Patents
Literature
2180 results about "Particle filter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
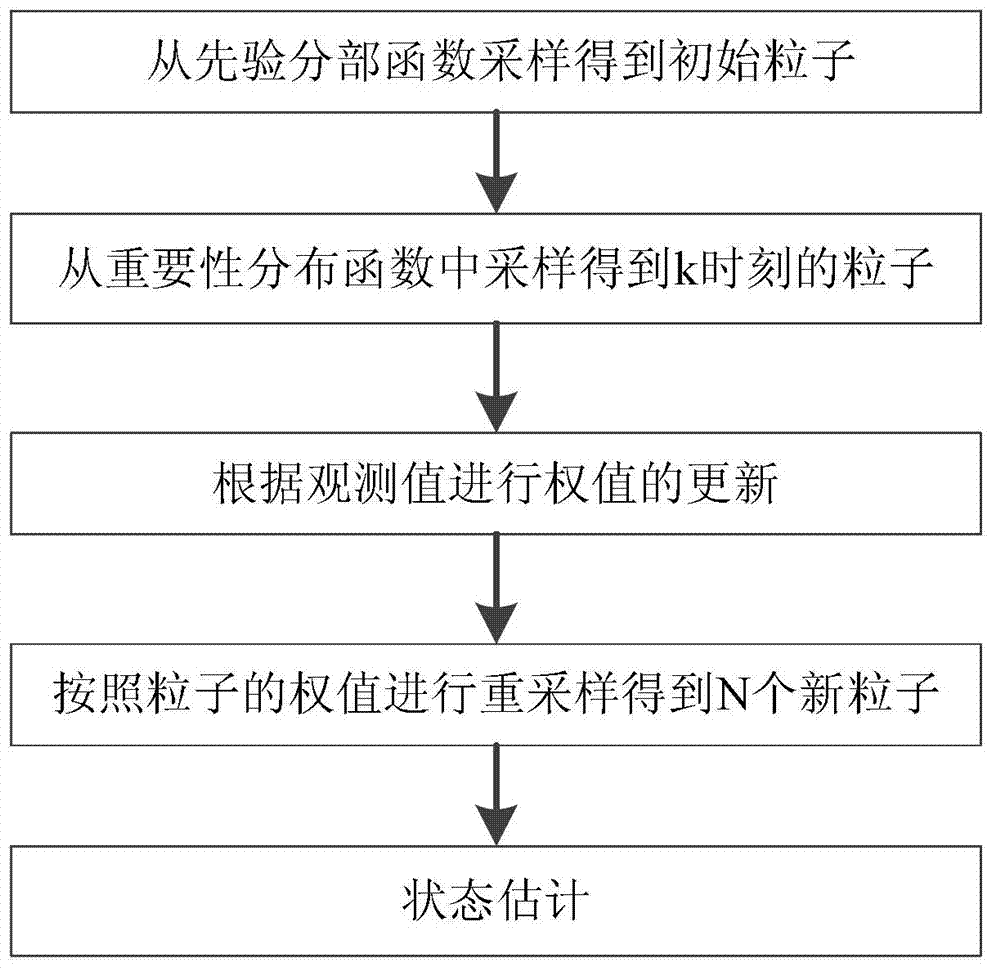
Particle filters or Sequential Monte Carlo (SMC) methods are a set of Monte Carlo algorithms used to solve filtering problems arising in signal processing and Bayesian statistical inference. The filtering problem consists of estimating the internal states in dynamical systems when partial observations are made, and random perturbations are present in the sensors as well as in the dynamical system. The objective is to compute the posterior distributions of the states of some Markov process, given some noisy and partial observations. The term "particle filters" was first coined in 1996 by Del Moral in reference to mean field interacting particle methods used in fluid mechanics since the beginning of the 1960s. The terminology "sequential Monte Carlo" was proposed by Liu and Chen in 1998.
Motion Tracking System
ActiveUS20080285805A1High precisionAccurate recordProgramme-controlled manipulatorPerson identificationMovement trackingKalman filter
Owner:XSENS HLDG BV
Tracking algorithm
A method of tracking an entity by monitoring a signal, the signal tending to vary spatially and be generally time-invariant, the entity moving from a first location within an area to a second location within the area, the method being suitable for use when the location of the source of the signal is unknown, the method comprising providing a plurality of particles for use with a particle filter, each particle being associated with a first particle location, a first particle location being an estimate of the first location of the entity, providing an estimate of the motion of the entity between the first location and the second location, using the estimate of the motion and using the particle filter, for each particle, updating the first particle location for that particle thereby producing an updated particle location, the updated particle location being an estimate of the second location of the entity, for each updated particle, estimating at least one expected signal parameter at the updated particle location, measuring a signal parameter at the second location of the entity, assigning a weight to each updated particle depending on the expected signal parameter estimated for that particle and the measured signal parameter, estimating the second location of the entity by determining a function of the weighted updated particles, and inputting the estimated location and measured signal parameter, as a location / parameter data set, to a database.
Owner:BAE SYSTEMS PLC
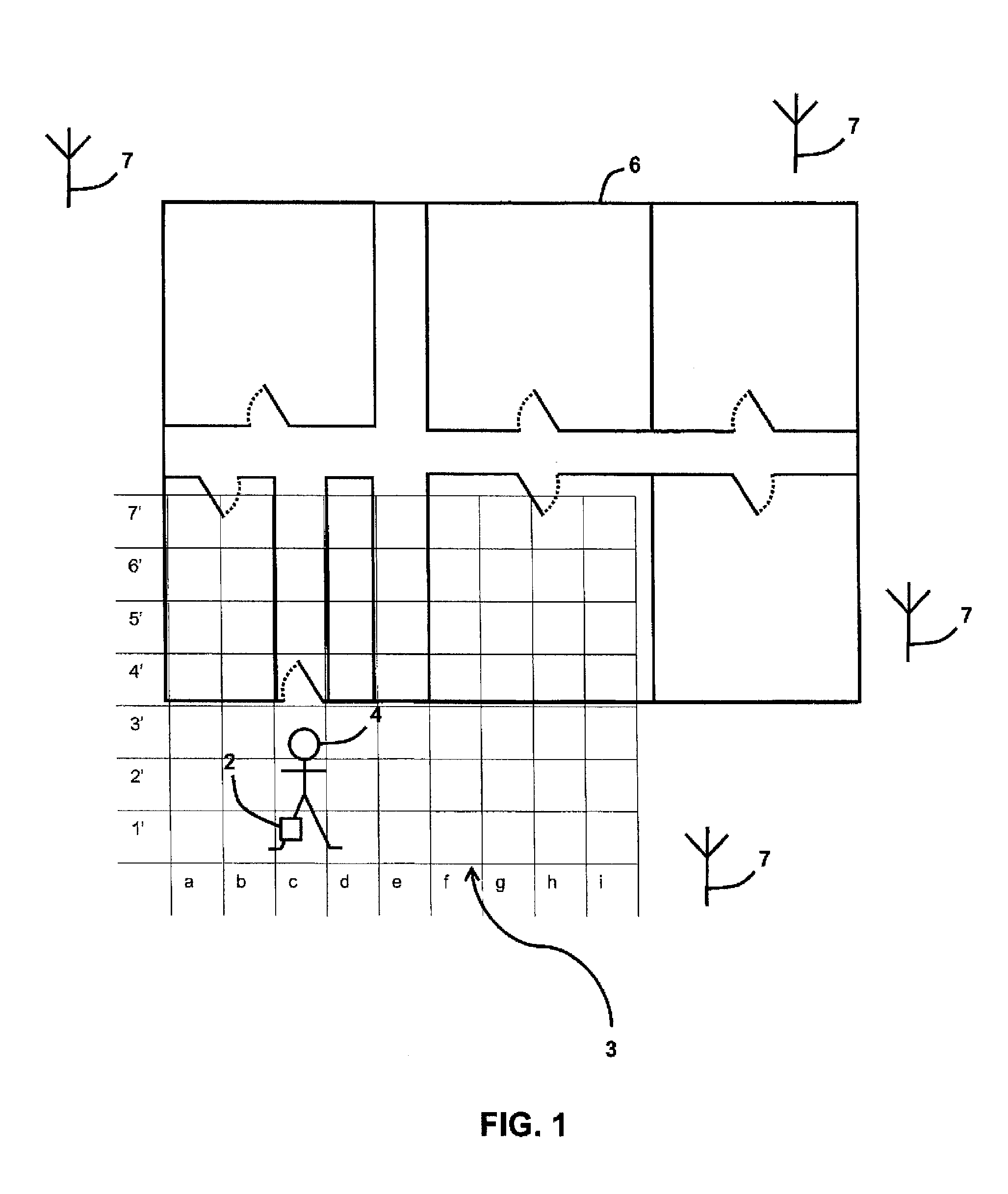
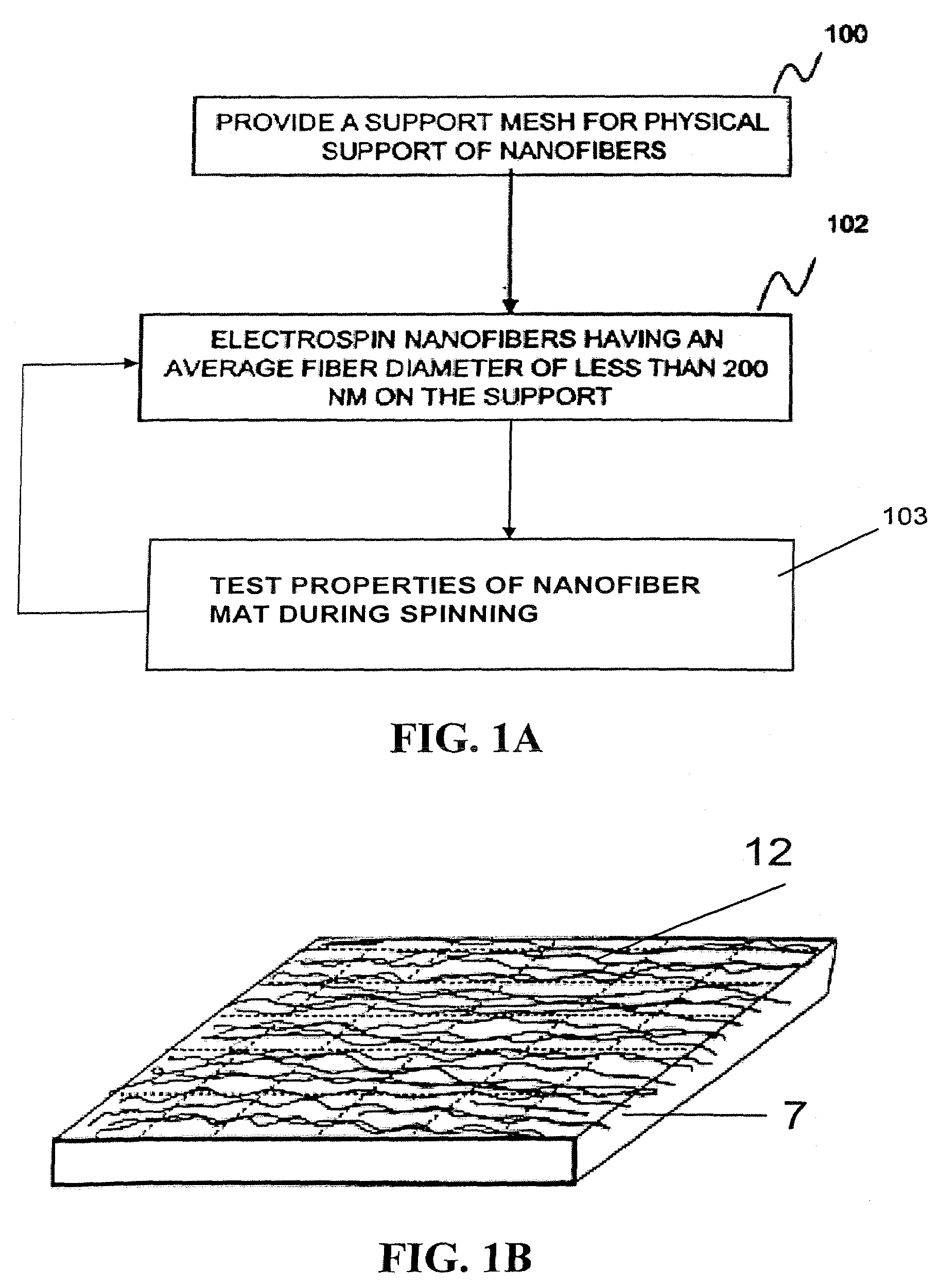
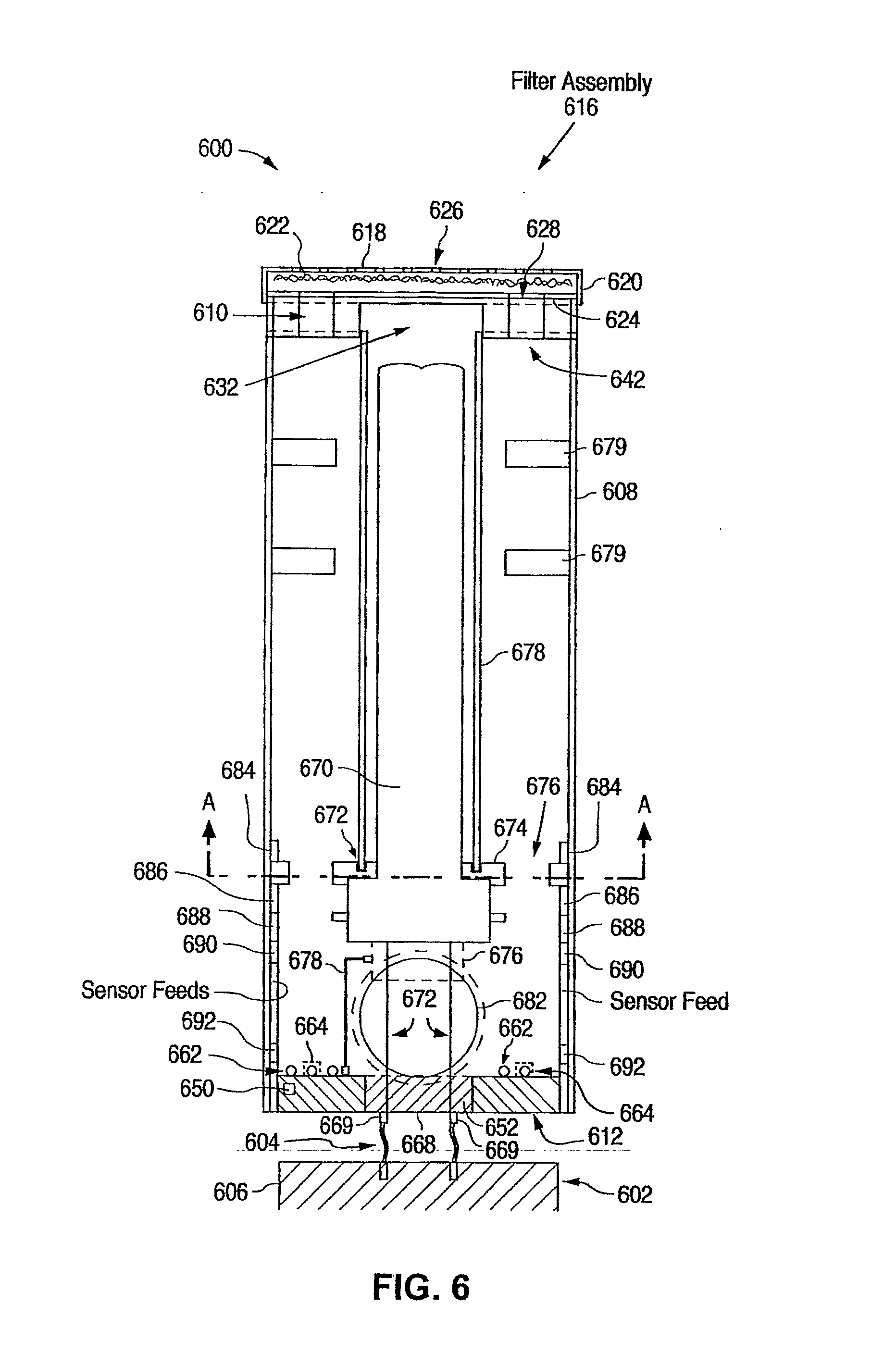
Particle filter system incorporating nanofibers
ActiveUS20080110342A1Electric discharge heatingFilament/thread formingElectric field modulationFiber
A filtration device including a filtration medium having a plurality of nanofibers of diameters less than 1 micron formed into a fiber mat in the presence of an abruptly varying electric field. The filtration device includes a support attached to the filtration medium and having openings for fluid flow therethrough. A device for making a filter material. The device includes an electrospinning element configured to electrospin a plurality of fibers from a tip of the electrospinning element, a collector opposed to the electrospinning element configured to collect electrospun fibers on a surface of the collector, and an electric field modulation device configured to abruptly vary an electric field at the collector at least once during electrospinning of the fibers. A method for making a filter material. The method provides a support having openings for fluid flow therethrough, electrospins nanofibers across an entirety of the openings, and abruptly varies an electric field at the collector at least once during electrospinning of the fibers.
Owner:RES TRIANGLE INST
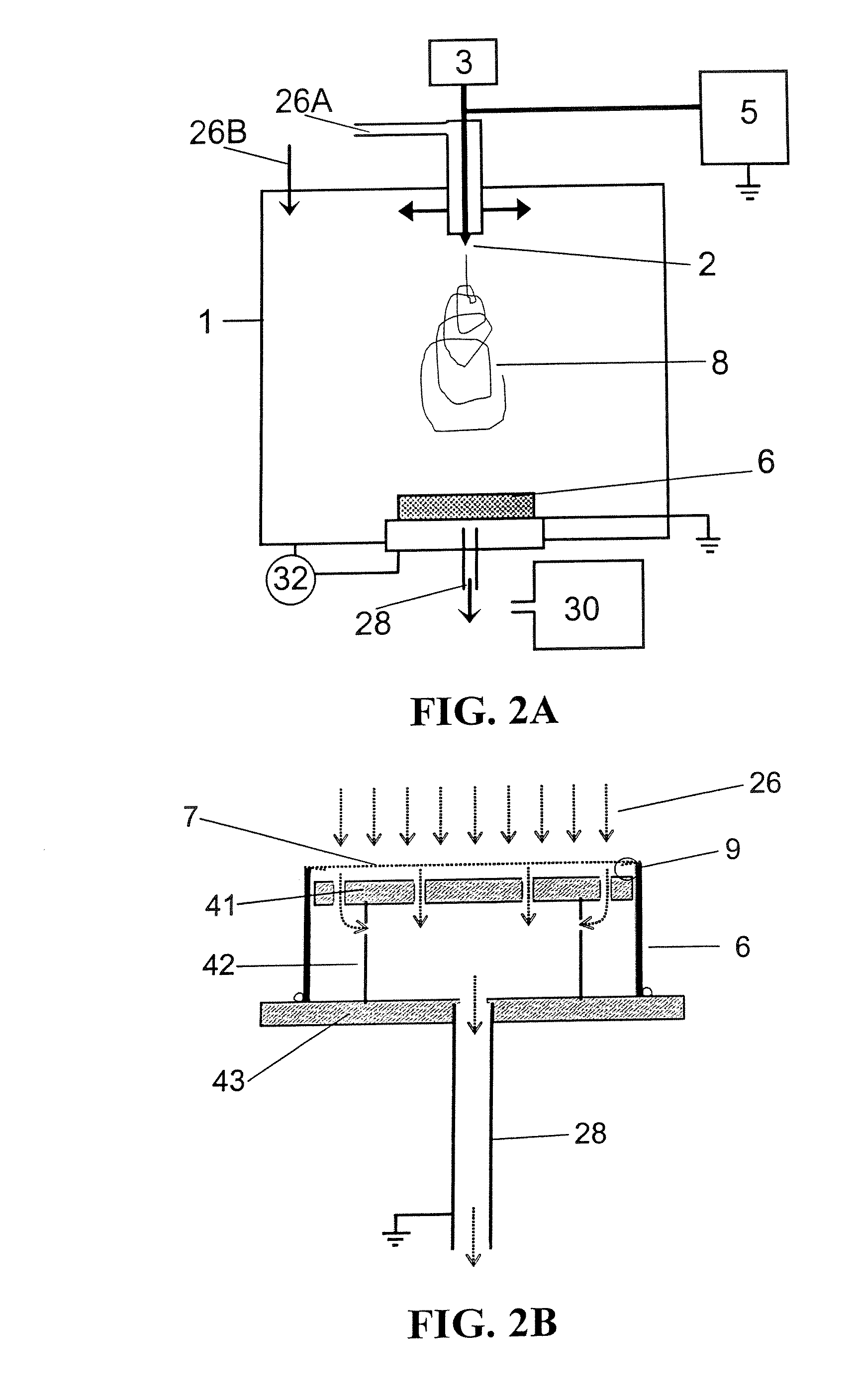
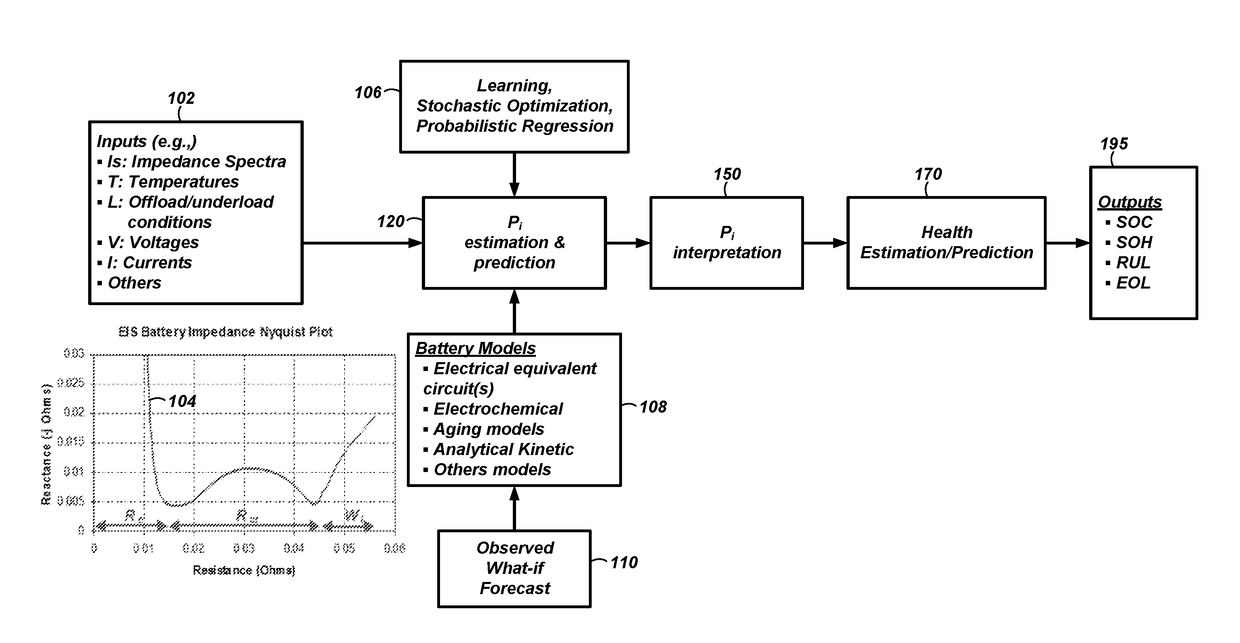
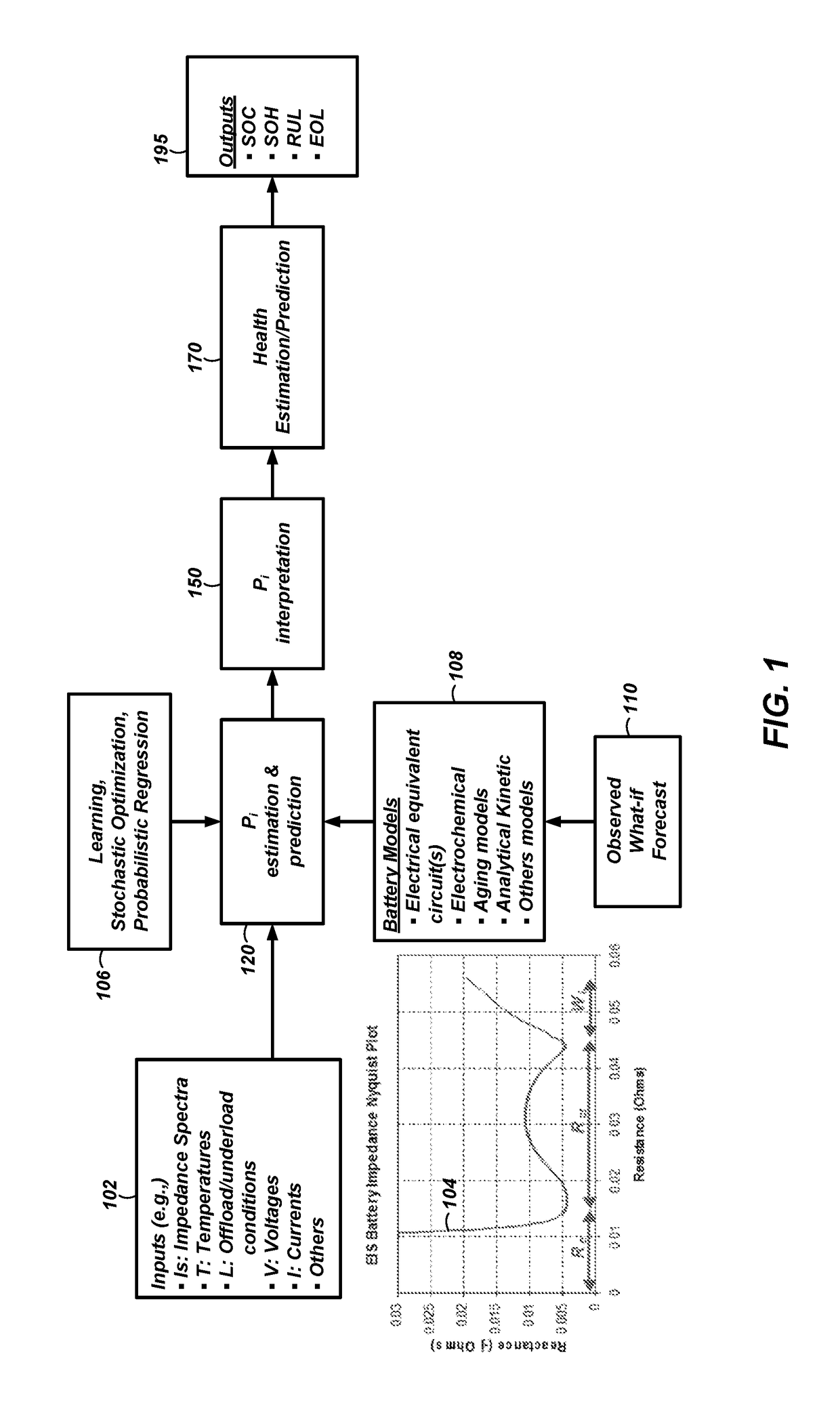
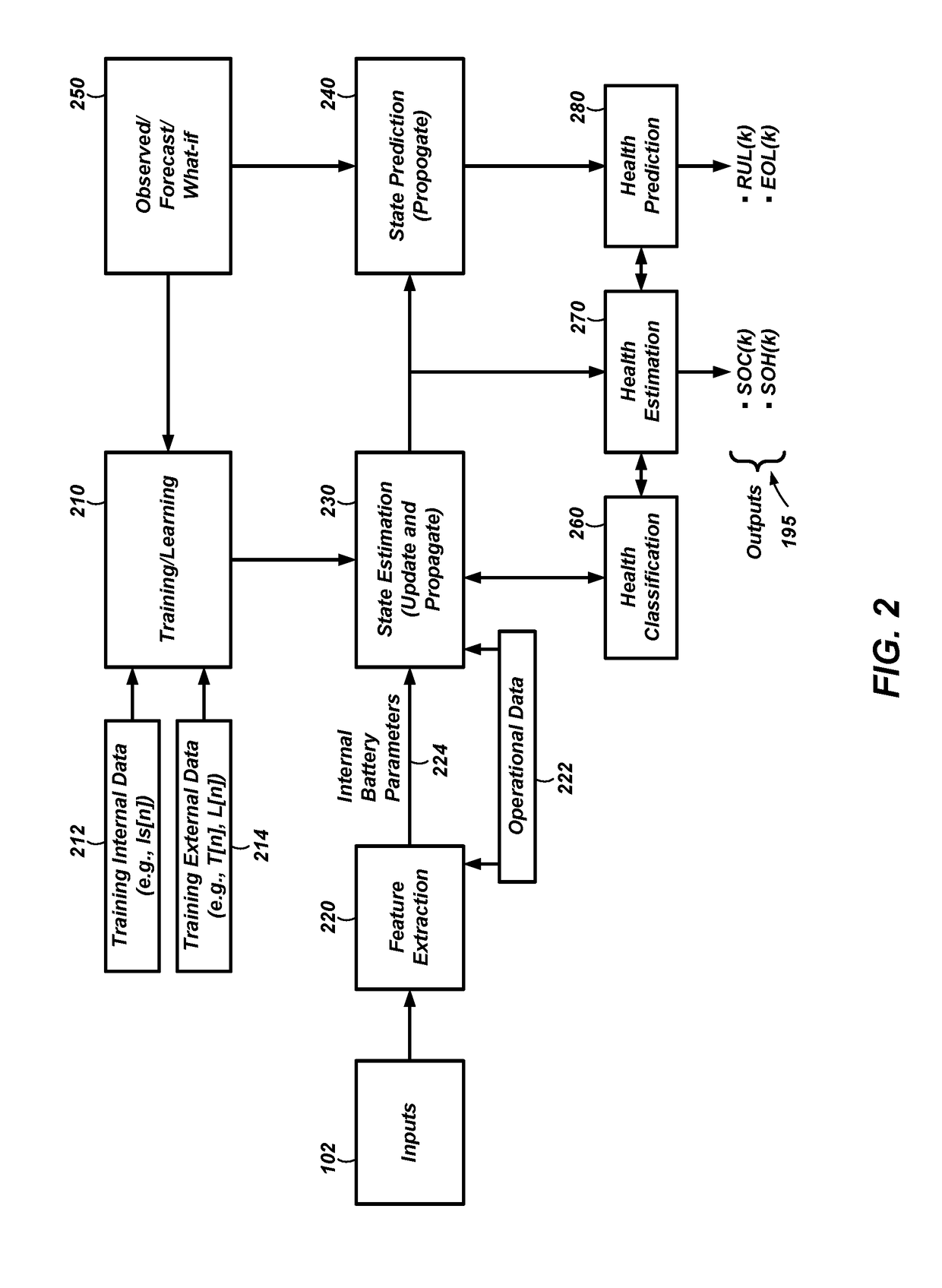
Systems and methods for estimation and prediction of battery health and performance
ActiveUS20180143257A1Testing/monitoring control systemsElectrical testingMoving averageState of health
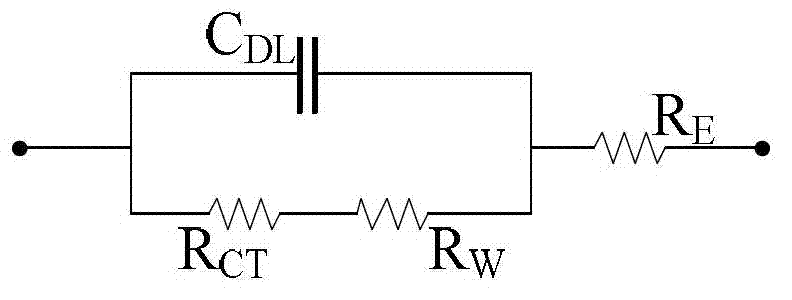
Systems and computer-implemented methods are used for analyzing battery information. The battery information may be acquired from both passive data acquisition and active data acquisition. Active data may be used for feature extraction and parameter identification responsive to the input data relative to an electrical equivalent circuit model to develop geometric-based parameters and optimization-based parameters. These parameters can be combined with a decision fusion algorithm to develop internal battery parameters. Analysis processes including particle filter analysis, neural network analysis, and auto regressive moving average analysis can be used to analyze the internal battery parameters and develop battery health metrics. Additional decision fusion algorithms can be used to combine the internal battery parameters and the battery health metrics to develop state-of-health estimations, state-of-charge estimations, remaining-useful-life predictions, and end-of-life predictions for the battery.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Power source for a dispersion compensation fiber optic system
InactiveUS6963685B2Minimize signalingIncrease bitrateCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmittersFrequency modulationDispersion compensation
Owner:OPTICAL HORIZONS CORP +1
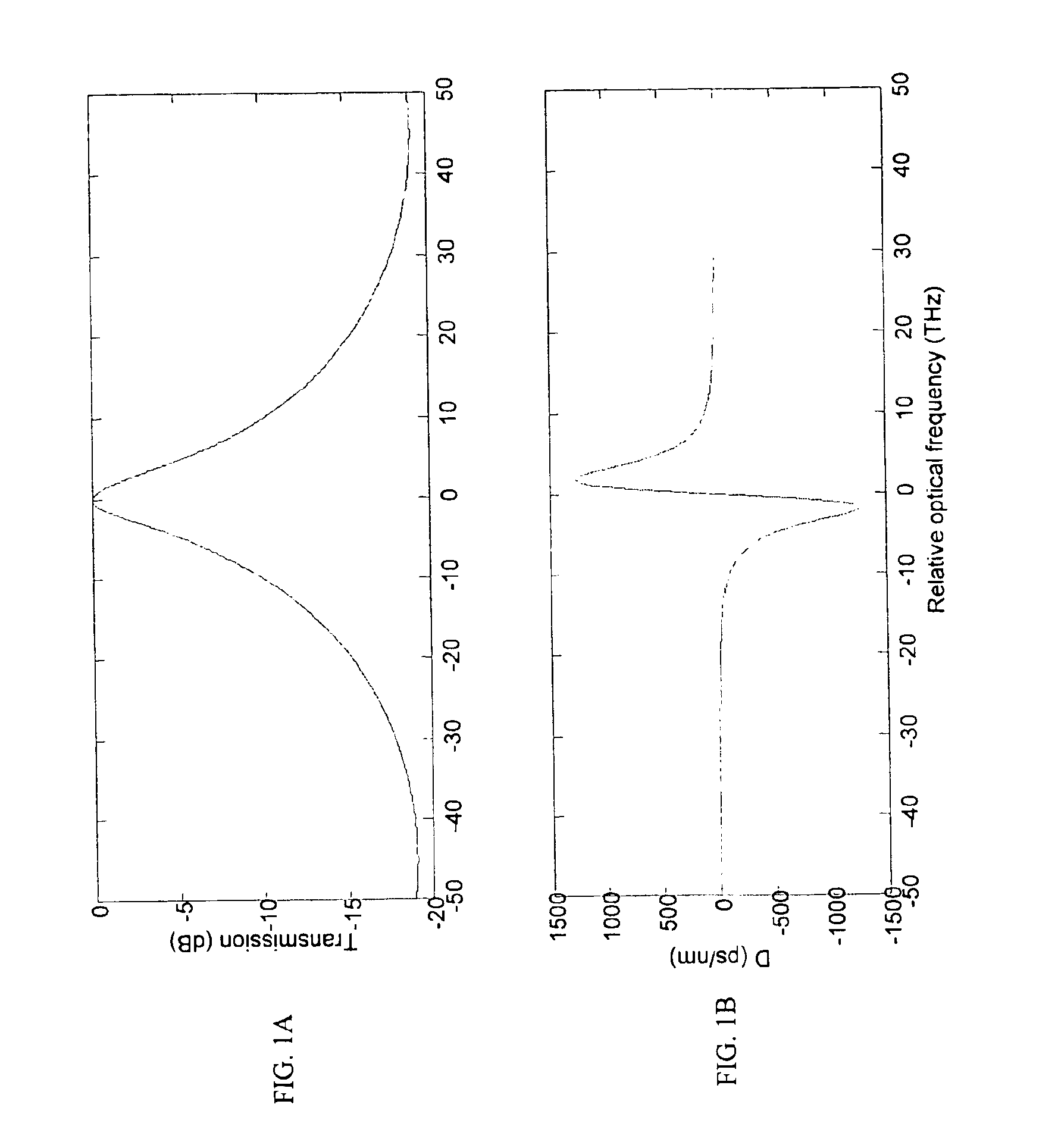
Methods and systems for averting or mitigating undesirable drilling events
InactiveUS6868920B2Avert and mitigate undesirable drilling eventAvert or mitigate undesirable drilling eventsConstructionsProbabilistic networksEnvironmental geologyParticle filter
A method and system for averting or mitigating undesirable drilling events during a drilling process is disclosed. The state of the drilling rig is detected, preferably automatically, based on surface and / or downhole measurement data. One or more undesirable drilling events are detected by correlating the acquired measurement data with the detected state. A drilling rig action is determined which averts or mitigates a detected undesirable drilling event. Finally, the drilling process is overridden by commanding performance of the action.The algorithm used in detecting the most likely rig state is preferably probabilistic in nature, and is even more preferably based on particle filtering techniques.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
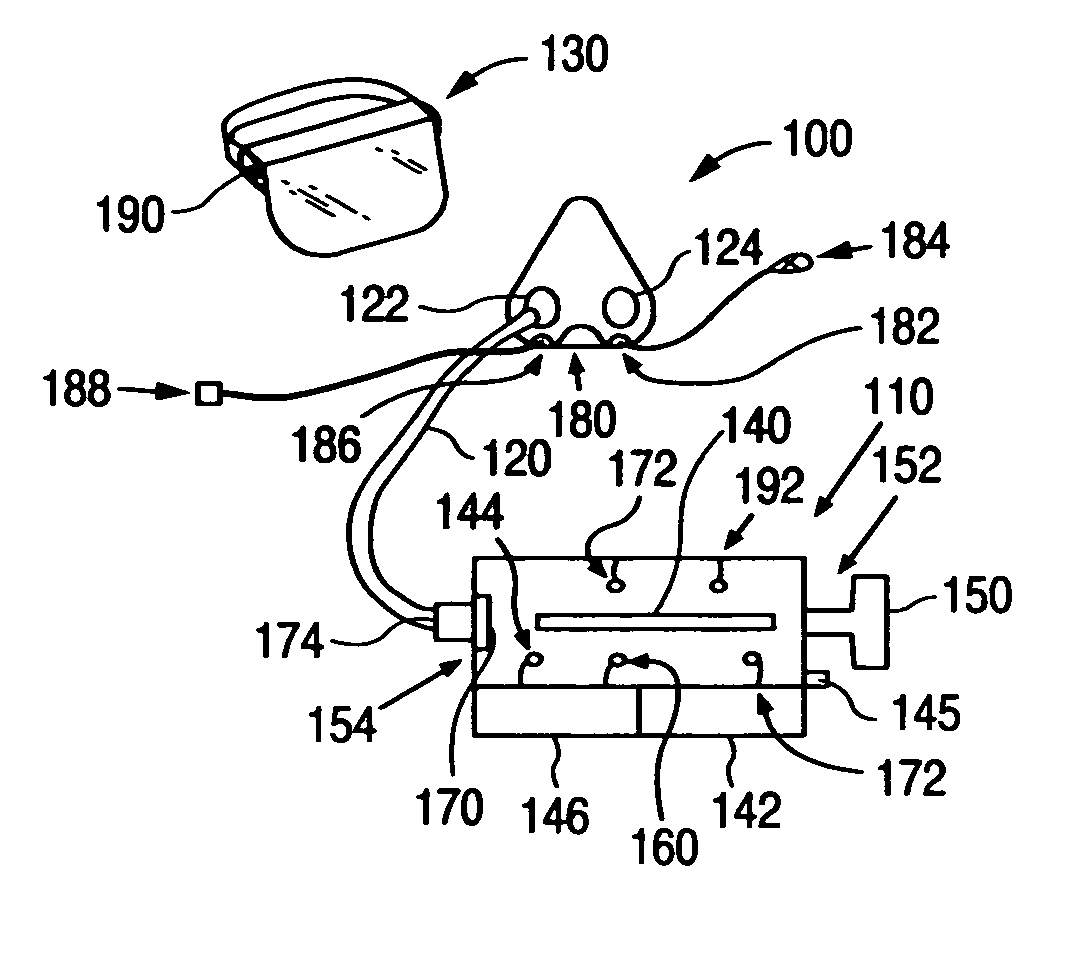
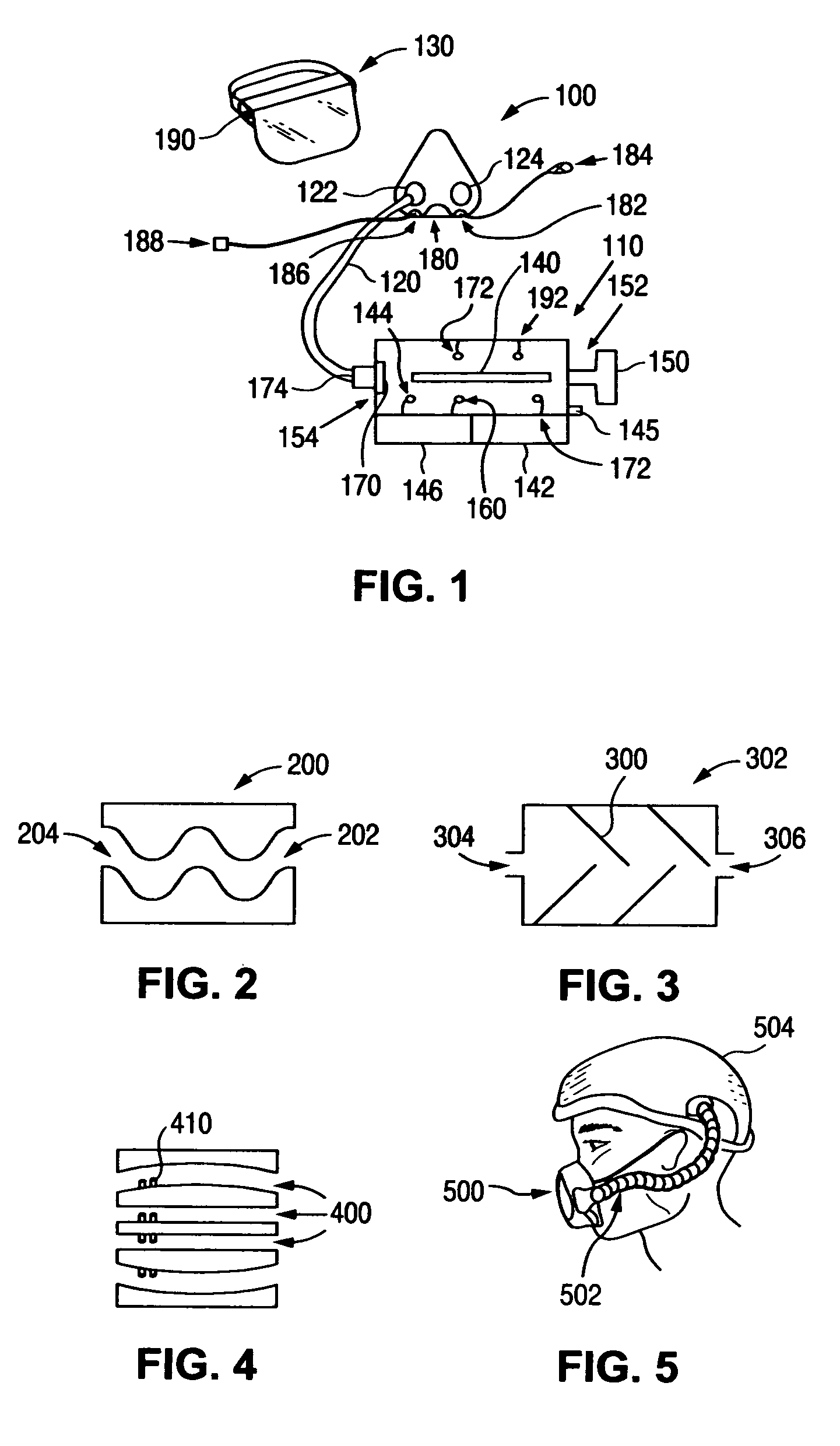
Air Supply Apparatus
InactiveUS20090004047A1Constant pressureDispersed particle filtrationBreathing filtersUltravioletHigh intensity
In an air sterilization system that includes a UV kill chamber for sterilizing air that is to be supplied to users, the effectiveness of killing or neutralizing pathogens is increased by including not only a UV light source of a certain intensity but also including a particle filter and providing short duration high intensity UV radiation. In the case of a user specific system that includes a face mask to supply air to a specific user, exhaled air from the face mask may be sterilized as well, either by using the same kill chamber or by using a separate kill chamber.
Owner:HUNTER ERIC C +4
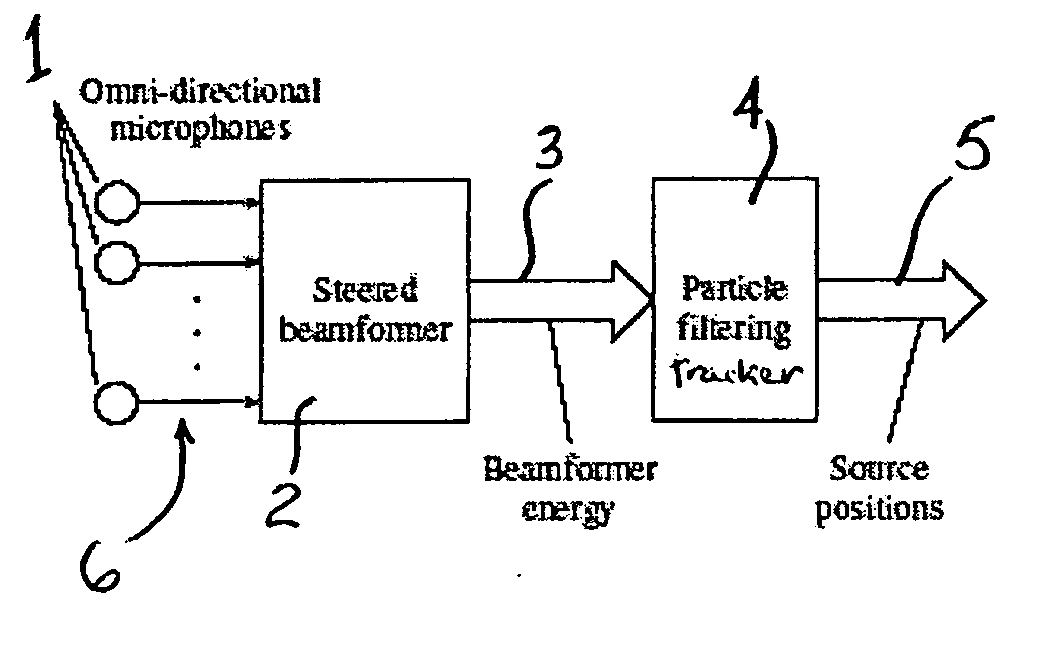
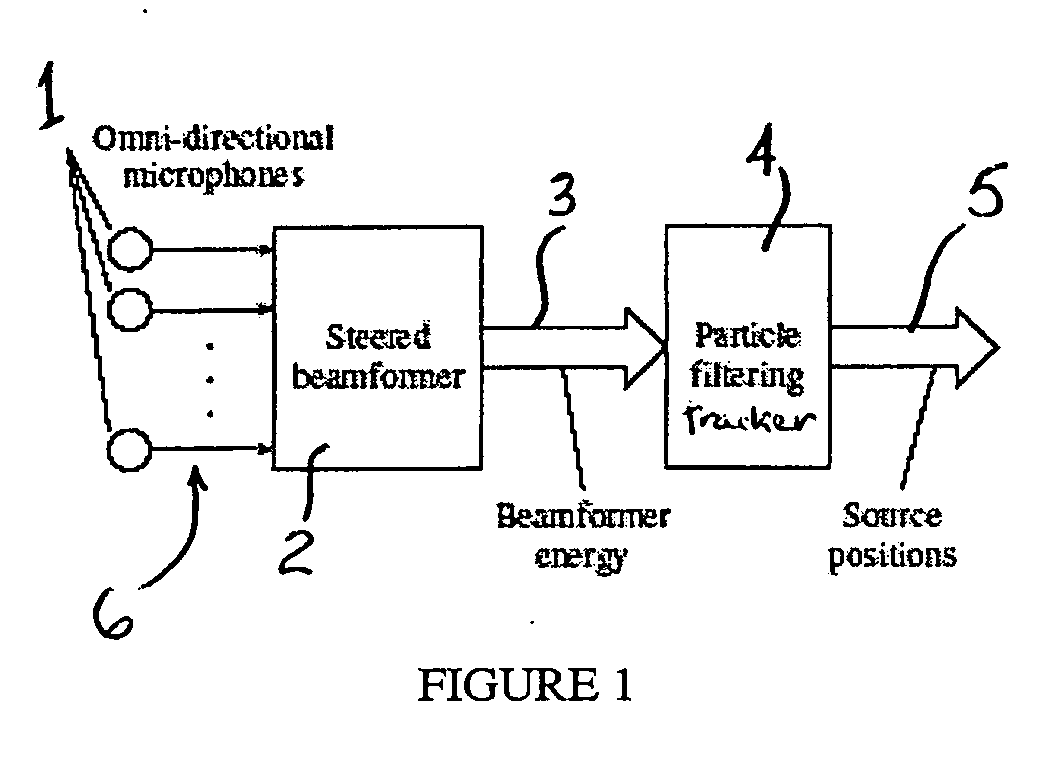
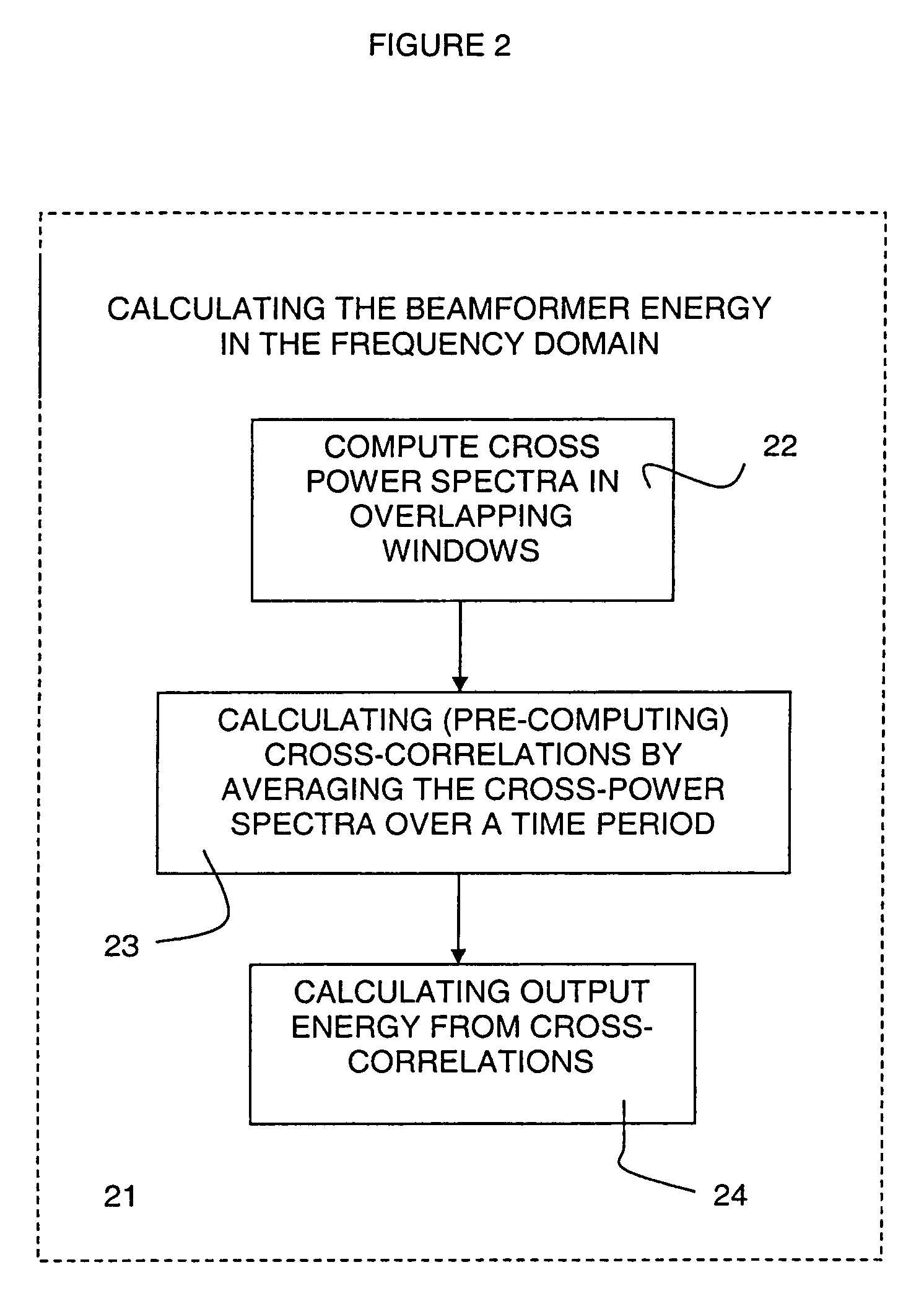
Robust localization and tracking of simultaneously moving sound sources using beamforming and particle filtering
The present invention relates to a system for localizing at least one sound source, comprising a set of spatially spaced apart sound sensors to detect sound from the at least one sound source and produce corresponding sound signals, and a frequency-domain beamformer responsive to the sound signals from the sound sensors and steered in a range of directions to localize, in a single step, the at least one sound source. The present invention is also concerned with a system for tracking a plurality of sound sources, comprising a set of spatially spaced apart sound sensors to detect sound from the sound sources and produce corresponding sound signals, and a sound source particle filtering tracker responsive to the sound signals from the sound sensors for simultaneously tracking the plurality of sound sources. The invention still further relates to a system for localizing and tracking a plurality of sound sources, comprising a set of spatially spaced apart sound sensors to detect sound from the sound sources and produce corresponding sound signals; a sound source detector responsive to the sound signals from the sound sensors and steered in a range of directions to localize the sound sources, and a particle filtering tracker connected to the sound source detector for simultaneously tracking the plurality of sound sources.
Owner:SCOPRA SCI & GENIE SEC
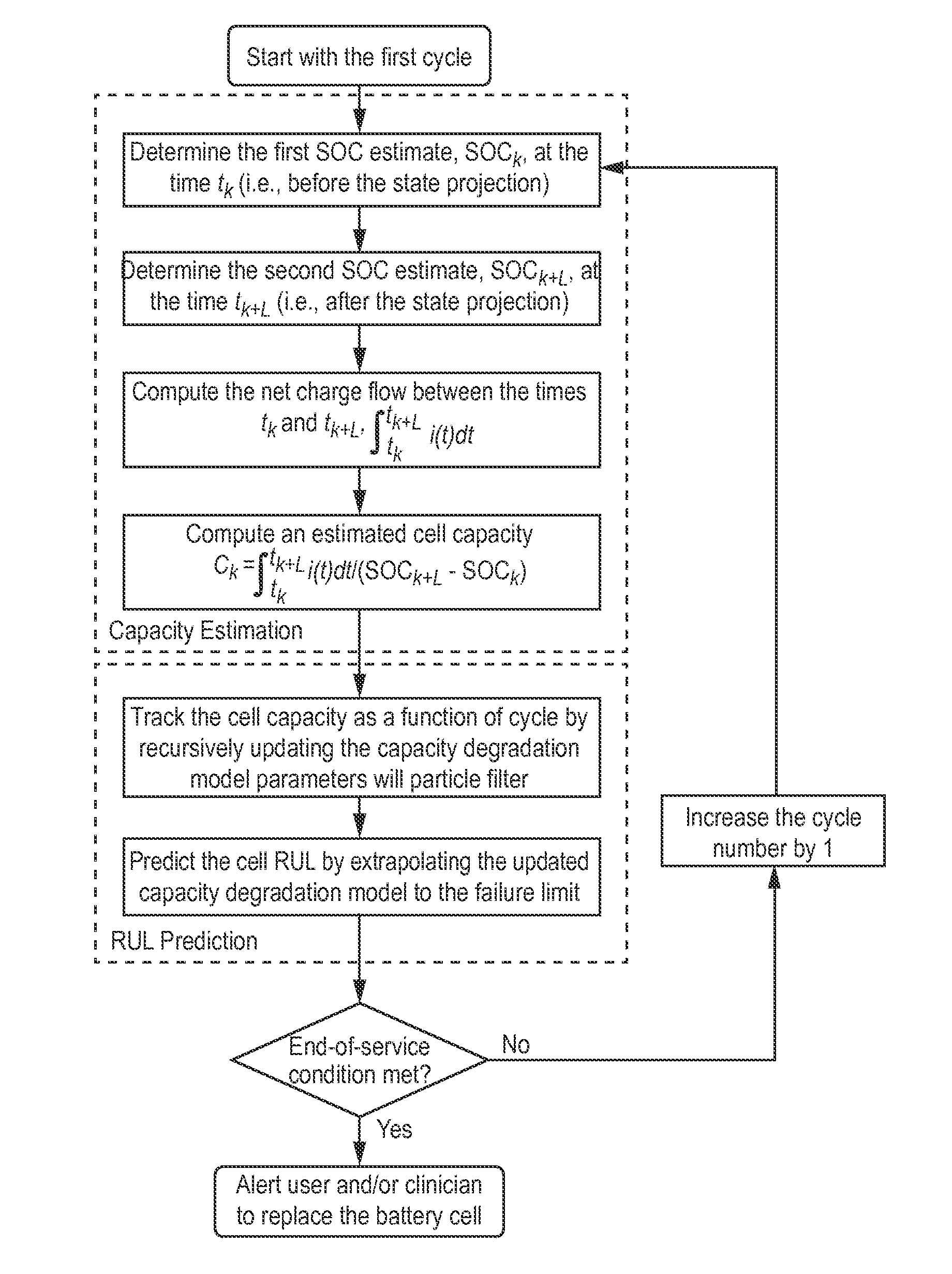
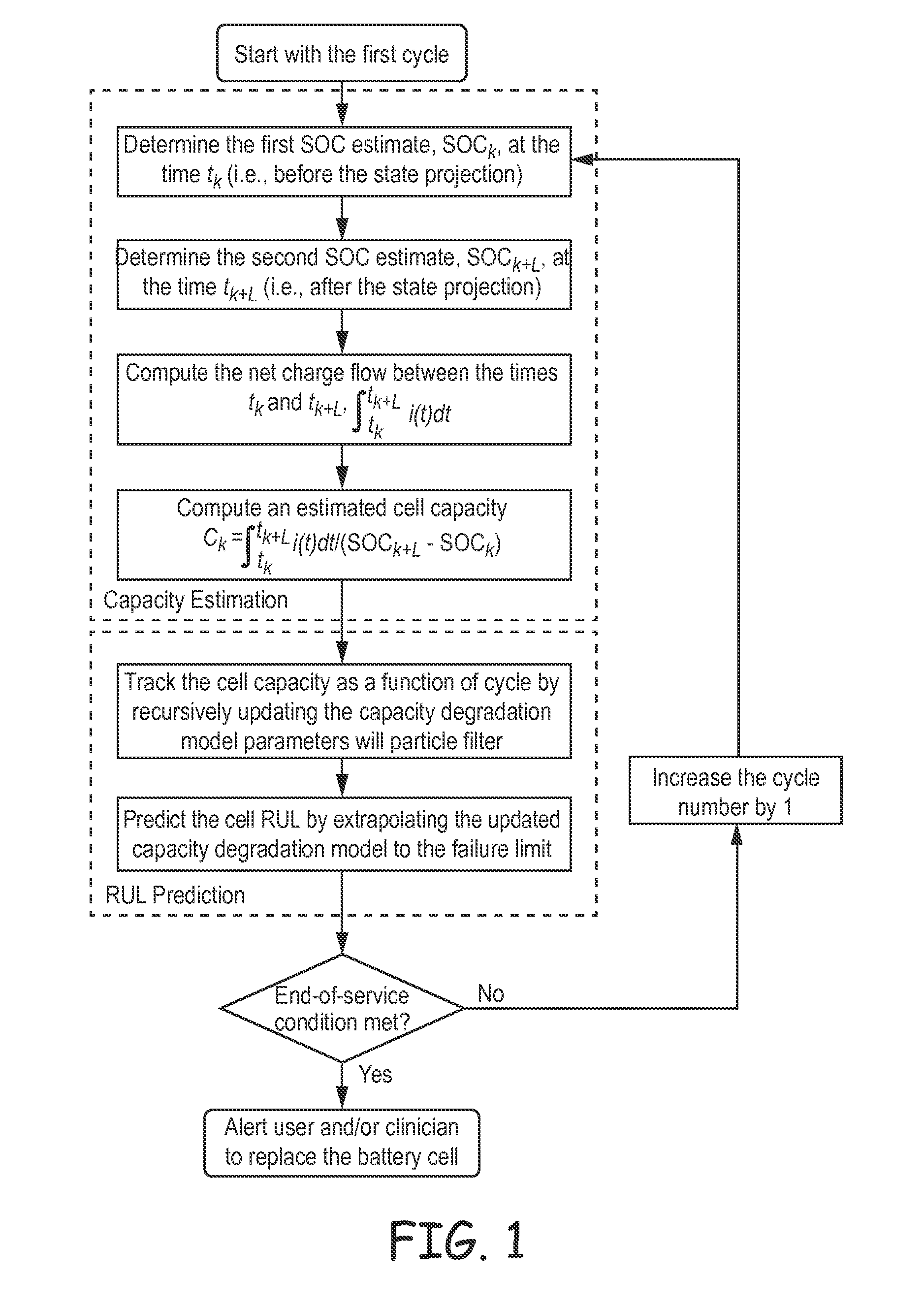
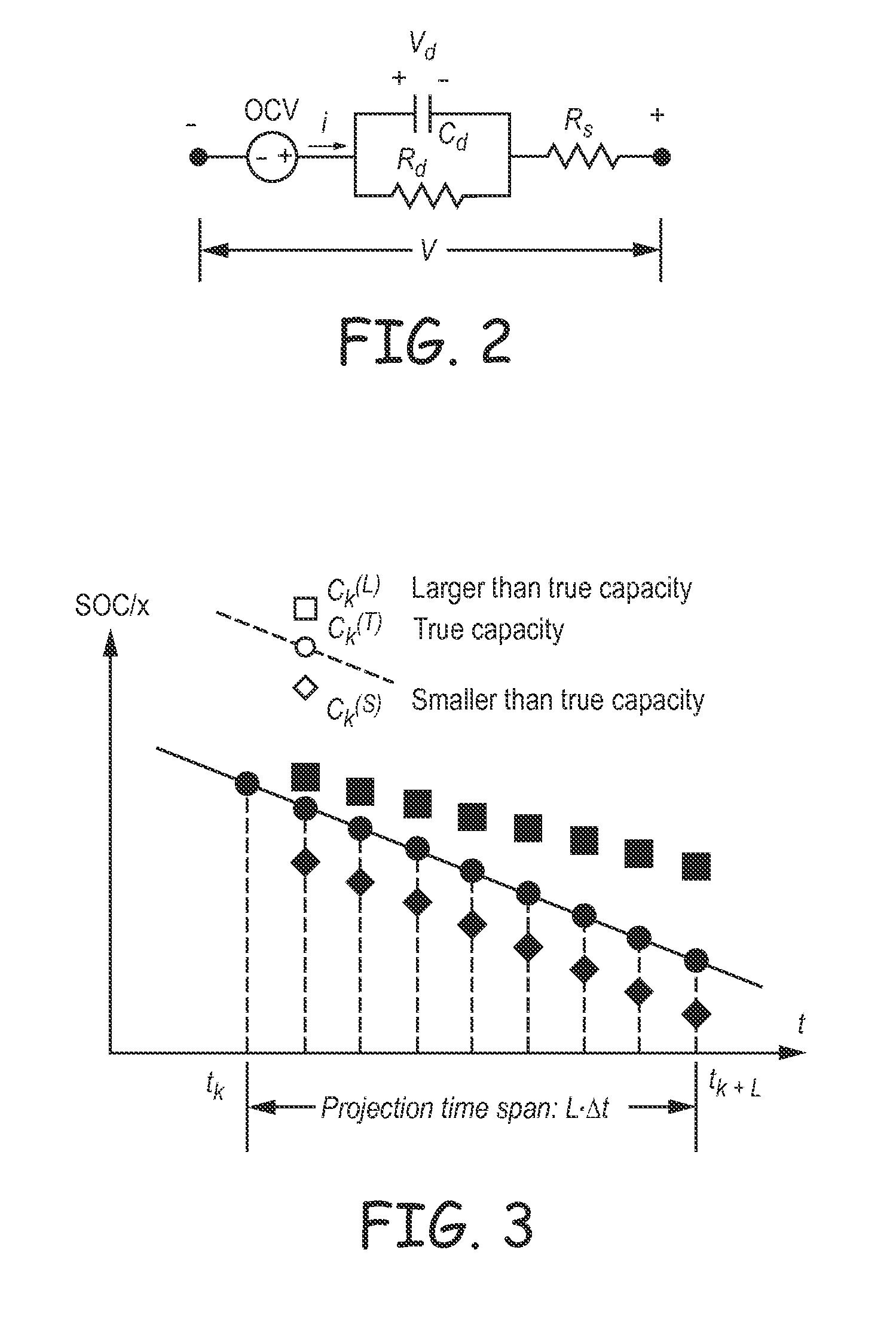
Method and System for Predicting Useful Life of a Rechargeable Battery
System and method for predicting the remaining useful life (RUL) of a rechargeable battery, such as a lithium-ion rechargeable battery. In a method, the capacity of the battery is determined based on at least changes of state of charge values estimated at a first and second time and a net charge flow of the battery and applying a particle filter to a capacity degradation formula using the determined capacity to form a capacity degradation model and determining the RUL using the capacity degradation model using a pre-defined end of service threshold. The system and method may be used to predict the RUL of a rechargeable battery in an implantable medical device.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
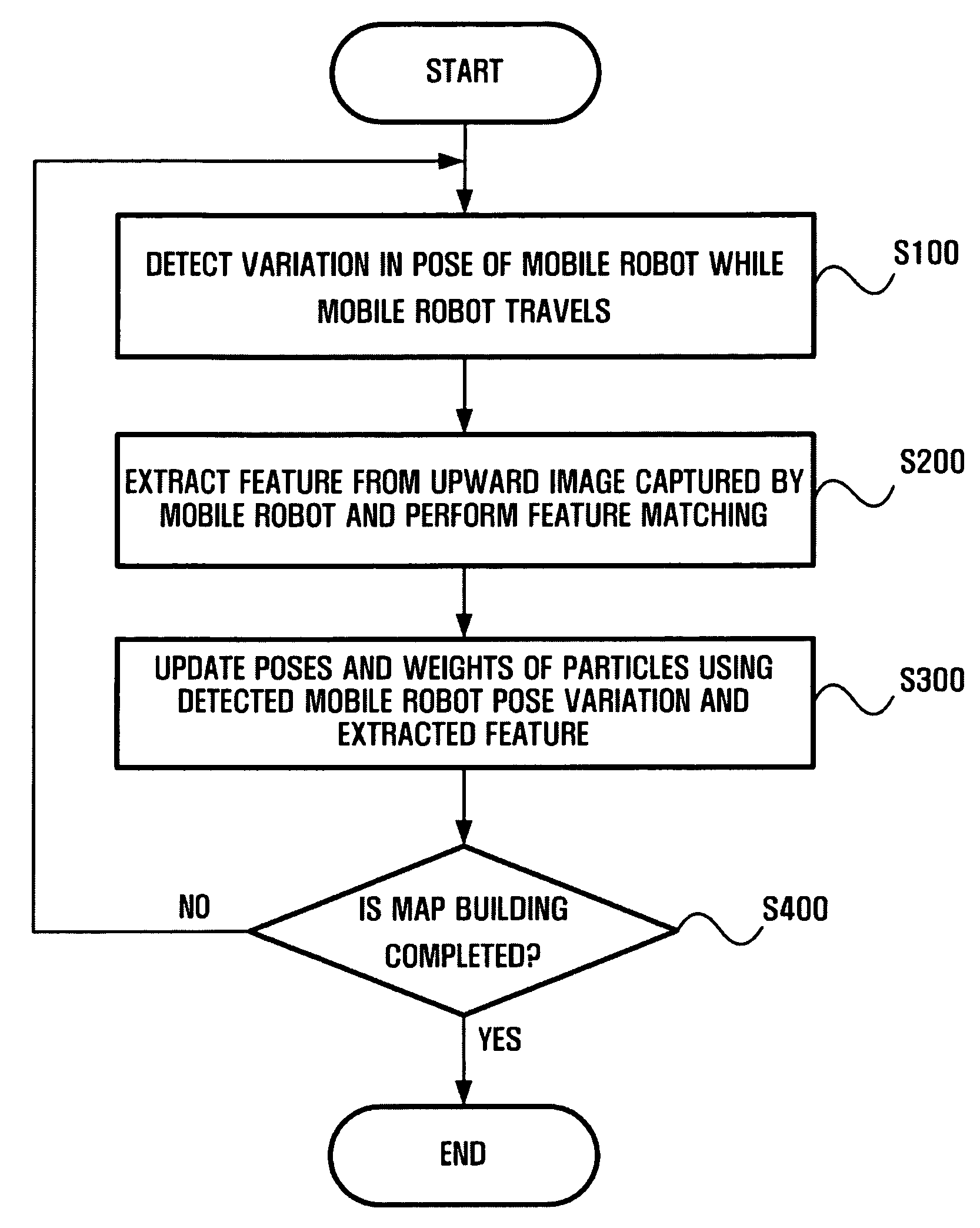
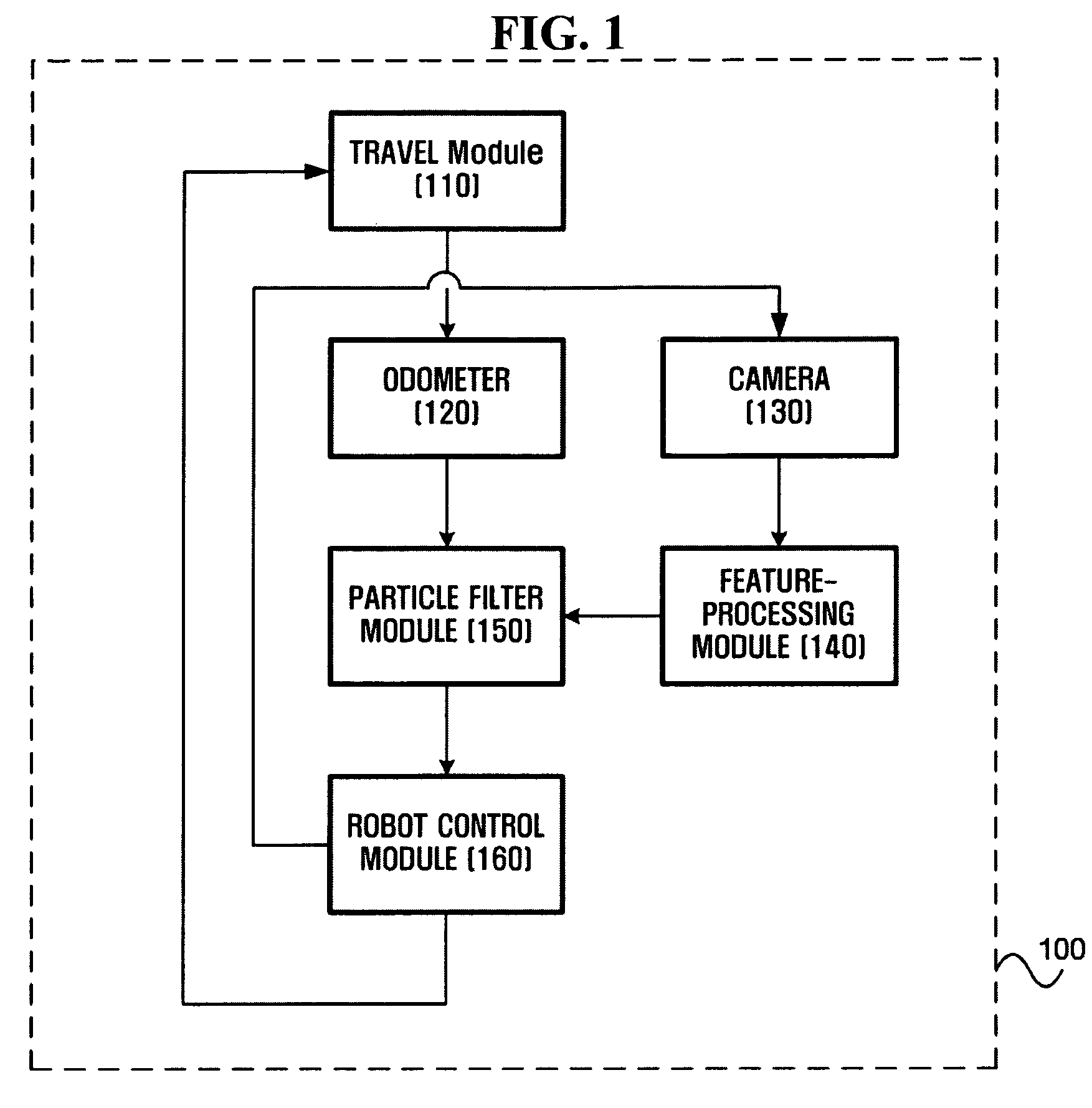
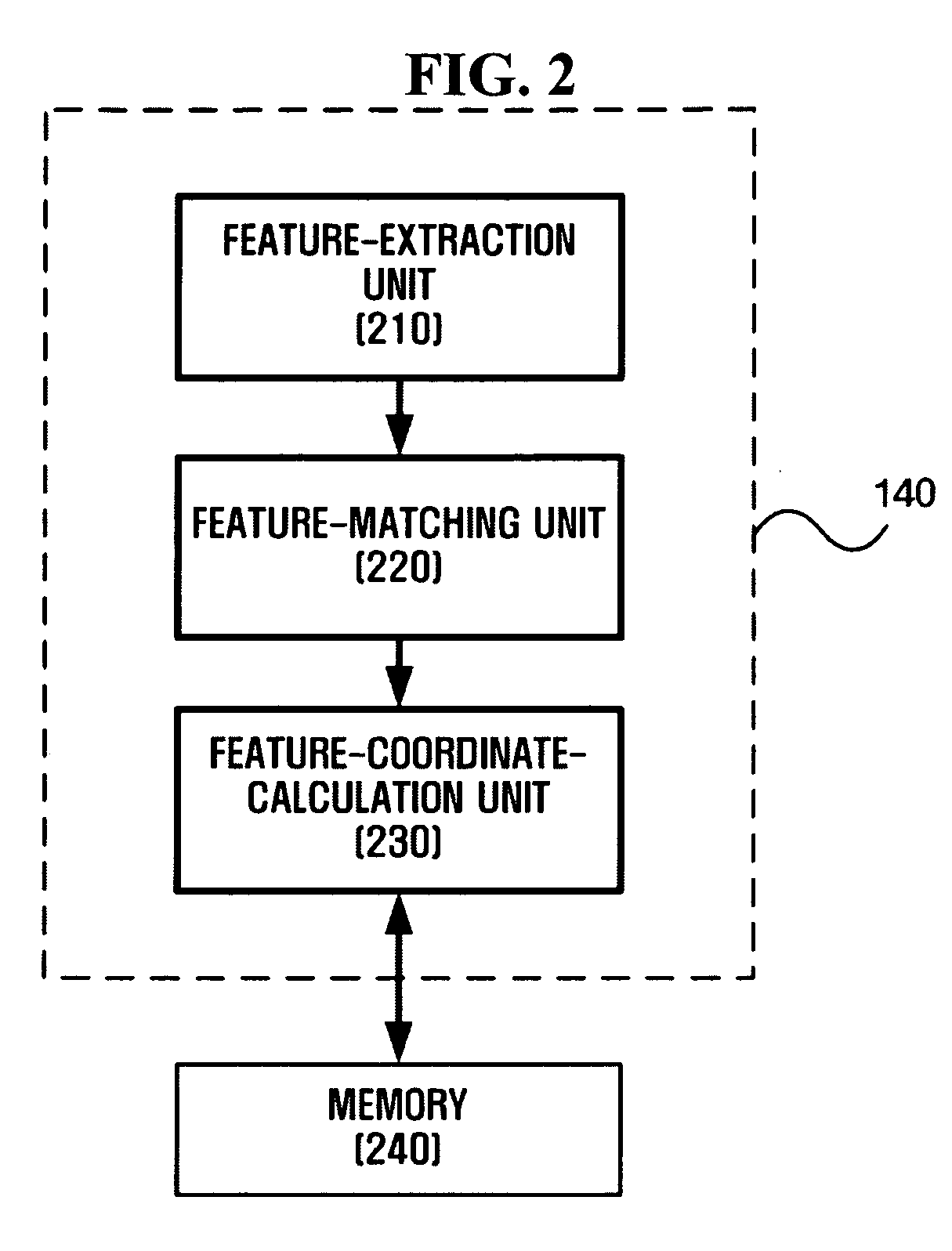
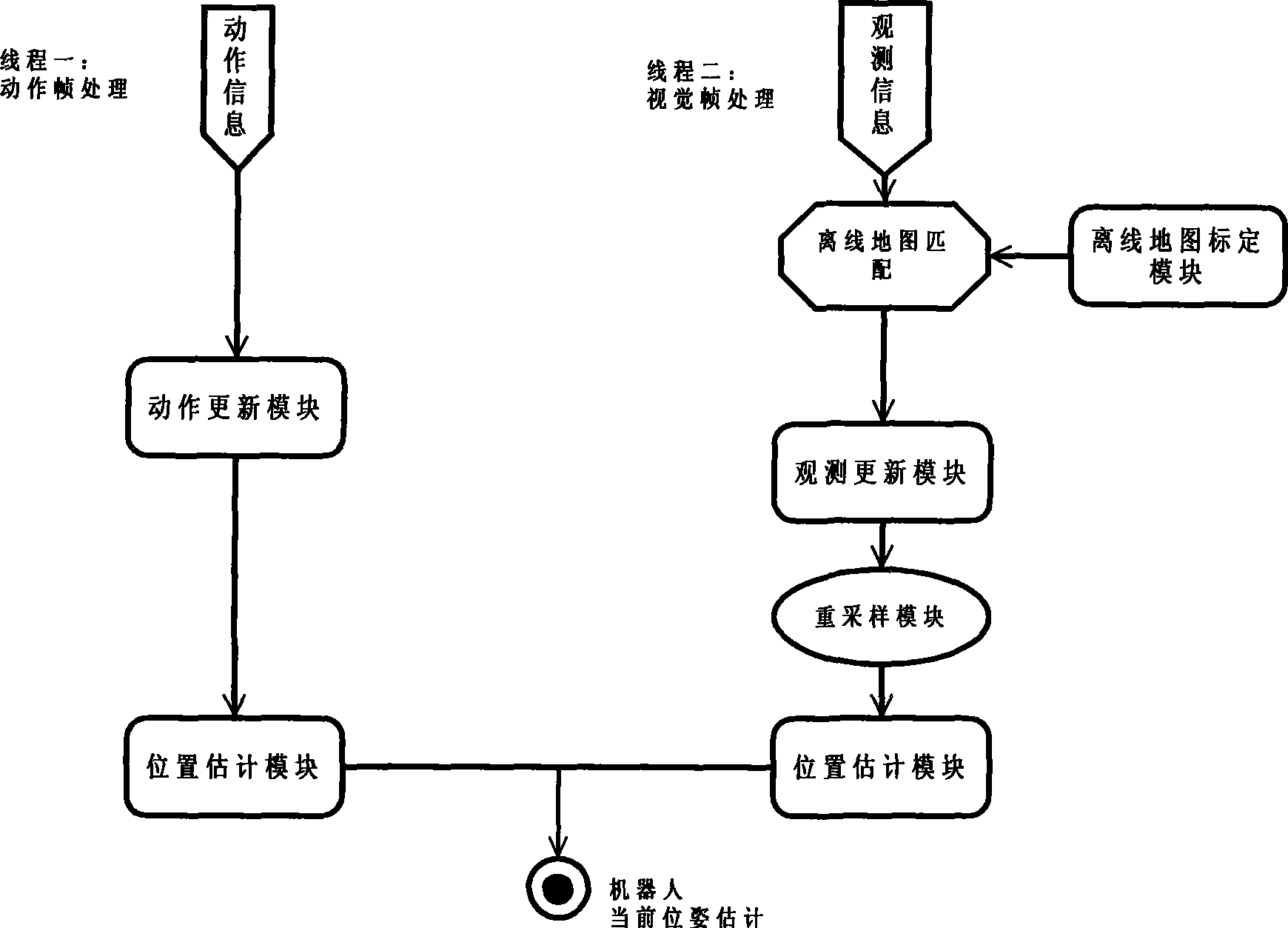
Method and apparatus for estimating pose of mobile robot using particle filter
ActiveUS20090024251A1Reduce the amount of memoryReduce the amount requiredProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorImage captureMobile robot
A method and apparatus for estimating the pose of a mobile robot using a particle filter is provided. The apparatus includes an odometer which detects a variation in the pose of a mobile robot, a feature-processing module which extracts at least one feature from an upward image captured by the mobile robot, and a particle filter module which determines current poses and weights of a plurality of particles by applying the mobile robot pose variation detected by the odometer and the feature extracted by the feature-processing module to previous poses and weights of the particles.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
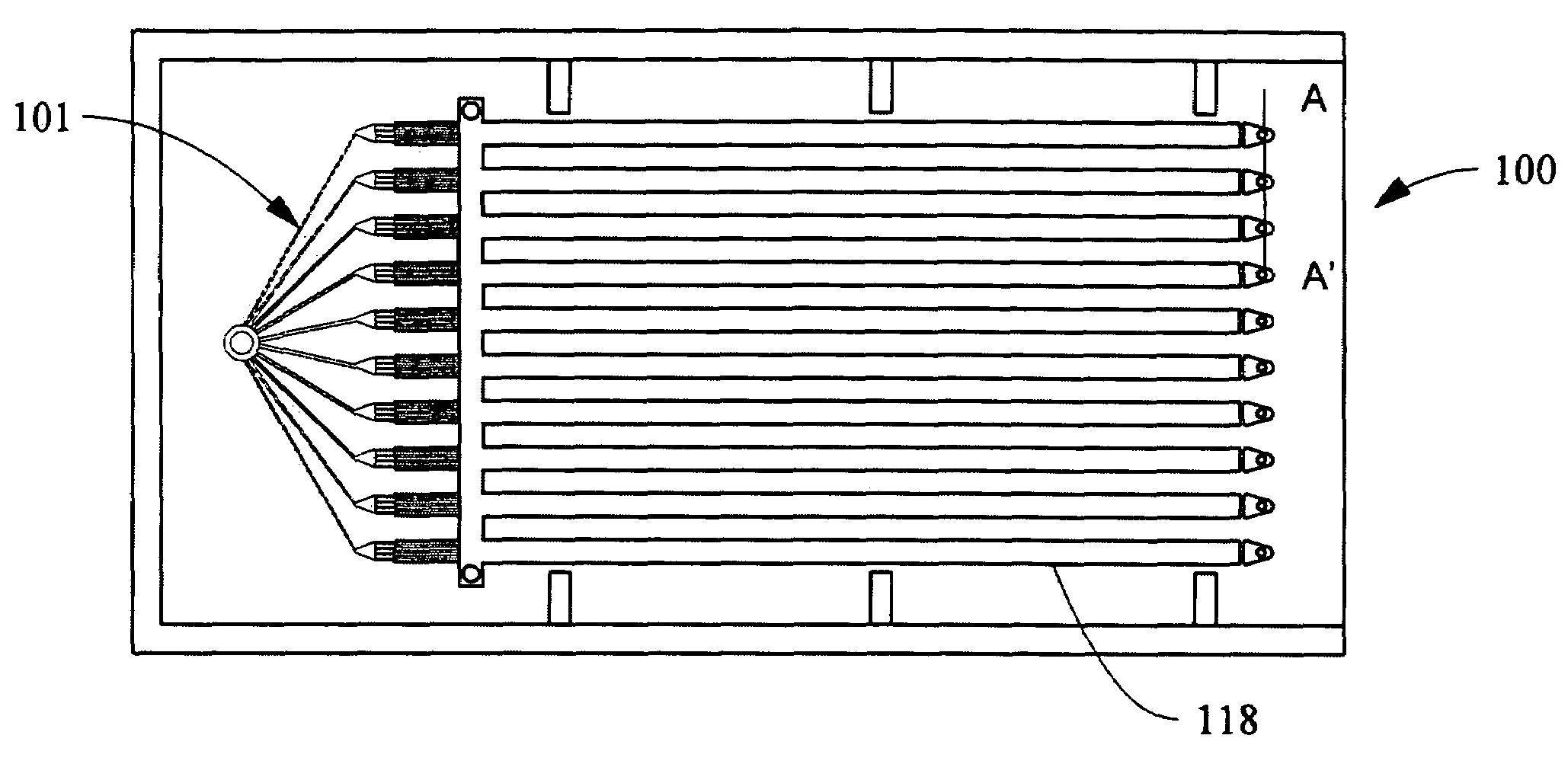
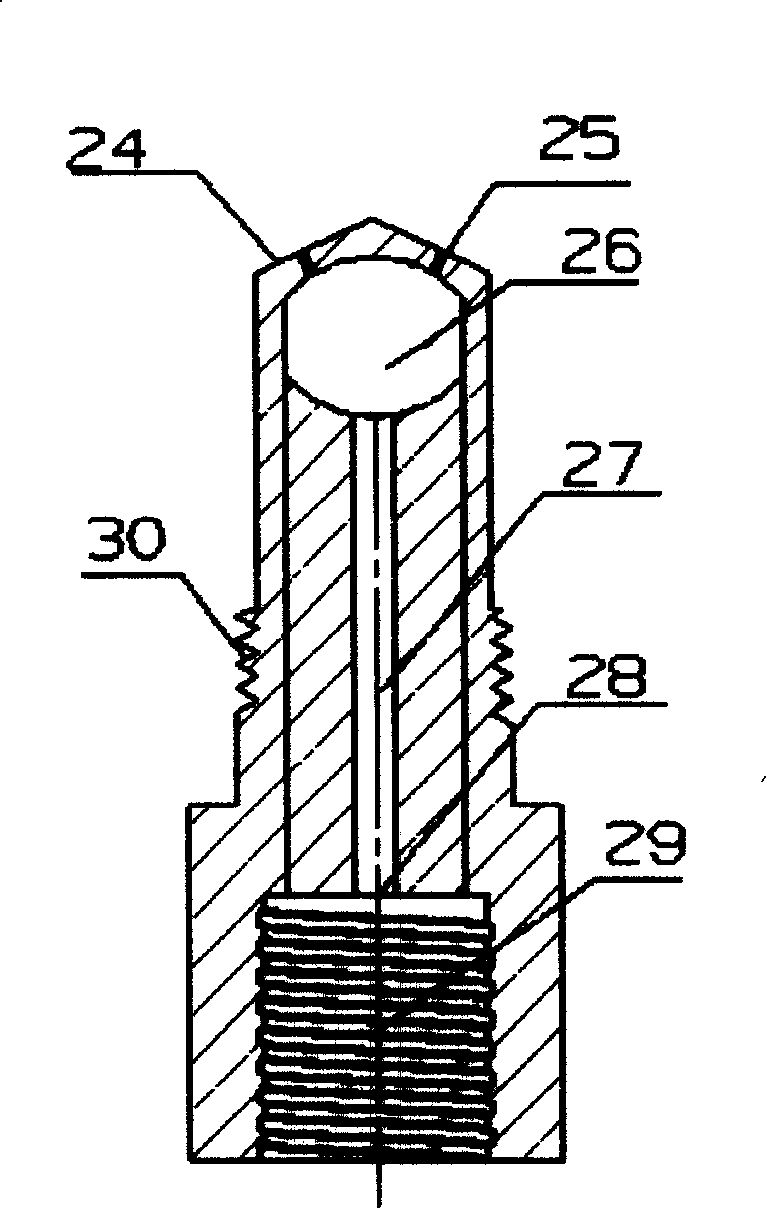
Bonded particle filters
InactiveUS7157043B2Significant portionMelt-holding vesselsMolten metal pouring equipmentsMolten metalMaterials science
An apparatus for filtering molten metal held in a vessel before the metal enters the dosing tube. The filtering apparatus includes an attachment portion that mounts to the dosing tube, a filter body connected to the attachment portion and a planar surface attached to an end of the filter body opposite the attachment portion. The filter body can include a beveled end opposite the attachment portion where the planar surface is attached. The apparatus can be made from a bonded-particle material made from silicon carbide or aluminum oxide held together by an aluminum-resistant binder.
Owner:METAULLICS SYST +1
Monolithic honeycomb structure made of porous ceramic and use as a particle filter
InactiveUS6582796B1Prevent the evaporation of the waterEasy curingInternal combustion piston enginesSilencing apparatusSodium BentoniteOxygen
A monolithic honeycomb-type structure useful in particular as a particle filter for exhaust gases from diesel engines has a number of passages that empty into the end faces of said monolith, but are alternately open and sealed. The monolith consists of a porous refractory material that comprises: 70 to 97% by mass of alpha and / or beta crystallographic-type silicon carbide that has at least one particle size and preferably at least two particle sizes, and 3 to 30% by mass of at least one bonding ceramic phase in the form of a micronic powder or particles that are obtained by atomization, comprising at least one simple oxide, for example, B2O3, Al2O3, SiO2, MgO, K2O, Li2O, Na2O, CaO, BaO, TiO, ZrO2 and Fe2O3 and / or at least one mixed oxide, for example, the alkaline aluminosilicates (of Li, Na, or K) or alkaline-earth aluminosilicates (of Mg, Ca, Sr or Ba), clays, bentonite, feldspars or other natural silico-aluminous materials. The production of the monolith comprises a calcination stage under an oxygen-containing atmosphere at a temperature up to 1650° C., but less than 1550° C.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
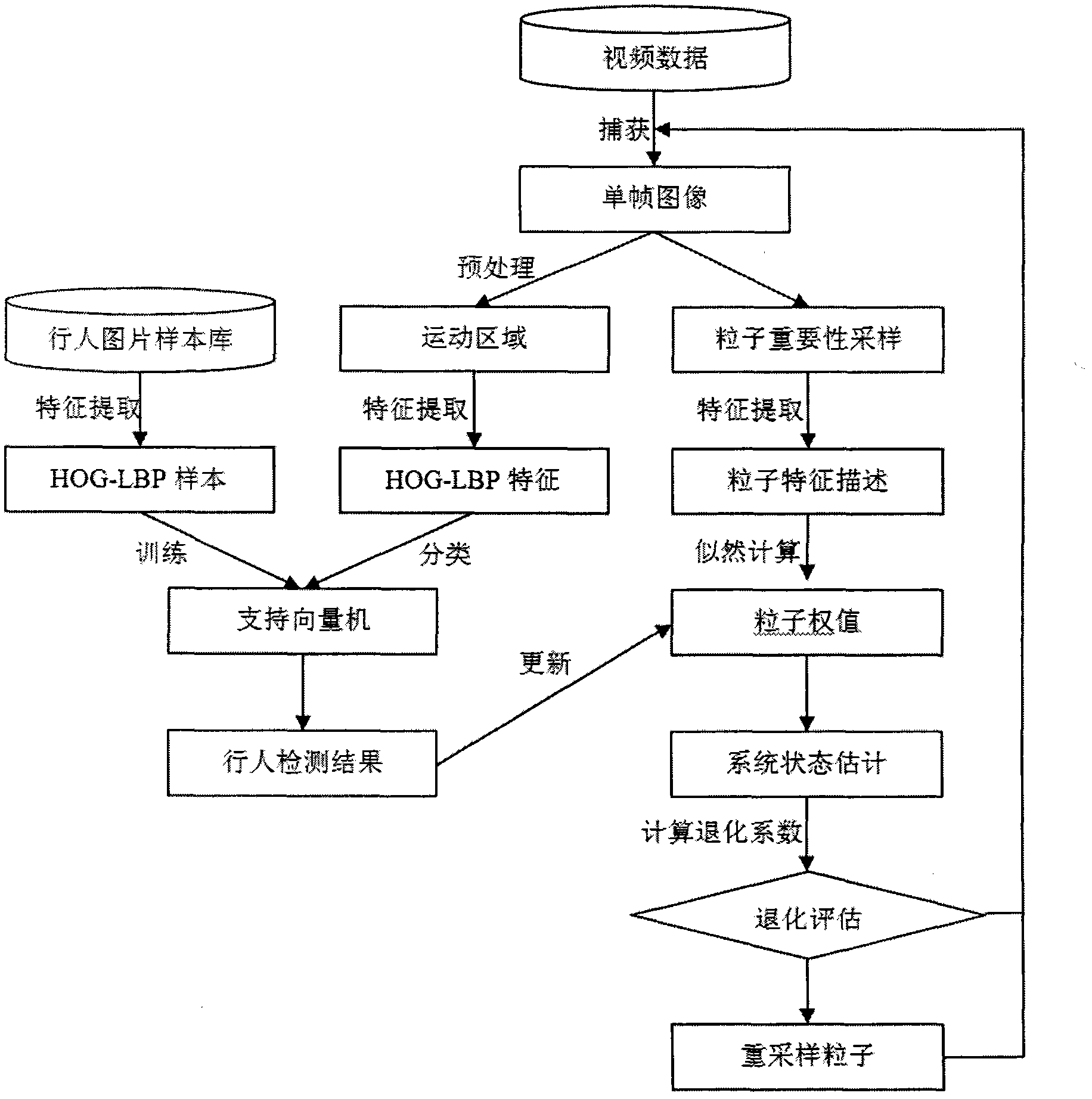
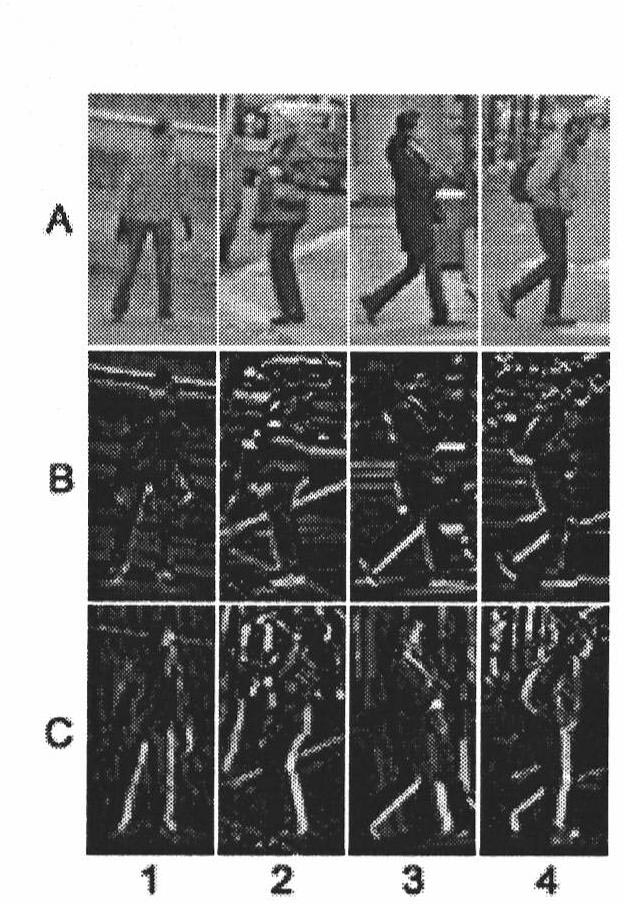
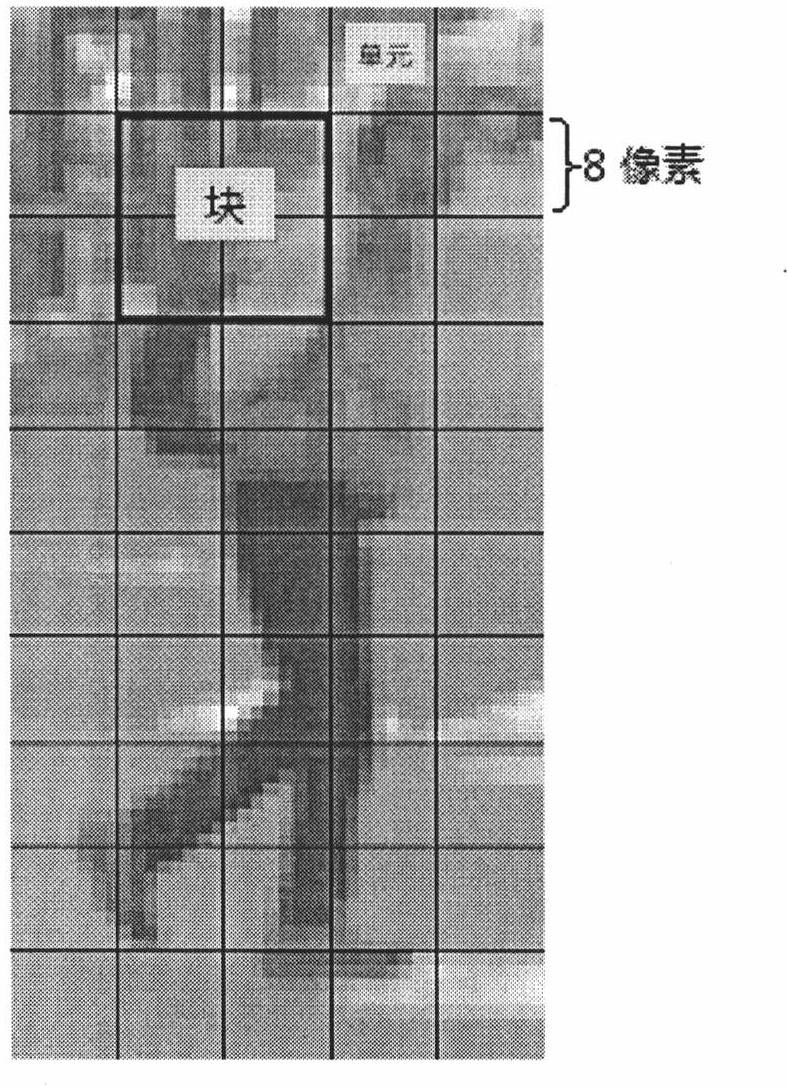
Pedestrian tracking method based on HOG-LBP
InactiveCN102663409AAvoid environmental impactOvercome occlusionImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionSupport vector machineFeature extraction
The invention discloses a pedestrian tracking method based on HOG-LBP, comprising the following steps of, A1, sample establishment; A2, feature extraction; A3, SVM model establishment; A4, classifier training; A5, video capture and pretreatment; A6, video pedestrian examination; A7, video pedestrian tracking: applying a particle filtering tracking method based on an HOG-LBP feature to track the pedestrian examined in step A6. The method firstly learns an image pedestrian mode through a support vector machine, and then classifies a moving area in a video sequence and inputs the result to a particle filtering machine to update the particle status, and finally realizes continuous tracking to pedestrian movement in the scene. Because the method collects pedestrian feature by adopting HOG-LBP and uses the particle filtering to track movement, it has good adaptability and stability to movement interleave and sheltering phenomenon in a scene and non-linear feature presented by the movement.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
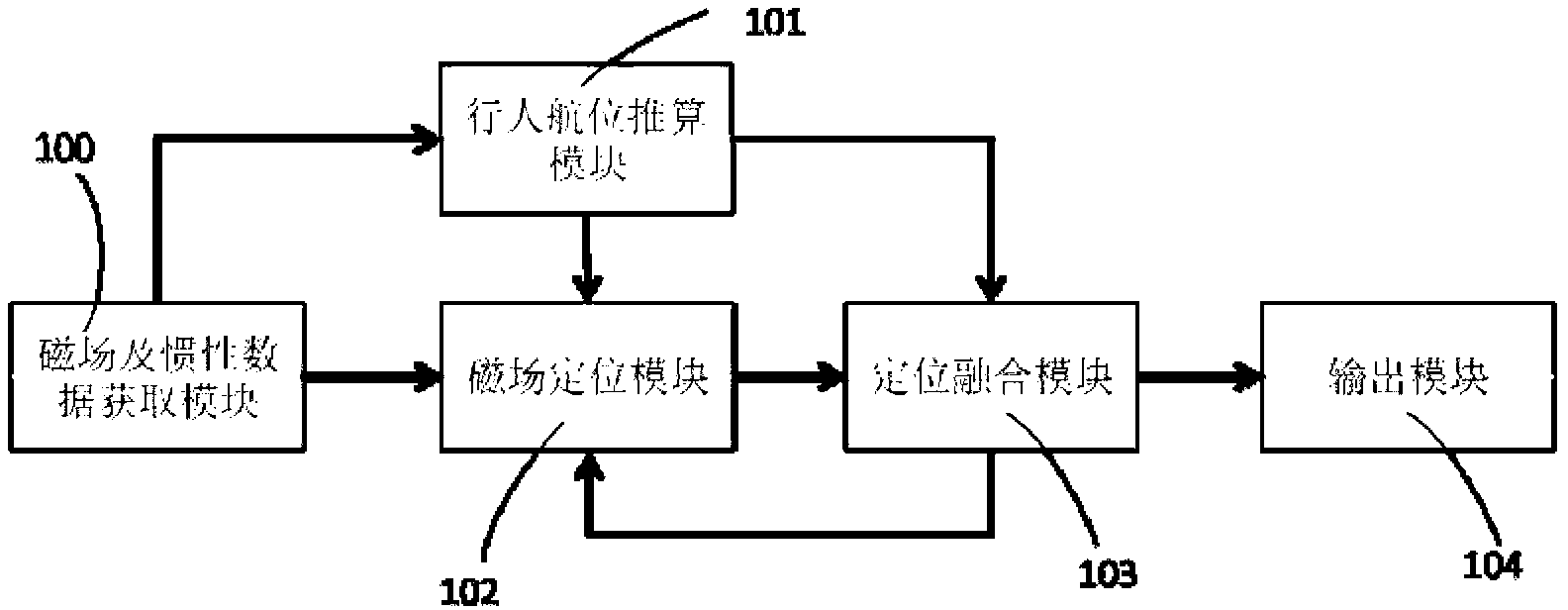
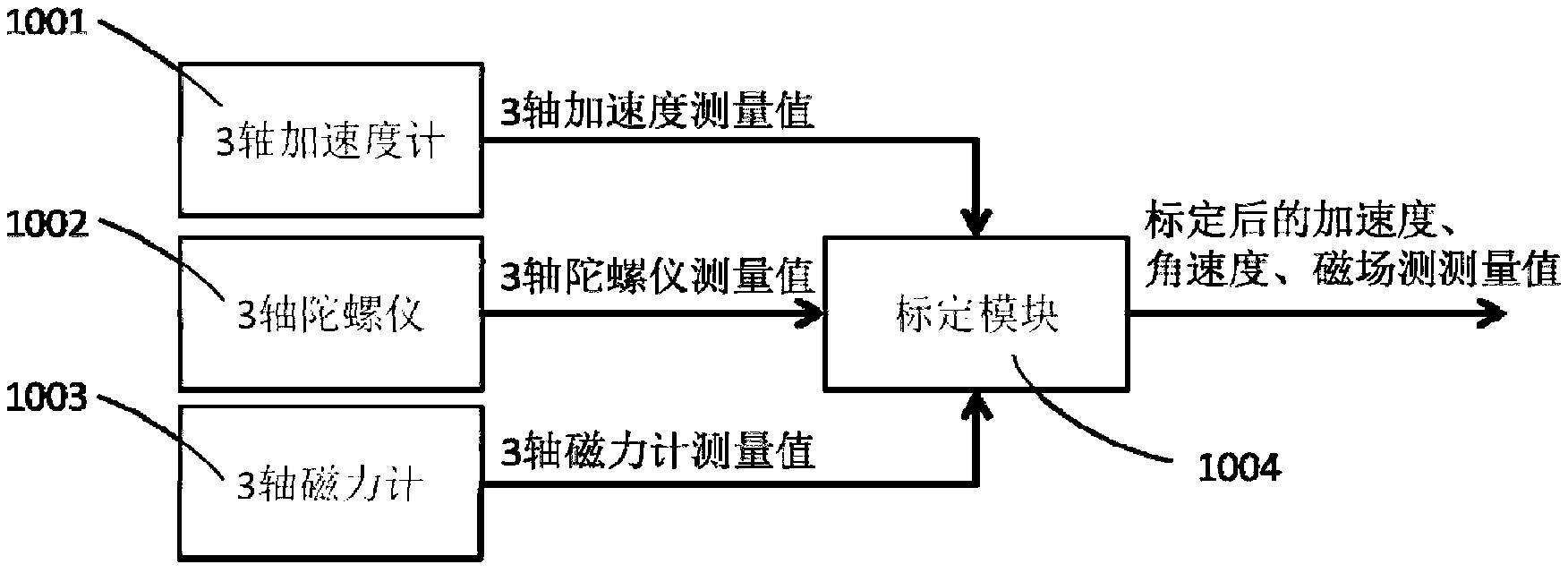
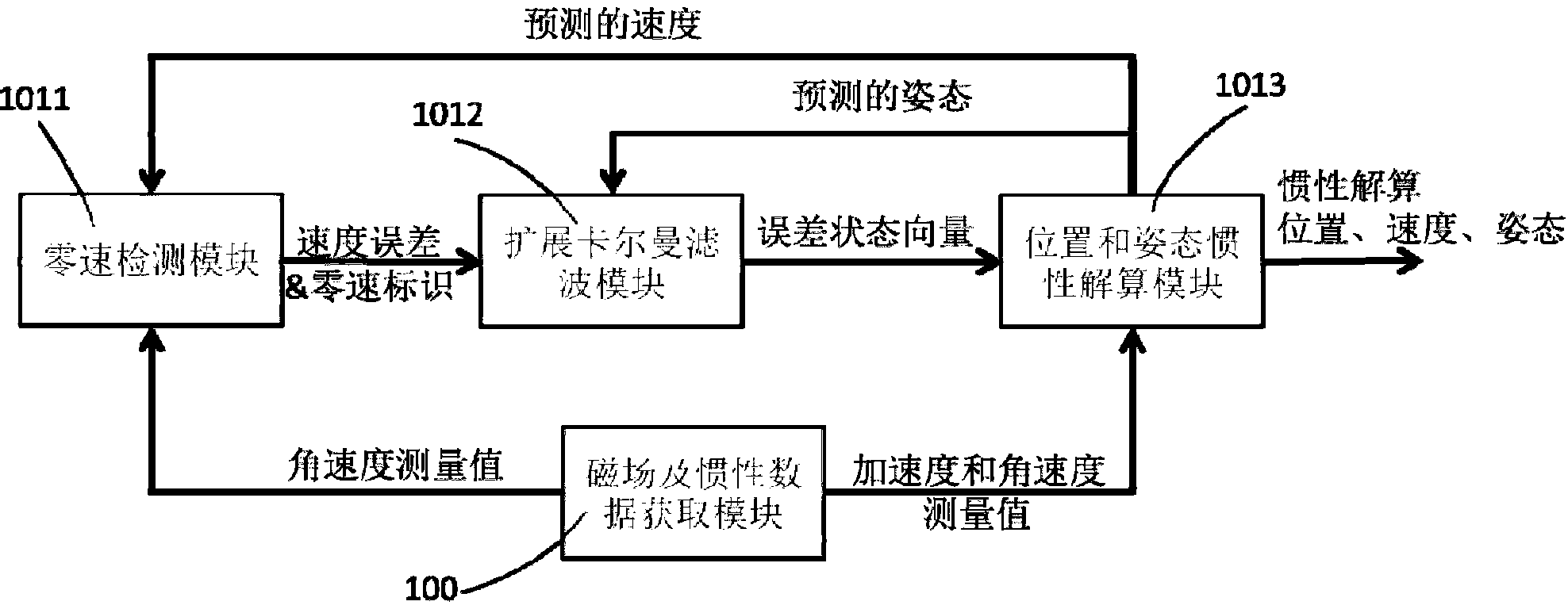
Pedestrian inertial positioning system based on indoor magnetic field feature assistance
ActiveCN103175529AThere is no need to lay out the problemReduce energy costsNavigation by terrestrial meansNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsTime–frequency analysisAngular velocity
The invention provides a pedestrian inertial positioning system based on indoor magnetic field feature assistance. The system comprises a magnetic field and inertial data obtaining module, a magnetic field positioning module, a pedestrian dead reckoning module, a positioning fusion module and an output module, wherein the magnetic field and inertial data obtaining module is used for acquiring magnetic field, accelerated speed and angular velocity information; the magnetic field positioning module is used for building a magnetic field feature library and carrying out time-frequency analysis on the magnetic field vector sequence in real time to extract the time-frequency feature, and matching with the magnetic field feature library to carry out magnetic field feature positioning; the pedestrian dead reckoning module is used for updating accelerated speed and angular velocity zero offset according to the condition that the step velocity discontinuity is zero during walking, judging the step number and calculating the step length and the direction of each step; the positioning fusion module is used for fusing a magnetic field feature positioning result and a pedestrian dead reckoning inertial positioning result by means of particle filter; and the output module is used for displaying a positioning result on web pages and terminals. The system provided by the invention has the characteristics of being independent from beacon during positioning, low in cost and consumption of positioning terminals, accurate in positioning result and adaptive to environment change.
Owner:MEDIASOC TECH
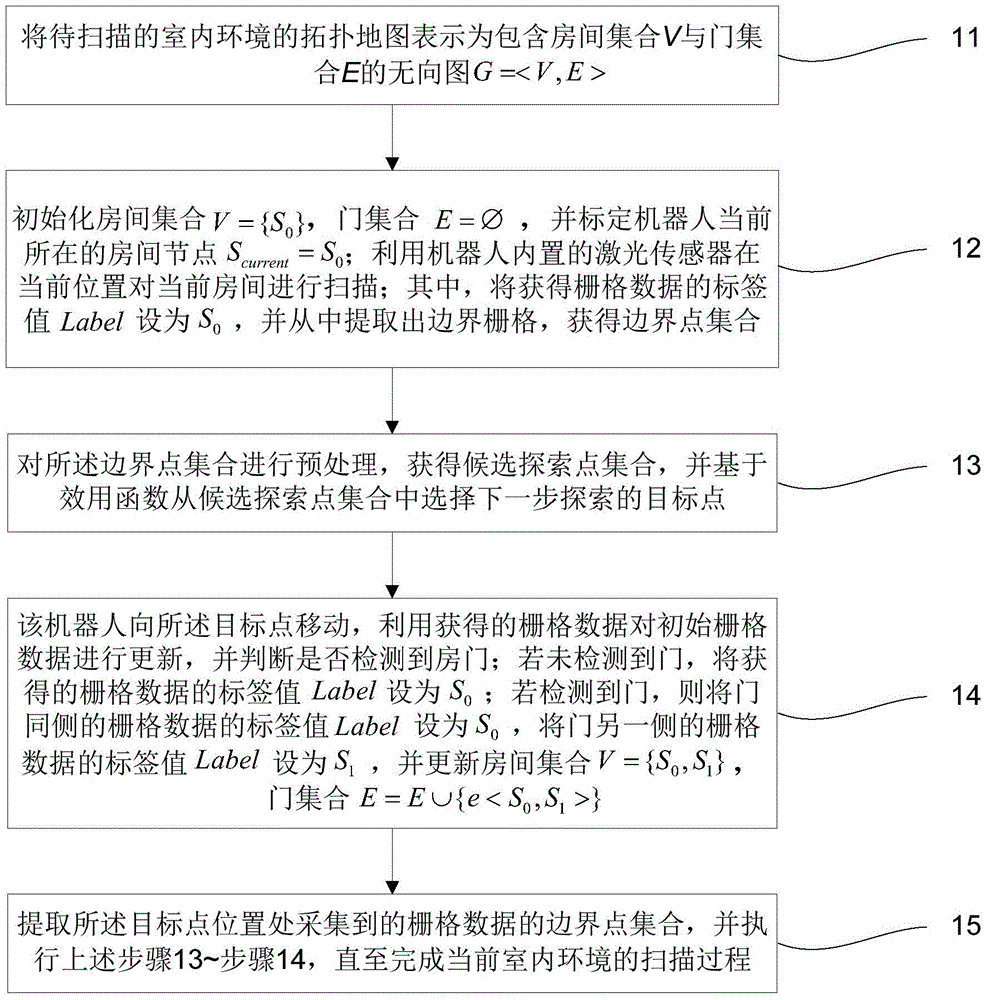
Indoor map building method for improving robot path planning efficiency
ActiveCN104898660AAvoid planningPosition/course control in two dimensionsSimultaneous localization and mappingTopological order
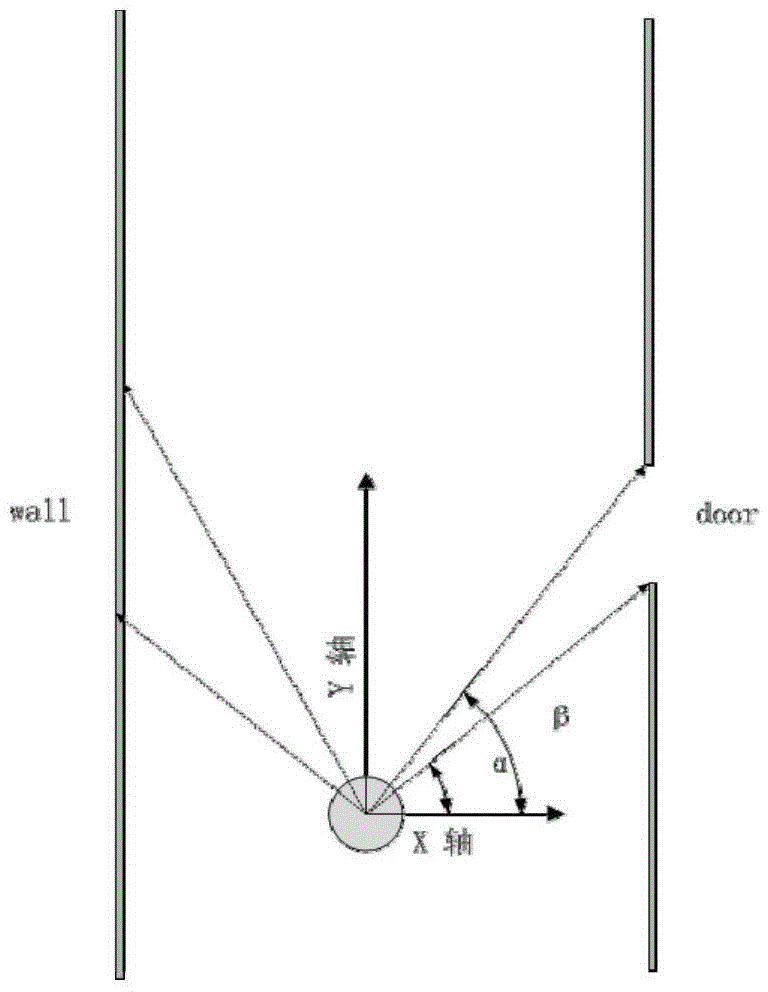
The invention discloses an indoor map building method for improving robot path planning efficiency. The method combines a topological map and a grid map, the planning problem happens in space represented by topological nodes, and planning of global space is avoided. In addition, laser is used for identifying a door in the indoor environment, a topological relationship between rooms is built, the process is merged in particle filter SLAM (simultaneous localization and mapping) algorithm, the grid map represented by the environment and the topological map based on the grid map can be obtained finally, and the path planning algorithm in robot navigation is simpler and more efficient.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Data-driven lithium ion battery cycle life prediction method based on AR (Autoregressive) model and RPF (Regularized Particle Filtering) algorithm
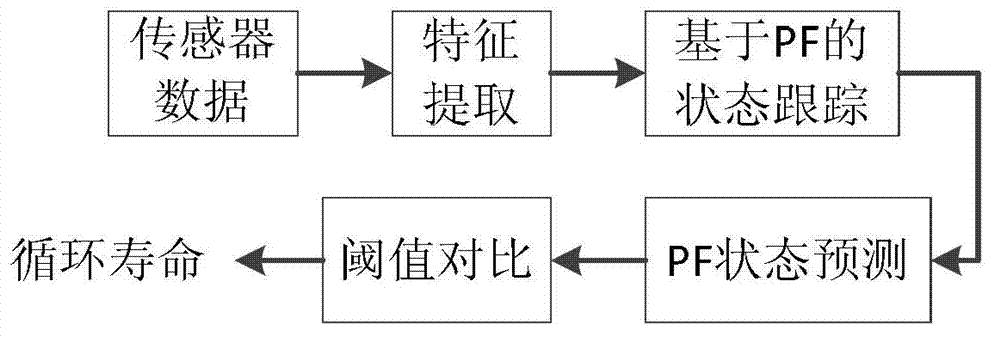
A data-driven lithium ion battery cycle life prediction method based on an AR (Autoregressive) model and an RPF (Regularized Particle Filtering) algorithm relates to a lithium ion battery cycle life prediction method and belongs to the technical field of data prediction. The invention solves the problems in the existing lithium ion battery cycle life prediction method that the model-based prediction method is complicated in modeling, and parameters are difficult to identify. The data-driven lithium ion battery cycle life prediction method combines time sequence analysis with particle filter method and comprises the following steps: the AR model is firstly utilized to realize the multi-step prediction on battery performance degradation process time sequence data; and then, aiming at the problem of uncertainty expression of the cycle life prediction result, the regularized particle filtering method is introduced, and a lithium ion battery cycle life prediction method framework is proposed. The method proposed by the invention can be used for effectively predicating the cycle life of a lithium ion battery and realizes the output of probability density distribution of the predication result, has good computational efficiency and uncertainty expression ability.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
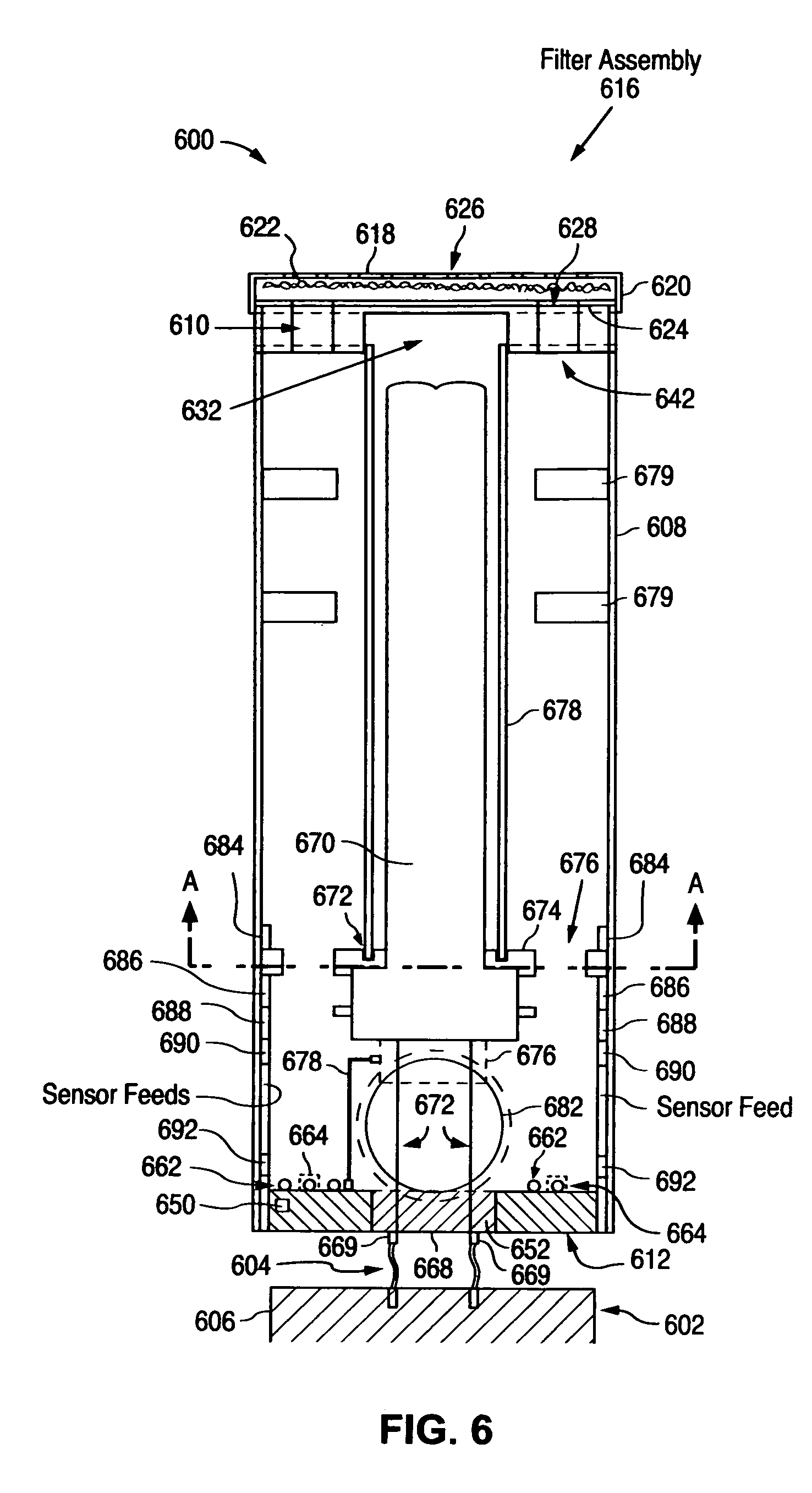
Air sterilization apparatus
InactiveUS20070101867A1Improve reflectivityCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentParticulatesEngineering
A portable sterilization apparatus that includes a face mask connected to a kill chamber having an ultraviolet source to destroy biological contaminants such as viruses, bacteria and fungi in air supplied to the mask, further includes a disposable particle filter in the kill chamber for filtering out particulates prior to irradiating the air with UV light, and in the case of a mercury vapor lamp UV source, a quartz sleeve surrounding the lamp. Valves are included in the face mask to limit carbon dioxide exhalation back into the kill chamber and to facilitate exhalation of air to the atmosphere.
Owner:NEXT SAFETY INC
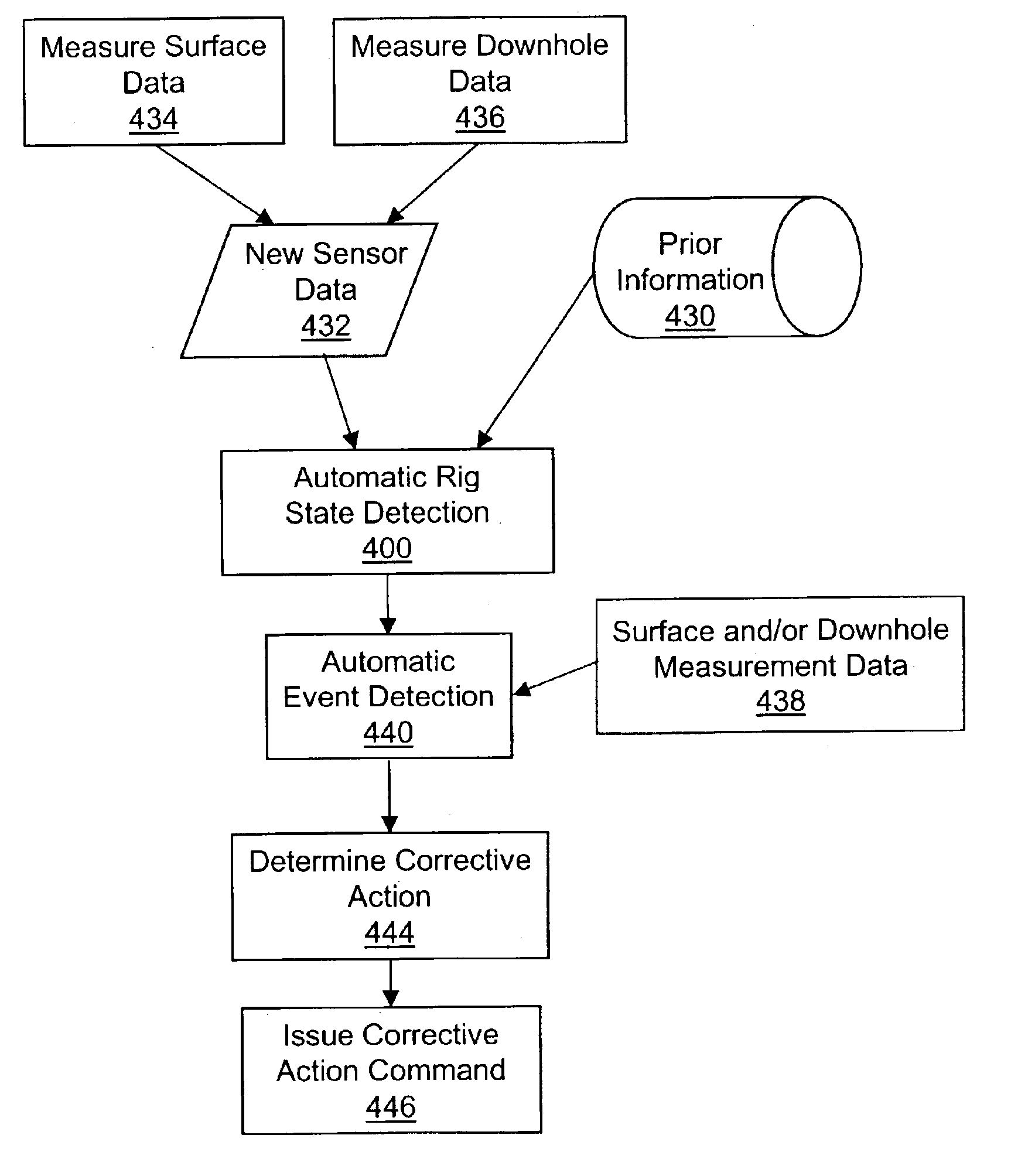
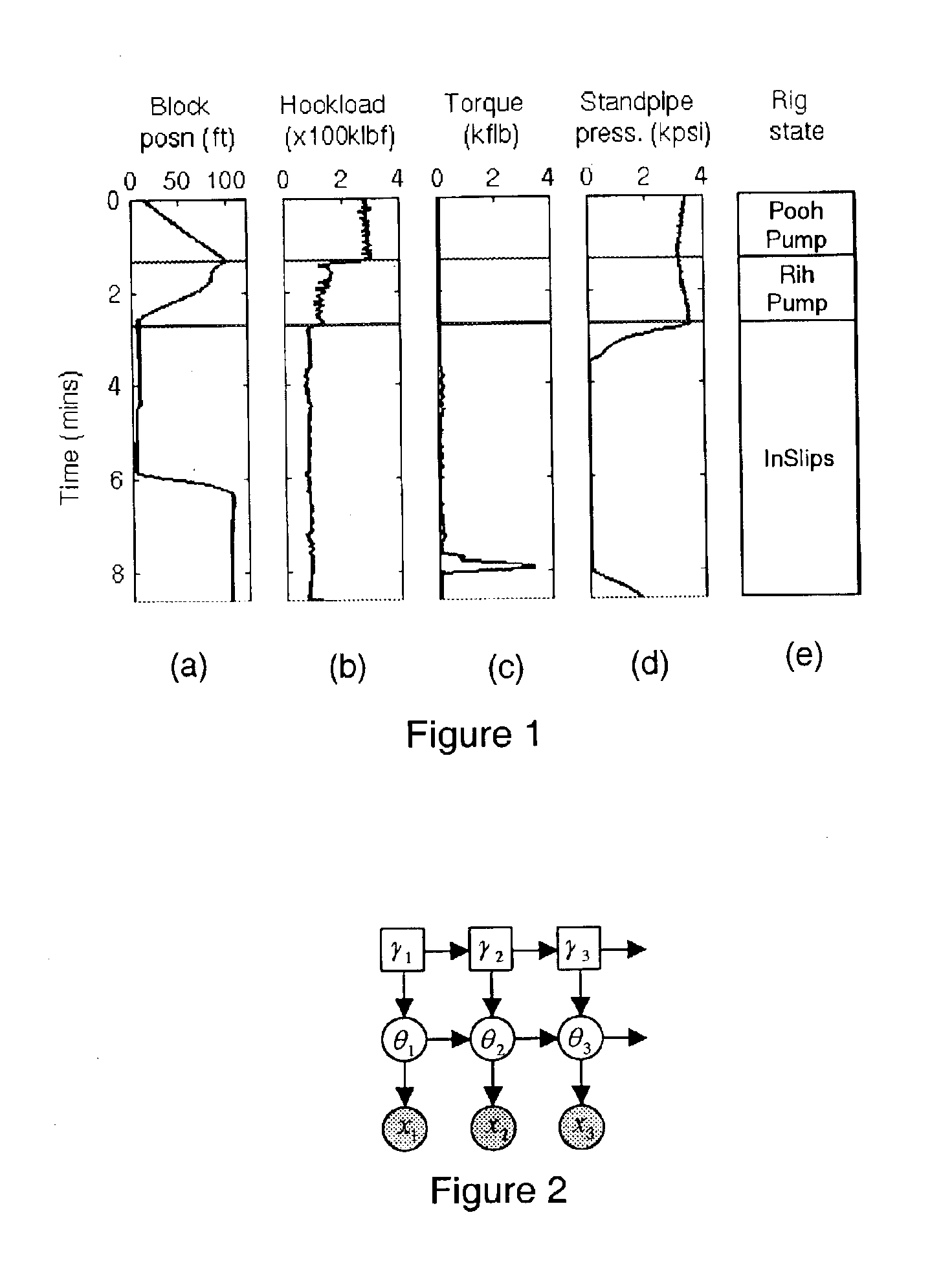
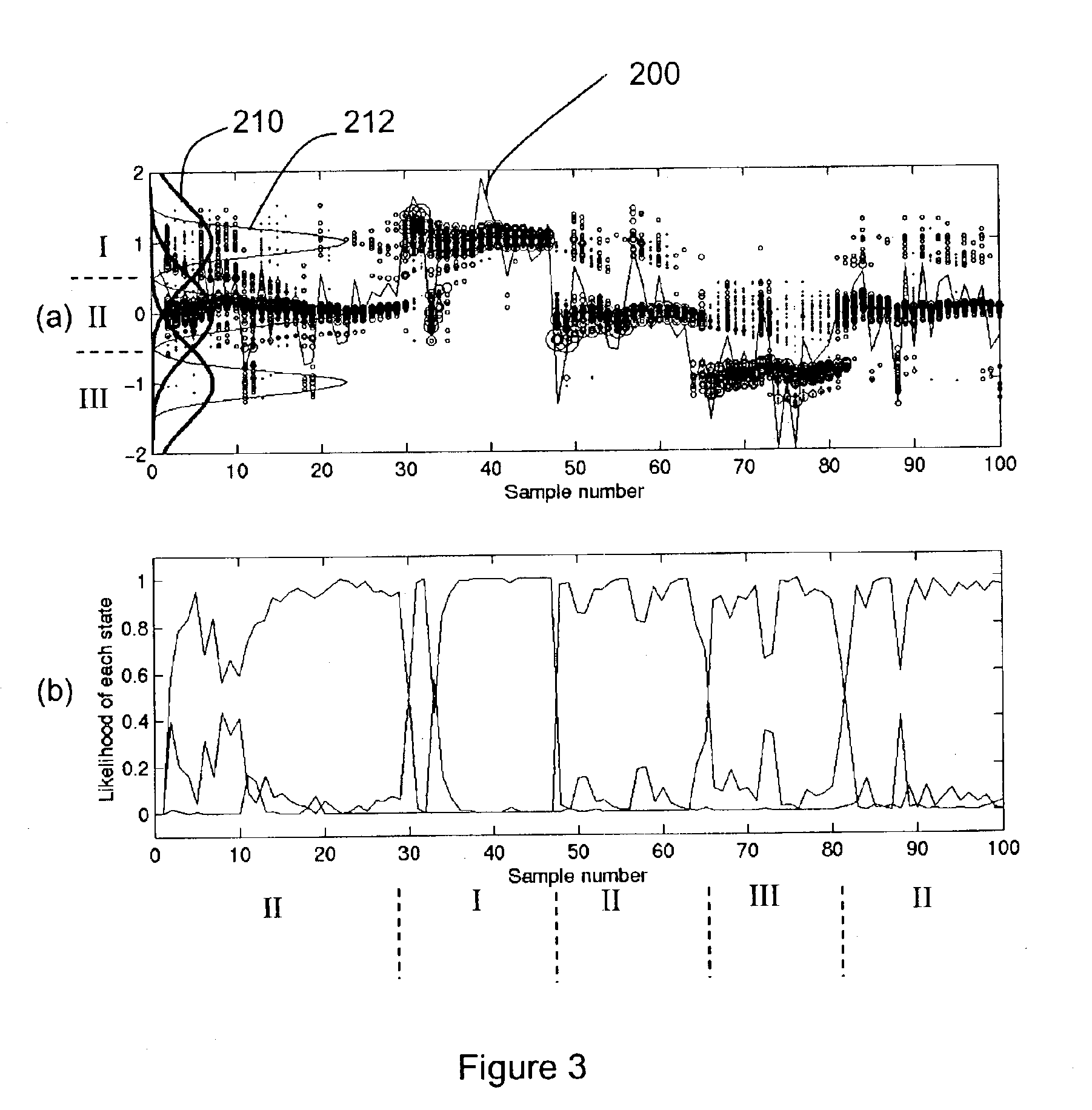
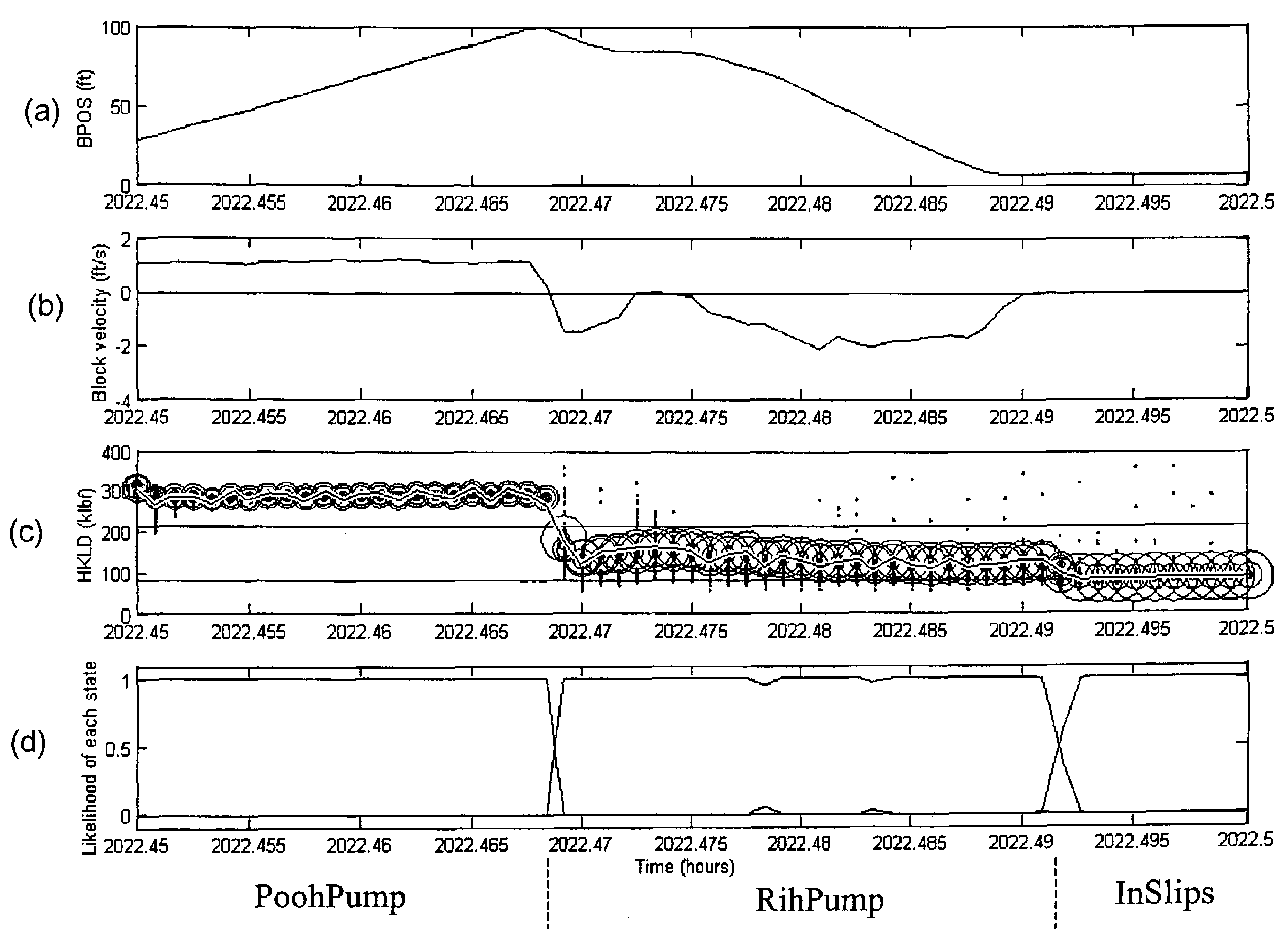
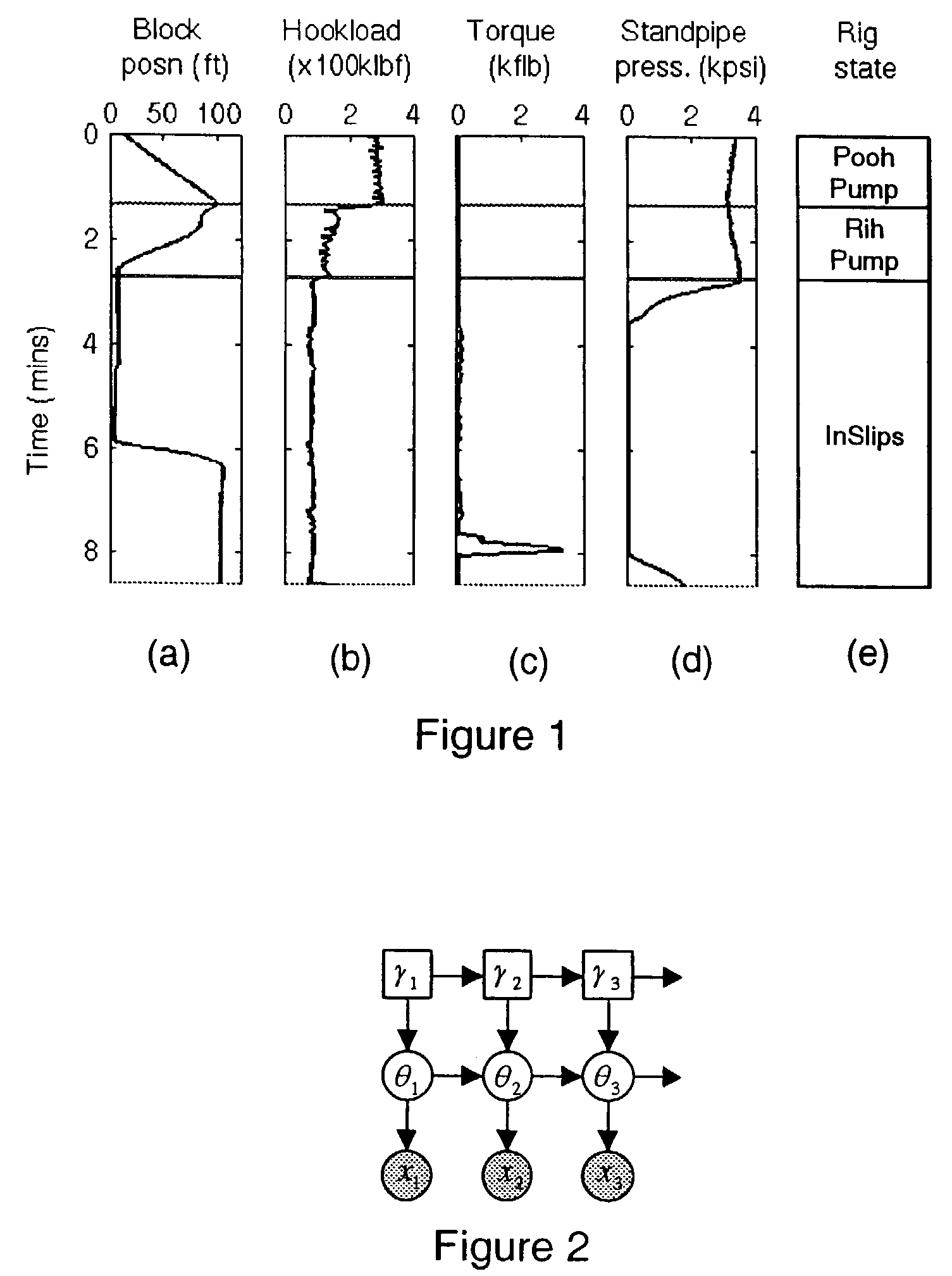
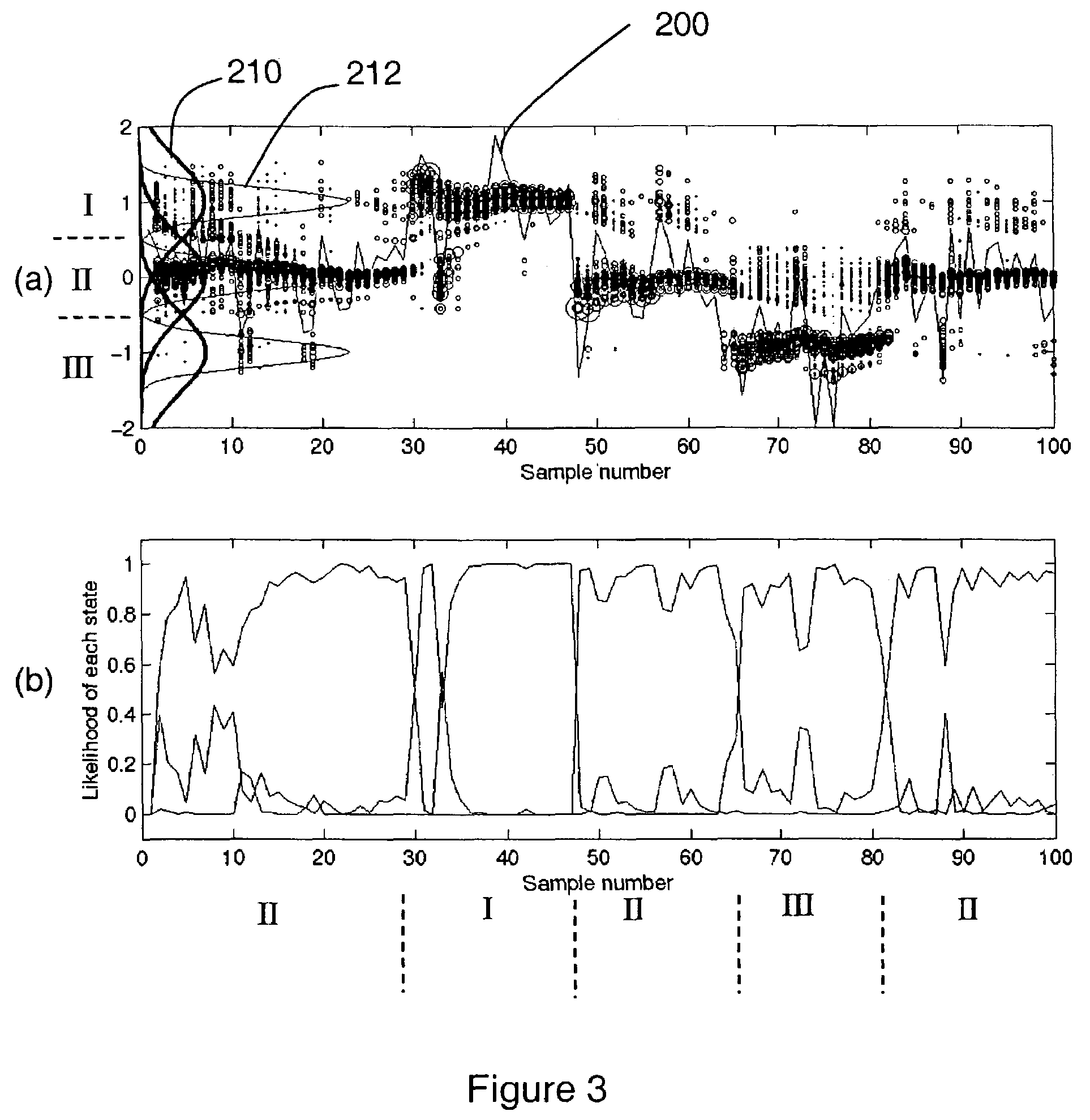
System and method for rig state detection
A method and system is disclosed for automatically detecting the state of a drilling rig during the drilling process of a wellbore. Two or more, but preferably four independent input data channels are received, each input data channel representing a series of measurements made over time during the drilling process. Based on the input channels the most likely state of the drilling rig is detected from at least three possible rig states. The detection method is preferably probabilistic and even more preferably based on particle filtering techniques. The preferred systems and methods disclosed are also capable of detecting events and displaying or notifying drilling personnel of the detected events and suggesting corrective action.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Microfabricated chemical reactor
InactiveUS6932951B1Components is relatively effectiveLower overall pressure dropChemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactorsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsChemical reactorEngineering
A microfabricated chemical reactor includes a plurality of lamina, an inlet port formed in at least one of the lamina, and an outlet port formed in at least one of the lamina. A continuous channel is formed in at least one of the lamina and provides fluid communication between the inlet port and the outlet port. In one configuration of the microfabricated chemical reactor, the reactor includes a particle filter disposed in the continuous channel and formed by one of the lamina, wherein the particle filter restricts flow through the continuous channel and retains catalyst or other particles within the continuous channel.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Air supply apparatus
InactiveUS20070102280A1Constant pressureProvide protectionGas treatmentDispersed particle separationUltravioletEngineering
In an air sterilization system that includes a UV kill chamber for sterilizing air that is to be supplied to users, the effectiveness of killing or neutralizing pathogens is increased by including not only a UV light source of a certain intensity but also including a particle filter and providing short duration high intensity UV radiation. In the case of a user specific system that includes a face mask to supply air to a specific user, exhaled air from the face mask may be sterilized as well, either by using the same kill chamber or by using a separate kill chamber.
Owner:NEXT SAFETY INC
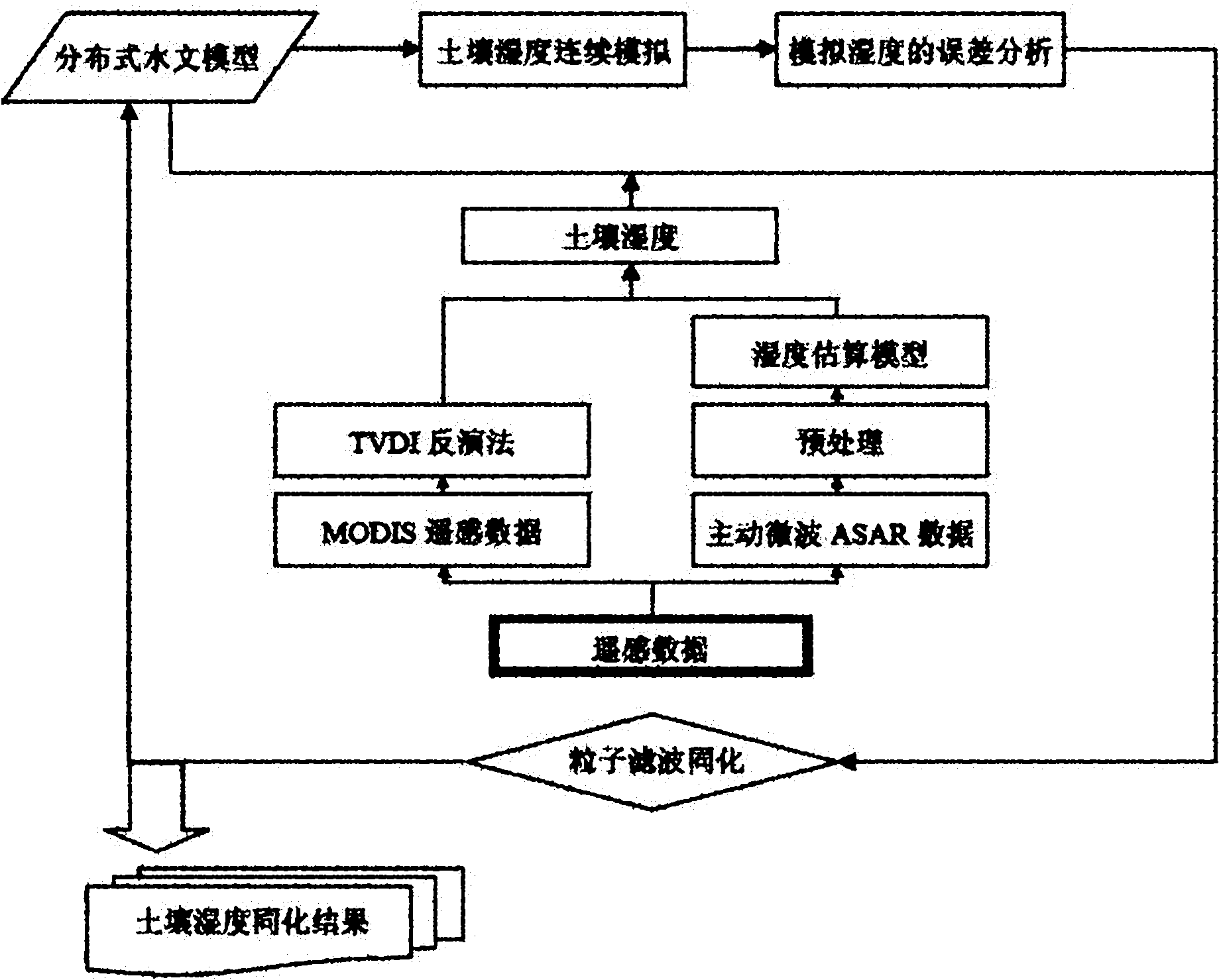
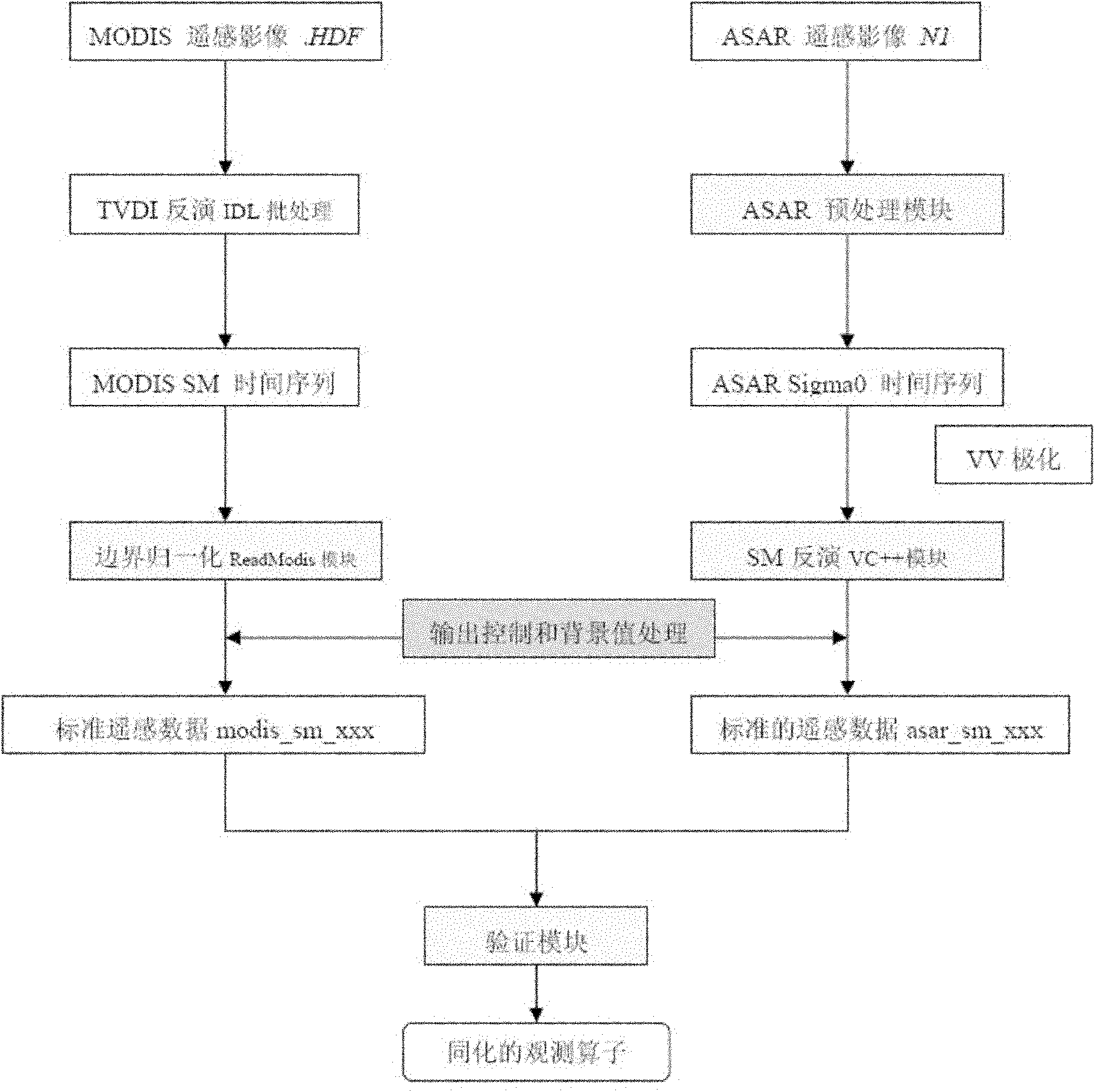
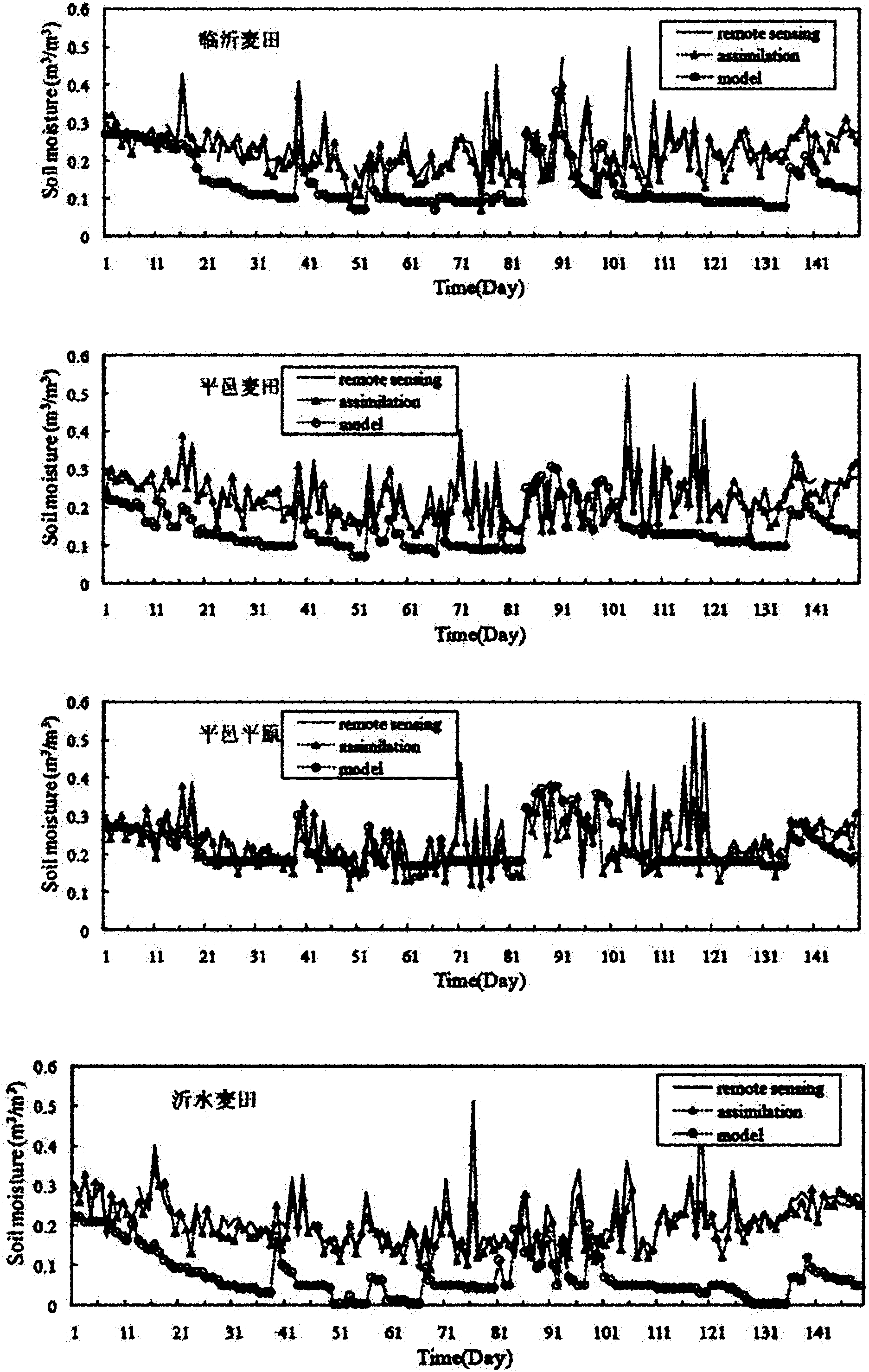
Method for assimilating remote sensing data of soil humidity in watershed scale
InactiveCN102034027AEfficient integrationGood day-to-day runoff simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSoil moisture contentDrainage basin
The invention provides a method for assimilating remote sensing data of soil humidity in a watershed scale. The method comprises the following steps of: improving a watershed runoff producing calculation module and developing a distributed hydrological model which is suitable for assimilating remote sensing soil humidity information and describes a soil hydrodynamic process; introducing a particle filtering sequence data assimilation method of information science, and continuously merging and assimilating new remote sensing observation data in a dynamic operation process of distributed hydrological process numerical simulation so as to acquire updated watershed soil humidity assimilated data during sequential assimilation; feeding the updated watershed soil humidity assimilated data back to a distributed hydrological model platform; and gradually estimating the time and space distribution pattern of watershed soil moisture content. Practices prove that by the method, not only high-precision and physically consistent watershed soil humidity data can be provided for research on hydrology, zoology, environment and agriculture, but also the foundation is laid for performing four-dimensional data assimilation processing on soil humidity data of an upper soil layer acquired by using remote sensing retrieval, and improving the precision of the model.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Automatic target tracking method and system by combining multi-characteristic matching and particle filtering
InactiveCN102184551ATelevision system detailsImage analysisScale-invariant feature transformComputer module
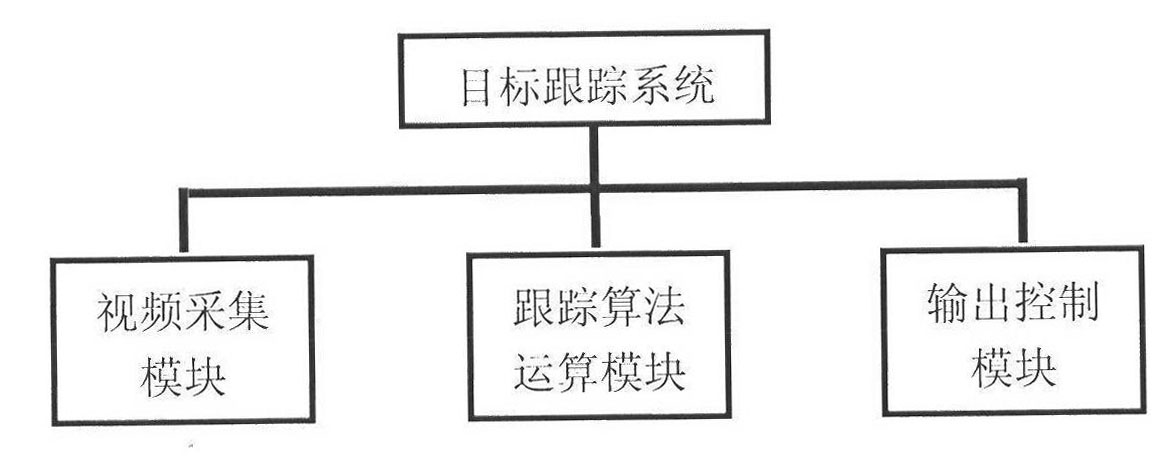
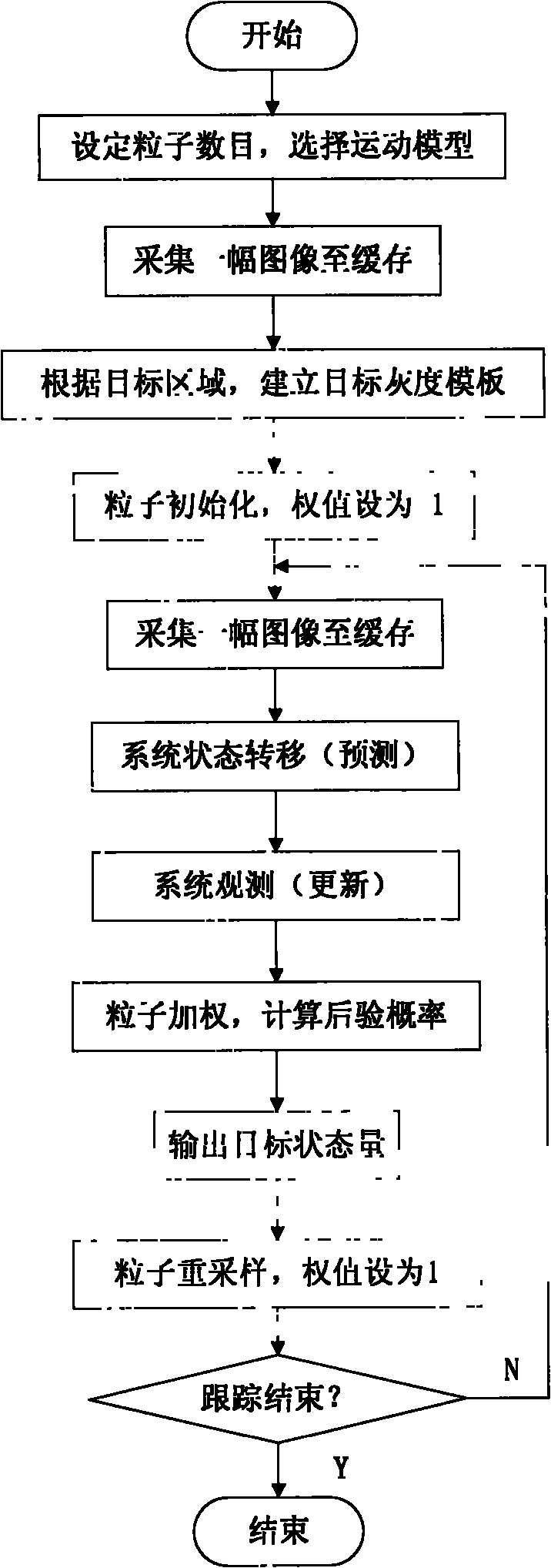
The invention relates to an automatic target tracking method and system by combining multi-characteristic matching and particle filtering. The target tracking system provided by the invention comprises a video acquisition module, a tracking algorithm computation module and an output control module, wherein the video acquisition module finishes the initialization of an acquisition card and the real-time acquisition of images; the tracking algorithm computation module comprises three tracking modes: the particle filtering tracking based on gray template region matching, the particle filtering tracking based on color probability distribution and the particle filtering tracking based on SIFT (scale invariant feature transform) characteristic matching, thereby realizing the target tracking of translation space and affine space; and the output control module utilizes the center of the target position obtained by tracking as a control command which is transmitted to a cloud deck, thereby realizing the motion of a camera along with a target object.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
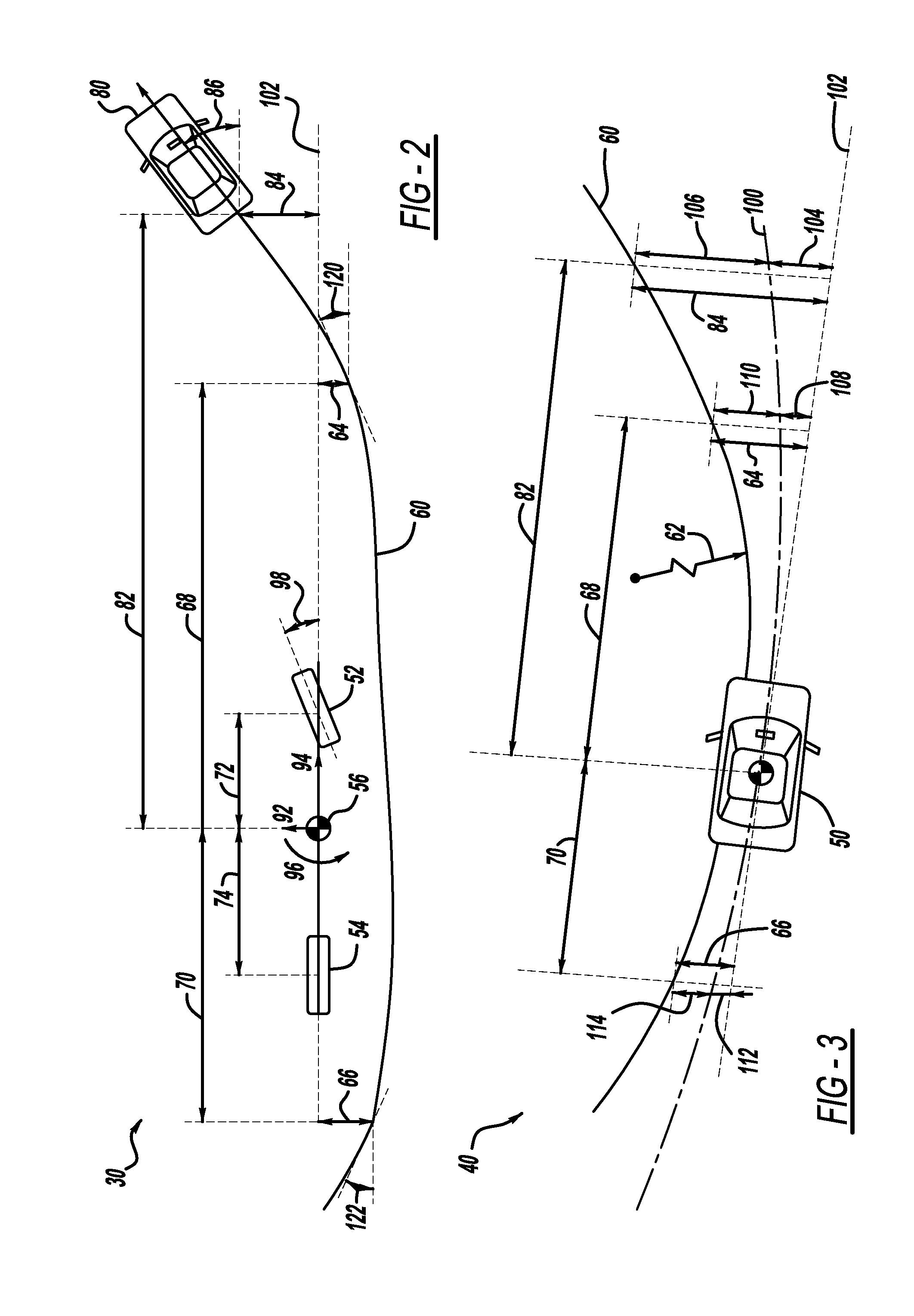
Lane fusion system using forward-view and rear-view cameras
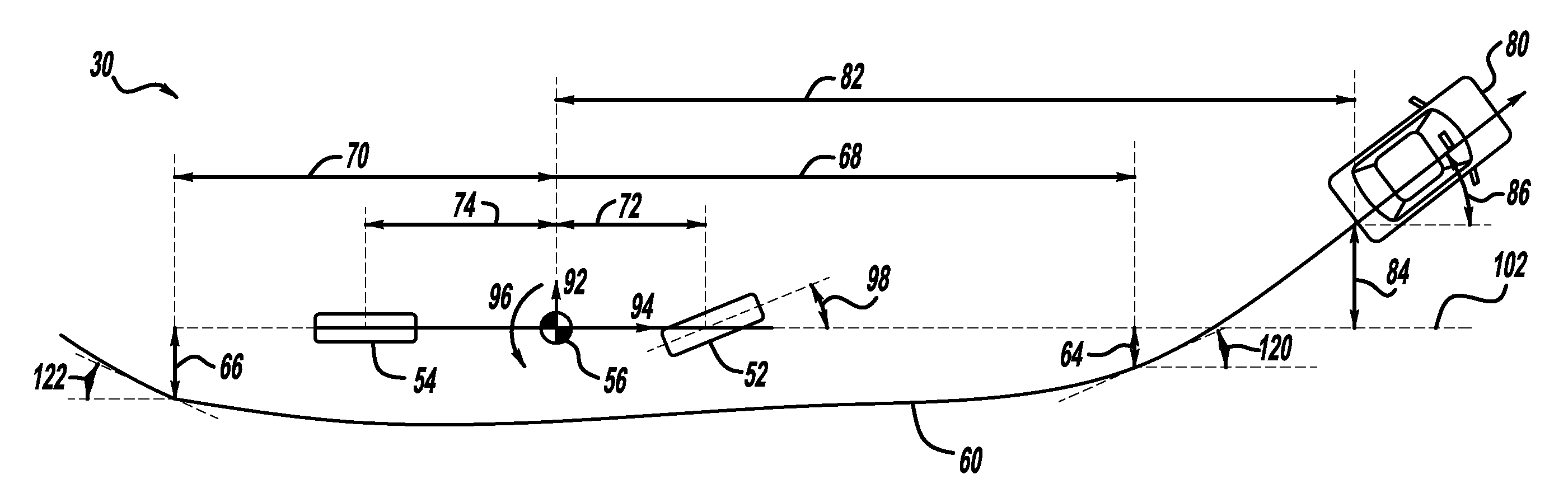
ActiveUS20120062747A1Character and pattern recognitionColor television detailsCamera imageVehicle dynamics
A method and system for computing lane curvature and a host vehicle's position and orientation relative to lane boundaries, using image data from forward-view and rear-view cameras and vehicle dynamics sensors as input. A host vehicle includes cameras at the front and rear, which can be used to detect lane boundaries such as curbs and lane stripes, among other purposes. The host vehicle also includes vehicle dynamics sensors including vehicle speed and yaw rate. A method is developed which computes lane curvature and the host vehicle's position relative to a lane reference path, where the lane reference path is derived from the lane boundaries extracted from a fusion of the front and rear camera images. Mathematical models provided in the disclosure include a Kalman filter tracking routine and a particle filter tracking routine.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
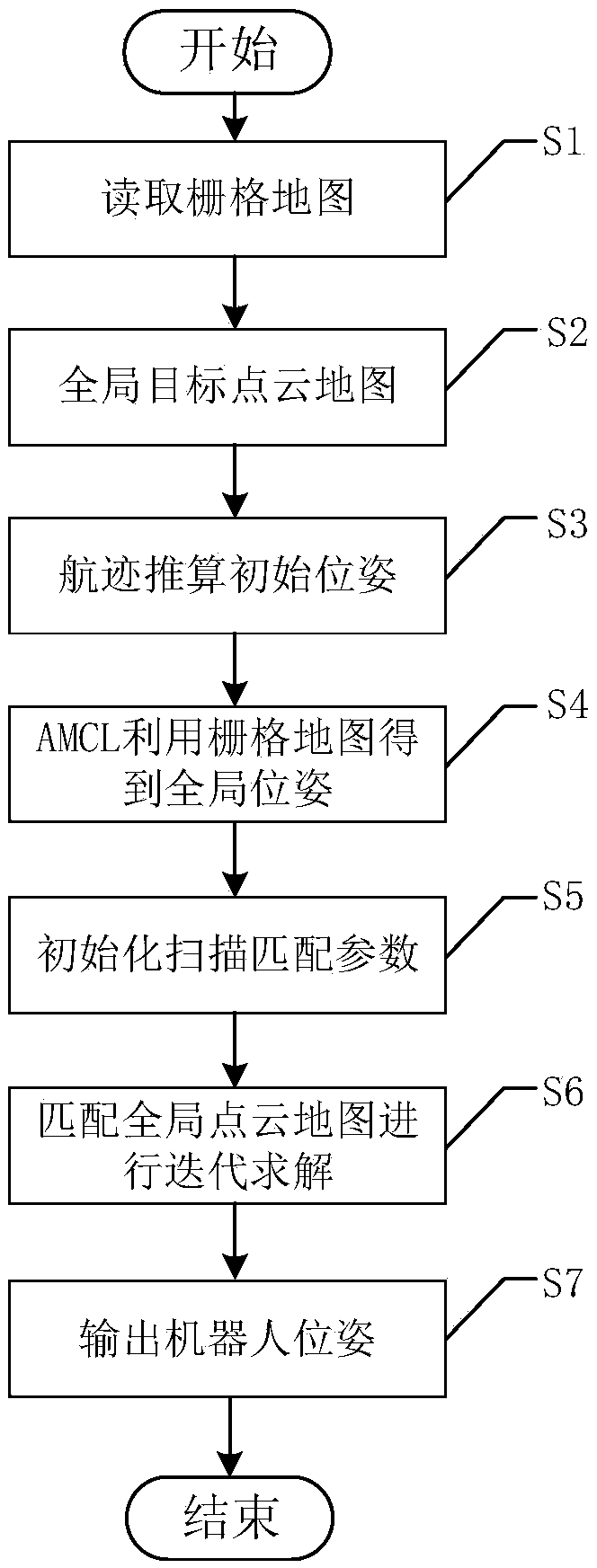
Mobile robot pose correction algorithm based on multi-level map matching
InactiveCN108917759AImprove global pose accuracyHigh positioning accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsRoboticsCorrection algorithm
The invention discloses a mobile robot pose correction algorithm based on multi-level map matching, which belongs to the technical fields of robotics and computer graphics. The algorithm of the invention uses a synchronous positioning and a composition algorithm to establish a global raster map, and combines a matching relationship between the current observation and the raster map to correct thetrack calculated by the track using an AMCL algorithm for reckoning the pose, so that the relatively accurate global pose information can be obtained, at the same time, the raster map is converted toa corresponding global target point cloud map, and the laser point cloud observed by the robot in real time is registered with the target point cloud map to further correct the global pose. The methodof the invention can obtain accurate global pose information and reduce the accumulation of long-distance positioning errors, and avoids the shortcomings of an existing particle filter technology that the pose solution is not accurate due to a limited particle space, the accuracy and efficiency of an ICP algorithm are too dependent on the initial pose, and efficient and accurate pose solution canbe realized.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
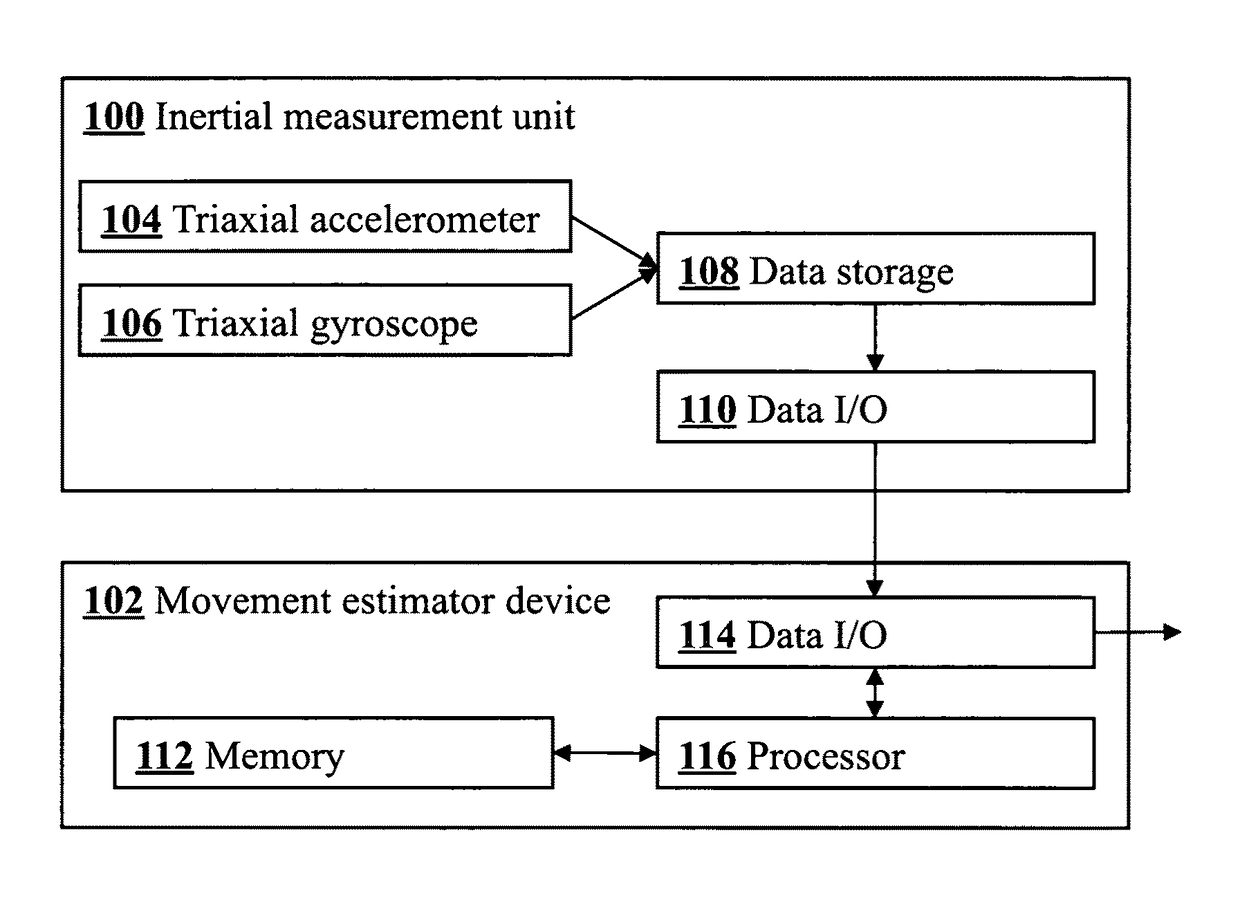
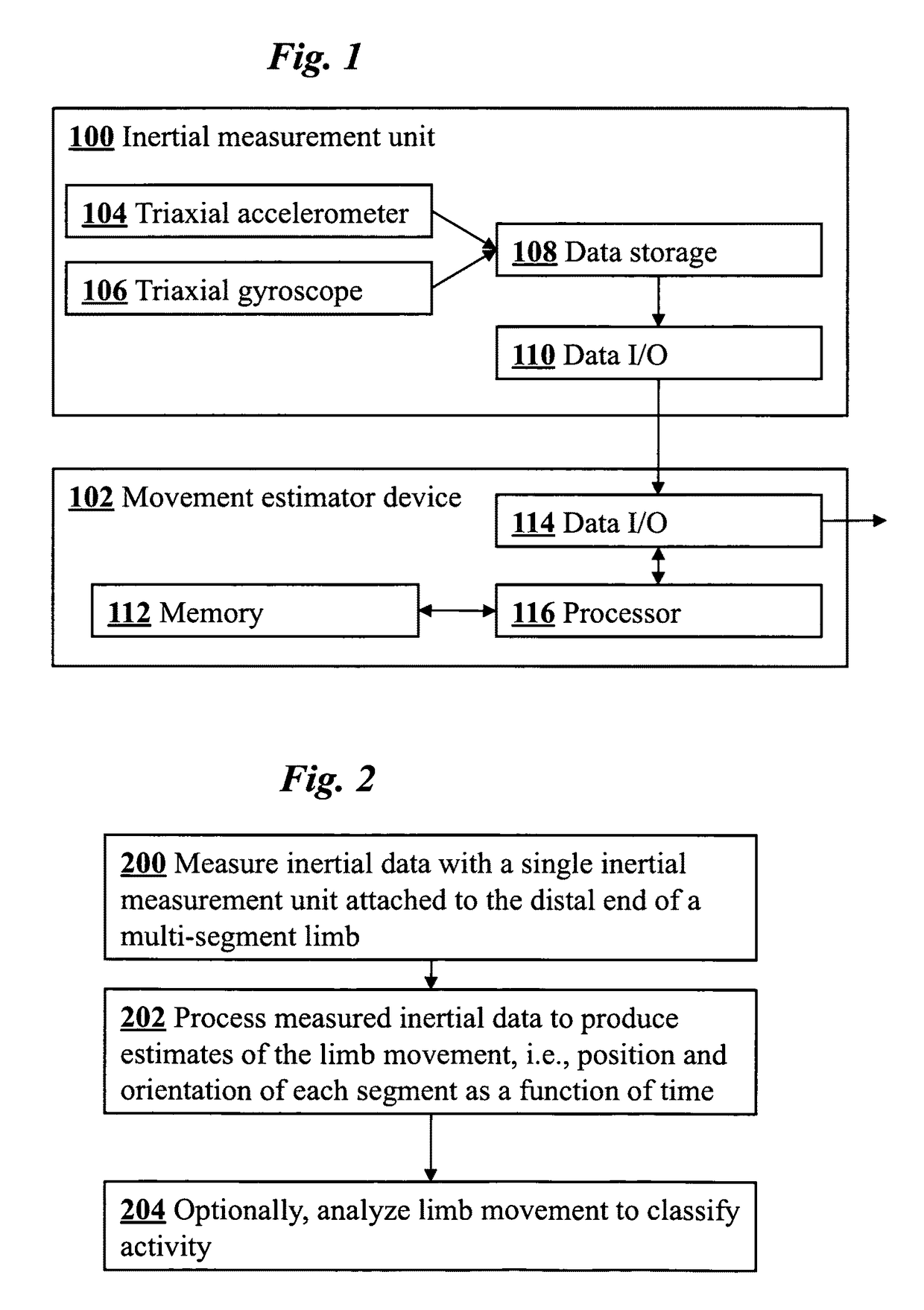
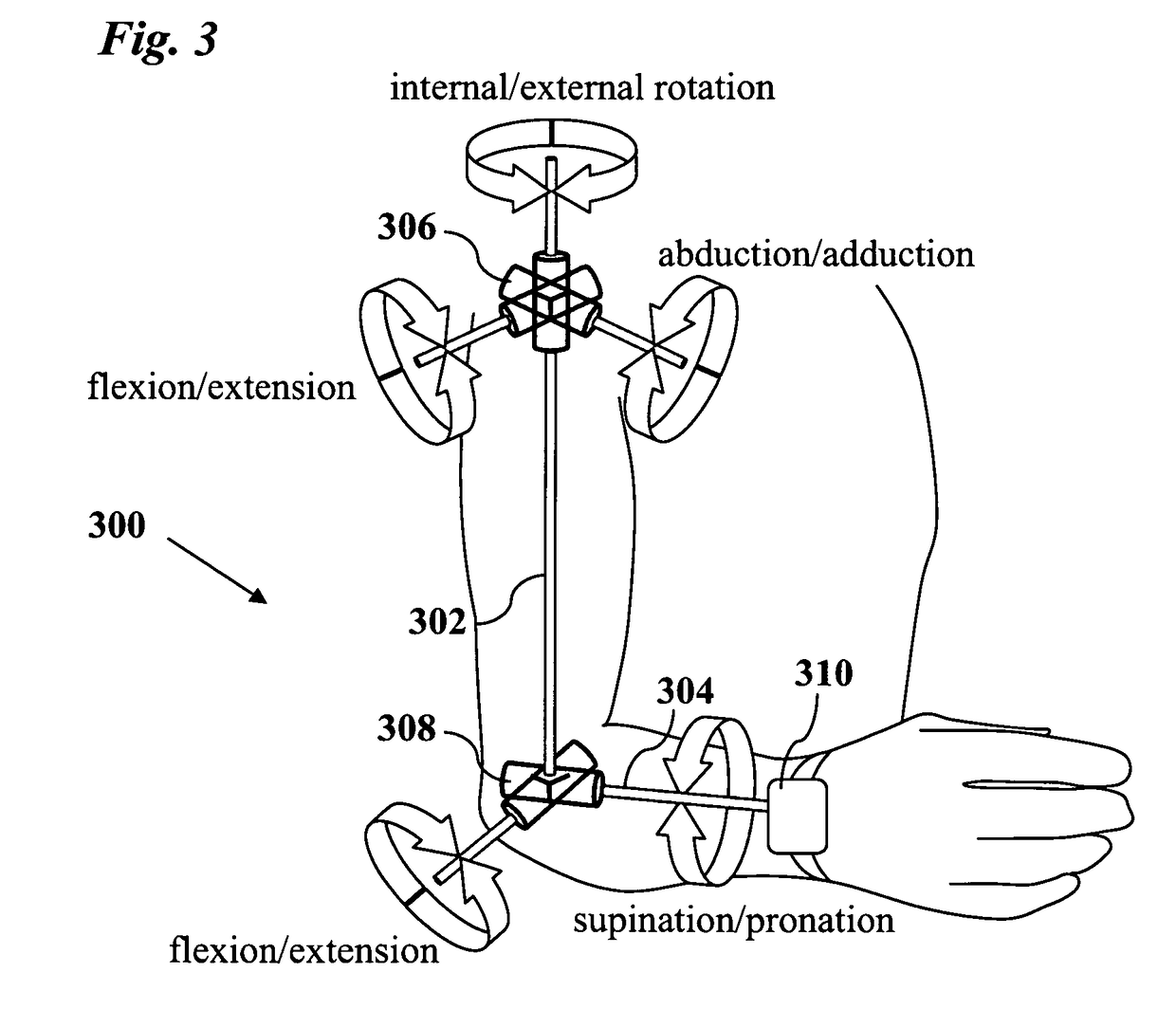
Joint angle tracking with inertial sensors
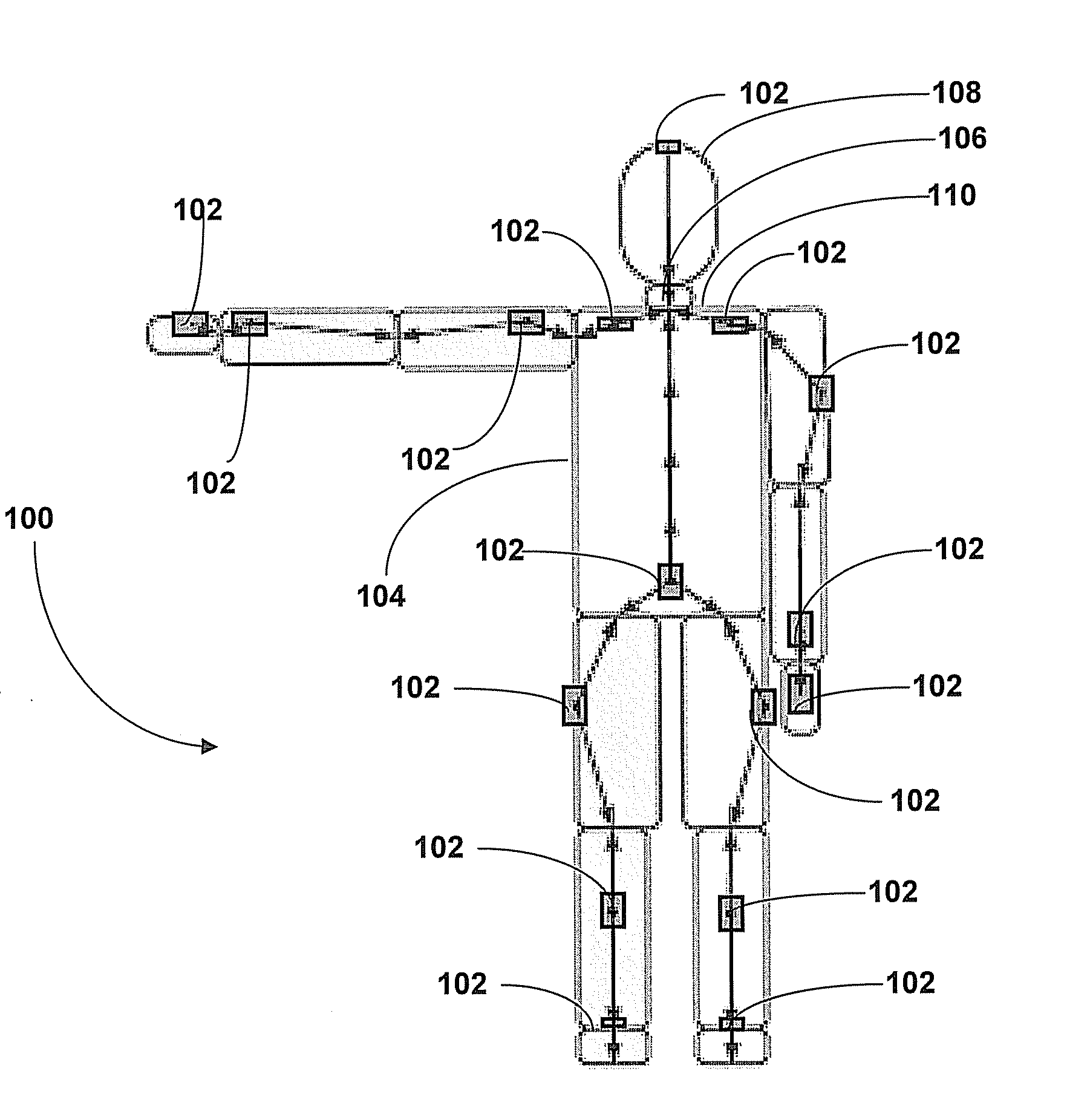
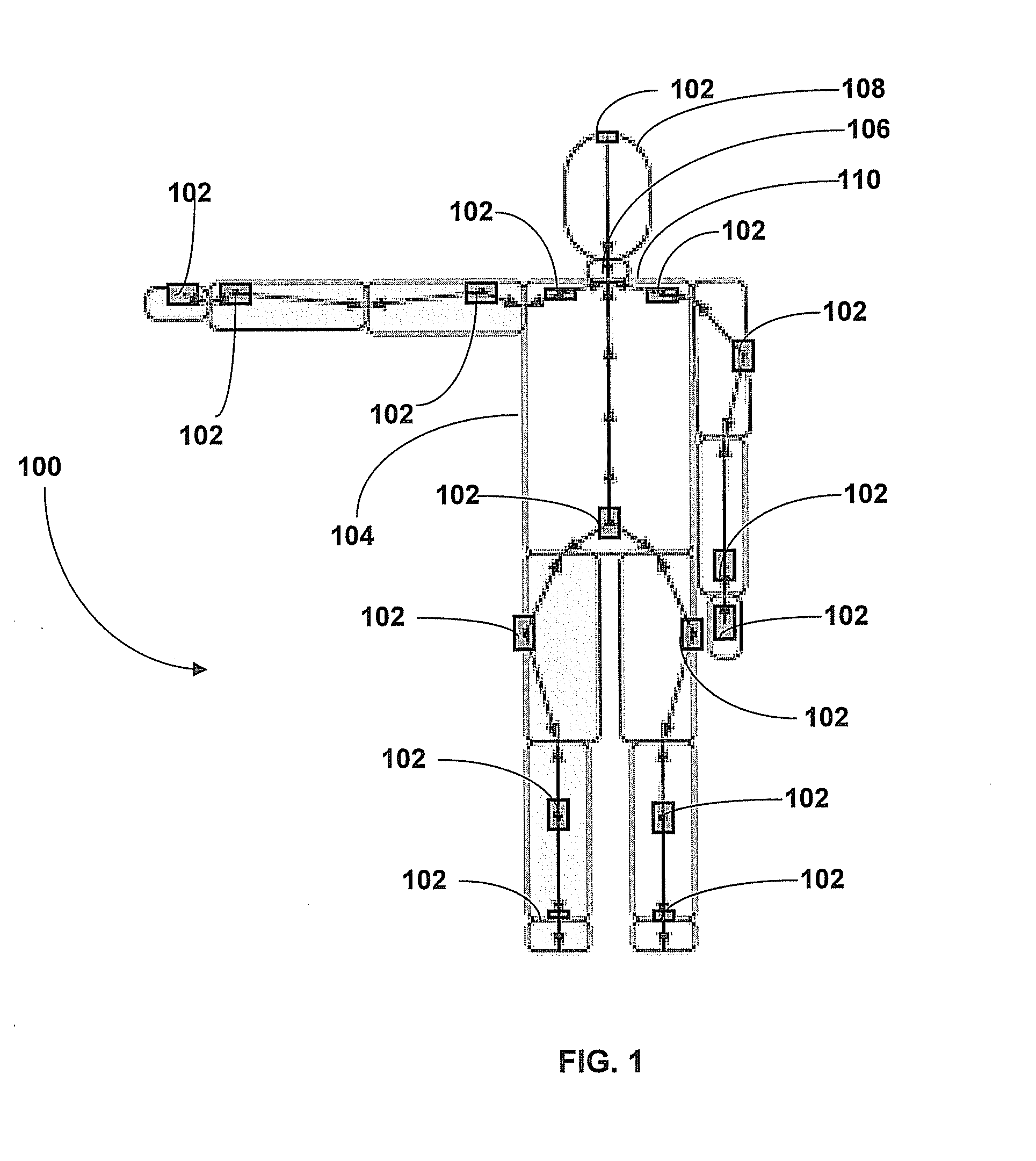
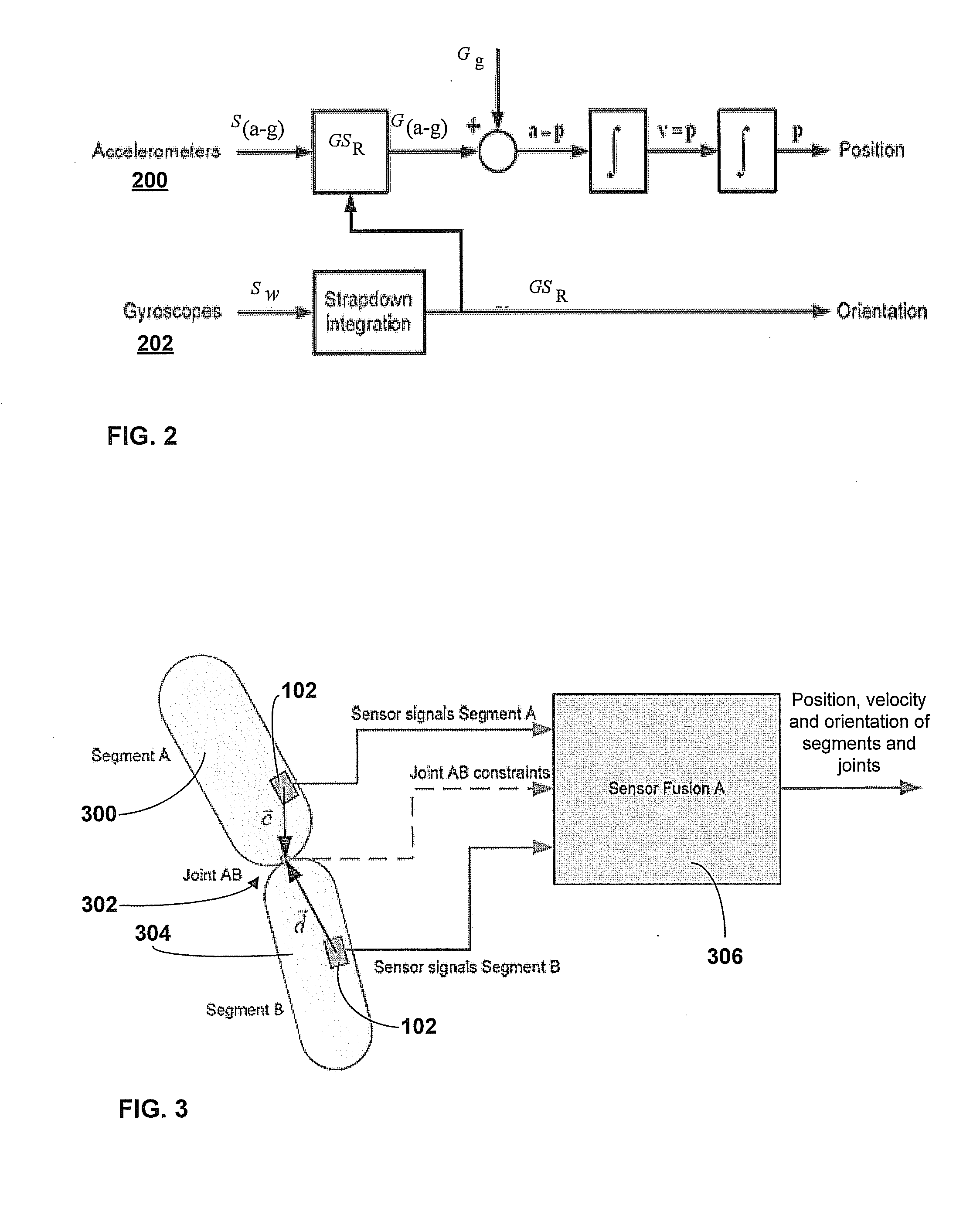
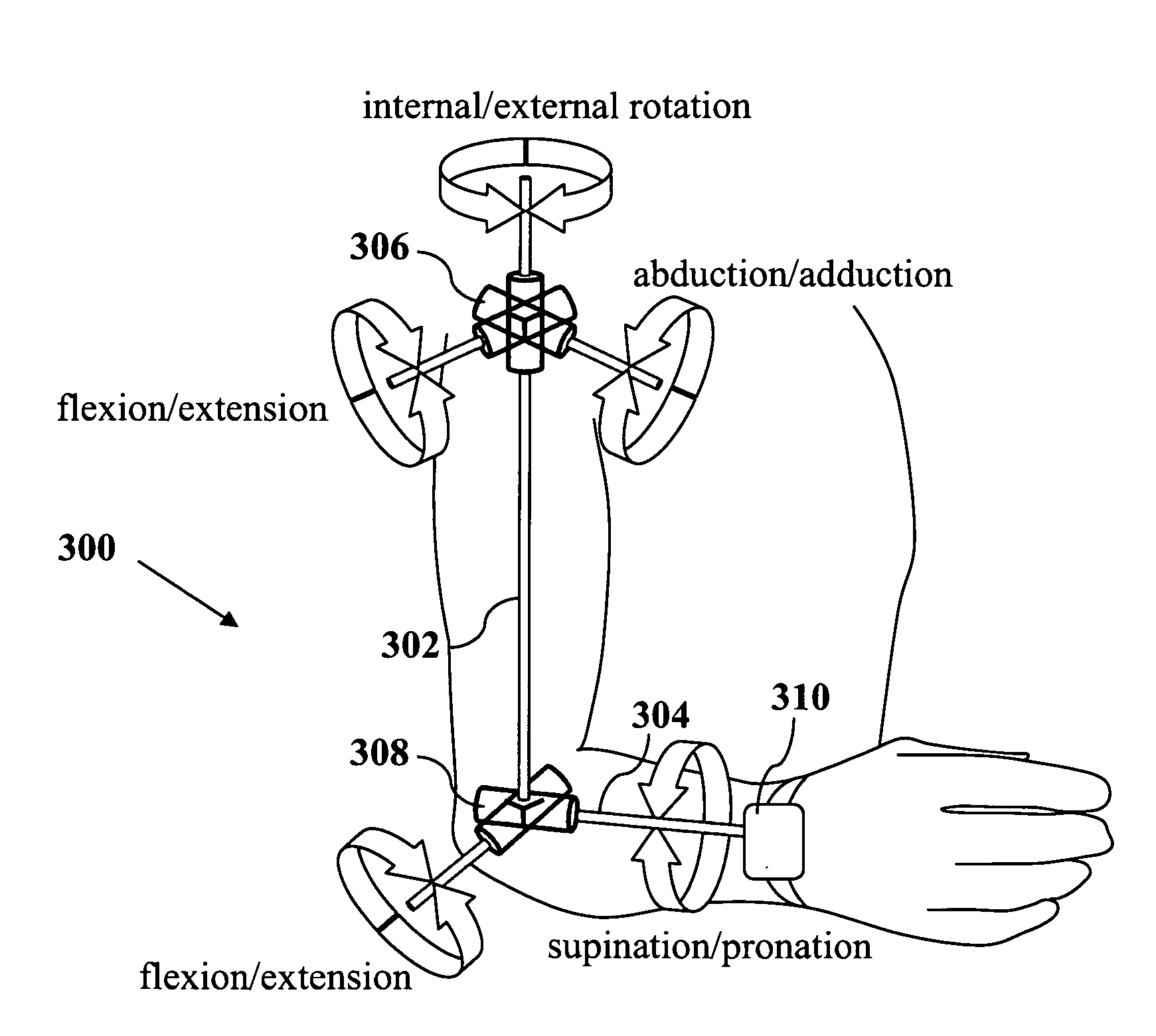
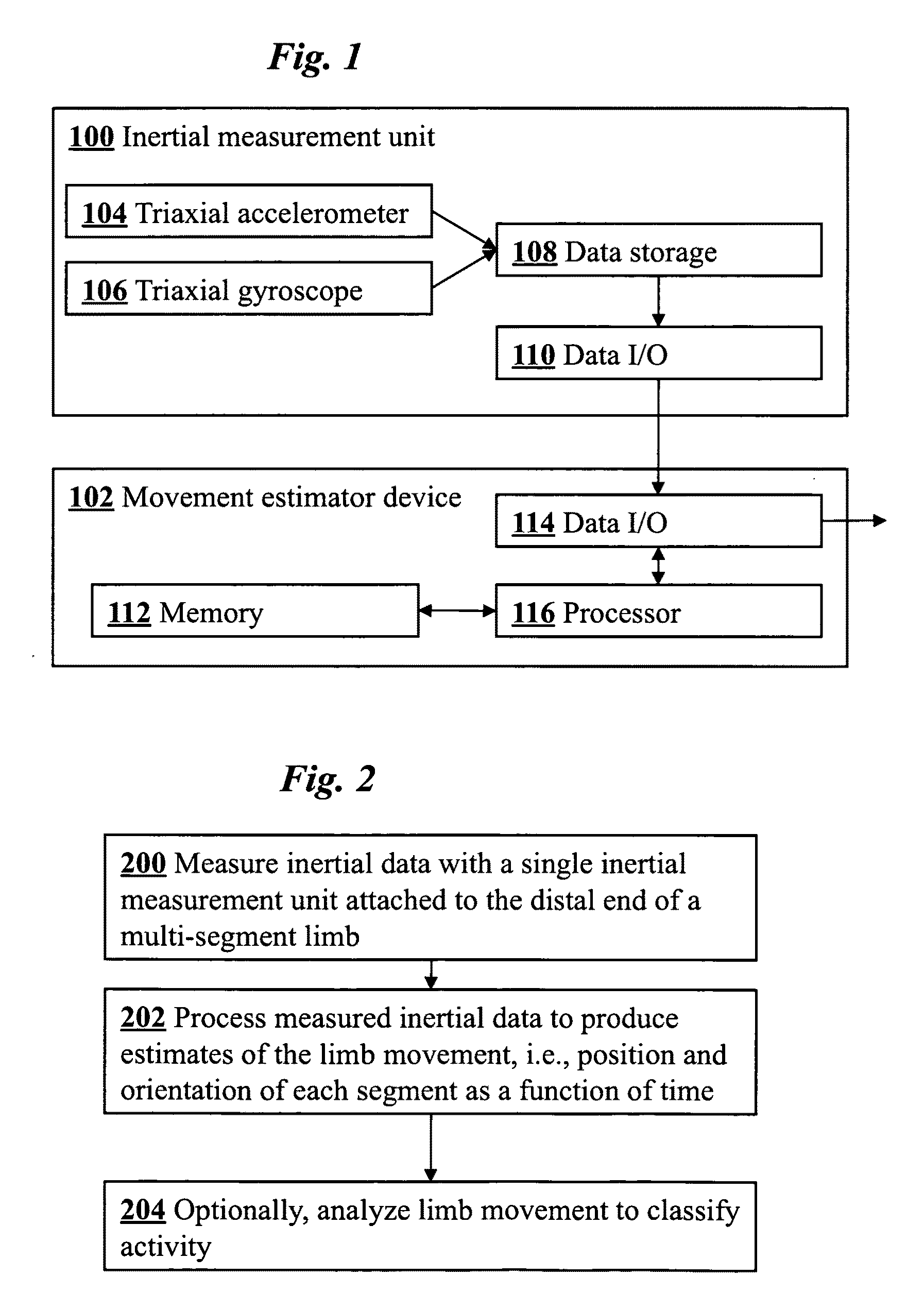
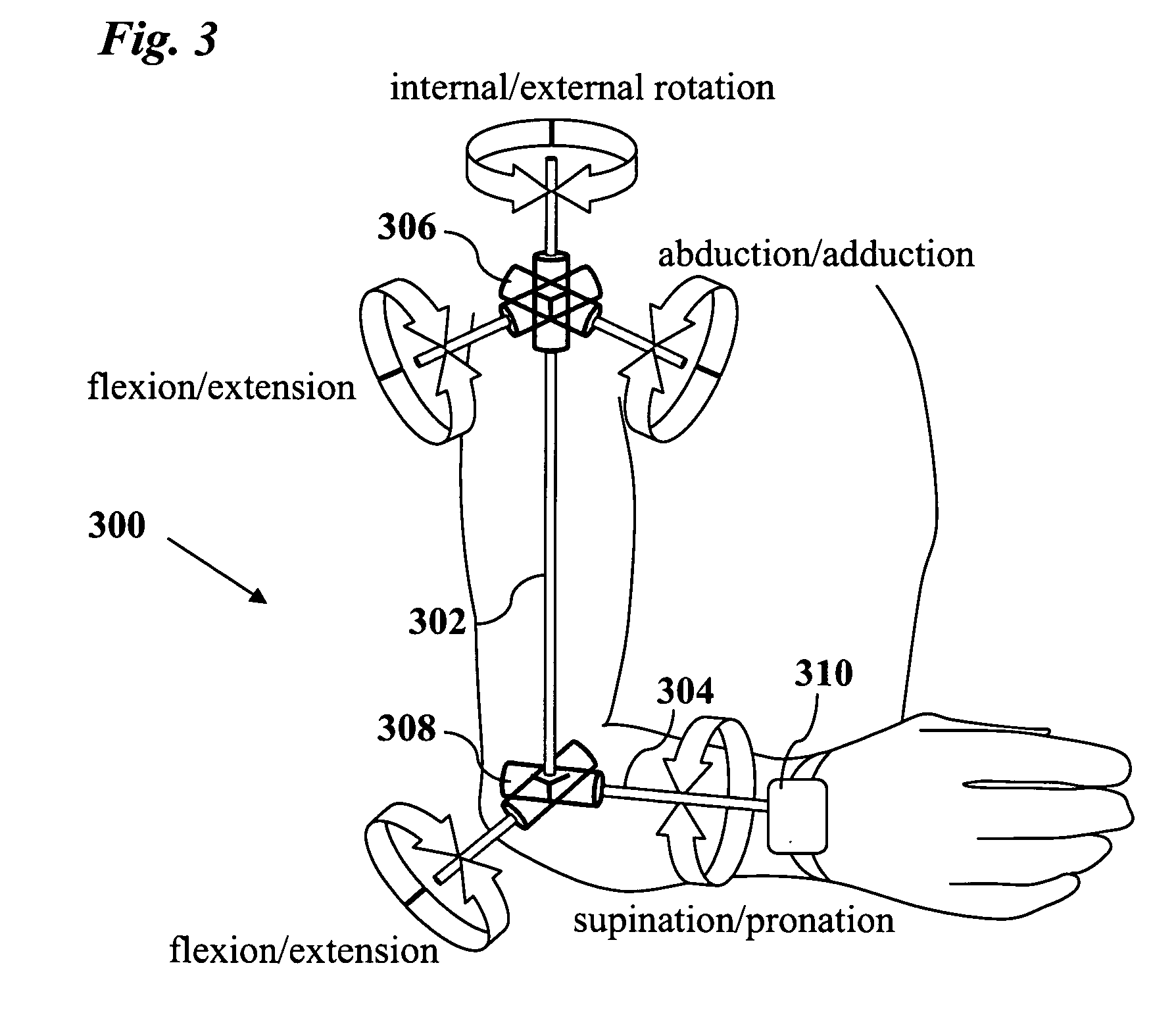
ActiveUS20090204031A1Accurate estimateAccurate trackingPerson identificationInertial sensorsEngineeringMulti segment
A method for estimating joint angles of a multi-segment limb from inertial sensor data accurately estimates and tracks the orientations of multiple segments of the limb as a function of time using data from a single inertial measurement unit worn at the distal end of the limb. Estimated joint angles are computed from measured inertial data as a function of time in a single step using a nonlinear state space estimator. The estimator preferably includes a tracking filter such as an unscented Kalman filter or particle filter. The nonlinear state space estimator incorporates state space evolution equations based on a kinematic model of the multi-segment limb.
Owner:OREGON ACTING BY & THROUGH THE STATE BOARD OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF THE PORTLAND STATE UNIV THE STATE OF
Systems and methods for precise sub-lane vehicle positioning
ActiveCN102529975AInstruments for road network navigationExternal condition input parametersOn boardCurve fitting
The invention relates to systems and methods for precise sub-lane vehicle positioning. A vehicle having an on-board computer, vehicle sensors, a satellite-positioning unit, a database storing a lane-level map performs a method to determine a new pose of the vehicle using map matching. The method includes the on-board computer of the vehicle receiving new data from at least one of the vehicle sensors and collecting measurements from the vehicle sensors. The method also includes the on-board computer of the vehicle computing propagation of vehicle pose with respect to consecutive time instances and performing a curve-fitting process. The method further includes the on-board computer of the vehicle performing a sub-routine of updating at least one observation model based on results of the curve-fitting process, performing a tracking sub-routine including using a probability distribution to update the vehicle pose in terms of data particles, and performing a particle filtering sub-routine based on the data particles to compute the new vehicle pose.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
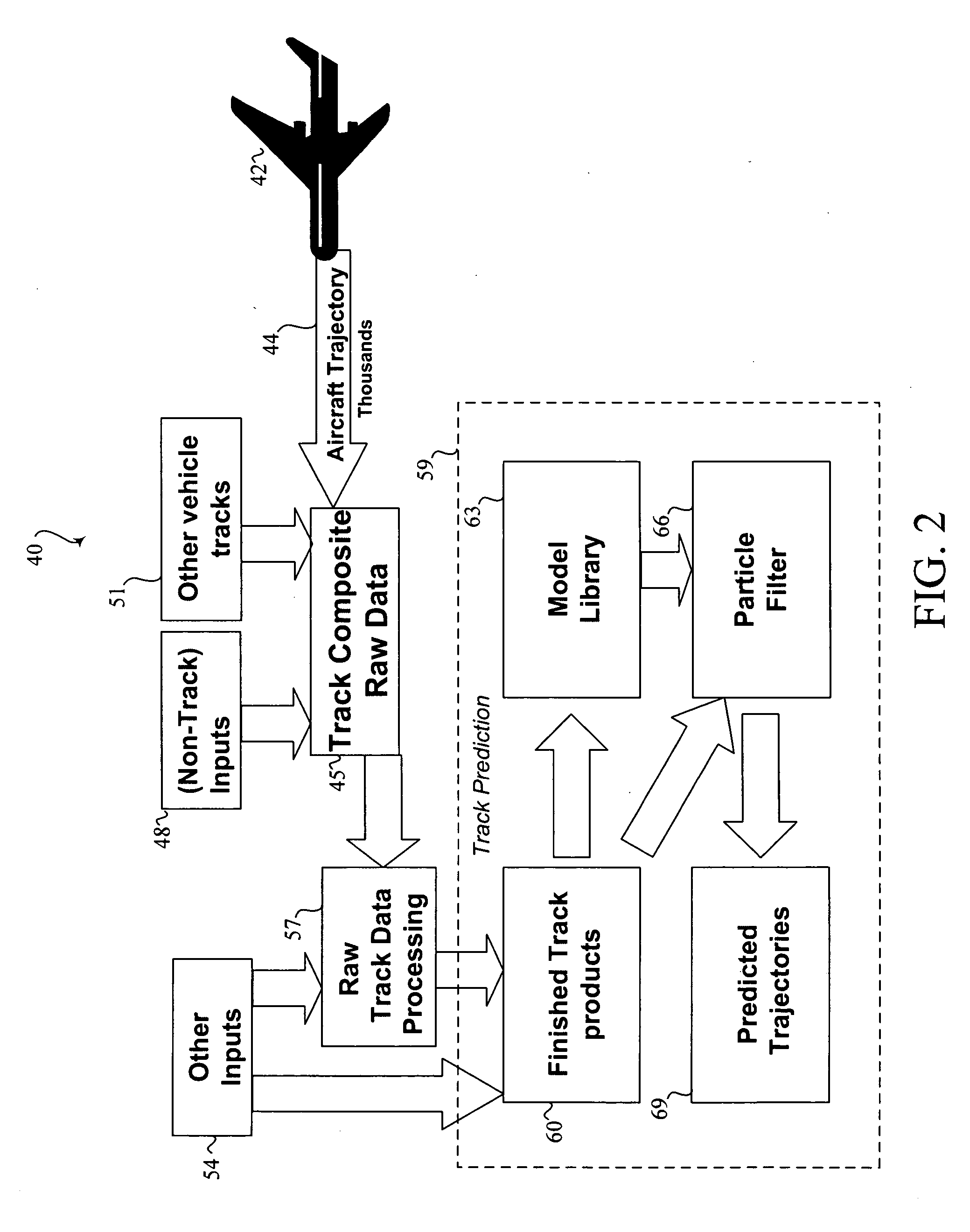
Trajectory prediction
InactiveUS20060224318A1Easy to predictEffective latencyPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsSimulationData signal
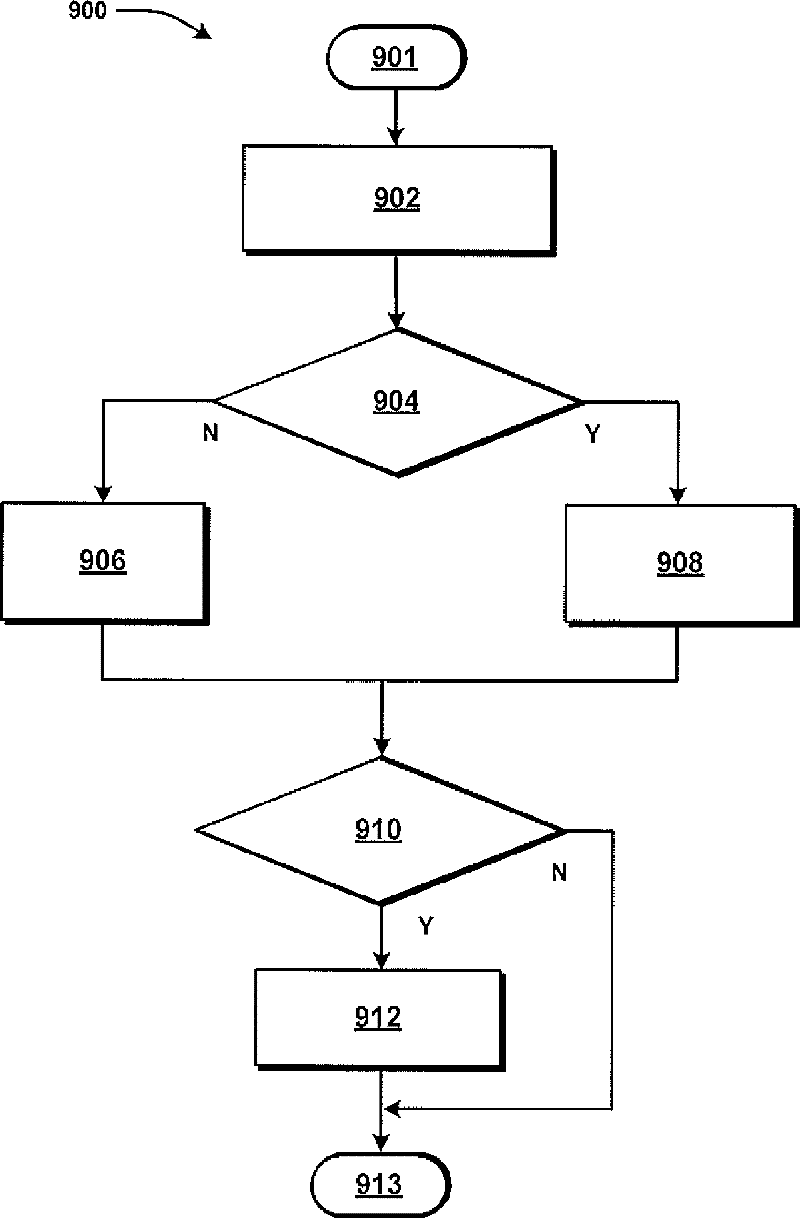
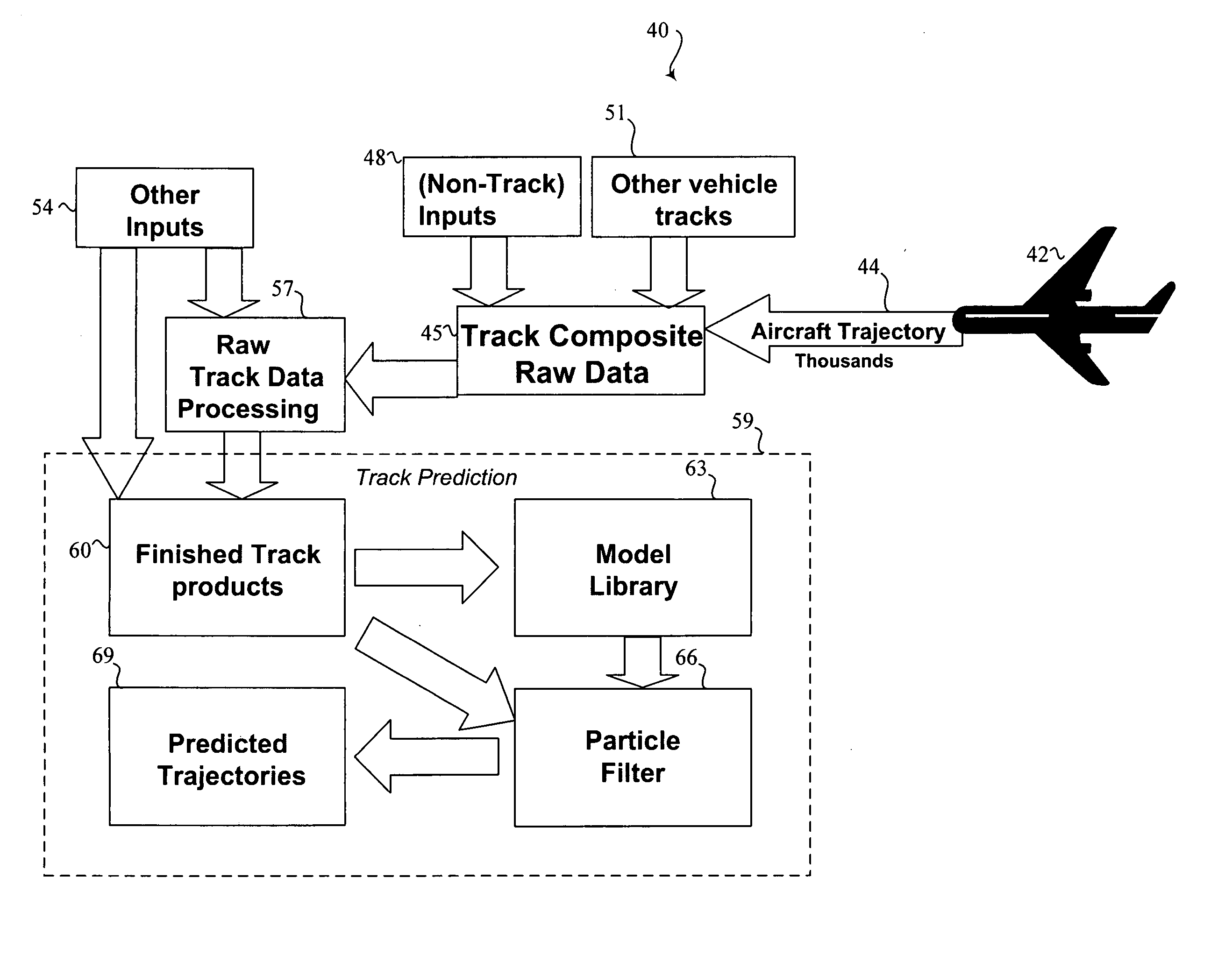
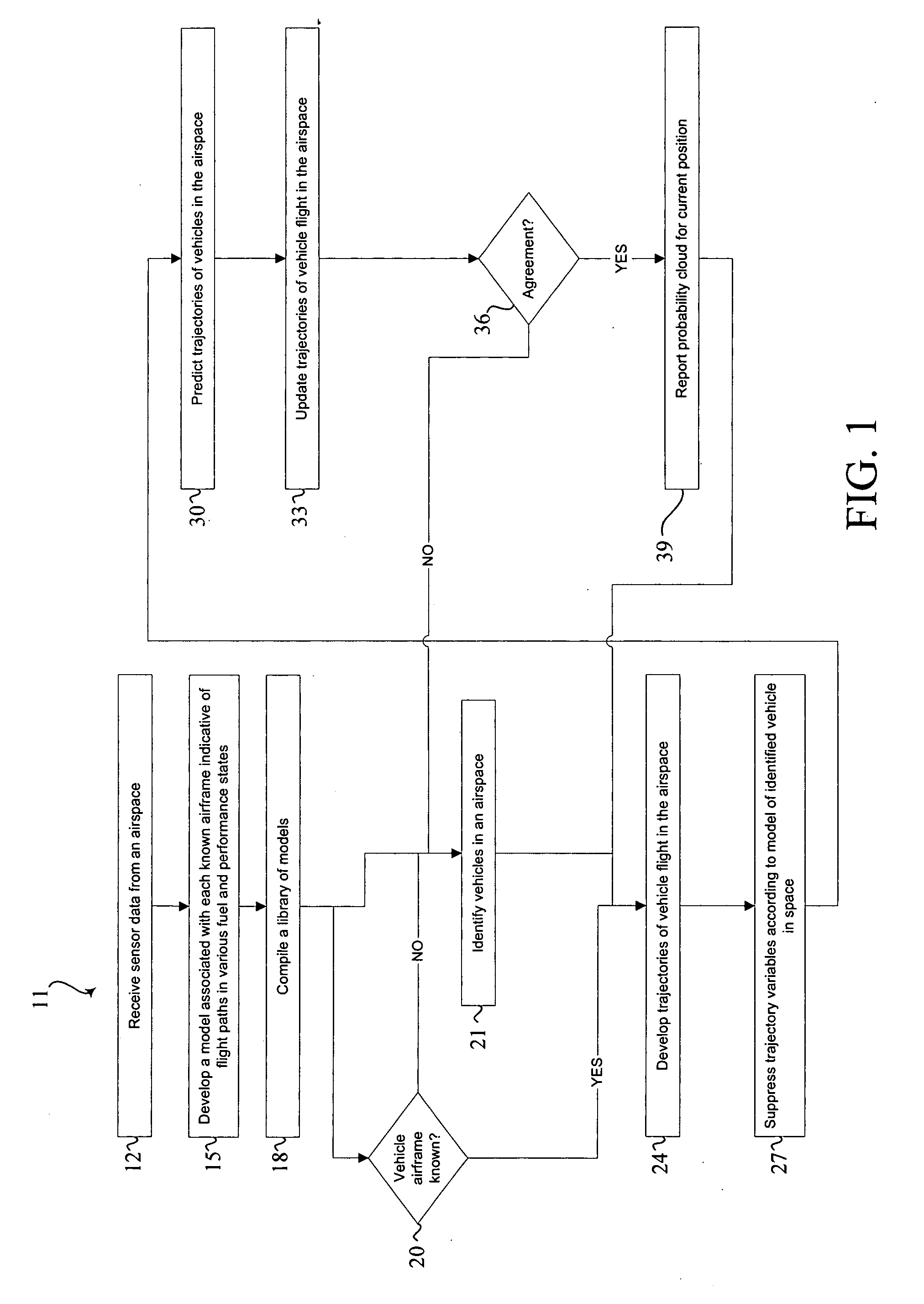
Methods and systems for improved prediction of the movement of vehicles through an airspace are disclosed. In one embodiment, a method for predicting movement of a vehicle in an airspace from a first location to a second location, the predicting based upon at least one data signal configured to communicate a plurality of sensor-perceived first locations of the vehicle includes time correlating the plurality of sensor perceived first locations. The plurality of sensor-perceived first locations are particle filtered to generate a plurality of confidences each corresponding with one of a plurality of predicted locations, each confidence representing a likelihood that the corresponding predicted location includes the second location.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Joint angle tracking with inertial sensors
ActiveUS9597015B2Accurately estimate and trackImprove usabilityPerson identificationInertial sensorsKaiman filterState space
A method for estimating joint angles of a multi-segment limb from inertial sensor data accurately estimates and tracks the orientations of multiple segments of the limb as a function of time using data from a single inertial measurement unit worn at the distal end of the limb. Estimated joint angles are computed from measured inertial data as a function of time in a single step using a nonlinear state space estimator. The estimator preferably includes a tracking filter such as an unscented Kalman filter or particle filter. The nonlinear state space estimator incorporates state space evolution equations based on a kinematic model of the multi-segment limb.
Owner:OREGON ACTING BY & THROUGH THE STATE BOARD OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF THE PORTLAND STATE UNIV THE STATE OF
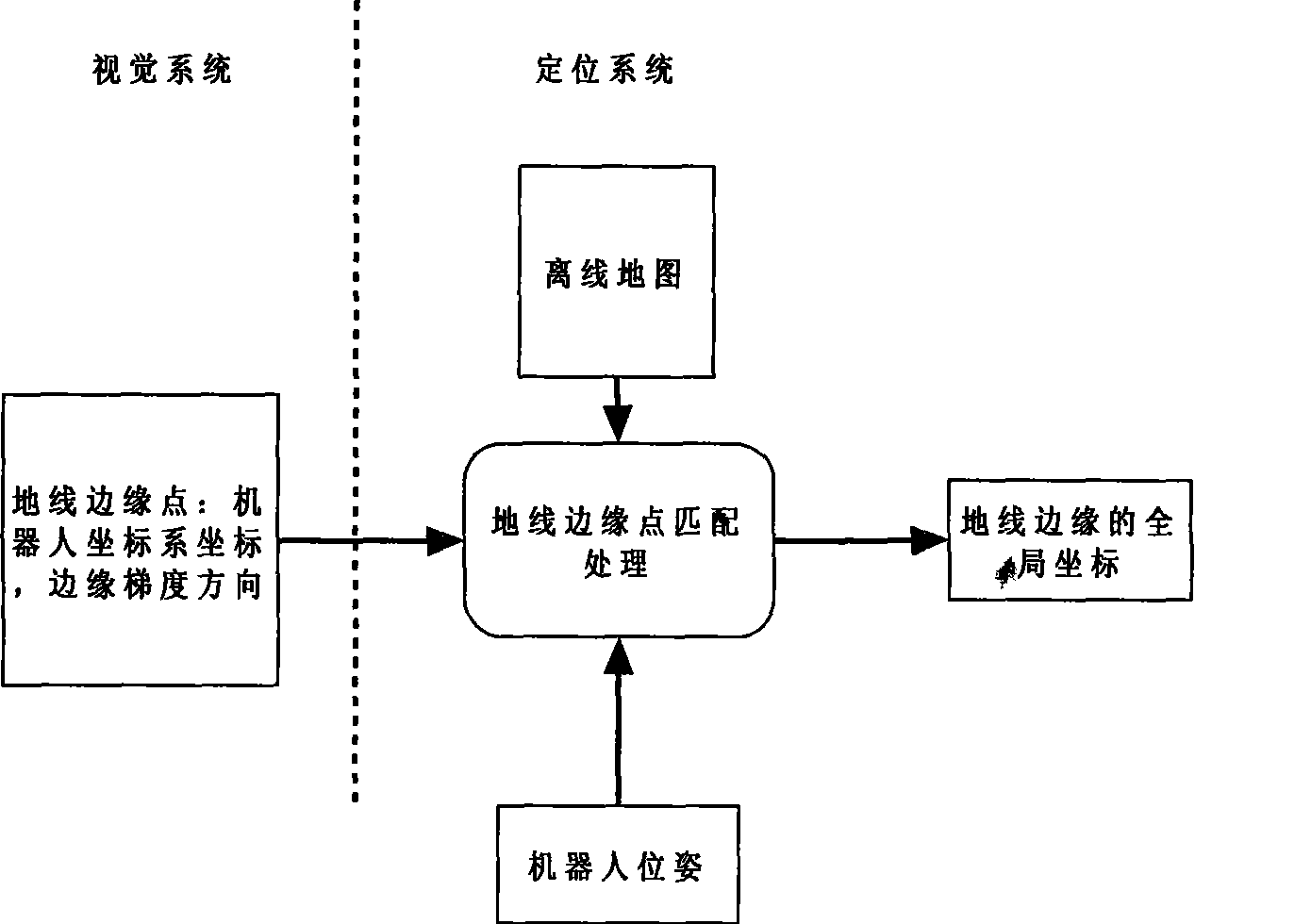
Walking robot positioning system based on monocular cam
ActiveCN101509781ASmall amount of calculationImprove real-time positioningInstruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsParticle densityEngineering
The invention discloses a travelling robot positioning system based on a single camera. In the system, a point model is adopted for representing an environmental model, an off-line map is calibrated, an action model and an observation model are established for carrying out position updating and road sign calibration, Monte Carto particle filter technology is adopted, particle swarm distribution with weights is adopted for representing robot pose estimation, the weights and the distribution of particles are updated through road sign matching processing, field particle distribution is rasterized, and a sub-region with maximal particle density is selected for positioning the robot. As an independent platform, the system greatly improves the map calibration technology on the environmental model, has great flexibility on the identification of ground line sections, and just needs re-calibration but not needs model re-establishment after environment change. The model reduces the matching complexity in visual processing and improves calculation efficiency. The Monte Carlo localization algorithm is expanded on the information integration processing technology, thus ensuring the real-time property and robustness of the system.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Diesel engine exhaust emission purifying system
InactiveCN101178020AImprove filtration efficiencyExhaust apparatusSilencing apparatusCombustion chamberIgnition coil
The invention discloses a purification system of vent gas of diesel engine. The purification system of vent gas of diesel engine essentially consists of a wall-flow diesel particle filter (DPF) and a heating regeneration device used for regeneration of the wall-flow diesel particle filter (DPF). The heating regeneration device consists of an electronic control unit (ECU), a combustion chamber and an ignition system. The ignition system comprises a spark plug, a high voltage wire and an ignition coil, a combustion air generating device and relevant pipes, ejector components and pipes, an oil nozzle, relevant temperature and pressure sensor and other gas paths, a valve of oil circuit and an automatic protection device. Compared with the prior art, the invention is characterized by reliable regeneration, efficient purification and no restriction of the way vehicle driving, etc.
Owner:YANTAI HUALONG BUSINESS MACHINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com