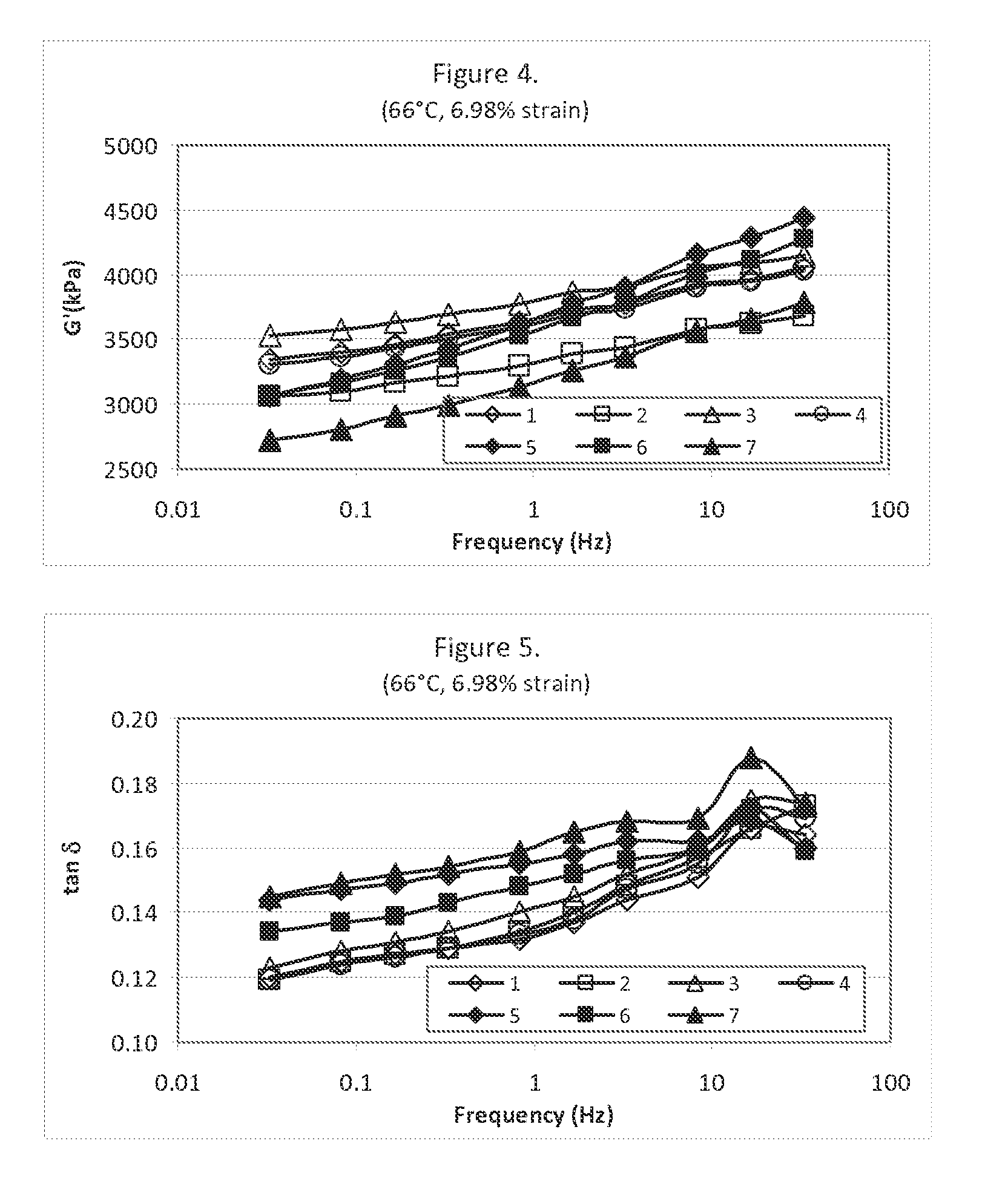
Patents
Literature
196 results about "Kenaf" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Kenaf [etymology: Persian], Hibiscus cannabinus, is a plant in the family Malvaceae also called Deccan hemp and Java jute. Hibiscus cannabinus is in the genus Hibiscus and is native to southern Asia, though its exact origin is unknown. The name also applies to the fibre obtained from this plant. Kenaf is one of the allied fibres of jute and shows similar characteristics.
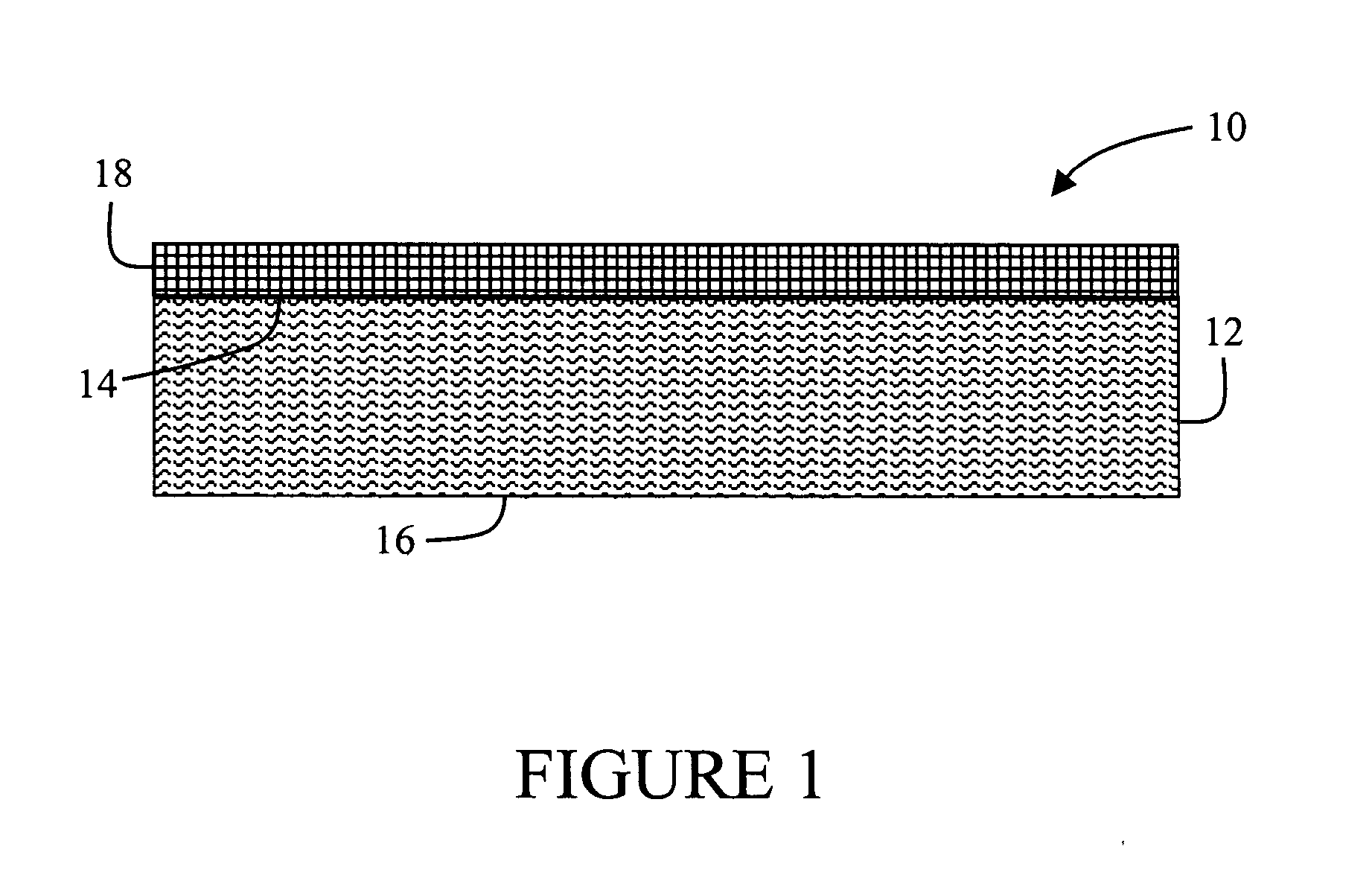
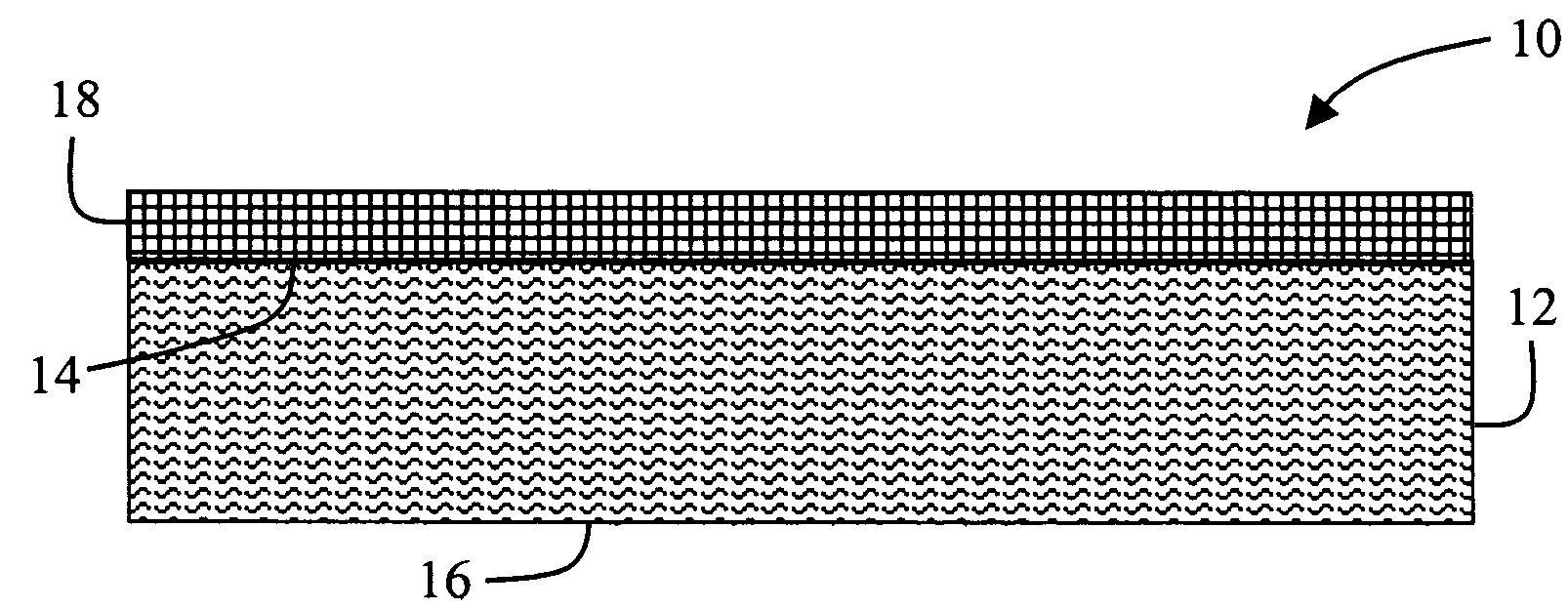
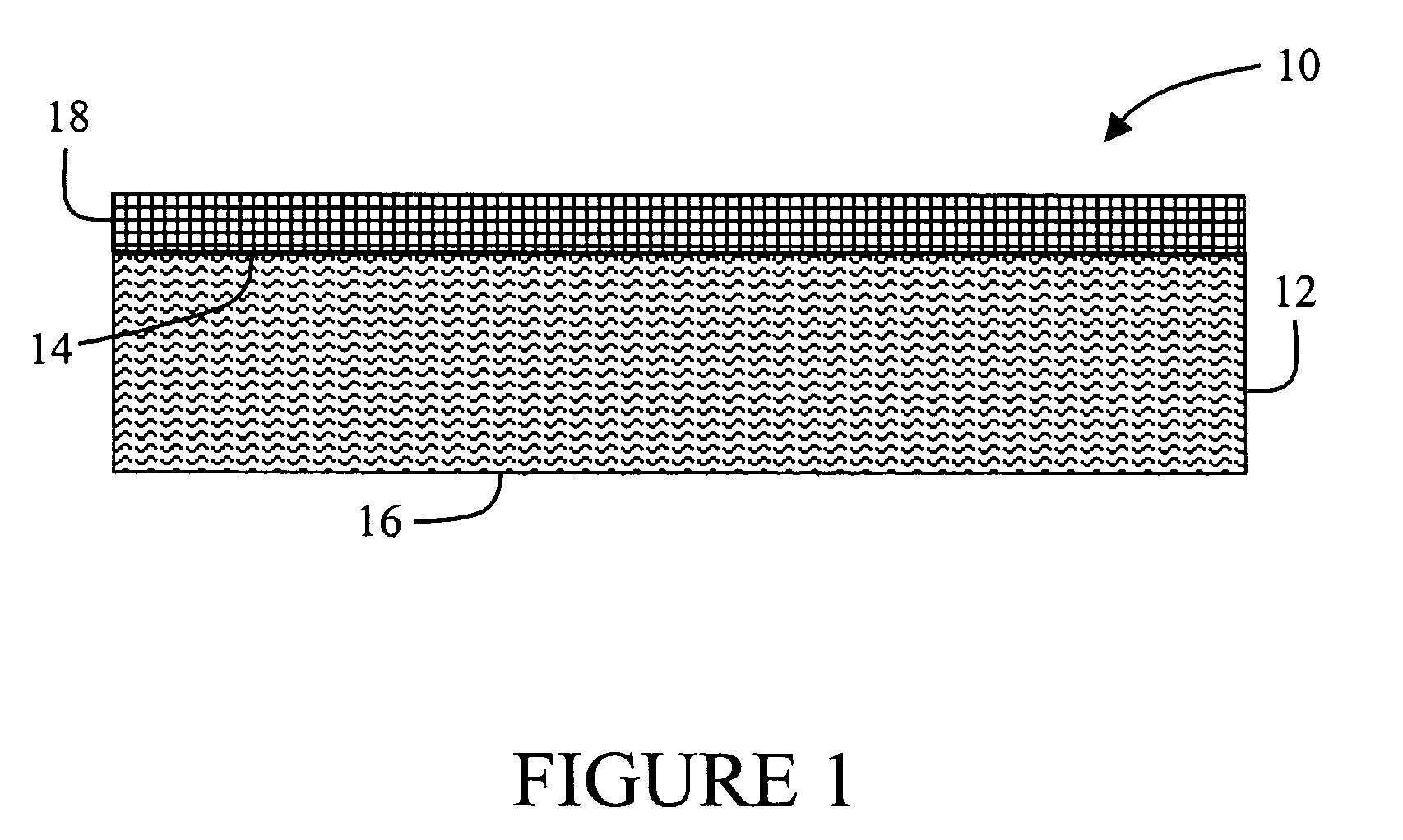
Composite thermoplastic sheets including natural fibers
A composite sheet material includes, in an exemplary embodiment a porous core that includes at least one thermoplastic material and from about 20 weight percent to about 80 weight percent of natural fibers based on a total weight of the porous core. The natural fibers include at least one of kenaf fibers, jute fibers, flax fibers, hemp fibers, cellulosic fibers, sisal fibers, and coir fibers.
Owner:HANWA AZDEL INC
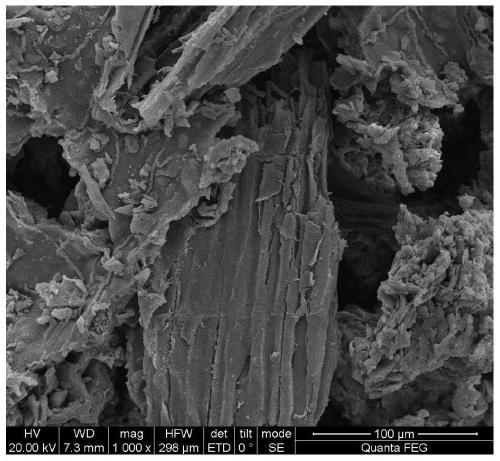
Kenaf stalk activated charcoal and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a flax straw activated carbon (flax carbon) and a preparation method thereof, which is obtained from flax straws which go through pretreatment, carbonization, activation, rinsing and drying and molding. The flax straw activated carbon prepared according to the invention has a specific surface area of 1200 to 1800m<2> / g, total pore volume is 0.8 to 1.0cm<3> / g. The particle diameter of the flax straw activated carbon is 0.001 to 10mm; benzene adsorptive value is 80 to 120mg / g; stacking density is 0.25 to 0.30g / m<3> and intensity is larger than 92 percent. The invention has an extremely good adsorptive property.
Owner:THE QUARTERMASTER EQUIPMENT RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF THE GENERAL LOGISITIC DEPARTME +1
Kenaf-fiber-reinforced resin composition
ActiveUS20060147695A1High mechanical strengthReduce biodegradationSynthetic resin layered productsRecord information storageKenafPolyresin
An object of the present invention is to provide a fiber-reinforced resin composition suitable for producing molded articles for products such as electrical and electronic equipment. The object has been achieved by a biodegradable resin composition containing a kenaf fiber, which contains a kenaf fiber in an amount of 10 to 50% by mass. In this case, the biodegradable resin is preferably a crystalline thermoplastic resin, particularly polylactic acid. The average fiber length (number average fiber length of the fibers excluding fragments) of the kenaf fiber is preferably 100 μm to 20 mm, and the kenaf fiber preferably contains a kenaf fiber having a fiber length of 300 μm to 20 mm. As the kenaf fiber, a fiber prepared from bast of kenaf is preferred.
Owner:NEC CORP
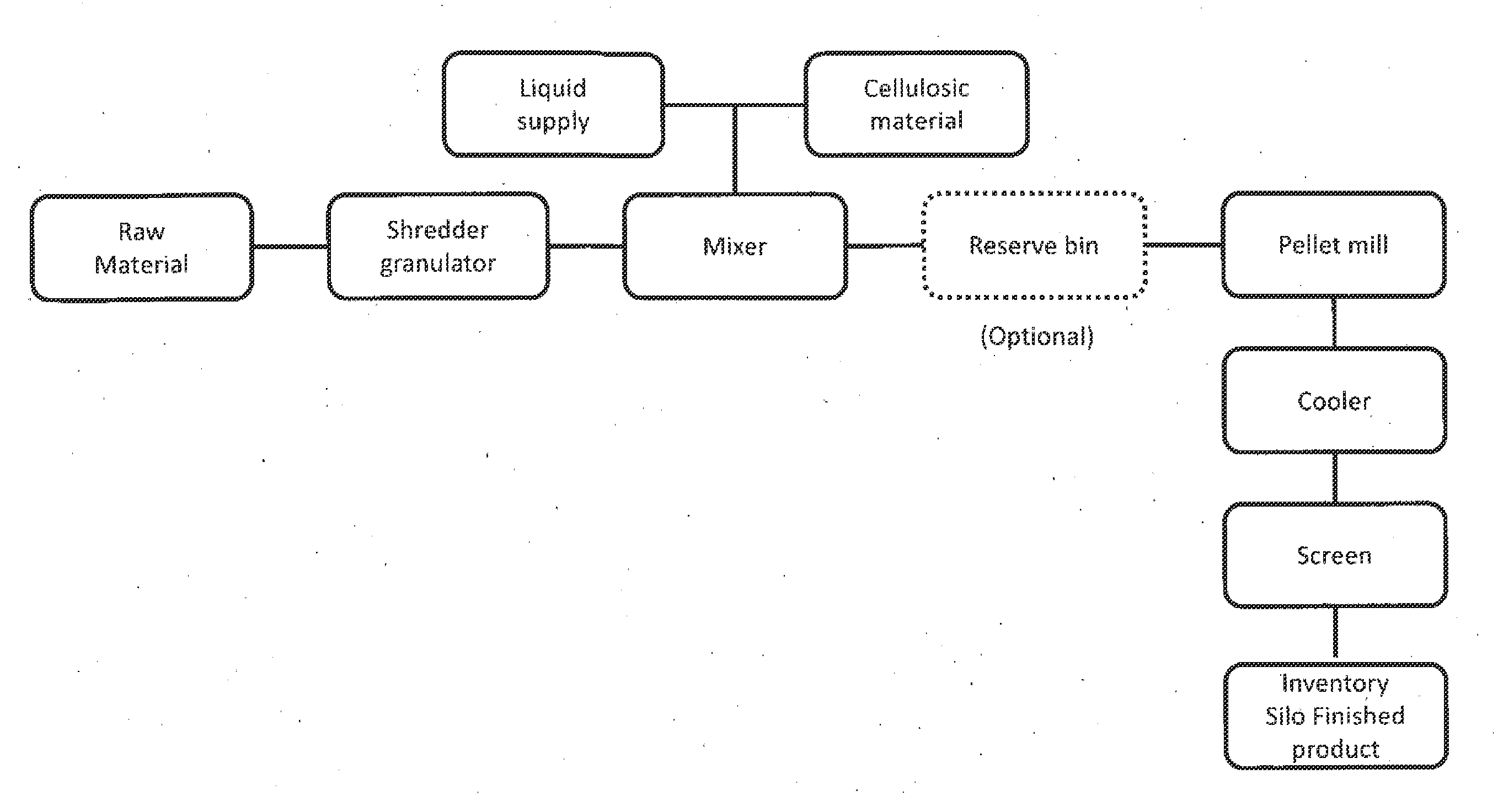
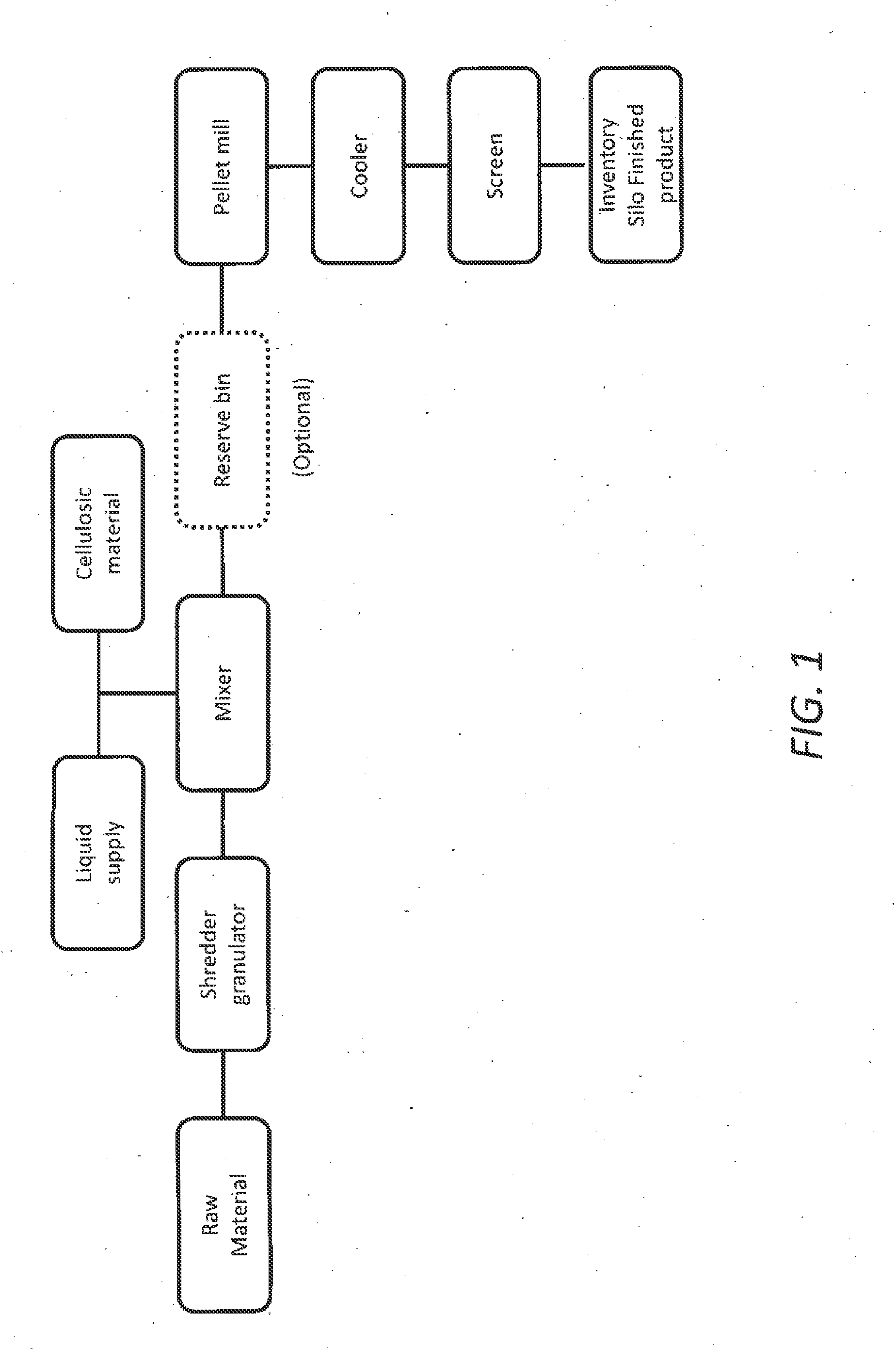
Multipurpose pellets and method of making same
A multipurpose pellet is provided comprising: from about 0.1% to about 100% by weight of a vegetable fiber chosen from cotton, bamboo fiber, rice fiber, esparto, papaya, coir, sisal, kapok, jute, ramie, flax, roselle hemp, hemp, kenaf, abaca, soybean fiber, okra fiber, vine fiber, banana fiber, rattan and nettlesjute; and from about 99.9% to about 0% by weight of cellulosic material.
Owner:LEFEBVRE ROBERT
Kenaf-fiber-reinforced resin composition
ActiveUS7445835B2Low costHigh biodegradation rateSynthetic resin layered productsRecord information storageKenafPolyresin
An object of the present invention is to provide a fiber-reinforced resin composition suitable for producing molded articles for products such as electrical and electronic equipment. The object has been achieved by a biodegradable resin composition containing a kenaf fiber, which contains a kenaf fiber in an amount of 10 to 50% by mass. In this case, the biodegradable resin is preferably a crystalline thermoplastic resin, particularly polylactic acid. The average fiber length (number average fiber length of the fibers excluding fragments) of the kenaf fiber is preferably 100 μm to 20 mm, and the kenaf fiber preferably contains a kenaf fiber having a fiber length of 300 μm to 20 mm. As the kenaf fiber, a fiber prepared from bast of kenaf is preferred.
Owner:NEC CORP
Preparation method for degummed kenaf fiber
The invention provides a preparation method for a degummed kenaf fiber. According to the method, vacuum technology, an enzyme system and ultrasonic technology are combined together for degumming of kenaf bast fibers. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out degumming on a kenaf fiber by using a mixed enzyme system, allowing enzyme liquid to fully penetrate into the fiber by using vacuum negative pressure technology and allowing gum macro-molecule insoluble in water to fracture and a part of lignin to be decomposed at the same time; and removing gum strongly bonding with the fiber by using low-frequency ultrasonic waves and finally, removing residual gum in tiny parts like micropores and slits by using high-frequency ultrasonic waves. The method overcomes the problems of a great amount of residual gum, rough fiber surface and the like in conventional degumming with a single biological enzyme, improves the quality of the degummed kenaf fiber and reduces the usage amount of the enzyme and chemicals.
Owner:于丰韬
Industrialized biological degumming technique for kenaf bast fiber
ActiveCN101503829AReduce occupancyReduce pollutionBacteriological rettingMicrobial agentNetwork structure
The invention discloses a factory biologic degumming process of kenaf bast. The process comprises the following steps: firstly, rolling kenaf bast till the kenaf bast loosens without damaging kenaf fiber, and carrying out activation and augmentation treatment of Erwinia carotovora microbial agent to obtain bacterial suspension; diluting the bacterial suspension and then carrying out immersion vaccination or spraying vaccination of the kenaf bast; carrying out immersion fermentation or wet fermentation of the kenaf bast till the kenaf bast turns blue and transversely torn kenaf pieces are in a network structure; inactivating the fermented kenaf bast by hot water; and then, cleaning the kenaf bast by high-pressure water while rolling the kenaf bast till kenaf fiber is obtained. The degumming process has the advantages of short degumming cycle, low production cost, less investment, less land occupation, low labor intensity, environmental protection, no pollution, stable product quality, and the like.
Owner:INST OF BAST FIBER CROPS CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Composite thermoplastic sheets including natural fibers
ActiveUS7431980B2Non-fibrous pulp additionSynthetic resin layered productsSisal fiberCellulose fiber
A composite sheet material includes, in an exemplary embodiment a porous core that includes at least one thermoplastic material and from about 20 weight percent to about 80 weight percent of natural fibers based on a total weight of the porous core. The natural fibers include at least one of kenaf fibers, jute fibers, flax fibers, hemp fibers, cellulosic fibers, sisal fibers, and coir fibers.
Owner:HANWA AZDEL INC
Methods for Treatment of Waste Activated Sludge
InactiveUS20110272350A1Reduce sludge disposal costsCost for disposalSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningSludge processingBiological bodyActivated sludge
A process for treating waste primary or activated sludge solids that have been removed to a digester phase of the activated sludge process through the use of powdered natural lignocellulosic materials (PNLM) and / or powdered kenaf core (PKC). These materials help this process by: (a) thickening of primary and / or waste activated sludge through adsorption, attached growth and achieving closer proximity of organisms by stimulating reduction of their associated ECP substance; (b) enhancing endogenous reduction of primary and / or waste activated sludge by thickening (see above) and improving the ratio of available carbon to available nitrogen by delivering a continuing gradual release of sugar from degrading PNLM and / or PKC; (c) enhancing the speed of endogenous reduction of primary and / or waste activated sludge—through higher efficiencies (same processes as above); and (d) improving dewatering characteristics of wasted primary and / or wasted activated sludge solids (through reduction and breakdown of ECP materials and higher densification of solids).
Owner:SKILLICORN PAUL +1
Composite fiber automobile interior board and production method thereof
InactiveCN102166842AImprove tensile propertiesGood filterability at high temperatureLaminationLamination apparatusSurface layerSisal fiber
The invention relates to a composite fiber automobile interior board and a production method thereof. The automobile interior board comprises a base layer and a non-woven or woven surface layer which is laminated on the at least one surface of the base layer, wherein the base layer consists of the following composite fibers: first fibers, namely polylactic acid fibers, second fibers, namely bastose selected from at least one of jute fibers, sisal fibers, ramie fibers, linen fibers, hemp fibers and kenaf fibers, and third fibers, namely basalt fibers in a weight percentage ratio of (20-70):(10-60):(10-60); and the surface layer consists of polylactic acid fibers. The composite fiber automobile interior board can be made into a three-dimensional deep drawing high-strength automobile interior board, and is safe, firm and environment-friendly when used as the base material of an automobile door inner board and a ceiling.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Clean paper making method by kenaf
InactiveCN101591866ACellulosic pulp after-treatmentNon-woody plant/crop pulpReactive oxygen radicalsUltraviolet lights
The invention is the pioneering invention in the paper making field, which is characterized by cutting kenaf is into small segments of 2-5cm, soaking the small segments and rolling to form fiber bundles by a thread rolling machine, conveying the fiber bundles to a stainless steel vessel, adopting potassium-based hydrogen peroxide and oxygen to generate hydroxyl free radical and active oxygen free radical with the catalysis of ultraviolet light at the temperature of 80 DEG C, discarding chromophoric group of lignin to form coarse pulp with whiteness being 60%ISO-85%ISO, then forming clean pulp without chlorine or contamination through discongesting, fine grinding, screening and deslagging. The invention is used for producing high-grade paper products such as cigarette paper, decorating paper, currency paper, and the like, and completely solves the two problems of serious contamination from paper making and harm to human body from chloride ion.
Owner:李朝旺
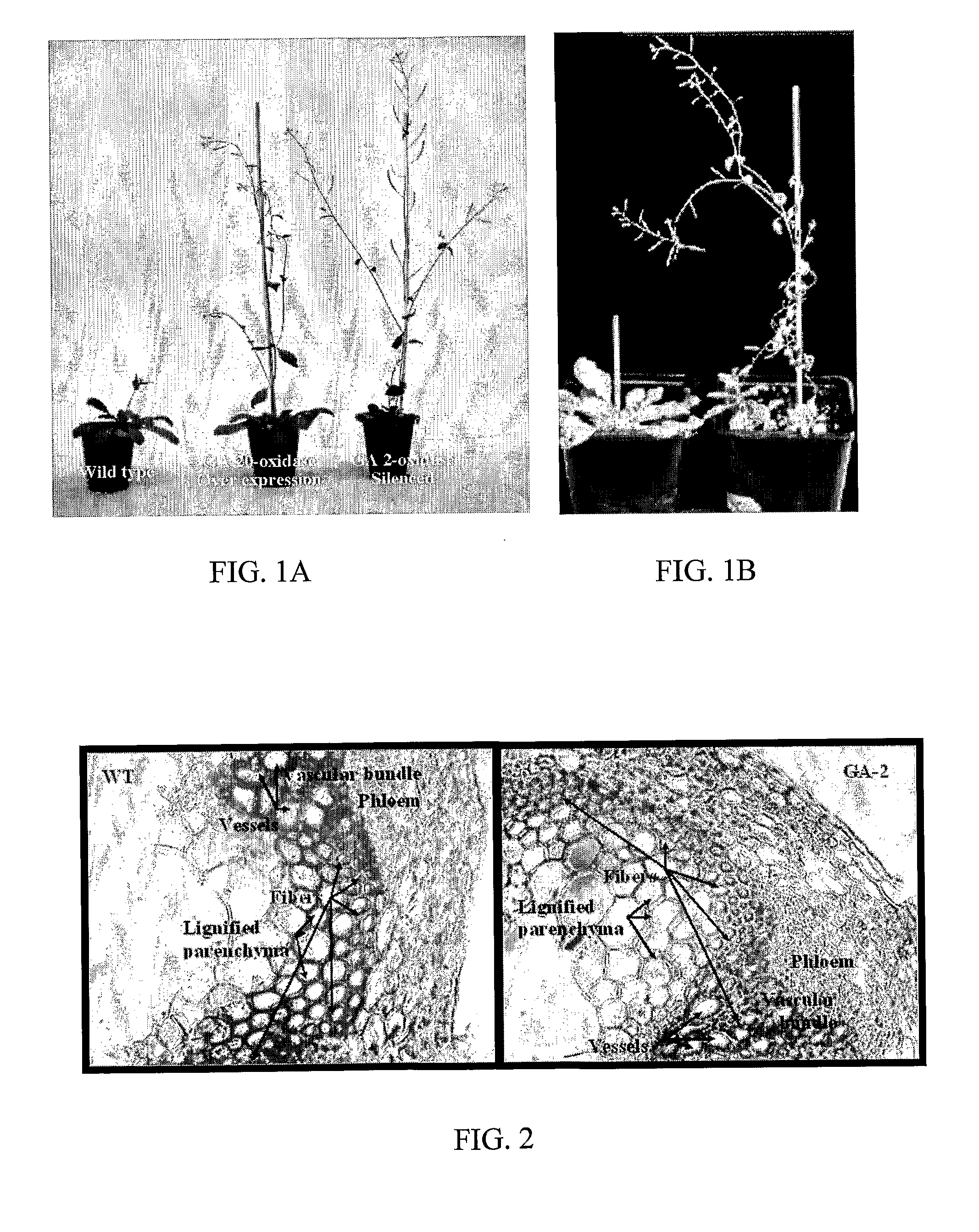
Compositions for silencing the expression of gibberellin 2-oxidase and uses thereof
InactiveUS20110004958A1Quick upgradeImprove the level ofSugar derivativesClimate change adaptationHibiscusNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention provides an isolated nucleic acid sequence encoding gibberellin 2-oxidase enzyme (GA 2-oxidase) of Hibiscus cannabinus. Furthermore, the present invention provides methods of silencing the expression of GA 2-oxidase gene via RNA interference for increasing fibers in plants, in particular in kenaf.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Method for production of molded article of plant- derived composite material, molded article of plant-derived composite material, method for production of plant-derived composite material, and plant-derived composite material
ActiveUS20100004358A1High mechanical strengthEfficient preparationIon-exchange process apparatusCosmetic preparationsPolymer sciencePresent method
The present invention provides a method for production of a molded article comprising a plant-derived composite material in which a plant-derived material is evenly dispersed and a plant-derived composite material molded article prepared therewith, and a method for production of a plant-derived composite material in which a plant-derived material is evenly dispersed and a plant-derived composite material prepared therewith. The present method for production of a molded article is a method for producing a molded article composed of a plant-derived composite material comprising a plant-derived material (e.g., a kenaf core) and a thermoplastic resin (e.g., polypropylene, polylactic acid), and comprises a process in which the plant-derived material is pressed to obtain raw-material pellets, a process in which the raw-material pellets and the thermoplastic resin are kneaded to obtain a plant-derived composite material, and a process in which the plant-derived composite material is molded into a molded article composed of the plant-derived composite material. The present molded article is obtained by the method.
Owner:TOYOTA BOSHOKU KK
Kenaf core/resin composite oil-absorption material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a kenaf core / resin composite oil-absorption material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method is characterized in that kenaf core waste in a textile industry is taken as a raw material to carry out graft copolymerization on oil-absorption resin and cellulose on the surfaces of kenaf core particles, so as to obtain a degradable kenaf core / resin composite high-oil-absorption resin. Compared with traditional inorganic oil-absorption materials and resin oil-absorption materials, the kenaf core / resin composite oil-absorption material and the preparation method have the advantages that the production cost can be substantially lowered, the waste of the textile industry is effectively utilized, and by utilizing a unique porous structure of a kenaf core, the oil absorption and keeping properties of the oil-absorption material are greatly improved; besides, after the kenaf core is subjected to graft copolymerization with the resin, the water absorbing capacity of the kenaf core is reduced, and the ratio of the oil absorbing capacity to the water absorbing capacity of the kenaf core is increased; the kenaf core simultaneously has the biodegradability of a straw and high water absorbing performance of the resin.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
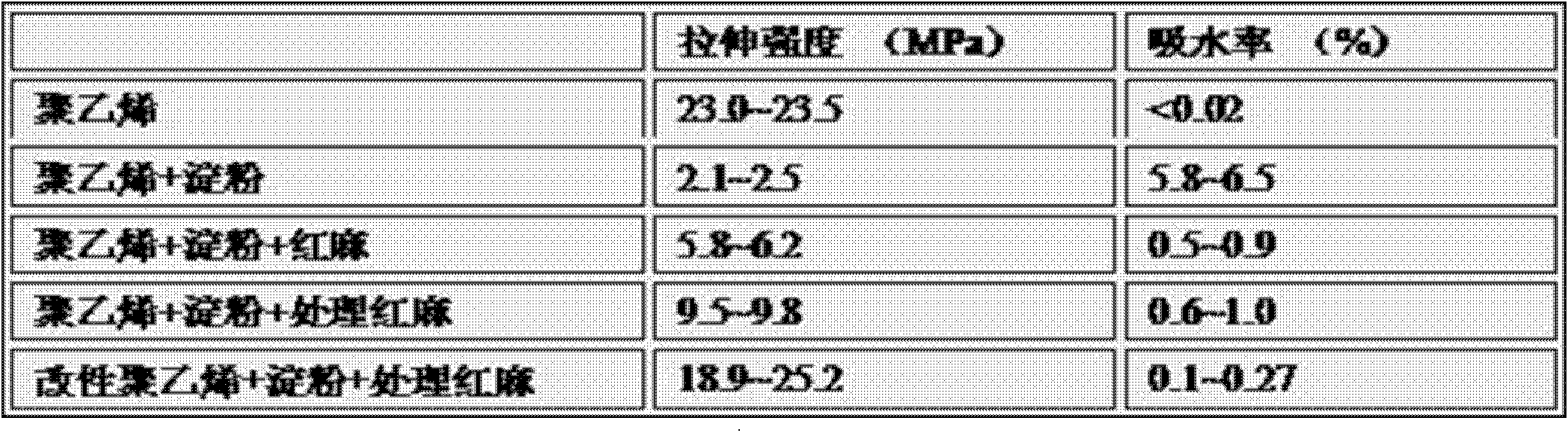
Degradable resin-starch-kenaf extruded plastic master batch
The invention belongs to the field of high polymer materials and in particular relates to a degradable resin-starch-kenaf extruded plastic master batch. The degradable resin-starch-kenaf extruded plastic master batch comprises the following components by volume percent: 30%-60% of polyethylene, 0-50% of starch and 5-40% of kenaf, wherein the polyethylene is composed of low-density polyethylene and maleic anhydride modified polyethylene in the volume ratio of (0.2-5):1. The extruded composite resin (master batch) material with higher tensile strength and good processing performance is prepared by virtue of a molecular design method; the biodegradation rate is 40%-70% in the presence of aerobiont; the using performance and the processing performance of the composite material are similar to those of the polyethylene, so that the material is green and environment-friendly, and therefore, the purposes of protecting the environment, efficiently utilizing the resources and lowering the cost are achieved.
Owner:赵振峰
Novel method for preparing Co3O4 spiral nanobelt by using three-dimensional porous kenaf stalk carbon as template
ActiveCN104843803AUnique shapeEasy to operateMaterial nanotechnologyCobalt oxides/hydroxidesNitrogenKenaf
The invention discloses a novel method for preparing a Co3O4 spiral nanobelt by using three-dimensional porous kenaf stalk carbon as a template. The novel method for preparing the Co3O4 spiral nanobelt by using three-dimensional porous kenaf stalk carbon as the template is as below: conducting high temperature calcination on a Co2 (OH)2(CO3)2 precursor grown in the three-dimensional porous kenaf stalk carbon template under nitrogen protection for the synthesis of a Co3O4 spiral nanobelt; and unlike the previously reported hydrothermal reaction, conducting calcination to prepare the Co3O4 cluster crystals. The method for preparing the Co3O4 spiral nanobelt has simple process and uses cheap and readily available raw materials; and the prepared Co3O4 spiral nanobelt has the advantages of large specific surface area, good catalytic activity and convenience for loading other materials.
Owner:郑州环智电子科技有限公司
Composites having leather-like characteristics
InactiveUS20130337711A1Permeable and breathableLayered productsWood working apparatusTriglycerideKenaf
This present invention is directed to the use of bio-based materials such as functionalized plant oils and natural fibers to provide substitutes for leather materials. The bio-based materials provide composites made with a range of natural fibers such as flax, cotton, jute and kenaf fibers, combined with natural plant oils (triglycerides) such as soy oil, linseed oil and their fatty acids. The natural fibers may be used in their as-delivered woven or nonwoven state and the triglycerides and fatty acids are chemically modified to allow them to react in a controlled manner giving predictable thermal and mechanical properties. The resulting material is a breathable, water resistant, leather-like material. This present invention is also directed to methods of making the substitutes for leather materials.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
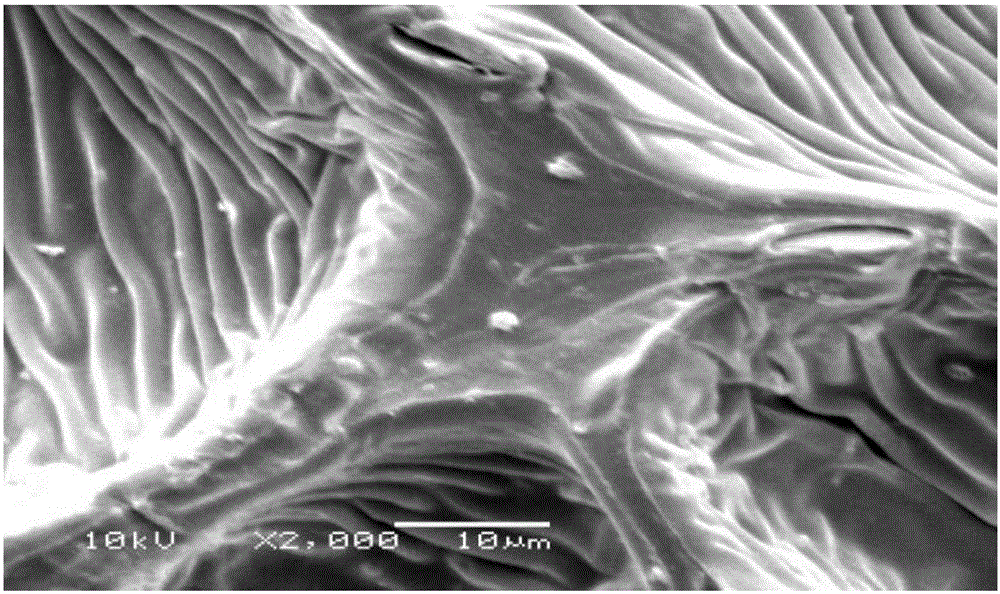
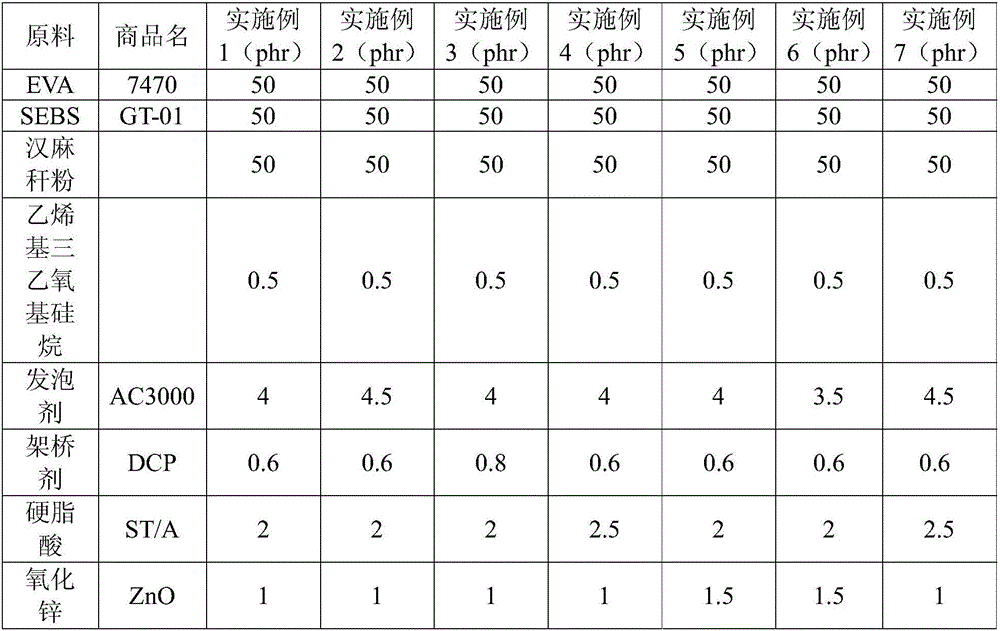
High-resilience aging-resistant EVA foamed material and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a high-resilience aging-resistant EVA foamed material and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps that 1, lignocellulose powder is modified through a silane coupling agent to obtain modified lignocellulose powder; 2, part of a hydrogenated styrene butadiene polymer, an ethylene-vinyl acetate polymer and the modified lignocellulose powder are added into an internal mixer to be mixed; 3, a foaming agent, a bridging agent, an activating agent and zinc oxide are added into the internal mixer to be mixed; 4, the materials mixed through the step 2 and the step 3 are granulated, injection foaming is conducted, cooling forming is conducted, and then the high-resilience aging-resistant EVA foamed material is obtained. After EVA is foamed by adding kenaf stalk powder, compressive deformation of EVA is obviously improved, and compressive deformation generated when EVA is foamed by adding the kenaf stalk powder is 15% higher than that generated when EVA is foamed without adding the kenaf stalk powder. A shoe insole made of the modified foamed body is light, durable, capable of reducing shock, high in resilience and good in tear resistance, and the EVA foamed material is suitable for various athletic and leisure shoe insoles and has an important application value.
Owner:湖北福力德鞋业有限责任公司 +2
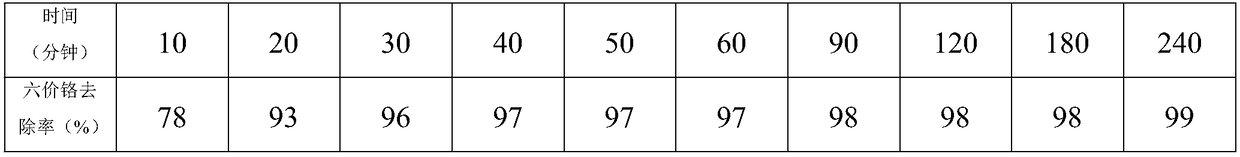
Magnetic biochar material for heavy metal waste water treatment and preparation method of magnetic biochar material
ActiveCN108311117ALow priceEase of mass productionOther chemical processesWater contaminantsAdsorption effectBiochar
The invention relates to a magnetic biochar material for heavy metal waste water treatment as well as a preparation method and a use of the magnetic biochar material. The material is prepared by taking kenaf biochar with large specific surface area and strong adsorption ability as a main body, combining the kenaf biochar with a bismuth ferrite material with the magnetism through chitosan, and performing crosslinking with glutaraldehyde. The preparation method concretely comprises the following steps of adding bismuth ferrite and the kenaf biochar material in thoroughly dissolved chitosan solution, enabling the three of the bismuth ferrite, the kenaf biochar material and the chitosan solution to be fully combined with mechanical stirring, using the glutaraldehyde as a crosslinking agent toenable the mechanical strength of the material to be strengthened, and grinding the dried materials to enable the specific surface area of the material to be further increased finally. The material has good adsorption effect to hexavalent chromium ions in heavy metal waste water, is strong in adsorption ability, liable in separation and recovery, low in preparation cost and simple in technology and is suitable for removal of the hexavalent chromium ions in waste water including smelting waste water, mine waste water, printing and dyeing waste water, chemical waste water and electroplating waste water.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
Method of producing a fiber board
InactiveUS20040187998A1High strengthGood moisture permeabilityCellulosic pulp after-treatmentDrafting machinesPolymer scienceVolumetric Mass Density
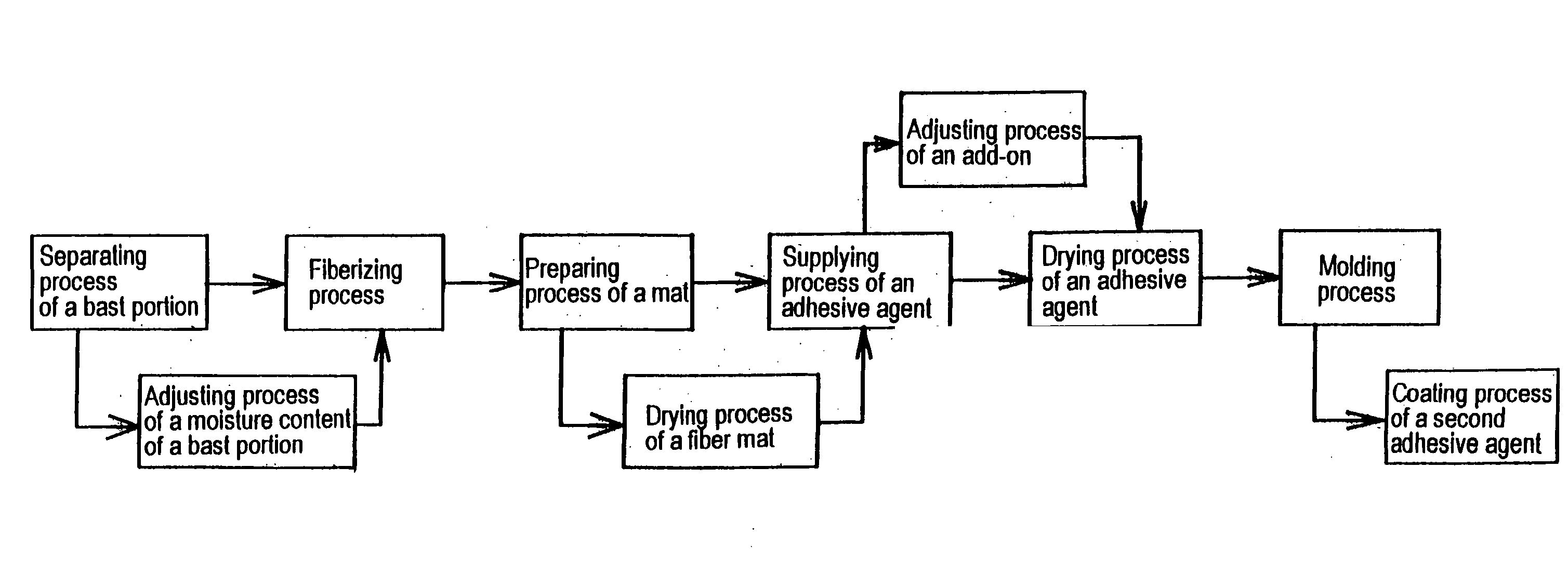
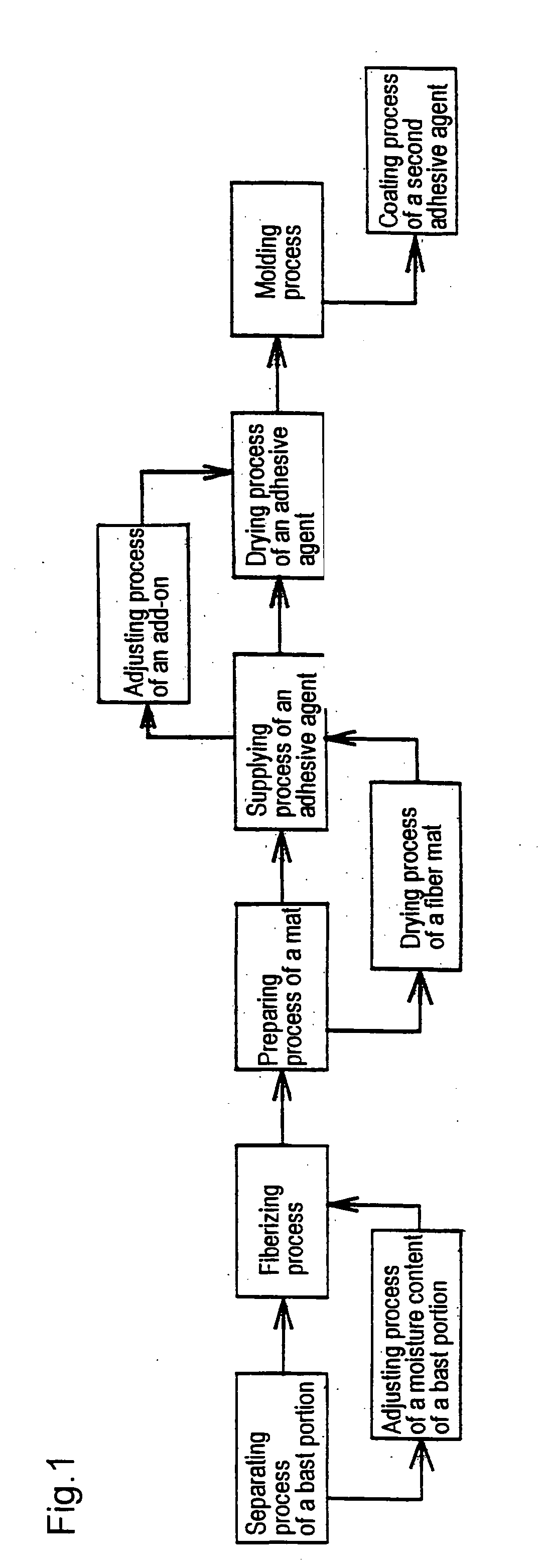
The present invention relates to a method of producing a fiber board characterized in that it comprises the following processes (a)-(f): (a) a separating process of a bast portion, (b) a fiberizing process by defibrating the bast portion of the kenaf, (c) a preparing process of a mat comprising the kenaf fibers having an average length of 10-200 mm and an average diameter of 10-300 mum, (d) a supplying process of an adhesive agent into the fiber mat, (e) a drying process of the adhesive agent, and (f) a molding process by heating said fiber mat under pressure to form a fiber board having a density of 600-900 kg / m<3>.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Method for producing fermentable sugar by red ramie bark fibre enzymolysis
ActiveCN101376905ALow lignificationImprove hydrolysis effectBiofuelsFermentationCelluloseLight pollution
The invention provides a method for producing fermentable sugar through the zymohydrolysis of kenaf bast fiber, in particular the invention provides a method for preparing sugar through the degradation of cellulose, which comprises the following steps: physical degumming, steam blasting and zymohydrolysis are conducted to the kenaf bast fiber, so as to produce the sugar. The fermentable sugar produced by the method can be used for the production of fuel ethanol, and is characterized by short treatment time, high conversion rate, light pollution and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI ZHONGWEI BIOCHEM
Backup board for machining process
InactiveUS20050176328A1Reduce material weightImprove workabilitySynthetic resin layered productsPrinted circuit aspectsPolymer scienceSurface layer
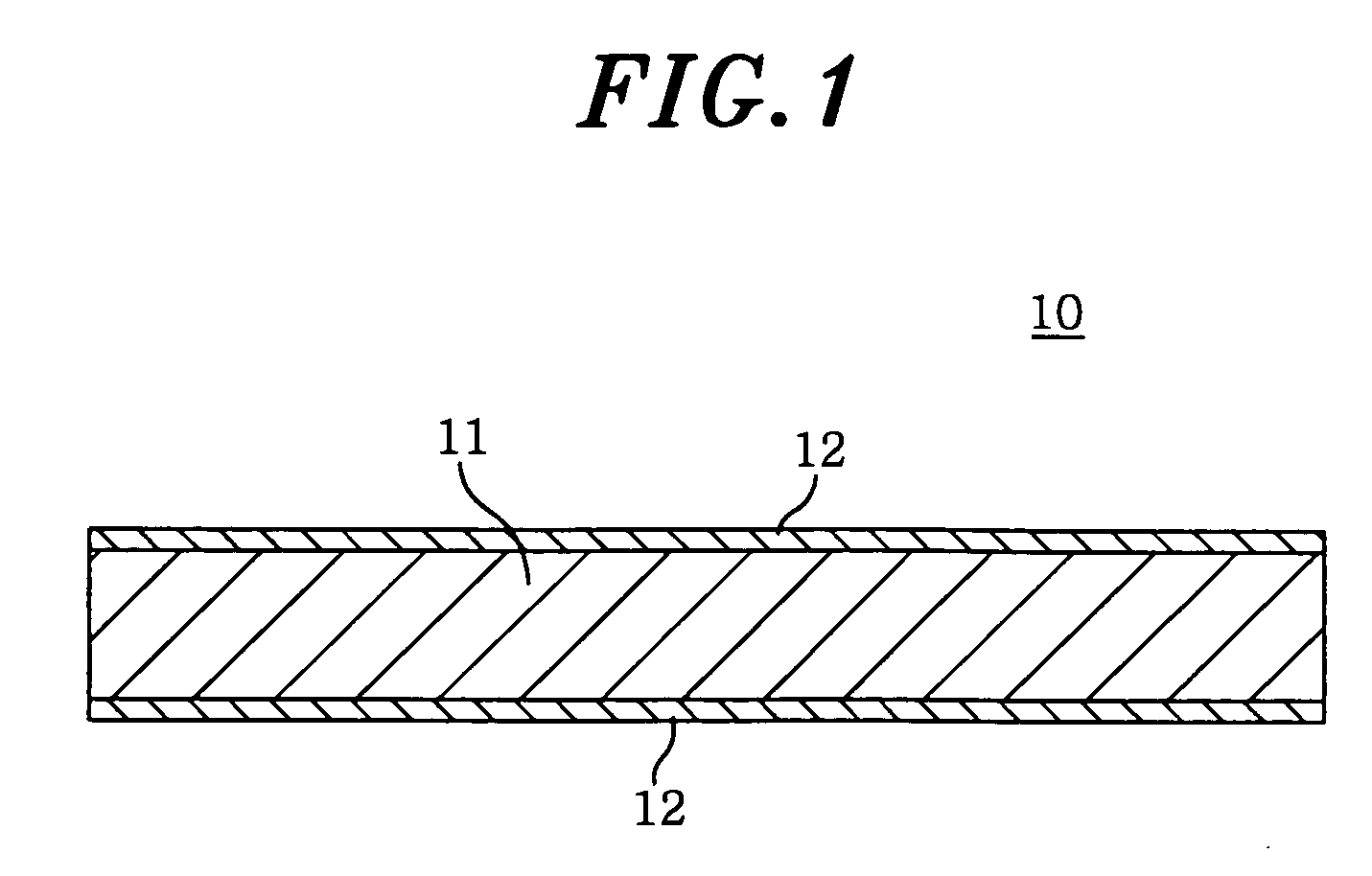
A backup board for use in a machining process includes a fibrous layer, at least one side of the fibrous layer being provided with a surface layer adhered and laminated thereon, wherein the surface layer is made of a cured paper impregnated with a thermosetting resin. The fibrous layer has a density of about 600˜900 kg / m3 and includes kenaf fibers adhered together by impregnating a thermosetting adhesive into a fibrous mat of the kenaf fibers, the kenaf fibers having an average length of about 10˜200 mm and an average diameter of about 10˜300 μm.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Natural fiber as core material in composite sandwich structure
InactiveUS20070149084A1Low costLight weightConstruction materialMagnetic materials for record carriersThermoplasticGlass fiber
A core component includes a natural fiber portion and a binder portion. The natural fiber portion and the binder portion are combined together, either partially or fully, so as to form a substantially homogenous material. Natural fibers can include: (1) bast fibers such as hemp, flax, kenaf, ramie, jute, and / or the like; (2) leaf fibers such as henequen, abaca, and / or the like; and (3) seed fibers such as cotton and / or the like. The core component can be used in conjunction with a composite structure, e.g., after formation of the core component, a reinforcing material (e.g., glass fibers, carbon fibers, aramid fibers and / or the like) can be placed on either side of the core component and injected with a resin material to form the composite structure. The resin material can be comprised of any number of polymeric materials, such as but not limited to thermoplastics, thermosets, and / or the like.
Owner:MAGNA INTERNATIONAL INC +1
Device and method for collection and biodegradation of hydrocarbon fluids
InactiveUS20070207533A1Water cleaningGeneral water supply conservationHydrocotyle bowlesioidesDecomposition
A portable, disposable device for the collection and bacteriological decomposition of liquid hydrocarbons including a pillow containing at least one member of the group consisting of (i) kenaf fibers / particles and (ii) a mixture of (a) natural, synthetic and / or oleophilic fibers / particles and (b)(i) one or more species of fungi selected from the group consisting of chaetonium indicum, chaetonium funicola, geotrichum candidum, macrophomina phaseolina, and trichoderma harziamum, and / or (b)(ii) one or more species of bacteria selected from the group consisting of bacillus subtillis, bacillus cereus sub group A and paenibacillus validus. The pillow may be quilted or otherwise constructed to define a plurality of chambers each containing the kenaf fibers / particles and / or the mixture of fibers / particles, fungi and / or bacteria. The device may further include a liquid impermeable pillow housing defining an opening to allow the liquid hydrocarbon to come into contact with the pillow. The pillow may define inter-connected channels for directing the flow of liquid hydrocarbons away from a contact point to evenly distribute the liquid hydrocarbons throughout the pillow. The upper and lower surfaces of the absorbent pillow may be constructed of different density fabric(s) and the pillow may define a sealed deflection area to further enhance the distribution of the liquid hydrocarbon throughout the pillow. A method of using the device includes the steps of: obtaining the device; placing the device proximate to a source of the liquid hydrocarbon and bringing the liquid hydrocarbon into contact with the device.
Owner:CALLAHAN & CHASE
Plant fiber reinforced polylactic acid composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a plant fiber reinforced polylactic acid composite material and a preparation method thereof. The plant fiber reinforced polylactic acid composite material comprises the following components in parts by weight: 12 to 26 parts of sisal fiber, 8 to 16 parts of kapok fiber, 5 to 19 parts of linen fiber, 6 to 18 parts of kenaf fiber, 2 to 7 parts of cotton fiber, 3 to 11 parts of palm fiber, 2 to 13 parts of bamboo fiber, 3 to 9 parts of coconut fiber, 3 to 14 parts of silicon dioxide and 22 to 45 parts of polylactic acid. The plant fiber reinforced polylactic acid composite material has the following advantages: (1) the interfacial property of the plant fiber and the polylactic acid of the plant fiber reinforced biodegradable composite material is high; (2) the composite material has high tensile strength and elongation at break.
Owner:苏州奥宇包装科技有限公司
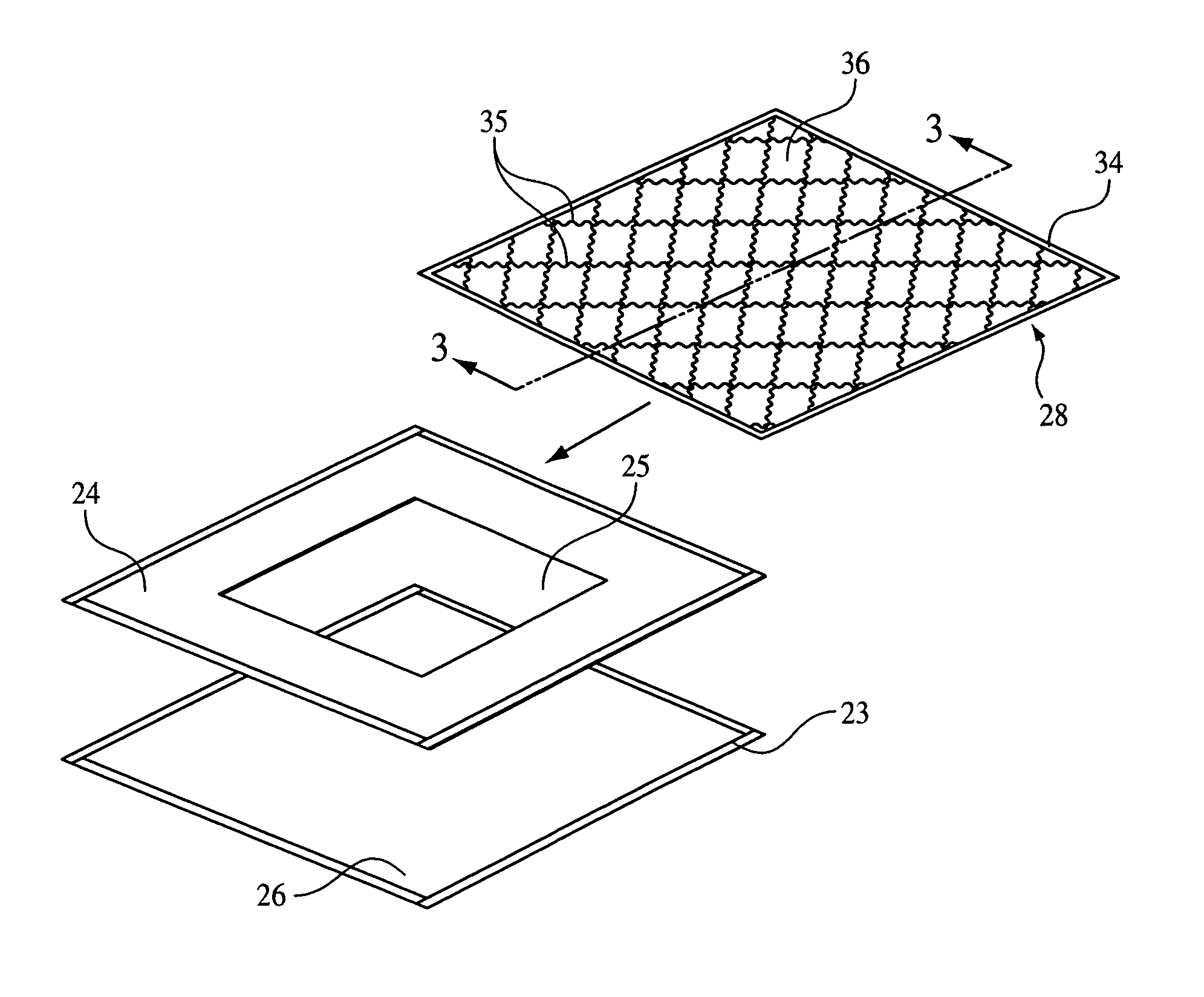
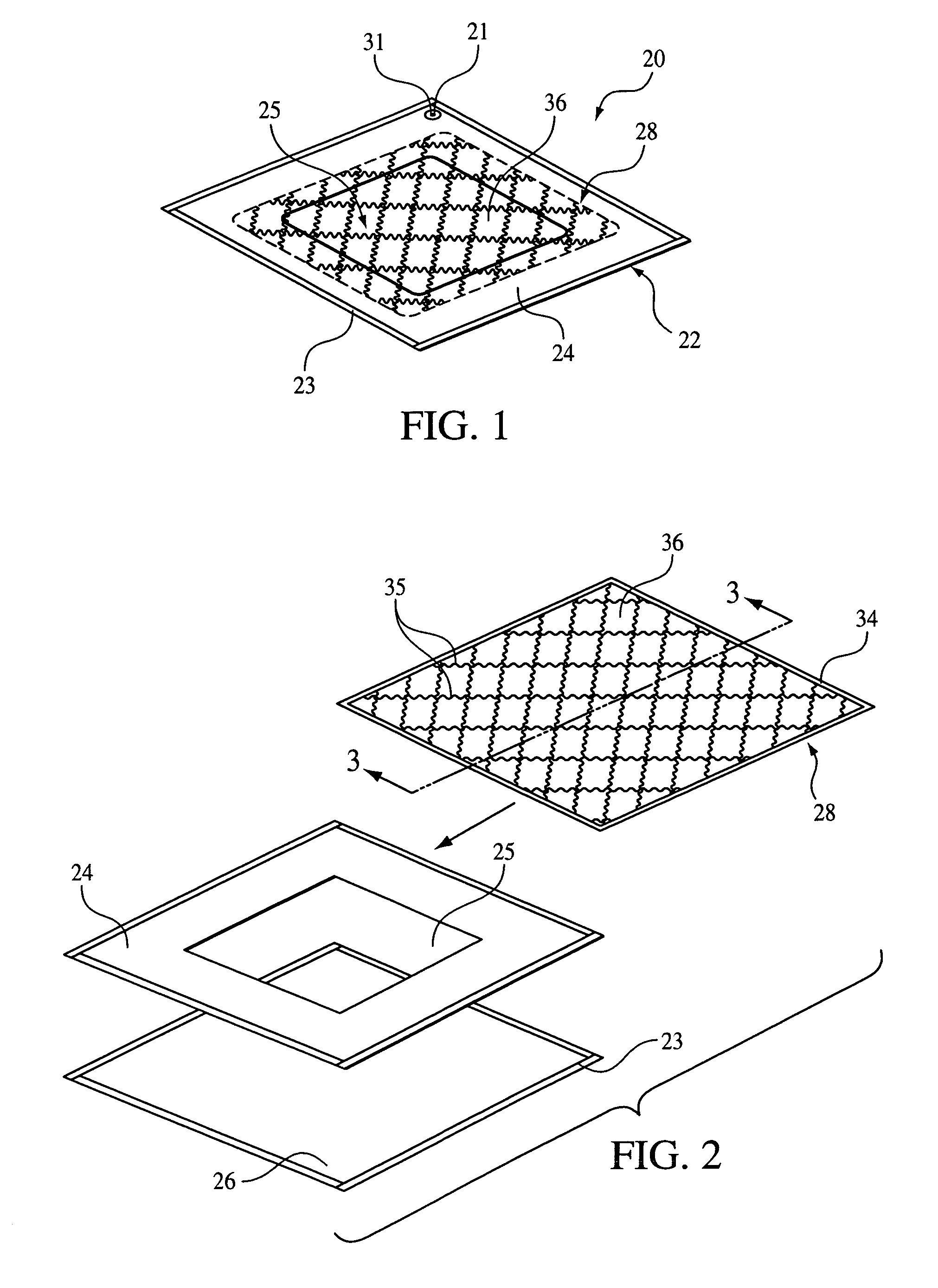
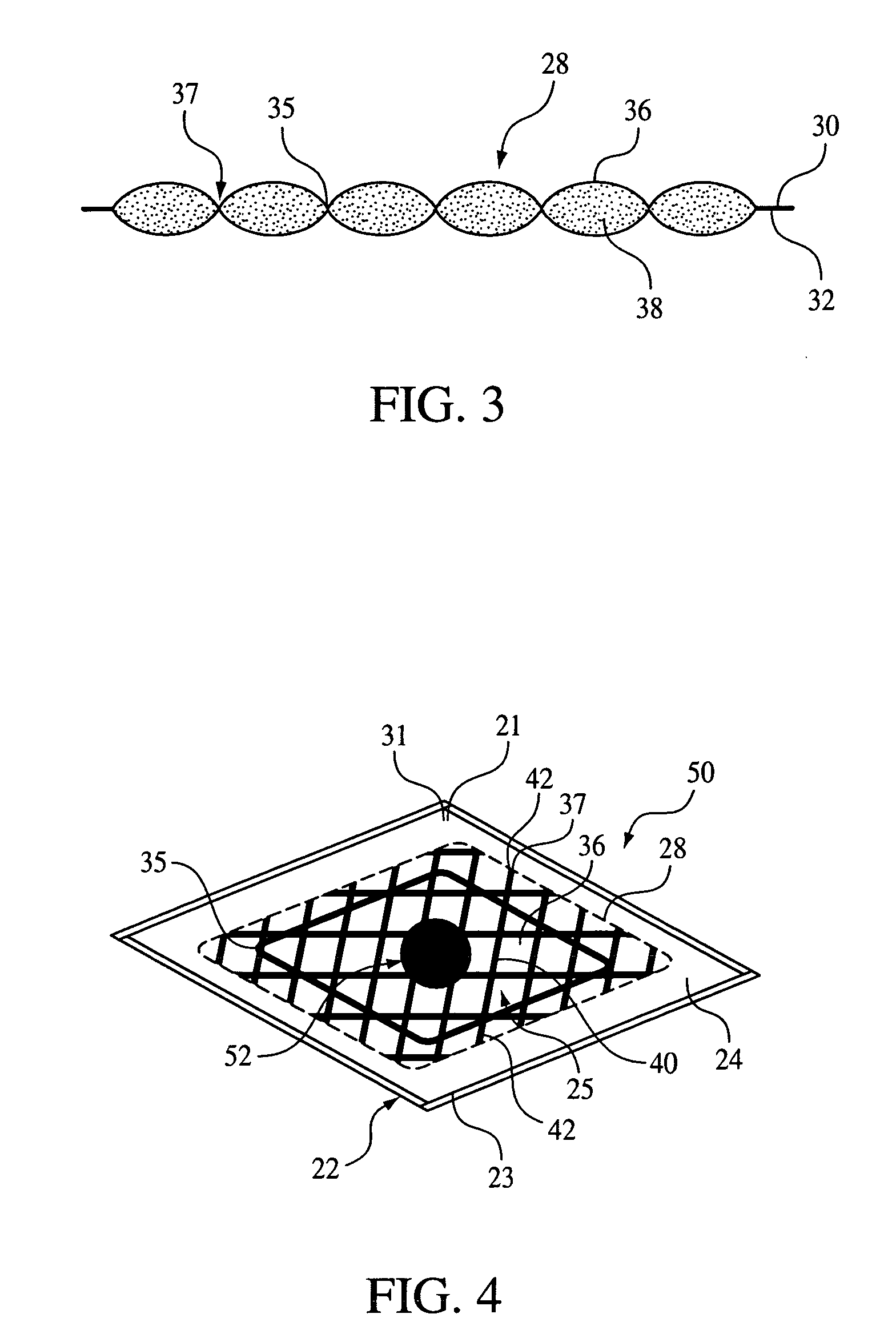
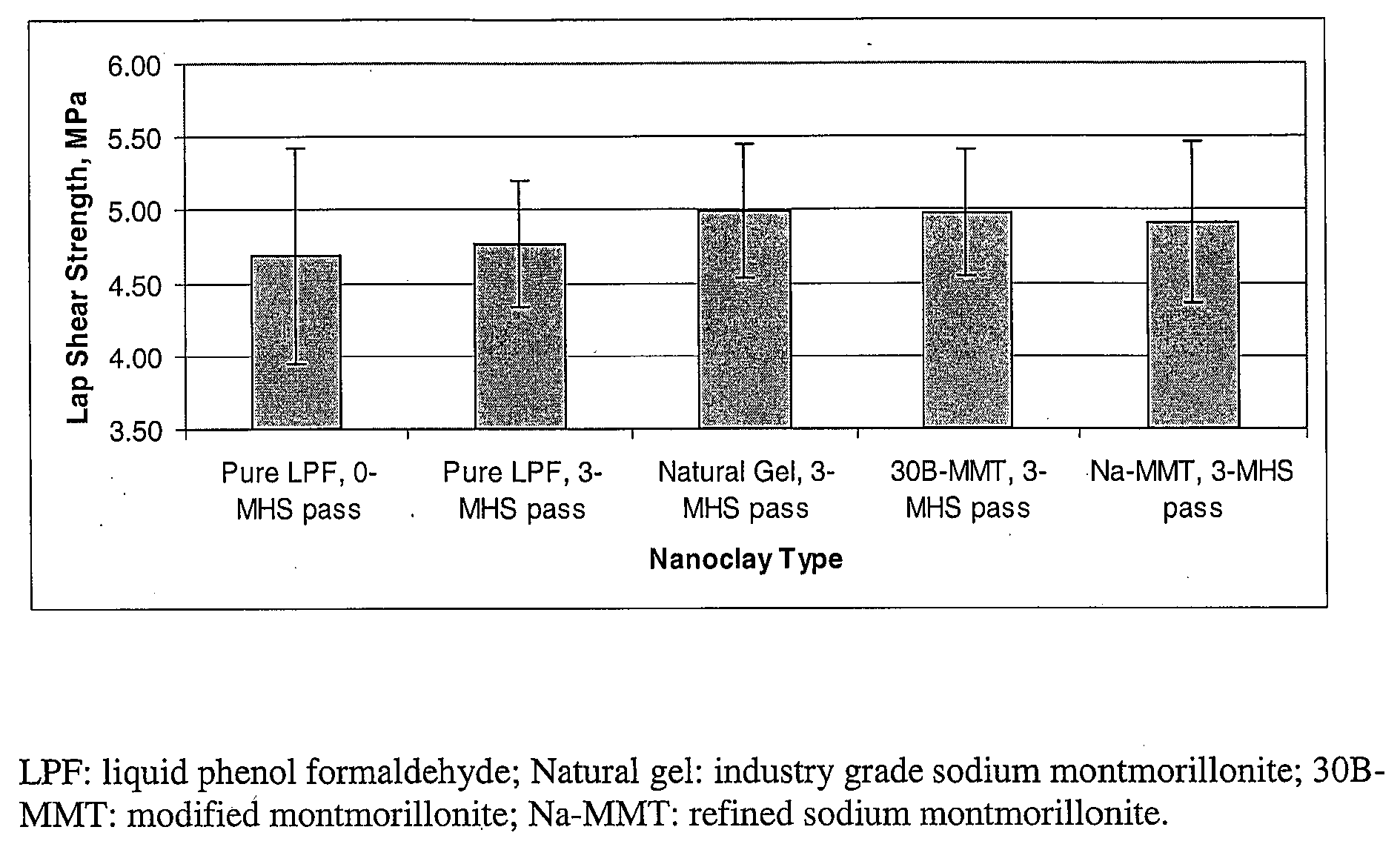
Phyllosilicate modified resins for lignocellulosic fiber based composite panels
InactiveUS20080234423A1Reduce usageLess-uneven propertyFibreboardPretreated surfacesHalloysiteNatural fiber
A method of forming a composite panel or board includes the step of adding phyllosilicate clay to a thermosetting resin and natural fibres. The natural fibres include hardwood fibre, softwood fibre, grain straw, hemp fibre, kenaf fibre, bagasse fibre, palm fibre, canola straw fibre, flax straw fibre, rapeseed straw fibre, wheat straw fibre, oat straw fibre, barley straw fibre, rice straw fibre or rye straw fibre. The thermosetting resin may include phenol formaldehyde, urea formaldehyde, melamine formaldehyde, melamine urea formaldehyde, or methylenediphenyl diisocynanate. The phyllosilicate clay may include nanoparticulate clay and may include natural, modified or synthetic forms of sodium montmorillonite, montmorillonite, nontronite, beidellite, volkonskoite, laponite, hectorite, saponite, sauconite, magadite, kenyaite, stevensite, vermiculite, halloysite, or hydrotactite.
Owner:ALBERTA RES COUNCIL INC
Kenaf reinforced rubber for power transmission belts
An elastomeric composition and a power transmission belt based on the elastomeric composition, wherein the composition includes kenaf fiber.
Owner:THE GATES CORP
Backup board for machining process
InactiveUS20070193680A1Less abrasionSacrificing their functionThread cutting machinesWood working apparatusAdhesiveKenaf
A backup board for use in a machining process includes a fibrous layer, at least one side of the fibrous layer being provided with a surface layer adhered and laminated thereon, wherein the surface layer is made of a cured paper impregnated with a thermosetting resin. The fibrous layer has a density of about 600˜900 kg / m3 and includes kenaf fibers adhered together by impregnating a thermosetting adhesive into a fibrous mat of the kenaf fibers, the kenaf fibers having an average length of about 10˜200 mm and an average diameter of about 10˜300 μm.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Adsorbent and process for producing adsorbent
InactiveUS20050202969A1Improve adsorption capacityHigh adsorption selectivityOther chemical processesCarbon compoundsLignin degradationLignin sulfate
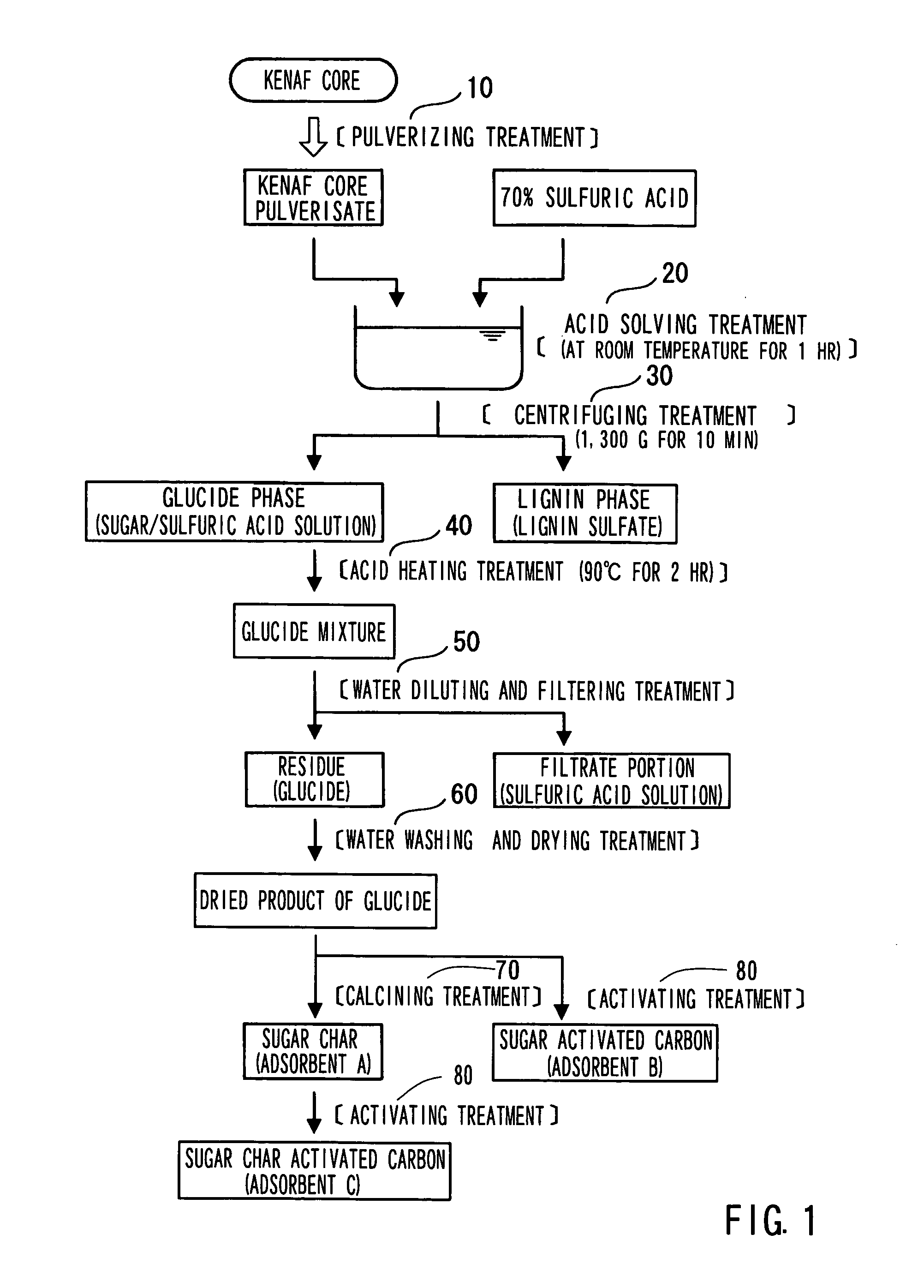
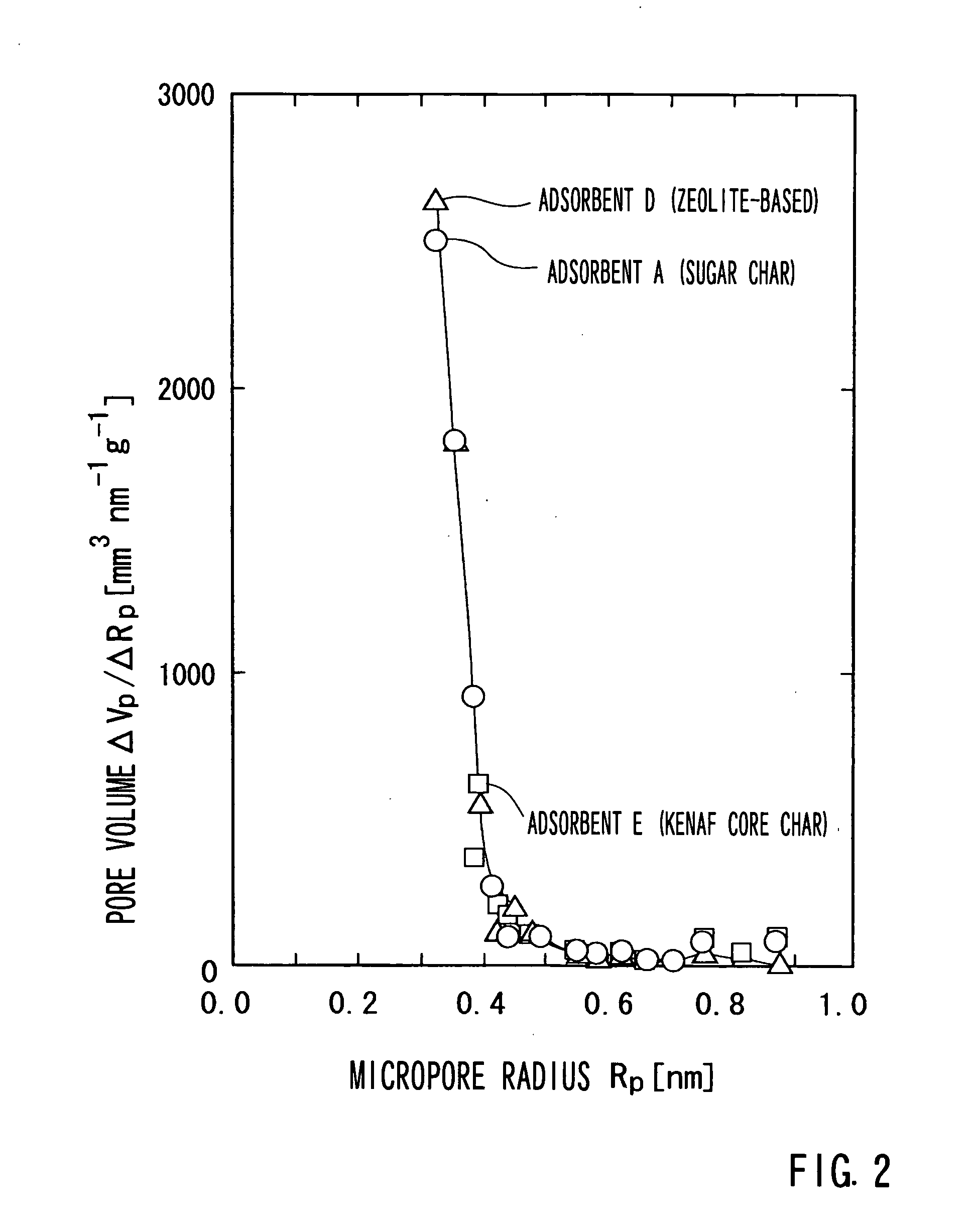
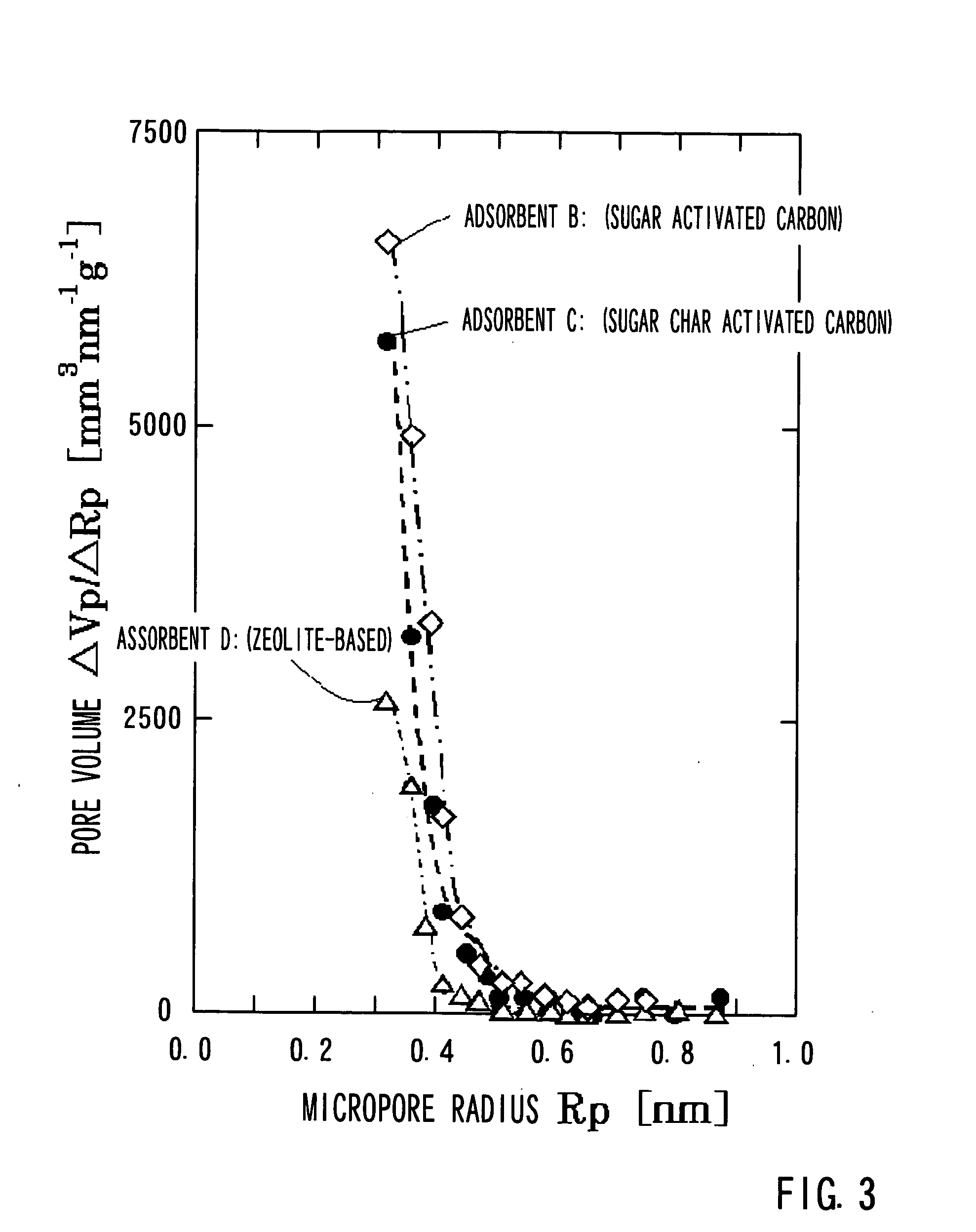
A kenaf core pulverized preparation obtained by a pulverization treatment 10 is dissolved in 70% sulfuric acid in an acid dissolving treatment 20 to obtain a glucide phase (sugar / sulfuric acid solution) The glucide phase is separated from a lignin phase (lignin sulfate) by a centrifuging treatment 30. The glucide phase is heated in the presence of sulfuric acid at 90° C. for about 2 hours by an acid heating treatment 40. Further, dilution of the glucide (residue) with water and filtration are carried out until a filtrate becomes neutral by a water diluting and filtering treatment 50. Washing with water and drying of the glucide are performed by a water washing and drying treatment 60. Thereafter, a sugar char that serves as an adsorbent A is obtained by a calcining treatment 70.
Owner:ARACO CORP
Biochar-based composite material, and preparation method and application thereof
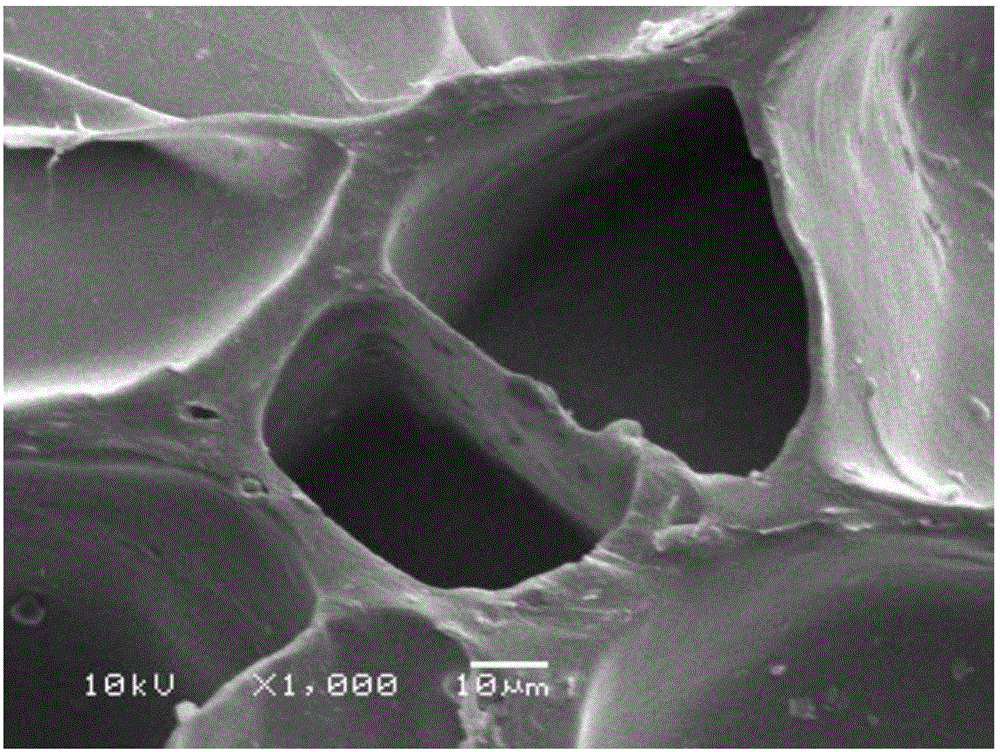
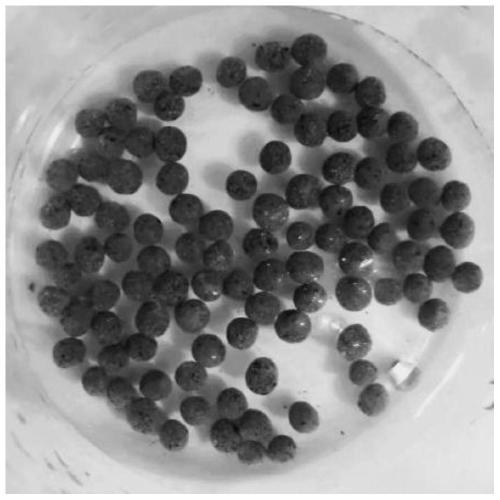
InactiveCN110252397AEasy to operateImprove performanceWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsKenafBiochar
The invention relates to a biochar-based composite material for water treatment, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The biochar-based composite material is prepared by using chitosan as a carrier and uniformly loading kenaf biochar and g-C3N4. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving chitosan, adding the kenaf biochar and g-C3N4 to obtain a mixed suspension, and dropwise adding the mixed suspension to a NaOH solution by using a syringe to obtain gel pellets having a uniform particle size. The biochar-based composite material has the advantages of simple preparation method, low cost, recyclability and high treatment efficiency. The material can be used for industrial wastewater treatment and repairing.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com