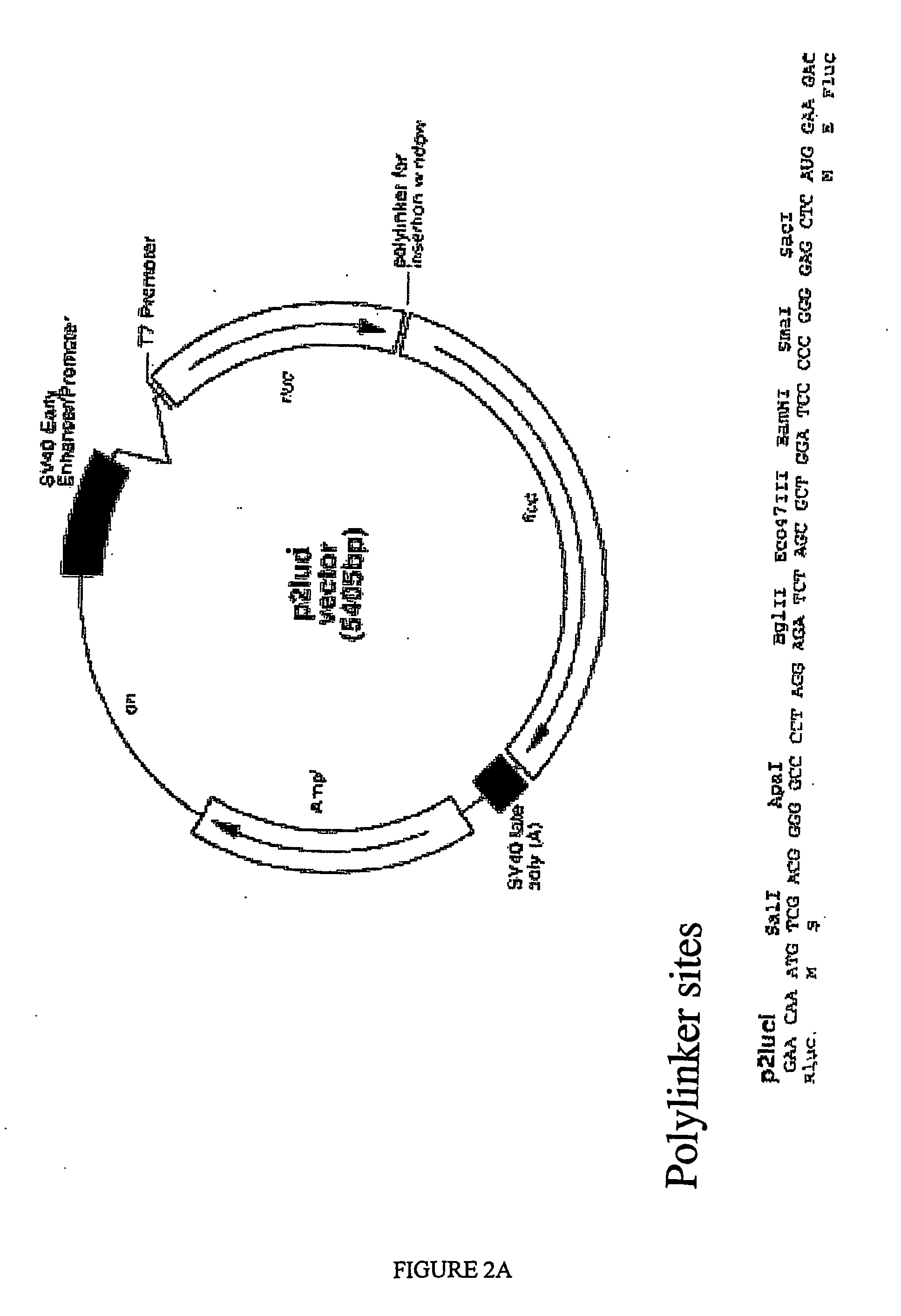
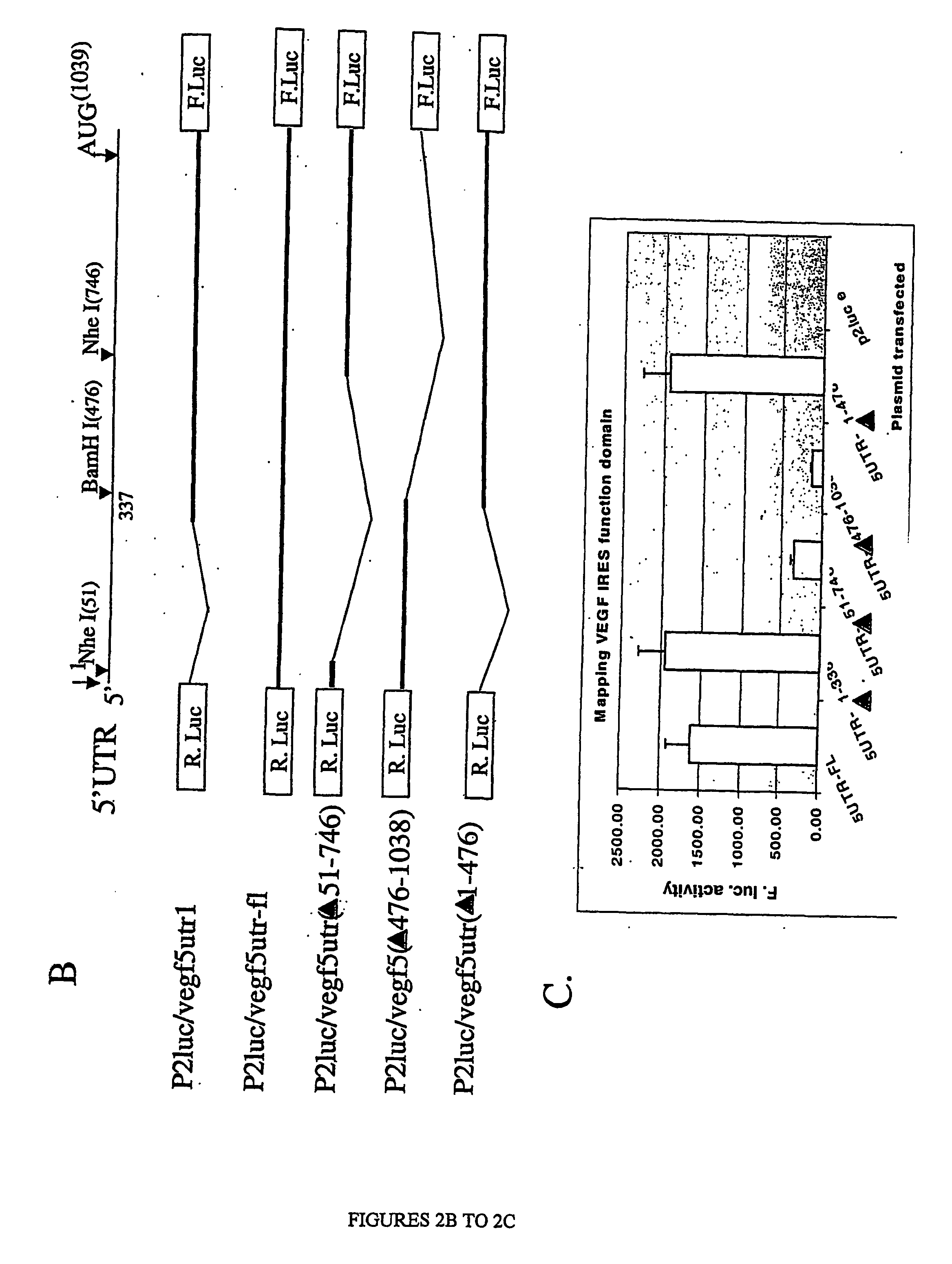
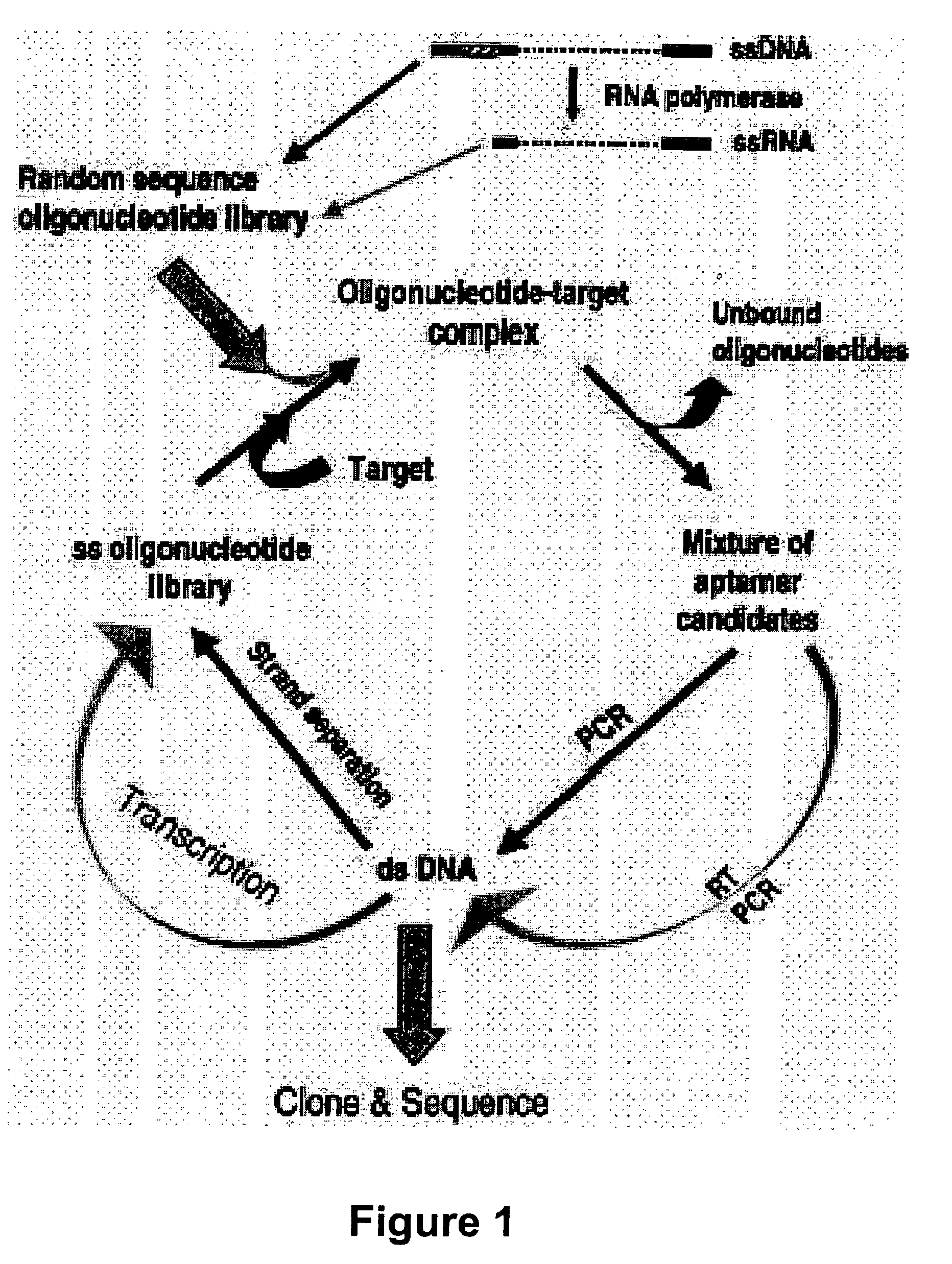
Patents
Literature
381 results about "Untranslated region" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In molecular genetics, an untranslated region (or UTR) refers to either of two sections, one on each side of a coding sequence on a strand of mRNA. If it is found on the 5' side, it is called the 5' UTR (or leader sequence), or if it is found on the 3' side, it is called the 3' UTR (or trailer sequence). mRNA is RNA that carries information from DNA to the ribosome, the site of protein synthesis (translation) within a cell. The mRNA is initially transcribed from the corresponding DNA sequence and then translated into protein. However, several regions of the mRNA are usually not translated into protein, including the 5' and 3' UTRs.
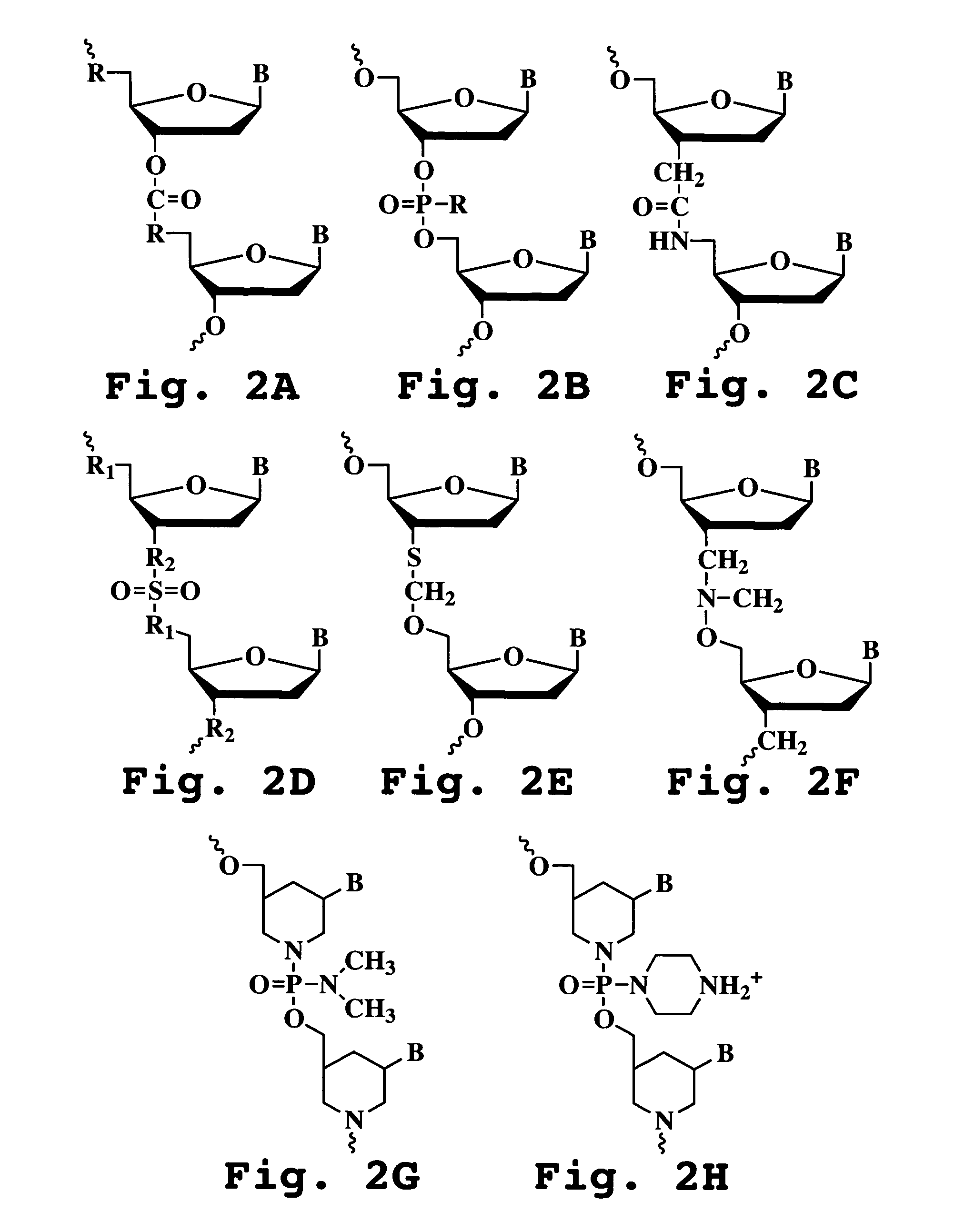
Method of eliminating inhibitory/instability regions from mRNA
InactiveUS6174666B1Microbiological testing/measurementVirus peptidesImmunodeficiency virusInstability
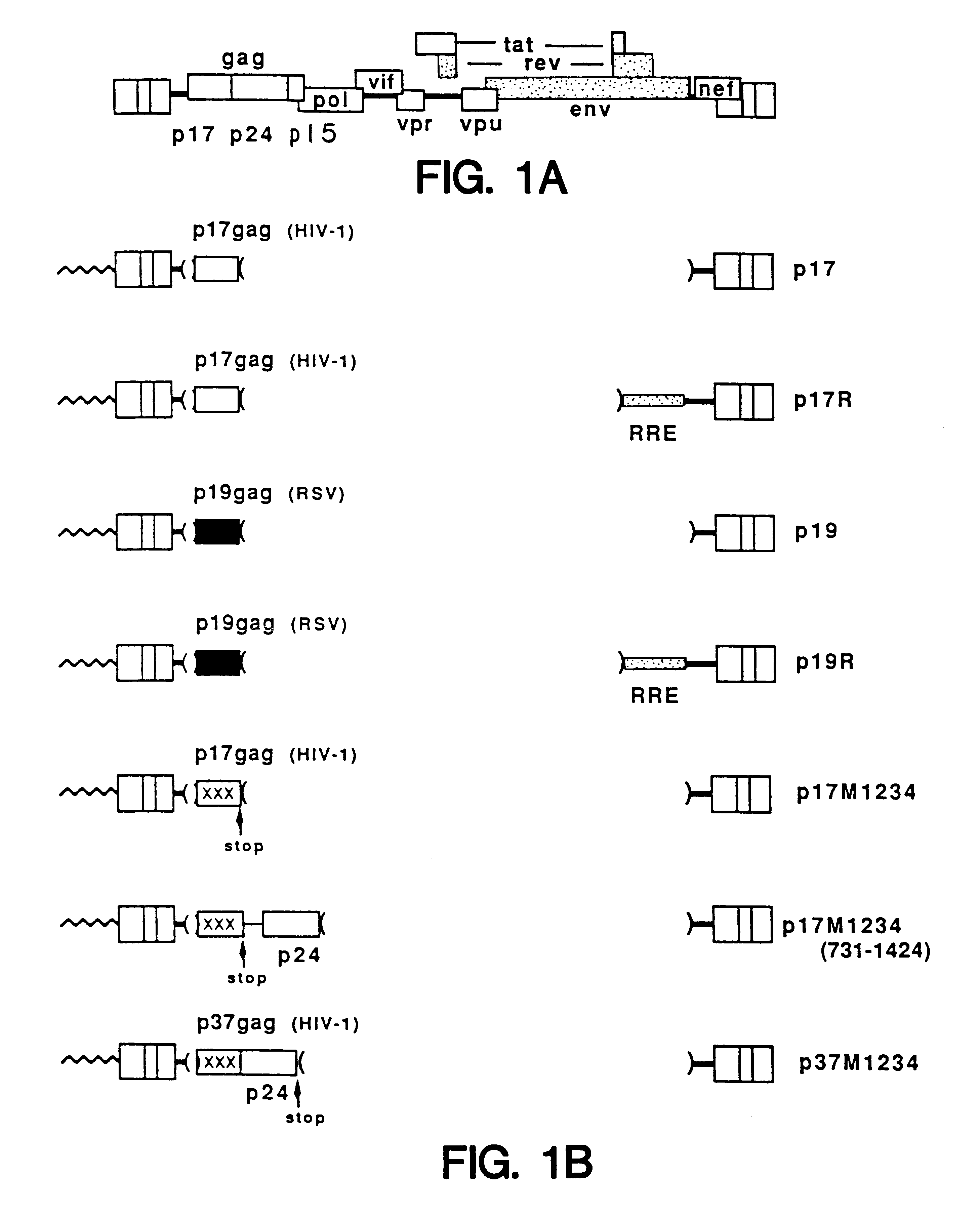
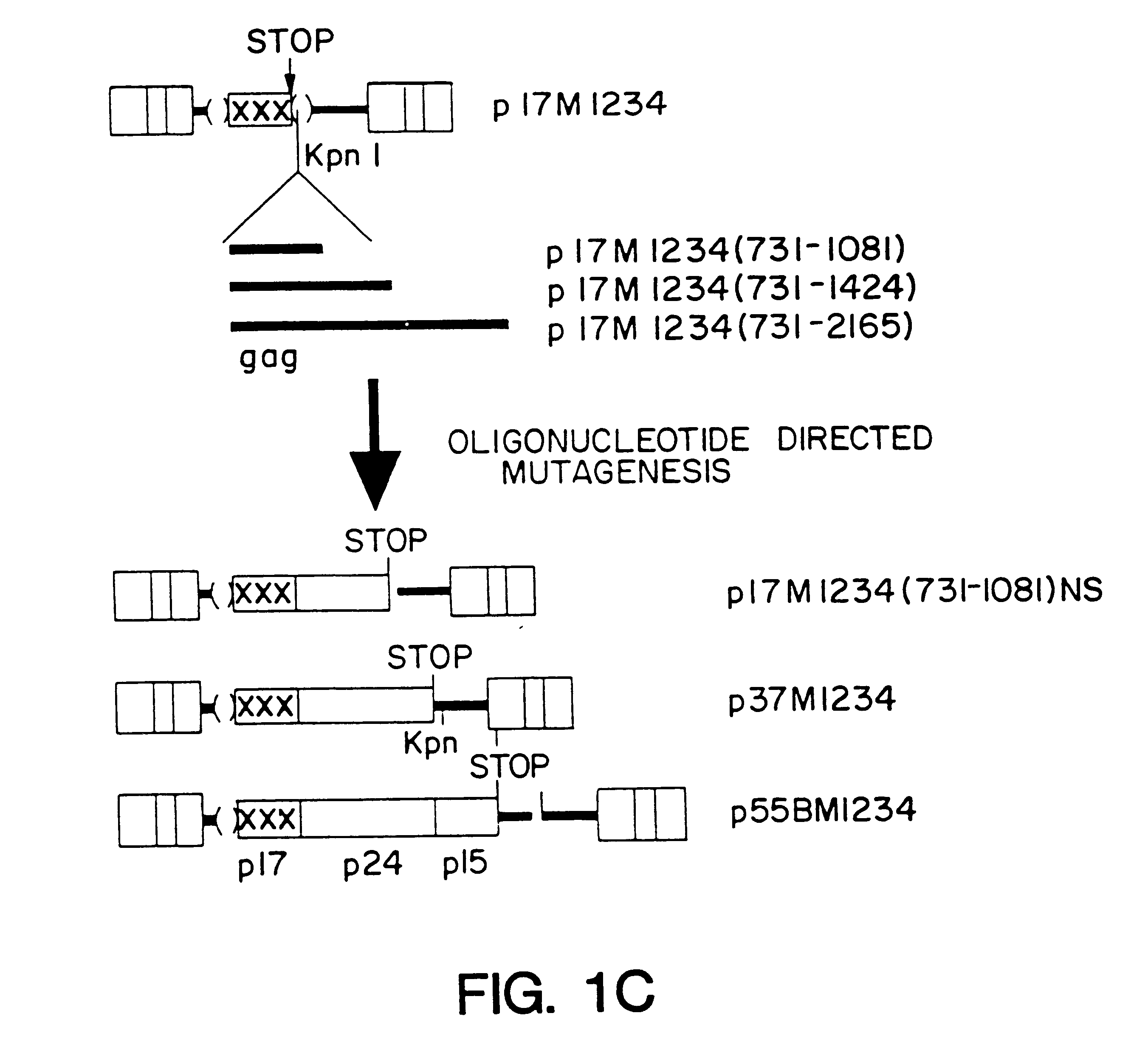
A method of locating an inhibitory / instability sequence or sequences within the coding region of an mRNA and modifying the gene encoding that mRNA to remove these inhibitory / instability sequences by making clustered nucleotide substitutions without altering the coding capacity of the gene is disclosed. Constructs containing these mutated genes and host cells containing these constructs are also disclosed. The method and constructs are exemplified by the mutation of a Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1 Rev-dependent gag gene to a Rev-independent gag gene. Constructs useful in locating inhibitory / instability sequences within either the coding region or the 3' untranslated region of an mRNA are also disclosed.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Use of regulatory sequences in transgenic plants
The present invention provides DNA sequences that function as 3′ untranslated regions (3′UTR) in plants. The 3′UTR's stabilize associated recombinant transcripts such that expression is improved. The invention further provides plant expression cassettes and recombinant plant that comprise a claimed 3′UTR.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Synthetic 5'UTRs, Expression Vectors, and Methods for Increasing Transgene Expression
ActiveUS20100293625A1Increase transgene expressionImprove stabilityVectorsSugar derivativesReticulum cellIntein
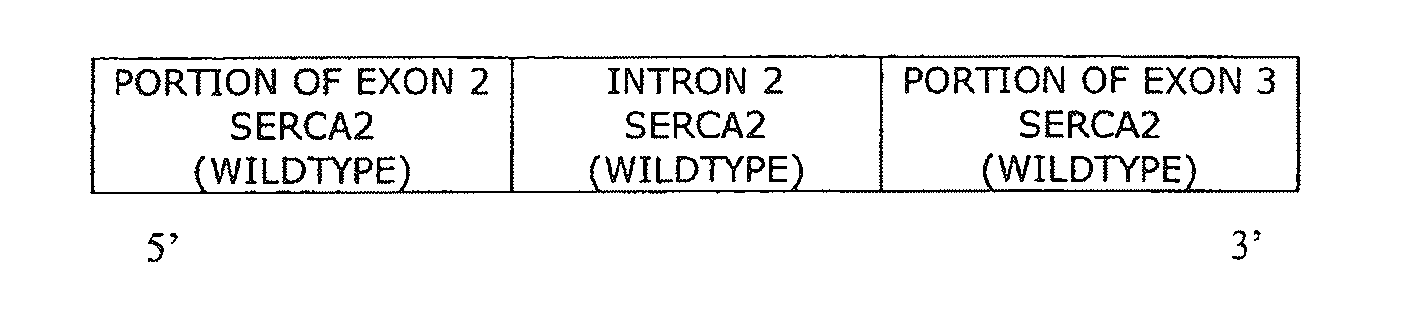
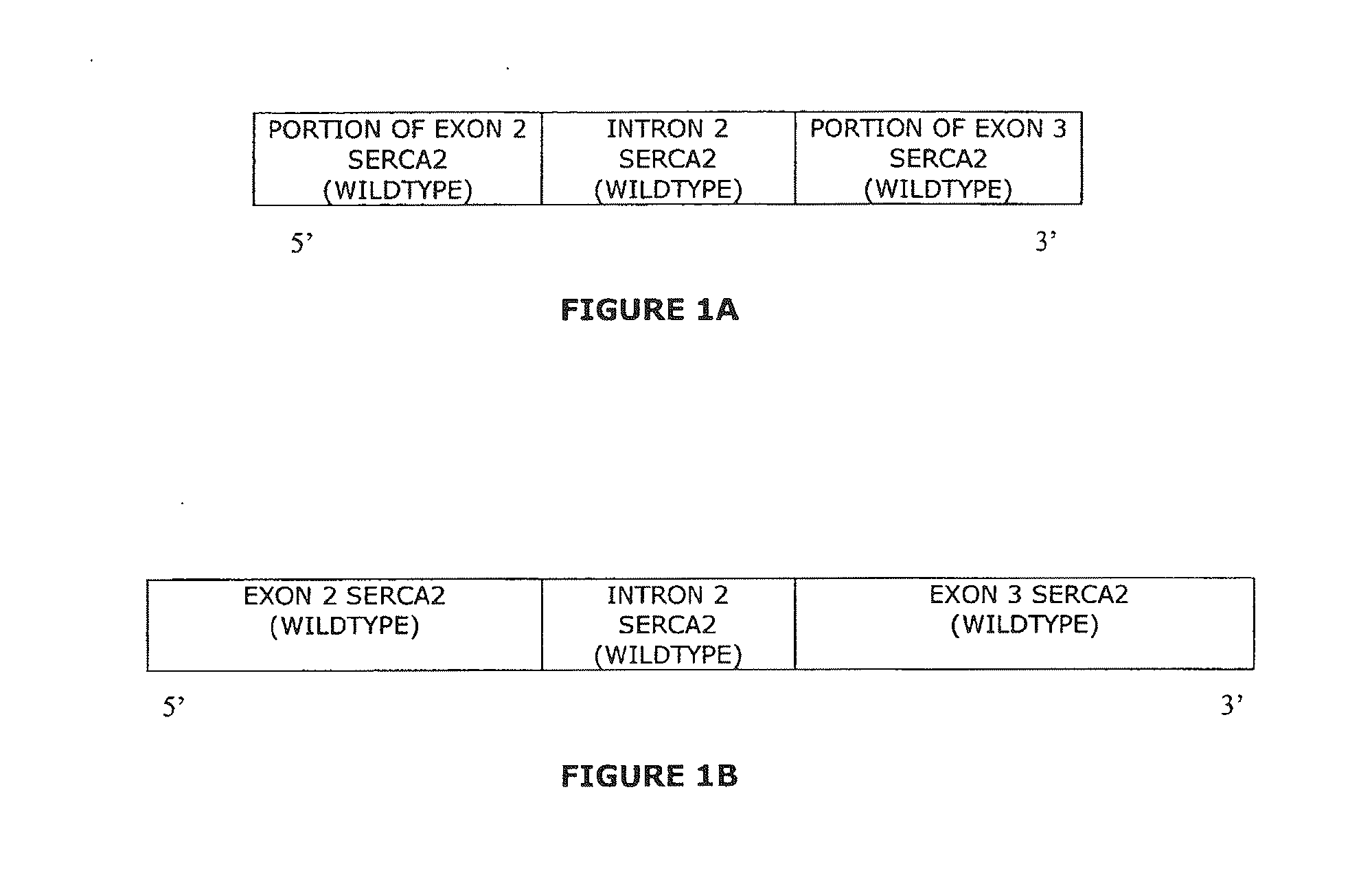
The present invention provides synthetic 5′UTRs comprising a first polynucleotide fragment and a second polynucleotide fragment, wherein the first polynucleotide fragment comprises at least one splice site of a first eukaryotic gene, the second polynucleotide fragment comprises at least a portion of 5′ untranslated region of a second eukaryotic gene, and the first polynucleotide fragment is located 5′ of the second polynucleotide fragment. In one embodiment, the first polynucleotide fragment comprises the second intron of a sarcoplasmic / endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase gene and the second polynucleotide fragment comprises at least a portion of the 5′ untranslated region (5′UTR) of a eukaryotic casein gene. The synthetic 5′UTRs are useful for increasing the expression of a transgene when positioned between a promoter and a transgene within an expression vector. The present invention also provides vectors comprising synthetic 5′UTRs and methods for increasing the expression of a transgene using synthetic 5′UTRs.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
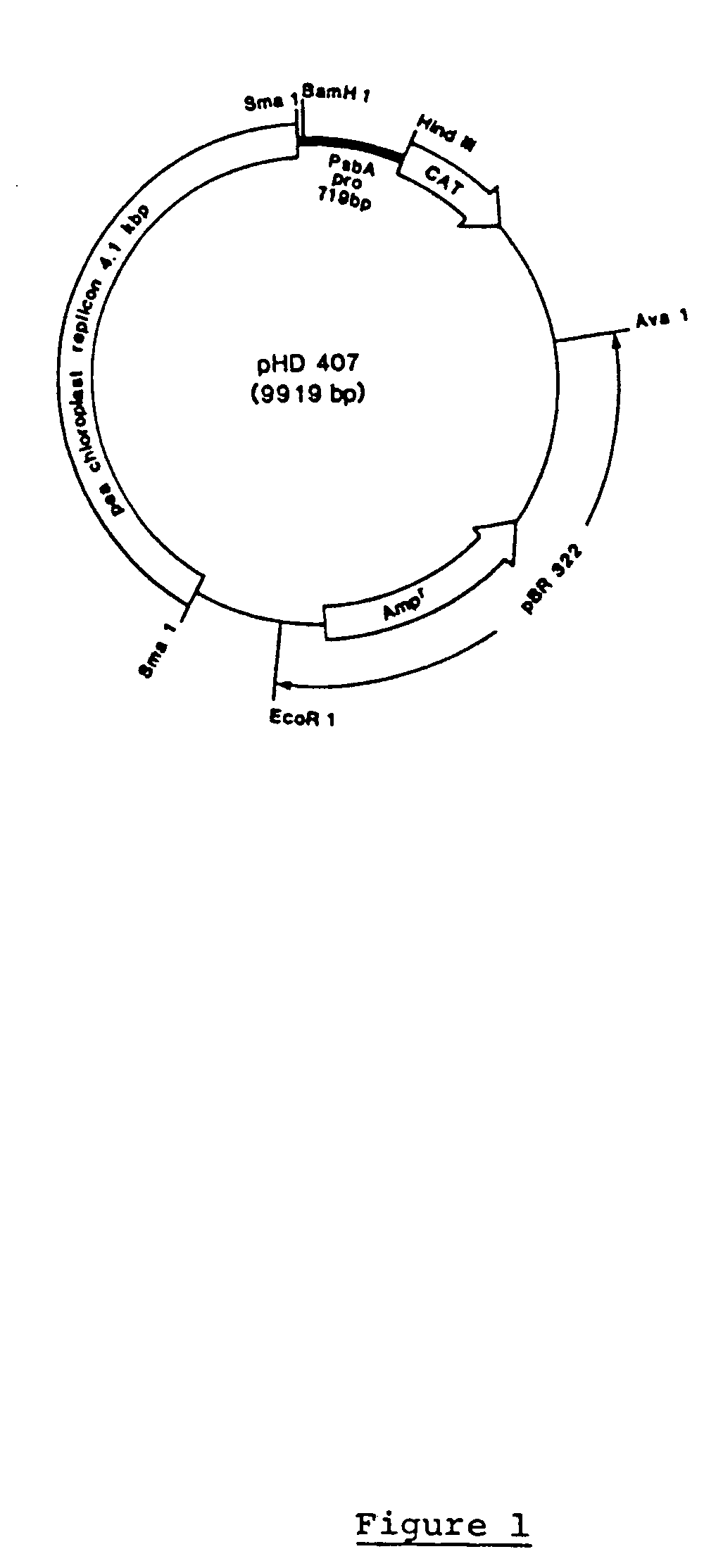
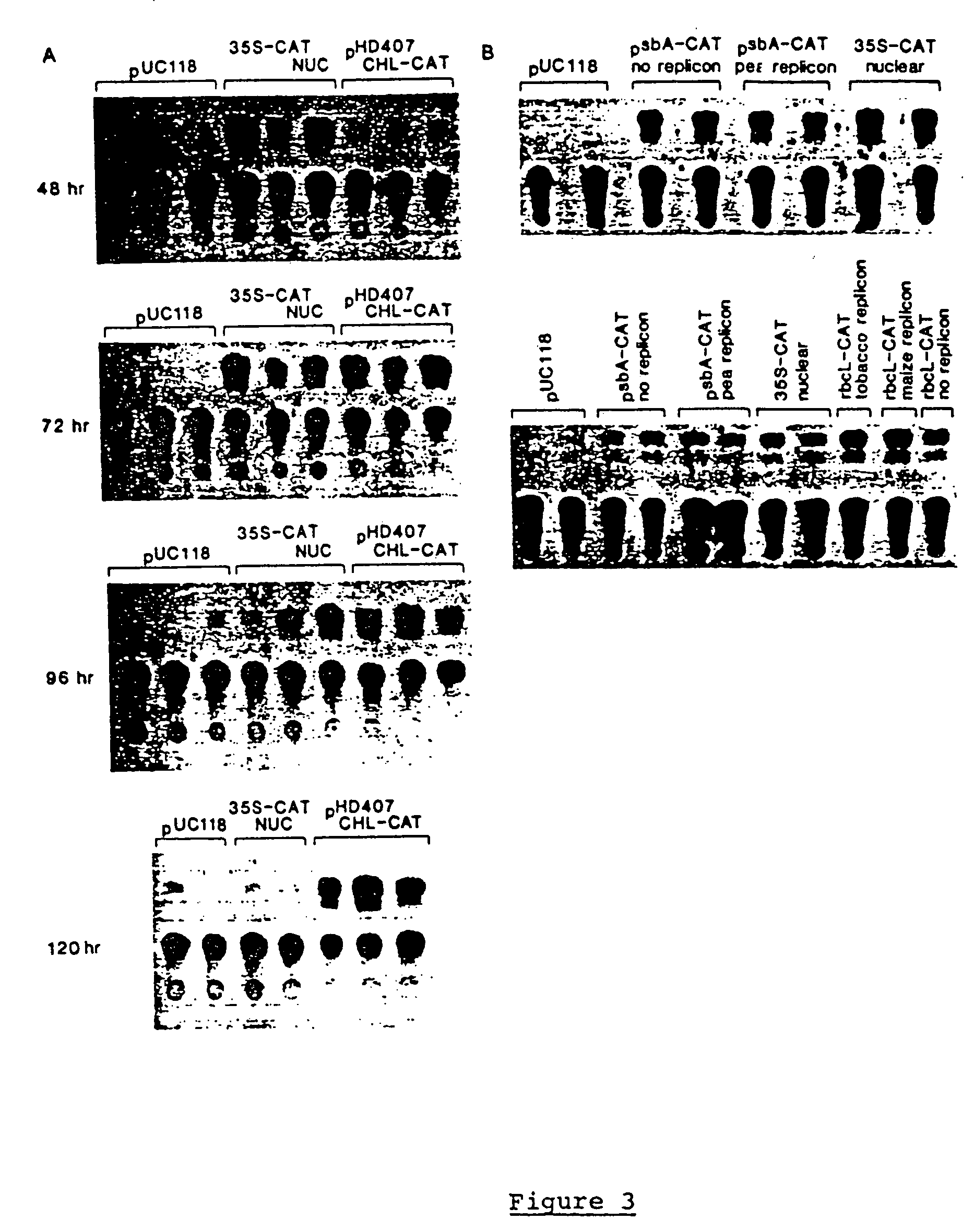
Genetic engineering of plant chloroplasts
Novel chimeric constructions and methods for their use are provided for expression of exogenous genes in a plant chloroplast. Particularly, expression is achieved by the use of a chloroplast or bacterial 5′ untranslated region in the expression cassette. The expression cassette may be integrated into the chloroplast genome by the use of chloroplast DNA flanking sequences, or may replicate autonomously if provided with a chloroplast origin of replication. Plants and cells containing the transformed chloroplasts are also provided. The constructs may be used with both monocotyledenous and dicotyledenous chloroplasts.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
Peptide display arrays
InactiveUS20120270748A1Improve throughputDone relatively cheaplyNucleotide librariesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPeptide displayDiscrete set
The present invention provides arrays, methods of constructing arrays, and methods of use of such arrays. The arrays of the invention comprise a substrate with two or more discrete constructs or discrete sets of constructs associated on the surface of the substrate, optionally via a linker molecule. The constructs include an oligonucleotide comprising a region encoding a peptide of interest and an affinity tag and an untranslated region, a fusion peptide comprising both the peptide of interest and the affinity tag and a capture agent that forms a binding pair with the affinity tag.
Owner:PROGNOSYS BIOSCI
Antisense antiviral compound and method for treating picornavirus infection
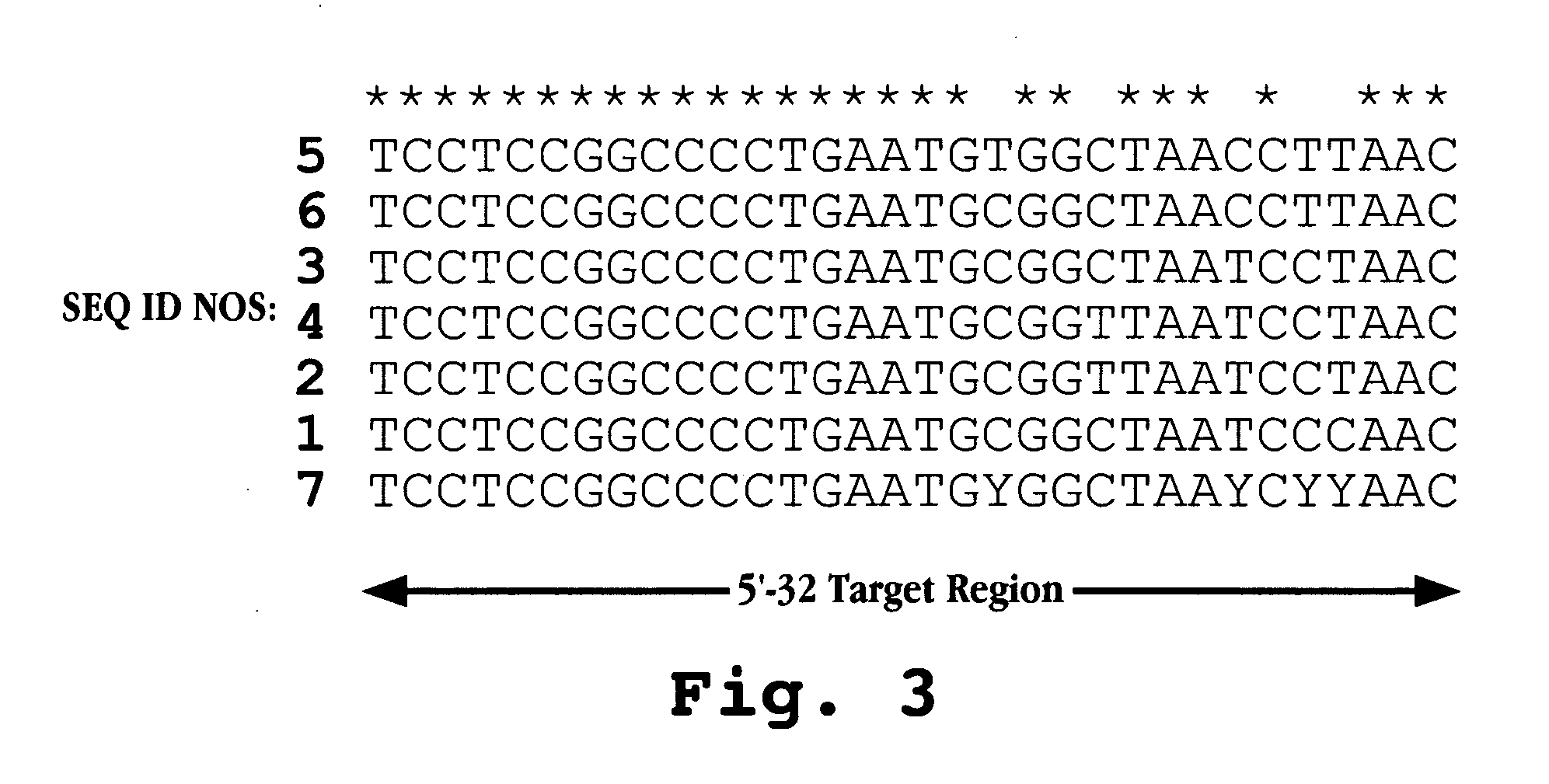
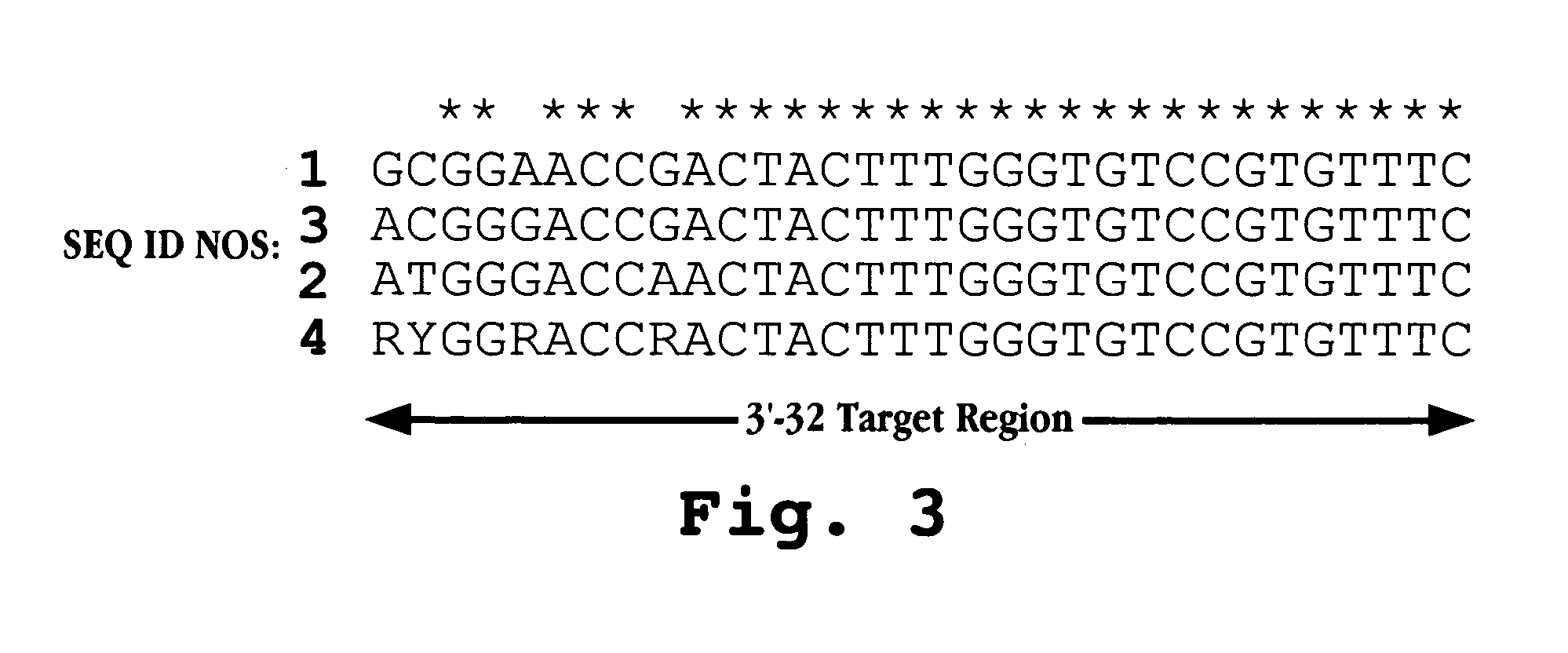
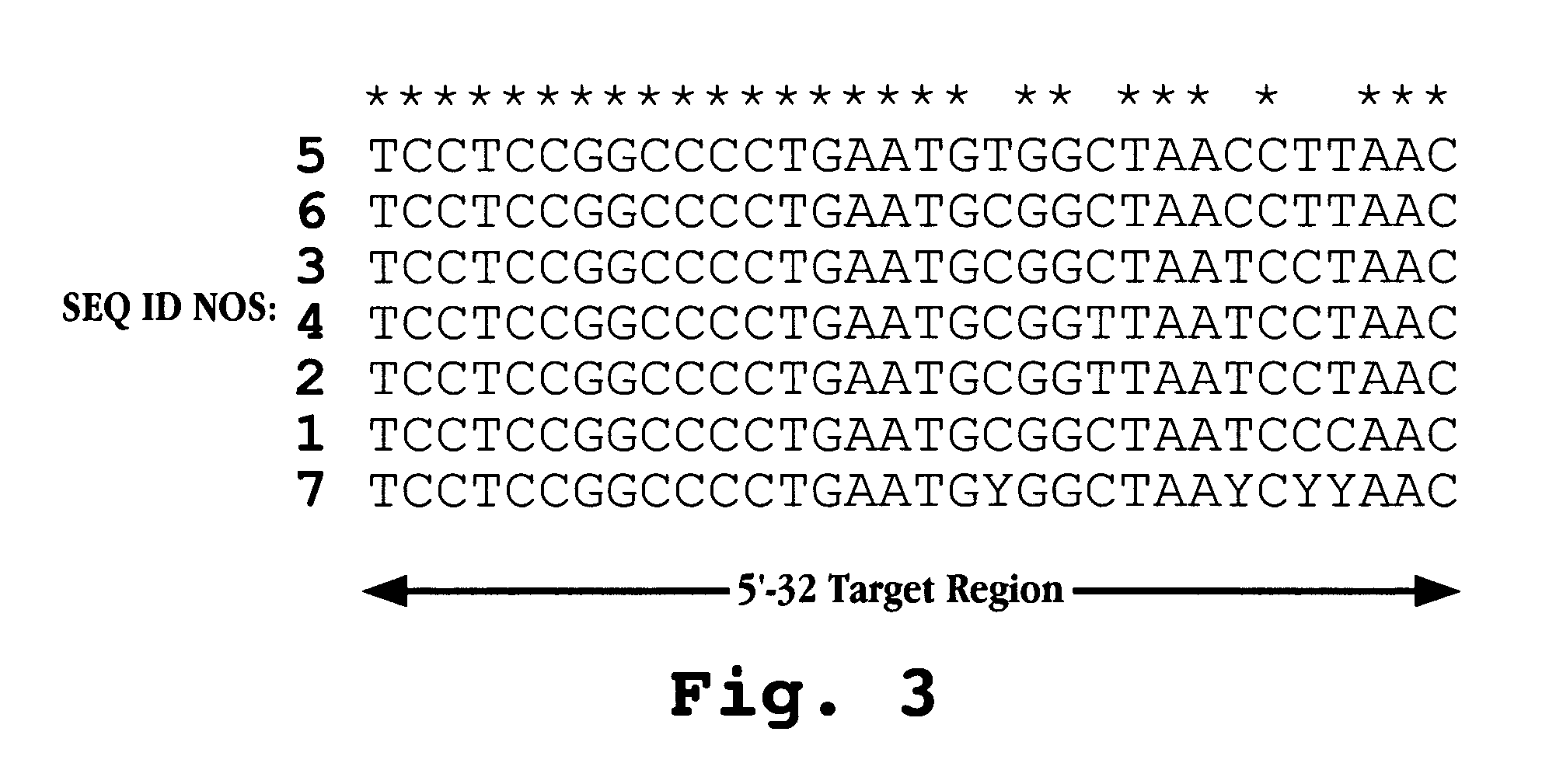
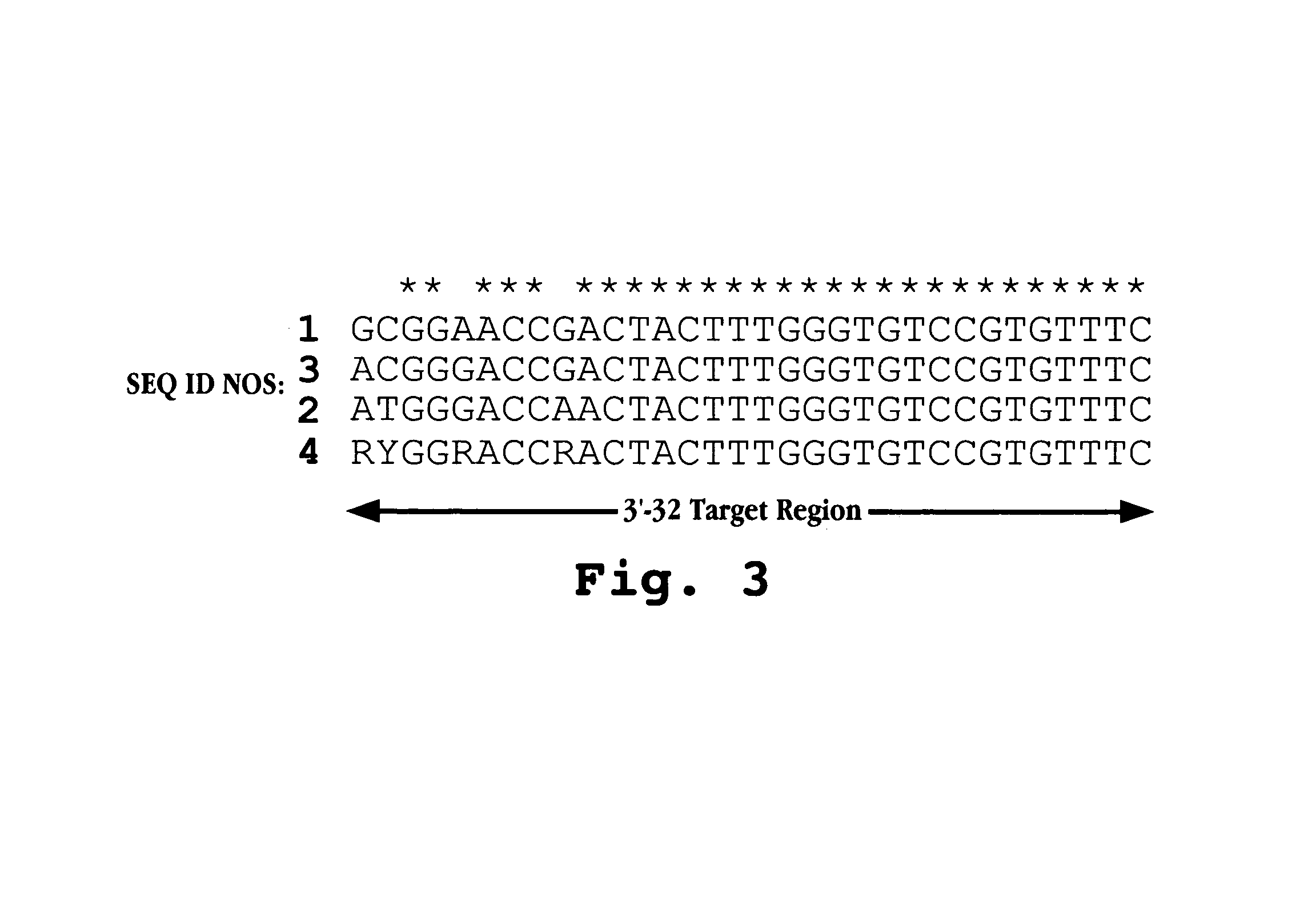
The invention provides antisense antiviral compounds and methods of their use and production in inhibition of growth of viruses of the Picornaviridae family and in the treatment of a viral infection. The compounds are particularly useful in the treatment of Enterovirus and / or Rhinovirus infection in a mammal. The antisense antiviral compounds are substantially uncharged, morpholino oligonucleotides have a sequence of 12-40 subunits, including at least 12 subunits having a targeting sequence that is complementary to a region associated with viral RNA sequences within a 32 nucleotide region of the viral 5′ untranslated region identified by SEQ ID NO:7.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Synthetic 5'UTRs, Expression Vectors, and Methods for Increasing Transgene Expression
InactiveUS20110247090A1High expressionImprove stabilitySugar derivativesFermentationNucleotideReticulum cell
The present invention provides synthetic 5′UTRs comprising a first polynucleotide fragment and a second polynucleotide fragment, wherein the first polynucleotide fragment comprises at least one splice site of a first eukaryotic gene, the second polynucleotide fragment comprises at least a portion of 5′ untranslated region of a second eukaryotic gene, and the first polynucleotide fragment is located 5′ of the second polynucleotide fragment. In one embodiment, the first polynucleotide fragment comprises the second intron of a sarcoplasmic / endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase gene and the second polynucleotide fragment comprises at least a portion of the 5′ untranslated region (5′UTR) of a eukaryotic casein gene. The synthetic 5′UTRs are useful for increasing the expression of a transgene when positioned between a promoter and a transgene within an expression vector. The present invention also provides vectors comprising synthetic 5′UTRs and methods for increasing the expression of a transgene using synthetic 5′UTRs.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Antisense antiviral compound and method for treating picornavirus infection
The invention provides antisense antiviral compounds and methods of their use and production in inhibition of growth of viruses of the Picornaviridae family and in the treatment of a viral infection. The compounds are particularly useful in the treatment of Enterovirus and / or Rhinovirus infection in a mammal. The antisense antiviral compounds are substantially uncharged, including partially positively charged, morpholino oligonucleotides have a sequence of 12-40 subunits, including at least 12 subunits having a targeting sequence that is complementary to a region associated with viral RNA sequences within a 32 nucleotide region of the viral 5′ untranslated region identified by SEQ ID NO:4.
Owner:AVI BIOPHARMA
Compositions and methods for inhibiting viral replication
The present invention relates to a double-stranded ribonucleic acid (dsRNA) having a nucleotide sequence which is less that 30 nucleotides in length and which is substantially identical to at least a part of a 3′-untranslated region (3′-UTR) of a (+) strand RNA virus, such as HCV, as well as pharmaceutical compositions comprising the dsRNA, together with a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The pharmaceutical compositions are useful for treating infections and diseases caused by the replication or activity of the (+) strand RNA virus, as well as methods for inhibiting viral replication.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARMA INC
Modulation of Gene Expression Using Oligomers That Target Gene Regions Downstream of 3' Untranslated Regions
Gene expression can be selectively modulated by contacting a cell with an oligomer that targets a gene region downstream of a ′3-UTR, thereby increasing or decreasing the expression of the target gene.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
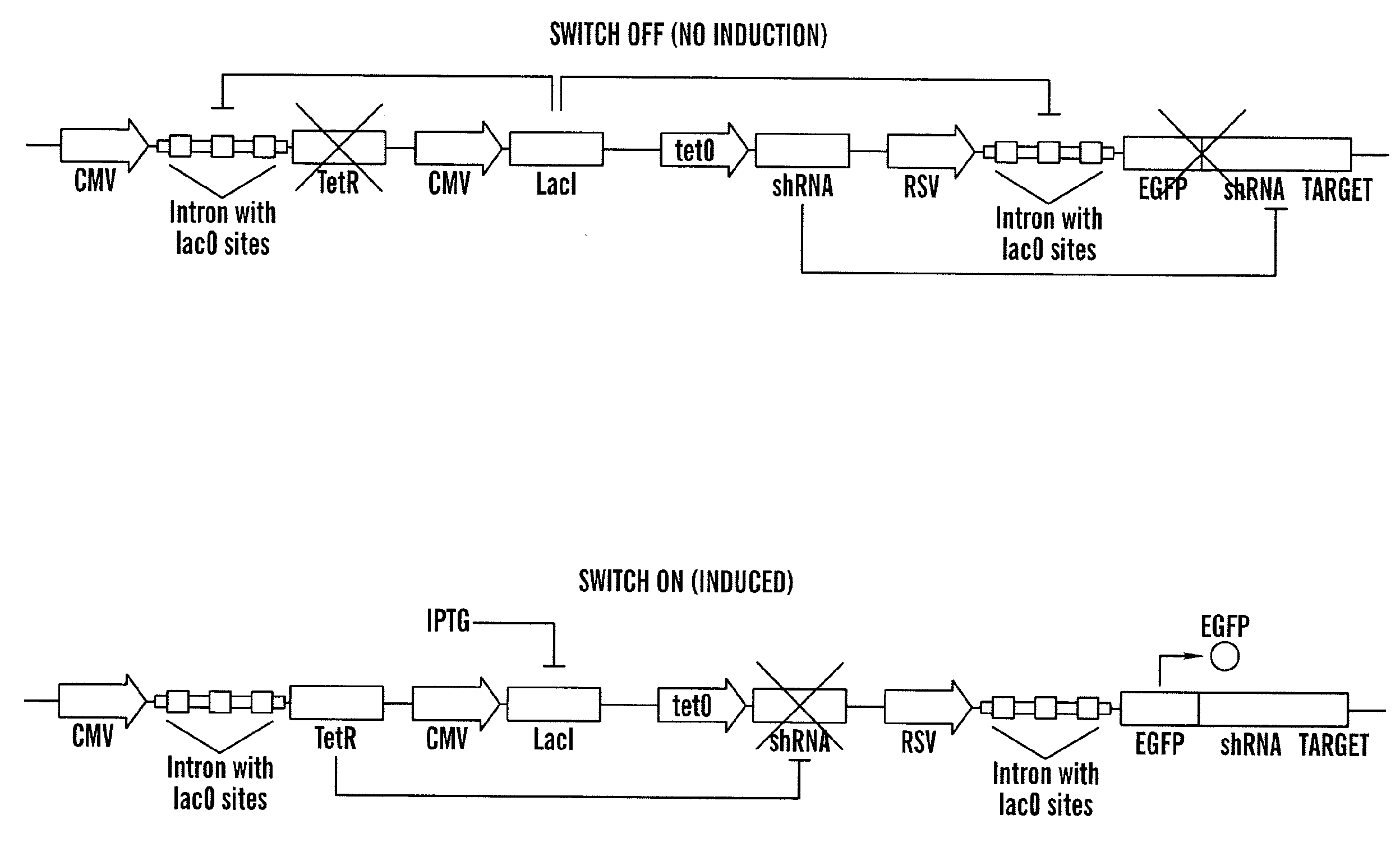
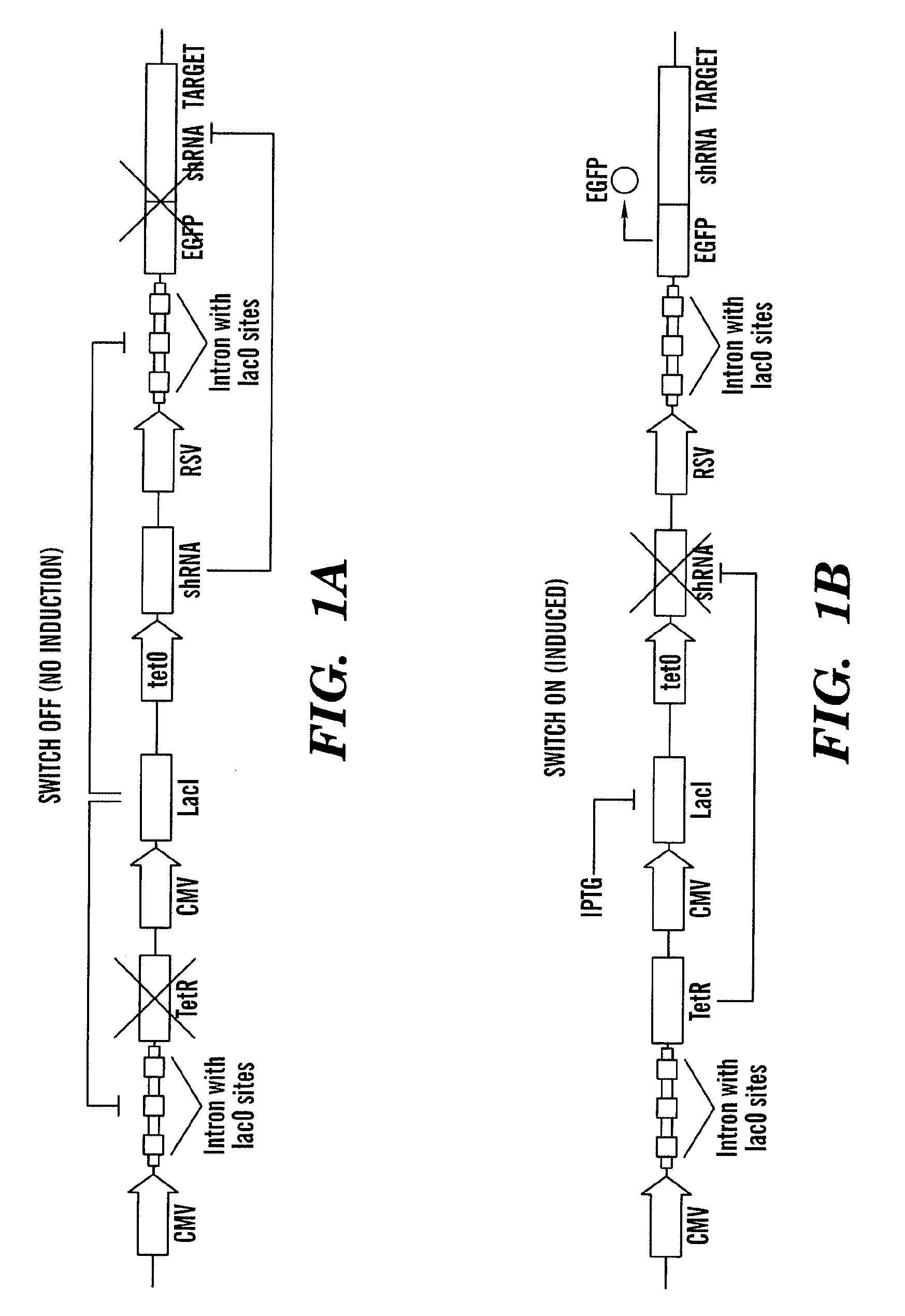
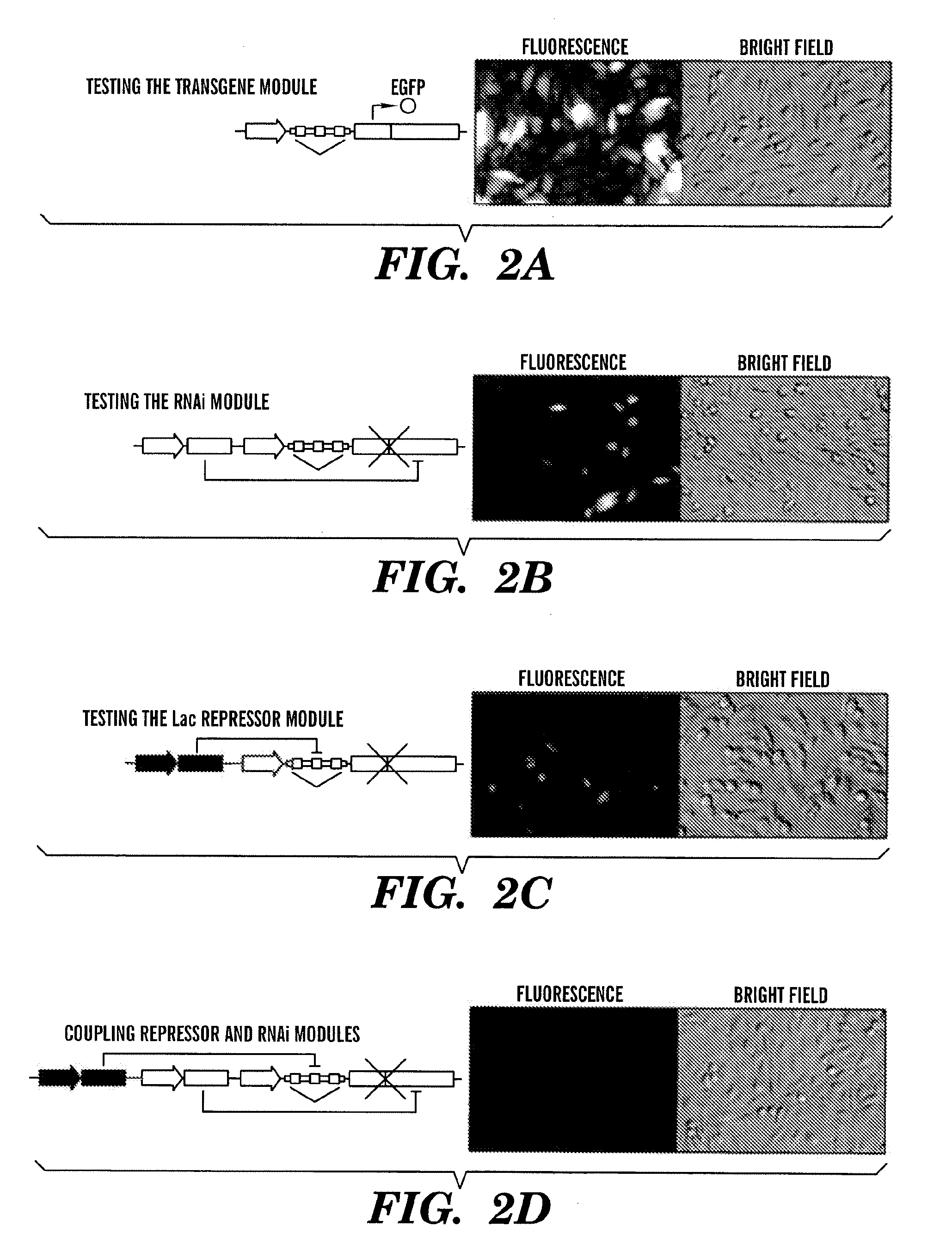
Tunable genetic switch for regulating gene expression
ActiveUS20100175141A1Eliminating background expressionInhibit expressionBiocideGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseBinding site
The present invention relates generally the field of genetics, in particular methods, compositions and systems for controlling the inducible expression of transgenes, while eliminating background expression of transgene expression. The present invention relates to methods of use of the compositions and systems as disclosed herein for controlling the inducible expression of transgenes while eliminating background expression of transgene expression, such as use in, for example, the in generation of transgenic animals, use in therapeutic application and use in assays. In some embodiments, the present invention relates to a system of controlled expression of RNAi molecules which target binding sites in the untranslated regions of transgene, thereby the expression of the transgene is modulated and leakiness is reduced. The compositions and methods of the present invention can be used to for therapy, prophylaxis, research and diagnostics in diseases and disorders which afflict mammalian species, generation of transgenic animals, in the study of biological processes as well as for enhance performance of agricultural crops.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Methods for identifying compounds that modulate untranslated region-dependent gene expression and methods of using same
InactiveUS20070111203A1Reduced stabilityReduces translation efficiencyCompound screeningPeptide librariesHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsHigh-throughput screening
The present invention relates to methods for identifying compounds that modulate untranslated region-dependent expression of a target gene. The invention particularly relates to using untranslated regions of a target gene or fragments thereof linked to a reporter gene to identify compounds that modulate untranslated region-dependent expression of a target gene. The methods of the present invention provide a simple, sensitive assay for high-throughput screening of libraries of compounds to identify pharmaceutical leads.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
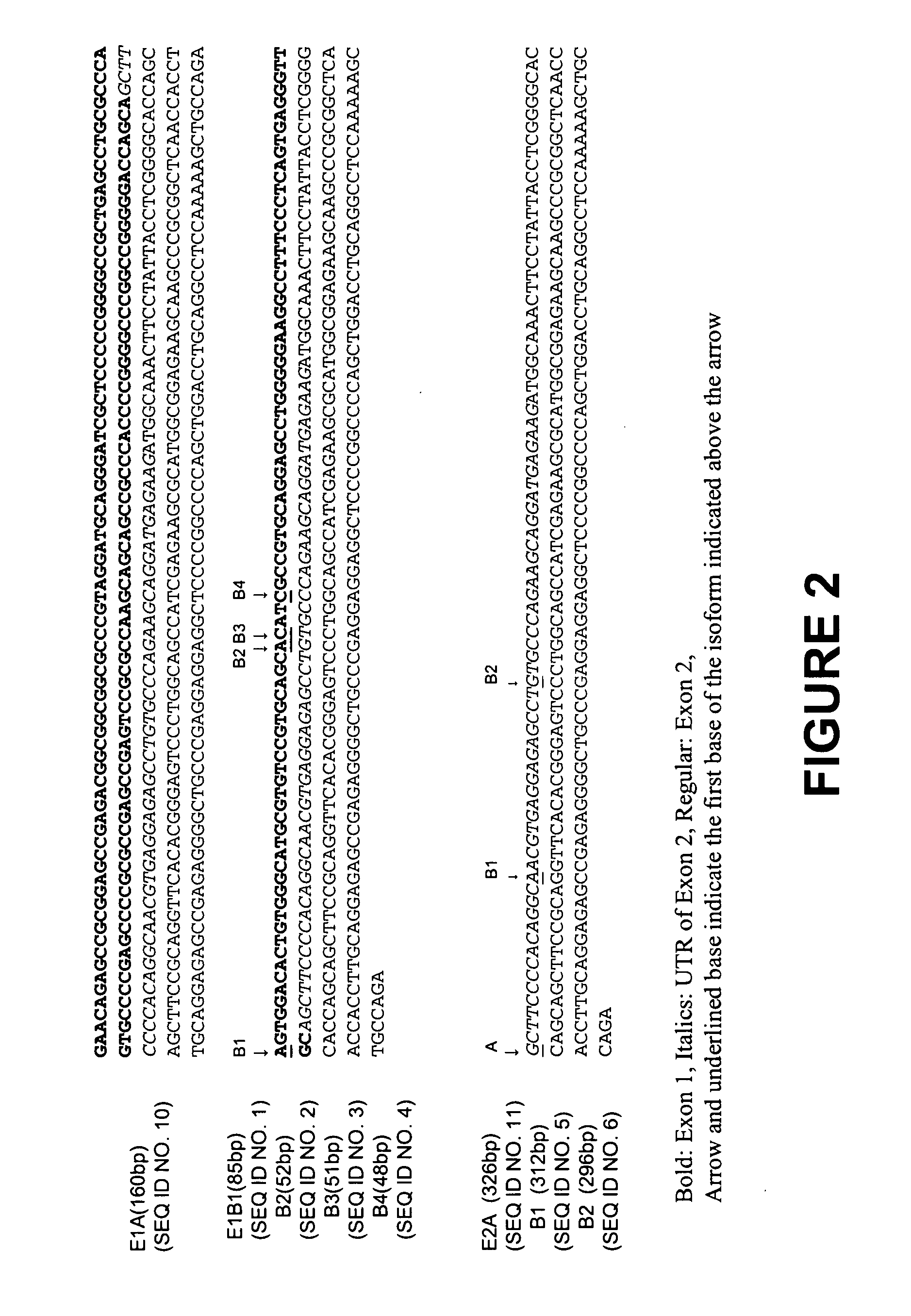
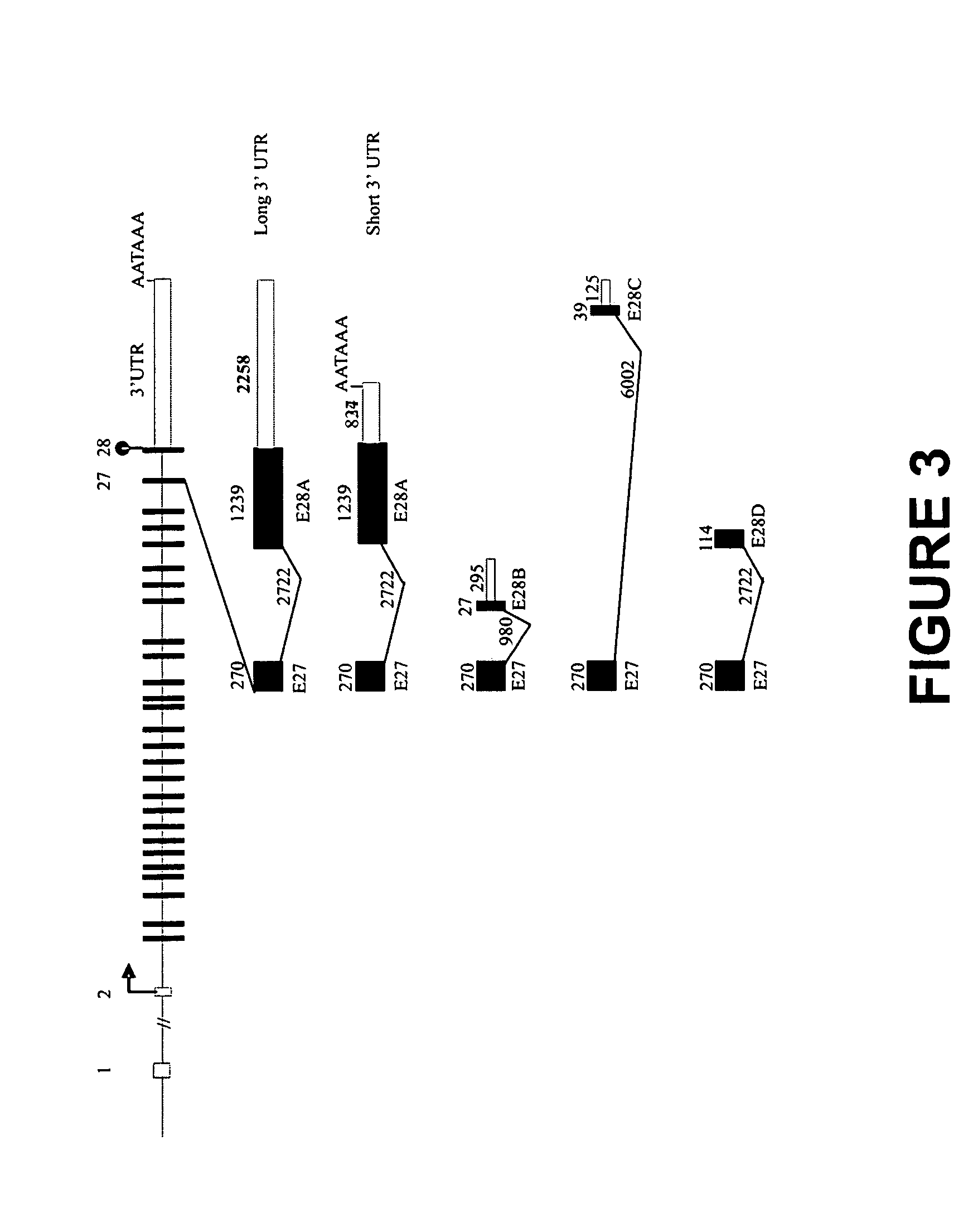
Human sodium channel isoforms
The present invention relates to novel isoforms in or near the 5′ untranslated region (upstream of the start codon) and the 3′ untranslated region (down stream of the start codon) which correlates with an increased risk of heart disease. These isoforms are various spliced variants of the wild-type sodium channel mRNA. Preferably, the isoforms that correlate with heart disease are E1B1 (SEQ ID NO. 1), E1B2 (SEQ ID NO. 2), E1B3 (SEQ ID NO. 3), E1B4 (SEQ ID NO. 4), E2B1 (SEQ ID NO. 5), E2B2 (SEQ ID NO. 6), E28B (SEQ ID NO. 7), E28C (SEQ ID NO. 8), and E28D (SEQ ID NO. 9).
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS +2
Modified Human Hepatitis C Virus Genomic RNA That can be Autonomously Replicated
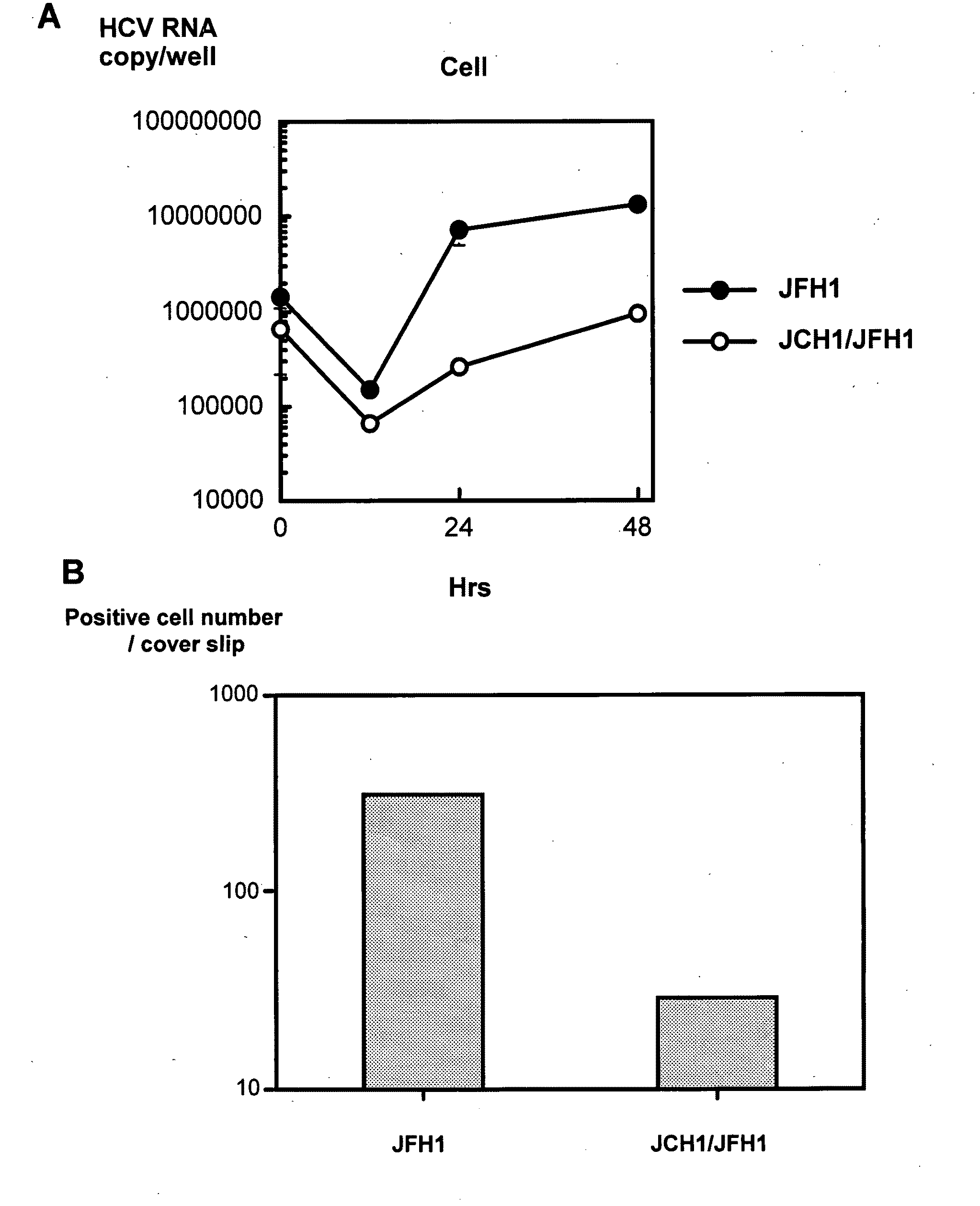
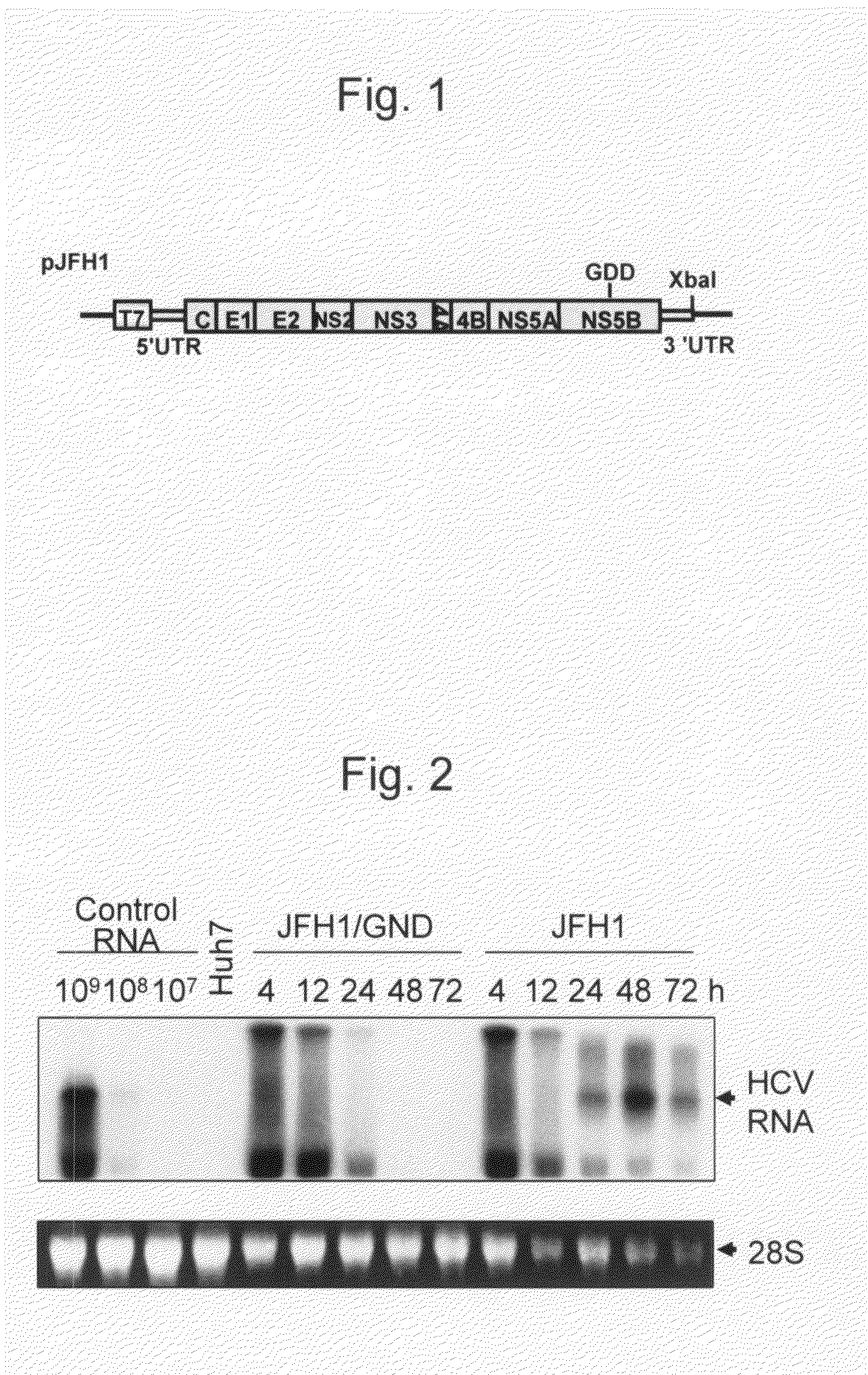
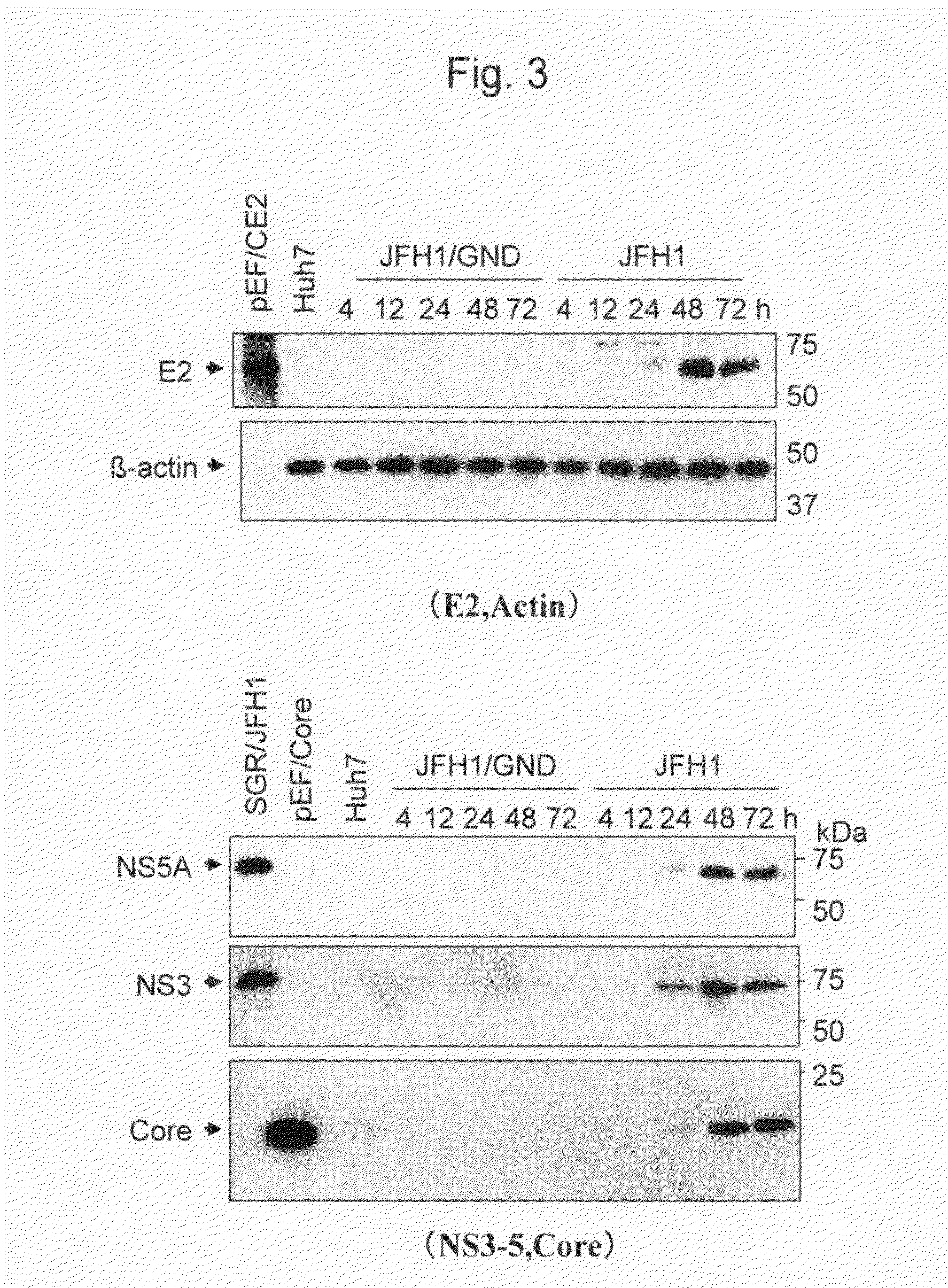
ActiveUS20090176200A1Easy to useSsRNA viruses positive-senseGenetic material ingredientsNucleotideGenetics
The present invention provides modified hepatitis C virus genomic RNA, comprising nucleotide sequences of genomic RNA portions of two or more types of hepatitis C viruses, which comprises a 5′ untranslated region, a core protein coding sequence, an E1 protein coding sequence, a p7 protein coding sequence, an E2 protein coding sequence, an NS2 protein coding sequence, an NS3 protein coding sequence, an NS4A protein coding sequence, an NS4B protein coding sequence, an NS5A protein coding sequence, an NS5B protein coding sequence, and a 3′ untranslated region, and which can be autonomously replicated. In particular, the present invention relates to modified hepatitis C virus genomic RNA, which can be autonomously replicated by substitution of the RNA sequence portion encoding NS3, NS4, NS5A, and NS5B proteins of hepatitis C virus genomic RNA with a partial RNA sequence encoding NS3, NS4, NS5A, and NS5B proteins of a JFH1 strain shown in SEQ ID NO: 1.
Owner:TORAY IND INC +1
Method for treating enterovirus or rhinovirus infection using antisense antiviral compounds
The invention provides antisense antiviral compounds and methods of their use and production in inhibition of growth of viruses of the Picornaviridae family and in the treatment of a viral infection. The compounds are particularly useful in the treatment of Enterovirus and / or Rhinovirus infection in a mammal. The antisense antiviral compounds are substantially uncharged, morpholino oligonucleotides have a sequence of 12-40 subunits, including at least 12 subunits having a targeting sequence that is complementary to a region associated with viral RNA sequences within a 32 nucleotide region of the viral 5′ untranslated region identified by SEQ ID NO:7.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
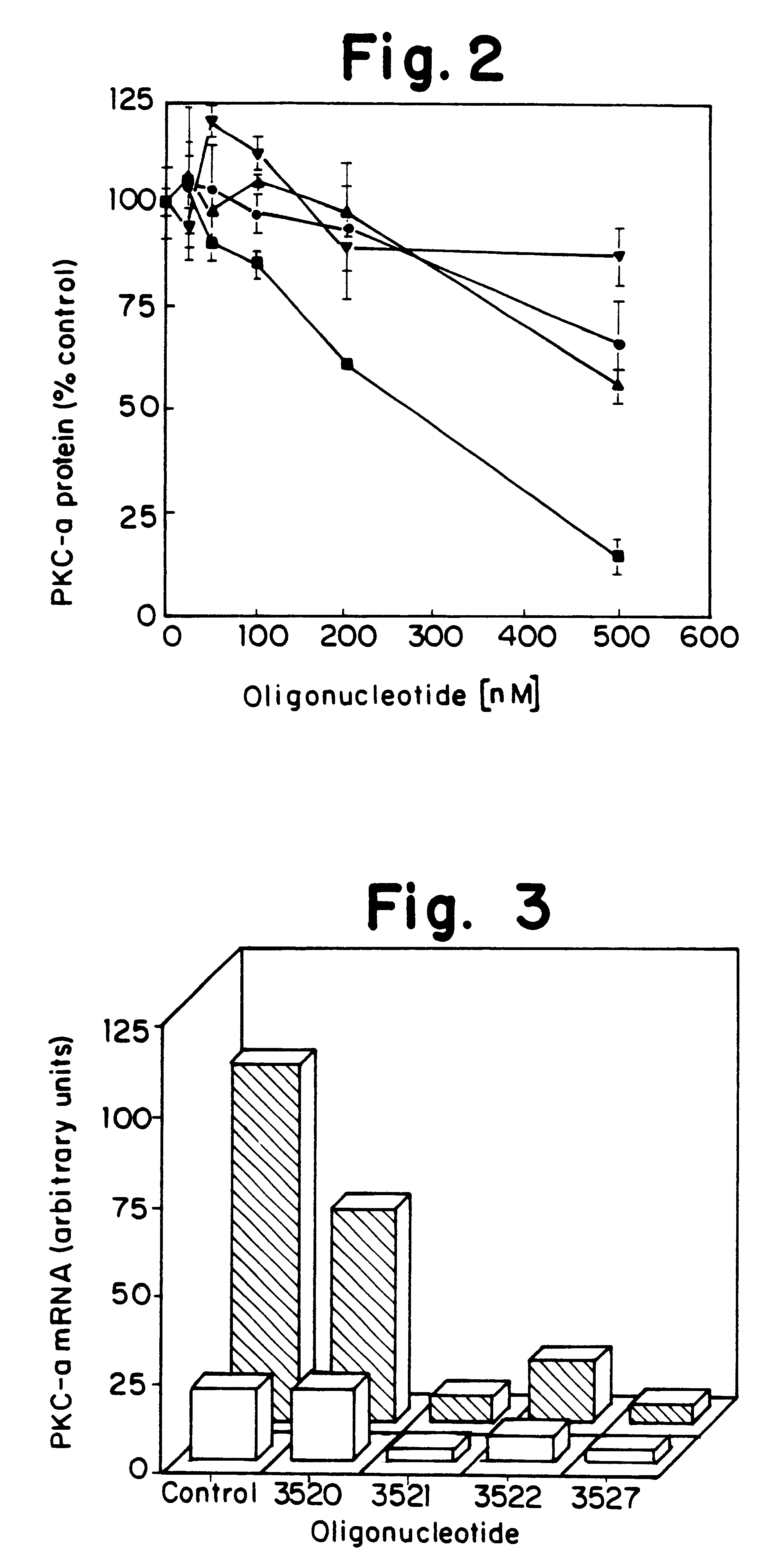
Antisense oligonucleotides which have phosphorothioate linkages of high chiral purity and which modulate betaI, betaII, gamma, delta, Ε, ζ and eta isoforms of human protein kinase C
InactiveUS6339066B1Modulate its functionImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsDiseasePkc delta
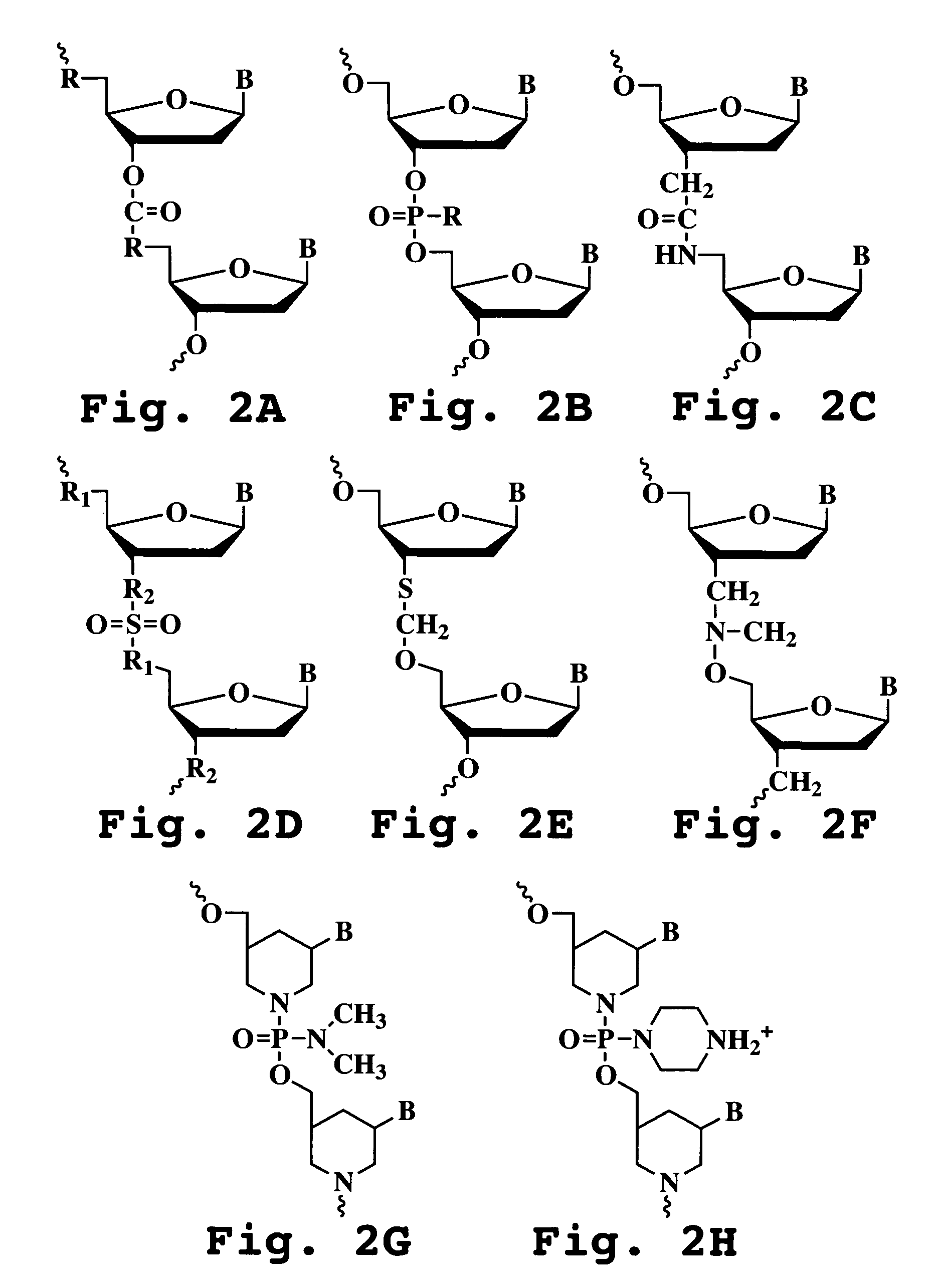
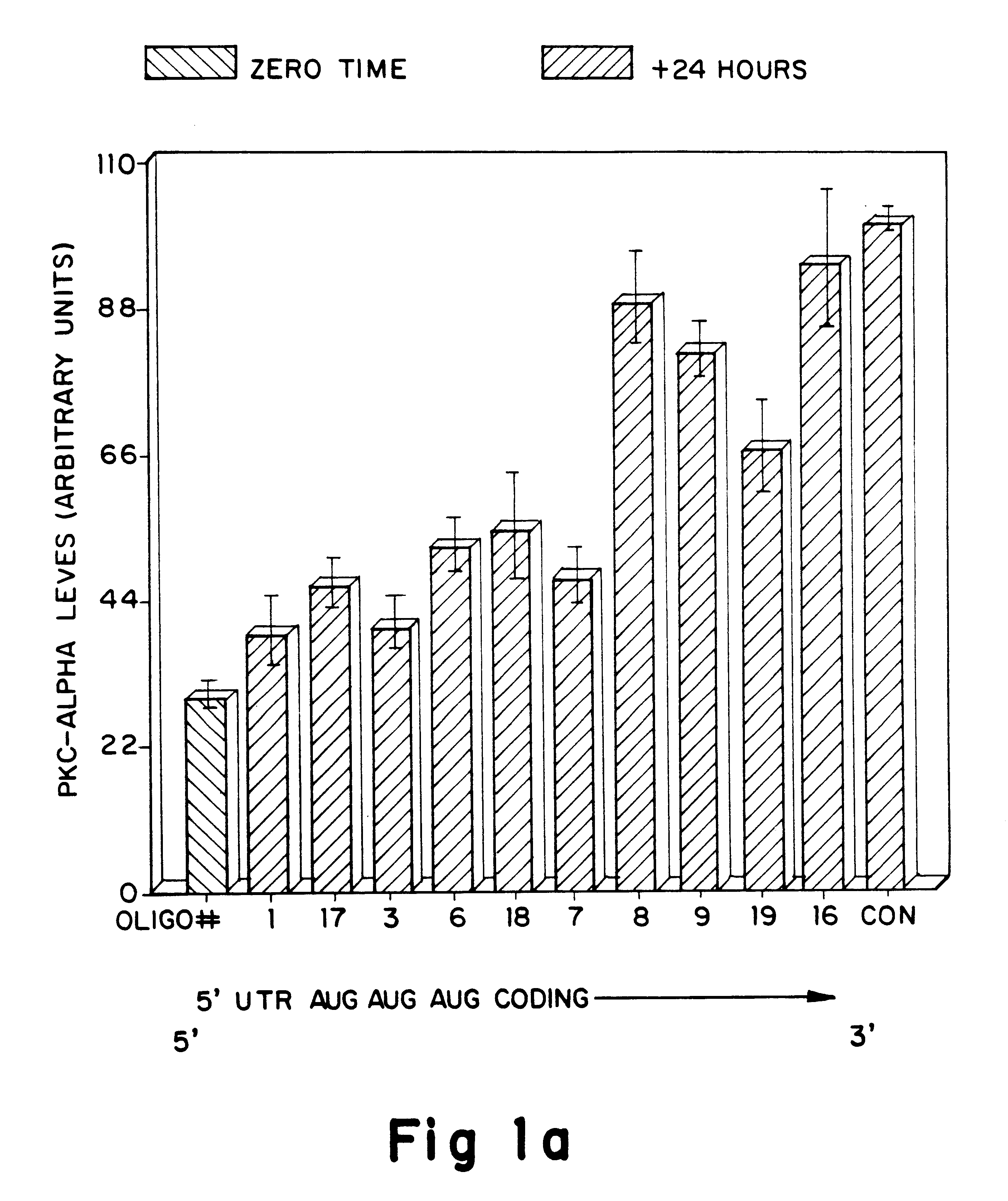
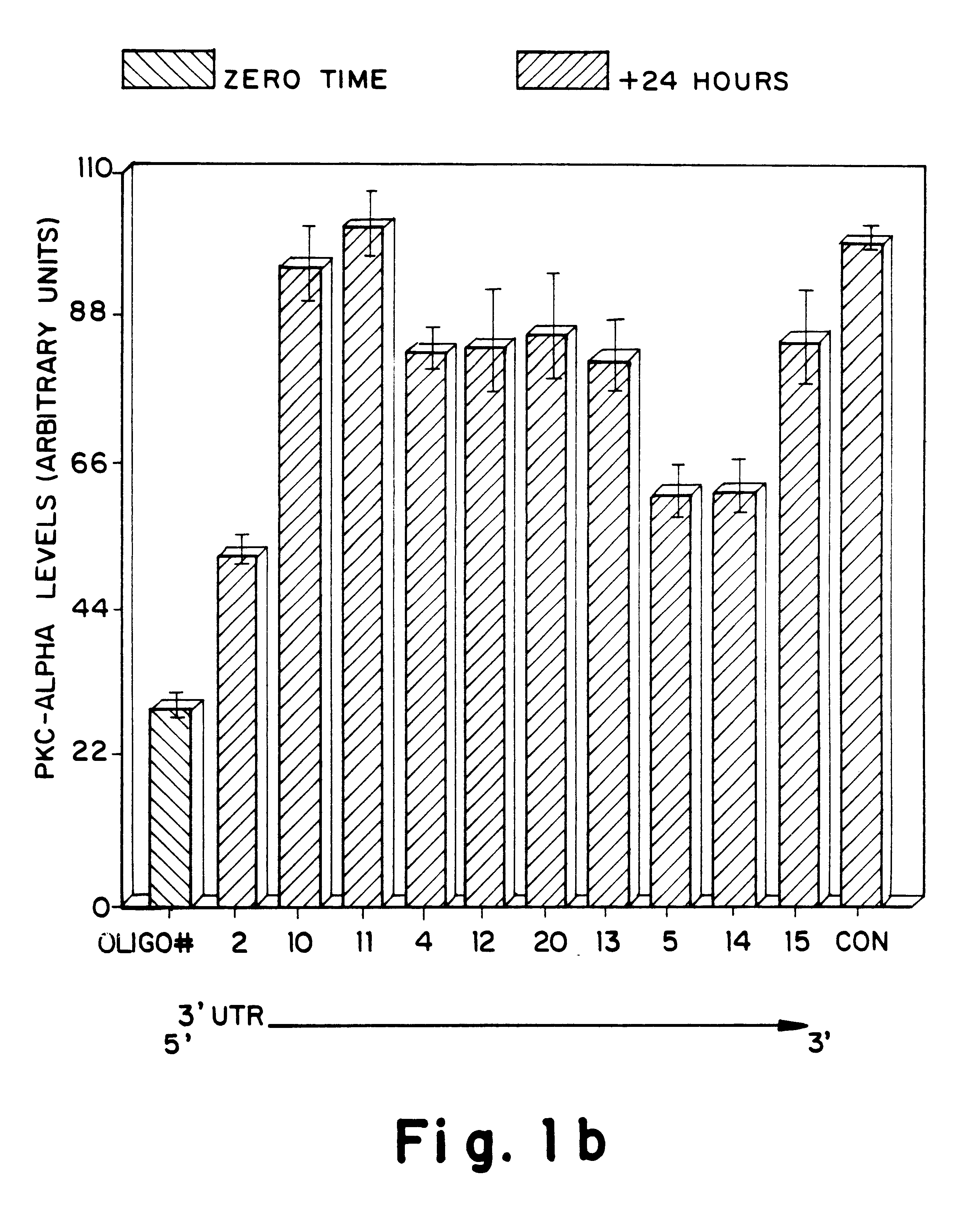
Compositions and methods are provided for the treatment and diagnosis of diseases associated with the expression of one or more of the betaI, betaII, gamma, delta, epsi, ζ or eta isoforms (isozymes) of protein kinase C (PKC). Oligonucleotides are provided which are targeted to nucleic acids encoding PKC-betaI, PKC-betaII, PKC-gamma, PKC-delta, PKC-epsi, PKC-ζ or PKC-eta. Provided herein are oligonucleotides specifically hybridizable with a translation initiation site, 5'-untranslated region, 3'-untranslated region or other targeted region of a betaI, betaII, gamma, delta, epsi, ζ or eta isoform of PKC, wherein at least about 75% of the nucleoside units of a given oligonucleotide are joined together by a stereospecific (i.e., Sp or Rp) phosphorothioate 3' to 5' linkages. In preferred embodiments, the oligonucleotides of the disclosure additionally contain one or more chemical modifications. Also disclosed are methods of using the oligonucleotides of the invention for modulating the expression of at least one of the betaI, betaII, gamma, delta, epsi, ζ or eta isoforms of PKC and for treating animals suffering from disease amenable to therapeutic intervention by modulating the expression of one or more of the betaI, betaII, gamma, delta, epsi, ζ or eta isoforms of PKC.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
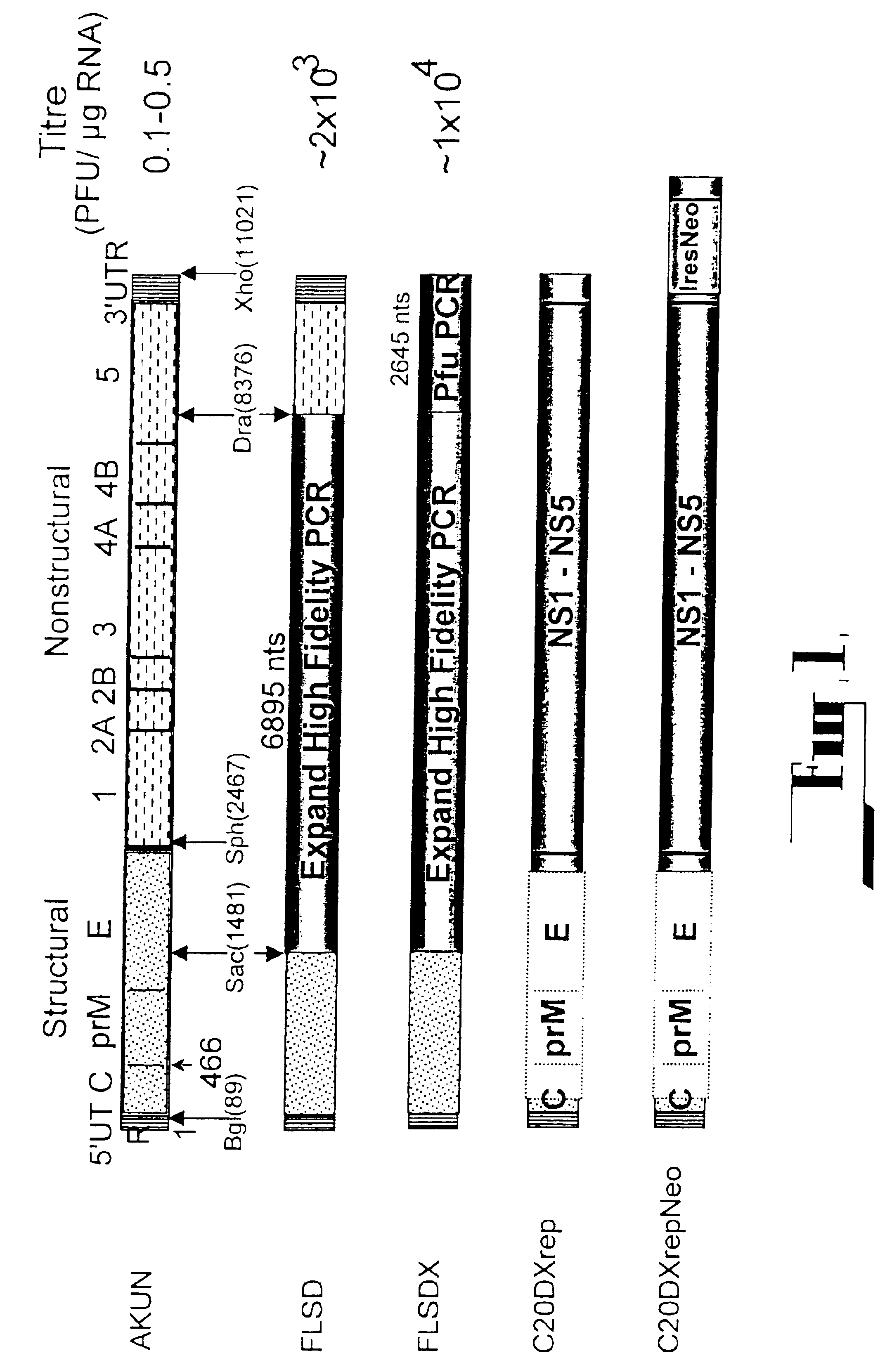
Flavivirus expression and delivery system
InactiveUS6893866B1High expressionImprove translation efficiencySsRNA viruses positive-senseVectorsNucleotideStructural protein
The present invention provides a gene expression system comprising: a) a self-replicating expression vector of flavivirus origin which includes the flavivirus 5′ untranslated region (UTR), at least a portion of the 5′ coding region for flavivirus core protein, the nucleotide sequence coding for the flavivirus non-structural proteins, and the complete or most of the 3′-terminal sequence of the flavivrus 3′UTR, required for self-replication of flavivirus genomic material, which vector is adapted to receive at least a nucleotide sequence without disrupting its replication capabilities; and b) at least a second vector that is capable of expressing flavivirus structural protein(s) and any other proteins required for packaging of the self-replicating expression vector into flavivirus viral particles which vector is engineered to prevent recombination with the self-replicating vector when in its presence.
Owner:REPLIKUN BIOTECH
SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) molecular marker related with back fat thickness trait of pig and detection method of SNP molecular marker
ActiveCN105255870AEarly detectionQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEnzyme digestionNucleotide
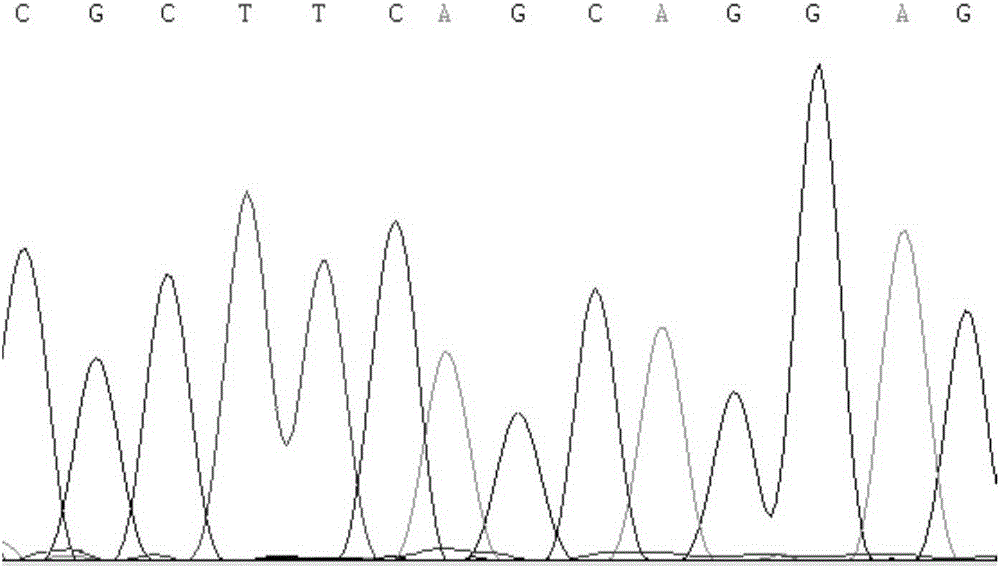
The invention provides an SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) molecular marker related with a back fat thickness trait of a pig and a detection method of the SNP molecular marker. By detecting exon regions of MARK4 (Microtubule Affinity-Regulating Kinase) genes of different pig species, one SNP locus (G-A) is found to exist at 55th basic group (mRNA (Messenger Ribonucleic Acid) total-length 2581th base group) in 3 minute UTR (Untranslated Region) of the MARK4 gene, an allele A is positively correlated with low back fat trait, and an allele G is positively correlated with high back fat trait. The invention provides the method for detecting the SNP molecular marker. Pig genomic DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) to be detected is amplified by using a primer pair with the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1-2 and is subjected to enzyme digestion by using pstI; if an enzyme-digested product is 251bp, a base group at a mutation is A; if the enzyme-digested product is 218bp, a base group at the mutation is G. According to the method provided by the invention, the back fat thickness of the pig can be predicted early, quickly and effectively at low cost; the SNP molecular marker can be used as a useful molecular marker for genetic improvement of the pig species.
Owner:湘潭市家畜育种站
Cis/trans riboregulators
ActiveUS20070136827A1Easy to controlInhibition of translationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOpen reading frameBinding site
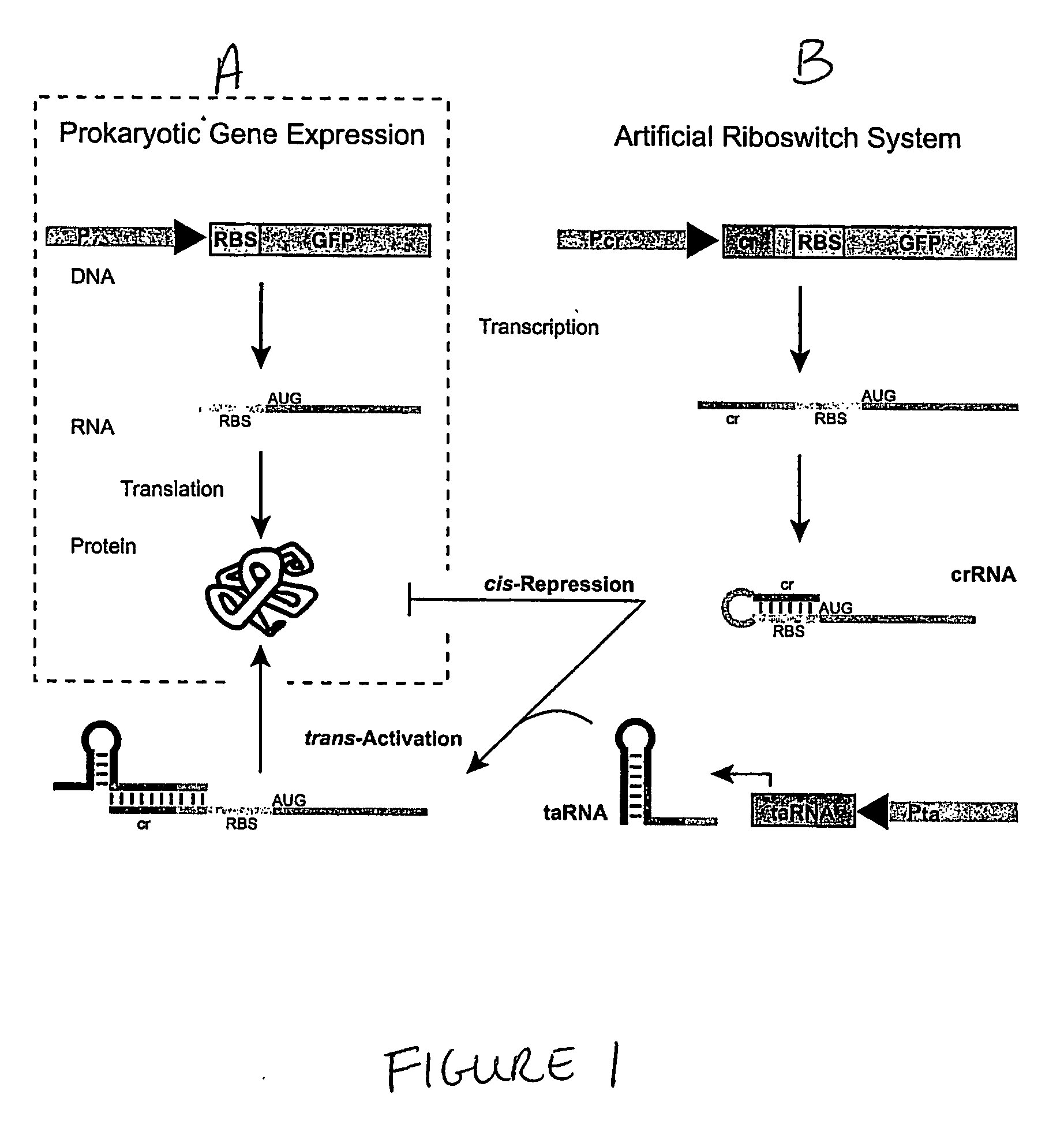
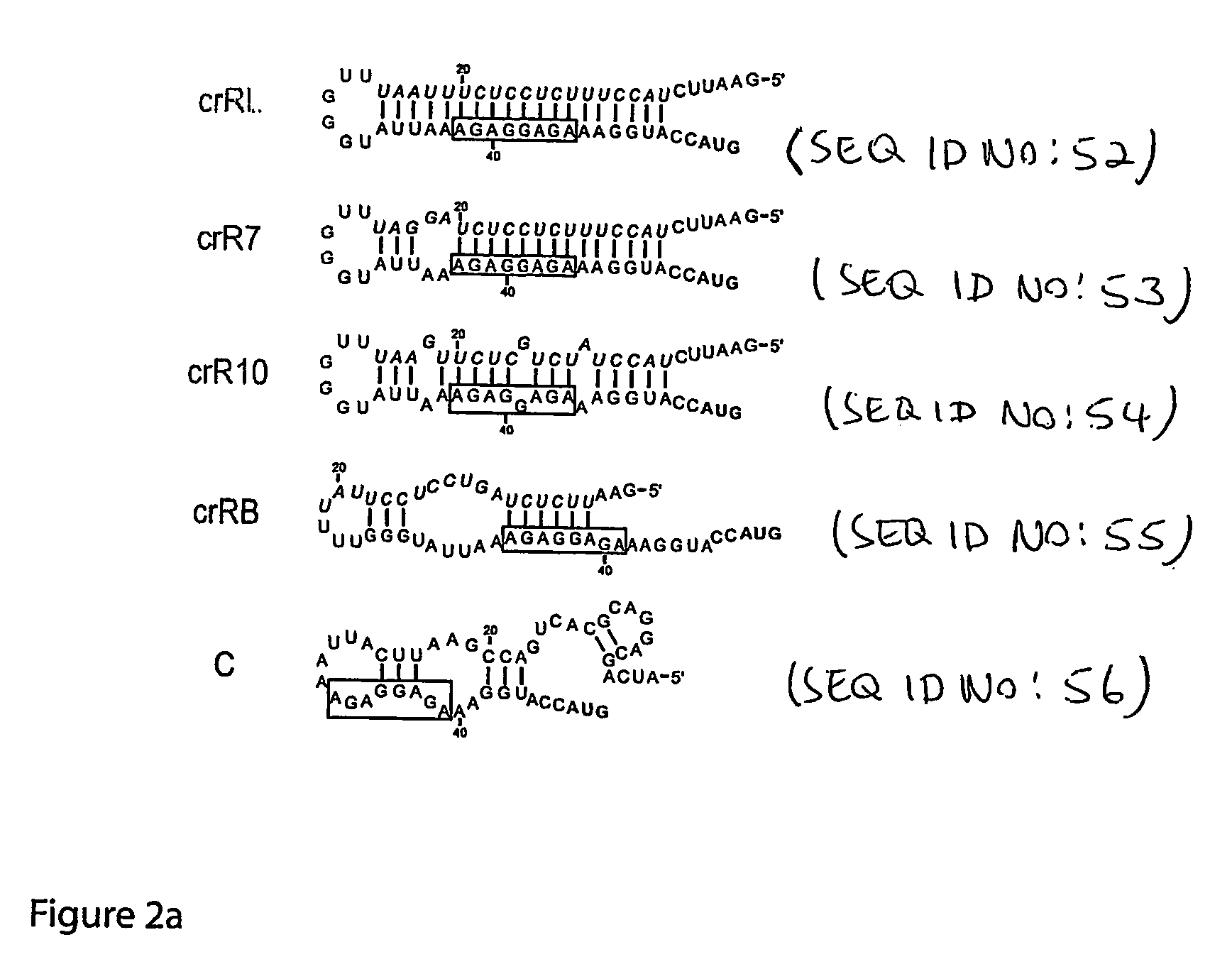
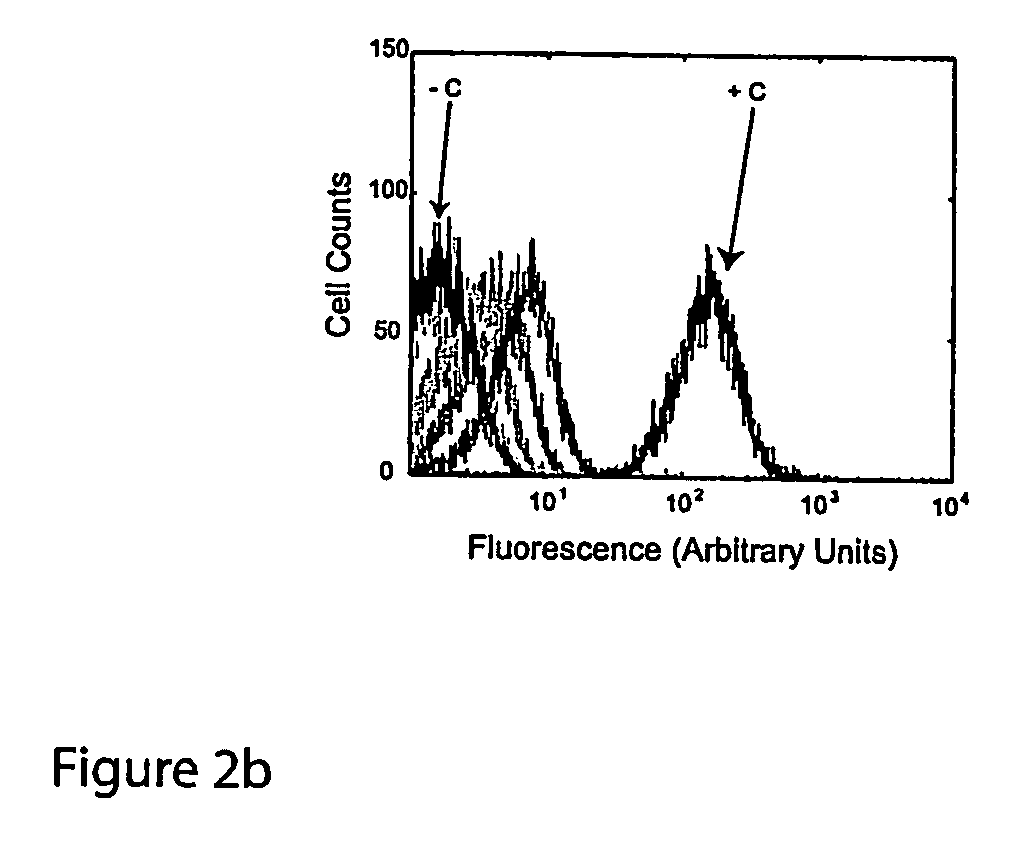
The present invention provides nucleic acid molecules, DNA constructs, plasmids, and methods for post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression using RNA molecules to both repress and activate translation of an open reading frame. Repression of gene expression is achieved through the presence of a regulatory nucleic acid element (the cis-repressive RNA or crRNA) within the 5′ untranslated region (5′ UTR) of an mRNA molecule. The nucleic acid element forms a hairpin (stem / loop) structure through complementary base pairing. The hairpin blocks access to the mRNA transcript by the ribosome, thereby preventing translation. In particular, in embodiments of the invention designed to operate in prokaryotic cells, the stem of the hairpin secondary structure sequesters the ribosome binding site (RBS). In embodiments of the invention designed to operate in eukaryotic cells, the stem of the hairpin is positioned upstream of the start codon, anywhere within the 5′ UTR of an mRNA. A small RNA (trans-activating RNA, or taRNA), expressed in trans, interacts with the crRNA and alters the hairpin structure. This alteration allows the ribosome to gain access to the region of the transcript upstream of the start codon, thereby activating transcription from its previously repressed state.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
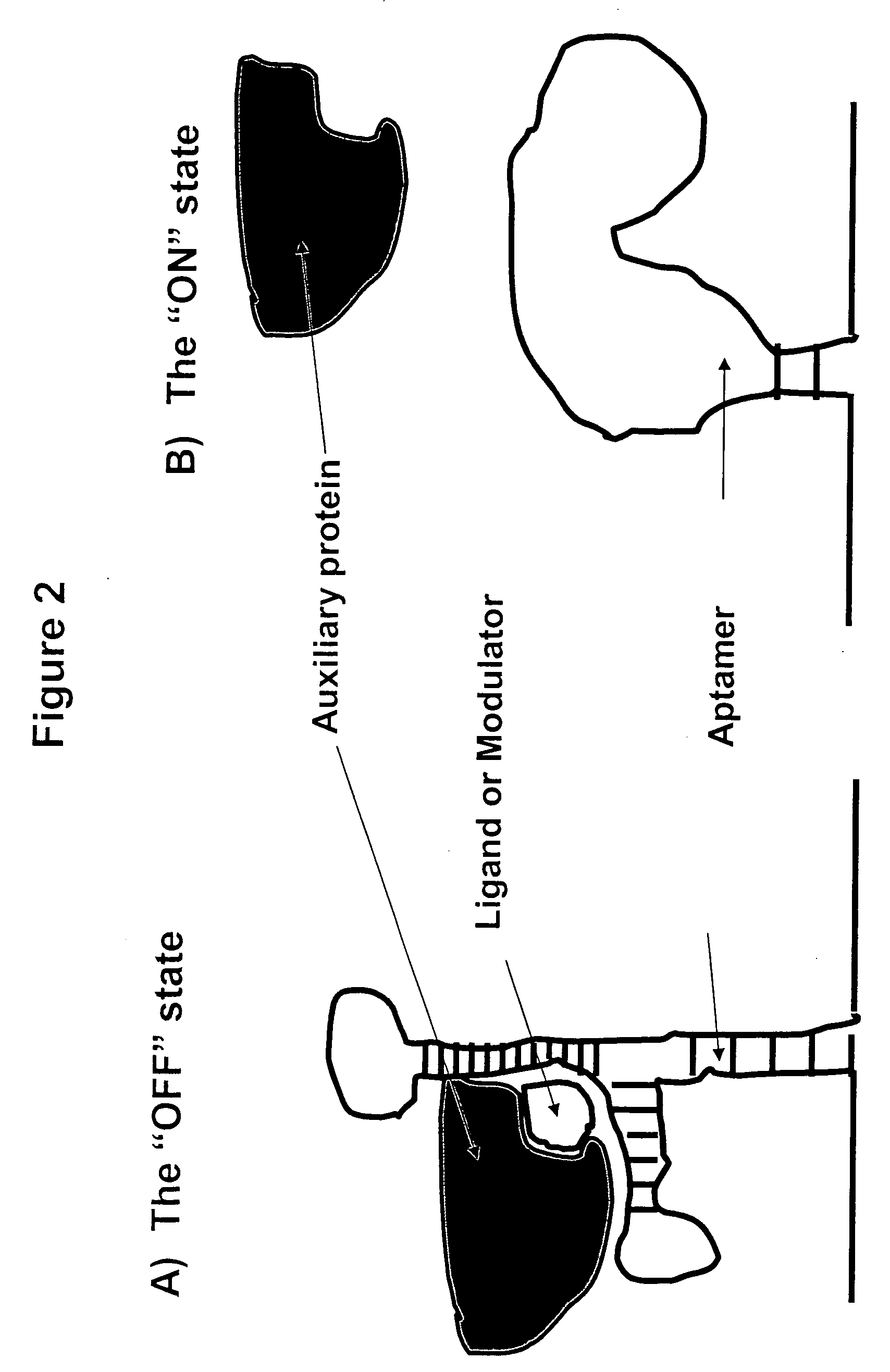
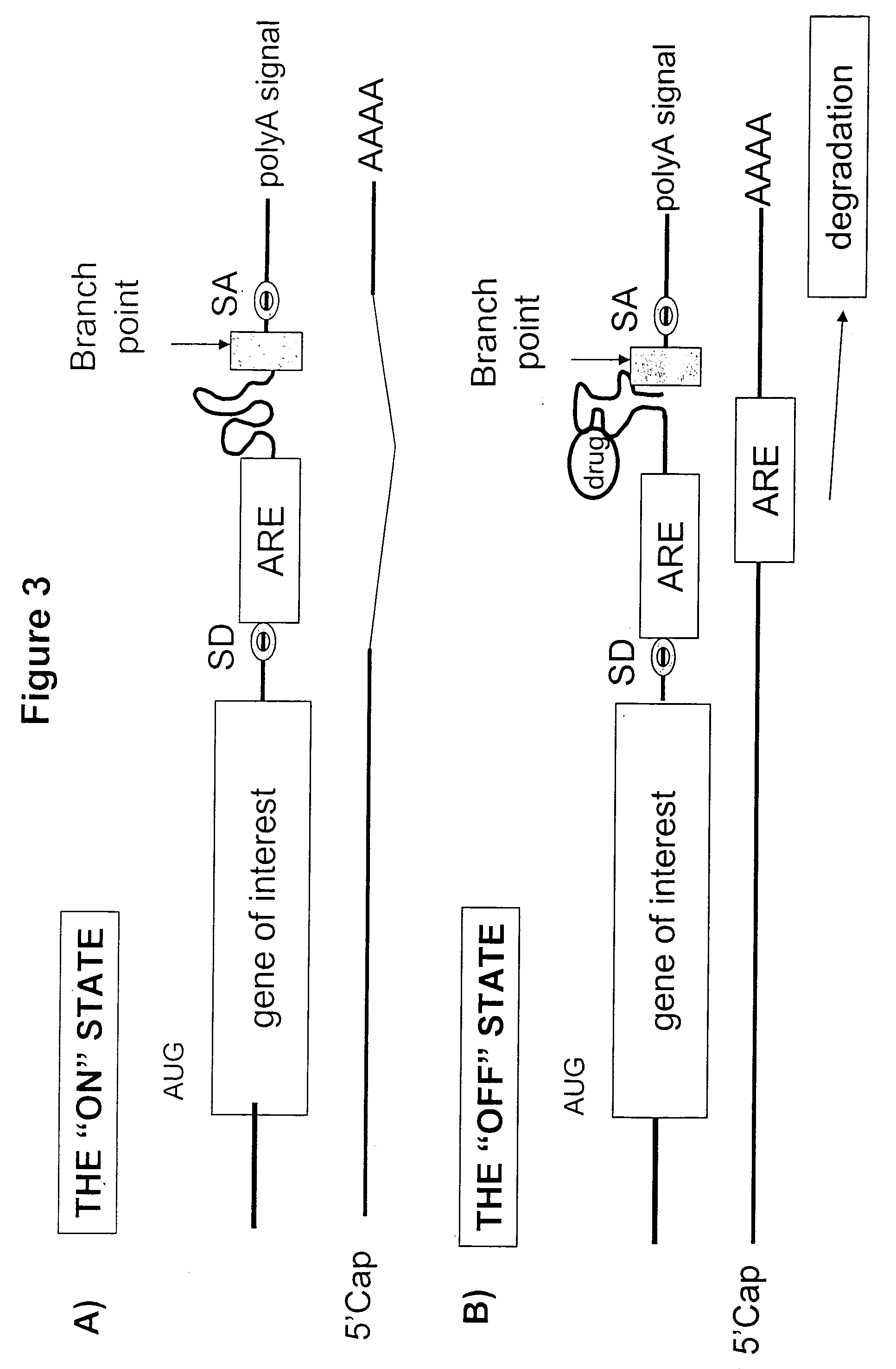
Gene regulation with aptamer and modulator complexes for gene therapy
Provided is an improved method for controlling gene expression in vivo through the use of a gene switch comprising one or more aptamer sequences operably linked to or incorporated into the untranslated regions (UTRs) of a transgene or nucleotide sequence of interest. Also provided are expression vectors having aptamer sequences located within the 3′ UTR, the 5′ UTR and between the genes of a multicistronic mRNA, as well as methods of using the expression vectors for controlling or regulating gene expression.
Owner:JOLLY DOUG +4
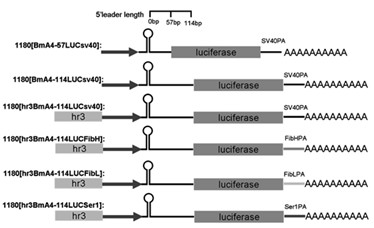
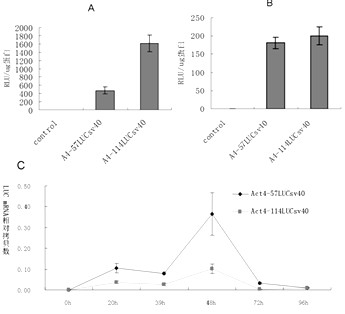
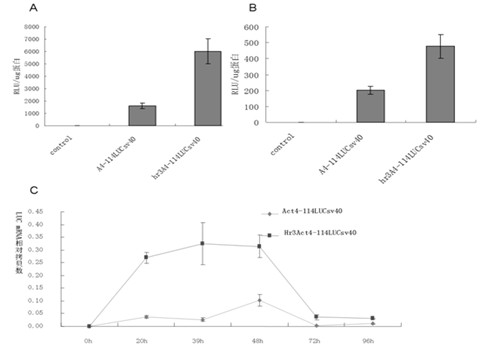
Enhancer Hr3
ActiveCN102492692AIncrease transcriptional activityImprove expression levelVector-based foreign material introductionDNA preparationRestriction sitePromoter
The invention relates to enhancer Hr3 adopting the nucleotide sequence shown in the SEQIDNO: 1. The enhancer Hr3 can be used for preparing and recombining heterologous protein by bombyx mori. The invention further relates to a recombination carrier containing the enhancer Hr3, and the recombination carrier is prepared in such a manner that the enhancer Hr3 is connected with a Nco1 restriction site at the upstream of a promoter of a carrier containing no enhancer through the Nco1 restriction site of the enhancer Hr3. In the invention, functional elements such as the first grade enhancer, activating transcription factor IE1, untranslated region sequences (5' UTR and 3' UTR) and the like which are expressed by intensifier are identified in the cellular level, and an efficient and stable sericin I expression system is built by integrating optimum elements on the basis, so that efficient expression recombination heterologous protein can be made of middle silk gland of transgenic bombyx mori.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Cold-inducible expression vector
InactiveUS6479260B1Improve efficiencyAppropriate useSugar derivativesDepsipeptidesCancer researchRegulatory region
A vector which is characterized in containing each of the following elements:(1) a promoter which shows its action in the host to be used;(2) regulatory region for regulating the action of the promoter of (1); and(3) a region which codes for the 5'-untranslated region derived from cold-shock protein gene mRNA or a region which codes for the region where substitution, deletion, insertion or addition of at least one base is applied to the said untranslated region.
Owner:TAKARA HOLDINGS
Methods for Detecting The Presence of Expanded CGG Repeats in the FMR1 Gene 5' Untranslated Region
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Antisense antiviral compound and method for treating picornavirus infection
The invention provides antisense antiviral compounds and methods of their use and production in inhibition of growth of viruses of the Picornaviridae family and in the treatment of a viral infection. The compounds are particularly useful in the treatment of Enterovirus and / or Rhinovirus infection in a mammal. The antisense antiviral compounds are substantially uncharged, including partially positively charged, morpholino oligonucleotides have a sequence of 12-40 subunits, including at least 12 subunits having a targeting sequence that is complementary to a region associated with viral RNA sequences within a 32 nucleotide region of the viral 5′ untranslated region identified by SEQ ID NO:4.
Owner:AVI BIOPHARMA
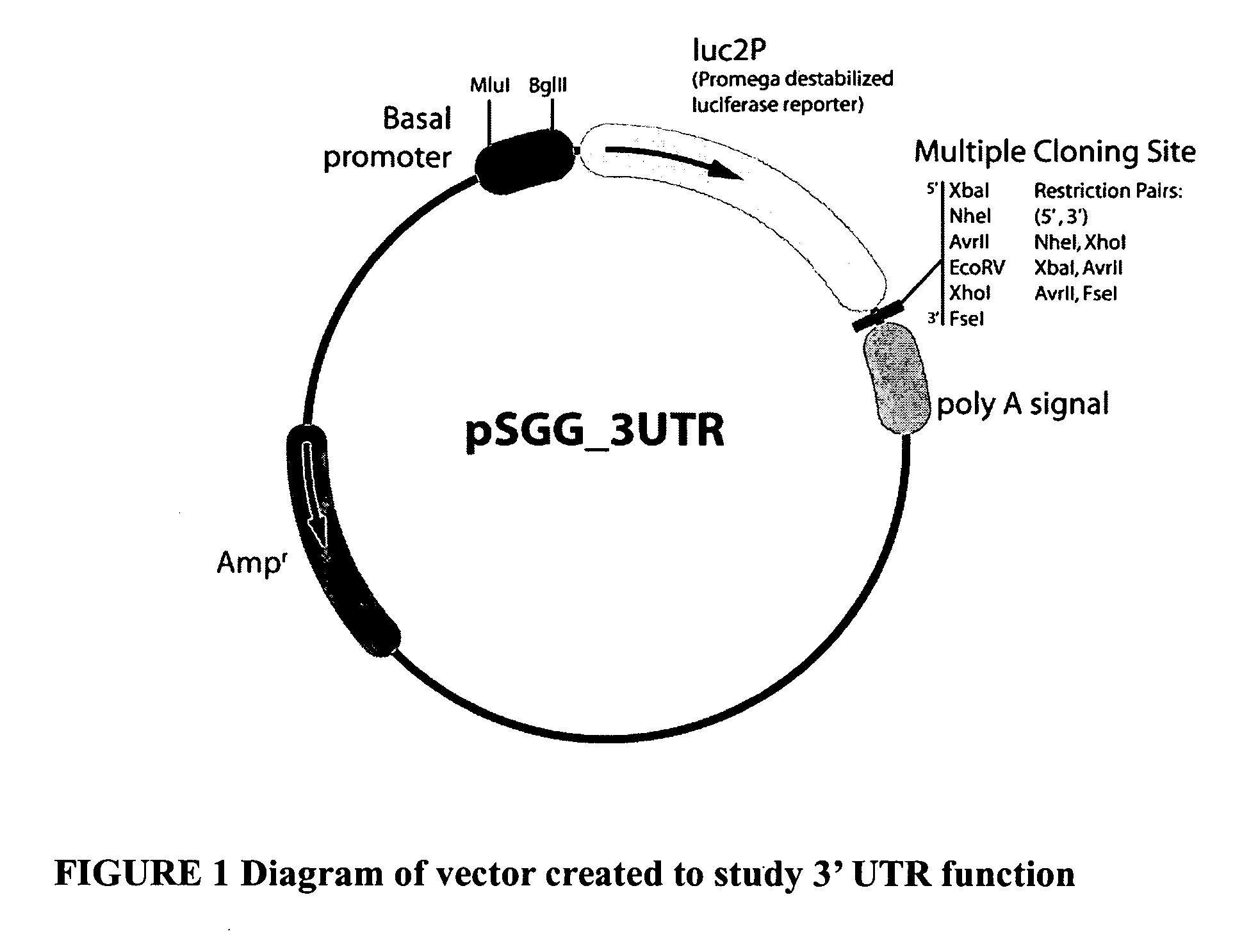
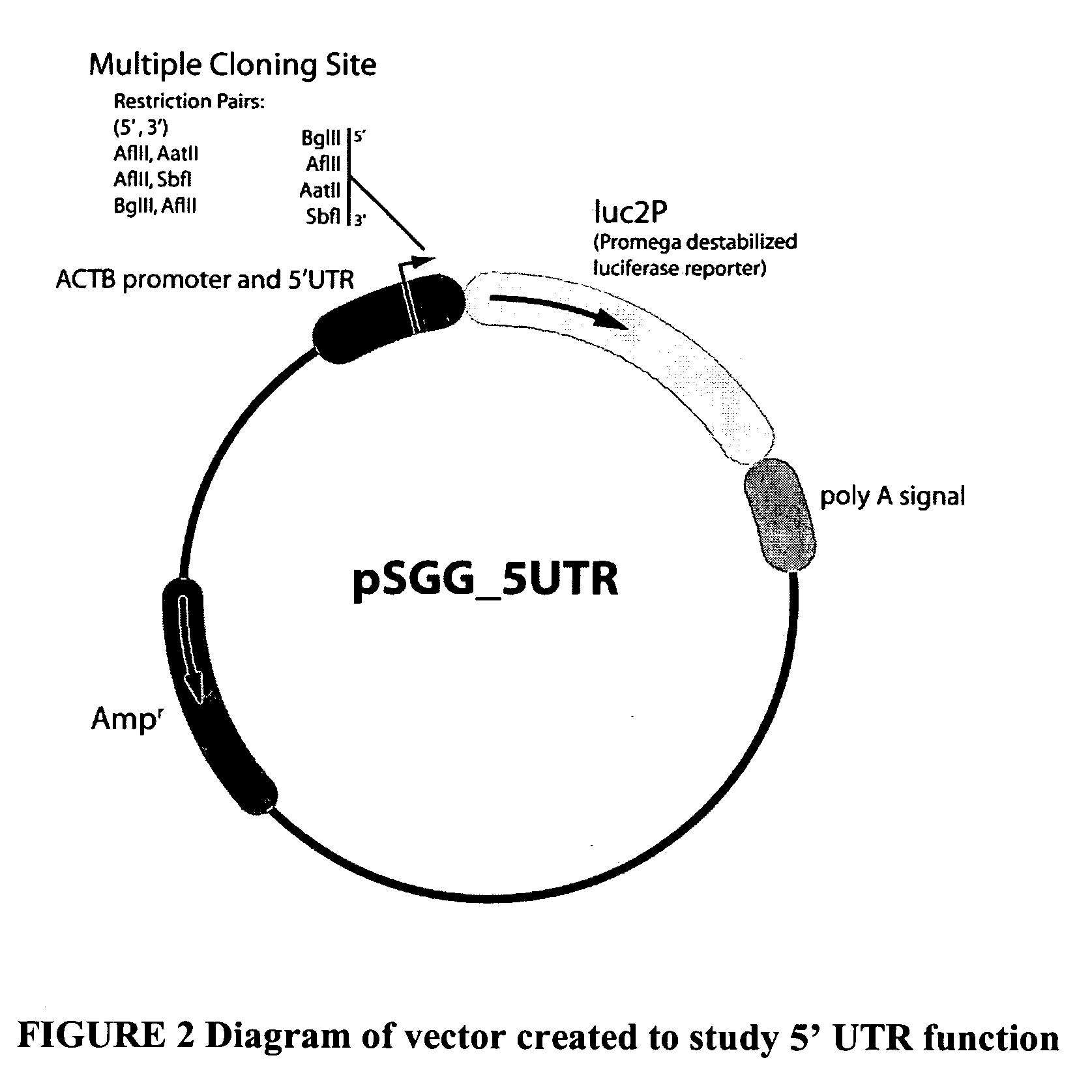
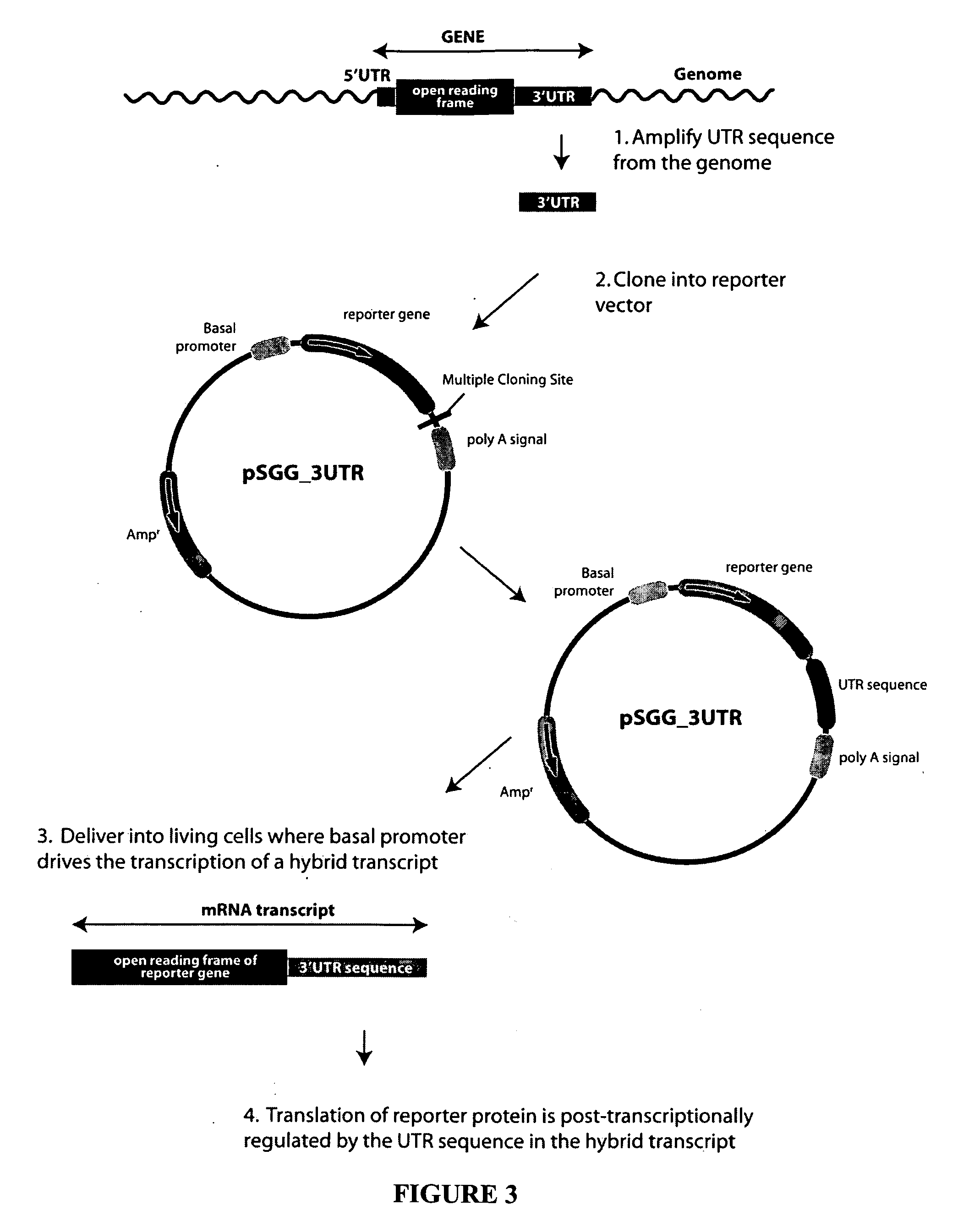
Functional arrays for high throughput characterization of regulatory elements in untranslated regions of genes
InactiveUS20080220983A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementTrans-regulatory elementOpen reading frame
This invention provides libraries of expression constructs having different untranslated regions (UTR) from a genome. The expression constructs include transcription regulatory sequences operably linked with a reporter gene and a 5′ UTR, a 3′ UTR or both, wherein the translation of the reporter gene is under the regulatory control of control regions in the UTR sequence. The libraries of this invention are useful for determining the impact of regulatory sequences in the UTRs on translation of open reading frames under a variety of conditions, such as different cellular environments.
Owner:SWITCHGEAR GENOMICS
Genetic marker related to porcine semen quality traits and application
The present invention belongs to the technical field of screening and application of pig genetic markers, and in particular relates to a genetic marker related to porcine semen quality traits and application, the genetic marker is a gene obtained by cloning of a pig RNF4 gene 3 'untranslated region, the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) can be used as a genetic marker of the porcine semen quality traits, a nucleotide sequence of the genetic marker is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 3 or SEQ ID NO: 4, the sequence SEQ ID NO: 3 or SEQ ID NO: 4 has an allelic gene mutation at 487bp, and AluI-RFLP polymorphism is caused by the allelic gene mutation. Screening step of the method are as follows: extraction of genomic DNA from pig blood, primer design, PCR amplification, PCR product cloning, sequencing, sequence comparing analysis, single nucleotide polymorphism detection, marking and semen quality trait correlation analysis. The genetic marker can be used in pig marker assisted selection.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Primers, kit and method for detection of human BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutation
ActiveCN105586427AStrong specificityStrong targetingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationInteinMicrobiology
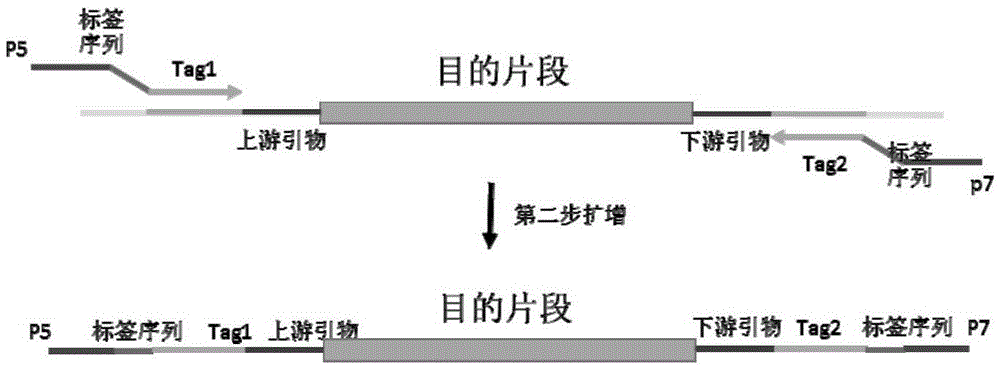
The invention discloses primers, a kit and a method for detection of human BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutation. The upstream primers are in a sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 1,3,5,7,9-193, and meanwhile the universal primer Tag1 is added to the 5' end of the sequence; the downstream primers are in a sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 2,4,6,8,10-194, and meanwhile the universal primer Tag2 is added to the 5' end of the sequence. The upstream primers with a P5 sequence and a sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 221-236 and the downstream primers with a P7 sequence and a sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 197-220 are also included. Through the primers, the kit and the method, mutation of all exons of BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, a connection region between the exons and introns, an untranslated region and a promoter region can be detected rapidly, accurately, easily and conveniently.
Owner:AMOY DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
METHODS FOR REGULATION OF p53 TRANSLATION AND FUNCTION
ActiveUS20090149377A1Reducing and eliminating p53-dependent neuronal deathSuppressing tissue agingPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsRibosomal proteinP53 Tumor Suppressor Protein
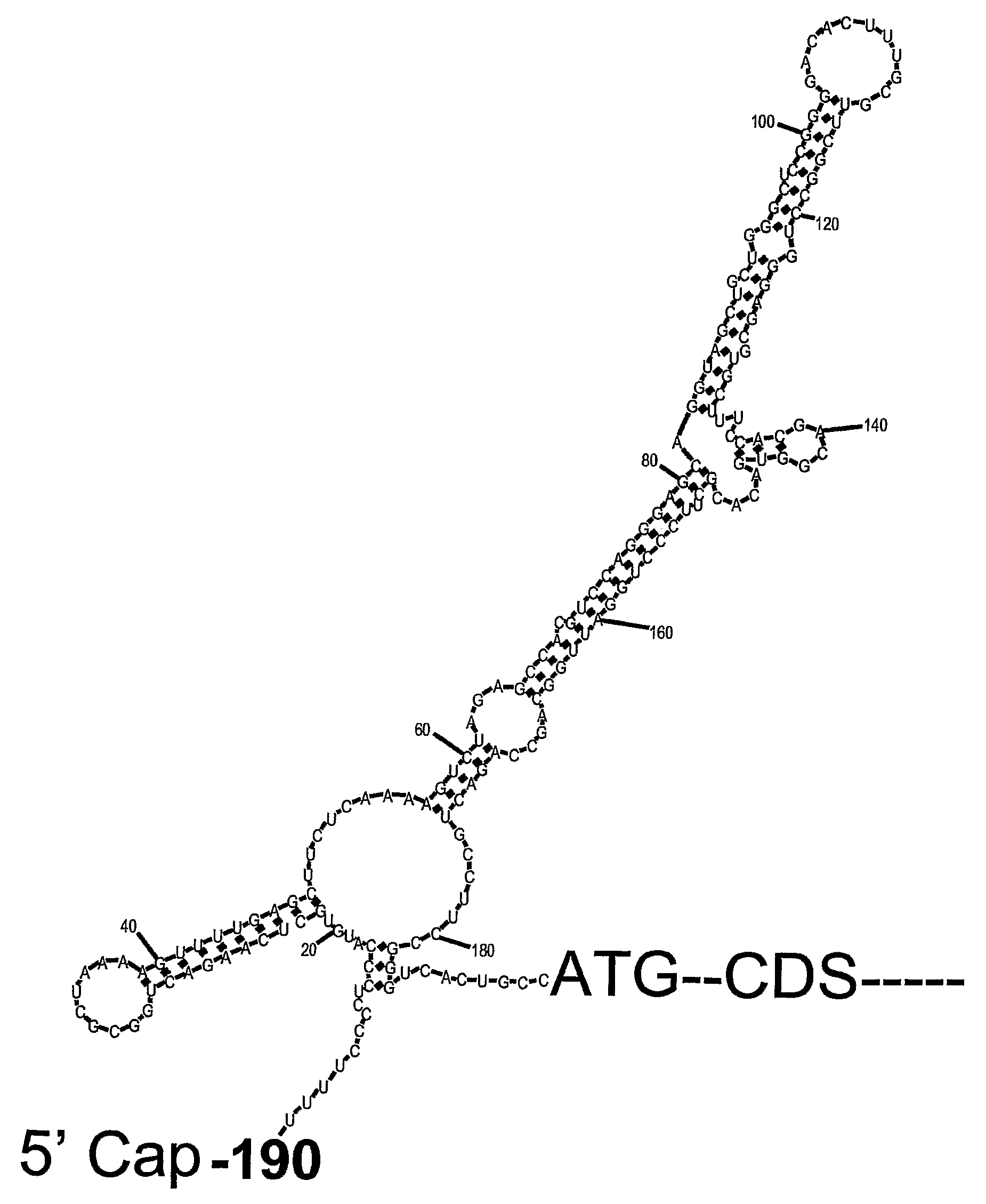
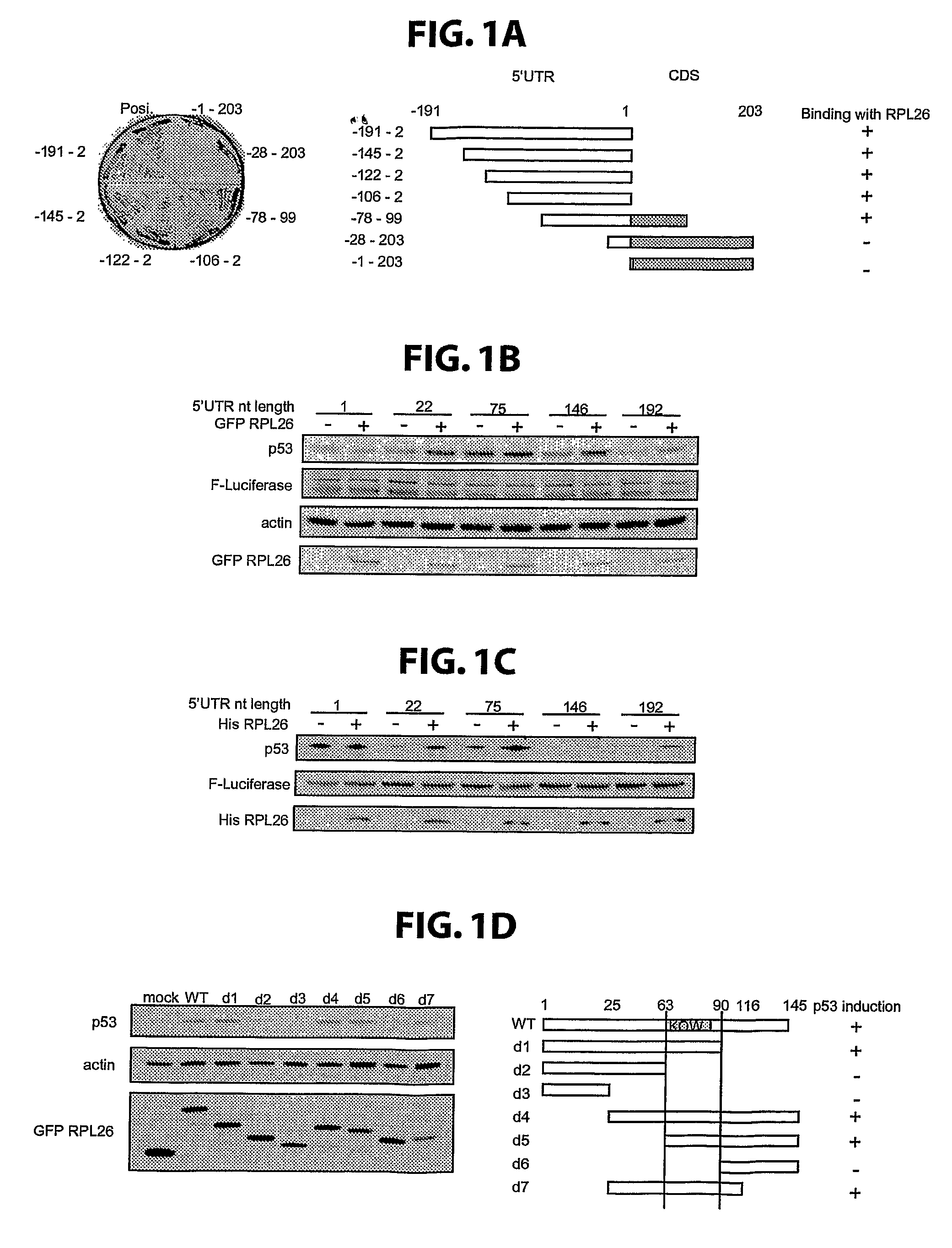
The present invention relates to novel methods for modulating the activity of p53 tumor suppressor protein by affecting p53 translational regulation. More specifically, the invention relates to novel methods for modulating p53 mRNA translation in a cell by affecting a function of a p53 5′-untranslated region (5′UTR), including its interaction with proteins such as Ribosomal Protein L26 (RPL26), nucleolin, and p53. The invention also relates to the use of these methods for treating cancer, neurodegenerative disorders and minimizing the negative effects of cellular stresses.
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC
Methods and compositions for detecting rhinoviruses
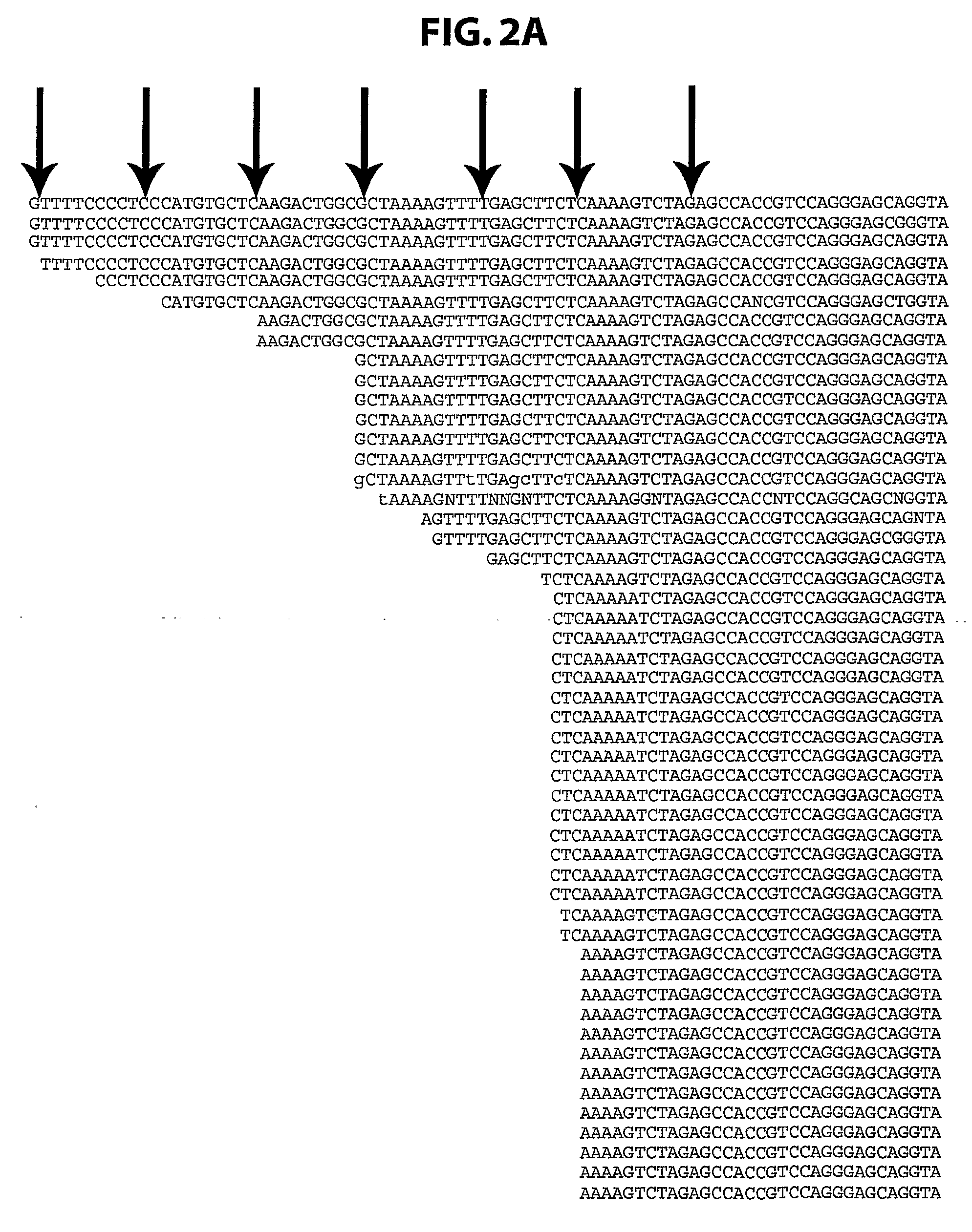
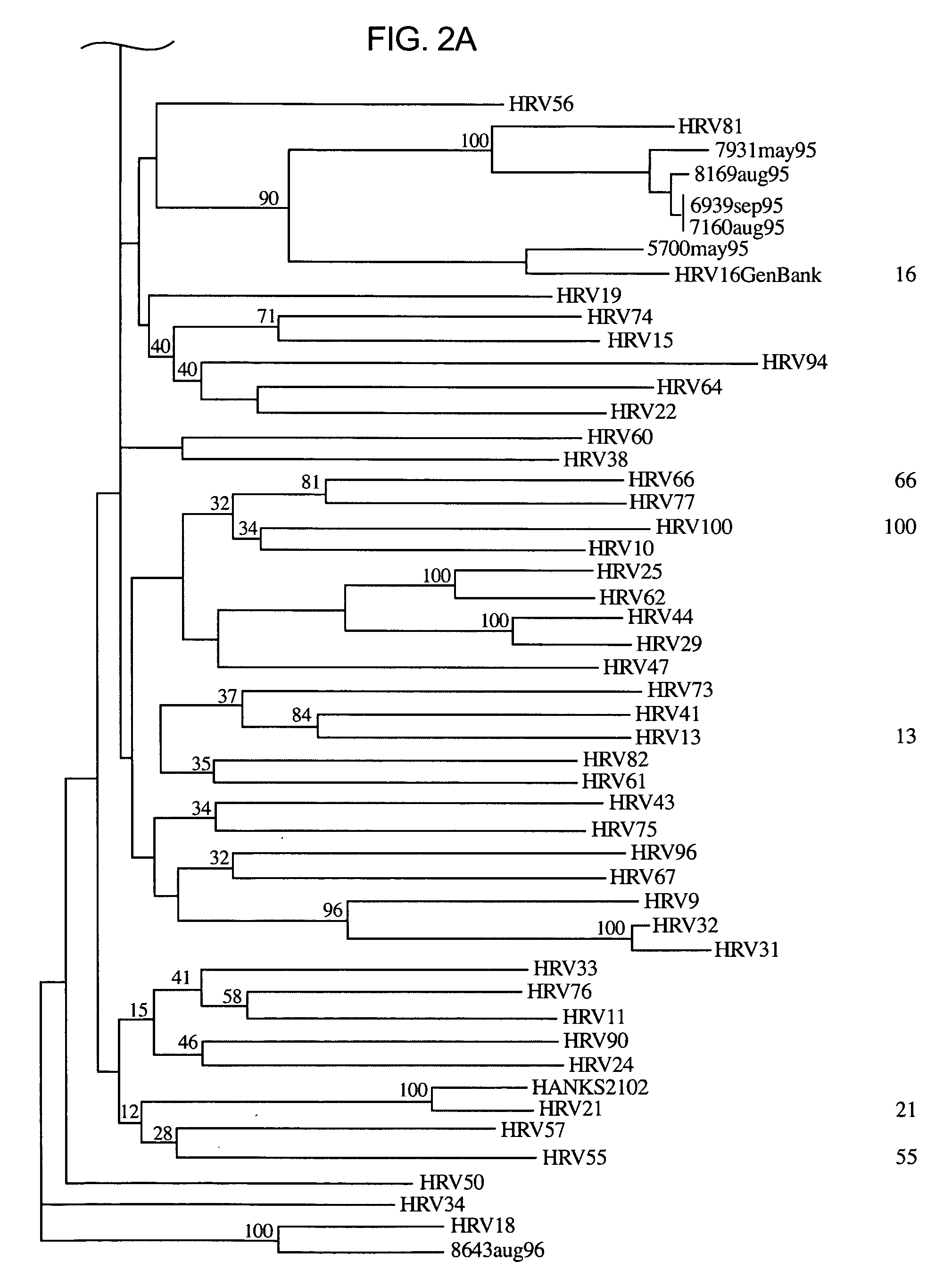
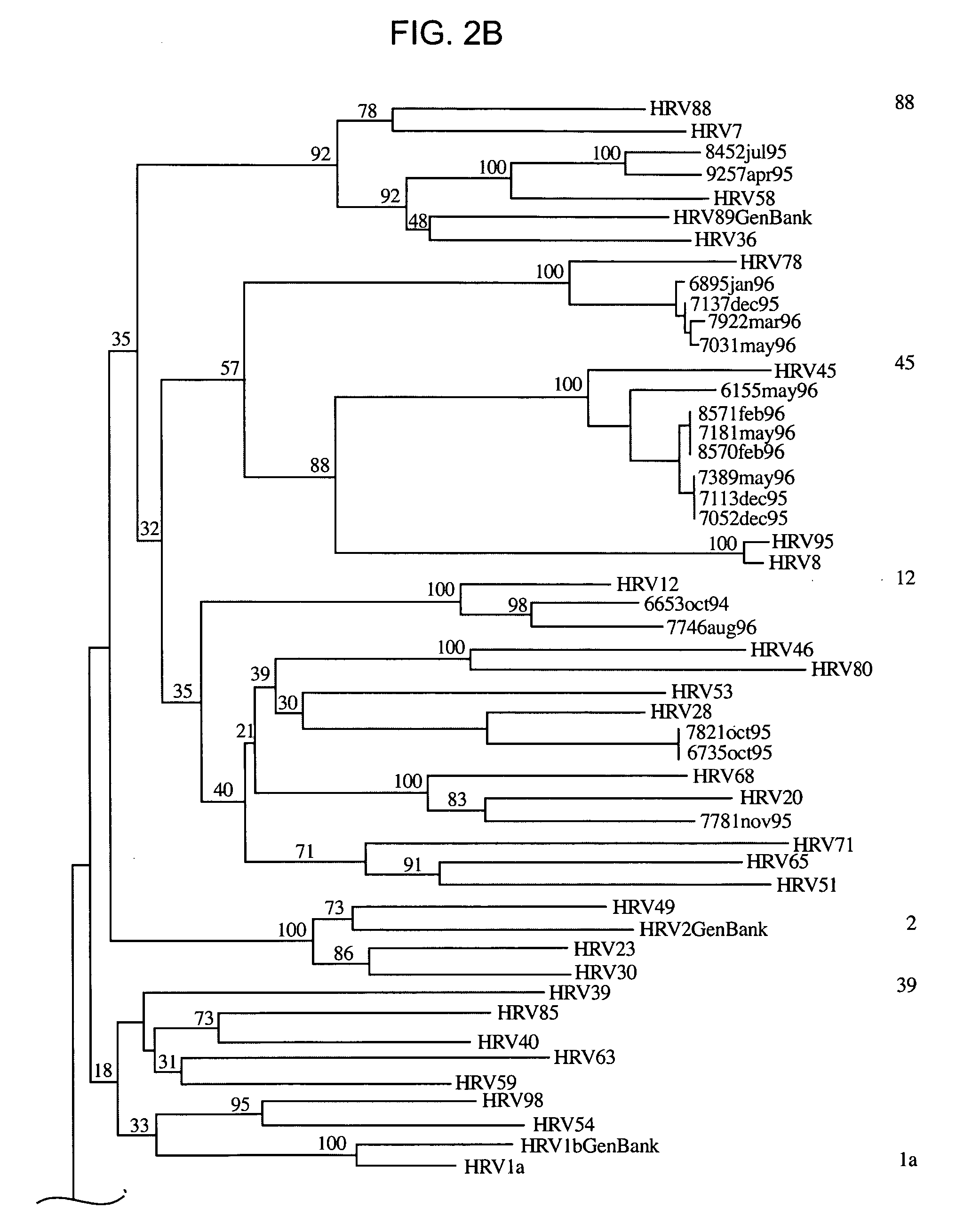
The invention provides methods and compositions for rapid, sensitive, and highly specific nucleic acid-based (e.g., DNA based) detection of human rhinovirus (HRV) in a sample. In general, the methods involve detecting a target nucleic acid having a target sequence of a conserved 5′ untranslated region of the HRV genome. The invention also features compositions, including primers, probes, and kits, for use in the methods of the invention.
Owner:FOCUS DIAGNOSTICS
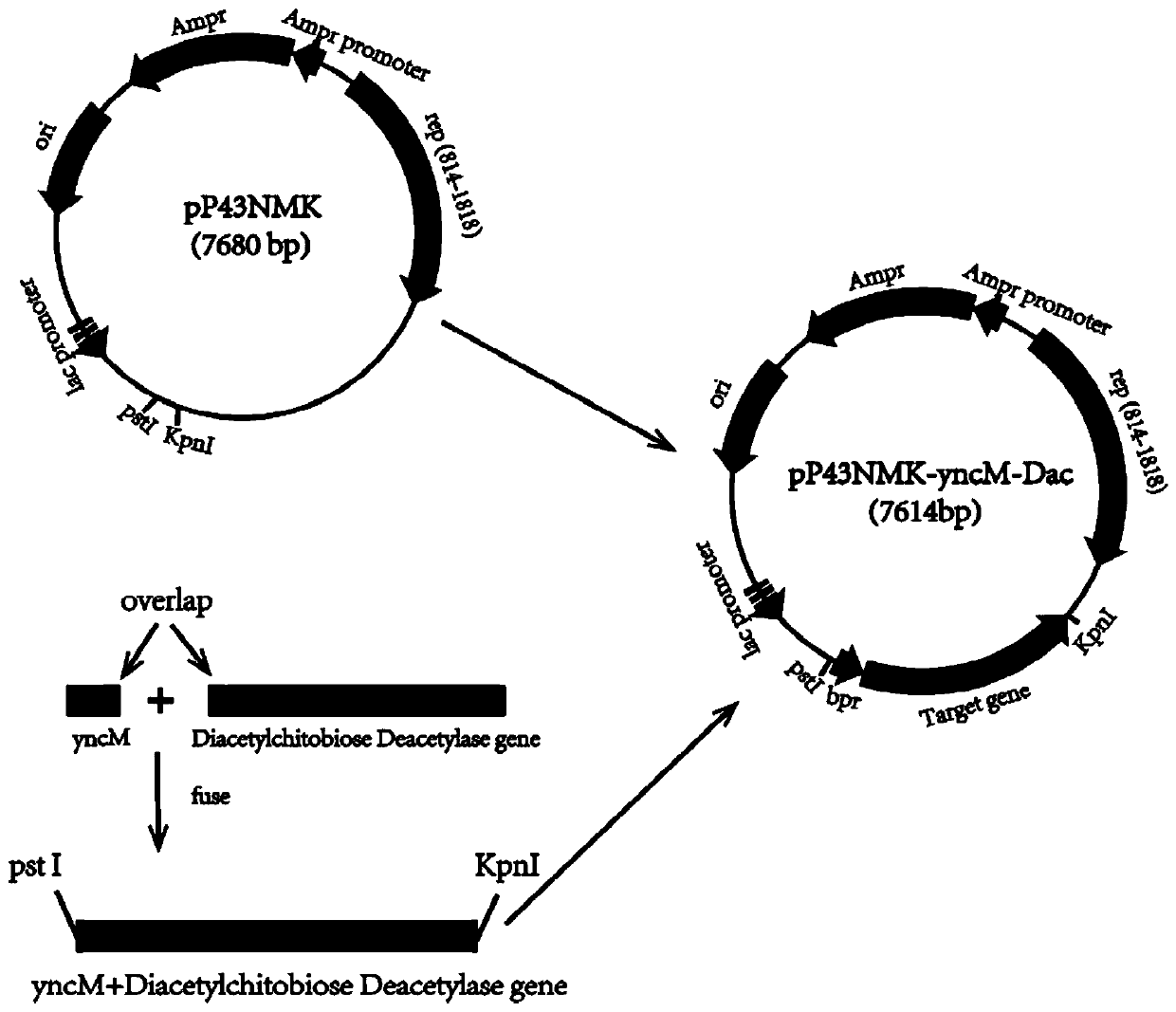
Construction and application of engineering bacteria secreting and expressing chitosan deacetylase
ActiveCN109777761AHigh expressionSimplify separation and purification stepsOrganic active ingredientsBacteriaHeterologousProtein target
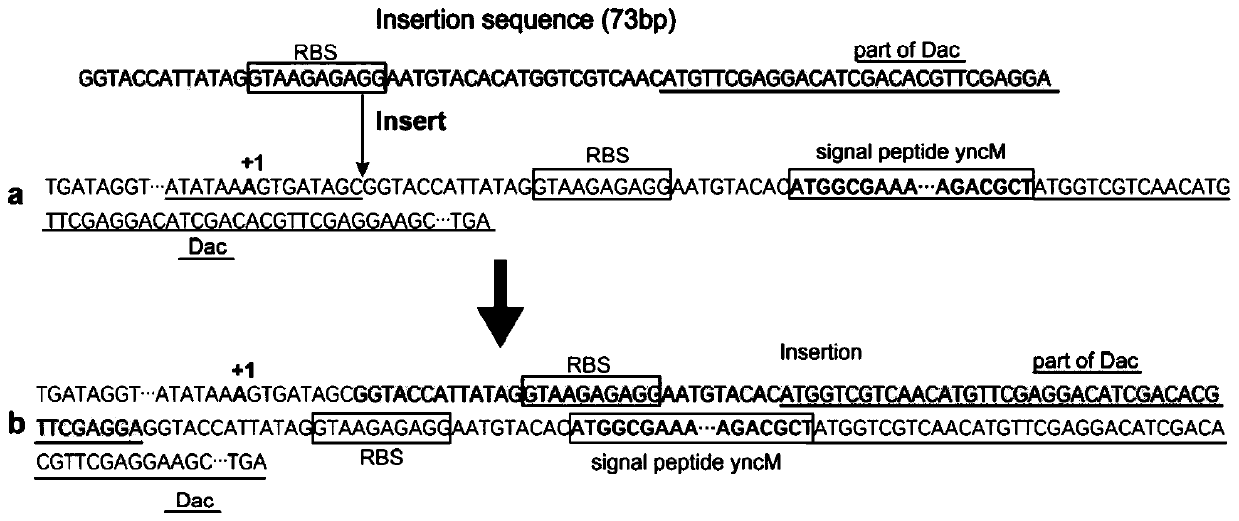
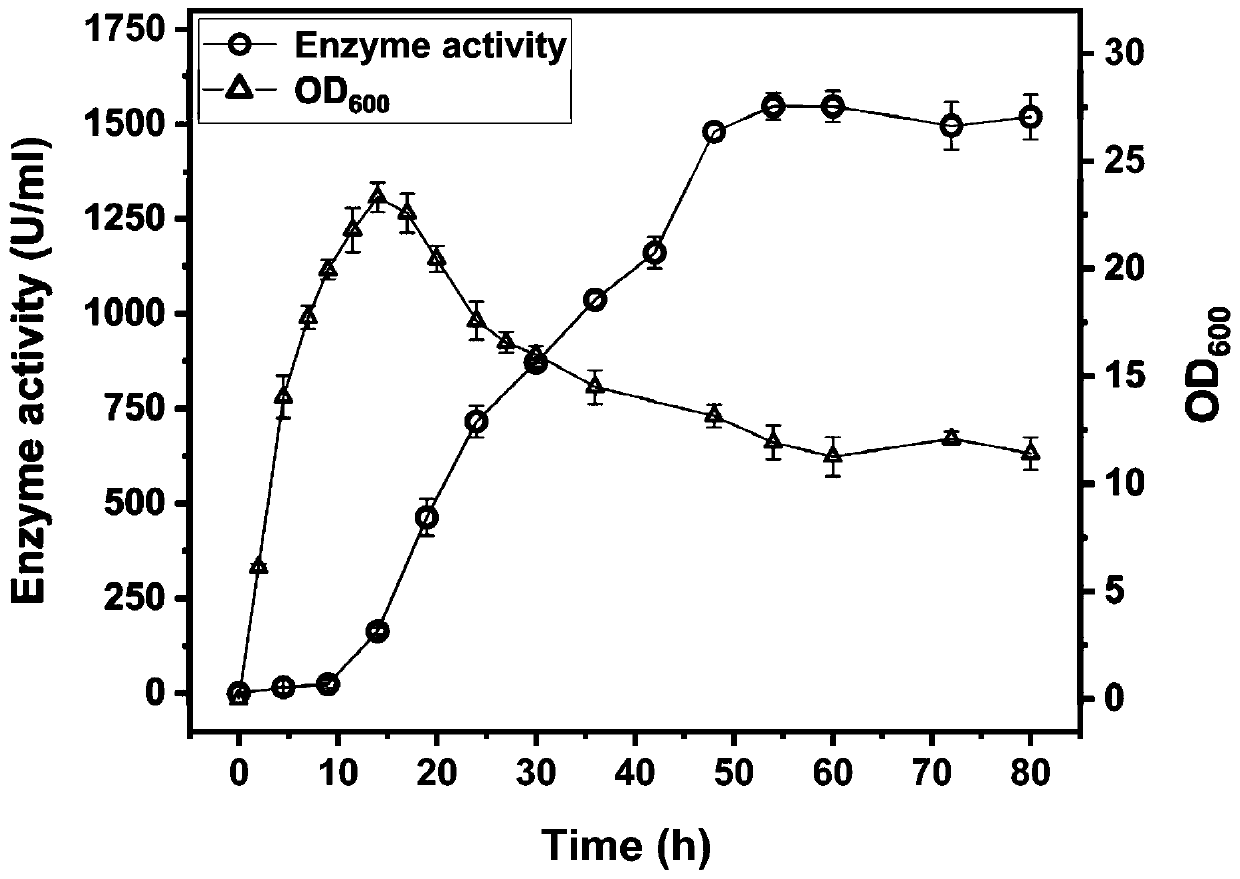
The invention discloses a construction and application of an engineering bacteria secreting and expressing chitosan deacetylase, belonging to the technical field of fermentation engineering. The construction firstly constructs a recombinant Bacillus subtilis secreting and expressing chitosan deacetylase gene by a different source, and adds a signal peptide fragment yncM in the recombinant vector for a first time, wherein the signal peptide can secrete target protein chitosan deacetylase outside cells of the recombinant Bacillus subtilis, and obtain mutants in a non-translation region at 5' end, so that the expression of the target protein is significantly increased and steps of subsequent enzyme separation and purification are greatly simplified. The enzyme activity of obtained chitosan deacetylase is up to 1548.7 U / mL and the yield of chitosan deacetylase is up to 620 mg / L when fermentation medium is fermented and cultured for 50-60 hours. And meanwhile, the method has the advantages of low production cost, mild production conditions, simple purification process, safe operation and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com