Patents
Literature
889results about "Vegetable material" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
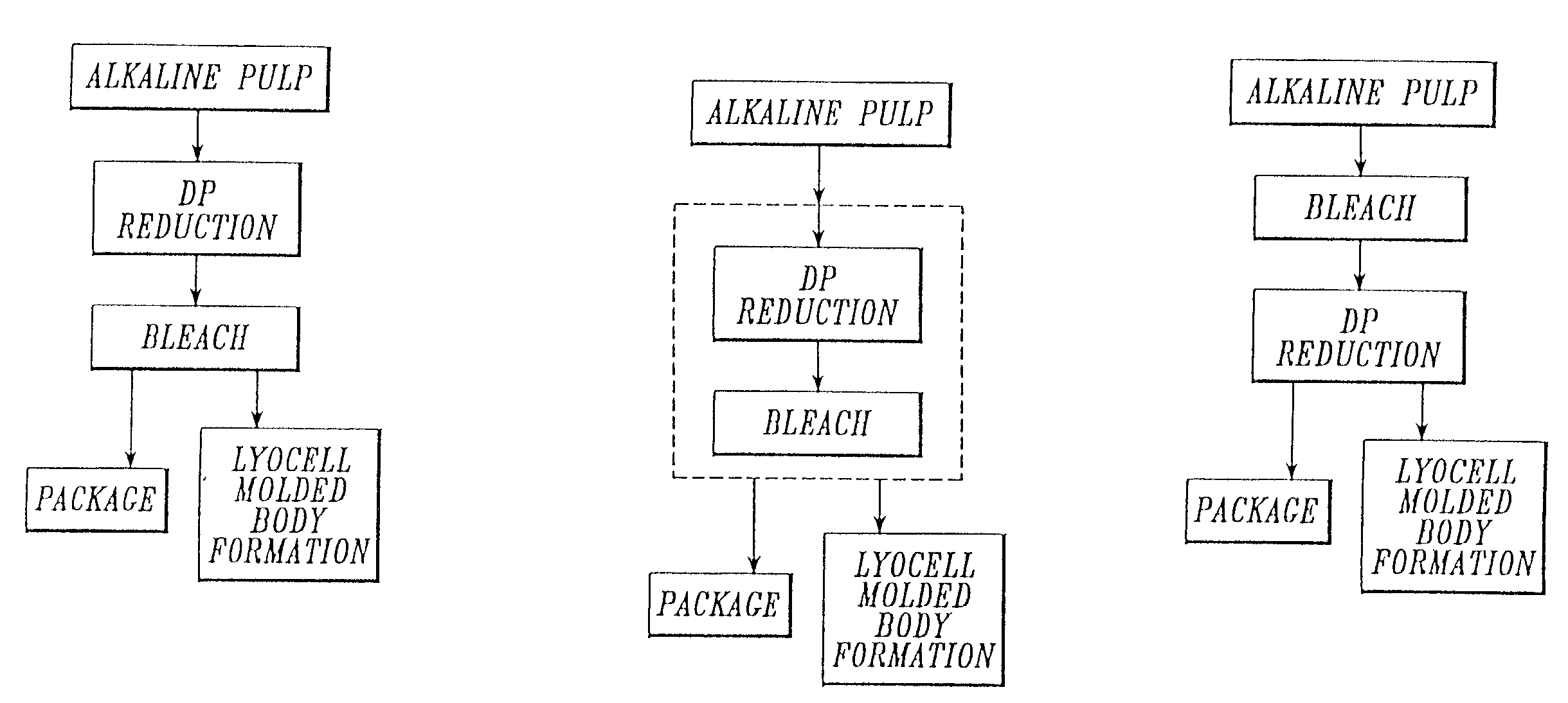
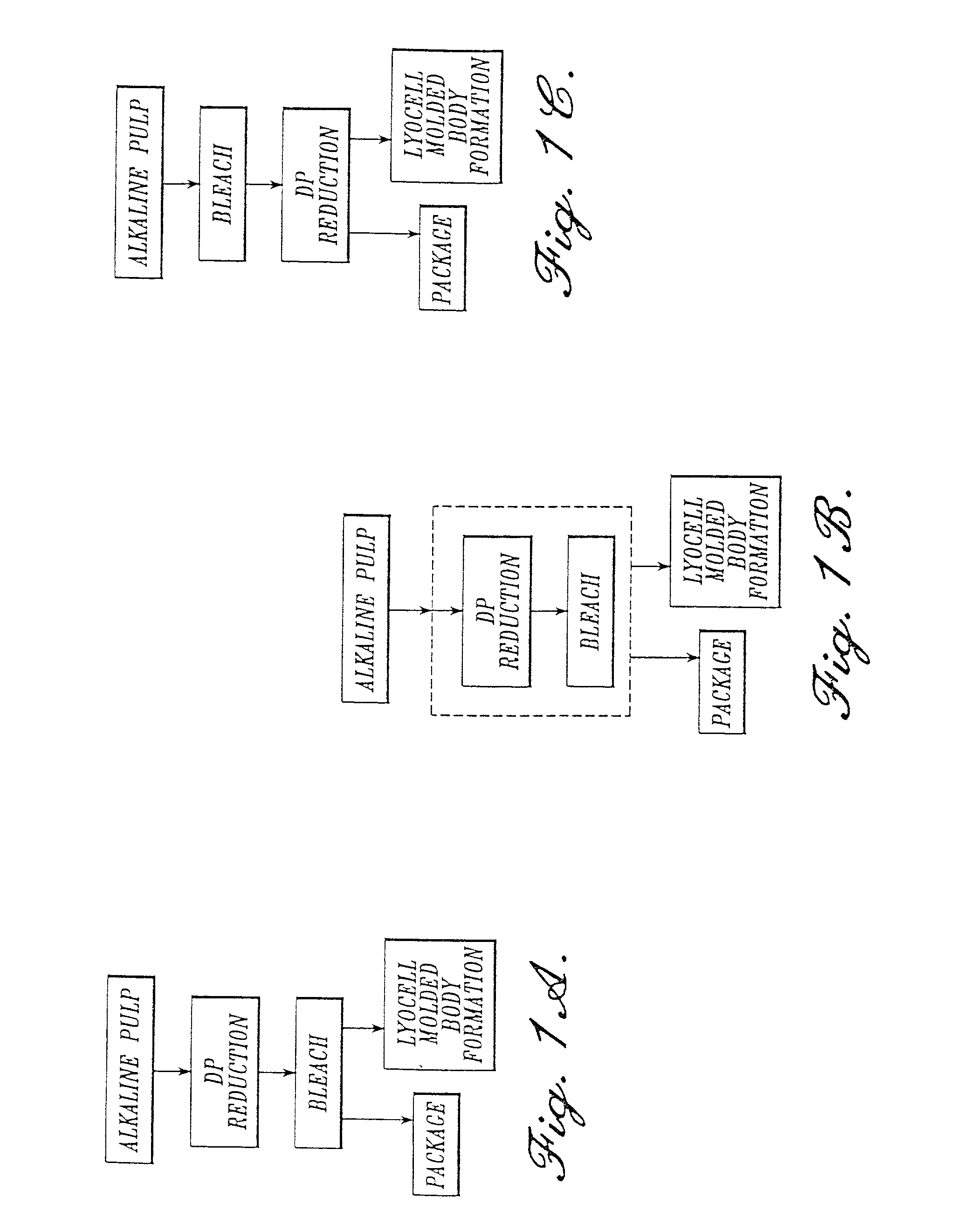
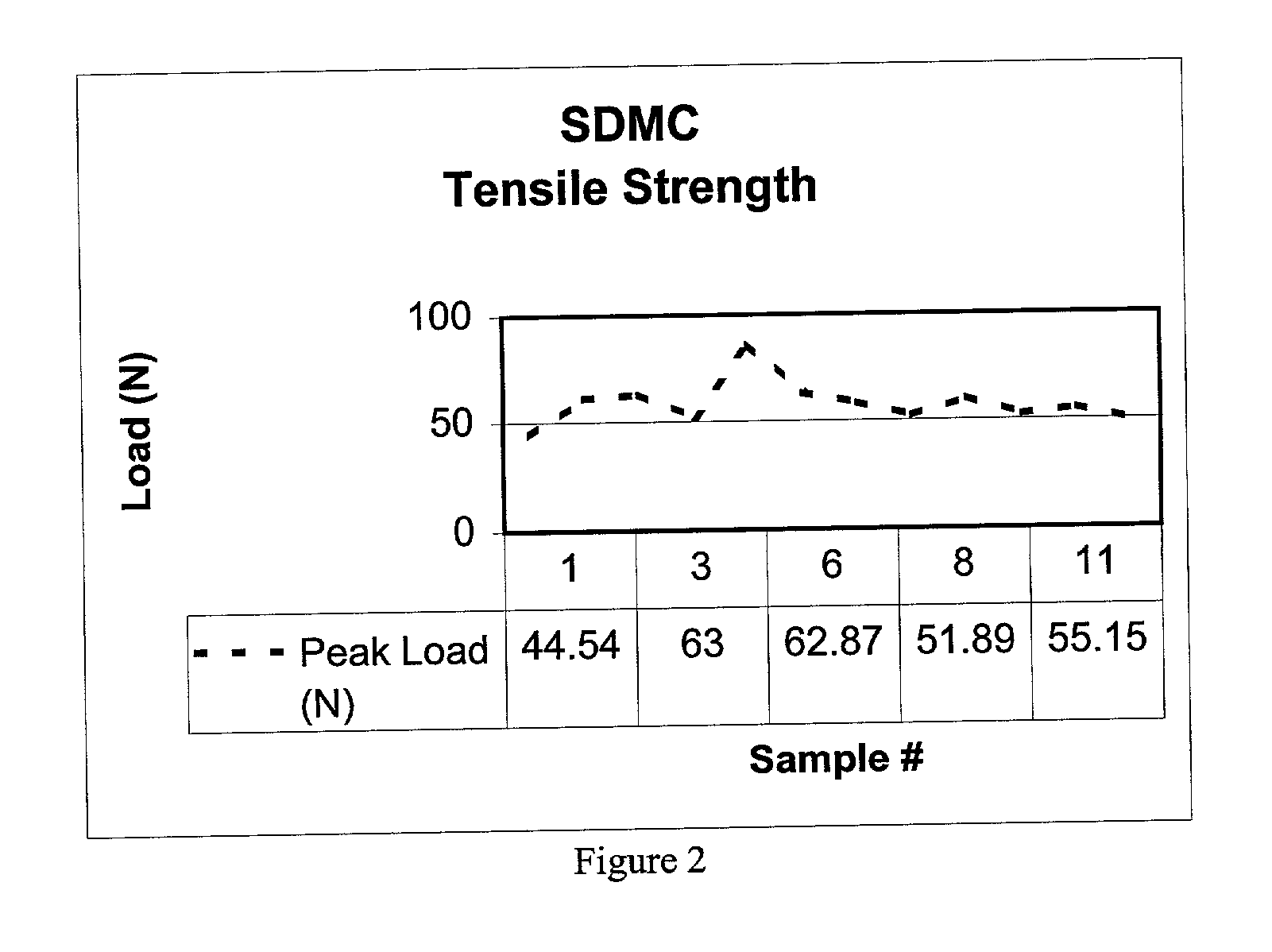
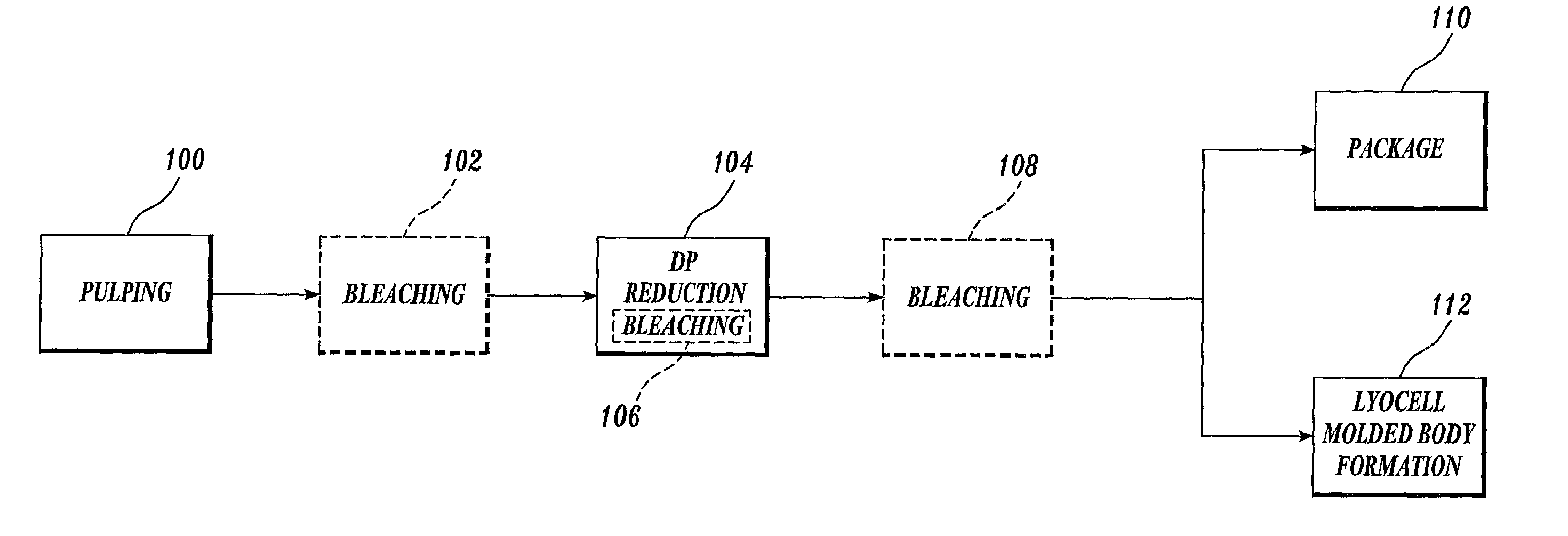
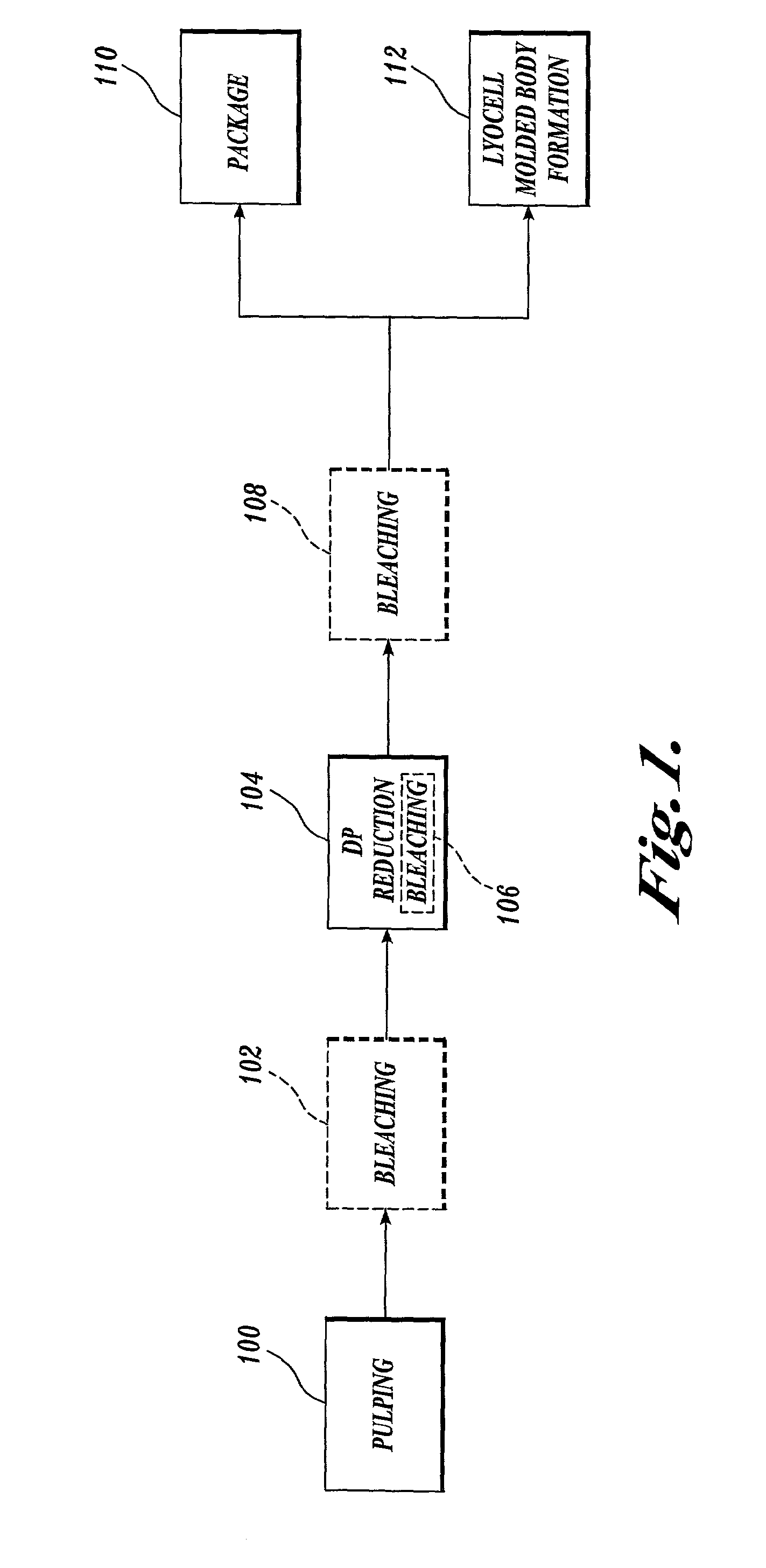
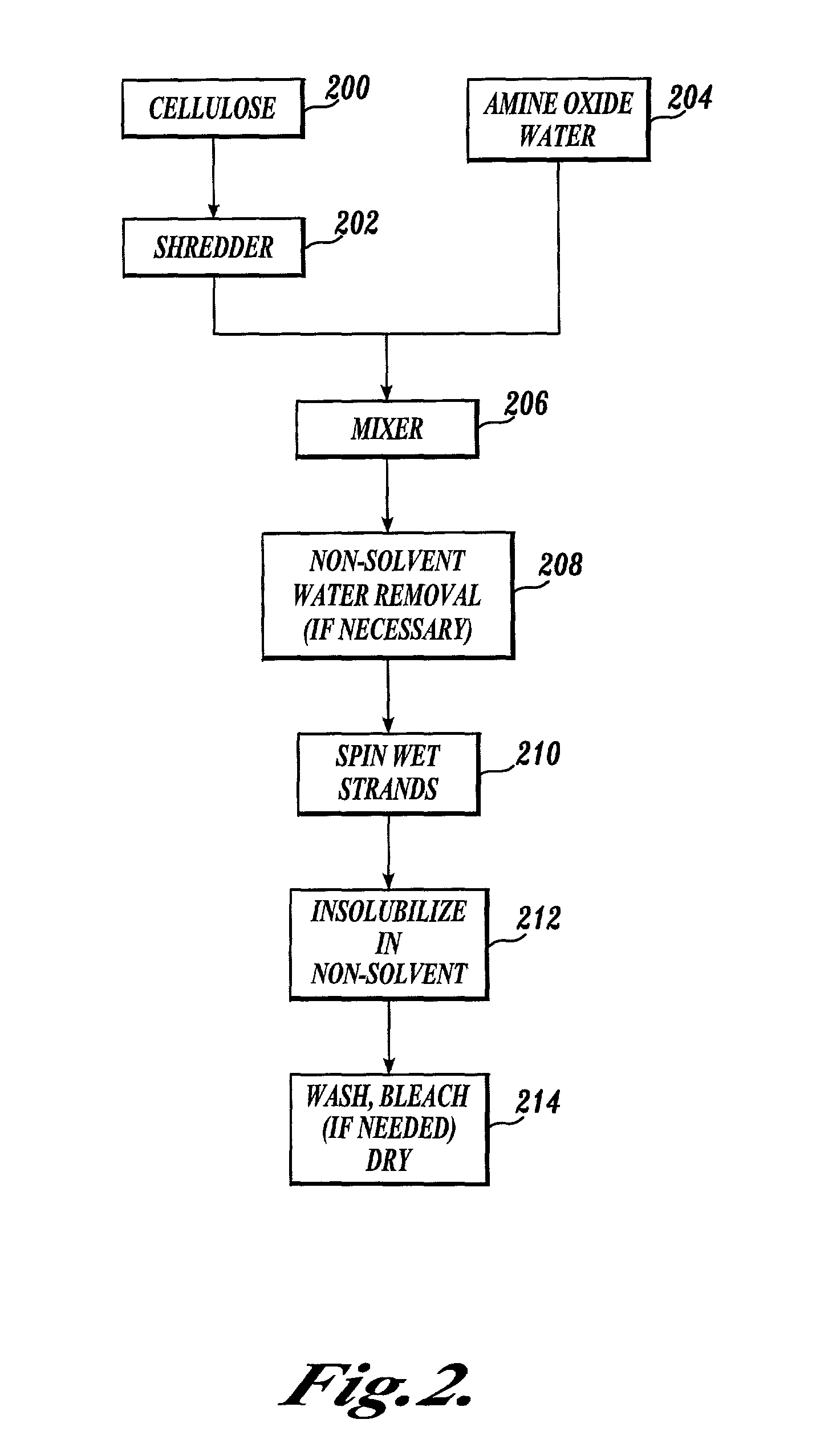
Process for making a composition for conversion to lyocell fiber from an alkaline pulp having low average degree of polymerization values
InactiveUS7083704B2Reducing hemicellulose contentIncreasing copper numberPulp properties modificationMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentHemicelluloseLyocell
The present invention provides compositions, useful for making lyocell fibers, having a high hemicellulose content, a low copper number and including cellulose that has a low average degree of polymerization (D.P.) and a narrow molecular weight distribution. Further, the present invention provides processes for making compositions, useful for making lyocell fibers, by contacting an alkaline pulp having a high hemicellulose content of at least about 7% with an oxidant sufficient to reduce the average degree of polymerization to about 200 to 1100 without substantially reducing the hemicellulose content or increasing the copper number of the pulp.
Owner:INT PAPER CO
Bamboo chip treatment and products
InactiveUS20050161852A1Equally distributedVoid space is smallWood working apparatusAbsorbent padsEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
Thin elongated bamboo chips are produced and then are softened and dried. The softening of the chips reduces void spaces which uses less glue and produces stronger members. The chips are then joined together with glue under pressure to form a bamboo board. By varying the depth and length of the chip form, the member produced can form a board, chipboard, beams, or columns of any size. Additional boards may be produced and glued together to form a larger board, beam, or column. Several chipboard layers fabricated in large sheets and glued together will form ‘multi-ply bamboo’, a bamboo substitute for plywood. Once cured, the member is kiln dried and sealed for moisture. The resulting bamboo member's strength and geometrical form is stable and consistent enough to be used as a structural grade member for frames, homes, buildings, and furniture.
Owner:DECKER EMIL GUY +1
Highly refined fiber mass, process of their manufacture and products containing the fibers
The present invention comprises an improved method for refining cellulose that produces a highly refined cellulosic material. The method comprises soaking raw material from primarily parenchymal cell wall structures in an aqueous solution which need not contain an agent to modify the fiber (e.g., a mild alkalizing or alkaline agent and / or solution) using reduced temperatures and pressures, and refining the material with a plate refiner so that a waste water stream is reduced in volume. The mass is dried to produce the HRC fiber. The HRC fiber displays a water retention capacity of about 25 to at least about 56 g H2O / g dry HRC and retains moisture under conditions that are ordinarily used to remove moisture from materials. The highly refined fiber product can also provide excellent thickening properties and can be used in a wide variety of materials, including edible materials.
Owner:FIBERSTAR INC
Solvent method high-wet-modulus bamboo fiber and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101694019AEasy to operateReduce energy consumptionMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentVegetable materialFiberCellulose
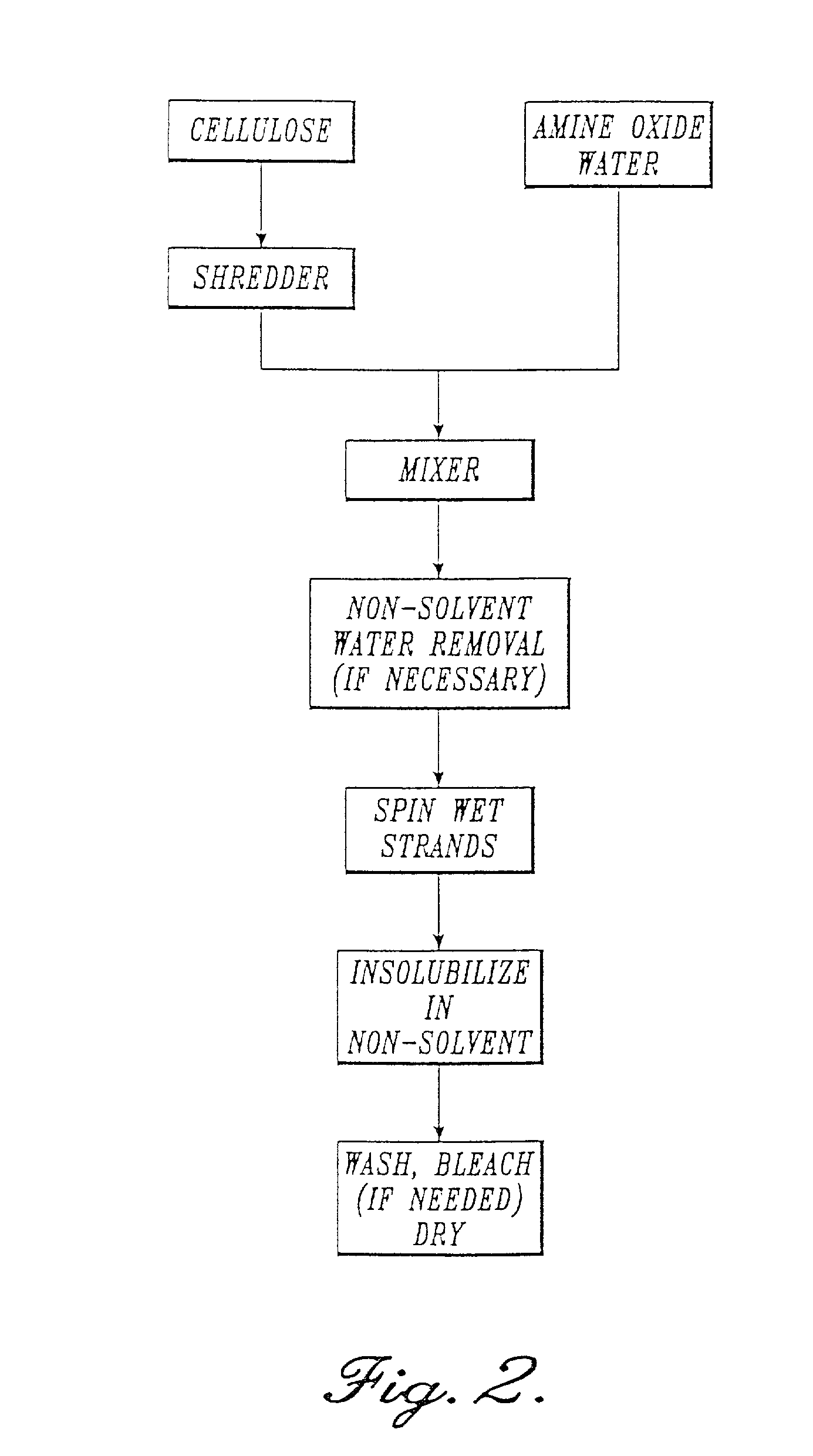
The invention discloses a solvent method high-wet-modulus bamboo fiber and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the bamboo fiber comprises the following steps: activation, adding bamboo pulp into deionized water, adjusting the pH value, adding cellulase for activation, and then adding alkali to adjust the pH value; squeezing, vacuum dewatering and squeezing; pre-dissolving, adding water solution containing 50-88% of N-methyl morpholine-N-oxide; dissolving, entering a dissolving machine, heating, vacuumizing, dehydrating, dissolving, homogenizing and defoaming; spinning, spraying through a spinneret plate, and molding by adopting a dry wet spinning; washing; whitening; oiling; and drying. The preparation method has simple operation, no industrial pollution, low energy consumption and high safety performance, and is applicable to manufacturing the solvent method bamboo fiber by large-scale industrialized continuous production; furthermore, the bamboo fiber prepared by the method not only maintains the natural physical and chemical properties of the bamboo fiber, but also generates no harmful chemical residue and has higher wet modulus.
Owner:SHANGHAI LYOCELL FIBER DEV
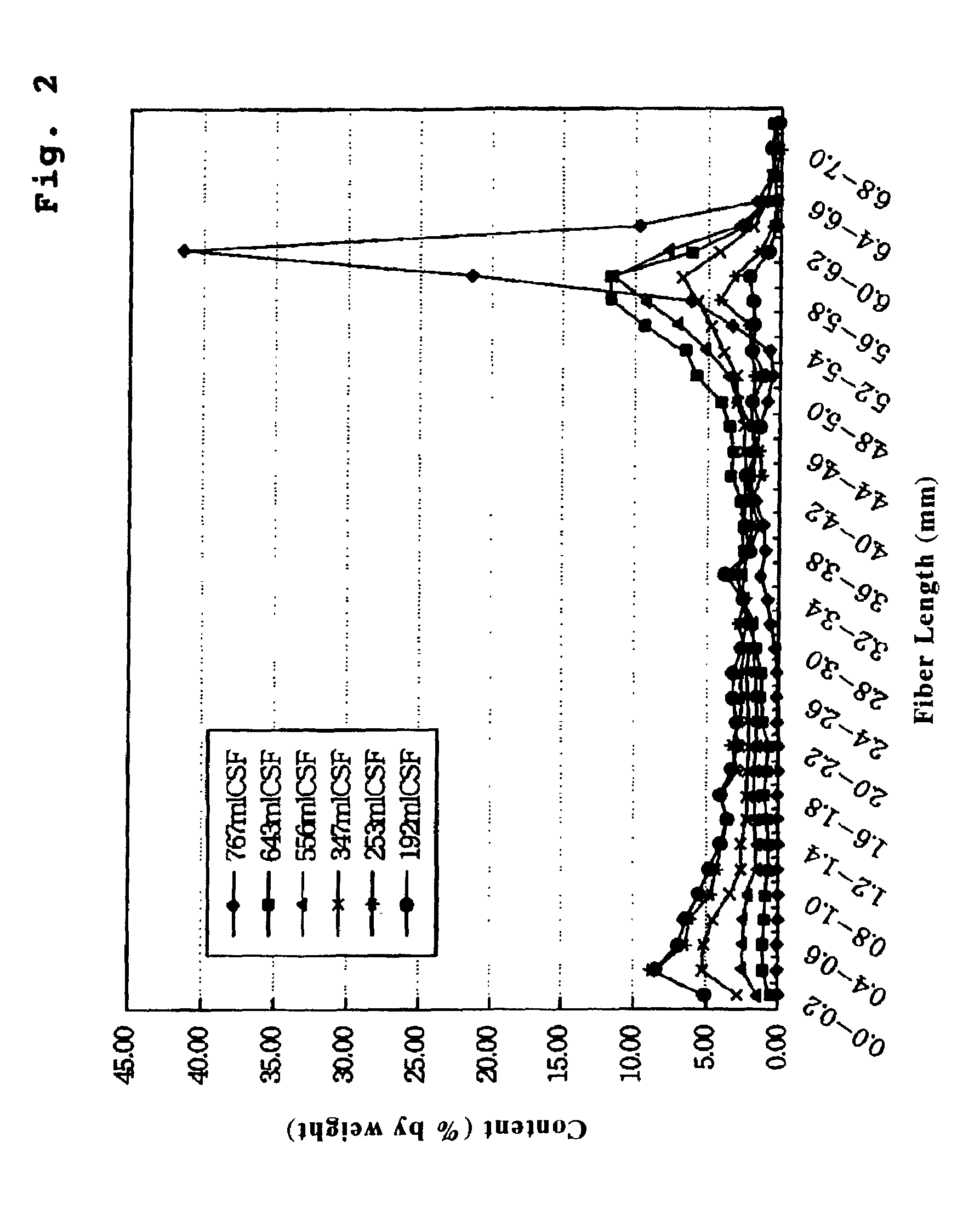
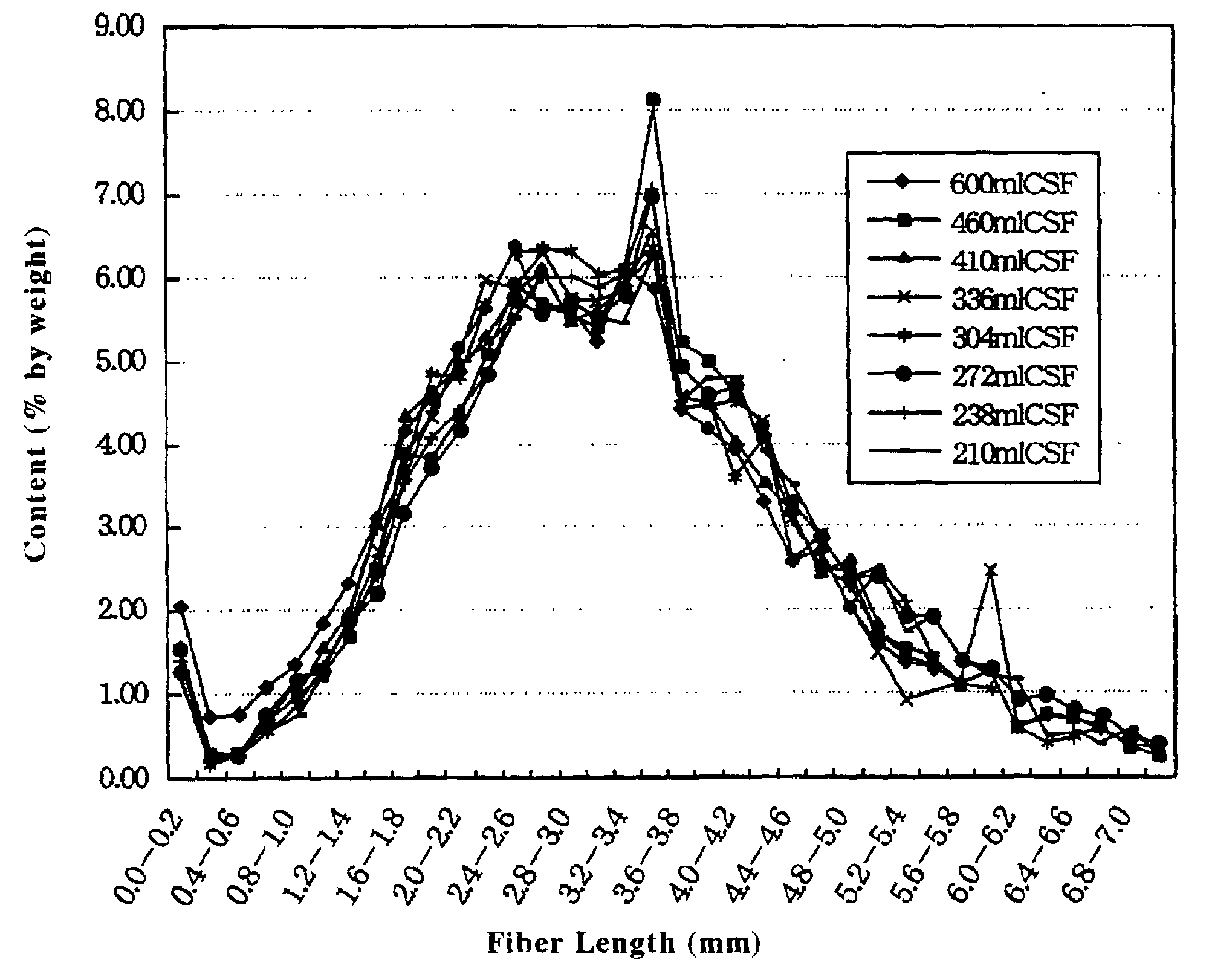
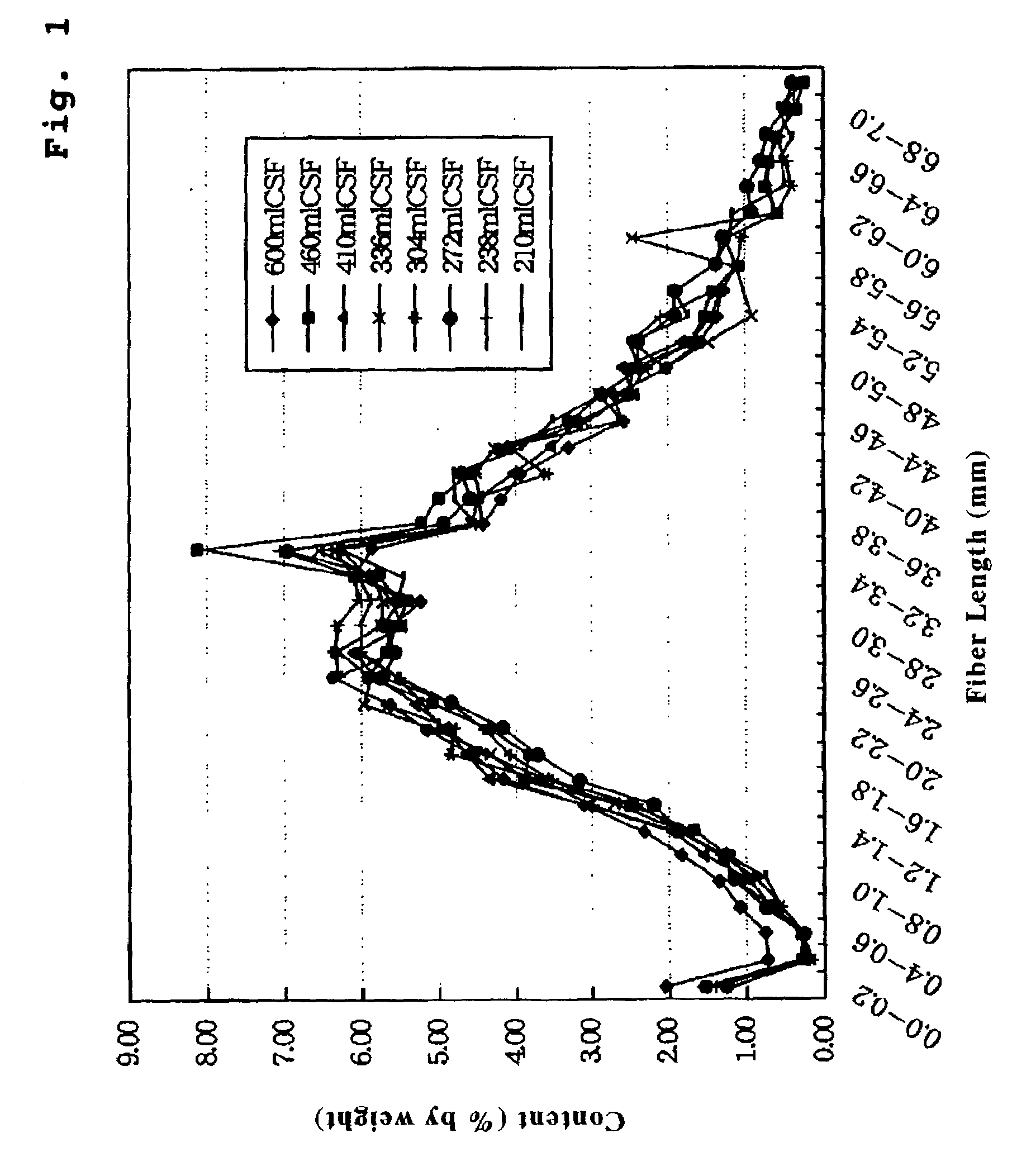
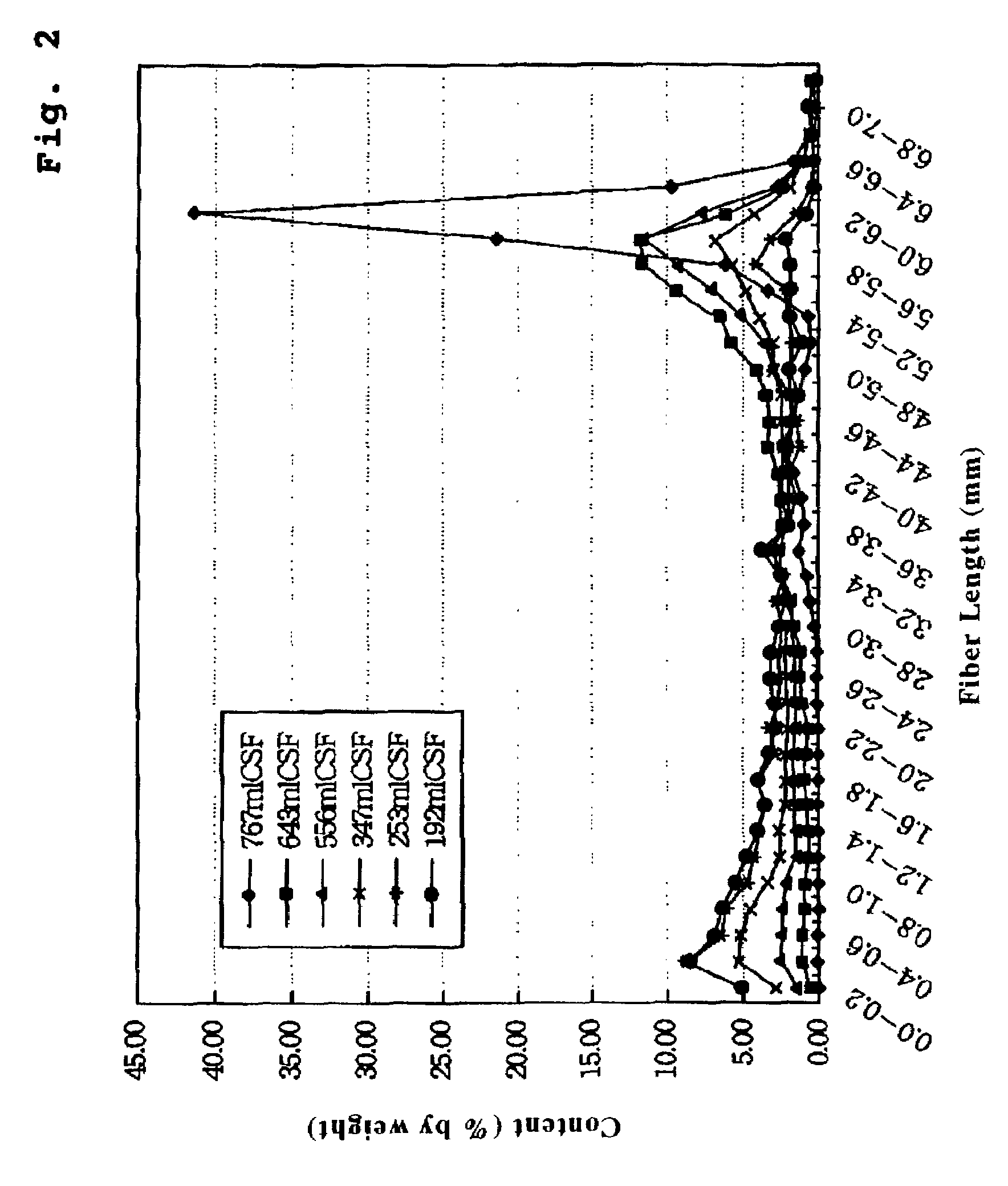
Water-disintegratable sheet and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS7241711B2Good wettingImprove dry strengthNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperFiberPolymer science
Disclosed is a water disintegratable sheet of which fibers are hydroentangled about each other. The water disintegratable sheet includes: at least one kind of primary fibers having a fiber length of at most 10 millimeter; and bast / leaf fibers having a Canadian Standard freeness value of at most 600 milliliter and a fiber length of at most 10 millimeter.
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP
Water-disintegratable sheet and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS7250382B2Reduce manufacturing costImprove balanceNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperFiberSheet material
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP
Method for producing pulp and lignin
InactiveUS20040244925A1Pretreatment with acid reacting compoundsPulp bleachingCellulosePtru catalyst
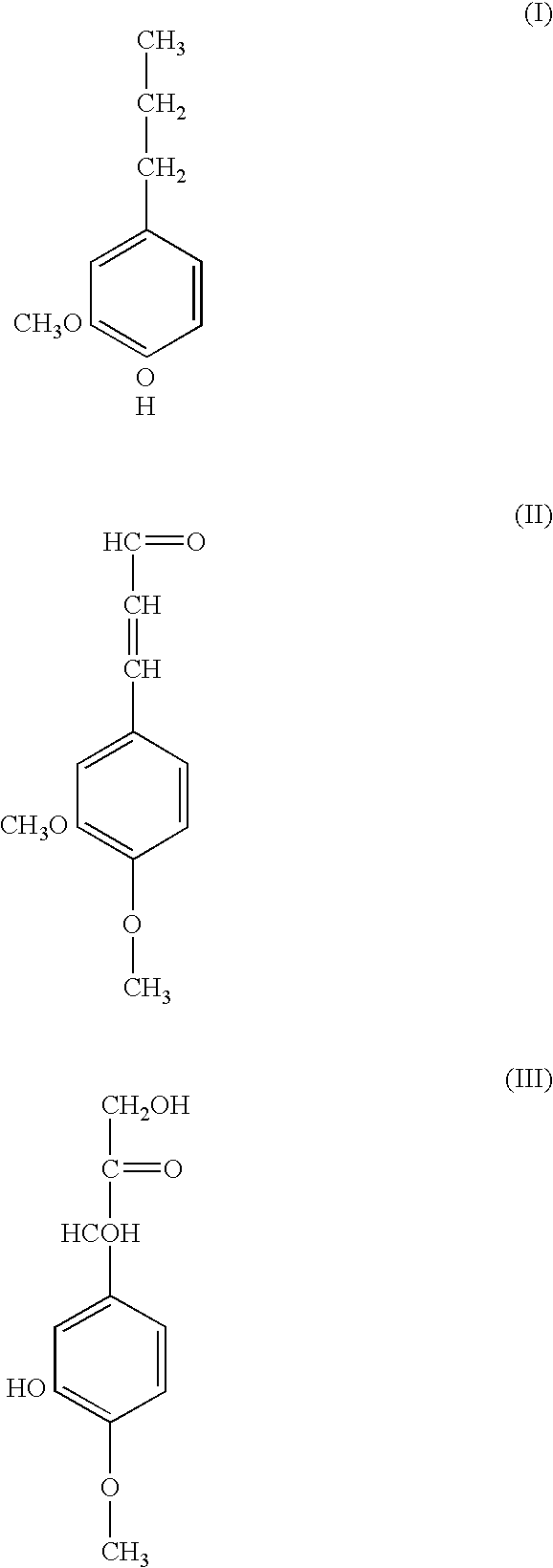
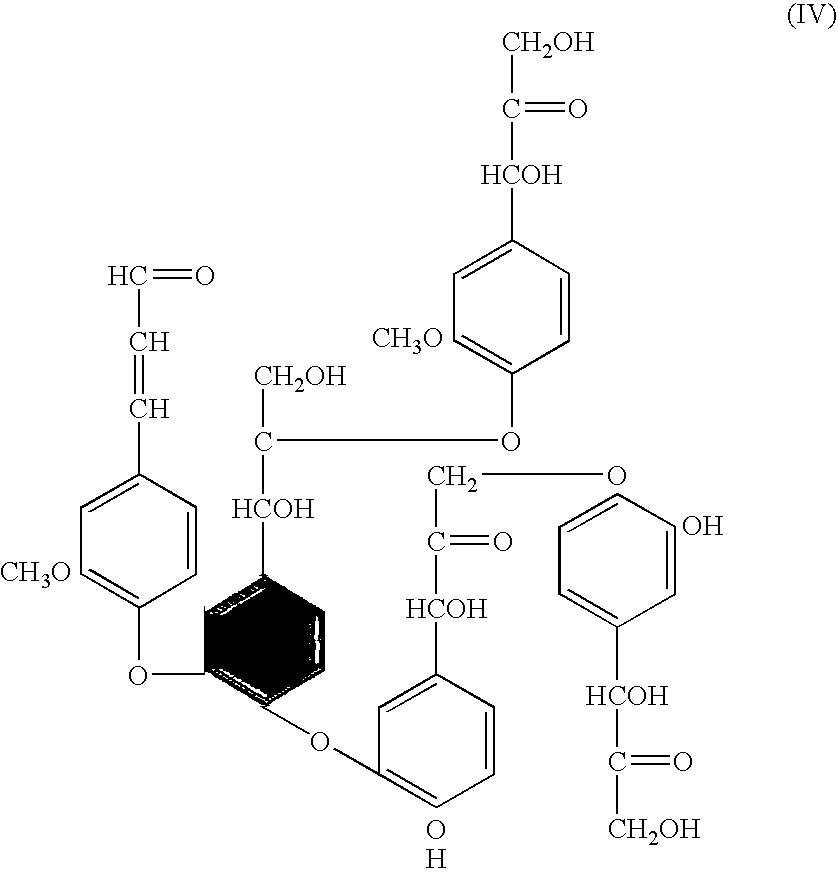
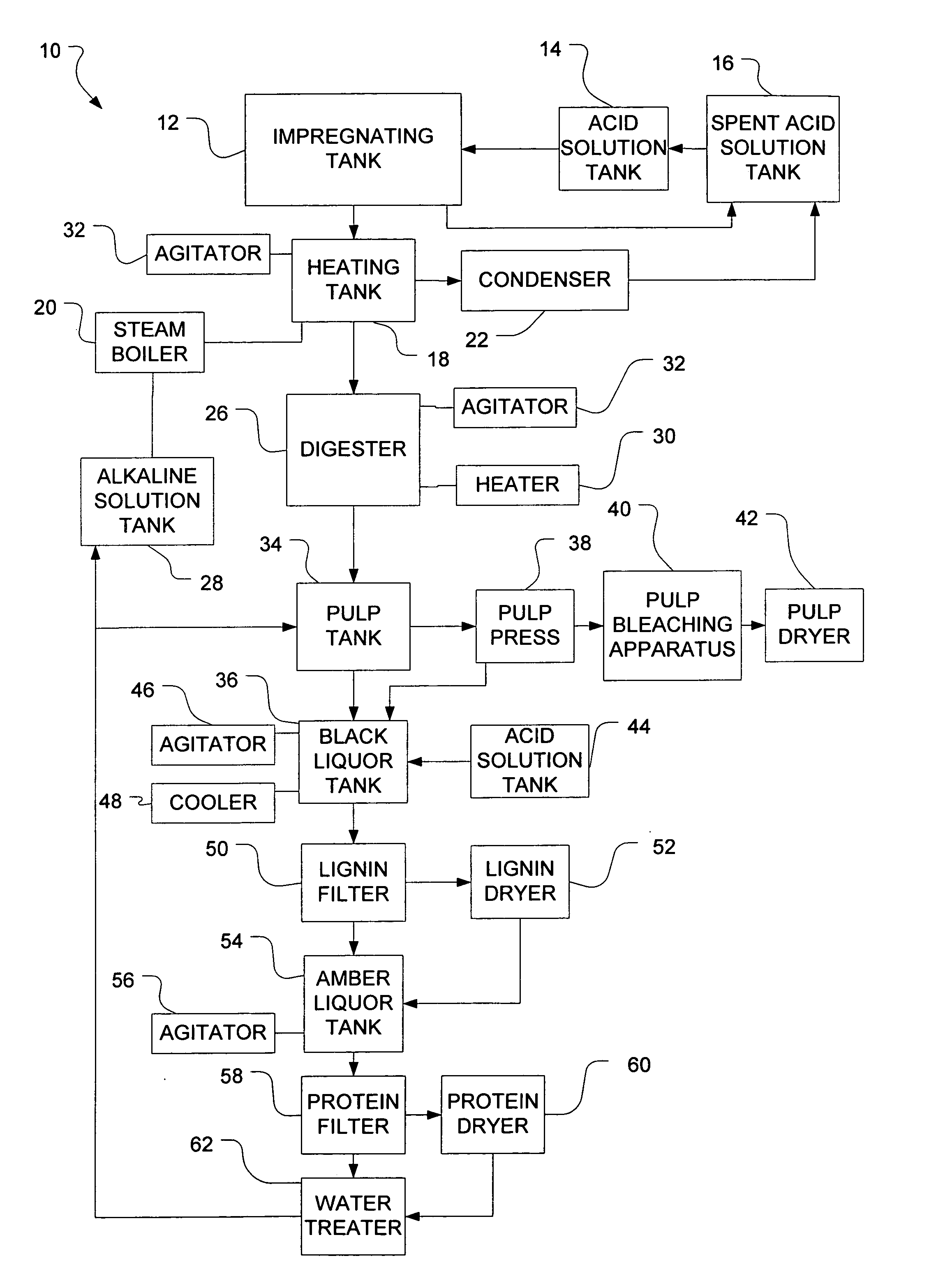
The invention provides for methods for producing pulp (comprising cellulose) and lignin from lignocellulosic material, such as wood chips. The methods involve acid catalyzed hydrolysis. Lignocellulosic material having a relatively high moisture concentration can be used as the starting material. The lignocellulosic material is impregnated with an acid (preferably nitric acid) and heated. During the heating lignin is depolymerized at relatively low temperatures, and the acid catalyst is distilled off. The acid catalyst can be collected and recycled after impregnation and heating. The lignocellulosic material is then digested in an alkaline solution under heat, dissolving the lignin and allowing the pulp to be removed. Acid is added to the black liquor to precipitate the lignin which is then removed. The resultant amber liquor can be further processed into other ancillary products such as alcohols and / or unicellular proteins.
Owner:PACIFIC PULP RESOURCES
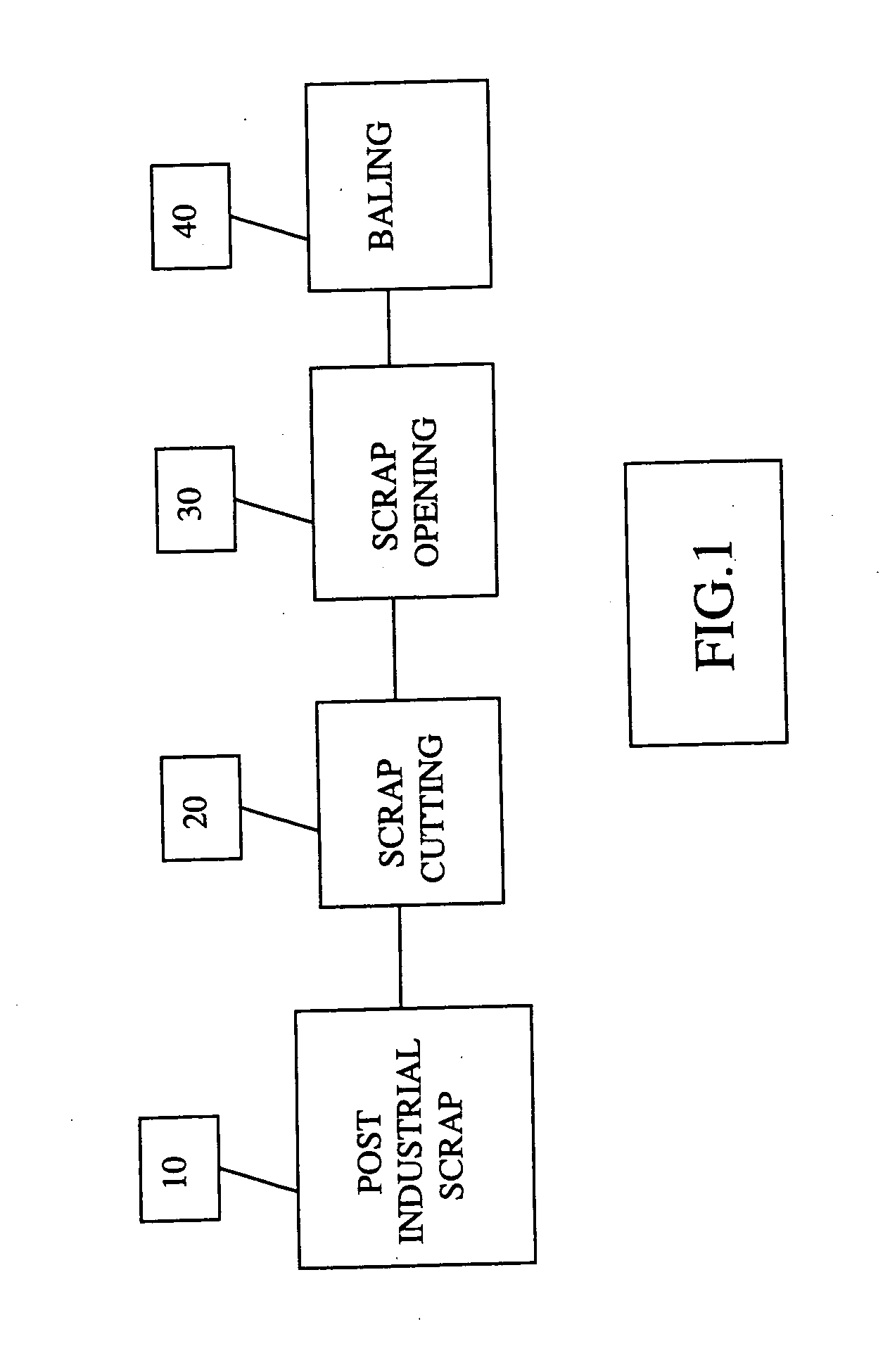
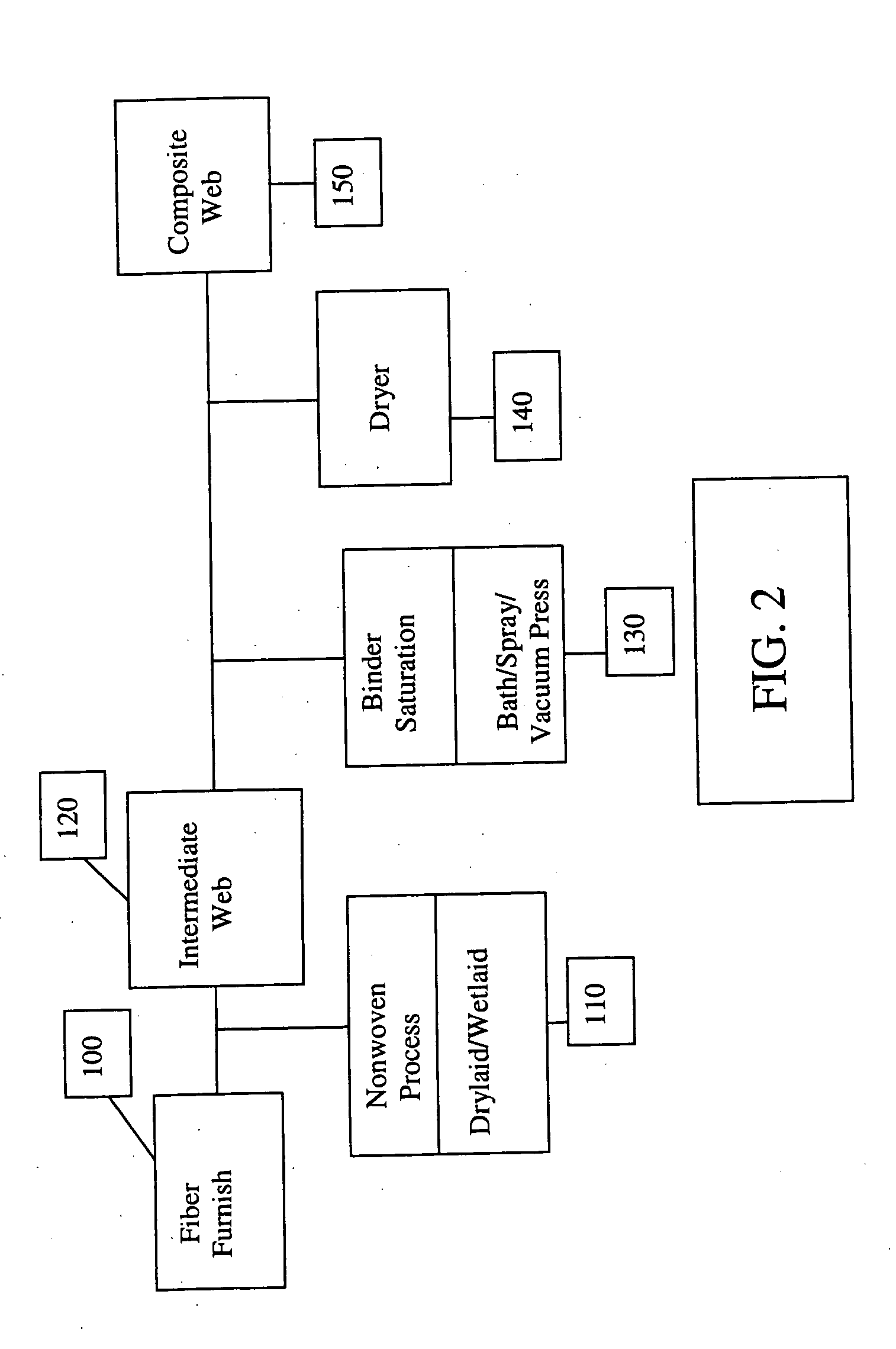
Composite web and process for manufacture from post-industrial scrap
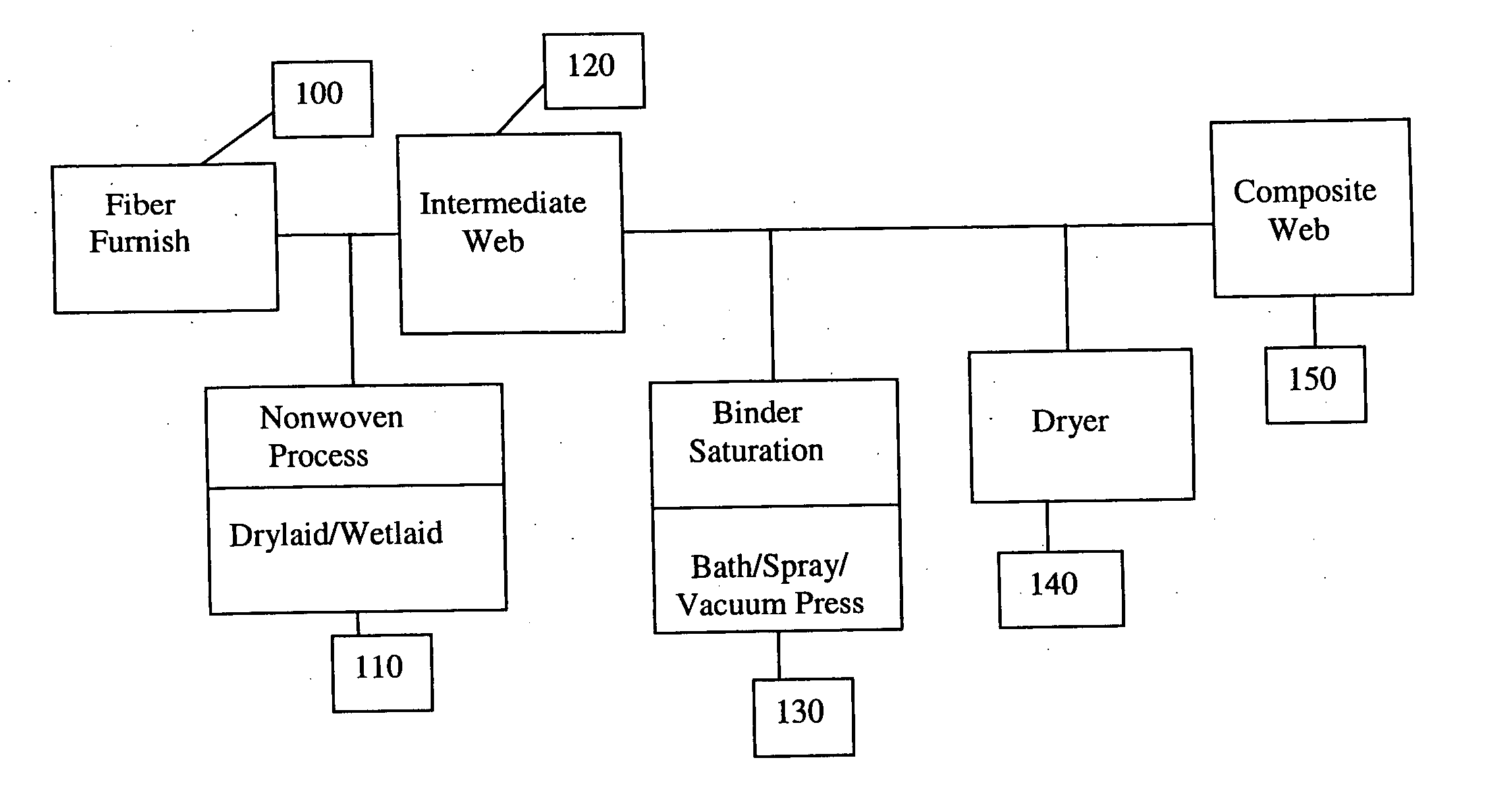
A composite web and process for manufacture from post-industrial scrap wherein the fibers are pre-opened and cut to an average fiber length of about 4 mm. A scrap fiber component and a cellulosic component of such fibers are blended into a fiber furnish. The scrap fiber component includes at least 15% synthetic fibers and may include a blend of natural fibers, high melting point synthetic fibers, and low melting point synthetic fibers. The cellulosic component may include post-industrial cotton fibers which may be refined before blending with the scrap fiber component. The fiber furnish is processed into an intermediate web such as by a drylaid or a wetlaid nonwoven process. The intermediate web is saturated with a latex binding agent and pressed and / or dried to form a composite web capable of further processing into molded or formed consumer or industrial products. The process is capable of producing a high basis weight composite web.
Owner:SSI TECH INC
Process for making a flowable and meterable densified fiber particle
InactiveUS7201825B2Speed up the flowEasy to transportFibreboardNon-fibrous pulp additionCellulose fiberDiscrete particle
Discrete particles of cellulosic material are flowable and meterable. They are easily dispersible in an aqueous or a dry medium. The particles comprise singulated cellulose fibers that have been densified. The particles have a density of at least 0.3 g / cc.
Owner:WEYERHAEUSER NR CO
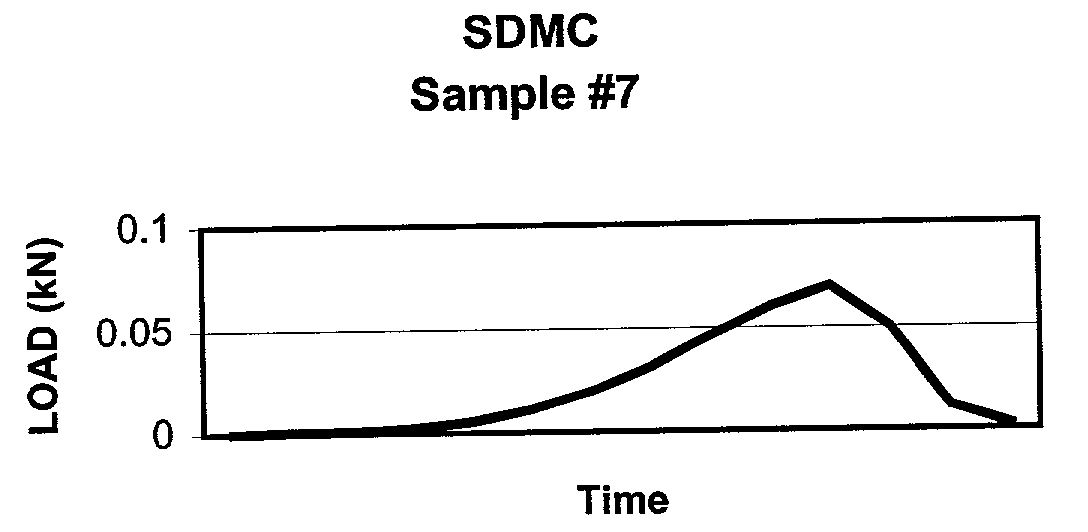
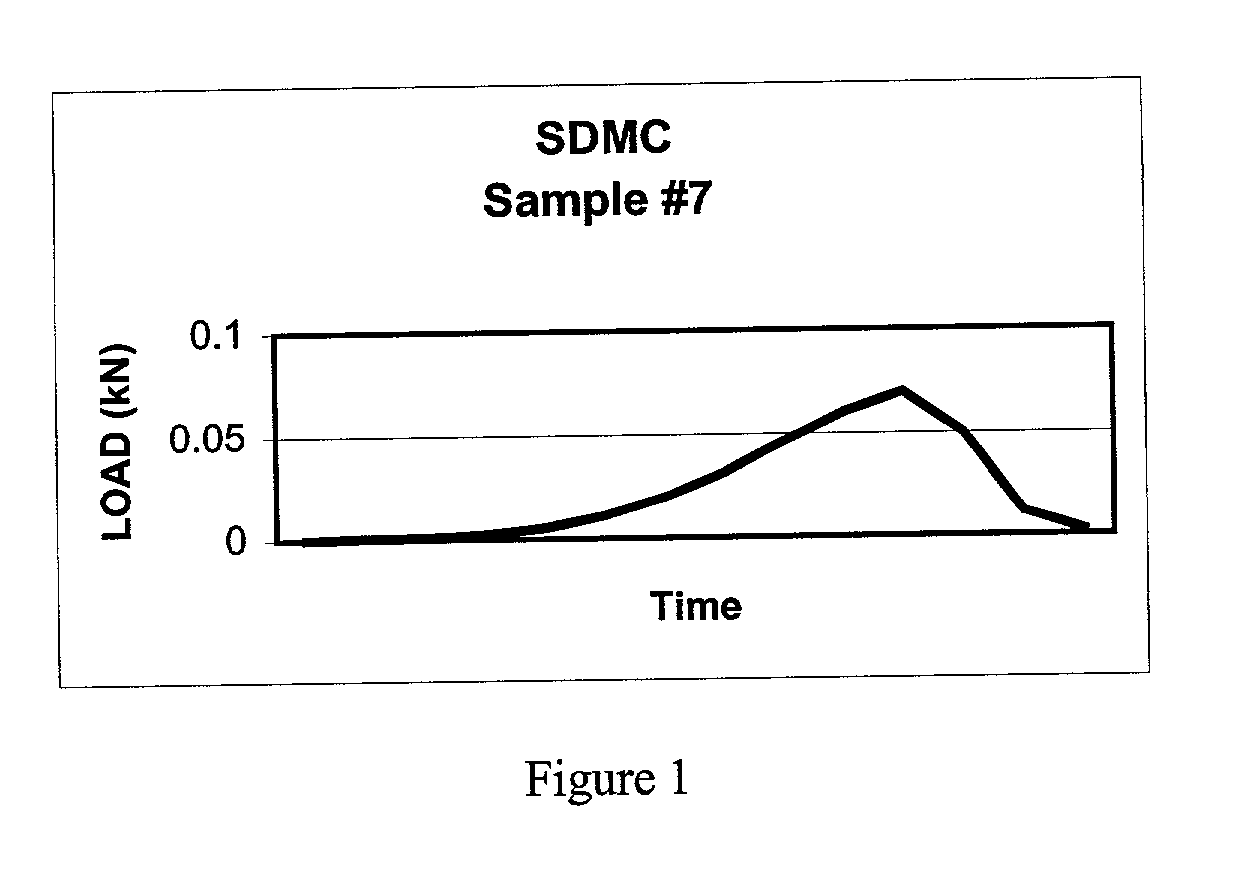
Solvent dehydrated microbially-derived cellulose for in vivo implantation
InactiveUS20020107223A1Less inter-fibril surface tensionReduce surface tensionOrganic active ingredientsBiocideCelluloseOrganic chemistry
A solvent dehydrated microbially-derived cellulose material is described for use as an implantable material in general and plastic surgery.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Hemp-material viscose fiber and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN101130885AQuality improvementHigh whitenessWet spinning methodsVegetable materialAfter treatmentHemp plant
The present invention discloses a method for preparing hemp viscose fiber by using hemp plant and hemp visose fiber prepared by adopting said method. Said method includes the following steps: preparing raw material, digesting, washing material, pulping, removing sand, bleaching, water-washing, fiber-making, impregnating, pressing, pulverizing, aging, xanthating, dissolving, mixing, filtering, defoaming, spinning, drawing, cutting and making after-treatment.
Owner:CHTC HELON
Process for making composition for conversion to lyocell fiber from sawdust
InactiveUS7090744B2Reduce the degree of polymerizationReduce contentPulp properties modificationMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentCopperHemicellulose
A process for making a composition for conversion to lyocell fiber where the process comprises pulping a raw material in a digester to provide an alkaline pulp, wherein the raw material comprises sawdust in an amount greater than 0 % up to 100 %; and contacting the alkaline pulp comprising cellulose and at least about 7 % hemicellulose under alkaline conditions with an amount of an oxidant sufficient to reduce the average degree of polymerization of the cellulose to within the range of from about 200 to about 1100, without substantially reducing the hemicellulose content of the pulp or substantially increasing the copper number.
Owner:INT PAPER CO
High polymerization degree cotton pulp and method for making the same
InactiveCN101130886AHigh fiber contentHigh whiteness valueVegetable materialCotton fibreDegree of polymerization
The present invention discloses a cotton pulp with high degree of polymerization and method for preparing said cotton pulp with high degree of polymerization by using cotton linters as raw material. Said preparation method includes the following steps: preparing raw material, digesting, washing material, pulping, removing sand, bleaching, acid treatment, water-washing, filtering and pulp-making, etc.
Owner:CHTC HELON
Preparation and application of cellulose mixed fibre using ion liquid as solvent
InactiveCN101089249AImprove protectionGood for healthFilament/thread formingVegetable materialIonSolvent
The present invention relates to a method for preparing cellulose polyblend fiber by using ionic liquid as solvent and its application method. Said preparation method includes the following steps: (1), uniformly mixing pulverized cellulose, chitin / chitosan and ionic liquid, dissolving them for 1-80 h at 25-160 deg.C so as to obtain the uniform stable spinning solution whose total solid content is 3-40%; (2), filtering and defoaming, then making the spinning solution be passed through single-hole or multi-hole spinneret, and fed into a coagulating bath and solidified, its spinning speed is 5-150 m / min; and (3), plasticizing, drawing, washing, bleaching, oiling and drying so as to obtain the invented cellulose polyblend fiber product. The spinning solution prepared by aid invention also can be used for preparing hollow fiber membrane, specially, can be used for making artificial organ and membrane for water purifier.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Bamboo fiber composite base material and method for manufacturing automotive interior trim part
InactiveCN102896843APromote growthIncrease productionLamination ancillary operationsSynthetic resin layered productsVascular bundlePolyester
The invention relates to a composite material for manufacturing an automotive interior trim part. The bamboo fiber composite base material for manufacturing the automotive interior trim part is prepared by taking thermoplastic synthetic fibers (polypropylene PP, polyethylene PE or polyester PET and the like) as a bonding substrate and bamboo fibers as a reinforcing material through hot pressing. The bamboo fiber composite base material is characterized in that the bamboo fibers are prepared by sawing natural bamboo into pieces with length required by production, removing parenchyma from the bamboo by mechanical, physical, chemical and biological methods and directly extracting vascular bundle bamboo fibers from the bamboo, and have the length of 60 to 150mm, the diameter of 0.3 to 1.5mm, the strength of 60 to 120MPa and the water content of 10 to 12 percent. The automotive interior trim part can be subjected to press forming when the bamboo fiber composite base material covers artificial leather, leather or a knitted or non-woven fabric for surface decoration.
Owner:喻云水
Preparation of original bamboo fiber by bioenzyme method
The invention discloses a method to make bamboo origin fiber that the process includes following steps: cutting the bamboo and dissecting into sheet, adding to boiling water, taking out and crushing, hammering to filament, adding into pressure cooker to boil, dipping the processed bamboo filament into solution that contains biology enzyme to gain fibrin fiber, cleaning, whitening, oil pumping, softening, shredding the fibrin fiber, the bamboo origin fiber would be gained.
Owner:苏州市利飞纺织品有限公司
Degumming technology of mulberry bark
InactiveCN101638811AImprove production rateAvoid damageVegetable materialBacteriological rettingFiberCellulase
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF IND TECH
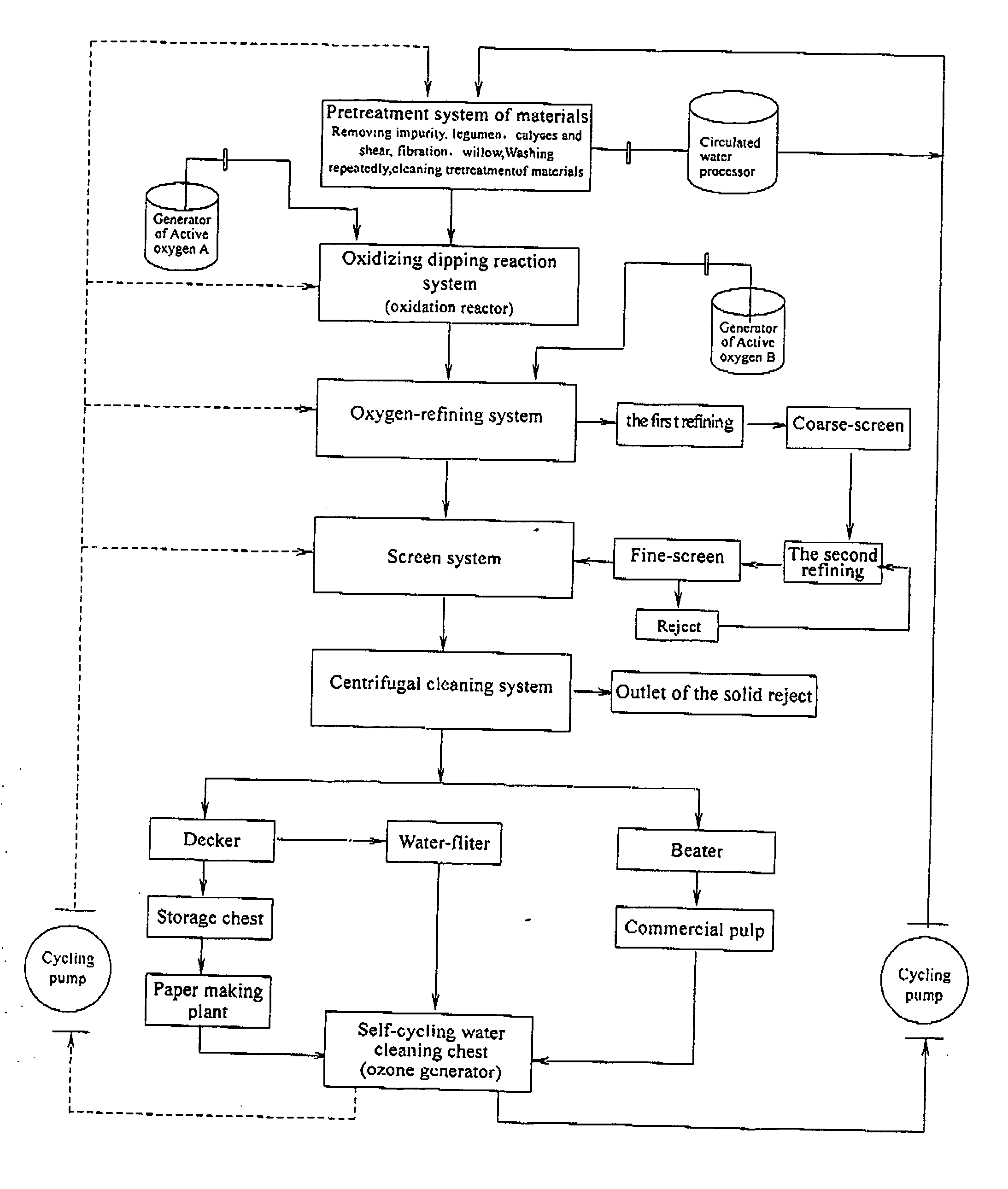
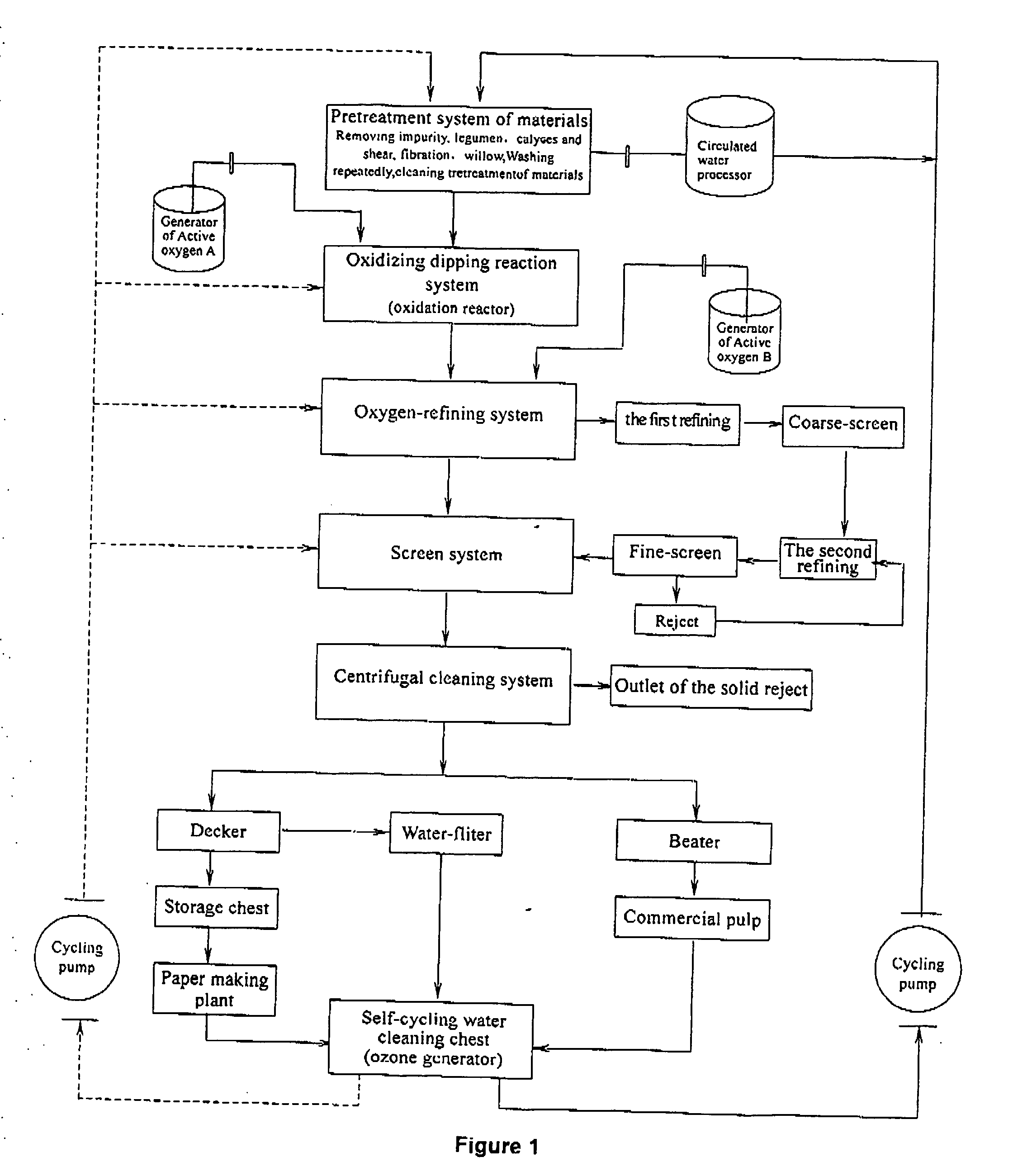
Fully Closed, Zero Discharge, Clean Oxidizing Pulping Technology and Process
InactiveUS20070272377A1Avoid pollutionSave energyPulp properties modificationPulp bleachingFiberLignin degradation
The aim of the present invention is to provide a close-loop, zero discharge and clean oxidation pulping method and technology. In accordance with present invention, it takes advantage of active oxygen free radical generated by reduction reaction of molecular oxygen in process reactor to transform and separate lignin to change chromophoric group in the intercellular space and obtain paper pulp. The conventional pulping technologies which use harmful polluting chemicals such as acid, alkaline, chlorine, anthraquinone and so on are basically changed in the present invention. The cooking and bleaching process, generating severe pollution, can be avoided. The abundant yearly grown fiber materials can be utilized in this process, and water and energy can be saved. The present invention can cut down production cost and have excellent social, economic and environmental performance.
Owner:MEI XIUQUAN
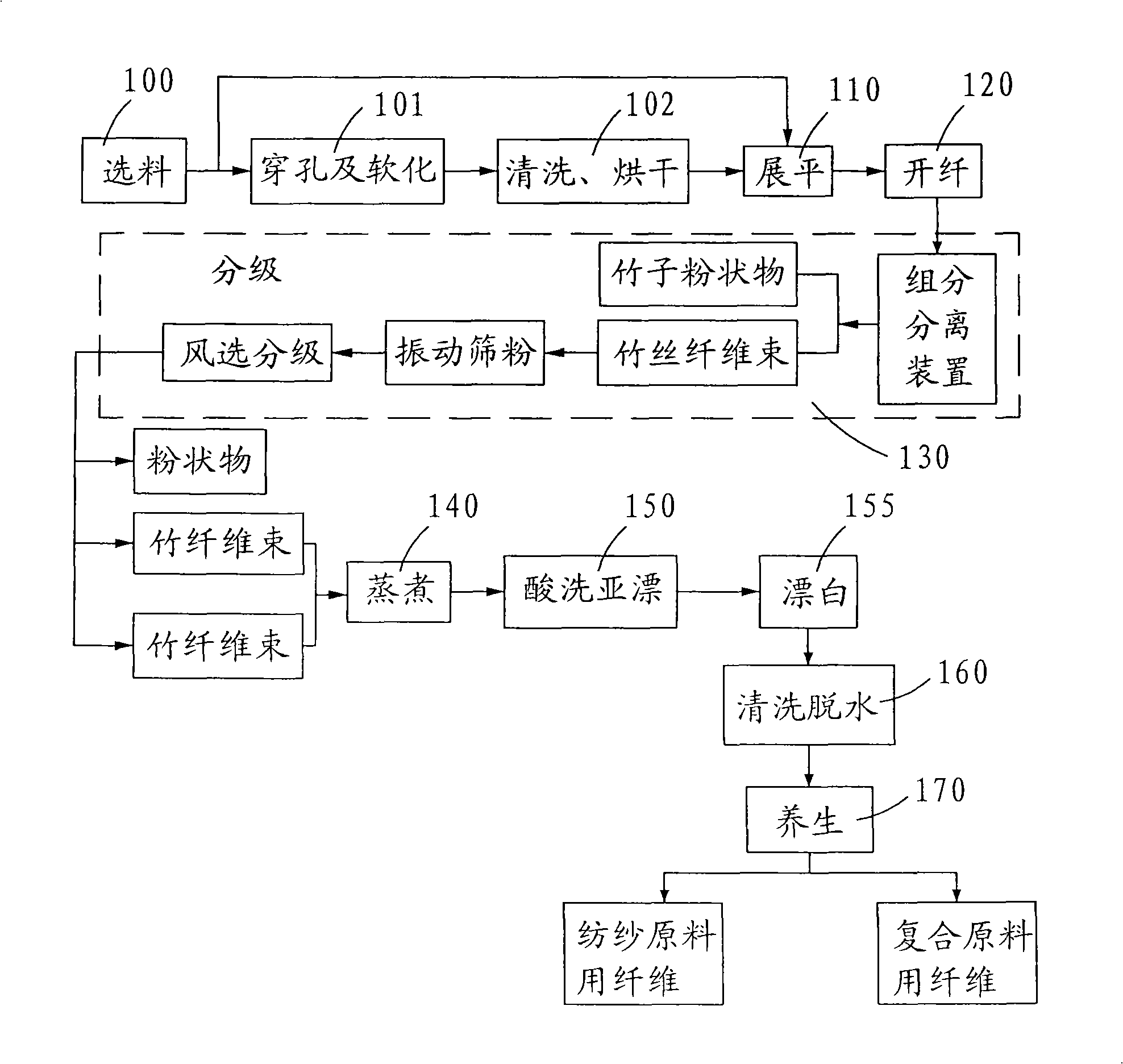
Pieparation method for fabricating raw bamboo into spinnable bamboo fibers
A method for preparing primary bamboo to be spinnable bamboo fibre includes cutting bamboo into pieces, placing prepared bamboo pieces in pressure container for obtaining coarse fibre, using mildew aqueous solution to remove lignin, pectin, sugar and fat out from the fibre; rolling and dividing the fibre, bleaching and rinsing the fibre for softening; dewatering and adding reinforcer to enhance fibre strength; using emulsifier to process fibre for having desired compliance and drying it for obtaining spinnable bamboo fibre.
Owner:刘忆萍
Process for producing bamboo fiber
InactiveCN101537648AReduce processing costsReduce pollutionWood working apparatusVegetable materialResource utilizationChemistry
The invention discloses a process for producing a bamboo fiber, comprising the following steps of selecting raw materials, extending, splitting, classifying, stewing and cooking, pickling, cleaning, dehydrating, curing and the like, thus preparing the bamboo fiber with the fineness of 0.03-0.08mm and the length of 30-80mm. The process can lead a whole bamboo to be extended by a special tool and subsequently and directly processed without being cut; furthermore, the processed bamboo fiber is longer, finer and more uniform, the utilization ratio of the resource is high, the cost is low and the quality of the product is stable.
Owner:FUJIAN DANHAI MATTRESS
Hemp-like bast fibre flash explosion-high temperature boiling combination degumming technique
The flash bursting and high temperature digesting process for degumming hemp bast fiber includes pre-treatment, flash bursting and high temperature digesting to eliminate residual pectin, hemicellulose and lignin from hemp bast fiber, and raise the fiber fracturing degree and softness. The flash bursting and high temperature digesting process has ideal degumming effect, obvious non-fiber component eliminating effect and less pollution, and the degummed hemp bast fiber has high cellulose rate, high fiber fracturing degree and high fiber flexibility.
Owner:THE QUARTERMASTER EQUIPMENT RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF THE GENERAL LOGISITIC DEPARTME
Tissue Products Containing Microalgae Materials
Dry products, and particularly dry tissue substrates, including a blend of conventional papermaking fibers and microalgae are disclosed herein. Use of a cationic retention aid in the dry tissue substrates helps to provide a tissue sheet retaining the microalgae without being detrimental to tissue properties such as caliper, bulk, air permeability, slough and absorbent capacity. Additionally, use of a flocculating agent may agglomerate the microalgae and make it easier to retain the microalgae within the tissue sheet.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Process for making bamboo fiberfill and articles thereof
InactiveUS20090101294A1Small sizeNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperFiberEngineering
A process for producing bamboo fiberfill from raw bamboo fiber includes, obtaining a bale of the raw bamboo fiber, picking up and separating the raw bamboo bale fiber into tufts of bamboo fiber with a bale opener, feeding the bamboo fiber tufts into a blending hopper configured to blend the bamboo fiber tufts, feeding the blended bamboo fiber tufts into a beater configured to open the bamboo fiber tufts, and feeding the opened bamboo fiber tufts into a fine opener configured to reduce the size of the opened bamboo fiber tufts and refine the opened bamboo fiber tufts into the bamboo fiberfill, wherein the bamboo fiberfill has a fiber length of about 30 millimeters to about 60 millimeters and a linear density of about 0.5 denier to about 5.0 denier.
Owner:FAIRFIELD PROCESSING CORP
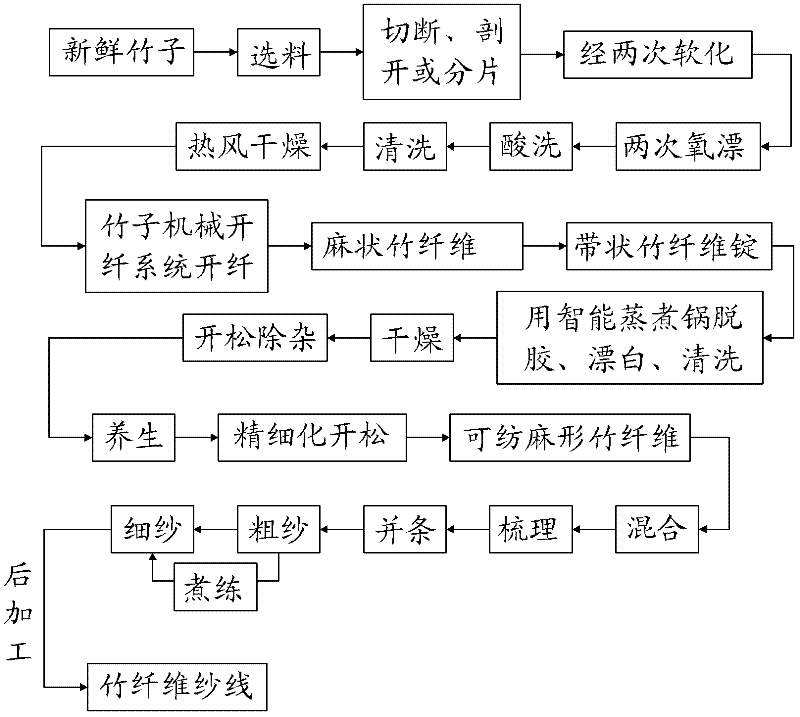
Production process for linen bamboo fibers, spinnable linen bamboo fibers and bamboo fiber yarns
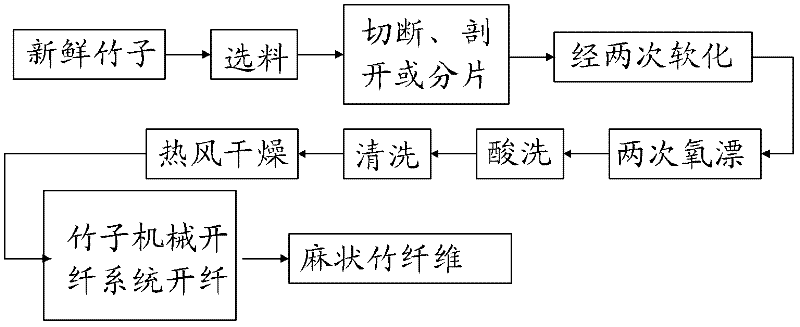
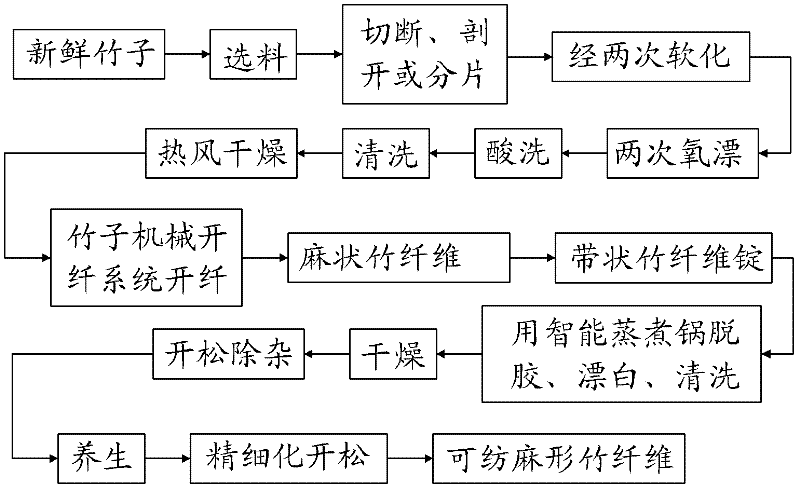
ActiveCN102242403AQuality improvementHigh strengthVegetable materialMechanical fibre separationYarnSoftening
The invention relates to a production process for linen bamboo fibers, spinnable linen bamboo fibers and bamboo fiber yarns. The production process comprises the following steps: sawing a fresh bamboo into pieces according to a certain length and then respectively soaking the pieces in different biologic softening solutions or cooking the pieces in specially prepared softening solutions at high temperature; after cleaning the pieces, heating and airing the pieces, and then feeding the pieces into a bamboo mechanical splitting system, thereby preparing the linen bamboo fibers; processing the linen bamboo fibers into strip-shaped bamboo fiber spindles; putting the strip-shaped bamboo fiber spindles into an intelligent steam cooker in turn, thereby degumming, bleaching and cleaning the strip-shaped bamboo fiber spindles; after drying the strip-shaped bamboo fiber spindles, opening and removing impurities, thereby acquiring the spinnable linen bamboo fibers; and sending the spinnable linen bamboo fibers into a yarn-forming integrated system, and performing the processes of opening, cotton-blending, carding, drawing and yarn-forming, thereby finally acquiring the bamboo fiber yarns. The bamboo fibers prepared by using the production process are linen, longer, thinner, more uniform and softer. The average fineness of the bamboo fibers can reach 400-600 metric counts. The bamboo fibers can be purely spun or fully blended with fibers such as cotton, linen, and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +1
Pulp treatment and process
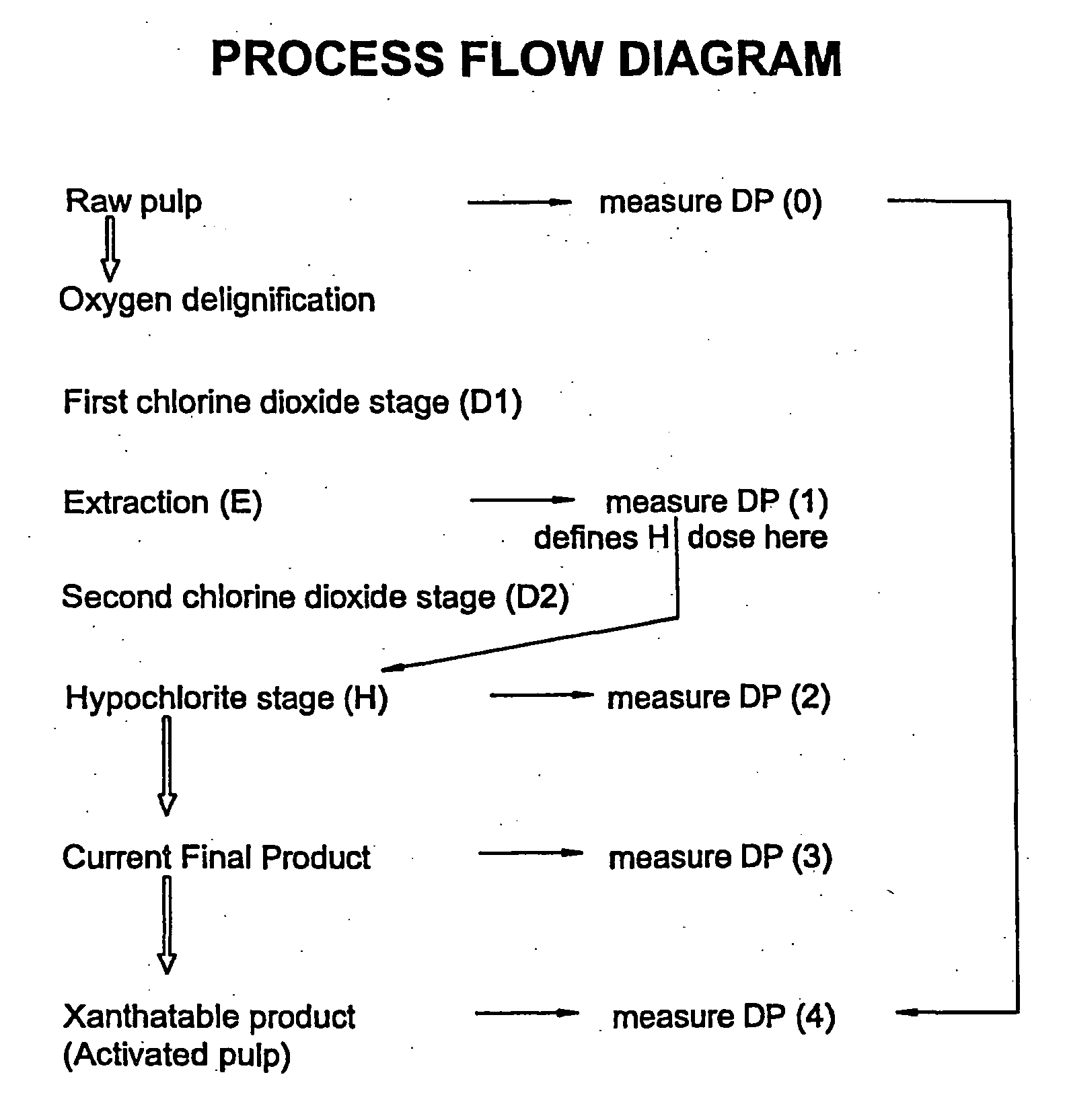
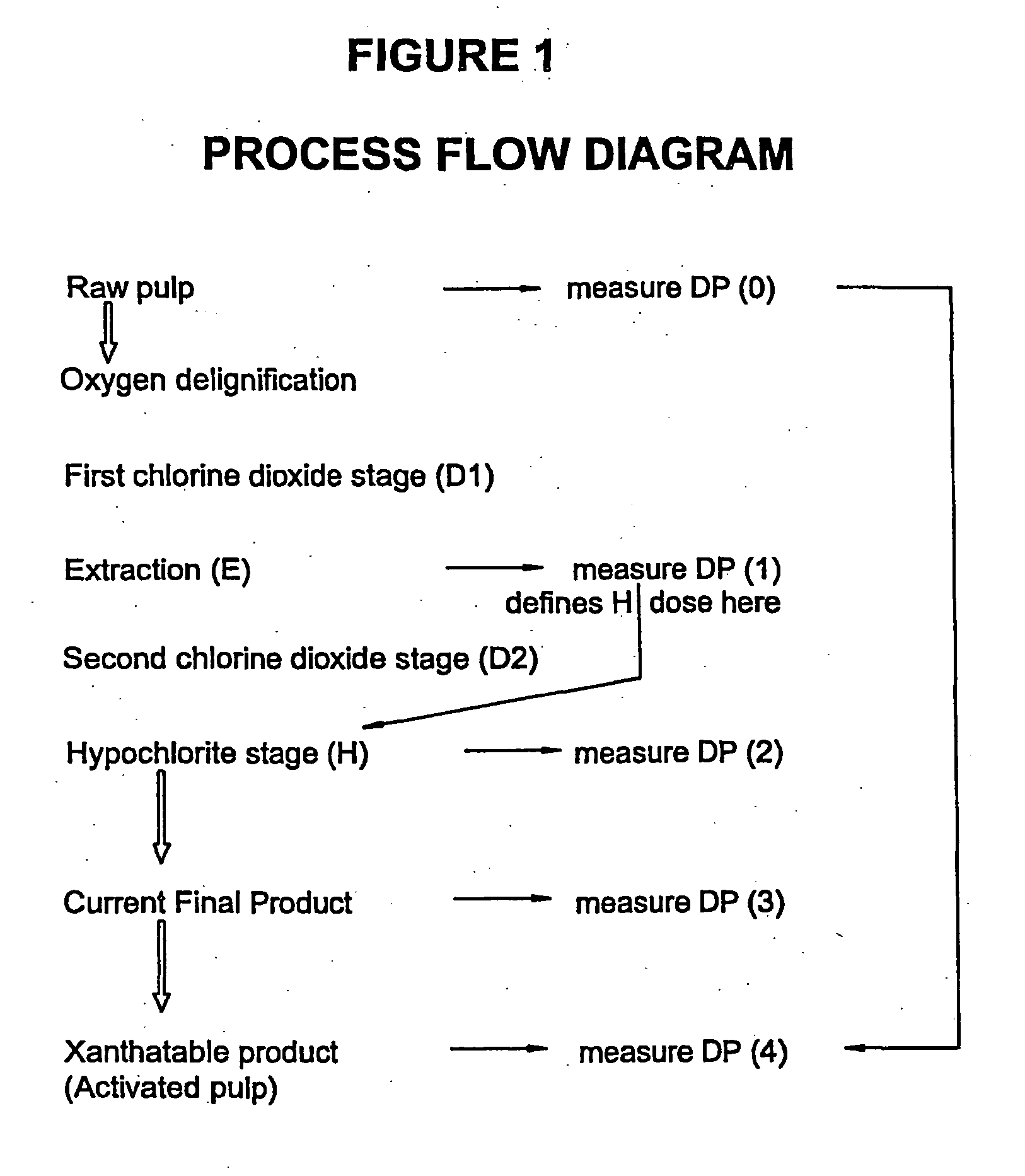
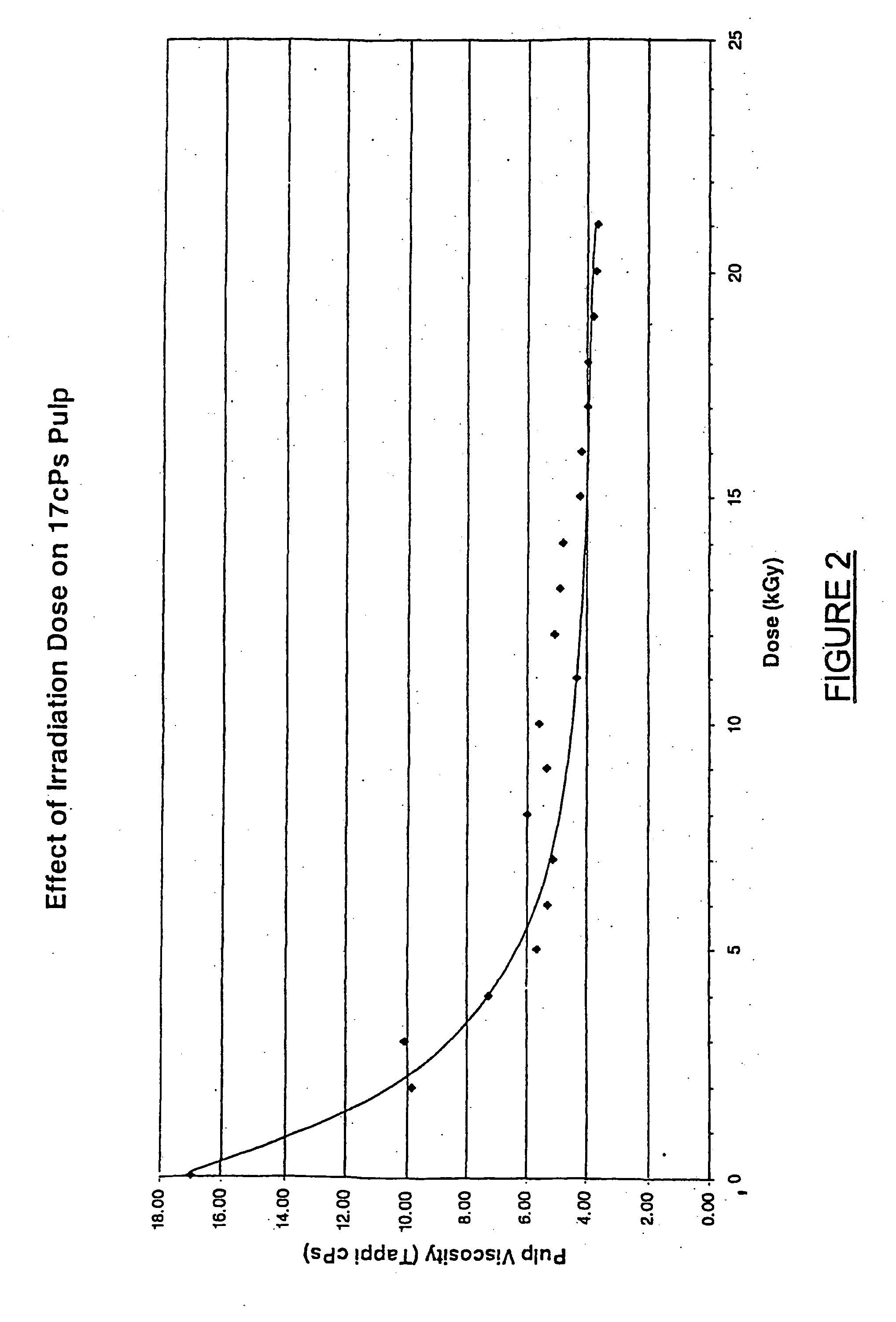
InactiveUS20040129394A1Reduce environmental problemsSmall DP rangeElectrolysis componentsWood treatment detailsPulp treatmentCompound (substance)
This invention provides a process for treating chemical woodpulp, or chemical cellulose including cotton linter, including the step of applying an electron processing technology (EPT) step to chemical woodpulp, or chemical cellulose, as the case may be, on an in-line basis to provide control of pulp viscosity or degree of polymerisation (DP). The invention also provides a method of process control in treating the aforementioned woodpulp or cellulose, including the step of using radiation dose-viscosity relationship curve for applying an EPT step on an in-line basis. The in-line EPT step may, in one form of the invention, replace and hence eliminate a chemical DP reduction step.
Owner:SAPPI LTD
Boiling-off method for bast fibre and bast fibre produced by the same
InactiveCN1772976AAchieve economyFully reflect the scientific concept of developmentVegetable materialEngineeringWater content
The present invention discloses a degumming method of bast fibre. Said method includes the following steps: soaking bast fibre in water for 40-80 min, making its water content is 60-100%, then placing the water-contained bast fibre into a steam explosion tank, making steam explosion under the condition of that its pressure is 1.3-1.7 MPa and the pressure-retaining time is 3-8 min, taking out the bast fibre, washing said bast fibre with water and drying so as to obtain the invented degummed bast fibre.
Owner:北京赛特瑞科技发展有限公司
Physical preparation method of natural bamboo fibers
ActiveCN102560695AImprove the bactericidal effectFineness slenderVegetable materialMechanical fibre separationDeodorantHigh pressure
The invention provides a physical preparation method of natural bamboo fibers. Through original bamboo cutting, rolling and slicing, dipping, primary high temperature and high pressure cooking, water washing, rolling and splitting, secondary high temperature and high pressure cooking, secondary water washing, ultrasonic vibratory splitting, bamboo fibers combing as well as screening and drying procedures, the natural bamboo fibers are prepared by using middle materials of Hunan annual moso bamboos as raw materials for preparing the natural bamboo fibers. By using the physical preparation method of the natural bamboo fibers, provided by the invention, the bactericidal capability of the bamboo fibers are improved while natural antibacterial, bacteriostatic, mothproofing, deodorant and ultraviolet resistant functions of the bamboo fibers are kept; and obvious breakthrough are made in fineness, strength, residual gum content and other aspects of the made 100% natural bamboo fibers.
Owner:湖南欧林雅服饰有限责任公司
Process for producing hemp-like bamboo fibers
ActiveCN102206873AStable separationGood flexibilityVegetable materialMechanical fibre separationHigh pressureFlax fiber
The invention relates to a process for producing hemp-like bamboo fibers, which comprises the following steps of: sawing bamboo according to certain length, flattening, soaking in intermediate temperature softening solution for 3 to 24 hours or cooking by using tailor-made softening solution at a high temperature under high pressure for 15 to 60 minutes, draining, feeding into a fiber separator, rolling, kneading, tearing, combing, opening and the like to prepare the hemp-like bamboo fibers; putting the hemp-like bamboo fibers into a bamboo fiber purifying reactor, performing alkali boiling, bleaching, cleaning and curing; and opening, decontaminating and regularly combing the hemp-like bamboo fibers by using a hackling machine or a middle cutting machine to prepare hemp-like spinnable bamboo fibers. By the method, the hemp-like bamboo fibers can be produced; and the fibers are regular, uniform and soft, have the characteristics of large length, high strength, low fineness and the like, and have spinnability similar to that of hemp and flax fibers.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Soft and strong fibrous structures and methods for making same
ActiveUS20110168342A1Negatively strengthNegatively softnessNon-fibrous pulp additionMechanical working/deformationPolymer scienceFiber structure
Soft and strong fibrous structures and more particularly soft and strong fibrous structures that contains less softwood fibers than known fibrous structures and methods for making such soft and strong fibrous structures are provided.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Degumming method of fabric
The invention relates to a degumming method for hemp fiber, in particular to a method for combined application of chemical with super critical CO2 fluid degumming. Wherein, before carrying out super critical CO2 fluid degumming, the hemp fiber first goes through chemical treatment, then super critical degumming is carried out under low and hi pressure respectively. The invention can obviously reduce the non-cellulose composition for example lignin, etc. in hemp fiber, is of an ideal degumming effect, with obviously improved cellulose ratio, very good softening effect of fiber, hence improved process quality of hemp fiber; the invention additionally overcomes the shortcoming associated with prior degumming way such as high pollution, etc., and is of high economic efficiency.
Owner:THE QUARTERMASTER EQUIPMENT RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF THE GENERAL LOGISITIC DEPARTME
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com