Patents
Literature
43 results about "Exome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The exome is the part of the genome composed of exons, the sequences which, when transcribed, remain within the mature RNA after introns are removed by RNA splicing and contribute to the final protein product encoded by that gene. It consists of all DNA that is transcribed into mature RNA in cells of any type, as distinct from the transcriptome, which is the RNA that has been transcribed only in a specific cell population. The exome of the human genome consists of roughly 180,000 exons constituting about 1% of the total genome, or about 30 megabases of DNA. Though composing a very small fraction of the genome, mutations in the exome are thought to harbor 85% of mutations that have a large effect on disease. Exome sequencing has proved to be an efficient strategy to determine the genetic basis of more than two dozen Mendelian or single gene disorders.
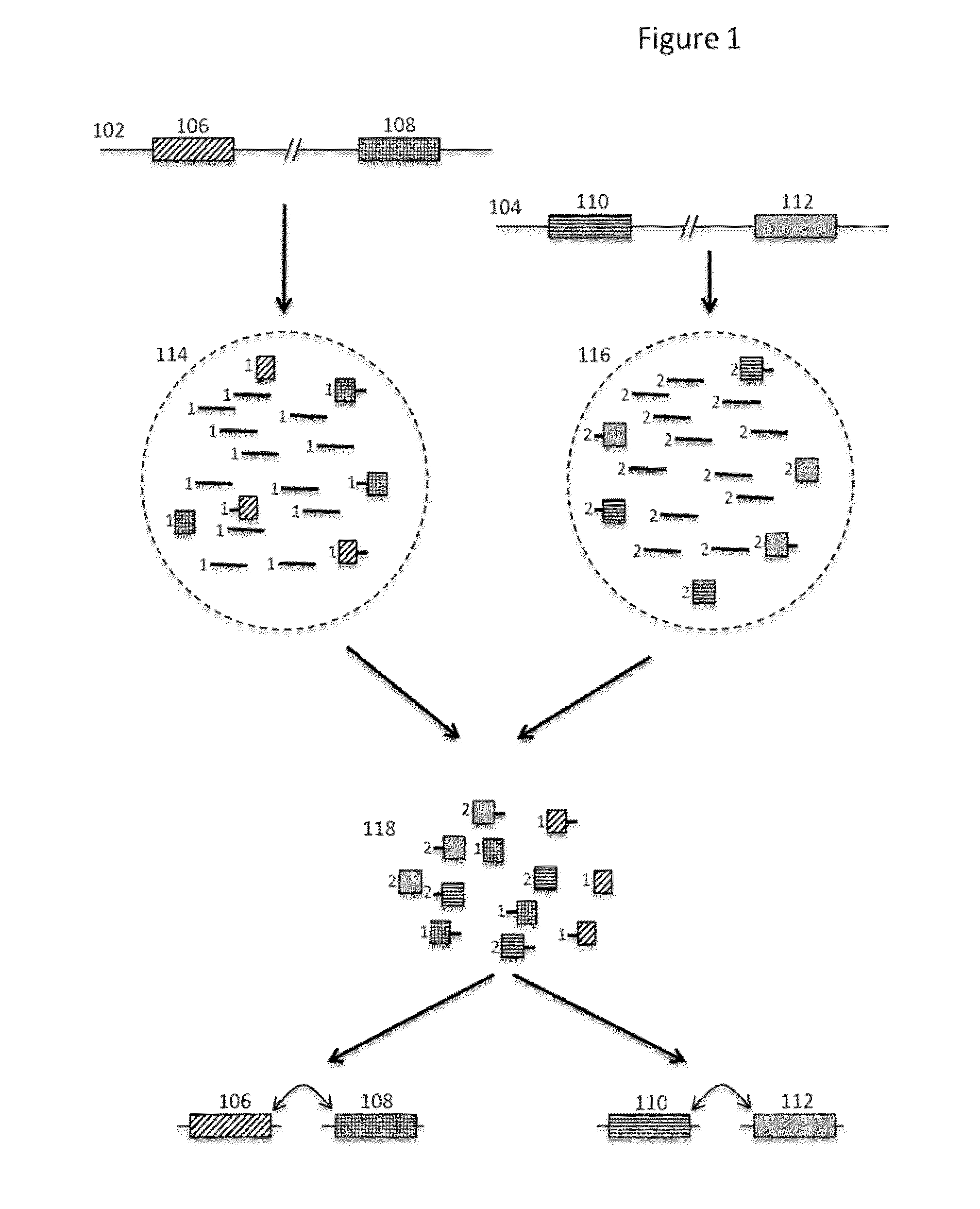
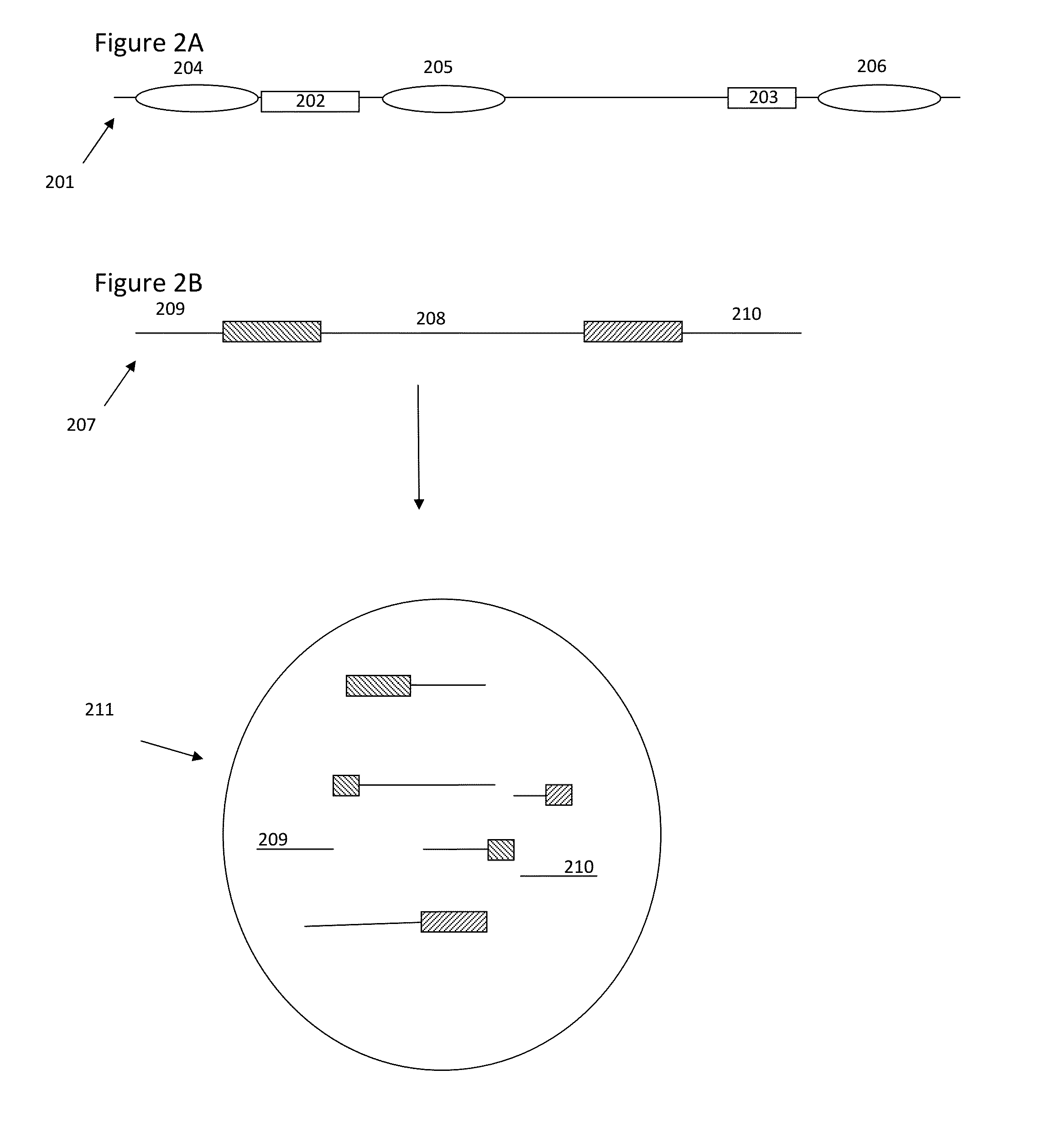
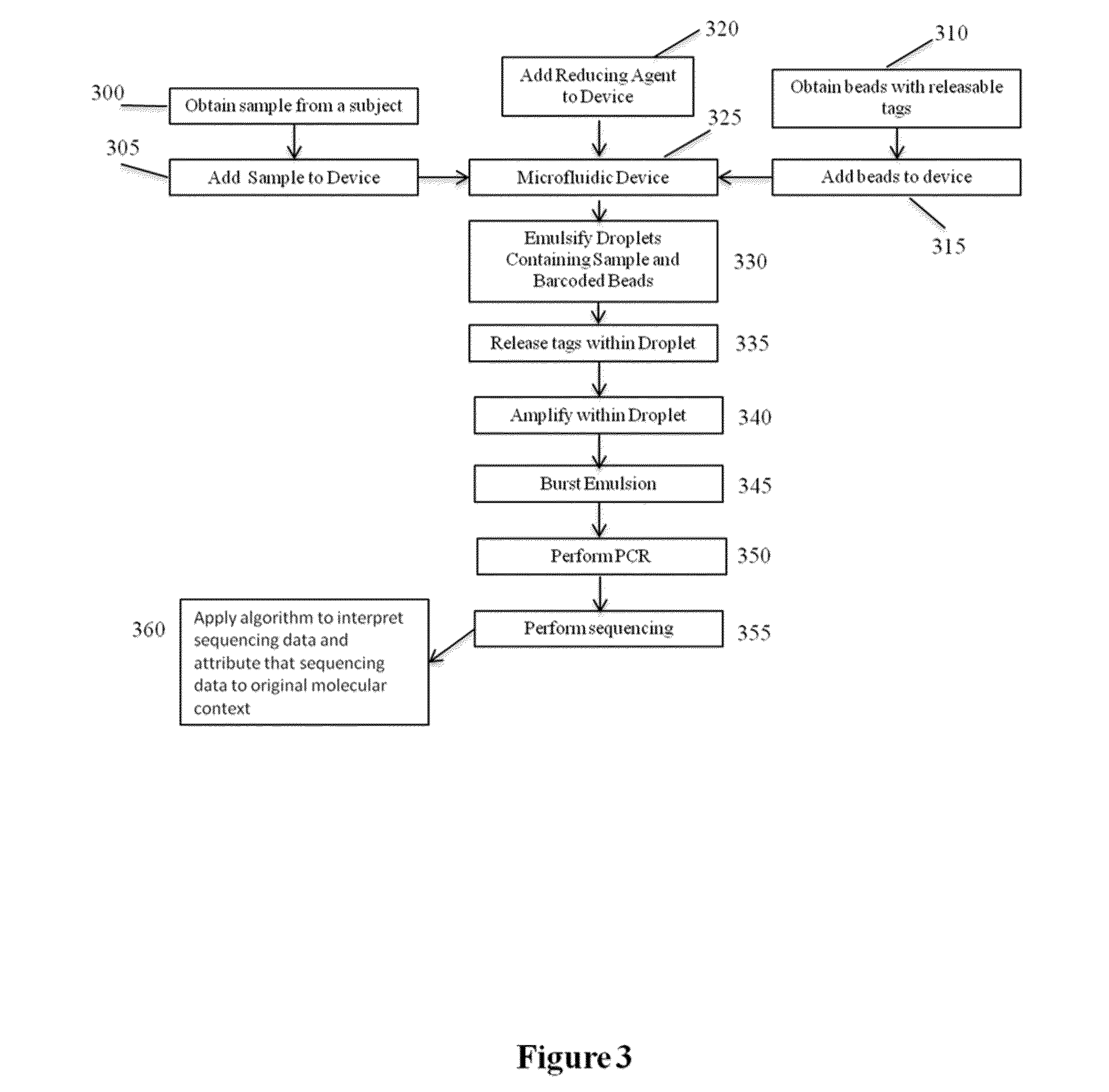
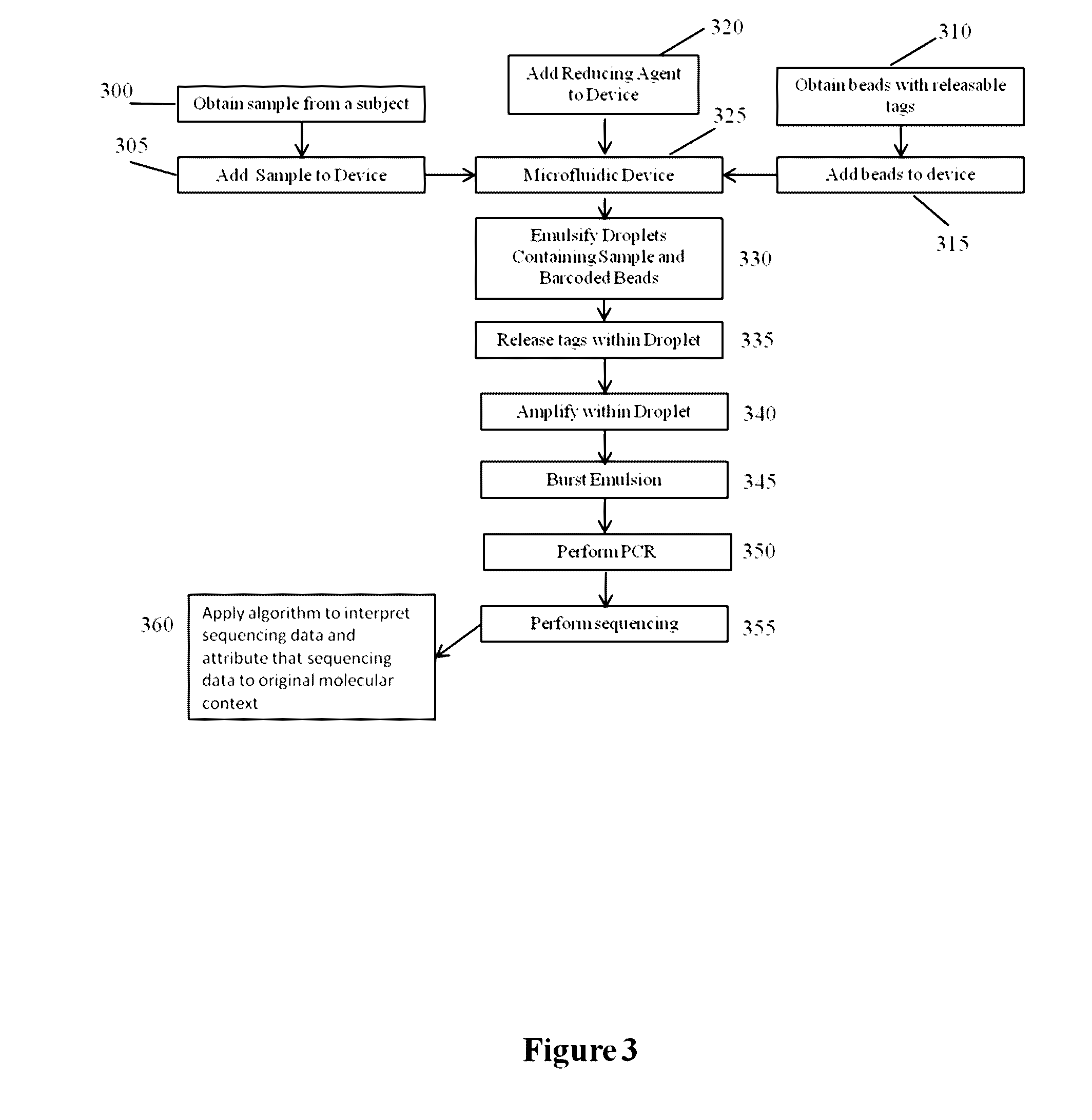
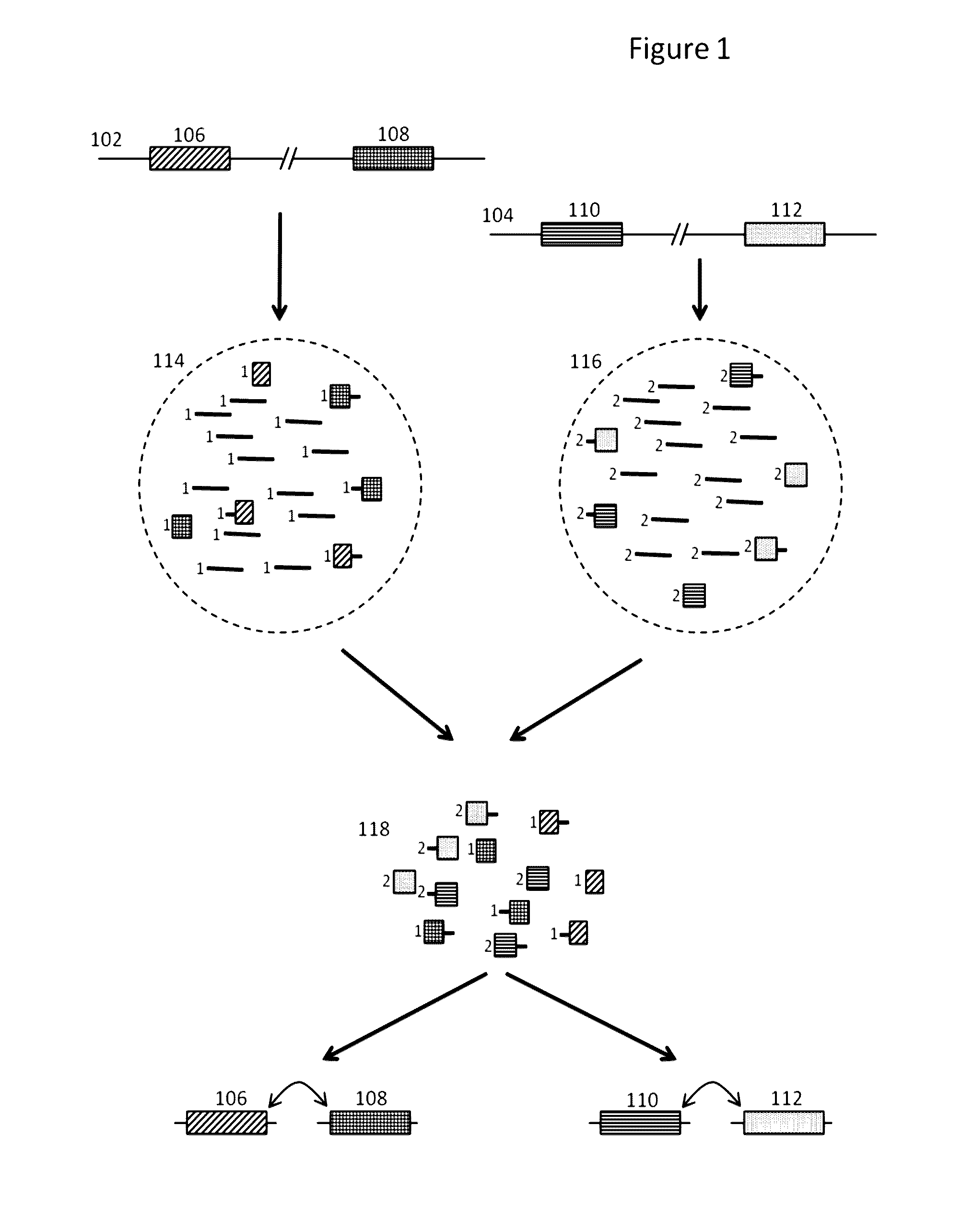
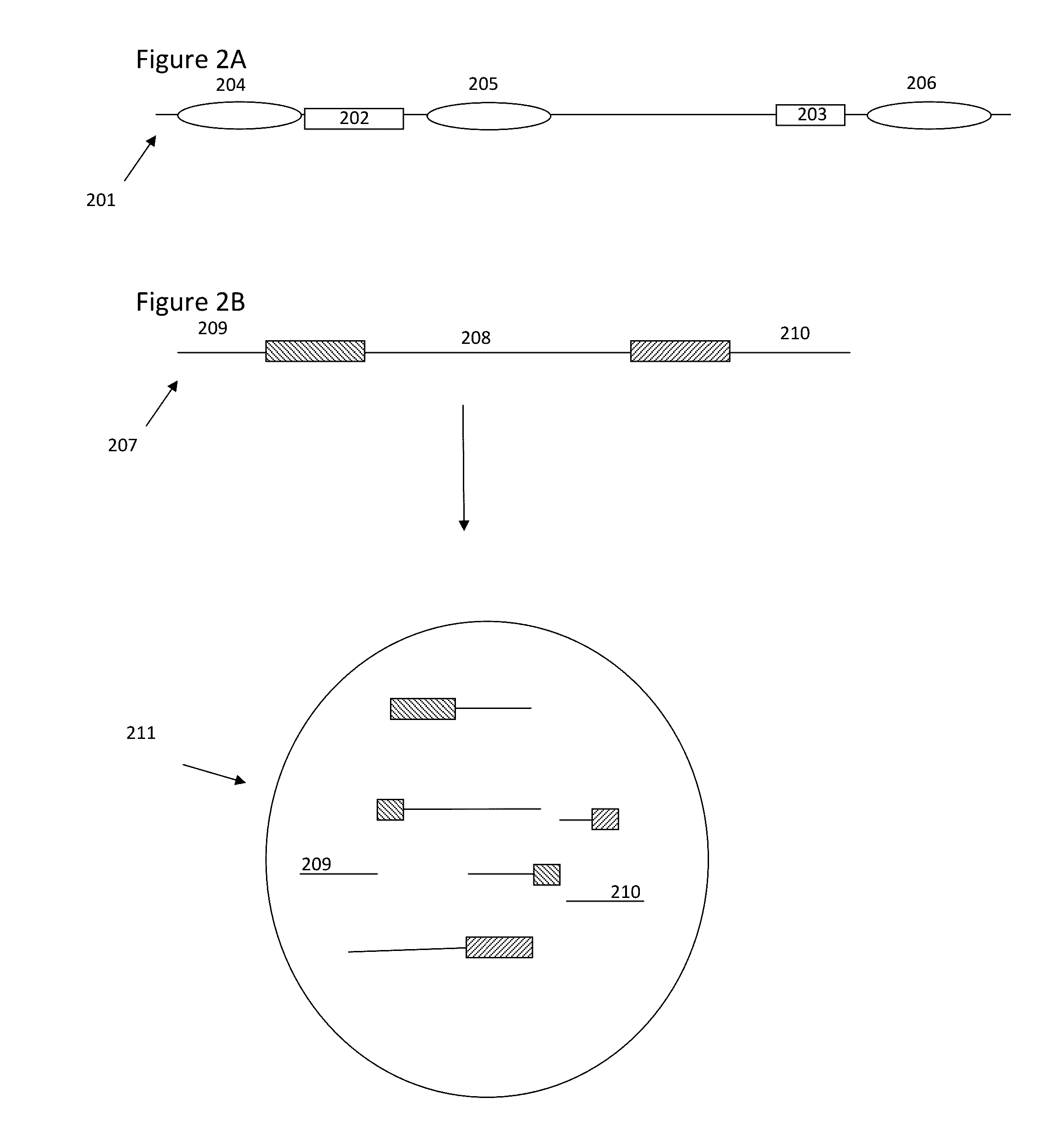
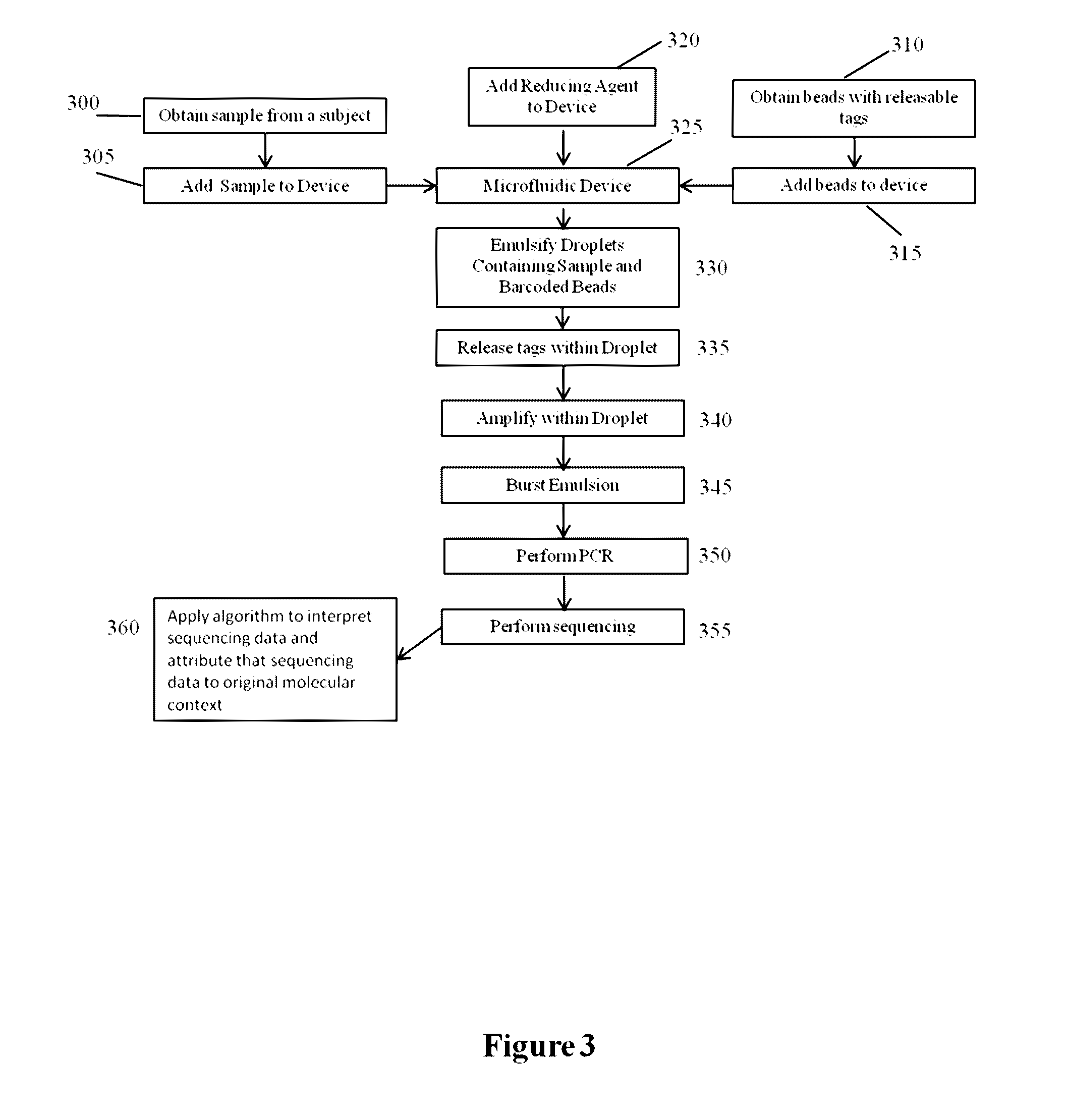
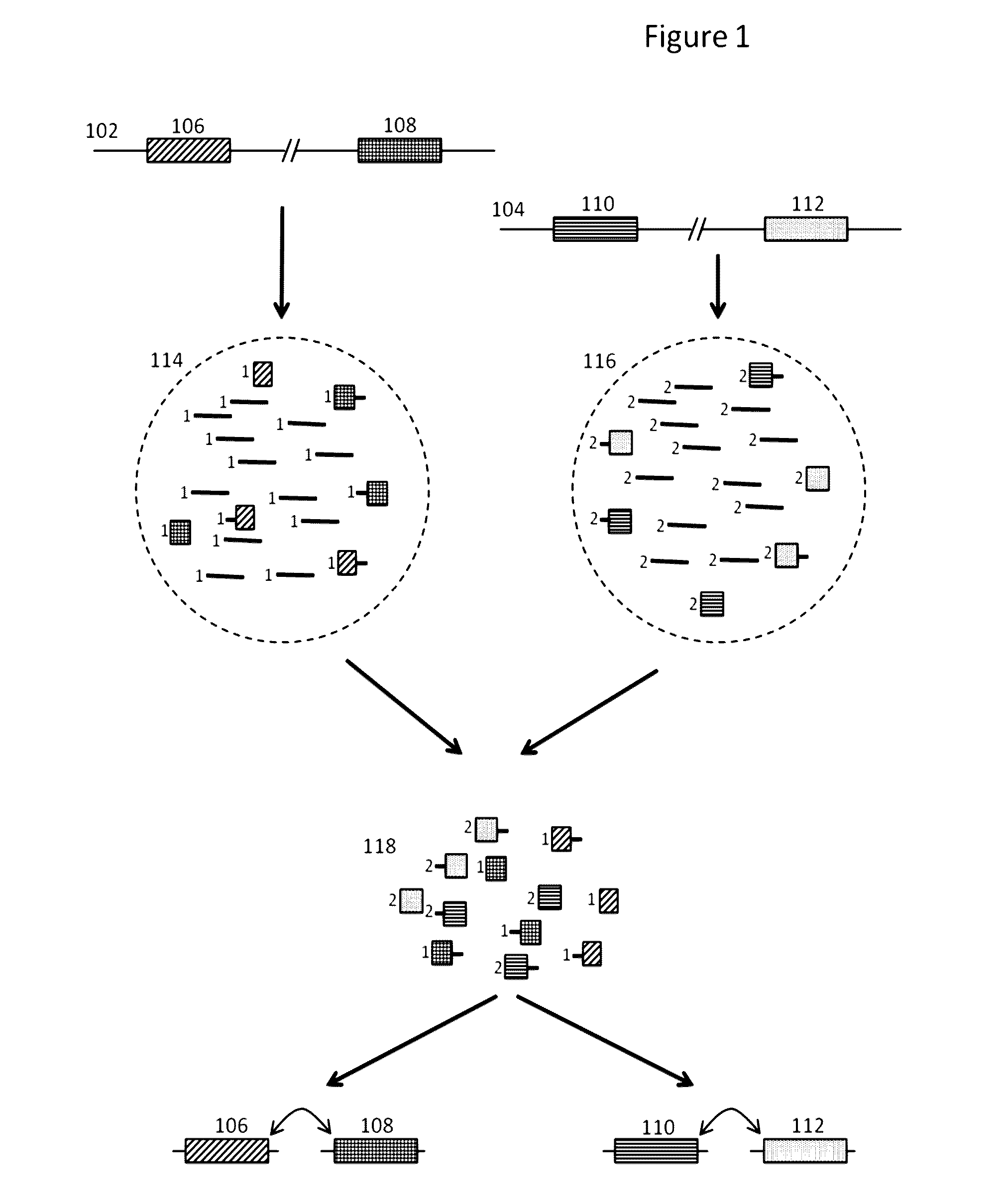
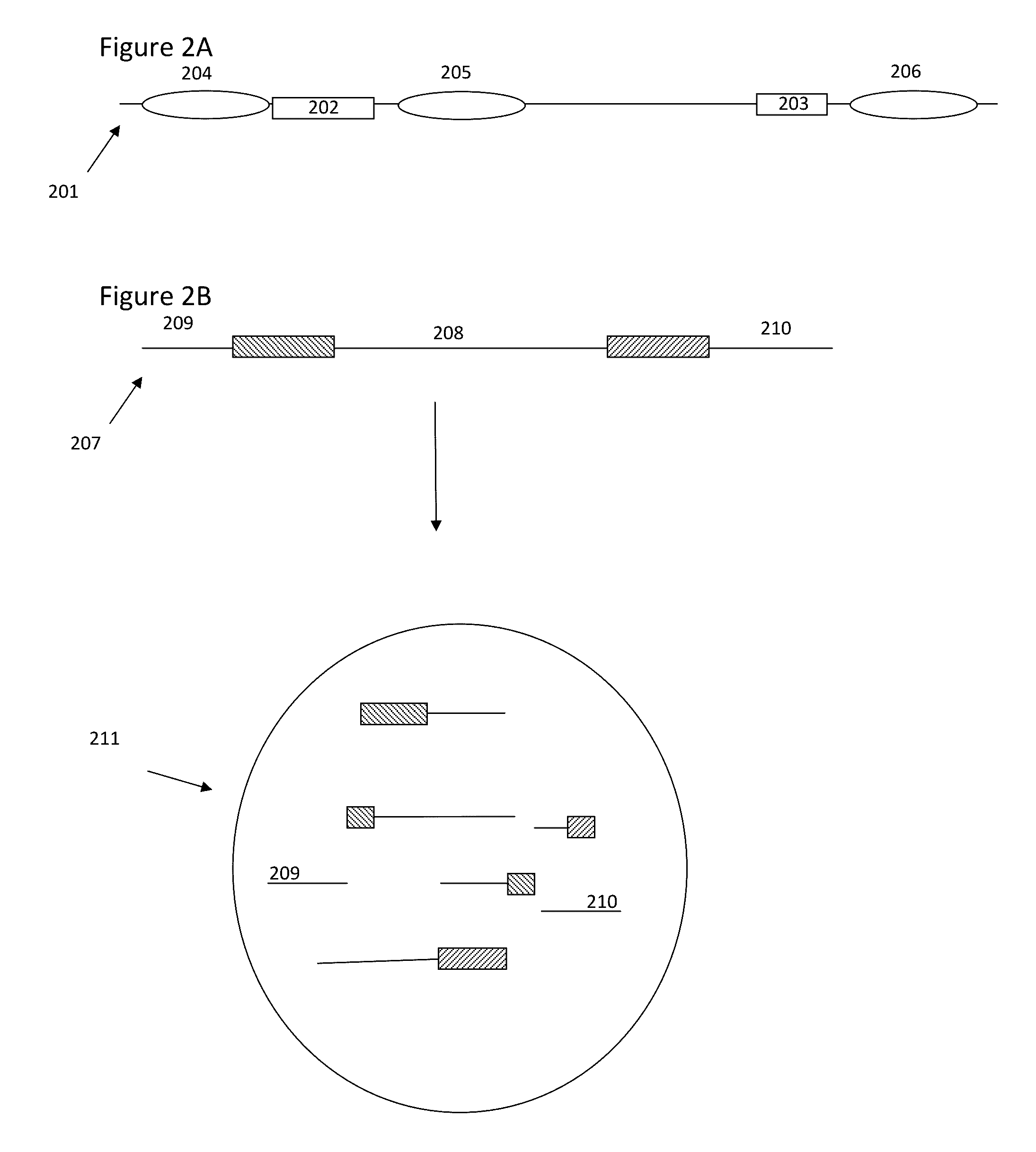
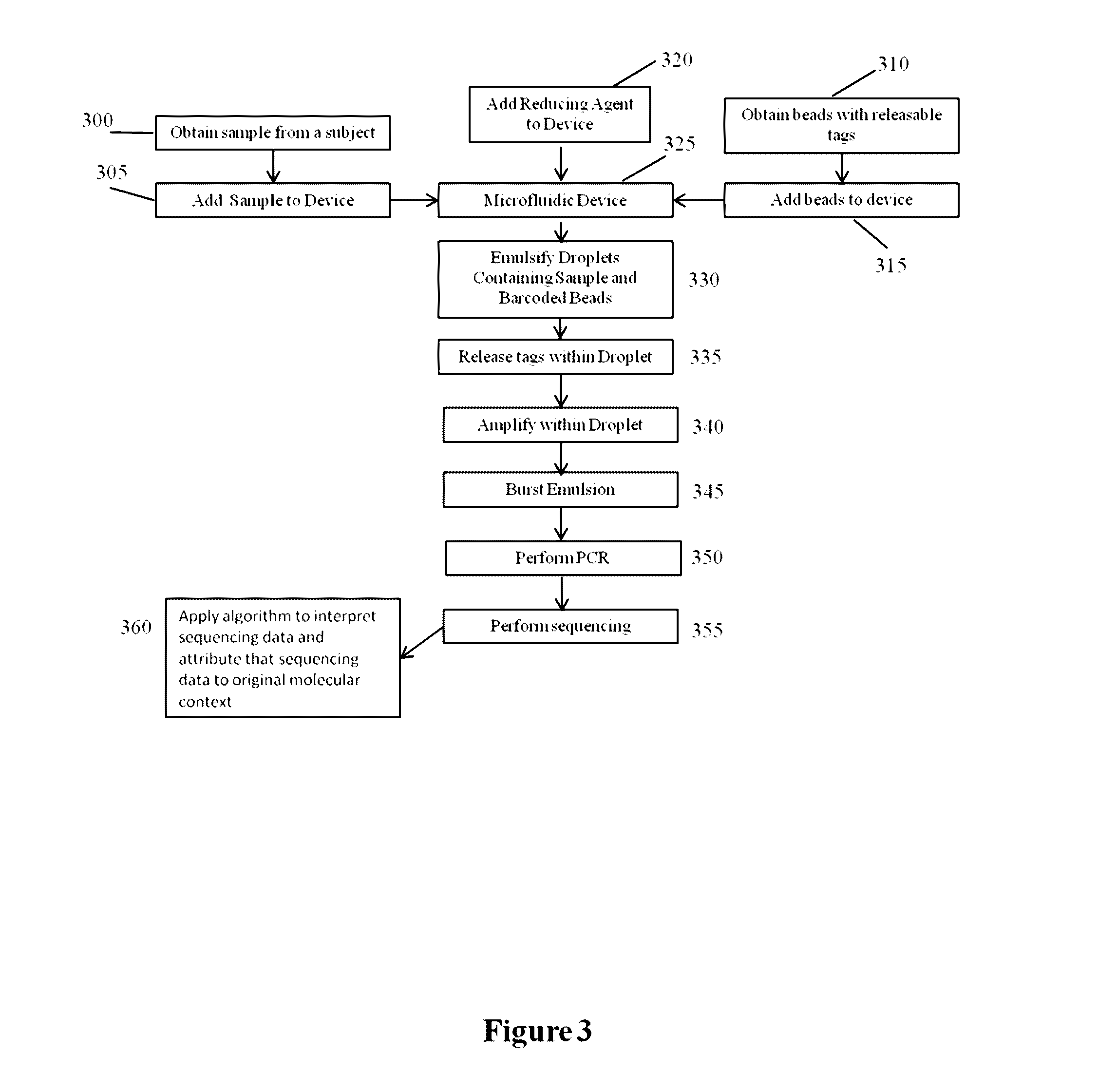
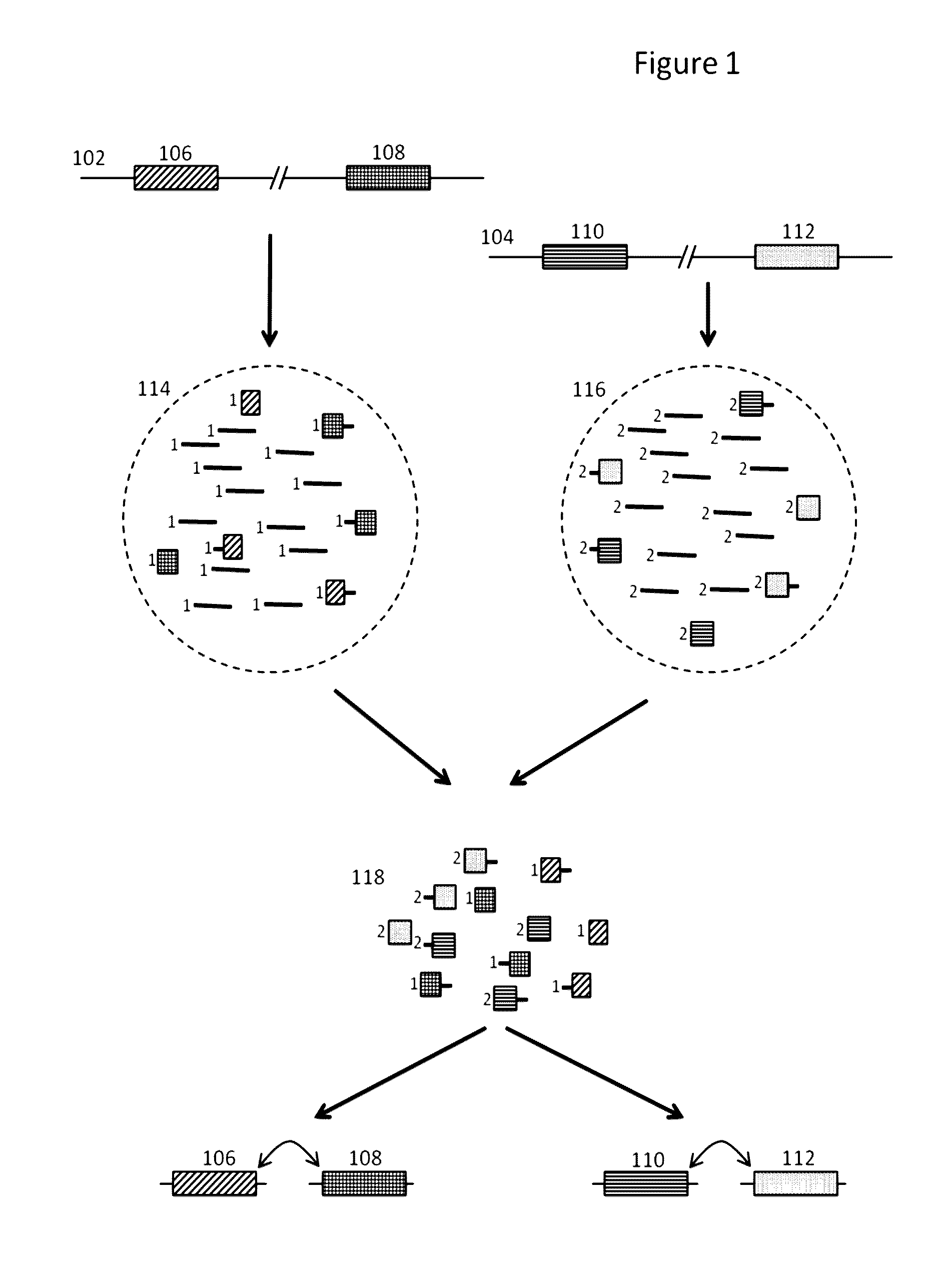
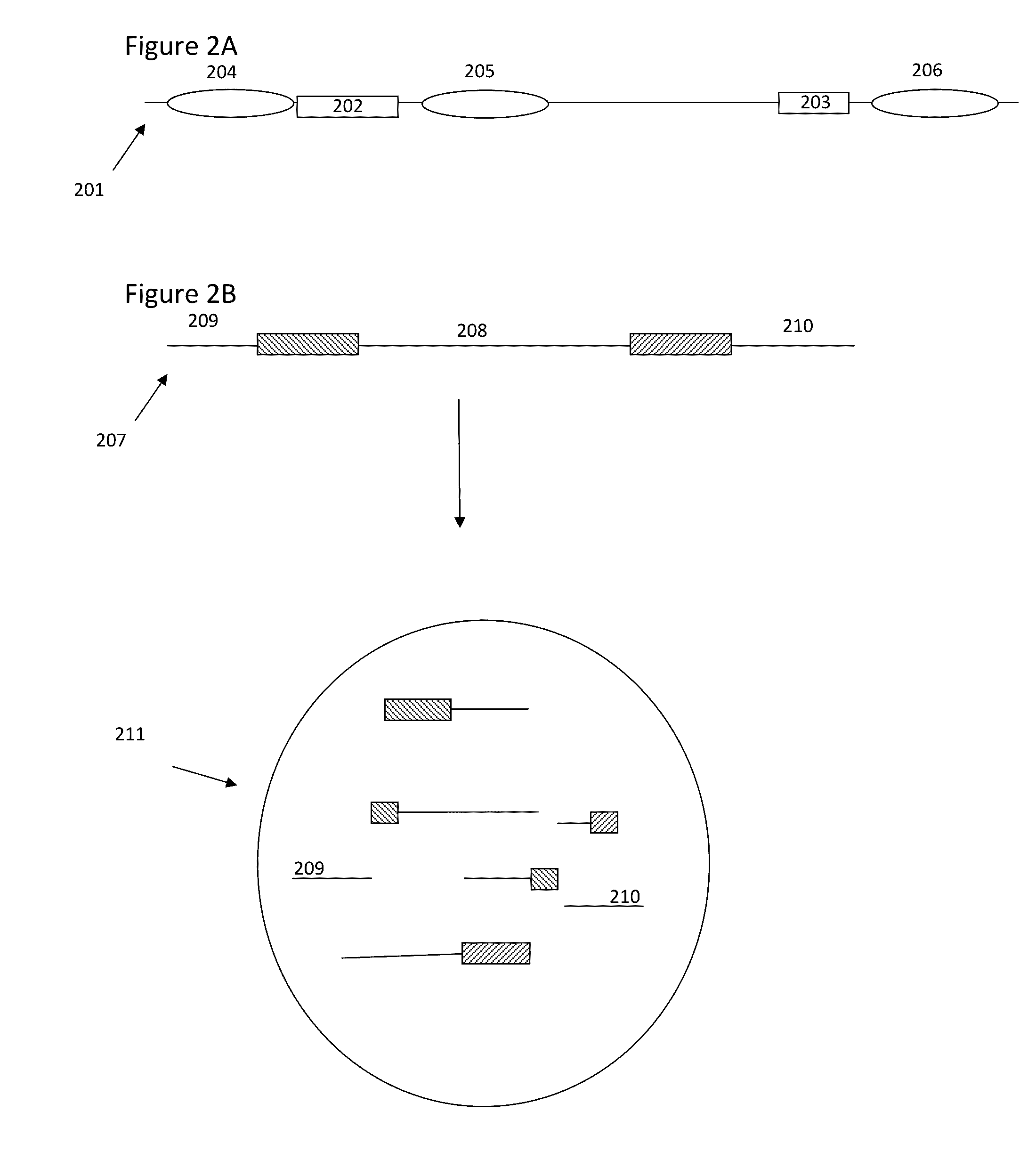
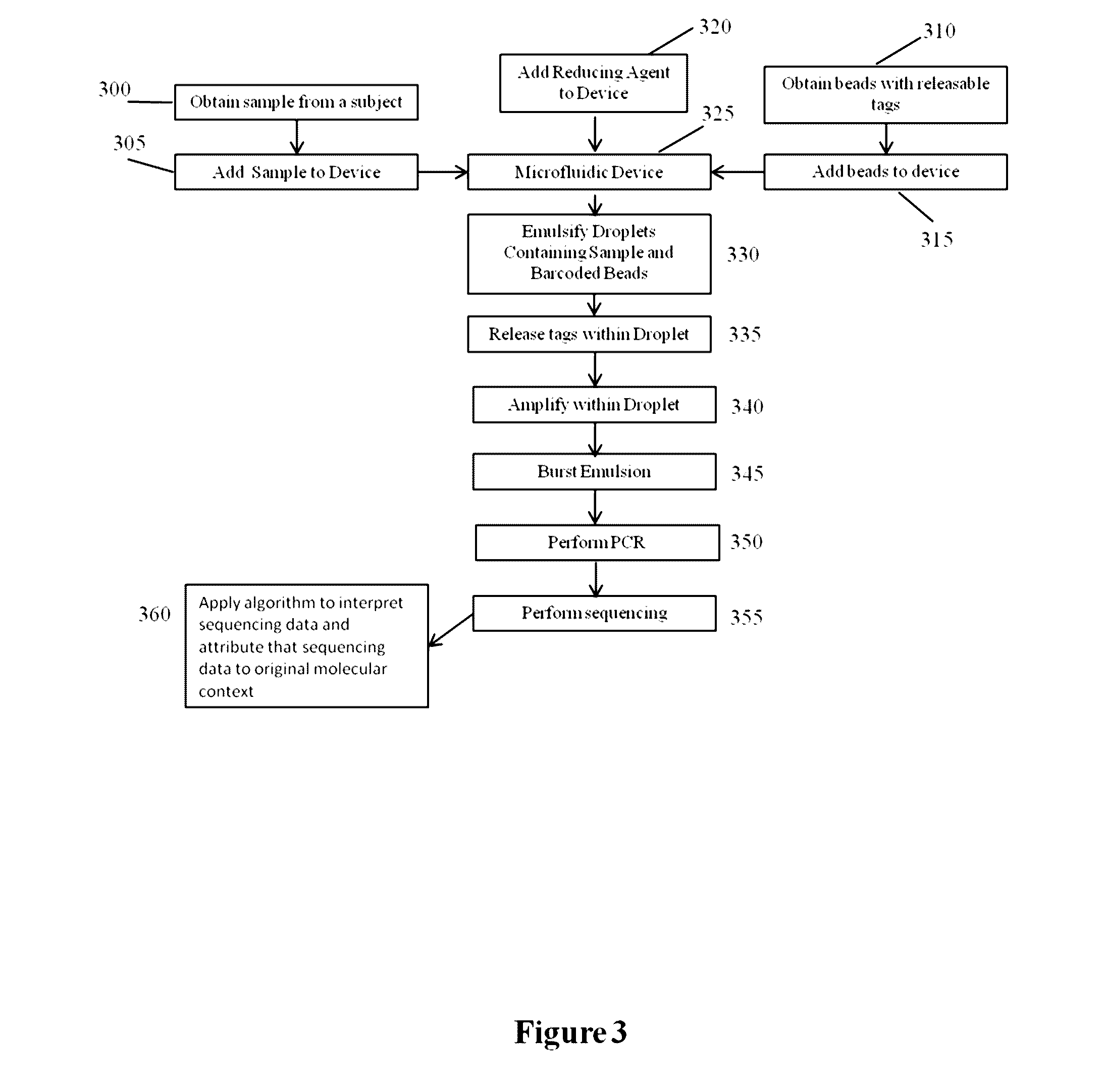
Methods and compositions for targeted nucleic acid sequencing
InactiveUS20160122817A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationInteinNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention is directed to methods, compositions and systems for capturing and analyzing sequence information contained in targeted regions of a genome. Such targeted regions may include exomes, partial exomes, introns, combinations of exonic and intronic regions, genes, panels of genes, and any other subsets of a whole genome that may be of interest.
Owner:10X GENOMICS
Methods and compositions for targeted nucleic acid sequencing
Owner:10X GENOMICS
Methods and compositions for targeted nucleic acid sequencing
The present invention is directed to methods, compositions and systems for capturing and analyzing sequence information contained in targeted regions of a genome. Such targeted regions may include exomes, partial exomes, introns, combinations of exonic and intronic regions, genes, panels of genes, and any other subsets of a whole genome that may be of interest.
Owner:10X GENOMICS
Methods and compositions for targeted nucleic acid sequencing
Owner:10X GENOMICS
Methods and compositions for targeted nucleic acid sequencing
The present invention is directed to methods, compositions and systems for capturing and analyzing sequence information contained in targeted regions of a genome. Such targeted regions may include exomes, partial exomes, introns, combinations of exonic and intronic regions, genes, panels of genes, and any other subsets of a whole genome that may be of interest.
Owner:10X GENOMICS
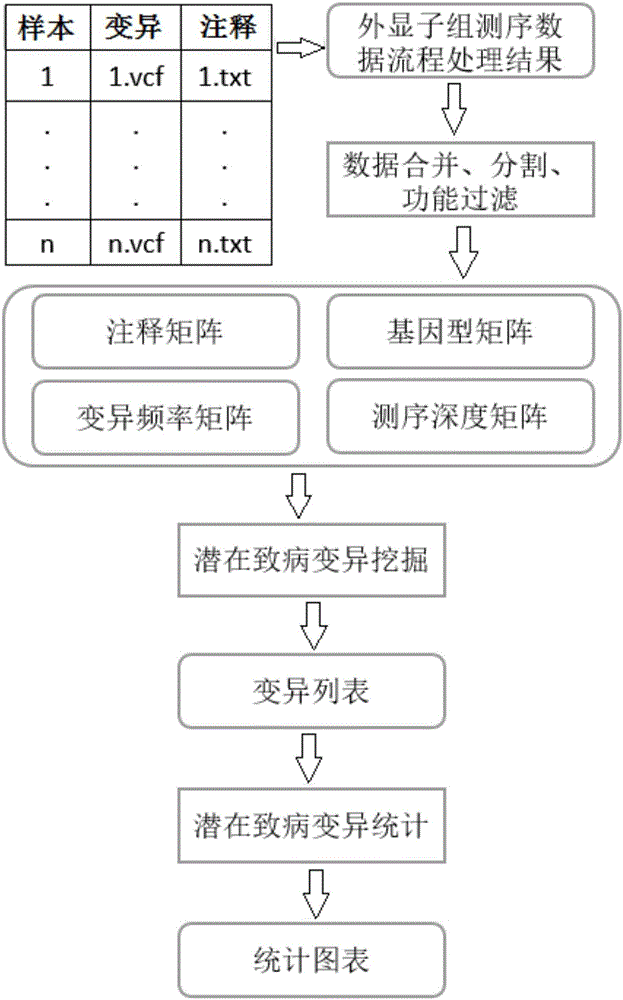
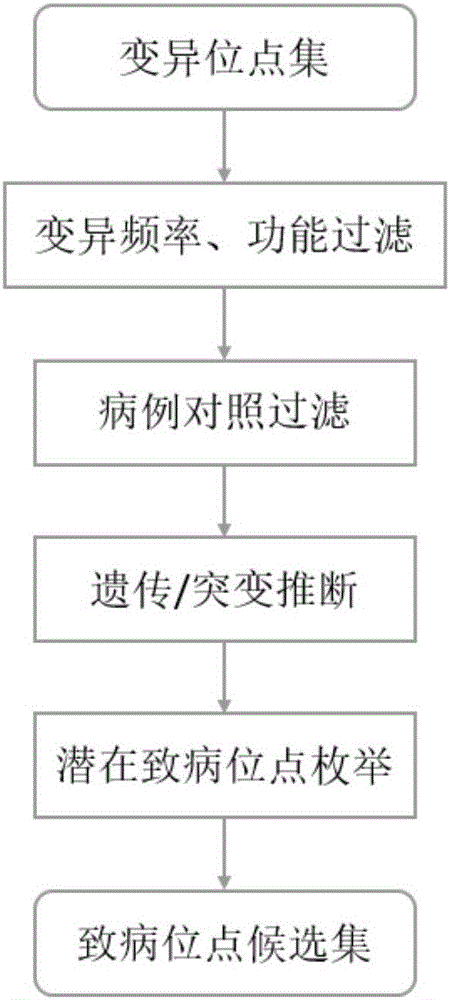
System for detecting potential pathogenic variants of exome based on family
InactiveCN105861697ASolve the problem of mining potential pathogenic variantsImprove heterogeneityMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsFiltrationScreening algorithm
The invention provides a system for detecting potential pathogenic variants of exome based on a family. The system comprises a comment integration module for reading a result file of exome sequencing data processing flow, a matrix segmentation module for extracting variants in all samples t, solving a union set and then combining all the samples to form a matrix, a potential pathogenic variant mining module for extracting variant information from the obtained matrix for being enumerated, evaluating pathogenicity of individual variants and combined double-site variants to obtain a list of potential pathogenic variants, and a potential pathogenic variant recording module for recording occurrence of a site in each sample and a target gene and displaying with icons. Output results of conventional exome sequencing low processing are used as input conditions to complete the integration and basic filtration of data; a candidate set of potential pathogenic variants is obtained according to a special variant screening algorithm, so that the system provided by the invention solves the problem of mining of potential pathogenic variants of sequencing data with high heterogeneity, high mutation rate and high noise.
Owner:WANKANGYUAN TIANJIN GENE TECH CO LTD
Repeat sequences of the ca125 gene and their use for diagnostic and therapeutic interventions
InactiveUS20070015907A1Survival and metastatic advantageExtend the life of ovarian carcinoma patientsOrganic active ingredientsFungiEscherichia coliBinding site
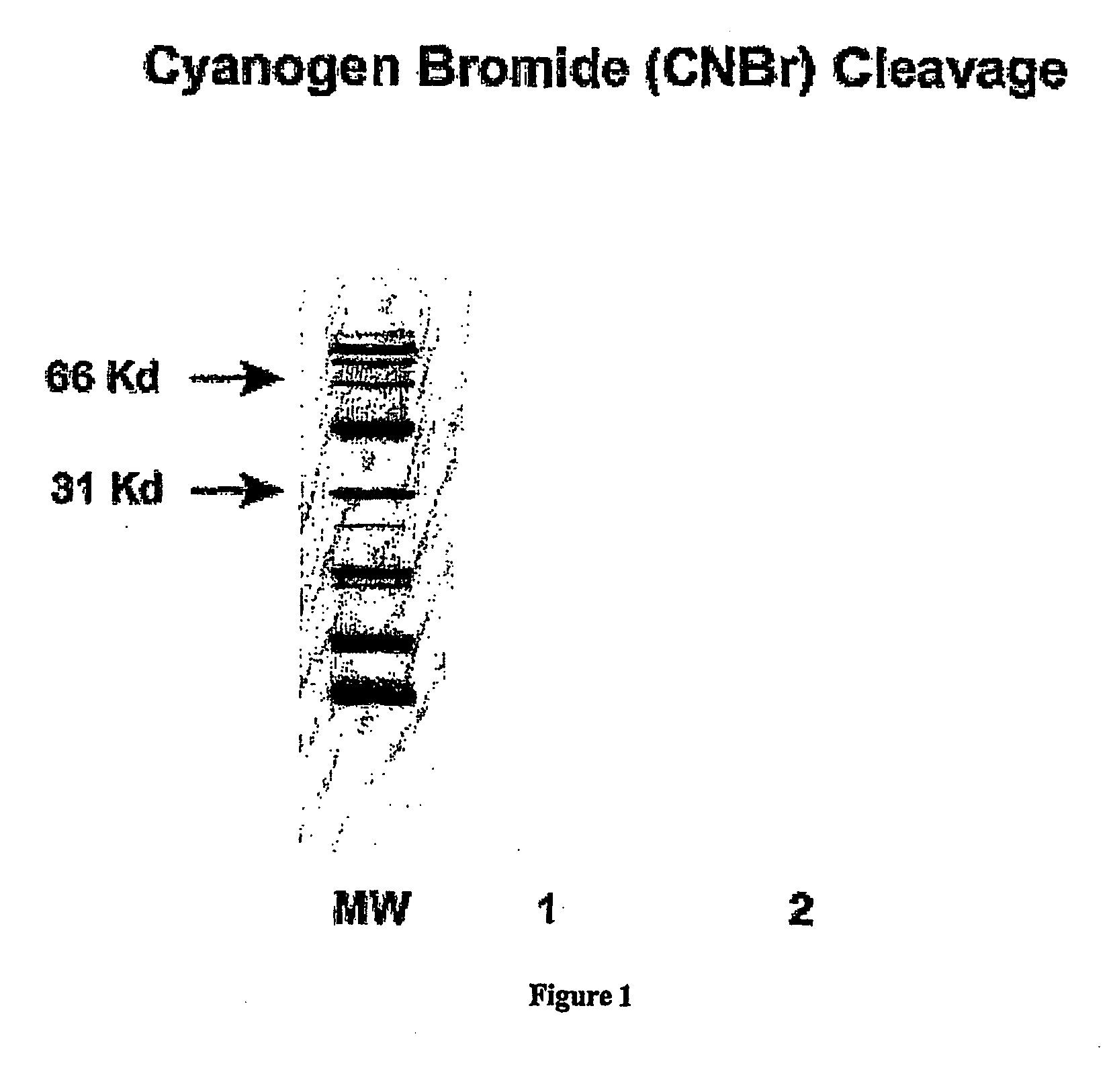
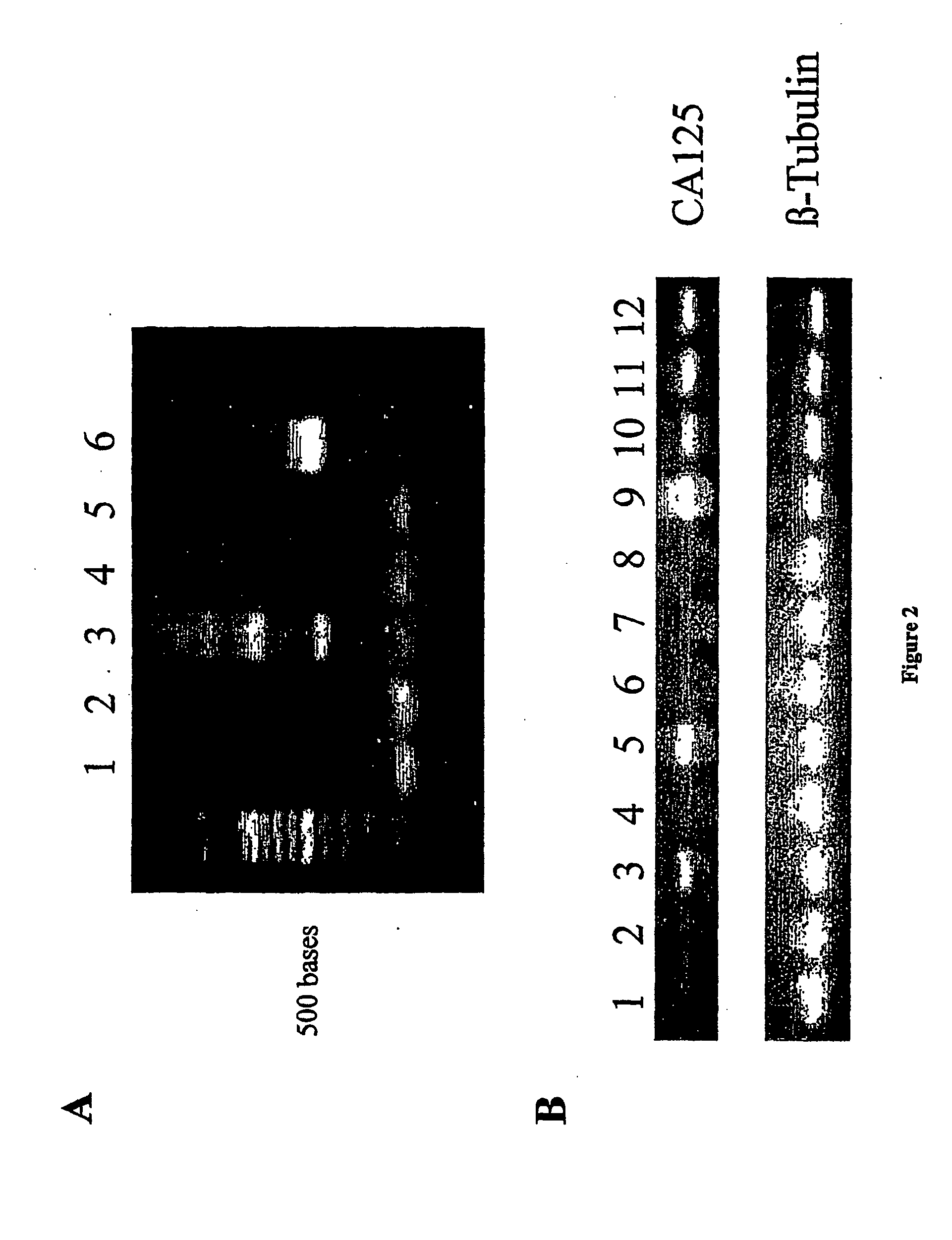
The CA125 gene has been cloned and multiple repeat sequences as well as the carboxy terminus have been identified. The CA125 molecule comprises three major domains: an extracellular amino terminal domain (Domain 1); a large multiple repeat domain (Domain 2); and a carboxy terminal domain (Domain 3) which includes a transmembrane anchor with a short cytoplasmic domain. The amino terminal domain is assembled by combining five genomic exons, four very short amino terminal sequences and one extraordinarily large exon. This domain is dominated by its capacity for O-glycosylation and its resultant richness in serine and threonine residues. Additionally, an amino terminal extension is present, which comprises four genomic exons. The amino acid composition of the amino terminal extension was found to be consistent with the amino acid composition of the amino terminal domain. The molecular structure is dominated by a repeat domain comprising 156 amino acid repeat units, which encompass the epitope binding sites. More than 60 repeat units have been identified, sequenced, and contiguously placed in the CA125 domain structure. The repeat units encompass an interactive disulfide bridged C-enclosure and the site of OC125 and M11 binding. The repeat sequences demonstrated 70-85% homology to each other. Expression of the repeats was demonstrated in E. coli. The CA125 molecule is anchored at its carboxy terminal through a transmembrane domain and a short cytoplasmic tail. The carboxy terminal also contains a proteolytic cleavage site approximately 50 amino acids upstream from the transmembrane domain, which allows for proteolytic cleavage and release of the CA125 molecule. Any one of the repeat domains has the potential for use as a new gold standard for detecting and monitoring the presence of the CA125 antigen. Further, the repeat domains or other domains, especially the c-terminal to the repeat domain also provide a basis for the development of a vaccine, which would be useful for the treatment of ovarian cancer and other carcinomas where CA125 is elevated.
Owner:BIOVENTURES LLC
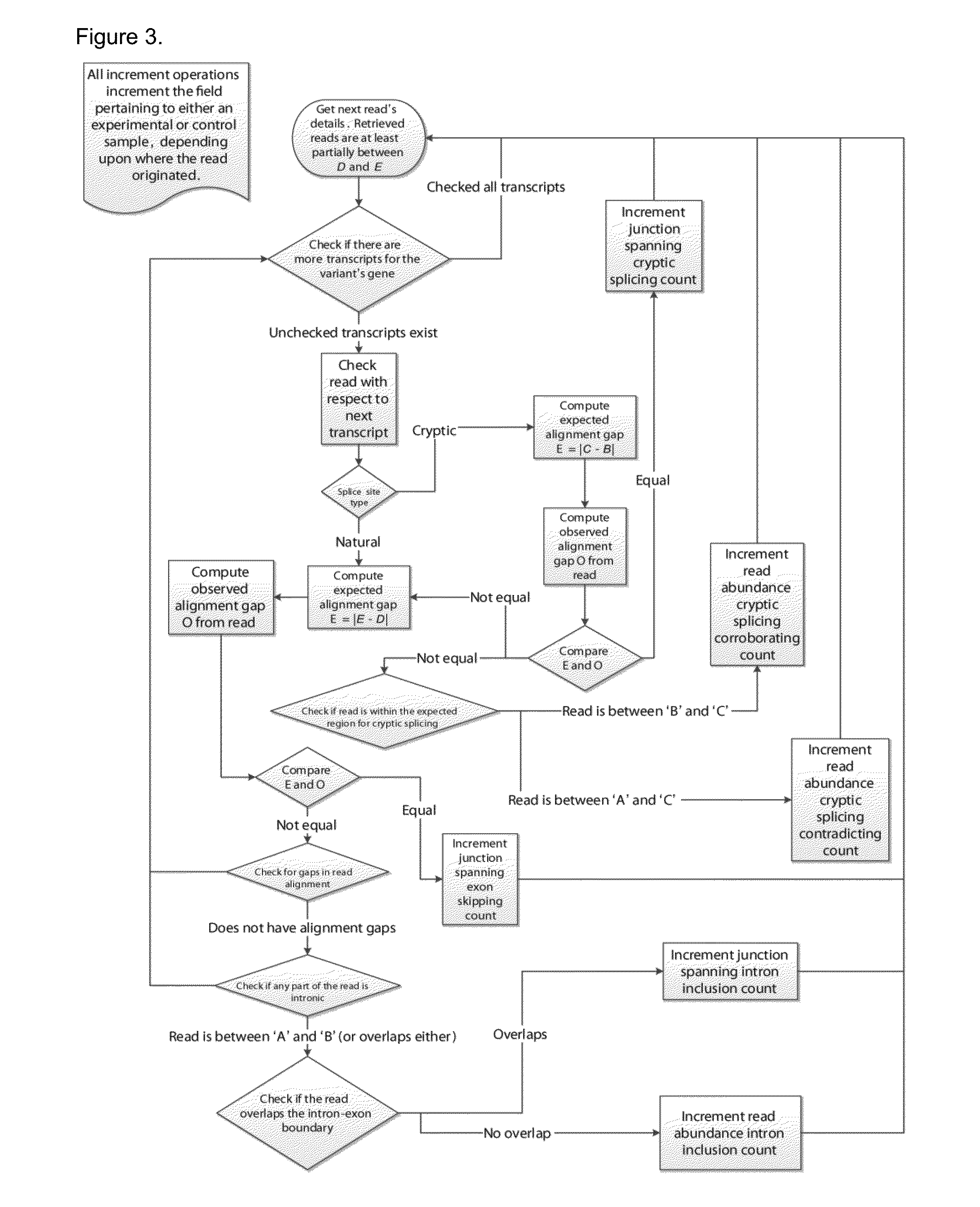
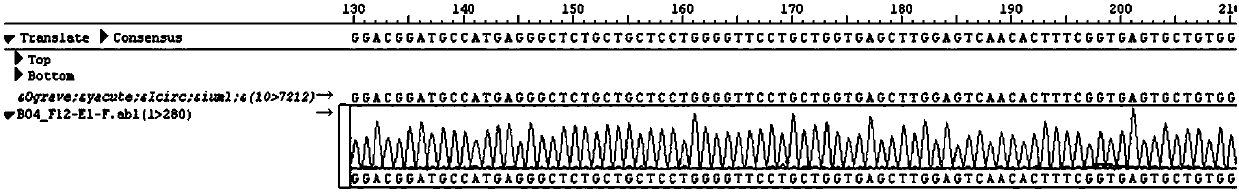
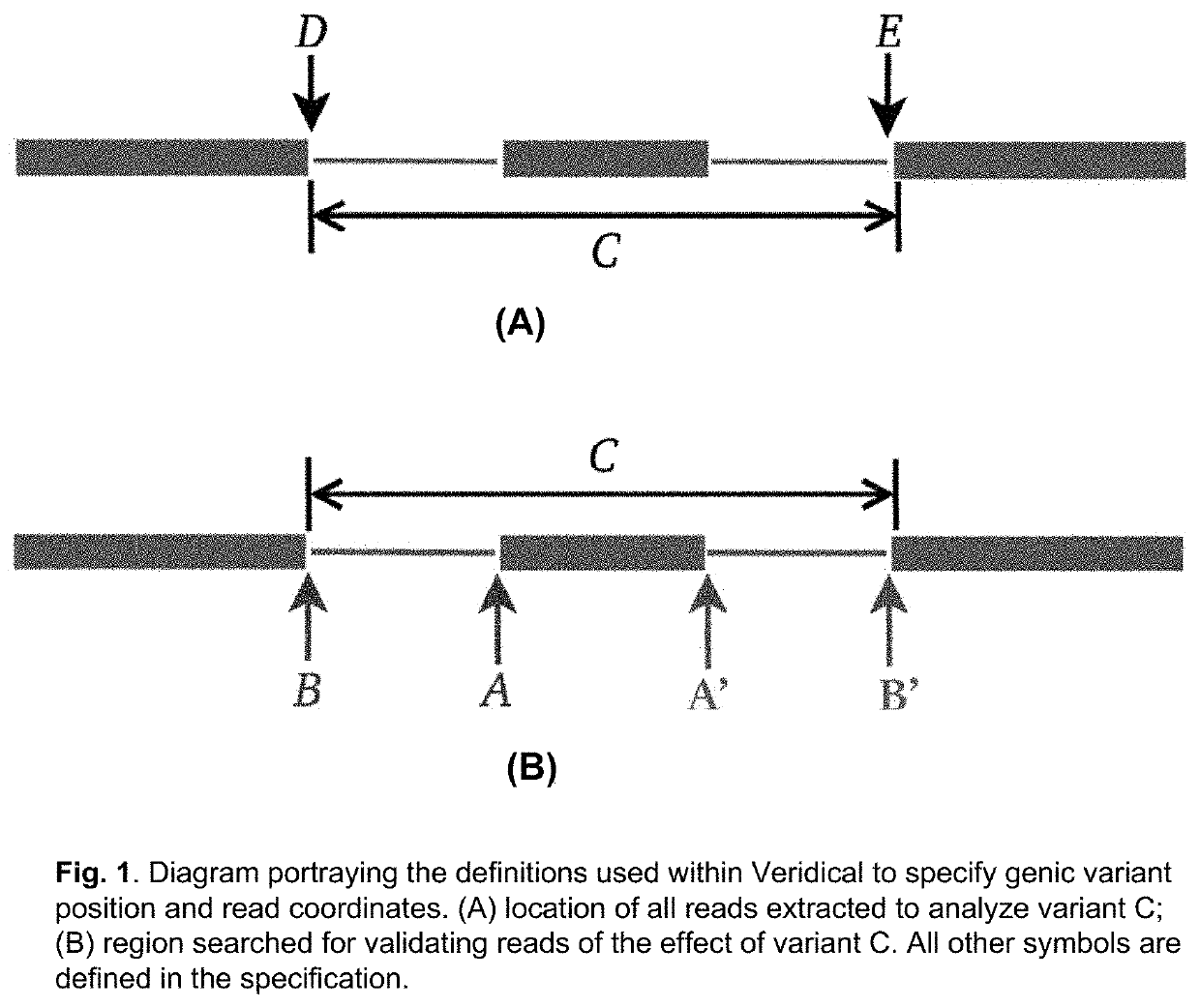
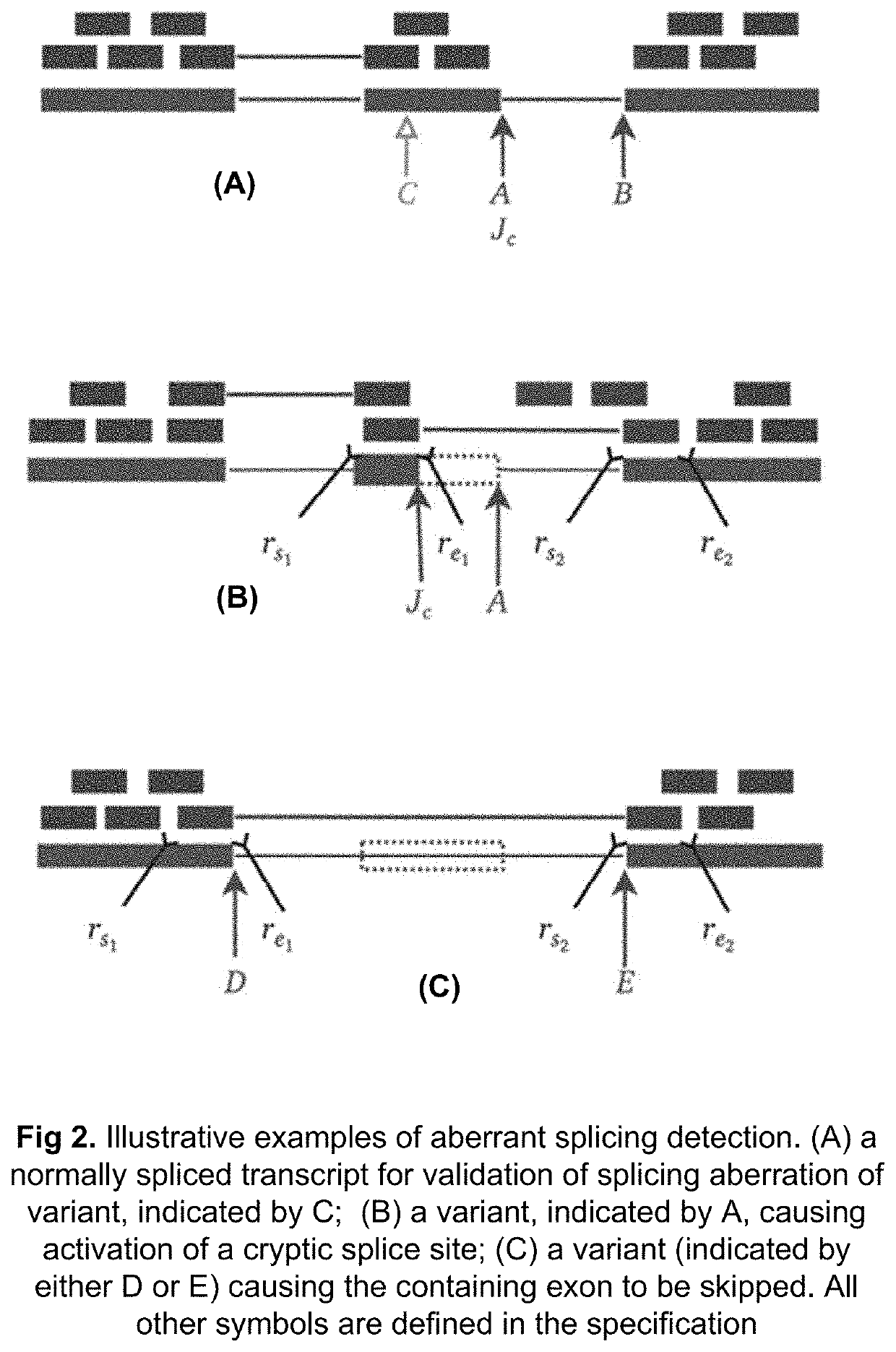
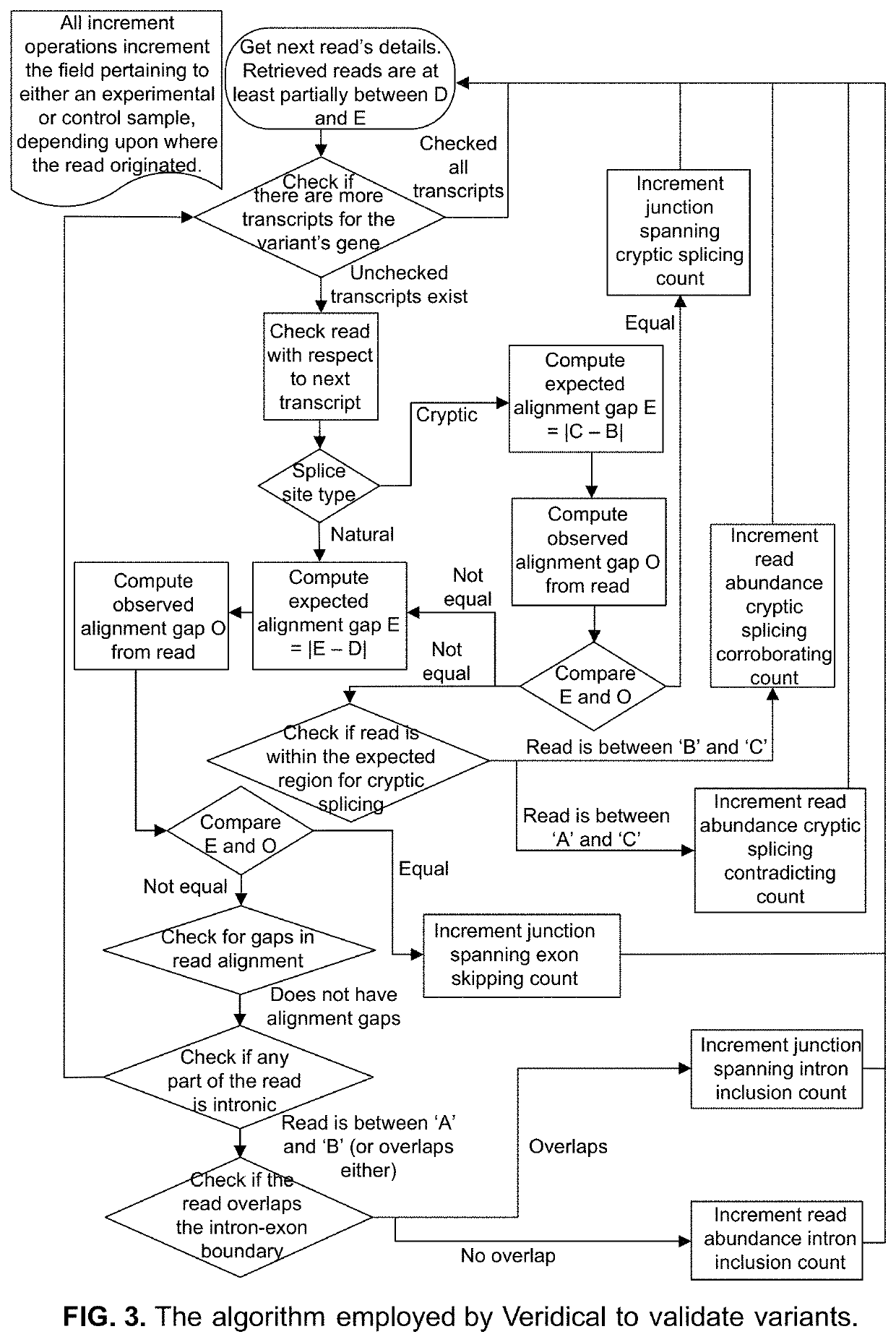
Method of Validating mRNA Splciing Mutations in Complete Transcriptomes
InactiveUS20150254397A1Accurate detectionAvoid changeMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningTissue sampleVariome
A method is described for the automatic validation of DNA sequencing variants that alter mRNA splicing from nucleic acids isolated from a patient or tissue sample. Evidence the a predicted splicing mutation is demonstrated by performing statistically valid comparisons between sequence read counts of abnormal RNA species in mutant versus non-mutant tissues. The method leverages large numbers of control samples to corroborate the consequences of predicted splicing variants in complete genomes and exomes for individuals carrying such mutations. Because the method examines all transcript evidence in a genome, it is not necessary a priori to know which gene or genes carry a splicing mutation.
Owner:CYTOGNOMIX
Tumor mutation burden standard substance, and preparation method and kit thereof
ActiveCN111118167AAccurate measurementFit closelyMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsPaired samplesReference product
The invention provides a tumor mutation burden standard substance, and a preparation method and application thereof. The tumor mutation burden standard substance is obtained by mixing extracted genomeDNA of 6 pairs of paired cell lines according to a certain proportion. Through whole exon sequencing, a gradient reference substance is sequenced; and a tumor mutation burden value of the corresponding gradient reference substance is calculated through a specific biological information algorithm. For a detection limit reference product, a tumor cell sample is diluted by a normal cell sample in paired samples; and a droplet digital PCR method is used for verifying the dilution proportion for ensuring the mixing to conform to the expectation, so that the complexity of clinic samples and the specificity and sensitivity of an inspection and testing system are simulated to a maximum degree. The product can be used for evaluating the performance of tumor mutation burden detection products, andcan also be used for algorithm optimization or detection flow process optimization of the tumor mutation burden. The tumor mutation burden standard substance is applicable to high-flux sequencing strategies of whole exon and targeted genome or exome subsets.
Owner:菁良科技(深圳)有限公司
Systems and methods for clonal replication and amplification of nucleic acid molecules for genomic and therapeutic applications
PendingUS20170067097A1Efficient productionCreate efficientlyMicrobiological testing/measurementChromosomal regionHaplotype
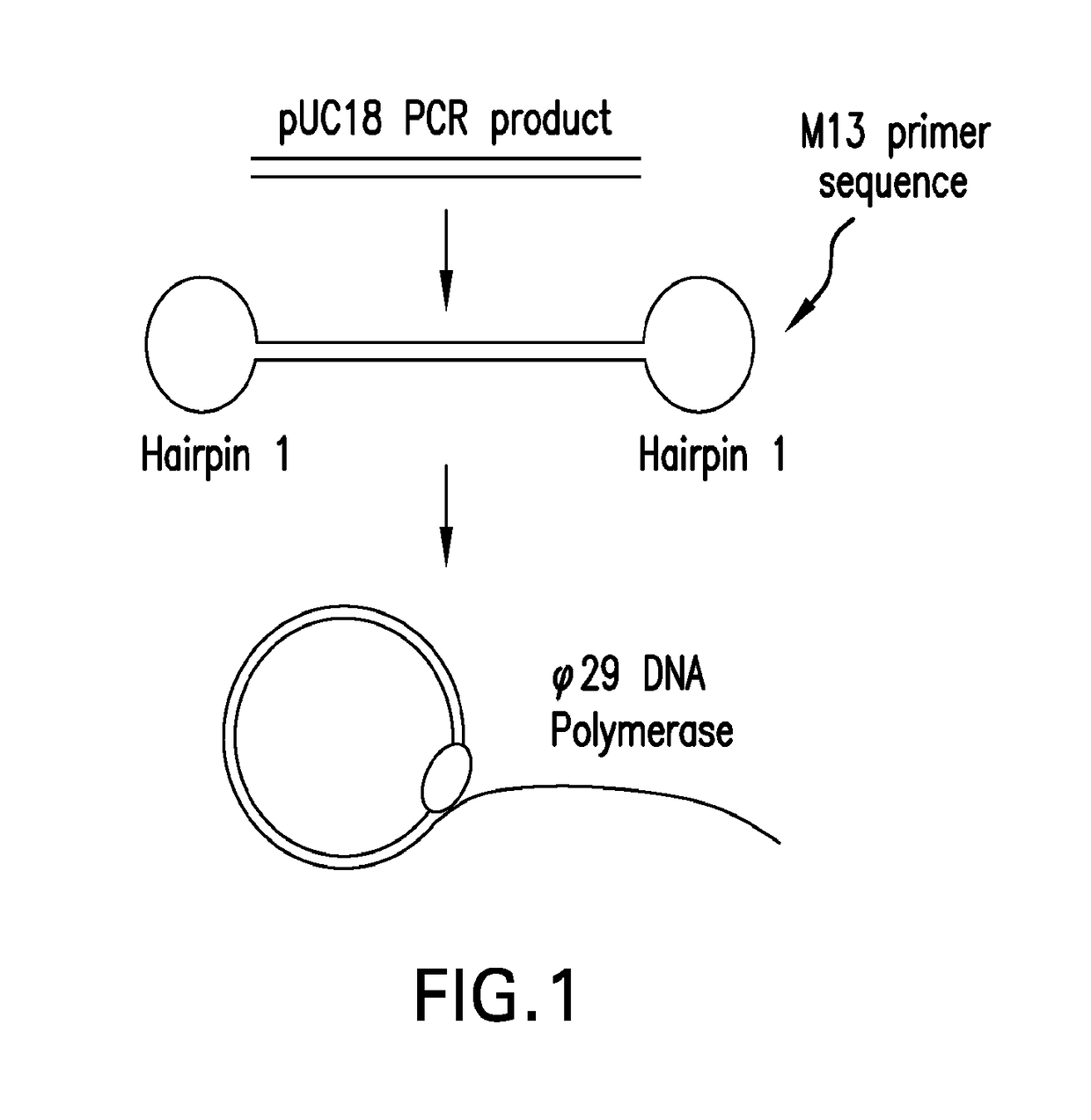
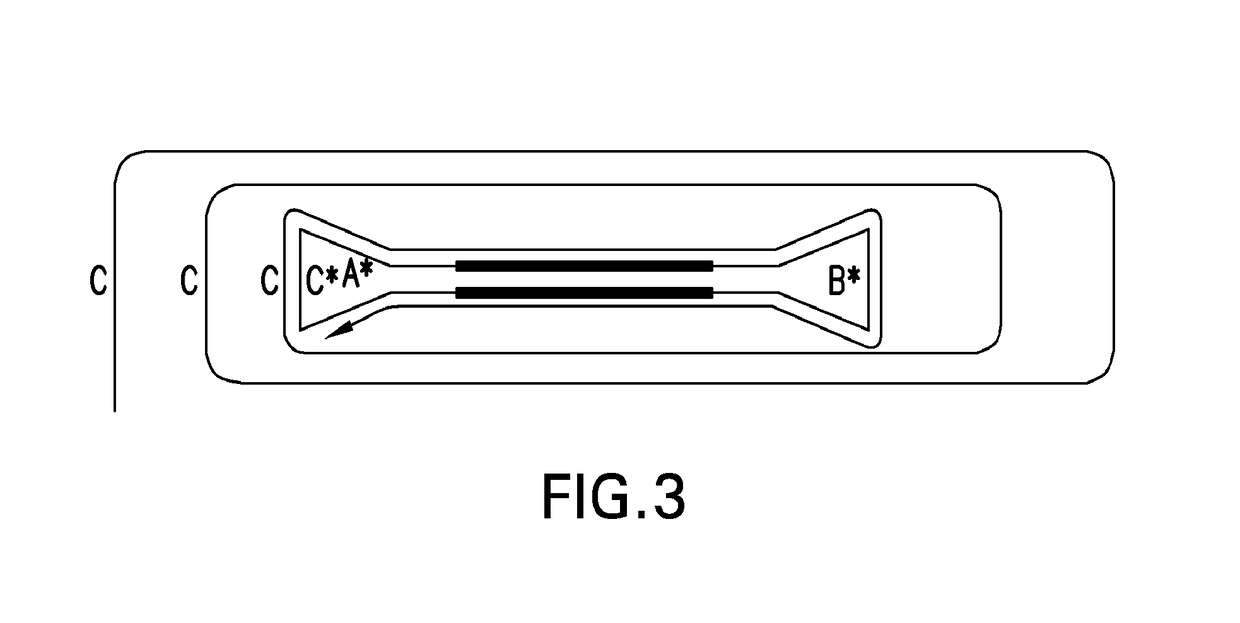
The present invention provides for methods, reagents, apparatuses, and systems for the replication or amplification of nucleic acid molecules from biological samples. In one embodiment of the invention, the nucleic molecules are isolated from the sample, and subjected to fragmenting and joining using ligating agents of one or more hairpin structures to each end of the fragmented nucleic molecules to form one or more dumbbell templates. The one or more dumbbell templates are contacted with at least one substantially complementary primer attached to a substrate, and subjected to rolling circle replication or rolling circle amplification. The resulting replicated dumbbell templates or amplified dumbbell templates are used in numerous genomic applications, including whole genome de novo sequencing; sequence variant detection, structural variant detection, determining the phase of molecular haplotypes, molecular counting for aneuploidy detection; targeted sequencing of gene panels, whole exome, or chromosomal regions for sequence variant detection, structural variant detection, determining the phase of molecular haplotypes and / or molecular counting for aneuploidy detection; study of nucleic acid-nucleic acid binding interactions, nucleic acid-protein binding interactions, and nucleic acid molecule expression arrays; and testing of the effects of small molecule inhibitors or activators or nucleic acid therapeutics.
Owner:REDVAULT BIOSCI
Deafness-related gene capture kit and application thereof
ActiveCN111378736AHigh detection specificityImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseaseNucleotide
The invention discloses a deafness-related gene capture kit and an application thereof. The invention provides a capture probe. The capture probe is as shown in 1) or 2) which are described in the specification, wherein 1) the capture probe is composed of probes as shown in sequences 1 to 113 in a sequence table; 2) the capture probe is composed of derivatives of probes in 1); and the derivative of each probe is a probe which is obtained by substituting and / or deleting and / or adding one or more nucleotides to each probe in 1) and has the same function. According to the deafness-related gene capture kit provided by the invention, target region sequencing analysis is carried out on a whole exon group or a deafness-related genome (respectively accounting for 1% and 0.01% of the whole genome)of a hereditary deafness patient; and most pathogenic mutation information of the disease is captured.
Owner:迈基诺(重庆)基因科技有限责任公司
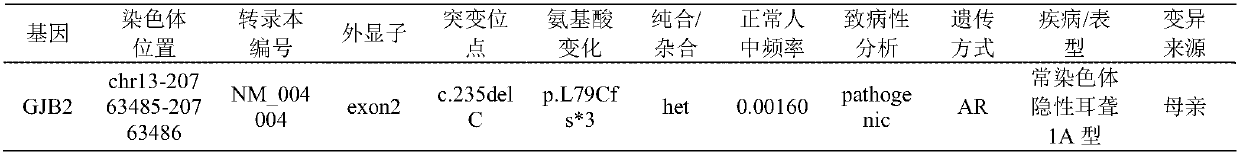
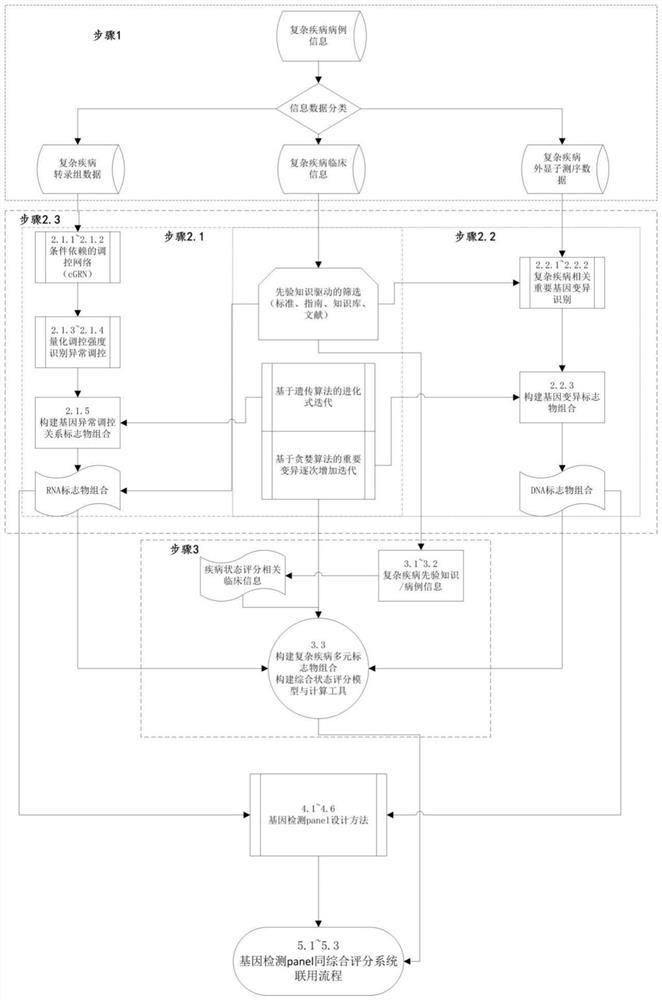
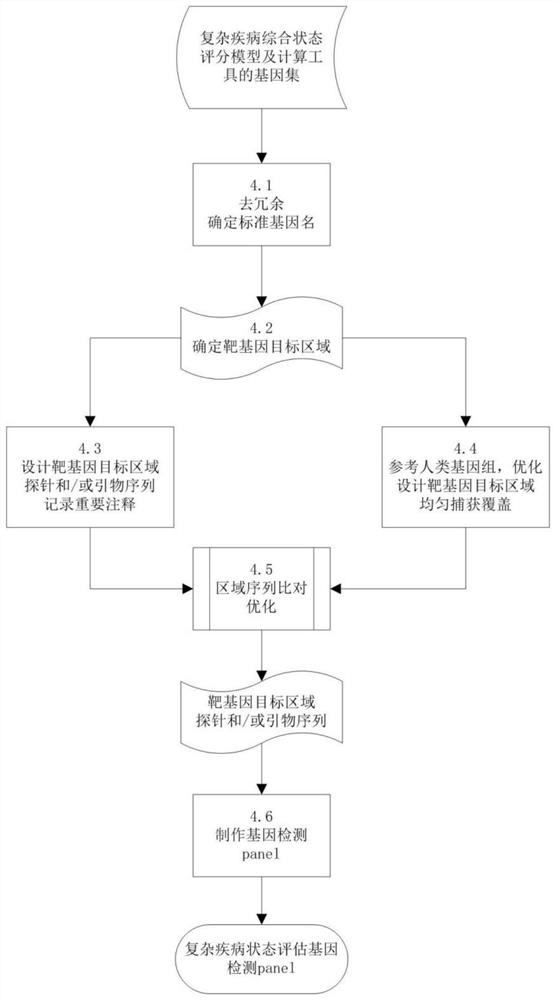
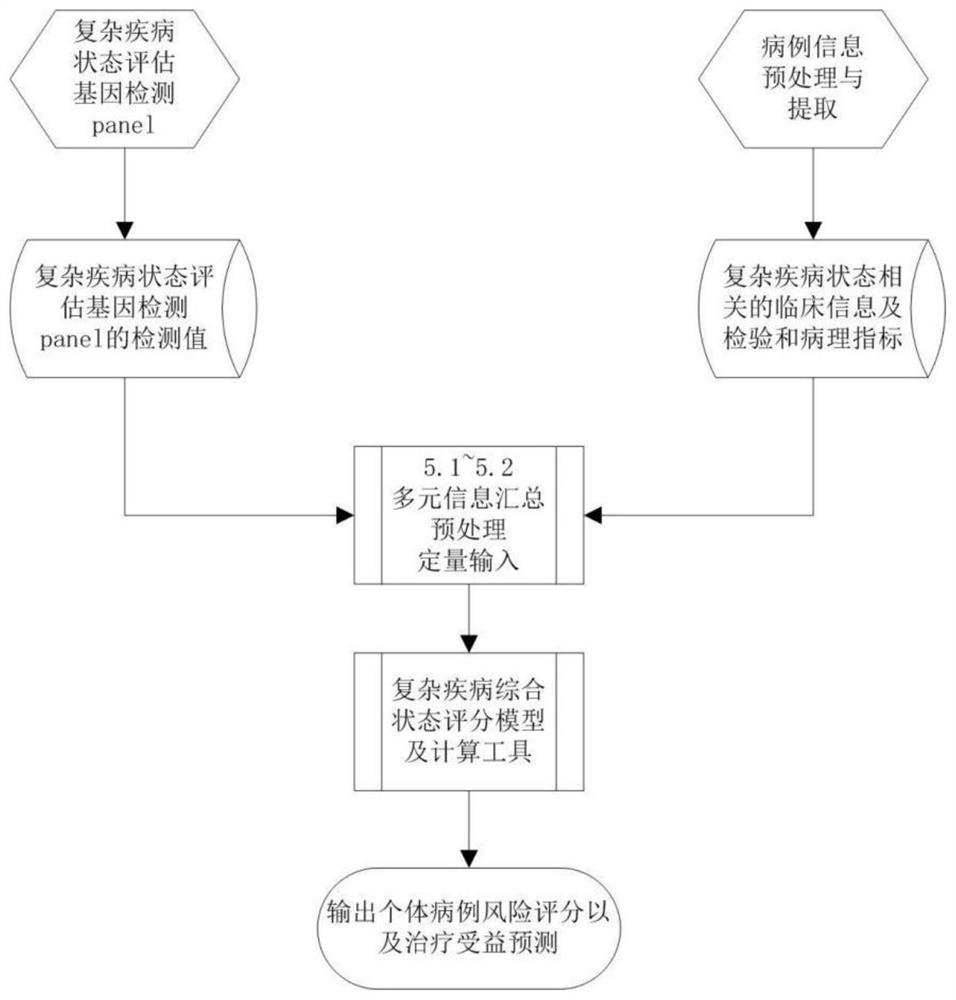
Complex disease state evaluation method based on high-throughput sequencing data and clinical phenotype construction and application
PendingCN111863137AImprove capture efficiencyFlexible adjustmentBiostatisticsMedical automated diagnosisExonPancreatic ductal
The invention relates to the field of gene detection and bioinformatics, and discloses a method for mining complex disease markers based on transcriptome data, exon group / genome data and clinical phenotypes. The invention designs a set of calculation method for constructing a complex disease state evaluation model by integrating high-throughput sequencing data and clinical phenotypes, the calculation method is applied to targeted medication of colorectal cancer, pancreatic ductal cancer and pancreas ductal cancer, biomarkers related to diseases are screened respectively, and the correspondingdisease state evaluation model is formed. The marker considering both accuracy and mechanism interpretability is constructed through the method and can be used for prognosis evaluation of complex diseases, treatment effect prediction, treatment scheme assistant decision making and the like.
Owner:上海朴岱生物科技合伙企业(有限合伙)
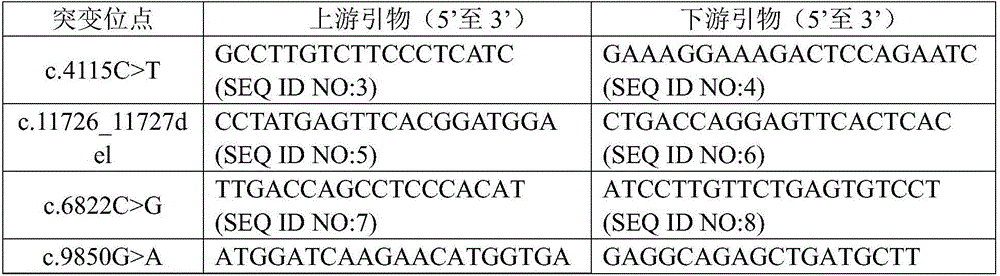
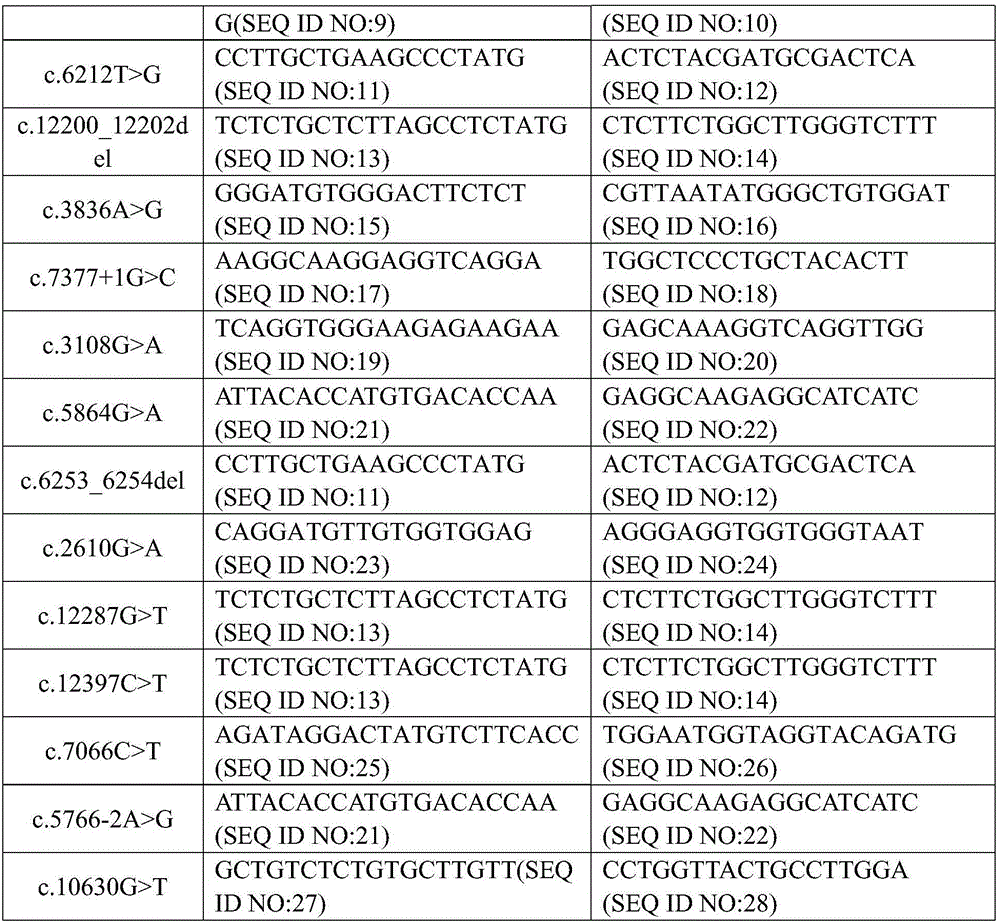
Kit and method for detecting whole exomes of ADAMTS13 gene
InactiveCN106868174AEasy to operateThe process is convenient and fastMicrobiological testing/measurementForward primerThrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
The invention discloses a kit and a method for detecting whole exomes of the ADAMTS13 gene. The kit comprises 26 pairs of forward primers and reverse primers for amplifying and covering whole exome sequences of the ADAMTS13 gene, wherein a segment of M13-F primer sequence with the length being 18bp is added at the 5' terminal of an upstream primer of PCR amplification, and a segment of M13-R primer sequence with the length being 16bp is added at the 5' terminal of a lower primer of PCR amplification. Based on the Sanger sequencing method, 1 pair of universal primers M13 is adopted as the sequencing primers, then the mutation condition of the whole exome sequences of the ADAMTS13 gene is detected, and the kit is used for genetic diagnosis for patients suffering from thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
Owner:杭州艾迪康医学检验中心有限公司
MMAF virulence gene novel mutation and application thereof
InactiveCN107176993AMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisVirulent characteristicsResearch Object
The invention discloses an MMAF virulence gene novel mutation and application thereof, and relates to virulence genes, novel mutation of an MMAF virulence gene DNAH1 is firstly found. A plurality of affected families and affected individuals of the MMAF are taken as study objects for sequencing and comparing exomes of the affected individuals in the families to find that DNAH1 genes of different patients have different gene mutations which are used for detecting various sperm tail paramorphia (MMAF).
Owner:厦门市妇幼保健院 +1
Method of identifying a gene associated with a disease or pathological condition of the disease
ActiveUS10787708B2Improves genotype accuracy of resultDifferentiates rareMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsDiseaseExon
A method of identifying a gene associated with a disease or pathological condition of the disease includes: a) obtaining a first group of exome sequences from a first population suffering from the disease or pathological condition and a second group of exome sequences from a second population not having the disease or pathological condition; b) identifying one or more variants in the first group by comparing it with the second group, and optionally with a public database, to generate a first set of variant data; c) applying a variant quality score calibration tool with a truth sensitivity threshold to remove false-positive variants having a sensitivity lower than the threshold and background variants from the first set of variant data so as to obtain a second set of variant data; d) removing synonymous variants from the second set of variant data to obtain a third set of variant data; and e) identifying one or more deleterious variants from the third set of variant data using a gene burden analysis, optionally generating a fourth set of variant data.
Owner:MACAU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
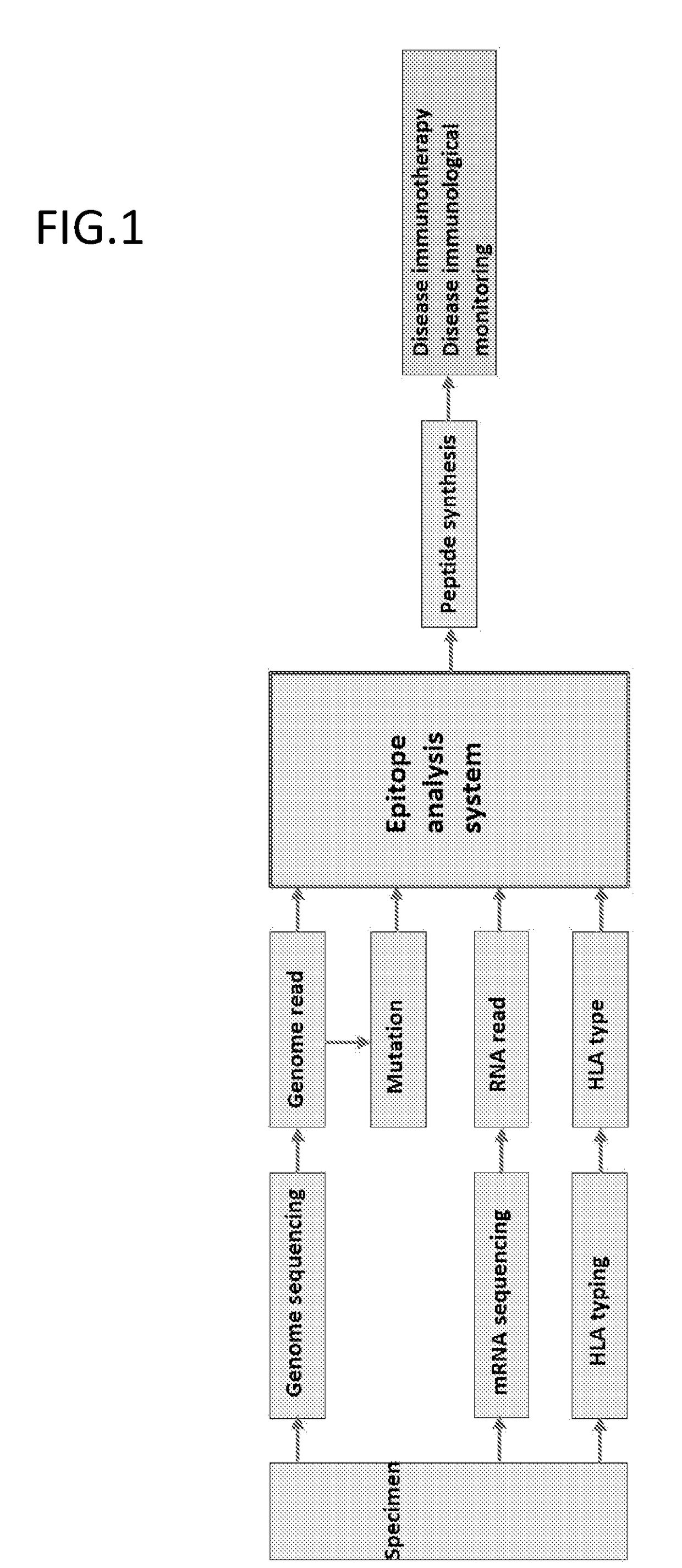
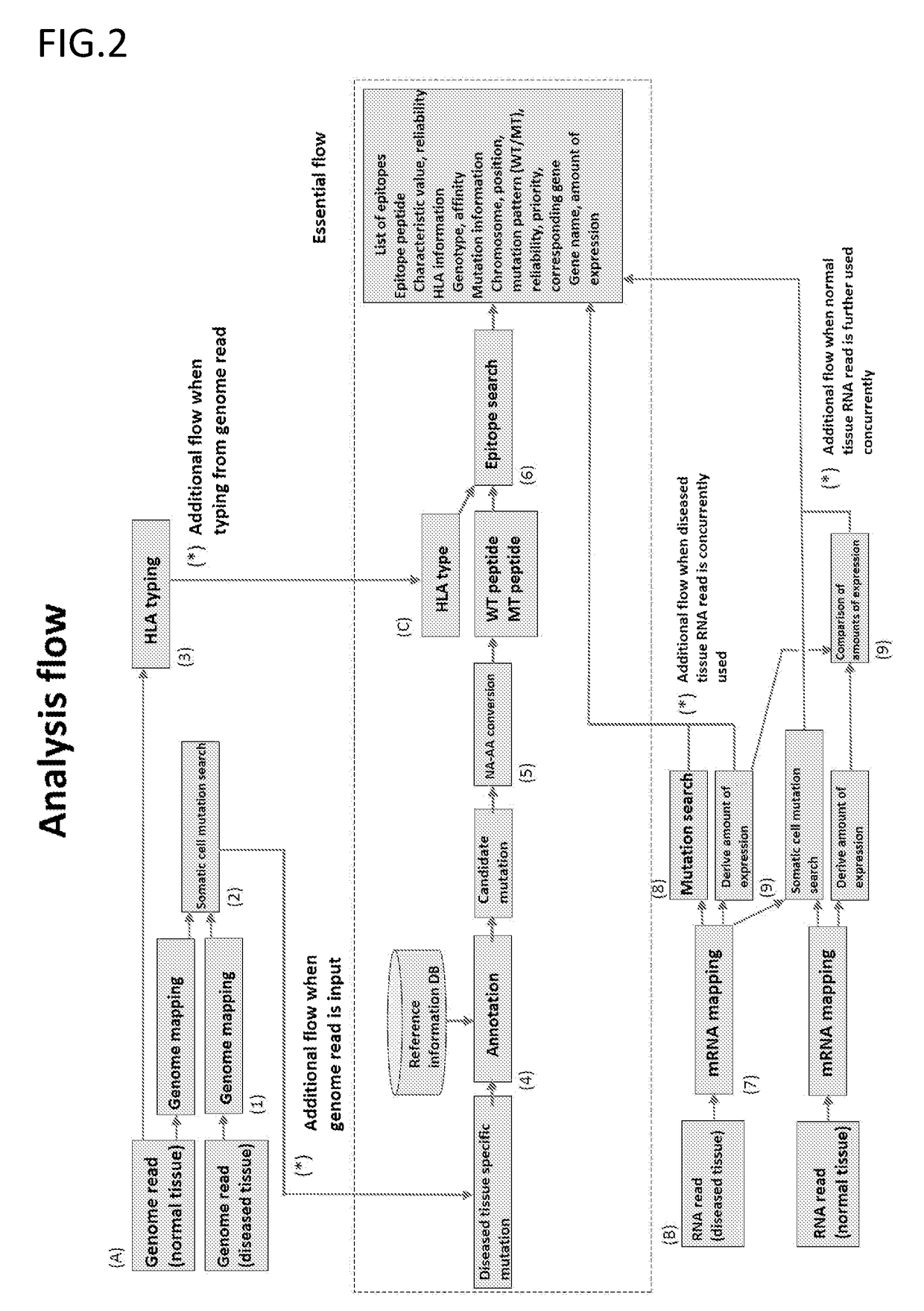
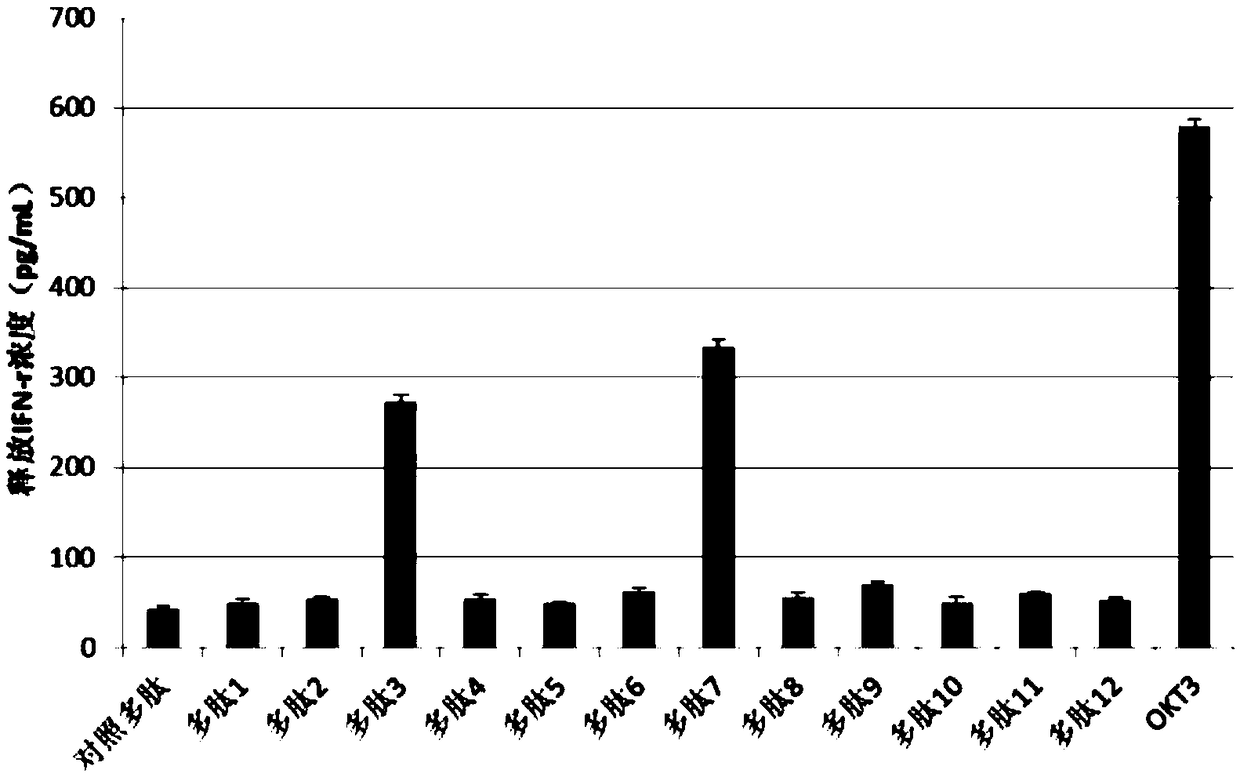
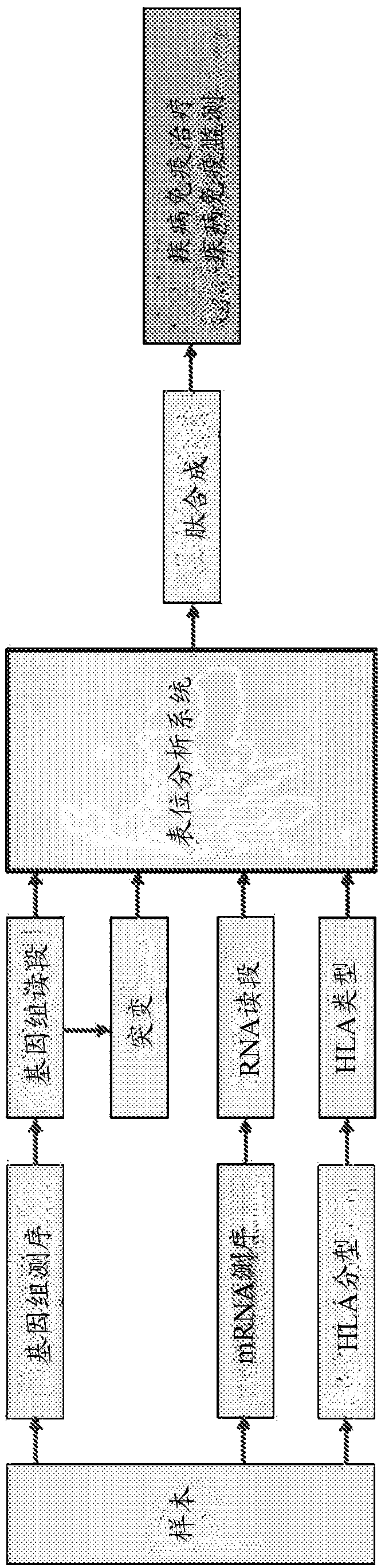
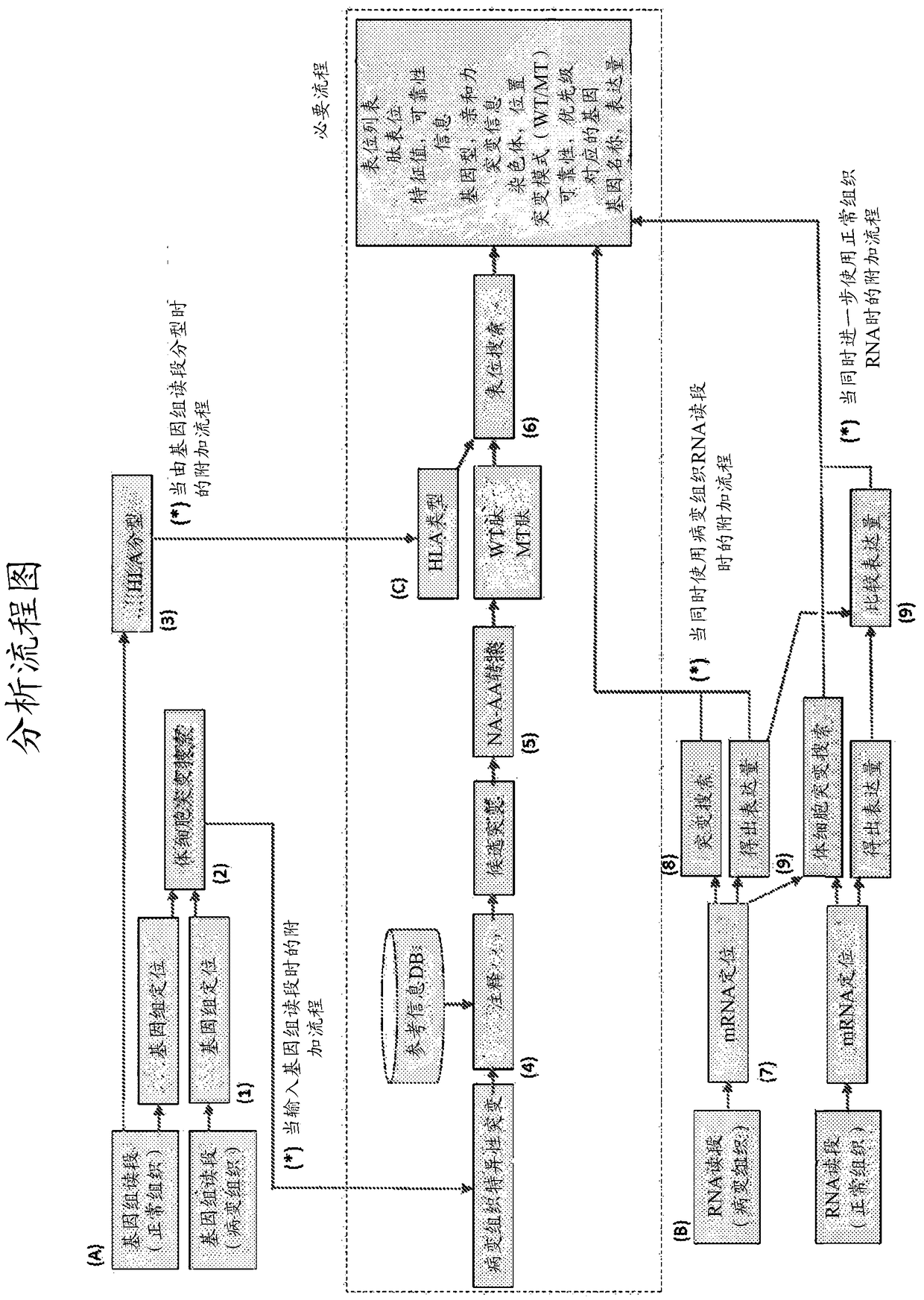
Monitoring and diagnosis for immunotherapy, and design for therapeutic agent
PendingUS20190080044A1Effective immunotherapyEffective immunological monitoringMicrobiological testing/measurementData visualisationDiseaseEpitope
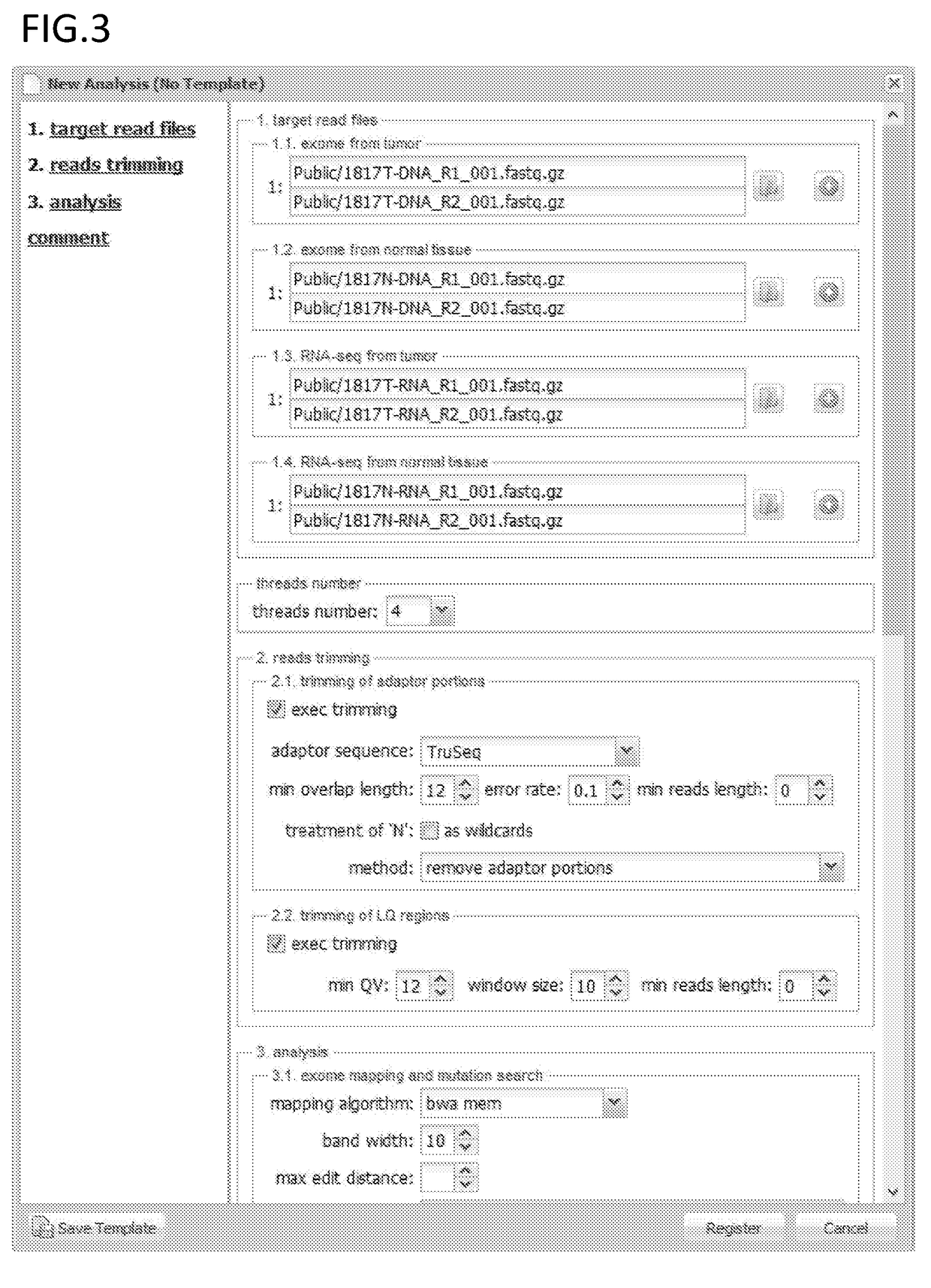
The present invention provides a method for producing a peptide for the treatment (in particular, immunotherapy), monitoring, or diagnosis of a disease in a subject. This method is achieved by obtaining information pertaining to a genome read, for example an exome read, of the subject and a mutation thereof, and, as necessary, information regarding the RNA sequence of the subject and information regarding the MHC type of the subject, analyzing an epitope related to the mutation on the basis of the information pertaining to the genome read (for example, the exome read) and the mutation, arbitrary information from the RNA sequence, the MHC type information, and information regarding the disease, and producing a peptide, as necessary, on the basis of information regarding the epitope
Owner:REPERTOIRE GENESIS
Variants of alpha-fetoprotein coding and expression sequences
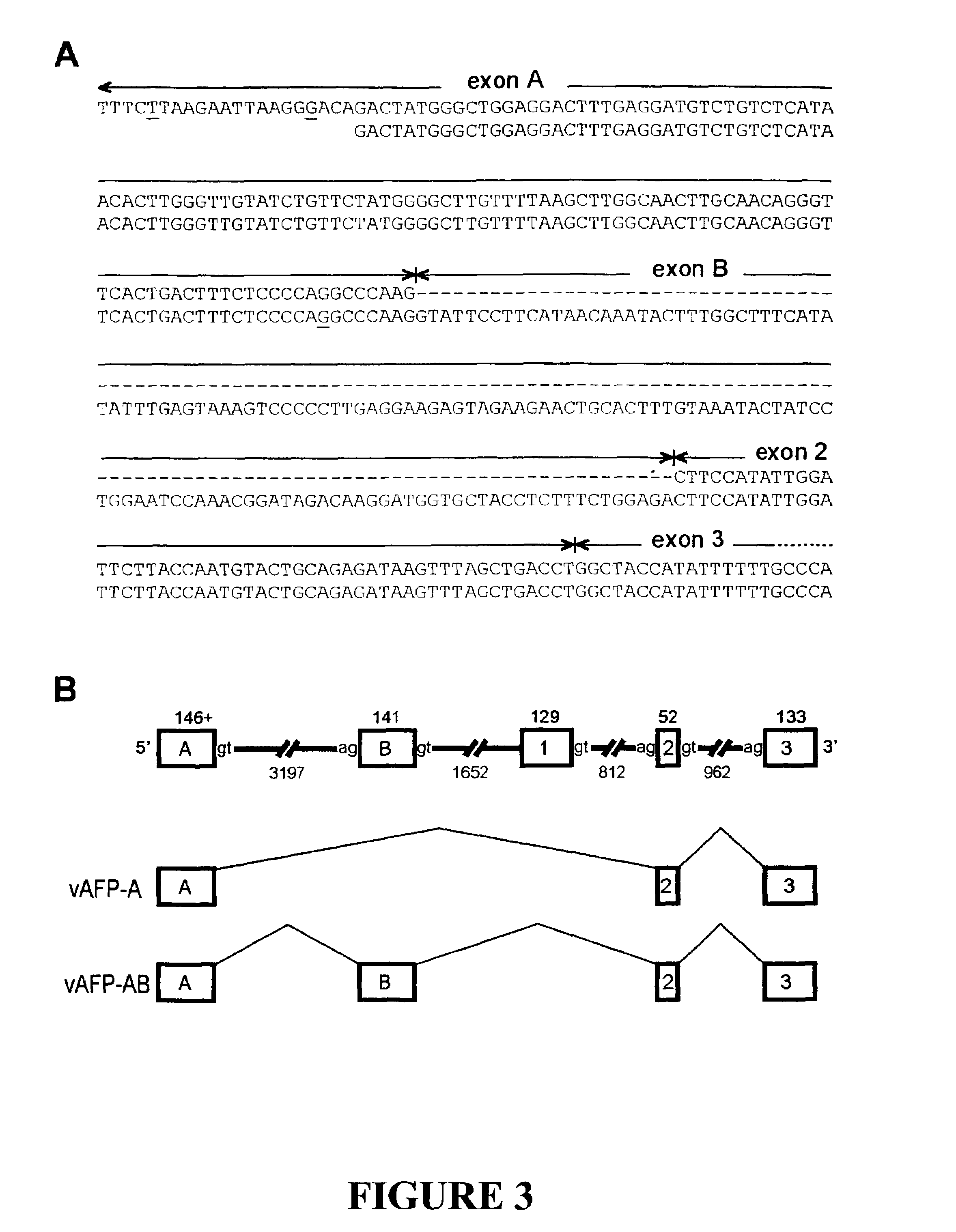
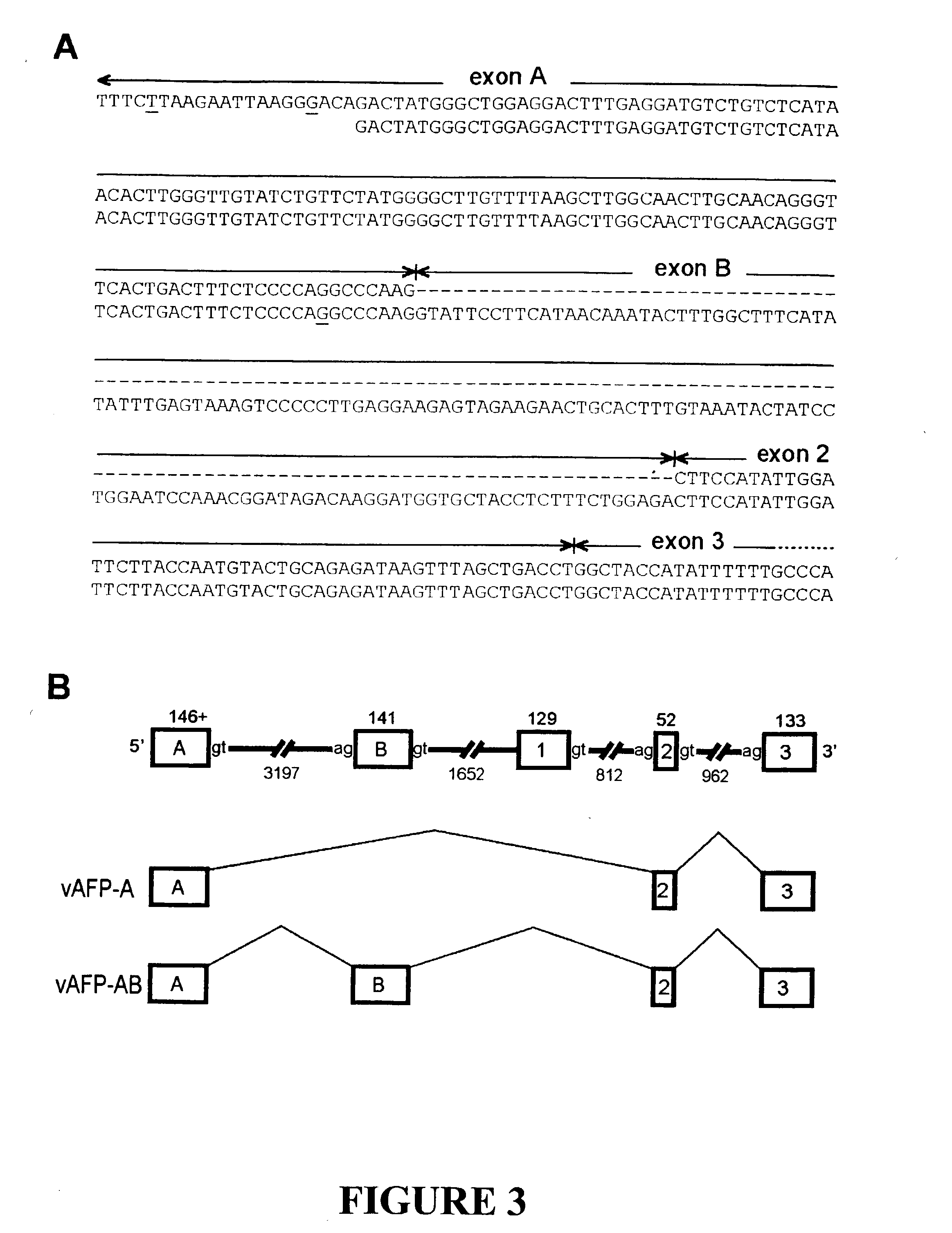
The invention discloses the sequences of variant forms of alpha-fetoprotein transcripts that have been identified in human hemopoietic progenitors but not in differentiated mature cells. The variant forms of AFP (vAFP) cDNA sequences isolated from a multipotent hemopoietic cell line, K562, differ from the authentic AFP transcript, consisting of 15 exons, by lacking only exon 1. Instead of exon 1, vAFP transcripts use an additional one or two exons located in the 5′-untranslated region of the AFP gene. K562 expressed selectively vAFP, whereas a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line, HepG2, showed no detectable expression of vAFP. In normal adult tissues, vAFP transcripts is detected in the bone marrow, thymus and brain, but not the spleen, suggesting the expression occurs in normal hemopoietic progenitors. Moreover, CD34+Lin− hemopoietic stem / progenitor cells purified by flow cytometric sorting also express the variant transcripts.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Construction method of whole-genome exon sequence capture probe
The invention relates to a kit for capturing a whole-genome exon sequence. The kit is a target sequence capture system based on the hybridization principle. An exon capture probe is designed, and a large quantity of exomes are obtained by hybridization to perform high-throughput sequencing and human whole genome comparison; and then, data analysis is performed, and the capture efficiency is calculated. The kit provided by the invention can provide high-quality target sequence enrichment, and has high specificity, high accuracy and excellent reproducibility in whole genome exon sequencing; the whole genome exon sequencing becomes the most effective policy for identifying the disease-causing gene of the Mendel disease; and the kit is also applied to the study and clinical diagnosis of the gene susceptible to complex diseases, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING CENT FOR PHYSICAL & CHEM ANALYSIS
Method for identifying novel minor histocompatibility antigens
InactiveUS20150226740A1Peptide/protein ingredientsLibrary screeningSpectroscopyMinor histocompatibility antigen
A novel method for human minor histocompatibility antigen (MiHA) discovery, novel MiHAs identified using this method, as well as uses of the novel MiHAs, are described. One of the features of the novel method is the inclusion of personalized translated transcriptome and / or exome in the database used for peptide identification by mass spectroscopy (MS). Candidate MiHAs are identified by comparing the personalized transcriptome and / or exome to a reference genome and / or to the transcriptome and / or exome of an HLA-matched subject.
Owner:UNIV DE MONTREAL
Variants of alpha-fetoprotein coding and expression sequences
The invention discloses the sequences of variant forms of alpha-fetoprotein transcripts that have been identified in human hemopoietic progenitors but not in differentiated mature cells. The variant forms of AFP (vAFP) cDNA sequences isolated from a multipotent hemopoietic cell line, K562, differ from the authentic AFP transcript, consisting of 15 exons, by lacking only exon 1. Instead of exon 1, vAFP transcripts use an additional one or two exons located in the 5'-untranslated region of the AFP gene. K562 expressed selectively vAFP, whereas a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line, HepG2, showed no detectable expression of vAFP. In normal adult tissues, vAFP transcripts is detected in the bone marrow, thymus and brain, but not the spleen, suggesting the expression occurs in normal hemopoietic progenitors. Moreover, CD34+Lin- hemopoietic stem / progenitor cells purified by flow cytometric sorting also express the variant transcripts.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Sexual dysplasia-related gene capture kit and application thereof
ActiveCN110904212AHigh detection specificityImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseasePhysiology
The invention discloses a sexual dysplasia-related gene capture kit and an application thereof. The sexual dysplasia-related gene capture kit carries out target region sequencing analysis on the wholeexon group or the sexual dysplasia-related genome (respectively accounting for 1% and 0.01% of the whole genome) of a patient with hereditary dysplasia, most pathogenic mutation information of the disease is captured, and the kit has the advantages of small required sample amount, low cost and high throughput, can detect many samples, and promotes discovery of new pathogenic variation of hereditary dysplasia. The sexual dysplasia-related gene mutation site selected by the invention covers common hot spot mutation and other unusual mutation sites of Chinese people. The high throughput of the kit makes sexual dysplasia-related genes in people comprehensively screened, so the kit is of great significance to improving population quality and benefiting the society.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Personalized vaccine
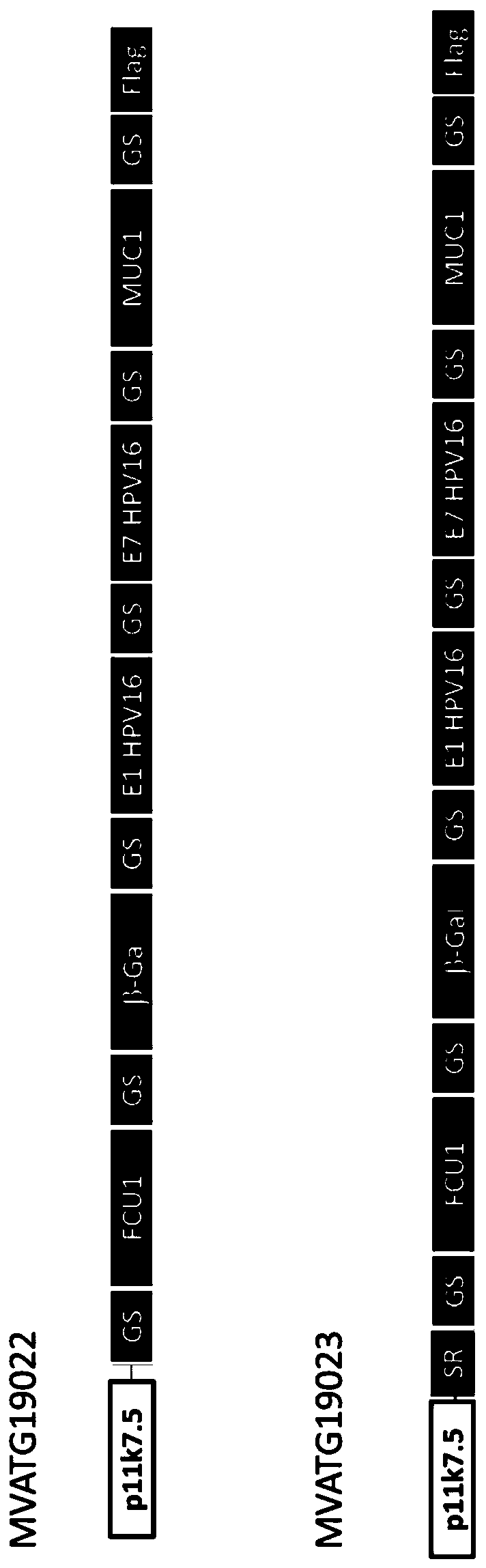
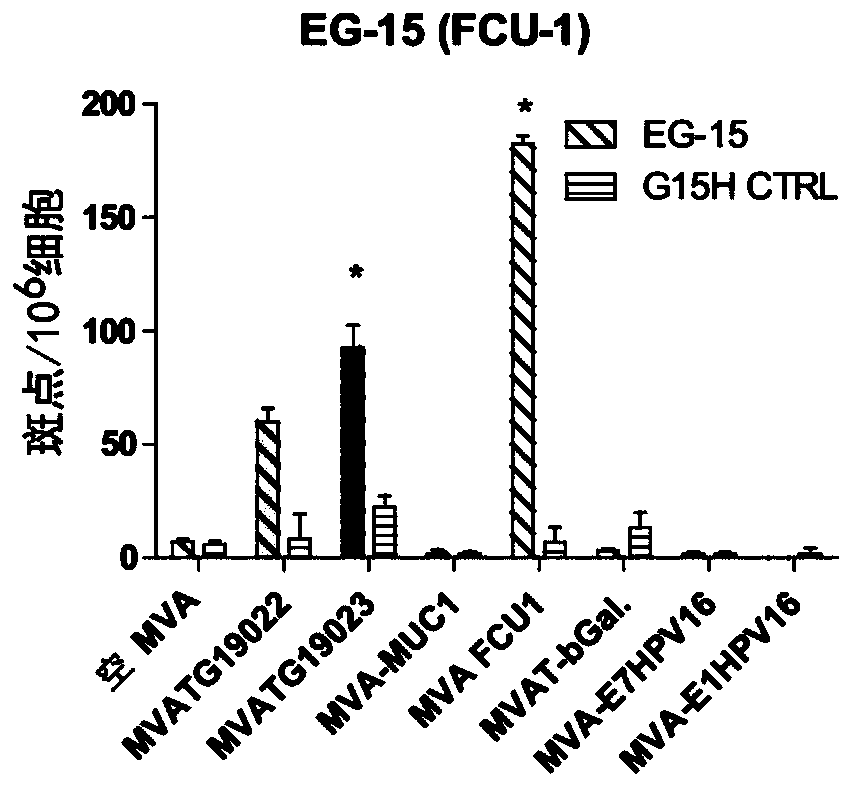
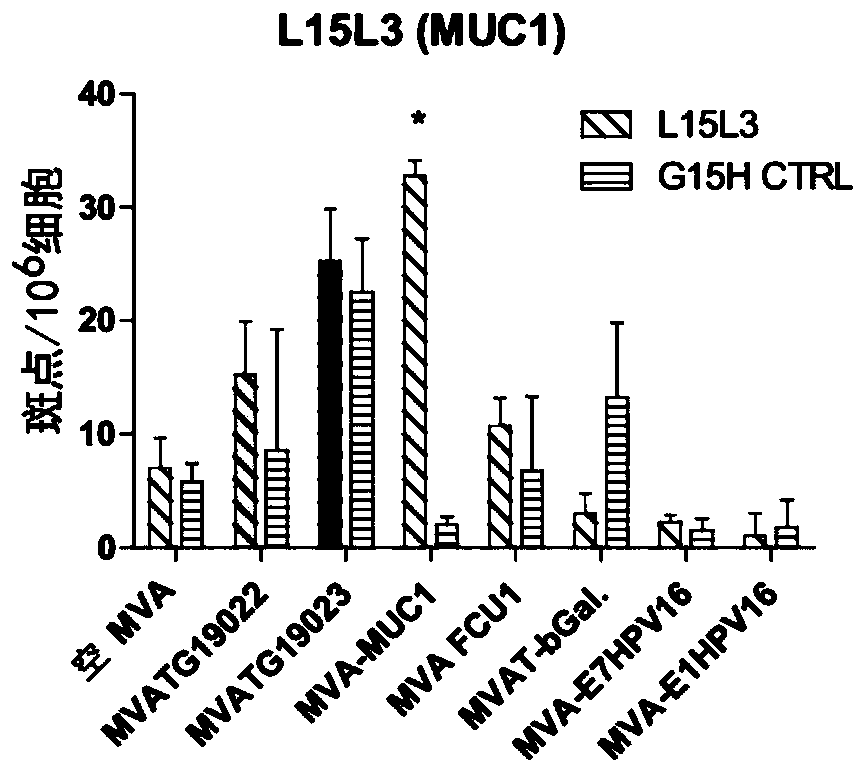
The present invention generally relates to a personalized cancer vaccine comprising a recombinant poxvirus encoding one or more neopeptide(s) or a composition comprising such a recombinant poxvirus and a pharmaceutically acceptable vehicle as well as the use of said personalized cancer vaccine for treating a cancerous subject in need thereof. A specific embodiment is directed to a method of providing such a vaccine or composition comprising an identification step comprising a) extracting the DNA from a tumor sample and a non-tumor sample, b) selecting target regions, preferably the entire coding regions of the genome (exome), c) sequencing said target regions (e.g. the exome) from said extracted DNAs and d) identifying one or more tumor-specific mutation(s) by comparing the DNA sequences obtained from said tumor and non-tumor samples. Embodiments also include a method of treating cancer or preventing its relapse comprising administration of such a personalized cancer vaccine. The invention is of very special interest in the field of personalized immunotherapy, specifically for stimulating T cell immune response.
Owner:TRANSGENE SA
Rice aroma gene of paddy rice and constructing process and use of expression vector including the rice aroma gene
InactiveCN1810974ABreed fastFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionStart codonBac clone
The present invention relates to rice breeding gene technology in biotechnology field, and is rice aroma gene of paddy rice and the constructing process and use of expression vector including the rice aroma gene. The rice aroma gene of paddy rice has nucleotide of total length of 9066 bases and including 1242 bases in start codon ATG upstream, 5859 bases in the gene region and 1965 bases in the termination codon TAA downstream, coding area comprising 15 exons, and gene sequence as changed betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase coding gene Badh with an 8 base deletion in the 7-th exon. Through cutting the integral rice aroma gene of paddy rice of the positive BAC clone with the limiting cleavage sites HindIII on two sides of the rice aroma gene of paddy rice Badh and cloning to expression vector pCAMBIA1302, the expression vector of rice aroma gene of paddy rice may be obtained and may be used in breeding excellent rice variety.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
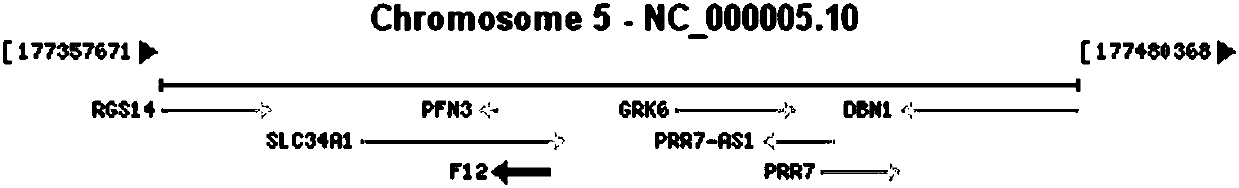
Primer, kit and method for detecting gene mutation of blood coagulation factor XII (F12)
InactiveCN107841554AImprove stabilityThere will be no missed detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPrenatal diagnosisSanger sequencing
The invention discloses a primer and a method for detecting gene mutation related to congenital deficiency of blood coagulation factor XII. The method comprises the following steps: performing amplification testing on 14 pairs of primers in a whole-exome sequence in a hot spot region of blood coagulation factor XII (F12); and adopting Sanger sequencing techniques and sequencing primers. Accordingto the primer and method disclosed by the invention, mutation of genes related to the congenital deficiency of blood coagulation factor XII can be rapidly detected. The method disclosed in the invention has accurate results, is capable of aiding diagnosis of the congenital deficiency of blood coagulation factor XII and has important reference significance on early intervention, early treatment andantenatal diagnosis.
Owner:南京艾迪康医学检验所有限公司
Method of validating mRNA splicing mutations in complete transcriptomes
A method is described for the automatic validation of DNA sequencing variants that alter mRNA splicing from nucleic acids isolated from a patient or tissue sample. Evidence of a predicted splicing mutation is demonstrated by performing statistically valid comparisons between sequence read counts of abnormal RNA species in mutant versus non-mutant tissues. The method leverages large numbers of control samples to corroborate the consequences of predicted splicing variants in complete genomes and exomes for individuals carrying such mutations. Because the method examines all transcript evidence in a genome, it is not necessary a priori to know which gene or genes carry a splicing mutation.
Owner:CYTOGNOMIX
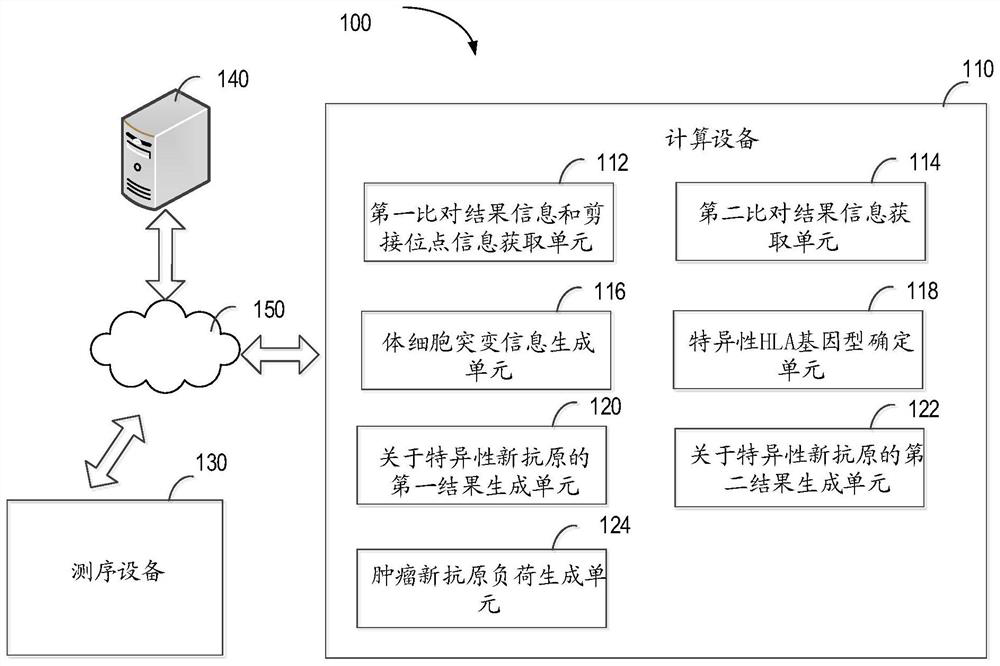
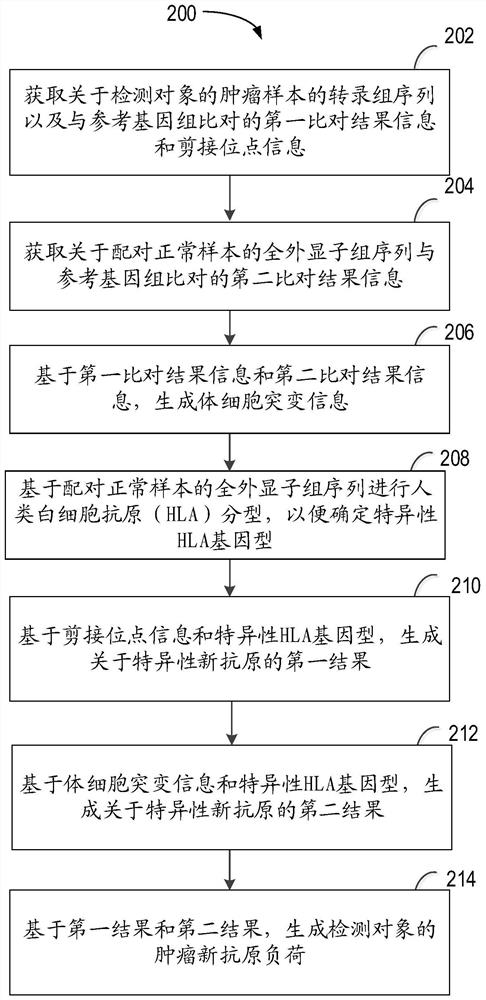
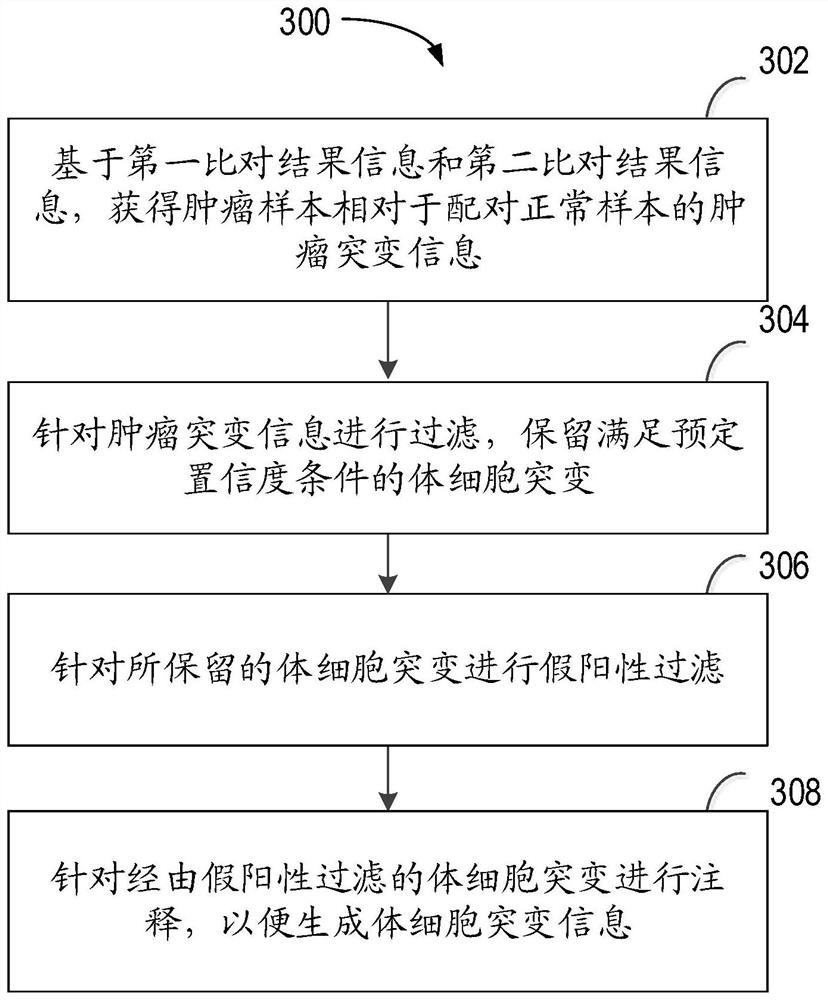
Method for detecting tumor neoantigen load, computing device and computer storage medium
The invention relates to a method for detecting tumor neoantigen load, computing equipment and a computer storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a transcriptome sequence related to a tumor sample, and first comparison result information and splicing site information which are compared with a reference genome; obtaining a whole exome sequence of the paired normal sample and a whole exome sequence of the paired normal sample in second comparison result information compared with the reference genome; generating somatic mutation information based on the first comparison result information and the second comparison result information; determining a specific HLA genotype; generating a first result about the specific neoantigen based on the splicing site information and the specific HLA genotype; generating a second result about the specific neoantigen based on the somatic mutation information and the specific HLA genotype; and generating the tumor neoantigen load of the detected object based on the first result and the second result. According to the invention, the comprehensiveness and reliability of tumor neoantigen load detection can be effectively improved.
Owner:CARRIER GENE TECH SUZHOU CO LTD +1
Abnormal sexual development related gene capture kit and its application
ActiveCN110904212BHigh detection specificityImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseaseMedicine
The invention discloses a sexual development abnormality-related gene capture kit and application thereof. The sexual developmental abnormality-related gene capture kit provided by the present invention is to perform target region sequencing on the whole exome or sexual developmental abnormality-related genome (accounting for 1% and 0.01% of the whole genome respectively) of patients with hereditary sexual developmental abnormality Analysis, which captures most of the pathogenic mutation information of the disease, has the advantages of small sample size, low cost, and high throughput, and can detect more samples, which promotes the identification of new pathogenic mutations of genetic abnormalities. Find. The genetic mutation sites related to abnormal sexual development selected in the present invention cover common hotspot mutations and other uncommon mutation points in Chinese. The high-throughput of the kit can comprehensively screen the genes related to abnormal sexual development in the population, which is of great significance for improving the quality of the population and benefiting the society.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
LRFF cell construction method
InactiveCN109136268AStrong target specificityLess prone to off-target effectsGenetically modified cellsBlood/immune system cellsPeripheral blood mononuclear cellWilms' tumor
The invention provides an LRFF cell construction method, human peripheral blood is used to sequence ctDNA or a whole exome of a tumor tissue, a mutation site is screened to predicate an epitope, and the sequence of an expression gene of a mutation polypeptide is connected and synthesized; meanwhile, a lentiviral vector is constructed, a lentivirus is packaged, an APC (Antigen Presenting Cell) is transfected to finish the transformation of a specific LV cell, the APC is cultured in vitro together with a PBMC (Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell) separated from the peripheral blood, the effectiveaccurate polypeptide is screened, a common T cell is transformed into an LRFF cell having more accurate lethality through the second impact stimulated by the accurate polypeptide; and the lethality ofthe T cell on a tumor cell is improved. The provided LRFF cell is widely applied to the individualized accurate treatment of a solid tumor.
Owner:BEIJING DCTY BIOTECH CO LTD
Monitoring and diagnosis for immunotherapy, and design for therapeutic agent
PendingCN109072227ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDiseaseEpitope
The present invention provides a method for producing a peptide for the treatment (in particular, immunotherapy), monitoring, or diagnosis of a disease in a subject. This method is achieved by obtaining information pertaining to a genome read, for example an exome read, of the subject and a mutation thereof, and, as necessary, information regarding the RNA sequence of the subject and information regarding the MHC type of the subject, analyzing an epitope related to the mutation on the basis of the information pertaining to the genome read (for example, the exome read) and the mutation, arbitrary information from the RNA sequence, the MHC type information, and information regarding the disease, and producing a peptide, as necessary, on the basis of information regarding the epitope.
Owner:REPERTOIRE GENESIS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com