Patents
Literature
234 results about "Skew angle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The term ‘angle of skew’ or ‘skew angle is basically the angle between a normal/perpendicular to the alignment/centerline of the bridge and the centerline of the pier .
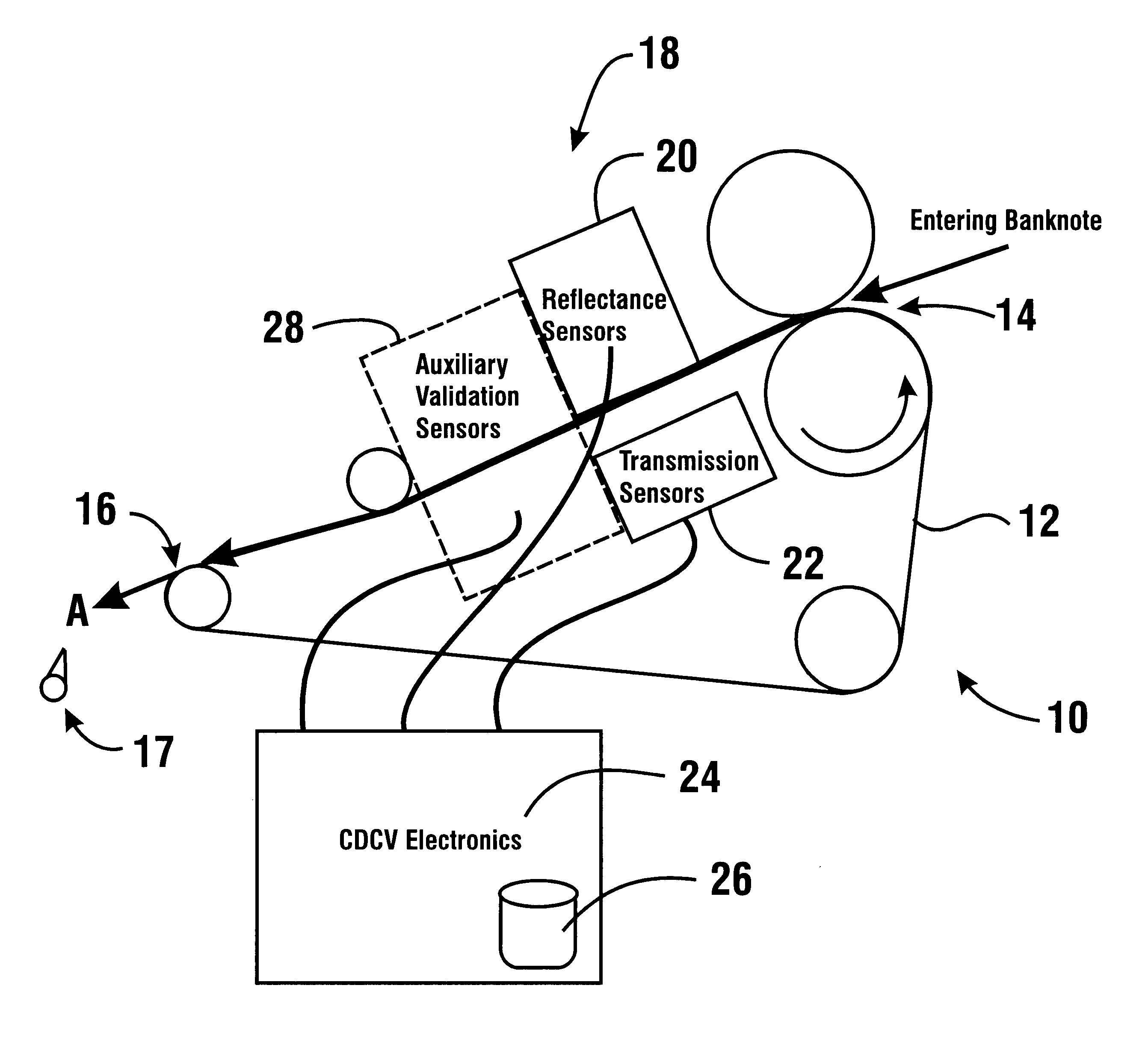
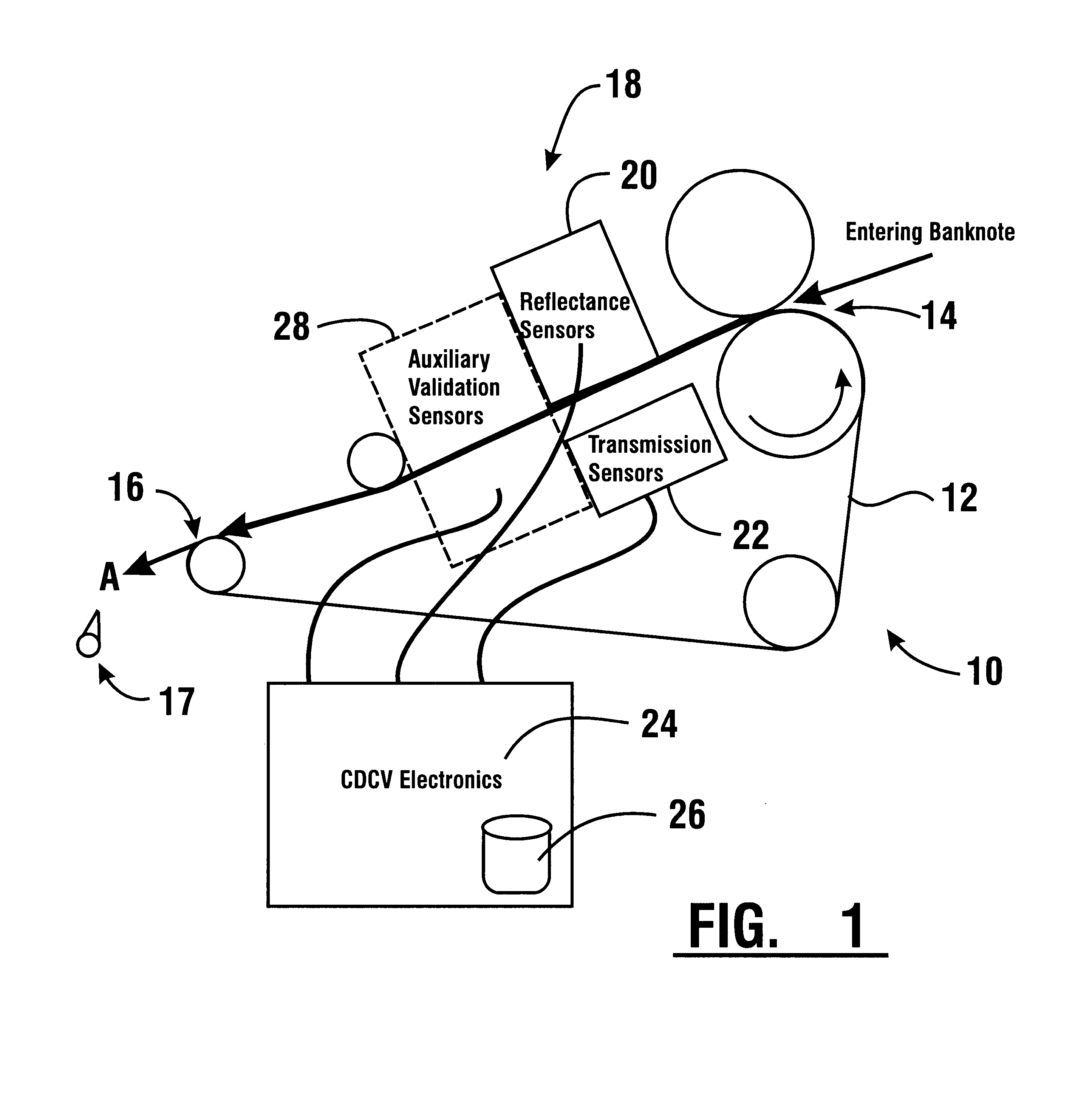
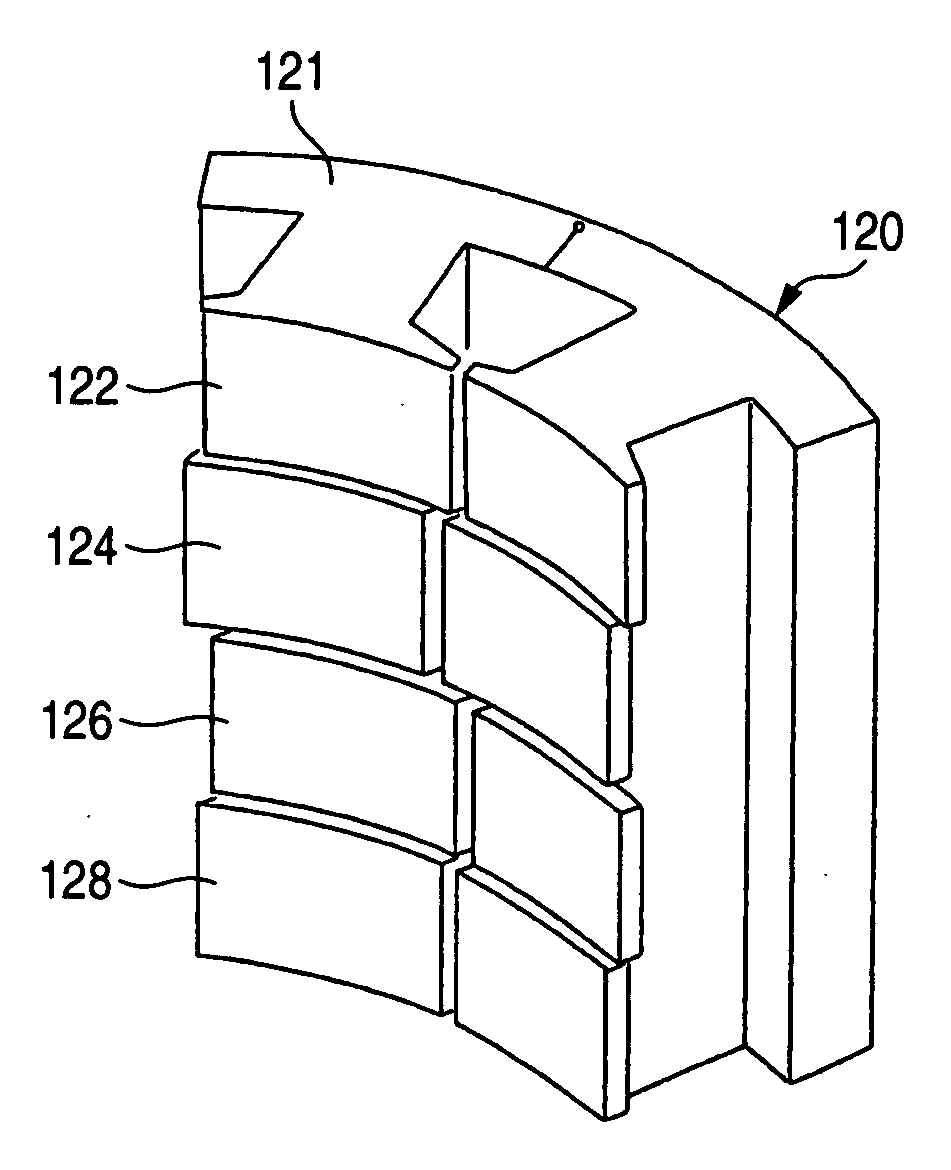
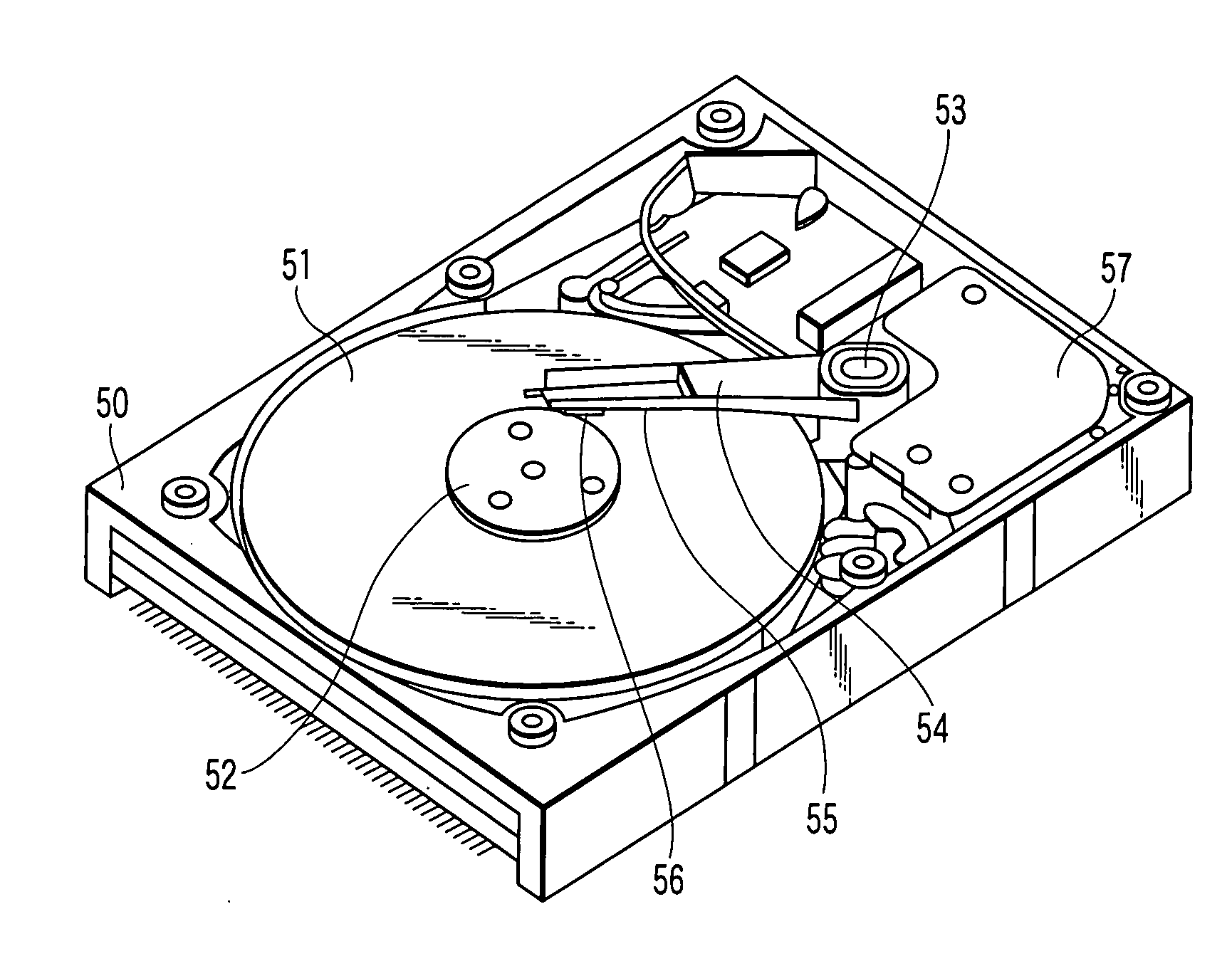
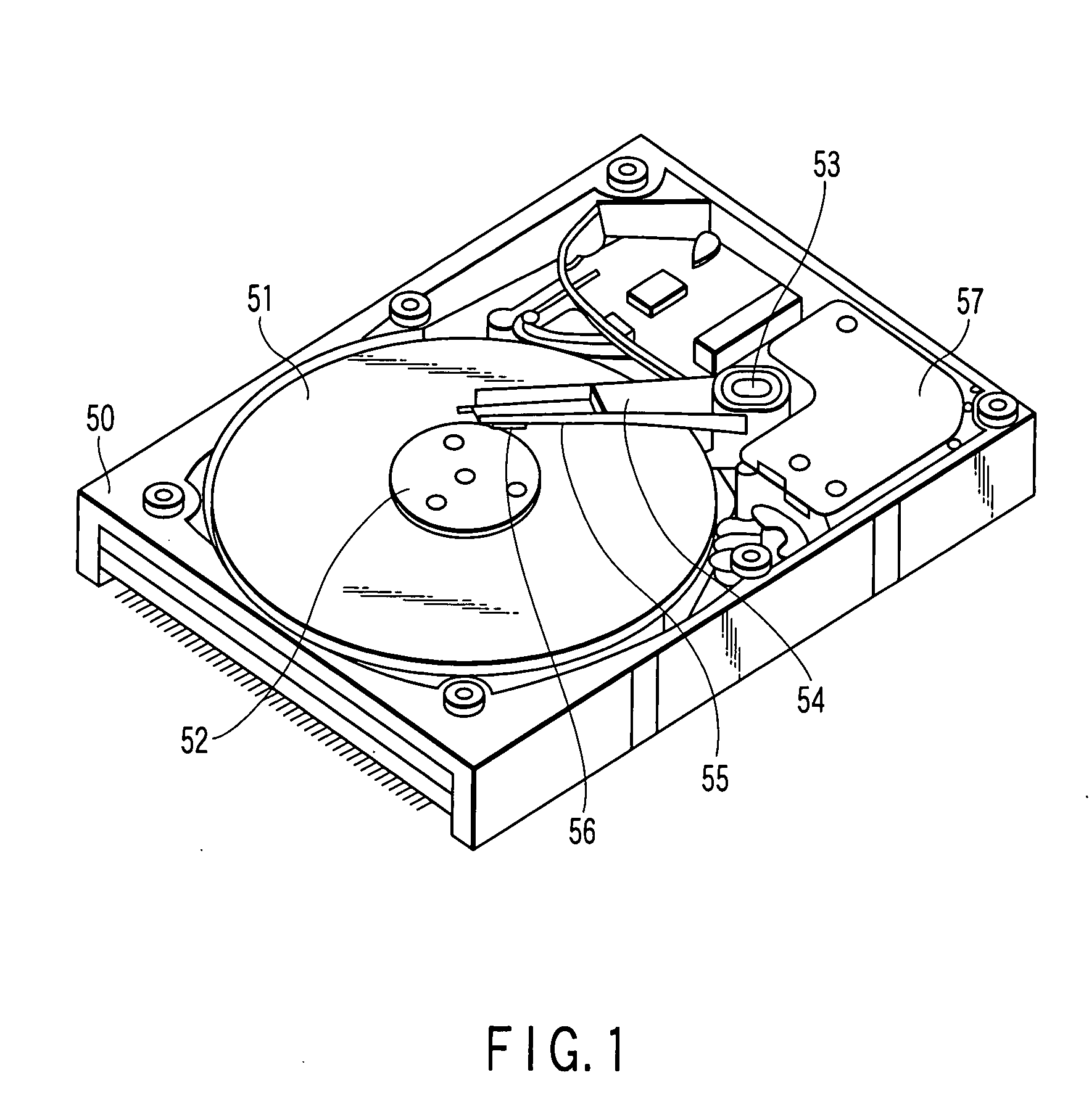
Apparatus and method for processing bank notes and other documents in an automated banking machine
InactiveUS6573983B1Easy to operateAvoid the needPaper-money testing devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansValue setSkew angle
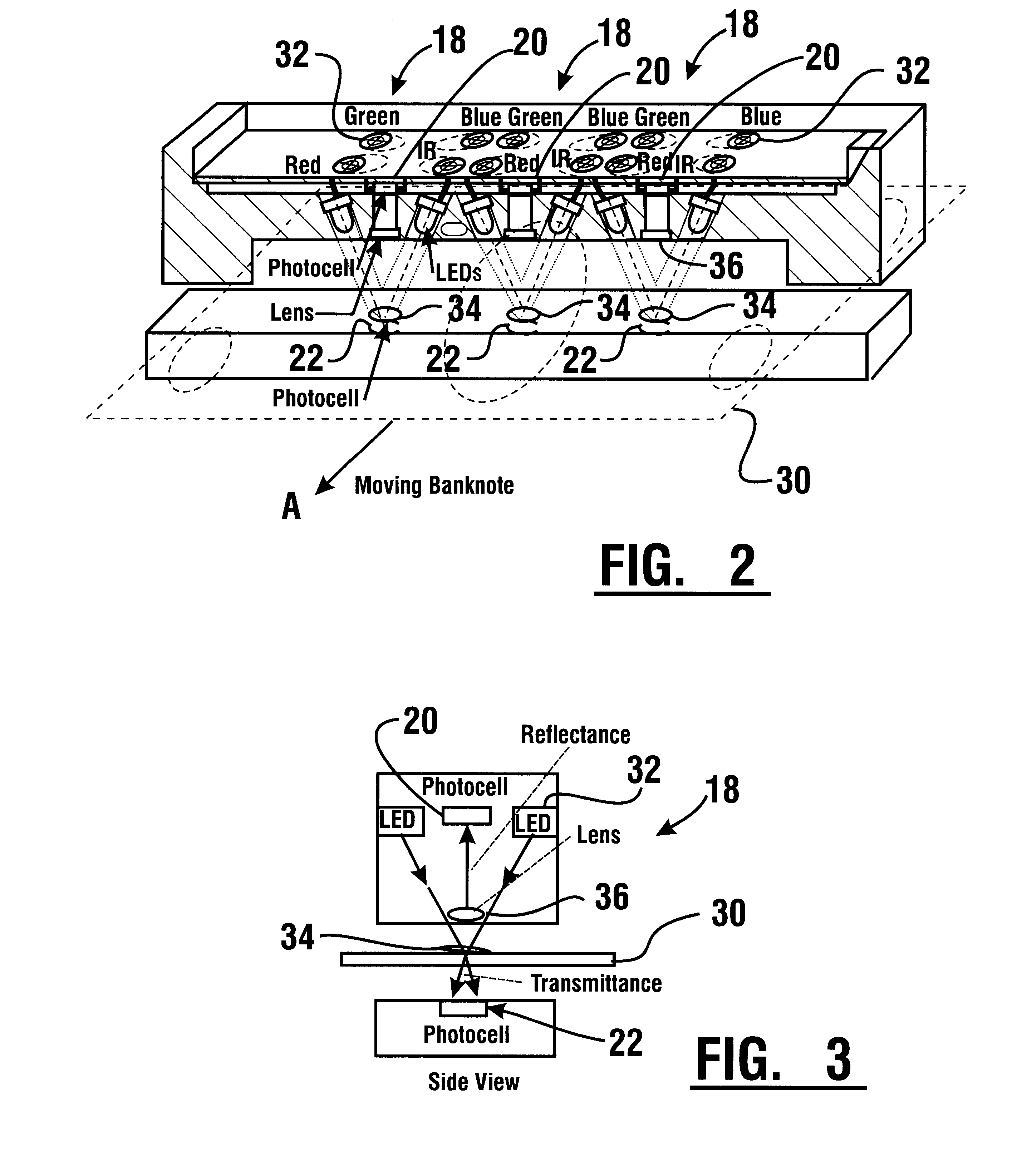
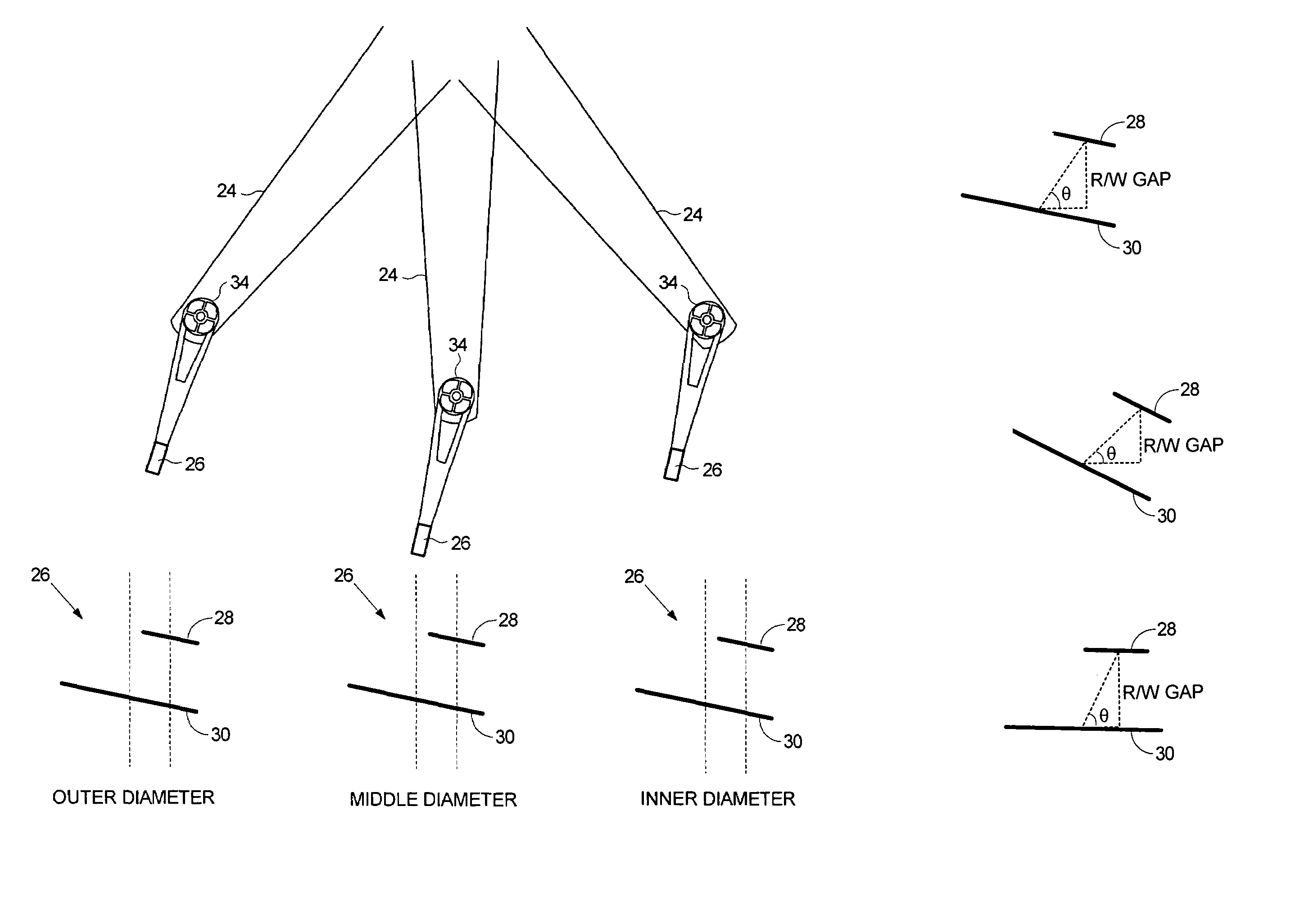
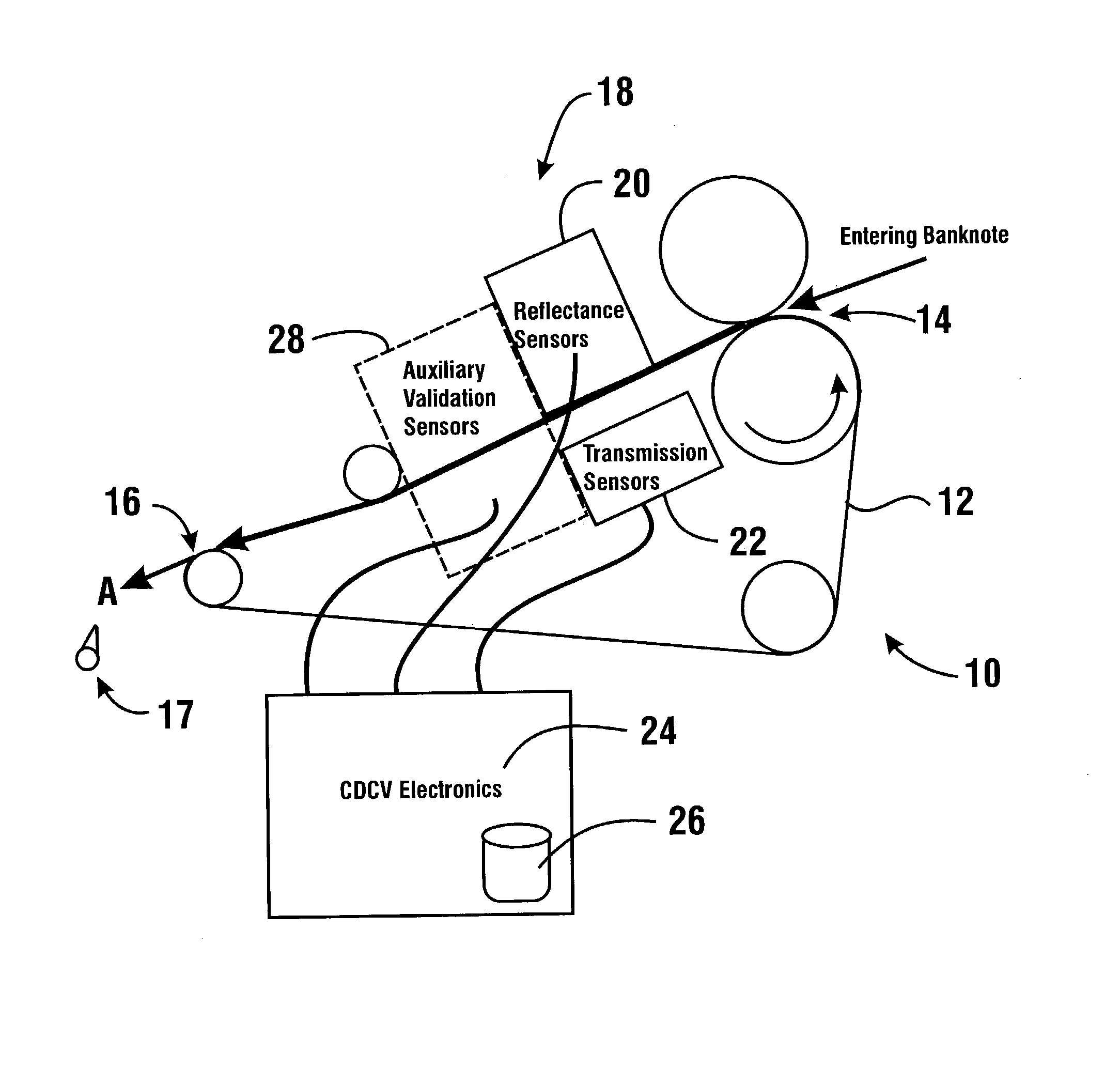
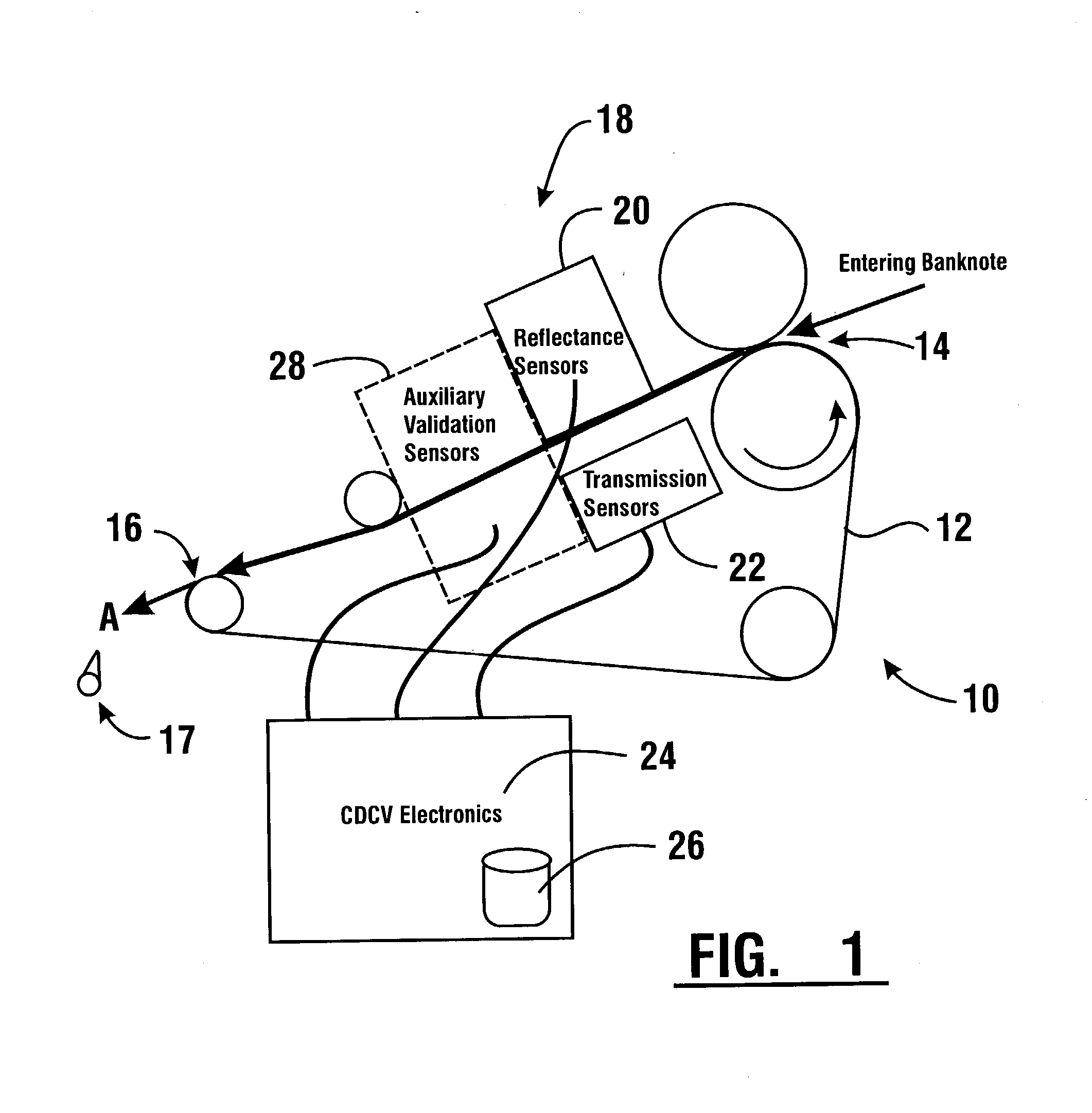
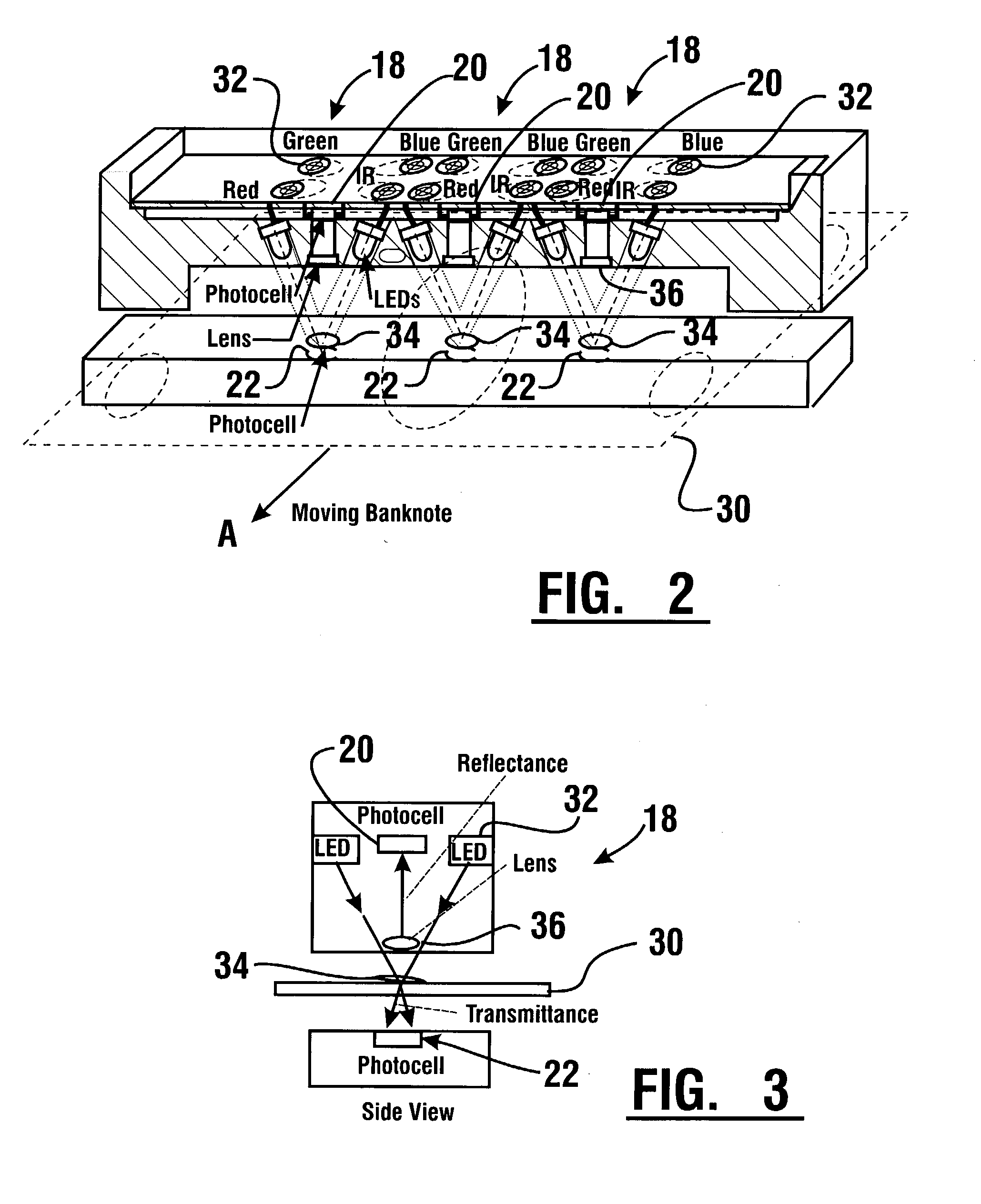
An apparatus and method for determining a type and / or a condition of a note passing through the apparatus includes a note transport (12) which moves the note past sensing assemblies (18). Each sensing assembly includes emitters (32). Each of the emitters produces radiation at a different wavelength. The sensing assemblies include a reflectance detector (20) and a transmission detector (22) which are disposed on opposed sides of the passing note. The emitters direct radiation onto test spots (34) on the passing note. Reflectance values are generated from radiation reflected from each type of emitter to the reflectance detector. Transmission values are generated from radiation transmitted from an emitter through each test spot to the transmission detector. A control circuit produces a sensed value set including the reflectance and transmission values from each of the emitters in each of the sensing assemblies. The control circuit also determines an angle of skew of the passing note. Memories (138) include templates of values corresponding to transmission and reflectance values for known note types in a number of note positions. The control circuit generates stored value sets from the templates and skew angle. The control circuit further calculates a value representative of a level of correlation between the sensed value set and each of the stored value sets. The control circuit determines the highest level of correlation between all the stored value sets which is indicative of the note type and / or a condition thereof Various types of sensing assemblies can be used including sensing assemblies that are also suitable for capturing image data from notes or instruments processed in an automated banking machine.
Owner:DIEBOLD NIXDORF
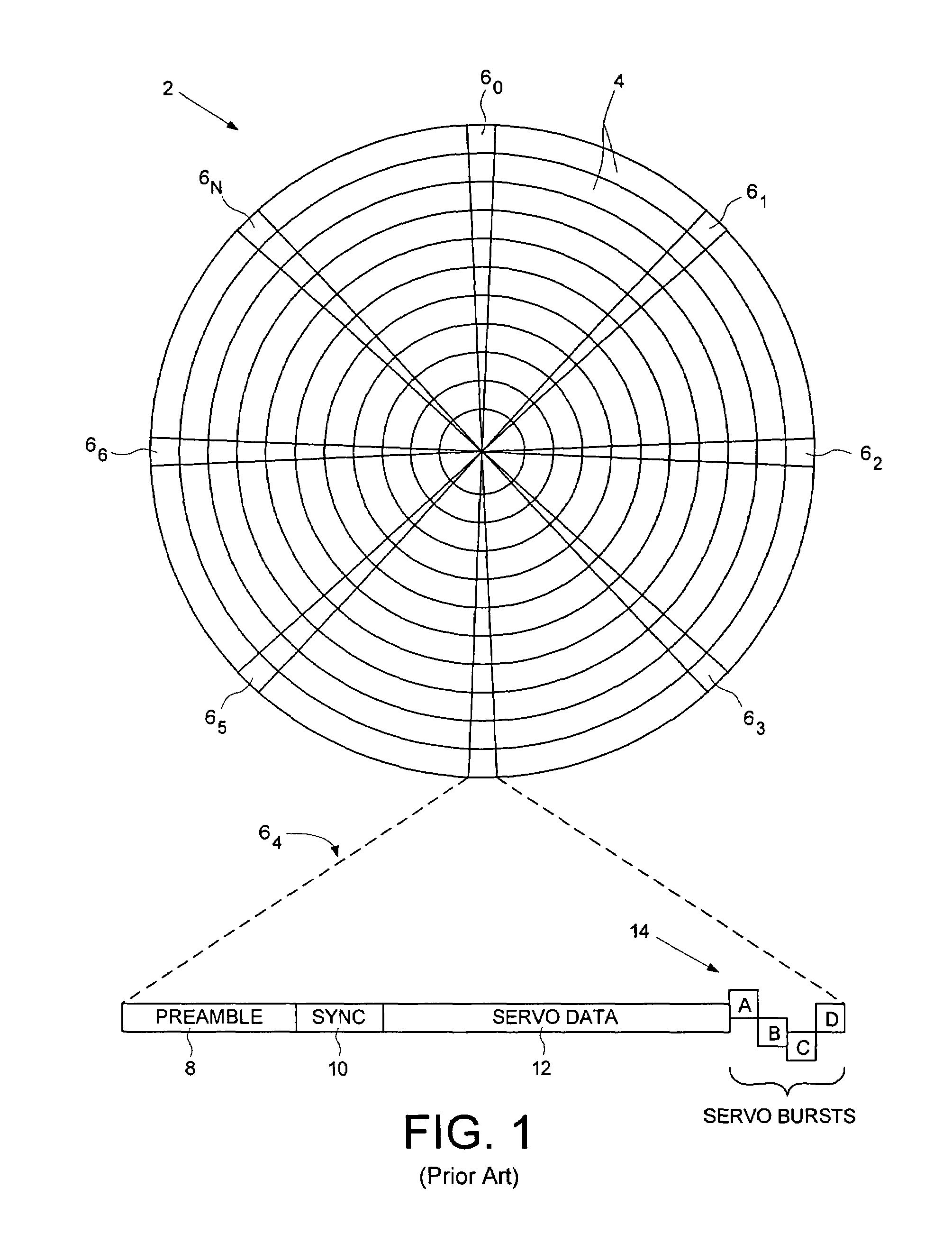
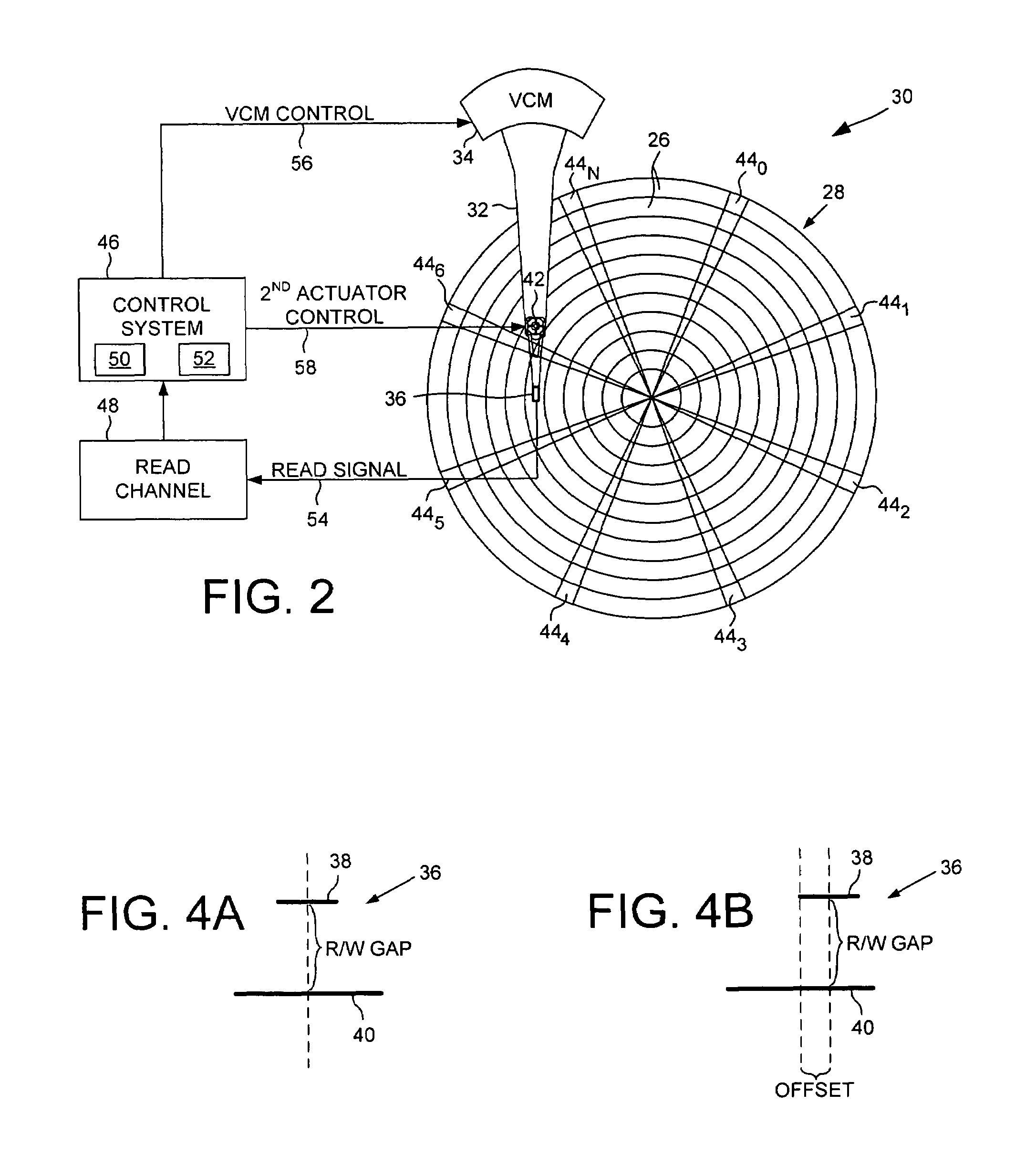
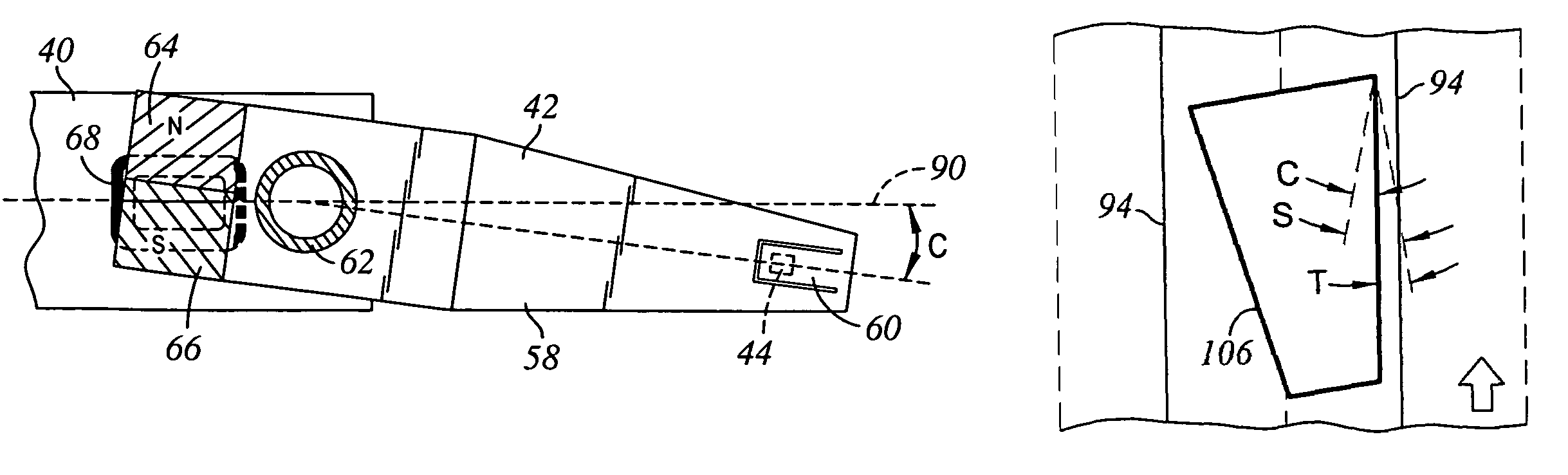
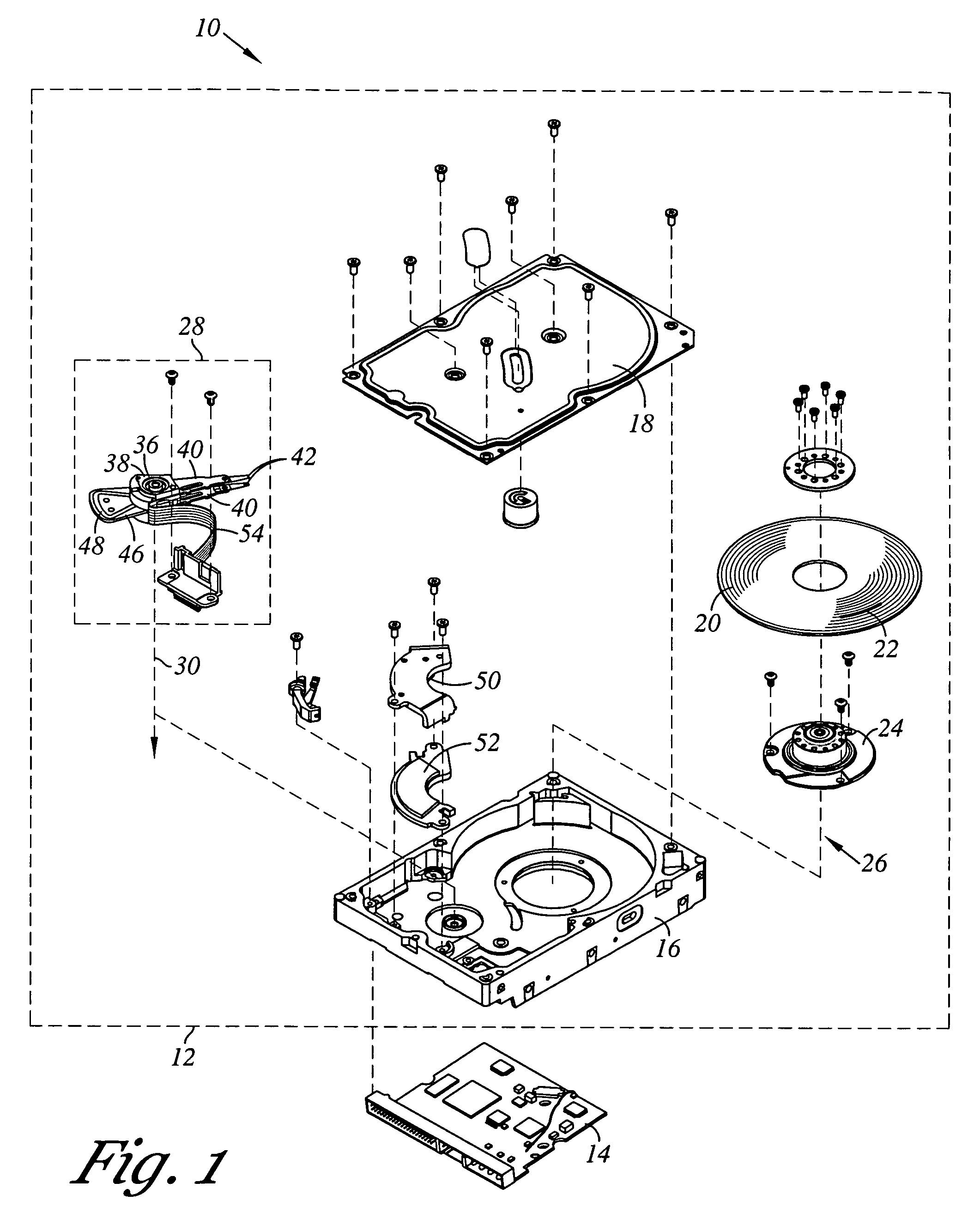
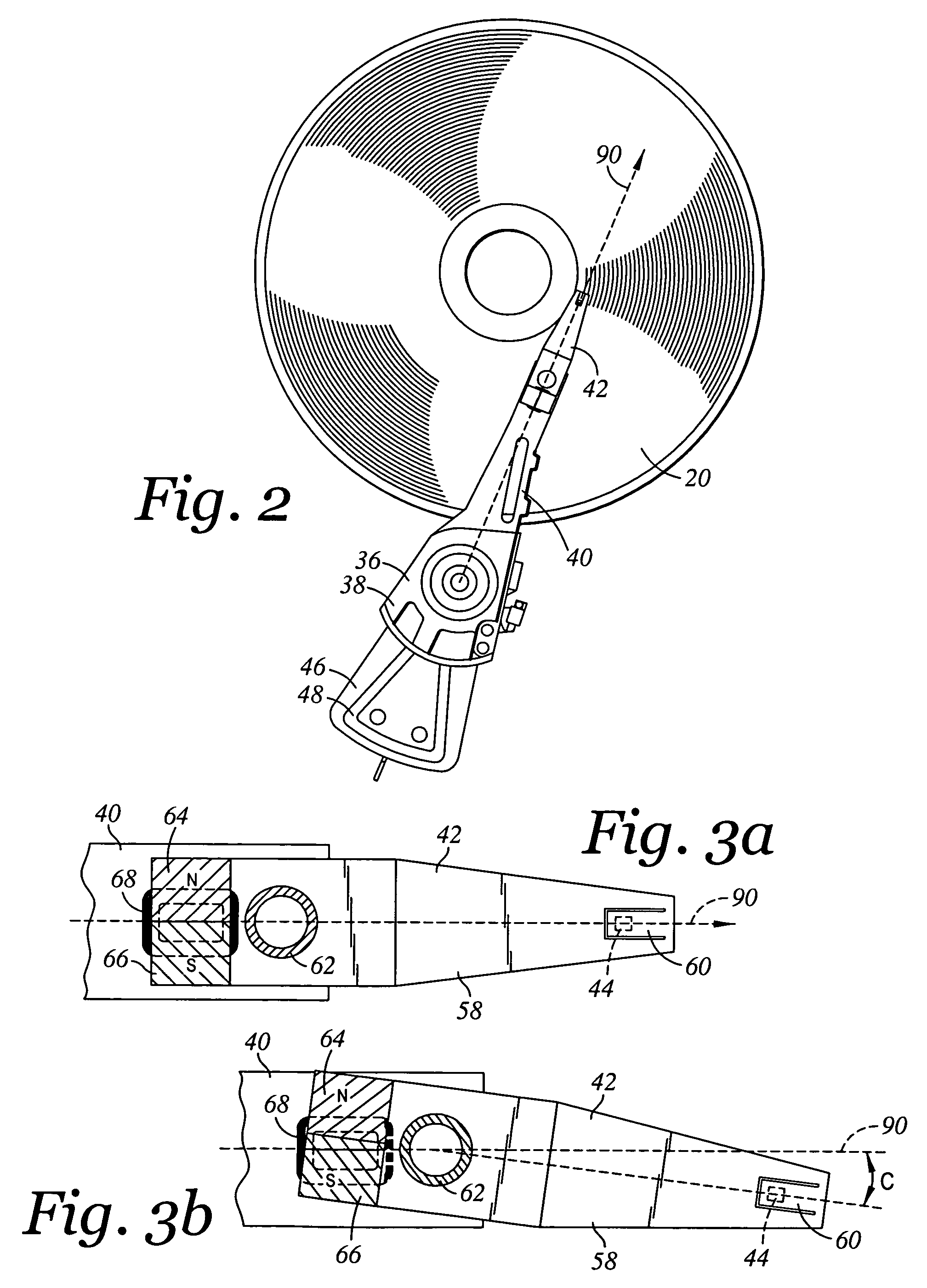
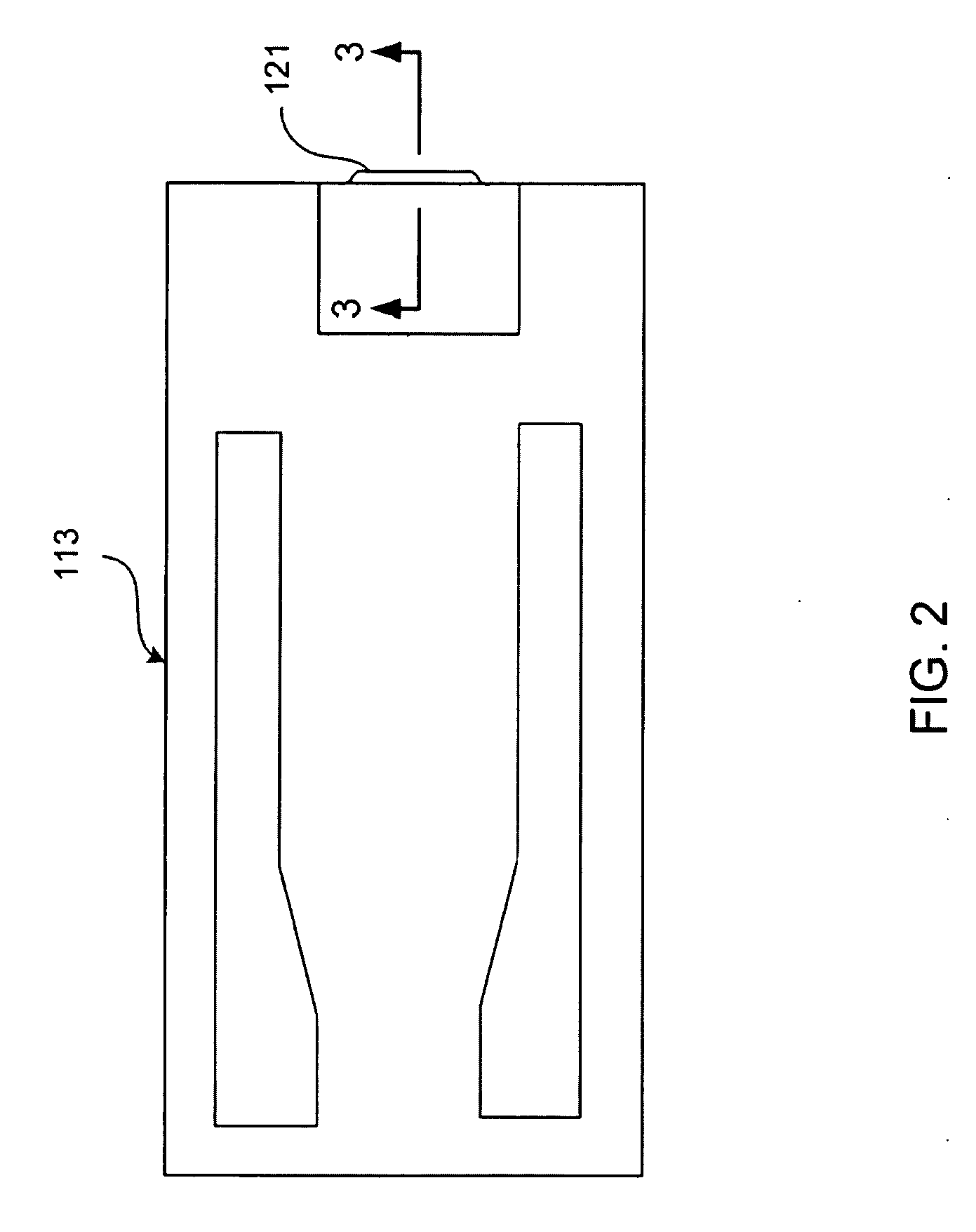
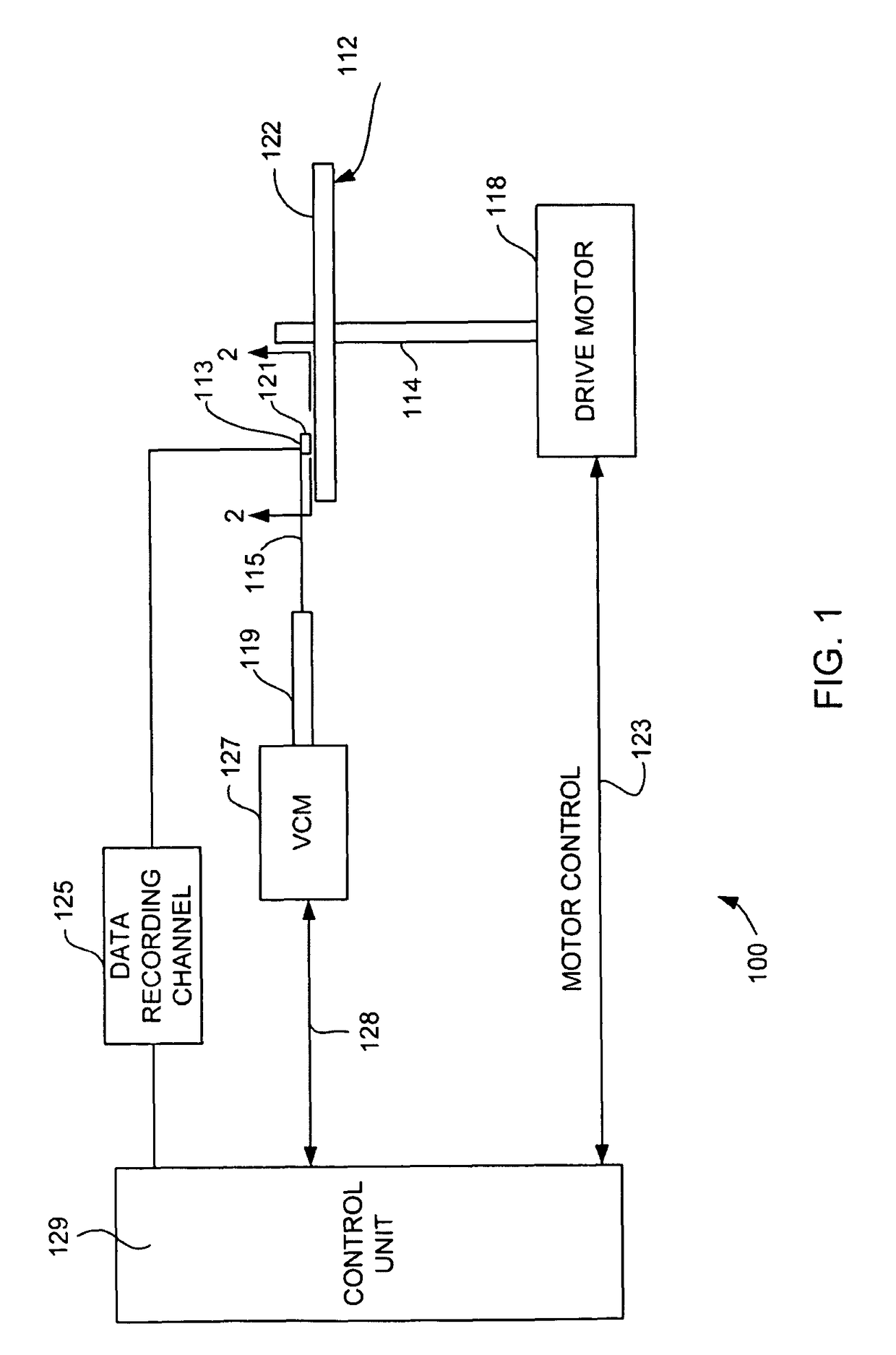
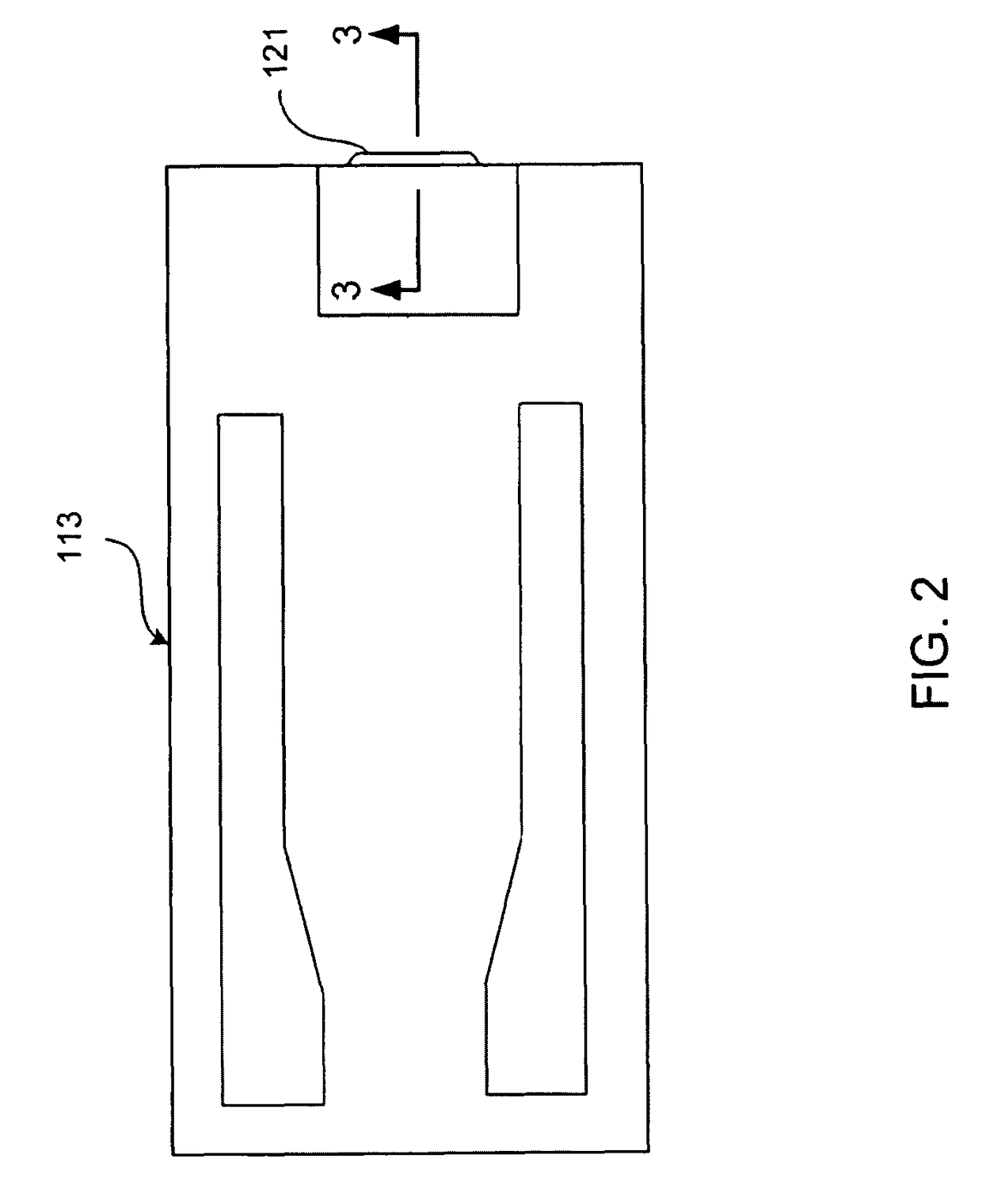
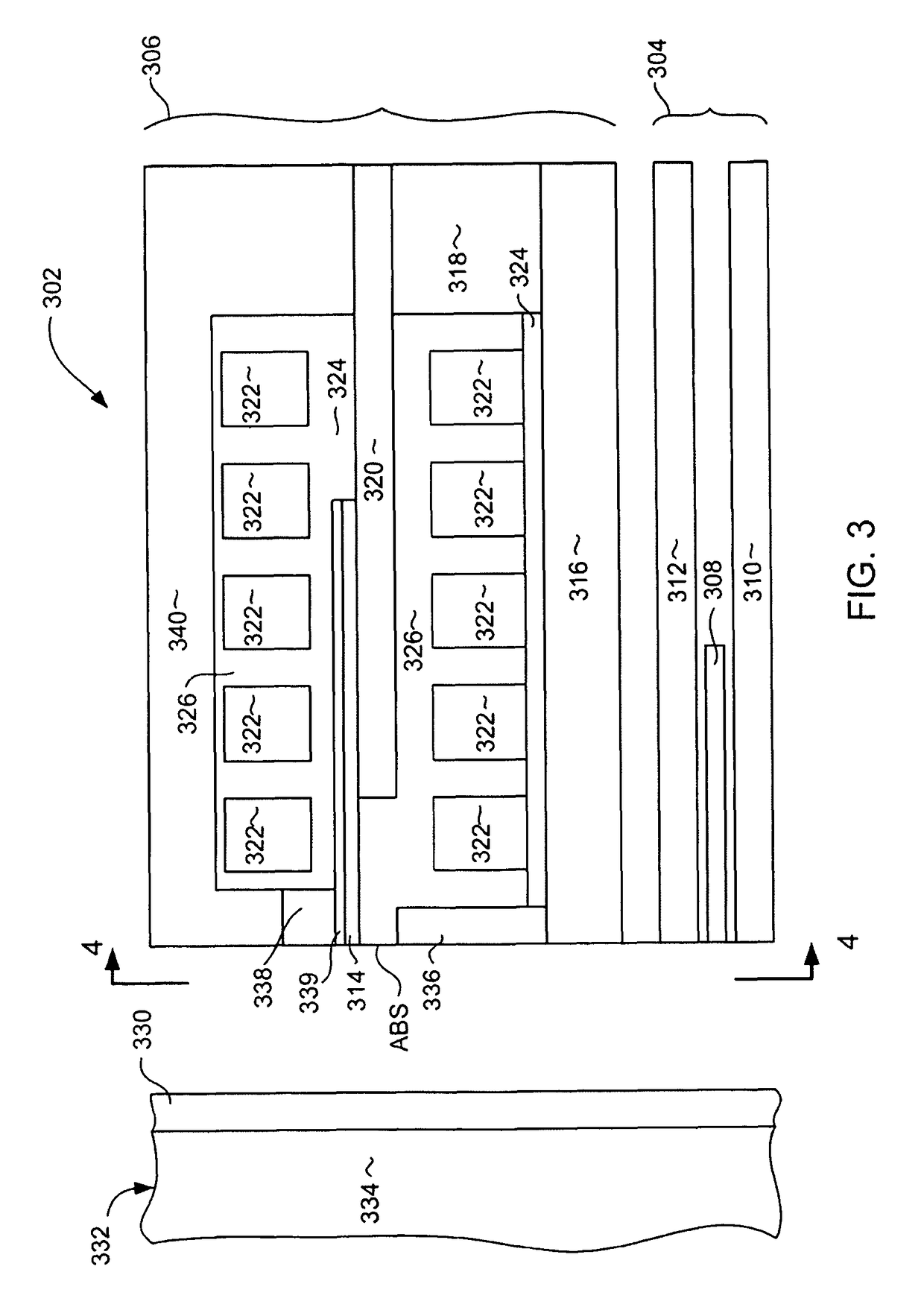
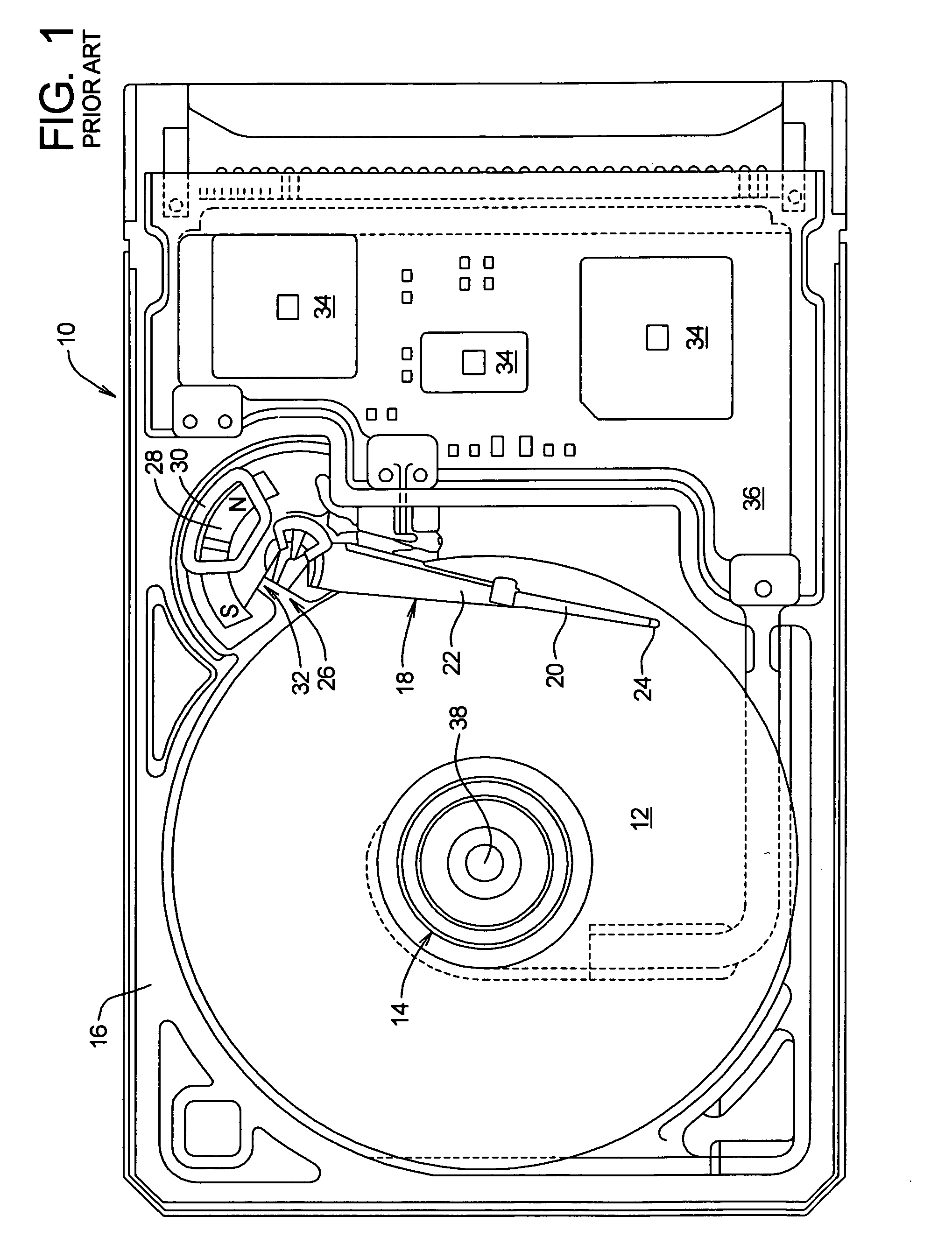
Servo writing a disk drive using a secondary actuator to control skew angle
InactiveUS7489464B1Constant skewConstant track densityDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageSkew angleActuator
A method of servo writing a plurality of servo sectors to a disk of a disk drive to define a plurality of data tracks is disclosed. The disk drive comprises the disk, an actuator arm, a head coupled to a distal end of the actuator arm, wherein the head comprises a read element and a write element. A voice coil motor (VCM) rotates the actuator arm about a pivot to actuate the head radially over the disk, and a secondary actuator adjusts a skew angle for the head while using the write element to write the servo sectors to the disk.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
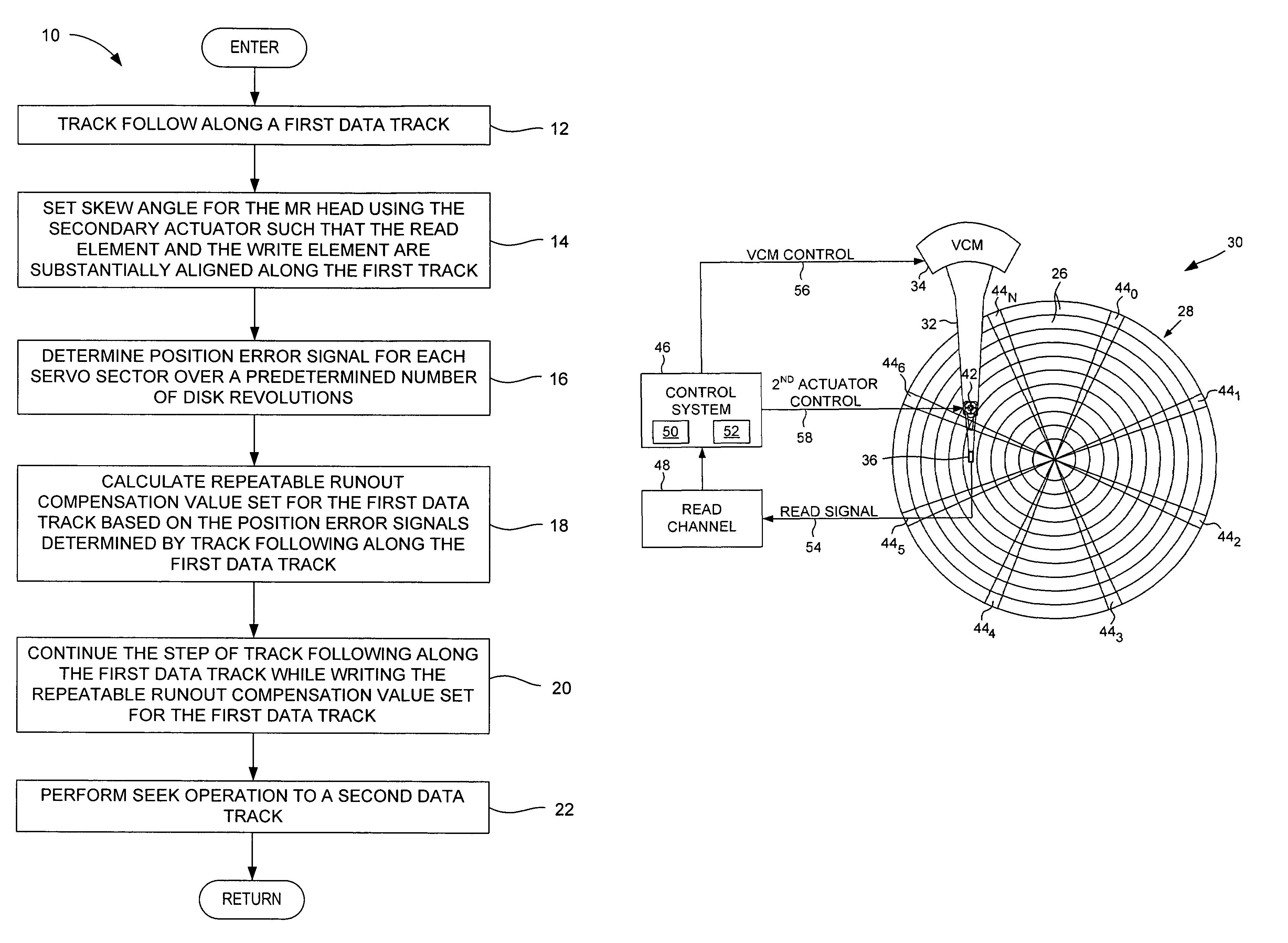
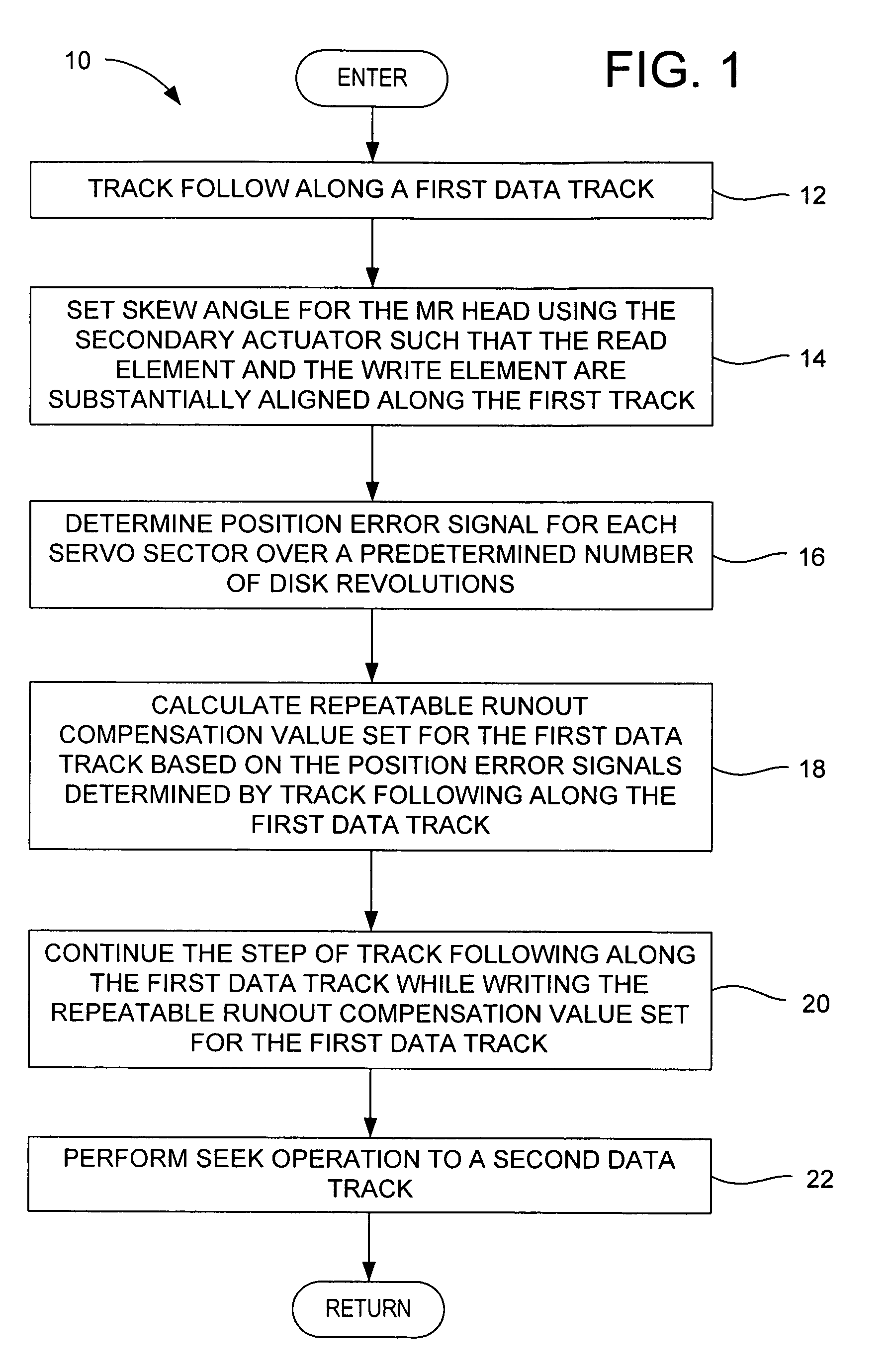
Magnetic disk drive and method for efficiently determining and storing RRO compensation values using a secondary micro-actuator
A method is disclosed for efficiently determining and writing repeatable runout (RRO) compensation value sets for data tracks on a magnetic disk in a disk drive. The disk drive has a magnetoresistive (MR) head having a read element and a separate write element, and a secondary actuator coupled to the end of a primary actuator for adjusting a head skew angle. In the method, the head skew angle is set such that the read and write elements are substantially aligned along the first track. A position error signal for each servo sector is determined over a predetermined number of disk revolutions during track following along a first data track. An RRO compensation value set is calculated for the first data track based on the position error signals. The RRO compensation value set is written for the first data track. A seek operation is then performed to a second data track.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method of operating a disk drive including rotating a perpendicular write head to reduce a difference between skew and taper angles, and a disk drive
InactiveUS7215514B1Reduce the differenceRecord information storageAlignment for track following on disksSkew angleEngineering
A method of operating a disk drive including providing the disk drive. The disk drive includes a disk with data tracks and an actuator with a slider including a perpendicular magnetic write head. The write head includes leading and trailing sides defining a taper angle. The write head and the actuator define a maximum skew angle with respect to the data tracks. The maximum skew angle being greater than the taper angle. The method further includes rotating the slider during operation of the disk drive to reduce a difference between the skew and taper angles for aligning the write head with the data tracks.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
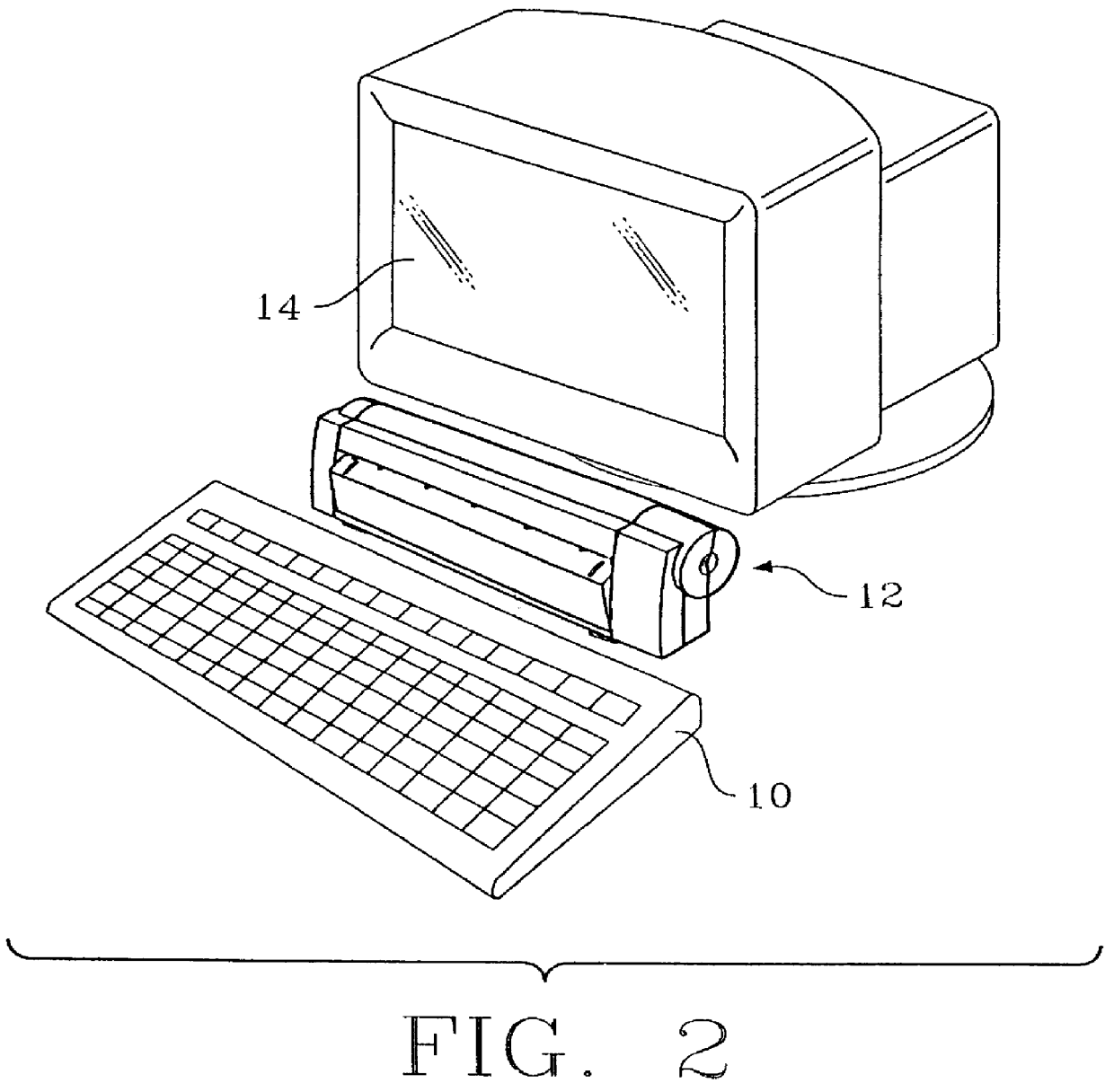
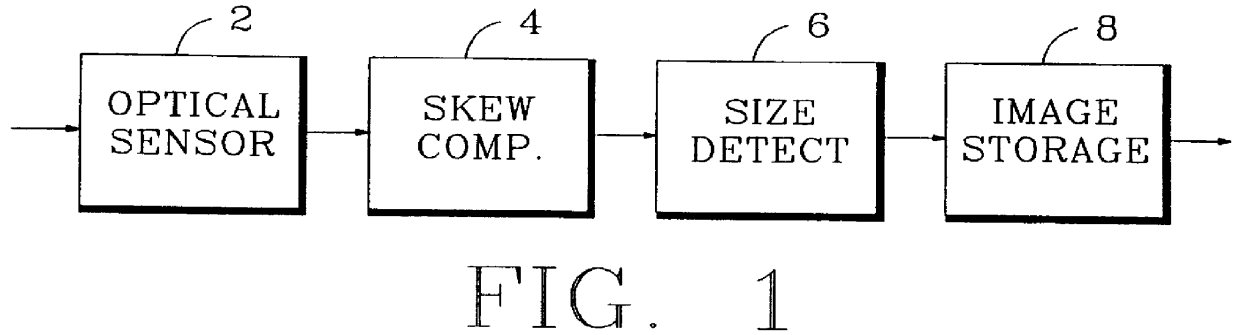
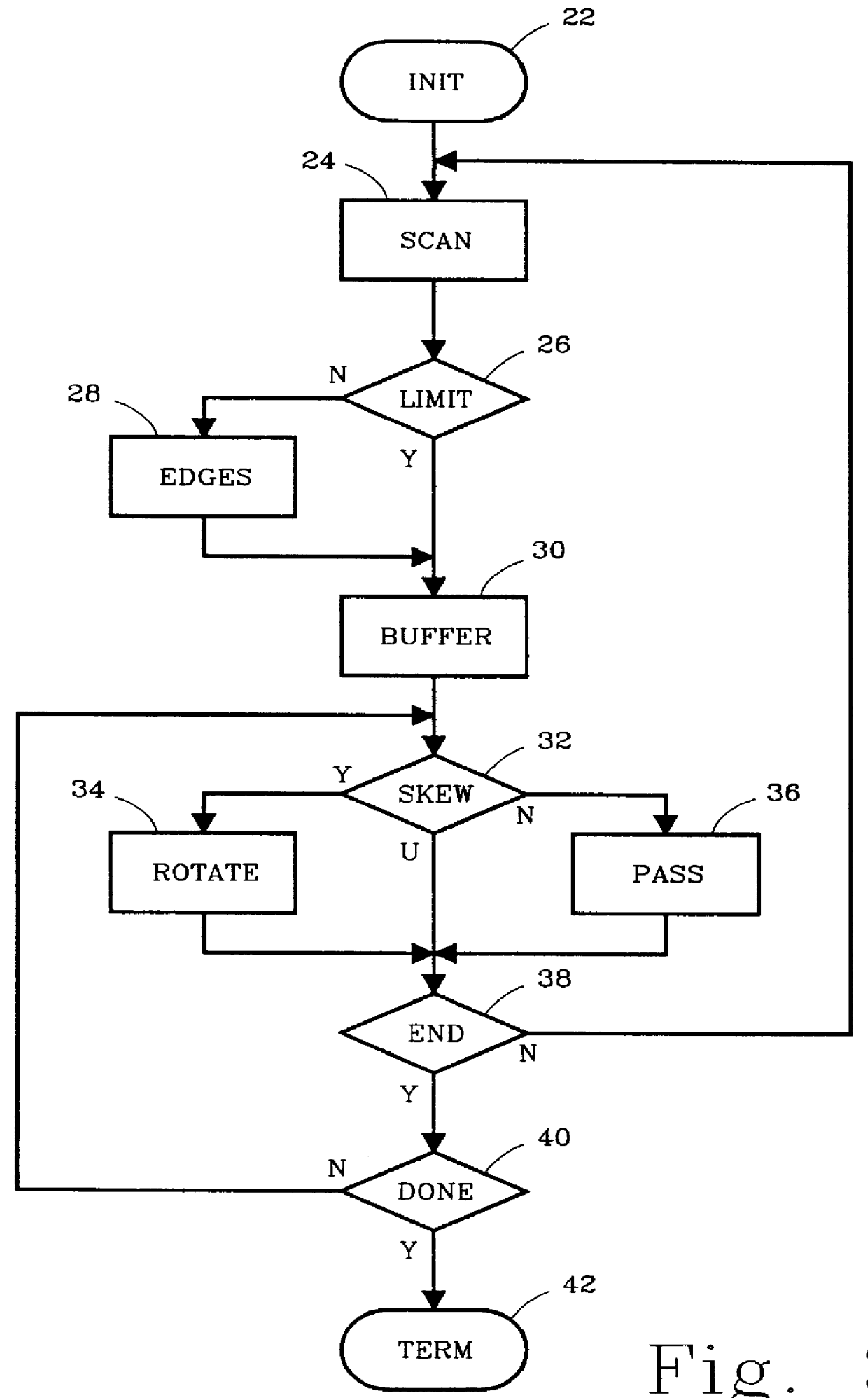
Method and apparatus for near real-time document skew compensation
InactiveUS6064778AReduce the amount of memoryReduce delaysCharacter recognitionPictoral communicationComputer graphics (images)Skew angle
A document imaging system detects skew and / or size of a document. In one embodiment, a document imaging system generates scanning signals representing the documents, analyxes the scanning signals to detect one more edges of the document before the entire lenght of the document is scanned, establishes a skew angle between the detected edges and a reference orientation, and modifies the scanning signals to compensate for skew while the document is being scanned. In another embodiment, a document imaging system detects one or more edges of a document, defines a polygon having sides substantially congruent with the detected edges, and establishes the size of the document in response to the polygon.
Owner:PRIMAX ELECTRONICS LTD
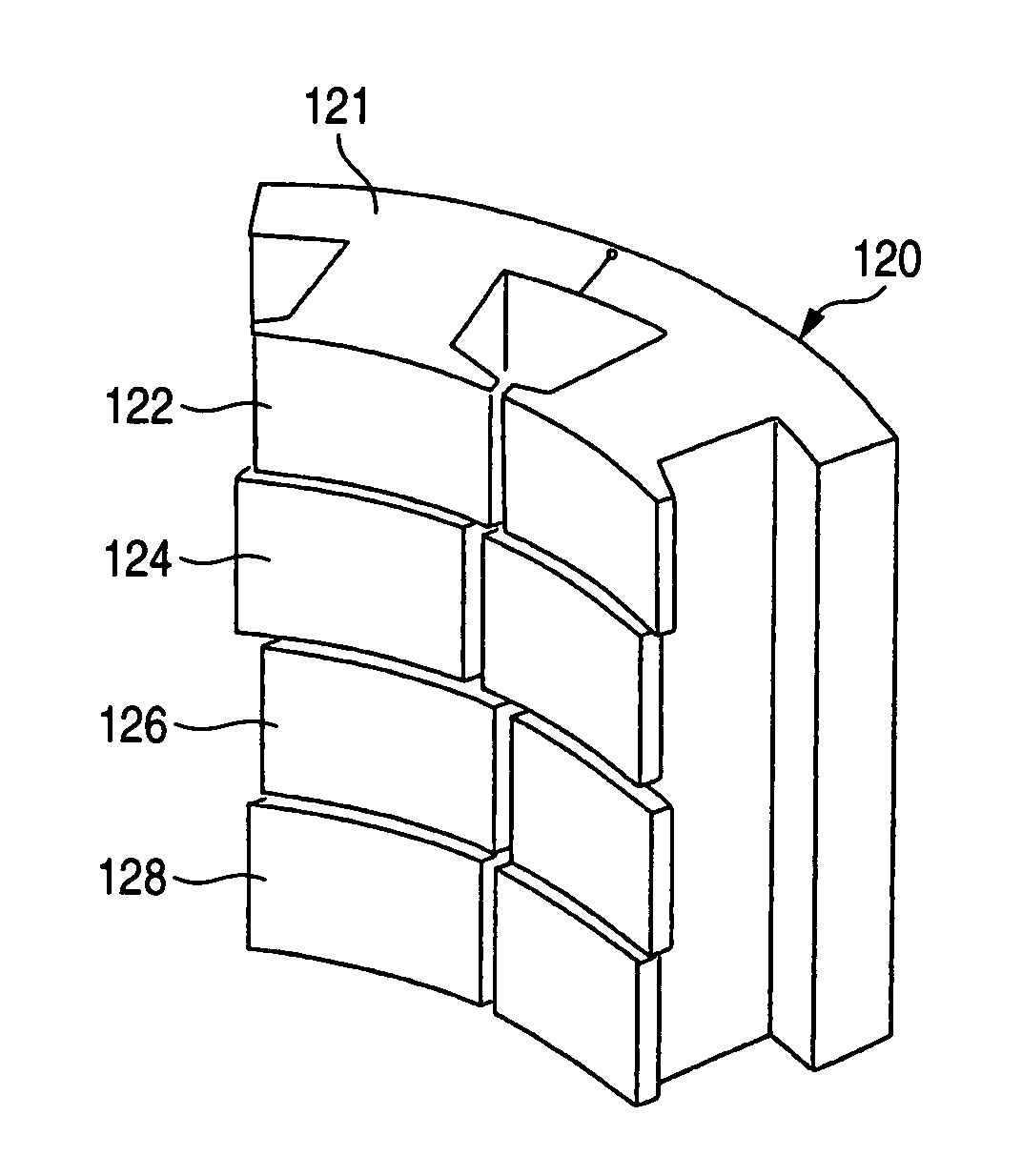
Permanent-magnet rotating machine
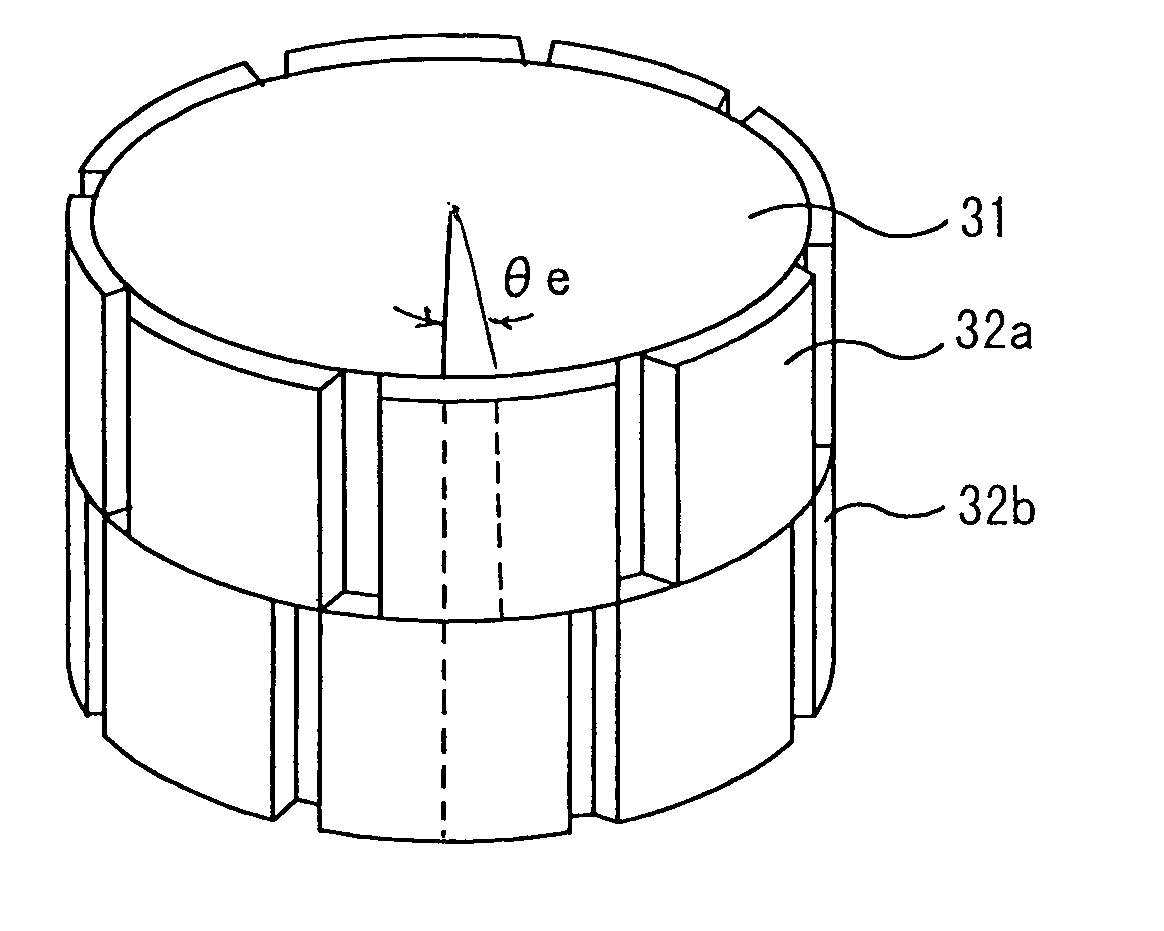
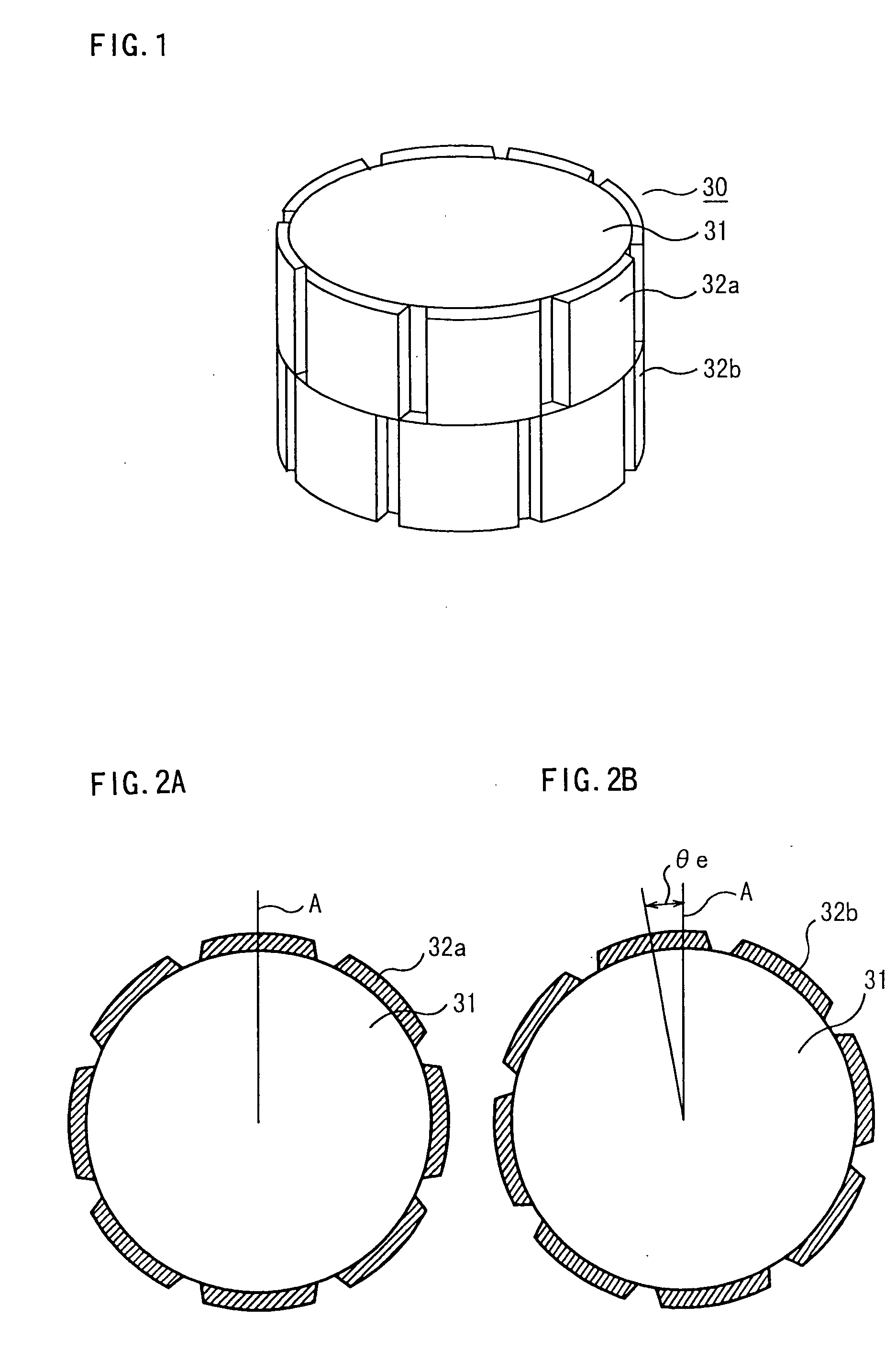
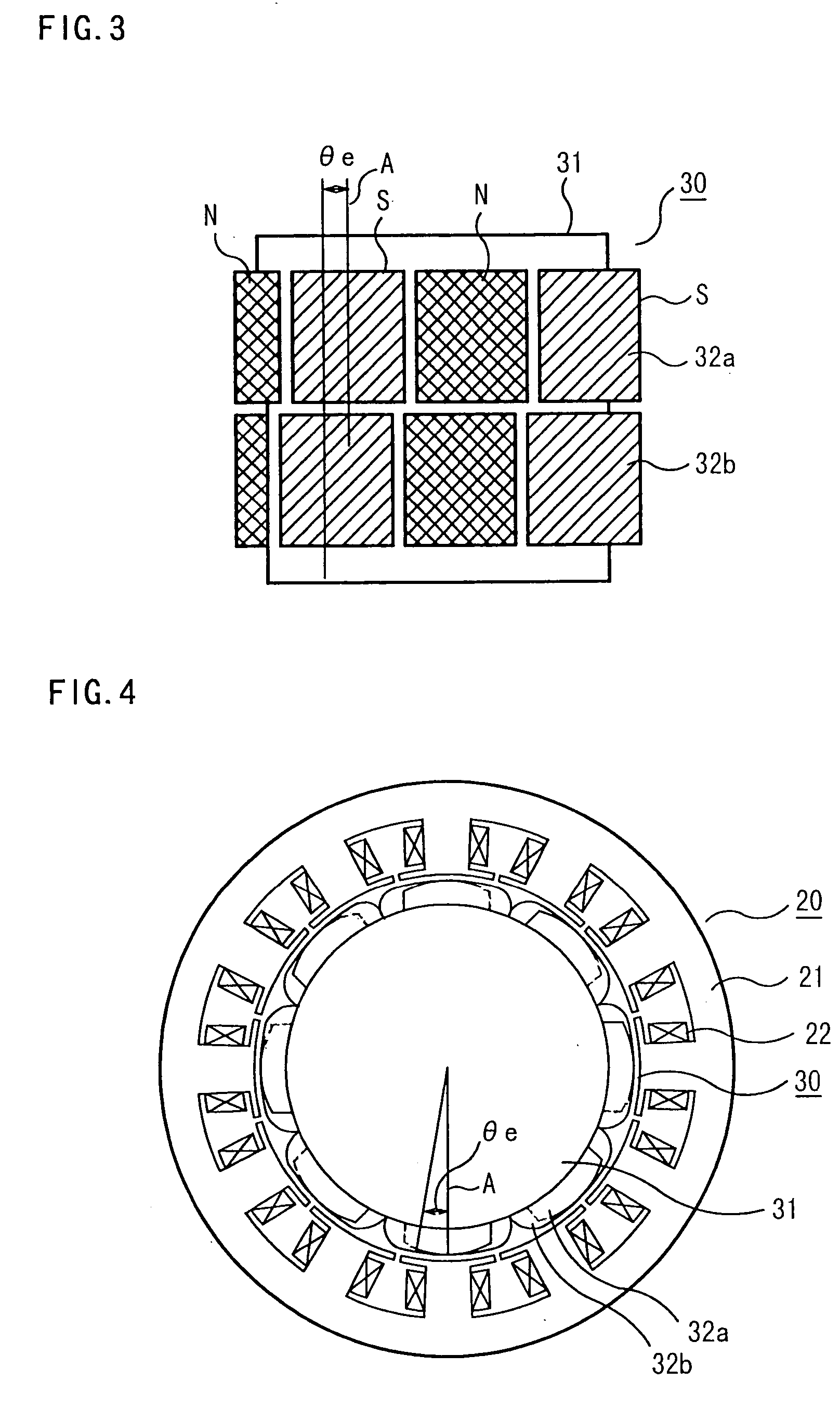
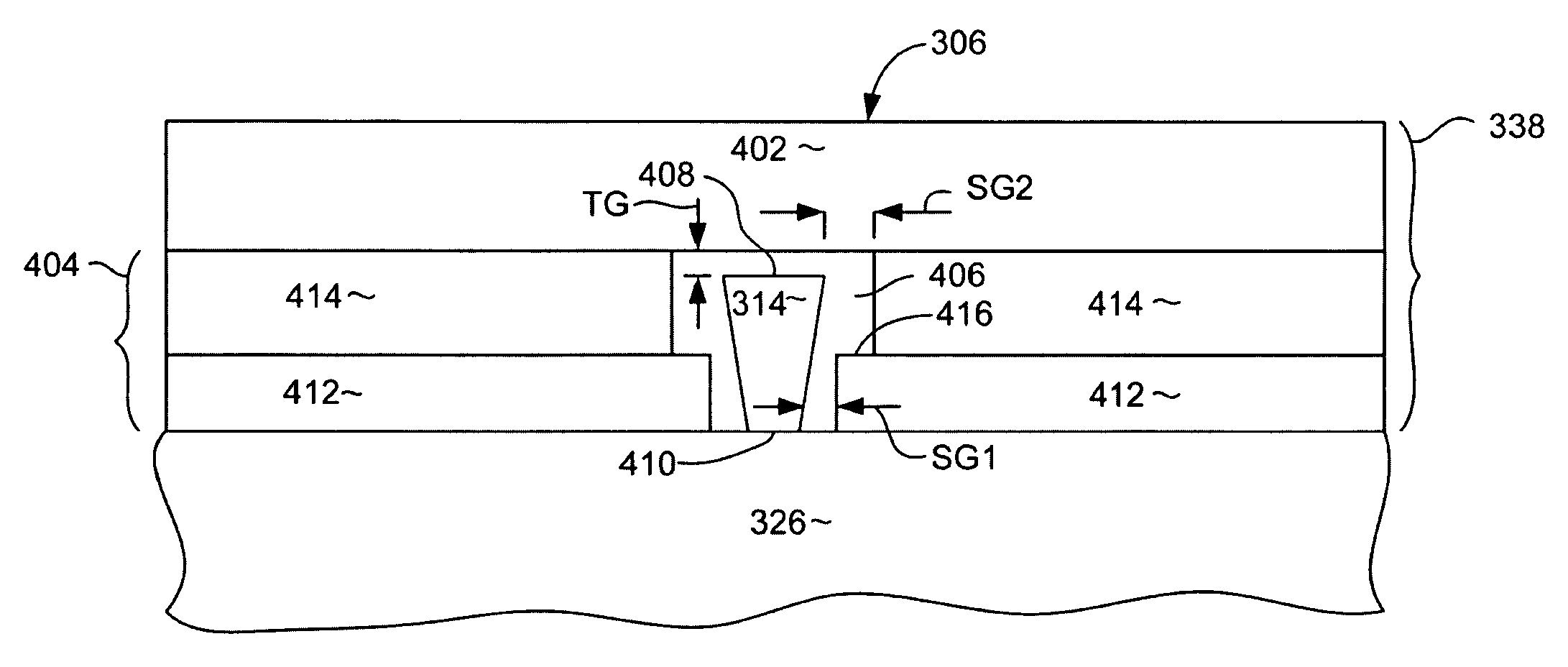
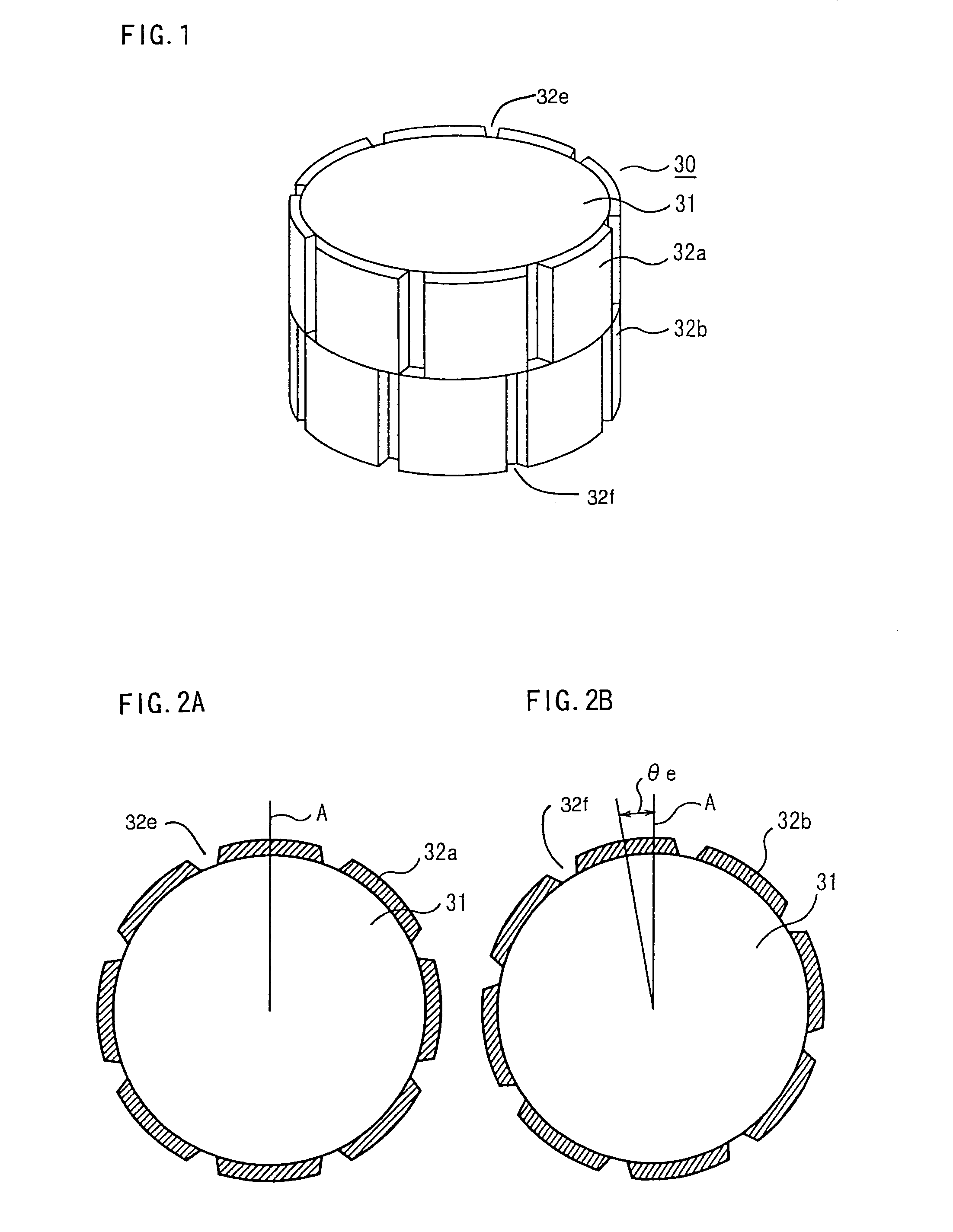
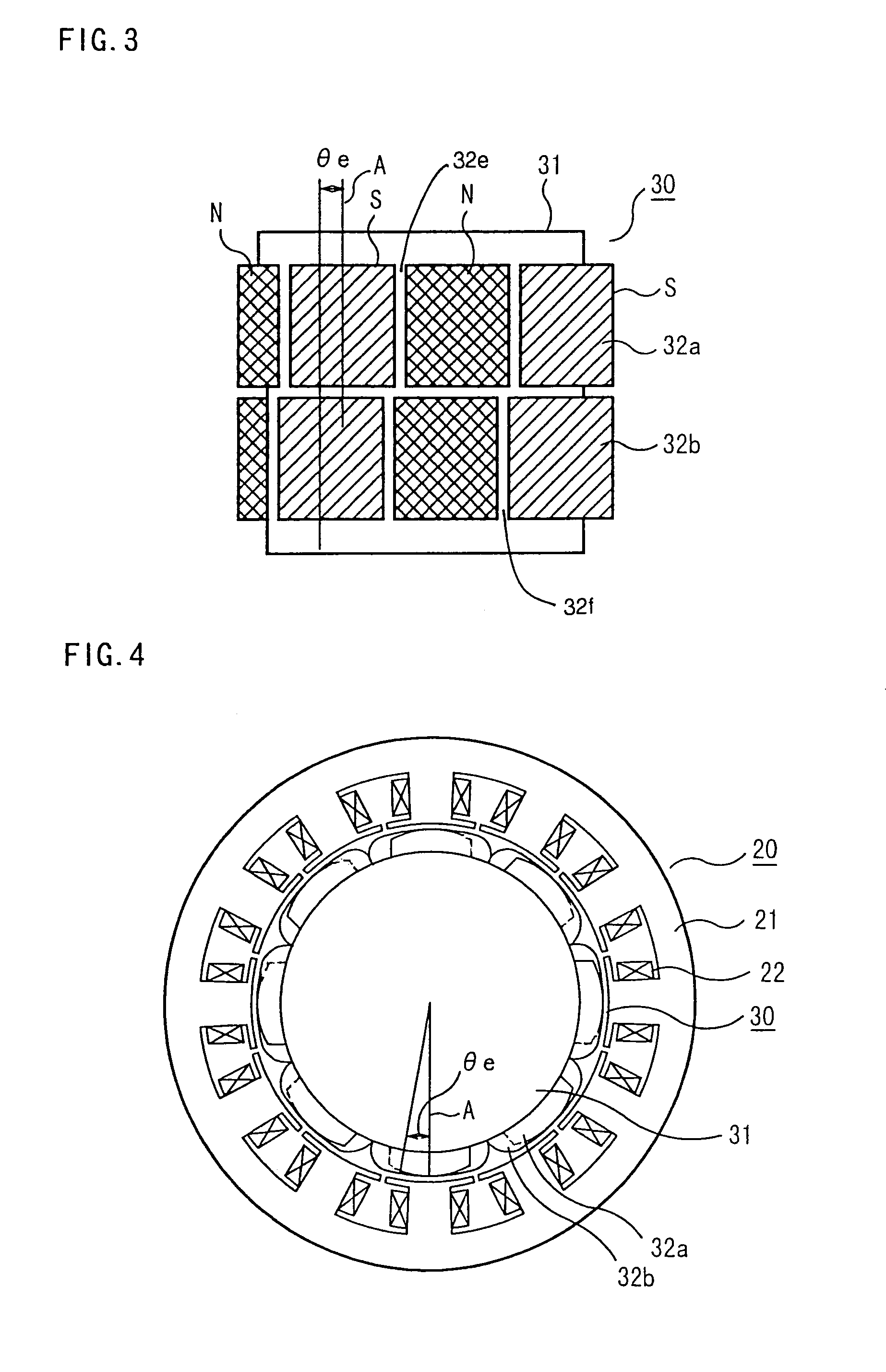
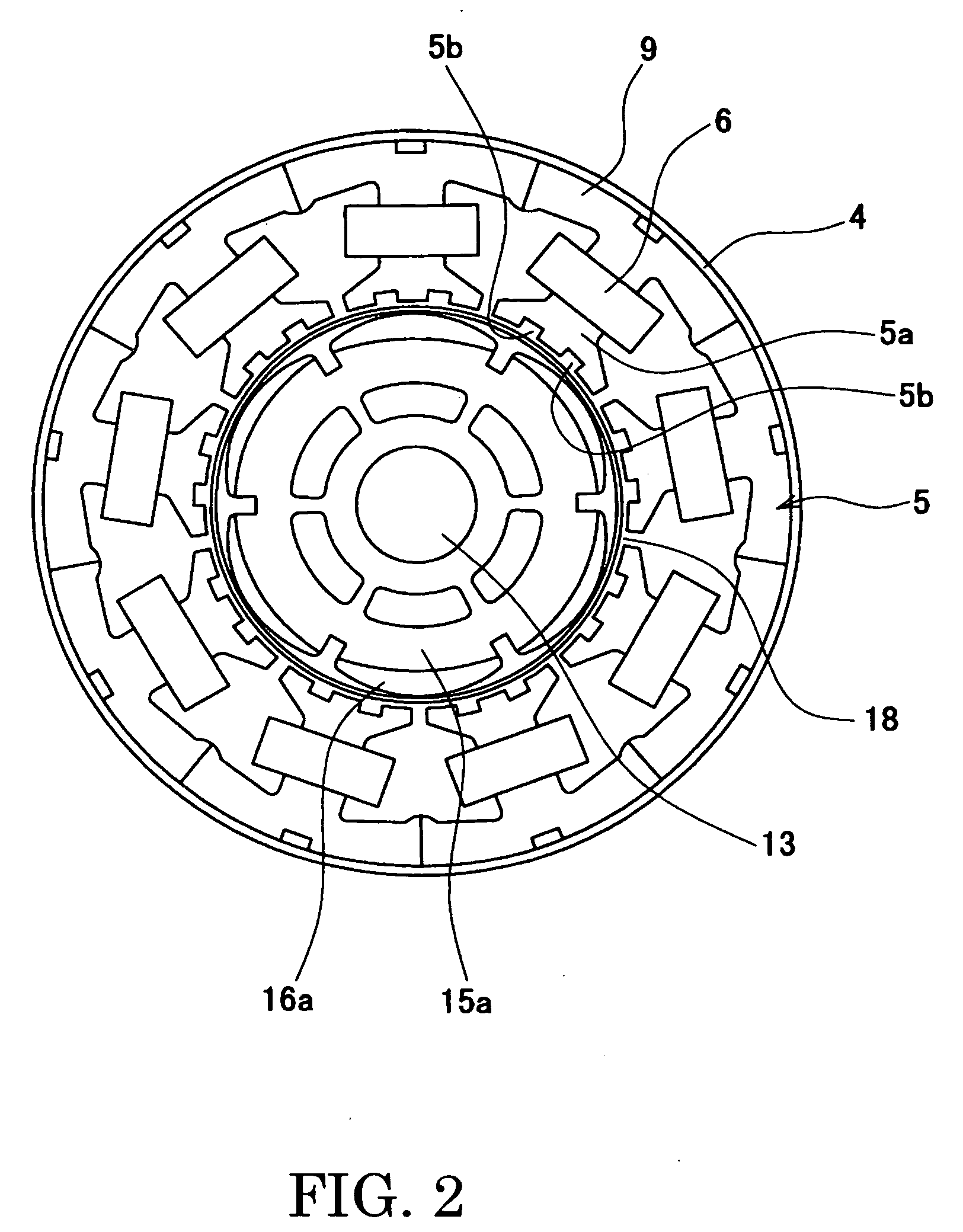
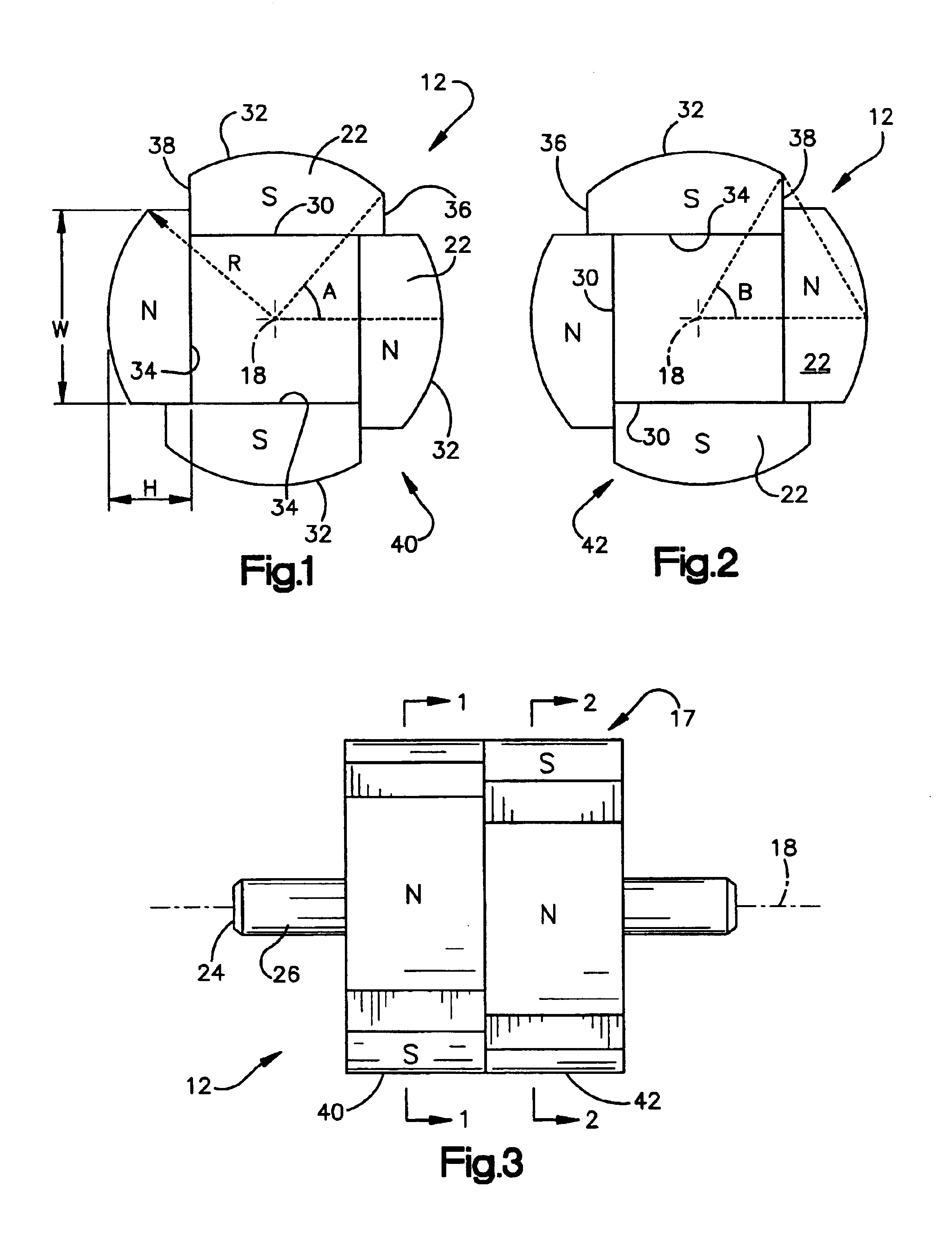
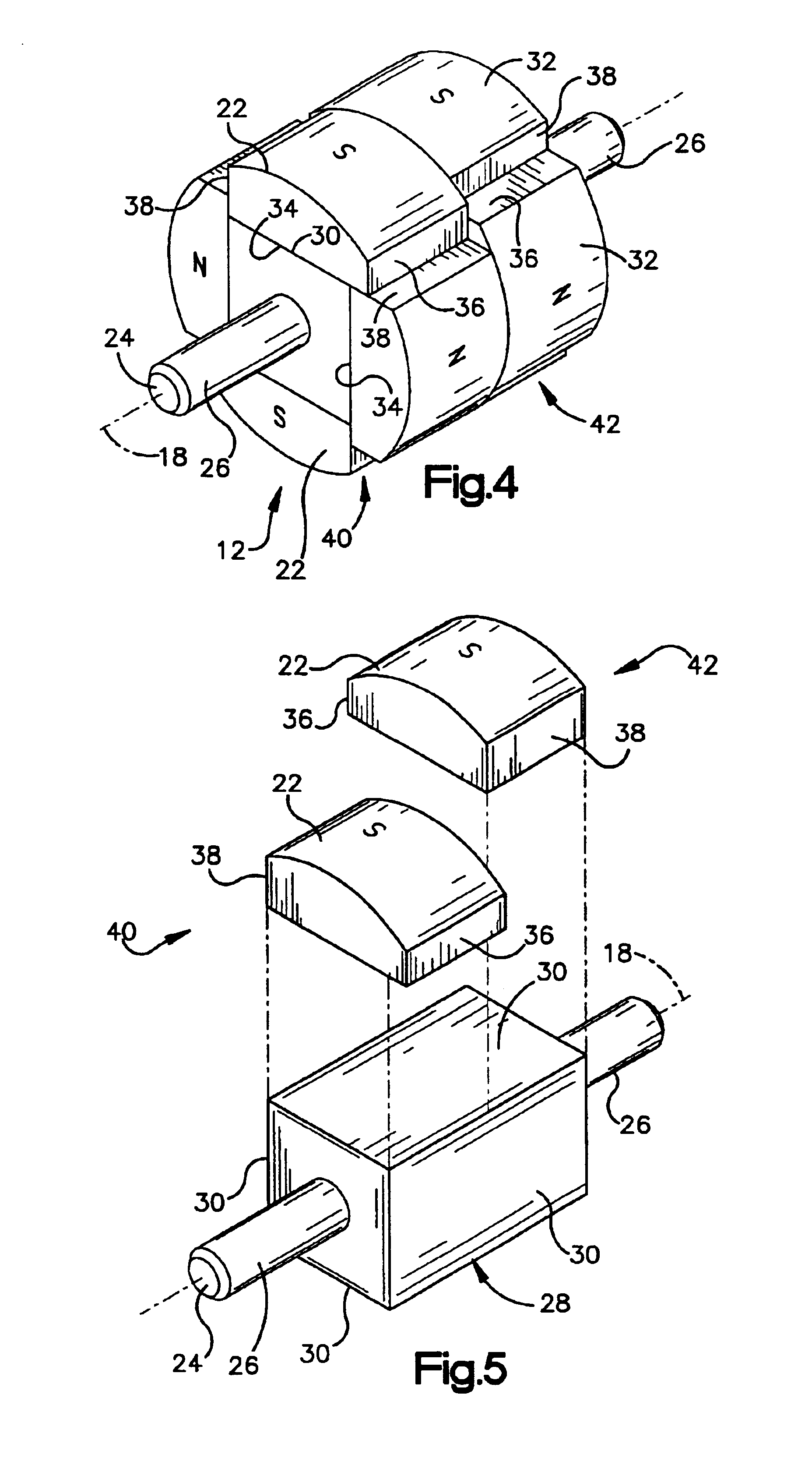
ActiveUS20040124728A1Efficiently reduce cogging torque and torque ripplesMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsLower limitSkew angle
A permanent-magnet rotating machine includes a rotor having a rotor core carrying on its curved outer surface multiple permanent magnets arranged in two rows along an axial direction in such a manner that the permanent magnets in one row are skewed from those in the other row in a circumferential direction by a row-to-row skew angle (electrical angle) thetae, and a stator having a cylindrical stator core in which the rotor is disposed, the stator core being provided with stator coils for producing a rotating magnetic field for rotating the rotor. A lower limit of the row-to-row skew angle thetae is set at a value larger than 30 degrees (electrical angle). A cogging torque ratio, or the ratio of a cogging torque occurring in the absence of skew to a cogging torque occurring when the permanent magnets are skewed, at a row-to-row skew angle of 30 degrees is calculated based on the relationship between the cogging torque ratio and the row-to-row skew angle thetae and B-H curve properties of the stator core, and an upper limit of the row-to-row skew angle thetae is set at a value not larger than its maximum value at which the cogging torque ratio does not exceed the calculated cogging torque ratio at 30 degrees.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Perpendicular write head having a modified wrap-around shield to improve overwrite, adjacent track interference and magnetic core width dependence on skew angle
ActiveUS20090168240A1Improved write field strengthReduced skew adjacent track interferenceRecord information storageHeads for perpendicular magnetisationsLeading edgeSkew angle
A magnetic write head for perpendicular magnetic data recording. The write head includes an wrap around trailing shield structure for improved write field strength, reduced skew related adjacent track interference and magnetic core width. The trailing wrap around shield includes a side shield that is separated from sides of the write pole by a side gap that is narrower near the leading edge of the write pole and wider near the trailing edge of the write pole.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Perpendicular write head having a modified wrap-around shield to improve overwrite, adjacent track interference and magnetic core width dependence on skew angle
ActiveUS8120874B2High strengthShorten the trackManufacture head surfaceRecord information storageLeading edgeSkew angle
A magnetic write head for perpendicular magnetic data recording. The write head includes an wrap around trailing shield structure for improved write field strength, reduced skew related adjacent track interference and magnetic core width. The trailing wrap around shield includes a side shield that is separated from sides of the write pole by a side gap that is narrower near the leading edge of the write pole and wider near the trailing edge of the write pole.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
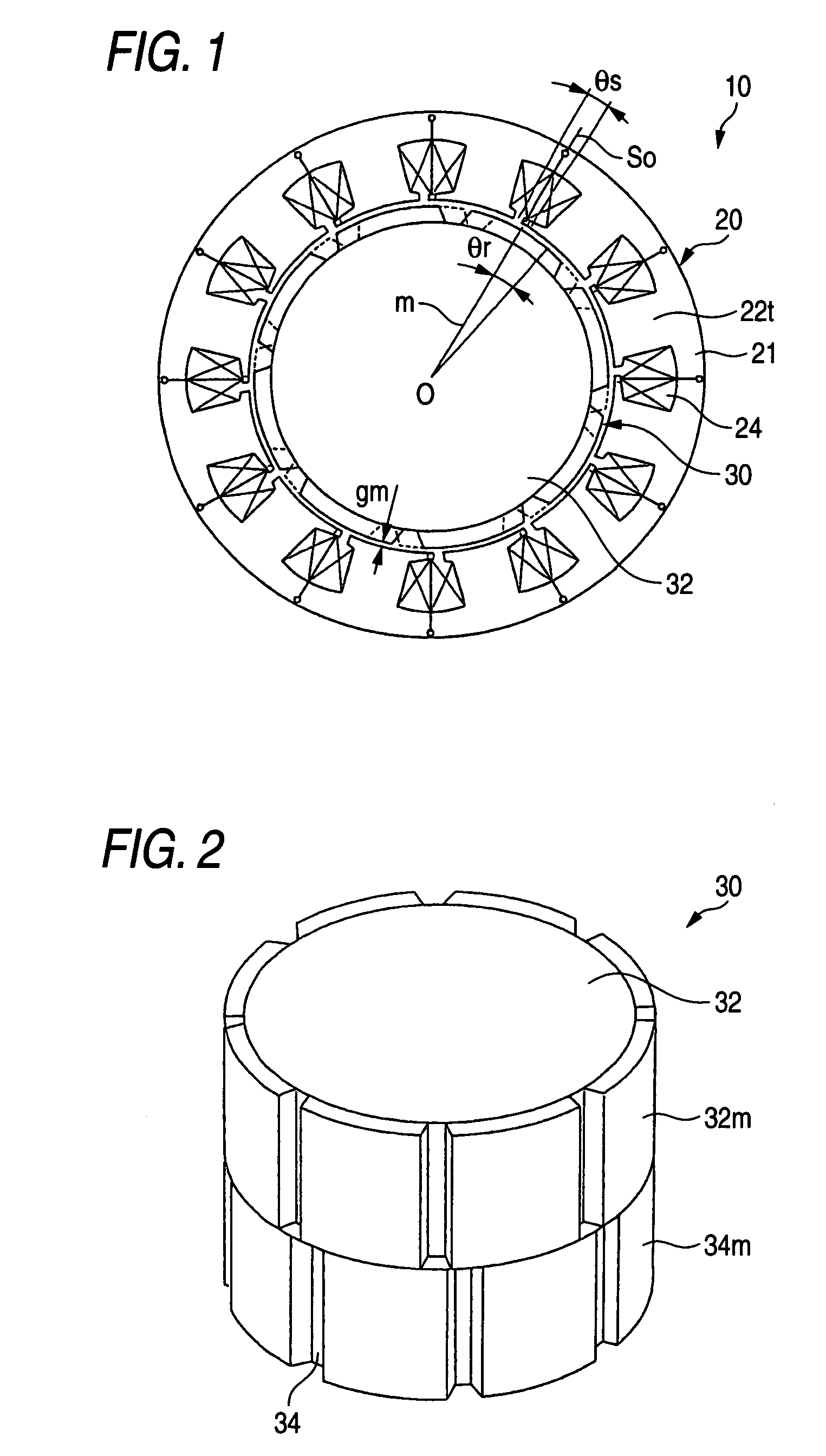
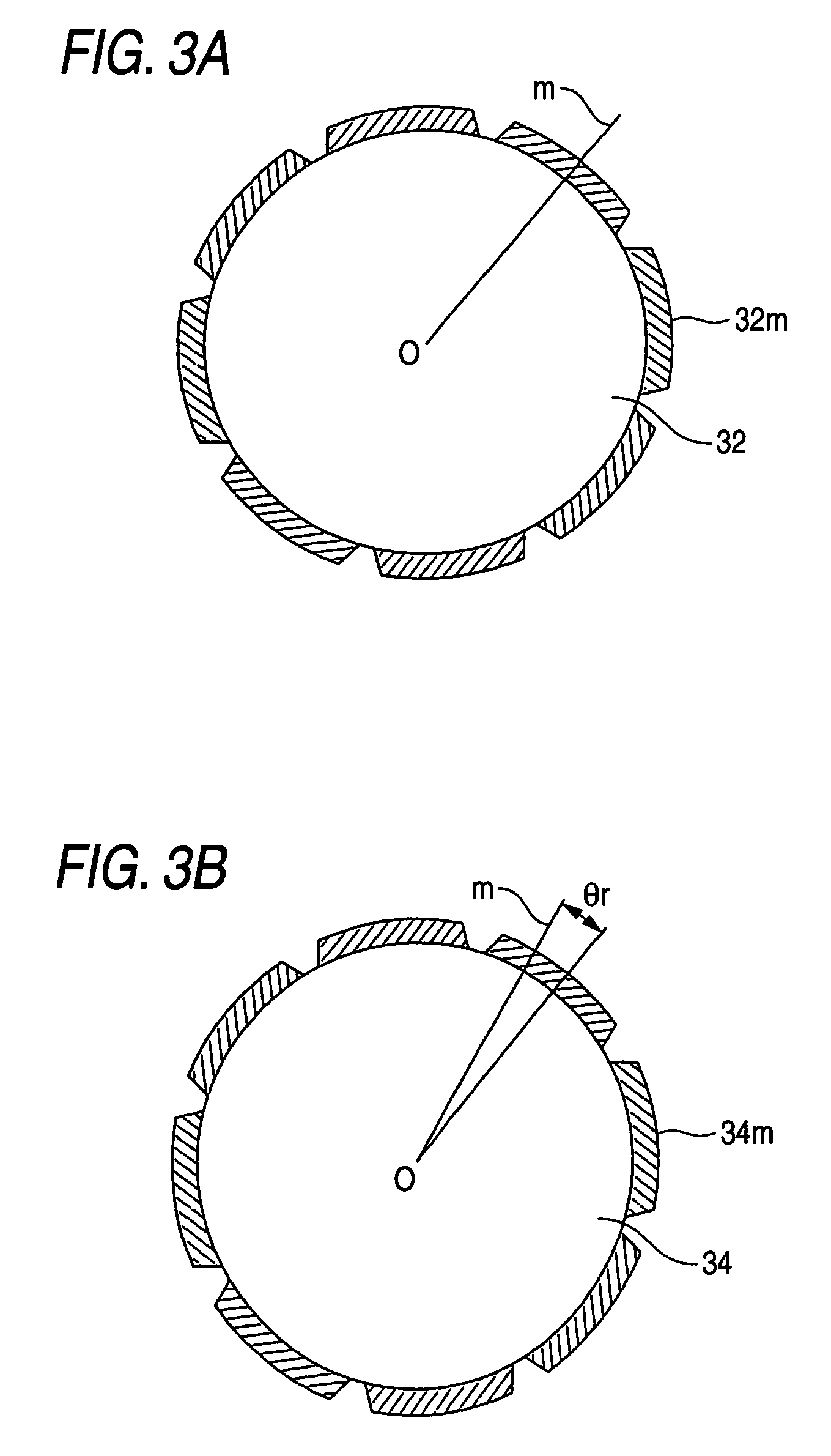
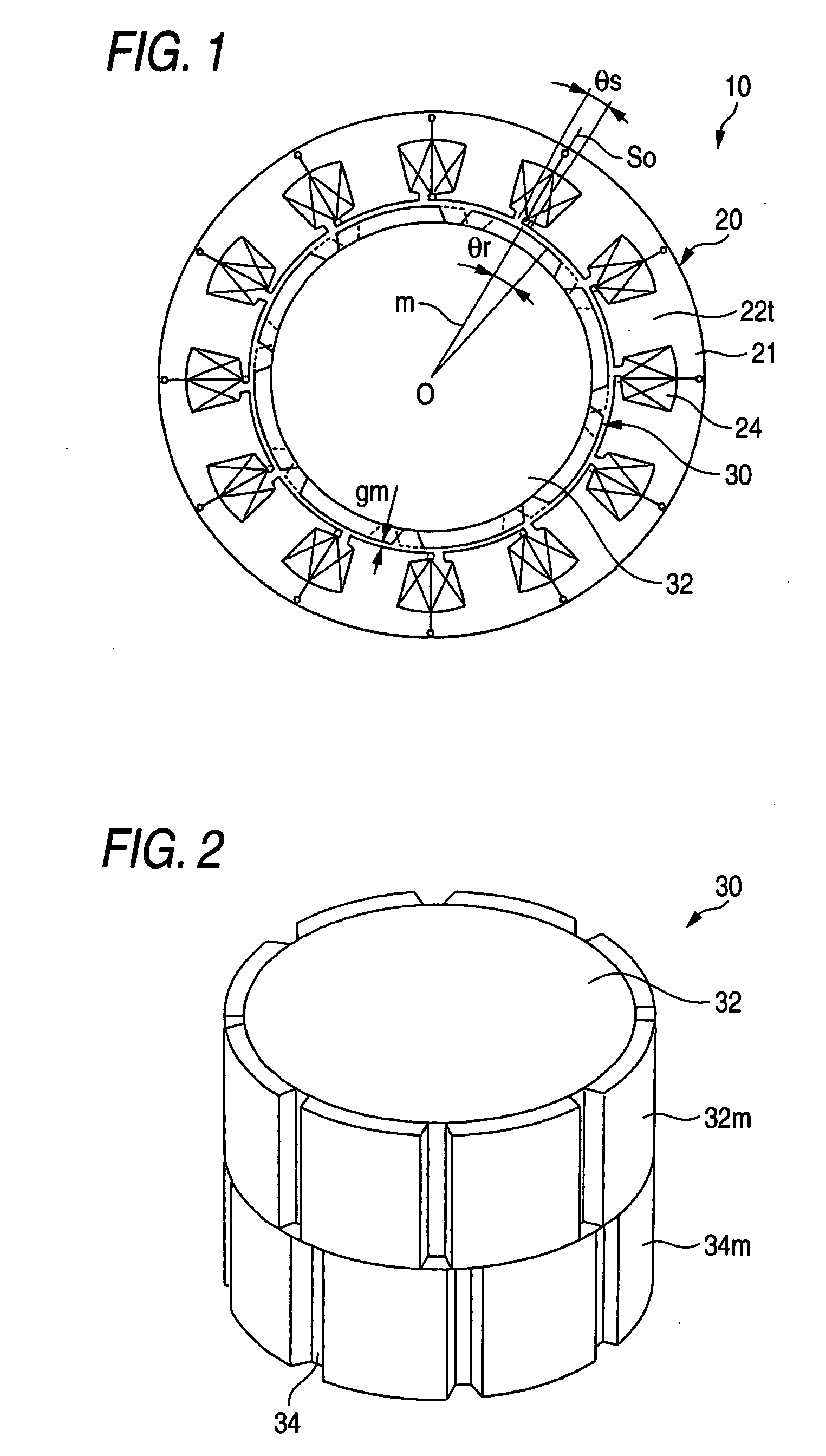
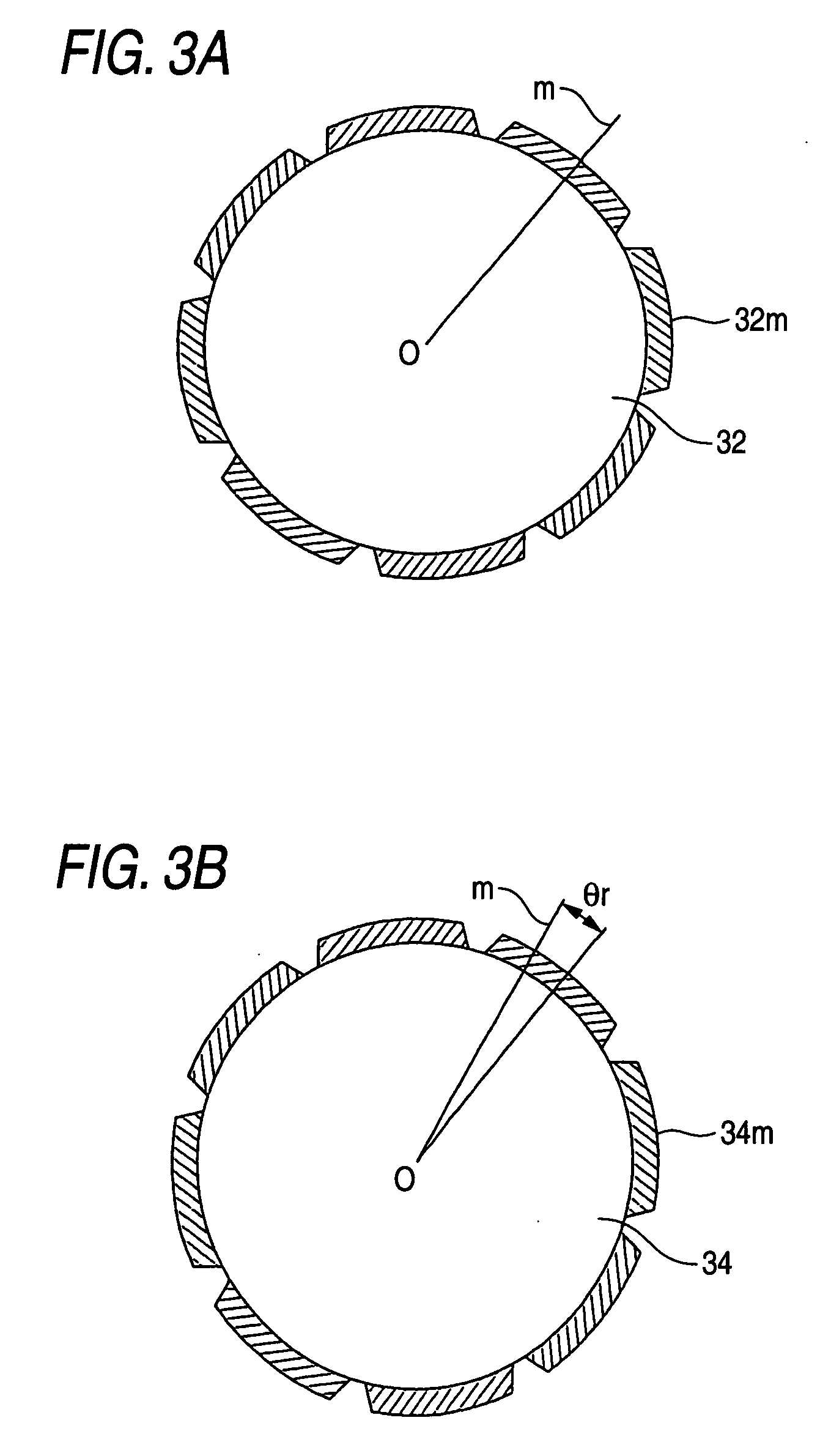
Permanent magnet electric motor with reduced cogging torque
ActiveUS7342338B2Simple constitutionEasy constructionSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsSkew anglePermanent magnet motor
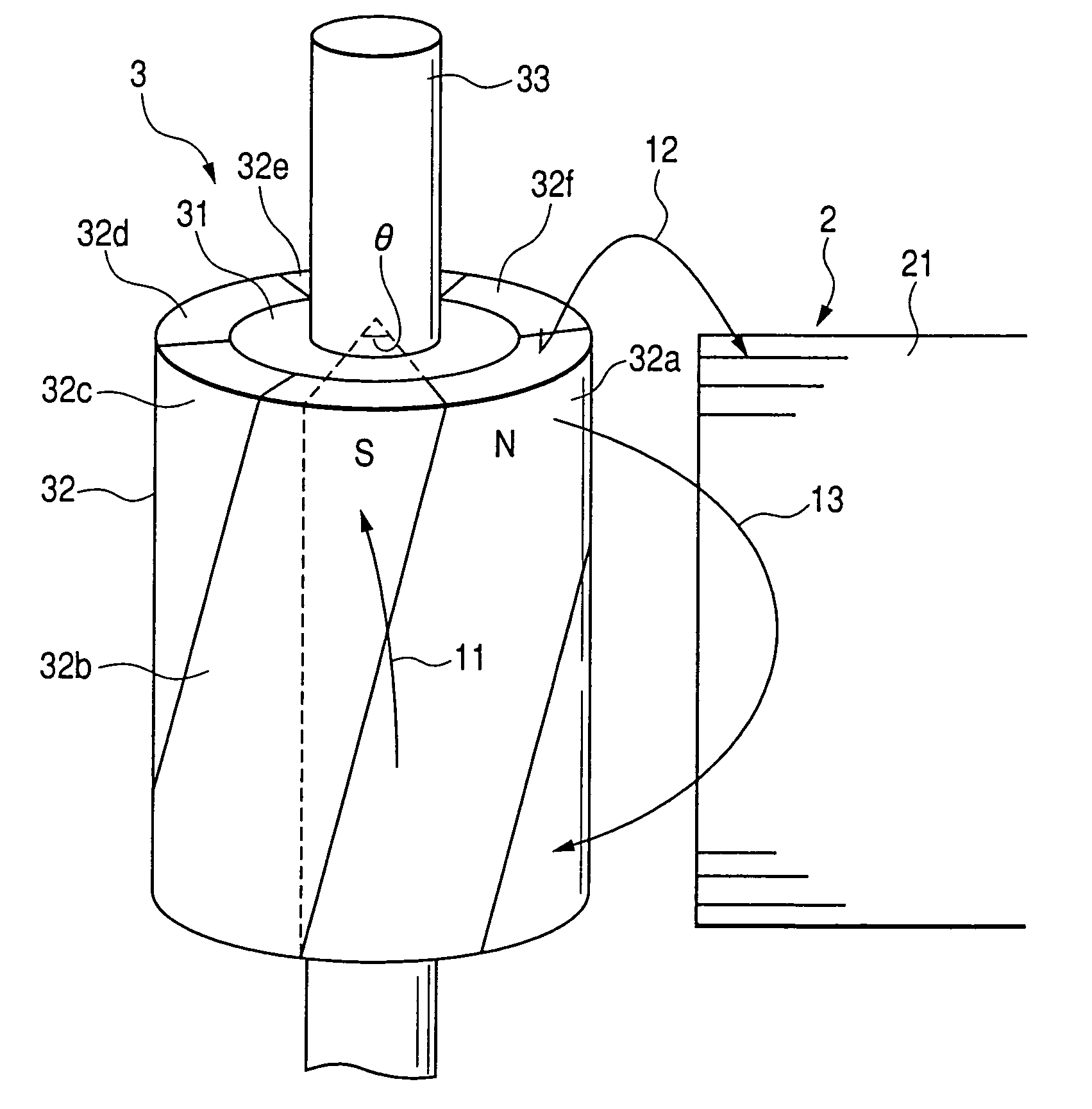
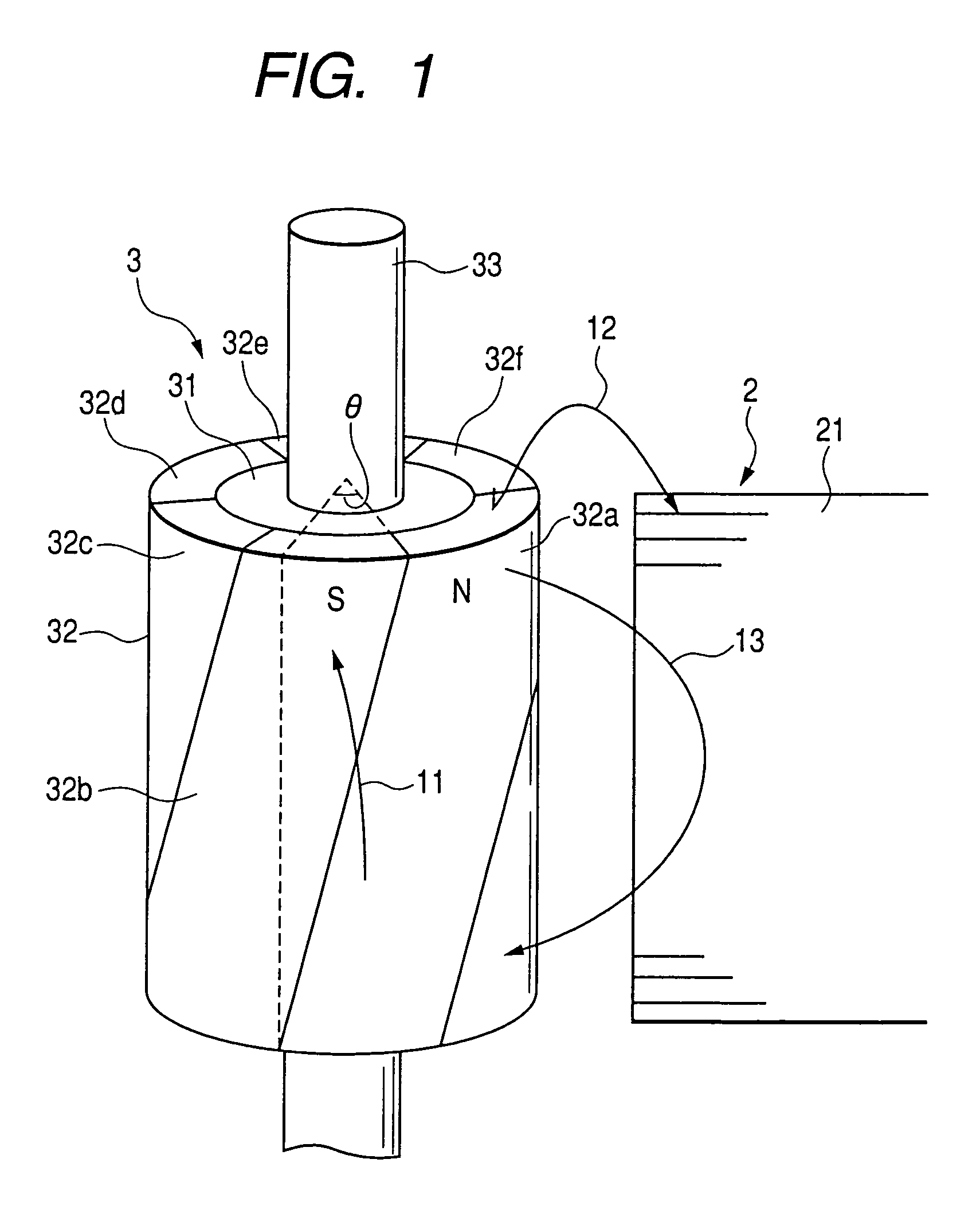
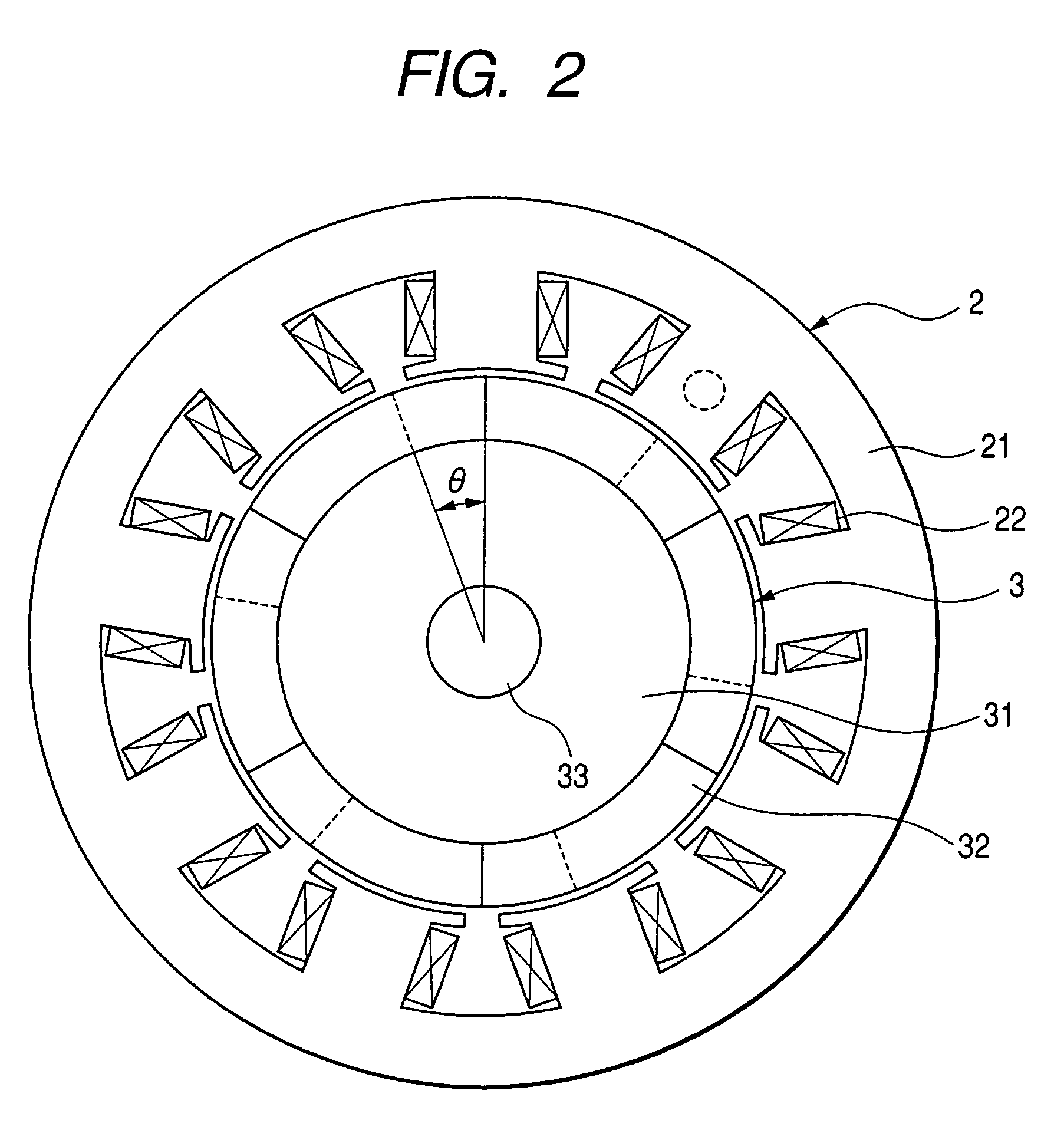
A permanent magnet electric motor 10 comprises a rotor 30 provided with two stages of permanent magnets in the axial direction on an outer circumferential face of a rotor iron core, and having a shaft shifted by a stage skew angle θr in electrical angle to decrease a first frequency component of cogging torque in the circumferential direction of the rotor iron core between two stages of the permanent magnets, a stator iron core 21 of cylindrical shape provided with the stator winding for producing a rotating magnetic field causing the rotor 30 to be rotated, and a stator 20 dividing the stator iron core 21 into plural blocks in the axial direction, and shifted by a stage skew angle θs in electrical angle to decrease a second frequency component of the cogging torque in the circumferential direction of the stator iron core 21.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Permanent-magnet rotating machine
ActiveUS7067948B2Efficiently reduce cogging torque and torque ripplesMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsLower limitSkew angle
A permanent-magnet rotating machine includes a rotor having a rotor core carrying on a curved outer surface multiple permanent magnets arranged in two rows along an axial direction. The permanent magnets in one row are skewed from those in the other row in a circumferential direction by a row-to-row skew angle (electrical angle) θe. A stator having a tubular stator core in which the rotor disposed includes stator coils for producing a rotating magnetic field for rotating the rotor. A lower limit of the row-to-row skew angle θe larger than 30 degrees (electrical angle). A ratio of cogging torque occurring in the absence of skew to cogging torque occurring when the permanent magnets are skewed, at a row-to-row skew angle of 30 degrees is calculated based on the cogging torque ratio, the row-to-row skew angle θe, and B-H curve properties of the stator core. An upper limit of the row-to-row skew angle θe is not larger than the maximum value at which the cogging torque ratio does not exceed the calculated cogging torque ratio at 30 degrees.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Apparatus and method for correlating a suspect note deposited in an automated banking machine with the depositor
InactiveUS20030210386A1Easy to operateAvoid the needPaper-money testing devicesCharacter and pattern recognitionValue setSkew angle
An apparatus and method for determining a type and / or a condition of a note passing through the apparatus includes a note transport (12) which moves the note past sensing assemblies (18). Each sensing assembly includes emitters (32). Each of the emitters produces radiation at a different wavelength. The sensing assemblies include a reflectance detector (20) and a transmission detector (22) which are disposed on opposed sides of the passing note. The emitters direct radiation onto test spots (34) on the passing note. Reflectance values are generated from radiation reflected from each type of emitter to the reflectance detector. Transmission values are generated from radiation transmitted from an emitter through each test spot to the transmission detector. A control circuit produces a sensed value set including the reflectance and transmission values from each of the emitters in each of the sensing assemblies. The control circuit also determines an angle of skew of the passing note. Memories (138) include templates of values corresponding to transmission and reflectance values for known note types in a number of note positions. The control circuit generates stored value sets from the templates and skew angle. The control circuit further calculates a value representative of a level of correlation between the sensed value set and each of the stored value sets. The control circuit determines the highest level of correlation between all the stored value sets which is indicative of the note type and / or a condition thereof. Various types of sensing assemblies can be used including sensing assemblies that are also suitable for capturing image data from notes or instruments processed in an automated banking machine.
Owner:DIEBOLD NIXDORF
Magnetic head and magnetic disc drive
InactiveUS7508619B2Preventing a side eraseImprove featuresDriving/moving recording headsManufacturing heads with multiple gapsSkew angleMagnetic poles
Embodiments in accordance with present invention provide a magnetic head and a magnetic disc drive capable of preventing a side erase while providing excellent recording characteristics. According to one embodiment, in order to prevent the side erase in an increased skew angle state, a first magnetic pole surface is formed in such a shape that the projection area of the first magnetic pole surface follows a track edge positioned on the boundary side in the track in the state where the first magnetic pole surface is positioned on the track at the innermost periphery thereof included in a first region. Likewise, to prevent the side erase in the increased skew angle state, a second magnetic pole surface is formed in such a shape that the projection area of the second magnetic pole surface follows a track edge positioned on the boundary side with respect to a track in the state where the second magnetic pole surface is positioned on the track at the outermost periphery thereof included in a second region.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Permanent magnet type motor
ActiveUS20060244335A1Reduce leakage fluxSimple constitutionMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsSkew anglePermanent magnet motor
A permanent magnet electric motor 10 comprises a rotor 30 provided with two stages of permanent magnets in the axial direction on an outer circumferential face of a rotor iron core, and having a shaft shifted by a stage skew angle θr in electrical angle to decrease a first frequency component of cogging torque in the circumferential direction of the rotor iron core between two stages of the permanent magnets, a stator iron core 21 of cylindrical shape provided with the stator winding for producing a rotating magnetic field causing the rotor 30 to be rotated, and a stator 20 dividing the stator iron core 21 into plural blocks in the axial direction, and shifted by a stage skew angle θs in electrical angle to decrease a second frequency component of the cogging torque in the circumferential direction of the stator iron core 21.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
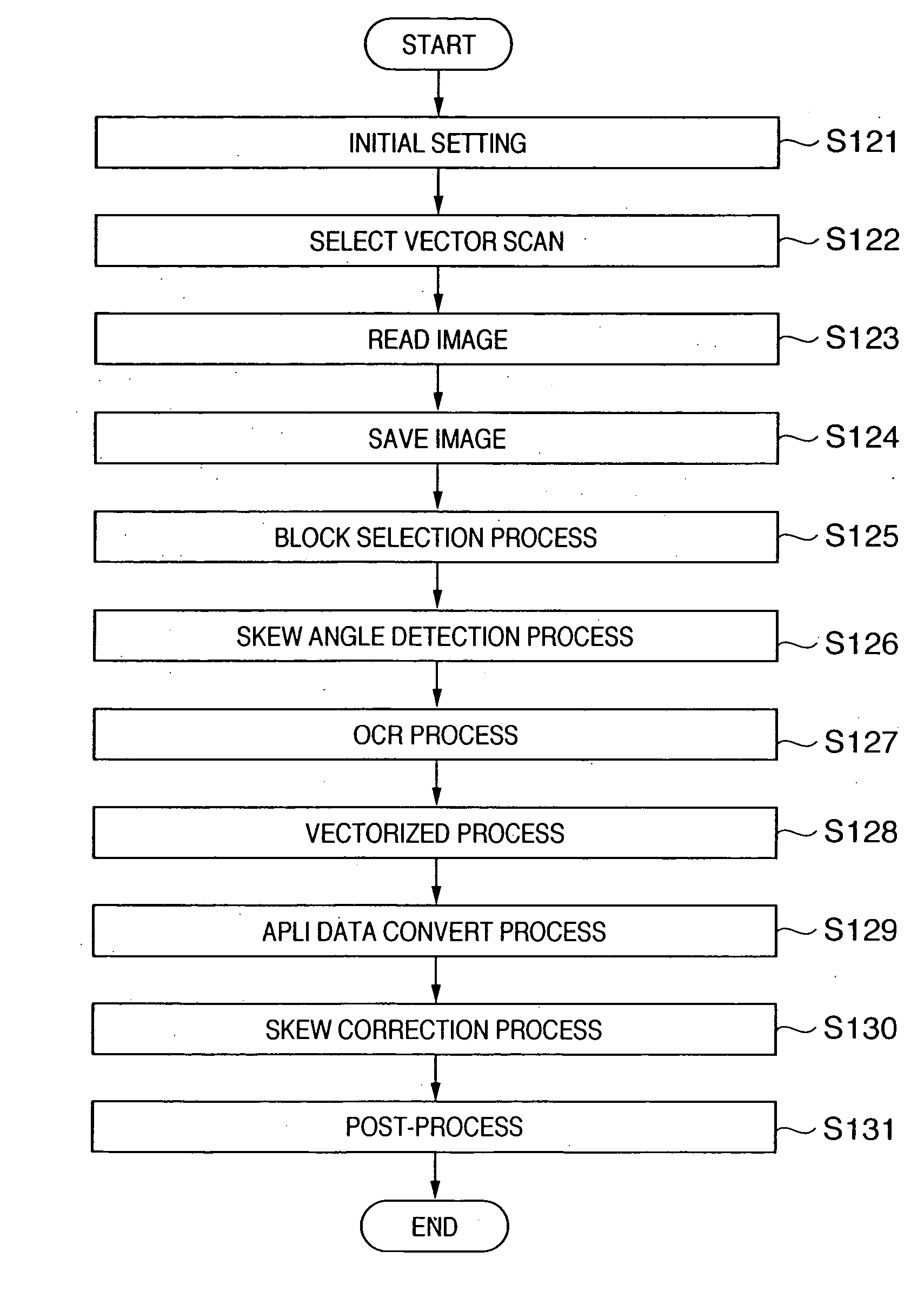
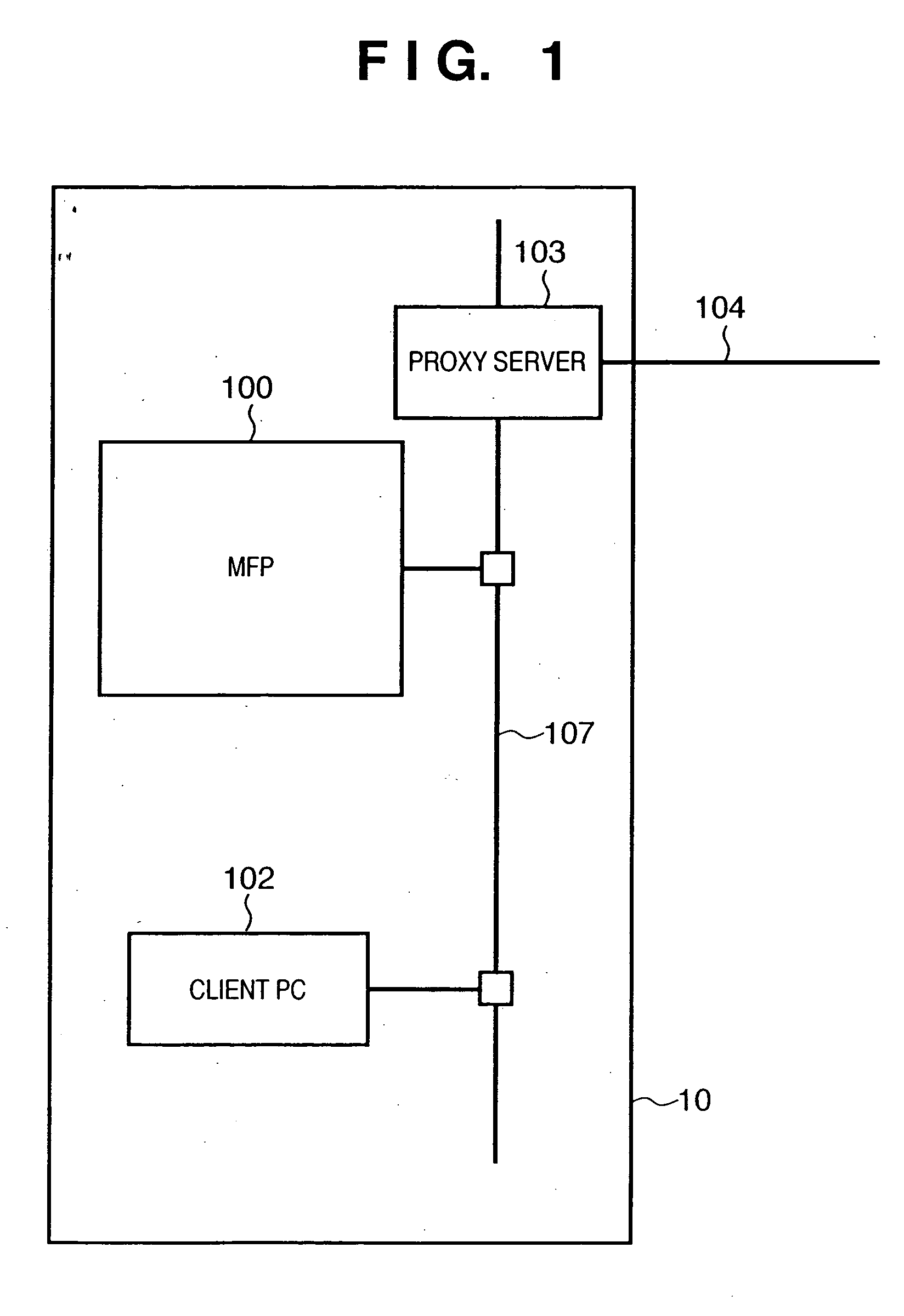
Image processing apparatus, information processing apparatus, control method therefor, and program
InactiveUS20050271296A1Improve accuracyEnsure correct executionImage analysisGeometric image transformationInformation processingImaging processing
Input image data is divided into a plurality of blocks. The skew angle of each divided block with respect to a predetermined direction is detected. Image data input from an input unit is converted into vector data for each divided block. The vector data corresponding to the divided block is corrected on the basis of the detected skew angle of each block.
Owner:CANON KK
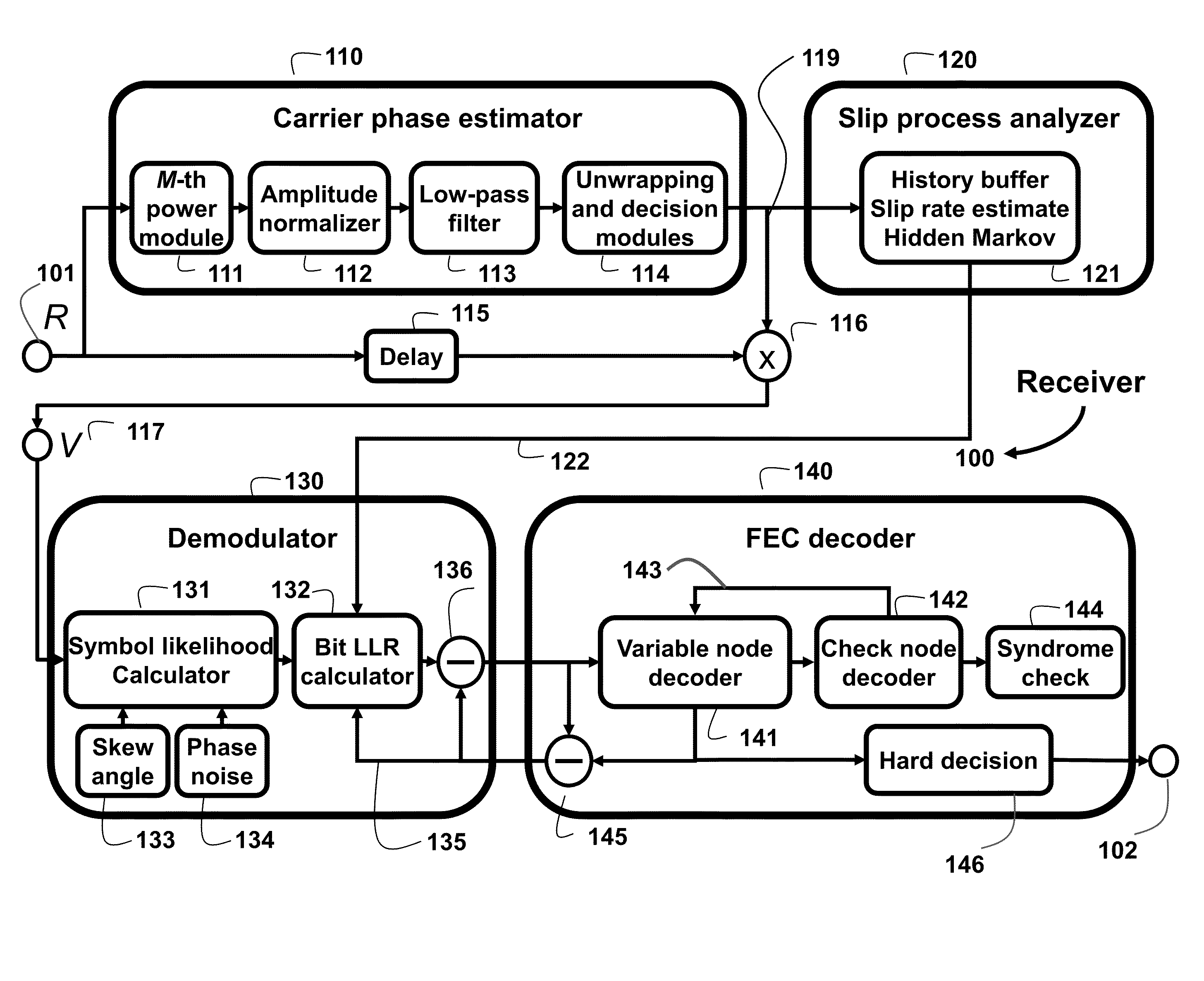
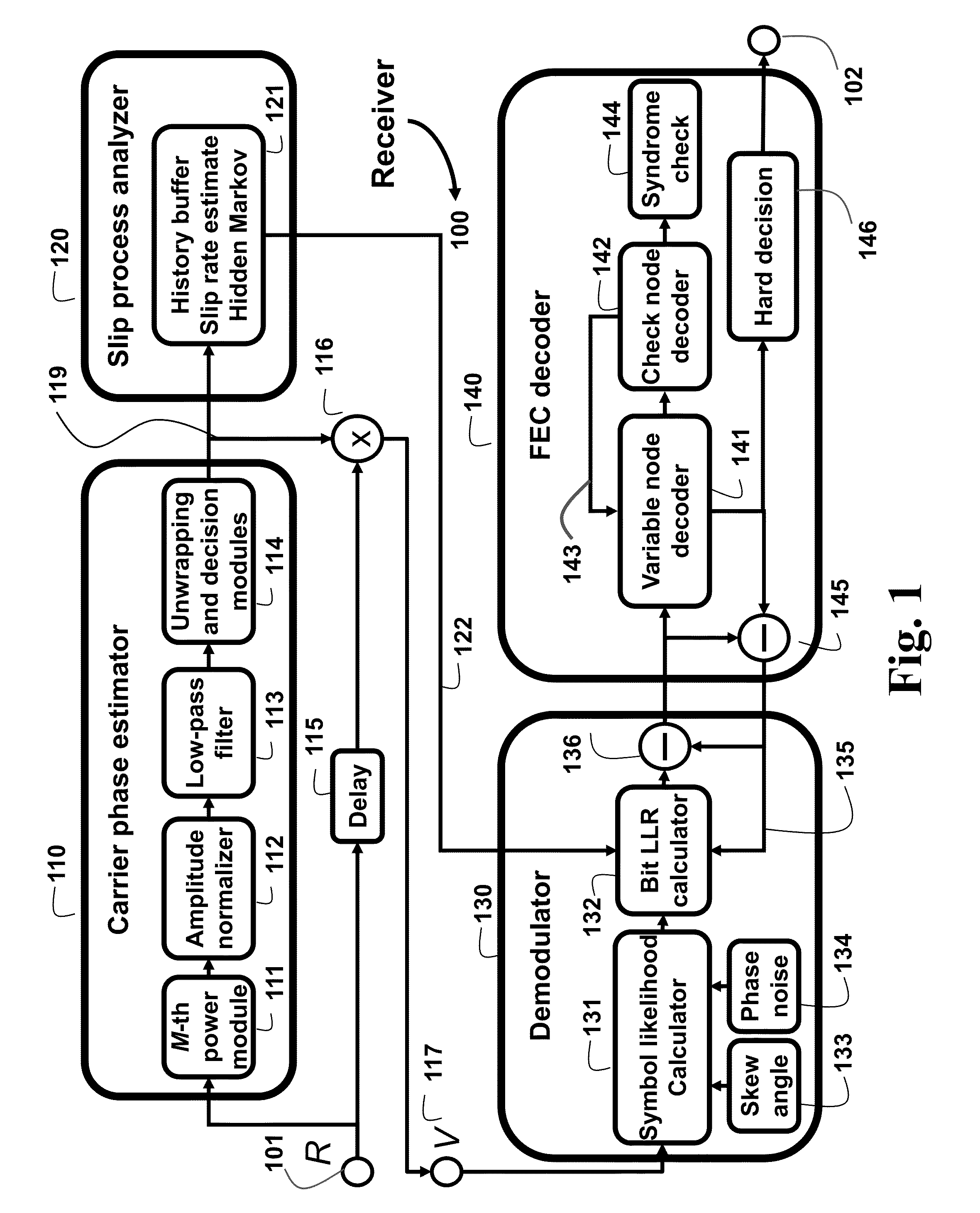
System and Method for Recovering Carrier Phase in Optical Communications
ActiveUS20160065315A1Improve performanceError minimizationError preventionSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansSkew angleHide markov model
The embodiments of the invention provide methods to deal with problems of cycle slips, angular skew, and residual phase noise for high-speed optical communications employing any arbitrary high-order multi-dimensional modulation formats. The embodiments use a slip process analyzer, a skew angle estimator, and a phase noise variance estimator to provide feedforward soft-decision information of a carrier phase recovery (CPE) for more accurate likelihood calculation based on a high-order hidden Markov model (HMM). The log-likelihood calculation can be done jointly in dual polarization with joint Markov state transition. Some embodiments use a kernel filter or a particle filter for log-likelihood calculation.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Method for manufacturing perpendicular magnetic recording head having inverted trapezoidal main magnetic pole layer
InactiveUS6952867B2InhibitionImprove performanceManufacture head surfaceElectrical transducersSkew angleMagnetic poles
The side edge of the main magnetic pole layer is prevented from protruding in the track width direction even when a skew angle is generated by forming the main magnetic pole layer of the opposing face opposing the recording medium as an inverted trapezoid, thereby enabling the occurrence of side fringing to be prevented.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Current-perpendicular-to-the-plane (CPP) magnetoresistive (MR) sensor structure with stacked sensors for minimization of the effect of head skew
ActiveUS9099125B1Manufacturing heads with multiple gapsRecord information storageRadial positionSkew angle
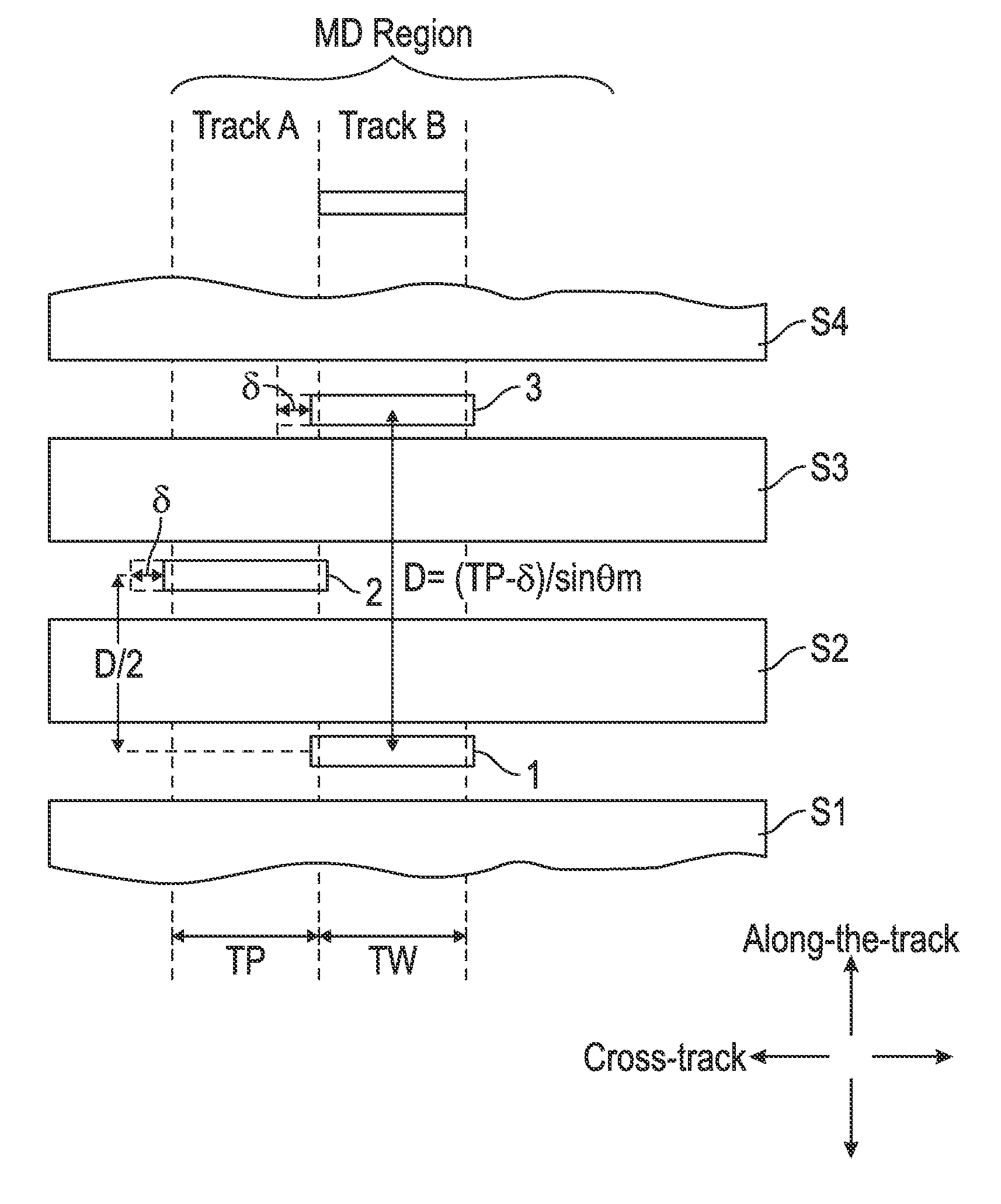
A two-dimensional magnetic recording (TDMR) multi-sensor read head has three stacked sensors separated by magnetic shields. The lower sensor is the primary sensor that is always aligned with the target track. The middle sensor is spaced laterally from the lower sensor a distance substantially equal to the track pitch (TP). The upper sensor is aligned with the lower sensor. The spacing D between the lower and upper sensors is selected to be related to TP and a maximum skew angle, where the skew angle is the angle between a line orthogonal to the sensor and the data track that varies with radial position of the head. The read head is connected to circuitry that selects two of the three sensors to be the active sensors depending on the radial position of the head and thus the skew angle of the head.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Permanent magnet type magnetic field generating apparatus
InactiveUS7760059B2Improve uniformityLow skew angleMagnetic measurementsPermanent magnetsSkew angleMagnetization
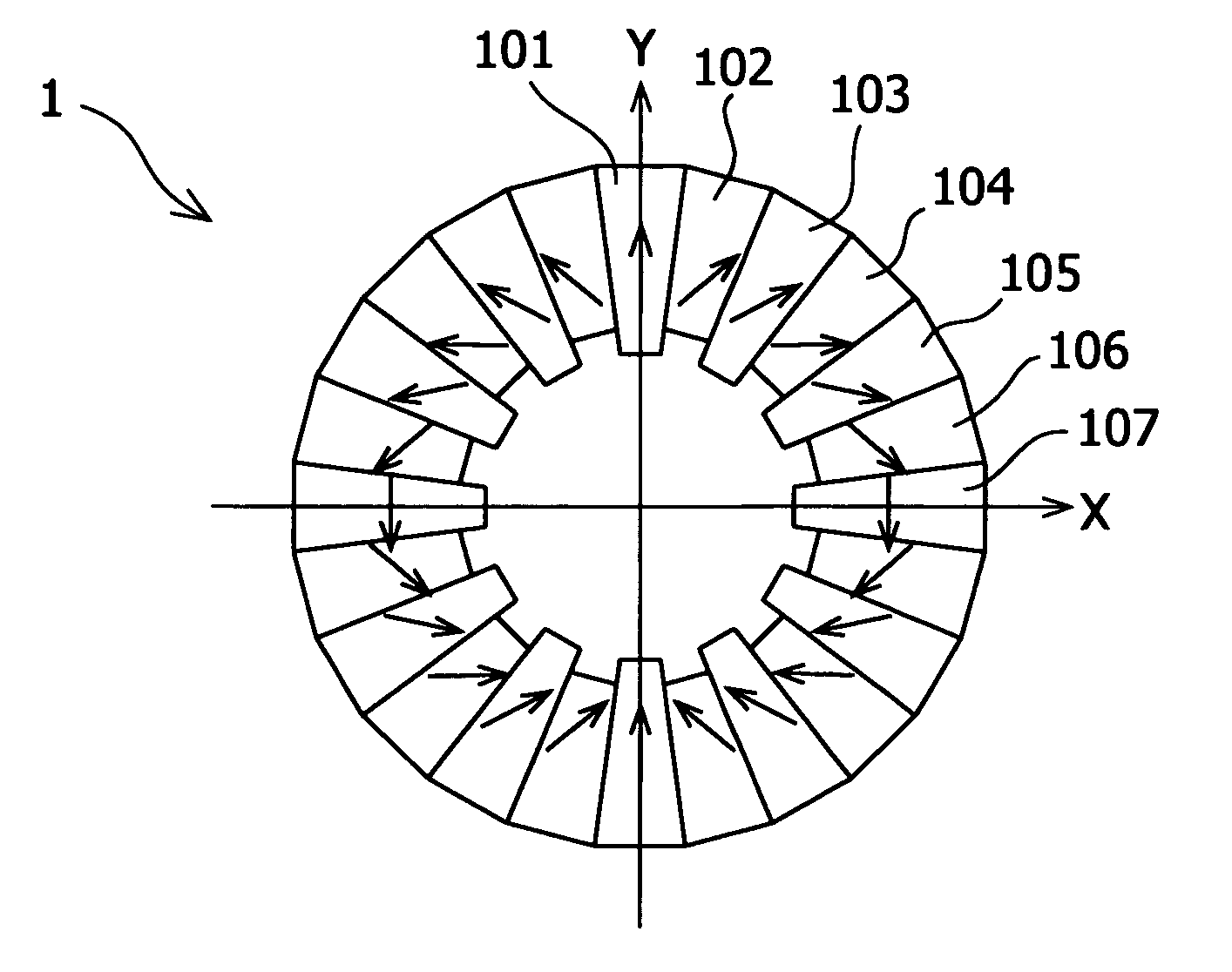
It is an object of the present invention to achieve a magnetic field with high uniformity and low skew angle in a dipole ring magnetic field generating apparatus. There is provided a permanent magnet type magnetic field generating apparatus comprising: a plurality of permanent magnet pieces disposed in a ring shape so that a substantially unidirectional magnetic field is generated in a space within the ring, the permanent magnet pieces having the magnetization direction undergoing one rotation over a half-circumference of the ring, the permanent magnet pieces having substantially the same magnetic strength, and the permanent magnet pieces being disposed so as to form indentations and protrusions toward a center axis of the ring, or having a shape having indentations and protrusions facing the center axis.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
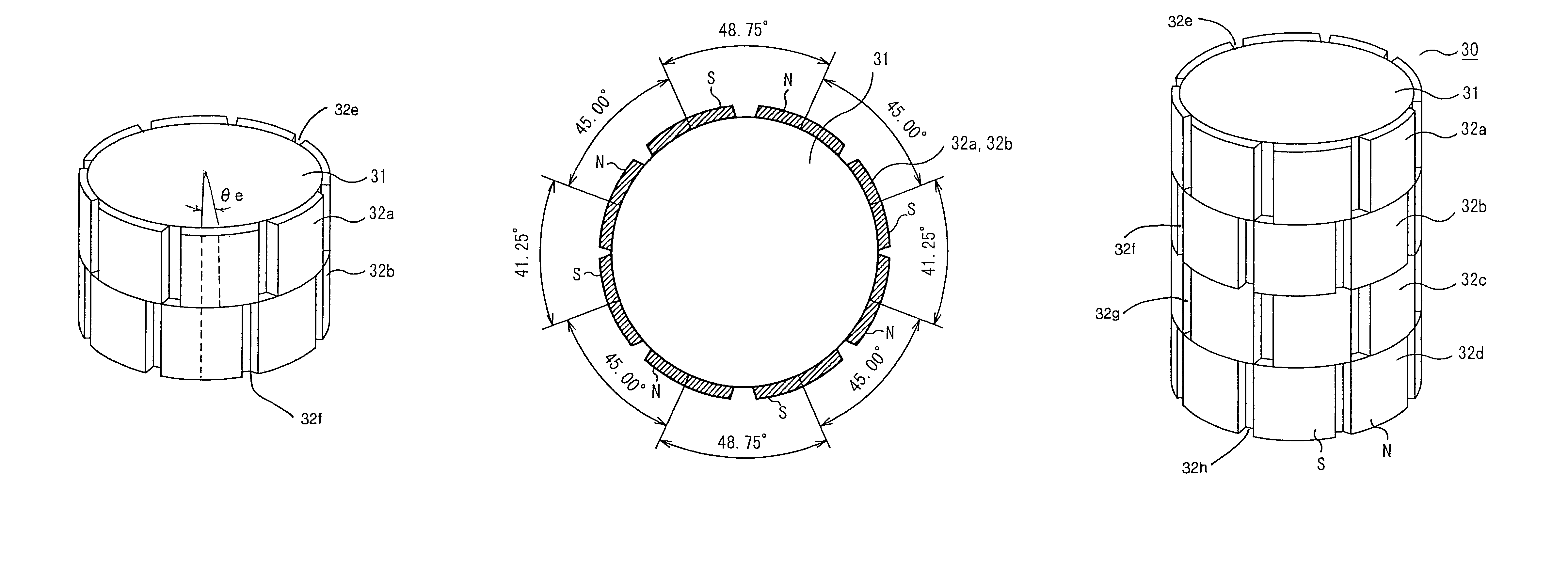
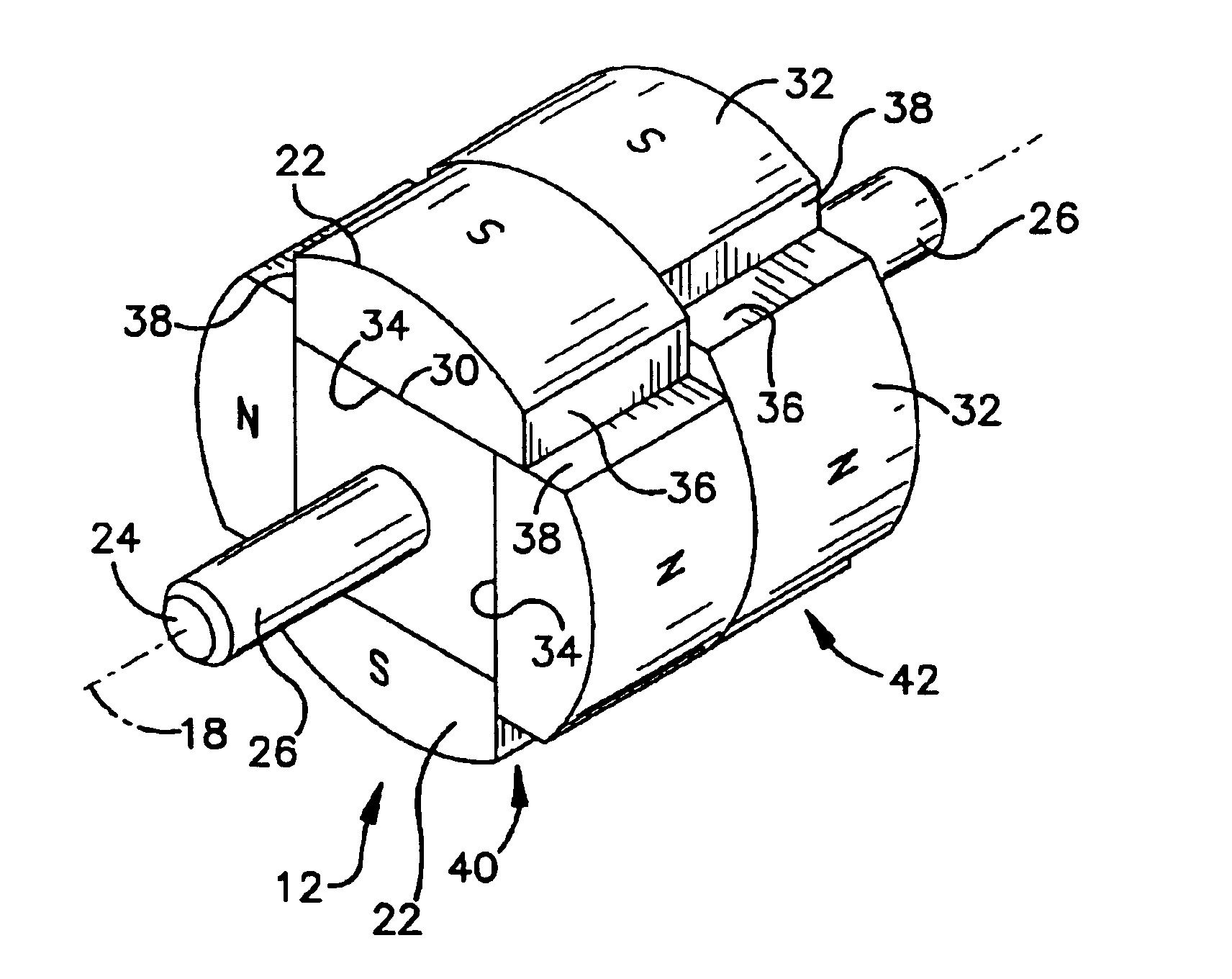
Brushless motor
ActiveUS20090224621A1Large outputImprove balanceMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsBrushless motorsSkew angle
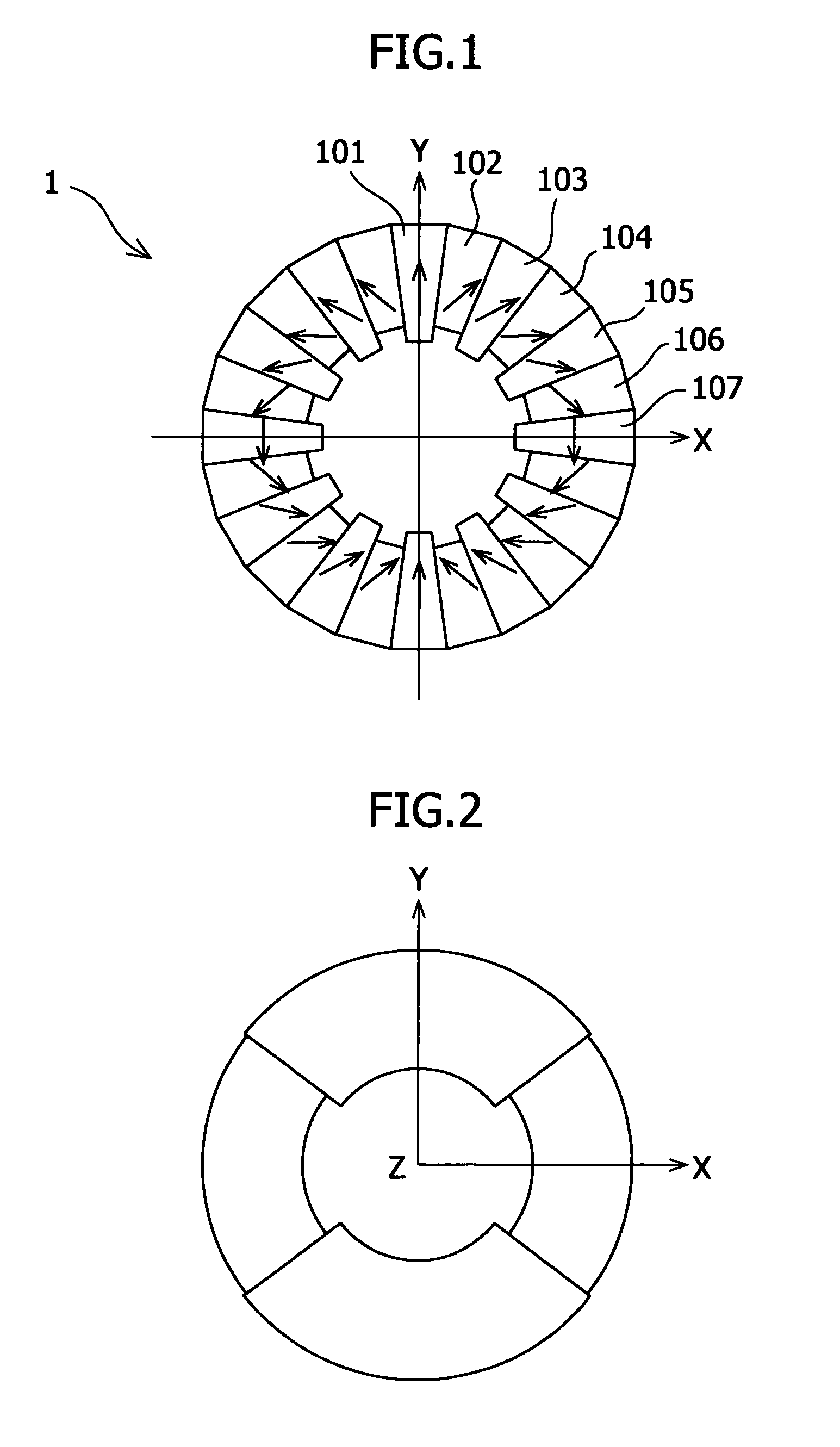
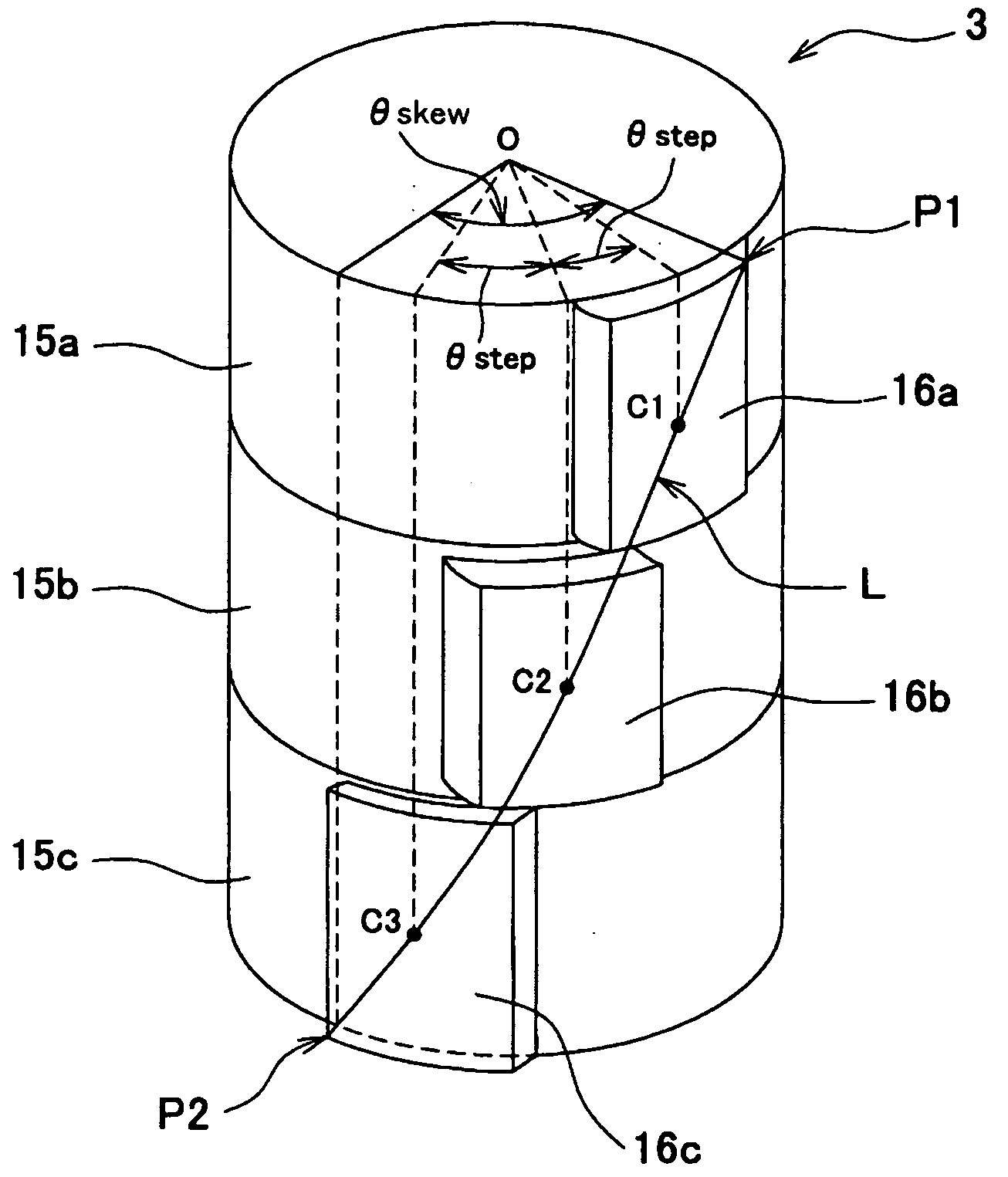
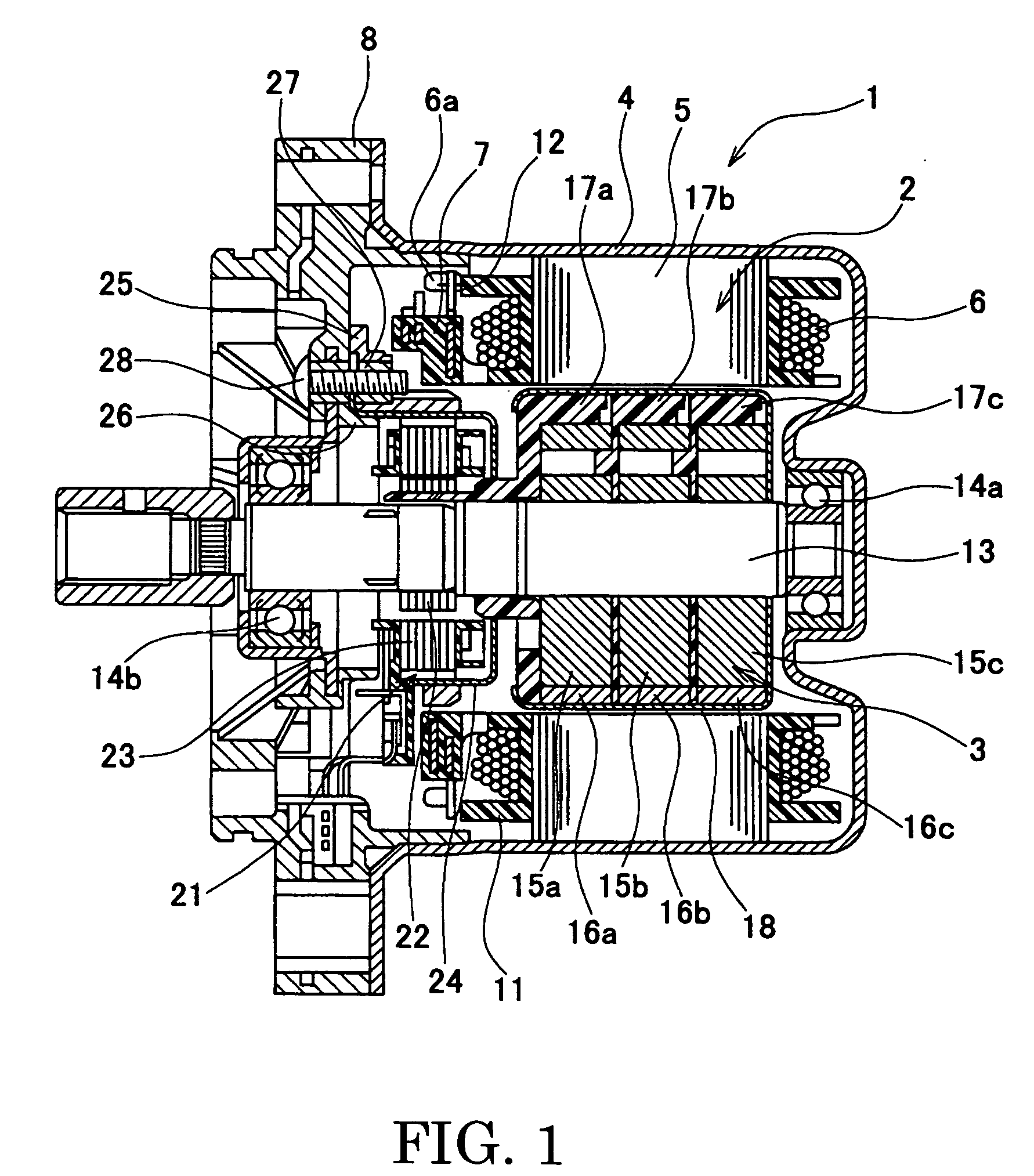
In a brushless motor including a rotor having 2n poles and a stator having 3n slots, segment magnets arranged, in three columns, in the axial direction, thus constituting rotor poles. The segment magnets of adjacent columns, which are identical in polarity, are displaced in the circumferential direction, thus forming a three-stage step-skew structure. The skew angle θskew of each segment magnet is set to an electrical angle of 60° to 75°. The center angle of θm of each segment magnet is set to 46.8° to 52.7°.
Owner:MITSUBA CORP
Magnetic disk apparatus
According to one embodiment, there is provided a magnetic disk apparatus having a magnetic disk having magnetic dot lines each including magnetic dots arrayed at equal intervals in a down track direction, and a read / write head which uses a plurality of adjacent magnetic dot lines as one track and sequentially performs read and write on the magnetic dots included in the magnetic dot lines constituting the track, in which the magnetic dots included in each of the magnetic dot lines in each track of the magnetic disk are displaced in the down track direction from the magnetic dots included in the adjacent dot line in the track depending on a possible skew angle between the read / write head and the track so that the magnetic dots are sequentially accessed by the read / write head.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Structure improvement of the pillow
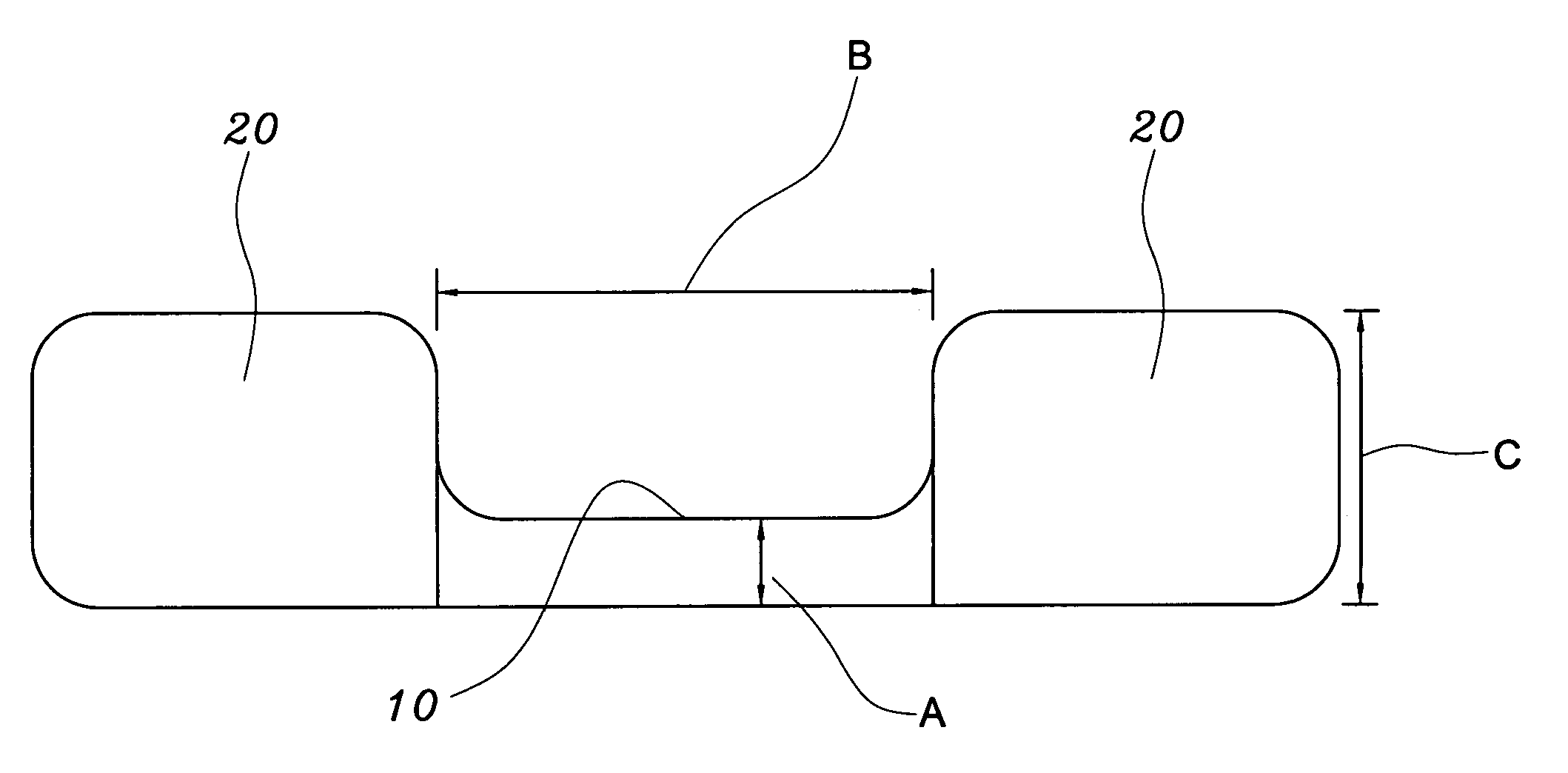
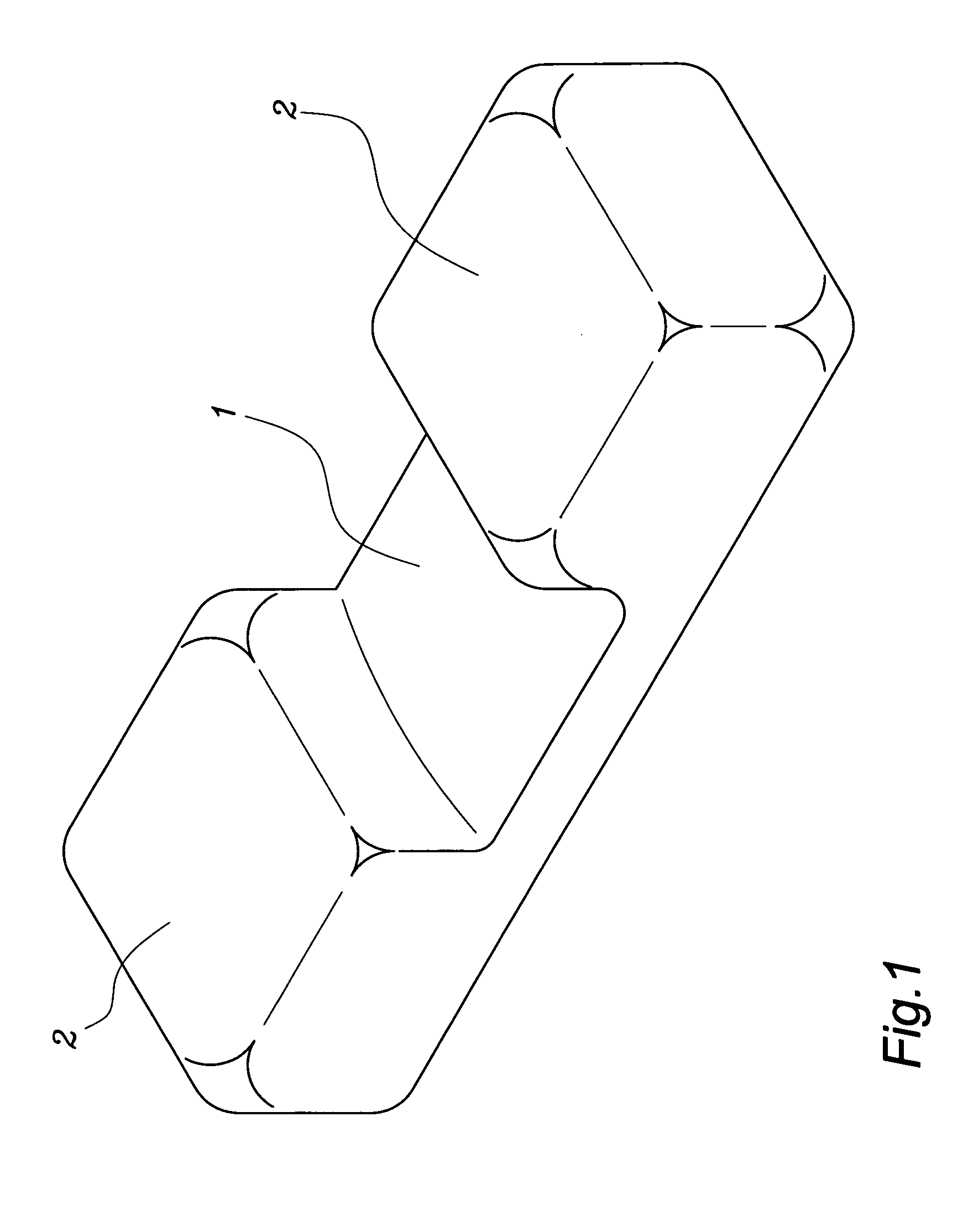
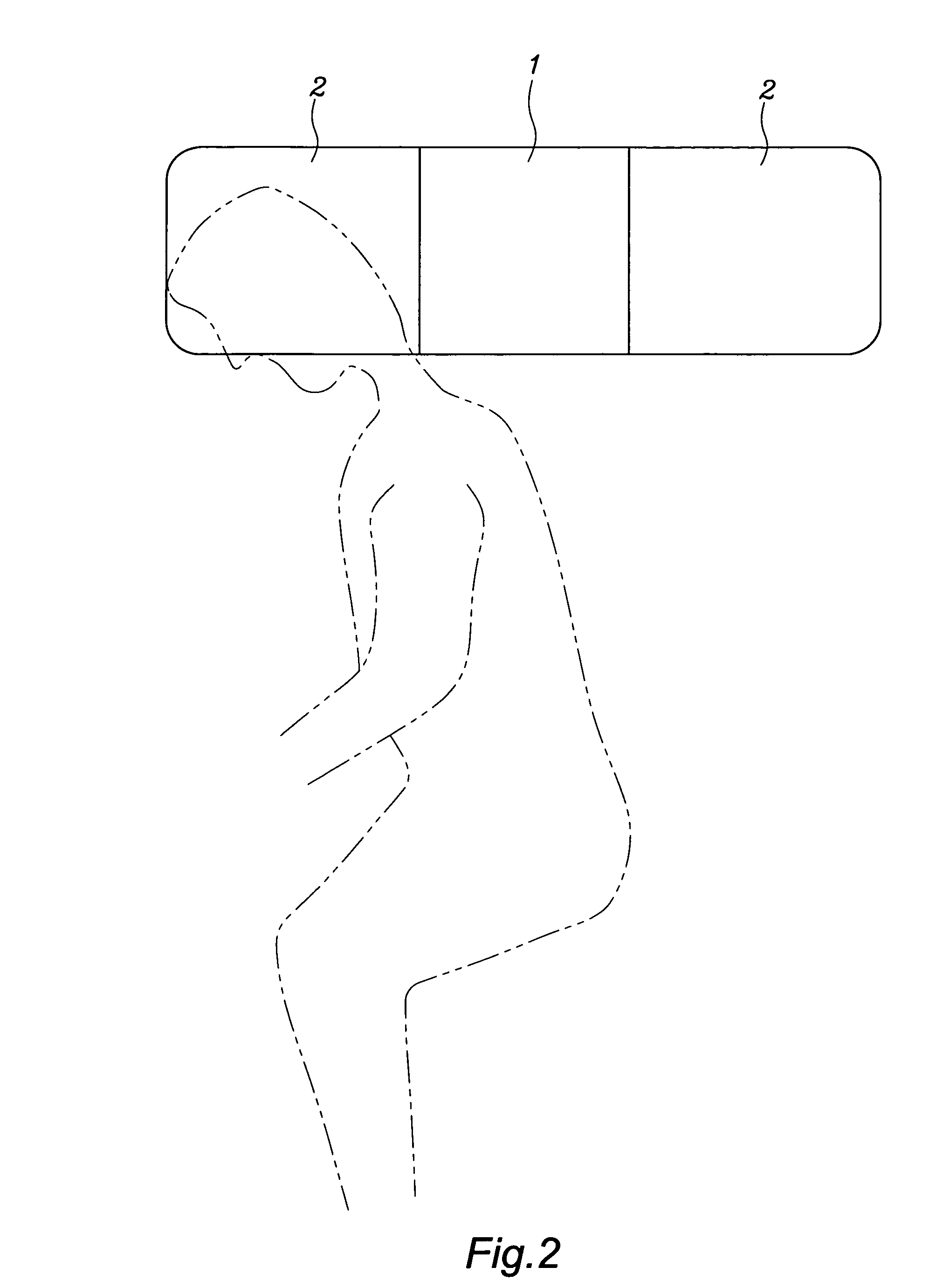
InactiveUS20080282474A1Improve sleep qualitySave storage spacePillowsBlanketSkew angleProne position
The present invention relates to an “structure improvement of the pillow”, which comprises a central main pillow and two lateral sub-pillows, wherein, said central main pillow is trapezoid in dimension with height of pillow top and central length such that the height of pillow top approximately equals the distance between the outer hind skull surface to the outer surface of the normal arched cervical vertebra when people lies on one's back while the height of central length approximately equals the distance between the outer side surface of two ears of human head with slight clearance for tolerance; said lateral sub-pillow is trapezoid in dimension with height of pillow top and the height of pillow top approximately equals the distance between the outer side skull surface to the outer side surface of the shoulder when people lies on one's side; The characterized is that a pair of symmetrical skew-angled arrangement for said central main pillow and each of said two lateral sub-pillows is formed in disposal so that the user head can be exactly placed on and closely supported by one of the two lateral sub-pillows completely when the user lies on one's side sleeping posture; Besides, a sunken dent space is created on the central top of the lateral sub-pillow so that the user ear will be not pressed without uncomfortable feeling.
Owner:HUANG SHIH JUNG
Brushless DC motor with stepped skewed rotor
InactiveUS6906443B2Magnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsSkew angleElectric machine
A brushless DC permanent magnet motor having a step skewed rotor including a rotor shaft having a portion having a substantially uniform cross sectional configuration defined by N planar sides of substantially equal length and width wherein N is equal to the number of poles of the motor, first and second annular sets of N number of substantially identically shaped bread loaf magnets one of which is attached to each of the N planar sides of the rotor shaft wherein the magnets of the first set have their orientation reversed with respect to the magnets of the second set and the magnets of the first set are offset or skewed by a predetermined skew angle from the magnets of the second set of magnets to form a stepped skewed rotor.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED
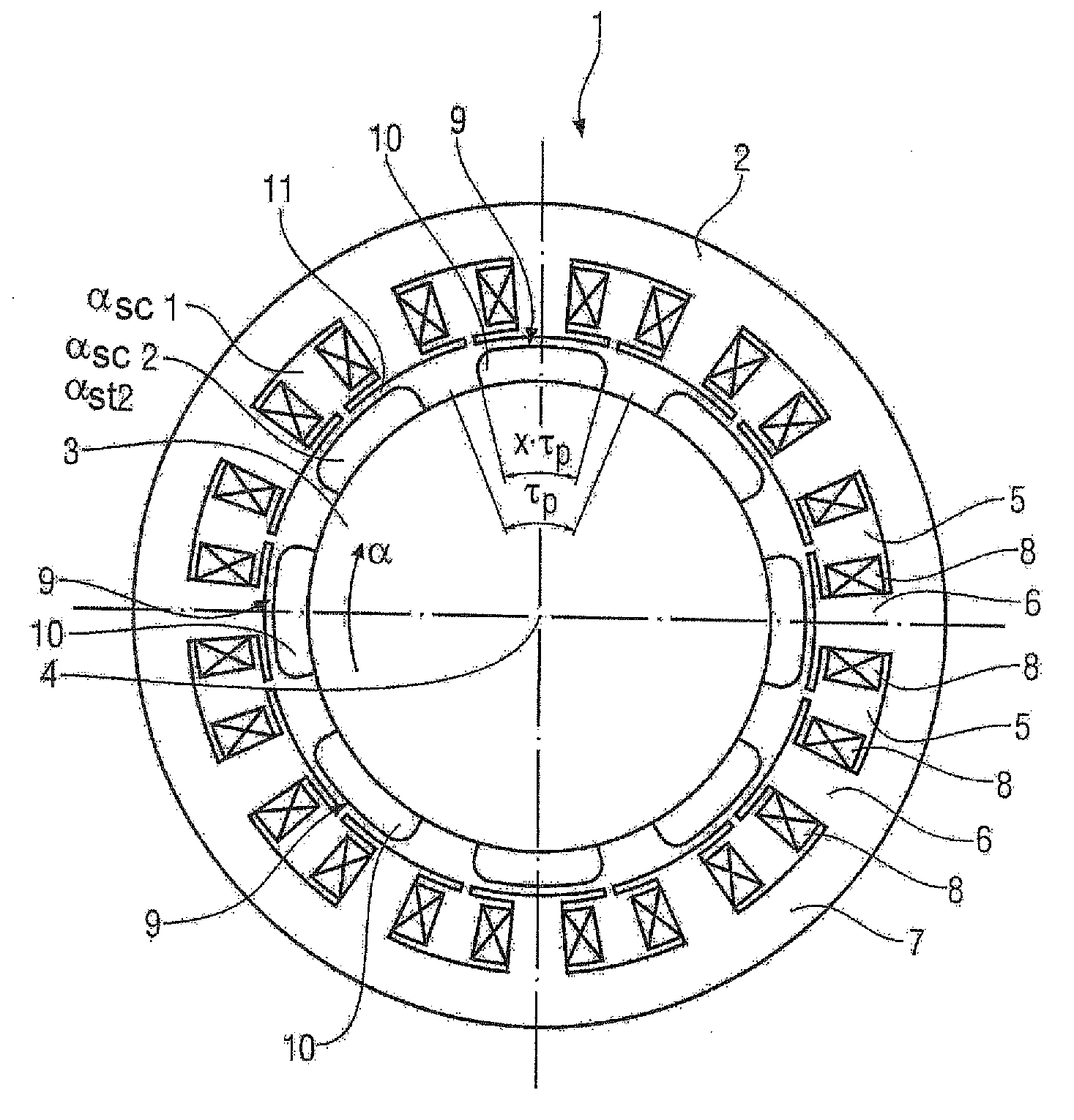
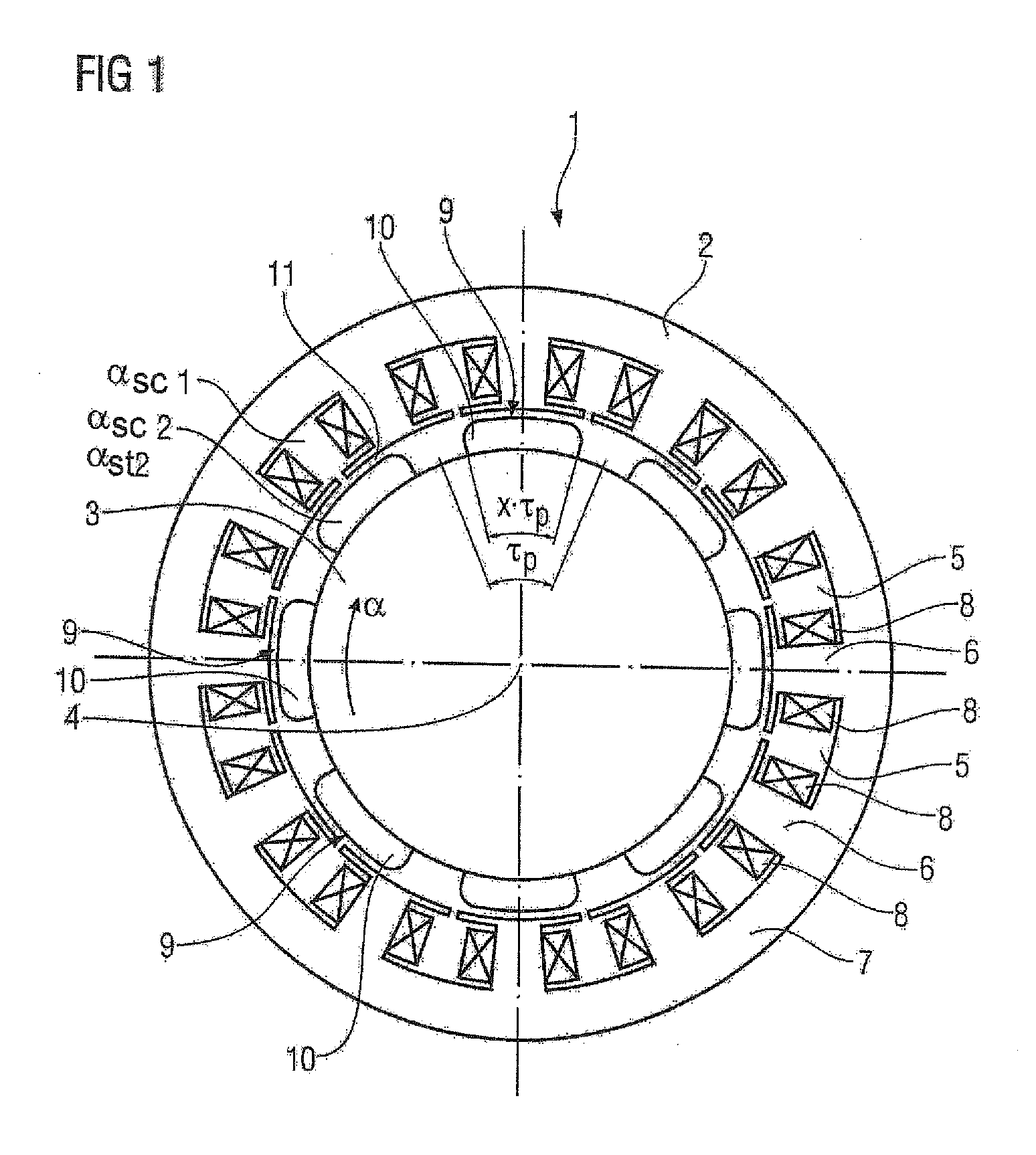
Permanent-magnet synchronous machine with suppression means for improving the torque ripple
InactiveUS20100264770A1Easy to manufactureEasy to solveMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsPermanent magnet synchronous machineSkew angle
A permanent-magnet synchronous machine for suppressing harmonics includes a stator and a rotor with permanent magnets. Each permanent magnet represents a magnetic pole and is, when viewed in the circumferential direction of the rotor, shaped as a parallelogram or an arrow. The pole coverage is less than one. The permanent magnets are staggered at a staggering angle, wherein the permanent magnets of one pole are arranged in the axial direction with an increasing offset of a circumferential angle in relation to a first permanent magnet of this pole. Each permanent magnet is skewed at a skew angle defined by a circumferential angle of a projection of a tip portion of the parallelogram or arrow. The optimal skew and staggering angles are calculated from the design parameters for the stator and the number of pole pairs and the number of poles in the axial direction of the rotor.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Permanent magnetic rotating machine
ActiveUS7034424B2High output densityHigh magnetic flux densityMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsSkew angleMagnetic poles
A permanent magnet rotating machine includes a rotor with a permanent magnet having circumferential magnetic poles with a skew at boundaries between magnetic poles of the permanent magnet, and a stator having a stator iron core in an almost cylindrical shape and convex poles protruding inwardly, the rotor being disposed within the stator. A skew angle of the skew is smaller than a theoretical angle θs (electrical angle) and larger than one-half the theoretical angle θs, wherein the theoretical angle θs is defined as,θs=180×(number of magnetic poles in the rotor) / smallest integer of which both the number of magnetic poles in the rotor and the number of magnetic poles in the stator are factors) [deg.].
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
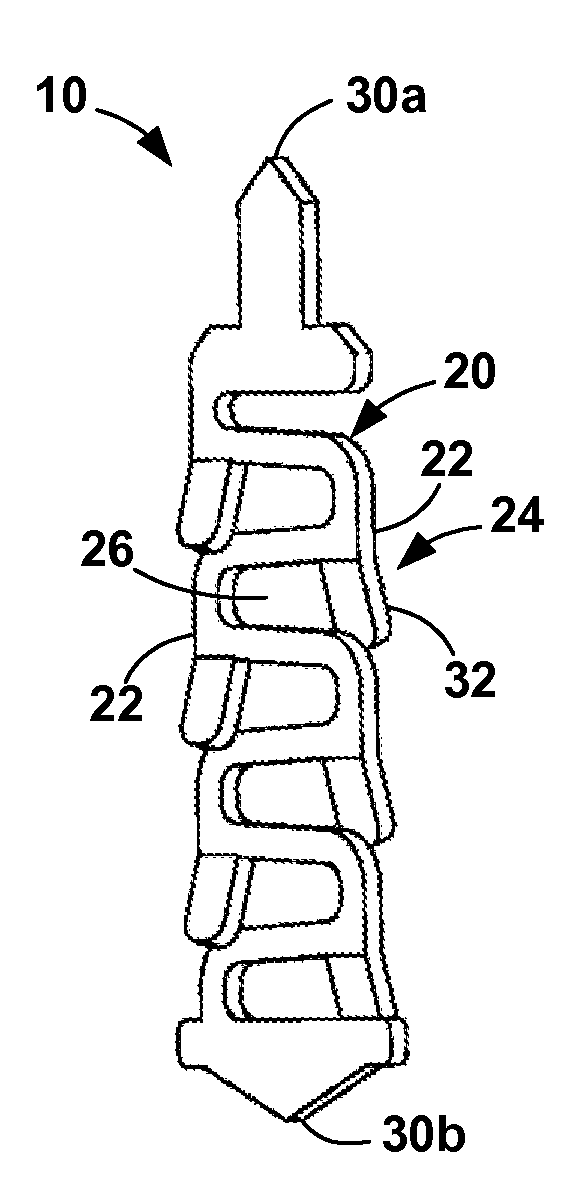
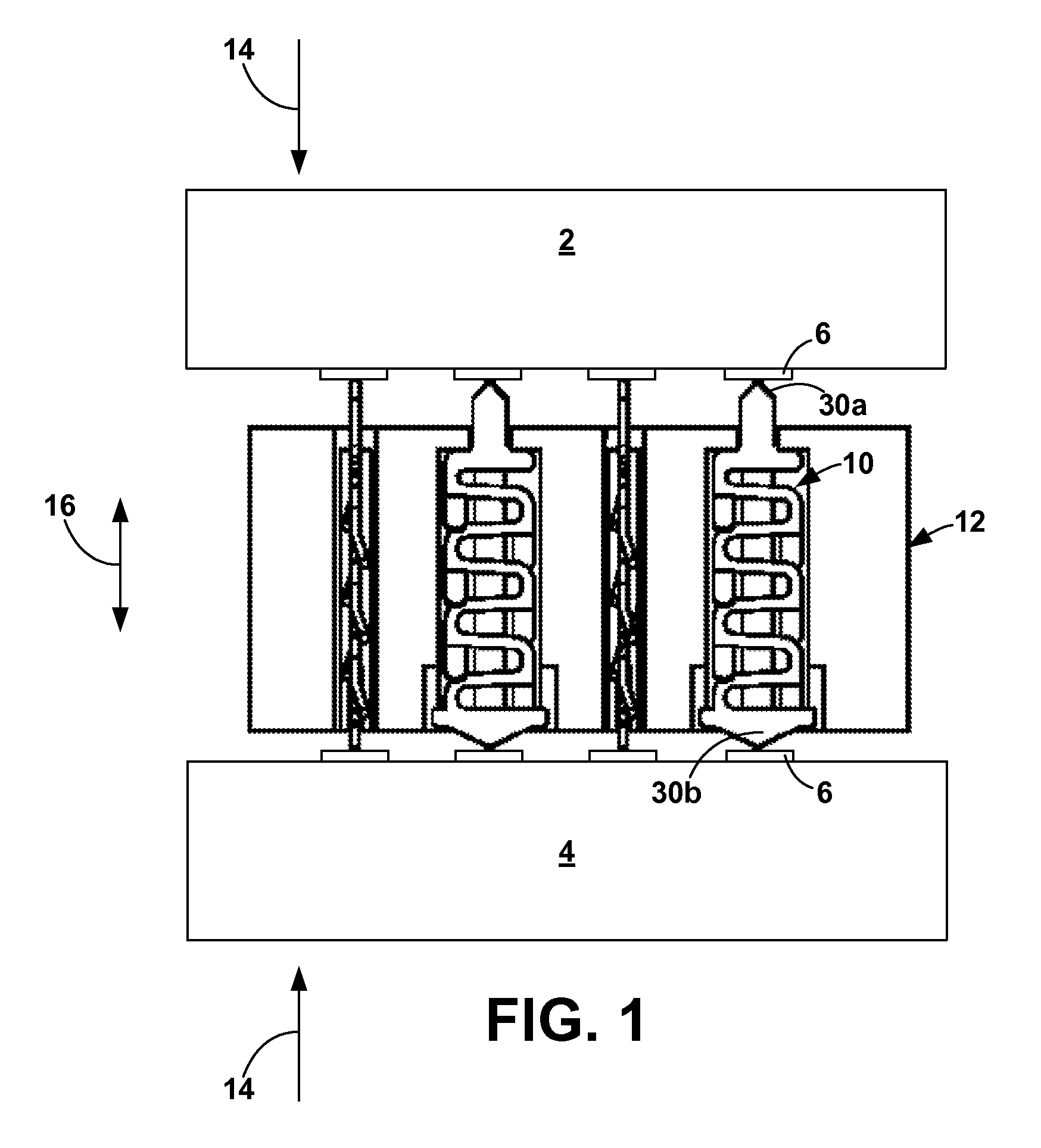
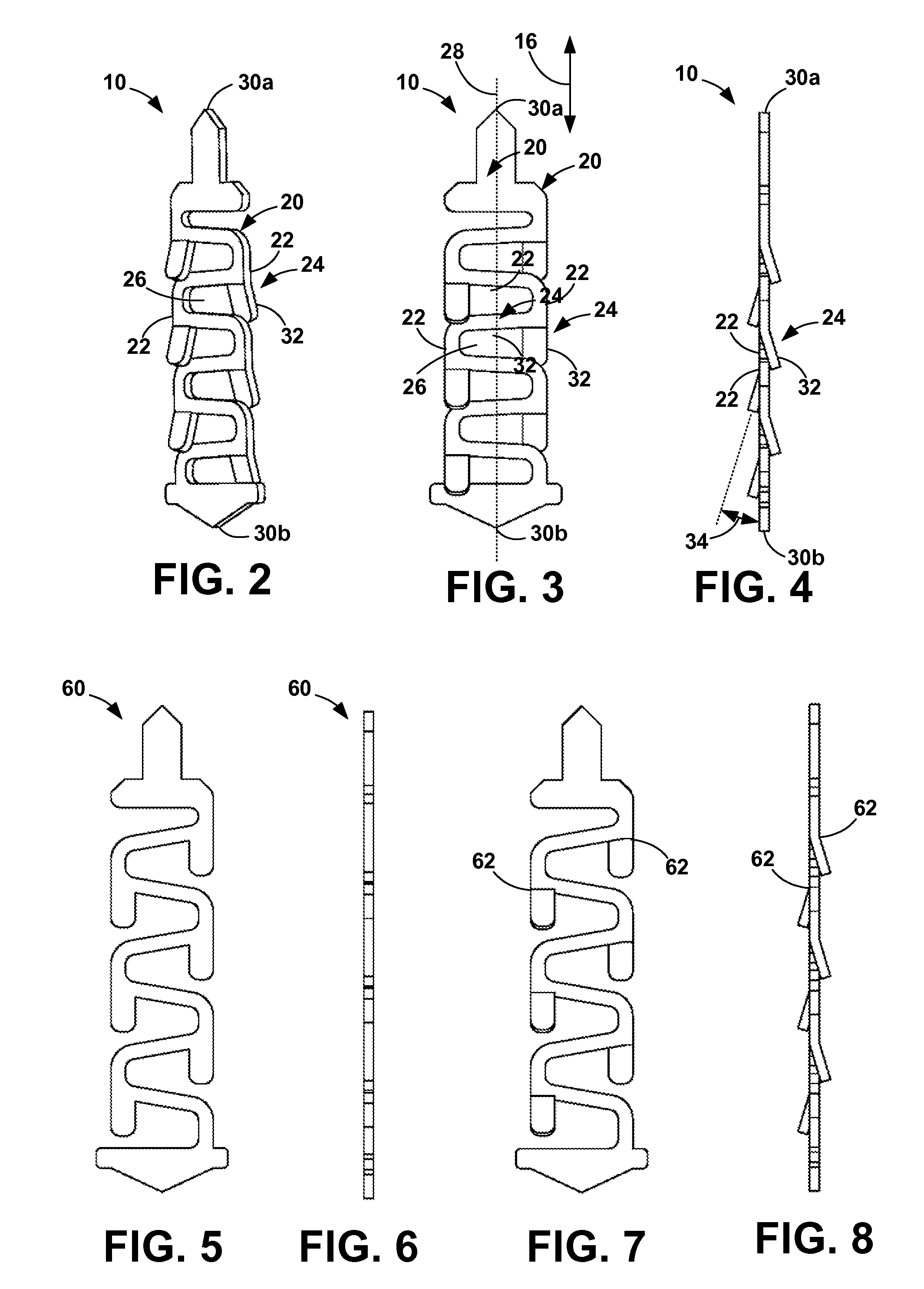
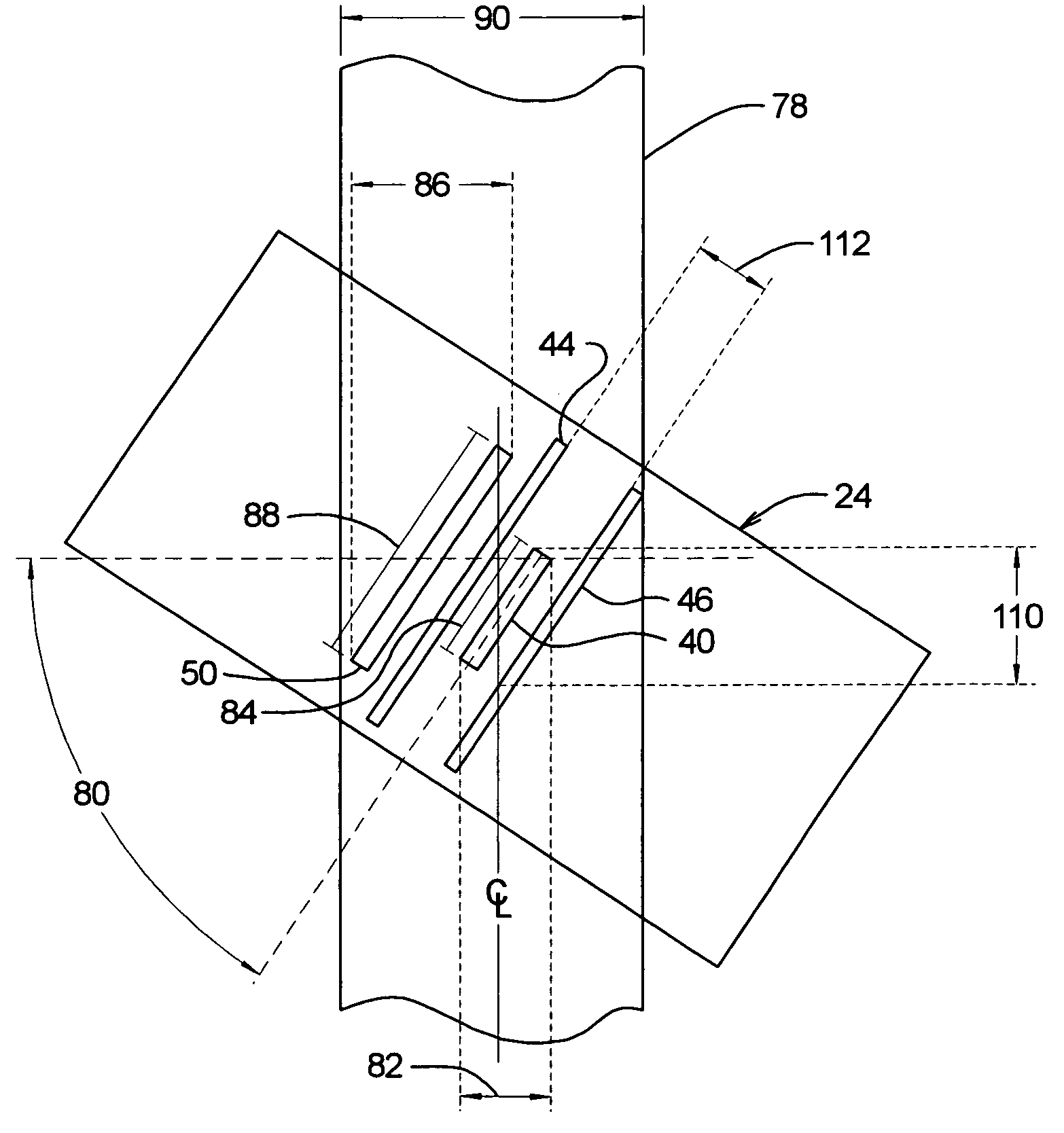
Compliant electrical contact and assembly
ActiveUS7556503B2Sufficient complianceReduce manufacturing costElectrically conductive connectionsCoupling contact membersShunt DeviceSkew angle
A compliant electrical contact and an assembly employing a plurality of the contacts that provides an interface between two electrical devices. The contact has a convoluted spring with convolutions and a contact point at each end. In one contact embodiment, the convolutions have appendages which electrically short adjacent convolutions throughout a significant portion of the compression range of the contact. An appendage may be a single finger that extends from one convolution toward the adjacent convolution, a pair of opposed fingers that extend toward each other from adjacent convolutions, or machined edges on adjacent convolutions. In some configurations, the fingers or a surface on the appendage or fingers are at a skew angle to the direction of compression. In another contact embodiment, a shunt attached at one contact point and parallel to the spring spans most or all of the convolutions longitudinally. The shunt electrically shorts adjacent convolutions by wiping on the abutting surface of the shunt or by a wiper extending from the convolution to the shunt. Alternatively, the shunt electrically shorts the two contact points, bypassing the convolutions. The contact is placed within a through aperture in a dielectric panel that has openings at each end through which the contact points protrude.
Owner:ARDENT CONCEPTS INC
Method and apparatus for reducing effective track width through highly skewed head angles
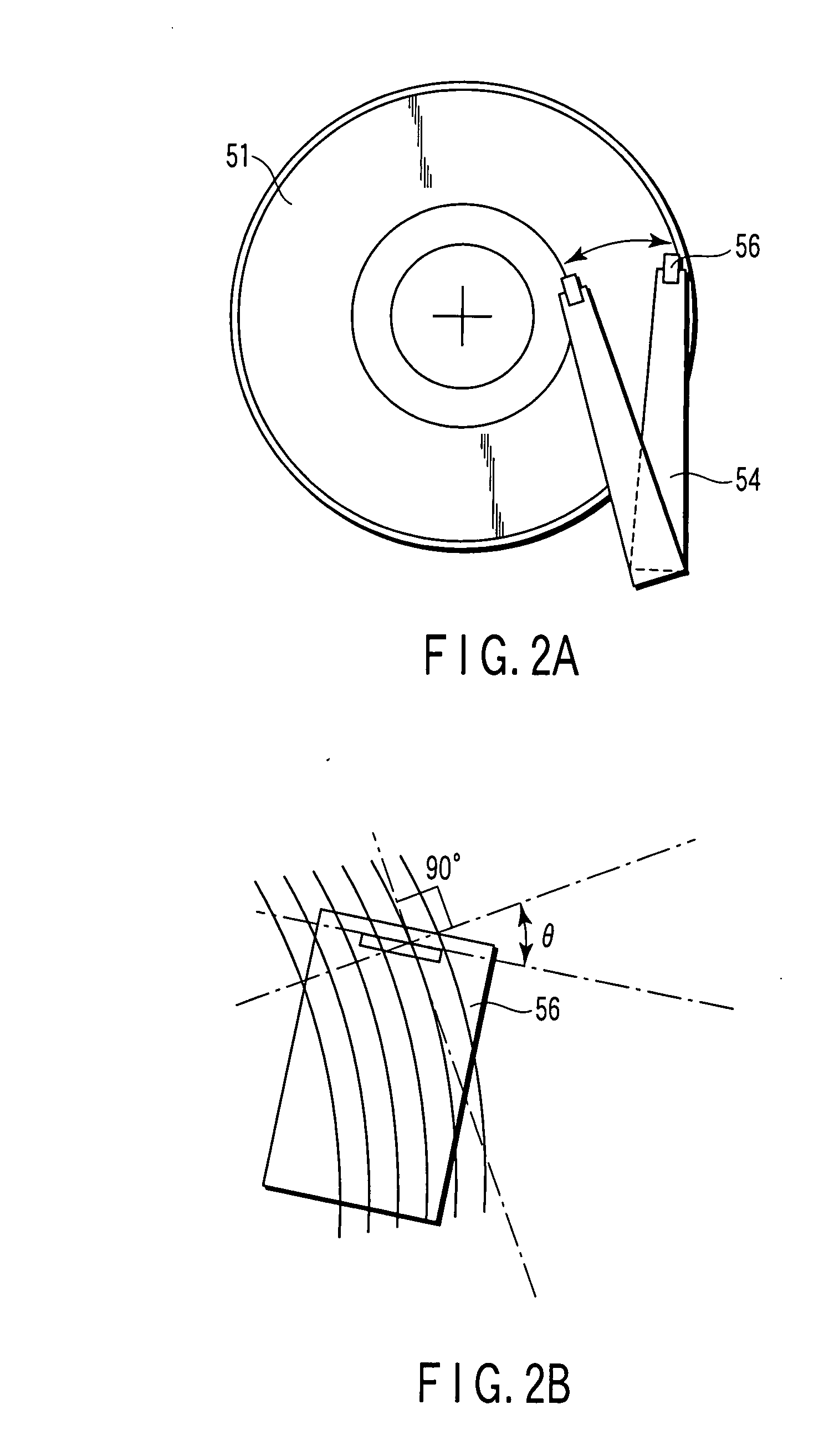
InactiveUS7193807B1Shorten the lengthOptimization rangeRecord information storageAlignment for track following on disksComputer hardwareSkew angle
A disk drive provides increased read and write element widths and tolerances, and also provides reduced track widths. The head with the read and write elements has a large skew angle relative to the tracks on the disk. The skew angle reduces the effective width of the read and write elements. Based on this reduction in effective width, the physical width of the read and write elements may be increased. Furthermore, the width of the tracks may be reduced instead of, or in addition to, the increased read and write element width.
Owner:MAXTOR
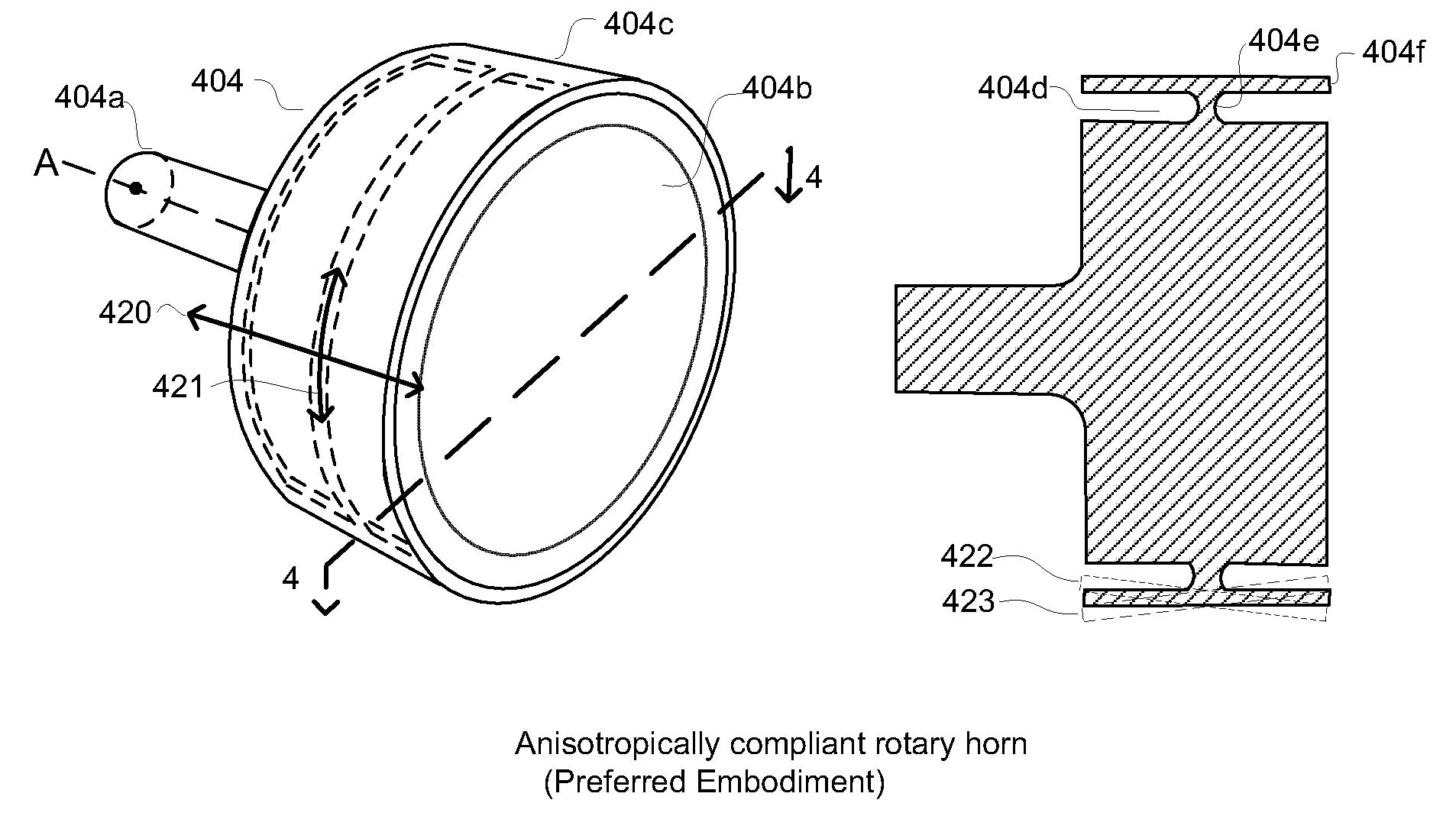
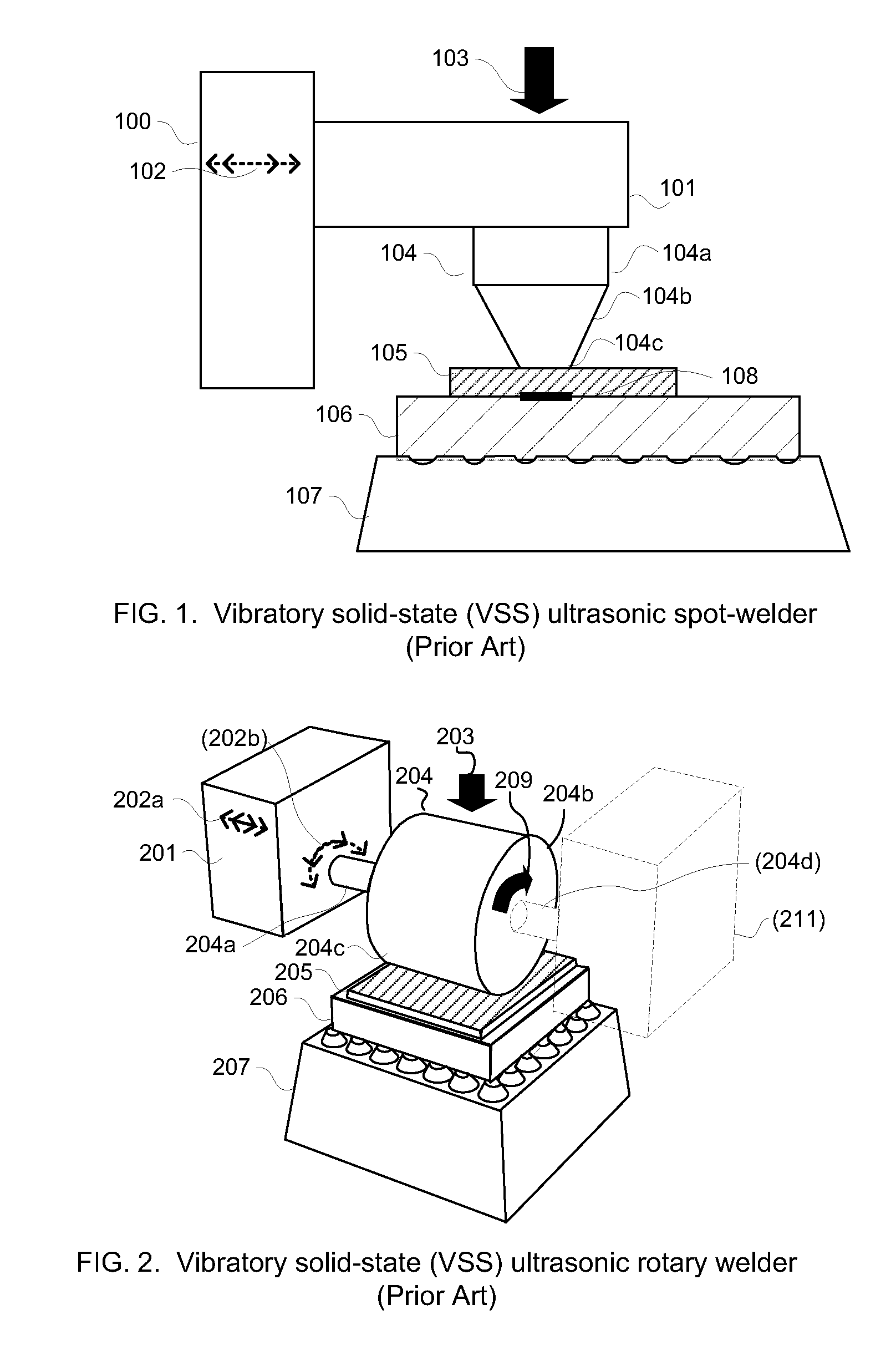
Anisotropically compliant horns for ultrasonic vibratory solid-state bonding
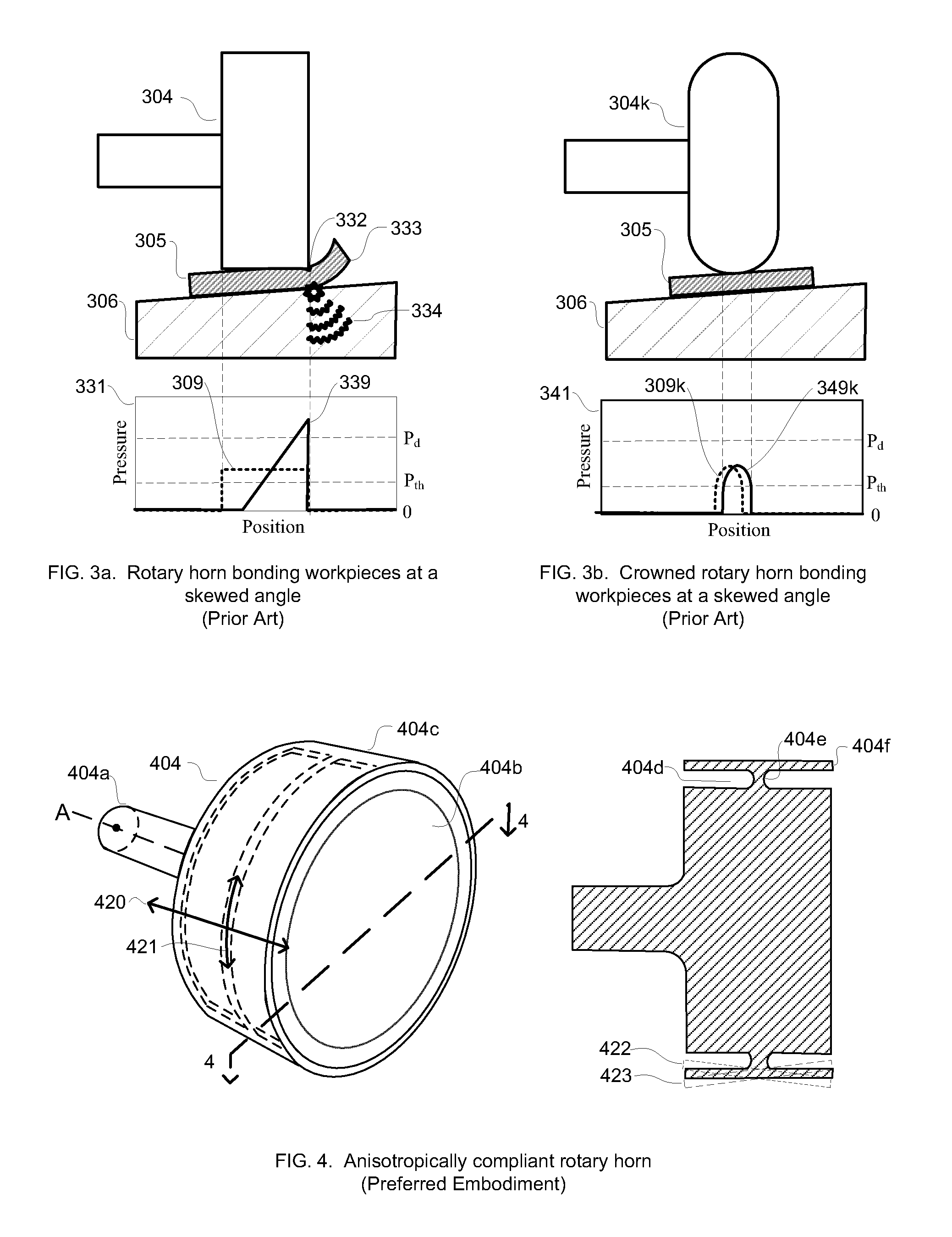
InactiveUS20100040903A1Minimize complianceReduce areaWelding/cutting auxillary devicesSolid-state devicesBond energySonification
A horn for vibratory solid-state ultrasonic welding of metals and similarly-behaved materials “self-levels” to produce wide continuous seams or large-area spot-welds between delicate workpieces without damage, even if the workpieces are not perfectly flat and parallel to the nominal toolface angle. The horn toolface flexes under pressure to conform to skew-angled workpieces because it is disposed on a tool head supported by a tool neck cut from the tool body. The tool head, the tool neck, or both are anisotropically compliant. When resonances are properly optimized for typical VSS modes of vibration, atypical but useful localized modes are excited at the compliant toolface edges, actually intensifying the bond energy where one might normally expect unwanted damping. Various design approaches optimize the characteristics of the tool head and tool neck to various materials and bonding configurations. The horns can be configured for use with existing ultrasonic welders.
Owner:FOREFRONT INNOVATIVE TECH
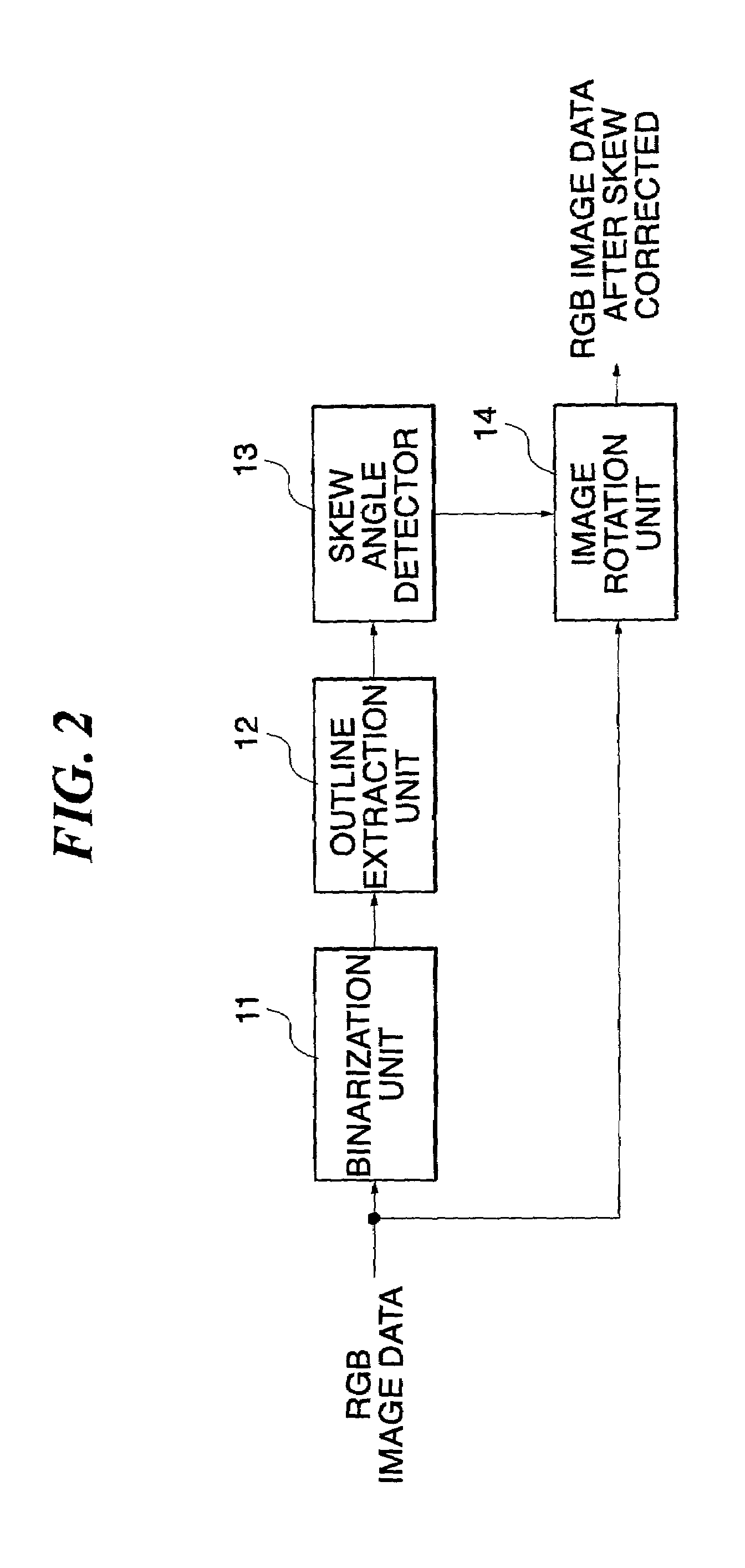
Device and method for correcting skew of an object in an image
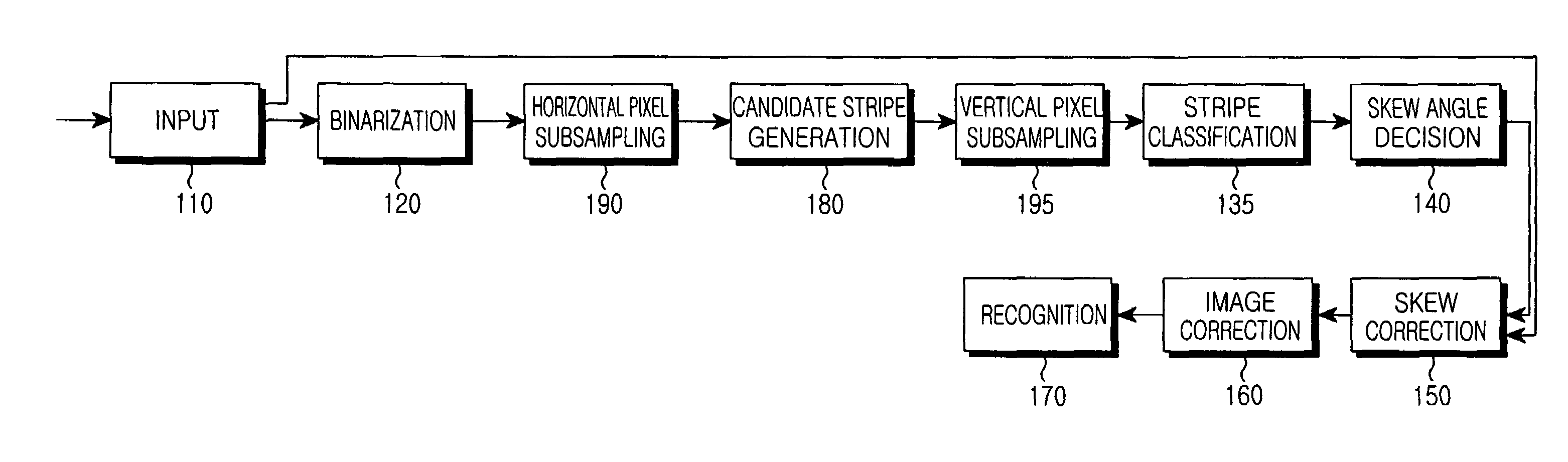
InactiveUS7340110B2Reduce horizontal pixelsReduce vertical pixelsImage enhancementCharacter recognitionPattern recognitionSkew angle
A device and method for correcting a skew of an object in an image. The device and method comprises an input part for receiving an image; a binarization part for binarizing pixels of the image into pixels having brightness values for character pixels and background pixels; a candidate stripe generation part for generating candidate stripes by performing dilation on character regions of the binarized image. The device and method further comprises a stripe classification part for classifying candidate stripes having a predetermined eccentricity and blob size among the candidate stripes, as valid stripes; a skew angle decision part for calculating direction angles of the classified stripes, and determining a direction angle having the largest count value as a skew angle; and a skew correction part for correcting a skew of an image by rotating the mage by the skew angle.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Twist drill
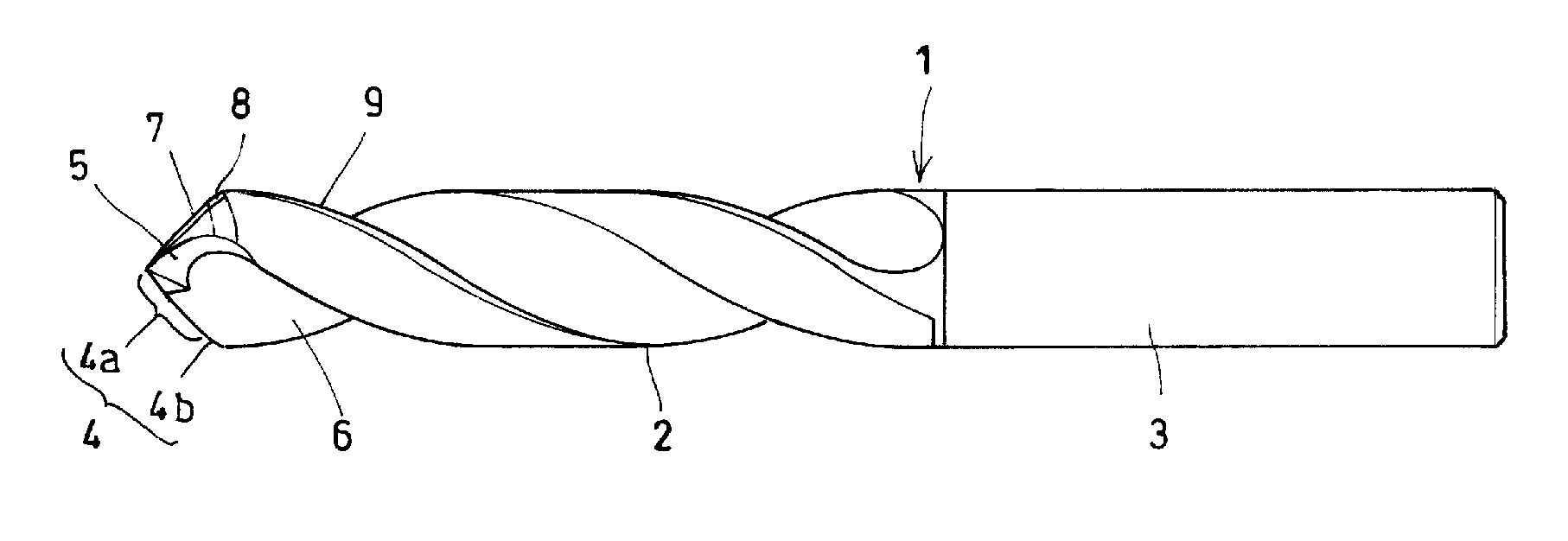
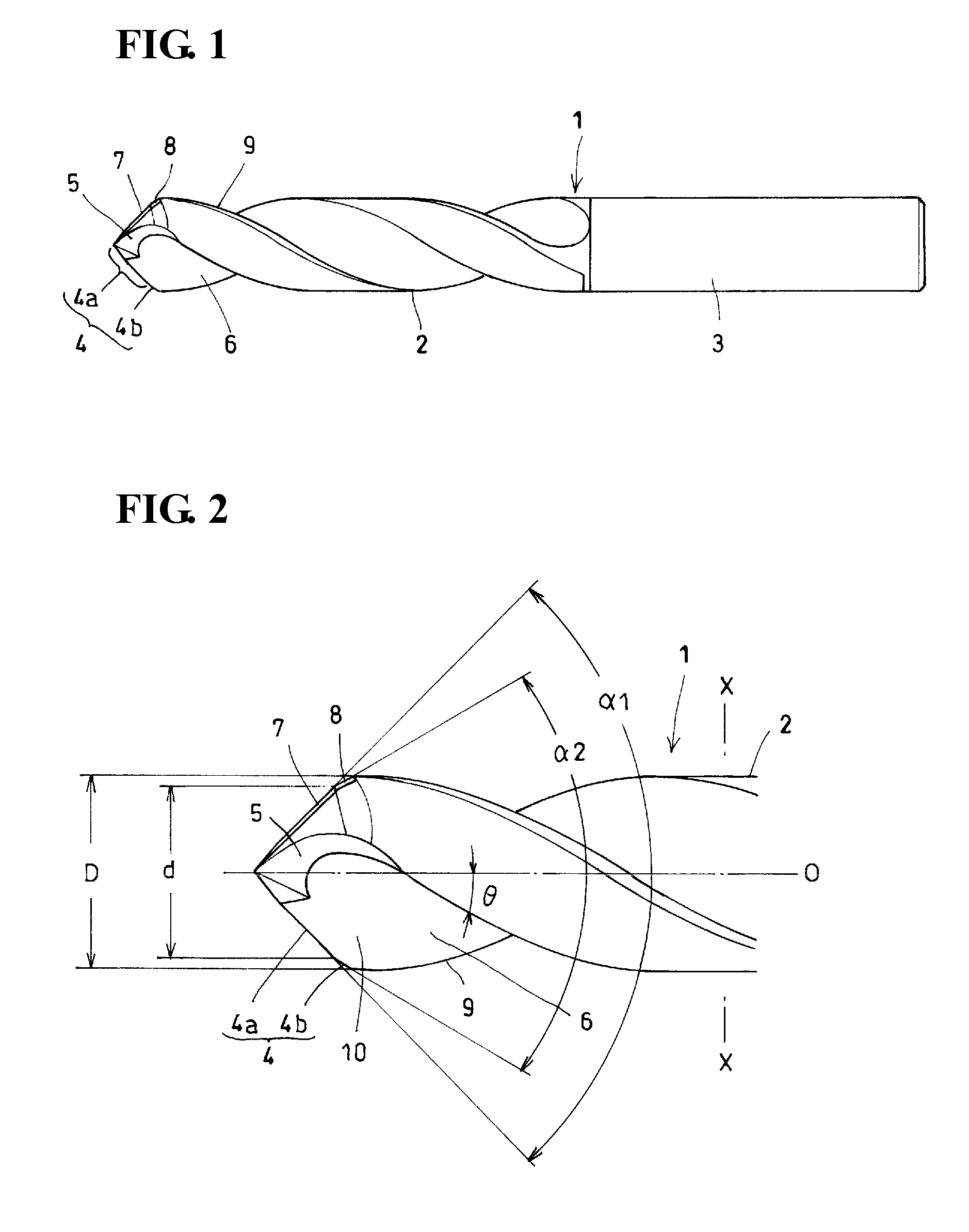
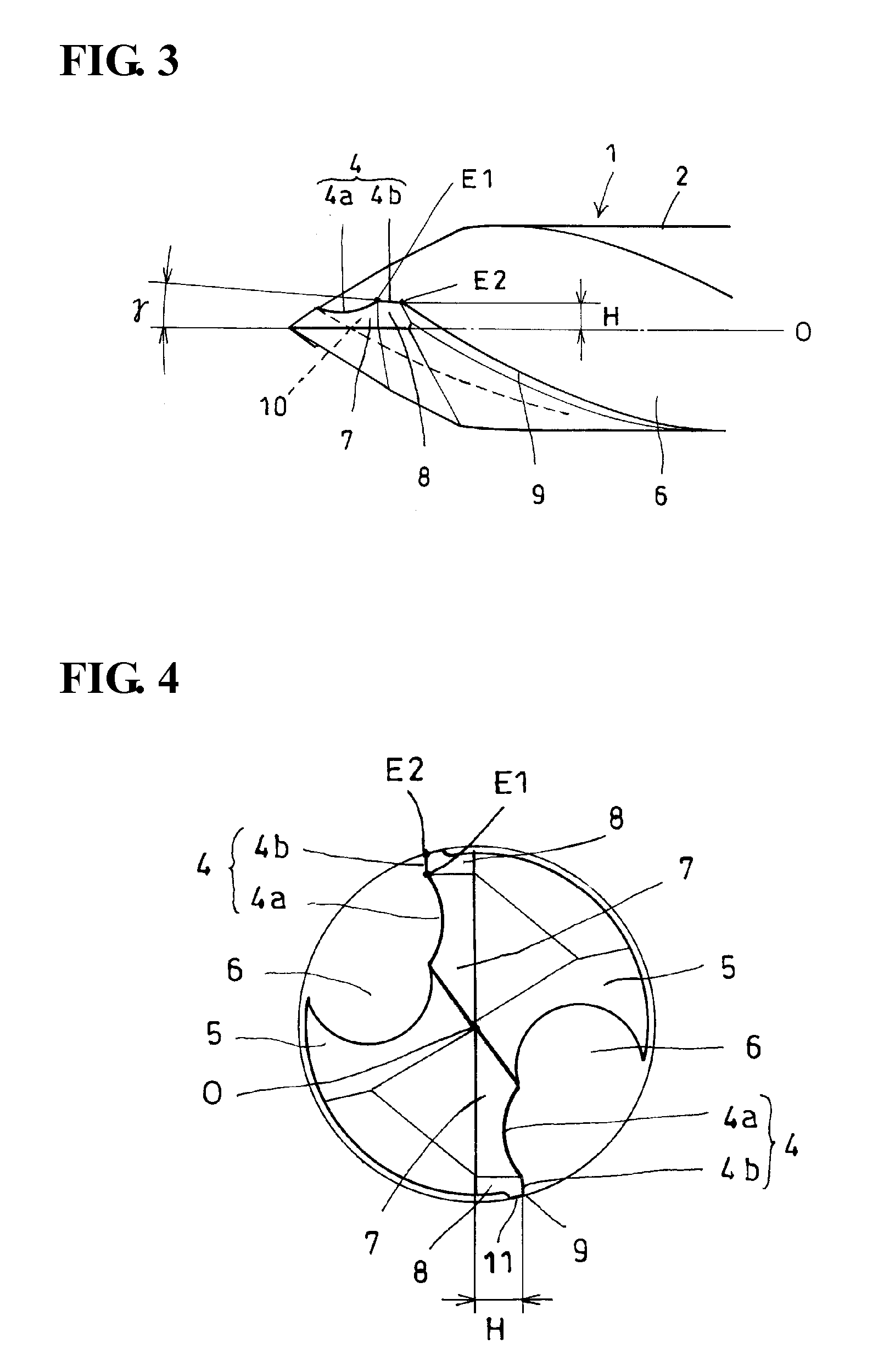
InactiveUS20110081215A1High quality drillingSmall liftWood turning toolsTransportation and packagingFluteLeading edge
Provided is a double-angle twist drill that increases the quality of drilling without increasing the amount of manufacturing work or the like. A secondary cutting edge 4b is substantially parallel to the rotation axis O of the drill, and at least a rake face 10 of the secondary cutting edge is included in the flute face of a helical flute 6. A part of the flute face of the helical flute that is located along a leading edge 9 is convexly curved with respect to the normal direction of rotation of the drill, so that the secondary cutting edge 4b having a small skew angle with respect to the rotation axis can be formed as a ridge at which the flute face intersects a second flank face.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC HARDMETAL CORP
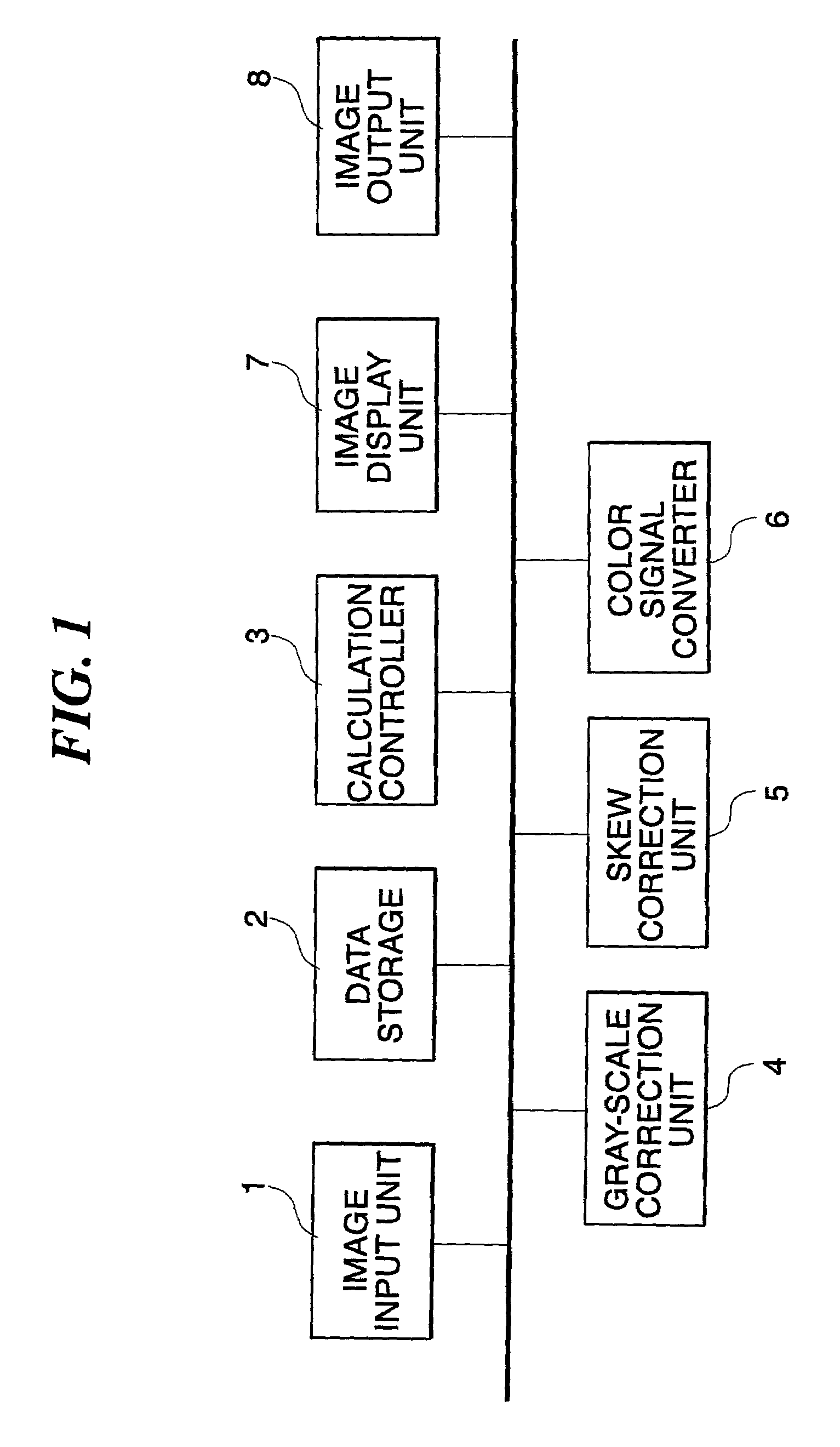
Image processing device, image processing method, and recording medium storing image processing program
InactiveUS7016552B2Accurate detectionImage analysisGeometric image transformationImaging processingSkew angle
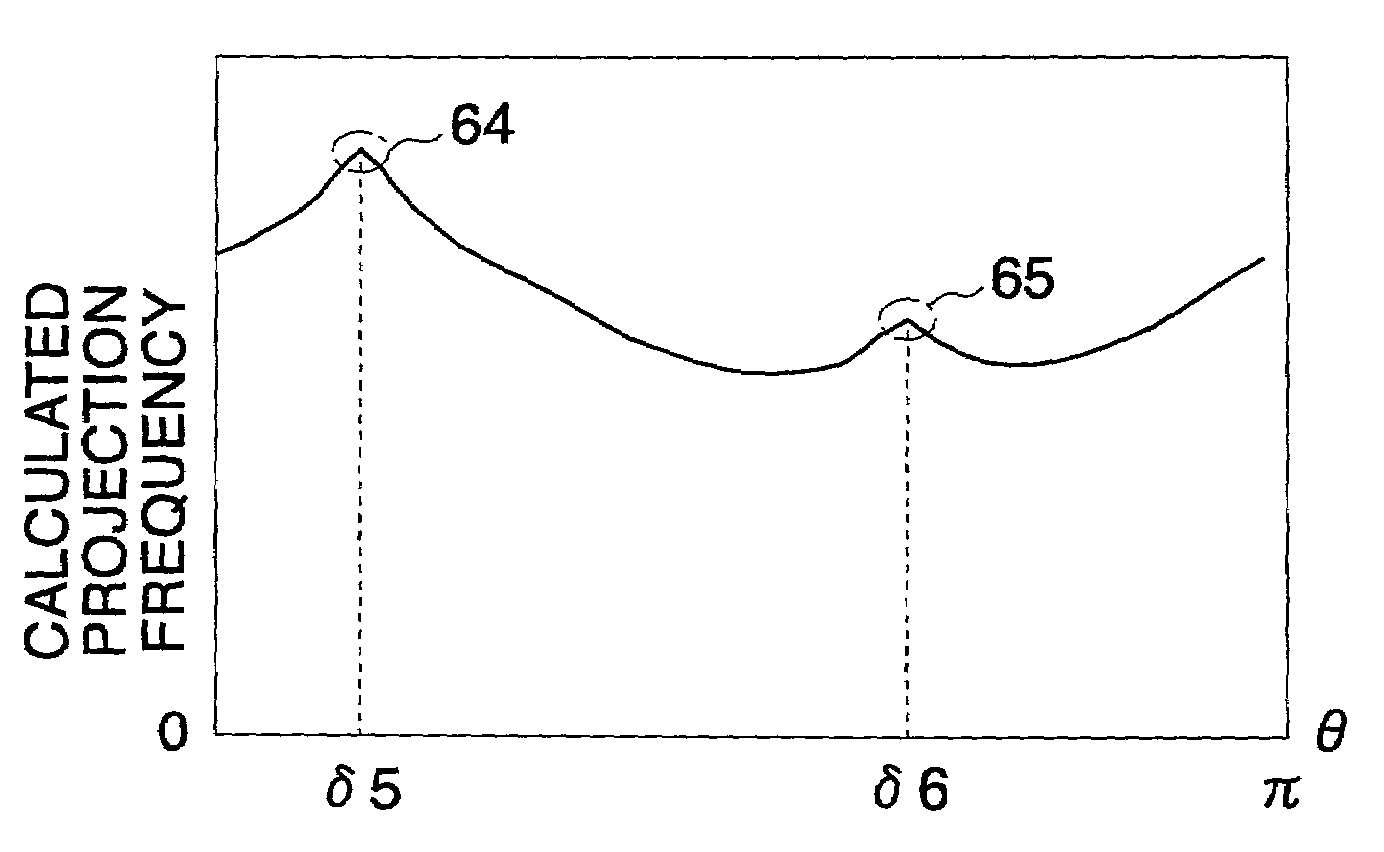
A Hough transform unit executes Hough transform to HIGH pixels of outline binary image data inputted thereto, and stores the calculation result in a Hough space data storage. A Hough space data calculating / projecting unit sequentially reads out data stored in the Hough space data storage, executes a specific calculation, and thereafter stores the calculation result sequentially in a calculated projection data storage. An angle detector sequentially reads out calculated frequency data stored in the calculated projection data storage, calculates the maximal value of the data read out, and detects an angle that gives the maximal value as the skew angle. The image processing device, being thus configured, allows detecting and correcting the skew angle with high accuracy, even when the input image contains image elements such as photograph images and dot images.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com