Patents
Literature
6795 results about "Ultrasonic vibration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
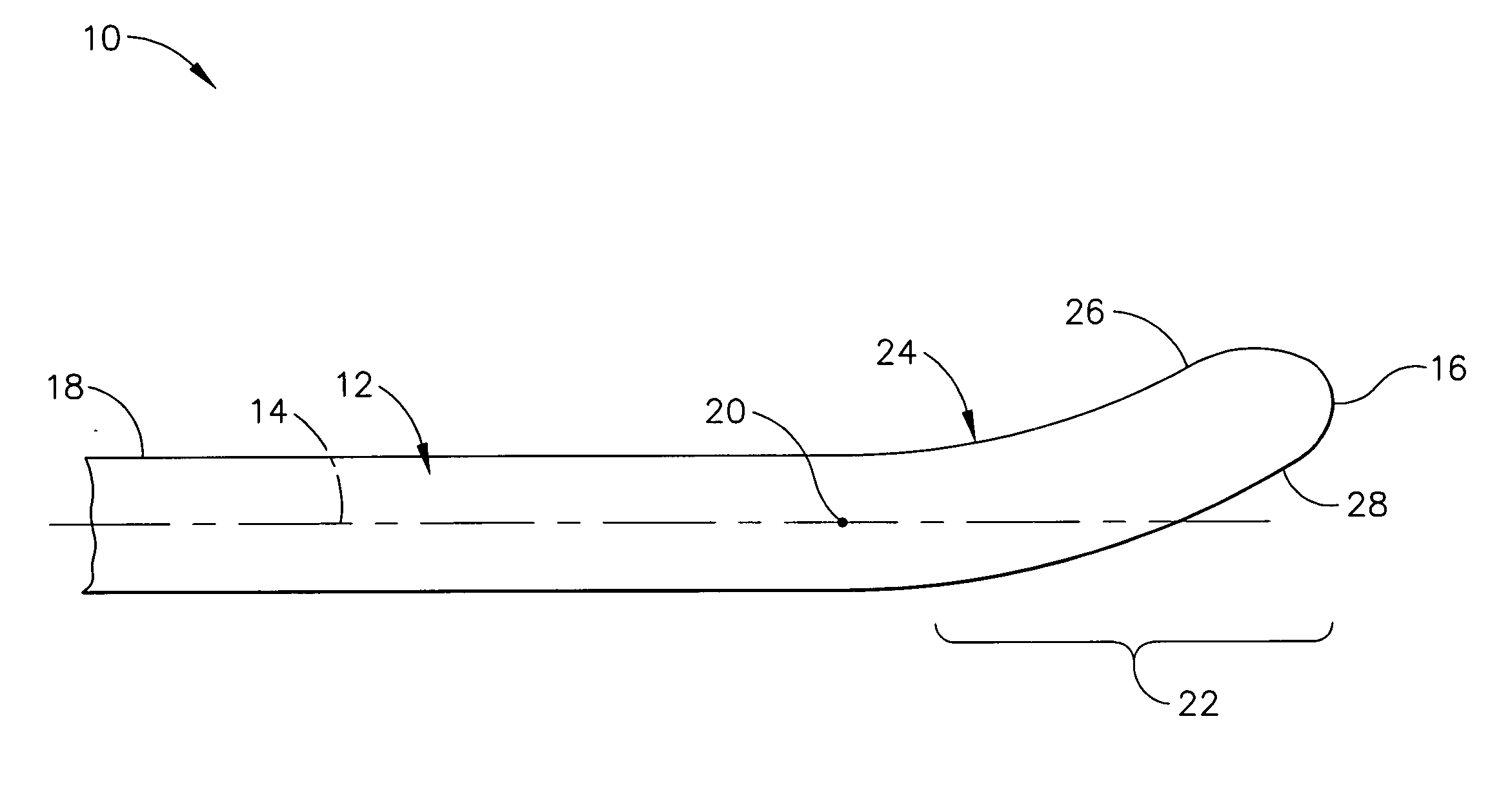
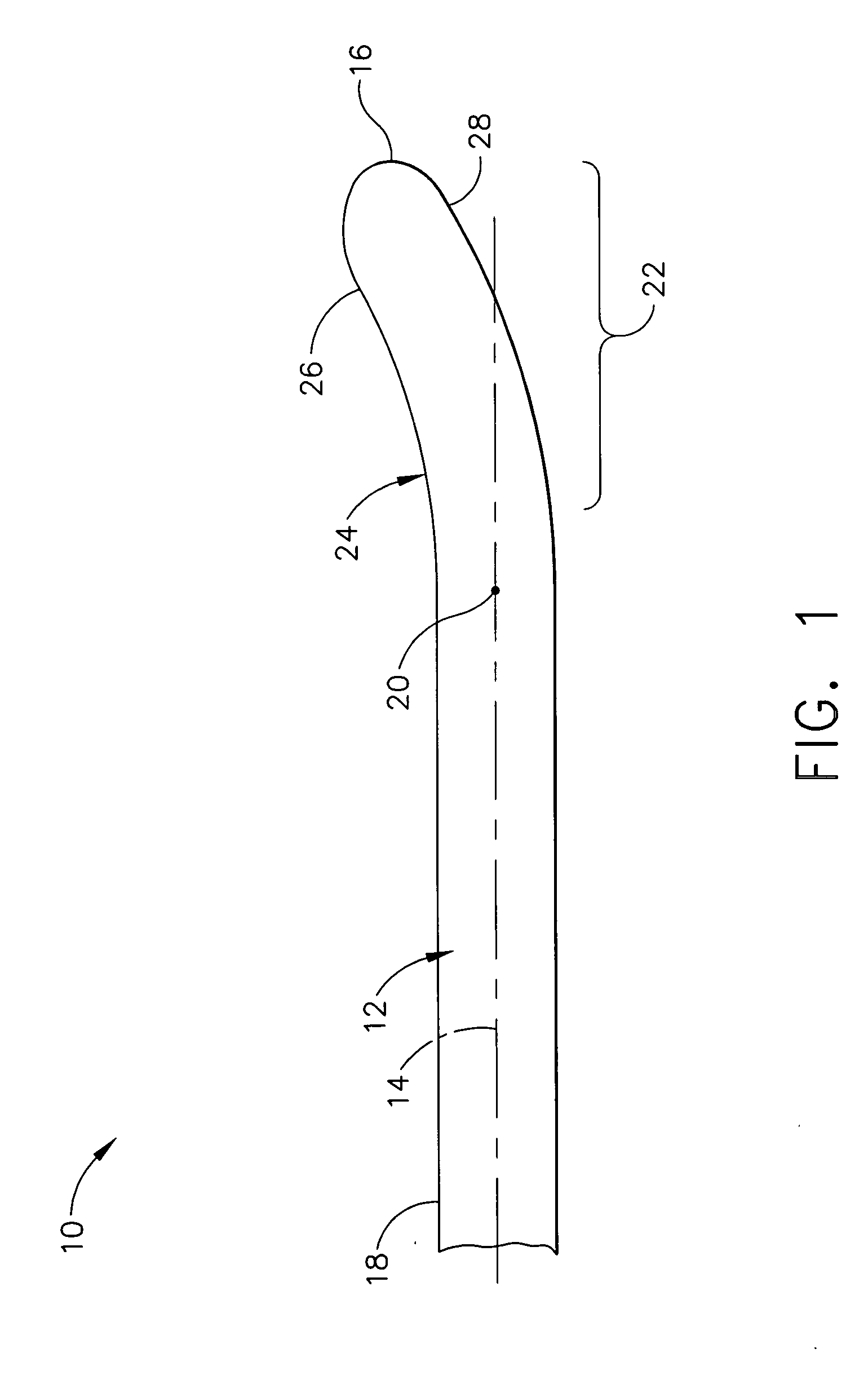
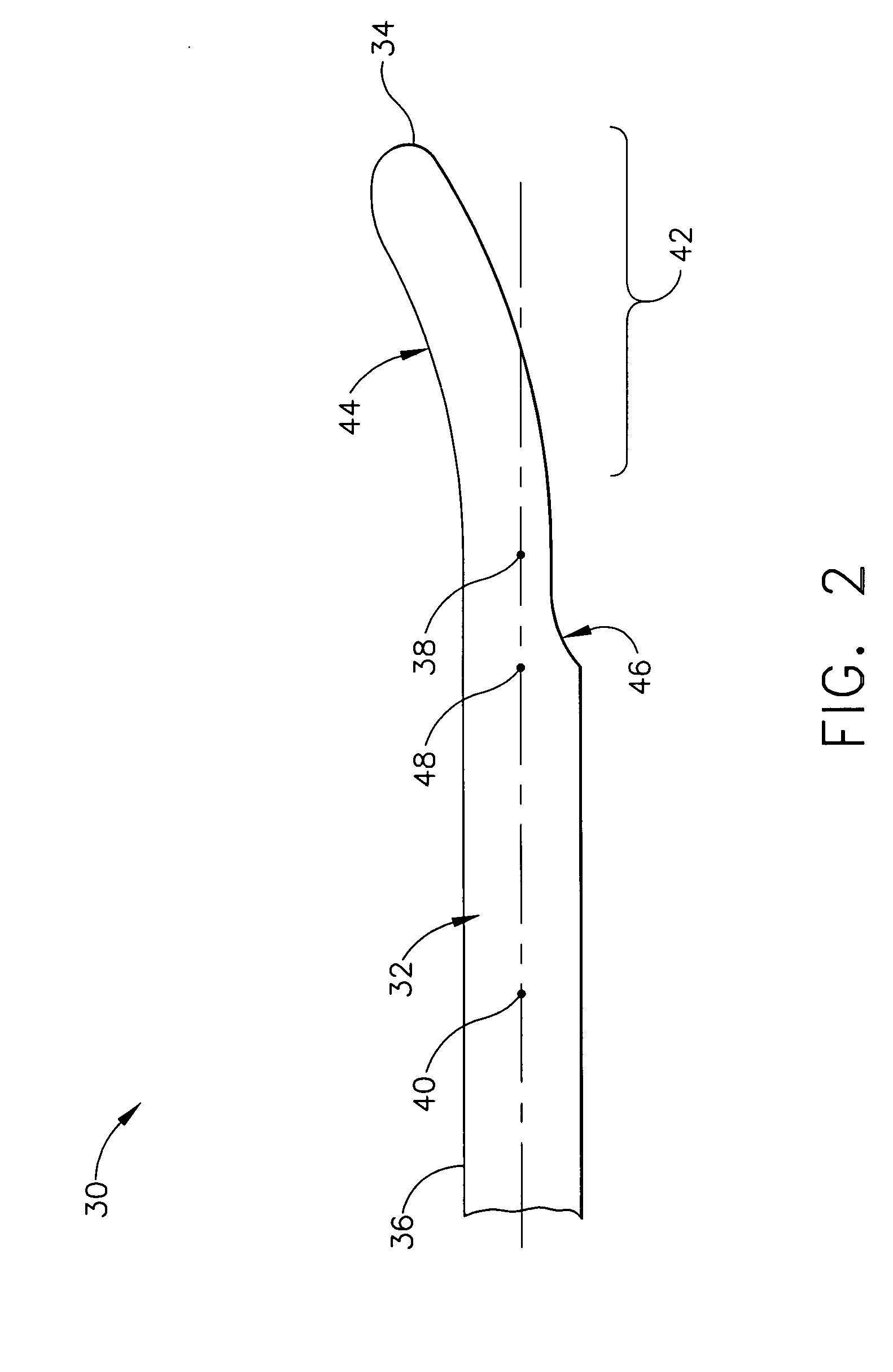
Ultrasonic vibration-assisted (UVA) machining is a process which makes use of a micro-scale high frequency vibration applied to a cutting tool to improve the material removal effectiveness. Its principle is to make the tool-workpiece interaction a microscopically non-monotonic process to facilitate chip separation and to reduce machining forces.
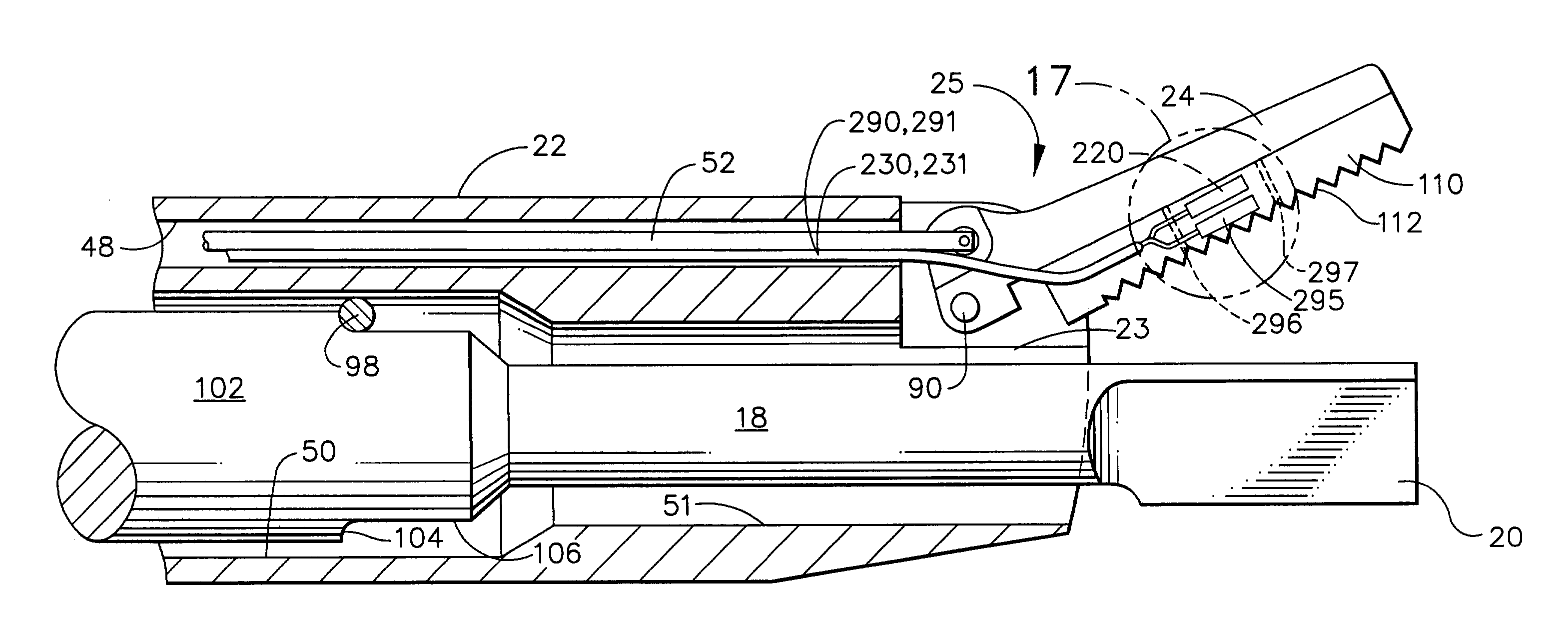
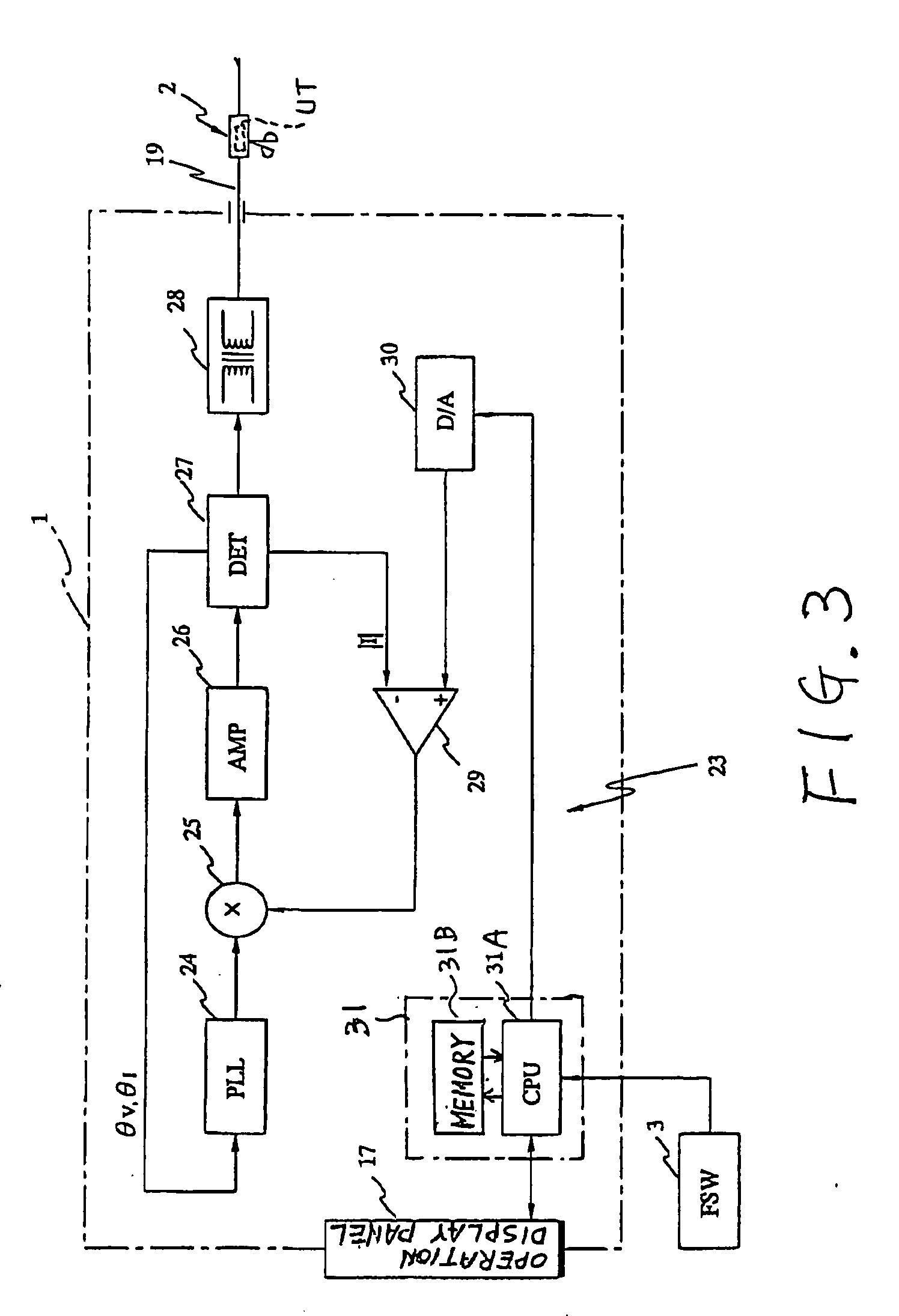
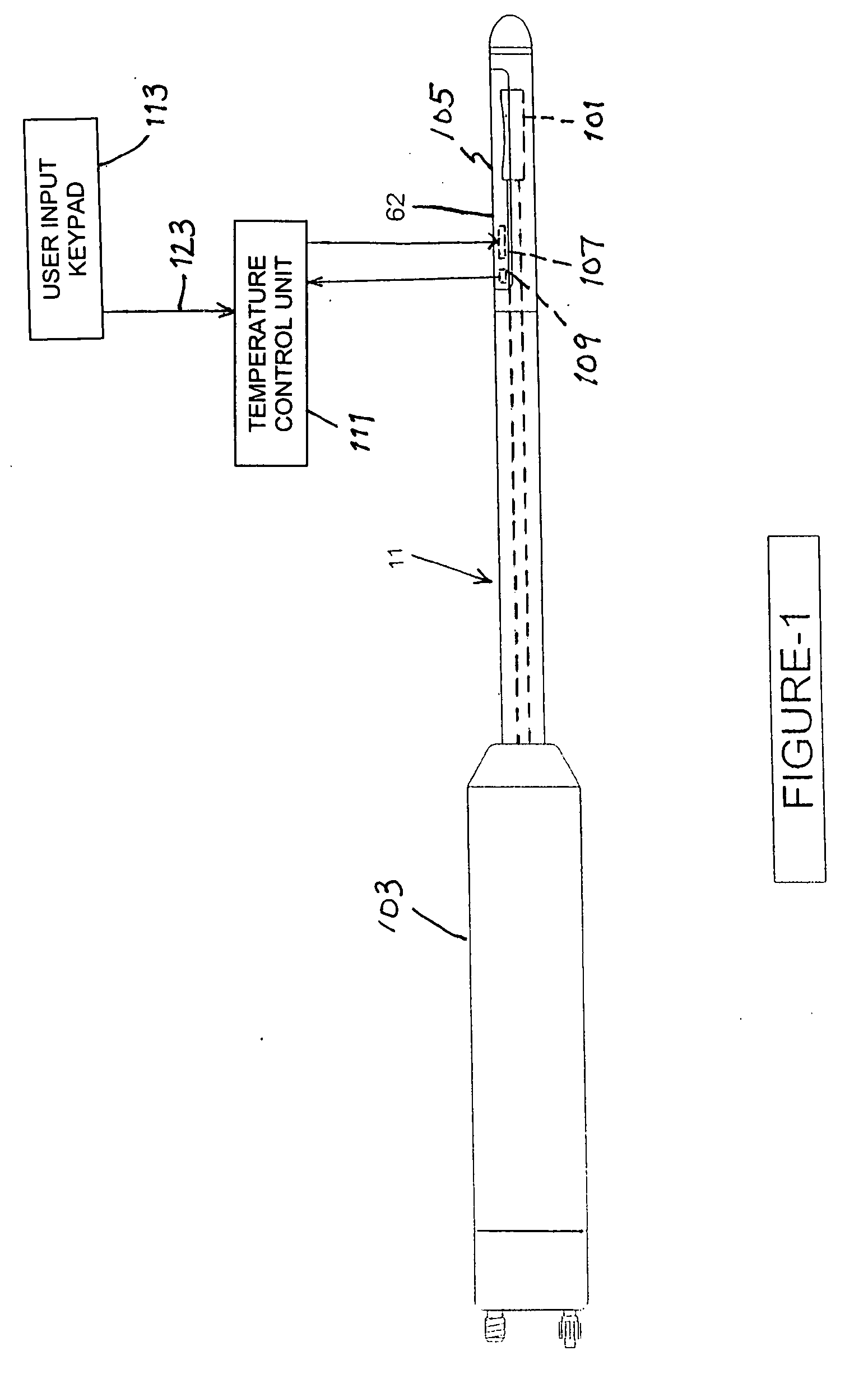
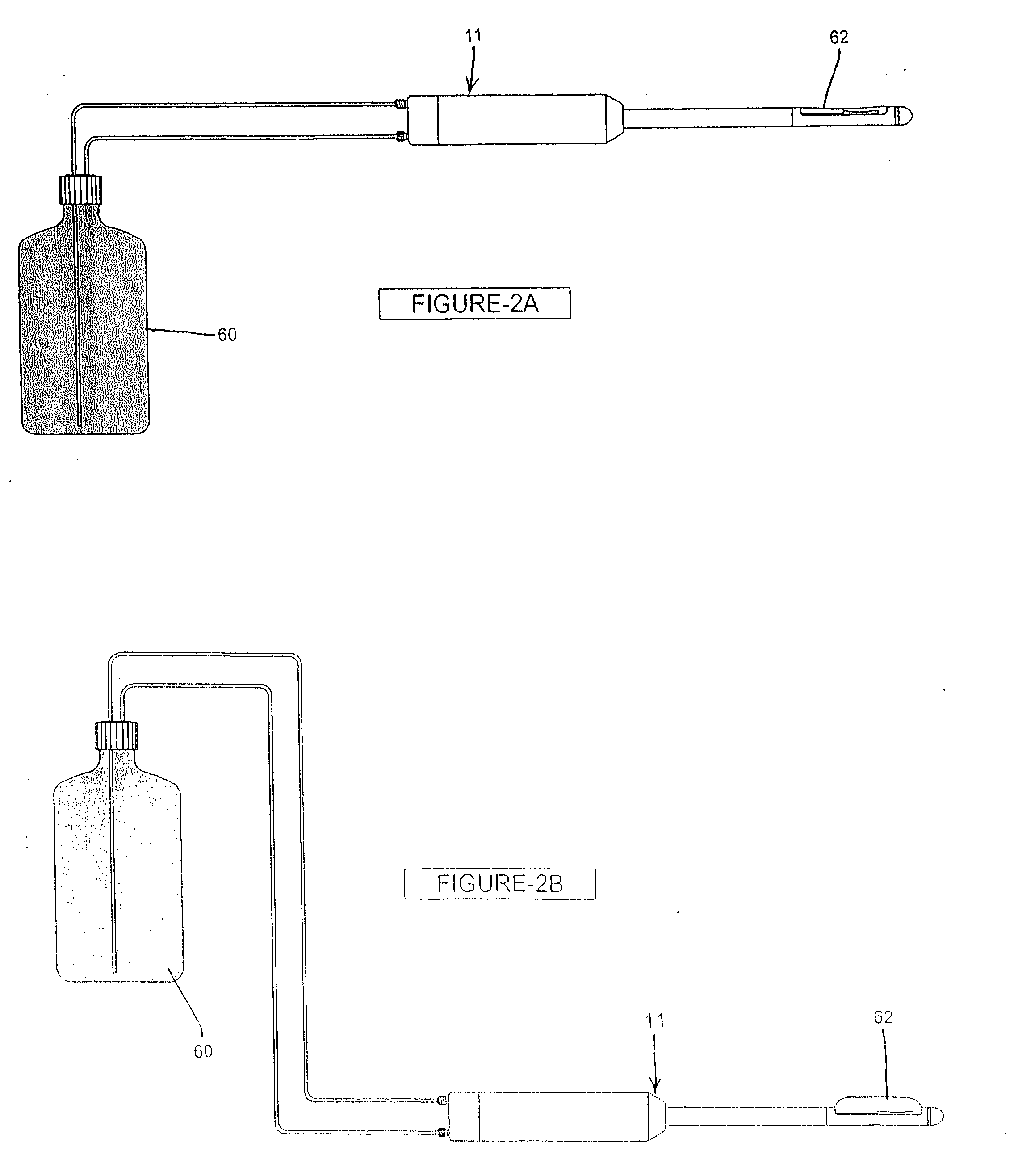
Feedback control in an ultrasonic surgical instrument for improved tissue effects
A temperature monitoring device and / or method which control the tissue temperature at the end-effector of a therapeutic ultrasonic cutting and coagulating instrument as the tissue is being heated with ultrasonic vibrations from the end-effector. One or more temperature sensors are located at the end-effector, preferably on a clamping member. The temperature sensors measure the temperature of the tissue engaged by the end-effector either directly or indirectly. An alternate method and apparatus provides an electrical tissue impedance measure in combination with an ultrasonic cutting and coagulating instrument to provide active feedback control of an ultrasonic generator.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
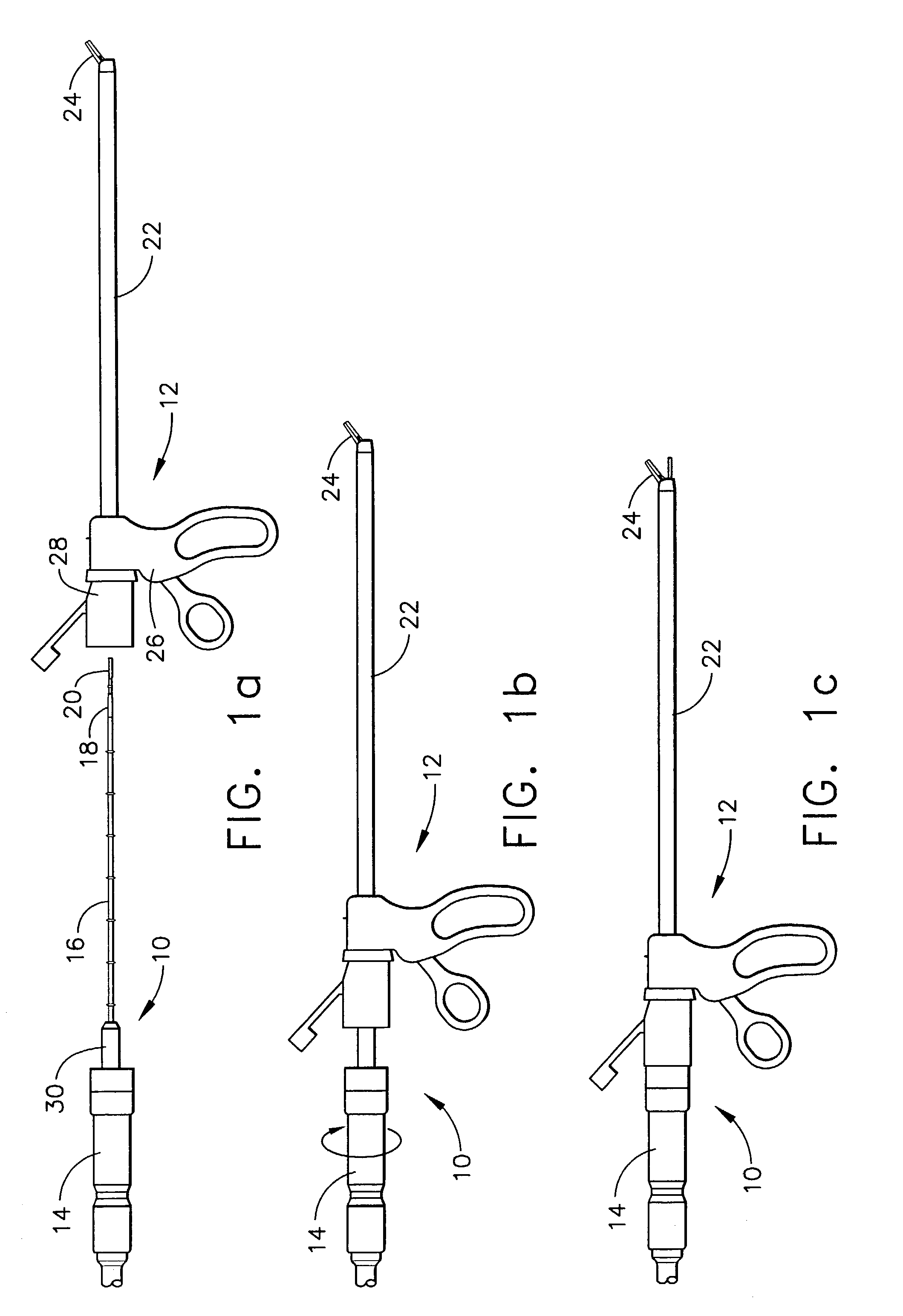
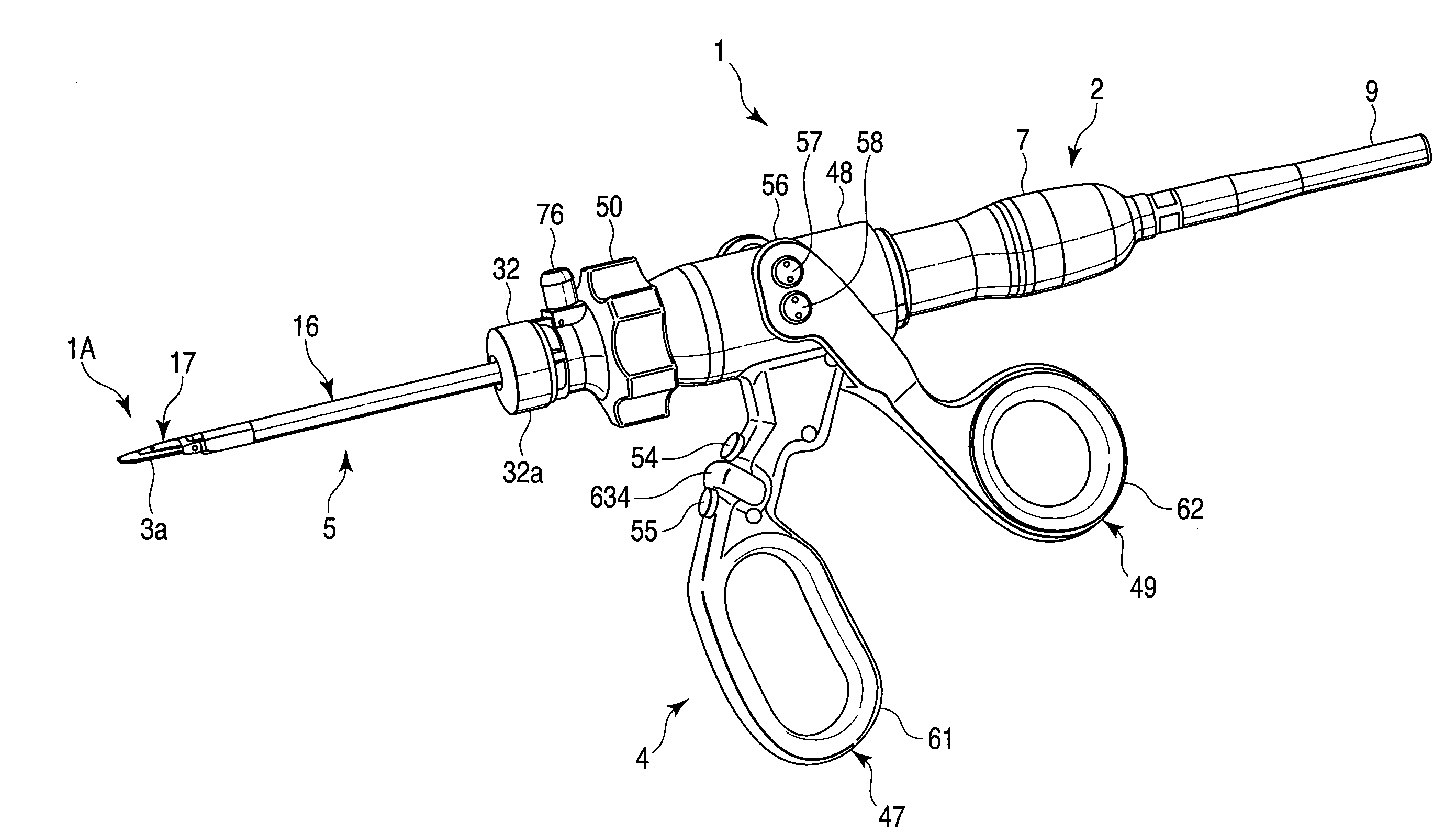
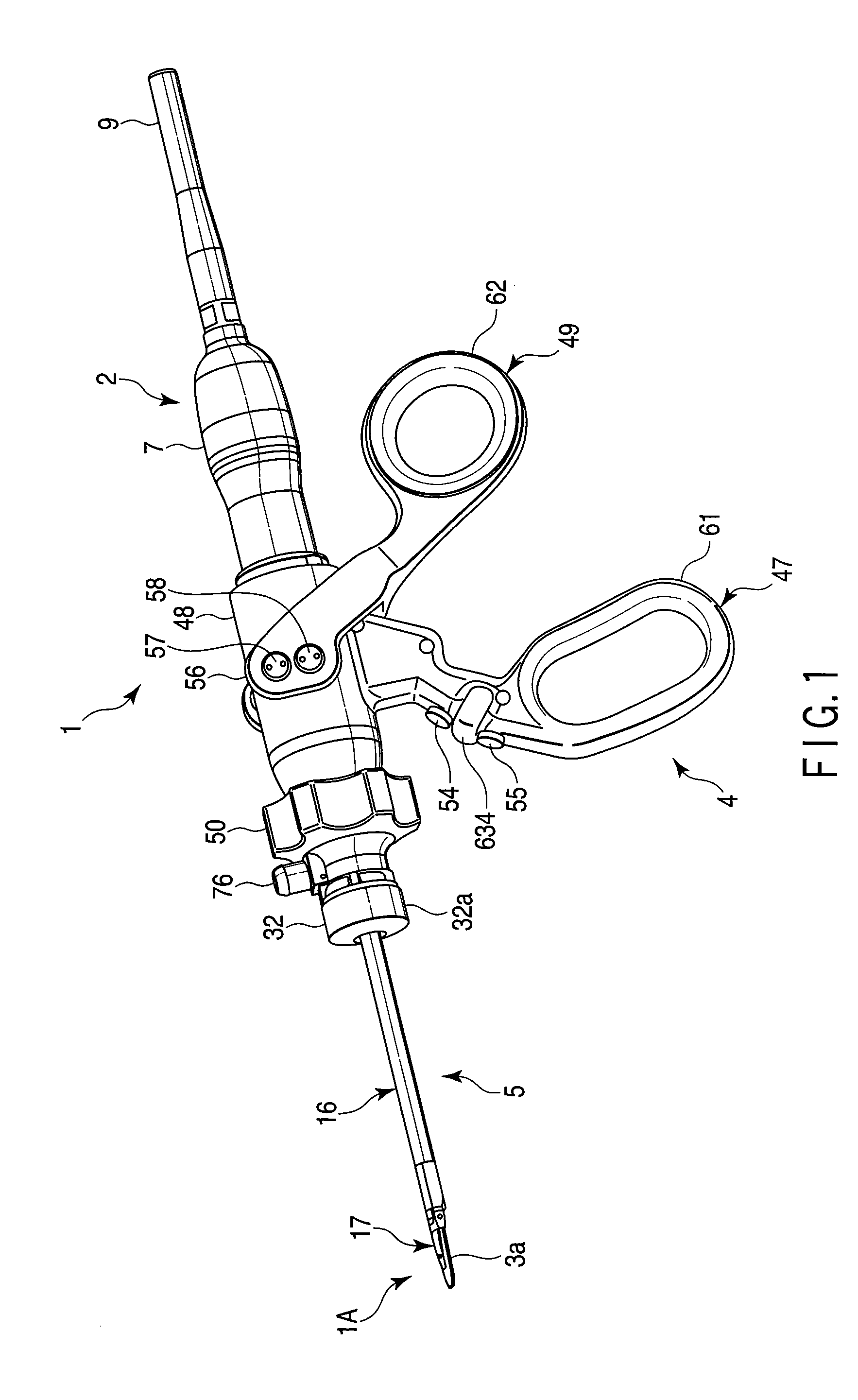
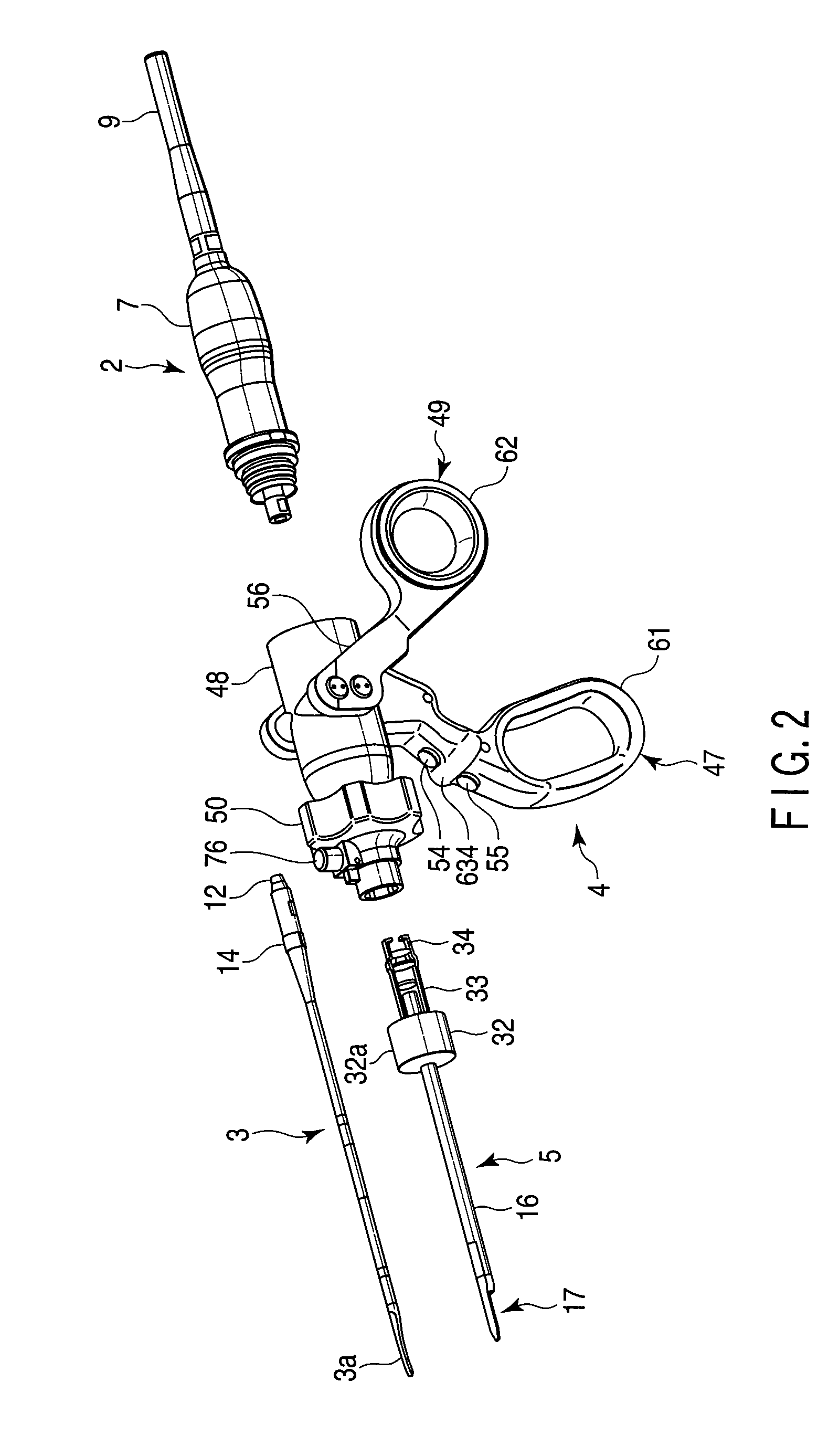
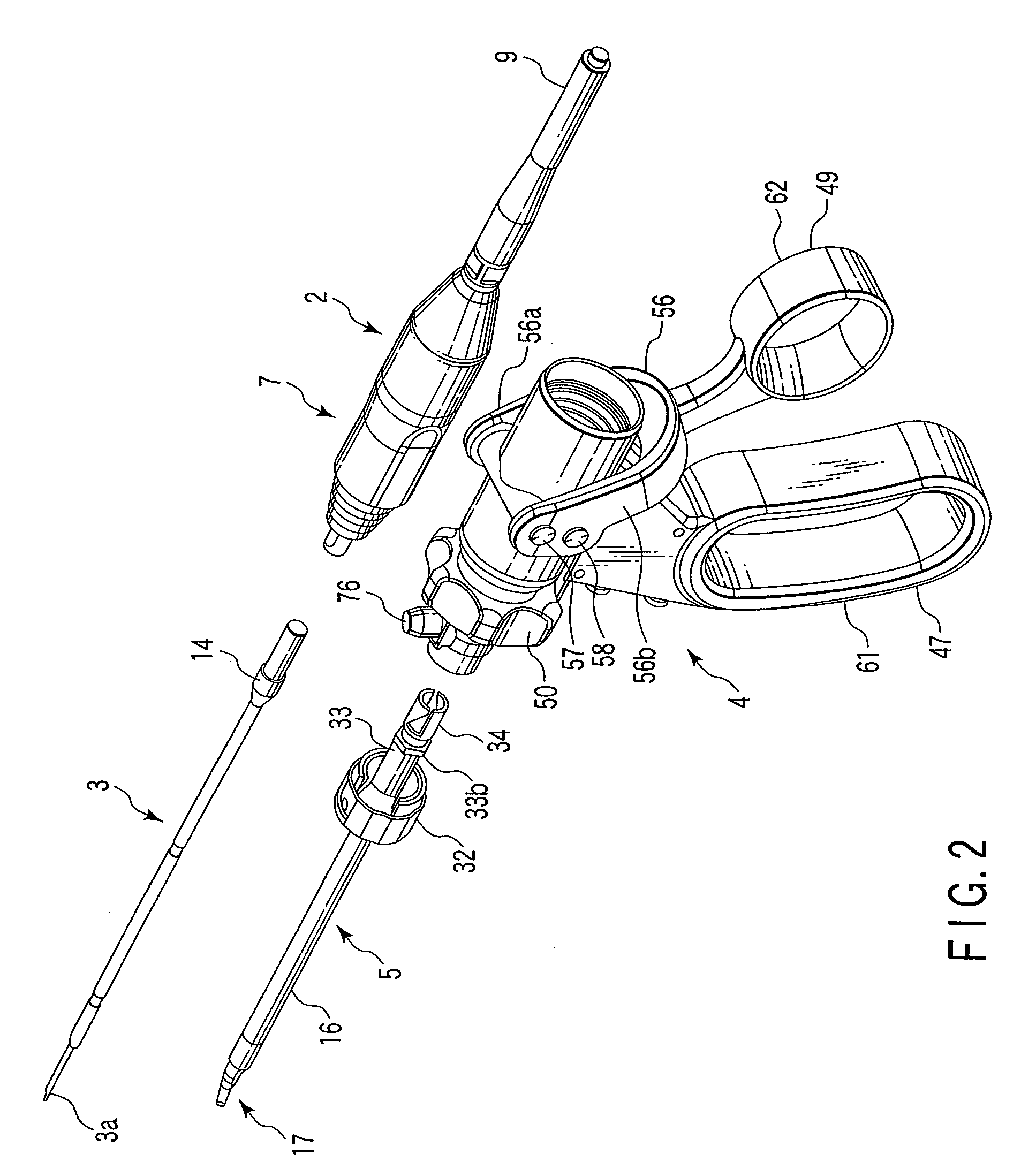
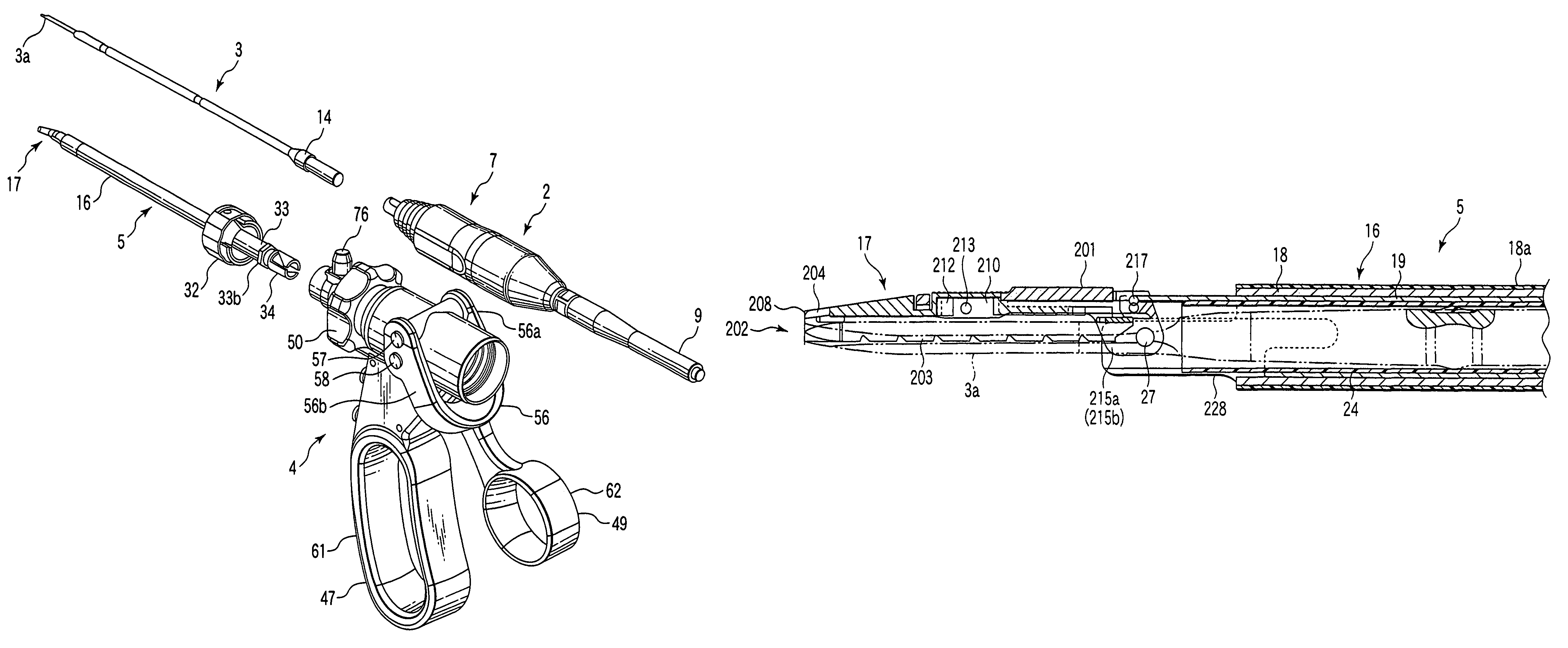
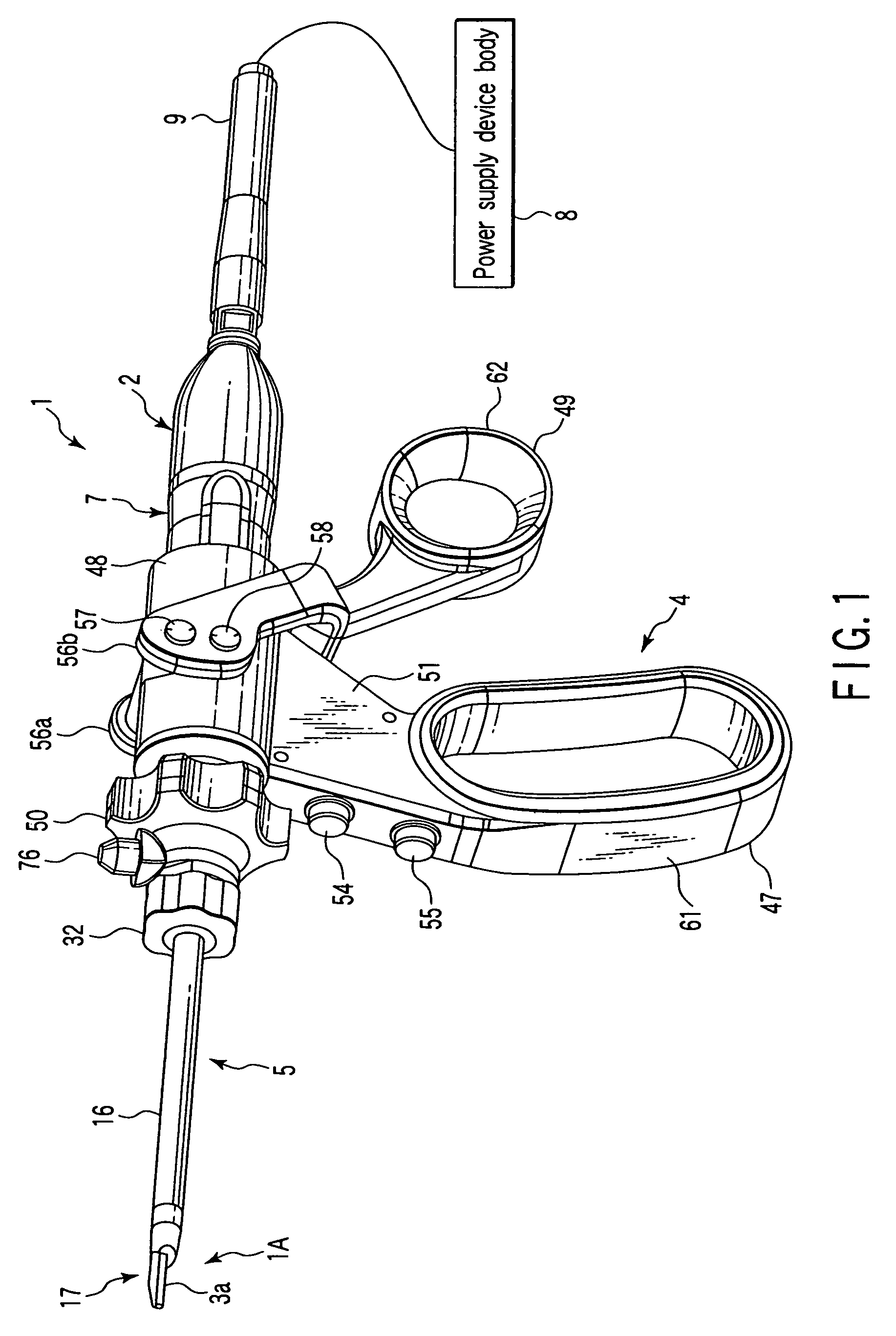
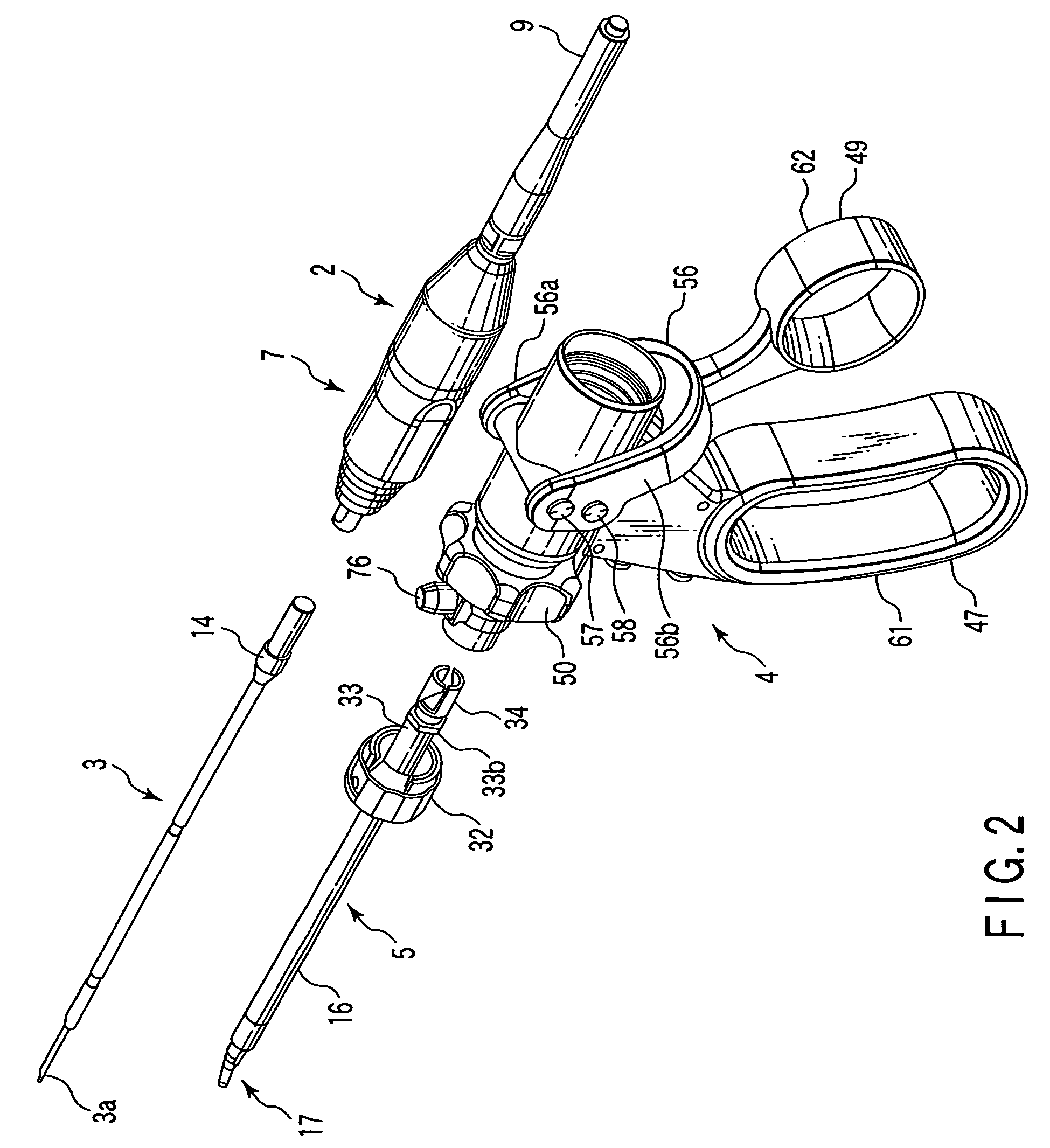
Surgical instrument
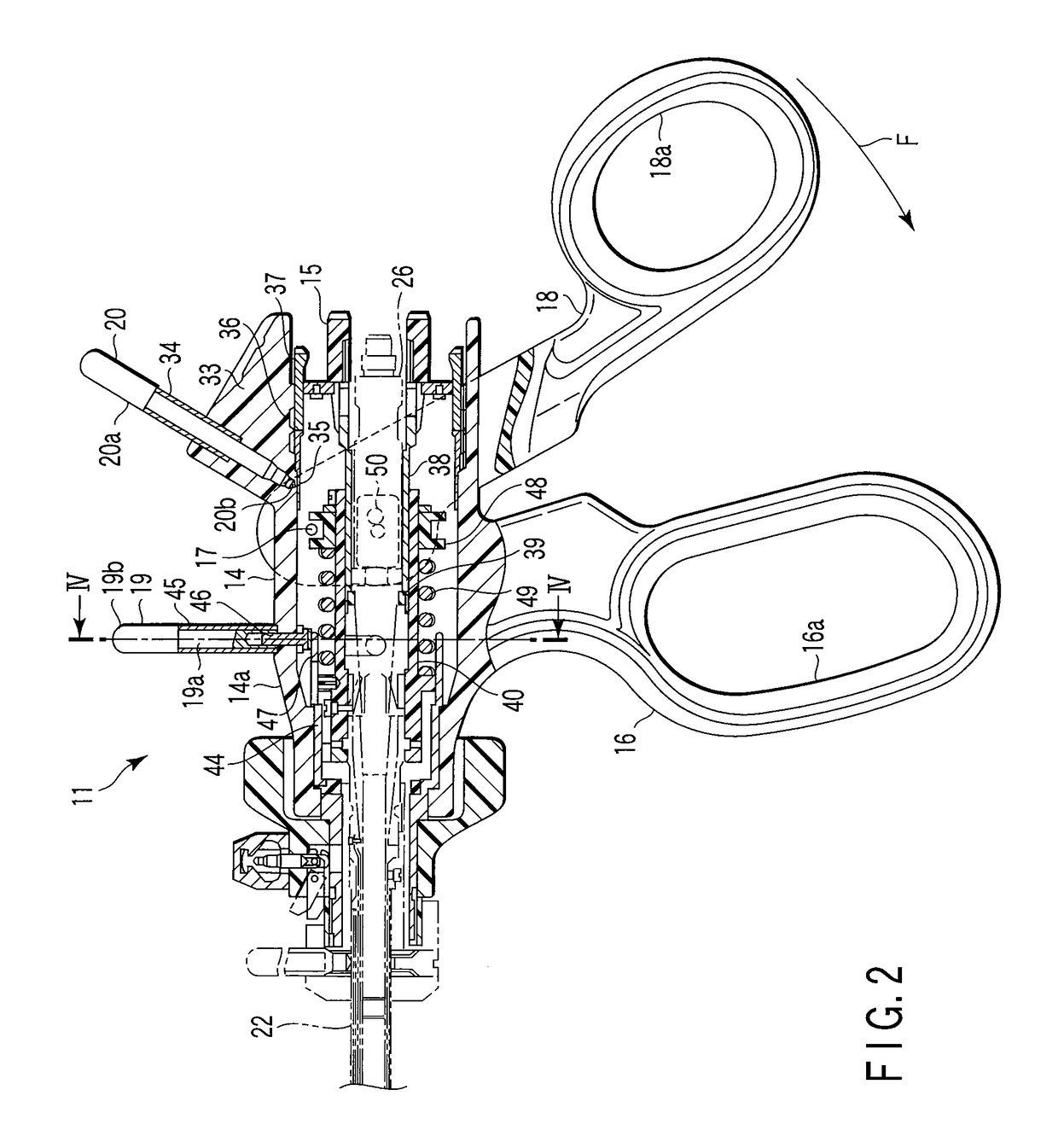
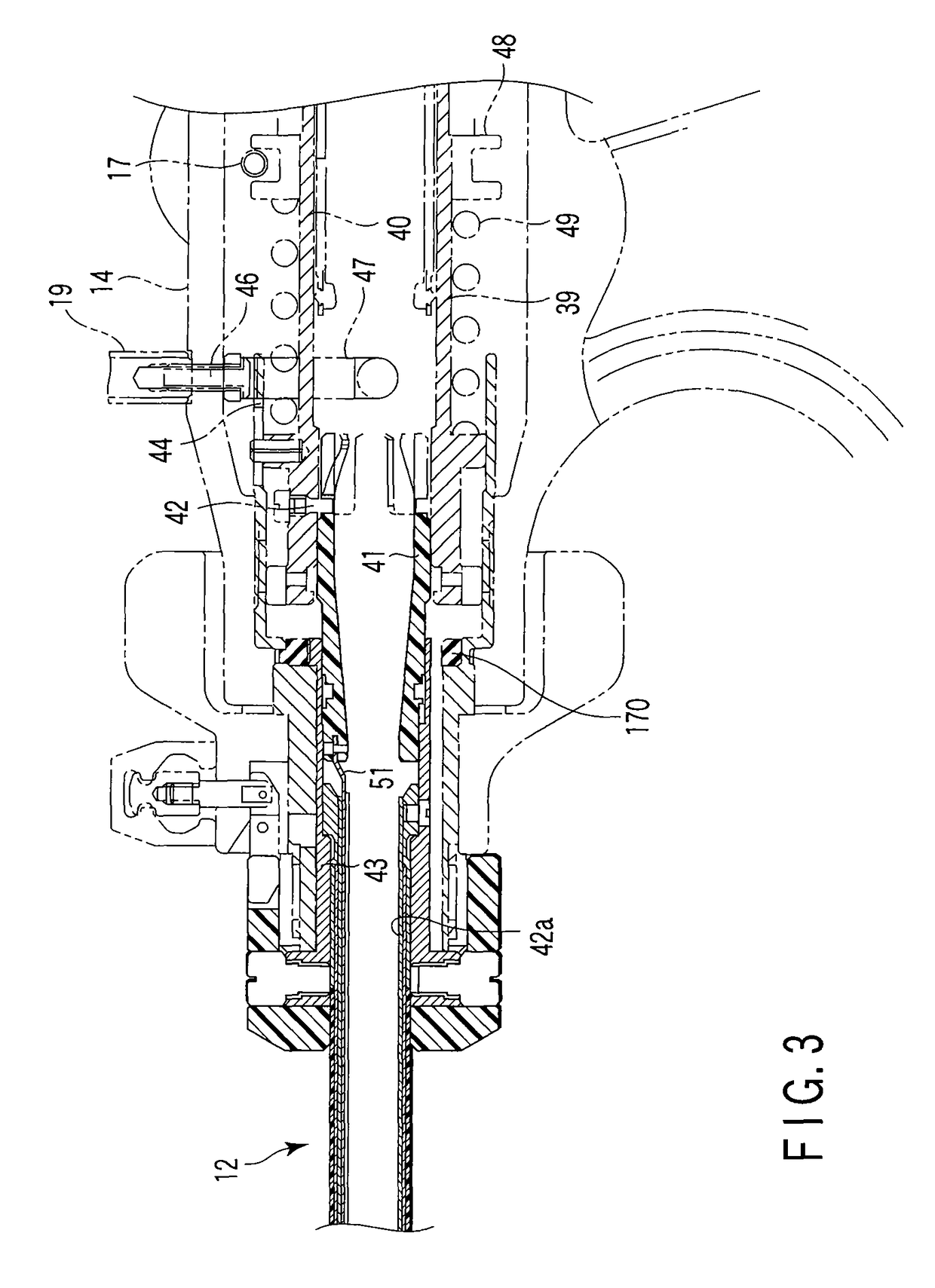
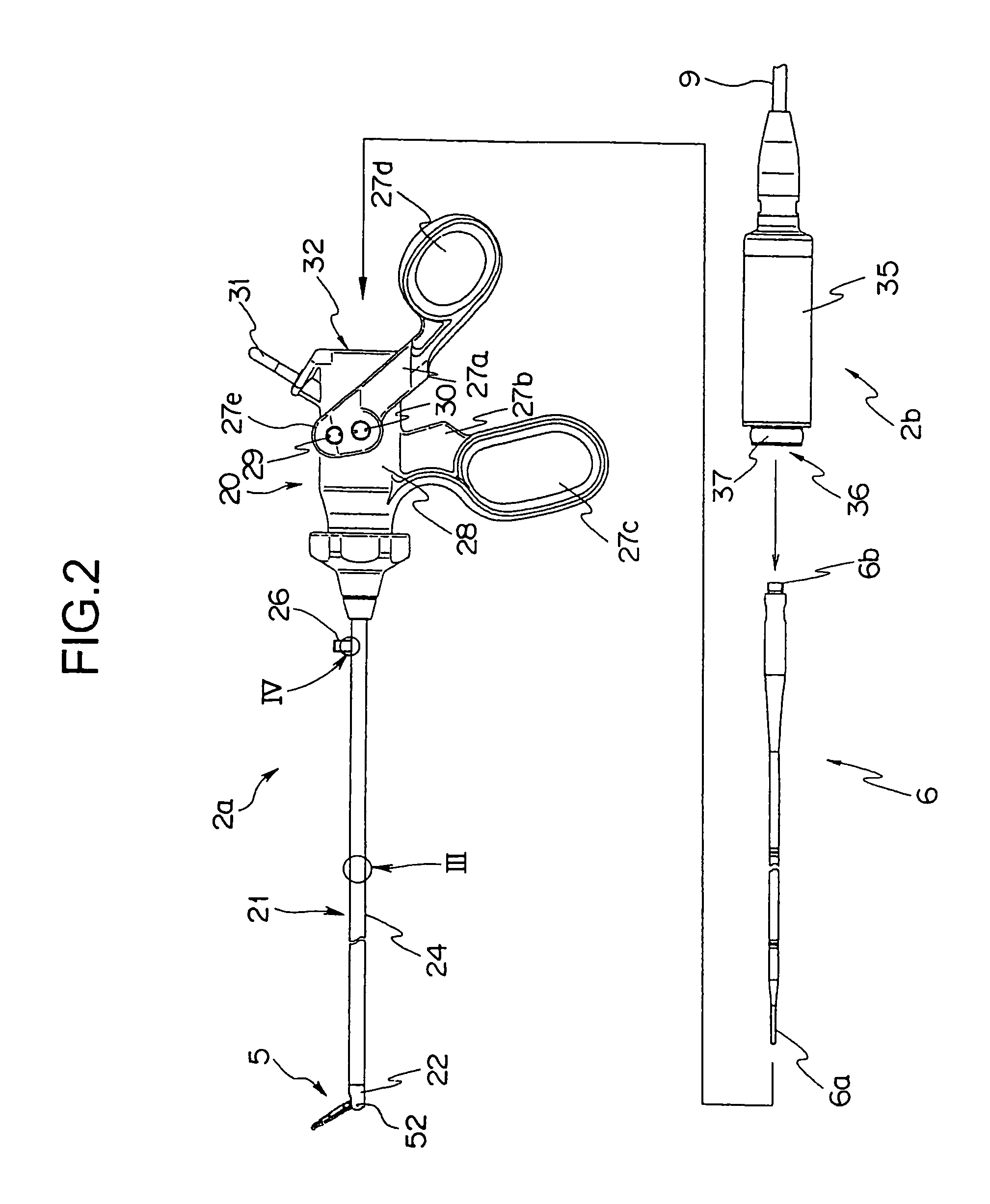
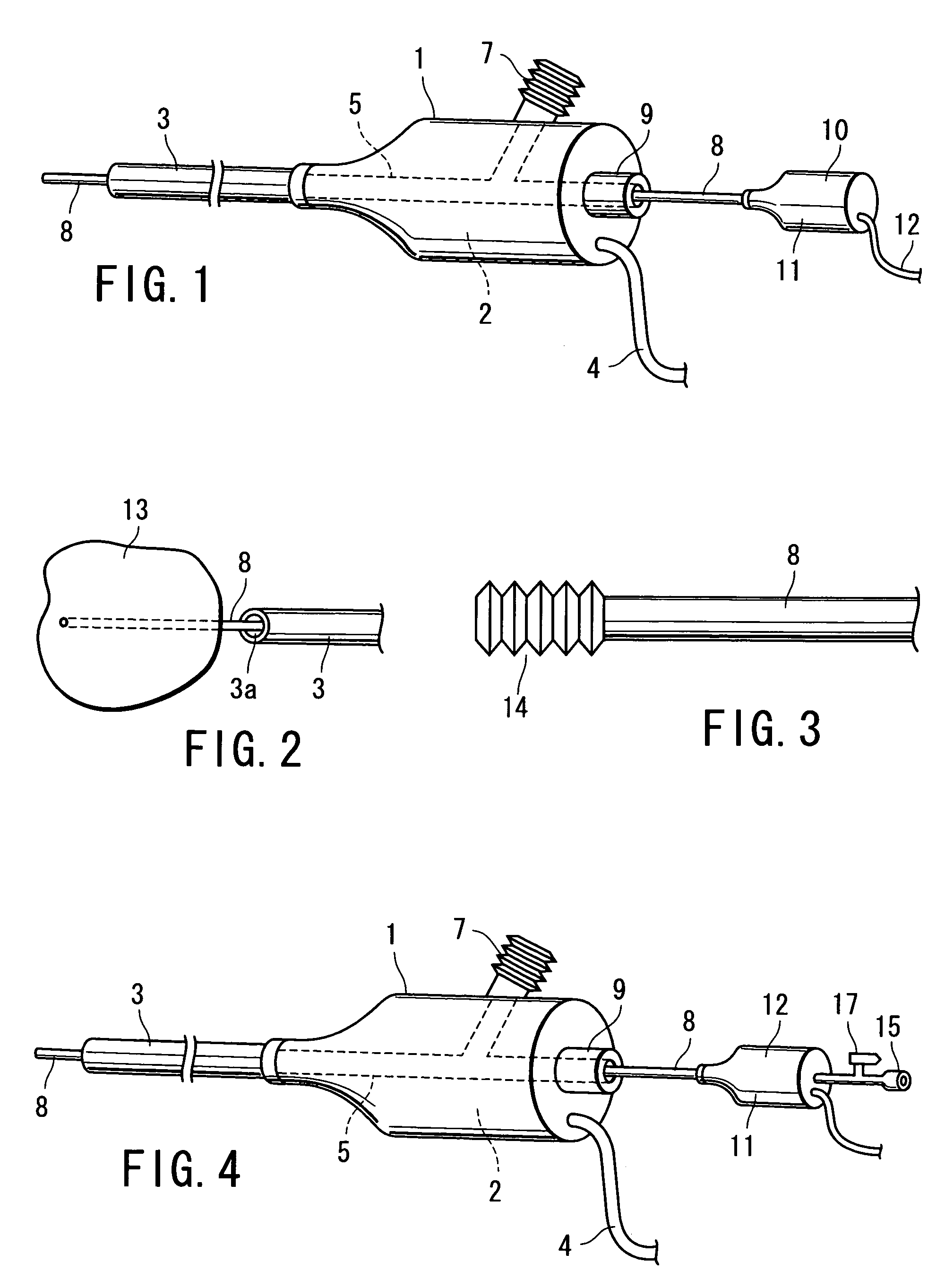
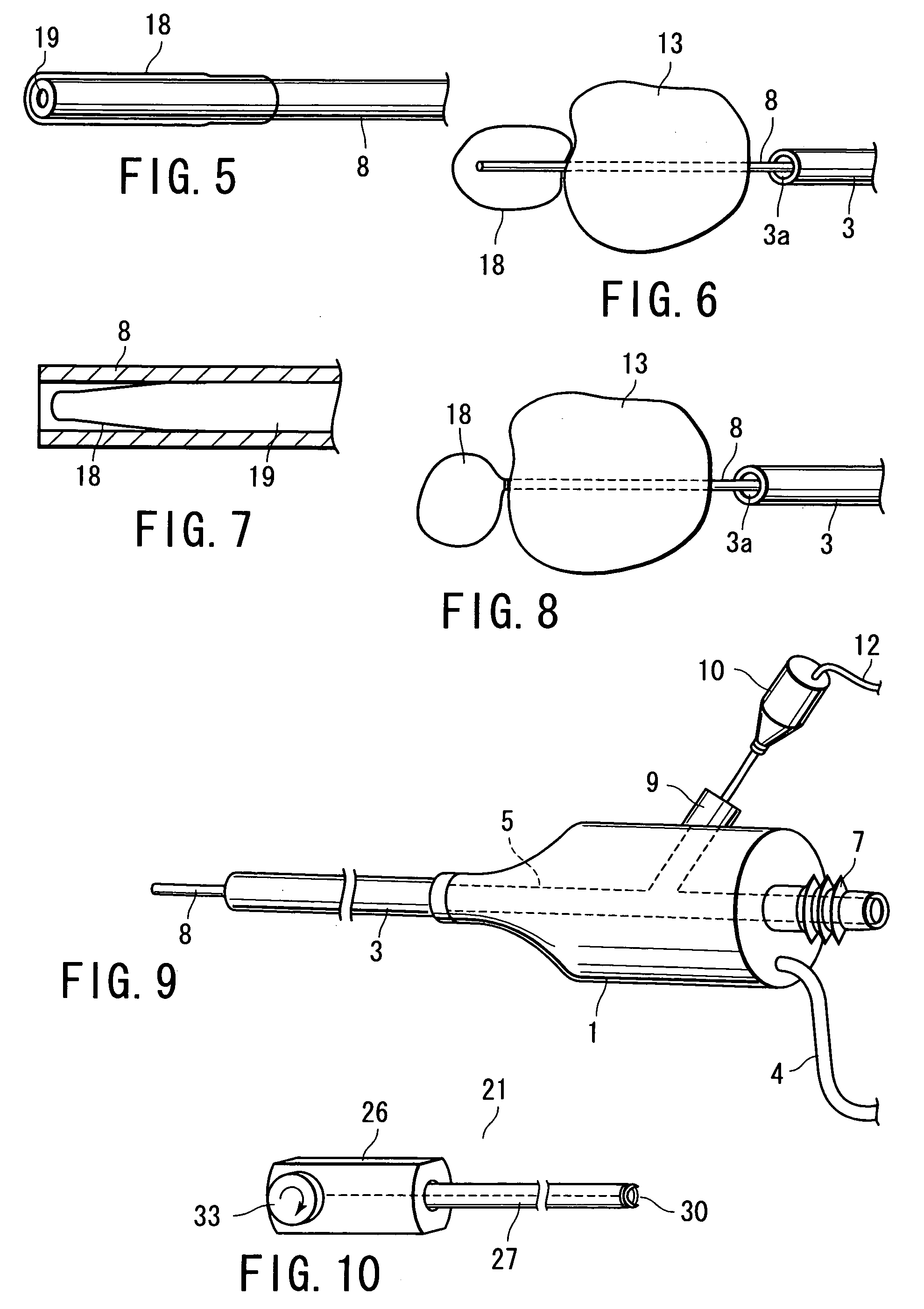
A surgical instrument has a first grasping member, a second grasping member which is provided to the first grasping member to open and close to the first grasping member, and grasps a living tissue between them, an ultrasonic coagulation-cutting unit which includes an ultrasonic vibrating portion provided in one of the first and second grasping members and connected to an ultrasonic transducer to generate ultrasonic vibration, and a pressing portion provided in the other of the first and second grasping members, and facing the ultrasonic vibrating portion, the pressing portion and the ultrasonic vibrating portion pressing the living tissue between them, and a high-frequency coagulation unit which includes a first electrode provided in the first grasping member, and a second electrode provided in the second grasping member, the first electrode and the second electrodes facing each other to coagulate the living tissue.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
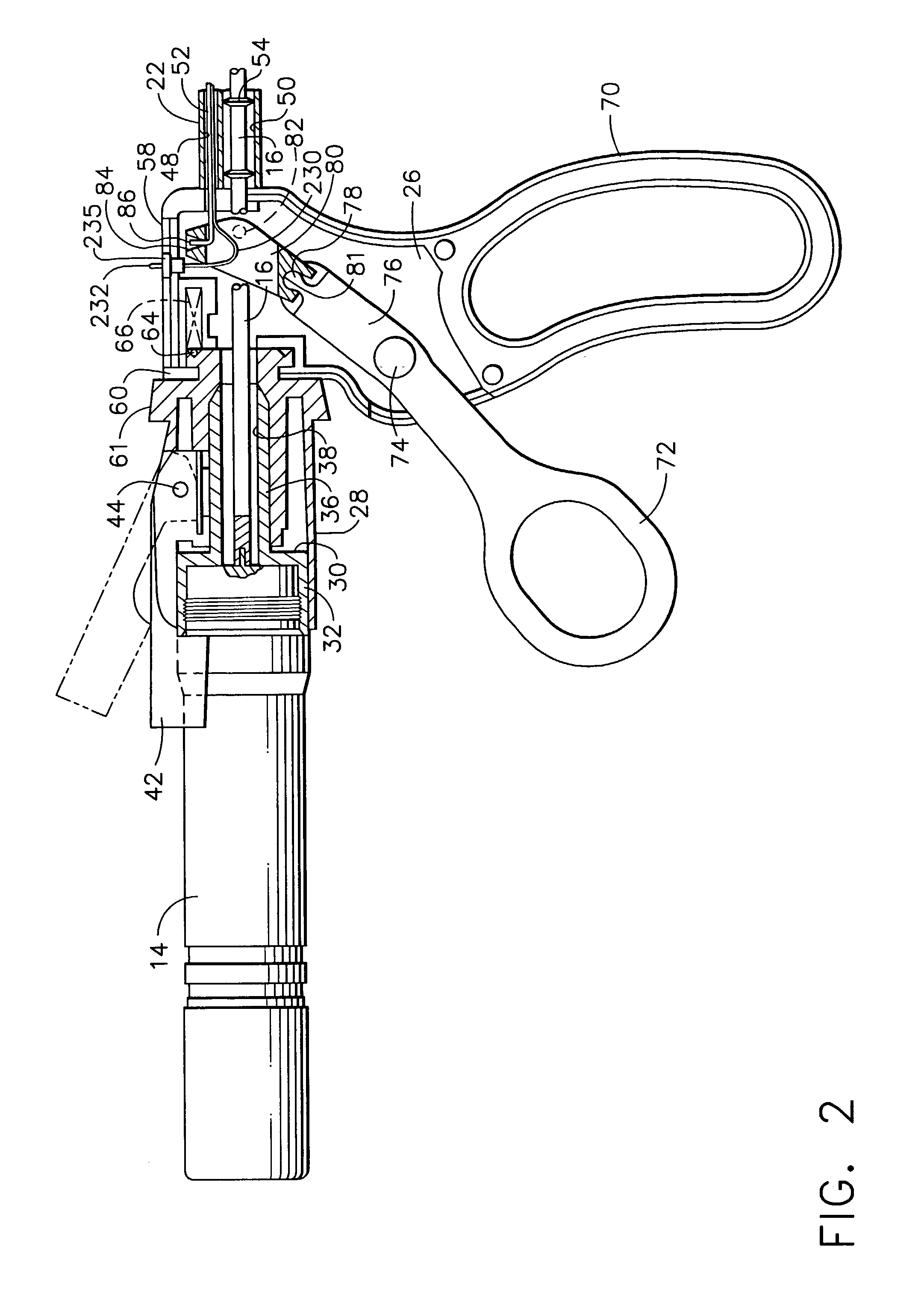
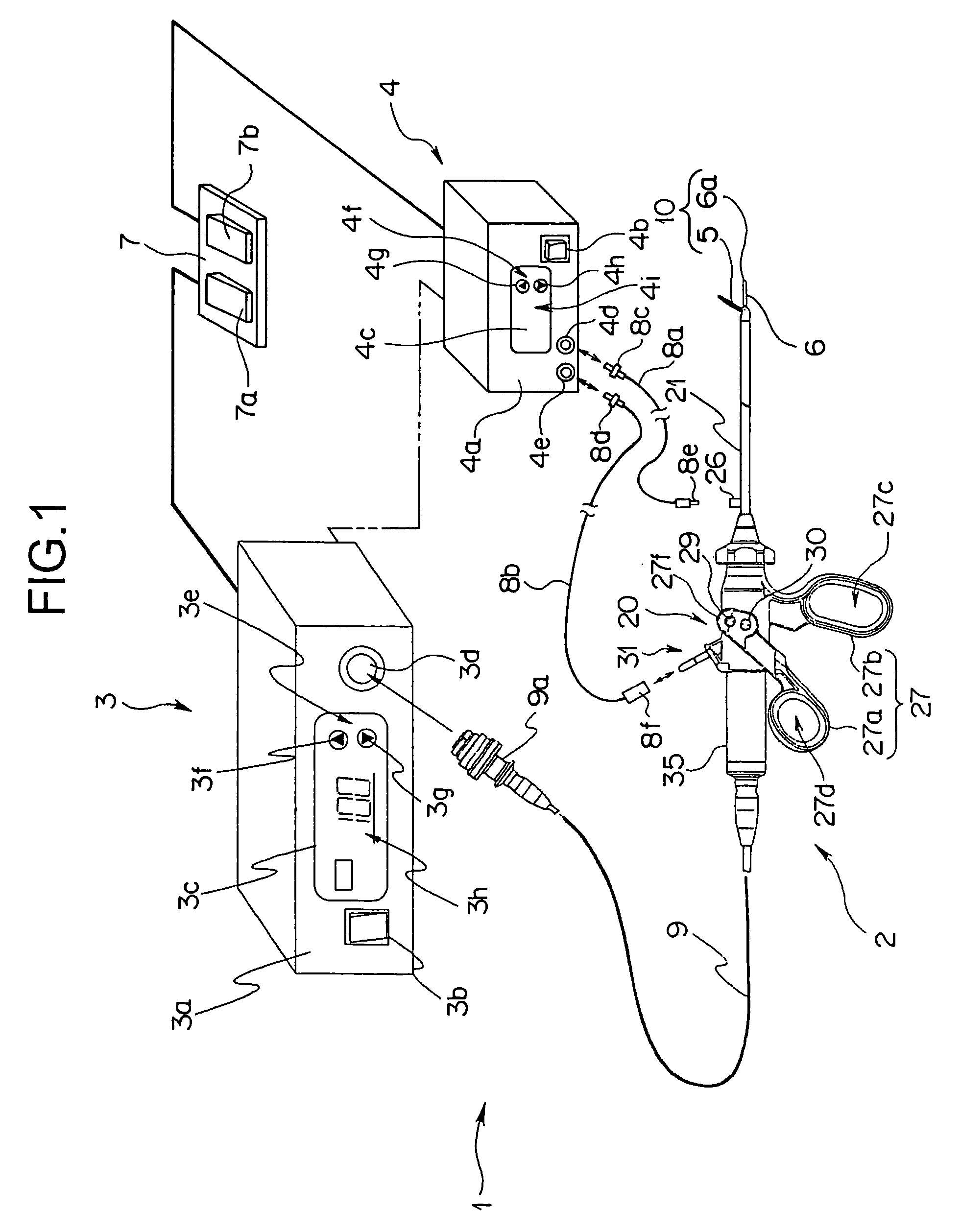
Ultrasonic coagulation and cutting apparatus
An ultrasonic coagulation and cutting apparatus includes: an ultrasonic transducer for a treatment using ultrasonic vibrations on body tissue; a probe for transmitting generated ultrasonic vibrations to the distal end thereof; a movable gripping member for cooperating with the outer surface of the probe in gripping therebetween body tissue; an operation unit operated to move the gripping member; an operation transmitting member for transmitting the operation of the operation unit to the gripping member; and high frequency power supply connecting portions for electrically connecting the probe and the gripping member to predetermined portions of a high frequency power supply for a treatment using high frequency current on the body tissue. At least coagulation of the body tissue using high frequency current is started in a first gripping state. Cutting of the body tissue using ultrasonic vibrations generated by the ultrasonic transducer is started in a second gripping state.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
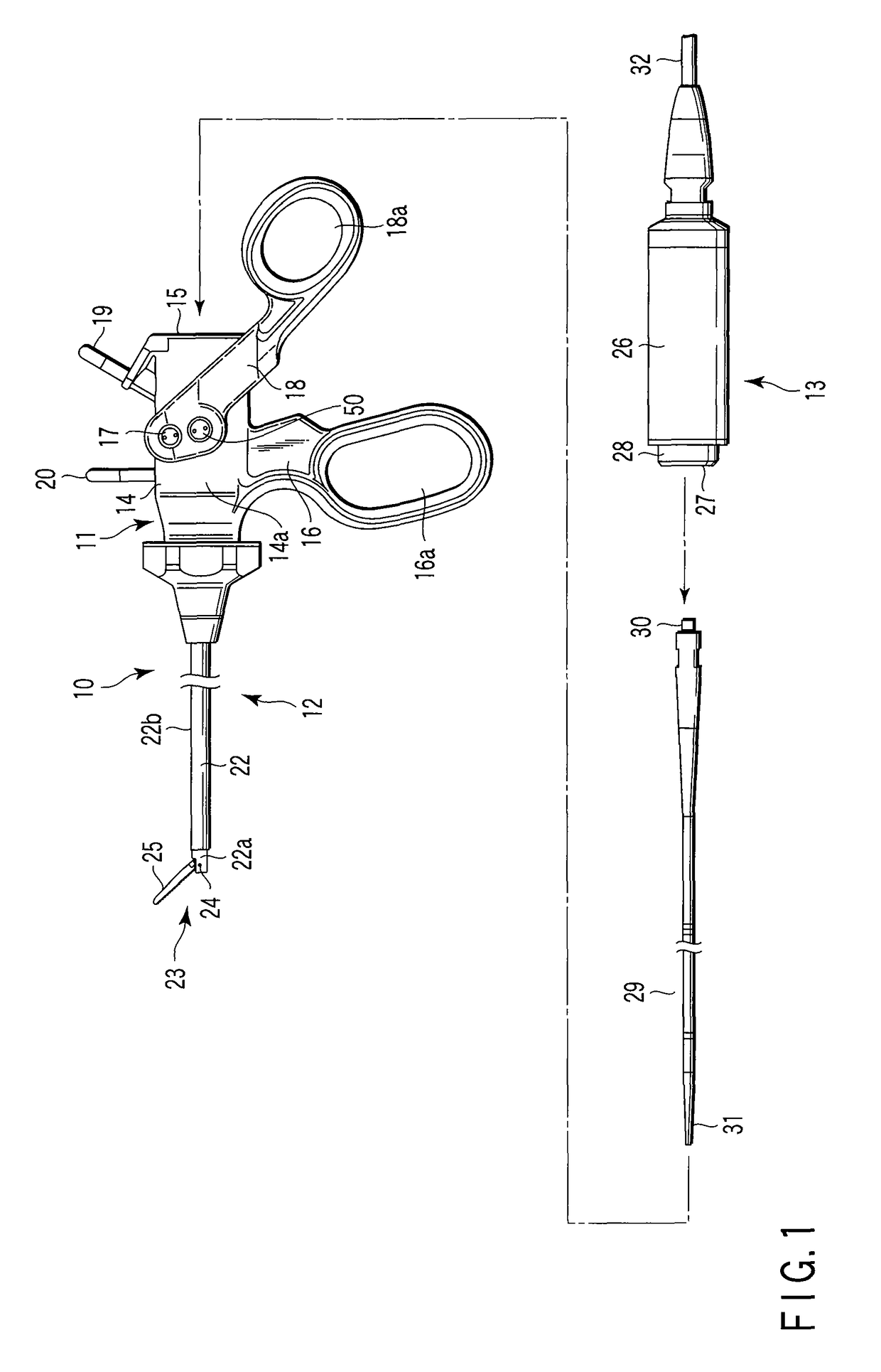
Ultrasonic forceps
Ultrasonic forceps adapted for use in open surgical forceps. The device is provided in the form of traditional open surgery forceps or tweezers, and the transmitting rod which transmits ultrasonic vibration from a proximally located transducer to the distally mounted welding horn runs through a lumen in one of the arms of the forceps.
Owner:STARION INSTR
Ultrasonic orthopedic surgical device with compound ultrasound vibration
InactiveUS20060030797A1Improve cutting efficiencyAvoid local accumulationChiropractic devicesEye exercisersVibration amplitudeDrive motor
An orthopedic surgical device with compound ultrasound vibration that comprises a handpiece, a surgical cutter fixed on the anterior top of the handpiece, and an ultrasound signal generator. Inside the outer casing of said handpiece, there are provided: an ultrasound transducer for transforming the ultrasound signals from said ultrasound signal generator into ultrasound mechanical waves; a horn (or amplitude transformer) for amplifying vibration amplitude of ultrasound mechanical waves generated from said transducer and then transmitting the amplified ultrasound mechanical waves to said surgical cutter to lead to longitudinal vibration of the surgical cutter; a driving motor fixed in the back end of said handpiece for driving said ultrasound transducer and horn to accomplish the movement of swing and rotation; an adapter provided between said driving motor and said transducer for supplying ultrasonic electrical signals generated by said ultrasound signal generator to said ultrasound transducer.
Owner:ZHOU ZHAOYING +3
Ultrasonic surgical apparatus with treatment modes selectable
InactiveUS20050288659A1Reliably coagulationShort timeSurgical instruments for heatingTransducerEngineering
An ultrasonic surgical apparatus comprises a treatment device with an ultrasonic transducer driven to generate ultrasonic vibration, an operation device outputting a signal commanding the transducer to start driving in response to an operator's operation, and a driver driving the transducer by supplying current thereto. The apparatus further comprises a controller controlling the driver. The controller controls the driver using selectively a first output control pattern and a second output control pattern. The first output control pattern is set to supply the current of a first current value under control of constant current control in response to the signal from the operation device, while the second output control pattern is set to supply the current of a second current value in response to the signal from the operation device and then the current is reduced in amount as the time counted from starting the supply elapses.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Surgical operating apparatus
A surgical operating apparatus includes a sheath provided with a distal end part and a proximal end part, an apparatus main body to be coupled to the proximal end part of the sheath, a probe which is provided with a distal end part and a proximal end part, is inserted into the sheath, and transmits ultrasonic vibration from the proximal end part side to the distal end part side, a jaw which is turnably supported at the distal end part of the sheath, and is operated to be opened or closed between a closed position at which the jaw is engaged with the distal end part of the probe, and an opened position at which the jaw is separated from the distal end part of the probe, a handle which is provided in the apparatus main body, and operates the opening / closing operation of the jaw, a slider section which is provided in the apparatus main body, and is advanced / retreated to be moved in a central axis direction of the probe between a first movement position corresponding to the opened position of the jaw and a second movement position corresponding to the closed position of the jaw in accordance with the operation of the handle, and a notification mechanism for notifying of a state where the slider section has moved by an amount equal to or larger than a predetermined amount on the way thereof from the first movement position to the second movement position.
Owner:OLYMPUS MEDICAL SYST CORP
Ultrasound treatment system
InactiveUS7780659B2Improve mobilityShorten the timeSurgical instruments for heatingArtificial legsUltrasonic vibrationPerfusion
An ultrasound treatment system in accordance with the present invention comprises an ultrasonic transducer, a handpiece, a probe, a sheath, a clamping member, an operation unit, an operating member, a suction base, and a perfusion base. The ultrasonic transducer generates ultrasonic vibrations. The handpiece has the ultrasonic transducer incorporated therein and serves as an operation unit. The probe is connected to the ultrasonic transducer, and serves as a vibration transmitting member for transmitting ultrasonic vibrations to a distal member realizing a stationary portion that is a treatment portion for treating a living tissue. The sheath serves as a protecting member for shielding the probe. The clamping member is opposed to the distal member at the distal end of the sheath, and realizes a movable portion that is another treatment portion for clamping a living tissue in cooperation with the distal member. The operation unit is manipulated for clamping a living tissue with the clamping member and distal member or freeing the living tissue therefrom.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
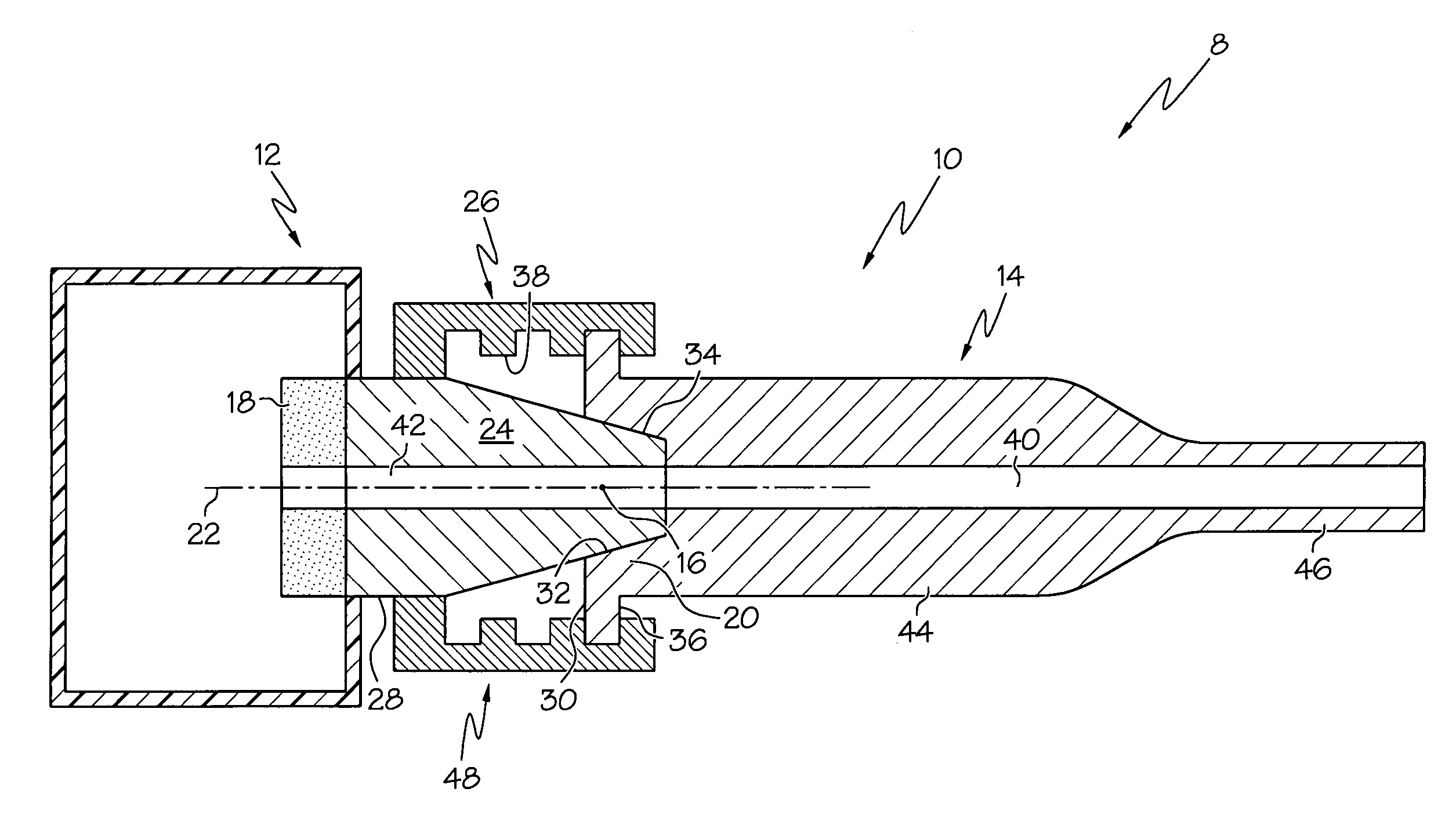
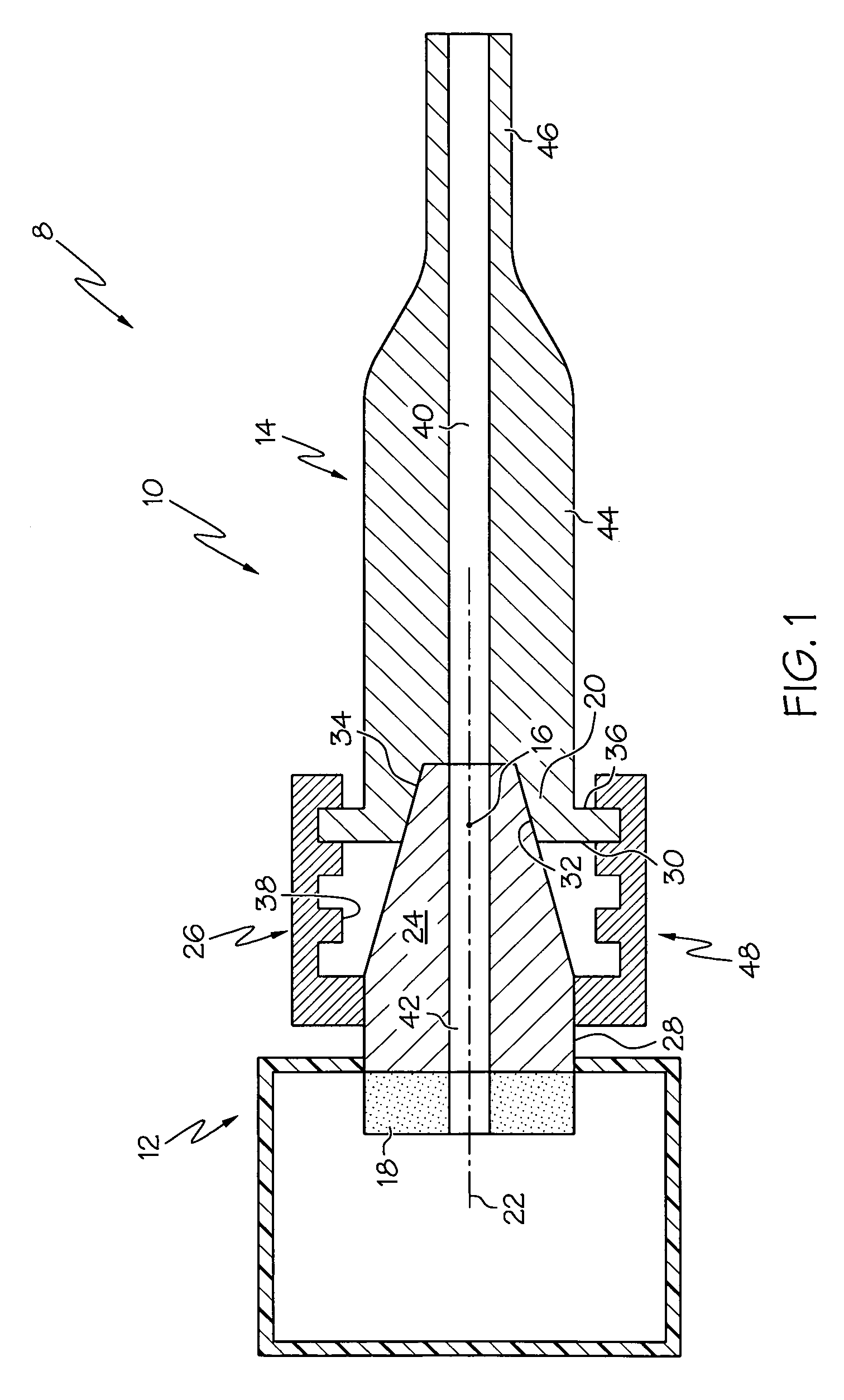
Elevated coupling liquid temperature during HIFU treatment method and hardware
InactiveUS20080281200A1Avoid necrosisEnhanced couplingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyLiquid temperatureUltrasonic vibration
A medical procedure utilizes a high-intensity focused ultrasound instrument having an applicator surface, a liquid-containing bolus or expandable chamber acting as a heat sink, and a source of ultrasonic vibrations, the applicator surface being a surface of a flexible wall of the bolus, the source of ultrasonic vibrations being in operative contact with the bolus. The applicator surface is placed in contact with an organ surface of a patient, the source is energized to produce ultrasonic vibrations focused at a predetermined focal region inside the organ, and a temperature of liquid in the bolus is controlled while the applicator surface is in contact with the organ surface to control temperature elevation in tissues of the organ between the focal region and the organ surface to necrose the tissues to within a desired distance from the organ surface.
Owner:US HIFU
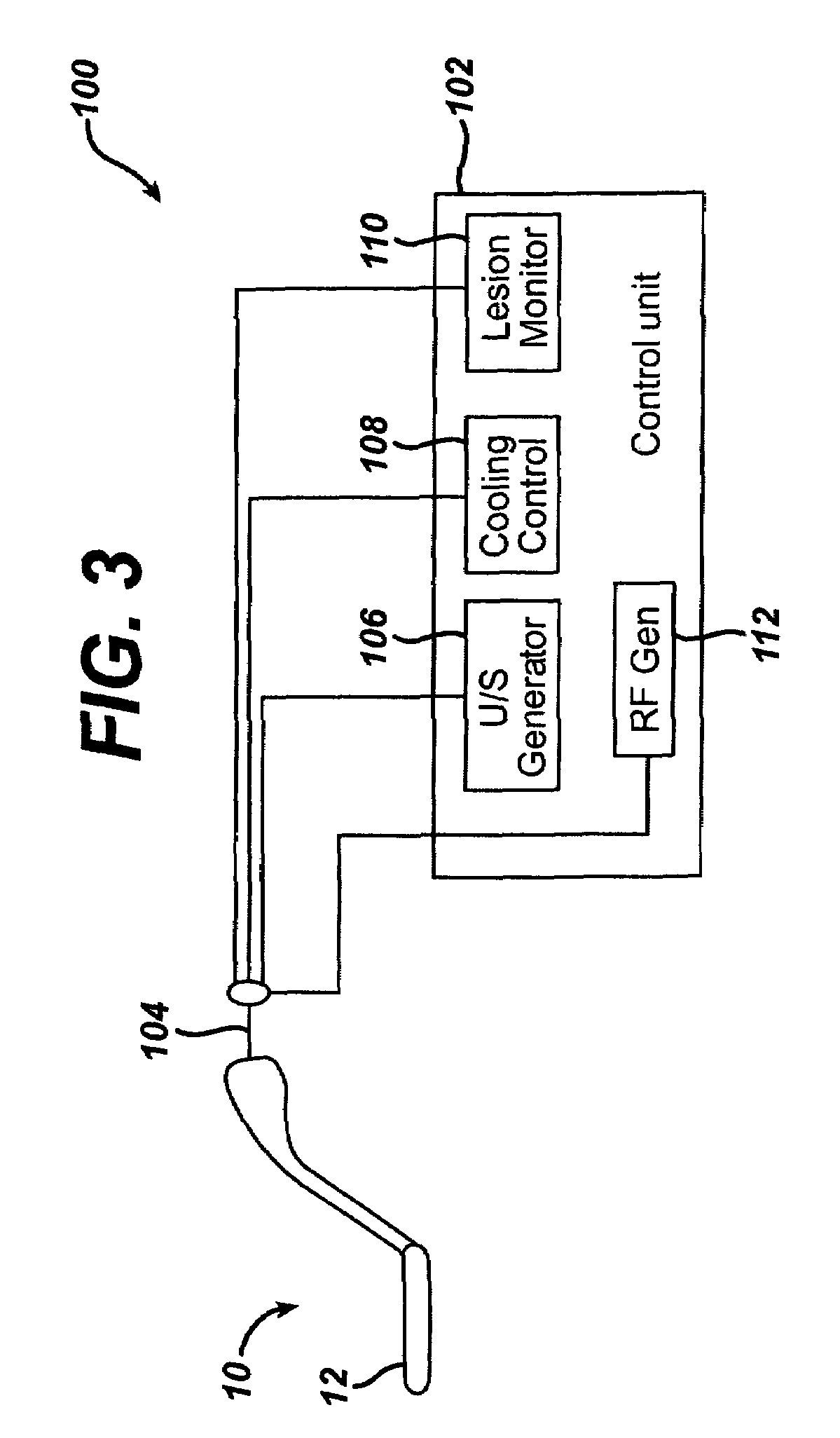
System for creating linear lesions for the treatment of atrial fibrillation
ActiveUS7037306B2Minimize damageFast formingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsChiropractic devicesUltrasonic vibrationLesion
A system for forming linear lesions in tissue, the system comprising a control unit having an ultrasound vibration driving section, and an ultrasonic applicator operatively connected to the control unit. The ultrasonic applicator comprises an ultrasonic transducer having an acoustic window, and an ultrasonic vibratory element, the ultrasonic vibratory element having a convergent shape with a focus located in the direction of the acoustic window. An air gap is adjacent to the ultrasonic vibratory element in an opposite direction from the focal point. The system further comprises means for controlling the depth of the lesion formed in the tissue.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Ultrasonic treatment appliance
InactiveUS6887252B1Minimize occurrenceImprove resectionSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsUltrasonic vibrationBiomedical engineering
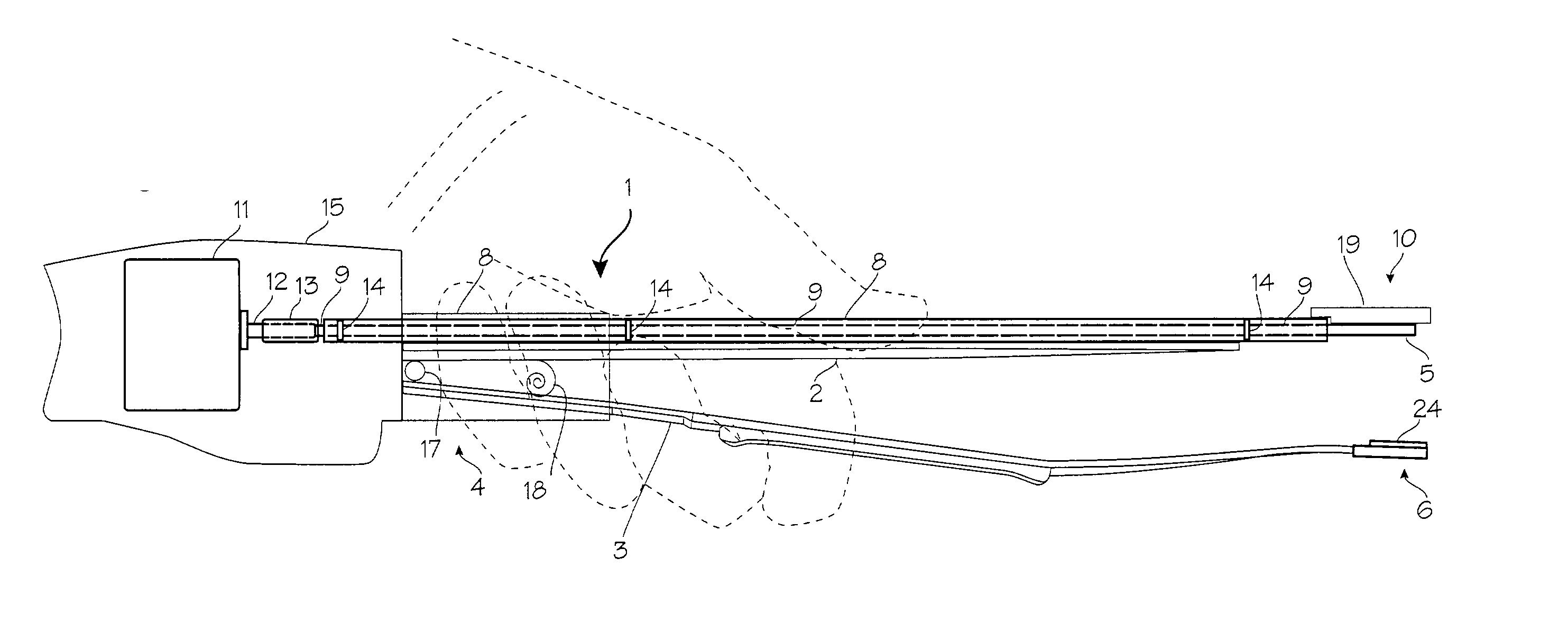
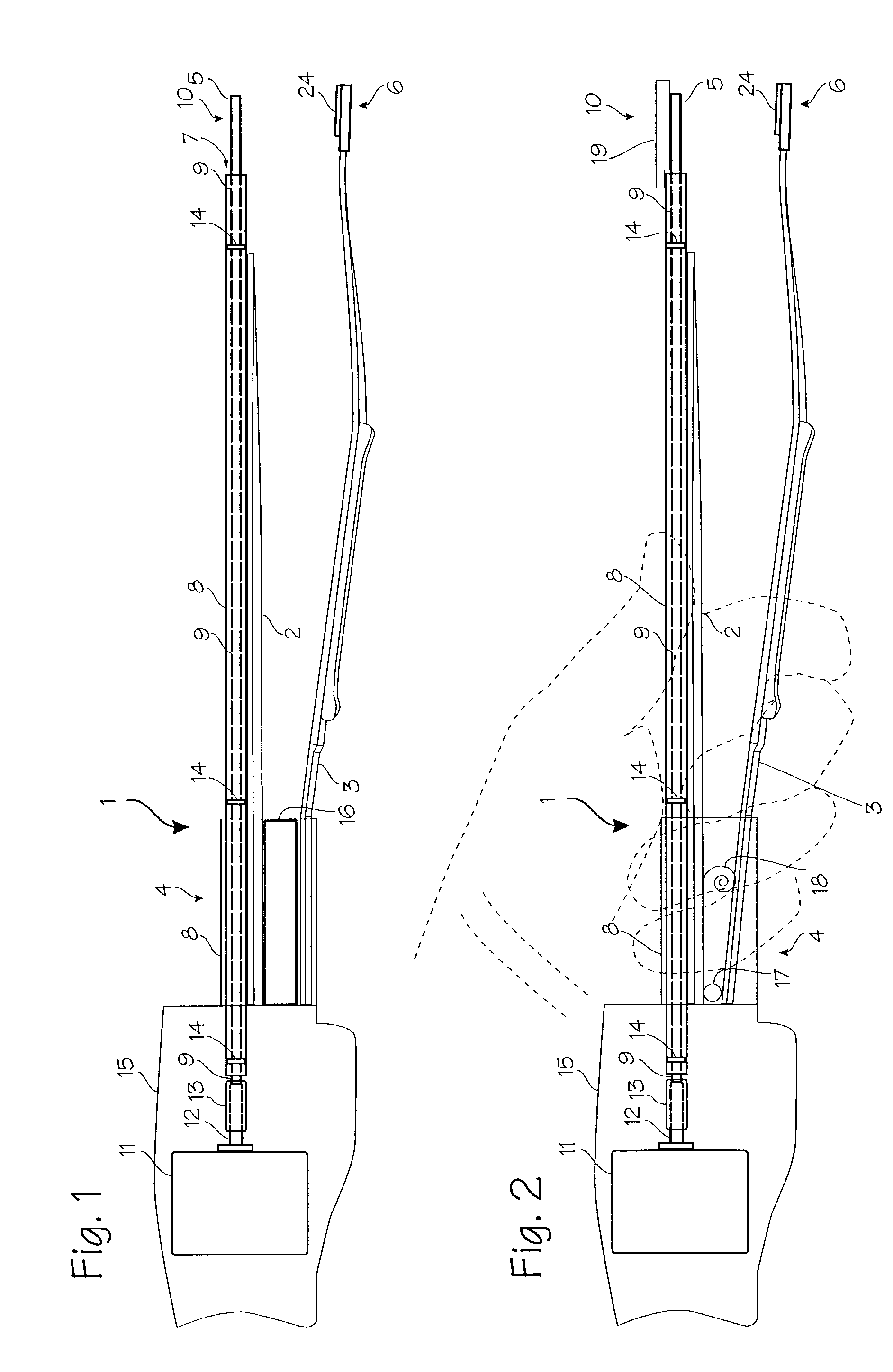
An ultrasonic treatment appliance includes a handpiece with a built-in ultrasonic transducer, and an elongated probe extending forward from the handpiece and connected to the ultrasonic transducer in order to propagate ultrasonic vibrations. The ultrasonic treatment appliance further comprises a distal probe part formed as an integral part of or independently of the probe at the distal end of the probe, and a clamping portion opposed to the distal probe part so that the clamping portion can open or close freely, the clamping portion being freely attachable thereto or detachable therefrom.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Ultrasonic surgical blade having transverse and longitudinal vibration
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT +1
Medical ultrasound system and handpiece and methods for making and tuning
InactiveUS20070232928A1Small sizeIncrease displacementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryUltrasonographyUltrasonic sensor
Several embodiments of medical ultrasound handpieces are described each including a medical ultrasound transducer assembly. An embodiment of a medical ultrasound system is described, wherein the medical ultrasound system includes a medical ultrasound handpiece having a medical ultrasound transducer assembly and includes an ultrasonically-vibratable medical-treatment instrument which is attachable to a distal end of the transducer assembly. An embodiment of a medical ultrasound system is described, wherein the medical ultrasound system has a handpiece including a medical ultrasound transducer assembly and including a housing or housing component surrounding the transducer assembly. A method for tuning a medical ultrasound handpiece includes machining at least a distal non-threaded portion of an instrument-attachment stud of the transducer assembly to match a measured fundamental frequency to a desired fundamental frequency to within a predetermined limit. A method for making a medical ultrasound transducer assembly determines acceptable gains for gain stages of the transducer assembly.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT +1
Ultrasonic wave generating/transmitting apparatus
InactiveUS7001335B2Avoid feverAvoid contactUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsEngineeringUltrasonic vibration
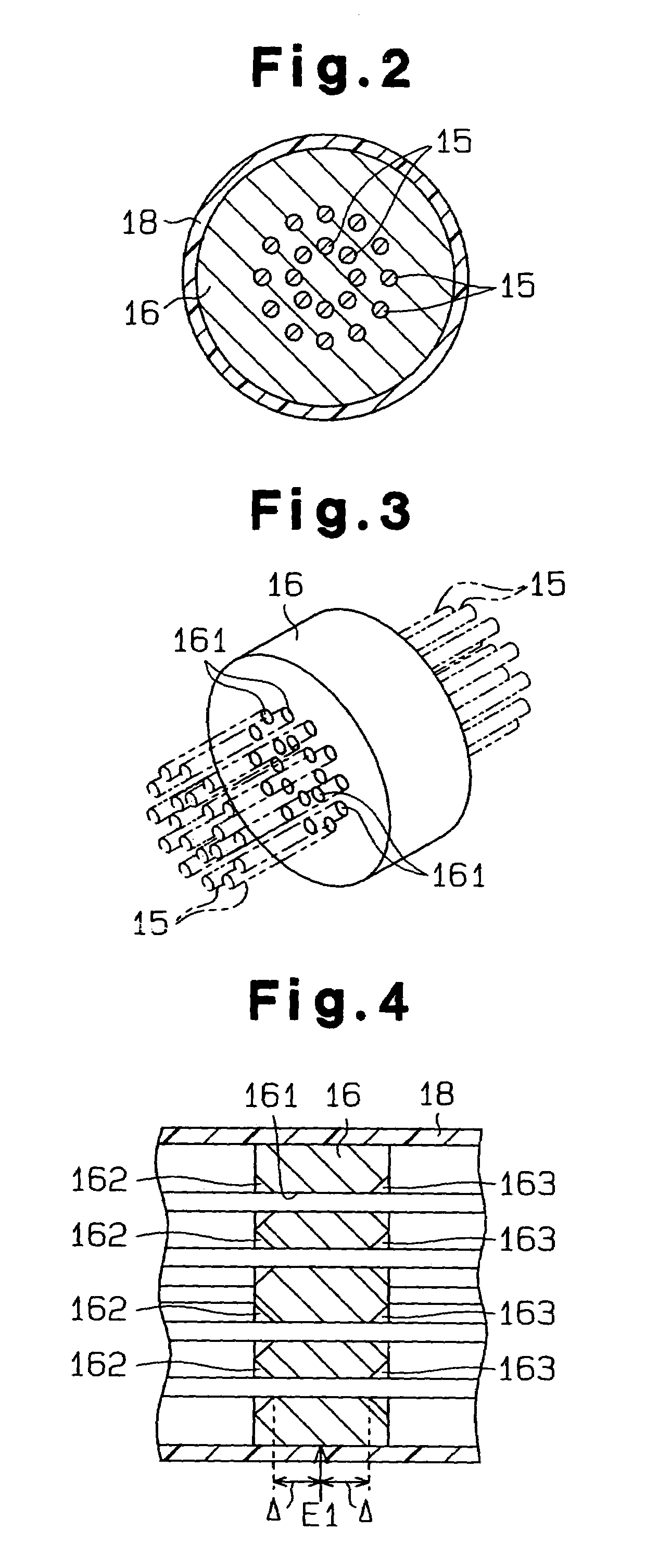
Disclosed is an ultrasonic generating and transmitting apparatus equipped with a transmission section for transmitting ultrasonic vibration from a vibration section. A plurality of linear members for transmitting ultrasonic vibration and binding plates which bind the linear members in such a state as to be apart from one another are provided. The transmission section is comprised of the linear members and the binding plates.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
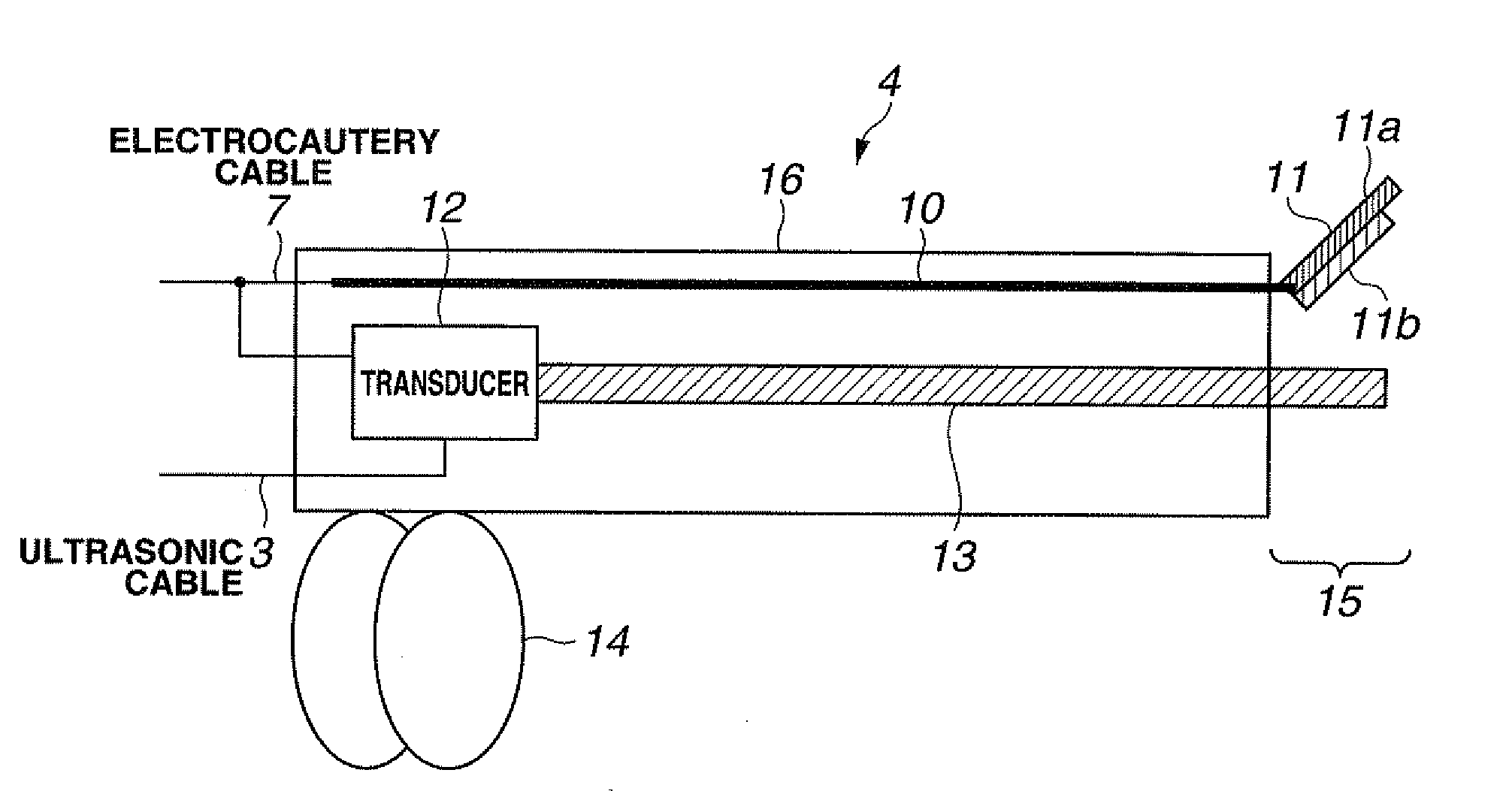
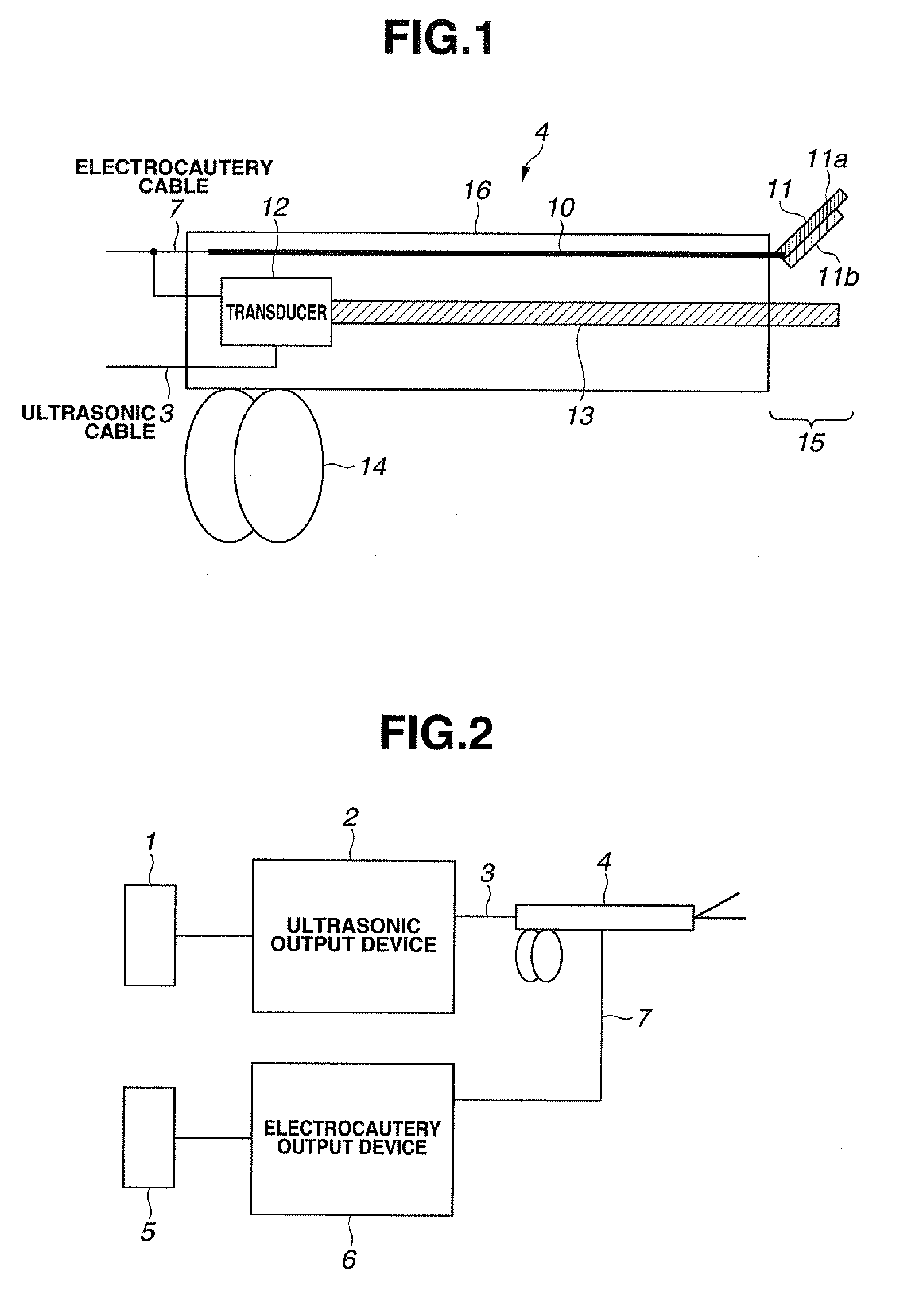
Relay device and ultrasonic-surgical and electrosurgical system
InactiveUS20080125768A1Ultrasound therapySurgical instruments for heatingEngineeringELECTROSURGICAL DEVICE
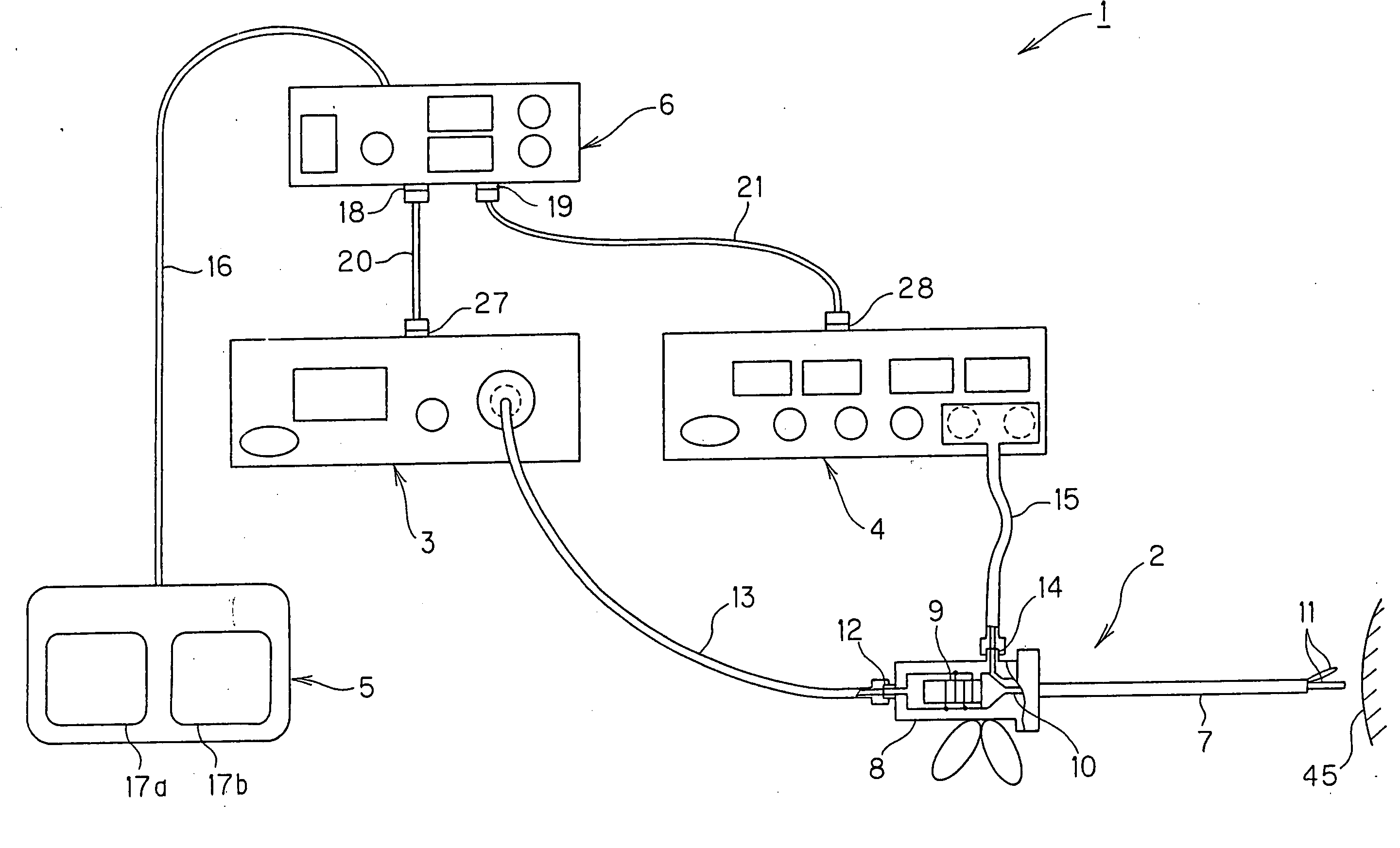
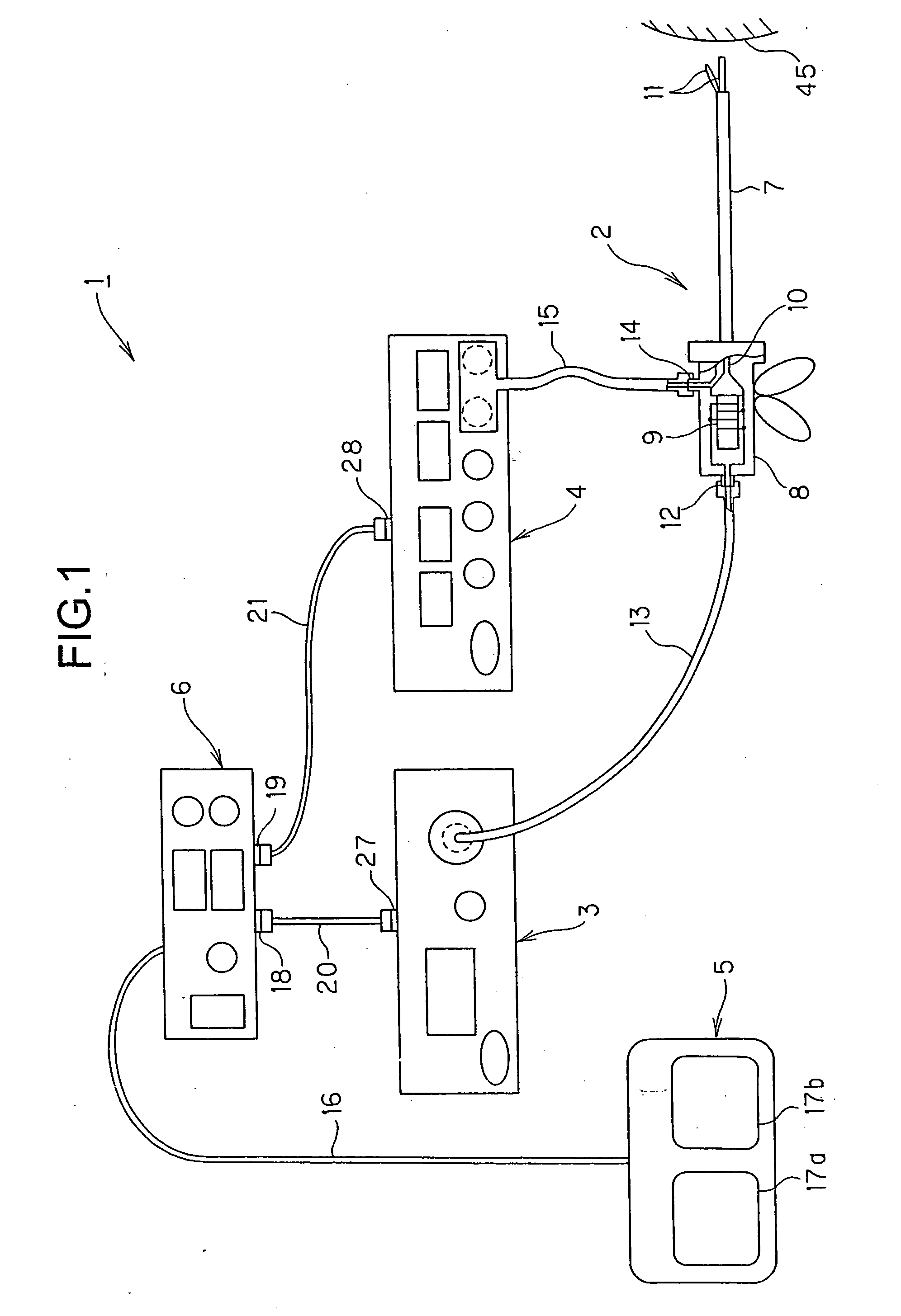
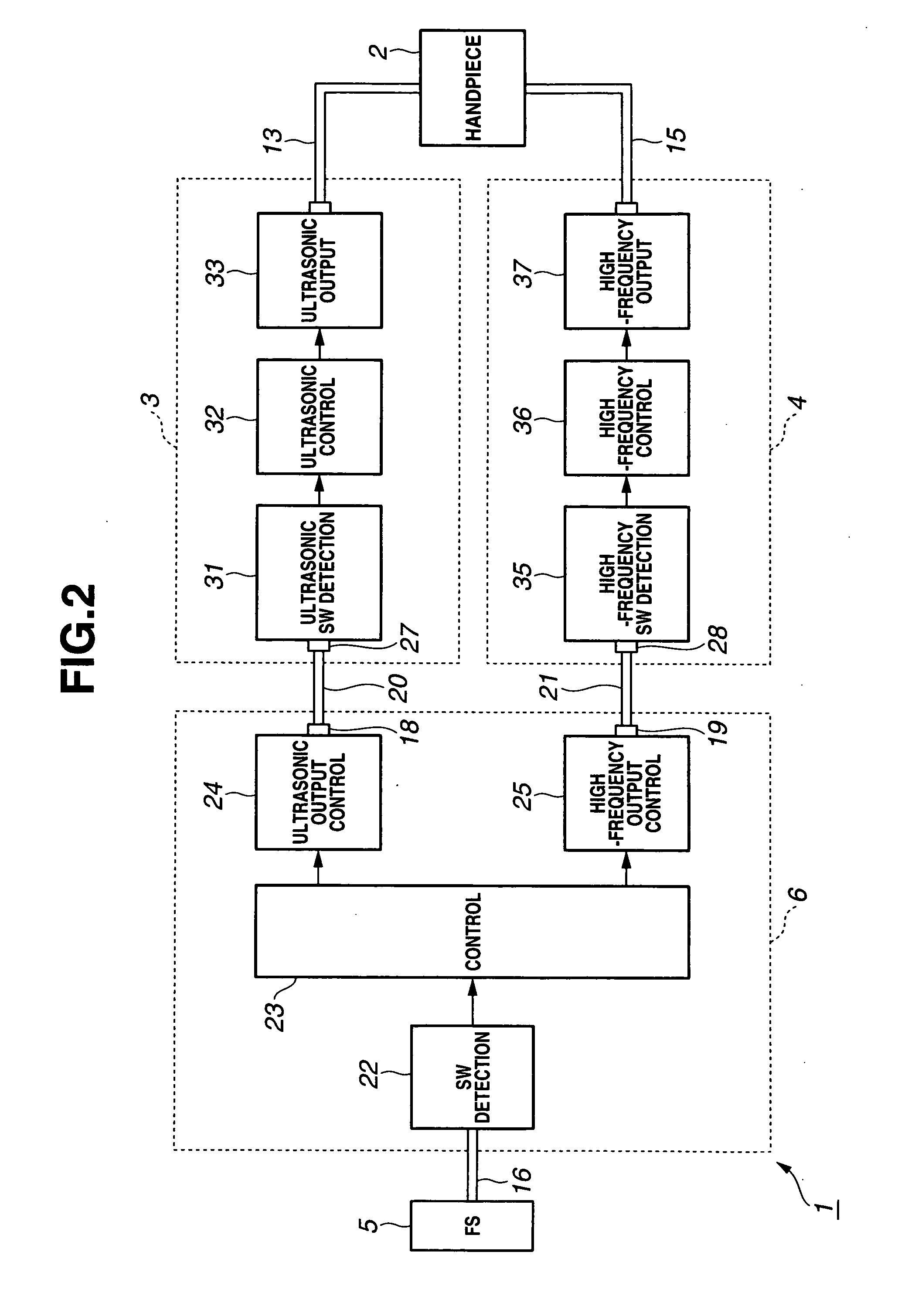
A relay device relays signals between a single switch unit and each of an ultrasonic surgical device that supplies an ultrasonic signal and an electrosurgical device that supplies a high-frequency signal, the switch unit being used for on / off control of outputs of the ultrasonic surgical device and the electrosurgical device, the ultrasonic surgical device and the electrosurgical device being connected to an ultrasonic / high-frequency treatment instrument capable of performing an ultrasonic treatment using ultrasonic vibration in accordance with the supplied ultrasonic signal and performing a high-frequency treatment in accordance with the supplied high-frequency signal. The relay device includes a switch detection unit for detecting the turn-on / off of the switch unit, a switch element for outputting a switch signal, which is used for on / off control of outputs of the ultrasonic signal and the high-frequency signal, to each of the ultrasonic surgical device and the electrosurgical device in accordance with a detection output of the switch detection unit, and a control unit for performing on / off control of the switch signal of the switch element in accordance with the detection output to control at least one of an output timing and an output mode of each of the ultrasonic signal and the high-frequency signal.
Owner:OLYMPUS MEDICAL SYST CORP
Ultrasonic medical device and method
InactiveUS7285895B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTransducerConvex side
Owner:CRESCENDO TECH
Calculus manipulation apparatus
An ultrasonic lithotripter comprising a first transmission probe which has a hollow portion in the form of a through hole and transmits ultrasonic vibration and a superfine second transmission probe which can be passed through the hollow portion of the first transmission probe. An object of manipulation is held by means of the second transmission probe as it is manipulated by means of the first transmission probe.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Surgical instrument
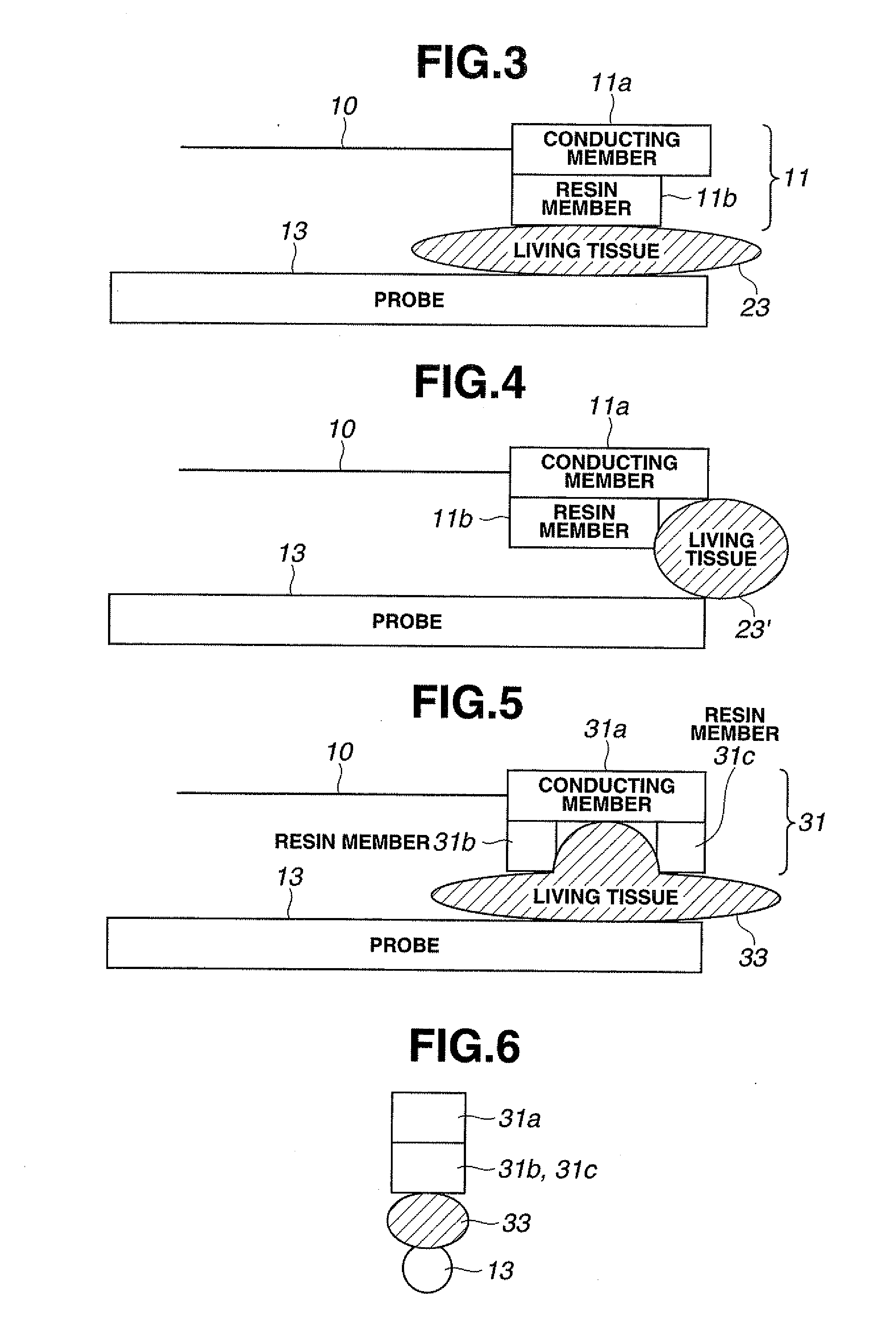
InactiveUS20090270771A1Efficiently conductedUltrasound therapyChiropractic devicesBiological bodyPower flow
A surgical instrument is provided including: an ultrasonic transducer for generating ultrasonic vibration; an ultrasonic probe for transmitting the ultrasonic vibration generated by the ultrasonic transducer to a distal end portion; a grasping member capable of grasping a living tissue as an object to be treated between the grasping member and a distal end portion of the ultrasonic probe by moving between positions close to and distant from the distal end portion of the ultrasonic probe; a conductive member configured of a conductive material for supplying high-frequency current to the living tissue, the conductive member being provided to the grasping member; and a non-conductive member configured of a non-conductive material and formed in a shape for blocking a contact between the conductive member and the ultrasonic probe and exposing a part of one surface of the conductive member on the ultrasonic probe side, the non-conductive member being provided to the grasping member so as to be located between the conductive member and the ultrasonic probe, thereby allowing high-frequency current to be effectively conducted to a living tissue.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Ultrasonic lead screw motor
InactiveUS6940209B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPressure infusionUltrasonic vibrationAxial force
An apparatus for driving a threaded shaft assembly that contains a threaded shaft with an axis of rotation and, engaged therewith, a threaded nut. Subjecting the threaded nut to ultrasonic vibrations causes the threaded shaft to simultaneously rotate and translate in the axial direction. The threaded shaft is connected to a load that applies an axial force to the threaded shaft.
Owner:NEW SCALE TECH
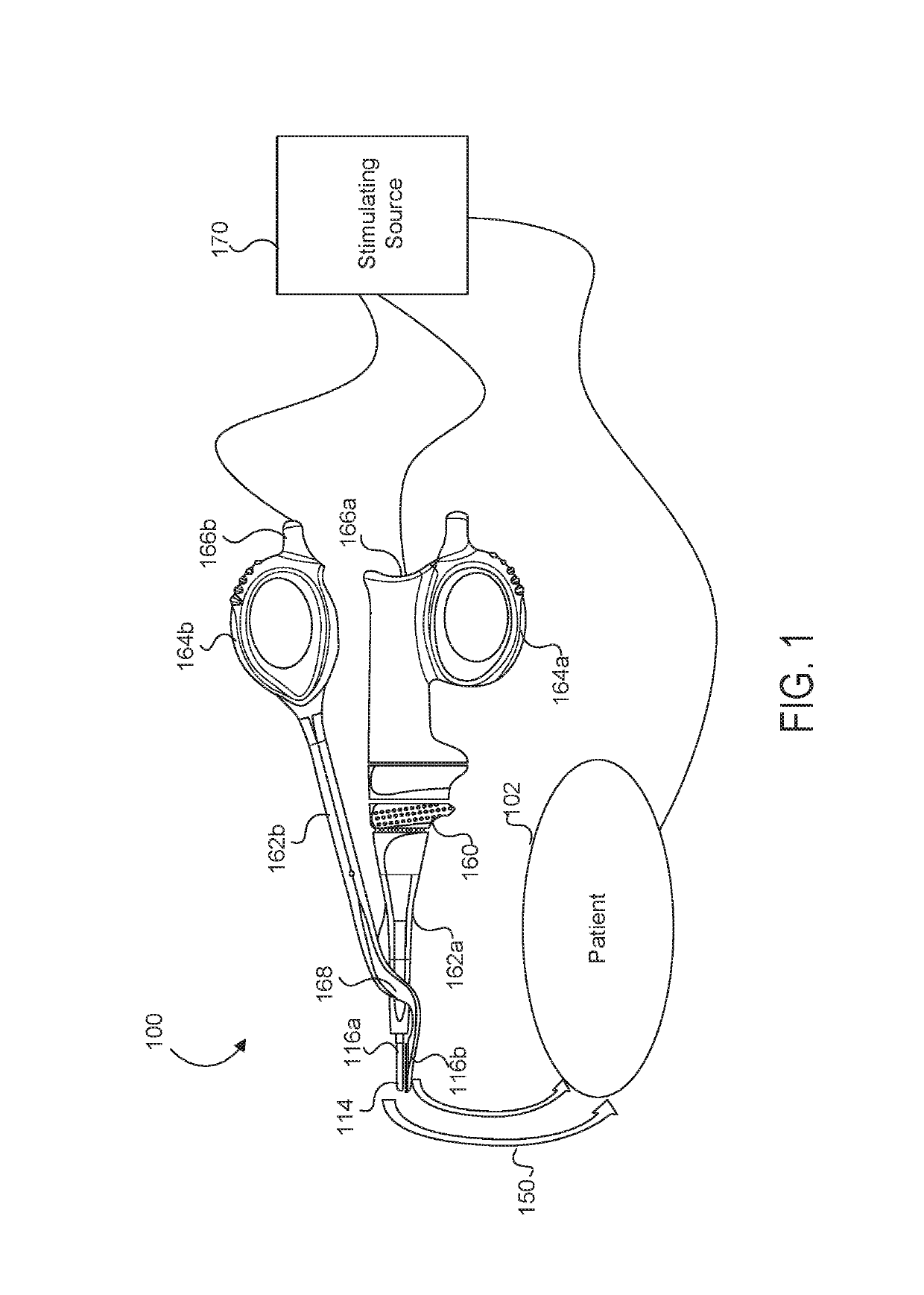
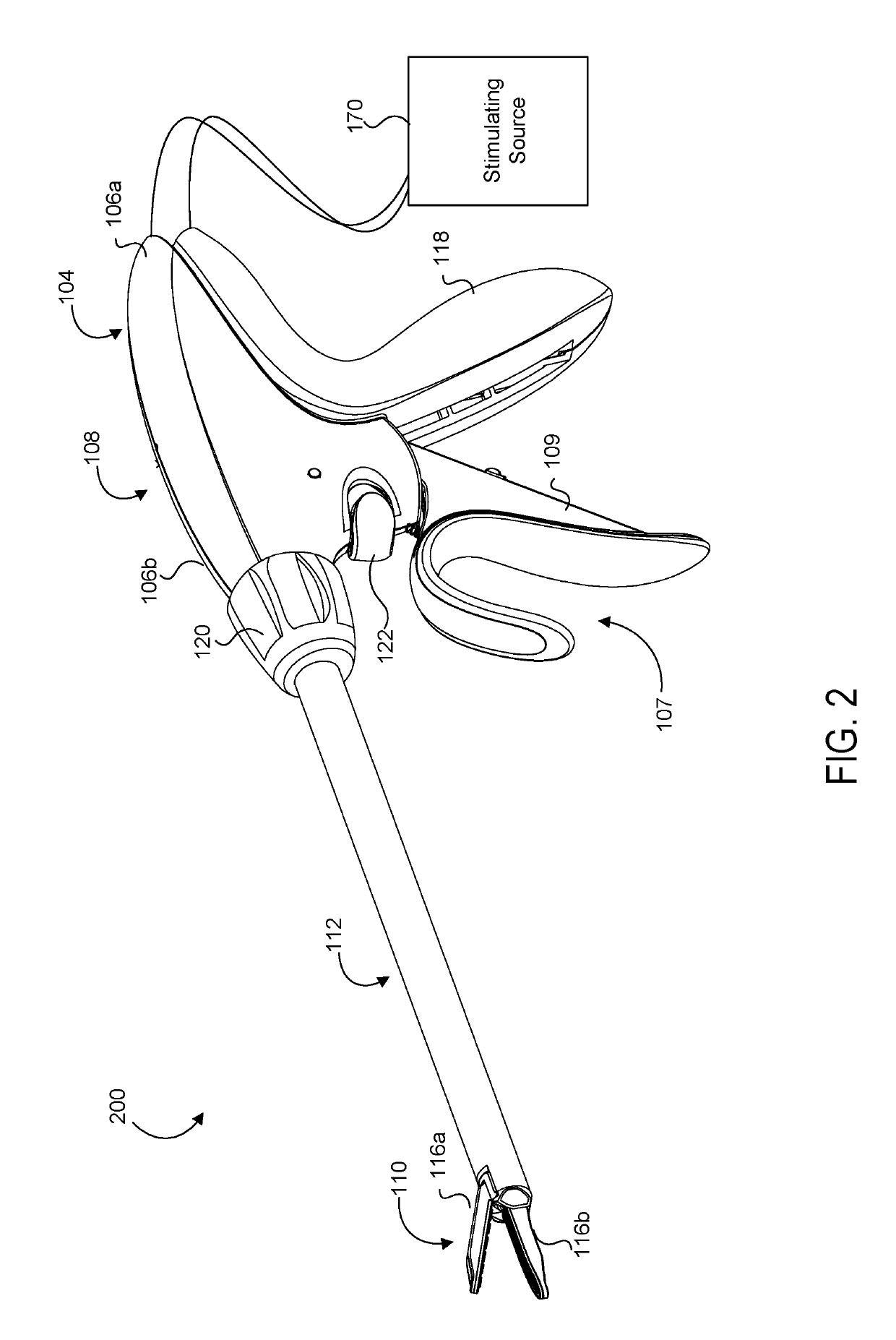
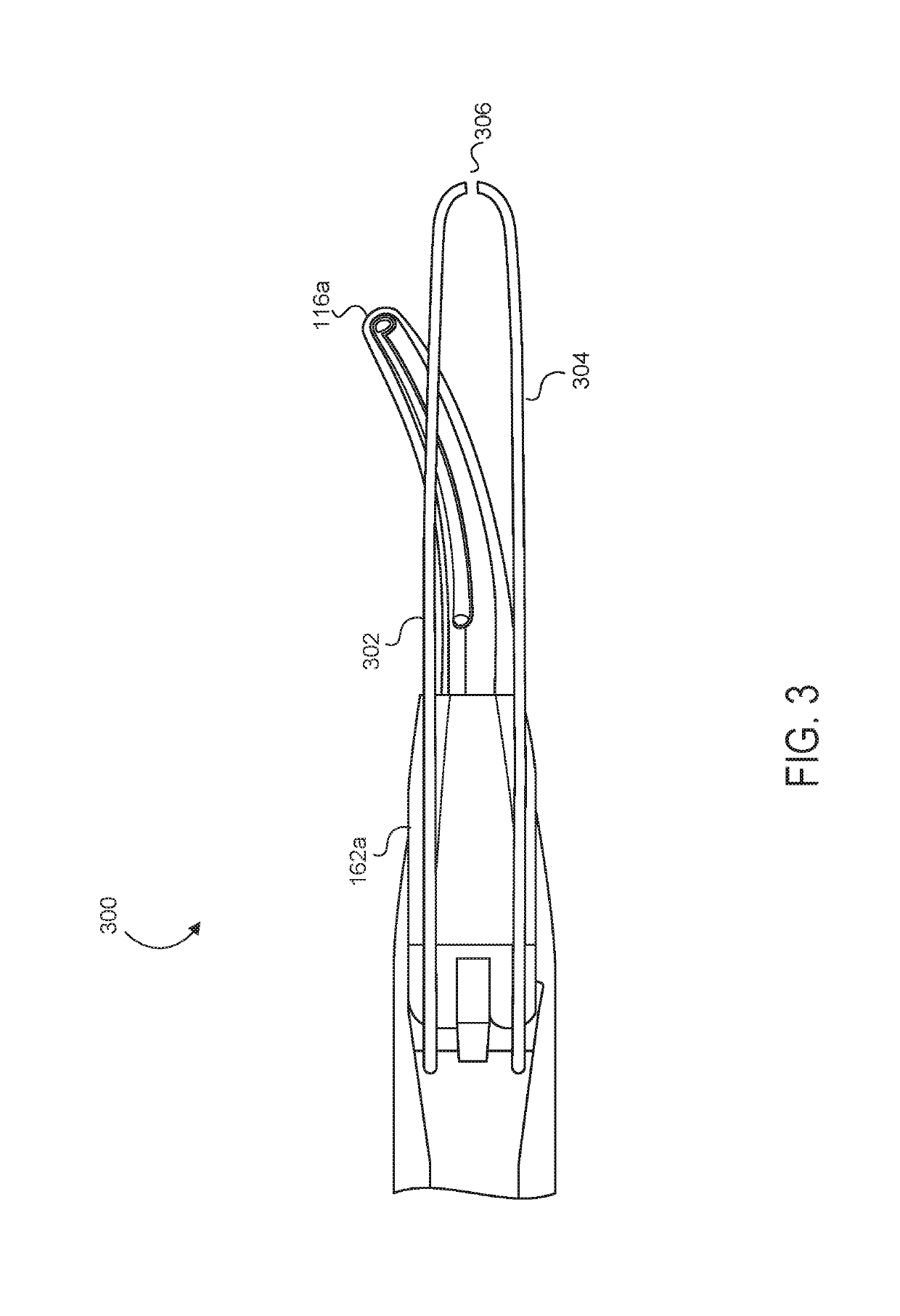
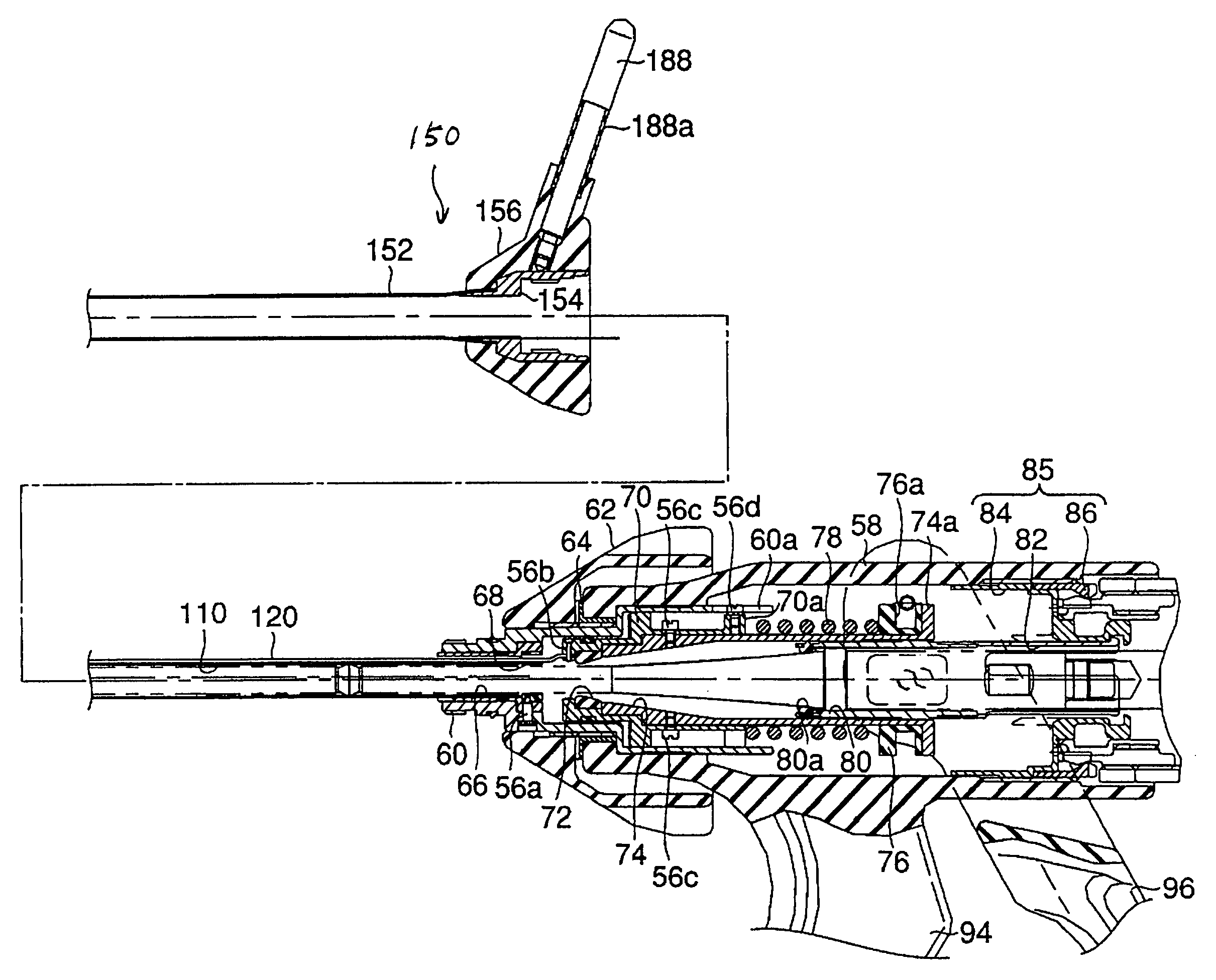
Medical device with a bilateral jaw configuration for nerve stimulation
ActiveUS10456193B2Spinal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsSacral nerve stimulationUltrasonic vibration
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
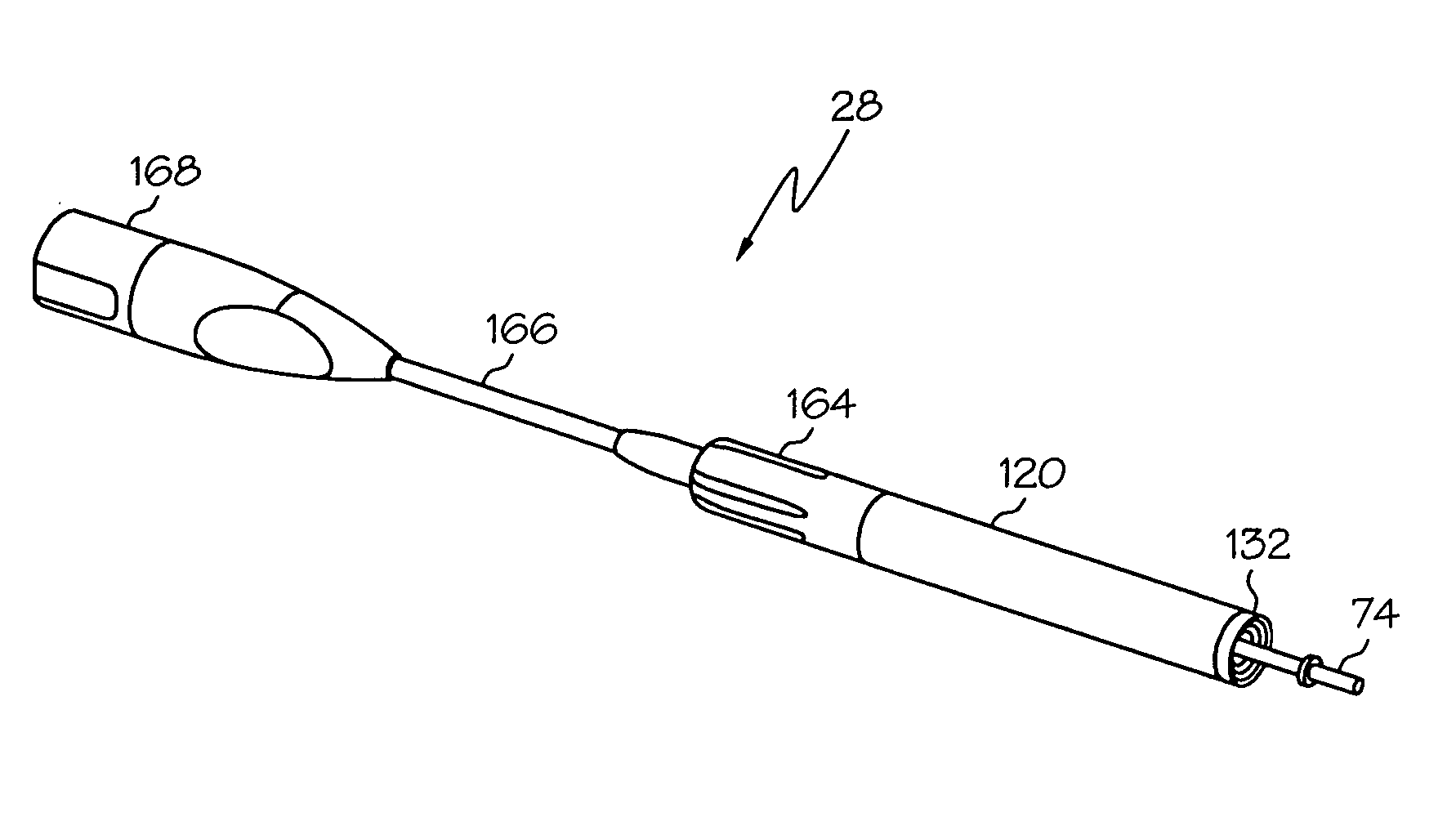
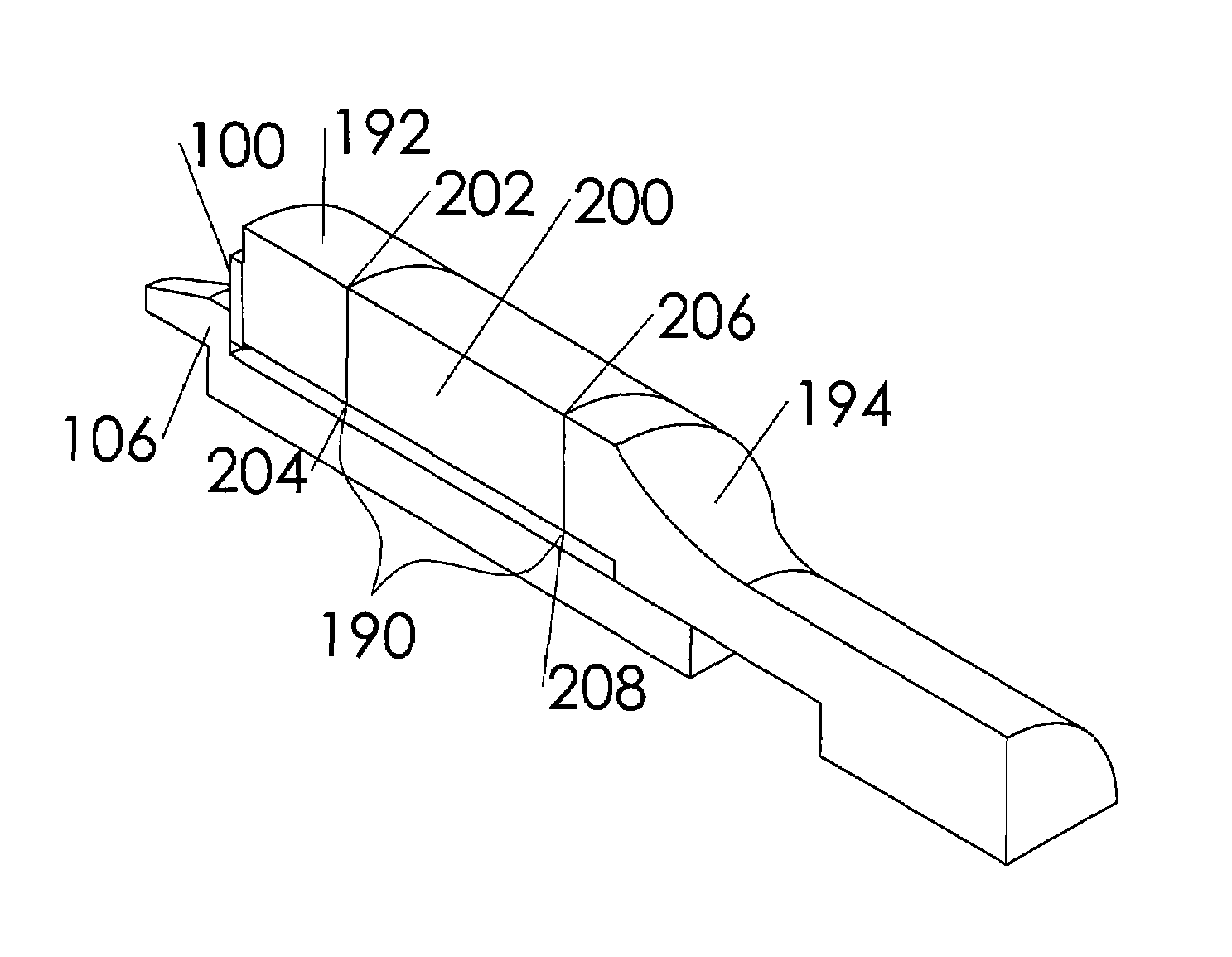
Treatment apparatus and treatment device for surgical treatments using ultrasonic vibration
ActiveUS7799045B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSurgical treatmentTransducer
An ultrasonic treatment device comprises a transducer unit, probe unit, and a main unit. The transducer unit comprises an ultrasonic transducer generating ultrasonic vibration in response to supply of power. The probe unit has a treatment member at a distal end thereof. The probe unit is detachably loaded to the transducer unit, and is equipped with an ultrasonic probe transmitting the ultrasonic vibration to the distal end of the treatment member when the transducer unit is loaded to the probe unit. The main unit is manually grasped by an operator. The probe unit with the transducer unit loaded thereto is detachably loaded to the main unit. The main unit has a cylindrical insert through which the ultrasonic probe is inserted to have the treatment member protruded outwardly when the probe unit is loaded. The main unit further has an outer sheath detachably covering an outer surface of the insert.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Chip manufacturing method
ActiveUS20150343559A1Efficiently formGlass reforming apparatusGlass severing apparatusLight beamUltrasonic vibration
A chip having a desired shape is formed from a platelike workpiece. The chip manufacturing method includes a shield tunnel forming step of applying a pulsed laser beam to the workpiece from a focusing unit included in a pulsed laser beam applying unit along the contour of the chip to be formed, with the focal point of the pulsed laser beam set at a predetermined depth from the upper surface of the workpiece, thereby forming a plurality of shield tunnels inside the workpiece along the contour of the chip to be formed. Each shield tunnel has a fine hole and an amorphous region formed around the fine hole for shielding the fine hole. In a chip forming step, ultrasonic vibration is applied to the workpiece to break the contour of the chip where the shield tunnels have been formed, thereby forming the chip from the workpiece.
Owner:DISCO CORP
Hook shaped ultrasonic cutting blade
ActiveUS20080009848A1Fast cutting speedDifficult to guideSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical sawsSurgical bladeUltrasonic vibration
An ultrasonic surgical blade has a blade body and a shank. The shank is fixed at one end to the blade body and is operatively connectable at an opposite end to a source of ultrasonic vibrations. The shank has a longitudinal axis. The blade body is eccentrically disposed relative to the axis.
Owner:MISONIX INC
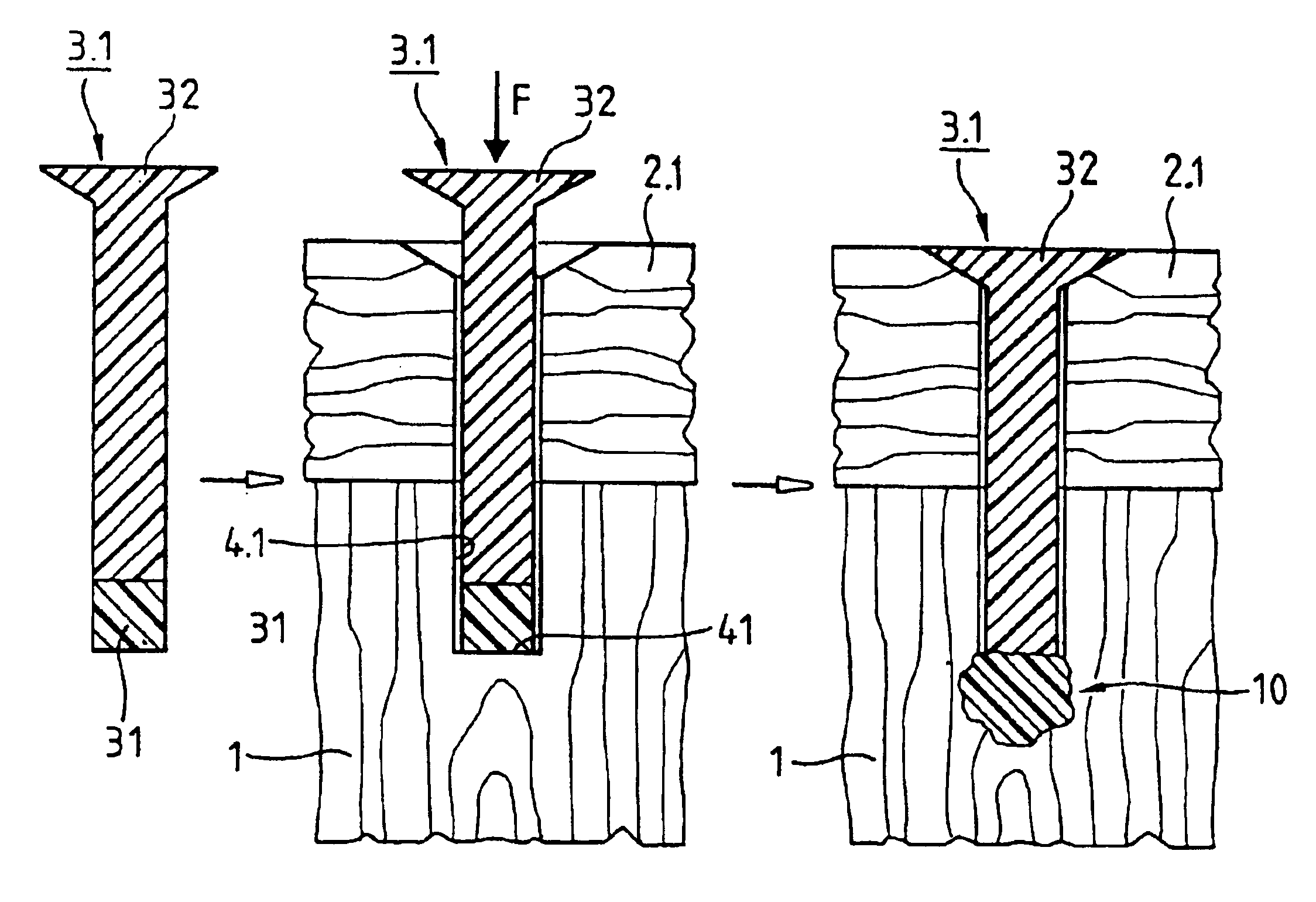
Process for anchoring connecting elements in a material with pores or cavities and connecting elements therefor
InactiveUS6913666B1Easy to reachReduce disadvantagesRivetsCylinder headsEngineeringUltrasonic vibration
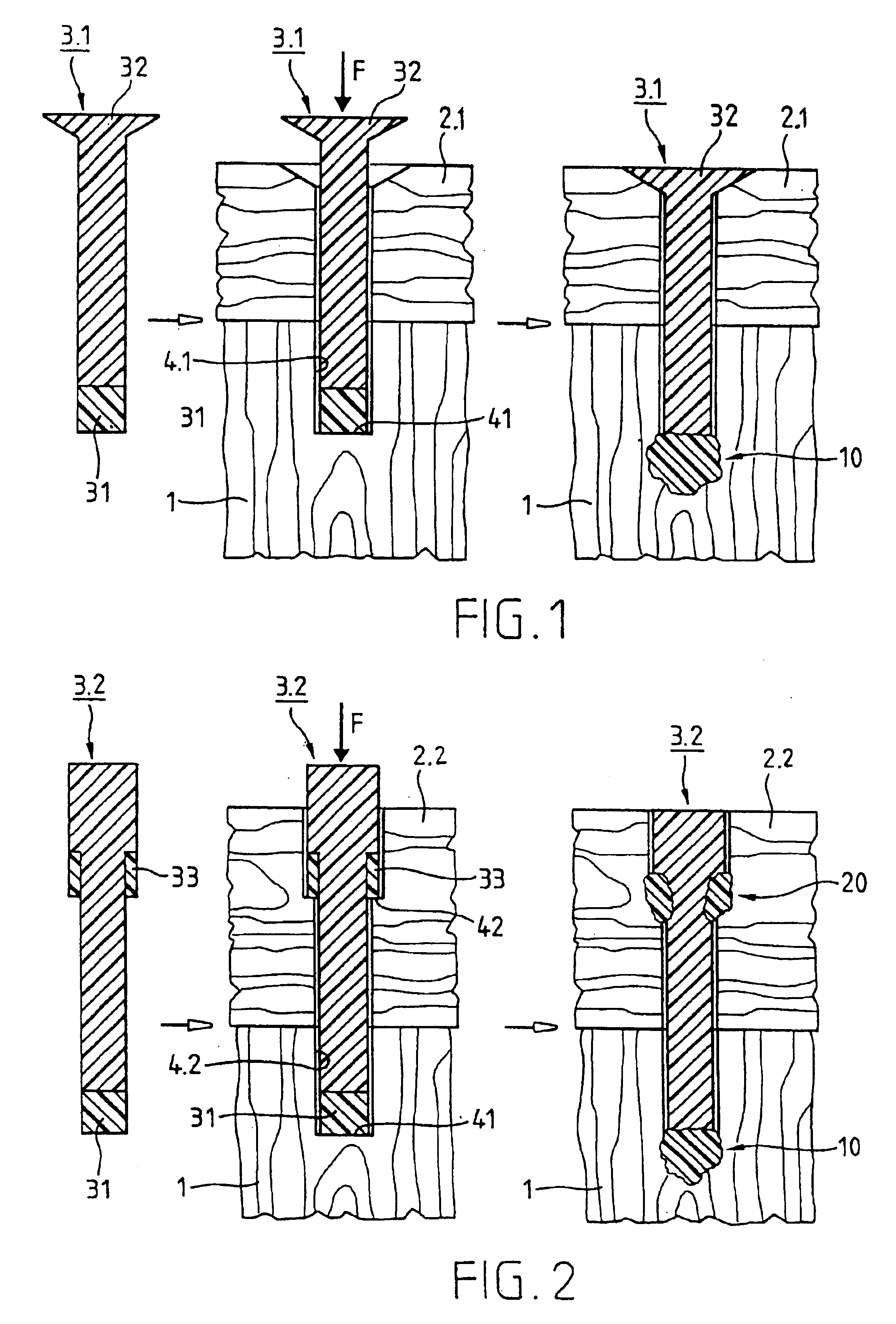
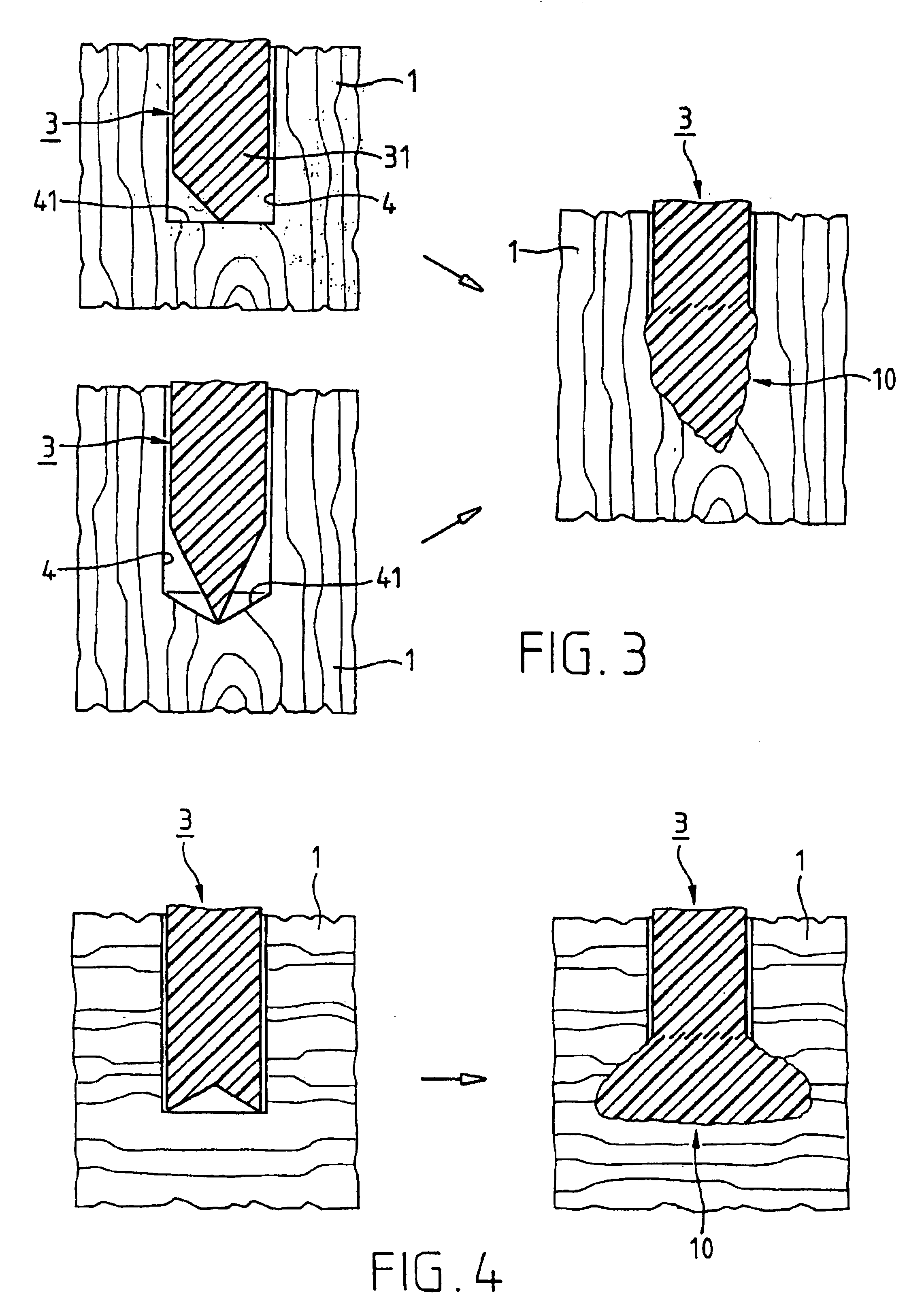
A joining pin (3.2) with which two parts (1 and 2) made from a porous material, particularly wood or a wood-like material, are to be joined together, is anchored in the porous material at predetermined anchoring points (31, 33). For this purpose, a bore (4.2) with a closed inner end (41) is made in the parts (1 and 2). The shape of this bore (4.2) is so matched to the joining pin (3.2) that it can be introduced substantially without force expenditure into the bore and is positionable in a first position. At least one predetermined anchoring point (31, 33) between the joining pin (3.2) and the wall of the bore (4.2) is formed when pressure is built up by pressing the joining pin (3.2) with a pressing force (F) more deeply into the bore to a second position. Energy is supplied in a planned manner to the joining pin (3.2) so that at the predetermined anchoring points (31, 33) the thermoplastic material of the joining pin (3.2) is plasticized. The locally plasticized plastic material is pressed by the local pressure into the porous material of the parts and forms local, macroscopic anchors (10, 20). The joining pin (3.2) is, e.g., made entirely from a thermoplastic material and the energy for plasticizing is supplied thereto by ultrasonic vibration.
Owner:WOODWELDING
Surgical operating apparatus
InactiveUS20090088785A1Increase rangeReduce manufacturing costUltrasound therapySurgical instruments for heatingSurgical operationDistal portion
A surgical operating apparatus includes a sheath having a distal end portion and a proximal end portion; a shaft-shaped probe body which is inserted in the sheath and has a distal end portion and a proximal end portion, and in which ultrasonic vibration is transmitted; a jaw which is rotatably supported on the distal end portion of the sheath and has a first electrode section which is one of bipolar electrodes; a probe distal end portion which is provided at the distal end portion of the probe body, is engaged with the jaw, and constitutes a second electrode section which is the other of the bipolar electrodes; and a driving member including a tubular body section, which is inserted in the sheath slidably in an axial direction of the sheath, and an operation section which is provided on a distal end side of the body section and has a connection section for connection to the jaw, the driving member rotating the jaw by a sliding operation of the body section, wherein a tube body of the body section has, on an inner peripheral surface side thereof, an insulation tube which effects electrical insulation between the probe body and the body section, and the insulation tube has a projection portion which projects forward of the body section.
Owner:OLYMPUS MEDICAL SYST CORP
Hook shaped ultrasonic cutting blade
ActiveUS8814870B2Less dead boneSmall incisionSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical sawsSurgical bladeEngineering
Owner:MISONIX INC
Surgical operating apparatus
ActiveUS8147488B2Prevent slippingInhibit wearSurgical needlesChiropractic devicesSurgical operationMedicine
A surgical operating apparatus includes a sheath, a probe body which is inserted through the sheath, and in which ultrasonic vibration is configured to be transmitted, a probe distal end portion which is provided at a distal end portion of the probe body and configured to function as one of bipolar electrodes, and a jaw which is rotatably supported on a distal end portion of the sheath, has an engaging surface which is engaged with the probe distal end portion, and has a second electrode section which is the other of the bipolar electrodes, wherein the jaw includes, at a distal end portion of the engaging surface for engagement with the probe distal end portion, a distal end chip which tolerates a positional displacement relative to the probe distal end portion when the jaw is engaged with the probe distal end portion.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
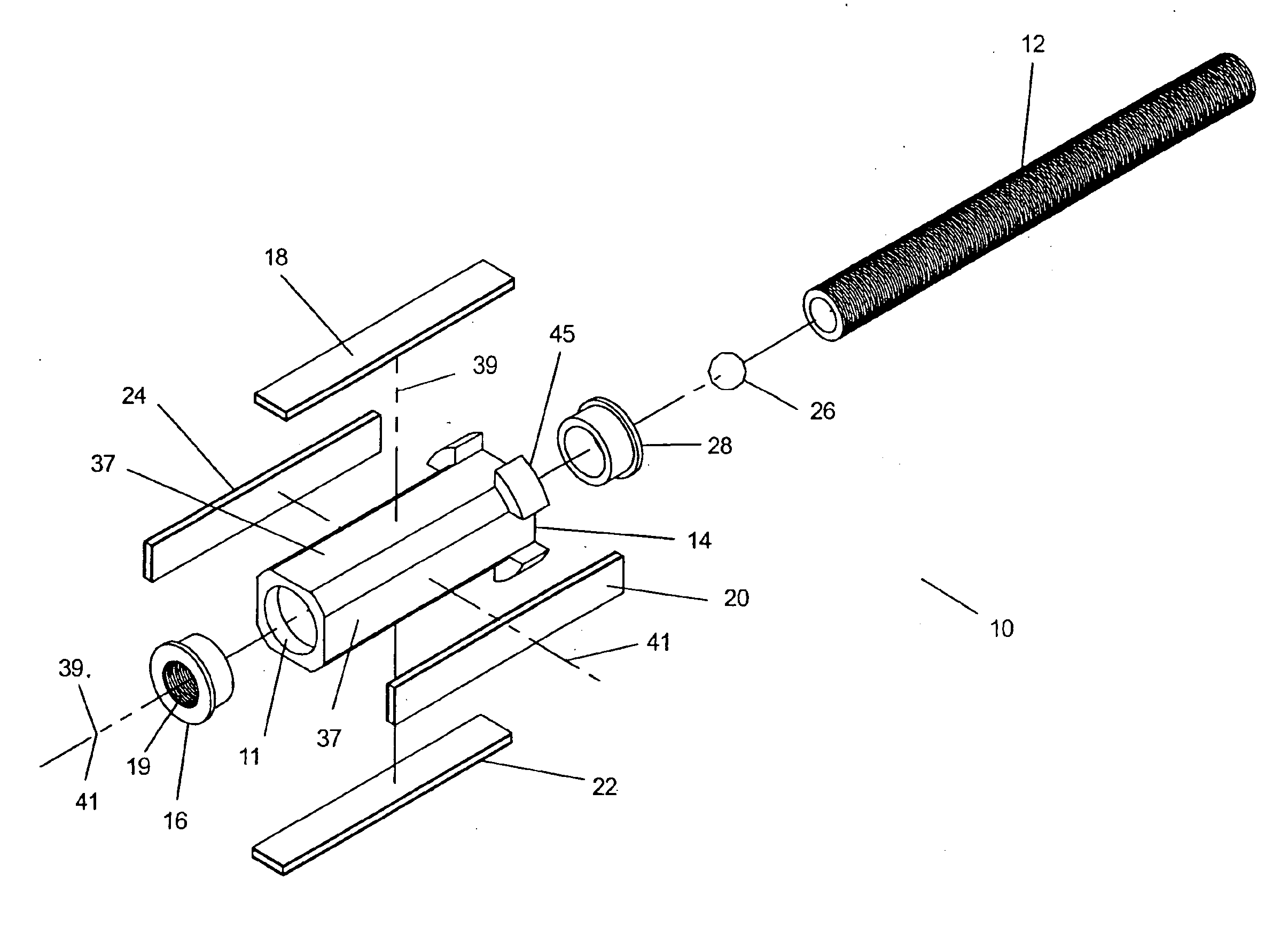
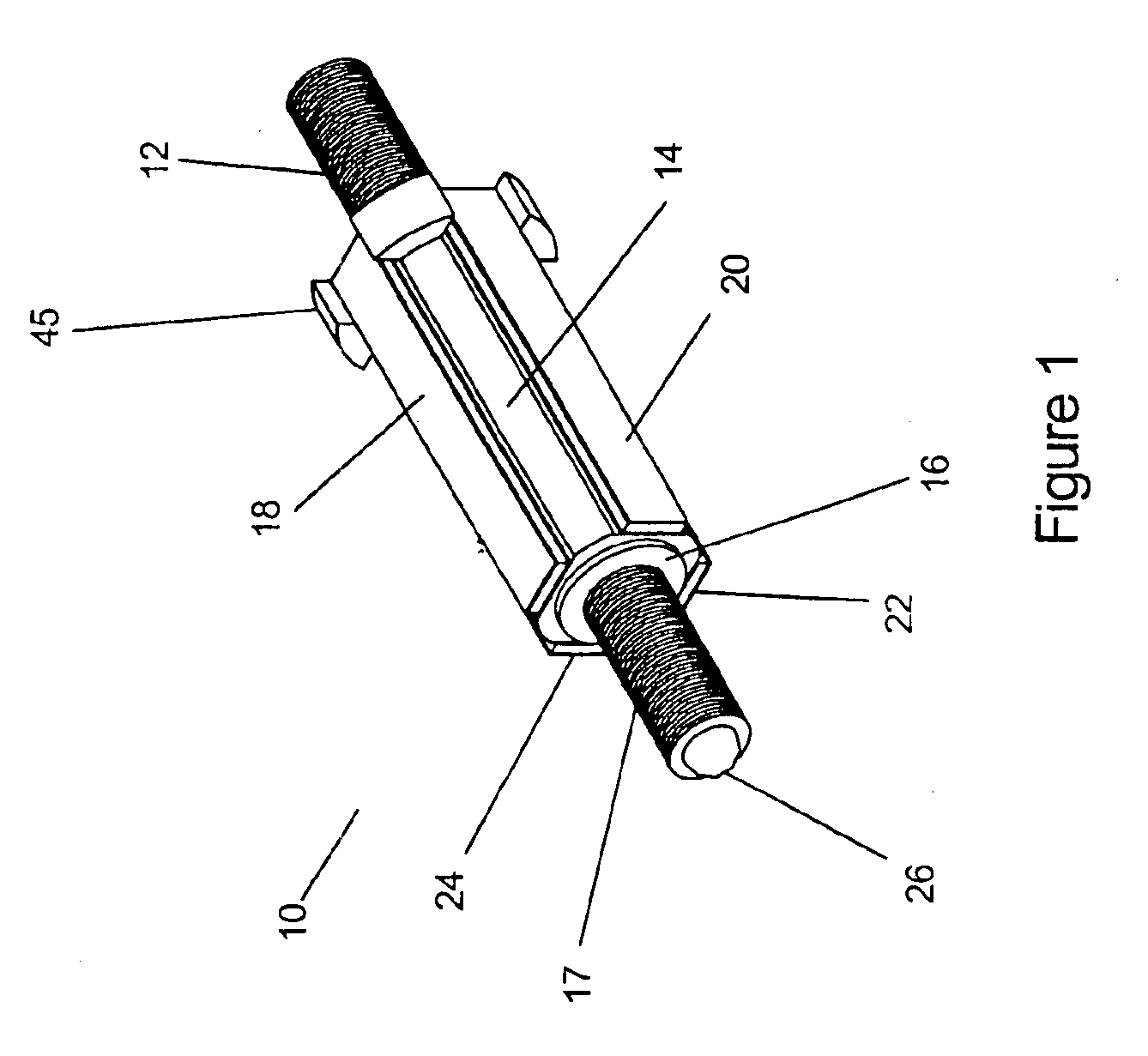
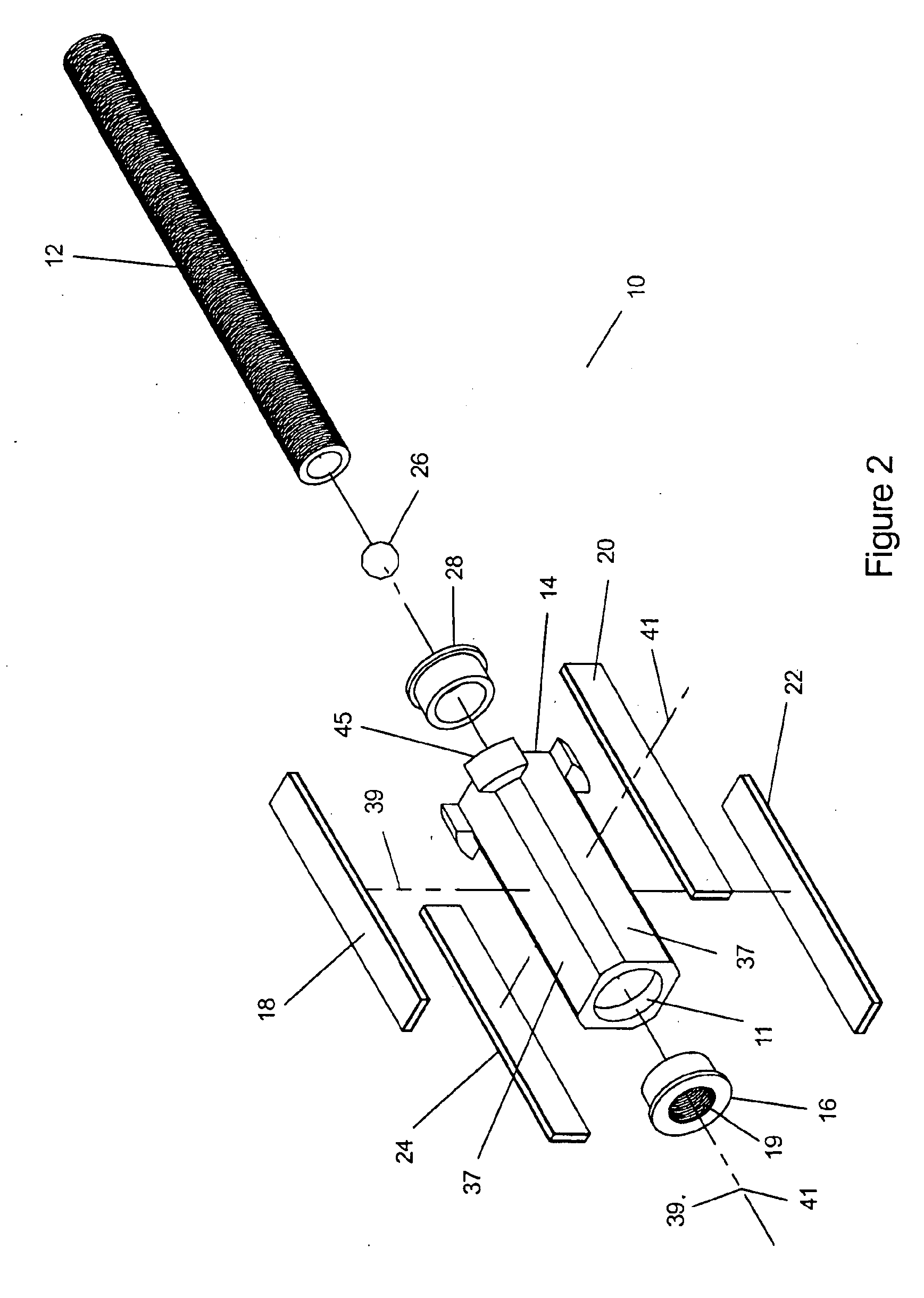
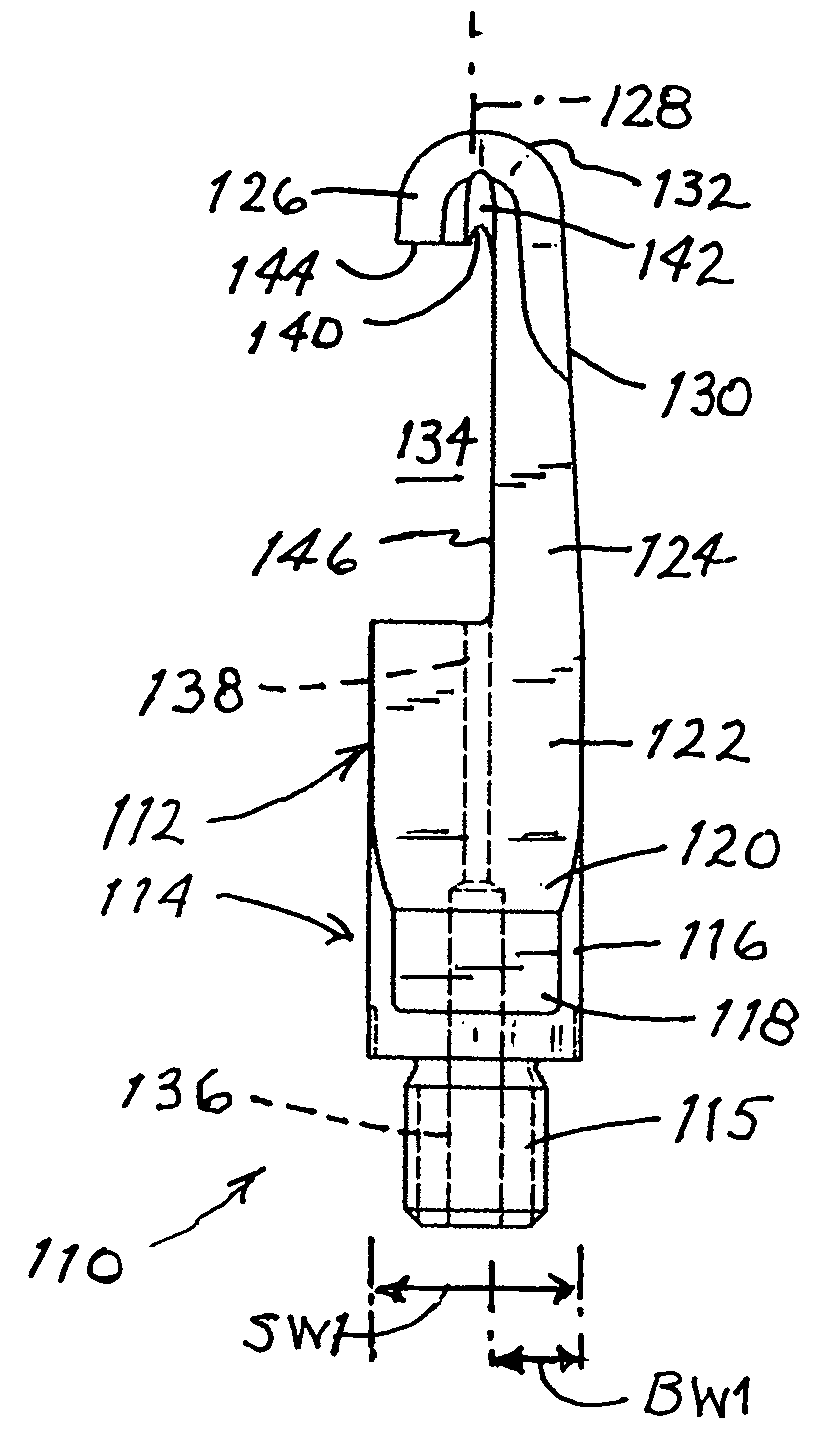
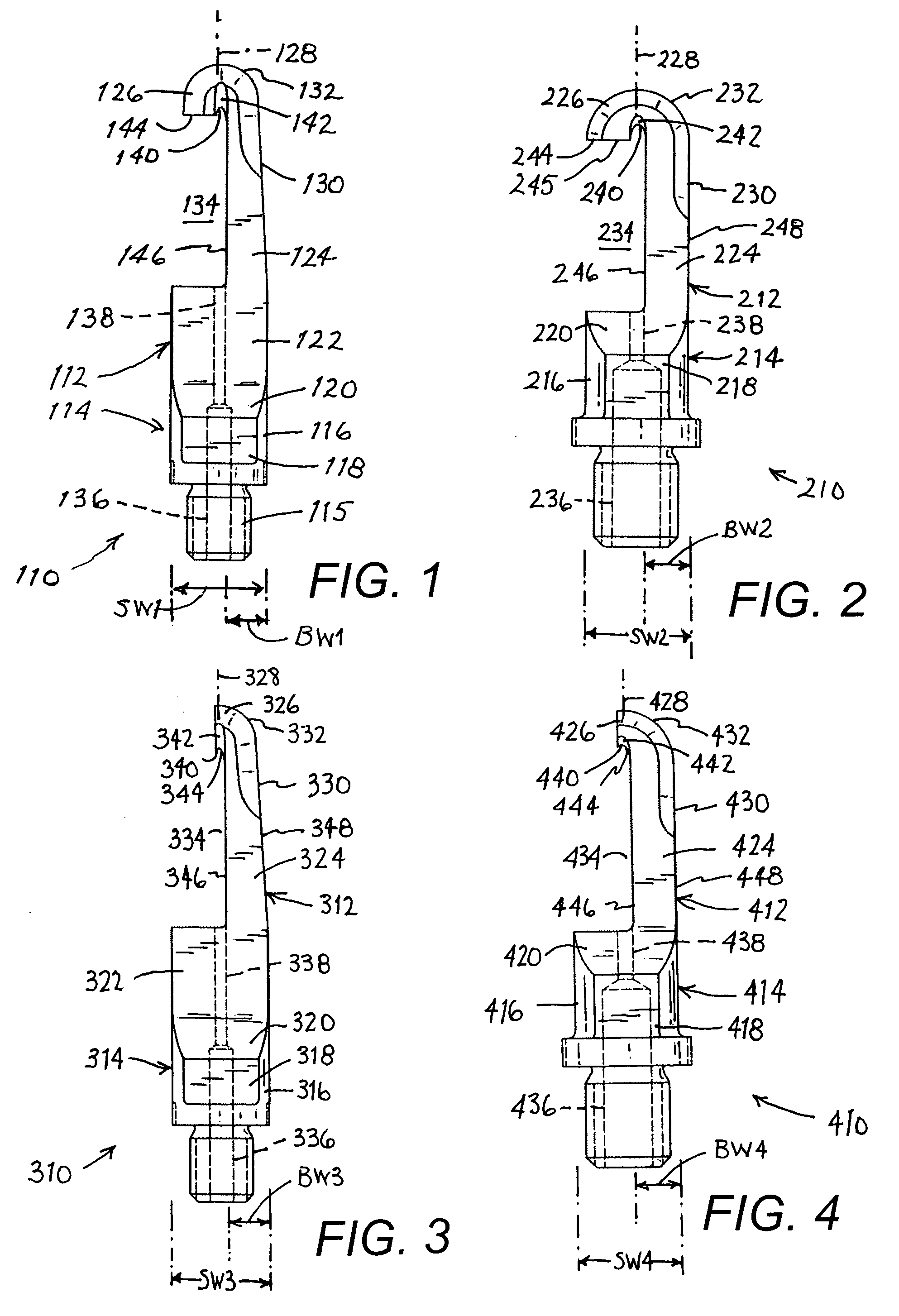
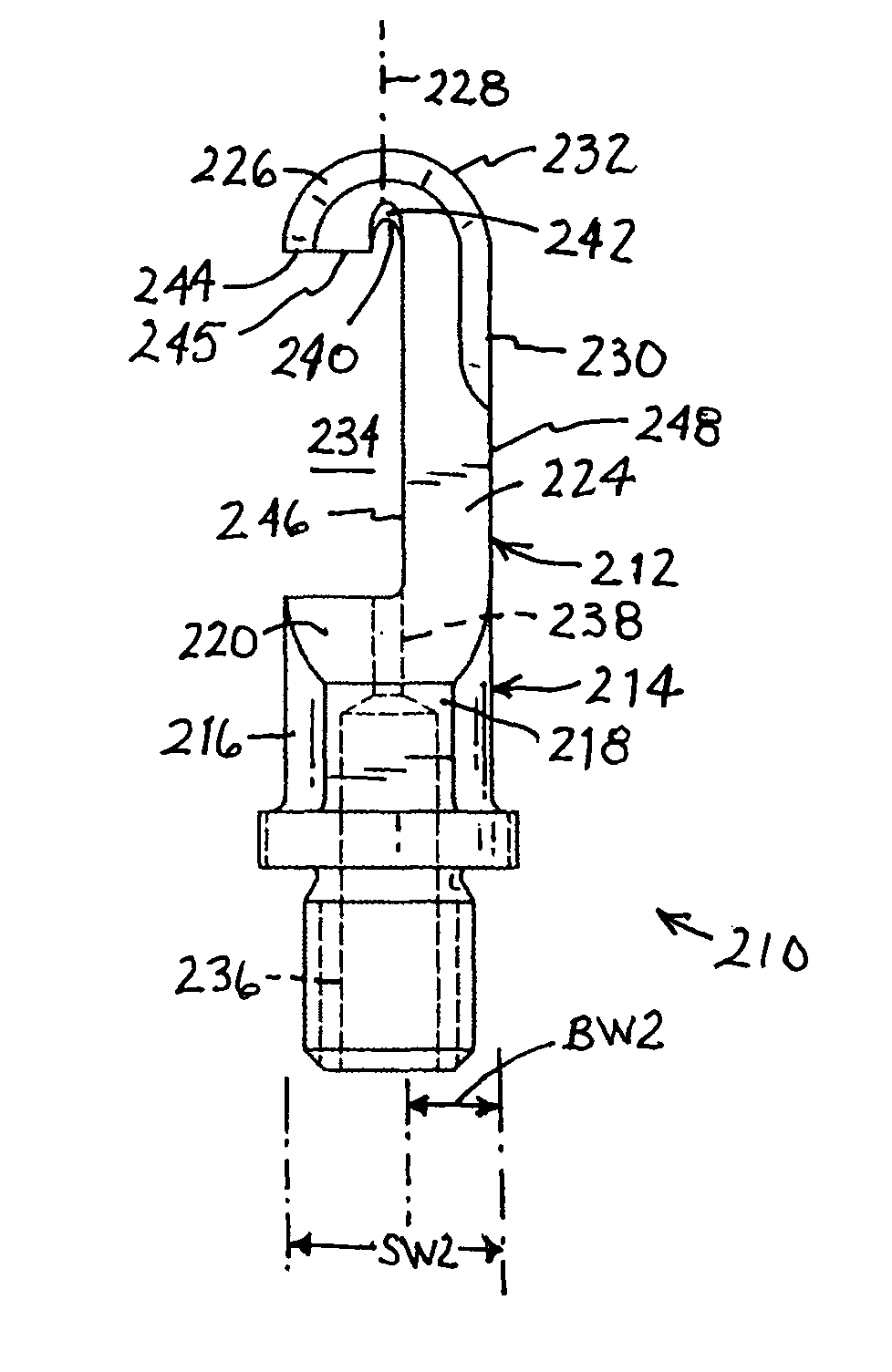
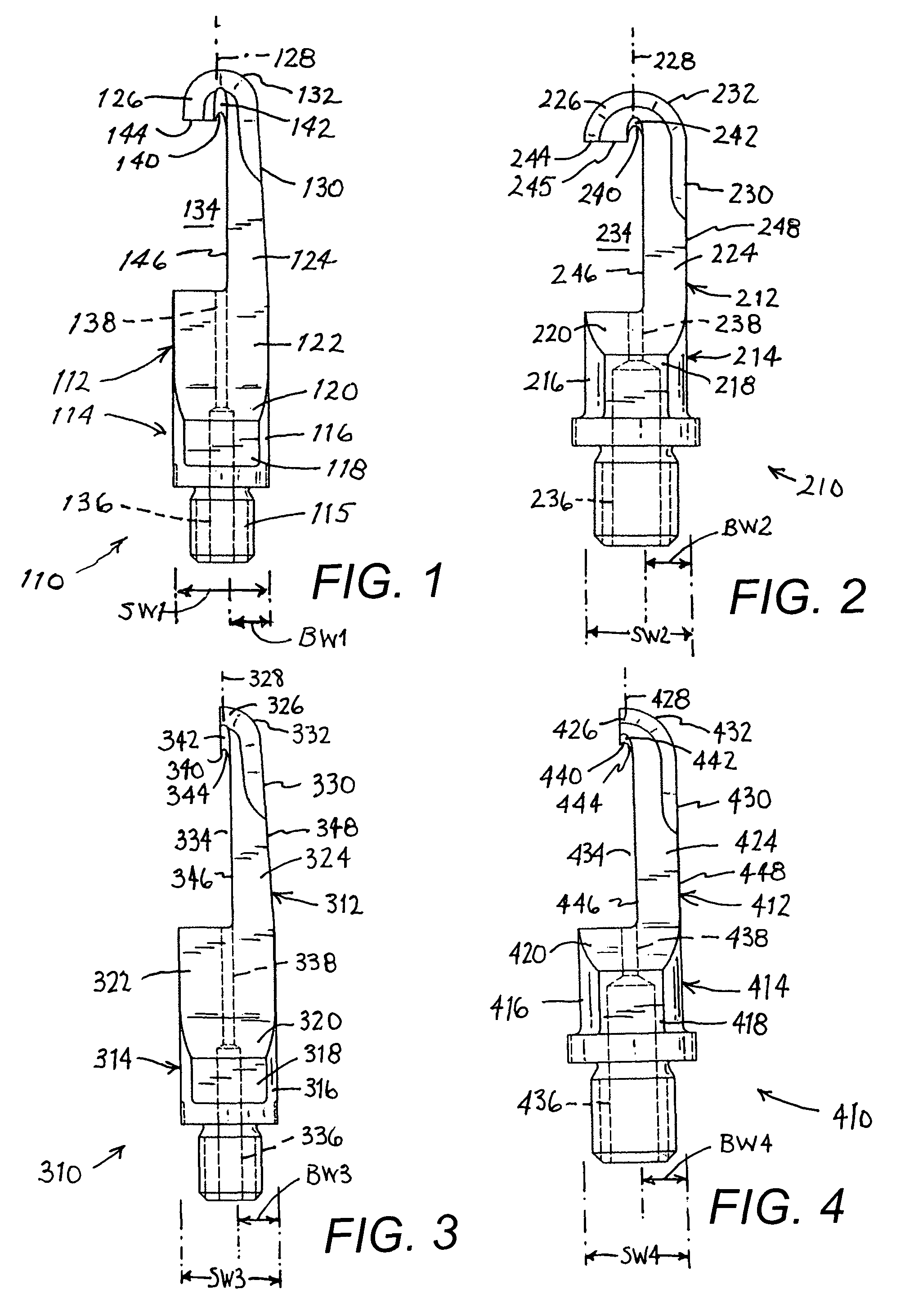
Ultrasonic medical instrument and medical instrument connection assembly
An ultrasonic medical instrument having a handpiece and medical ultrasonic blade assembly including a vibration antinode, a handpiece, and a medical ultrasonic blade. The blade is threadably engaged by the handpiece proximate the vibration antinode. The blade is in ultrasound-transmitting physical contact with the handpiece proximate the vibration antinode and apart from where the medical ultrasonic blade is threadably engaged by the handpiece. A medical-instrument connection assembly for transmitting ultrasonic vibrations includes first, second, and third connecting members. The first connecting member is adapted to be ultrasonically vibrated and has a longitudinal axis. The second connecting member is capable of being positioned to be substantially coaxially aligned with the longitudinal axis and in ultrasound-transmitting physical contact with the first connecting member. The third connecting member surrounds, and is rotatably or fixedly attached to, the second connecting member and is threadably engageable with the first connecting member.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
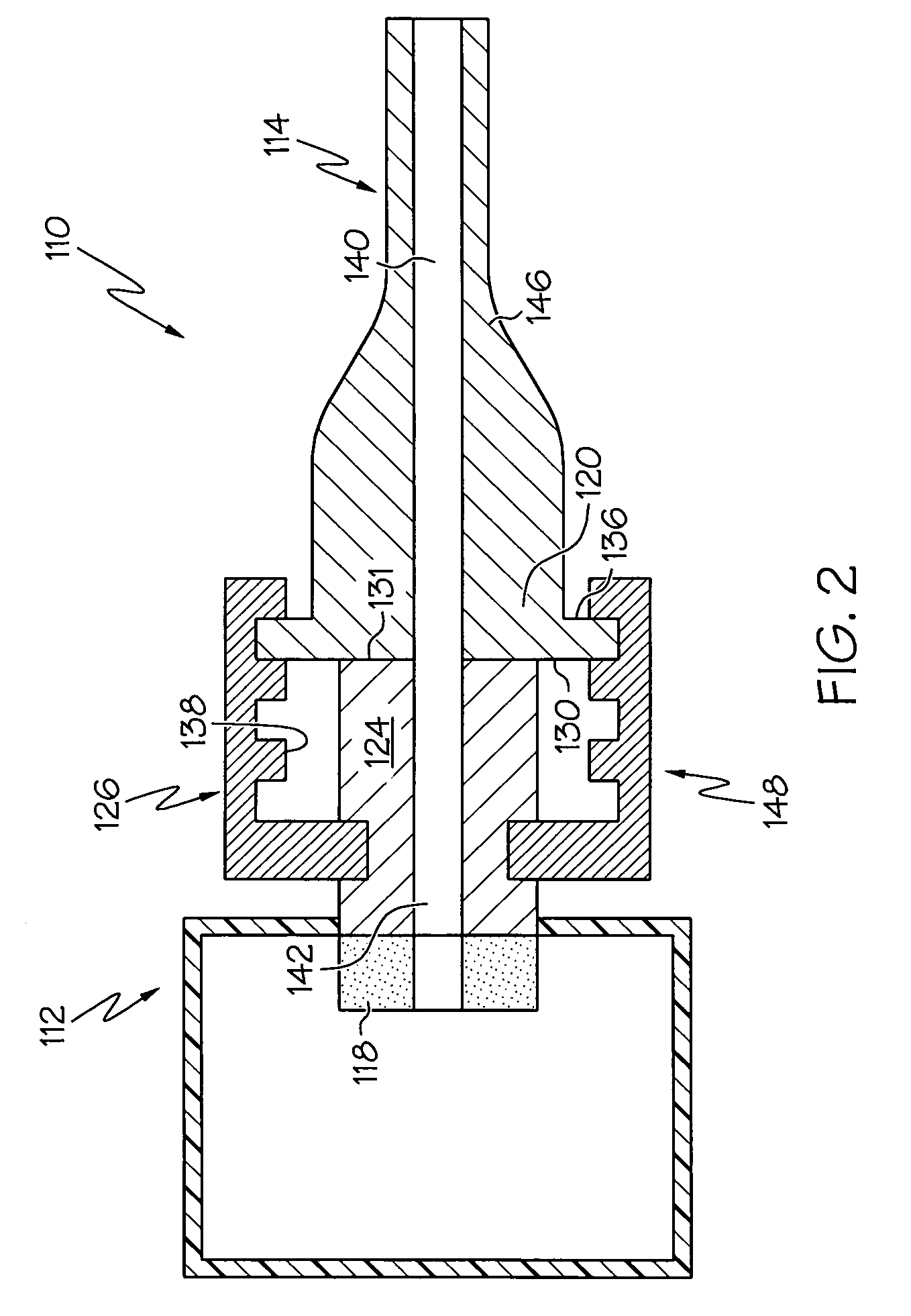
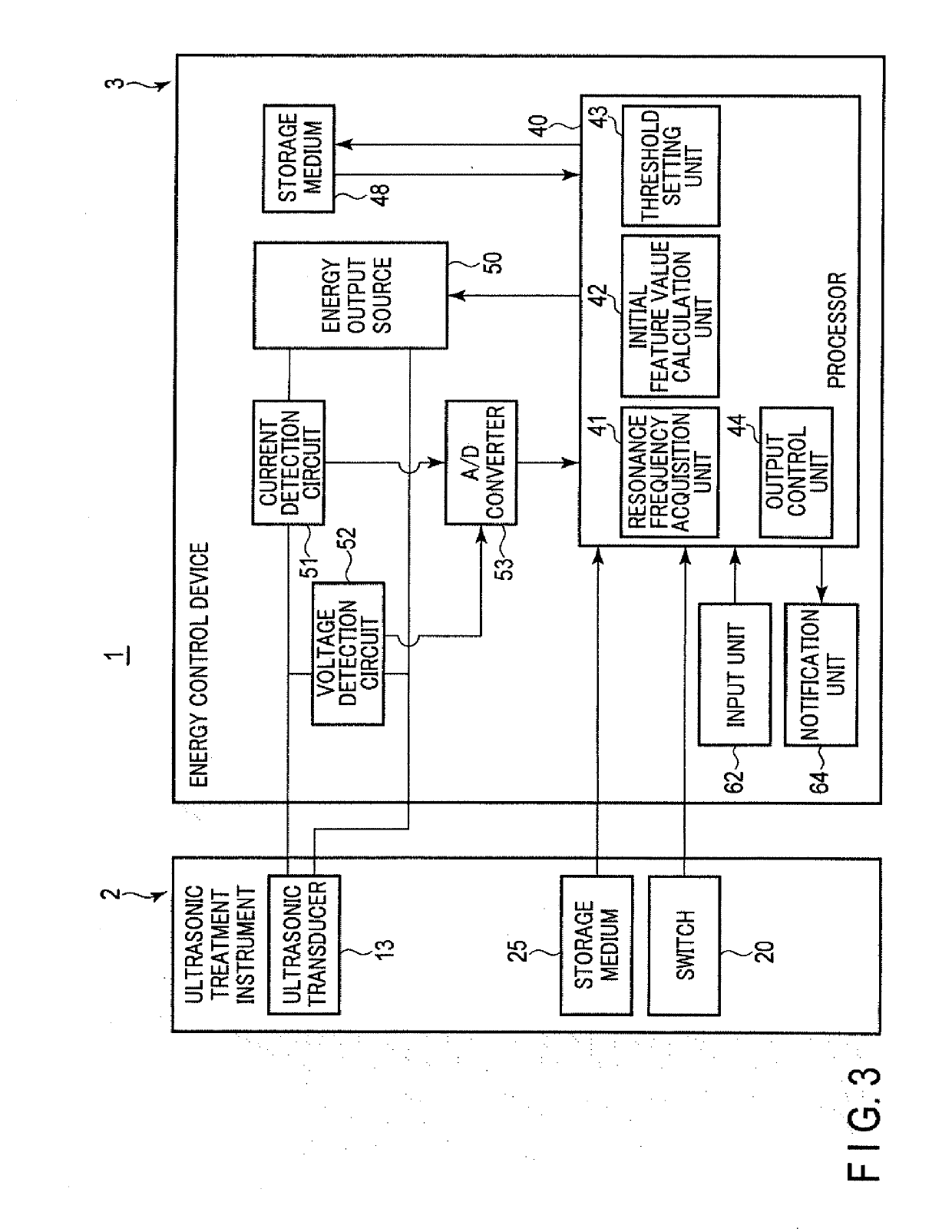
Energy control device and treatment system
An energy control device supplies power to an ultrasonic treatment instrument including an end effector performing treatment using ultrasonic vibration generated by an ultrasonic transducer. The energy control device includes an energy source configured to output the power to the ultrasonic transducer, and an integrated circuit. The integrated circuit is configured to: acquire a resonance frequency of a vibration system including the ultrasonic transducer; calculate an initial feature value relating to the resonance frequency after a start of an output of the power; set a threshold based on the initial feature value; and perform causing the energy source to stop or reduce the output of the power to the ultrasonic transducer based on a relationship between the resonance frequency and the threshold, or notifying the relationship between the resonance frequency and the threshold.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
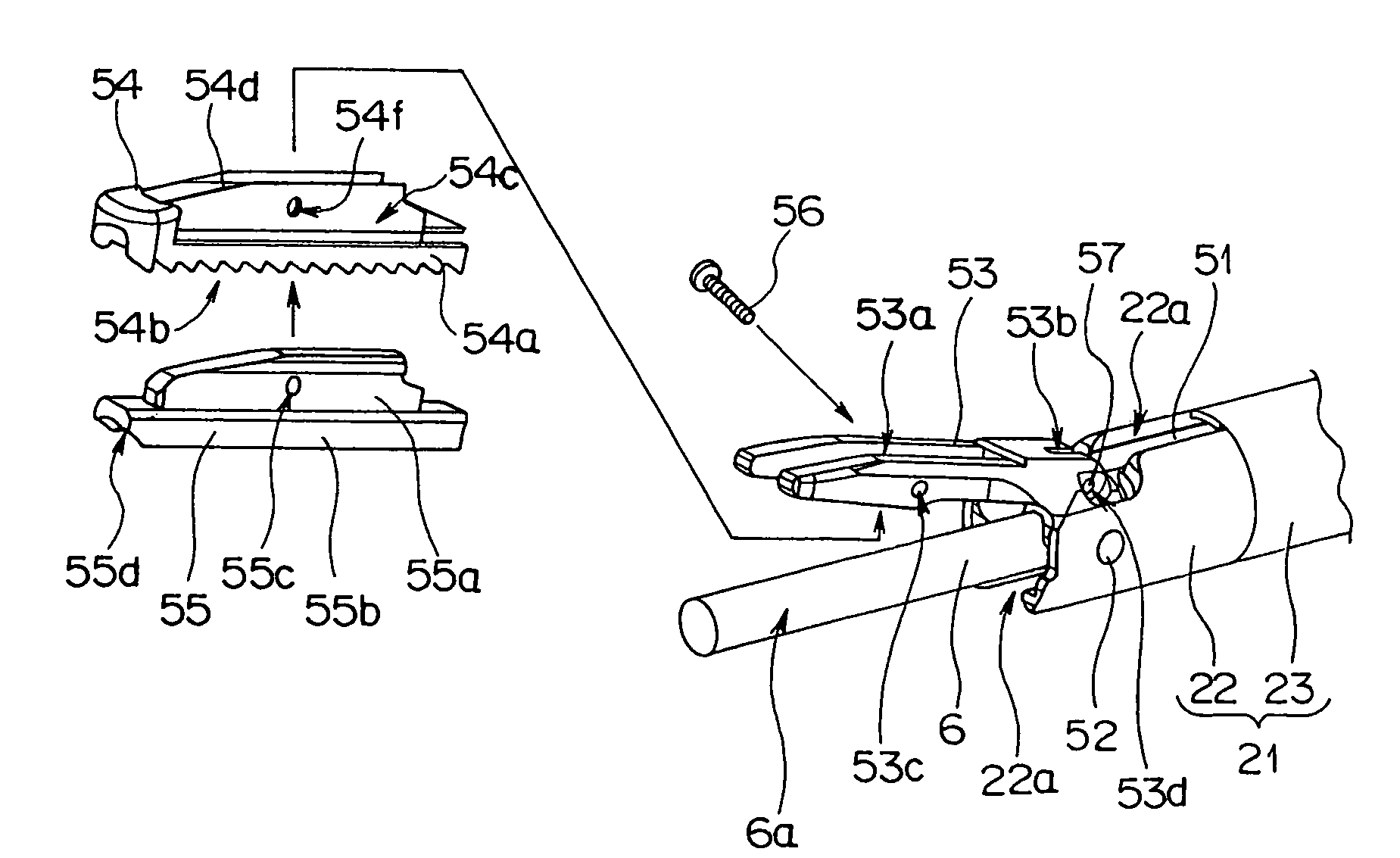
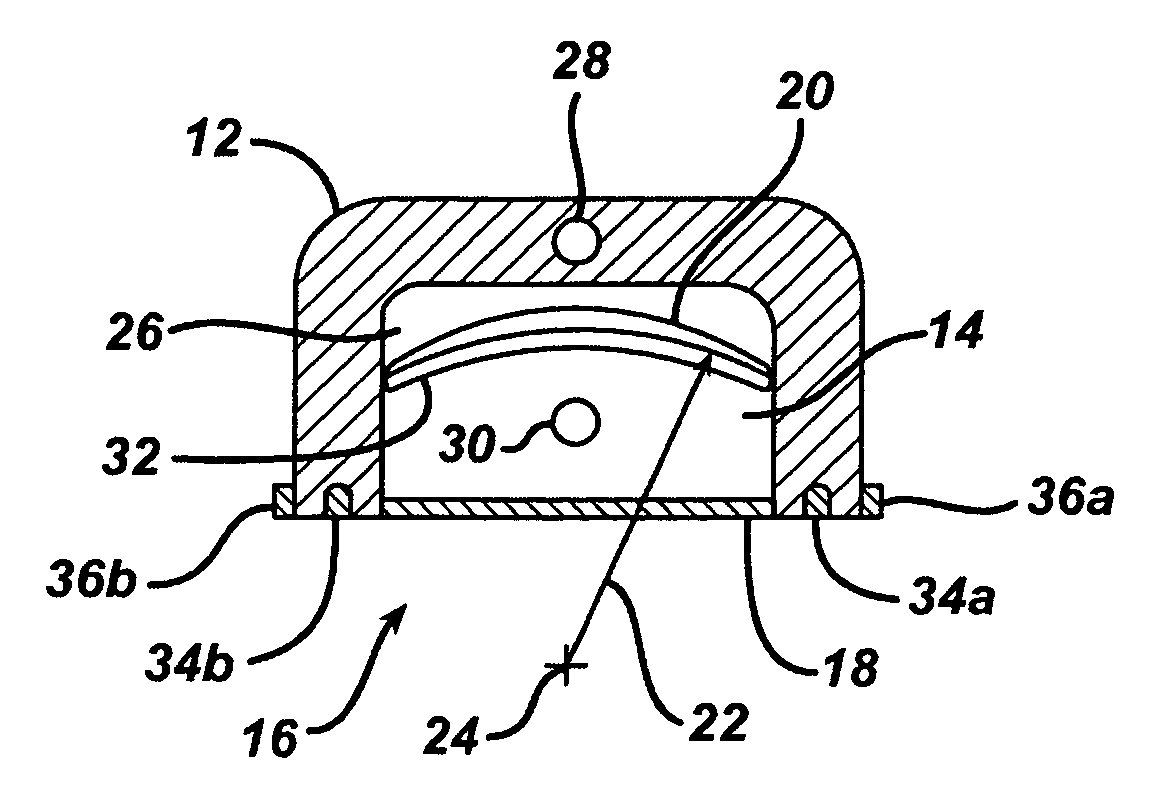
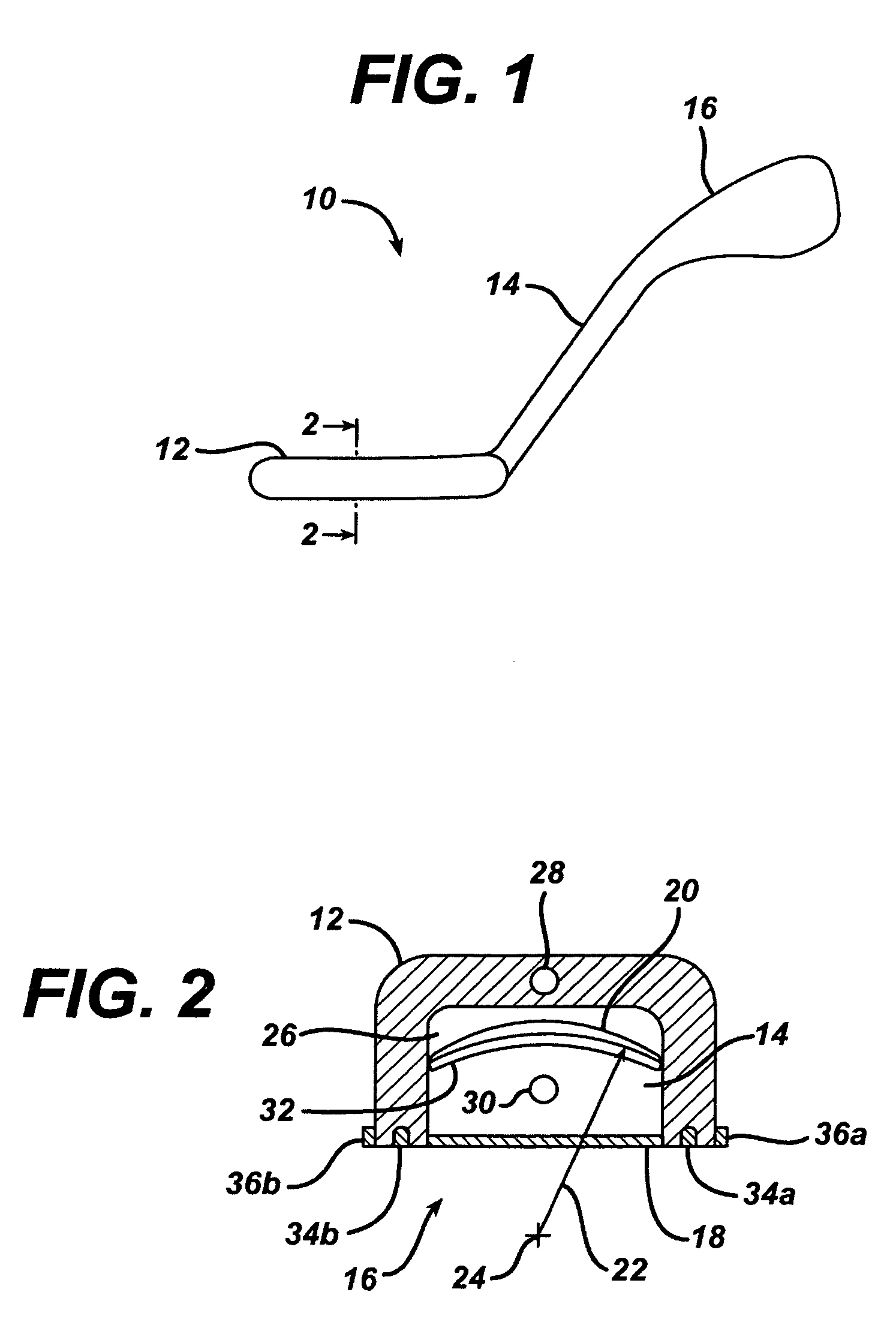
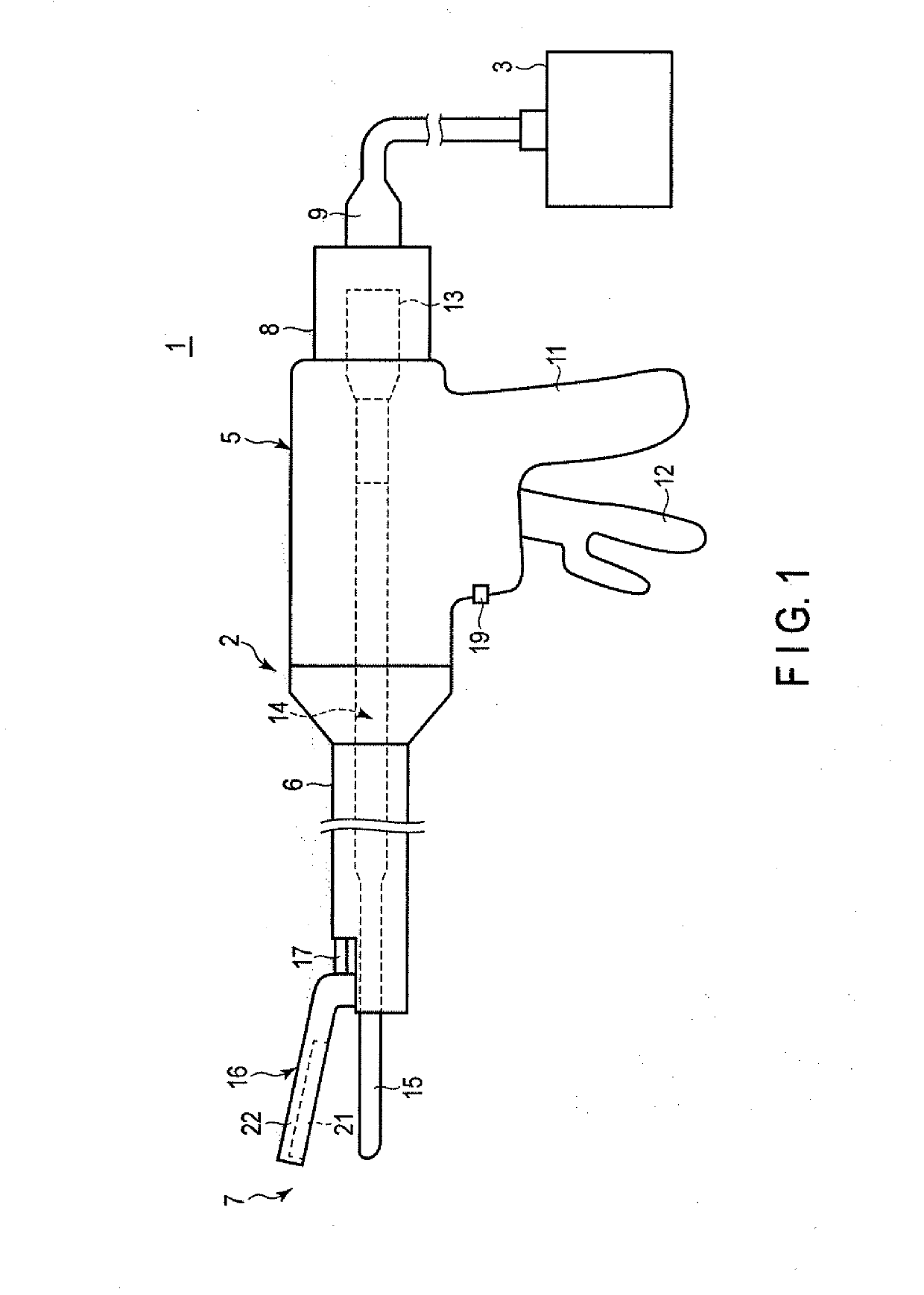
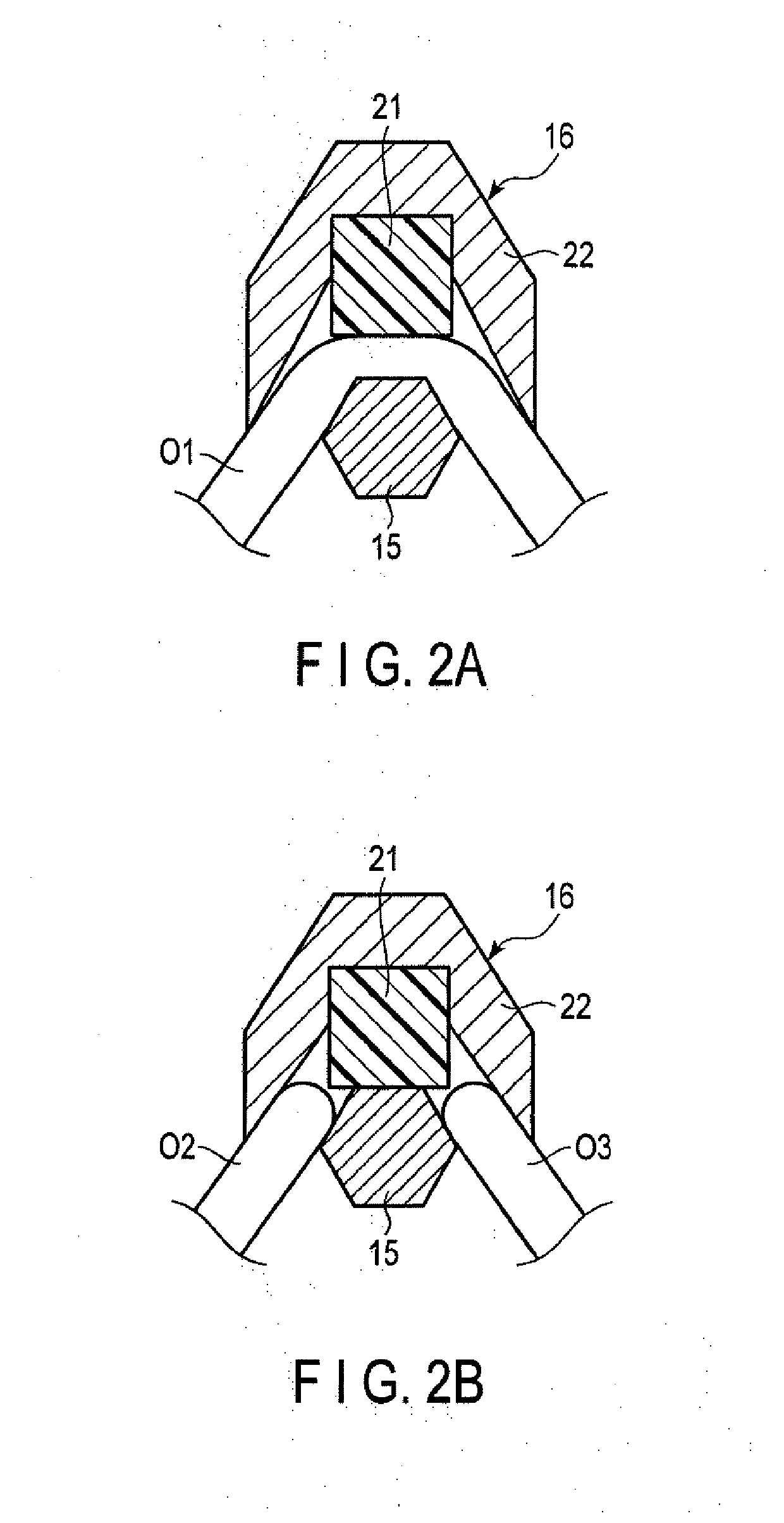
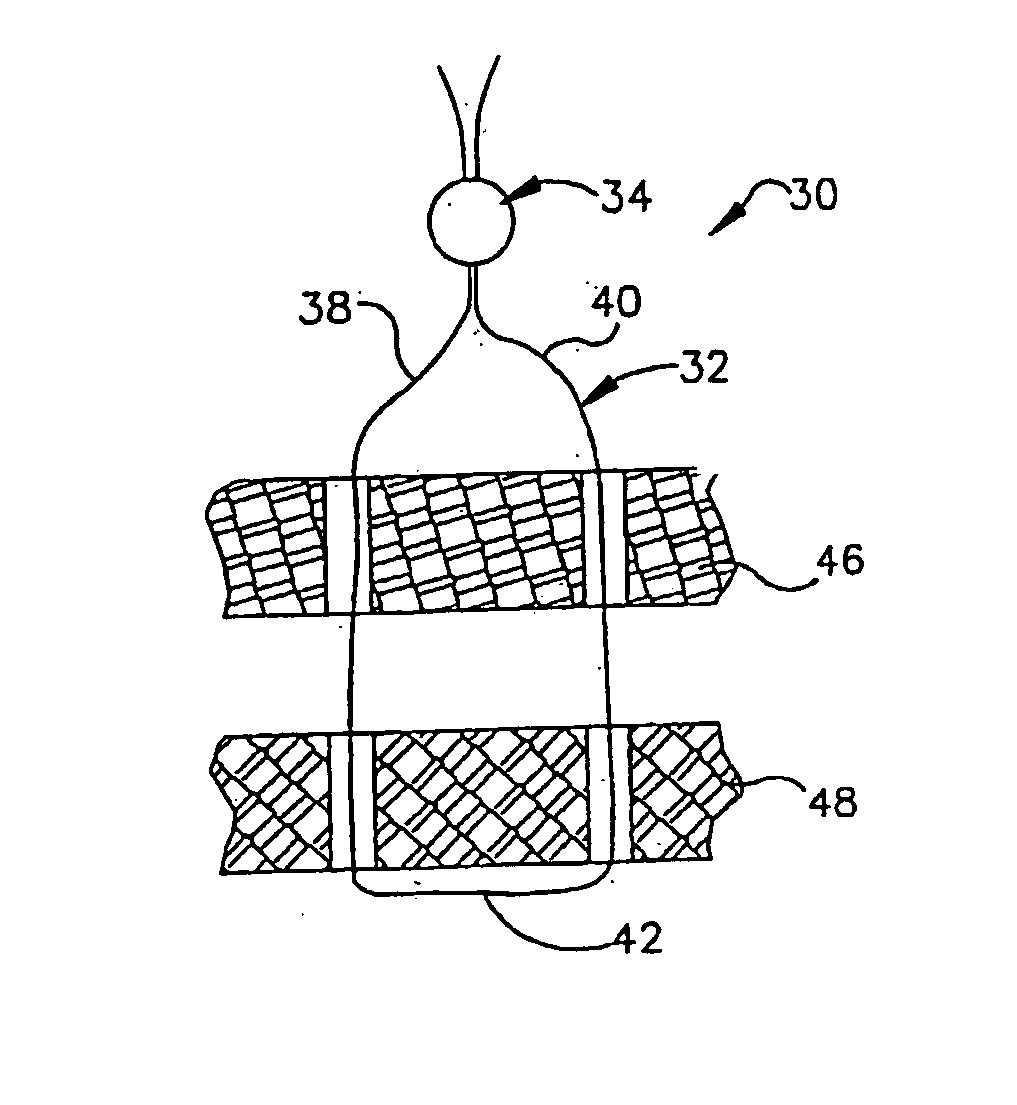
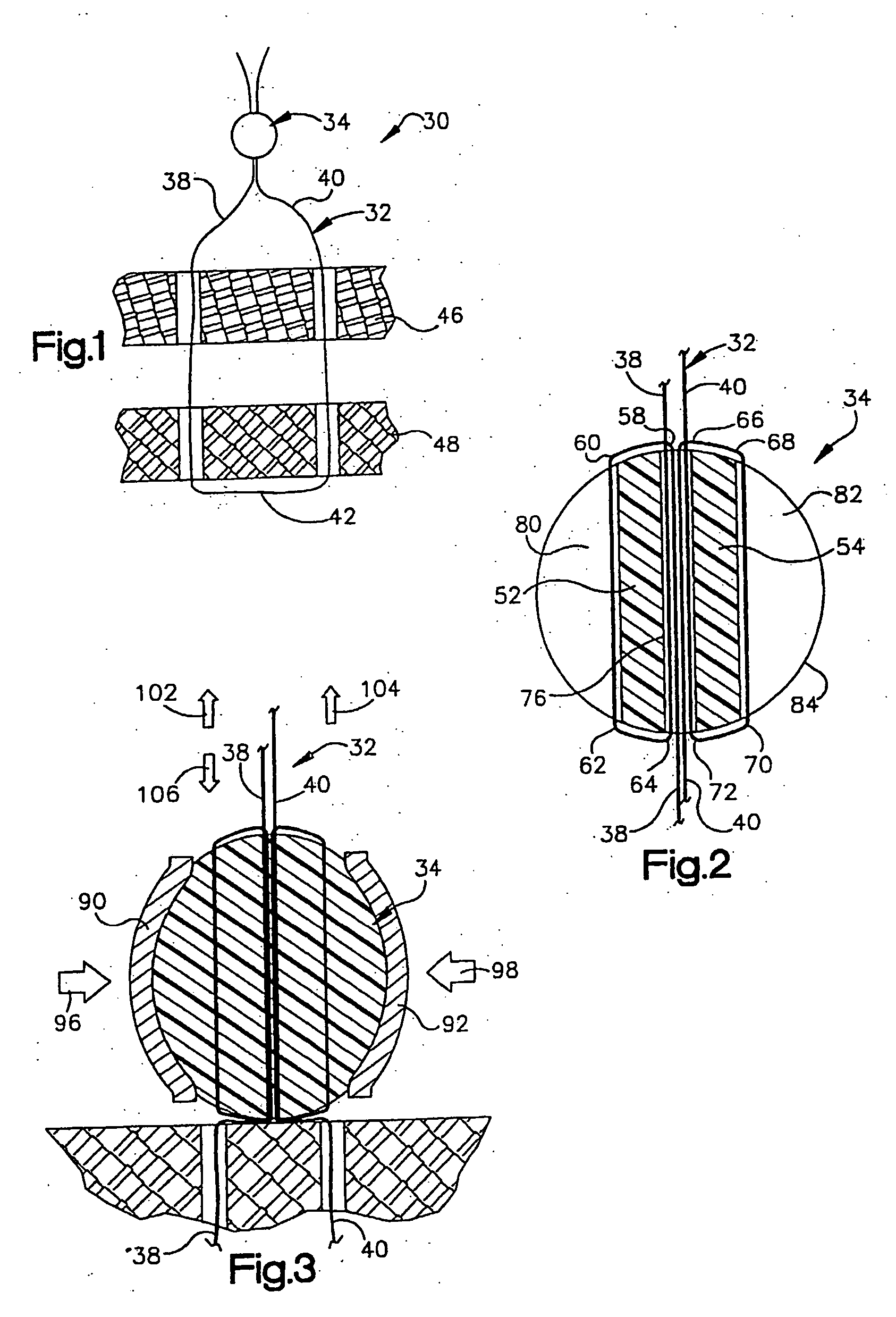
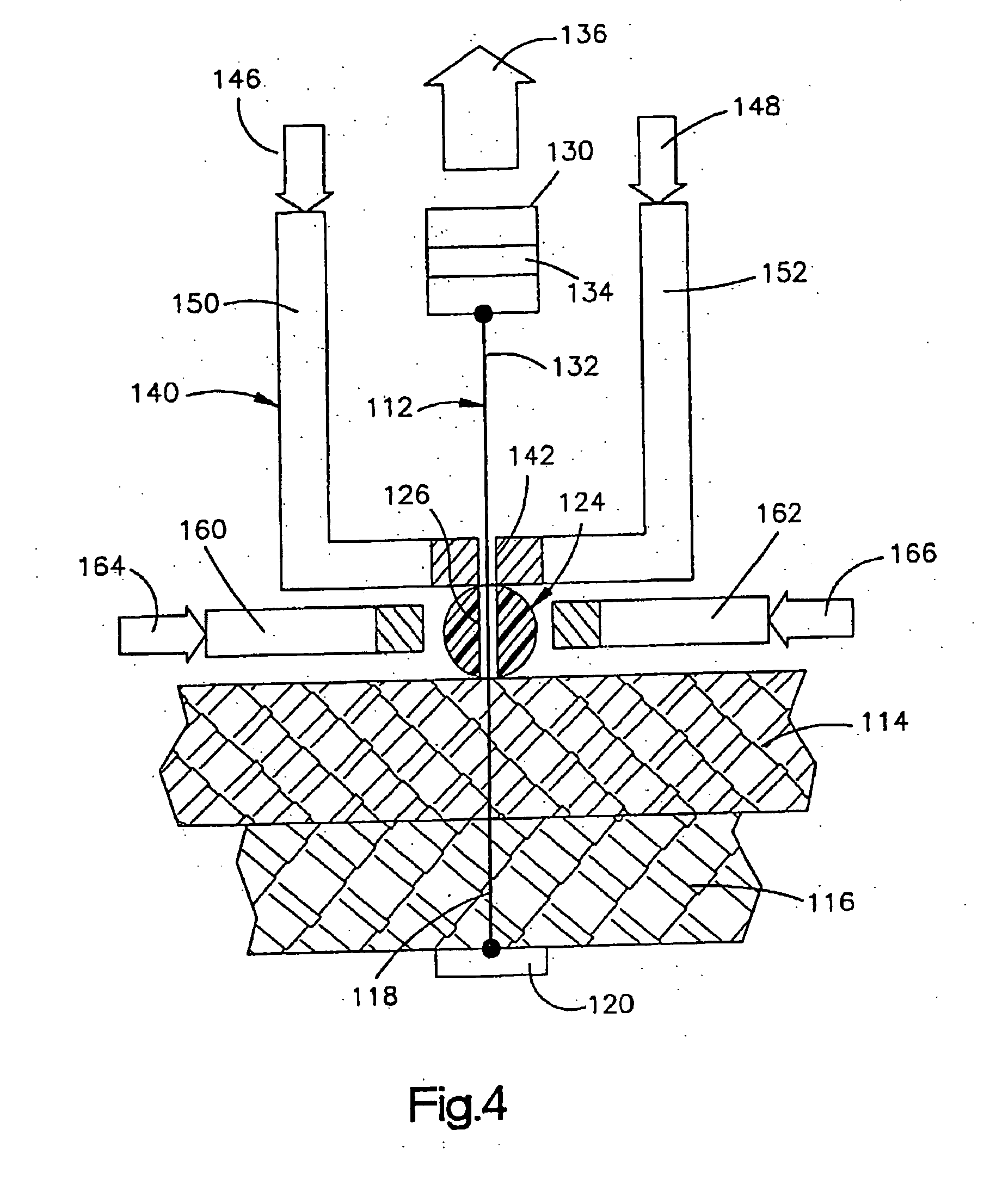
Method of using ultrasonic vibration to secure body tissue
A suture and a suture retainer are positioned relative to body tissue. Ultrasonic vibratory energy is utilized to heat the suture retainer and effect a bonding of portions of the suture retainer to each other and / or to the suture. Portions of the body tissue may be pressed into linear apposition with each other and held in place by cooperation between the suture and the suture retainer. The suture retainer may include one or more portions between which the suture extends. The suture retainer may include sections which have surface areas which are bonded together. If desired, the suture may be wrapped around one of the sections of the suture retainer. The suture retainer may be formed with a recess in which the suture is received. If desired, the suture retainer may be omitted and the sections of the suture bonded to each other.
Owner:P TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com