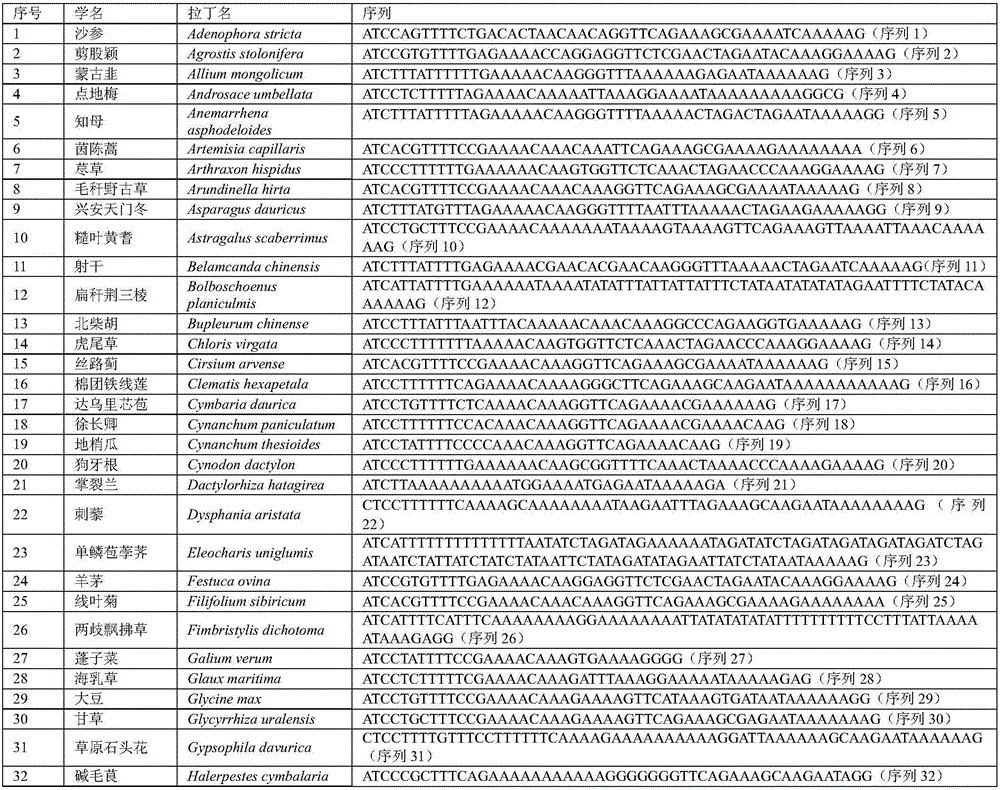
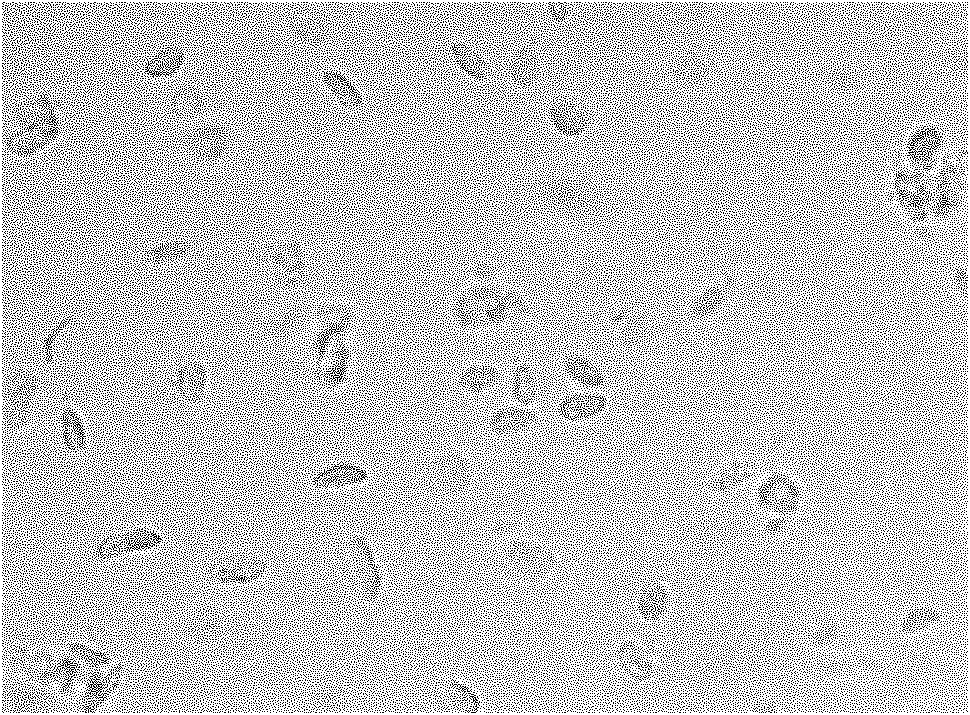Patents
Literature
48 results about "Chloroplast DNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
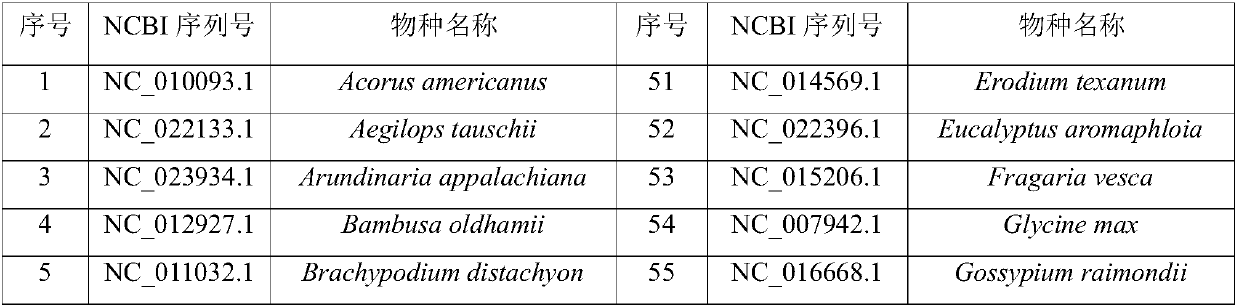
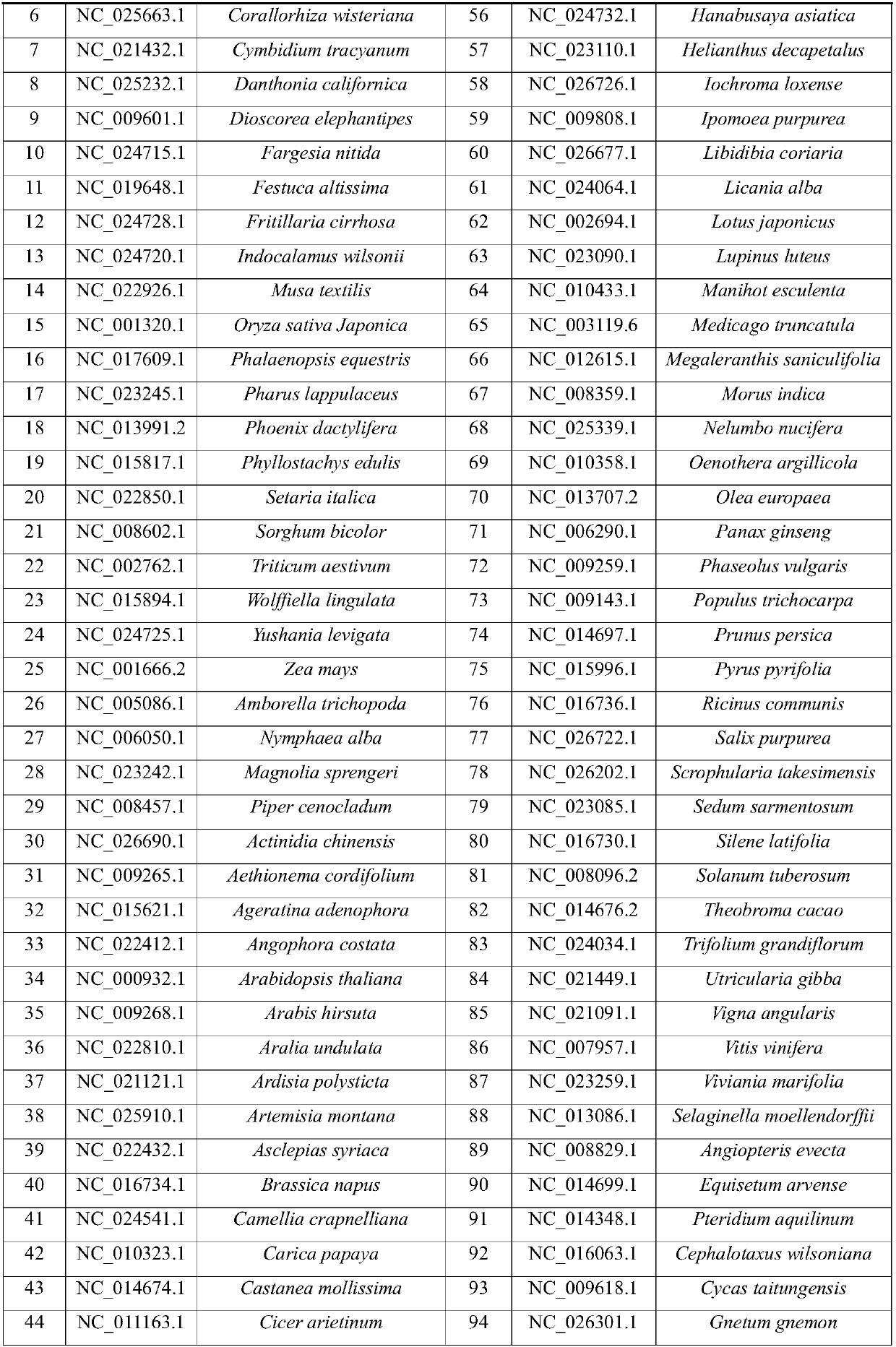
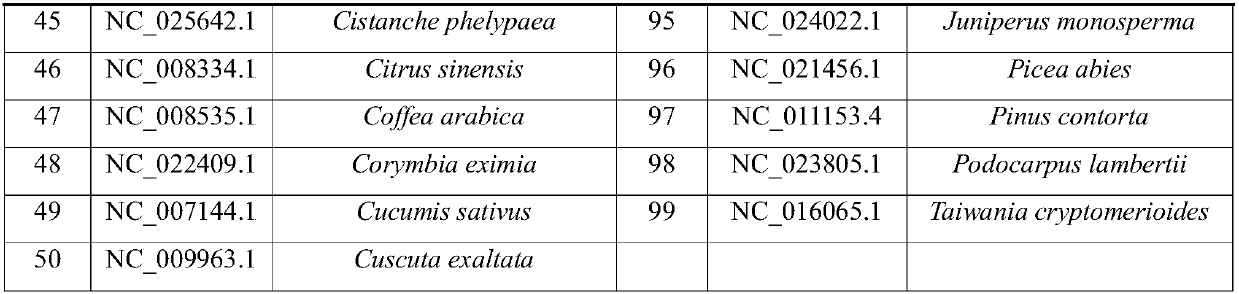
Chloroplasts have their own DNA, often abbreviated as cpDNA. It is also known as the plastome when referring to genomes of other plastids. Its existence was first proven in 1962, and first sequenced in 1986—when two Japanese research teams sequenced the chloroplast DNA of liverwort and tobacco. Since then, hundreds of chloroplast DNAs from various species have been sequenced, but they are mostly those of land plants and green algae—glaucophytes, red algae, and other algae groups are extremely underrepresented, potentially introducing some bias in views of "typical" chloroplast DNA structure and content.
Genetic engineering of plant chloroplasts
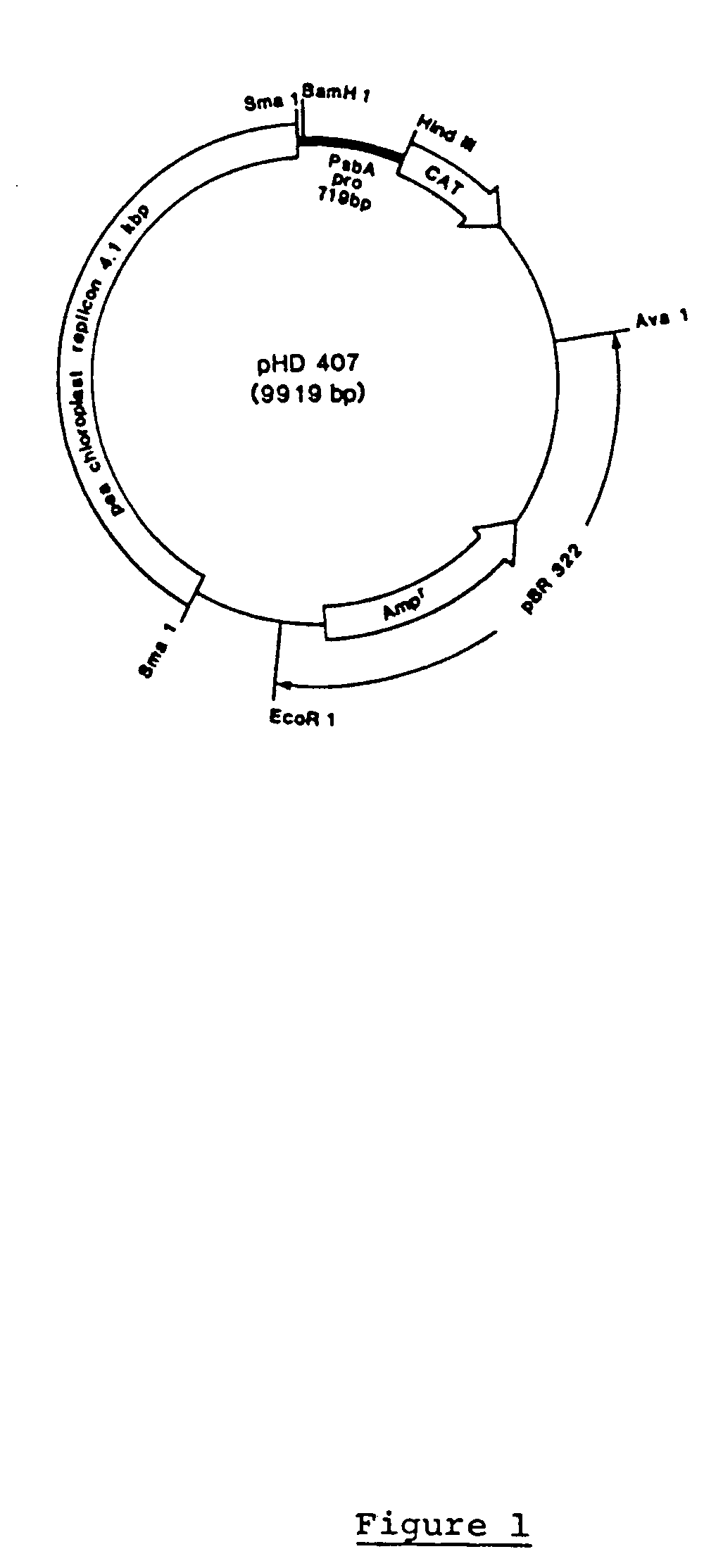
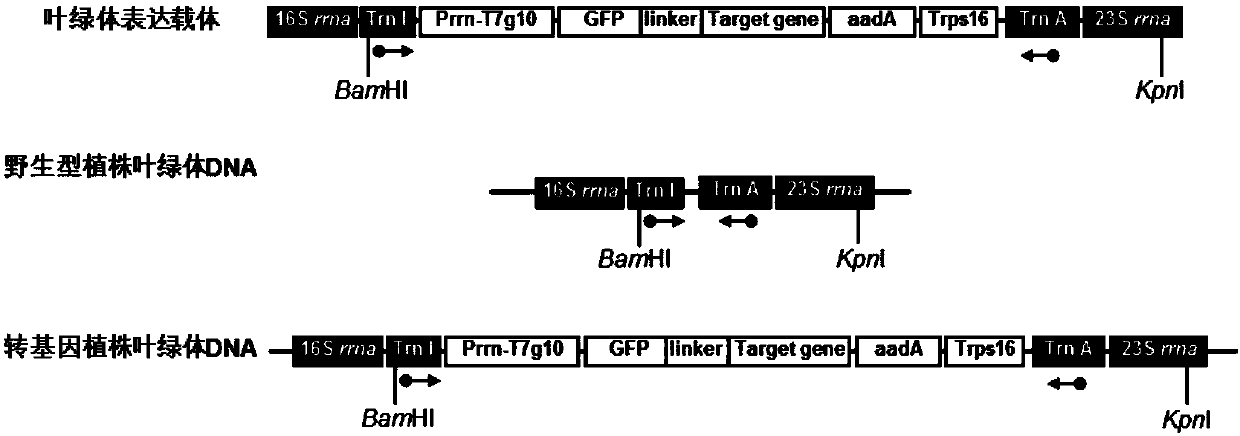
Novel chimeric constructions and methods for their use are provided for expression of exogenous genes in a plant chloroplast. Particularly, expression is achieved by the use of a chloroplast or bacterial 5′ untranslated region in the expression cassette. The expression cassette may be integrated into the chloroplast genome by the use of chloroplast DNA flanking sequences, or may replicate autonomously if provided with a chloroplast origin of replication. Plants and cells containing the transformed chloroplasts are also provided. The constructs may be used with both monocotyledenous and dicotyledenous chloroplasts.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
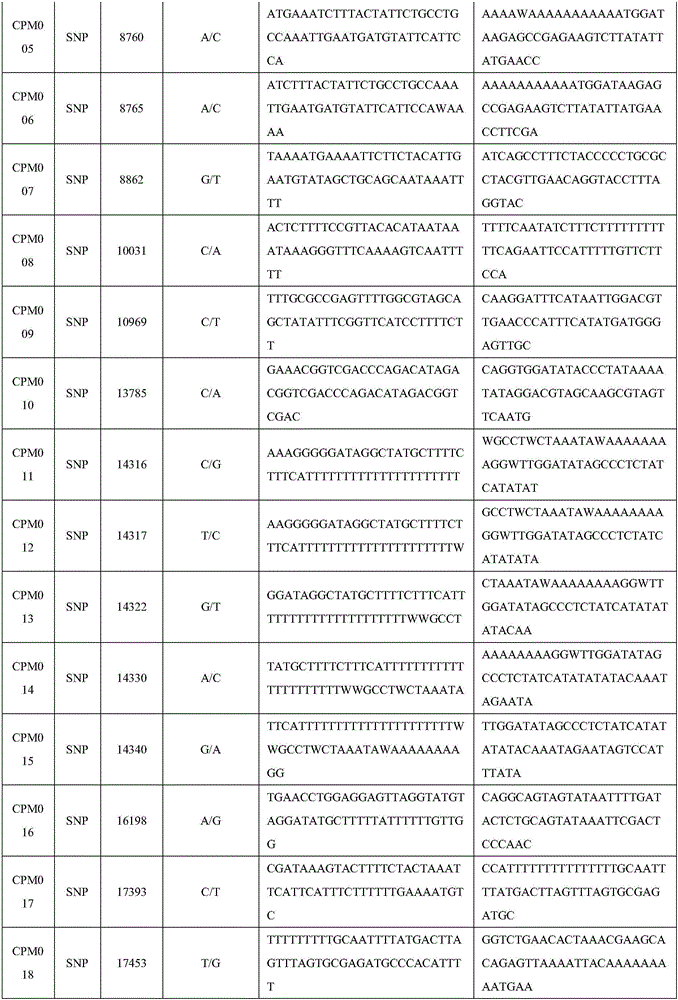
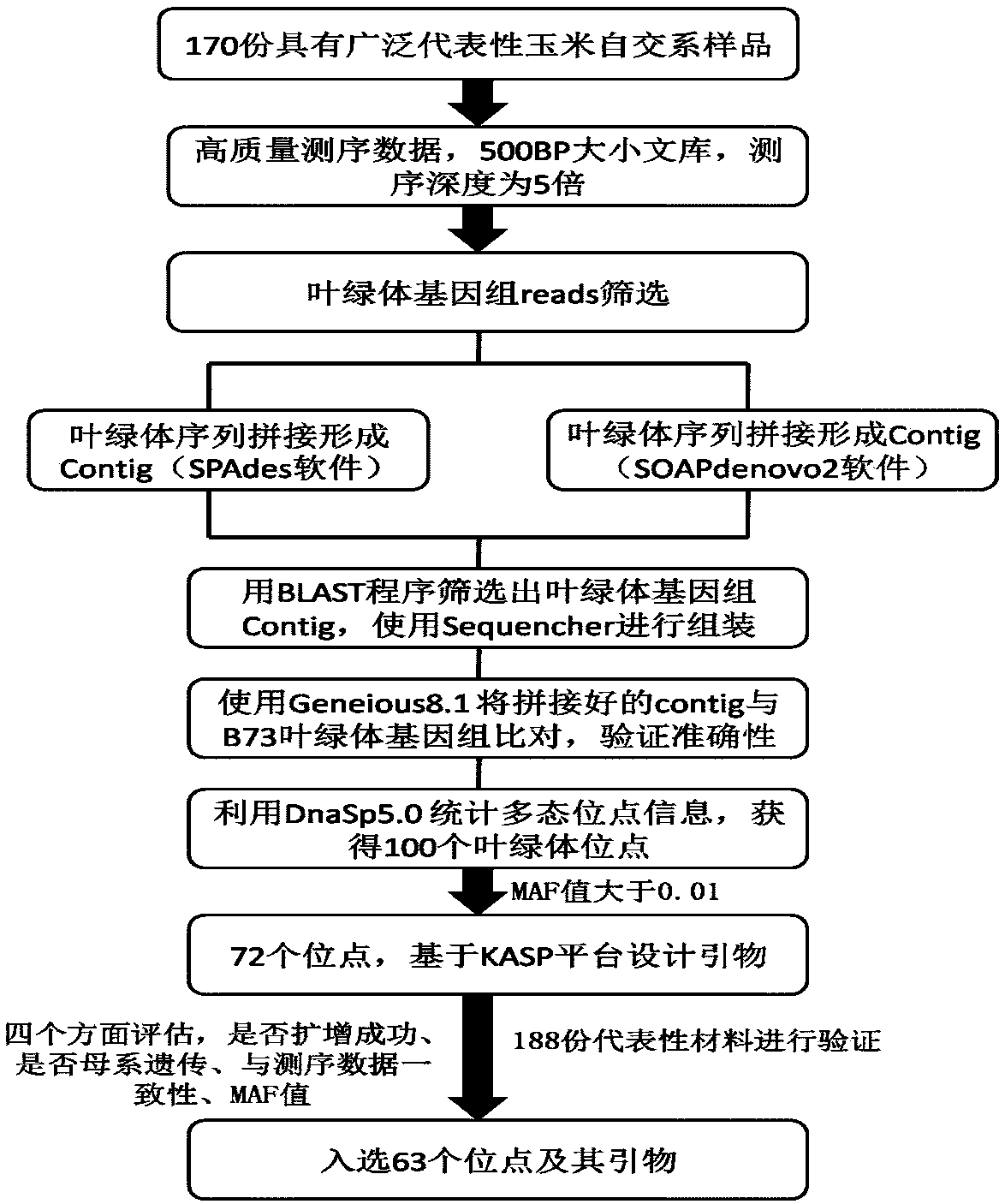
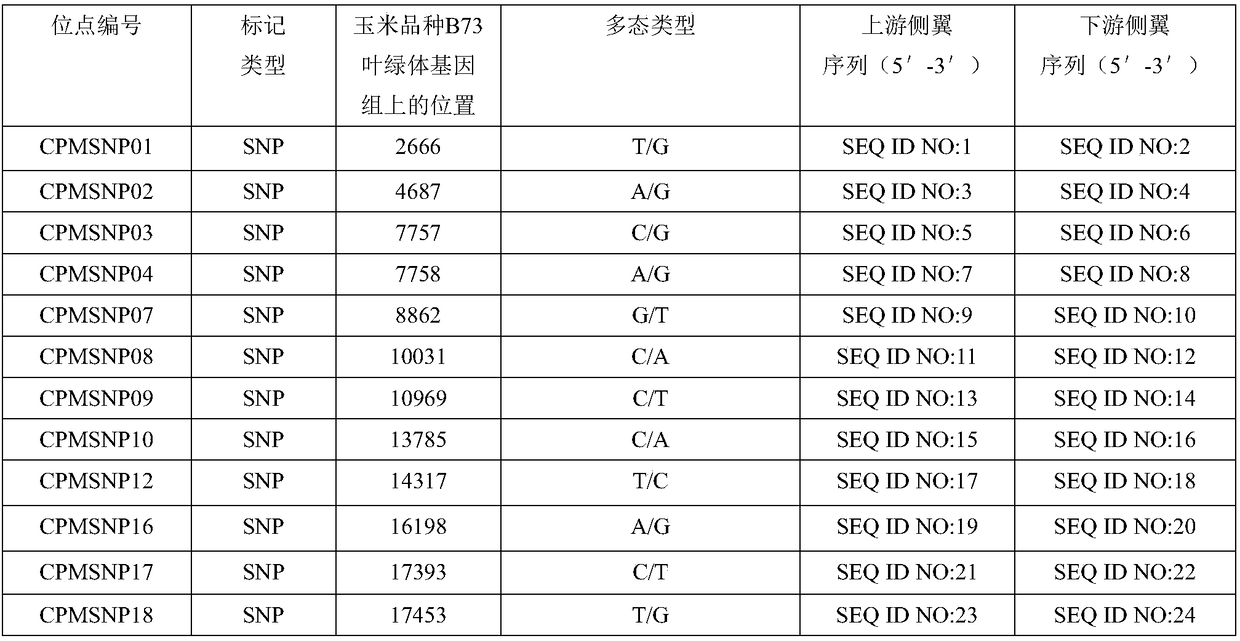
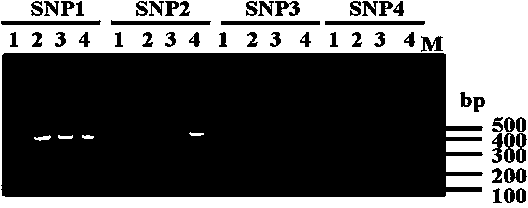
Set of chloroplast SNP and INDEL molecular marker combination for maternal traceability of maize
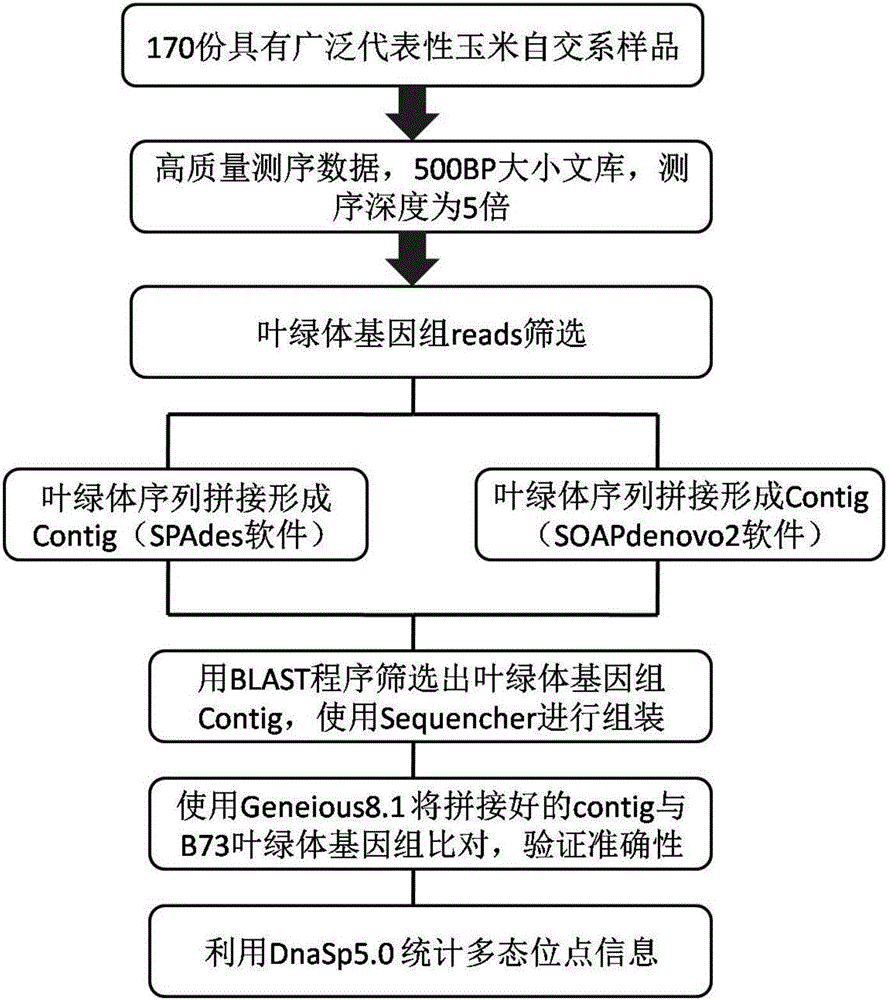
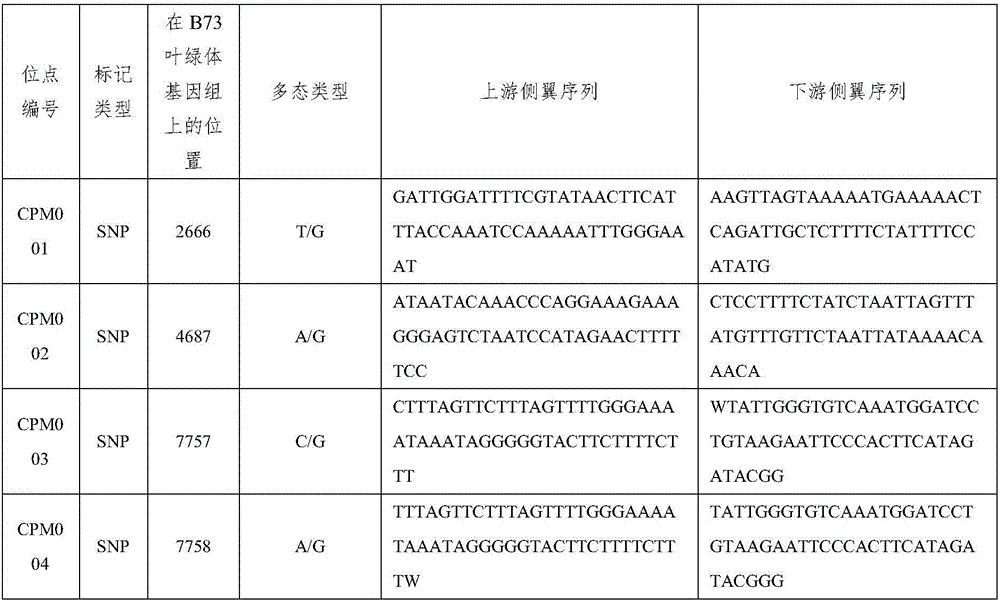
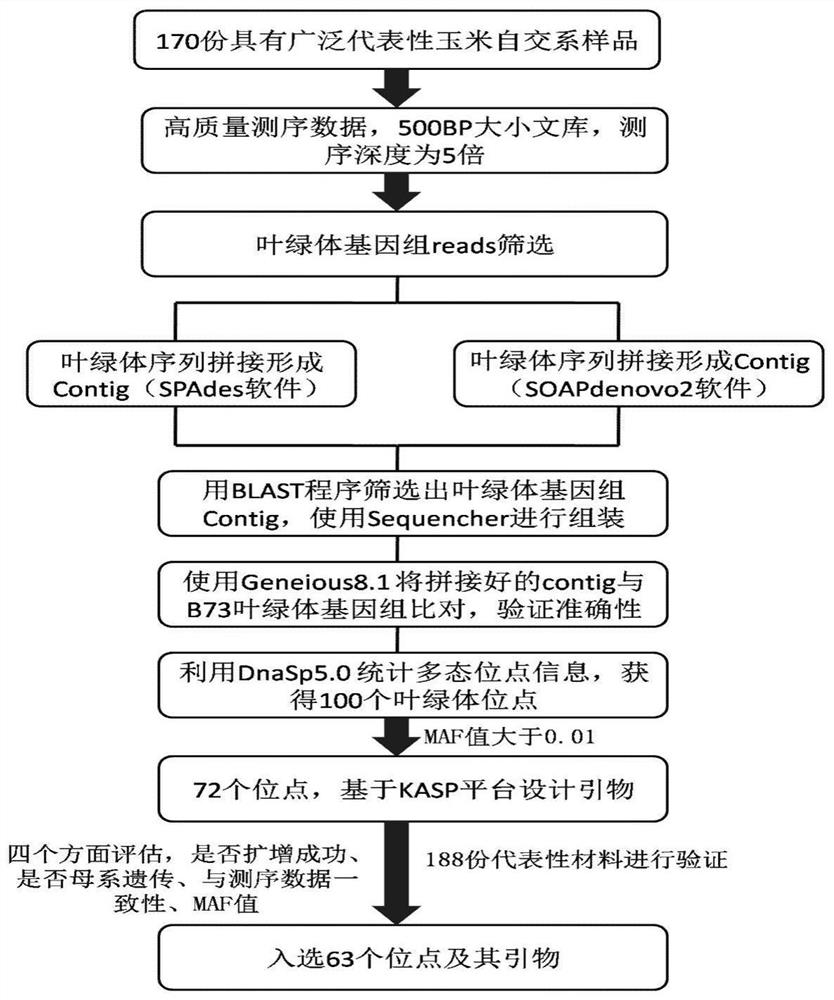
The invention relates to a set of chloroplast SNP and INDEL molecular marker combination for maternal traceability of maize. On the basis of high quality resequencing data, the invention develops a set of maize chloroplast genome polymorphic locus combination, the polymorphic loci are CPM001-CPM100, which include 96 SNP loci and 4 IDNEL loci. The 100 chloroplast loci can be applied to construction of a maize chloroplast DNA fingerprint database, parental traceability, and reciprocal cross identification. Through application of the chloroplast polymorphic loci, the range of available marker loci for maize on the genomic level is expanded; and a new idea and method are provided for maize varieties, germplasm resource identification, genetic relationship evaluation, cytoplasmic genetic characteristics and other studies.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Vector mediated organelle transfection
ActiveUS20070011759A1High expressionFunction increaseSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsEucaryotic cellDNA construct
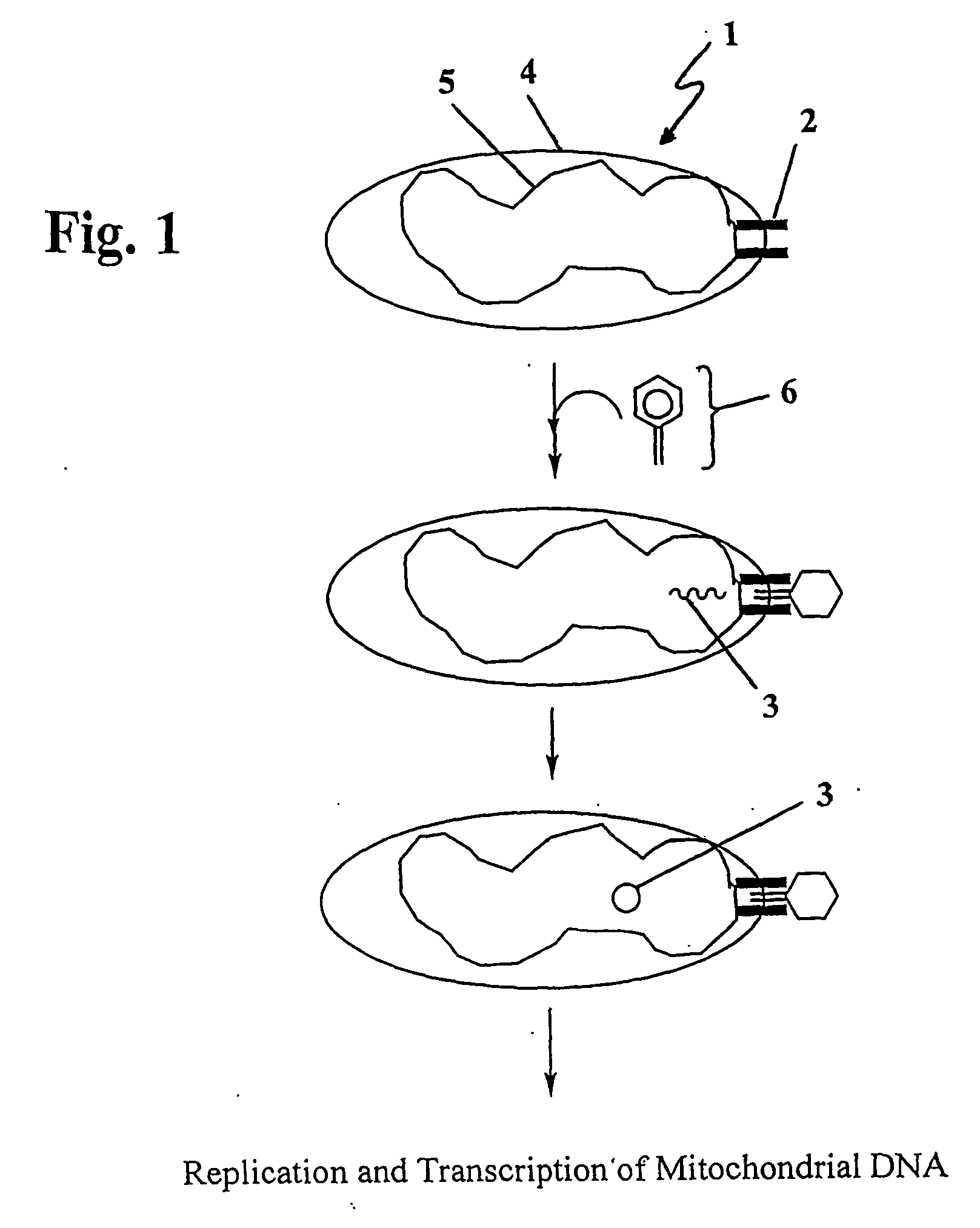
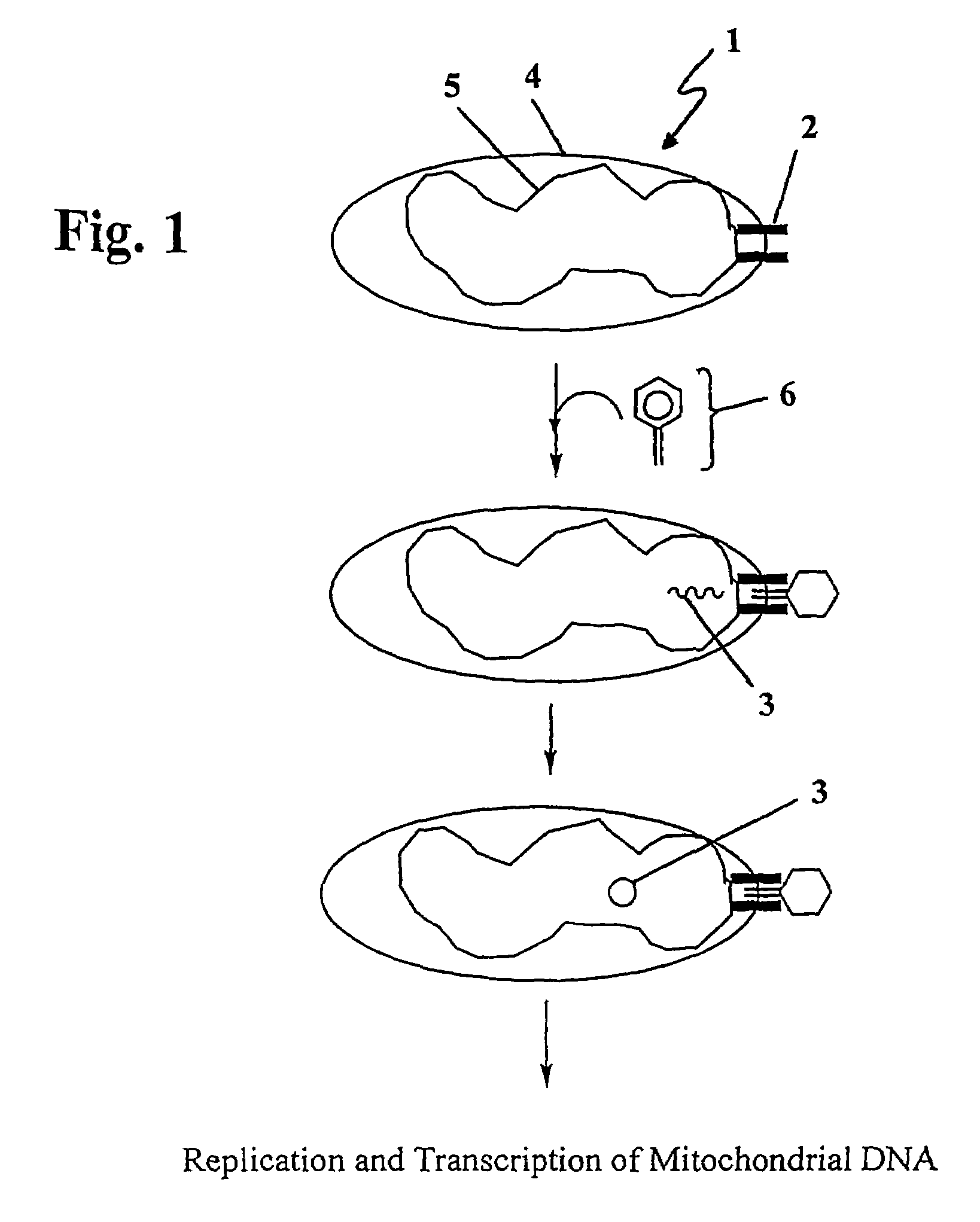
The present invention provides compositions and methods for direct transfection of mitochondria and chloroplast DNA in living cells. More particularly, the present invention is based on the use of viral vectors that specifically bind to receptors uniquely found on the target organelle. In one embodiment, as shown in FIG. 1, a eukaryotic cell containing an organelle (1) that has been modified to express a viral receptor (2) on the organelle's surface is provided. A viral vector (6) comprising a desired recombinant DNA construct (3) is introduced into the cytosol of the cell, wherein the viral vector binds to its receptor and introduces the recombinant DNA into the interior of the organelle.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Method for separating cotton chloroplast DNA
InactiveCN101117634AQuality improvementHigh yieldFermentationPlant genotype modificationSucroseSaccharum
The present invention belongs to the cotton genetic engineering technical field, in particular to a new method for separating the chloroplast DNA of cotton. The present invention includes: young and tender leaves are taken as material, and are fully homogenated by a common domestic juicer, four kinds of buffer solutions of A, B, C, and D are utilized, the leaves are centrifuged at a general velocity, and the cotton chloroplast DNA pure can be finally obtained successively by the separating and the cracking of the chloroplast as well as the separating and the purifying of the chloroplast DNA (cpDNA). The quality of the chloroplast DNA prepared and separated by the present invention is higher, and the UV spectrophotometer measuring shows that the D260 nm / D280 nm of a DNA sample prepared by the present invention is set between 1.6 and 1.8; the leaf sample yields up to 1-10 microgram cpDNA per gram. After being verified, taking the separated cpDNA as the template can completely satisfy the common molecular biological operation needs such as the specific enzyme restriction, the RAPD, the PCR, the clone of target gene sequences, and so on. Compared with the prior art, the present invention does not need a hypervelocity centrifugal machine, and equipments and steps of centrifugalization through the sucrose density gradient are also not needed.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
A method for identification of distant hybrid offspring of peony and peony
InactiveCN102260736AEffective selection processMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular identificationMolecular genetics
The invention relates to a method for identifying plant hybrid progeny, in particular to a method for identifying distant hybrid progeny of peony and peony. The identification method provided by the invention comprises: identification and screening of hybrid seedling early form, identification of female parent by chloroplast DNA, identification of male parent by SSR molecular marker. Through the combination of morphology and molecules, identify hybrid offspring, identify true and false hybrids, study and summarize the relationship between true hybrid seedlings and parents, determine the heritable external morphological indicators, and obtain a reasonable hybrid at the molecular genetic level The genetic distance between the species and the parent, the degree of kinship, and finally a reasonable identification standard system is established on the basis of morphological and molecular genetics, so that the later selection process can be carried out effectively.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for rapidly discriminating species of cotton
InactiveCN103468672AEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA barcodingBarcode
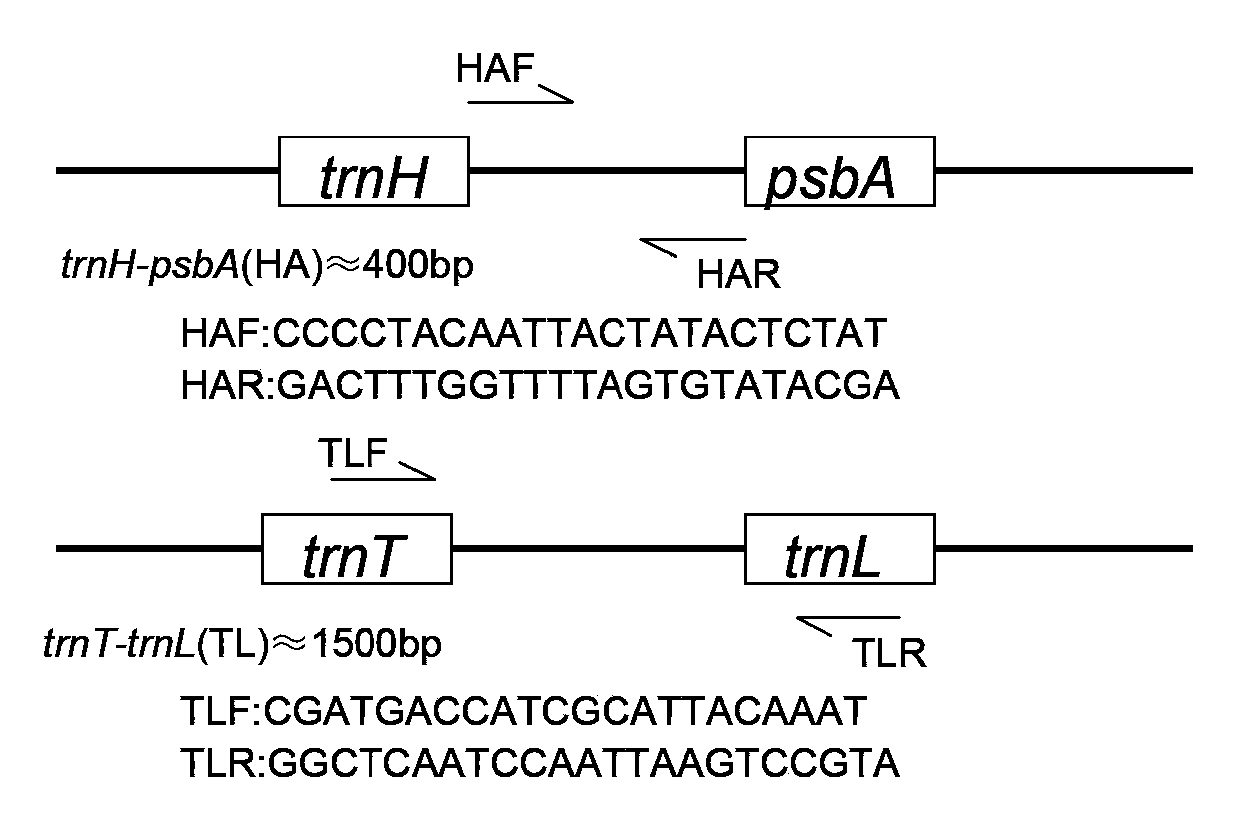
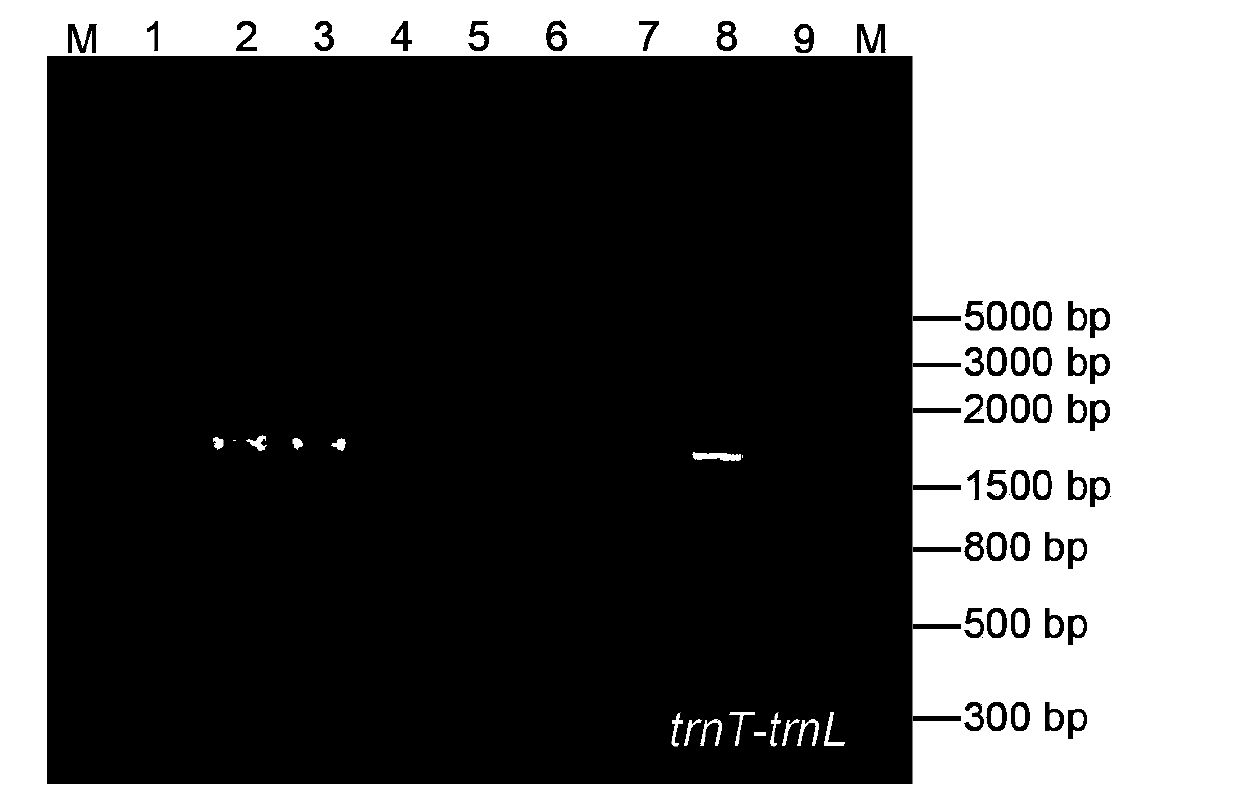
The invention relates to the molecular biology field, and concretely relates to a cotton species DNA barcode and a method for rapidly and accurately identifying the species of cotton. The method comprises the following steps: sampling, carrying out total DNA extraction, carrying out PCR amplification, cloning, sequencing, and carrying out sequence alignment. In the invention, cotton chloroplast genome specific primer pair total DNA is adopted to carry out specific amplification of trnT-trnL and trnH-psbA sequences, so convenience, fastness, no individual extraction of chloroplast DNA are realized; a combination of the trnT-trnL and trnH-psbA sequences adopted as the cotton species DNA barcode has a moderate length, has a high cotton species identification capacity, and can rapidly identifies the cotton species. The method does not rely on traditional identification classification experiences, and has the advantages of simple operation and high accuracy.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
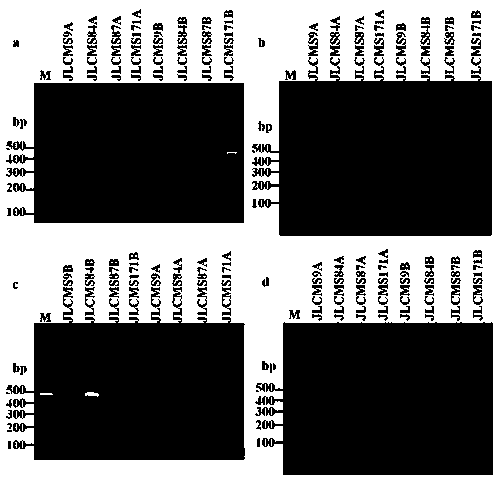
Molecular markers of maize chloroplast genome and its application in cultivar identification
ActiveCN108486266AGuaranteed accuracyImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationReciprocal crossGermplasm
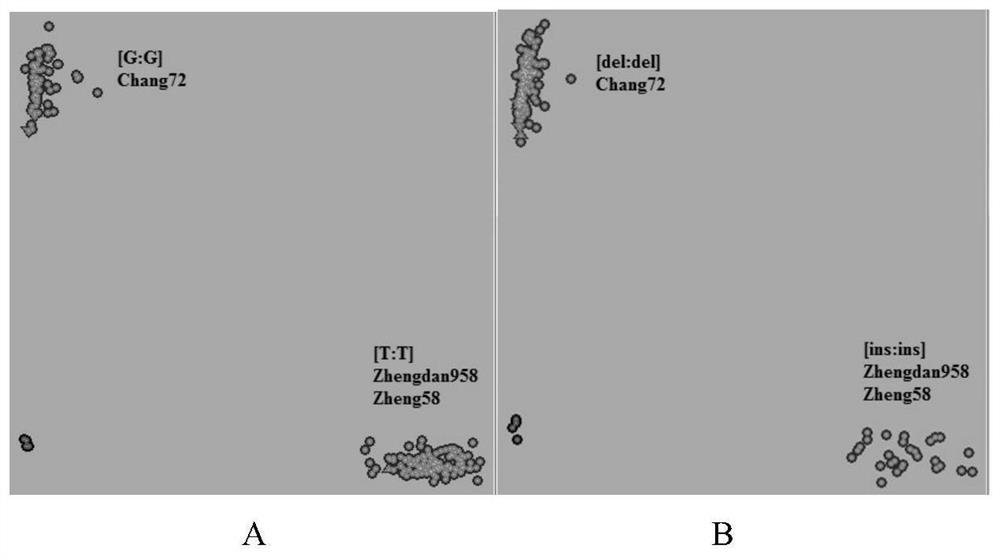
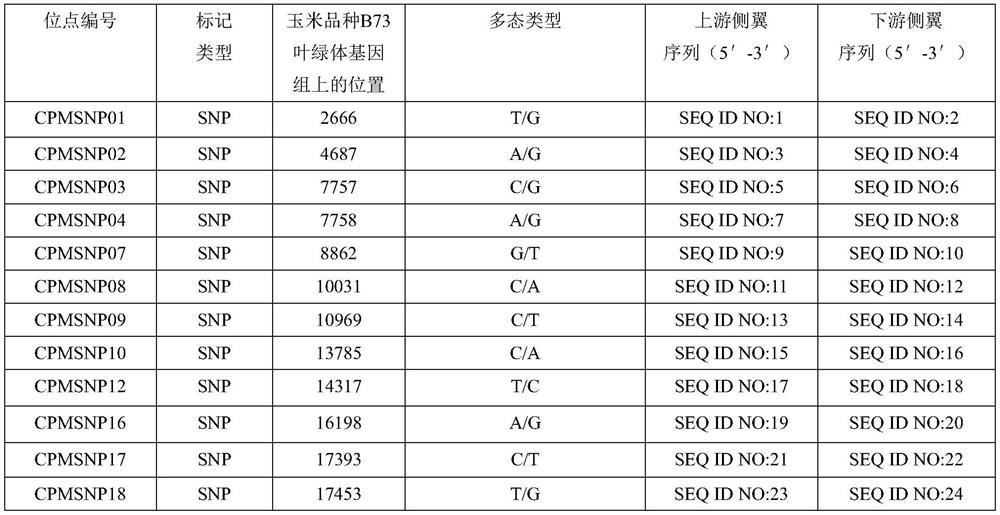
The invention provides molecular markerd of a maize chloroplast genome and its application in cultivar identification. The molecular markerd comprise 57 SNP markers and 6 InDel markers. The 63 molecular markers and primers developed according to the markers can be used in any one of the following: (1) constructing a corn variety chloroplast DNA-SNP and InDel fingerprint database, (2) carrying outcorn maternal line traceability analysis, and (3) performing reciprocal cross identification on corn samples. Through the application of the chloroplast polymorphic primer composition, the range of available marker sites of the corn is expanded at the genome level and the new ideas and technical means are provided for the study of maize variety and germplasm resource identification, genetic relationship evaluation and cytoplasmic genetic characteristics.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Method for identifying soybean male sterile cytoplasm through SNP marks of chloroplast DNA
ActiveCN104004853AMark stableImprove reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyChloroplast
The invention provides a method for identifying soybean male sterile cytoplasm through SNP marks of chloroplast DNA. The method can also be applied to distinction of a soybean cytoplasmic male sterile line and a maintainer line containing normal cytoplasm. The method includes the following steps of extracting the seed genome DNA of the soybean cytoplasmic male sterile line and the seed genome DNA of the maintainer line to serve as amplification templates, selecting four pairs of the SNPs marks of the chloroplast DNA, and designing a pair of primers on the side wing sequences of each pair of SNPs respectively to conduct PCR amplification. The PCR products obtained through amplification conduct identification on the difference between the length of the enzyme-digested products of the sterile line and the length of the enzyme-digested products of the maintainer line through digestion of restriction enzymes. According to the method, the soybean male sterile cytoplasm and normal fertile cytoplasm can be rapidly and accurately identified. The method can also be used for detecting the maintainer line which contains fertile cytoplasm and is mixed in the sterile line containing sterile cytoplasm in the breeding process of the sterile line, and provides guarantees for the purity requirement in the production process of soybean sterile line seeds.
Owner:JILIN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
High-purity and high-quality extraction method of chloroplast DNA of strip-leaf plants
The invention discloses a method for extracting chloroplast DNA of strip-leaf plants. The method comprises the following steps that A, the protoplasts of leaves are acquired by means of making mechanical injuries on the leaves and enzymolysis treatment in combination, wherein the acquired protoplasts contain chloroplasts, mitochondria and nuclei; B, impurities in the acquired products from step A are removed by differential centrifugation treatment to conduct crude extraction of the chloroplasts; C, the impurities in the acquired products from step B are removed by density gradient centrifugation to conduct purification of the chloroplasts; D, extraction is conducted on the acquired products from step C by means of a Tiangen rapid biochemical plant genome DNA extraction system to obtain high-purity chloroplast DNA. With the method for extracting the chloroplast DNA of the strip-leaf plants, high-purity and high-quality extraction can be conducted on the chloroplast DNA of the strip-leaf plants.
Owner:唐山润泽粮油食品有限公司
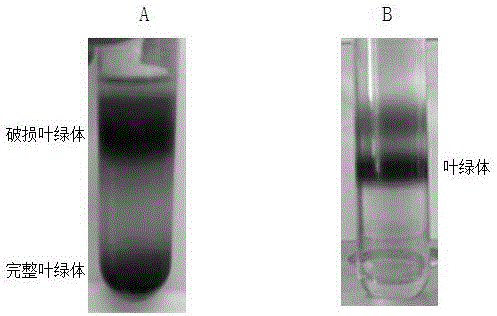
Preparation method of wheat complete chloroplasts
InactiveCN105907697AShort preparation timeEasy procedureCell dissociation methodsPlant cellsBiotechnologyQuantitative determination
The invention belongs to the technical field of biotechnology, and relates to the technical field of plant complete cell organ separation, in particular to a simple and rapid preparation method of wheat complete chloroplasts. The method comprises the following steps of 1, preparing a Percoll gradient; 2, preprocessing a wheat sample; 3, performing density gradient centrifuging on the wheat sample; 4, completing extraction of the chloroplasts. The Percoll is adopted as a medium for gradient centrifuging, wheat complete and damaged chloroplasts can be distinguished, the preparation time is short, the procedure is simple and convenient, the sufficient and complete chloroplasts are obtained, quantitative determination is performed, and then the chloroplasts can be precisely applied to extraction of chloroplast function protein, membrane protein, matrix protein and chloroplast DNA and various follow-up researches.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
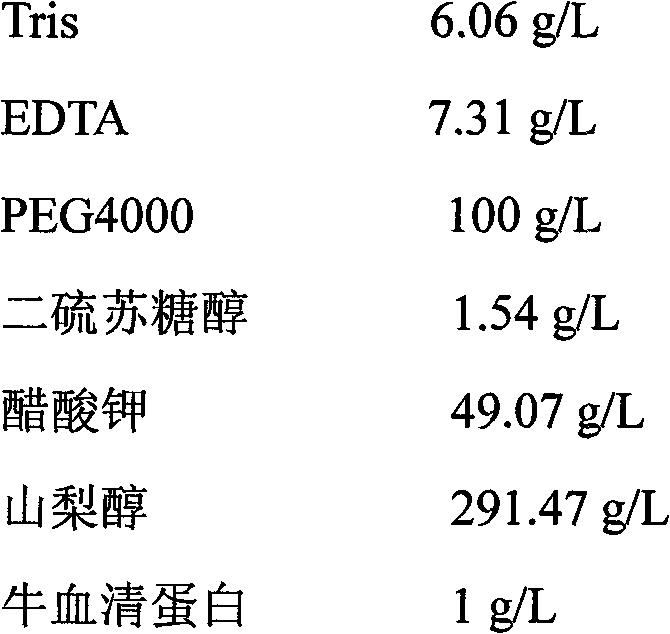
Complete chloroplast long-time isolated culture method
The invention discloses a complete chloroplast long-time isolated culture method. Sterile seedling cotyledons of cucumber, tobacco and spinach are used as materials respectively; citric acid, NaCl, Tris and ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) are used as chloroplast extraction reagents of main components; complete chloroplast (figure 1) is separated by the operations of grinding, gauze filtration, differential centrifugation and the like of the plant materials; and MnCl2, MgSO4, NaCl, sorbitol and the like are used as culture reagents of the main components, and the isolated chloroplast is subjected to liquid culture. After being cultured in vitro for about 20 days, the chloroplast still keeps green and is microscopically normal (figure 2), and the membrane structure is complete (figure 3). In two weeks of isolated culture, the chloroplast is split and propagated to reach relatively stable number (figure 4). Proved by isolated transformation and exogenous gene detection of the chloroplast, the DNA in the chloroplast cultured for long time is not degraded (figure 5). The method can provide convenience and a new path for basic theories and application research of chloroplast function, genetic transformation, cell engineering and the like.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Camellia polymorphic chloroplast genome microsatellite molecular marker primers and method for screening and discriminating related species
ActiveCN109337997AEfficient developmentAvoid the Phenomenon of "Misidentification"Microbiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCapillary electrophoresisGenetic diversity
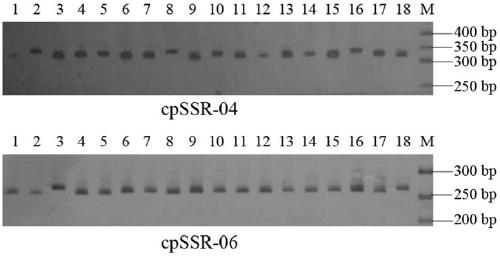
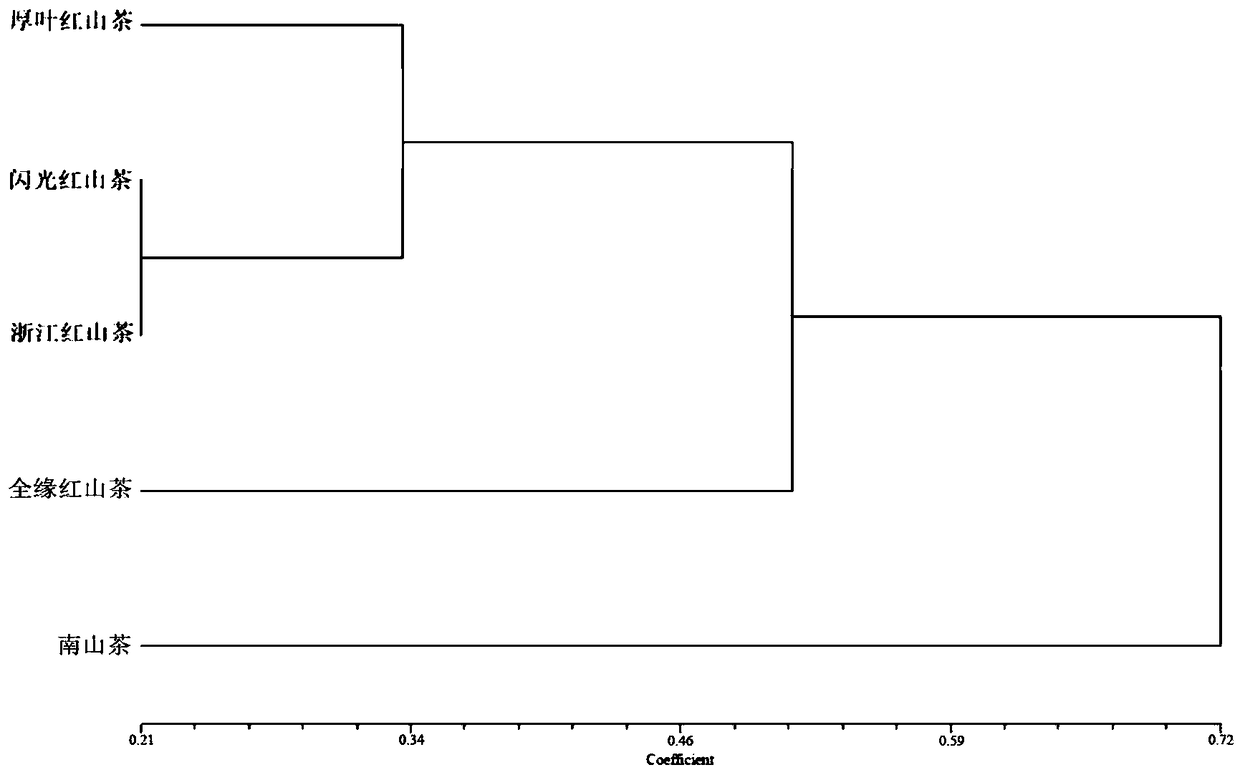
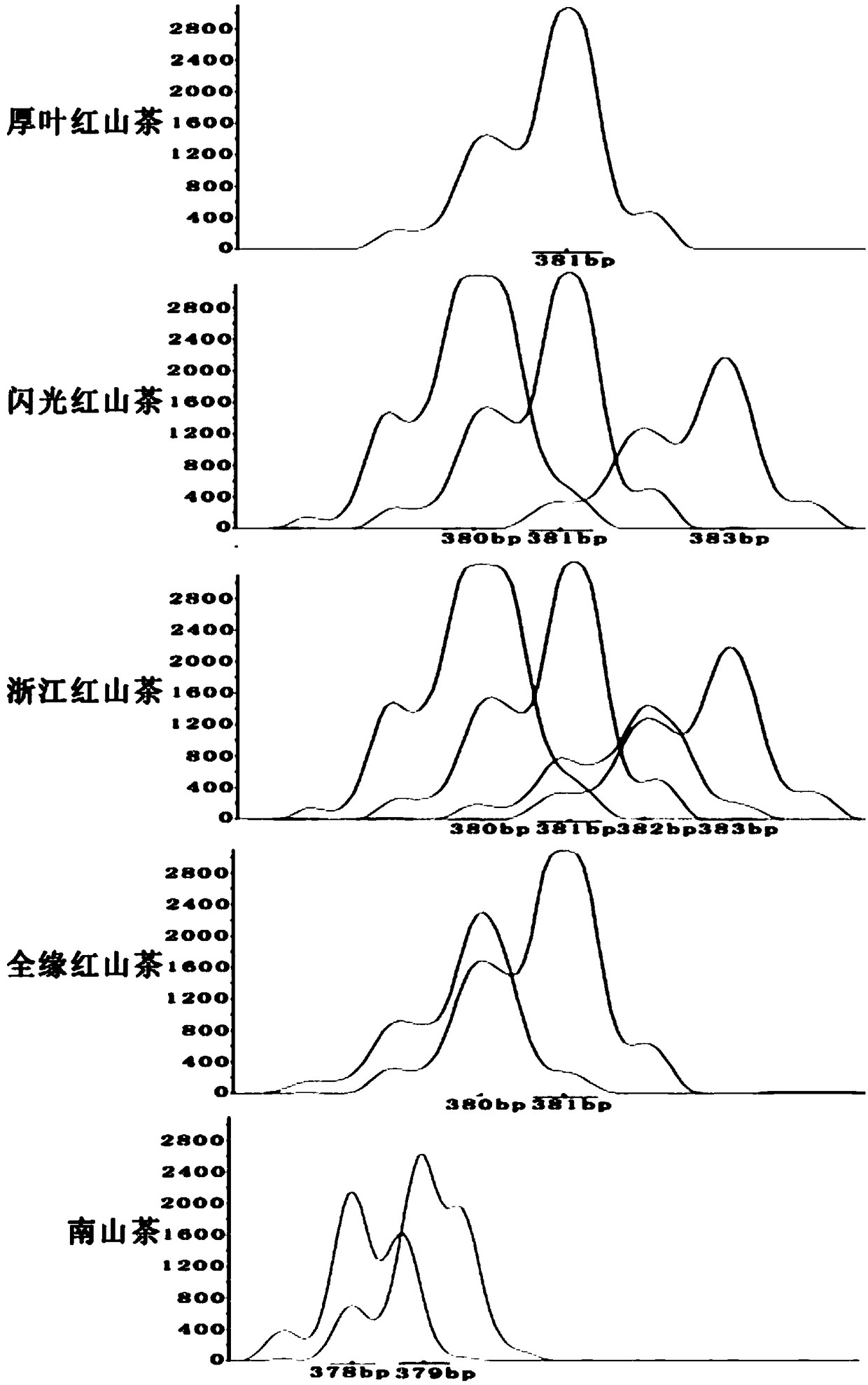
The invention belongs to the technical field of forestry molecular biology and particularly relates to camellia polymorphic chloroplast genome microsatellite molecular marker primers and a method forscreening and discriminating related species. Based on the relative consistency of camellia species chloroplast DNA sequence microsatellite sites, cpSSR primers are designed aiming at the specific microsatellite sites with interspecies variation; DNA of different camellia species is execrated, mixed with the primers and amplified and then is subjected to electrophoresis detection; finally, the 16pairs of camellia polymorphic chloroplast genome microsatellite molecular marker primers are obtained. The method for discriminating the related species comprises the following steps: extracting bothDNA of Zhejiang red camellia and DNA of related species of the Zhejiang red camellia, performing capillary electrophoresis separation by adopting the polymorphic primers, and separating and discriminating the related species according to PCR product fragments. The primer screening method provided by the invention is quick, efficient and widely applicable to other plant species with chloroplast genome sequence information; an obtained polymorphic cpSSR marker can be used for the systematic classification of camellia plants, related species discrimination, genetic diversity analysis and other studies.
Owner:JIANGXI ACAD OF FORESTRY
Method for extracting deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) from mature kenaf laminas
InactiveCN102533729APrevents Oxidative InterferenceReduce extraction timeDNA preparationGenomicsEnzyme digestion
The invention belongs to the field of plant molecular biology, and particularly relates to a method for efficiently and stably extracting deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) from mature kenaf laminas. According to the invention, a method for extracting genome DNA from kenaf laminas by a cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB) method is improved and optimized on the basis of a traditional kenaf genome DNA extraction method by combining with the characteristic that the mature kenaf laminas contain polysaccharide and polyphenol. The kenaf genome DNA obtained by applying the method for efficiently and stably extracting the DNA from the mature kenaf laminas has clear strips and do not have tailings; OD260 / OD280 is 1.7-1.9; enzyme digestion is complete; the quality and the yield of the kenaf genome DNA obtained by applying the method for efficiently and stably extracting the DNA from the mature kenaf laminas are higher than that of the kenaf genome DNA obtained by applying an improved sodium dodecyl sulfonate (SDS) method. The kenaf genome DNA can be used for amplifying chloroplast DNA and mitochondria DNA. A working foundation is laid for further developing researches on genomics of kenaf and bast-fibre plants thereof and subcellular genomics.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Method for efficiently obtaining chloroplast DNA sequencing data and application thereof
ActiveCN110042148AGuaranteed randomnessFull Coverage GuaranteedMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisNucleic acid sequencingPlant evolution
The present application discloses a method for efficiently obtaining chloroplast DNA sequencing data and an application thereof. The method comprises steps of constructing a non-redundant chloroplastsequence set by using a chloroplast nucleic acid sequence set; designing probes according to the non-redundant chloroplast sequence set, capturing chloroplast DNA fragments of whole genome of samplesto be detected, and then performing sequencing to obtain the chloroplast DNA sequencing data. The method can directly capture the chloroplast DNA fragments from the whole genome of the samples to be detected, is simple and convenient to operate, and has relatively low requirements for sample quality. The method has wide applicability, can capture the plant chloroplast DNA of different evolutionarybranches, has no preference for capture regions, can ensure wide coverage of the data produced by the sequencing, is especially suitable for obtaining the large-scale relatively large evolutionary branch chloroplast DNA sequencing data and lays foundation for in-depth study of large-scale plant evolution and hereditary.
Owner:SHENZHEN BGI AGRI & CYCLE ECONOMIC TECH
Method for extracting DNA of algae chloroplast
InactiveCN102732503AHigh yieldTo achieve the separation effectDNA preparationWater bathsGenomic sequencing
The invention relates to a method for extracting a DNA of an algae chloroplast. The method comprises the following steps of carrying out pulp homogenization of fresh or frozen algae as a raw material by a tissue pulp homogenization machine, adding a buffer solution A into the homogenate obtained by the previous step, carrying out centrifugation by a centrifugal force of 3000 to 6000xg, collecting precipitates, adding a buffer solution B into the precipitates, carrying out water bath pyrolysis at a temperature of 60 to 70 DEG C for 1 to 2 hours, removing denatured proteins of the lysate, adding CsCl and Hoechst 33258 into the lysate, carrying out centrifugation by a centrifugal force of 36000 to 40000xg for 8 to 12 hours, taking out a stripe containing a DNA of an algae chloroplast, removing Hoechst 33258, adding 2.5 to 3.5M of sodium acetate, double distilled water and isopropanol into the stripe, standing at a temperature of -20 DEG C for 20 to 40 minutes, carrying out centrifugation by a centrifugal force of 12000 to 16000xg for 15 to 30 minutes to obtain precipitates, and carrying out purification to obtain the DNA of the algae chloroplast. Compared with the prior art, the method simplifies extraction processes, has simple and feasible processes, improves an extraction ratio and purity of a DNA of an algae chloroplast, realizes an algae (fresh algae) chloroplast DNA yield of 150 to 200 micrograms per gram, and can fully satisfy requirements of conventional molecular biology processes such as genomic sequencing, specific enzyme digestion, random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD), polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and target gene sequence cloning.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MARINE DEV RES INST
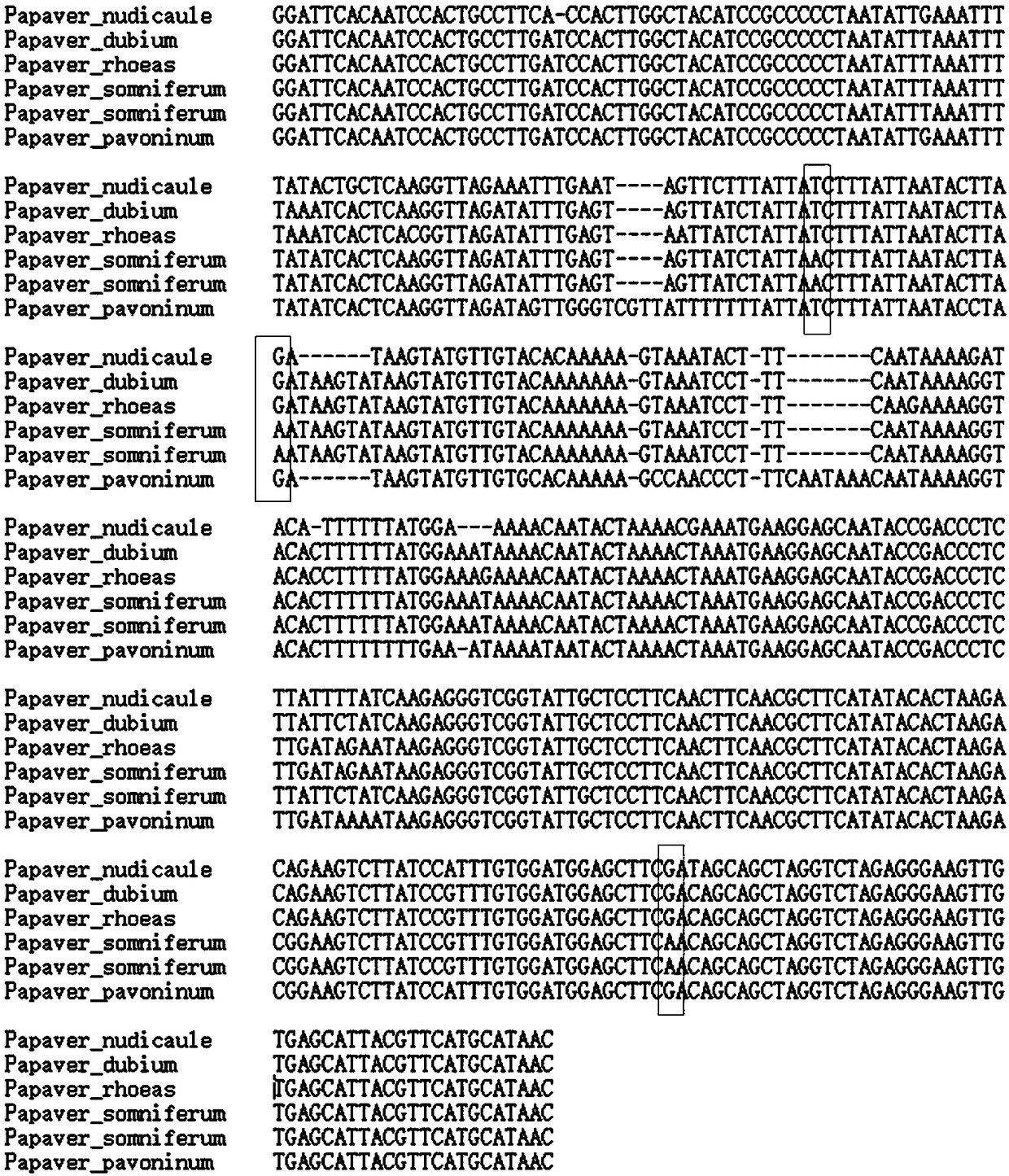
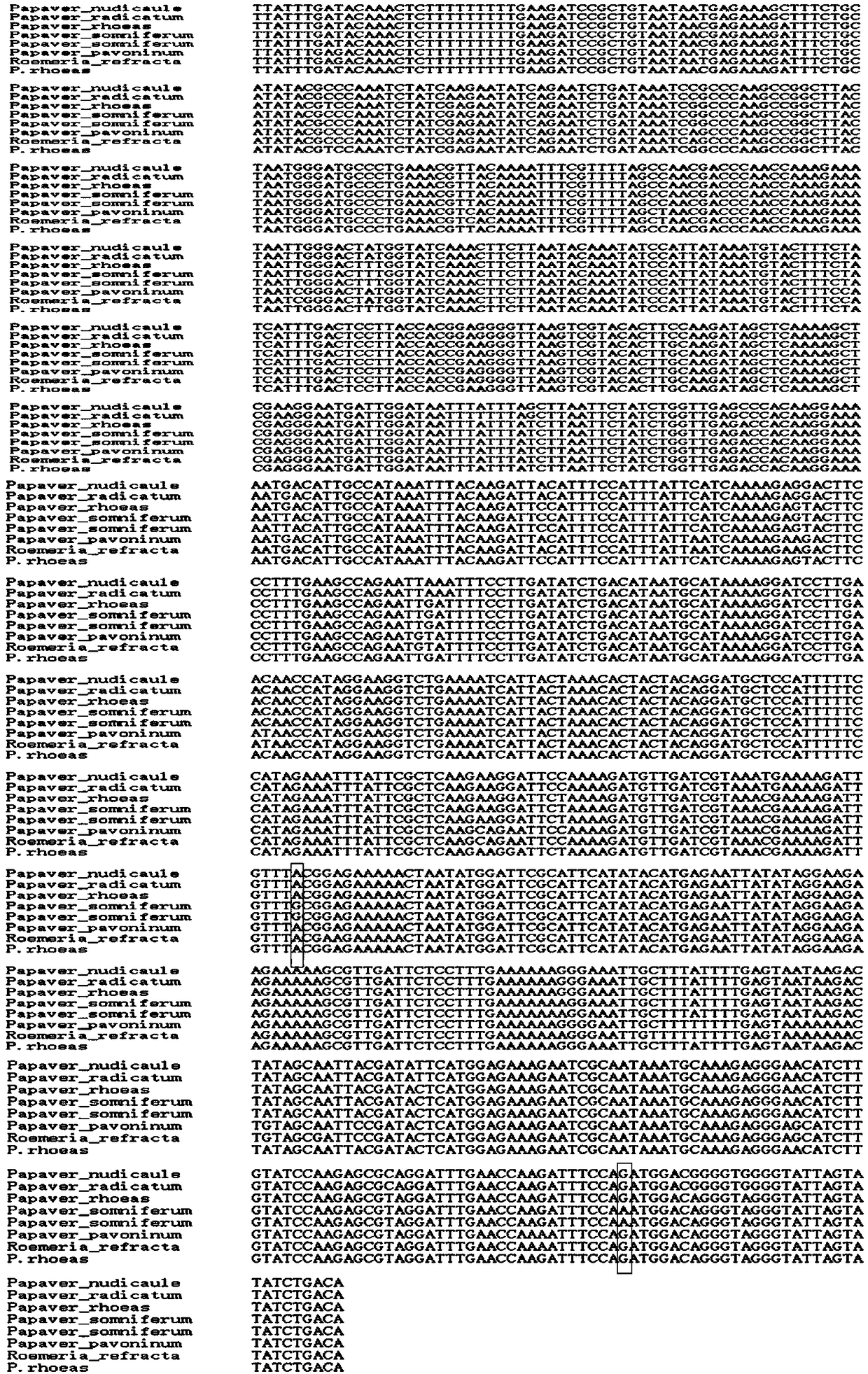
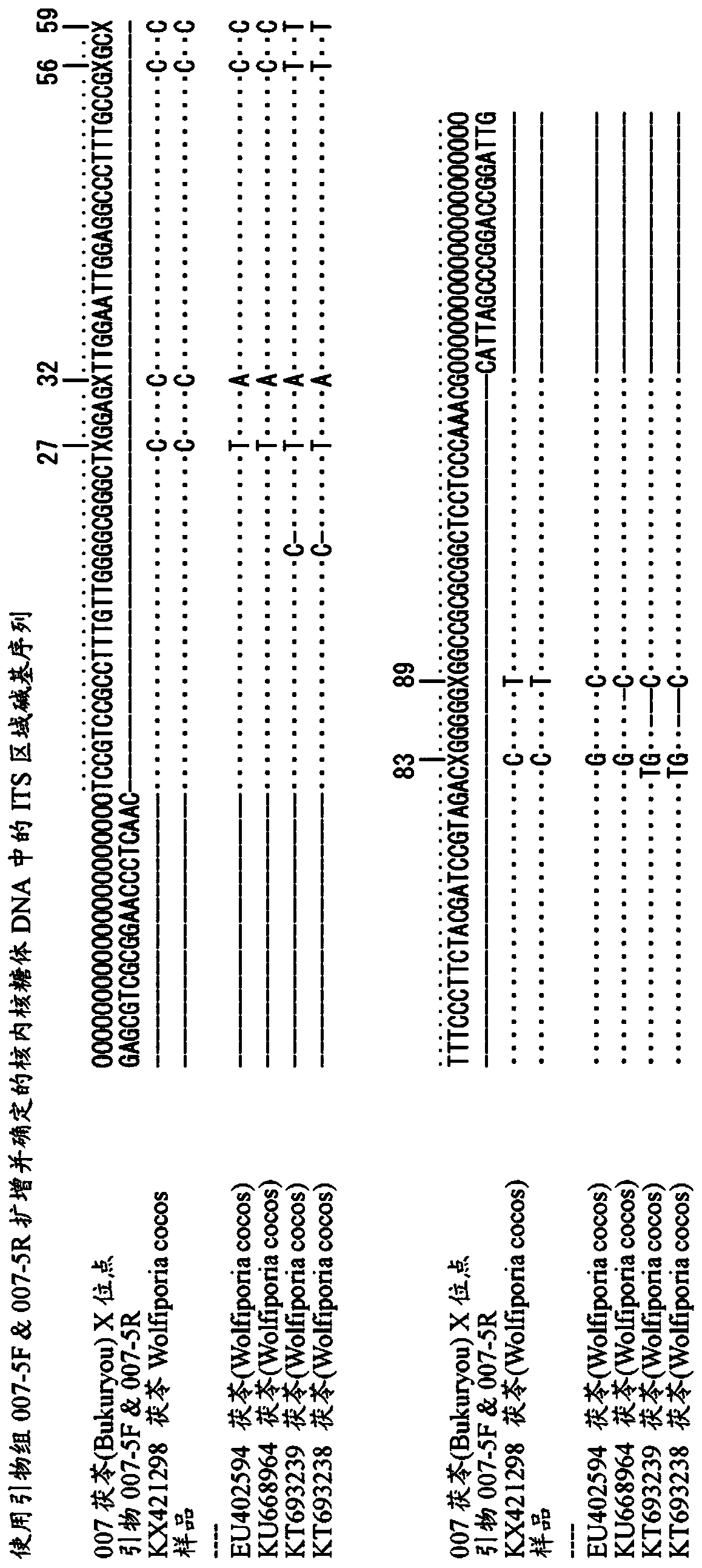
Method for identifying opium poppy by using chloroplast DNA bar code
InactiveCN108396070AImprove accuracyRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA barcodingChloroplast
The invention provides a method for identifying papaveraceae papaver opium poppy (opium) by using chloroplast gene DNA bar code. According to the method, the distribution region of papaver plants is widely surveyed; samples in a plurality of places are collected; a database of a chloroplast sequence of the plant in the papaver is built; through comparison, special information sites of the opium poppy are discovered; in the sequence with the total length of 2645bP, the site at105bp is A; the site at 121bp is A; the site at 333bp is A; the site at 748bp is T; the site at 1539bp is G; the site at1751bp is A; the site at 2392bp is G; the site at 2604bp is A. By using the differences between the sites and other species, the opium poppy can be fast and accurately identified.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
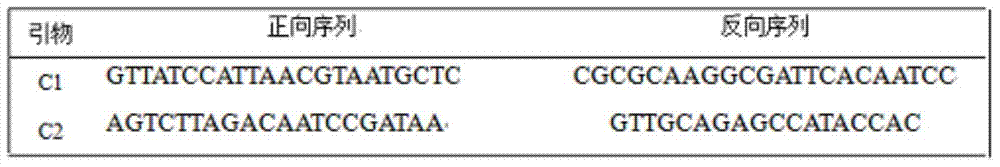
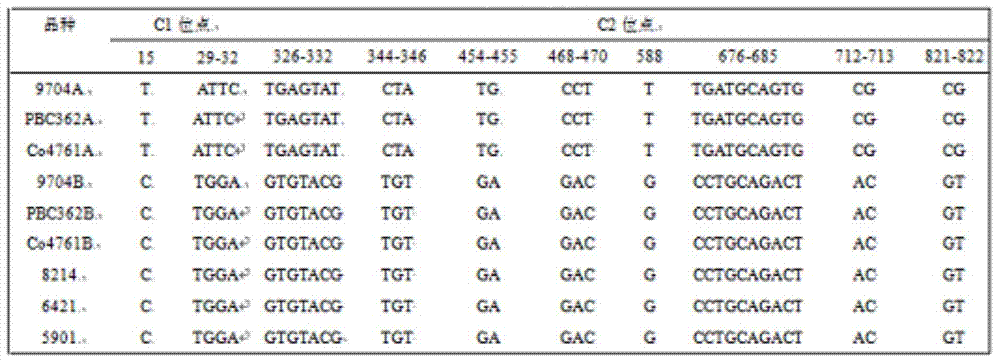
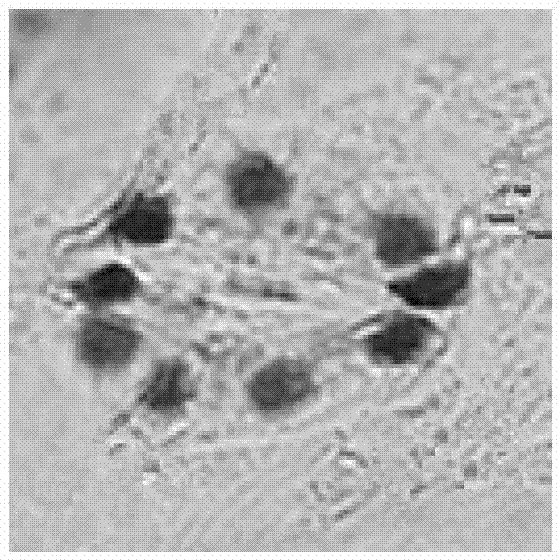
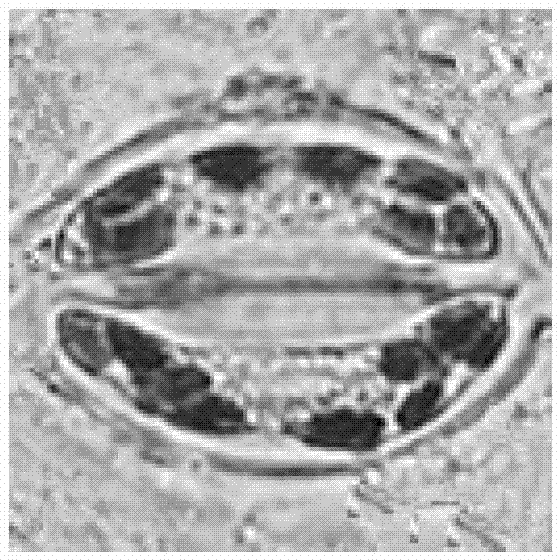
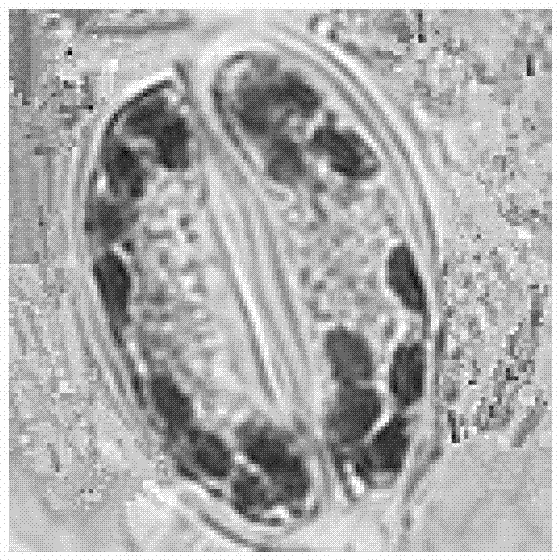
Method for detecting chloroplast DNAs to identify cytoplasmic male sterile line of hot pepper
InactiveCN104513856AEasy to identifyEfficient and accurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyHot peppers
The invention discloses a method for detecting chloroplast DNAs to identify cytoplasmic male sterile line of hot pepper. The method comprises the following steps: taking the leaves of hot pepper as a material, extracting total DNAs in the leaves, carrying out PCR amplification by using chloroplast primers (C1 and C2), carrying out clone sequencing on amplification products, and then making a comparison with chloroplast DNA molecular fingerprints of the cytoplasmic male sterile line of hot pepper, namely identifying the cytoplasmic male sterile line of hot pepper simply, efficiently and accurately. The method for detecting chloroplast DNAs to identify the cytoplasmic male sterile line of hot pepper disclosed by the invention, the clone sequencing is carried out on the PCR amplification products of the chloroplast primers (C1 and C2) only when the cytoplasmic male sterile line of hot pepper is identified, and then a comparison is made, so that the cytoplasmic male sterile line of hot pepper can be identified simply, efficiently and accurately.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF ARTS & SCI +1
Identification method of interspecific hybrids of Brassica campestris and Brassica napus
InactiveCN102768210AImprove accuracyAccurate identificationInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsStomaCuticle
The invention discloses an identification method of interspecific hybrids of Brassica campestris and Brassica napus, falling into the technical field of plant cytology. The method includes collecting the 4th-7th leaves of a plant in the seedling stage, tearing to collect hypoderm tissues of lower parts of the leaves, staining with iodine-potassium iodide solution, observing stomata under an optical microscope, measuring major / minor axis values of guard cells, calculating perimeter values of the guard cells with an ellipse model while observing and counting chloroplasts, recording 15 data per leaf, and identifying with parents as controls. For Brassica campestris, stoma guard cells have perimeter smaller than 58.90 micrometer and chloroplast count of 9-11; for Brassica napus, stoma guard cells have perimeter greater than 75.83 micrometer and chloroplast count of 19-20; while, for the to-be-identified material, if more than ten stomata simultaneously satisfy that guard cells have perimeter of 58.90-75.83 micrometer and chloroplast count of 14-16, it is determined that the plant is interspecific hybrids F1 of Brassica campestris and Brassica napus, otherwise it is false hybrid.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
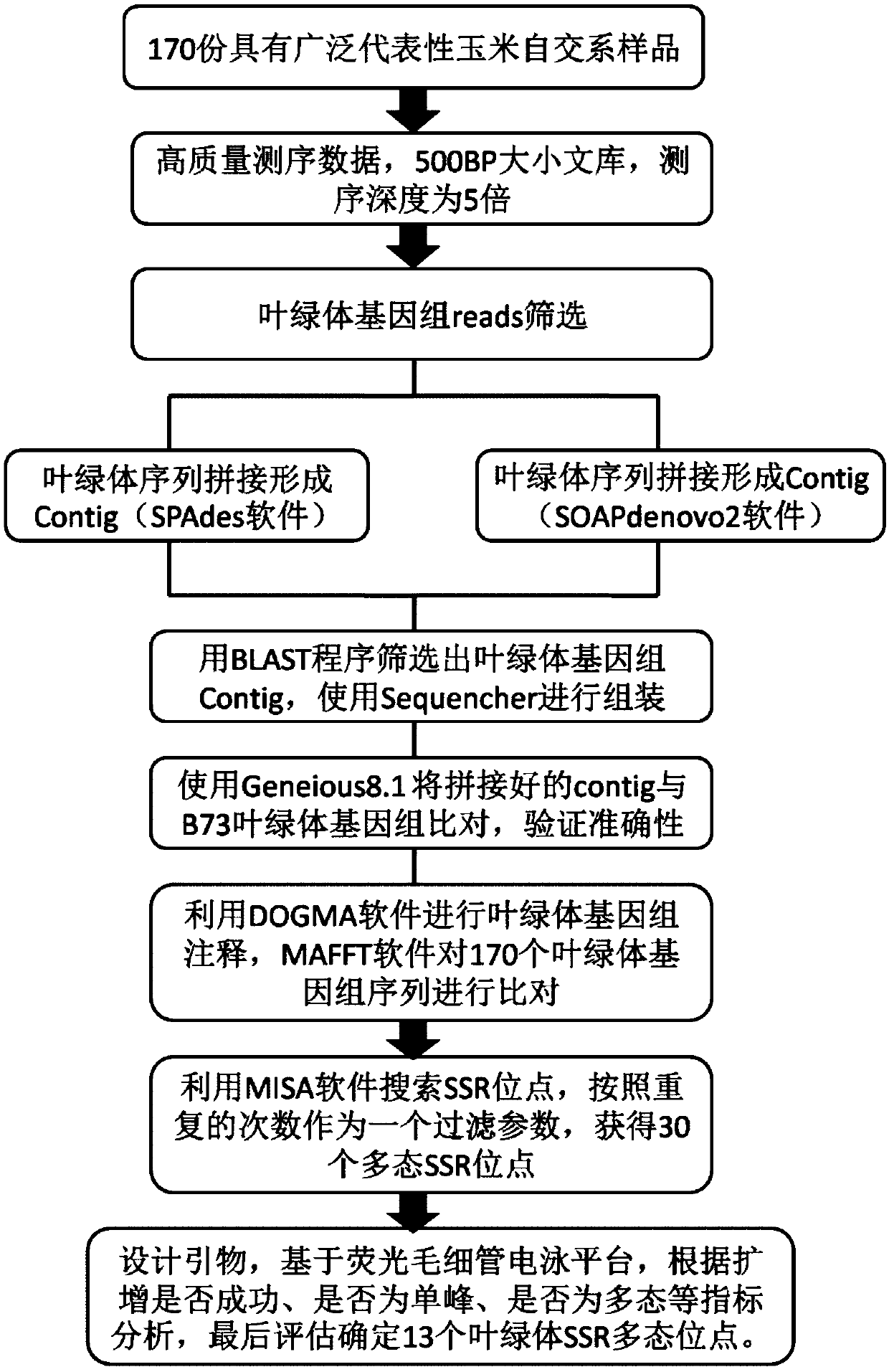
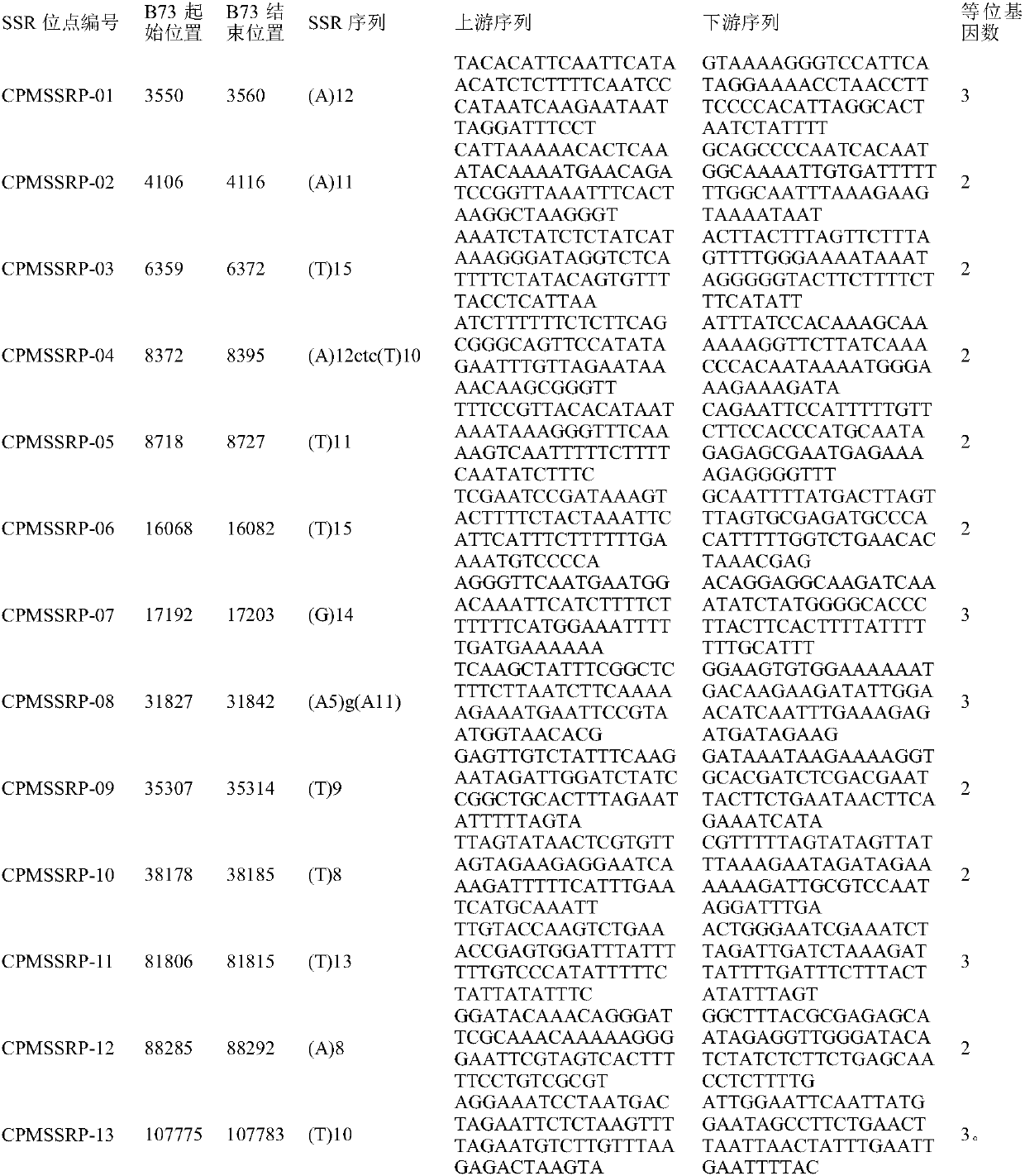
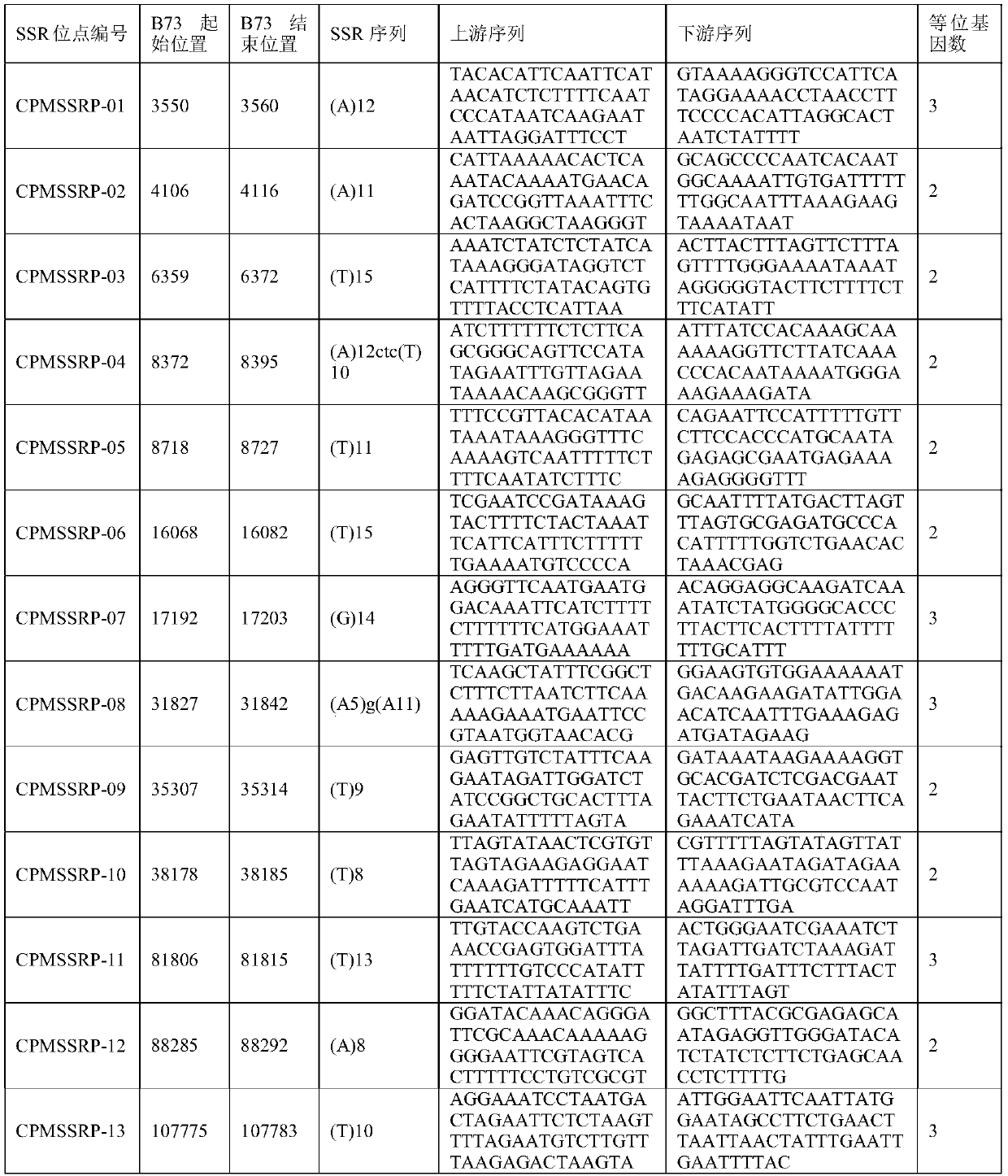
Corn chloroplast genome SSR site and application in variety identification
ActiveCN108676906AGuaranteed accuracyImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGermplasmChloroplast
The invention provides a corn chloroplast genome SSR site and application in variety identification. According to the corn chloroplast genome SSR site disclosed by the invention, accuracy and high efficiency of an obtained chloroplast polymorphic site are ensured by representative sample selection, high-quality sequencing data and accurate data analysis; 13 chloroplast SSR polymorphic sites can befinally determined by choosing a corn material with a wide source and rich phenotypes and gene types, based on a spliced corn material chloroplast genome sequence and by adoption of MISA software tosearch SSR. When the SSR sites are utilized, (1) a corn variety chloroplast DNA-SSR fingerprint database can be constructed, (2) a corn sample maternal line can be traced and analyzed, and (3) a cornsample can be reciprocally crossed and identified. When the chloroplast SSR site disclosed by the invention is used, a usable marker site range of corns can be expanded on the genome level; thus, a novel idea and a novel method are provided for researches on corn variety and germplasm resource identification, genetic relationship evaluation, cytoplasmic inheritance characteristics and the like.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
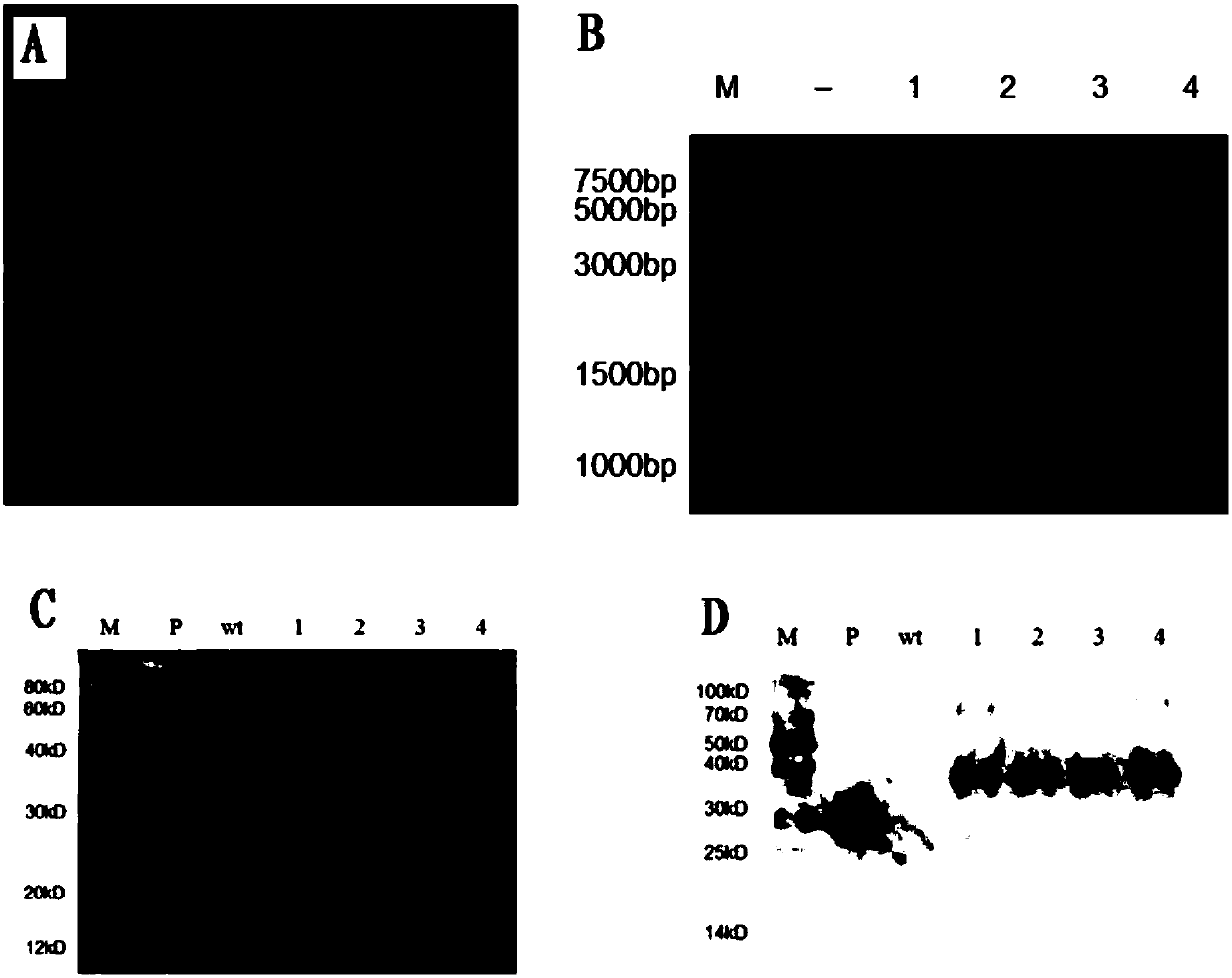
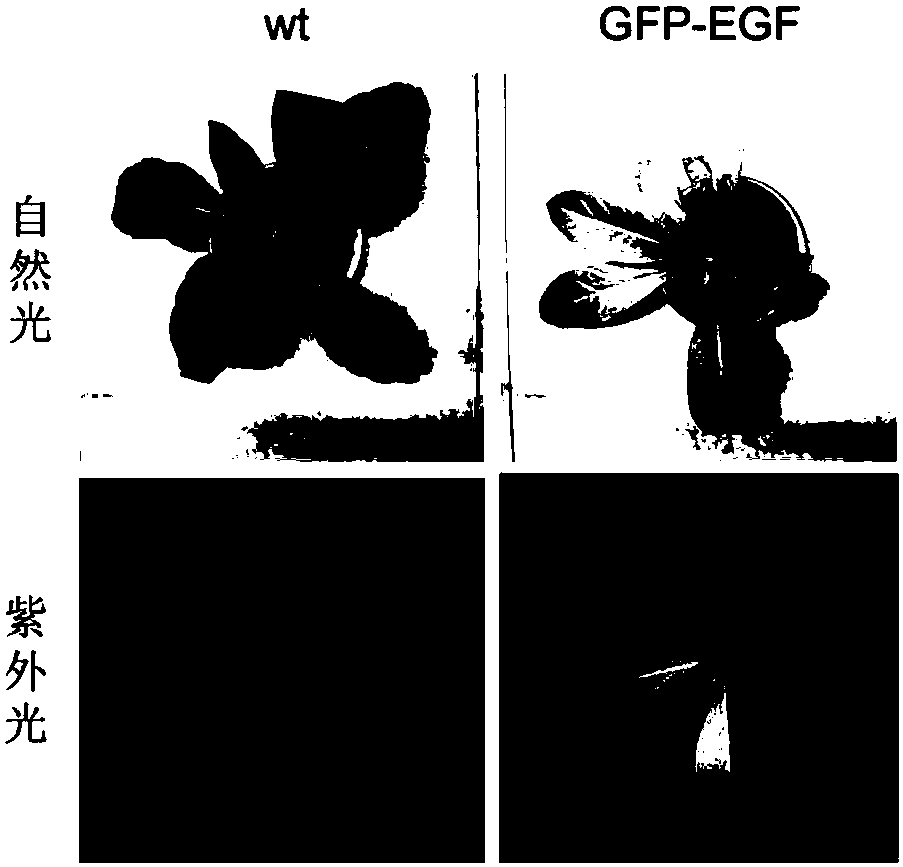
Chloroplast-expressed human epidermal growth factor (hEGF) protein and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108034003AEligible for commercial productionPeptide preparation methodsVector-based foreign material introductionNicotiana tabacumHuman epidermal growth factor receptor
The invention discloses a chloroplast-expressed human epidermal growth factor (hEGF) protein and a preparation method thereof. The amino acid sequence of the protein is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The invention further discloses a tobacco chloroplast expression vector pWYP23404 for producing the epidermal growth factor hEGF protein. The preparation method of the protein comprises the following steps: building the tobacco chloroplast expression vector pWYP23404, performing tobacco chloroplast transformation and homogenization screening on an EGF (Epidermal Growth Factor) gene to obtain a homogenization plant of a tobacco chloroplast-transformed hEGF gene, and analyzing the hEGF expression amount in the chloroplast-transformed gene tobacco plant; purifying the hEGF protein to obtain the chloroplast-expressed epidermal growth factor hEGF protein. By adopting the chloroplast-expressed hEGF protein and the preparation method thereof, a GFP (Green Fluorescent Protein)-fused protein of the hEGF isexpressed efficiently in a tobacco chloroplast, and commercial production conditions are realized.
Owner:JILIN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Primer group and crude drug identification method using primer group
PendingCN111378777AAvoid mixingEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyChloroplast
An aim of the present invention is to develop and provide a means for accurately identifying whether or not a plant to be detected, which is a candidate crude drug after processing, is a base plant, and identifying the candidate crude drug as a target crude drug and an identification method using the means. For various crude drugs, a primer group capable of stably acquiring base sequence information from a processed to-be-detected plant and amplifying a specific region in genome DNA or chloroplast DNA of a base plant with a specific base sequence in the base plant is designed. The invention provides the primer group and a crude drug identification method using the primer group.
Owner:TSUMURA
Chloroplast DNA extracting method of sonneratia plant
The invention discloses a chloroplast DNA extracting method of a sonneratia plant. The method comprises the following steps: performing dark treatment on leaves of the sonneratia plant first, performing homogenate, centrifugal treatment and filtration to obtain filtrate, namely sonneratia plant chloroplast, then adding cracking buffering liquid into the obtained chloroplast for fully cracking, firstly extracting the obtained cracking mixture solution by using phenol, then extracting by using phenol-chloroform, centrifuging to obtain a precipitate, dissolving the obtained precipitate, and performing RNase digestion to obtain the chloroplast DNA of the sonneratia plant, wherein the concentration of lauryl sodium sulfate in the cracking buffering liquid is 3.5 to 4.5 percent. By utilizing the method, high-quality and high-purity chloroplast DNA of the sonneratia plant is extracted, separated and obtained successfully, and the method is of great significance to analyze evolutionary relationship of the sonneratia plant, design an SSR primer to analyze the genetic diversity of the existing sonneratia plant population, analyze the expansion and evolution of exotic sonneratia plant at home and the like, and has a broad promotion and application prospect.
Owner:LINGNAN NORMAL UNIV
Method for analyzing otis tarda food source plant through feces DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
ActiveCN106381337APromoting the development of research on feeding ecologyReduce manpower consumptionMicrobiological testing/measurementStool dnaAnimal feces
The invention discloses a method for analyzing an otis tarda food source plant through feces DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid). The method comprises the following steps of (1) using trnL gene amplification primer pairs with different base tags for respectively amplifying multiple trnL gene segments in otis tarda feces to be measured, so as to obtain the multiple trnL gene segments in the otis tarda feces to be measured added with different base tag sequences; (2) mixing the multiple trnL gene segments in the otis tarda feces to be measured added with the different base tag sequences, so as to obtain mixed segments, high-throughput sequencing the mixed segments, so as to obtain multiple sequencing sequences of the trnL gene segments in the otis tarda feces to be measured; (3) comparing the multiple sequencing sequences of the trnL gene segments in the otistarda feces to be measured with an eciophyte chloroplast DNA trnL complete sequence database and a common trnL bar code database, judging the otis tarda food source plant to be measured according to the homology of sequences in the sequencing sequences and the two databases, and calculating the percentage of a plant ingested by an otis tarda according to a sequence bar number. The method for analyzing the otis tarda food source plant through feces DNA provided by the invention provides a technical support for researching feeding habit preference of animals and recipes.
Owner:RES INST OF FORESTRY NEW TECH CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
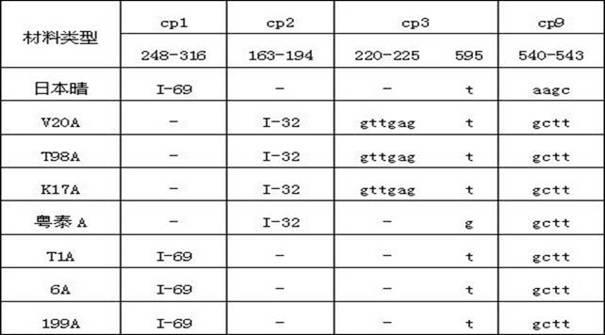
Method for identifying cytoplasm type of three-line sterile rice by detecting chloroplast DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid)
InactiveCN102605054AEasy to identifyEfficient identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnology3-deoxyribose
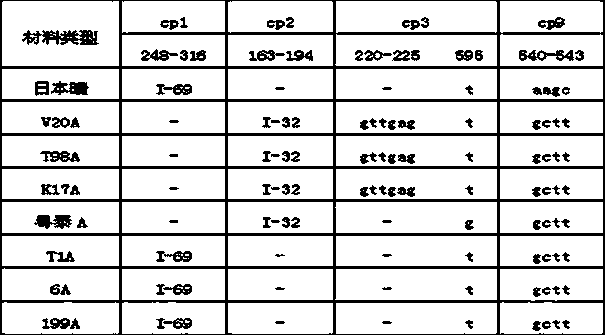
The invention discloses a method for identifying the cytoplasm type of three-line sterile rice by detecting chloroplast DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid). The method comprises the steps of: taking rice leaves as material, extracting chloroplast DNA in the leaves, carrying out PCR (polymerse chin rection) amplification by using chloroplast primers cp1, cp2, cp3 and cp9, cloning and sequencing the amplified product, and comparing the result with chloroplast DNA molecular fingerprinting of the three-line sterile rice so as to simply and efficiently identify the cytoplasm type of the three-line sterile rice.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
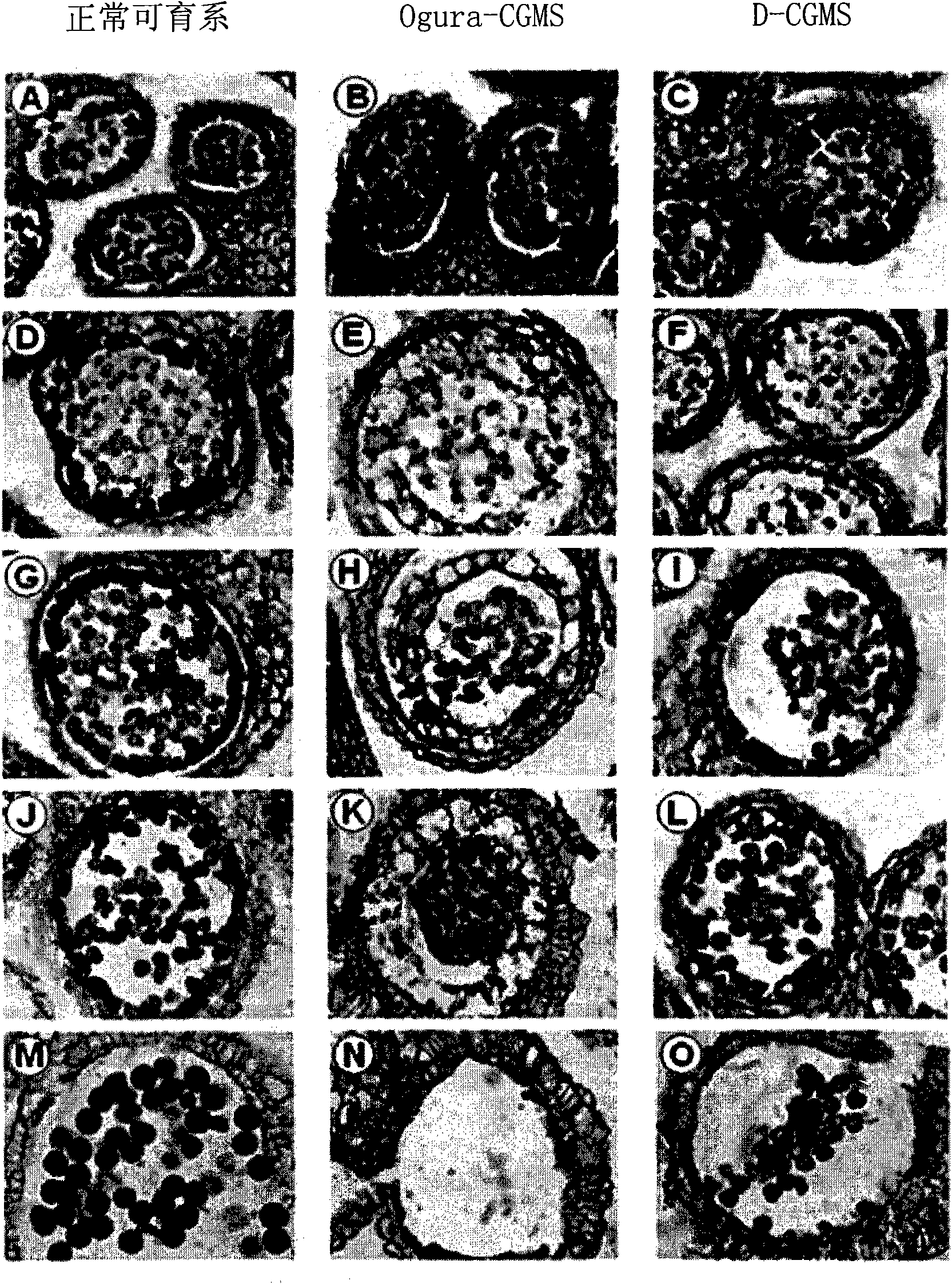
A method for producing a hybrid seed using plant of novel cytoplasmic-genic male sterility raphanus sativus line and DNA markers for selecting the plant of said raphanus sativus line
ActiveCN101679982AQuick selectionEasy to breedMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringHybrid seedNucleotide
The present invention relates to a method for producing hybrid seeds using a novel Cytoplasmic-Genic Male Sterility (CGMS) Raphanus sativus line plant and DNA markers for the selection of the same, more precisely a novel CGMS (D-CGMS) Raphanus sativus line plant, a method for producing hybrid seeds using the same, chloroplast DNA-based markers for the selection of the D-CGMS Raphanus sativus lineplant having the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ. ID. NO: 5, mitochondrial DNA-based SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) markers for the selection of the D-CGMS Raphanus sativus line plant located on the 171st nucleotide of the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ. ID. NO: 12. The D-CGMS Raphanus sativus line plant of the present invention can be effectively used for the production of hybrid seeds owing to its high stability of male sterility. The chloroplast DNA-based markers and mitochondrial DNA-based SNP markers for the selection of D- CGMS Raphanus sativus line plants can be very effective in the selection of D-CGMS Raphanus sativus line plants during breeding process.
Owner:DONGBU HITEK CO LTD
Electrotransformation method of isolated chloroplast of cucumis stativum
InactiveCN103966255AImprove efficiencyShort timeMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionPlant cellChloroplast
The invention relates to an electrotransformation method of isolated chloroplast of cucumis stativum. The method comprises the following steps: by taking chloroplast separated from sterile cotyledon of cucumis stativum as a raw material, establishing an electrotransformation system of isolated chloroplast of cucumis stativum in proper volume and under proportion of chloroplast concentration and expression vectors; after transformation, carrying out short-time incubation, centrifugalization and DNase I digestion of chloroplast to carry out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) and RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction) identification by taking extracted transformed chloroplast DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) and RNA (Ribonucleic Acid). The result shows that the chloroplast expression vector not only can be efficiently transformed to chloroplast, but also expression of an exogenous gene can be detected in the transcriptional level. The method provided by the invention can be used for overcoming the problems that the chloroplast of a higher plant cell is long in transformation period, difficult in technology and high in cost and the like, and provides an effective novel path for establishment of the higher plant chloroplast transformation vector, identification of the functions of key elements and basic theory and application and research of regulation of chloroplast gene expression and cell engineering and the like.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Vector mediated organelle transfection
InactiveUS7741112B2High expressionFunction increaseSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsDNA constructViral vector
The present invention provides compositions and methods for direct transfection of mitochondria and chloroplast DNA in living cells. More particularly, the present invention is based on the use of viral vectors that specifically bind to receptors uniquely found on the target organelle. In one embodiment, as shown in FIG. 1, a eukaryotic cell containing an organelle (1) that has been modified to express a viral receptor (2) on the organelle's surface is provided. A viral vector (6) comprising a desired recombinant DNA construct (3) is introduced into the cytosol of the cell, wherein the viral vector binds to its receptor and introduces the recombinant DNA into the interior of the organelle.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Method for identifying cytoplasm type of three-line sterile rice by detecting chloroplast DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid)
InactiveCN102605054BEasy to identifyEfficient identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnology3-deoxyribose
The invention discloses a method for identifying the cytoplasm type of three-line sterile rice by detecting chloroplast DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid). The method comprises the steps of: taking rice leaves as material, extracting chloroplast DNA in the leaves, carrying out PCR (polymerse chin rection) amplification by using chloroplast primers cp1, cp2, cp3 and cp9, cloning and sequencing the amplified product, and comparing the result with chloroplast DNA molecular fingerprinting of the three-line sterile rice so as to simply and efficiently identify the cytoplasm type of the three-line sterile rice.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Molecular Markers of Maize Chloroplast Genome and Its Application in Variety Identification
ActiveCN108486266BVerify accuracyGood amplification effectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGermplasmChloroplast
The invention provides a molecular marker of maize chloroplast genome and its application in variety identification. The molecular markers include 57 SNP markers and 6 InDel markers, and these 63 molecular markers and primers developed according to each marker can be applied in any of the following: (1) constructing maize variety chloroplast DNA-SNP, InDel fingerprint database; (2) Carry out traceability analysis of maize parent line; (3) Carry out reciprocal cross identification of corn samples. Through the application of chloroplast polymorphic primer combinations, the range of available marker sites in maize has been expanded at the genome level; new ideas and technical means have been provided for the identification of maize varieties, germplasm resources, genetic relationship evaluation, and cytoplasmic genetic characteristics.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Primer pair for microalgae identification and application thereof
ActiveCN113462808AMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationBiotechnologyChaetoceros muelleri
The invention provides a primer pair for microalgae identification, wherein the primer pair is cpDNAB2F: 5'-TCTTATGGTCACAAGCTTTCCA-3', and cpDNAB2R: 5'-CTGTCATACCATATGTGCTTCC-3'. According to the present invention, the 21 microalgae are subjected to PCR amplification by using the primer pair so as to respectively obtain the unique chloroplast DNA bar code sequences, wherein the 11 microalgae such as Seminavis robus, Nitzschia palea, Chaetoceros muelleri, Picocystis salina and the like can be identified into the species, and the other microalgae species can be identified into the genus, such that the repeatability is good, the stability and the reliability are good, and the detection is rapid.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com