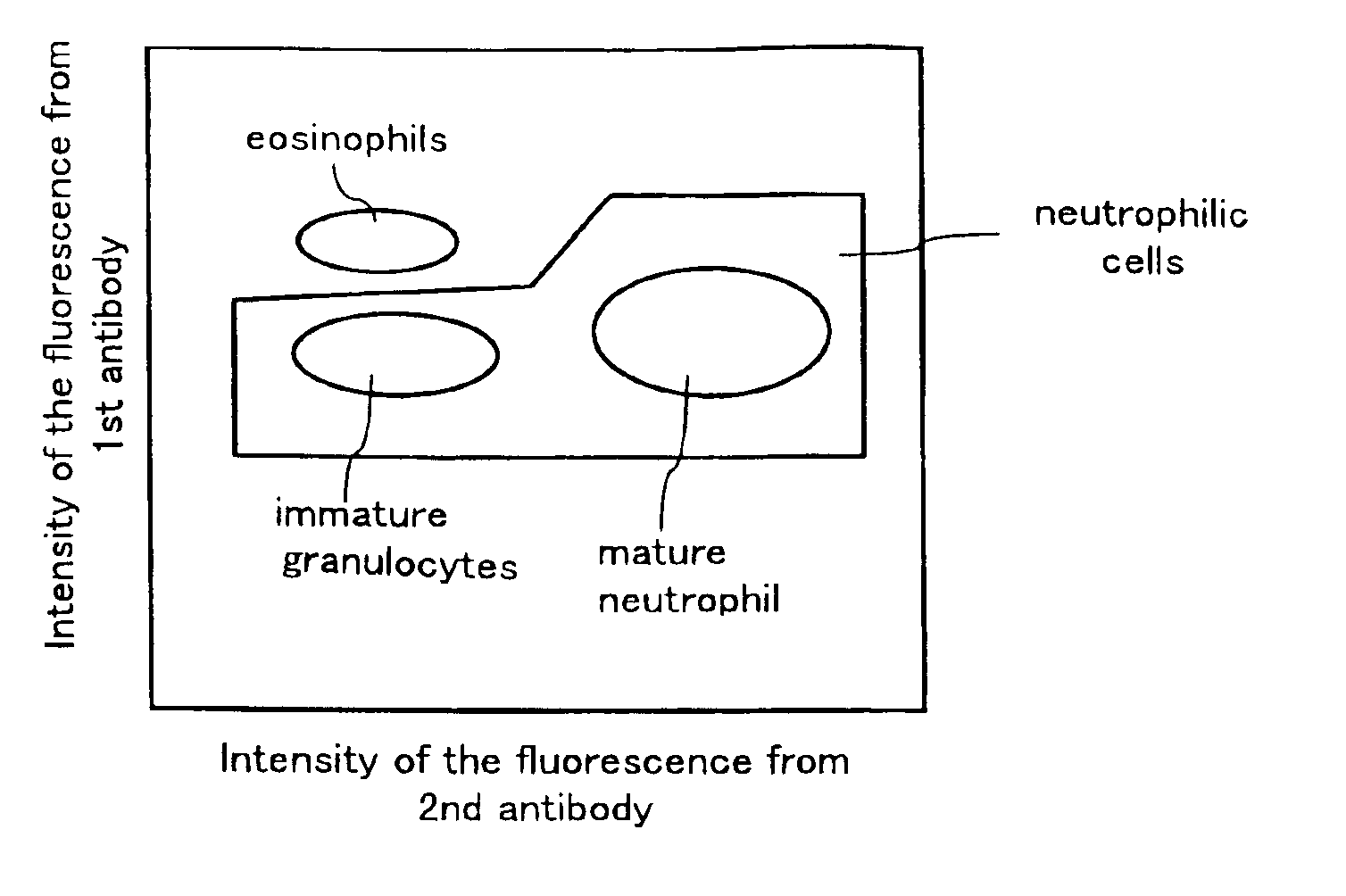
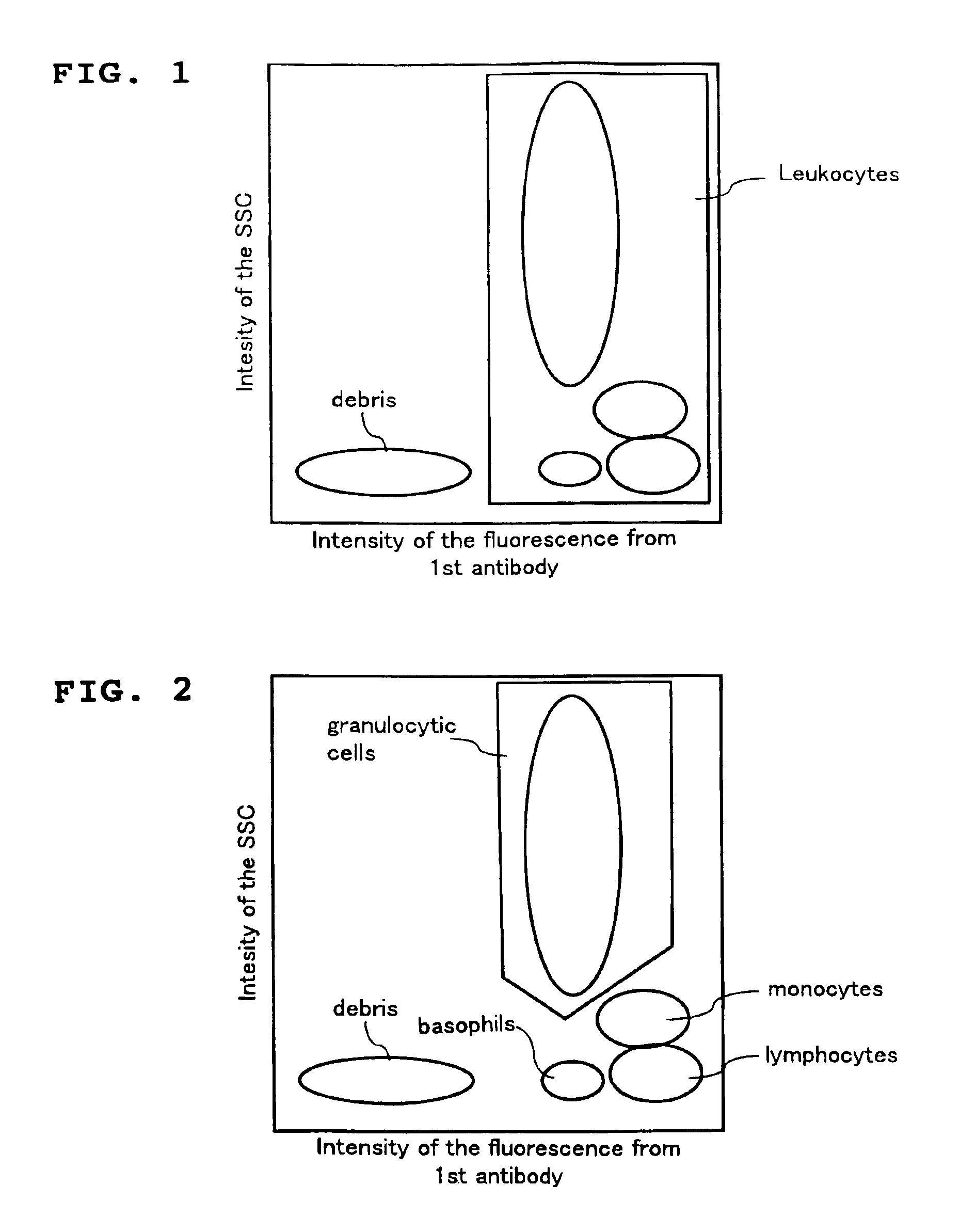
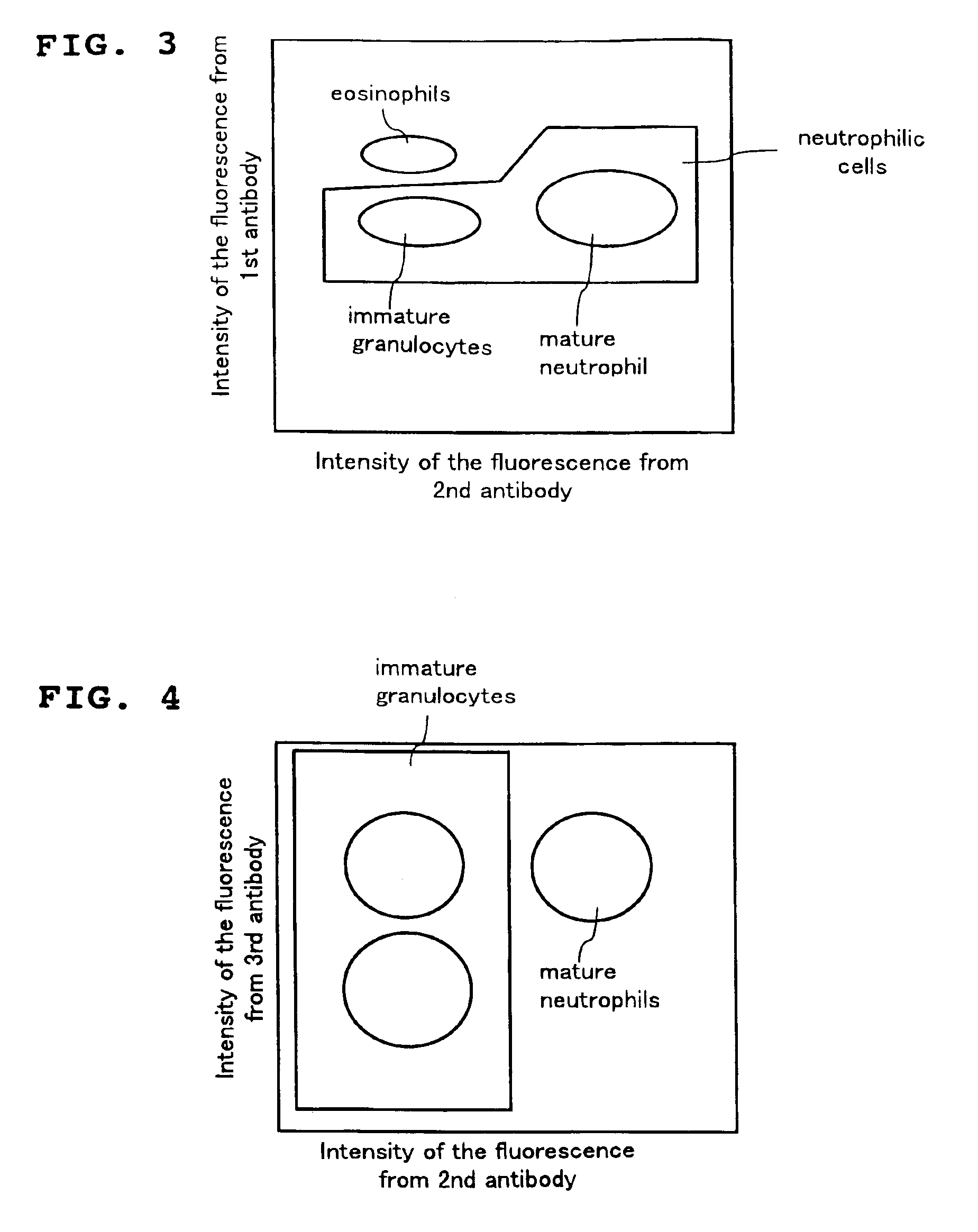
A method for classifying and counting leukocytes comprises the steps of: (1) adding to a hematological sample the following fluorescence-labeled antibodies labeled with fluorescent dyes which emit fluorescences distinguishable from each other; (a) a first fluorescence-labeled antibody (1st antibody) which bonds specifically to leukocytes, (b) a second fluorescence-labeled antibody (2nd antibody) which bonds to at least one kind of neutrophilic cells, and (c) a third fluorescence-labeled antibody (3rd antibody) which bonds to at least one kind of immature granulocytic cells, in order to stain leukocytic cells in the sample, and removing erythrocytes from the sample; (2) analyzing the resulting sample using a flow cytometer to measure at least one scattered light signal and three separate fluorescence signals; (3) defining a group of granulocytic cells on the basis of intensity of the scattered light and intensity of fluorescence from the 1st antibody; (4) defining neutrophilic cells in the defined group of granulocylic cells on the basis of the intensity of the fluorescence from the 1st antibody and intensity of fluorescence from the 2nd or 3rd antibody; (5) classifying the defined group of the neutrophilic cells into groups of neutrophilic cells different in degree of maturity on the basis of the intensity of the fluorescence from the 2nd antibody and the intensity of the fluorescence from the 3rd antibody, and counting the number of cells in each of the groups.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Method for evaluating a patients biological condition
This invention is concerned with a method for evaluating the dynamic biological state of a patient, said method, which involves measuring several elements or substances contained in the blood and interpreting results of the measurements carried out, comprising the following steps (1°) taking a sample of blood from the patient to be examined; (2°) determining hematic substances serving as metabolic and / or tissue parameters; (3°) measuring, on the basis of the determination of step (2°), the totality or part of indexes J1 to J157 defined in the disclosure; and (4°) comparing at least part of said indexes J1 to J157 with similar values obtained at steps (2°) and (3°) on subjects already identified as healthy, to dynamically assess the biological state of the patient to be examined. This invention is also concerned with a software product for executing on a computer steps (3°) and (4°).
Owner:ENDOGENICS
Method of classifying and counting leucocytes
ActiveUS20080176274A1Low costAccurate classificationMicrobiological testing/measurementIndividual particle analysisStainingWhite blood cell
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Method for discriminating platelets from red blood cells
ActiveUS20070105230A1Efficient modificationEasy to distinguishSamplingDead animal preservationMedicineRefractive index
A method for discriminating and quantifying platelets within an analyzed blood sample involves initially diluting the blood sample with a ghosting reagent that causes a change in the index of refraction of the cell. Owing to the change in the index of refraction, light scattered from the ghosted red blood cells will be substantially reduced relative to light scattered from platelets. This results in locations of platelets within a scatterplot of the analyzed blood sample to fall within a region distinguishable from those containing normal red blood cells, fragmented red blood cells, and microcytic red blood cells.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
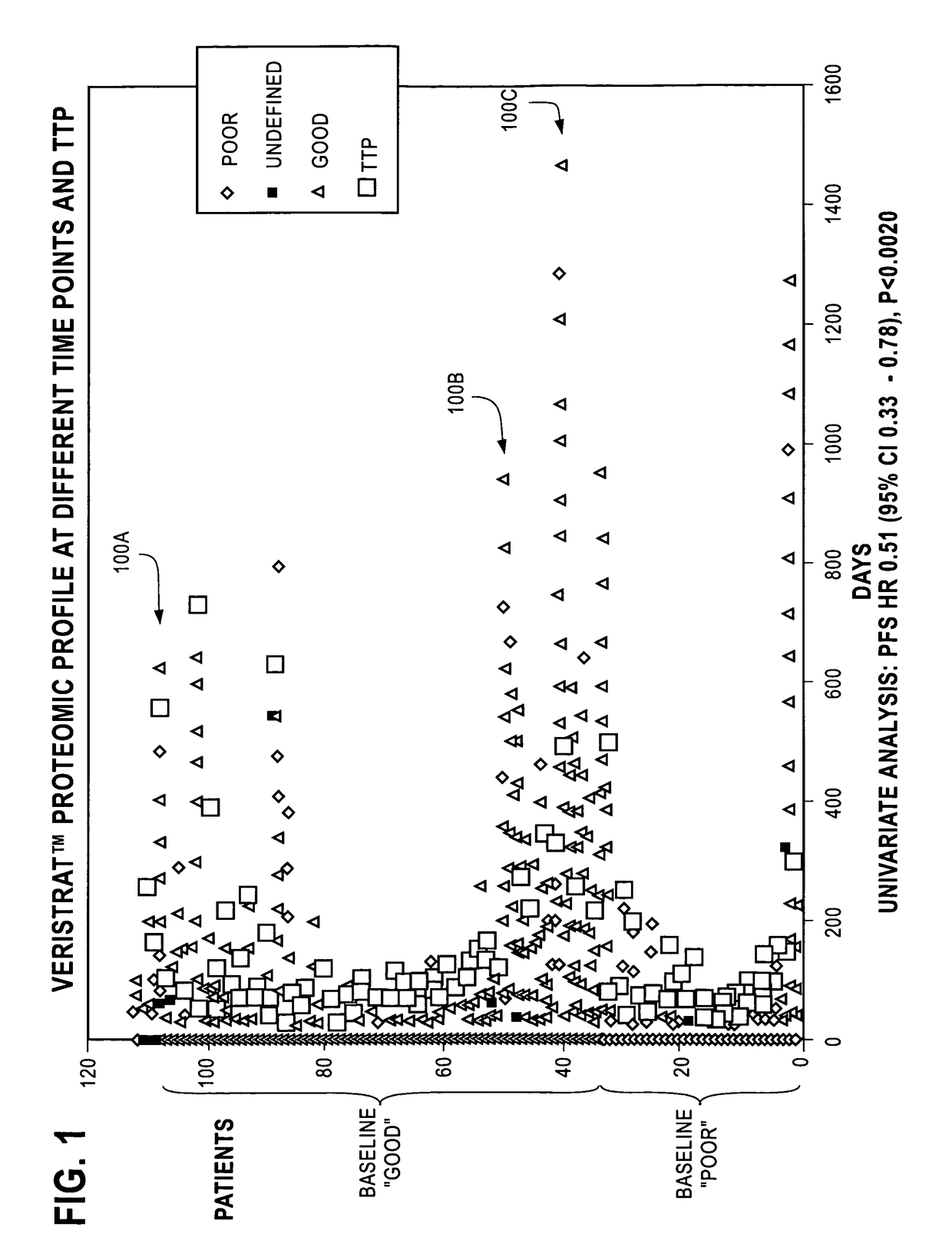
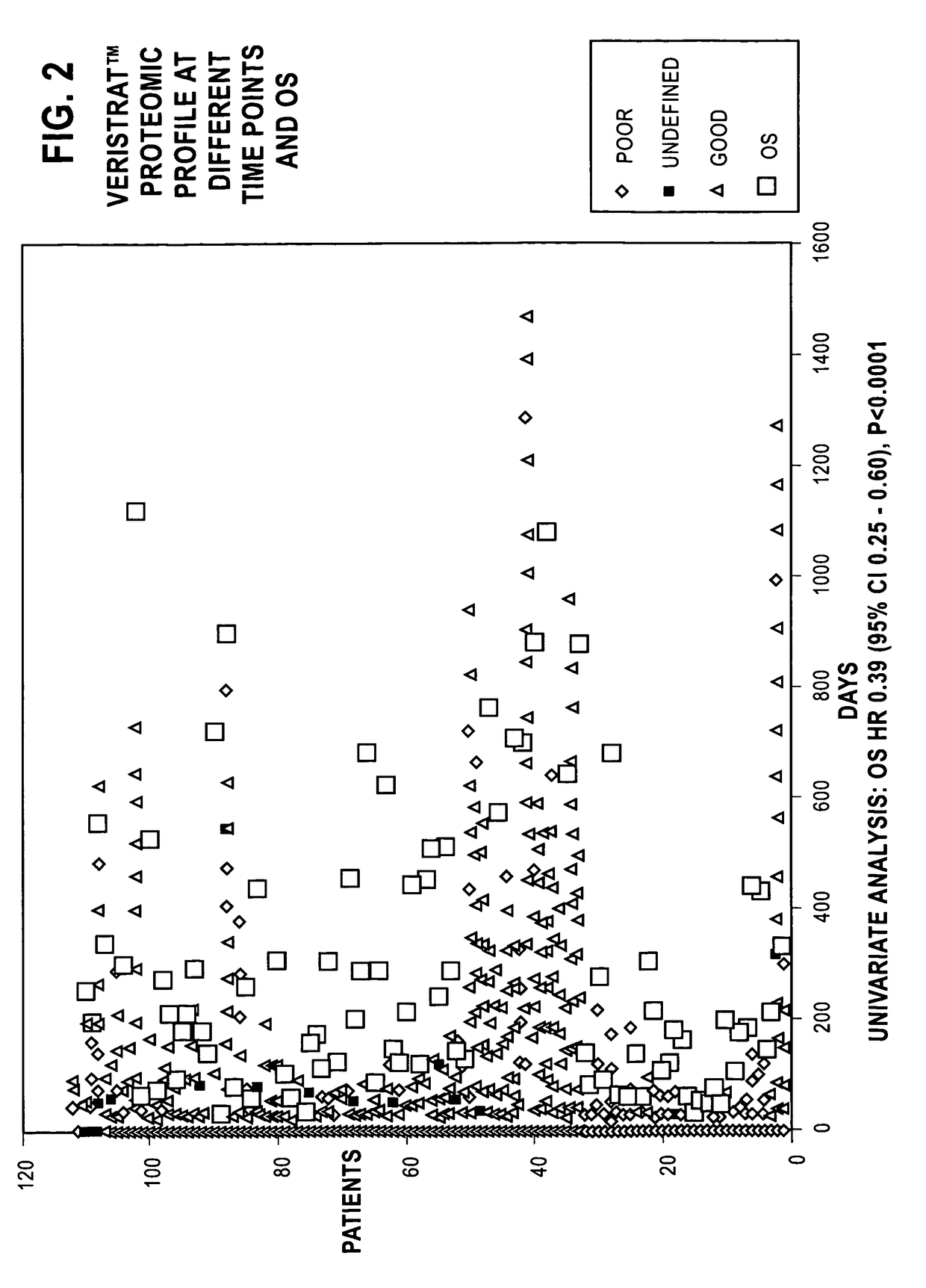
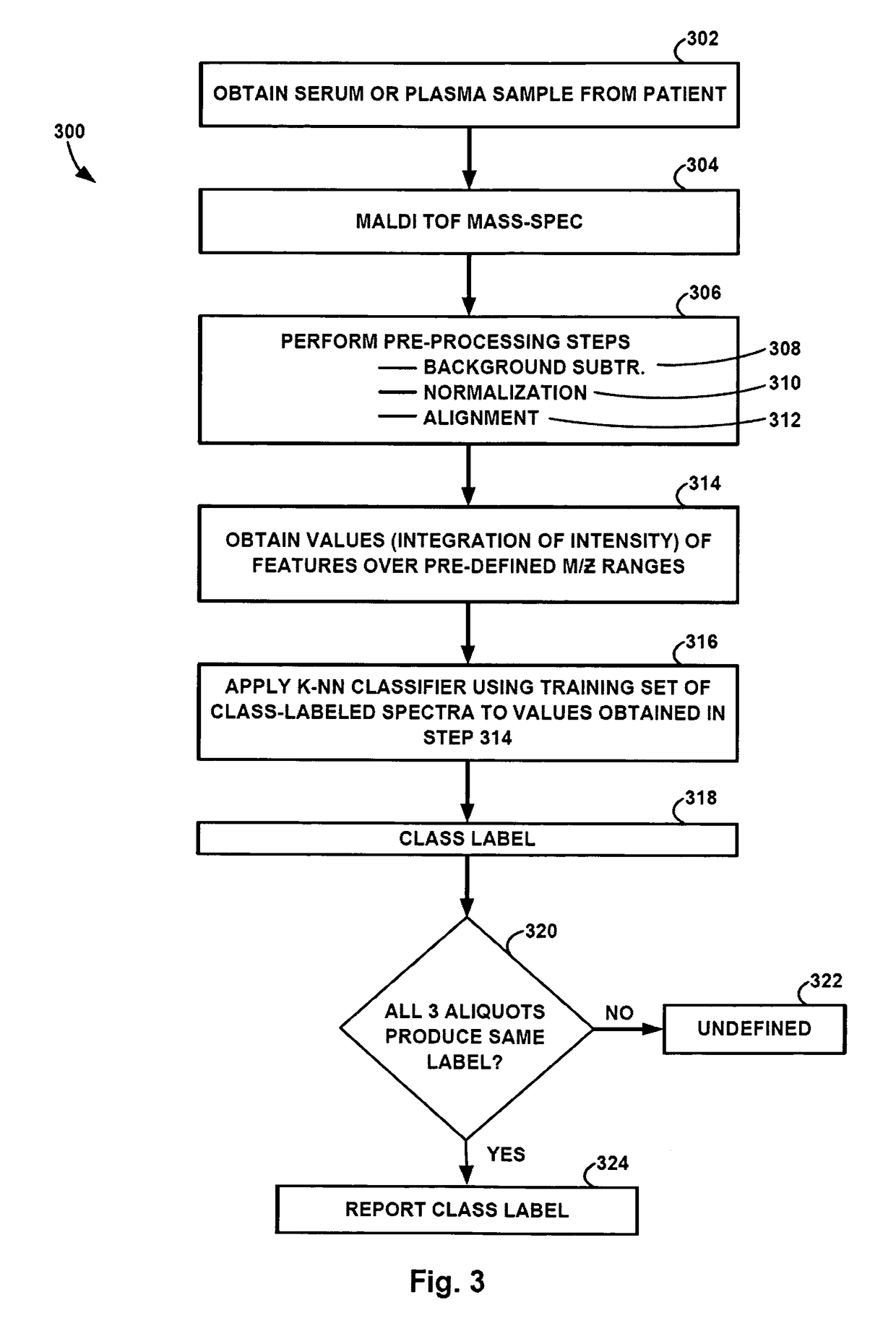
Monitoring treatment of cancer patients with drugs targeting EGFR pathway using mass spectrometry of patient samples
Owner:BIODESIX
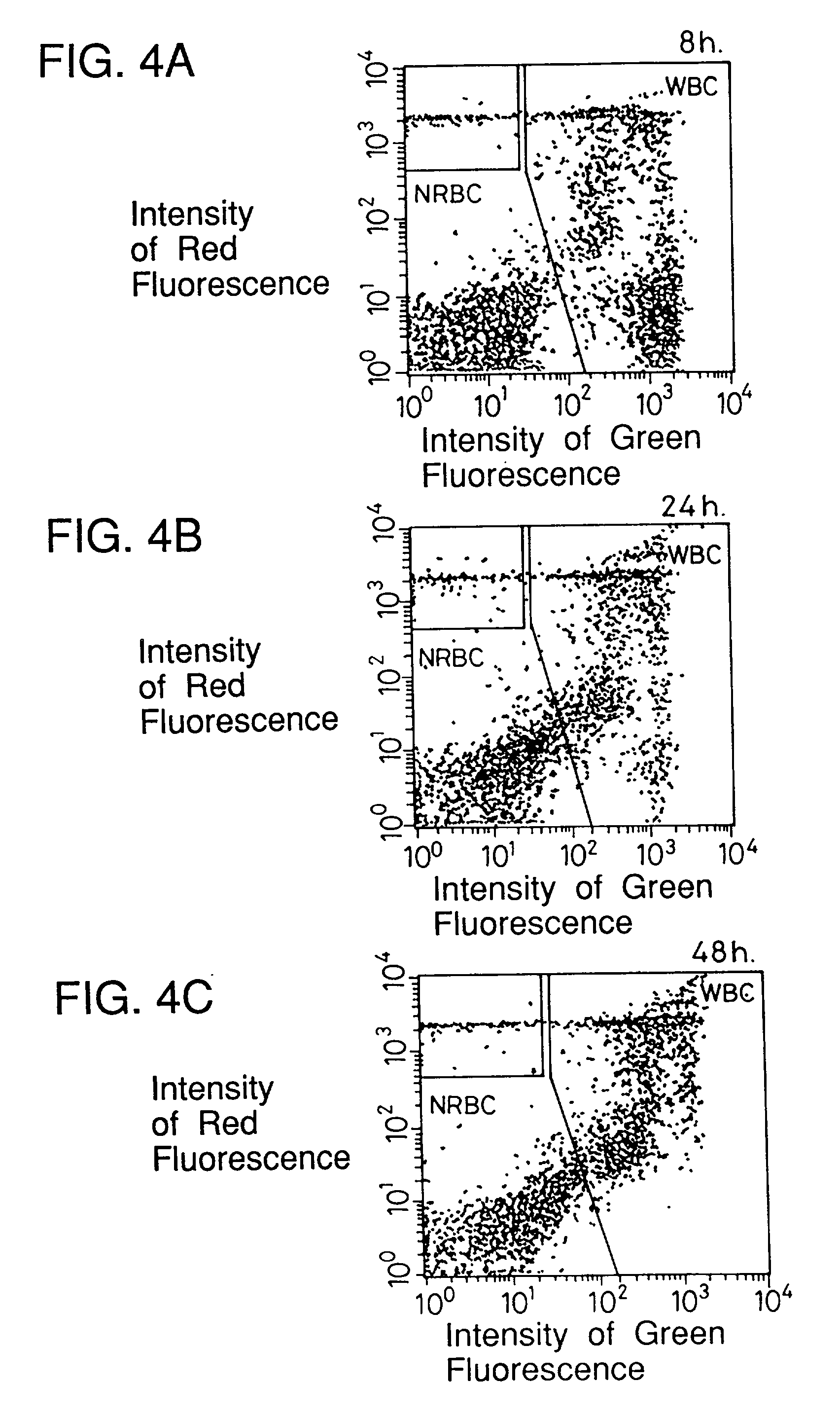
Process for discriminating and counting erythroblasts
InactiveUS20020006631A1Microbiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceRed blood cellWhite blood cell
A method for discriminating and counting erythroblasts comprises the steps of: (i) staining leukocytes in a hematologic sample by adding a fluorescent labeled antibody capable of binding specifically with leukocytes to the hematologic sample; (ii) raising the permeability only of cell membranes of erythroblasts in the hematologic sample to a nucleotide fluorescent dye which does not permeate a cell membrane usually, the nucleotide fluorescent dye having a fluorescent spectrum capable of being distinguished from that of a fluorescent labeling compound of the fluorescent labeled antibody in step (i); (iii) staining nuclei of the erythroblasts in the hematologic sample with the nucleotide fluorescent dye; (iv) subjecting the hematologic sample to flowcytometry to detect at least two fluorescent signals from each cell; and (v) discriminating and counting the erythroblasts from difference in intensity between the at least two fluorescent signals.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
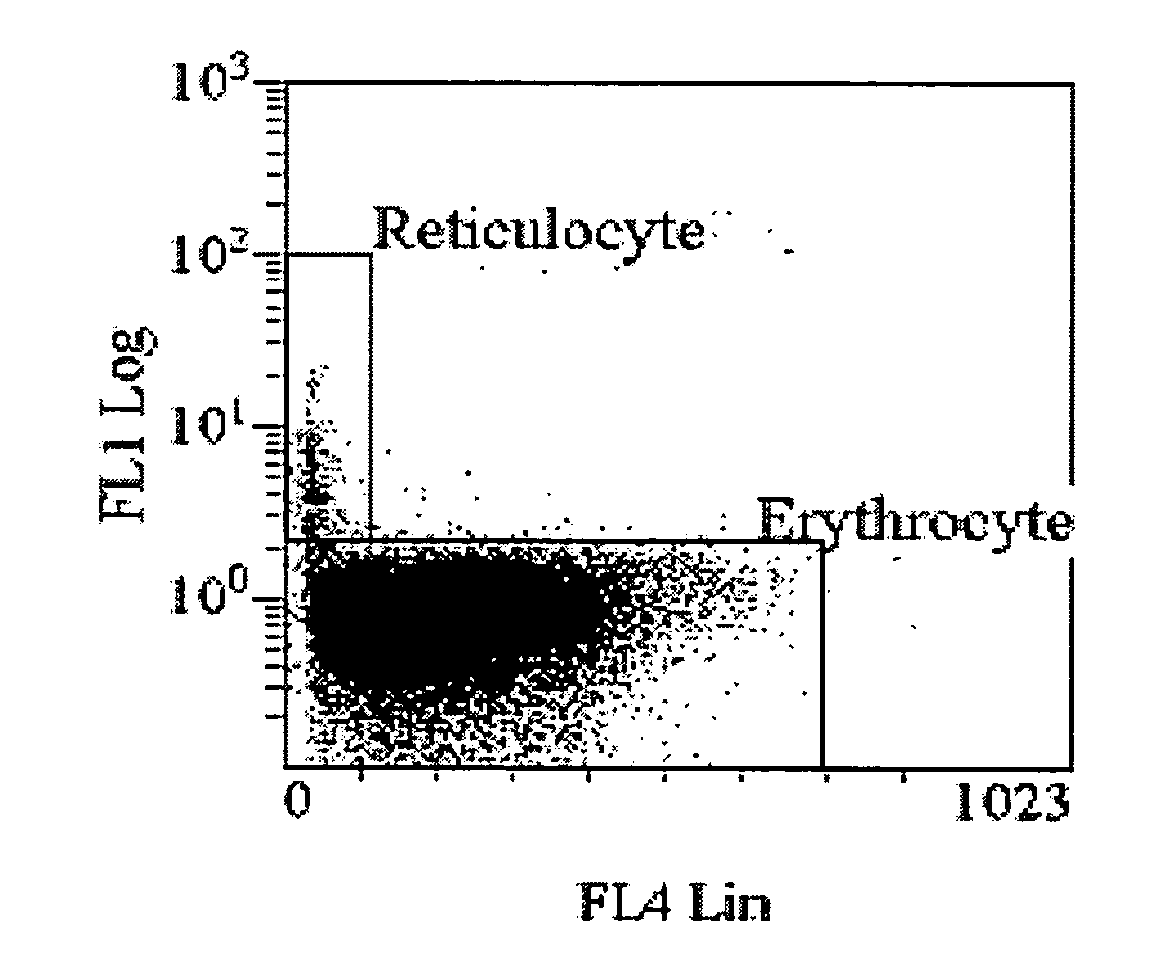
Method of measurement of cellular hemoglobin
ActiveUS20070020612A1Prevent further reactionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingFluorescenceCell membrane
A method of measuring cellular hemoglobin of a blood sample includes mixing a blood sample with a permeation reagent, and incubating the sample mixture to permeate cellular membrane of red blood cells and to cause hemoglobin aggregation within the cells; adding a neutralization reagent to inhibit further reactions of the permeation reagent; performing a cell-by-cell measurement of side scatter signals of the red blood cells in the sample mixture on a flow cytometer; and obtaining cellular hemoglobin (Hgbcell) of each red blood cell using the obtained side scatter signals. The method further includes measuring cellular hemoglobin of reticulocytes (Hgbretic) by differentiating reticulocytes using a simultaneous fluorescence measurement. The method also includes measuring cellular percentage of a hemoglobin variant in mature red blood cells or reticulocytes by adding a fluorescent antibody in the neutralization reagent and detecting fluorescence signals of antibody bound hemoglobin variant.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
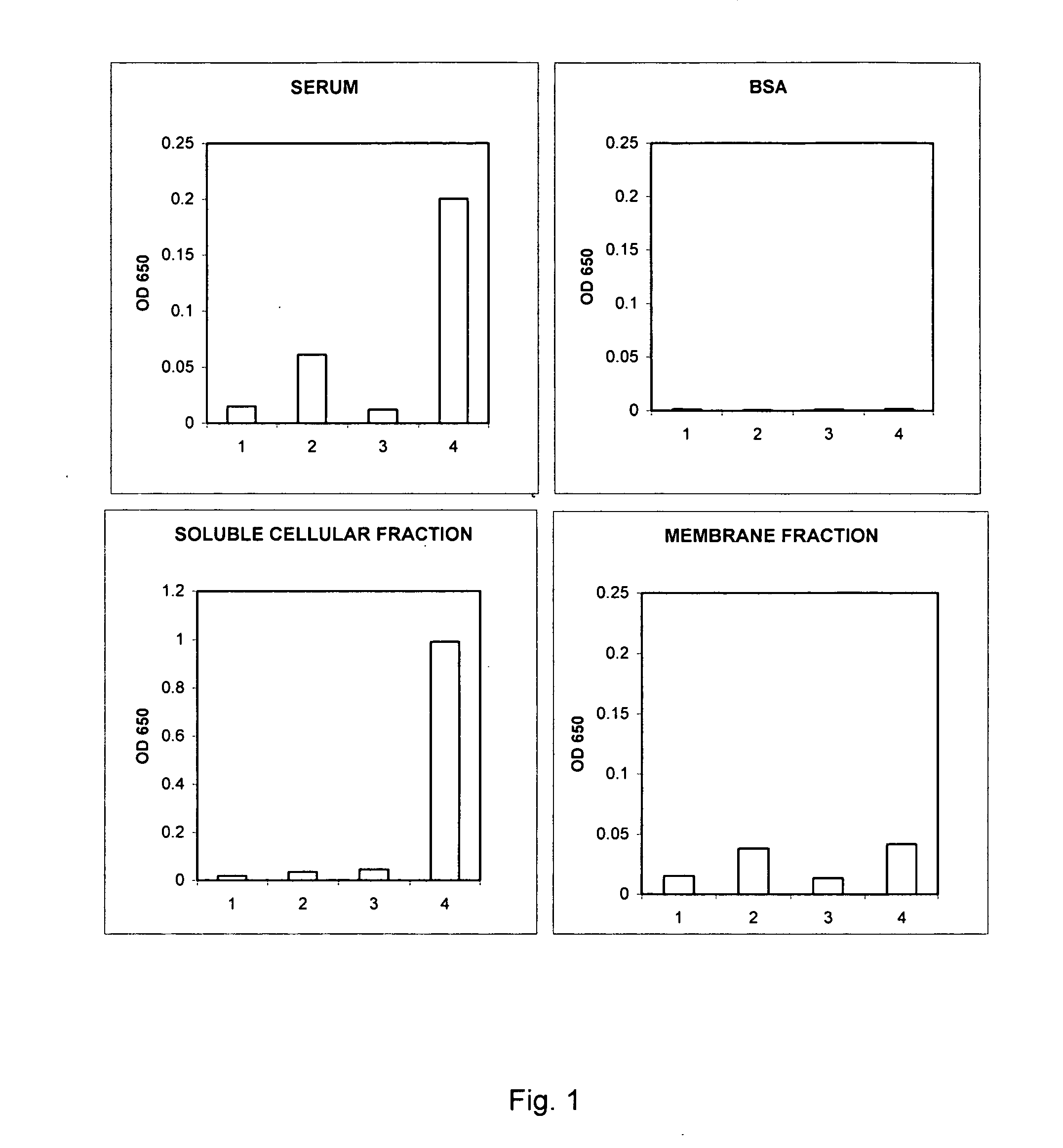
Diagnosis and monitoring of systemic lupus erythematosus and of scleroderma
ActiveUS20050037441A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRed CellSclerosis skin
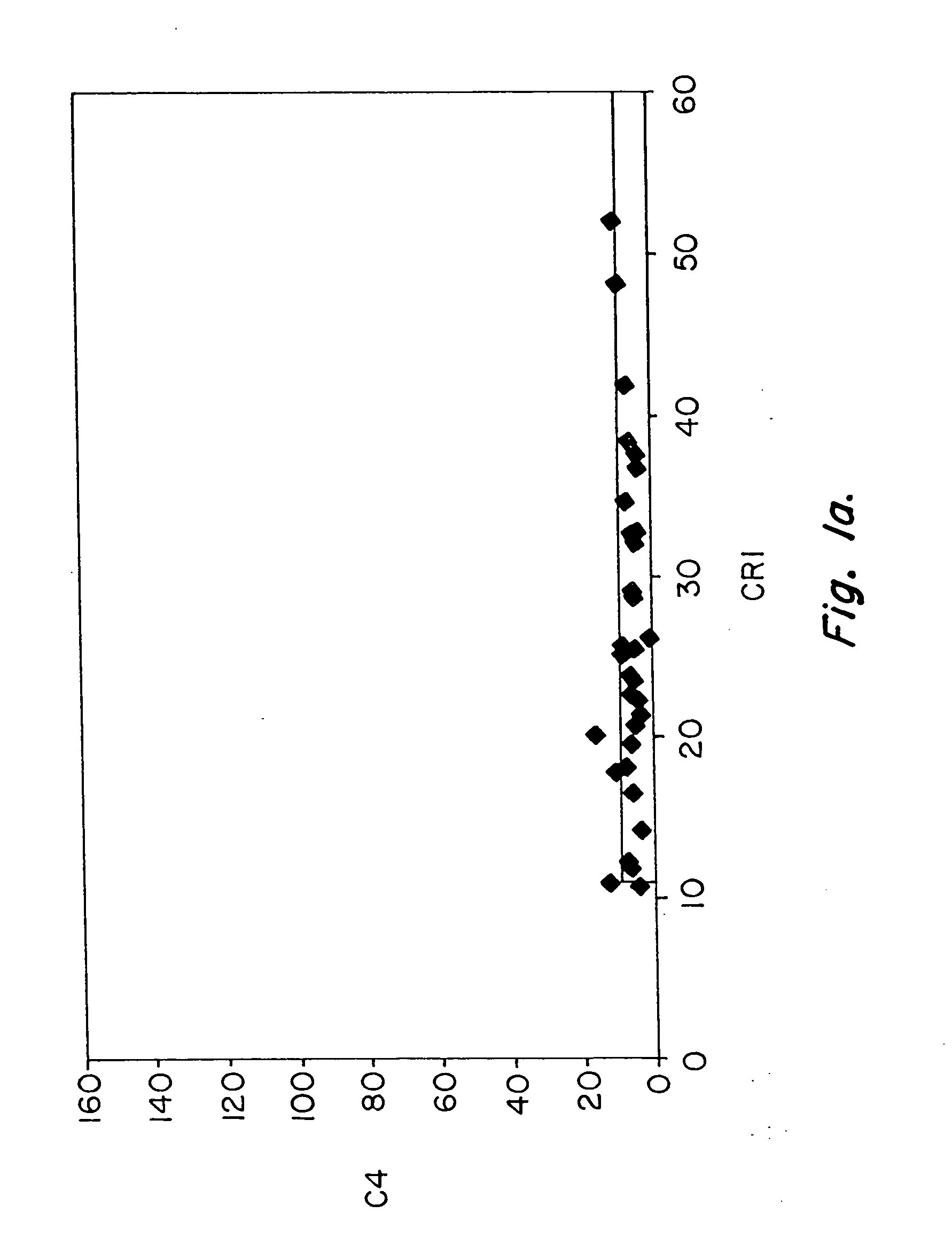
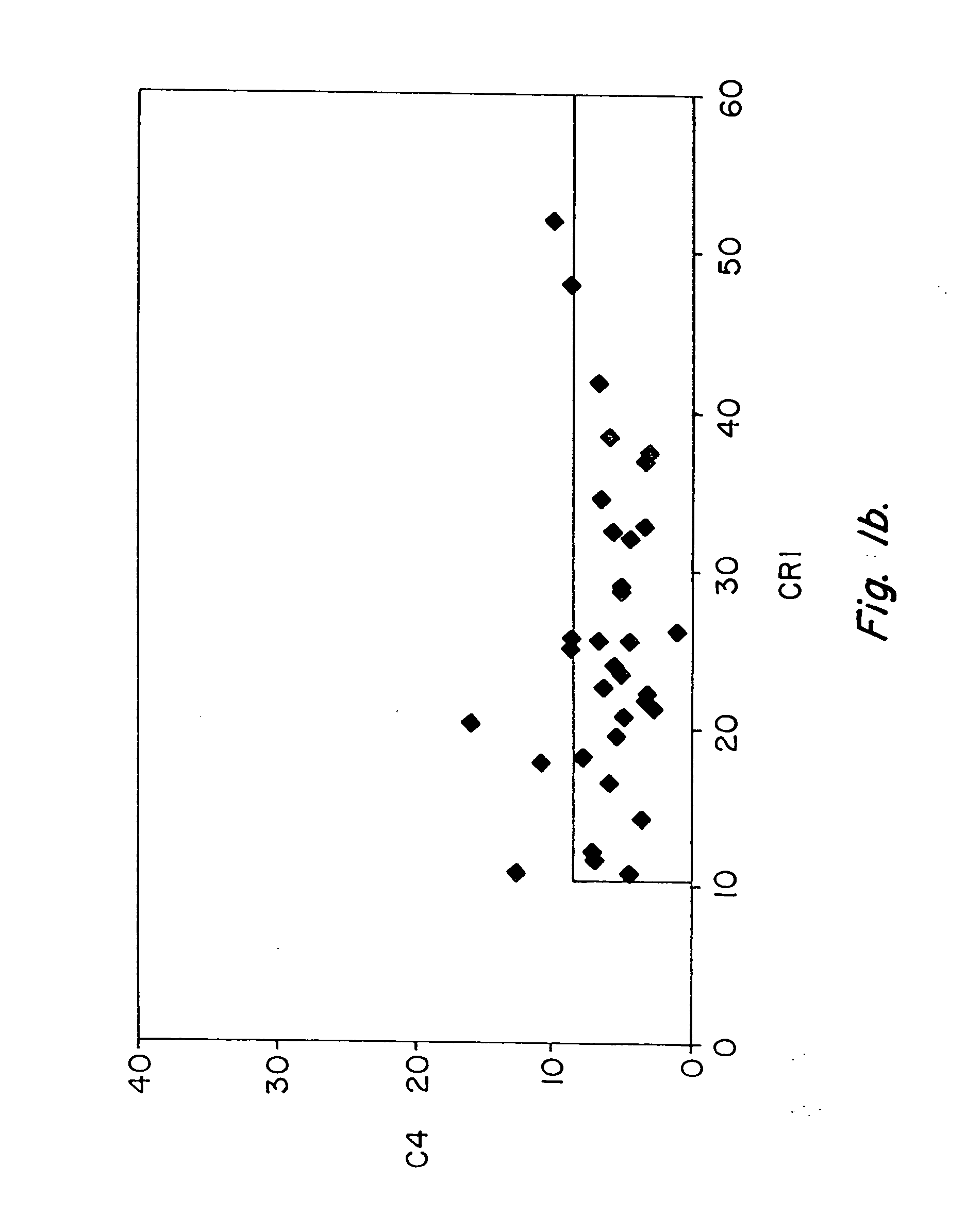
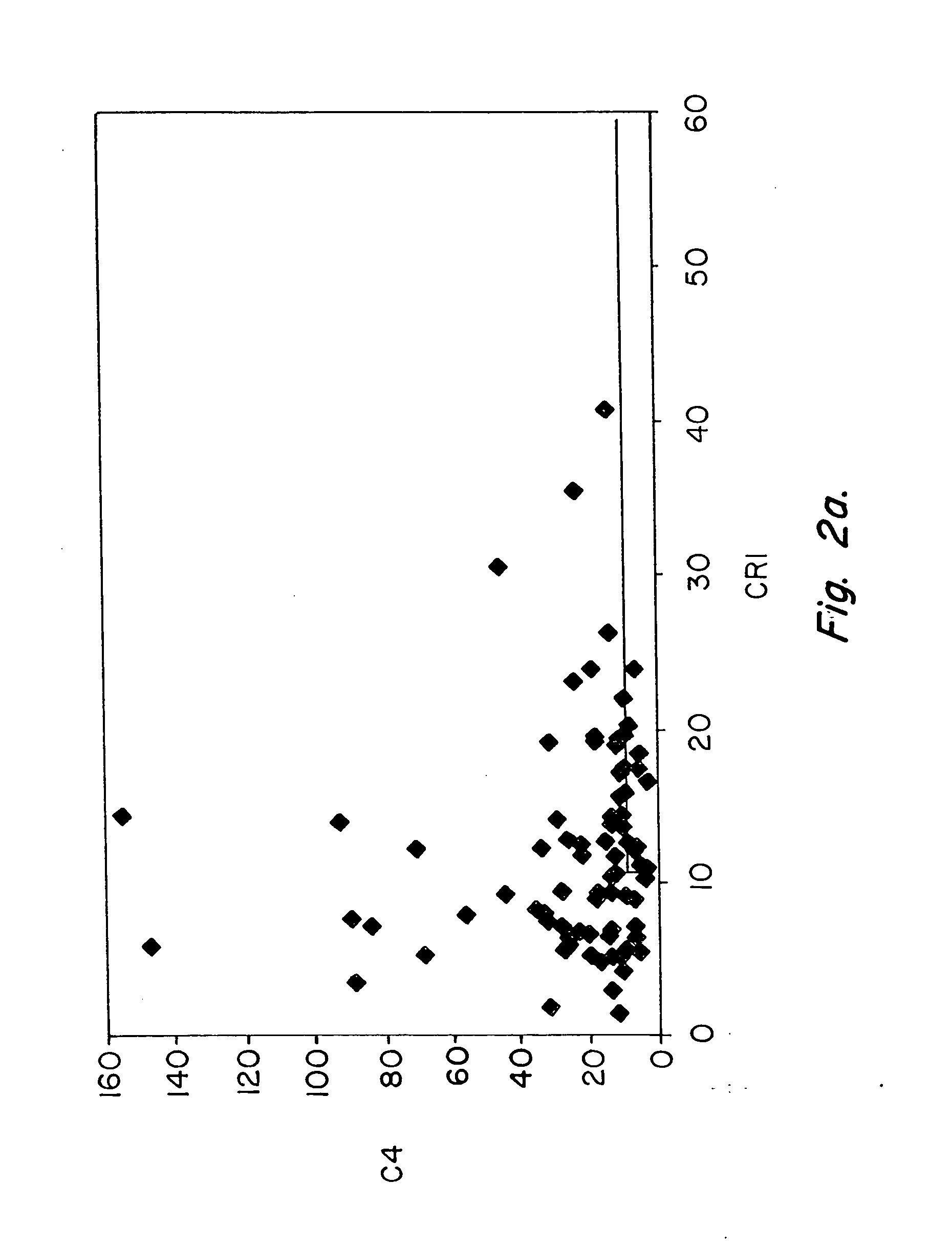
Methods for diagnosing and monitoring systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) or scleroderma by determining, in a blood sample from the individual being diagnosed or monitored, complement component C4d deposited on surfaces of red blood cells in the sample, and optionally also determining complement receptor CR1 deposited on the red blood cell surfaces. For diagnosis this is compared with the quantity of C4d (and optionally CR1) present on red blood cells of normal individuals. For monitoring it is compared with a value in a sample or samples previously obtained from the individual patient.The comparison may be made with individual values for C4d and CR1 and / or with a ratio of the two found in normal individuals.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
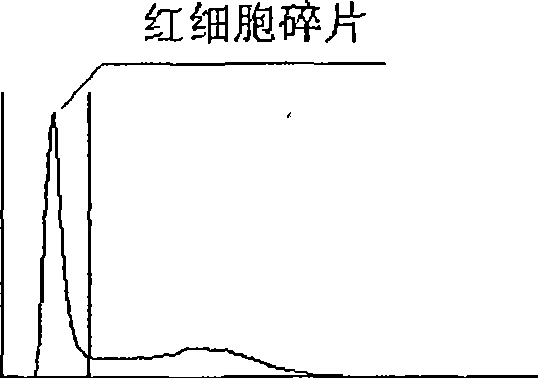
Method for recognizing erythrocyte chips
ActiveCN101464245AImprove accuracyIndividual particle analysisBiological testingWhite blood cellBlood cell analysis
A method for indentifying red cell fragments is used for blood cell analysis with cell counting by the resistance method, and comprises the following steps: A. counting white blood cells in a blood sample, drawing a white blood cell column diagram, and recording the full width at half maximum of each particle pulse during the process of particle pulse signal identification; B. locating an area A with possible existence of red cell fragments and an area B without any red cell fragments on the white blood cell column diagram, and determining whether the existence of red cell fragments interfering with white blood cell counting is true in the area A according to the comparison between the distribution of the full width at half maximum of particle pulse in the area A and in the area B; and C. in the case of disturbance caused by red cell fragments, determining the position, in which the interference peak of red cells ends, and correcting the count value of white blood cells according to the ending position of the interference peak of the red cells. The method achieves the effect of improving the accuracy of the result of white blood cell counting and the accuracy of white blood cell classification.
Owner:深圳迈瑞动物医疗科技股份有限公司
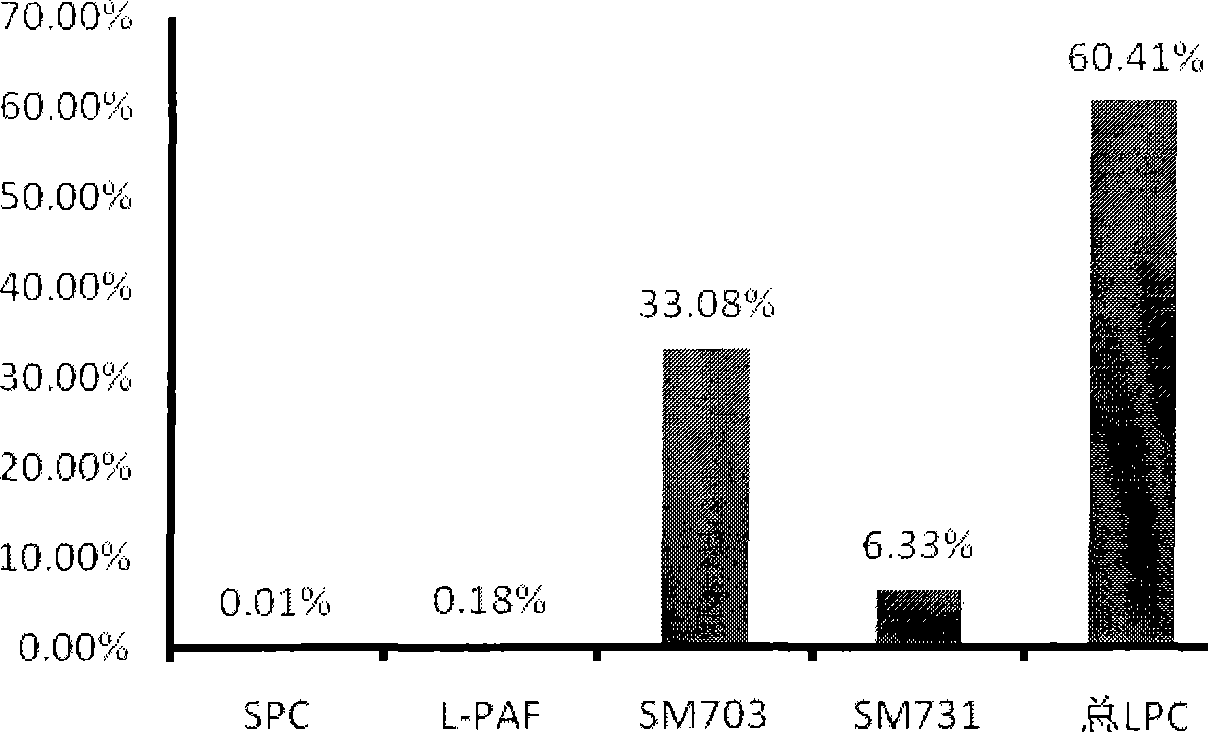
Production and use of reagent kit for measurement of lipide molecule content in human blood sample and colorectal carcinoma diagnosis
The invention relates to the measurement for the lipid molecule content in a human blood sample as well as the preparation and the application of a colon cancer or rectum cancer diagnosis reagent kit, in particular to the extraction of lipid molecules in a human blood sample and the content measurement thereof as well as the definition of colon cancer or rectum cancer lipid molecule marks. In addition, the invention also discloses the details about the detection of a few colon cancer or rectum cancer lipid molecule marks in a blood sample and provides a reagent kit which is formed according to the lipid molecule marks and used for colon cancer or rectum cancer diagnosis. According to the content of the lipid molecule marks in the sample, the possibility for a patient suffering the colon cancer or rectum cancer can be diagnosed from the sample through special calculation and analysis, and the invention also provides a new means for the healing efficacy analysis in the colon cancer or rectum cancer treatment.
Owner:桑建利
Nucleated Red Blood Cell Analysis System and Method
ActiveUS20120282599A1Eliminate distractionsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRed blood cellFluorescence
Systems and methods for analyzing blood samples, and more specifically for performing a nucleated red blood cell (nRBC) analysis. The systems and methods screen a blood sample by means of fluorescence staining and a fluorescence triggering strategy, to identify nuclei-containing particles within the blood sample. As such, interference from unlysed red blood cells (RBCs) and fragments of lysed RBCs is substantially eliminated. The systems and methods also enable development of relatively milder reagent(s), suitable for assays of samples containing fragile white blood cells (WBCs). In one embodiment, the systems and methods include: (a) staining a blood sample with an exclusive cell membrane permeable fluorescent dye; (b) using a fluorescence trigger to screen the blood sample for nuclei-containing particles; and (c) using measurements of light scatter and fluorescence emission to distinguish nRBCs from WBCs.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
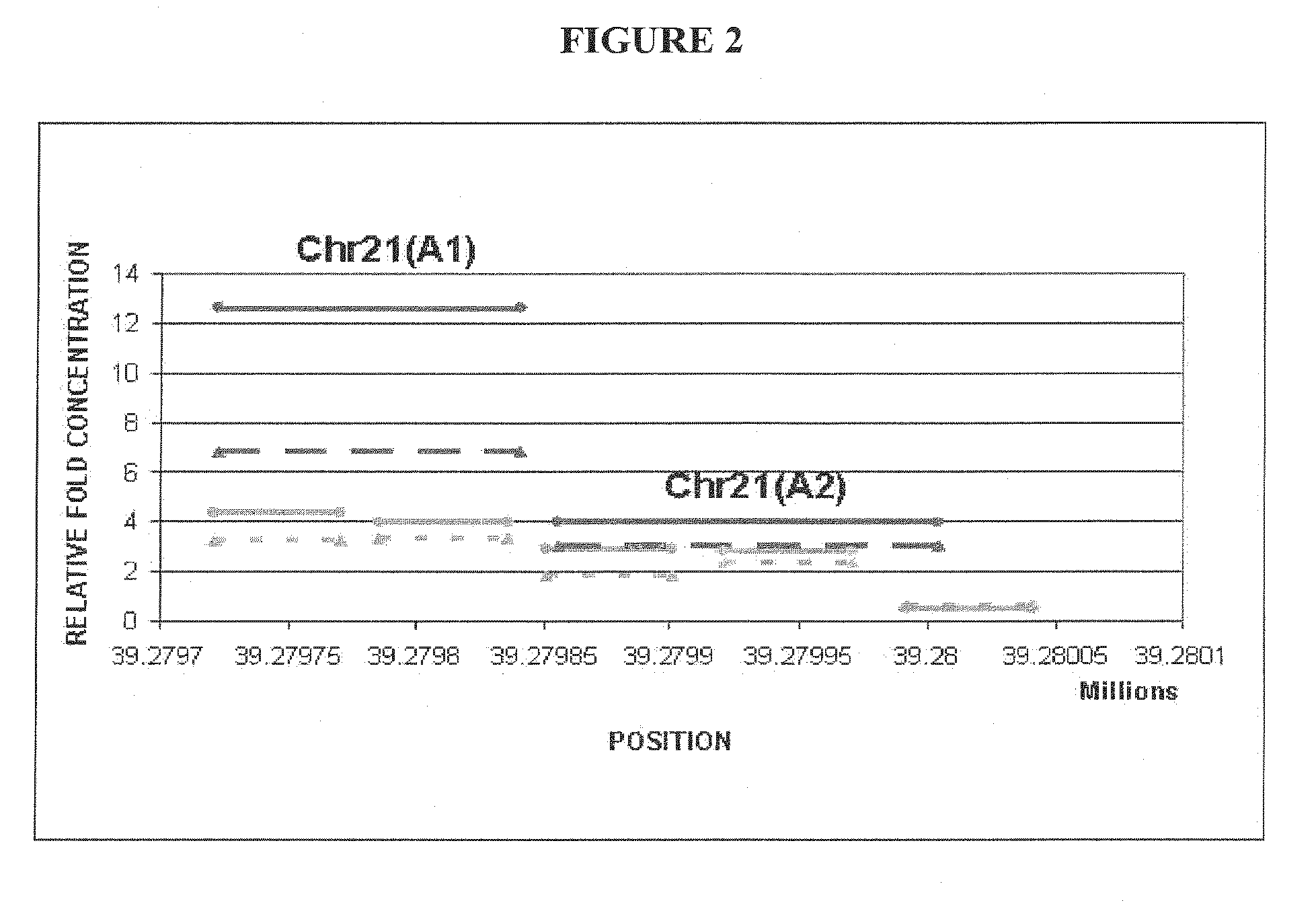
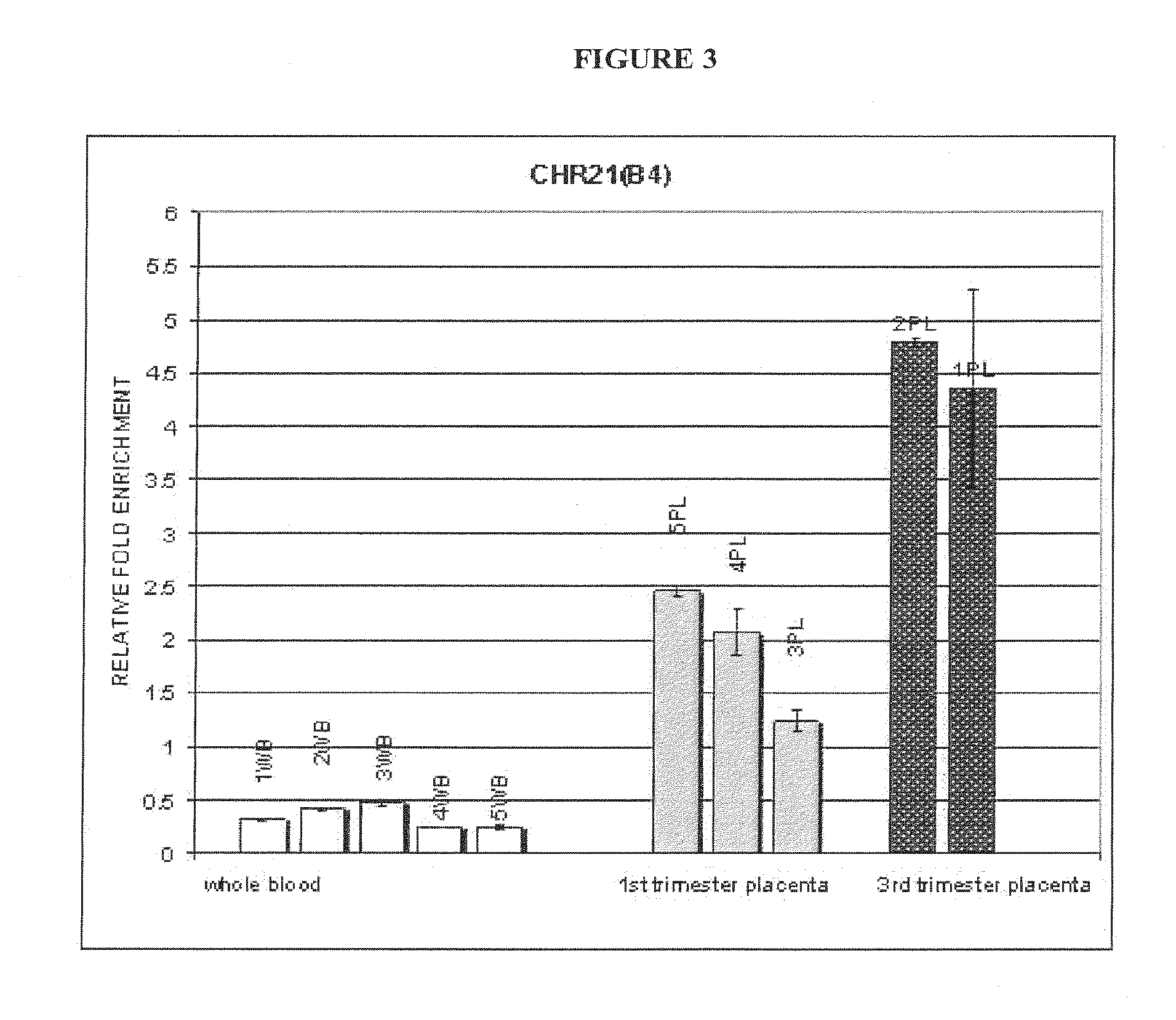
Methods and compositions for noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of fetal aneuploidies
ActiveUS20120282613A1Accurate predictionDiagnosing fetal aneuploidiesSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMethylated DNA immunoprecipitationAdult female
The invention provides methods and compositions for noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of fetal aneuploidies. A large panel of differentially methylated regions (DMRs) have been identified. Certain of these DMRs are hypomethylated in adult female blood DNA and hypermethylated in fetal DNA, whereas others are hypermethylated in adult female blood DNA and hypomethylated in fetal DNA. Moreover, DMRs that are hypomethylated in adult female blood DNA and hypermethylated in fetal DNA have been shown to accurately predict a fetal aneuploidy in fetal DNA present in a maternal blood sample during pregnancy. In the methods of the invention, hypermethylated DNA is physically separated from hypomethylated DNA, preferably by methylated DNA immunoprecipitation.
Owner:NIPD GENETICS PUBLIC CO LTD
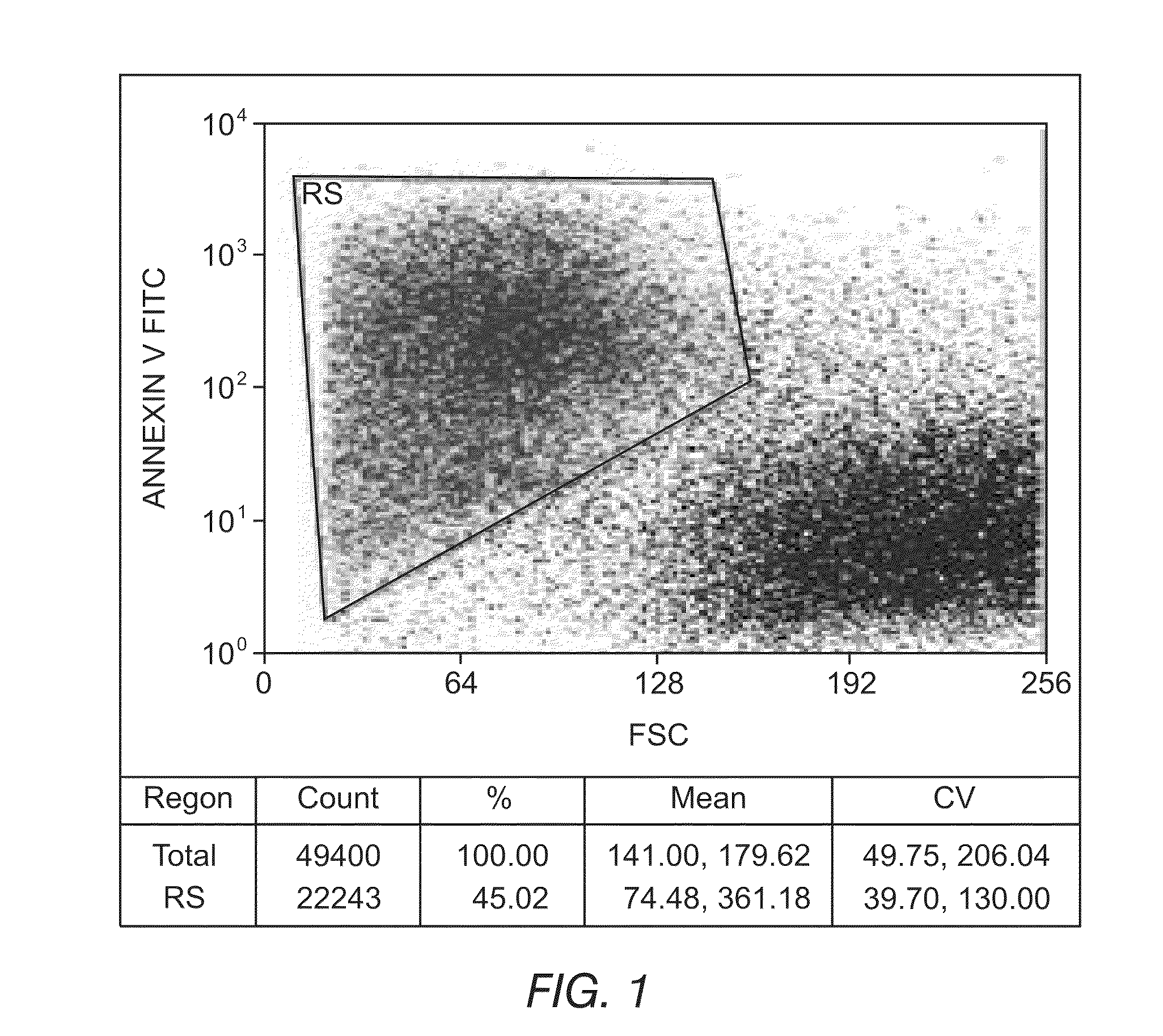
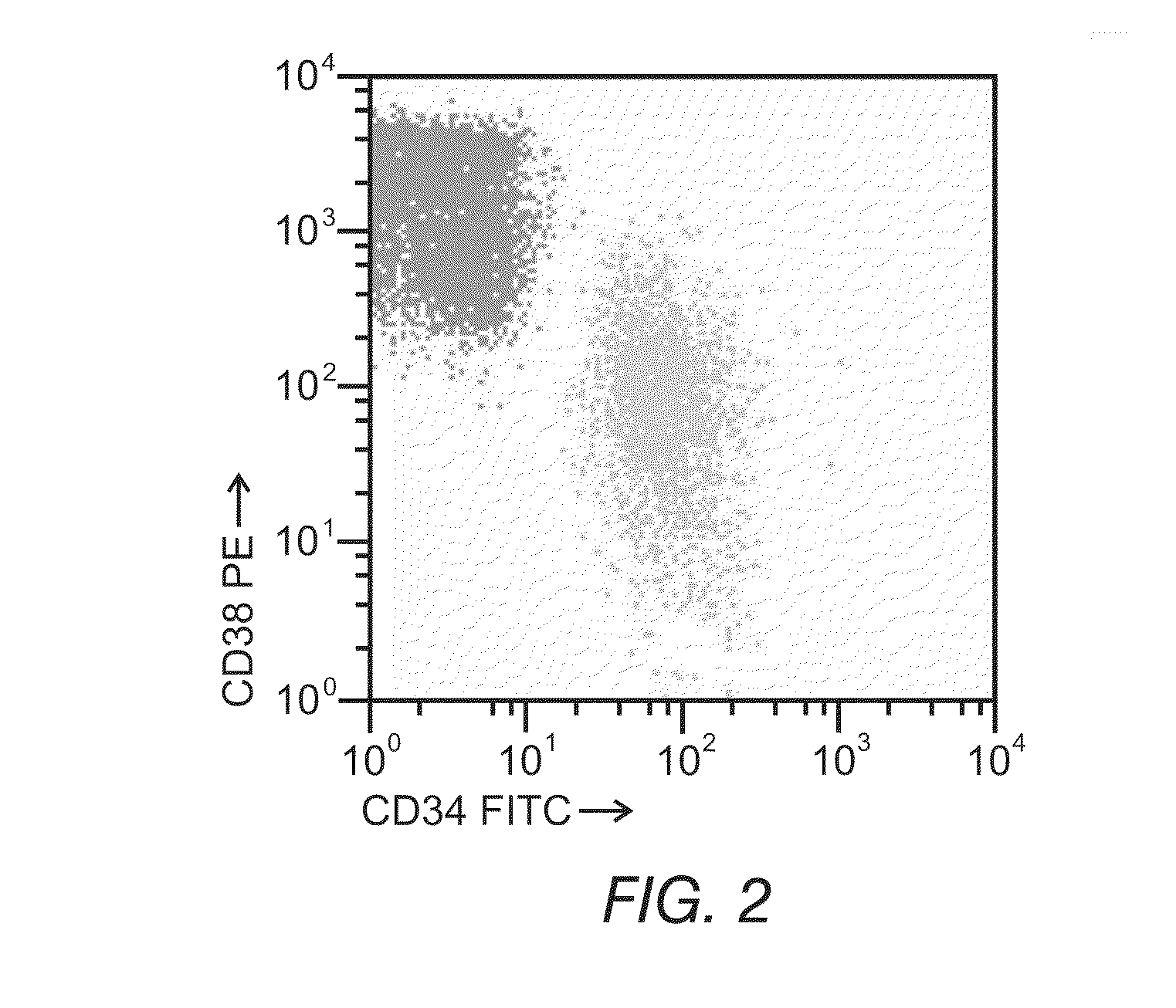
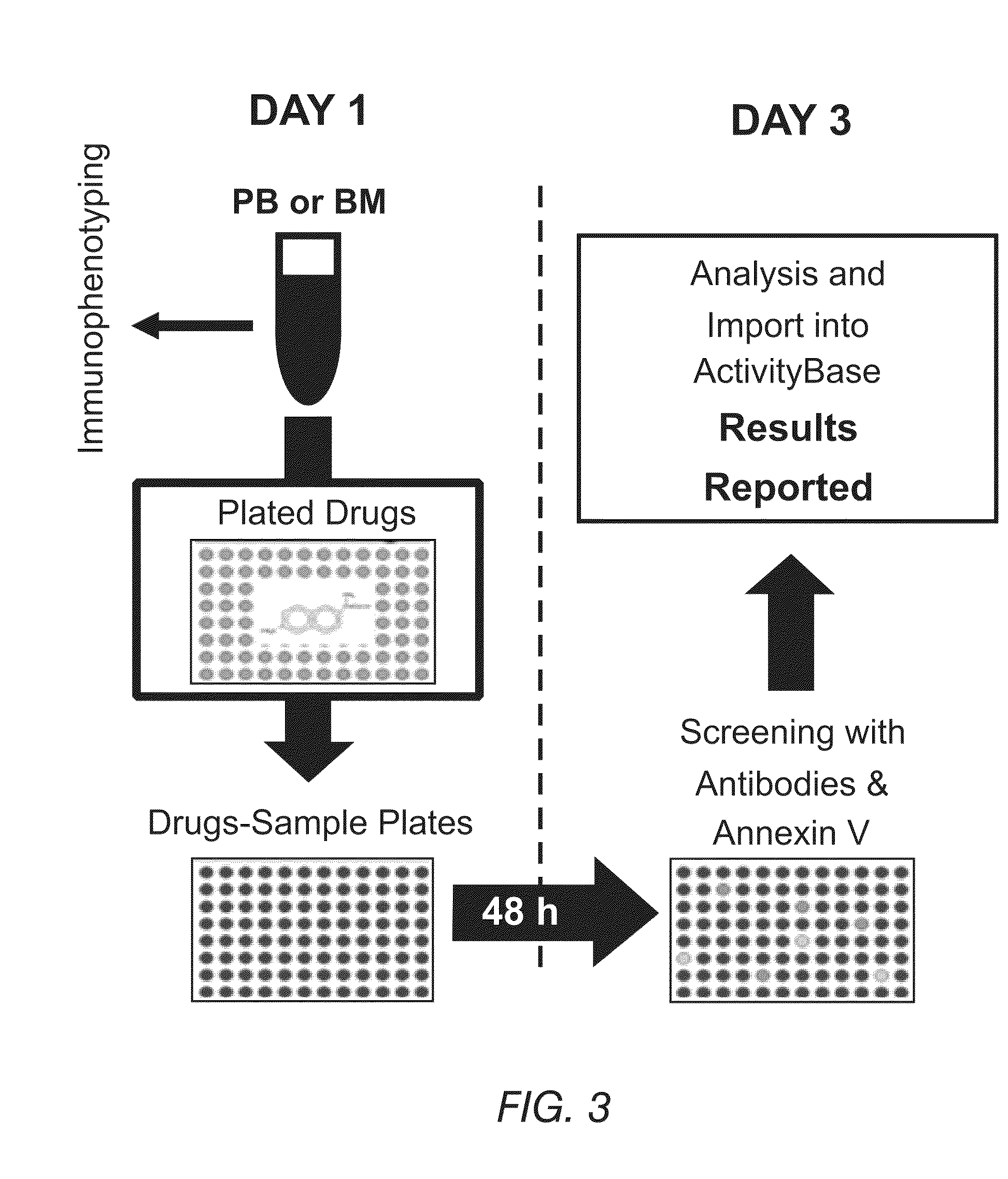
Methods for providing personalized medicine test ex vivo for hematological neoplasms
InactiveUS20100298255A1Quick analysisAccurate parameter estimatesBiocideBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCytotoxic drugApoptosis
Described herein are methods, devices, and compositions for providing personalized medicine tests for hematological neoplasms. In some embodiments, the methods comprise measuring the efficacy of inducing apoptosis selectively in malignant cells using any number of potential alternative combination drug treatments. In some embodiments, the ex vivo testing is measured using a recently extracted patient hematological samples. In other embodiments, the efficacy is measured ex vivo using an automated flow cytometry platform. For example, by using an automated flow cytometry platform, the evaluation of hundreds, or even thousands of drugs and compositions, can be made ex vivo. Thus, alternative polytherapy treatments can be explored. Non-cytotoxic drugs surprisingly induce apoptosis selectively in malignant cells ex vivo. In some embodiments, the methods described herein comprise evaluating non-cytotoxic drugs.
Owner:VIVIA BIOTECH SL
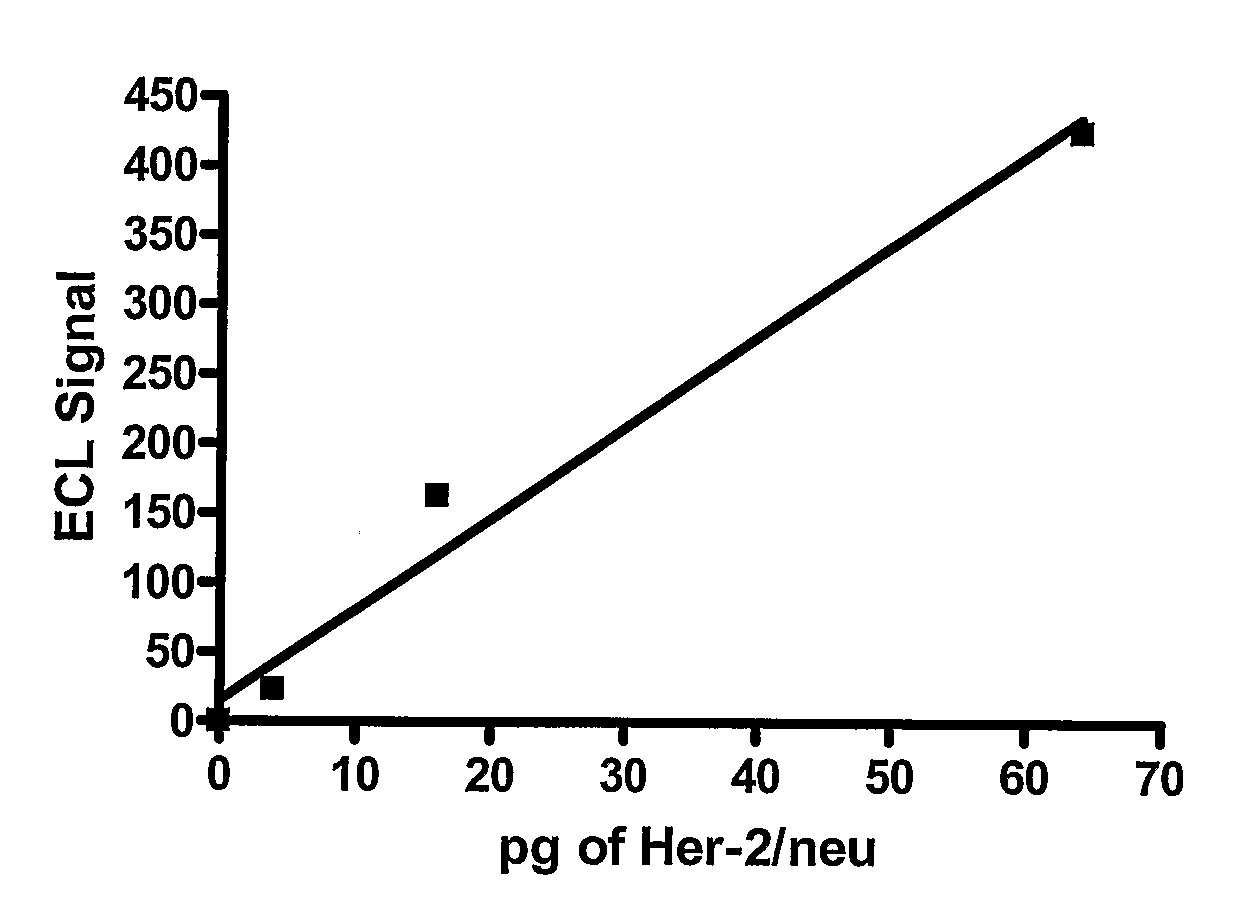
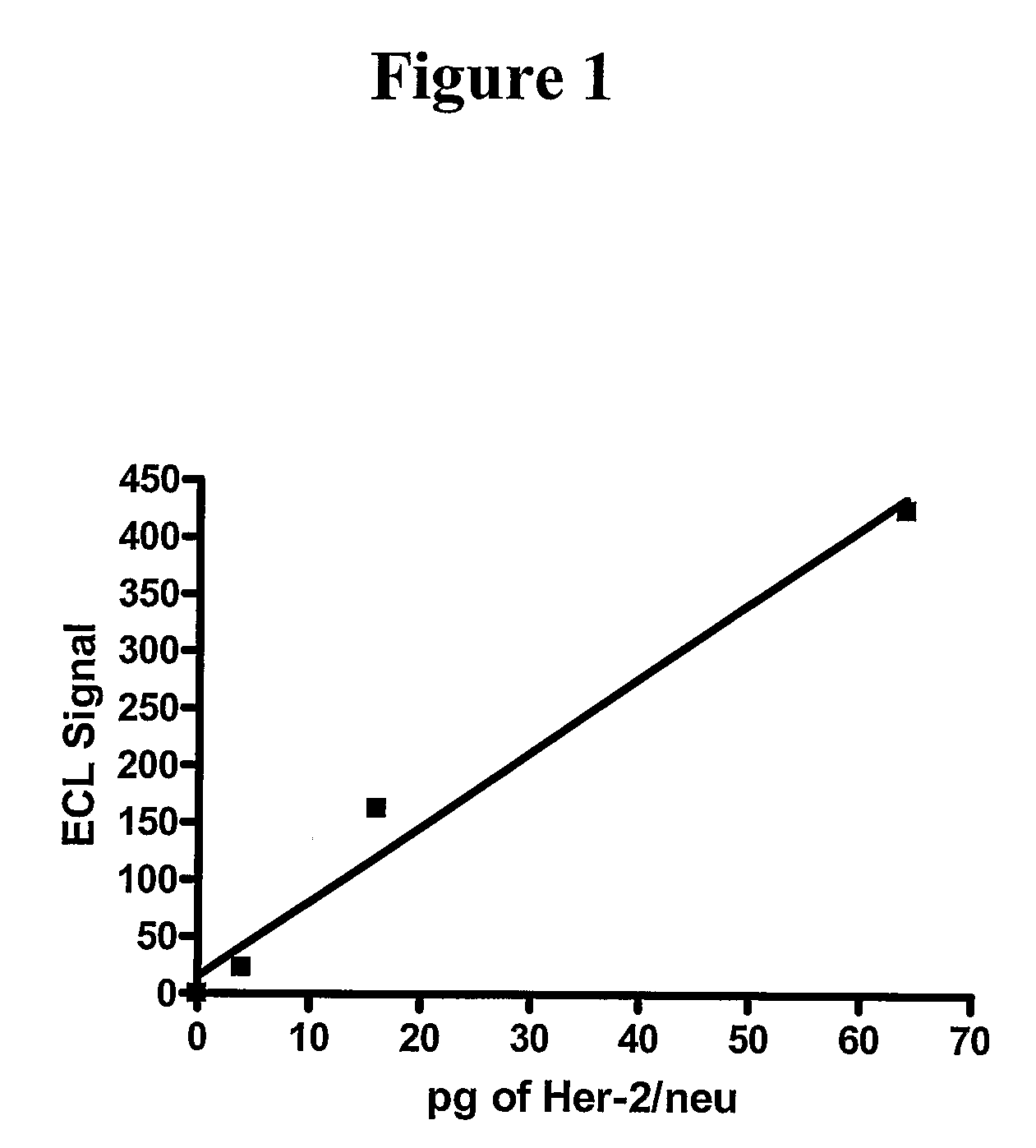
Detection of Elevated Levels of Her-2/Neu Protein on Circulating Cancer Cells and Treatment
InactiveUS20080261243A1Biological material analysisImmunoglobulinsAnticarcinogenCirculating cancer cell
The expression of Her-2 / neu protein on circulating cancer cells in a blood sample is detected by isolating the cancer cells from the blood sample and then performing on the isolated cancer cells a sensitive Her-2 / neu immunoassay. A positive result indicates the expression of Her-2 / neu on cancer cells in the blood sample. This method can be used to identify cancer patients who are likely to benefit from treatment with an anticancer agent that targets Her-2 / neu, such as trastuzumab (HERCEPTIN).
Owner:WELLSTAT BIOLOGICS CORP
Method and apparatus for determining anticoagulant therapy factors
InactiveUS20110224292A1BiocideAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionAnti coagulationCoagulation reagent
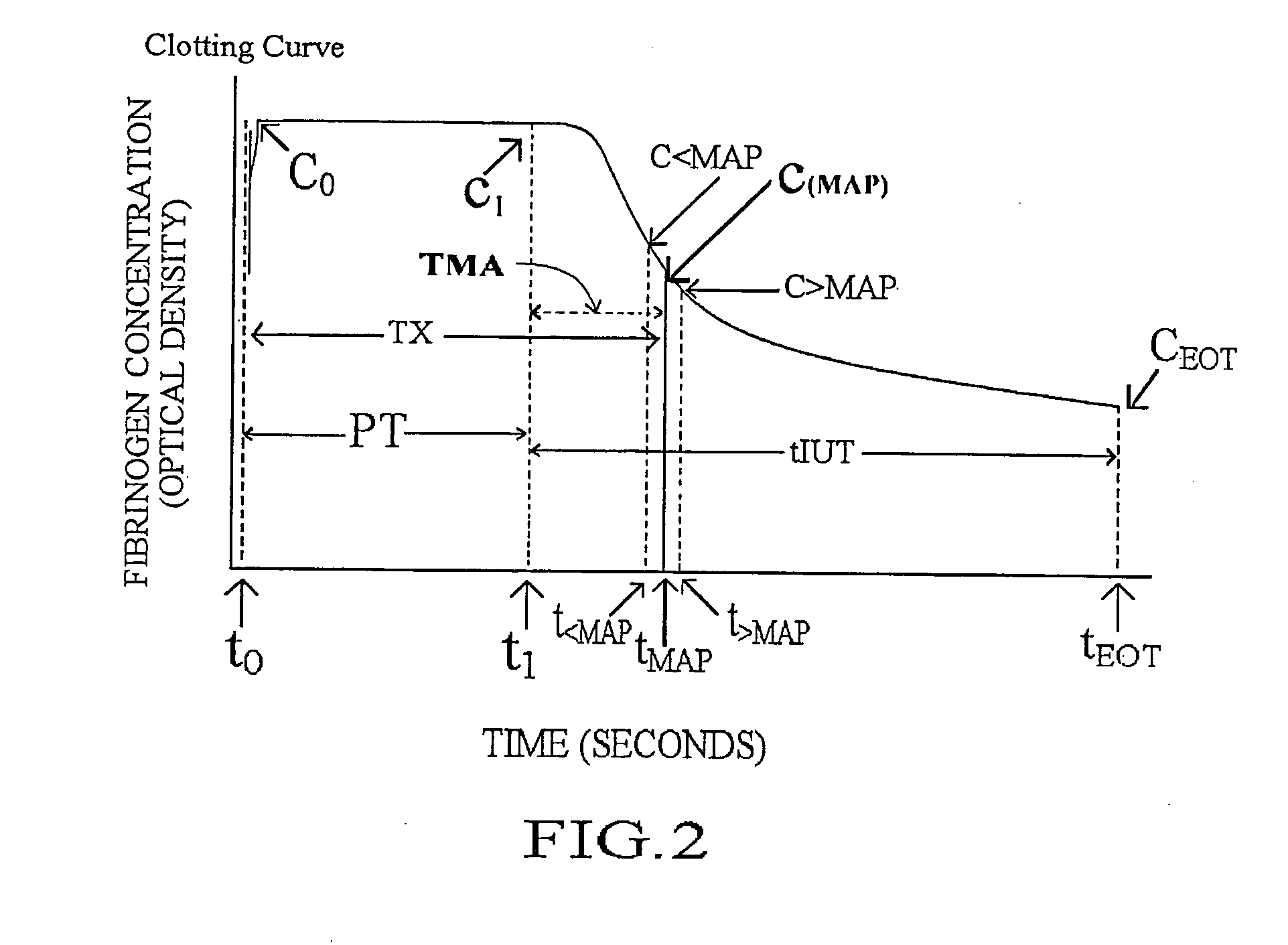
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for determining new anticoagulant therapy factors for monitoring oral anticoagulant therapy to help prevent excessive bleeding or deleterious blood clots that might otherwise occur before, during or after surgery. The inventive methods and apparatus provide an International Normalization Ratio (INR) based on a coagulation reaction with a blood sample of a living being. Embodiments include methods and apparatus for determining an anticoagulant therapy factor without requiring use of a mean normal prothrombin time determination or an ISI, and may be carried out with the patient sample and a coagulation reagent, where the coagulation reagent may be selected from a number of coagulation reagents. One embodiment provides an INRs value which is determined from a prothrombin time (PT or T1) of a patient blood sample and a theoretical end of test time (TEOT), where a theoretical clotting area is used to determine the INRs value according to the expression, INRs=T1*TEOT*MUL, where MUL is a multiplier that takes into account pixel parity and sampling times. The INRs may be used to determine a course of treatment for a patient or other living being without regard to the specific coagulation regent used to generate the coagulation data (e.g., time and optical activity values).
Owner:WADA
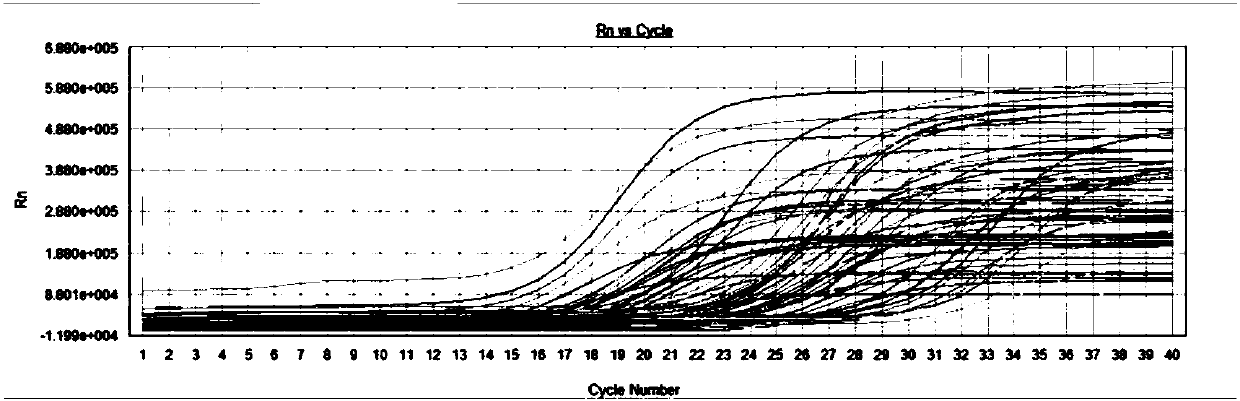
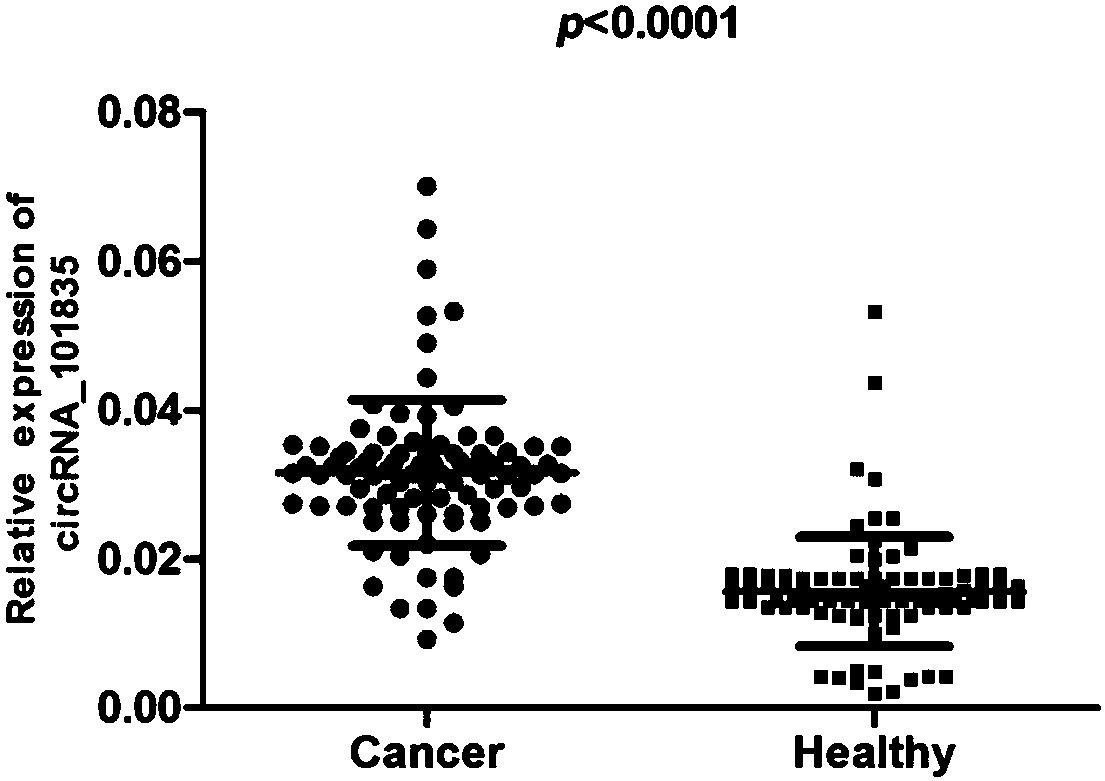
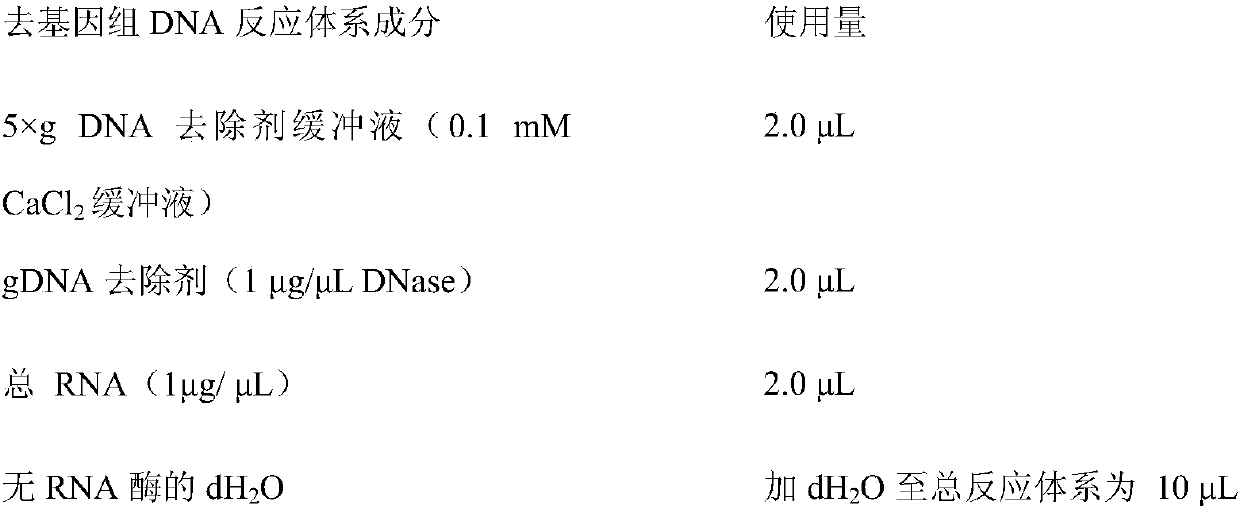
Primers, kit and method to detect circular DNA circRNA_101835 and their application
InactiveCN107858435AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescencePolymerase chain reaction
The invention relates to primers, kit and method to detect circular DNA circRNA_101835 and their application. The primers to detect circular DNA circRNA_101835 are involved. The kit includes a blood sample RNA extracting reagent, the primers, a genome-removed DNA reaction system, a reverse transcription reaction system, and a qPCR (quantitative polymerase chain reaction) operation reaction system.The invention discloses expression of the circular DNA circRNA_101835 in people with gastric cancer and normal people and the use of fluorescence quantitative PCR to detect the circular DNA circRNA_101835. The circular DNA circRNA_101835 is suitable for assisted diagnosis of gastric cancer and evaluation on cancer treatment effect and prognosis condition.
Owner:ZHENJIANG NO 1 PEOPLES HOSPITAL
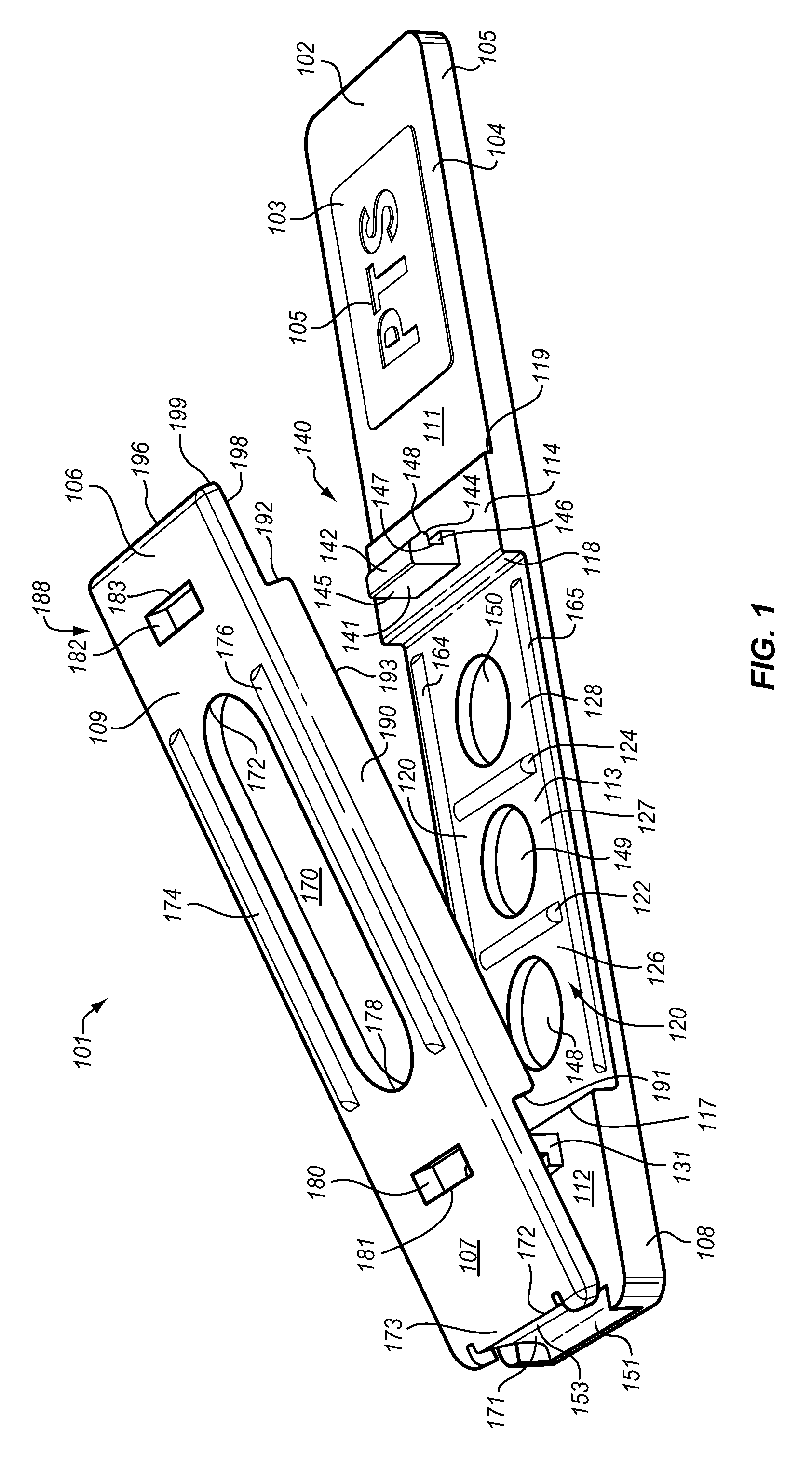
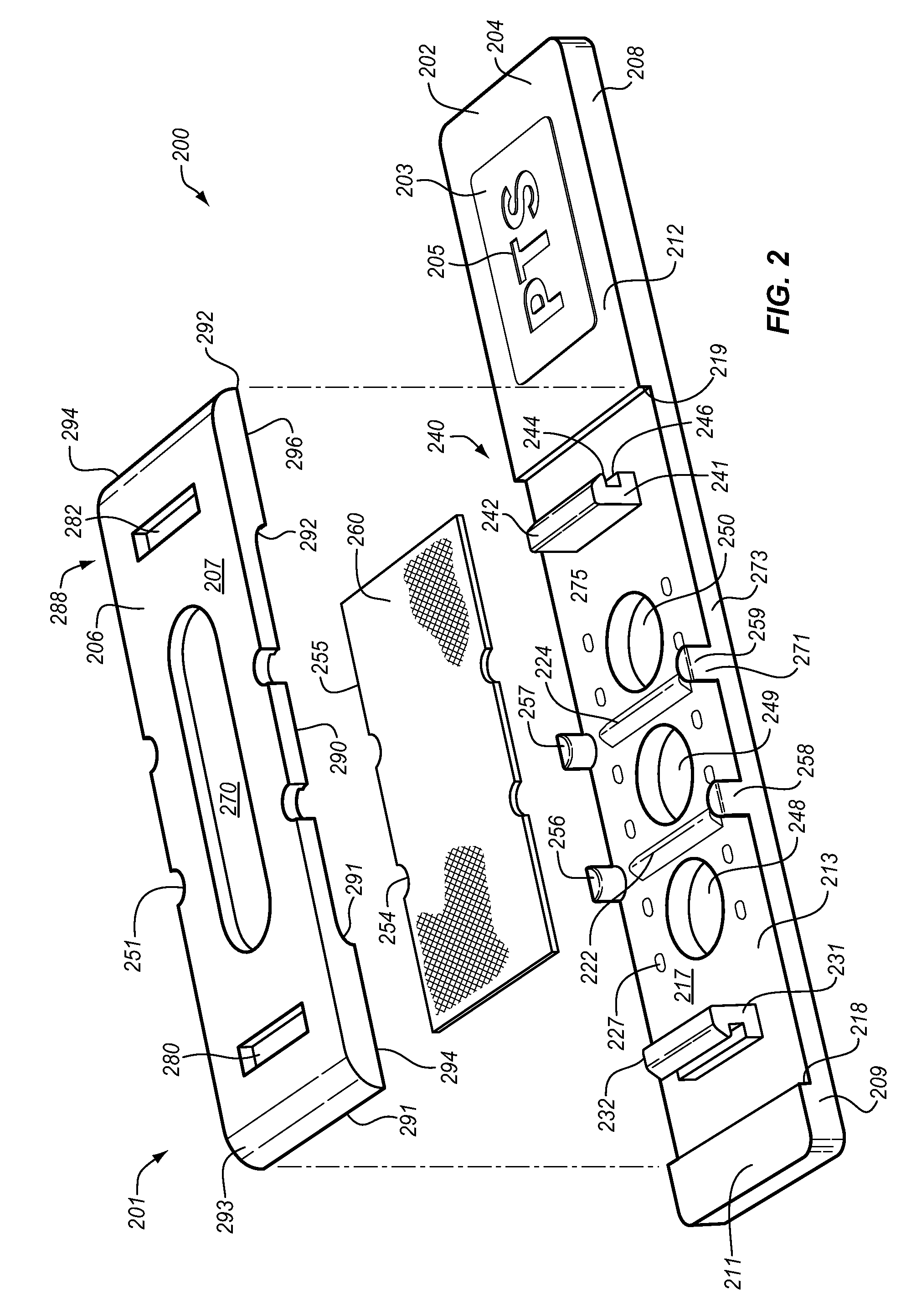
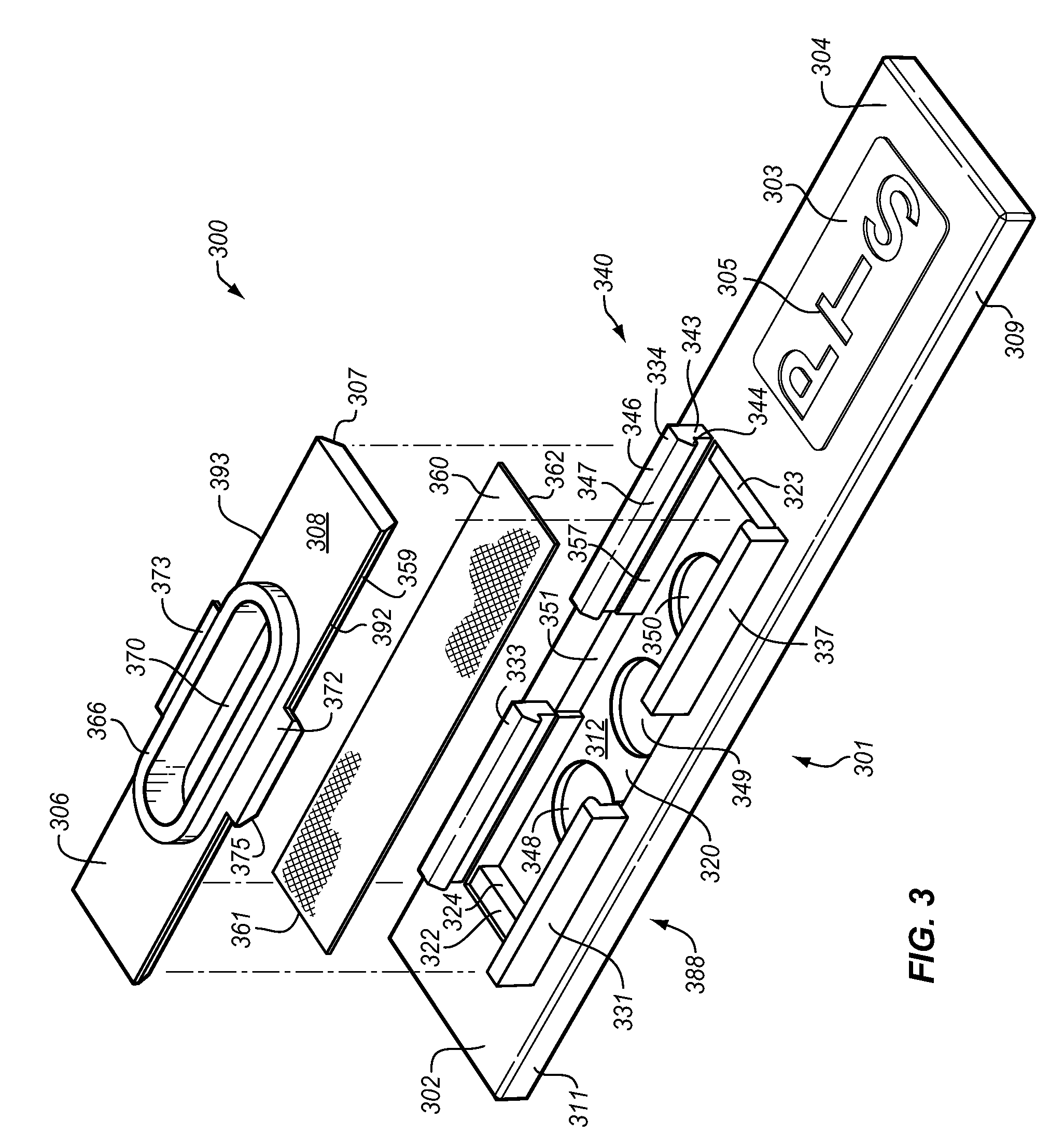
Single-use test device for imaging blood cells
This present invention relates generally to devices, systems, and methods for performing bioimaging at the microscopic scale and, more particularly, to devices and systems including a disposable testing device configured to perform bioimaging at the microscopic scale, and methods of performing the bioimaging using the disposable testing device. In some aspects, a testing device is provided for imaging blood cells in a blood sample. The testing device having a sample entry port for receiving the blood sample; a sample testing conduit fluidically connected to the sample entry port, the sample testing conduit including: (i) a planar member, (ii) a transparent planar member, and (iii) a plurality of spacer elements having an average spacer height and disposed between the planar member and the transparent planar member; and an imager chip forming at least a portion of the planar member.
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com