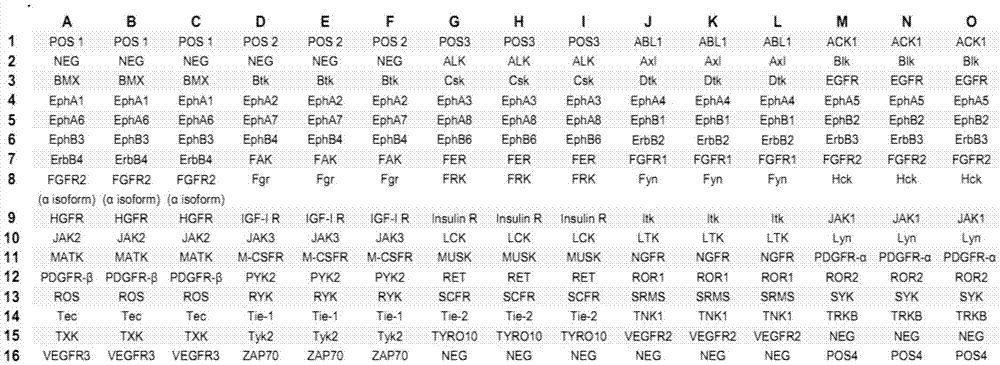
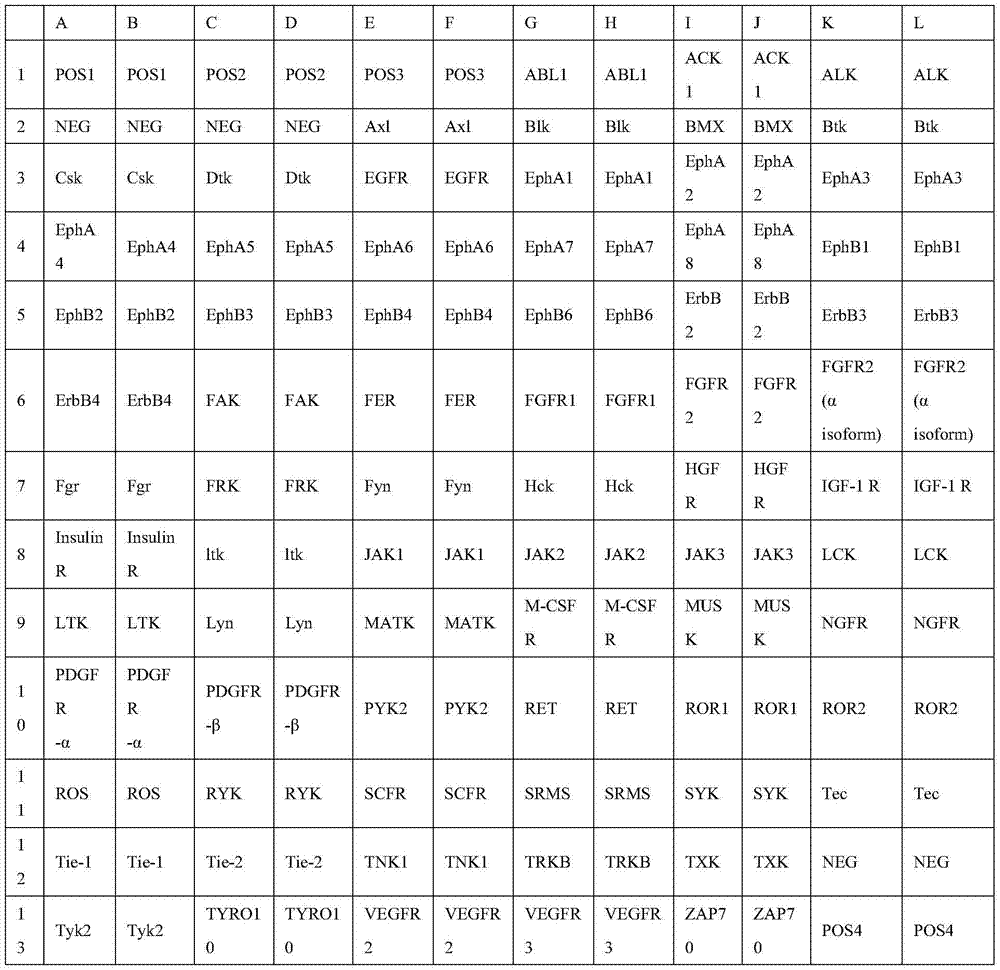
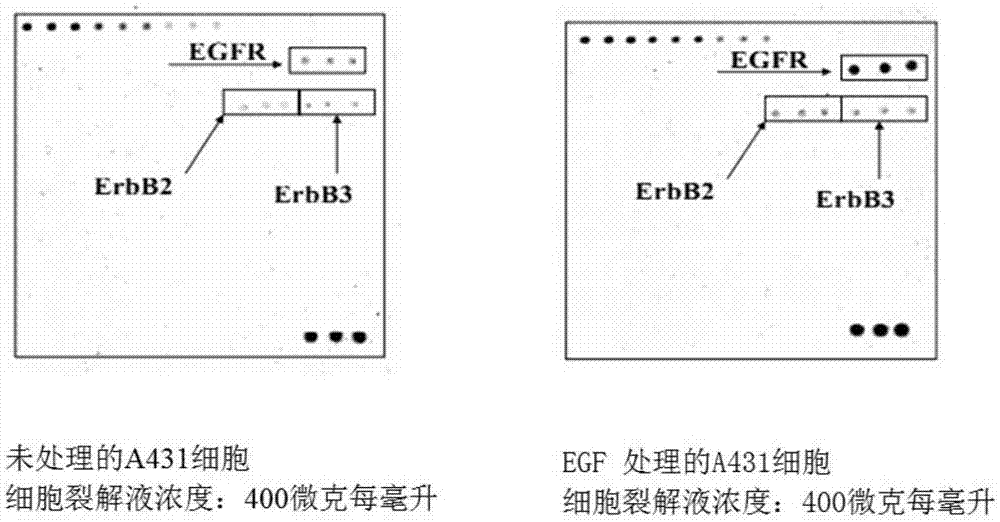
Patents
Literature
270 results about "Immunoprecipitation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
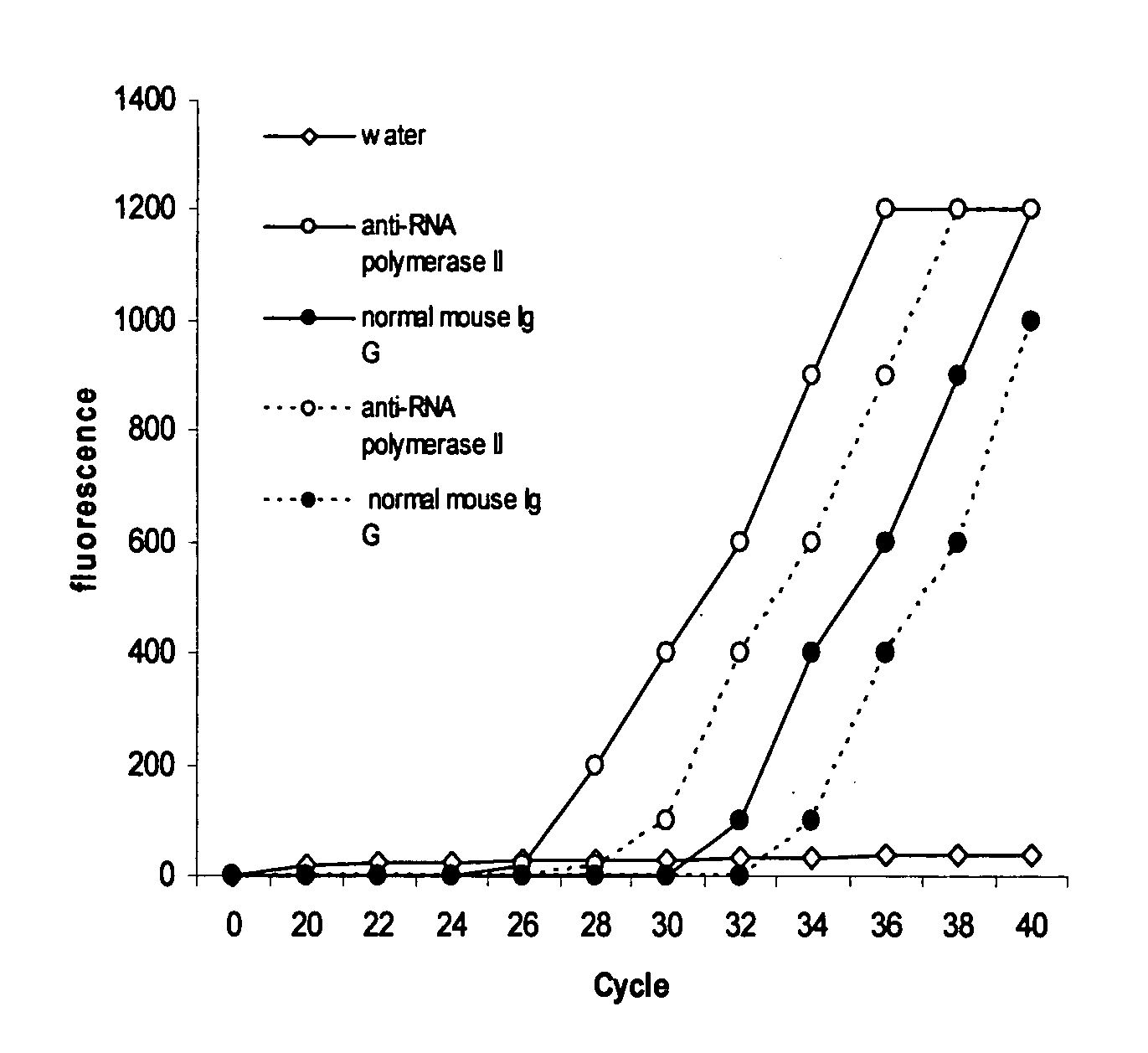
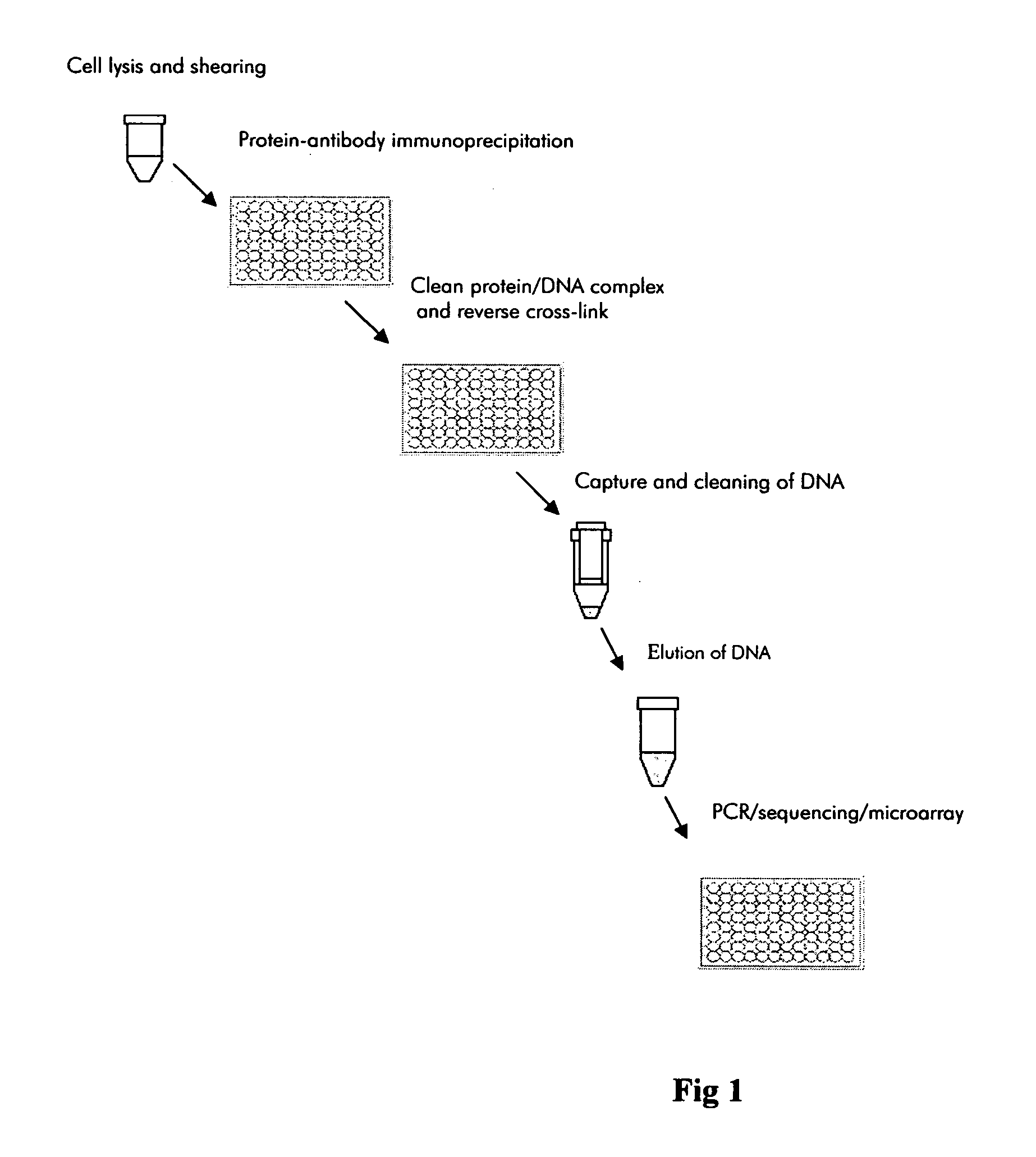
Immunoprecipitation (IP) is the technique of precipitating a protein antigen out of solution using an antibody that specifically binds to that particular protein. This process can be used to isolate and concentrate a particular protein from a sample containing many thousands of different proteins. Immunoprecipitation requires that the antibody be coupled to a solid substrate at some point in the procedure.
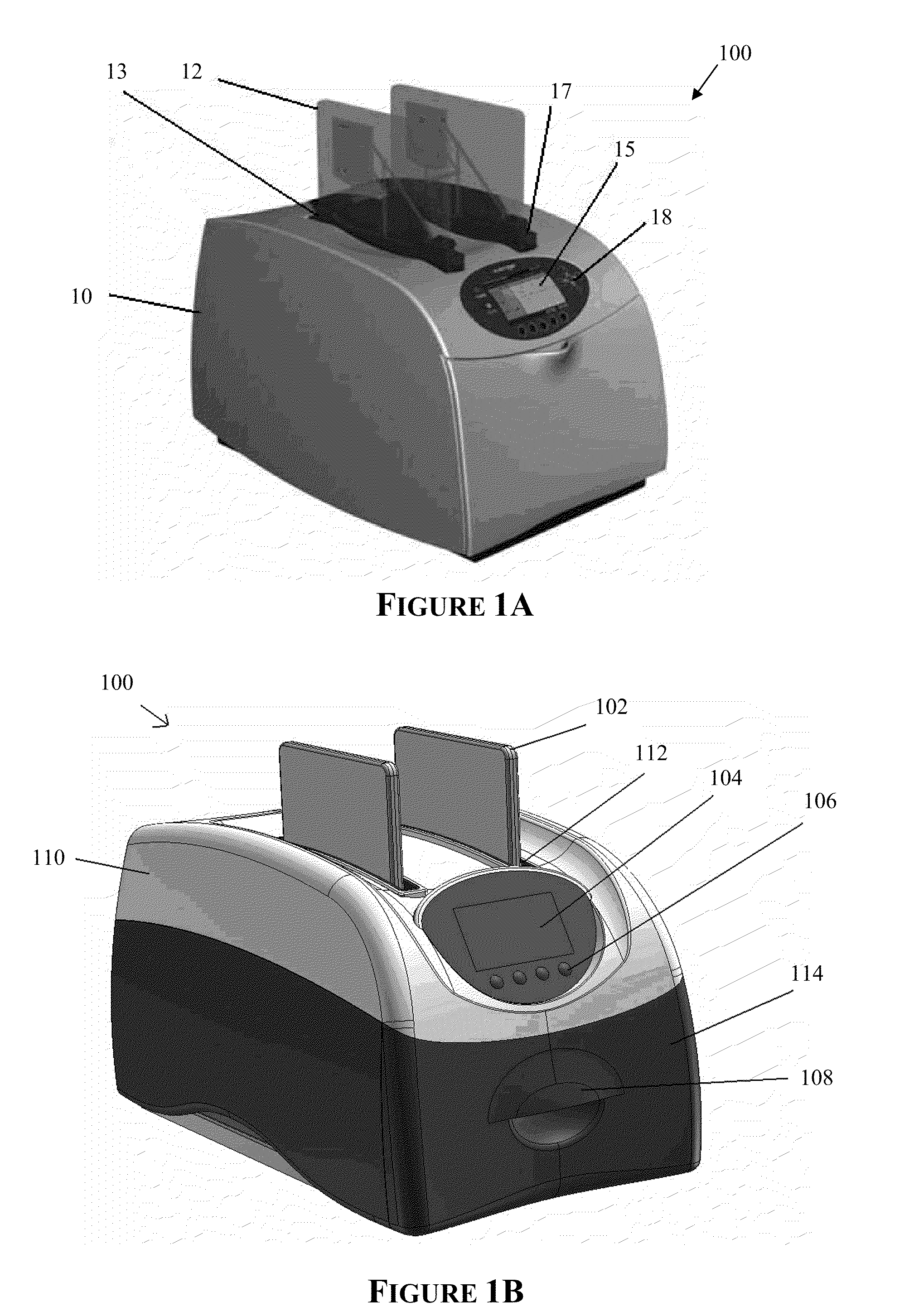
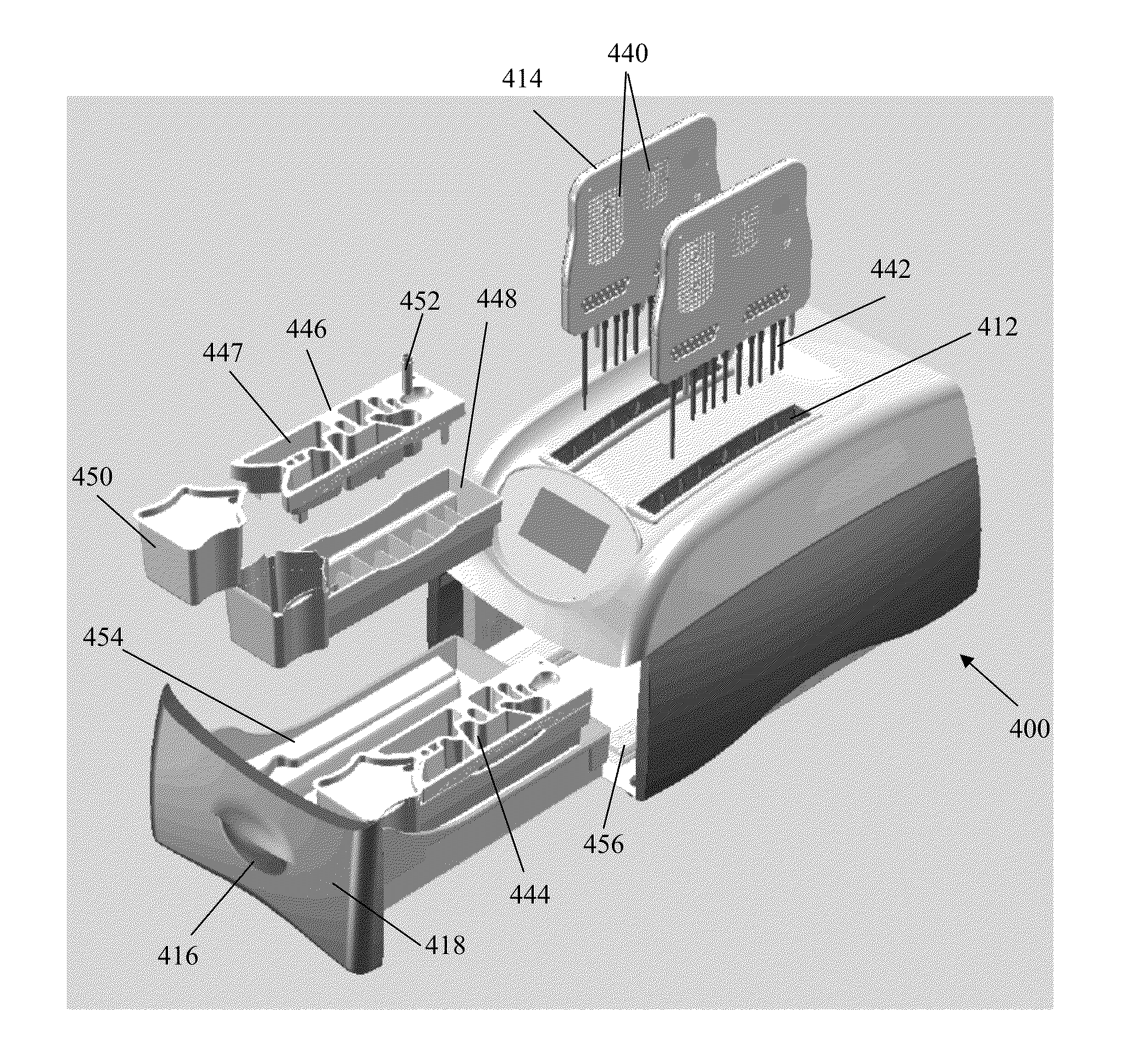
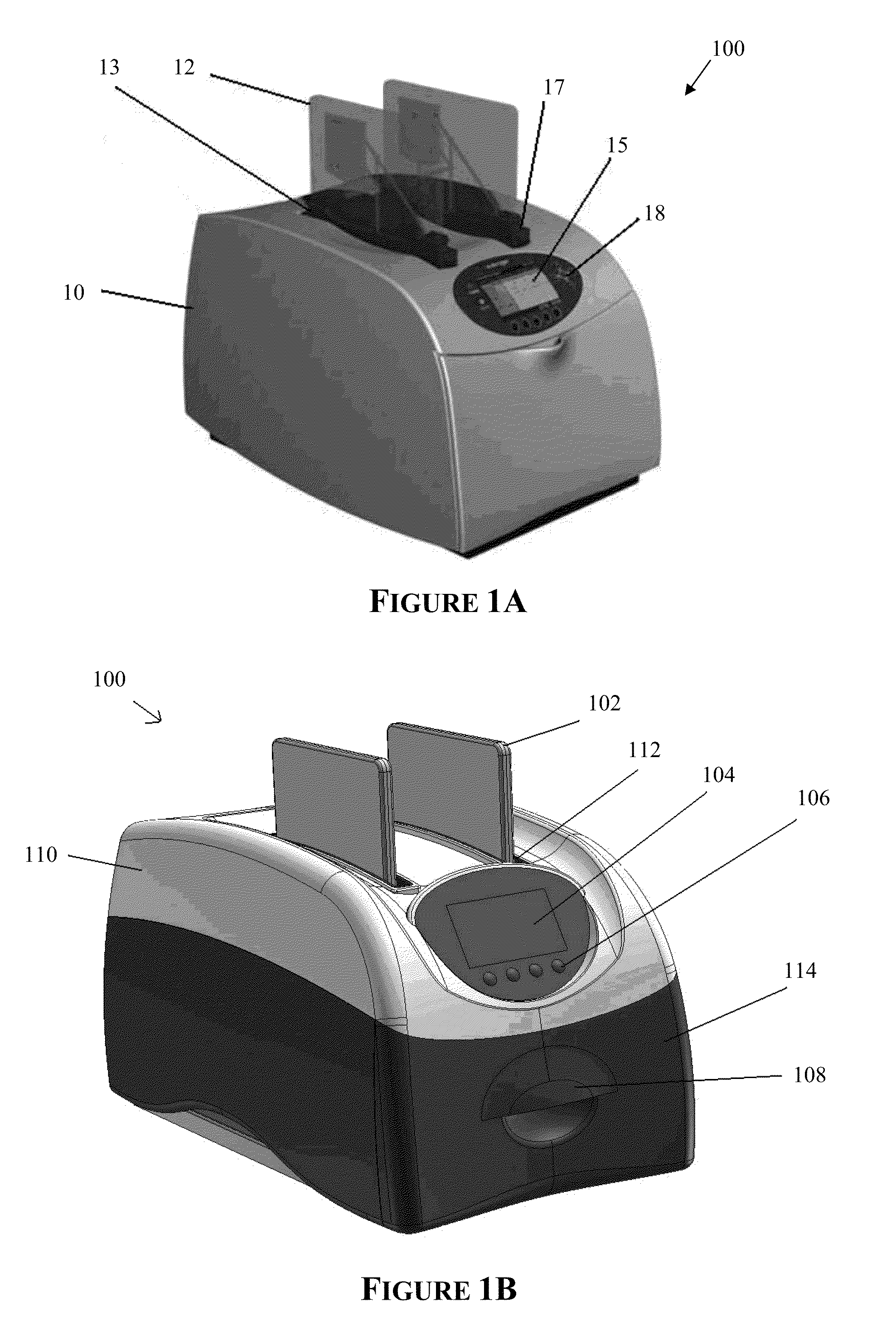
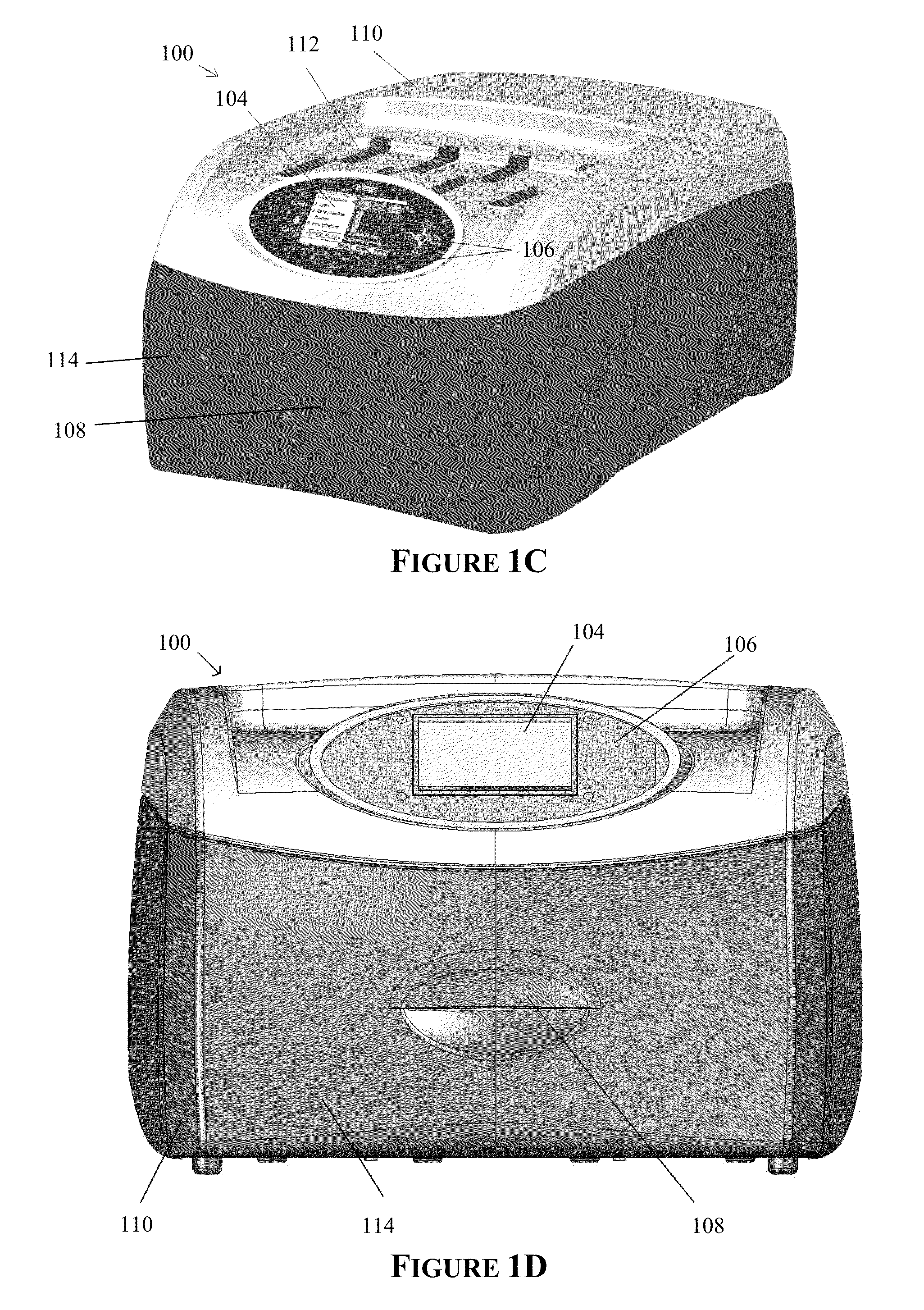
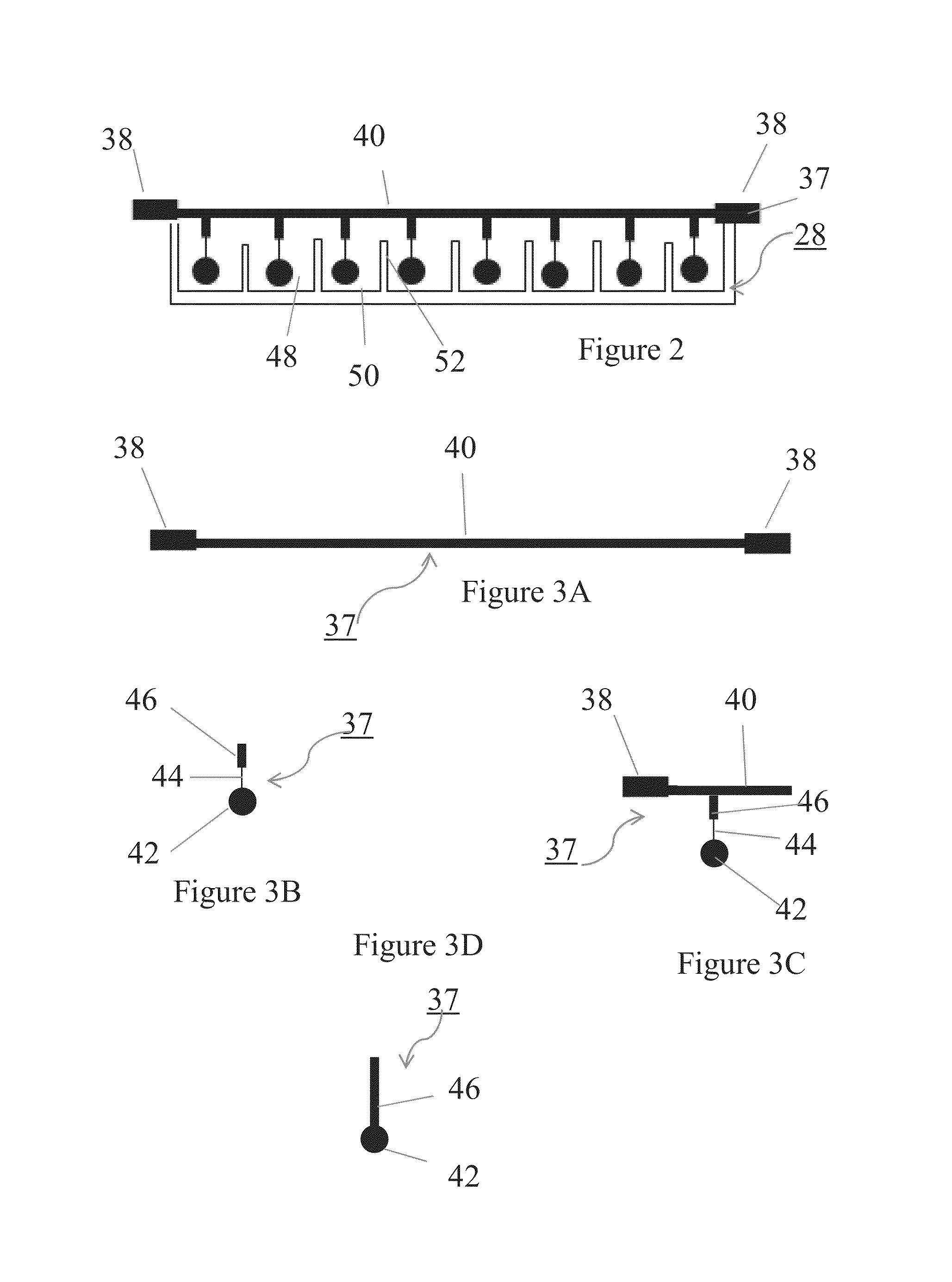
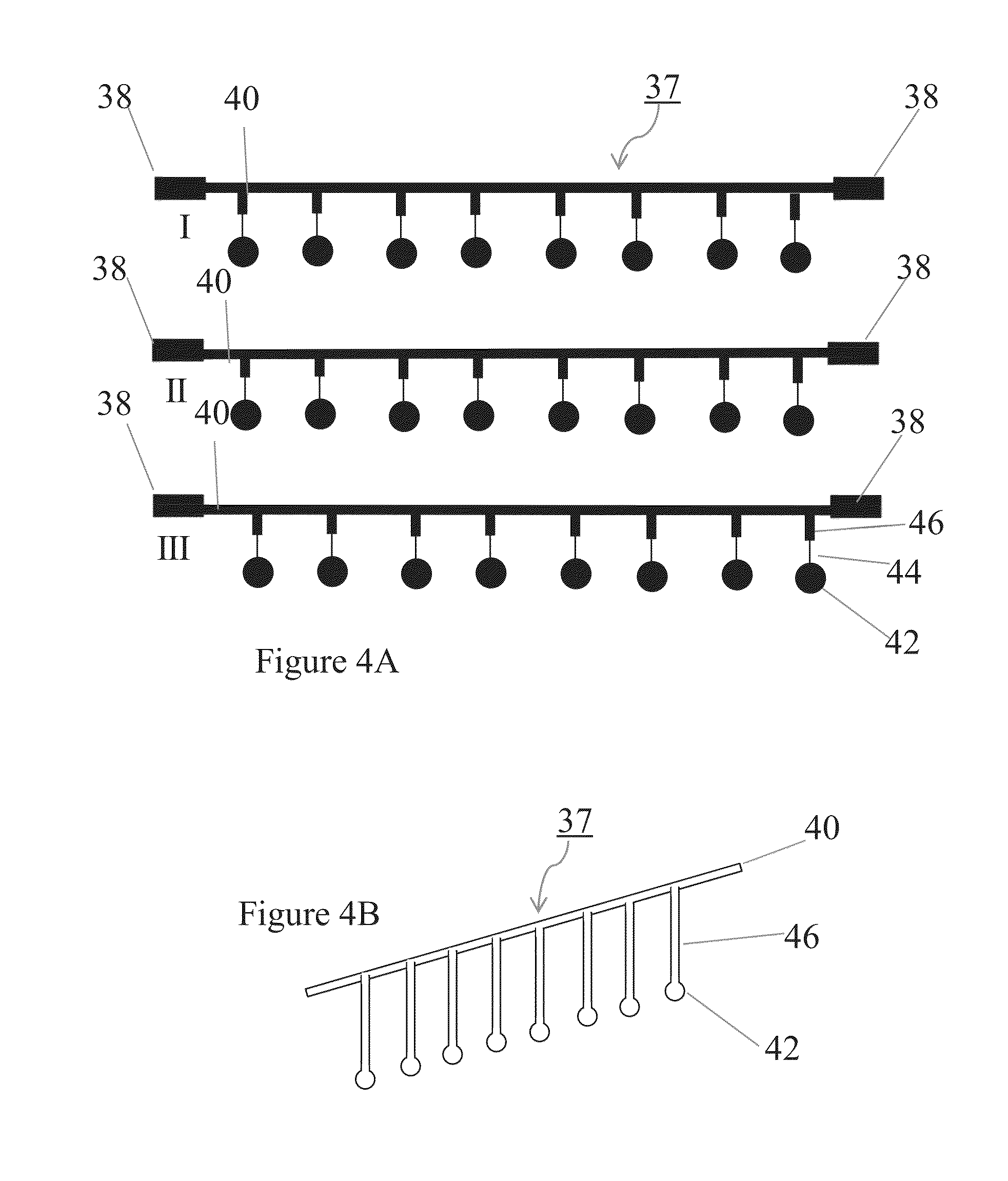
Apparatus for and method of processing biological samples
The present invention provides systems, devices, apparatuses and methods for automated bioprocessing. Examples of protocols and bioprocessing procedures suitable for the present invention include but are not limited to: immunoprecipitation, chromatin immunoprecipitation, recombinant protein isolation, nucleic acid separation and isolation, protein labeling, separation and isolation, cell separation and isolation, food safety analysis and automatic bead based separation. In some embodiments, the invention provides automated systems, automated devices, automated cartridges and automated methods of western blot processing. Other embodiments include automated systems, automated devices, automated cartridges and automated methods for separation, preparation and purification of nucleic acids, such as DNA or RNA or fragments thereof, including plasmid DNA, genomic DNA, bacterial DNA, viral DNA and any other DNA, and for automated systems, automated devices, automated cartridges and automated methods for processing, separation and purification of proteins, peptides and the like.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Rapid way to obtain high expression clones of mammalian cells using a methylcellulose and immunoprecipitation screening method
InactiveUS20050118652A1High throughput screeningImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsPeptide preparation methodsHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsScreening method
The invention provides a genetic screening method for identifying a transfected cell expressing the polypeptide of interest. The methods allows for high throughput screening of recombinant cells for elevated levels of expression of the polypeptide of interest. The invention also provides capture media, formulations and methods of making and using thereof.
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
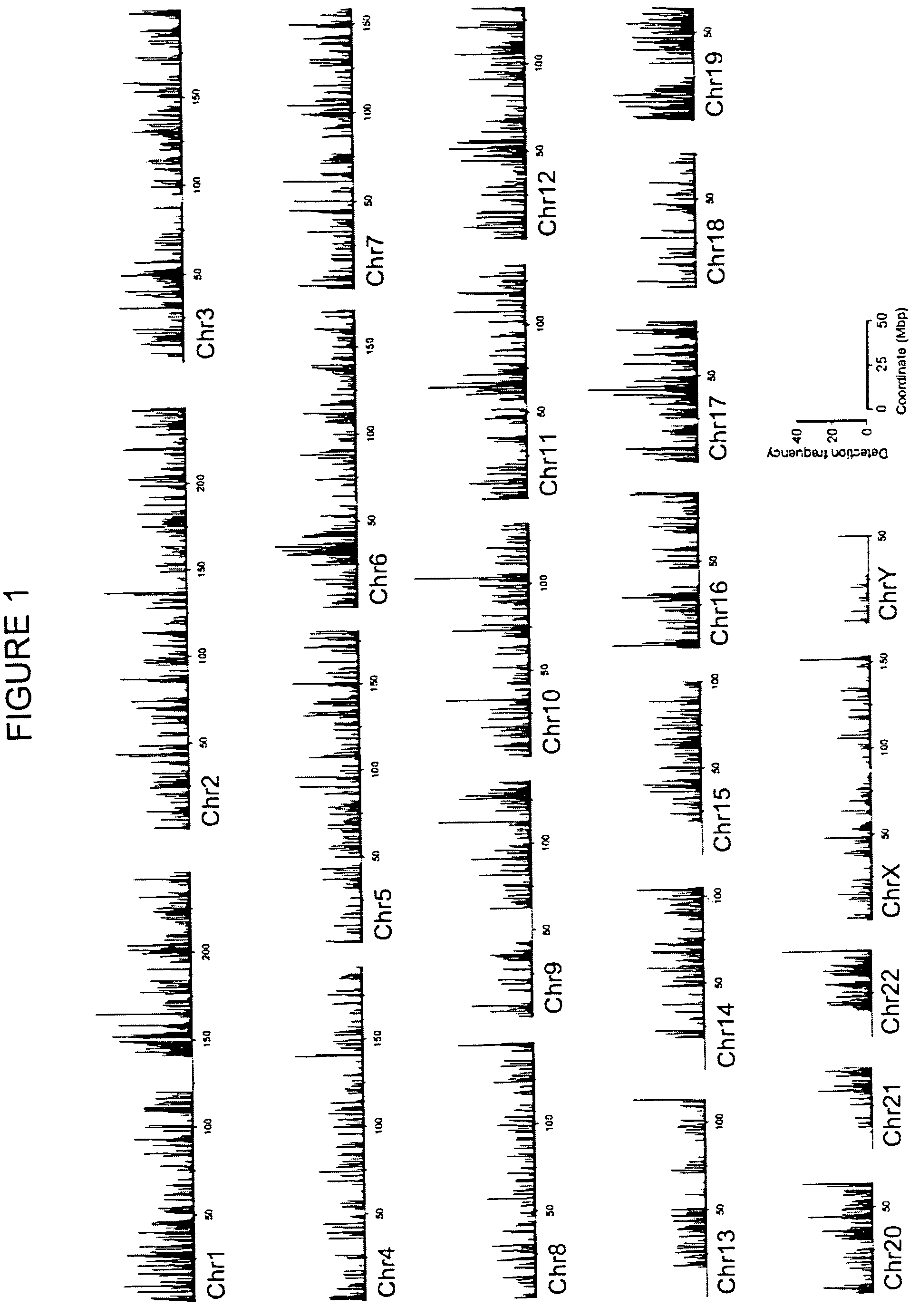
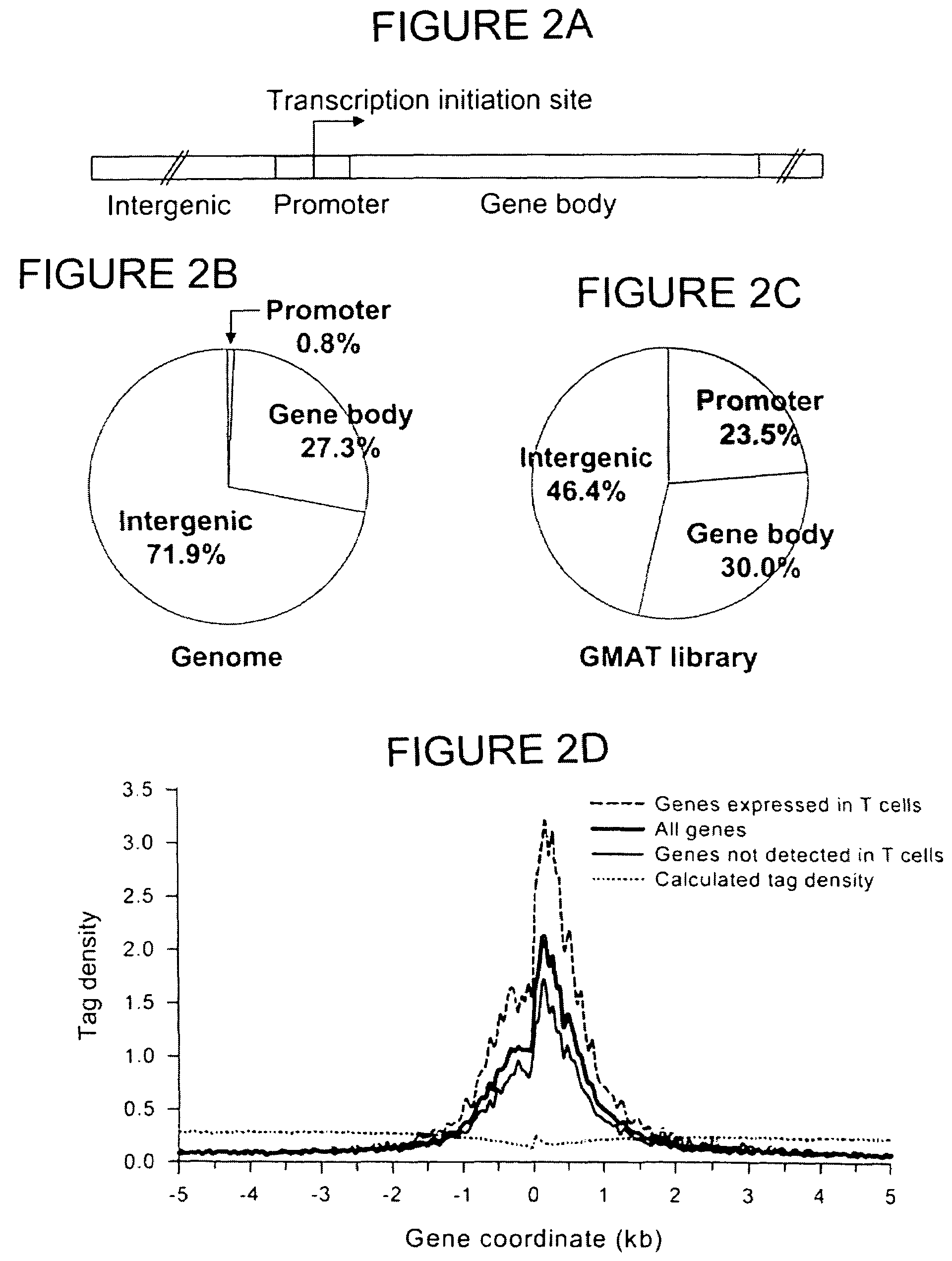
Method of identifying active chromatin domains
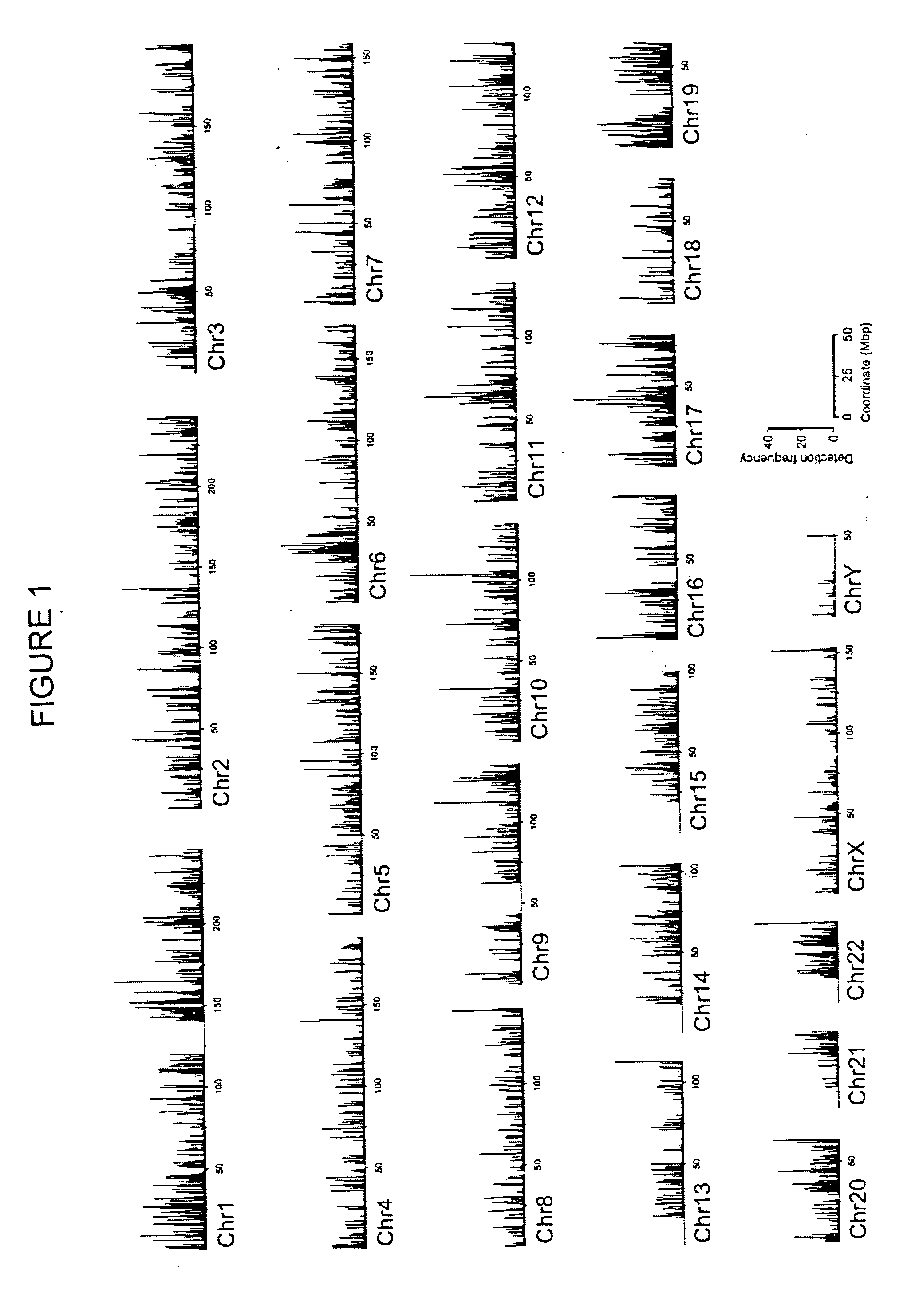
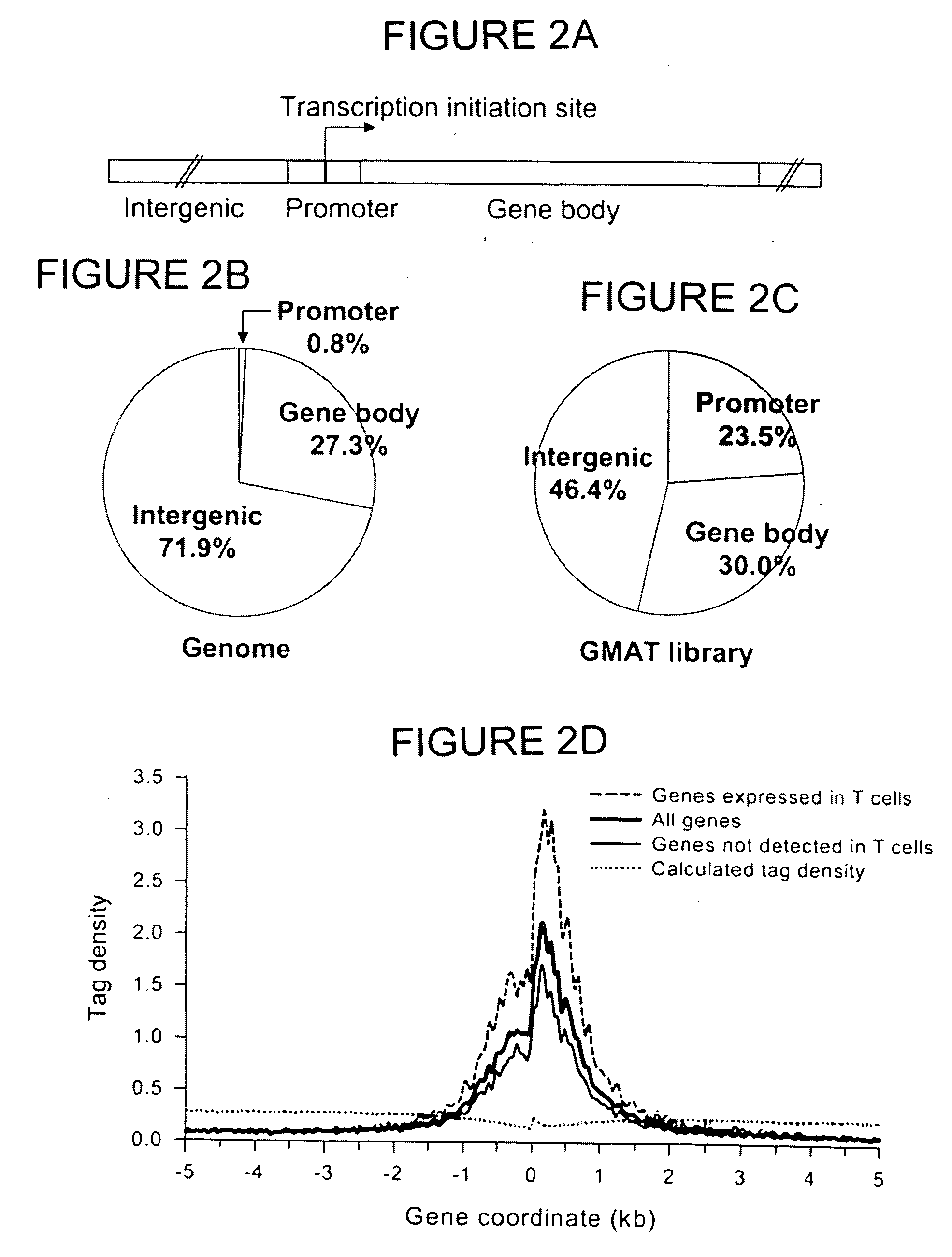
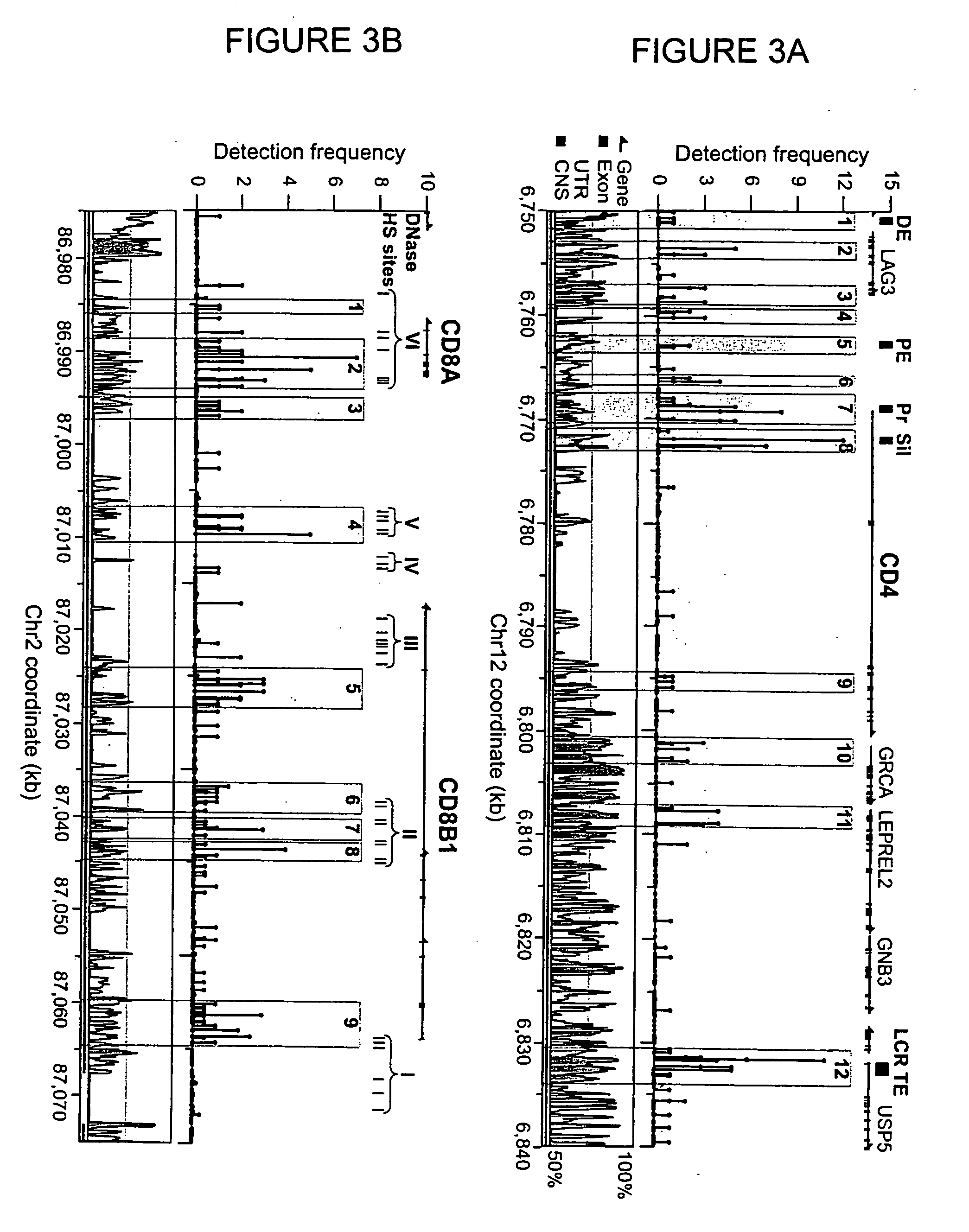
The invention provides a method of mapping DNA-protein interactions within a genome by fixing living cells to cross-link DNA and proteins, lysing the cells, and isolating chromatin by immunoprecipitation. DNA is purified and a SAGE protocol is performed on the purified DNA to produce GMAT-tag sequences, which are compared to a genomic sequence of the living cells to map DNA-protein interactions. The invention further provides a method of identifying an active chromatin domain and a method of identifying aberrant chromatin acetylation, wherein chromatin immunoprecipitation is performed using an antibody recognizing acetylated histone protein.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE US REPRESENTED BY THE SEC
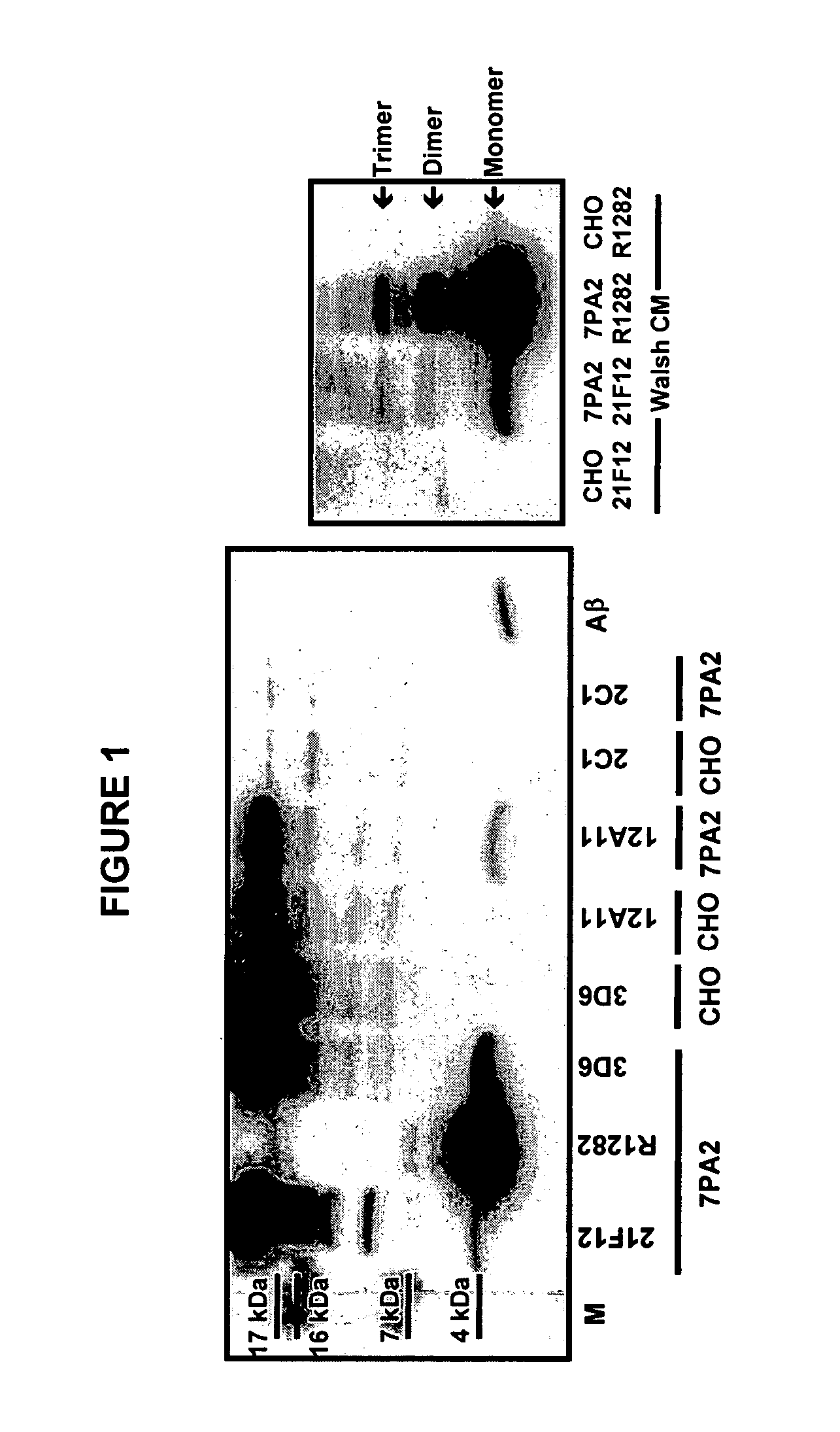
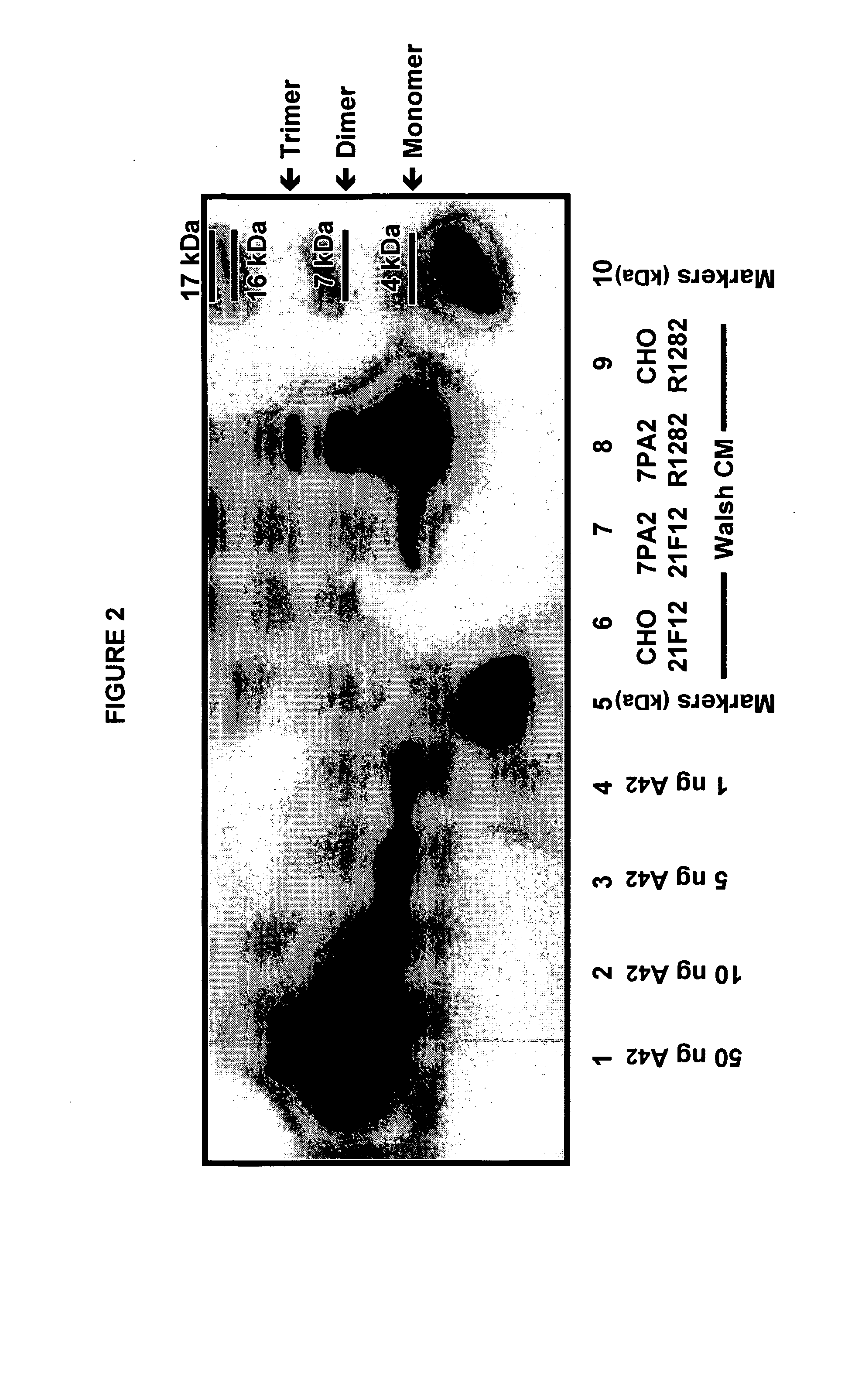
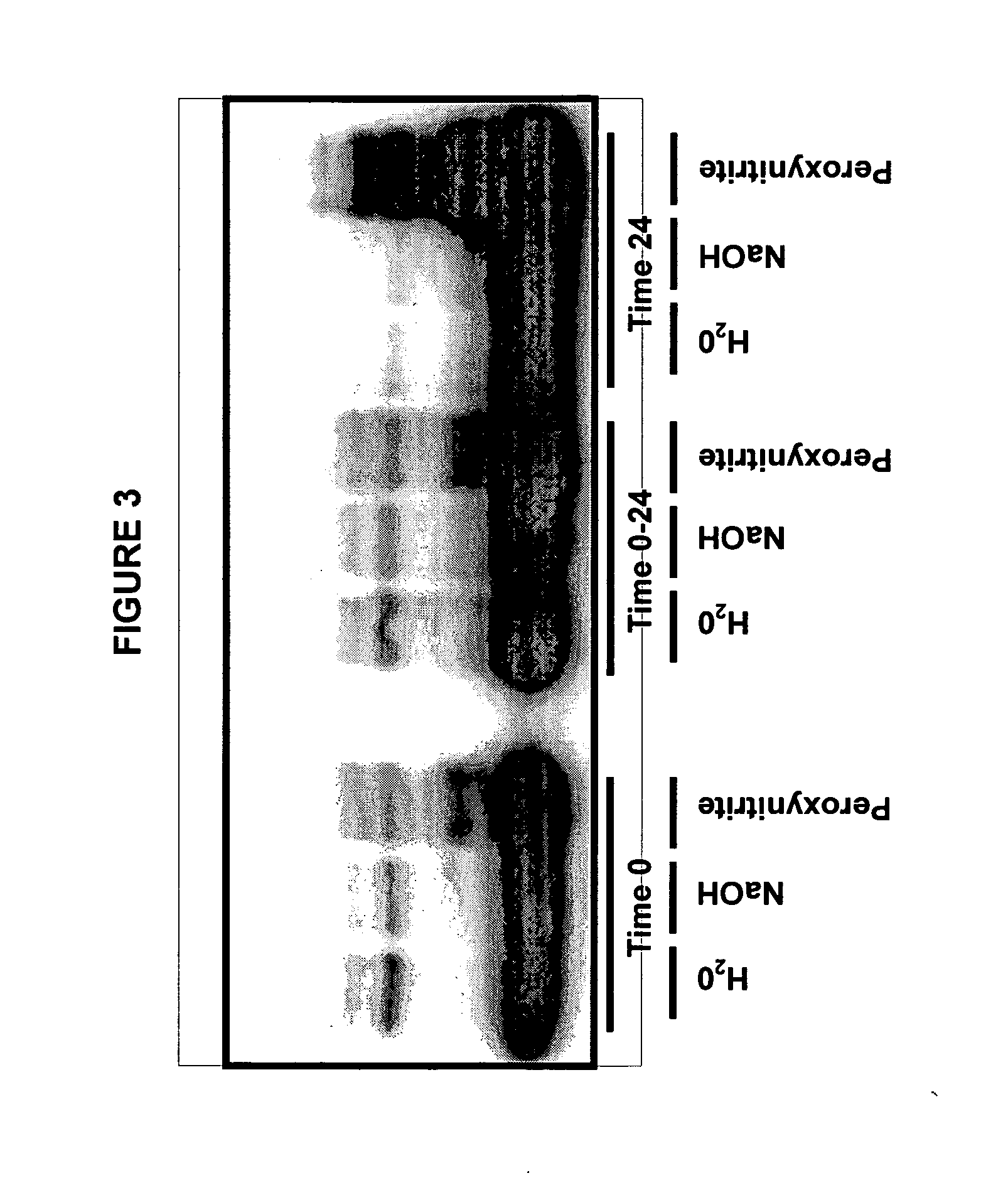
Immunoprecipitation-based assay for predicting in vivo efficacy of beta-amyloid antibodies
InactiveUS20060240486A1Rapid improvement in cognitionImprove bindingCompound screeningApoptosis detectionAβ oligomersAmyloid
In various aspects, the present invention provides methods and kits for predicting the therapeutic efficacy of an immunological reagent, identifying an immunological reagent having therapeutic efficacy, or both, for the treatment of an amyloidogenic disorder by comparing the amount of Aβ monomer in an Aβ preparation which binds to the immunological reagent to an amount of one or more Aβ oligomers in the Aβ preparation which bind to the immunological reagent to determine a relative bound amount, and predicting the efficacy of the immunological reagent, identifying an immunological reagent having therapeutic efficacy, or both, for the treatment of an amyloidogenic disorder based at least on the relative bound amount.
Owner:JANSSEN ALZHEIMER IMMUNOTHERAPY +1
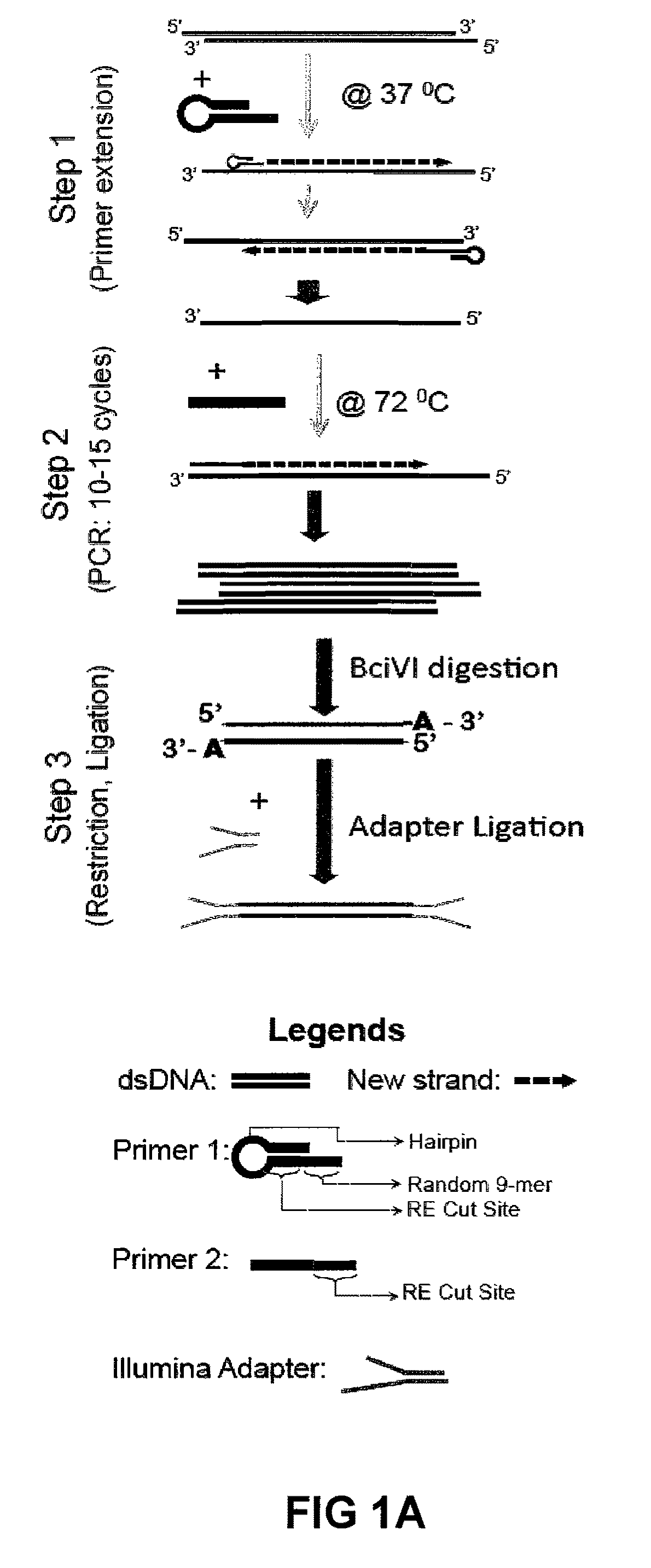
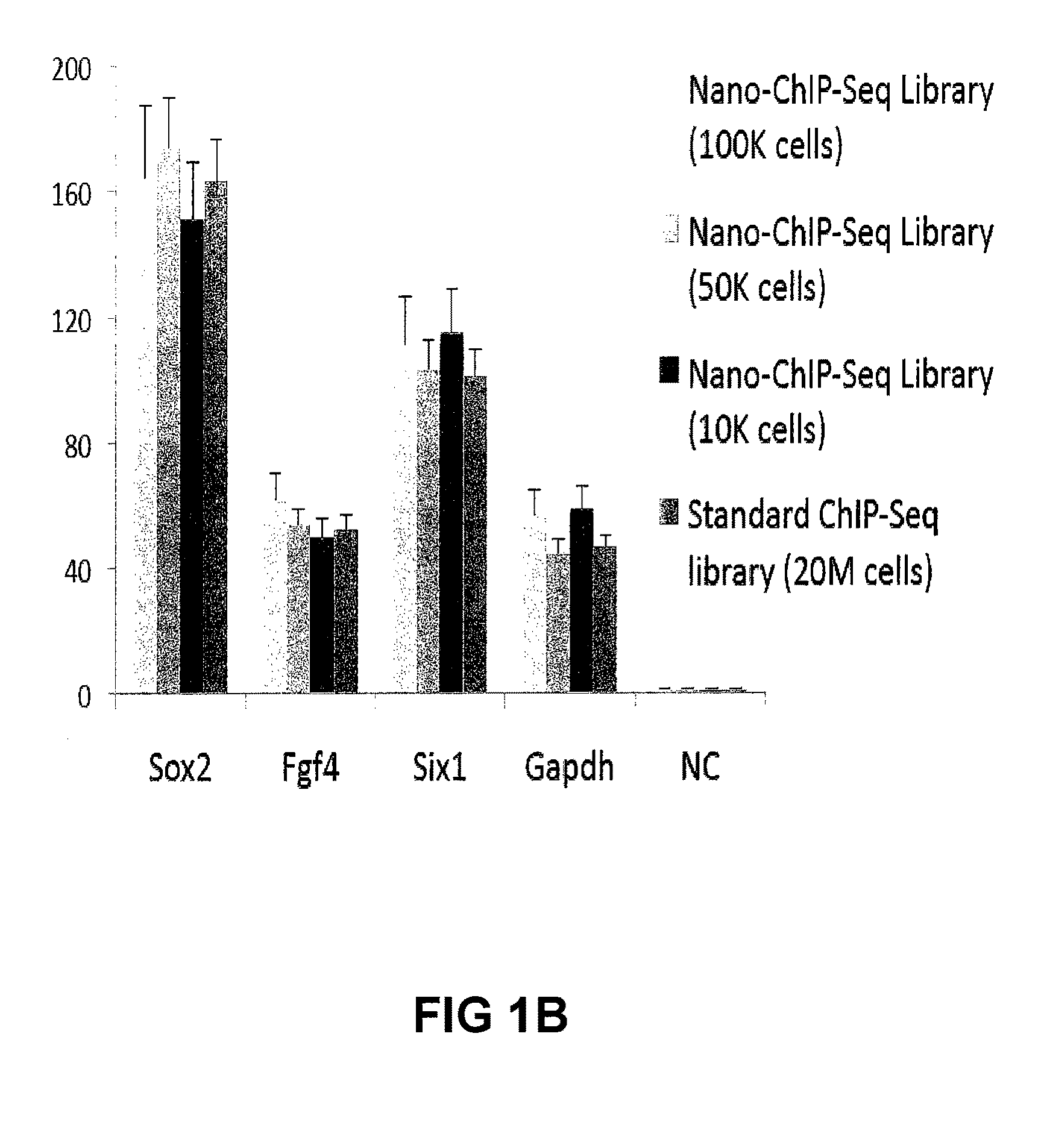
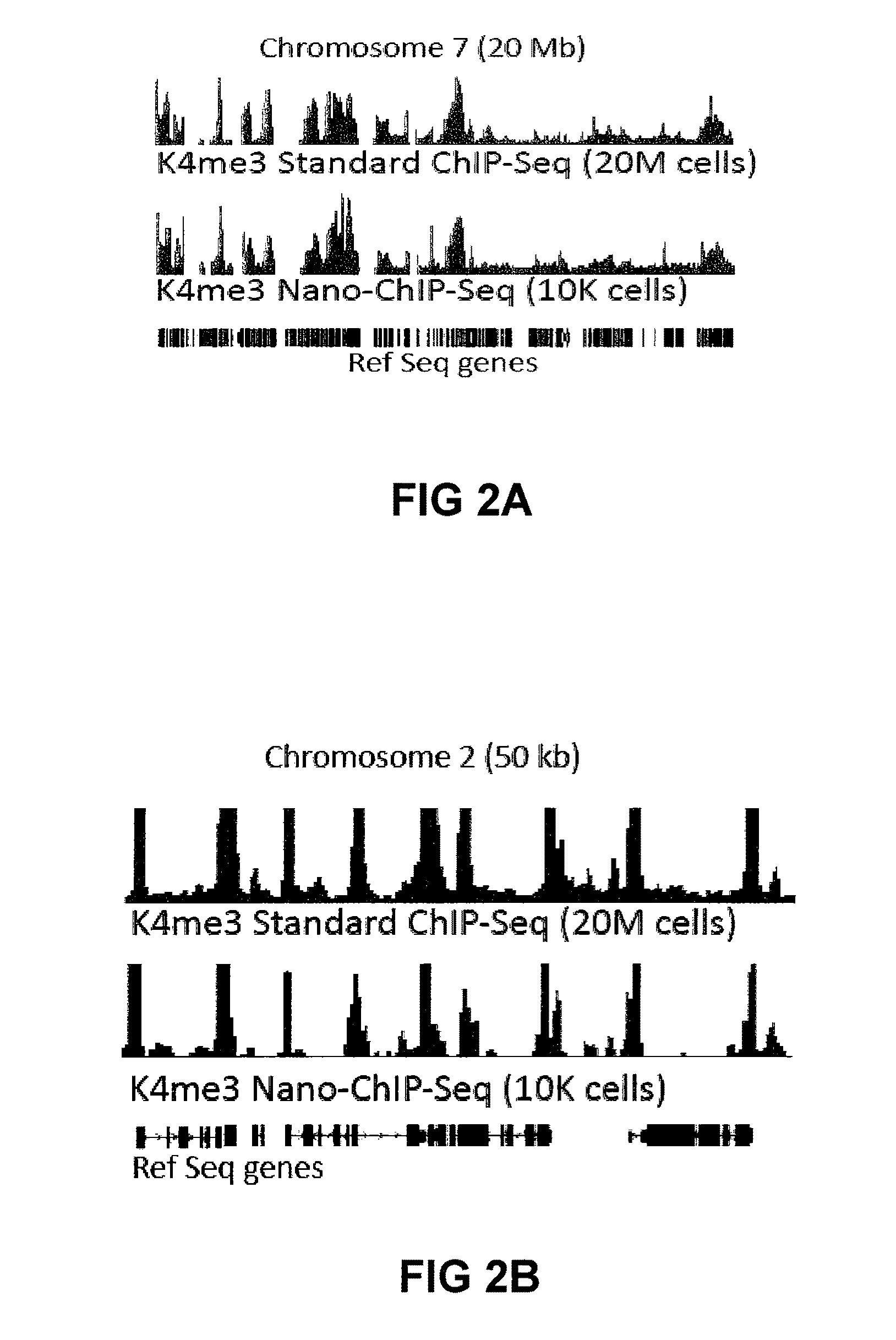
Methods For Preparing Sequencing Libraries
ActiveUS20110189677A1Reduce the amount requiredSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementImproved methodOrder of magnitude
Improvements in chromatin immunoprecipitation-high throughput sequencing techniques has allowed the creation of chromatin maps from limited biological sample sizes that cannot be evaluated using conventional chromatin immunoprecipitation-sequencing protocols. For example, a modified universal primer is utilized that incorporates restriction enzymes into chromatin immunoprecipitation fragments before amplification. The improved method allows the sample sizes to be several orders of magnitude less than that required for standard ChIP-Seq techniques.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
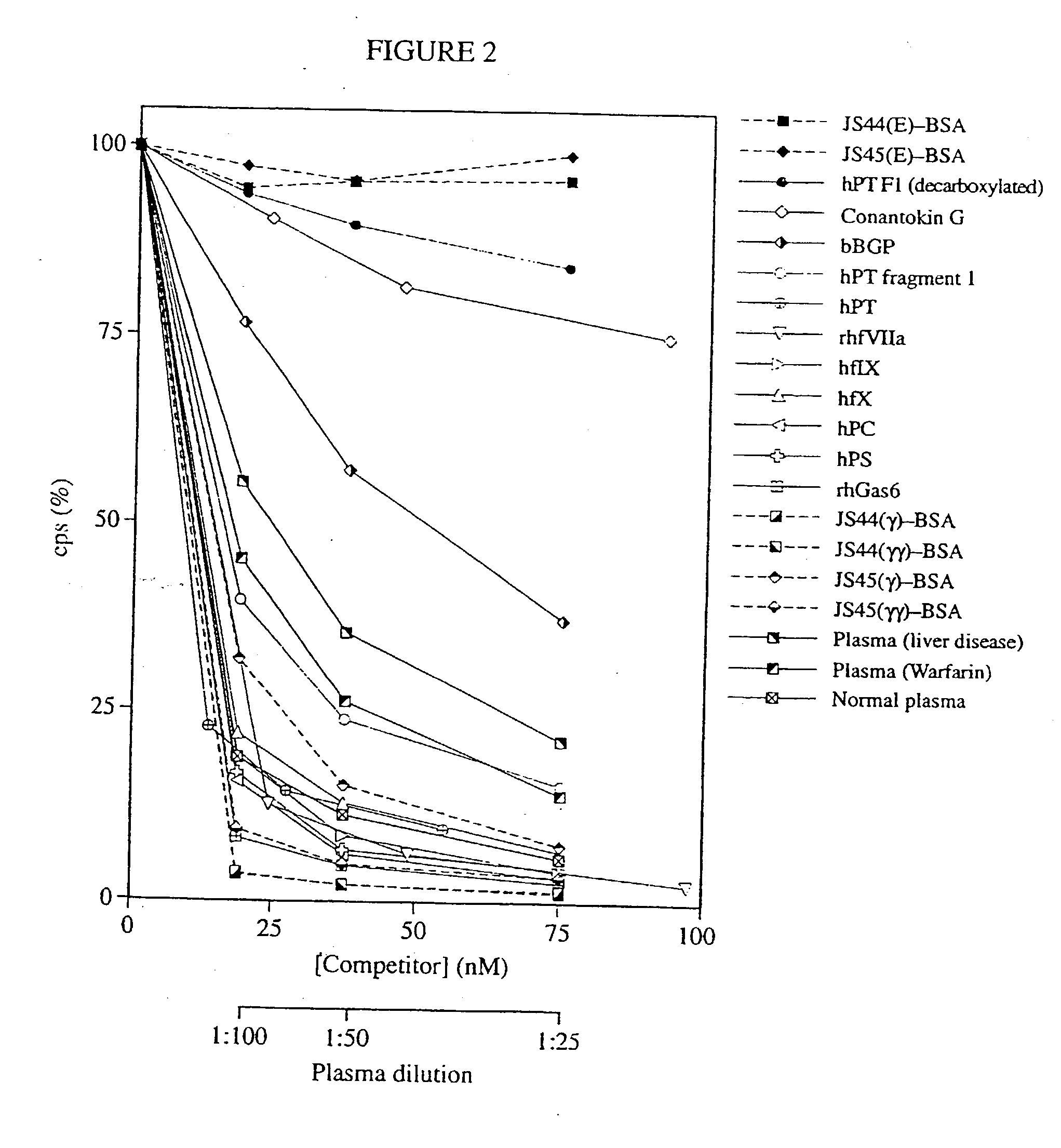
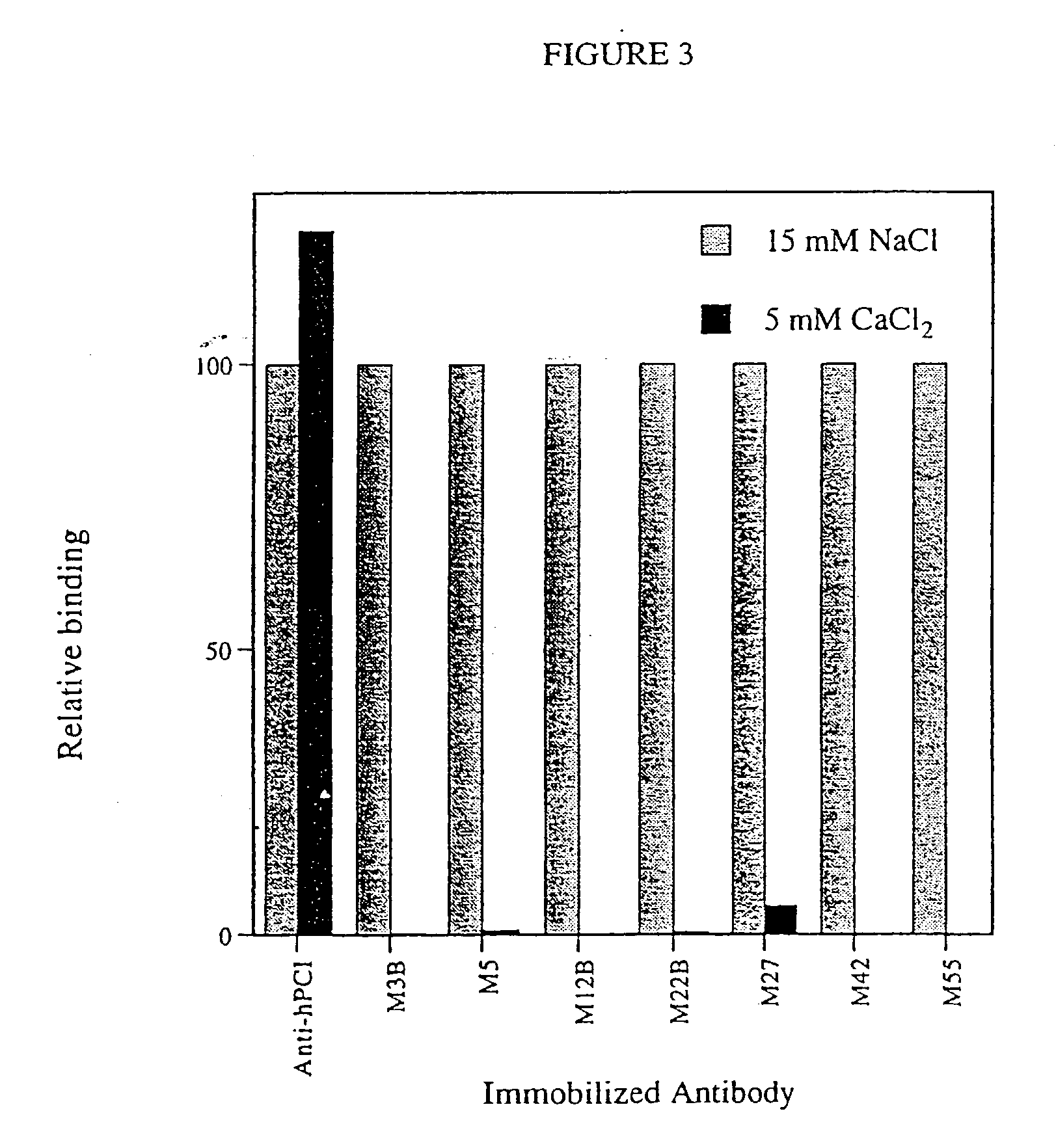
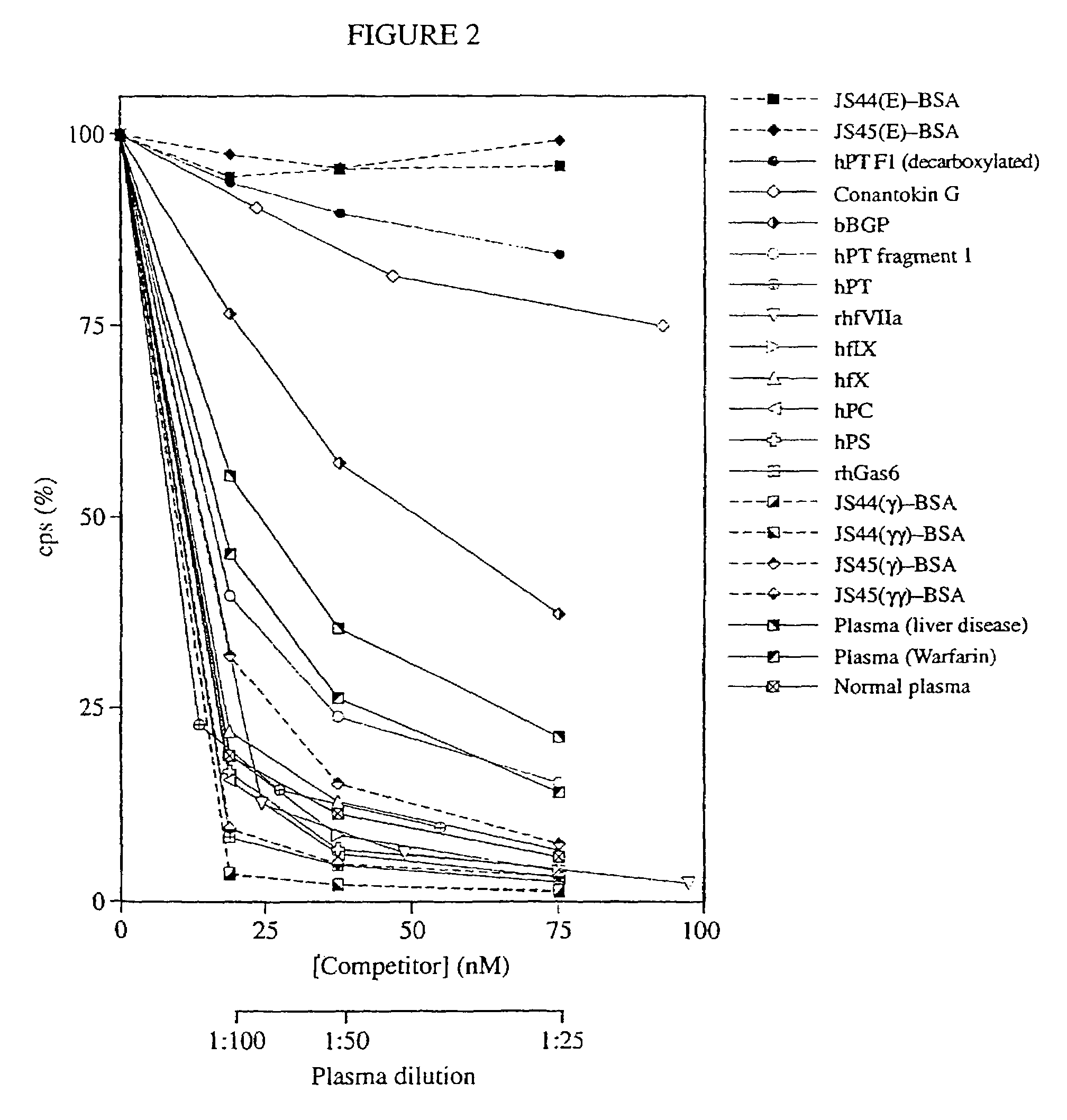
Antibodies binding a gamma carboxyglutamic acid displaying epitope
Antibodies are described, which are suitable for identification of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid (Gla), said antibodies having an ability of identifying Gla residues in proteins and / or peptides, while not reacting with glutamic (Glu) residues in corresponding proteins and / or peptides. Methods for the preparation and identification of said antibodies as well as methods for detection of Gla in biological fluids, tissue extracts, tissue specimens, in which methods said antibodies are used, are also described. There is also described the use of said antibodies for immunopurification of Gla-containing proteins or peptides by, for instance, immunoprecipitation or immunoaffinity chromatography.
Owner:BIOMEDICA DIAGNOSTICS INC +1
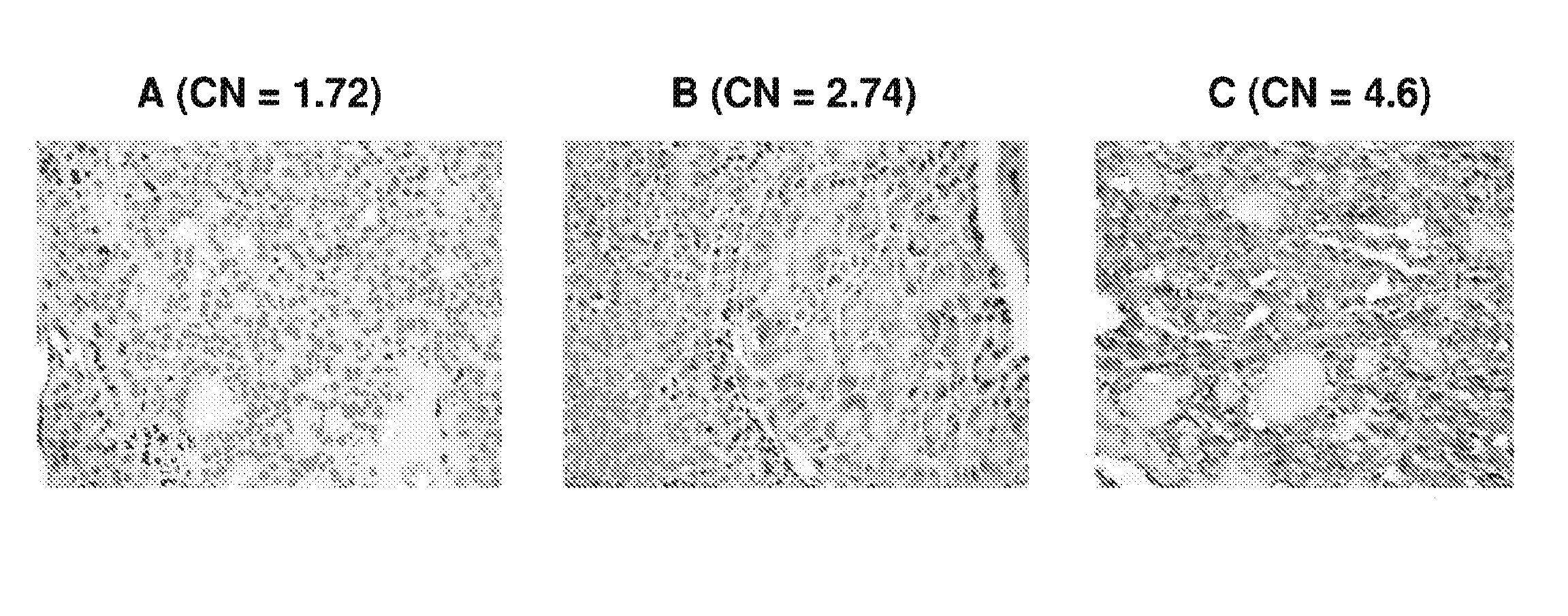
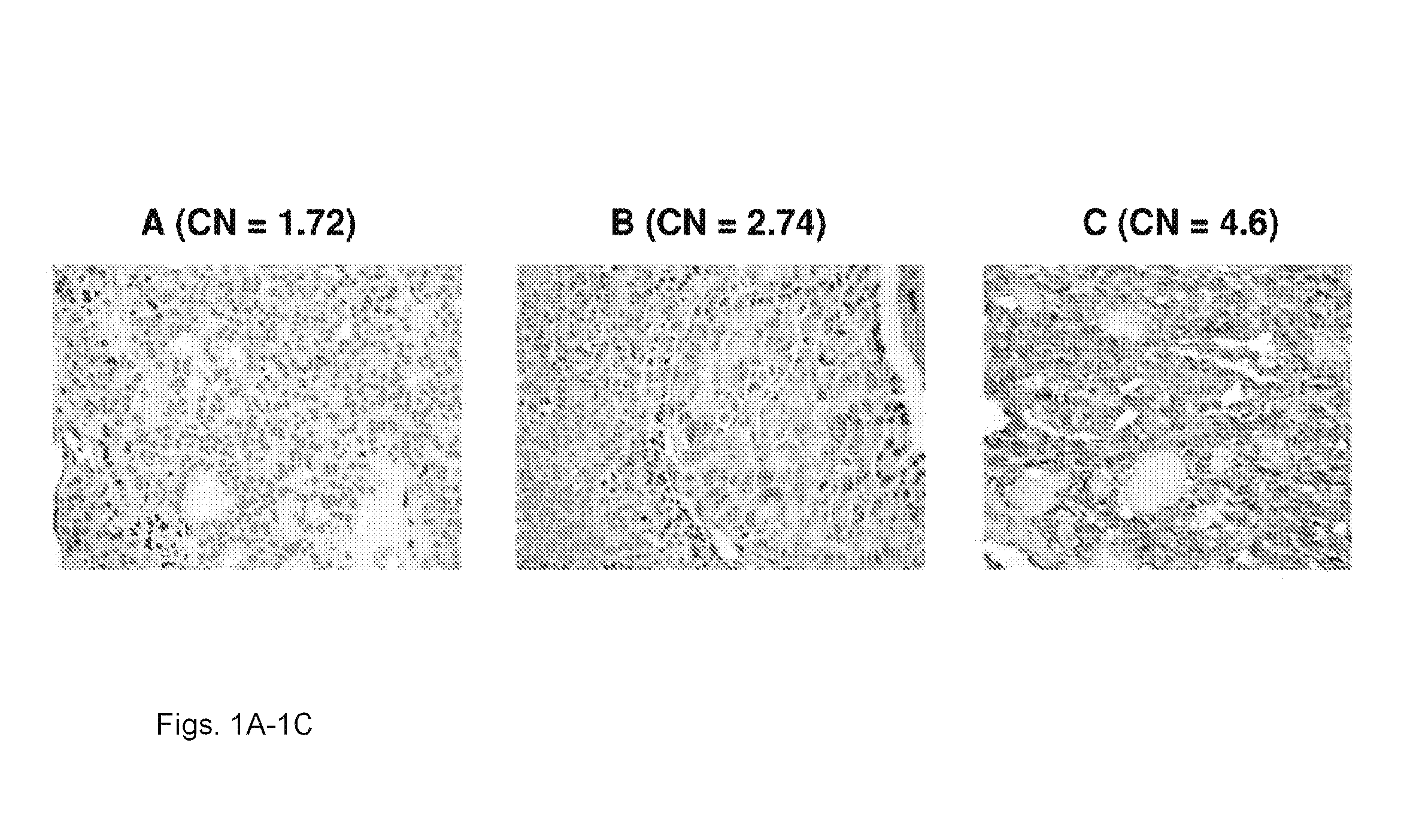
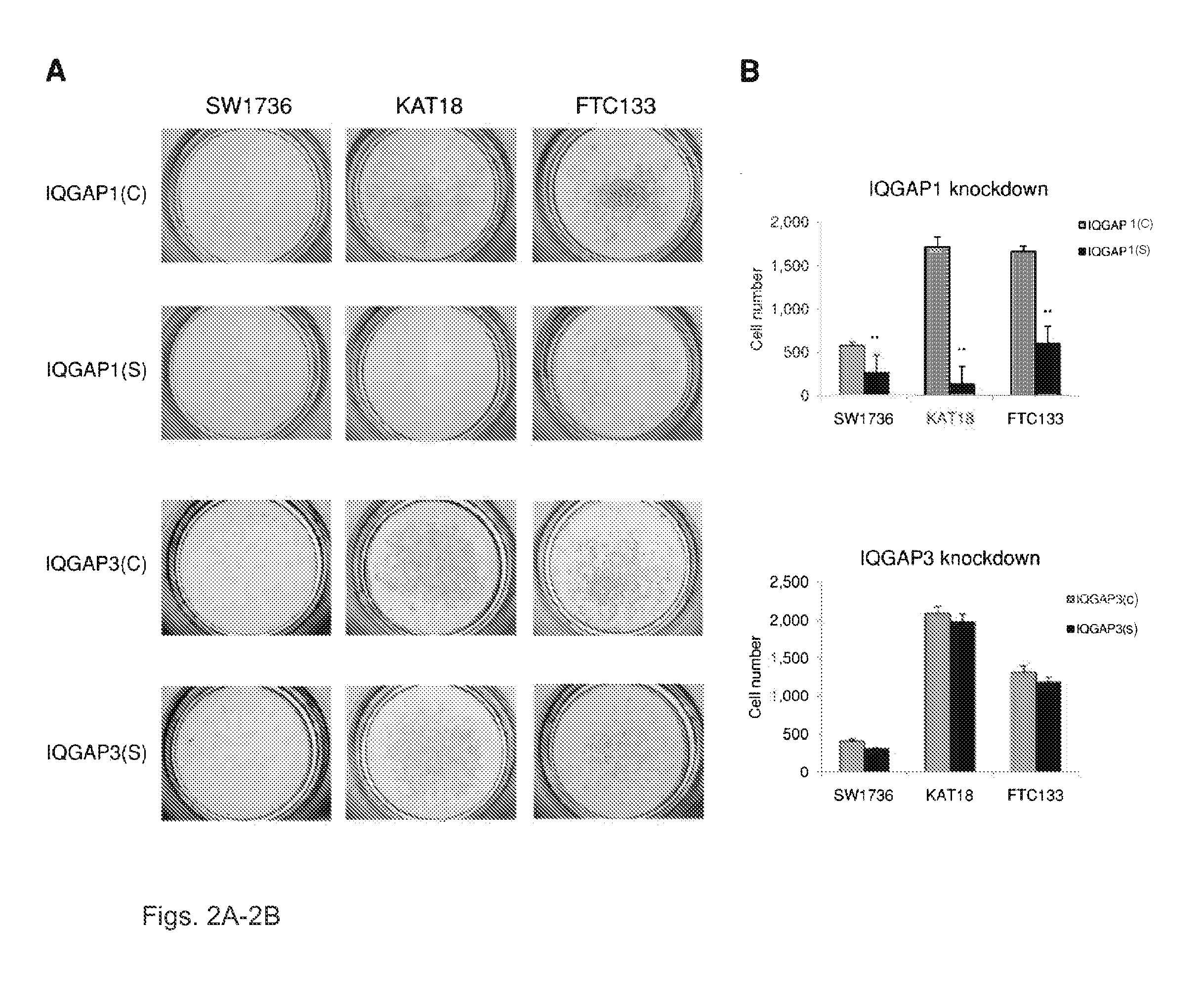
Genetic amplification of IQGAP1 in cancer
ActiveUS9157123B2Diminish invasivenessReduce spreadOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesCell invasionFollicular thyroid cancer
We examined IQGAP1 copy gain and its relationship with clinicopathologic outcomes of thyroid cancer and investigated its role in cell invasion and molecules involved in the process. We found IQGAP1 copy number (CN) gain ?3 in 1 of 30 (3%) of benign thyroid tumor, 24 of 74 (32%) follicular variant papillary thyroid cancer (FVPTC), 44 of 107 (41%) follicular thyroid cancer (FTC), 8 of 16 (50%) tall cell papillary thyroid cancer (PTC), and 27 of 41 (66%) anaplastic thyroid cancer, in increasing order of invasiveness of these tumors. A similar tumor distribution trend of CN ?4 was also seen. IQGAP1 copy gain was positively correlated with IQGAP1 protein expression. It was significantly associated with extrathyroidal and vascular invasion of FVPTC and FTC and, remarkably, a 50%-60% rate of multifocality and recurrence of BRAF mutation-positive PTC (P=0.01 and 0.02, respectively). The siRNA knock-down of IQGAP1 dramatically inhibited thyroid cancer cell invasion and colony formation. Co-immunoprecipitation assay showed direct interaction of IQGAP1 with E-cadherin, a known invasion-suppressing molecule, which was upregulated when IQGAP1 was knocked down. IQGAP1, through genetic copy gain, plays an important role in the invasiveness of thyroid cancer and represents a useful prognostic marker and therapeutic target for this and other cancers.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Compositions and methods for regulating sas1r
InactiveUS20100183617A1Preserve ovarian reserveCompound screeningApoptosis detectionSperm proteinEmbryo
The present invention provides compositions and methods useful for regulating fertilization and for use as a contraceptive based on the discovery herein of an oocyte specific protein, SAS1R (Sperm Acrosomal SLLP1 Receptor), which is a sperm protein receptor. Six SAS1R variants, including the full length SAS1R, were identified. mSLLP1 and SAS1R co-localized to oocytes and to acrosomes of acrosome-reacted sperm. Interactions between mSLLP1 and SAS1R were demonstrated by far-western analysis, in a yeast two-hybrid system under stringent selection conditions, and by immunoprecipitation of SAS1R by anti-mSLLP1 as well as the converse. Purified recombinant SAS1R was found to have protease activity, to inhibit fertilization in-vitro, and to induce an immune response in females. Together, the results suggest SAS1R is a proteolytically active, oocyte and early embryo specific oolemmal metalloprotease receptor for the sperm intra-acrosomal ligand SLLP1 and is a target for regulating fertilization and as a contraceptive.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Methods and compositions for noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of fetal aneuploidies
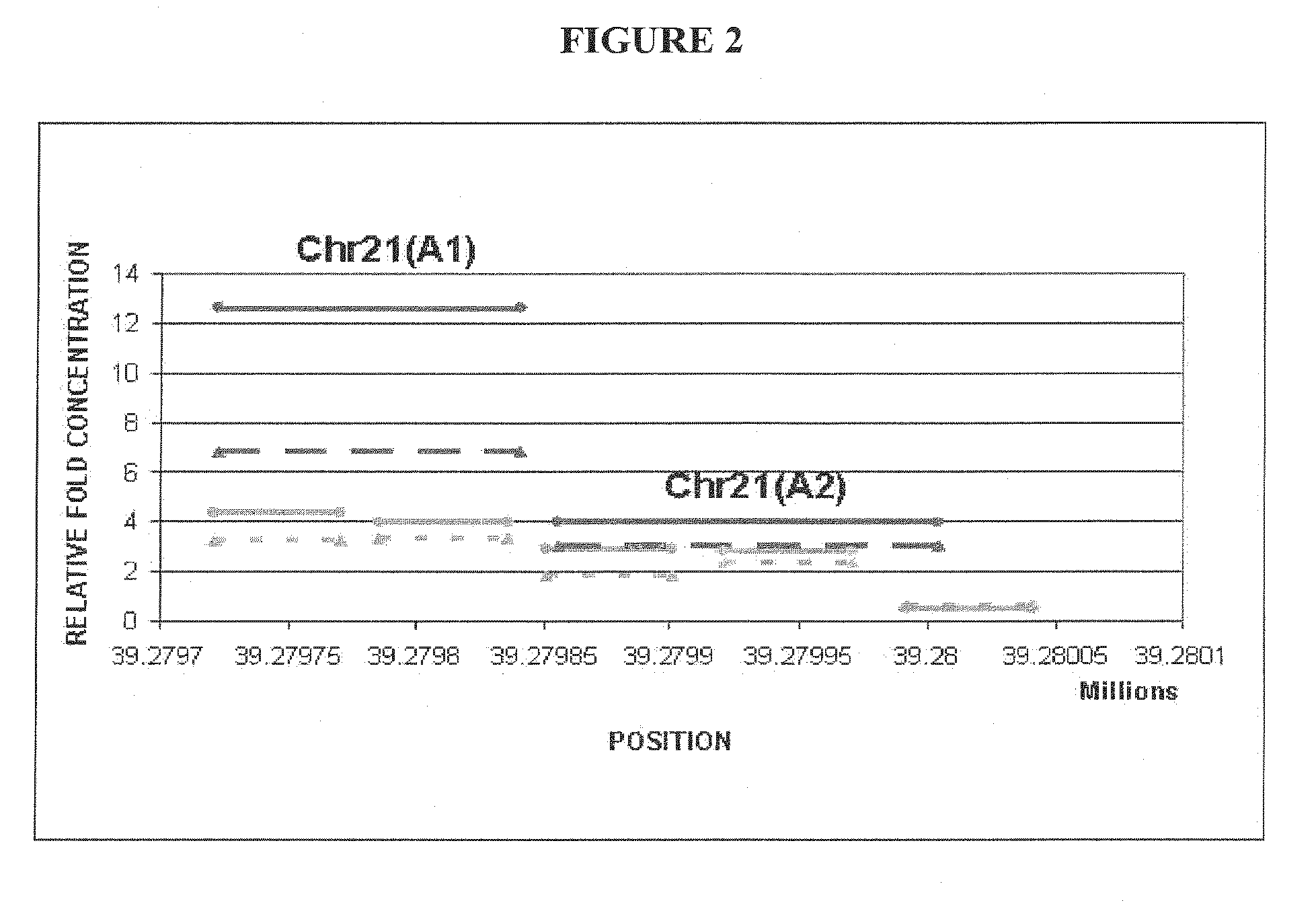
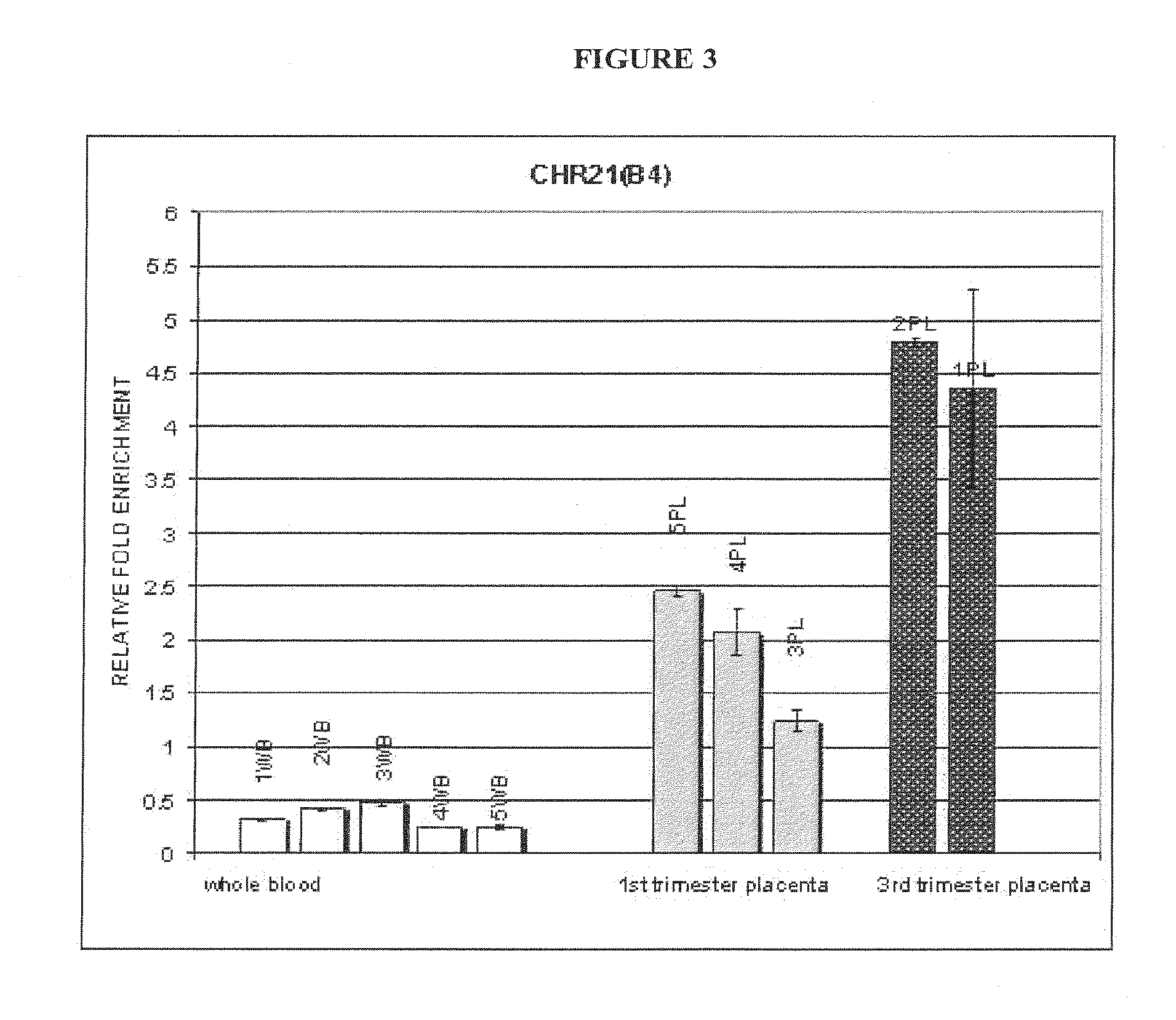
ActiveUS20120282613A1Accurate predictionDiagnosing fetal aneuploidiesSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMethylated DNA immunoprecipitationAdult female
The invention provides methods and compositions for noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of fetal aneuploidies. A large panel of differentially methylated regions (DMRs) have been identified. Certain of these DMRs are hypomethylated in adult female blood DNA and hypermethylated in fetal DNA, whereas others are hypermethylated in adult female blood DNA and hypomethylated in fetal DNA. Moreover, DMRs that are hypomethylated in adult female blood DNA and hypermethylated in fetal DNA have been shown to accurately predict a fetal aneuploidy in fetal DNA present in a maternal blood sample during pregnancy. In the methods of the invention, hypermethylated DNA is physically separated from hypomethylated DNA, preferably by methylated DNA immunoprecipitation.
Owner:NIPD GENETICS PUBLIC CO LTD
Methods of rapid chromatin immunoprecipitation
InactiveUS20070141583A1Reduce degradationAchieved rapidly and efficientlyMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid reductionIn vivoImmunoprecipitation
Owner:LI WEIWEI +1
High-throughput sequencing method for methylated DNA and use thereof
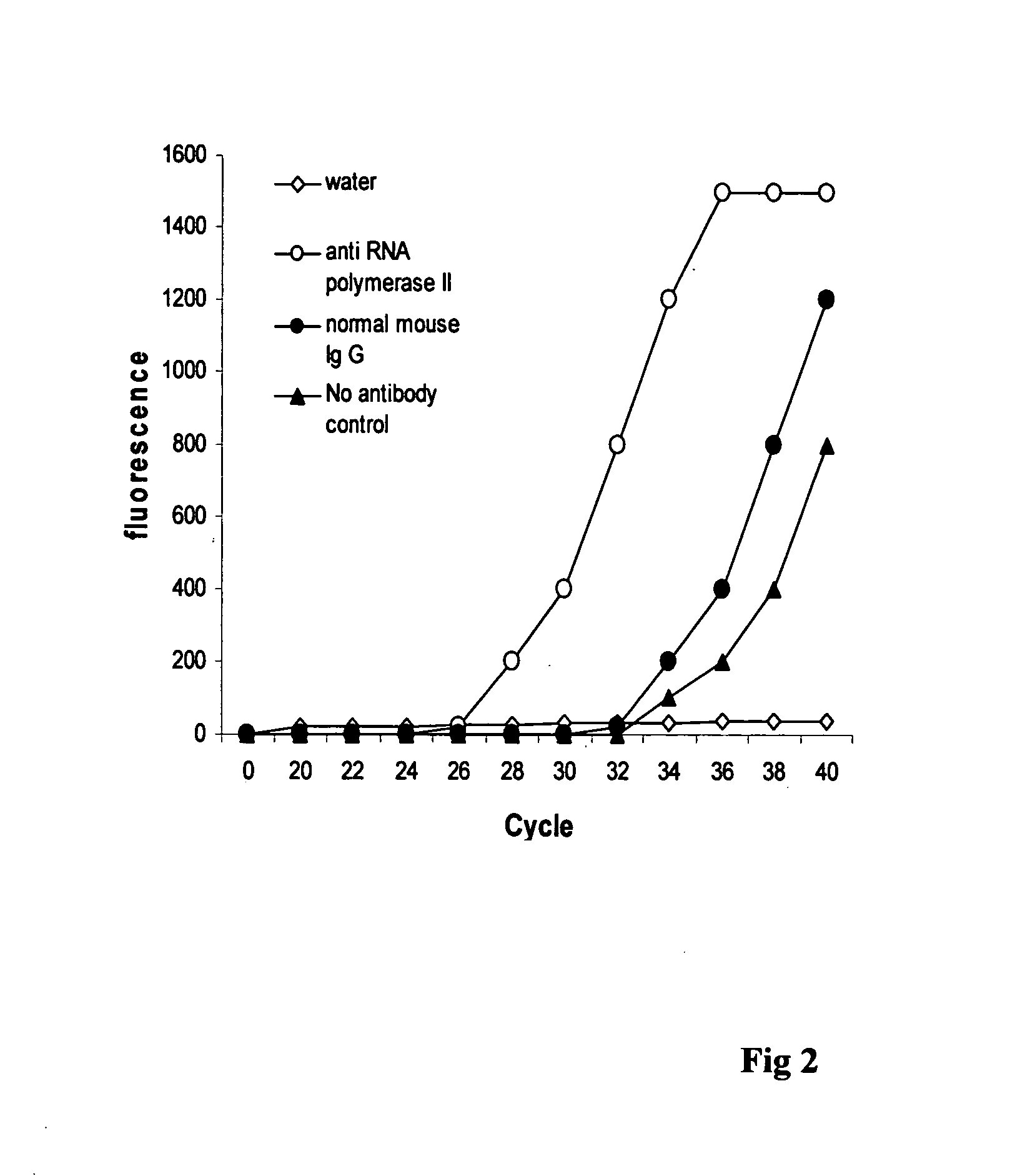
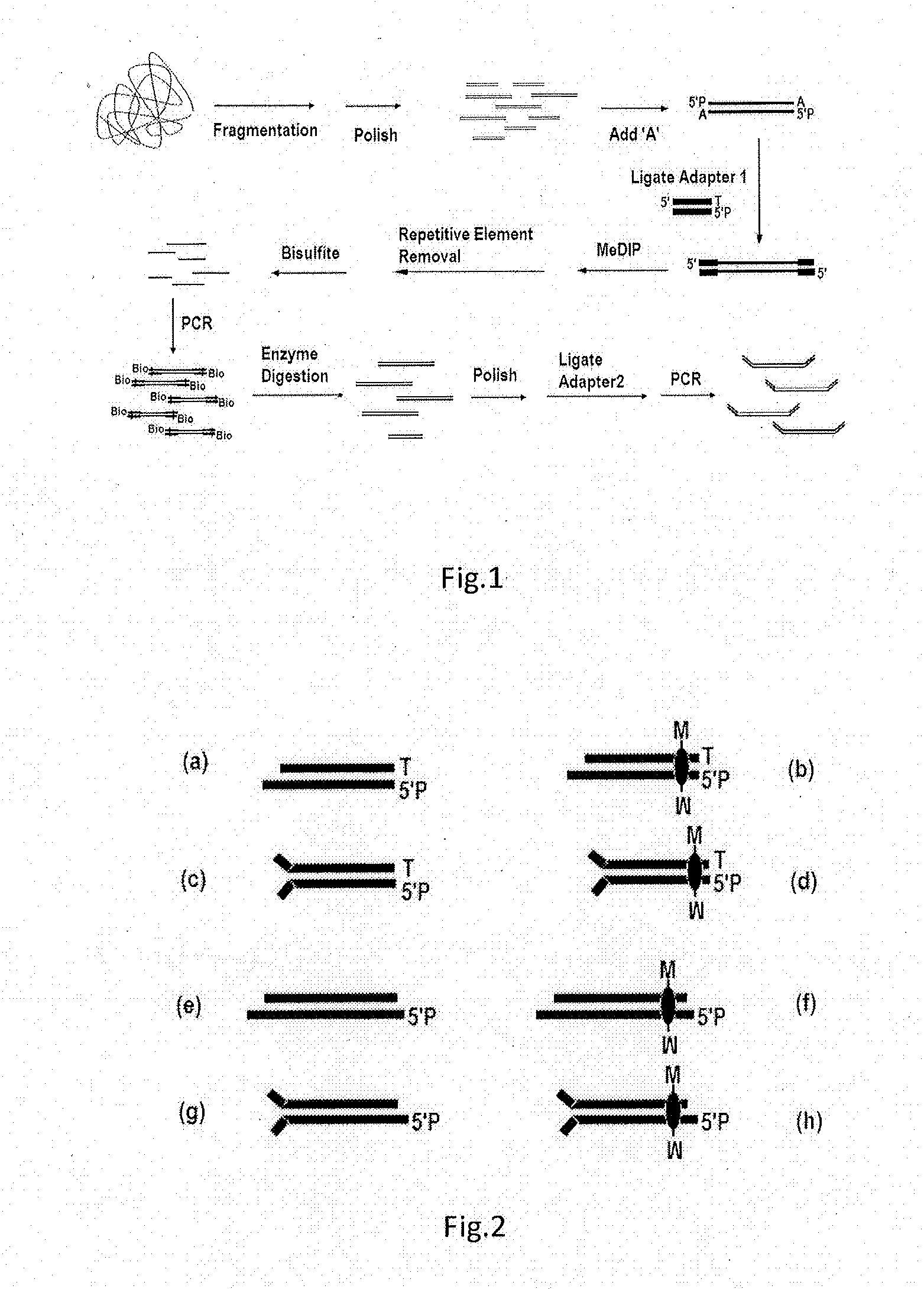
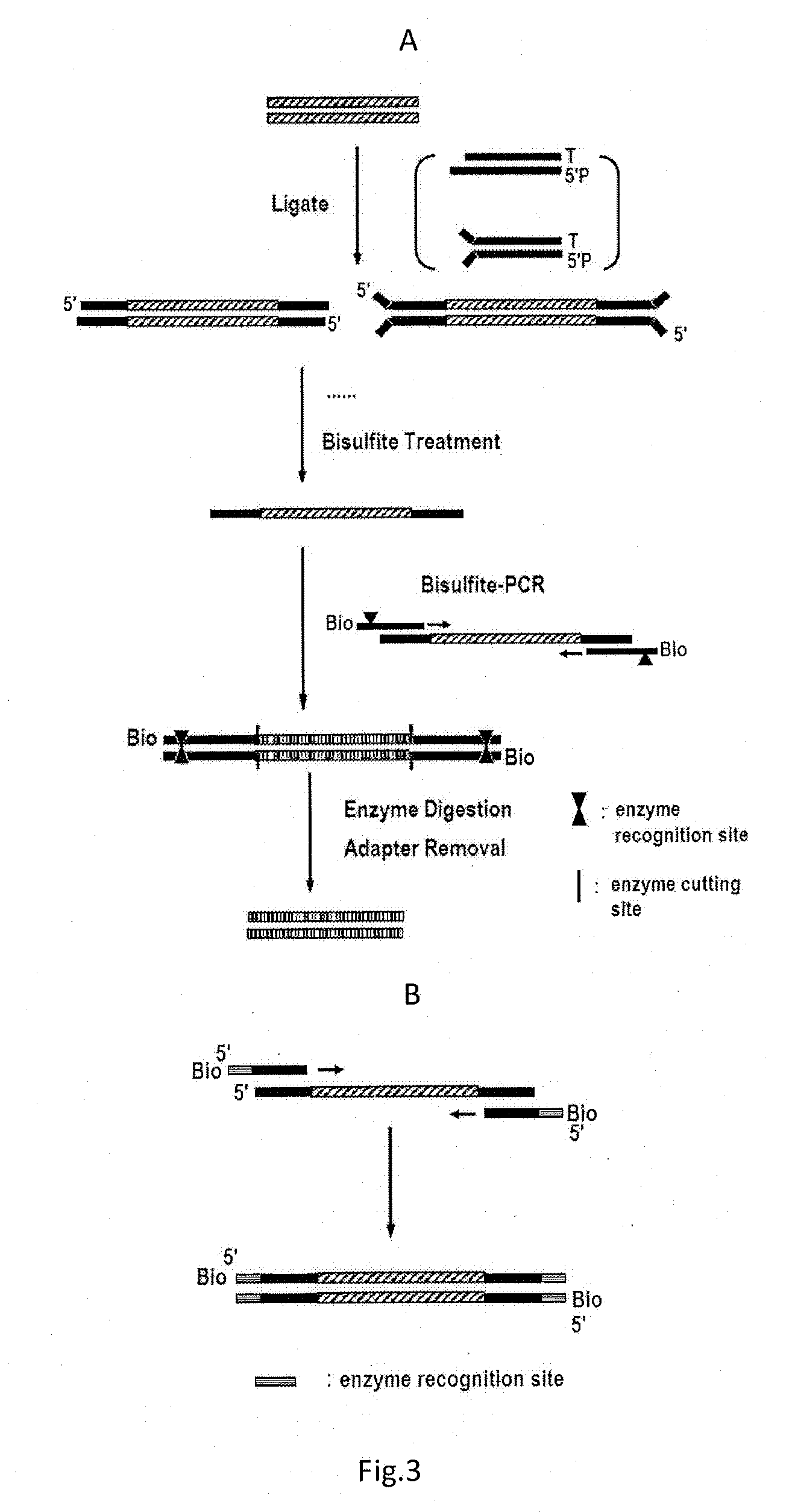
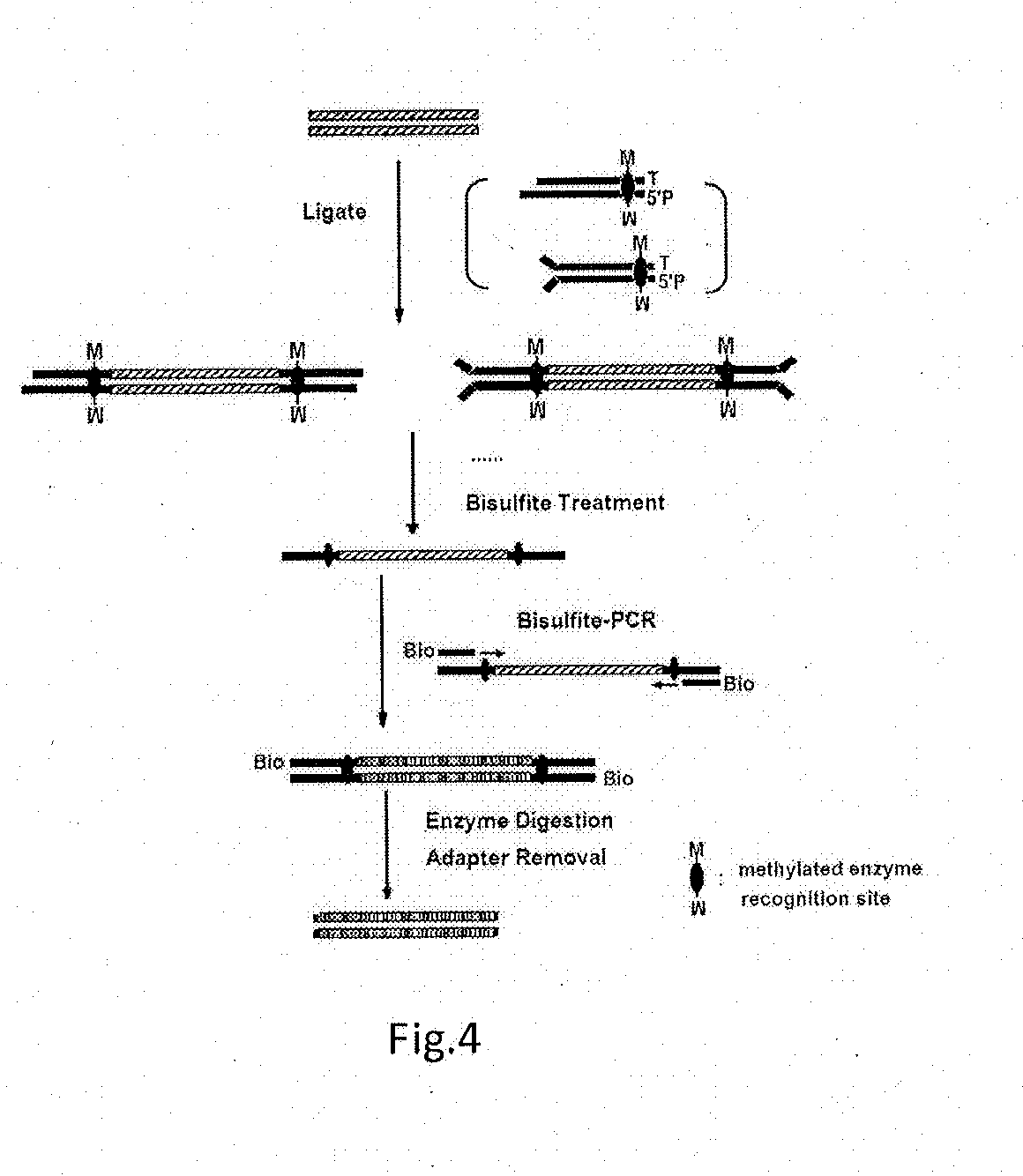
ActiveUS20130244885A1Improve digestion efficiencyDigestion efficiencyNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementRepetitive SequencesMethylated DNA immunoprecipitation
The present invention provides a high-throughput sequencing method for methylated DNA, and use thereof. Particularly, the present invention provides a high-throughput sequencing method for methylated DNA, which combines methylated DNA immunoprecipitation, removal of repetitive sequences, and bisulfite treatment. The site of sequencing library will be decreased, and the cost will be reduced by using the method disclosed in the present invention.
Owner:INST OF PSYCHOLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
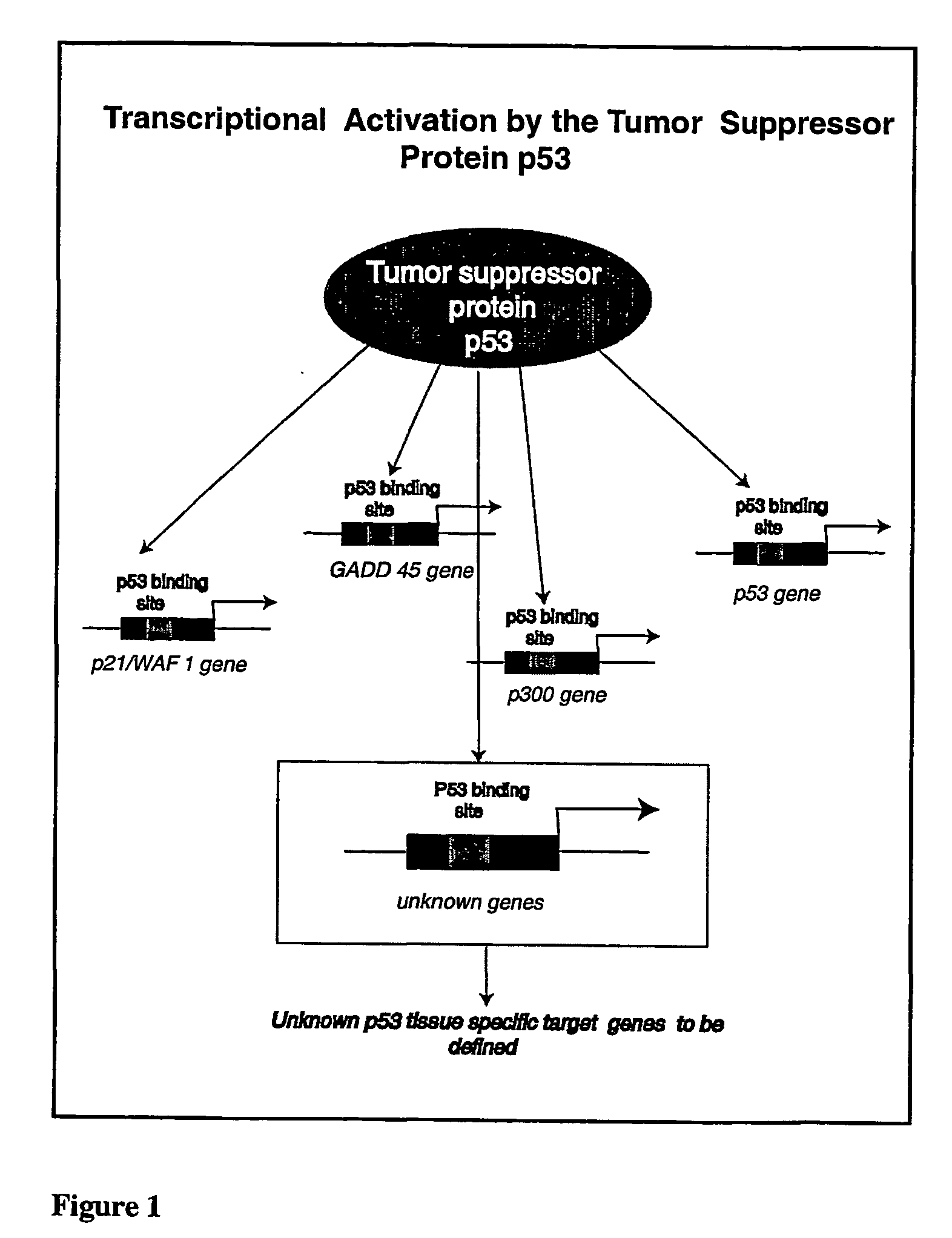
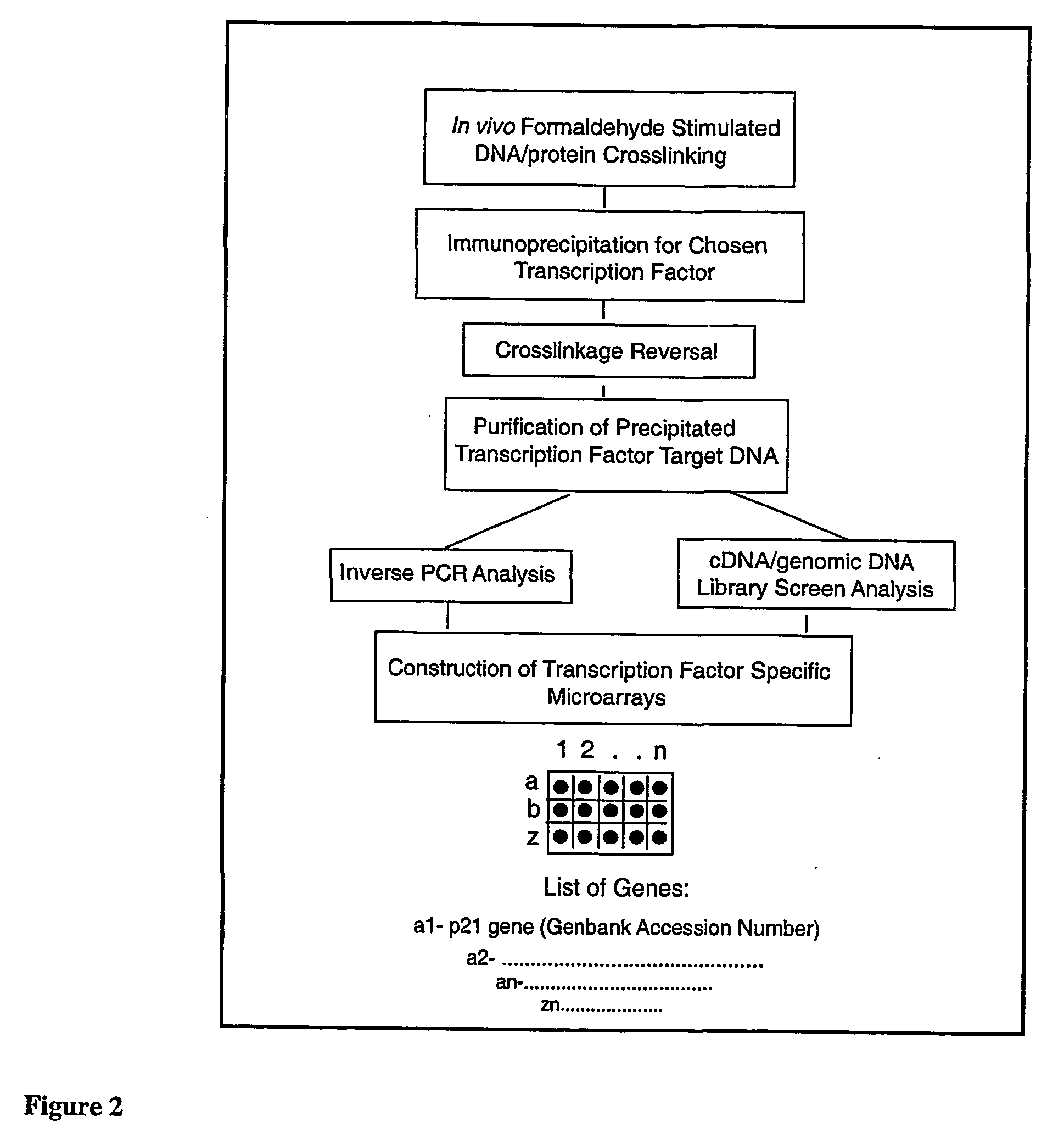
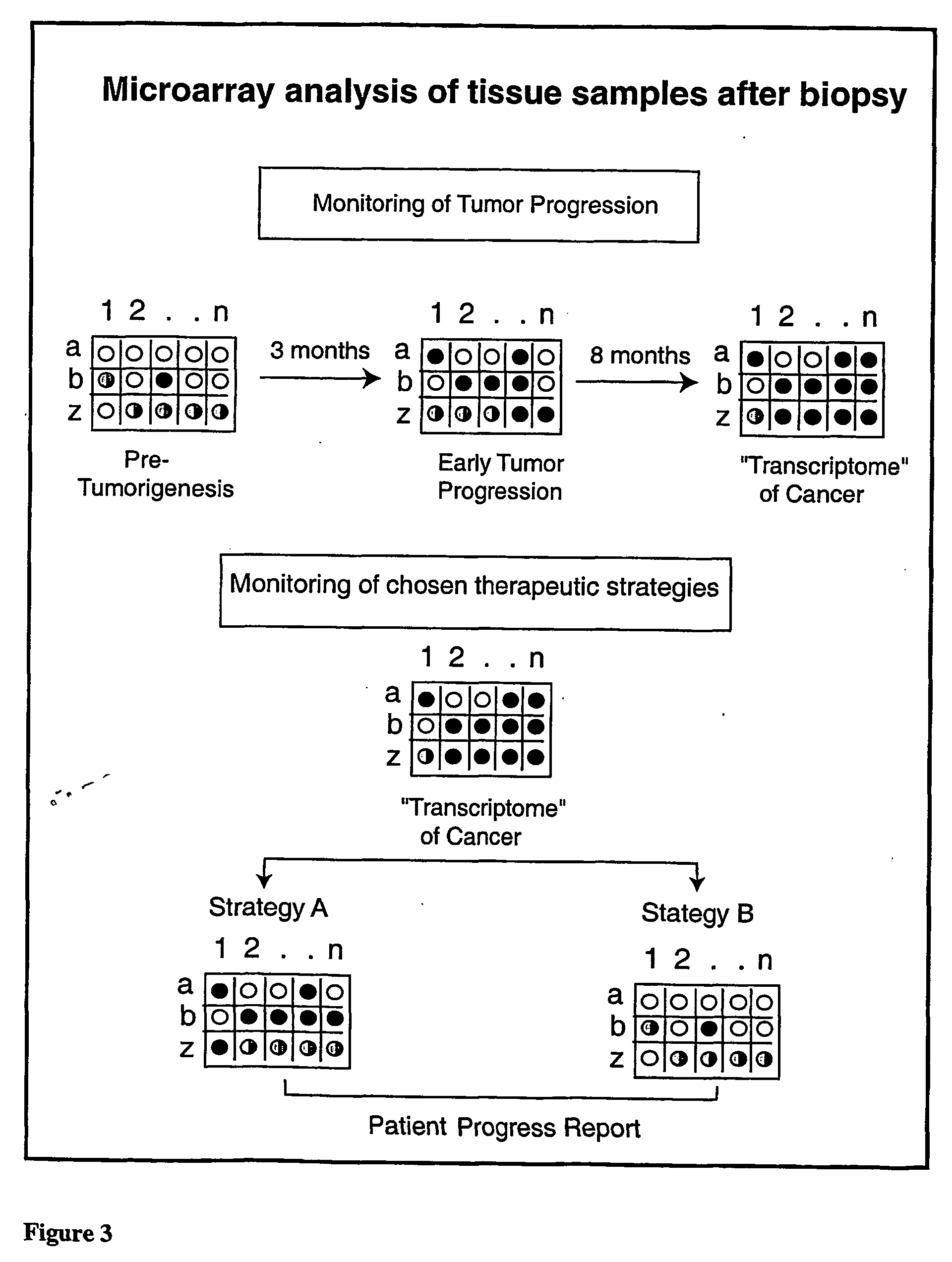
Micro-arrayed organization of transcription factor target genes
InactiveUS20050079492A1Decreasing acquisitionDecreased background random sequenceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationProtein targetImmunoprecipitation
The following invention outlines methodologies for the construction and utilization of transcription factor direct target gene microarrays of both DNA and corresponding protein / peptide target origin. The technology entails the array / microarray annotation and organization of transcription factor direct loci and corresponding protein products identified through modified and improved versions of chromosomal immunoprecipitation (CHIP) and molecular cloning procedures. It allows for the formulation of physiologically directed arrays which result in a thorough, focused characterization of the genetic and biochemical regulation occurring within a give population of cells or a given tissue. Arrays and microarrays of direct targets for any given transcription factor created utilizing this technology are substantially more clinically relevant for purposes of medical diagnostics and patient prognostics than conventional microarrays due to the physiologically focused nature and the transcription factor targets. In addition, the characterization and array organization of transcription factor target protein products and the assessment of their interactions with other proteins and / or small molecules is of critical importance for the purposes of understanding cellular and ultimately the design of therapeutics for human anomalies.
Owner:BURS JR ROBERT M +2
Lyophilized viper antivenin and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101816789AHigh potencyGuaranteed curative effectAntinoxious agentsMammal material medical ingredientsMass ratioBlood plasma
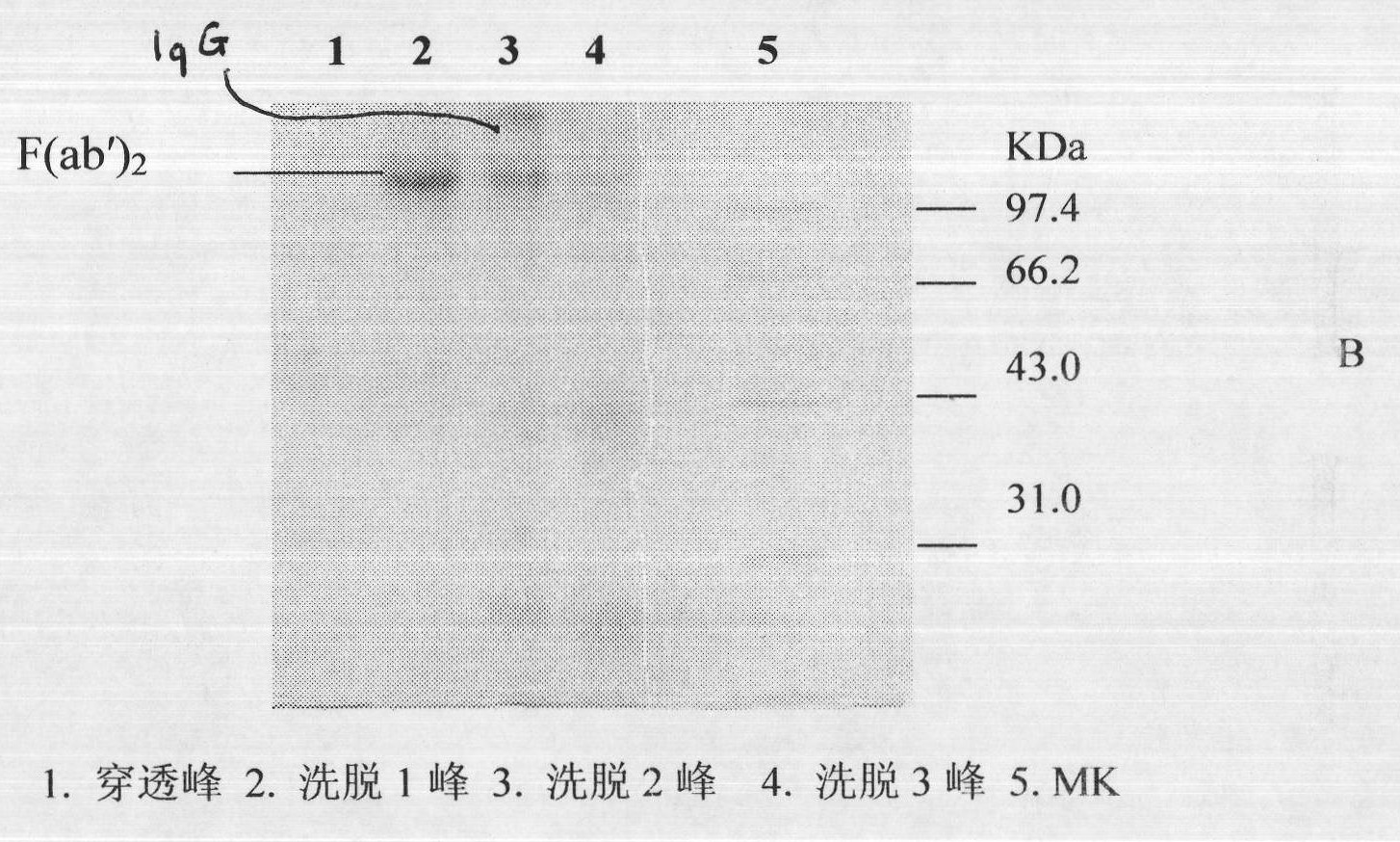
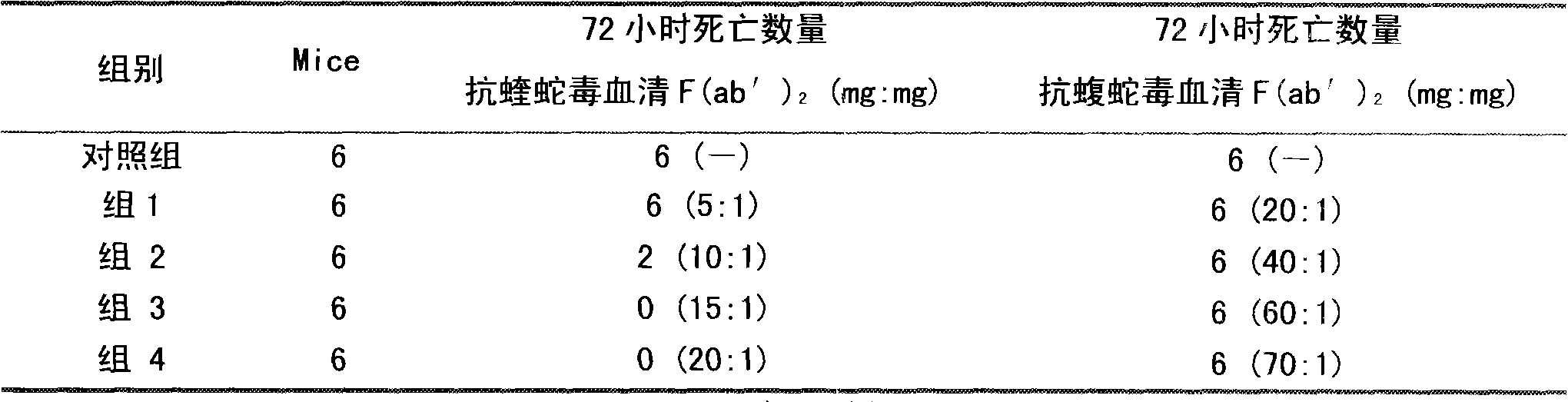
The invention discloses a lyophilized viper antivenin and a preparation method thereof, belonging to biochemical products, more particularly relating to an antivenin and a preparation technology thereof. The mass ratio of the antivenin and viper venom is 15:1, which can specifically neutralize the viper venom injected to mouse; as determined by immunodiffusion, the immunoprecipitation line appears in case that the ratio of viper antivenin F(ab')2 in lyophilized form to viper venom is 8:1; and other detected items conform to the quality standard of antivenin in Chinese Pharmacopoeia 2010. The detection of Phenyl-Sepharose (low-sub) FF column chromatography result shows that: activity is centralized at eluting peak 1, micromolecule impurity proteins are centralized at penetration peal, eluting peak 2 and eluting peak 3. According to the technology of the invention, immune blood plasma is resulted from viper venom immune horse, IgG is prepared by salting out the immune blood plasma, and F(ab')2 active fragment is obtained after the IgG is subject to enzymolysis and purification by a hydrophobic column. The lyophilized viper antivenin has strong specificity, high potency and more than 85% of the purity of antivenin F(ab')2 in lyophilized form.
Owner:浙江健博生物科技股份有限公司
Affinity matrices with enhanced visibility for molecular pull-down and immunoprecipitation applications
InactiveUS6887377B2Low non-specific protein binding capabilityEasy to monitorIon-exchanger regenerationLoose filtering material filtersMoietyImmunoprecipitation
An affinity matrix for use in affinity based molecular pull down and immunoprecipitation procedures. The affinity matrix comprises a polymeric support, a dye attached to a fraction of the polymeric support to enable optical detection of the polymeric support, and an affinity ligand other than the dye attached to a fraction of the polymeric support for the capture of a molecule.Also provided is a method for the isolation of a biomolecule from an aqueous solution. The method comprises combining the aqueous solution with an affinity matrix comprising a polymeric support and separating the affinity matrix from the aqueous solution. A dye is attached to a fraction of the polymeric support which enables optical detection and monitoring of the affinity matrix and, accordingly, reduces the likelihood of the loss of affinity matrix during the separation step. In addition, an affinity ligand other than the dye is also attached to a fraction of the polymeric support for the capture of the biomolecule.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
ELISA kit for detecting Salmonella pullorum antibody
ActiveCN103995126AReduce stressImprove featuresBiological material analysisBiological testingAntigenElisa kit
An ELISA kit for detecting a Salmonella pullorum antibody is established by screening Salmonella pullorum dominant antigen GroEL through an immunoprecipitation technology, expressing GroEL recombinant protein through utilizing a prokaryotic expression vector, and utilizing an antigen protein. The kit can reduce the response of chicken in the detection process of the Salmonella pullorum antibody, and can improve the detection specificity and the sensitivity.
Owner:WENS FOOD GRP CO LTD
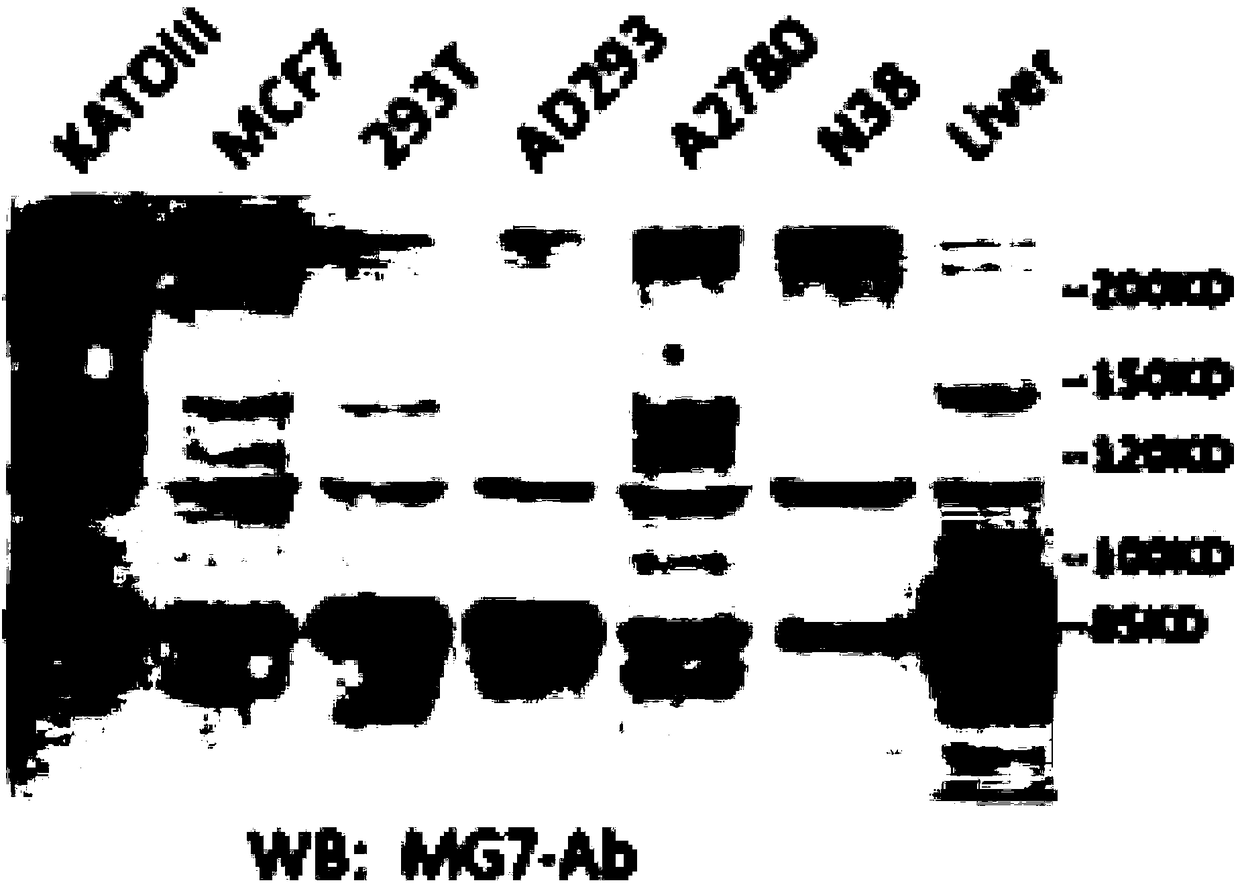
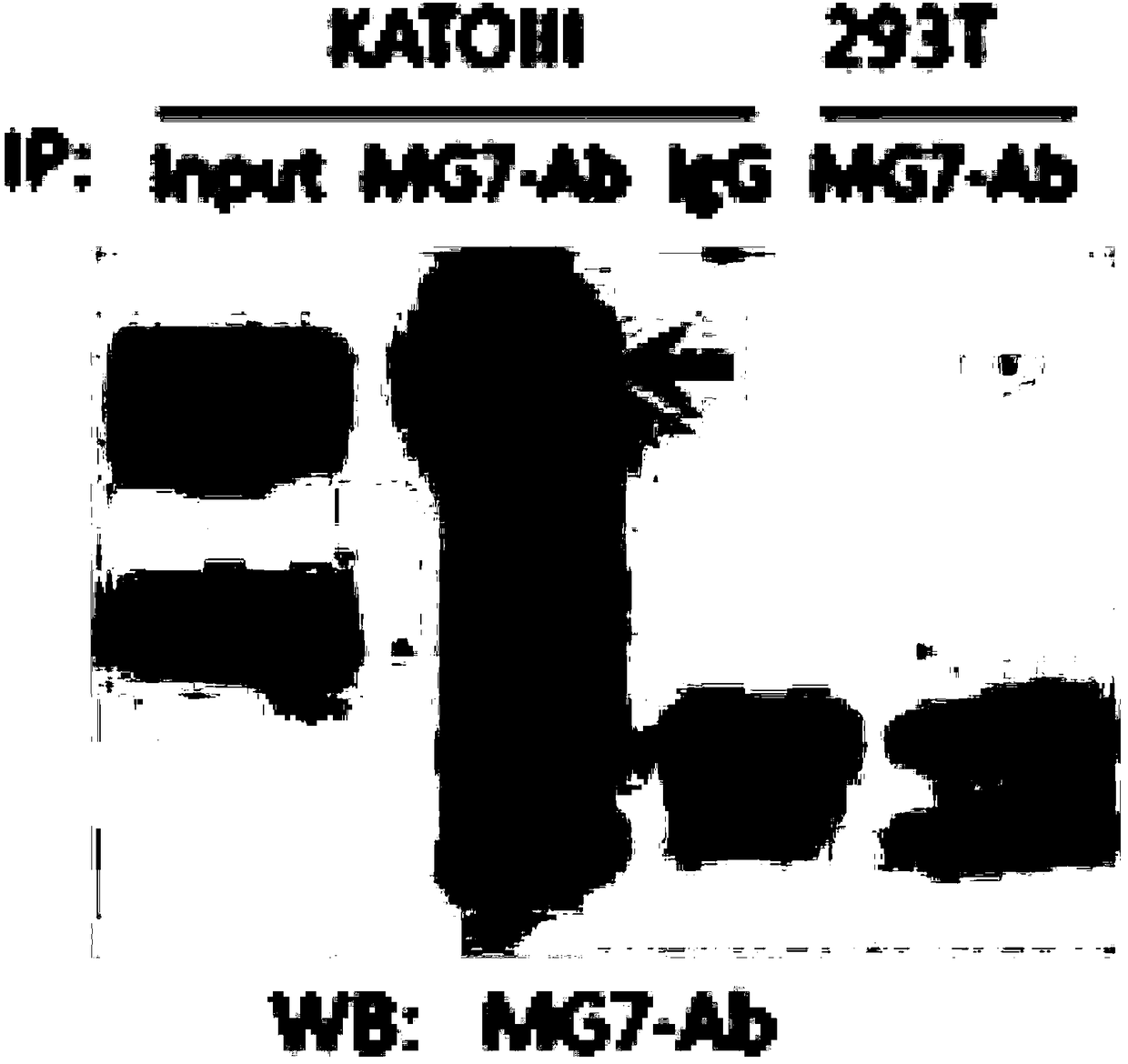
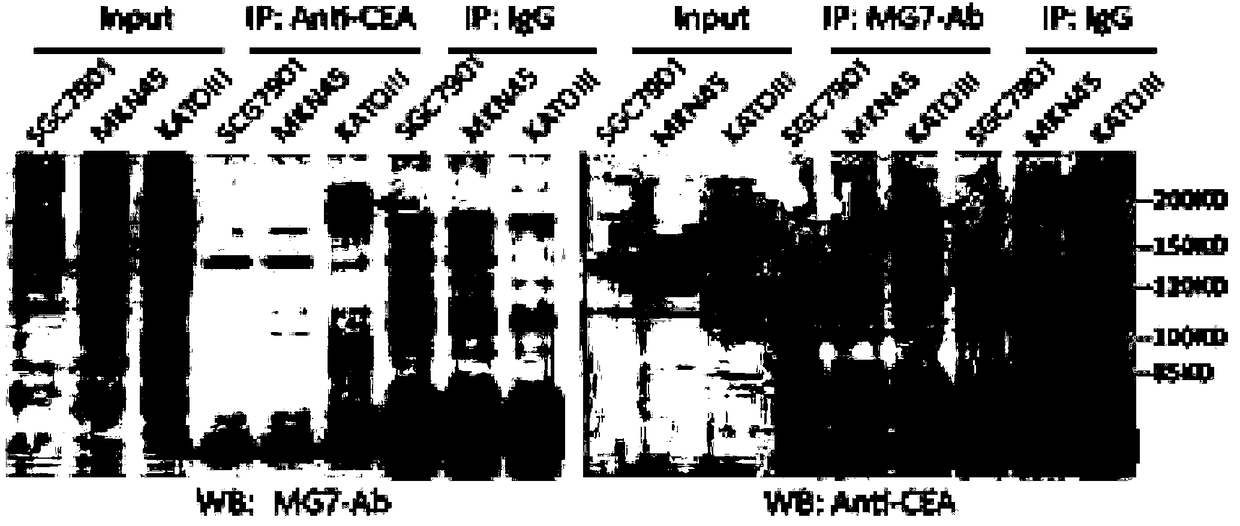
Anti-human CEACAM5 monoclonal antibody and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108341876AHigh affinityImprove featuresMicroorganism based processesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsStainingImmunoprecipitation
The invention discloses an anti-human CEACAM5 monoclonal antibody and a preparation method and application thereof, and the anti-human CEACAM5 monoclonal antibody is produced by a mouse hybridoma cellline with the accession number CCTCC NO: C2016129. The preparation method comprises the following steps: S1, immunizing a mouse with whole cell protein, lysed by human gastric cancer cells, as an immunogen; S2, fusing spleen cells of the immunized mouse obtained in the step S1 with mouse myeloma cells; S3, selecting a hybridoma cell line stably secreting antibodies after cell cloning occurs during the cell fusing in the step 2; and S4, preparing the anti-human CEACAM5 monoclonal antibody from the hybridoma cell line stably secreting the antibodies obtained in the step 3. The monoclonal antibody can be used to prepare a composition for treating a malignant tumor. The anti-human CEACAM5 monoclonal antibody can be widely used in various routine operations such as flow cytometry, immunohistochemical staining and immunoprecipitation.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
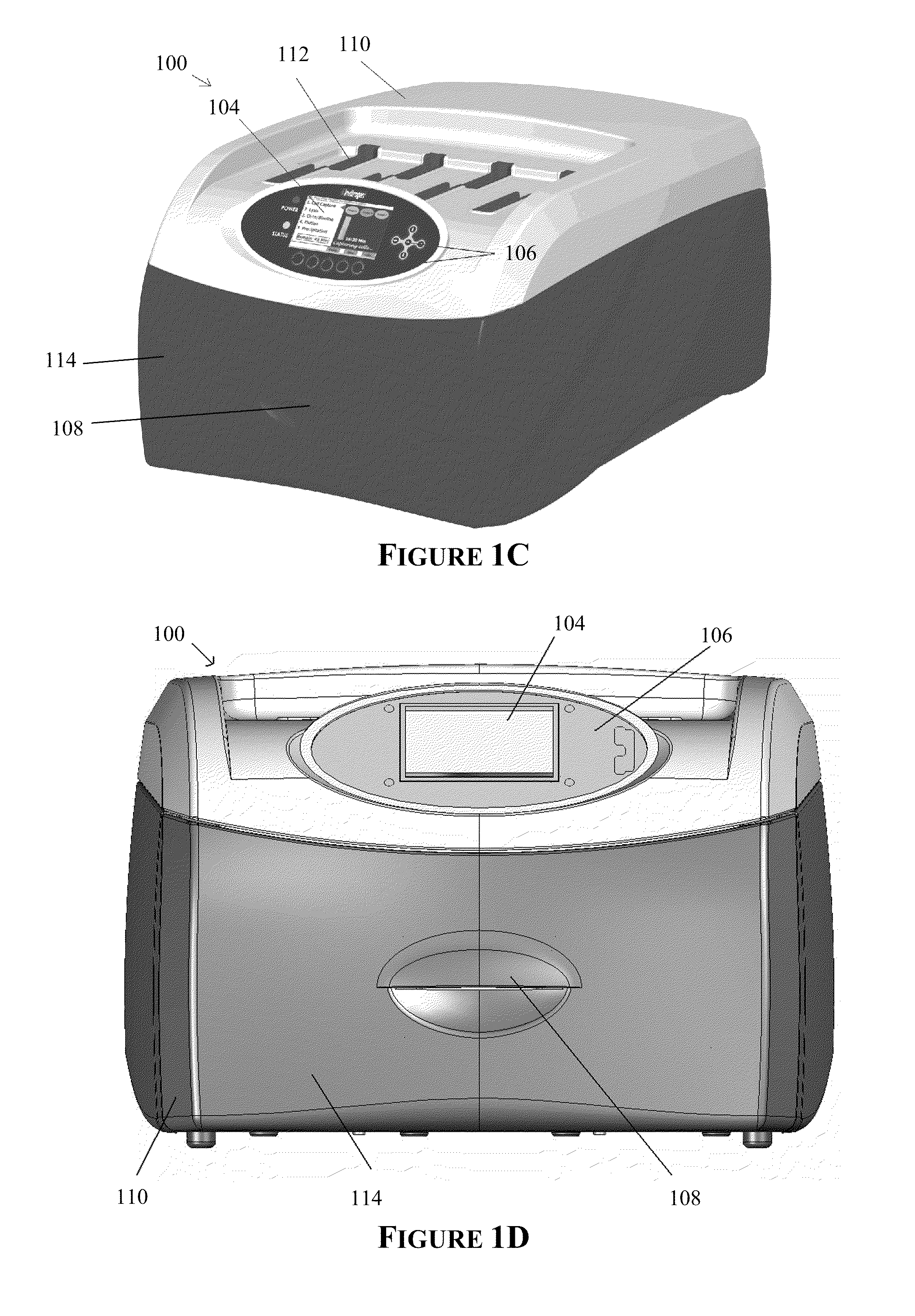
Apparatus for and method of processing biological samples
ActiveUS20130040376A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusWestern blotGenomic DNA
The present invention provides systems, devices, apparatuses and methods for automated bioprocessing. Examples of protocols and bioprocessing procedures suitable for the present invention include but are not limited to: immunoprecipitation, chromatin immunoprecipitation, recombinant protein isolation, nucleic acid separation and isolation, protein labeling, separation and isolation, cell separation and isolation, food safety analysis and automatic bead based separation. In some embodiments, the invention provides automated systems, automated devices, automated cartridges and automated methods of western blot processing. Other embodiments include automated systems, automated devices, automated cartridges and automated methods for separation, preparation and purification of nucleic acids, such as DNA or RNA or fragments thereof, including plasmid DNA, genomic DNA, bacterial DNA, viral DNA and any other DNA, and for automated systems, automated devices, automated cartridges and automated methods for processing, separation and purification of proteins, peptides and the like.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Antibodies binding a gamma carboxyglutamic acid displaying epitope
InactiveUS7439025B2Quick selectionComponent separationHybrid cell preparationTissue extractsImmunoprecipitation
Antibodies are described, which are suitable for identification of γ-carboxyglutamic acid (Gla), said antibodies having an ability of identifying Gla residues in proteins and / or peptides, while not reacting with glutamic (Glu) residues in corresponding proteins and / or peptides. Methods for the preparation and identification of said antibodies as well as methods for detection of Gla in biological fluids, tissue extracts, tissue specimens, in which methods said antibodies are used, are also described. There is also described the use of said antibodies for immunopurification of Gla-containing proteins or peptides by, for instance, immunoprecipitation or immunoaffinity chromatography.
Owner:BIOMEDICA DIAGNOSTICS INC +1
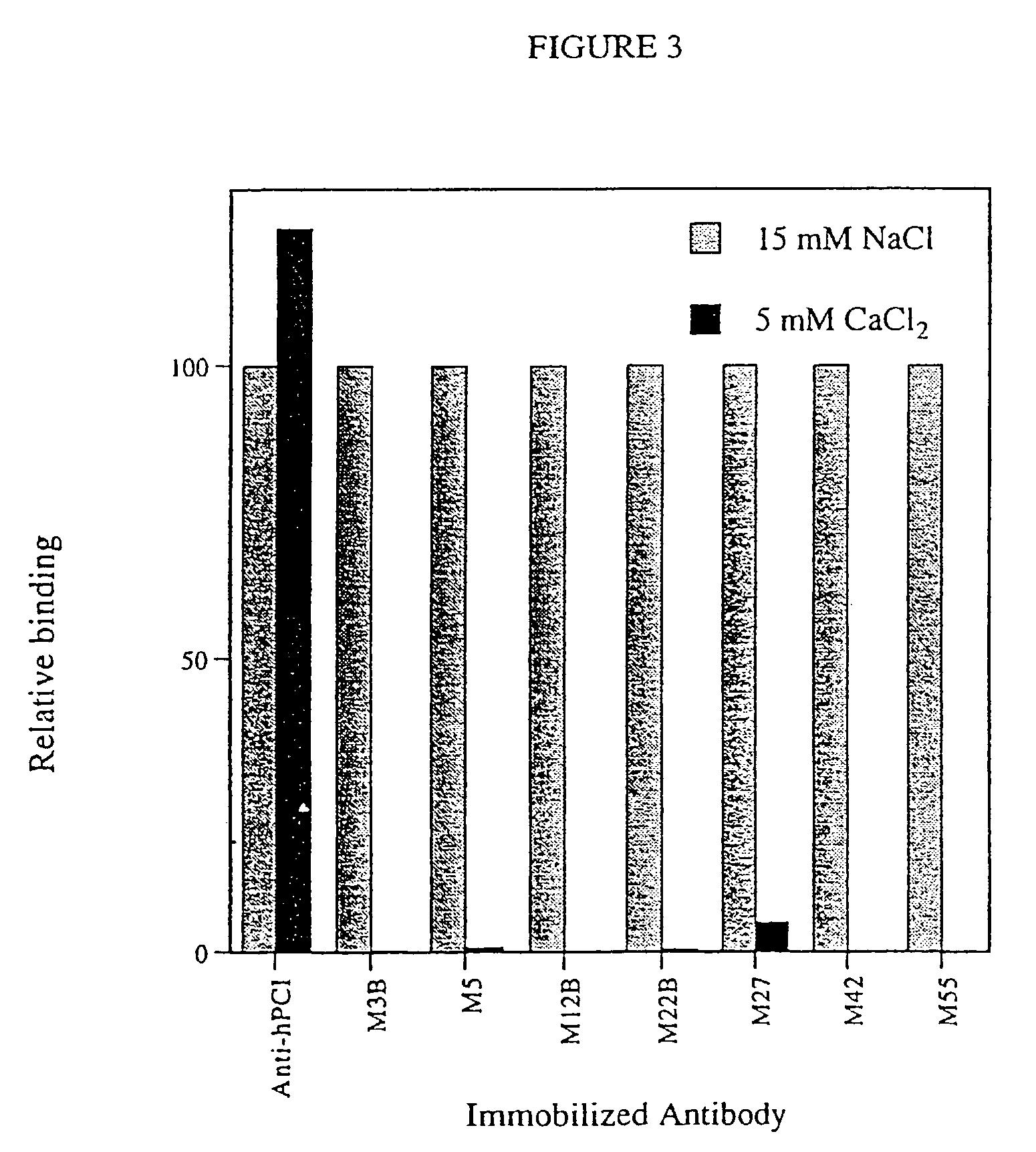
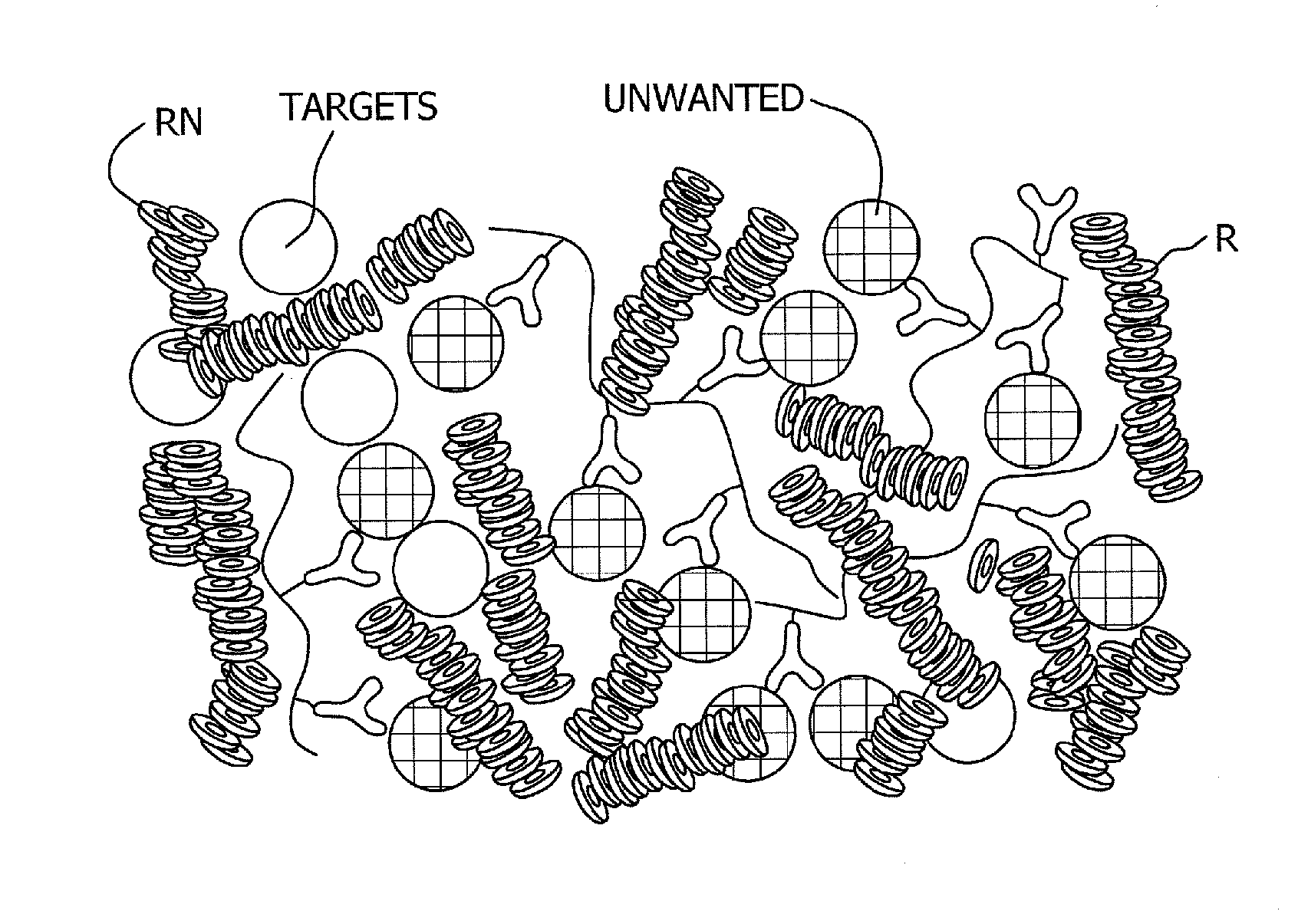
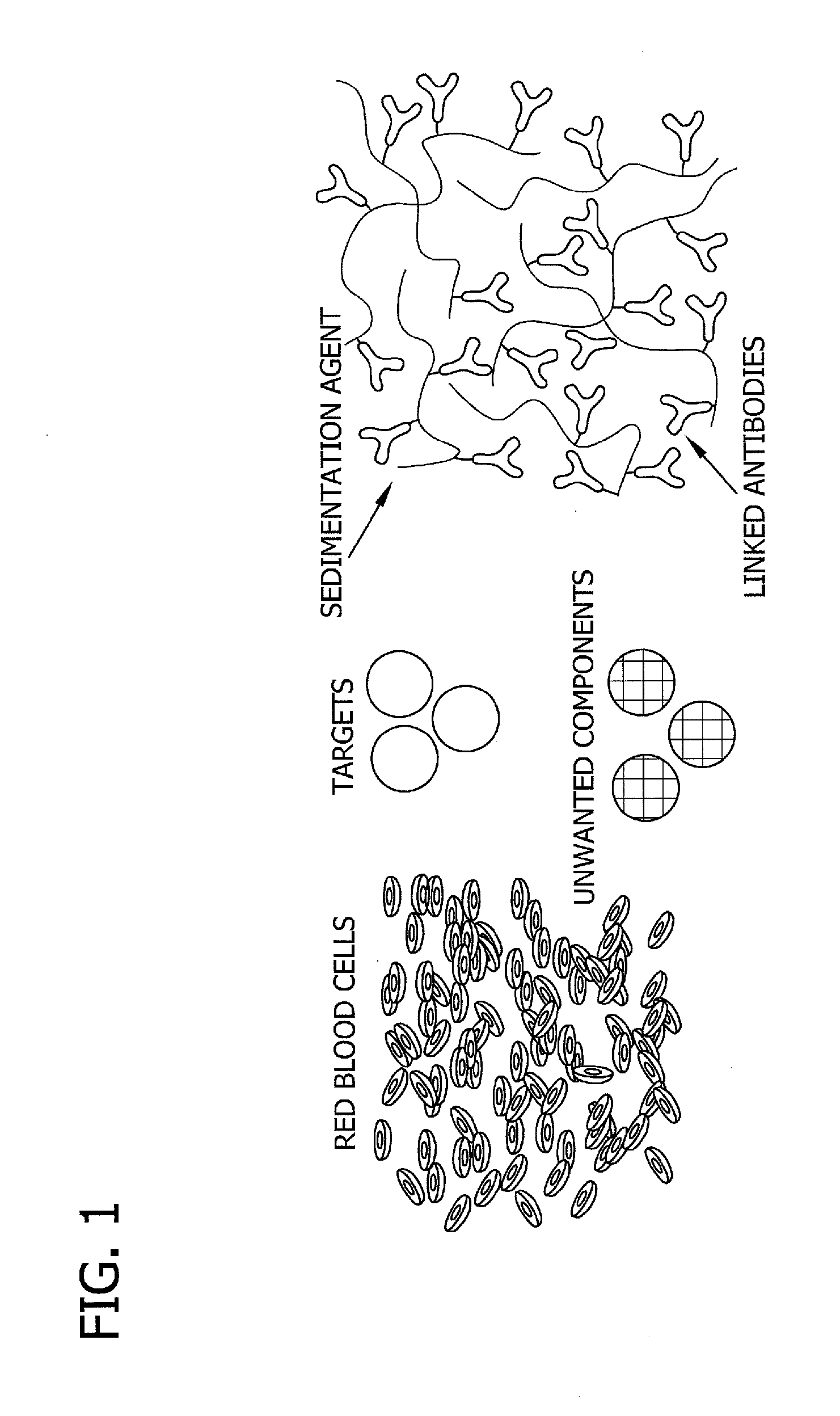
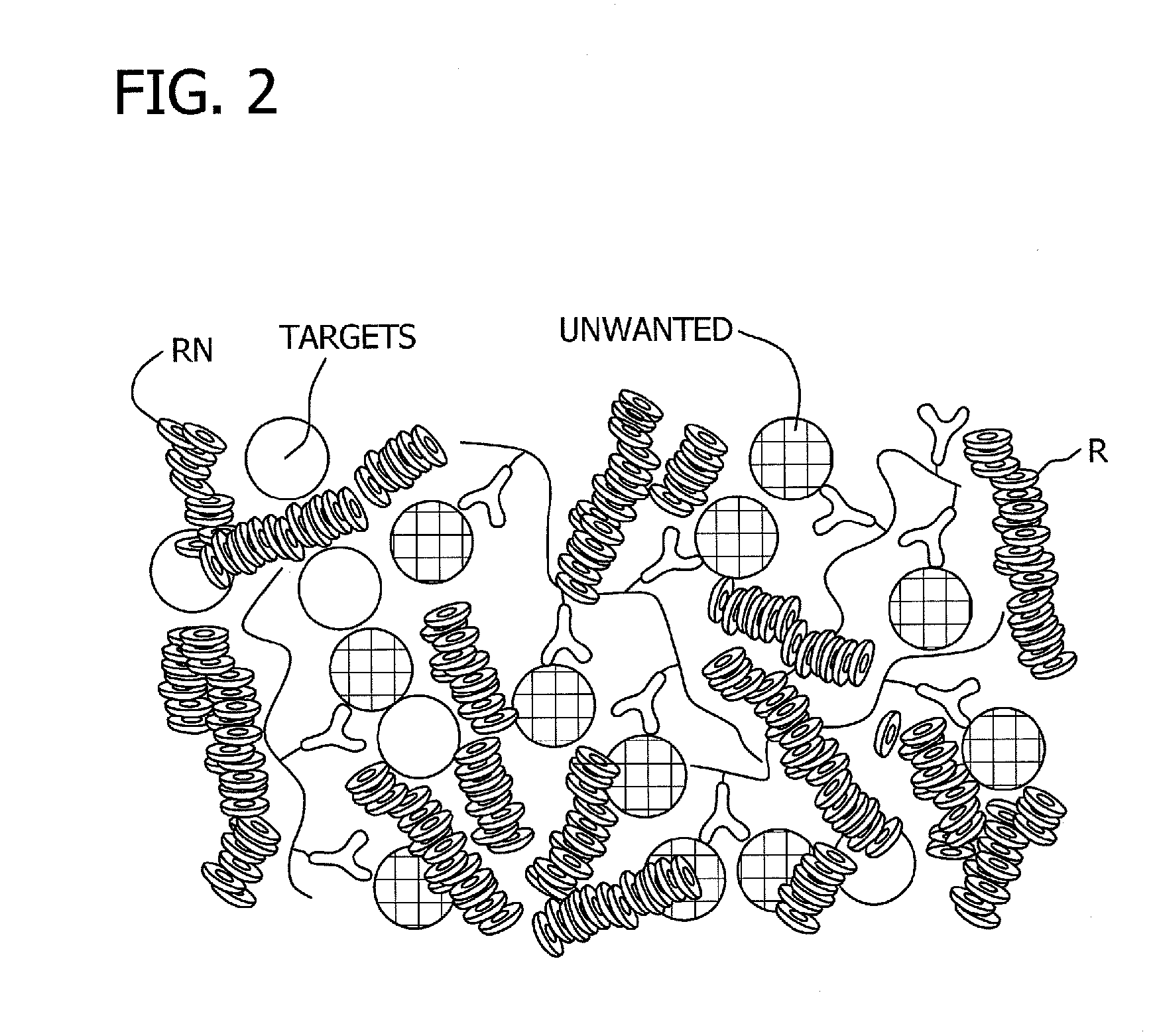
Antibody-linked immuno-sedimentation agent and method of isolating a target from a sample using same
InactiveUS20130266930A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisRed blood cellAntigen binding
The present disclosure is directed to antibody-linked immuno-sedimentation agent, the antibody being linked to a sedimentation agent by a non-antigen binding region of the antibody, and a method of isolating a target from a sample using the antibody-linked immuno-sedimentation agent. The methods involve forming a mixture including a sample with an antibody linked immuno-sedimentation agent and red blood cells under conditions sufficient to form red blood cell rouleaux and allow antibody-antigen binding.
Owner:CYTOSED
Detection of Antibodies
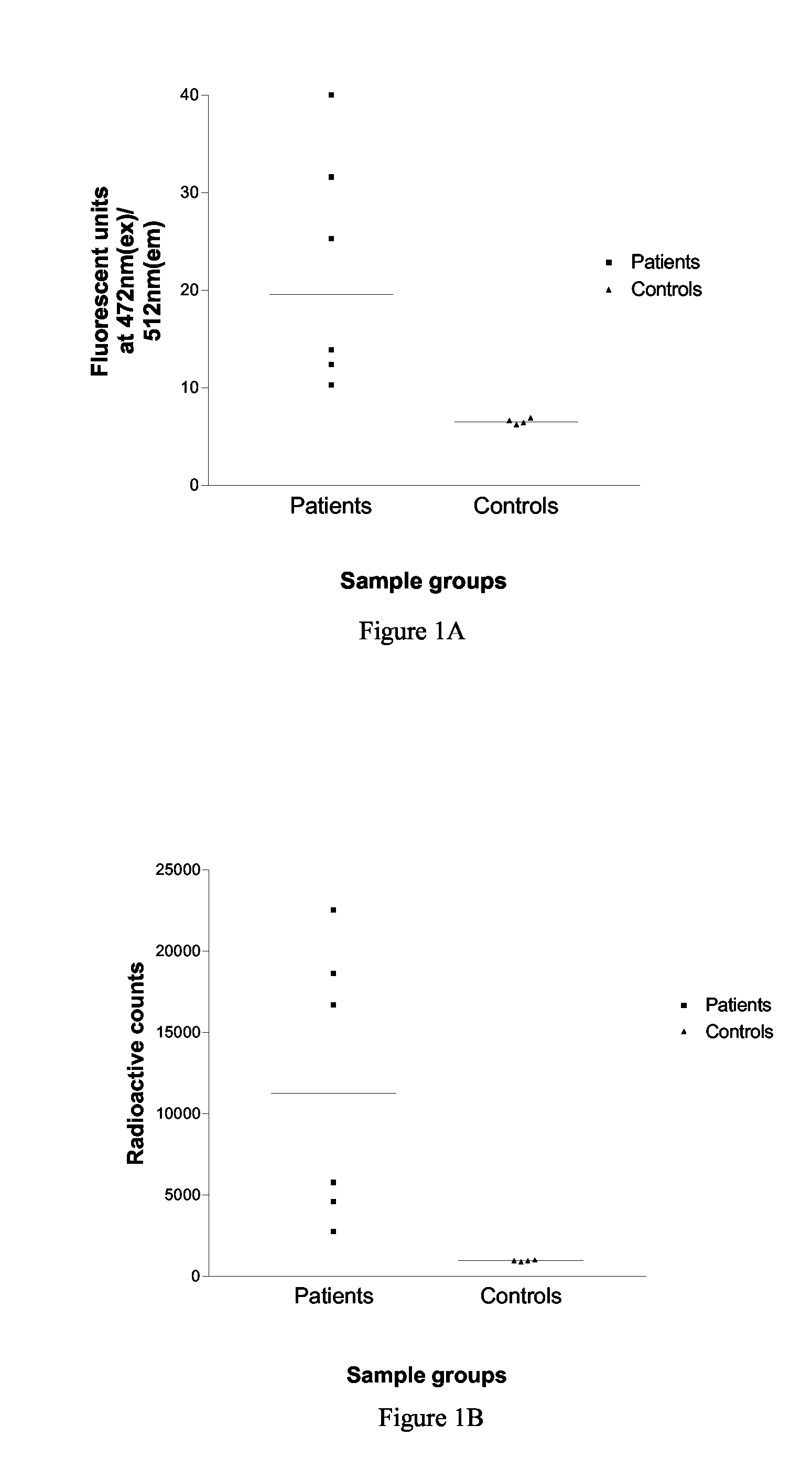
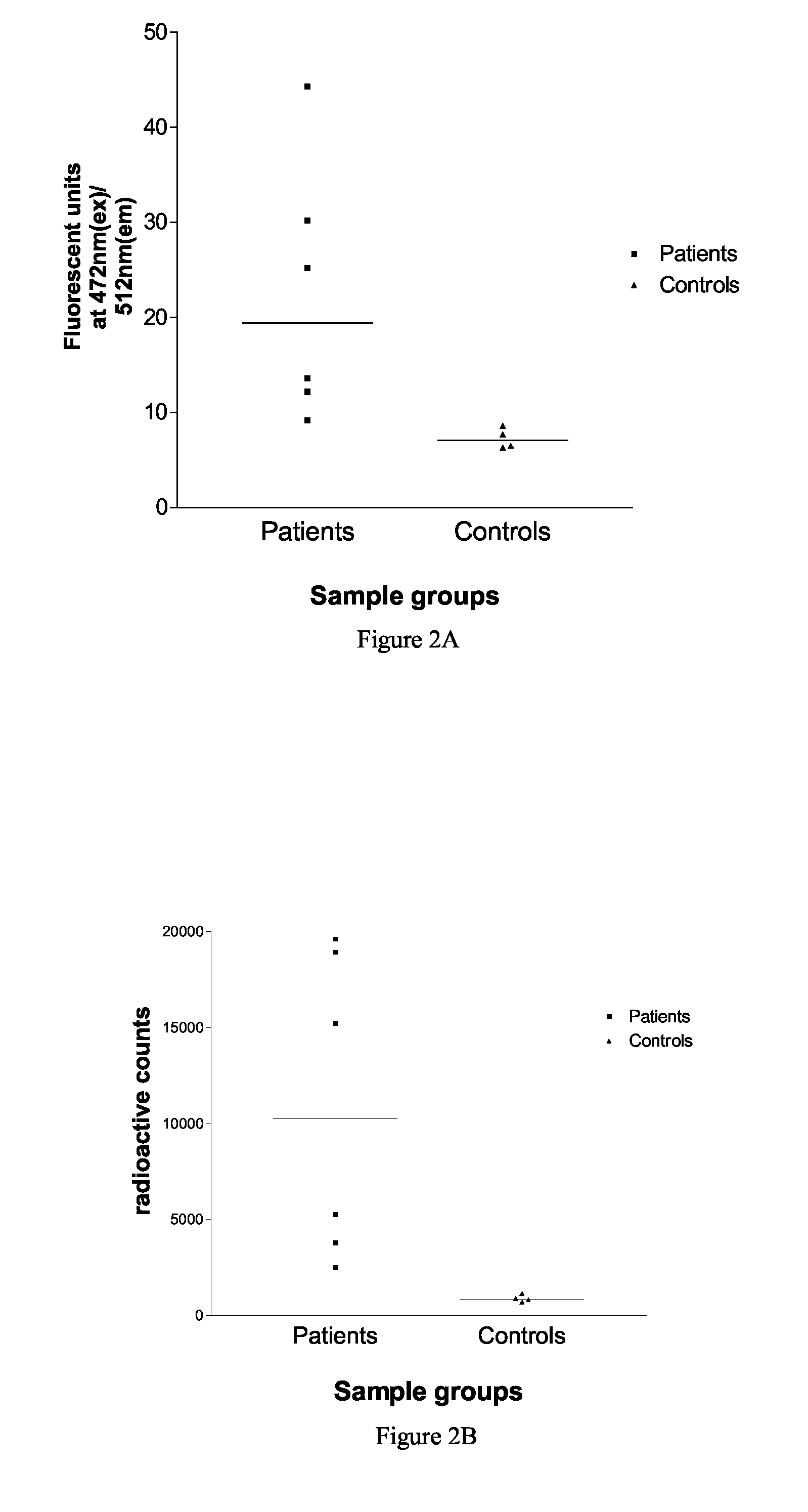
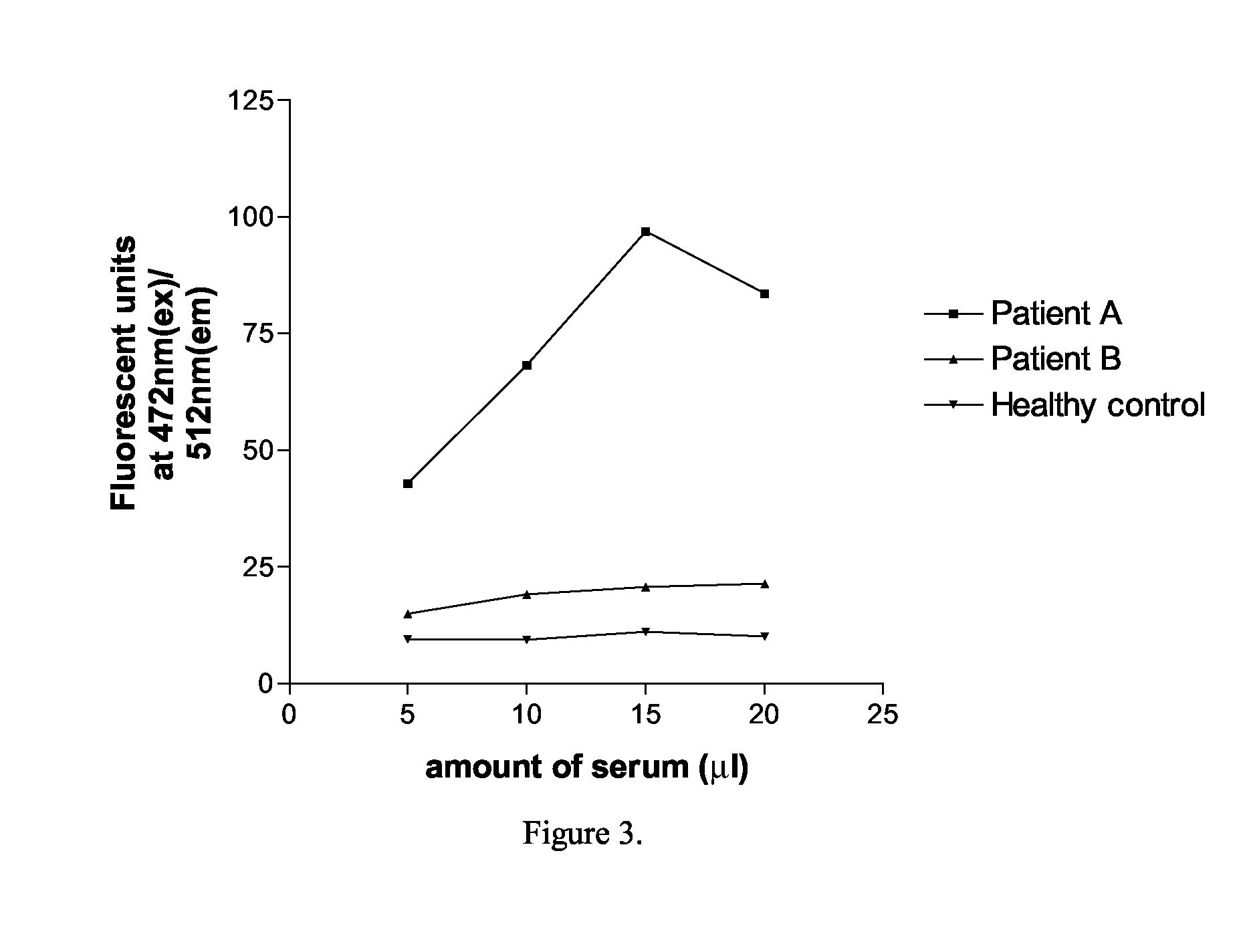
InactiveUS20090029388A1Efficient methodImprove the signal-to-background ratioBiological testingAutoimmune diseaseWater Channel Proteins
The present invention relates to a method for detecting antibodies against a target antigen in a sample which comprises contacting the sample with labelled target antigen, subjecting the sample to immunoprecipitation to precipitate antibodies in the sample and detecting the presence of antibodies against the target antigen in the sample by means of the presence of labelled target antigen in the immunoprecipitate, wherein the labelled target antigen is a fusion protein comprising the target antigen and a fluorescent protein label and the presence of labelled target antigen in the immunoprecipitate is detected by means of the fluorescence of the fluorescent label. The method is particularly suitable for use where the target antigen is an autoantigen and can also be used to identify autoantigens implicated in a particular autoimmune disorder by screening serum samples from patients with a clinical phenotype indicative or suggestive of an autoimmune disorder and suitable controls. The target protein may be from the cys-loop acetyl choline receptor ion channel gene superfamily, the voltage-gated calcium, sodium or potassium ion channel gene superfamily, the glutamate receptor gene family, a receptor tyrosine kinase, or other membrane associated channels such as aquaporin gene family.
Owner:BEESON DAVID
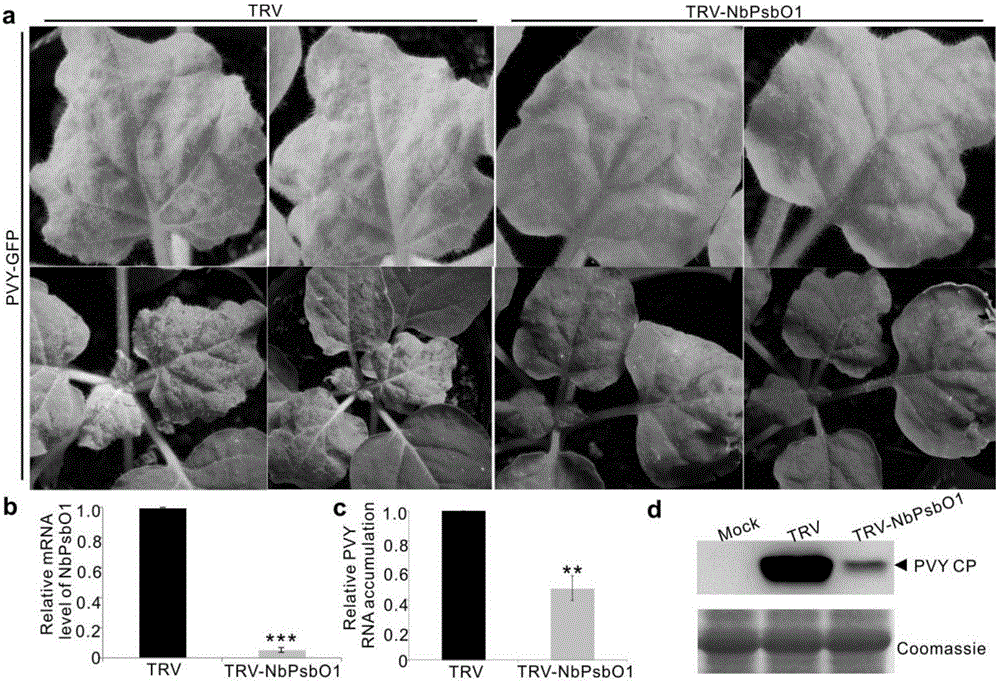
Screening and application of plant antiviral new target PsbO1
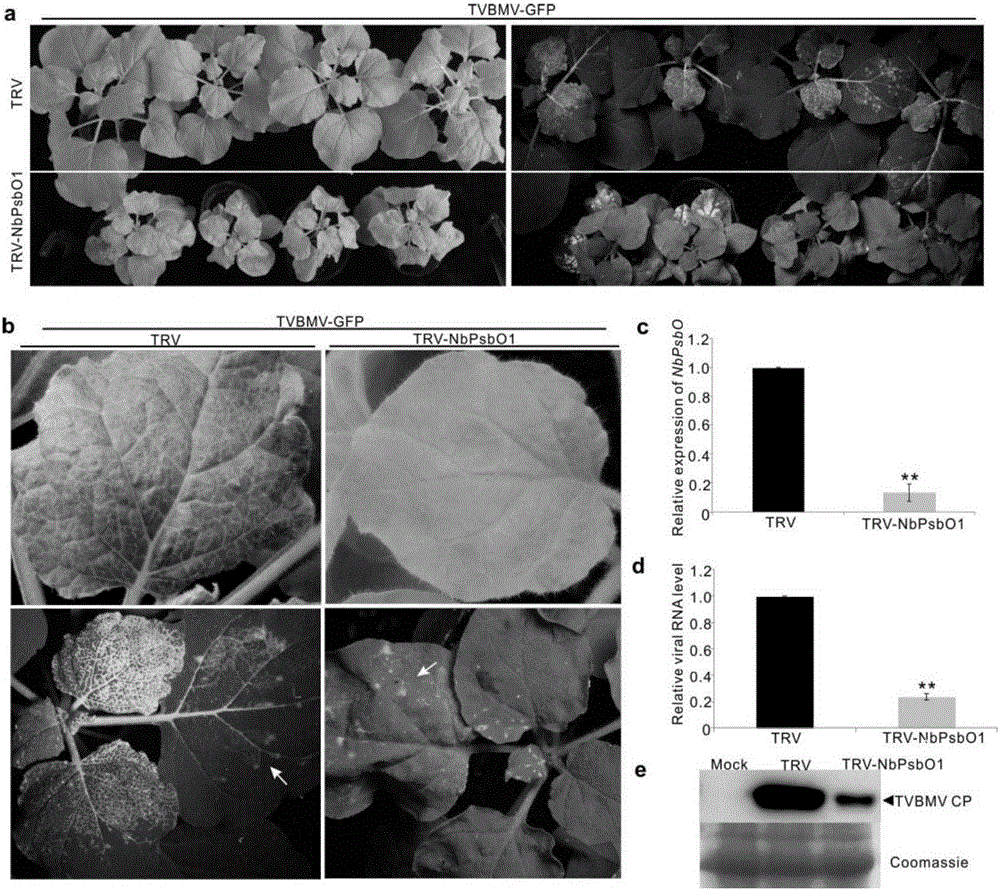
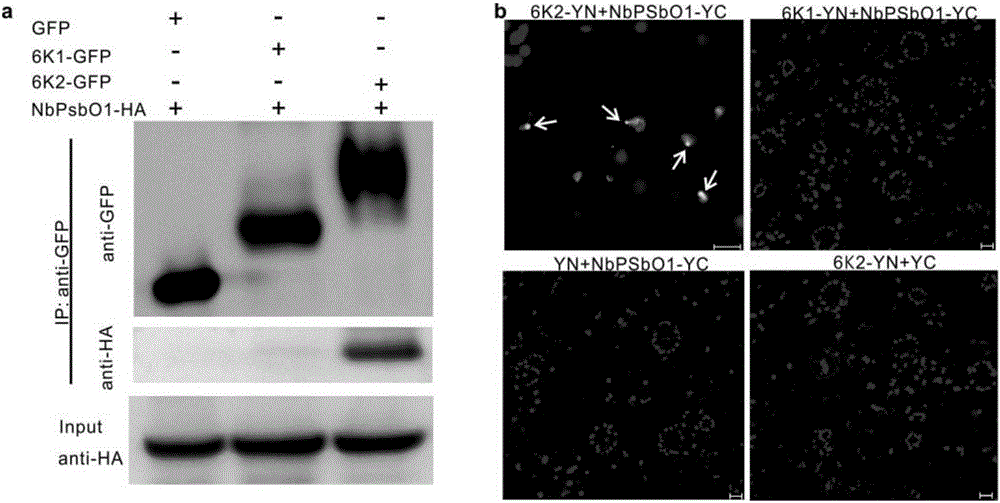
InactiveCN106699857AReduce infestationPlant peptidesGenetic engineeringNicotiana tabacumPotato virus Y PVY
The invention relates to the field of plant antiviral genetic engineering, and provides a plant antiviral new target. On the basis of tobacco vein banding mosaic virus infection cloning, photosystem II oxygen-evolving complex protein PsbO1 is screened through immunoprecipitation and mass spectrography, and a PbsO1 gene is obtained through reverse transcription PCR amplification. Immunoprecipitation and bimolecular fluorescence complementation prove that the PsbO1 can interact with the tobacco vein banding mosaic virus 6K2. Reduction in expression of the PsbO1 gene enables an infected plant to generate resistance to the tobacco vein banding mosaic virus and potato virus Y.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
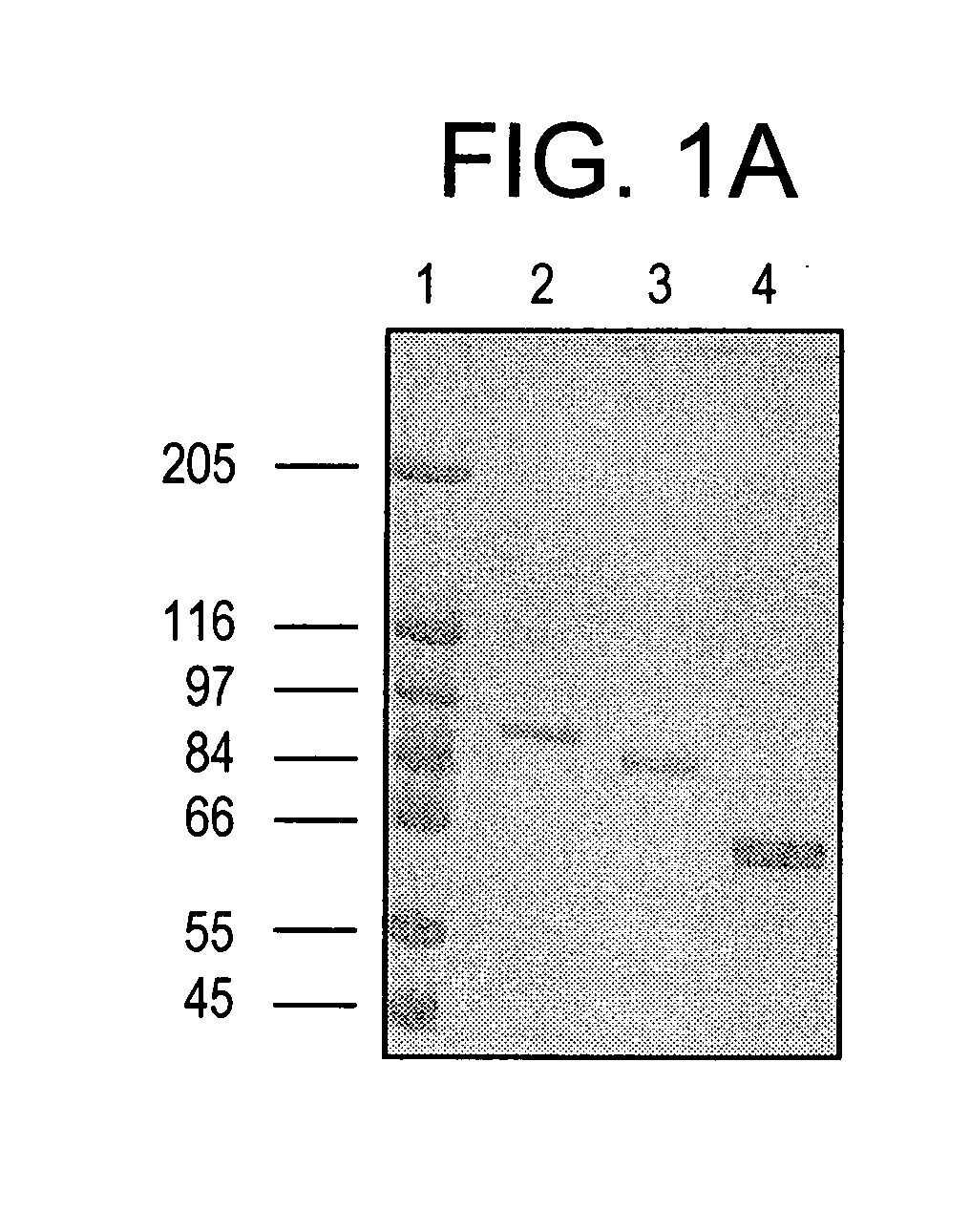
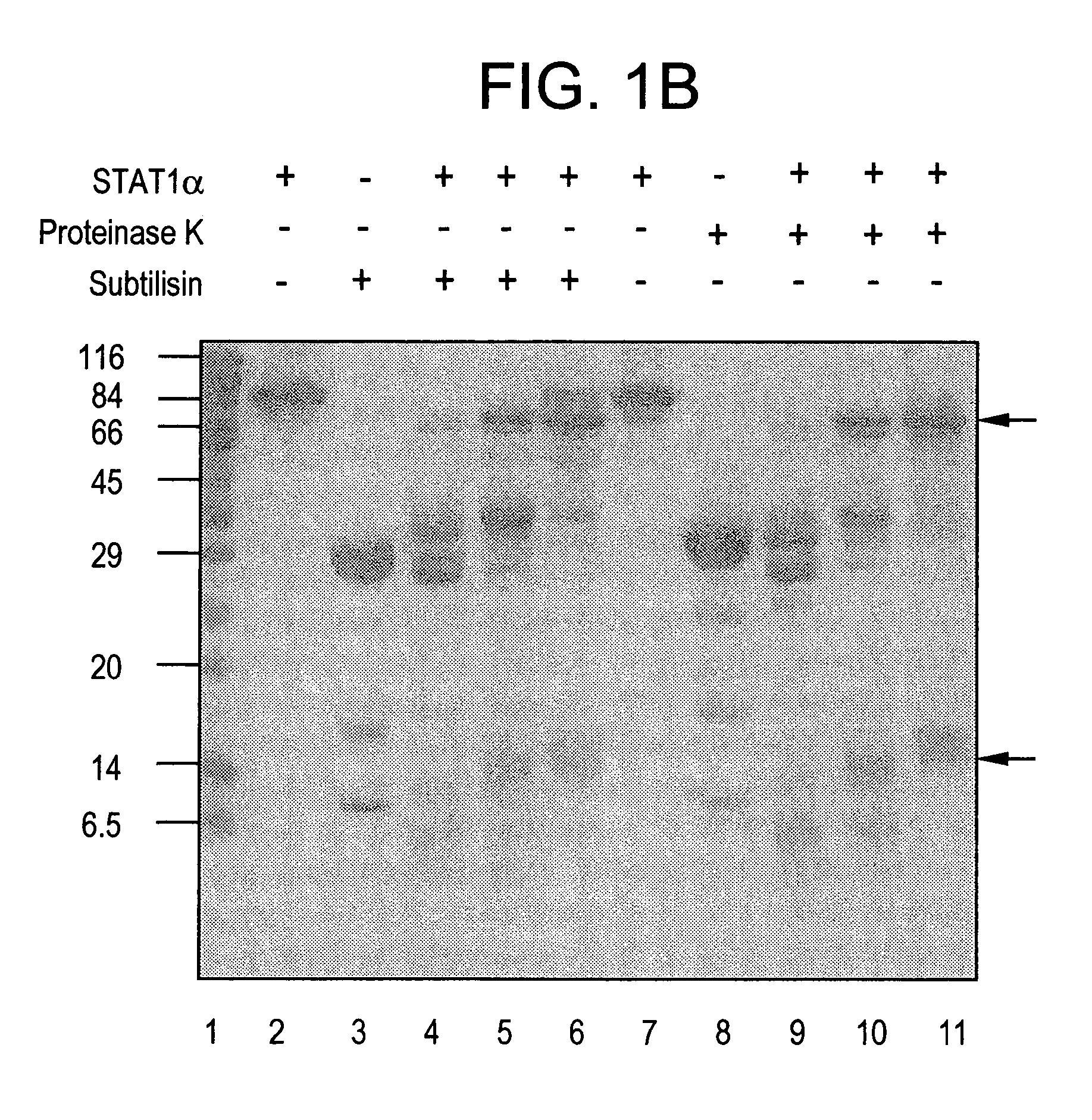
Purified Stat proteins and methods of purifying thereof
InactiveUS20060160152A1High binding affinityImprove throughputCompound screeningVirusesEscherichia coliCysteine thiolate
The present invention describes methods of producing milligram quantities of three forms of purified Stat1 protein from recombinant DNA constructs. In addition, the Stat proteins may be isolated in their phosphorylated or nonphosphorylated forms (Tyr 701). The proteins can be produced in baculovirus infected insect cells, or E. coli. A compact domain in the amino terminus of Stat1α was isolated and found to enhance DNA binding due to its ability to interact with a neighboring Stat protein. A relatively protease-resistant recombinant truncated form of the Stat protein was isolated in 40-50 mg quantities. Purification of the Stat proteins were performed after modifying specific cysteine residues of the Stat proteins to prevent aggregation. Activated EGF-receptor partially purified from membranes by immunoprecipitation was shown to be capable of in vitro catalysis of the phosphorylation of the tyrosine residue of Stat1 known to be phosphorylated in vivo. Techniques are enclosed to separate the phosphorylated from the nonphosphorylated Stat proteins. The techniques disclosed are general for Stat proteins and may be used to isolate large quantities of purified Stat 2, 3, 4, 5A, 5B and 6. Methods for using purified Stat proteins, truncated Stat proteins, or Stat N-terminal fragments for drug discovery are also disclosed.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Yunnan red pear PybMYB gene as well as prokaryotic expression vector and application thereof
InactiveCN103146710AStrong specificityPrecise positioningImmunoglobulins against plantsPlant peptidesEscherichia coliImmunoprecipitation
The invention discloses a Yunnan red pear PyMYB gene through pigment synthesis regulation and trichome development regulatory protein as well as a prokaryotic expression vector thereof and an application of the prokaryotic expression vector. The PyMYB gene is cloned from red fruit peel of Yunnan red pear NO.1 by using a RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) technology, and then the gene is expressed in escherichia coli Rosetta (DE3) by using the prokaryotic expression vector and is purified by a GST (Glutathione S-transferase) gel column purification method to obtain a Yunnan red pear PyMYB purified protein, wherein the Yunnan red pear PyMYB purified protein is used for the preparation of a PyMYB specific antibody and the application thereof in a PyMYB protein expression detection and immunoprecipitation, a chromatin co-immunoprecipitation and a fusion protein sedimentation experiment. The antibody prepared by the invention is strong in specificity, can accurately detect subcellular localization of the PyMYB protein, and is used for verifying protein interaction in the co-immunoprecipitation experiment, efficiently separating the protein and DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) segment combined by the PyMYB protein and detecting the expression of the antibody in a transgenic plant.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
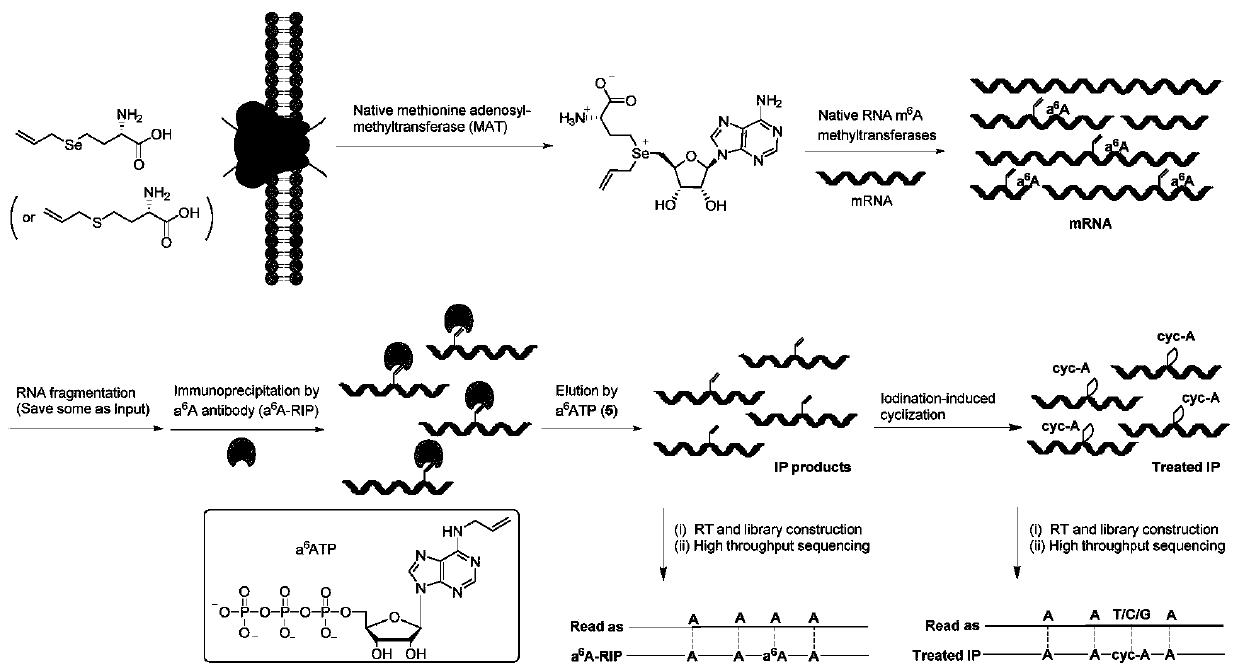
Method and kit for detecting RNA N6-methyladenosine modification at single-base resolution in range of whole transcriptome
ActiveCN111154837AAccurate resolutionHigh precisionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingBase JChemical treatment
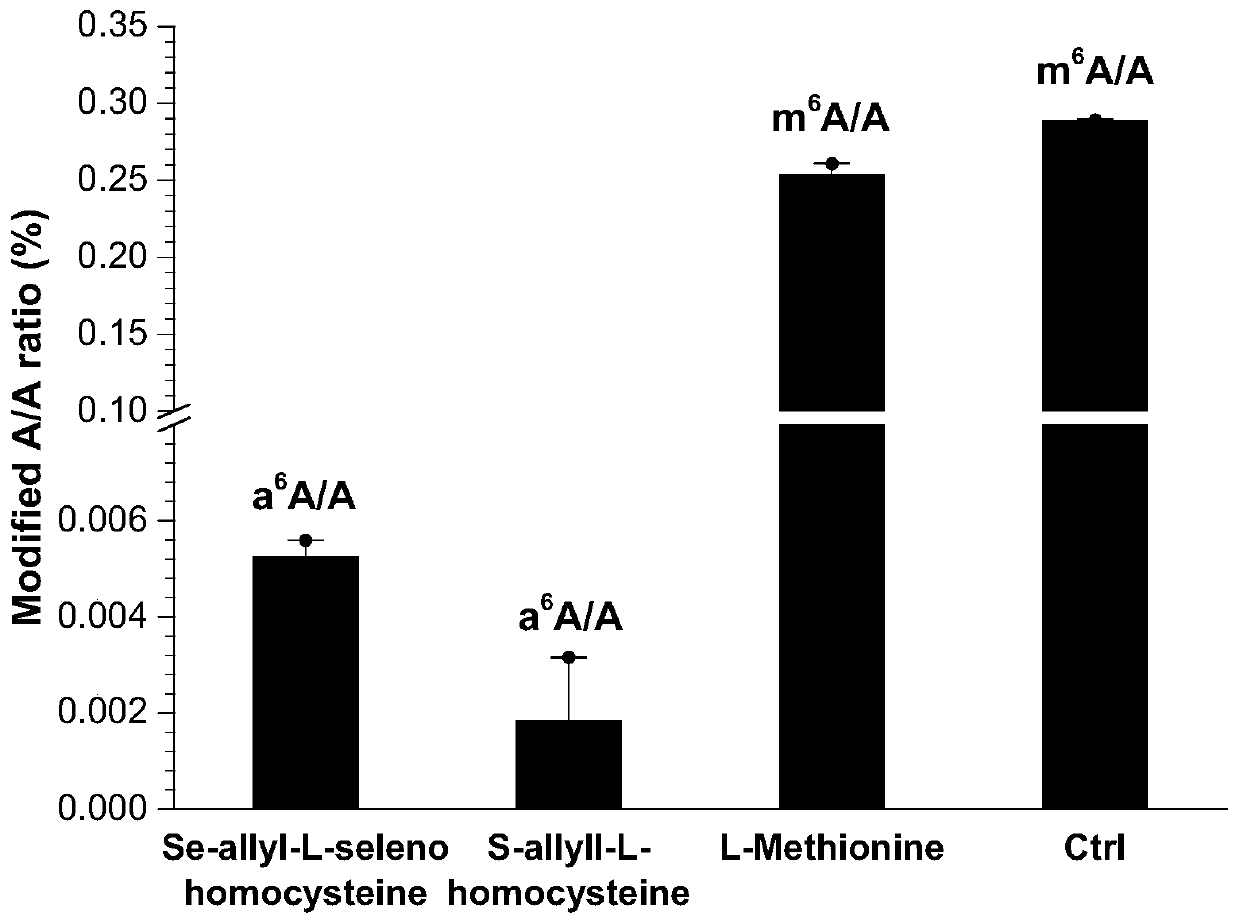
The invention provides a method and kit for detecting RNA N6-methyladenosine modification at single-base resolution in a range of a whole transcriptome. According to the method, on the basis of an N6-allyl label of in-vivo ribonucleic acid (RNA) adenine and chemical treatment, base mutation of the in-vivo ribonucleic acid (RNA) adenine in a process of reverse transcription into DNA is induced, andthen a mutation site is recognized by means of nucleic acid sequencing, so that an a6A site is obtained, and the a6A site is a site originally modified by m6A in cell RNA. By means of the method, thespecific label of N6-allyladenine in a cell is achieved for the first time, and the label not only can be used for replacing an N6-methyladenosine site in the cell, but also can be positioned by means of mutation sequencing. Compared with existing gene sequencing technologies applied to m6A detection, the method for detecting RNA N6-methyladenosine modification at single-base resolution in the range of the whole transcriptome has the advantage that due to the fact that the mutation site can be accurate down to single-base resolution, the precision of m6A site detection based on m6A antibody immunoprecipitation and a massively parallel sequencing method which are currently and generally adopted is improved, so that the method for detecting RNA N6-methyladenosine modification at single-baseresolution in the range of the whole transcriptome is a direct high-throughput single-base identification method.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
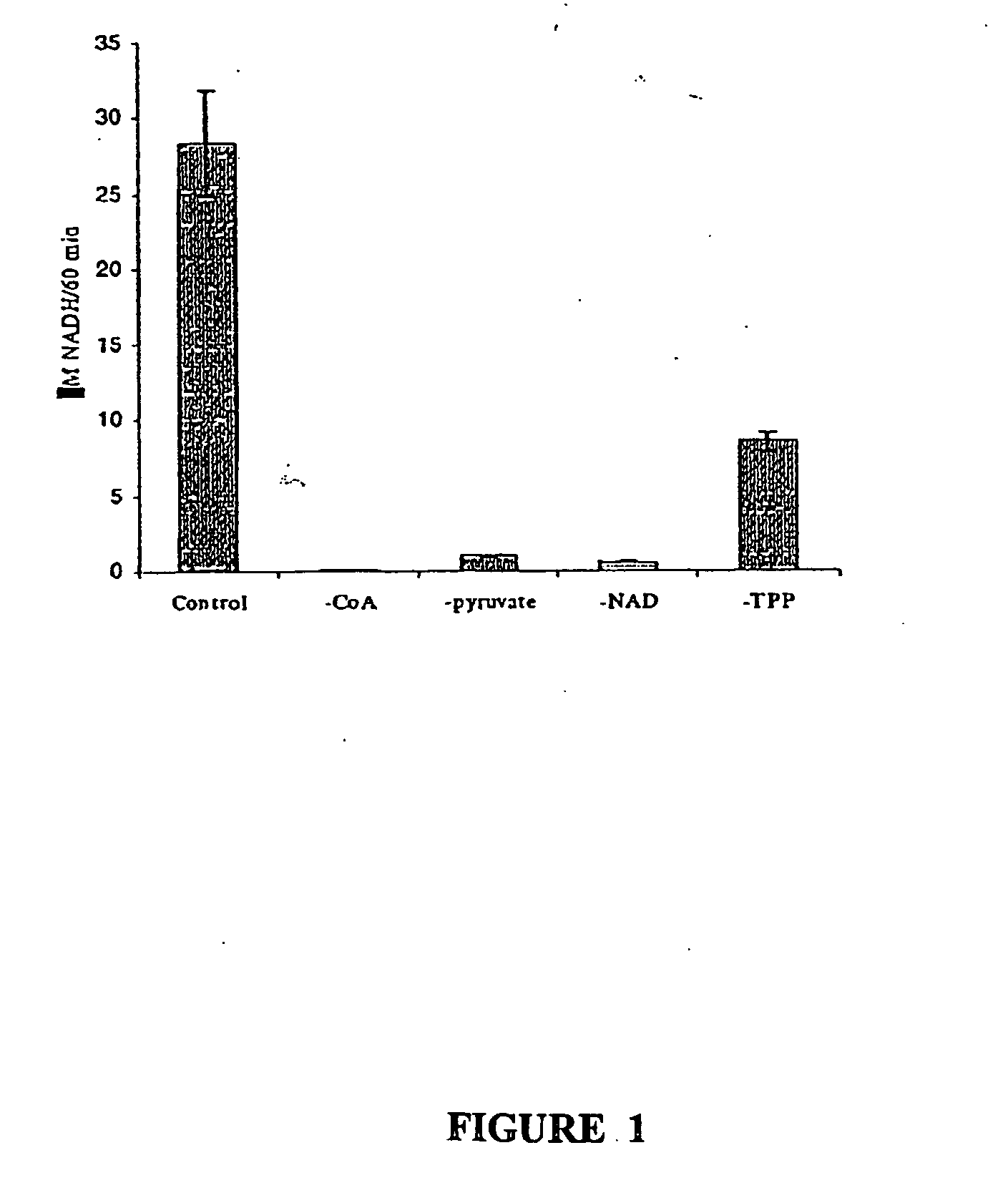
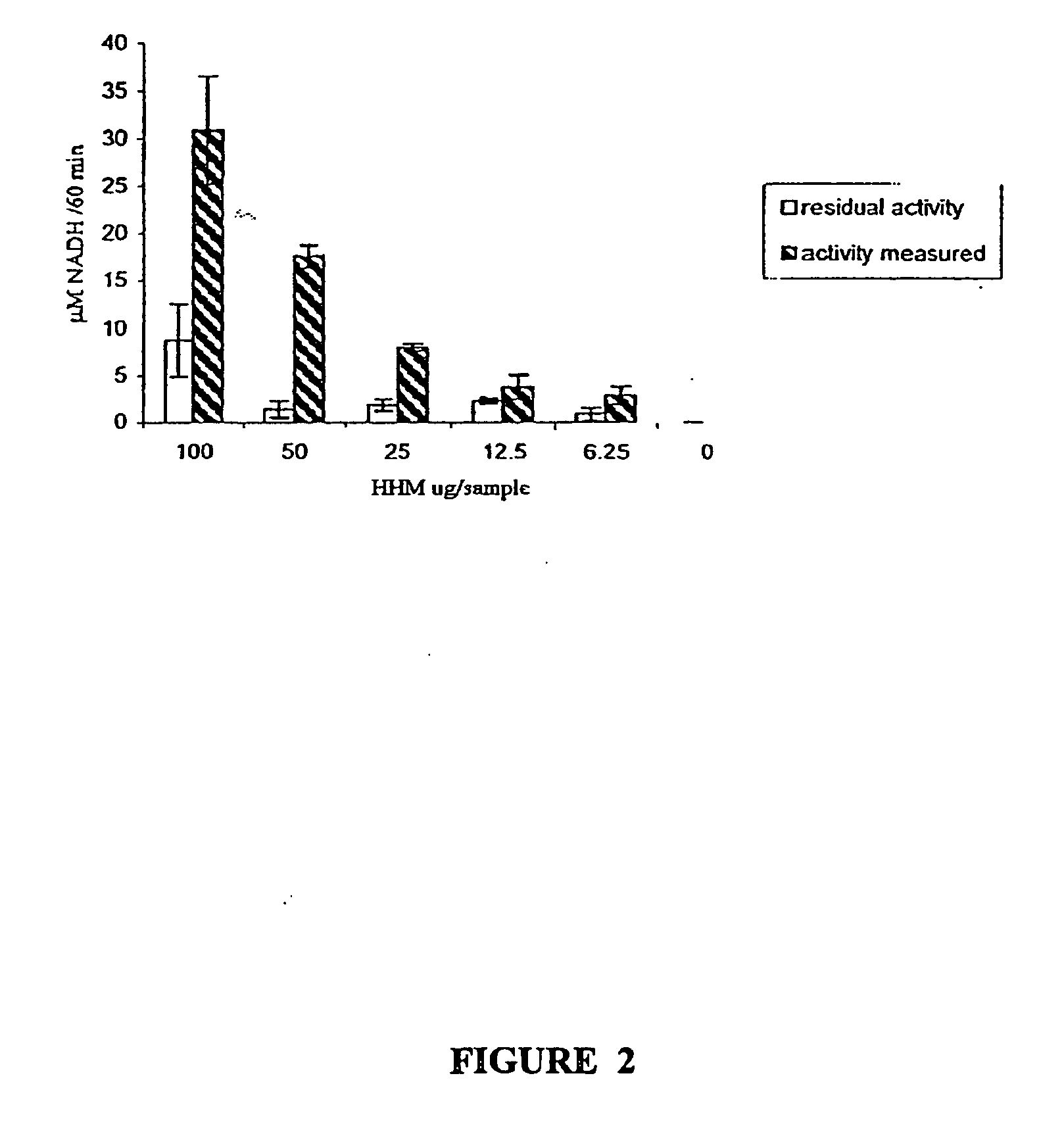
Immunocapture-based measurements of mammalian pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
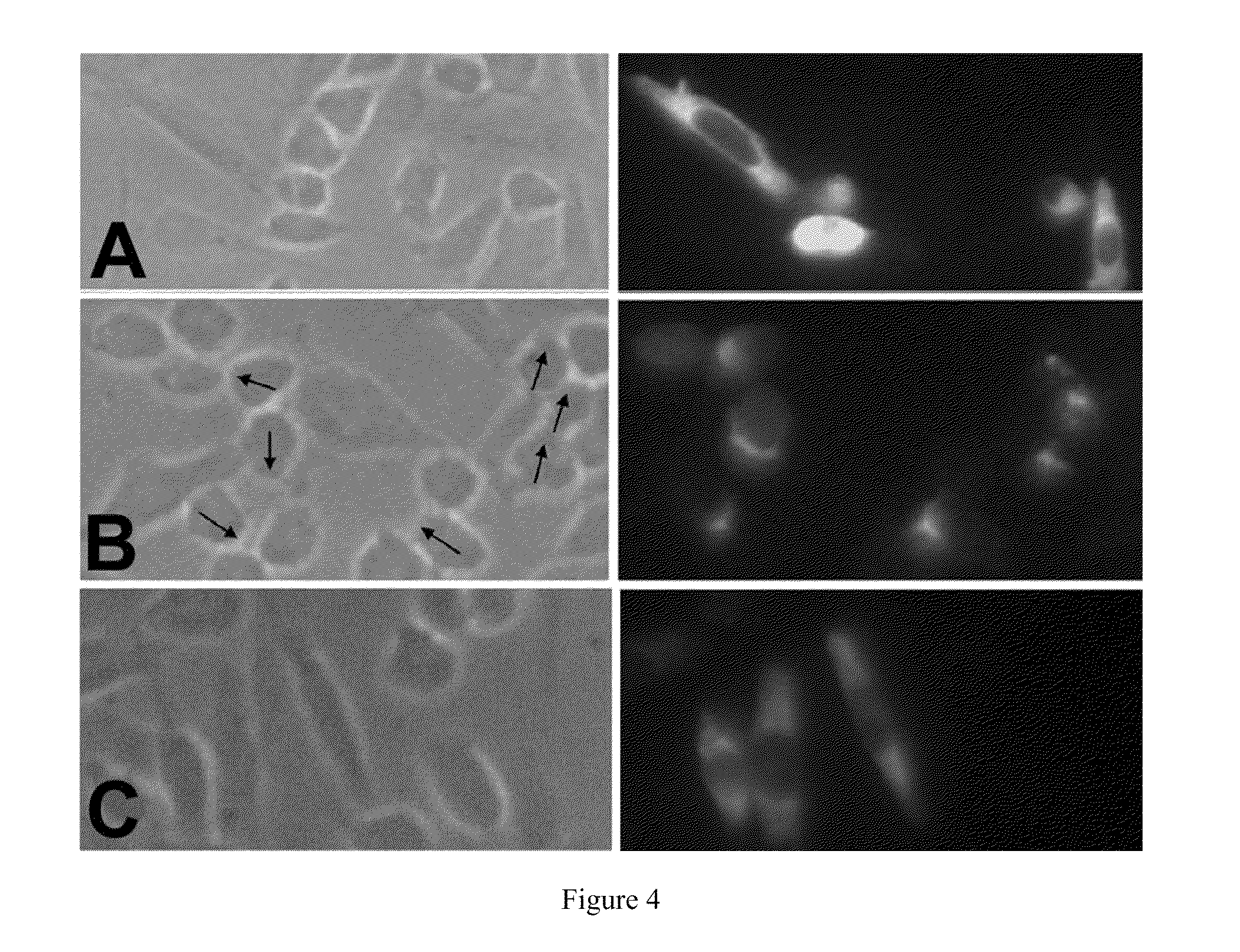
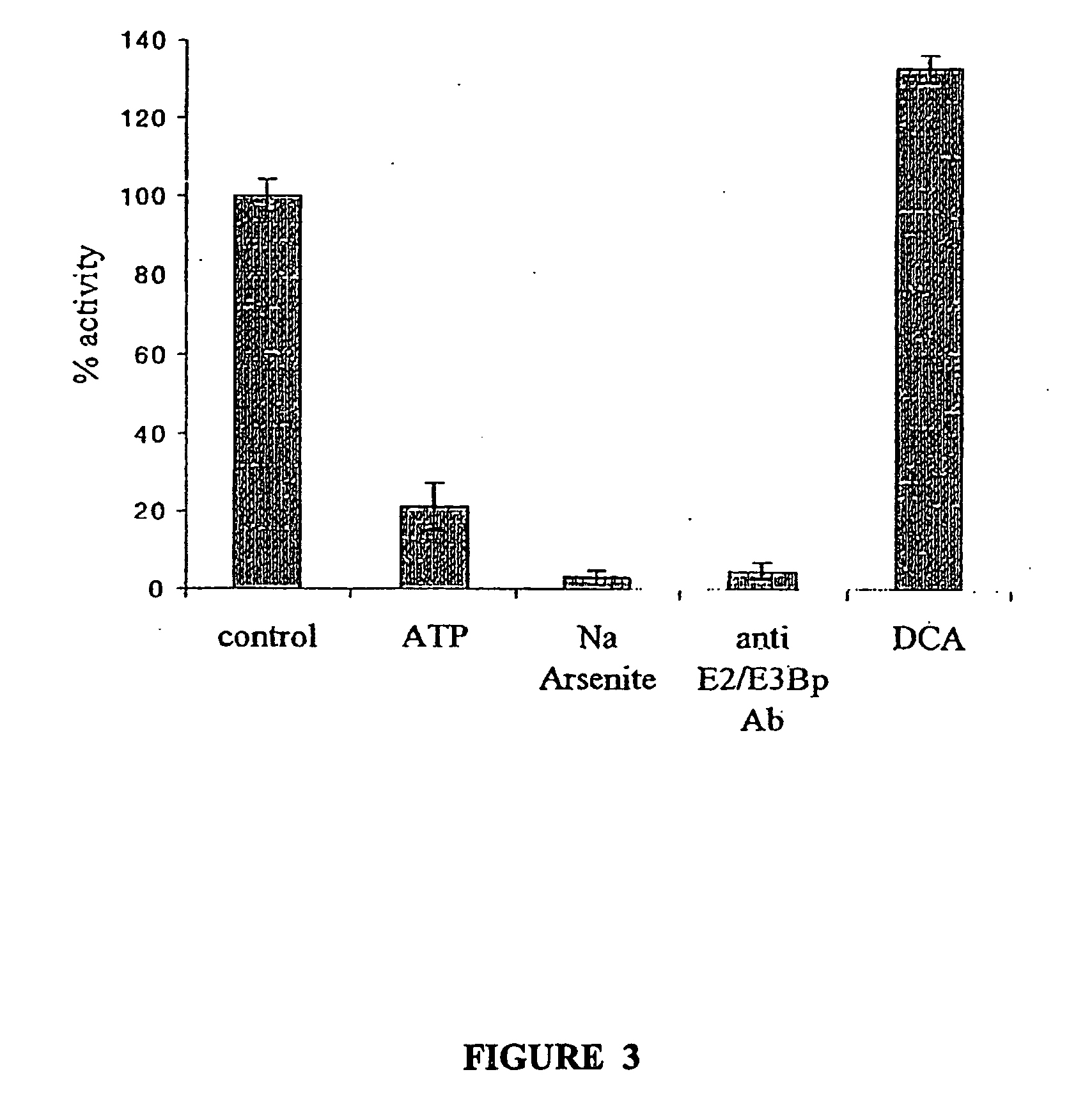
The present invention is based on the discovery that an antibody specific for PDH complex can be used to immunoprecitate PDH complex from the patient sample in an active state. Therefore the anti-PDH complex specific antibody can be used to determine the amount of and / or active state of PDH in a patient sample. The invention immunoassay methods for determining the amount and / or active state of PDH complex present in a patient sample are useful for screening to identify individuals having symptoms indicating malfunction of PDH complex. For example, the invention methods can be used to screen individuals for symptoms of onset of the diabetic state, such as insulitis, and for diagnosing late onset diseases, such as diabetes, Alzheimer's and the like.
Owner:MITOSCI
Plasma biomarker tool for the diagnosis of liver cancer comprising liver carboxylesterase 1 and liver cancer screening method
ActiveUS8198038B2Efficient detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisFluorescenceScreening method
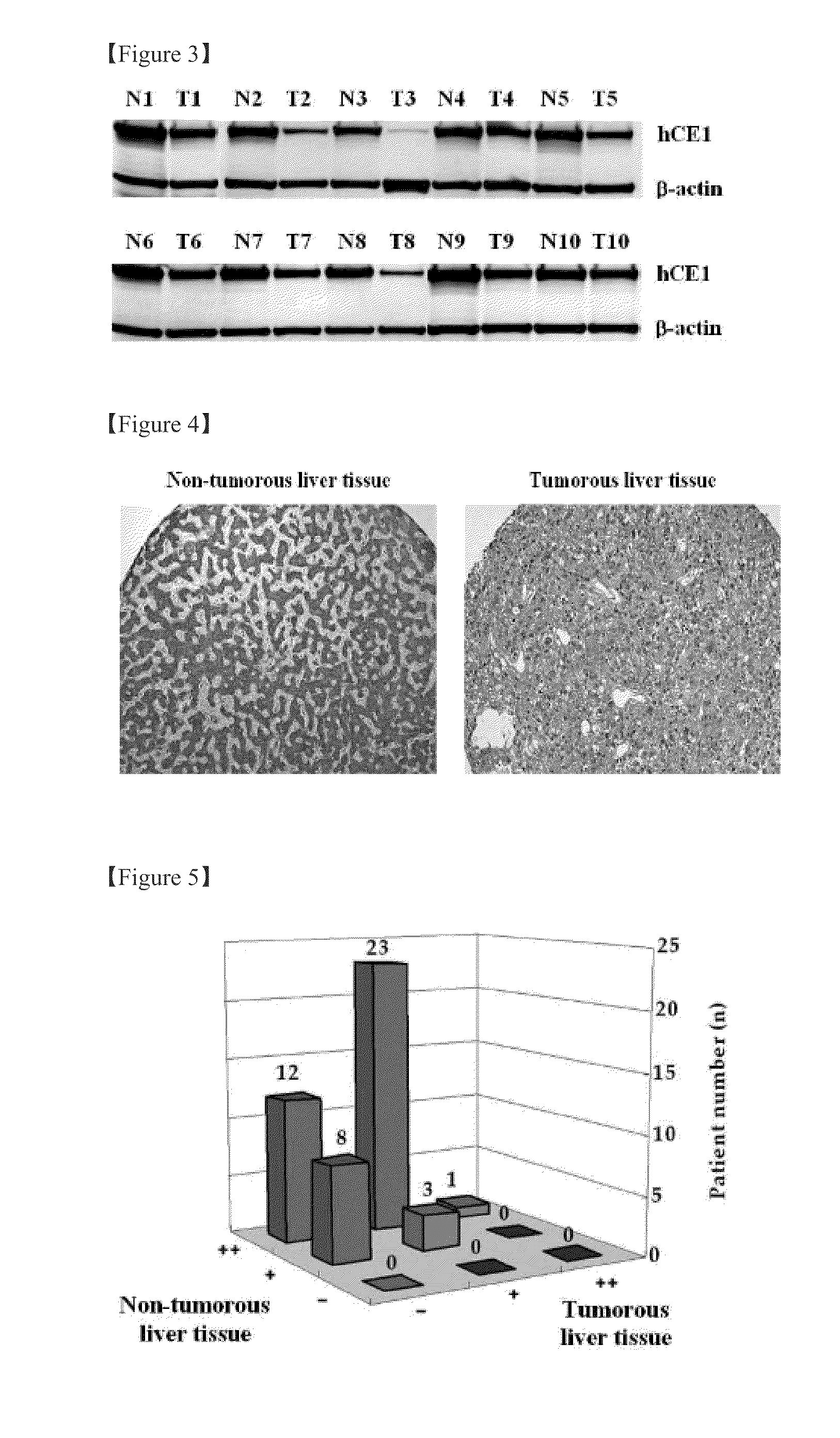
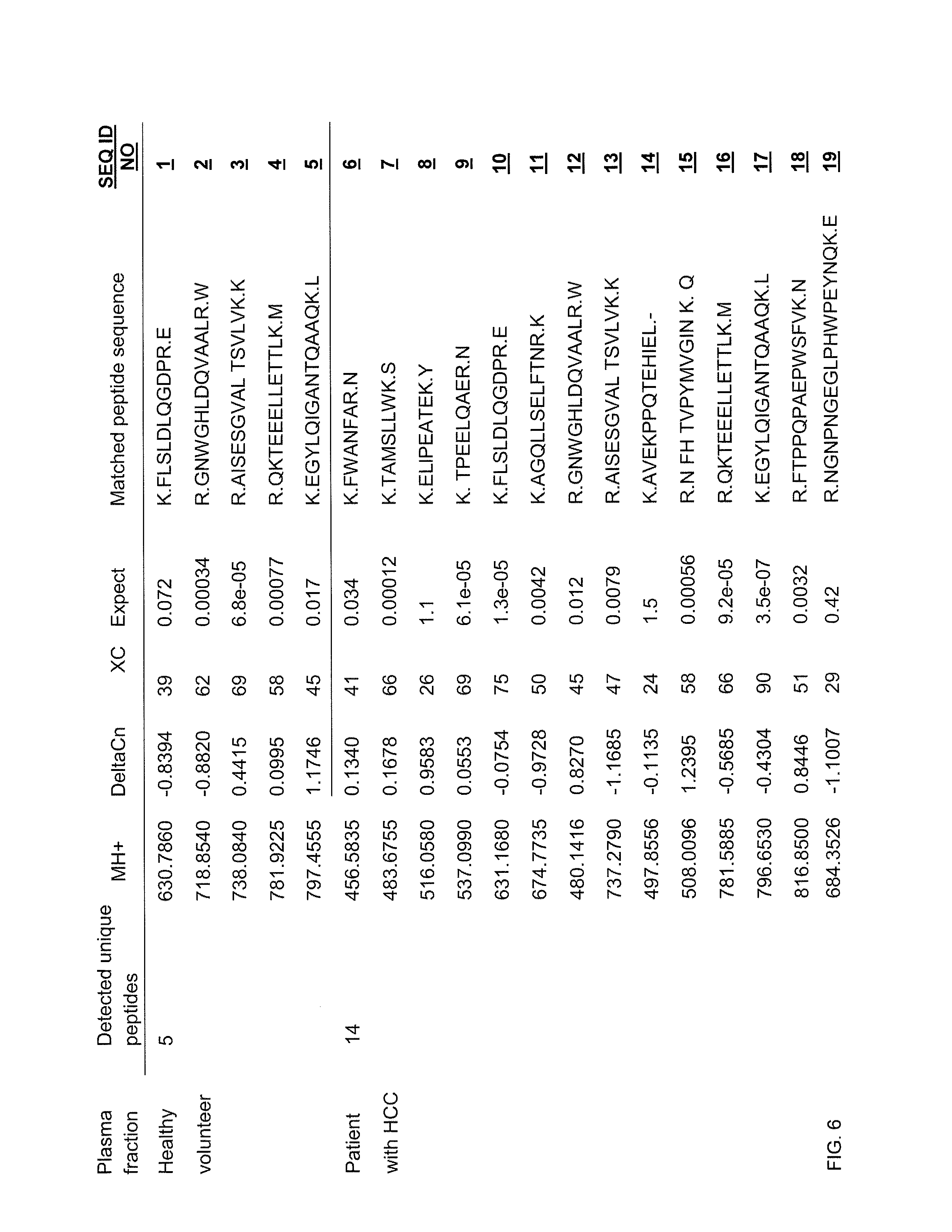
The present invention relates to a plasma biomarker for diagnosing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), in particular to the discovery of a protein in plasma using 2-D fluorescence differential gel electrophoresis (2-D DIGE), immunoprecipitation and Nano-liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (Nano-LC-MS / MS) system that was unknown on the basis of conventional techniques. By demonstrating the presence of liver carboxylesterase 1 (hCE1) in human plasma and confirming that its secretion level is higher in patients with HCC than in healthy volunteers, this invention may be used as a screening method to diagnose HCC at an early stage.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
Device and method to perform multiplex assays and target enrichment
A device termed the MobileArray™ device and methods, which form the MobileArray™ system, are disclosed for performing multiplex assays, target enrichment or purification. The device and methods disclosed enable the performing of multiplex assays, target enrichment or purification in a simplified manner. The MobileArray™ device gains the advantages and applications of the advanced multiplexing platforms, but does not require the special expensive equipment, reagents, software or dedicated operators. In addition, the MobileArray™ system can also be utilized in immunoprecipitation and target enrichment or purification in a multiplex manner. Furthermore, the MobileArray™ system can be integrated in an automated procedure. The MobileArray™ system makes it possible to apply multiplexing protocols in routine clinical practice, food safety inspection and general life science research laboratories.
Owner:DIGITAL BIOTECH LLC
Method of identifying active chromatin domains
The invention provides a method of mapping DNA-protein interactions within a genome by fixing living cells to cross-link DNA and proteins, lysing the cells, and isolating chromatin by immunoprecipitation. DNA is purified and a SAGE protocol is performed on the purified DNA to produce GMAT-tag sequences, which are compared to a genomic sequence of the living cells to map DNA-protein interactions. The invention further provides a method of identifying an active chromatin domain and a method of identifying aberrant chromatin acetylation, wherein chromatin immunoprecipitation is performed using an antibody recognizing acetylated histone protein.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE US REPRESENTED BY THE SEC
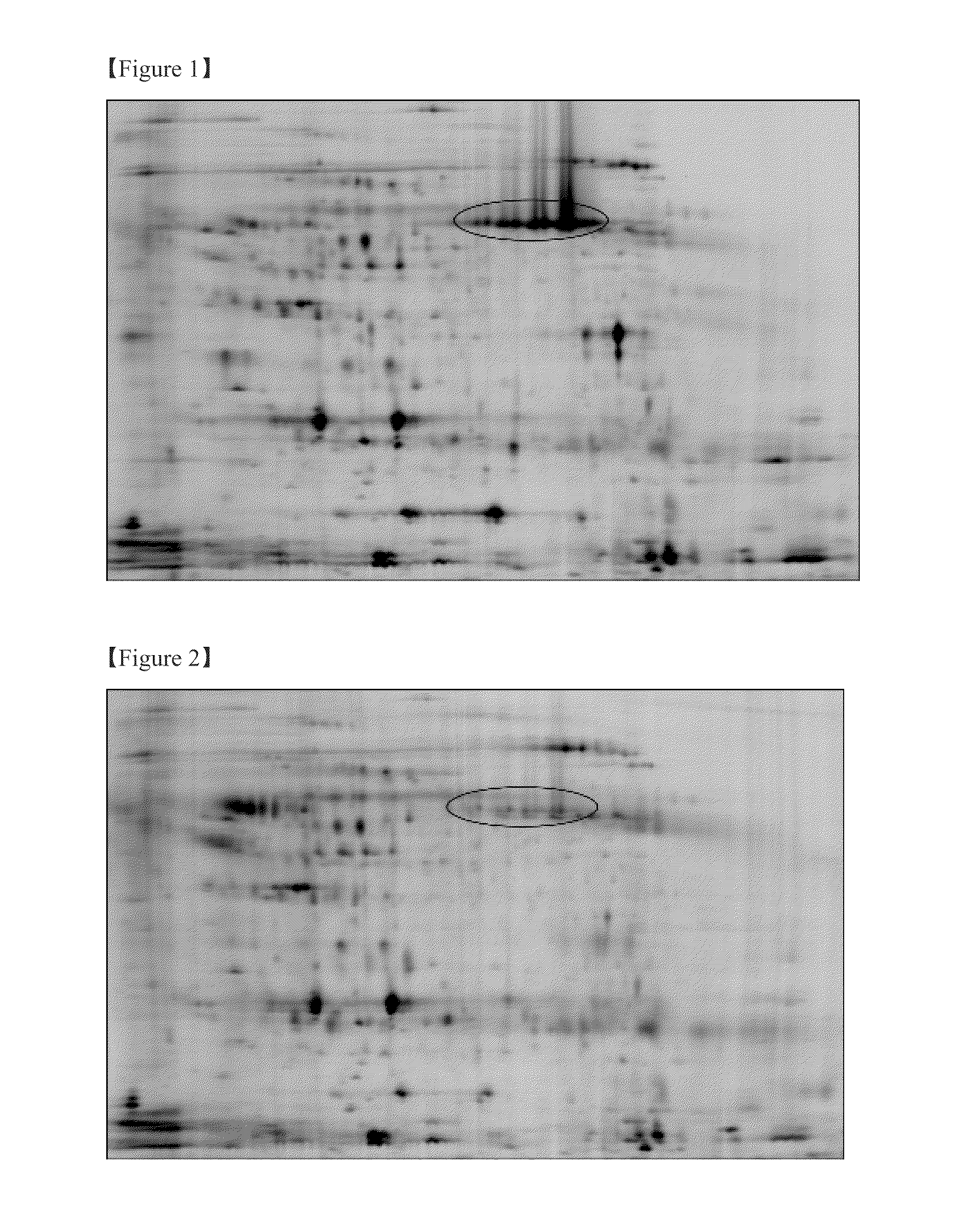
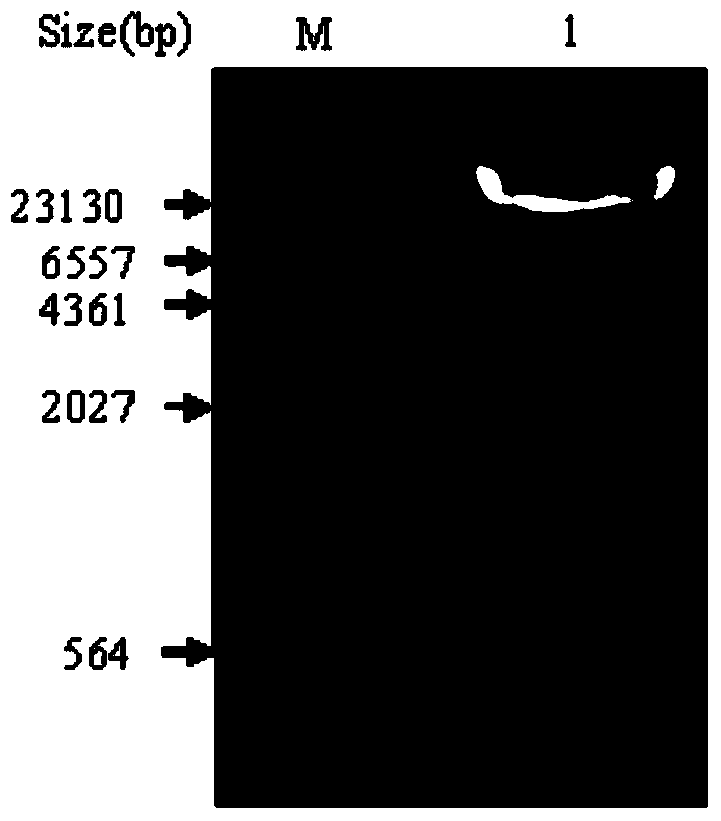
Yunnan red pear [delta]PybHLH gene and prokaryotic expression vector and application thereof
The present invention discloses a biological synthesis of a Yunnan red pear anthocyanidin and a specific segment [delta]PybHLH of a trichome generating developmental regulation protein PybHLH gene and a prokaryotic expression vector thereof. By cloning the specific fragment [delta]PybHLH from Yunnan red pears through RT-PCR technology, and constructing a prokaryotic expression vector thereof and expressing in escherichia coli, a Yunnan red pear [delta]PybHLH purified protein is obtained. The Yunnan red pear [delta]PybHLH purified protein is applied to the preparation of a PybHLH specific antibody which can be used for a PybHLH expression detection, immunoprecipitation and chromatin immunization coprecipitation. The antibody has a strong specificity, can accurately detect subcellular positioning of the PybHLH protein, efficiently conduct the purification of the PybHLH protein, separate proteins and DNA fragments combined by the PybHLH protein and detect expressing condition thereof in transgenic plants.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Phosphorylation antibody chip kit for detecting human receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK)
ActiveCN106918698ASimplified steps for fixing to glass slidesHigh sensitivityBiological material analysisBiological testingBiotin-streptavidin complexPhosphorylation
The invention relates to a phosphorylation antibody chip kit for detecting human RTK. The phosphorylation antibody chip kit for detecting human RTK comprises: a solid-phase vector, which is a standard film or slide coated with a specific antibody; a cleaning solution, which comprises a 20X concentrated cleaning solution of 0.1% Tween-20 and a dilution solution thereof; a sample diluting solution; a dilution solution used for diluting the antibody and HRP-streptavidin; a biotinylated detection antibody mixture; a 300X concentrated fluorescein-streptavidin solution; a sample treating solution, which is a 2X cell lysis buffer; and the specific antibody, which is targeted to 71 proteins. The RTK phosphorylation antibody chip kit provided by the invention can rapidly, simply and accurately determine the situations of phosphorylation of 71 proteins in a RTK pathway through one experiment; and pathway activation in cells can be rapidly detected by monitoring the phosphorylation changes of proteins in an experimental model system without complicated immunoprecipitation and blotting.
Owner:RAYBIOTECH INC GUANGZHOU
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com






![Yunnan red pear [delta]PybHLH gene and prokaryotic expression vector and application thereof Yunnan red pear [delta]PybHLH gene and prokaryotic expression vector and application thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/b9c76cd0-e691-49d8-9672-ca8f208bbd5e/120113150934.PNG)
![Yunnan red pear [delta]PybHLH gene and prokaryotic expression vector and application thereof Yunnan red pear [delta]PybHLH gene and prokaryotic expression vector and application thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/b9c76cd0-e691-49d8-9672-ca8f208bbd5e/120113150937.PNG)
![Yunnan red pear [delta]PybHLH gene and prokaryotic expression vector and application thereof Yunnan red pear [delta]PybHLH gene and prokaryotic expression vector and application thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/b9c76cd0-e691-49d8-9672-ca8f208bbd5e/120113150940.PNG)