Patents
Literature
3487 results about "Sound quality" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sound quality is typically an assessment of the accuracy, fidelity, or intelligibility of audio output from an electronic device. Quality can be measured objectively, such as when tools are used to gauge the accuracy with which the device reproduces an original sound; or it can be measured subjectively, such as when human listeners respond to the sound or gauge its perceived similarity to another sound.
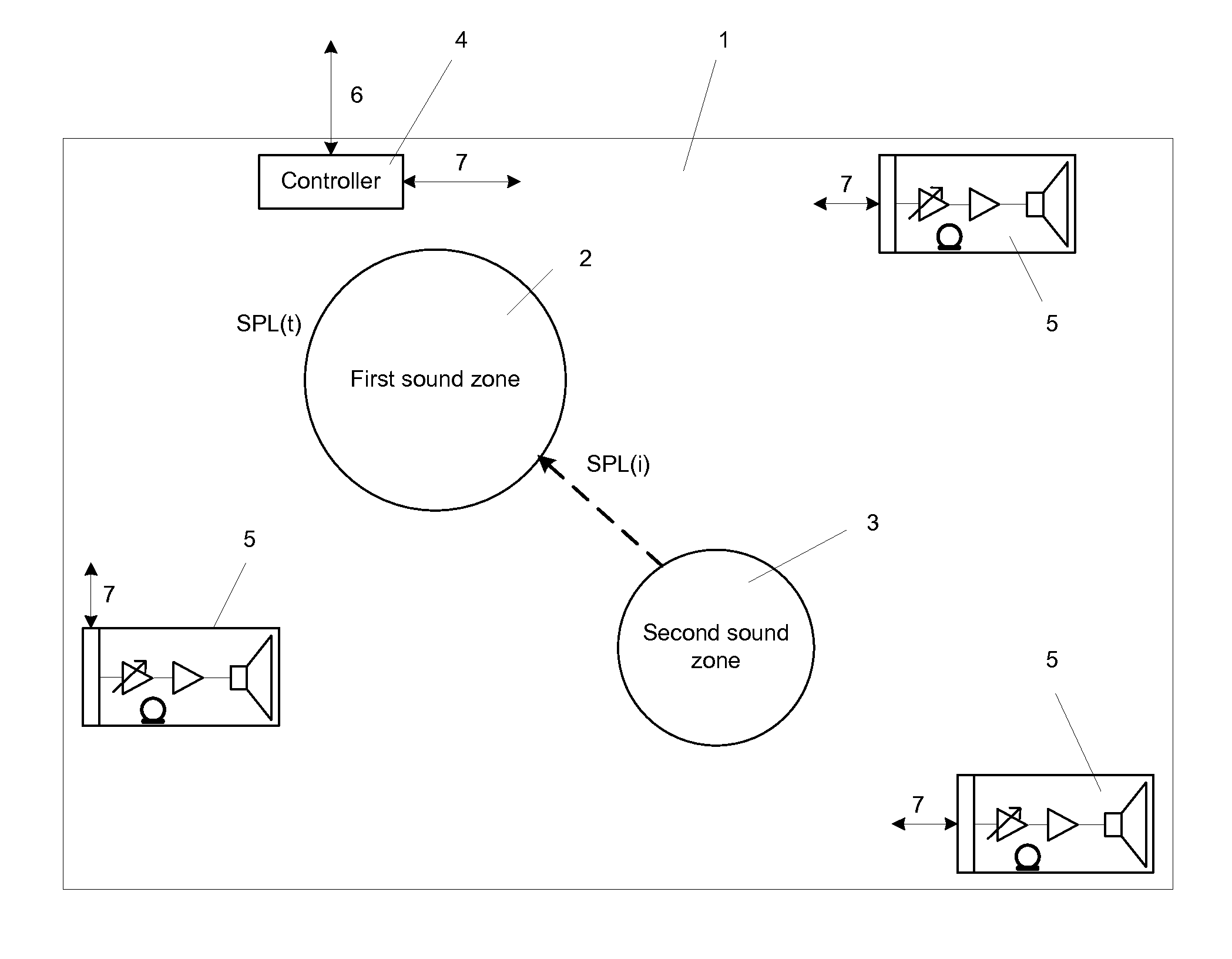
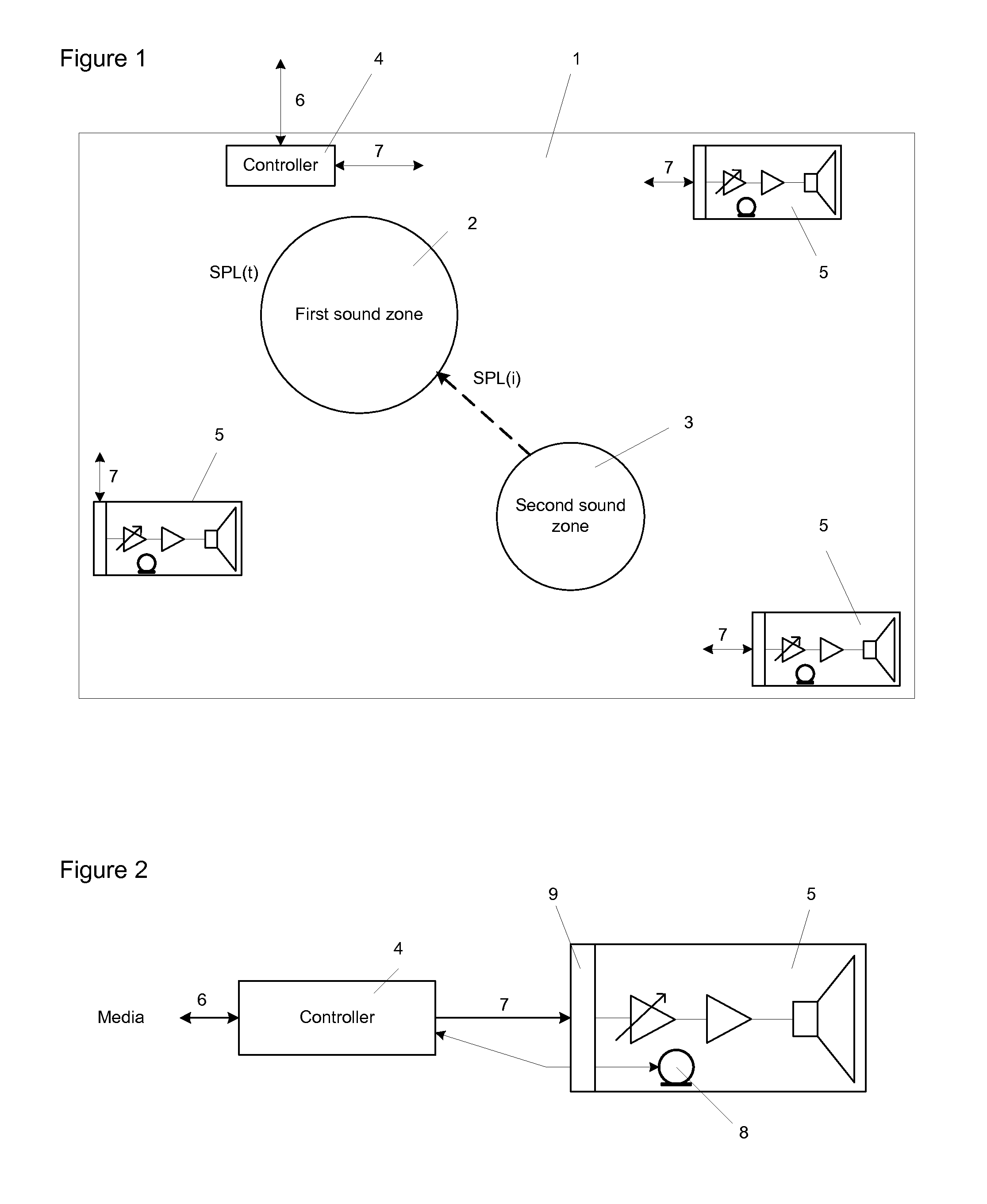
System for optimizing the perceived sound quality in virtual sound zones
ActiveUS20130230175A1Stereophonic circuit arrangementsStereophonic systemsOperation modeSound quality
The invention discloses a system applied to optimize the perceived sound quality in virtual sound zones. The system includes a method to establish a threshold of acceptability for an interfering audio programme on a target audio programme. The method includes physical parameters like target programme and interferer programme which combined with the scenarios: information gathering, entertainment and reading and / or working, constitutes modes of operations that may be processed and controlled by a system controller.
Owner:BANG & OLUFSEN
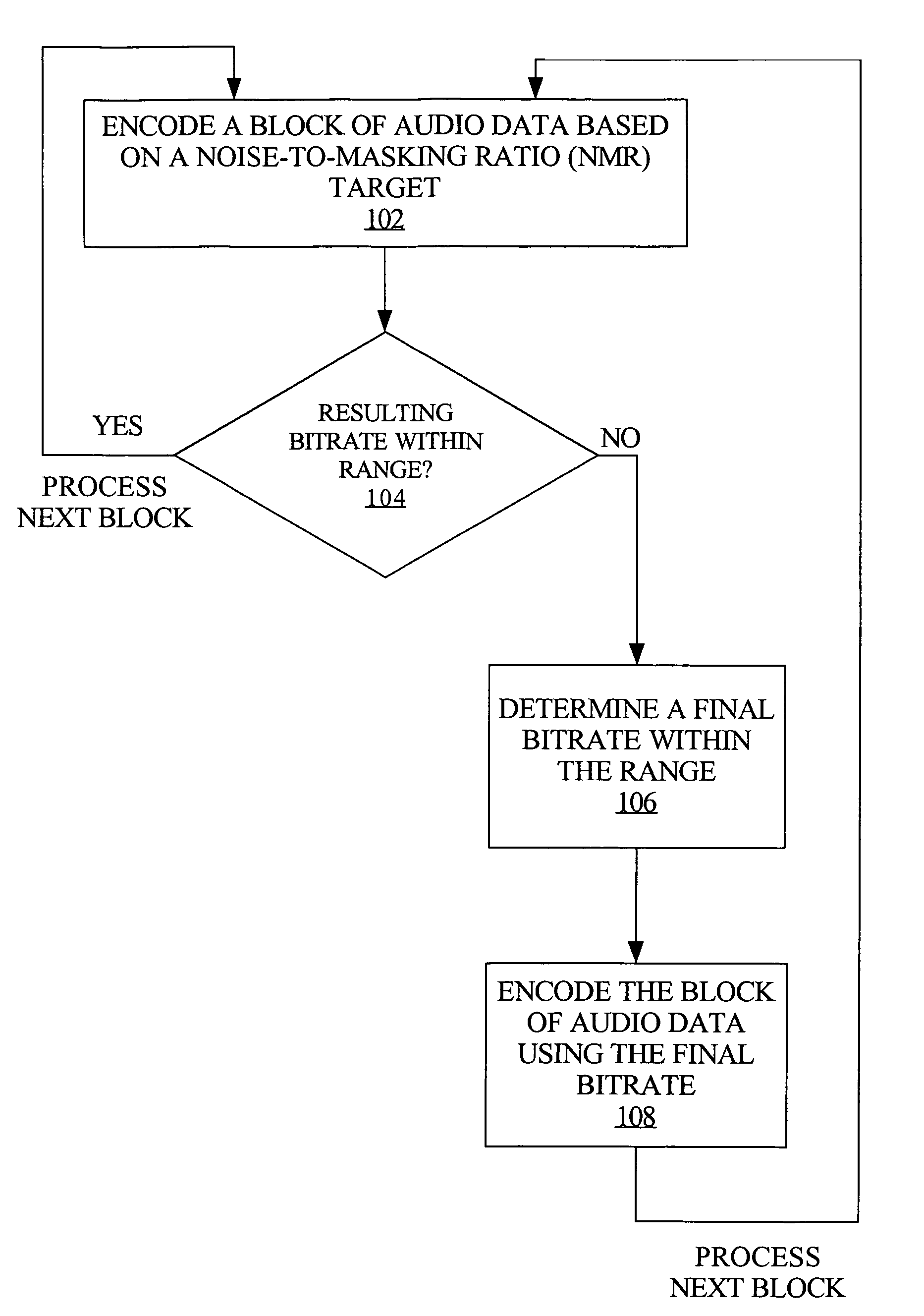
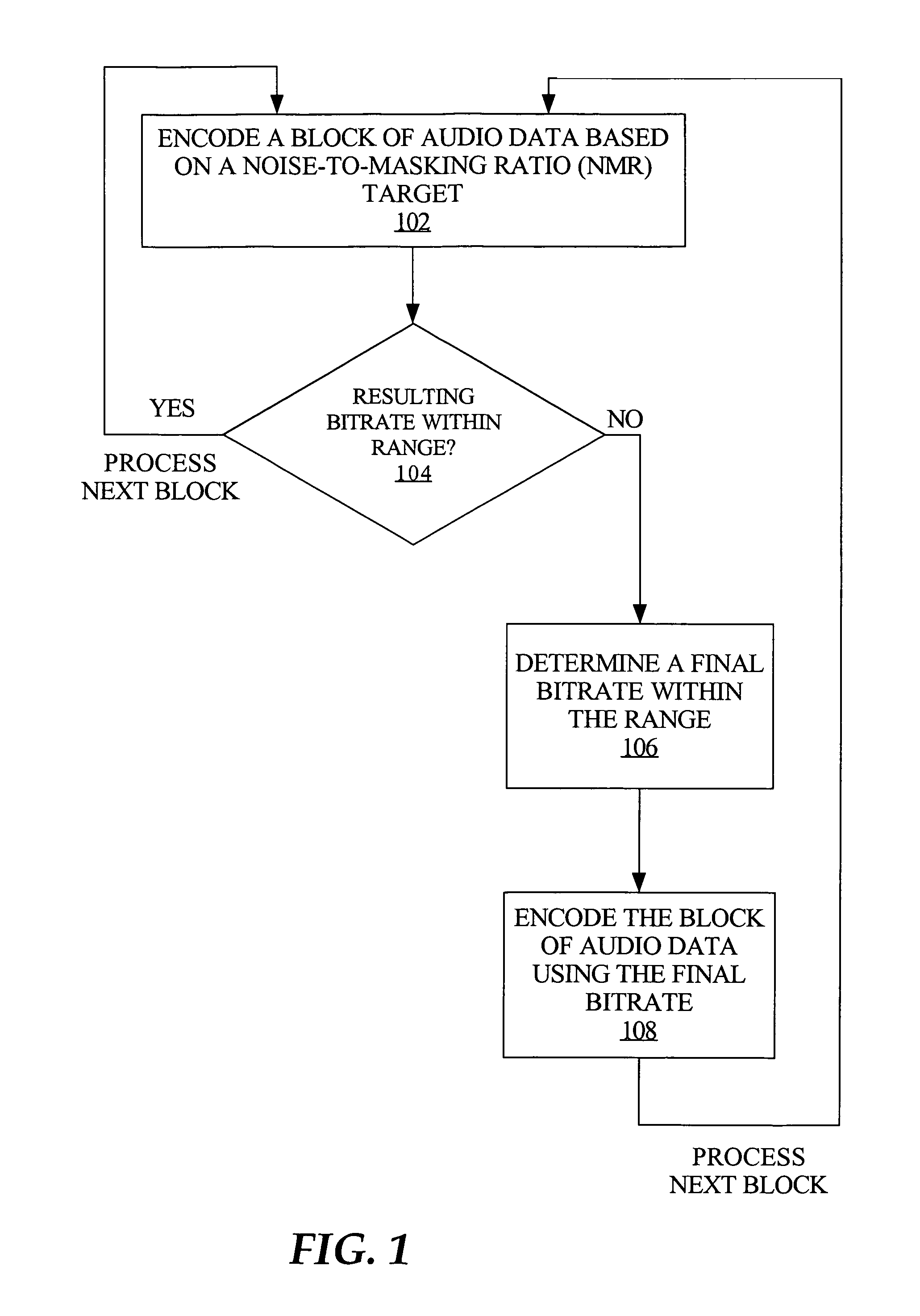
Bitrate constrained variable bitrate audio encoding
ActiveUS7634413B1Excessively high bitratesImprove sound qualitySpeech analysisCoding blockSound quality
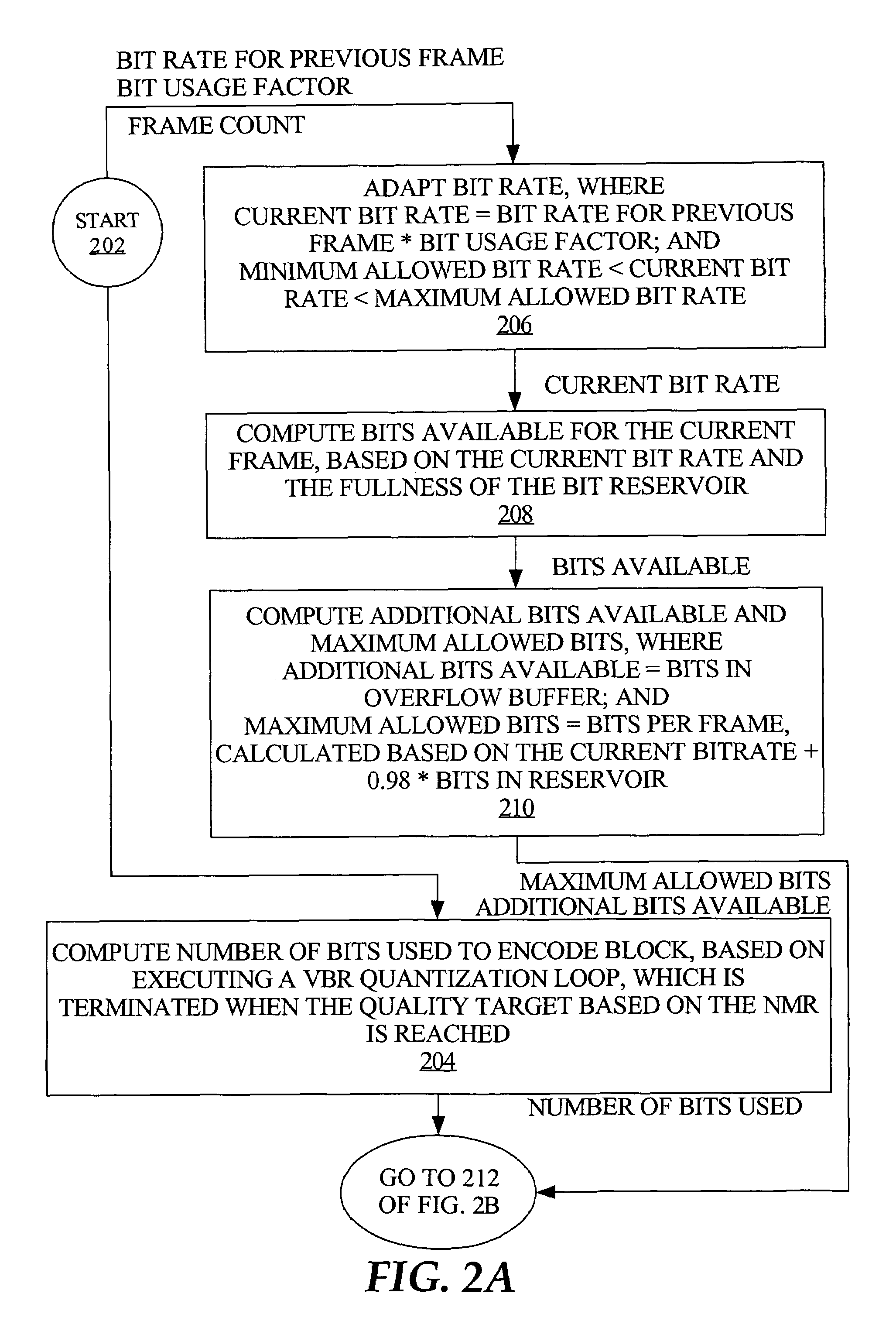
A hybrid audio encoding technique incorporates both ABR, or CBR, and VBR encoding modes. For each audio coding block, after a VBR quantization loop meets the NMR target, a second quantization loop might be called to adaptively control the final bitrate. That is, if the NMR-based quantization loop results in a bitrate that is not within a specified range, then a bitrate-based CBR or ABR quantization loop determines a final bitrate that is within the range and is adaptively determined based on the encoding difficulty of the audio data. Excessive bitrates from use of conventional VBR mode are eliminated, while still providing much more constant perceptual sound quality than use of conventional CBR mode can achieve.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and apparatus for diphone aliasing
The present invention improves upon electronic speech synthesis using pre-recorded segments of speech to fill in for other missing segments of speech. The formalized aliasing approach of the present invention overcomes the ad hoc aliasing approach of the prior art which oftentimes generated less than satisfactory speech synthesis sound output. By formalizing the relationship between missing speech sound samples and available speech sound samples, the present invention provides a structured approach to aliasing which results in improved synthetic speech sound quality. Further, the formalized aliasing approach of the present invention can be used to lessen storage requirements for speech sound samples by only storing as many sound samples as memory capacity can support.
Owner:APPLE INC
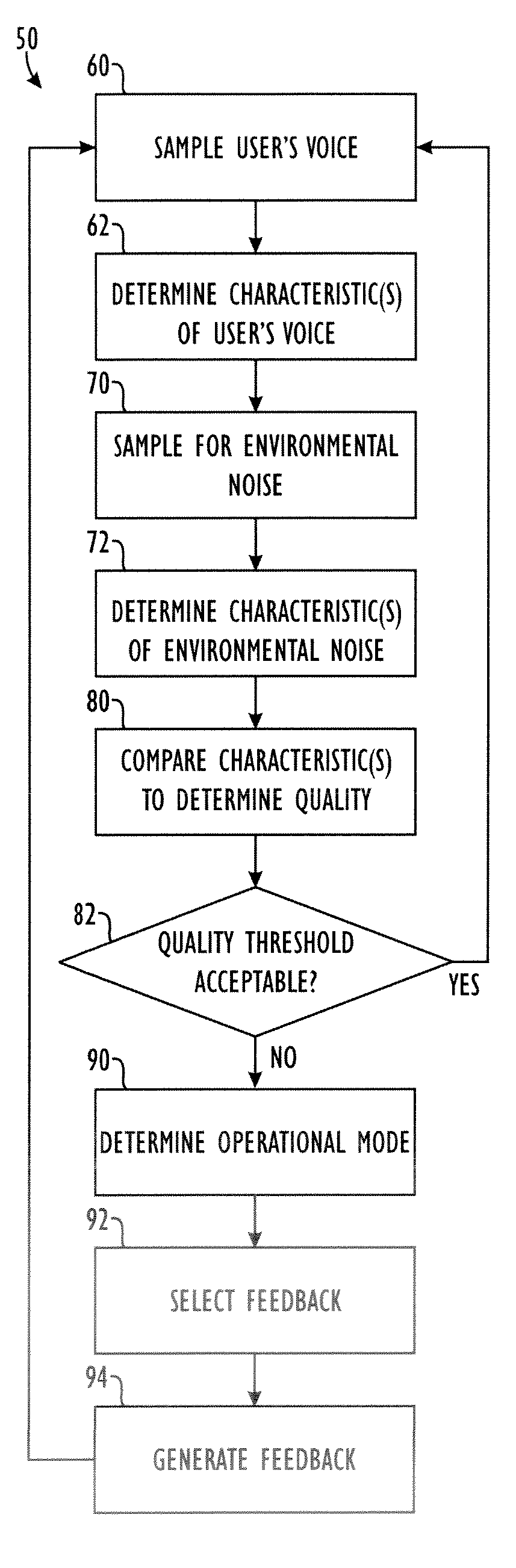
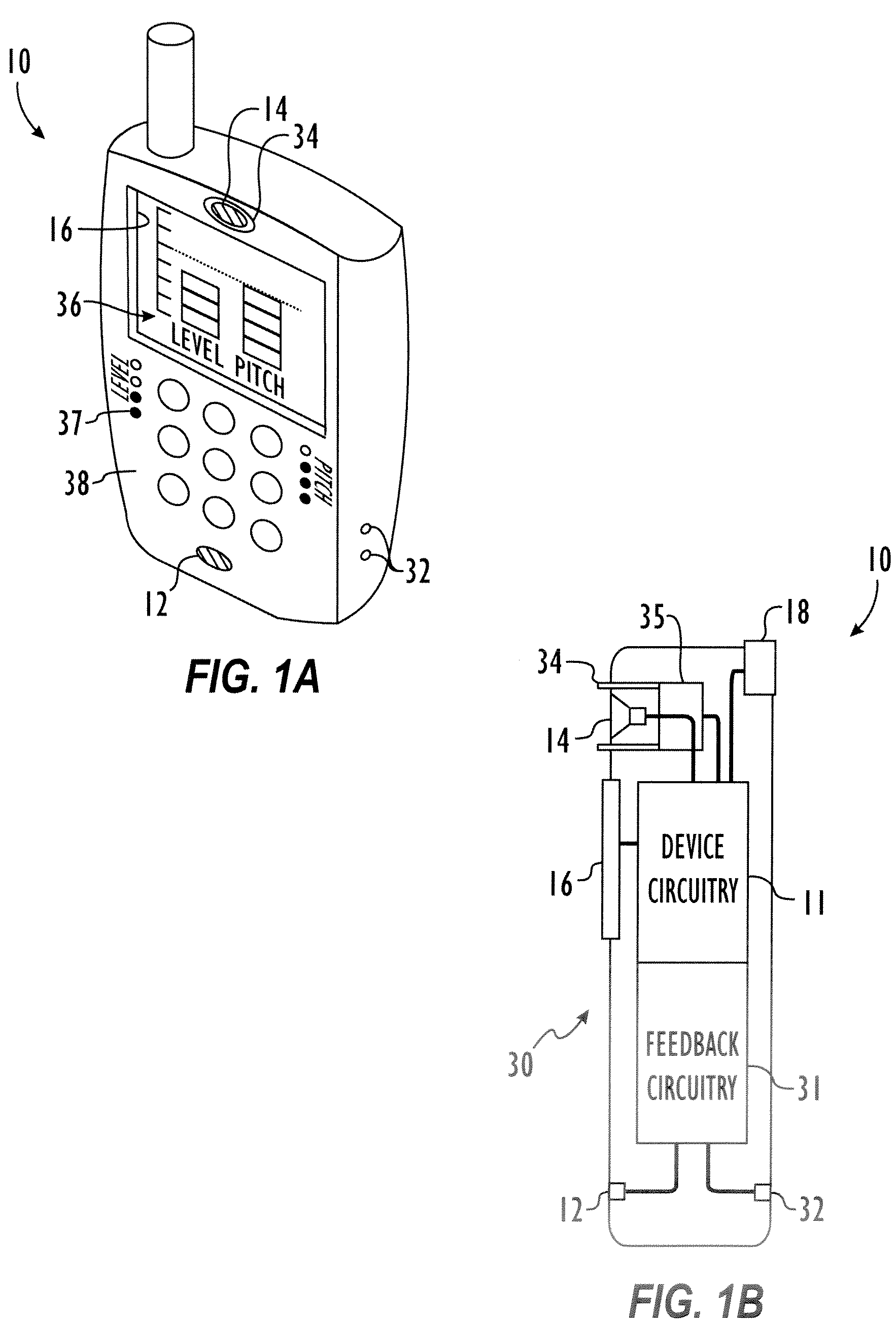
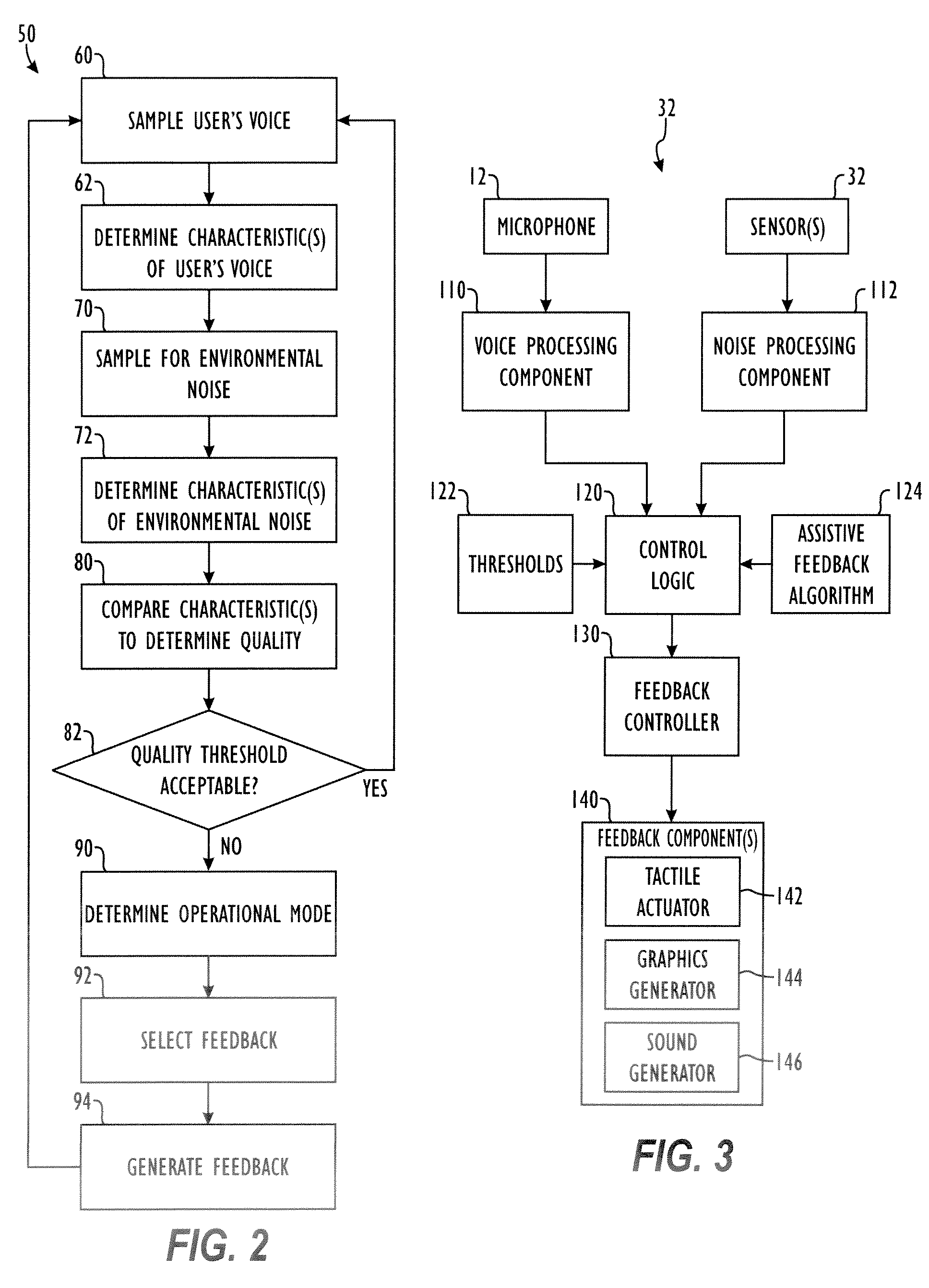
Method and apparatus for providing feedback of vocal quality to a user
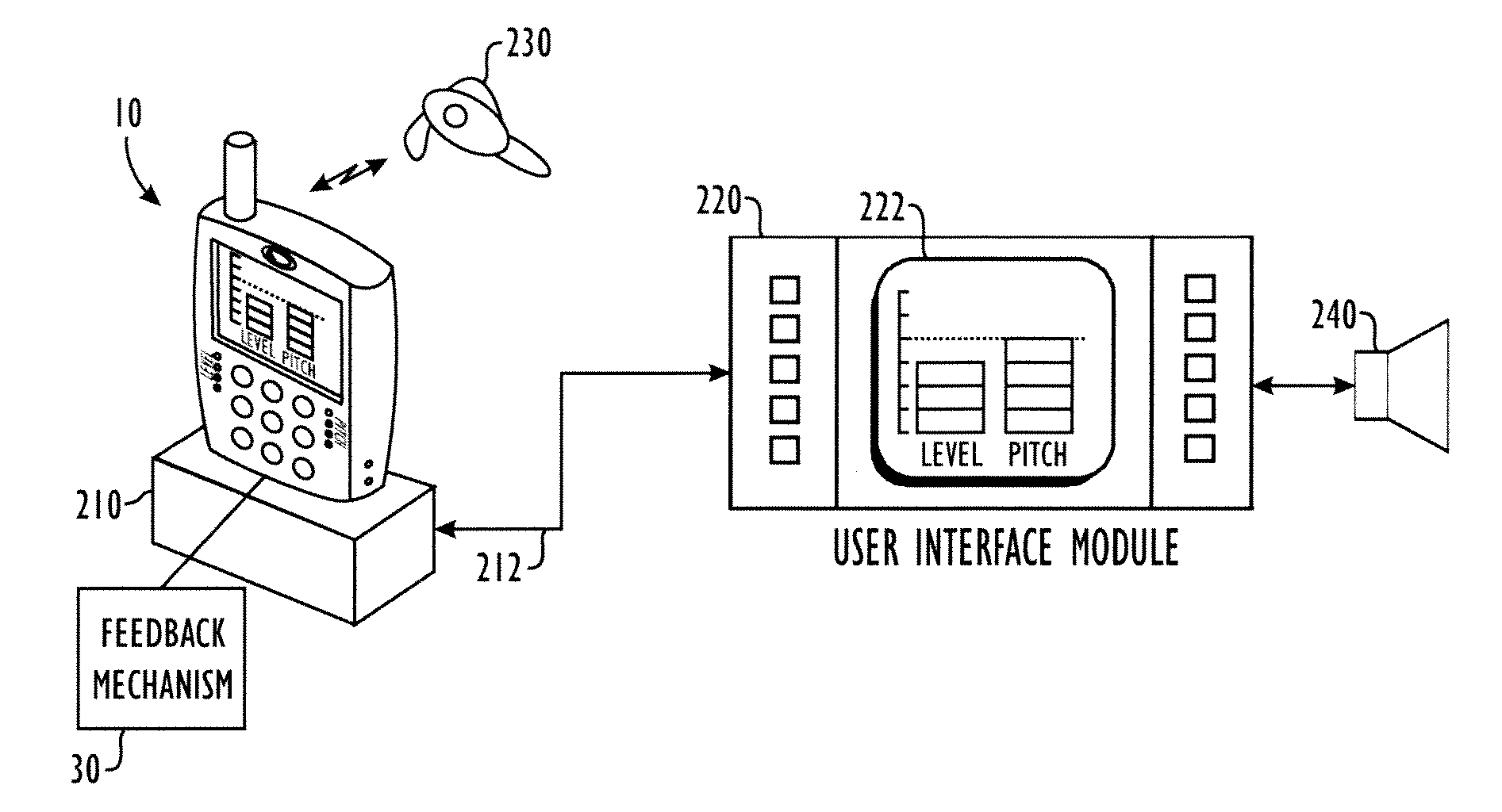
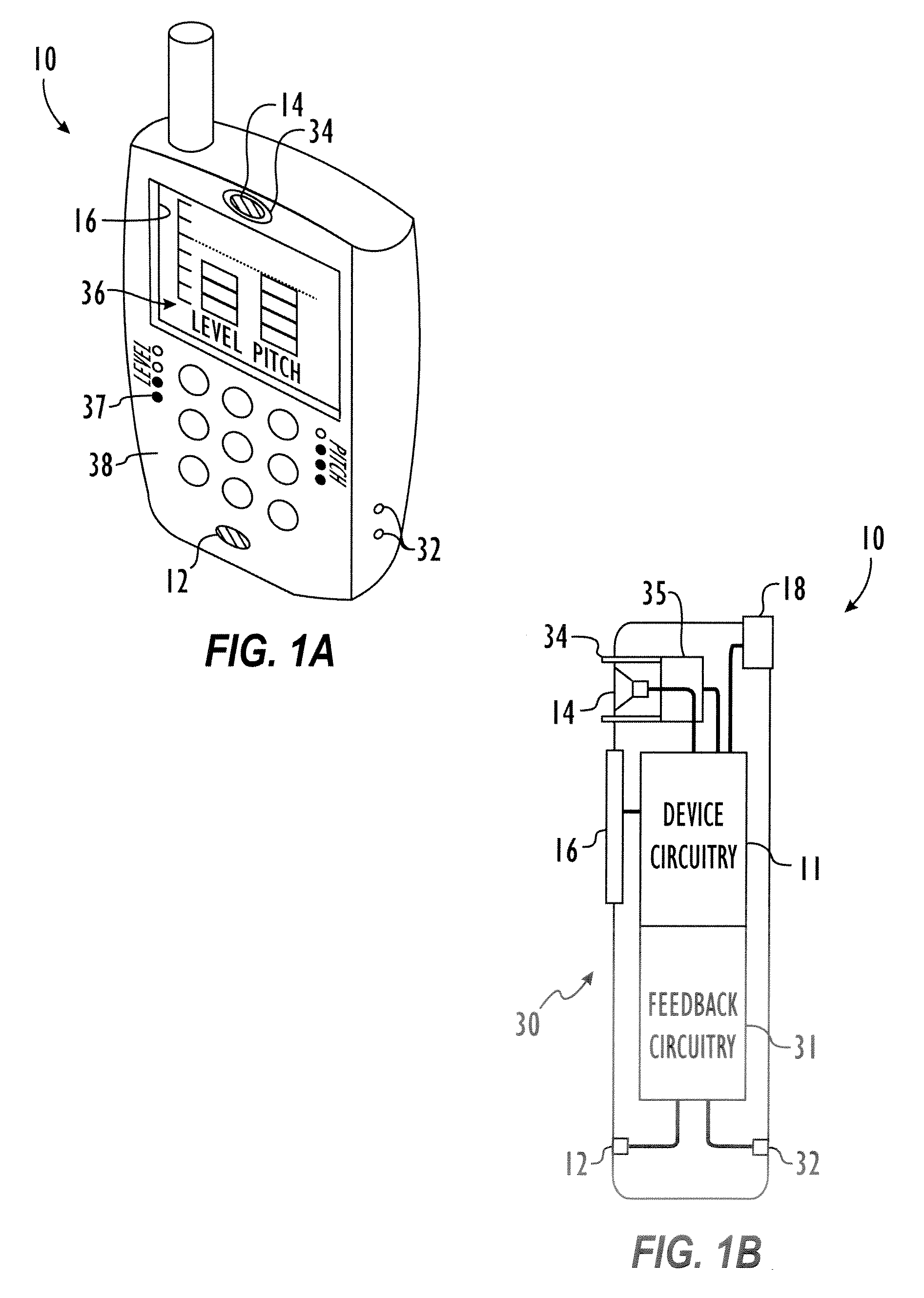
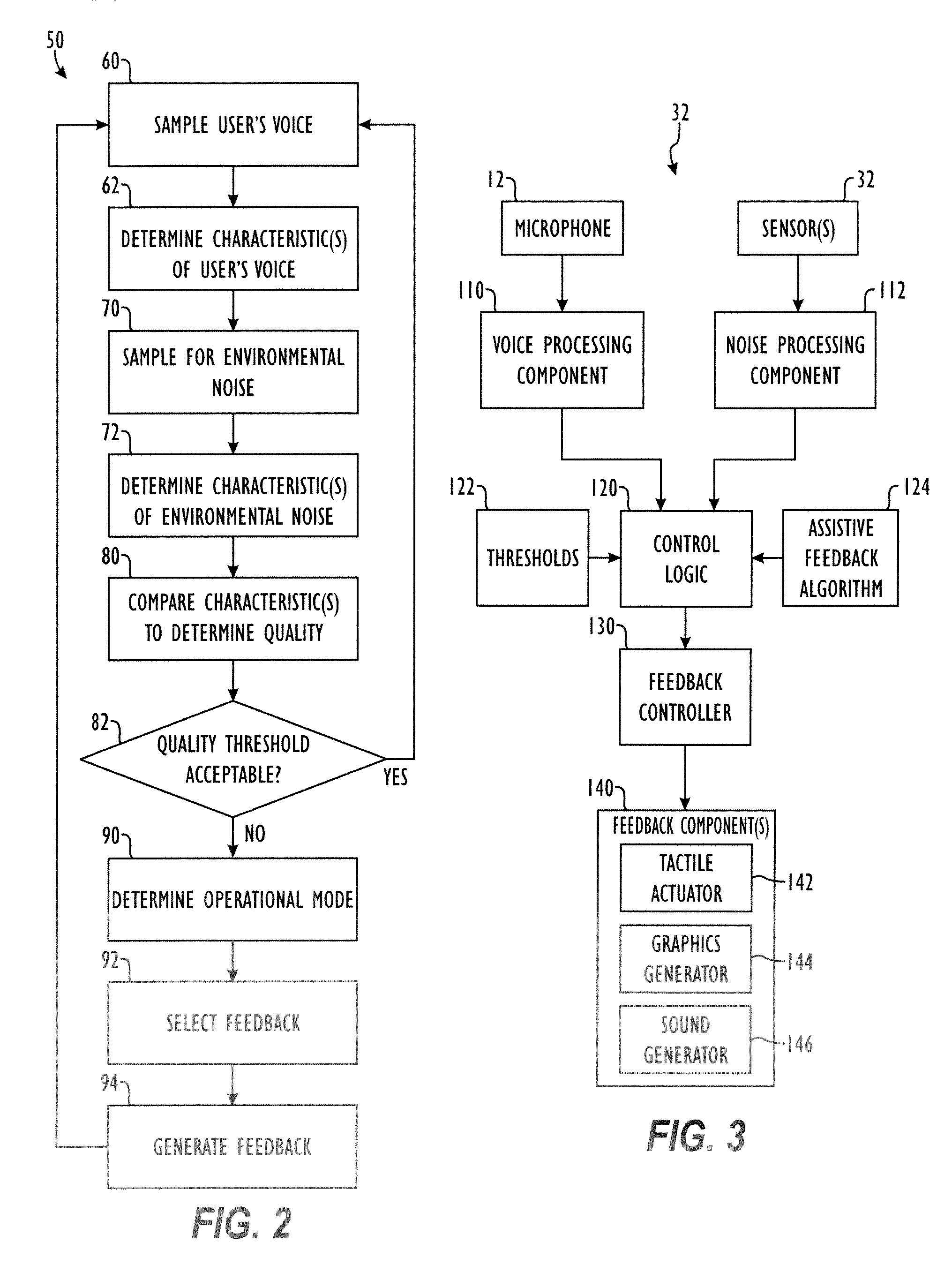
Embodiments of the invention relate to a feedback mechanism that informs a user of a communication device to adjust the volume, pitch, tone or other characteristic of his voice so as to compensate for noise in the surrounding environment. The feedback mechanism includes feedback circuitry that analyzes audio signals from the microphone and preferably from one or more additional environmental noise sensors. From the analysis, the feedback circuitry determines characteristics of the user's voice and characteristics of the environmental noise, and provides an analysis of how the user might modify his voice to best compensate for environmental noise. This analysis results in an indication to the user, such as through a vibration, a sound, or graphical indication on the device, which tells the user whether and to what extent the user should adjust a characteristic of his voice to best overcome such environmental noise.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
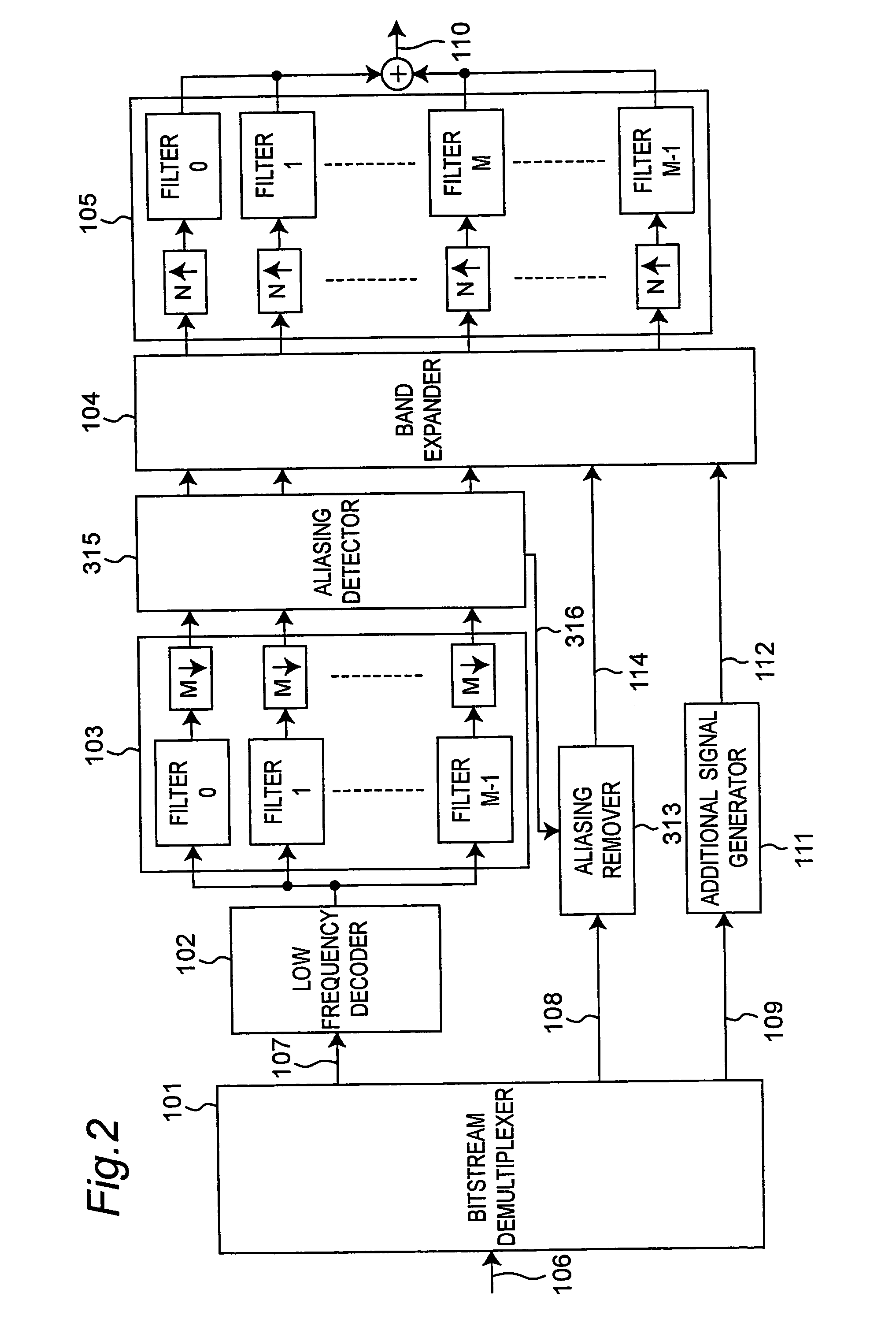
Audio decoding apparatus and method
ActiveUS20050149339A1Suppress aliasingPrevent degradationSpeech analysisCode conversionSound qualityAudio frequency
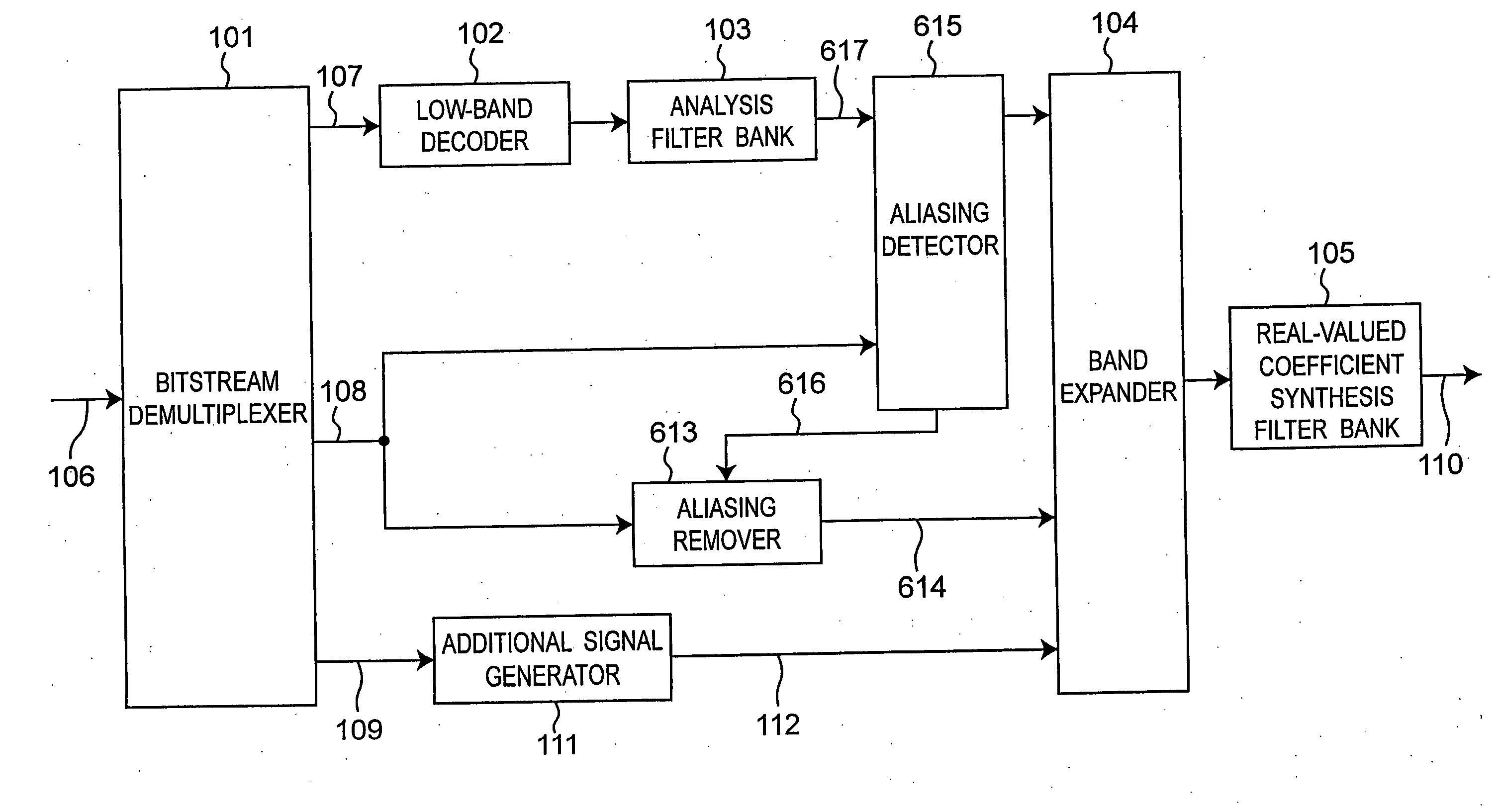
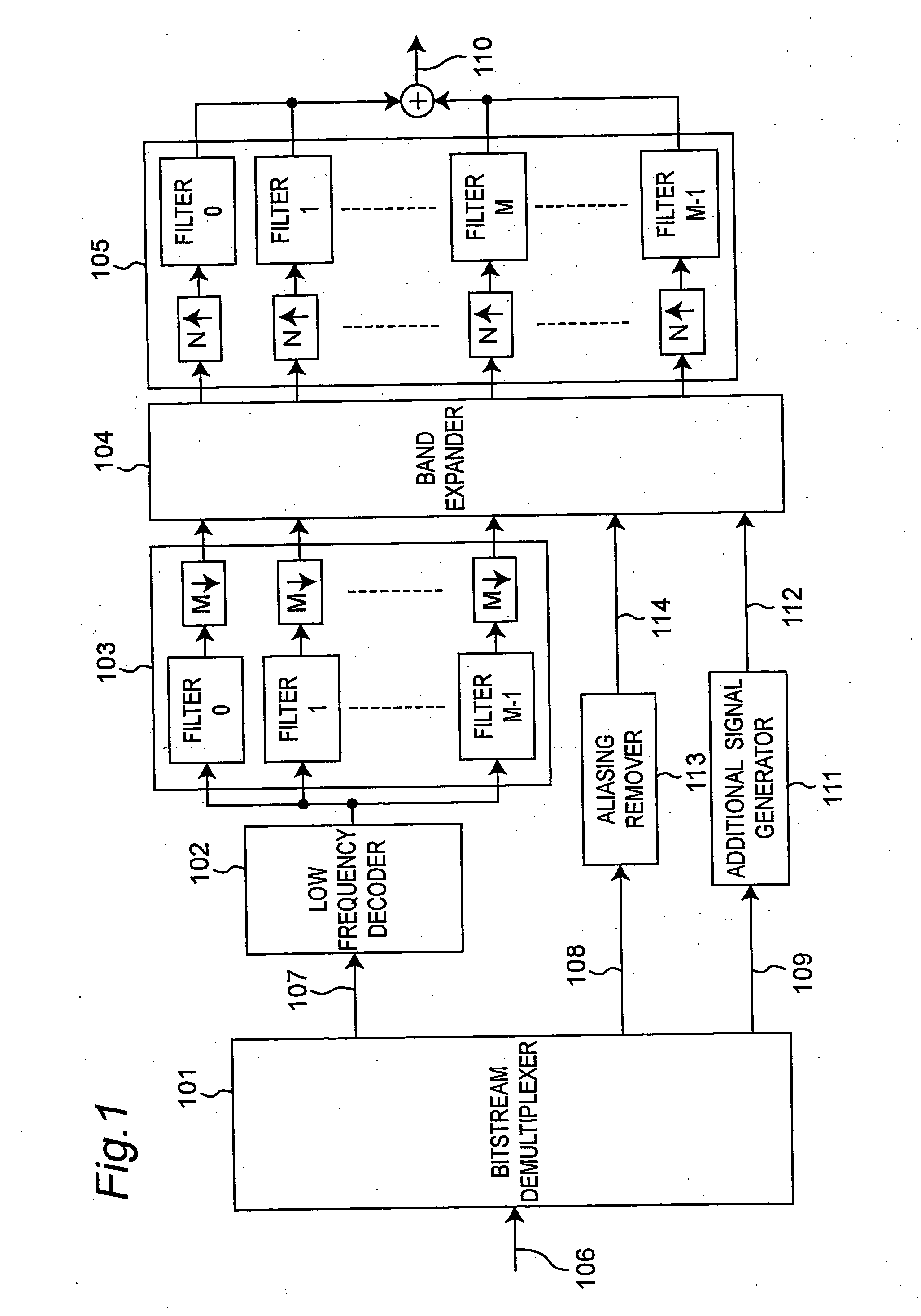
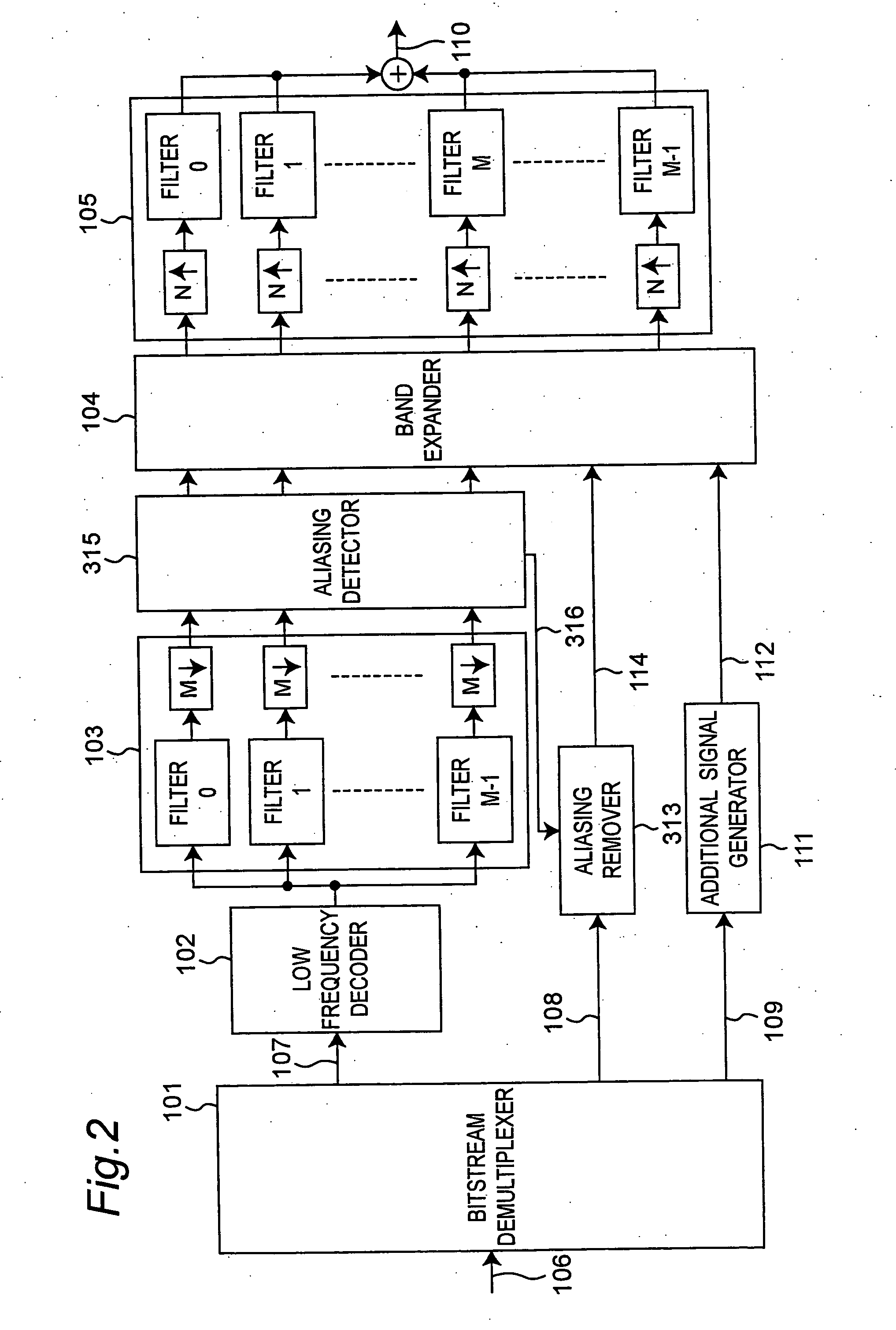
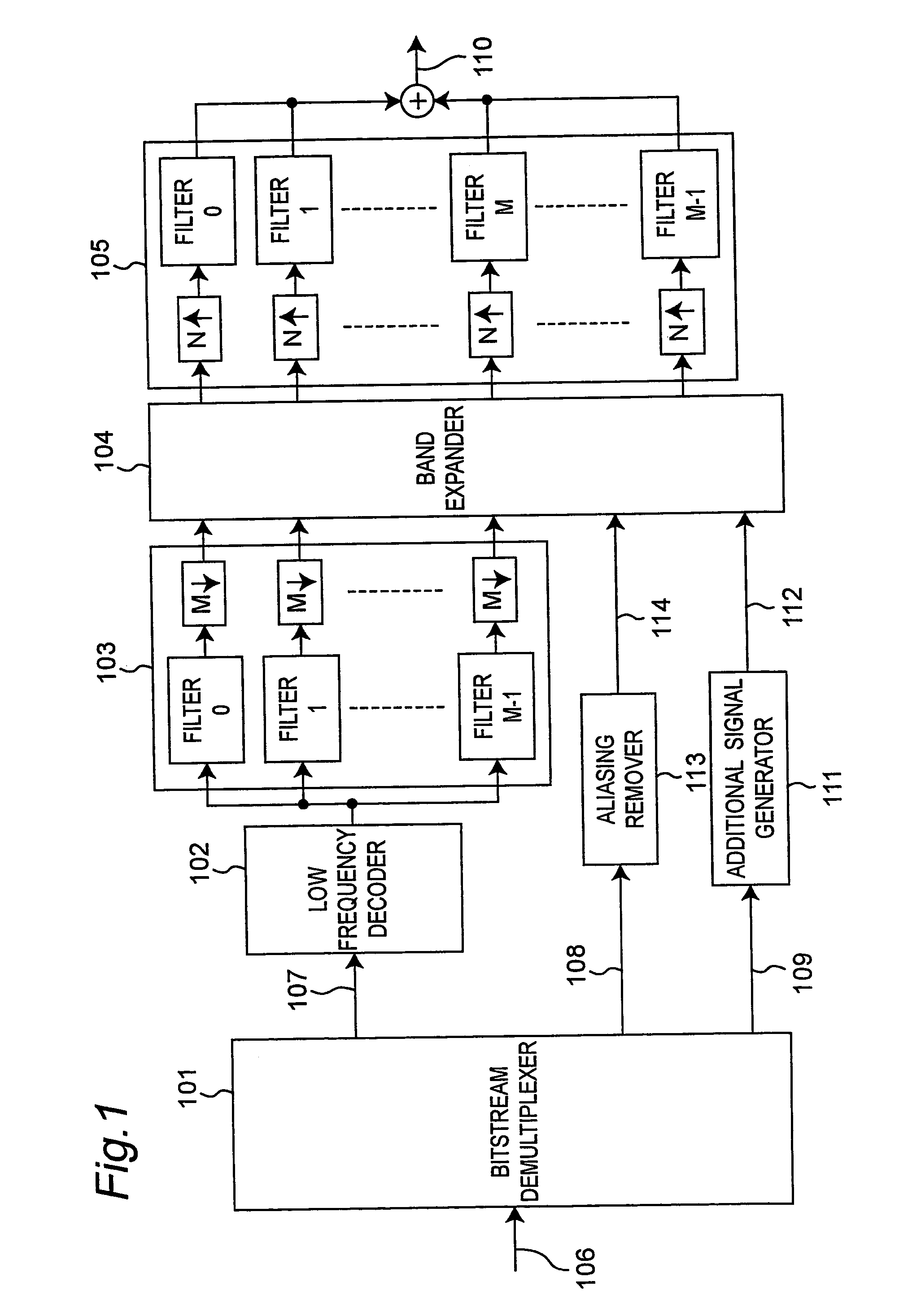
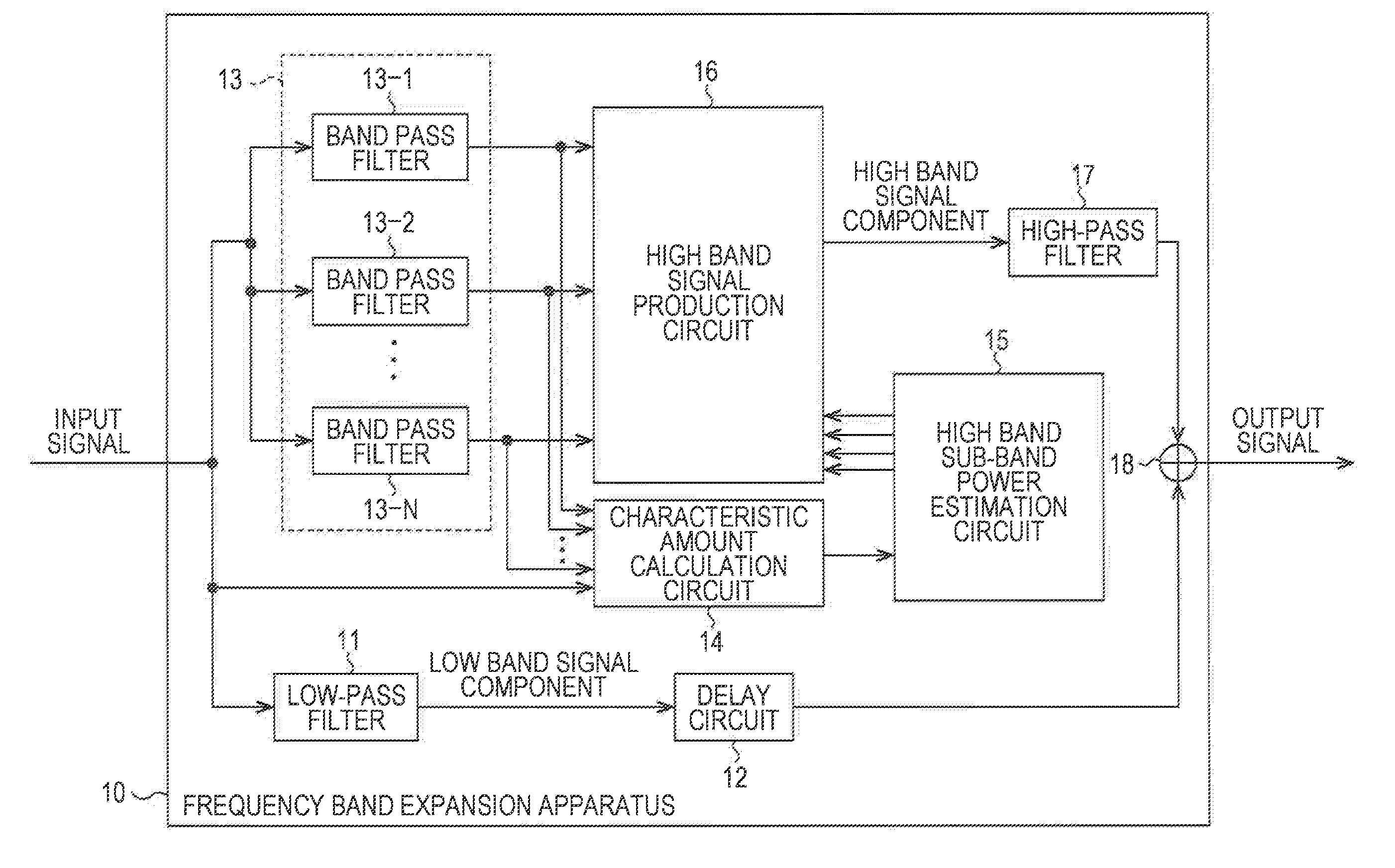
An audio decoding apparatus decodes high frequency component signals using a band expander that generates multiple high frequency subband signals from low frequency subband signals divided into multiple subbands and transmitted high frequency encoded information. The apparatus is provided with an aliasing detector and an aliasing remover. The aliasing detector detects the degree of occurrence of aliasing components in the multiple high frequency subband signals generated by the band expander. The aliasing remover suppresses aliasing components in the high frequency subband signals by adjusting the gain used to generate the high frequency subband signals. Thus occurrence of aliasing can be suppressed and the resulting degradation in sound quality can be reduced, even when real-valued subband signals are used in order to reduce the number of operations.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
Audio decoding apparatus and method for band expansion with aliasing adjustment
InactiveUS7069212B2Reduce in quantityImprove sound qualityCode conversionSpeech synthesisSound qualityComputer science
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
Enhancing audio using a mobile device
ActiveUS20160035337A1Gain controlVolume compression/expansion in untuned/low-frequency amplifiersNoise levelSound quality
Embodiments disclosed herein enable detection and improvement of the quality of the audio signal using a mobile device by determining the loss in the audio signal and enhancing audio by streaming the remainder portion of audio. Embodiments disclosed herein enable an improvement in the sound quality rendered by rendering devices by emitting an test audio signal from the source device, measuring the test audio signal using microphones, detecting variation in the frequency response, loudness and timing characteristics using impulse responses and correcting for them. Embodiments disclosed herein also compensate for the noise in the acoustic space by determining the reverberation and ambient noise levels and their frequency characteristics and changing the digital filters and volumes of the source signal to compensate for the varying noise levels.
Owner:CAAVO INC
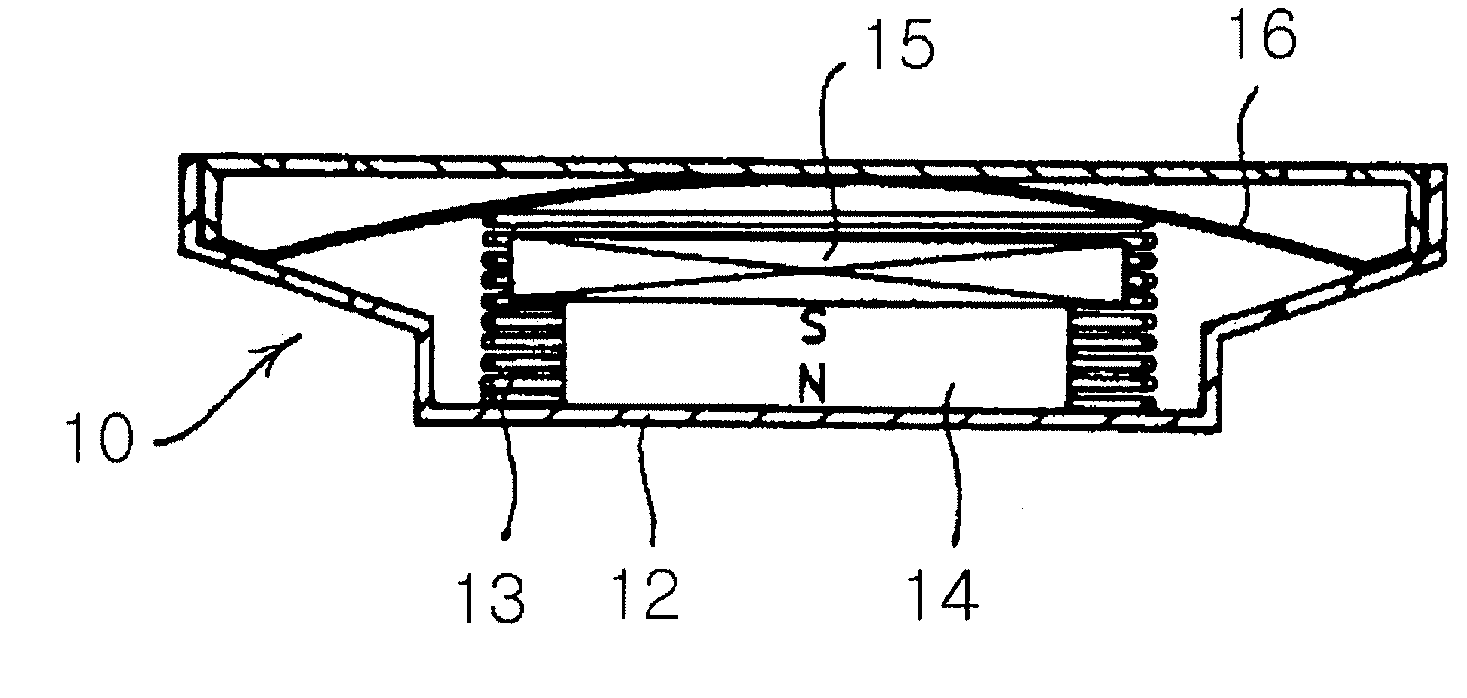
Acoustic Diaphragm and Speaker Having the Same
InactiveUS20080260188A1Good physical propertiesImprove sound qualityFibre diaphragmsPolymeric diaphragmsFiberNanofiber
Disclosed herein is an acoustic diaphragm for converting electrical signals into mechanical signals to produce sounds. The acoustic diaphragm comprises carbon nanotubes or graphite nanofibers as major materials. Preferably, the carbon nanotubes or graphite nanofibers are included or dispersed in the acoustic diaphragm. Since the acoustic diaphragm has excellent physical properties in terms of elastic modulus, internal loss and strength, it can effectively achieve superior sound quality and high output in a particular frequency band as well as in a broad frequency band.
Owner:KH CHEM CO LTD
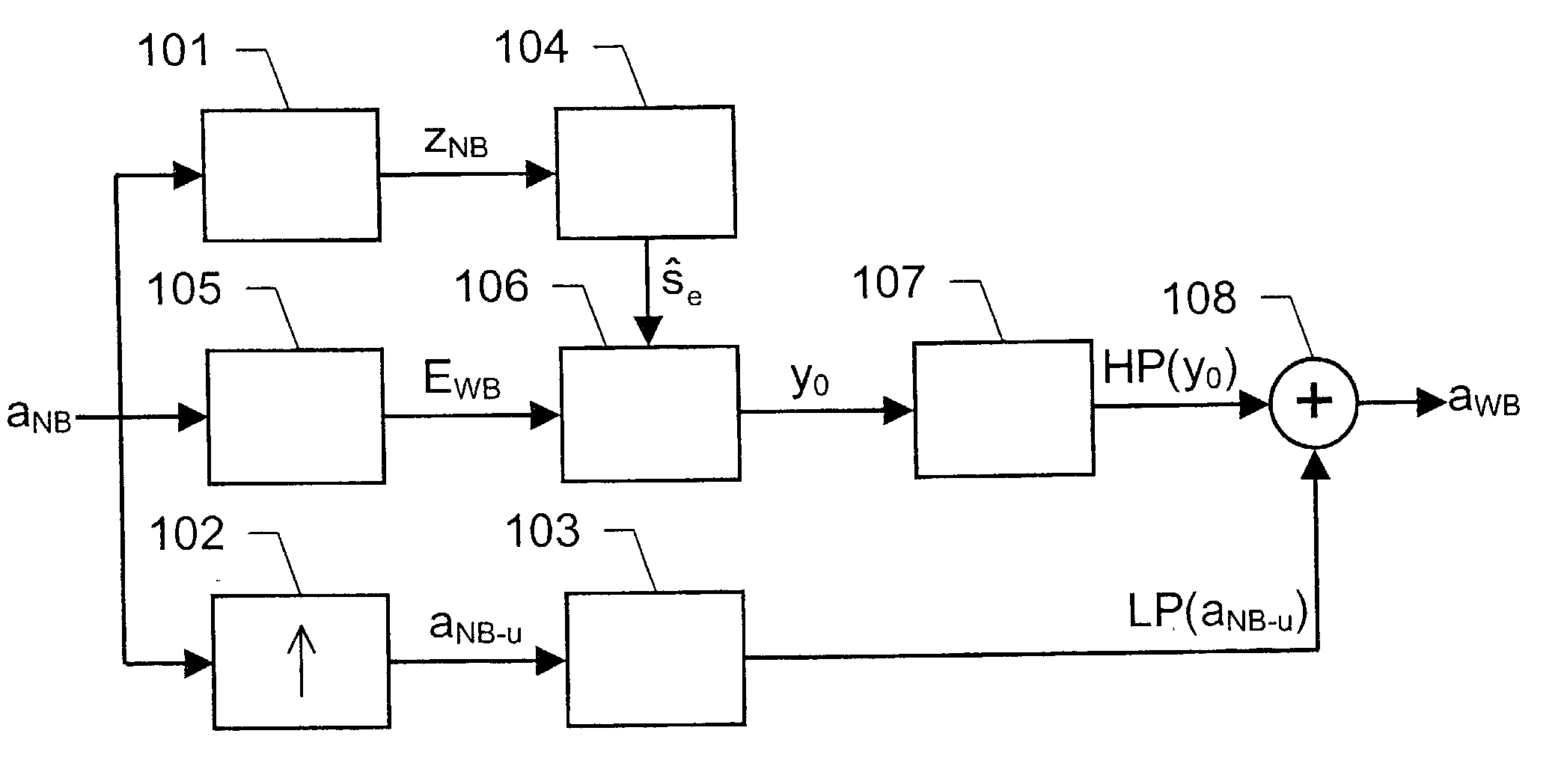
Bandwidth extension of acoustic signals
InactiveUS20030009327A1Reduce the amount requiredImprove sound qualitySpeech synthesisBandwidth extensionFrequency spectrum
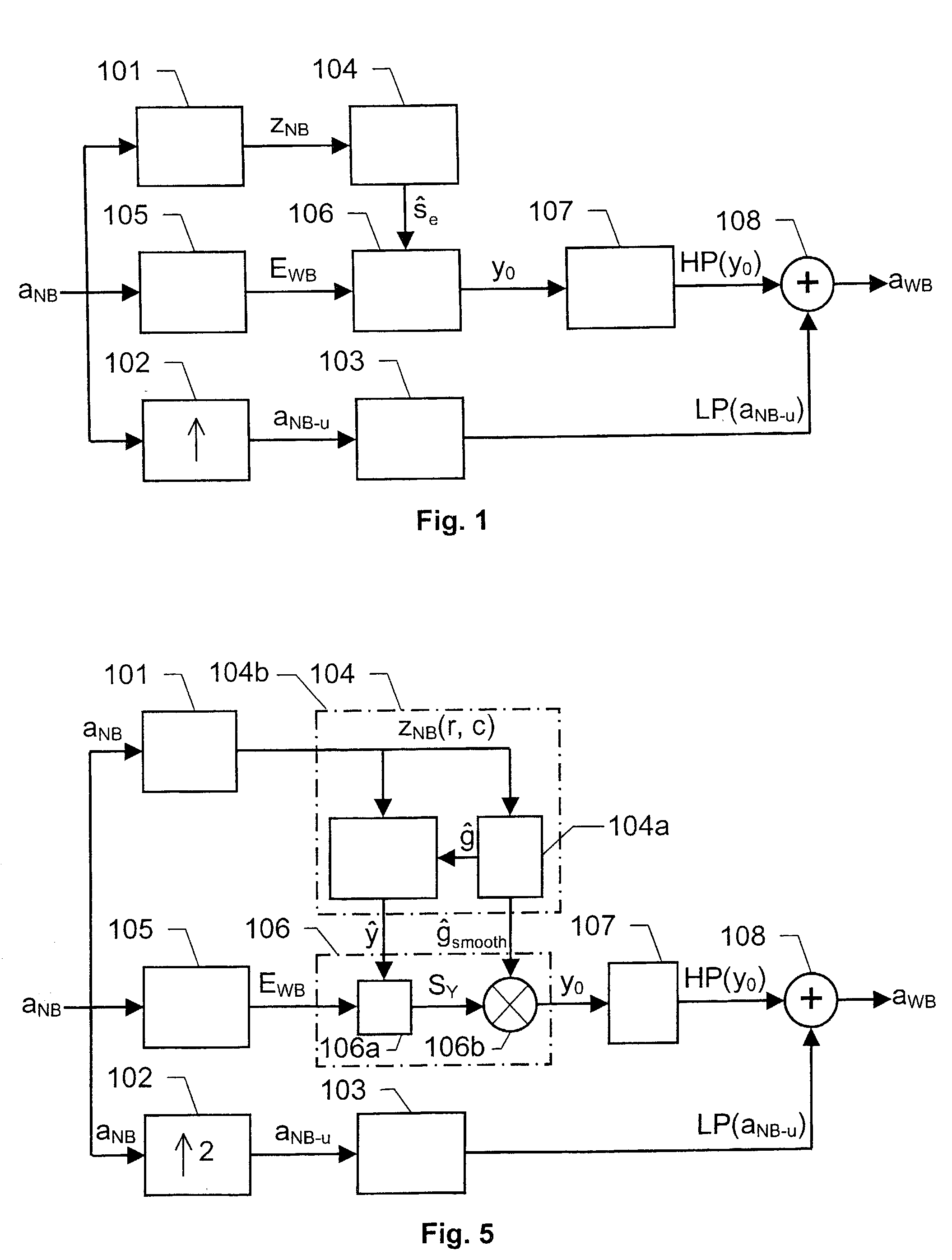
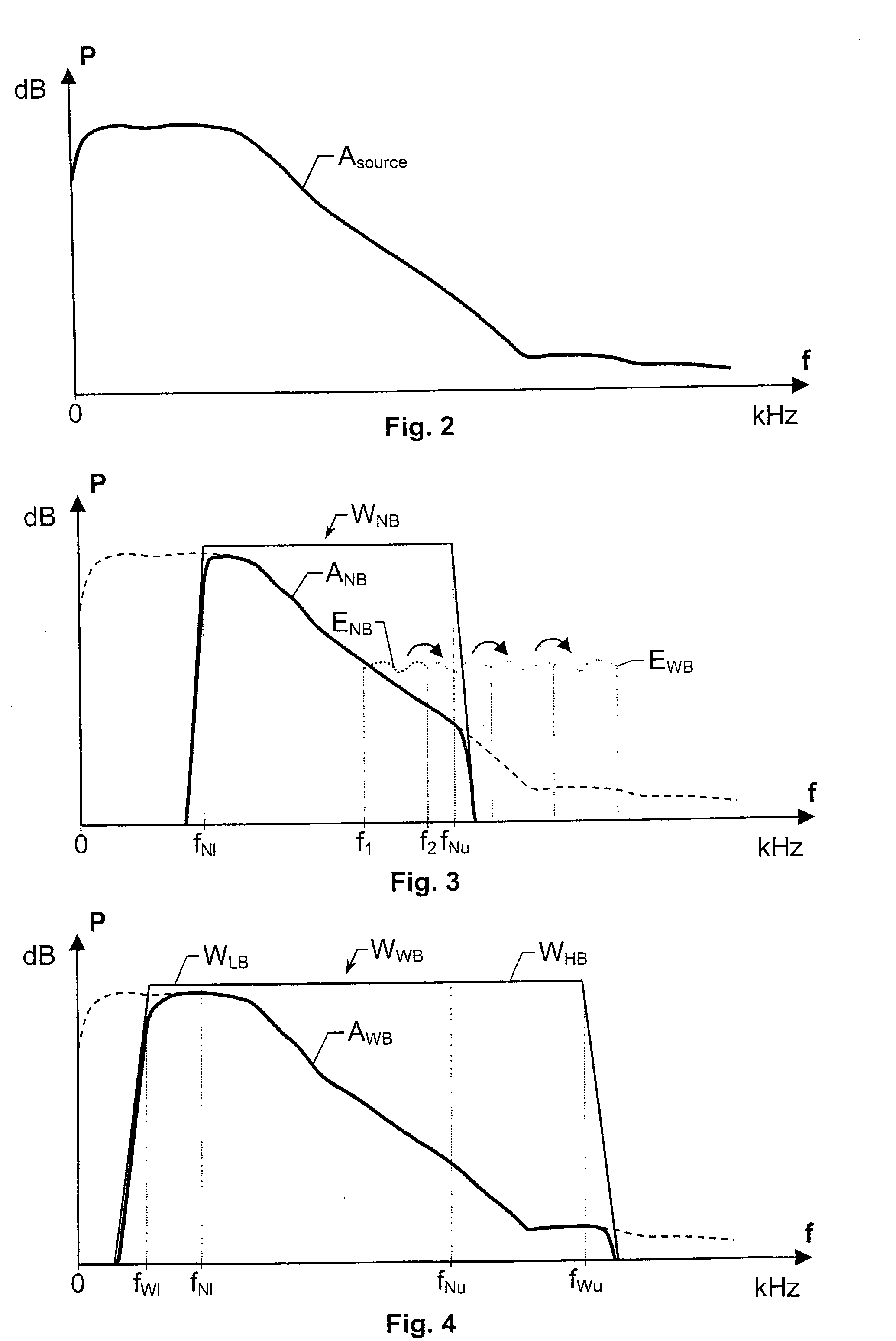
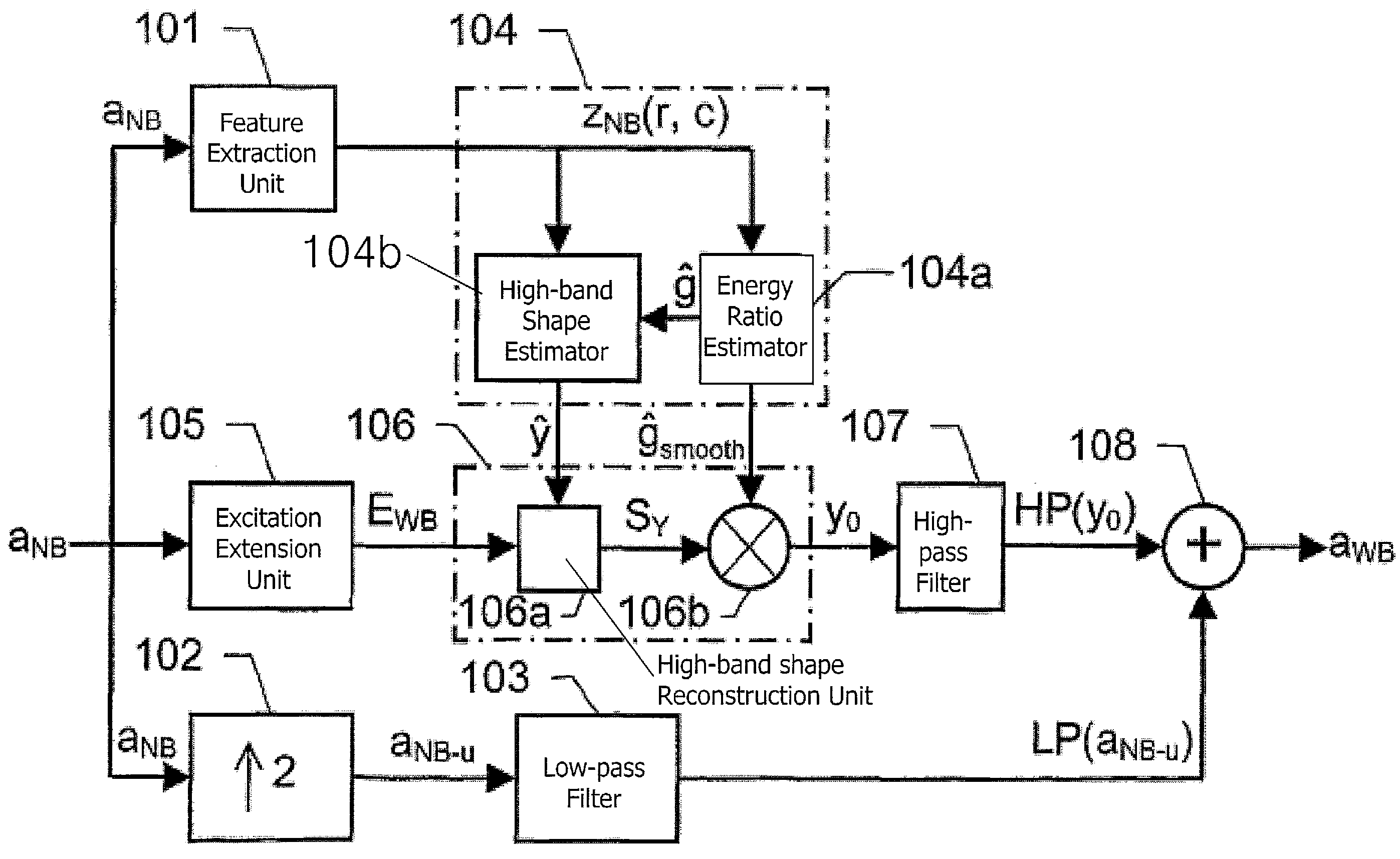
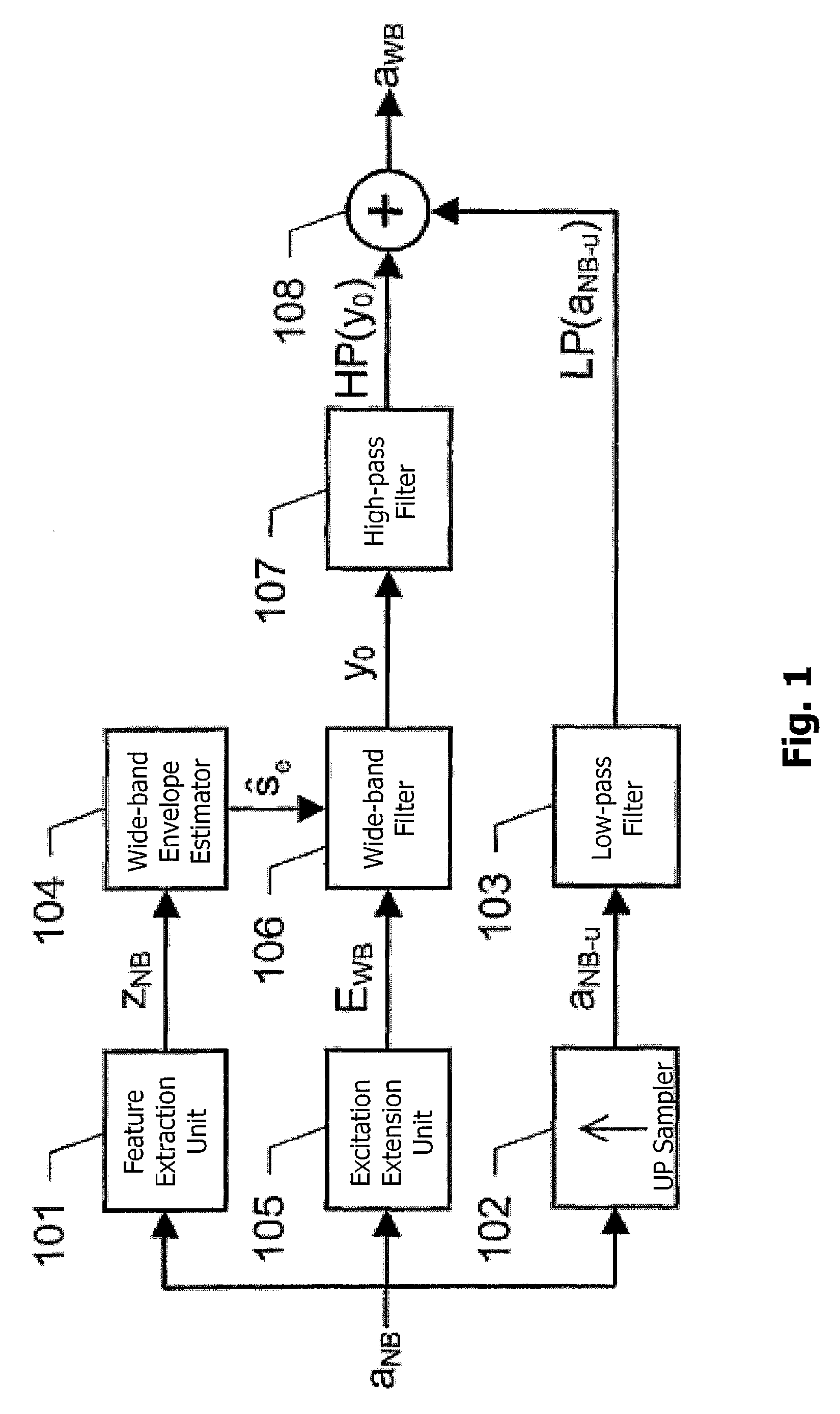
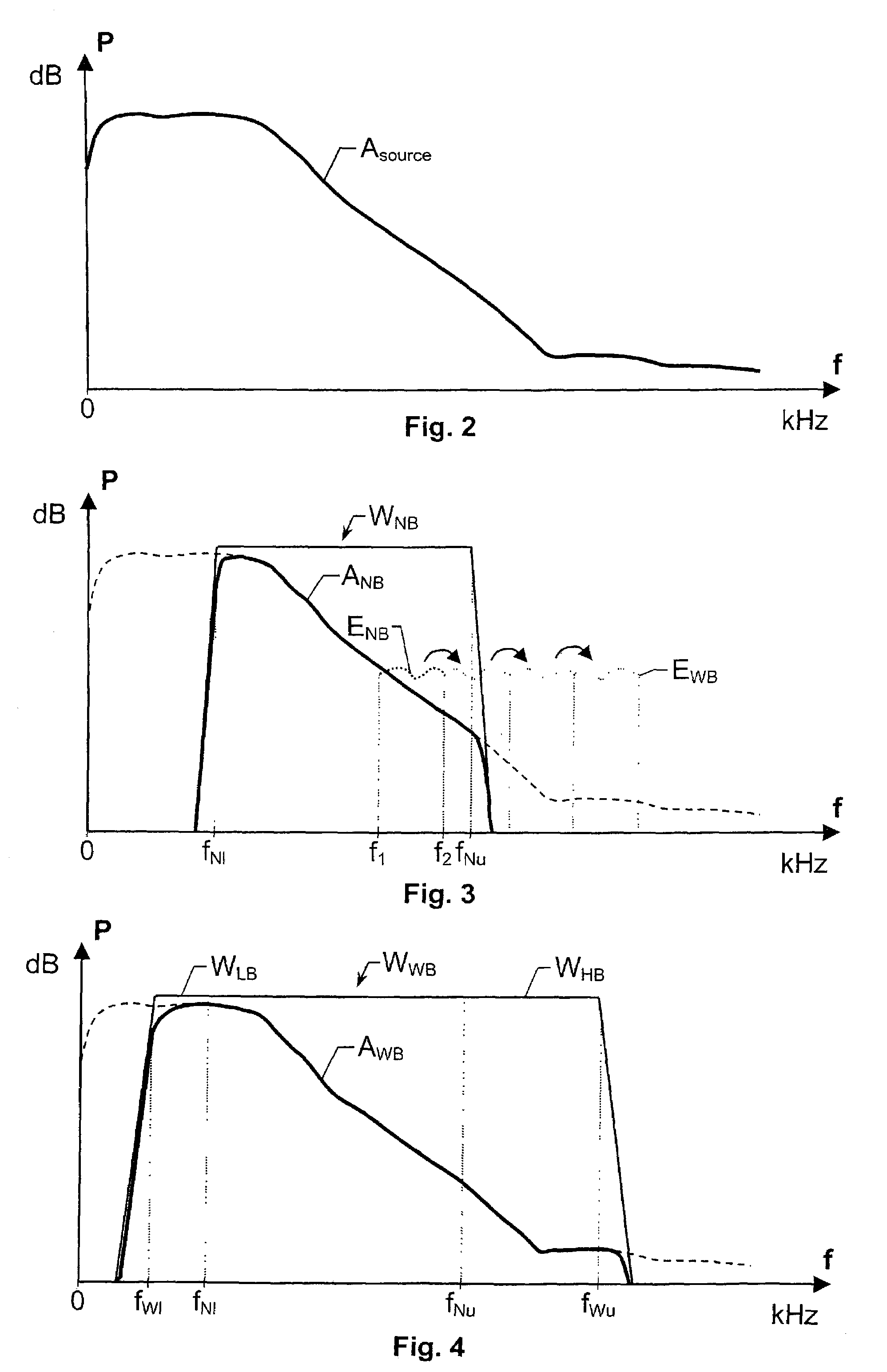
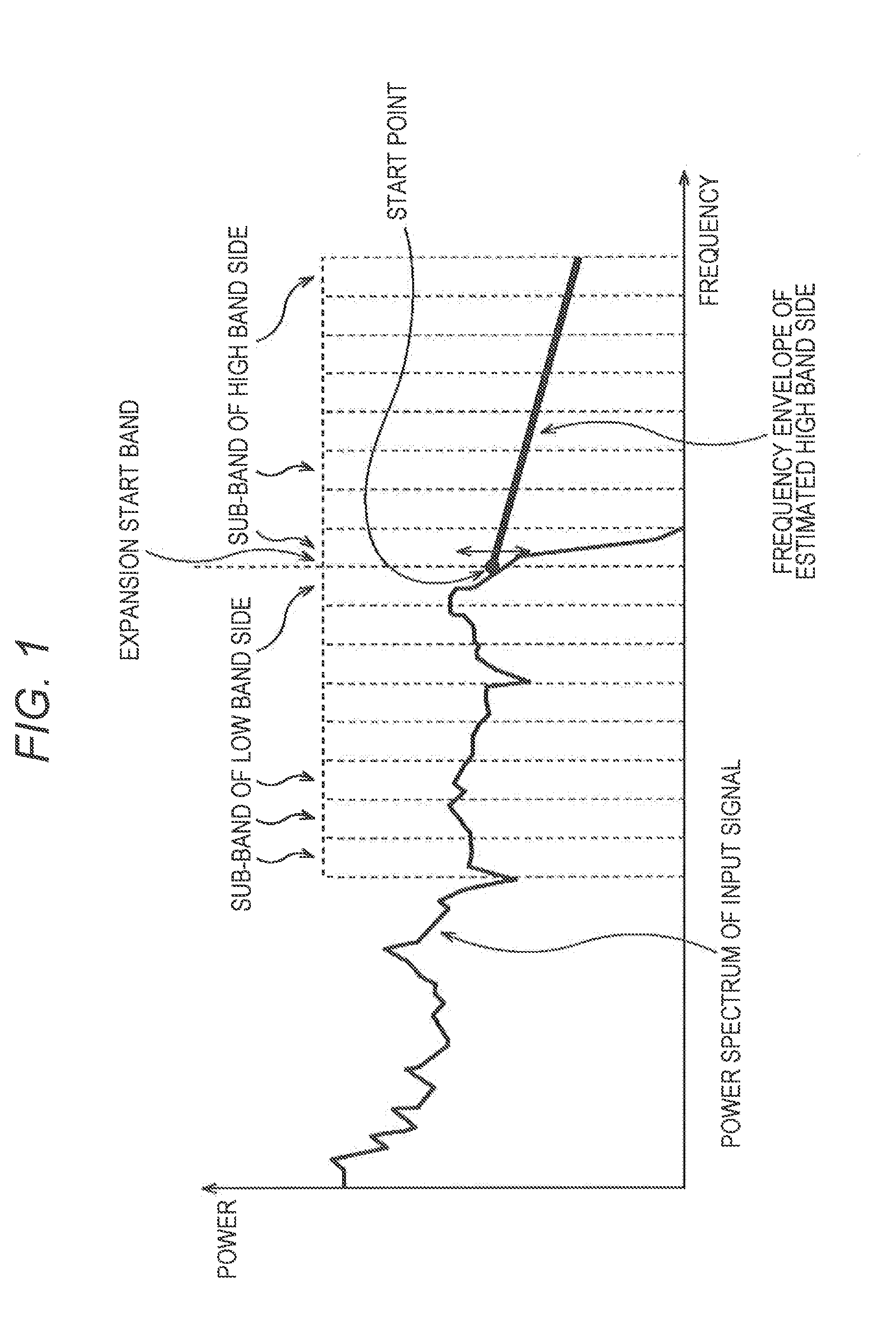
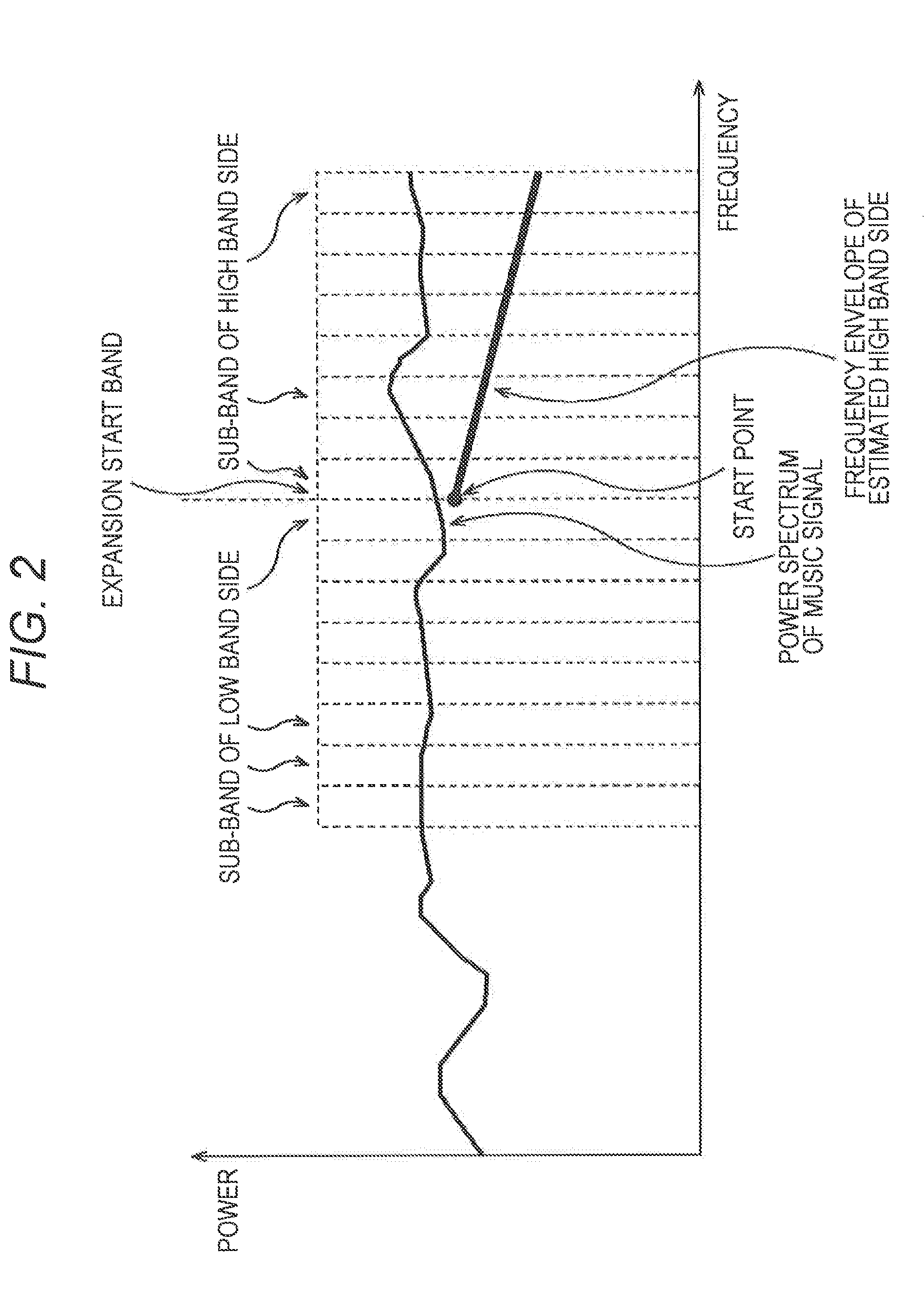
The present invention relates to a solution for improving the perceived sound quality of a decoded acoustic signal. The improvement is accomplished by means of extending the spectrum of a received narrow-band acoustic signal (aNB). According to the invention, a wide-band acoustic signal (aWB) is produced by extracting at least one essential attribute (zNB) from the narrow-band acoustic signal (aNB). Parameters, e.g. representing signal energies, with respect to wide-band frequency components outside the spectrum (ANB) of the narrow-band acoustic signal (aNB) are estimated based on the at least one essential attribute (zNB). This estimation involves allocating a parameter value to a wide-band frequency component, based on a corresponding confidence level. For instance, a relatively high parameter value is allowed to be allocated to a frequency component if it has a comparatively high degree certainty. In contrast, a relatively low parameter value is only allowed to be allocated to a frequency component if it is associated with a comparatively low degree certainty.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
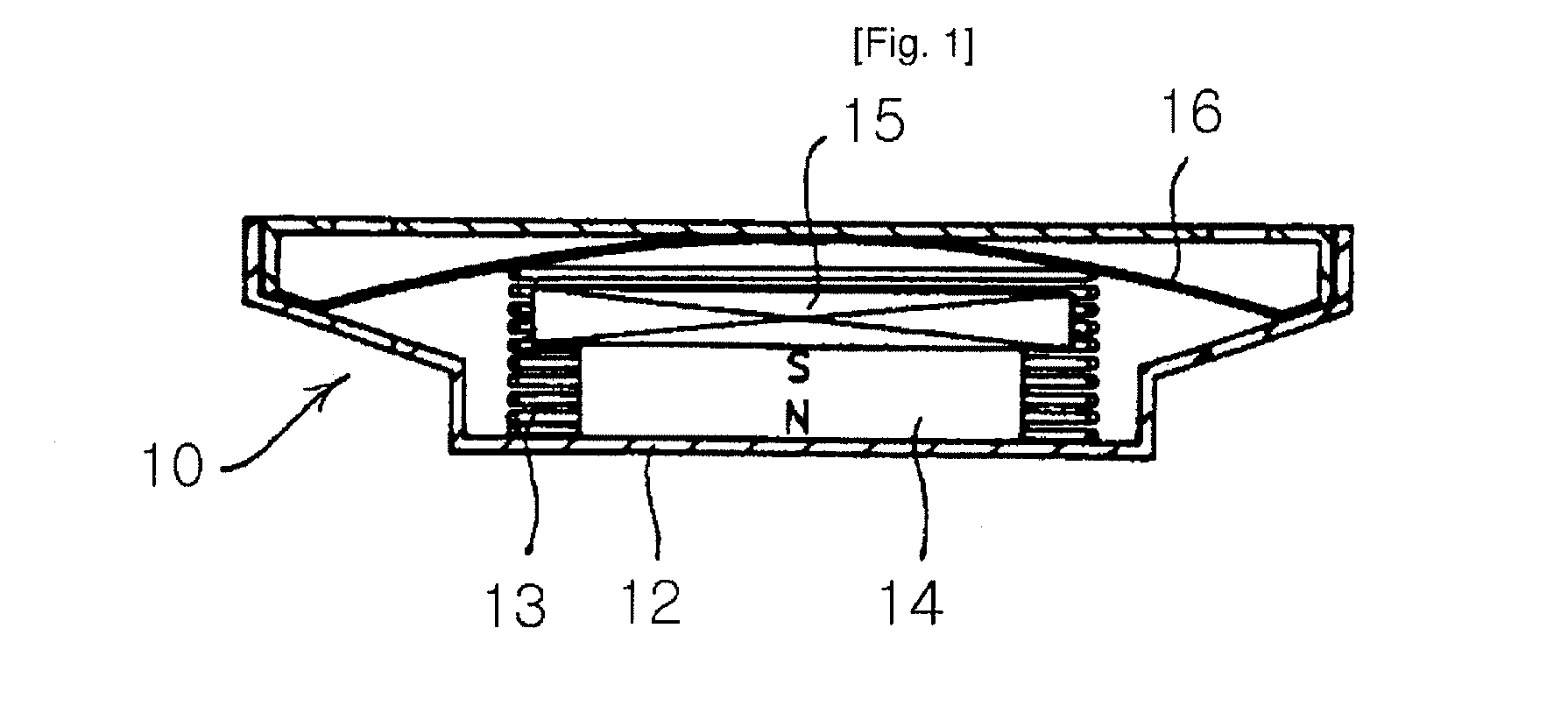
Acoustic Diaphragm and Speakers Having the Same
InactiveUS20090045005A1Good physical propertiesImprove sound qualityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersNanotechnologyFiberNanofiber
Disclosed herein is an acoustic diaphragm for converting electrical signals into mechanical signals to produce sounds. The acoustic diaphragm comprises carbon nanotubes or graphite nanofibers as reinforcing agents. Preferably, the carbon nanotubes or graphite nanofibers are included or dispersed in the acoustic diaphragm or coated on the surface of the acoustic diaphragm. Since the acoustic diaphragm has excellent physical properties in terms of elastic modulus, internal loss, strength and density, it can effectively achieve superior sound quality and a high output in a particular frequency band as well as in a broad frequency band.
Owner:KH CHEM CO LTD
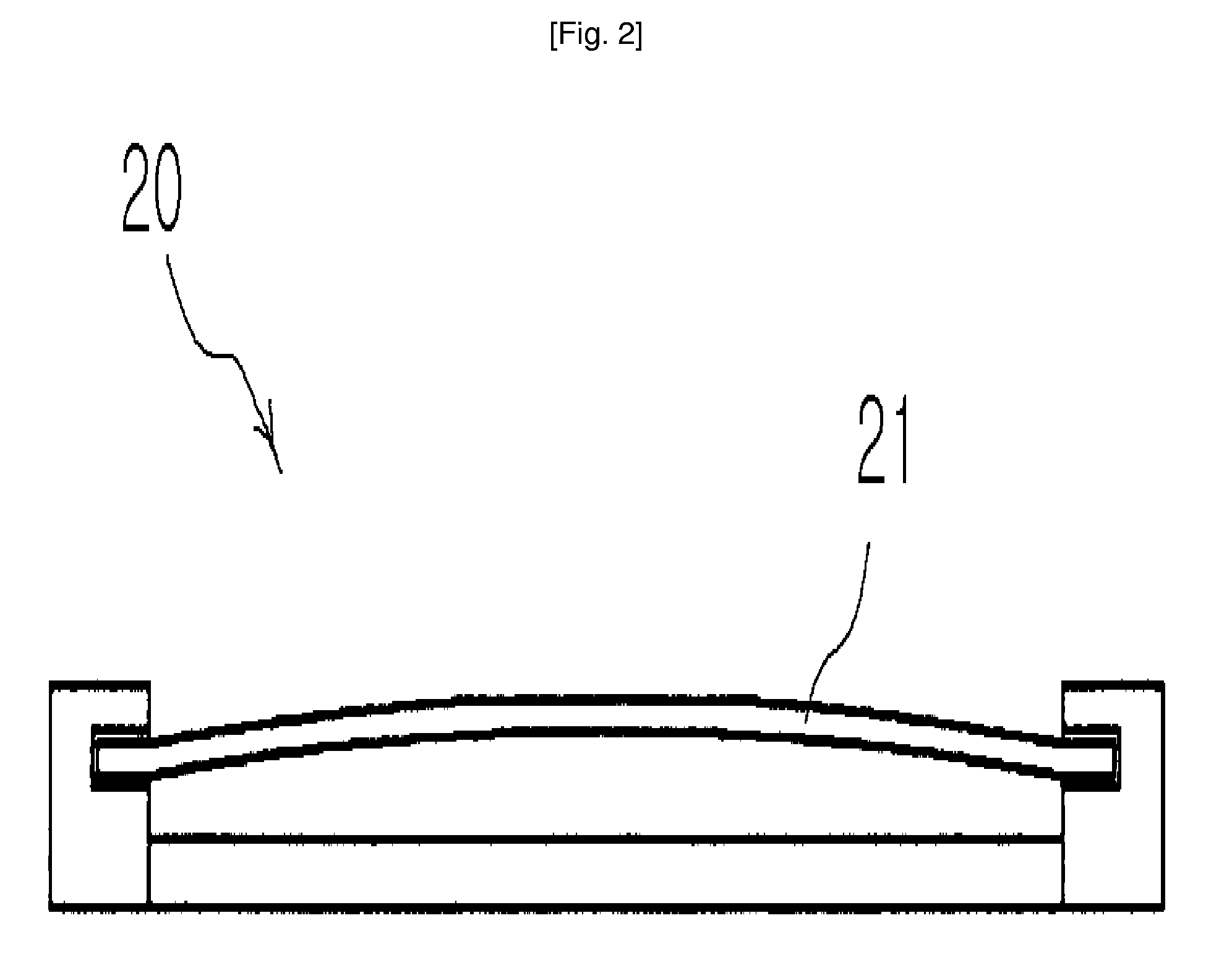
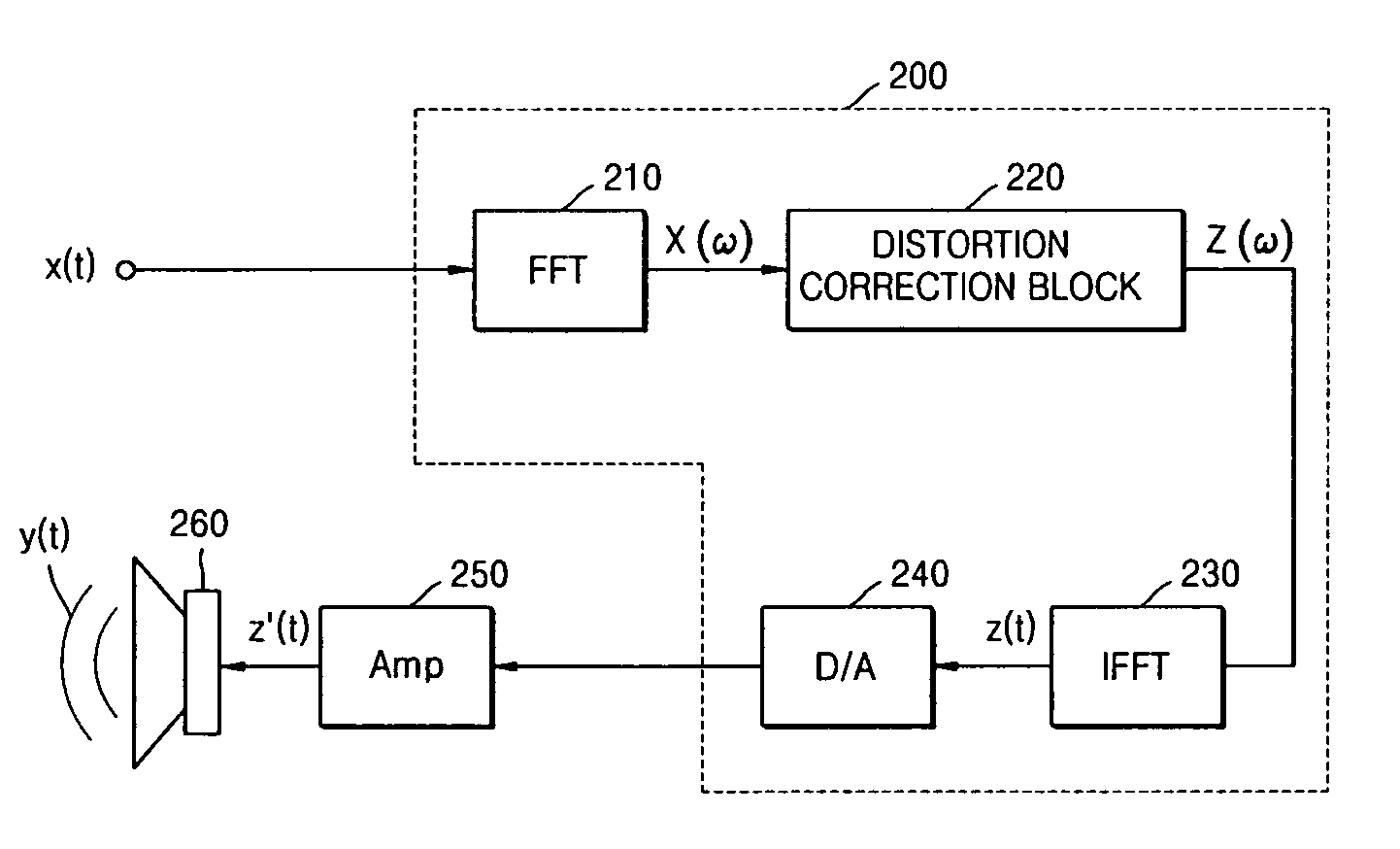
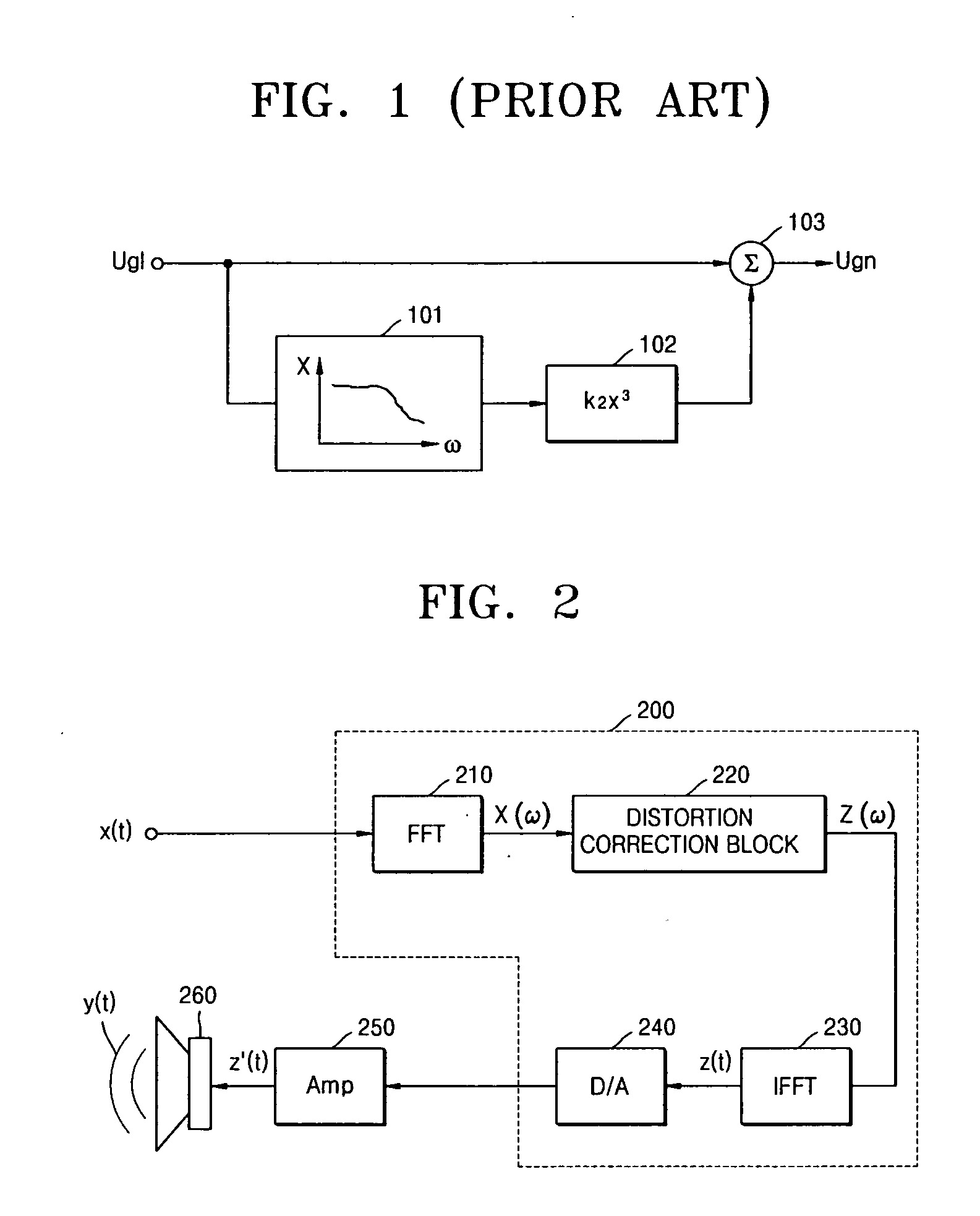
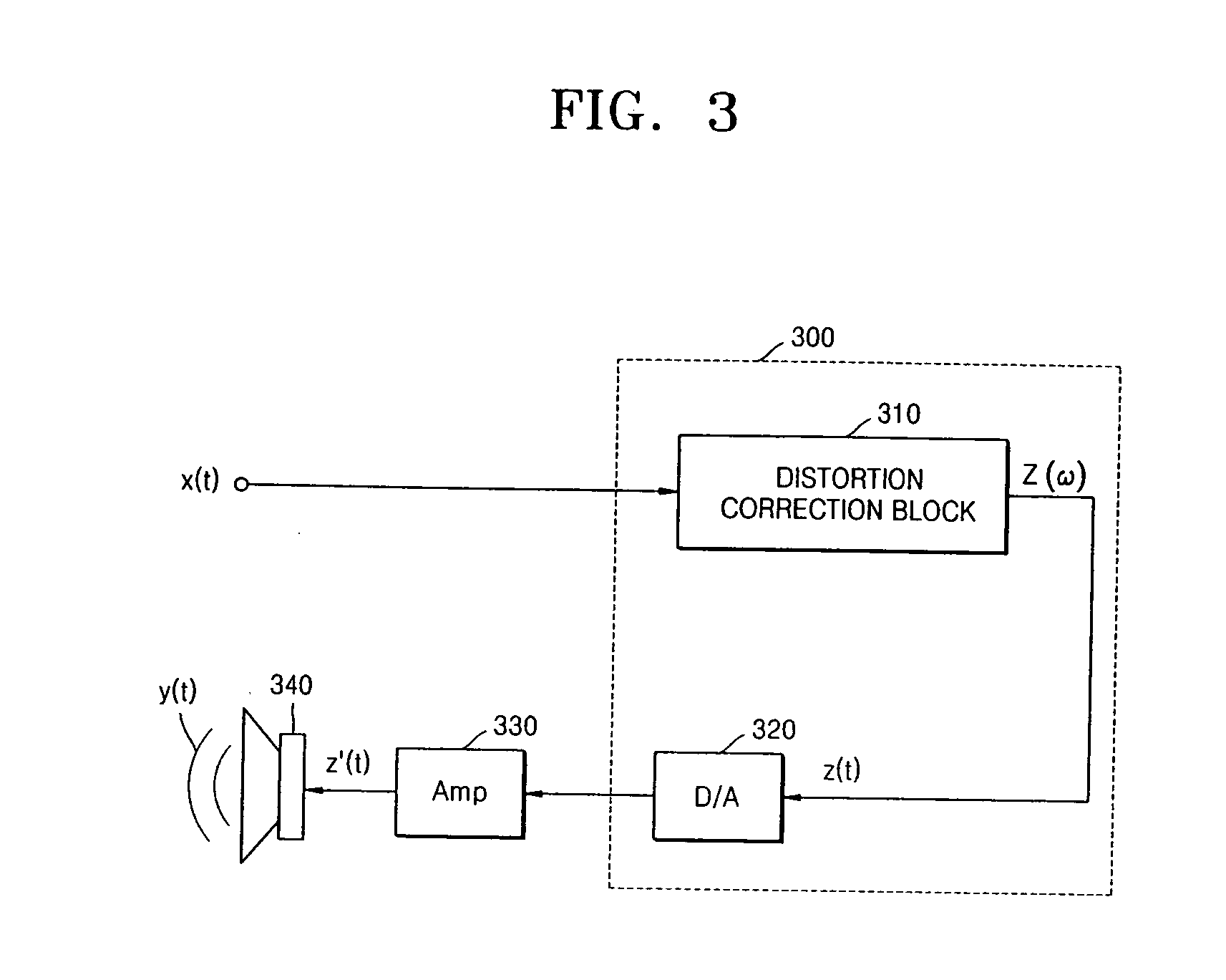
Method and apparatus for compensating for nonlinear distortion of speaker system
InactiveUS20050047606A1Improve output signal qualityEasy to implementTransducer circuit dampingFrequency response correctionTime domainViscous damping
A method and an apparatus for compensating for nonlinear distortion are provided to divide audio signals reproduced in a nonlinear speaker system into linear and nonlinear components in a time domain and a frequency domain, and then generate inversely-corrected signals by means of an inverse filtering scheme, so that it is possible to further consider a variety of nonlinear distortion characteristics such as viscous damping and structural damping which have not been reflected in the conventional lumped parameter method, and thus to obtain better sound quality.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Audio decoding device, decoding method, and program
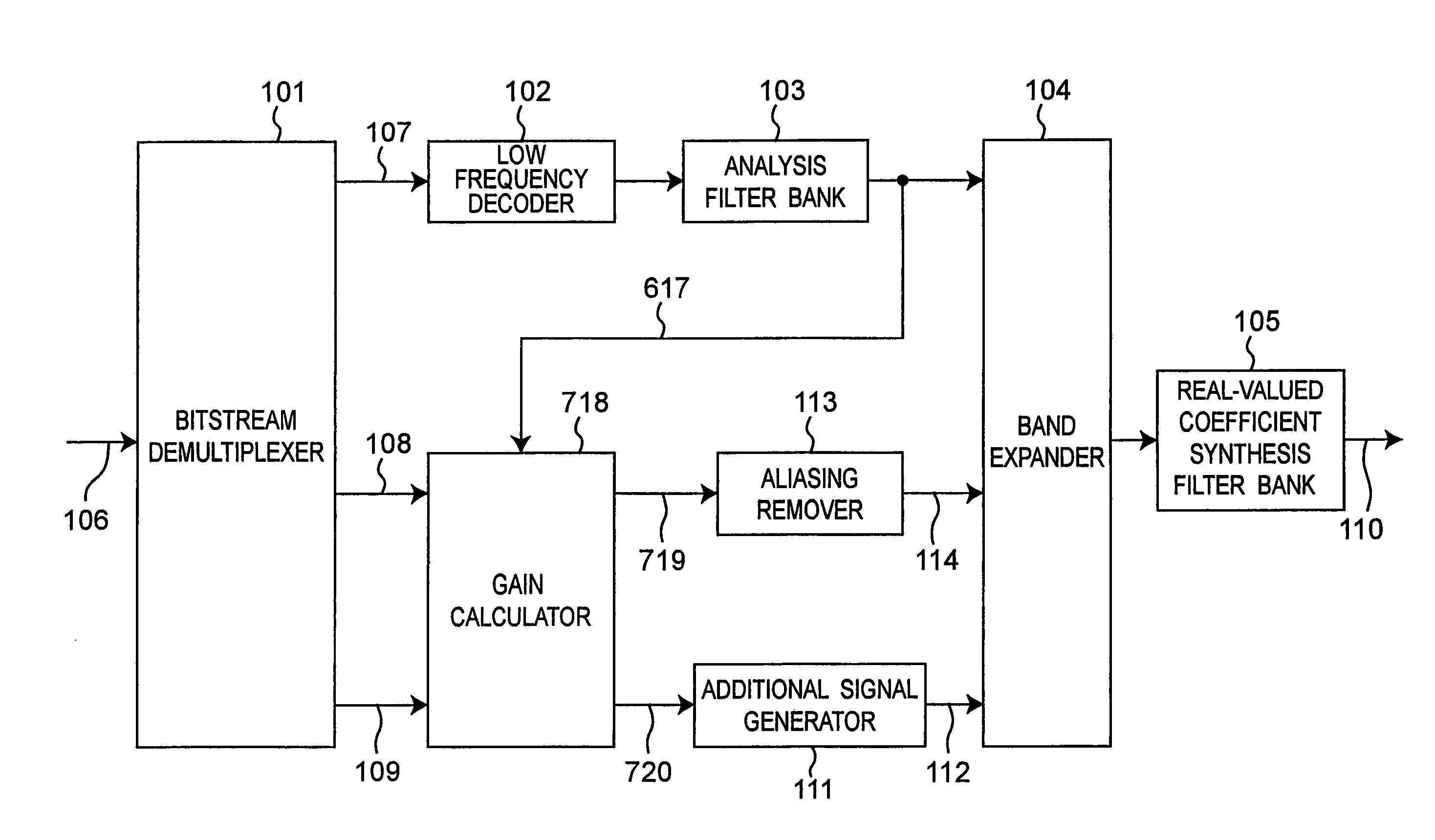
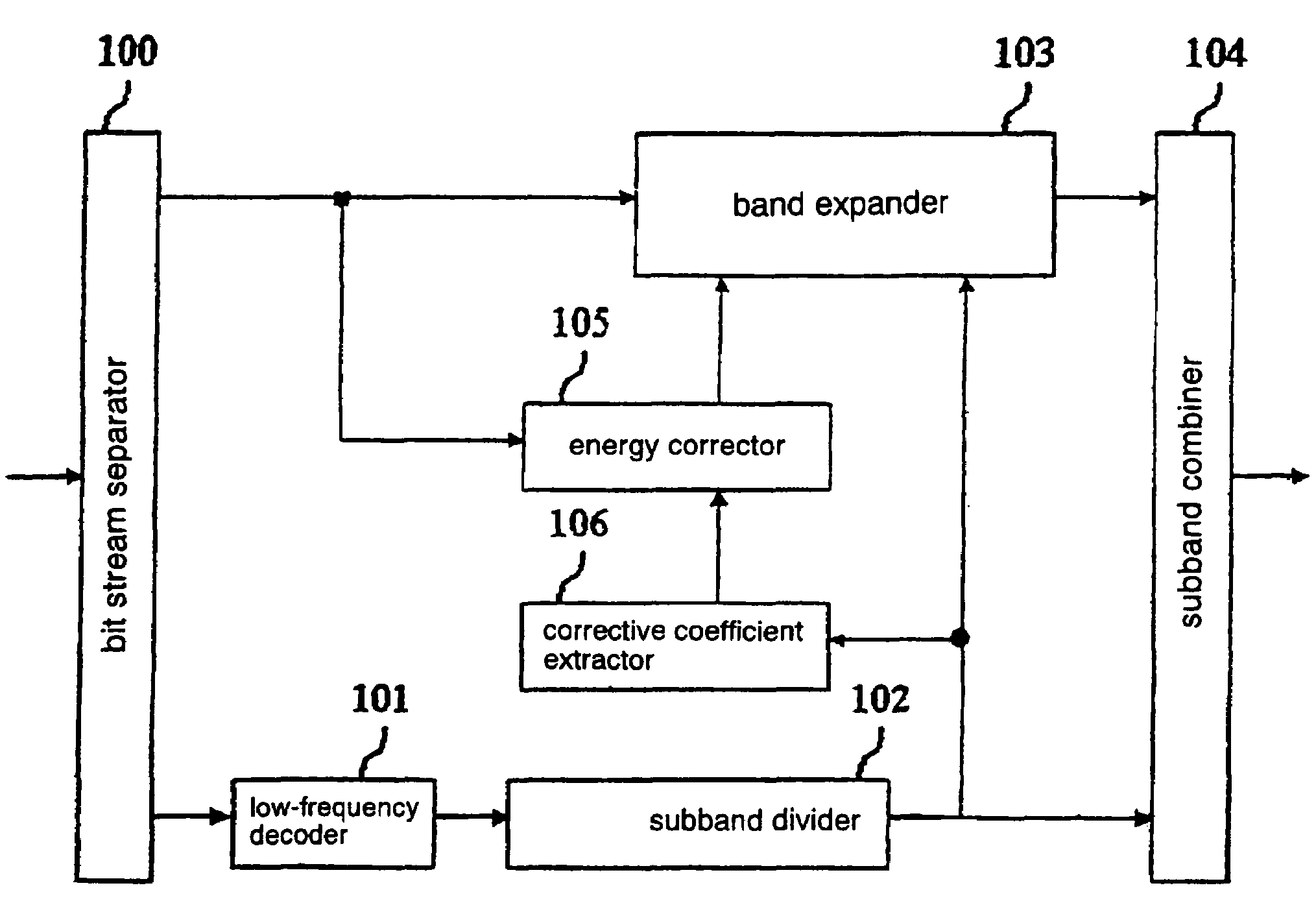
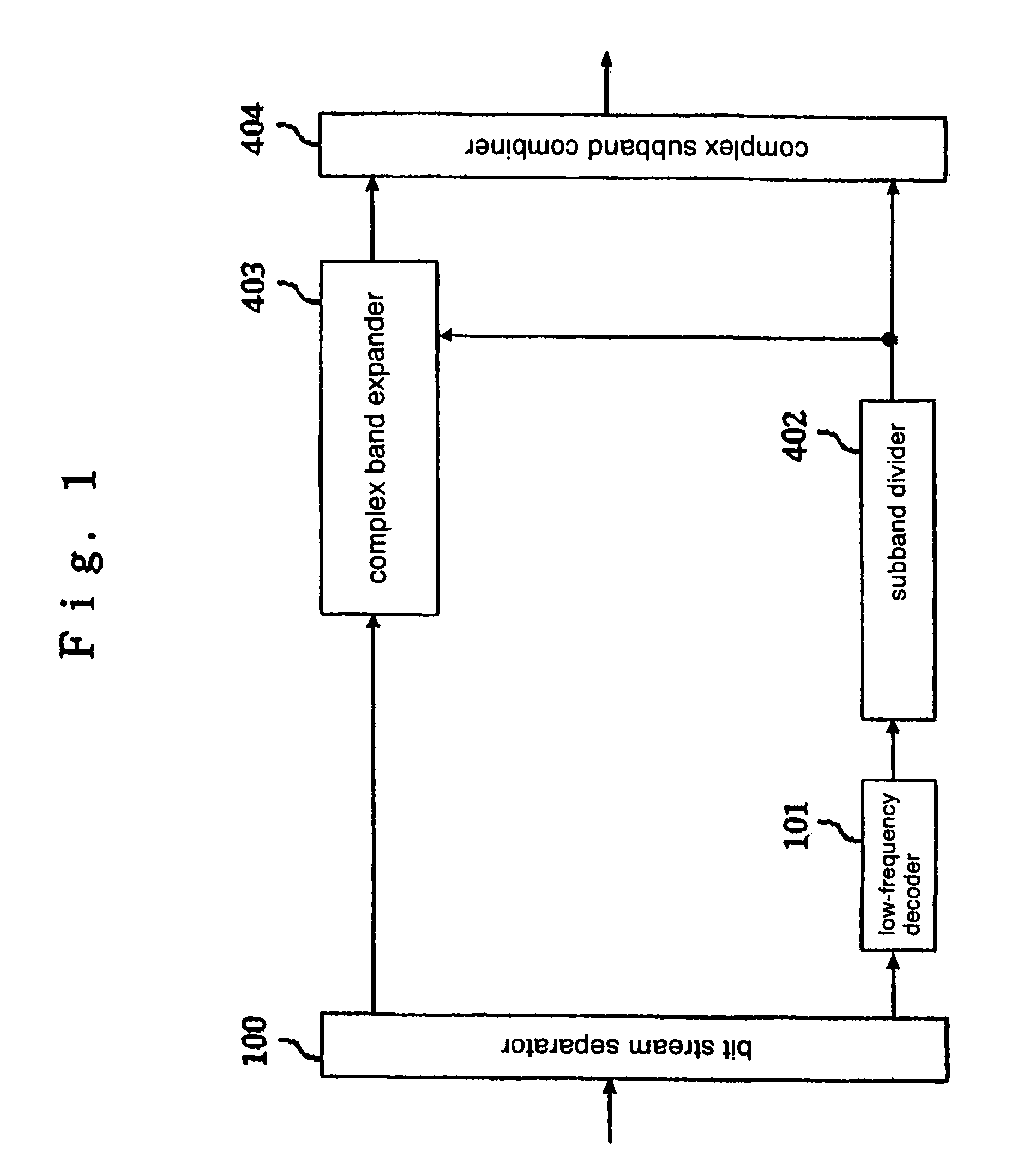
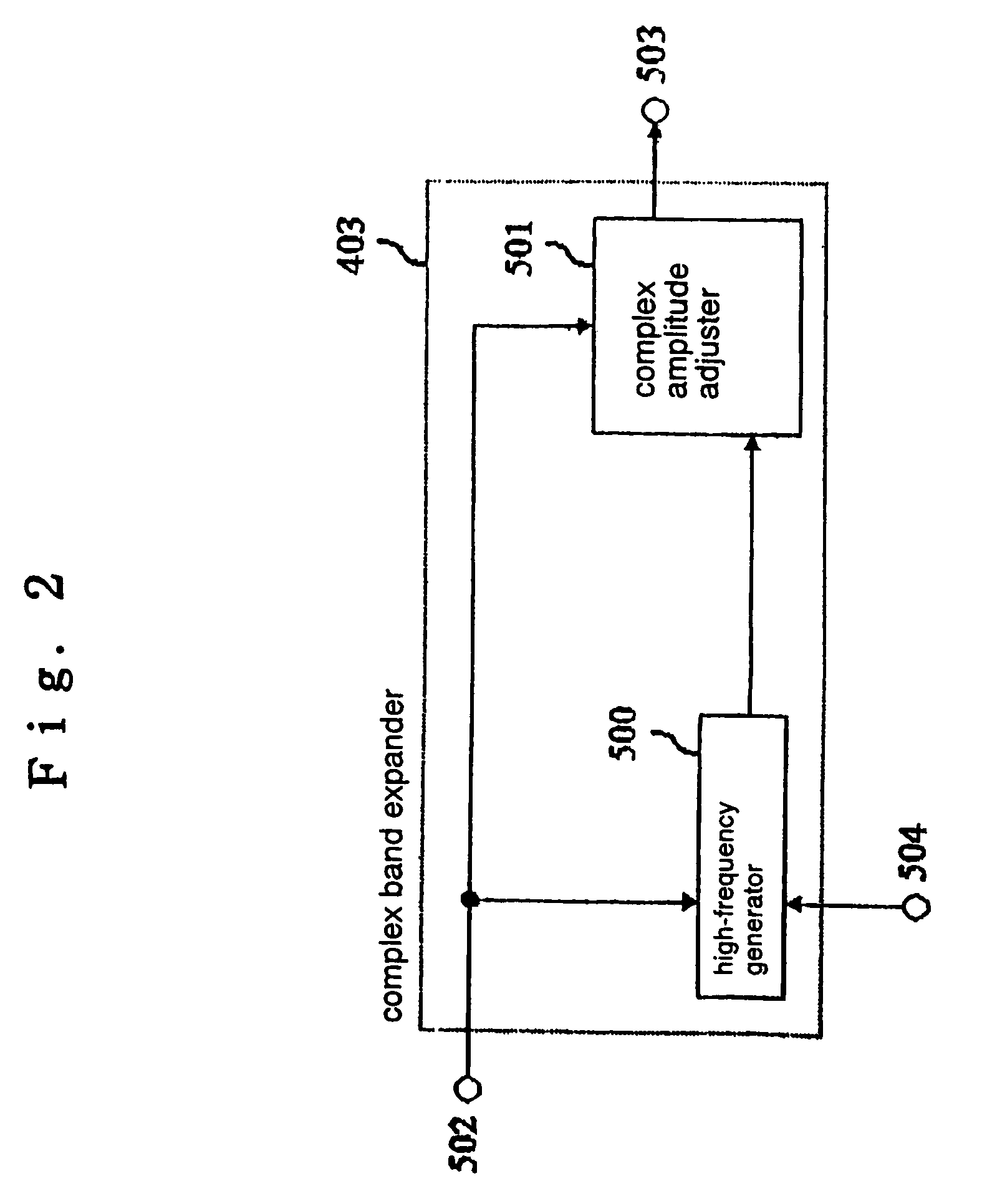
ActiveUS7555434B2Reduce the amount of calculationImprove sound qualitySpeech analysisCode conversionDecoding methodsSound quality
An energy corrector (105) for correcting a target energy for high-frequency components and a corrective coefficient calculator (106) for calculating an energy corrective coefficient from low-frequency subband signals are newly provided. These processors perform a process for correcting a target energy that is required when a band expanding process is performed on a real number only. Thus, a real subband combining filter and a real band expander which require a smaller amount of calculations can be used instead of a complex subband combining filter and a complex band expander, while maintaining a high sound-quality level, and the required amount of calculations and the apparatus scale can be reduced.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
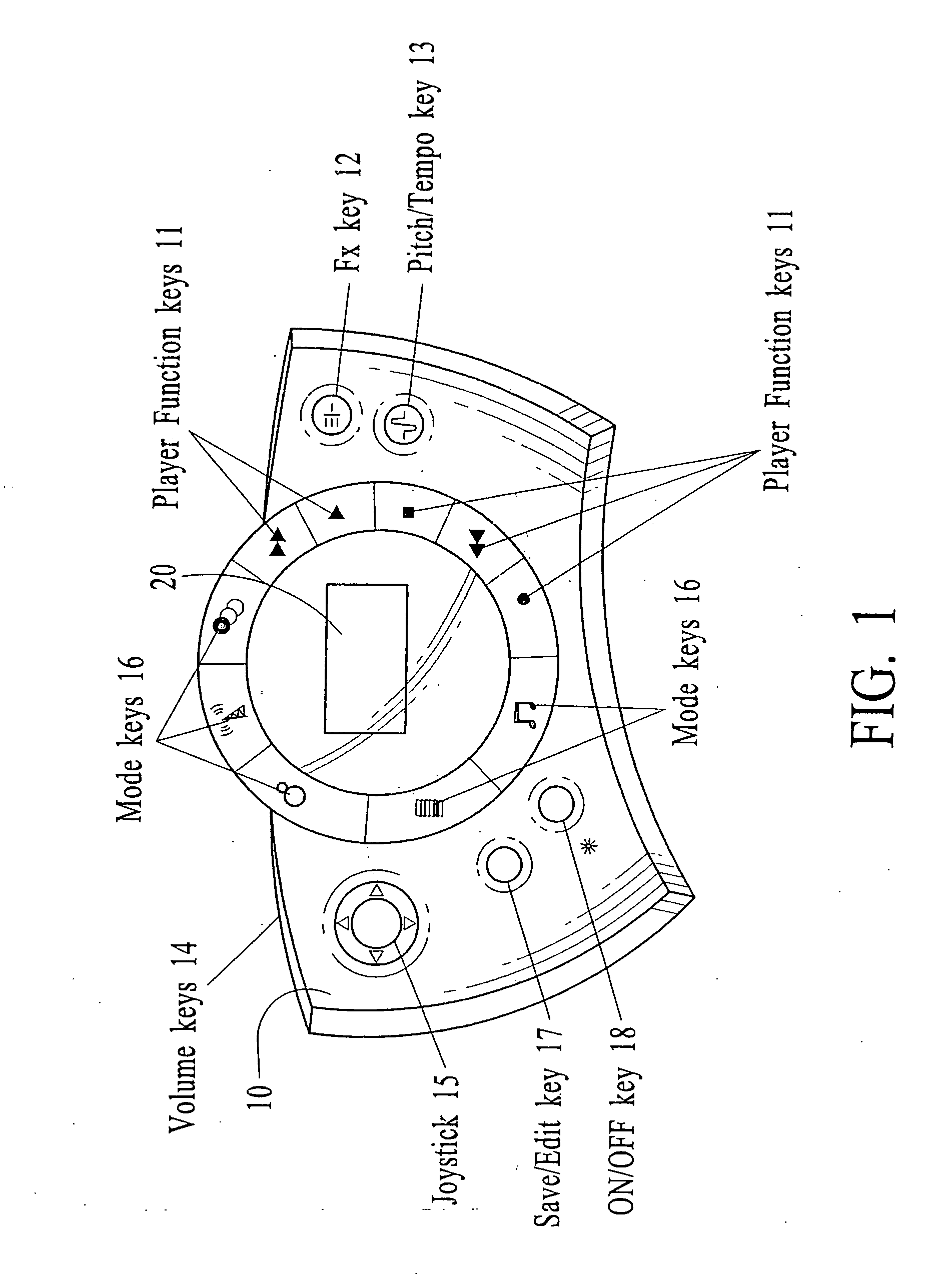
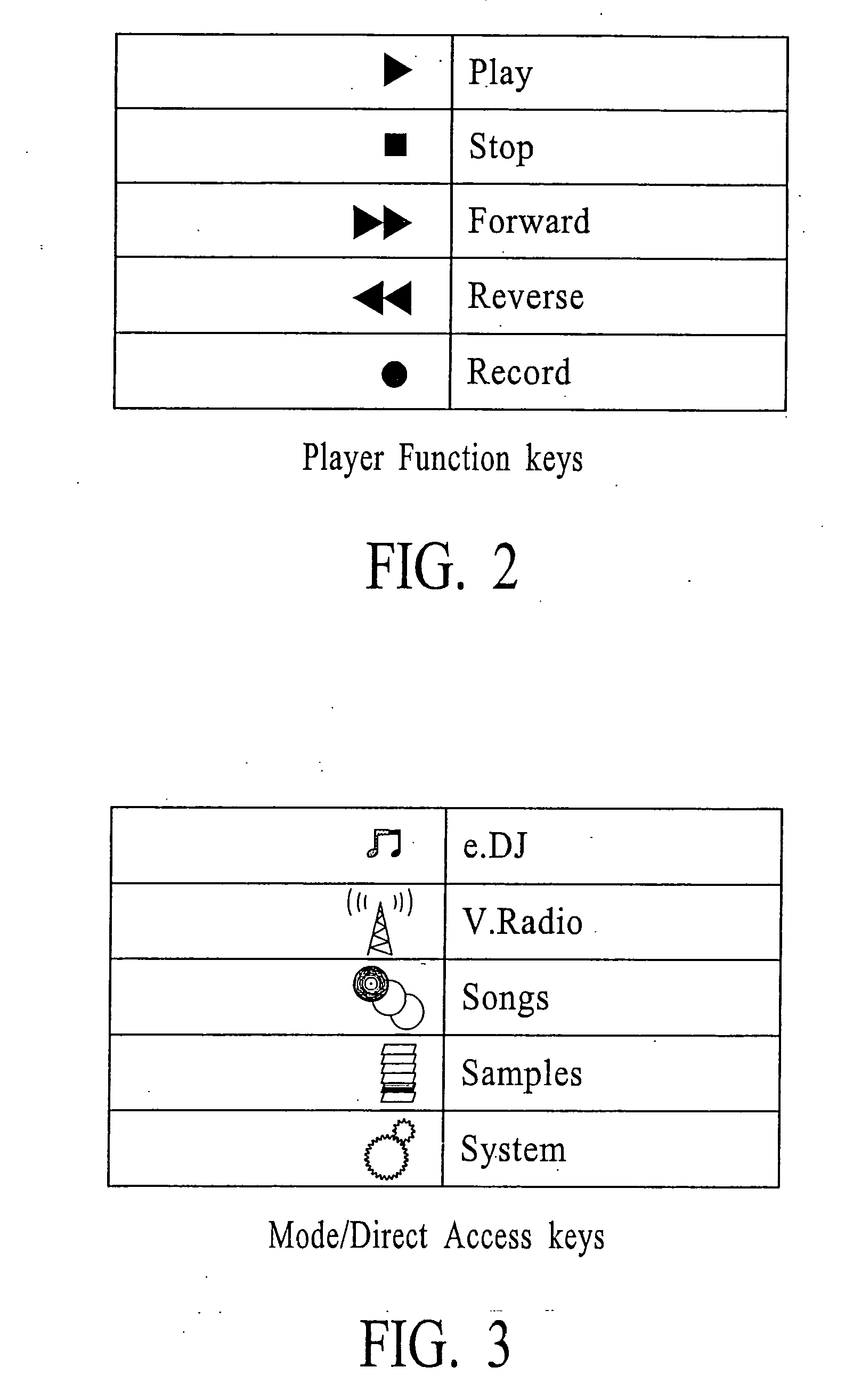
Systems and Methods for Portable Audio Synthesis
InactiveUS20080156178A1Create efficientlyEfficiently stored and/processedGearworksMusical toysAudio synthesisDisplay device
Systems and methods for creating, modifying, interacting with and playing music are provided, particularly systems and methods employing a top-down process, where the user is provided with a musical composition that may be modified and interacted with and played and / or stored (for later play). The system preferably is provided in a handheld form factor, and a graphical display is provided to display status information, graphical representations of musical lanes or components which preferably vary in shape as musical parameters and the like are changed for particular instruments or musical components such as a microphone input or audio samples. An interactive auto-composition process preferably is utilized that employs musical rules and preferably a pseudo random number generator, which may also incorporate randomness introduced by timing of user input or the like, the user may then quickly begin creating desirable music in accordance with one or a variety of musical styles, with the user modifying the auto-composed (or previously created) musical composition, either for a real time performance and / or for storing and subsequent playback. In addition, an analysis process flow is described for using pre-existing music as input(s) to an algorithm to derive music rules that may be used as part of a music style in a subsequent auto-composition process. In addition, the present invention makes use of node-based music generation as part of a system and method to broadcast and receive music data files, which are then used to generate and play music. By incorporating the music generation process into a node-subscriber unit, the bandwidth-intensive systems of conventional techniques can be avoided. Consequently, the bandwidth can preferably be also used of additional features such as node-to-node and node to base music data transmission. The present invention is characterized by the broadcast of relatively small data files that contain various parameters sufficient to describe the music to the node / subscriber music generator. In addition, problems associated with audio synthesis in a portable environment are addressed in the present invention by providing systems and methods for performing audio synthesis in a manner that simplifies design requirements and / or minimizes cost, while still providing quality audio synthesis features targeted for a portable system (e.g., portable telephone). In addition, problems associated with the tradeoff between overall sound quality and memory requirements in a MIDI sound bank are addressed in the present invention by providing systems and methods for a reduced memory size footprint MIDI sound bank.
Owner:MEDIALAB SOLUTIONS
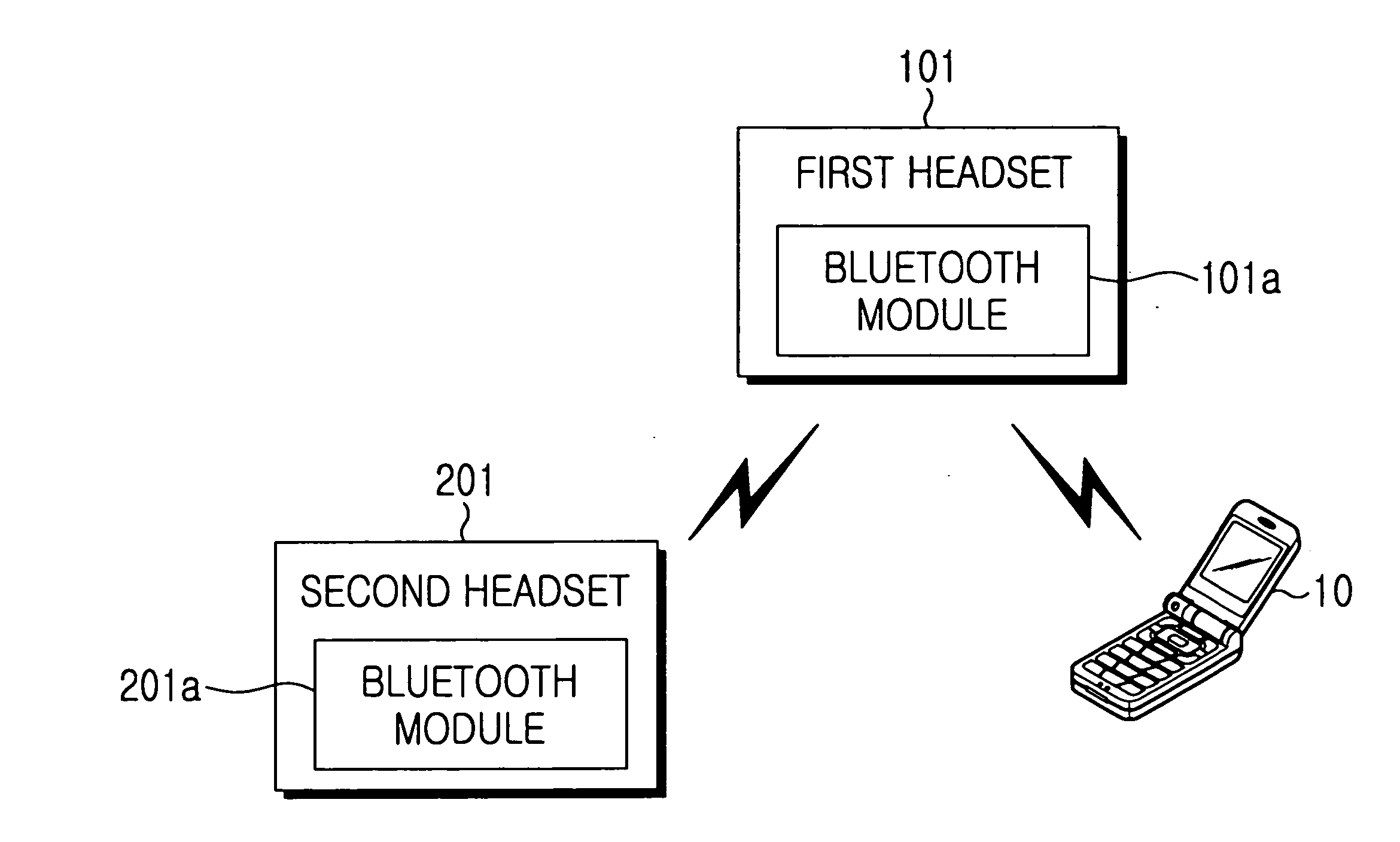
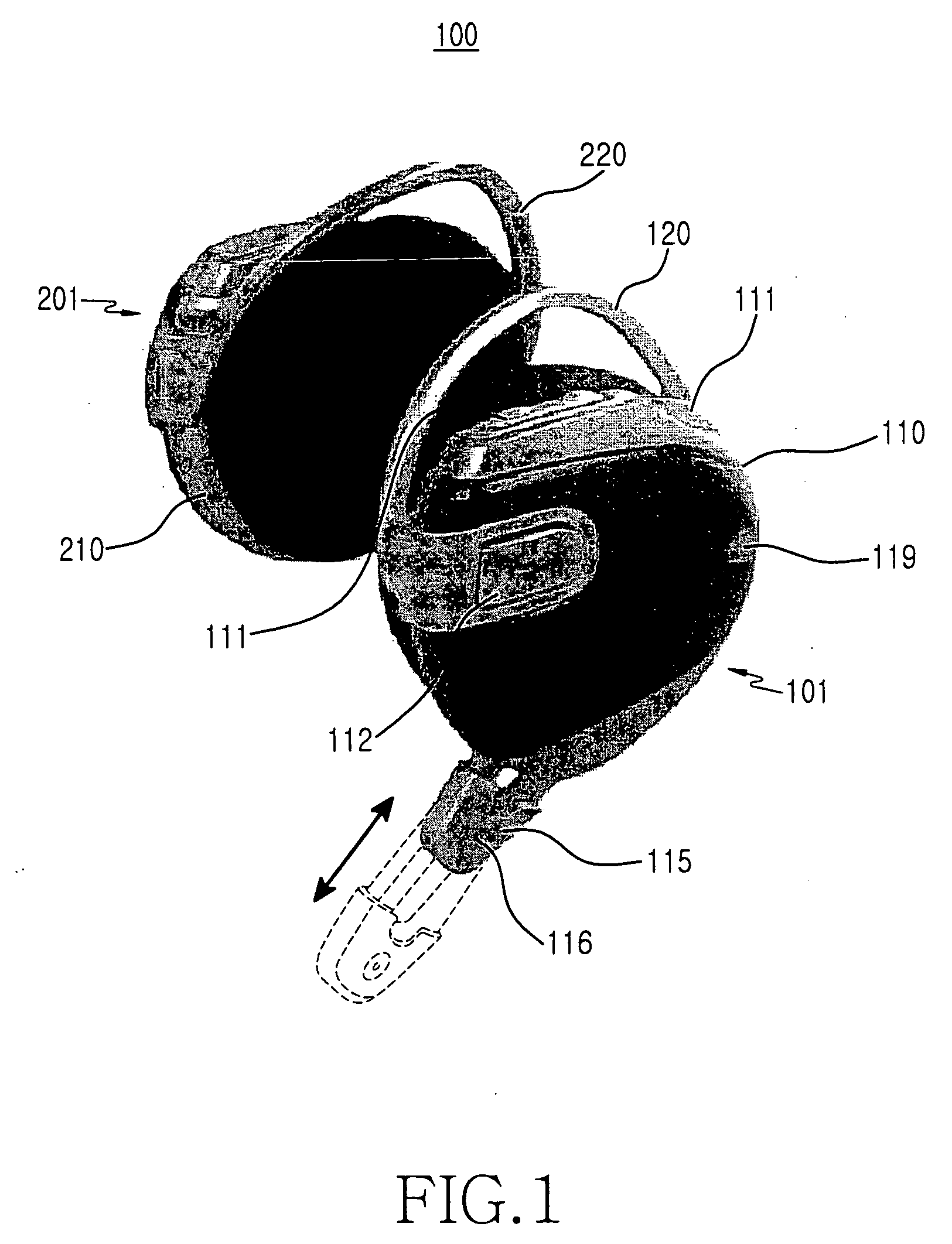
Wireless stereo headset
ActiveUS20060251277A1MicrophonesHeadphones for stereophonic communicationVoice communicationSound quality
Disclosed is a wireless stereo headset. The wireless stereo headset includes a first headset including a speaker unit and a Bluetooth® enabled module, for converting sound signals received from a device, transmitting the sound signals into sounds and outputting the sounds, and a second headset including a speaker unit and a Bluetooth® enabled module, for selectively receiving a portion of the sound signals which are converted into sounds and outputting the sounds, thereby accomplishing mono sound by using the first headset according to a user's request or achieving stereo sound by using the first and second headsets. The wireless stereo headset can perform voice communication by using only the first headset, while accomplishing stereo sounds by using both the first and second headsets, thereby using the wireless stereo headset to enjoy an improved sound quality.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Display unit for refrigerator
ActiveUS20050134472A1Improve sound qualityPrevent penetrationLighting and heating apparatusSignalling system detailsIntermediate frequencyResonance
The present invention relates to a display unit for a refrigerator for improving sound quality. A display having a TV receiving function is installed at a front surface of a refrigerator door. A mounting panel with a plurality of speaker holes formed therein is also installed around an edge of the display. A speaker is mounted to a rear surface of the mounting panel on a portion where the speaker holes are formed. Further, a resonance box is installed to enclose the speaker such that low and middle frequency sound can be transmitted forward to the outside. A sound transmission tube that communicates with the speaker hole is formed at a front portion of the resonance box. In addition, a sound absorbing material is covered on an inner rear surface of the resonance box that faces the rear of the speaker.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Resonance chamber of a cellular phone
InactiveUS20050190941A1Good resonance effectFinal product manufacturePrinted circuit aspectsInterior spaceEngineering
A cellular phone having a first opening for delivering voice on a shell is provided. A printed circuit board (PCB) is disposed within an inner space enclosed by the shell and divides the inner space into a first acoustic room and a second acoustic room. A speaker is disposed within the first acoustic room and electrically connects the PCB. A through hole is formed on the PCB to communicate the first acoustic room and the second acoustic room to increase the size of total resonance chamber for improving resonance effect in low frequency voices. Furthermore, at least a second opening is formed on the shell to communicate the first acoustic room or the second acoustic room to the environment for flattening the resonance curve to improve the voice quality.
Owner:CLAM CORP
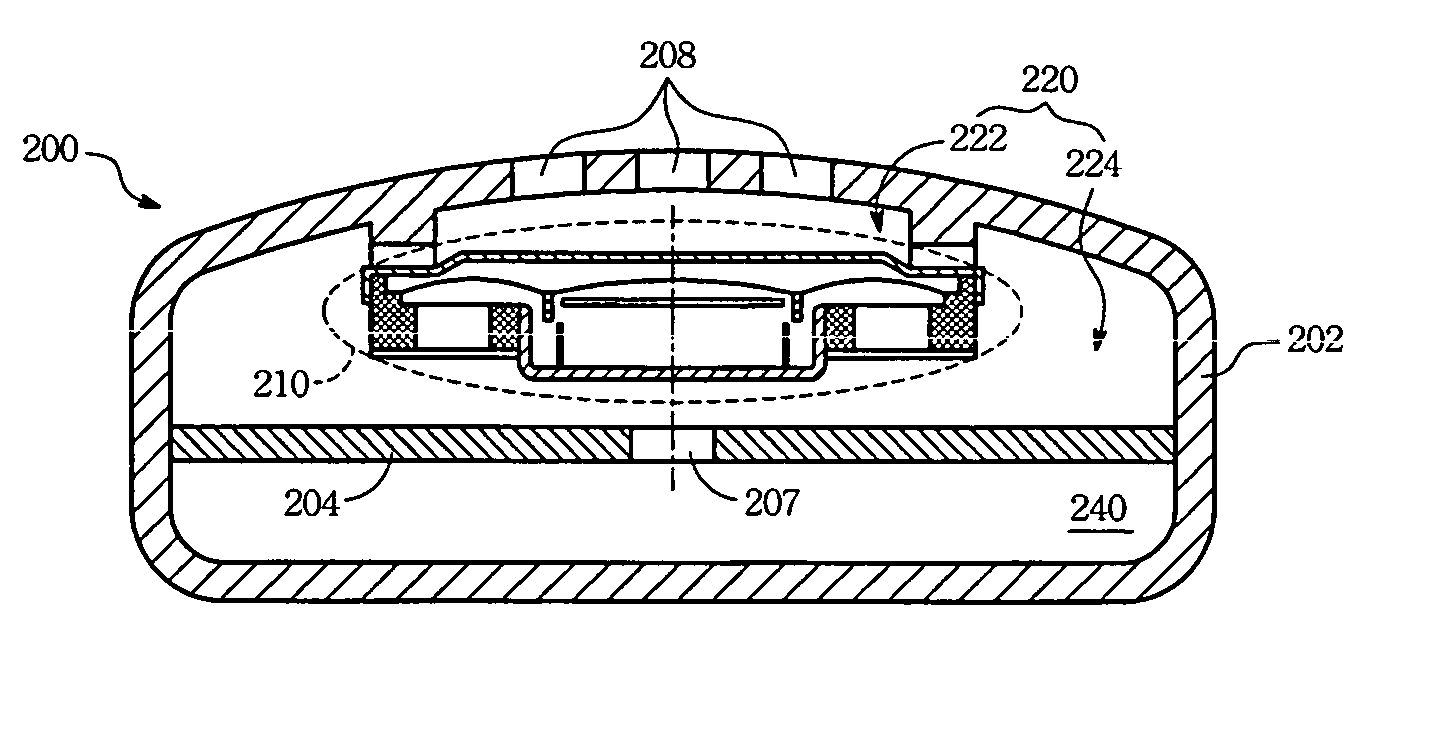
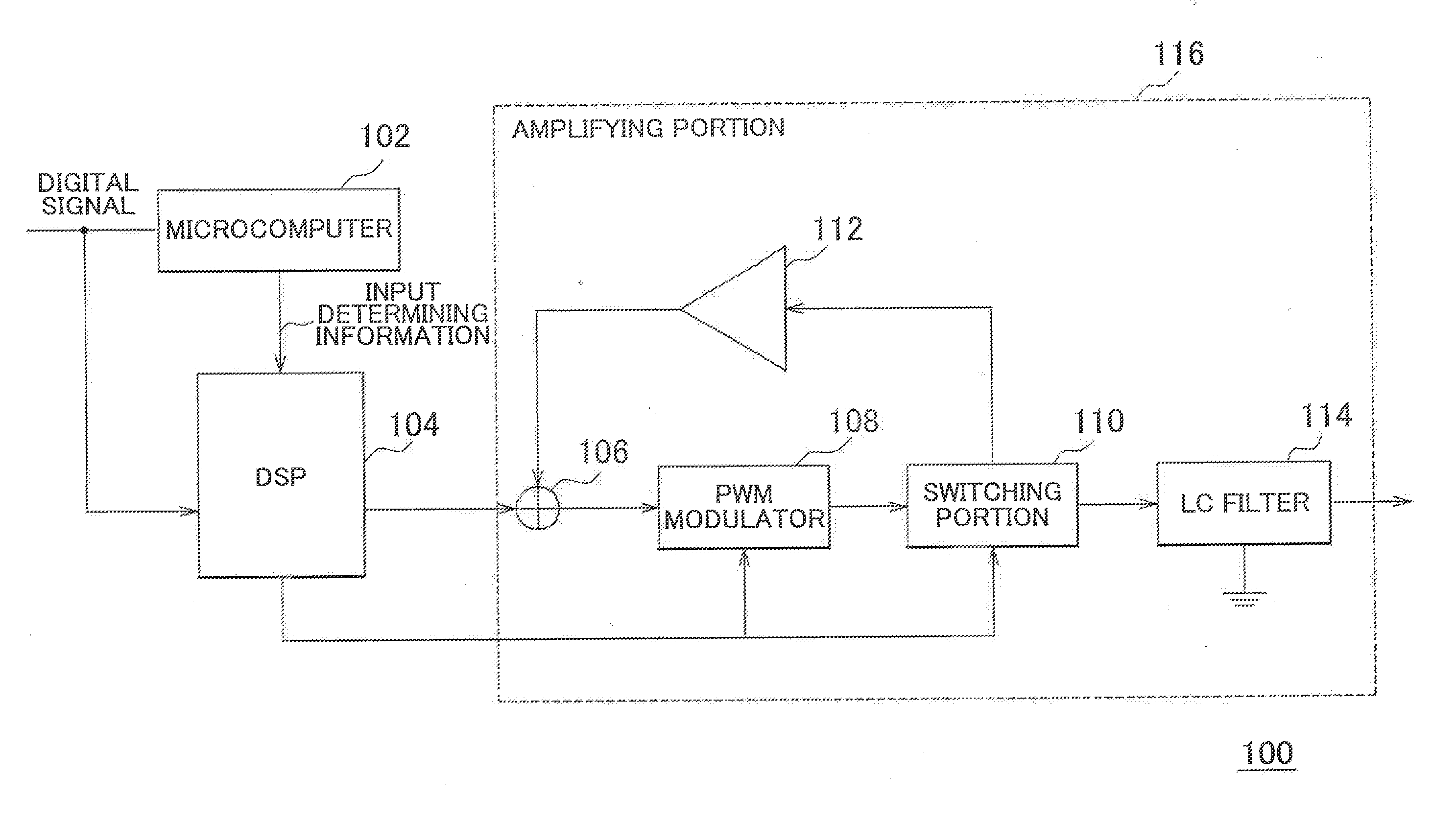
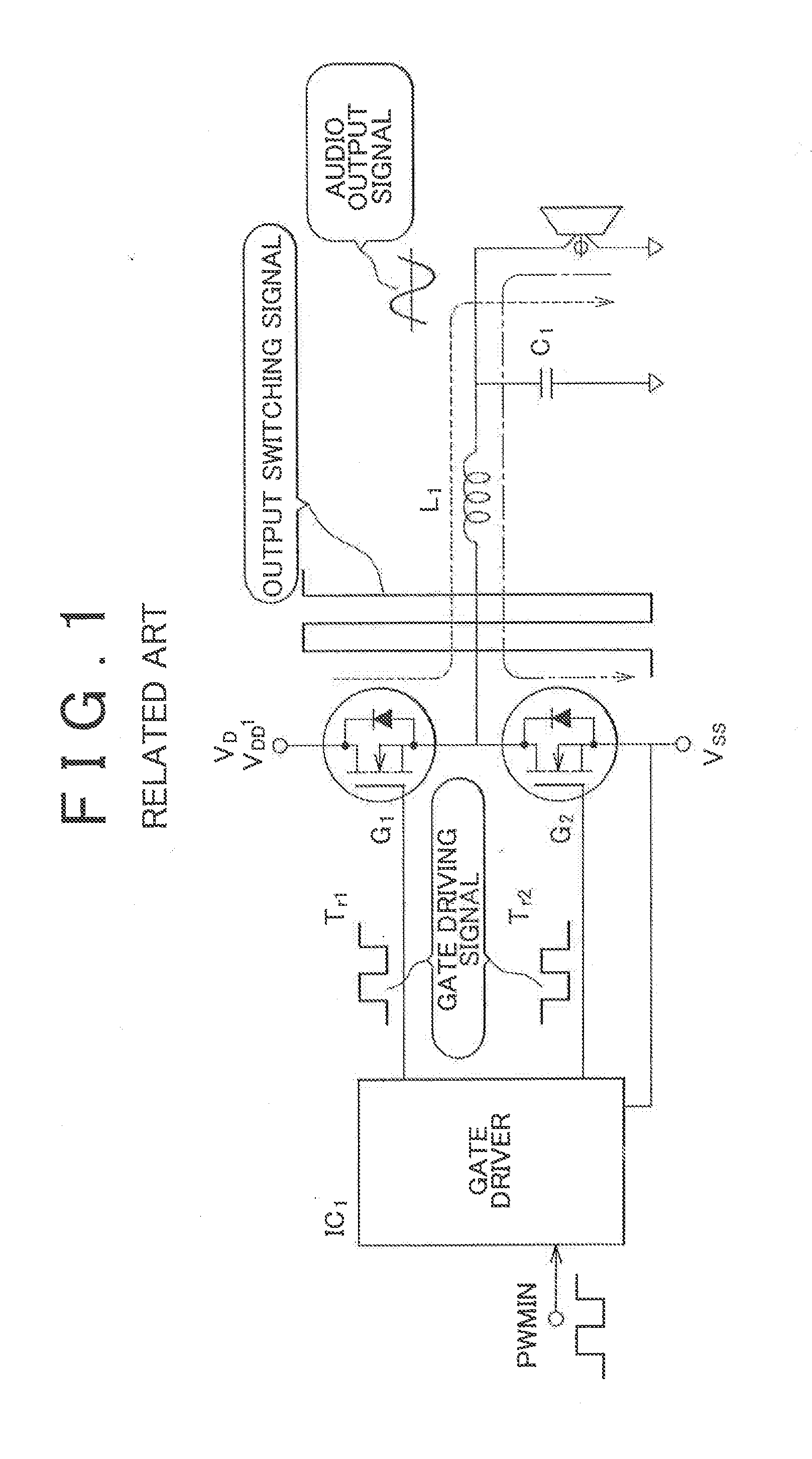
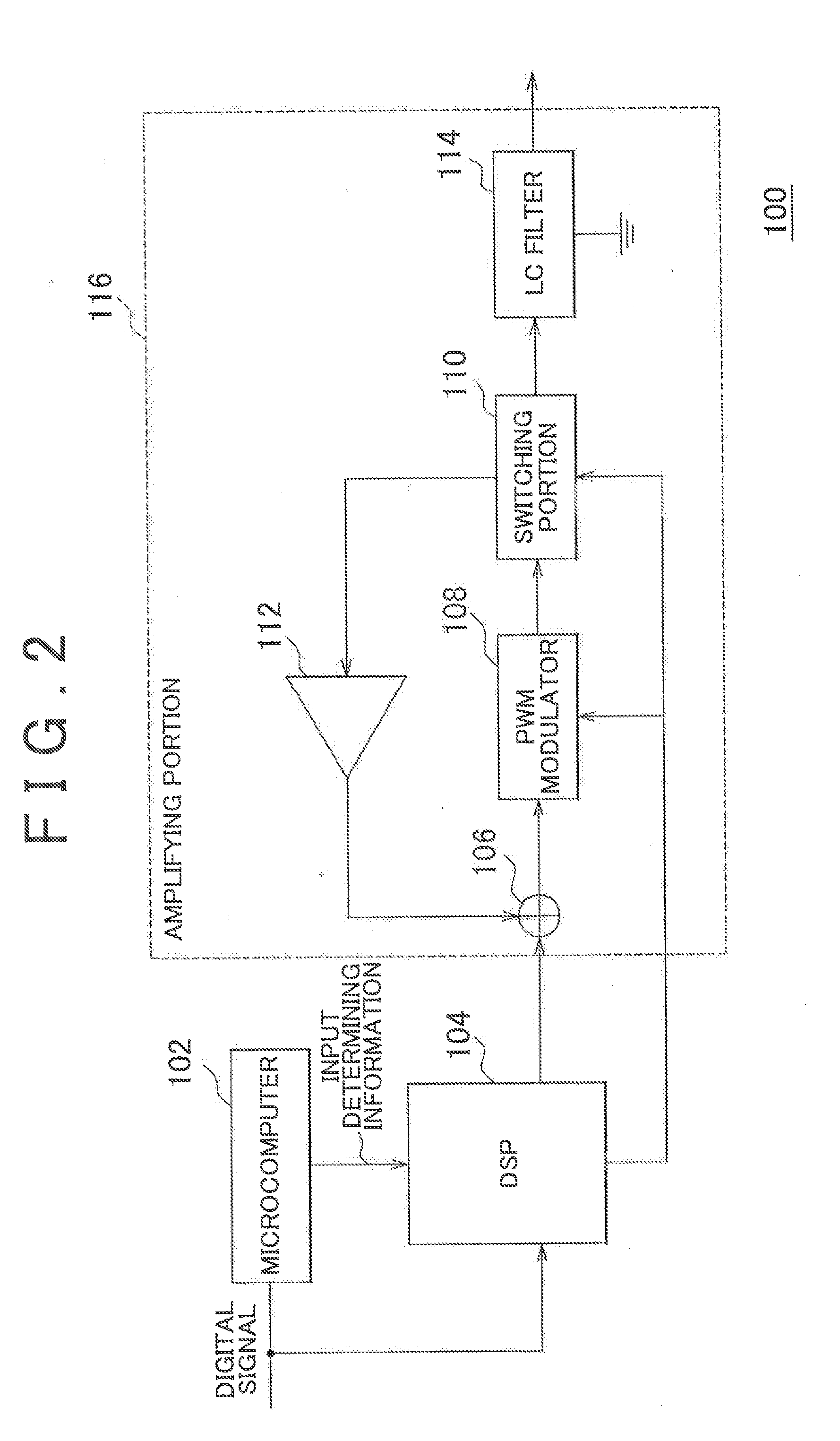
Amplifier and amplifying method
InactiveUS20130163789A1Reduce power consumptionAmplifier combinationsTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsAudio power amplifierSound sources
An amplifier that modulates a carrier frequency according to a digital signal and amplifies the modulated signal includes a determining portion that determines at least one of a sound quality required for the digital signal, a sound source of the digital signal, and a type of sound of the digital signal, a carrier frequency setting portion that sets a carrier frequency according to a result of the determination, and a pulse-width modulating portion that pulse-width modulates the carrier frequency according to the digital signal.
Owner:HARMAN INT JAPAN +1
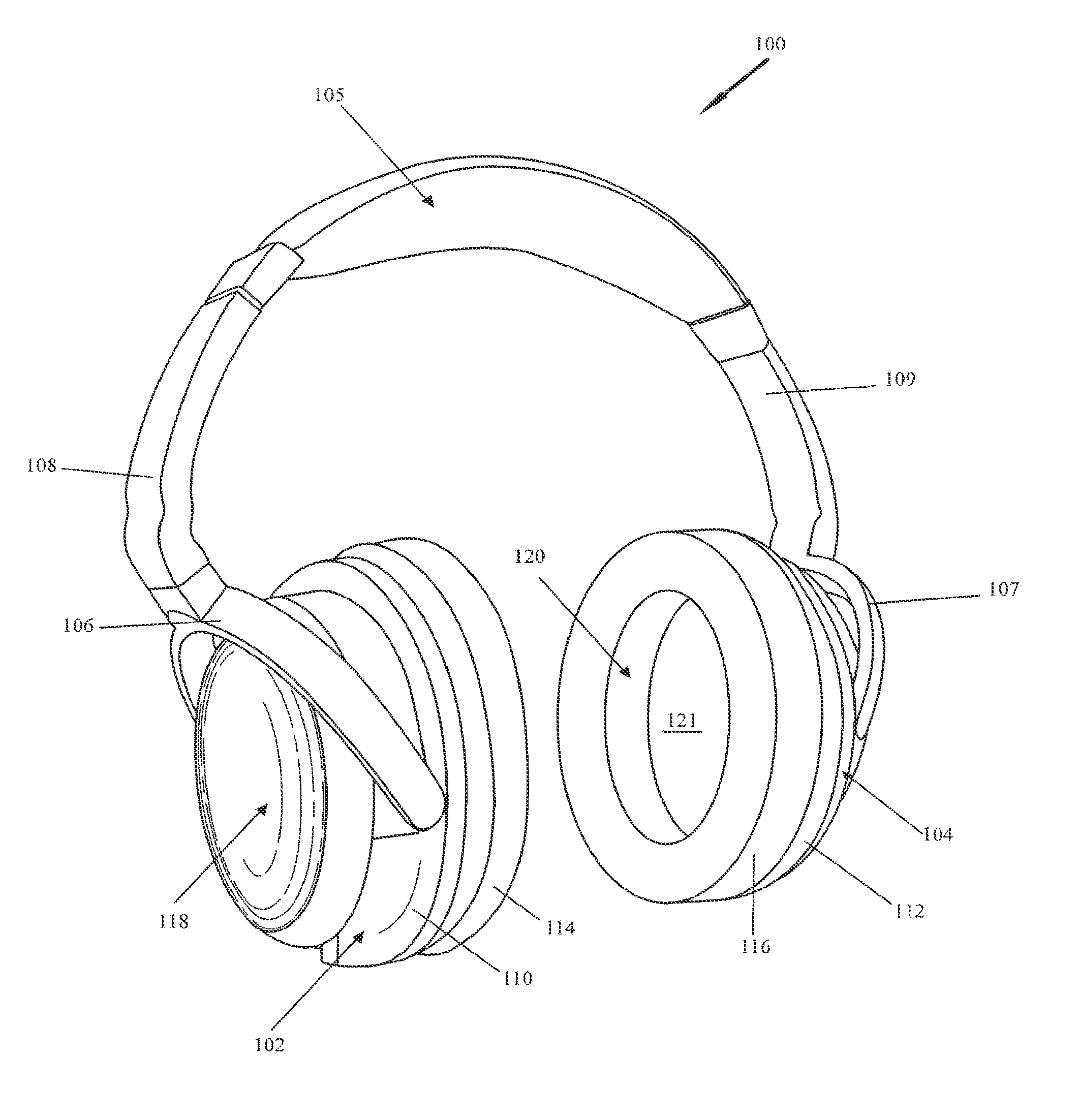
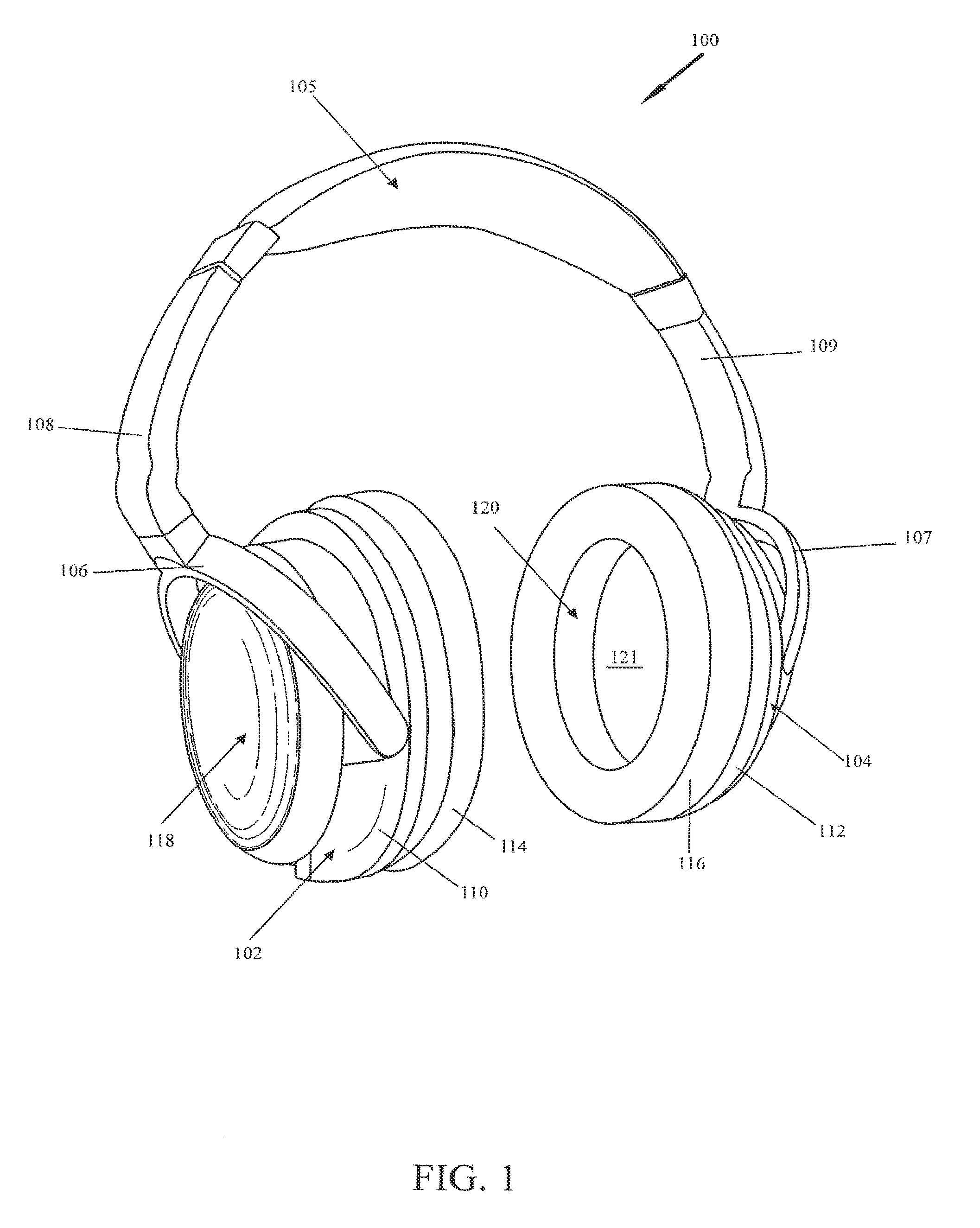
Headphone apparatus
A single chamber headphone apparatus and earcup design is provided which enhances wearer comfort, reduces headphone weight, facilitates ease of use, maintenance and operation by providing an improved internal chamber and battery cap configuration. Sound quality is improved by eliminating acoustic problems associated with two-chamber headset designs. A volume balance control is also provided.
Owner:ABLE PLANET
Bandwidth extension of acoustic signals
InactiveUS7359854B2Improved bandwidth extension solutionEnhanced perceived sound qualitySpeech synthesisBandwidth extensionFrequency spectrum
A solution for improving the perceived sound quality of a decoded acoustic signal is accomplished by extending the spectrum of a received narrow-band acoustic signal (aNB). A wide-band acoustic signal (AWB) is produced by extracting at least one essential attribute (zNB) from the narrow-band acoustic signal (aNB). Parameters, e.g., representing signal energies, with respect to wide-band frequency components outside the spectrum (ANB) of the narrow-band acoustic signal (aNB), are estimated based on the at least one essential attribute (zNB). This estimation involves allocating a parameter value to a wide-band frequency component, based on a corresponding confidence level.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
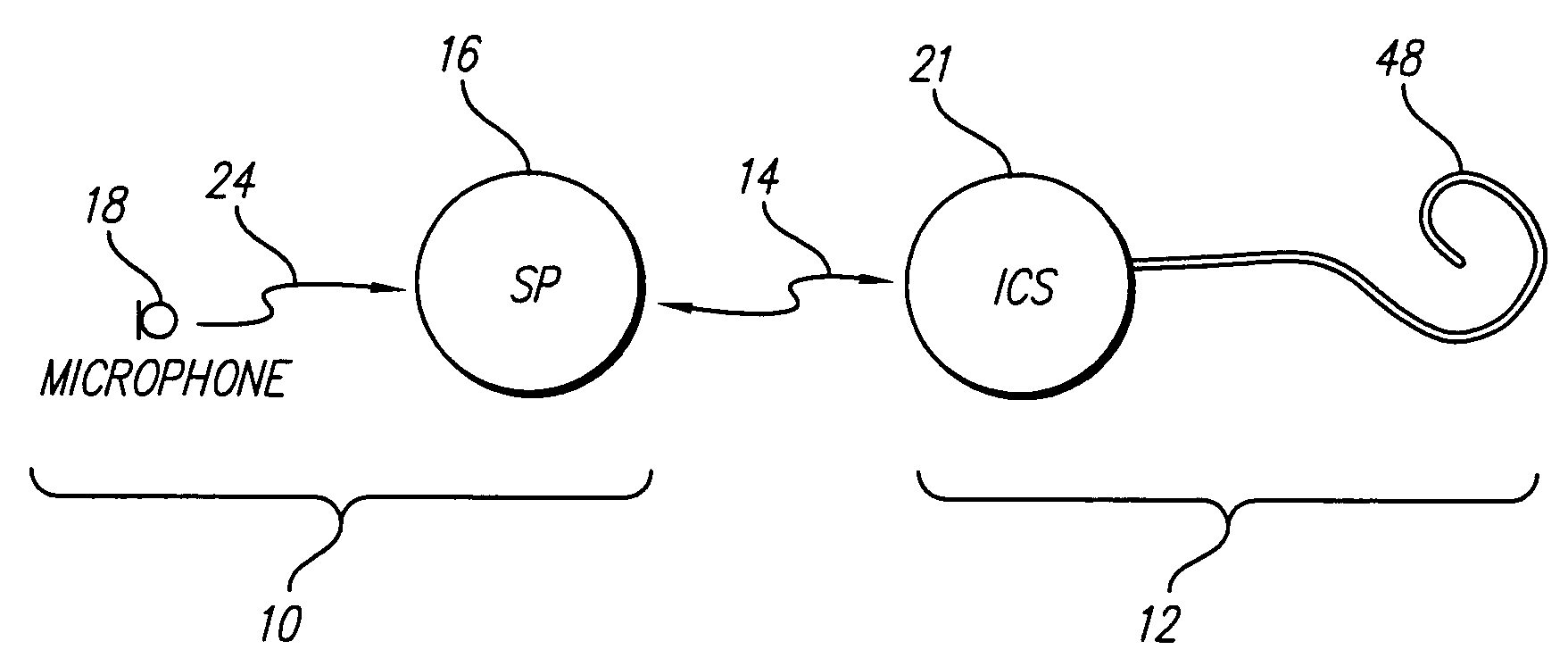
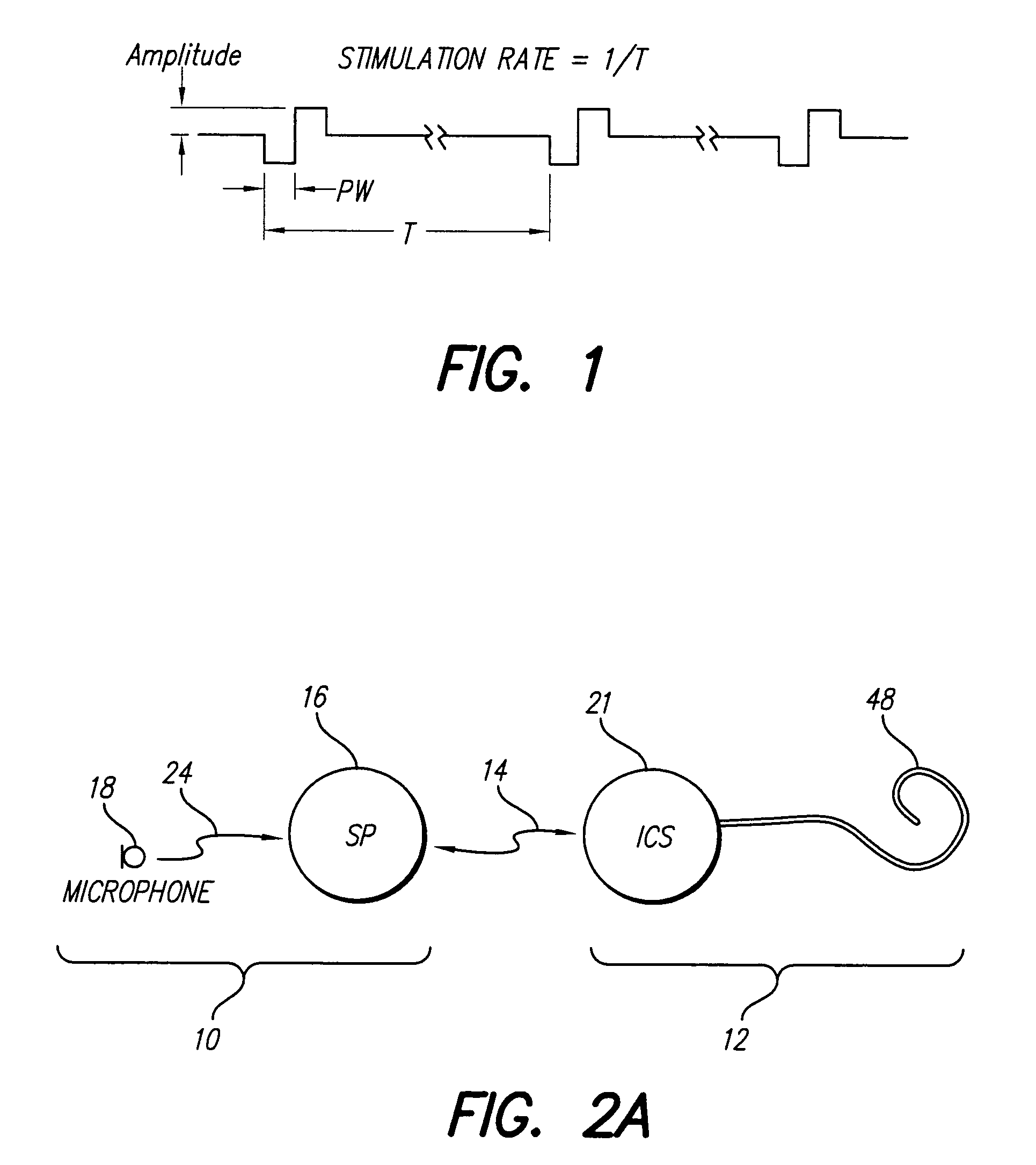
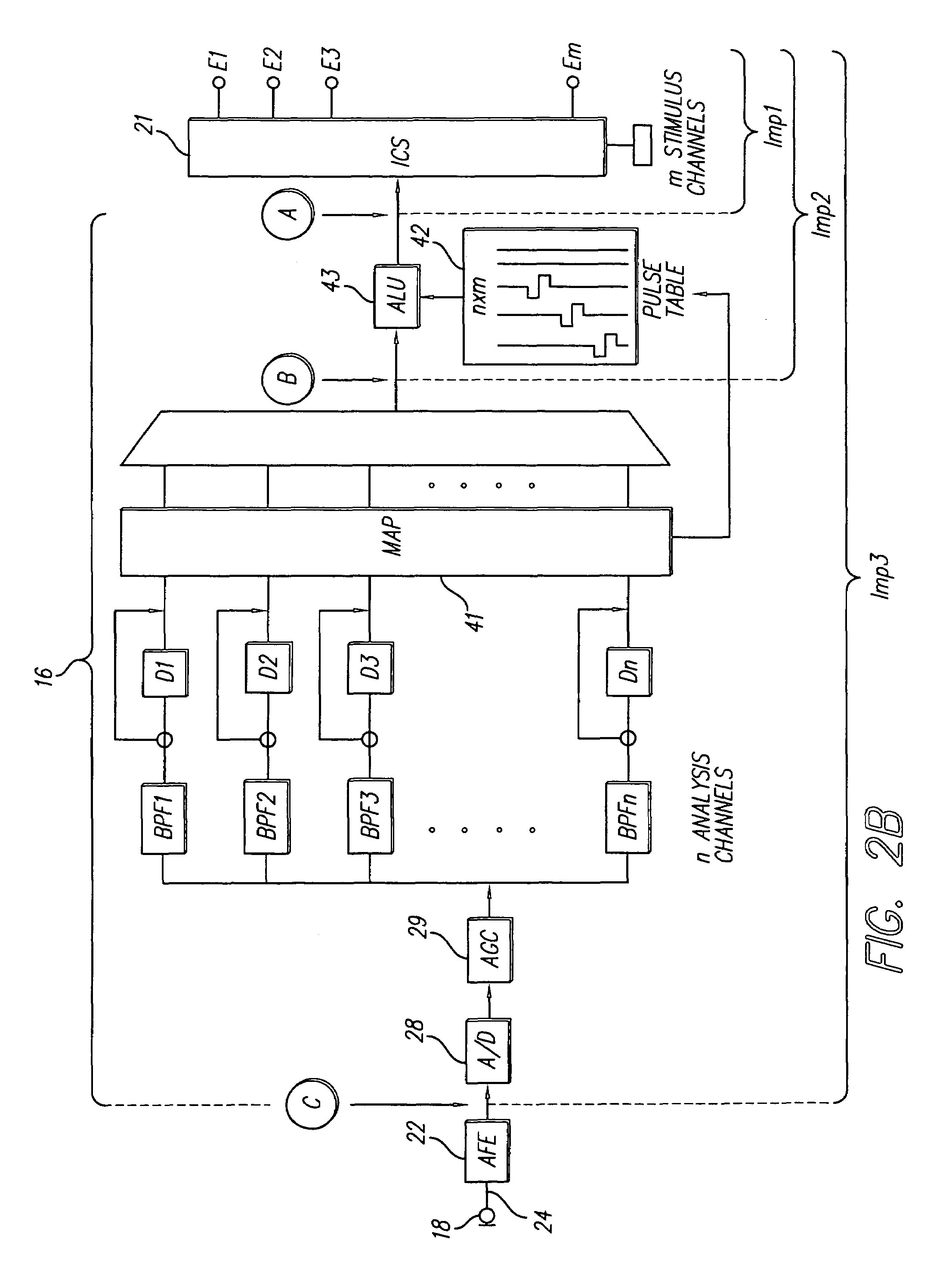
Optimizing pitch and other speech stimuli allocation in a cochlear implant
ActiveUS7251530B1Easy to controlImprove sound qualityElectrotherapyAudiometeringOctaveCochlear implantation
Errors in pitch (frequency) allocation within a cochlear implant are corrected in order to provide a significant and profound improvement in the quality of sound perceived by the cochlear implant user. In one embodiment, the user is stimulated with a reference signal, e.g., the tone “A” (440 Hz) and then the user is stimulated with a probe signal, separated from the reference signal by an octave, e.g., high “A” (880 Hz). The user adjusts the location where the probe signal is applied, using current steering, until the pitch of the probe signal, as perceived by the user, matches the pitch of the reference signal, as perceived by the user. In this manner, the user maps frequencies to stimulation locations in order to tune his or her implant system to his or her unique cochlea.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONICS AG
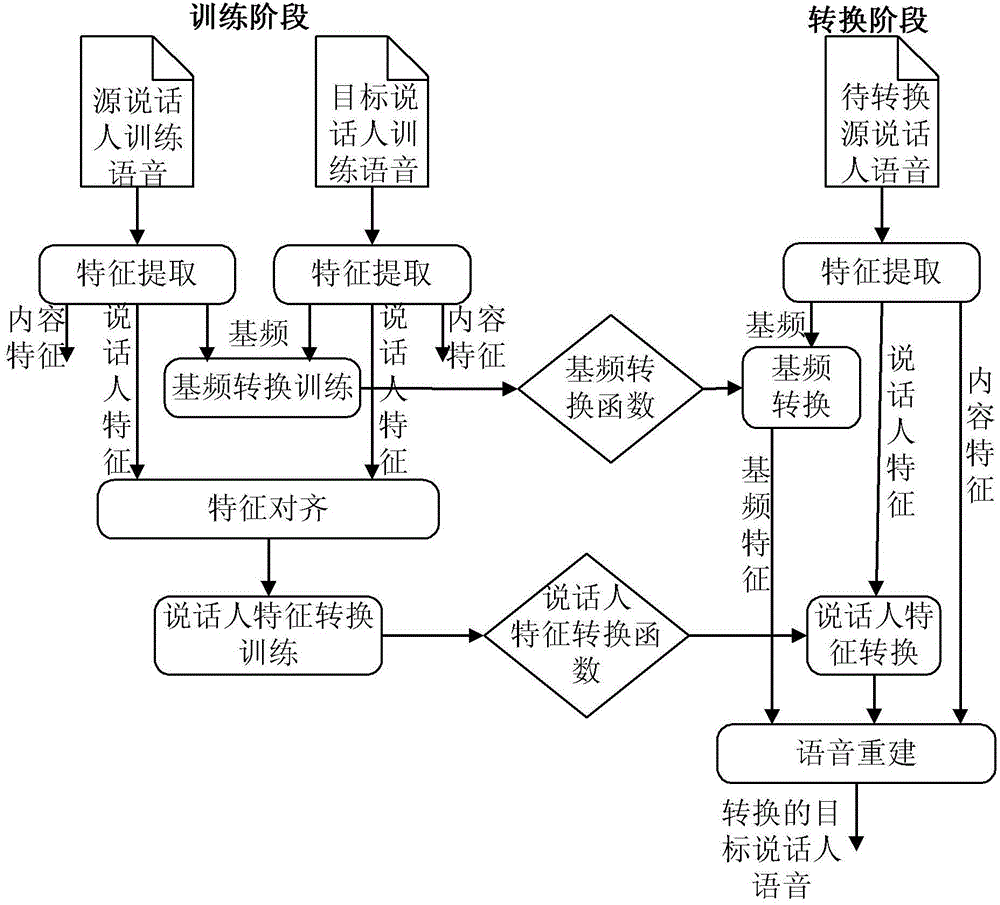
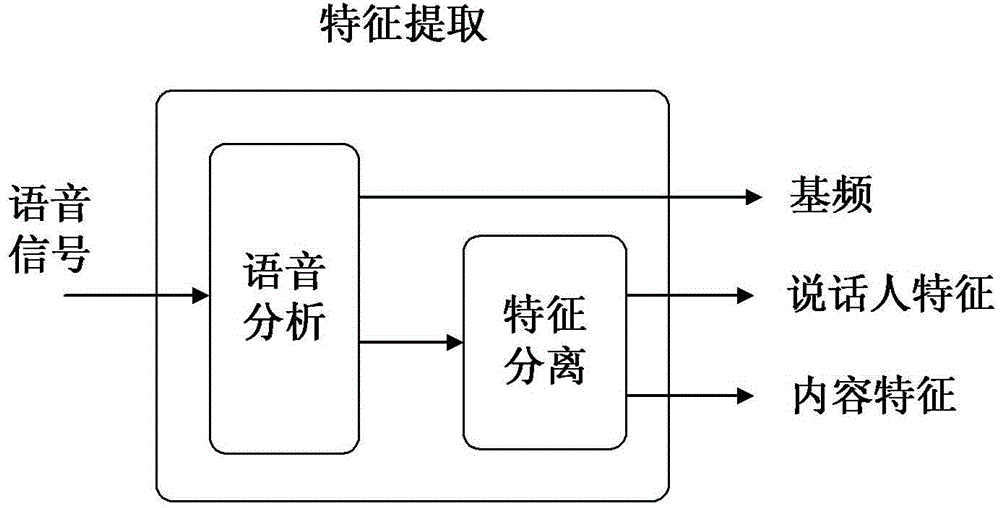
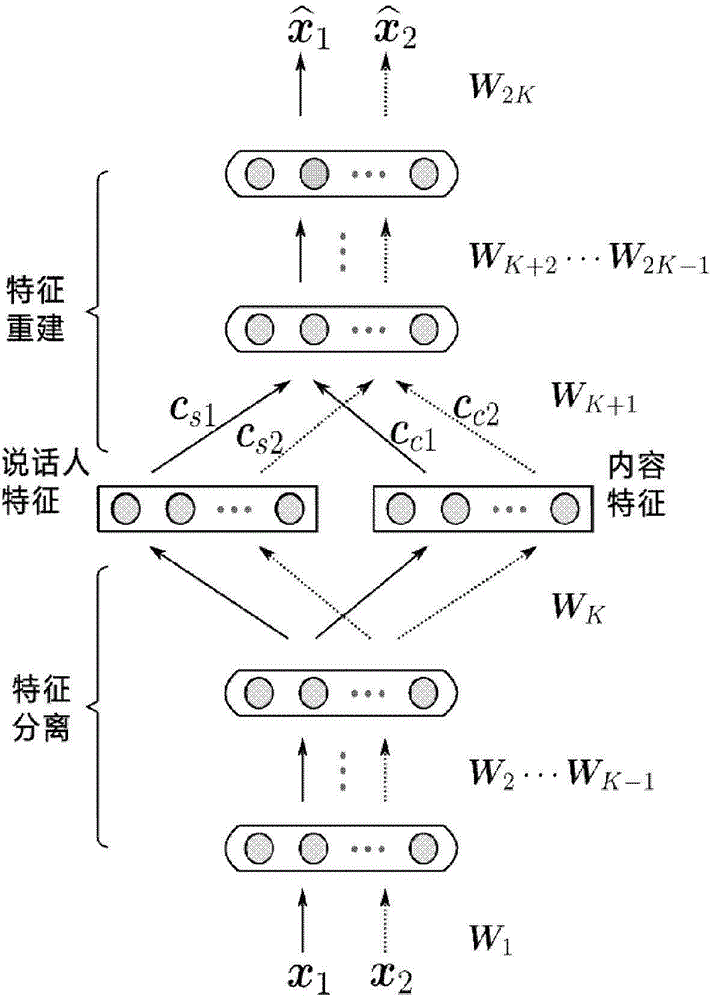
Conversion method for sound of speaker
ActiveCN102982809AAchieve separationMeet the needs of processing tasksSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumSound quality
The invention discloses a conversion method for sound of a speaker. The method comprises a training stage and a conversion stage, wherein the training stage comprises the steps of respectively extracting a fundamental frequency characteristic, a speaker characteristic and a content characteristic from training voice signals of a source speaker and a target speaker, constructing a fundamental frequency conversion function according to the fundamental frequency characteristic, and constructing a speaker conversion function according to the speaker characteristic. The conversion stage comprises the steps of extracting a fundamental frequency characteristic and a spectrum characteristic from a voice signal to be converted of the source speaker, using the fundamental frequency conversion function and the speaker conversion function obtained in the training stage to convert the fundamental frequency characteristic and the speaker characteristic extracted from the voice signal to be converted, obtaining the converted fundamental frequency characteristic and the speaker characteristic, and synthesizing voices of the target speaker according to the obtained converted fundamental frequency characteristic, the speaker characteristic and the content characteristic in the voice signal to be converted. The method is easy to realize, and the converted sound quality and similarity are higher.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method and apparatus for providing feedback of vocal quality to a user
Embodiments of the invention relate to a feedback mechanism that informs a user of a communication device to adjust the volume, pitch, tone or other characteristic of his voice so as to compensate for noise in the surrounding environment. The feedback mechanism includes feedback circuitry that analyzes audio signals from the microphone and preferably from one or more additional environmental noise sensors. From the analysis, the feedback circuitry determines characteristics of the user's voice and characteristics of the environmental noise, and provides an analysis of how the user might modify his voice to best compensate for environmental noise. This analysis results in an indication to the user, such as through a vibration, a sound, or graphical indication on the device, which tells the user whether and to what extent the user should adjust a characteristic of his voice to best overcome such environmental noise.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
Remote audio device management system
ActiveUS20050002535A1Conveniently formedEnhances audio acquisition qualityTelevision conference systemsColor television detailsSound qualityManagement system
An audio device management system (ADMS) manages remote audio devices via user selections in video links. The system enhances audio acquisition quality by receiving and processing human suggestions, forming customized two-way audio links according to user requests, and learning audio pickup strategies and camera management strategies from user operations. The ADMS control interface for a remote user provides a multi-window GUI that provides an overview window and selection display window. The ADMS provides users with more flexibility to enhance audio signals according to their needs and makes it more convenient to form customized two-way audio links without requiring users to remember a list of phone numbers. The ADMS also automatically manages available microphones for audio pickup based on microphone sound quality and the system's past experience when users monitor a structured audio environment without explicitly expressing their attentions in the video window.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Signal processing apparatus and signal processing method, encoder and encoding method, decoder and decoding method, and program
ActiveUS20130028427A1Improve sound qualitySpeech analysisStereophonic arrangmentsDecoding methodsSound quality
The present invention relates to a signal processing apparatus and a signal processing method, an encoder and an encoding method, a decoder and a decoding method, and a program capable of reproducing music signal having a better sound quality by expansion of frequency band.An encoder sets an interval including 16 frames as interval section to be processed, outputs high band encoded data for obtaining the high band component of an input signal and low band encoded data obtained by encoding the low band signal of the input signal for each section to be processed. In this case, for each frame, a coefficient used in estimation of the high band component is selected and the section to be processed is divided into continuous frame segments including continuous frames from which the coefficient with the same section to be processed is selected. In addition, high band encoded data is produced which includes data including information indicating a length of each continuous frame segment, information indicating the number of continuous frame segments included in the section to be processed and a coefficient index indicating the coefficient selected in each continuous frame segment. The present invention is applicable to the encoder.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method and apparatus to extract important spectral component from audio signal and low bit-rate audio signal coding and/or decoding method and apparatus using the same
InactiveUS20070016404A1Broadcast information characterisationBroadcast circuit arrangementsDecoding methodsFrequency spectrum
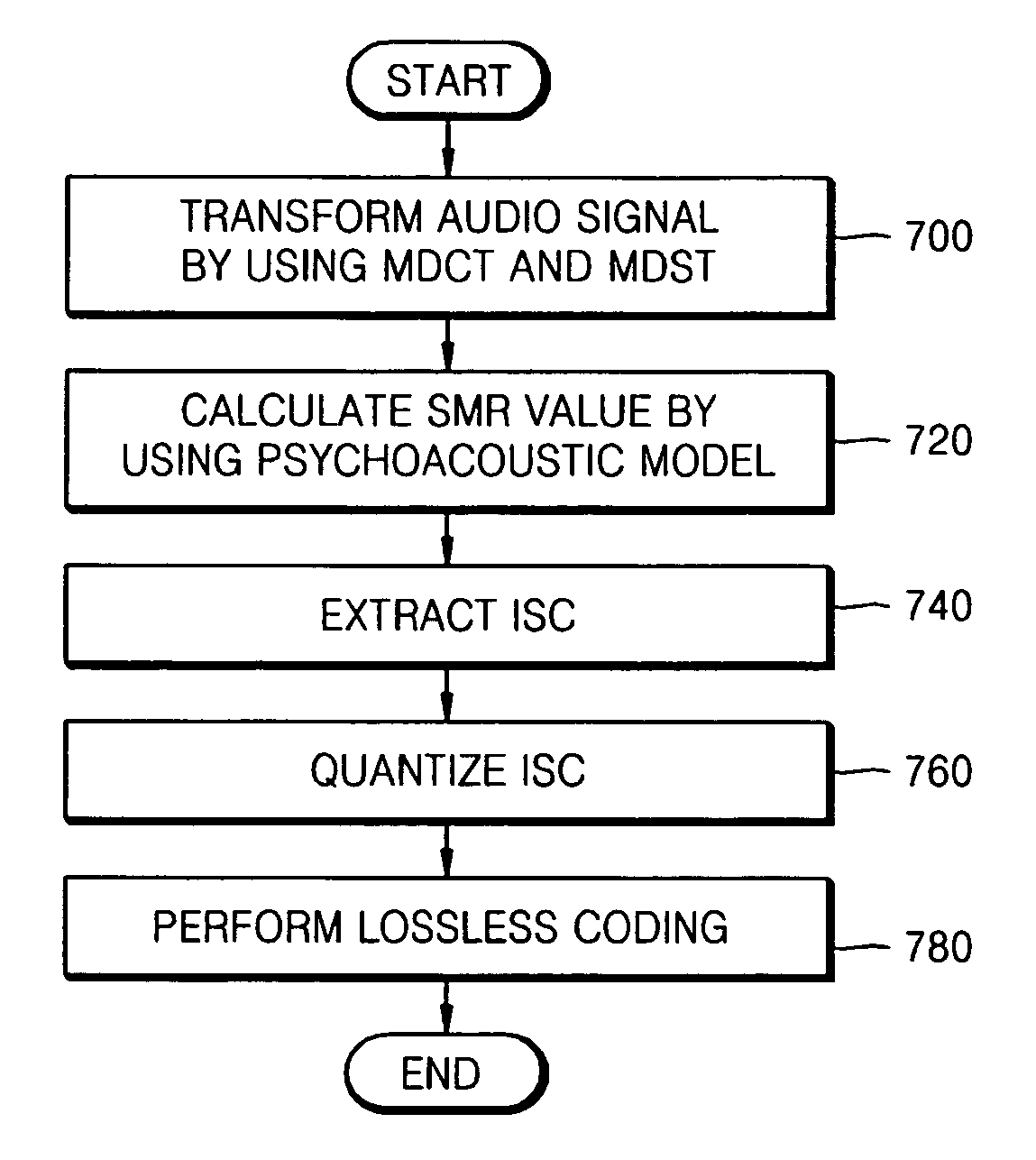
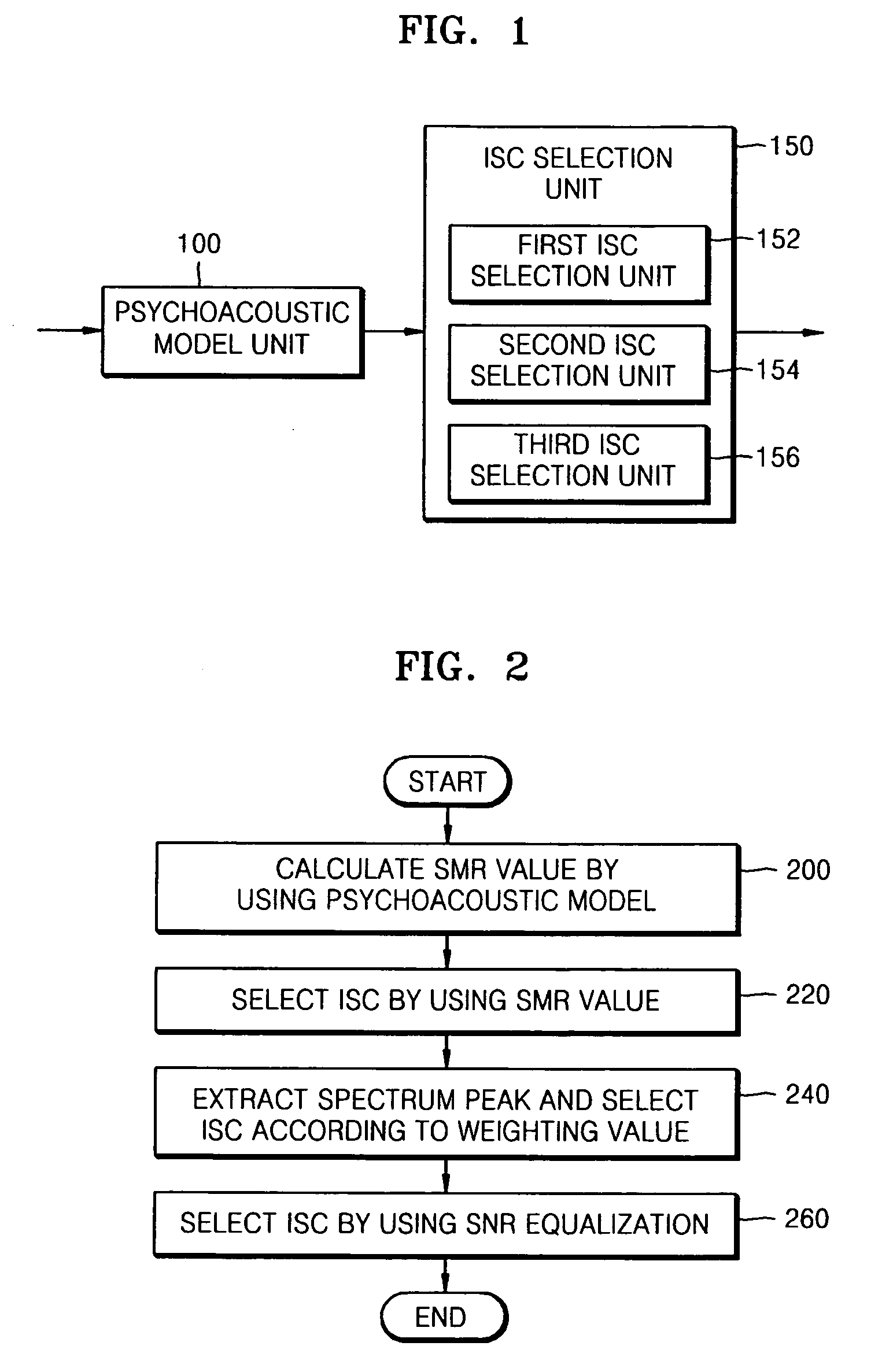
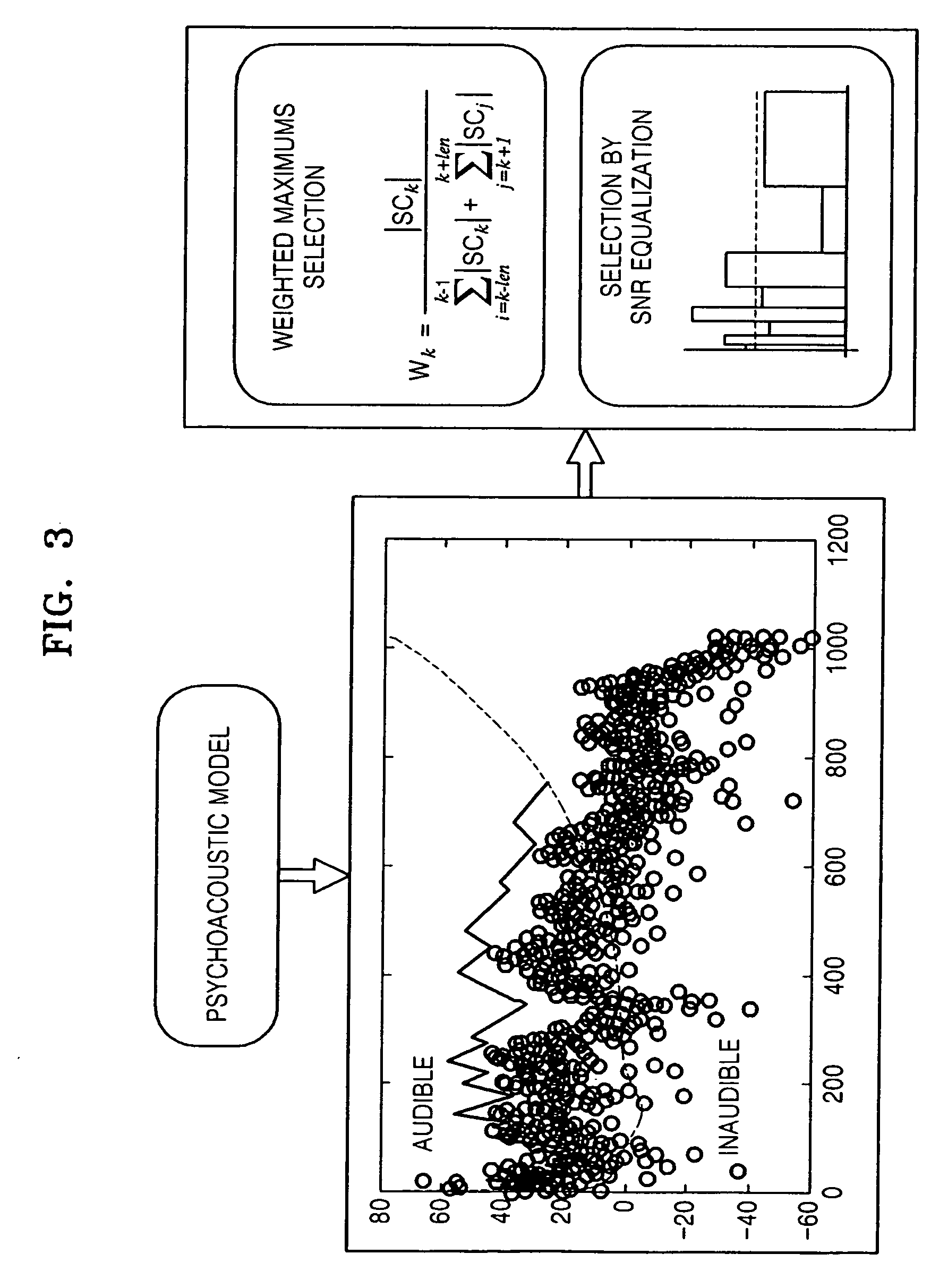
An method and apparatus to extract an audio signal having an important spectral component (ISC) and a low bit-rate audio signal coding / decoding method using the method and apparatus to extract the ISC. The method of extracting the ISC includes calculating perceptual importance including an SMR (signal-to-mark ratio) value of transformed spectral audio signals by using a psychoacoustic model, selecting spectral signals having a masking threshold value smaller than that of the spectral audio signals using the SMR value as first ISCs, and extracting a spectral peak from the audio signals selected as the ISCs according to a predetermined weighting factor to select second ISCs. Accordingly, the perceptual important spectral components can be efficiently coded so as to obtain high sound quality at a low bit-rate. In addition, it is possible to extract the perceptual important spectral component by using the psychoacoustic model, to perform coding without phase information, and to efficiently represent a spectral signal at a low bit-rate. In addition, the methods and apparatus can be employed in all the applications requiring a low bit-rate audio coding scheme and in a next generation audio scheme.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Speaker for mobile terminals and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20050220320A1Thin structureWide frequency characteristicTransducer detailsGeotextilesEngineeringSound quality
Disclosed herein are a speaker for mobile terminals which has a slim structure and has a wide frequency characteristic and an excellent high frequency distortion characteristic, thus accomplishing an excellent sound quality, and a method of manufacturing the speaker.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
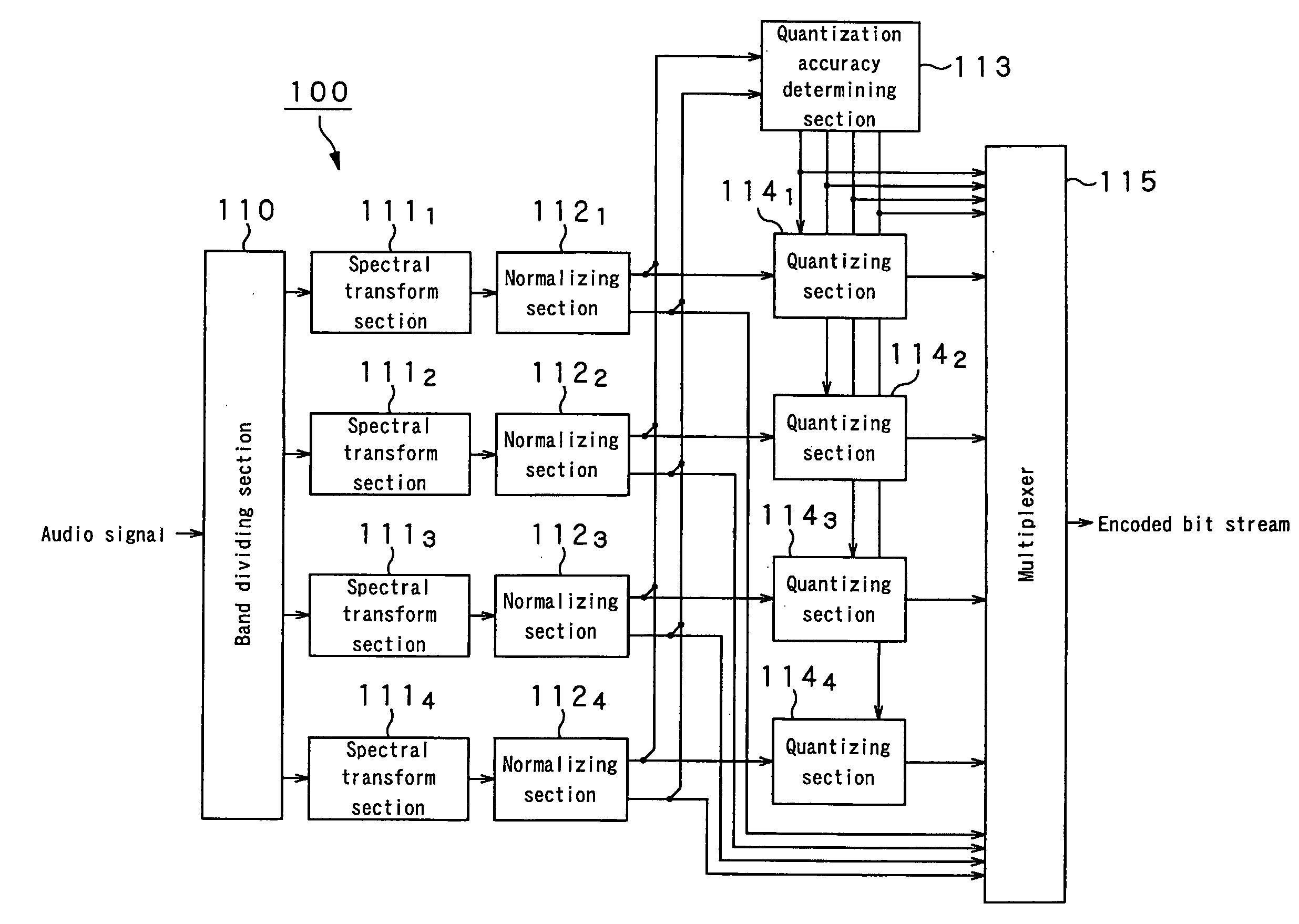
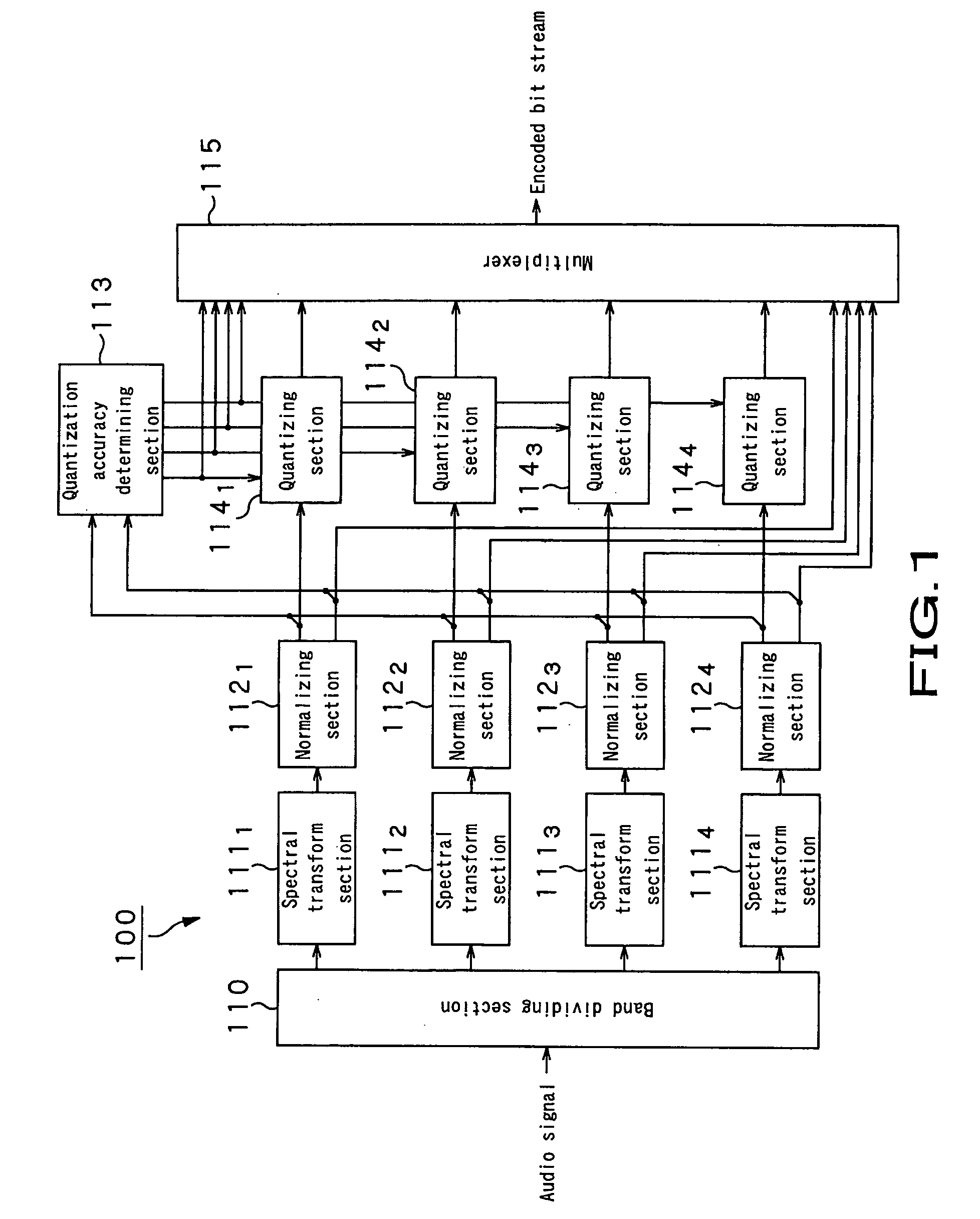
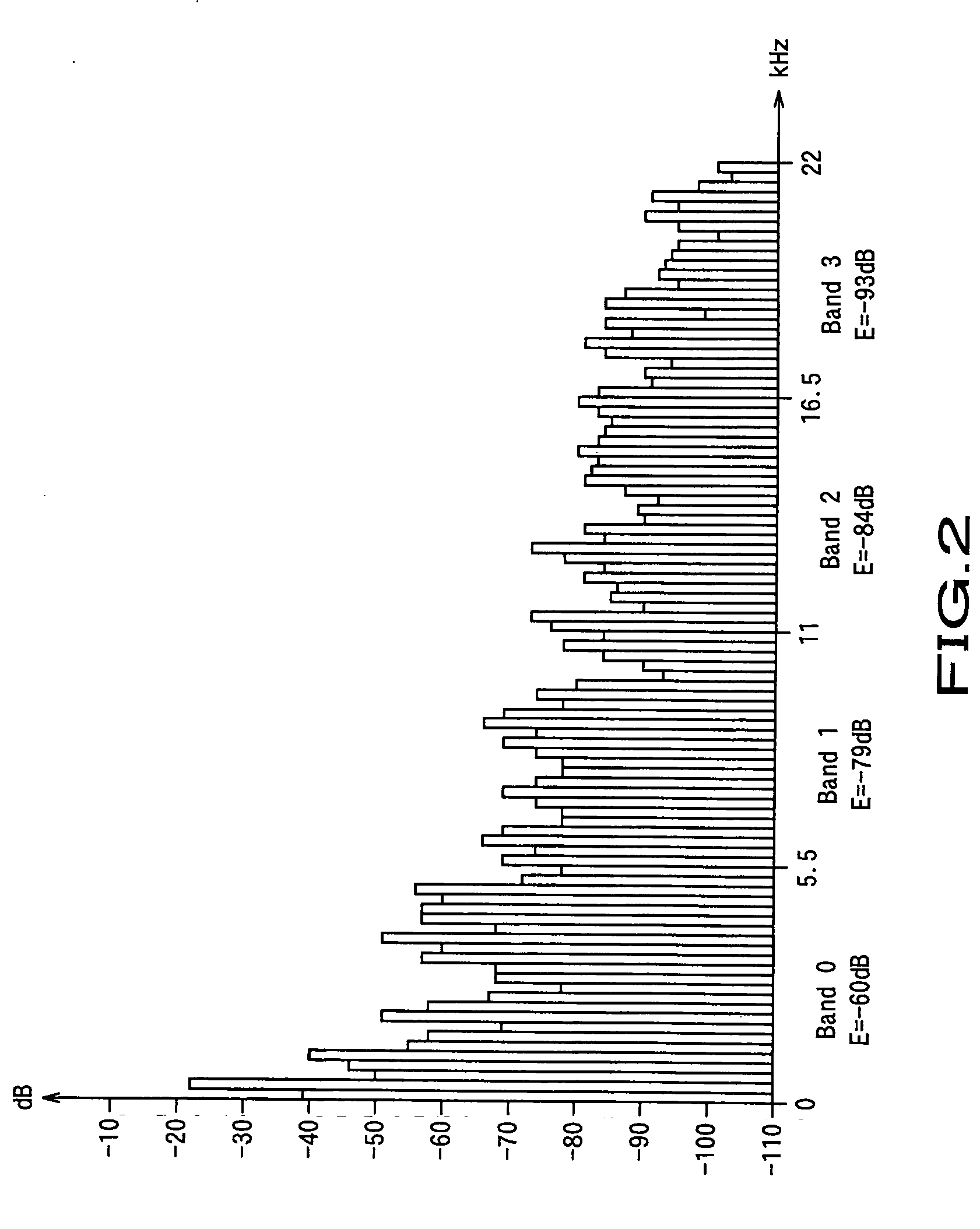
Audio signal encoding apparatus and audio signal encoding method
InactiveUS20050267744A1Prevent any auditory problemImprove sound qualitySpeech analysisCode conversionAuditory senseFrequency spectrum
Any disagreement of the power level before encoding an audio signal and the power level after encoding the audio signal is adjusted to improve the sound quality to the auditory sense. The present invention provides an audio signal encoding apparatus comprising, a band dividing section that divides an input audio signal by a plurality frequency sub-bands, a spectral transform section that transforms the audio signal of each frequency sub-band into a spectral signal, a normalizing section that normalizes each spectral signal by means of a scale factor and generates a normalized spectral signal, a quantizing section that quantizes each normalized spectral signal and generates a quantized spectral signal, a scale factor adjusting section that adjusts the value of the scale factor used by the normalizing section according to the normalized spectral signal and the quantized spectral signal, and an encoding section that encodes at least each quantized spectral signal and the scale factor used by the normalizing section or the scale factor adjusted by the scale factor adjusting section. The scale factor adjusting section is adapted to compare the absolute value of the difference of the energy of the normalized spectral signal and the energy of the quantized spectral signal with a first threshold value for each frequency sub-band and, if the absolute value of the difference is greater than the first threshold value, adjust the value of the scale factor used by the normalizing section so as to make the absolute value of the difference of the energies not greater than a second threshold value.
Owner:SONY CORP
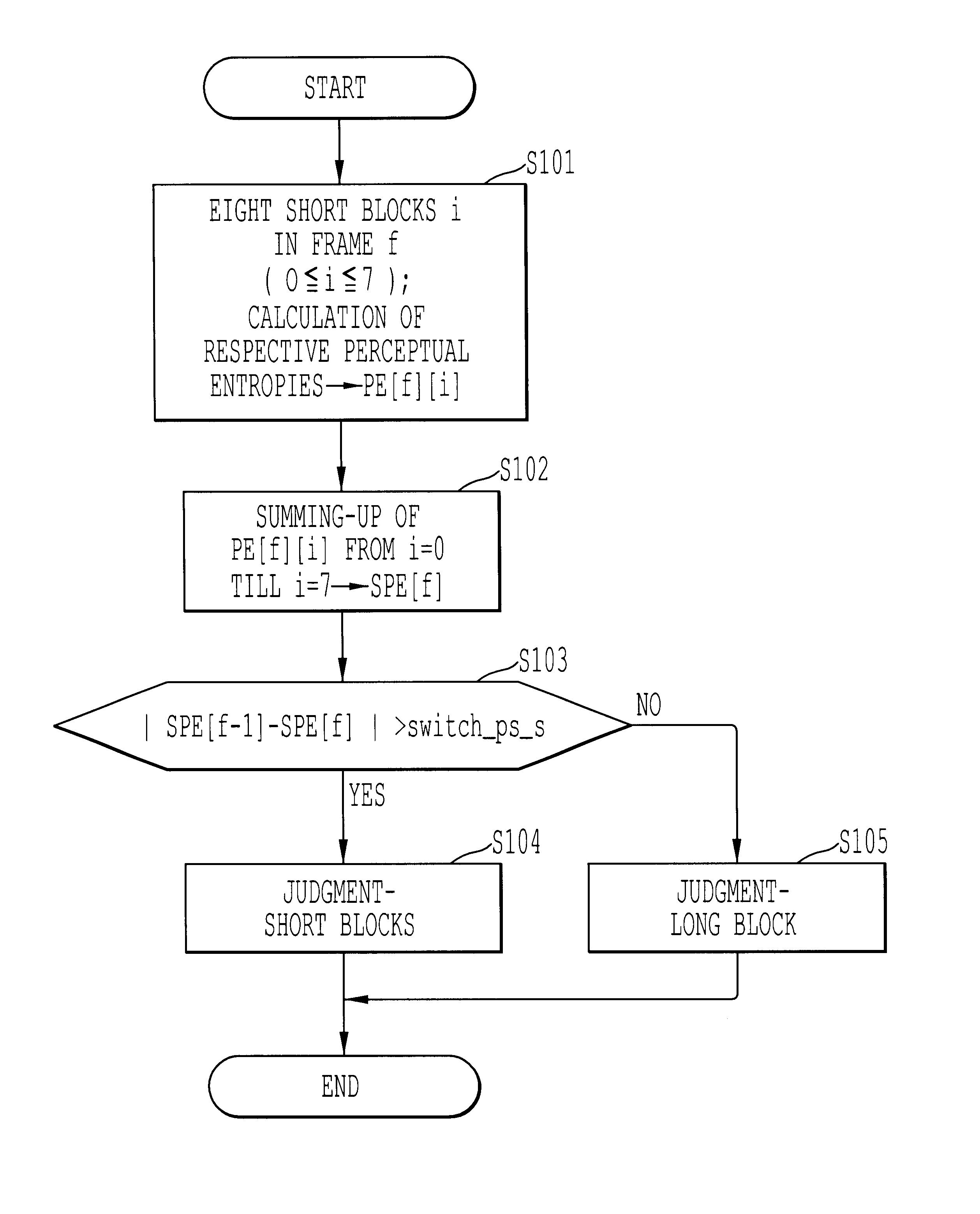
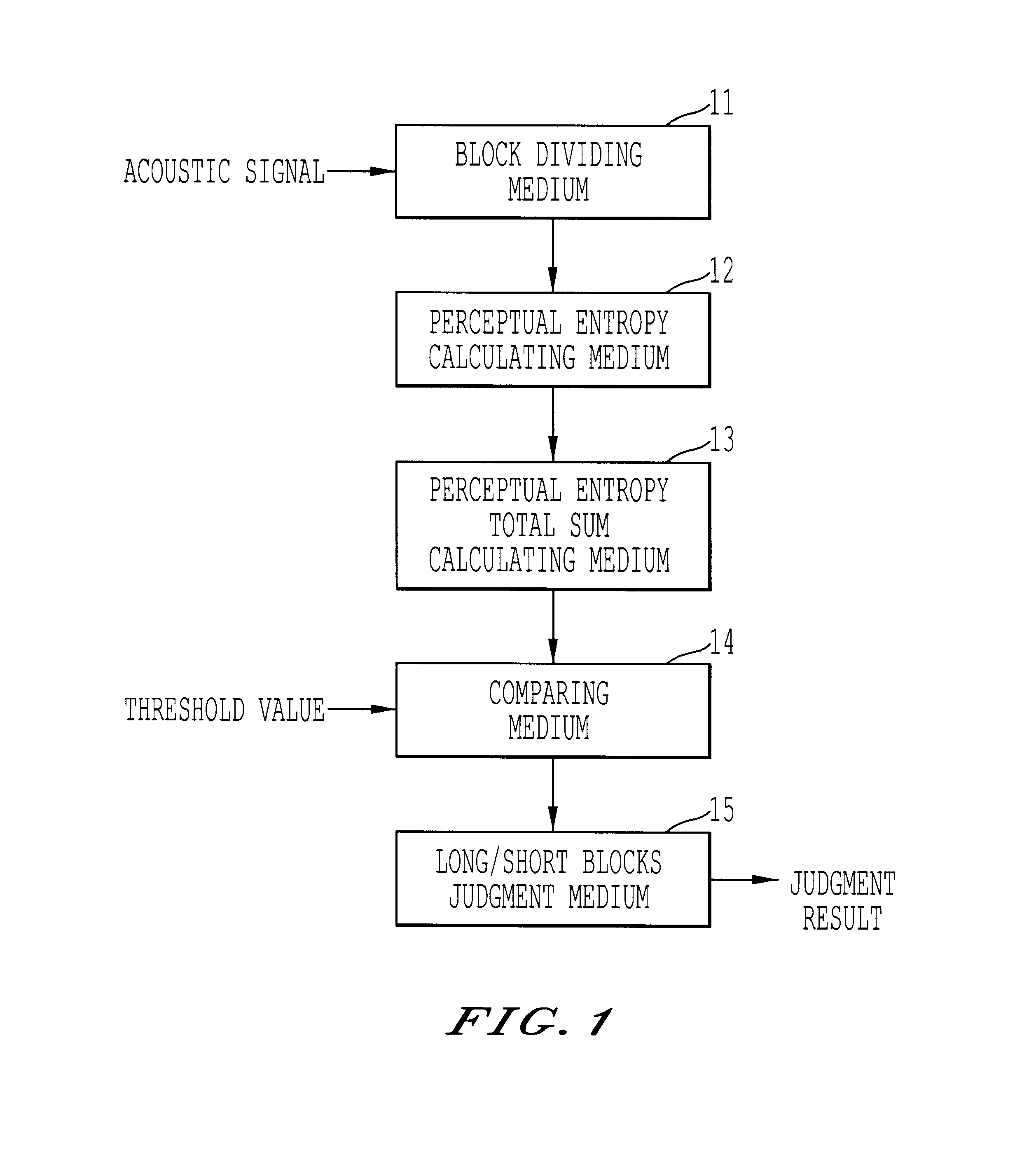
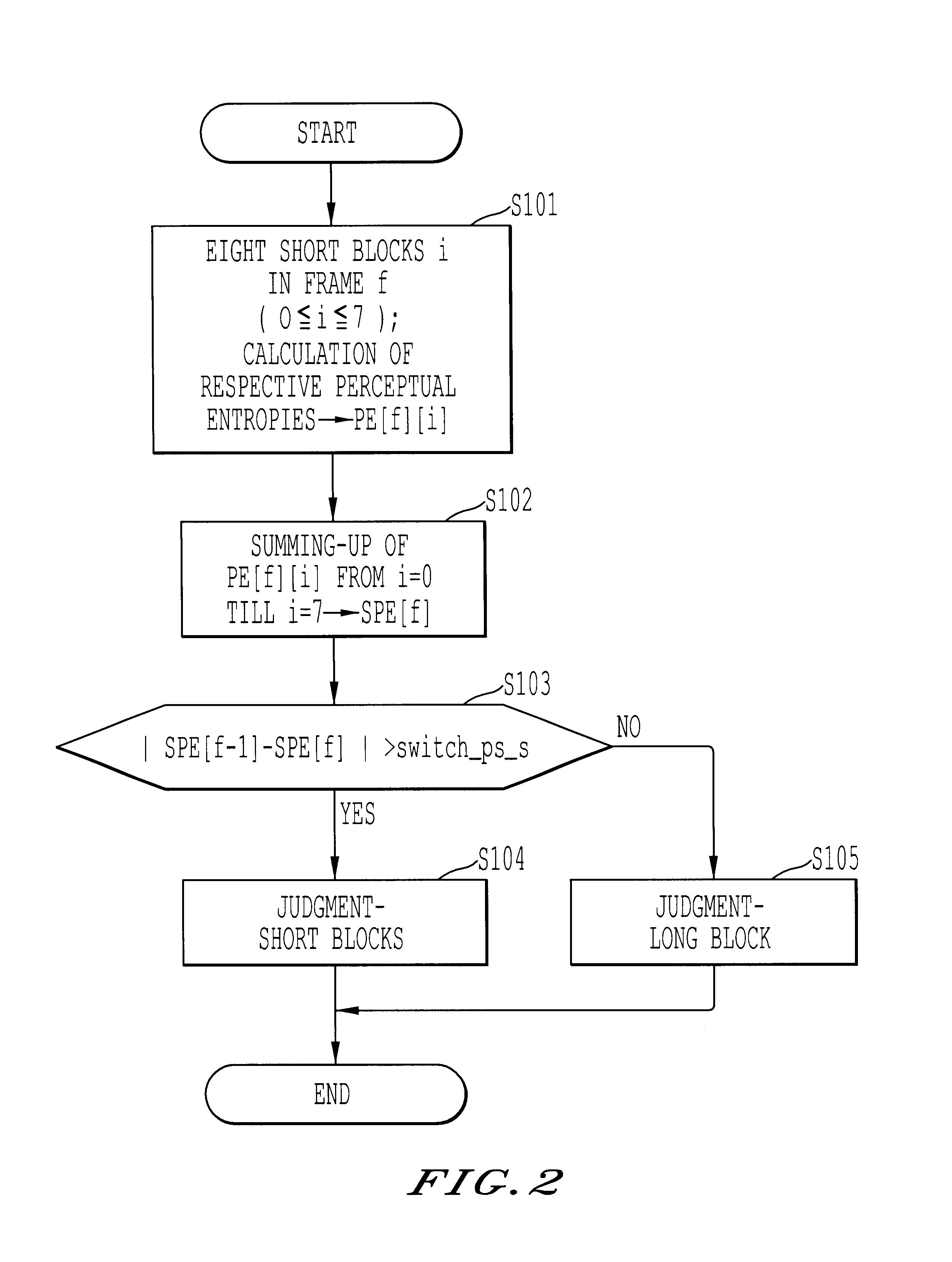
Method, apparatus, and medium of digital acoustic signal coding long/short blocks judgement by frame difference of perceptual entropy
A digital acoustic signal coding apparatus, a method of coding the digital acoustic signal, and a recording medium for recording a program of coding the digital acoustic signal are respectively realized. It is possible to provide the digital acoustic signal coding method and apparatus, in which, corresponding to the difference between the sampling frequencies of the input acoustic signal, short blocks can be suitably classified into groups without deteriorating sound quality and the suitability of using either long / short blocks can be judged. The coding apparatus is composed of a calculation medium for calculating the sensation entropy of an input acoustic signal per each of the respective short sensation blocks; a sensation entropy sum total calculation medium for obtaining a total sum in a frame of the sensation entropy; a comparison medium for comparing an absolute value of the difference between the respective total sums of the sensation entropy of successive two frames with a previously determined threshold value; and a long / short block judgment medium for judging whether a long block or short blocks should be used to convert a block of the input acoustic signal on the basis of the comparison result.
Owner:RICOH KK
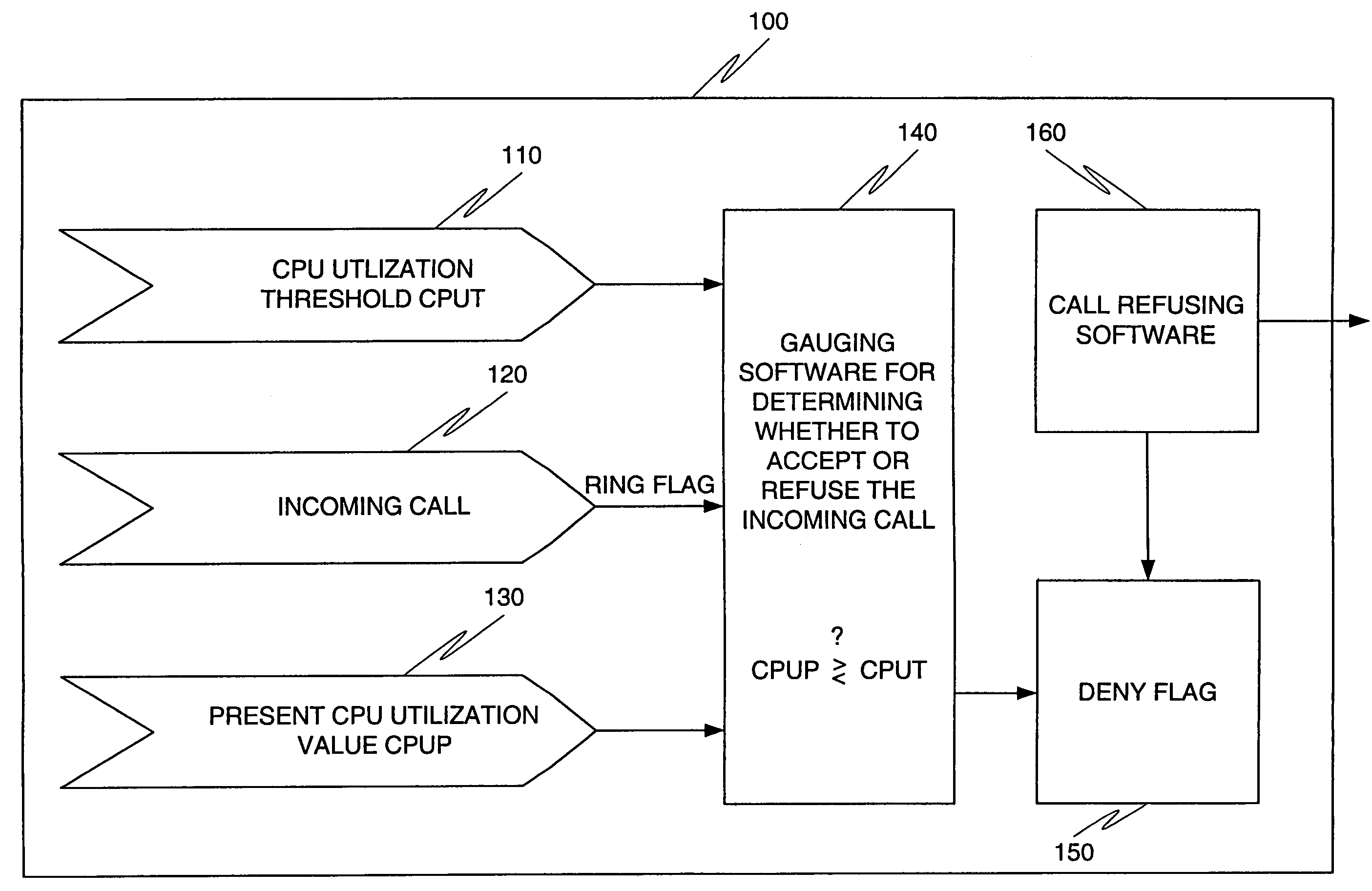
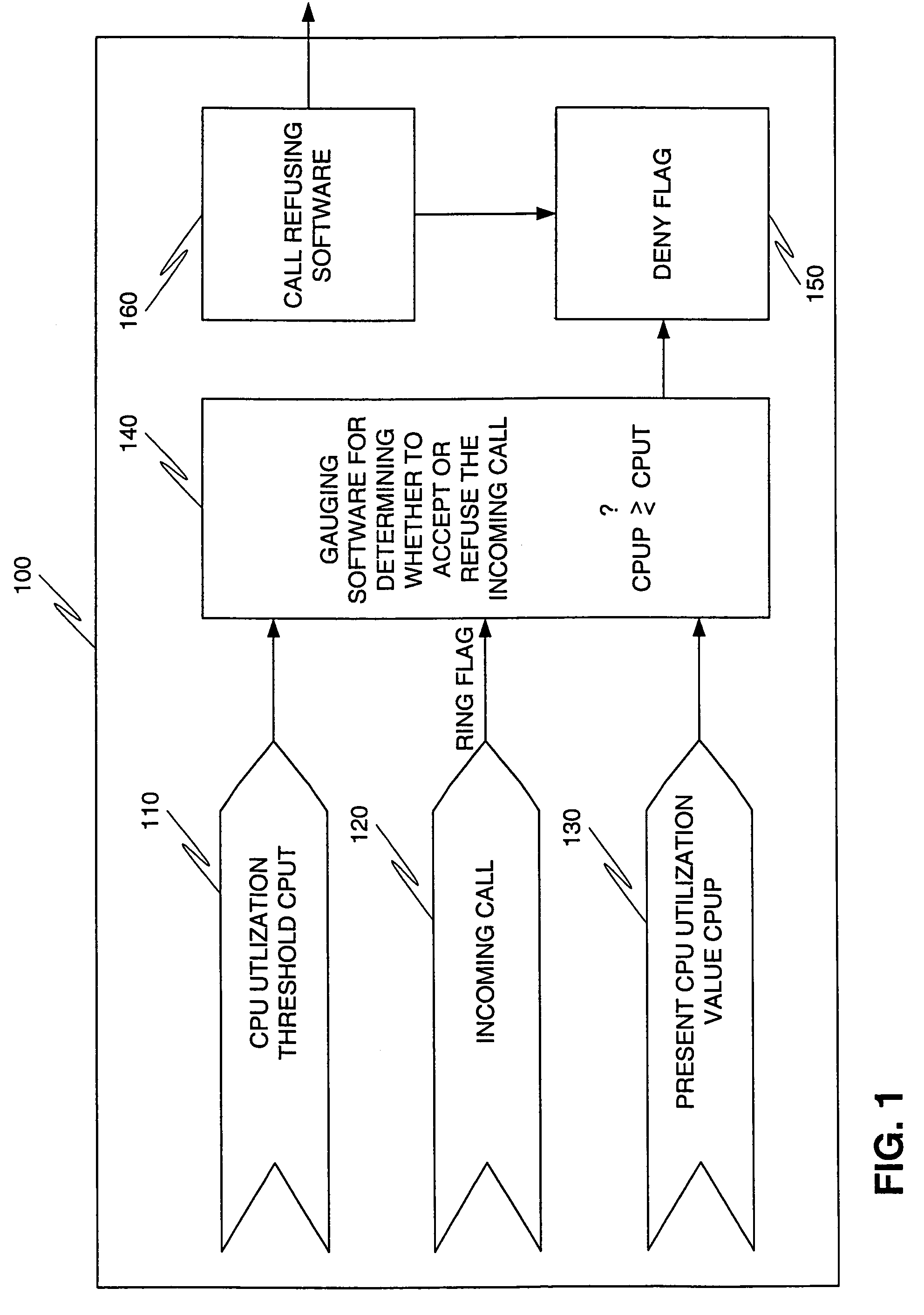
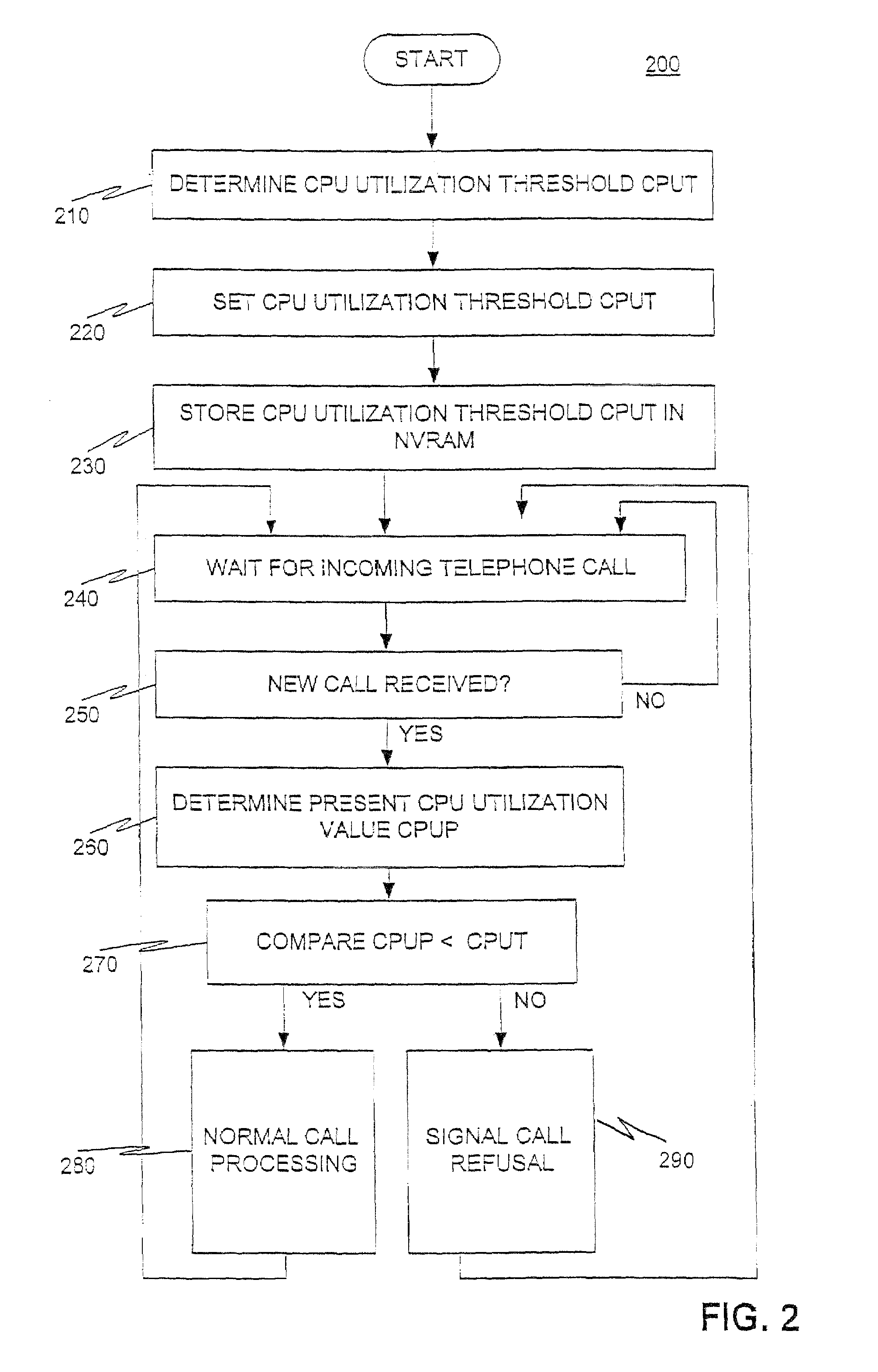
Program and method for preventing overload in a packet telephony gateway
InactiveUS7277384B1Prevent overloadError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsSound qualityPacket telephony
A program and a method for a gateway are provided to deny incoming calls to prevent overload. The program provides a maximum CPU utilization threshold CPUT, which is set by the user. When a new incoming call is presented to the packet telephony gateway, the program checks a present CPU utilization CPUP. If the present CPU utilization CPUP is greater than the threshold, the call is refused. This insures that sound quality of the calls currently being handled is maintained, and that existing calls are never dropped.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
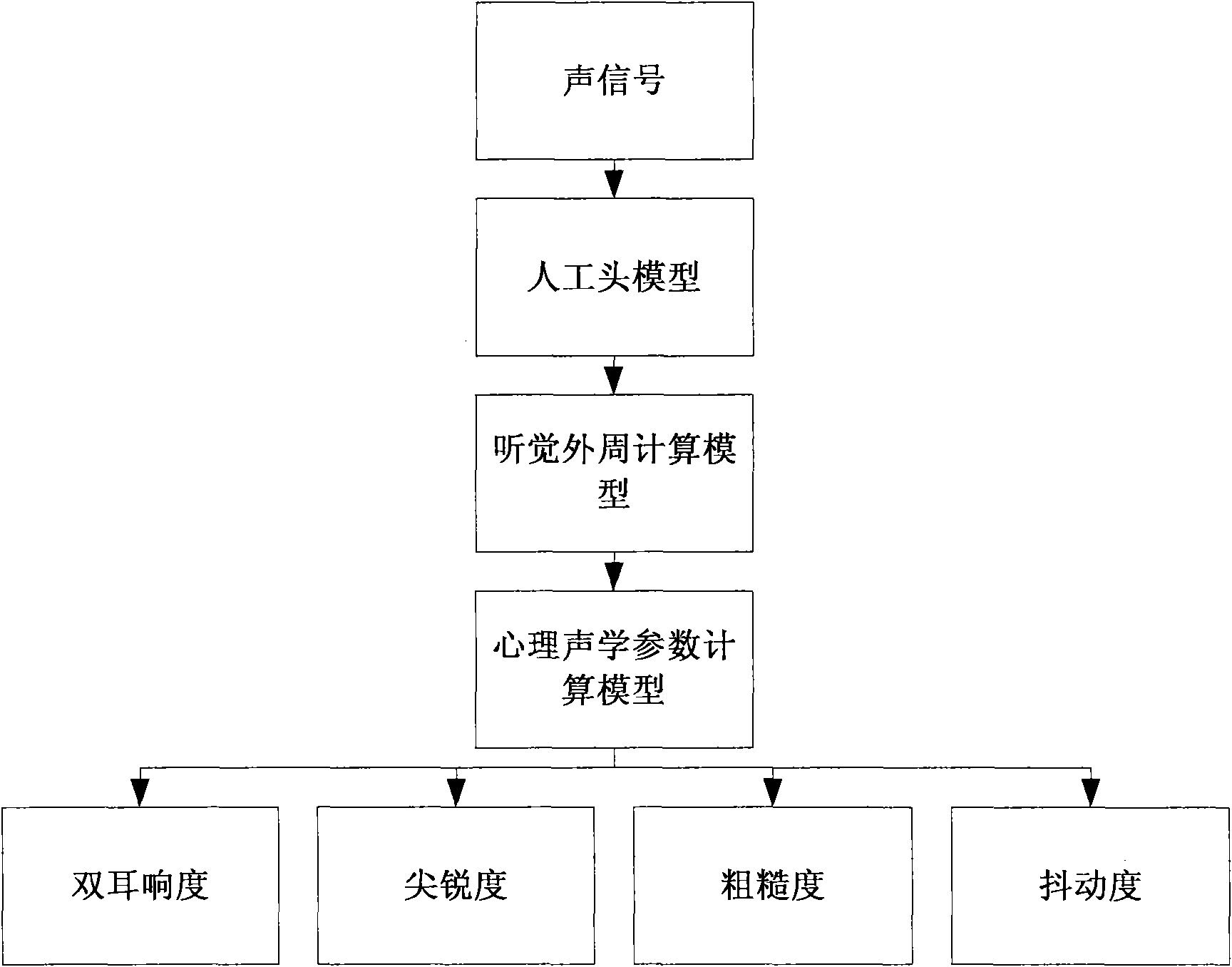
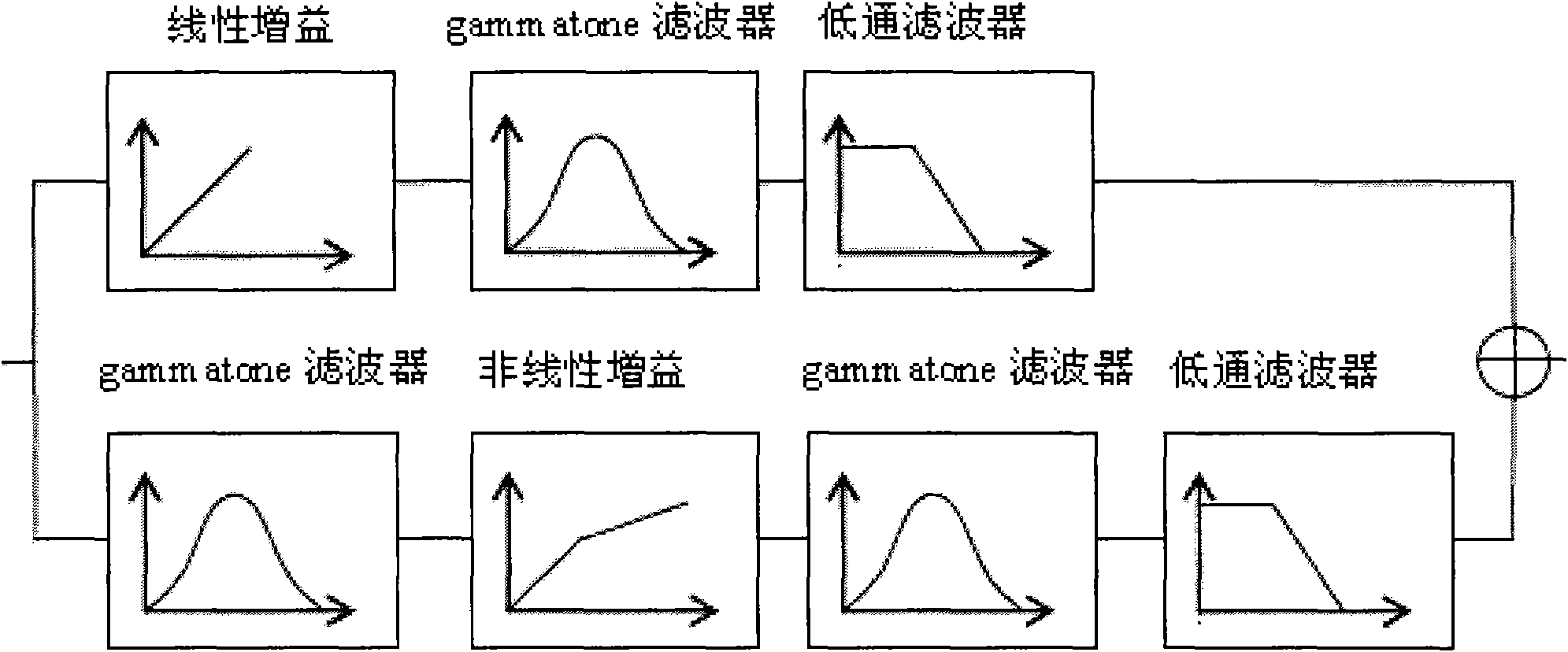
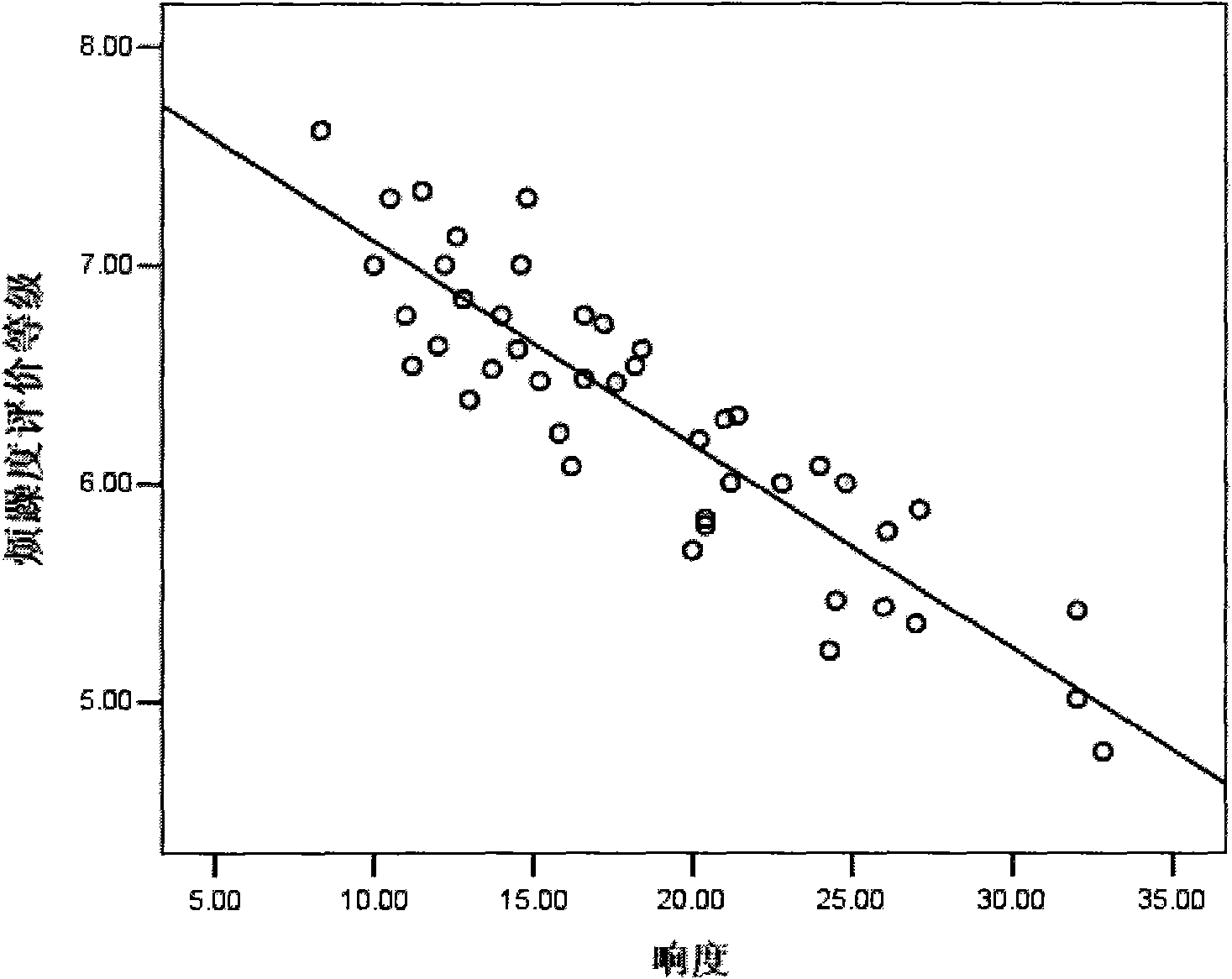
Method for objectively and quantifiably evaluating noise fret degree in vehicle based on auditory model
InactiveCN101672690AImprove performanceOvercoming complexityVibration measurement in fluidPsychotechnic devicesHuman bodyProcess mechanism
The invention relates to a method for objectively and quantifiably evaluating noise fret degree in a vehicle based on an auditory model, in particular to an evaluation method of psychoacoustics and vehicle sound quality. The method comprises the following steps: designing a dummy head model; imitating a processing mechanism of the middle ear and the inner ear of a human body to the sound by usingan auditory peripheral calculation model; collecting vehicle noise signals under the working conditions of uniform, accelerated and idle speed; pre-treating the noise sample and processing the loudness in specification; obtaining a psychoacoustics parameter by using a sound quality calculation model; obtaining subjective evaluation result test data by using a grouped and paired comparison method;calculating and painting a correlated scatter plot chart between each parameter and the ranking value of the subjective evaluation result; and analyzing and calculating to obtain the objectively quantifiable model of the subjective fret degree under each working condition. The invention can realize the psychoacoustic parameter calculation of objectively evaluating the sound quality with differentvehicle types, gears and speeds, wherein the calculated value has good pertinence and consistency with the evaluated result of the subjective evaluation method. The invention has stable evaluated result and high reliability, and can improve the sound quality and competitiveness of vehicles combined with the design of new CAE cars.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com