Patents
Literature
45052 results about "Instrumentation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Instrumentation is a collective term for measuring instruments that are used for indicating, measuring and recording physical quantities such as flow, temperature, level, distance, angle, or pressure. The term has its origins in the art and science of scientific instrument-making.
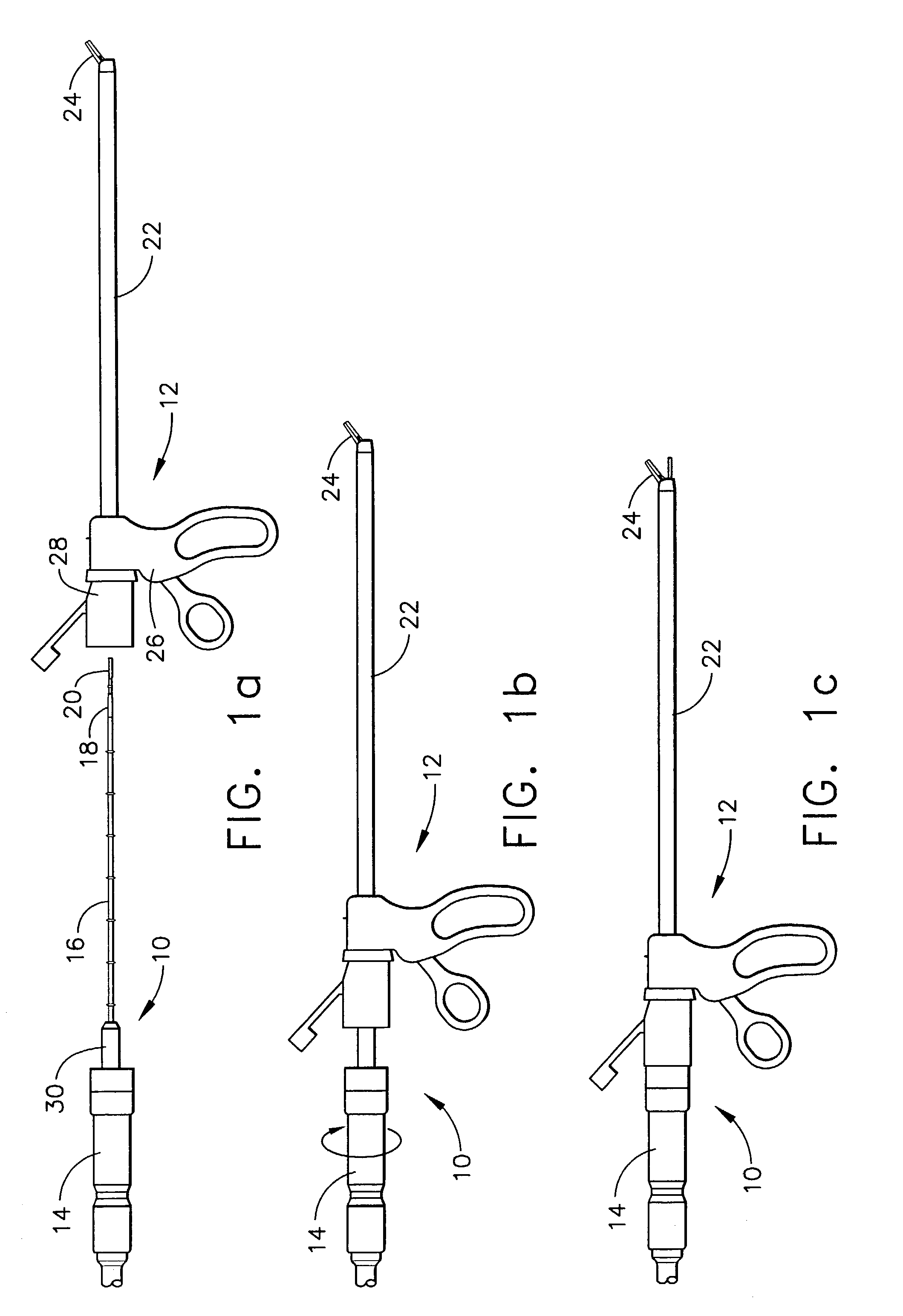
Methods and apparatus for performing transluminal and other procedures
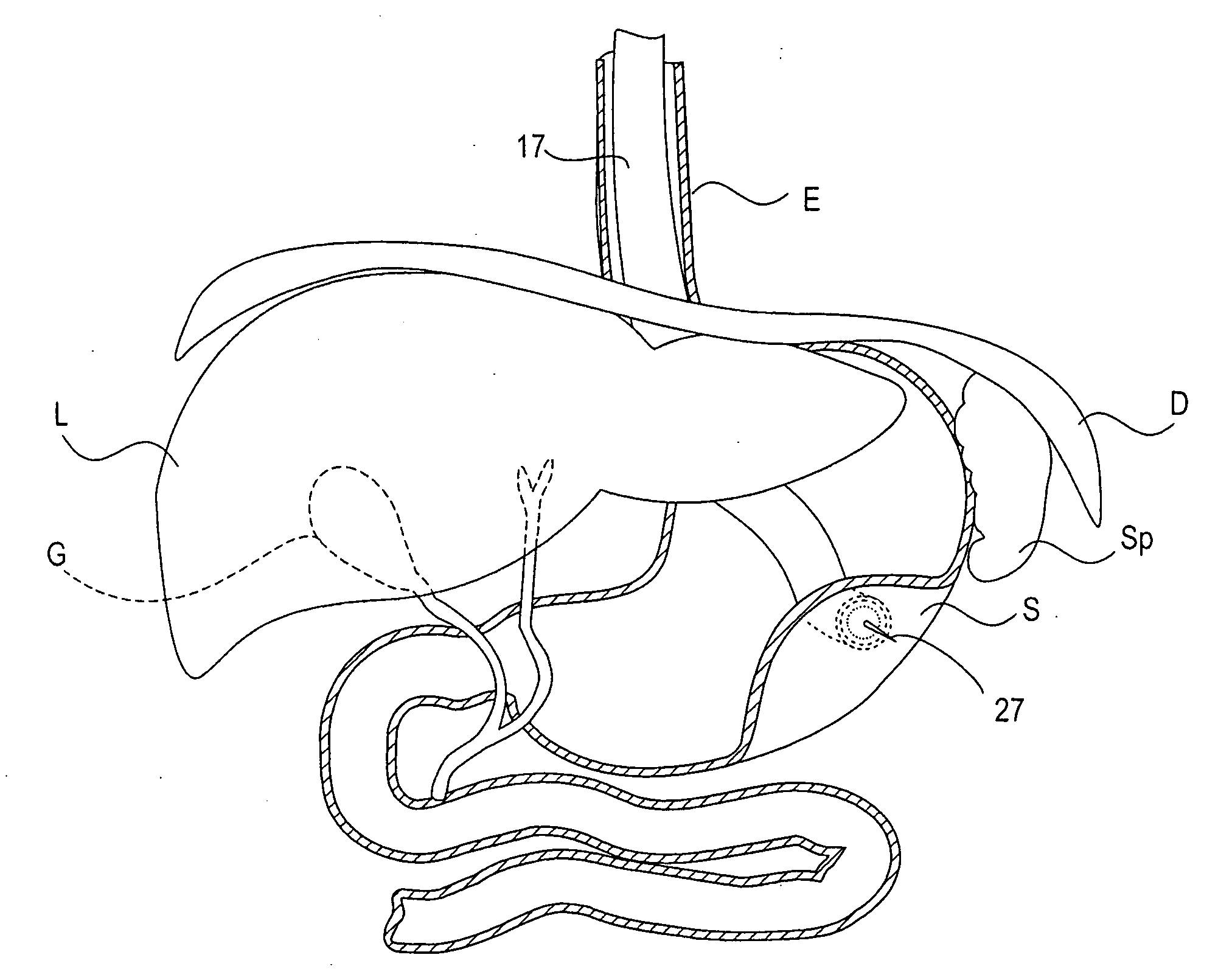
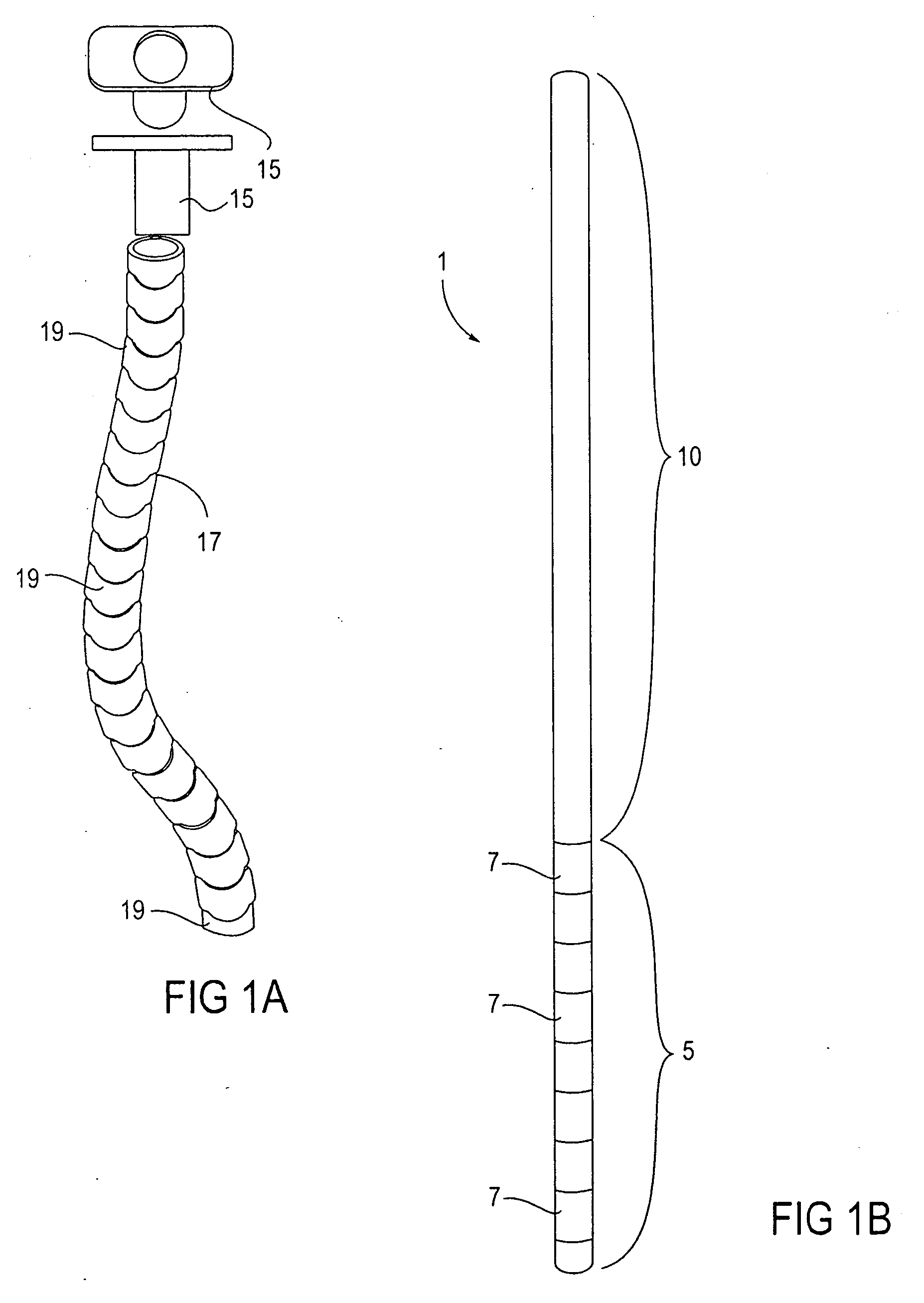
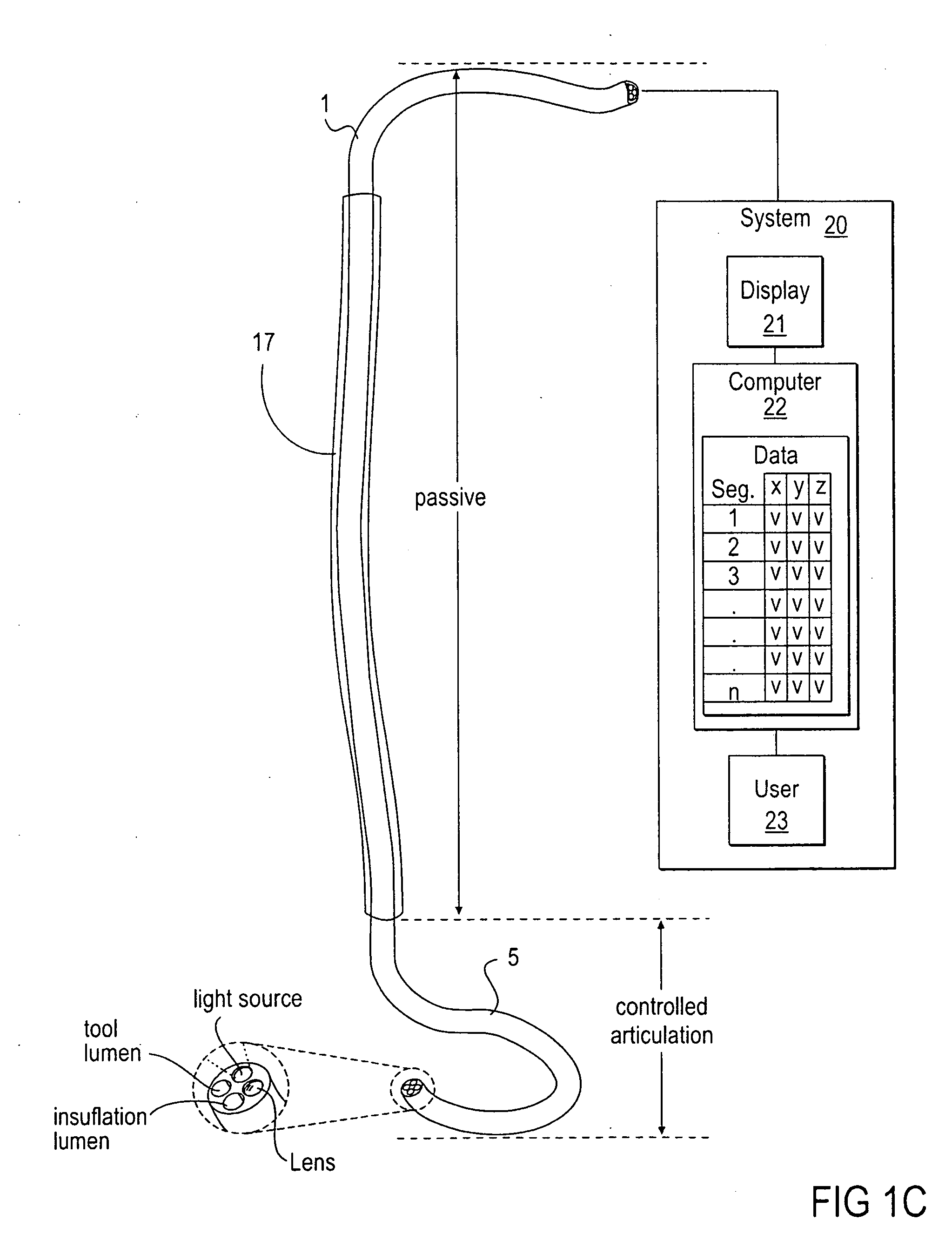
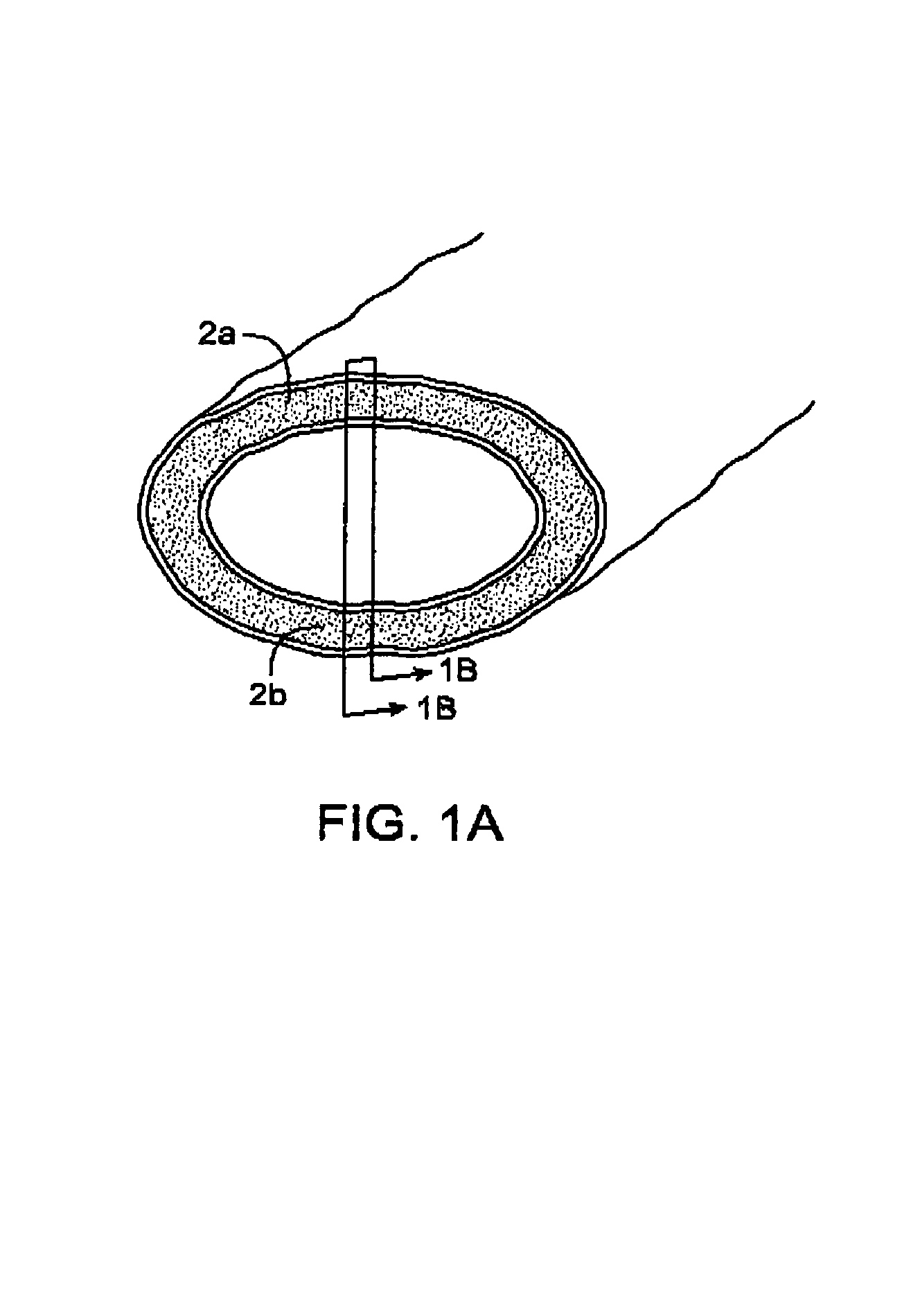
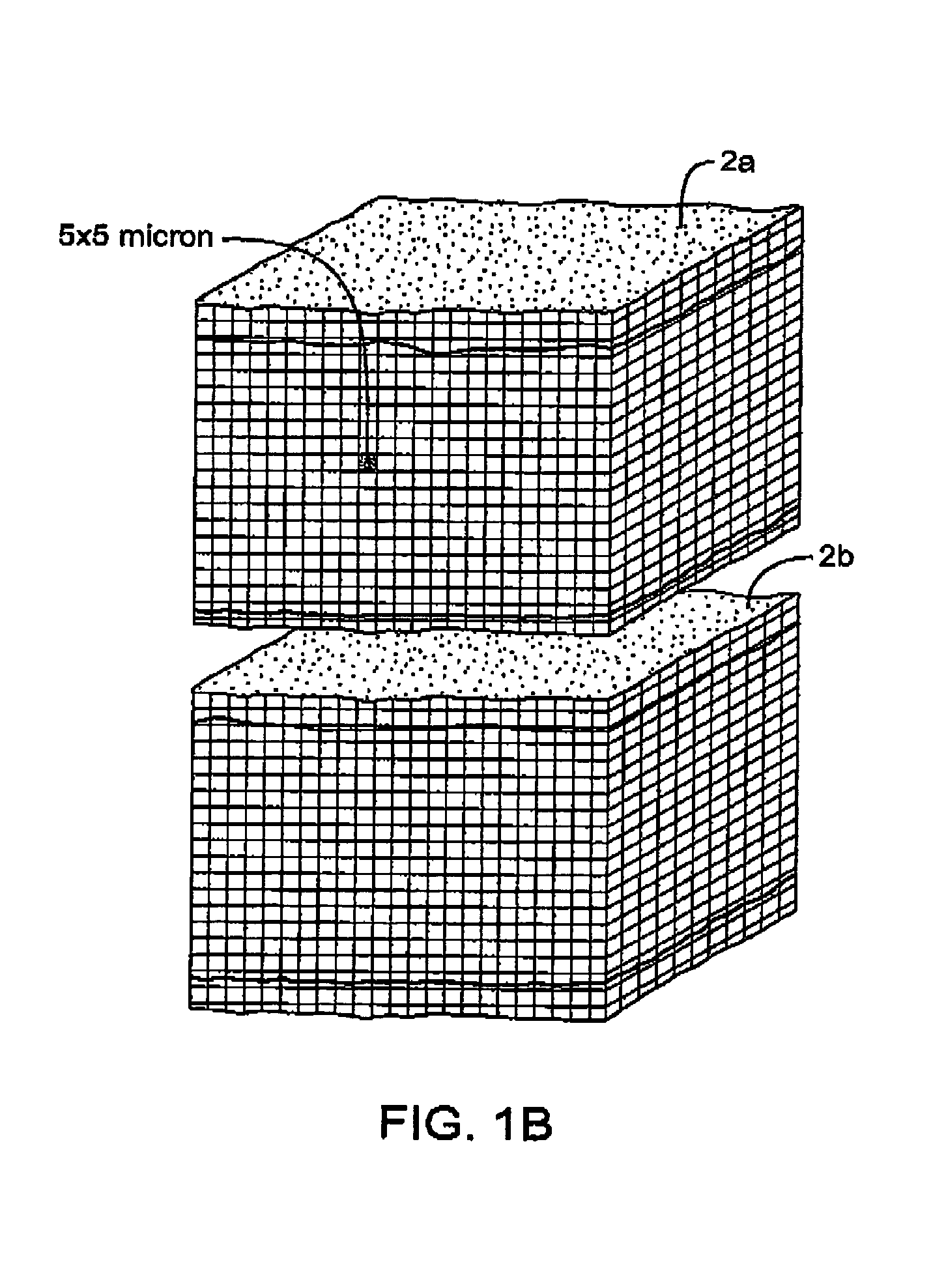
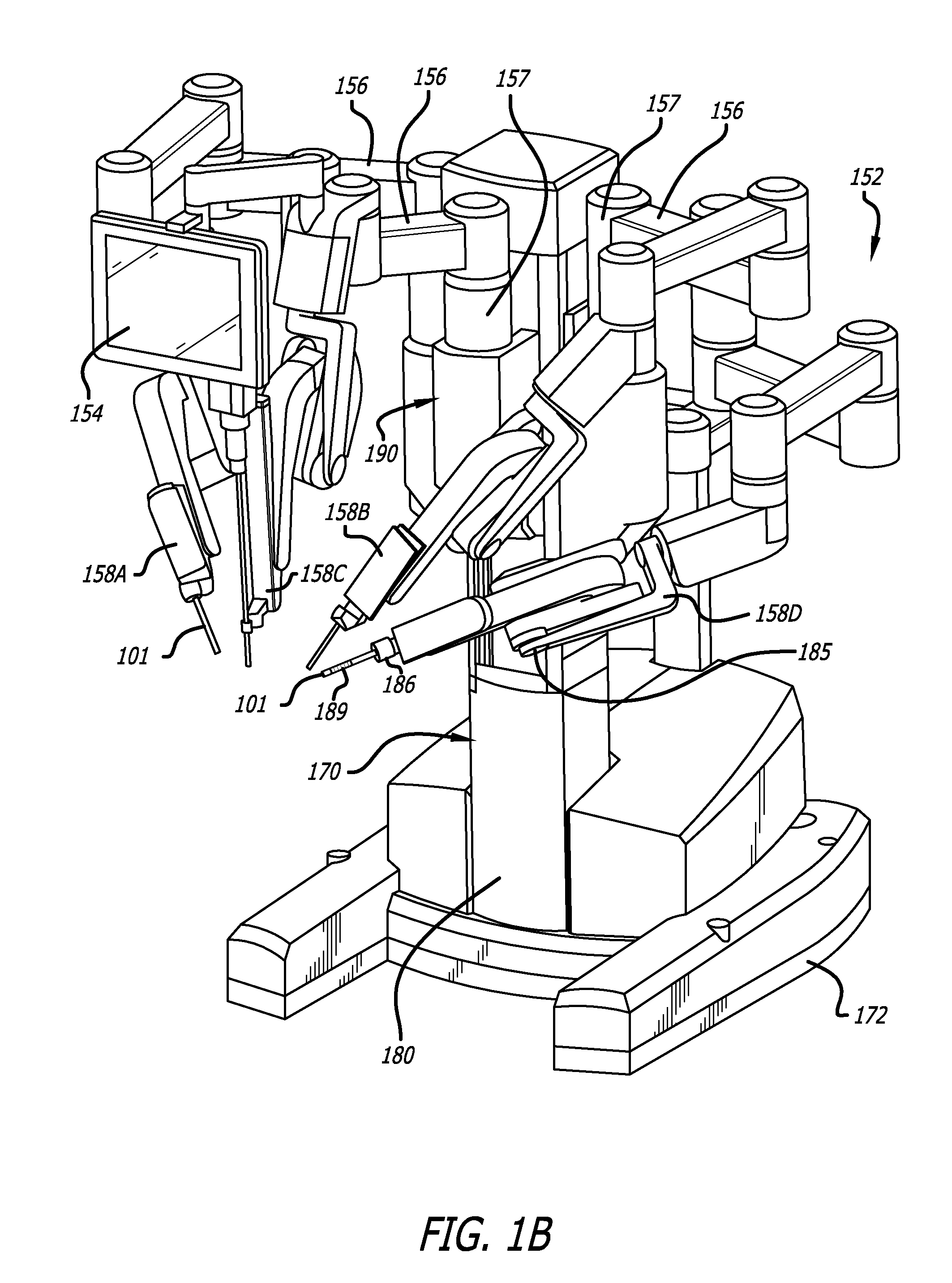
InactiveUS20070135803A1Prevent overflowPrevent leakageSuture equipmentsEar treatmentSurgeryInstrumentation
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
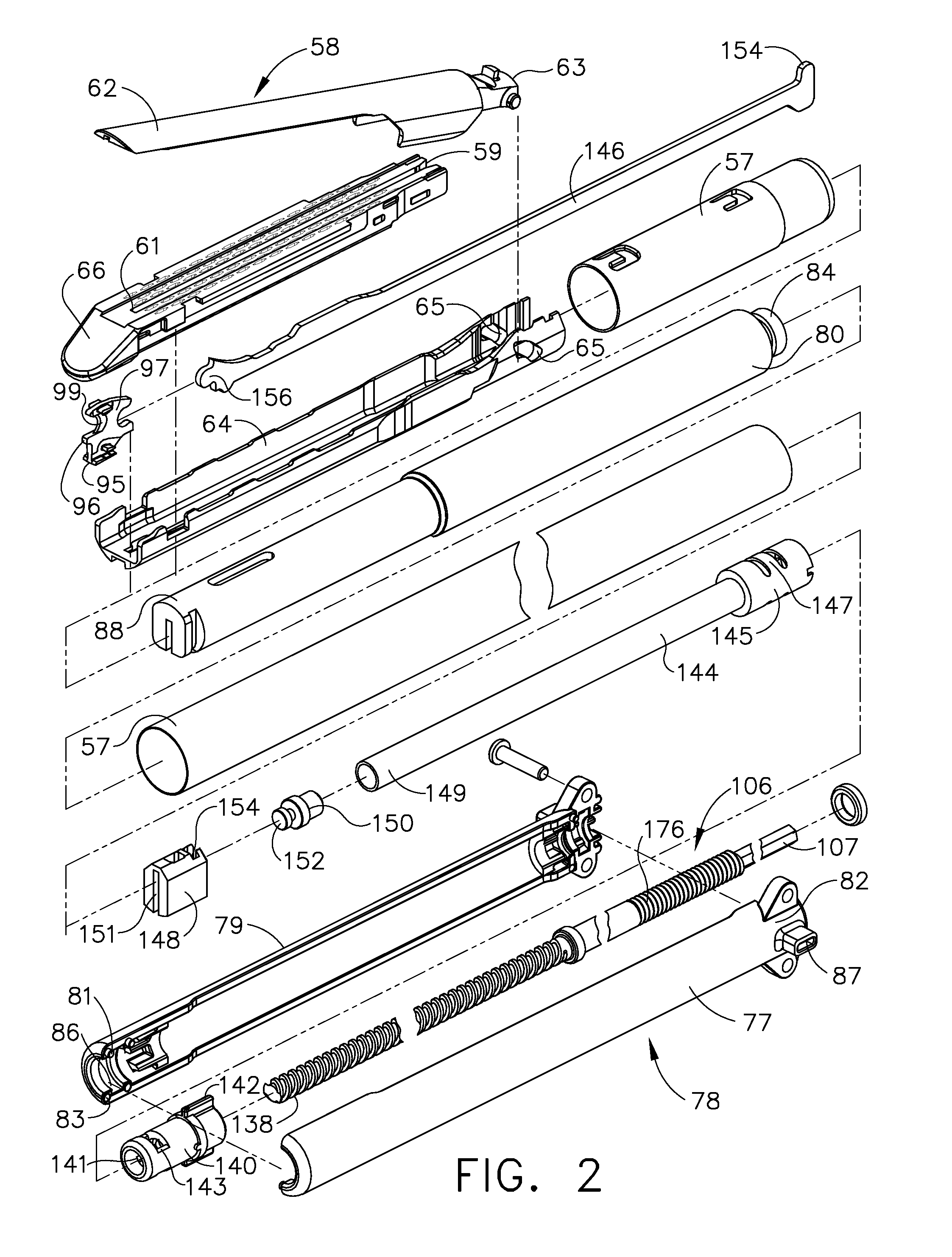
Electrosurgical working end with replaceable cartridges
InactiveUS7041102B2Reduce conductancePrevent any substantial dehydrationSurgical instruments for heatingCoatingsEngineeringMedical device
An electrosurgical medical device and method for creating thermal welds in engaged tissue that carries the electrosurgical components in a disposable cartridge. The instrument also can carry a blade member in a disposable cartridge, thus making the instrument system inexpensive to use. In another embodiment, the electrical leads of the cartridge have a surface coating of a thermochromic material to provide the physician with a visual indicator of operational parameters when applying energy to tissue.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
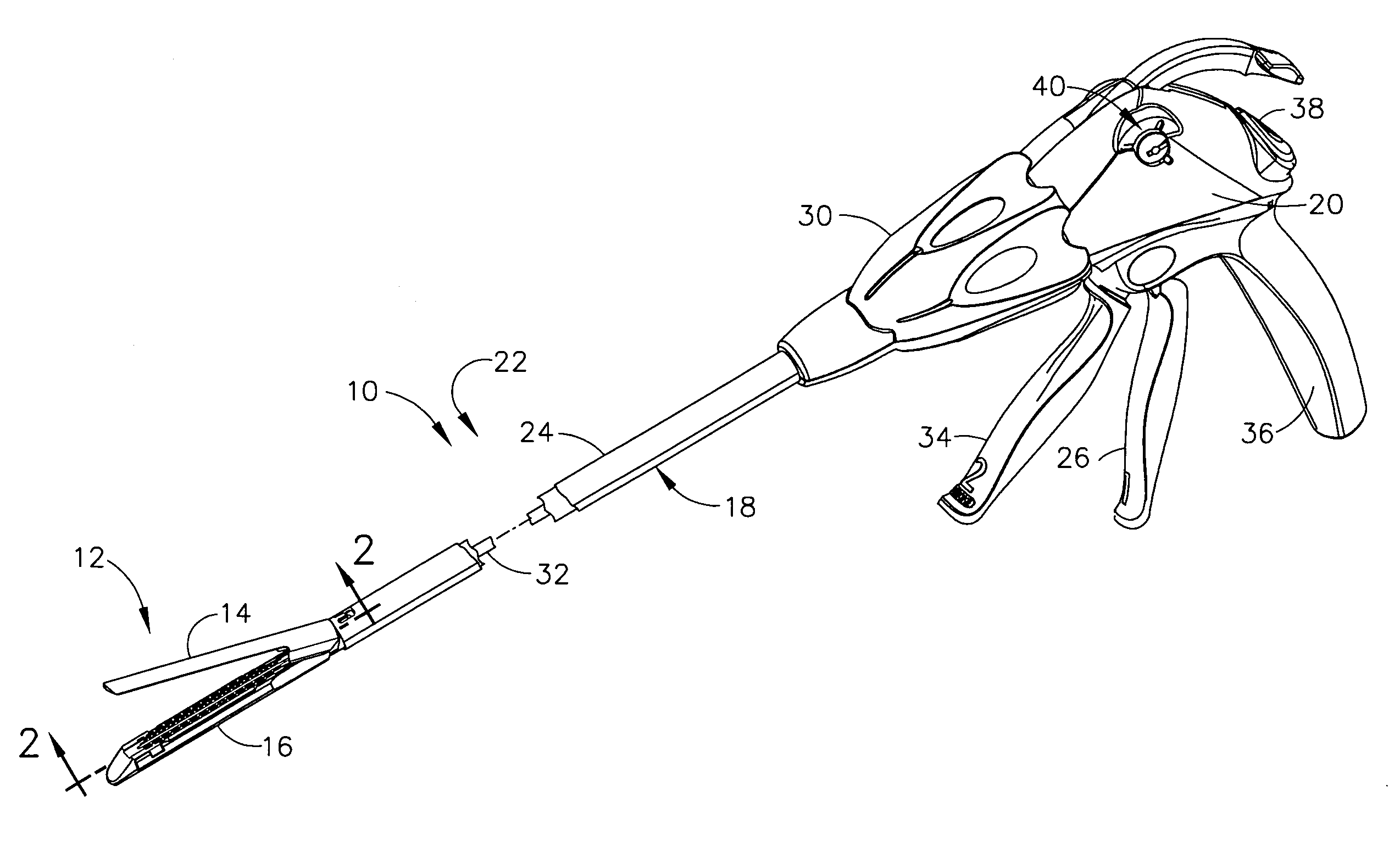
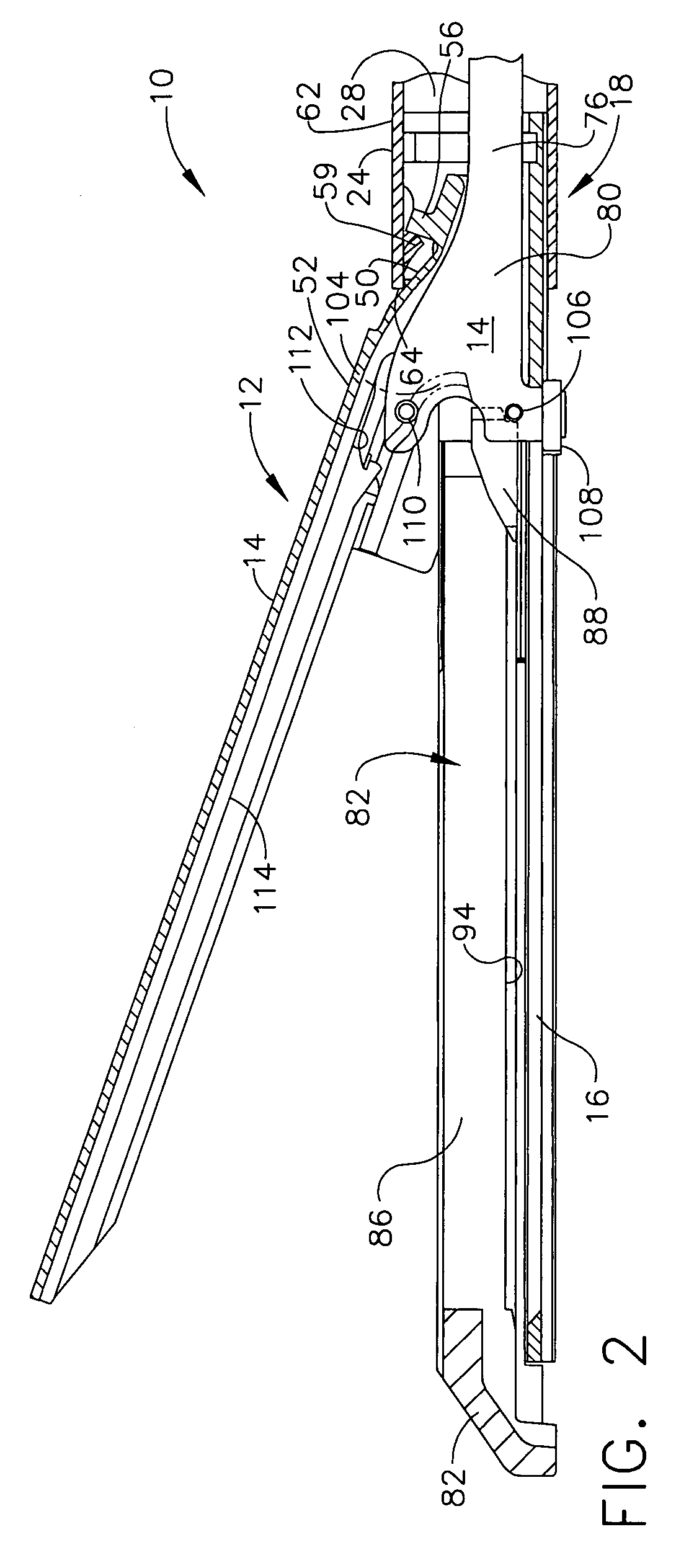
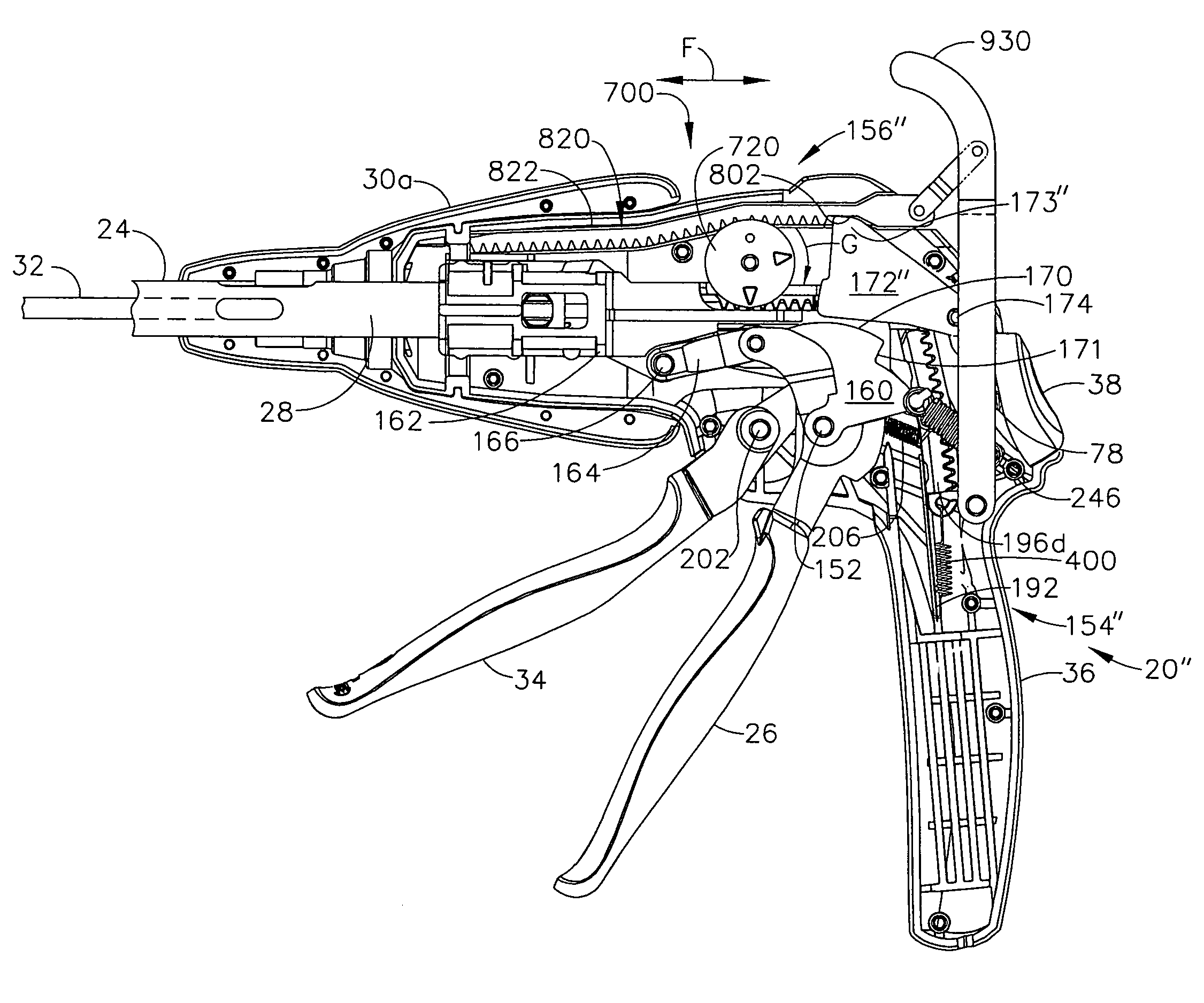
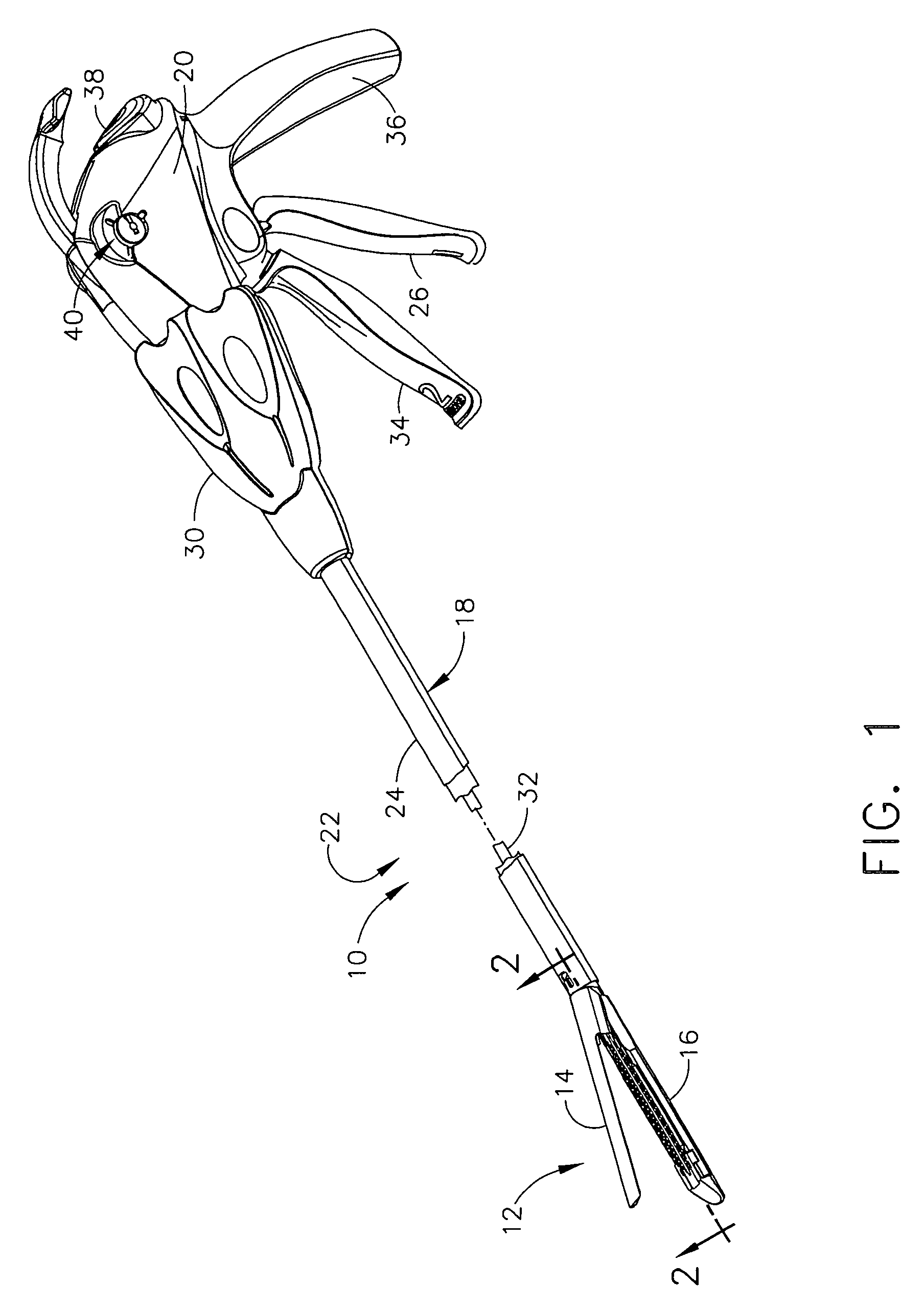
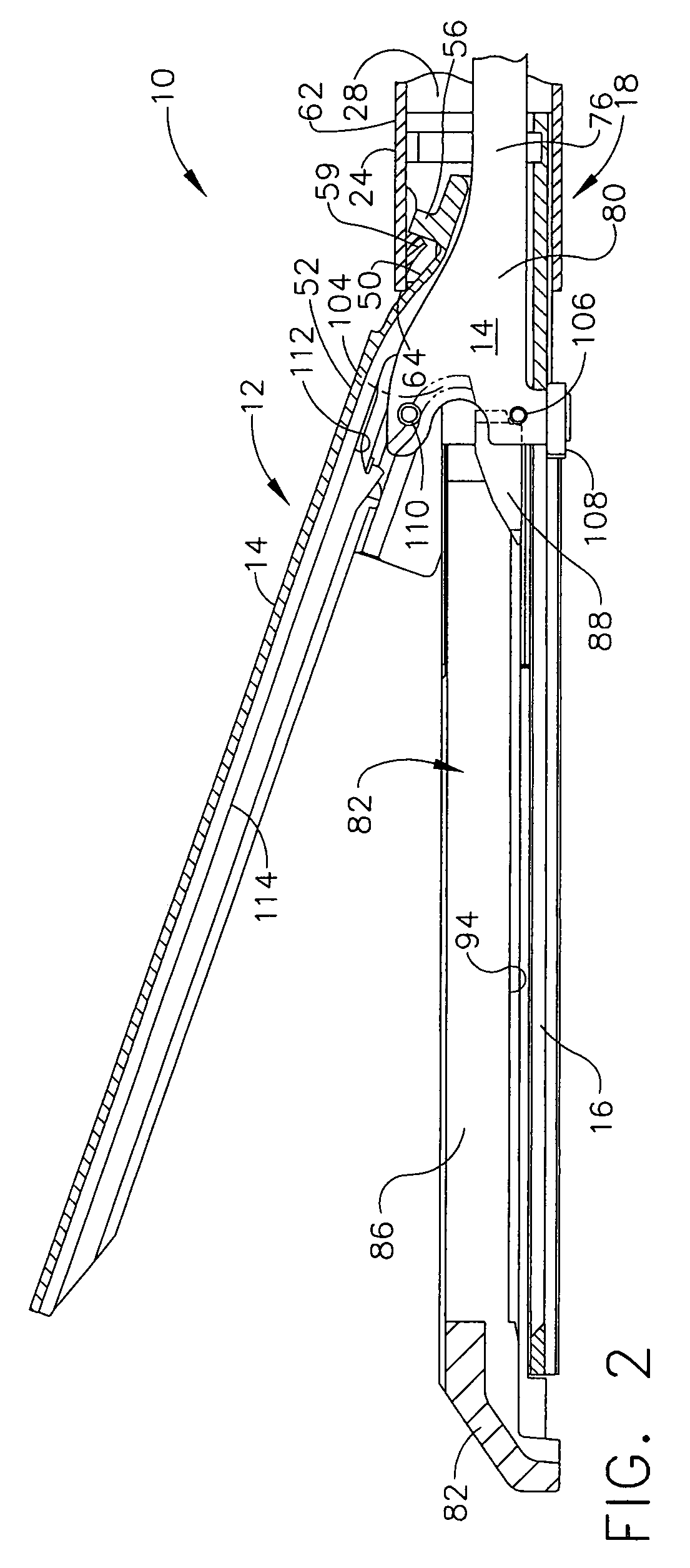
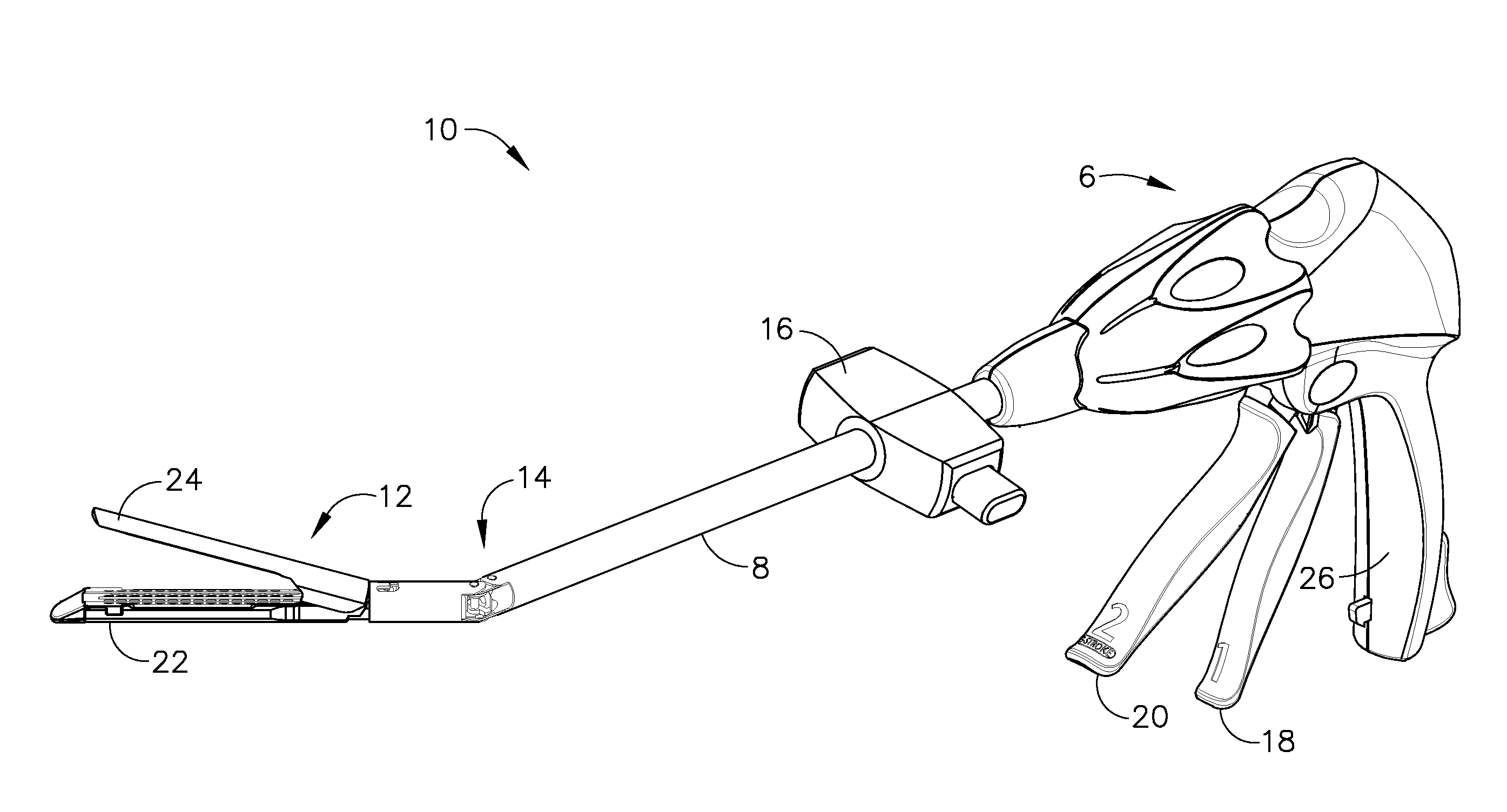
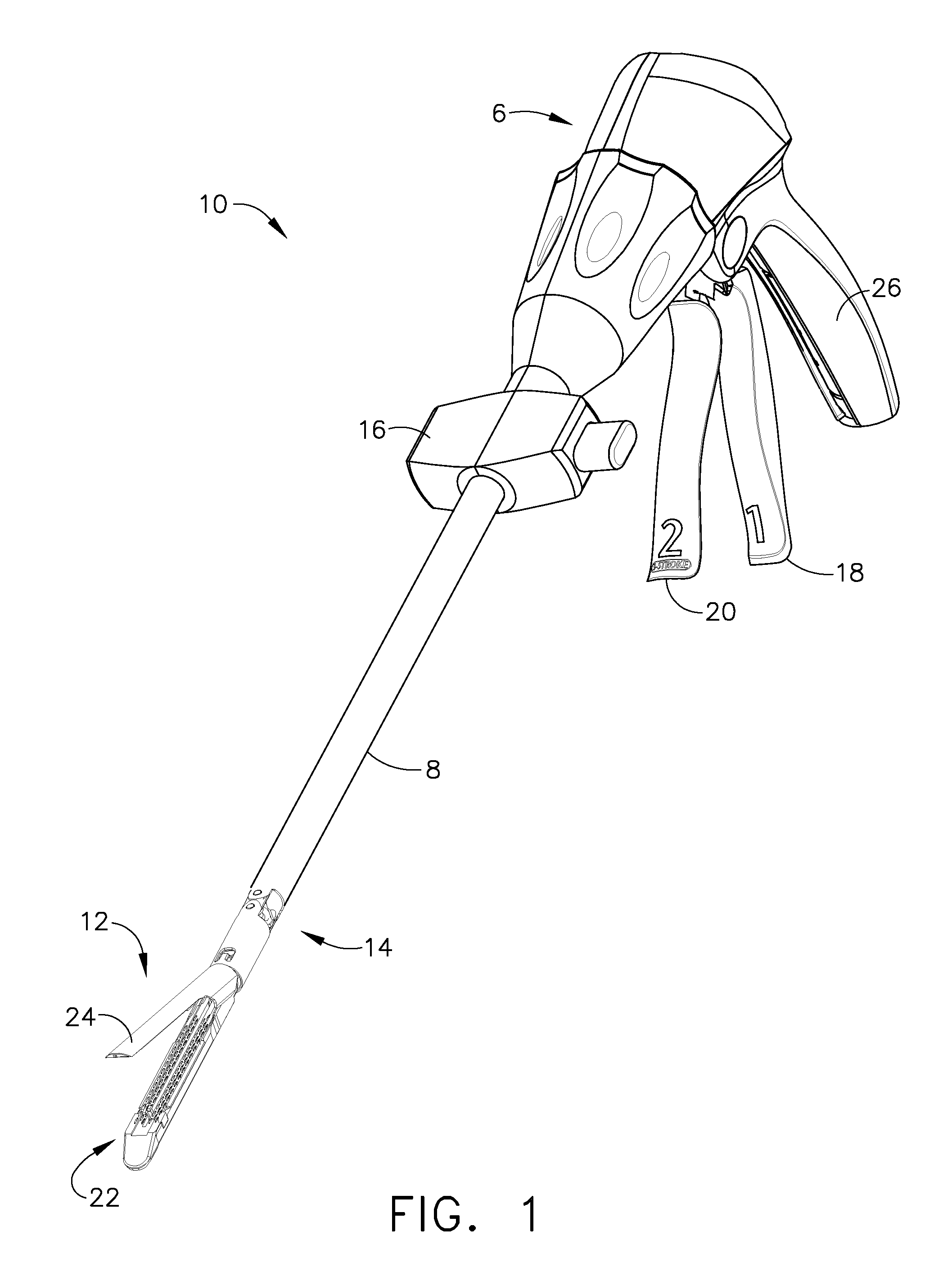
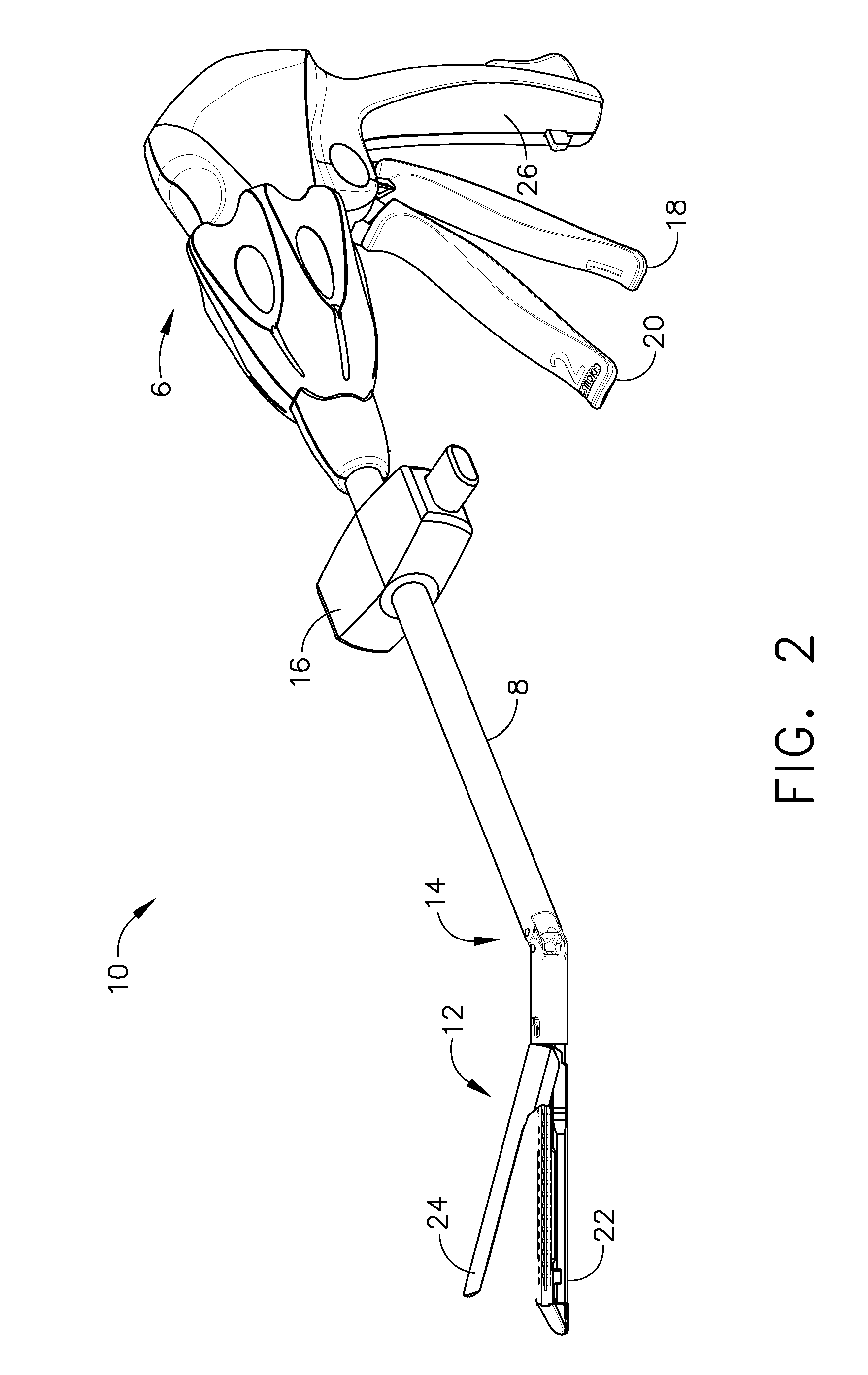
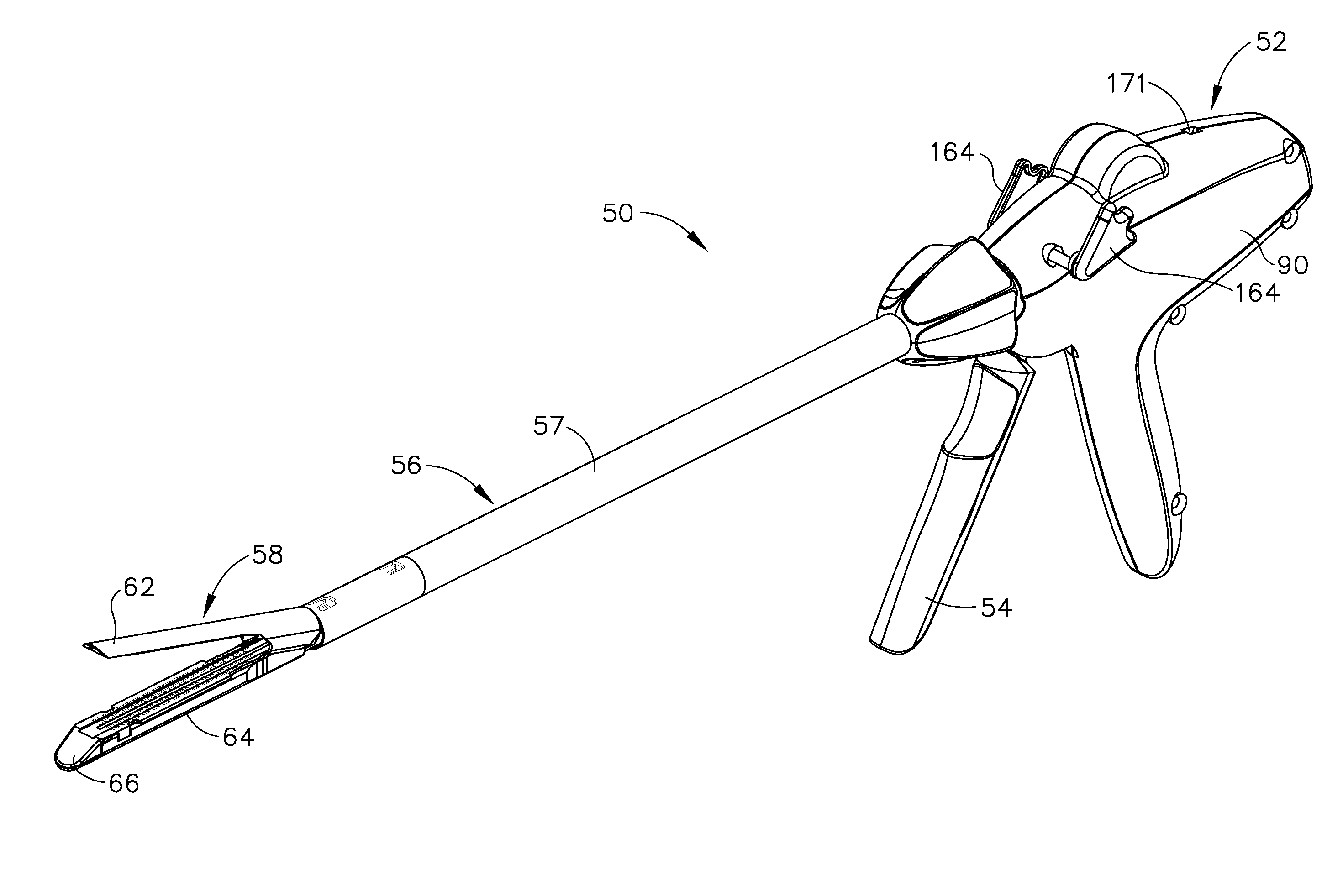
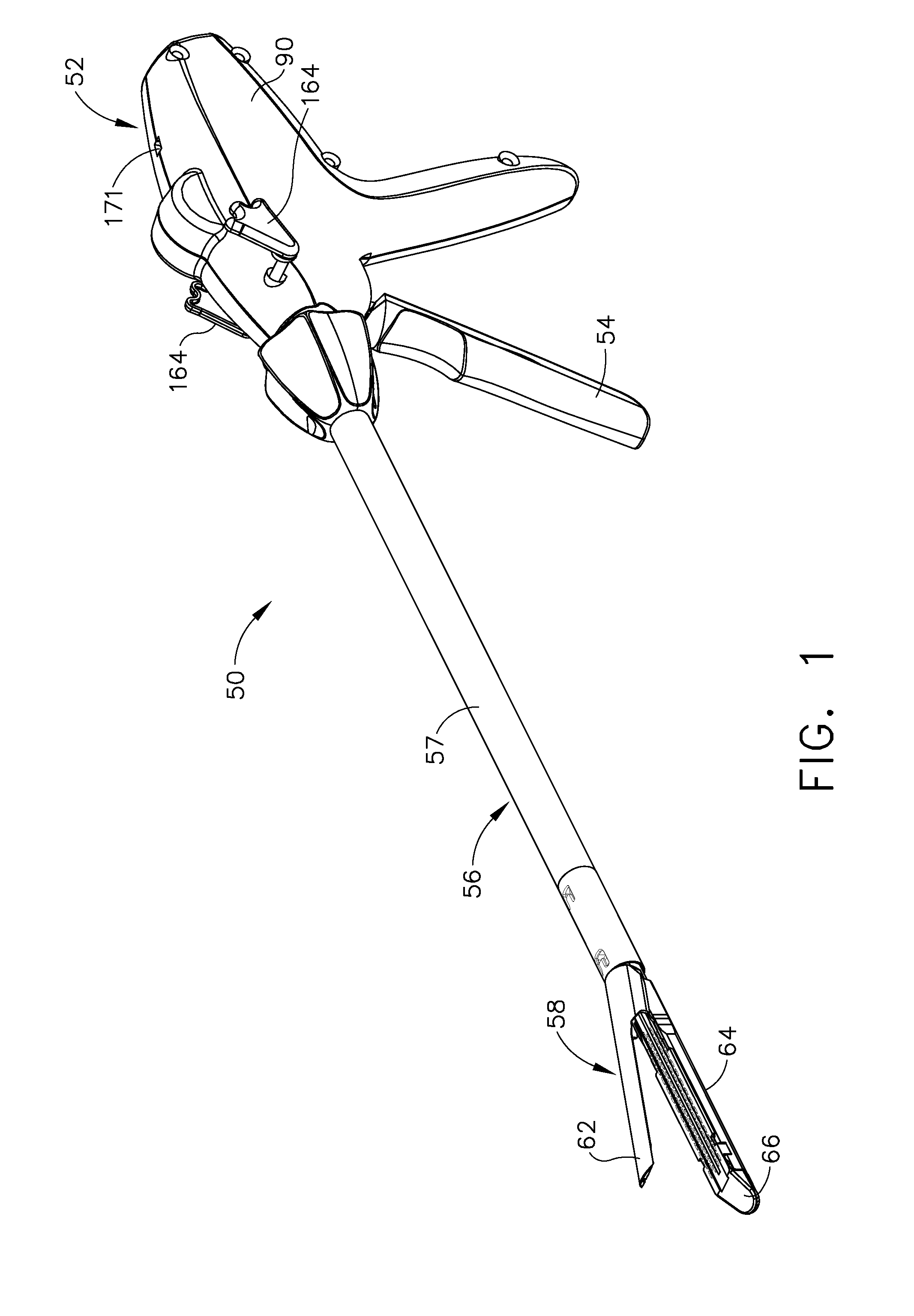
Surgical stapling and cutting instrument with manually retractable firing member
A surgical stapling and severing instrument particularly suited to endoscopic procedures incorporates a handle that produces separate closing and firing motions to actuate an end effector. In particular, the handle produces multiple firing strokes in order to reduce the required amount of force required to fire (i.e., staple and sever) the end effector. A linked transmission reduces the required handle longitudinal length, yet achieves a rigid, strong configuration when straightened for firing. A traction biased firing mechanism avoids binding in driving this straightened linked rack. The instrument further has a manually actuatable retraction system that does not require the use of additional springs or other mechanisms to generate retraction forces which must be overcome when generating the forces necessary to fire the device. In various embodiments, the retraction system provides a visual indication to the surgeon as to how far firing has progressed.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
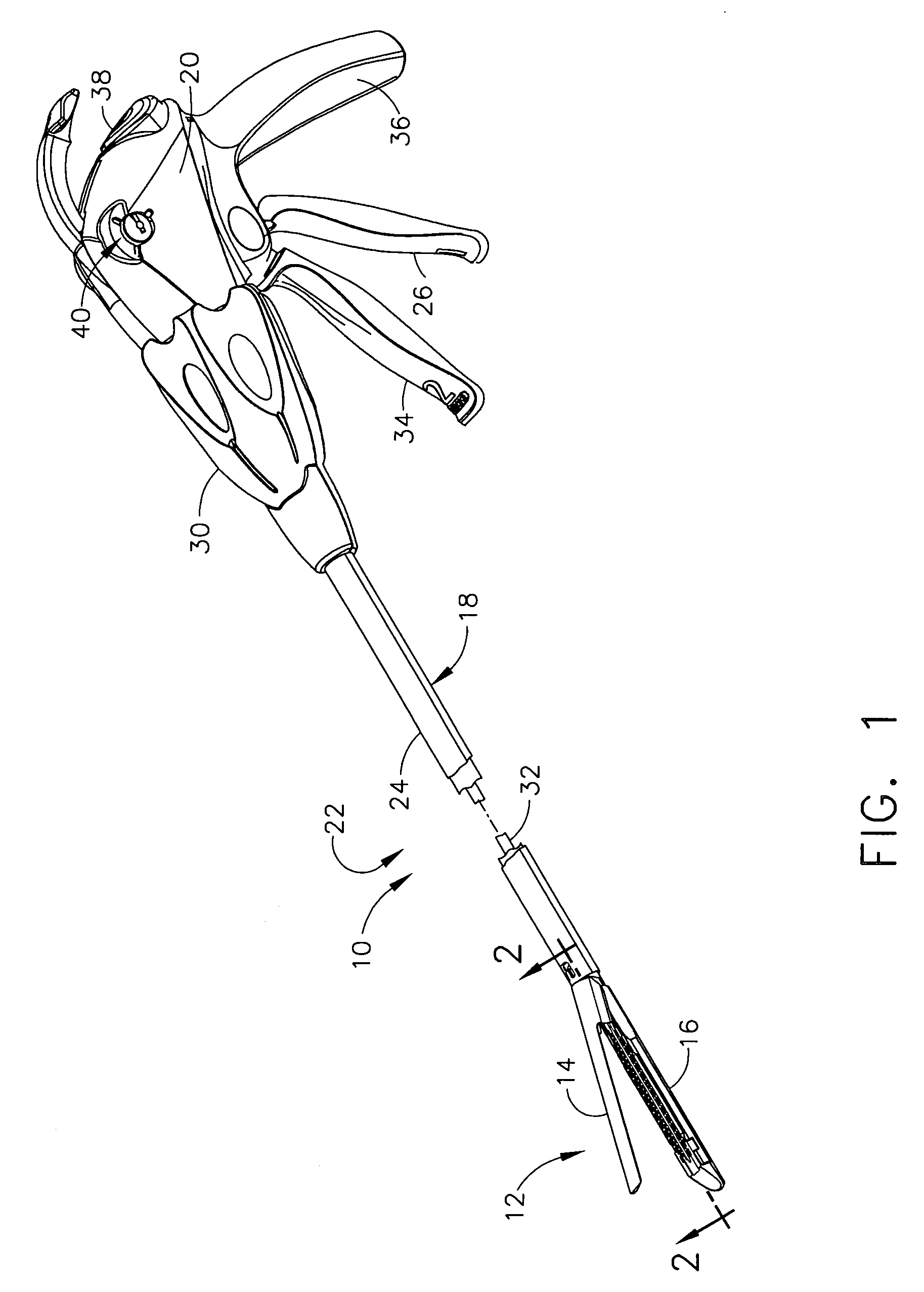
Surgical stapling and cutting instrument with travel-indicating retraction member
A surgical stapling and severing instrument particularly suited to endoscopic procedures incorporates a handle that produces separate closing and firing motions to actuate an end effector. In particular, the handle produces multiple firing strokes in order to reduce the required amount of force required to fire (i.e., staple and sever) the end effector. A linked transmission reduces the required handle longitudinal length, yet achieves a rigid, strong configuration when straightened for firing. A traction biased firing mechanism avoids binding in driving this straightened linked rack. The instrument further has a manually actuatable retraction system that does not require the use of additional springs or other mechanisms to generate retraction forces which must be overcome when generating the forces necessary to fire the device. In various embodiments, the retraction system provides a visual indication to the surgeon as to how far firing has progressed.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Smart recognition apparatus and method
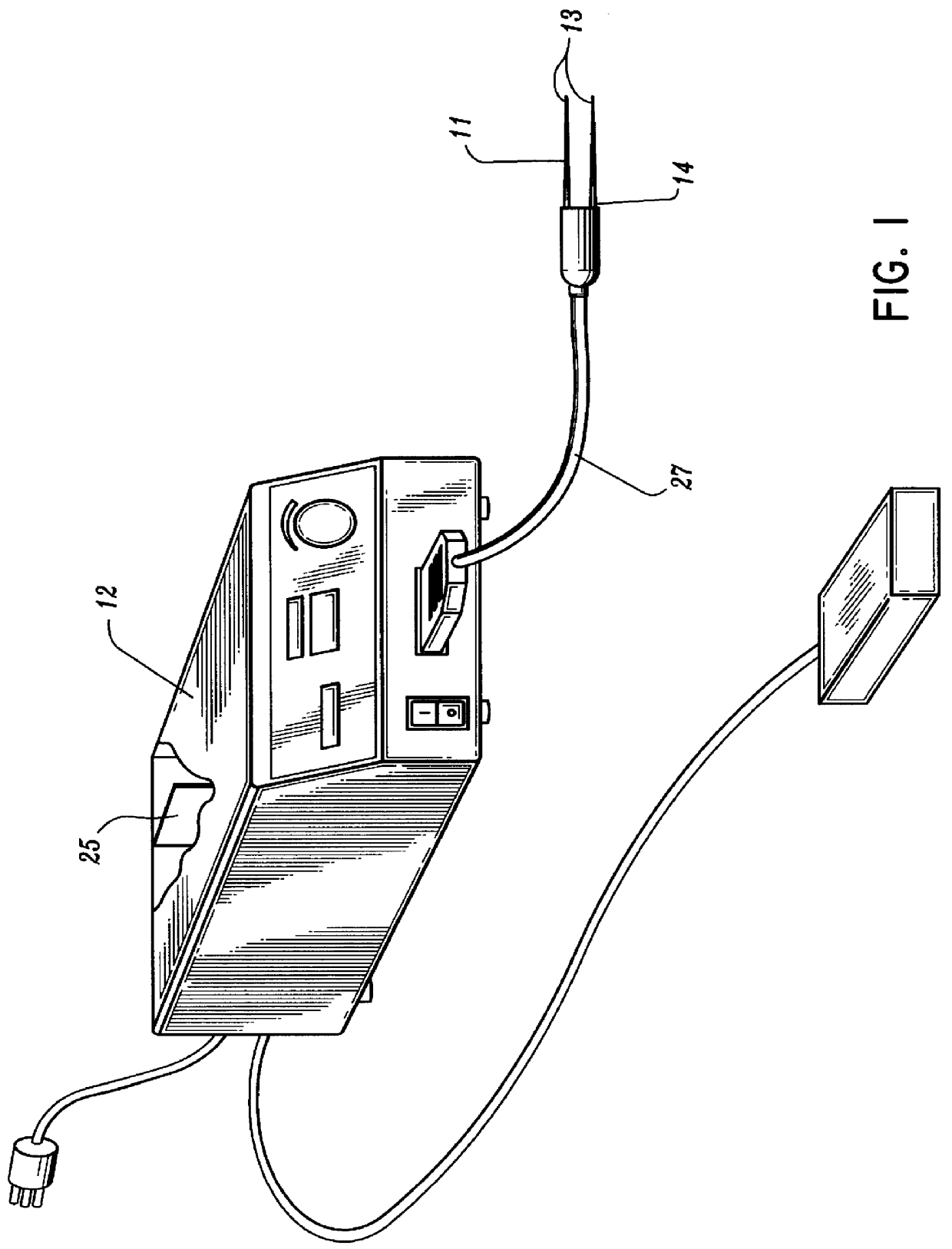
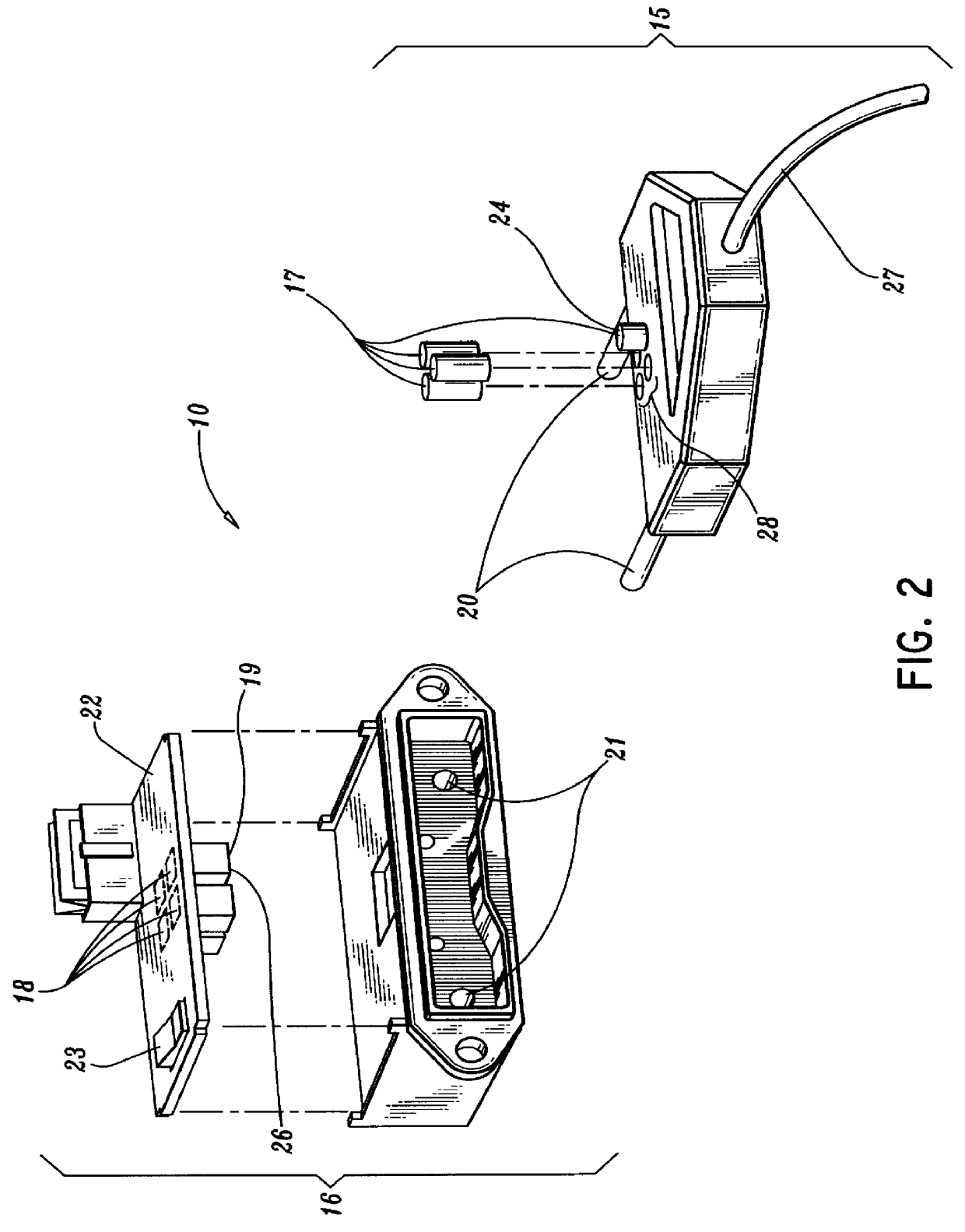
A qualifying connection for an instrument attaches to a source of electrosurgery energy to and the instrument and has first and second parts coupled to the instrument and the source, respectively. Optical couplings on the connection transmit invisible energy to identify the instrument and are proximate on the first and second parts. A light modifier on the first part is proximal to the second part for modification of radiation in the infrared wavelengths so infrared transmitters encode signals and non contact coded proximity detectors on the second part are the coupled detectors. Non contact coded proximity detectors respond to modified infrared light establishing an Nth bit identification code. An infrared light supply in the source pass from the transmitters across the communicating couplings for encoding signals by modification of the infrared light with a light modifier. Mechanical attachments include conjugating male and female portions physically extending between the parts for mating engagement. The attachments juxtaposition the parts when the attachments geometrically conjugate to geographically positioning the couplings proximate for communicating. The attachments have one or more conductors for delivery of high frequency energy from the source to the instrument. A cable fits between the first part of the connection and the instrument and has electrical conductors for carrying energy passing through the first part of the connection from the source to the instrument. An identifying circuit couples to the second part and responds to invisible light optically communicated across the couplings for verifying the type of instrument connected by the cable to the source.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Tissue pad for use with an ultrasonic surgical instrument
InactiveUS20060079874A1Effectively smooths out abusive tissue forceSurgical instrument detailsSurgical forcepsBiological activationSurgical department
An ultrasonic clamp coagulator assembly that is configured to permit selective cutting, coagulation and clamping of tissue during surgical procedures. An elongated portion of the instrument can be configured for endoscopic applications and has an outside diameter of less than 6 mm. The construction includes a clamping mechanism, including a clamp arm pivotally mounted at the distal portion of the instrument, which is specifically configured to create a desired level of tissue clamping forces, exceeding 4 pounds when the trigger is fully closed. The clamping mechanism includes a two-piece pad design and pad material that enables the higher tissue clamping forces and a force-limiting mechanism that effectively smooths out abusive tissue forces. The assembly also features hand activation configured to provide an ergonomical grip and operation for the surgeon. Hand switches are placed in the range of the natural swing of the surgeon's thumb, whether gripping the surgical instrument right-handed or left handed.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
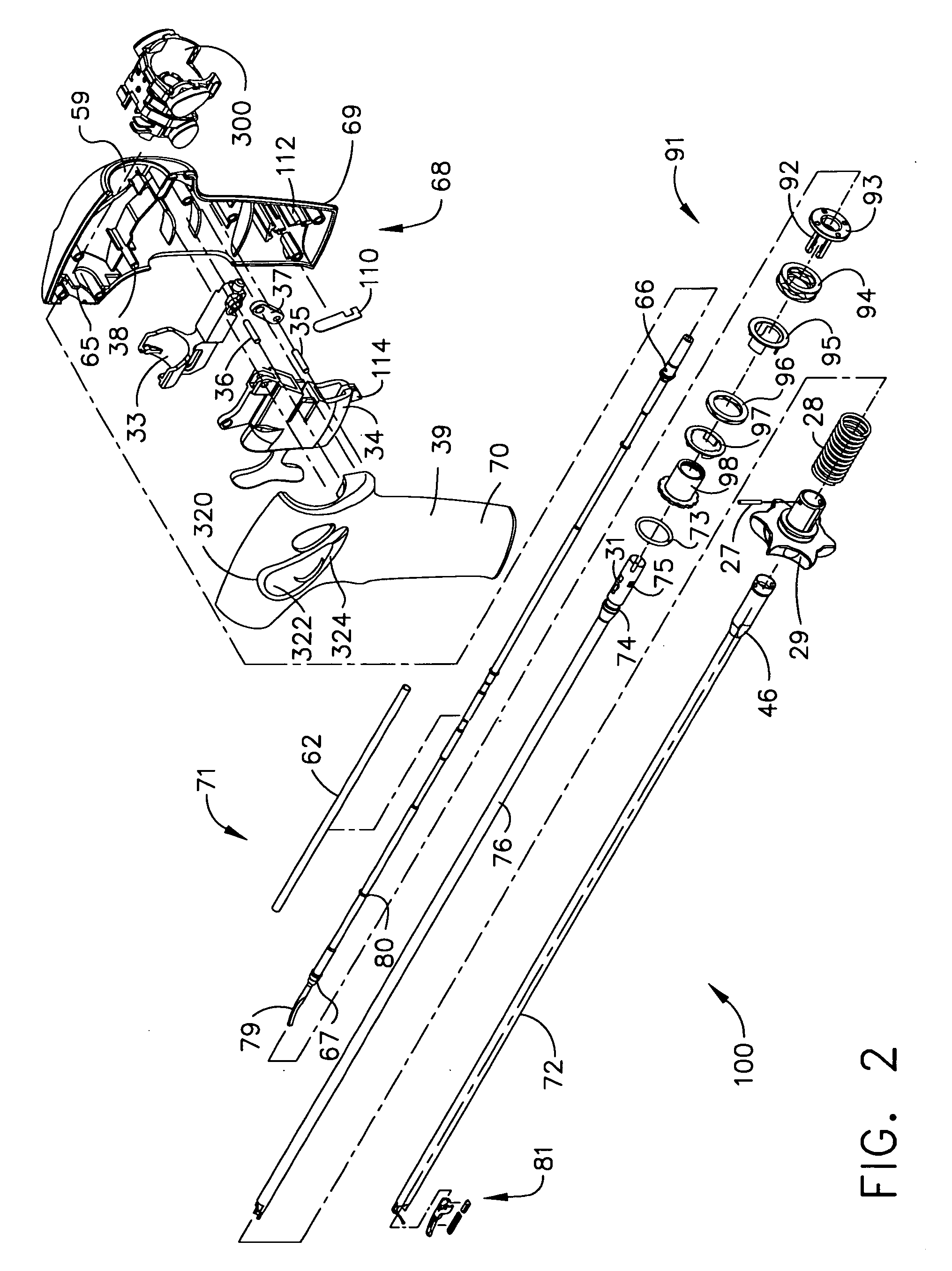
Apparatus and method for performing a bypass procedure in a digestive system
Surgical instrumentation and methods for performing a bypass procedure in a digestive system incorporate laparoscopic techniques to minimize surgical trauma to the patient. The instrumentation includes an outer guide member dimensioned for insertion and passage through an esophagus of a patient and defining an opening therein extending at least along a portion of the length of the outer guide member, an elongate anvil delivery member at least partially disposed within the opening of the outer guide member and being adapted for longitudinal movement within the outer guide member between an initial position and an actuated position and an anvil operatively engageable with the delivery member. The anvil includes an anvil rod defining a longitudinal axis and an anvil head connected to the anvil rod. The anvil head is at least partially disposed within the opening of the outer guide member when in the initial position of the delivery member and is fully exposed from the distal end of the outer guide member upon movement of the delivery member to the actuated position.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
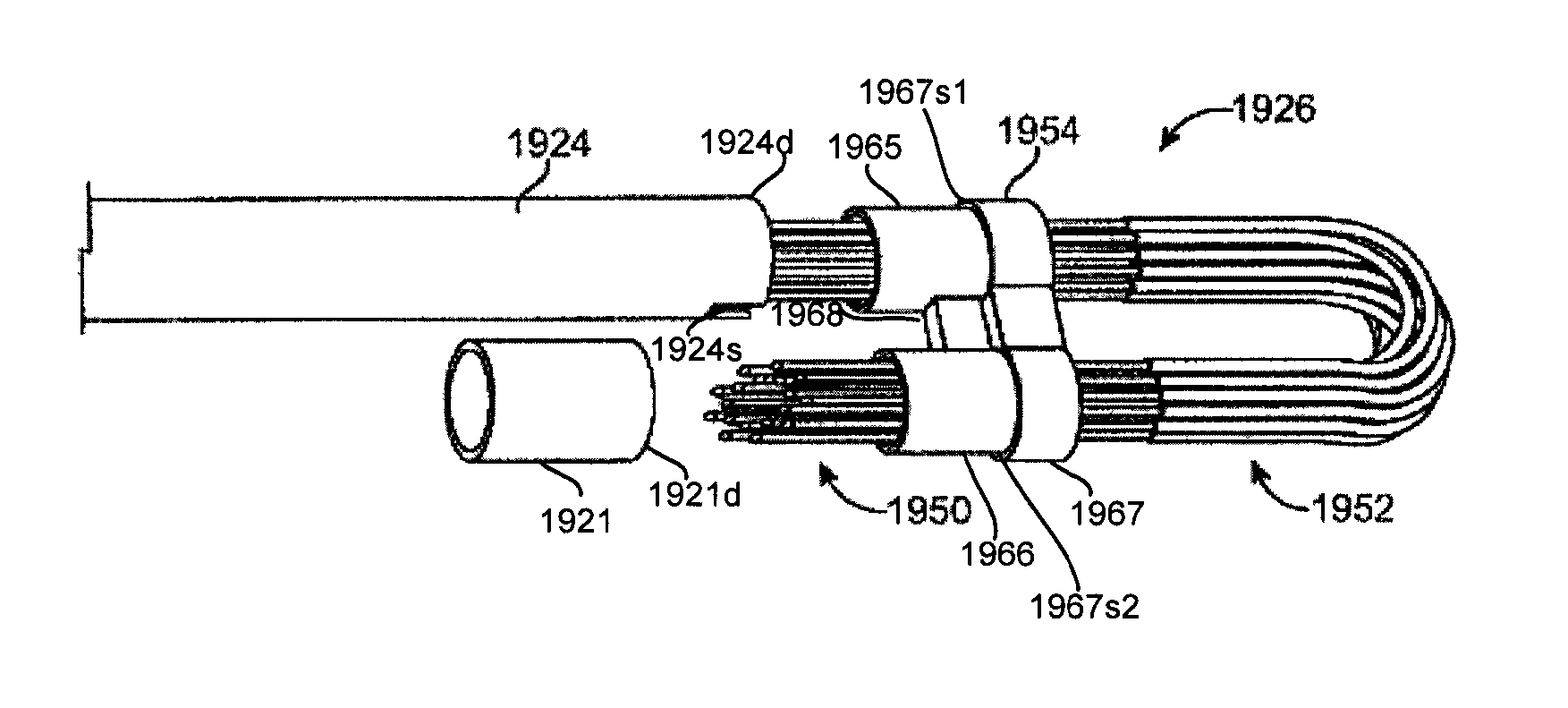
Robotically-controlled end effector
The present invention is directed to a surgical instrument with a robotics system, a memory device and an end effector having an elongate channel, knife position sensor(s) and a firing bar coupled to a knife. In response to drive motions initiated by the robotics system, the firing bar may translate within the elongate channel. As the firing bar translates, the sensor(s) transmit a signal to the memory device. The position of the knife may be determined from the output signals and may be communicated to the robotics system or instrument user. The sensors may be Hall Effect sensors.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
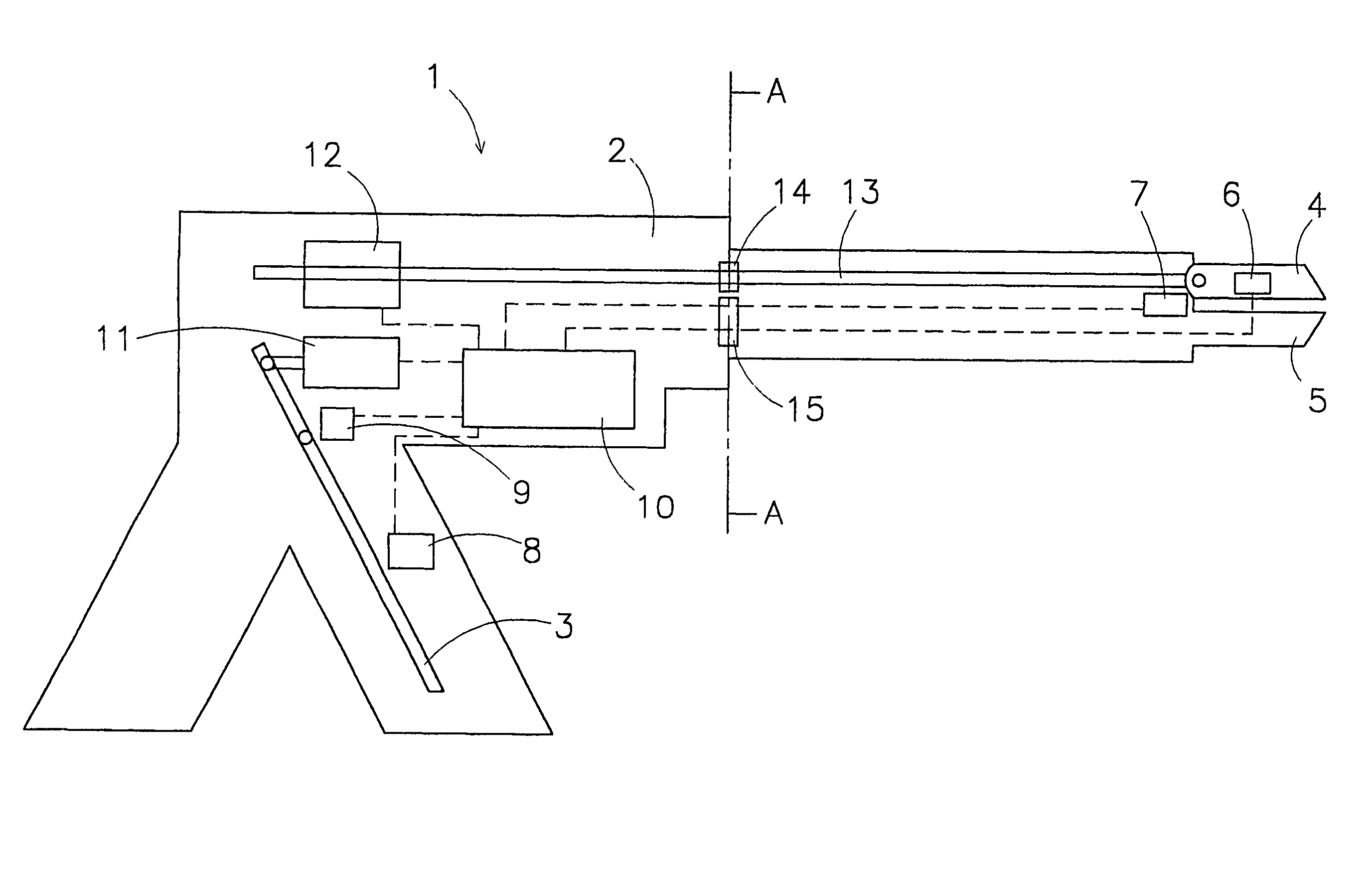
Surgical instrument
InactiveUS7300450B2Easy to handleFlexible in movementDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsLess invasive surgeryEngineering
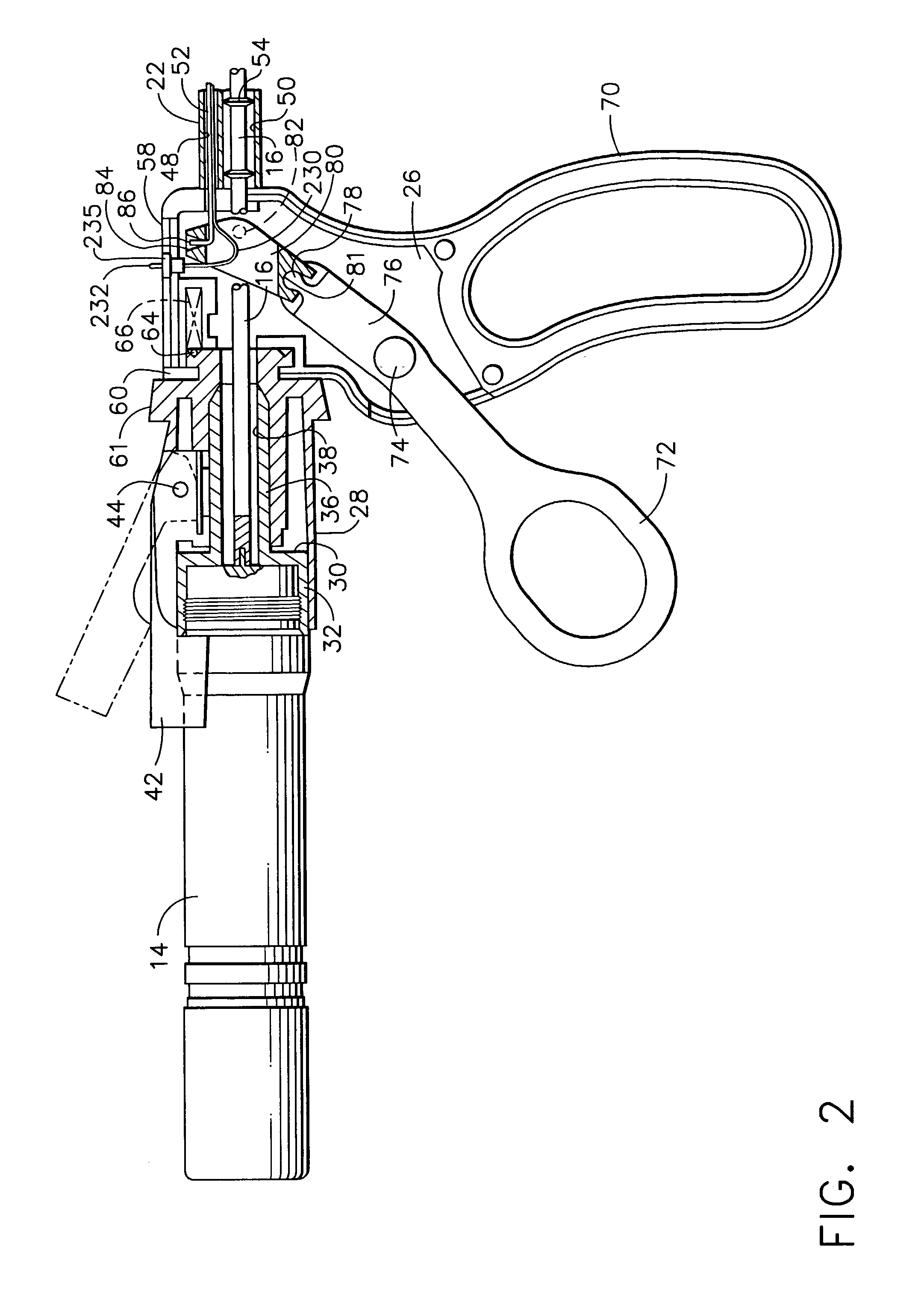
The invention relates to an instrument for surgery, in particular minimally invasive surgery. The instrument includes means for feeding back a force which is exerted on the working element of the instrument to the operating element. These means include at least a first force sensor for measuring the force which is exerted on the working element, a control unit and a first actuator. On the basis of a signal which originates from the first force sensor, the control unit controls at least the first actuator in order to control the operating element. Furthermore, the means preferably include a first position sensor for measuring a position of the working element with respect to the frame. The control unit advantageously determines an impedance which the working element is subject to as a result of the presence of a tissue or the like, on the basis of which impedance the control unit controls at least the first actuator.
Owner:VLEUGELS HLDG
Feedback control in an ultrasonic surgical instrument for improved tissue effects
A temperature monitoring device and / or method which control the tissue temperature at the end-effector of a therapeutic ultrasonic cutting and coagulating instrument as the tissue is being heated with ultrasonic vibrations from the end-effector. One or more temperature sensors are located at the end-effector, preferably on a clamping member. The temperature sensors measure the temperature of the tissue engaged by the end-effector either directly or indirectly. An alternate method and apparatus provides an electrical tissue impedance measure in combination with an ultrasonic cutting and coagulating instrument to provide active feedback control of an ultrasonic generator.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Electrosurgical system
InactiveUS6893435B2Sufficient powerImproving impedanceSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsEngineeringRadio frequency
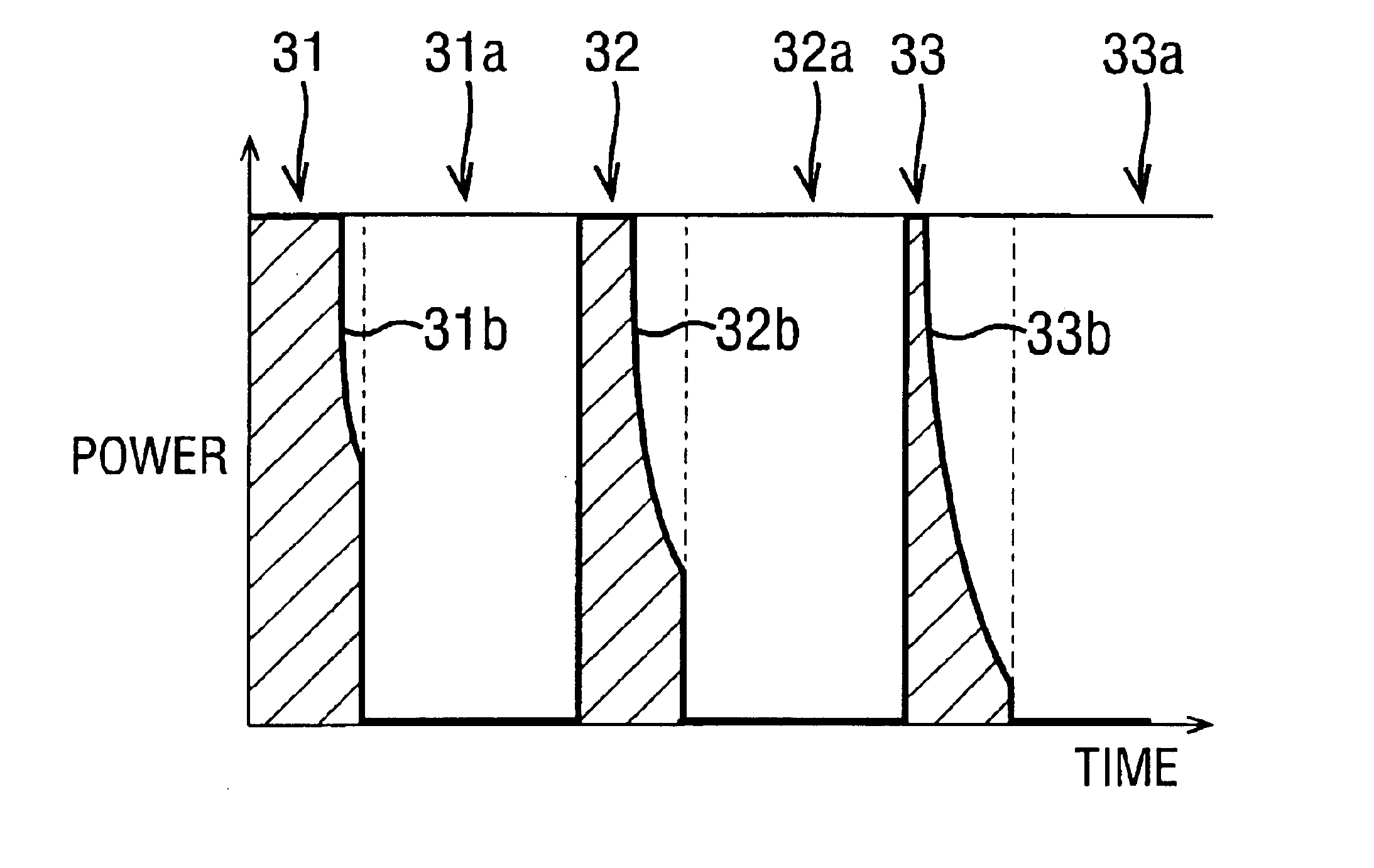
An electrosurgical system has an electrosurgical generator and a bipolar electrosurgical instrument, the generator being arranged to perform a treatment cycle in which radio frequency energy is delivered to the instrument as an amplitude-modulated radio frequency power signal in the form of a succession of pulses characterized by periods of a least 100 milliseconds between successive pulses and by a predetermined pulse mark-to-space ratio. Energy delivery between pulses is substantially zero and the mark-to-space ratio is typically 1:4 or less. Each burst is of sufficiently high power to form vapor bubbles within tissue being treated and the time between successive pulses is sufficiently long to permit condensation of the vapor. The treatment cycles may each include an initial period and a subsequent period, the pulse duty cycle being increased or energy being delivered continuously in the subsequent period in order that tissue coagulation can be achieved quickly despite increasing tissue impedance.
Owner:GYRUS MEDICAL LTD
Laparoscopic tissue thickness and clamp load measuring devices
A surgical instrument having opposed jaws that can be selectively moved between open and closed positions. Various embodiments include components for measuring the thickness of tissue clamped between the opposed jaws. Some embodiments are configured to ascertain the amount of compressive force that is being applied to the tissue while the thickness of the tissue is being determined. The tissue thickness data is displayed on the instrument itself and / or on a display that is remote from the instrument. The various embodiments may comprise different types of surgical instruments such as surgical staplers and graspers. A jaw arrangement with jaws shaped to define a cradle that corresponds to a cross-sectional shape of an object is also disclosed. The components that generate the thickness data may be electrically or mechanically actuated.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
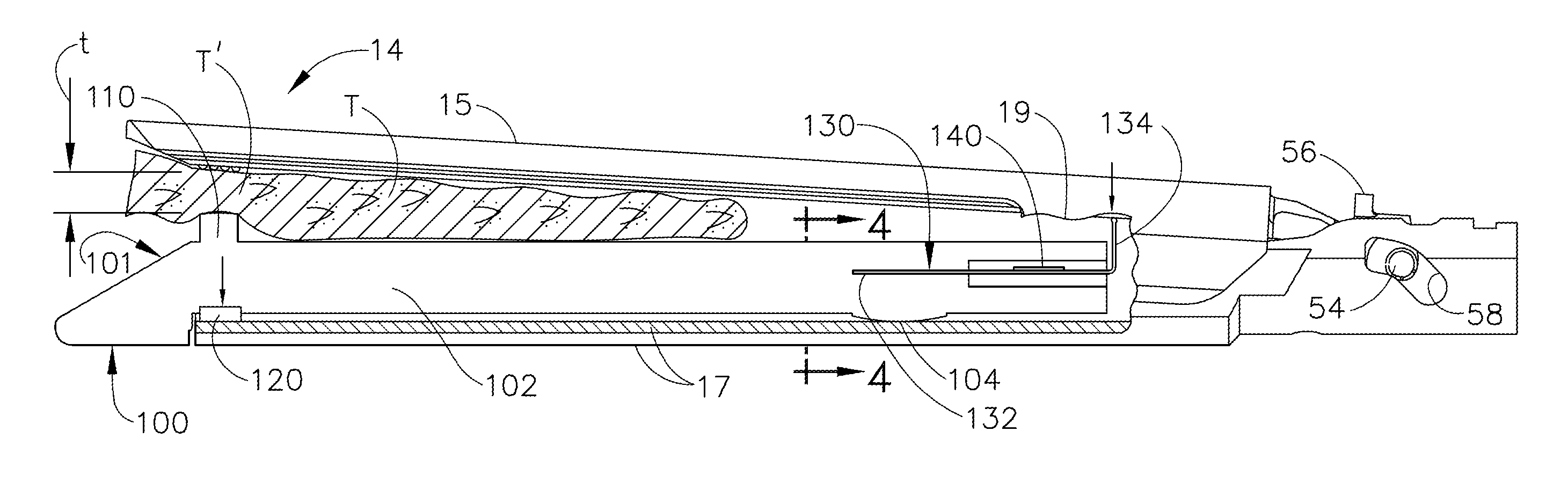
Surgical instrument
A surgical instrument comprising a tube shaft at the proximal end of which an instrument head for rotatably supporting an effector is pivotably supported and at the distal end of which an instrument handle is arranged which causes a pivot as well as a bending movement of the instrument head via a bending gear train and a rotation of the effector via a rotation gear train. In the rotation gear train, a motion compensating member is integrated and also is operated via the instrument handle when the bending gear train is operated, and drives the rotation gear train such that an operation of the rotation gear train caused by the pivoting movement of the instrument head, or parts thereof, is compensated.
Owner:TUEBINGEN SCI MEDICAL
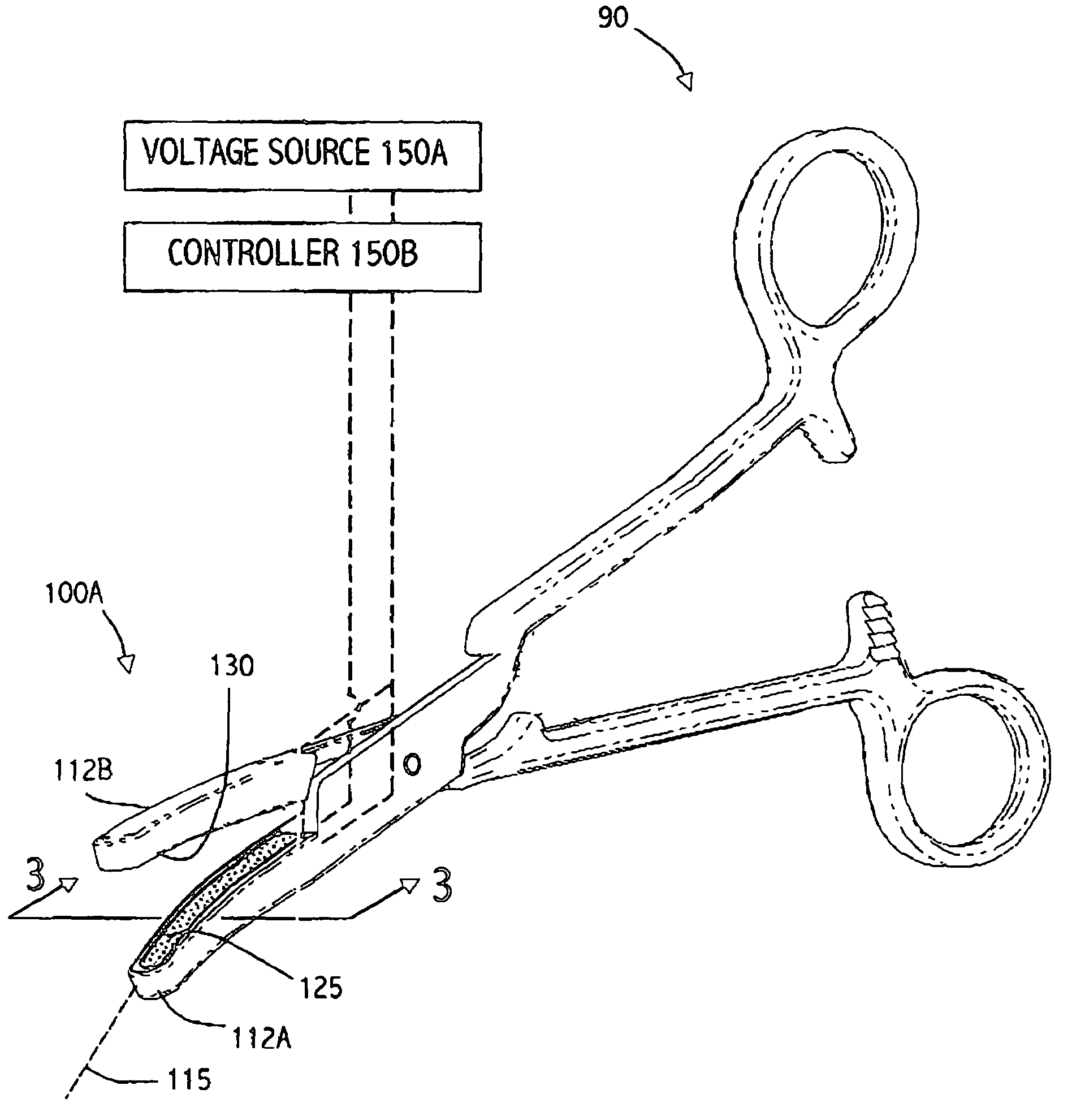
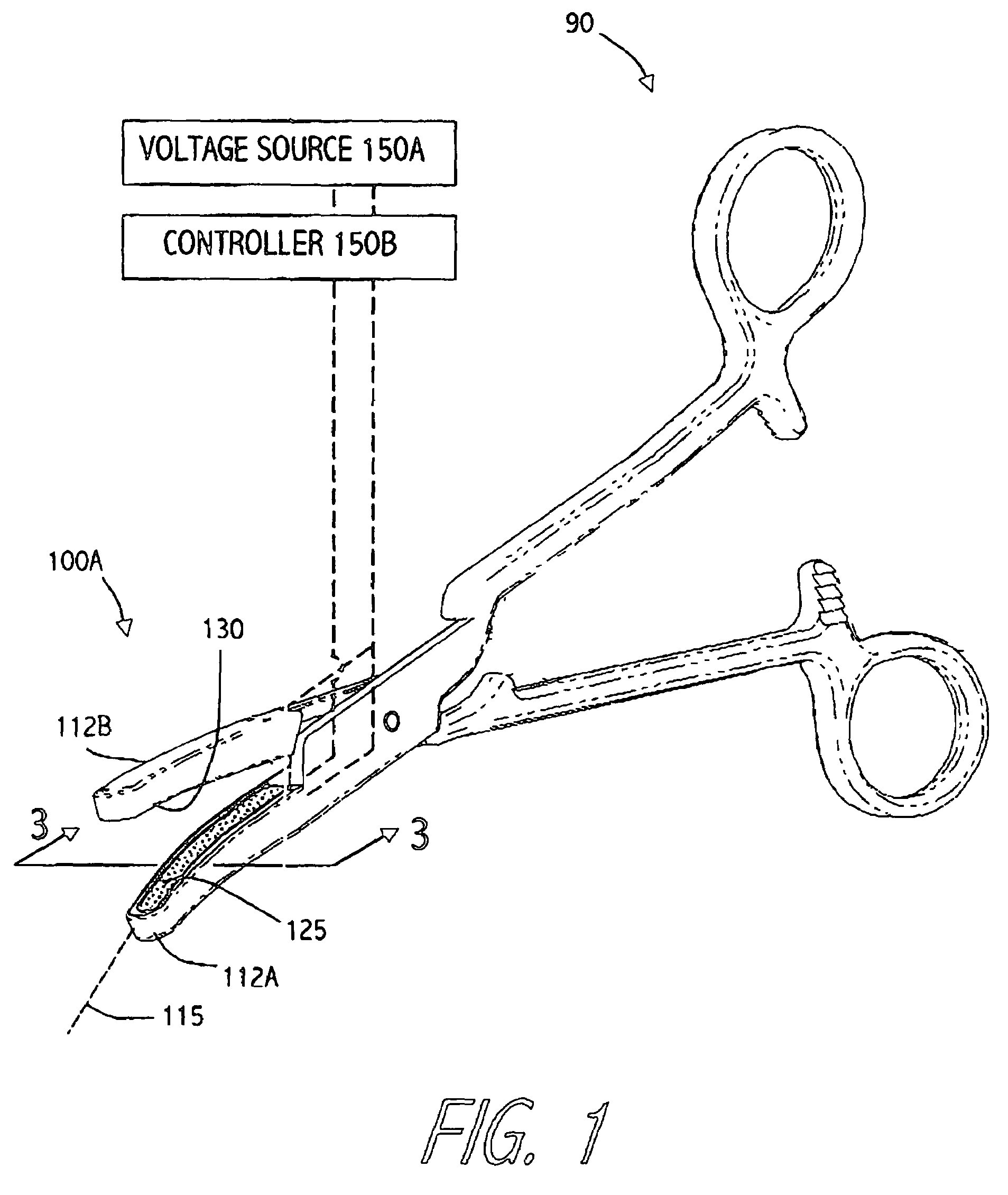
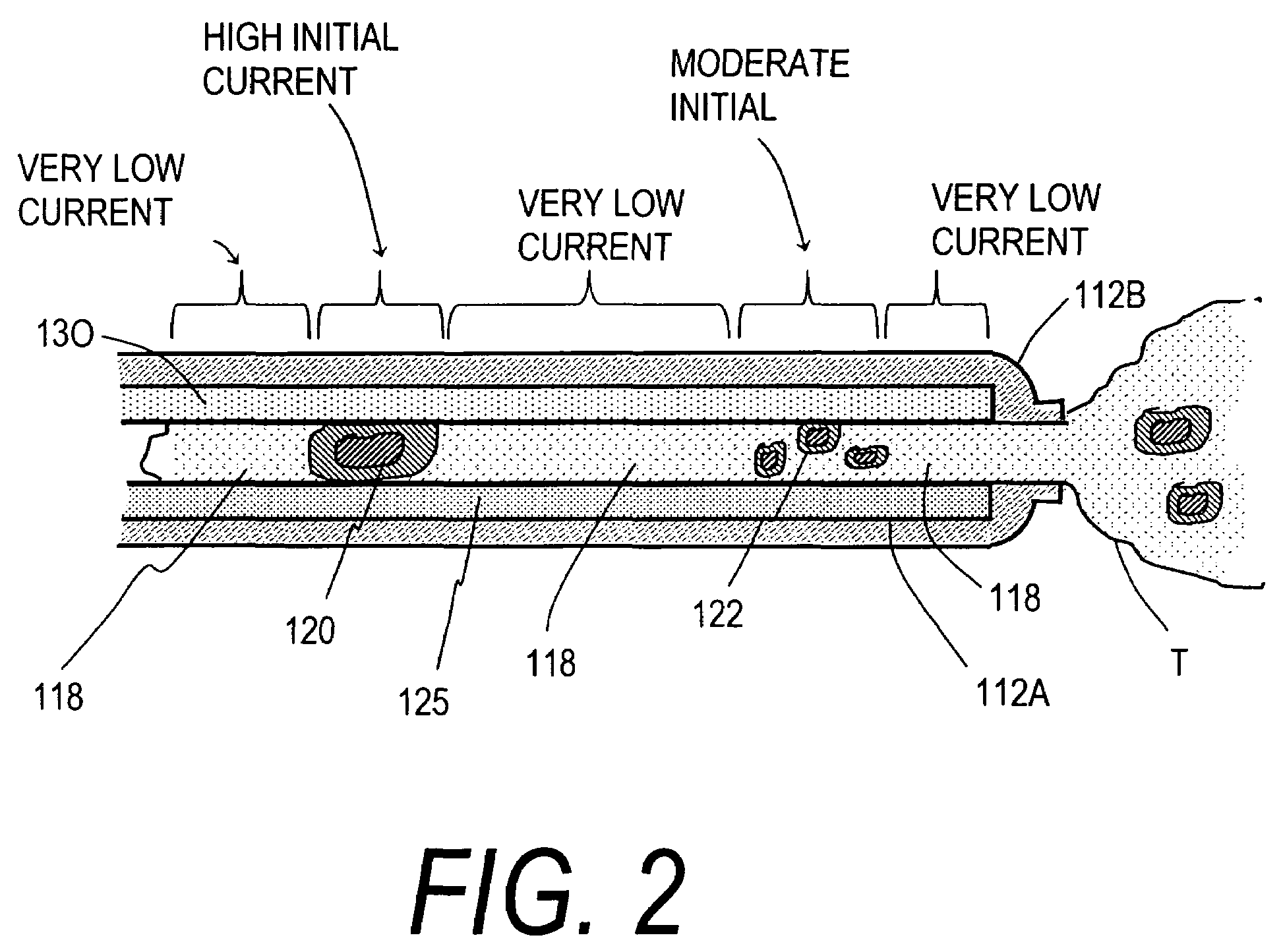
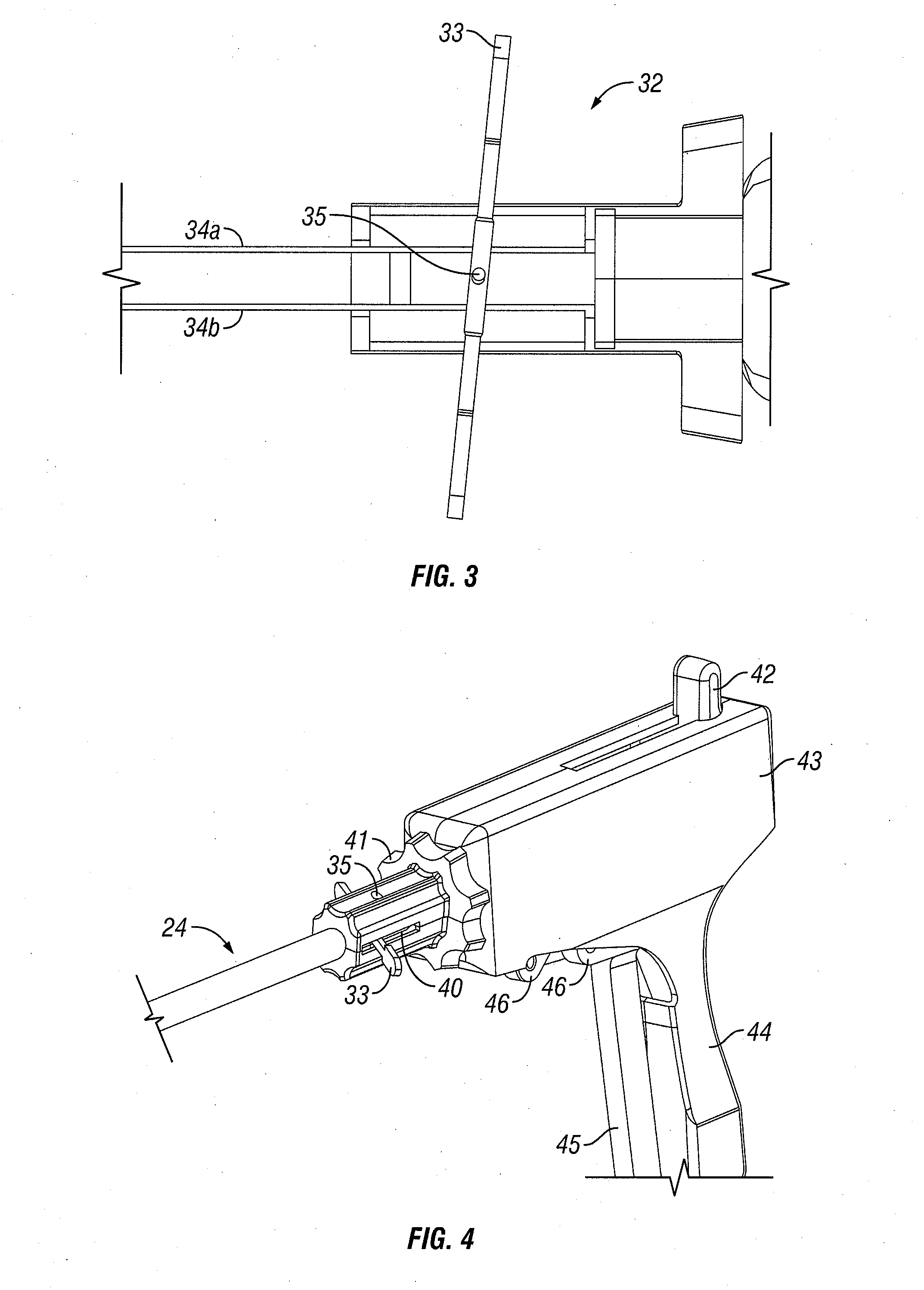
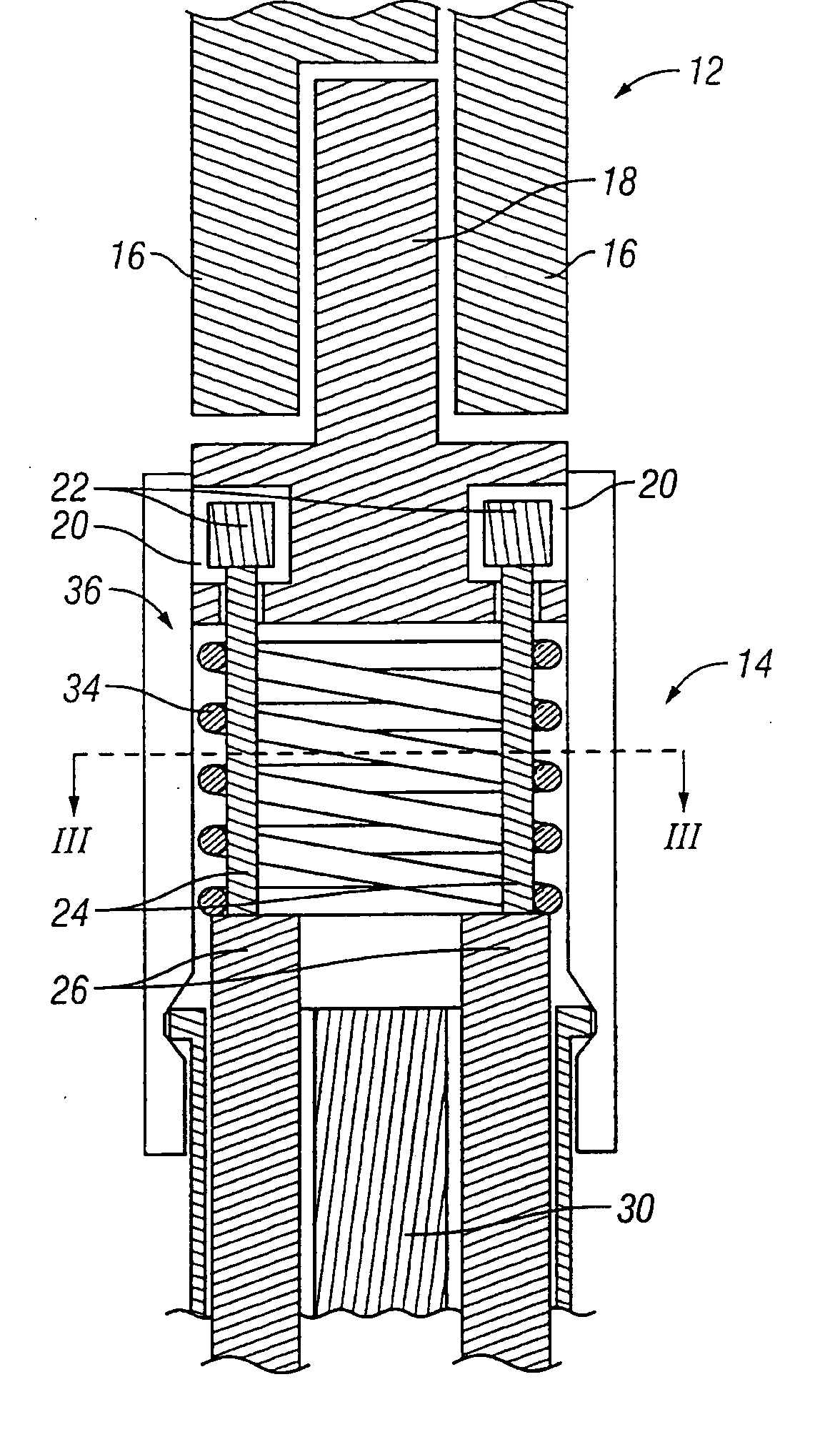
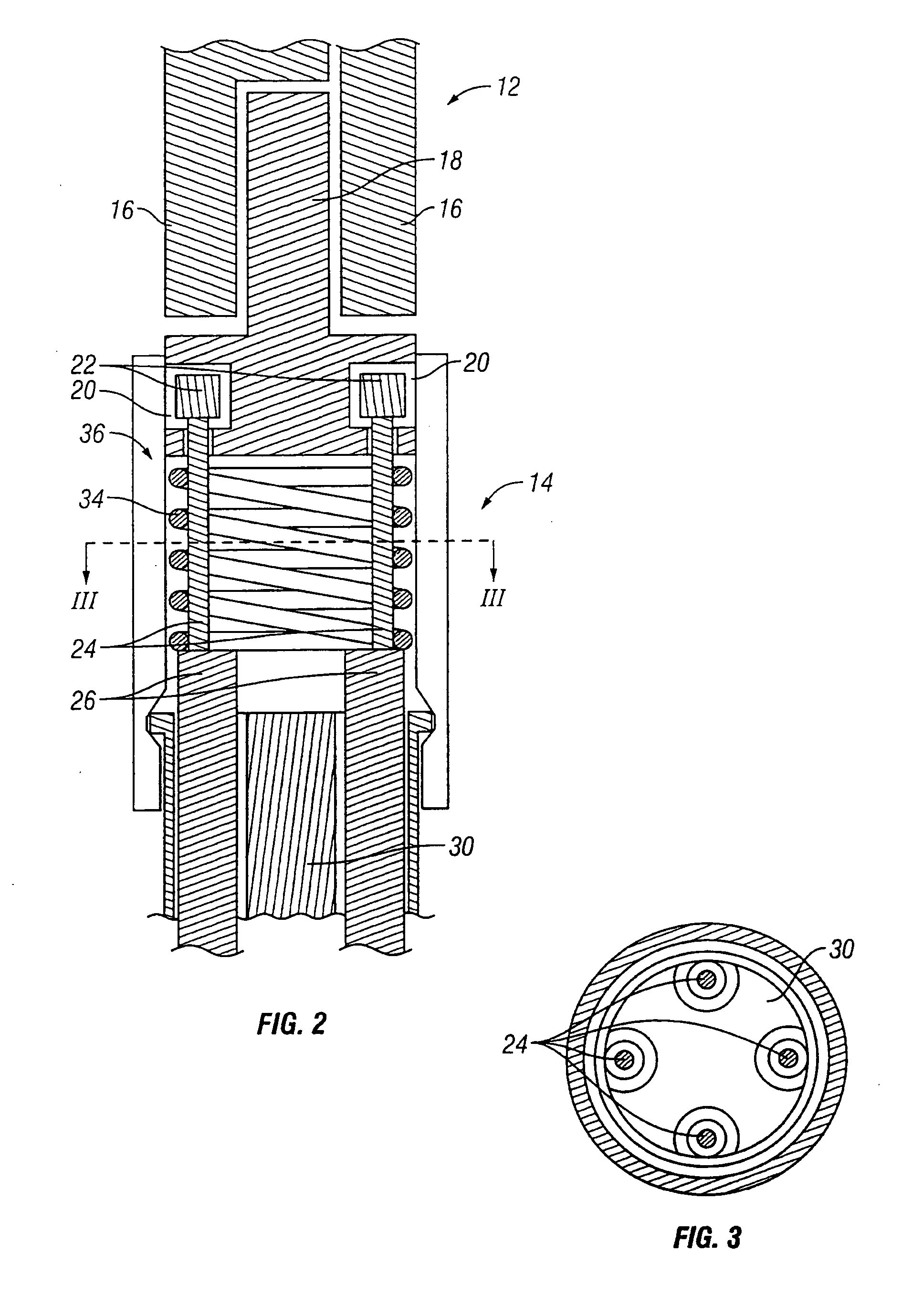
Surgical apparatus with indicator
InactiveUS7237708B1Facilitate communicationSuture equipmentsStapling toolsEngineeringSurgical department
An apparatus and system are disclosed for indicating relative positions of elements in a surgical apparatus. The indicating elements can include electrical circuitry that provides means for activating visual, audible or tactile indicators, thereby alerting the user that an event has occured with respect to the instrument.
Owner:UNITED STATES SURGICAL CORP
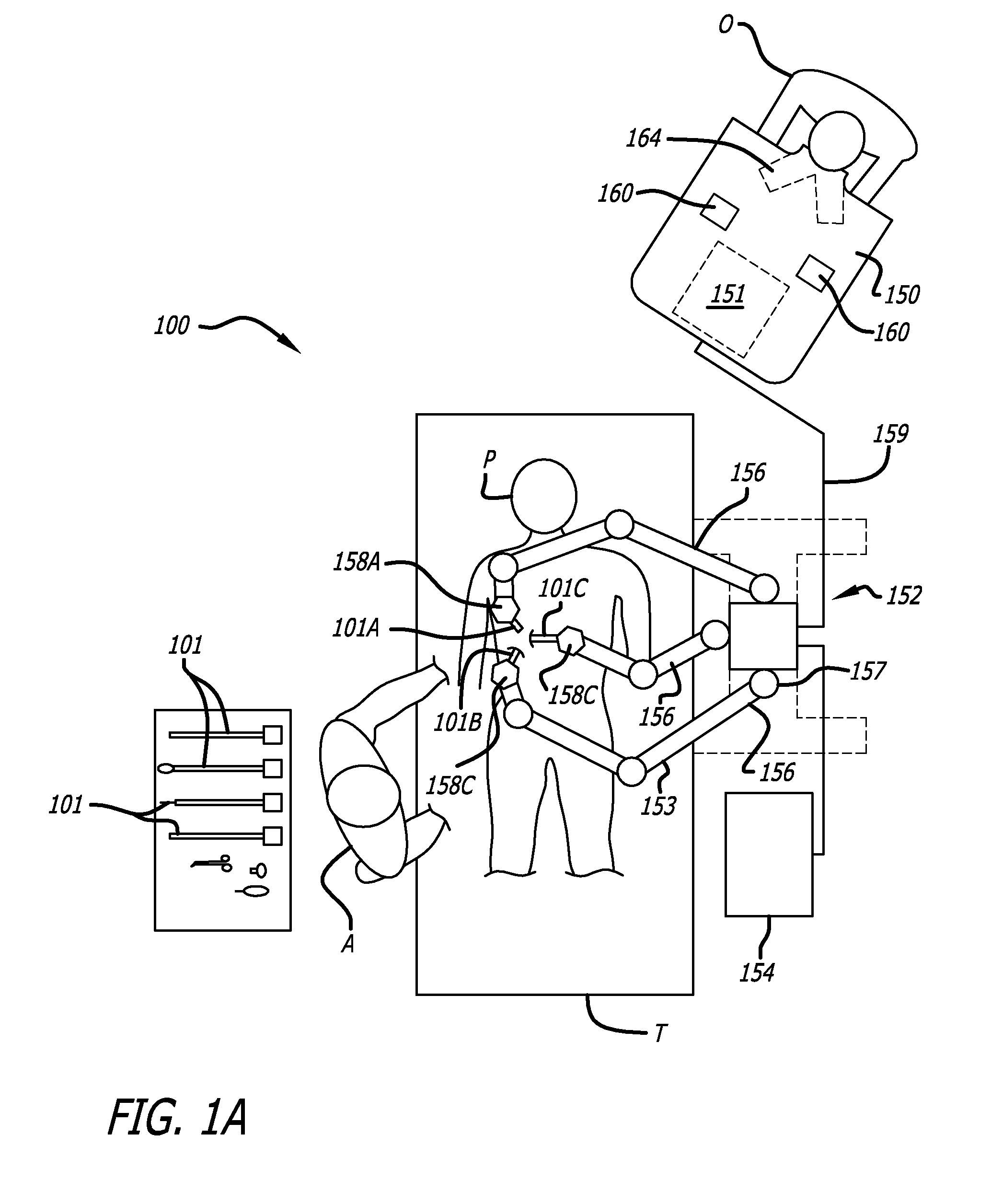
Method and apparatus for performing stereotactic surgery
A stereotactic navigation system for navigating an instrument to a target within a patient may include a stereotactic head frame, an imaging device, a tracking device, a controller and a display. The stereotactic head frame is coupled to the patient and is used to assist in guiding the instrument to the target. The imaging device captures image data of the patient and of the stereotactic head frame. The tracking device is used to track the position of the instrument relative to the stereotactic head frame. The controller receives the image data from the imaging device and identifies the stereotactic head frame in the image data and automatically registers the image data with navigable patient space upon identifying the stereotactic head frame, while the display displays the image data.
Owner:SURGICAL NAVIGATION TECH
Surgical instrument having a multiple rate directional switching mechanism
A surgical instrument having a remotely controllable user interface, and a firing drive configured to generate a rotary firing motion upon a first actuation of the remotely controllable user interface and a rotary refraction motion upon an other actuation of remotely controllable user interface. The instrument is such that when the remotely controllable user interface operates a first drive member, the first actuation advances a cutting member a first distance, wherein, when the remotely controllable user interface operates a second drive member, the other actuation retracts the cutting member a second distance, and wherein the second distance is greater than the first distance.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Electrosurgical probe and method of use
ActiveUS7169146B2Reduce the temperatureQuick changeSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsElectrical resistance and conductanceVolumetric Mass Density
An electrosurgical instrument that allows precise modulation of active Rf density in an engaged tissue volume. The working end of the instrument has a tissue-contacting surface of a conductive-resistive matrix that is variably resistive depending on its temperature. The matrix comprises a positive temperature coefficient (PTC) polymeric material hat exhibits very large increases in resistivity as any local portion increases beyond a selected temperature. In a method of use, the polymeric PTC material senses the temperature of engaged tissue in a manner akin to pixel-by-pixel sensing and thereby changes its resistance in a corresponding pixel-by-pixel manner. The instrument further carries cooling means to cause accelerated thermal relaxation of the PTC matrix during use to make the engagement surface highly responsive to temperature changes that in turn alter the matrix between being electrically conductive and electrically resistive.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
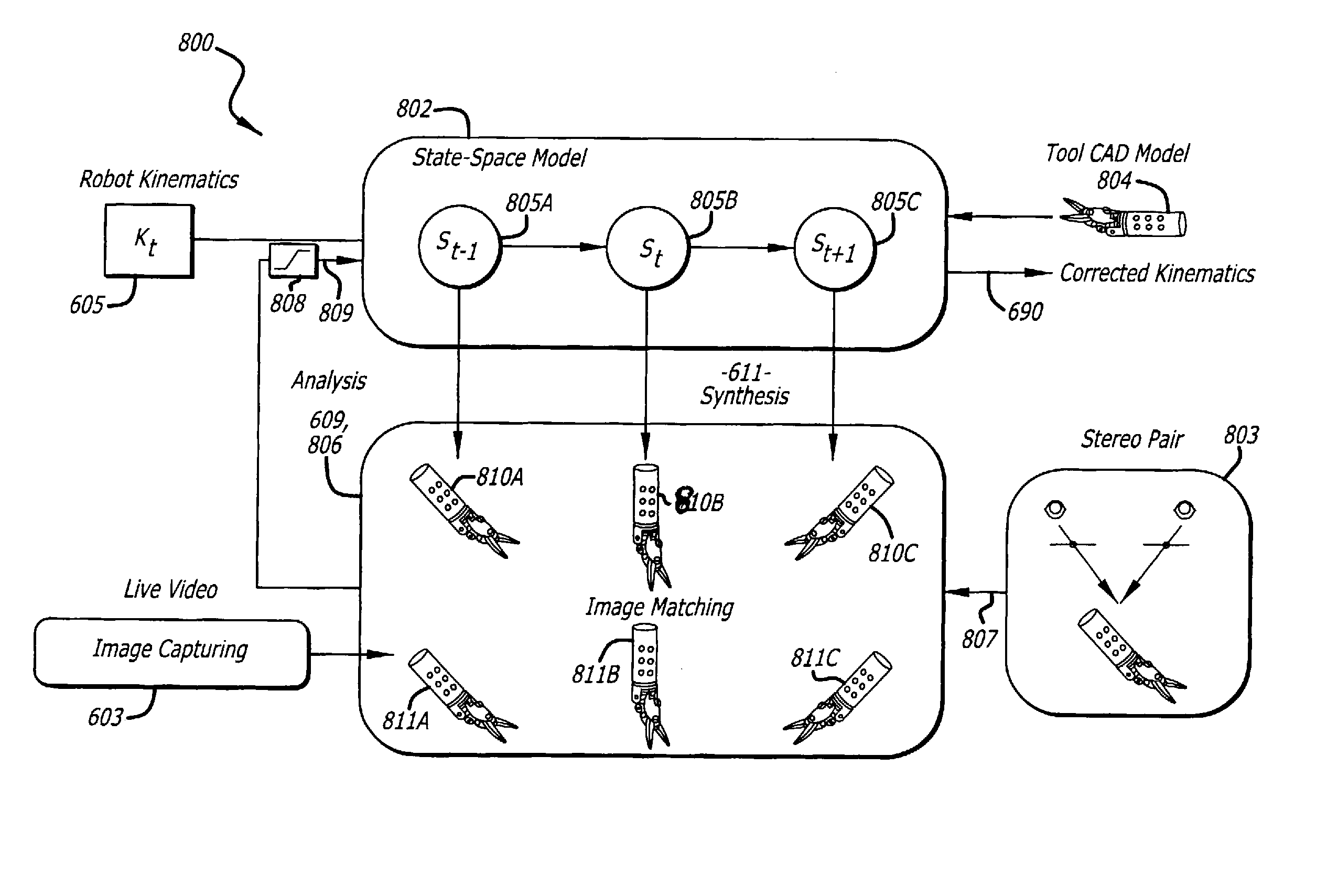
Methods and systems for robotic instrument tool tracking with adaptive fusion of kinematics information and image information
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
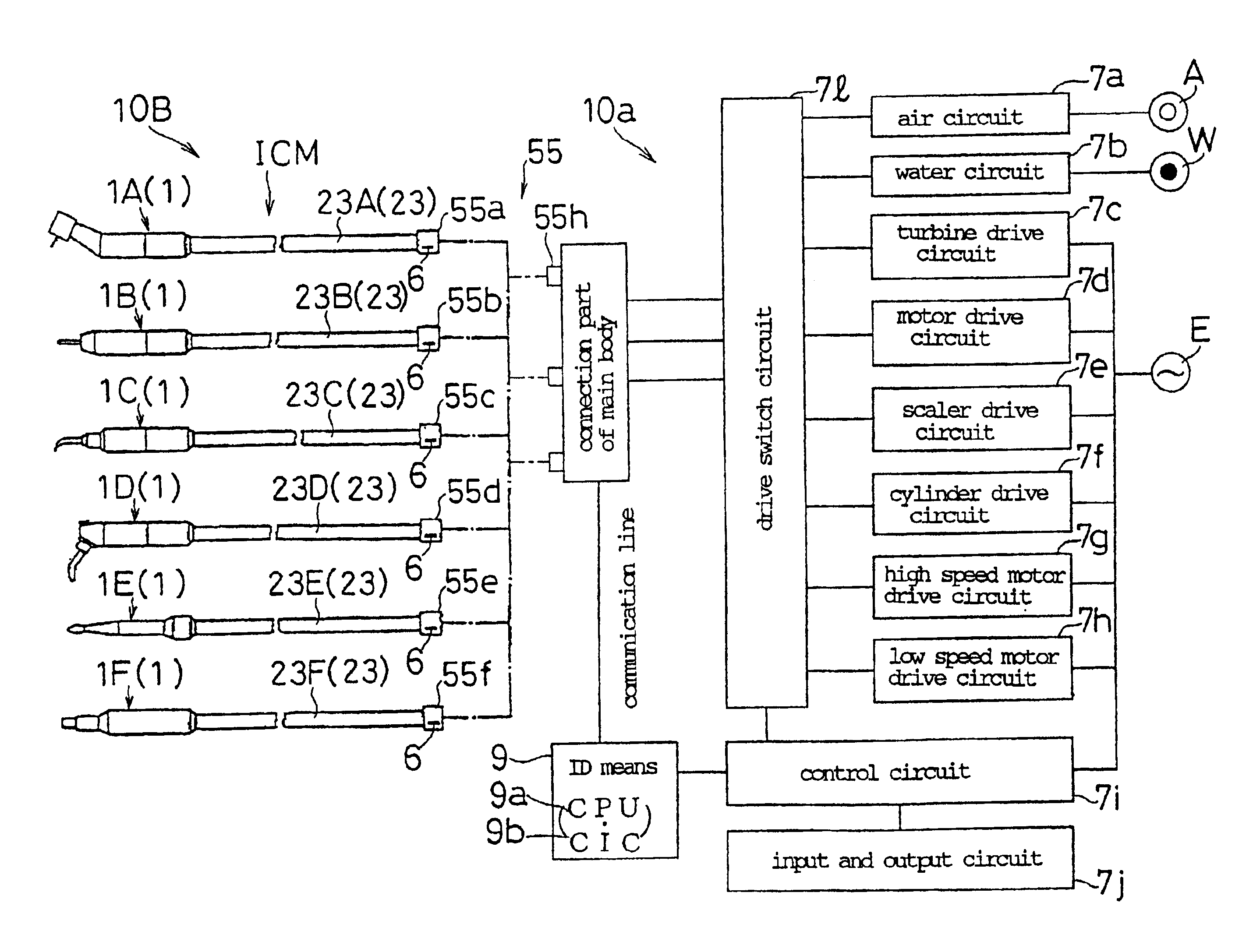
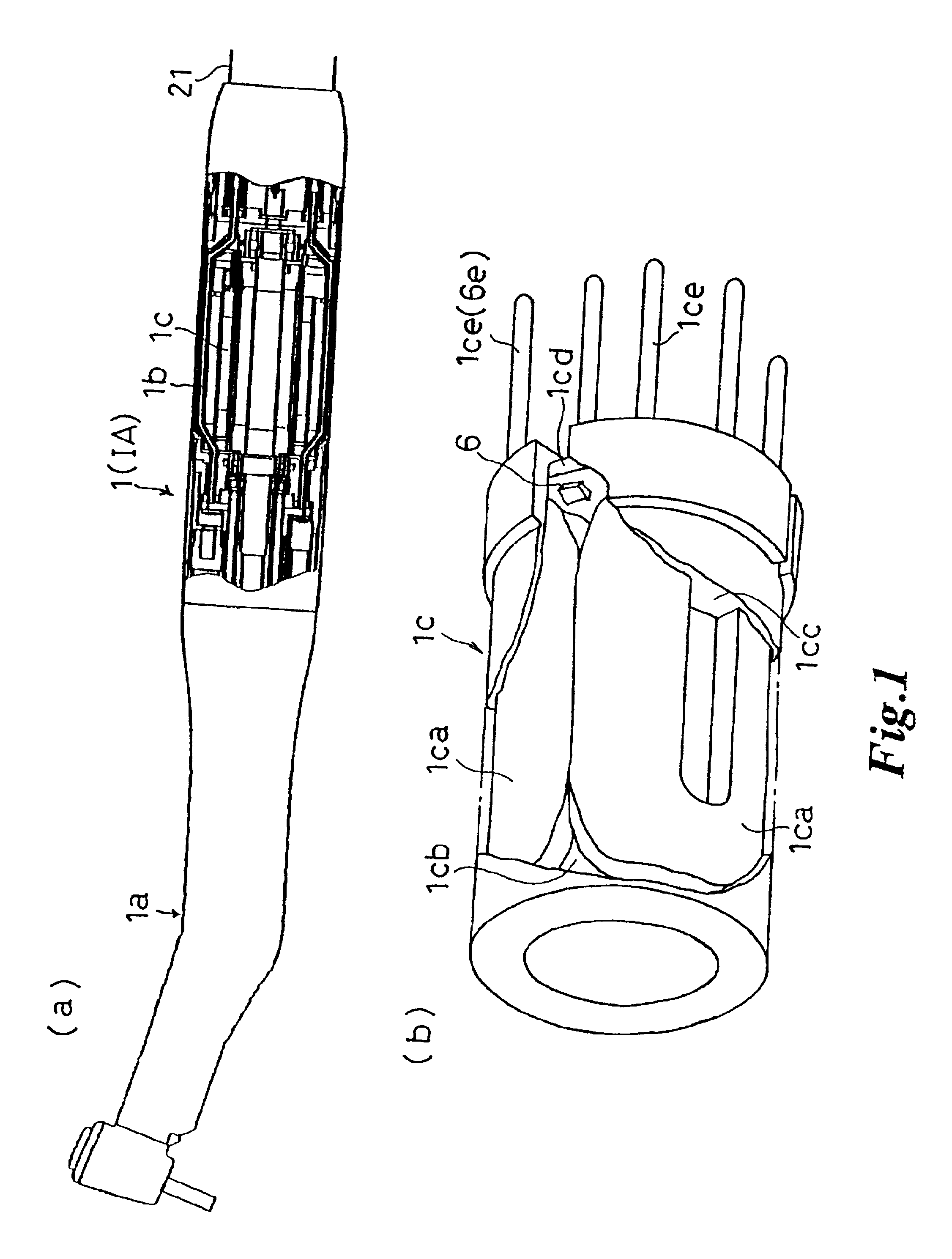
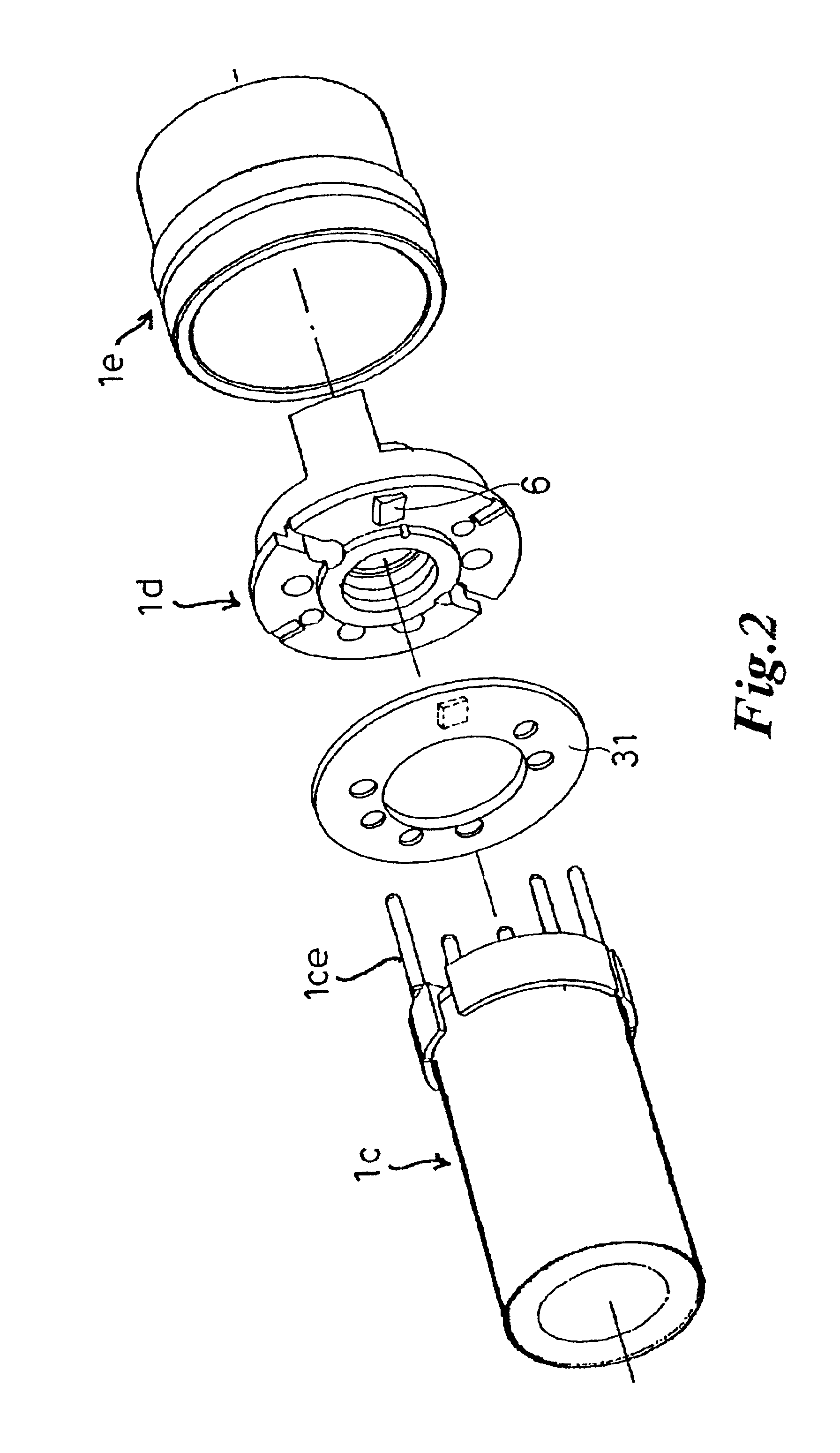
Identification type instrument assembly, identification type adapter, identification type tube, and medical apparatus using them
InactiveUS6899538B2Easily and surely specifiedImprove the problemDiagnosticsSurgeryMedical deviceBiomedical engineering
An identification type instrument assembly detachably connected to a main body of a medical apparatus for use in diagnosis and treatment. The instrument assembly is provided with identification signal output means for actively outputting unique self-identification signals prepared in advance under a predetermined procedure, and the connected instrument assembly can be specified in the main body by the identification signals outputted from the identification signal output means when the instrument assembly is connected to the main body.
Owner:MORITA MFG CO LTD
Sealed surgical access device
InactiveUS7052454B2” laparoscopy is greatly facilitatedFulfil requirementsEar treatmentCannulasCouplingEngineering
A surgical access device is adapted to facilitate access through an incision in a body wall having an inner surface and an outer surface, and into a body cavity of a patient. The device includes first and second retention members adapted to be disposed in proximity to the outer surface and the inner surface of the body wall, respectively. A membrane extending between the two retention members forms a throat which is adapted to extend through the incision and form a first funnel extending from the first retention member into the throat, and a second funnel extending from the second retention member into the throat. The throat of the membrane has characteristics for forming an instrument seal in the presence of an instrument and a zero seal in the absence of an instrument. The first retention member may include a ring with either a fixed or variable diameter. The ring can be formed in first and second sections, each having two ends. Couplings can be disposed between the ends to accommodate variations in the size of the first retention member. The first retention member can also be formed as an inflatable toroid, a self-expanding foam, or a circumferential spring. A plurality of inflatable chambers can also provide the surgical access device with a working channel adapted for disposition across the body wall. A first retention member with a plurality of retention stations functions with a plurality of tethers connected to the membrane to change the shape of the membrane and the working channel. A stabilizing platform can be used to support the access device generally independent of any movement of the body wall.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Electrosurgical system
ActiveUS7220260B2Avoid failureReduce voltageDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingRadio frequency signalElectrical impedance
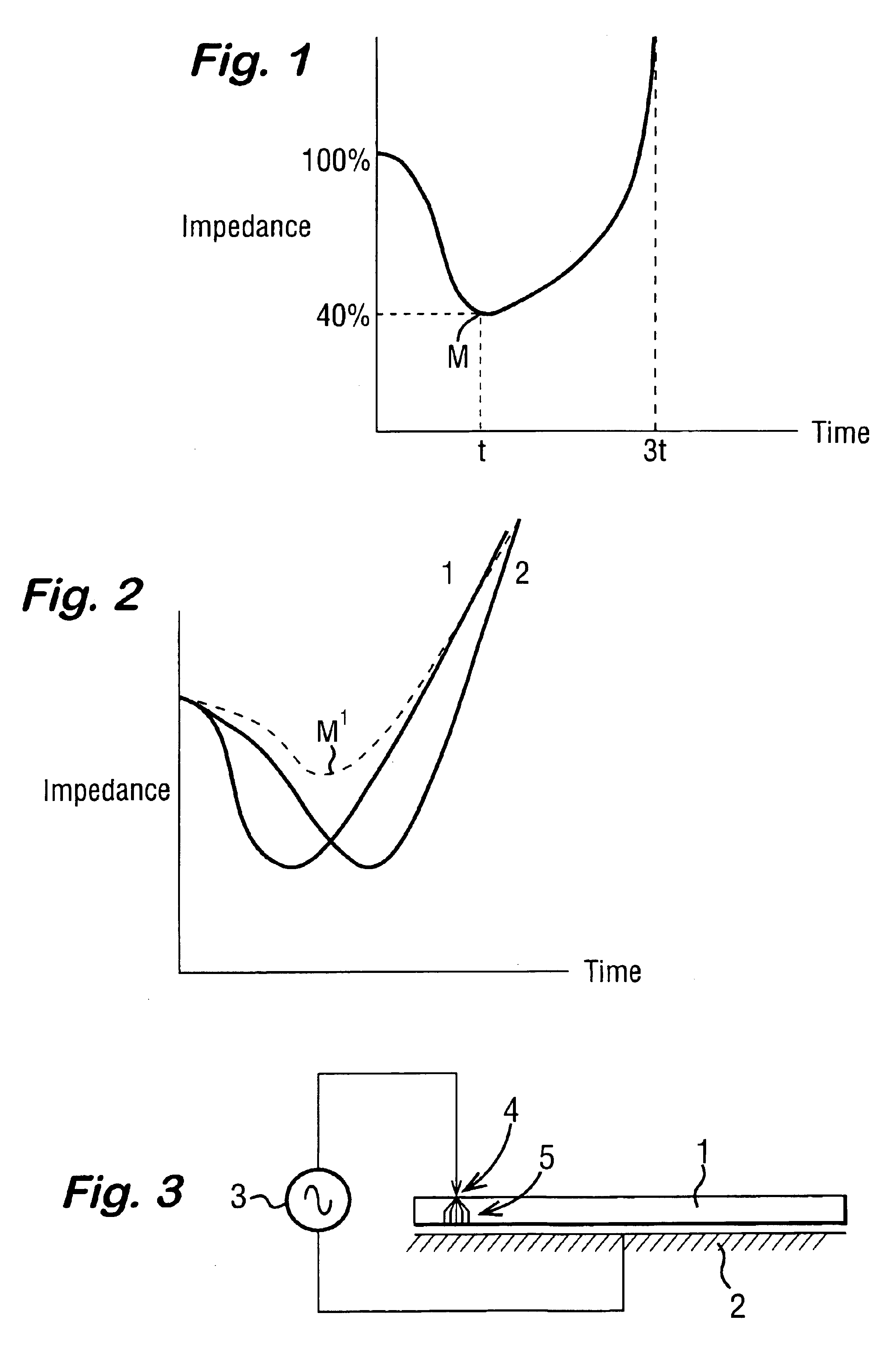
An electrosurgical system comprises a generator and an instrument including a first electrode, a second electrode, and an insulating spacer separating the first and second electrodes. The generator repeatedly measures a characteristic of the radio frequency output such as the impedance between the first and second electrodes. The generator analyses the impedance measurements, and interrupts the radio frequency signal when the rate of change of the impedance is such as to indicate the onset of a “flare-out”. In this way, the power is reduced before the flare-out leads to permanent damage or failure of the instrument.
Owner:GYRUS MEDICAL LTD
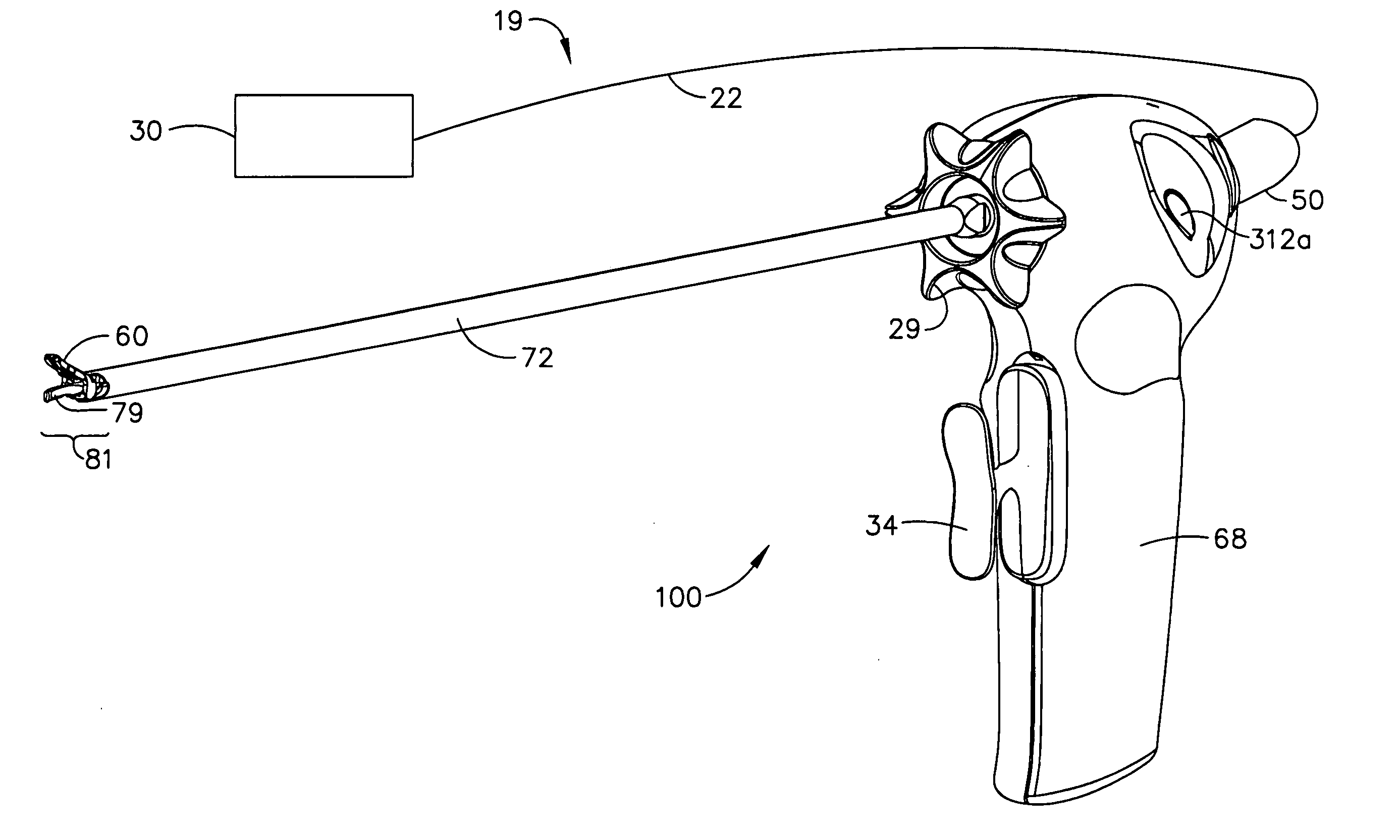
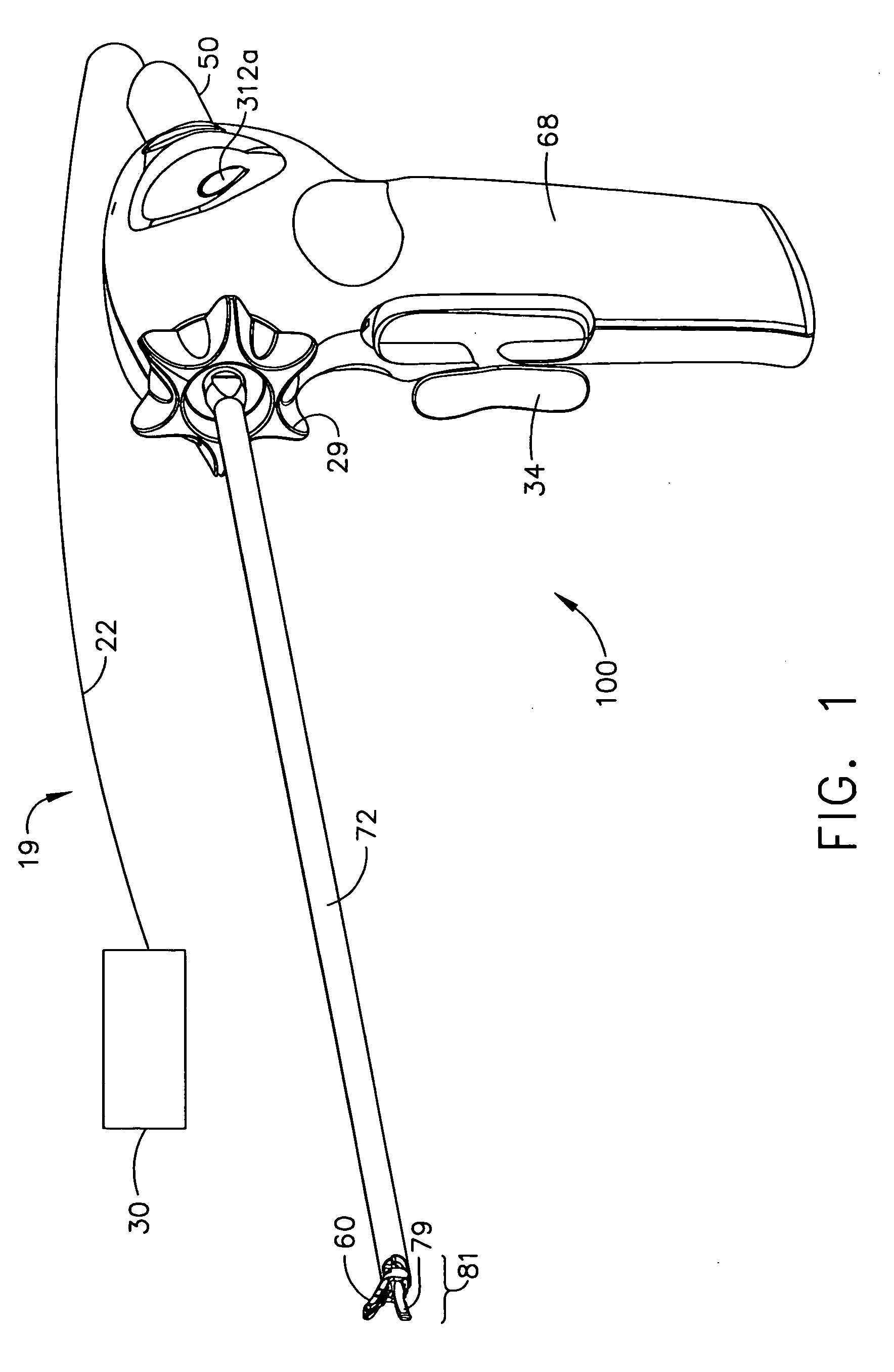
Method and apparatus for articulating the wrist of a laparoscopic grasping instrument
InactiveUS20090198272A1Avoid relative motionDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsAbdominal cavityLocking mechanism
A medical instrument has a set of opposing jaws that can be articulated, both left and right, from centerline. The instrument has a proper bend radius and support for the jaw actuation member and cutter driving member. The bendable support for the drive members comprises tightly wound coil springs. Another embodiment of the invention controls the degree of articulation at the handle of the laparoscopic instrument. A further embodiment of the invention incorporates a locking mechanism to prevent motion of the wrist while the user performs other operations on the device. The locking mechanism also includes an indexing feature with which the user can index and choose the necessary amount of angle between preset angles.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
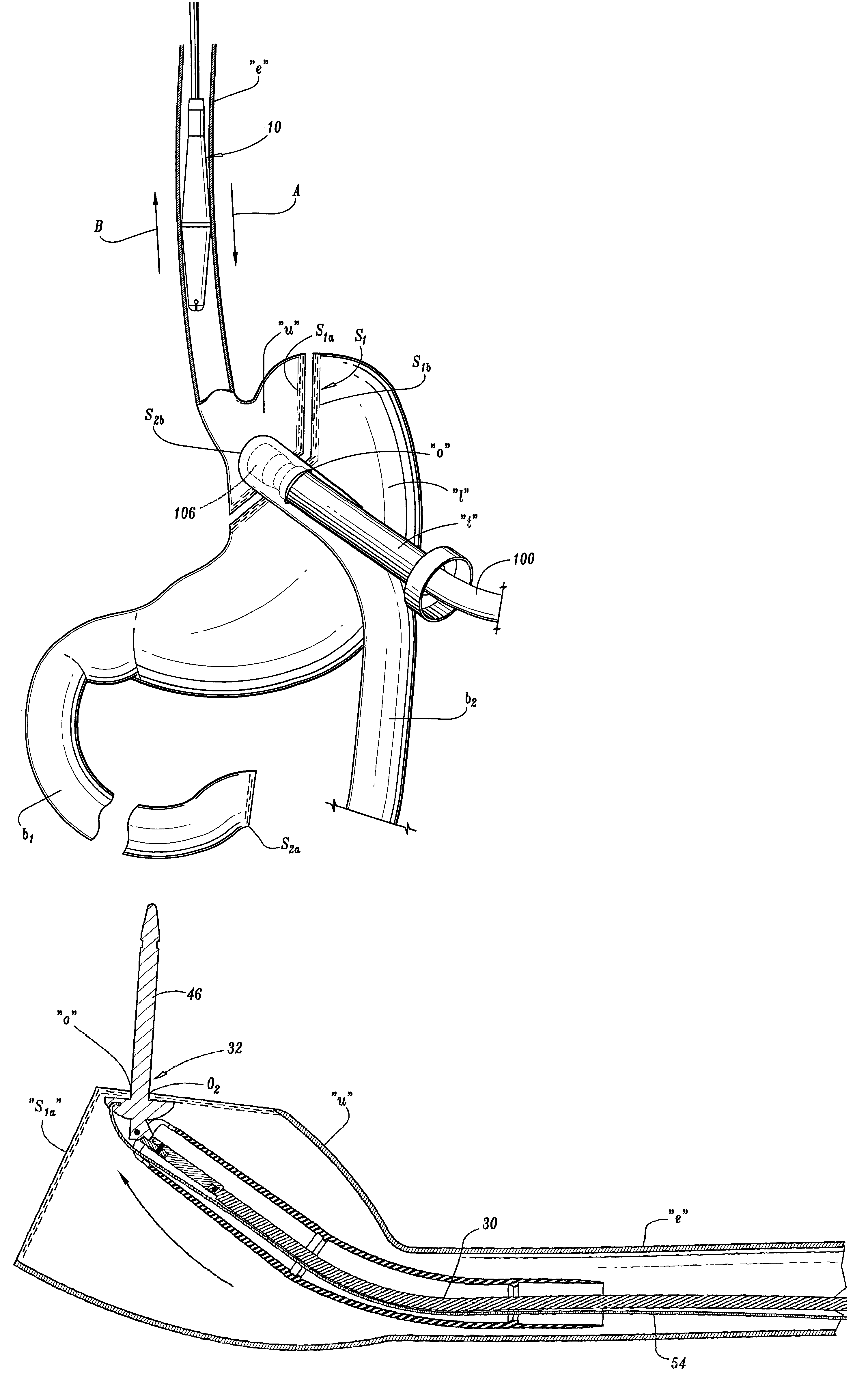
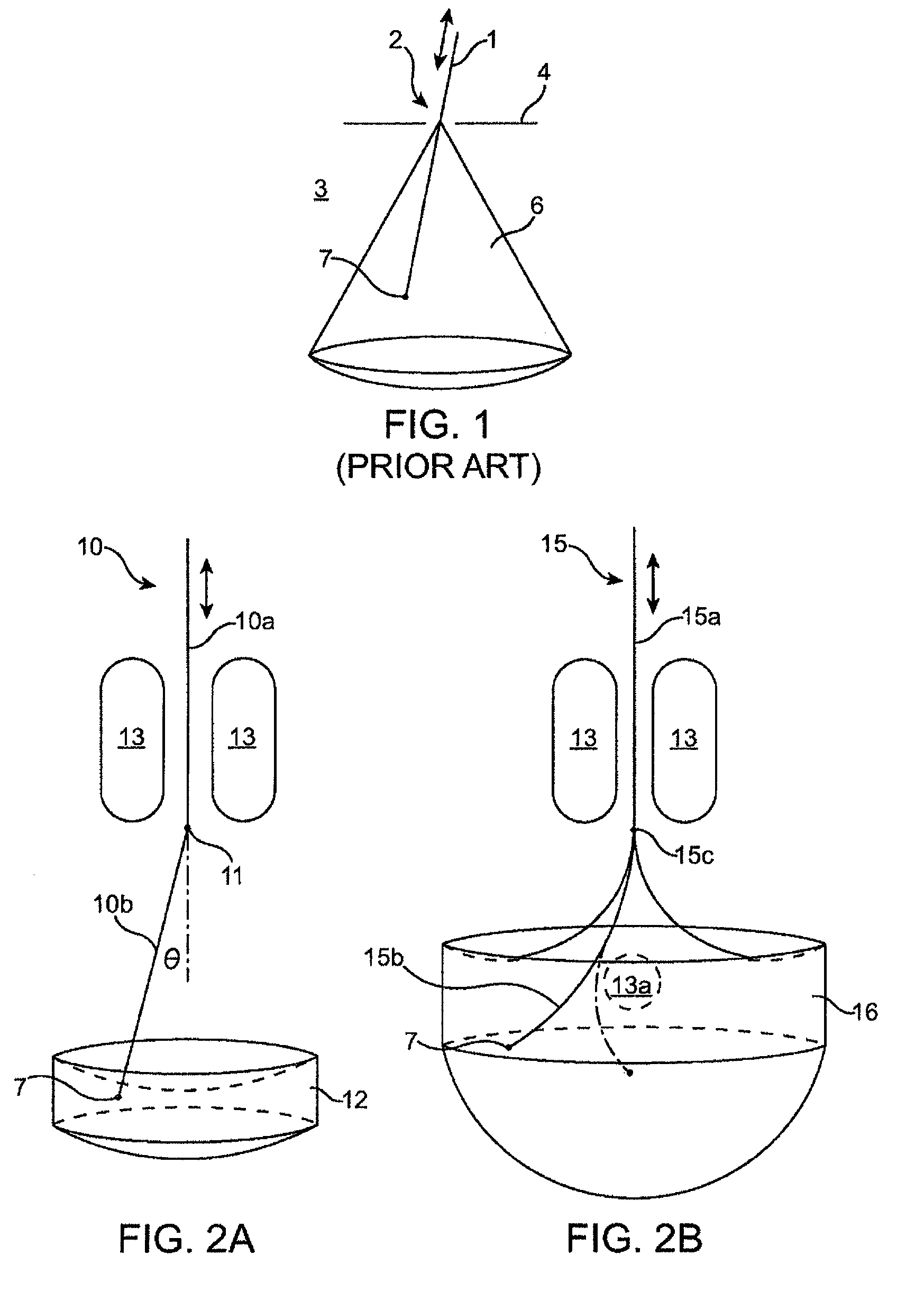
Cardiac tissue ablation instrument with flexible wrist
The present invention is directed to an articulate minimally invasive surgical instrument with a flexible wrist to facilitate the safe placement and provide visual verification of the ablation catheter or other devices in Cardiac Tissue Ablation (CTA) treatments. In one embodiment, the instrument is an endoscope which has an elongate shaft, a flexible wrist at the working end of the shaft, and a vision scope lens at the tip of the flexible wrist. The flexible wrist has at least one degree of freedom to provide the desired articulation. It is actuated and controlled by a drive mechanism located in the housing at the distal end of the shaft. The articulation of the endoscope allows images of hard-to-see places to be taken for use in assisting the placement of the ablation catheter on the desired cardiac tissue. The endoscope may further include couplings to releasably attach an ablation device / catheter or a catheter guide to the endoscope thereby further utilizing the endoscope articulation to facilitate placement of the ablation catheter on hard-to-reach cardiac tissues. In another embodiment, the articulate instrument is a grasper or any other instrument with a flexible wrist and a built-in lumen to allow an endoscope to insert and be guided to the distal end of the instrument.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL
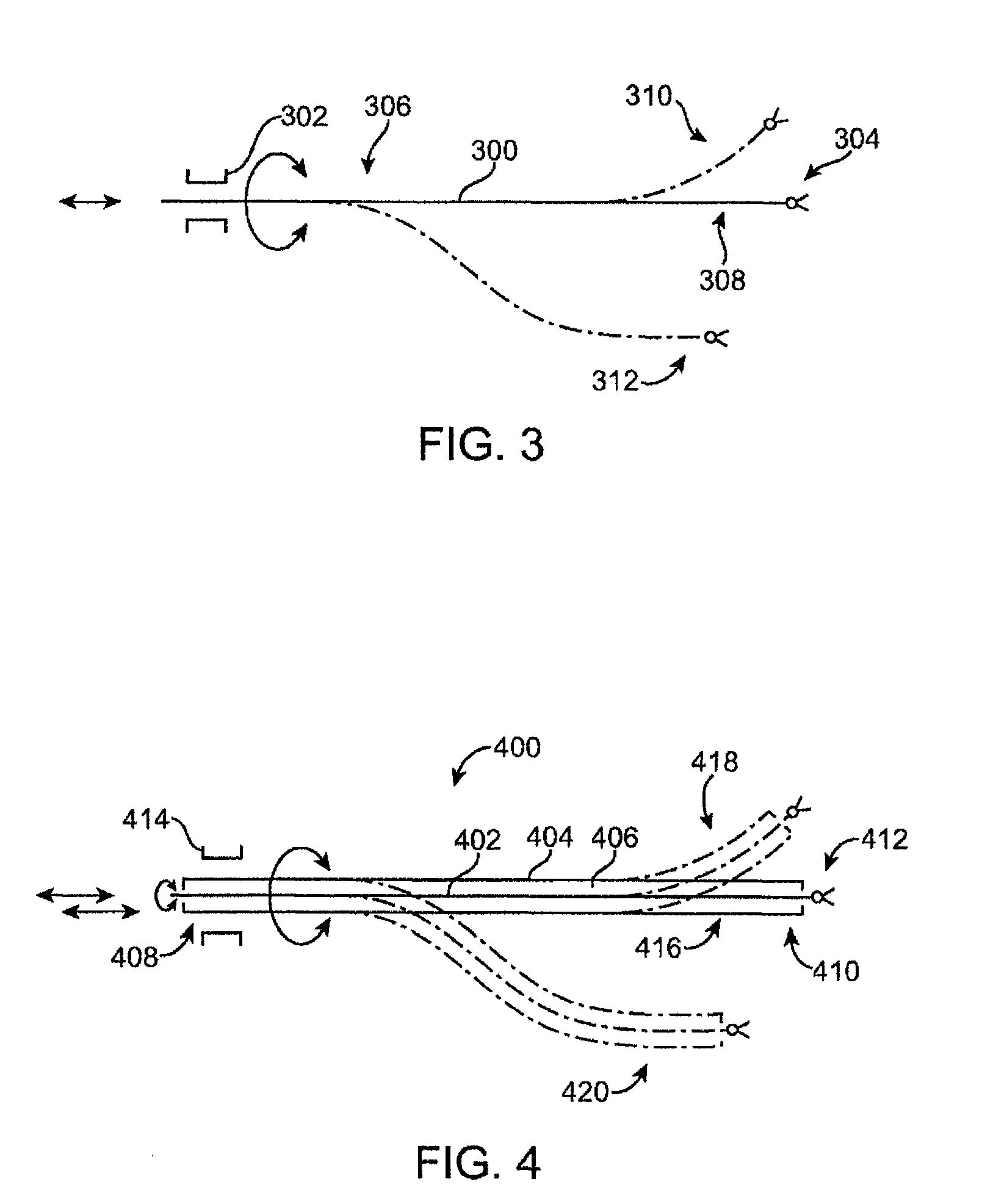
Retrograde instrument
A minimally invasive surgical instrument includes a U-turn mechanism that transmits actuating forces around a U-turn. The U-turn mechanism is coupled between segments of the instrument and has a bend radius that is smaller than flexible arms having a similar cross section diameter. The actuating forces transmitted by the U-turn mechanism are used to move distal components of the instrument, such as an end effector and a wrist mechanism.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
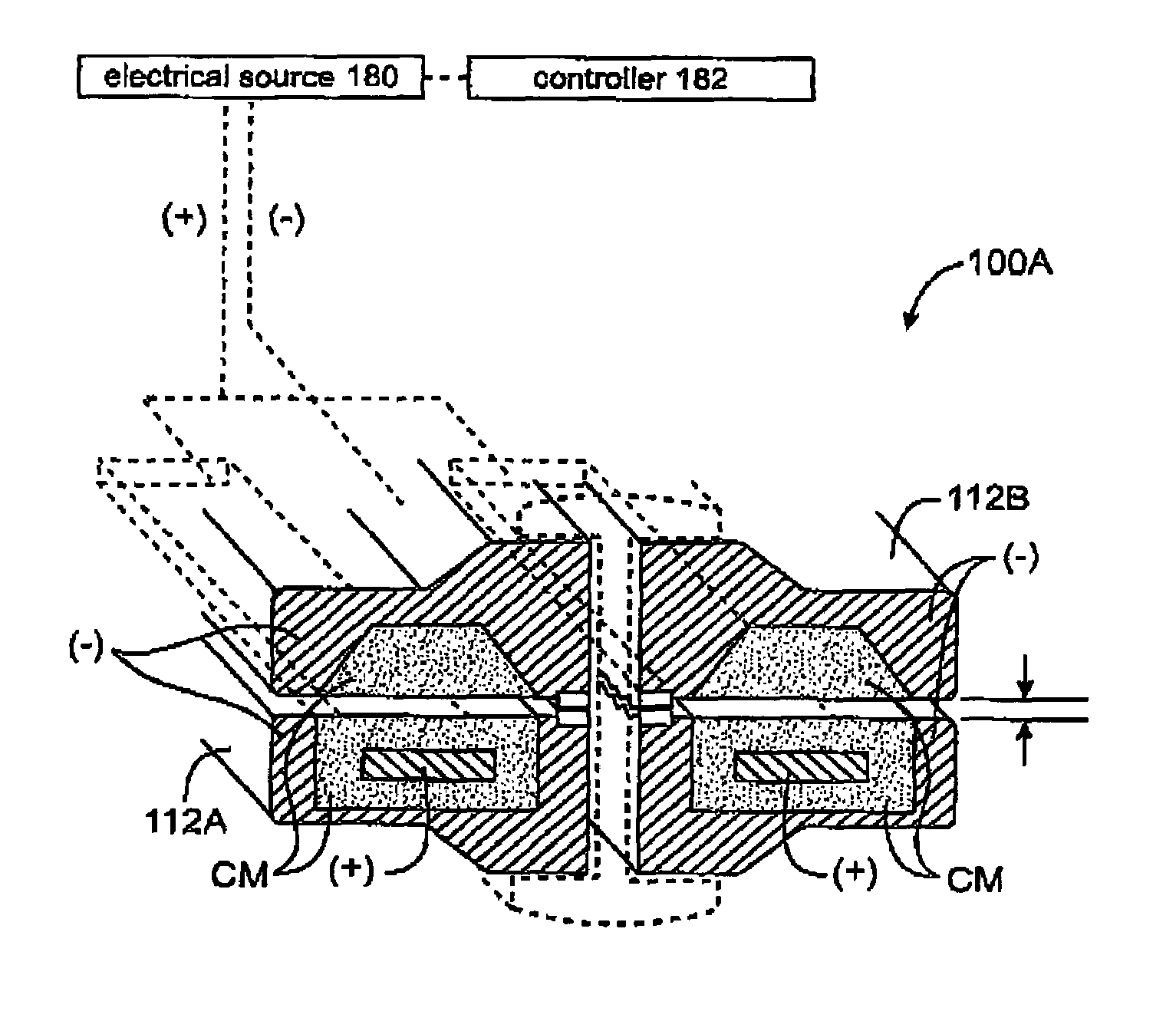
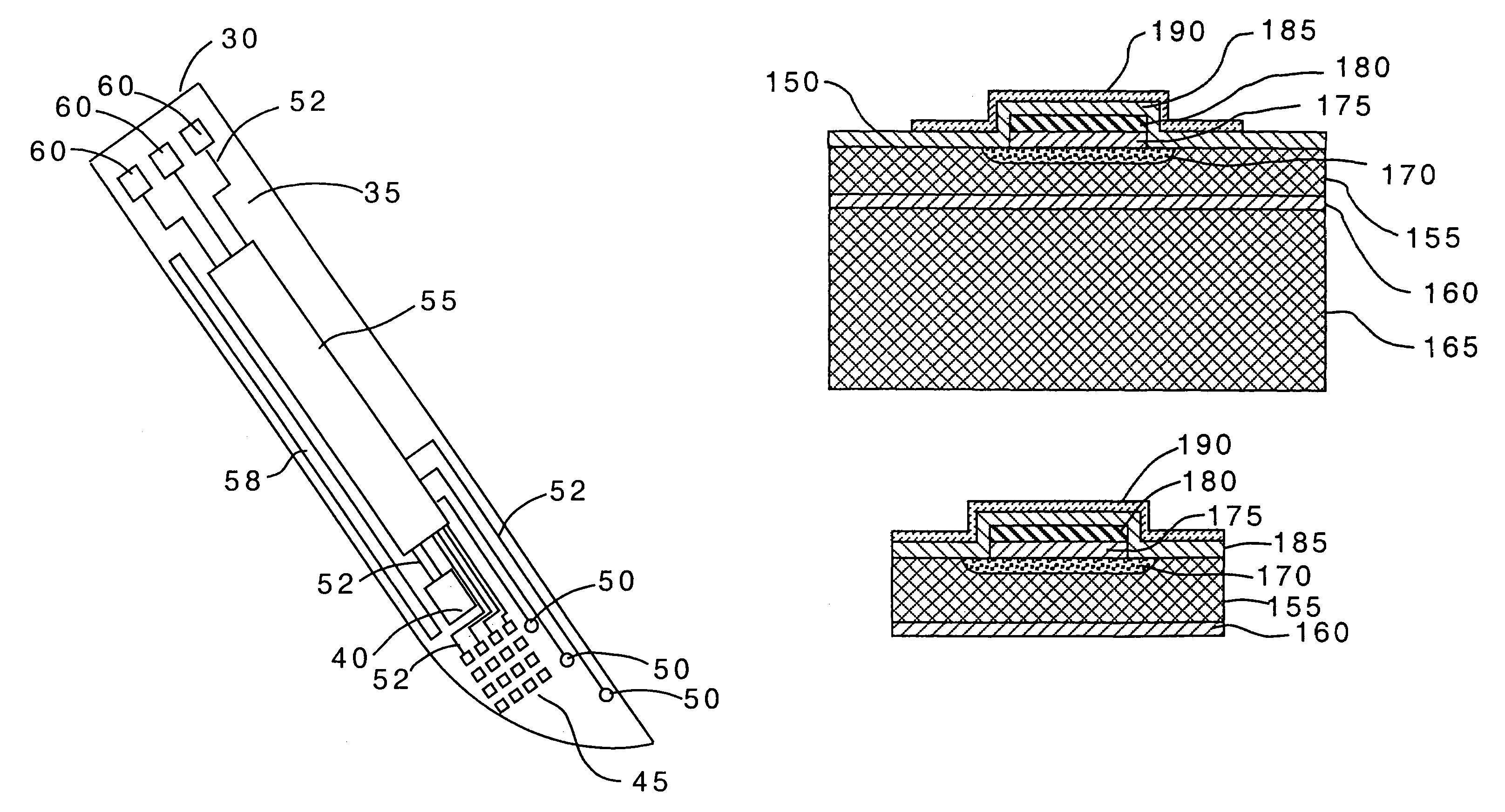
Method of making a cutting instrument having integrated sensors
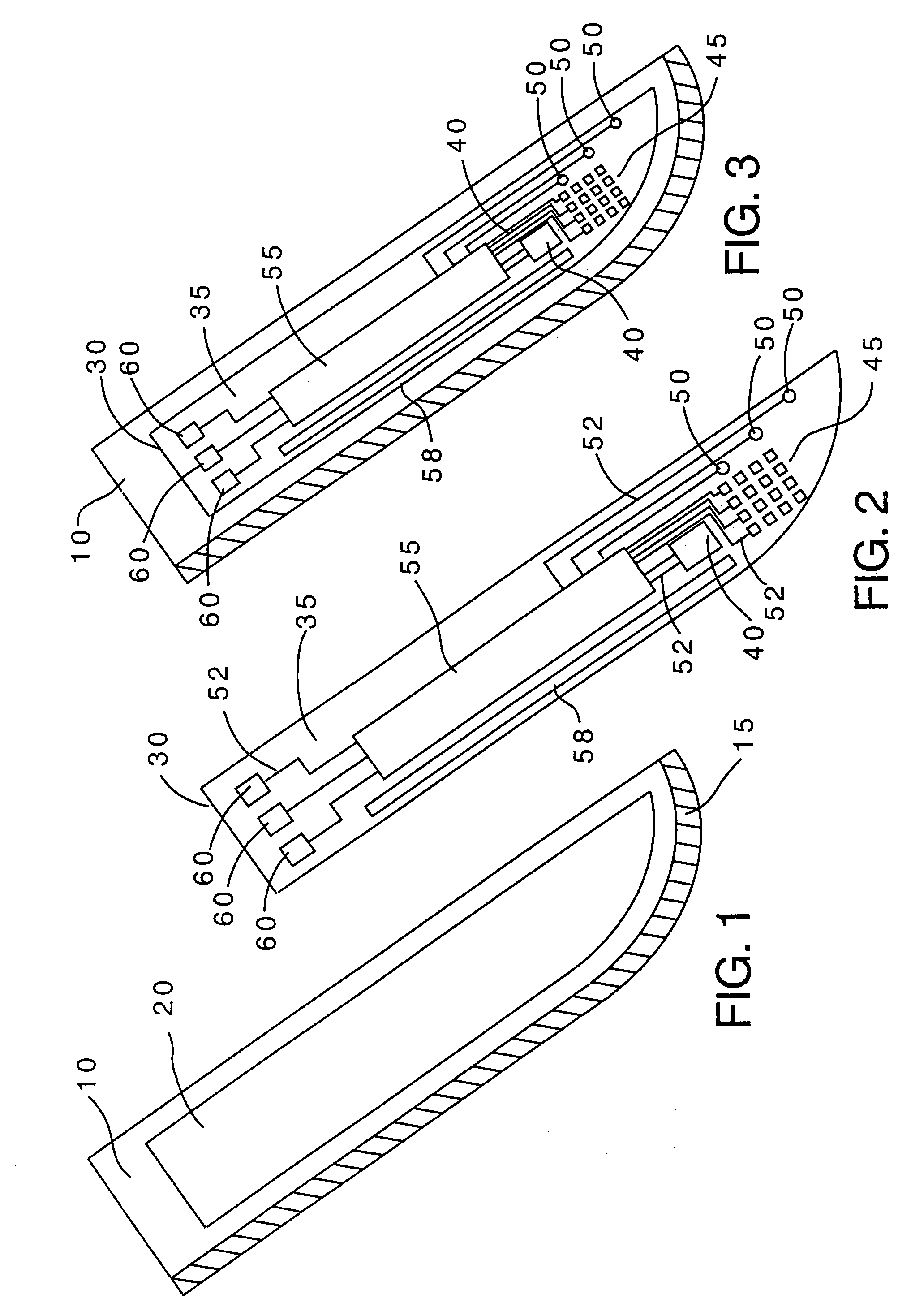
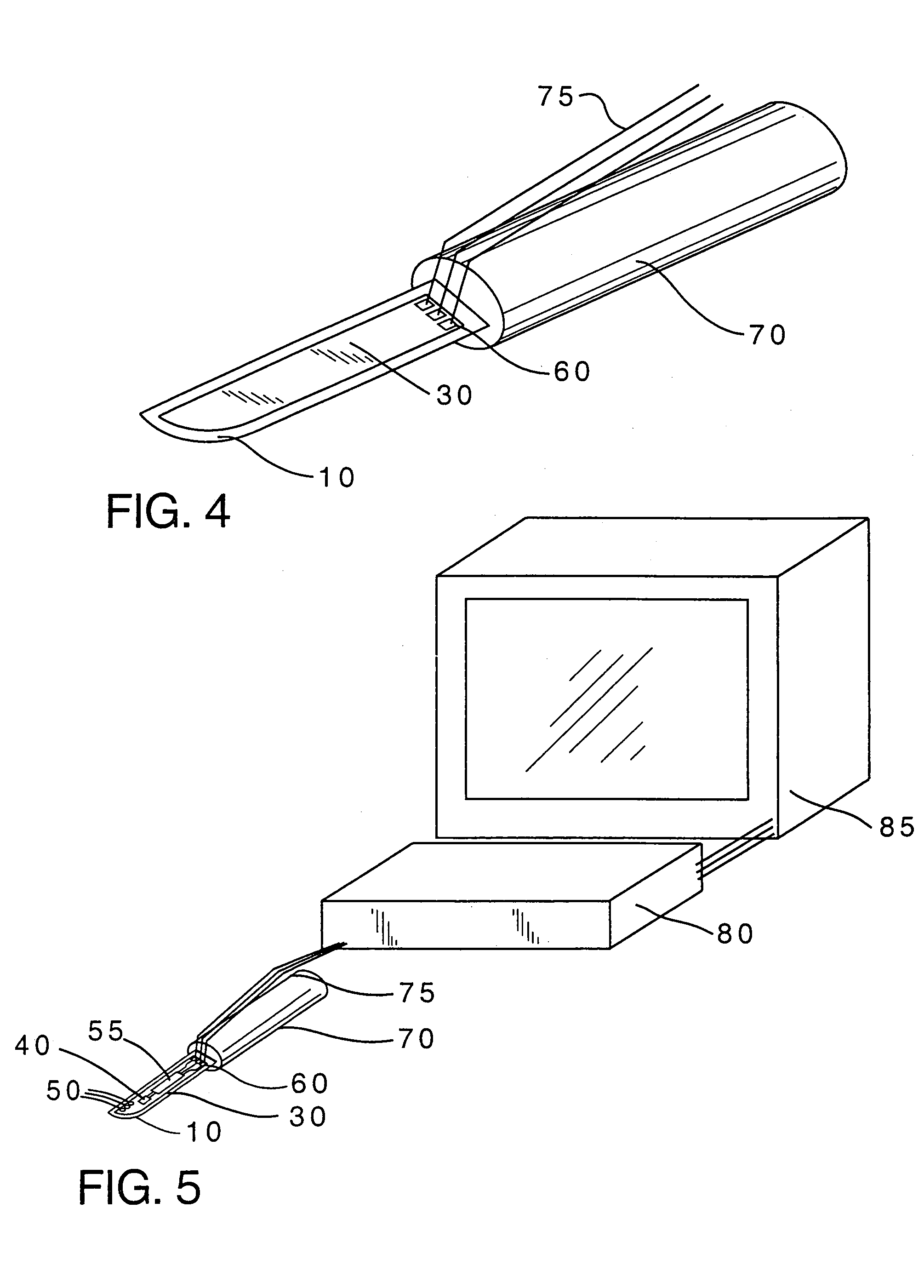
A cutting instrument including a metal blade has a recess formed therein and a semiconductor substrate affixed to the blade in the recess. The semiconductor substrate includes at least one sensor formed thereon. The sensor formed on the semiconductor substrate may comprise at least one or an array of a strain sensors, pressure sensors, nerve sensors, temperature sensors, density sensors, accelerometers, and gyroscopes. The cutting instrument may also further include a handle wherein the blade is affixed to the handle and the semiconductor substrate is electrically coupled to the handle. The handle may then be coupled, either physically or by wireless transmission, to a computer that is adapted to display information to a person using the cutting instrument based on signals generated by one or more of the sensors formed on the semiconductor substrate. The computer or handle may also be adapted to store data based on the signals generated by one or more of the sensors. A method of making said cutting instrument includes the steps of at least one sensor being formed on a semiconductor wafer and a layer of photoresist being applied on a top side of the semiconductor wafer according to a pattern that matches the defined shape of the semiconductor substrate. The portion of the semiconductor wafer not covered by the photoresist is removed and thereafter the photoresist is removed from the semiconductor wafer, thereby leaving the semiconductor substrate having a defined shape and at least one sensor formed thereon. The semiconductor substrate having a defined shape and at least one sensor formed thereon is then affixed to a metal blade in a recess formed in said blade.
Owner:VERIMETRA
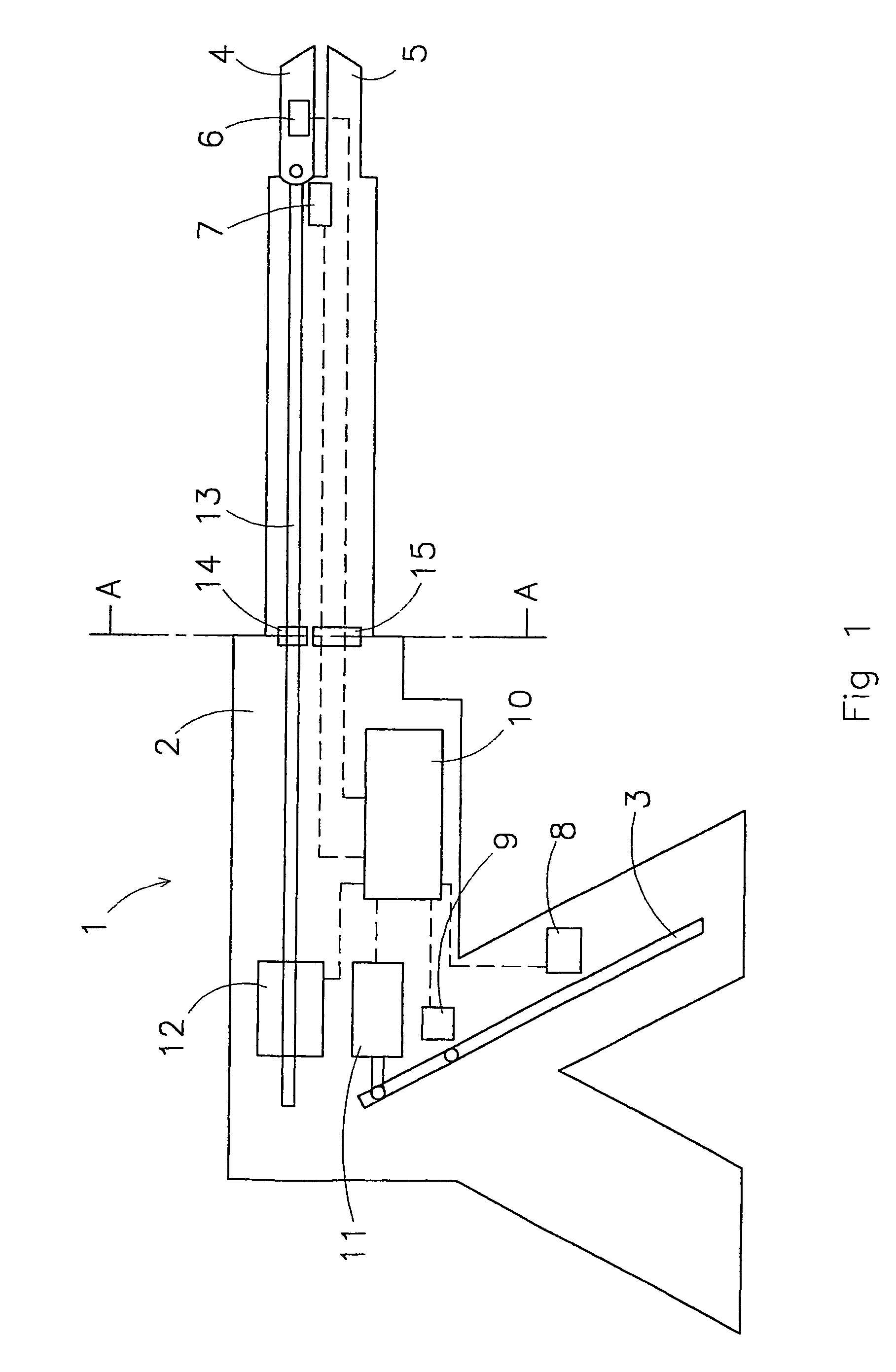
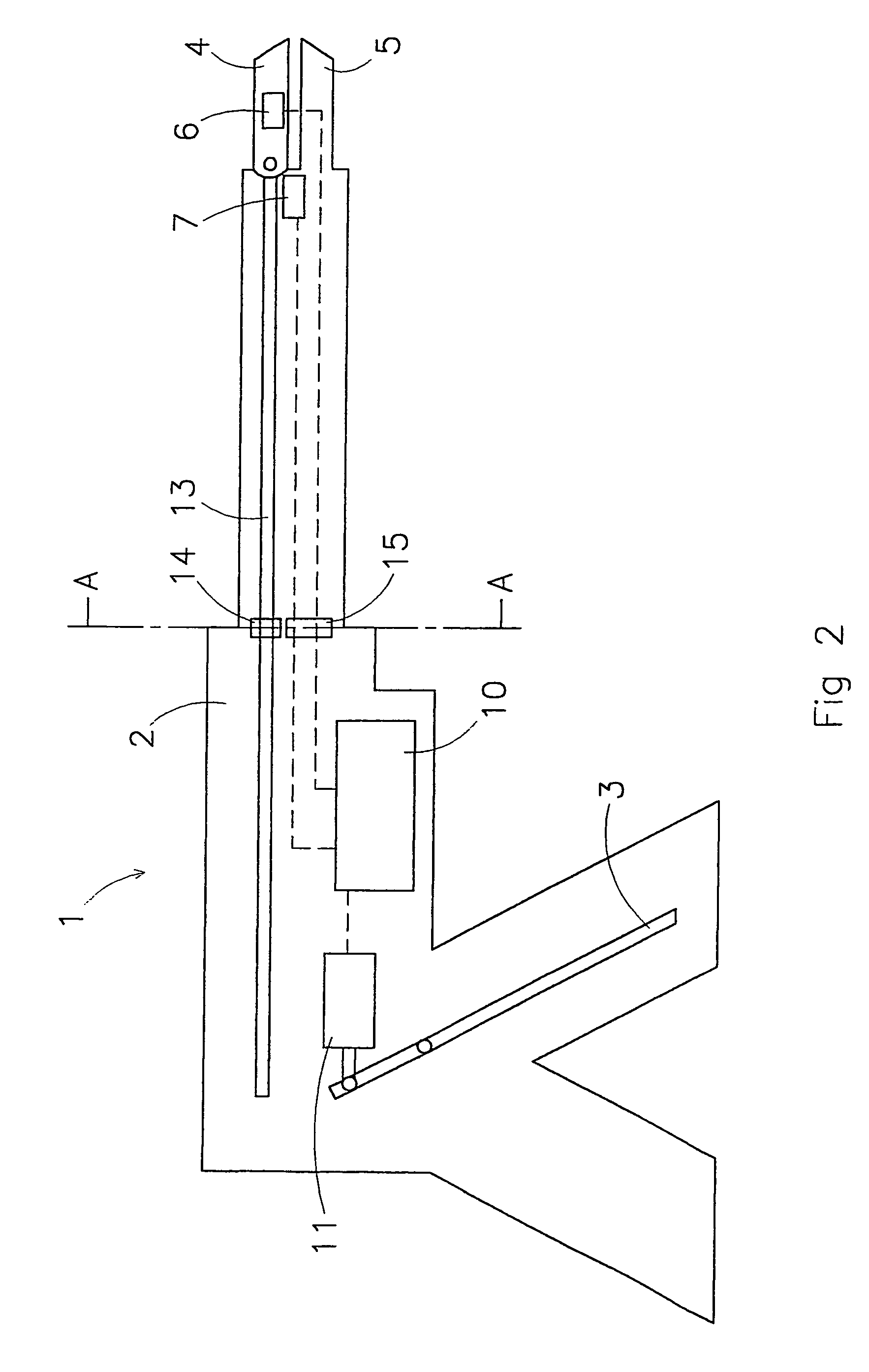
Device for introducing and positioning surgical instruments and corresponding method
InactiveUS20090204108A1Precise and simple and quick insertionPrecise positioningDiagnosticsSurgical drapesSurgical operationEngineering
This invention relates to a device (20) for inserting and positioning surgical instruments (10) in the body of a patient, with an outer cover (22), into which outer cover (22) at least a front part (11) of the surgical instrument (10) is insertable, and which outer cover (22) is removable for positioning the surgical instrument (10) at the point of application, the outer cover (22) being pulled away from the front part (11) of the surgical instrument (10) by means of a pulling device (21). In particular, the outer cover (22) is able to be pulled backwards over the front part (21) <sic. (11)> of the surgical instrument (10), and the surgical instrument (10), or respectively its front part, is able to be uncovered again, so that the function assigned to the surgical instrument (10) is able to be carried out unimpeded. The outer cover (22) can be returned to the starting position, in particular also by means of a return device. The outer cover (22) is preferably able to be controlled by means of the pulling device (21) using the handle (15) of the surgical instrument (10).
Owner:STEFFEN RUDOLF
Shape lockable apparatus and method for advancing an instrument through unsupported anatomy
Apparatus and methods are provided for placing and advancing a diagnostic of therapeutic instrument in a hollow body organ of a tortuous or unsupported anatomy, comprising a handle, an overtube, a distal region having an atraumatic tip. The overtube may be removable from the handle, and have a longitudinal axis disposed at an angle relative to the handle. The overtube may be selectively stiffened to reduce distension of the organ caused by advancement of the diagnostic or therapeutic instrument. The distal region permits passive steering of the overtube caused by deflection of the diagnostic or therapeutic instrument while the atraumatic tip prevents the wall of the organ from becoming caught or pinched during manipulation of the diagnostic or therapeutic instrument.
Owner:USGI MEDICAL CORP
Surgical instrument for orthopedic surgery
ActiveUS8221424B2Safe foraminal decompressionDiagnosticsEndoscopic cutting instrumentsTool bitSurgical instrumentation
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Medical device
A medical device includes a medical instrument with a transponder detachably fixed to the medical device. The transponder serves as a data medium about specific information of the medical instrument. The medical device further includes a data exchange mechanism for exchanging data with the transponder. When a medical treatment is to be performed, the medical instrument is placed to a receiving mechanism for receiving the medical instrument separated from the transponder, while the transponder is placed to the data exchange mechanism which is placed locally apart or locally placed different from the receiving mechanism so that disadvantageous influences of the medical treatment do not affect the transponder.
Owner:SCHMID +2
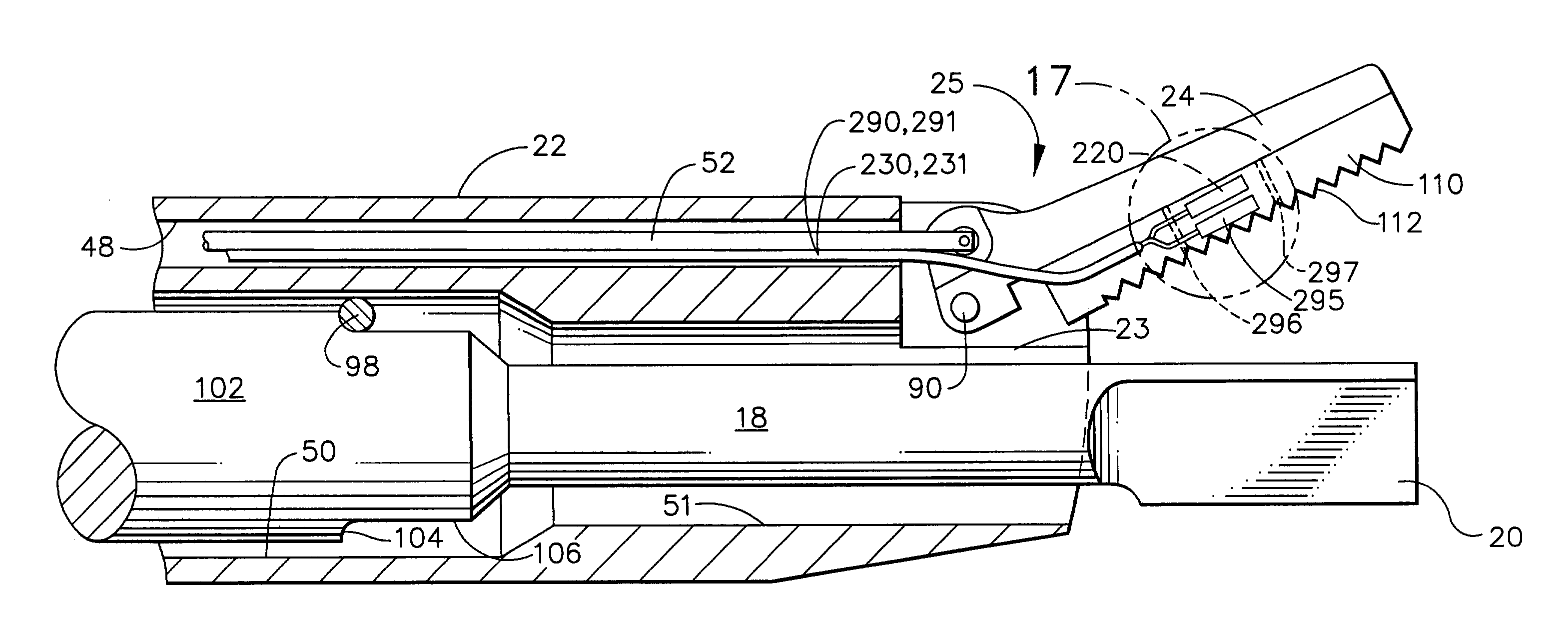
End effector identification by mechanical features
According to one aspect of the present disclosure, a surgical instrument is disclosed. The instrument includes a handle portion, a body portion extending distally from the handle portion and defining a first longitudinal axis and a loading unit. The loading unit includes a tool assembly, the loading adapted to be coupled to the body portion. The instrument also includes a sensor tube movably positioned within the body portion, the sensor tube adapted to engage the loading unit and a load switch coupled to a microcontroller. The load switch is adapted to be actuated by the sensor tube when the sensor tube is engaged by the loading unit being inserted into the body portion.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com