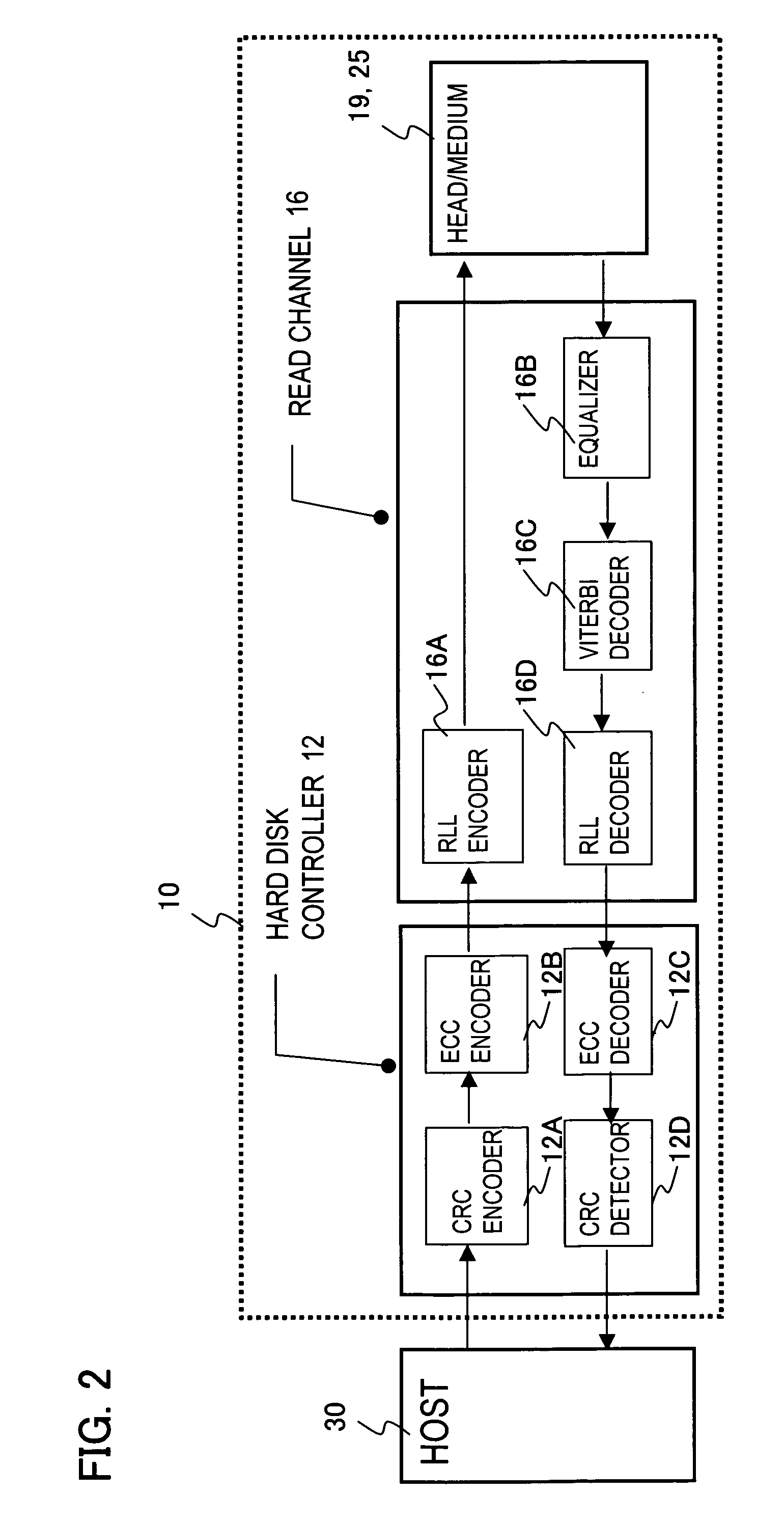
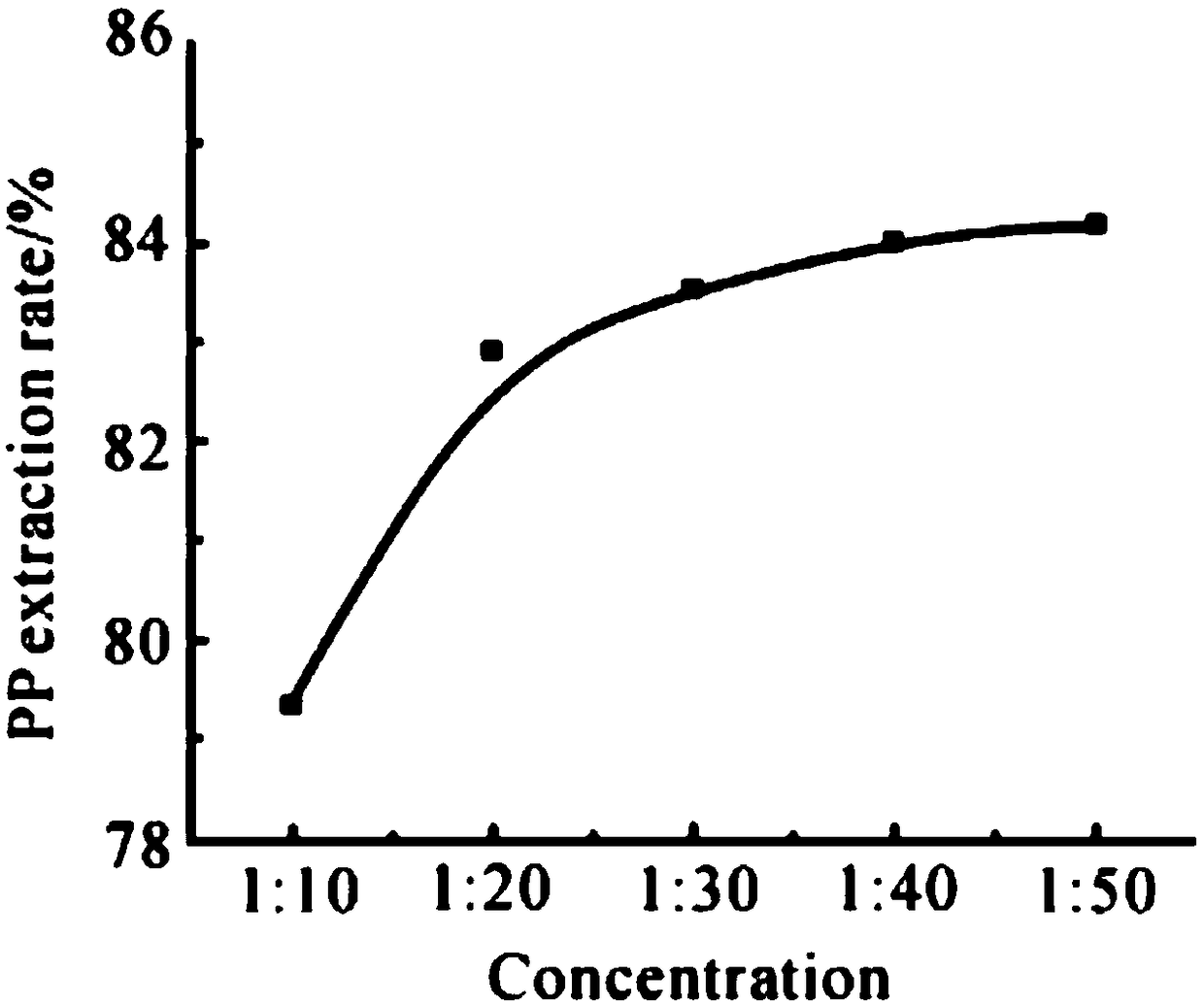
Patents
Literature
57 results about "Thermal relaxation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
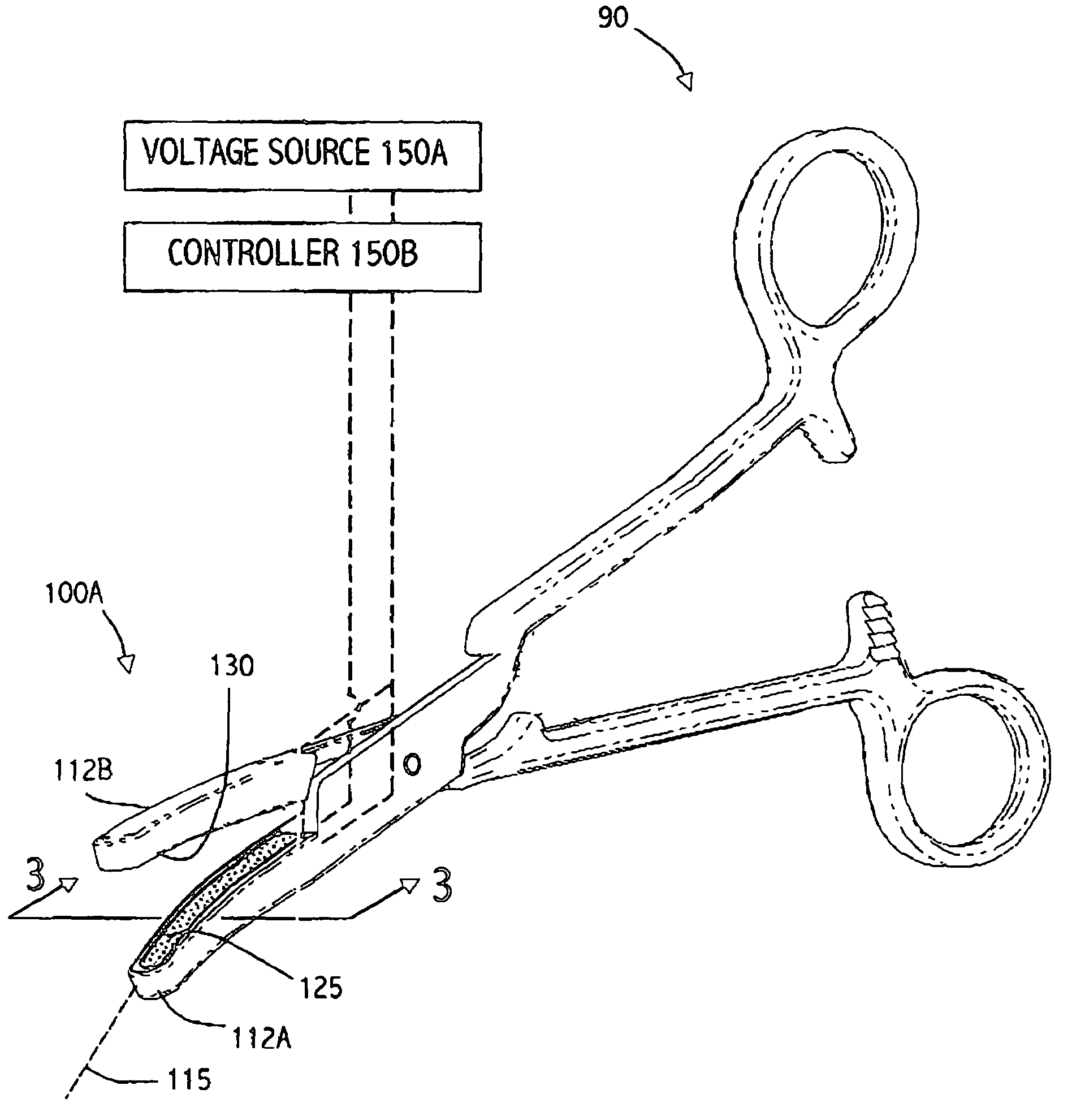
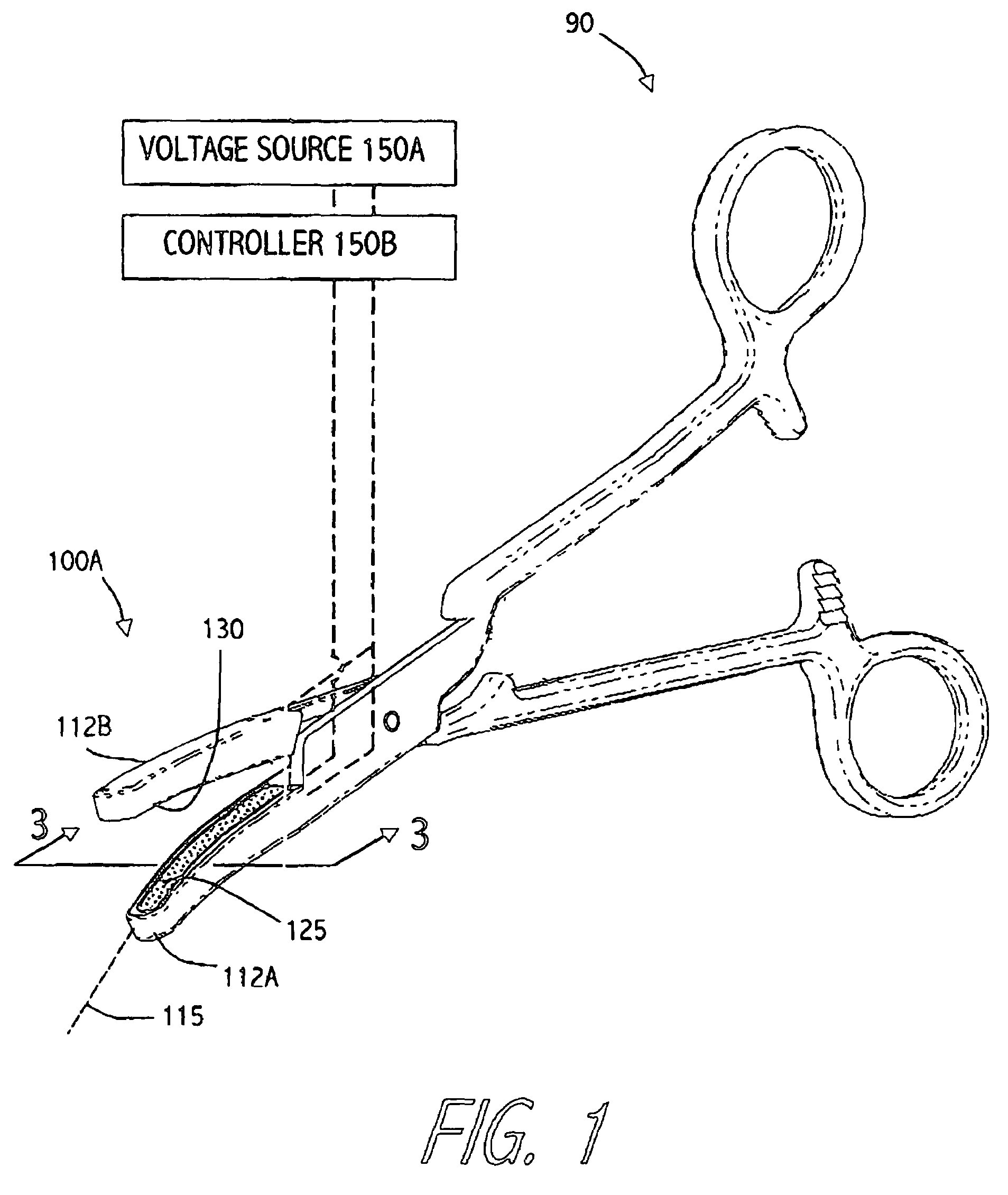
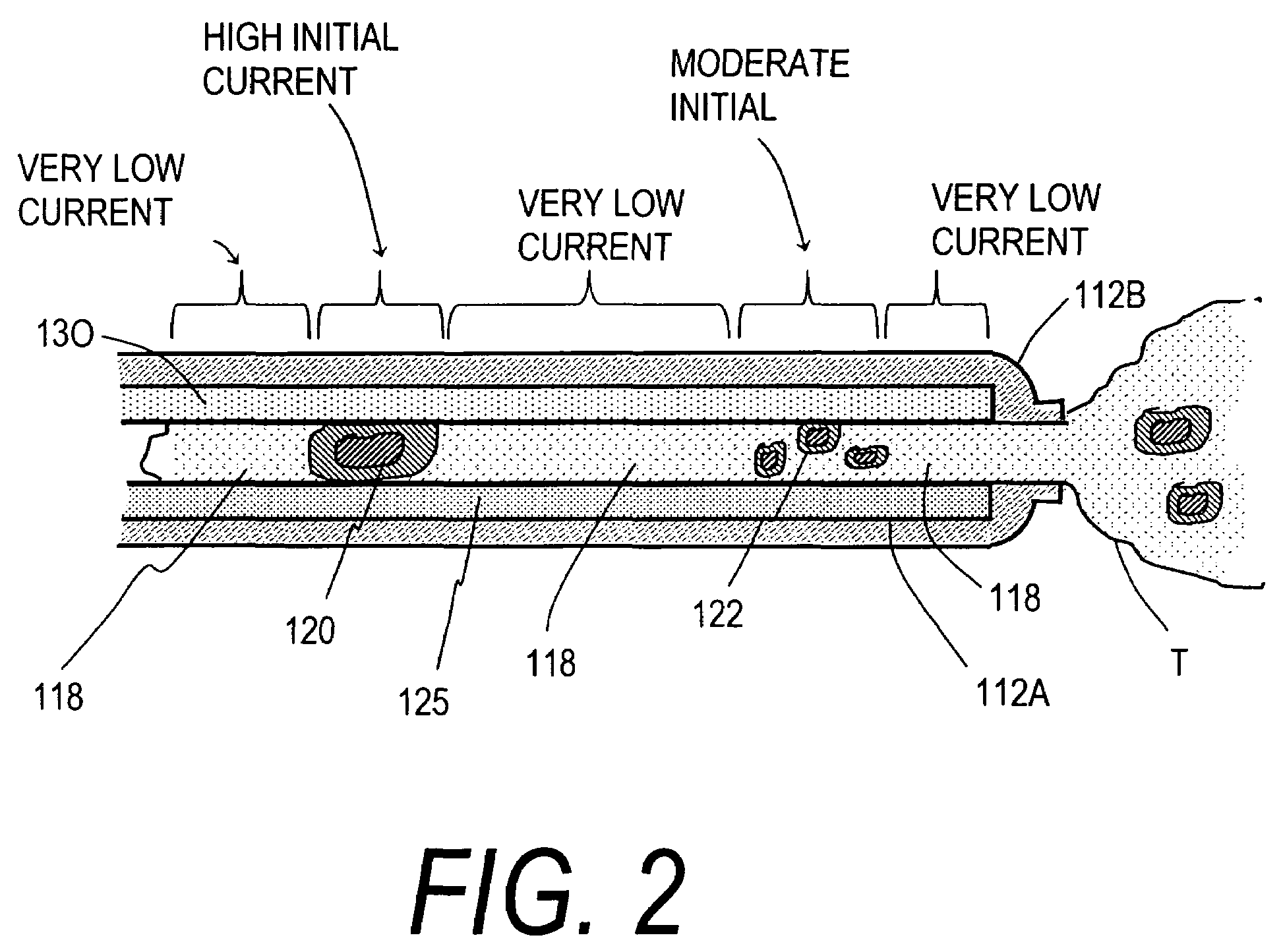
Electrosurgical probe and method of use
ActiveUS7169146B2Reduce the temperatureQuick changeSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsElectrical resistance and conductanceVolumetric Mass Density
An electrosurgical instrument that allows precise modulation of active Rf density in an engaged tissue volume. The working end of the instrument has a tissue-contacting surface of a conductive-resistive matrix that is variably resistive depending on its temperature. The matrix comprises a positive temperature coefficient (PTC) polymeric material hat exhibits very large increases in resistivity as any local portion increases beyond a selected temperature. In a method of use, the polymeric PTC material senses the temperature of engaged tissue in a manner akin to pixel-by-pixel sensing and thereby changes its resistance in a corresponding pixel-by-pixel manner. The instrument further carries cooling means to cause accelerated thermal relaxation of the PTC matrix during use to make the engagement surface highly responsive to temperature changes that in turn alter the matrix between being electrically conductive and electrically resistive.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
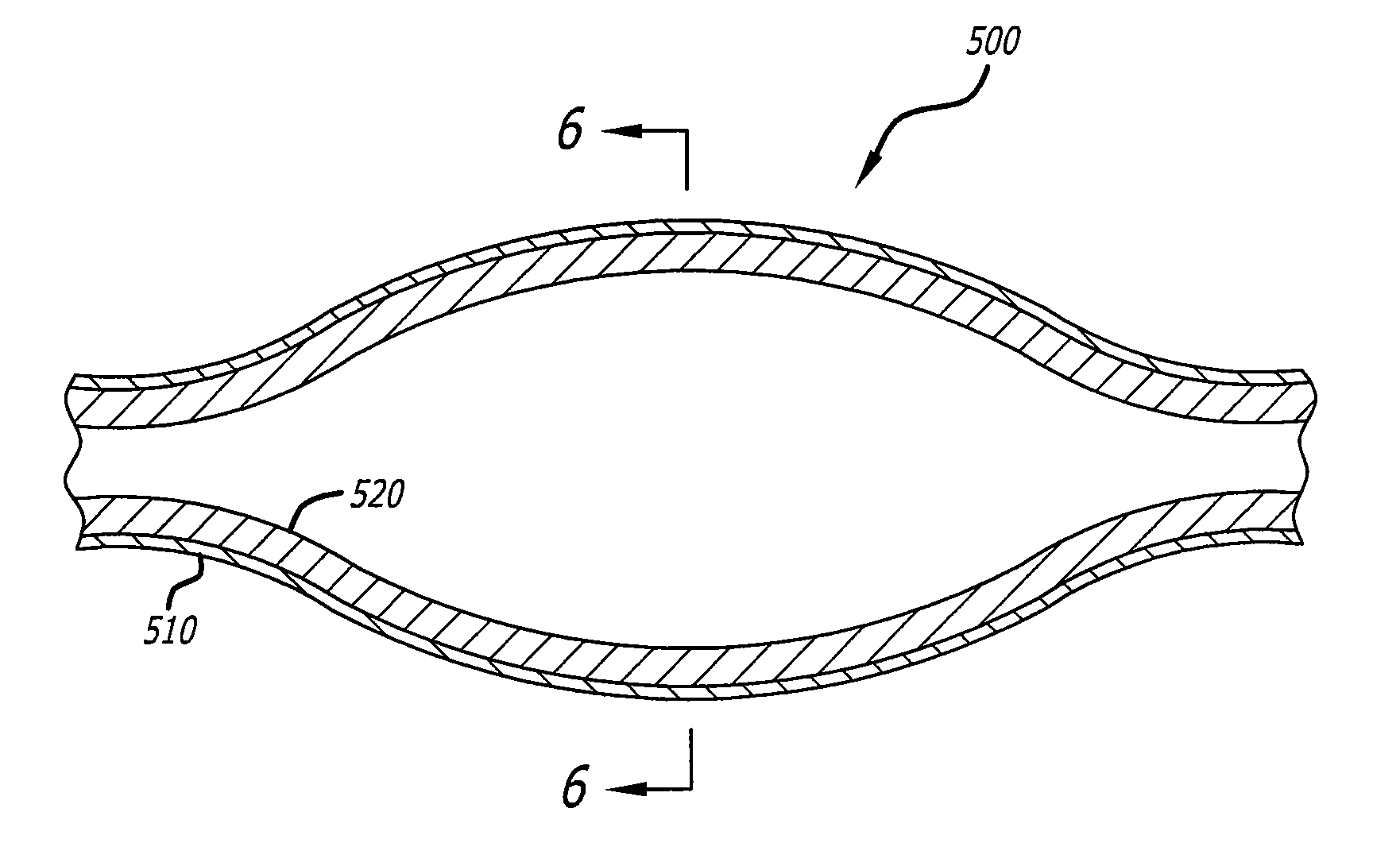
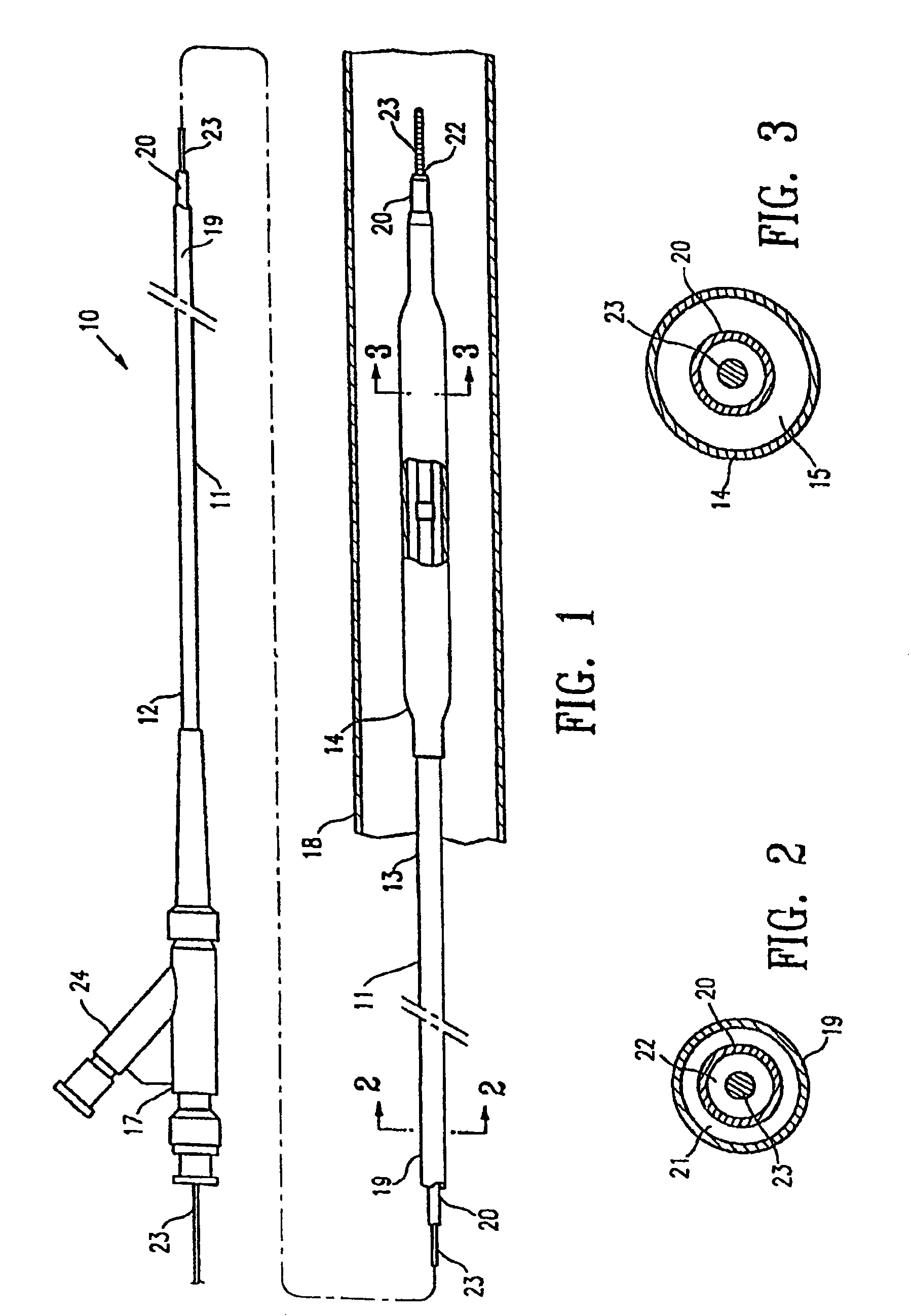
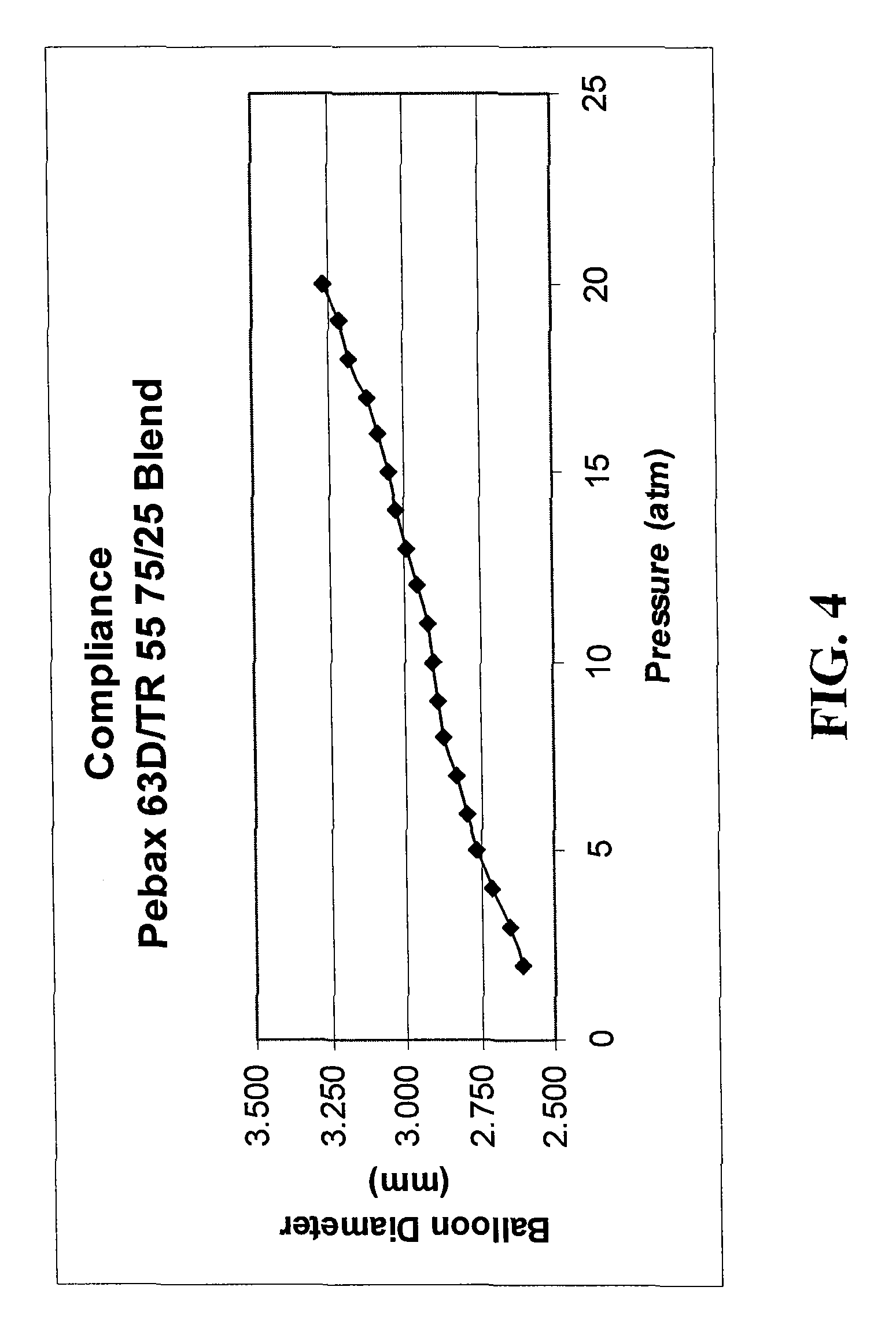
Robust multi-layer balloon
A multilayer balloon catheter is formed to have an inner layer and an outer layer, where the outer layer is adapted to resist shredding and premature rupture. The outer layer is formed of a material having a glass transition temperature that is lower than the transition or melting temperature of the inner layer. By forming the balloon on a mold at a temperature between the glass transition temperature of the outer layer and the glass transition or melting temperature of the inner layer, the outer layer will undergo a thermal relaxation that will alleviate some of the axial orientation of the polymer chains that develop during the formation of the multilayer balloon. This relaxation leads to a resistance to shredding when the balloon is expanded during operation.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Ground source heat pump well field design and control strategy for large tonnage
InactiveUS7647773B1Optimal Control StrategyEasy to operateCollector components/accessoriesLighting and heating apparatusModularityGood practice
The present invention features geothermal systems that use of a well field open loop scheme by interconnecting the well field through a system of mains and controlled branches, the latter composed of multiple (2-5) wells. The proposed design lends itself to the use of modular well field kits that minimize installation cost, insures equal return water distribution to the active wells, creates standardization and insures best practices. The benefits of individual branch control include the ability to serve the building load in staged delivery, thereby minimizing well field parasitic load, and maximizing the time available for well field thermal relaxation and availability.
Owner:AMERICAN REFINING GRP
Processing technology of arc-shaped spring
ActiveCN102501009ASmall thermal relaxation rateLarge momentary torqueFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesStress reliefMaterials science
The invention relates to a processing technology of a large-radian arc-shaped spring. The processing technology is characterized by comprising the following procedures of: spring coiling: primary stress relief annealing; spring grinding; spring bending into an arc-shaped spring; secondary stress relief annealing; shot blasting; hot-strong pressing; sorting; angular rigidity and torque test; fatigue life test; and surface antirust treatment. According to the forming technology of the arc-shaped spring provided by the invention, the arc-shaped spring with the free angle of being more than 45 degrees can be effectively formed, the thermal relaxation rate of the spring is less than 2%, the instantaneous torque is large, the fatigue life is 1 million times, and the technical problems of low finished product rate and incapability for normal use of the large-radian arc-shaped spring in the prior art are solved.
Owner:HANGZHOU FUCHUN SPRING
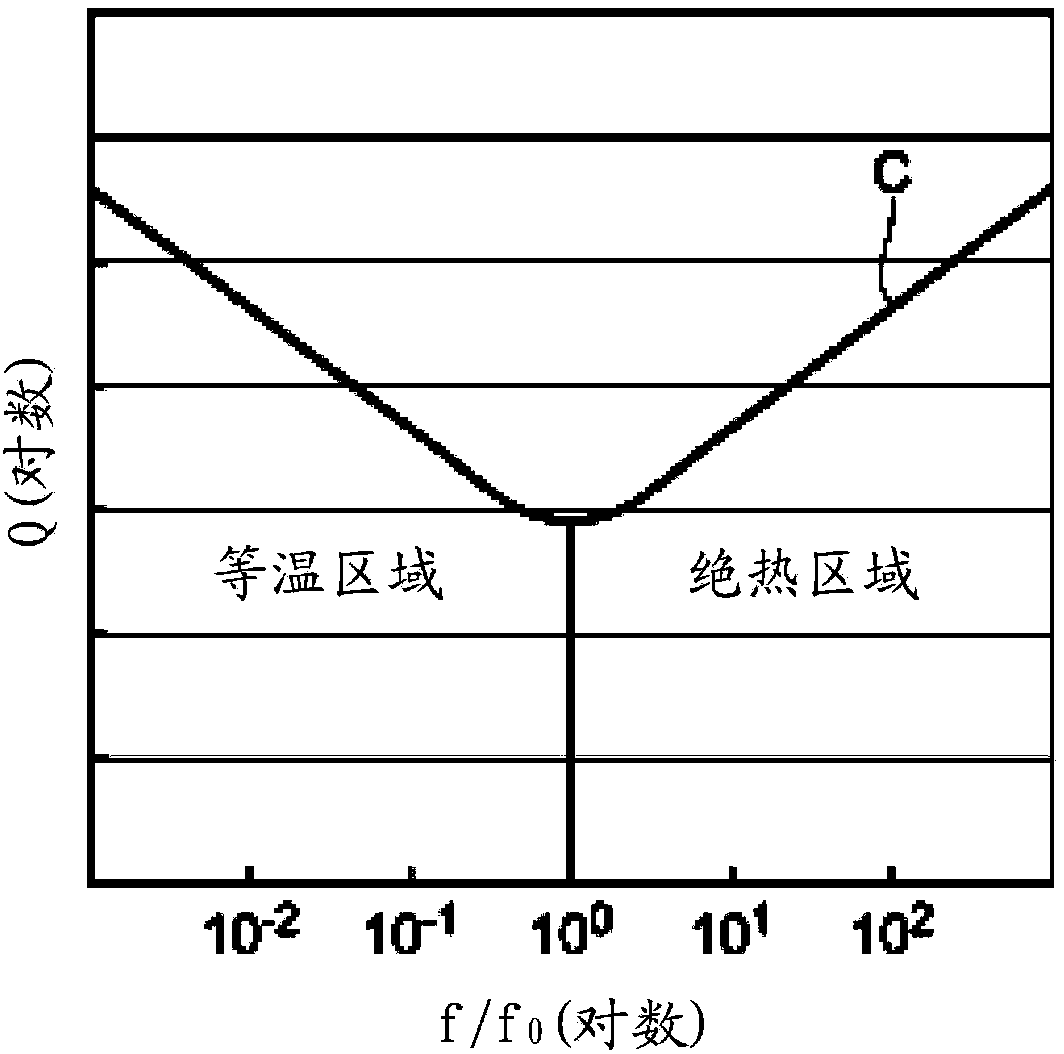
Resonator element, resonator, and oscillator
InactiveUS20120007685A1Improve the vibration effectAvoid heat conductionImpedence networksOscillations generatorsMechanical resonanceEngineering
A resonator element includes: at least one resonating arm extending, wherein the resonating arm has a mechanical resonance frequency which is higher than a thermal relaxation frequency thereof, the resonating arm has a groove portion, the groove portion includes a bottom portion, a first side surface that extends along the longitudinal direction of the resonating arm and comes into contact with the opened principal surface and the bottom portion, and a second side surface that faces the first side surface with the bottom portion disposed therebetween and comes into contact with the opened principal surface and the bottom portion, and the groove portion has a non-electrode region which extends from a part of the first side surface close to the bottom portion to a part of the second side surface close to the bottom portion and in which no electrode is provided.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
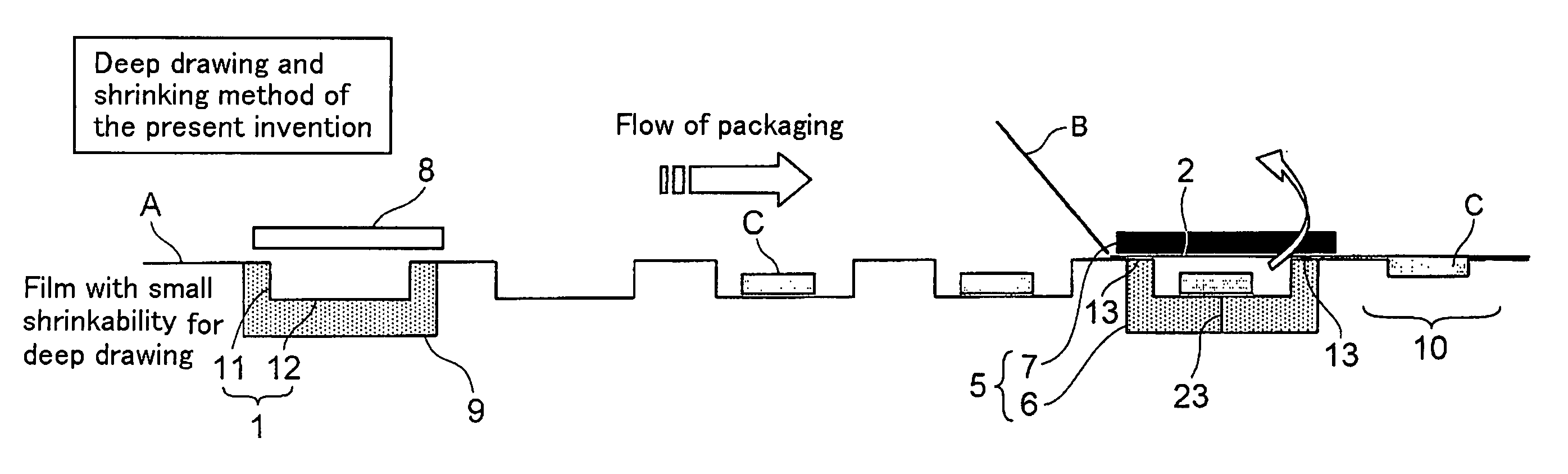
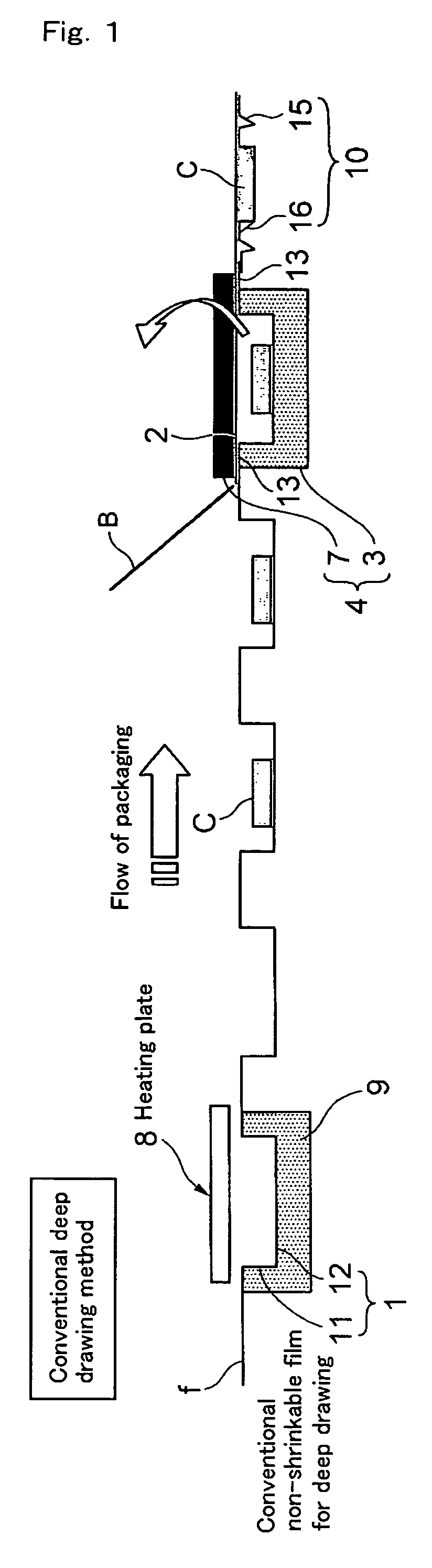
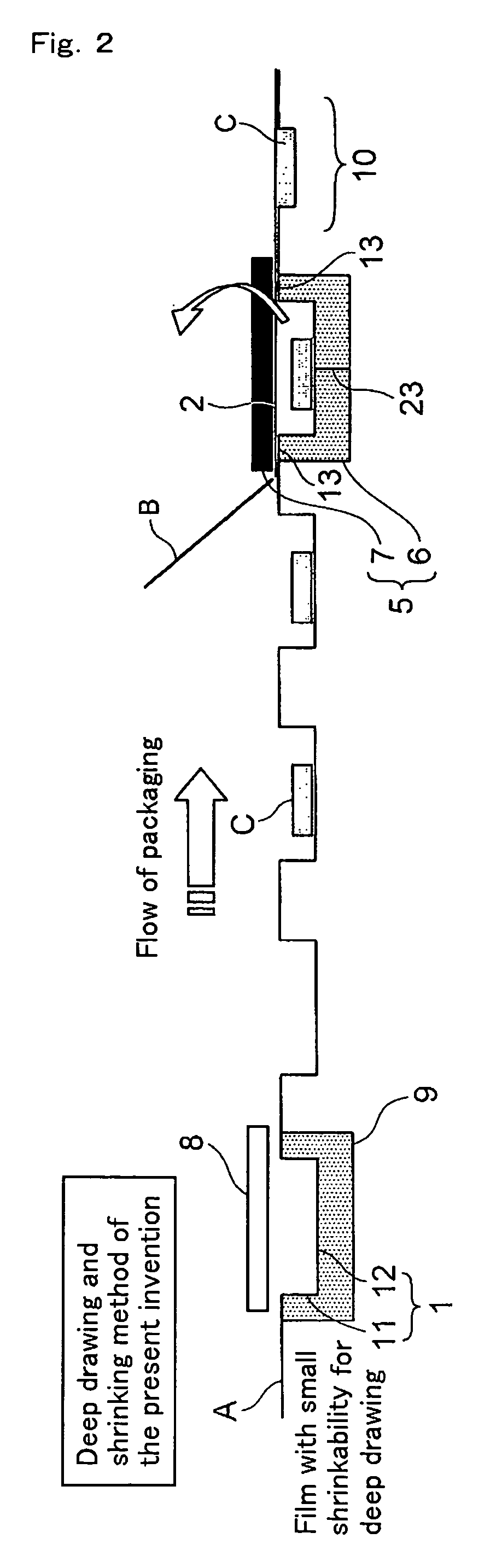
Deep draw packing method and film with small shrinkability for deep draw packing
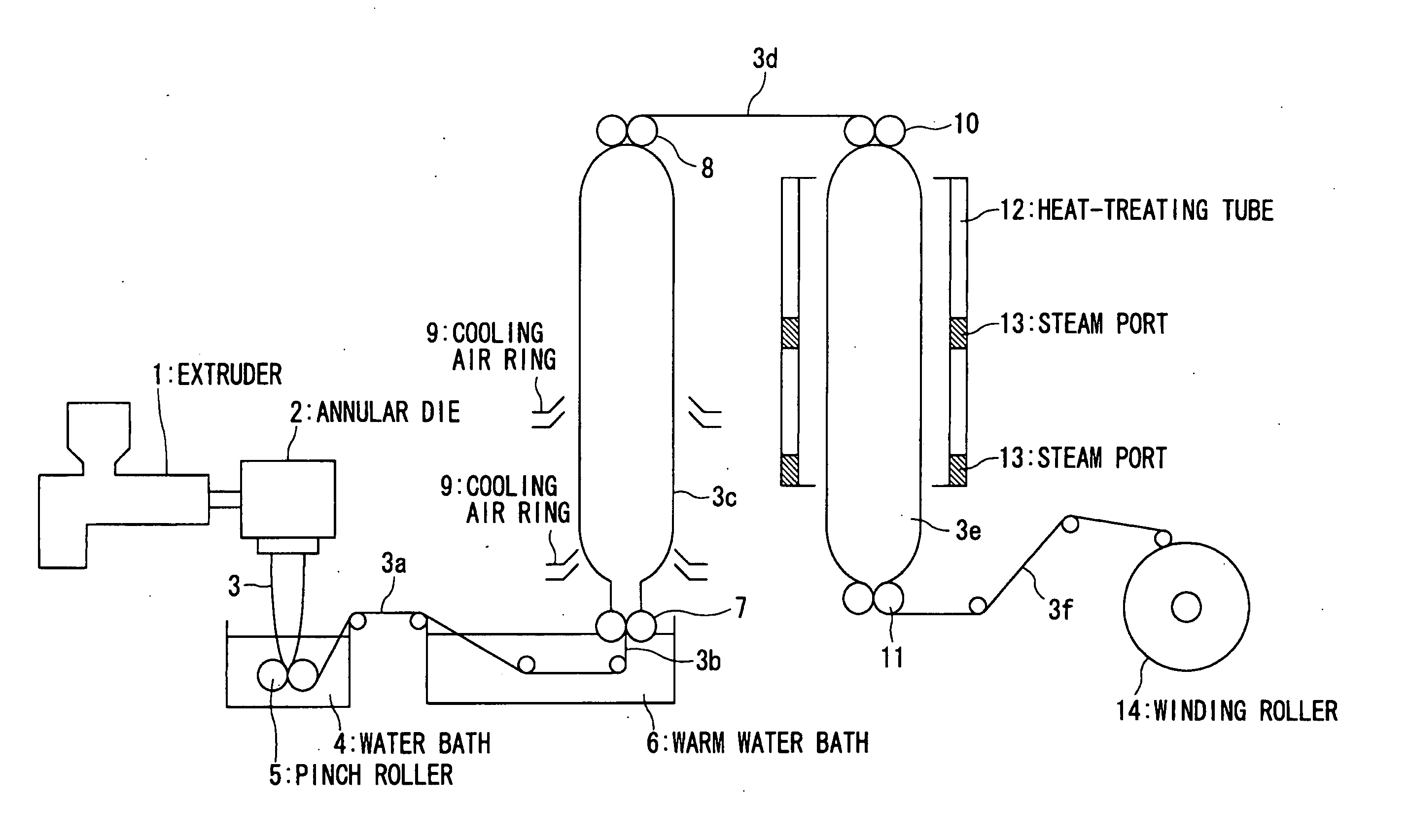
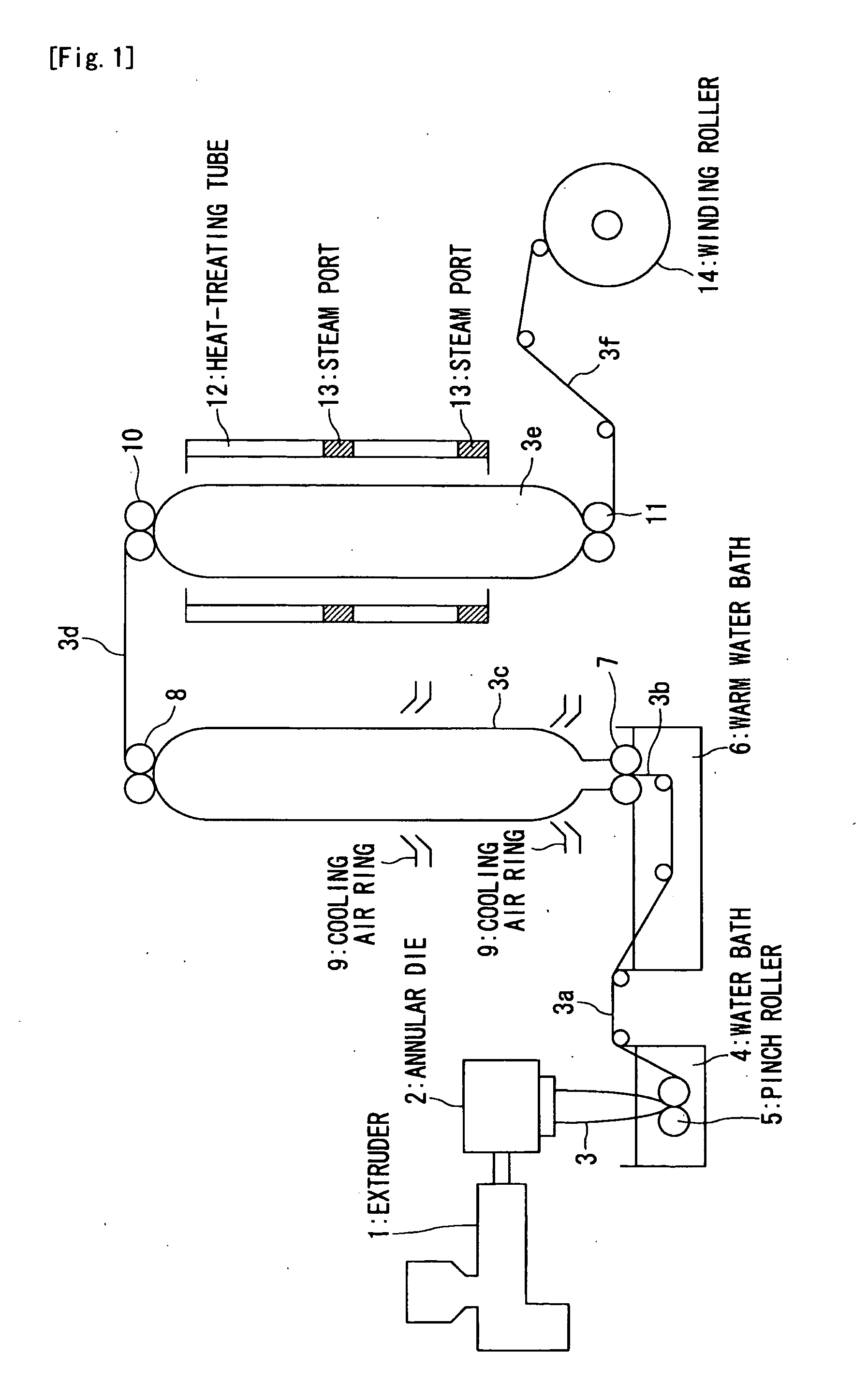
Deep draw packaging includes placing an object (C) in a concave container portion (1) formed by molding a film with small shrinkability (A), that is a film having a residual thermal shrinkage rate at 100° C. of 1 to 15 %. The film (A) is formed by stretching a film having deep draw moldability and then thermally relaxing the film. The film has a surface which is formed of a heat sealable material which becomes the inner wall of the container portion. The concave container portion (1) is thereafter transferred to to a vacuum packaging apparatus (5) where it is covered by a cover portion (2) formed of a film (B) which can be heat welded to the film (A). A side face portion (11) and a bottom face portion (12) of the concave container portion (1) are thermally shrunk into close contact with the object (C). Less curling is exhibited when an upper peripheral portion (13) of the concave container portion (1) is sealed with the film (B).
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
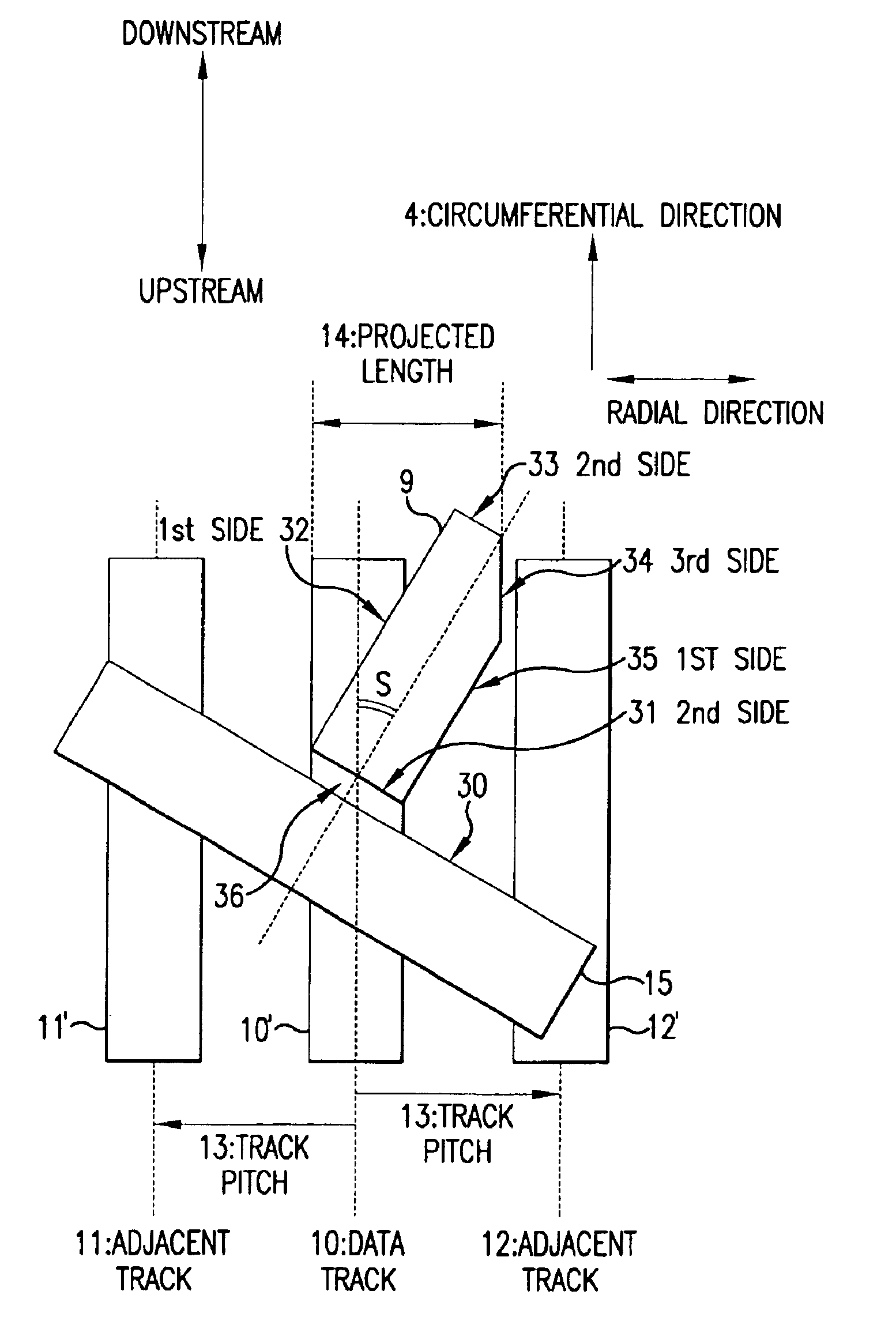
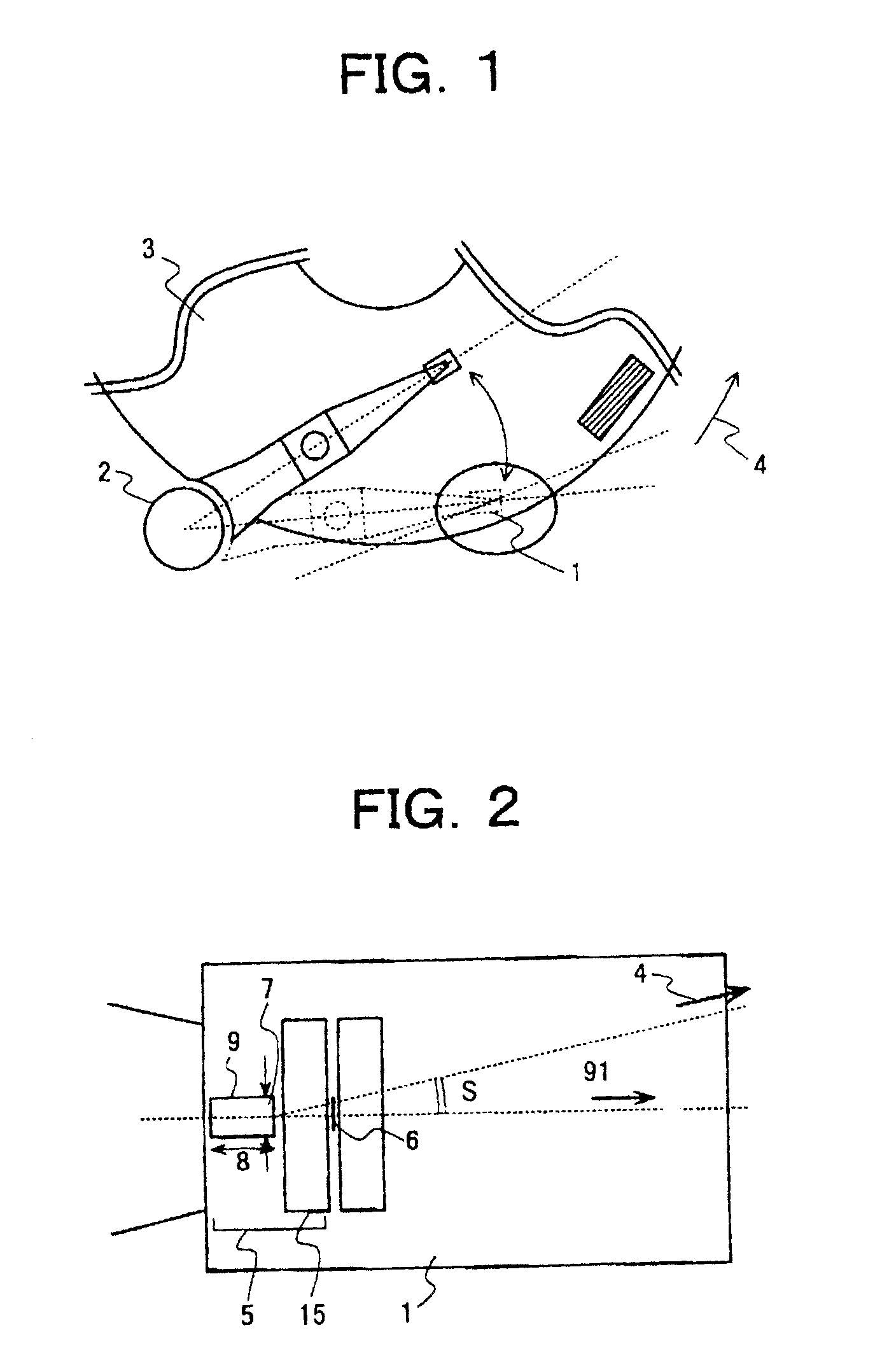
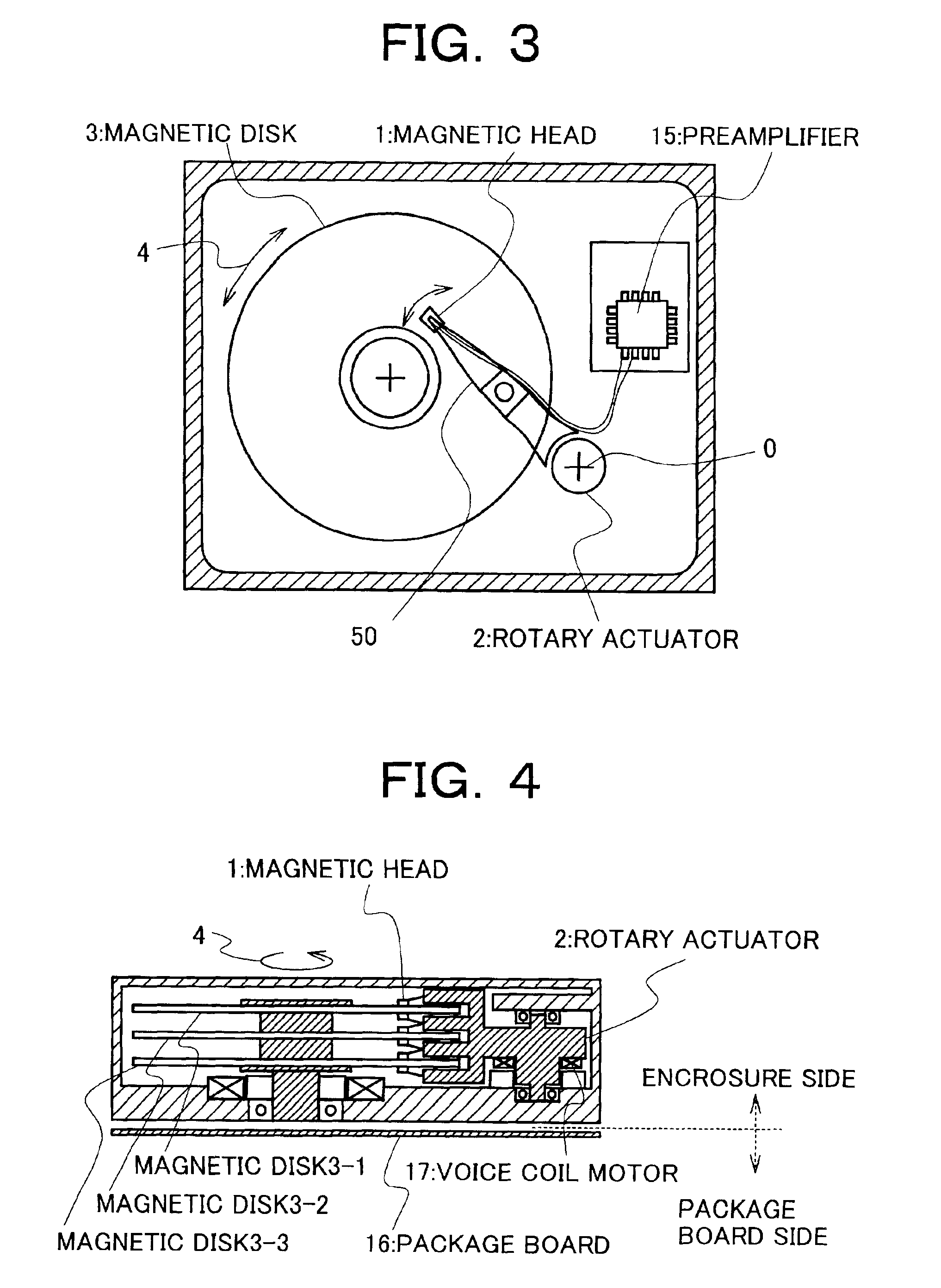
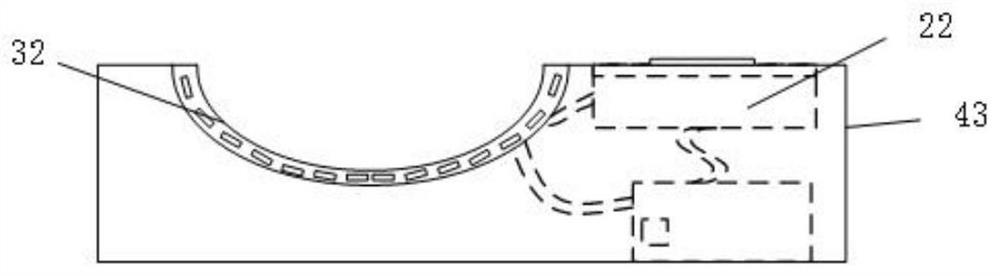
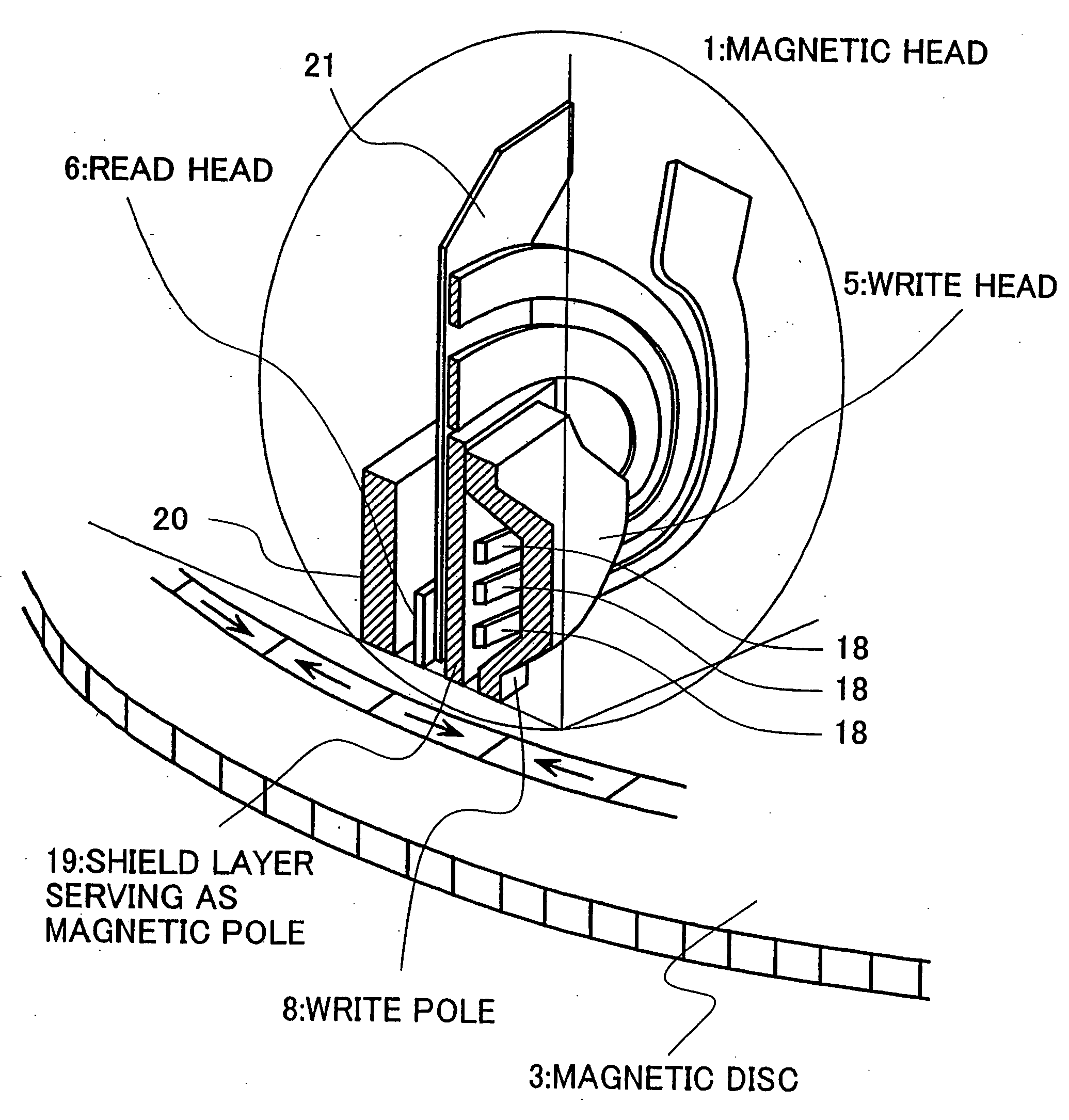
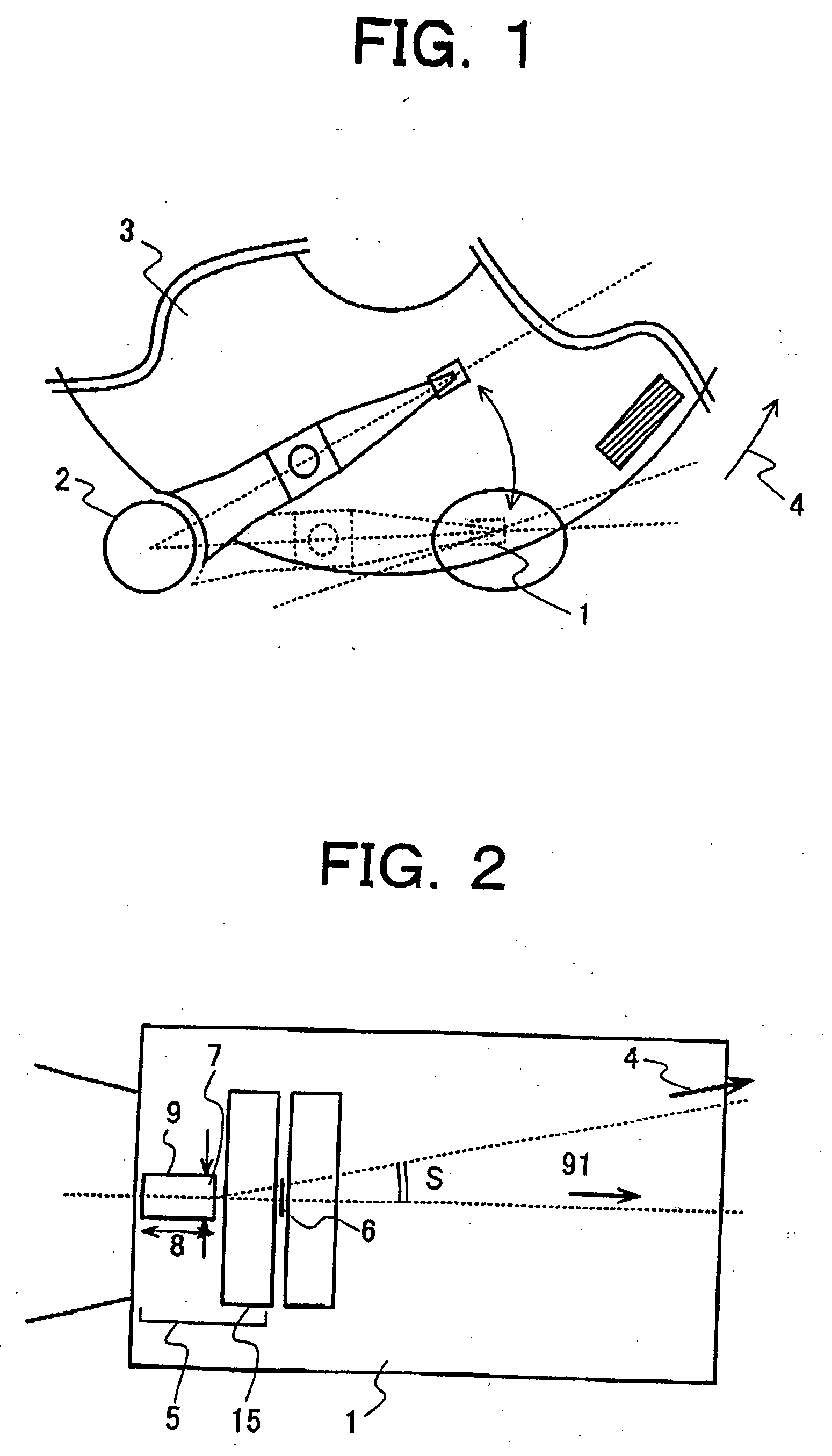
Magnetic head with high reliability of the data protection, magnetic disk apparatus including the magnetic head and the method of recording information on the magnetic disk apparatus without miserasing the previously recorded data
InactiveUS6940690B2Suppress accelerationThermal decay is not easily acceleratedManufacture head surfaceHeads using thin filmsSkew angleMagnetic poles
There are provided a magnetic head and a magnetic disk apparatus wherein an upper magnetic pole is so shaped that, at a position where skew angle is maximum, the maximum of its projected length in the radial direction of a magnetic disk is not more than the track pitch of the magnetic disk, whereby acceleration of thermal relaxation of information recorded on adjacent tracks is obviated even in an area where the skew angle is large.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH JAPAN LTD +1
Self-stimulated Raman scattering laser of In-Band pump
InactiveCN101807774AHigh beam qualityReduce thermal effectsLaser using scattering effectsDielectricStimulate raman scattering
The invention discloses a self-stimulated Raman scattering laser of an In-Band pump, which comprises a laser pump source, a laser energy transfer optical fiber, a first planoconvex lens for collimation, a second planoconvex lens for focusing, a reflection mirror of a resonator cavity, a laser gain dielectric crystal, a laser output mirror and a laser collimating mirror which are sequentially arranged, wherein pump light outputted by the laser pump source is transmitted to the first planoconvex lens via the laser energy transfer optical fiber, collimated by the first planoconvex lens, focused by the second planoconvex lens and further focused on the end surface of the laser gain dielectric crystal, the laser gain dielectric crystal produces stimulated radiation after absorbing the pump light, when the radiation of fundamental frequency light in the resonator cavity exceeds the self-stimulated Raman scattering threshold of the laser gain dielectric crystal, the produced Raman laser is collimated and outputted by the laser collimating mirror. The self-stimulated Raman scattering laser can improve the self-stimulated Raman scattering conversion rate, eliminate the thermal relaxation process from the pump energy level to the laser energy level of electrons of the conventional pump way, improve the quantum efficiency, reduce the heat and increase the self-stimulated Raman scattering conversion rate.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Detection method of hot shear cutter material laser shock residual stress thermal relaxation
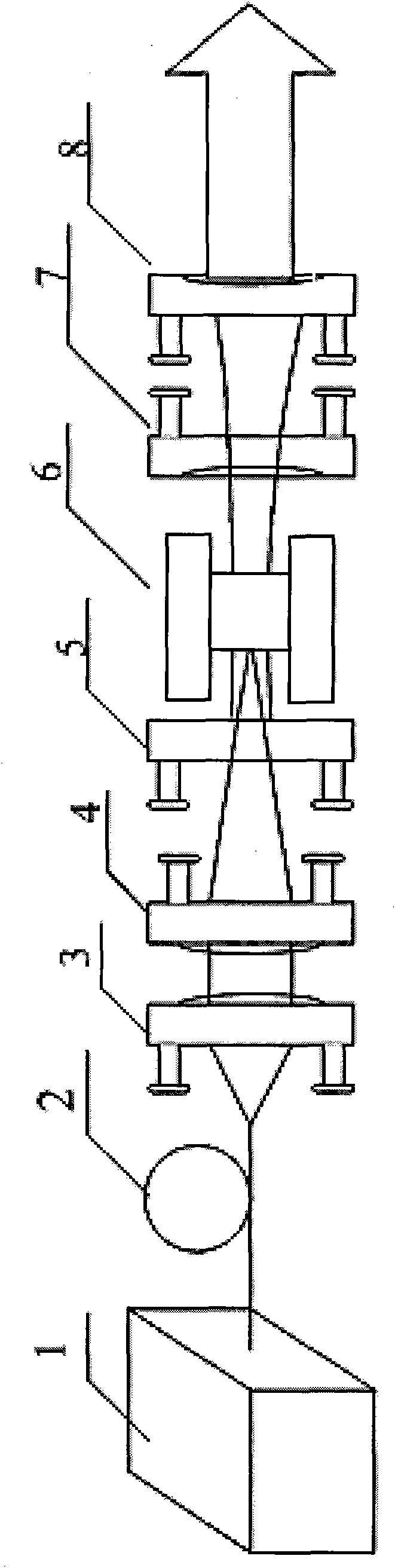
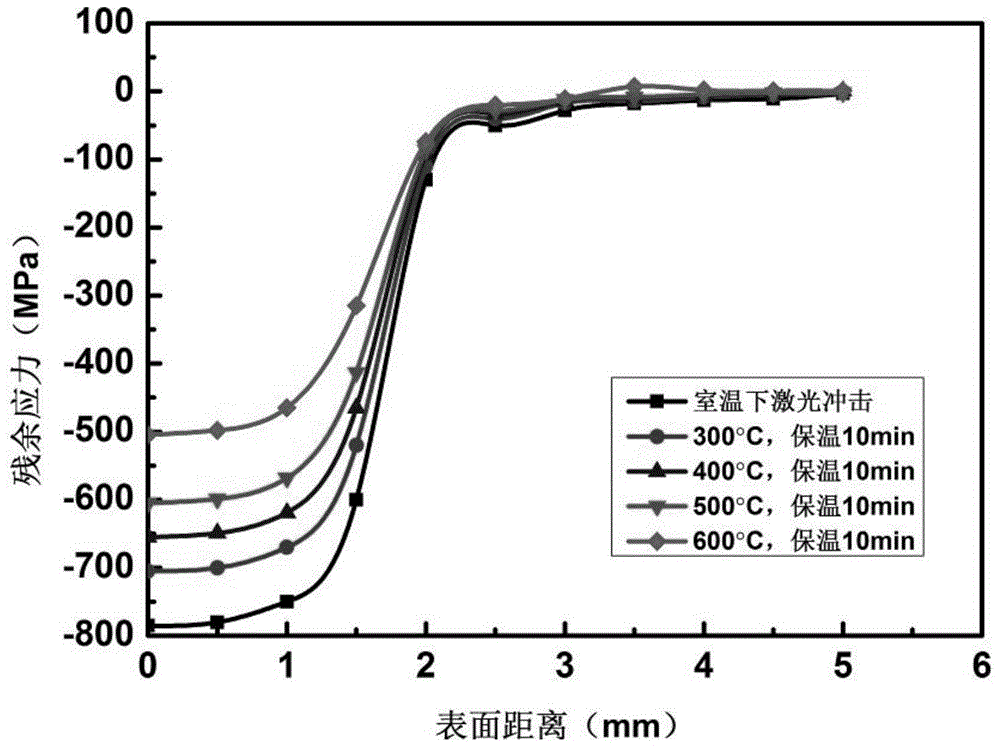
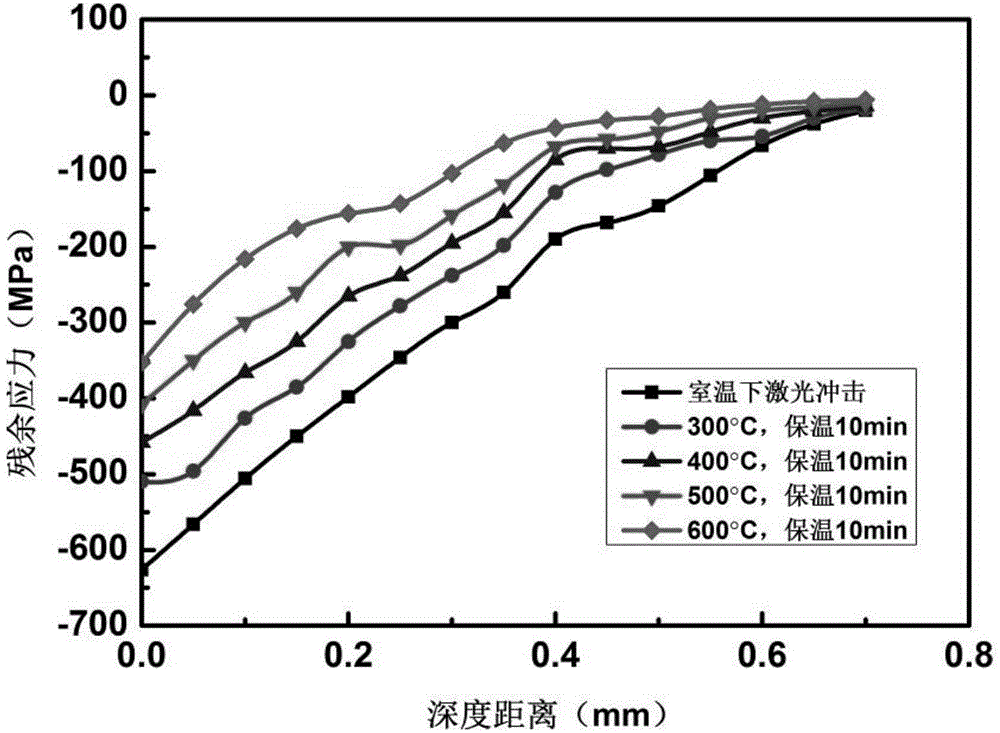
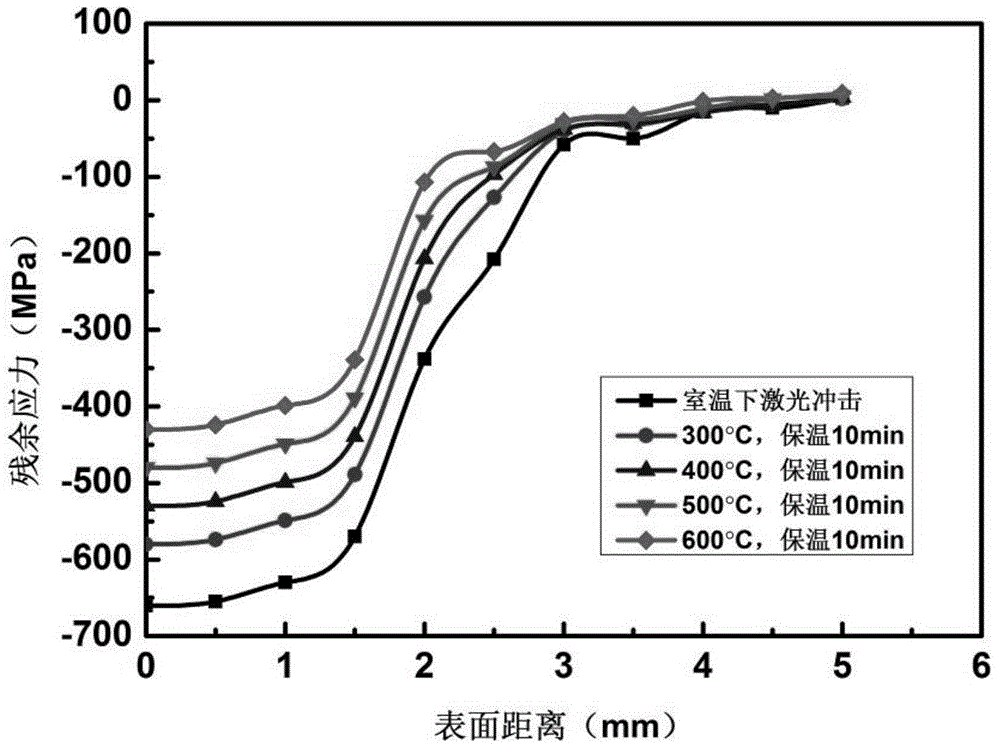
InactiveCN104833786ASimple and fast operationImprove detection efficiencyTesting metalsEnvironmental resistanceElement model
The invention provides a detection method of hot shear cutter material laser shock residual stress thermal relaxation. The detection method comprises following steps: a hot shear cutter material is cut into cuboid small pieces, and the length, width, and height of the cuboid small pieces are measured; a geometric model is constructed in simulation software ANSYS / LS_DYNA, and a finite element model is obtained via unit selection, mapped meshing, constitutive model selection, and boundary condition application; laser parameters are set, simulation of laser shock on the finite element model is carried out in a S-shaped light spot impact trajectory; surface residual stress and depth residual stress of the finite element model are measured after impact; at a same thermal holding time, temperature load of the finite element model is changed, and surface residual stress and depth residual stress of the finite element model are measured, so that residual stress thermal relaxation under different temperature load is obtained. Operation of the detection method is simple and convenient; detection efficiency is high; cost is low; the detection method is friendly to the environment; no pollution is caused; and optimum parameters can be provided for subsequent hot shear cutter impact modification.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
High strength low shrinkage polyester drawn yarn, and a process of preparing for the same
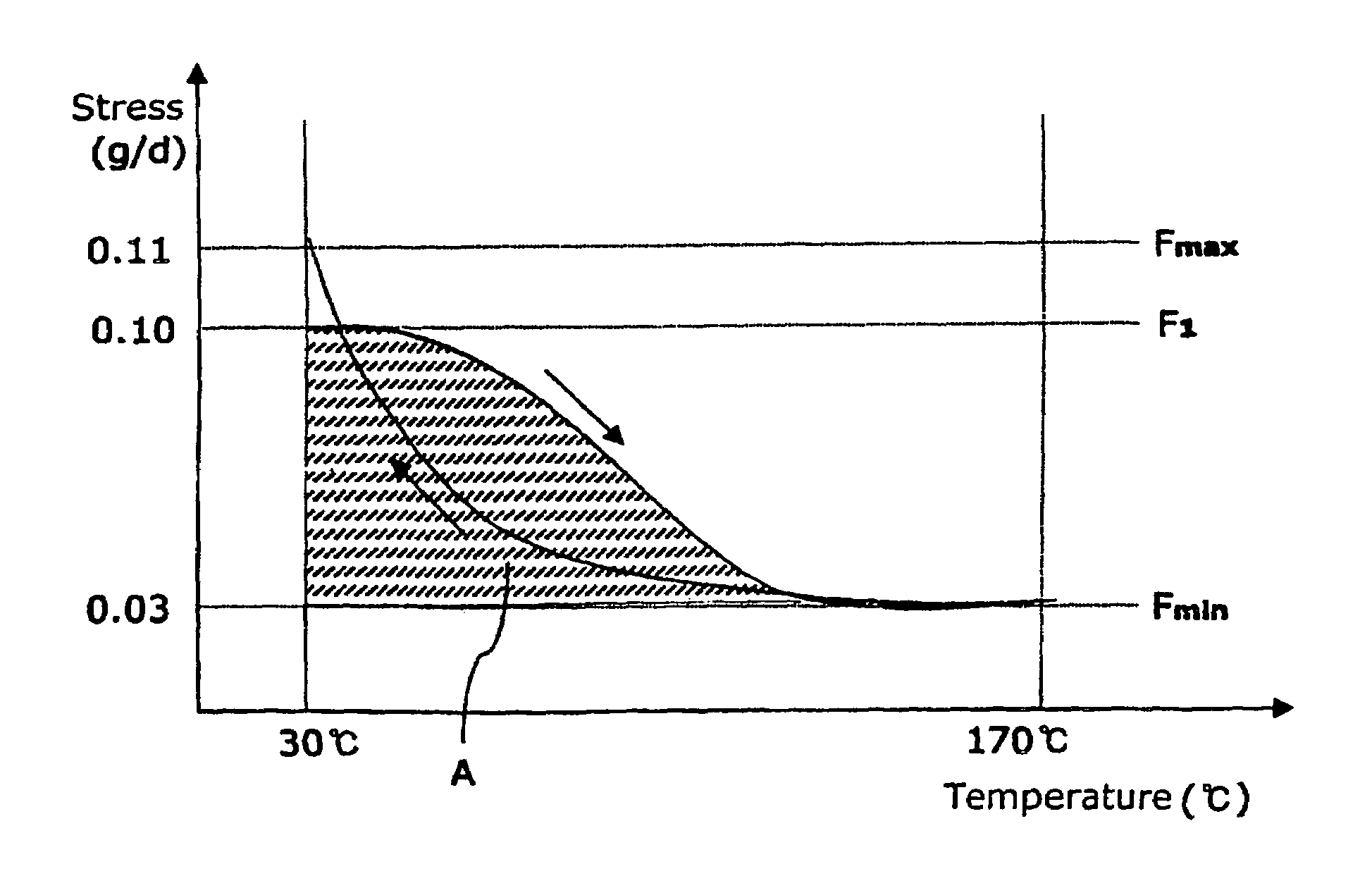
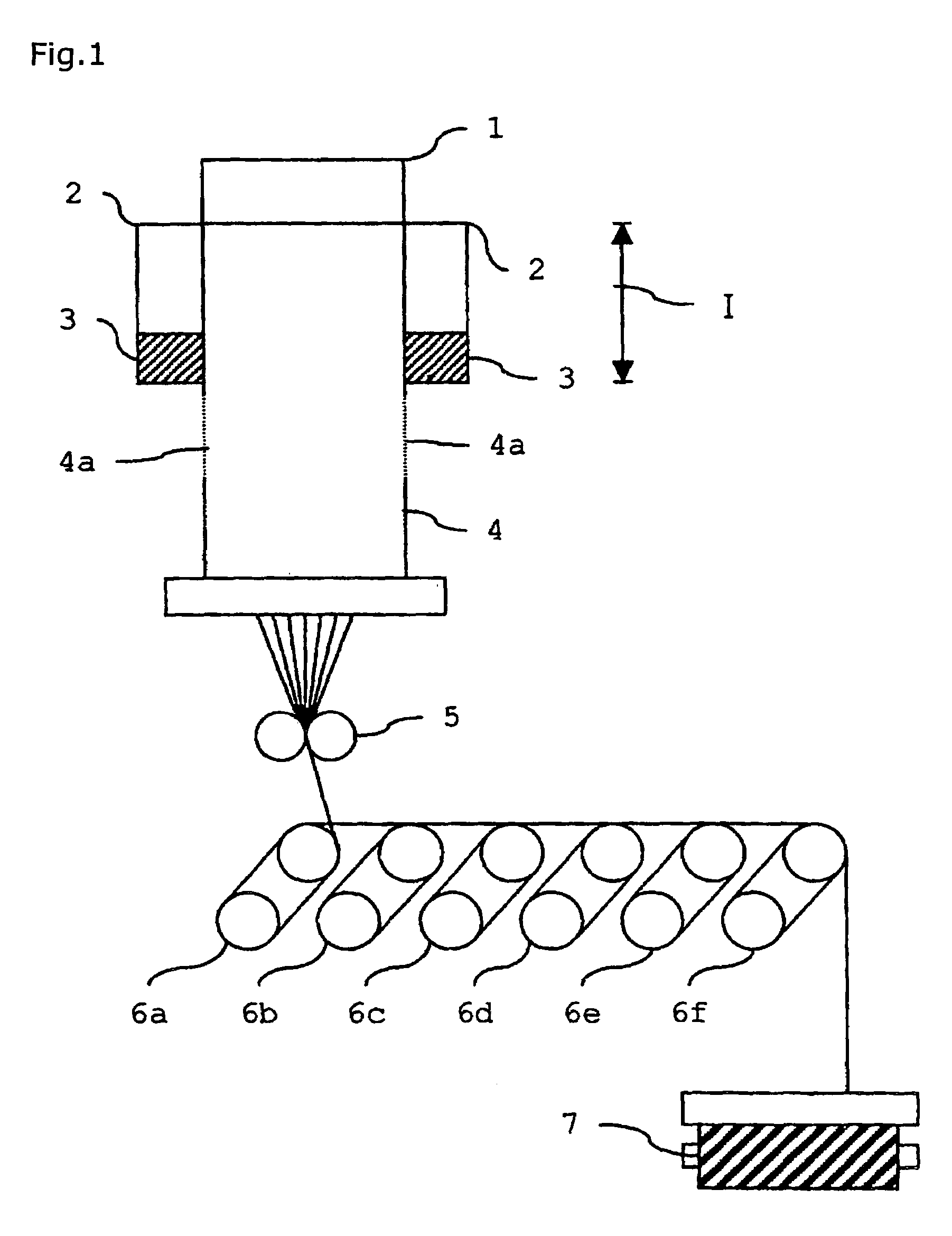
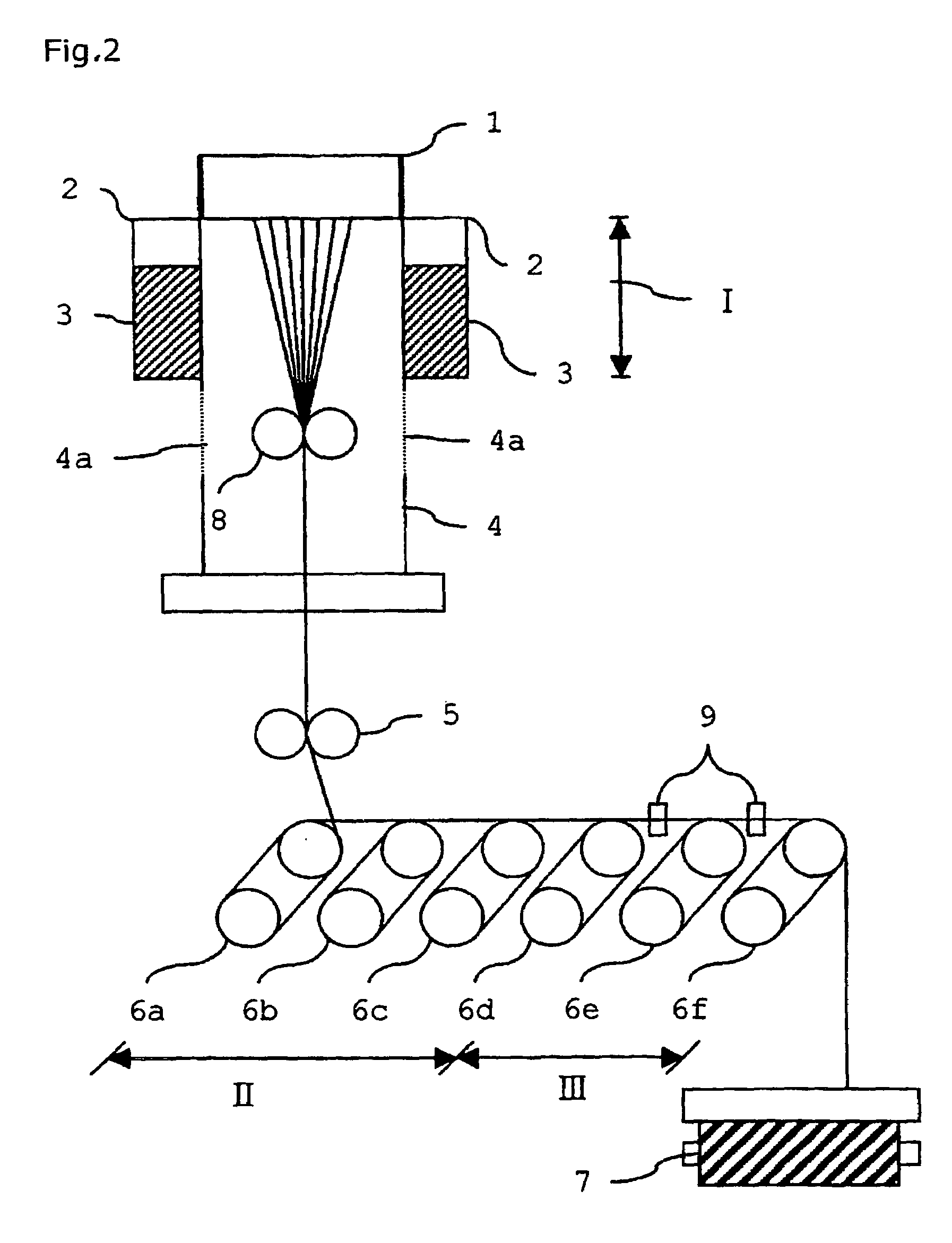
InactiveUS7198843B2Minimize form changeLow rate of changeSynthetic resin layered productsYarnYarnPolyester
The present invention discloses a high strength low shrinkage polyester drawn yarn used as industrial yarns and a process or producing the same. The strength low shrinkage polyester drawn yarn has a thermal relaxation stress change ratio of 5 to 100% and a thermal relaxation stress area ratio of 50 to 140% on a thermal relaxation and shrinkage stress curve with a final temperature set to 170% C. The process for producing a high strength low shrinkage polyester drawn yam by a direct spin draw (DSD) process in which a quenching delay region I is mounted, wherein the high strength low shrinkage polyester drawn yarn is produced in such methods that a spinning oil is attached to the yarn being spun with an oiling apparatus 8 mounted at the position 500 to 1,500 mm below from the lower bottom surface of the insulating board 3, the relaxation stress of the yarn is controlled with one or tow tension guides 9 mounted between Godet rollers of a relaxation region III, or both oiling apparatus 8 and tension guides 9 are mounted.
Owner:KOLON IND INC
Directly-pumping self-stimulated Raman scattering human eye safe waveband laser
InactiveCN101814695AImprove scattering efficiencyReduce thermal effectsLaser using scattering effectsActive medium materialStimulate raman scatteringElectron
The invention discloses a directly-pumping self-stimulated Raman scattering human eye safe waveband laser. The laser comprises a laser pumping source, a laser energy transmission fiber, a plano-convex lens collimator, a plano-convex focus lens, a cavity reflector, a laser gain medium crystal, a laser output mirror and a laser collimating lens, wherein pumping light output by the laser pumping source is transmitted to the plano-convex lens collimator through the laser energy transmission fiber; after being collimated, the pumping light is focused on the end face of the laser gain medium crystal through the plano-convex focus lens; the laser gain medium crystal absorbs the pumping light and generates stimulated radiation with a waveband of 1.3 microns; and when the radiation with the waveband of 1.3 microns surpasses a self-stimulated Raman scattering threshold value of the laser gain medium crystal, generated human eye safe waveband laser with the waveband of 1.5 microns is collimated and output by the output mirror. The laser has the advantages of enhancing self-stimulated Raman scattering conversion rate in the waveband of Nd3+1.3 microns, eliminating thermal relaxation process of electronics from a pumping energy grade to a laser energy grade in a conventional pumping mode, enhancing quantum efficiency and reducing heat.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Hot-rolled rod online EDC water bath toughening treatment method for high-strength bridge cable galvanized steel wire
ActiveCN108165716ALargest production sizeWide range of production specificationsFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesWater bathsHigh intensity
The invention relates to a hot-rolled wire rod online EDC water bath toughening treatment method for a high-strength bridge cable galvanized steel wire. After rolled materials are rolled through high-speed wire rods, and after spinning, the wire rods are subjected to linear thermal relaxation, and EDC water bath toughening heat treatment and on-line heat collection and heat preservation are carried out; the thermal relaxation temperature is 820 DEG C-880 DEG C, and the thermal relaxation time is 10s-60s; after water bath cooling is carried out on the wire rods after online wire heat relaxation, the water bath temperature is 93 DEG C-100 DEG C, and the water bath cooling time is 30s-90s; the temperature of the water outlet of the wire rods after being cooled through EDC water bath is controlled to be 520 DEG-600 DEG C; and after water is discharged from the wire rods, heat collection is carried out, the heat collection temperature is 200 DEG C-400 DEG C, and the heat collection and heatpreservation time is 30min-2h. The hot-rolled wire rod online EDC water bath toughening treatment method is suitable for producing the wire rods with the diameter of phi 12.0mm-phi 16.0mm for the bridge cable galvanized steel wires, the specification range of the wire rods is wider, the diameter of the wire rods is larger, the tensile strength of the galvanized steel wires for a bridge cable by the wire rods is larger than or equal to 1960MPa, the number of twisting times is larger than or equal to 15 times, and the cable galvanized steel wire with the performance fills the domestic production blank.
Owner:JIANGYIN XINGCHENG GOLD MATERIALS CO LTD
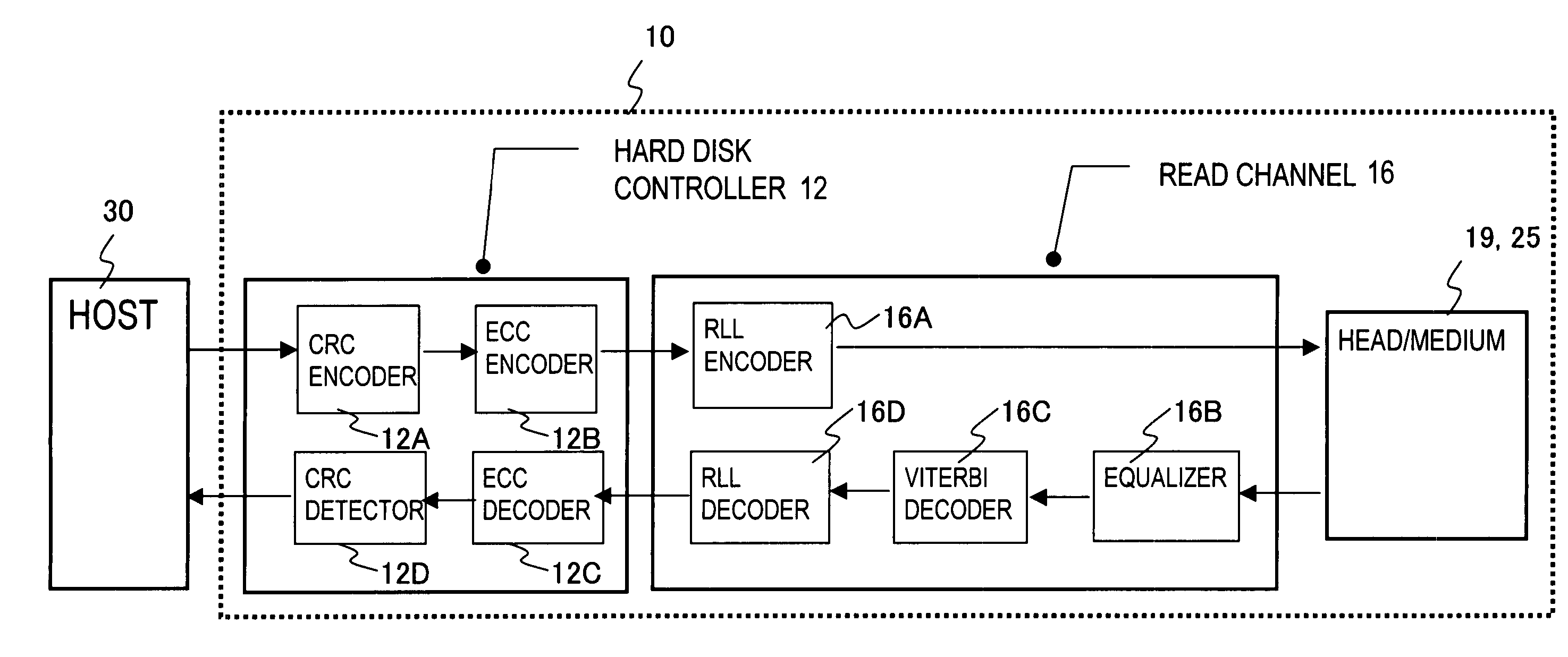
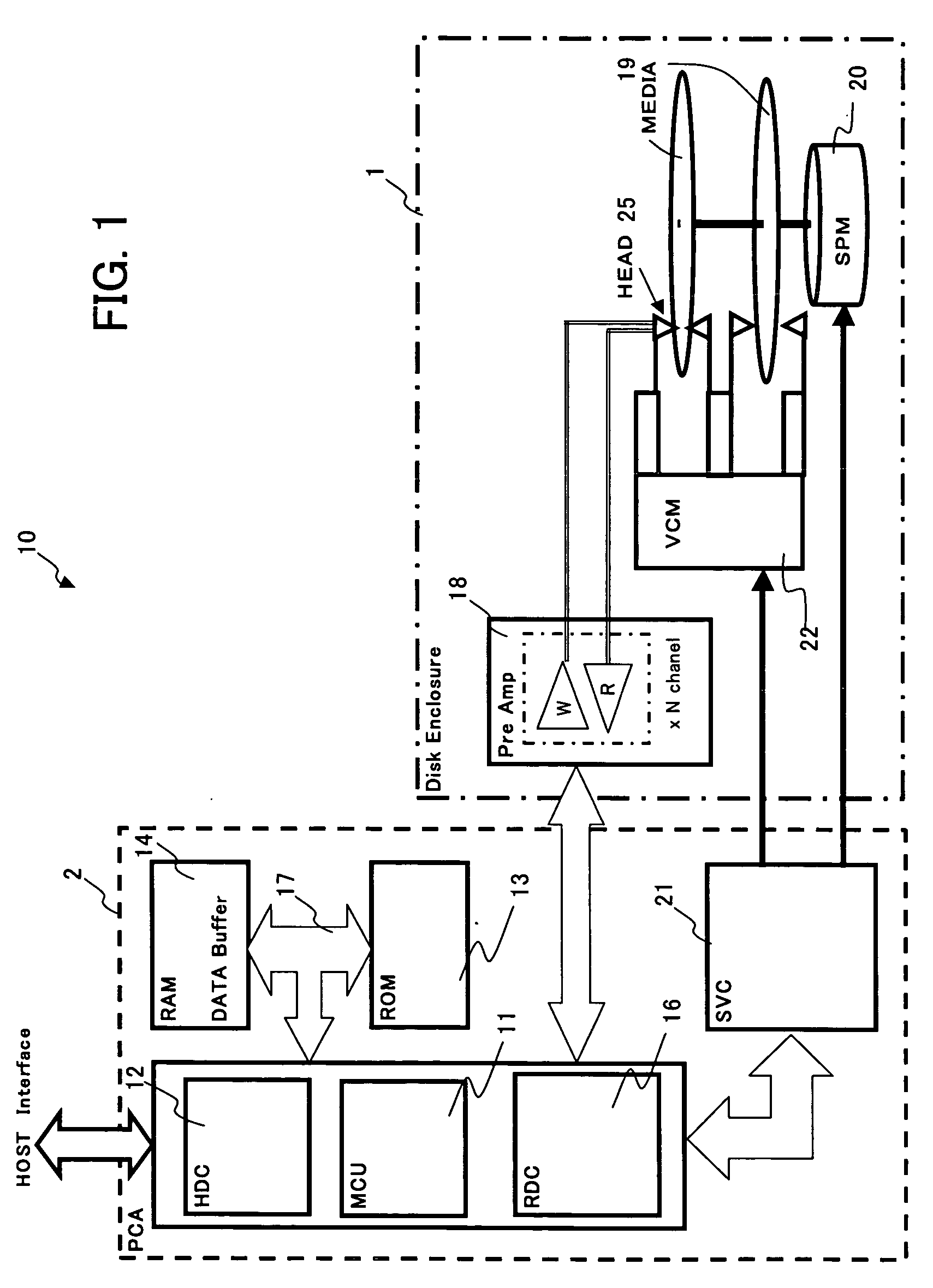
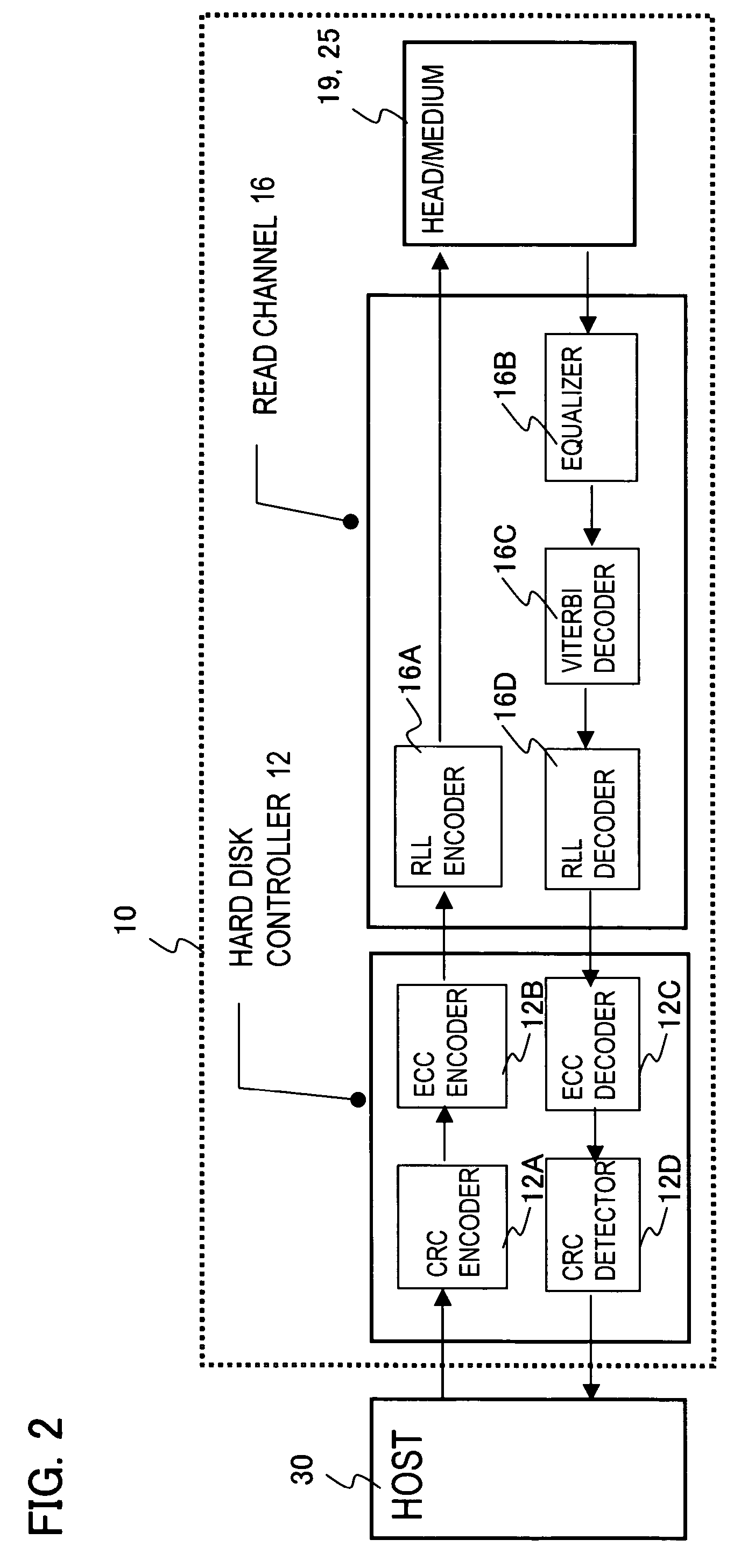
Data loss prevention method of a media storage device and media storage device
ActiveUS20070041118A1Accurate detectionSmall recording areaRecord information storageCarrier monitoringComputer hardwareData loss
A media storage device reads and writes data from and to a storage medium using a head and prevents in advance data loss due to thermal relaxation of data recorded on the storage medium. Table stores information which is related to a read error detected by a channel circuit in record units. The channel circuit measures information which is related to a read error and updates the information in the table. Further, data degradation is judged by this information which is related to the read error. Degradation of recorded data due to thermal relaxation can be detected accurately, and data loss can be prevented.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
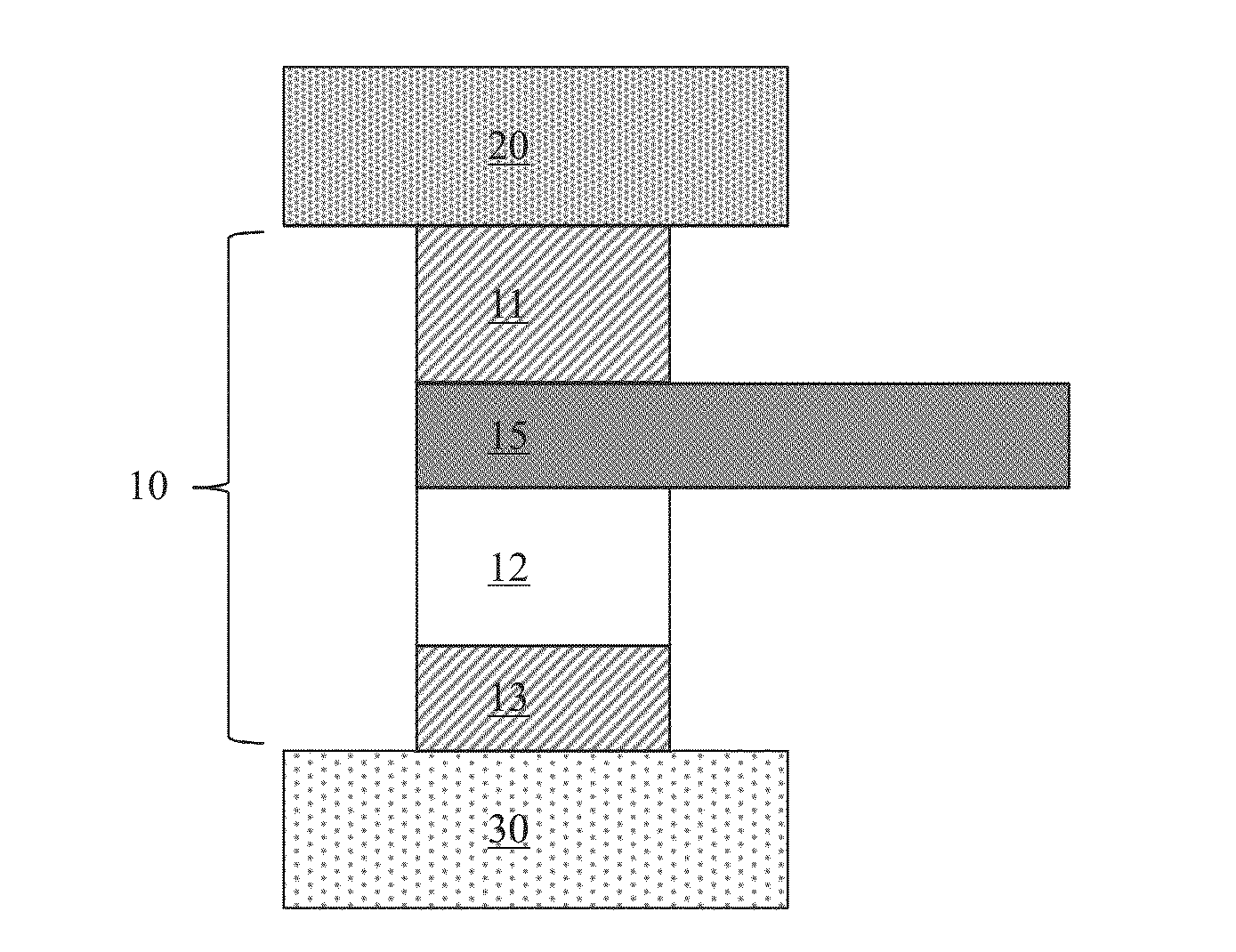
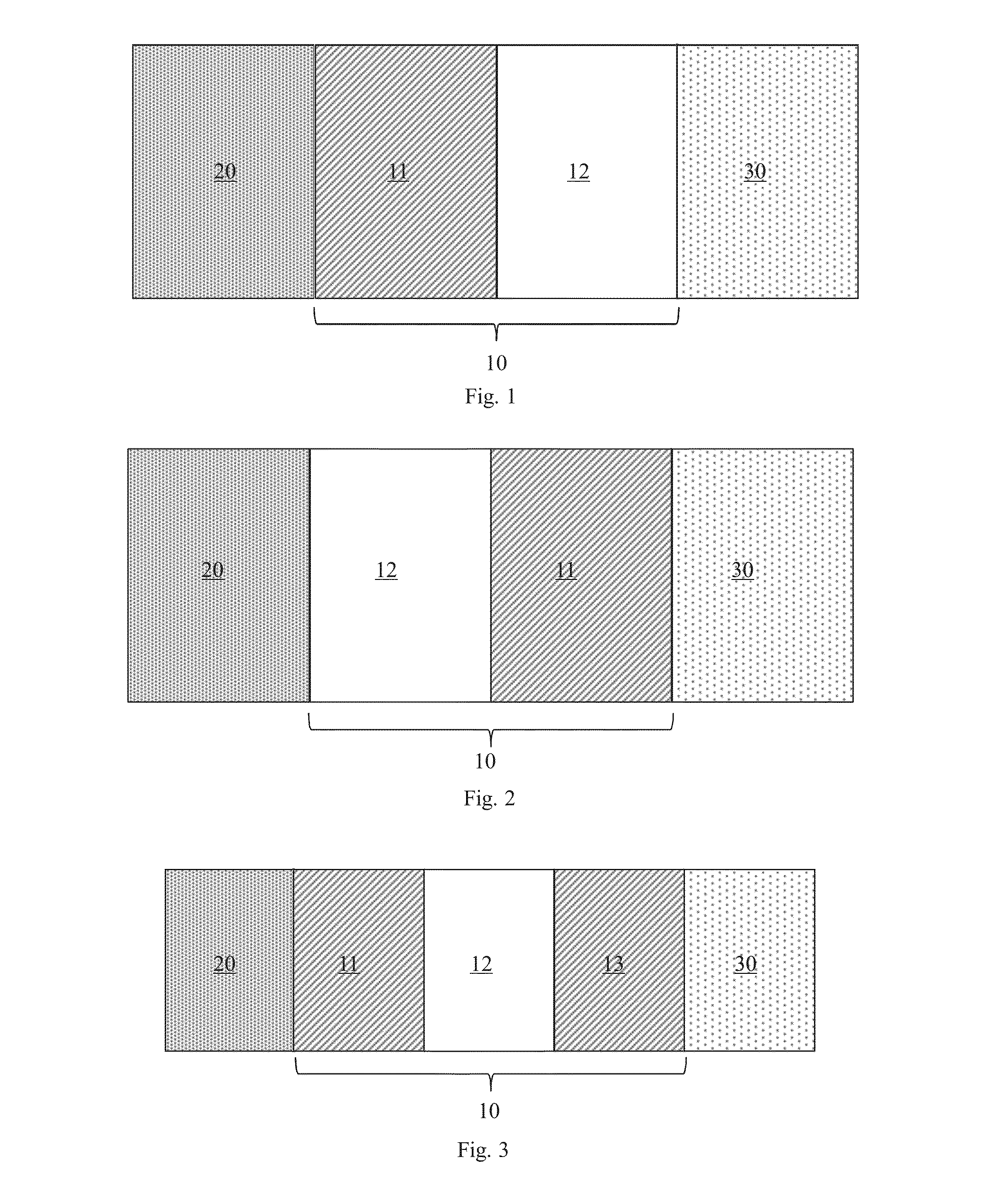
Thermal oscillator
ActiveUS9640748B2Easy to adjustControl DimensionsThermoelectric device with dielectric constant thermal changeThermoelectric deivce with magnetic permeability thermal changeThermodynamicsHeat flux
A thermal oscillator (10) for creating an oscillating heat flux from a stationary spatial thermal gradient between a warm reservoir (20) and a cold reservoir (30) is provided. The thermal oscillator (10) includes a thermal conductor (11) which is connectable to the warm reservoir (20) or to the cold reservoir (30) and configured to conduct a heat flux from the warm reservoir (20) towards the cold reservoir (30), and a thermal switch (12) coupled to the thermal conductor (11) for receiving the heat flux and having a certain difference between two states (S1, S2) of thermal conductance for providing thermal relaxation oscillations such that the oscillating heat flux is created from the received heat flux.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Segmented copolymer thermoplastic dielectric elastomer thin membrane and dielectric driver of thin membrane
The invention discloses a segmented copolymer thermoplastic dielectric elastomer thin membrane and a dielectric driver of the thin membrane. According to the segmented copolymer thermoplastic dielectric elastomer thin membrane and the dielectric driver of the thin membrane, the segmented copolymer thermoplastic dielectric elastomer thin membrane is subjected to a prestretching thermal relaxation technology, and a thinner self-supporting dielectric elastomer without fixing by a frame can be obtained; the driving performance of the dielectric elastomer is also improved, the driving voltage of the dielectric elastomer is lowered, the breakdown field strength of the dielectric elastomer is improved, and the area deformation of the dielectric elastomer is improved. In addition, through asymmetric prestretching thermal relaxation treatment, the dielectric elastomer with anisotropic mechanical properties can be obtained and can be used for drivers with anisotropic driving performance under frameless driving, and important significance is achieved on manufacturing of anisotropic flexible drivers and flexible robots by adopting the dielectric elastomer.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
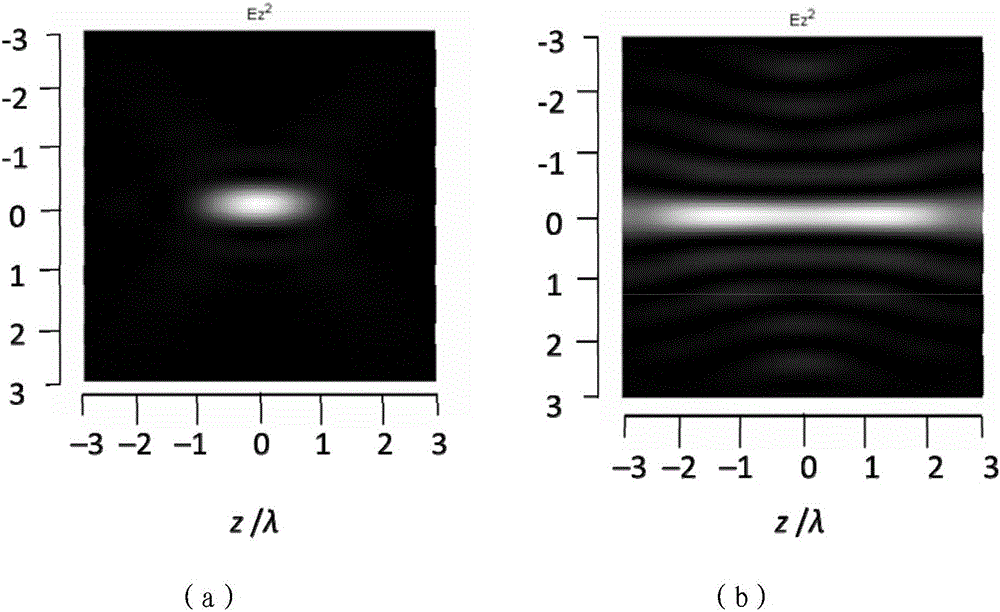
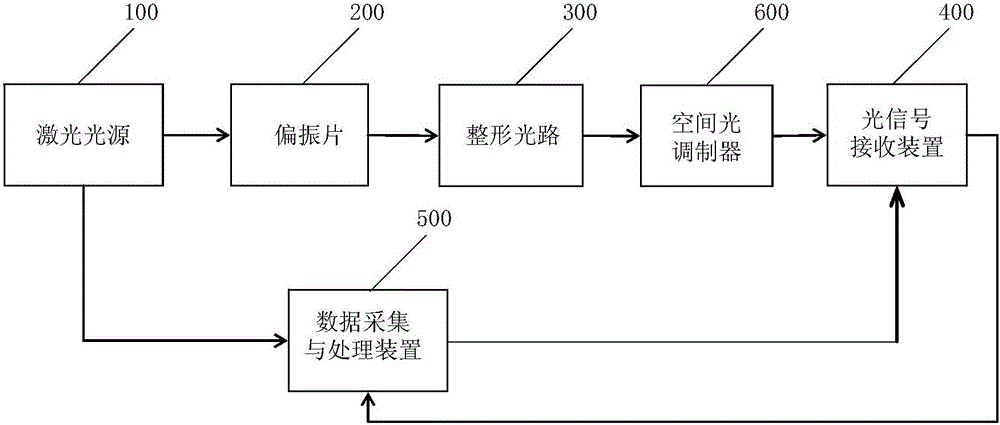
Photoacoustic microscope system
InactiveCN106066306ATake advantage ofSolve the problem of luminous flux lossMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotoacoustic microscopySpatial light modulator
The invention discloses a photoacoustic microscope system. Pulse laser is emitted through a laser source, the pulse laser goes through a polarizing film and then forms linearly polarized light, the linearly polarized light is subjected to collimation and beam expanding under the action of a shaping light path and then is emitted to the surface of a spatial light modulator, the modulated pulse light irradiates tissue, a photoacoustic signal reception device located at the other end of the tissue receives a photoacoustic signal and transforms the acoustic signal into an electric signal, a data acquisition and processing device acquires the electric signal and stores the data and a 3D image and a cross section image of the tissue are obtained through 3D reconstruction. The spatial light modulator is used in the light path so that optical focal depth is substantially increased and large-focal depth and high-resolution photoacoustic imaging is realized. The photoacoustic microscope system is free of an axicon for producing Bessel light beams, solves the problem of an axicon luminous flux loss, is free of two laser irradiation processes at a short time interval for Bessel light beam sidelobe influence elimination, simplifies experiment device design and part costs and prevents high energy thermal relaxation effect-caused damage to biological tissue.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Thermal oscillator
ActiveUS20160112050A1Easy to adjustControl DimensionsThermoelectric device with dielectric constant thermal changeRadiation pyrometryElectrical conductorHeat flux
A thermal oscillator (10) for creating an oscillating heat flux from a stationary spatial thermal gradient between a warm reservoir (20) and a cold reservoir (30) is provided. The thermal oscillator (10) includes a thermal conductor (11) which is connectable to the warm reservoir (20) or to the cold reservoir (30) and configured to conduct a heat flux from the warm reservoir (20) towards the cold reservoir (30), and a thermal switch (12) coupled to the thermal conductor (11) for receiving the heat flux and having a certain difference between two states (S1, S2) of thermal conductance for providing thermal relaxation oscillations such that the oscillating heat flux is created from the received heat flux.
Owner:IBM CORP
Data loss prevention method of a media storage device and media storage device
ActiveUS7643237B2Improve accuracyAvoid data lossRecord information storageCarrier monitoringComputer hardwareSignal quality
A media storage device which reads and writes data from and to a storage medium using a head prevents in advance data loss due to thermal relaxation of data recorded on the storage medium. Management information is created, in units of received write commands, for holding the recording areas on the storage medium of the write data and signal quality information; the management data is stored in a management table, and signal quality is measured, updated, and used in re-recording judgements, in write command units. Thermal relaxation state management can be performed in write command units; thermal relaxation processing is simple, and moreover degradation of recorded data due to thermal relaxation can be detected accurately, and data loss can be prevented.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
High strength low shrinkage polyester drawn yarn, and a process of preparing for the same
InactiveUS20060145391A1High ratio drawingReduce maintenanceSynthetic resin layered productsCeramic shaping apparatusPolyesterYarn
The present invention discloses a high strength low shrinkage polyester drawn yarn used as industrial yarns and a process or producing the same. The strength low shrinkage polyester drawn yarn has a thermal relaxation stress change ratio of 5 to 100% and a thermal relaxation stress area ratio of 50 to 140% on a thermal relaxation and shrinkage stress curve with a final temperature set to 170% C. The process for producing a high strength low shrinkage polyester drawn yam by a direct spin draw (DSD) process in which a quenching delay region I is mounted, wherein the high strength low shrinkage polyester drawn yarn is produced in such methods that a spinning oil is attached to the yarn being spun with an oiling apparatus 8 mounted at the position 500 to 1,500 mm below from the lower bottom surface of the insulating board 3, the relaxation stress of the yarn is controlled with one or tow tension guides 9 mounted between Godet rollers of a relaxation region III, or both oiling apparatus 8 and tension guides 9 are mounted.
Owner:KOLON IND INC
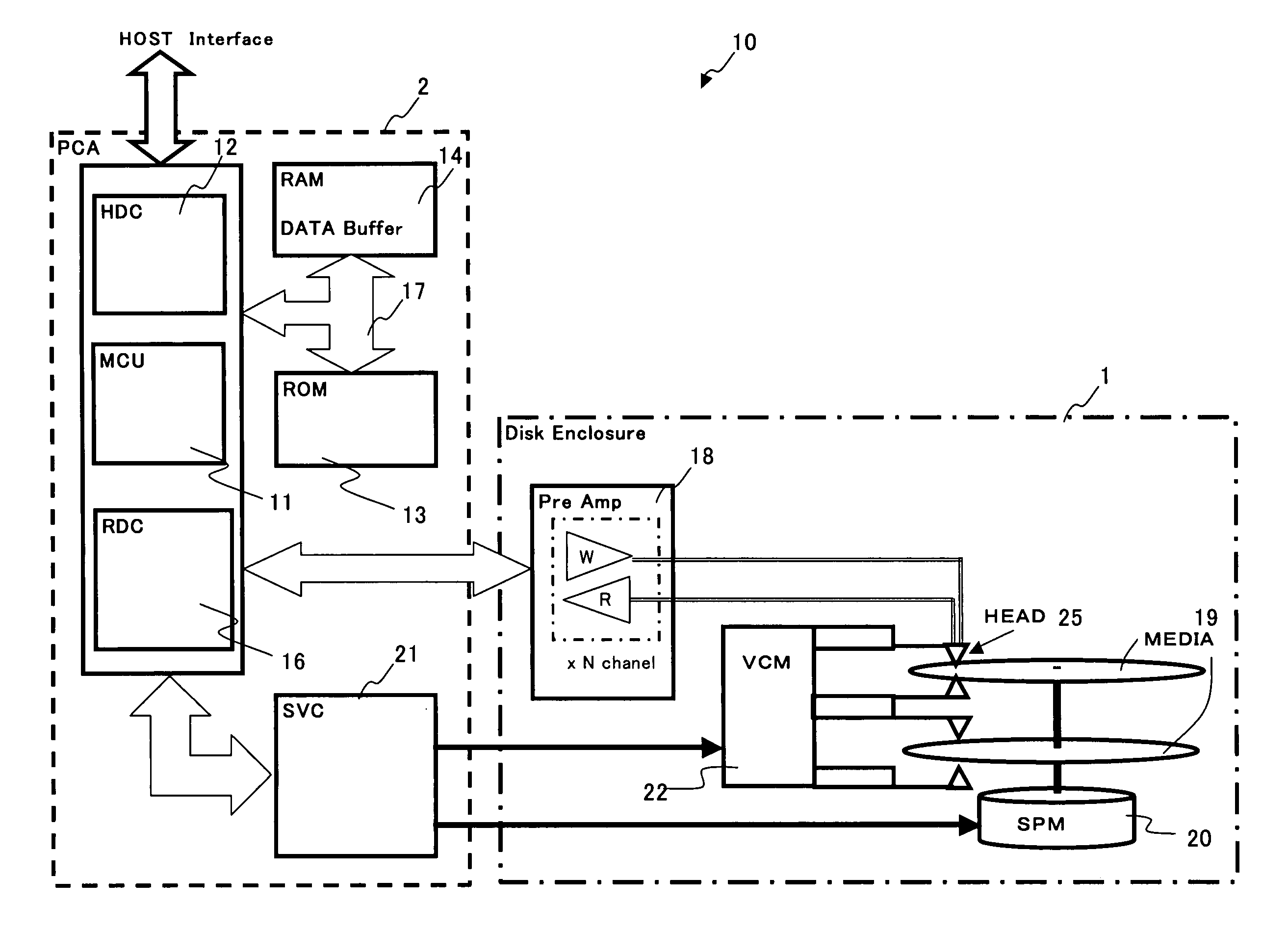
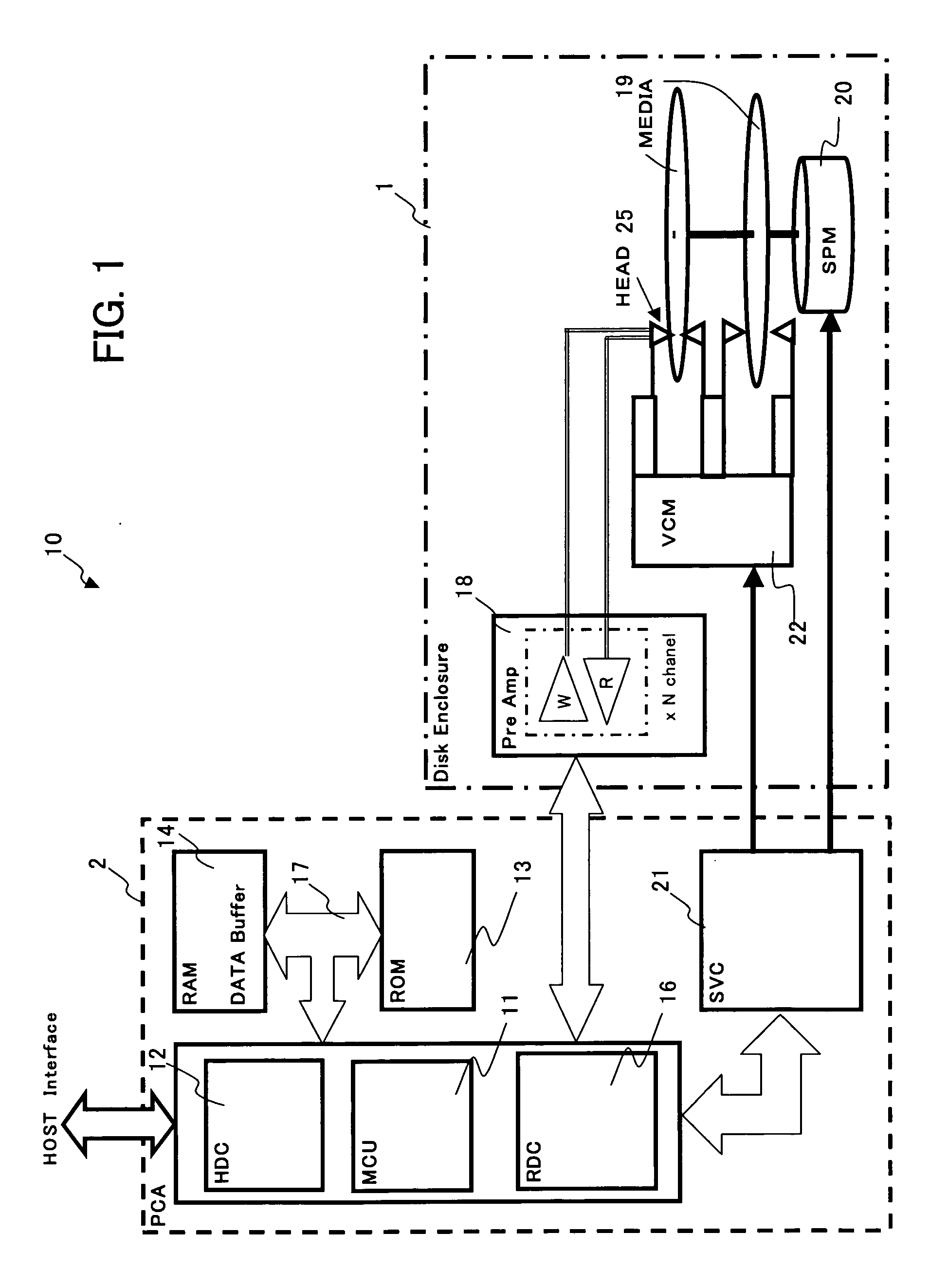
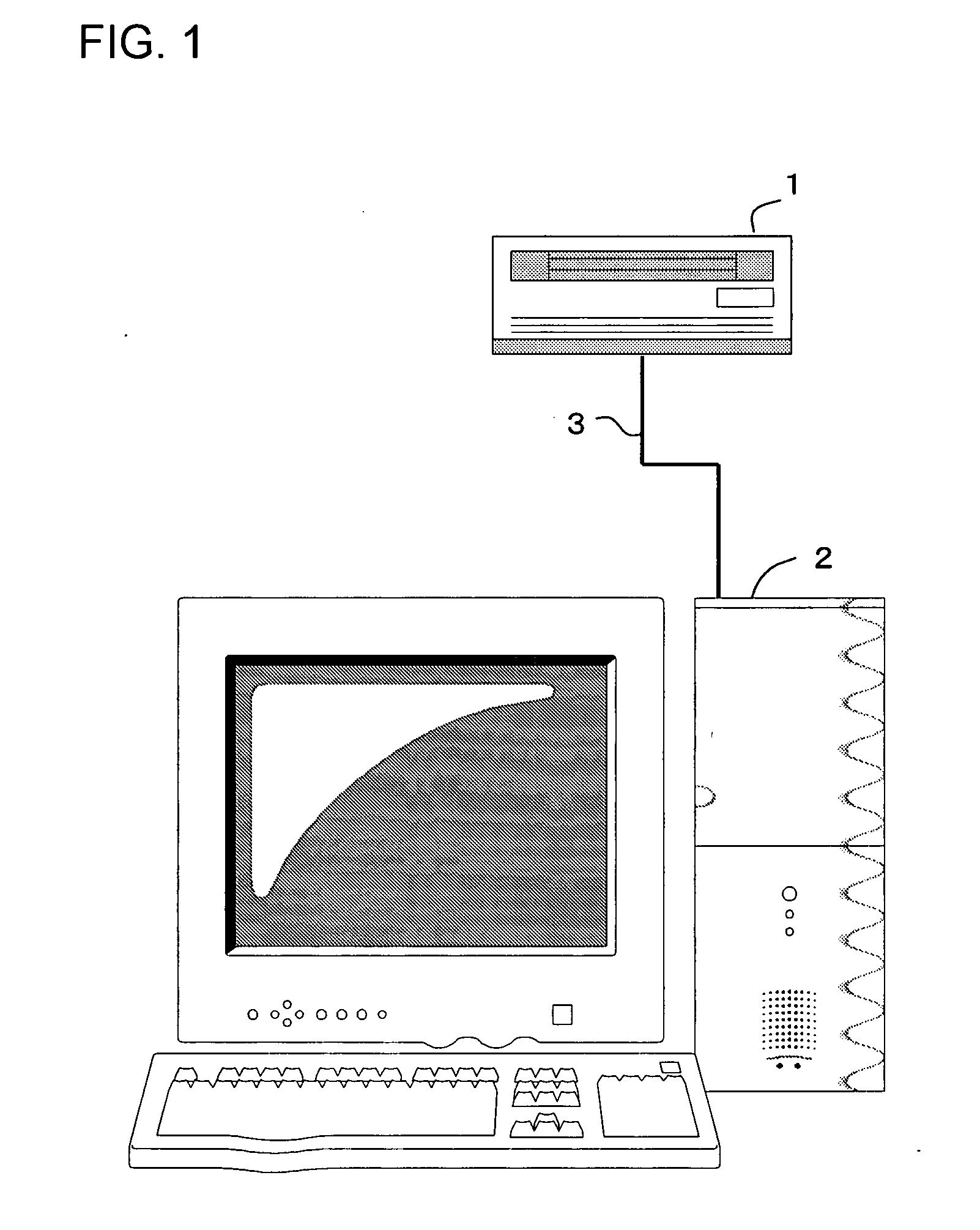
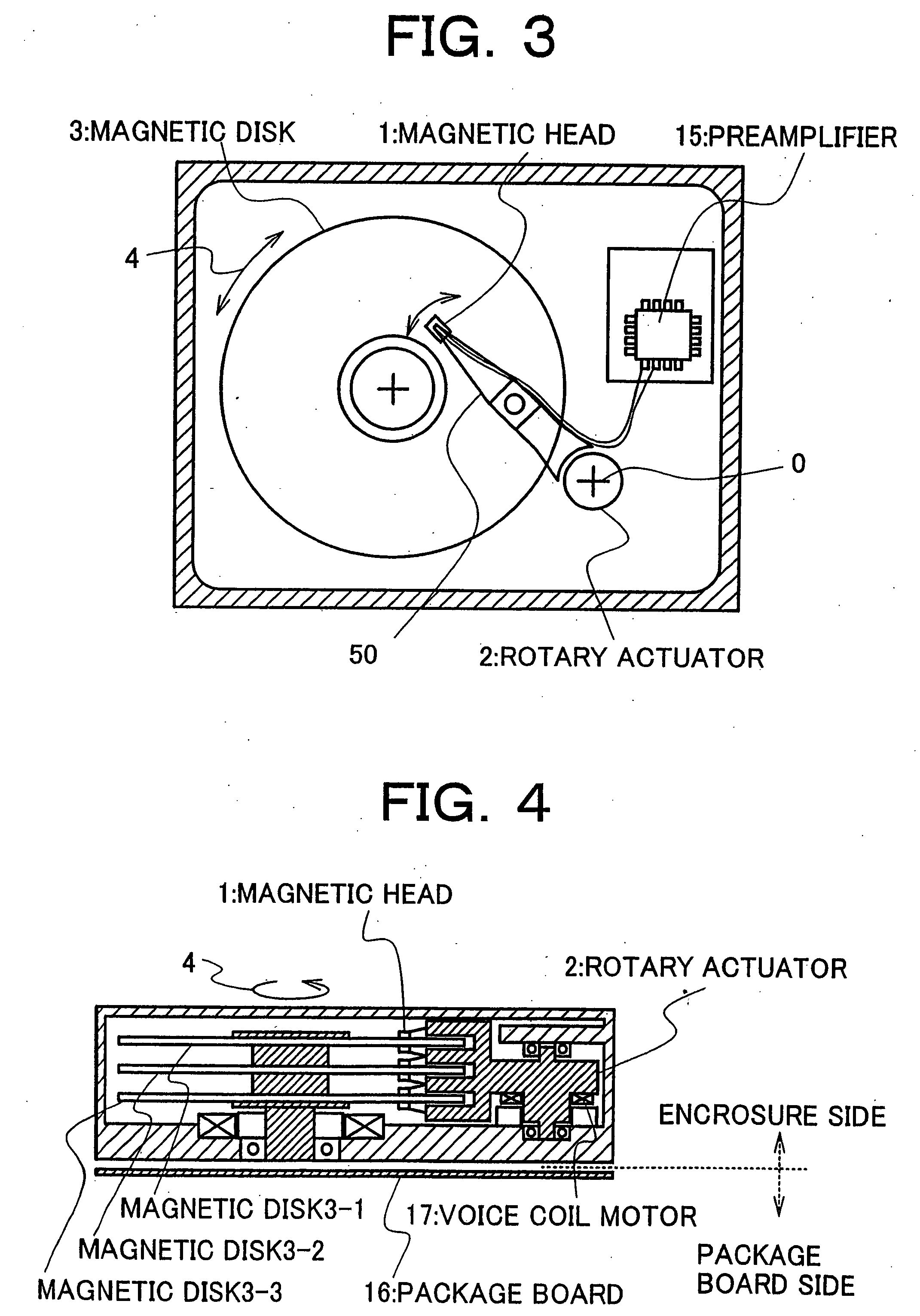
Magnetic disk read/write device and method of evaluation of thermal relaxation degradation in magnetic disk read/write device
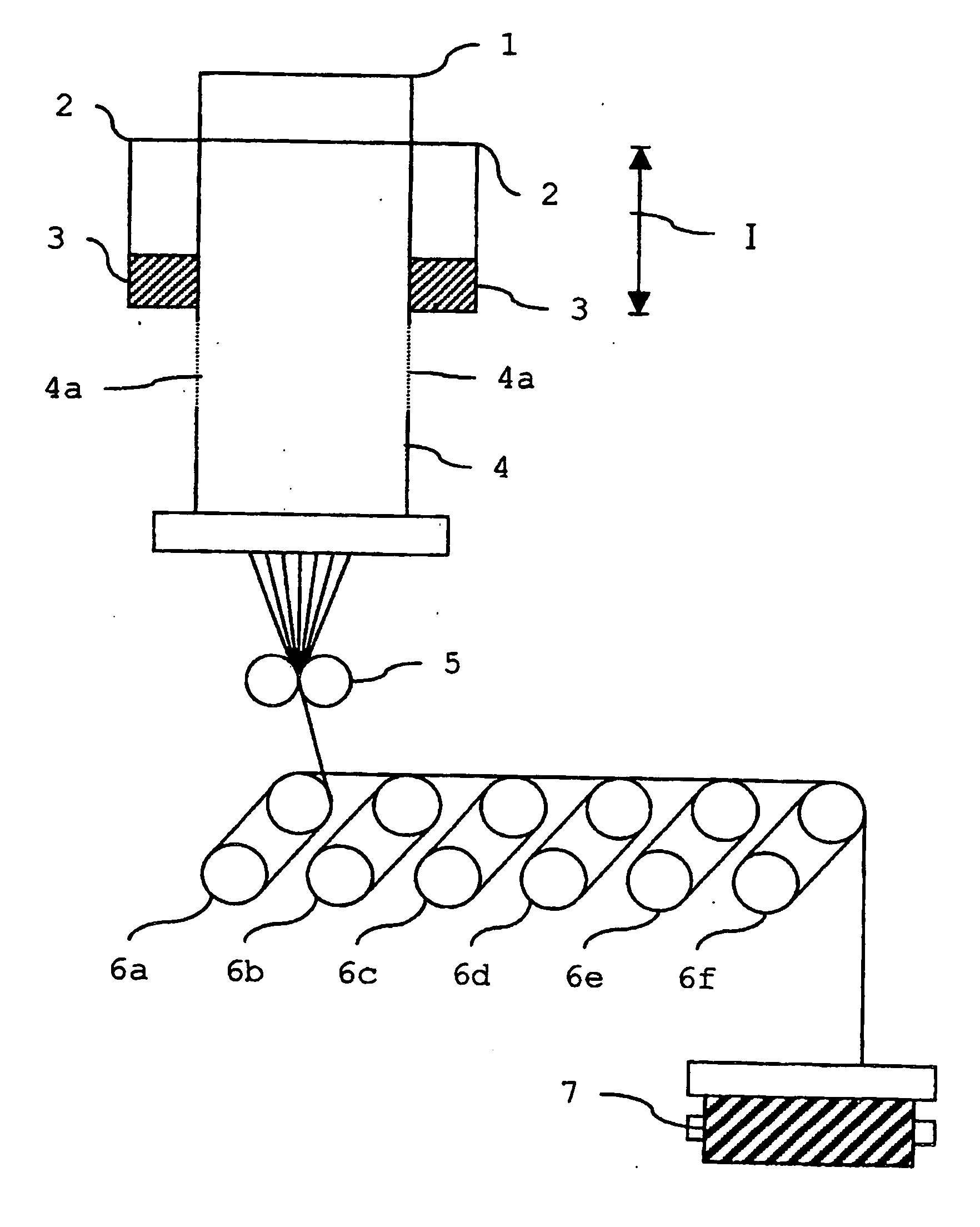
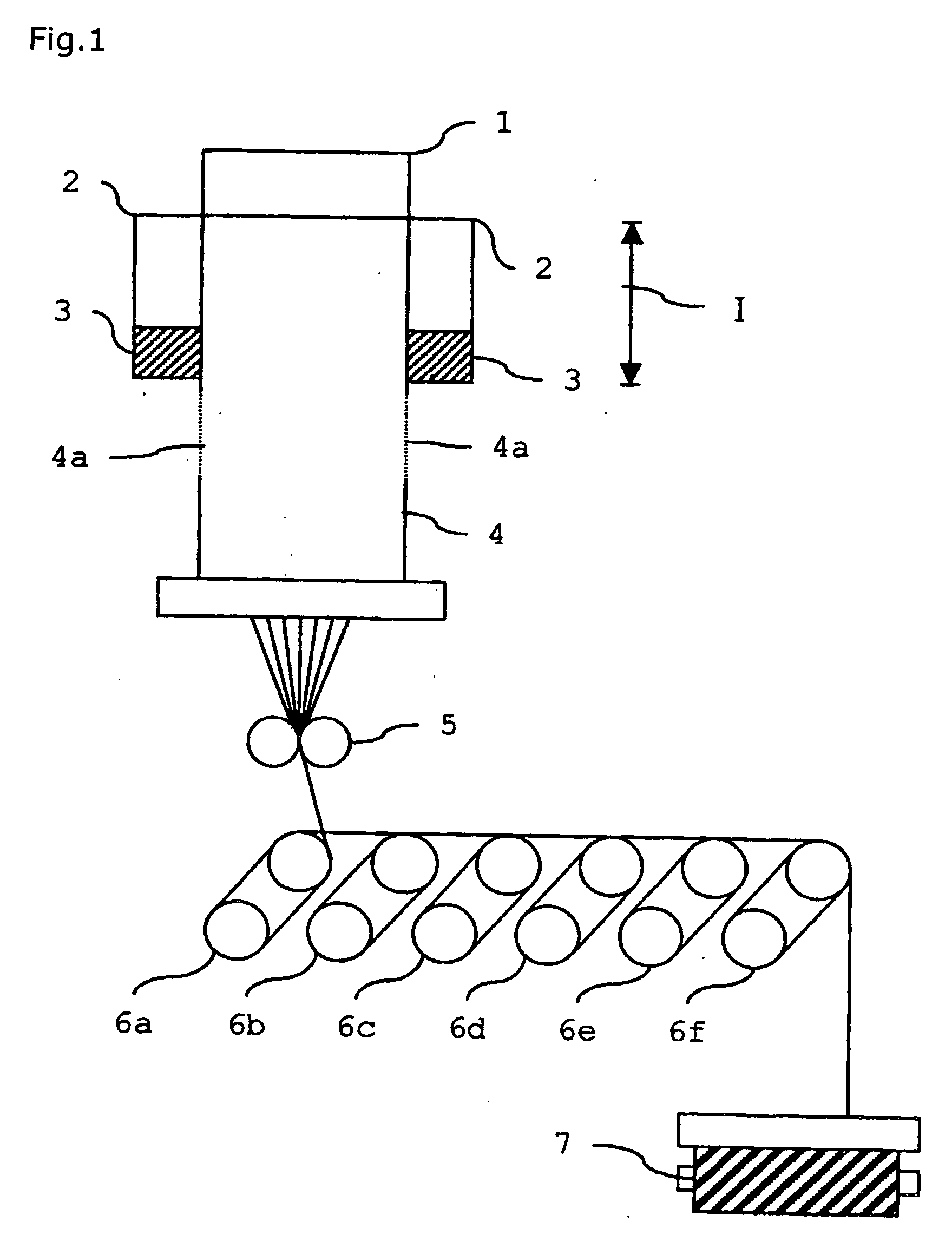
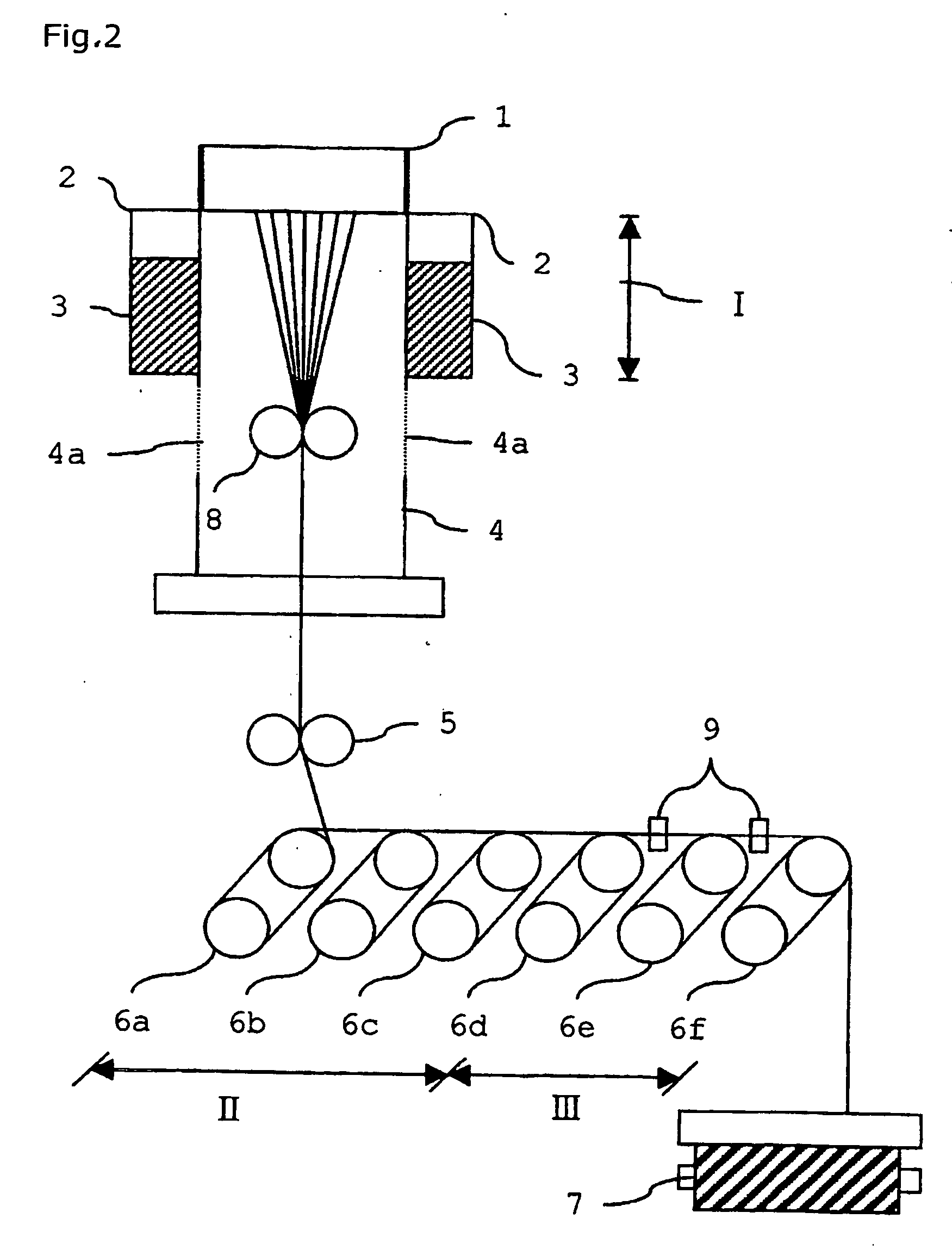
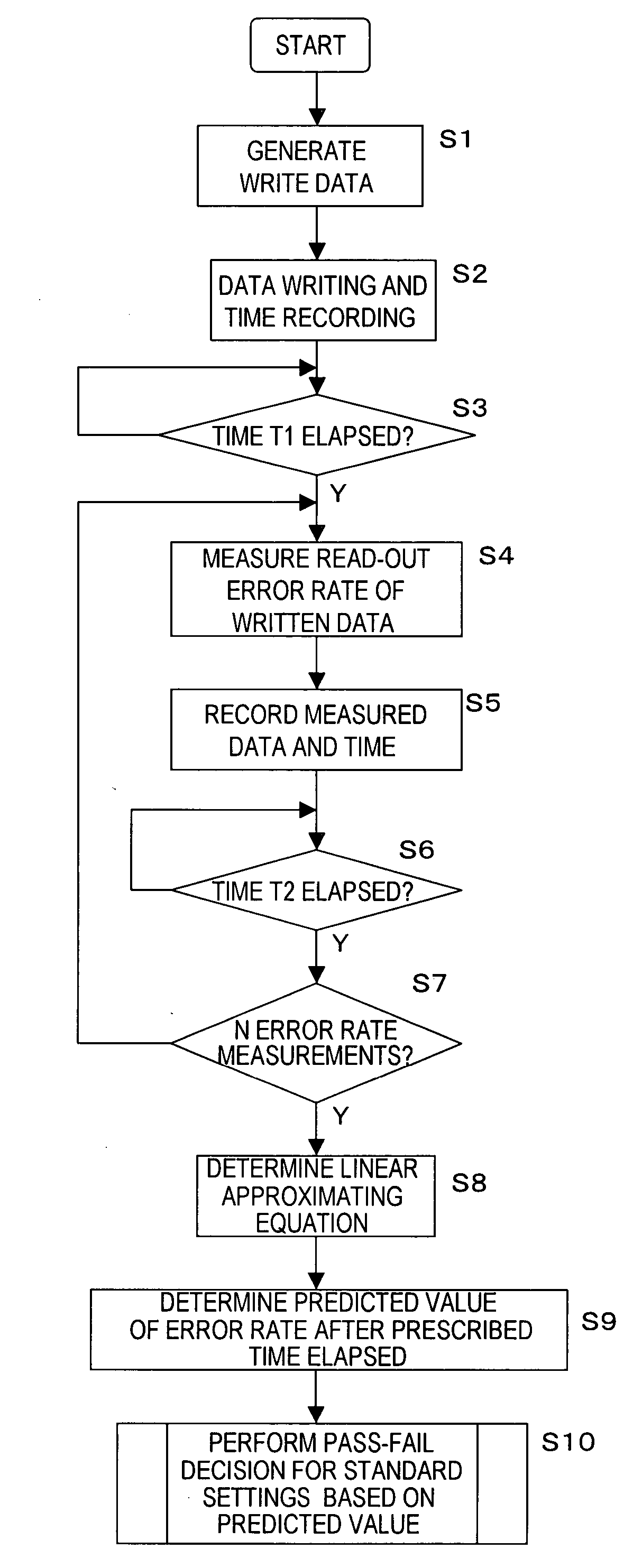
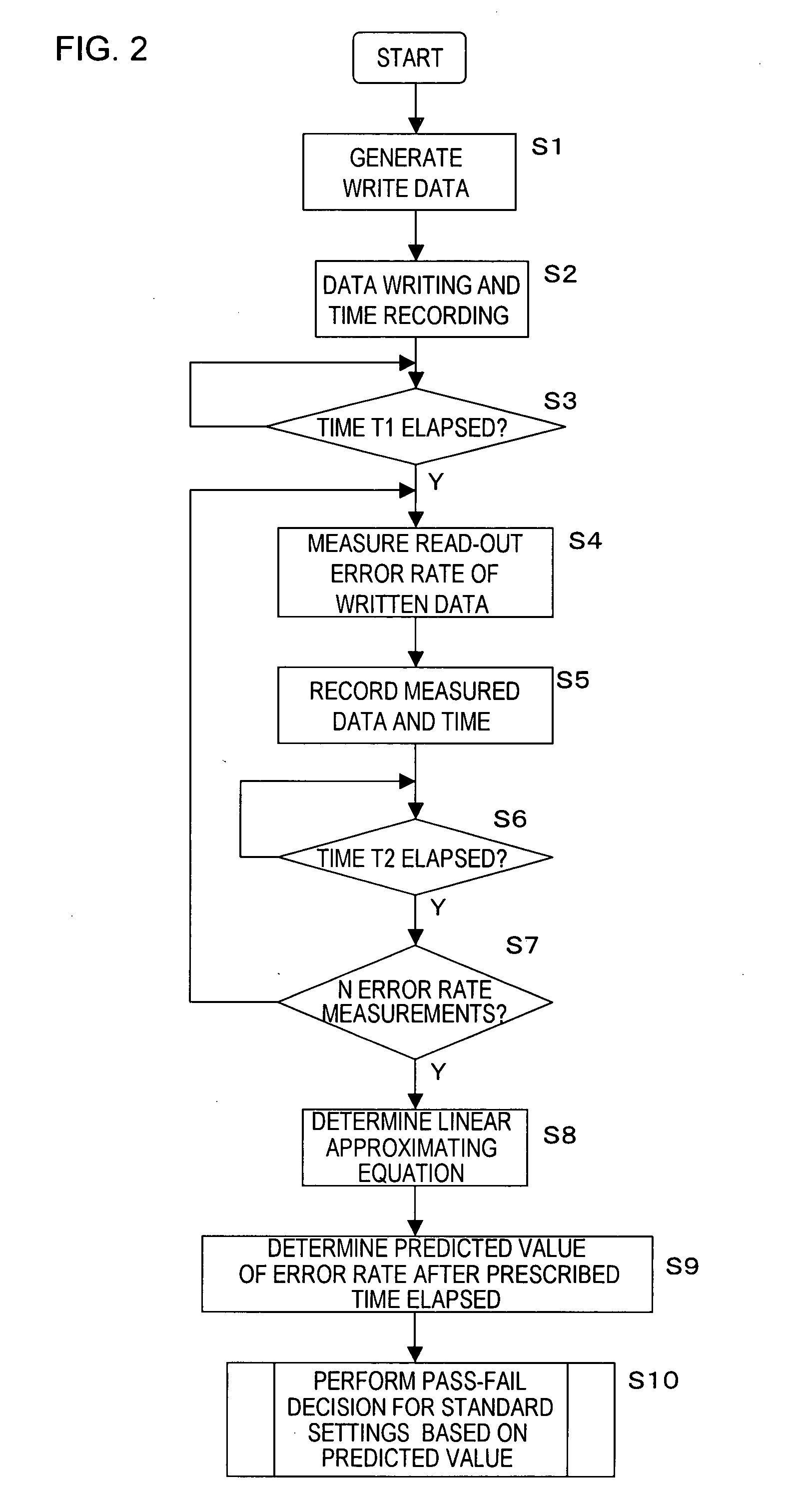
A method of evaluating thermal relaxation in magnetic recording, and a pass-fail decision method for a magnetic disk read / write device which satisfies lifetime assurance conditions, are provided. The pass-fail decision method for a magnetic disk read / write device is a method of thermal relaxation degradation in a magnetic disk read / write device comprising a magnetic disk and a head which writes to and reads out from the magnetic disk, wherein prescribed signals are written to and recorded on the magnetic disk; the written and recorded signals are repeatedly read out at fixed time intervals over a prescribed time period; the error rate is measured for each reading-out; the relation between the logarithm of the elapsed time and the measured error rate is linearly approximated; and the error rate of the magnetic disk read / write device at a time exceeding the prescribed period is evaluated.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Preparation method of PBT porous fibers
InactiveCN109234832AImprove performanceLarge specific surface areaFilament/thread formingMonocomponent polyesters artificial filamentPolymer scienceFiltration
The invention relates to a preparation method of PBT porous fibers, and belongs to the technical field of porous fibers. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing spinning grade PBT and spinning grade PP, and then drying PBT raw materials to remove moisture in the raw materials; mixing PBT and PP uniformly according to proportions and then carrying out melt blendingto prepare a blend alloy; then preparing blended nascent fibers by using a twin-screw mixing extruder; asymmetrically cooling the nascent fibers, then performing cold drawing on the nascent fibers, and carrying out thermal relaxation to obtain protofilaments; and preparing the PBT porous fibers by fully soaking the obtained protofilaments in a xylene solution, taking out the protofilaments, cleaning the protofilaments with ethanol, and drying the protofilaments. According to the preparation method provided by the invention, the performance of PBT is improved through melt blending spinning, andthen dispersed phase PP is dissolved by xylene to prepare the PBT porous fibers. The preparation process of the method is simple and the cost is low; pore structures appear on the surfaces of and inside the obtained fibers; the specific surface area of the fibers is large, the filtration resistance is small, and the adsorption capacity is high, so that the porous fibers have excellent hollow heatpreservation performance.
Owner:TAICANG RONGWEN SYNTHETIC FIBER
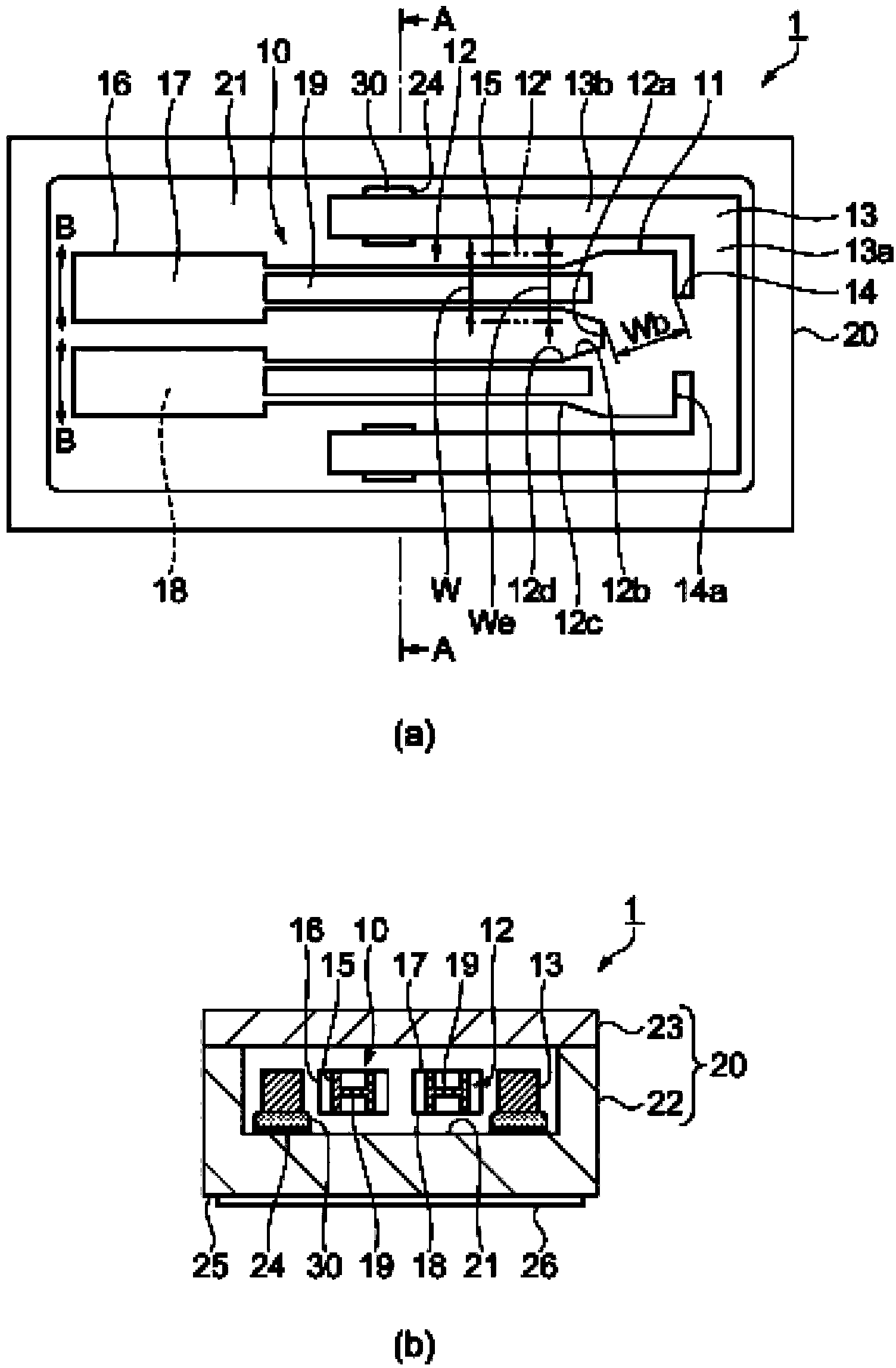
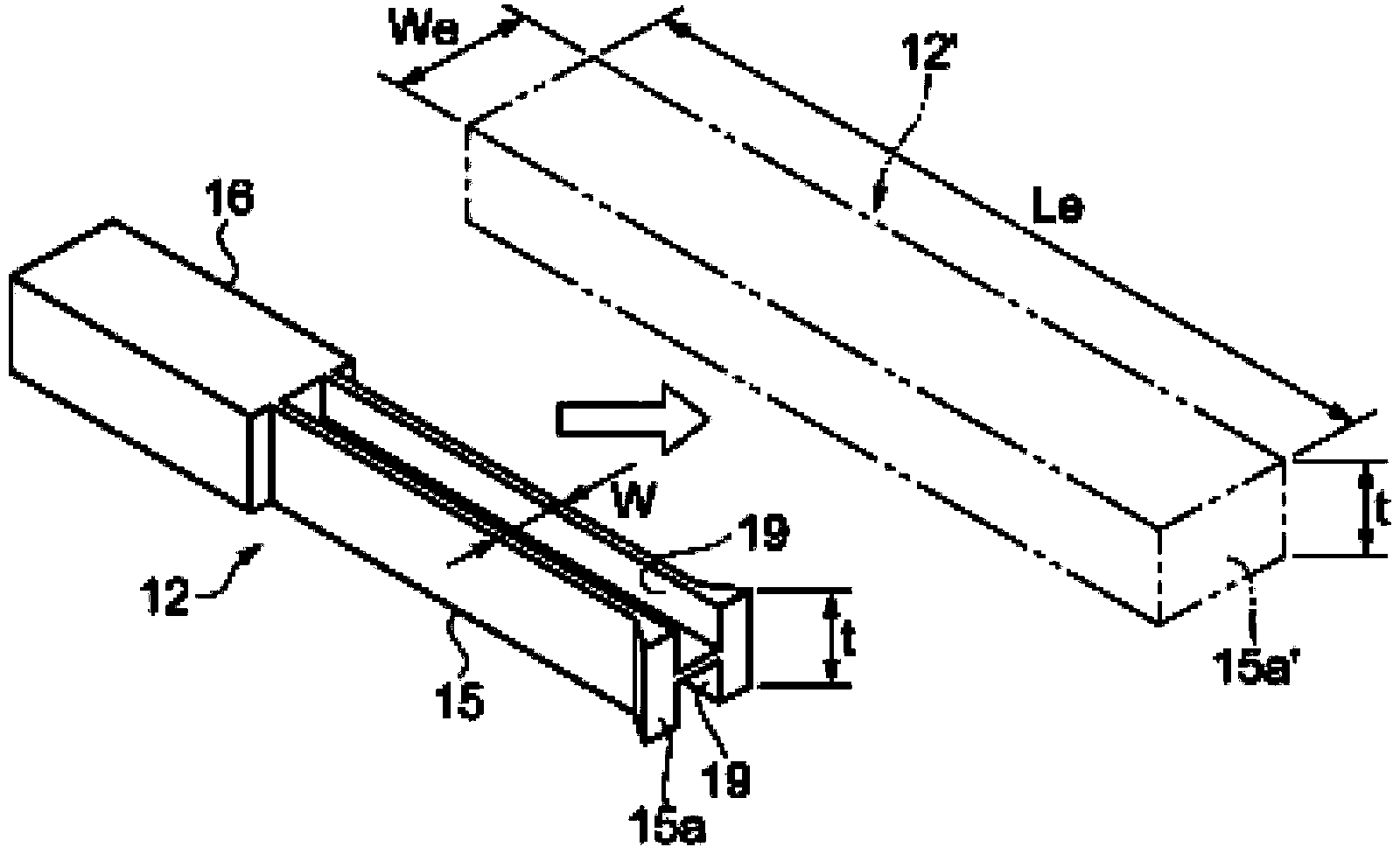
Vibrating reed, vibrator, vibration device, sensor, and electronic device
InactiveCN103731118AImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionEngineeringCrotch
The invention provides a vibrating reed, a vibrator, a vibration device, a sensor, and an electronic device. The vibrating reed includes a base having a notch between one end and the other end, a pair of vibrating arms extending from one end of the base in a first direction when in top view, and a support section connected with the other end of the base when in top view, wherein a mechanical resonant frequency f of the vibrating arms is higher than a thermal relaxation frequency f0 of the vibrating arms, and assuming that a closest approach distance between the outer edge of the notch and the outer edge of a crotch section formed between the vibrating arms is a base flexion width Wb, and an arm width of the hypothetical vibrating arm is an effective arm width We, a relationship of Wb>We is satisfied, wherein a cross-sectional shape of the hypothetical vibrating arm along a plane comprising a second direction crossing the first direction and a thickness direction of the vibrating arm is a rectangle, the mechanical resonant frequency of the hypothetical vibrating arm is equal to the mechanical resonant frequency f of the vibrating arm, the thermoelastic loss is equivalent to the thermoelastic loss of the vibrating arm, and the thickness is equal to the thickness of the vibrating arm.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Heat-shrinkable multi-layer film for deep-draw forming, and process for production thereof
ActiveUS20130136906A1Good heat shrinkabilityHigh degreeLamination ancillary operationsSynthetic resin layered productsMultilayer membranePolymer science
A polyamide resin-based heat-shrinkable multilayer film having excellent heat shrinkability and strength, as well as a high degree of deep A polyamide resin-based heat-shrinkable multilayer film having excellent heat shrinkability and strength, as well as a high degree of deep drawability as represented a shorter side-basis draw ratio (D / L) in excess of 0.6 between a maximum draw depth (D) and a shorter side length (L) of a mold opening is provided. The multilayer film is characterized by including a surface layer (a) comprising a thermoplastic resin, an intermediate layer (b) comprising a polyamide resin, and a surface layer (c) comprising a sealable resin, wherein (A) the intermediate layer (b) comprises a mixture of an aliphatic polyamide having a melting point of at least 180° C., and an amorphous aromatic polyamide comprising a polycondensation product of an aliphatic diamine with is ophthalmic acid and terephthalic acid as main acid components, including 25-45 wt. % of the amorphous aromatic polyamide, and has a thickness exceeding 25% and at most 50% of a total thickness of whole layers, and exhibiting: (B) tensile stresses at an elongation of 100% as measured in a tensile test at 100° C., including 3-22 N in at least one of a longitudinal direction (MD) and a transverse direction (TD) and an average of MD and TD values of 3-20N, and (C) a shrinkage in hot water at 90° C. of 3 to 20% in each of MD and TD. The film is produced through a process of strictly controlling biaxial stretching ratios and heat-relaxation ratios.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
LED pulsed light hair removal instrument
ActiveCN111772790AHigh light efficiencyQuick responseElectrical apparatusSurgical instrument detailsPulse controlHair follicle
The invention relates to an LED pulsed light hair removal instrument. The LED pulsed light hair removal instrument comprises an LED light source module, a sensor module, an interaction module and a pulse control module, wherein the LED light source module is used for generating pulsed light, and light parameters of the pulsed light are obtained through calculation based on thermal relaxation of multiple cells of hair follicles and peripheral tissues of the hair follicles; the sensor module is used for acquiring working data; the interaction module is used for receiving a control command; and the pulse control module is used for controlling the LED light source module to work according to the working data and the control command. The hair removal instrument is small in size, stable in workand good in treatment effect.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN FUDAN JOINT INNOVATION CENT +1
Data loss prevention method of a media storage device and media storage device
ActiveUS20070041114A1Accurate detectionSmall recording areaRecord information storageCarrier monitoringComputer hardwareSignal quality
A media storage device which reads and writes data from and to a storage medium using a head prevents in advance data loss due to thermal relaxation of data recorded on the storage medium. Management information is created, in units of received write commands, for holding the recording areas on the storage medium of the write data and signal quality information; the management data is stored in a management table, and signal quality is measured, updated, and used in re-recording judgements, in write command units. Thermal relaxation state management can be performed in write command units; thermal relaxation processing is simple, and moreover degradation of recorded data due to thermal relaxation can be detected accurately, and data loss can be prevented.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
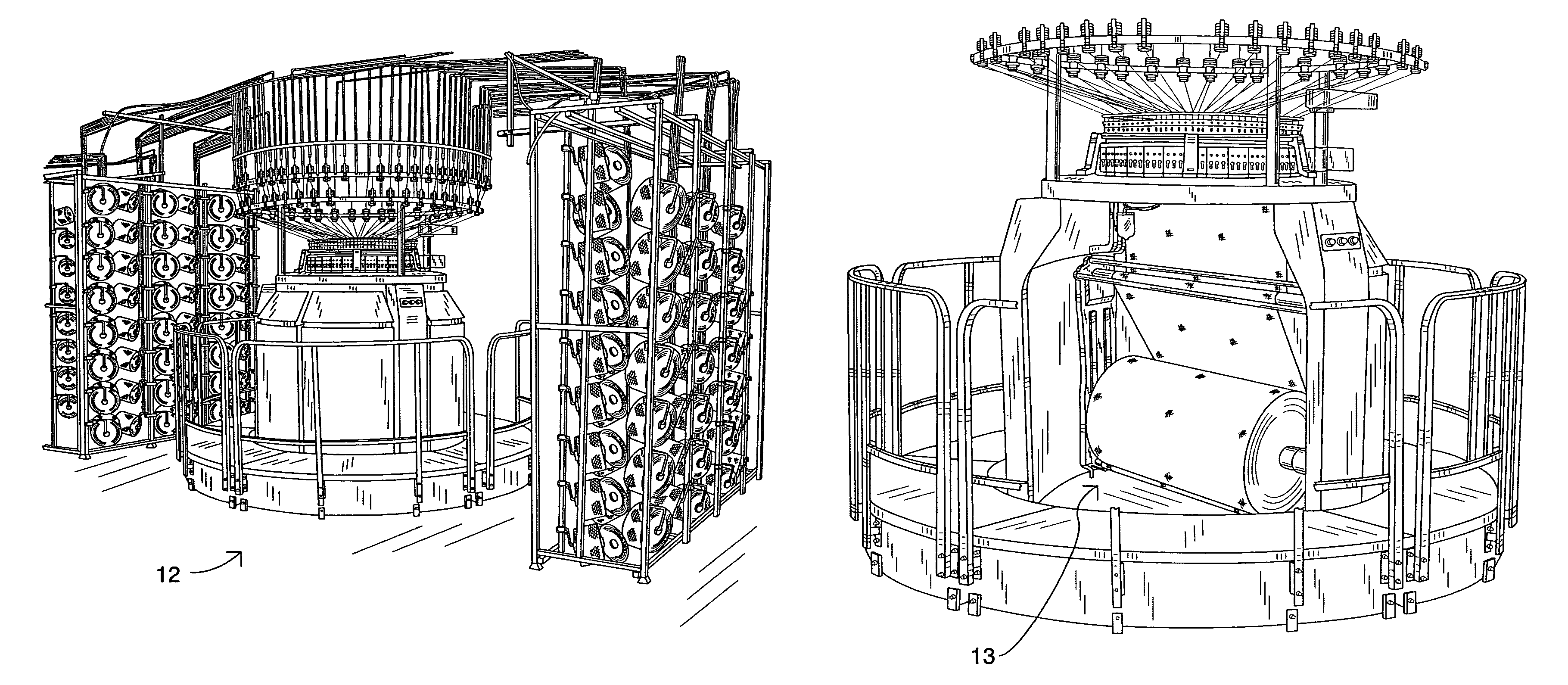
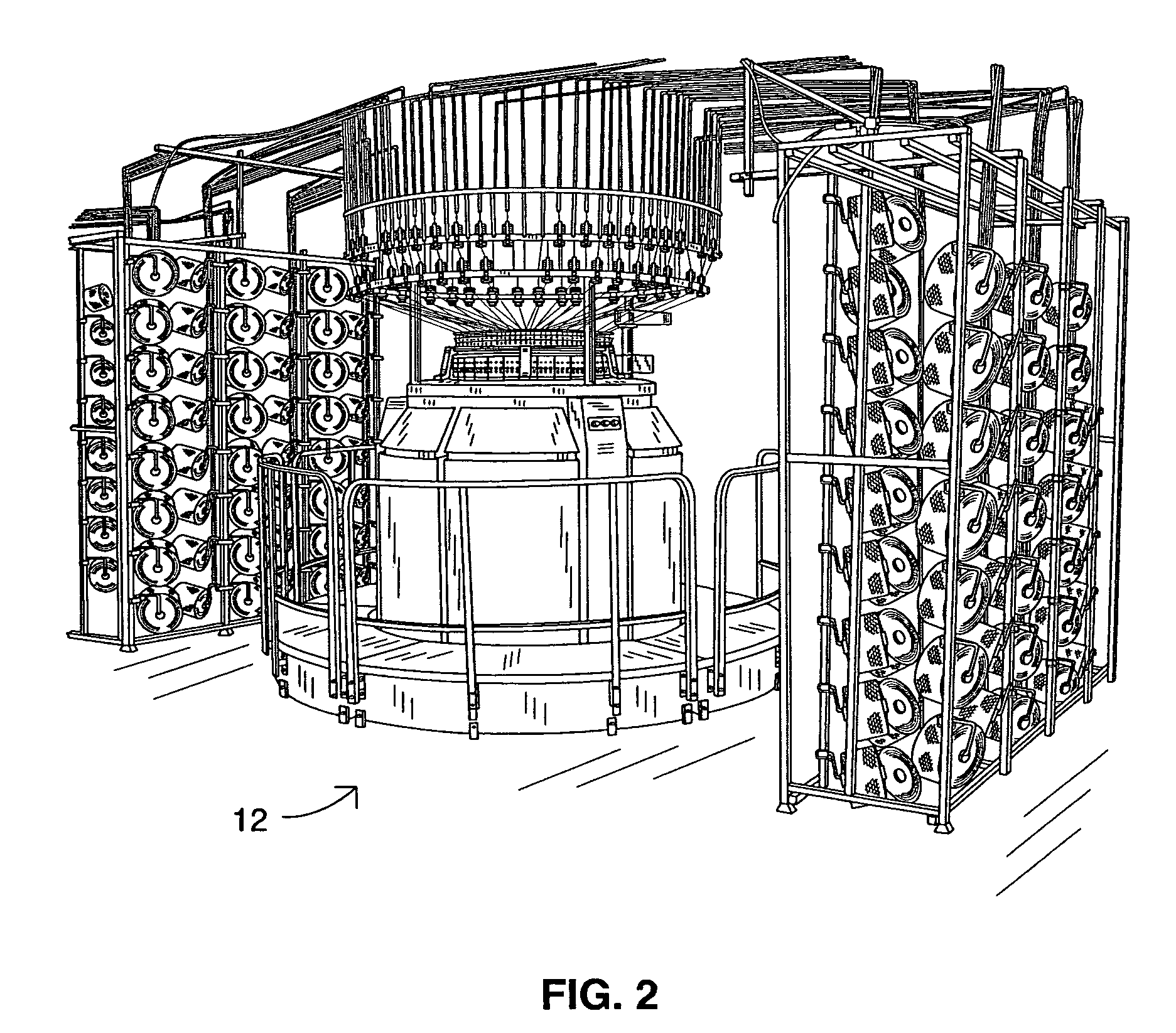
Apparatus for forming an unbalanced, circular knit fabric and a coated fabric produced therefrom
An apparatus for forming an unbalanced, circular knit fabric for coating in a subsequent operation, the apparatus comprising: a circular knitting station; and a thermal relaxation station downstream from the circular knitting station for relaxing the fabric in all directions. In the preferred embodiment of the invention, the apparatus includes a slitting station downstream from the circular knitting station. Also in the preferred embodiment, the apparatus includes a thermal finishing station downstream from the thermal relaxation station for setting the desired width of the fabric thereby also setting the desired stretch of the fabric in its length direction. A coated fabric, the coated fabric comprising a circular knitted, single knit fabric substrate, wherein the stretch of the fabric in the wale direction is greater than the stretch of the fabric in the course direction. In the preferred embodiment of the invention, the coated fabric further includes an outer coating. Also in the preferred embodiment, the fabric is formed by a four feed repeat.
Owner:TEX TECH COATINGS LLC
Magnetic head with high reliability of the data protection, magnetic disk apparatus including the magnetic head and the method of recording information on the magnetic disk apparatus without miserasing the previously recorded data
InactiveUS20060028752A1Thermal decay is not easily acceleratedGrowth inhibitionManufacture head surfaceHeads using thin filmsSkew angleMagnetic poles
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH JAPAN LTD
Self-stimulated Raman scattering laser of In-Band pump
InactiveCN101807774BHigh beam qualityReduce thermal effectsLaser using scattering effectsDielectricStimulate raman scattering
The invention discloses a self-stimulated Raman scattering laser of an In-Band pump, which comprises a laser pump source, a laser energy transfer optical fiber, a first planoconvex lens for collimation, a second planoconvex lens for focusing, a reflection mirror of a resonator cavity, a laser gain dielectric crystal, a laser output mirror and a laser collimating mirror which are sequentially arranged, wherein pump light outputted by the laser pump source is transmitted to the first planoconvex lens via the laser energy transfer optical fiber, collimated by the first planoconvex lens, focused by the second planoconvex lens and further focused on the end surface of the laser gain dielectric crystal, the laser gain dielectric crystal produces stimulated radiation after absorbing the pump light, when the radiation of fundamental frequency light in the resonator cavity exceeds the self-stimulated Raman scattering threshold of the laser gain dielectric crystal, the produced Raman laser is collimated and outputted by the laser collimating mirror. The self-stimulated Raman scattering laser can improve the self-stimulated Raman scattering conversion rate, eliminate the thermal relaxation process from the pump energy level to the laser energy level of electrons of the conventional pump way, improve the quantum efficiency, reduce the heat and increase the self-stimulated Raman scatteringconversion rate.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
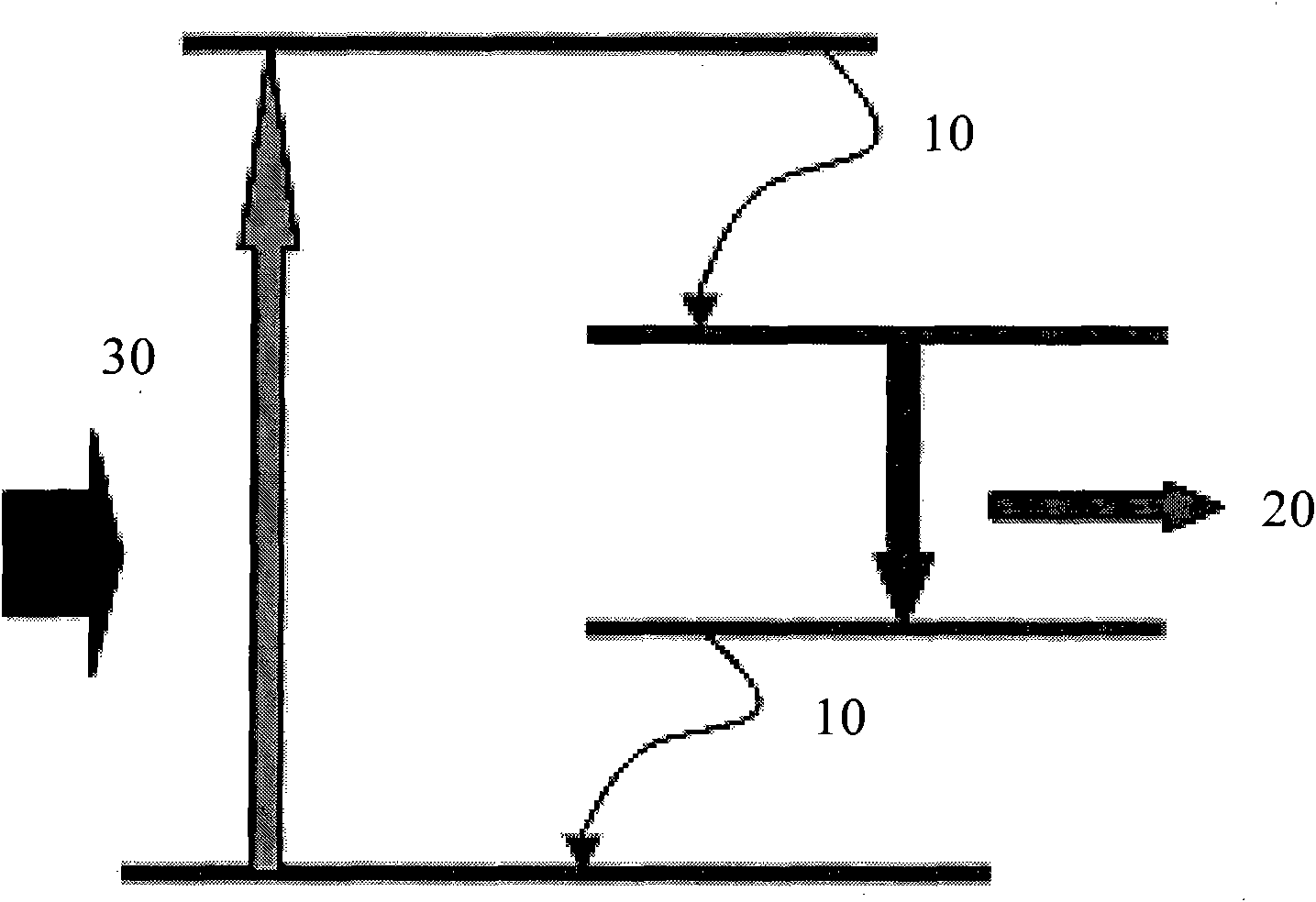
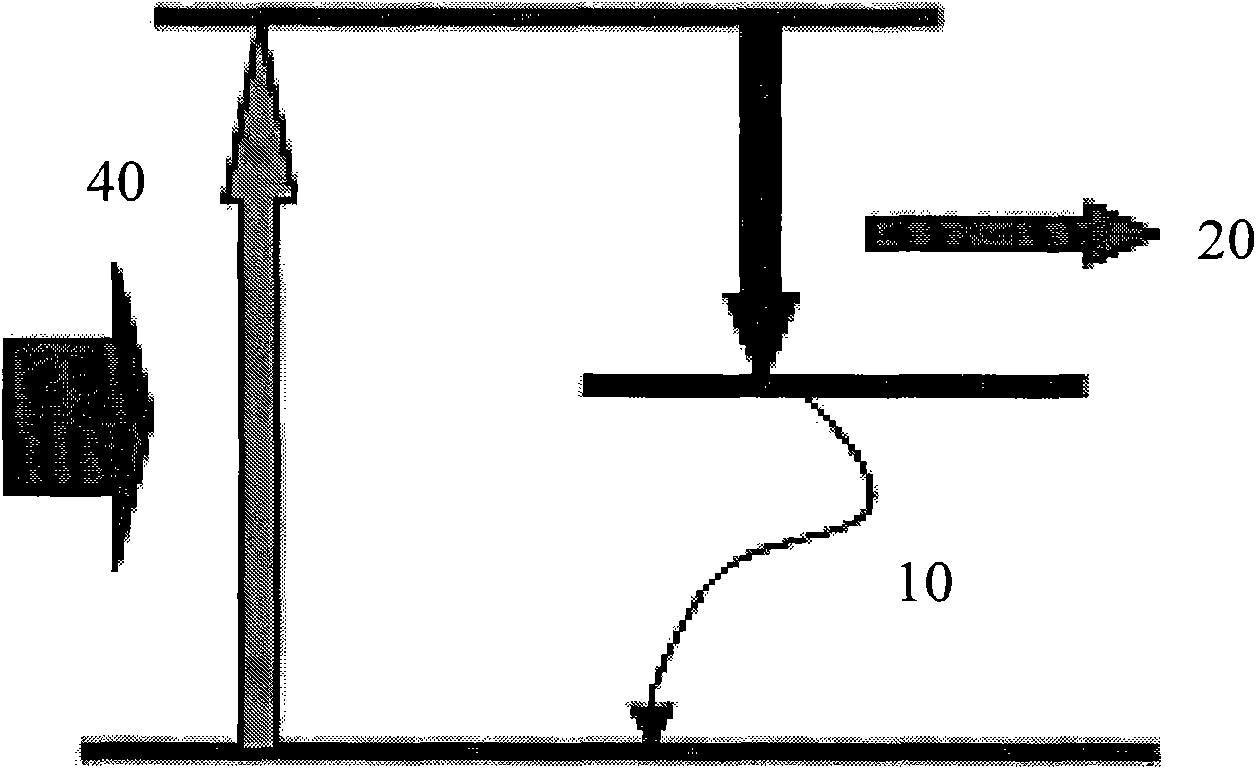
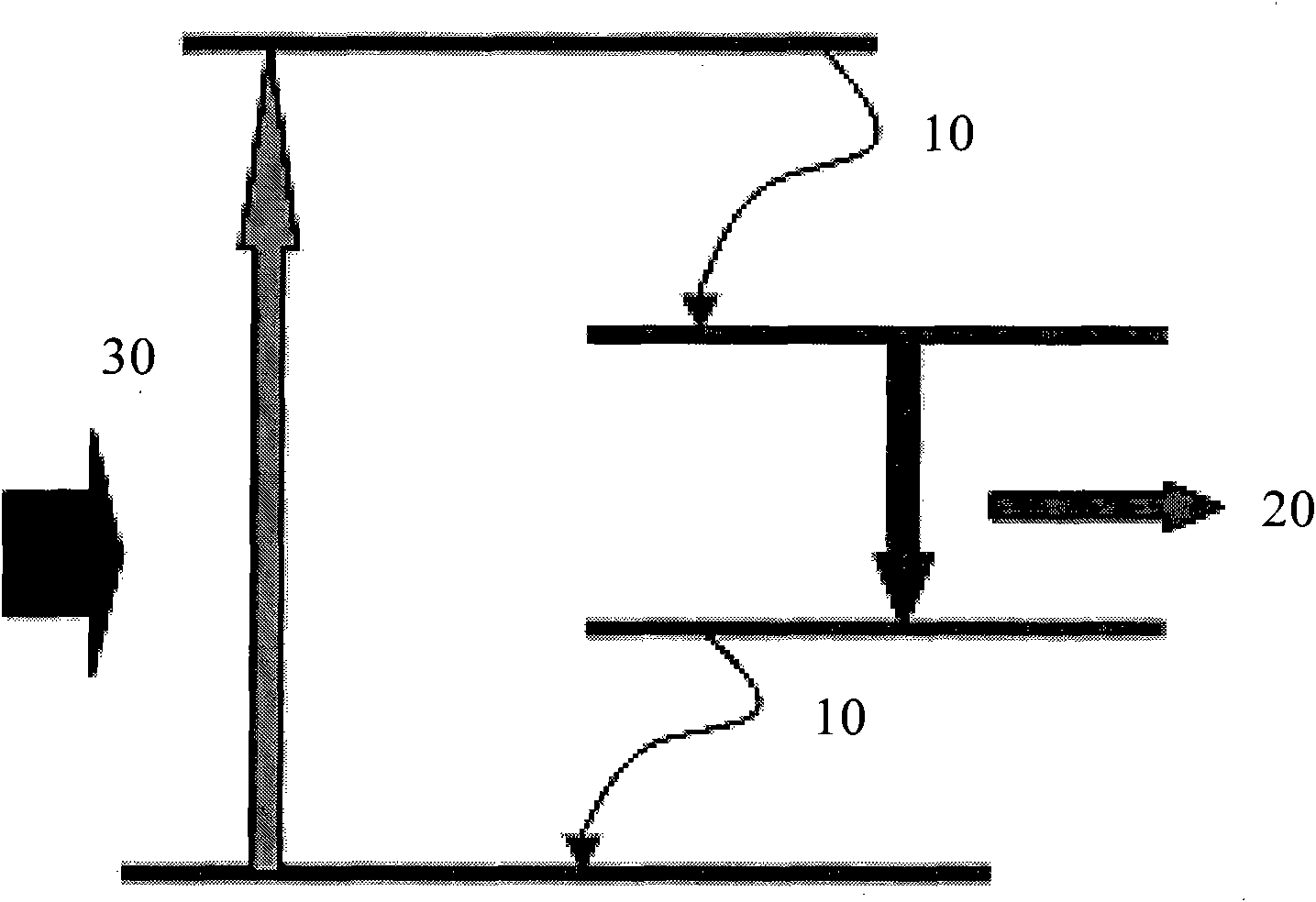
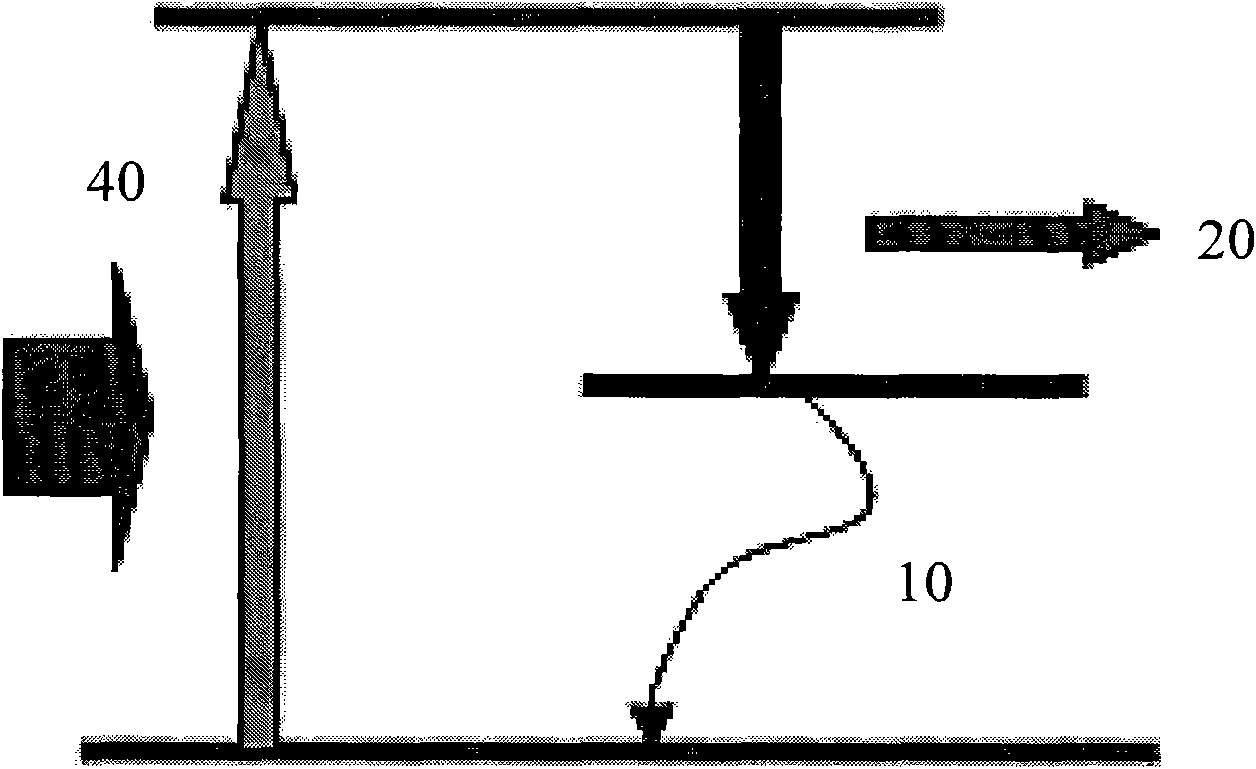
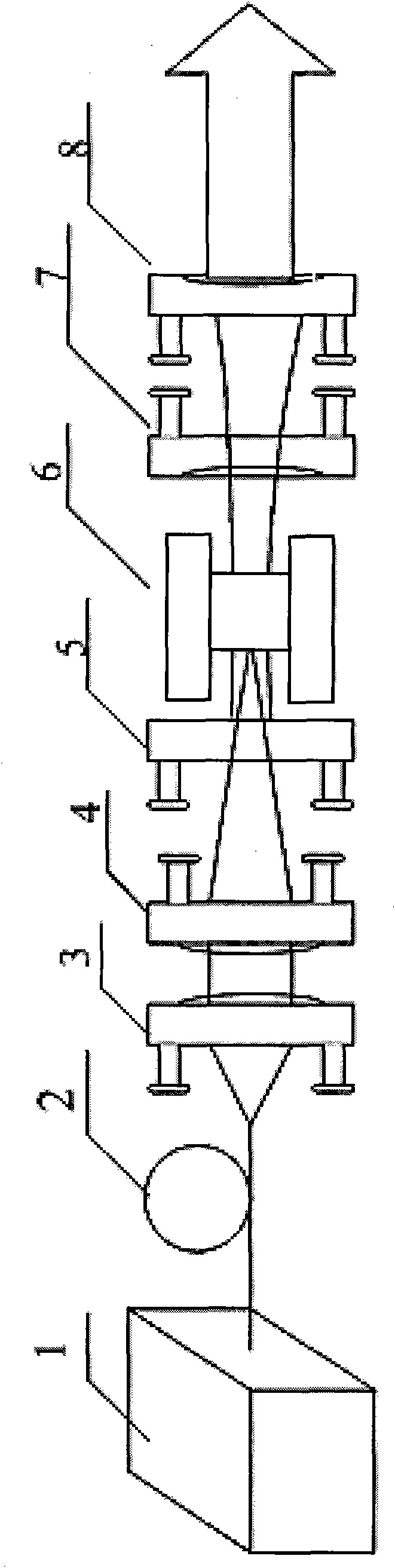
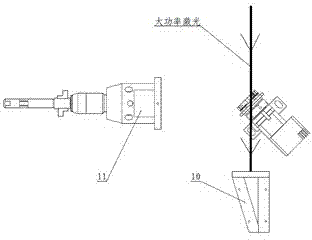
Method of realizing slow rise and slow drop control on laser output power
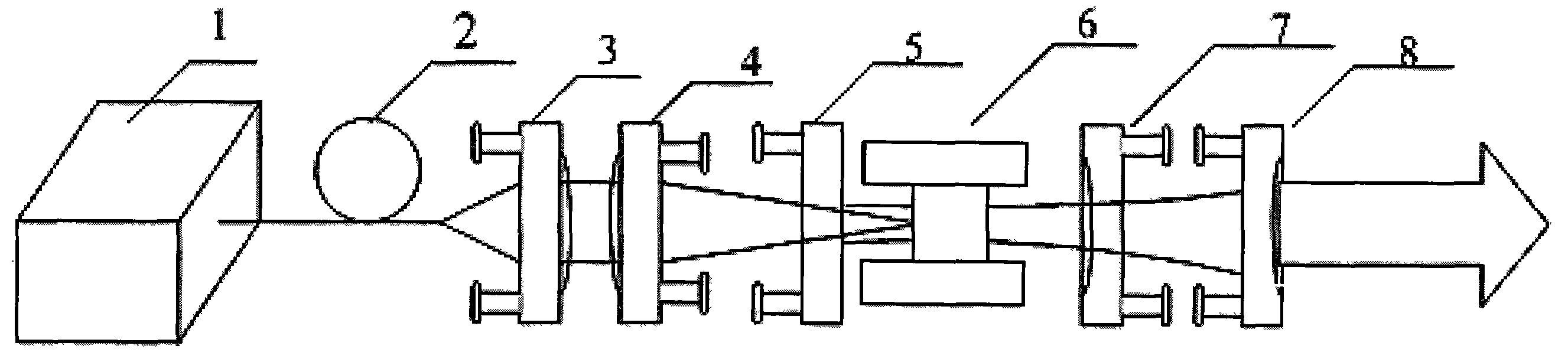
The invention discloses a method of realizing slow rise and slow drop control on laser output power. An optical gate device capable of adjusting and controlling laser energy output, a high-power laser energy absorption body (10), and a set of optical fiber coupler (11) are included. The method is characterized in that a control motor (1) drives a laser reflector (5) to perform reciprocating motion from a position I to a position II, the rotation speed of the control motor (1) can adjust a laser output power change curve during the process from the position I to the position II, and slow rise is realized; and the rotation speed of the control motor (1) can adjust a laser output power drop curve during the process from the position II to the position I, and slow drop is realized. According to the method of realizing slow rise and slow drop control on laser output power, the phenomenon of laser power overshoot as the solid laser is influenced by a thermal relaxation can be avoided, and the method can be effectively applied to an arc striking process, an arc stopping process and switch optical action in the laser welding field.
Owner:JIANGSU ZHONGKESIXIANG LASER TECH
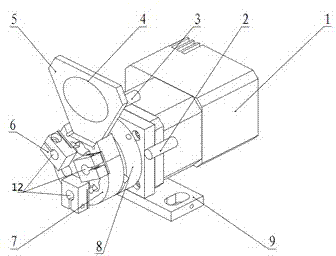
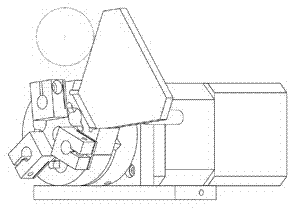
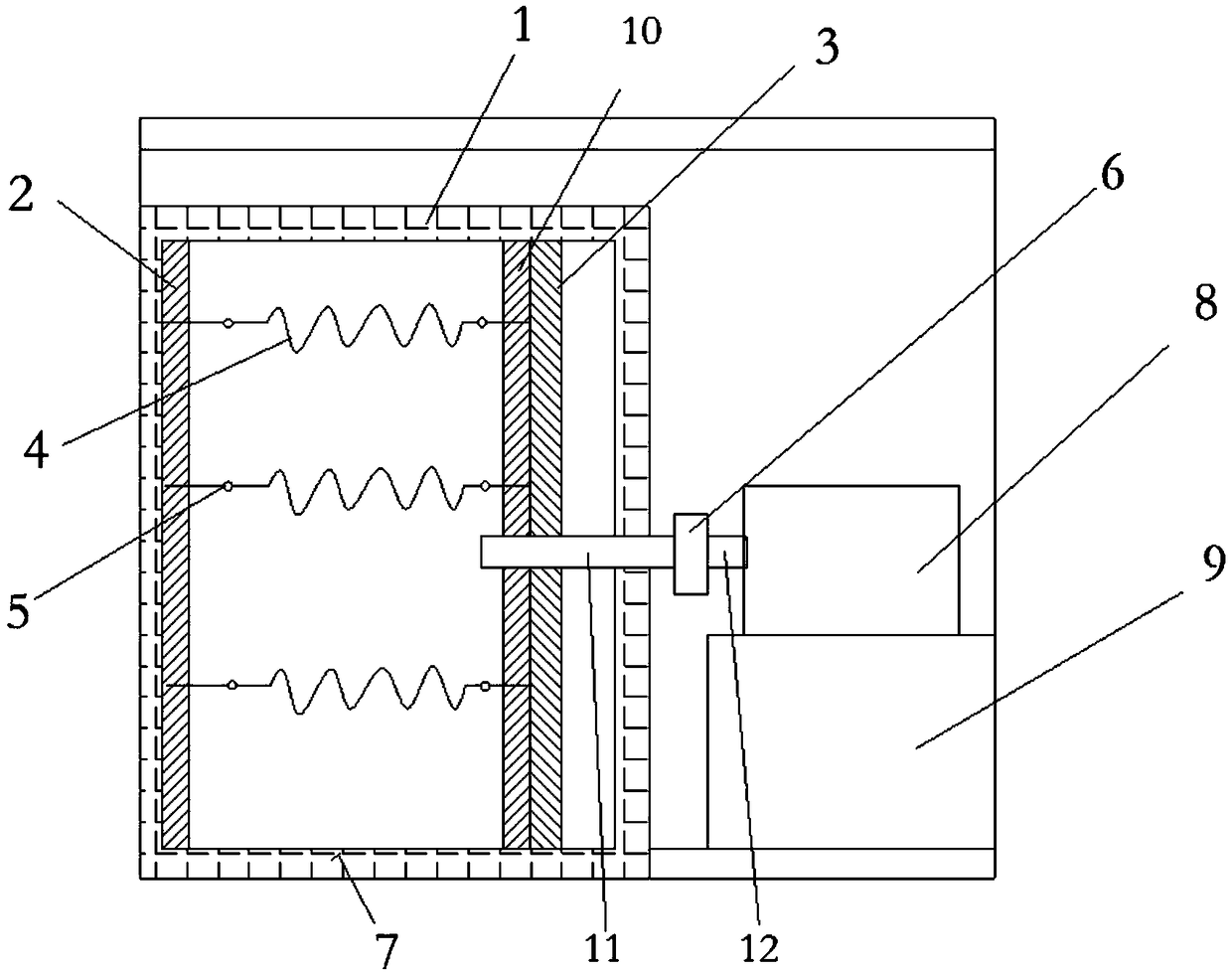
Spring thermal relaxation testing device
InactiveCN108152016AAccurate measurement and control of relaxation parametersMachine part testingEngineeringTime control
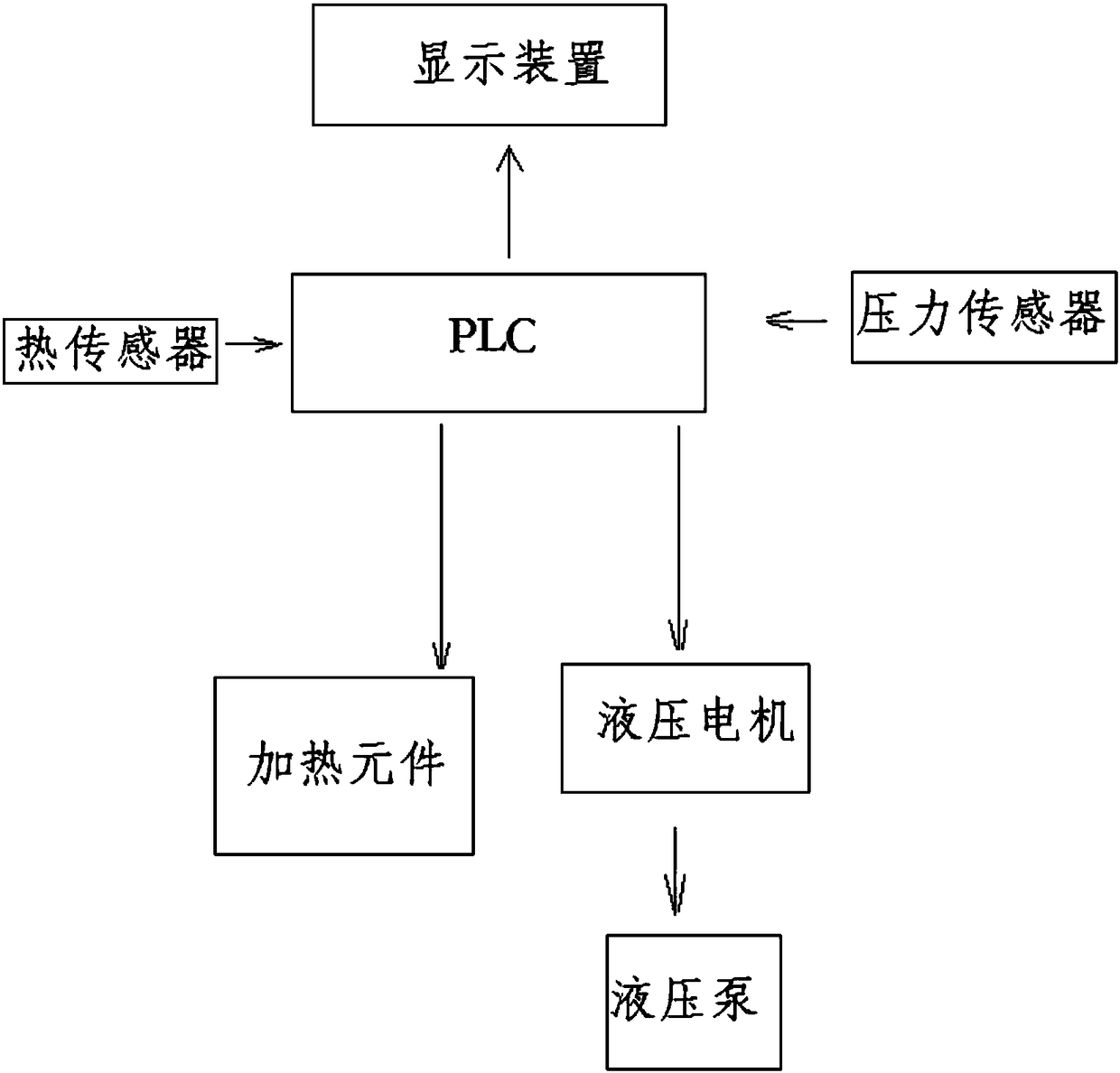
The invention discloses a spring thermal relaxation testing device, which comprises a high temperature box, wherein the high temperature box is internally provided with a fixed heating layer and a movable heating layer, the fixed heating layer and the movable heating layer are oppositely arranged, the fixed heating layer and the movable heating layer are internally provided with a heating element;the fixed heating layer and the movable heating layer are provided with hooks, and each spring is hung between two oppositely arranged hooks; the fixed heating layer is fixed with the inner wall of the high temperature box, the movable heating layer is fixed with a pull rod, the pull rod is connected with a tension meter, the tension meter is fixed with a hydraulic pull rod, and the hydraulic pull rod is driven by a hydraulic tank; the movable heating layer is externally provided with a heat preservation layer, and the heat preservation layer and the movable heating layer are fixed into a whole and arranged on a guide rail at the lower part of the high temperature box. The spring thermal relaxation testing device has the advantages that the heating temperature and received tension of thesprings can be controlled due to adoption of a temperature controller and a pressure control device which are controlled by a PLC, time control is performed according to a built-in time controller ofthe PLC, and thus relaxation parameters of the springs can be accurately measured and controlled.
Owner:凤城市凯驰内燃机配件有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com