Patents
Literature
288results about How to "Material efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
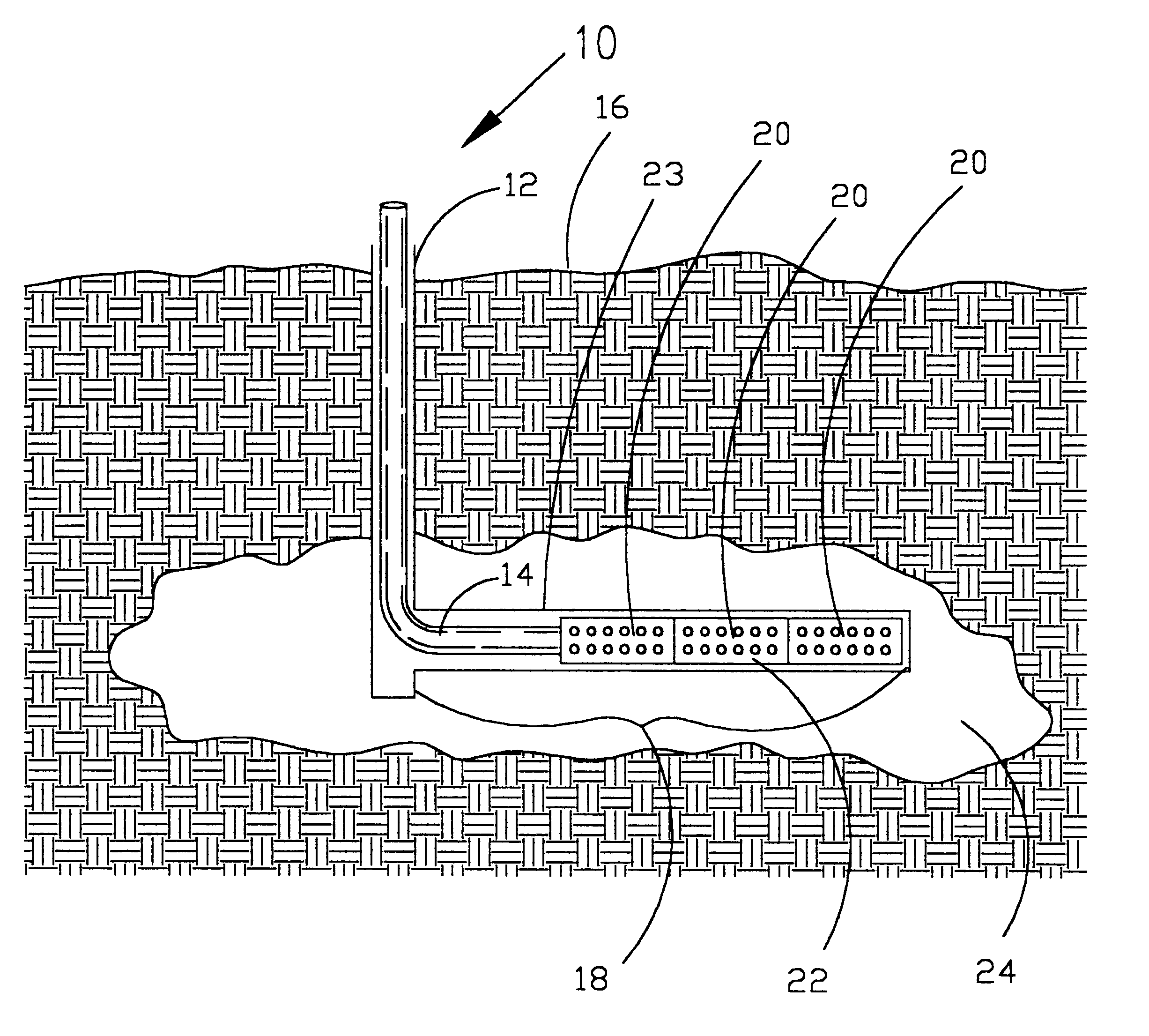
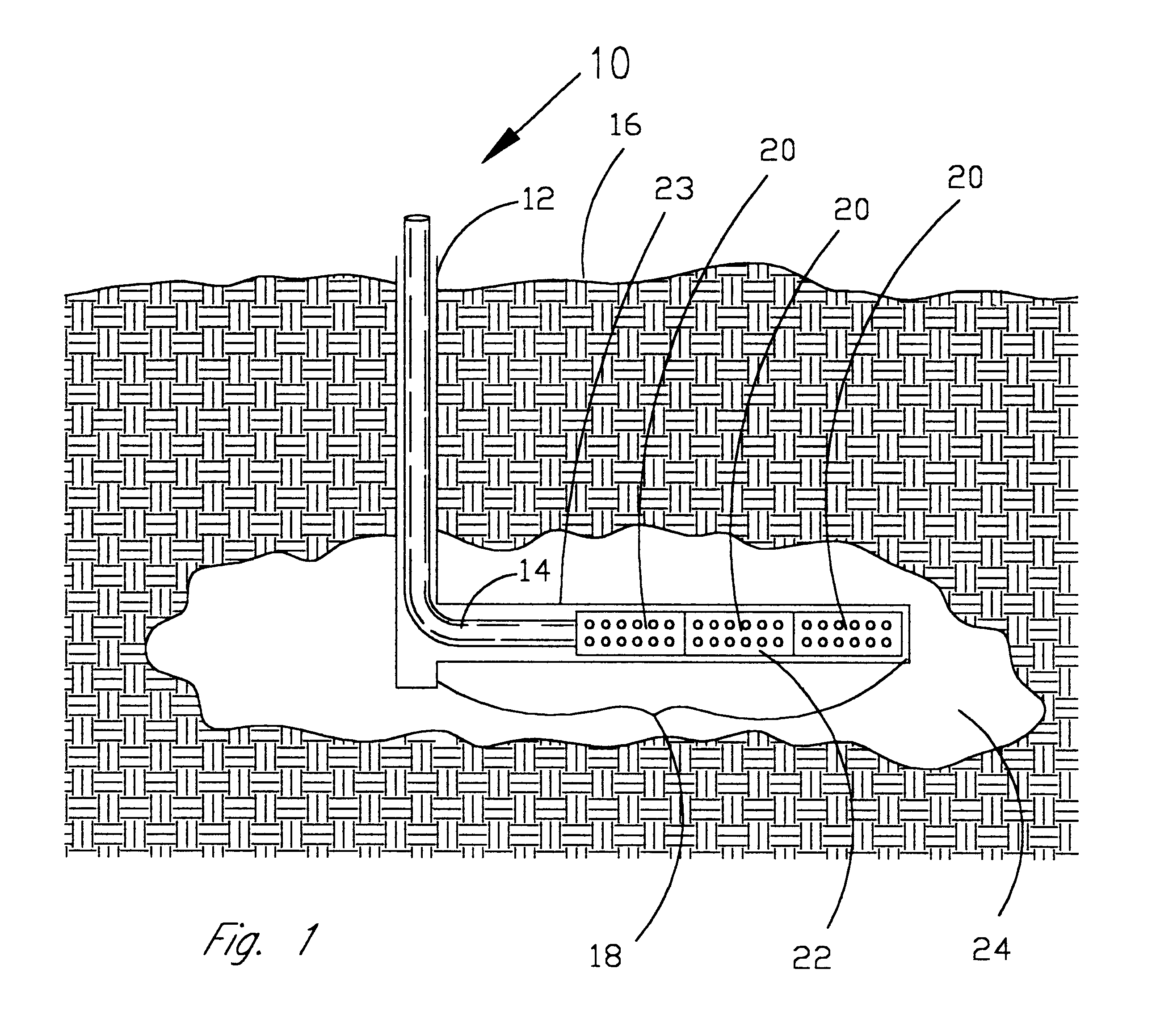
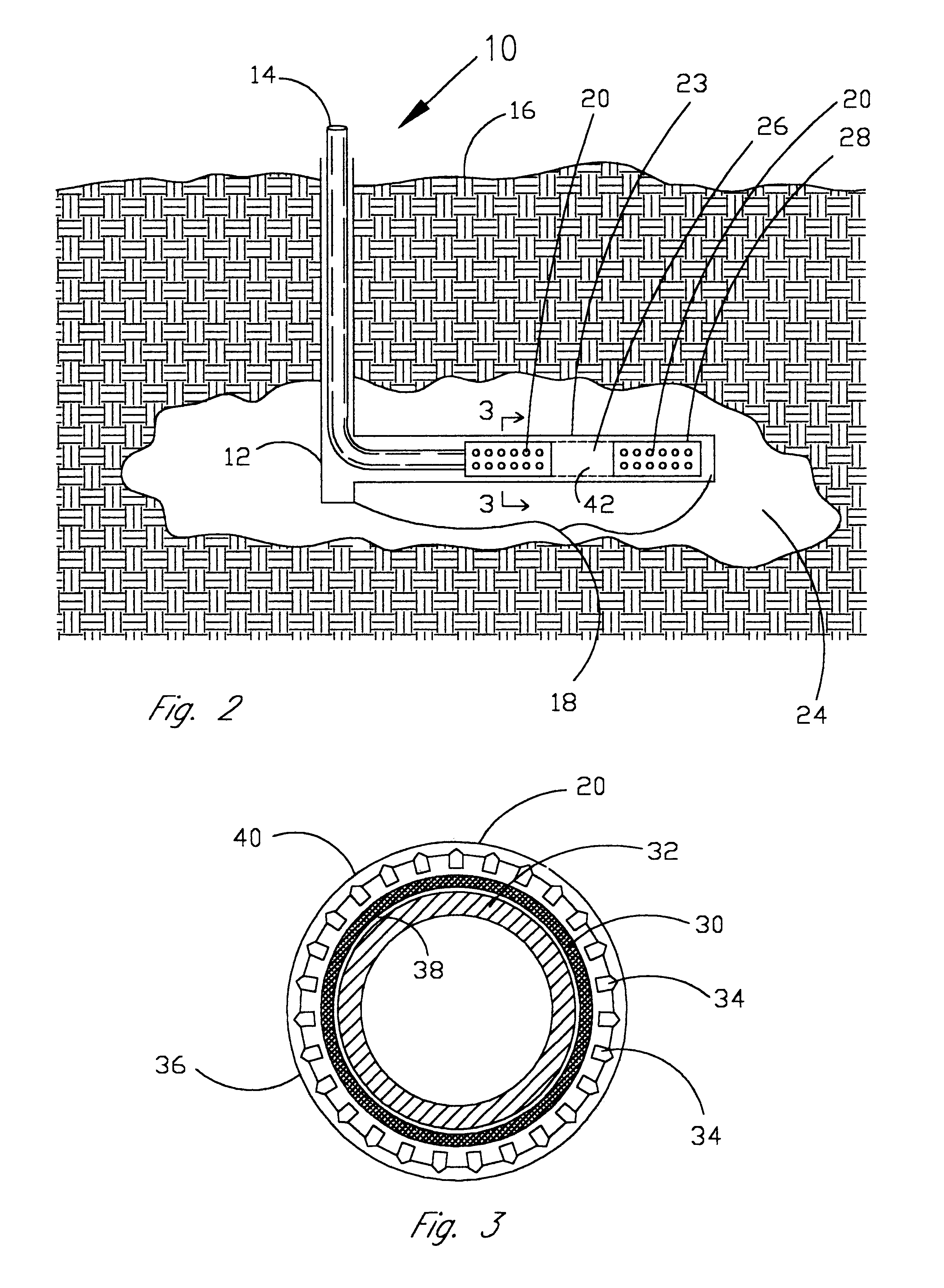
Product and process for coating wellbore screens
InactiveUS6394185B1Material efficiencyReduce interfacial tensionCleaning apparatusFluid removalEnzymeChemistry
Coatings for well screens that protect the screens from damage as they are inserted into the wellbore and once in the well, release reactive materials to react with and degrade potentially plugging materials such as drill solids, fluid filtercakes, fluid loss additives, and drilling fluids. The coatings can be specifically designed for individual well conditions and are comprised of a binder that either melts or dissolves within the wellbore and one or more reactive materials such as acids, enzymes, surfactants, chelants, oxidizers or free radical generators and the like which are released into the screen and the near wellbore area and which are effective in degrading or dissolving materials which could potentially plug the screen.
Owner:CONSTIEN VERNON GEORGE
Publishing layout wizard
InactiveUS6931591B1Expensive to maintainExpensive to updateCathode-ray tube indicatorsNatural language data processingGraphicsWeb browser
The present invention facilitates the specification and distribution of templated content materials by a content provider over an information exchange network such as the Internet. The present invention incorporates a system for managing inventories of graphical elements and their relationships to pre-defined page templates. A database capable of keeping track of users and their corresponding access privileges within the system is employed to monitor user activity. Ultimately, through the use of a software component delivered over the Internet for use within standard web browsers, end-users are able to populate templates under the constraints imposed by the rules of the manufacturers at the time of template design. These population elements which “fill in the blanks” of the pre-defined templates may be either of type IMAGE or TEXT. Image regions are populated by choosing from a subset of the entire image inventory, while TEXT types can be completely free form, with specific rules guiding justification, point size, font, and leading, or “fill in the blank” form with the same constraint rules as free form. Once the end user has met all of the criteria for a fully populated template, the system provides sophisticated means for downloading a high resolution file (such as a print-ready file or other file representation of the composed publication) which encapsulates all resources needed (layout, images, fonts, and constraint geometries) to fulfill the requirements of the publication. The downloaded file may be printed or published by electronic transfer, e.g., to a publisher for printing of the actual publication.
Owner:SAEPIO TECH
Light-Emitting Element, Display Device, Electronic Device, and Lighting Device
PendingUS20170025630A1Improve emission efficiencyReduce power consumptionIndium organic compoundsSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceTriplet state
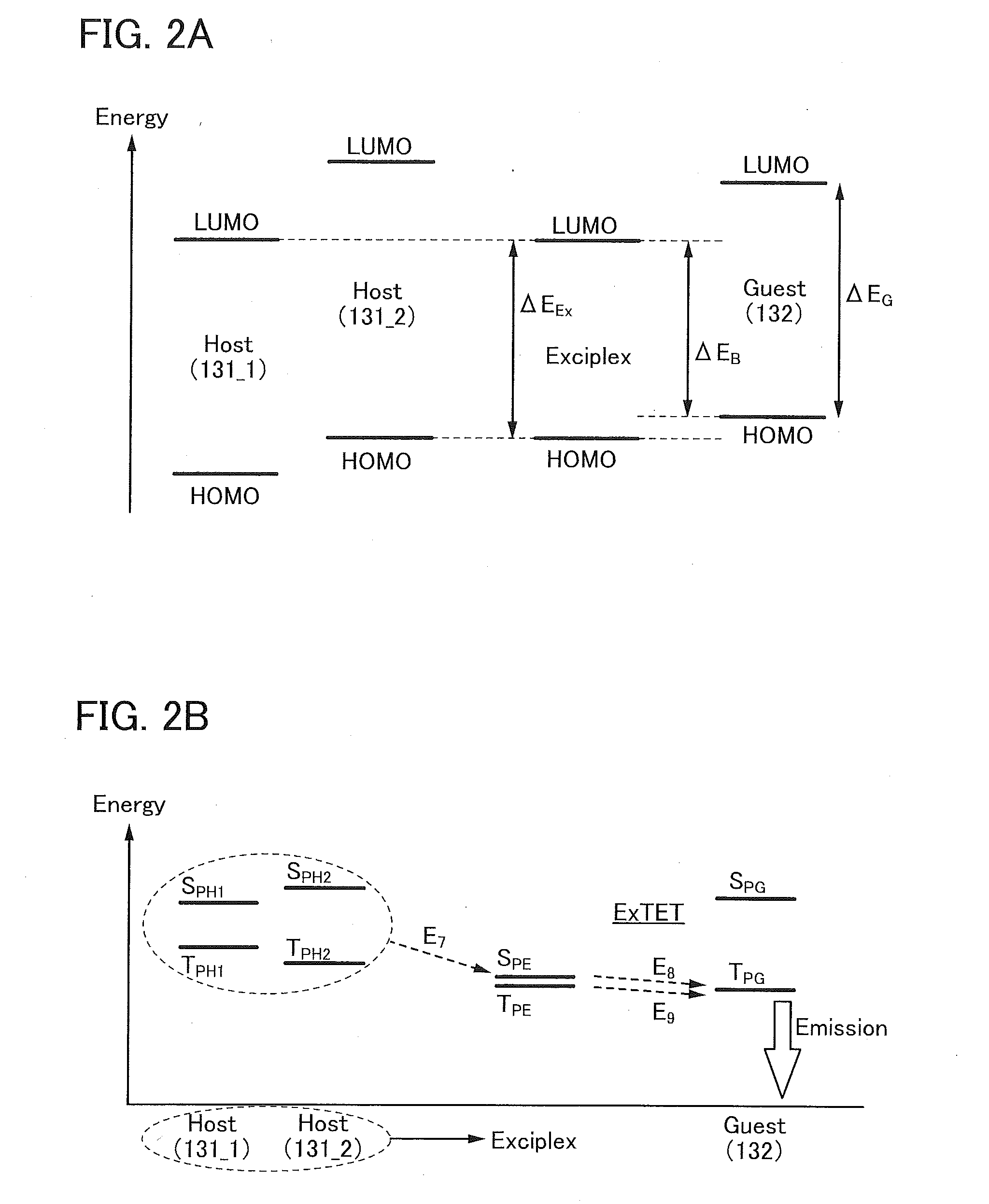
A light-emitting element with high emission efficiency. The light-emitting element includes a first organic compound, a second organic compound, and a guest material. The LUMO level of the first organic compound is lower than the LUMO level of the second organic compound. The HOMO level of the first organic compound is lower than the HOMO level of the second organic compound. The HOMO level of the guest material is higher than the HOMO level of the second organic compound. The energy difference between the LUMO level of the guest material and the HOMO level of the guest material is larger than the energy difference between the LUMO level of the first organic compound and the HOMO level of the second organic compound. The guest material has a function of converting triplet excitation energy into light emission. The first organic compound and the second organic compound form an exciplex.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Silicon composite particles, preparation thereof, and negative electrode material for non-aqueous electrolyte secondary cell
ActiveUS20050214644A1Improve cycle performanceMinimize changesSilicaNitrogen compoundsSilicon alloyInorganic compound
Silicon composite particles are prepared by sintering primary fine particles of silicon, silicon alloy or silicon oxide together with an organosilicon compound. Sintering of the organosilicon compound results in a silicon-base inorganic compound which serves as a binder. Each particle has the structure that silicon or silicon alloy fine particles are dispersed in the silicon-base inorganic compound binder, and voids are present within the particle.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Compositions and composites of cellulosic and lignocellulosic materials and resins, and methods of making the same
Owner:XYLECO INC
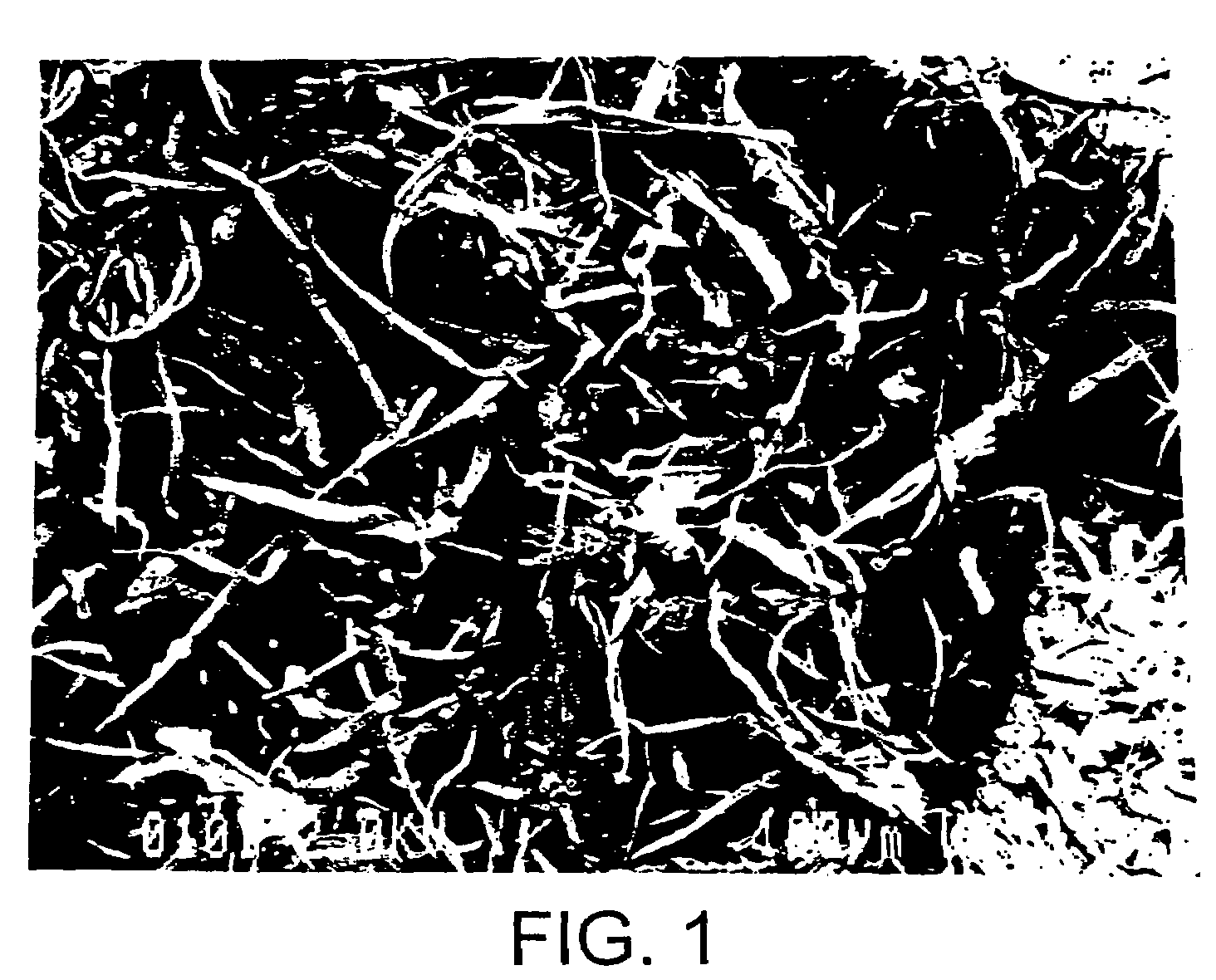
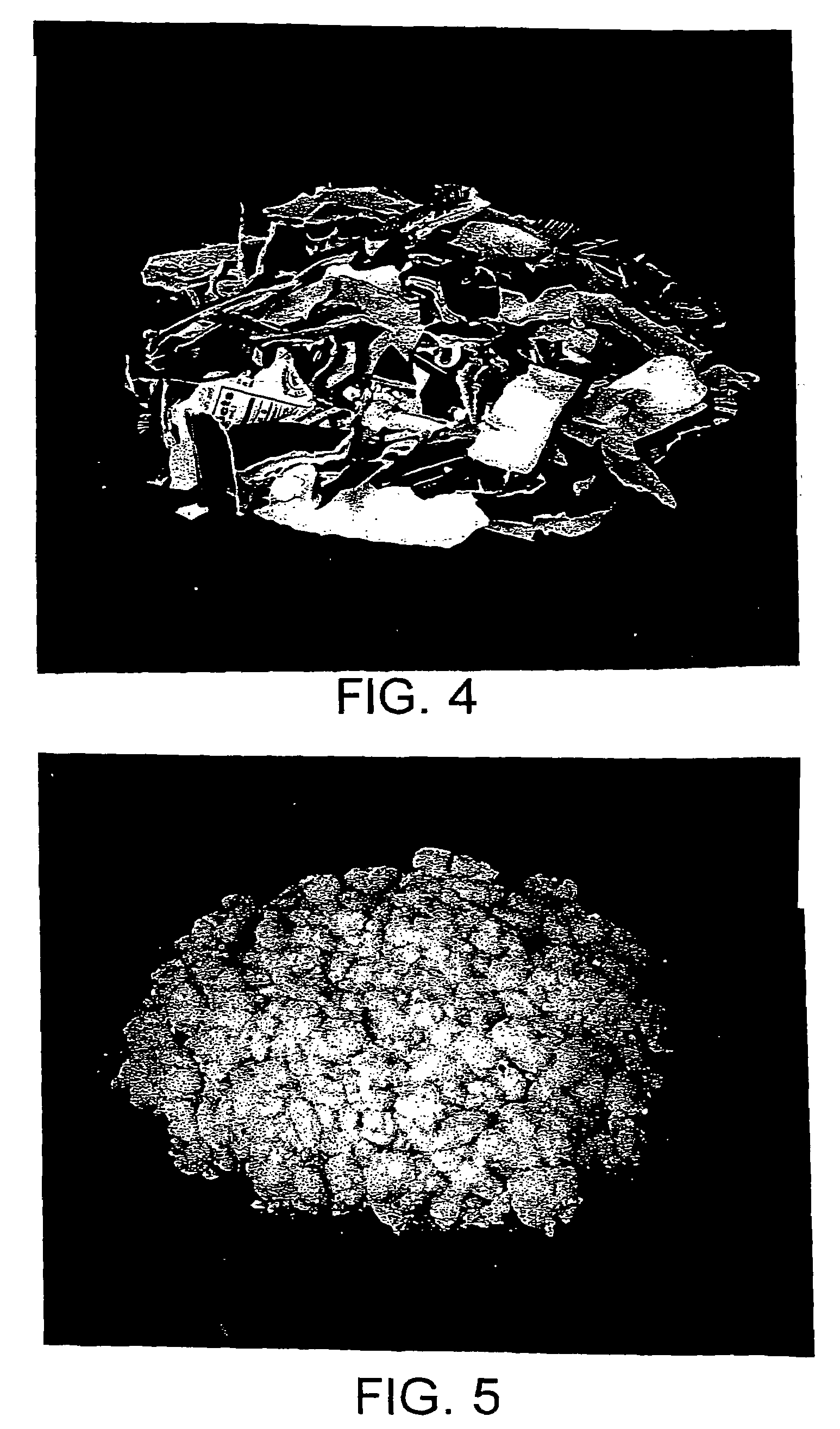
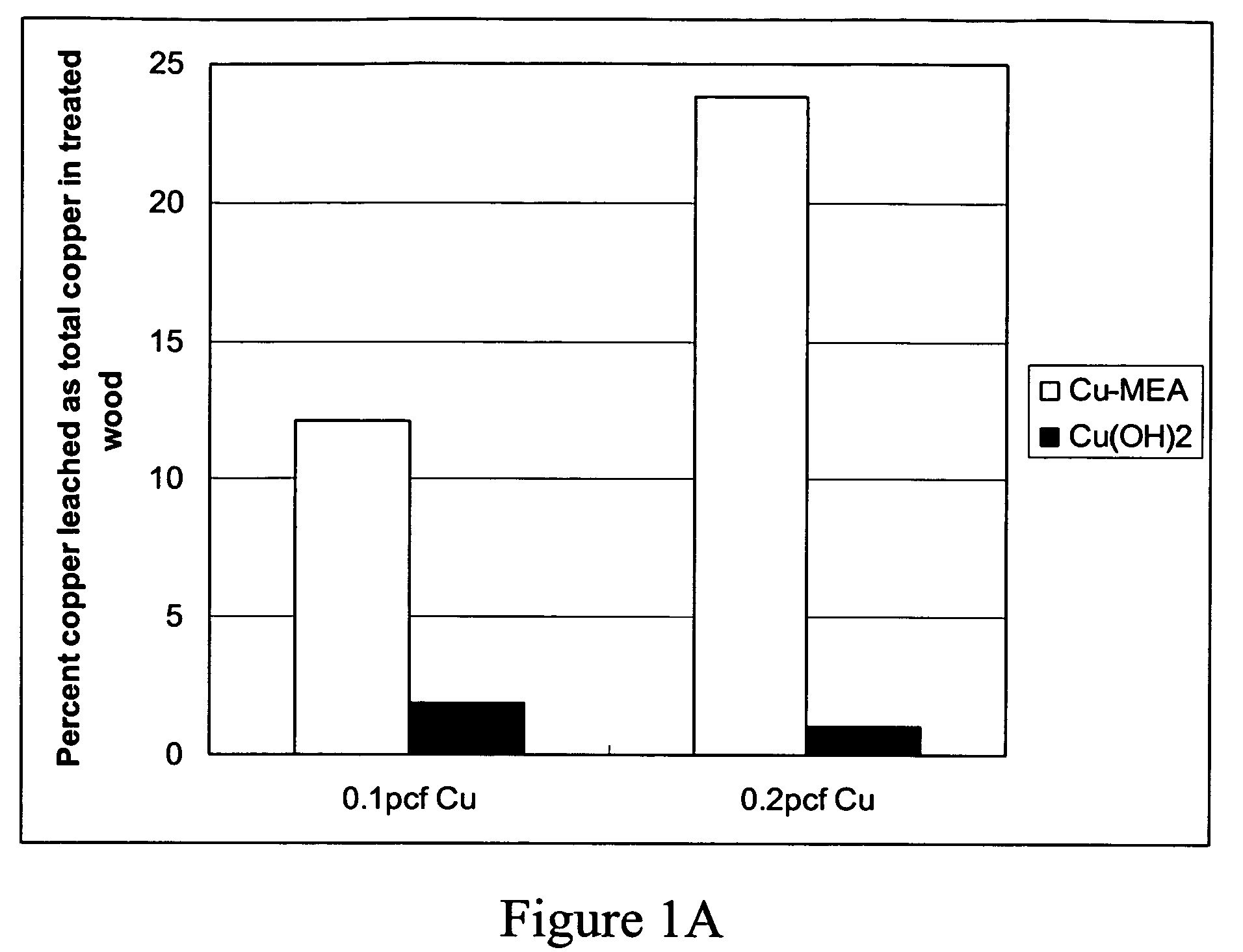
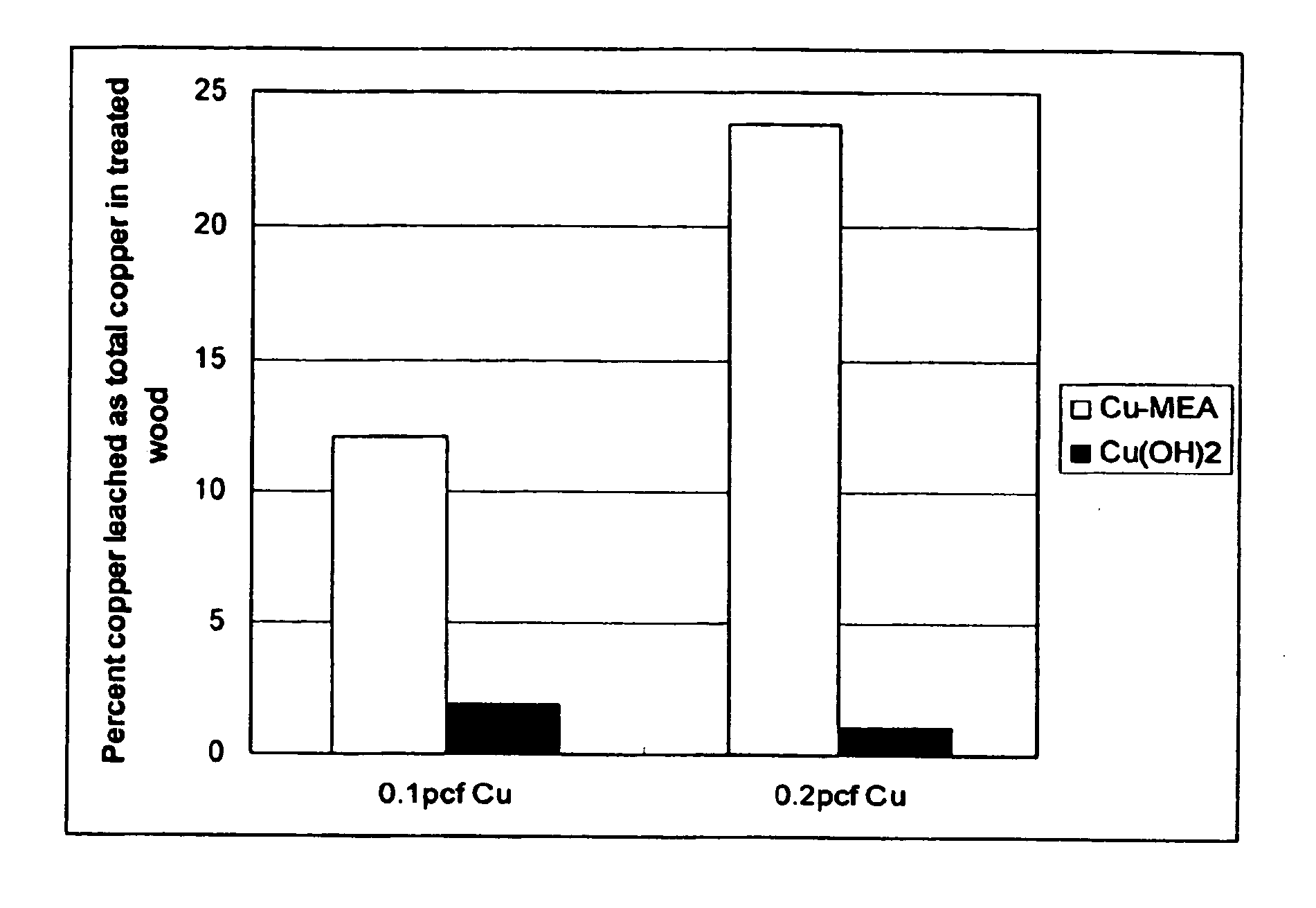
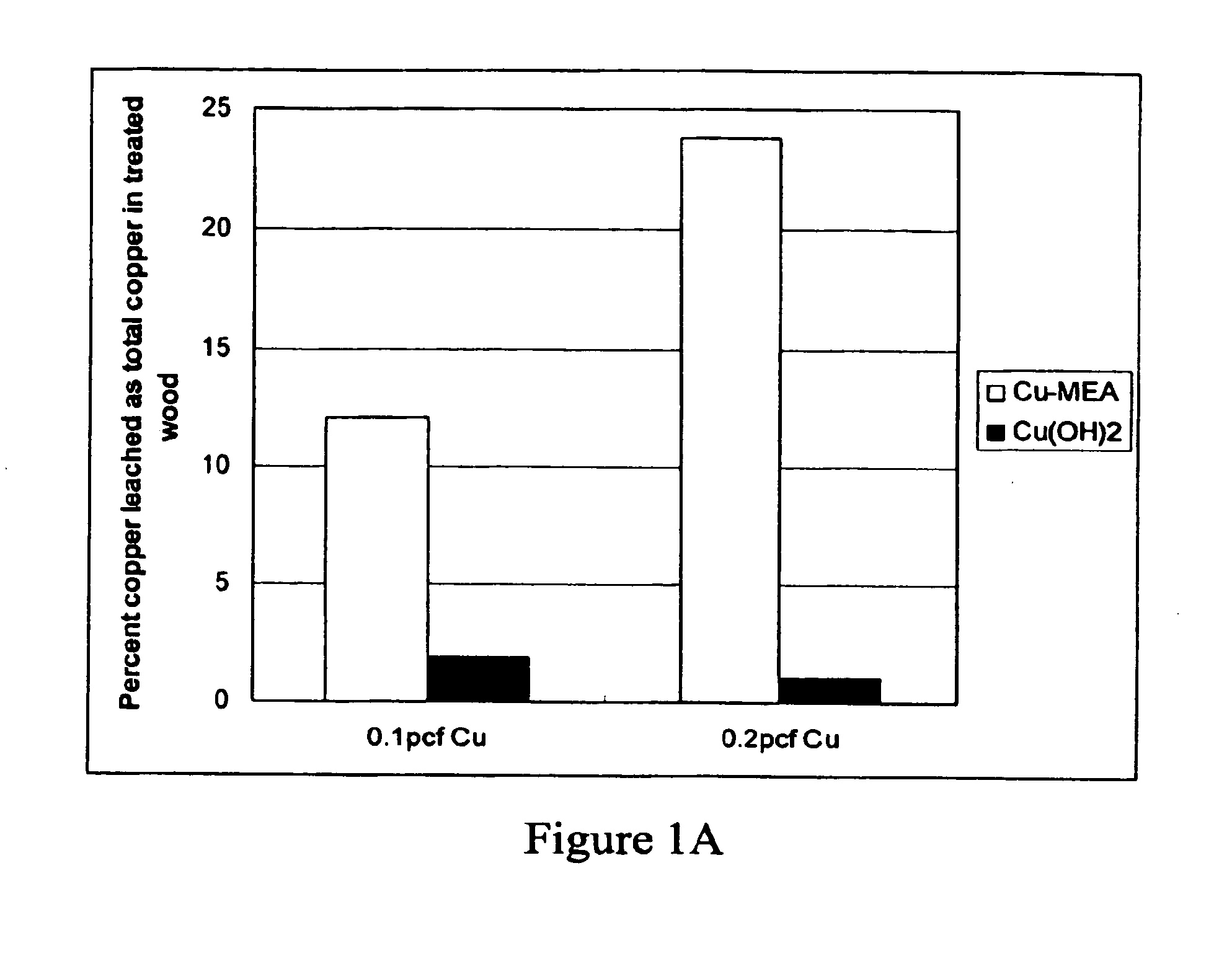
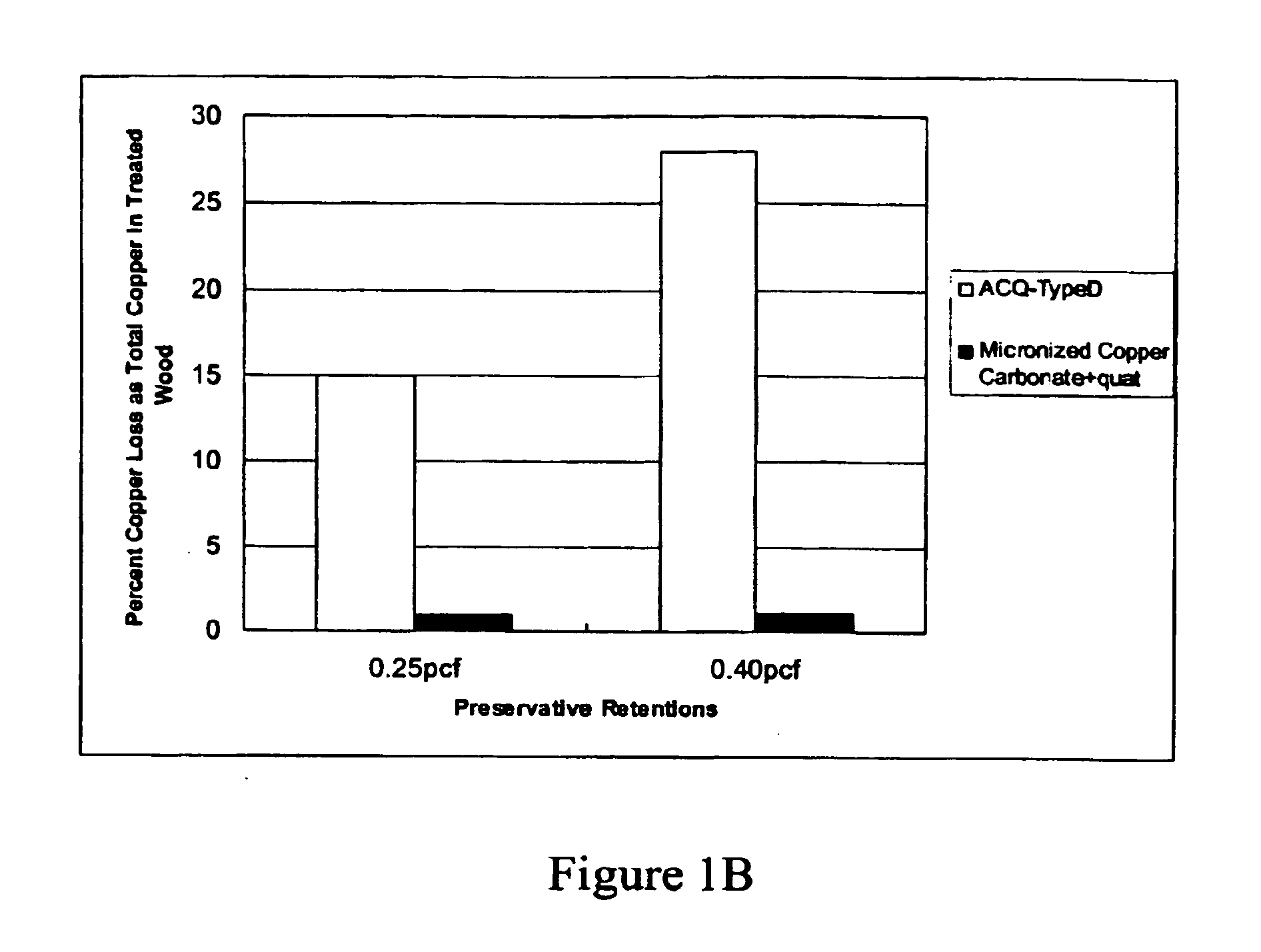
Micronized wood preservative formulations
ActiveUS20050118280A1Material efficiencyFibreboardHeavy metal active ingredientsPreservativeMaterials science
The present invention provides wood preservative compositions comprising micronized particles. In one embodiment, the composition comprises dispersions of micronized metal or metal compounds. In another embodiment, the wood preservative composition comprises an inorganic component comprising a metal or metal compound and organic biocide. When the composition comprises an inorganic component and an organic biocide, the inorganic component or the organic biocide or both are present as micronized particles. When compositions of the present invention are used for preservation of wood, the micronized particles can be observed as uniformly distributed within the wood and there is minimal leaching of the metal and biocide from the wood.
Owner:KOPPERS PERFORMANCE CHEM
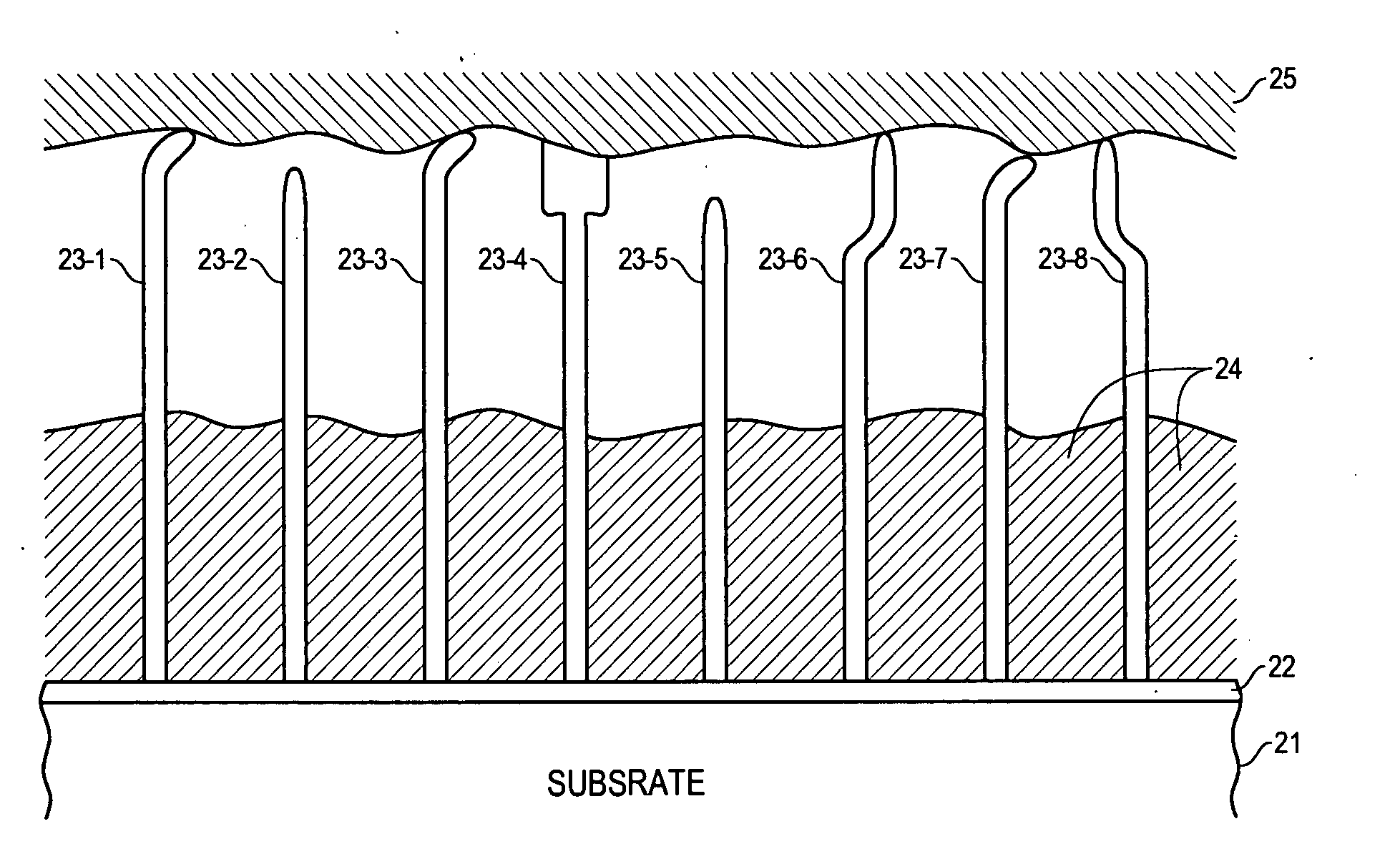
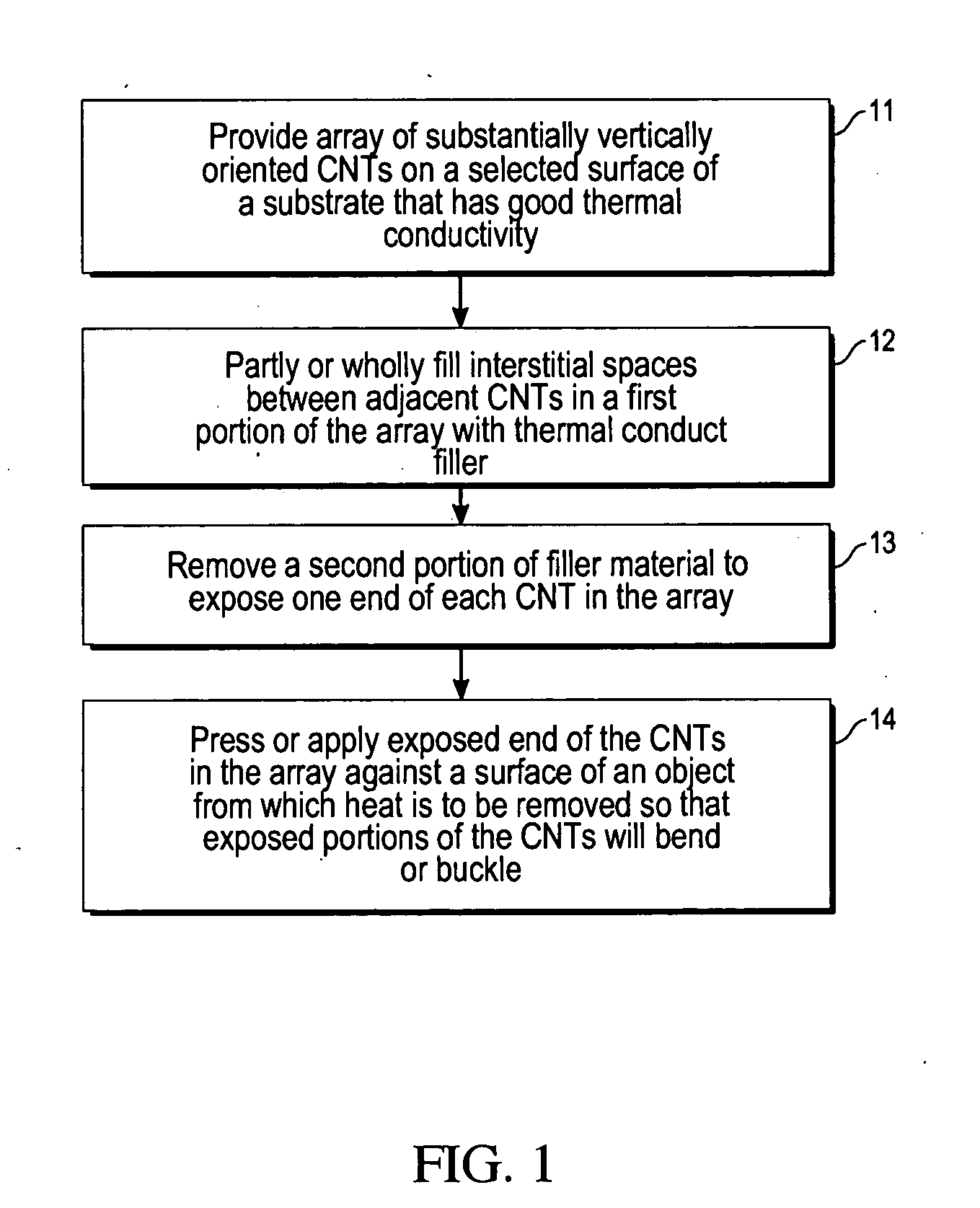
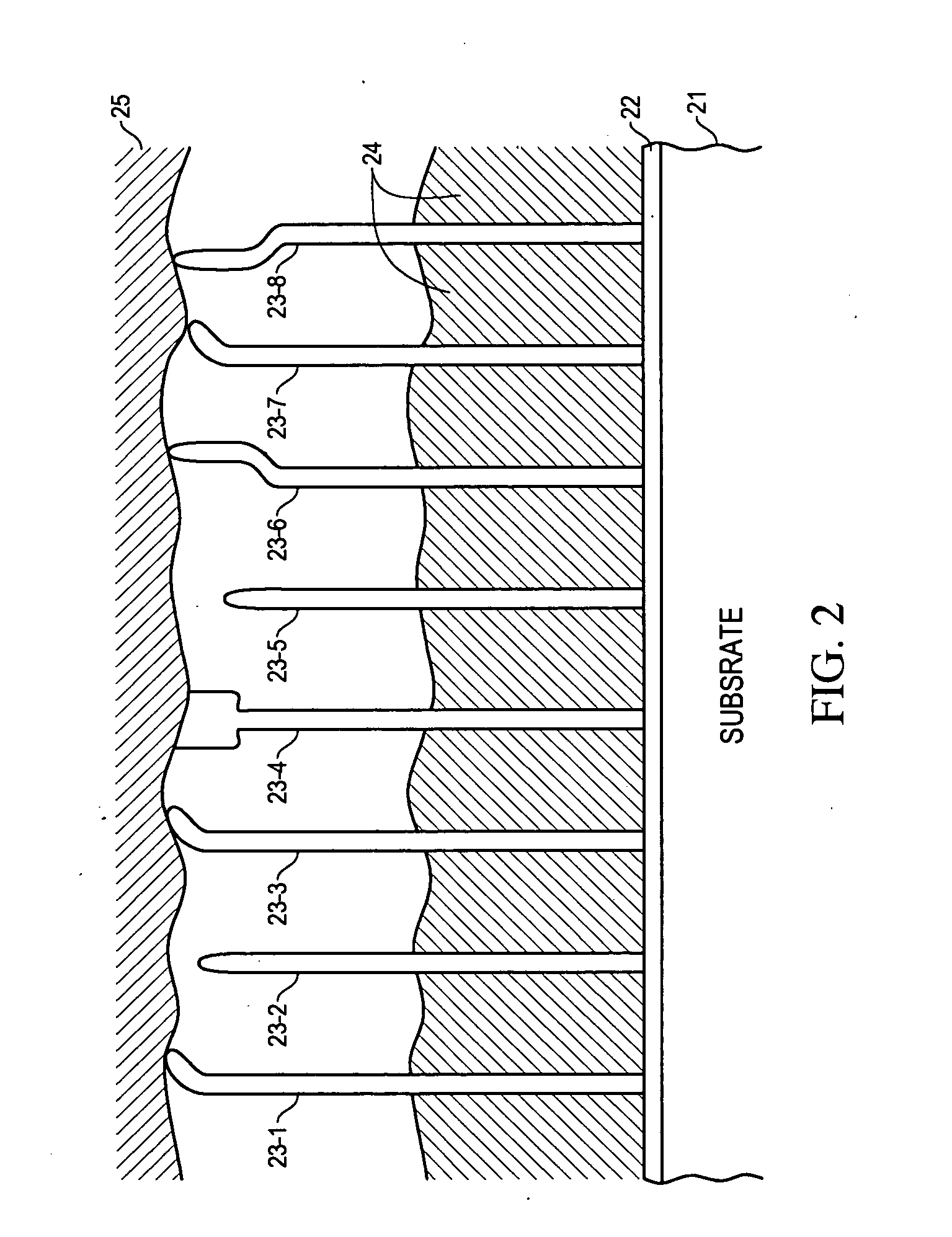
Nanoengineered thermal materials based on carbon nanotube array composites
InactiveUS20050224220A1High mechanical strengthImprove cooling effectMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHeat fluxFilling materials
A method for providing for thermal conduction using an array of carbon nanotubes (CNTs). An array of vertically oriented CNTs is grown on a substrate having high thermal conductivity, and interstitial regions between adjacent CNTs in the array are partly or wholly filled with a filler material having a high thermal conductivity so that at least one end of each CNT is exposed. The exposed end of each CNT is pressed against a surface of an object from which heat is to be removed. The CNT-filler composite adjacent to the substrate provides improved mechanical strength to anchor CNTs in place and also serves as a heat spreader to improve diffusion of heat flux from the smaller volume (CNTs) to a larger heat sink.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
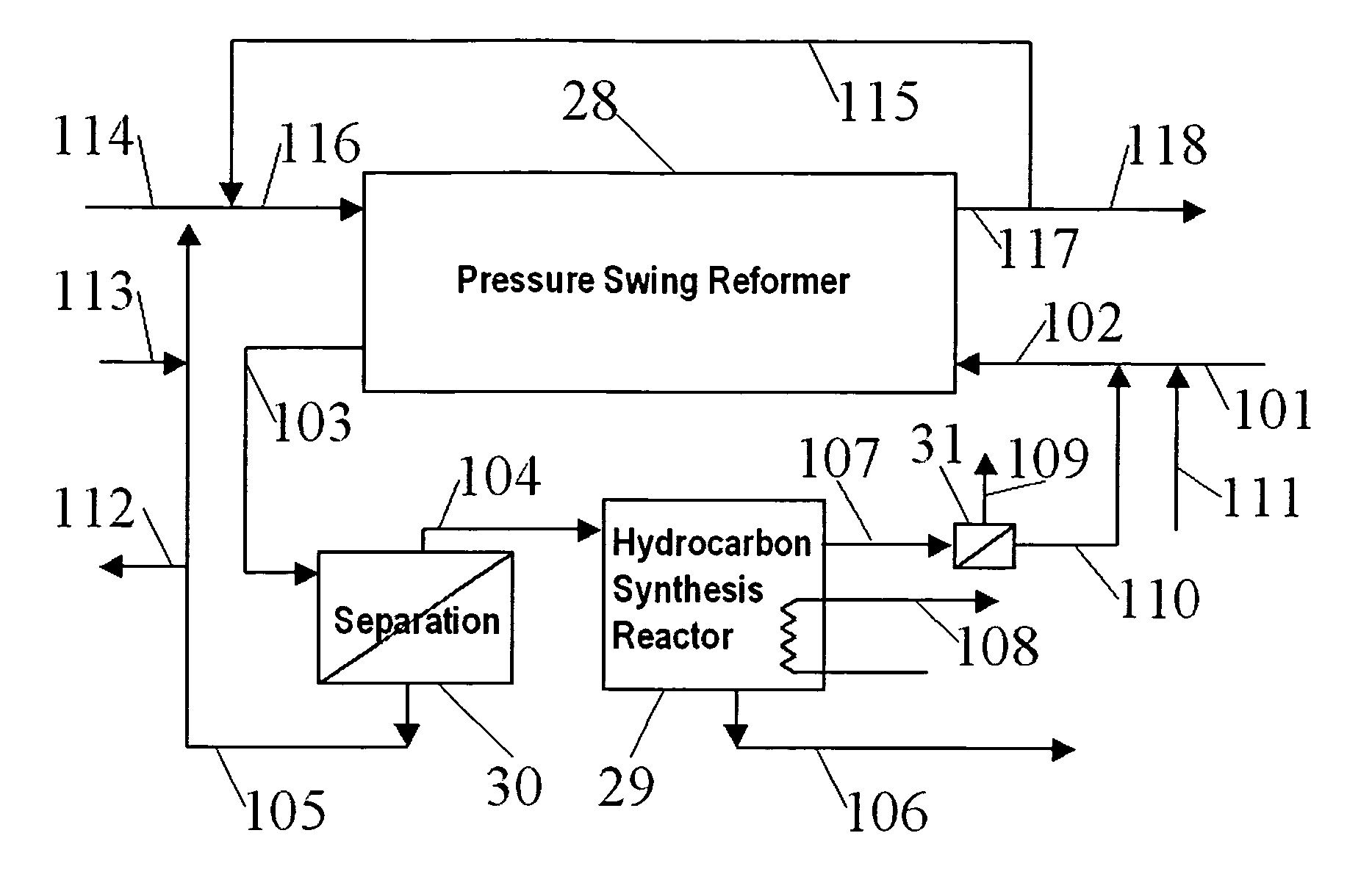
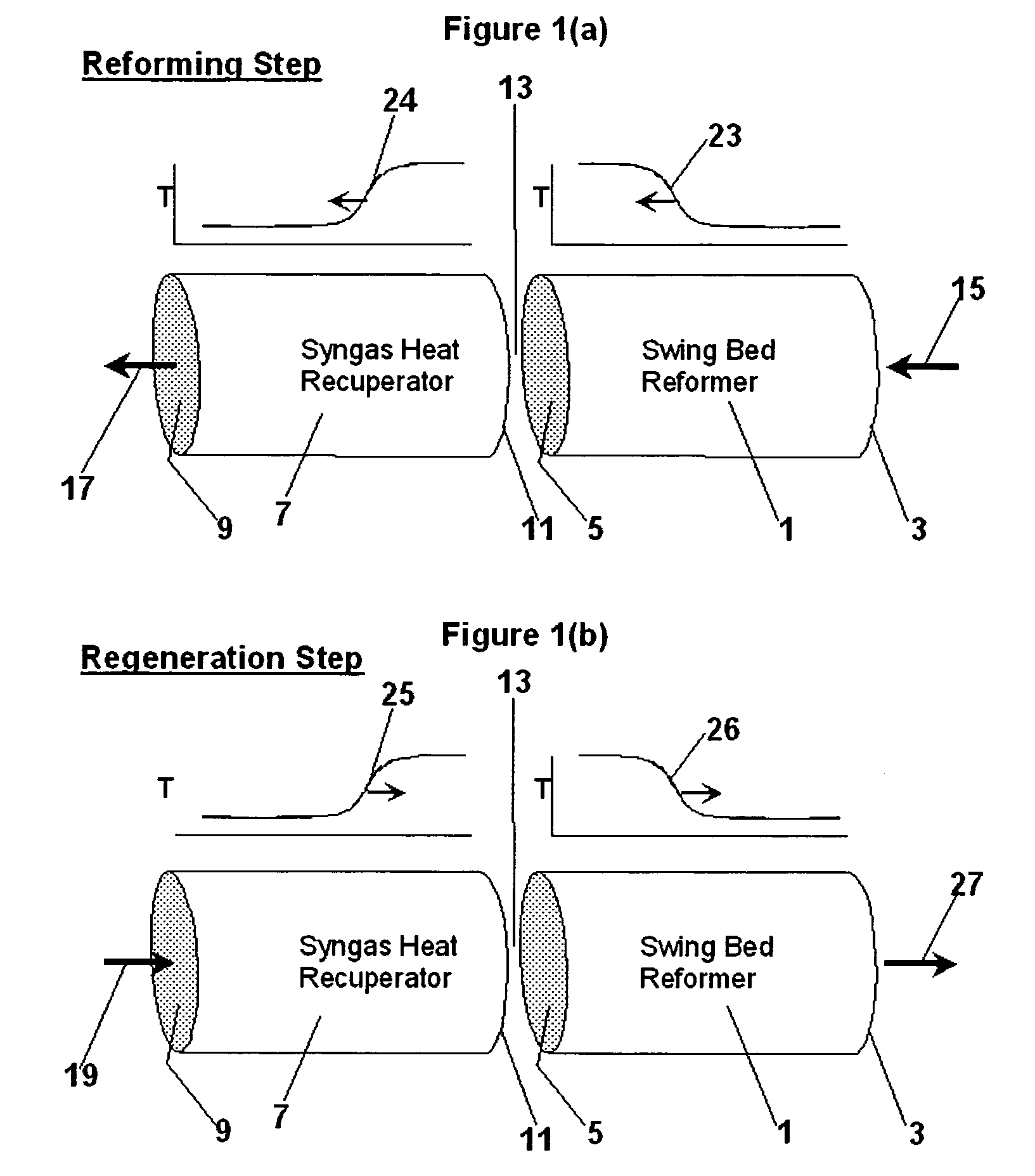
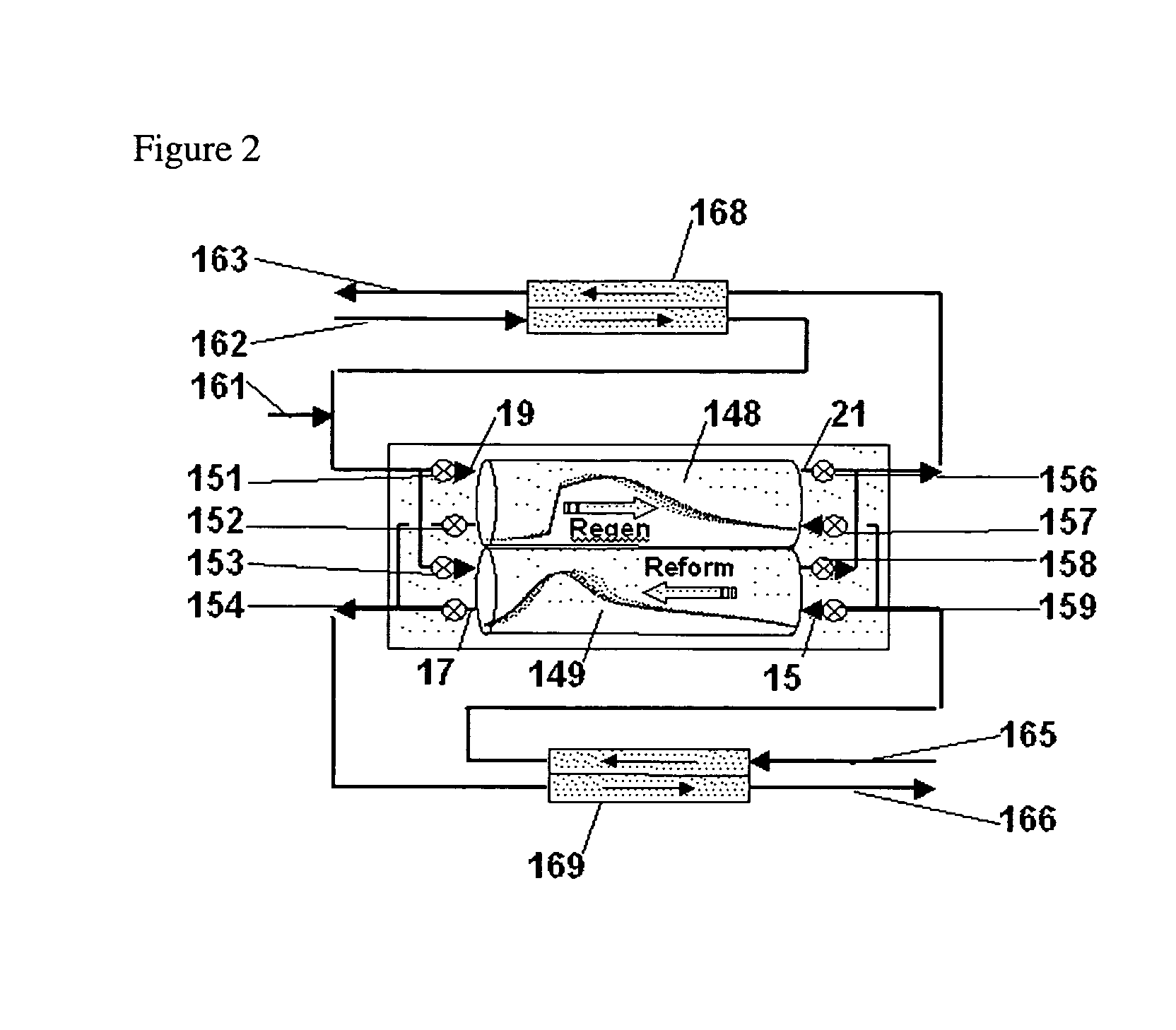
Hydrocarbon synthesis process using pressure swing reforming
ActiveUS7045553B2Material efficiencyAccelerates synthesis processOrganic compounds purification/separation/stabilisationHydrogenLiquid productSyngas
The invention provides a method for producing liquid hydrocarbons by first generating in a pressure swing reformer a synthesis gas stream having a mole ratio of H2:CO greater than 2:1. Then, a portion of the hydrogen is separated to produce a synthesis gas stream having a mole ratio of H2:CO of about 2:1 which steam is then introduced into a hydrocarbon synthesis reactor for conversion to liquid products.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Method for manufacturing composite piezoelectric substrate
ActiveUS20140173862A1Uniform thicknessMaterial efficiencyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyImpedence networksImpurityNanotechnology
In a method for manufacturing a composite piezoelectric substrate, a piezoelectric substrate and a supporting substrate are prepared, ions are implanted from a surface of the piezoelectric substrate to form a defective layer at a predetermined depth, impurities adhered to the surface of the piezoelectric substrate in which the defective layer is formed and / or a surface of the supporting substrate are removed to directly expose the constituent atoms of the surfaces and activate the surfaces, the supporting substrate is bonded to the piezoelectric substrate to form a bonded substrate body, the bonded substrate body is separated at the defective layer so that a separation layer between the surface of the piezoelectric substrate and the defective layer is separated from the piezoelectric substrate and bonded to the supporting substrate to form a composite piezoelectric substrate, and the surface of the separation layer of the composite piezoelectric substrate is smoothed.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
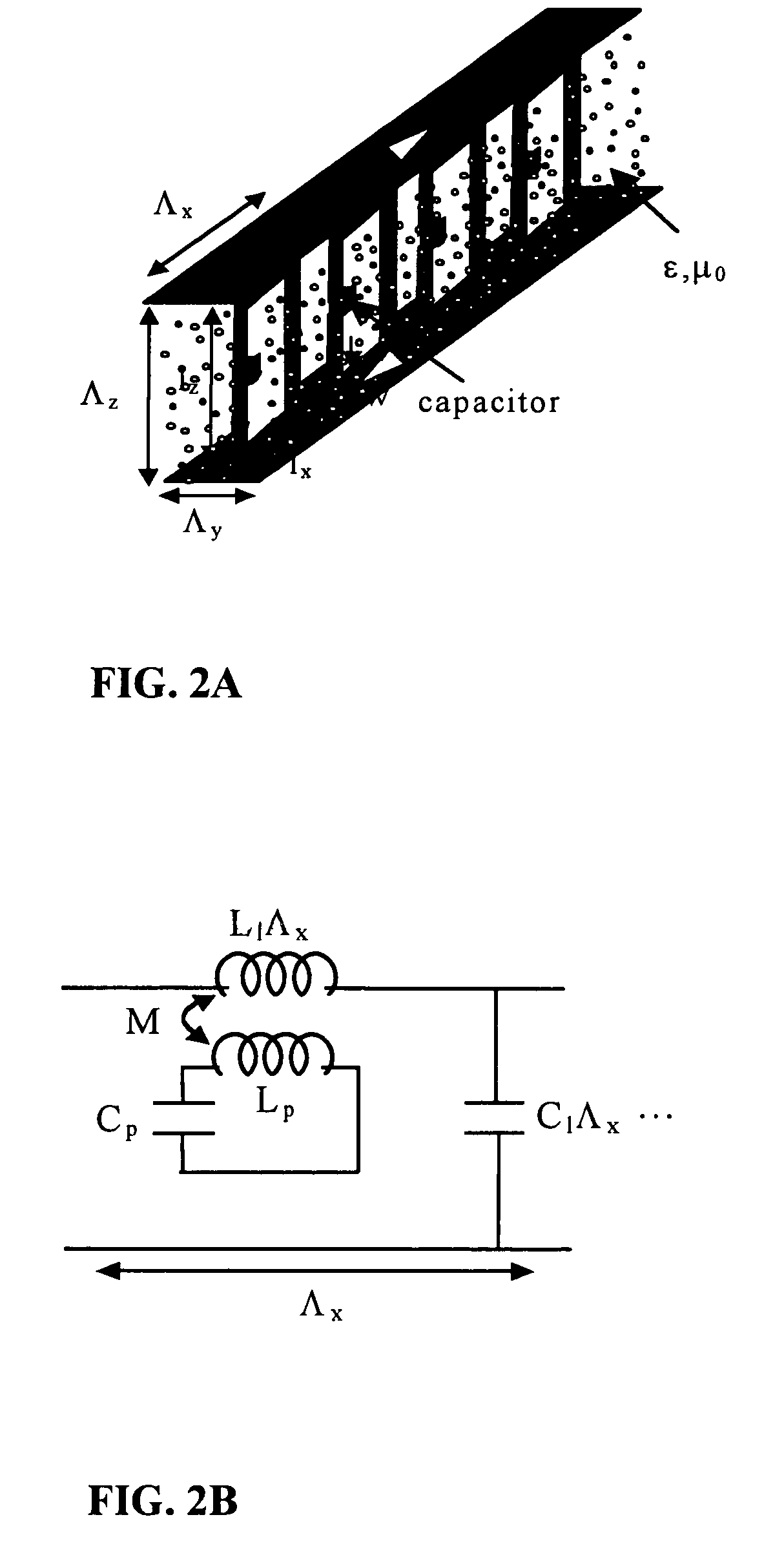
Electro-ferromagnetic, tunable electromagnetic band-gap, and bi-anisotropic composite media using wire configurations
InactiveUS20050146402A1High bandwidthSmall sizeRadiating elements structural formsResonatorsDielectricElectricity
An artificial electro-ferromagnetic meta-material demonstrates the design of tunable band-gap and tunable bi-anisotropic materials. The medium is obtained using a composite mixture of dielectric, ferro-electric, and metallic materials arranged in a periodic fashion. By changing the intensity of an applied DC field the permeability of the artificial electro-ferromagnetic can be properly varied over a particular range of frequency. The structure shows excellent Electromagnetic Band-Gap (EBG) behavior with a band-gap frequency that can be tuned by changing the applied DC field intensity. The building block of the electro-ferromagnetic material is composed of miniaturized high Q resonant circuits embedded in a low-loss dielectric background. The resonant circuits are constructed from metallic loops terminated with a printed capacitor loaded with a ferro-electric material. Modifying the topology of the embedded-circuit, a bi-anisotropic material (tunable) is examined. The embedded-circuit meta-material is treated theoretically using a transmission line analogy of a medium supporting TEM waves.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Compositions and composites of cellulosic and lignocellulosic materials and resins, and methods of making the same
InactiveUS20050200050A1Material efficiencyBiocidePulp properties modificationCellulosePolymer science
Owner:XYLECO INC
Plate material packing box, plate material transporting method, and plate material loading or unloading method
InactiveUS20070131574A1Avoid enteringEasy to storeOther accessoriesContainer/bottle contructionEngineeringHolding room
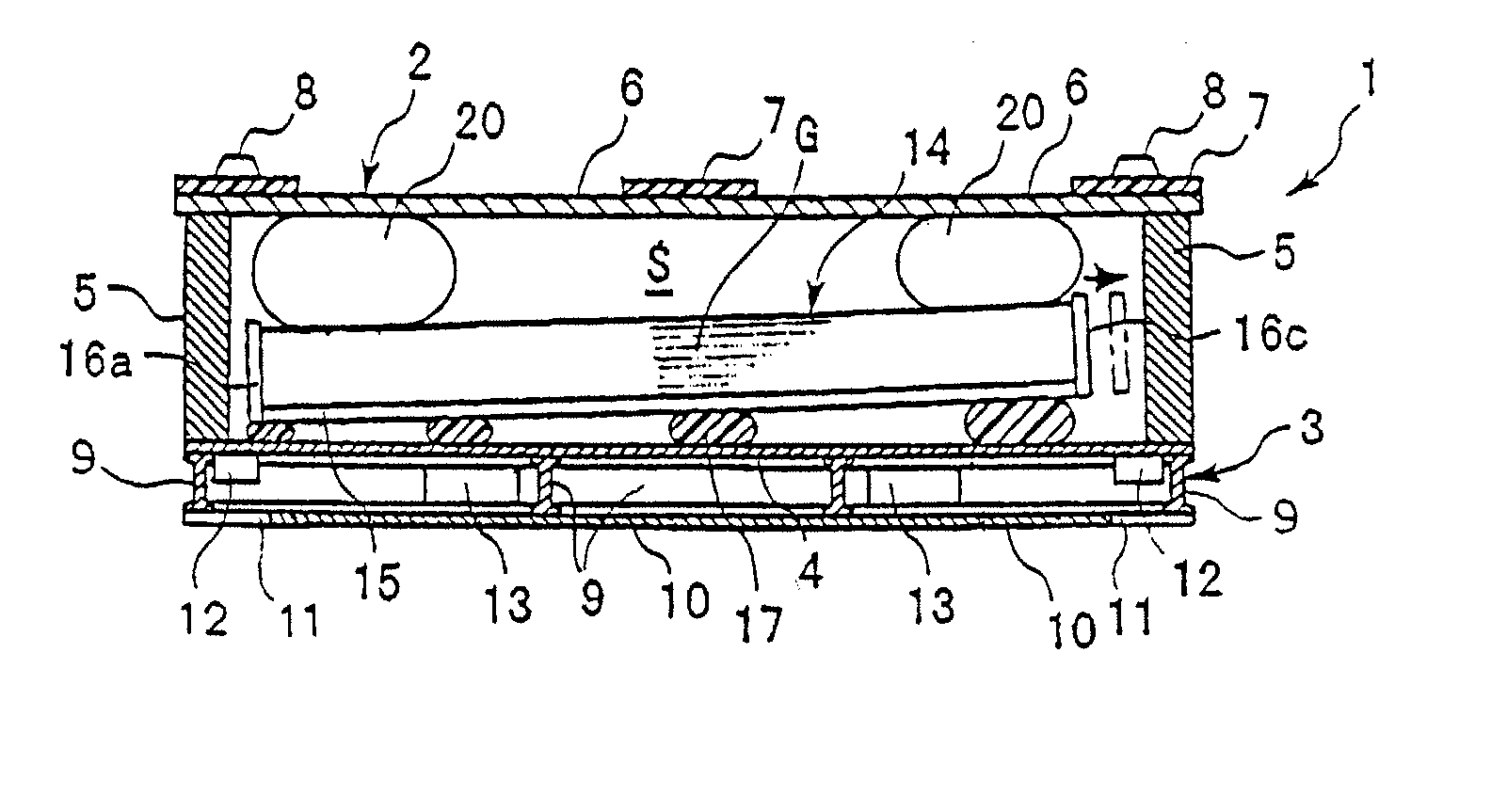
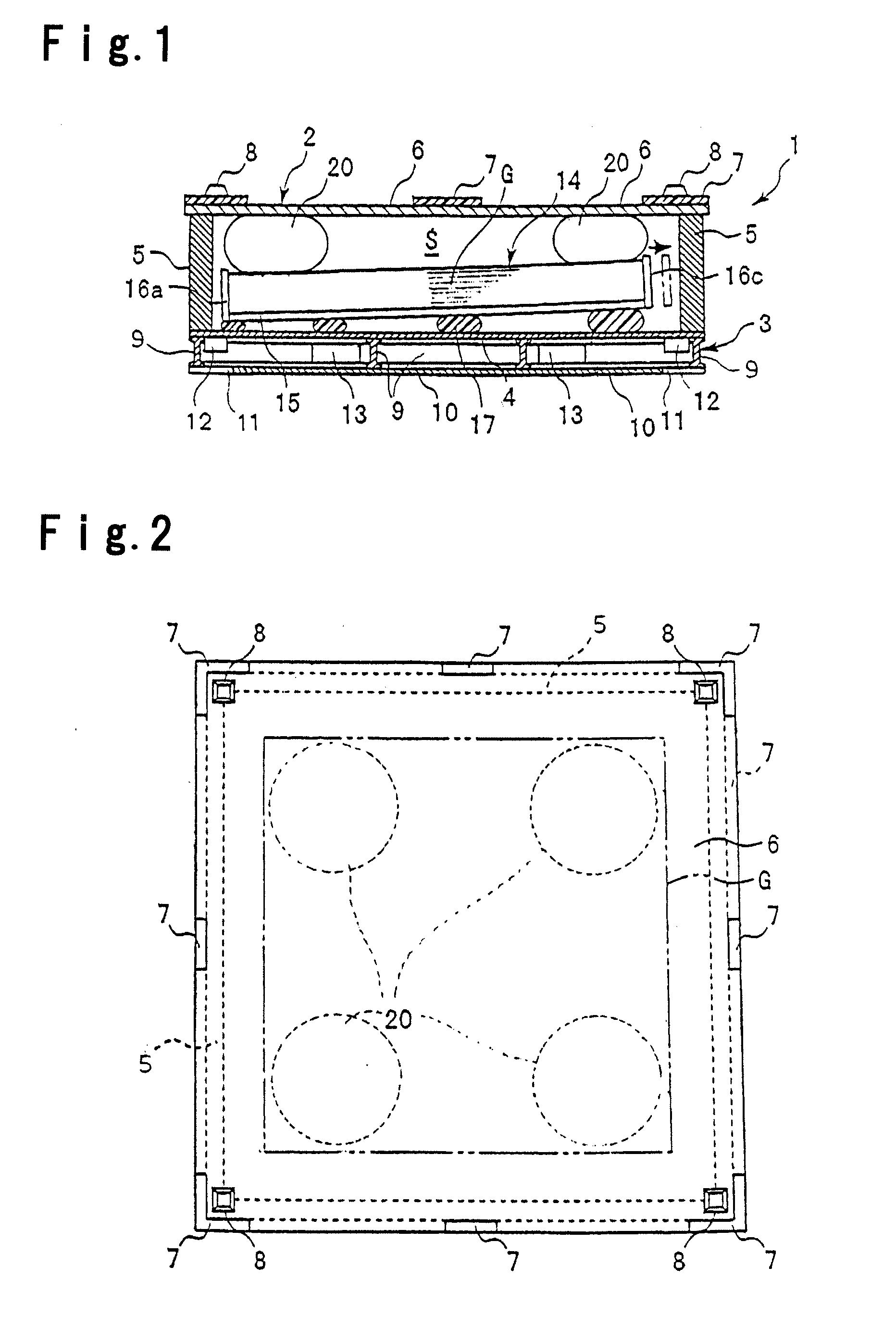
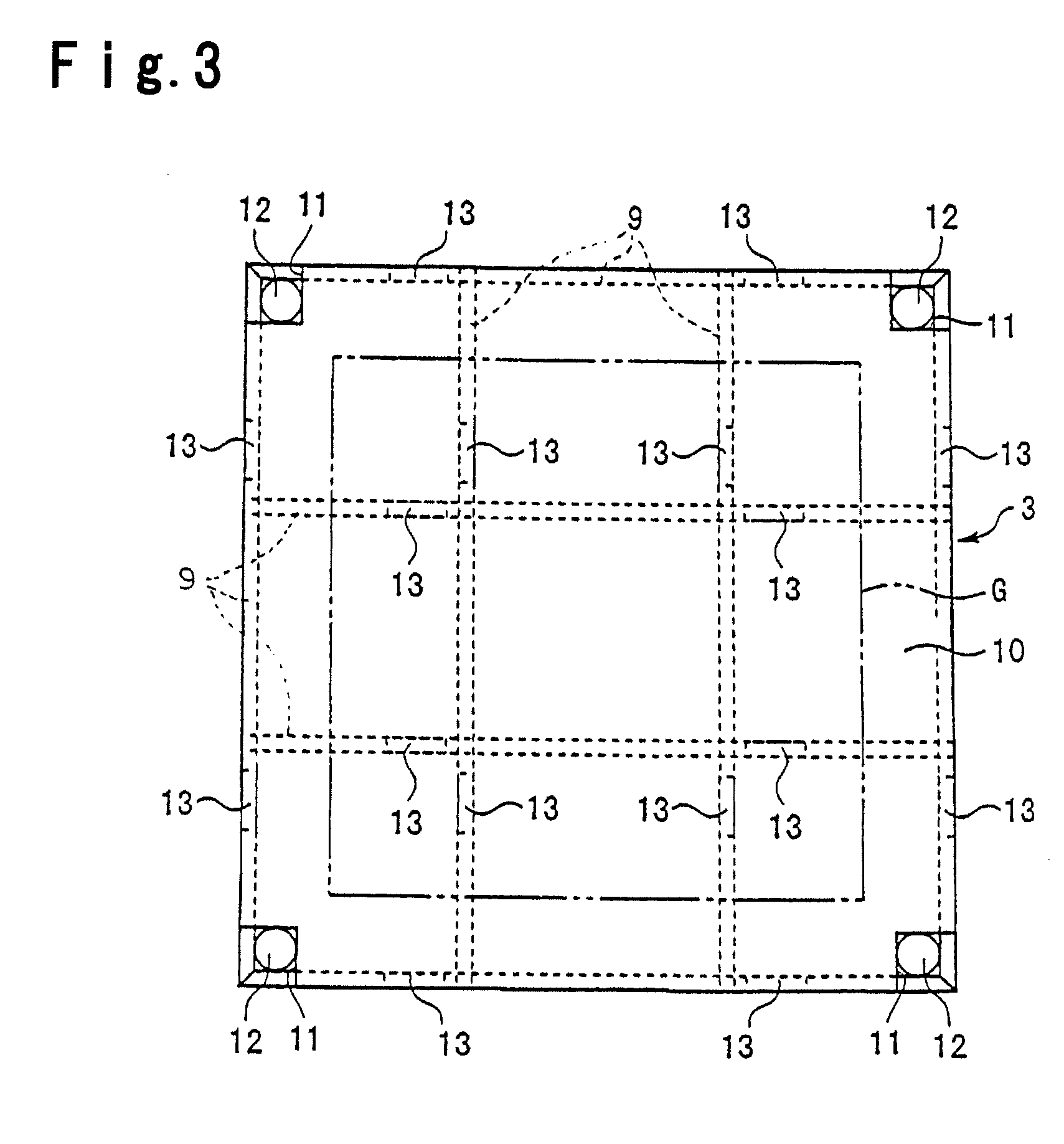
A plate material packing box capable of preventing dirt from entering thereinto, easily storable in a storage room with a low ceiling by reducing the height dimension during transportation, and capable of transporting plate materials efficiently and constantly; a plate material transporting method using such a plate material packing box; and a plate material loading or unloading method. The packing box comprises a pedestal 3 having an upper lining, a plate material storage box 14 put on the pedestal 3, and an upper cover 2 enclosing the plate material storage box 14 on the pedestal 3 and being detachable from the pedestal 3, wherein the plate material storage box 14 is an upwardly open support having a bottom plate 15 to have a plurality of plate materials G put thereon in a substantially horizontally stacked state, and side plate 16a to 16d along four sides of its periphery, the upper cover 2 is a downwardly open box having a top plate 6 covering the upper surface of the plate material storage box 14 and side frames 5 along four sides of its periphery; a vibration damper 17 is interposed between the pedestal 3 and the bottom plate 5; and a cushion material 20 is installed between the top plate 6 and the plate materials G put on the bottom plate 15.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Preparation of CIGS-based solar cells using a buffered electrodeposition bath
InactiveUS7297868B2Easy to handleLightweight productionElectrolytic coatingsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumSolar cell
A photovoltaic cell exhibiting an overall conversion efficiency of at least 9.0% is prepared from a copper-indium-gallium-diselenide thin film. The thin film is prepared by simultaneously electroplating copper, indium, gallium, and selenium onto a substrate using a buffered electro-deposition bath. The electrodeposition is followed by adding indium to adjust the final stoichiometry of the thin film.
Owner:DAVIS JOSEPH & NEGLEY
Apparatus and method for an ultrasonic medical device with variable frequency drive
InactiveUS20060116610A1Destroying effectTiming is simpleSurgeryChiropractic devicesCouplingTransducer
An apparatus and method for an ultrasonic medical device with a variable frequency drive for ablating a biological material comprises an ultrasonic probe having a proximal end, a distal end and a longitudinal axis therebetween; a transducer that drives the ultrasonic probe over a variable frequency range, creating a transverse ultrasonic vibration along at least a portion of the longitudinal axis of the ultrasonic probe; a coupling engaging the proximal end of the ultrasonic probe to a distal end of the transducer; and an ultrasonic energy source engaged to the transducer that produces an ultrasonic energy, wherein driving the ultrasonic probe over the variable frequency range allows for the ultrasonic energy to propagate around a bend of the ultrasonic probe to ablate the biological material in communication with the ultrasonic probe.
Owner:CYBERSONICS
Compact Device for Dual Transmutation for Isotope Production Permitting Production of Positron Emitters, Beta Emitters and Alpha Emitters Using Energetic Electrons
InactiveUS20080240330A1Promote coolingEasily removeConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsHigh energyRadiochemistry
A method and apparatus for directing high energy electrons to a converter material that emits gamma rays, which, in turn interact directly with parent isotopes to produce unstable, short-lived medical isotopes and product isotopes by the gamma, n reaction, or which interact with high-z materials to produce neutrons that then produce valuable isotopes by neutron capture in parent isotopes.
Owner:HOLDEN CHARLES S
Simplified warm-keeping body and warm-keeping cloth
ActiveUS20060135016A1Conveniently carriedEasy to storeLayered productsWoven fabricsElectrical and Electronics engineeringTextile
Owner:ASAHI KASEI FIBERS CORPORATION
Flourescent organic nanofibrils as sensory materials for explosives detection
ActiveUS20090233374A1Efficiently sensedEfficiently quenchedAnalysis using chemical indicatorsWeather/light/corrosion resistanceFiberFluorescence
The present invention relates to a class of fluorescent, organic nanofibrils, and particularly the films comprising entangled piling of these nanofibrils exhibiting effective quenching of their fluorescence upon exposure the vapor of explosives. The invention also relates to a sensor and a method for sensing the explosives vapor and other volatile organic compounds, including the explosives taggants through the modulation of the fluorescence of the nanofibril film and the electrical conductivity of the nanofibrils. The invention also relates to a development of synthetic methods, protocols and techniques that leads to production of various arylene-ethynylene macrocycle (AEM) molecules, which consist of a shape-persistent, toroidal scaffold in planar conformation, with minimal ring strain and highly tunable ring sizes (from 0.5 nm to above 10 nm). The invention also relates to an approach to optimization of the one-dimensional molecular arrangement along the long axis of the nanofibril, which provides increased exciton (excited state) migration (via cofacial intermolecular electronic coupling) and charge transport (via pi-electronic delocalization). A combination of long-range exciton migration and efficient charge transport makes the nanofibrils ideal as sensory materials for detecting explosives and other volatile organic compounds through both optical and electrical sensing mechanisms.
Owner:SOUTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY
Computer-implemented system capable of creating an advertisement
InactiveUS20050235201A1Expensive to maintainExpensive to updateNatural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsRule sets
A tool for the creation of graphically based customizable collateral materials needing localization from an online master inventory of supplied elements is disclosed. The tool includes an online channel to assist a content provider in making available all advertising graphics, materials and layouts that meet the content provider's specification and / or rule-set.
Owner:SAEPIO TECH
Manufacturing apparatus
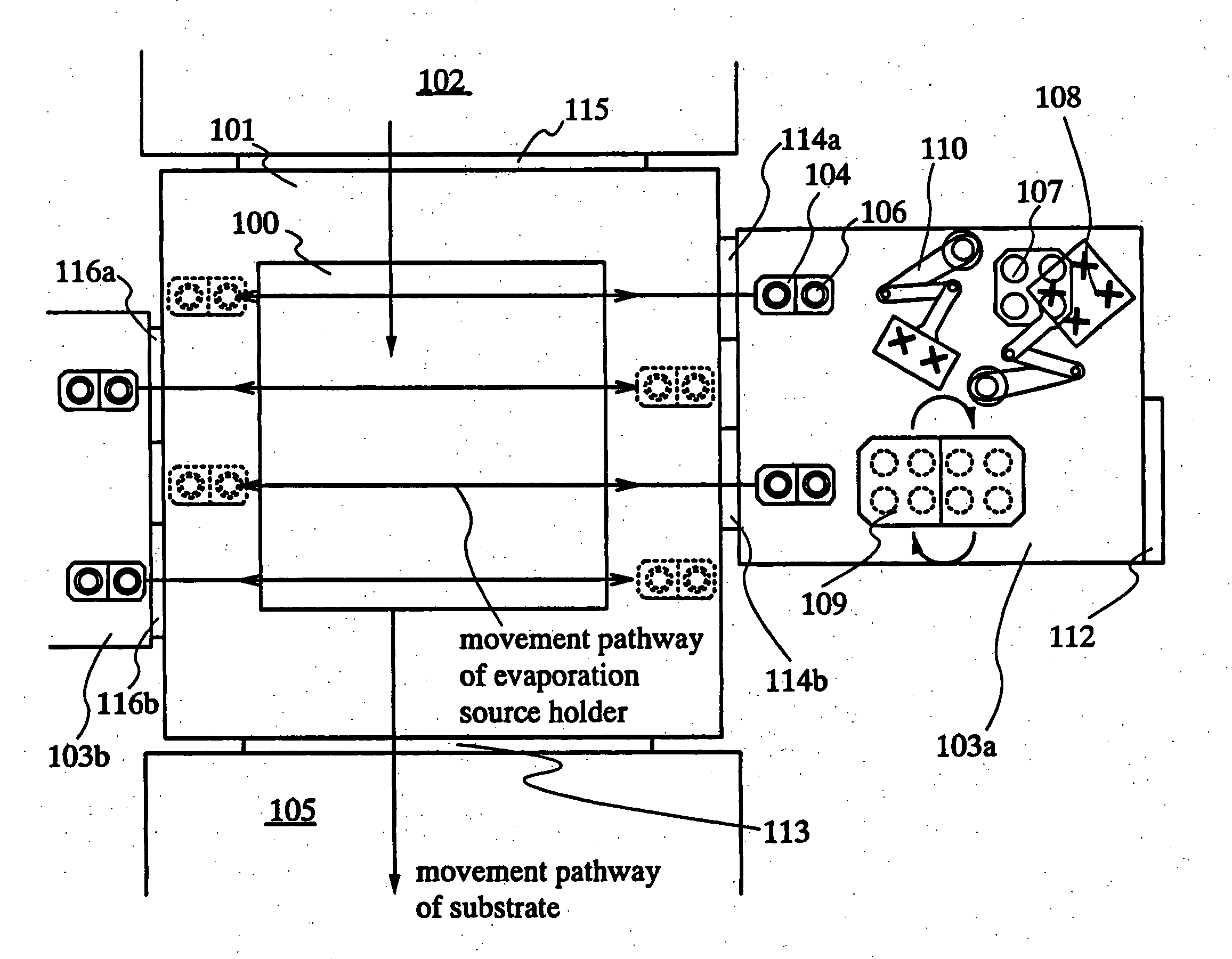
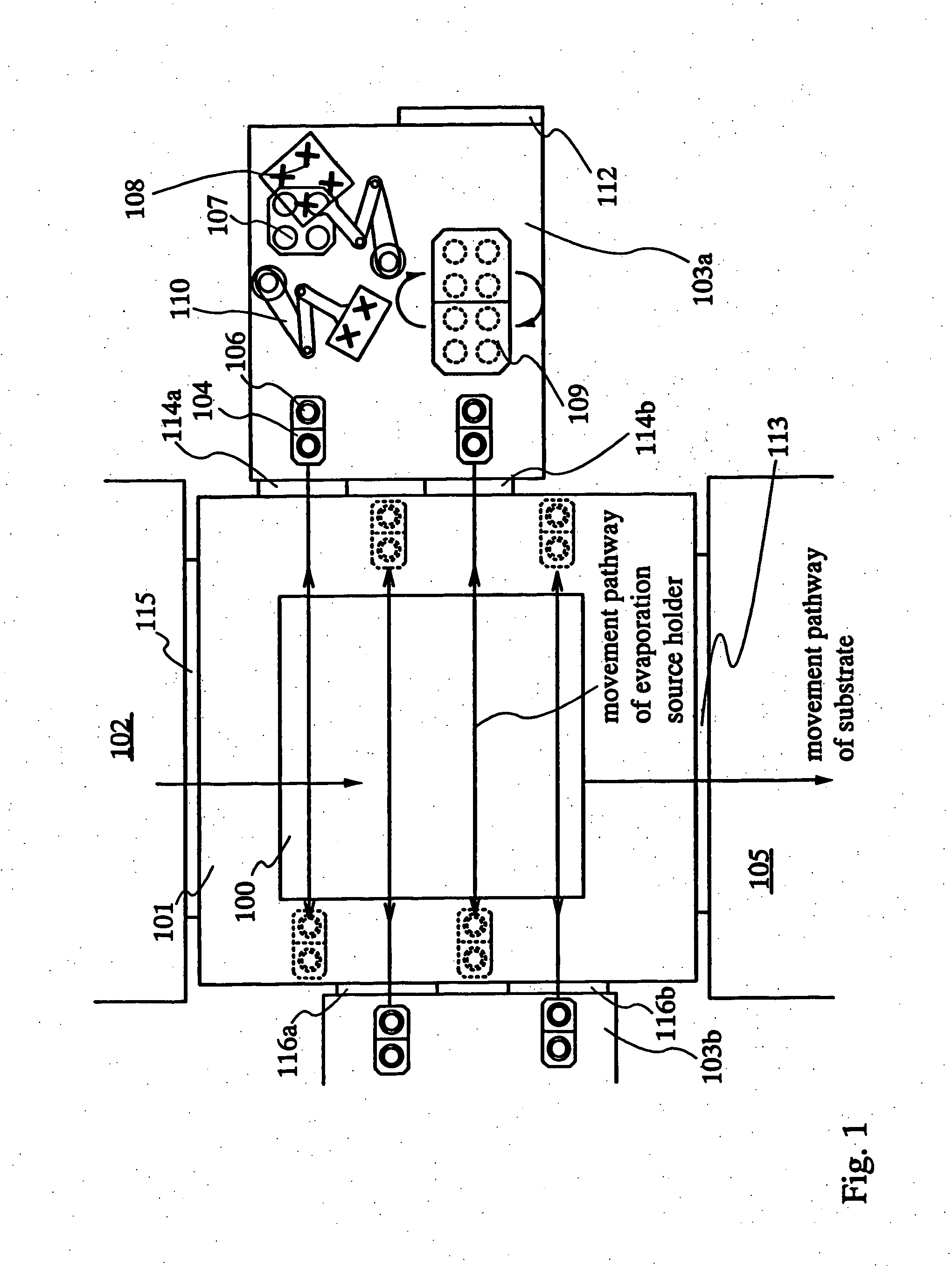
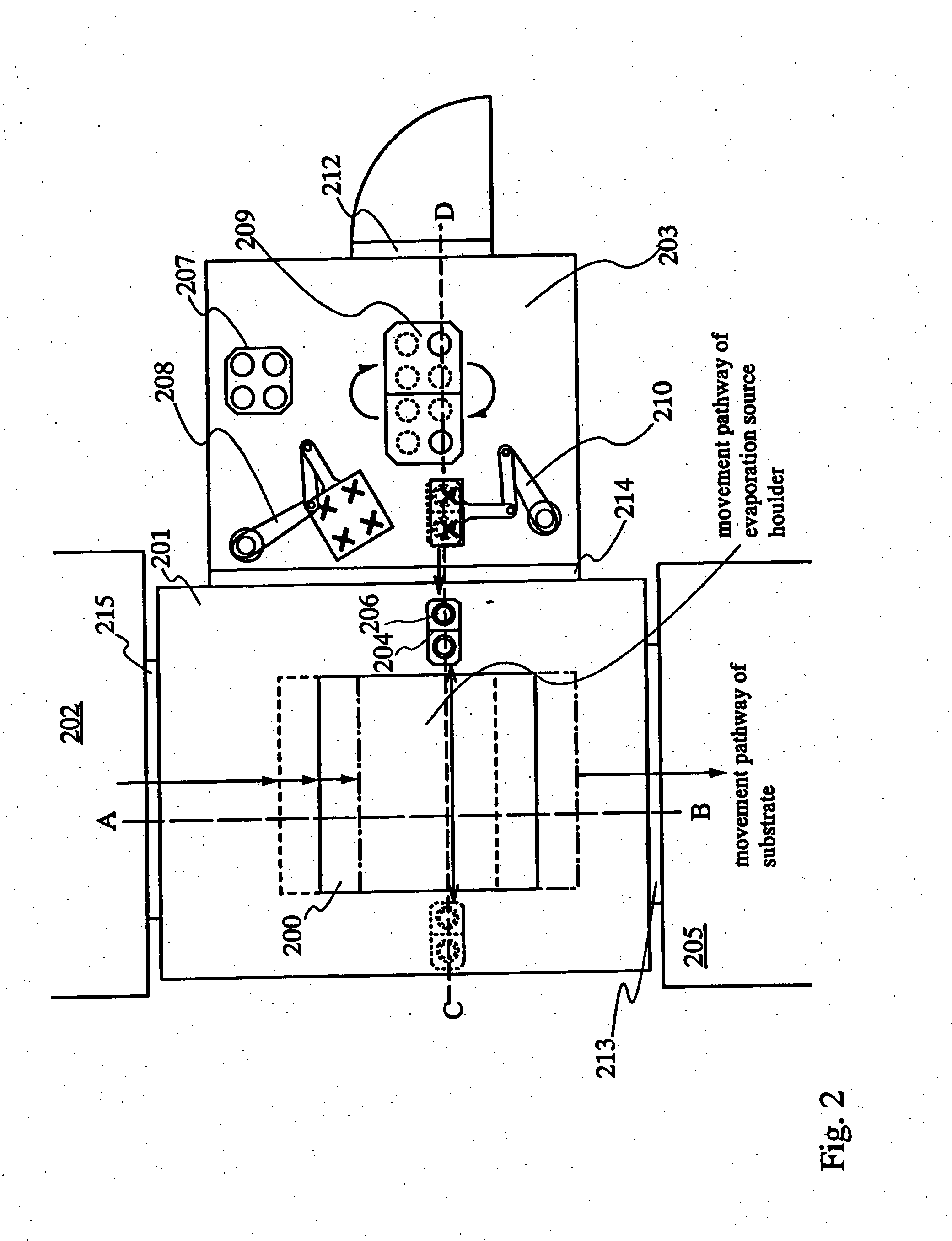
InactiveUS20070186852A1Material efficiencyReduce manufacturing costVacuum evaporation coatingSolid-state devicesCrucibleReciprocating motion
The purpose of the invention is increasing the efficiency of utilizing an EL material and providing a deposition method and a vapor deposition apparatus which is one of the film formation systems which are excellent in throughput and uniformity in film thickness in forming an EL layer. According to the invention, evaporation is performed by moving or reciprocating an evaporation source holder in which a plurality of containers (crucible) each encapsulating an evaporation material are set only in an X direction while moving a substrate at regular intervals. Further, in the plurality of evaporation source holders, film thickness meters of adjacent evaporation sources are disposed alternately so as to sandwich the movement pathway of the substrate.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
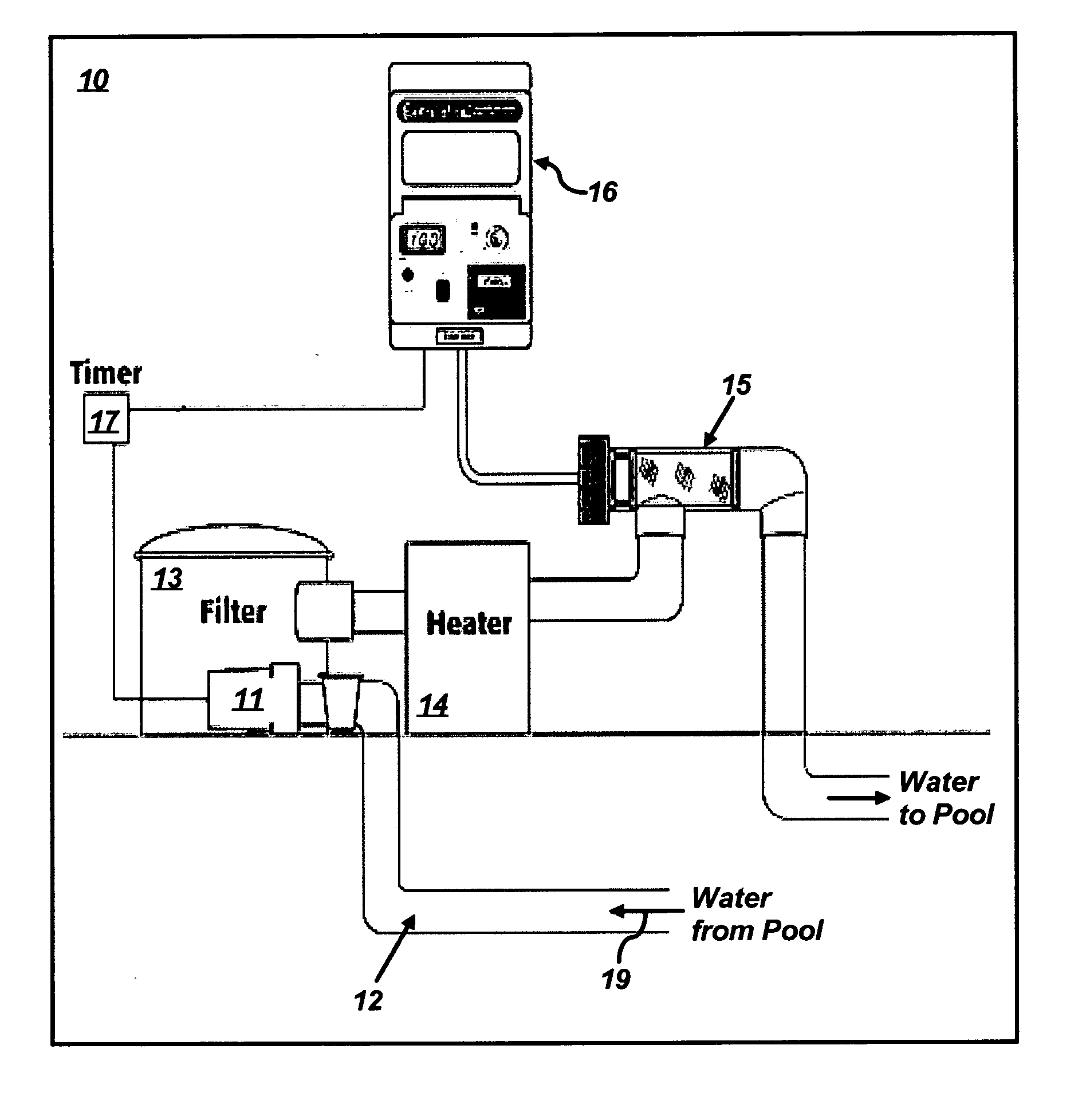
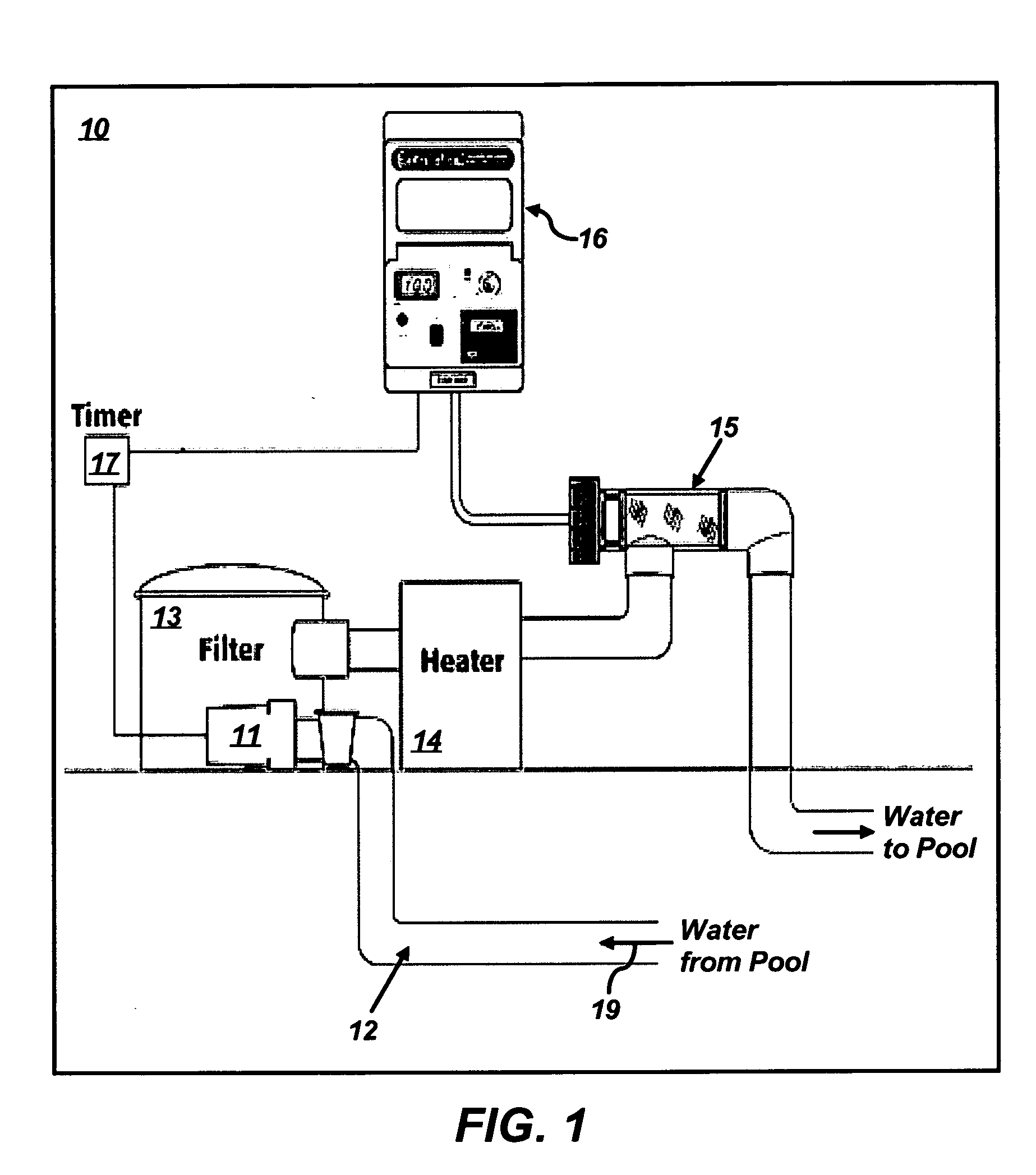
Swimming pool cleaning and sanitizing system
InactiveUS20060054568A1Increase oxidation reduction potentialExtend your lifeWater treatment parameter controlWater/sewage treatment with mechanical oscillationsAcoustic waveIonization
A cleaning and sanitation apparatus for cleaning a liquid, the apparatus comprising ionization means to produce ions having an algaecidal or bactericidal effect into the liquid, ultrasonic cleaning means to introduce sound waves into the liquid, and electronic oxidation means to increase the oxidation reduction potential of the liquid, wherein the ionization means, the ultrasonic cleaning means and the electronic oxidation means are operated simultaneously for a period to clean and sanitize the liquid in the absence of added salt, chlorine or other chemicals.
Owner:ENVIRO SWIM
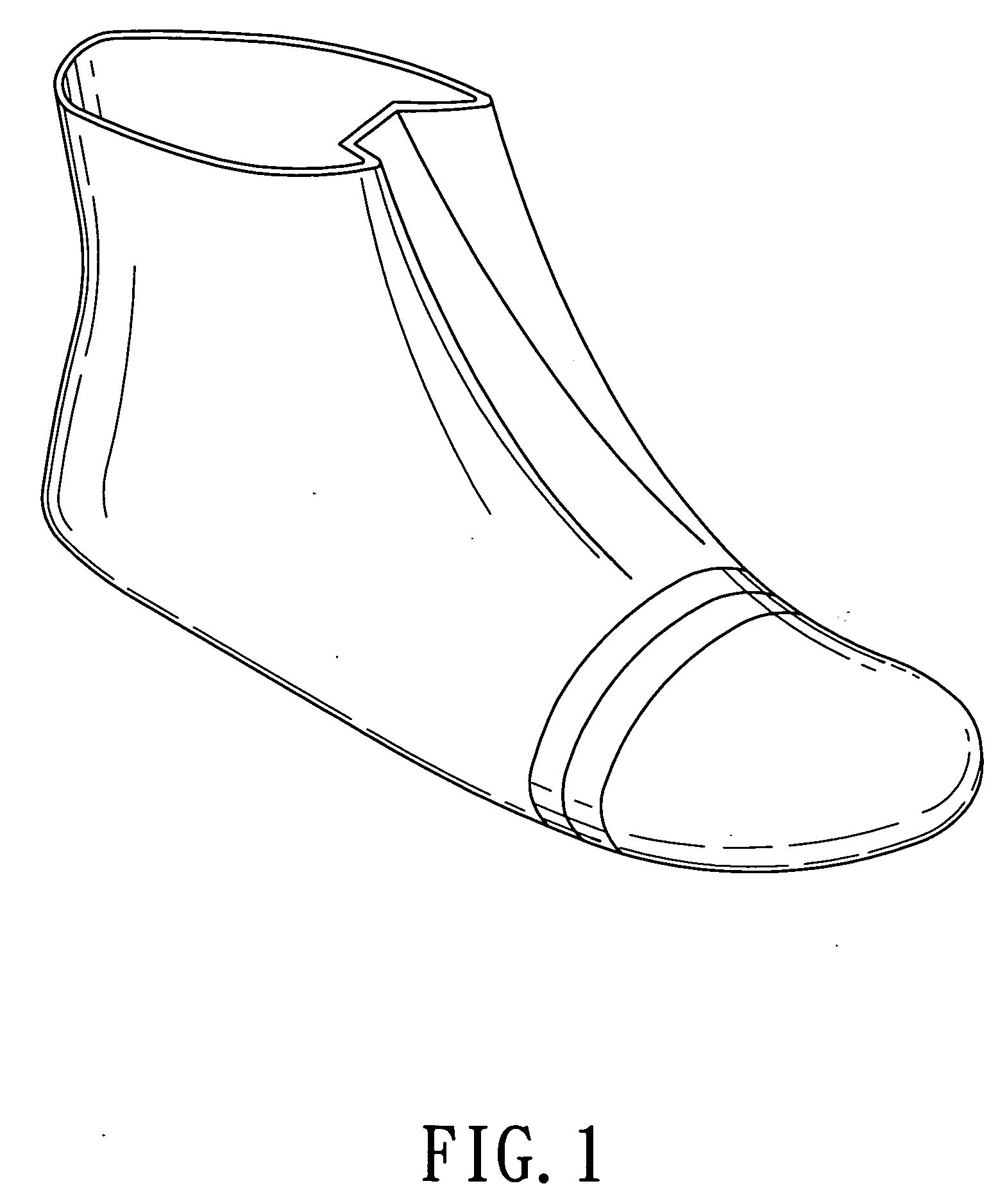
Shoe having an upper made of a waterproof breathable laminate
Owner:CHEN EDDIE
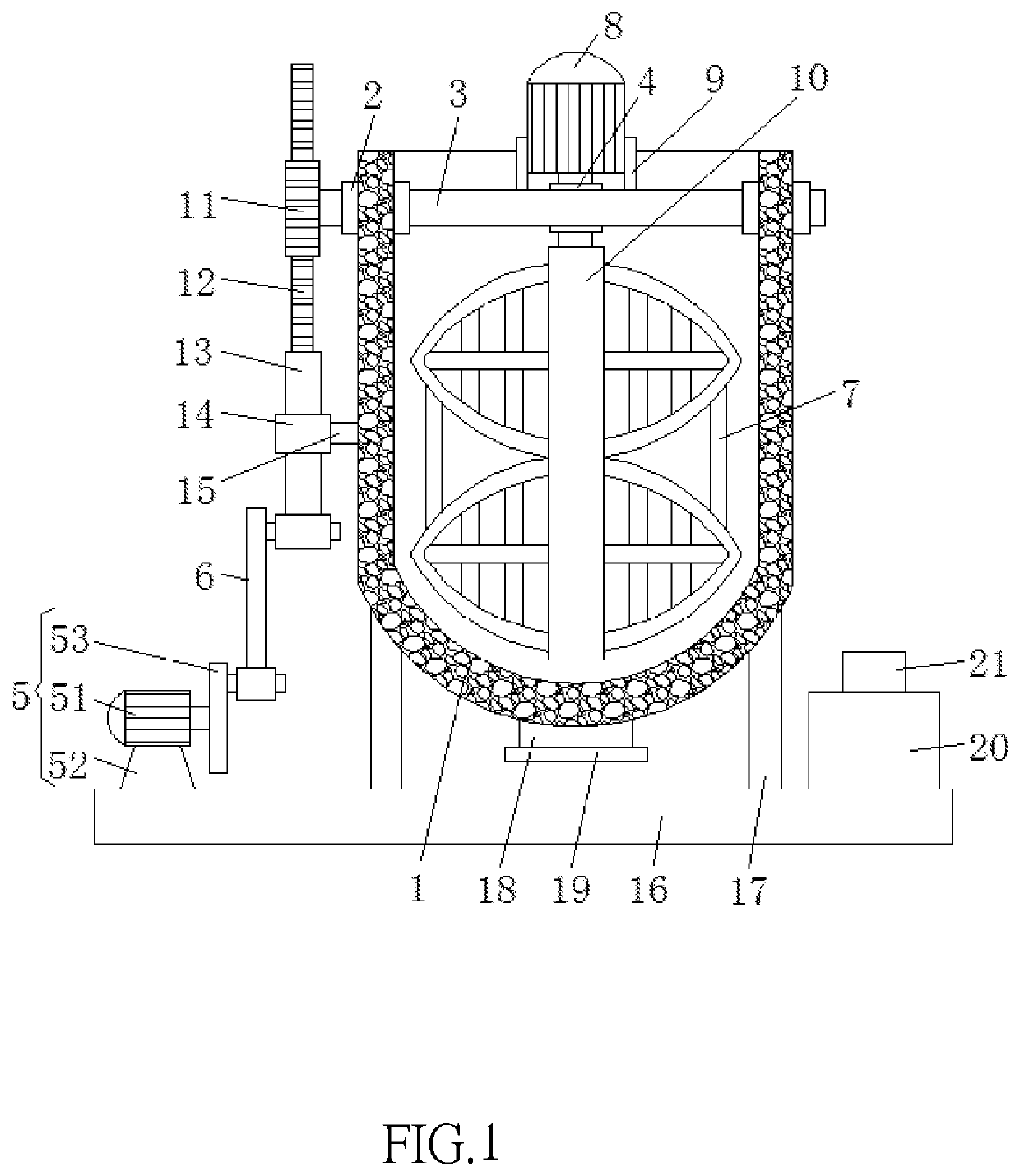
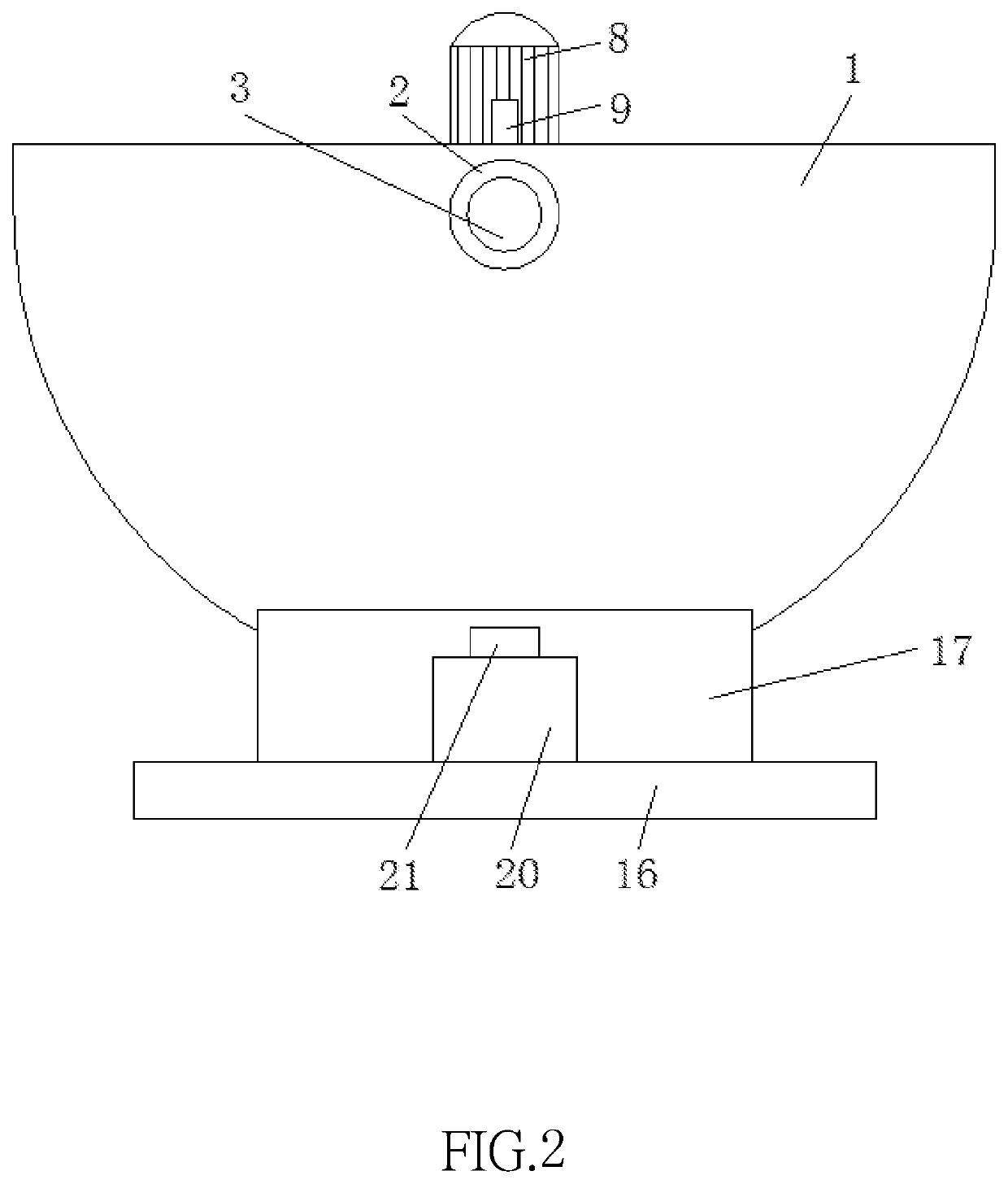
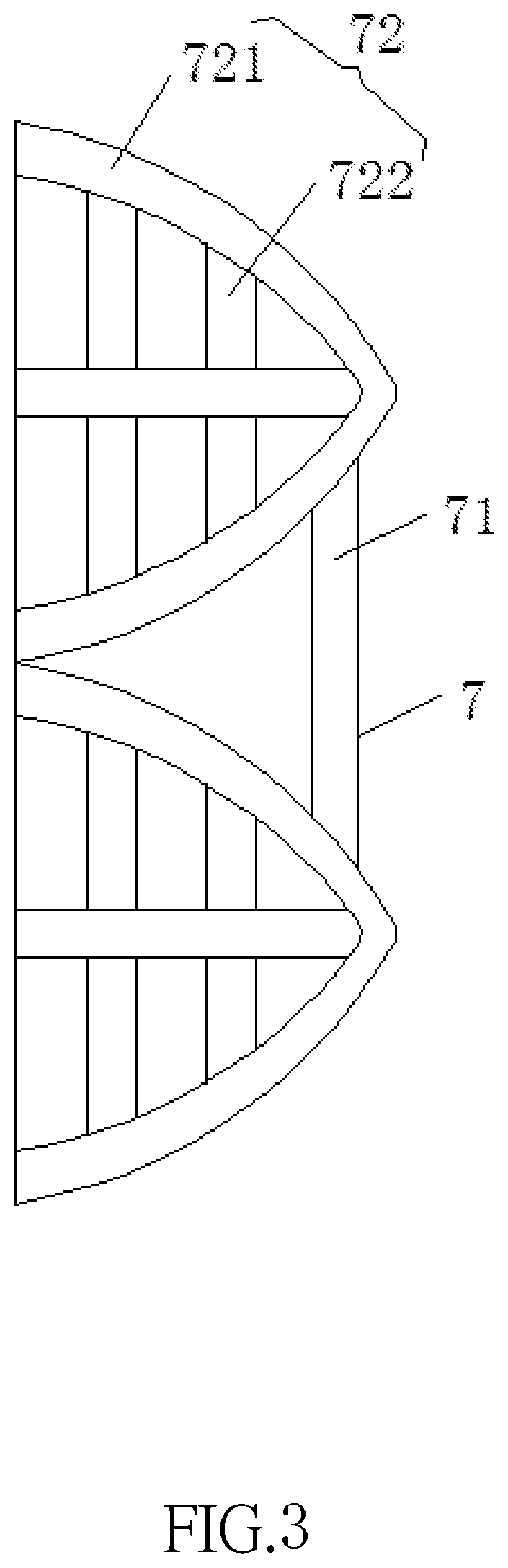
Electrically controlled mixing and blending apparatus for chemical liquid raw materials
ActiveUS20190366282A1Increase productivityReasonable designShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersTransportation and packagingRotational axisGear drive
An electrically controlled mixing and blending apparatus featuring high corrosion resistance and mixing efficiency includes a housing, a first bearing engaged to both sides of the housing, and the interior of both first bearings being coupled to a first rotating shaft, a second bearing engaged to a surface at the middle of the first rotating shaft and the interior of the second bearing being engaged to a surface of an output shaft of a first motor output shaft. Both sides of the first motor are fixedly coupled to a surface of the first rotating shaft through a first fixed rod. A gear drives the first motor, a blending rod and a stirring rack to swing in the front-rear direction through the first rotating shaft to increase the turbulence of the liquid raw materials, reduce the time required for mixing raw materials, and improve the production efficiency.
Owner:DONGGUAN UNIV OF TECH
Aromatic polycarbonate resin, electrophotographic photoconductor, dihydroxy diphenyl ether compound, and process of manufacturing dihydroxy diphenyl ether compound
InactiveUS20050106483A1Increased in sensitivity chemical sensitivityIncreased in optical sensitivity sensitivityDevelopersElectrographic process apparatusDiphenyl etherCompound a
A polycarbonate resin has a constitutional unit expressed by the following general formula (I): A1 represents an alkyl group which is substitutional or nonsubstitutional, and an aryl group which is substitutional or nonsubstitutional. A2,A3,A4,A5,A6 and A7 each represent one of a hydrogen atom, a halogen atom, an alkyl group which has 1 to 6 carbon atoms and is substitutional or nonsubstitutional.
Owner:RICOH KK
Laser selective cutting by impulsive heat deposition in the IR wavelength range for direct-drive ablation
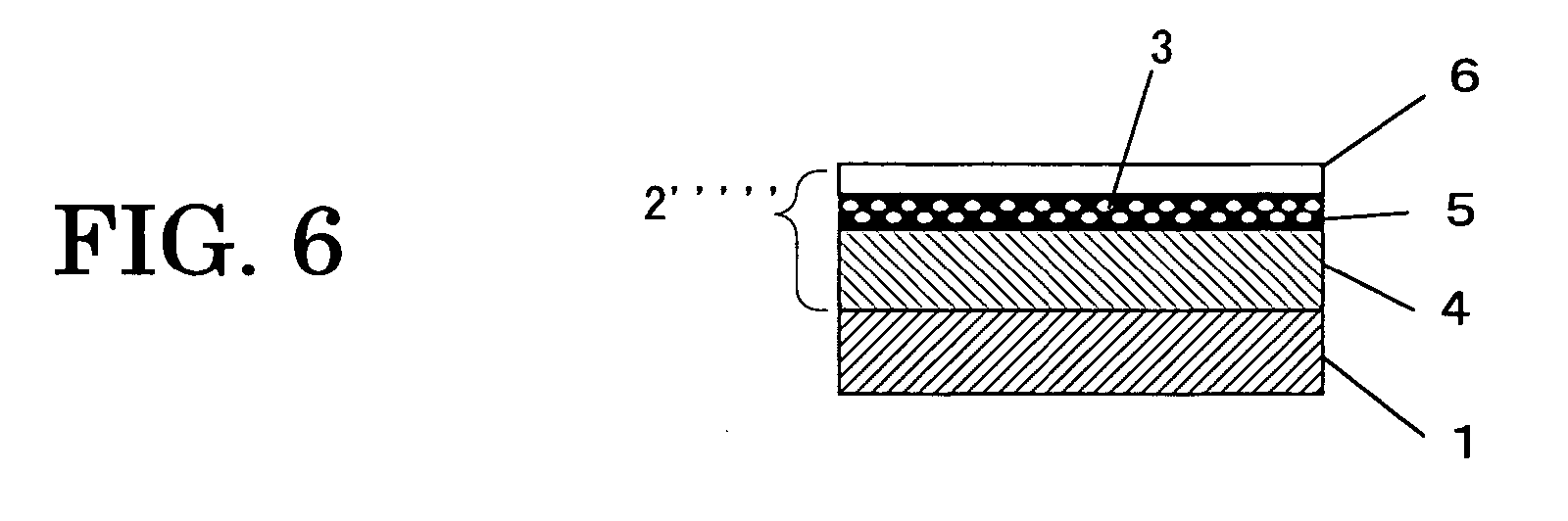
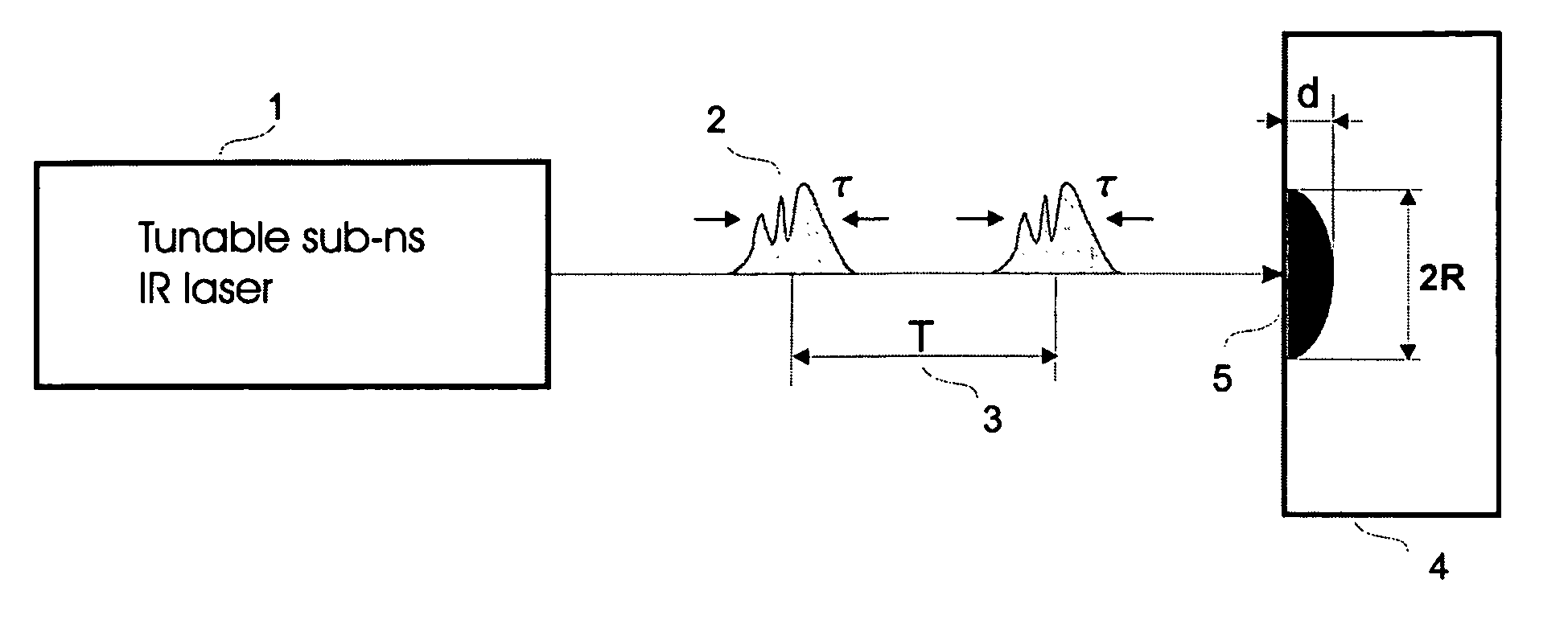
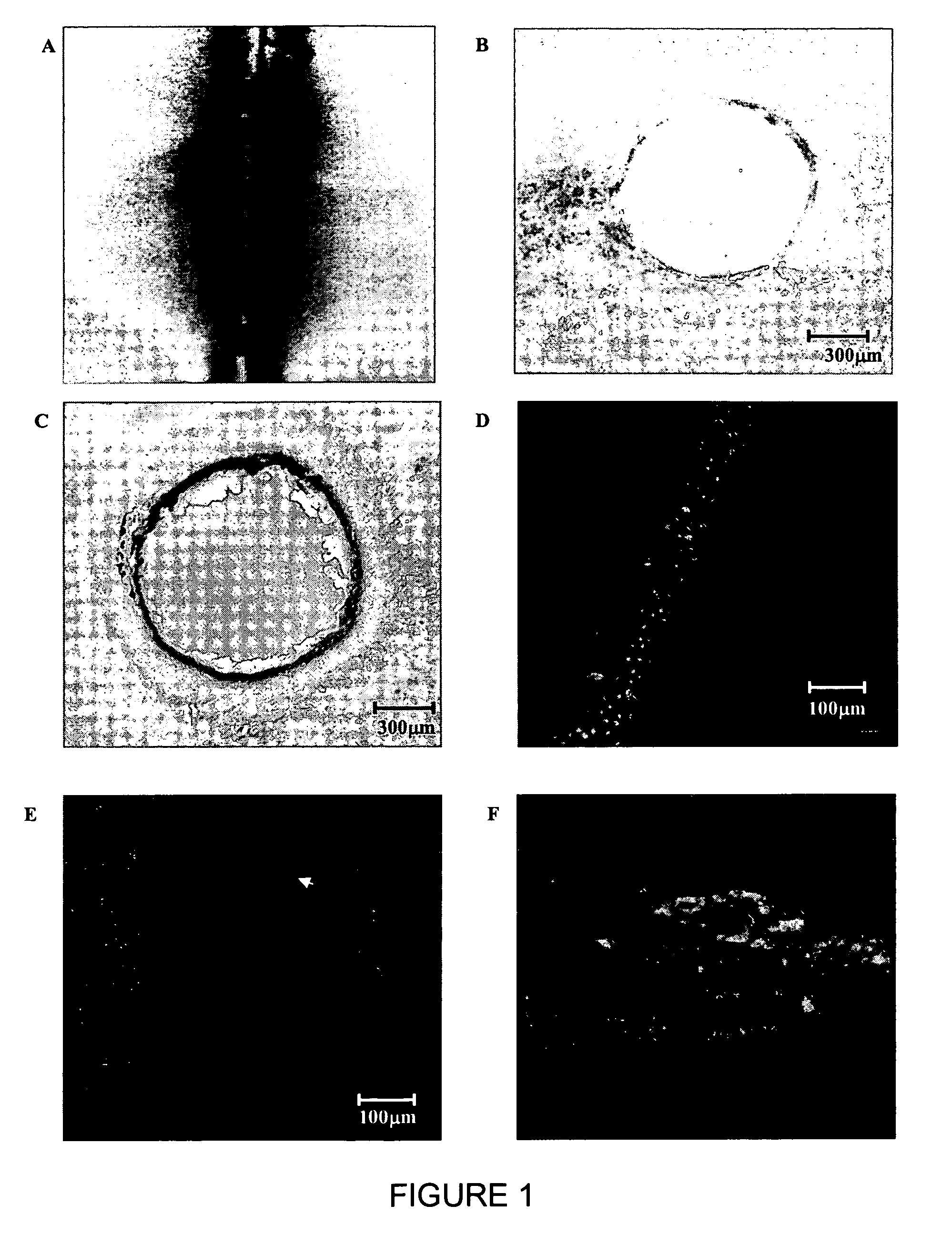
ActiveUS8029501B2Material efficiencyImprove efficiencySurgical instrument detailsLight therapyThermal dilatationHeat deposition
The present invention provides a method of laser processing of materials, specifically laser induced ablation processes for laser removal of material particularly important in medical and dental applications in which the laser removal of material should be done in such a way as to not damage any of the surrounding soft or hard biomaterial. The ablation process is achieved by impulsive heat deposition (IHD) by direct and specific excitation of short lived vibrations or phonons of the material in such a way as to not generate highly reactive and damaging ions through multiphoton absorption. The heat deposition and ensuing ablation process under prescribed time and wavelength conditions for laser irradiation is achieved faster than heat transfer to surrounding tissue by either acoustic or thermal expansion or thermal diffusion that otherwise would lead to excess heat related damage. The result is that all the deposited laser energy is optimally channelled into the ablation process in which the inertially confined stresses from both photomechanical expansion forces and thermally driven phase transitions and associated volume changes constructively interfere to drive the most efficient ablation process possible with minimal damage to surrounding areas by either ionizing radiation or heat effects. By choosing a specific range of wavelengths, spatial and temporal shaping of infrared laser pulses, the energy can be optimally deposited in a manner that further increases the efficiency of the ablation process with respect to minimizing collateral damage.
Owner:LIGHT MATTER INTERACTION INC
Support device for resonator
ActiveUS20110036897A1Large logarithmic decrementFaster sound propagation speedSolid-state devicesWelding/cutting auxillary devicesClassical mechanicsUltrasonic vibration
The purpose of this invention is to provide a support device for a resonator that can support the resonator at an optional location, can let the resonator vibrate with a specified vibration consistently, and can apply an ultrasonic vibration to objects efficiently. By inserting first clamping means and second clamping means, which comprise supporting member at least at each contacting portion, into first portion-to-be-supported and second portion-to-be-supported of resonator, the resonator is supported. As substances of the supporting member, substances that have a logarithmic decrement higher than 0.01 and lower than 1.0 and / or a sound propagation speed of more than 5900 m / s are suitable.
Owner:ADWELDS CORP
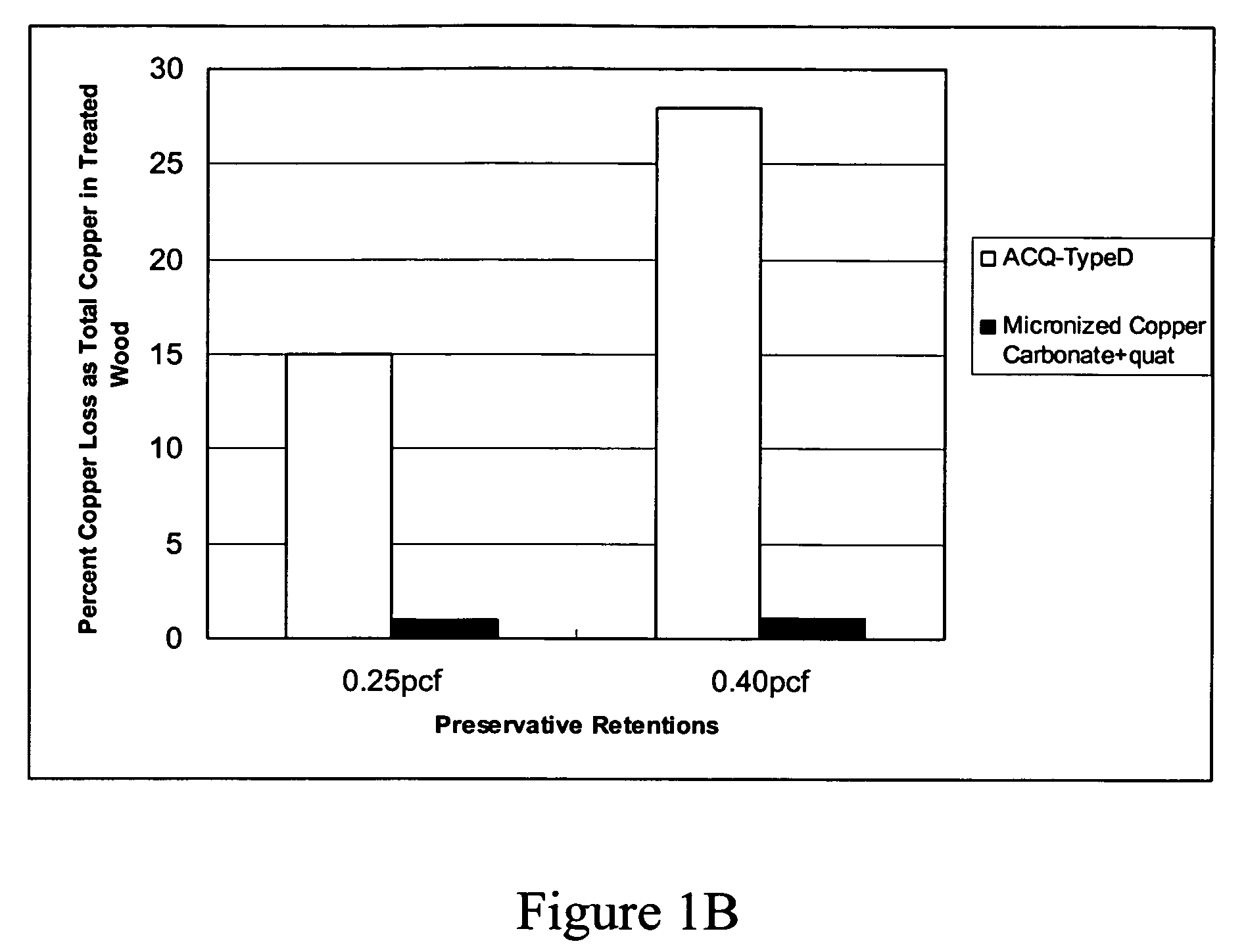
Micronized wood presservative formulations
ActiveUS20070193473A1Small sizePrevent flocculationBiocideDead animal preservationPreservativeMaterials science
The present invention provides wood preservative compositions comprising micronized particles. In one embodiment, the composition comprises dispersions of micronized metal or metal compounds. In another embodiment, the wood preservative composition comprises an inorganic biocide comprising a metal or metal compound and organic biocide. When the composition comprises an inorganic biocide and an organic biocide, the inorganic biocide or the organic biocide or both are present as micronized particles. When compositions of the present invention are used for preservation of wood, there is minimal leaching of the metal and biocide from the wood.
Owner:KOPPERS PERFORMANCE CHEM
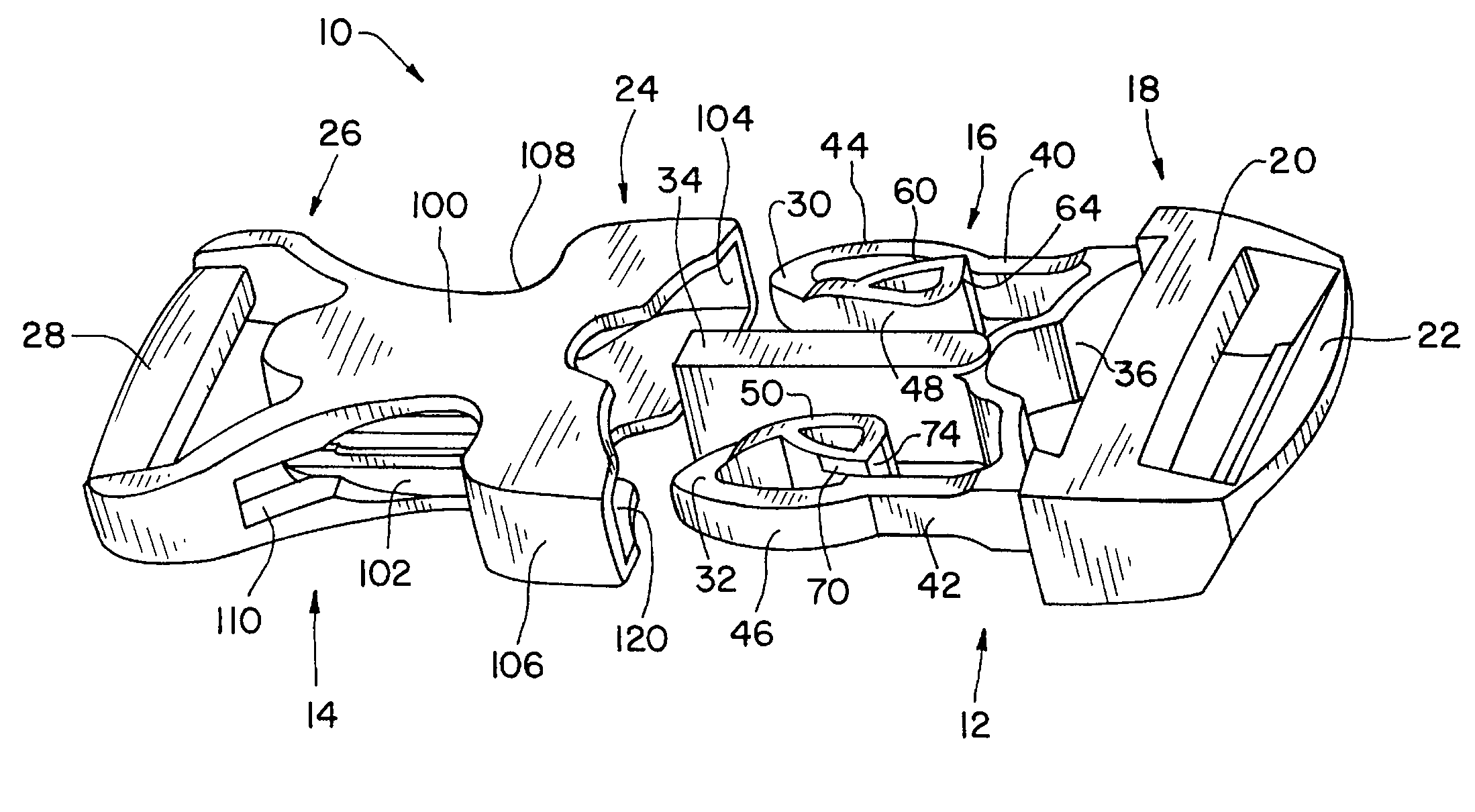
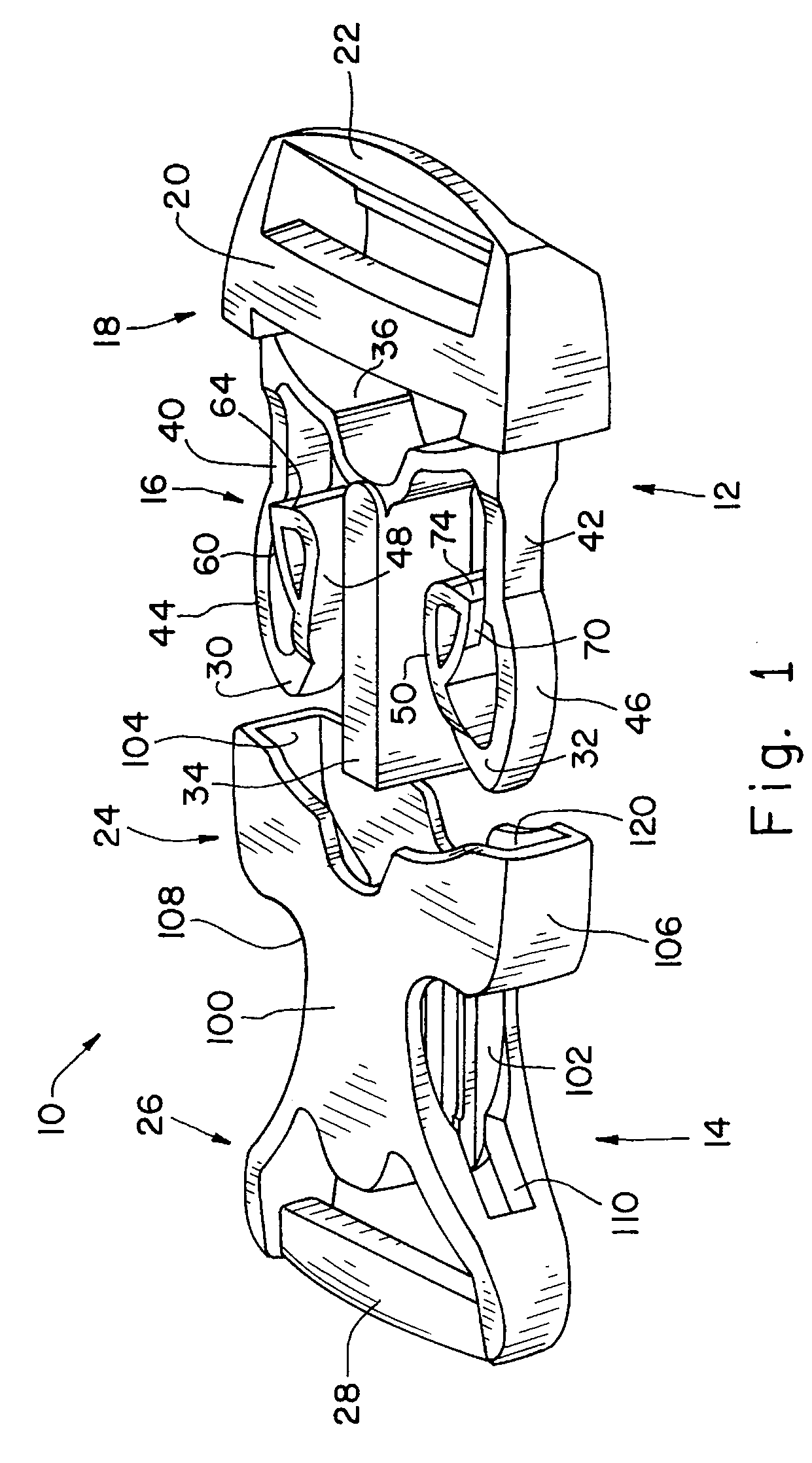
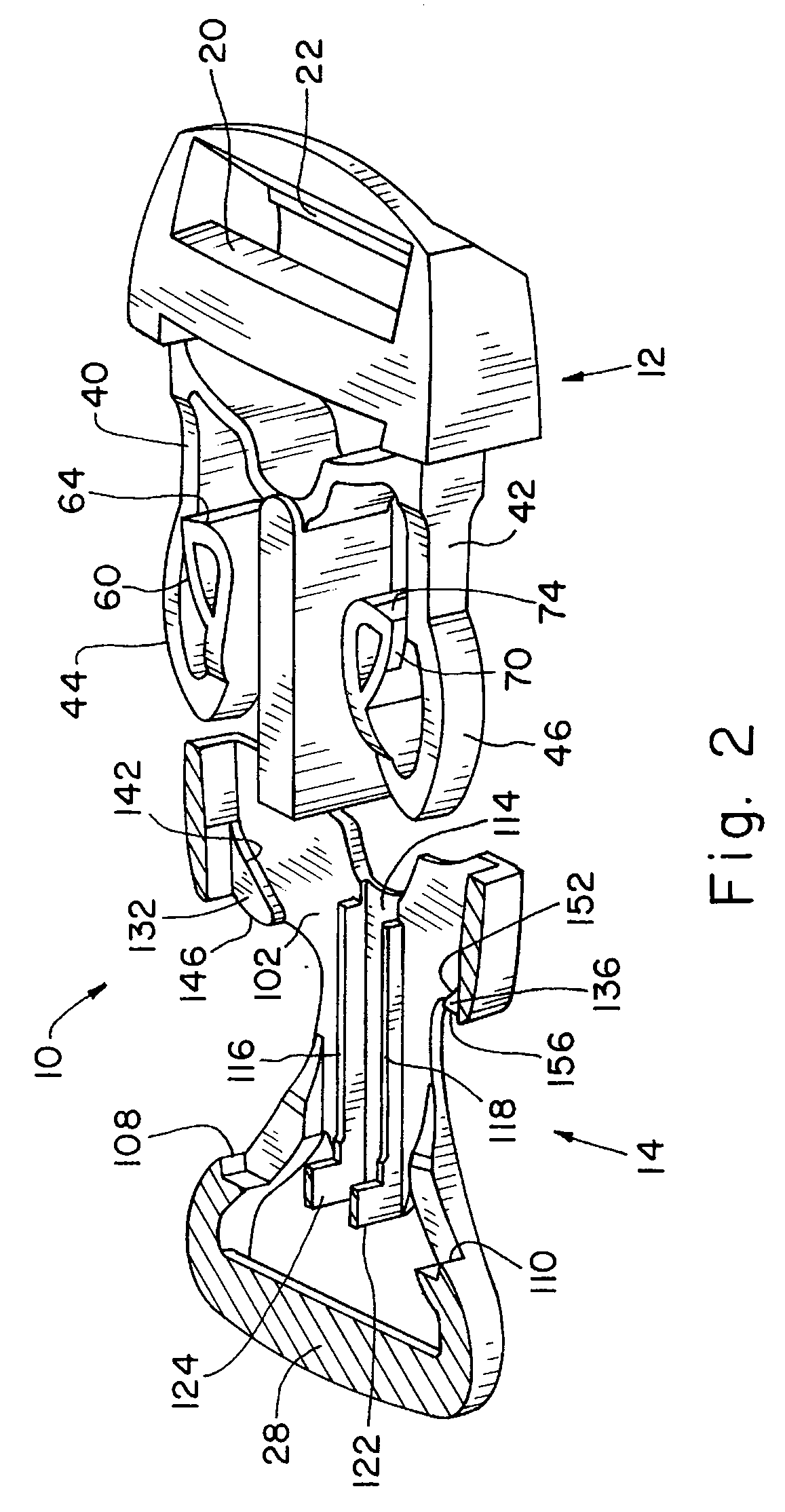
Buckle
ActiveUS20080134479A1Unlatches easilyHigh strengthSnap fastenersClothes buttonsMechanical engineering
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
Silicon composite particles, preparation thereof, and negative electrode material for non-aqueous electrolyte secondary cell
ActiveUS7790316B2Improve cycle performanceMinimize changesSilicaNitrogen compoundsSilicon alloyInorganic compound
Silicon composite particles are prepared by sintering primary fine particles of silicon, silicon alloy or silicon oxide together with an organosilicon compound. Sintering of the organosilicon compound results in a silicon-base inorganic compound which serves as a binder. Each particle has the structure that silicon or silicon alloy fine particles are dispersed in the silicon-base inorganic compound binder, and voids are present within the particle.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Alternating current rotatable sputter cathode
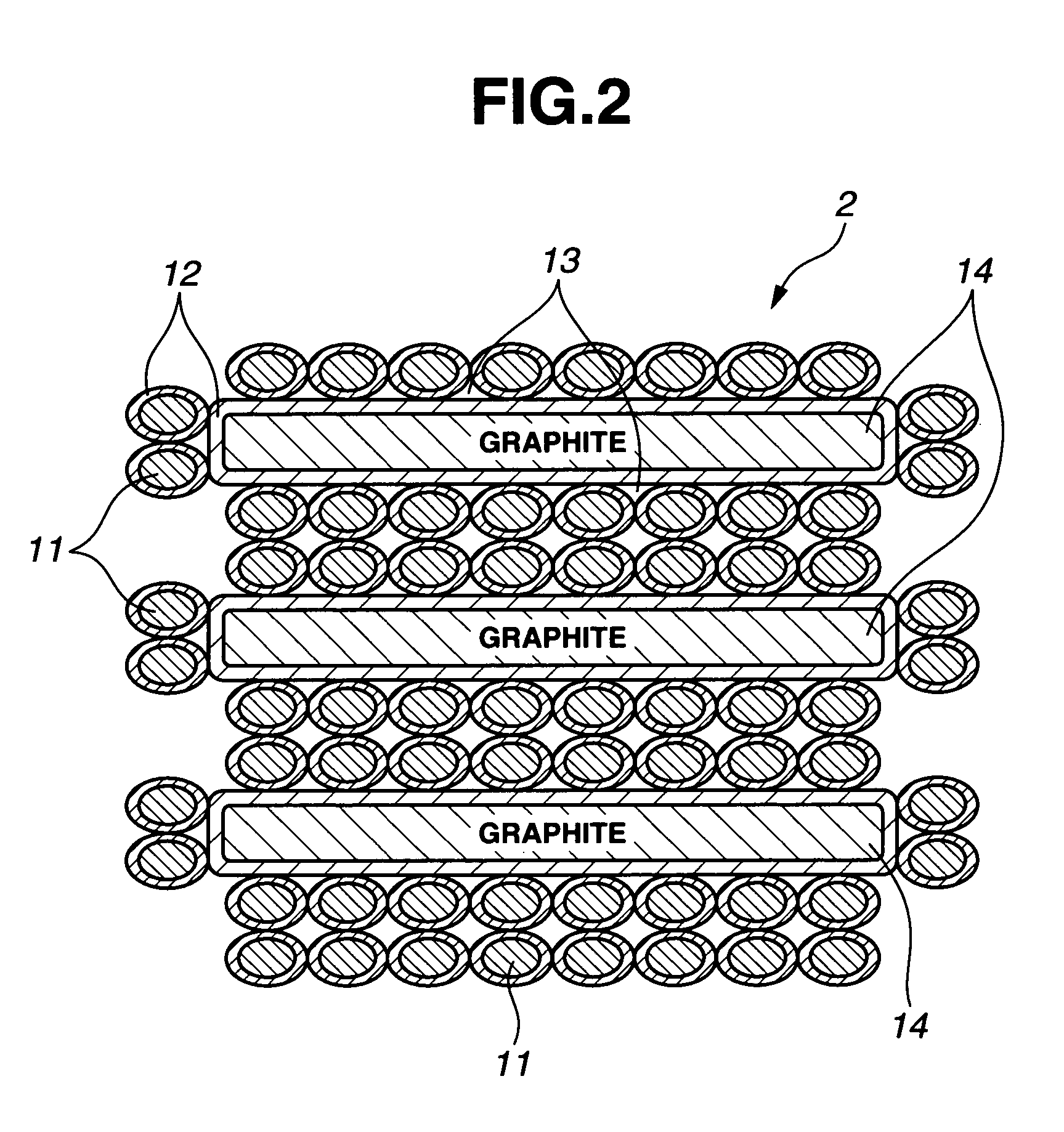
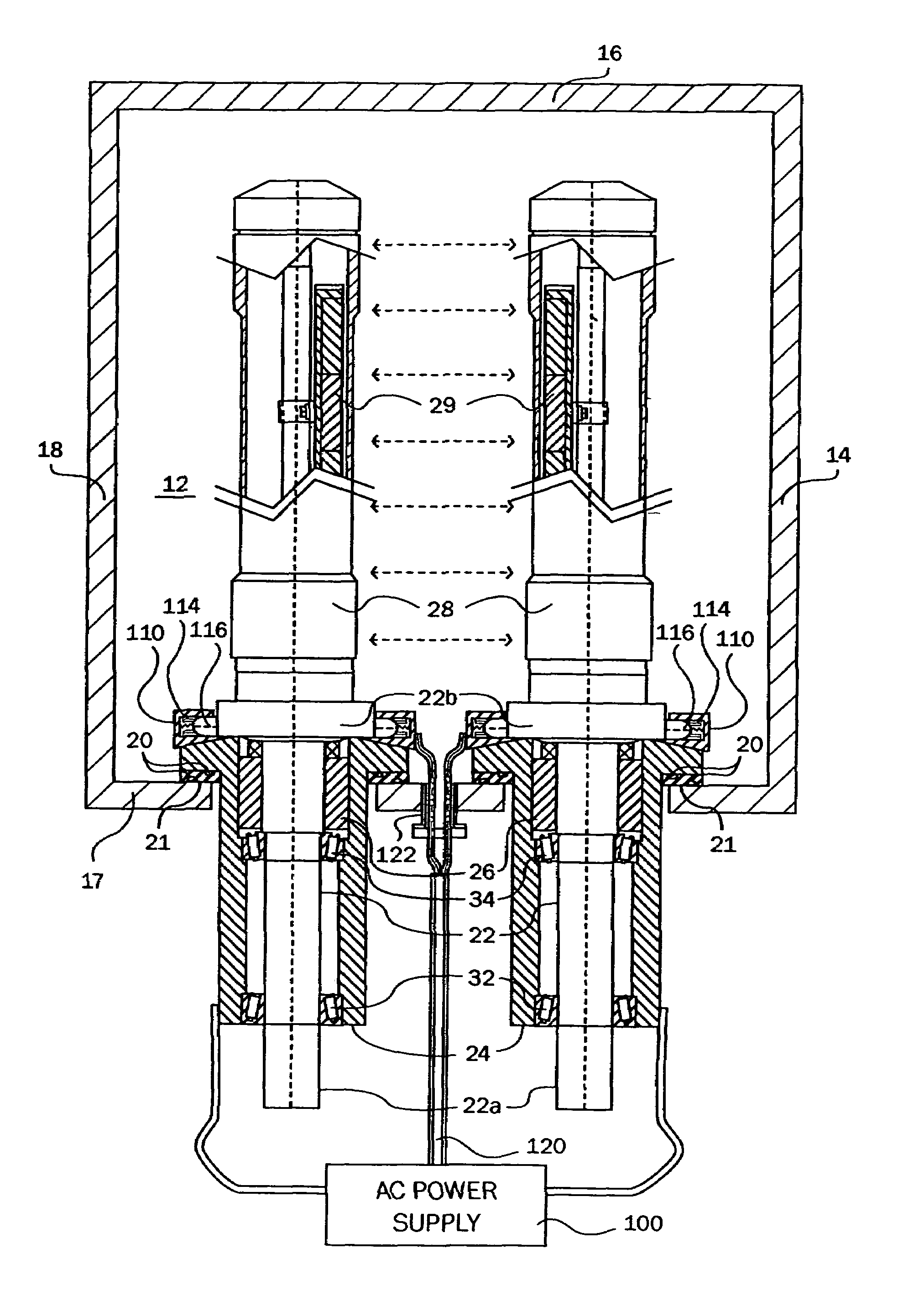
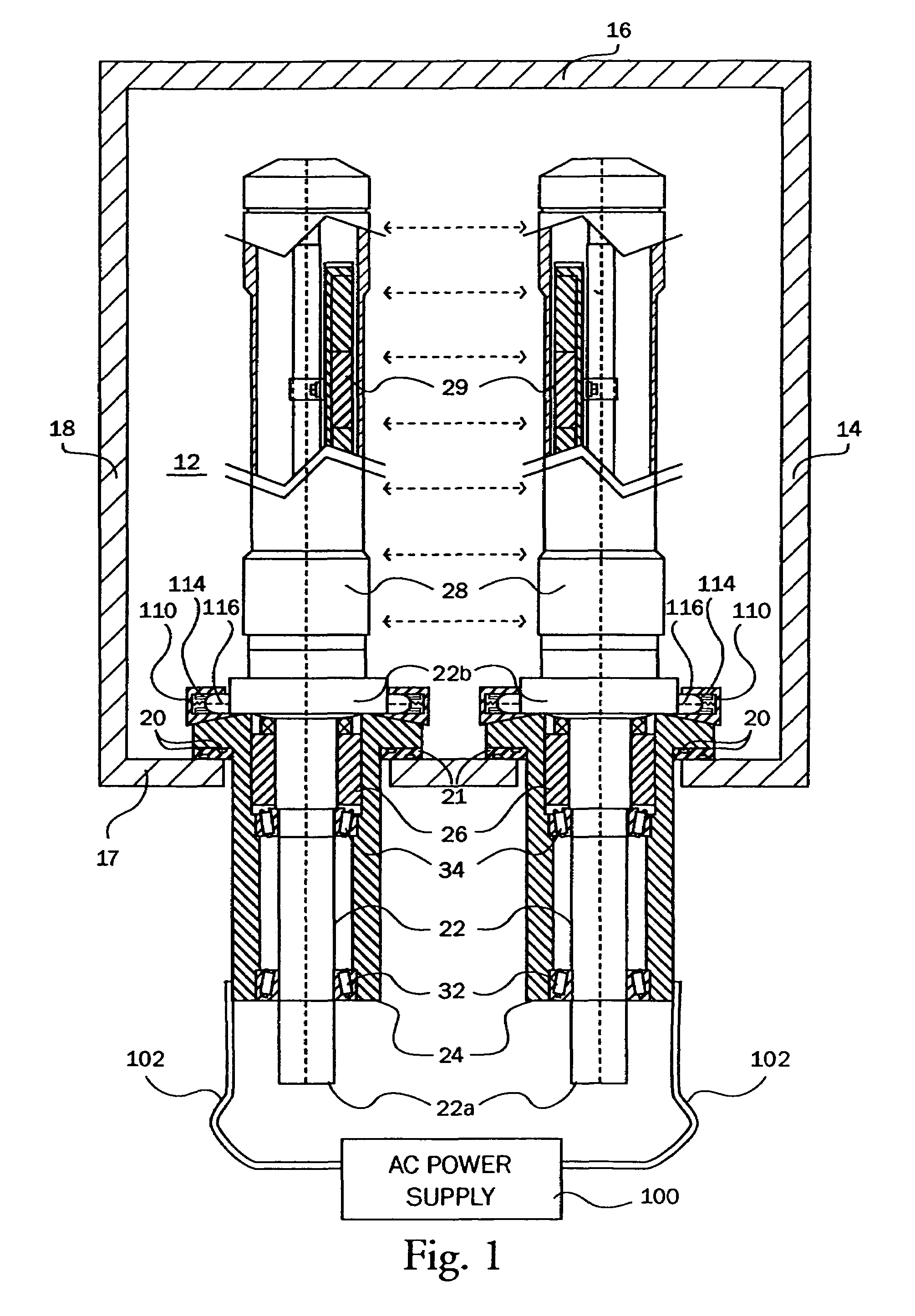
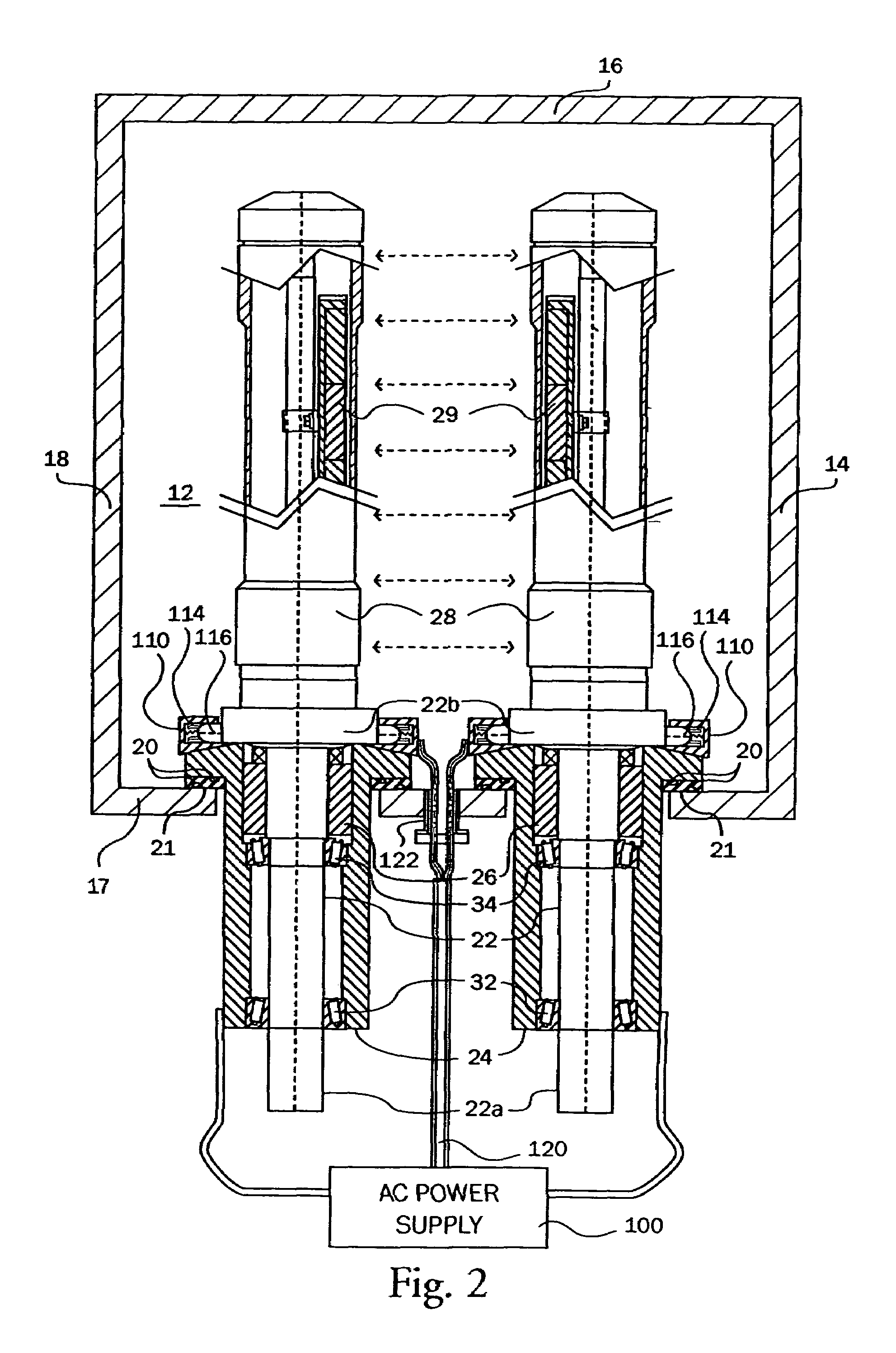
InactiveUS7399385B2Material efficiencyIncrease ratingsCellsElectric discharge tubesElectricityEngineering
The present invention is an alternating current rotary sputter cathode in a vacuum chamber. The apparatus includes a housing containing a vacuum and a cathode disposed therein. A drive shaft is rotatably mounted in the bearing housing. A rotary vacuum seal is located in the bearing housing for sealing the drive shaft to the housing. An at least one electrical contact is disposed between a power source and the cathode for transmittal of an oscillating or fluctuating current to the cathode. The electrical contact between the power source and the cathode is disposed inside of the vacuum chamber, greatly reducing, and almost eliminating, the current induced heating of various bearing, seals, and other parts of the rotatably sputter cathode assembly.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Sterilization Method
A method of sterilizing a material, said method comprising the steps of: (a) introducing a solution comprising peroxyacetic acid into a hot gaseous stream to produce a peroxyacetic acid vapor; and (b) contacting such peroxyacetic acid vapor with the material to be sterilized.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com