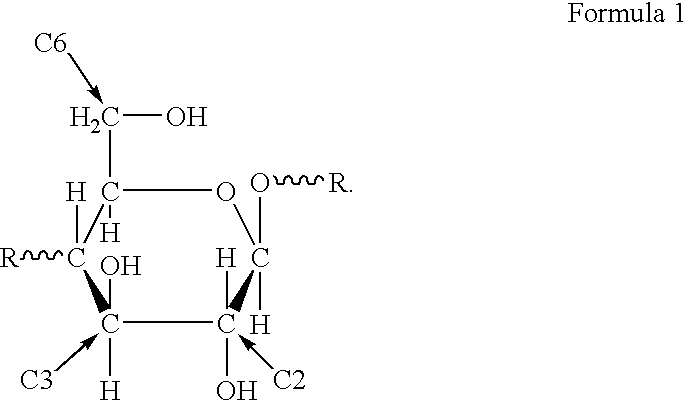Patents
Literature
929results about "Pulp properties modification" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
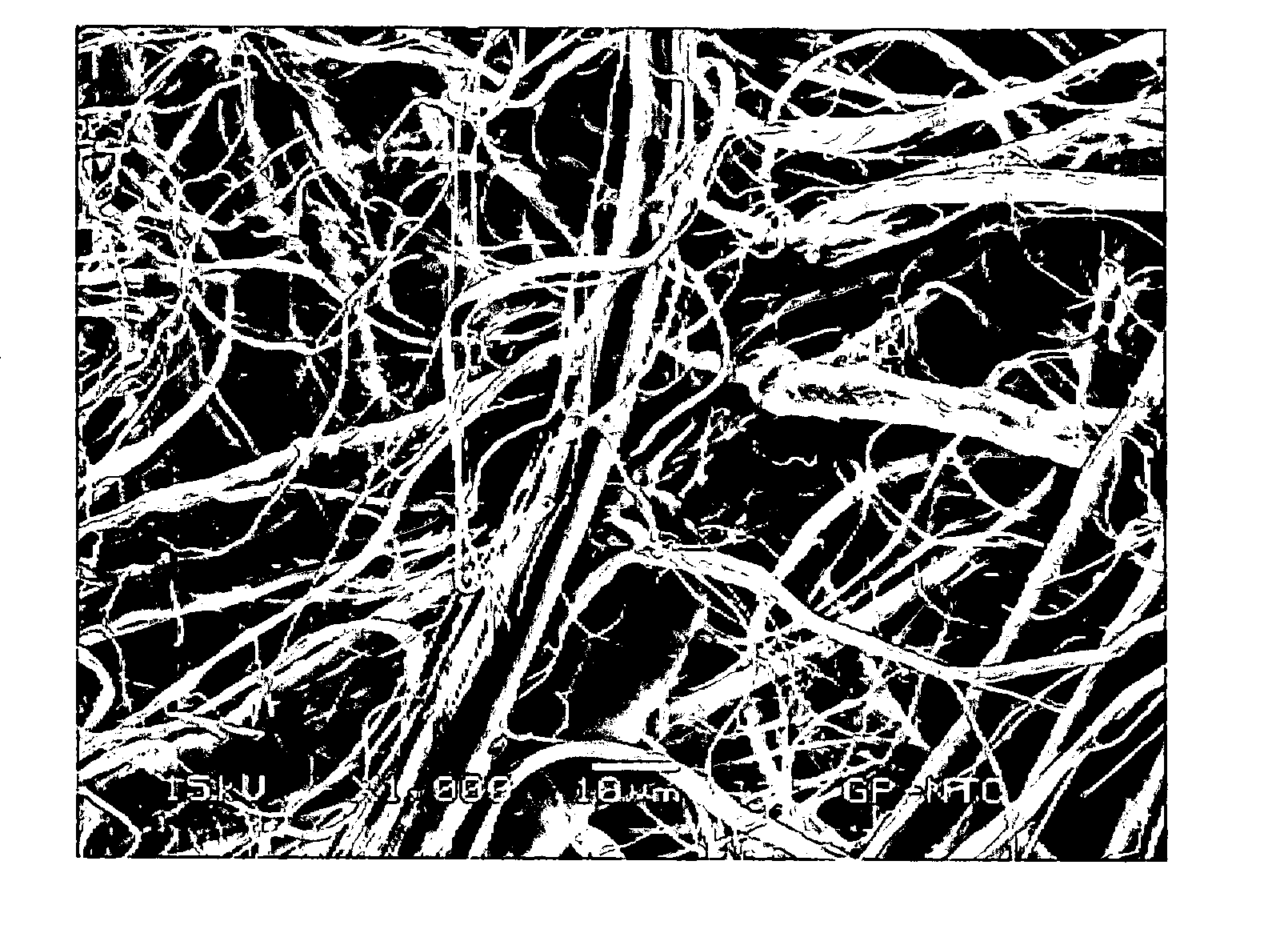
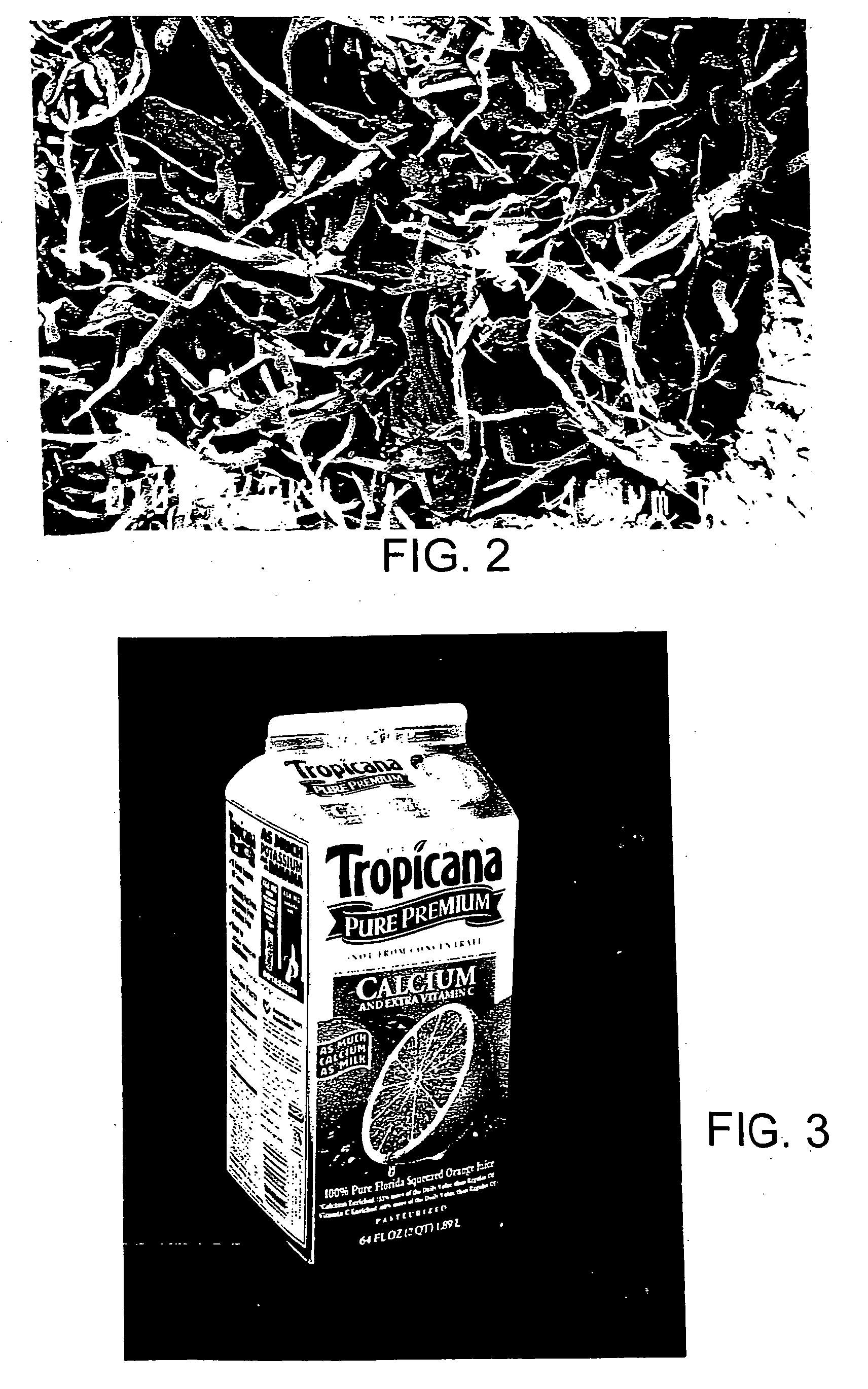
Method and apparatus for manufacturing microfibrillated cellulose fiber
ActiveUS7381294B2Efficient and stable productionQuality improvementNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperCellulose fiberSlurry
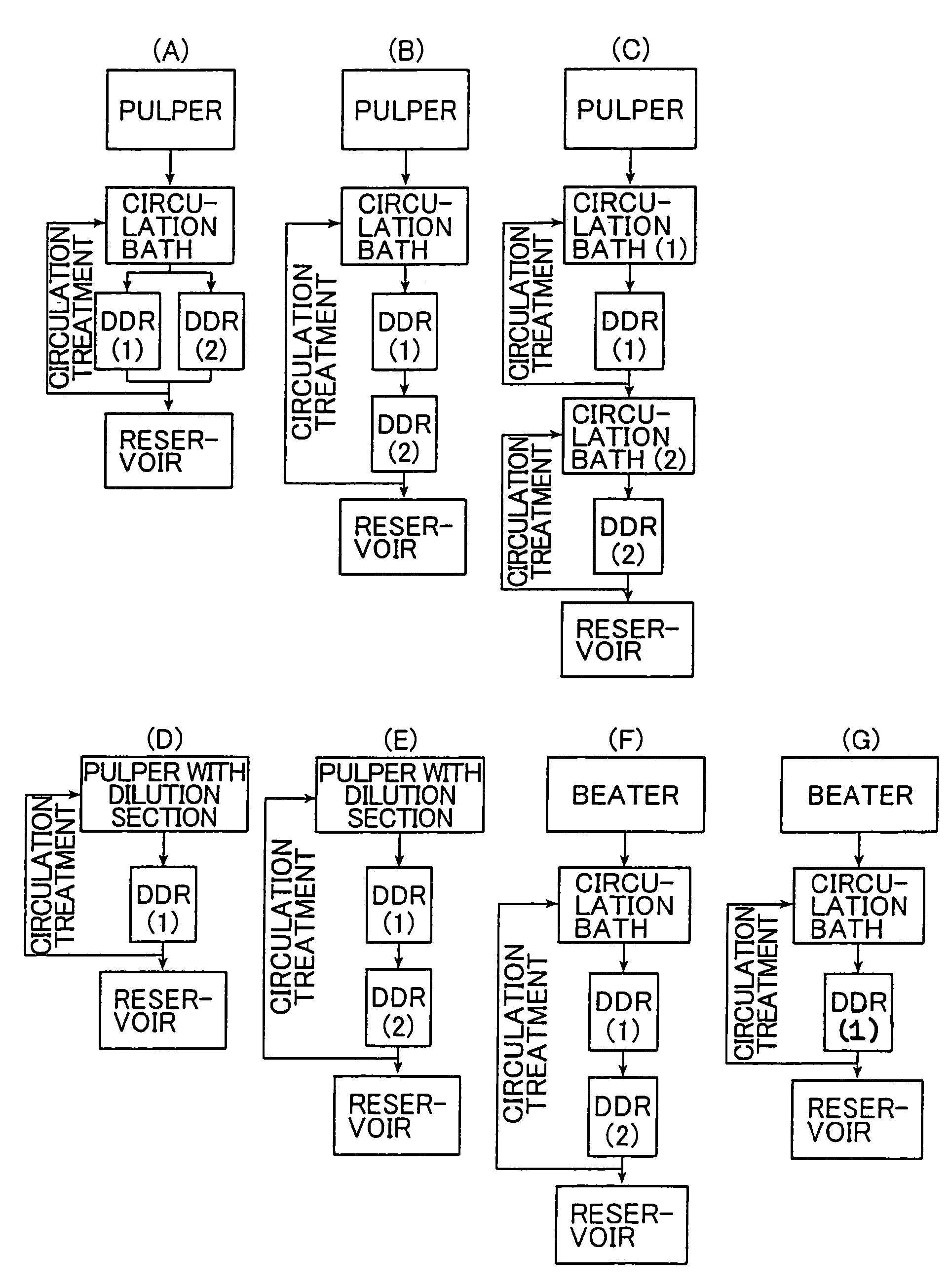
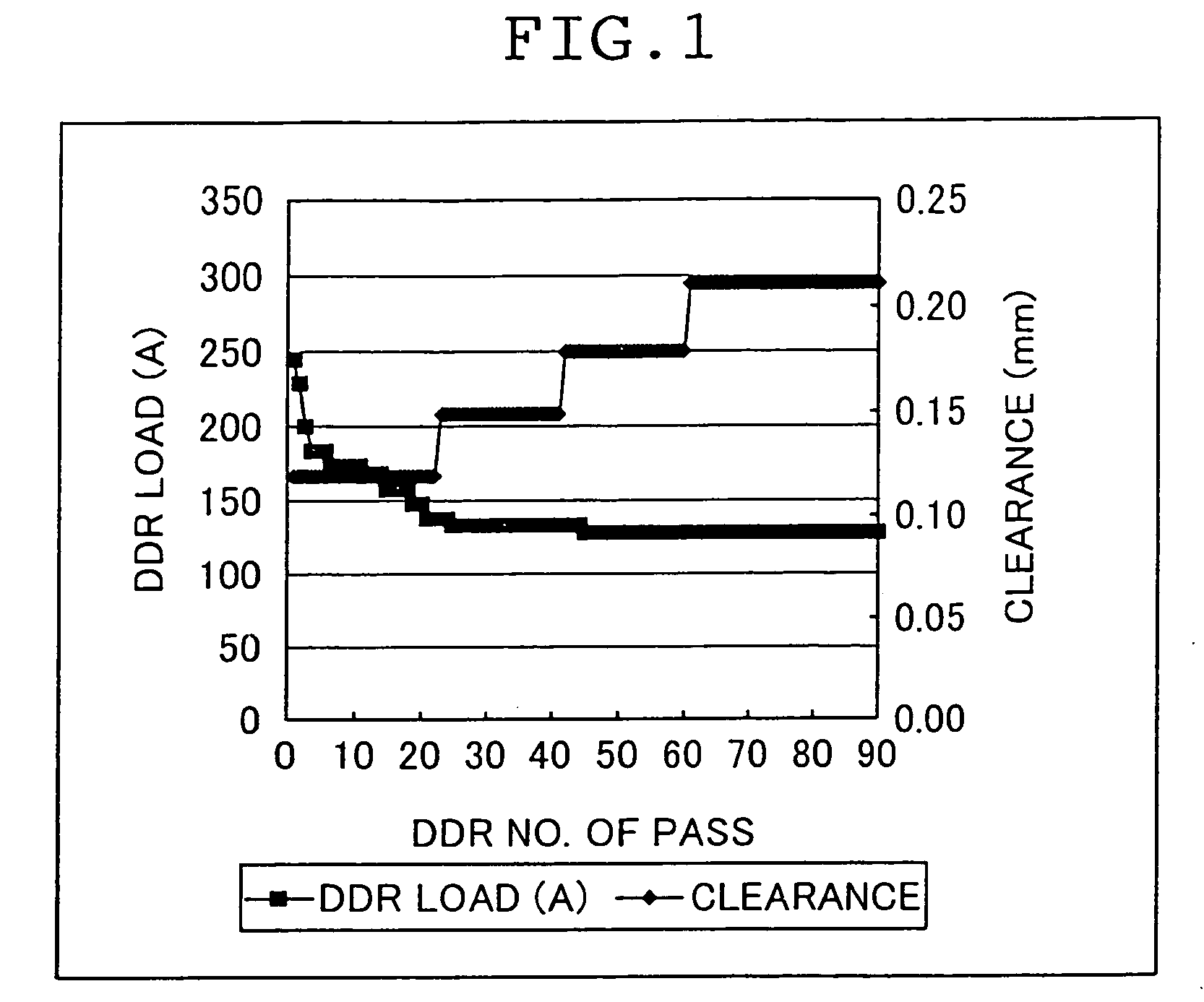
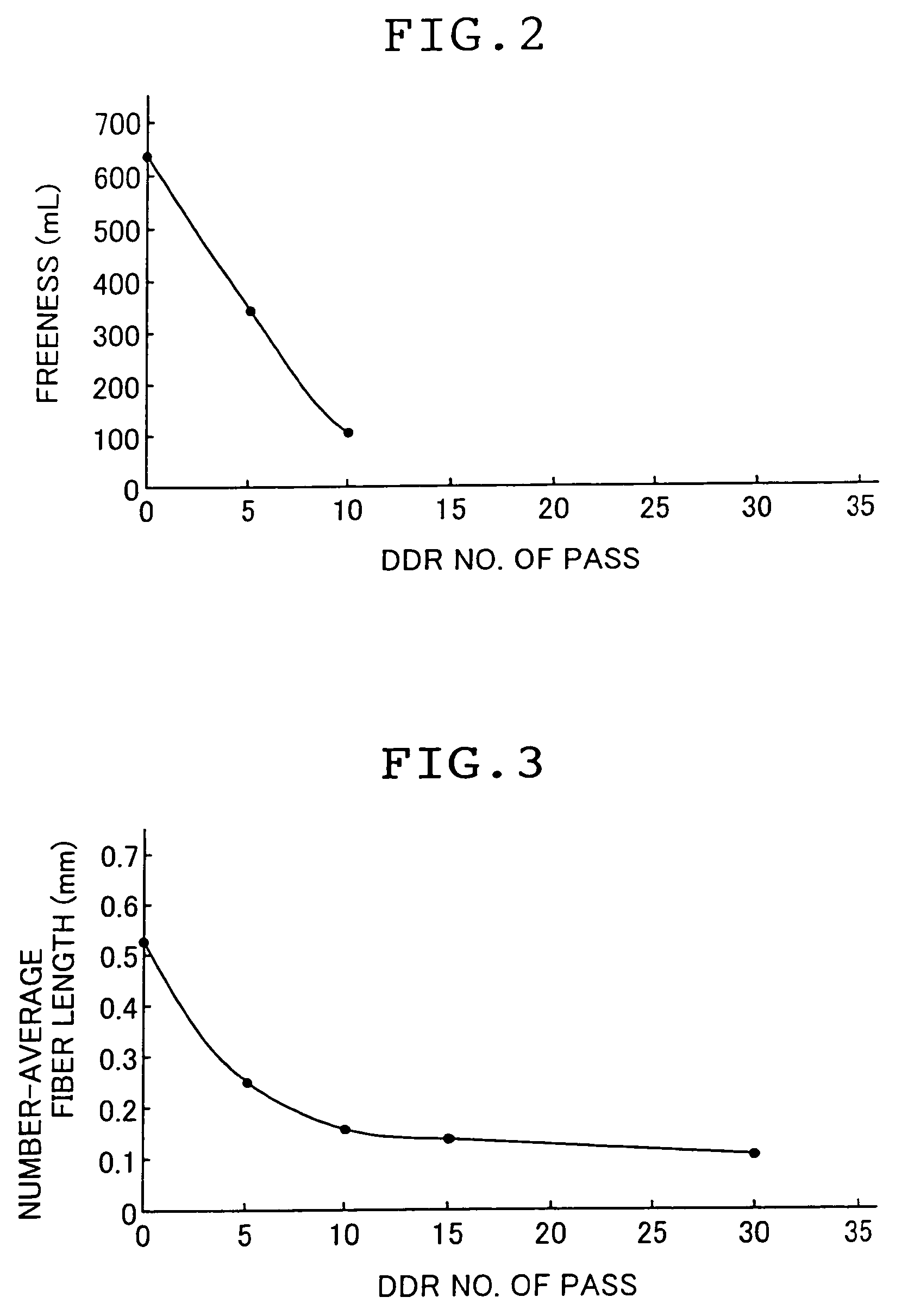
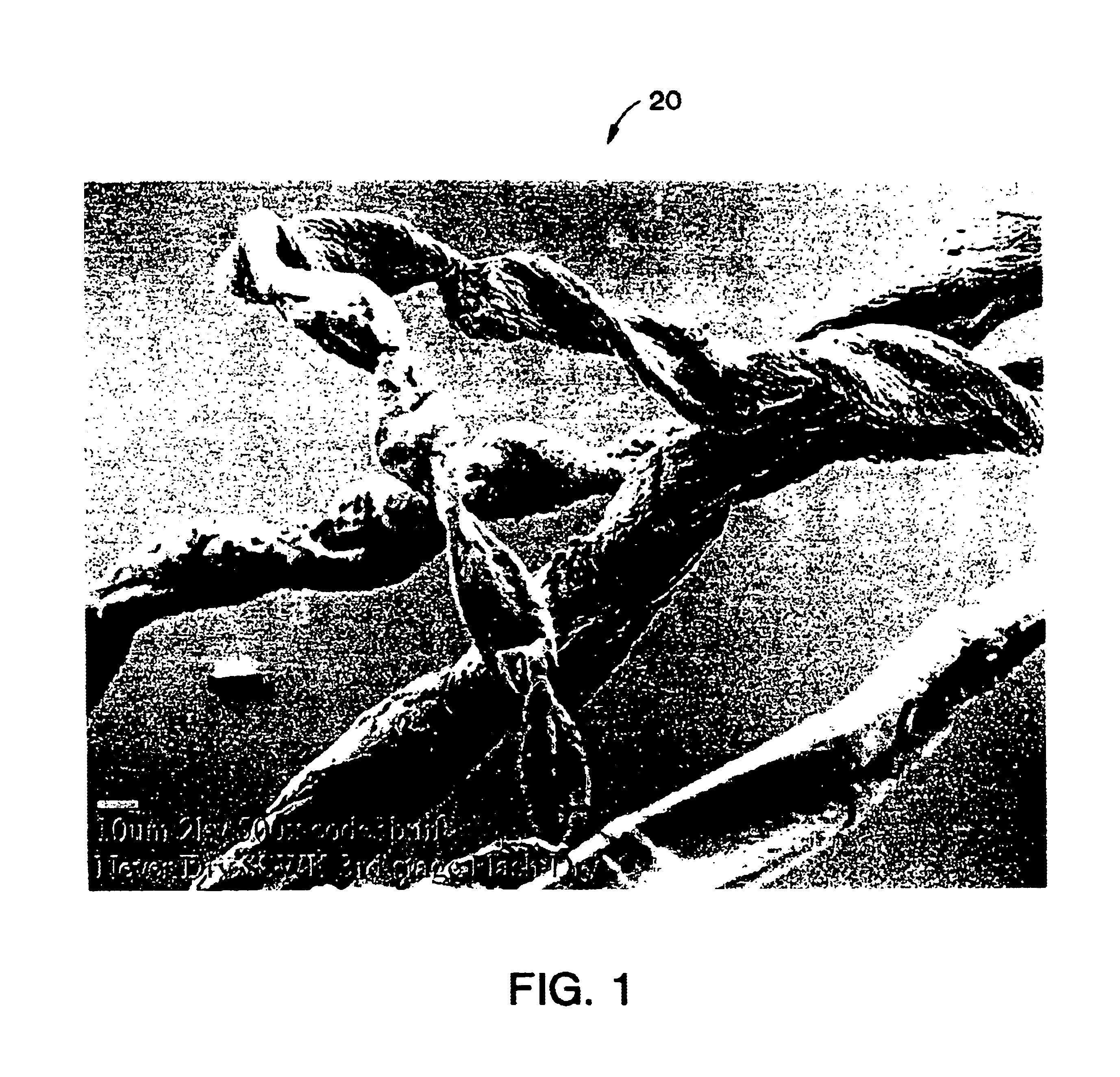
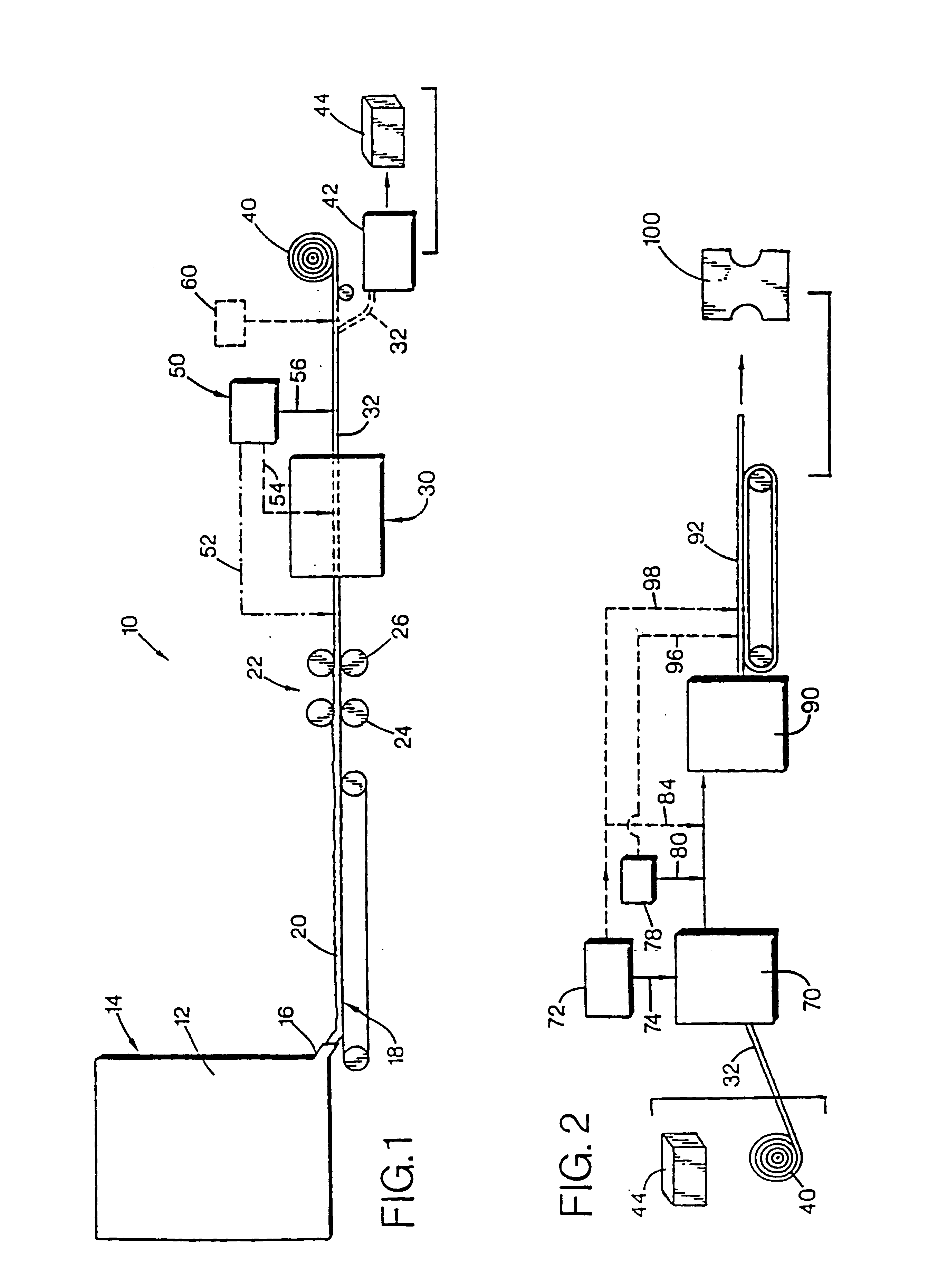
A method for producing a microfibrillated cellulose, which comprises subjecting a slurry containing a pulp having a solids concentration of 1 to 6 wt % to the treatment with a disc refiner repeatedly ten times or more, to thereby prepare a microfibrillated cellulose having a number average fiber length or 0.2 mm or less and an amount of water hold of 10 mL / g or more, the amount representing the volume of water capable of being held by a unit weight of the cellulose fiber. The method allows the production of a microfibrillated cellulose having high quality with stability and with good efficiency.
Owner:DSG INT LTD
Absorbent sheet having regenerated cellulose microfiber network
ActiveUS20070224419A1High wet/dry tensile ratioImprove consistencyNon-fibrous pulp additionPaper after-treatmentPolymer sciencePapermaking
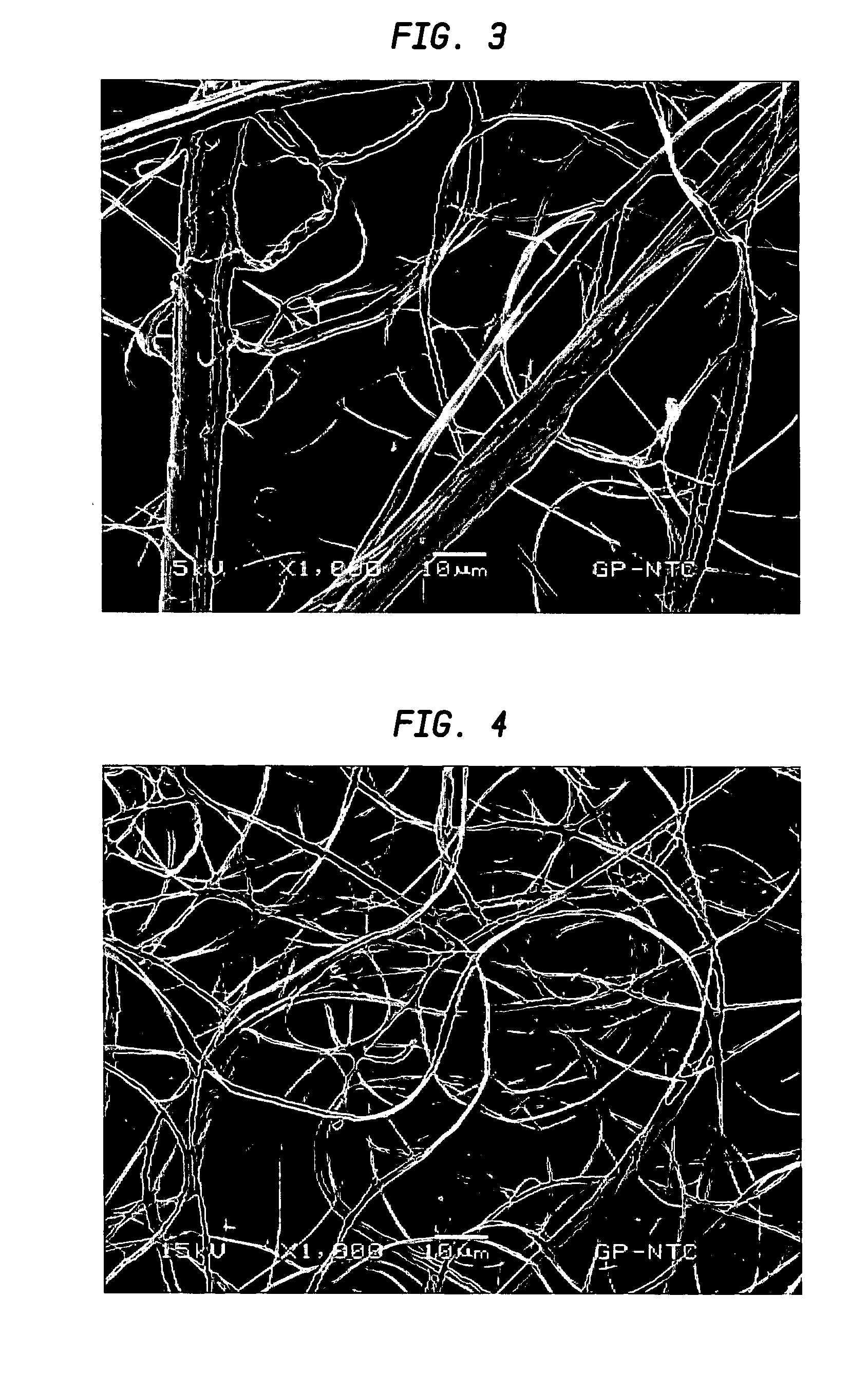
An absorbent paper sheet for tissue or towel includes from about 99 percent to about 70 percent by weight of cellulosic papermaking fiber and from about 1 percent to about 30 percent by weight fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber which was regenerated form a cellulosic dope utilizing a tertiary amine N-oxide solvent or an ionic liquid. Fibrillation of the microfiber is controlled such that it has a reduced coarseness and a reduced freeness as compared with unfibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber from which it is made and provides at least one of the following attributes to the absorbent sheet: (a) the absorbent sheet exhibits an elevated SAT value and an elevated wet tensile value as compared with a like sheet prepared without fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber; (b) the absorbent sheet exhibits an elevated wet / dry CD tensile ratio as compared with a like sheet prepared without fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber; (c) the absorbent sheet exhibits a lower GM Break Modulus than a like sheet having like tensile values prepared without fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber; or (d) the absorbent sheet exhibits an elevated bulk as compared with a like sheet having like tensile values prepared without fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber. In some embodiments, the pulp is pre-treated with debonder to enhance the wet / dry CD tensile ratio of the sheet.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
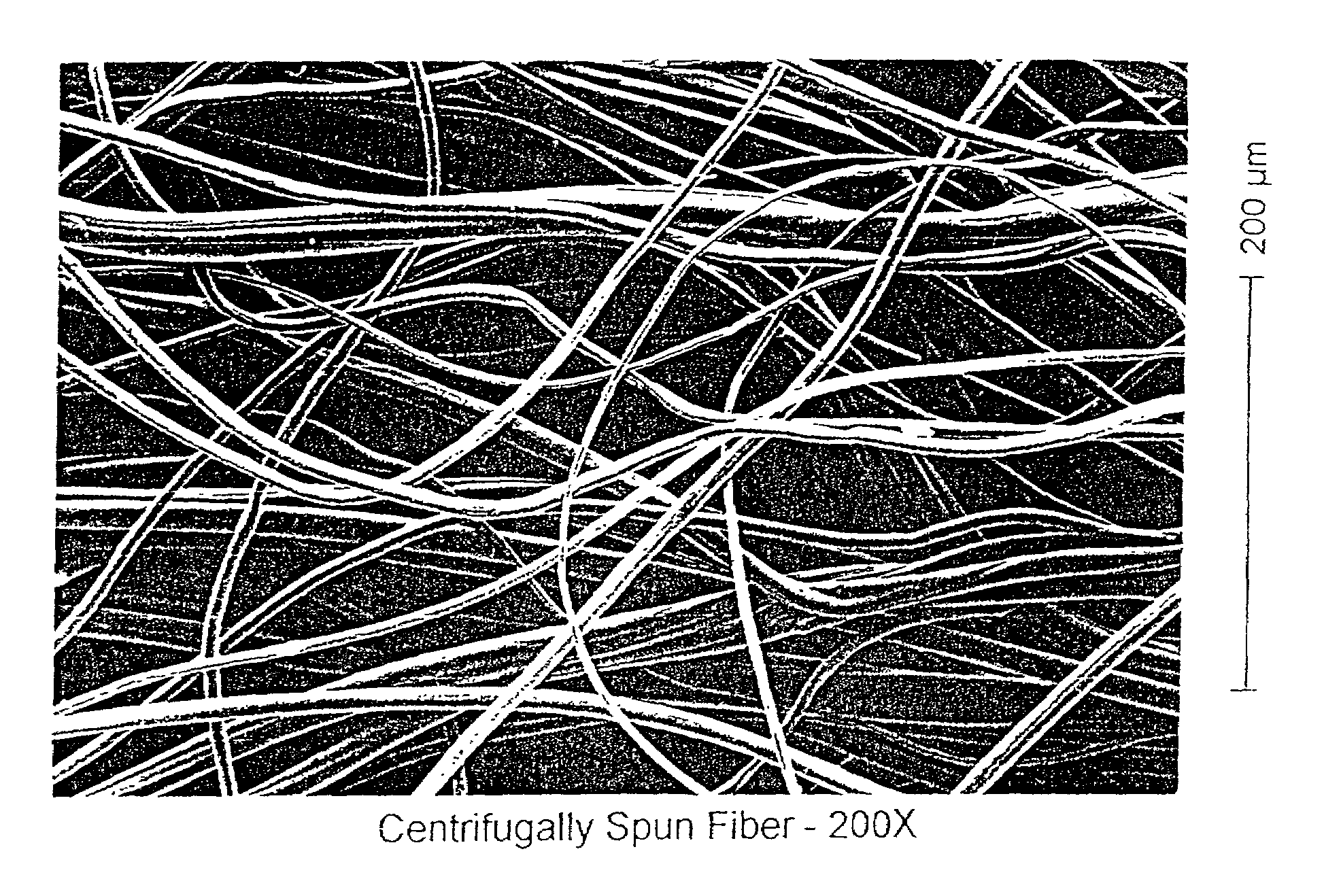
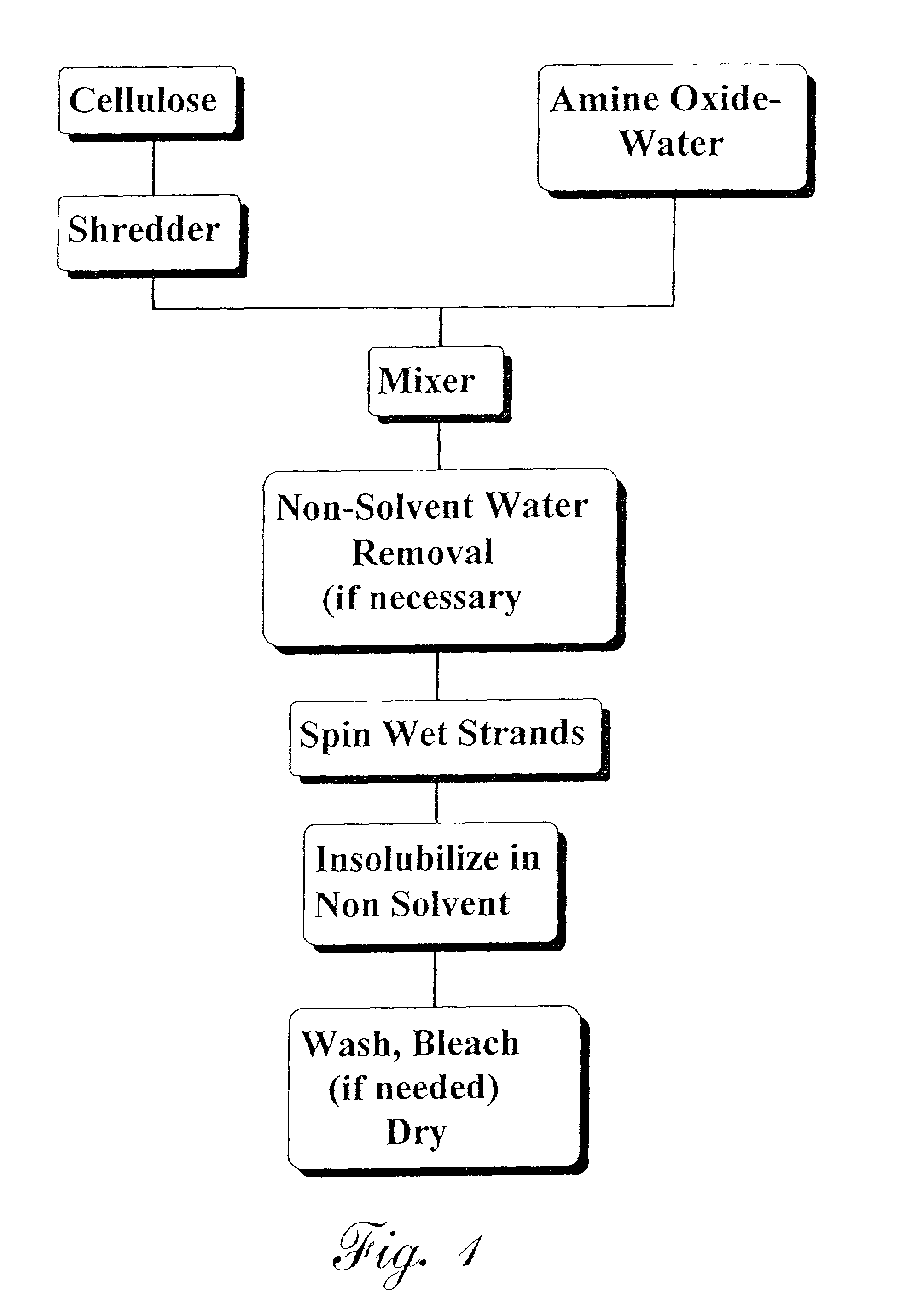
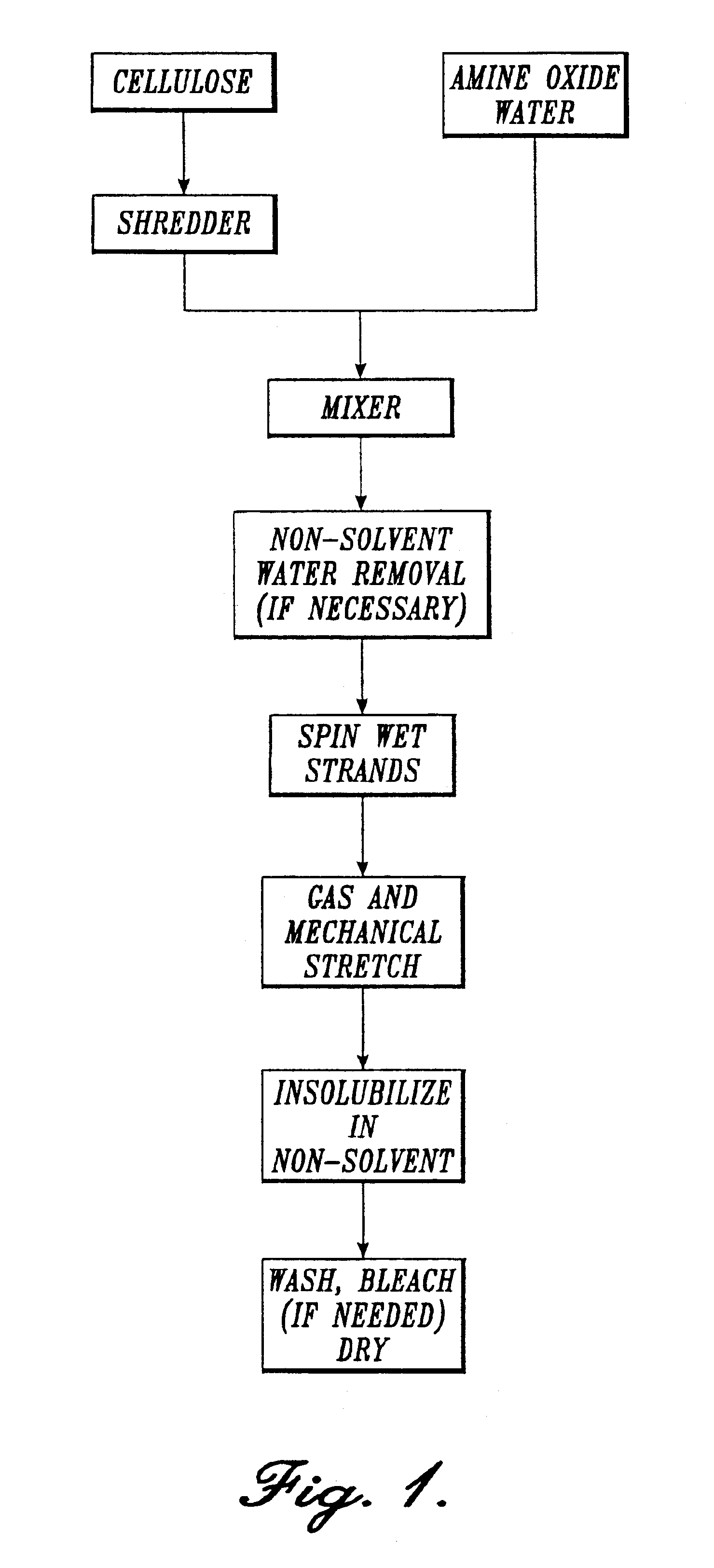
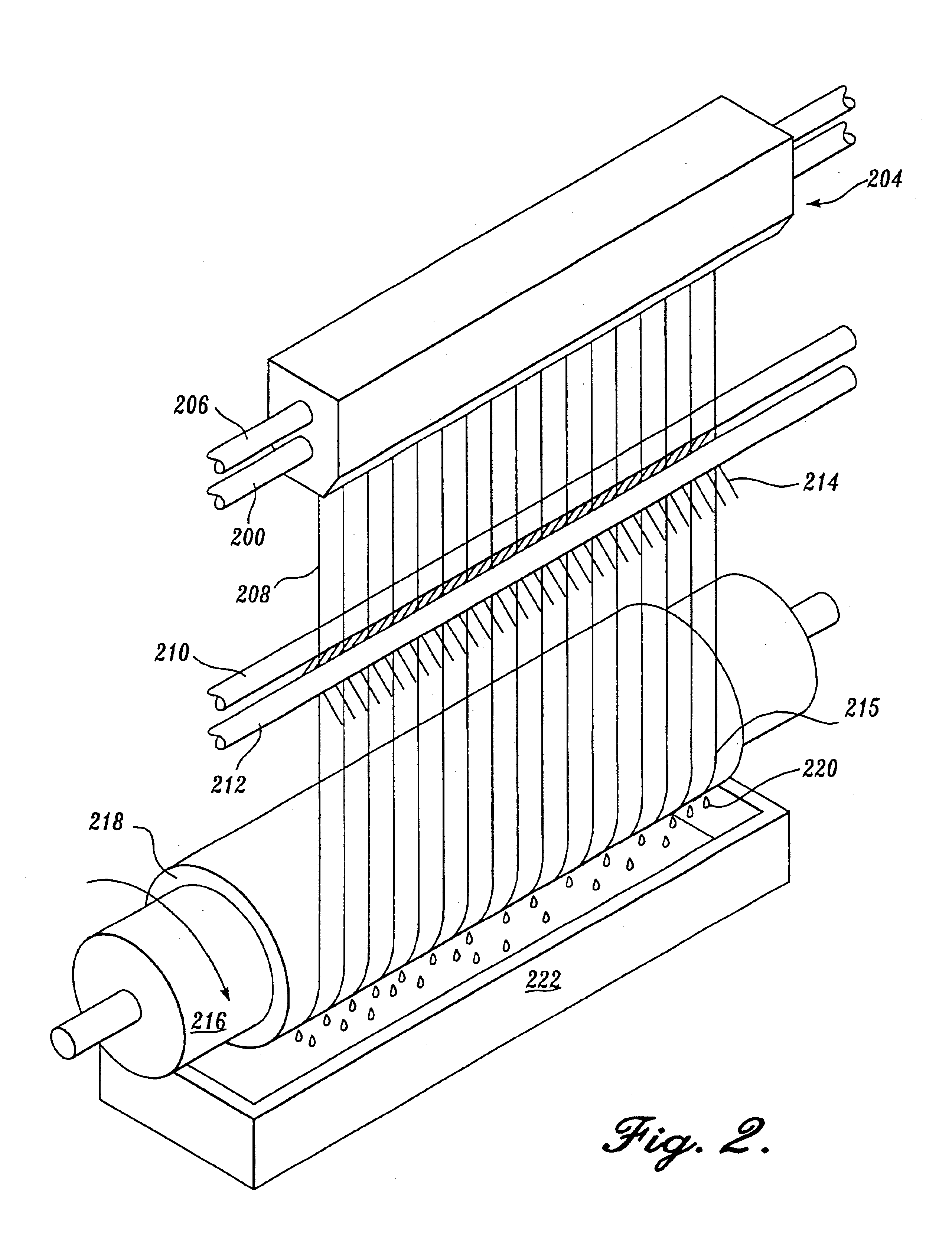
Lyocell nonwoven fabric
InactiveUS7067444B2Powerful solventLow tendency to fibrillatePulp properties modificationMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentMelt blowingNonwoven fabric
A lyocell nonwoven fabric having fibers characterized by pebbled surfaces and variable cross sections and diameters along the fibers and from fiber to fiber, is disclosed. The lyocell nonwoven fabric is produced by centrifugal spinning, melt blowing or spunbonding. The lyocell nonwoven fabric has fibers that can be made in the microdenier range with average weights as low as one denier or less. The lyocell nonwoven fabric has fibers with low gloss, a reduced tendency to fibrillate and have enhanced dye receptivity.
Owner:INT PAPER CO
Compositions and composites of cellulosic and lignocellulosic materials and resins, and methods of making the same
Owner:XYLECO INC
Method of producing and the use of microfibrillated paper
InactiveUS20100065236A1Non-fibrous pulp additionPulp properties modificationChemical structureEngineering
The present invention relates to a method of producing a cellulose based paper, the paper itself and the use thereof where the paper exhibits enhanced mechanical properties. The method involves providing a suspension of well dispersed modified cellulose at a low concentration. The properties and the chemical structure of the paper make it suitable for in vivo applications such as implant material.
Owner:SWETREE TECHOLOGIES AB
Method of preparing microfibrillar polysaccharide
ActiveUS20060289132A1Pulp properties modificationThin material handlingPolysaccharideOxidizing agent
The present invention relates to a method of preparing microfibrillar polysaccharide comprising treating a polysaccharide in an aqueous suspension comprising an oxidant and at least one transition metal, mechanically delaminating said polysaccharide such that microfibrillar polysaccharide is formed. The invention also relates to microfibrillar polysaccharide obtainable by the method.
Owner:KEMIRA OY
Methods for forming a fluted composite
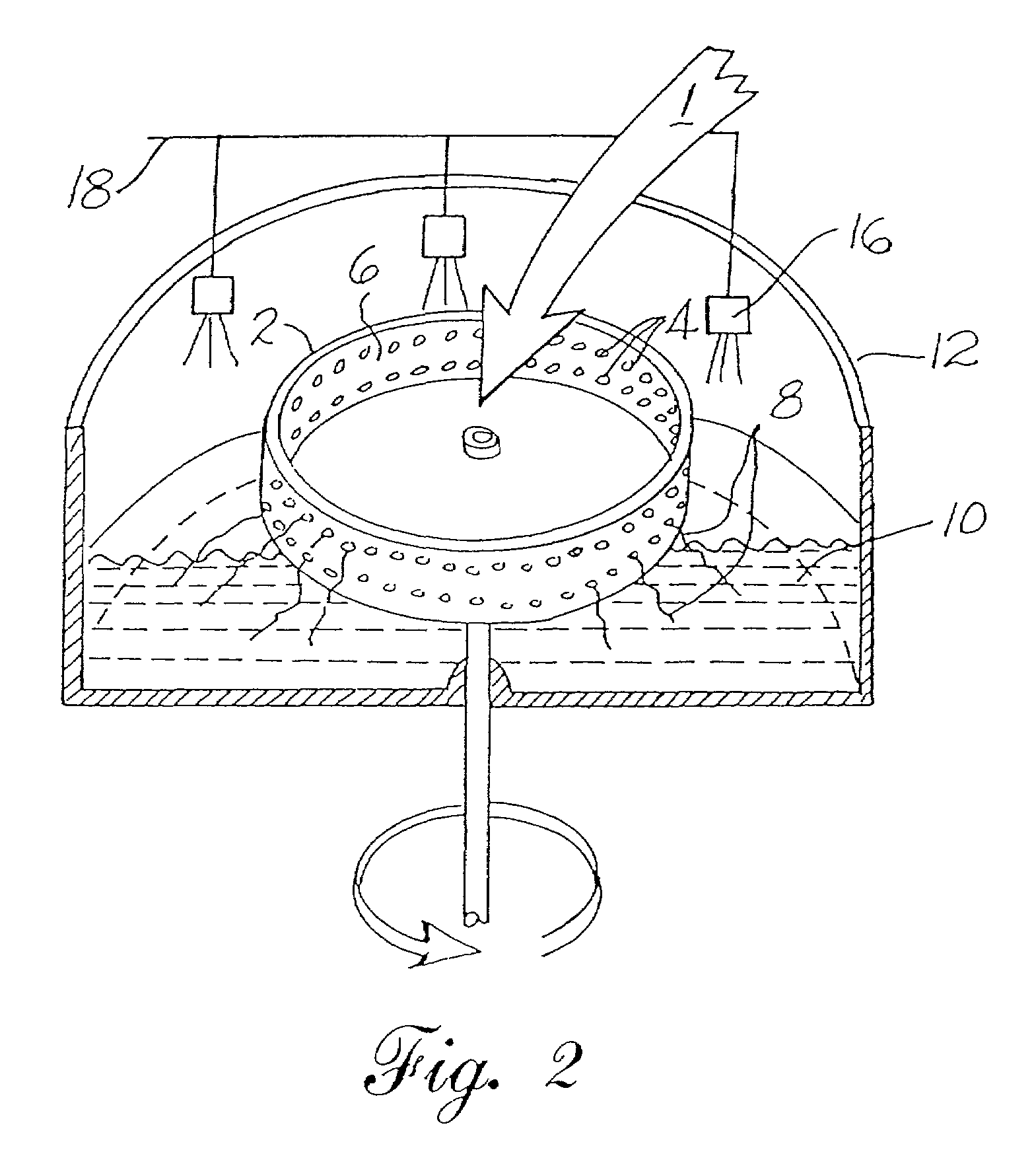
Methods for forming an absorbent fibrous composite containing absorbent material dispersed in bands through the composite and along the composite's length are disclosed. The methods generally include depositing a fibrous slurry on a foraminous support to form a web and depositing or injecting absorbent material into the web across its width to provide a web having absorbent material in bands along the composite's length. Drying the web provides a fluted absorbent composite. In one embodiment, the method is a wetlaid method and in another embodiment, the method is a foam-forming method. Preferably, the methods are twin-wire forming methods.
Owner:NAT INST FOR STRATEGIC TECH ACQUISITIONS & COMMLIZATION
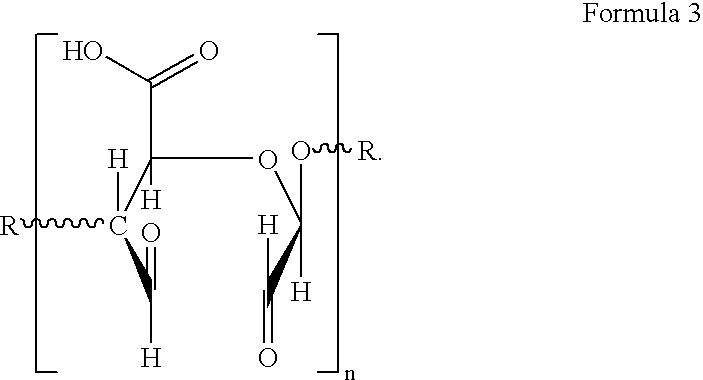
Oxidized polymeric carbohydrates and products made thereof
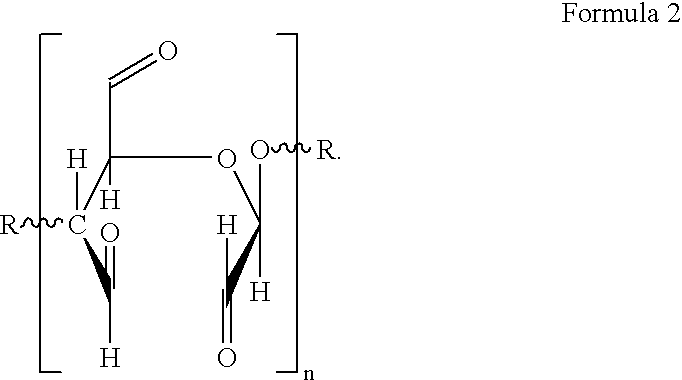
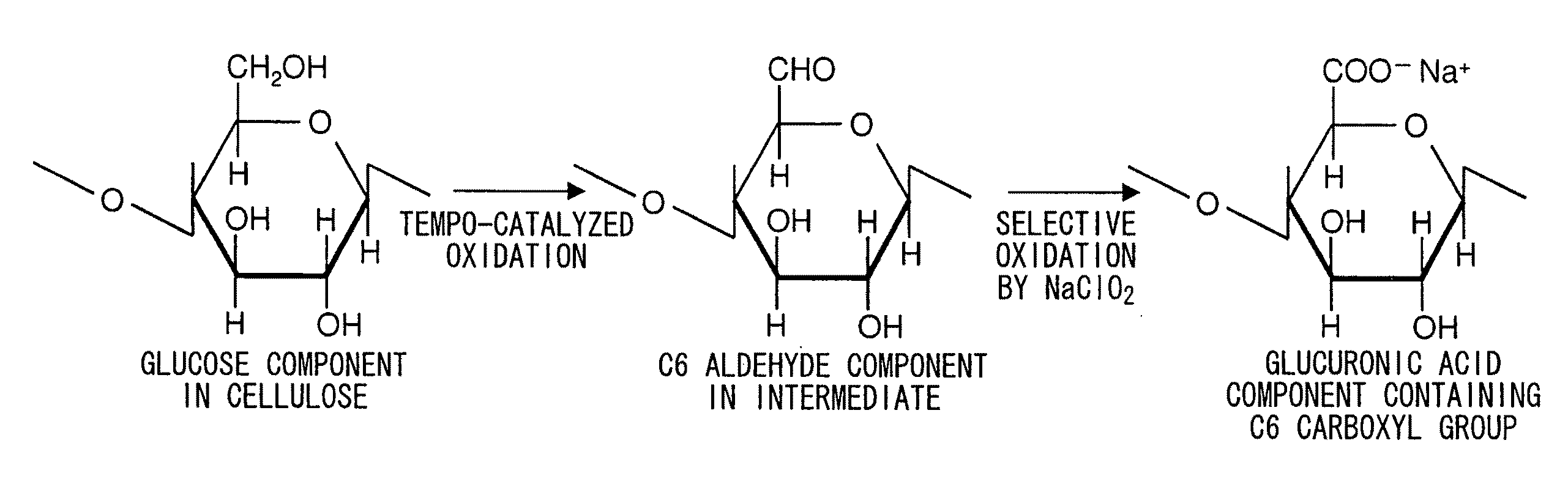
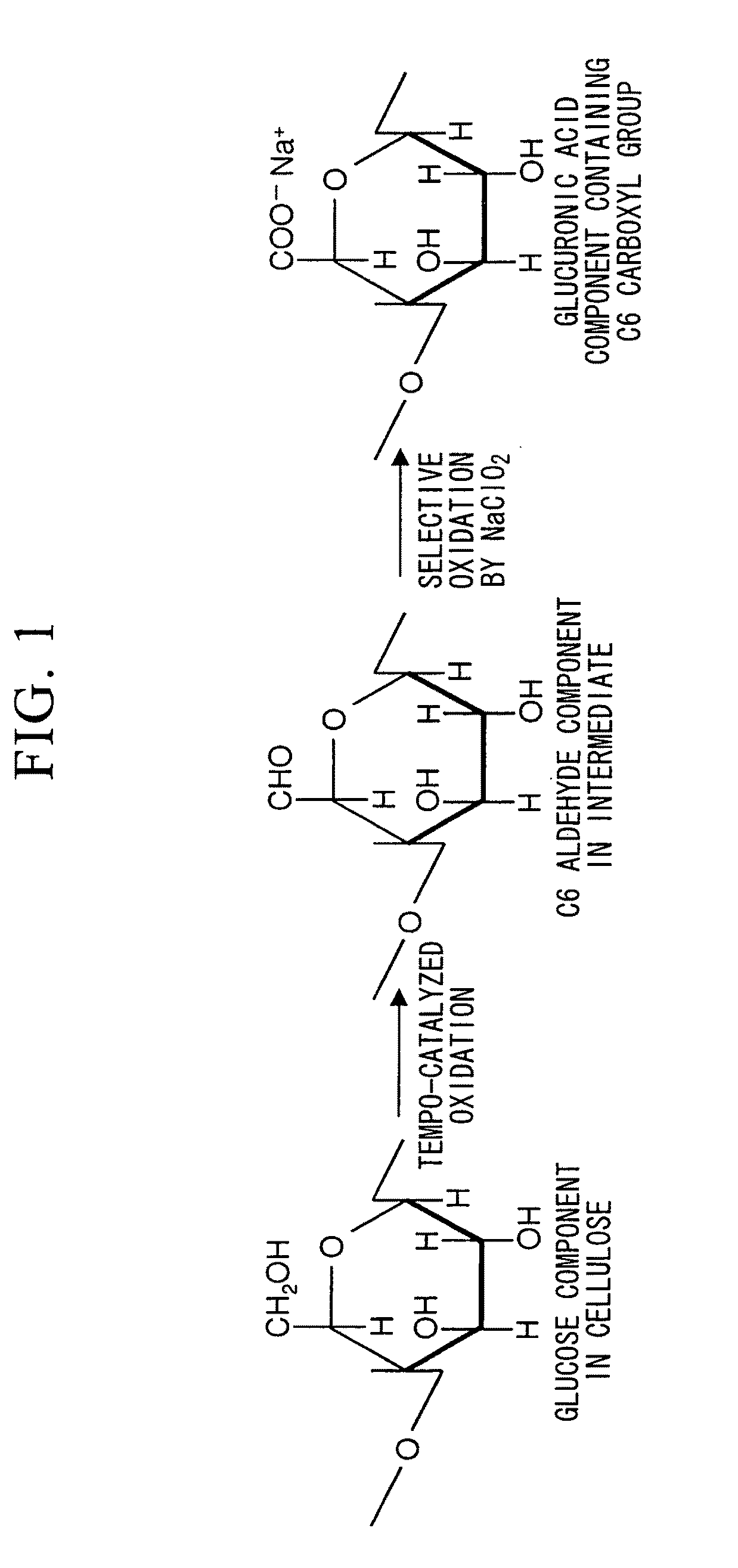
The present invention relates to a polysaccharide having functional groups, wherein said groups are aldehyde groups formed at positions C2 and / or C3 as well as at position C6 of the anhydroglucose units of the polysaccharide chain. Preferably the polysaccharide is a cellulosic fibrous material whose primary and secondary hydroxyl groups of the cellulose are oxidized into aldehyde groups at least in part by means of TEMPO oxidation and periodate oxidation.The invention also concerns a paper or nonwoven comprising the above polysaccharide. According to the invention a relative wet strength of more than 10% can be achieved.
Owner:SCA HYGIENE PROD AB
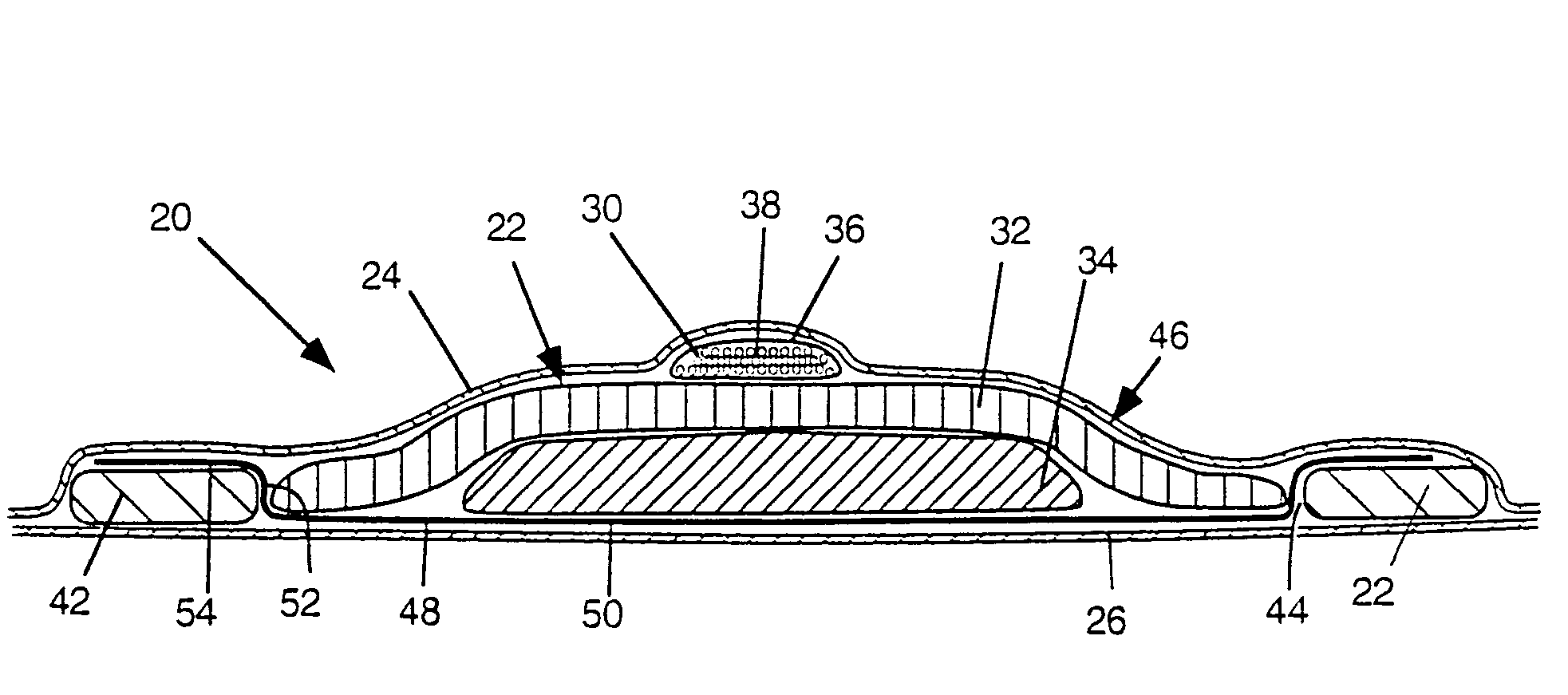
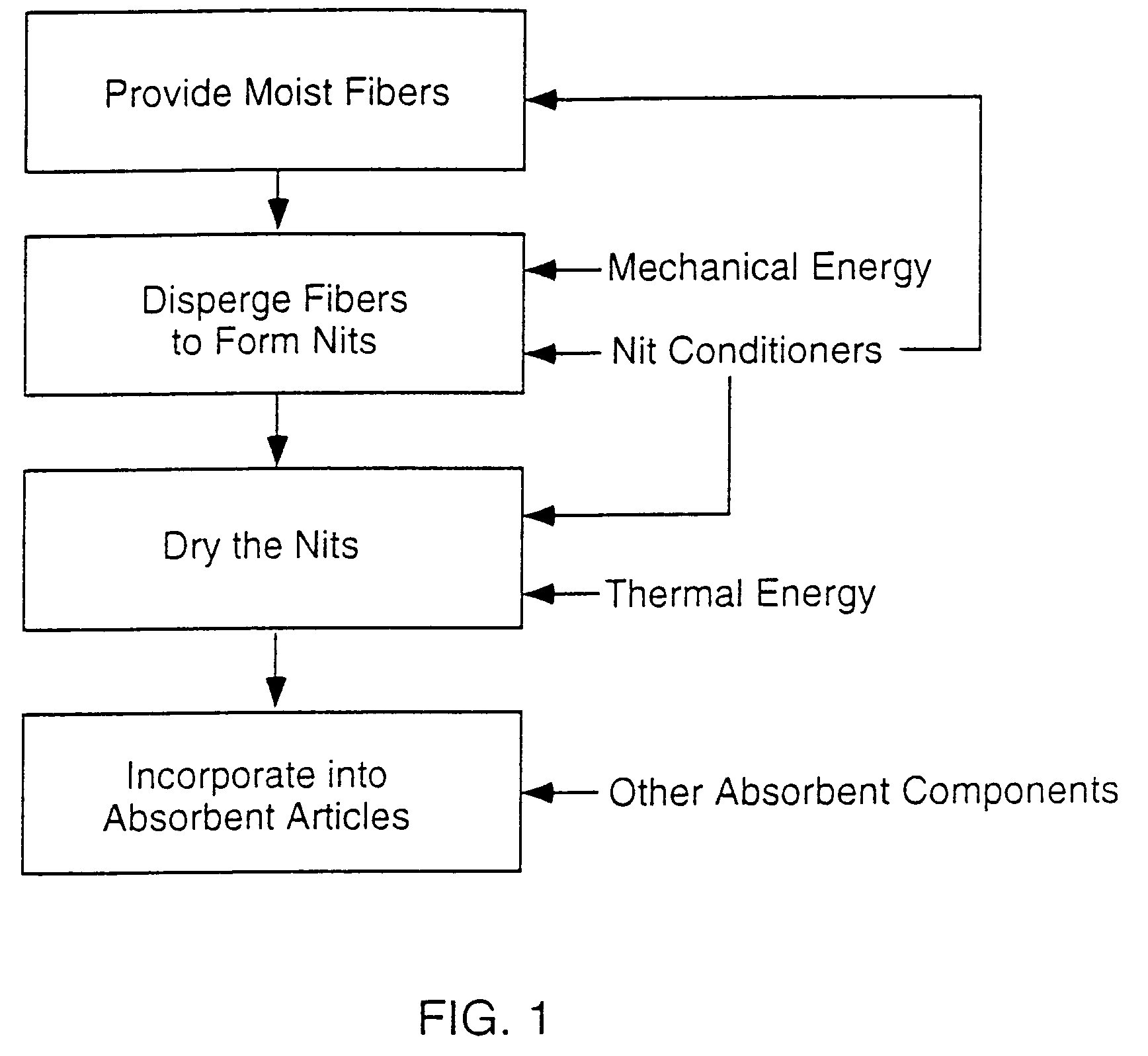
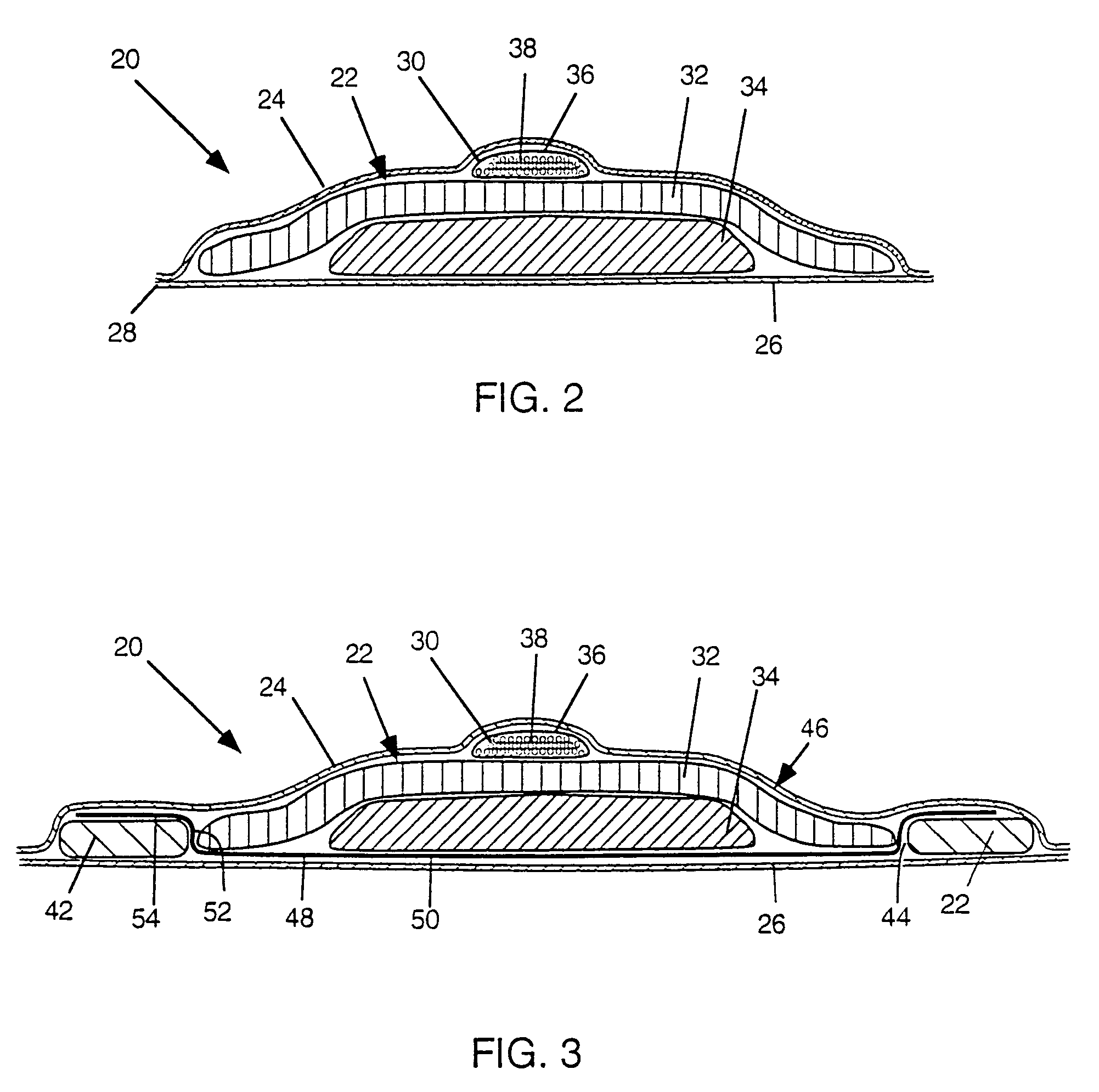
Absorbent articles with nits and free-flowing particles
Absorbent articles comprising fibrous nits and other free-flowing particles are disclosed. In one embodiment, an absorbent article is disclosed comprising free-flowing particles in a central portion which, in conjunction with other absorbent members, provides excellent body fit and good fluid handling performance. In another embodiment, good leakage control is provided by the combined effect of good intake and fluid handling performance of fibrous nits coupled with a wicking barrier between the nits and the longitudinal sides of the articles. An optional central rising member can further enhance the topography of the article when compressed by urging the portion comprising nits to deflect vertically upward.Methods of preparing cellulosic nits and incorporating them into absorbent articles are also described.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Absorbent sheet having regenerated cellulose microfiber network
An absorbent paper sheet for tissue or towel includes from about 99 percent to about 70 percent by weight of cellulosic papermaking fiber and from about 1 percent to about 30 percent by weight fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber which was regenerated form a cellulosic dope utilizing a tertiary amine N-oxide solvent or an ionic liquid. Fibrillation of the microfiber is controlled such that it has a reduced coarseness and a reduced freeness as compared with unfibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber from which it is made and provides at least one of the following attributes to the absorbent sheet: (a) the absorbent sheet exhibits an elevated SAT value and an elevated wet tensile value as compared with a like sheet prepared without fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber; (b) the absorbent sheet exhibits an elevated wet / dry CD tensile ratio as compared with a like sheet prepared without fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber; (c) the absorbent sheet exhibits a lower GM Break Modulus than a like sheet having like tensile values prepared without fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber; or (d) the absorbent sheet exhibits an elevated bulk as compared with a like sheet having like tensile values prepared without fibrillated regenerated cellulose microfiber. In some embodiments, the pulp is pre-treated with debonder to enhance the wet / dry CD tensile ratio of the sheet.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Ligno cellulosic materials and the products made therefrom
ActiveUS20060260773A1Reducing functional groupGood drainage propertyBiocidePaper after-treatmentCelluloseHypochlorite
A process comprising treating a lignocellulosic material preferably pulp in the presence of a transition metal catalyst with a oxidizing agent selected from a group consisting of hydrogen peroxide, hypochlorite, hypochlorous acid and any combination thereof to form a treated lignocellulosic material having a viscosity equal to or less than about 17 cp and having reducing functional groups selected from the group consisting of aldehyde and aldehyde type functional groups at the C6 and C1 positions but predominating at the C1 position.
Owner:INT PAPER CO
Method of preparing microfibrillar polysaccharide
Owner:KEMIRA OY
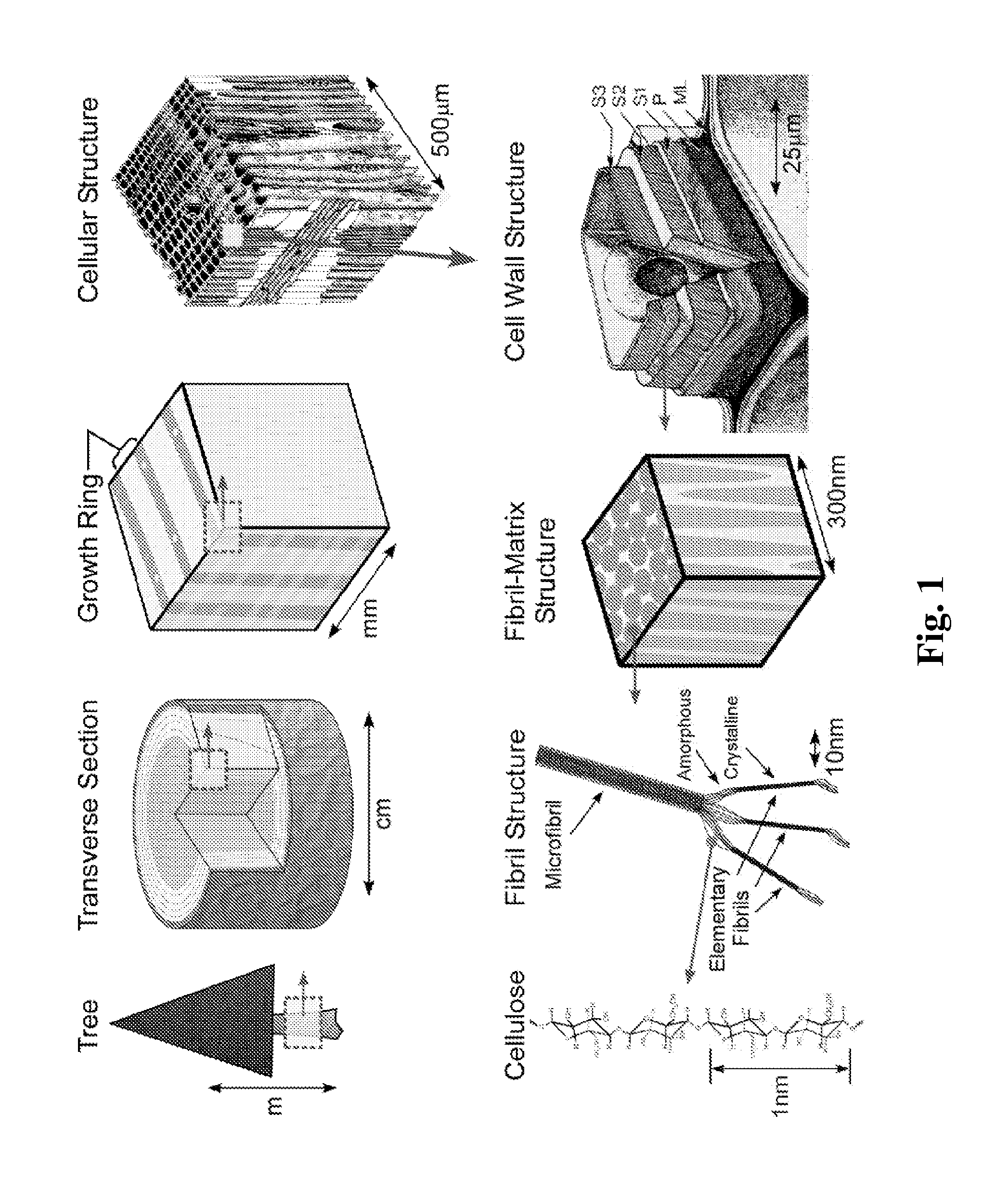
Cellulose nanofiber production method of same and cellulose nanofiber dispersion
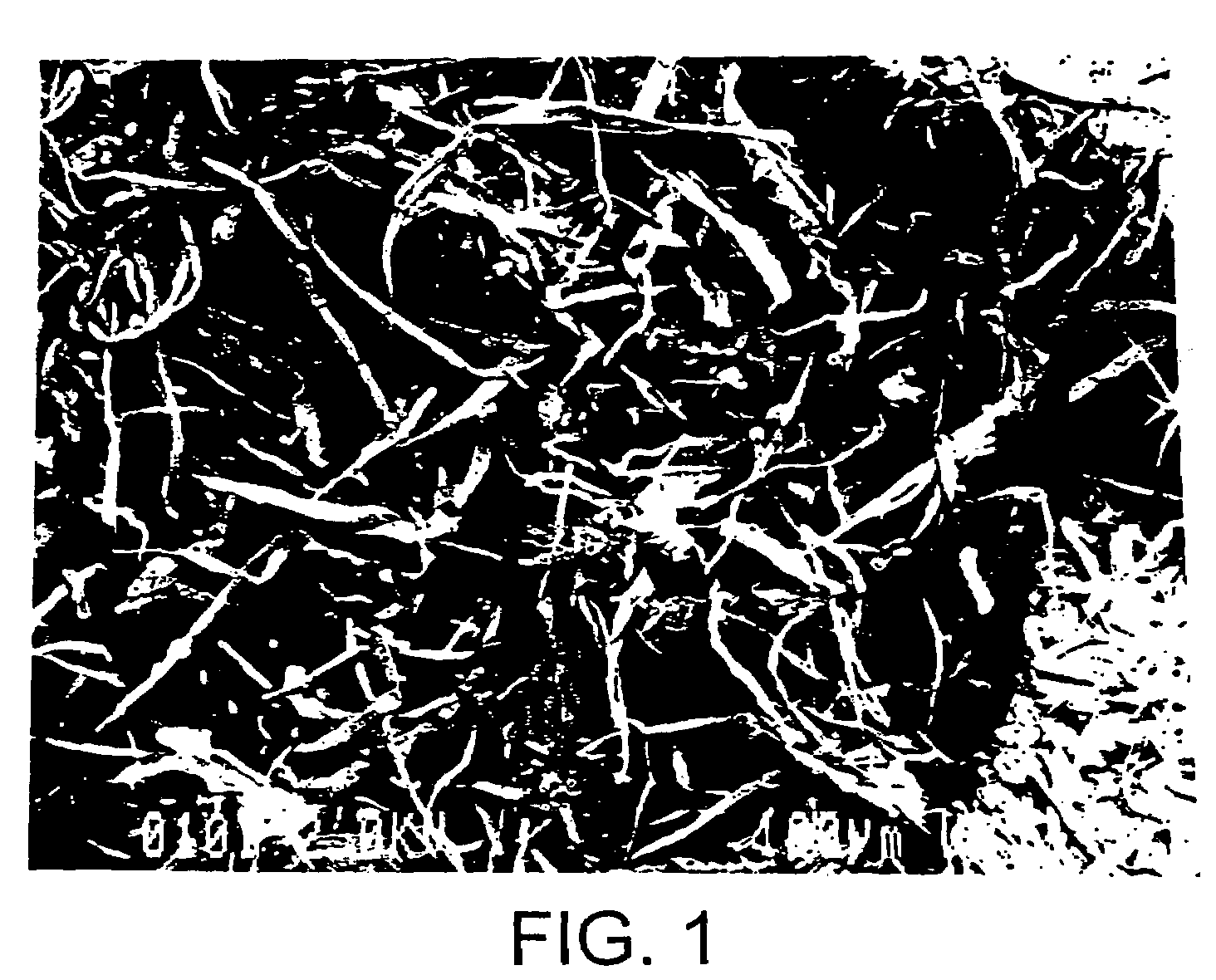
InactiveUS20100233481A1High degree of polymerizationHigh strengthNanotechPulp properties modificationCelluloseFiber
The cellulose nanofiber production method of the present invention comprises an oxidation treatment step for oxidizing native cellulose in a neutral or acidic reaction solution containing an N-oxyl compound and an oxidizing agent that oxidizes aldehyde groups, and a dispersion step for dispersing the native cellulose in a medium following the oxidation treatment step. According to the production method of the present invention, a cellulose nanofiber is provided that has long fibers and demonstrates high strength.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
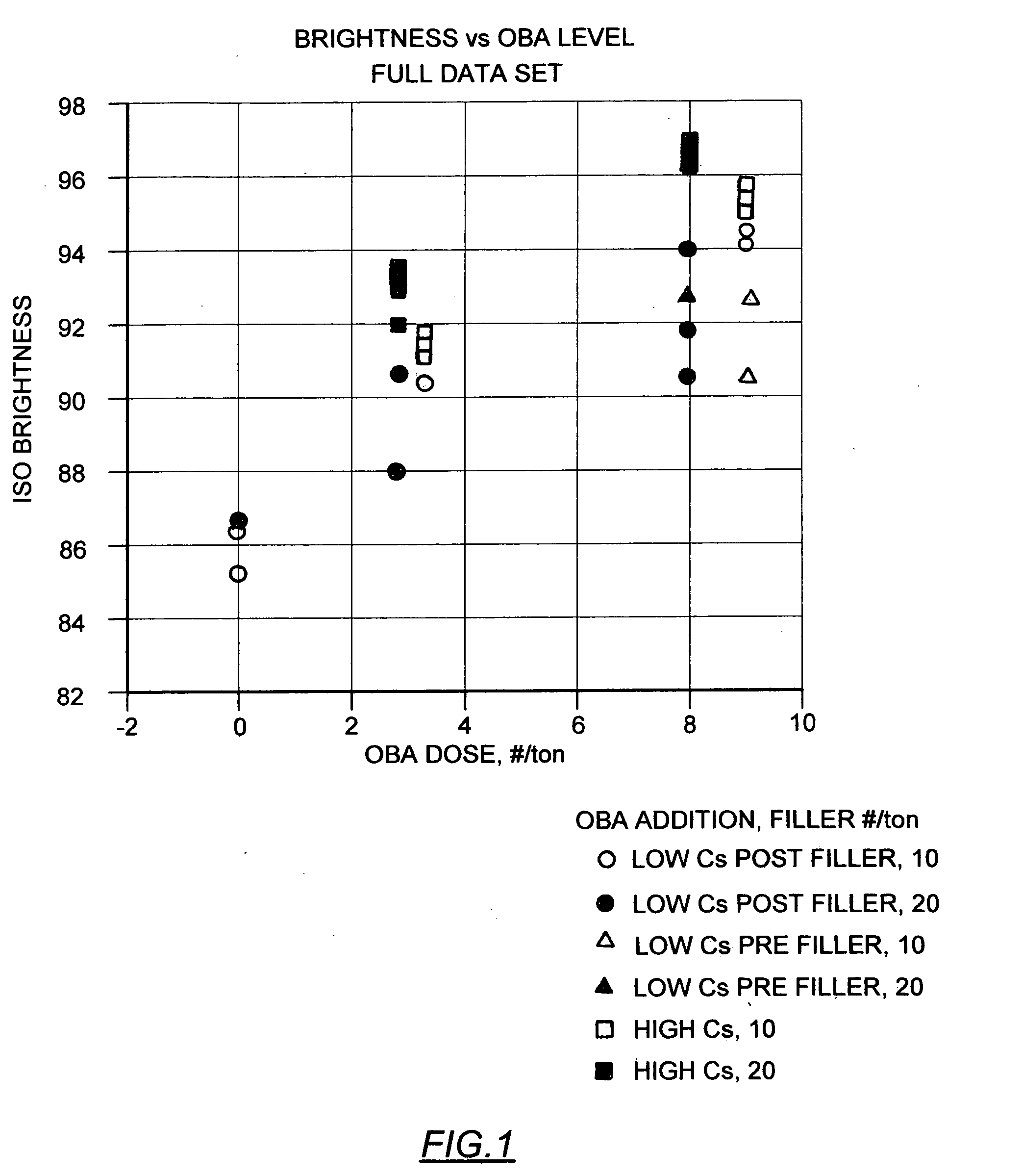
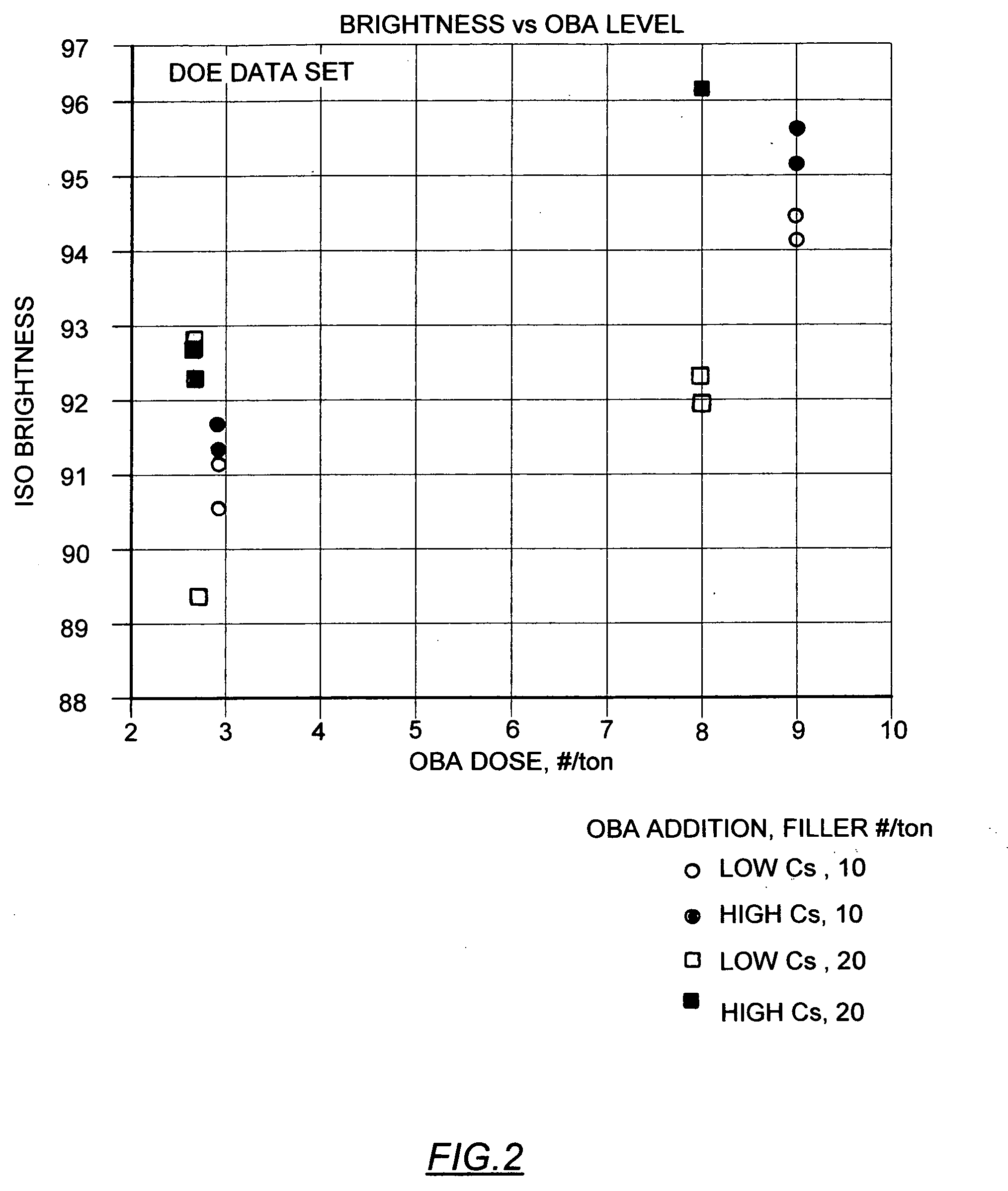
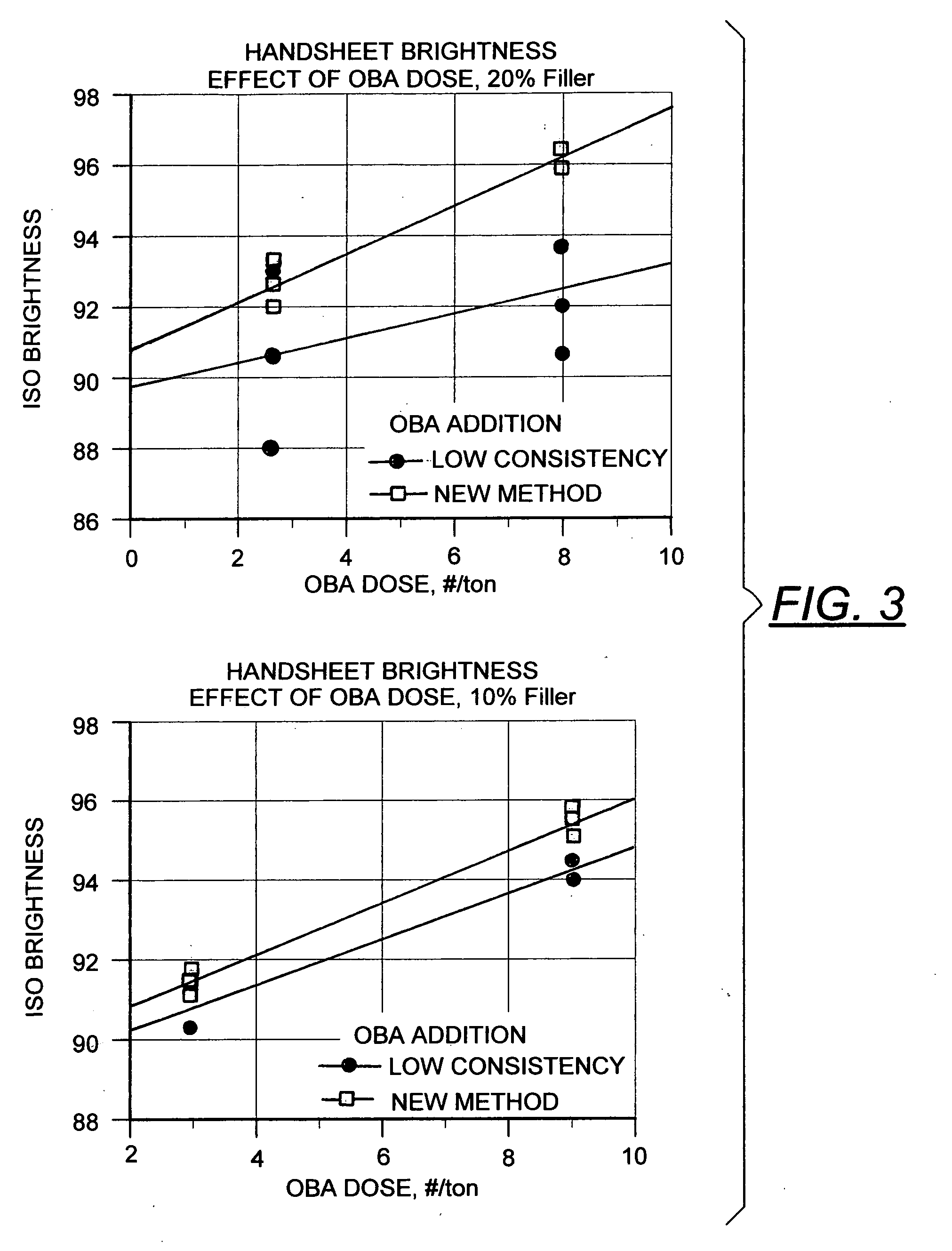
Pulp and paper having increased brightness
InactiveUS20070193707A1Natural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperPulp and paper industryBrightness perception
Owner:INT PAPER CO
Meltblown process with mechanical attenuation
InactiveUS6773648B2High speed spinningImprove productivityPulp properties modificationArtificial filament physical treatmentCelluloseUltrasound attenuation
Owner:WEYERHAEUSER NR CO
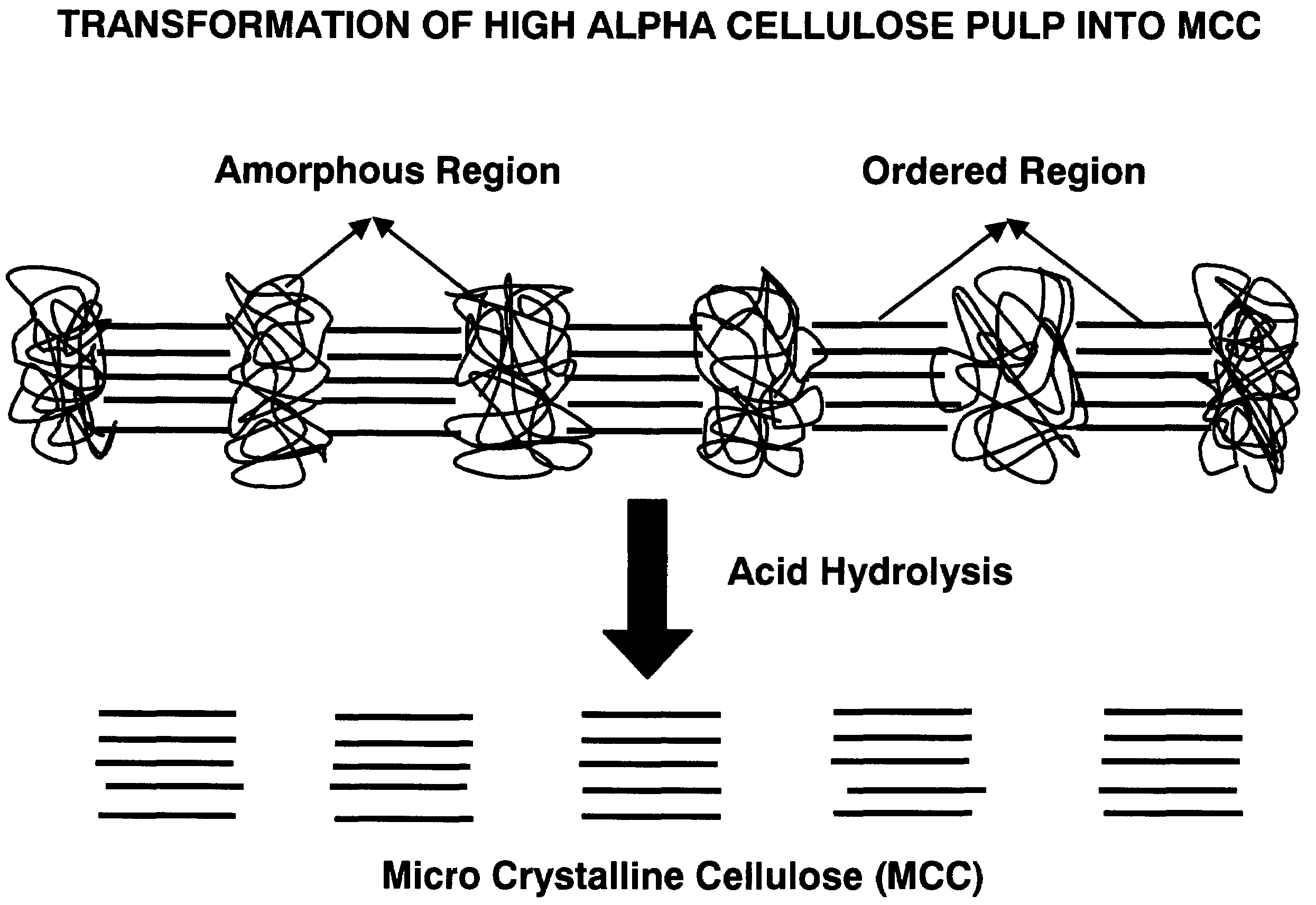
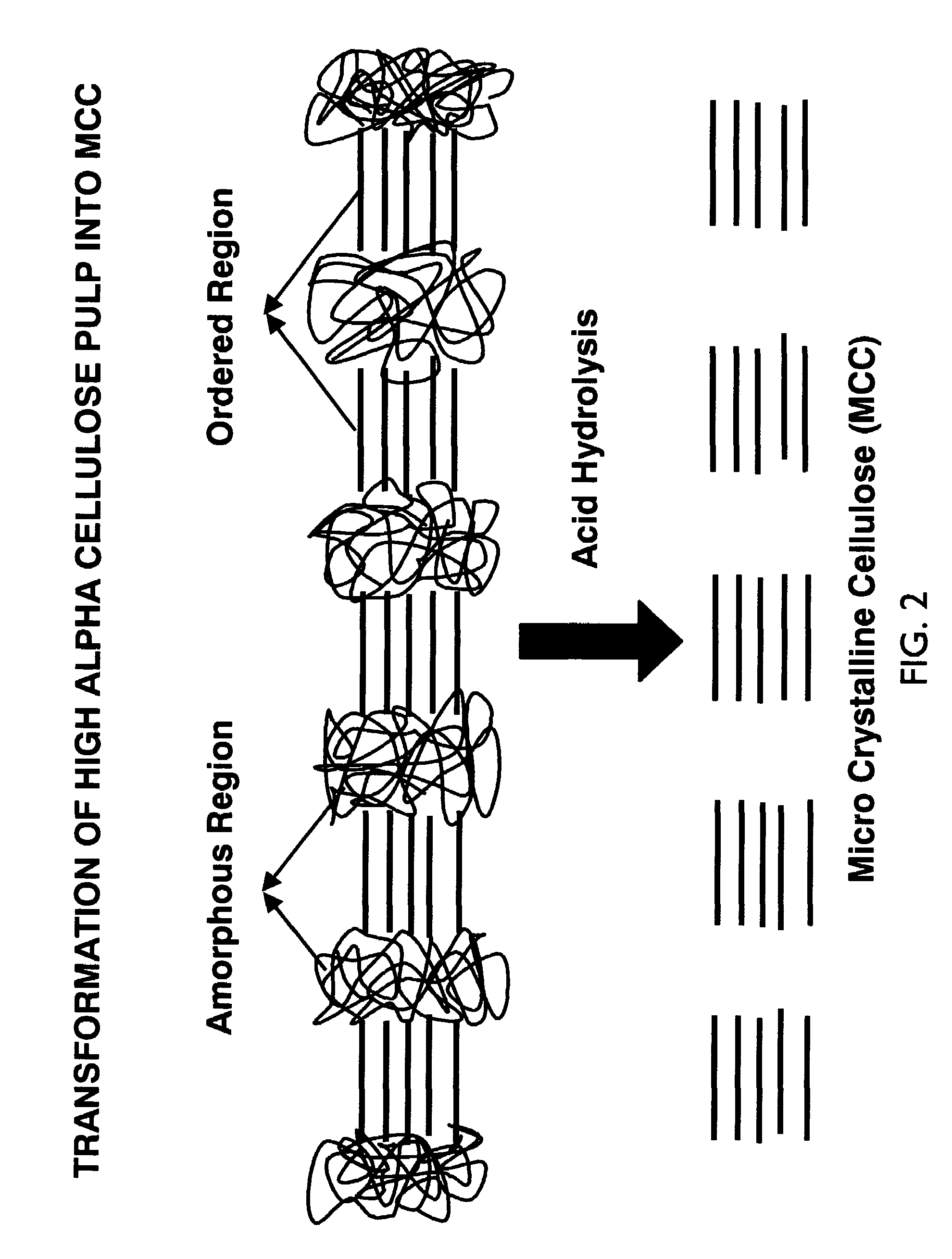
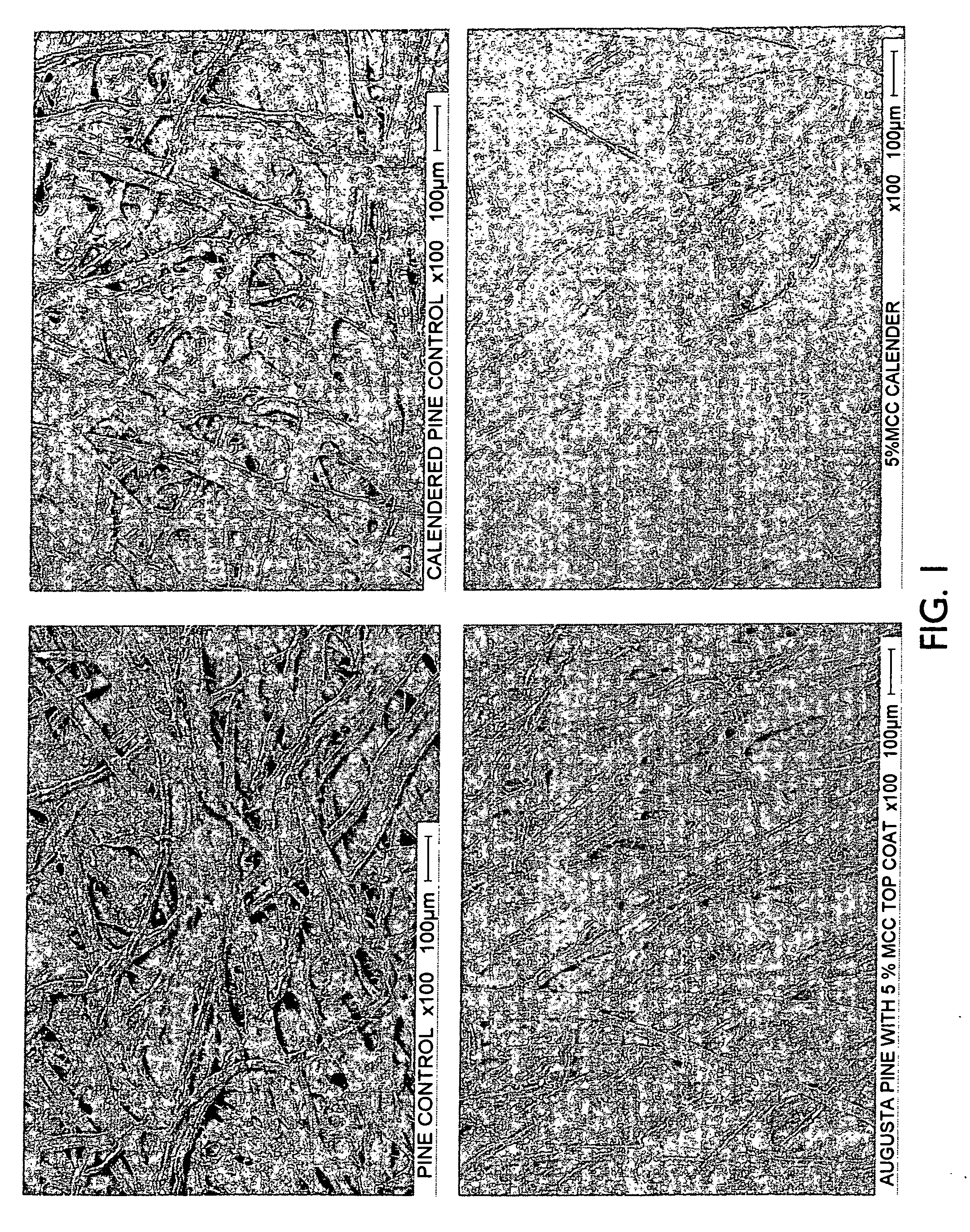
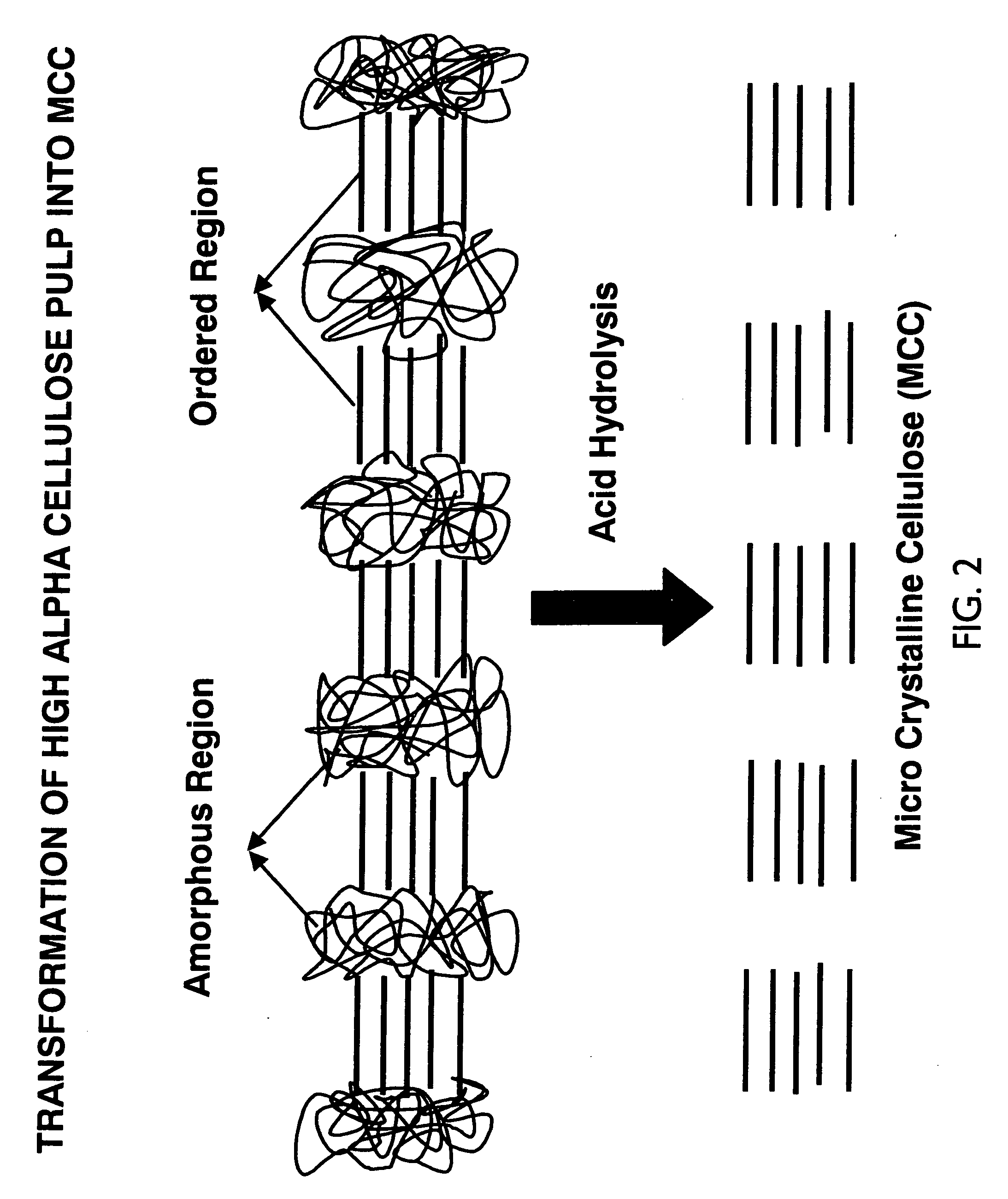
Surface treatment with texturized microcrystalline cellulose microfibrils for improved paper and paper board
InactiveUS7037405B2High binding capacityImprove abilitiesNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperFiberPaperboard
The present invention relates to the production of texturized microcrystalline cellulose from raw pulp material. This texturized microcrystalline cellulose can then be used for surface treatment of paper or paper board. Additionally, the texturized microcrystalline cellulose may be used as a starting material for production of paper or paper board.
Owner:INT PAPER CO
Paper or paperboard product and a process for production of a paper or paperboard product
InactiveUS20130180680A1Improve retentionGood strength performancePulp properties modificationSpecial paperCellulosePaperboard
The present invention relates to a paper or paperboard product comprising a furnish wherein said furnish comprises a cationic polymer in an amount of above 1.5% by weight, an anionic polymer and microfibrillated cellulose. The invention further relates to a process for the production of said product.
Owner:STORA ENSO OYJ
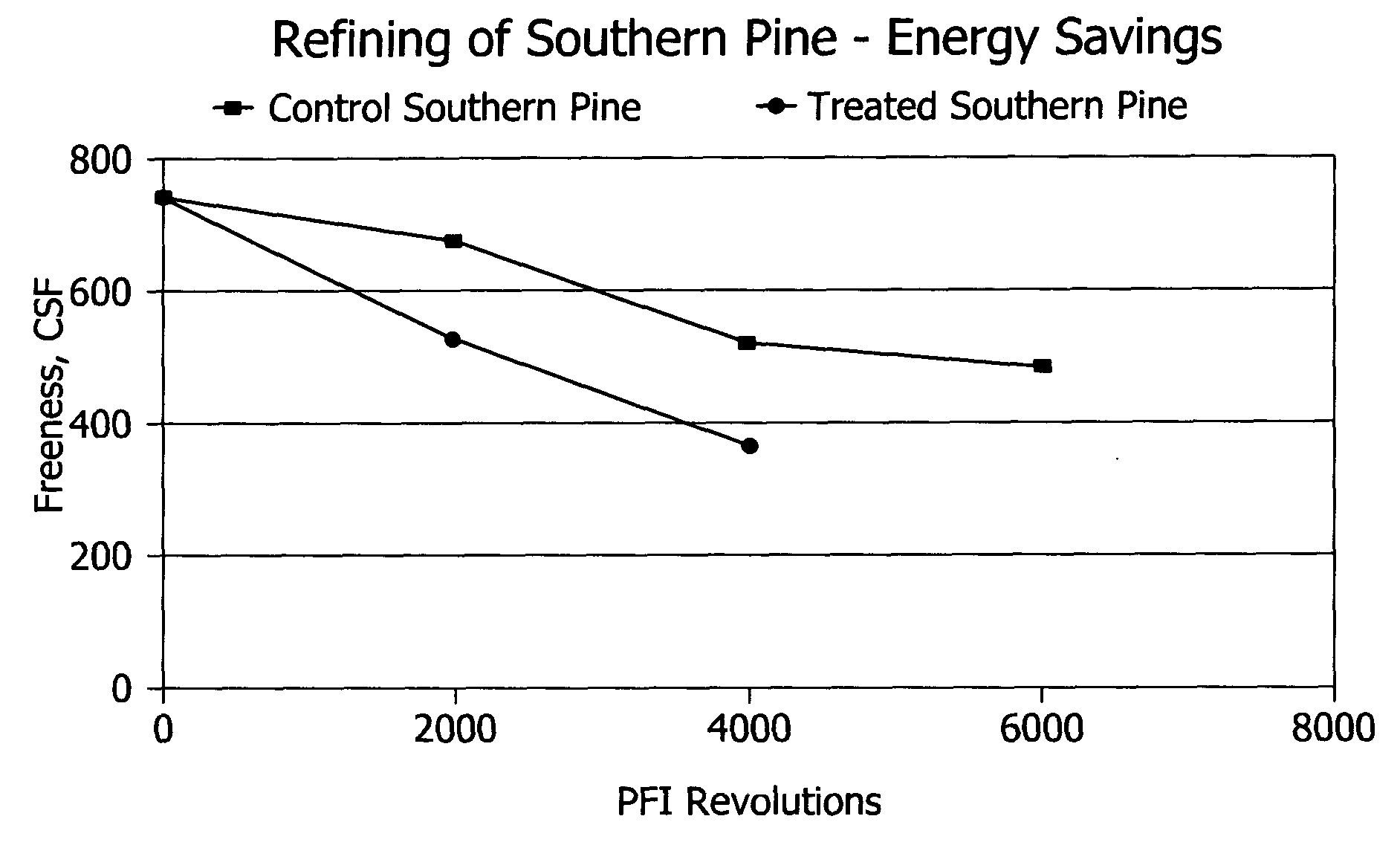
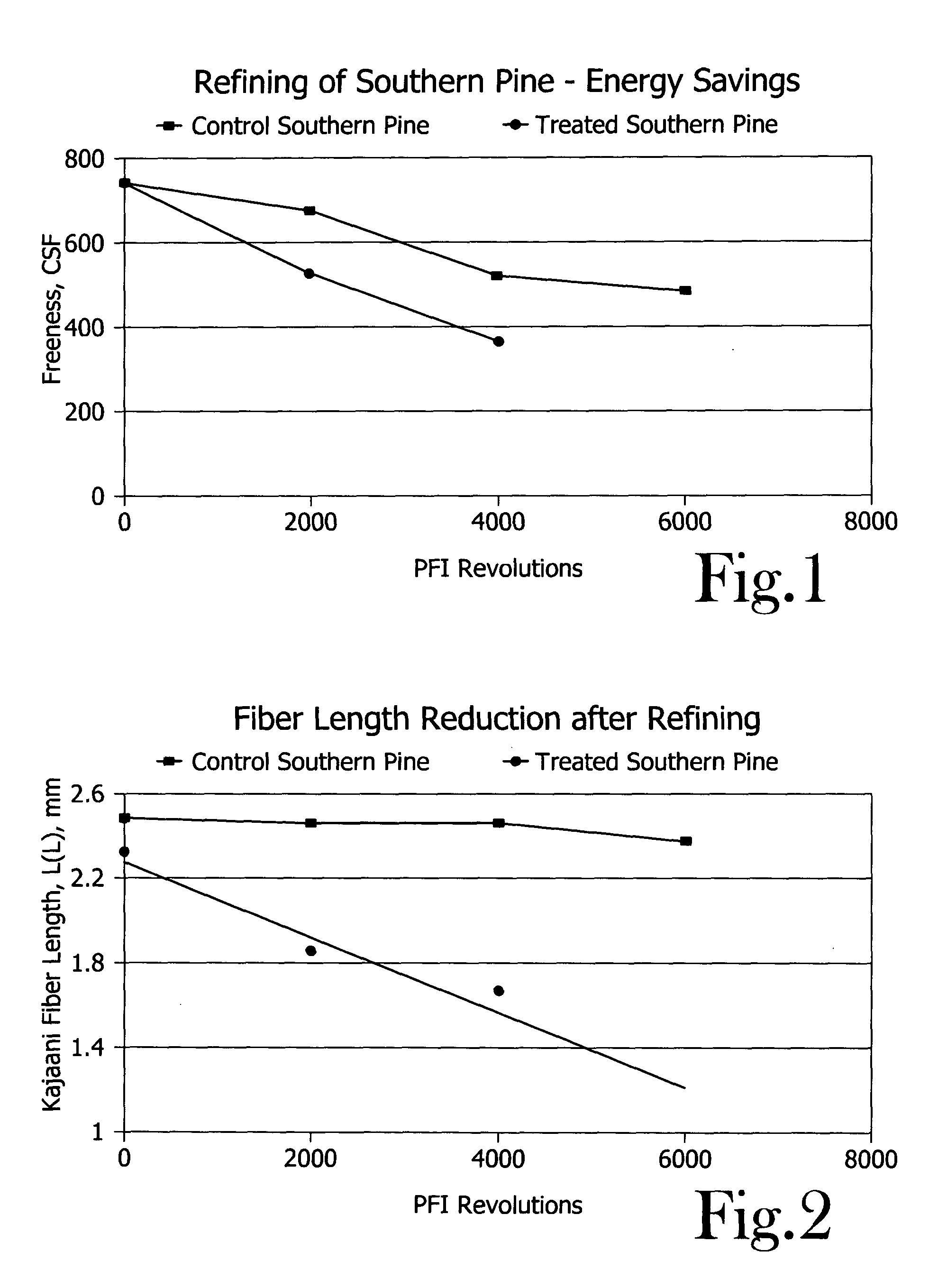
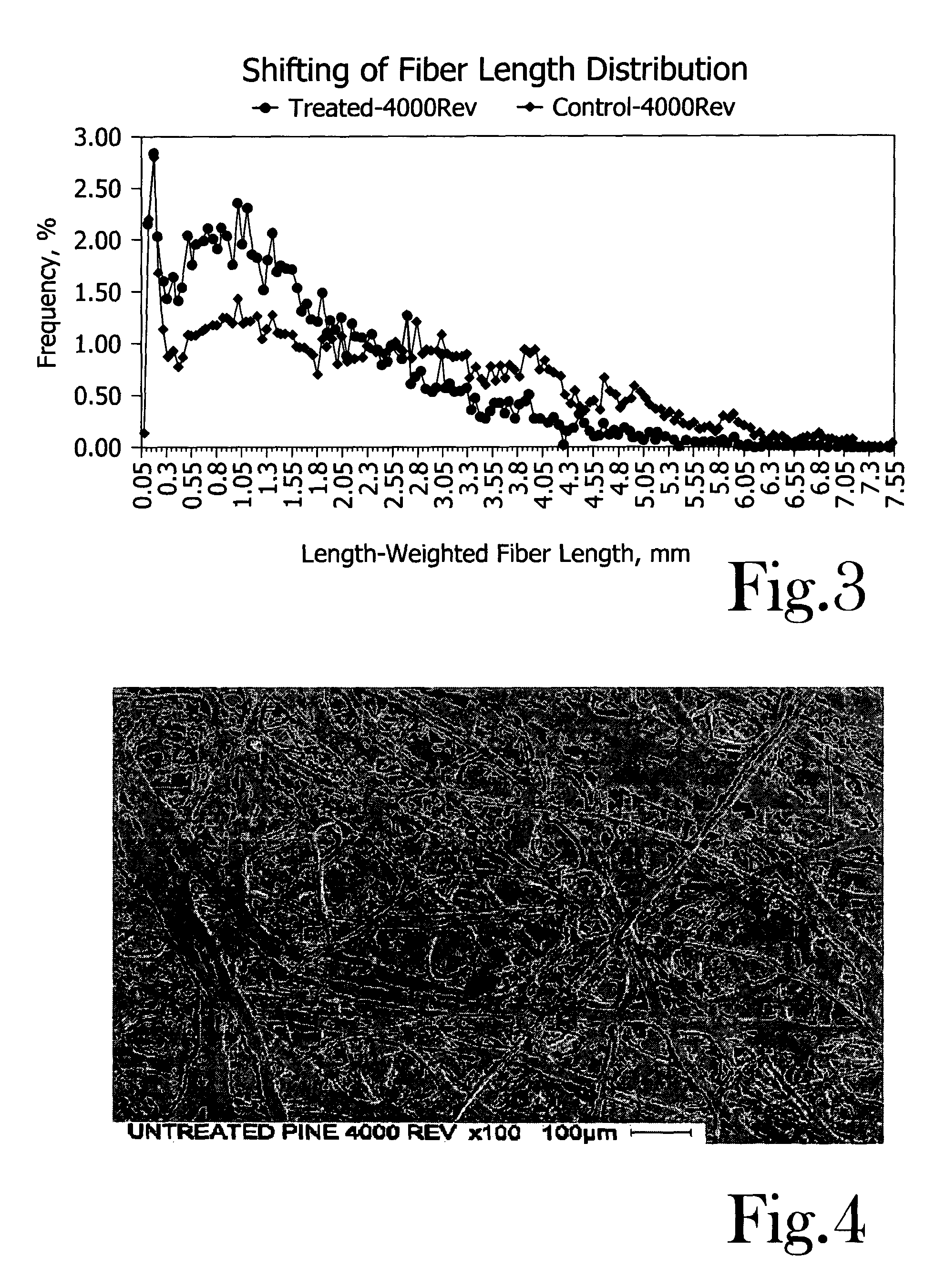
Chemical activation and refining of southern pine kraft fibers
InactiveUS20050061455A1Increase the pulp freenessEasy to drainPulp properties modificationPulp bleachingChemical treatmentCellulose fiber
A method for alteration of the morphology of cellulose fibers, particularly softwood fibers, by (a) subjecting the fibers to a metal ion-activated peroxide treatment carried out at a pH of between about 1 and about 9, preferably between 3 and 7, and (b) subjecting the treated fibers to a refining treatment thereby converts SW fibers to HW-like fibers in many respects. The metal ion-activated peroxide treatment has been noted to act on pulp cellulose and hemi-cellulose, causing oxidation and oxidative degradation of cellulose fibers. The chemical treatment of the pulp, taken alone, is not sufficient to attain the desired modification of the morphology of the fibers, however, subsequent refining or like mechanical treatment of the chemically-treated fibers to achieve a given degree of refinement of the fibers requires dramatically less refining energy to achieve a desired end point of refinement and to impart other desirable properties to the pulp. A pulp of modified SW fibers and a mixture of HW fibers and modified HW fibers are disclosed.
Owner:INT PAPER CO
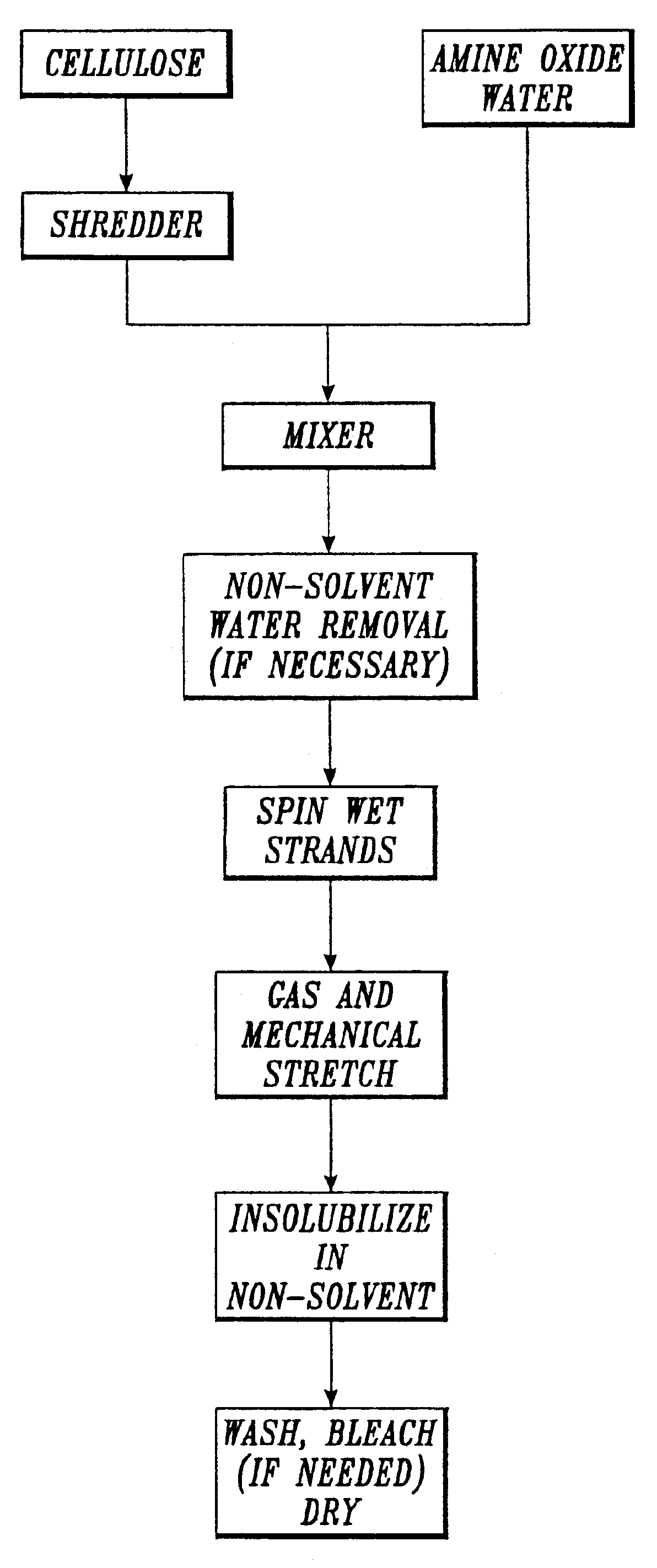
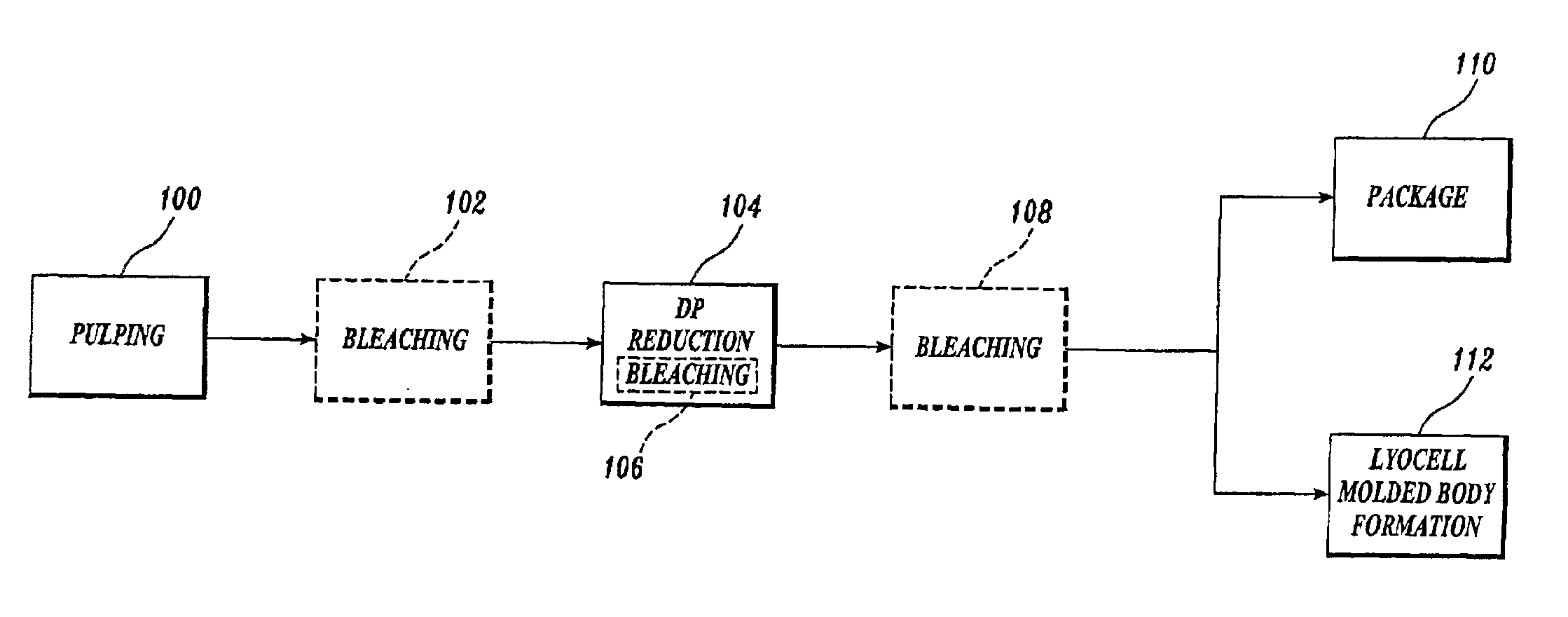
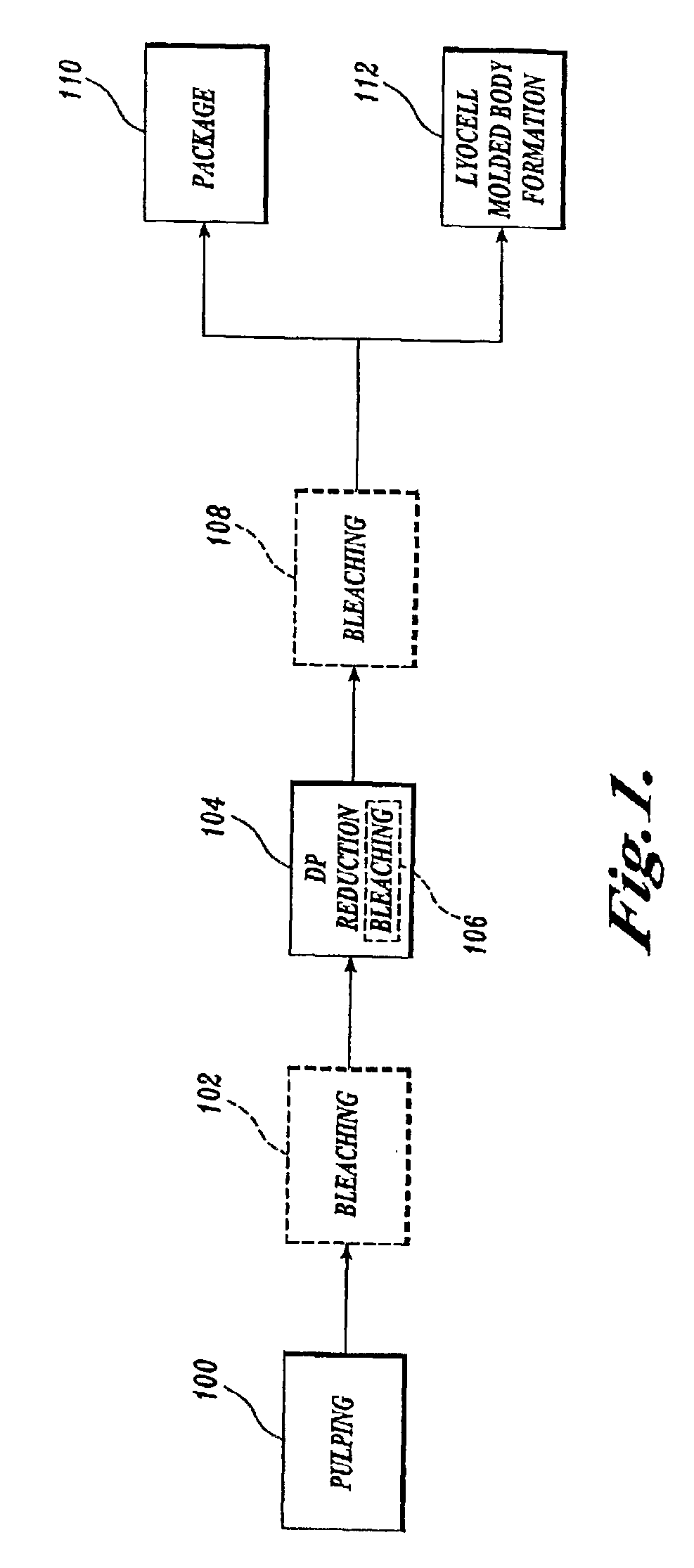
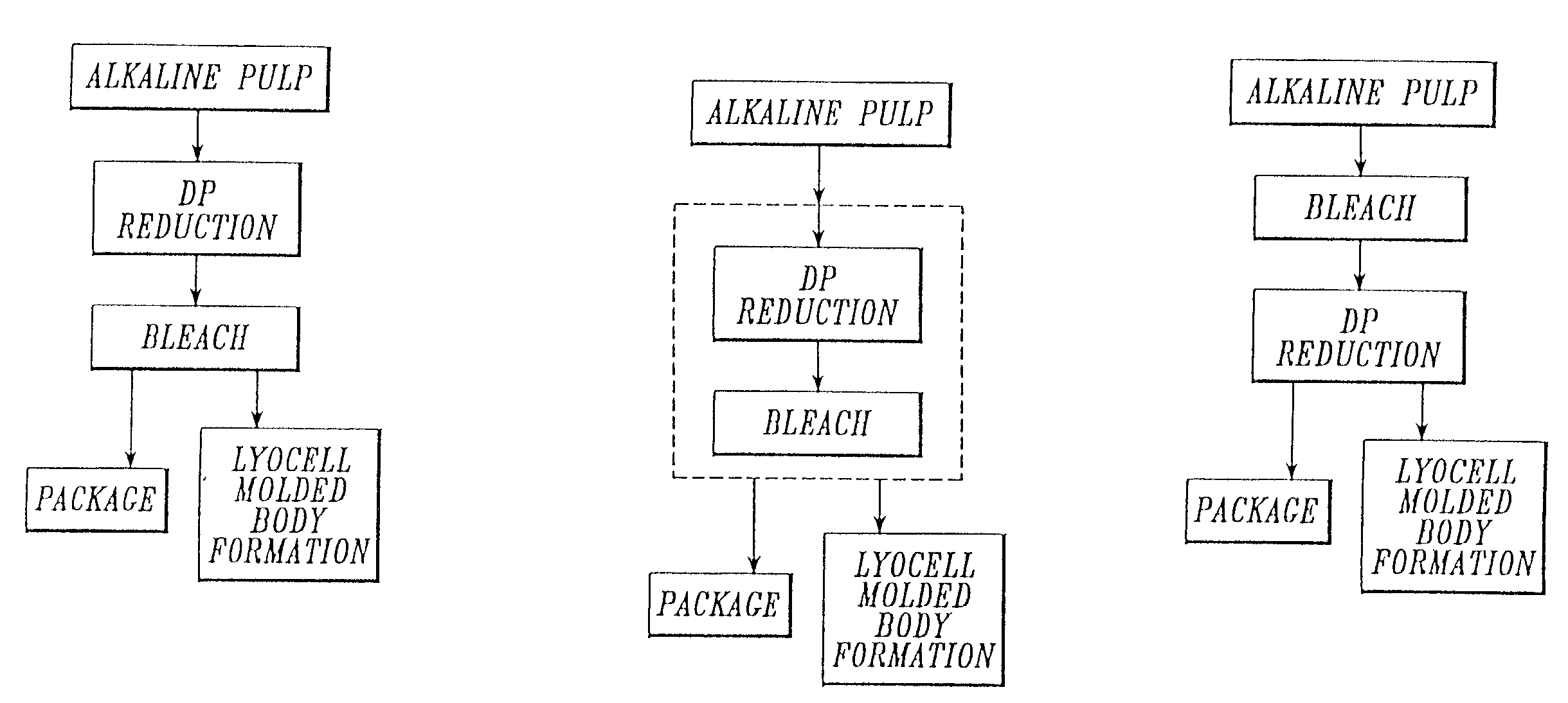
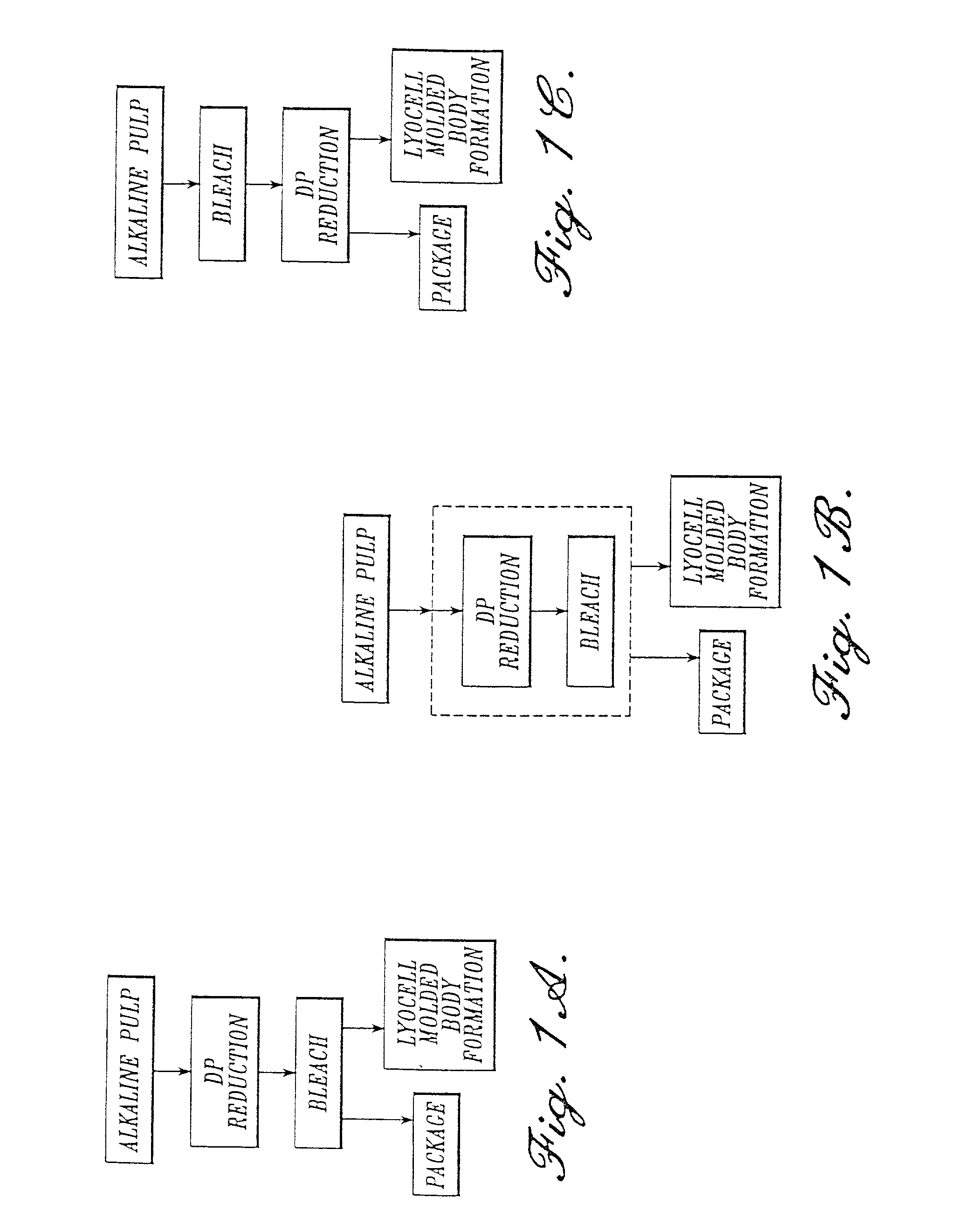
Process for making lyocell fiber from sawdust pulp
InactiveUS6861023B2Reducing average degree of polymerizationReduced hemicellulose contentPulp properties modificationArtificial filaments from cellulose solutionsCopperLyocell
A process for making lyocell fibers including the steps of pulping raw material in a digester to provide an alkaline pulp, wherein the raw material includes sawdust in an amount greater than 0% up to 100%; contacting the alkaline pulp including cellulose and at least about 7% hemicellulose under alkaline conditions with an amount of an oxidant sufficient to reduce the average degree of polymerization of the cellulose to the range of from about 200 to about 1100 without substantially reducing the hemicellulose content or substantially increasing the copper number of the pulp; and forming fibers from the pulp.
Owner:INT PAPER CO
Process for making a composition for conversion to lyocell fiber from an alkaline pulp having low average degree of polymerization values
InactiveUS7083704B2Reducing hemicellulose contentIncreasing copper numberPulp properties modificationMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentHemicelluloseLyocell
The present invention provides compositions, useful for making lyocell fibers, having a high hemicellulose content, a low copper number and including cellulose that has a low average degree of polymerization (D.P.) and a narrow molecular weight distribution. Further, the present invention provides processes for making compositions, useful for making lyocell fibers, by contacting an alkaline pulp having a high hemicellulose content of at least about 7% with an oxidant sufficient to reduce the average degree of polymerization to about 200 to 1100 without substantially reducing the hemicellulose content or increasing the copper number of the pulp.
Owner:INT PAPER CO
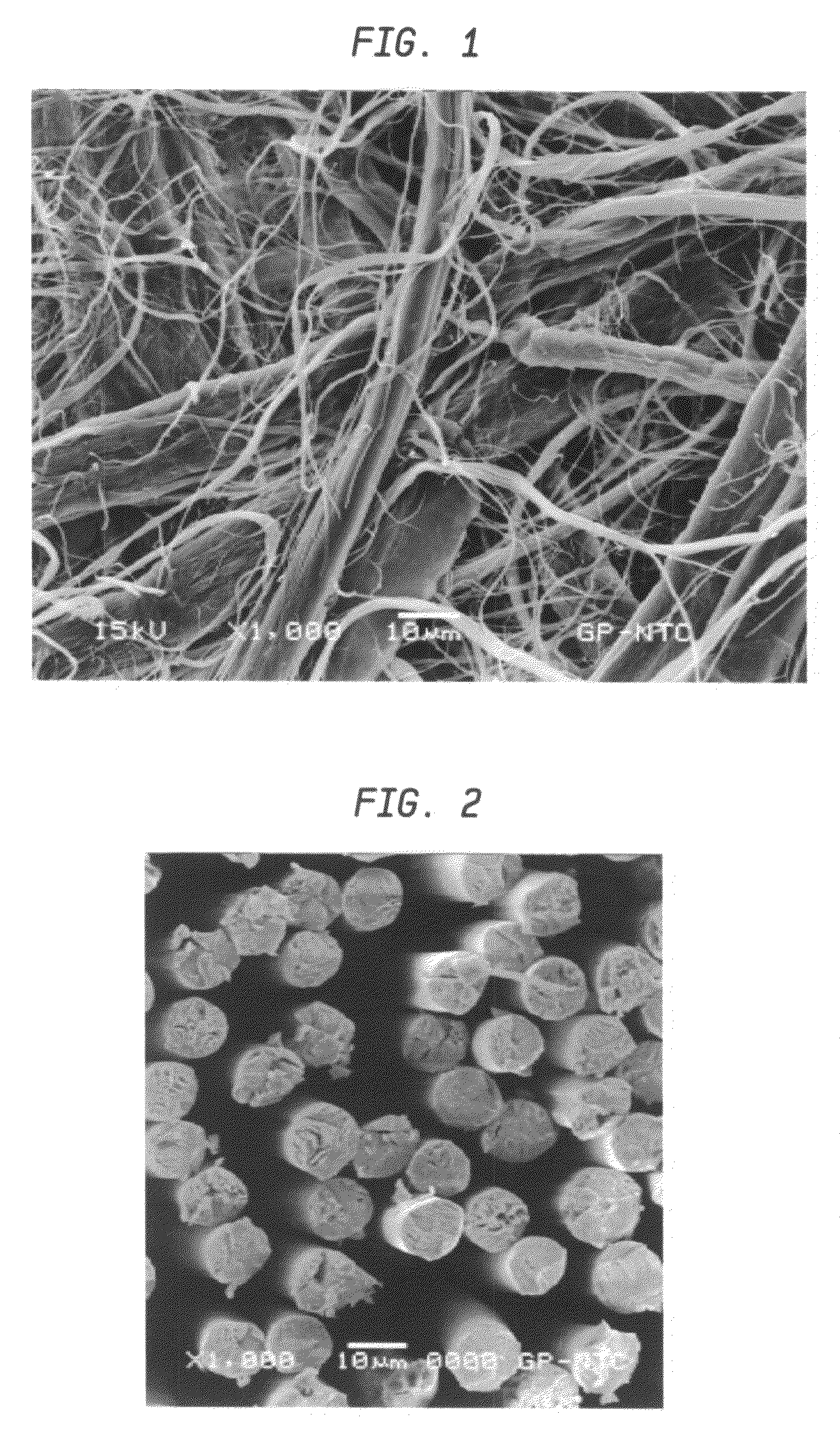
Method and apparatus for manufacturing microfibrillated cellulose fiber
ActiveUS20050194477A1Efficient and stable productionQuality improvementNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperCellulose fiberSlurry
A method for producing a microfibrillated cellulose, which comprises subjecting a slurry containing a pulp having a solids concentration of 1 to 6 wt % to the treatment with a disc refiner repeatedly ten times or more, to thereby prepare a microfibrillated cellulose having a number average fiber length or 0.2 mm or less and an amount of water hold of 10 mL / g or more, the amount representing the volume of water capable of being held by a unit weight of the cellulose fiber. The method allows the production of a microfibrillated cellulose having high quality with stability and with good efficiency.
Owner:DSG INT LTD
Wood pulp fiber morphology modifications through thermal drying
InactiveUS6837970B2High degreeIncreased formationPulp properties modificationPaper/cardboardFiberCross linker
A method of modifying a two-dimensional, flat fiber morphology of a never-been-dried wood pulp into a three-dimensional twisted fiber morphology without the aid of a chemical cross-linker. The method includes the steps of treating a never-been-dried wood pulp fiber slurry with a drying aid and thermally drying the wood pulp fiber slurry. The method may alternatively, or additionally, include the steps of spray drying a wood pulp fiber slurry and / or a slurry of a hydrophilic material, and flash drying the spray dried wood pulp fiber slurry and / or slurry of hydrophilic material.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Method for producing modified cellulose
InactiveUS20120043039A1Improve propertiesEfficient productionSpecial paperPaper after-treatmentFiberFiber suspension
The present invention provides a method for producing modified nanofibrillated cellulose characterized by bringing cellulosic material into a fiber suspension, adsorbing a cellulose derivative or polysaccharide or polysaccharide derivative onto fibers in said fiber suspension under special conditions and subjecting the obtained fiber suspension derivative to mechanical disintegration. A modified nanofibrillated cellulose obtainable by a method of the present invention is provided. Furthermore, the invention relates to the use of said modified nanotibrillated cellulose.
Owner:UPM-KYMMENE OYJ
Processes and apparatus for producing nanocellulose, and compositions and products produced therefrom
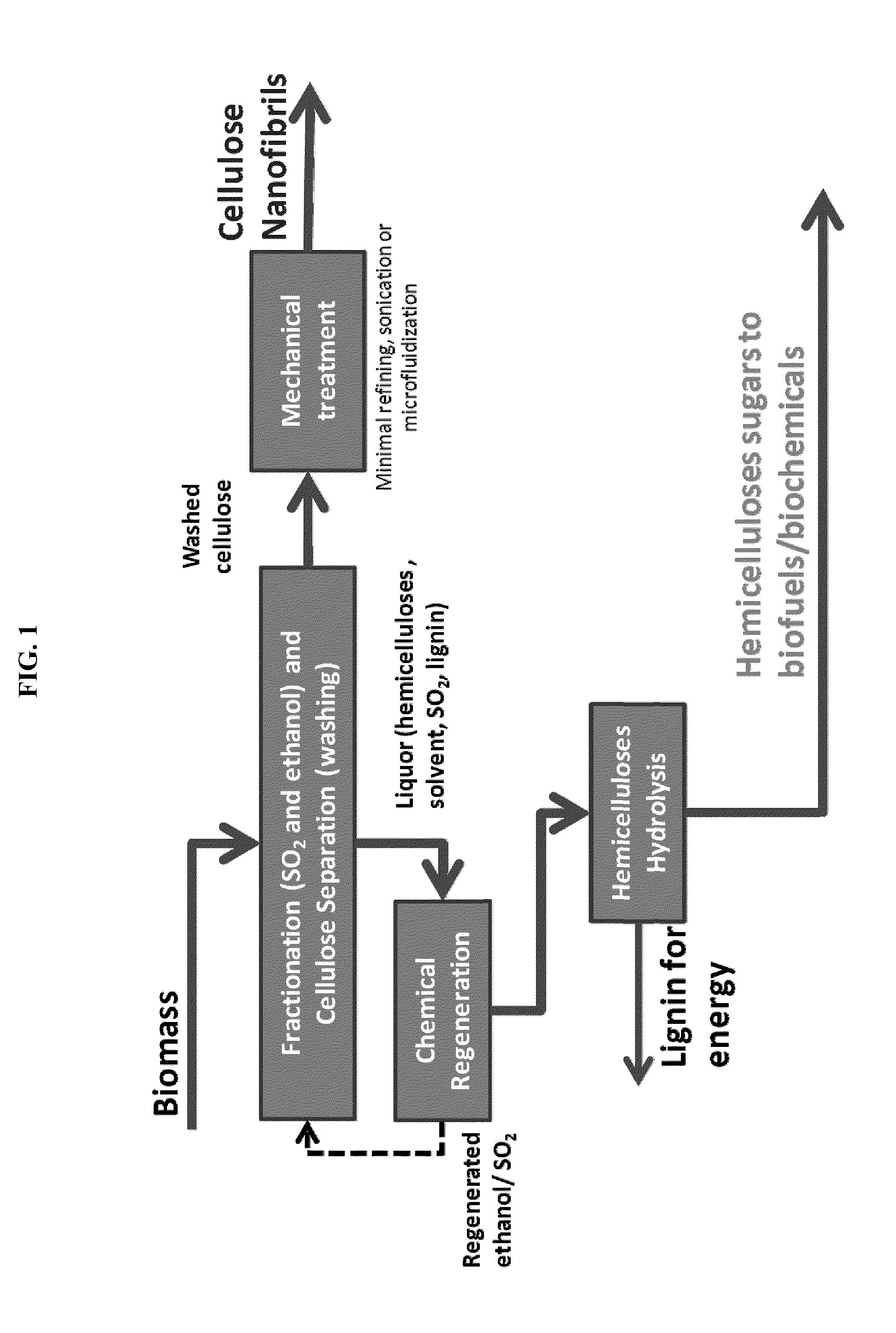
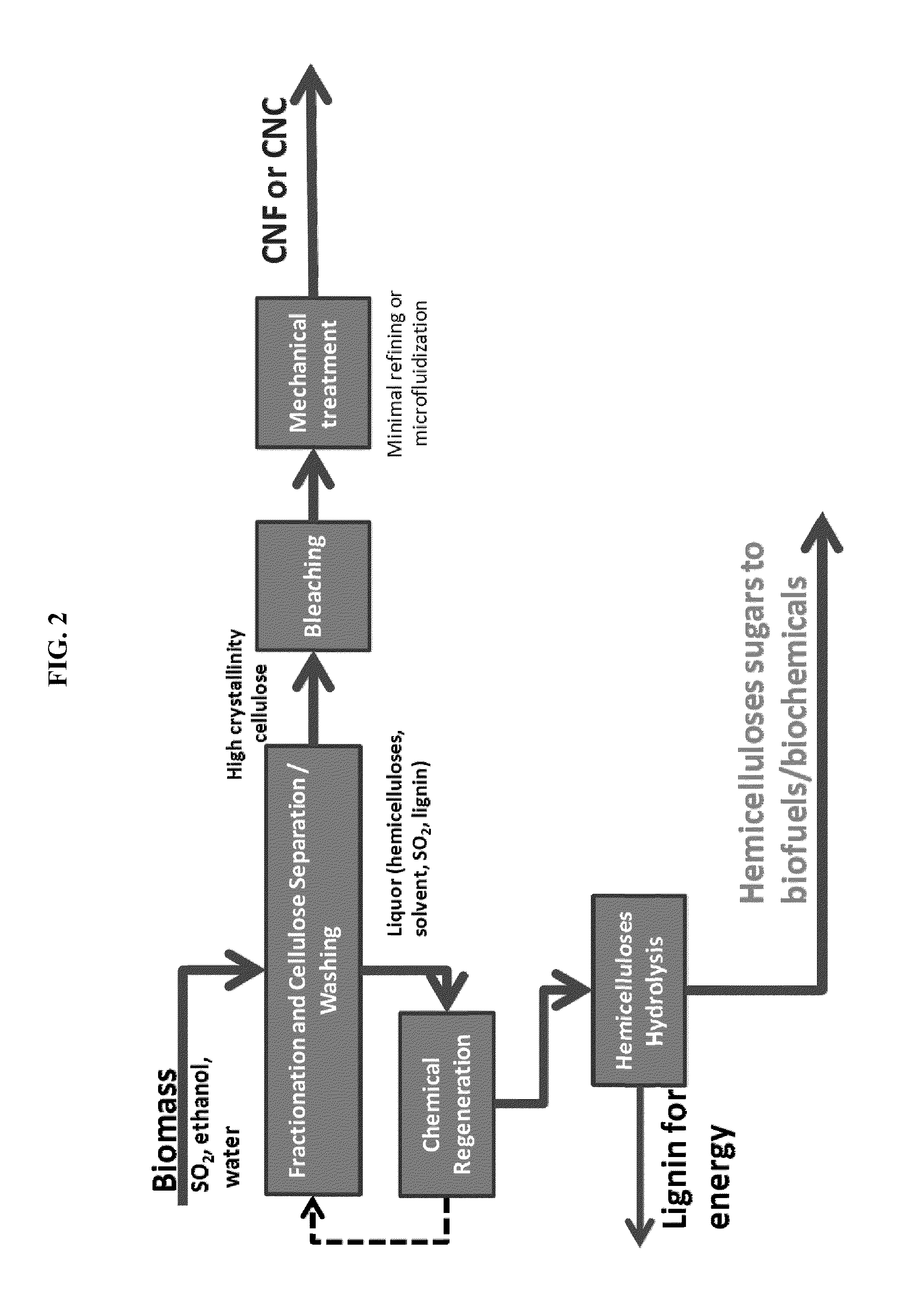
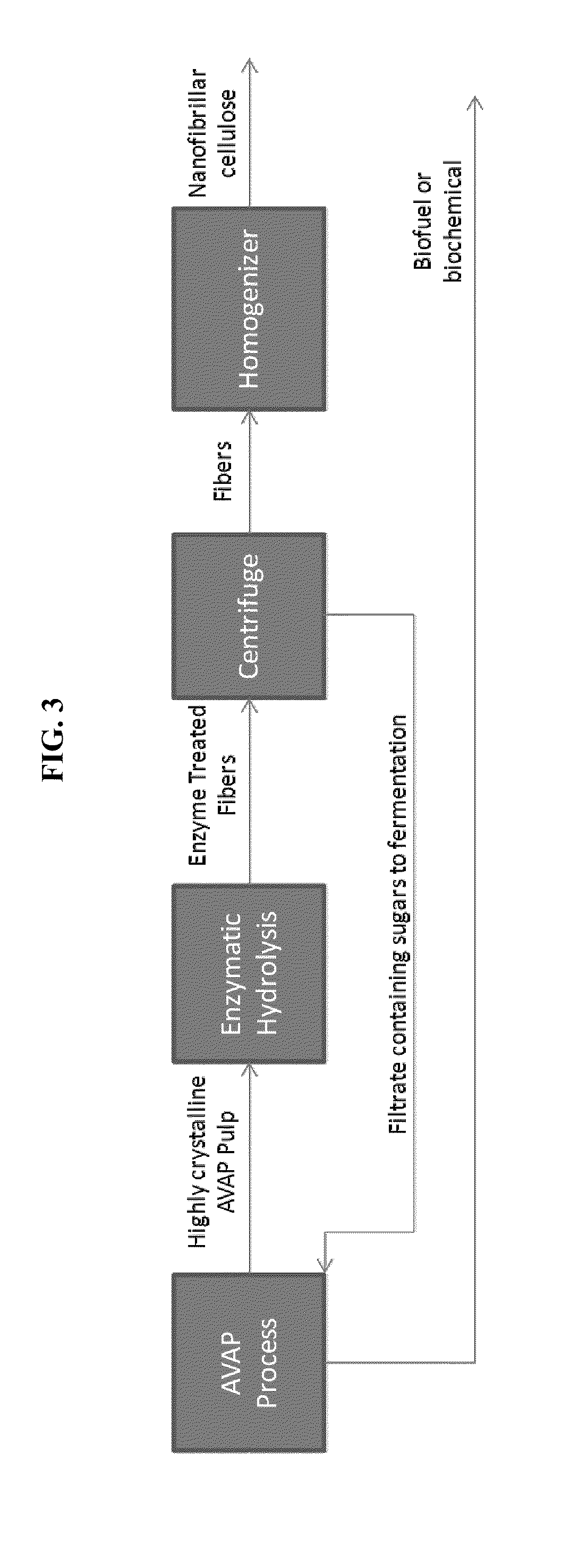
Processes disclosed are capable of converting biomass into high-crystallinity nanocellulose with surprisingly low mechanical energy input. In some variations, the process includes fractionating biomass with an acid (such as sulfur dioxide), a solvent (such as ethanol), and water, to generate cellulose-rich solids and a liquid containing hemicellulose and lignin; and mechanically treating the cellulose-rich solids to form nanofibrils and / or nanocrystals. The total mechanical energy may be less than 500 kilowatt-hours per ton. The crystallinity of the nanocellulose material may be 80% or higher, translating into good reinforcing properties for composites. The nanocellulose material may include nanofibrillated cellulose, nanocrystalline cellulose, or both. In some embodiments, the nanocellulose material is hydrophobic via deposition of some lignin onto the cellulose surface. Optionally, sugars derived from amorphous cellulose and hemicellulose may be separately fermented, such as to monomers for various polymers. These polymers may be combined with the nanocellulose to form completely renewable composites.
Owner:GRANBIO INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HOLDINGS LLC
Method of binding particles to binder treated fibers
InactiveUS7144474B1Efficiently and economically attachedIncreases absorptive efficiency of productNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperFiberHydrogen
Fiber treated with an organic nonpolymeric binder is combined with superabsorbent particles in order to bind the particles to the fiber. The nonpolymeric organic binder comprises binder molecules that include at least one functional group capable of forming a hydrogen bond or a coordinate covalent bond with the particles and at least one functional group capable of forming a hydrogen bond with the fiber. The superabsorbent particles have a hydrogen or coordinate covalent bonding functional site. The binder serves to bind the particles to the fiber through formation of hydrogen and / or coordinate covalent bonds.
Owner:WEYERHAEUSER CO
Surface treatment with texturized microcrystalline cellulose microfibrils for improved paper and paper board
InactiveUS20060144535A1High binding capacityImprove abilitiesNon-fibrous pulp additionSpecial paperFiberCardboard
The present invention relates to the production of texturized microcrystalline cellulose from raw pulp material. This texturized microcrystalline cellulose can then be used for surface treatment of paper or paper board. Additionally, the texturized microcrystalline cellulose may be used as a starting material for production of paper or paper board.
Owner:INT PAPER CO
Method of providing papermaking fibers with durable curl
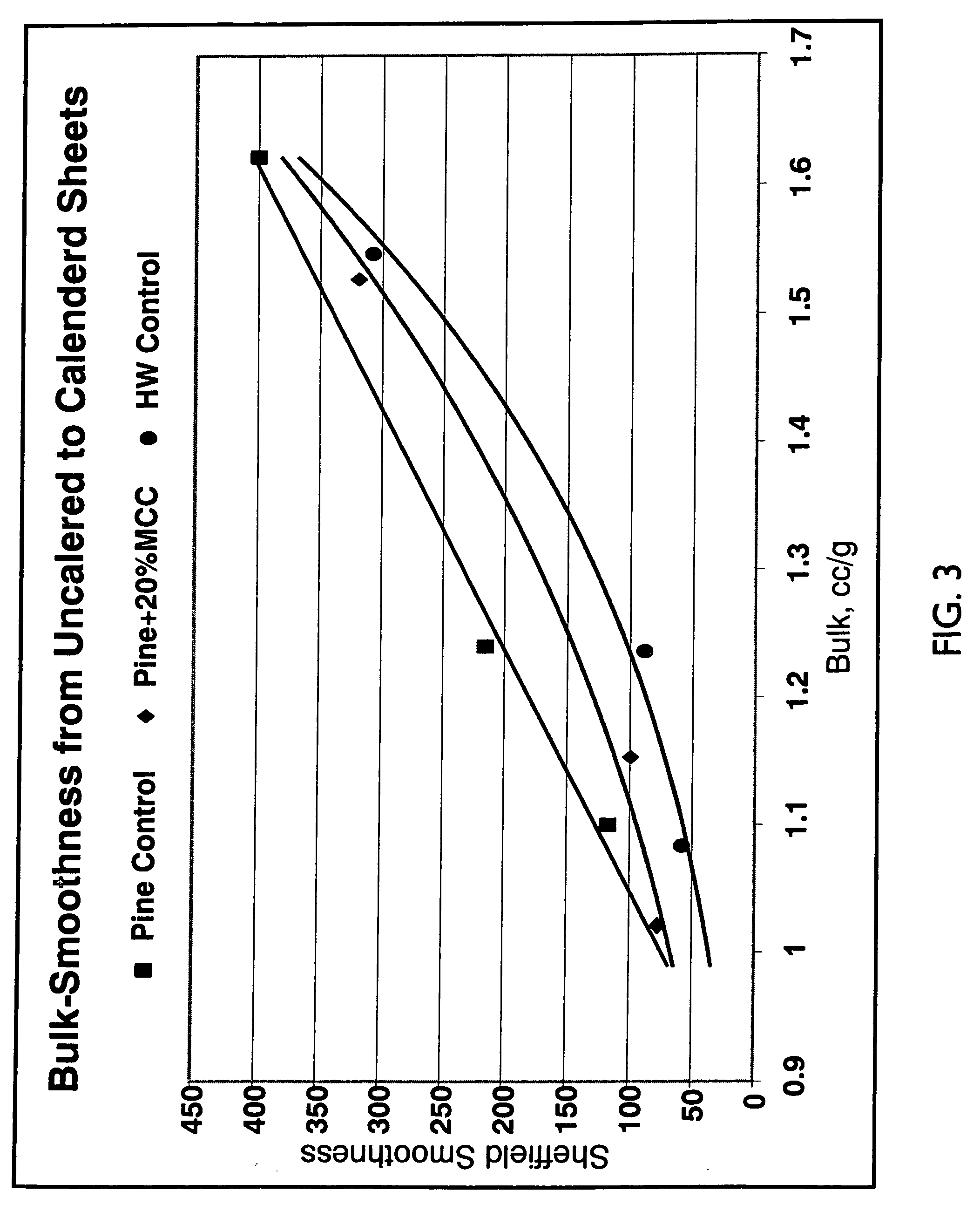
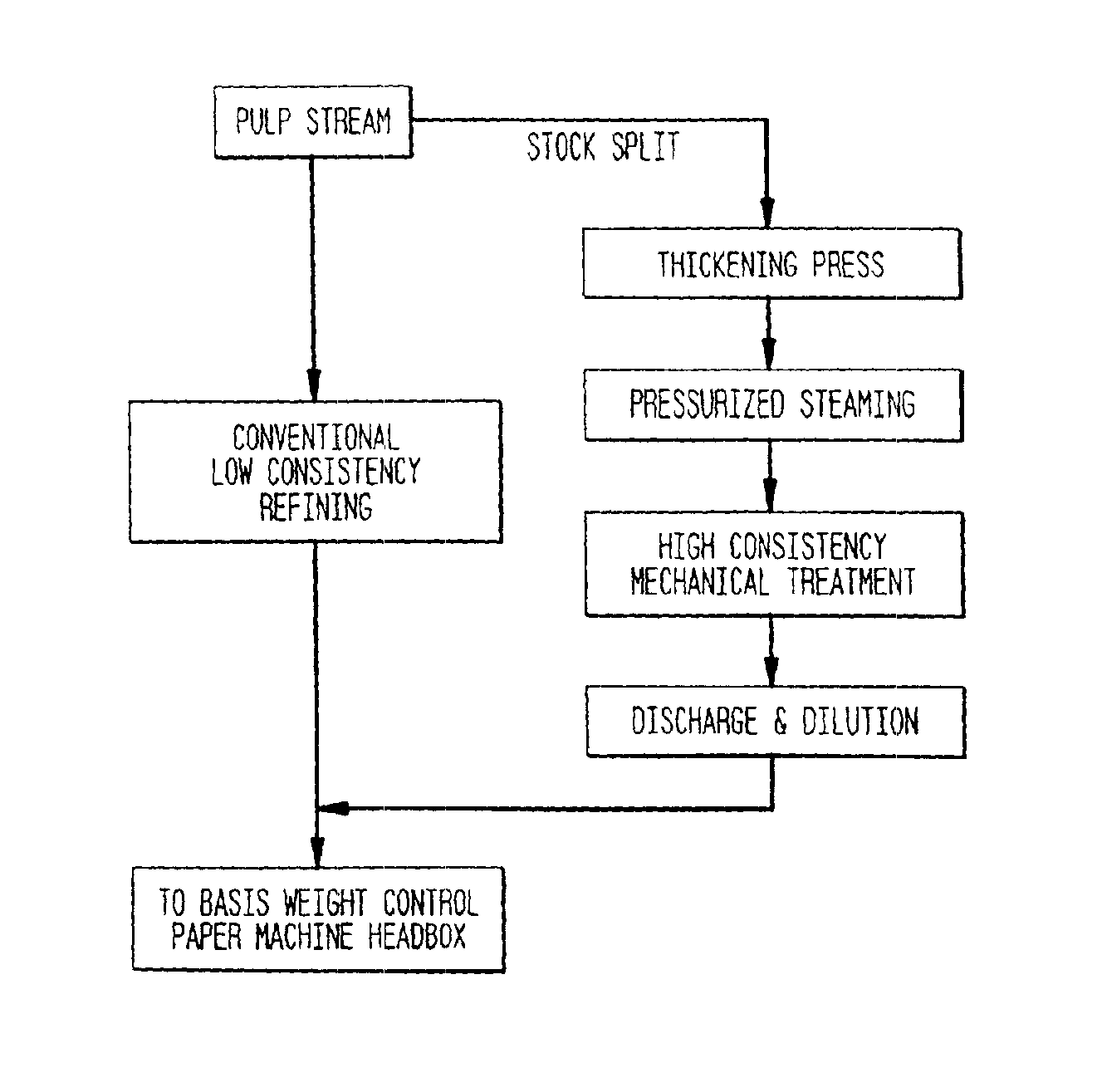
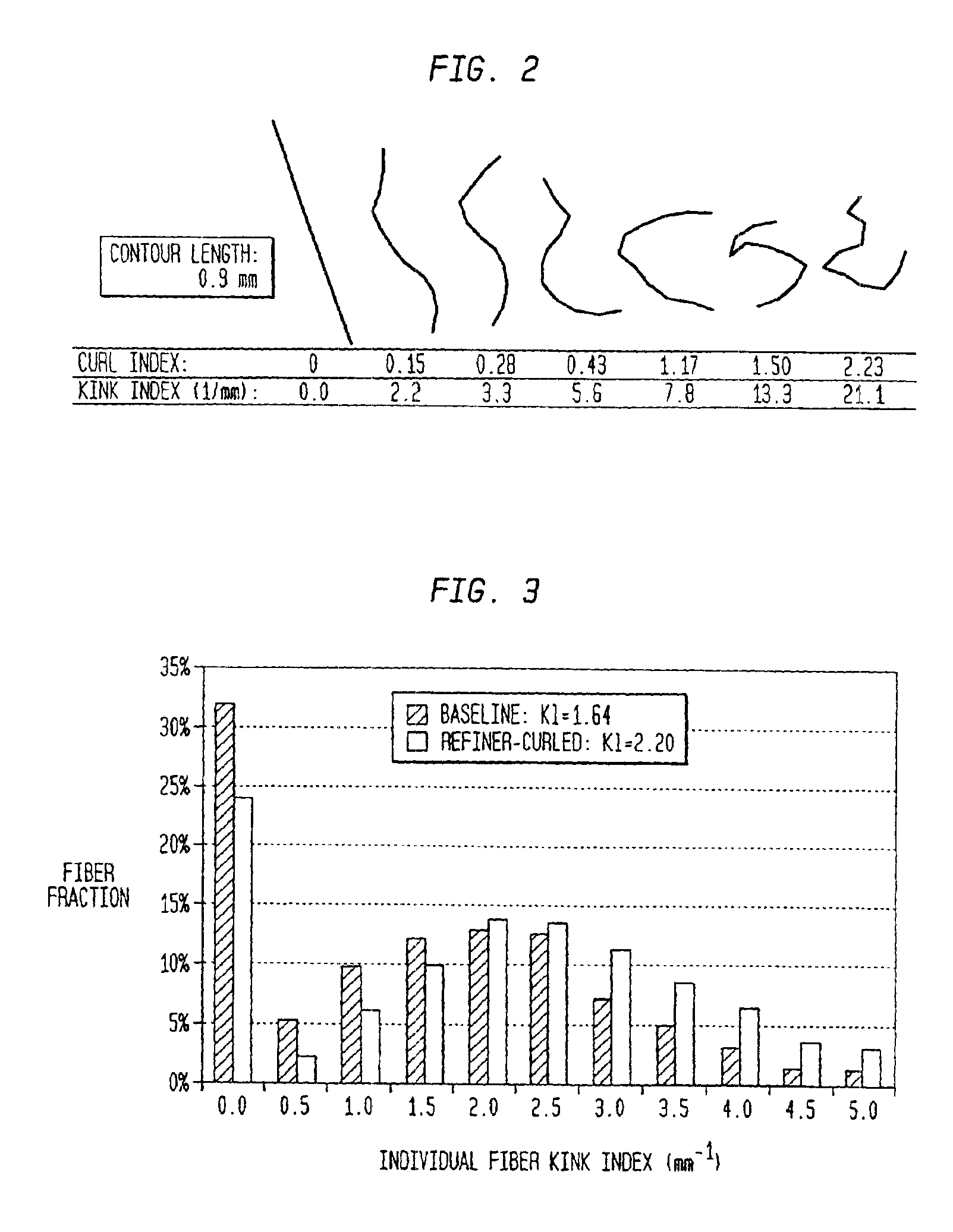
A process for producing high bulk cellulosic fiber exhibiting a durable elevated curl index includes: (a) concurrently heat treating and convolving cellulosic fiber pulp at elevated temperature and pressure at high consistency under conditions selected so as to preclude substantial fibrillation and attendant paper strength and fiber bonding development; and (b) recovering the pulp wherein the length weighted curl index of the treated fiber is at least about 20% higher than the length weighted curl index of the fiber prior to the heat treatment and convolving thereof. The curl imparted to the fiber persists upon treatment for 30 minutes in a laboratory disintegrator at 3000 rpm at 1% consistency at a temperature of 125° F. Moreover, the curl may be imparted to the fiber in a disk refiner at very short residence times, on the order of several seconds or less. In general, the process is carried out in the presence of saturated steam at a pressure of from about 5 to about 150 psig.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Compositions and composites of cellulosic and lignocellulosic materials and resins, and methods of making the same
InactiveUS20050200050A1Material efficiencyBiocidePulp properties modificationCellulosePolymer science
Owner:XYLECO INC
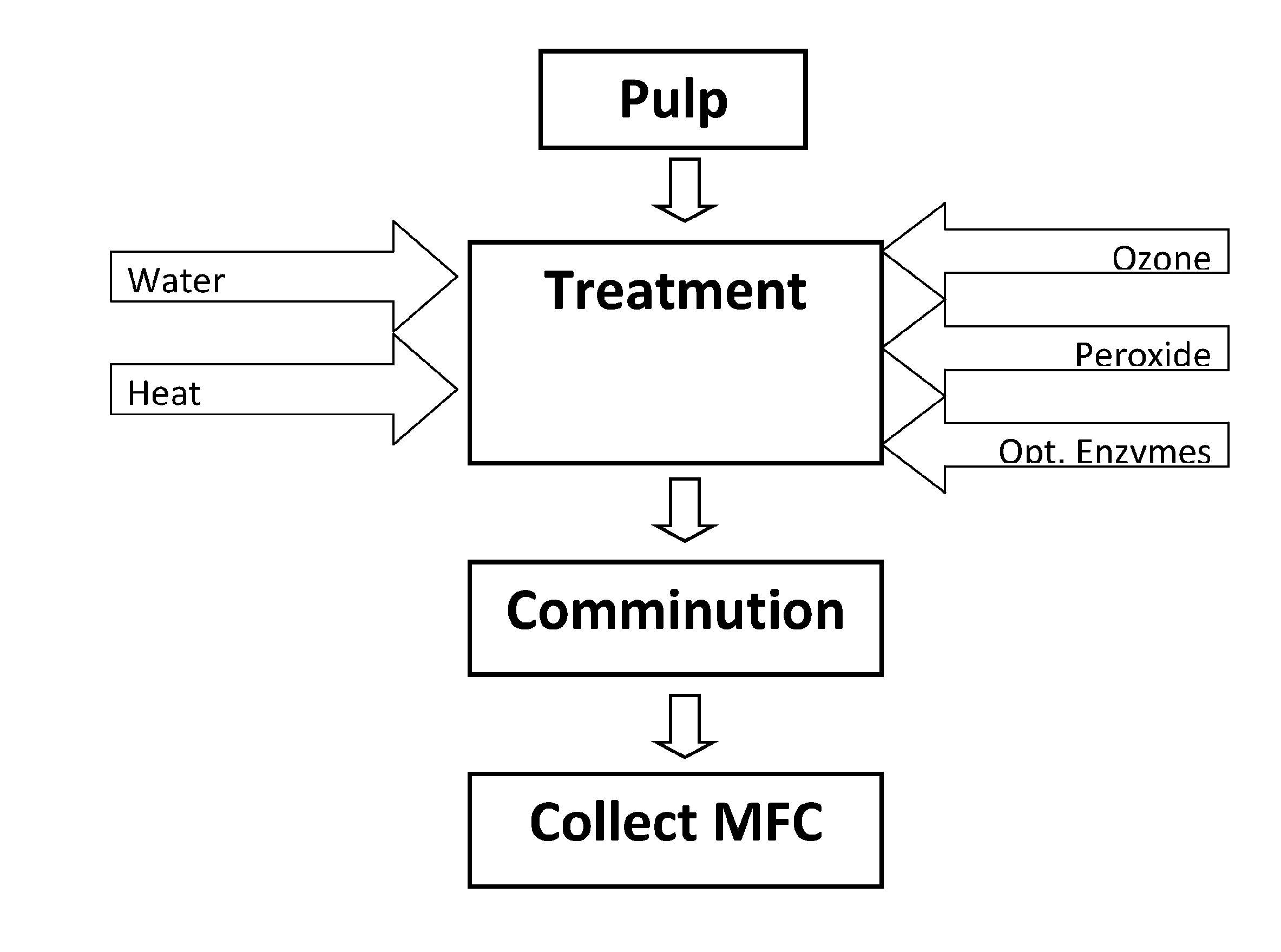
Energy Efficient Process for Preparing Nanocellulose Fibers
ActiveUS20150167243A1Improve efficiencyWeaken energySpecial paperPaper after-treatmentDepolymerizationNanofiber
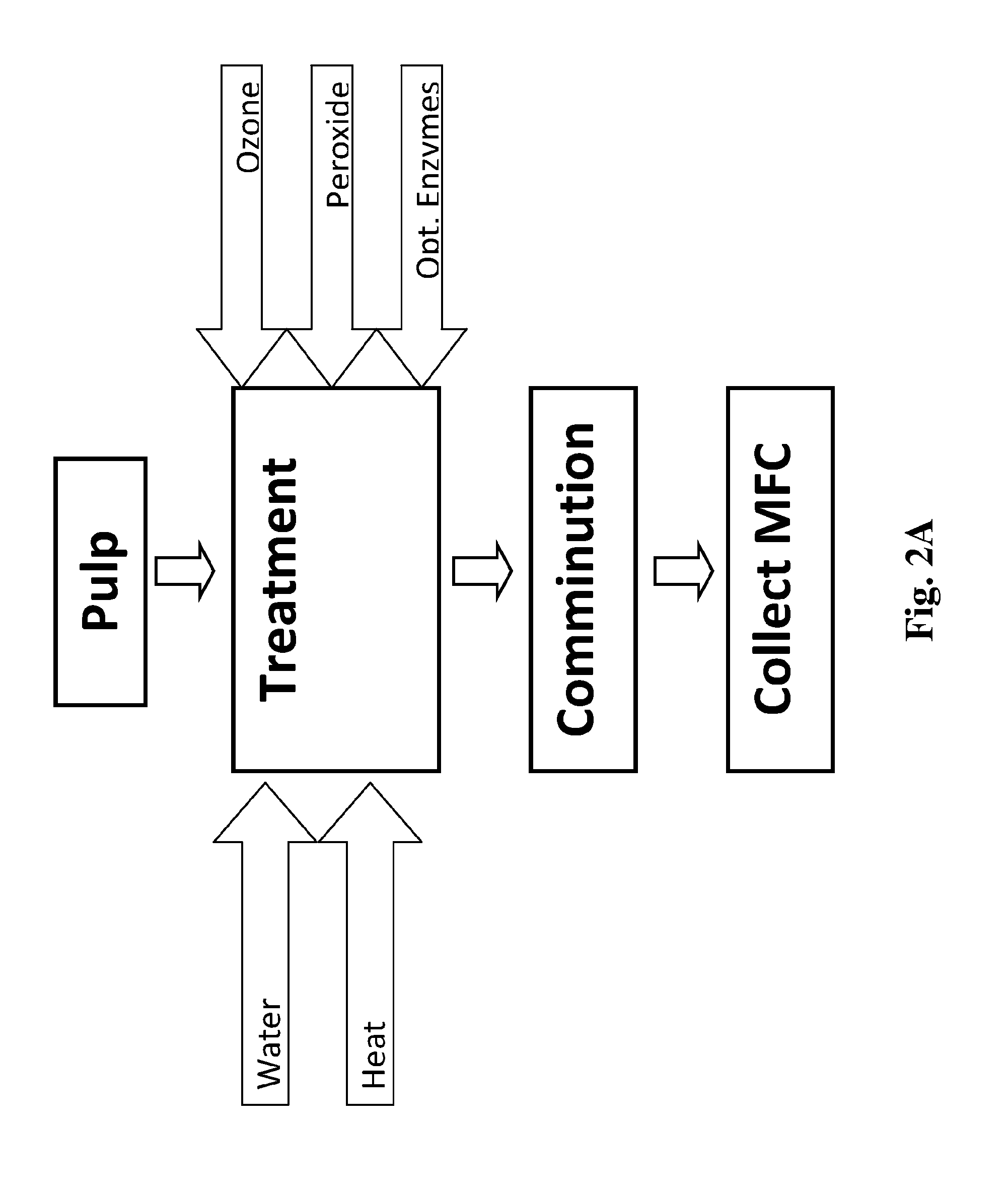
A scalable, energy efficient process for preparing cellulose nanofibers is disclosed. The process employs a depolymerizing treatment with one or both of: (a) a relatively high charge of ozone under conditions that promote the formation of free radicals to chemically depolymerize the cellulose fiber cell wall and interfiber bonds; or (b) a cellulase enzyme. Depolymerization may be estimated by pulp viscosity changes. The depolymerizing treatment is followed by or concurrent with mechanical comminution of the treated fibers, the comminution being done in any of several mechanical comminuting devices, the amount of energy savings varying depending on the type of comminuting system and the treatment conditions. Comminution may be carried out to any of several endpoint measures such as fiber length, % fines or slurry viscosity.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MAINE
Material for odor control
The present invention is directed to materials containing an enzyme inhibitor, including treated fibers, nonwovens, functional particles and processes for making these materials. These materials are useful in reducing or delaying onset of odor generation from various waste materials including human and animal elimination products.
Owner:BUCKEYE TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com