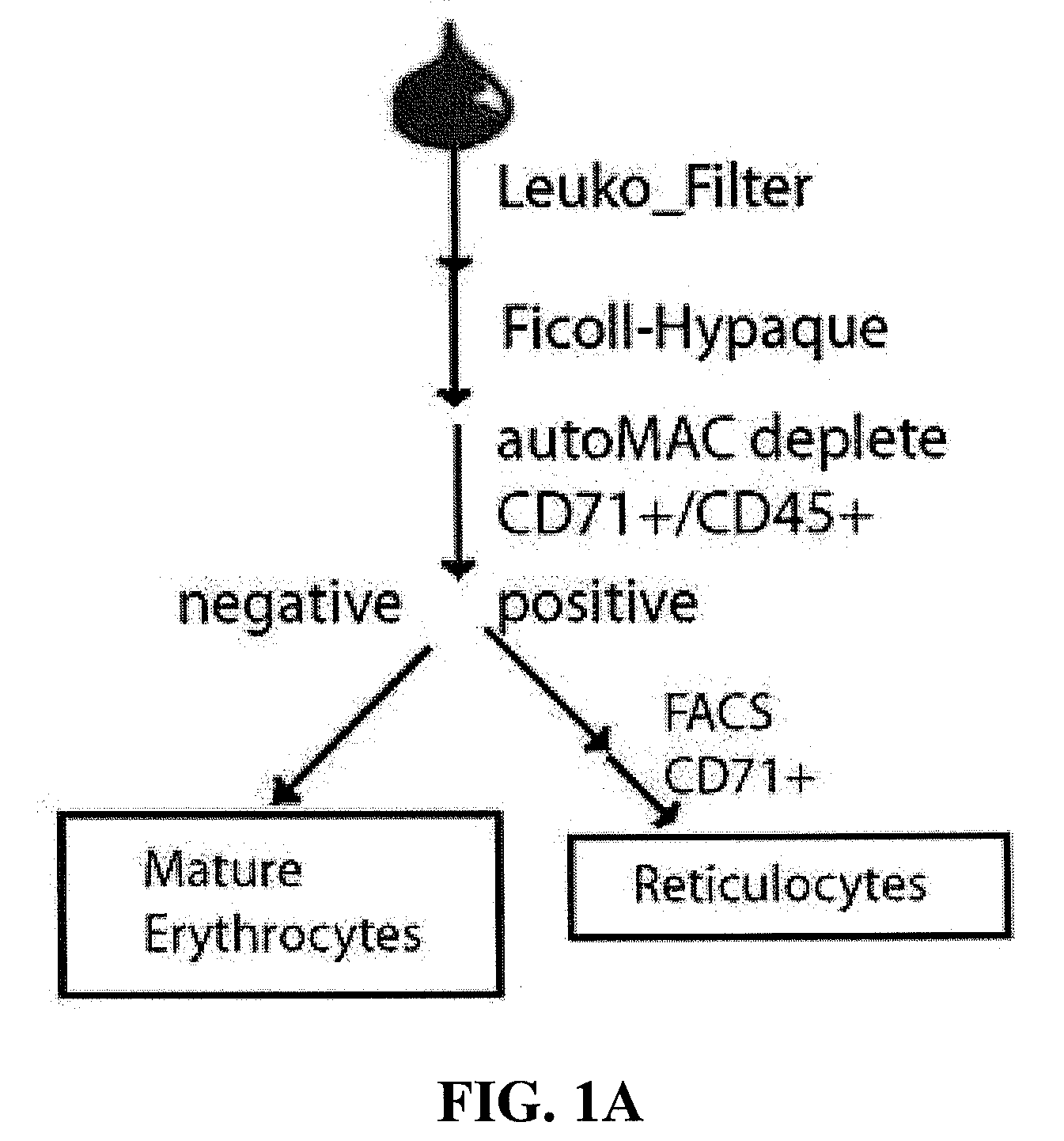
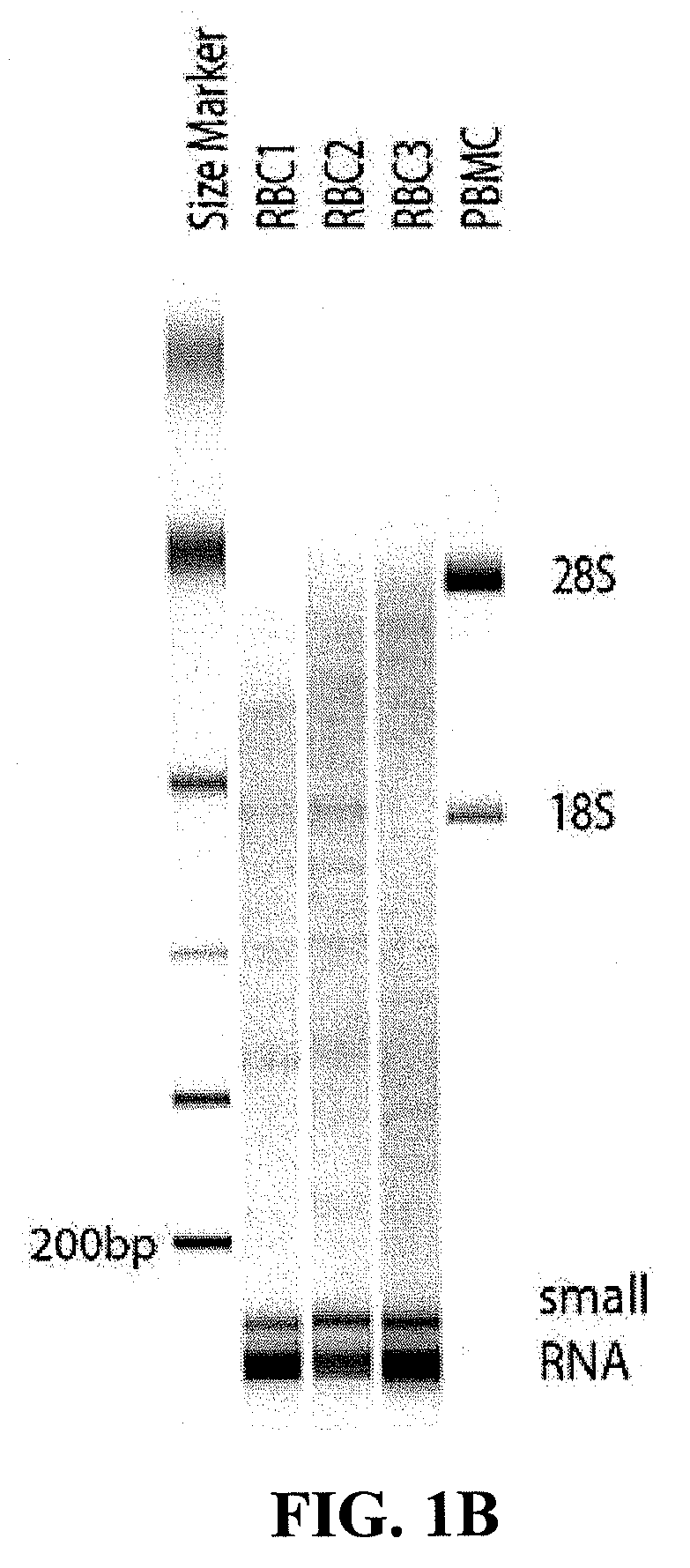
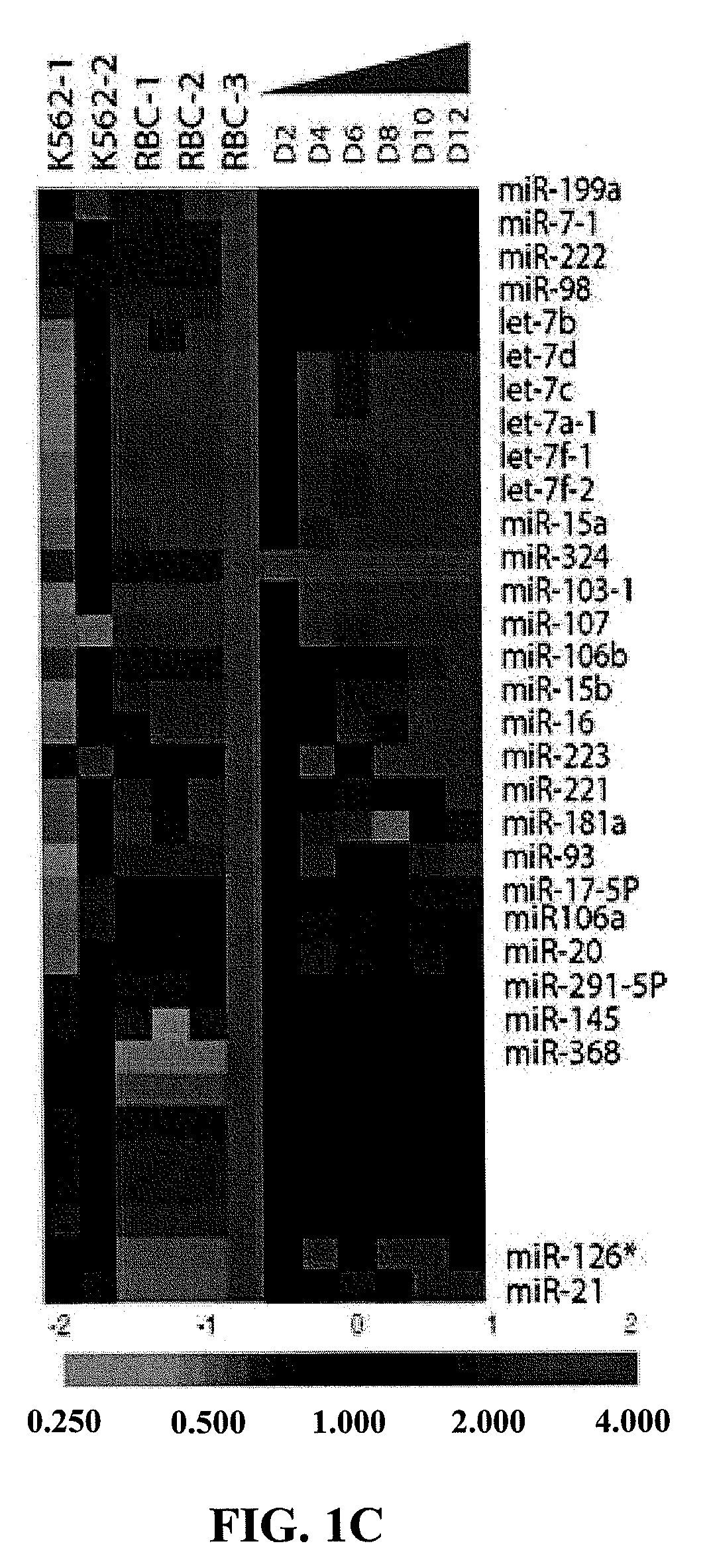
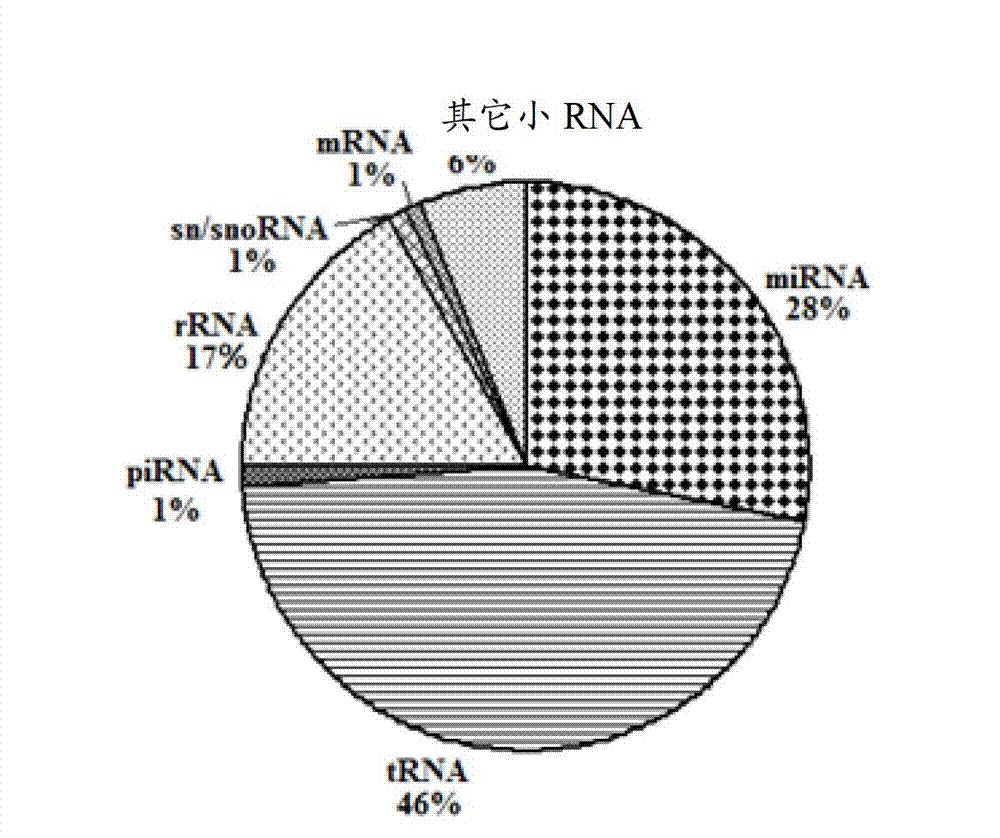
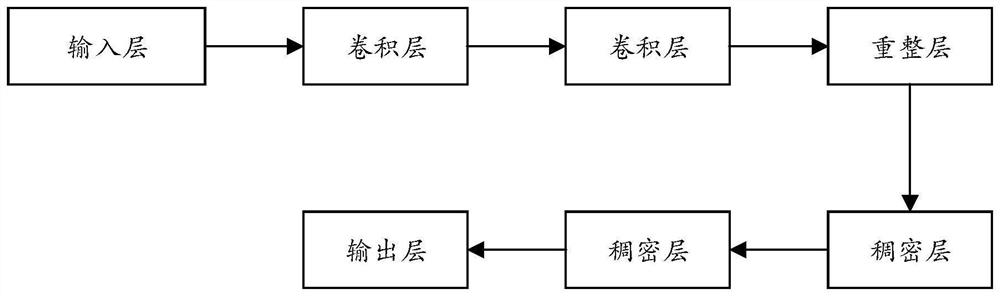
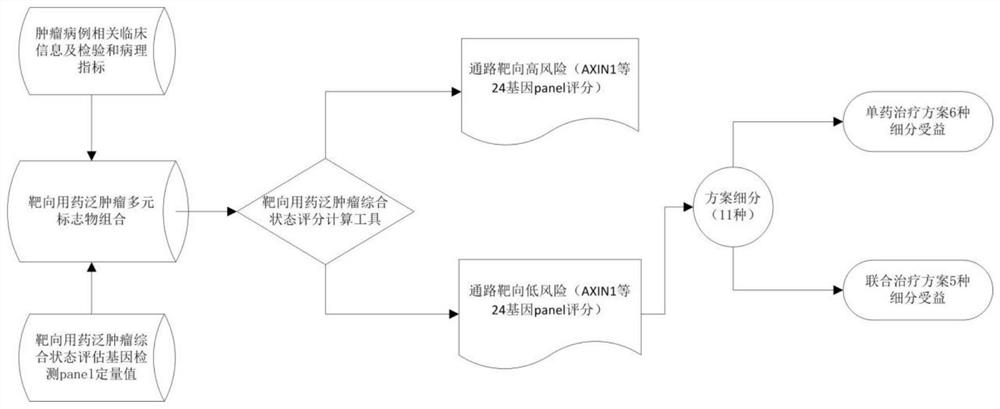
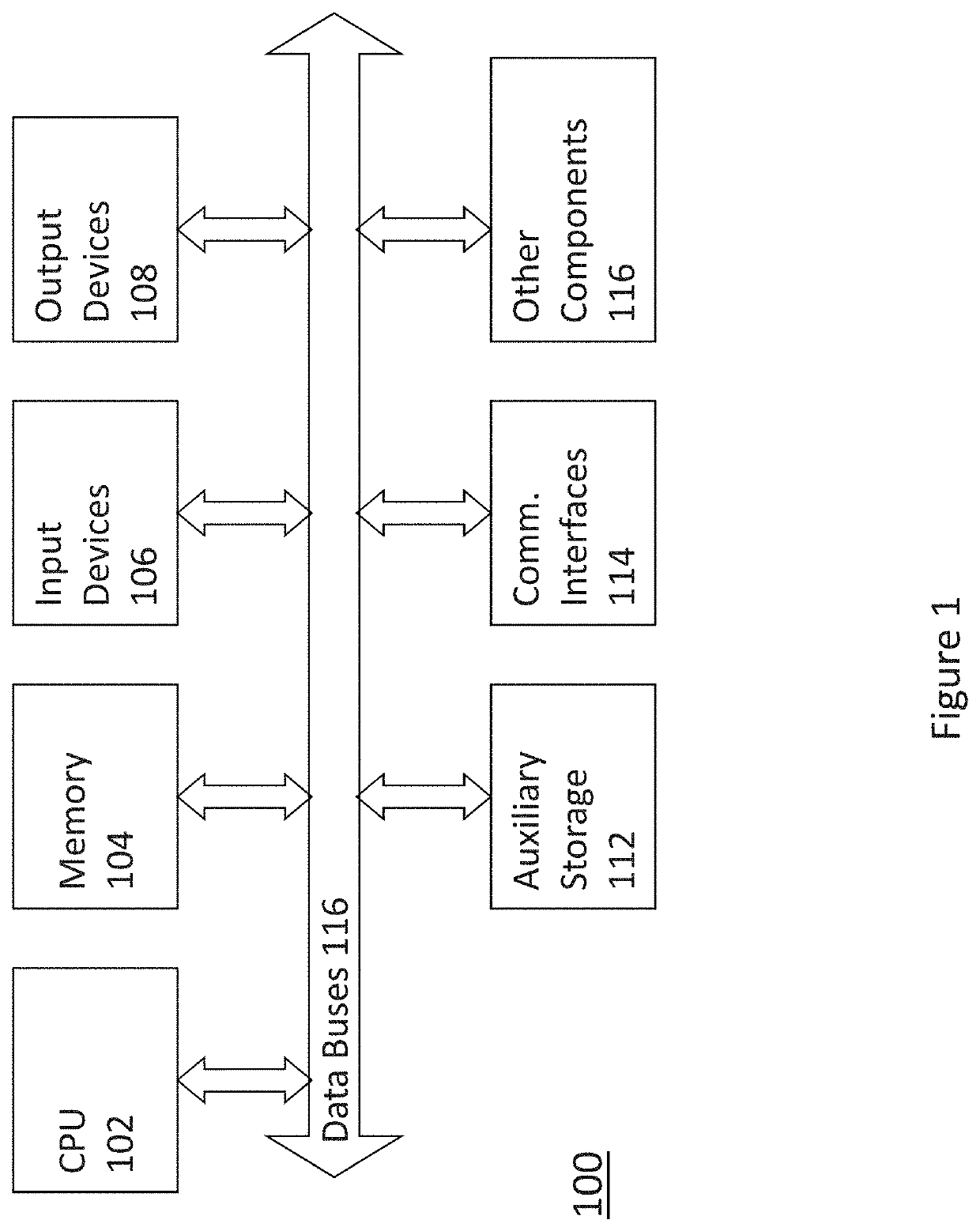
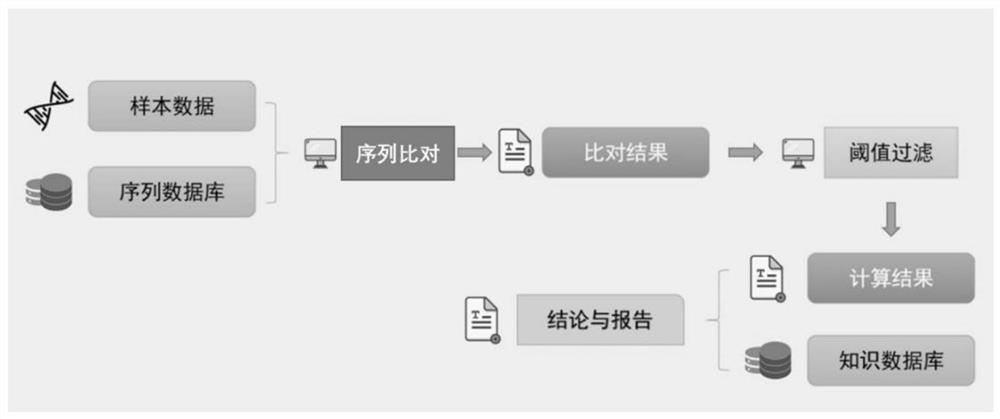
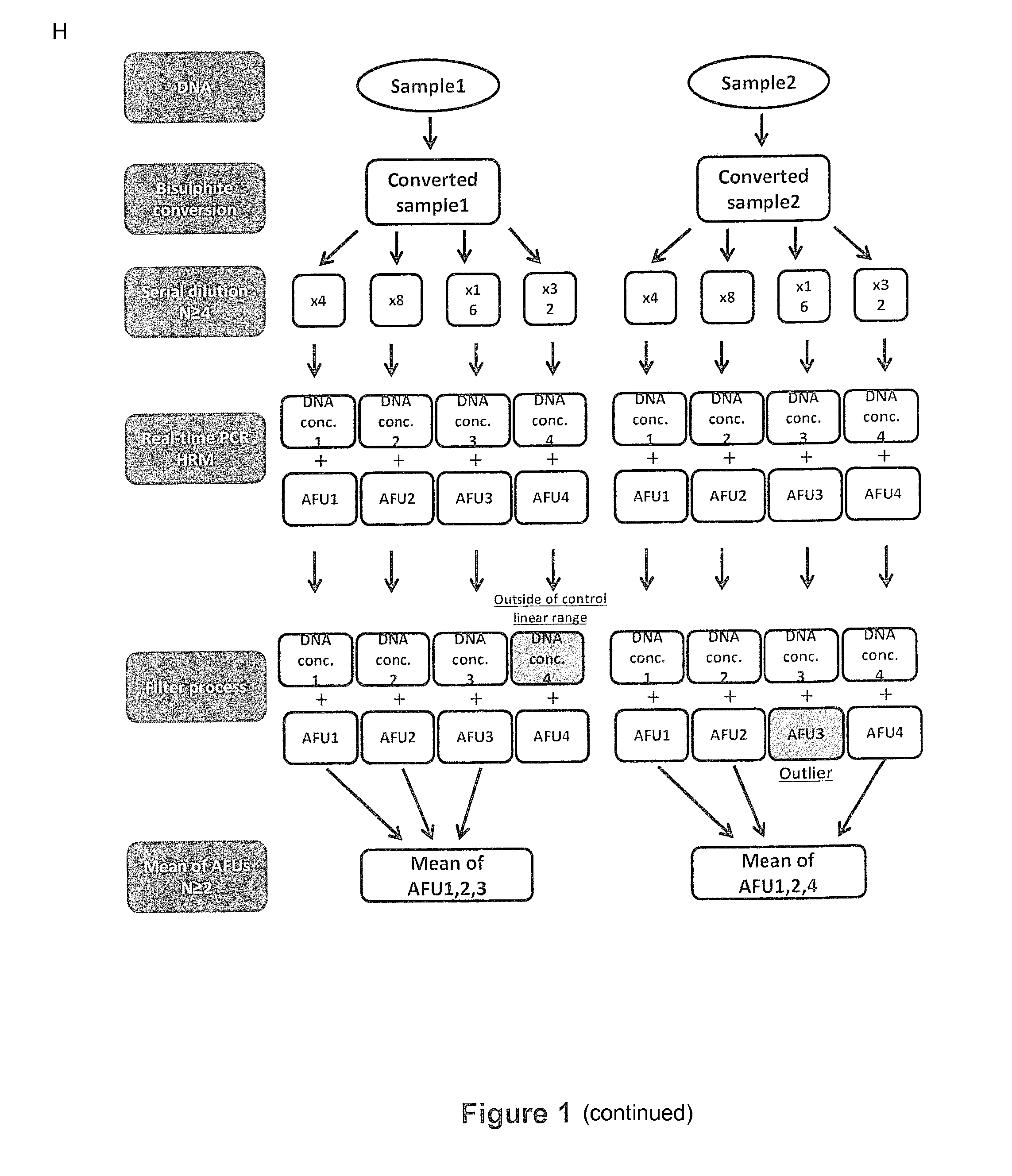
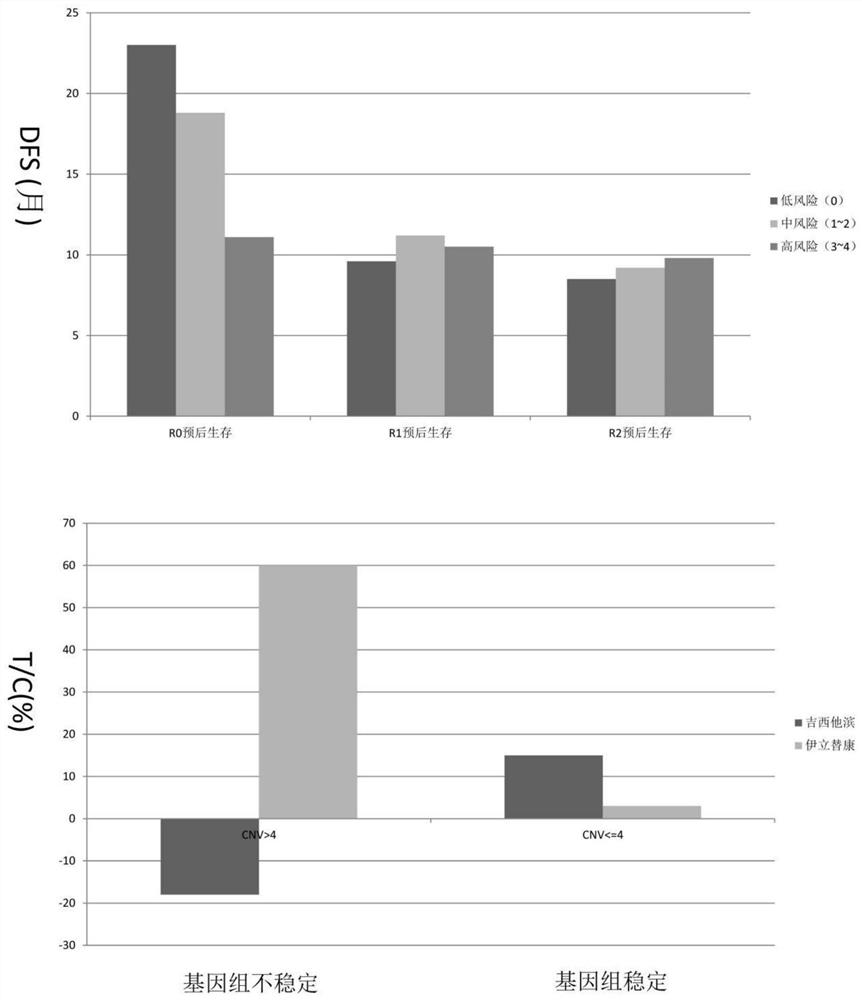
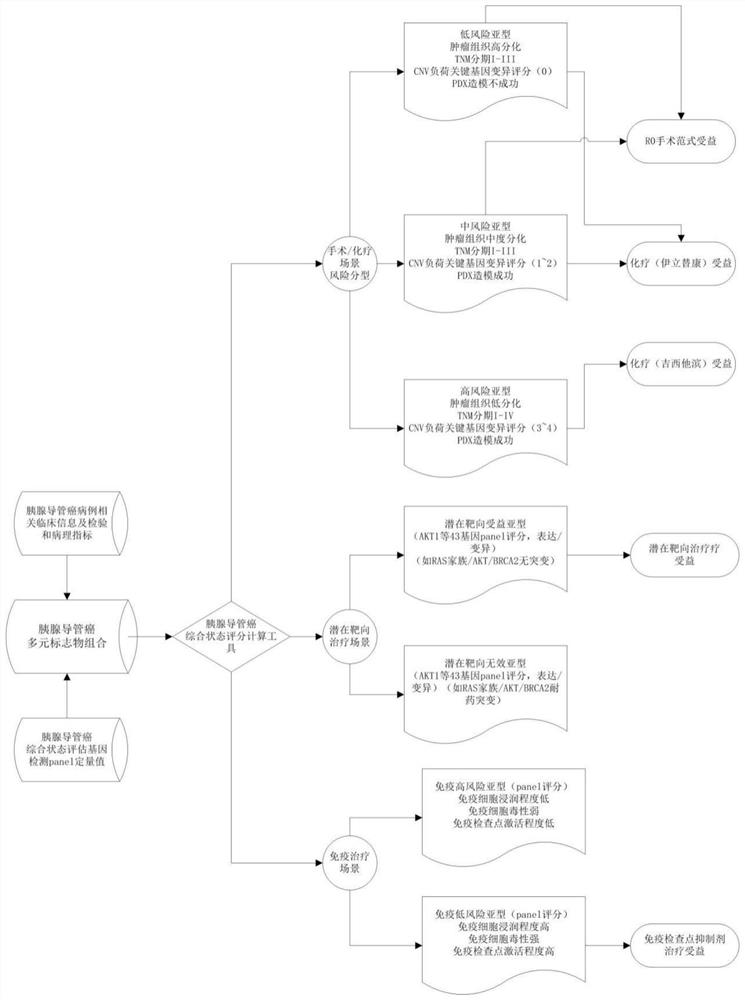
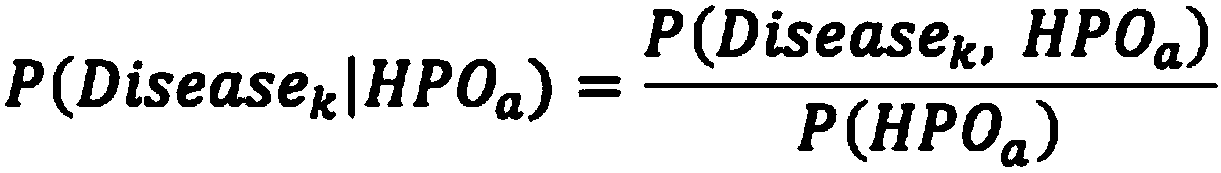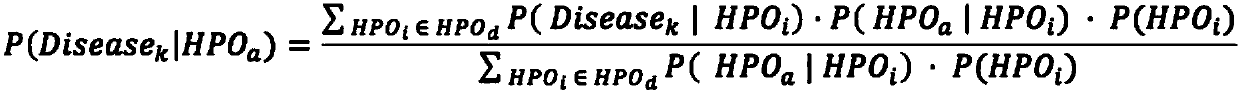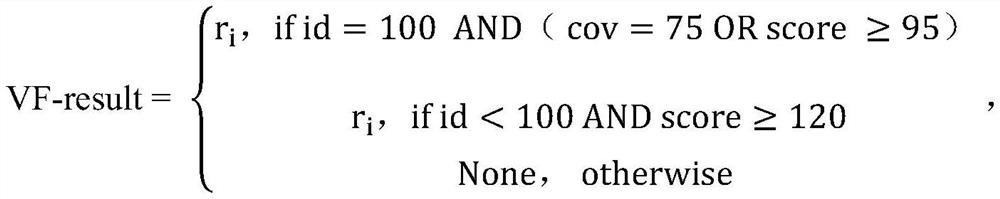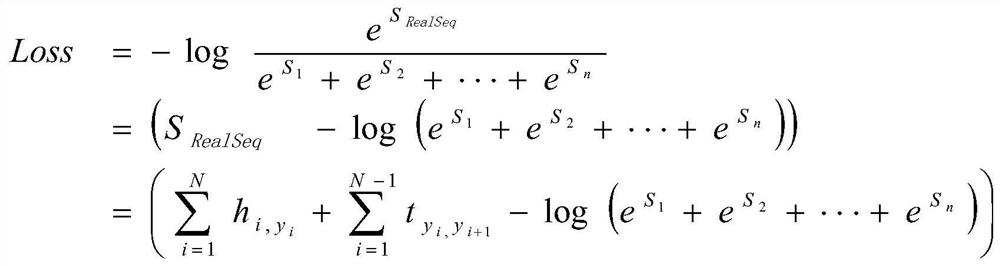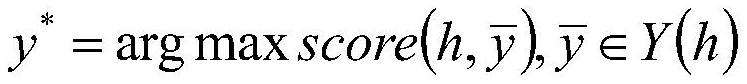Patents
Literature
70 results about "Clinical phenotype" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In this context, a phenotype would be any observable characteristic or trait of a disease, such as morphology, development, biochemical or physiological properties, or behavior, without any implication of a mechanism. A clinical phenotype would be the presentation of a disease in a given individual. Some organizations...
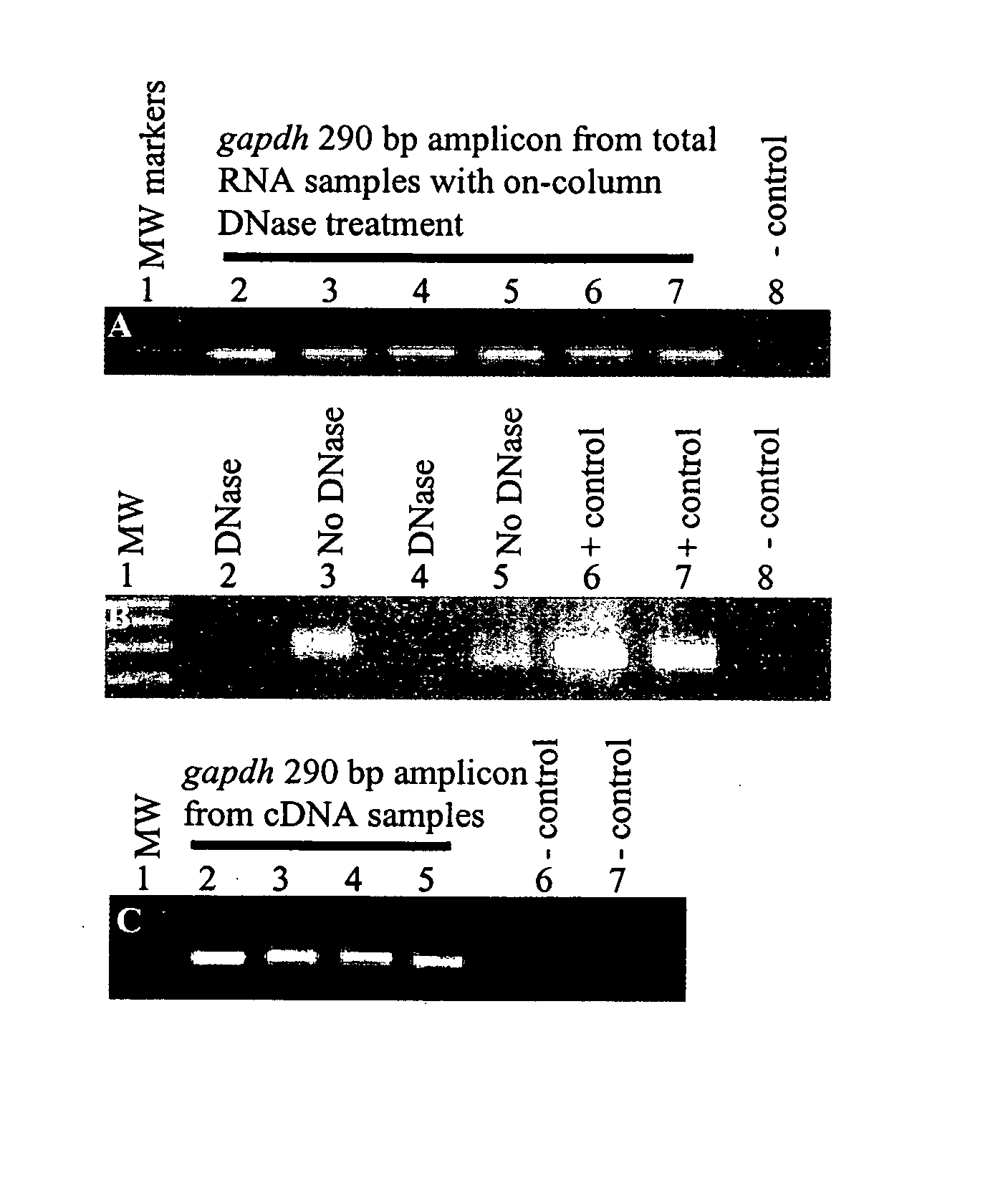
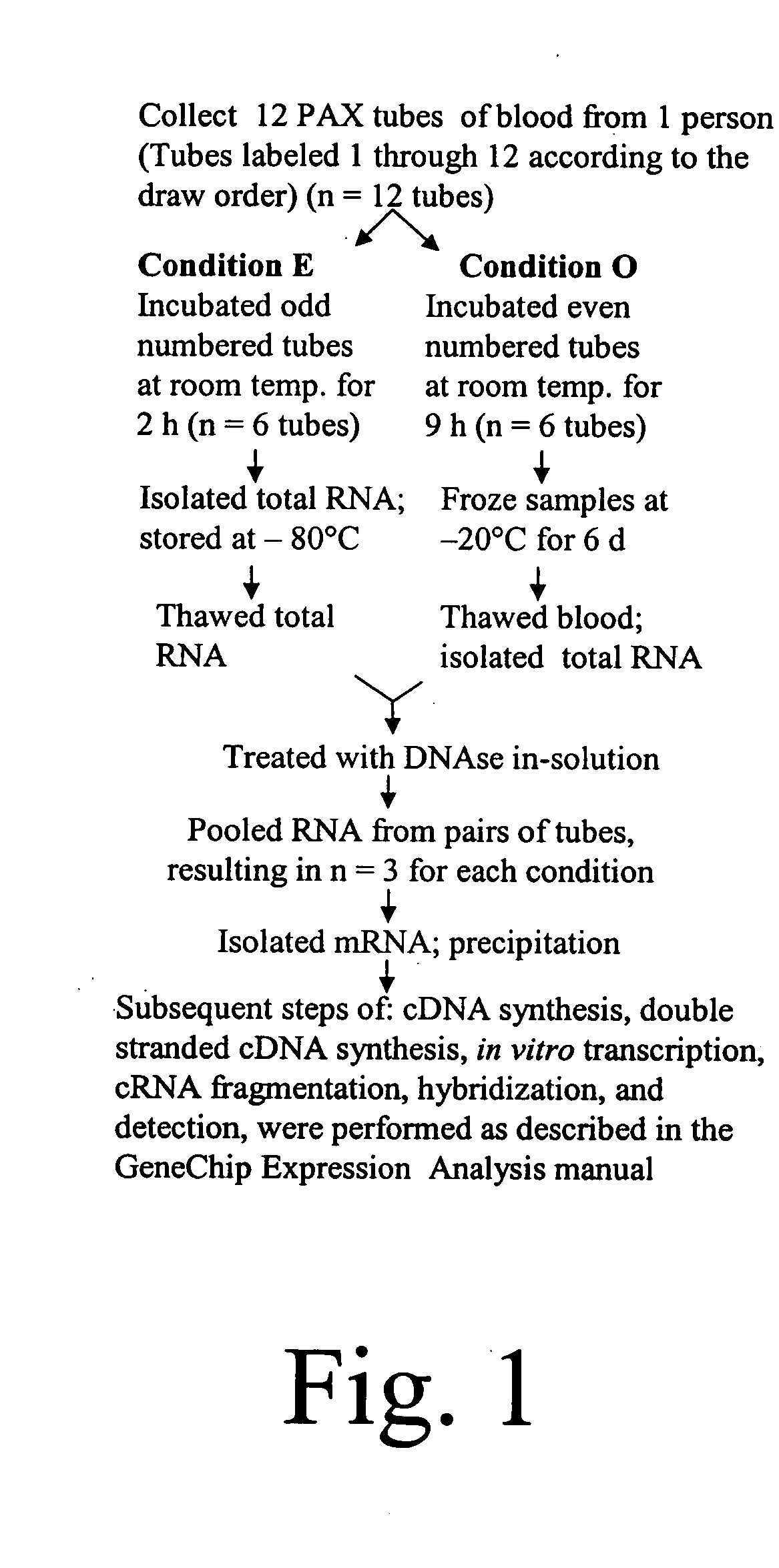
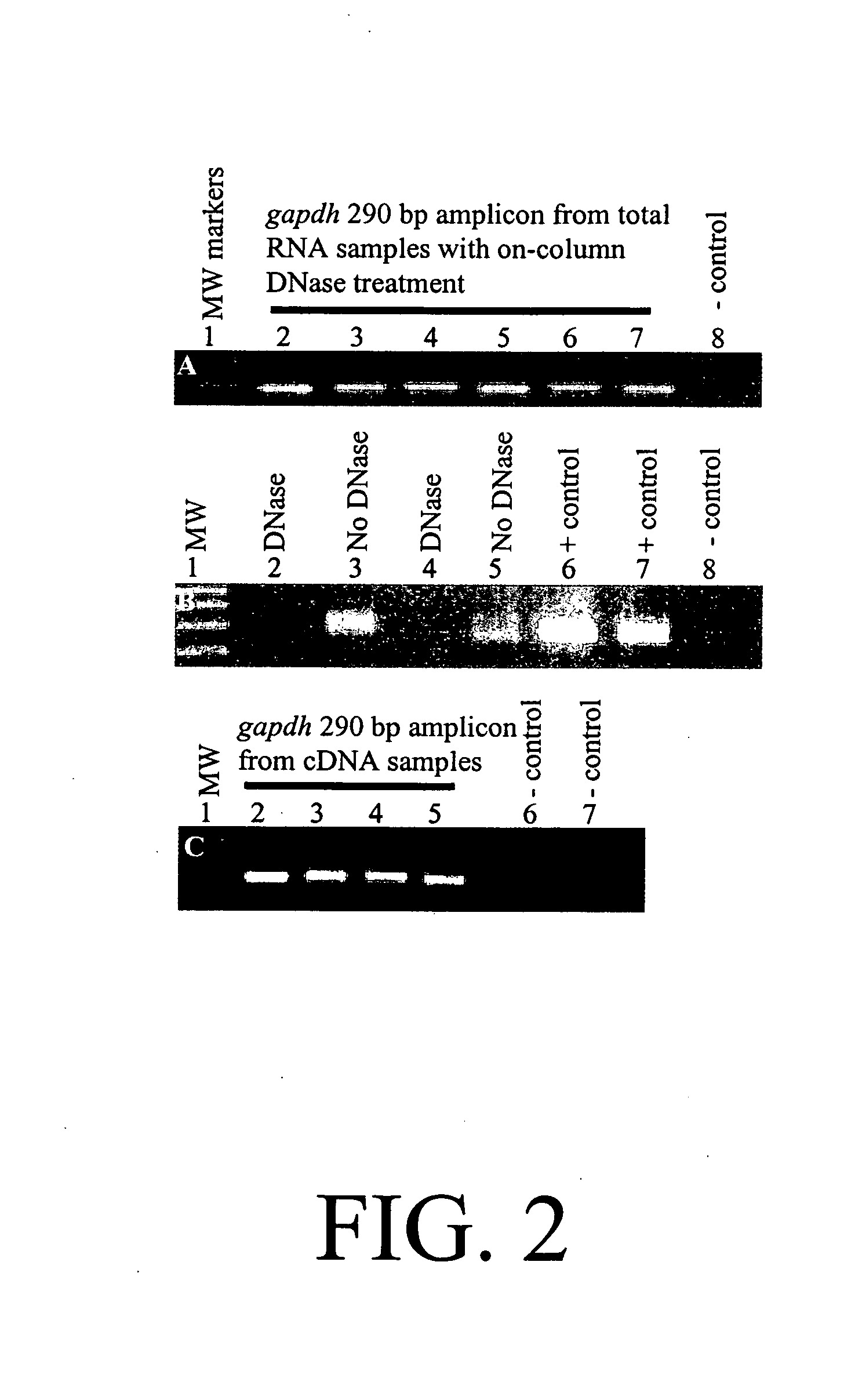
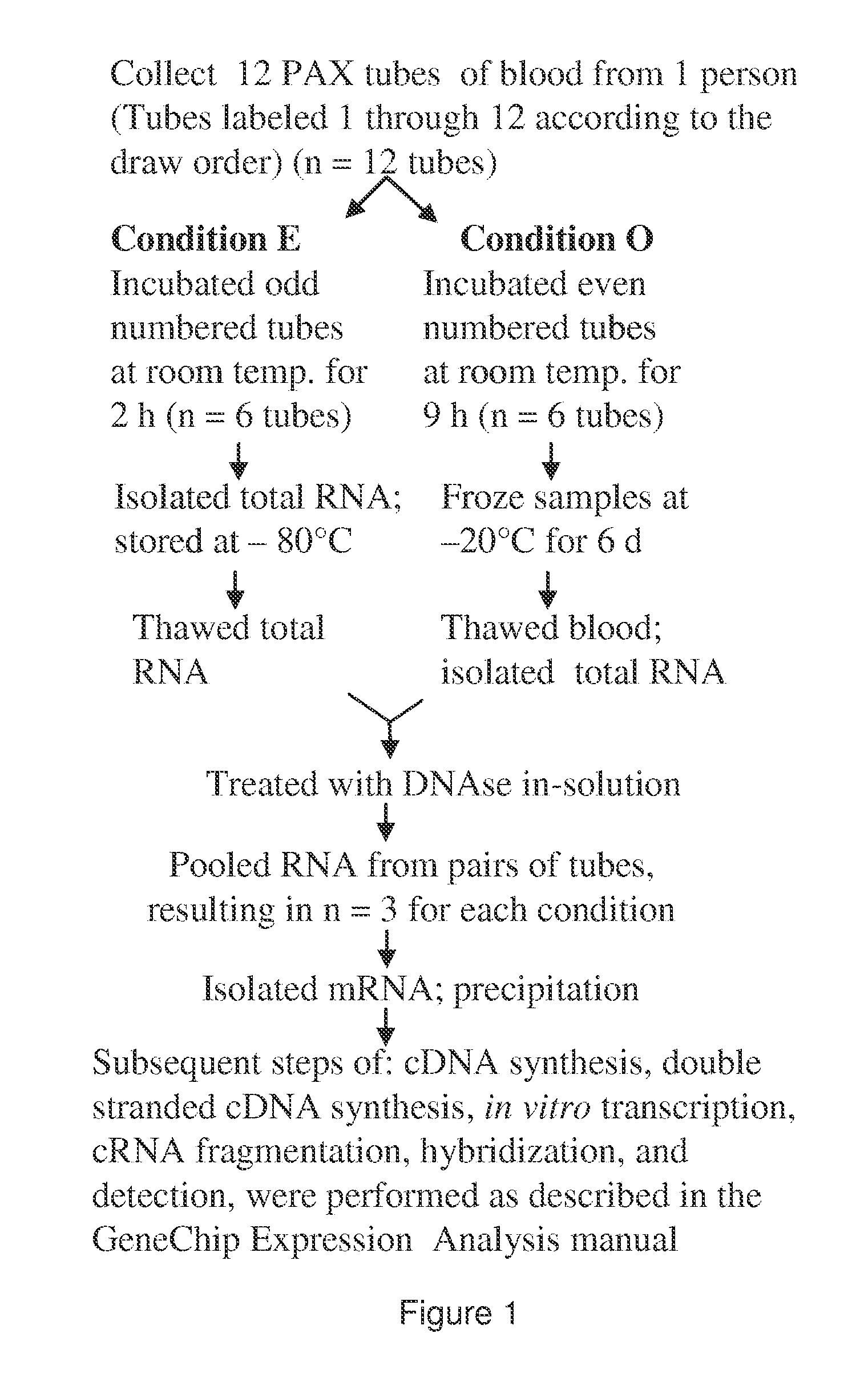
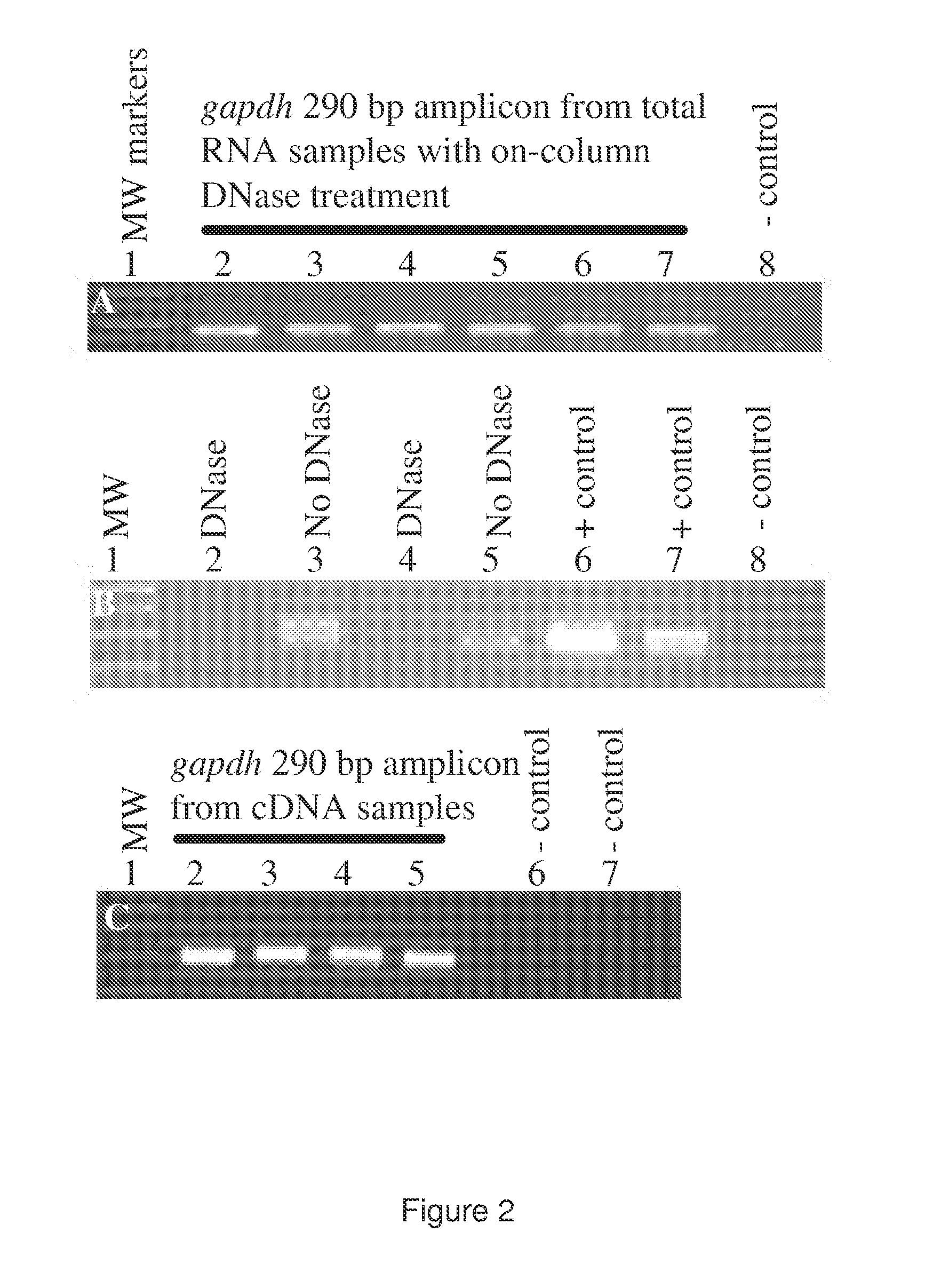
Diagnosis and prognosis of infectious diseases clinical phenotypes and other physiologic states using host gene expression biomarkers in blood
InactiveUS20080020379A1High sensitivityImprove reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementWhite blood cellHost gene
The present invention provides a specific set of gene expression markers from peripheral blood leukocytes that are indicative of a host response to exposure, response, and recovery infectious pathogen infections. The present invention further provides methods for identifying the specific set of gene expression markers, methods of monitoring disease progression and treatment of infectious pathogen infections, methods of prognosing the onset of an infectious pathogen infection, and methods of diagnosing an infectious pathogen infection and identifying the pathogen involved.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY +1
Diagnosis and Prognosis of Infectious Disease Clinical Phenotypes and other Physiologic States Using Host Gene Expression Biomarkers In Blood
InactiveUS20110183856A1High sensitivityImprove reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningWhite blood cellPhysiologic States
The present invention provides a specific set of gene expression markers from peripheral blood leukocytes that are indicative of a host response to exposure, response, and recovery infectious pathogen infections. The present invention further provides methods for identifying the specific set of gene expression markers, methods of monitoring disease progression and treatment of infectious pathogen infections, methods of prognosing the onset of an infectious pathogen infection, and methods of diagnosing an infectious pathogen infection and identifying the pathogen involved.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY +1
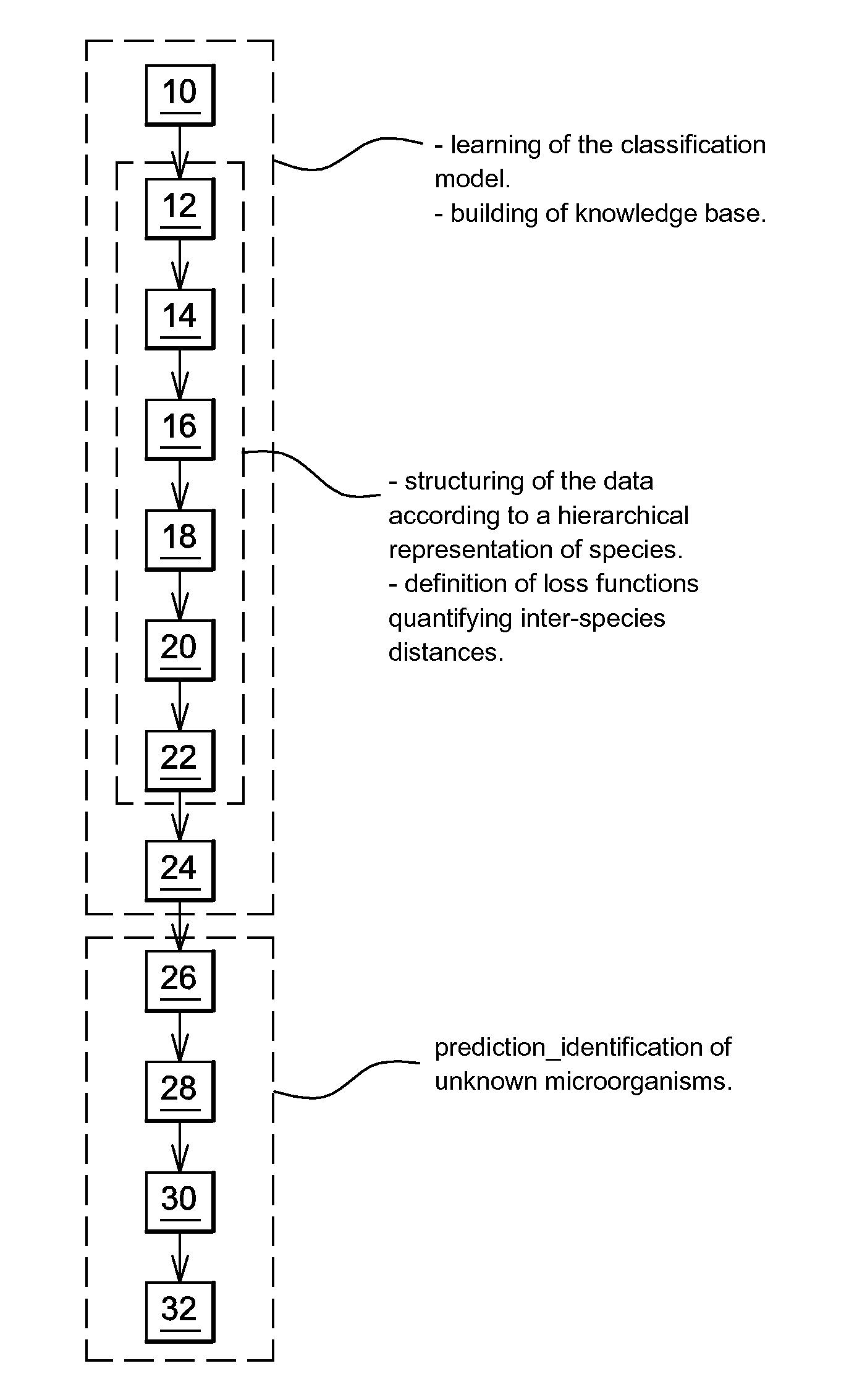
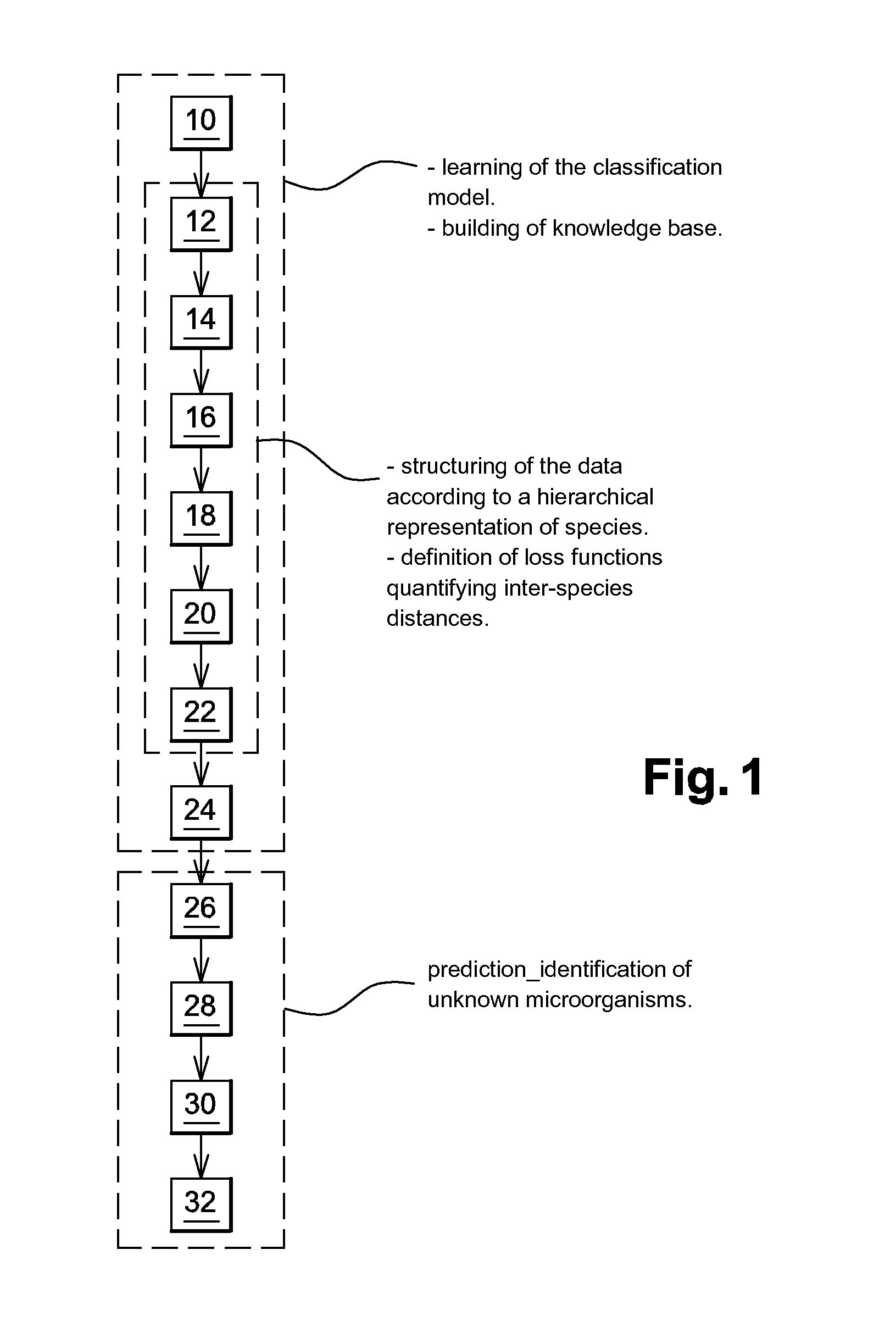
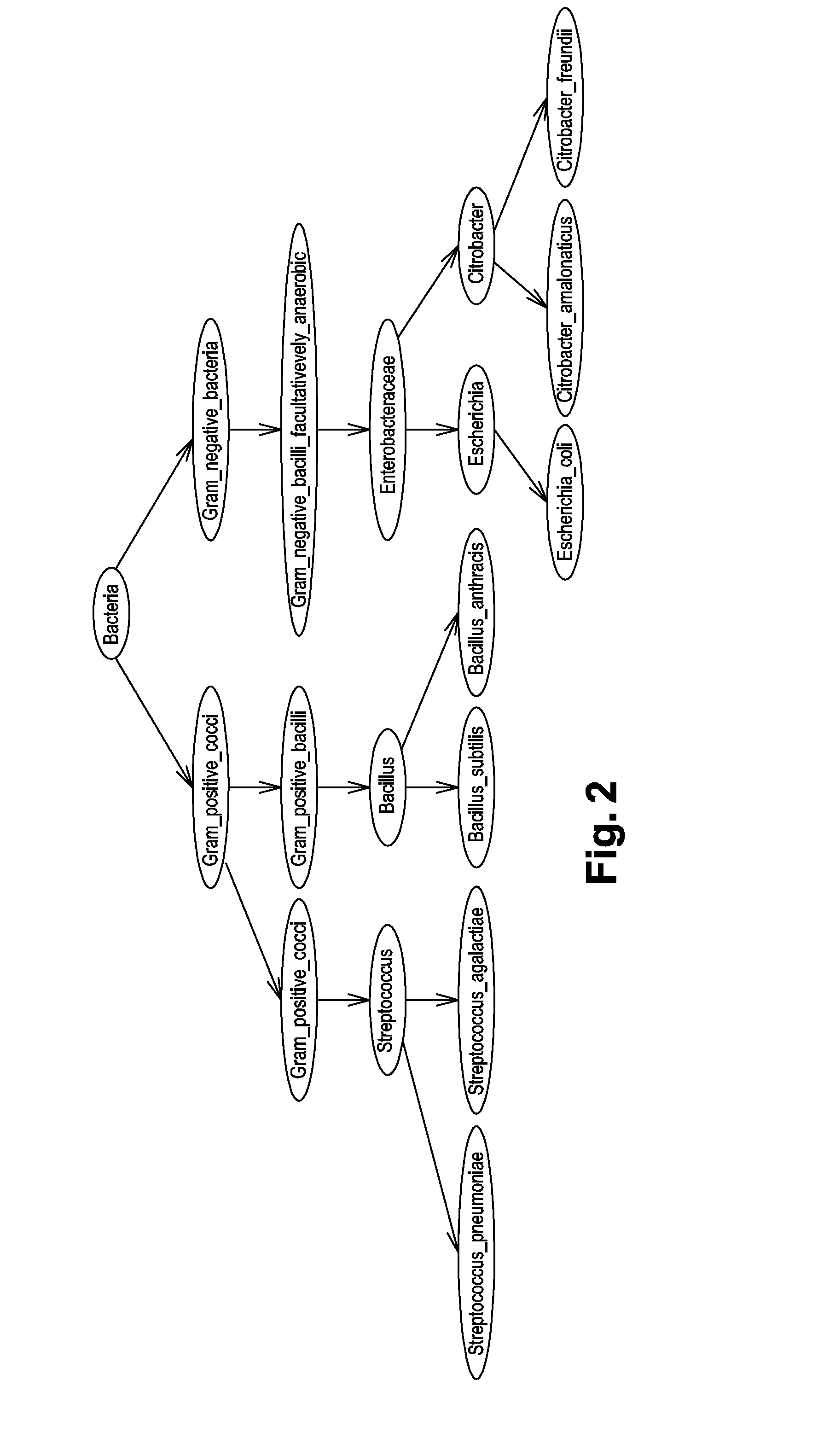
Identification Of Microorganisms By Spectrometry And Structured Classification
InactiveUS20150051840A1Minimize severityReliable identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsNODALMicroorganism
A method of identifying by spectrometry of unknown microorganisms from among a set of reference species, including a first step of supervised learning of a classification model of the reference species, a second step of predicting an unknown microorganism to be identified, including acquiring a spectrum of the unknown microorganism; and applying a prediction model according to said spectrum and to the classification model to infer at least one type of microorganism to which the unknown microorganism belong. The classification model is calculated by a structured multi-class SVM algorithm applied to the nodes of a tree-like hierarchical representation of the reference species in terms of evolution and / or of clinical phenotype and having margin constraints including so-called “loss” functions quantifying a proximity between the tree nodes.
Owner:BIOMERIEUX SA
Methods and compositions for the treatment of erythrocyte diseases
InactiveUS20090124566A1Extend your lifeImprove survivalOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseRed blood cell
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Duplex-seq-based ultralow-frequency mutation site detection analysis method
ActiveCN106599616AMeet the requirements of subsequent analysisIncrease diversitySequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsGeneticsBarcode
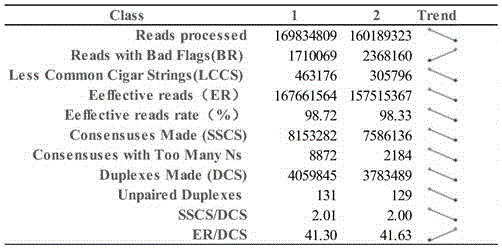
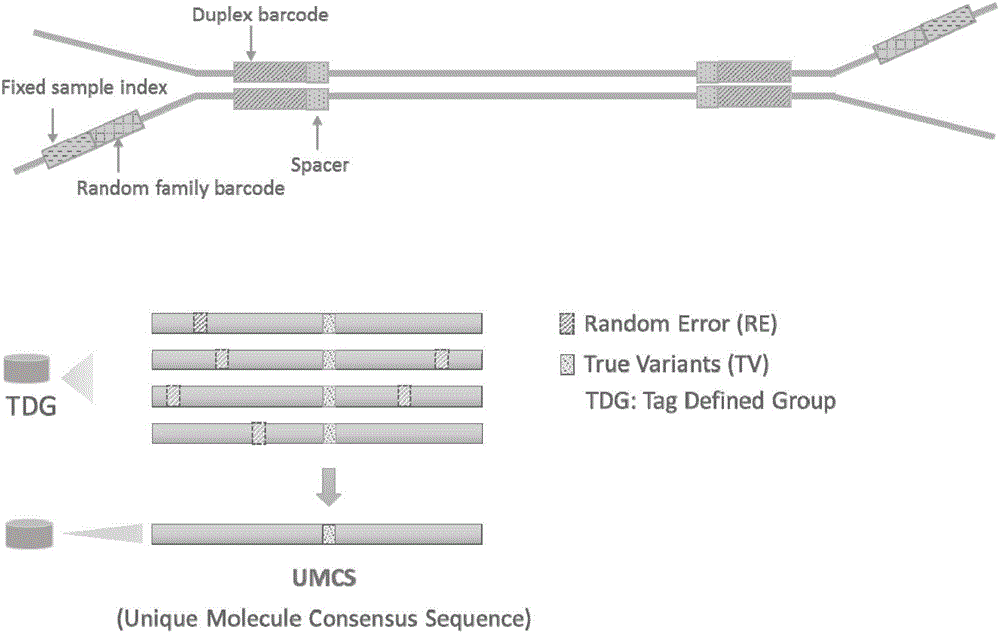
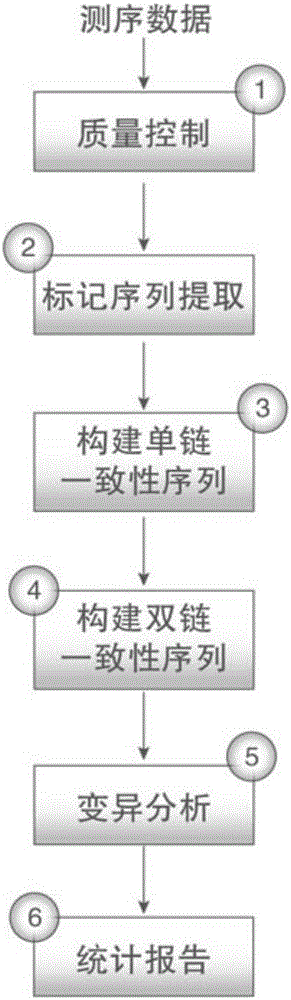
The invention discloses a duplex-seq-based ultralow-frequency mutation site detection analysis method. The method comprises the following steps of 1) assessing original sequencing data quality, reducing data noises, and providing effective data for subsequent analysis; 2) extracting a random barcode to a title line of each sequence of a sequence file, thereby facilitating subsequent quick retrieval of the barcode and creation of a consistency sequence; 3) creating the consistency sequence according to a family barcode and a duplex barcode, and excluding mutations introduced in a library creation process or a PCR process; 4) constructing a double-strand consistency sequence according to duplex-tag, and further excluding non-symmetric mutation sites in the sequence; 5) performing local quality correction on compared data, and performing low-frequency mutation site detection; performing annotation of three levels including a gene structure, a function and a clinical phenotype on the mutation sites; and 6) performing statistics on SSCS and DCS sequence number, comparison result and mutation site information, and outputting a visual chart.
Owner:SHANGHAI PASSION BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Analysis detection system for screening single gene hereditary disease pathogenic gene based on patient clinical symptom data and whole exome sequencing data
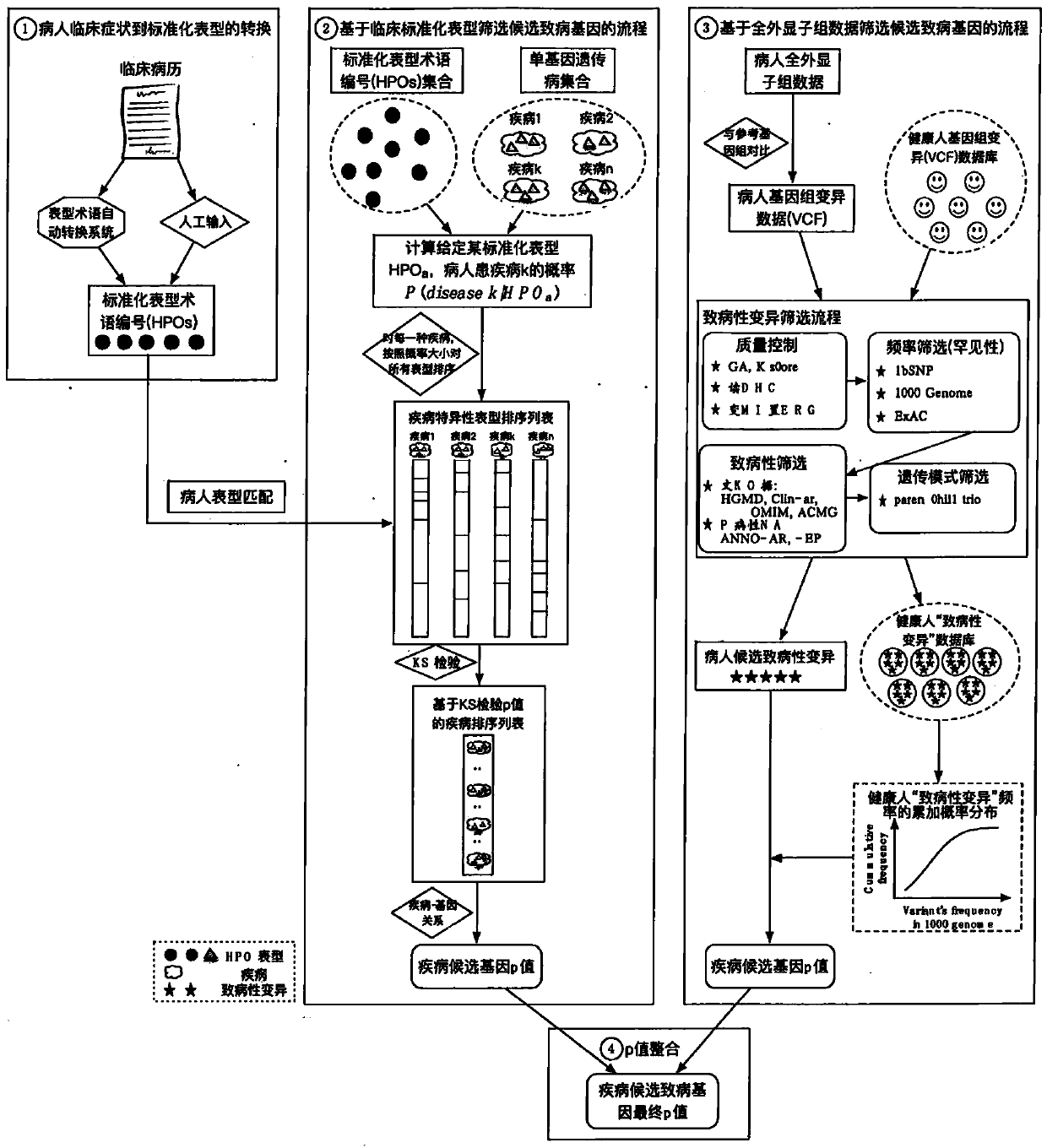
The invention relates to an automated analysis system for automatically screening the single gene disease and hereditary disease pathogenic gene based on patient clinical phenotype information and whole exome sequencing data. The system comprises four automatic analysis modules: (1) an automatic transferring subsystem for automatic transferring from patient clinical report to standardized phenotype term (HPO, human phenotype ontology); (2) an automatic analysis system for screening disease pathogenic gene based on patient standardized phenotype; (3) an automatic analysis system for screening disease pathogenic gene based on patient whole exome sequencing data; and (4) a p value integration system. The system adopts a possibility model to calculate the possibility of developing a certain single gene hereditary disease under the situation that a certain standard phenotype of the patient is provided, and utilizes a computer statistic check method to systematically evaluate the significance level of developing a certain single gene hereditary disease after all standard phenotype of the patient are provided, so as to accordingly achieve the purpose of screening candidate disease pathogenic gene based on clinical standard phenotype.
Owner:上海睿视健康科技有限公司
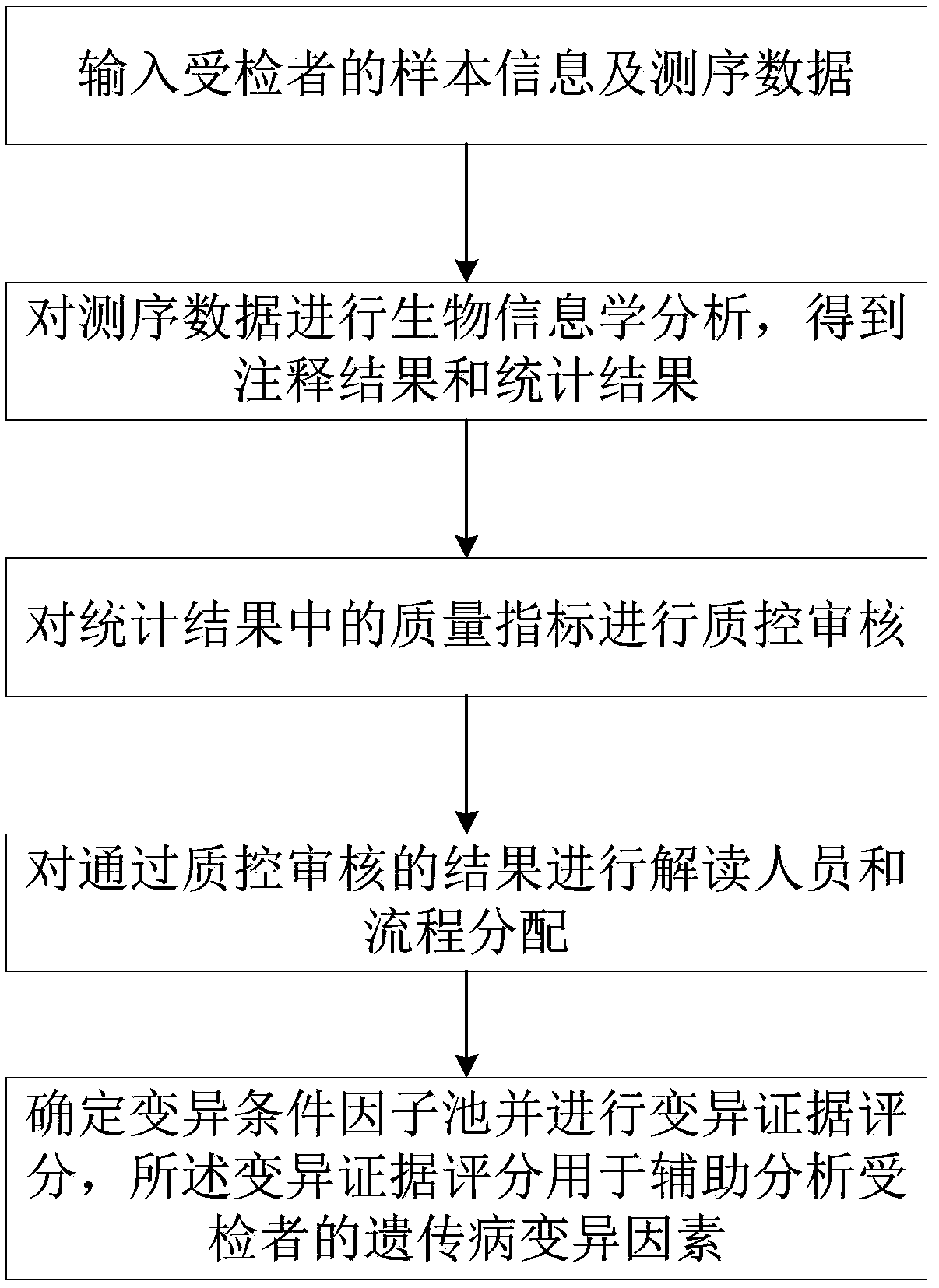
Data analysis method for genetic disease gene testing, system thereof and storage medium
ActiveCN109686439AAchieve semi-automatic interpretationImprove work efficiencyHealth-index calculationMedical automated diagnosisSemi automaticAnnotation
The invention discloses a data analysis method for genetic disease gene testing, a system thereof and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of inputting sample information and sequencing information of a testee; performing bioinformatics analysis on the sequencing data and obtaining an annotation result and a statistics result; performing quality control auditing on a quality index in astatistics result; performing interpretation personnel and flow distribution on a result which passes quality control auditing; determining a variation condition factor pool and performing variationevidence scoring, wherein the variation evidence scoring is used for assisted analysis for a genetic disease variation factor of the testee. The method and the system thereof perform bioinformatics analysis and quality control auditing based on the sequencing data, and performs interpretation personnel and flow distribution based on clinical phenotype information. Furthermore through variation evidence scoring, semi-automatic interpolation is realized and working efficiency is improved. Furthermore, a one-generation verifying primer database can be introduced, thereby greatly saving a primer designing process and reducing resource consumption. The data analysis method, the system thereof and the storage medium can be widely used for genetic disease gene sequencing data analysis and interpretation.
Owner:CAPITALBIO GENOMICS
Detection of Antibodies
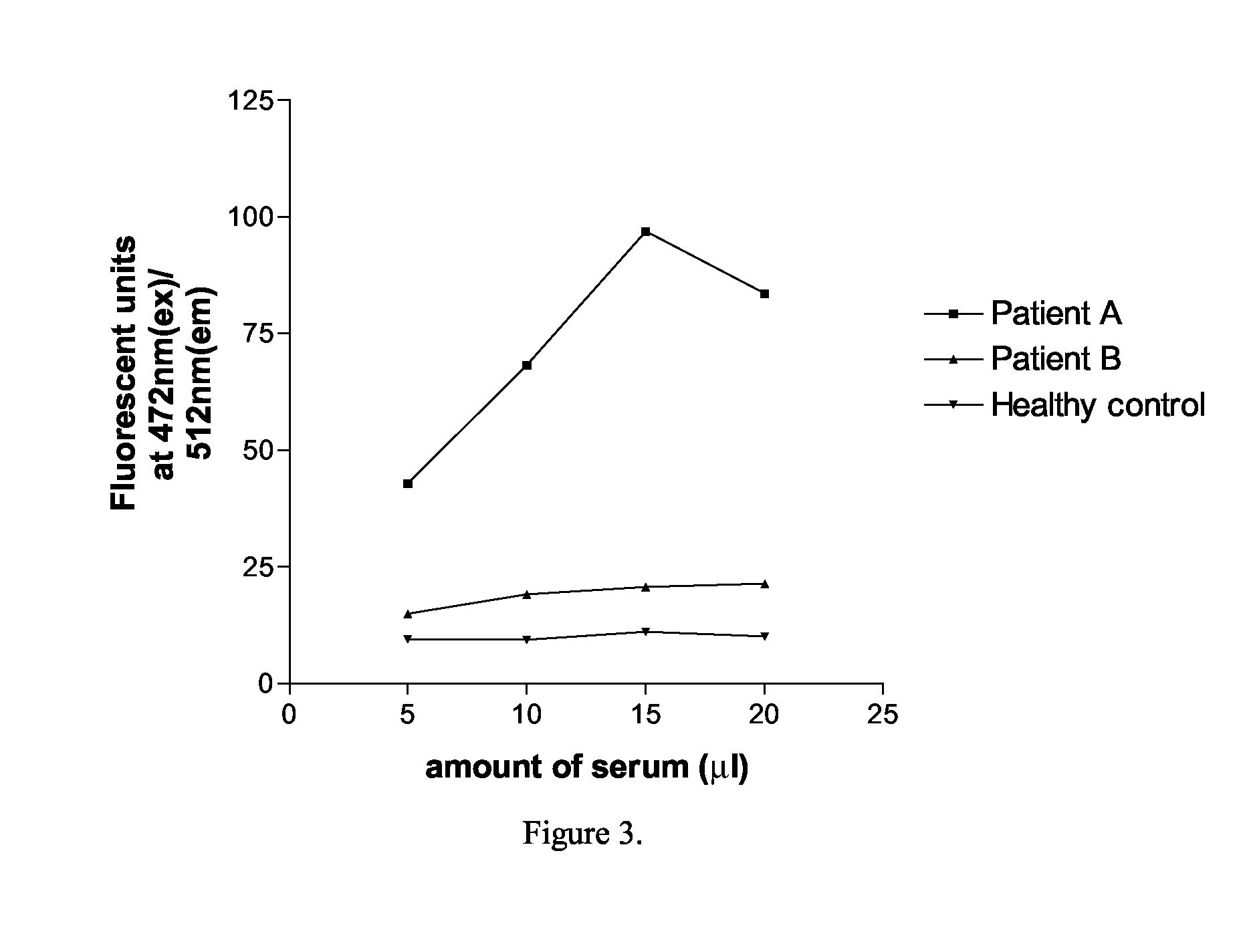
InactiveUS20090029388A1Efficient methodImprove the signal-to-background ratioBiological testingAutoimmune diseaseWater Channel Proteins
The present invention relates to a method for detecting antibodies against a target antigen in a sample which comprises contacting the sample with labelled target antigen, subjecting the sample to immunoprecipitation to precipitate antibodies in the sample and detecting the presence of antibodies against the target antigen in the sample by means of the presence of labelled target antigen in the immunoprecipitate, wherein the labelled target antigen is a fusion protein comprising the target antigen and a fluorescent protein label and the presence of labelled target antigen in the immunoprecipitate is detected by means of the fluorescence of the fluorescent label. The method is particularly suitable for use where the target antigen is an autoantigen and can also be used to identify autoantigens implicated in a particular autoimmune disorder by screening serum samples from patients with a clinical phenotype indicative or suggestive of an autoimmune disorder and suitable controls. The target protein may be from the cys-loop acetyl choline receptor ion channel gene superfamily, the voltage-gated calcium, sodium or potassium ion channel gene superfamily, the glutamate receptor gene family, a receptor tyrosine kinase, or other membrane associated channels such as aquaporin gene family.
Owner:BEESON DAVID
Disease diagnosis method and device and terminal equipment
InactiveCN109473169AImprove diagnostic efficiencyShorten the timeMedical automated diagnosisProteomicsDiagnosis methodsTerminal equipment
The invention is applicable to the technical field of disease diagnosis, and provides a disease diagnosis method and device and terminal equipment. The method comprises the steps of obtaining the clinical phenotype of a patient, and matching a disease list with the phenotype similar to the clinical phenotype in a database; analyzing and sifting disease-causing genes corresponding to all diseases in the disease list, and determining the disease-causing gene and the disease corresponding to the clinical phenotype. According to the method and device, the disease list with the phenotype similar tothe clinical phenotype is quickly obtained for analysis with the clinical phenotype as the core, the efficiency of making a definite diagnosis on the disease of the patient is improved, and the timeof a doctor and the patient is saved.
Owner:AEGICARE (SHENZHEN) TECH CO LTD
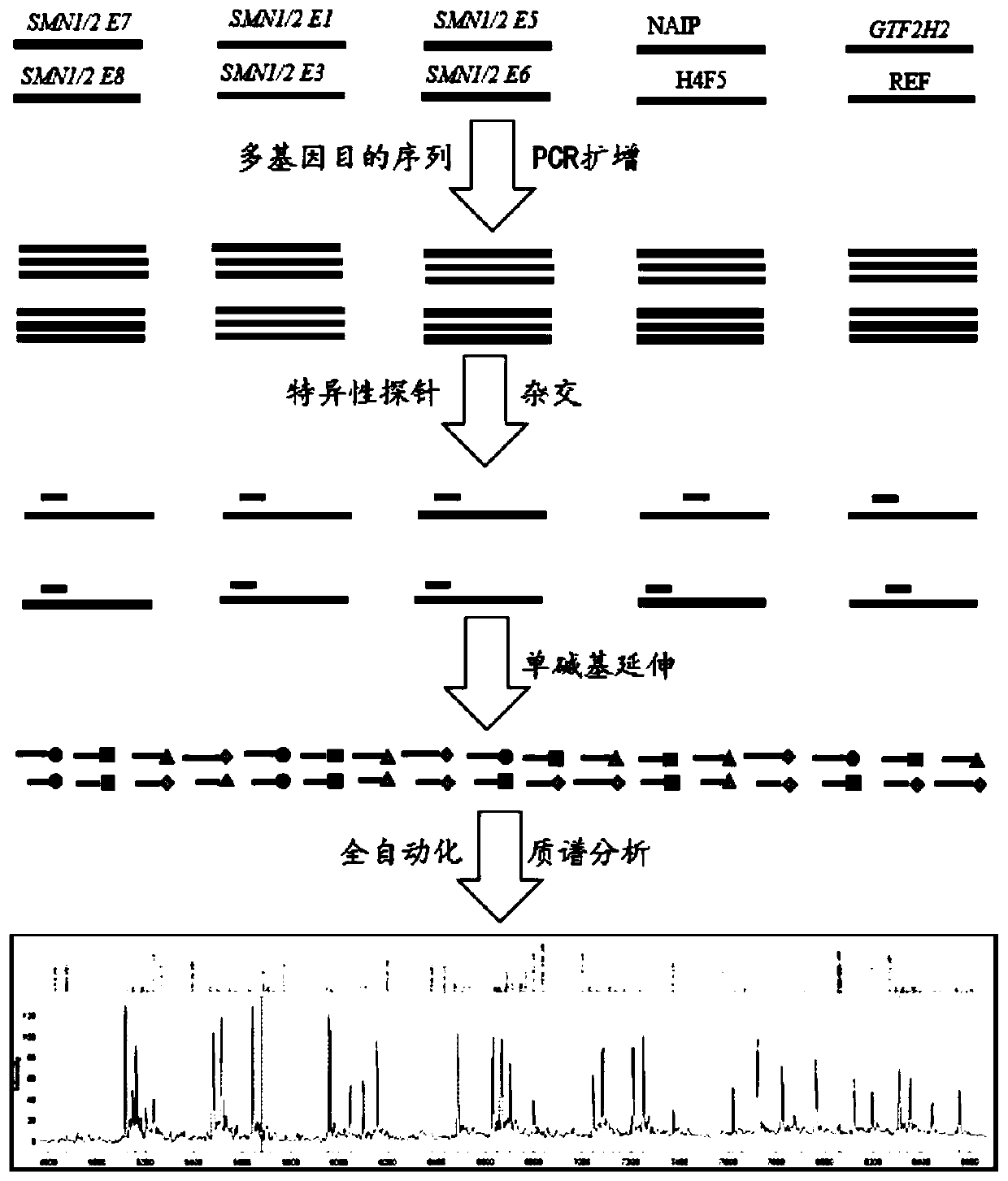
Time-of-flight mass spectrometry nucleic acid analysis method for detecting human spinal muscular atrophy gene mutation
ActiveCN110468192AImprove stabilityImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPrenatal diagnosisTime of flight
The invention discloses a time-of-flight mass spectrometry nucleic acid analysis method for detecting human spinal muscular atrophy gene mutation. A primer combination comprising an amplification primer and a mass spectrometry extension probe primer is utilized. According to the method, the copy numbers of sequences related to SMN1, SMN2, NAIP, H4F5 and GTF2H2 genes are quantitatively detected, and whether deletion, deletion number and multiple copies exist or not is analyzed, so that the clinical phenotype severity can be directly deduced; the method has good sensitivity, specificity, stability and accuracy, and effectively solves the technical bottleneck of false negative, false positive and the like; the operation is simple, the cost is relatively low, and the result is stable and reliable; the method is high in flux and low in cost, has general representativeness and universality, is easy to realize automatic and large-scale detection, and is suitable for large-scale population screening; genetic typing detection can be carried out on part of common SMN1 upper point mutations; and the requirements of large-scale population screening, prenatal diagnosis and conventional molecular diagnosis in current SMA prevention and treatment are met.
Owner:GUANGZHOU DARUI BIOTECH
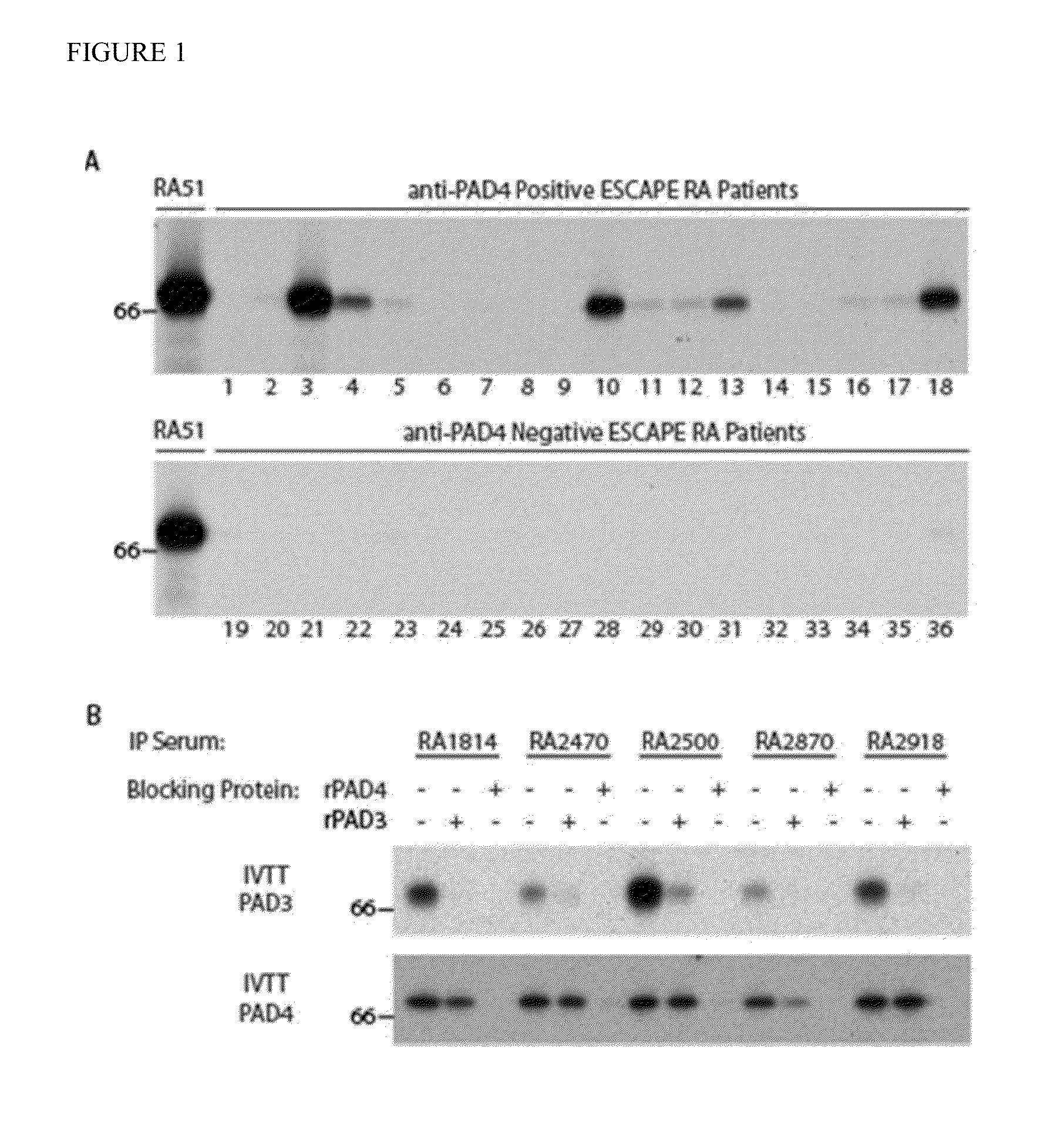
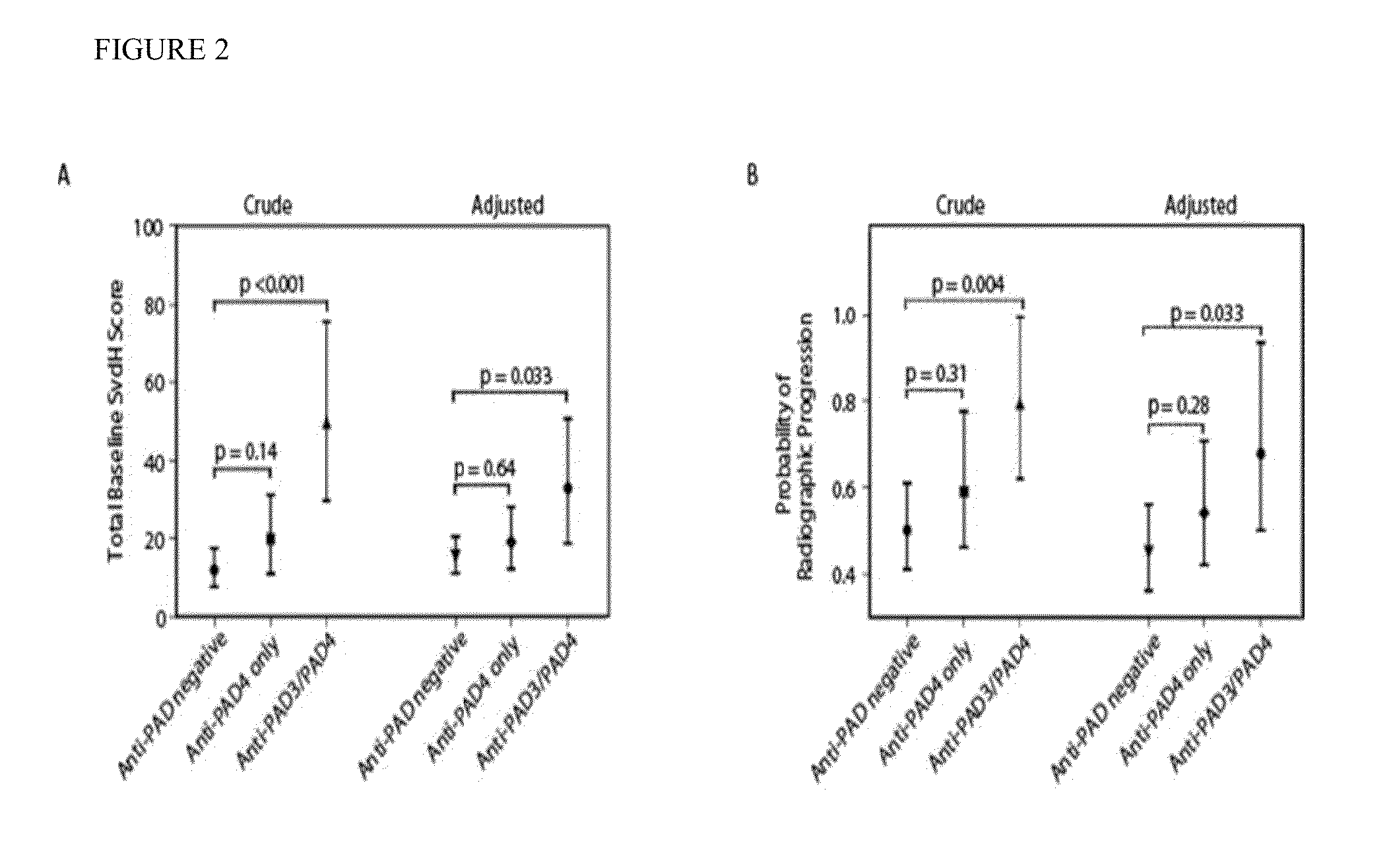
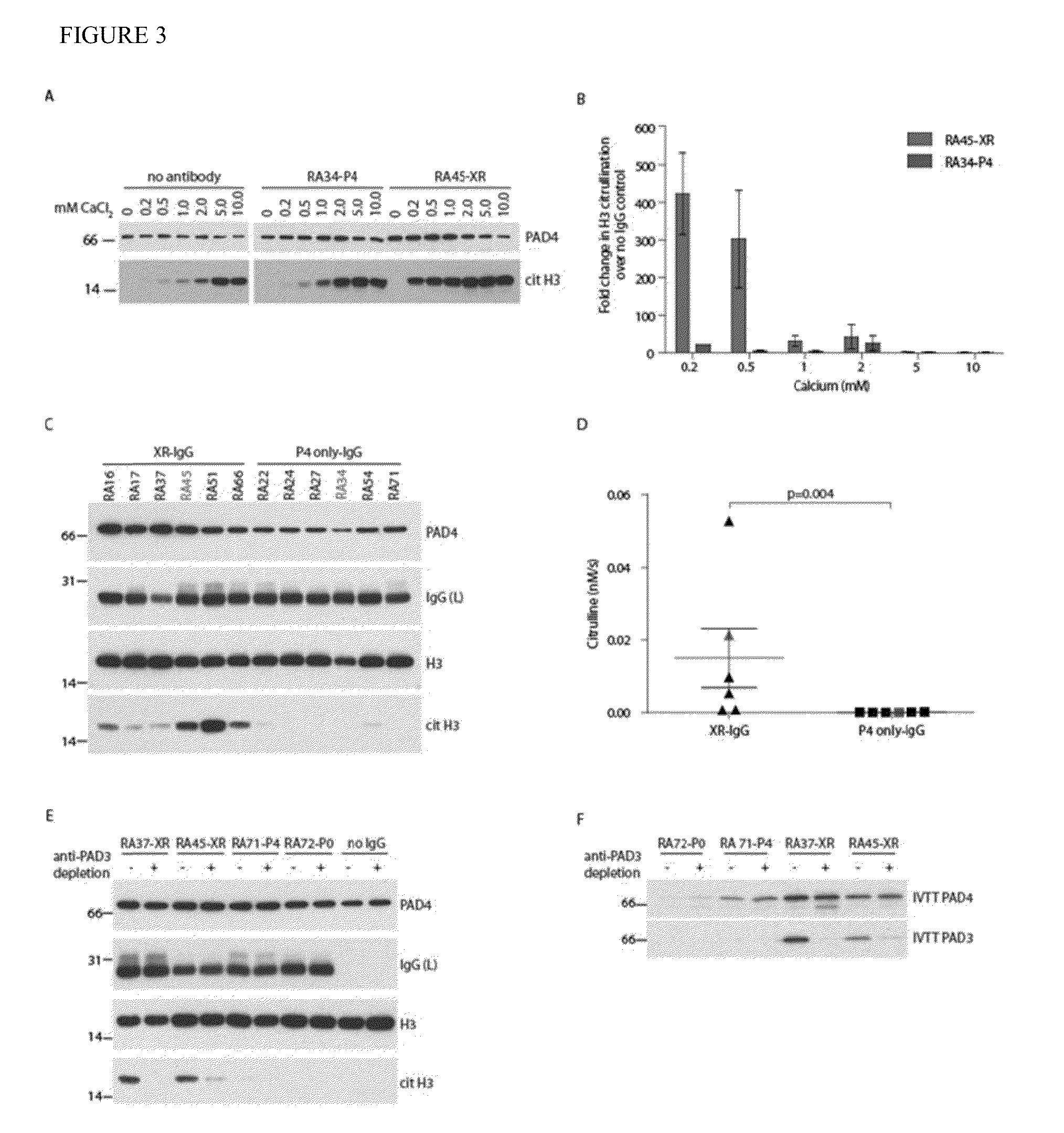
Human autoantibodies specific for pad3 which are cross-reactive with pad4 and their use in the diagnosis and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and related diseases
ActiveUS20140127720A1Improve enzymatic activityLower requirementDisease diagnosisBiological testingInterstitial lung diseaseAutoantibody
In one or more embodiments, the present invention provides a novel biomarker which provides a link between a distinct clinical phenotype and a biochemical effect of an autoantibody on an enzyme implicated in disease pathogenesis. In particular, the present invention provides an isolated or purified human autoantibody to PAD3 protein. Methods of diagnosis of subjects for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) using these antibodies as well as diagnosis of the severity of RA in the subject, and methods for monitoring treatment of a subject with RA are also provided. The biomarkers provided herein are also useful in the diagnosis of connective tissue-interstitial lung disease (CT-ILD) in patients having or suspected of having RA.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
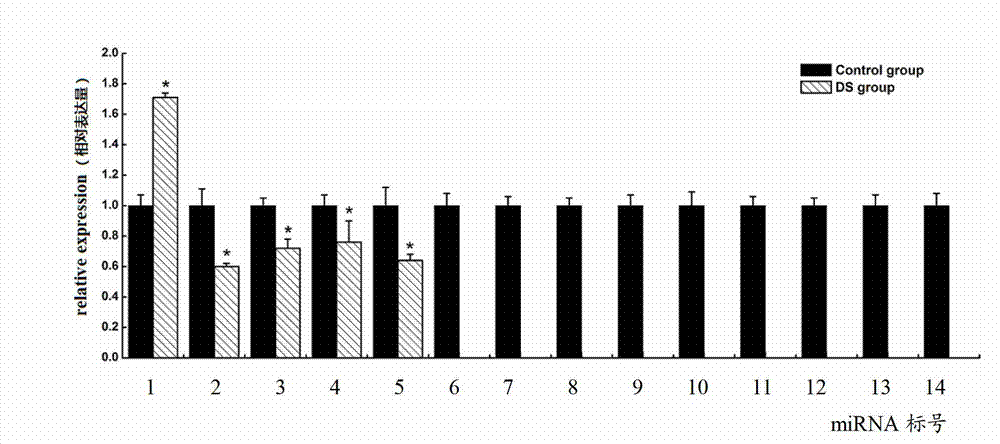
Down syndrome 21 chromosome miRNA differential expression map model, modeling method and application
ActiveCN103045736AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseaseDistribution characteristic
The expression map and the chromosome distribution characteristic of a DS (down syndrome) fetal genome-wide miRNAs are studied by an Illumina deep sequencing technology so as to obtain a down syndrome 21 chromosome-related miRNA differential expression map model, which consists of an up-regulated miRNA, four down-regulated miRNAs and 9 zero-expression miRNAs. miRNA molecules with significant difference and specific expression help to understand a molecular regulation mechanism for occurrence and development of a clinical phenotype of a DS disease and lay the foundation for further studying gene expression disorder of a DS patient genome-wide and a relationship between the gene expression disorder and relevant clinical symptoms.
Owner:徐勇
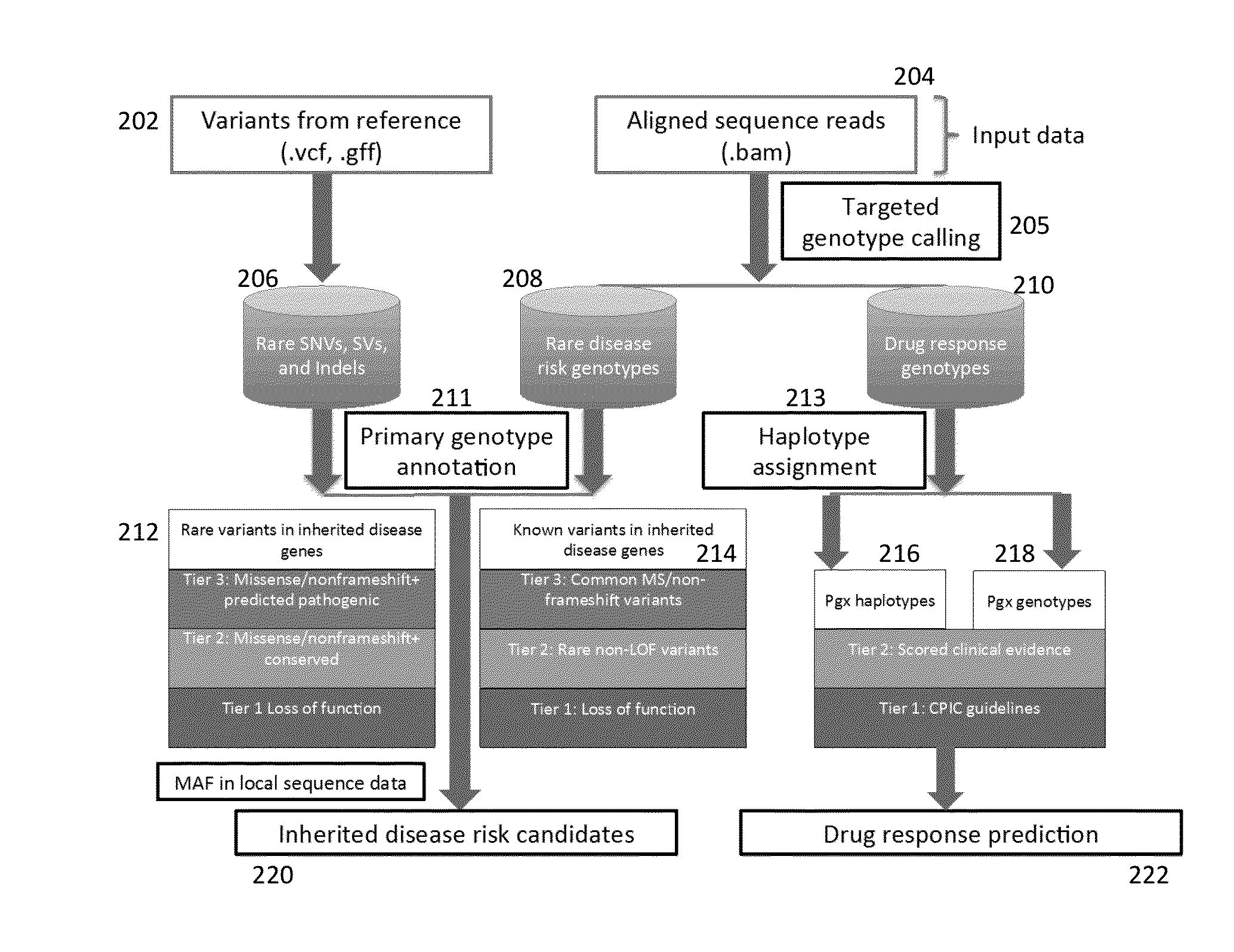
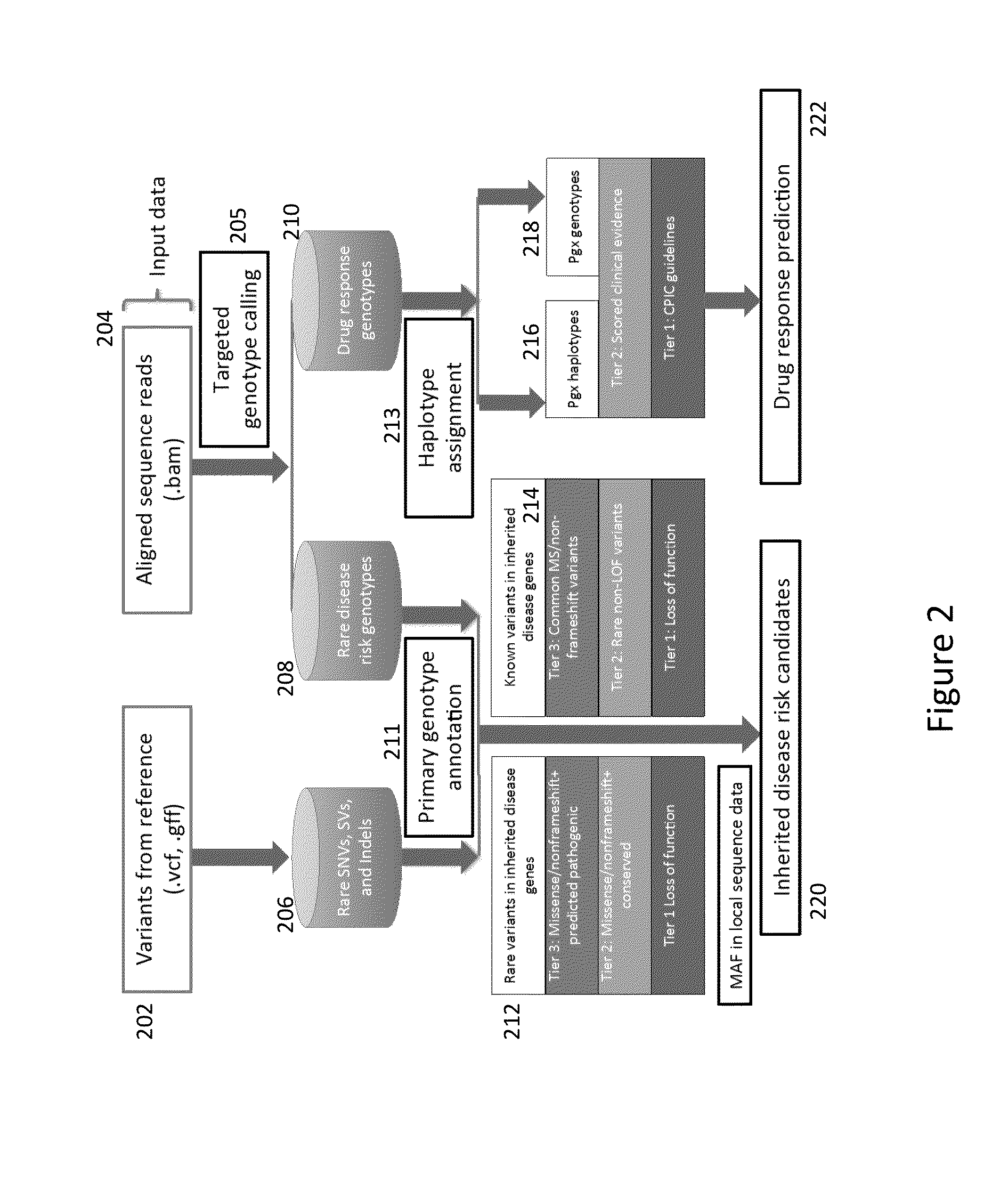
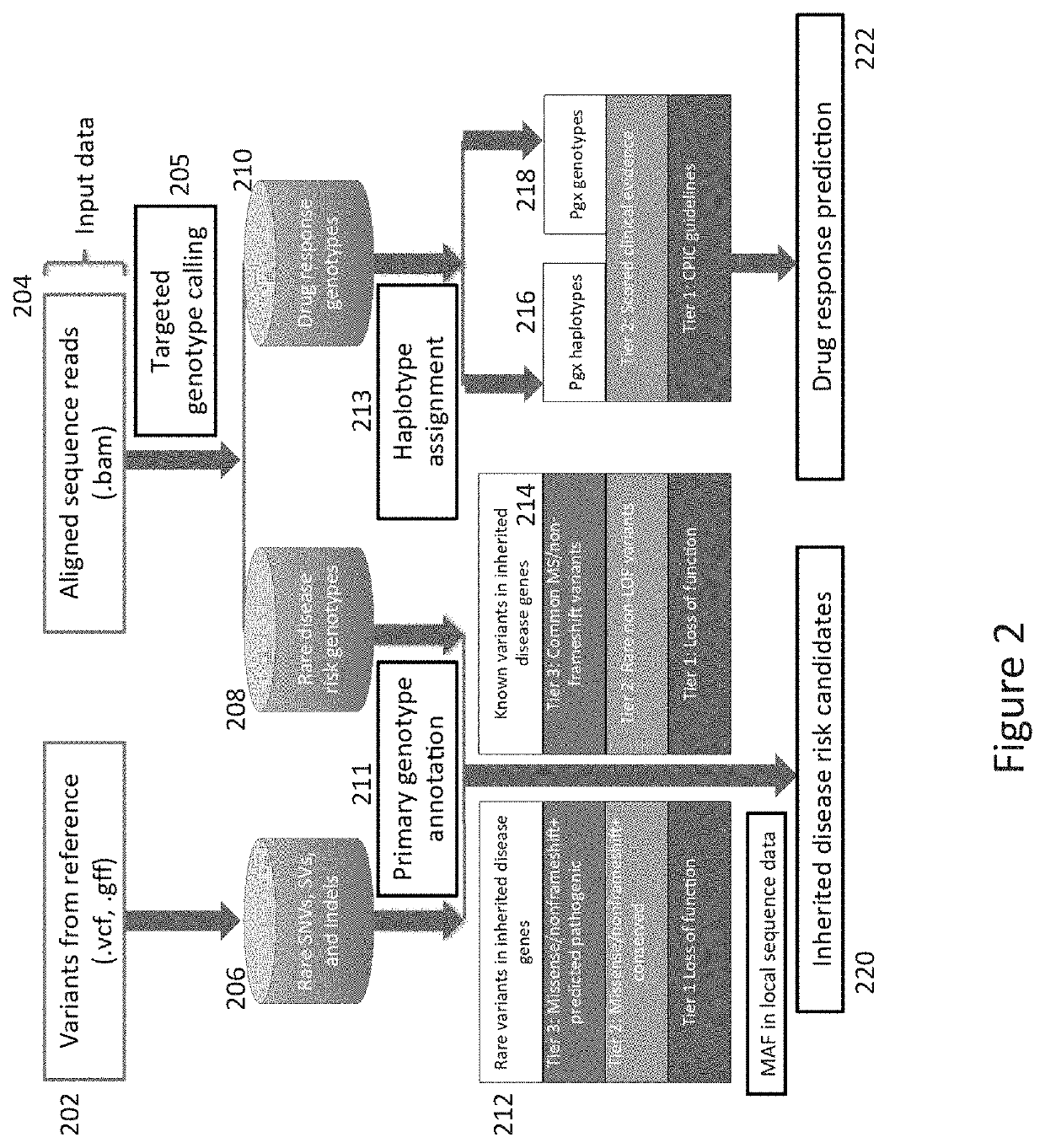
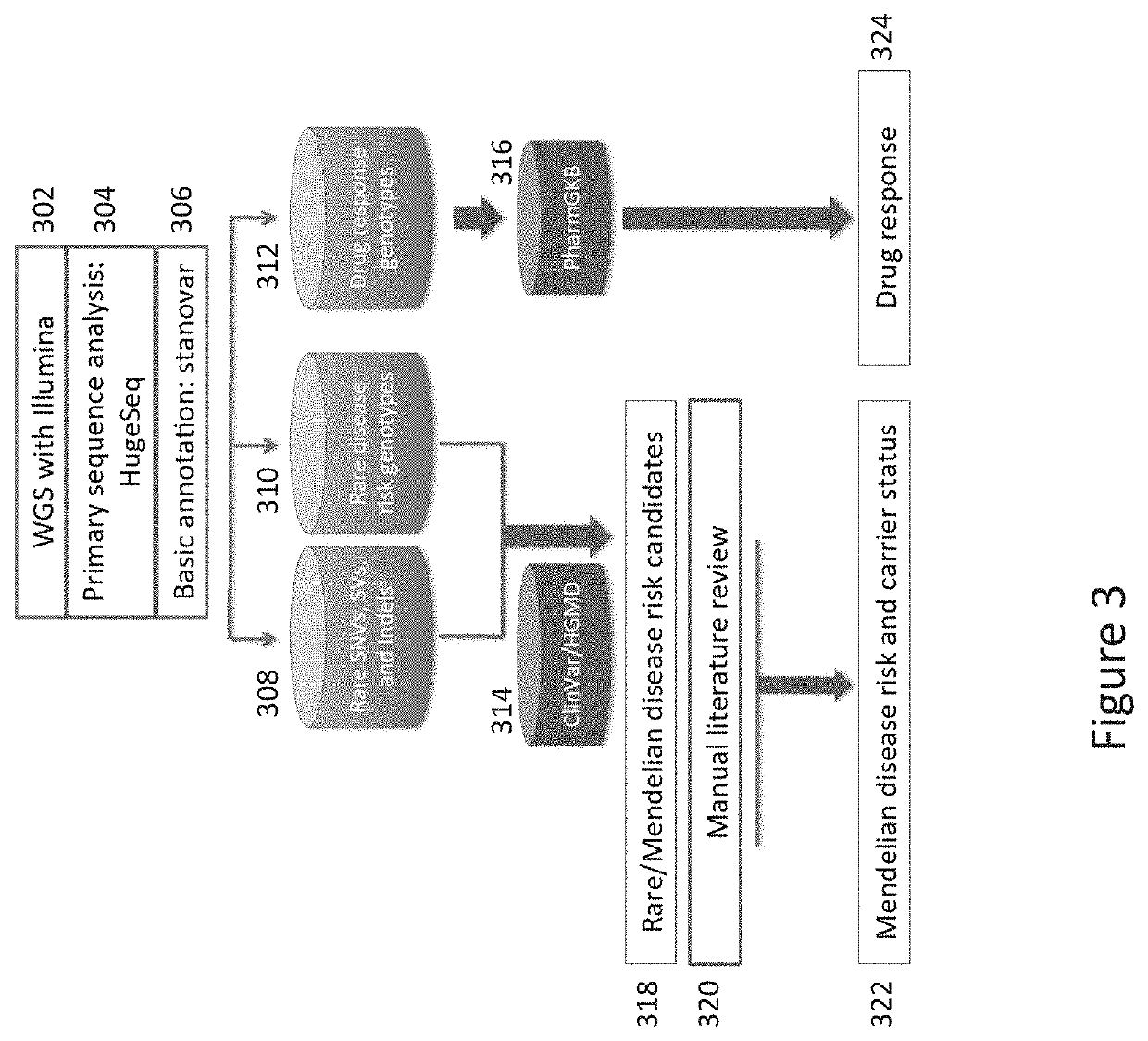
Method and System for Identifying Clinical Phenotypes in Whole Genome DNA Sequence Data
High throughput sequencing has facilitated a precipitous drop in the cost of whole genome human DNA sequencing, prompting predictions of a revolution in medicine via personalization of diagnostic and therapeutic strategies to individual genetics. Disclosed is a comprehensive series of methods for identification of genetic variants and medical genotypes, phasing genetic data and using Mendelian inheritance for quality control, and providing predictive genetic information about risk for rare disease phenotypes and response to pharmacological therapy in single individuals and father-mother-child trios.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
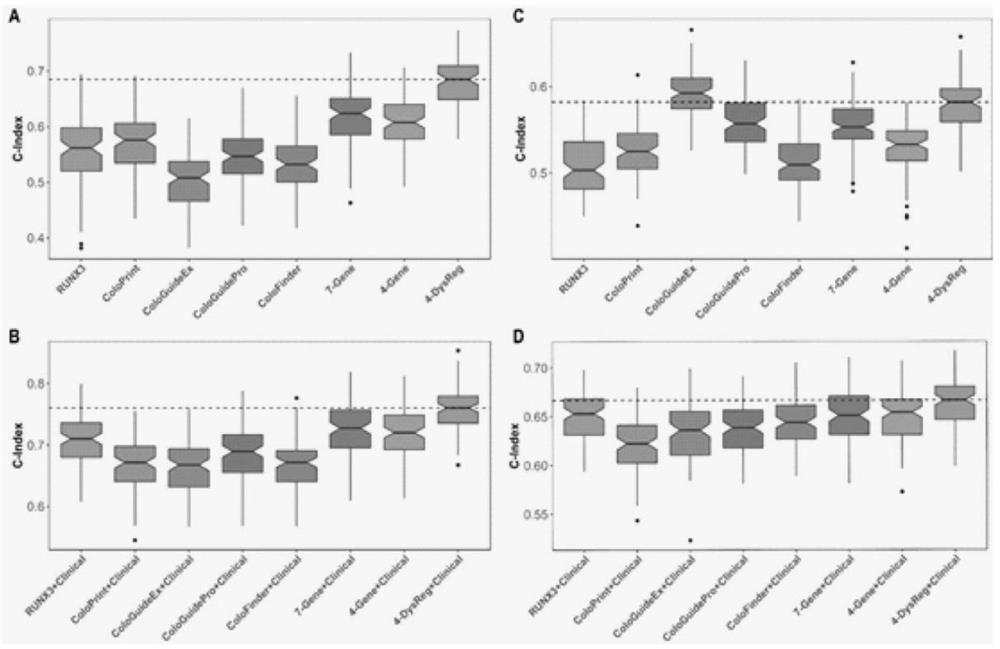
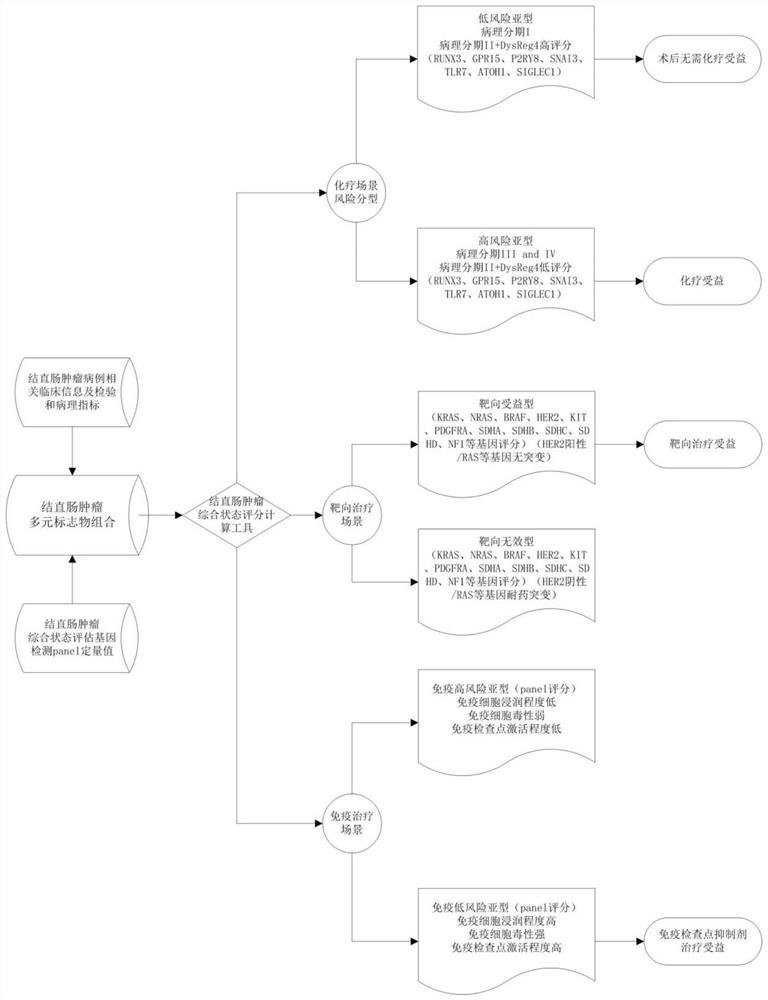
Method for constructing colorectal tumor state evaluation model and application
PendingCN111863126AImprove capture efficiencyFlexible adjustmentMedical automated diagnosisProteomicsBio informaticsTranscriptome
The invention relates to the field of gene detection and bioinformatics. The invention discloses an application of a complex disease state evaluation method constructed based on high-throughput sequencing data and clinical phenotypes in a colorectal tumor state evaluation model. The invention discloses a method for mining colorectal cancer markers based on transcriptome data, exon group / genome data and clinical phenotypes. The invention designs a set of calculation method for constructing a colorectal cancer state evaluation model by integrating high-throughput sequencing data and clinical phenotypes, biomarkers related to colorectal cancer are screened out, and a corresponding disease state evaluation model is formed. The markers considering both accuracy and mechanism interpretability are constructed through the method and can be used for colorectal cancer prognosis evaluation, treatment effect prediction, treatment scheme assistant decision making and the like.
Owner:上海市生物医药技术研究院
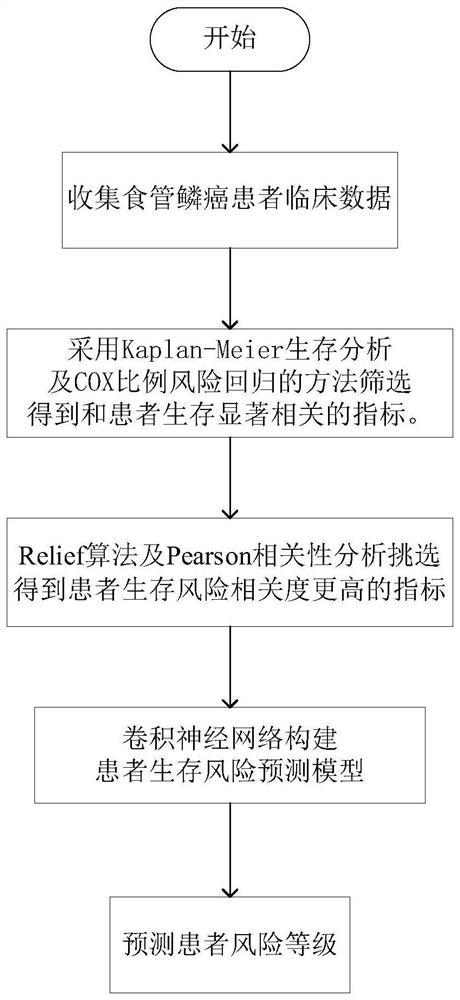
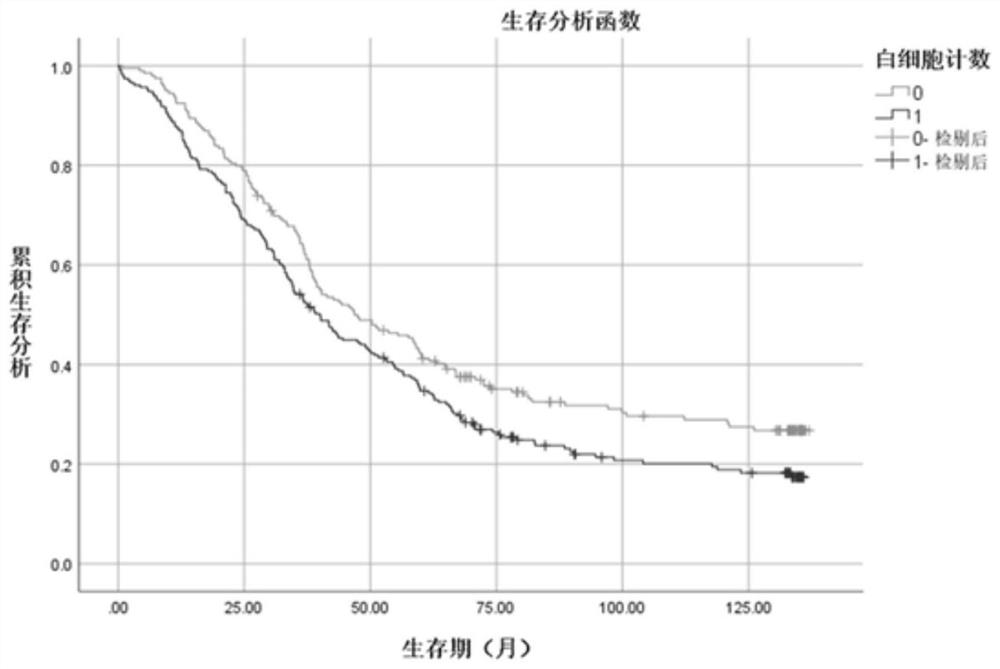
Esophageal squamous carcinoma patient survival risk prediction method based on convolutional neural network
InactiveCN113096810AImproved prognosisHealth-index calculationEpidemiological alert systemsSCC - Squamous cell carcinomaPatient survival
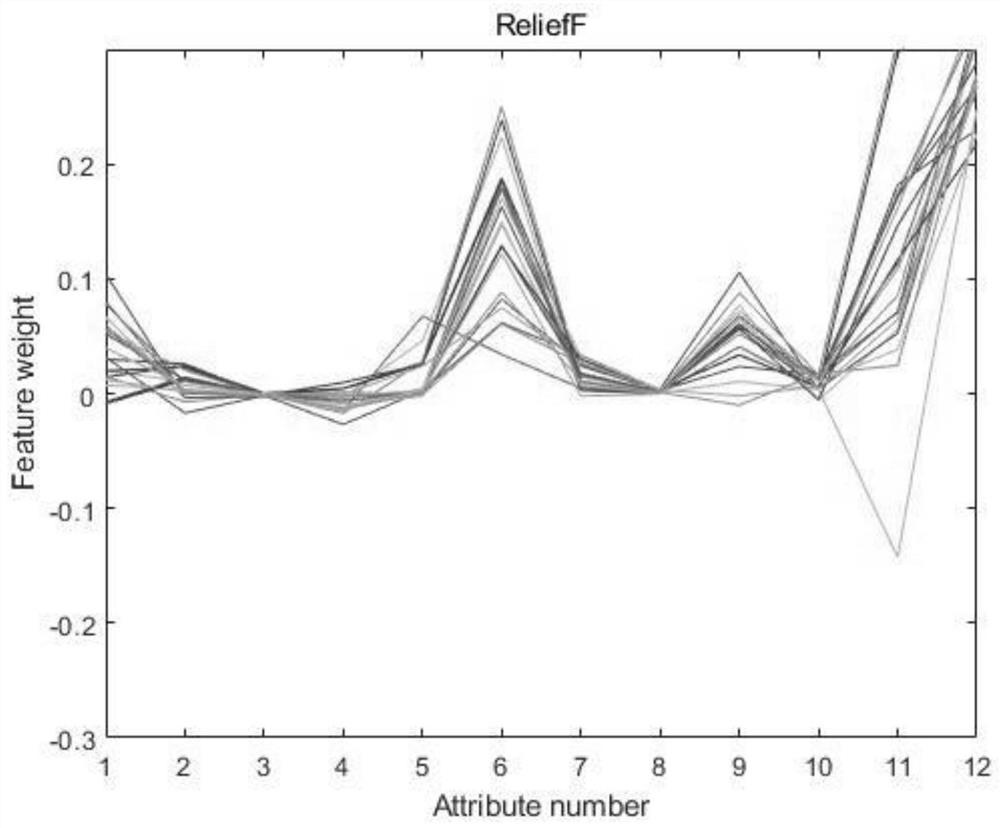
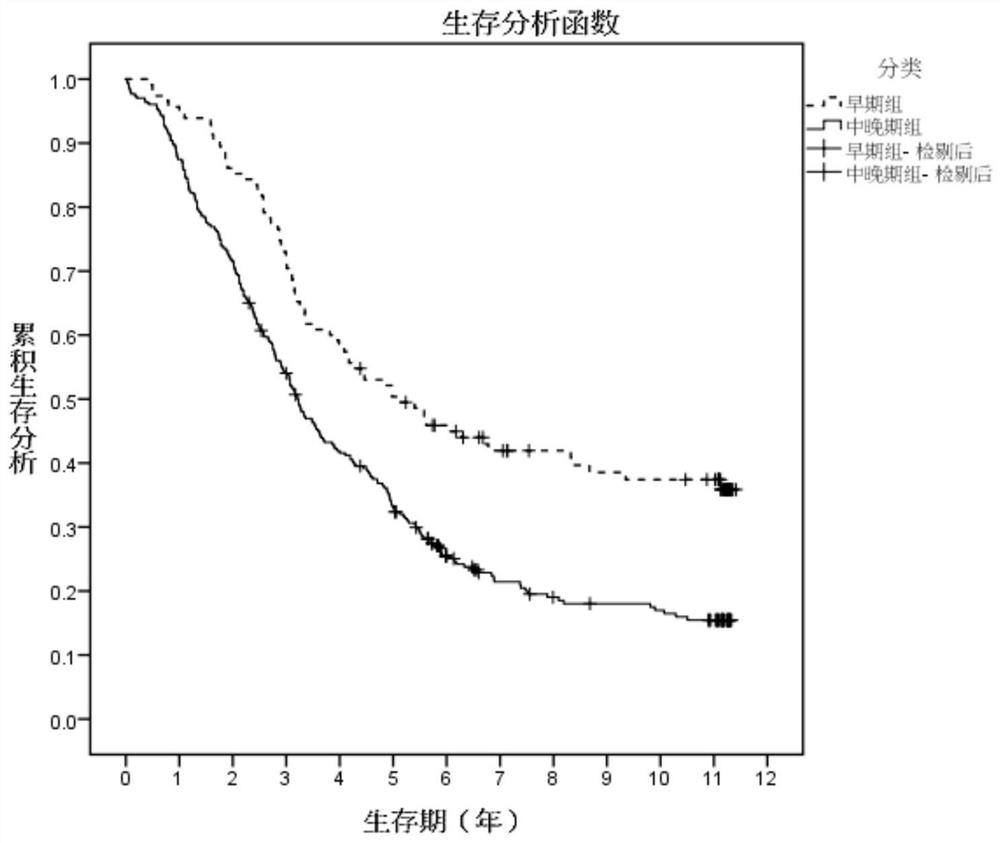
The invention provides an esophageal squamous carcinoma patient survival risk prediction method based on a convolutional neural network. The method comprises the steps of: collecting M clinical phenotype indexes and survival information of esophageal squamous carcinoma patients as original data; performing research by using a Kaplan-Meier method and a log-rank method to obtain a relationship between clinical phenotype indexes and lifetime information of the esophageal cancer patients; analyzing clinical phenotype indexes influencing survival prognosis of the patients by using Univariate Cox hazard analysis; extracting clinical phenotype indexes with higher correlation with the survival risk of the patients through a Relief feature selection algorithm and Pearson correlation analysis; and finally, constructing a survival risk prediction model of the esophageal squamous carcinoma patients by using a convolutional neural network and using clinical phenotype indexes with higher correlation, and further judging the prognosis survival risk of the patients. According to the method, the postoperative survival condition of the esophageal squamous carcinoma patients is accurately predicted, the prognosis risk prediction capability is improved, and the prognosis risk prediction cost is reduced.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
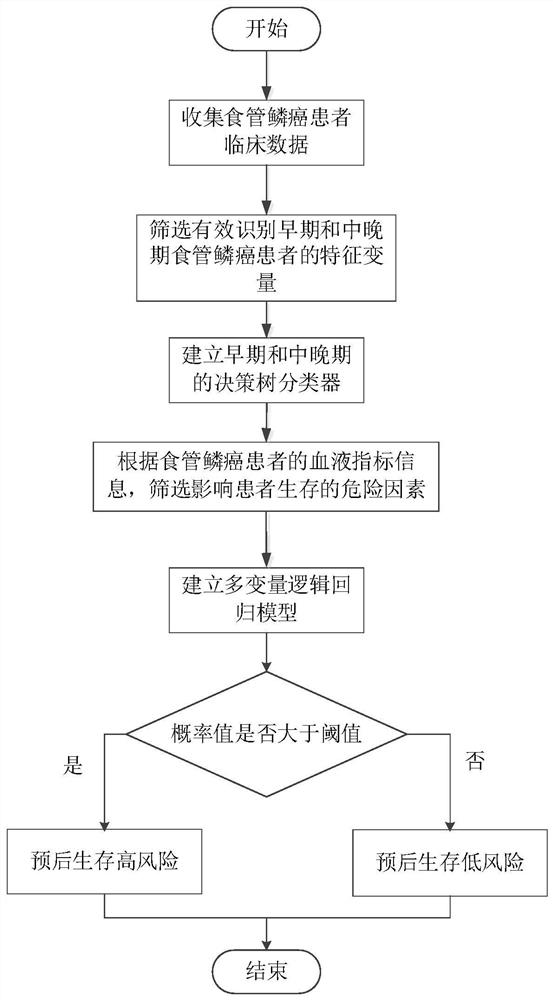
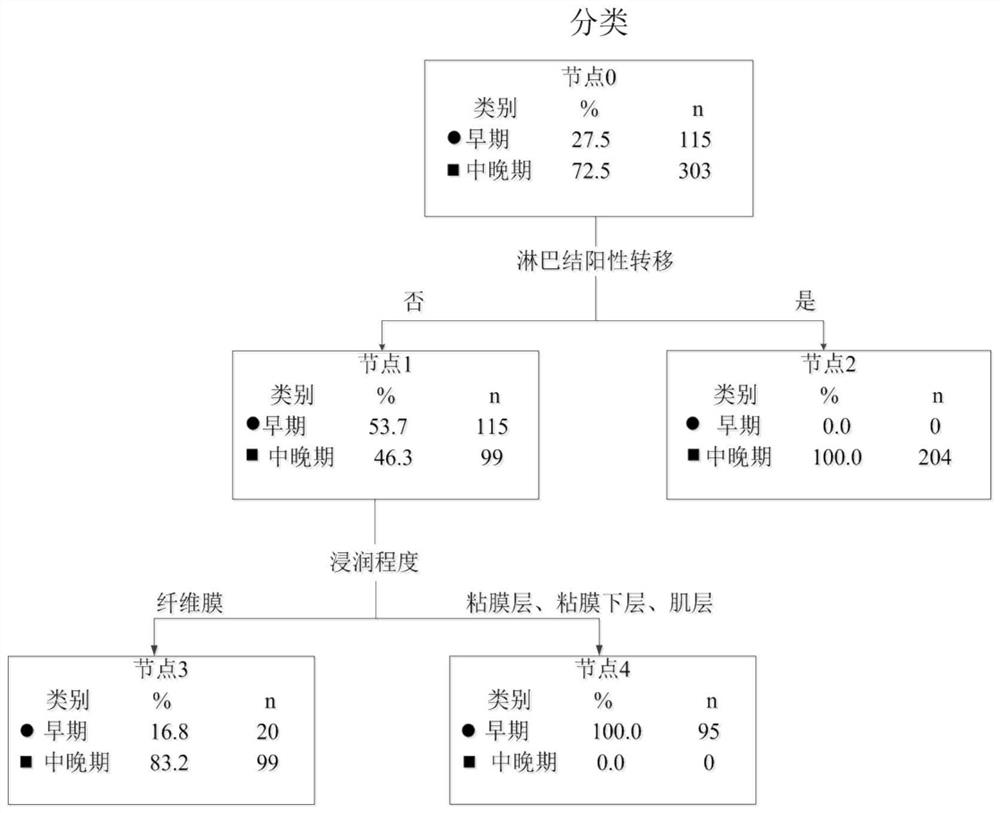
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma risk prediction method based on clinical phenotype and logistic regression analysis
ActiveCN112185549AEffective identification of characteristic variablesImprove the performance of risk predictionMedical data miningCharacter and pattern recognitionPatient survivalClinical phenotype
The invention provides an esophageal squamous cell carcinoma risk prediction method based on clinical phenotype and logistic regression analysis. The method is used for realizing prognosis survival risk assessment of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, screening out characteristic indexes according to clinical detection data of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients, and constructing a decision tree classifier according to the characteristic indexes; secondly, dividing the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients into early-stage esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients and middle-late-stage esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients by utilizing the decision tree classifier; then, obtaining blood index informationof the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patient one week before the operation, and screening out blood indexes with high correlation with the survival risk of the esophageal squamous cell carcinomapatient, and constructiung a logistic regression model; inputting the classified blood indexes of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patient into the logistic regression model to obtain a prognosis survival risk probability value of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patient; and judging the prognosis survival risk. According to the method, the postoperative survival state of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patient can be accurately judged, the risk prediction performance is improved, and the risk prediction cost is reduced.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Gene chip for screening primary cilium-related disease causative gene
InactiveCN105256378AUnderstanding Molecular MechanismsNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementClinical phenotypeRelated gene
The invention discloses a gene chip for screening a primary cilium-related disease causative gene. The gene chip comprises hundreds of probes. The probes are used for detecting a primary cilium-related disease related gene. The gene chip realizes purposeful gene screening on primary cilium-related disease clinical phenotype cases, can fast and effective identify causative genes, and provides basis for primary cilium-related disease early diagnosis and individual treatment.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Method and system for predicting disease risk
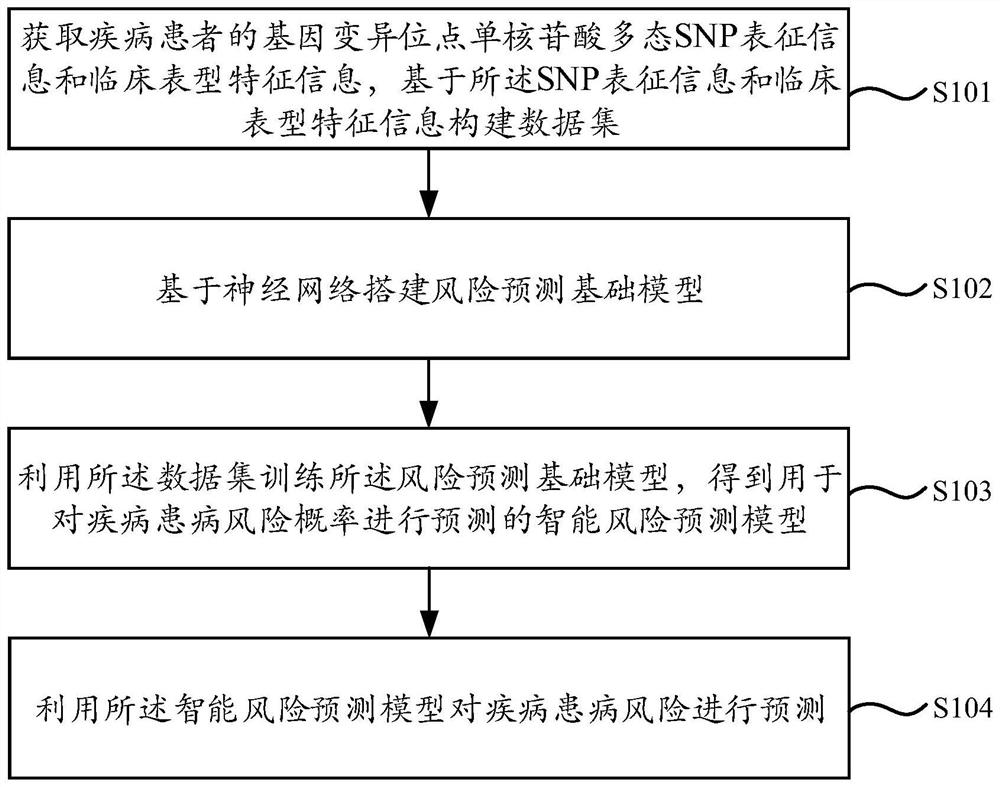
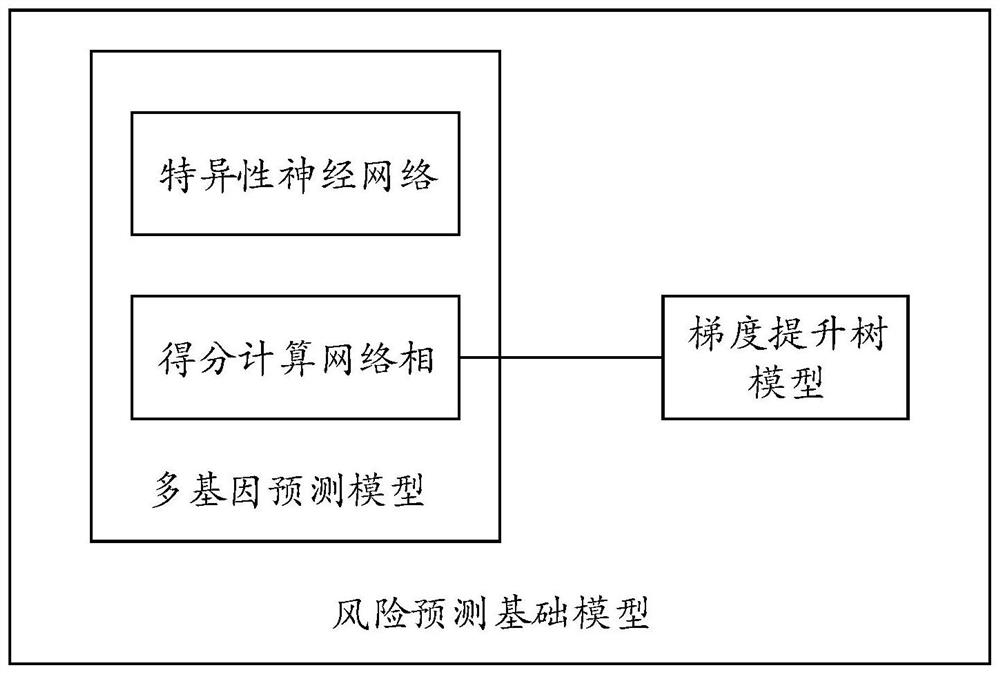
PendingCN114373547AImprove accuracyImprove robustnessHealth-index calculationProteomicsDisease riskData set
The invention provides a disease risk prediction method and system, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining gene variation site single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) characterization information and clinical phenotype feature information of a disease patient, and constructing a data set based on the SNP characterization information and the clinical phenotype feature information; building a risk prediction basic model based on a neural network; training the risk prediction basic model by using the data set to obtain an intelligent risk prediction model for predicting the disease risk probability; and performing performance evaluation on the intelligent risk prediction model. According to the scheme, deep learning is utilized to learn SNP characterization of a disease patient, meanwhile, the incidence relation between the SNP site and the disease can be captured through the deep learning model, and the accuracy of disease risk prediction can be effectively improved.
Owner:PING AN TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Method and application of pan-tumor targeted drug sensitivity state evaluation model constructed based on high-throughput sequencing data and clinical phenotypes
ActiveCN111640508ARealize integrated utilizationFlexible approachMedical simulationHybridisationTumor targetTumor targeting
The invention relates to the field of gene detection and bioinformatics, and discloses application of a state evaluation model constructed on the basis of high-throughput sequencing data and clinicalphenotypes to evaluation of the sensitivity state of a pan-tumor targeted drug. The invention discloses a method for mining a pan-tumor targeted drug marker based on transcriptome data, exon group / genome data and clinical phenotype, designs a set of calculation method for constructing a pan-tumor targeted drug sensitivity evaluation model by integrating the high-throughput sequencing data and clinical phenotype, screens out biomarkers related to tumor patient targeted drug sensitivity, and forms a pan-tumor targeted drug sensitivity state evaluation model. A marker considering both accuracy and mechanism interpretability is constructed through the method, and the method can be used for predicting a pan-tumor treatment effect, assisting in decision making of a treatment scheme and the like.
Owner:上海市生物医药技术研究院
Method and System for Identifying Clinical Phenotypes in Whole Genome DNA Sequence Data
High throughput sequencing has facilitated a precipitous drop in the cost of whole genome human DNA sequencing, prompting predictions of a revolution in medicine via personalization of diagnostic and therapeutic strategies to individual genetics. Disclosed is a comprehensive series of methods for identification of genetic variants and medical genotypes, phasing genetic data and using Mendelian inheritance for quality control, and providing predictive genetic information about risk for rare disease phenotypes and response to pharmacological therapy in single individuals and father-mother-child trios.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
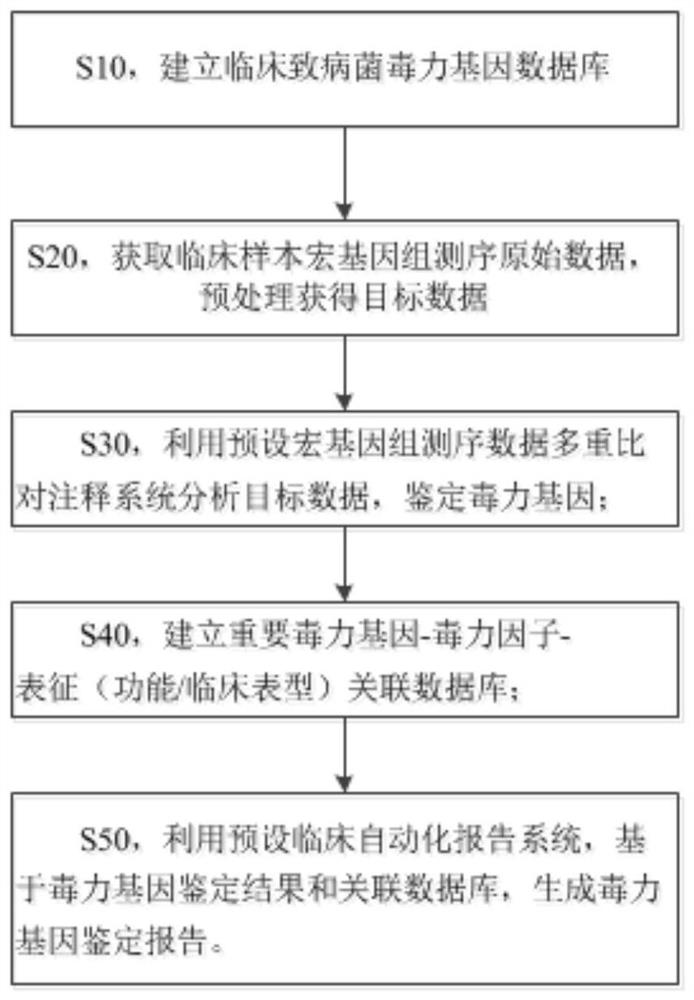
Metagenome-based clinical important pathogenic bacterium virulence gene detection method and system
ActiveCN113223618ATimely diagnosisTimely therapeuticBiostatisticsSequence analysisGenomic sequencingCerebrospinal fluid
The invention discloses a metagenome-based clinical important pathogenic bacterium virulence gene detection method and system. The method comprises the following steps: s10, establishing a clinical pathogenic bacterium virulence gene database; s20, acquiring clinical sample metagenome sequencing original data, and preprocessing the clinical sample metagenome sequencing original data to obtain target data; s30, analyzing the target data by using a preset metagenome sequencing data multiple comparison annotation system, and identifying virulence genes; s40, establishing an important virulence gene-virulence factor-characterization (function / clinical phenotype) associated database; s50, generating a virulence gene identification report based on the virulence gene identification result and the association database by using a preset clinical automatic report system. The system can perform virulence gene identification on metagenome sequencing data of clinical infection samples of different types (cerebrospinal fluid and the like), and multiple important virulence genes of multiple pathogenic bacteria in the samples are identified at a time. The system has good sensitivity and accuracy and helps doctors to perform diagnosis, treatment and prognosis in time.
Owner:HUGOBIOTECH BEIJING CO LTD +2
Accurate prediction method for pathogenic genetic variation
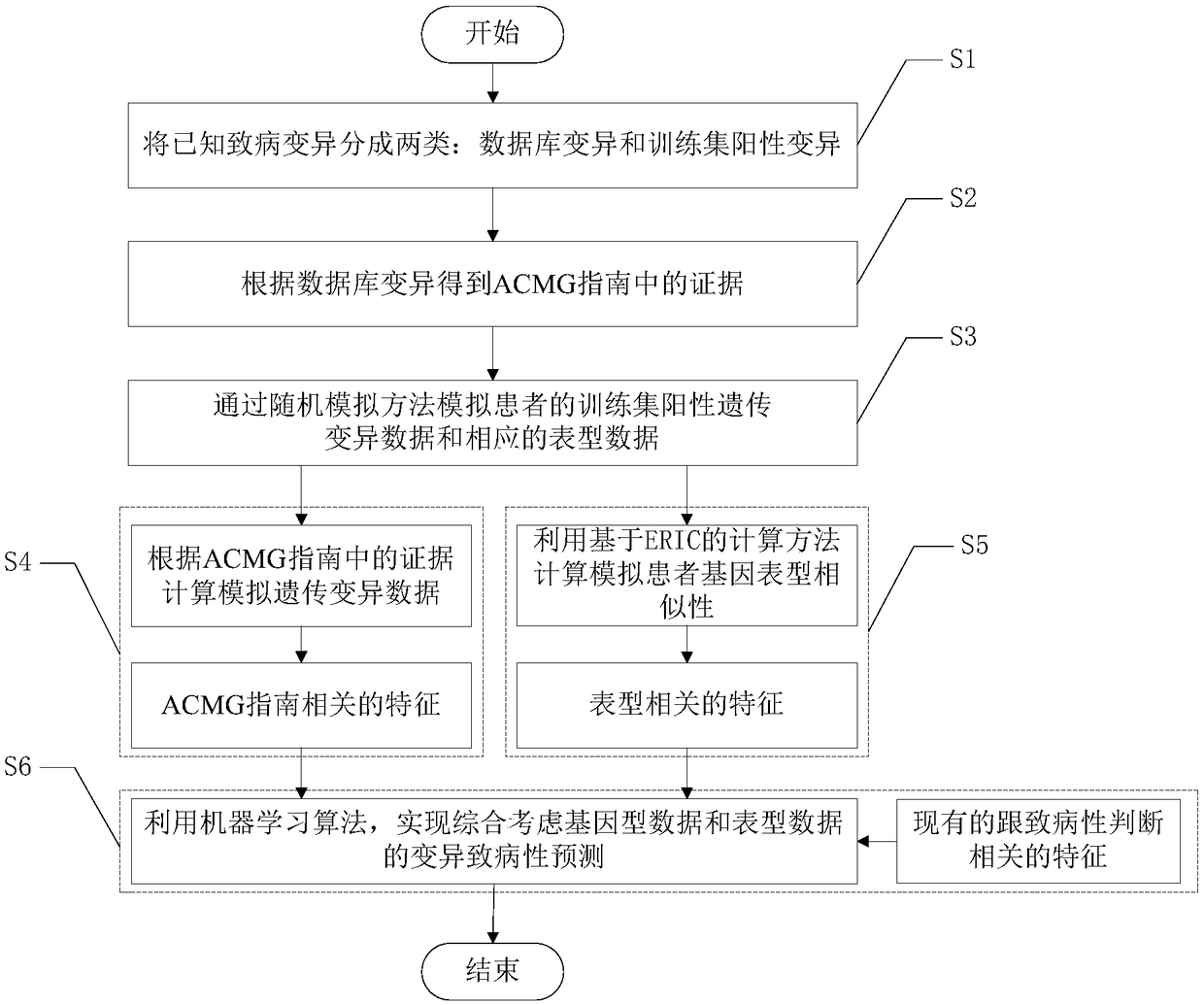
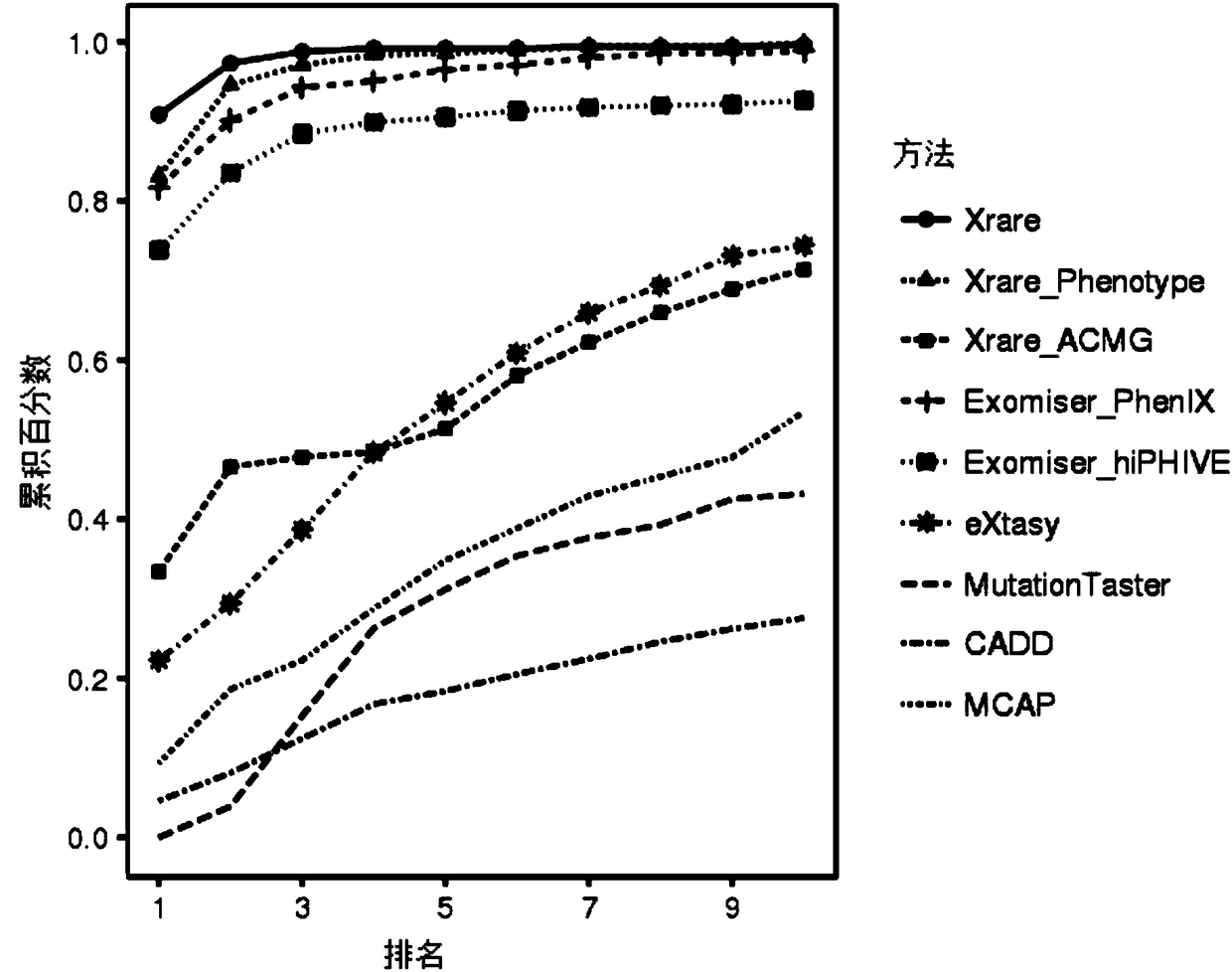
ActiveCN108363902AImprove interpretabilityImprove accuracyProteomicsGenomicsAlgorithmClinical phenotype
The invention discloses an accurate prediction method for pathogenic genetic variation. Known pathogenic variations are classified into two types: database variation and training set positive variation; partial evidences in an ACMG guide are obtained through the database variation; training set positive genetic variation data and corresponding phenotypic data of a patient are simulated through a random extraction method; guide related features are calculated; phenotype related features are calculated by utilizing an ERIC-based calculation method; and in combination with existing pathogenicityjudgment related features, and by utilizing a machine learning algorithm, variation pathogenicity prediction performed by comprehensively considering genotype data and phenotype data is realized. Themethod solves the problem that accurate prediction of variation pathogenicity cannot be performed due to incomplete clinical phenotype data, noises and inaccurate description in an actual scene.
Owner:成都奇恩生物科技有限公司
Complex disease state evaluation method based on high-throughput sequencing data and clinical phenotype construction and application
PendingCN111863137AImprove capture efficiencyFlexible adjustmentBiostatisticsMedical automated diagnosisExonPancreatic ductal
The invention relates to the field of gene detection and bioinformatics, and discloses a method for mining complex disease markers based on transcriptome data, exon group / genome data and clinical phenotypes. The invention designs a set of calculation method for constructing a complex disease state evaluation model by integrating high-throughput sequencing data and clinical phenotypes, the calculation method is applied to targeted medication of colorectal cancer, pancreatic ductal cancer and pancreas ductal cancer, biomarkers related to diseases are screened respectively, and the correspondingdisease state evaluation model is formed. The marker considering both accuracy and mechanism interpretability is constructed through the method and can be used for prognosis evaluation of complex diseases, treatment effect prediction, treatment scheme assistant decision making and the like.
Owner:上海朴岱生物科技合伙企业(有限合伙)
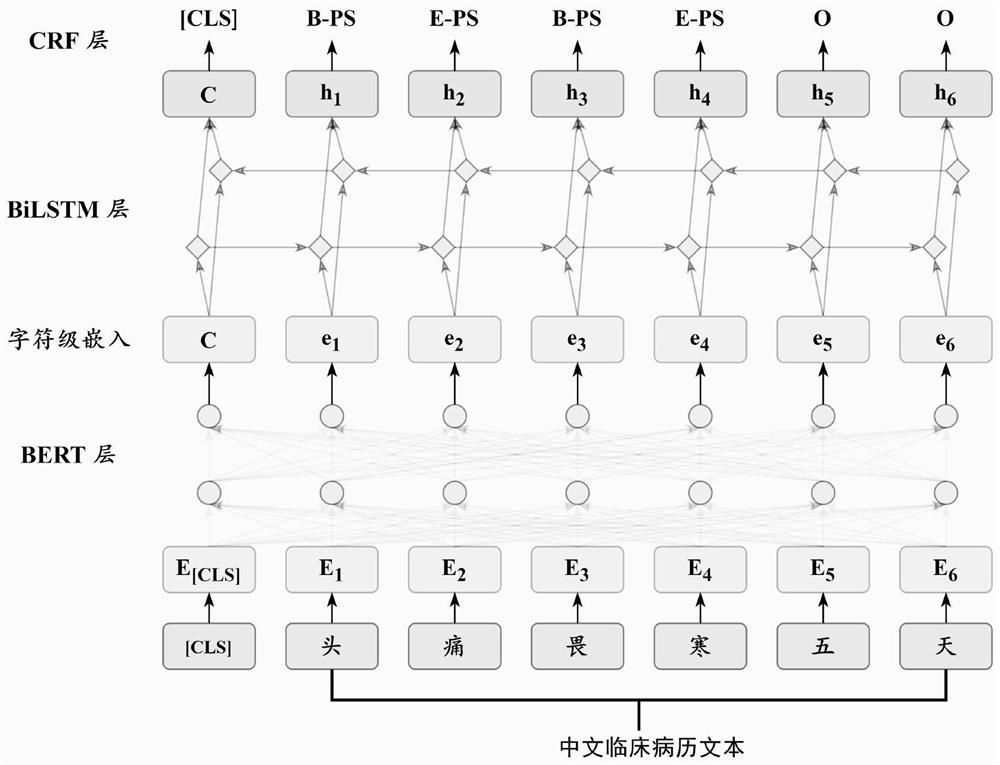
Chinese clinical phenotype fine-grained named entity recognition method and system
PendingCN114564959APrecisely structured dataCharacter and pattern recognitionNatural language data processingConditional random fieldMedical record
The invention provides a Chinese clinical phenotype-based fine-grained named entity recognition method and system, and belongs to the technical field of clinical medical record information processing, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the character-level embedded feature extraction of a clinical text through a natural language pre-training model BERT; integrating the character-level embedded features and the sequence features of the clinical text by using a bidirectional long and short word memory model BiLSTM, and carrying out feature coding to obtain tags; and carrying out decoding prediction on the tag by using a conditional random field (CRF) to obtain a named entity recognition result. According to the method, a clinical fine-grained phenotype entity standard data set for a fine-grained named entity experiment is established, negative symptoms and positive symptoms are distinguished, and more accurate structured data is provided for clinical analysis.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Gene panel for detecting single-gene genetic hypertension and application of gene panel
InactiveCN109750101AThe detection process is fastAchieve early detectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDetection rateDisease cause
The invention discloses a gene panel for detecting single-gene genetic hypertension and application of a gene panel. By means of the gene panel, potential pathogenic gene mutation of single-gene genetic hypertension can be screened out of massive genetic information by means of targeted high-throughput sequencing in combination of a bioinformatics analysis means, and the positive detection rate ofmutation sites of single-gene genetic hypertension and application can be remarkably increased. The detection result of the gene panel is combined with clinical phenotype of a patient, etiological diagnosis of single-gene genetic hypertension and application of gene panel can be effectively assisted, and therefore the clinical disease diagnosis rate is increased, a specific and effective intervention treatment scheme is implemented aiming to specific illness states, and the effects of early finding, early intervention and prognosis improvement on single-gene genetic hypertension are achieved.According to the technical scheme, the remarkable advantages of being high in gene detection speed, high in disease diagnosis accurate and the like are achieved.
Owner:FUWAI HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
Marfan syndrome detection kit based on FBN1 gene insertion mutation
ActiveCN114107452AHelp early treatmentReduce the prevalenceMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisBase JMarfan syndrome
The invention provides a Marfan syndrome detection kit based on FBN1 gene c.5688-5689 insertion mutation, and belongs to the technical field of molecular biological detection. Whole blood DNA of Marfan syndrome family members is subjected to base sequence analysis, c.5688-5689insG base insertion variation (p.Arg1897Glufs) of the FBN1 gene is detected in family diseased members, and the variation is not detected in non-diseased members in the family. By detecting whether a subject carries the FBN1 gene c.5688-5689 insertion mutation or not, a carrier of the variation can be detected, molecular diagnosis and family genetic analysis of the Marfan syndrome can be facilitated, meanwhile, the relationship between gene mutation and clinical phenotype can be researched, a basis is provided for antenatal diagnosis possibly needed in the future, and the application prospect is wide. Meanwhile, a new target spot is provided for research and development of medicines for treating Marfan syndrome.
Owner:SHENZHEN EYE HOSPITAL
Natural language processing method and system for clinical phenotype information of infertility
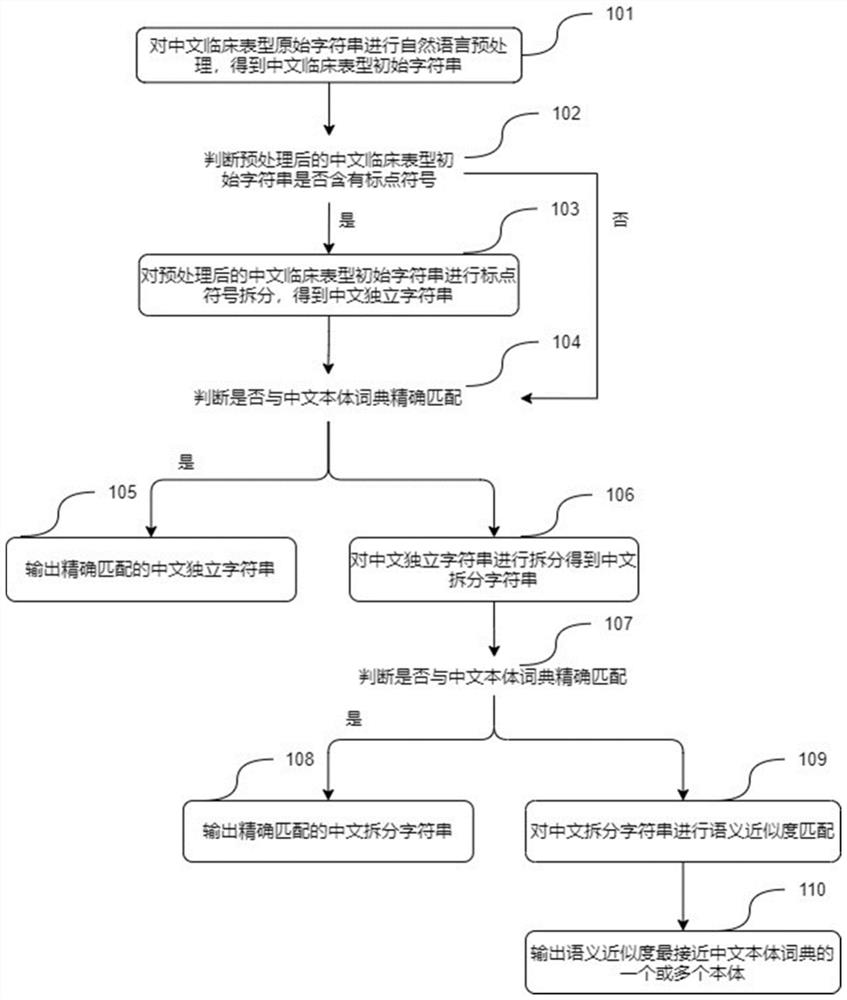
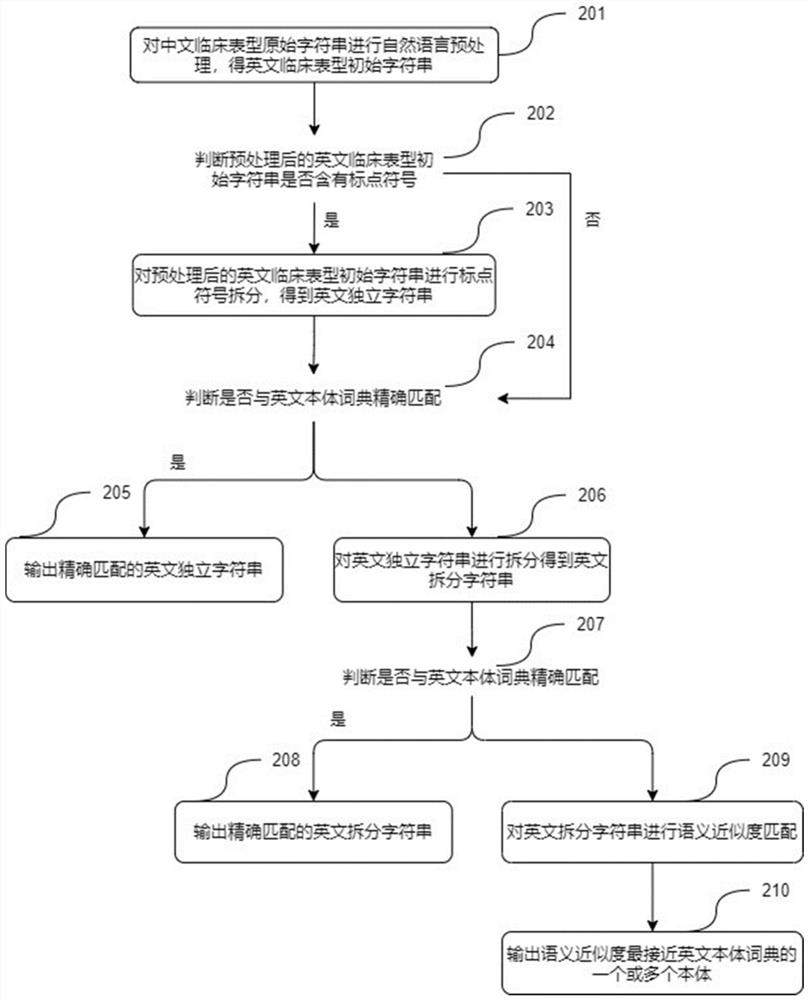
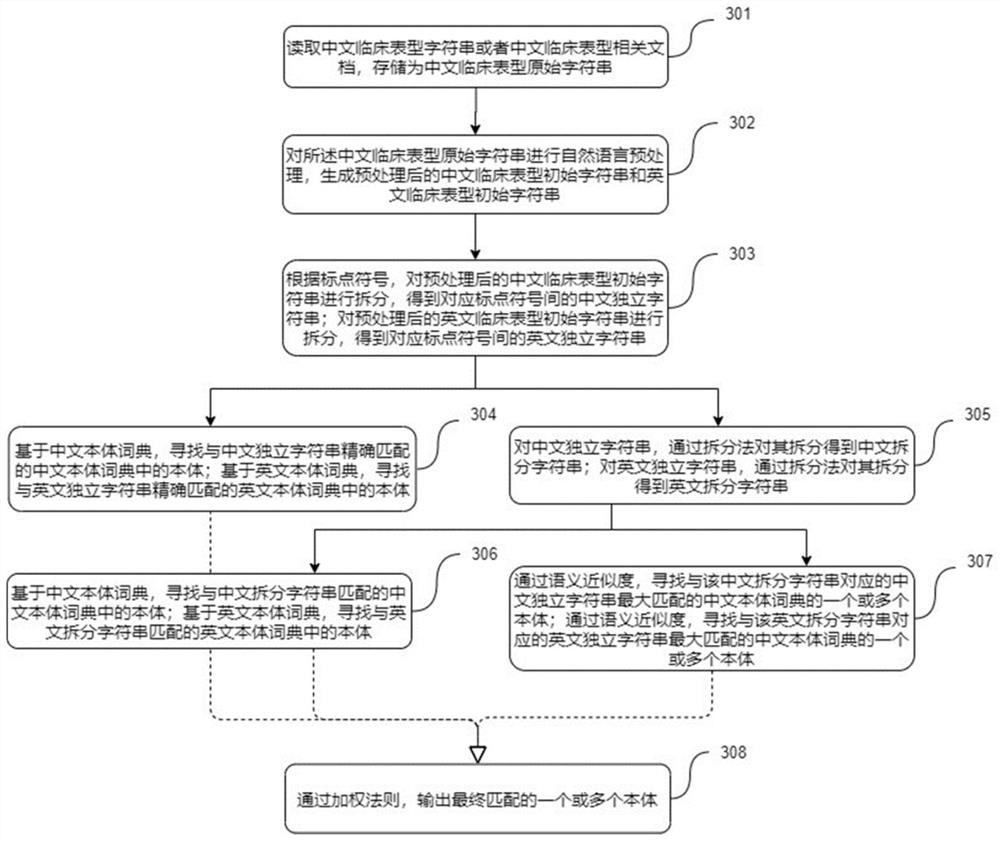
PendingCN112765318AQuick identificationInnovativeSemantic analysisText database queryingClinical phenotypeInfertility
The invention provides a natural language processing method and system for clinical phenotype information of infertility. A Chinese clinical phenotype original character string is converted into a Chinese and English clinical phenotype initial character string, an independent character string and a split character string through natural language preprocessing, punctuation mark splitting and field splitting methods; and based on a pre-established Chinese and English ontology dictionary, accurate matching and fuzzy matching are performed on the clinical phenotype initial character string, the independent character string and the split character string, and finally one or more ontologies matched with the Chinese and English ontology dictionary are output through a weighting rule. The fuzzy matching is intended to be calculated through semantic approximation. The invention further provides a natural language processing system and a medium. The natural language processing system comprises a reading module, a conversion module, a splitting module, a matching module and an output module. According to the method, the problem of quick matching of Chinese clinical phenotype information and the ontology dictionary is solved, and convenience is brought to all-exon sequencing analysis of diseases such as infertility and the like.
Owner:CARRIER GENE TECH SUZHOU CO LTD
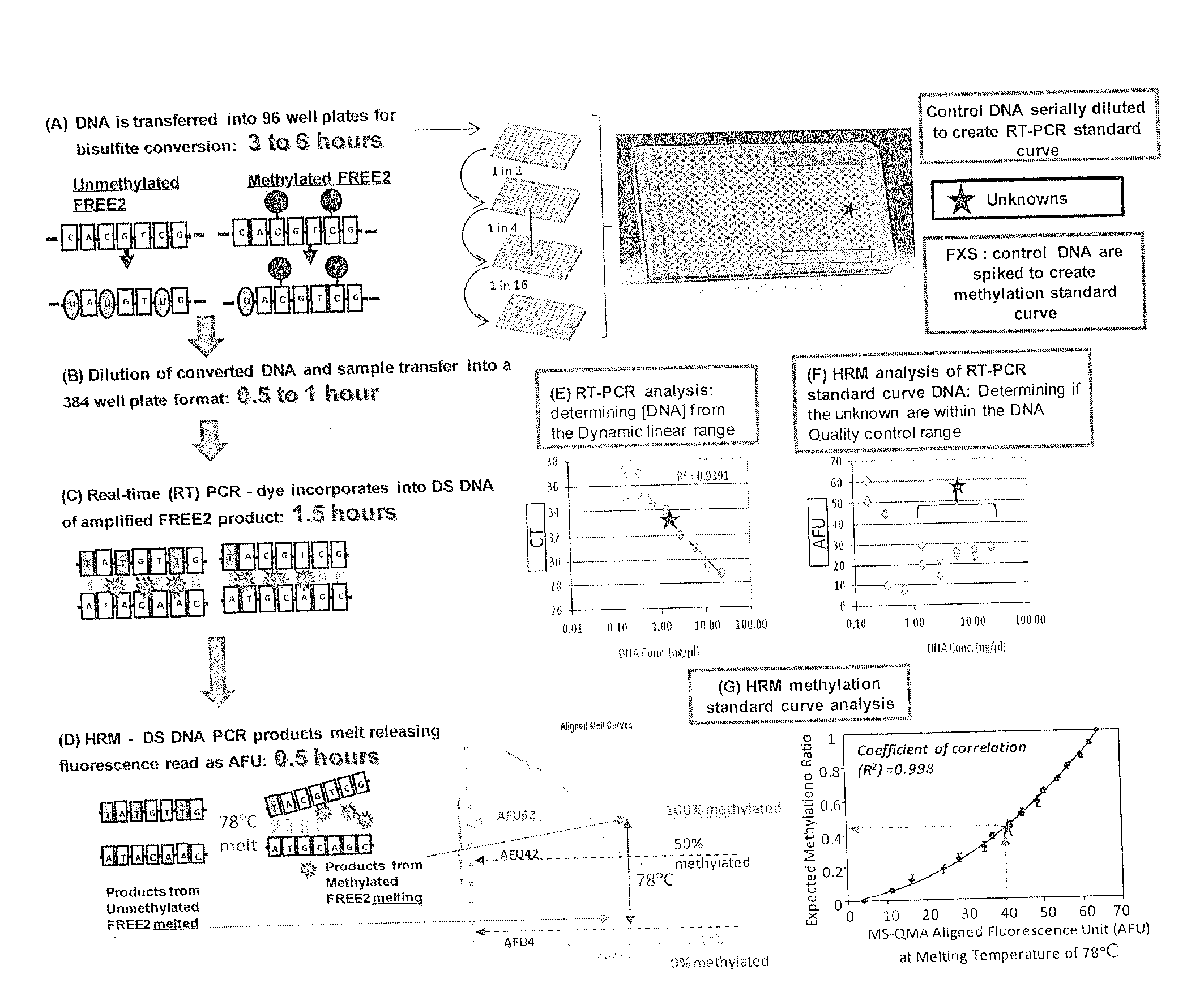
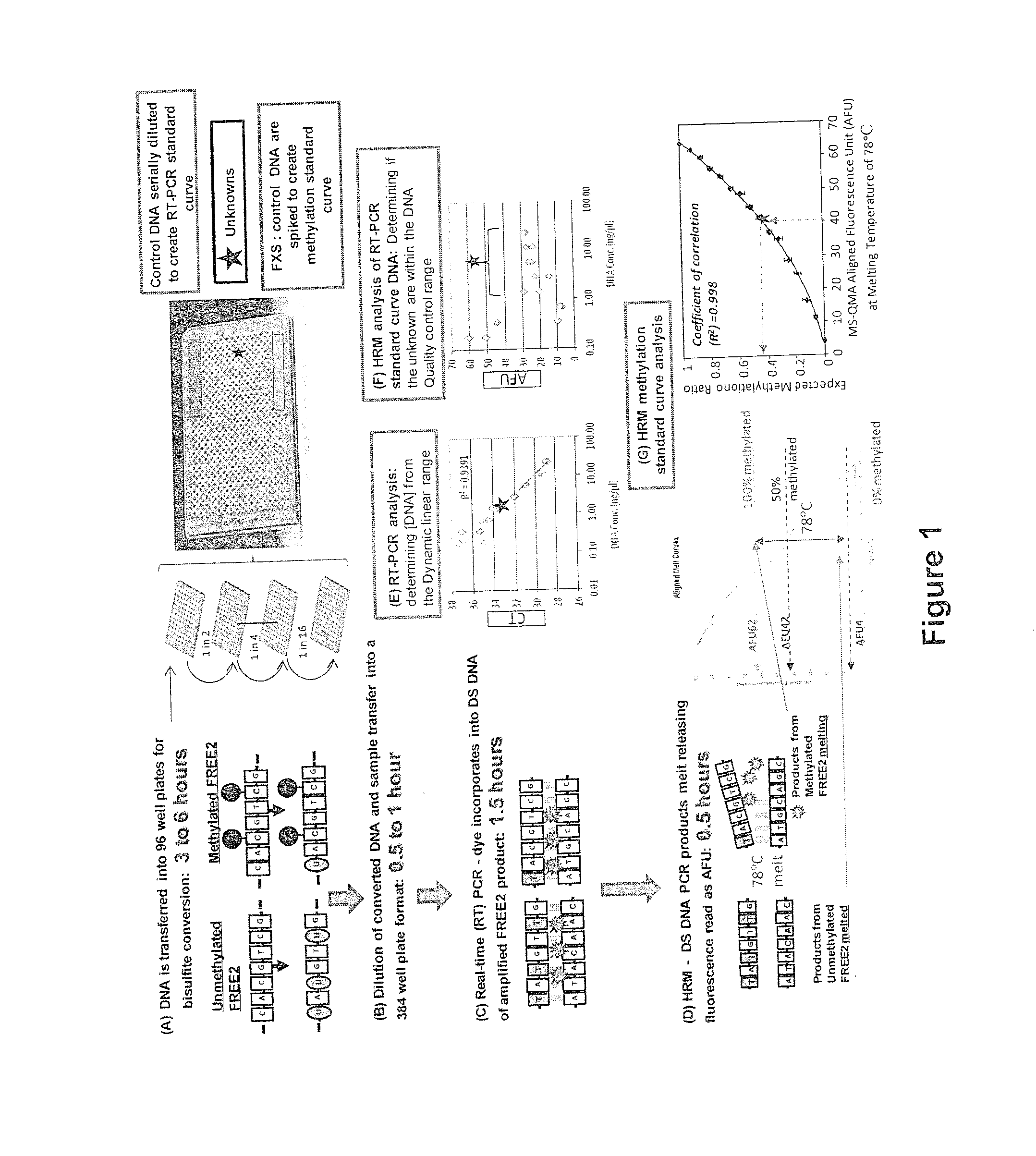
An assay for quantitating the extent of methylation of a target site
InactiveUS20160083792A1High throughput screeningSignificant diagnosticMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsAssayClinical phenotype
An assay quantifies the extent of methylation in a DNA sample. Kits and clinical diagnostic assays include assays to determine clinical phenotypes based on extent of methylation of a DNA target site.
Owner:MURDOCH CHILDRENS RES INST
Construction method and application of pancreatic ductal cancer state evaluation model
PendingCN111816315AImprove capture efficiencyFlexible adjustmentMedical data miningForecastingExonBiology
The invention relates to the field of gene detection and bioinformatics and discloses application of a complex disease state evaluation method constructed based on high-throughput sequencing data andclinical phenotypes in a pancreatic ductal carcinoma state evaluation model. The invention also provides a method for mining pancreatic ductal cancer complex disease markers based on transcriptome data, exon group / genome data and clinical phenotypes, designs a calculation method for constructing a pancreatic ductal cancer state evaluation model by integrating high-throughput sequencing data and clinical phenotypes, screens out biomarkers related to pancreatic ductal cancer and creates the corresponding disease state evaluation model. The markers having both accuracy and mechanism interpretability are constructed through the method, and can be used for pancreatic ductal cancer prognosis evaluation, treatment effect prediction, assistant decision making of treatment schemes and the like.
Owner:上海市生物医药技术研究院 +1
Compositions and methods for spinocerebellar ataxia
ActiveUS20060292604A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEtiologyAutosomal dominant cerebellar ataxia
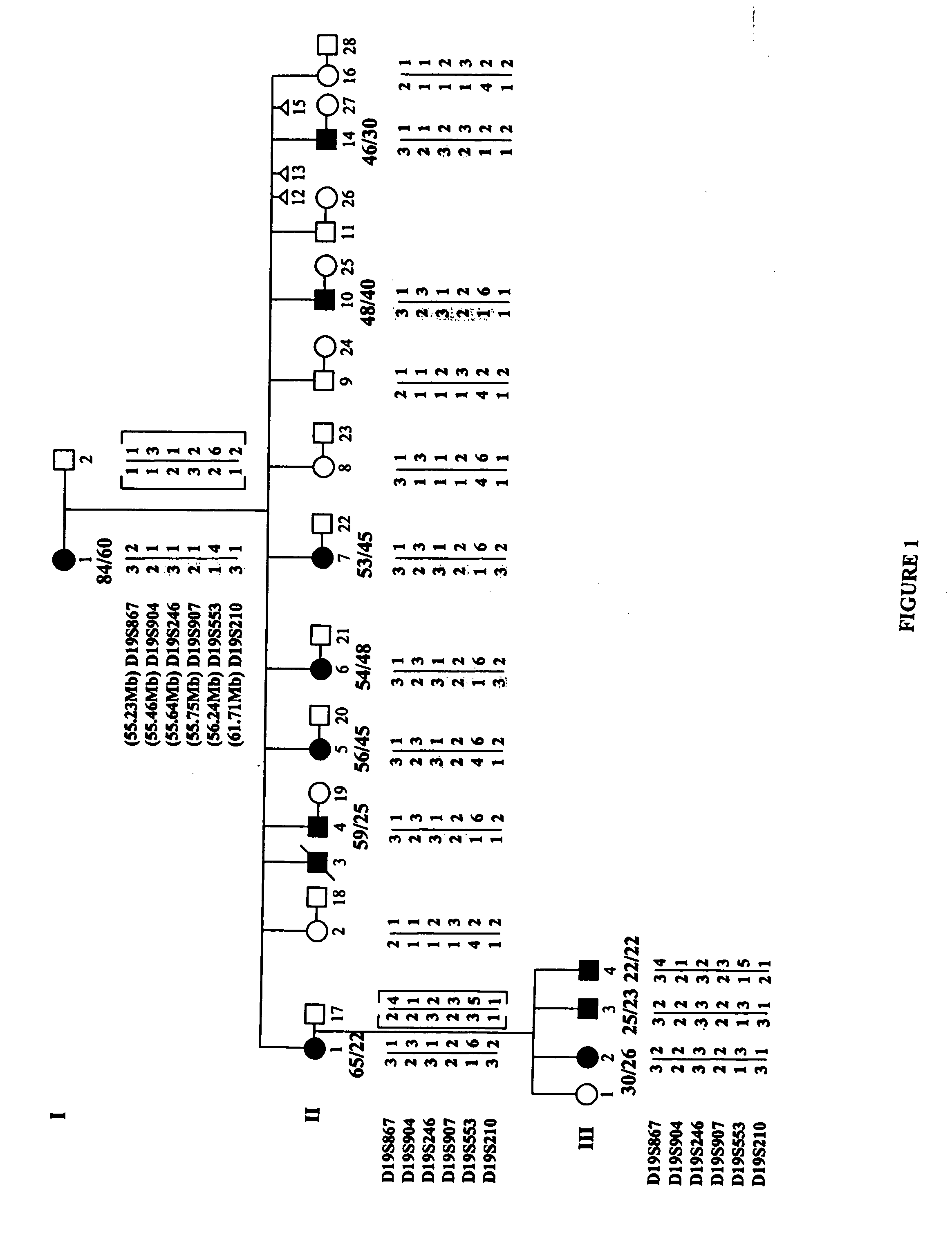
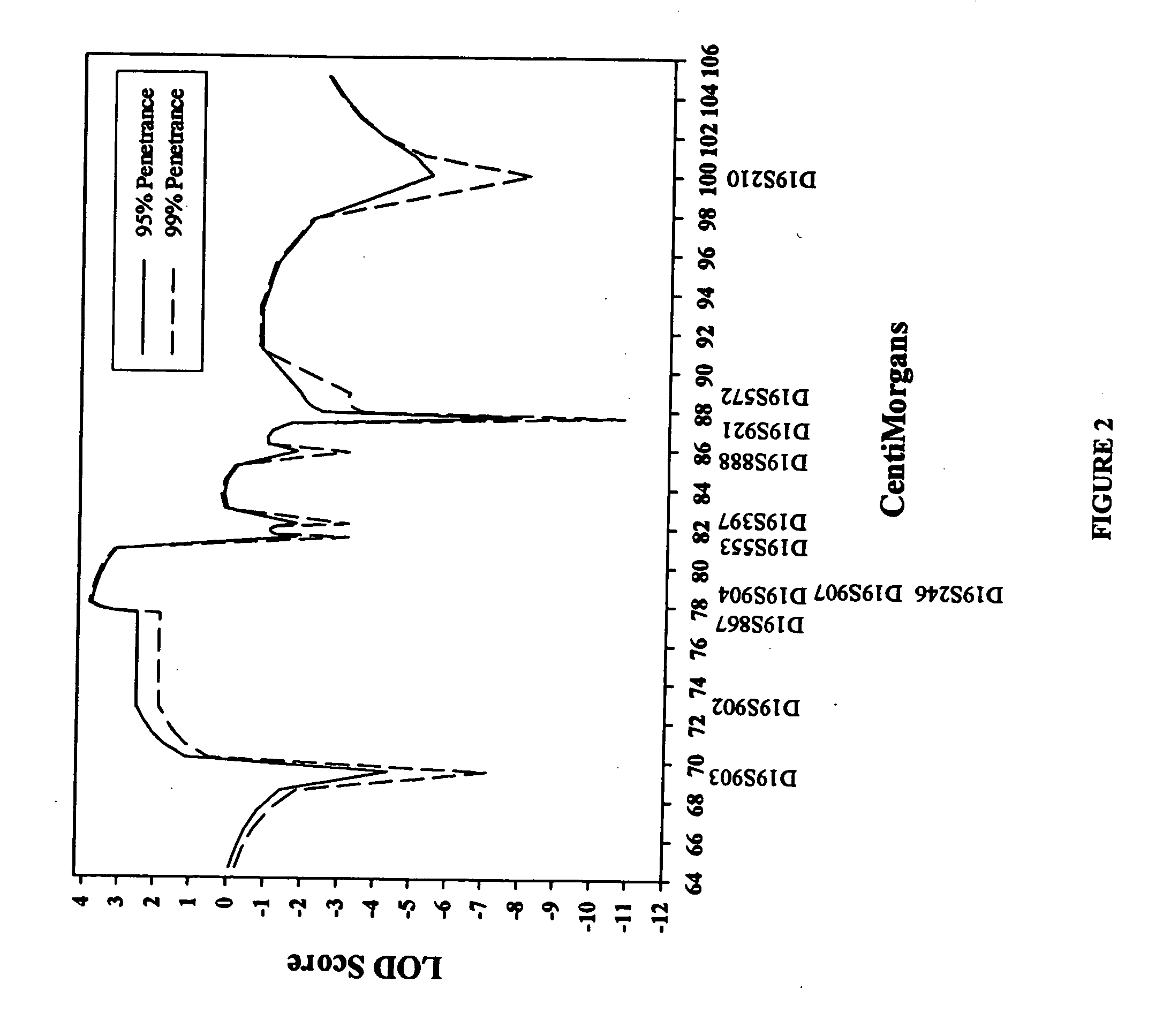
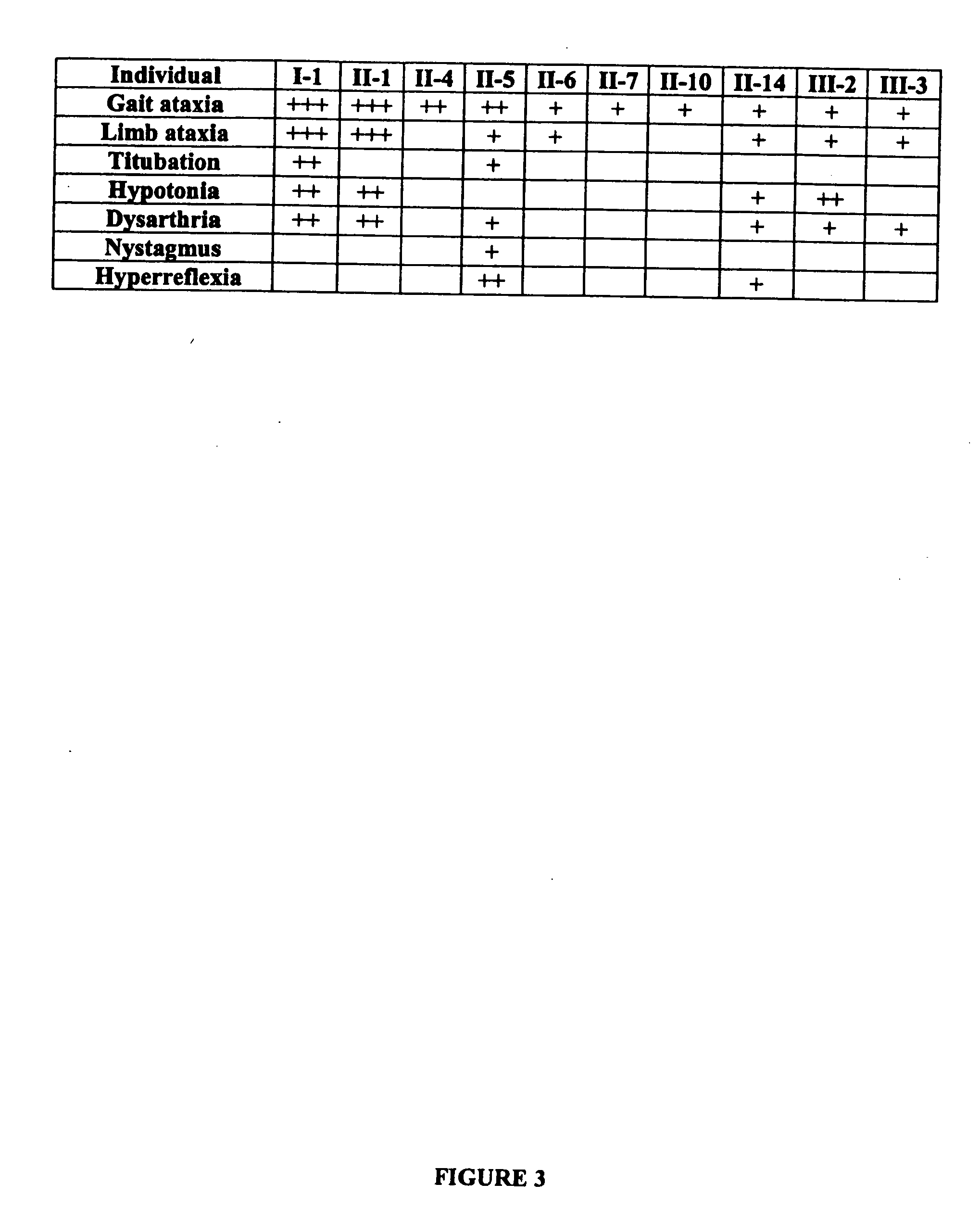
The autosomal dominant spinocerebellar ataxias (SCAs) represent a growing and heterogeneous clinical phenotype with ongoing discovery of causative etiologies. Methods: The authors collected DNA and clinically characterized a three-generation Filipino family segregating a dominant ataxia. Following elimination of several known SCA loci, a genome-wide linkage study was undertaken with additional fine mapping of 19q13. Results: Clinical characterization of affected family members revealed cerebellar signs including gait ataxia, limb ataxia / dysmetria, titubation, hypotonia, dysarthria, and nystagmus. Linkage was found in a ˜4 cM region of 19q13 bounded by markers D19S867 and D19S553, with a maximum LOD score of 3.89 at markers D19S904, D19S246, and D19S907. This region overlaps with, though markedly reduces the previously described SCA13 locus. Conclusion: An autosomal dominant cerebellar ataxia clinically distinguishable from SCA13 overlaps with the SCA13 locus on chromosome 19q13.3.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com