Patents
Literature
2142 results about "Signal parameter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
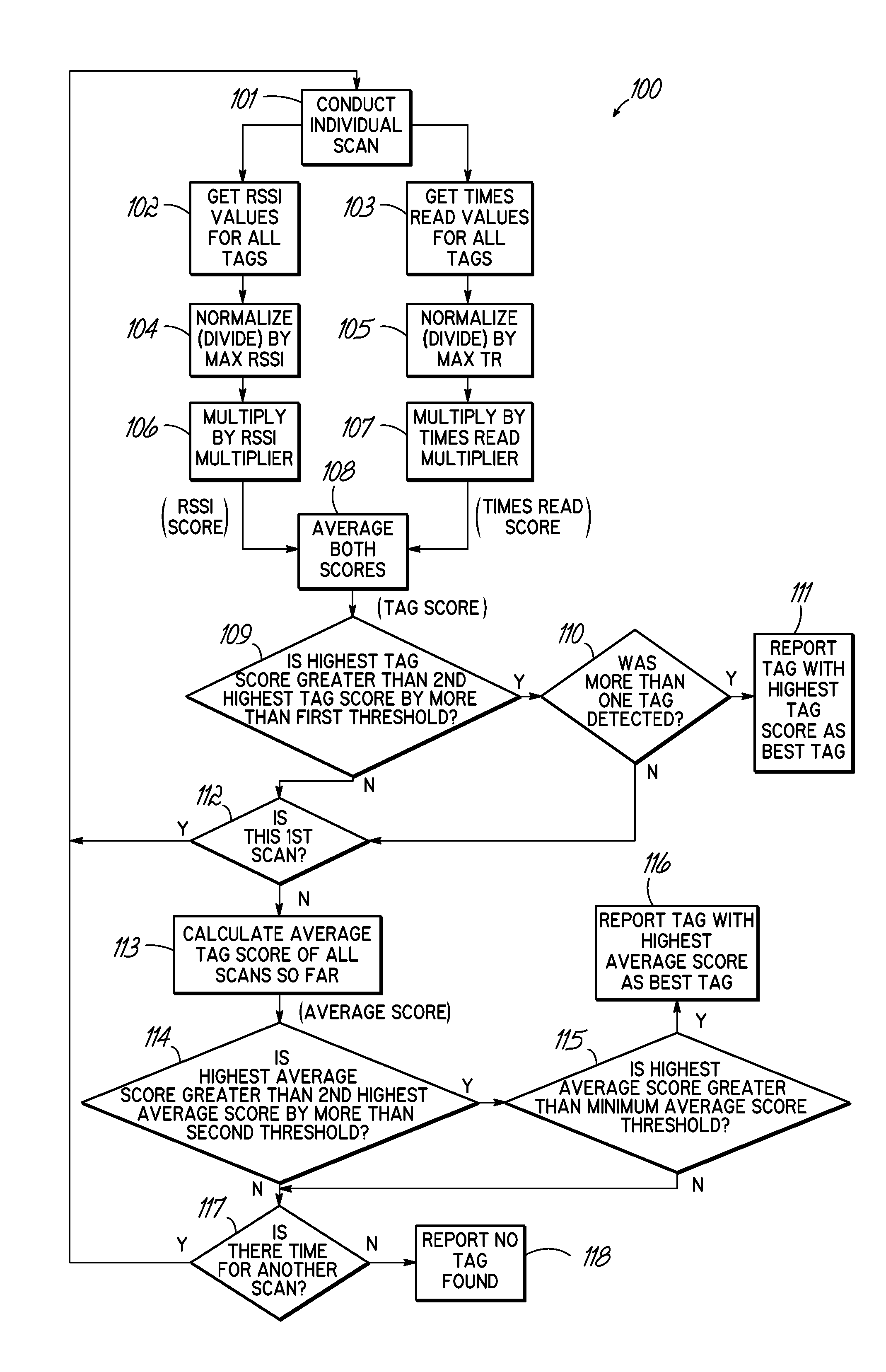
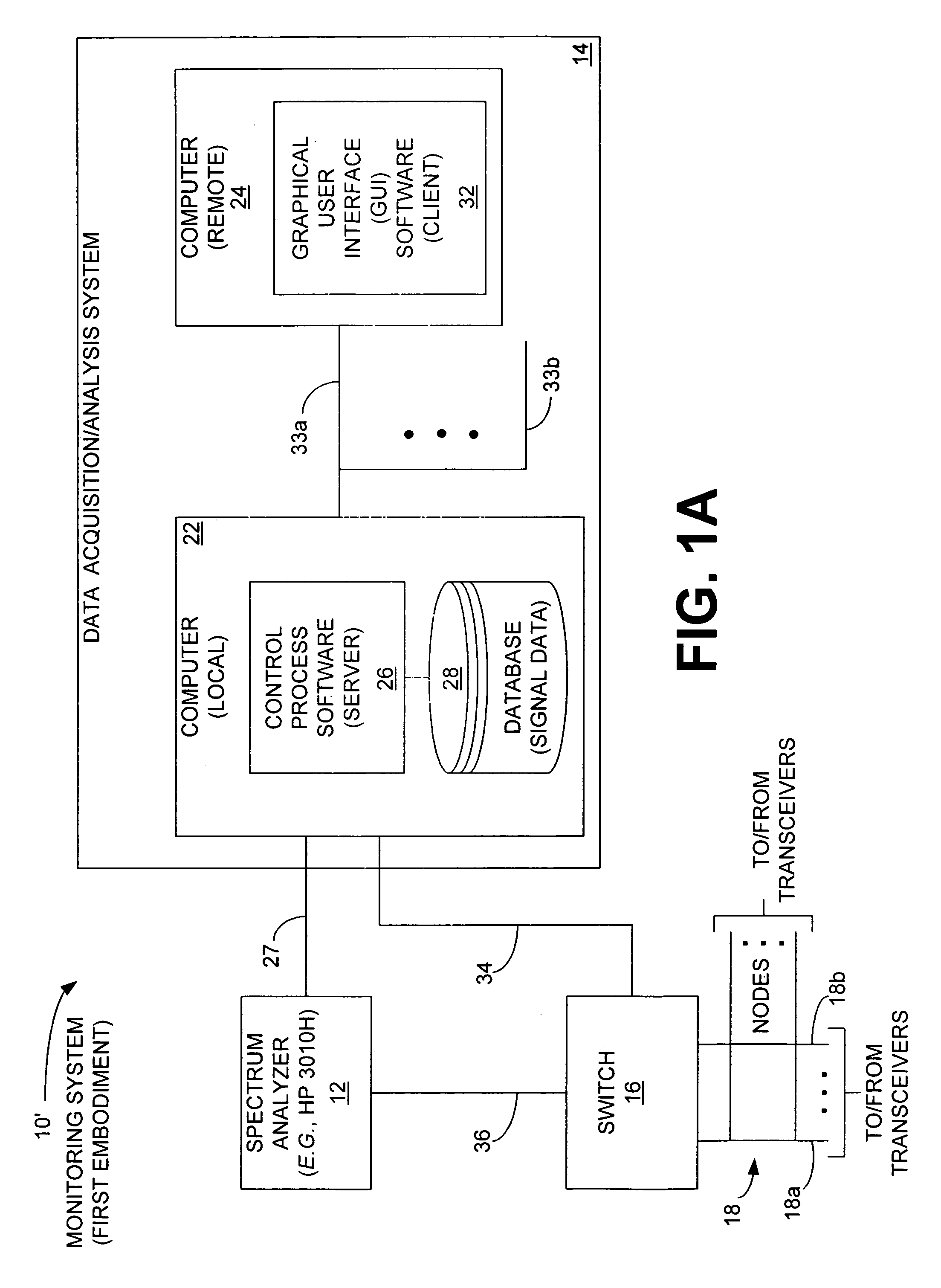
Method and system for correctly identifying specific RFID tags
ActiveUS8659397B2Electric signal transmission systemsMemory record carrier reading problemsComputer scienceSignal parameter
A system and method for identifying a specific RFID tag includes RFID reader circuitry, such as within an RFID reader, configured for sending and receiving RF signals to detect RFID tags and for obtaining signal parameter information associated with the RFID tags. Processing circuitry is configured for using the signal parameter information for one or more tags of the RFID tags and calculating a tag score for the one or more RFID tags. The processing circuitry is further configured for determining a specific RFID tag using the tag scores for the one or more RFID tags.
Owner:VOCOLLECT
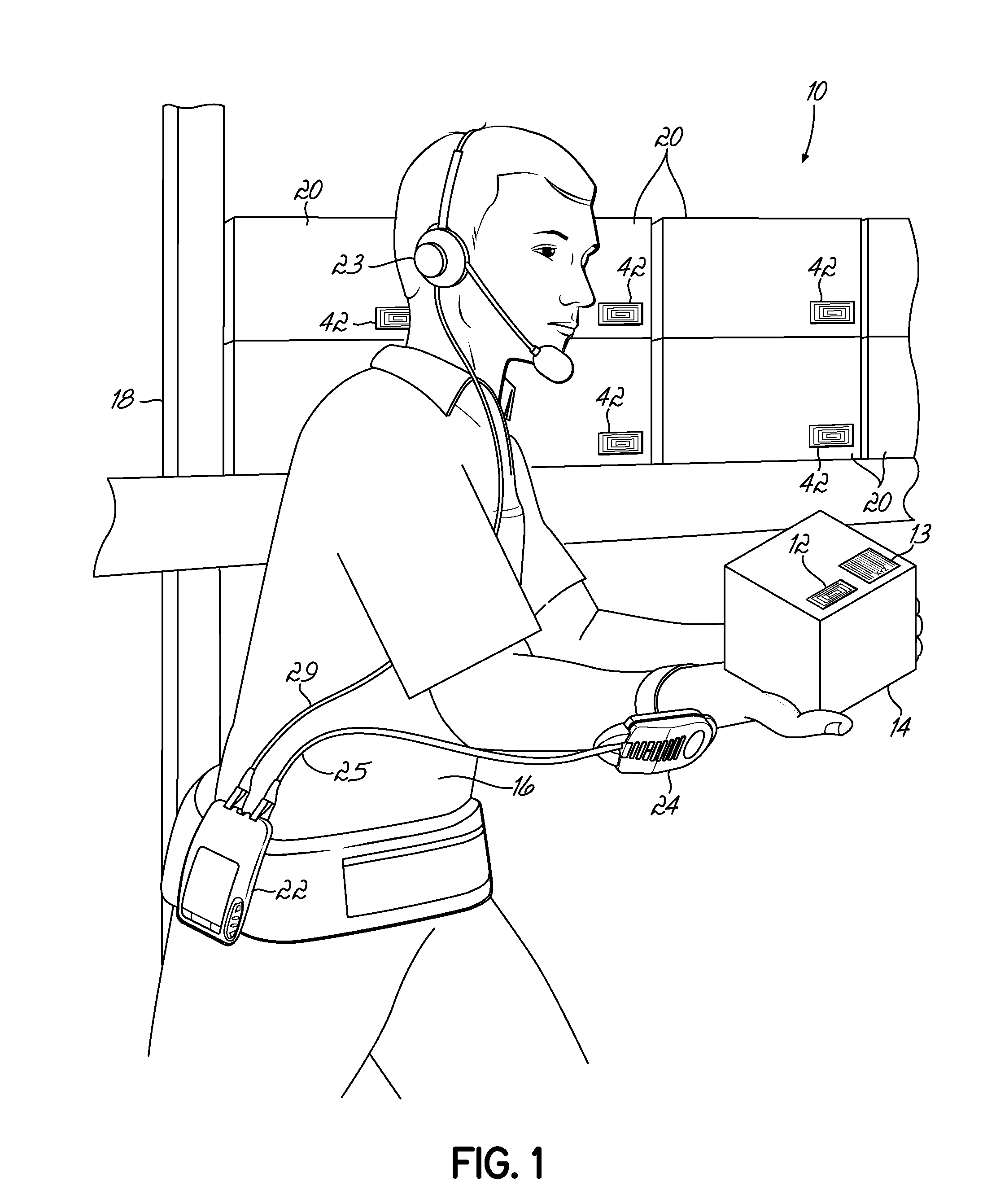
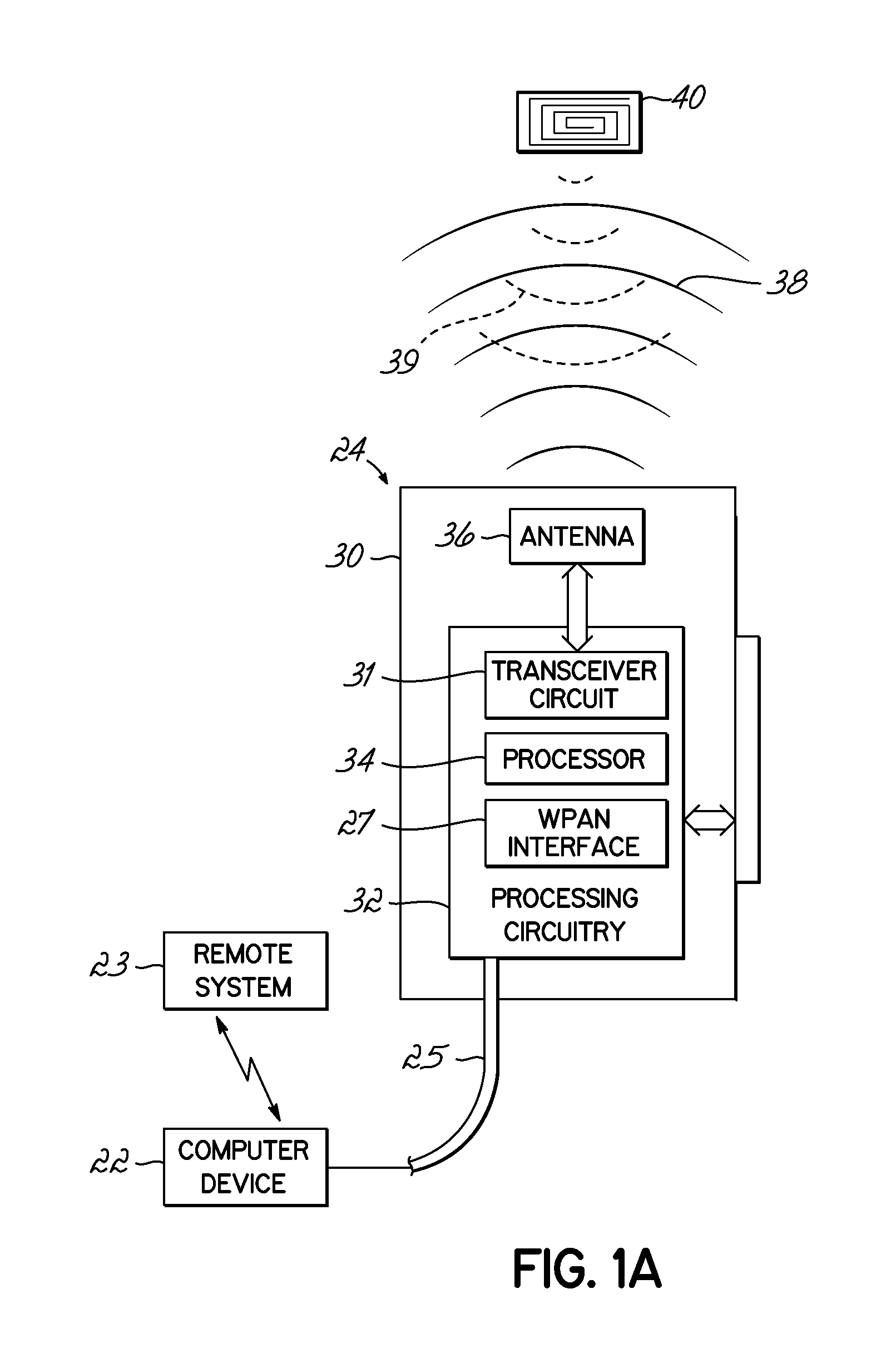
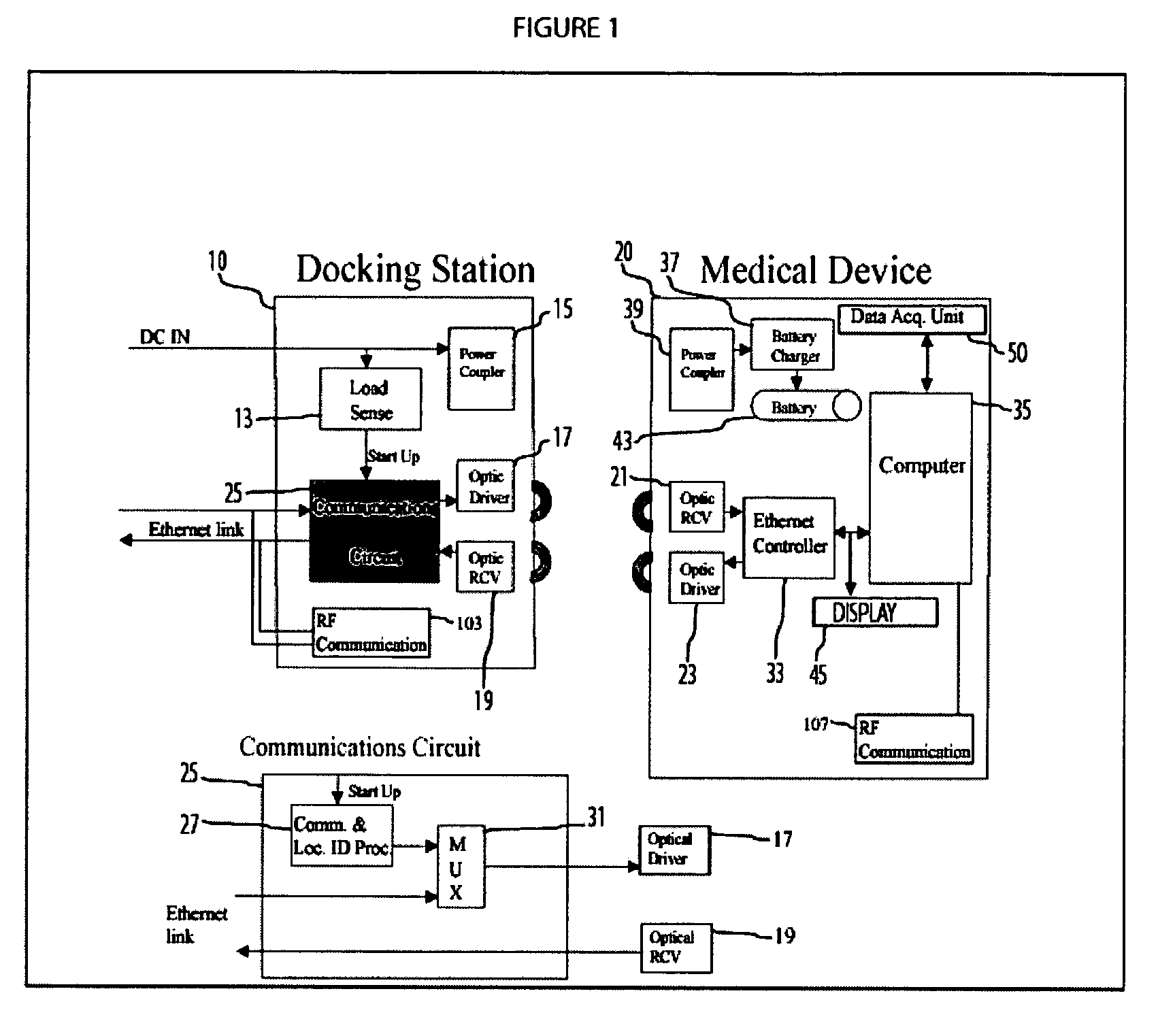
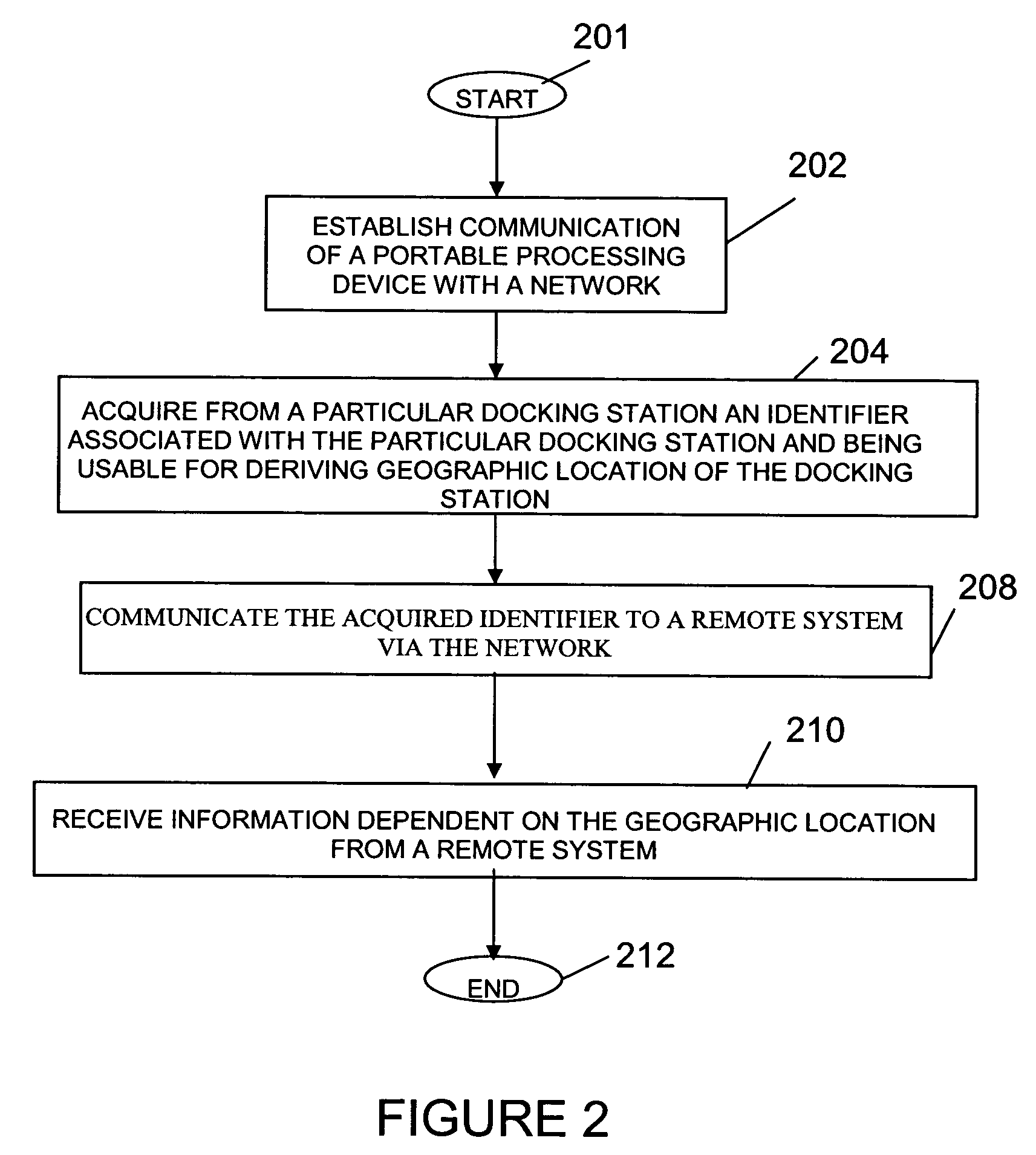
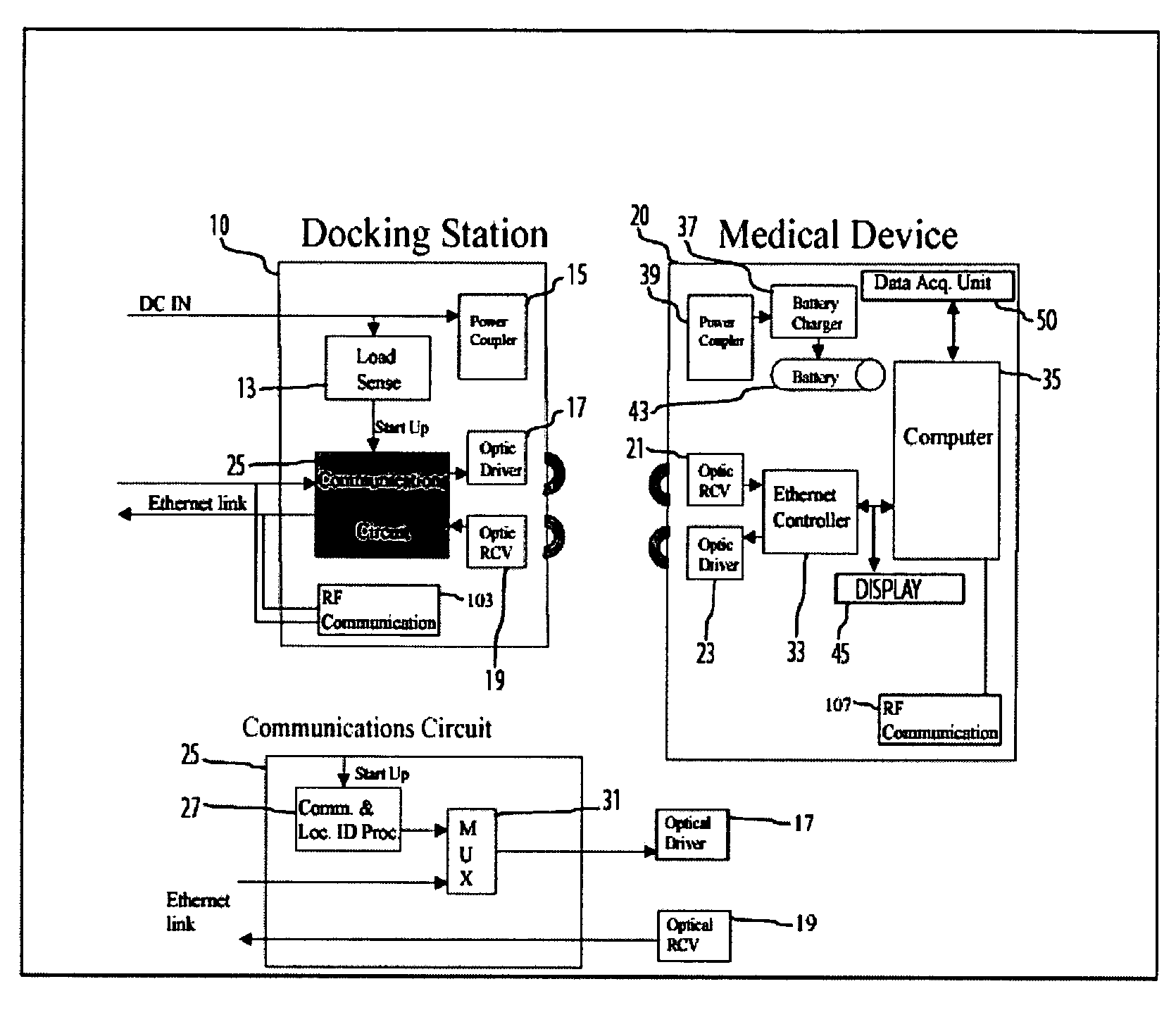
Portable patient monitoring system including location identification capability
A docking station advantageously provides a location identifier to a portable processing device which processes the location identifier to determine docking station location (and other information) and to upload settings and configuration information related to an identified location which is retained until a different docking station location is encountered. In a system for use in a docking station suitable for attaching to a portable patient monitoring device for processing signal parameters acquired from a patient, a power coupler couples power to provide electrical power to a portable processing device. An adaptive communication interface, in a first mode of operation, communicates an identifier associated with a particular docking station to the portable processing device, and in a second mode of operation, establishes connection of the portable processing device to a network.
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
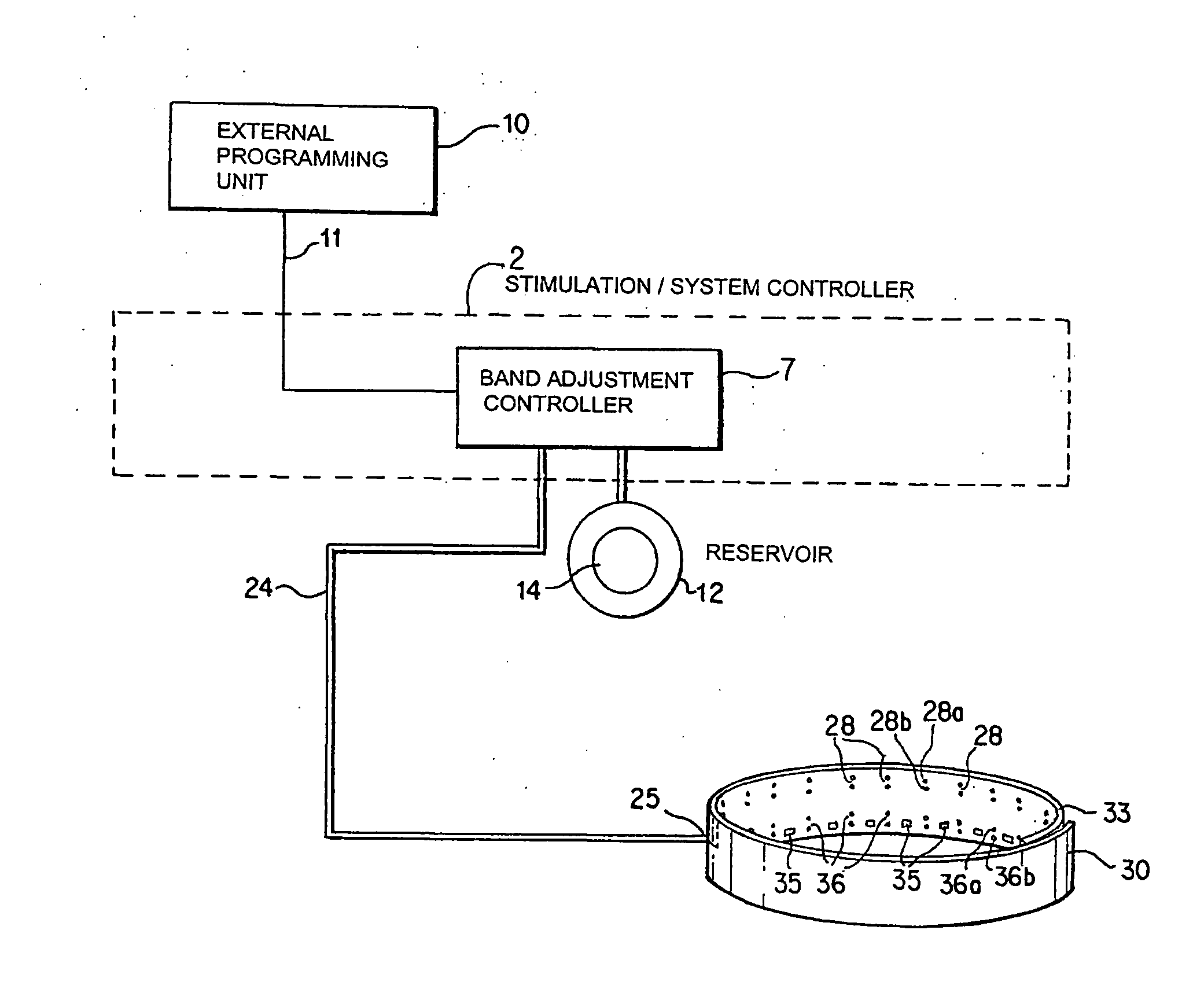
Noninvasively adjustable gastric band
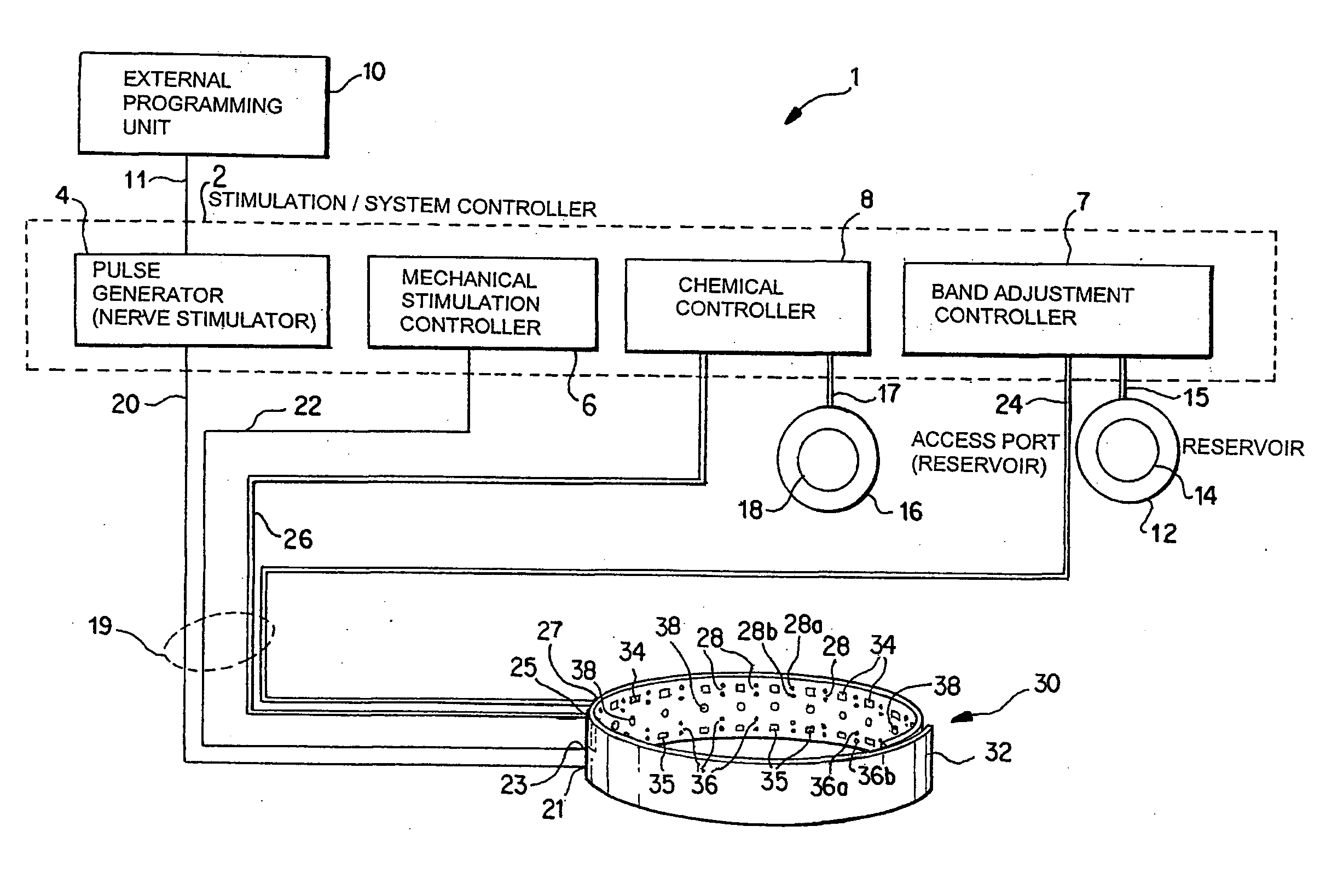
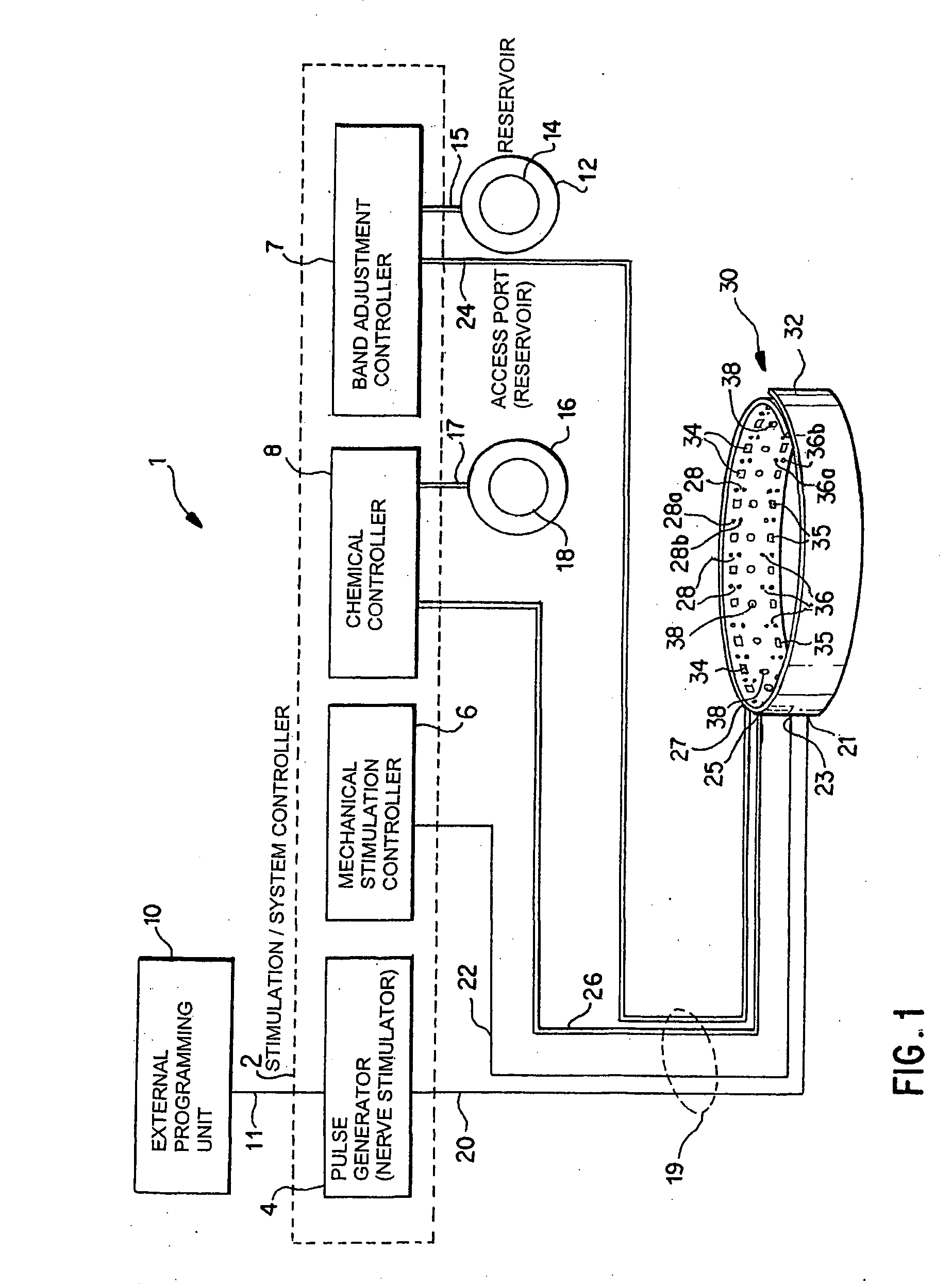
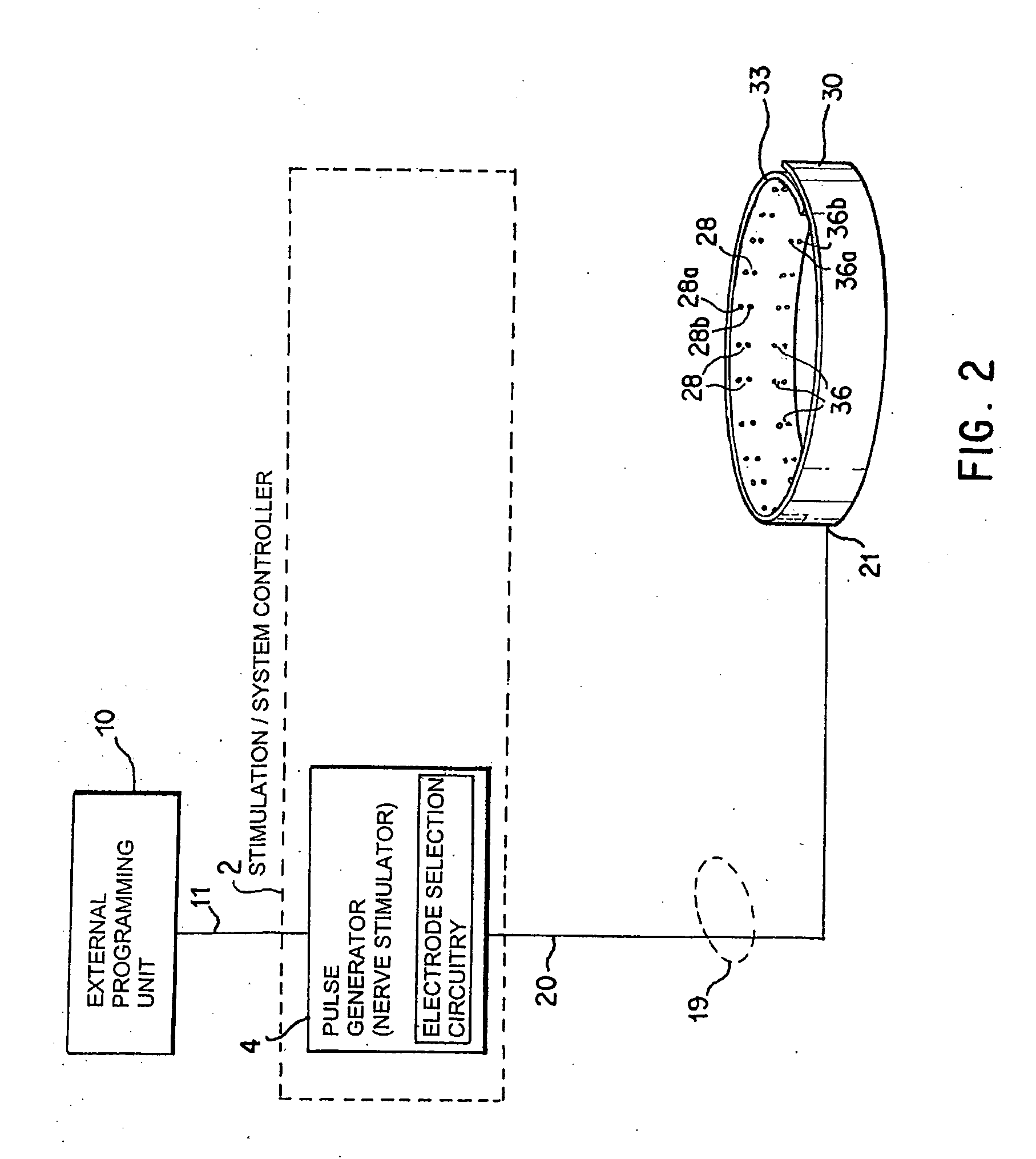
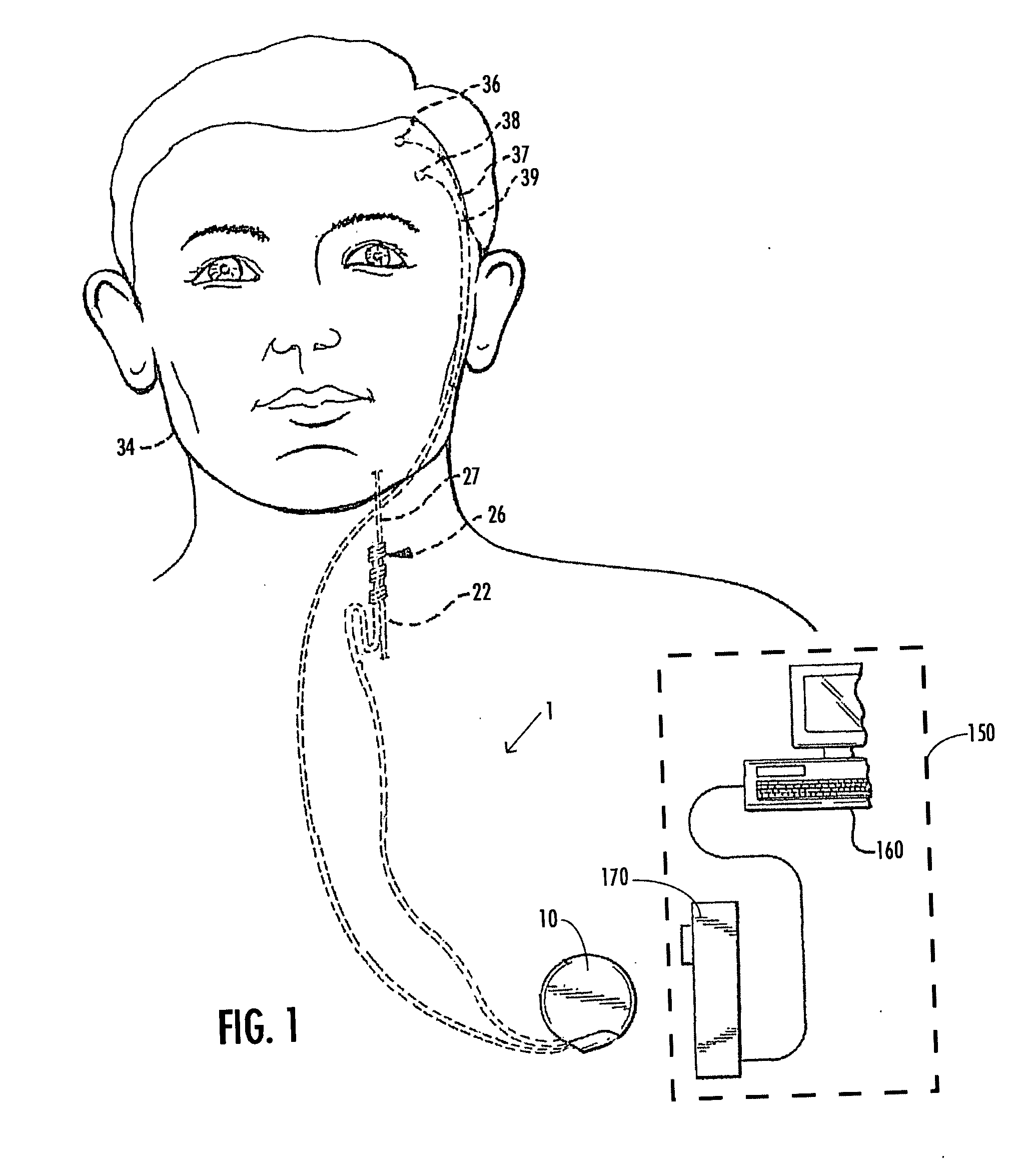
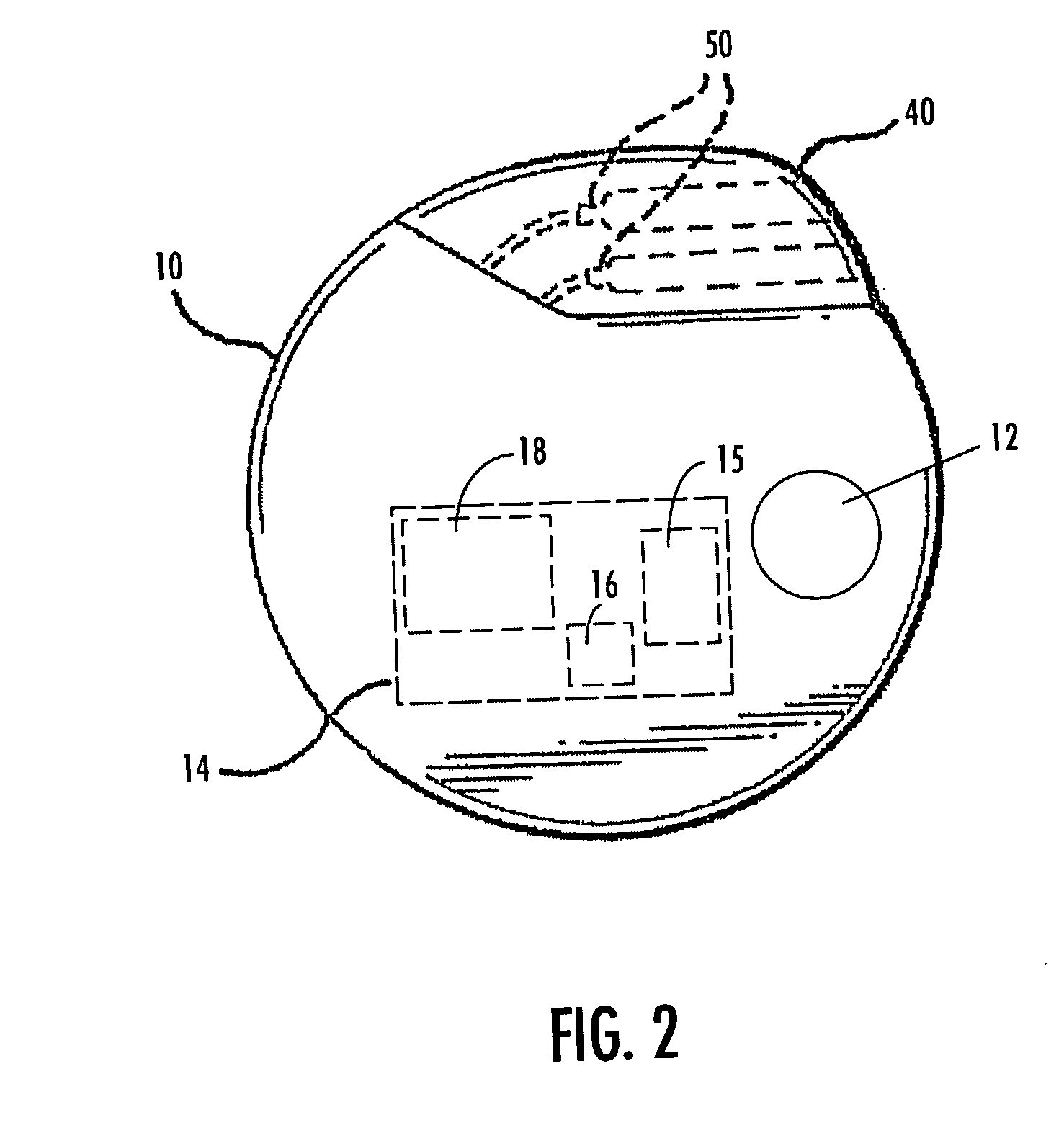
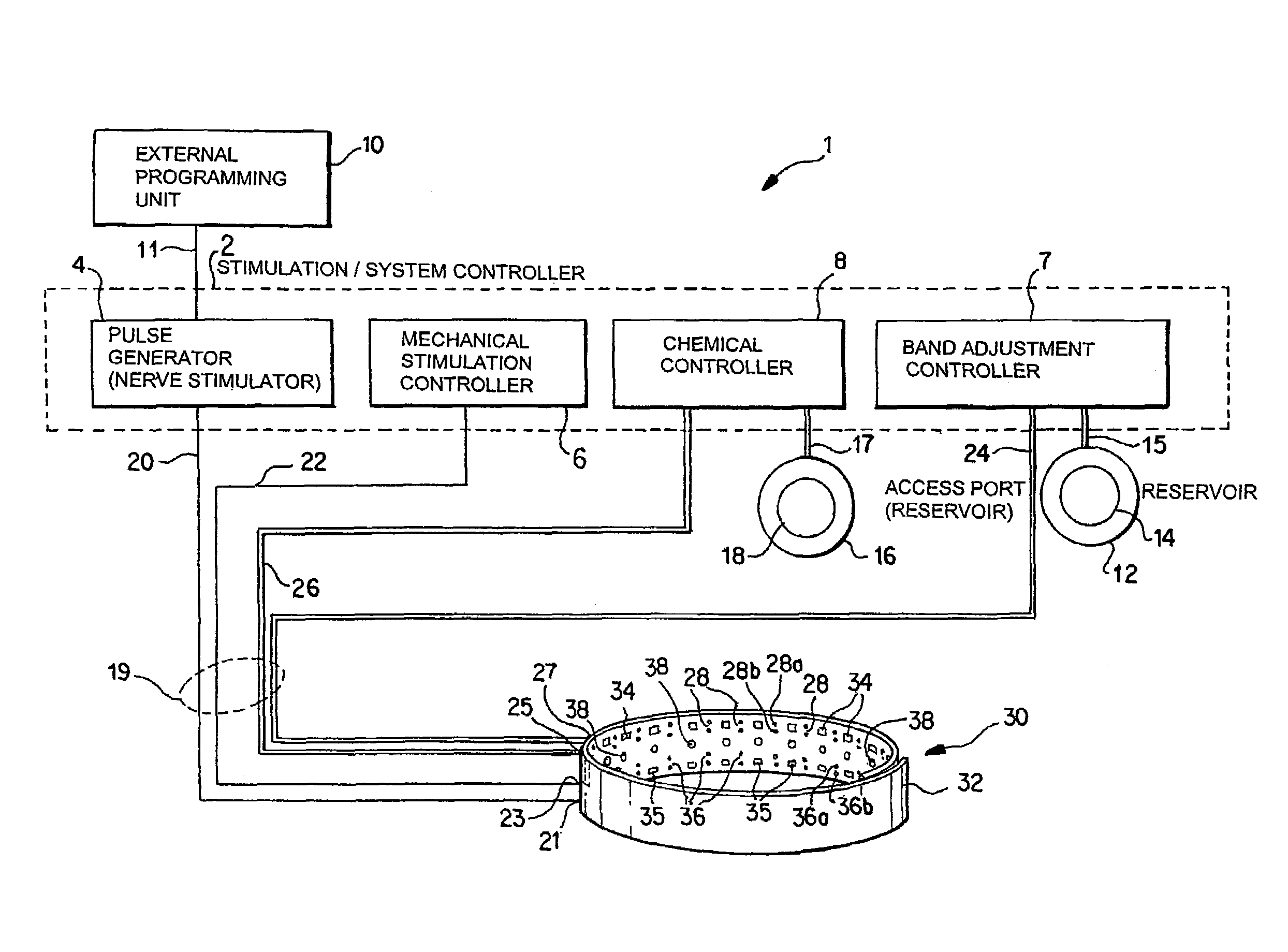
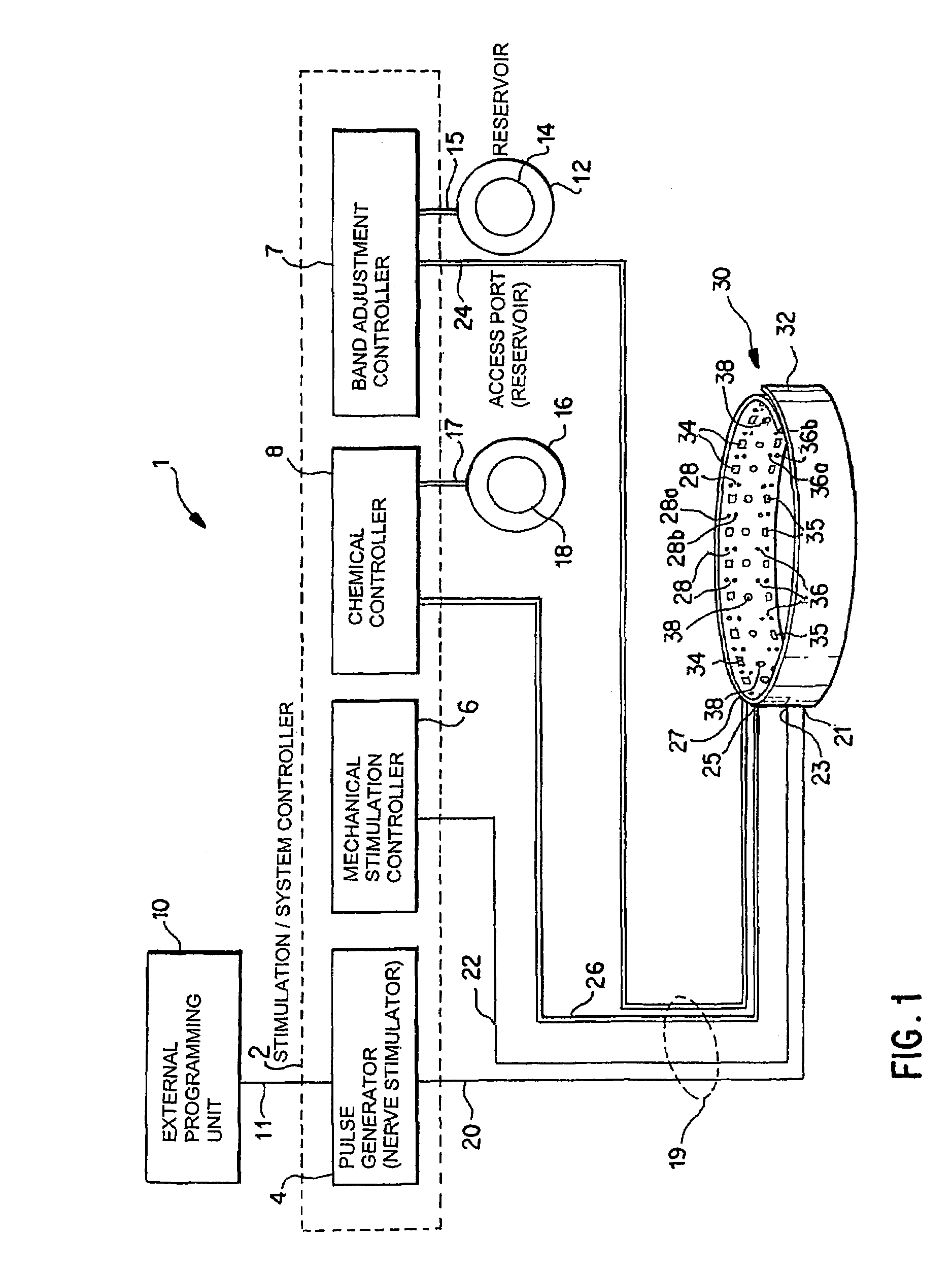
A method and apparatus for treatment of an eating disorder includes electrically, mechanically and / or pharmaceutically / chemically stimulating a of the vagus nerve of the lower esophagus, cardia, esophageal / cardia junction, cardia / fundus junction or upper stomach so as to induce afferent action potentials on the vagus nerve. The device may be noninvasively adjusted after implantation to provide increased or decreased restriction on the patient's gastrointestinal tract. Each stimulus may be administered as a series of programmed pulses of defined amplitude, duration and period, to evoke a responsive signal to the brain by the target nerve, effective for producing a temporary feeling of satiety in the person. An implantable stimulus generator may be operatively coupled to a nerve electrode, pressure device or chemical outlet to apply a defined signal to a selected nerve branch. The implantable stimulus generator is programmable to allow clinician programming of defined signal parameters effective to treat the eating disorder of the patient. Methods are also provided to identify electrodes nearest to a branch of the vagus nerve to apply an electrical stimulation signal with improved efficiency.
Owner:CYBERONICS INC
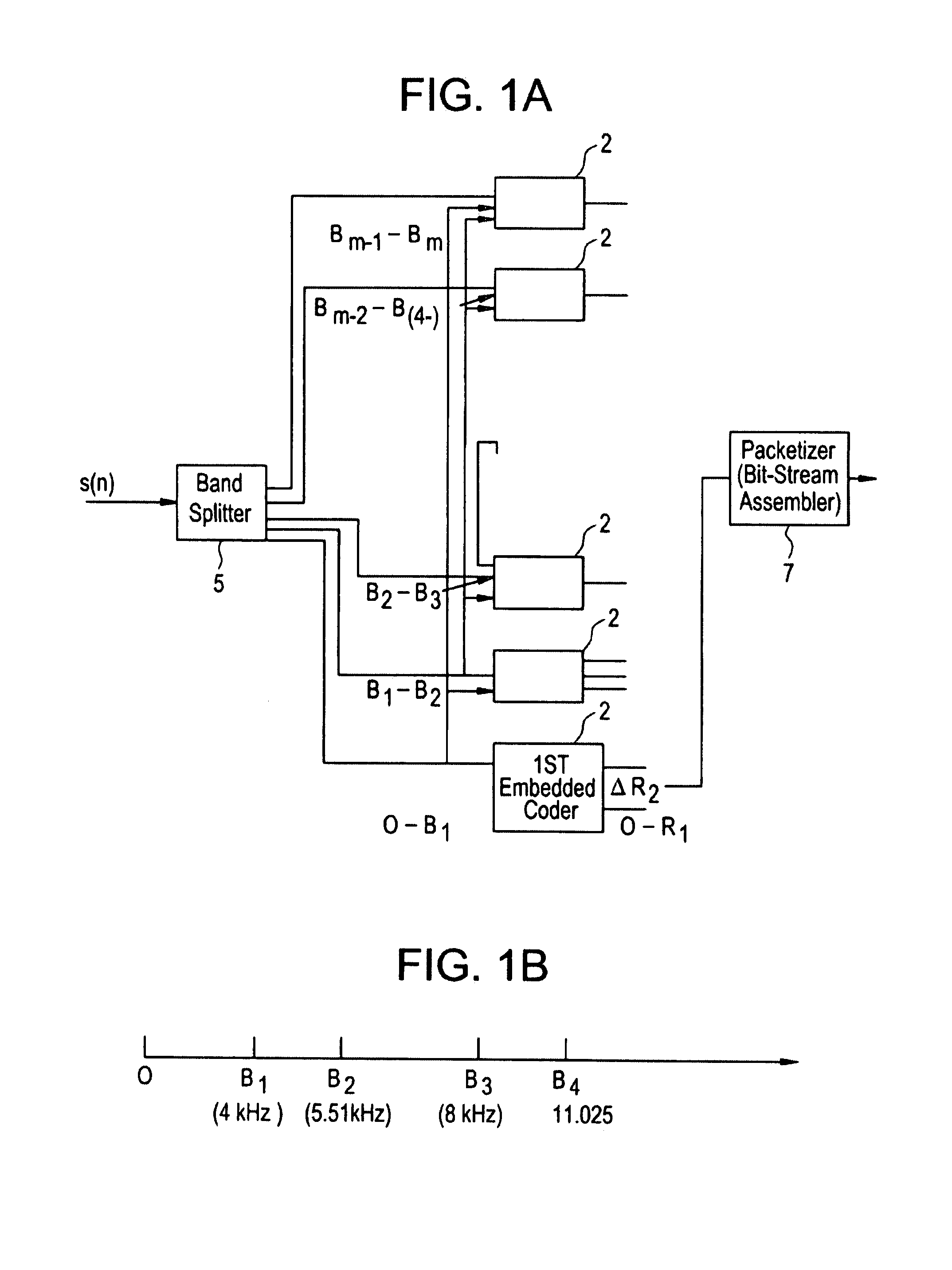
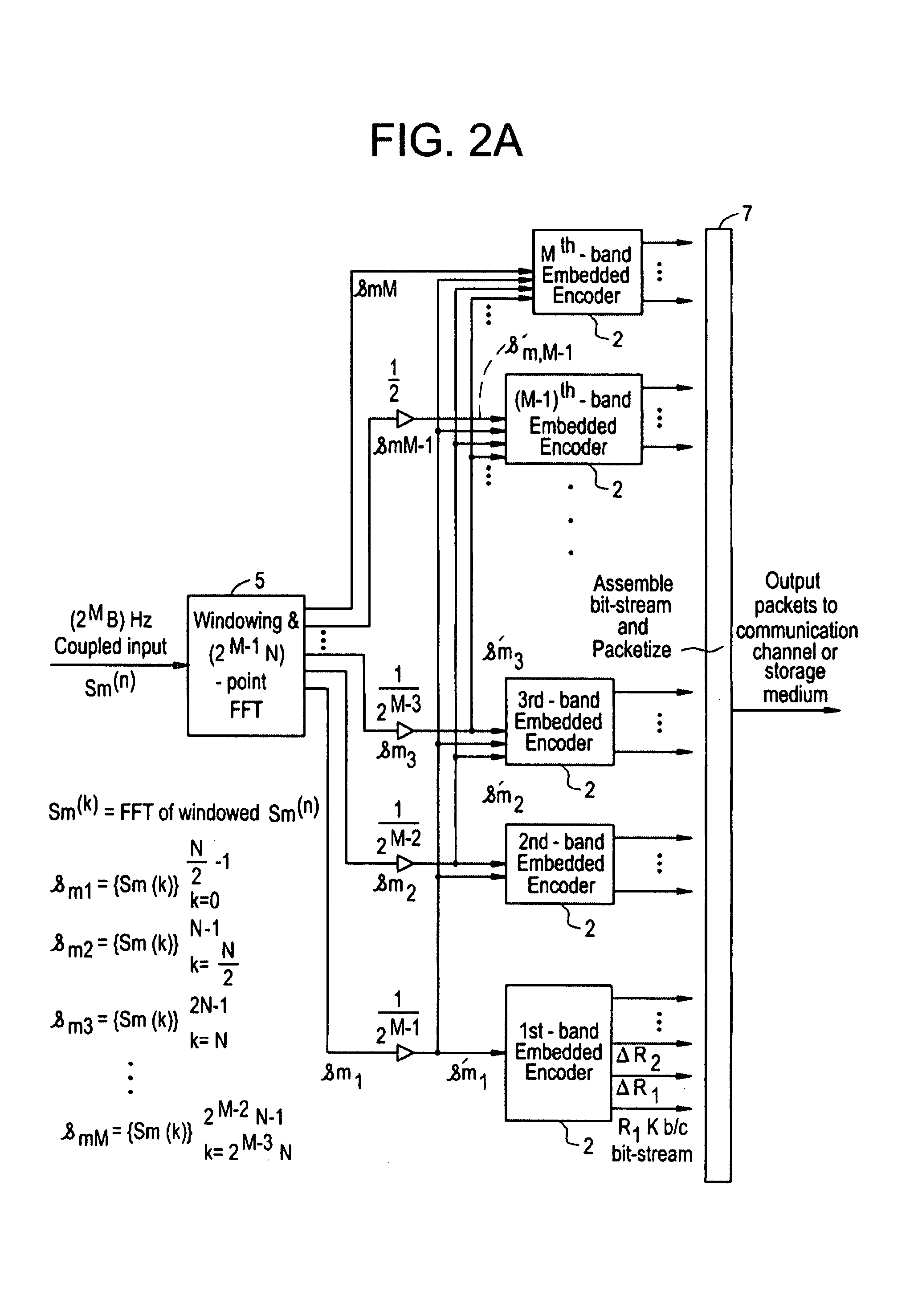
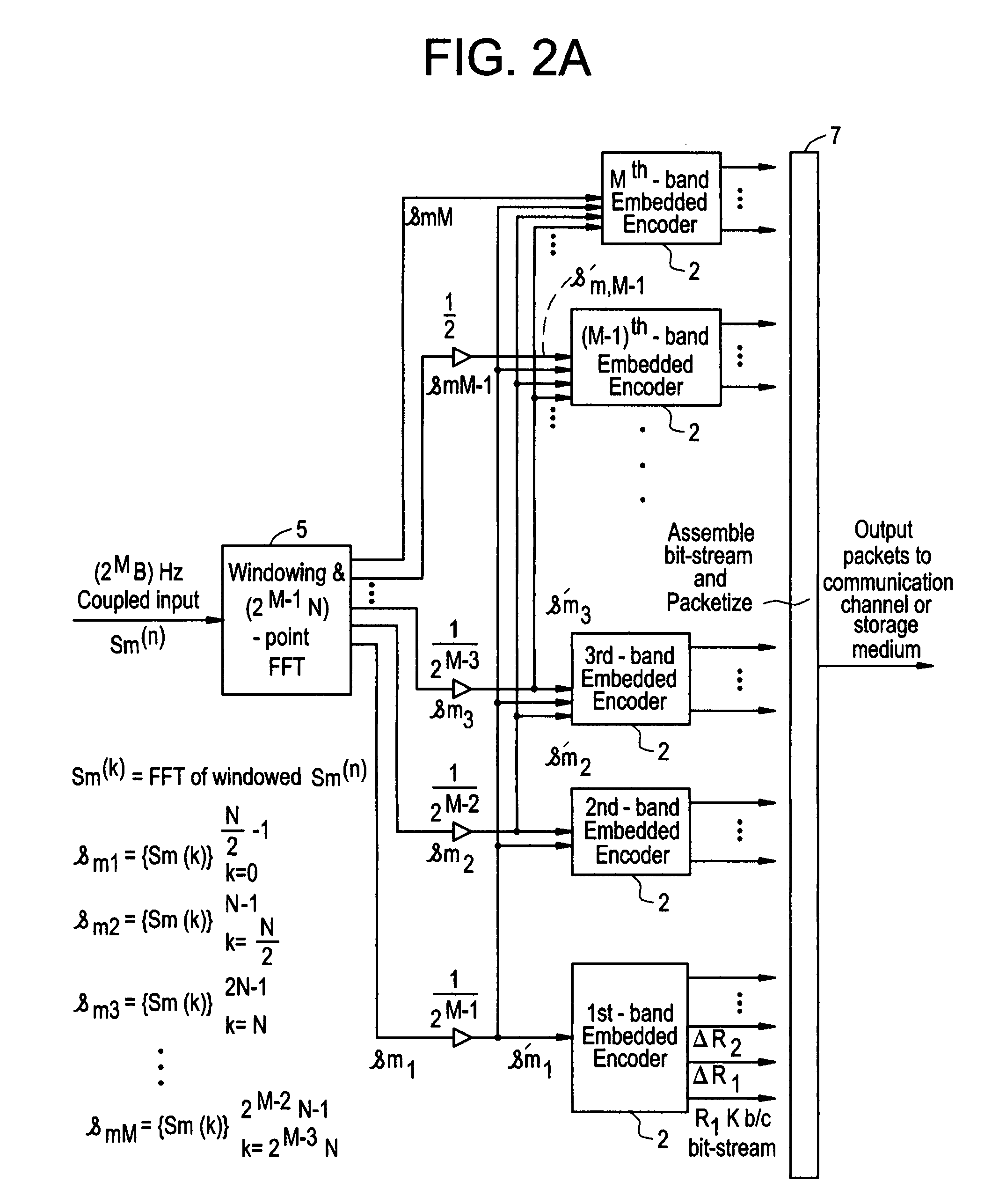
Scalable and embedded codec for speech and audio signals
InactiveUS7272556B1Improve signal reconstruction accuracyImprove reconstruction accuracySpeech analysisMultiple modesAudio signal flow
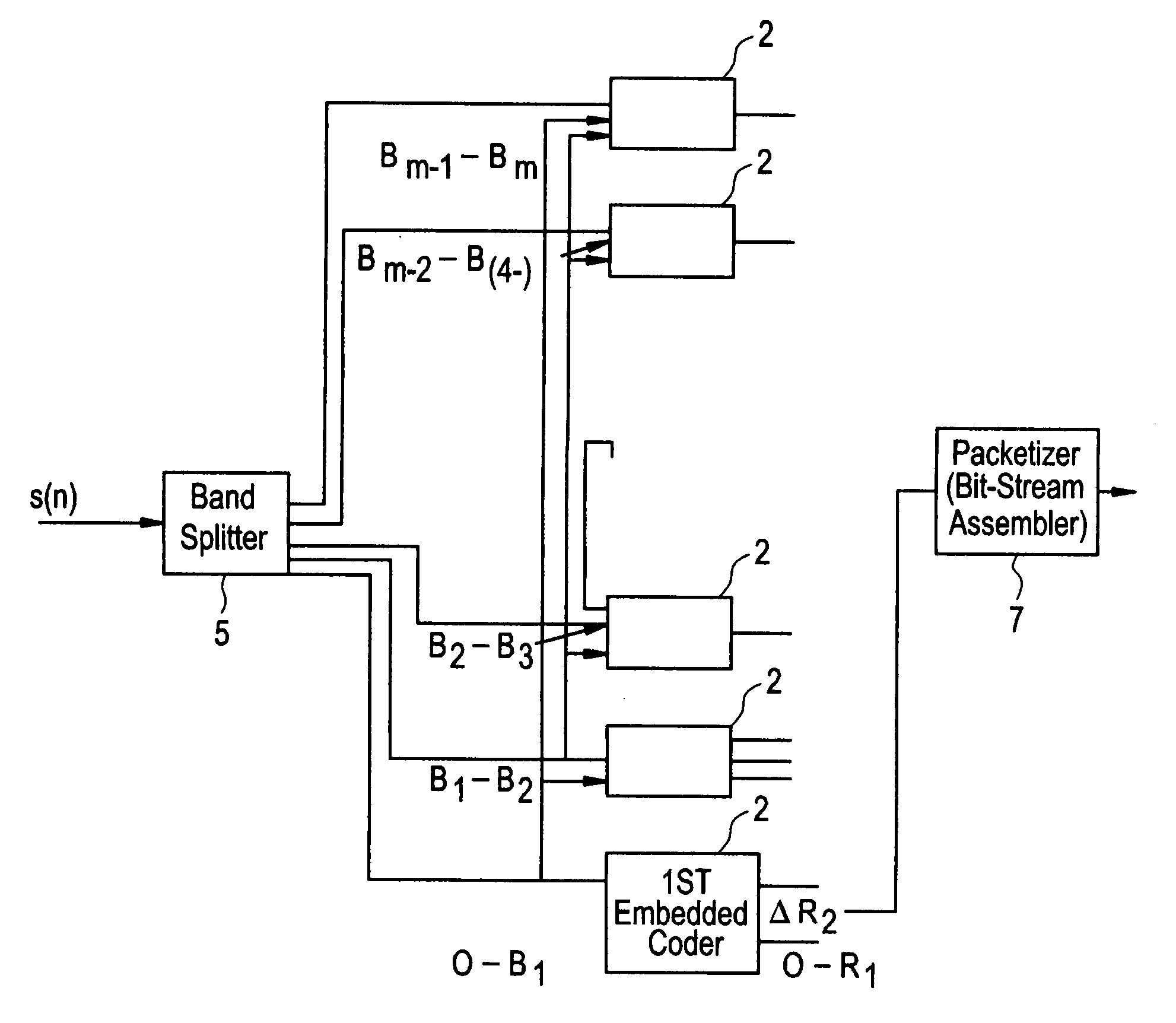
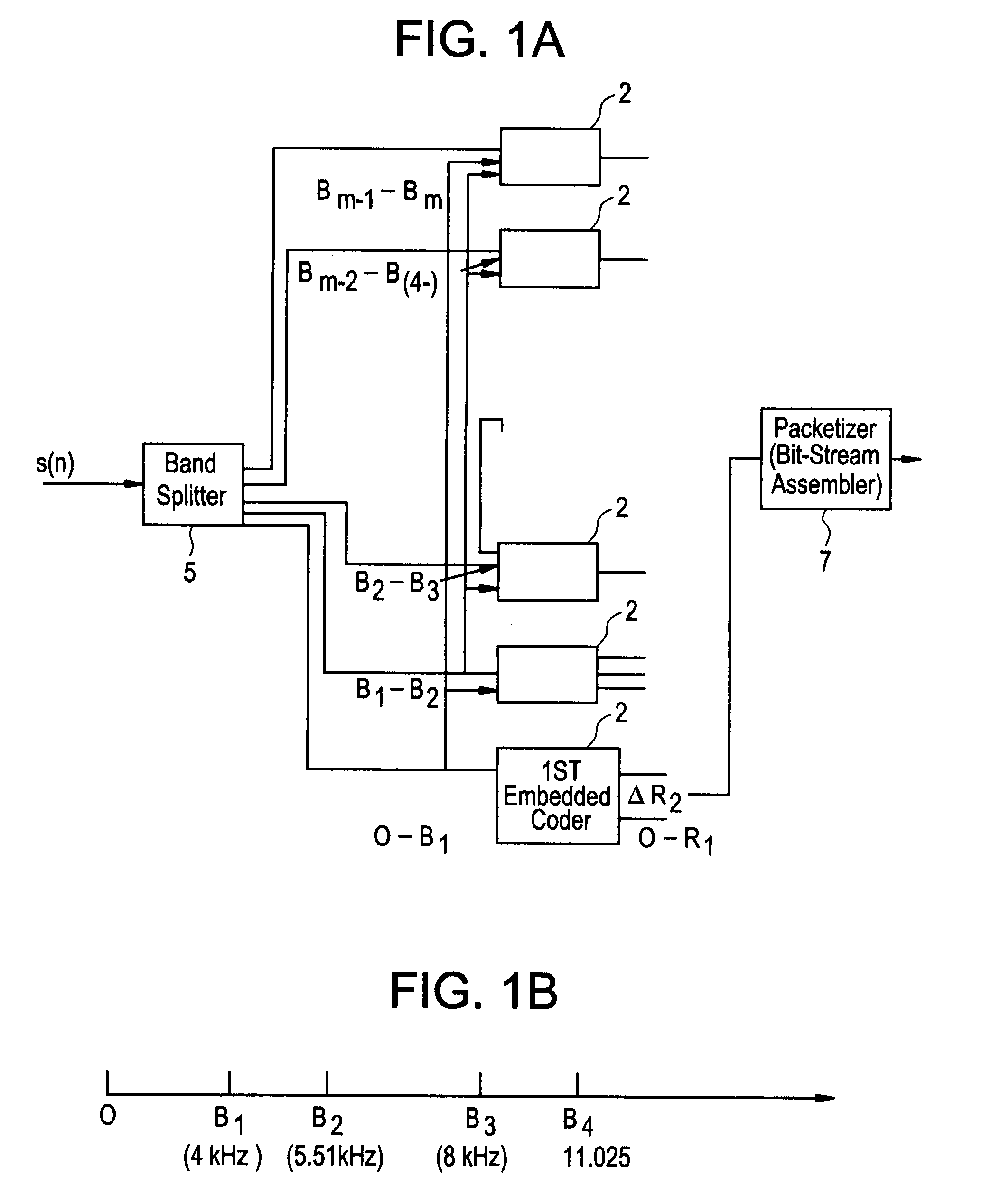
A system and method for processing of audio and speech signals is disclosed, which provide compatibility over a range of communication devices operating at different sampling frequencies and / or bit rates. The analyzer of the system divides the input signal in different portions, at least one of which carries information sufficient to provide intelligible reconstruction of the input signal. The analyzer also encodes separate information about other portions of the signal in an embedded manner, so that a smooth transition can be achieved from low bit-rate to high bit-rate applications. Accordingly, communication devices operating at different sampling rates and / or bit-rates can extract corresponding information from the output bit stream of the analyzer. In the present invention embedded information generally relates to separate parameters of the input signal, or to additional resolution in the transmission of original signal parameters. Non-linear techniques for enhancing the overall performance of the system are also disclosed. Also disclosed is a novel method of improving the quantization of signal parameters. In a specific embodiment the input signal is processed in two or more modes dependent on the state of the signal in a frame. When the signal is determined to be in a transition state, the encoder provides phase information about N sinusoids, which the decoder end uses to improve the quality of the output signal at low bit rates.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
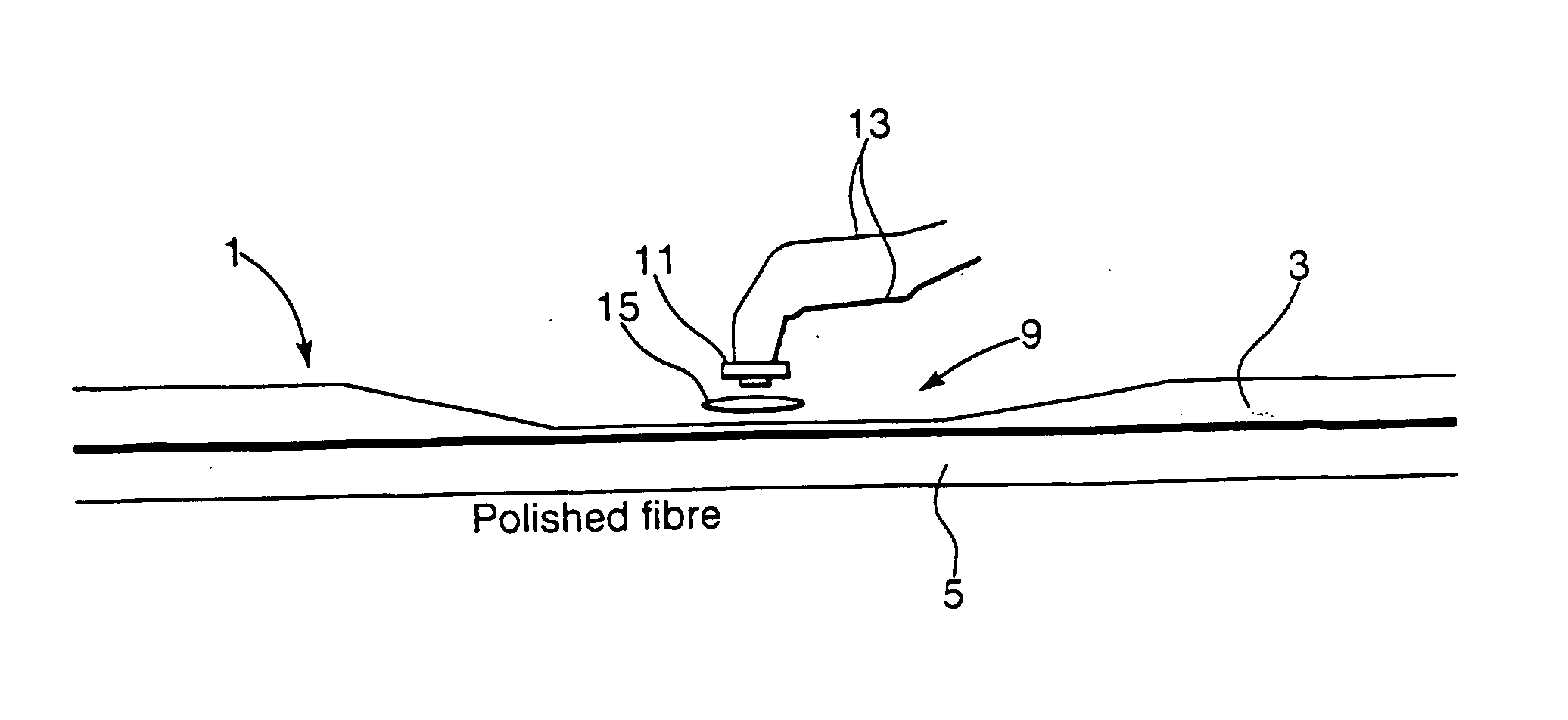
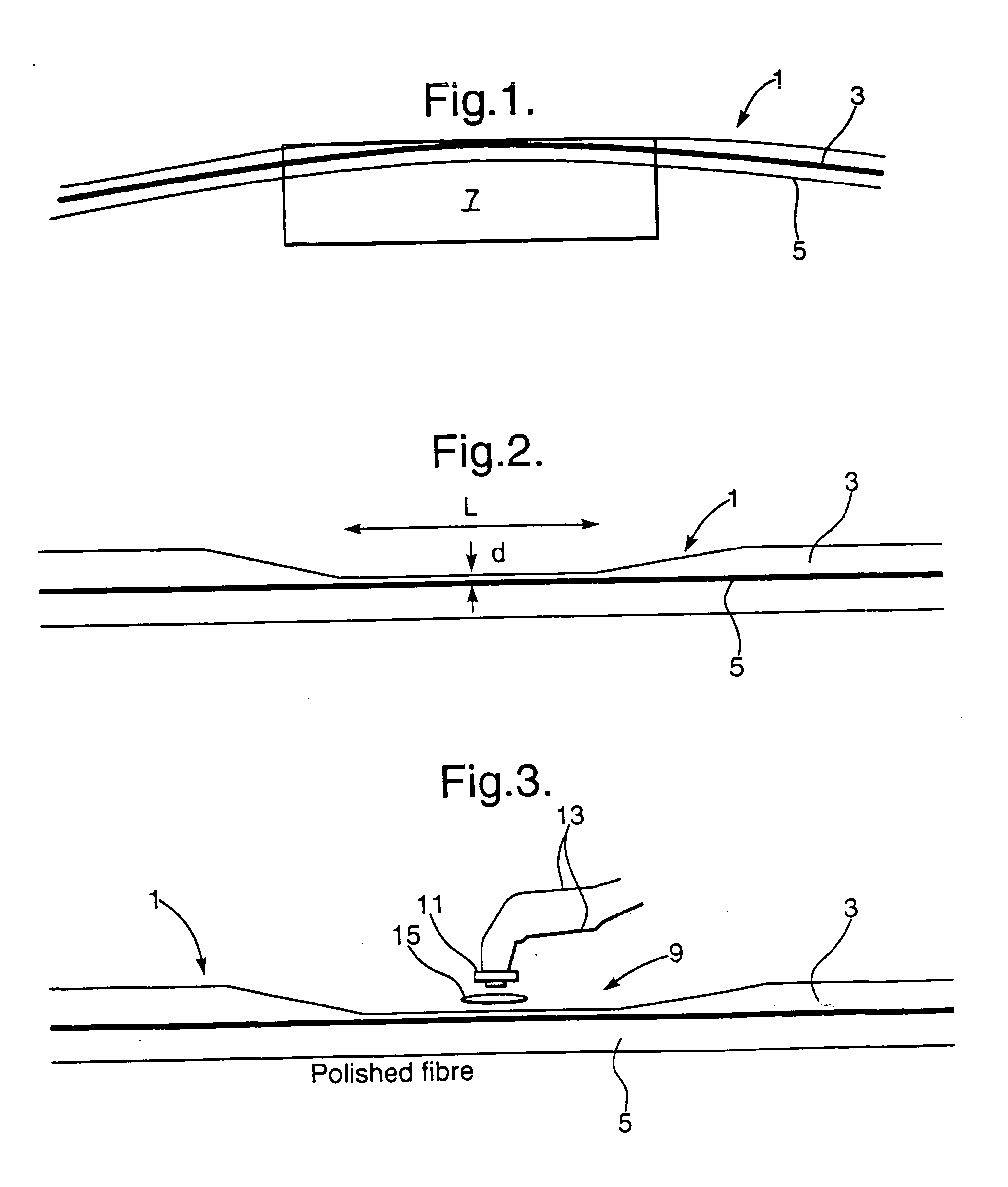
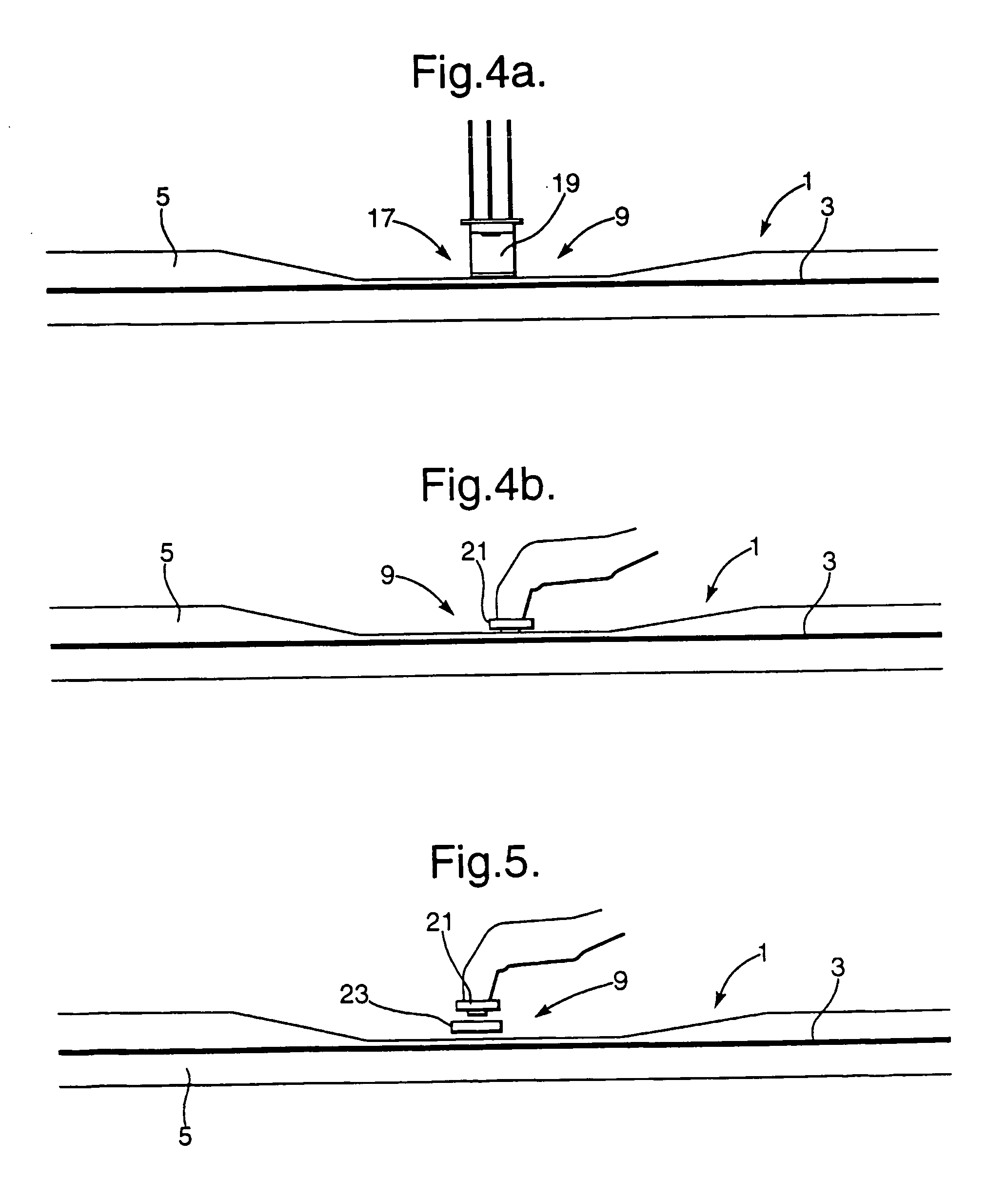
Monitor for an optical fibre and multi-guide optical fibre circuits and methods of making them
InactiveUS20050074208A1Easy to controlHigh yield preparationOptical measurementsCoupling light guidesEngineeringEvanescent wave
The invention relates to a monitor for monitoring at least one optical signal parameter in an opticl fibre having an access region of reduced cladding sufficient to allow access to the evanescent field. The monitor includes an optical element mountable adjacent to the access region of an optical fibre which optical element is capable of obtaining access to the evanescent field to enable use of the data therein to derive the at least one optical signal parameter.
Owner:BADCOCK RODNEY +2
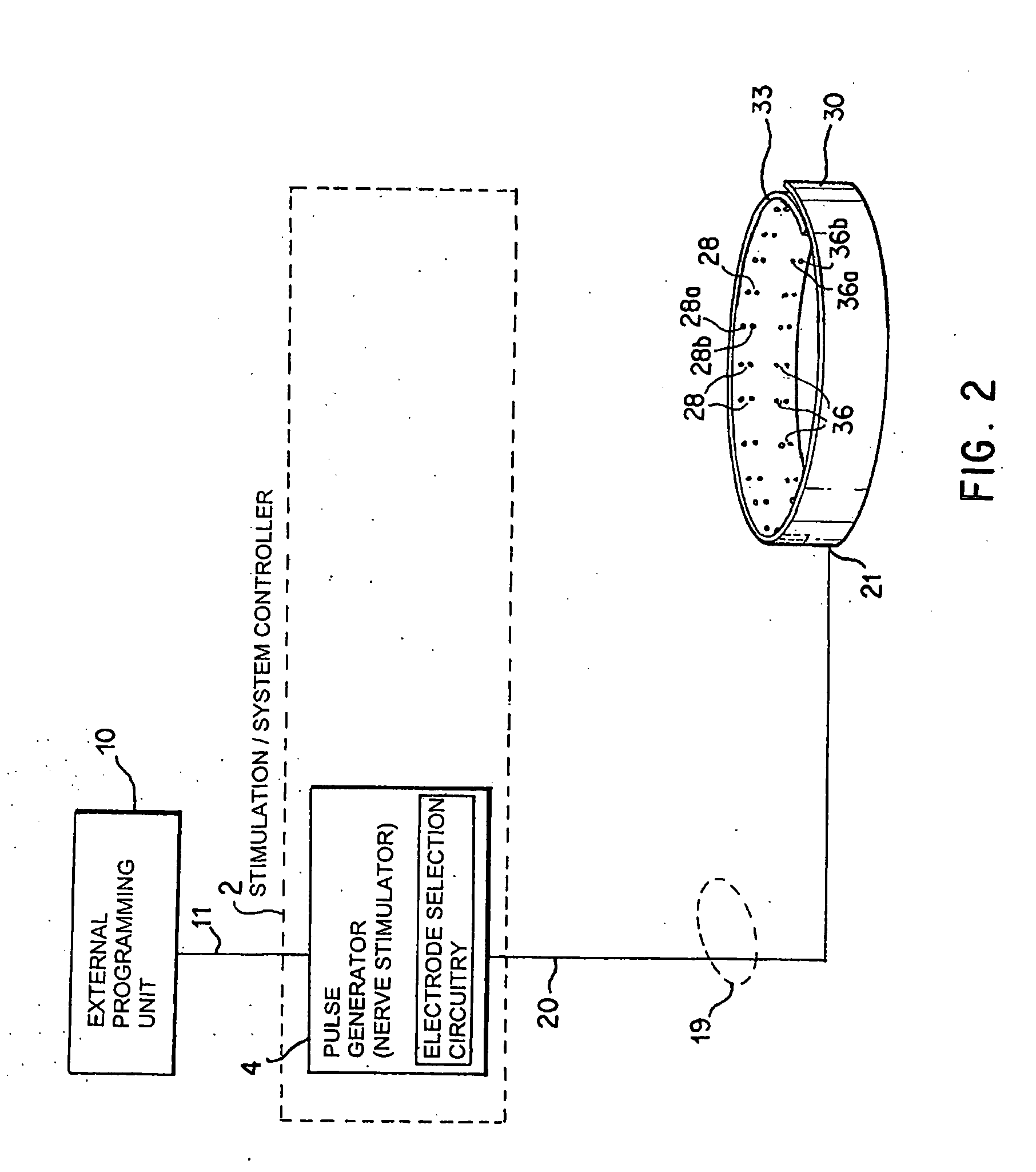
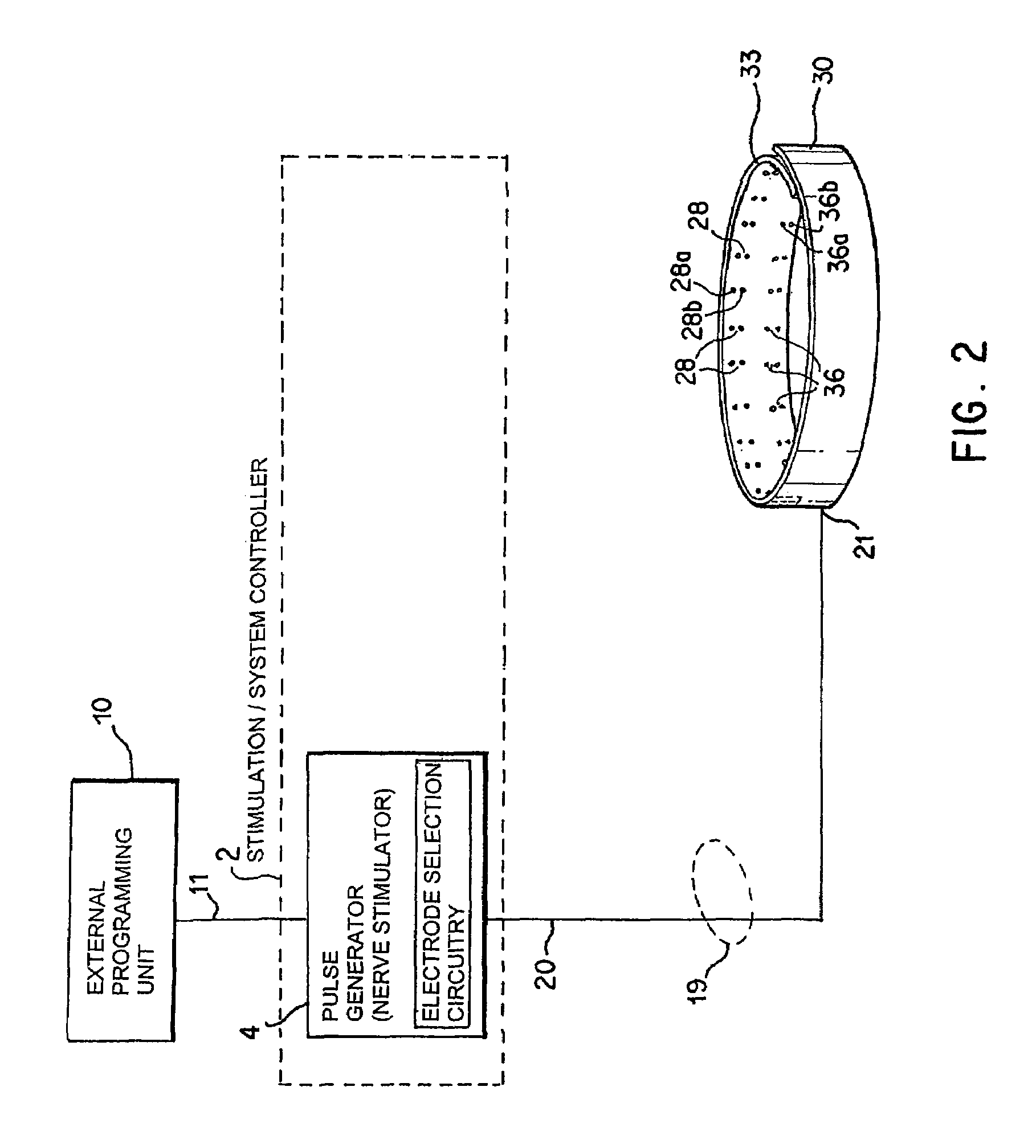
Selective stimulation systems and signal parameters for medical conditions
Devices, systems and methods are provided for targeted treatment of a variety of conditions, particularly conditions that are associated with or influenced by the nervous system, such as pain. Targeted treatment of such conditions is provided with minimal deleterious side effects, such as undesired motor responses or undesired stimulation of unaffected body regions. This is achieved by directly neuromodulating a target anatomy associated with the condition while minimizing or excluding undesired neuromodulation of other anatomies.
Owner:TC1 LLC
Location estimation in wireless telecommunication networks
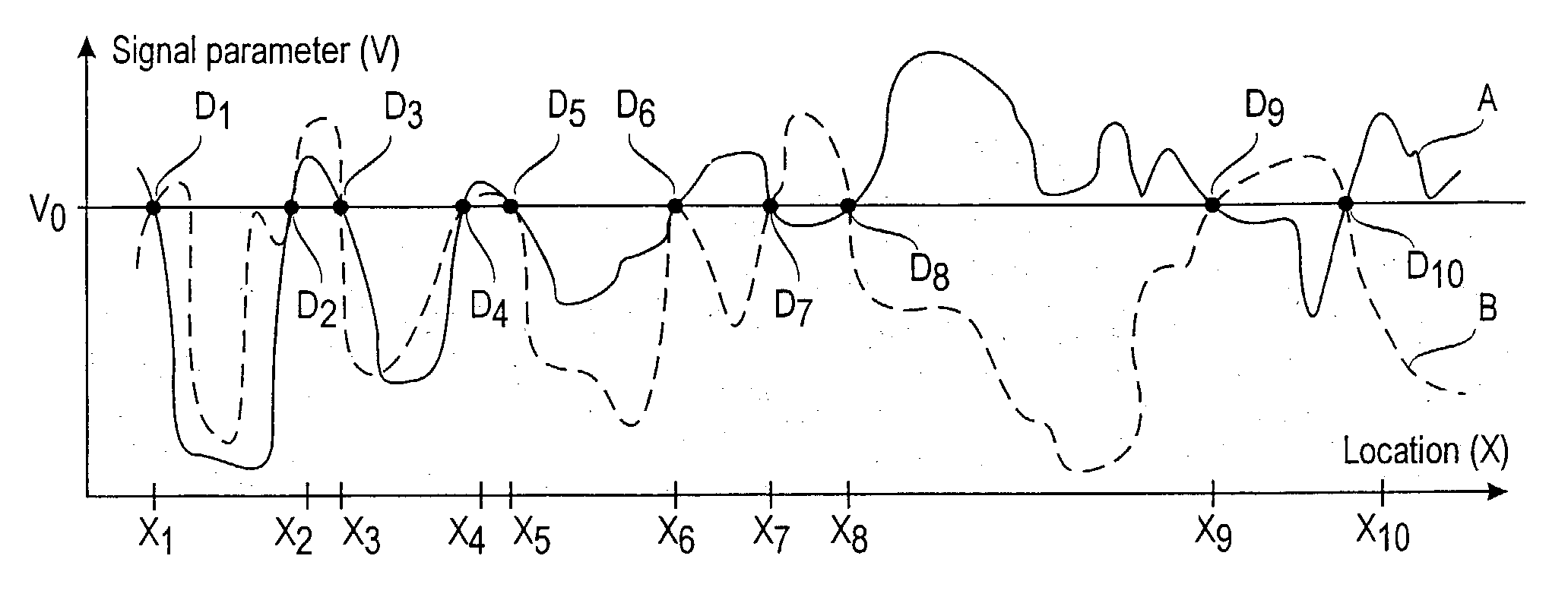
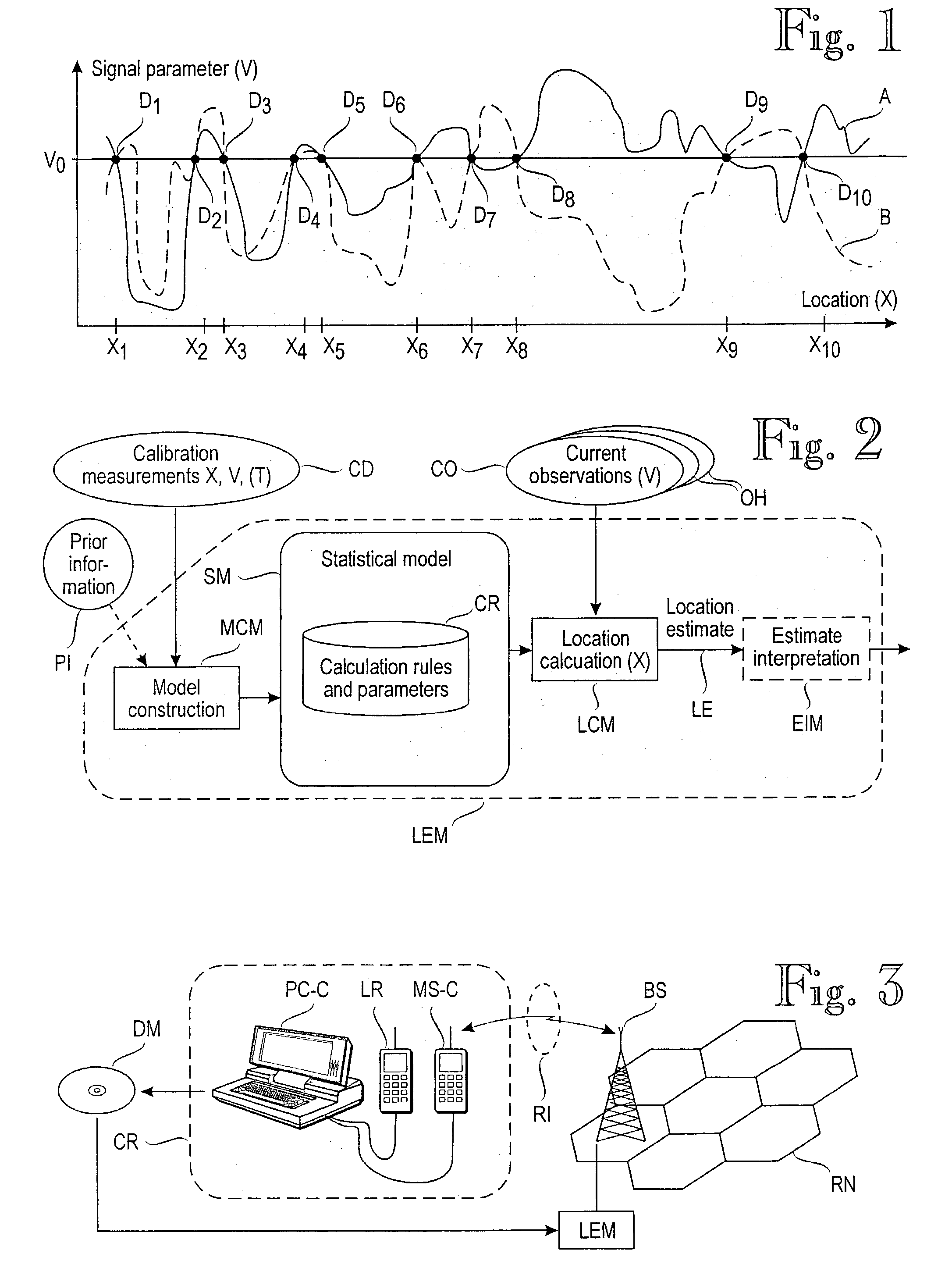
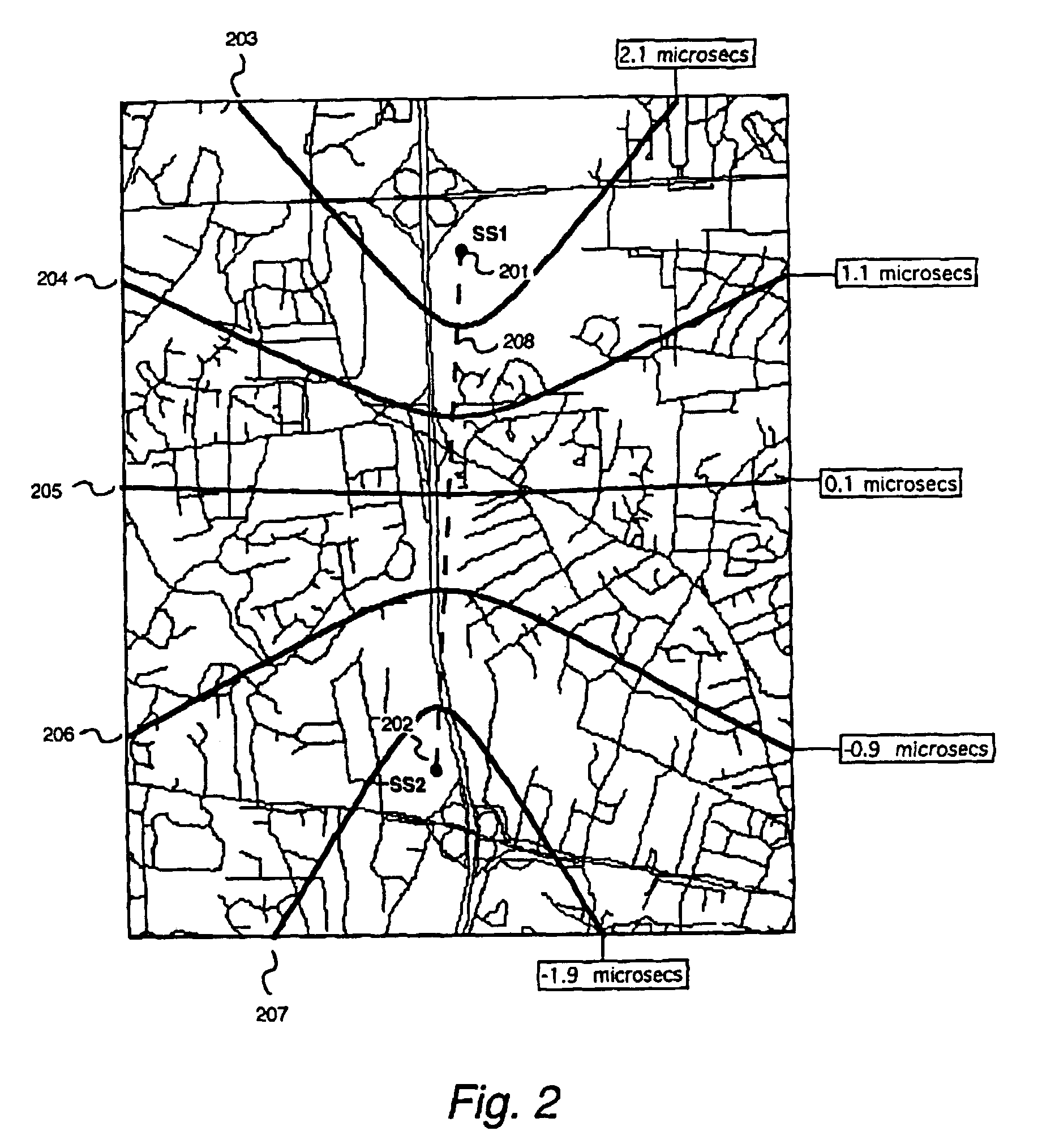
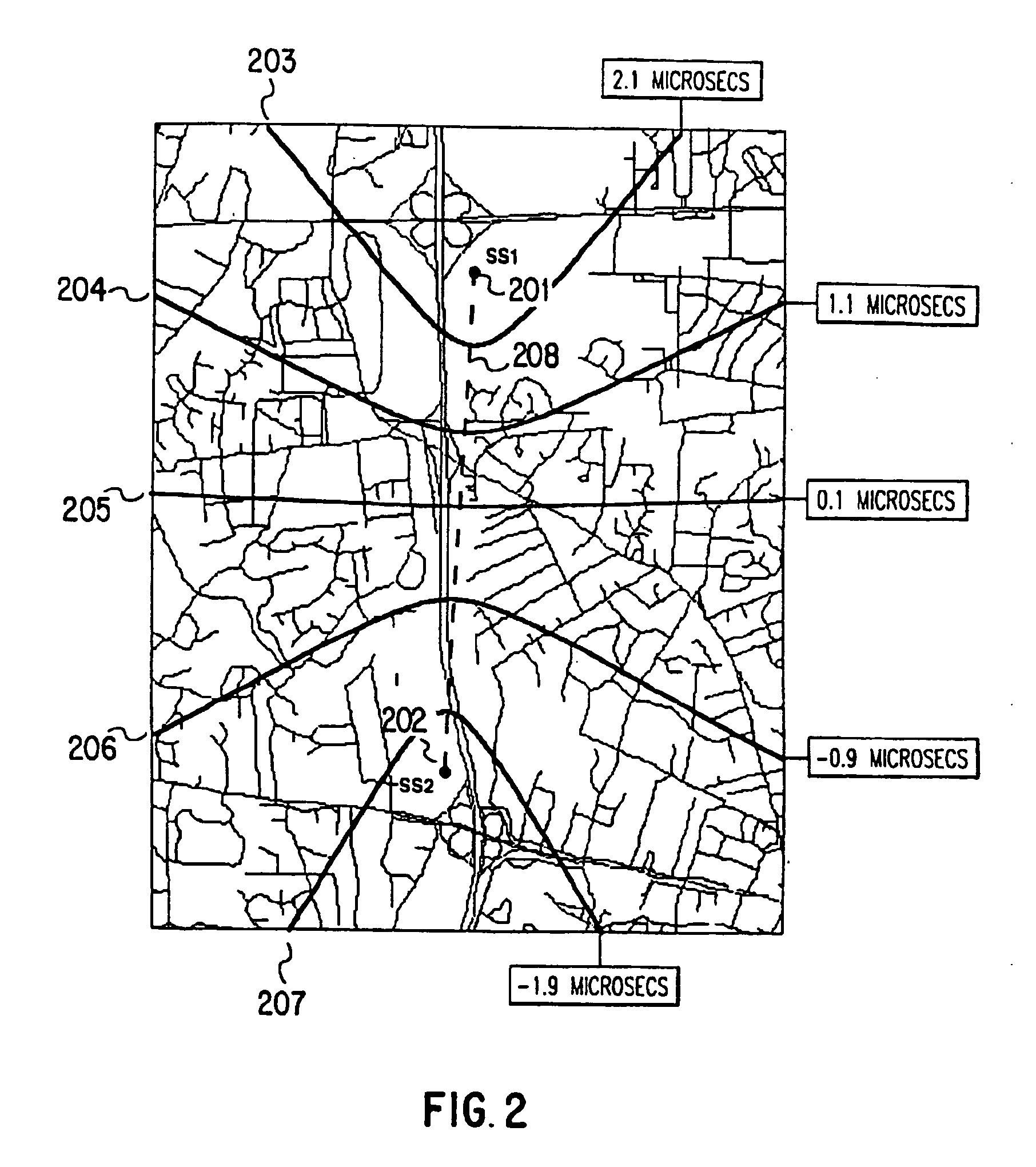
A method for estimating a receiver's location in a wireless communication environment having several channels. Each channel has at least one signal parameter that varies with location differently from the other channels. A set of calibration data is determined for each calibration point, each set including the location and at least one measured signal parameter for each of several channels. The calibration data serve as a basis for a statistical model of the signal parameters versus a receiver's location. A set of observed signal parameters is determined, the set including at least one signal parameter for each of several channels at the receiver's location. A location estimate approximating the location of the receiver is determined on the basis of the statistical model and the set of observed signal parameters.
Owner:AIRWAVE LOCATION TECH LLC
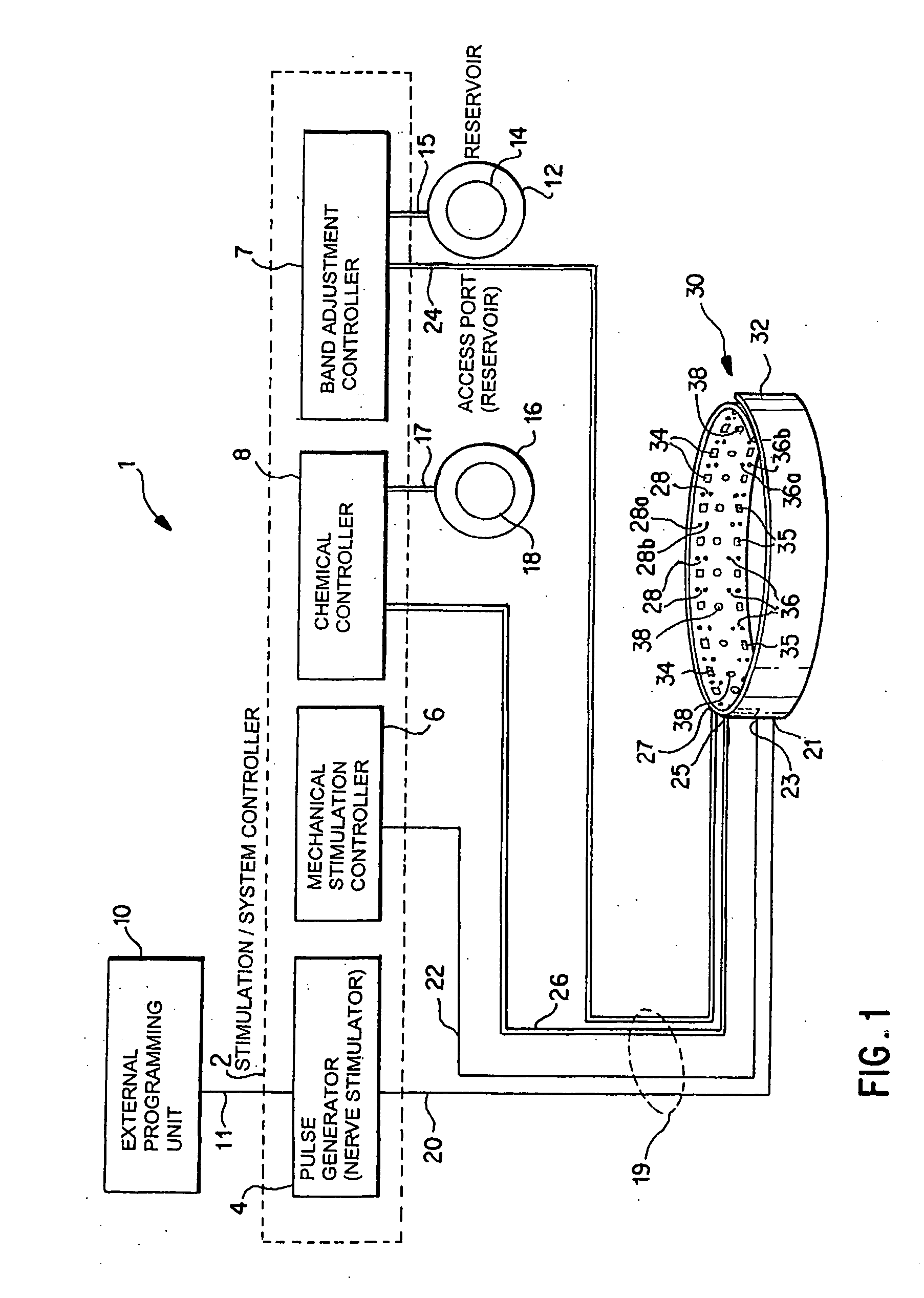
Identification of electrodes for nerve stimulation in the treatment of eating disorders
A method and apparatus for treatment of an eating disorder includes electrically, mechanically and / or pharmaceutically / chemically stimulating a of the vagus nerve of the lower esophagus, cardia, esophageal / cardia junction, cardia / fundus junction or upper stomach so as to induce afferent action potentials on the vagus nerve. The device may be noninvasively adjusted after implantation to provide increased or decreased restriction on the patient's gastrointestinal tract. Each stimulus may be administered as a series of programmed pulses of defined amplitude, duration and period, to evoke a responsive signal to the brain by the target nerve, effective for producing a temporary feeling of satiety in the person. An implantable stimulus generator may be operatively coupled to a nerve electrode, pressure device or chemical outlet to apply a defined signal to a selected nerve branch. The implantable stimulus generator is programmable to allow clinician programming of defined signal parameters effective to treat the eating disorder of the patient. Methods are also provided to identify electrodes nearest to a branch of the vagus nerve to apply an electrical stimulation signal with improved efficiency.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
Tracking algorithm
A method of tracking an entity by monitoring a signal, the signal tending to vary spatially and be generally time-invariant, the entity moving from a first location within an area to a second location within the area, the method being suitable for use when the location of the source of the signal is unknown, the method comprising providing a plurality of particles for use with a particle filter, each particle being associated with a first particle location, a first particle location being an estimate of the first location of the entity, providing an estimate of the motion of the entity between the first location and the second location, using the estimate of the motion and using the particle filter, for each particle, updating the first particle location for that particle thereby producing an updated particle location, the updated particle location being an estimate of the second location of the entity, for each updated particle, estimating at least one expected signal parameter at the updated particle location, measuring a signal parameter at the second location of the entity, assigning a weight to each updated particle depending on the expected signal parameter estimated for that particle and the measured signal parameter, estimating the second location of the entity by determining a function of the weighted updated particles, and inputting the estimated location and measured signal parameter, as a location / parameter data set, to a database.
Owner:BAE SYSTEMS PLC
Adaptive compression and decompression of bandlimited signals
InactiveUS7009533B1Less bandwidthLess storageCode conversionPictoral communicationAdaptive compressionSpectrum analyzer
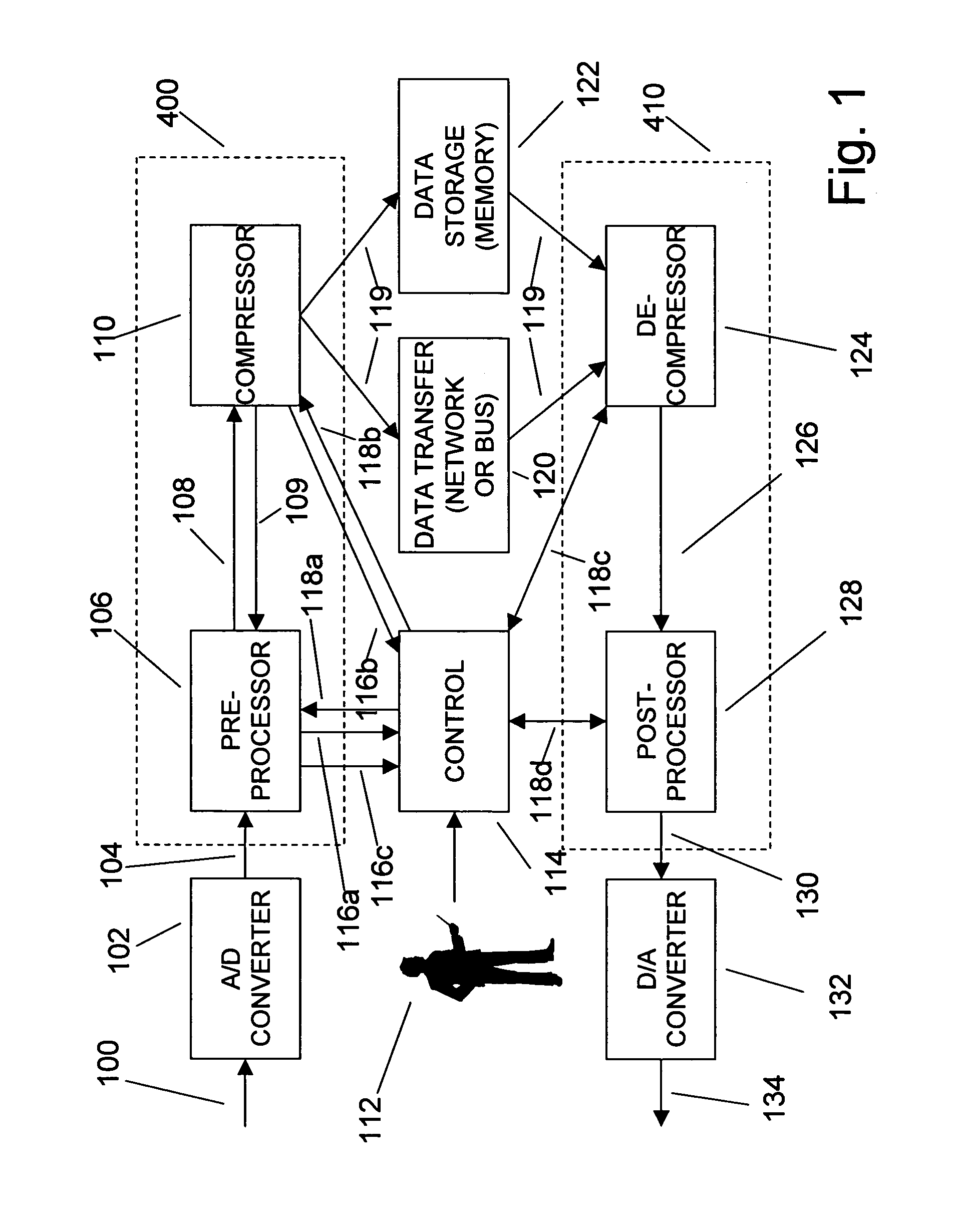
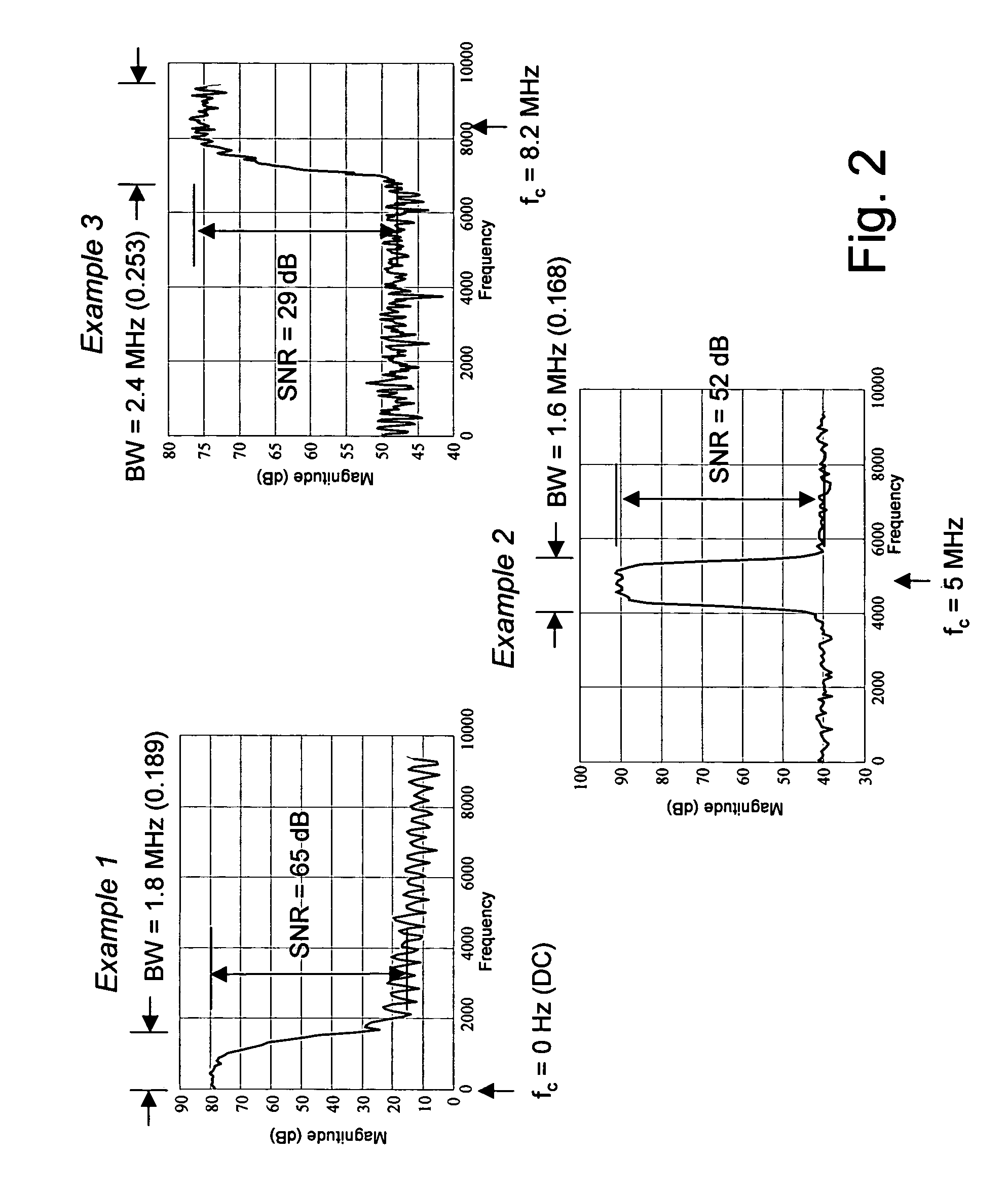
An efficient method for compressing sampled analog signals in real time, without loss, or at a user-specified rate or distortion level, is described. The present invention is particularly effective for compressing and decompressing high-speed, bandlimited analog signals that are not appropriately or effectively compressed by prior art speech, audio, image, and video compression algorithms due to various limitations of such prior art compression solutions. The present invention's preprocessor apparatus measures one or more signal parameters and, under program control, appropriately modifies the preprocessor input signal to create one or more preprocessor output signals that are more effectively compressed by a follow-on compressor. In many instances, the follow-on compressor operates most effectively when its input signal is at baseband. The compressor creates a stream of compressed data tokens and compression control parameters that represent the original sampled input signal using fewer bits. The decompression subsystem uses a decompressor to decompress the stream of compressed data tokens and compression control parameters. After decompression, the decompressor output signal is processed by a post-processor, which reverses the operations of the preprocessor during compression, generating a postprocessed signal that exactly matches (during lossless compression) or approximates (during lossy compression) the original sampled input signal. Parallel processing implementations of both the compression and decompression subsystems are described that can operate at higher sampling rates when compared to the sampling rates of a single compression or decompression subsystem. In addition to providing the benefits of real-time compression and decompression to a new, general class of sampled data users who previously could not obtain benefits from compression, the present invention also enhances the performance of test and measurement equipment (oscilloscopes, signal generators, spectrum analyzers, logic analyzers, etc.), busses and networks carrying sampled data, and data converters (A / D and D / A converters).
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Scalable and embedded codec for speech and audio signals
InactiveUS20080052068A1Improve reconstruction accuracySpeech analysisMultiple modesCommunication device
A system and method for processing of audio and speech signals is disclosed, which provide compatibility over a range of communication devices operating at different sampling frequencies and / or bit rates. The analyzer of the system divides the input signal in different portions, at least one of which carries information sufficient to provide intelligible reconstruction of the input signal. The analyzer also encodes separate information about other portions of the signal in an embedded manner, so that a smooth transition can be achieved from low bit-rate to high bit-rate applications. Accordingly, communication devices operating at different sampling rates and / or bit-rates can extract corresponding information from the output bit stream of the analyzer. In the present invention embedded information generally relates to separate parameters of the input signal, or to additional resolution in the transmission of original signal parameters. Non-linear techniques for enhancing the overall performance of the system are also disclosed. Also disclosed is a novel method of improving the quantization of signal parameters. In a specific embodiment the input signal is processed in two or more modes dependent on the state of the signal in a frame. When the signal is determined to be in a transition state, the encoder provides phase information about N sinusoids, which the decoder end uses to improve the quality of the output signal at low bit rates.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
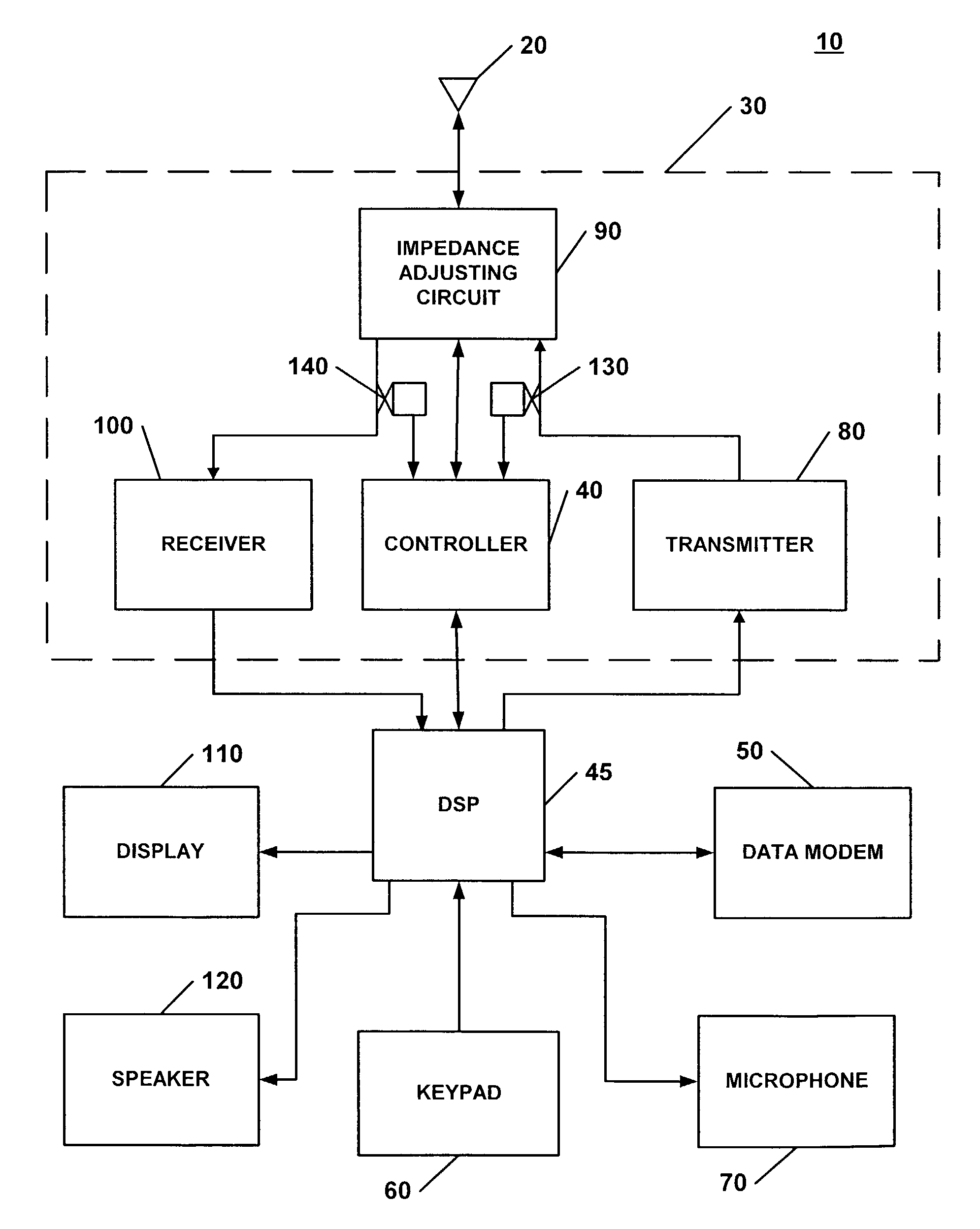
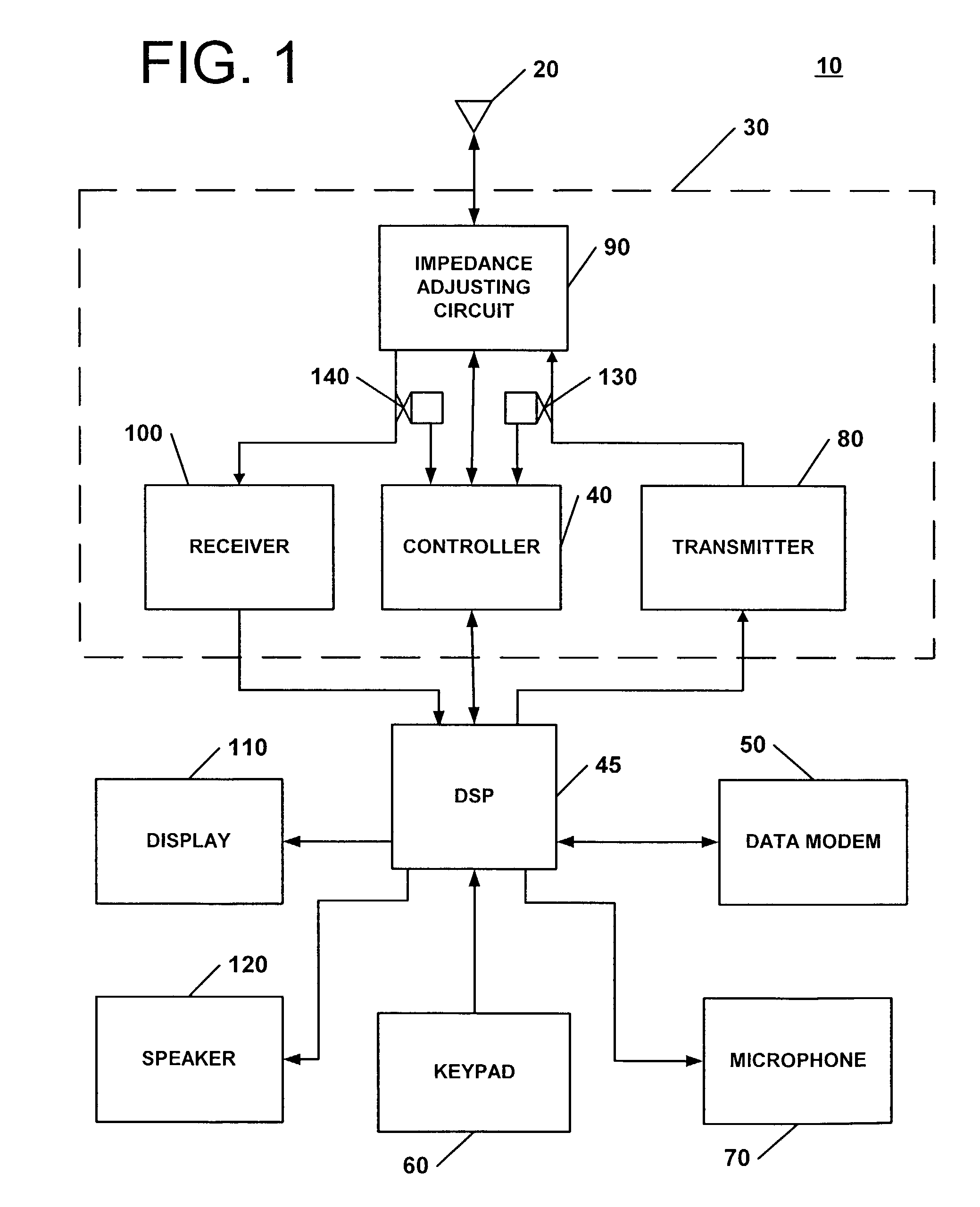
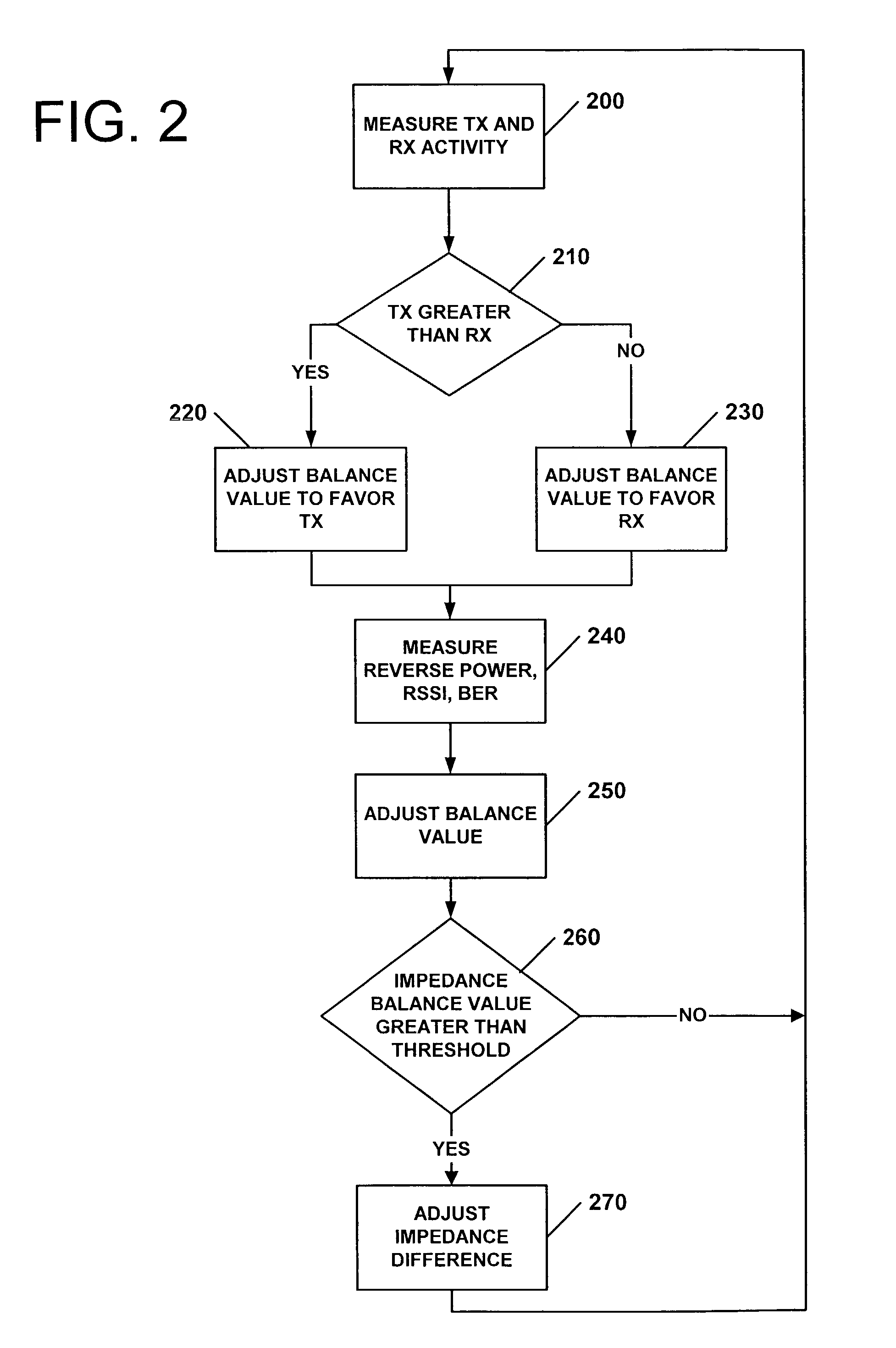
Apparatus and methods for tuning antenna impedance using transmitter and receiver parameters
InactiveUS6993297B2Reduce presented impedance differenceReduce impedance differenceMultiple-port networksResonant long antennasAntenna impedanceControl signal
According to some embodiments of the present invention, an impedance transformation circuit is provided for use with a transmitter, a receiver, and an antenna. The transmitter may provide transmission signals for transmission by the antenna. The antenna may provide received signals having an associated signal parameter to the receiver. The impedance transformation circuit includes an impedance adjusting circuit and a controller. The impedance adjusting circuit is connected between the antenna, the receiver, and the transmitter. The impedance adjusting circuit is configured to change an impedance difference presented between at least one of: 1) the transmitter and the antenna, and 2) the antenna and the receiver, in response to a control signal. The controller generates the control signal to change the presented impedance difference in response to a signal parameter.
Owner:SONY ERICSSON MOBILE COMM AB
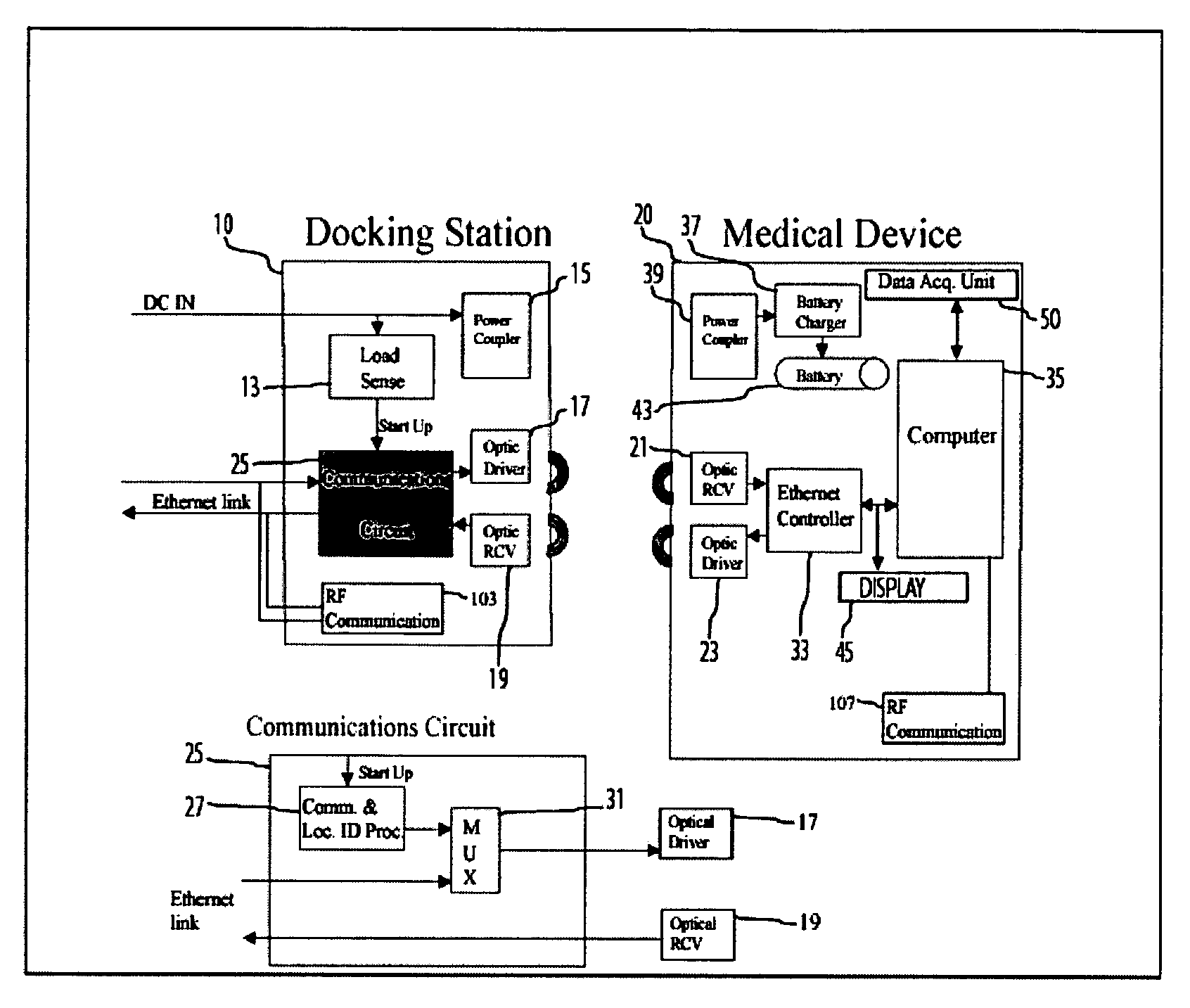
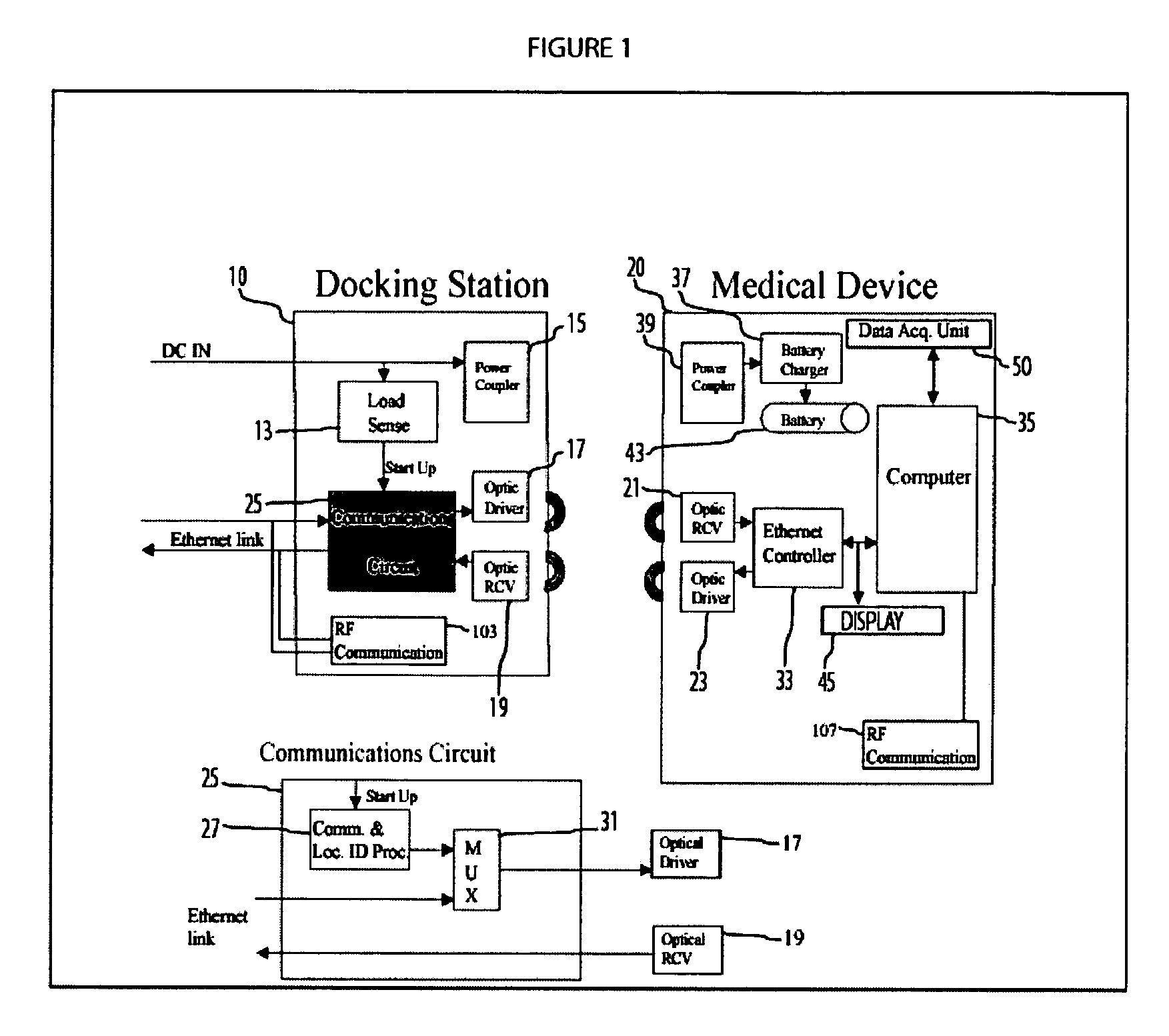
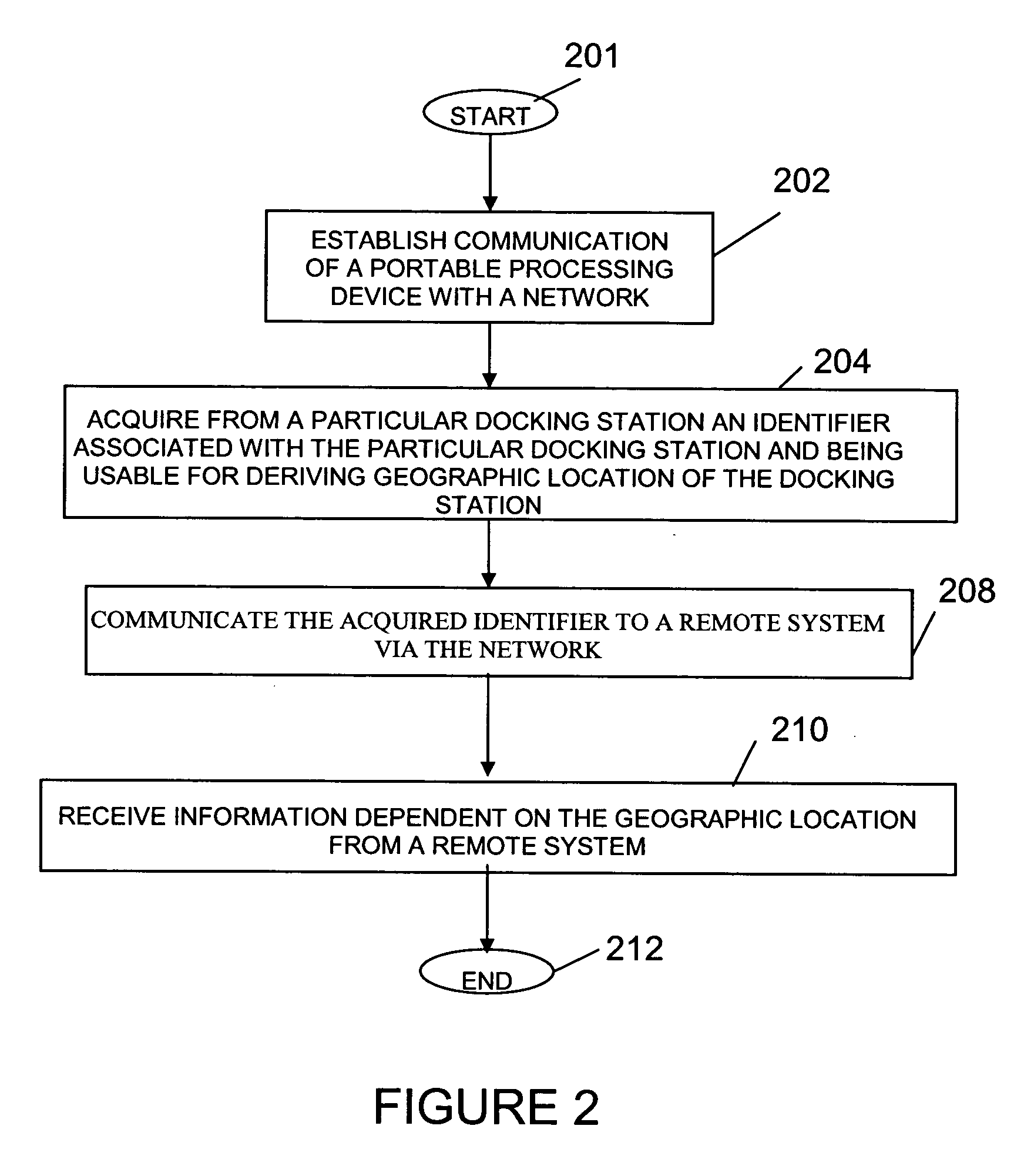
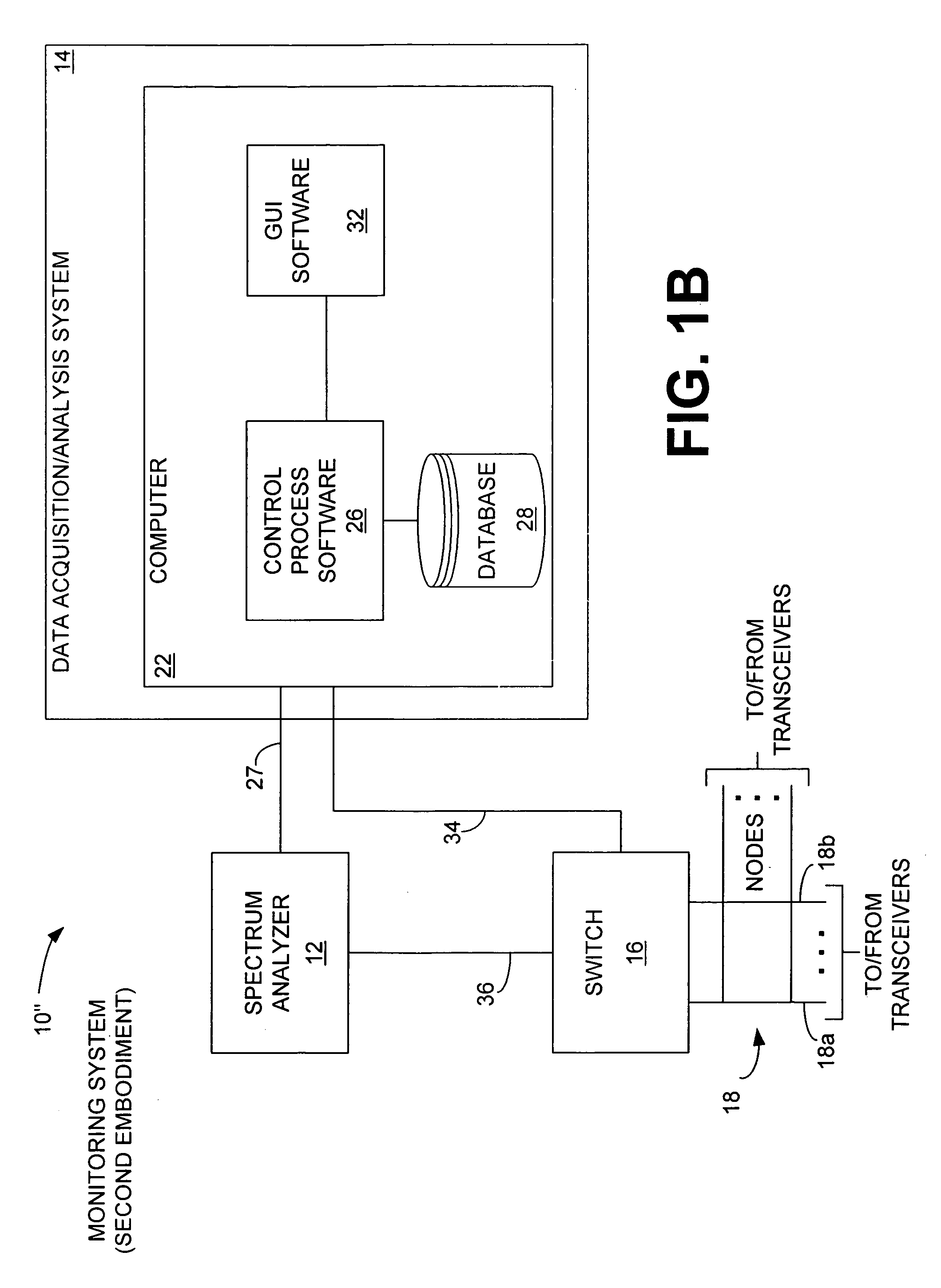
Portable patient monitoring system including location identification capability
ActiveUS20050033124A1Engagement/disengagement of coupling partsSurgeryDocking stationMonitoring system
A docking station advantageously provides a location identifier to a portable processing device which processes the location identifier to determine docking station location (and other information) and to upload settings and configuration information related to an identified location which is retained until a different docking station location is encountered. In a system for use in a docking station suitable for attaching to a portable patient monitoring device for processing signal parameters acquired from a patient, a power coupler couples power to provide electrical power to a portable processing device. An adaptive communication interface, in a first mode of operation, communicates an identifier associated with a particular docking station to the portable processing device, and in a second mode of operation, establishes connection of the portable processing device to a network.
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
Selective nerve stimulation for the treatment of eating disorders
ActiveUS20070027498A1Avoid problemsConvenient treatmentHead electrodesMedical devicesRegimenMedicine
A method and apparatus for treating persons suffering from an eating disorder includes direct or indirect stimulation of selected areas of the brain associated with a symptom of the eating disorder. The stimulation regimen is programmable to enable physician optimization of stimulation signal parameters to ameliorate at least one symptom of bulimia or another eating disorder. Certain embodiments employ deep brain stimulation and / or sensing together with cranial nerve stimulation and / or sensing.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
Identification of electrodes for nerve stimulation in the treatment of eating disorders
A method and apparatus for treatment of an eating disorder includes electrically, mechanically and / or pharmaceutically / chemically stimulating a of the vagus nerve of the lower esophagus, cardia, esophageal / cardia junction, cardia / fundus junction or upper stomach so as to induce afferent action potentials on the vagus nerve. The device may be noninvasively adjusted after implantation to provide increased or decreased restriction on the patient's gastrointestinal tract. Each stimulus may be administered as a series of programmed pulses of defined amplitude, duration and period, to evoke a responsive signal to the brain by the target nerve, effective for producing a temporary feeling of satiety in the person. An implantable stimulus generator may be operatively coupled to a nerve electrode, pressure device or chemical outlet to apply a defined signal to a selected nerve branch. The implantable stimulus generator is programmable to allow clinician programming of defined signal parameters effective to treat the eating disorder of the patient. Methods are also provided to identify electrodes nearest to a branch of the vagus nerve to apply an electrical stimulation signal with improved efficiency.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
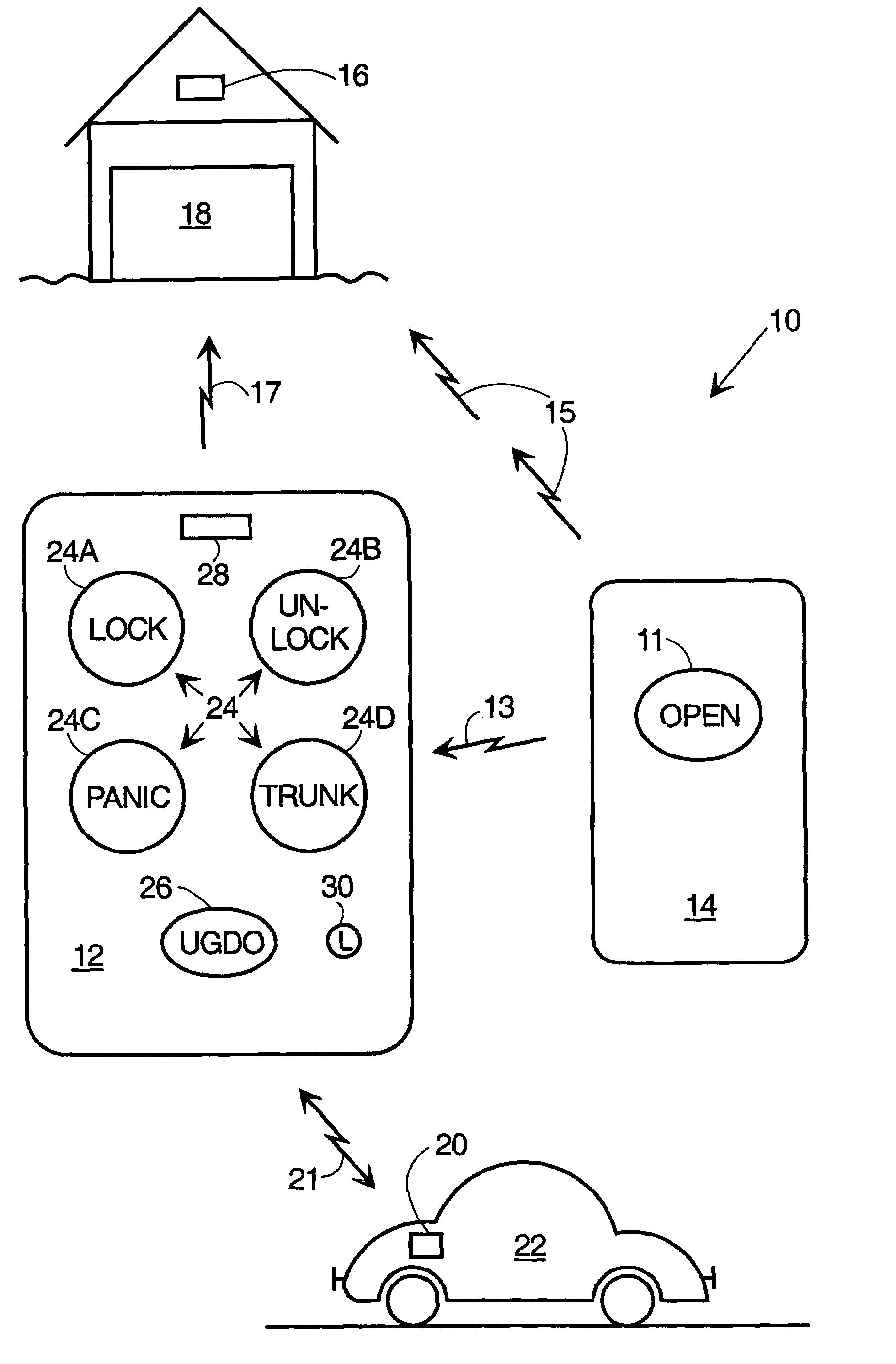
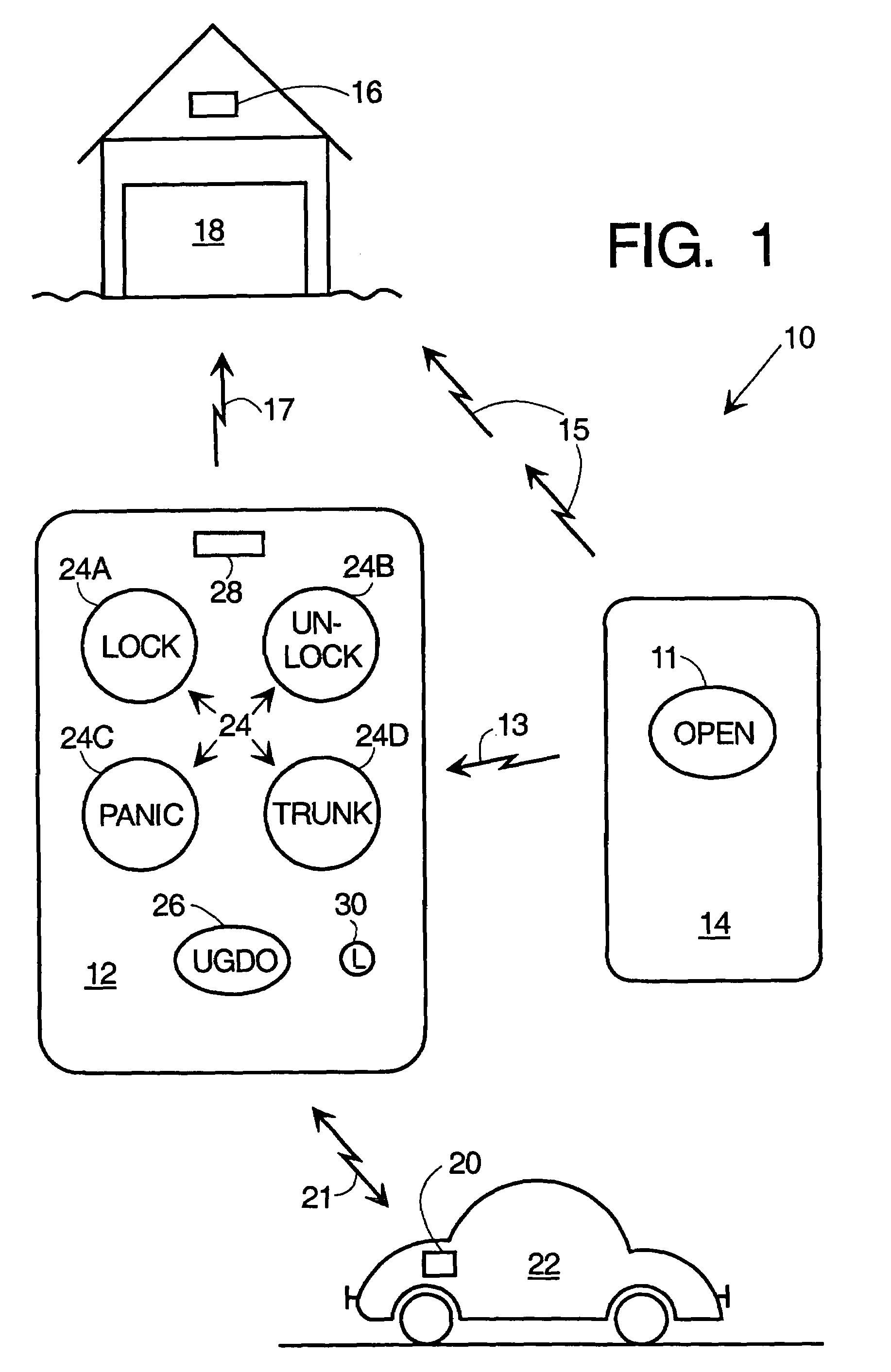
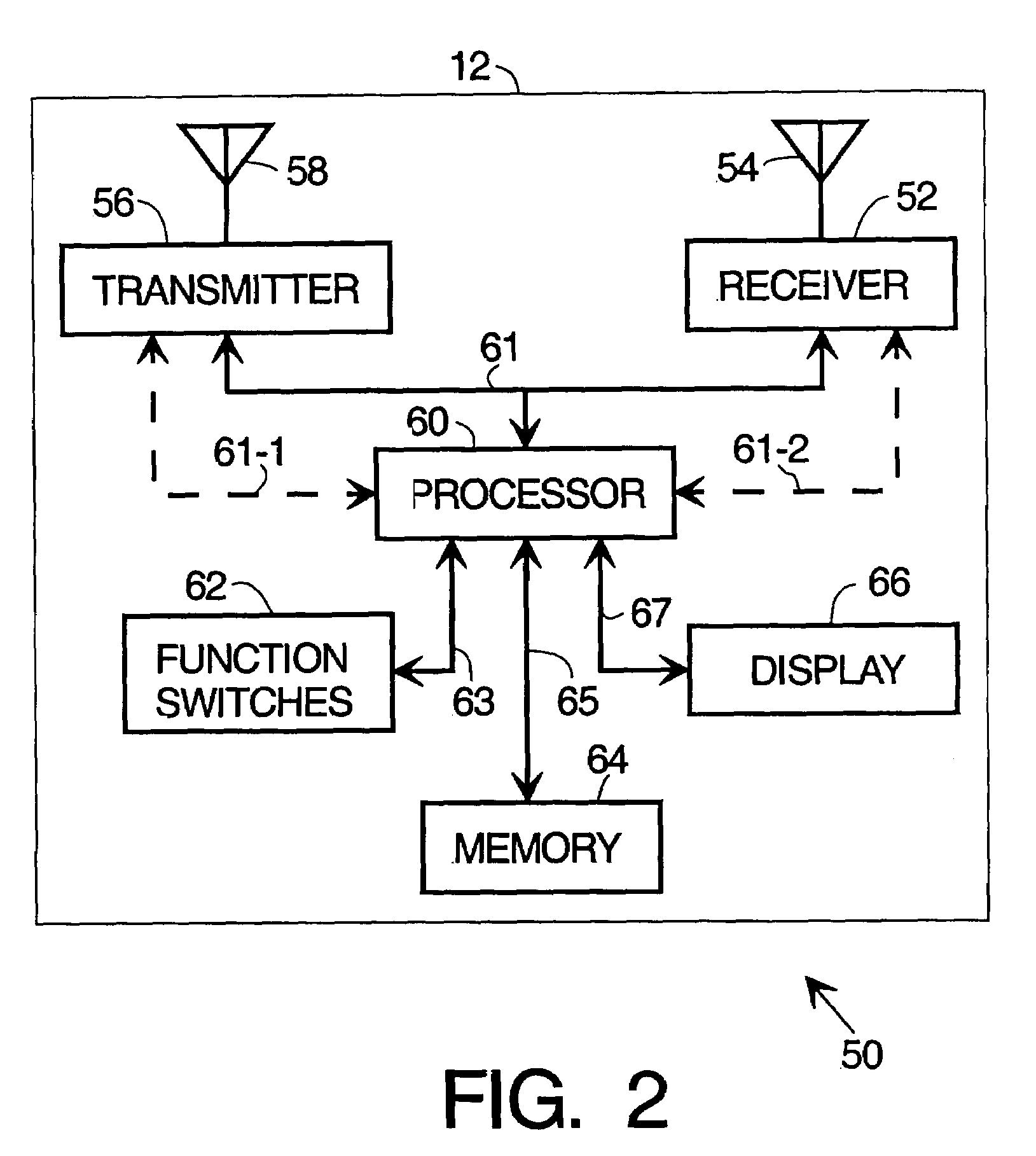
Combined garage door and keyless entry fob
InactiveUS7215238B2Digital data processing detailsAnti-theft devicesElectronic systemsDisplay device
Methods and apparatus are provided for a combined vehicle keyless entry and garage door (GD) opener fob. The fob comprises a receiver, transmitter, processor, memory, user activated function switches, and preferably a display. In a GD function learn mode, the fob memorizes the signal parameters of a GD activate signal received directly from a nearby GD opener. In the normal GD operate mode, the fob transmits a replica of the GD activate signal using the learned signal parameters stored in the memory. The optional display preferably tells the user that the learn mode is active, prompts the user to operate the nearby GD opener during the learn mode, indicates whether the learn operation was successful or not and shows when the fob has returned to normal (non-learn mode) operation. The GD modes of the fob are entirely self-contained and do not depend upon the vehicle electronics system.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
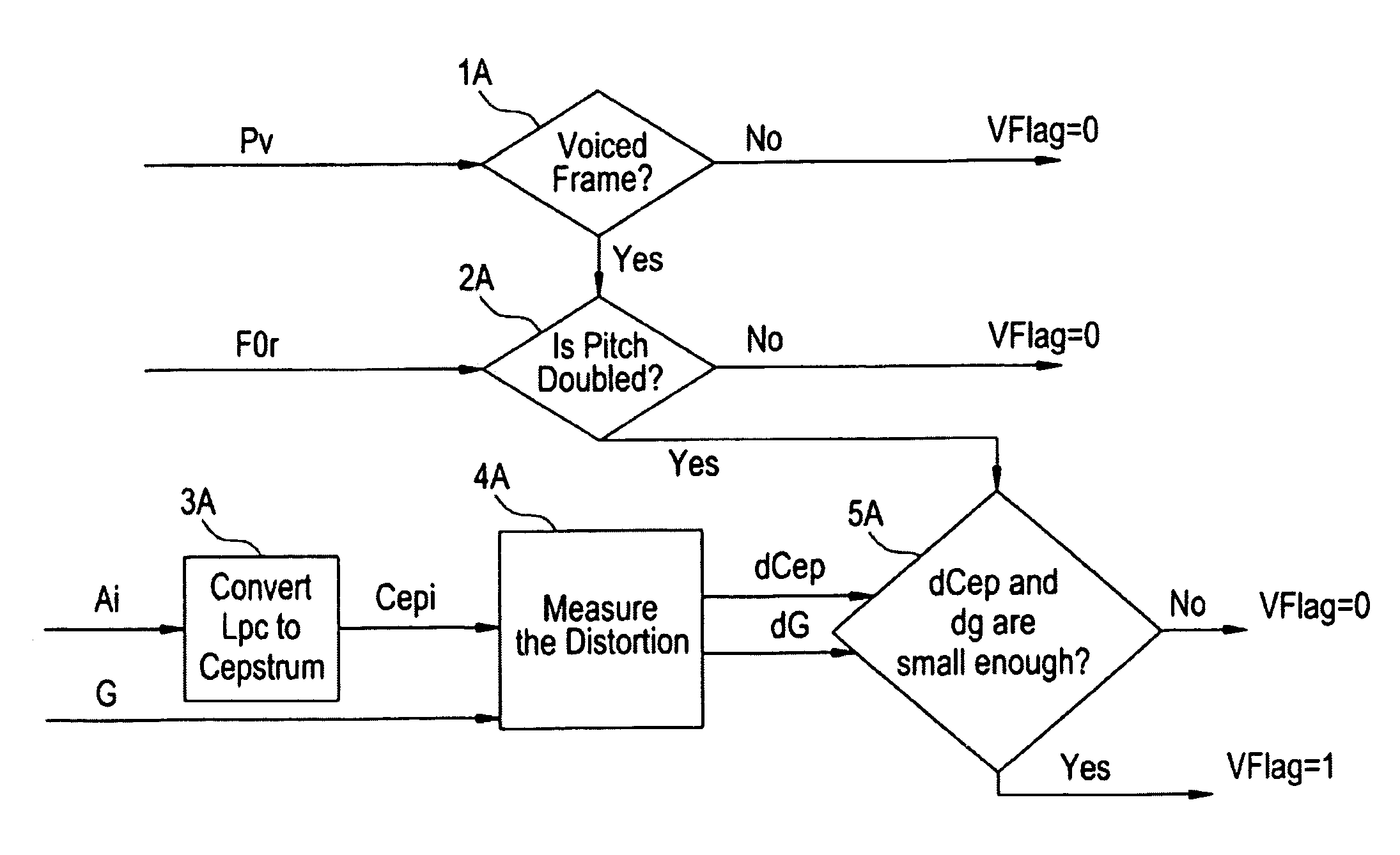
Method and an apparatus for voice activity detection
InactiveUS20120232896A1Easy to adaptFast processingSpeech recognitionDecision combinationSpeech sound
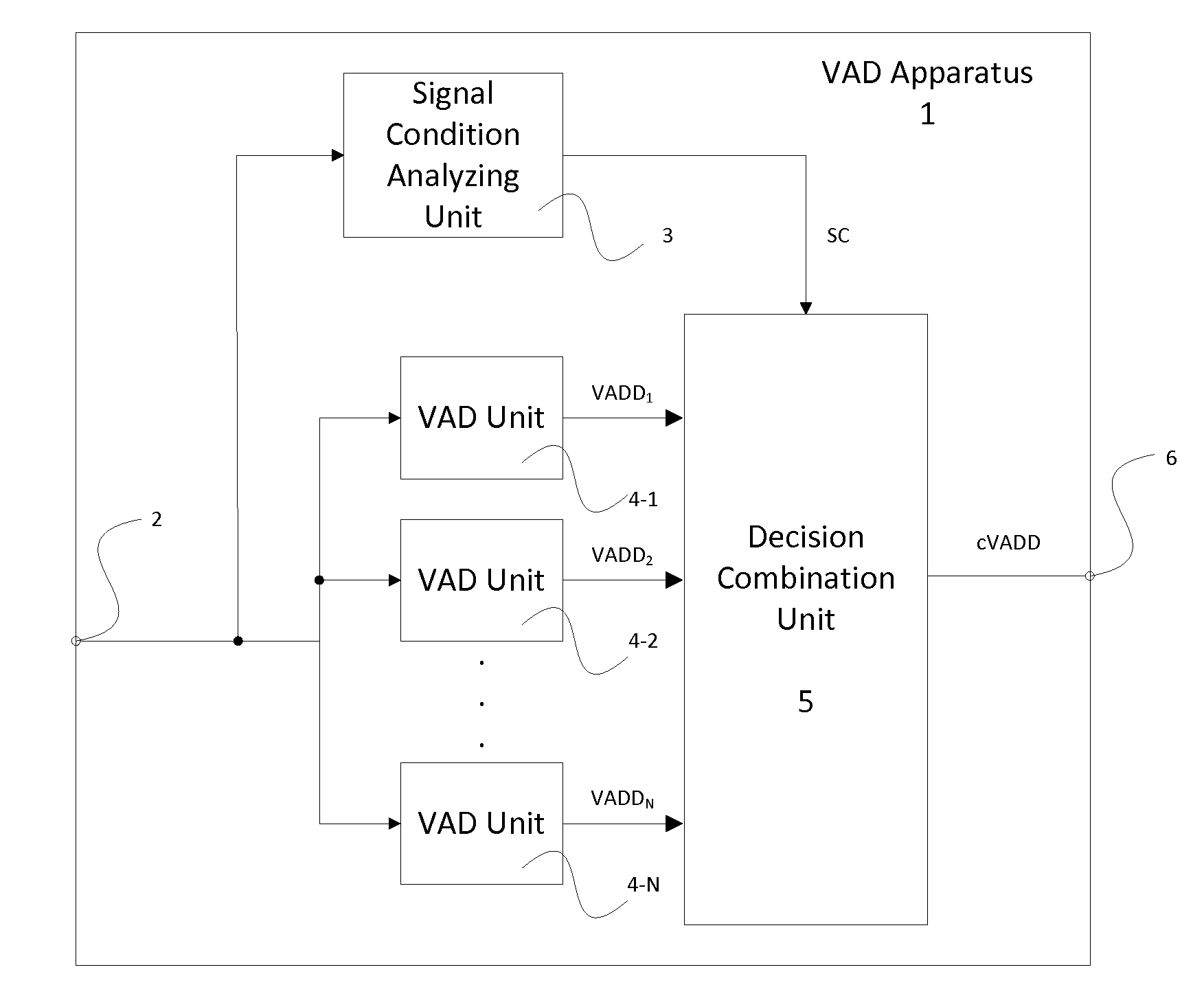
A voice activity detection apparatus (1) comprising: a signal condition analyzing unit (3) which analyses at least one signal parameter of an input signal to detect a signal condition SC of said input signal; at least two voice activity detection units (4-i) comprising different voice detection characteristics, wherein each voice activity detection unit (4-i) performs separately a voice activity detection of said input signal to provide a voice activity detection decision VADD; and a decision combination unit (5) which combines the voice activity detection decisions VADDs provided by said voice activity detection units (4-i) depending on the detected signal condition SC to provide a combined voice activity detection decision cVADD.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Monitoring system and method implementing failure time spectrum scan
InactiveUS7003414B1Spectral/fourier analysisTwo-way working systemsFrequency spectrumSpectrum analyzer
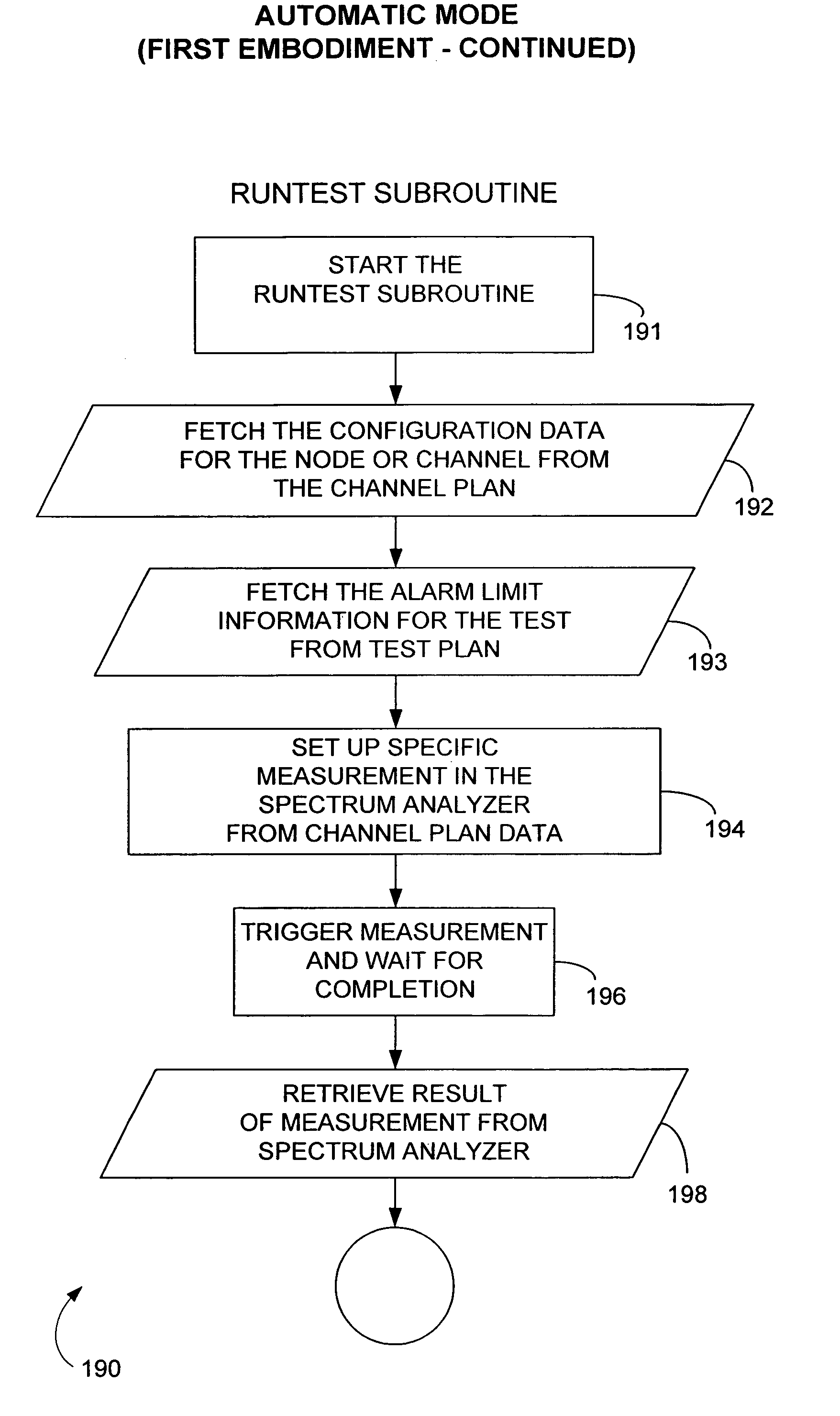
A channel plan with a corresponding test plan are implemented in connection with a plurality of nodes that communicate signals. The channel plan has one or more predefined specifications for each of one or more signal channels on each of the nodes. The channel plan enables a monitoring system to, among other things, conduct automatic periodic test plans, comprising tests, on the nodes, based upon the predefined data specified in the channel plan. Each test plan prescribes measurement of at least one signal parameter, pertaining to one or more nodes as a whole and / or to one or more channels contained within the nodes. The monitoring system includes a spectrum analyzer, a switch enabling the spectrum analyzer to interface with the nodes, and a controller controlling the switch and the spectrum analyzer. The controller is configured to enable creation of and display the channel plan and test plan, based upon user inputs. Notably, the controller can be configured to compare results from tests with alarm limits, specified in the test plan, to control the spectrum analyzer to perform a failure time spectrum scan when one or more test results exceed one or more alarm limits, and to generate a plot of power amplitude versus frequency over the frequency spectrum of the node at issue.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
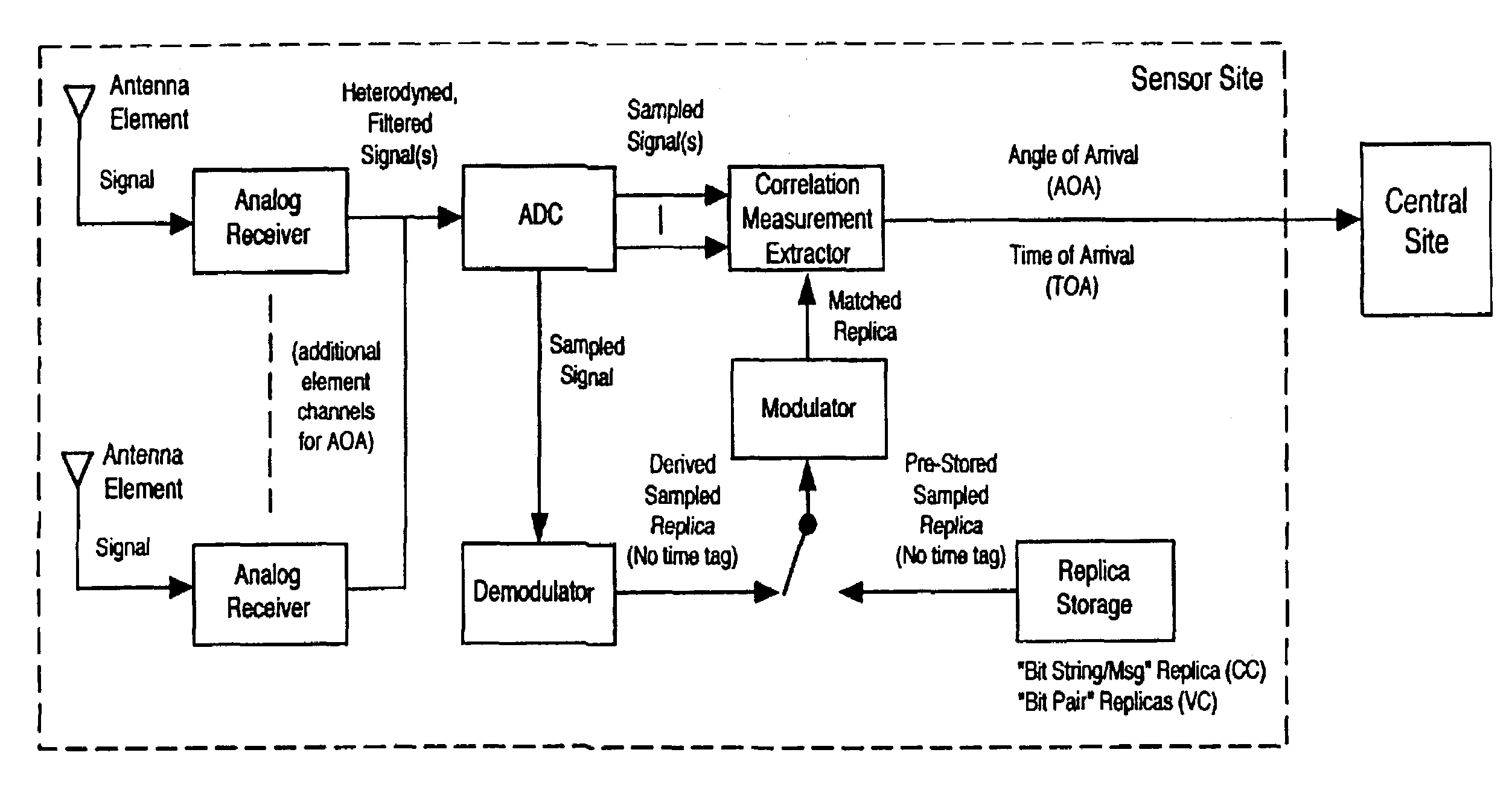
Robust, efficient, localization system
InactiveUS7340259B2Quick responseEasy to measure in real timeDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationLocalization systemCode division multiple access
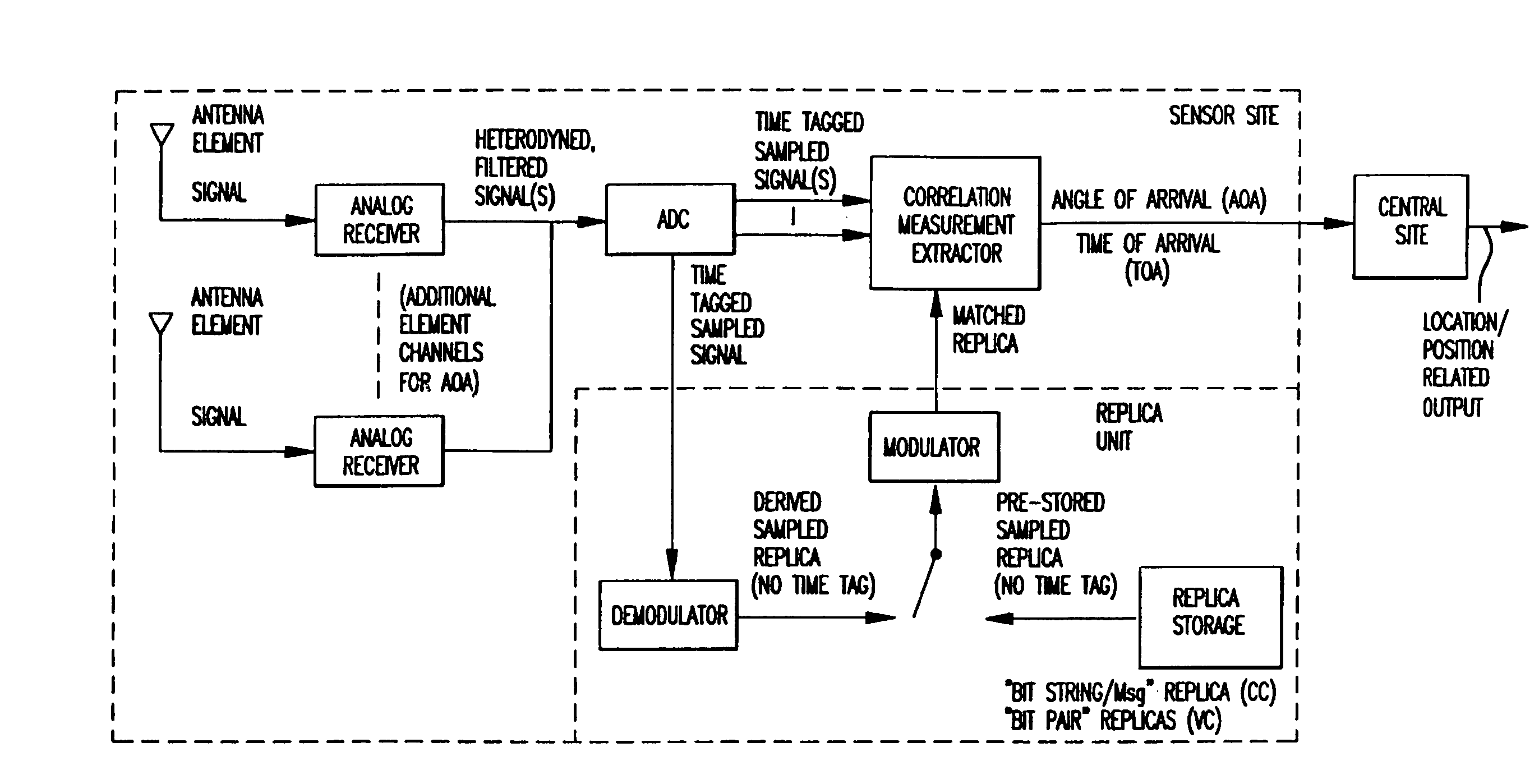
Replica correlation processing, and associated representative signal-data reduction and reconstruction techniques, are used to detect signals of interest and obtain robust measures of received-signal parameters, such as time differences of signal arrival and directional angles of arrival, that can be used to estimate the location of a cellularized-communications signal source. The new use in the present invention of signal-correlation processing for locating communications transmitters. This enables accurate and efficient extraction of parameters for a particular signal even in a frequency band that contains multiple received transmissions, such as occurs with code-division-multiple-access (CDMA) communications. Correlation processing as disclosed herein further enables extended processing integration times to facilitate the effective detection of desired communications-signal effects and replication measurement of their location-related parameters, even for the communications signals modulated to convey voice conversations or those weakened through propagation effects. Using prior, constructed, signal replicas in the correlation processing enables elimination of the inter-site communications of the signal representations that support the correlation analyses. Reduced-data representations of the modulated signals for voiced conversation, or for the variable components of data communications, are used to significantly reduce the inter-site communications that support the correlation analyses.
Owner:TRUE POSITION INC
Bandwidth extension of acoustic signals
InactiveUS20030009327A1Reduce the amount requiredImprove sound qualitySpeech synthesisBandwidth extensionFrequency spectrum
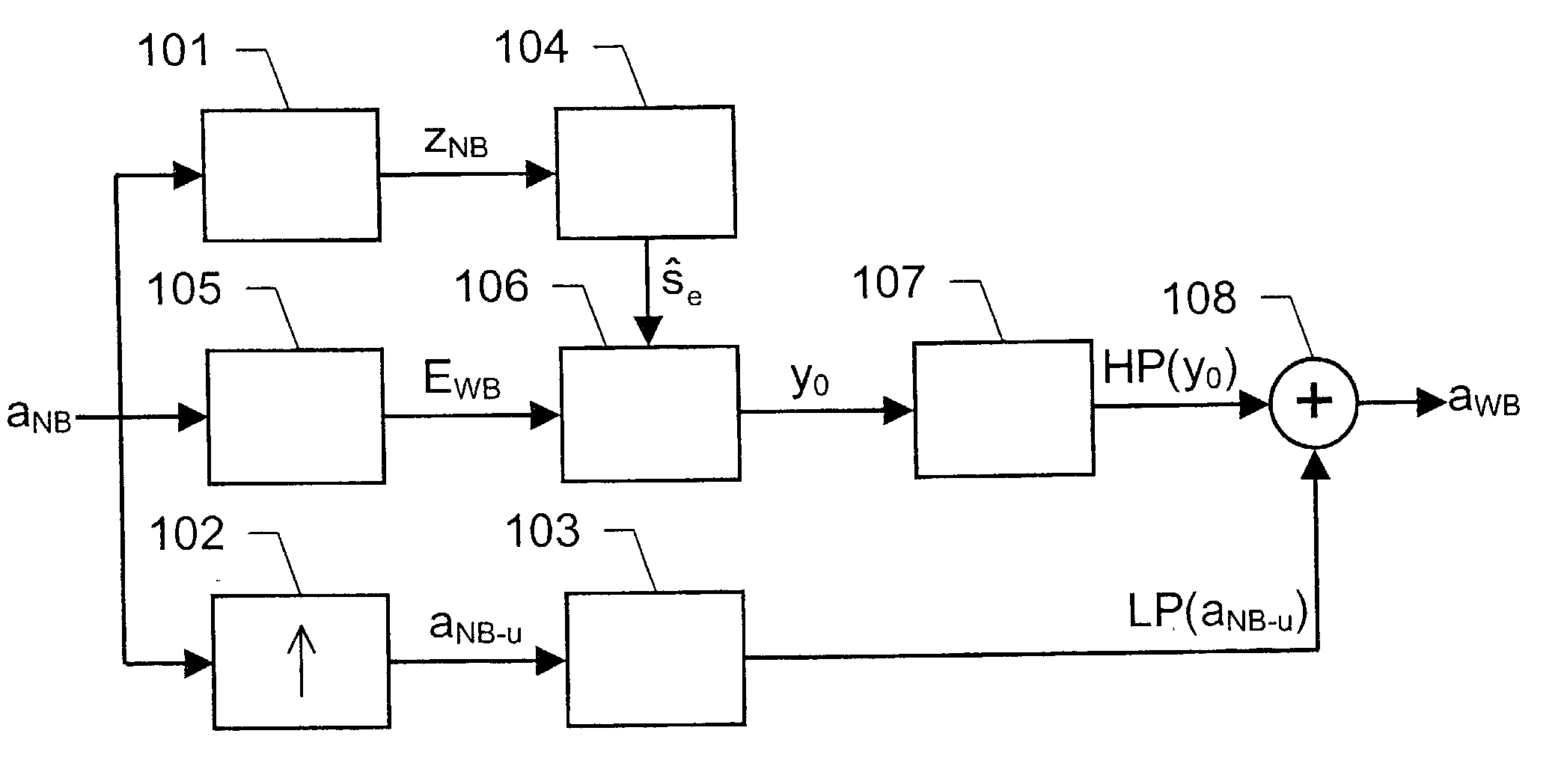
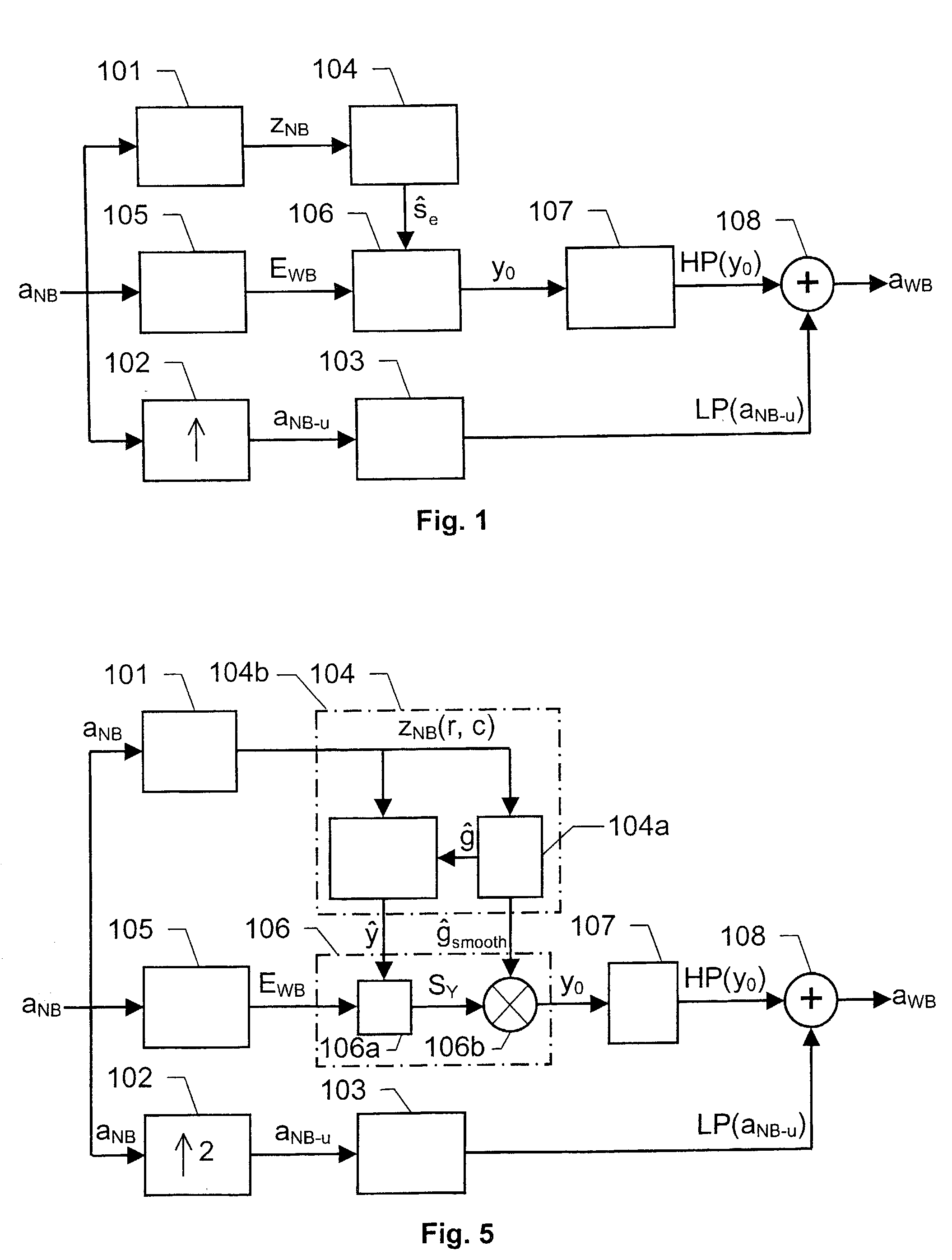
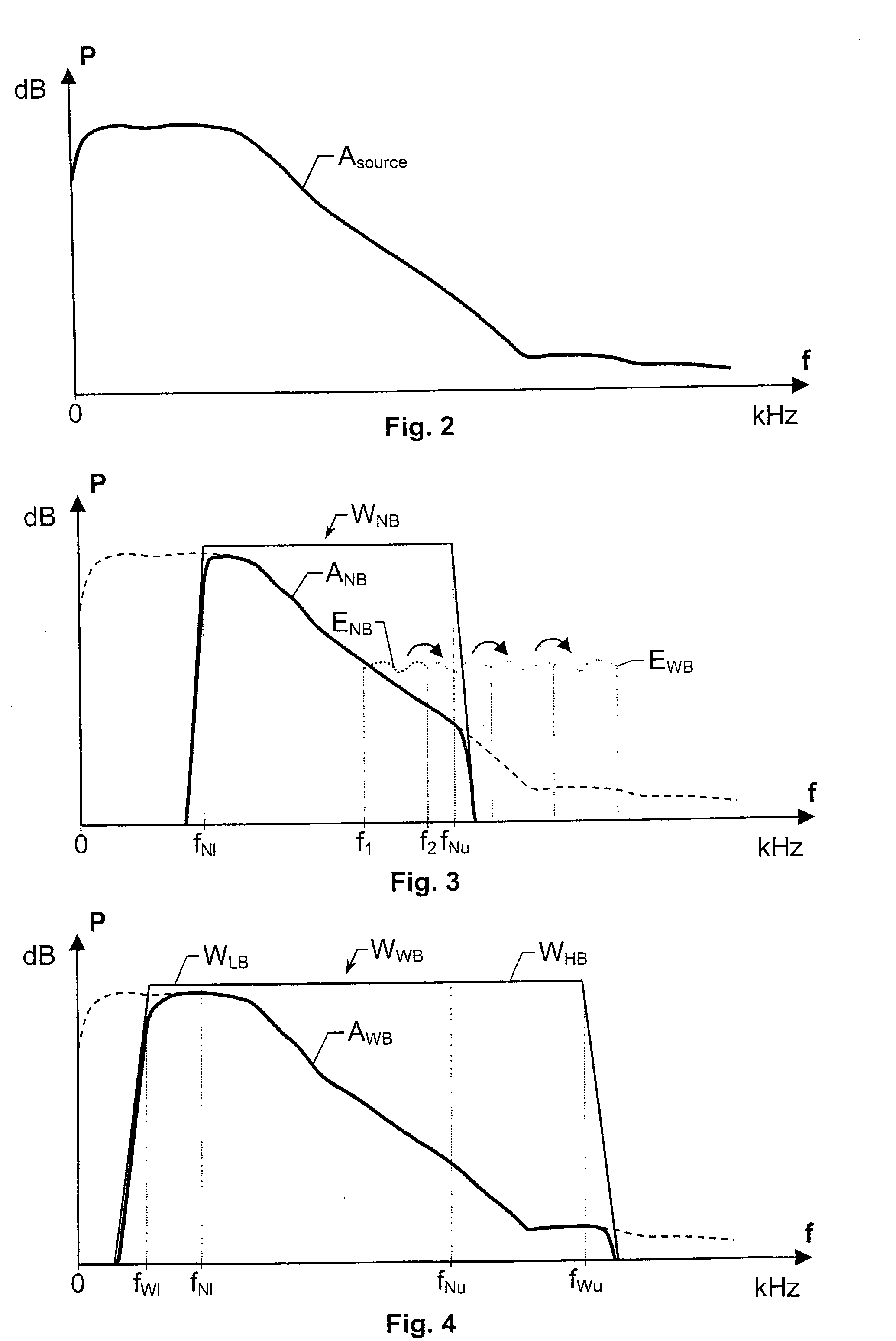
The present invention relates to a solution for improving the perceived sound quality of a decoded acoustic signal. The improvement is accomplished by means of extending the spectrum of a received narrow-band acoustic signal (aNB). According to the invention, a wide-band acoustic signal (aWB) is produced by extracting at least one essential attribute (zNB) from the narrow-band acoustic signal (aNB). Parameters, e.g. representing signal energies, with respect to wide-band frequency components outside the spectrum (ANB) of the narrow-band acoustic signal (aNB) are estimated based on the at least one essential attribute (zNB). This estimation involves allocating a parameter value to a wide-band frequency component, based on a corresponding confidence level. For instance, a relatively high parameter value is allowed to be allocated to a frequency component if it has a comparatively high degree certainty. In contrast, a relatively low parameter value is only allowed to be allocated to a frequency component if it is associated with a comparatively low degree certainty.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
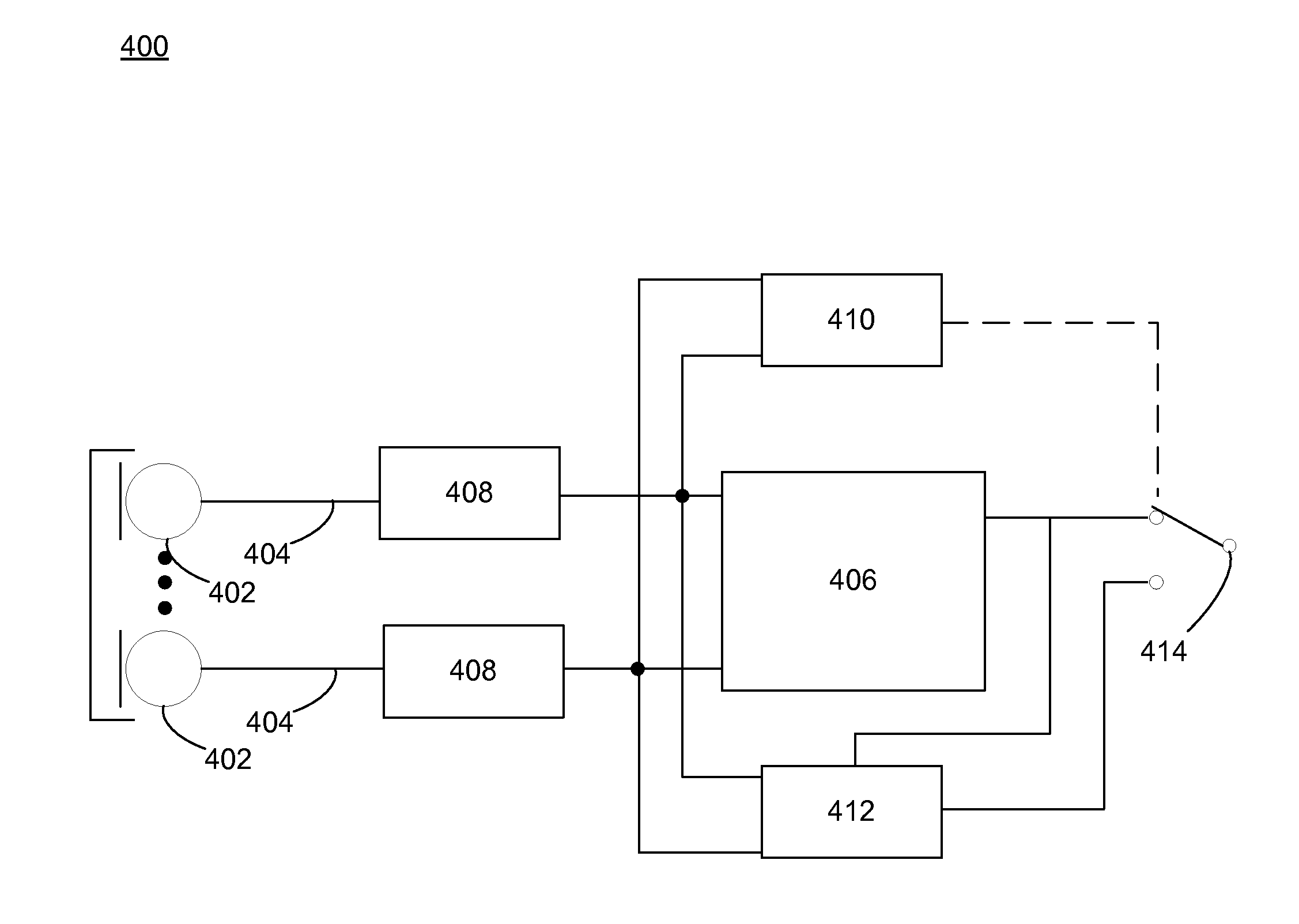
System and method for identifying suboptimal microphone performance
Embodiments disclosed herein may include determining a signal parameter of a first microphone and a second microphone associated with a computing device. Embodiments may include generating a reference parameter based upon at least one of the parameter of the first microphone and the parameter of the second microphone. Embodiments may include adjusting a tolerance of at least one of the first microphone and the second microphone, based upon the reference parameter. Embodiments may include receiving, at the first microphone, a first speech signal, the first speech signal having a first speech signal magnitude and receiving, at the second microphone, a second speech signal, the second speech signal having a second speech signal magnitude. Embodiments may include comparing at least one of the first speech signal magnitude and the second speech signal magnitude with a third speech signal magnitude and detecting an obstructed microphone based upon the comparison.
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
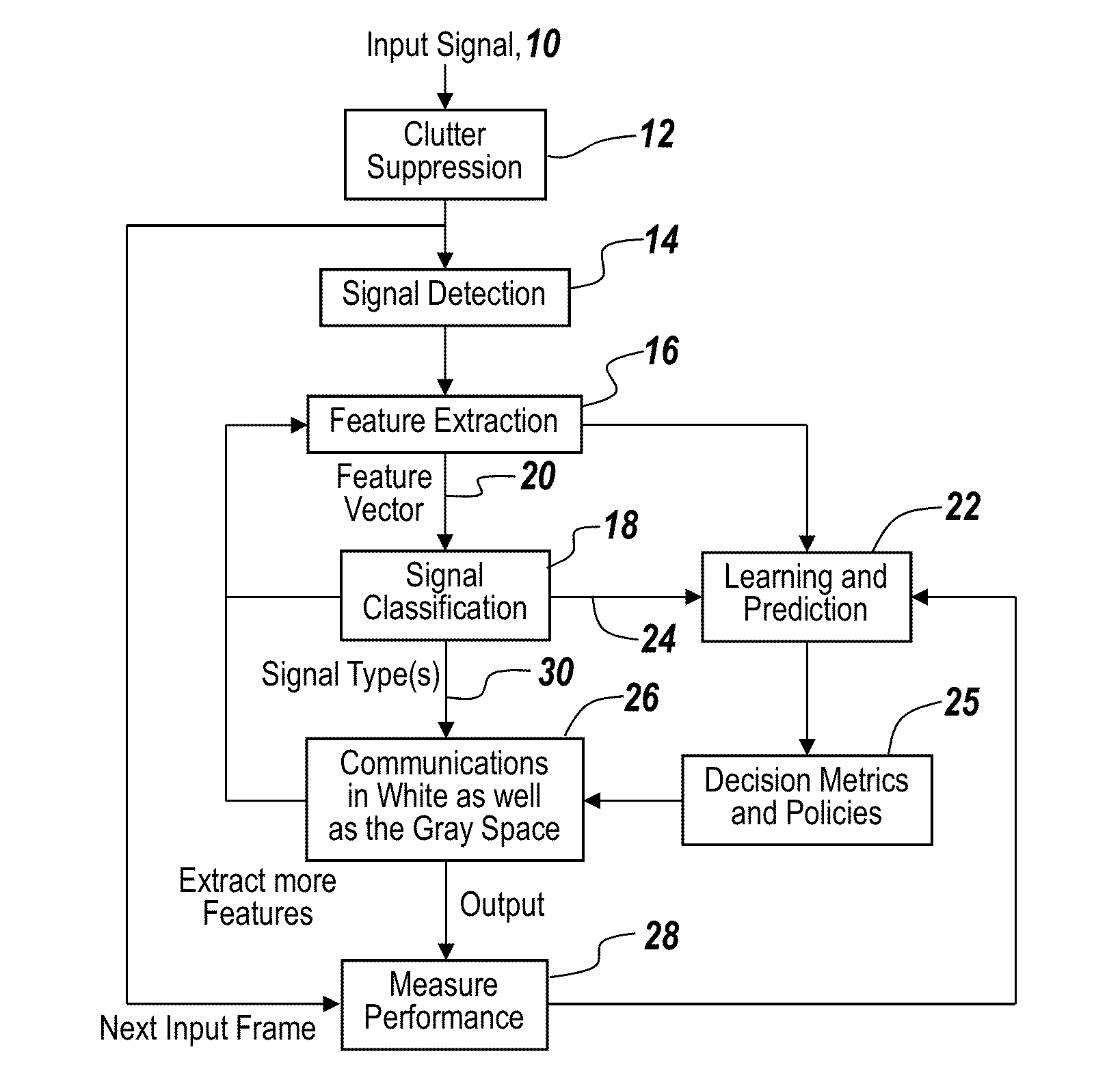
Cognitive radio methodology, physical layer policies and machine learning
ActiveUS20130288734A1Easy to adaptEasy to classifyAssess restrictionRadio transmissionCognitive communicationPhysical layer
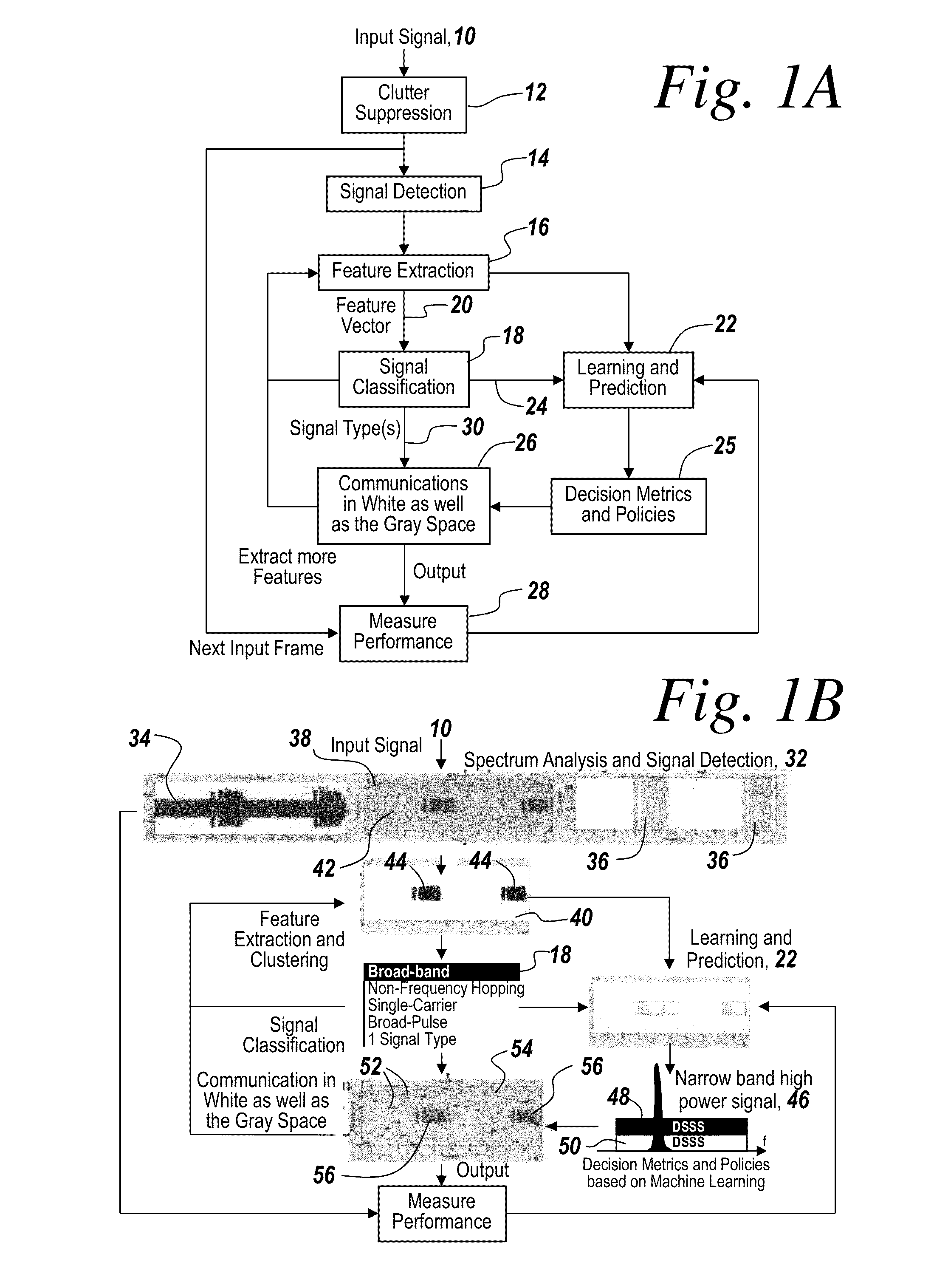
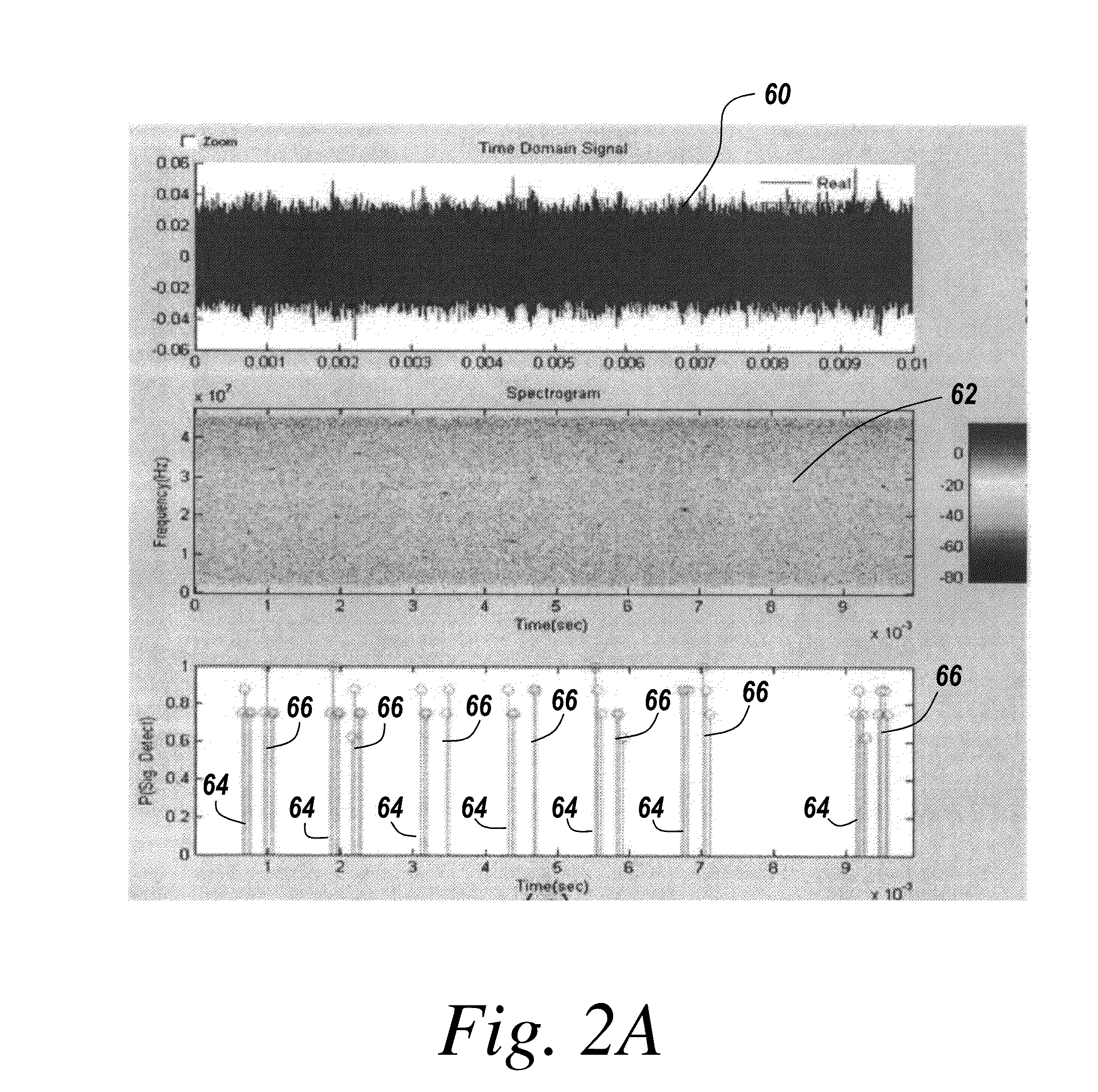
In a method of cognitive communication a system for generating non-interfering transmission, includes conducting radio scene analysis to find grey space using external signal parameters for incoming signal analysis without having to decode incoming signals.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTEGRATION INC
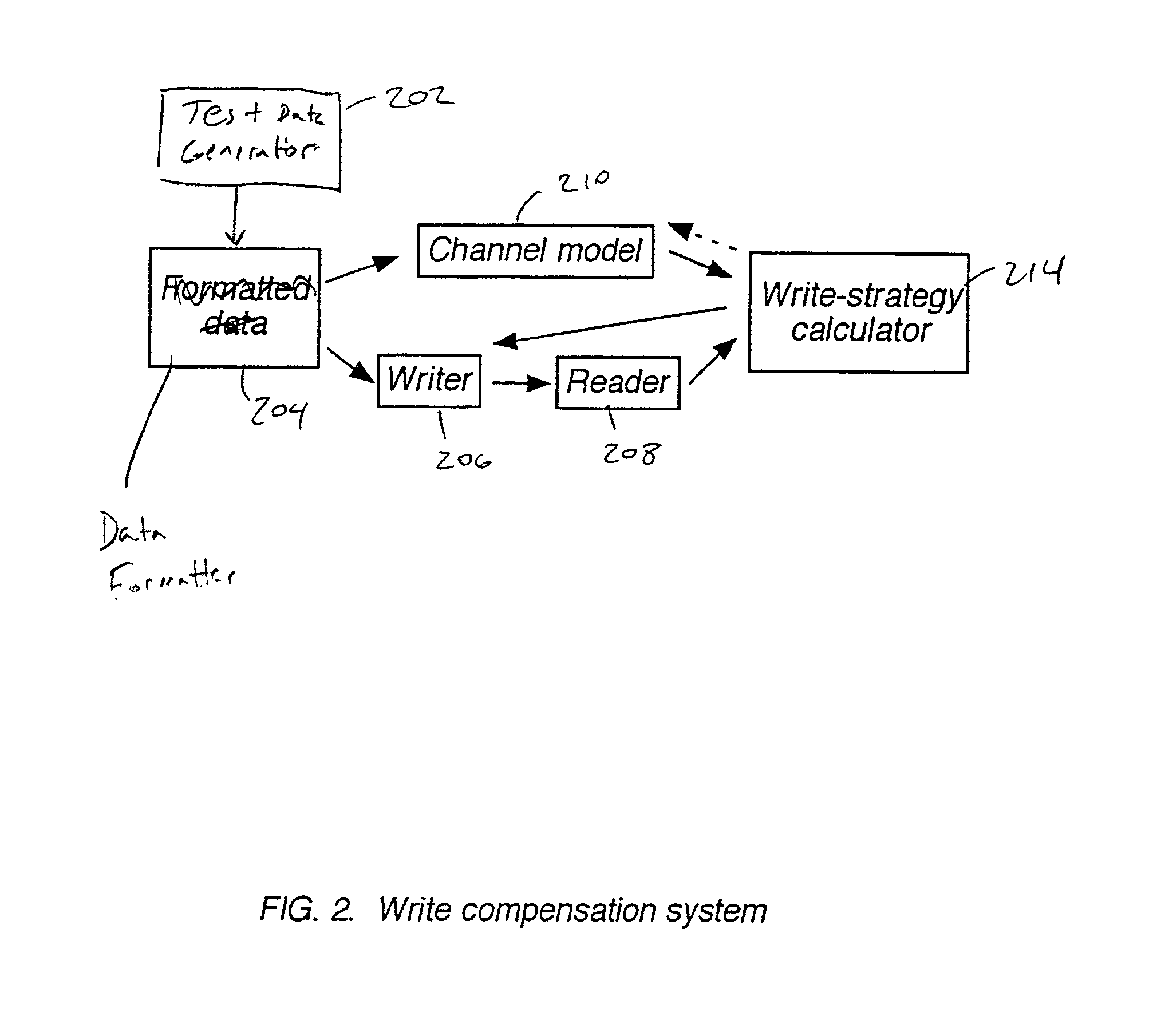
Write compensation for data storage and communication systems
InactiveUS20020126604A1Television system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersCommunications systemChannel sensitivity
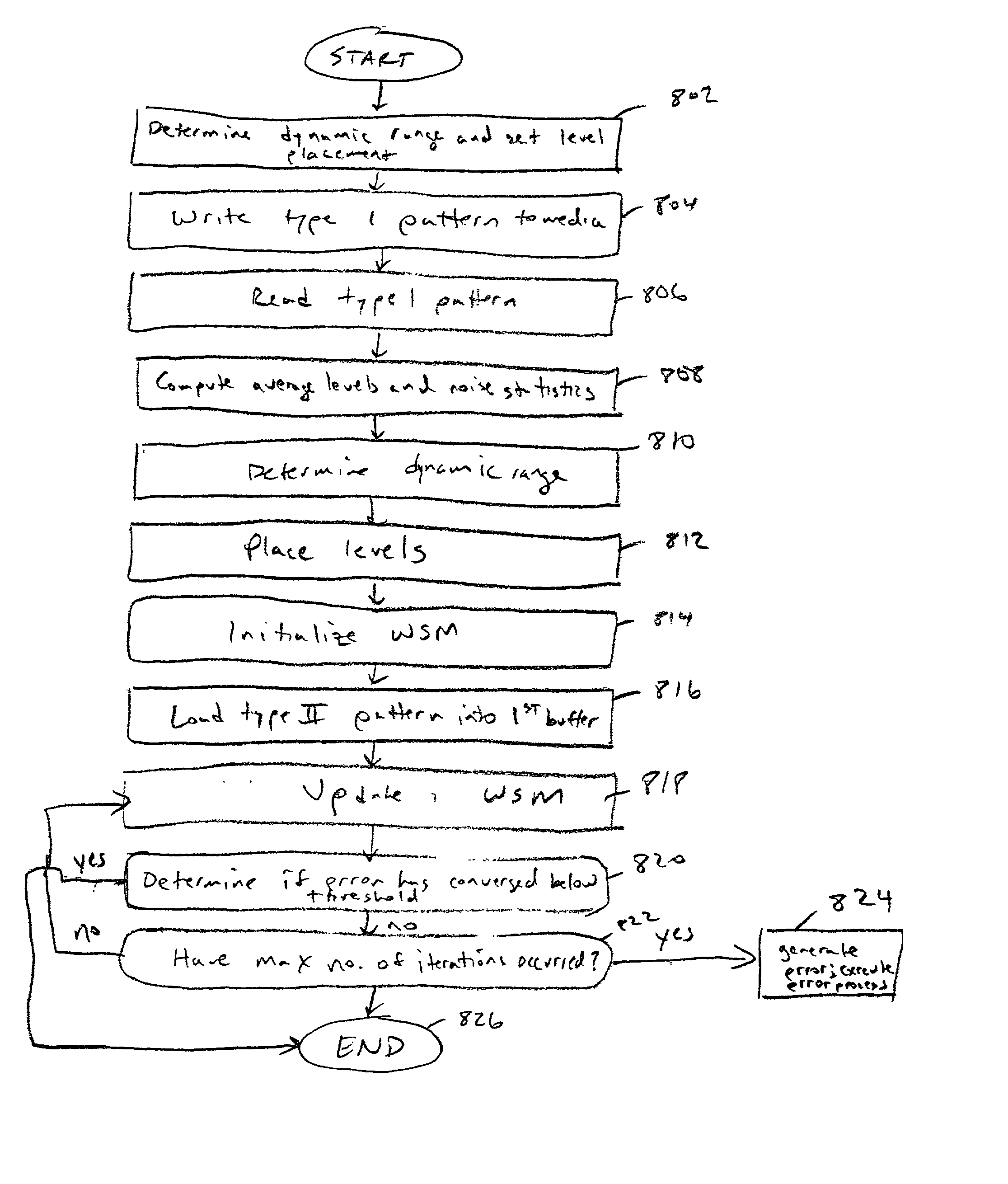
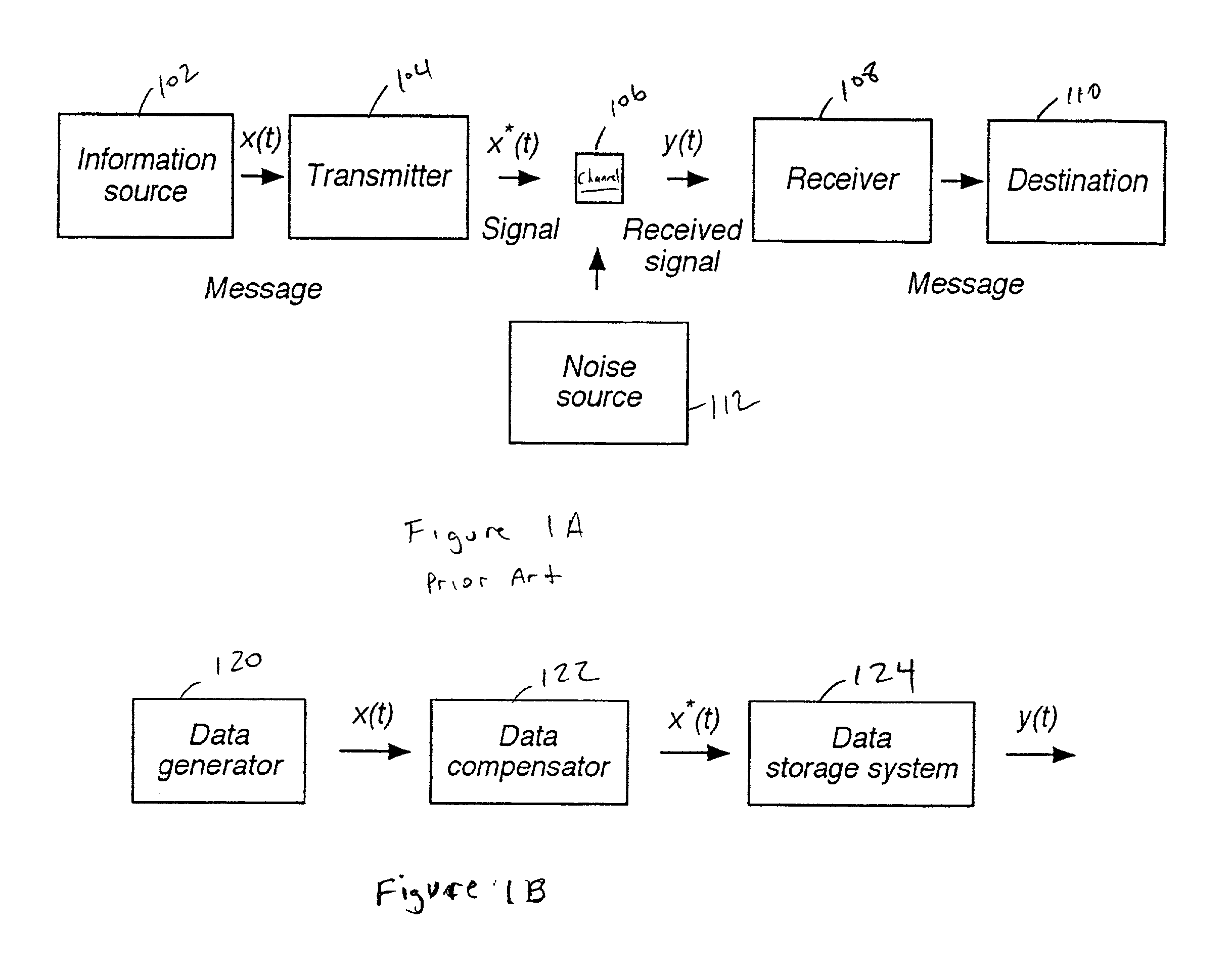
Methods and systems for write compensation for optimizing the performance of a data storage or communication channel are disclosed. In one embodiment, a method comprises determining channel sensitivity to modifications in write signal parameters, detecting systematic errors in a read signal recovered from data written with a first set of write parameters, and adjusting the write signal parameters by an amount determined from the channel sensitivity such that the systematic errors are reduced when data are written with the adjusted write parameters.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
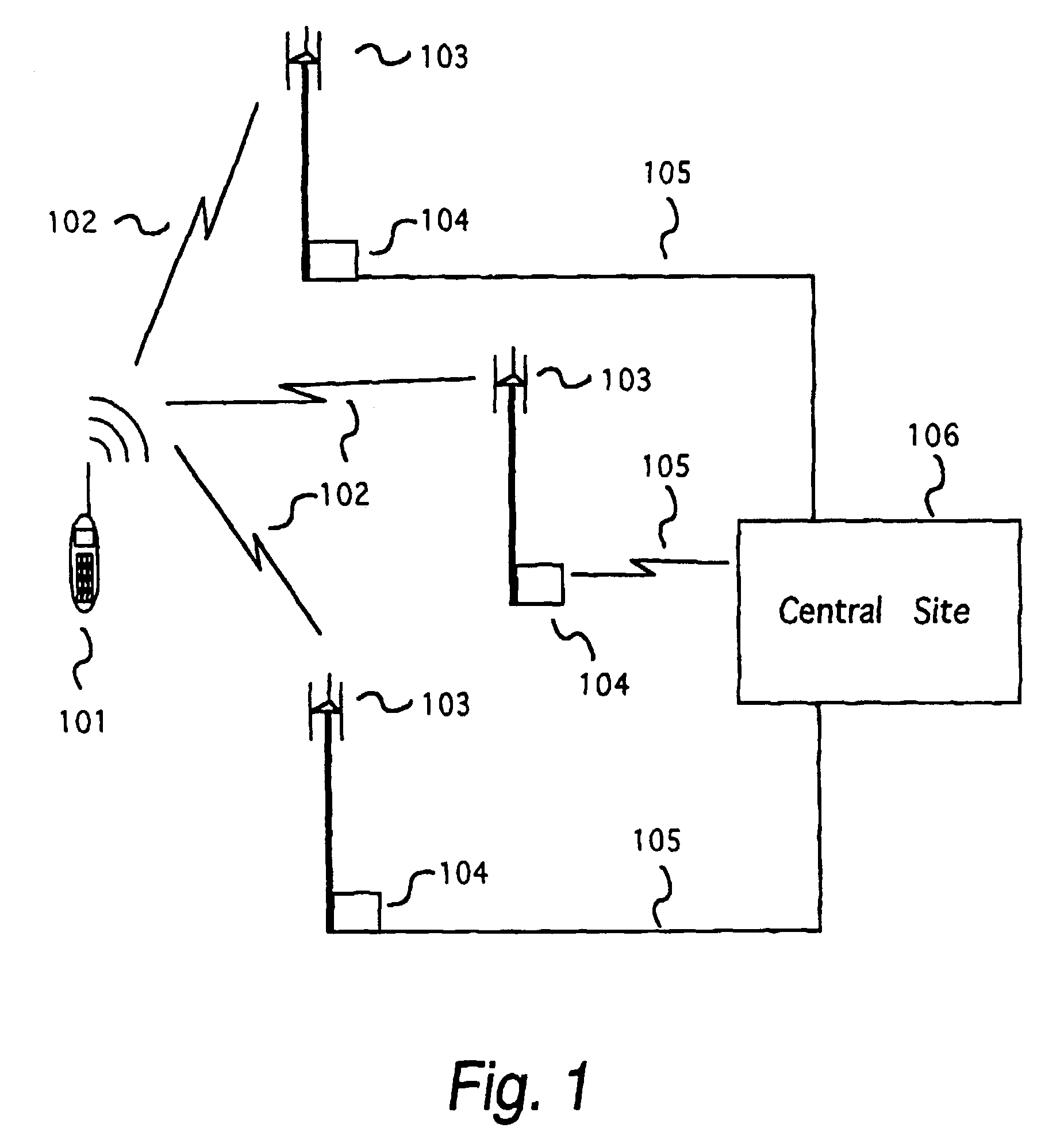
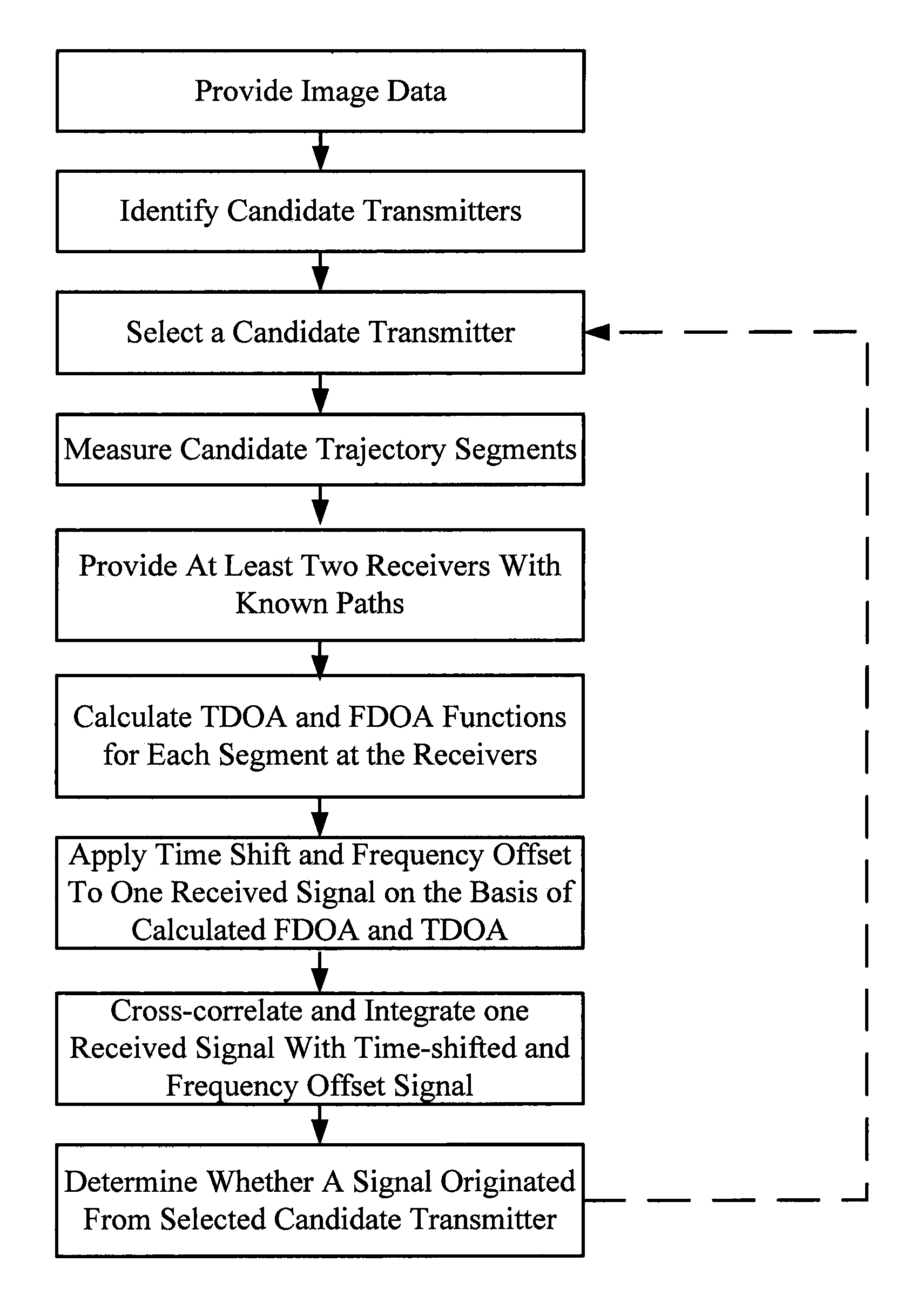
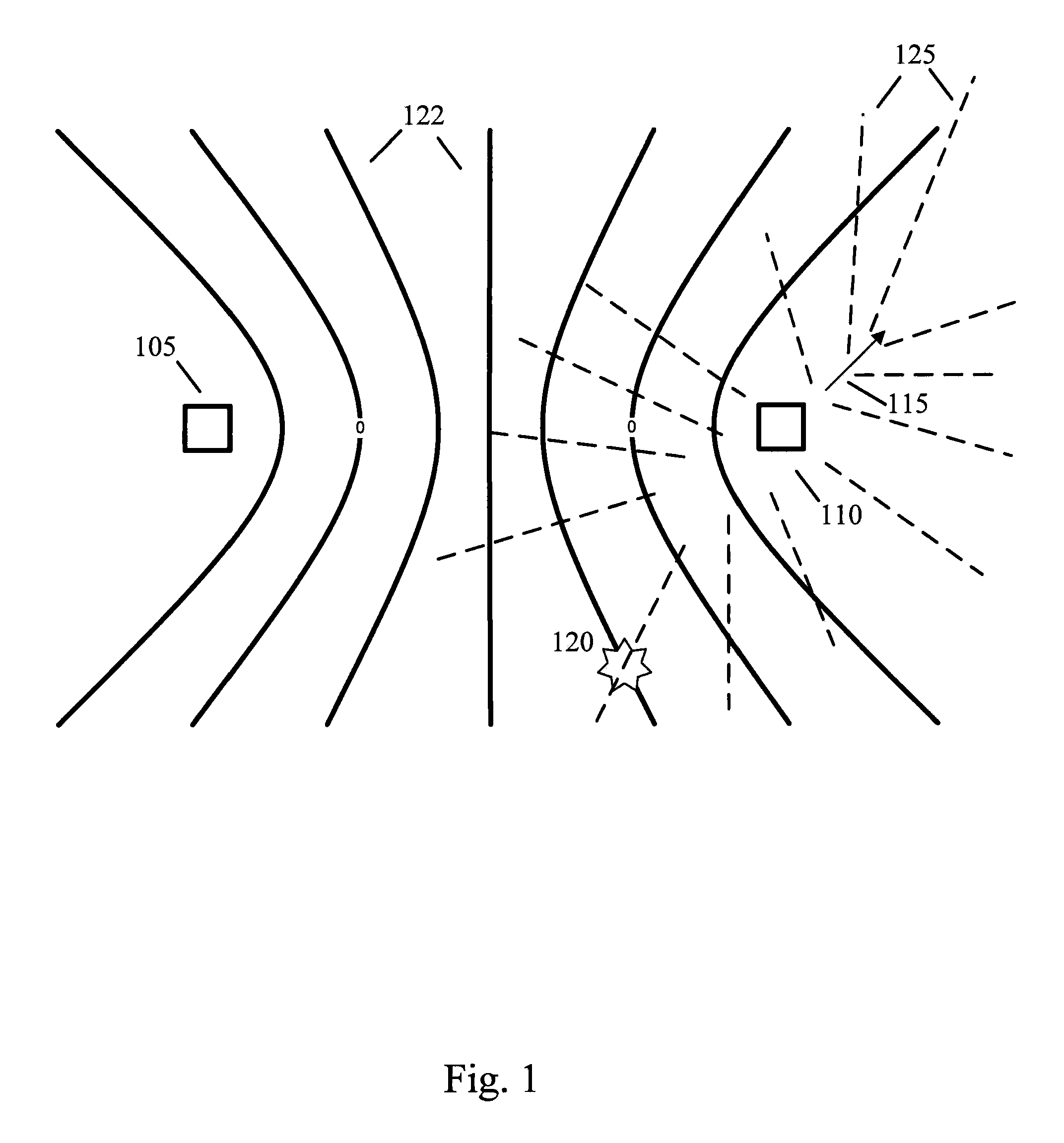
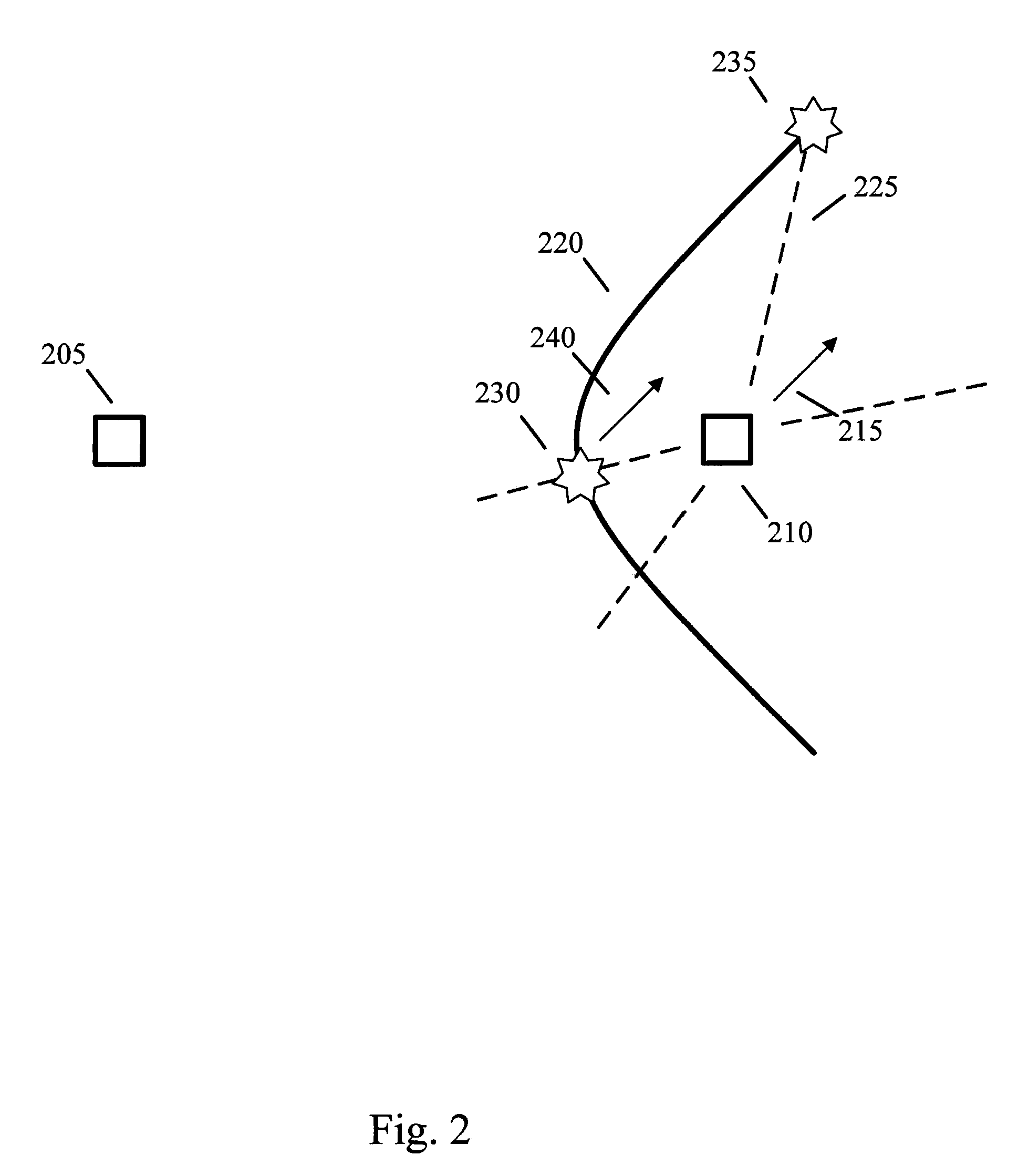
Method of Correlating Known Image Data of Moving Transmitters with Measured Radio Signals
ActiveUS20110074631A1Radio wave direction/deviation determination systemsPosition fixationEngineeringImaging data
Systems and methods of correlating potential transmitters with received radio signals is provided. Image data is provided including paths traveled by potential transmitter. Potential transmitters are identified within the image data along with path segments traveled by potential transmitters. A first and second transmitter calculate certain parameters of received signals assuming that signals originated along the path segments. The calculated signal parameters are then compared to measured signal parameter to determine whether a transmitter is associated with a particular path.
Owner:RINCON RES CORP
Acoustic impact detection and monitoring system
ActiveUS7607351B2Cost effectiveQuick checkMultiple-port networksVibration measurement in fluidHydrophoneTelecommunications link
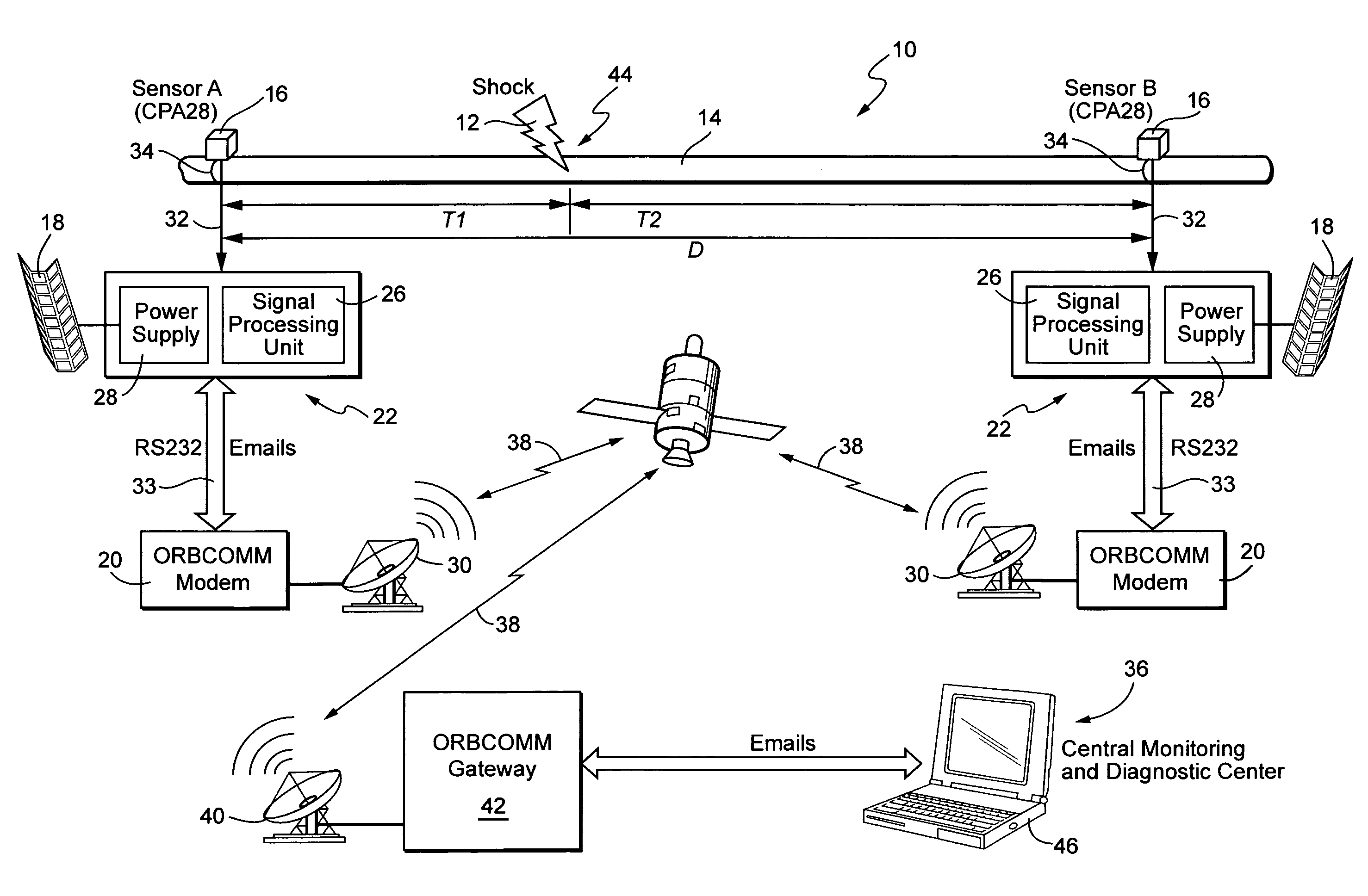
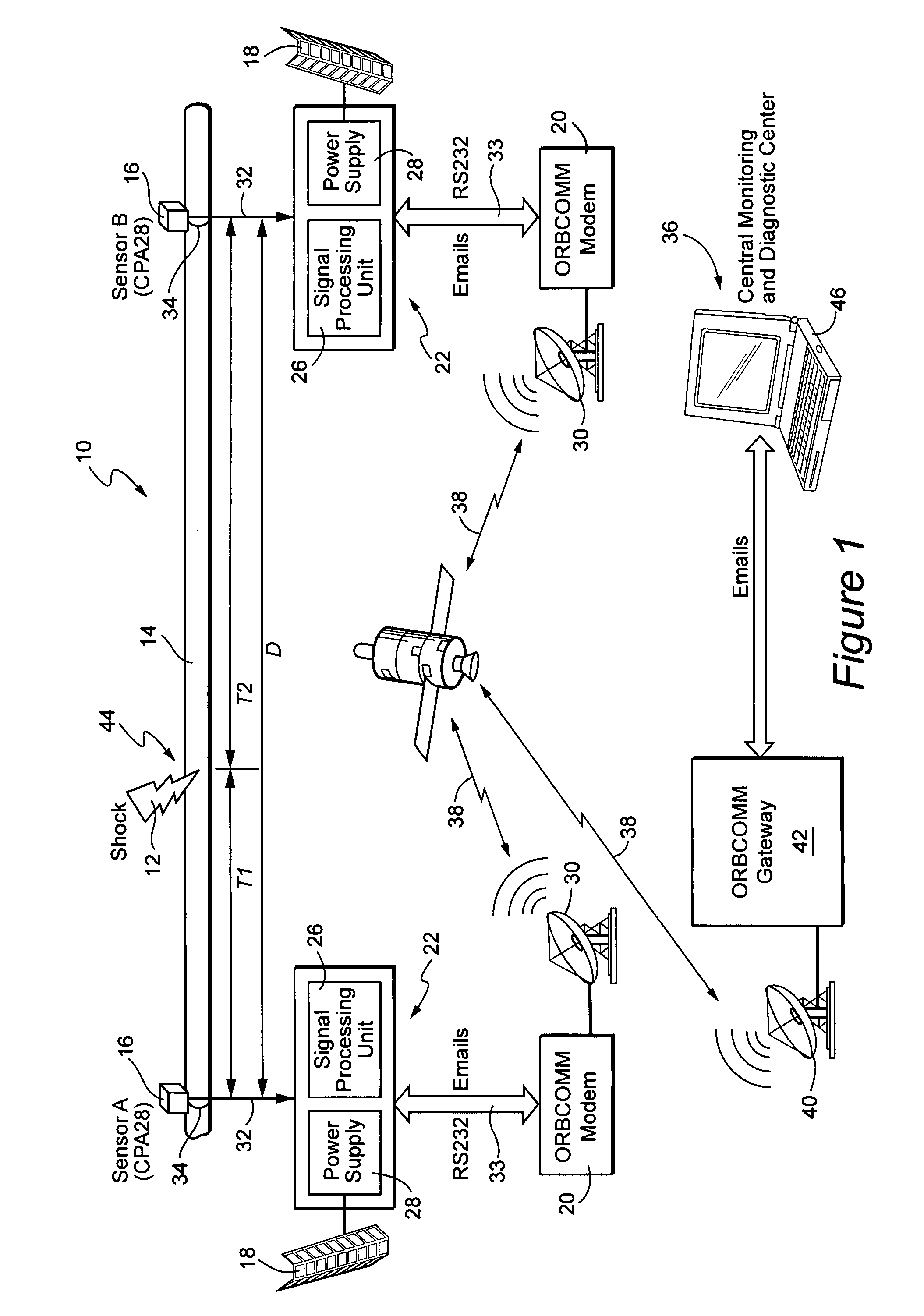
A system is disclosed for detecting and locating harmful impacts to pipelines using sensors placed along the pipeline. The exact spacing of sensors is site specific and is set with the goal of maximizing sensor spacing without reducing system performance and reliability. At each sensor location, preferably there are four basic components, i.e., a hydrophone, solar power components, and data processing and communications equipment. Each hydrophone directly measures the acoustic noise fluctuation in a pipe section, which propagates at long distances in the pipeline at the specific speed of sound for the particular type of pipe. If specific signal parameters exceed a programmed threshold, a detection message is generated and transmitted via a communications link to a central monitoring and diagnostic center.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Robust, Efficient, Localization System
InactiveUS20080161015A1Faster routingConvenient and effective detectionDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationLocalization systemCode division multiple access
Replica correlation processing, and associated representative signal-data reduction and reconstruction techniques, are used to detect signals of interest and obtain robust measures of received-signal parameters, such as time differences of signal arrival and directional angles of arrival, that can be used to estimate the location of a cellularized-communications signal source. The new use in the present invention of signal-correlation processing for locating communications transmitters. This enables accurate and efficient extraction of parameters for a particular signal even in a frequency band that contains multiple received transmissions, such as occurs with code-division-multiple-access (CDMA) communications. Correlation processing as disclosed herein further enables extended processing integration times to facilitate the effective detection of desired communications-signal effects and replication measurement of their location-related parameters, even for the communications signals modulated to convey voice conversations or those weakened through propagation effects. Using prior, constructed, signal replicas in the correlation processing enables elimination of the inter-site communications of the signal representations that support the correlation analyses. Reduced-data representations of the modulated signals for voiced conversation, or for the variable components of data communications, are used to significantly reduce the inter-site communications that support the correlation analyses.
Owner:TRUE POSITION INC
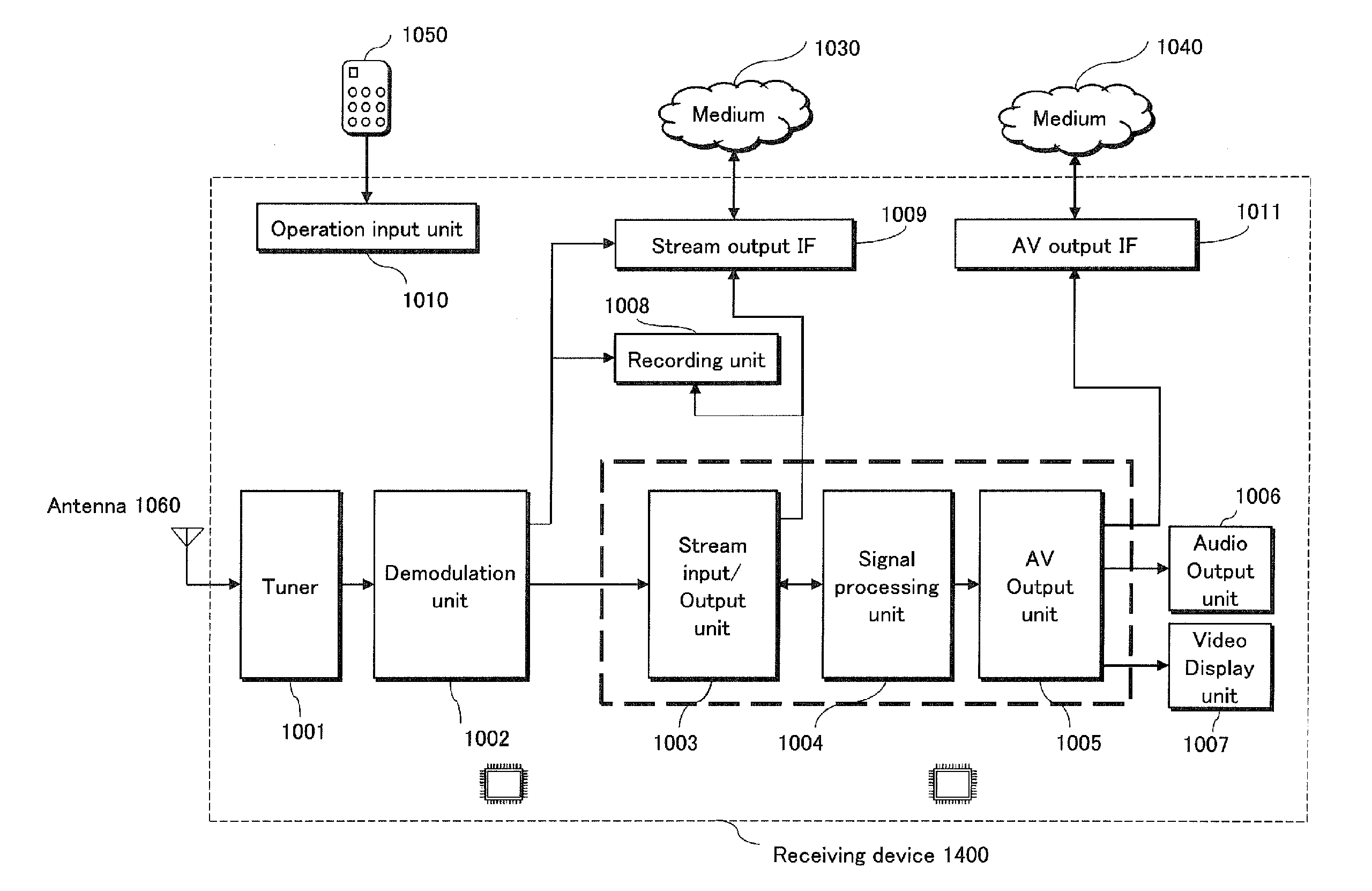
Transmission method, reception method, transmission apparatus, and reception apparatus
ActiveUS20120314762A1Improve transmission efficiencyReducing size of headerPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesSpecific information broadcast systemsAdaptive codingPhysical layer
The present invention relates to transmission and reception of digital broadcast in a digital broadcast network supporting a configuration of multiple physical layer pipes (PLPs). In particular, signalling parameters relating to a complete PLP are transmitted within layer 1 signalling related to the PLP. The baseband frames mapped on the pipe are configured according to this layer 1 signalling in the same way at the transmitter as they are demapped on the receiver side. The baseband frames are transmitted and received without including these parameters, in particular, at least one of parameters indicating (i) an input stream format, (ii) a single or a multiple input stream, (iii) constant or adaptive coding and modulation, (iv) presence of input stream synchronization, (v) presence of null packet deletion, or (vi) input stream identifier.
Owner:SUN PATENT TRUST
Method and system for directing a data message in a wireless communications network including multiple wireless systems
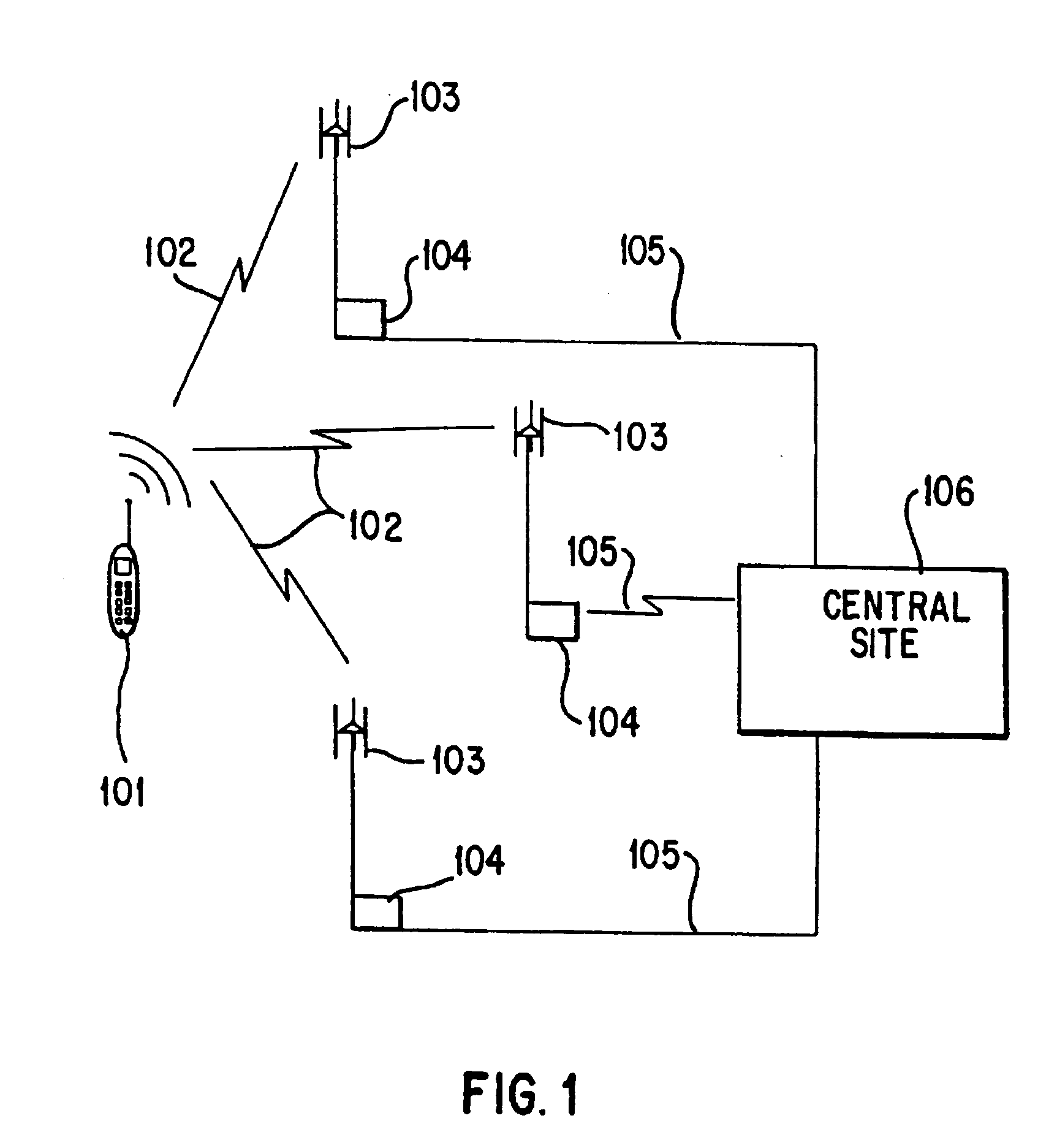
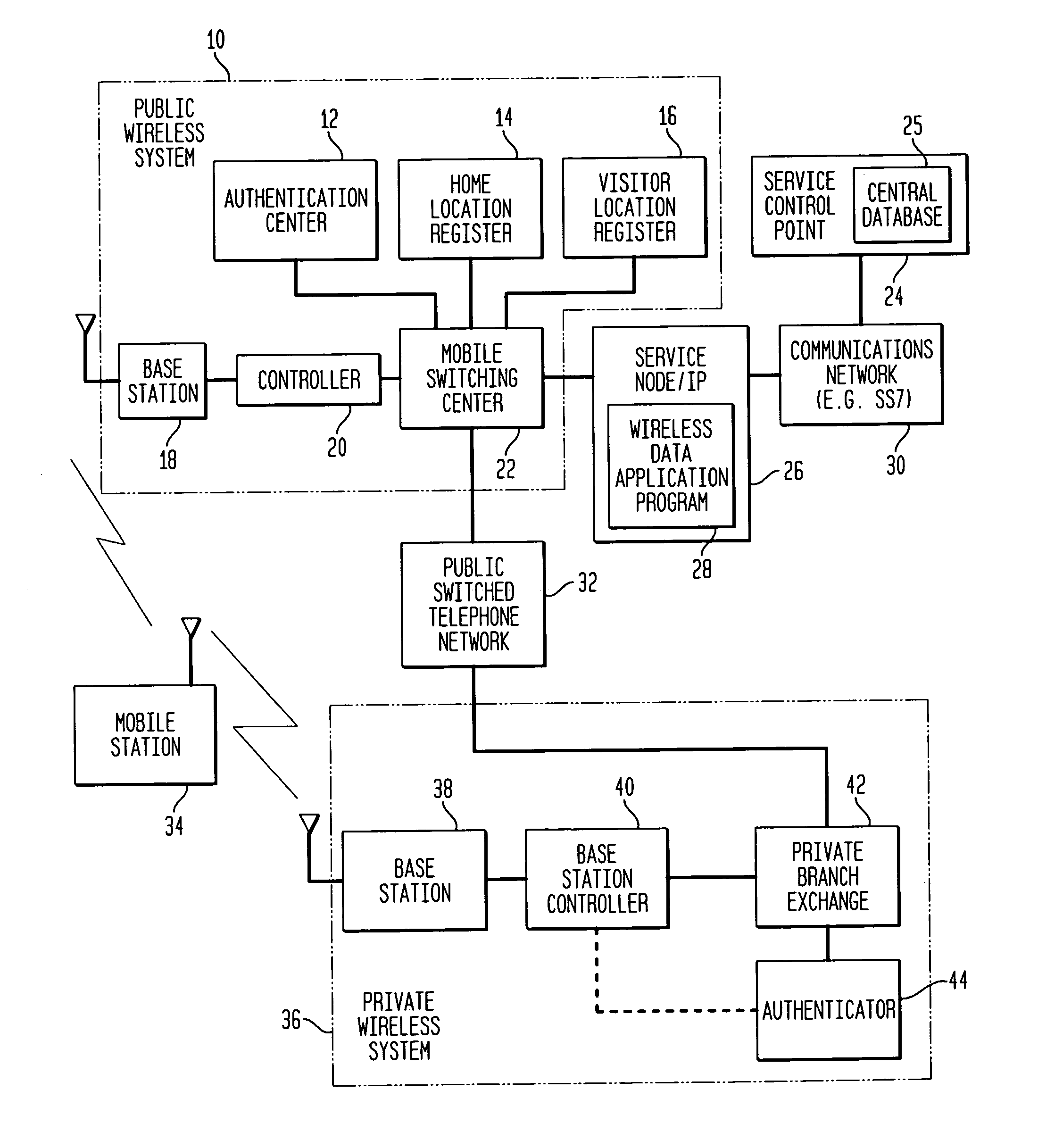
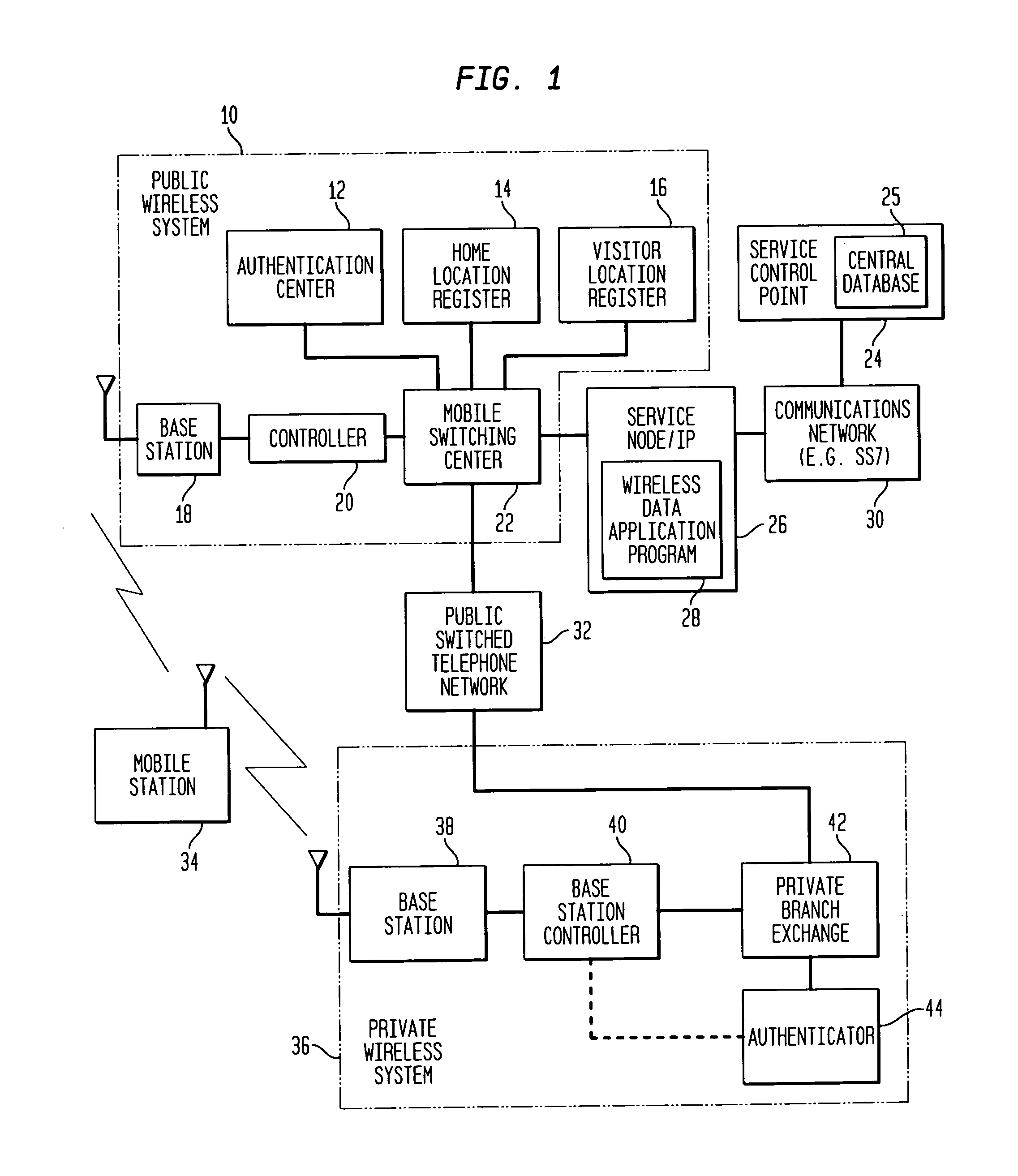
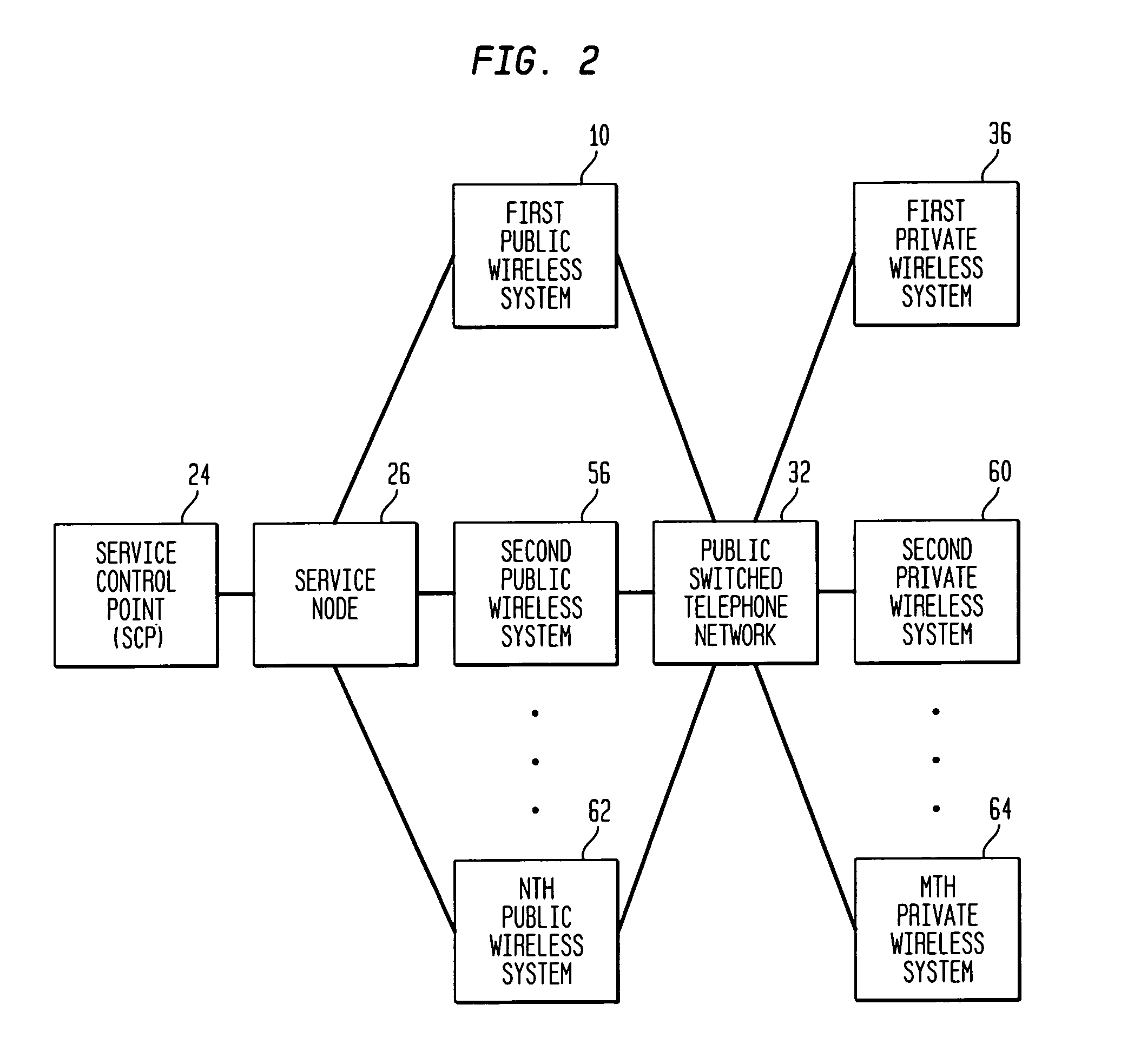
InactiveUS7171199B1Reduces inter-system signaling trafficUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsCommunications systemTransfer procedure
A mobile station scans for electromagnetic signals representing control channels of the public wireless system and the private wireless system. The mobile station measures a received signal parameter of at least one of the scanned control channels. The hybrid communications network may transfer the mobile station's service from the public wireless system to the private wireless system, if the measured signal parameter meets or exceeds a private target. Alternately, the hybrid communications system may transfer service from the private wireless system to the public wireless system, if the measured signal parameter meets or exceeds a public target. A service control point maintains a central database of user profiles updated in response to the transferring procedure. A service node redirects a data message for the mobile station through the public wireless system or through the private wireless system, as facilitated by the central database, to deliver the data message to the mobile station during its operation on an active one of the wireless systems.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
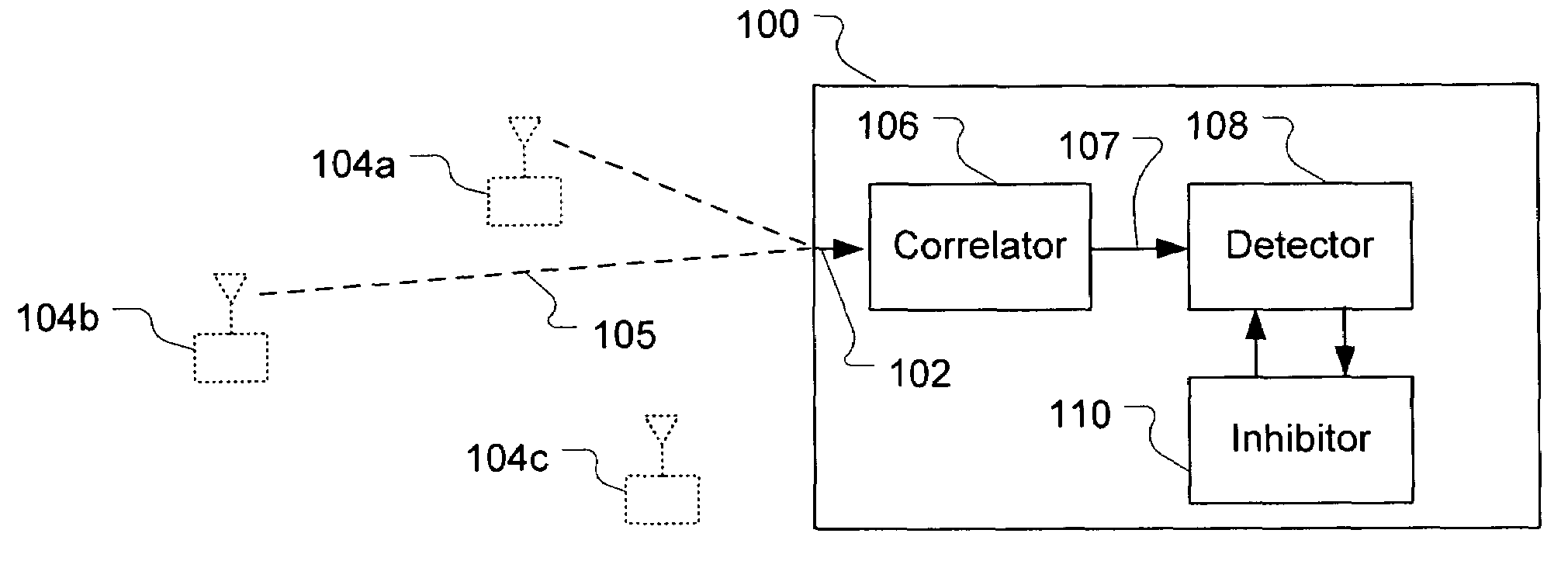
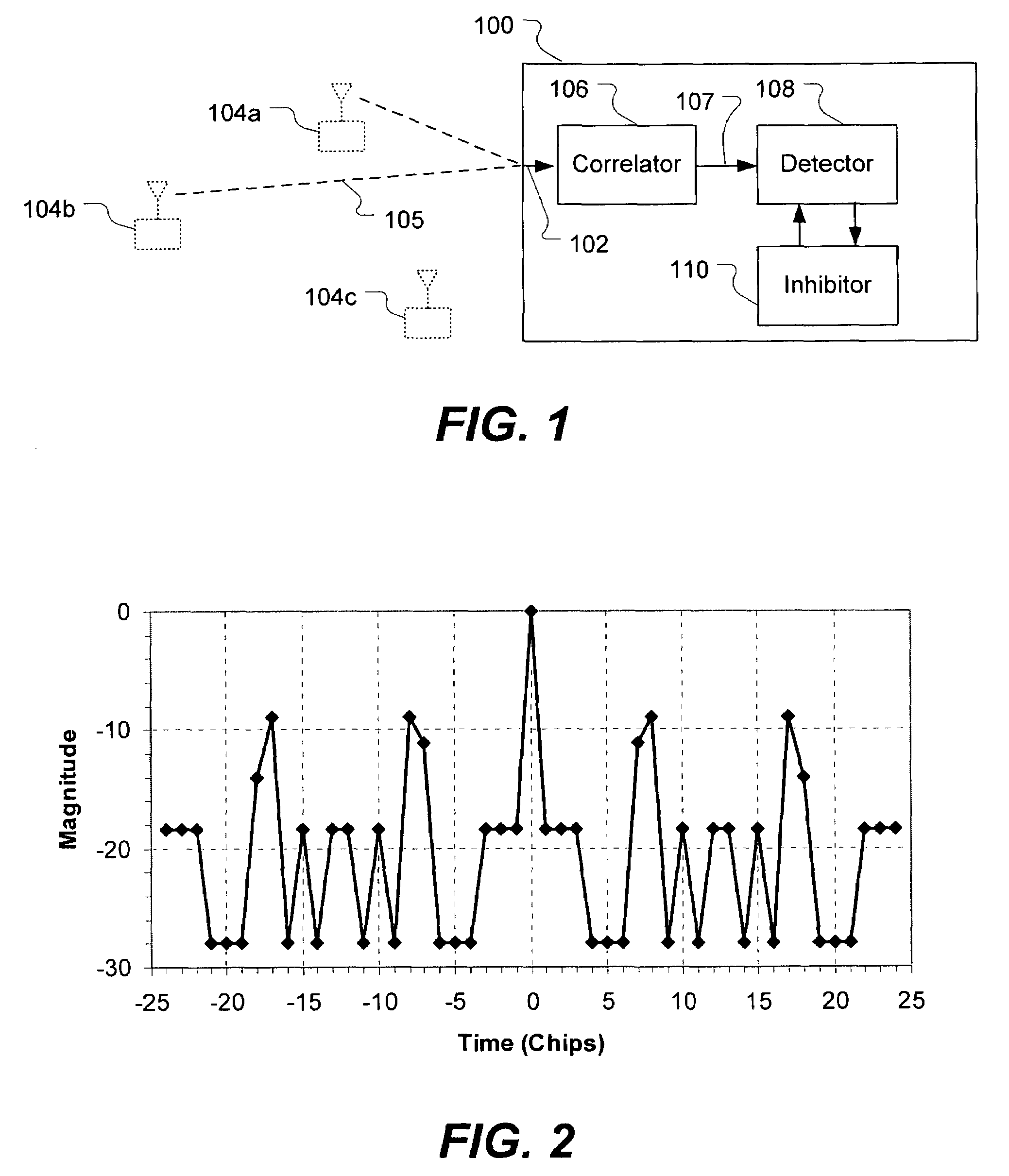
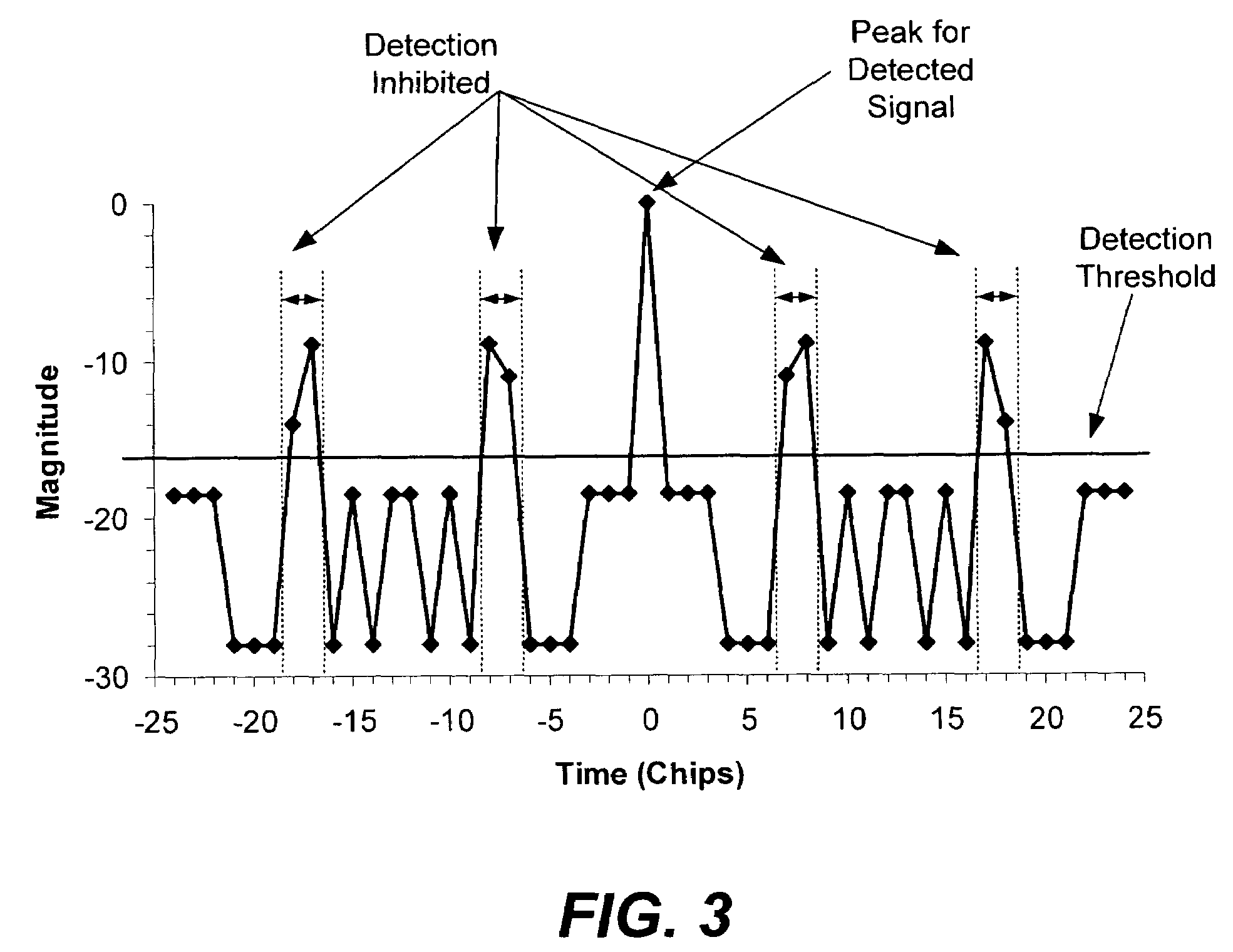
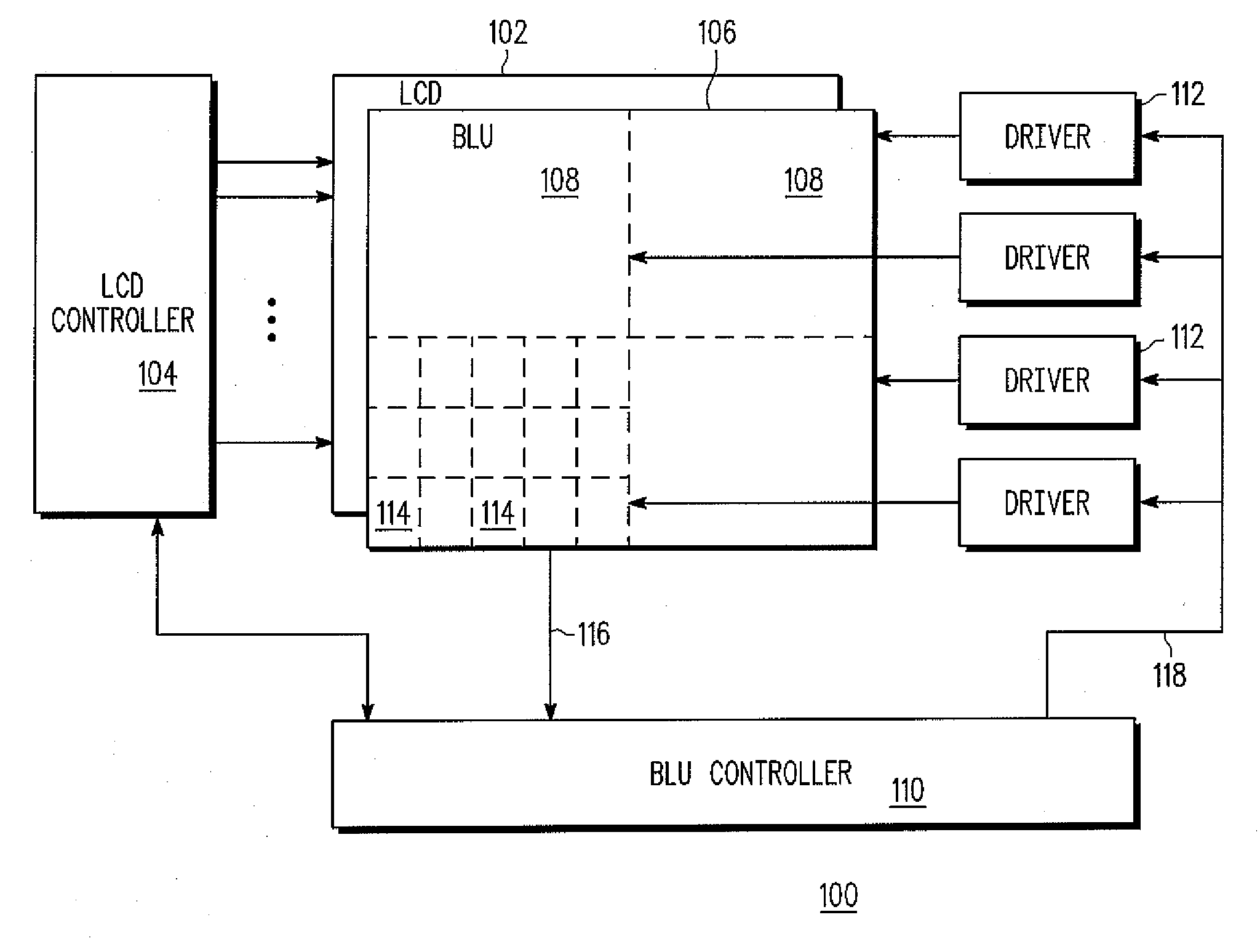
Spread spectrum signal detection with inhibiting for known sidelobe locations
A method and apparatus for detecting a spread spectrum signal is described. Signals can be detected using correlation techniques. When a signal is detected, declaring of signal presence is inhibited for offsets of signal parameters from the parameters of the detected signal, where the offset corresponds to a known sidelobe of the spreading code. This helps to reduce false detections caused by sidelobes of the spreading code.
Owner:L3 TECH INC
Method and apparatus for controlling light emitting diode
InactiveUS20080180414A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringLight-emitting diode
A method of driving an LED includes determining an operational parameter of the LED, determining a driving signal parameter for the LED, and generating a periodic driving signal for driving the LED. The generated periodic driving signal has a duty cycle that depends on the determined driving signal parameter and the determined operational parameter of the LED.
Owner:FREESCALE SEMICON INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com