Patents
Literature
418 results about "Cochlear implantation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
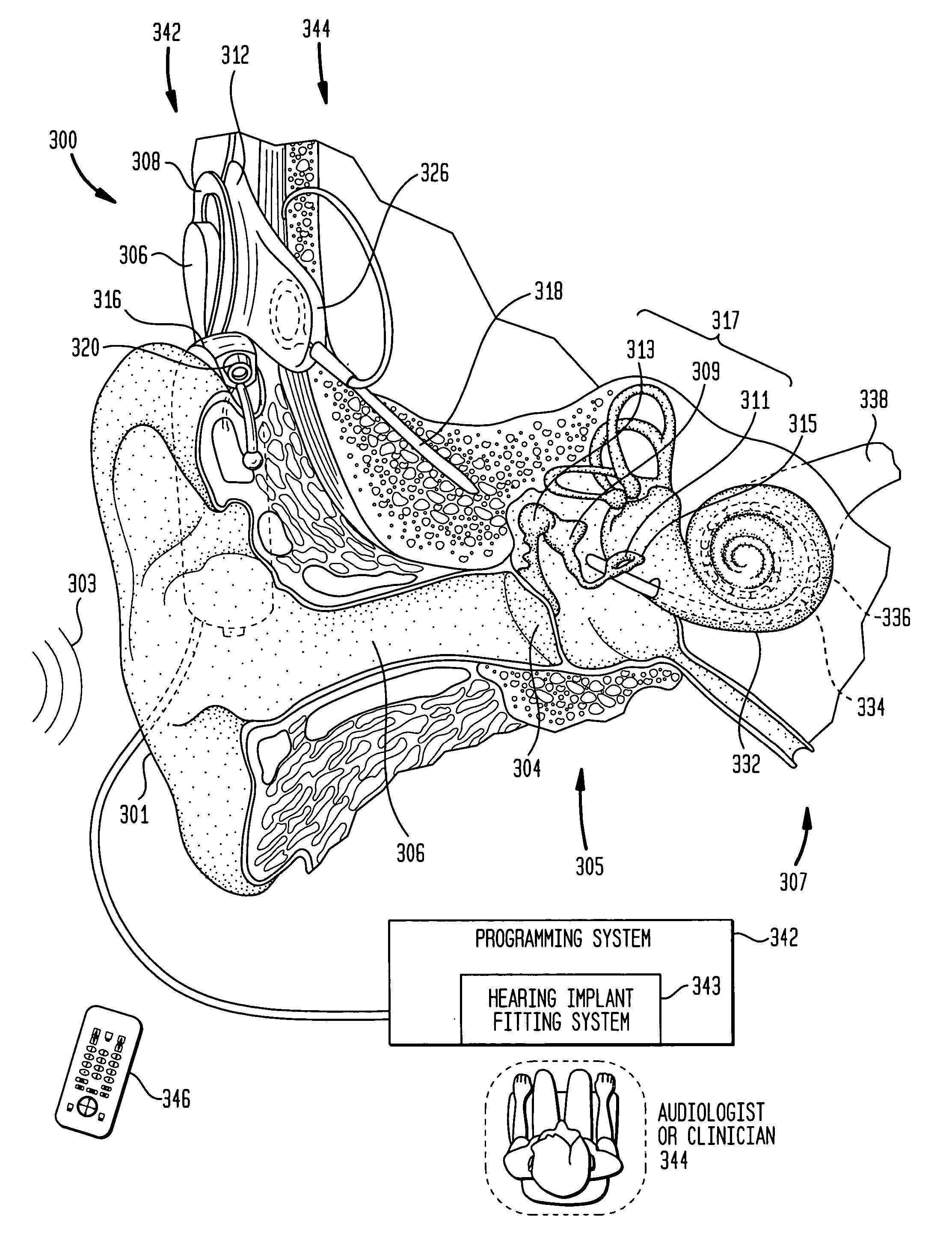
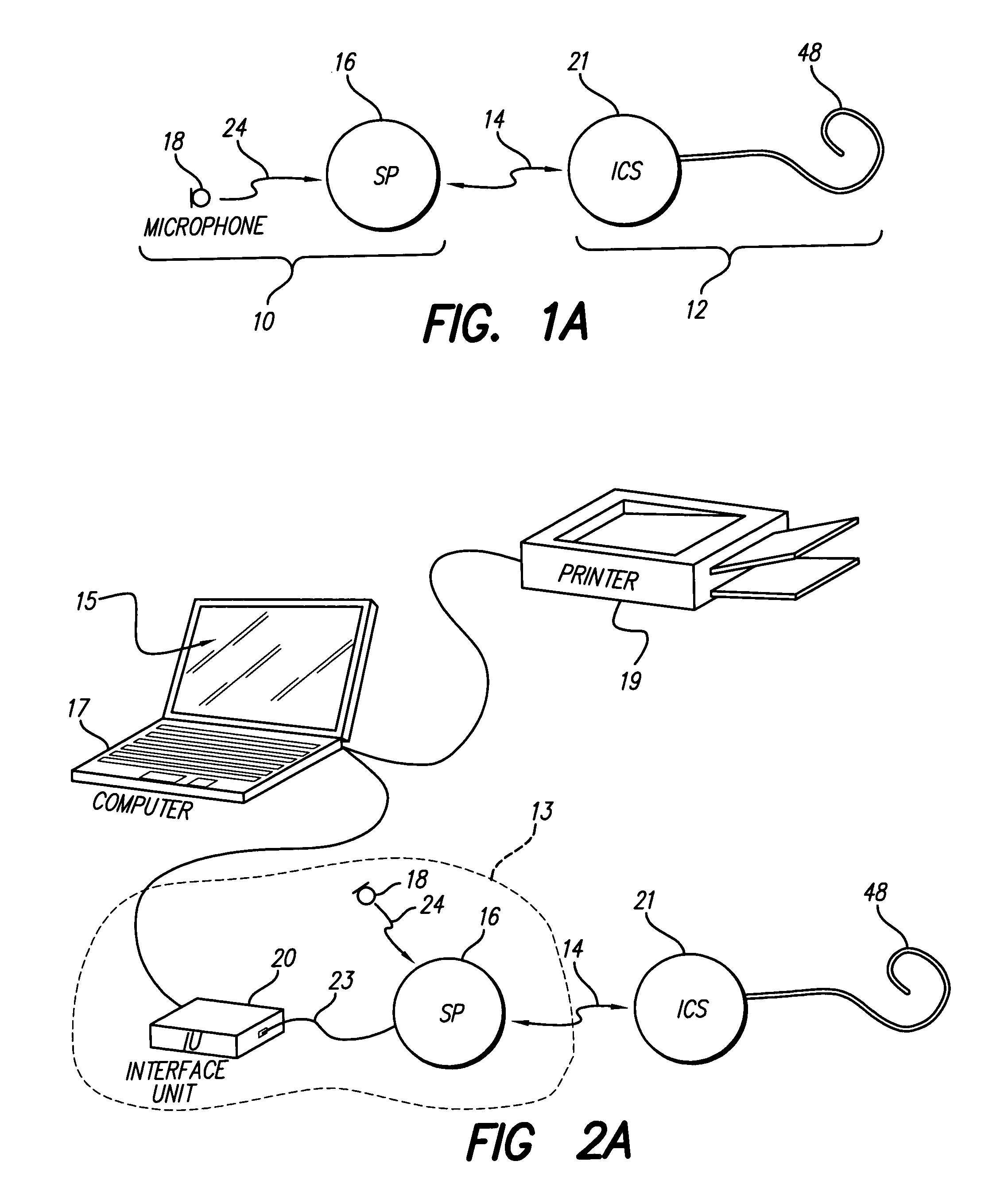
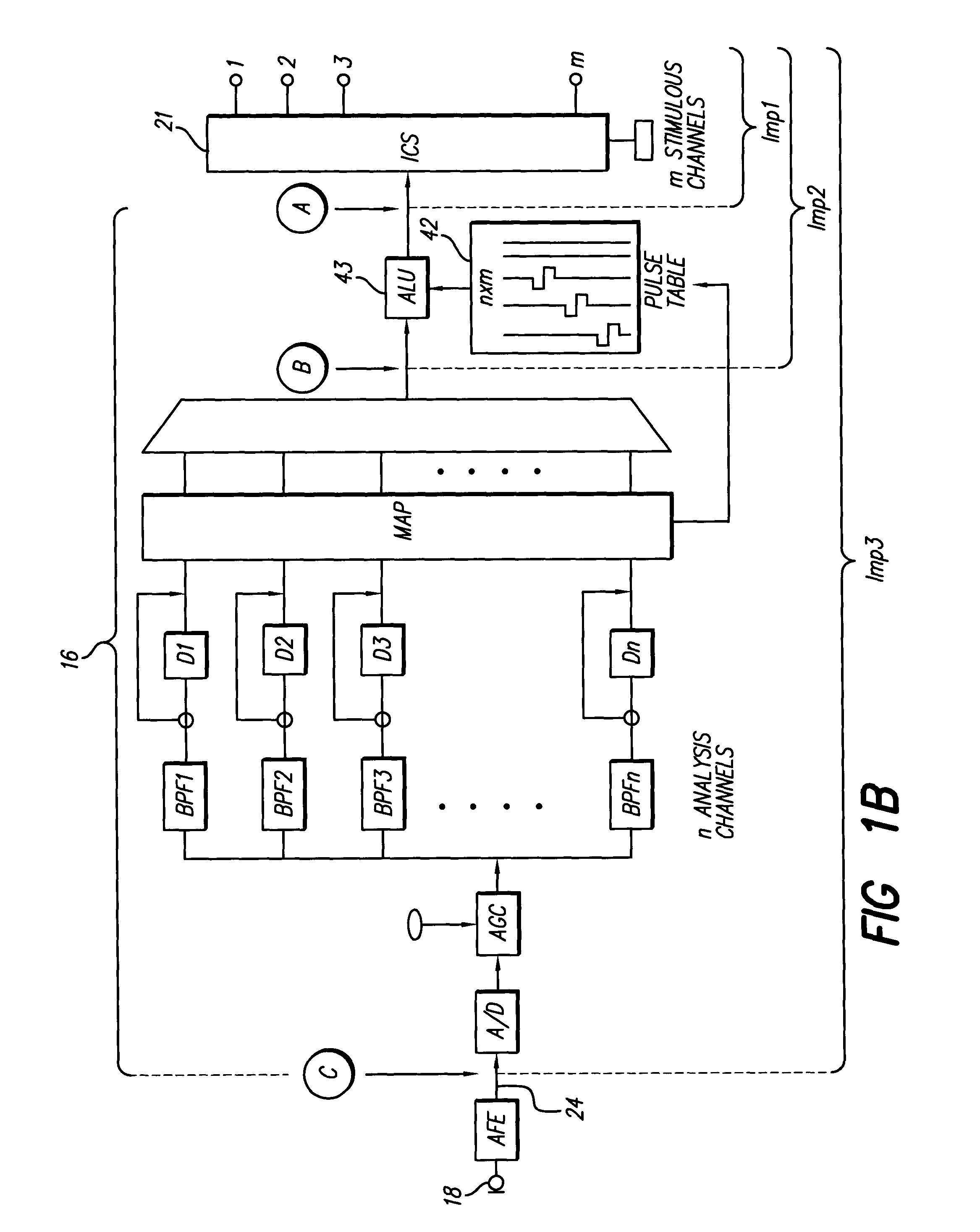
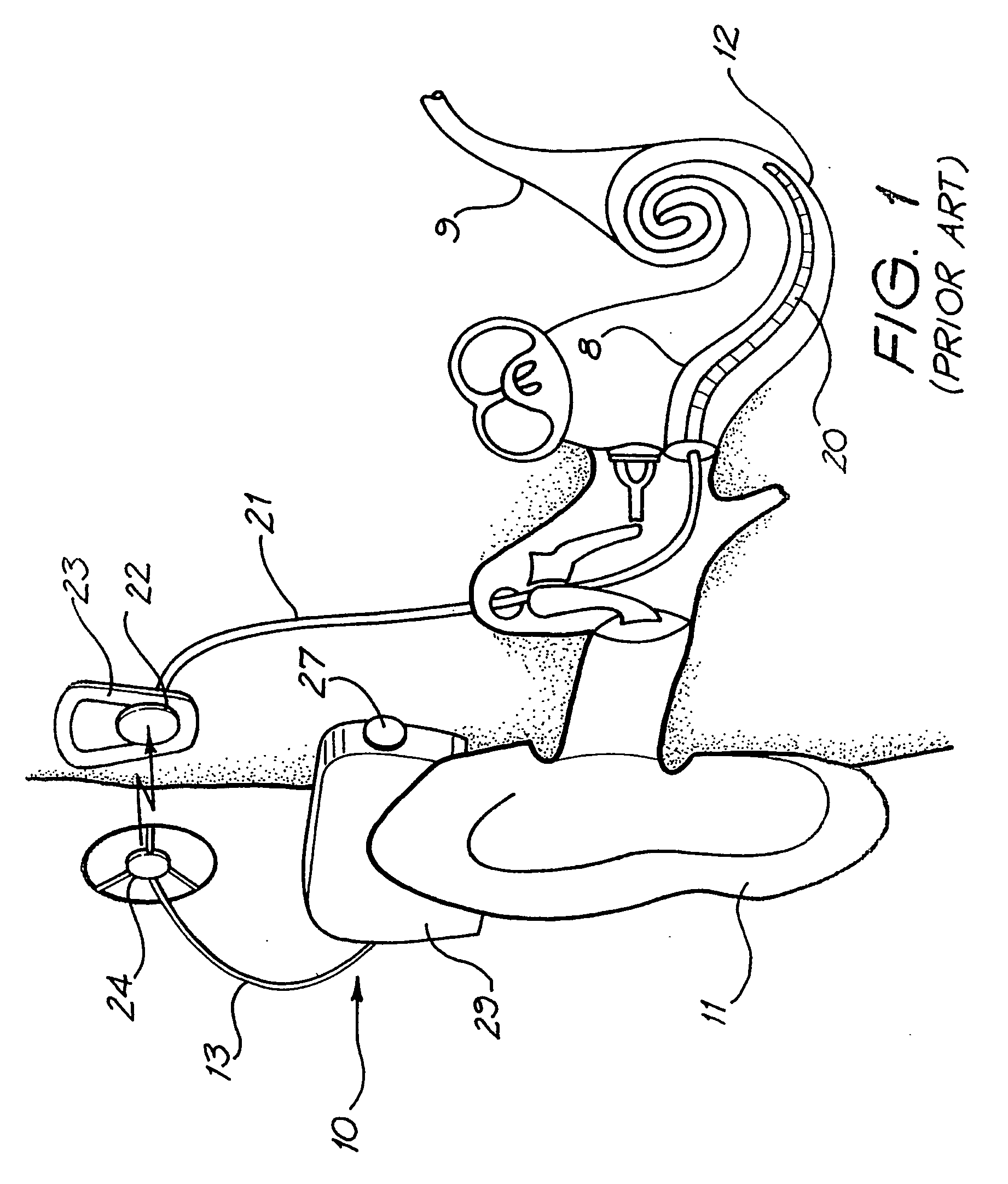
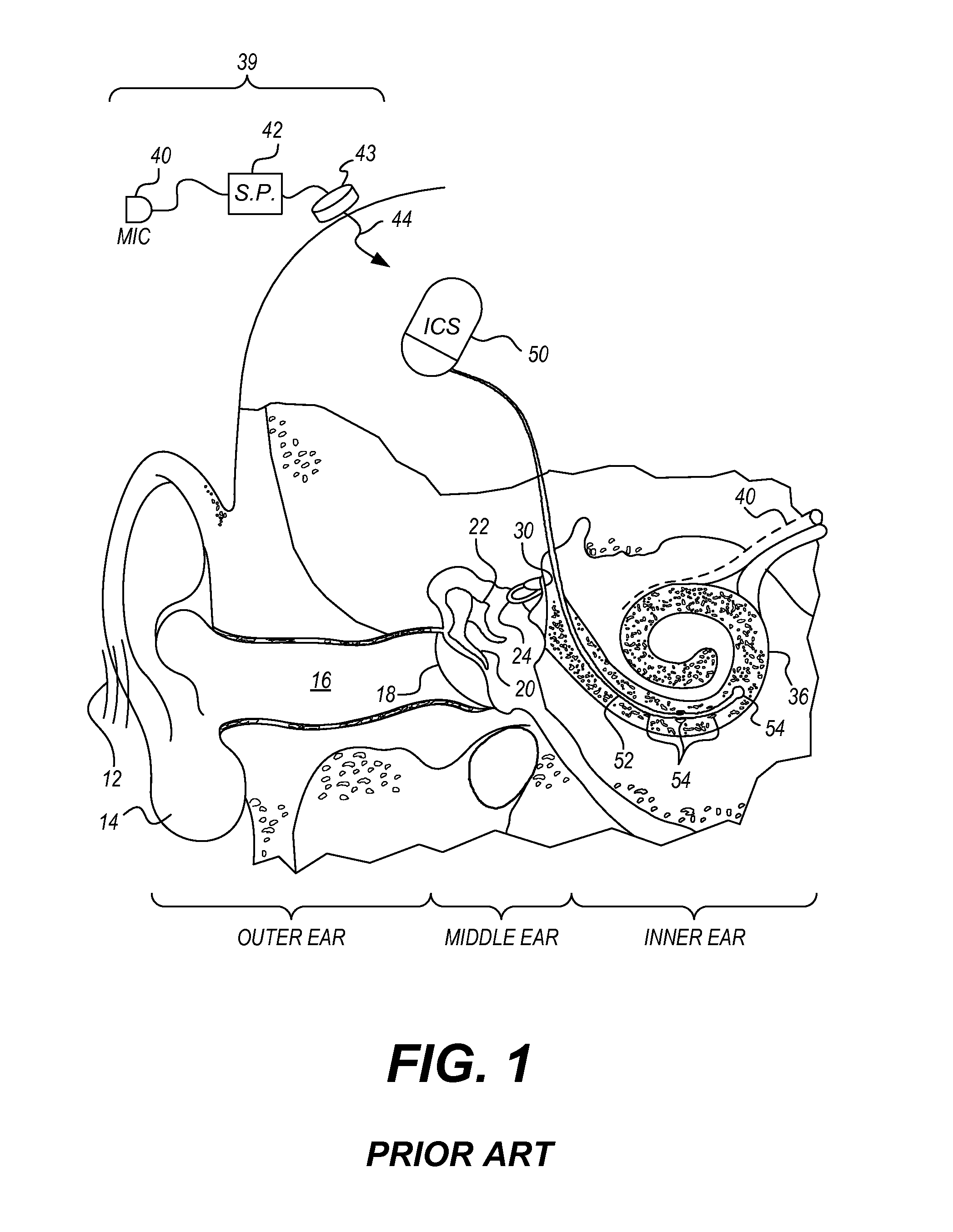
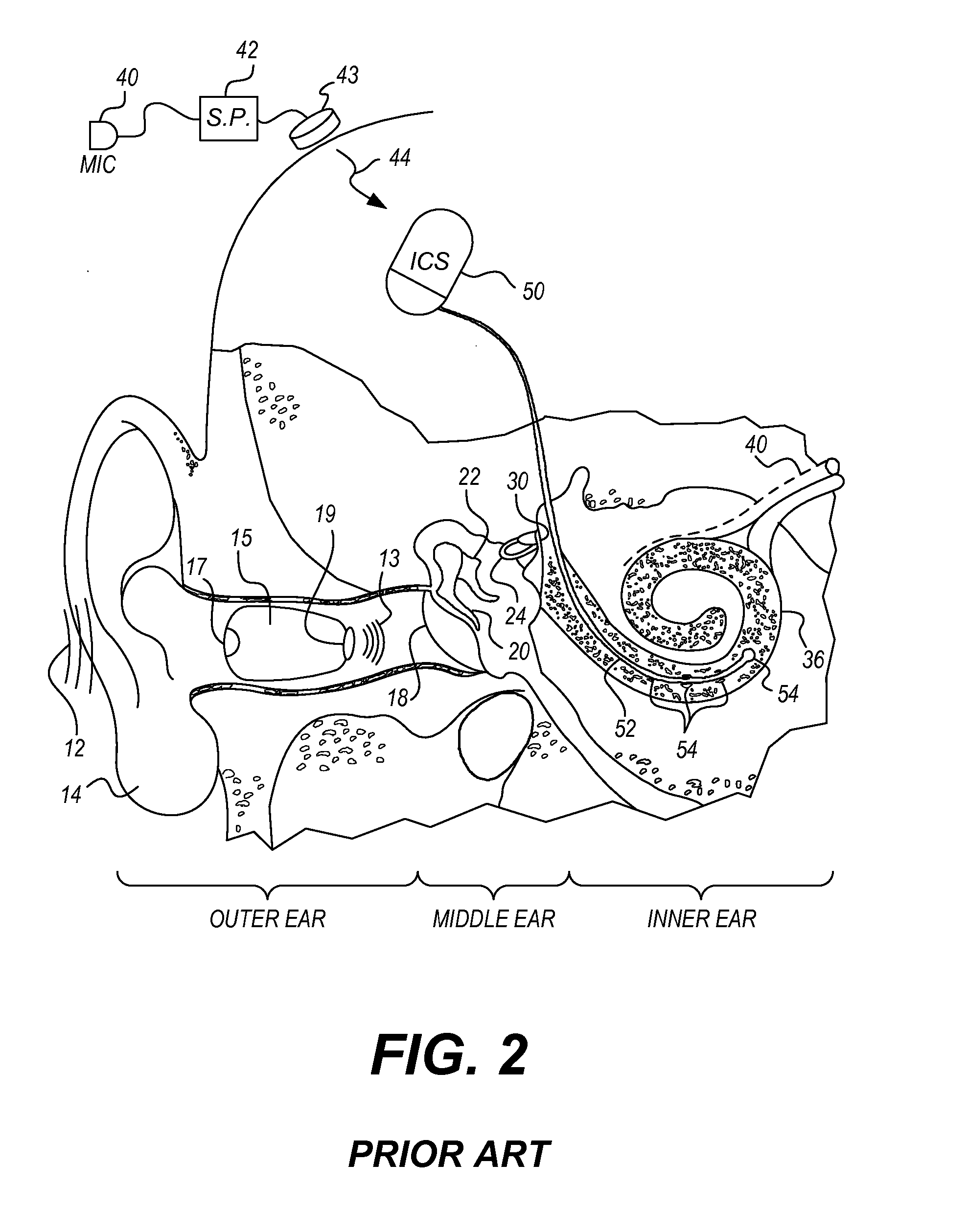
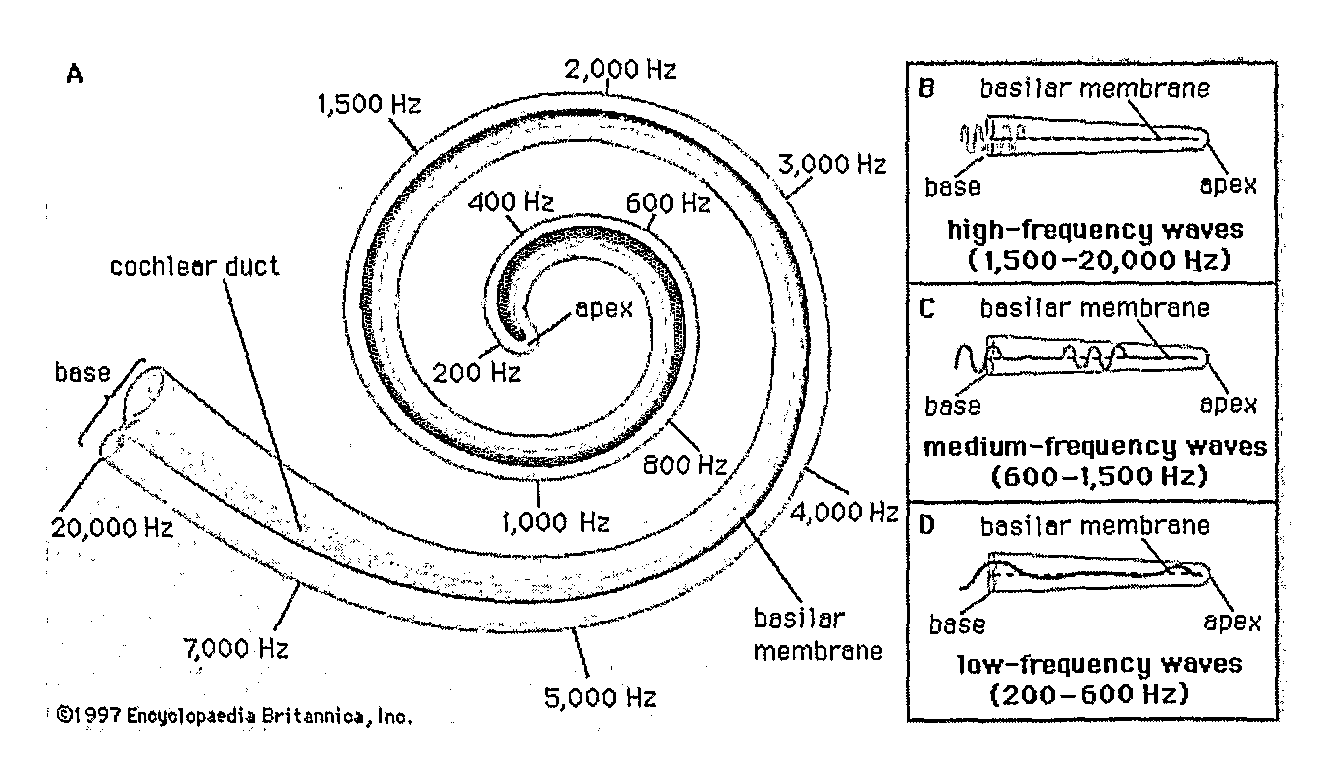
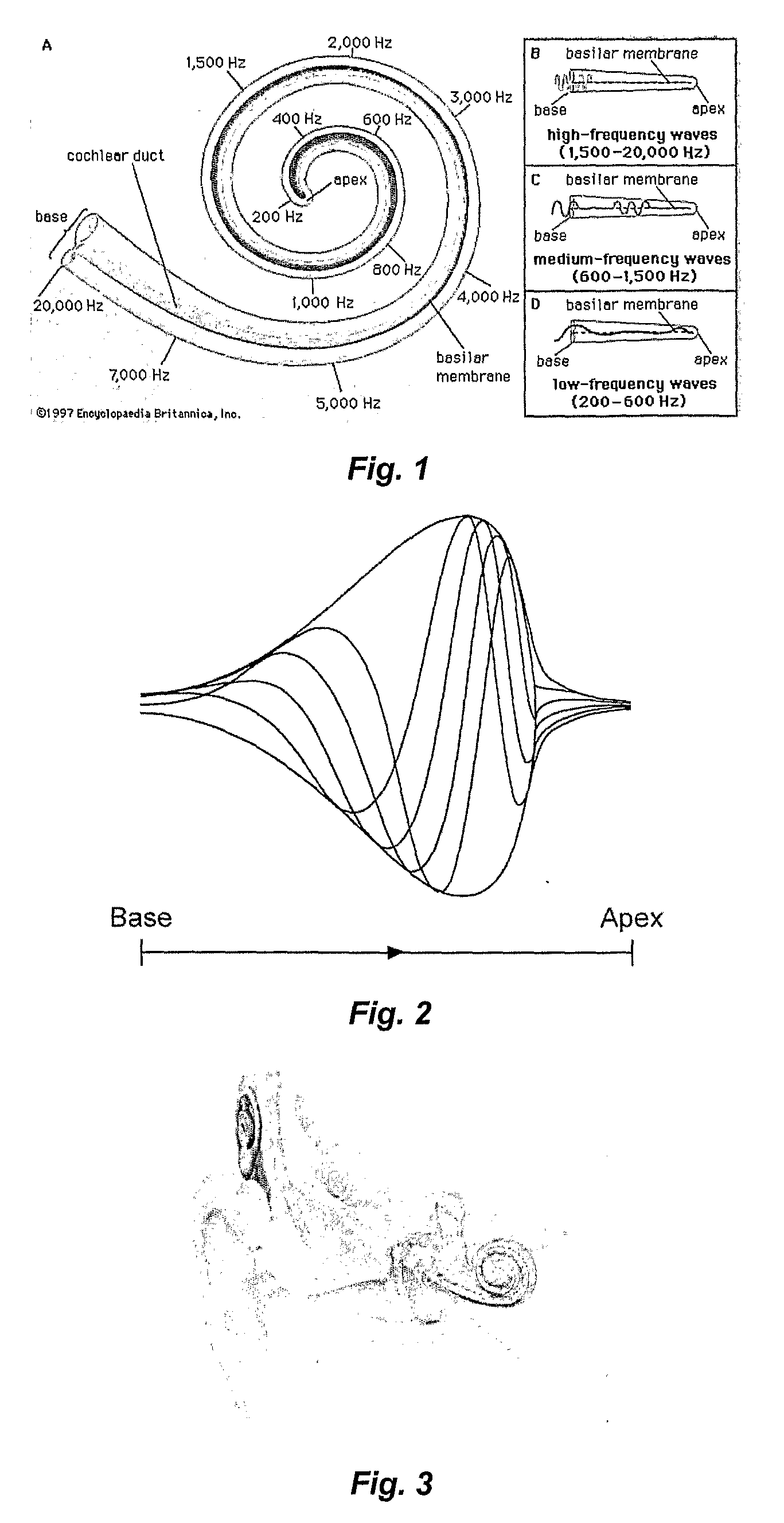
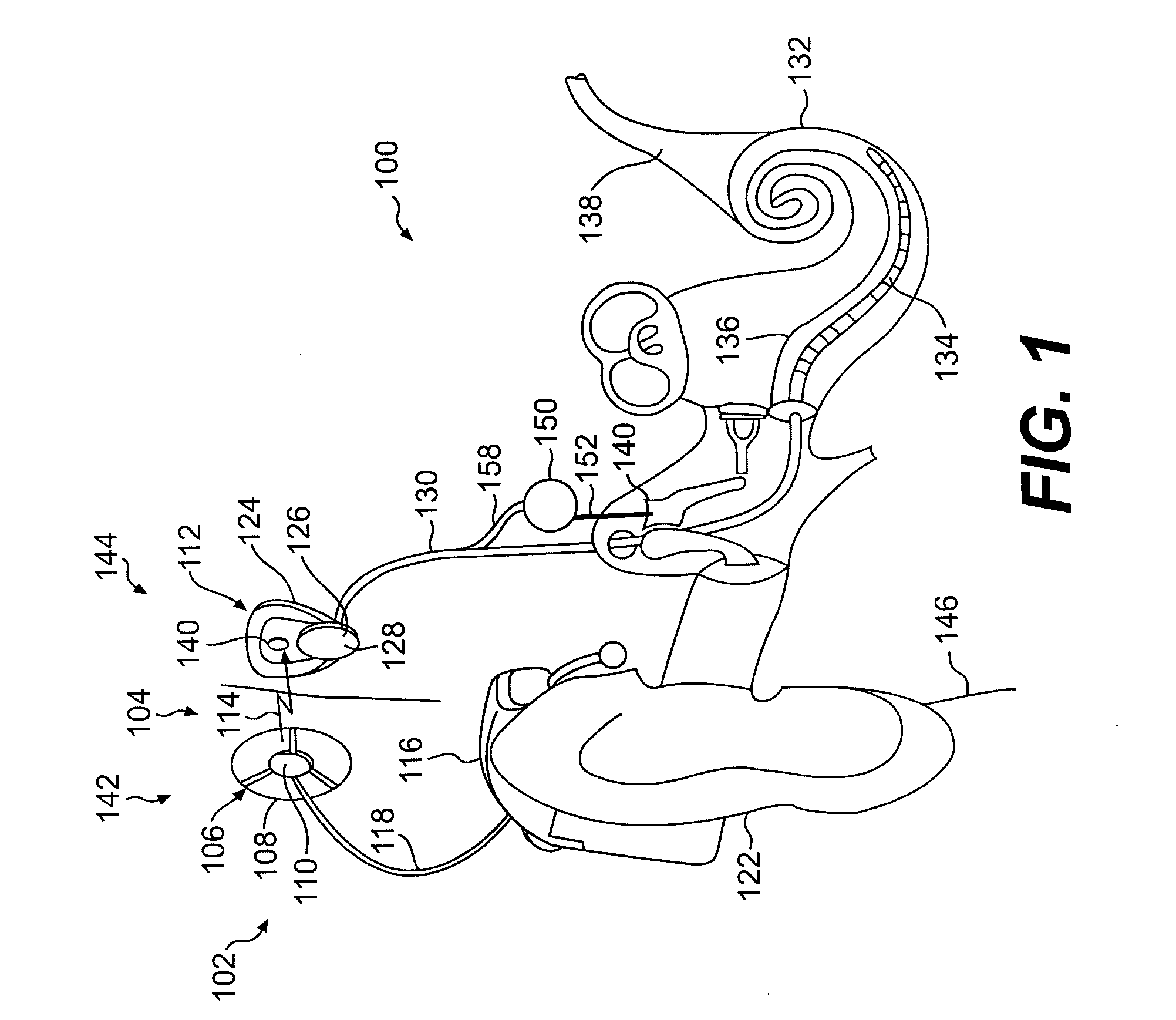
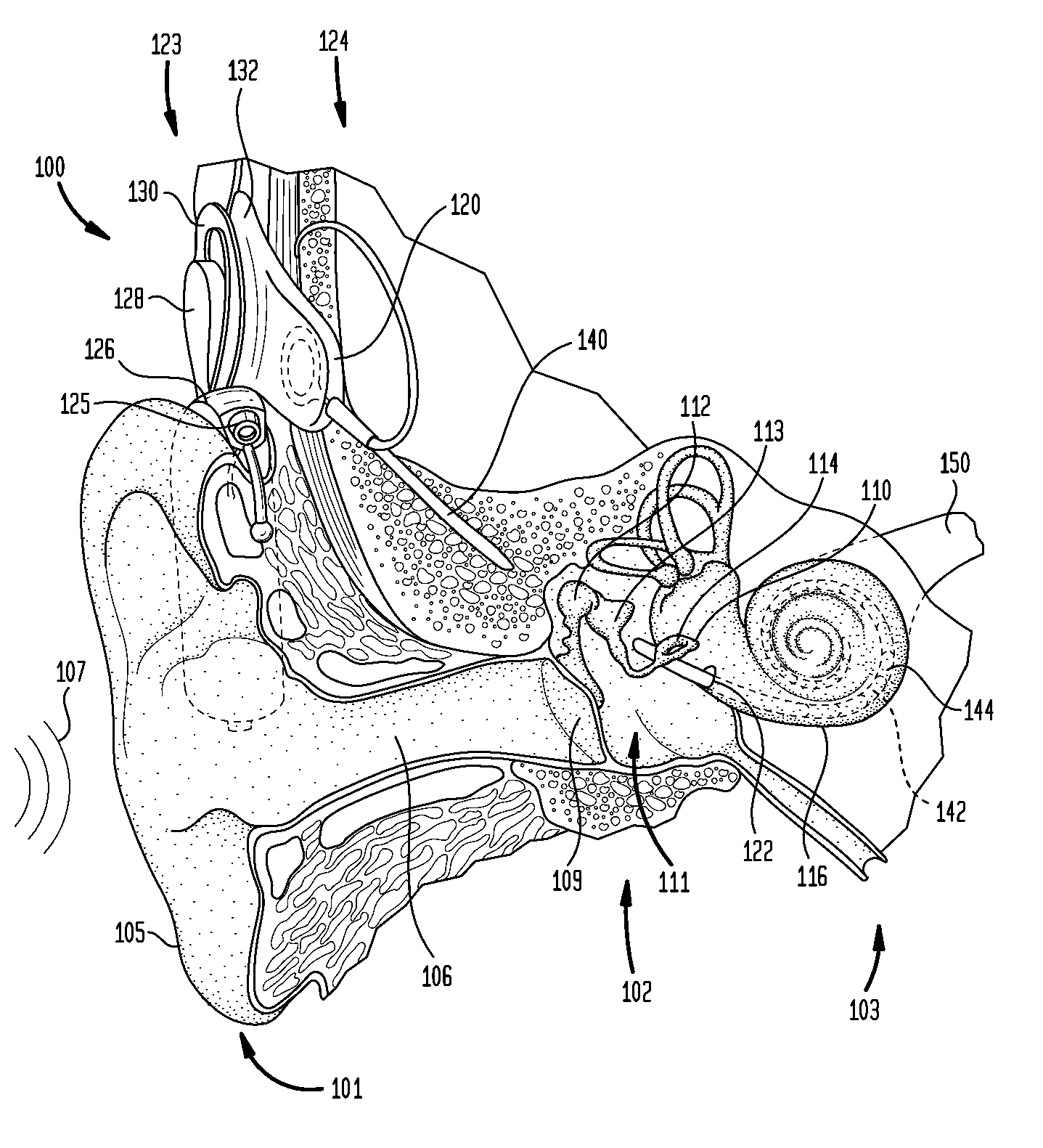
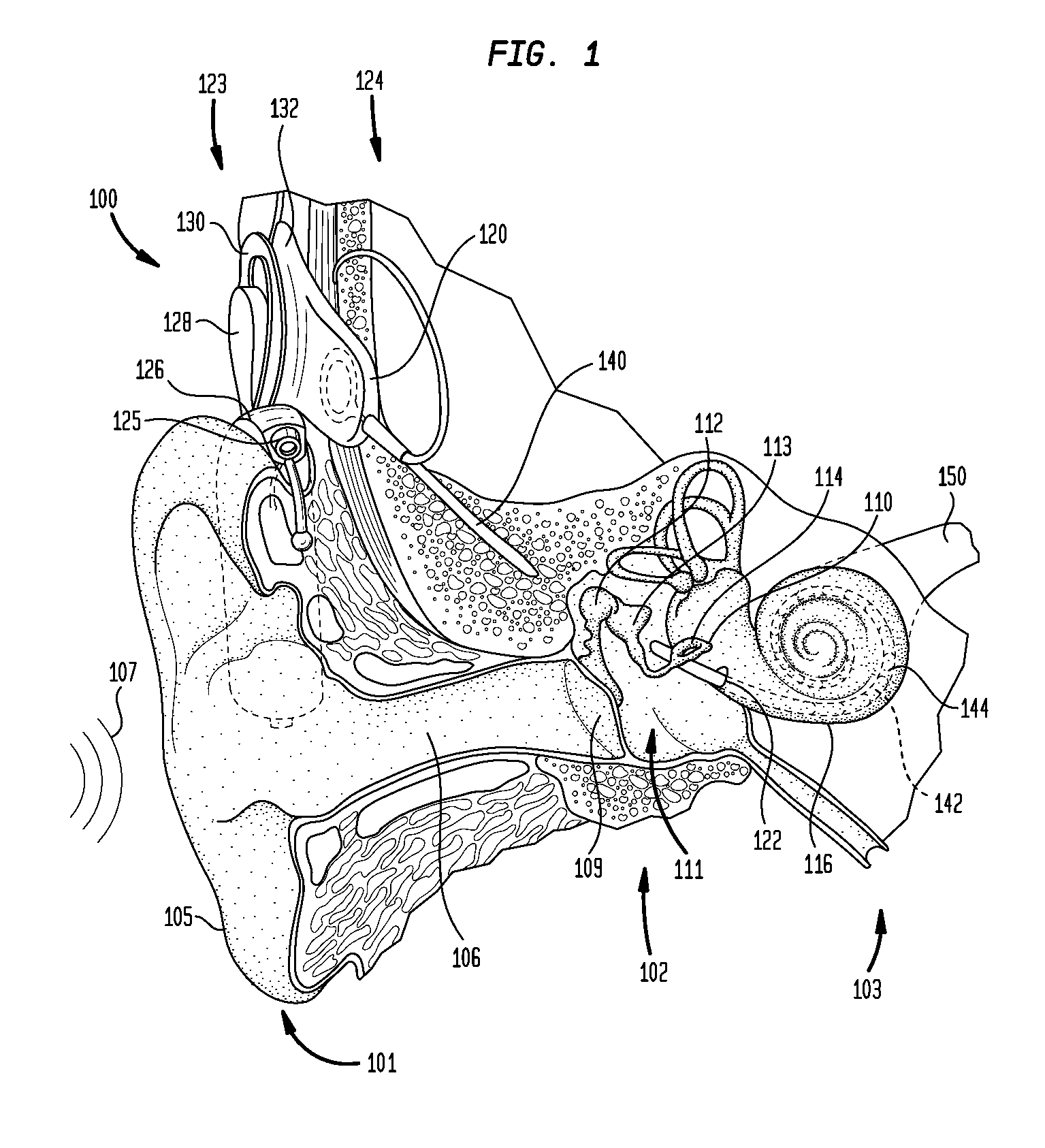
A cochlear implant ( CI) is a surgically implanted neuroprosthetic device that provides a sense of sound to a person with moderate to profound sensorineural hearing loss. Cochlear implants bypass the normal acoustic hearing process, instead replacing it with electric signals which directly stimulate the auditory nerve.
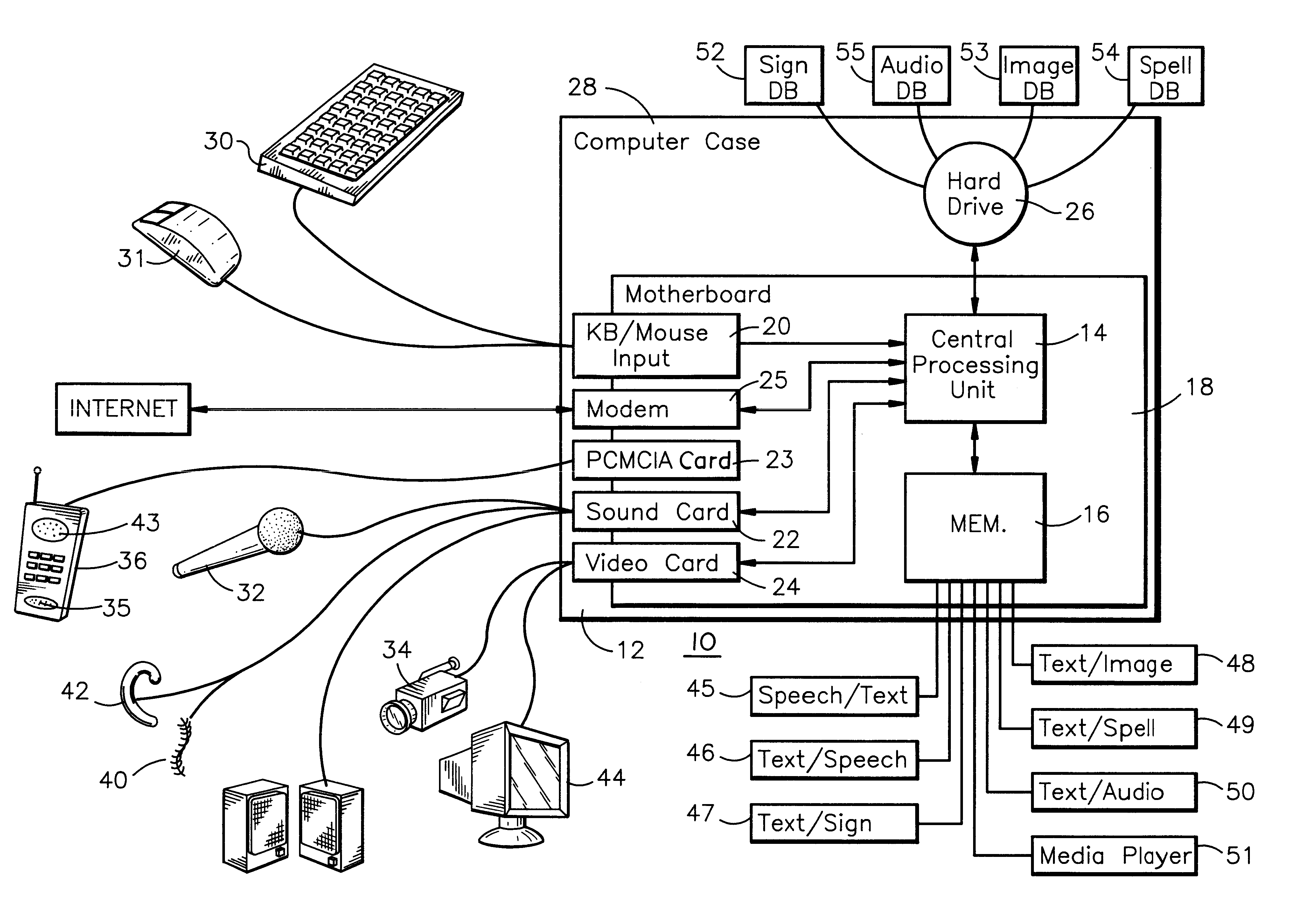
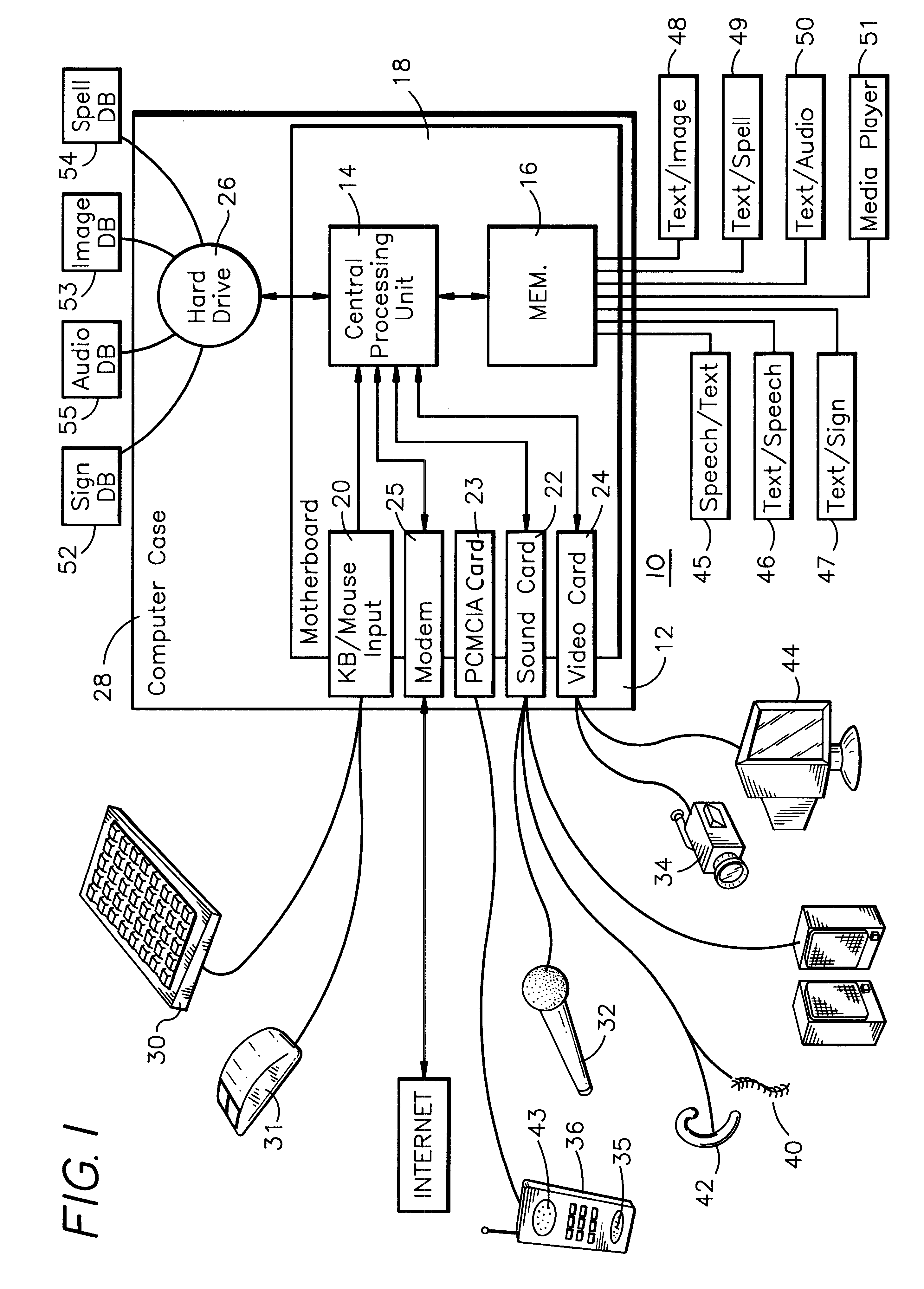
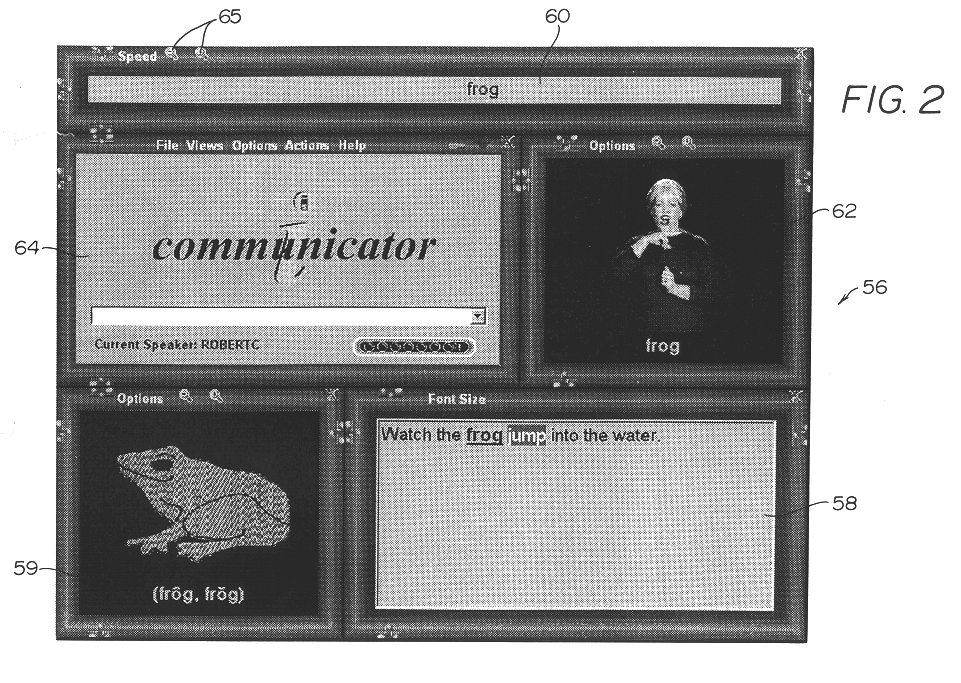
Electronic translator for assisting communications
InactiveUS6377925B1Hearing impaired stereophonic signal reproductionAutomatic exchangesData streamOutput device
An electronic translator translates input speech into multiple streams of data that are simultaneously delivered to the user, such as a hearing impaired individual. Preferably, the data is delivered in audible, visual and text formats. These multiple data streams are delivered to the hearing-impaired individual in a synchronized fashion, thereby creating a cognitive response. Preferably, the system of the present invention converts the input speech to a text format, and then translates the text to any of three other forms, including sign language, animation and computer generated speech. The sign language and animation translations are preferably implemented by using the medium of digital movies in which videos of a person signing words, phrase and finger spelled words, and of animations corresponding to the words, are selectively accessed from databases and displayed. Additionally the received speech is converted to computer-generated speech for input to various hearing enhancement devices used by the deaf or hearing-impaired, such as cochlear implants and hearing aids, or other output devices such as speakers, etc. The data streams are synchronized utilizing a high-speed personal computer to facilitate sufficiently fast processing that the text, video signing and audible streams can be generated simultaneously in real time. Once synchronized the data streams are presented to the subject concurrently in a method that allows the process of mental comprehension to occur. The electronic translator can also be interfaced to other communications devices, such as telephones. Preferably, the hearing-impaired person is also able to use the system's keyboard or mouse to converse or respond.
Owner:INTERACTIVE SOLUTIONS
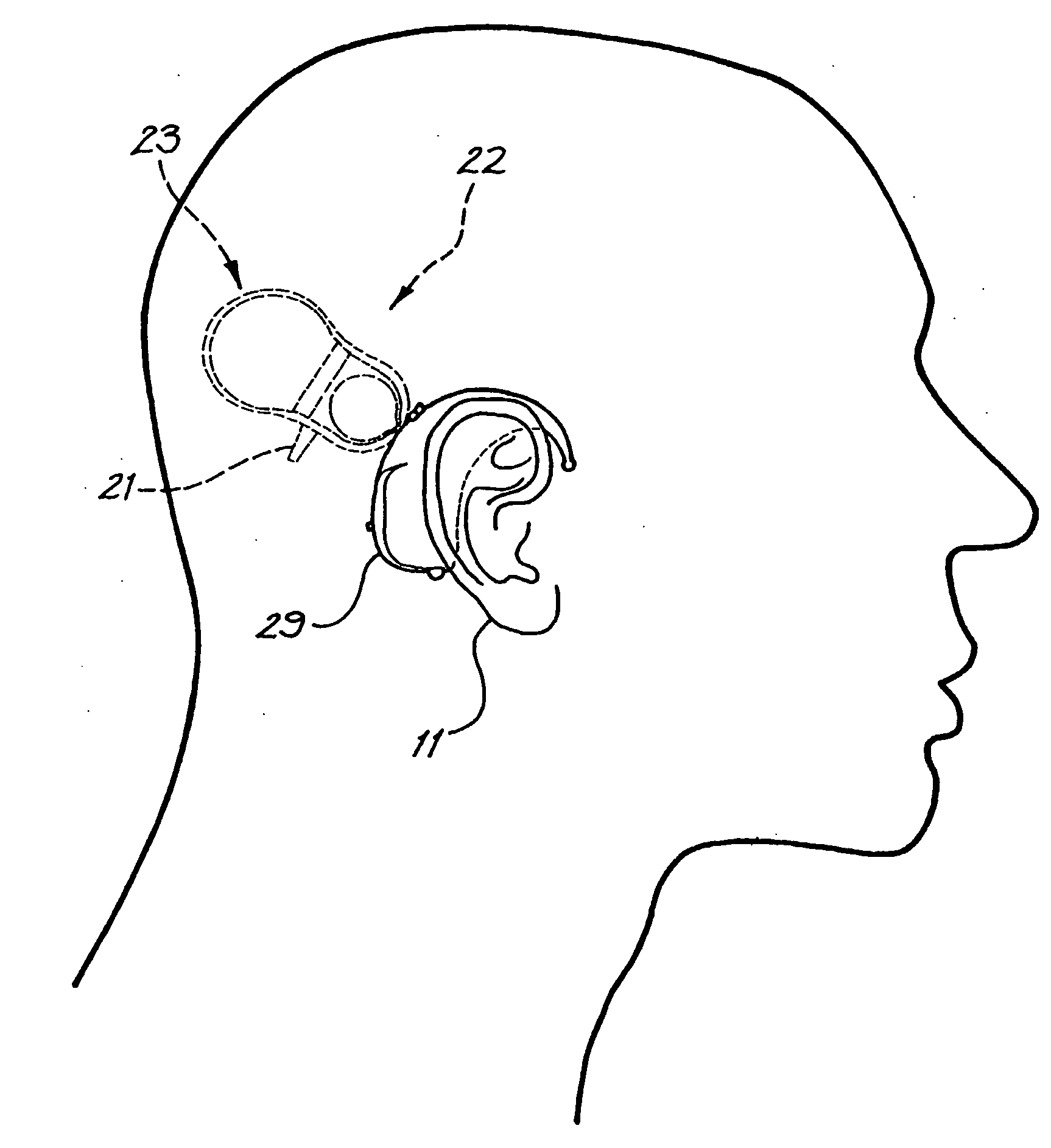
Totally implantable hearing prosthesis
ActiveUS20050020873A1Easy and safe to implantIncrease powerElectrotherapyImplantable hearing aidsCochlear implantationProsthesis
The invention comprises a totally implantable hearing prosthesis for hearing impaired persons. An inertial vibrational element is hermetically sealed and implanted in bone between the lateral and superior semicircular canals without breaching the integrity of the canals. The vibrational element is adapted to vibrate the walls of the canals and the fluids contained therein, thereby vibrating contiguous fluids within the cochlea thus stimulating hair cells and creating a hearing percept. The invention can also be adapted to be a tinnitus masking system, and / or used in combination with a coehlear implant hearing system.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Focused stimulation in a medical stimulation device
ActiveUS20060247735A1Narrowing of the stimulation regions minimizes or prevents this from occurringHead electrodesDeaf-aid setsCochlear implantationImplant electrode
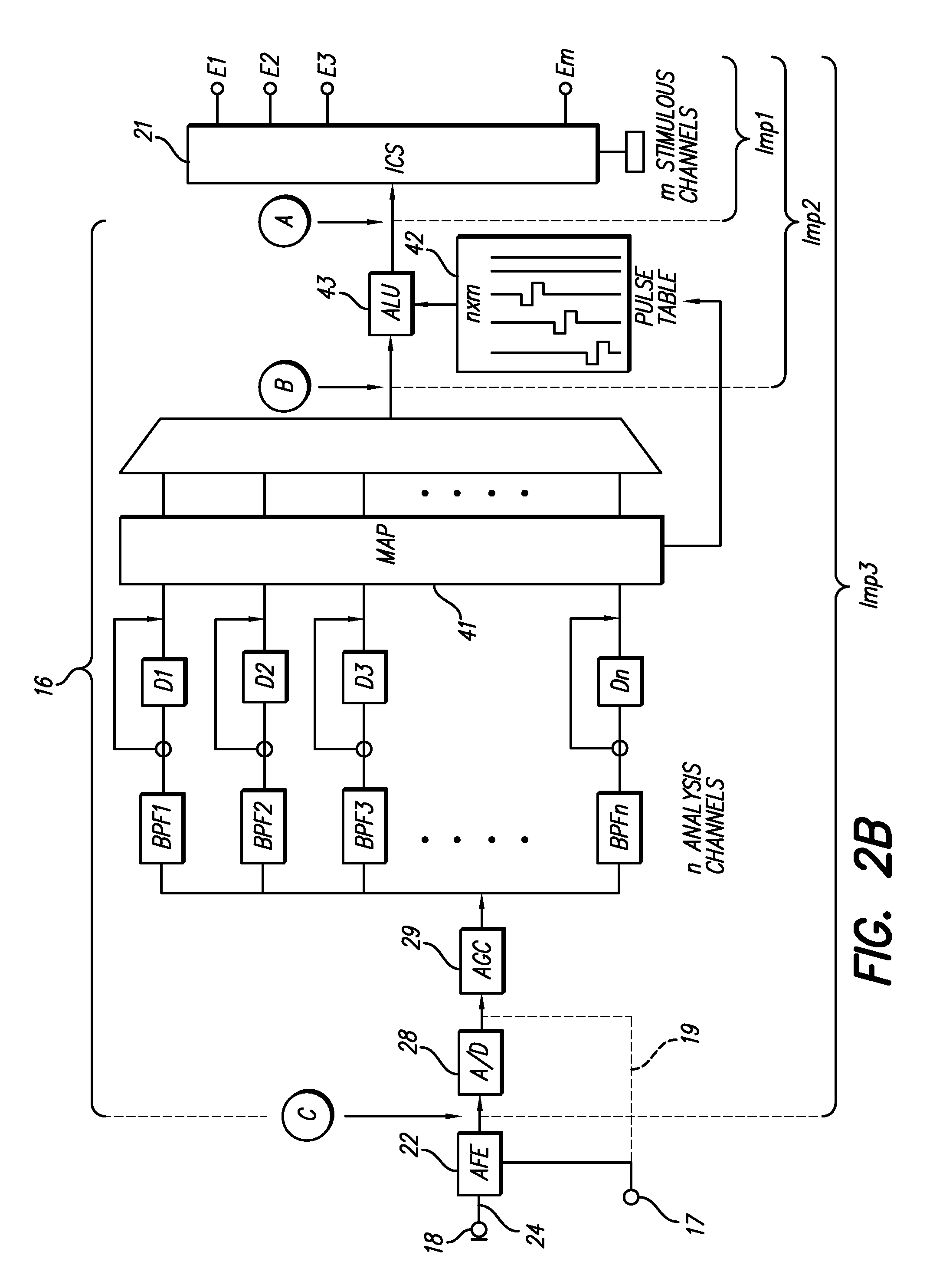
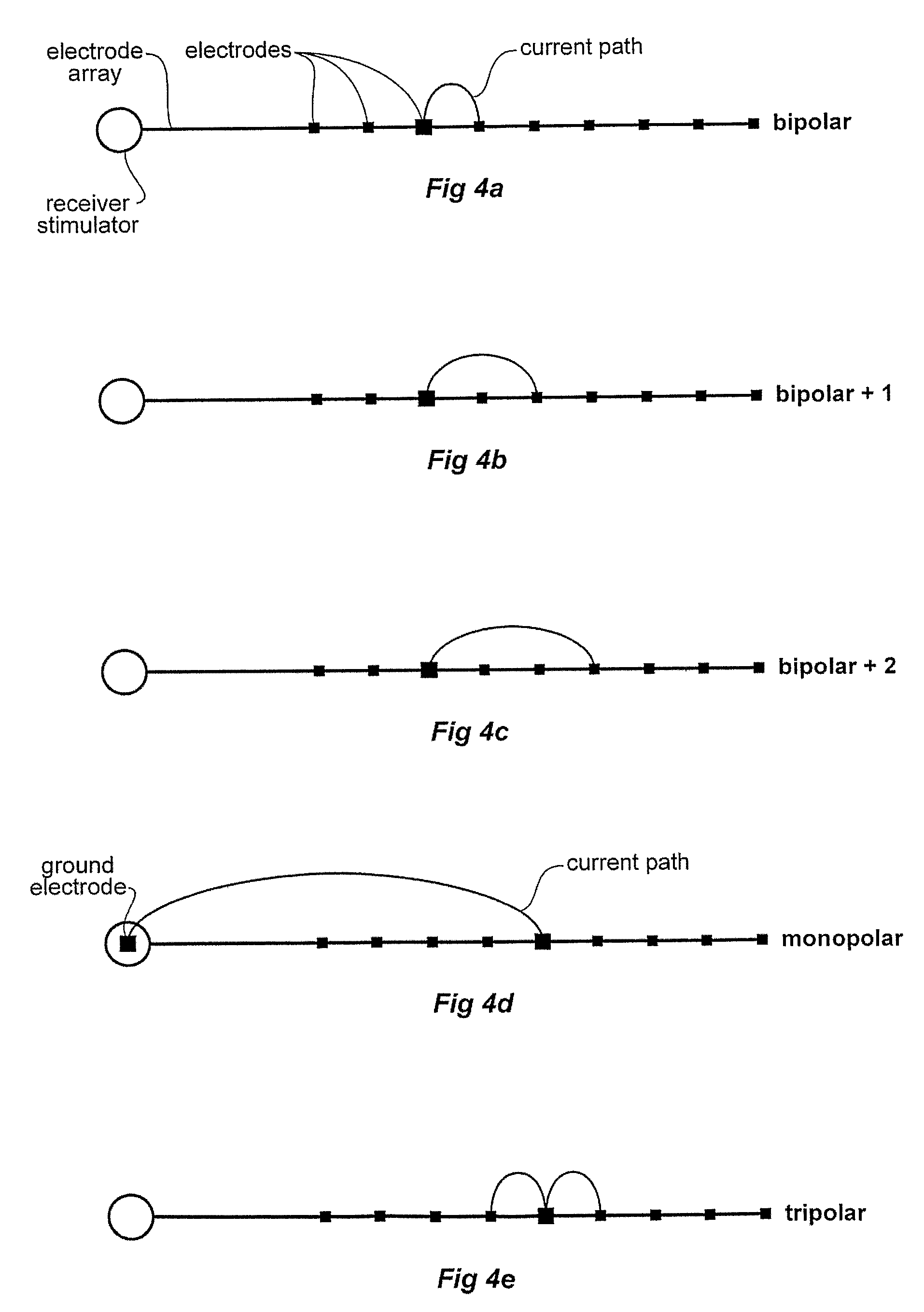
A medical stimulation device such as a cochlear implant configured to provide stimulation of one or more spatially-restricted contiguous portion(s) of the spiral array of auditory nerve fibers in the cochlear (“discrete stimulation regions”). Each discrete stimulation region is defined by the constructive and / or destructive interference of stimulating and limiting signals simultaneously applied to electrode channels of an implanted electrode array, the stimulating and limiting signals being determined based upon transimpedance measurements of intracochlear electrode channels of the implanted electrode array representing specific spread functions of an individual recipient. The stimulating signal is preferably applied through a targeted electrode channel; that is, one or more successive electrodes which is / are adjacent to the discrete stimulation region. The targeted electrode channel is selected to represent a sound based on the outputs of a sound processor to stimulate neural activity in the discrete stimulation region to thereby cause a percept of the represented sound. The size of the discrete stimulation region is defined by the limiting signal(s) applied to electrode channel(s) other than the targeted electrode channel, and which negate(s) current spread which would otherwise occur in response to the stimulating signal.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
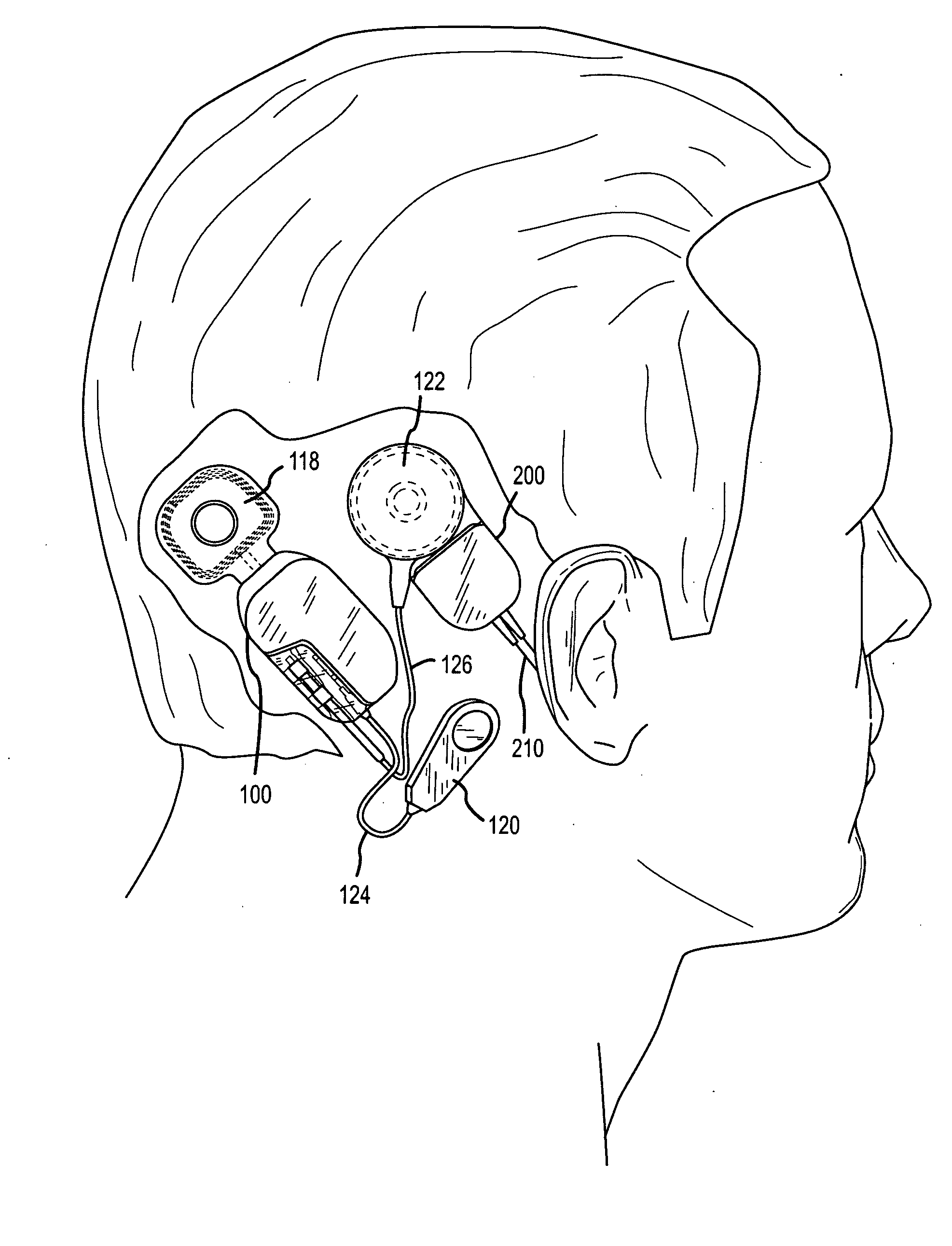
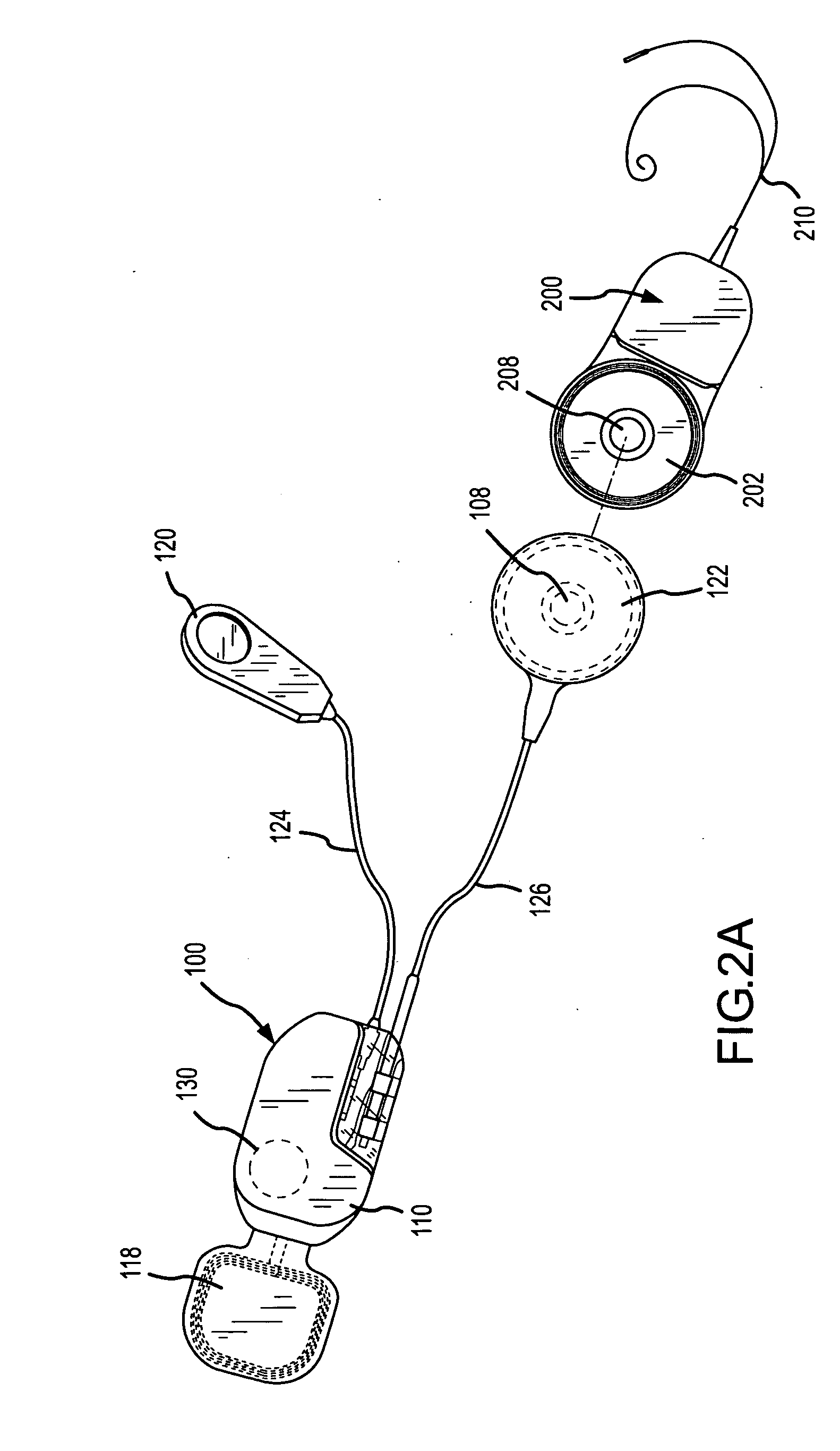
Integrated implantable hearing device, microphone and power unit
InactiveUS20060183965A1Easy accessAvoid difficultyElectrotherapyBehind the ear hearing aidsHearing apparatusElectric power
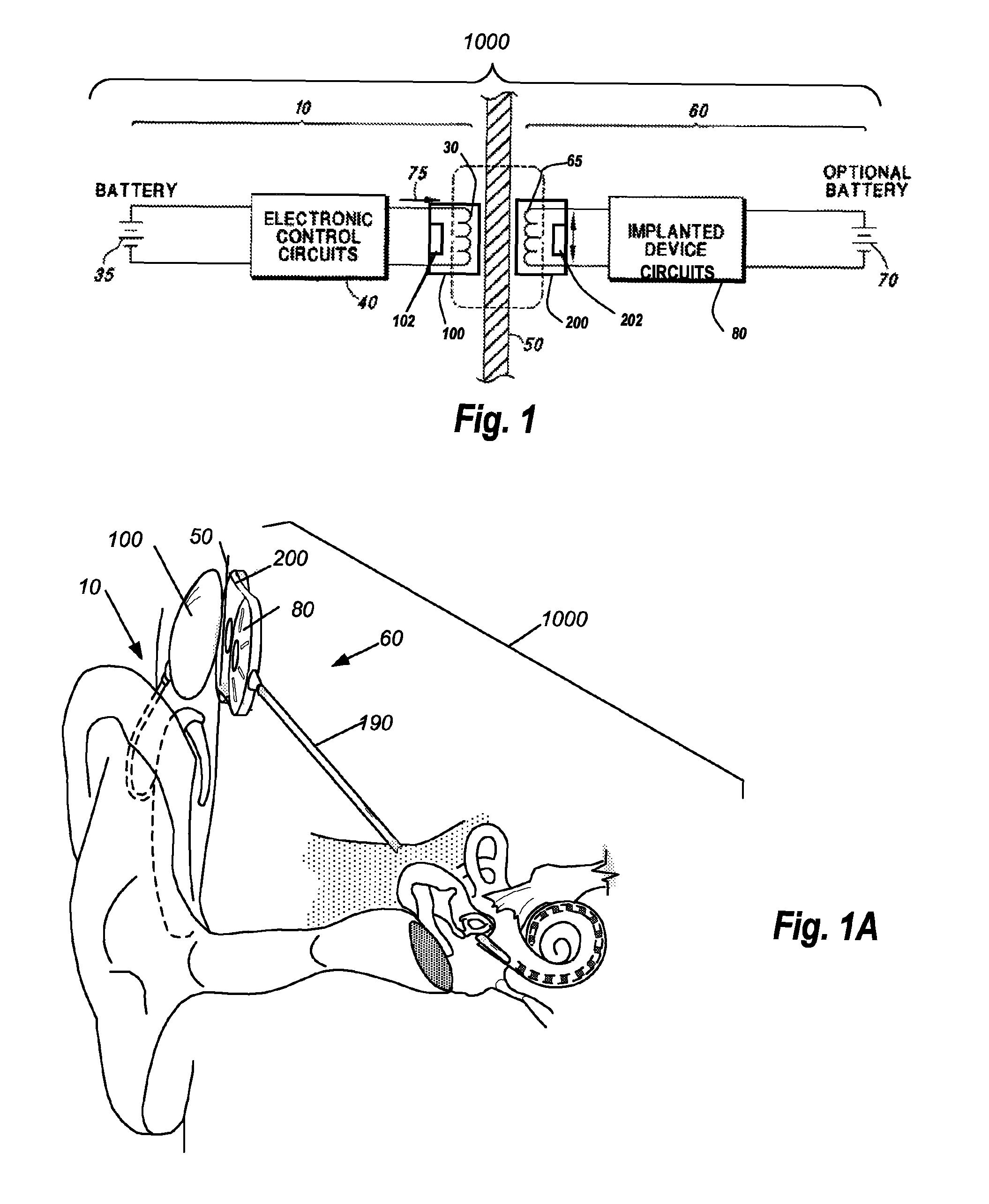
An implantable hearing unit is provided that includes an implantable microphone, a rechargeable power storage device and a speech signal processor. The hearing unit further includes a signal coupling device that is adapted for electrical interconnection to an implantable auditory stimulation device, which is operative to stimulate an auditory component of a patient. Such a stimulation device may include cochlear implants, brain stem stimulation systems, auditory nerve stimulation systems, and middle or inner ear transducer systems. The signal coupling device is operative to provide processed drive signals from the signal processor to the stimulation device as well provide power from the power storage device to operate the stimulation device. In one arrangement, the signal coupling device is a wireless coupling between first and second coils. In such an arrangement, the hearing unit may be utilized with an existing implanted stimulation device to make that device a fully implanted hearing system.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
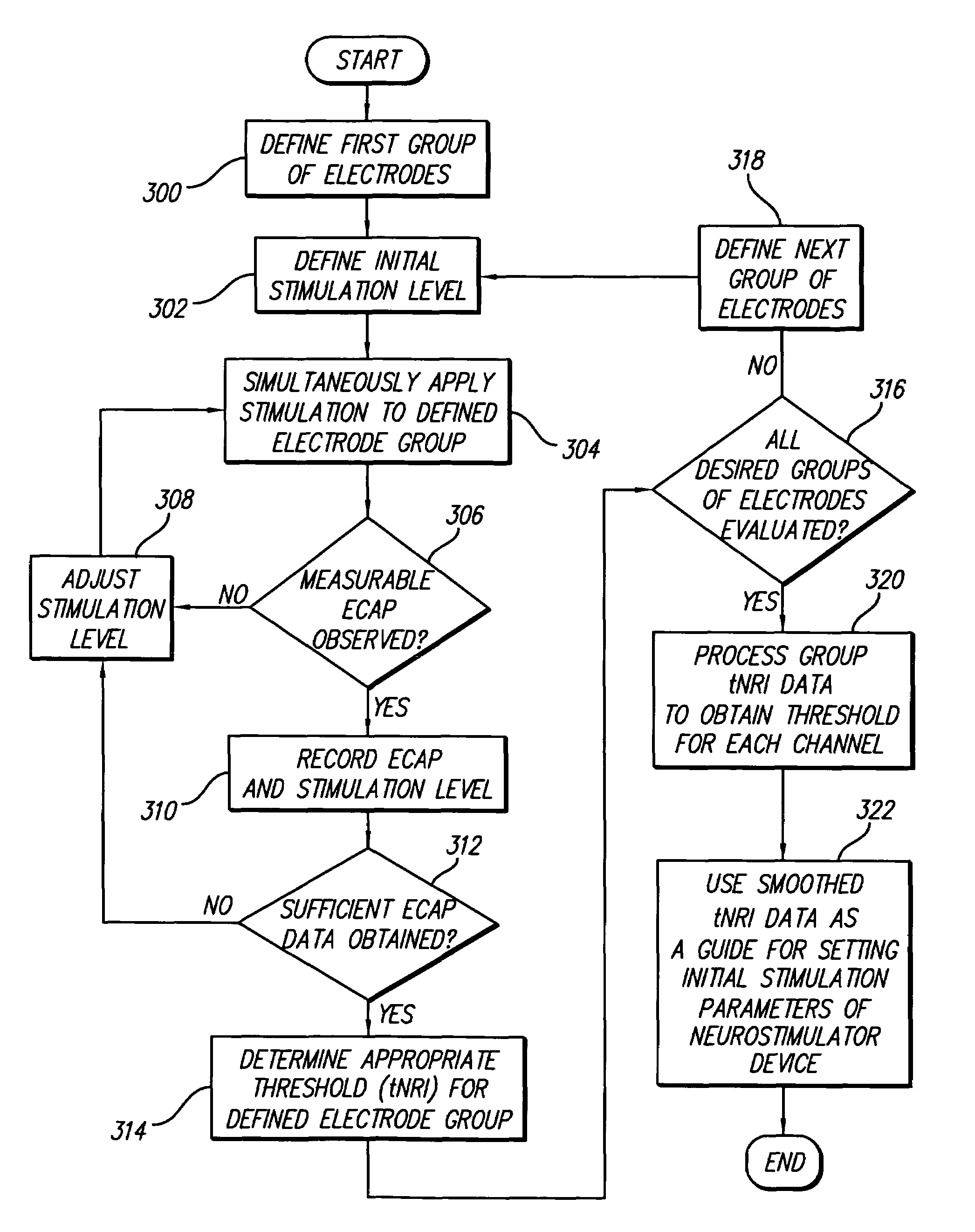
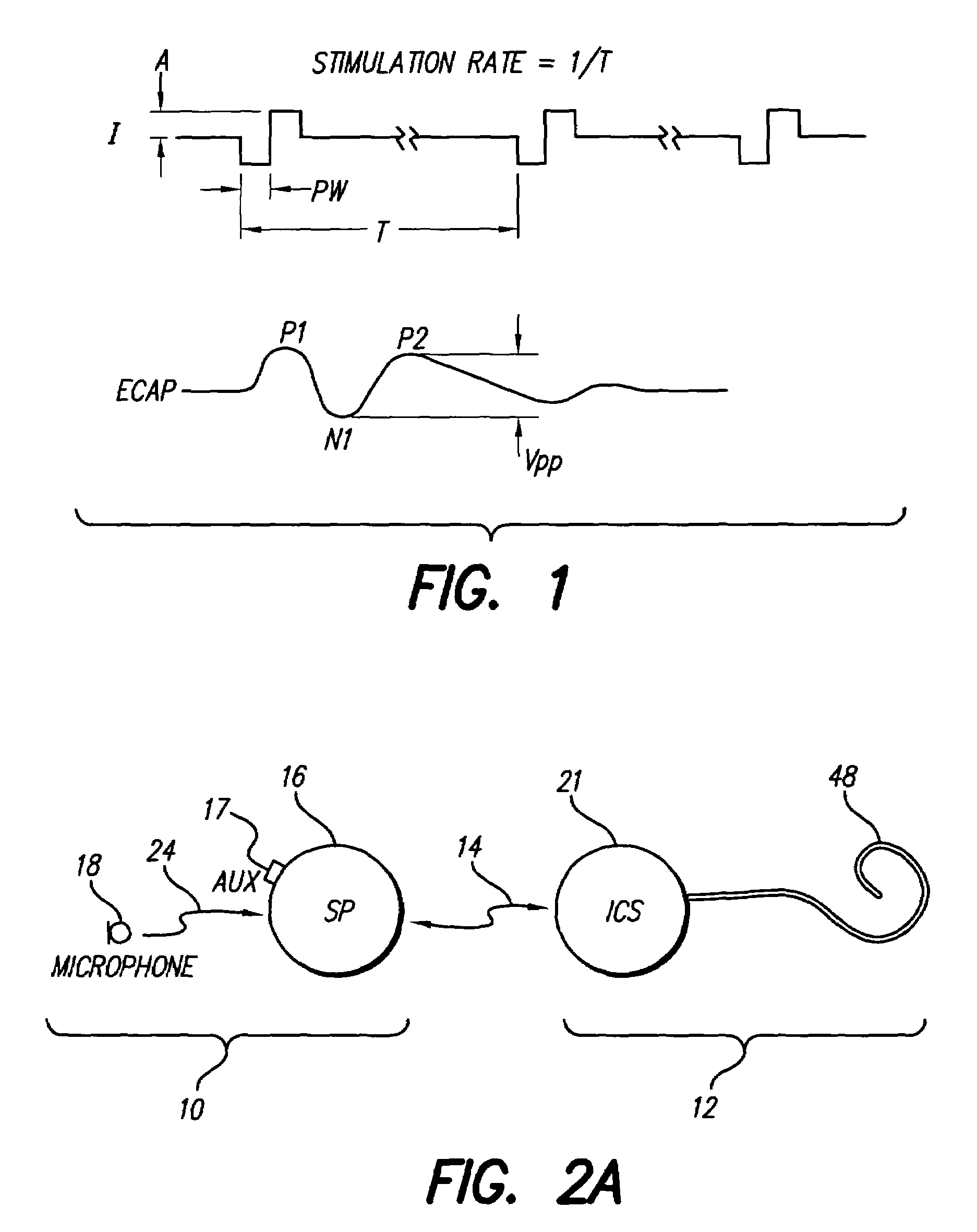
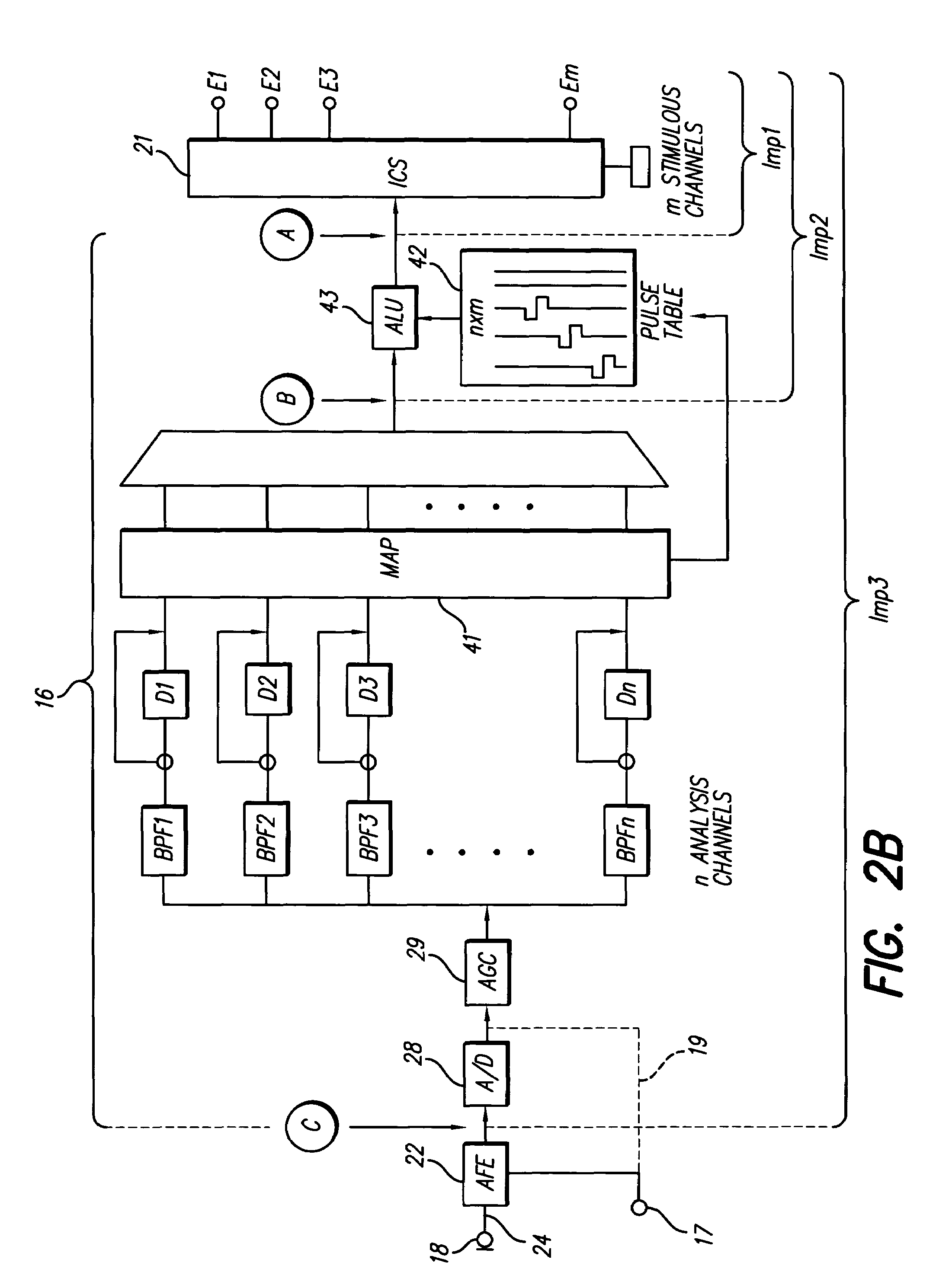
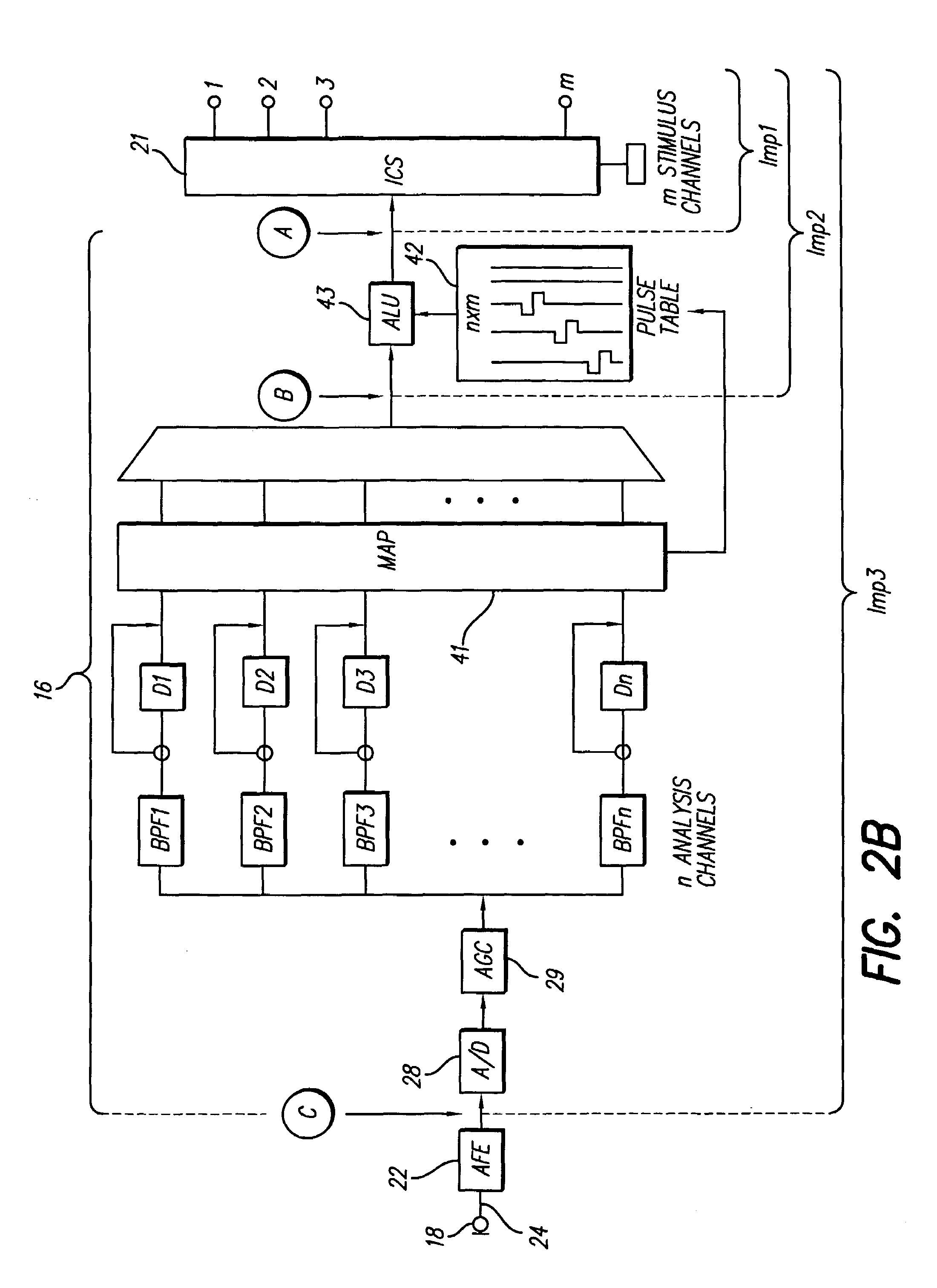
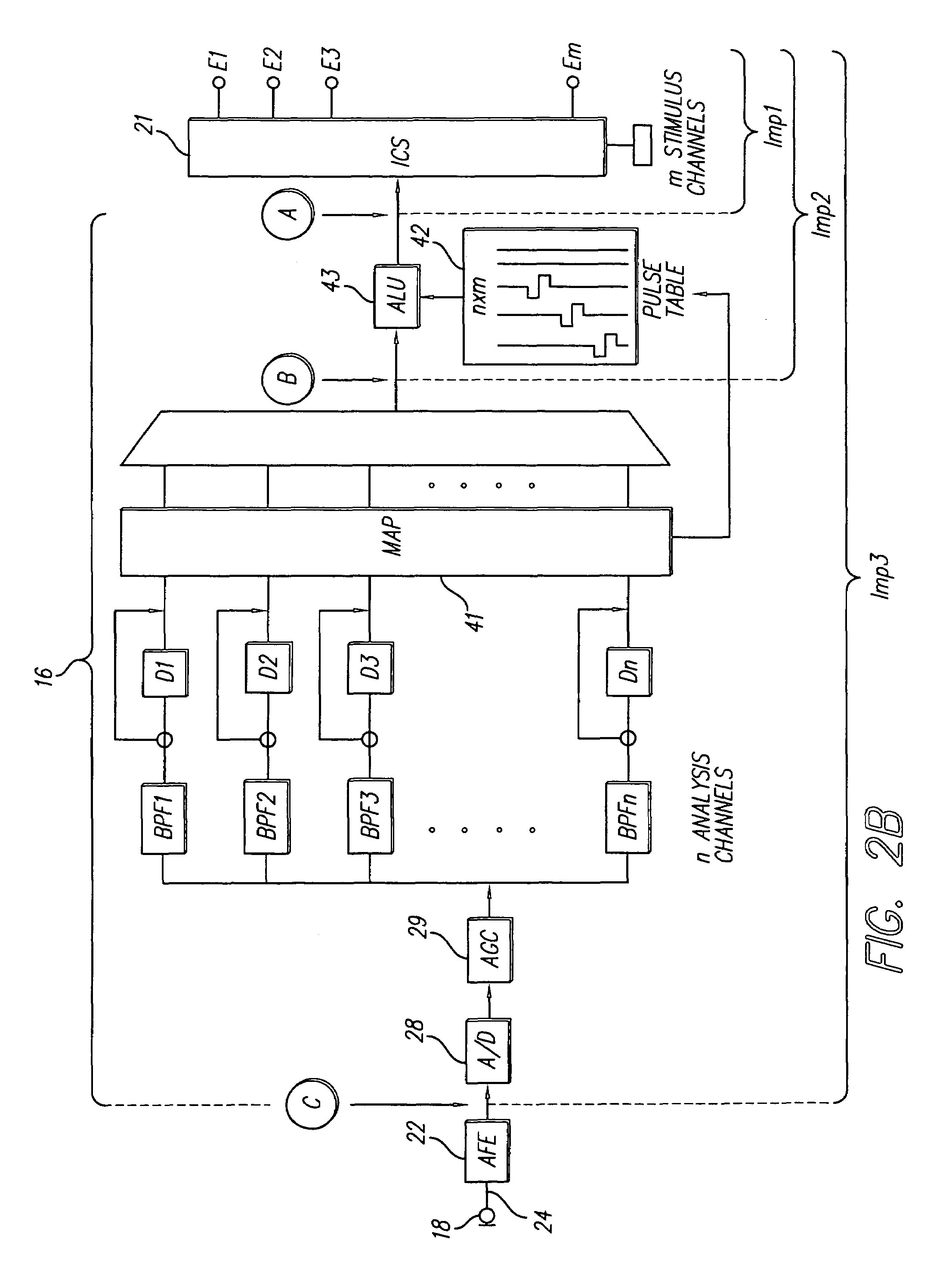
Method and system for generating a cochlear implant program using multi-electrode stimulation to elicit the electrically-evoked compound action potential
InactiveUS7206640B1Increase amplitudeConvenient recordingHead electrodesEvoked compound action potentialConfocal
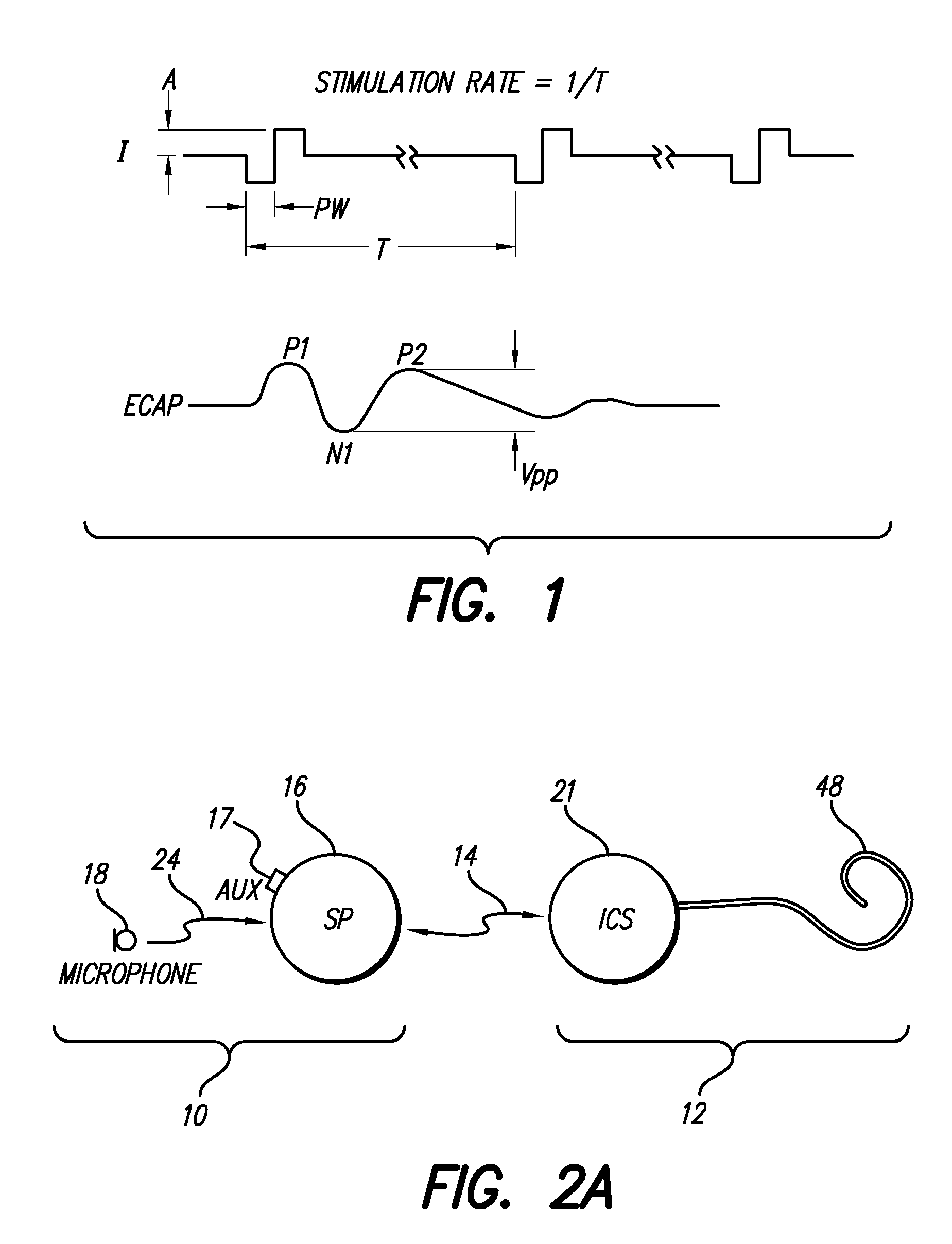
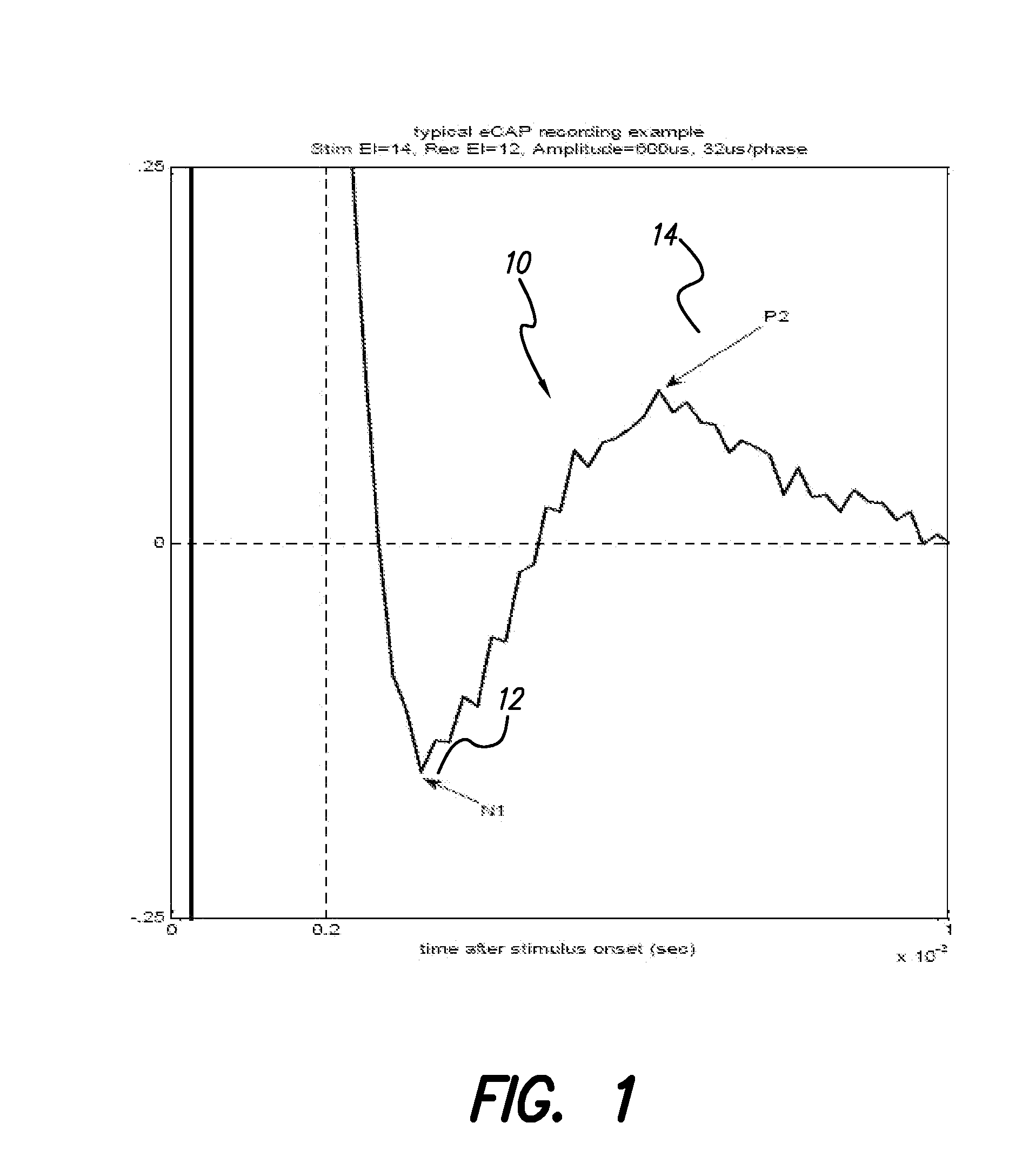
A multichannel cochlear implant system spatially spreads the excitation pattern in the target neural tissue by either: (1) rapid sequential stimulation of a small group of electrodes, or (2) simultaneously stimulating a small group of electrodes. Such multi-electrode stimulation stimulates a greater number of neurons in a synchronous manner, thereby increasing the amplitude of the extra-cellular voltage fluctuation and facilitating its recording. The electrical stimuli are applied simultaneously (or sequentially at a rapid rate) on selected small groups of electrodes while monitoring the evoked compound action potential (ECAP) on a nearby electrode. The presence of an observable ECAP not only validates operation of the implant device at a time when the patient may be unconscious or otherwise unable to provide subjective feedback, but also provides a way for the magnitude of the observed ECAP to be recorded as a function of the amplitude of the applied stimulus. From this data, a safe, efficacious and comfortable threshold level can be obtained which may be used thereafter as the initial setting of the stimulation parameters of the neurostimulation device, or to guide the setting of the stimulation parameters of the neurostimulation device.
Owner:ADVNACED BIONICS LLC
Enhanced methods for determining iso-loudness contours for fitting cochlear implant sound processors
InactiveUS7043303B1Simple processIncrease chanceElectrotherapyArtificial respirationHigh rateEqual-loudness contour
Methods are taught to simplify the cochlear implant fitting process for various cochlear prostheses and stimulation strategies, including high rate stimulation strategies. For instance, patient self-programming is made possible. In addition, auto-fitting is made possible (particularly useful for very young patients and other patients for whom it is challenging to obtain feedback) using iso-neural response contours which can be linearly transposed to arrive at iso-loudness contours. Furthermore, M iso-loudness contours (or iso-neural contours) can be linearly transposed to determine T iso-loudness contours. In addition, wider pulse widths can be used to generate an iso-loudness contour whose shape can be used (via linear transposition) to program high-rate, narrow pulse width stimulation.
Owner:ADVNACED BIONICS LLC
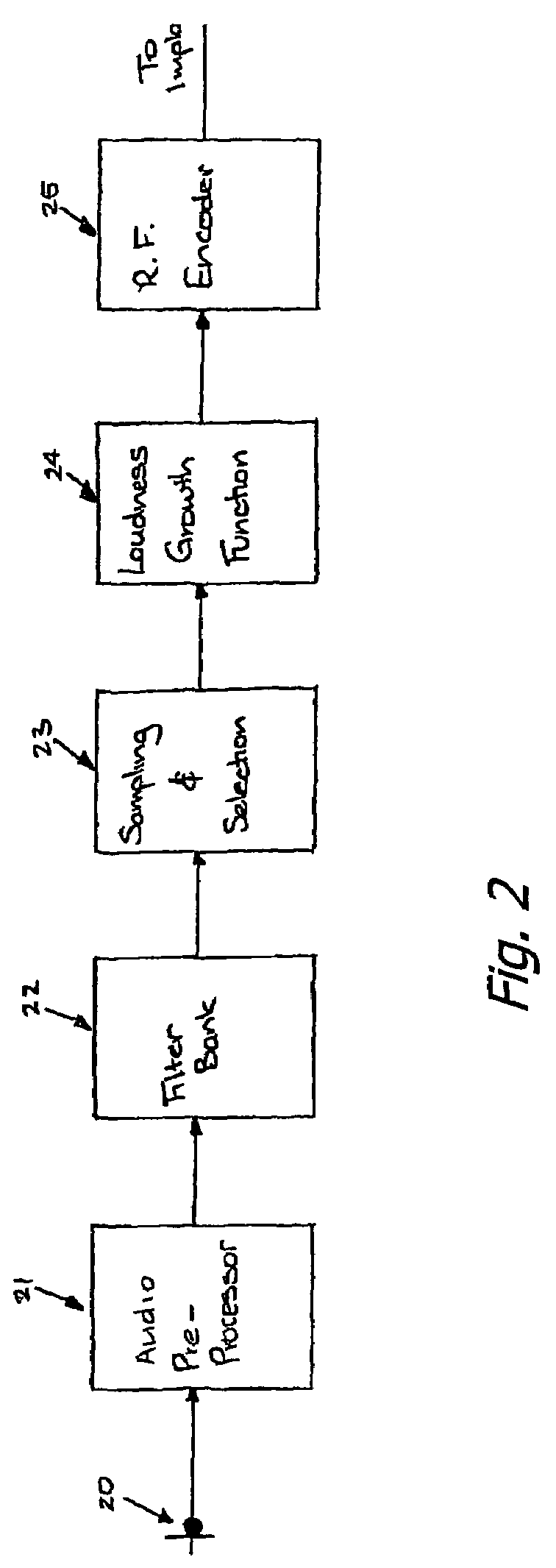
Sound-processing strategy for cochlear implants
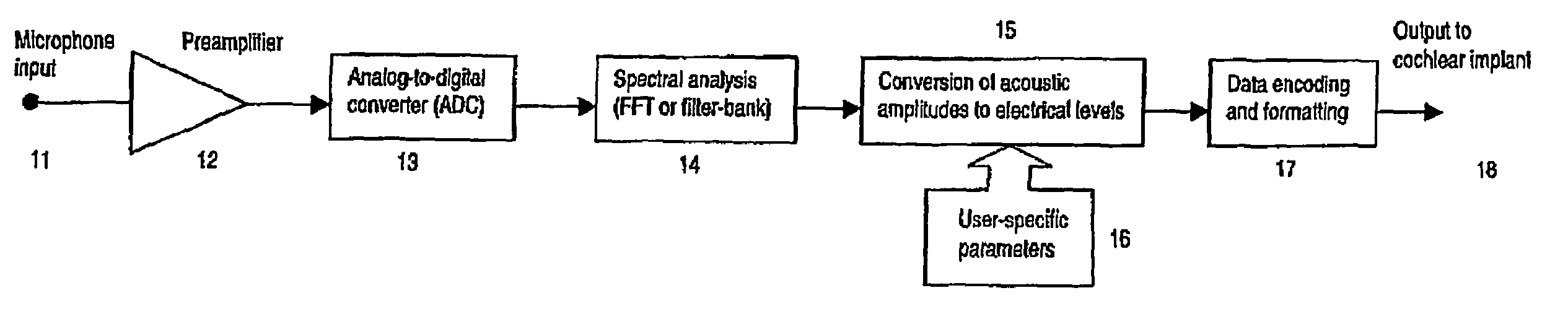
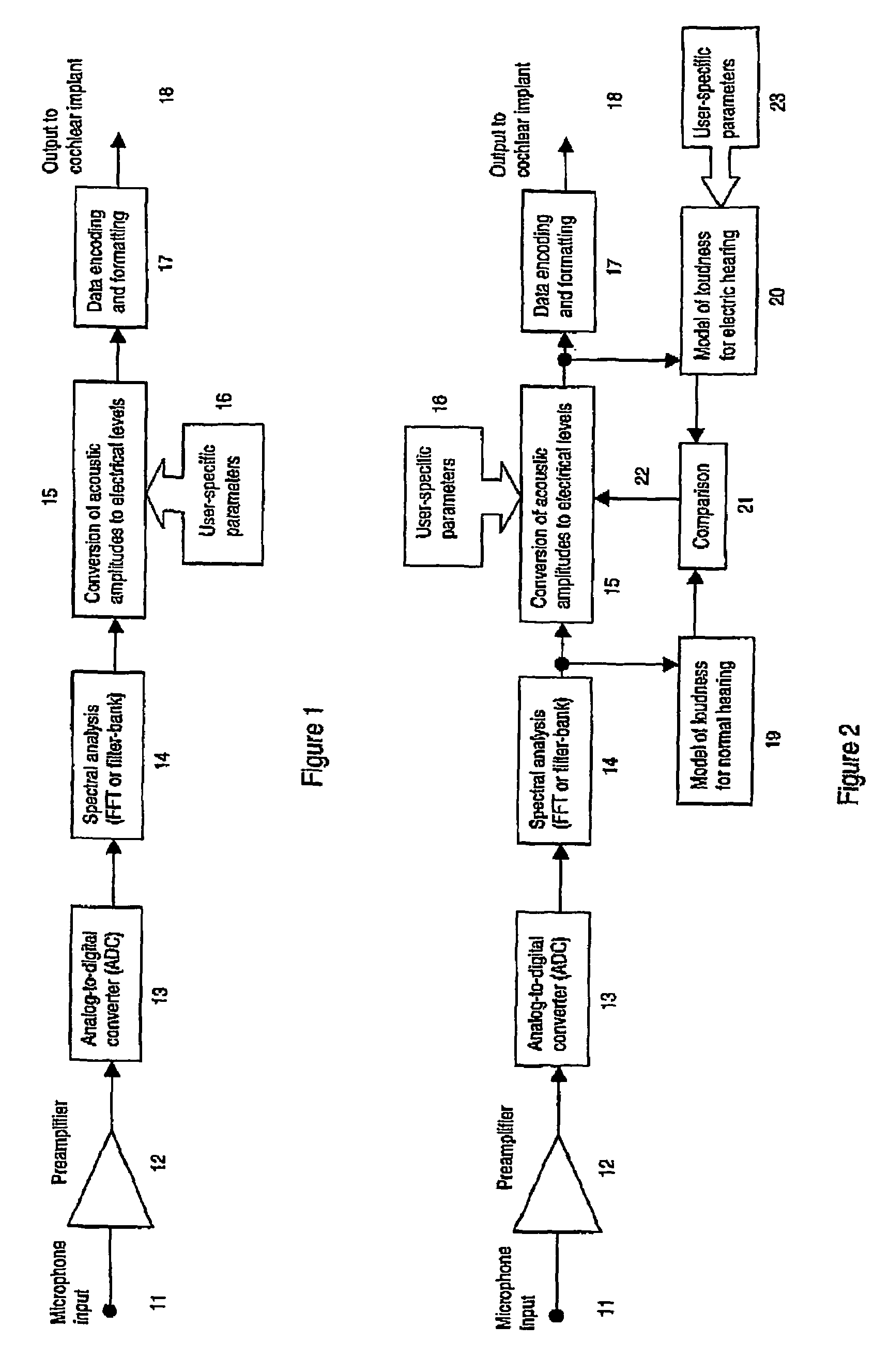
InactiveUS7171272B2Reduce the impactImprove speech clarityElectrotherapySpeech analysisCochlear implantationProsthesis
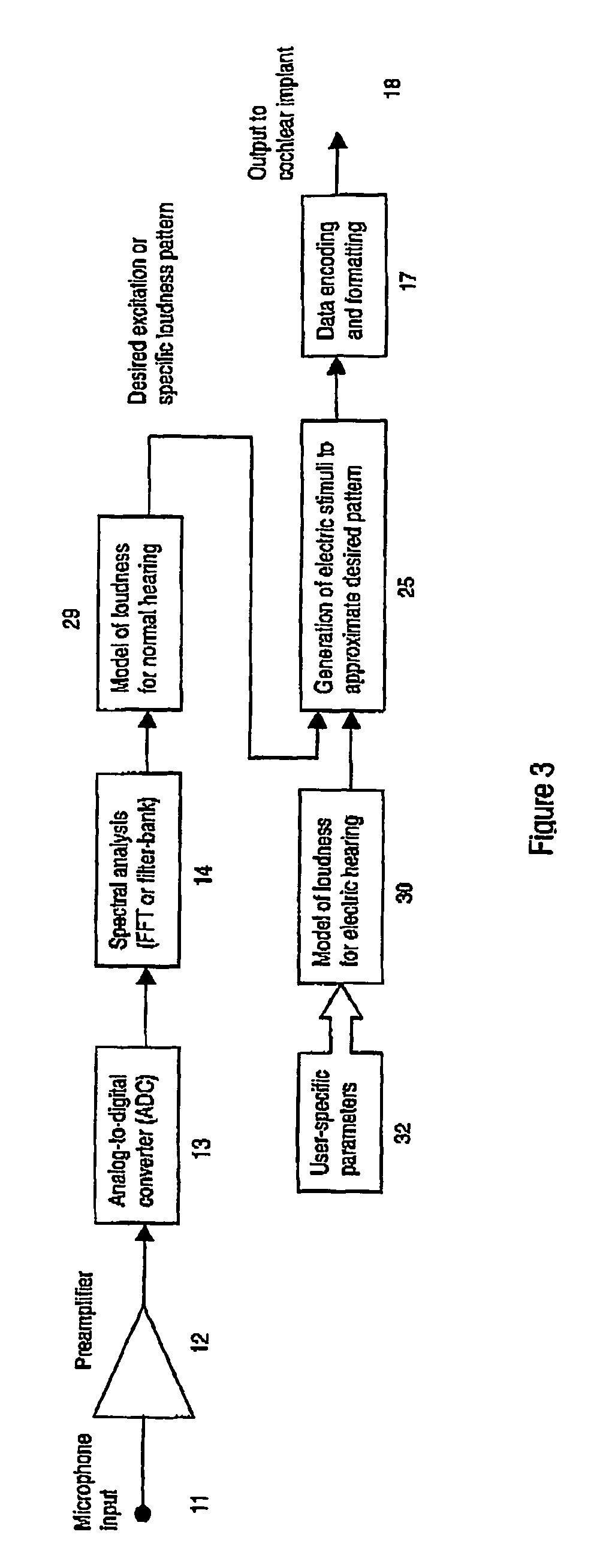
A sound processing method for auditory prostheses, such as cochlear implants, which is adapted to improve the perception of loudness by users, and to improve speech perception. The overall contribution of stimuli to simulated loudness is compared with an estimate of acoustic loudness for a normally hearing listener based on the input sound signal. A weighting is applied to the filter channels to emphasize those frequencies which are most important to speech perception for normal hearing listeners when selecting channels as a basis for stimulation.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE
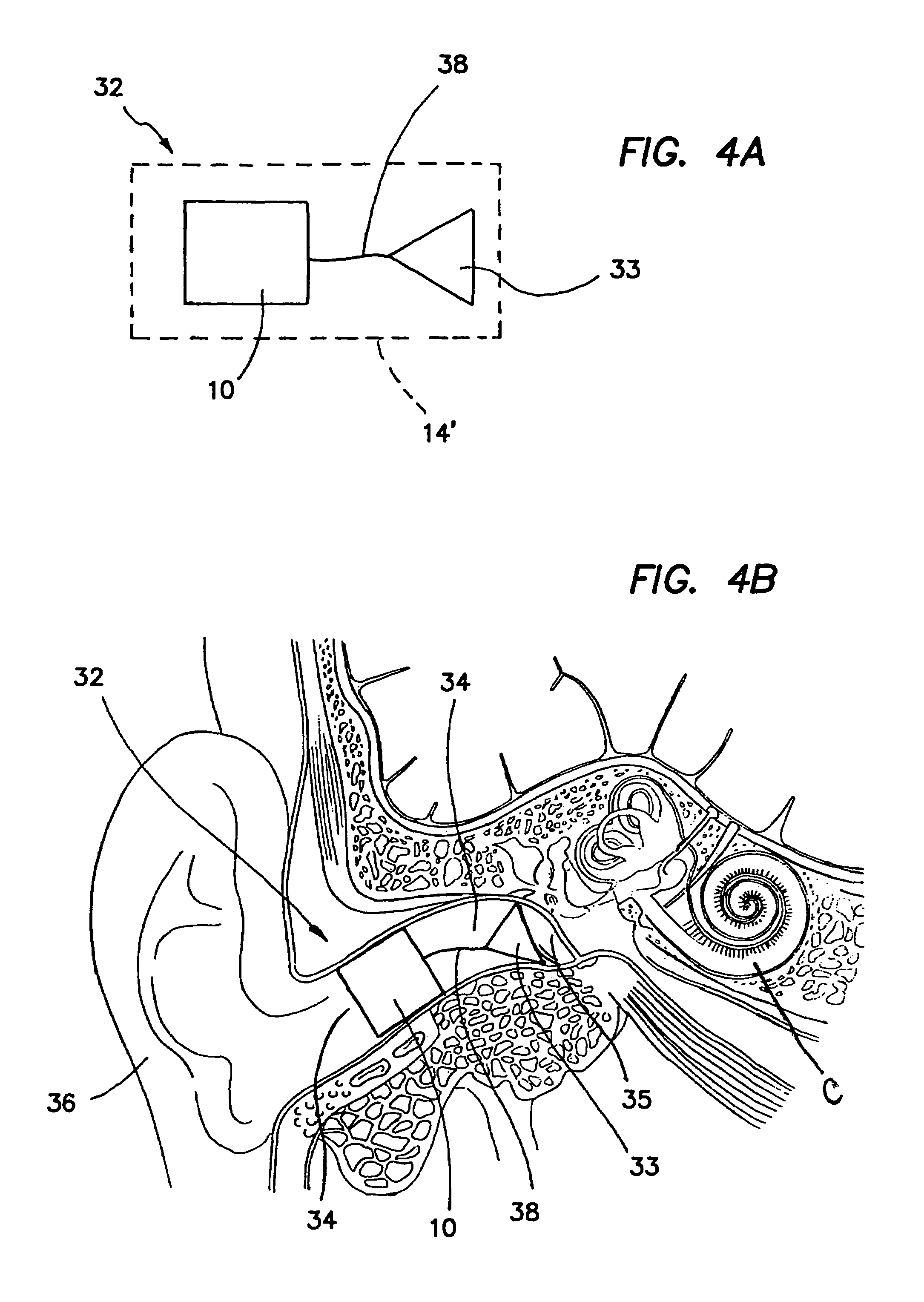
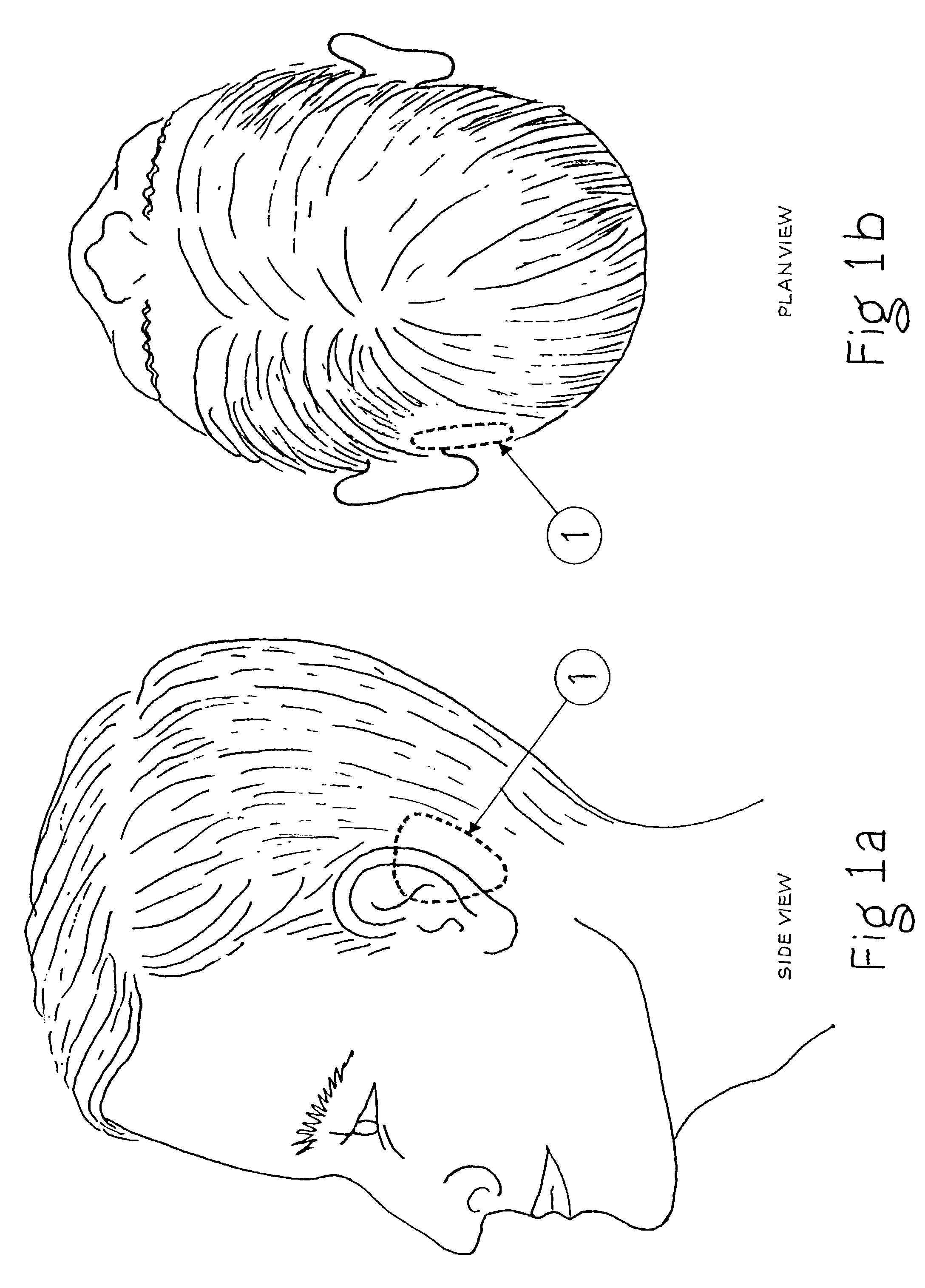
Fixation system for an implantable medical device
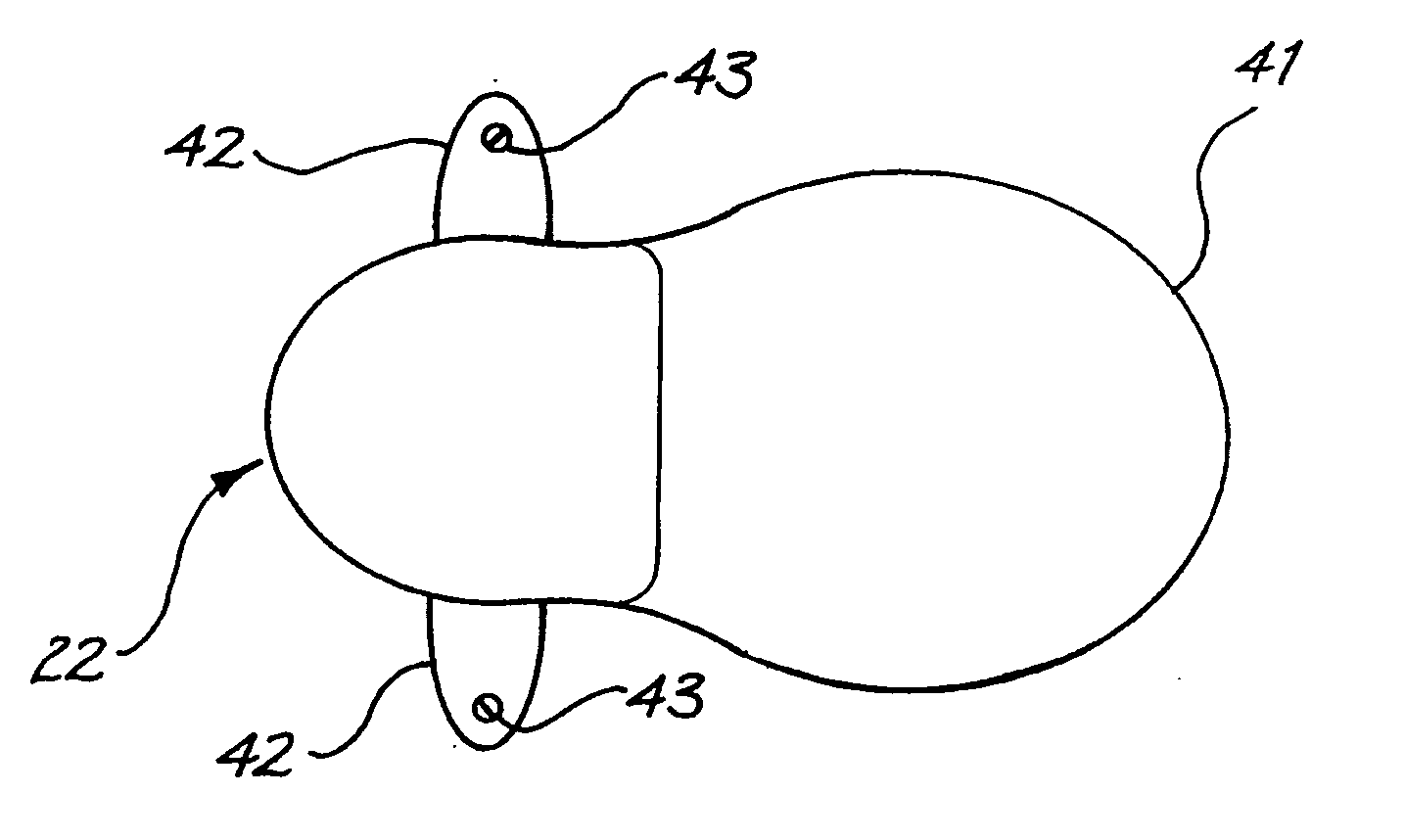
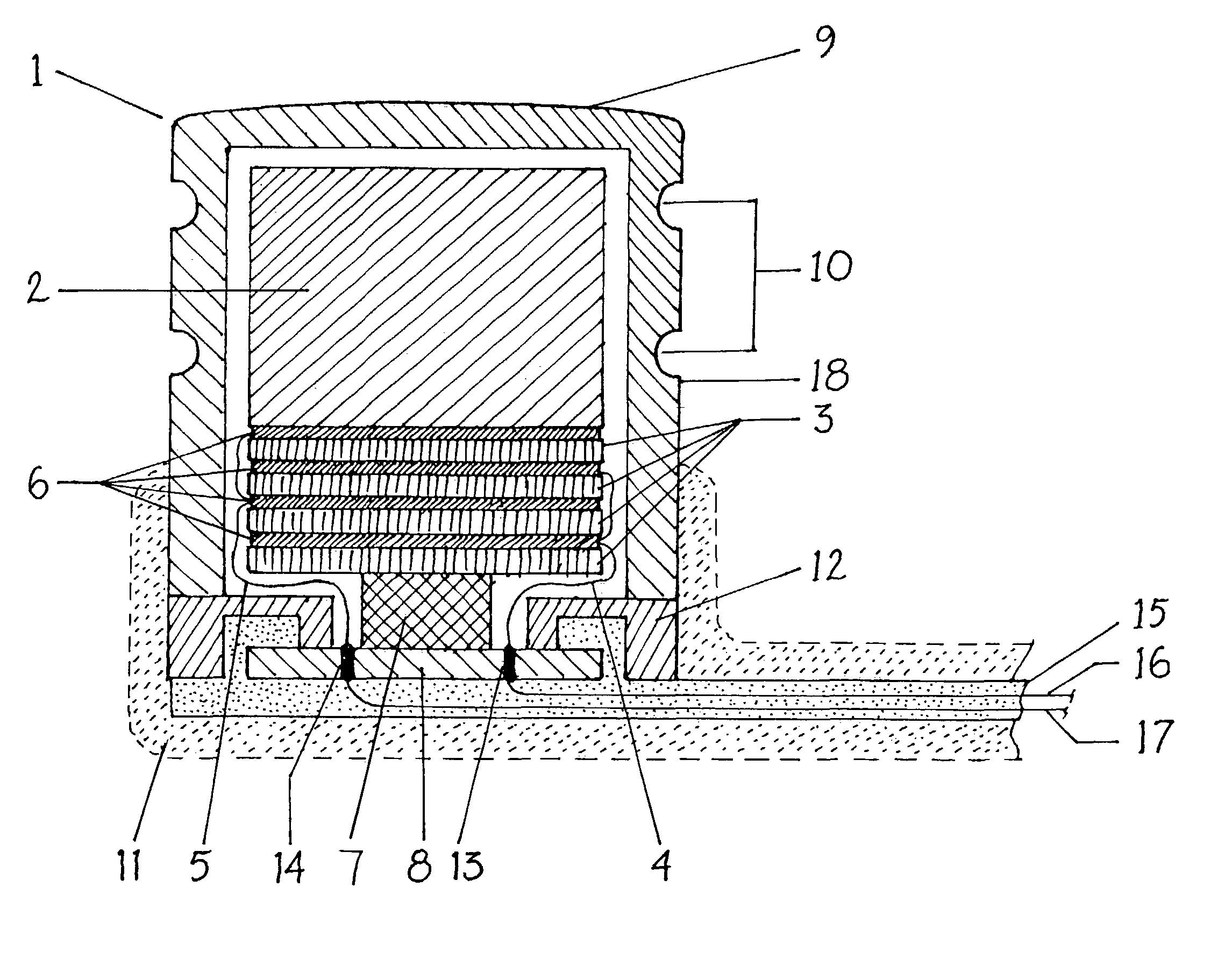
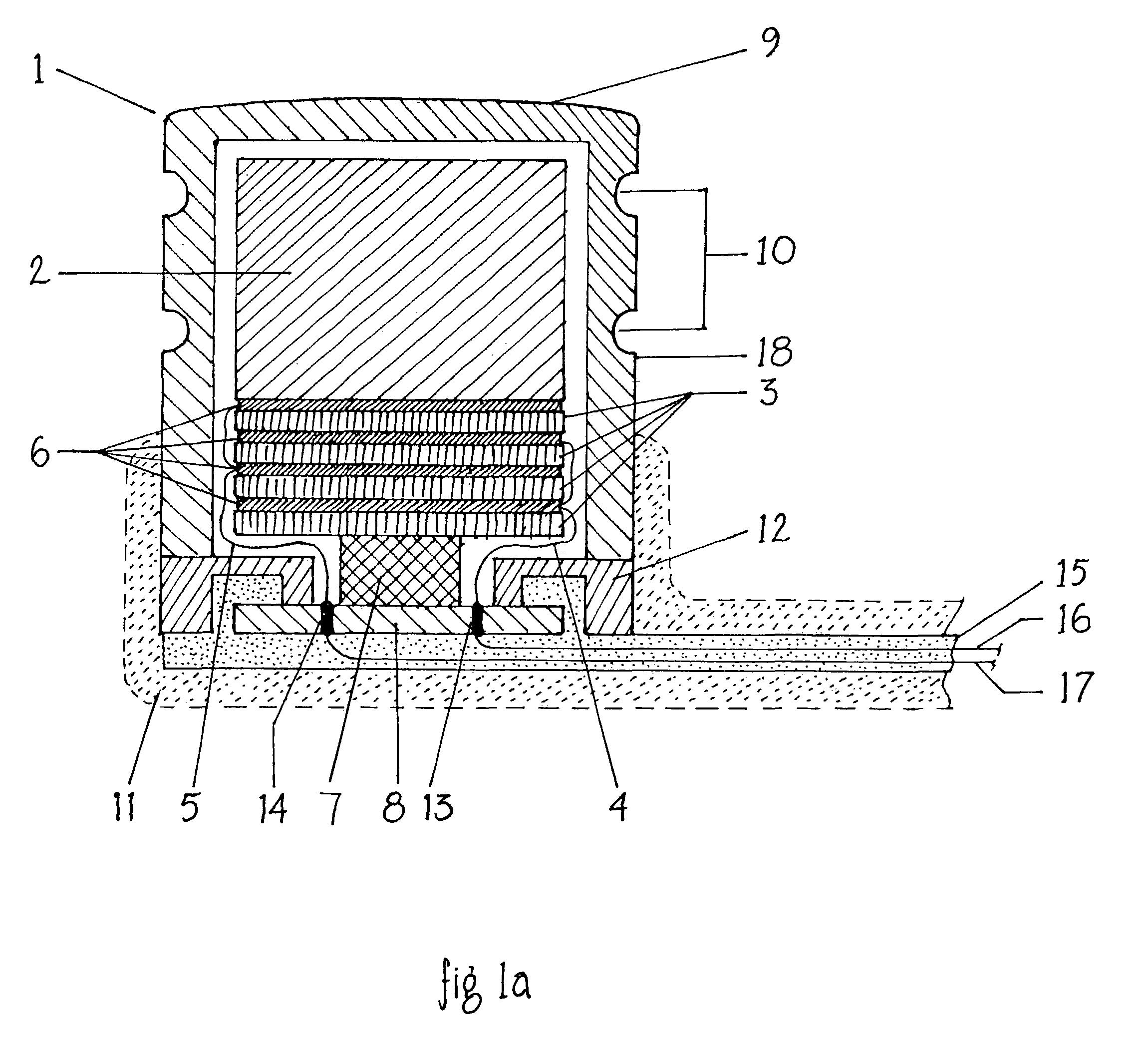
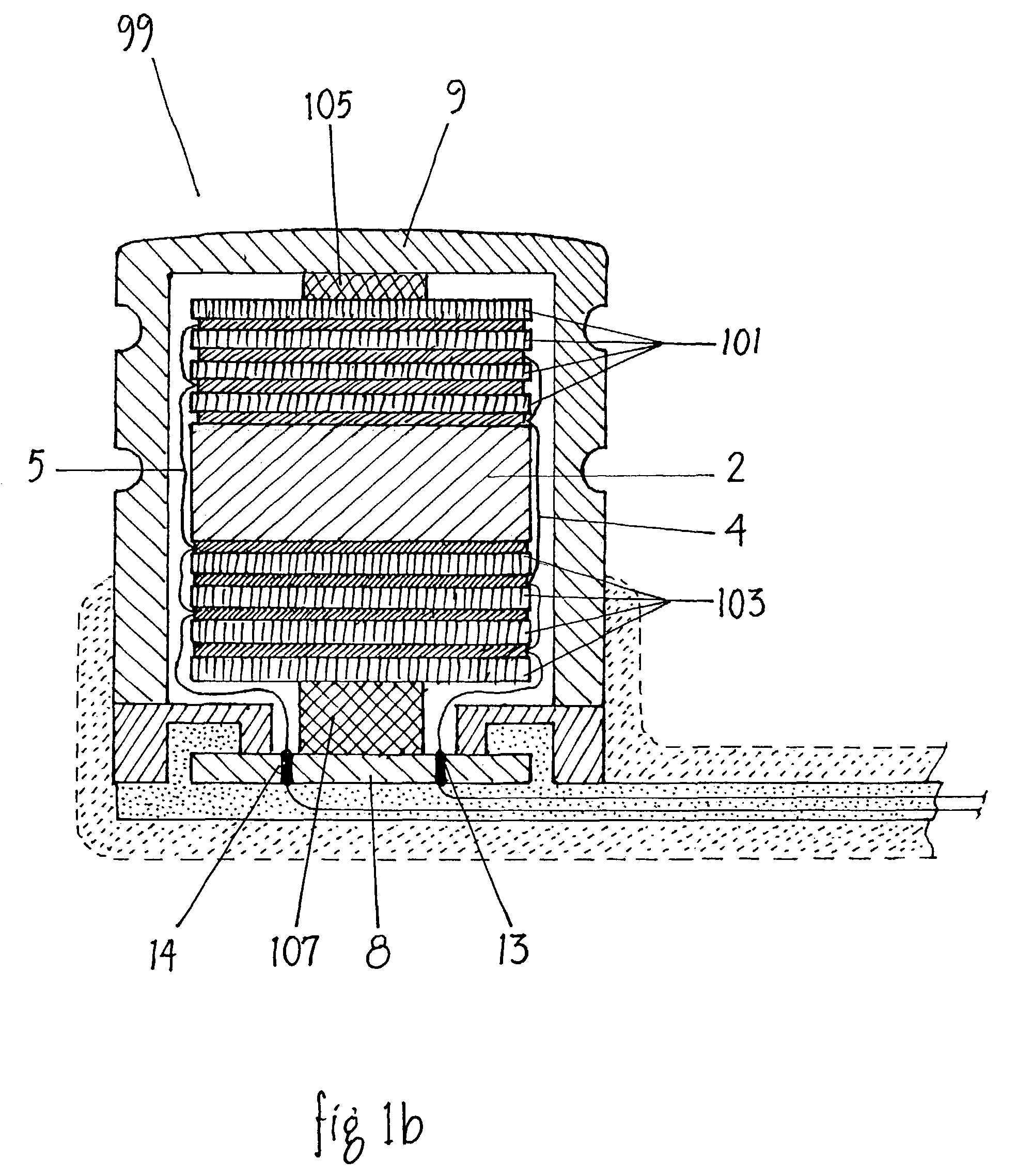
A medical implant, such as an implantable component (22) of a tissue-stimulating prosthesis. One example of such a prosthesis being a cochlear implant. The component (22) is adapted to be implanted at or adjacent a tissue surface within the recipient, such as a bone surface. The component (22) has a housing and at least one flange (42) extending outwardly therefrom. The flange (42) can be secured to the tissue surface via a tissue fixation device, such as a bone screw (43).
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Cochlear implant
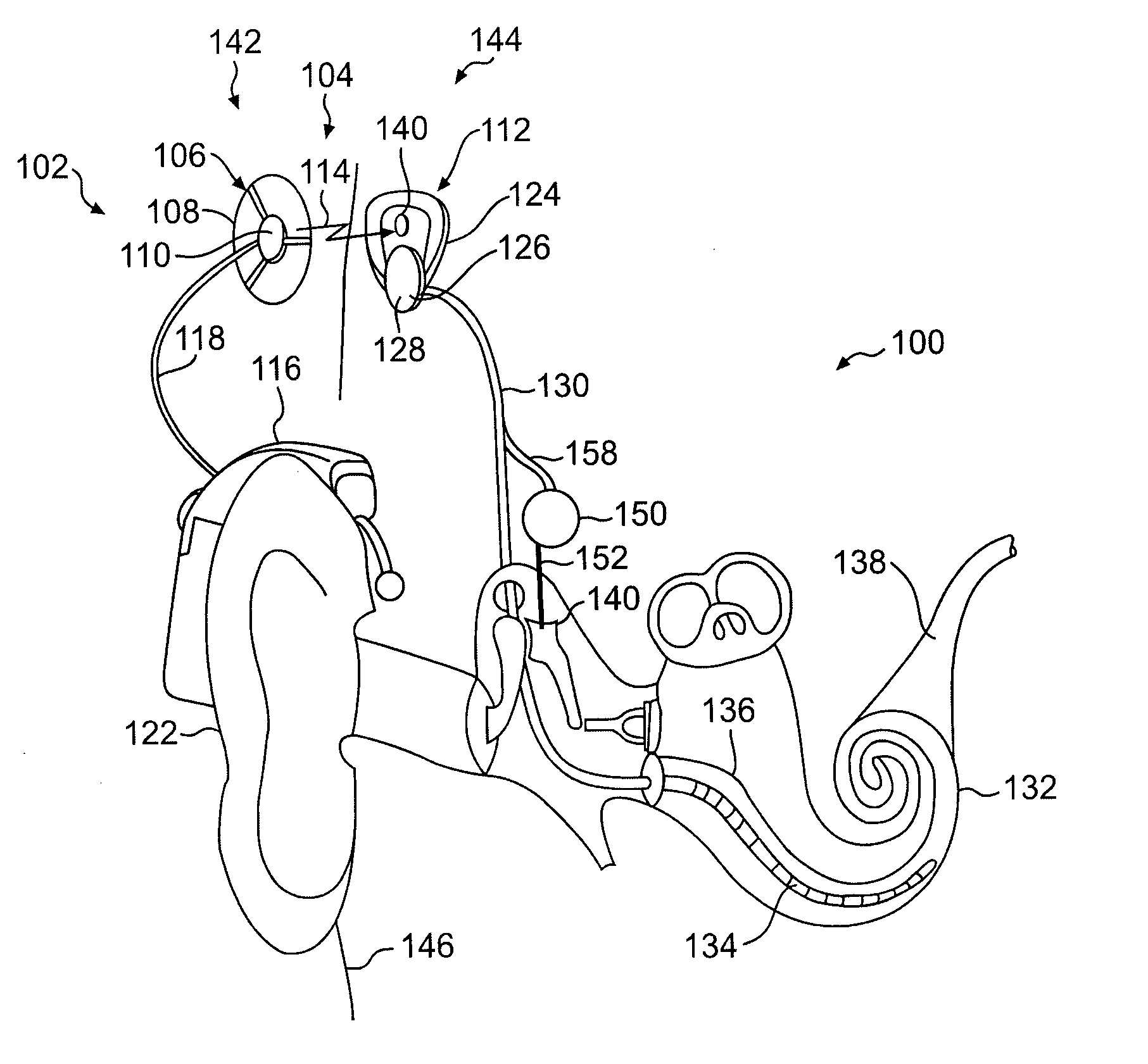
An implantable component (30) of a cochlear implant system comprising a housing for a stimulator unit (31) that is adapted to output one or more stimulation signals and an electrode assembly (30) adapted to apply electrical stimulation in accordance with the output of the stimulator unit (31). On implantation, the housing is positionable such that the electrode assembly (20) extends from the housing at least initially in a downward orientation toward the mastoid cavity before entering the cochlea. An external component (50, 60 or 70) of a cochlear implant system comprising a support for mounting to the ear of an recipient and an external signal transmitter coil (53) wherein the signal transmitter coil (53) is movably mounted to at least a portion of the support.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Optimizing cochlear implant electrode selection
InactiveUS6915166B1Contribute more to speech perception performanceImprove performanceElectrotherapyDeaf-aid setsCochlear implantationImplant electrode
A method is described to allow for better selection of electrodes for neural stimulation, for example in a cochlear implant. A series of stimuli, at different stimulation levels, are provided at each electrode to be tested, and the neural response to each stimulus is measured, using an implanted electrode. A value is then calculated relating stimulus level to response, to allow the relative responsiveness of electrodes to be determined. This can then be used as the basis for a stimulation map used to select which electrodes are stimulated and at what level.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Optical waveguide vibration sensor for use in hearing aid
InactiveUS7444877B2Vibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPolymer optical waveguideLoudspeaker
A directionally-sensitive device for detecting and processing vibration waves includes an array of polymeric optical waveguide resonators positioned between a light source, such as an LED array, and a light detector, such as a photodiode array. The resonators which are preferably oriented substantially perpendicularly with respect to incoming vibration waves, vibrate when a wave is detected, thus modulating light signals that are transmitted between the light source and the light detector. The light detector converts the modulated light into electrical signals which, in a preferred embodiment, are used to drive either the speaker of a hearing aid or the electrode array of a cochlear implant. The device is manufactured using a combination of traditional semiconductor processes and polymer microfabrication techniques.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
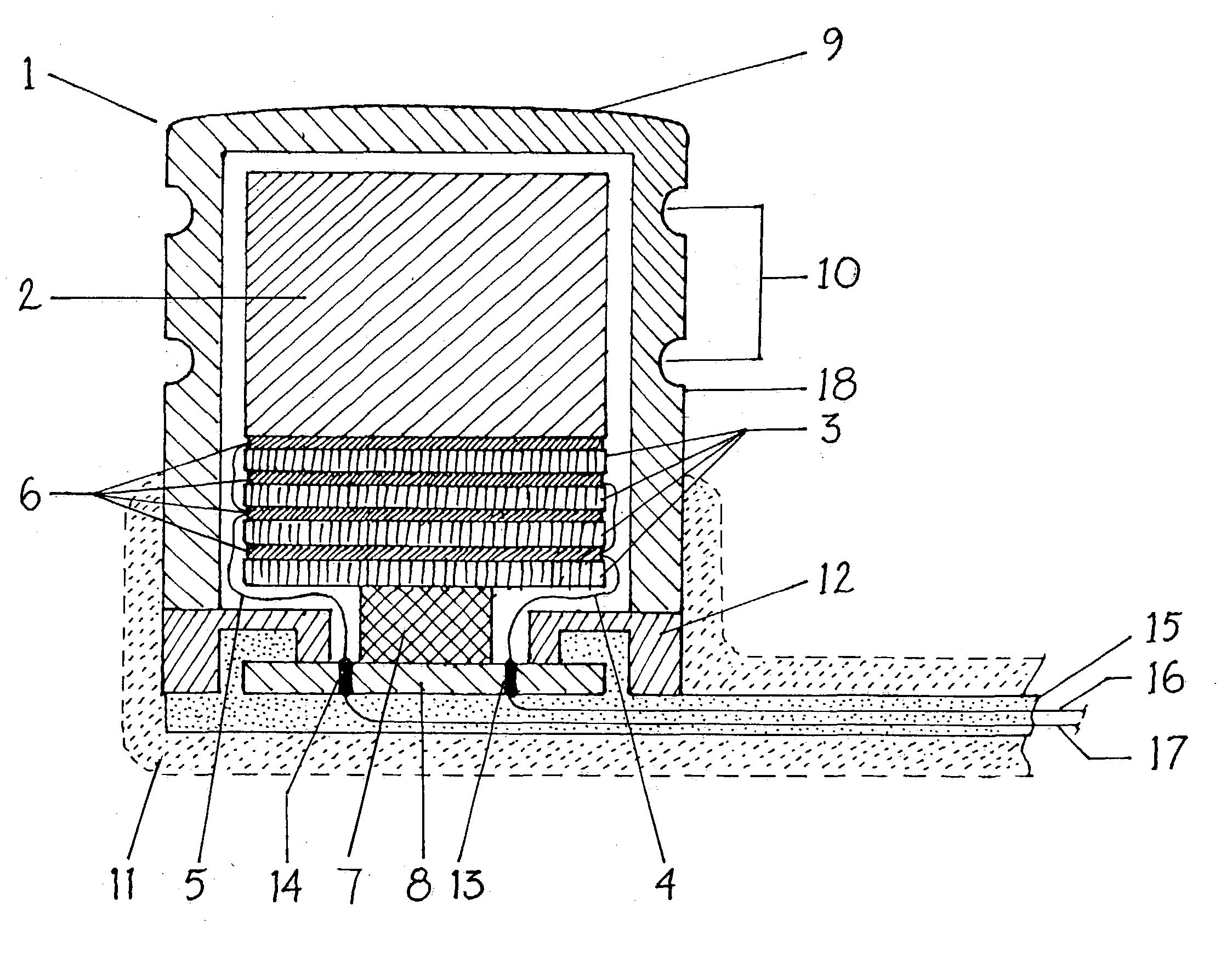
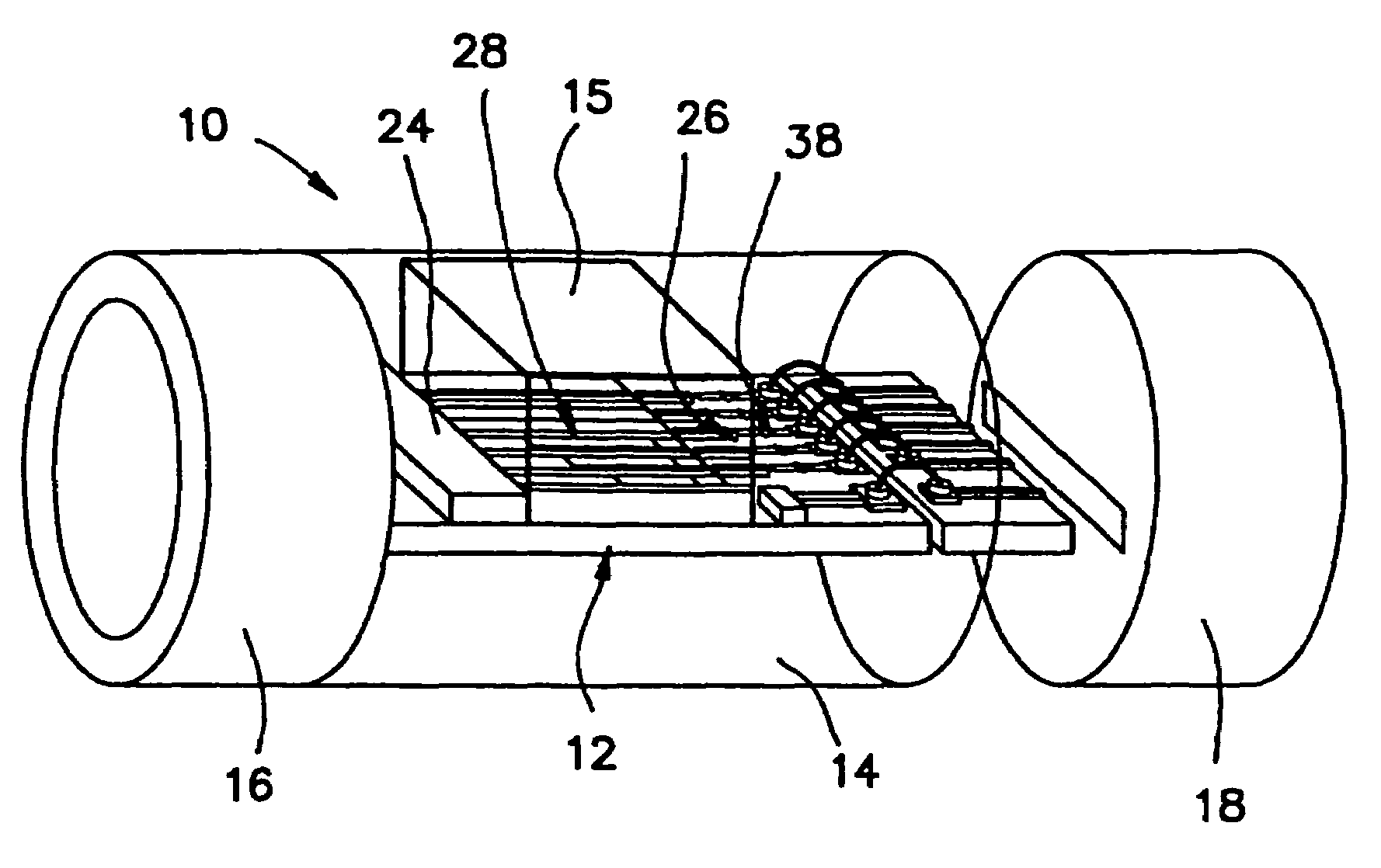
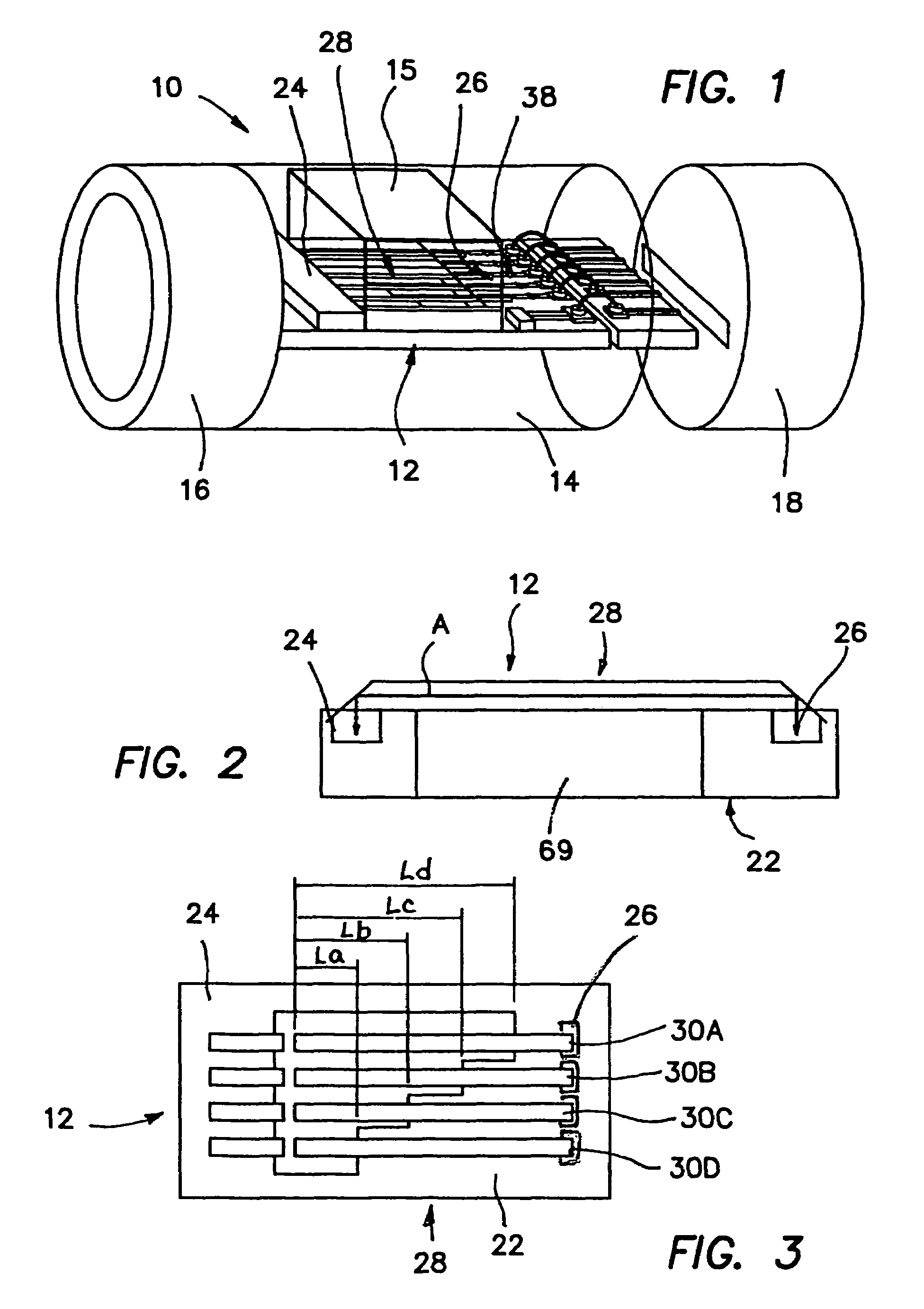
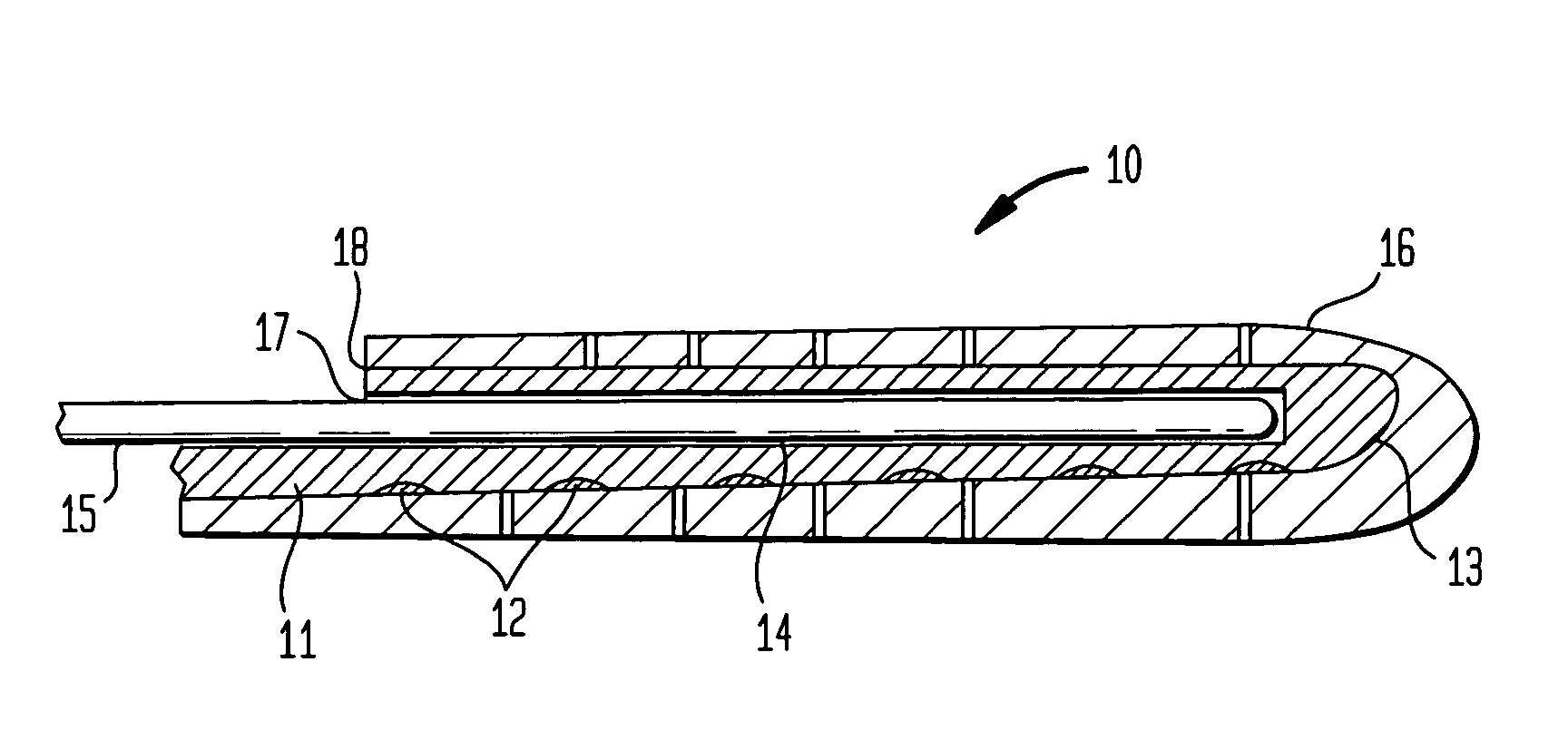
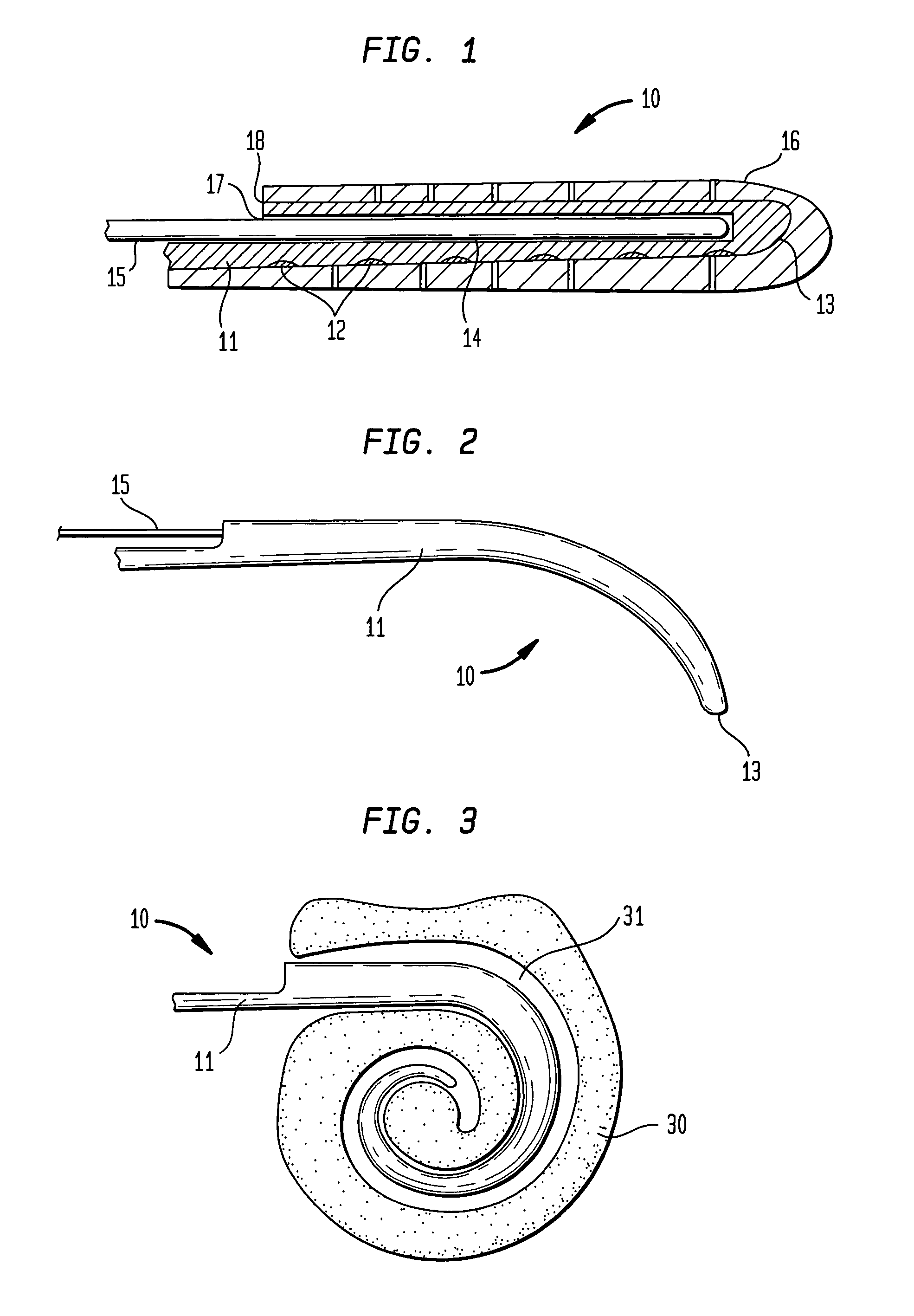
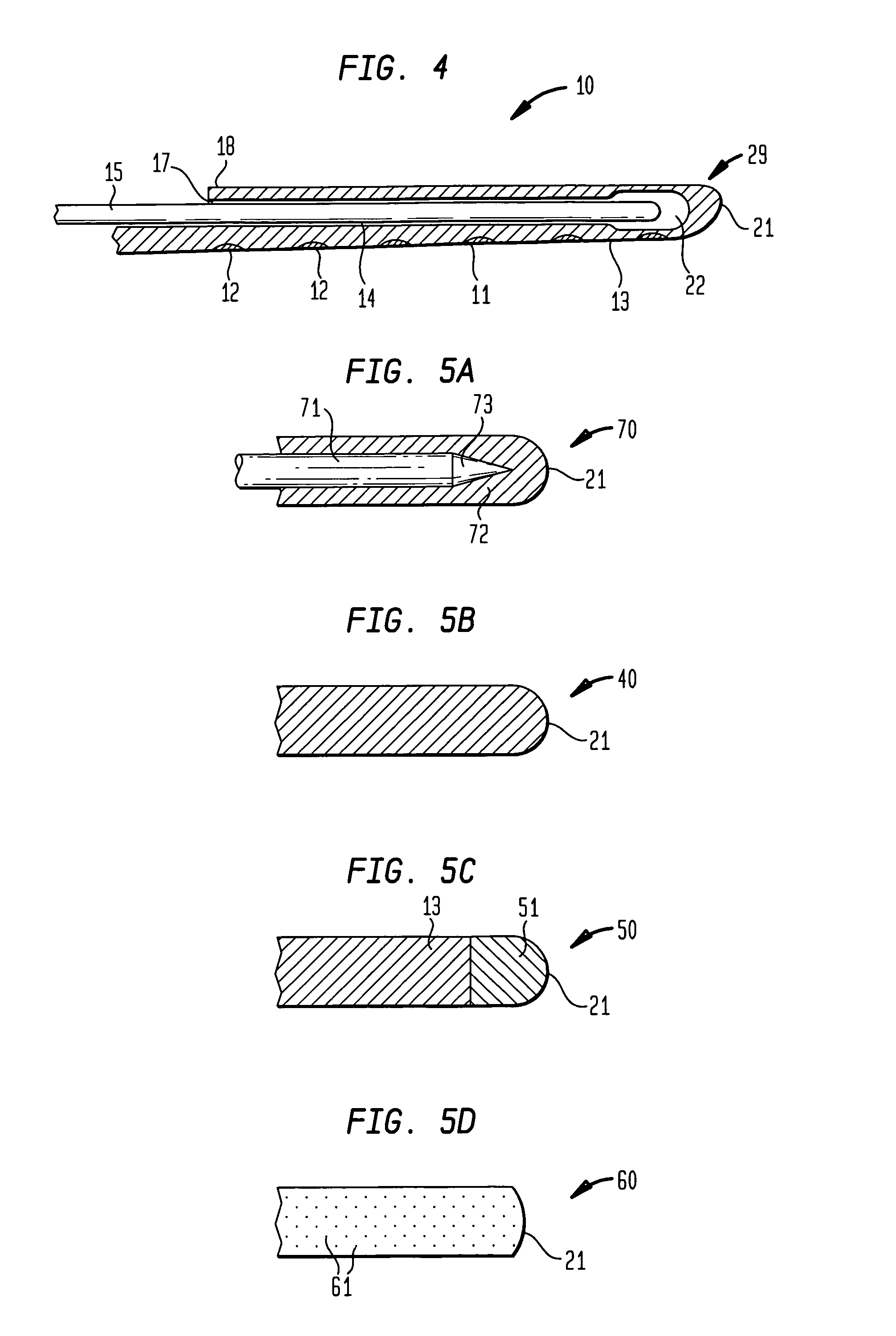
Cochlear implant electrode and method of making same
ActiveUS7319906B2Increase stiffnessImprove complianceHead electrodesExternal electrodesFilling materialsCochlear implantation
A cochlear stimulation lead and method of making an aggressively curved electrode array are provided. In one embodiment of the lead, while the curved section of the lead is curled further beyond the originally molded curvature and held in this position, a filling channel is filled up with a filling material that is hardened or cured in this held position. The resulting lead has a tip curvature that is more curved than the originally molded curvature.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONICS AG
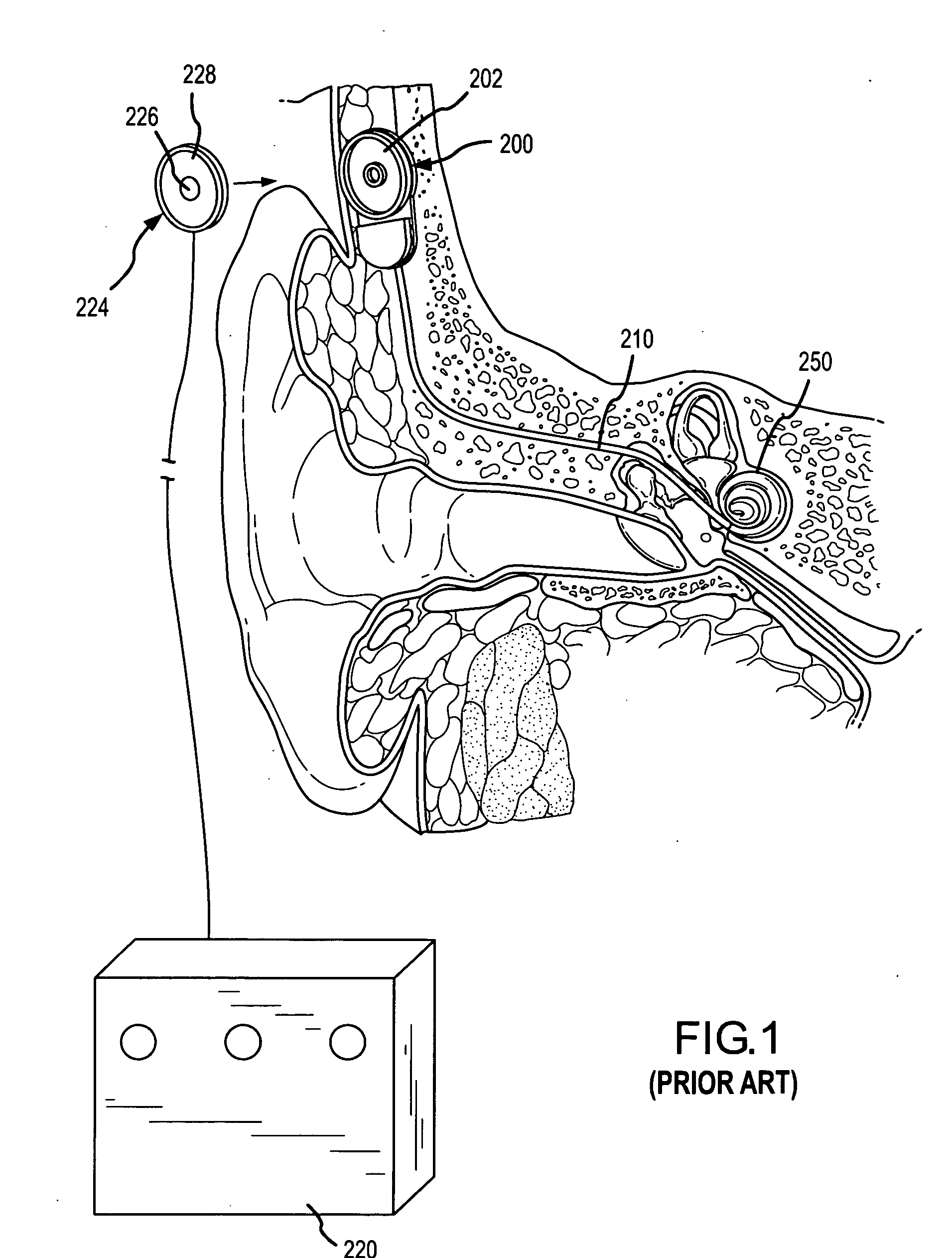
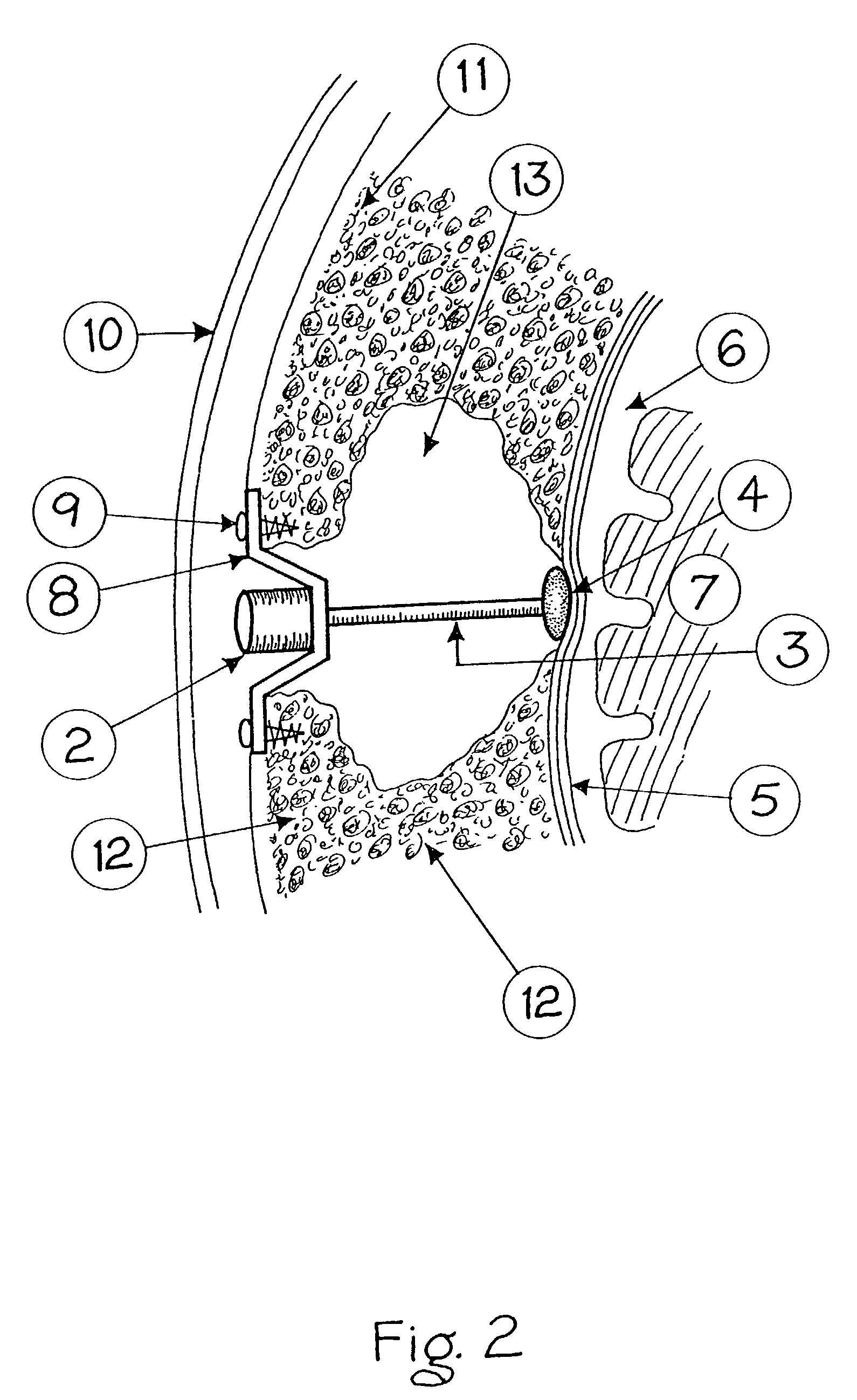
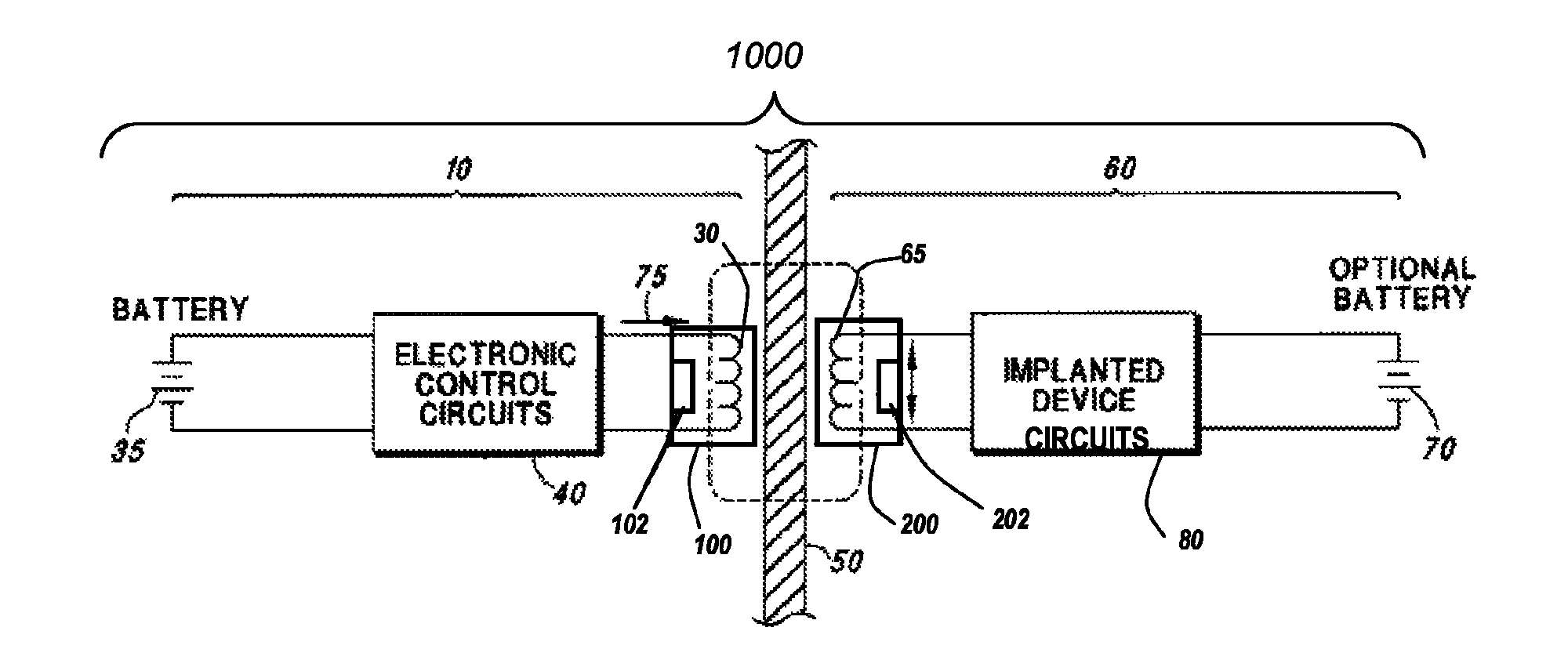
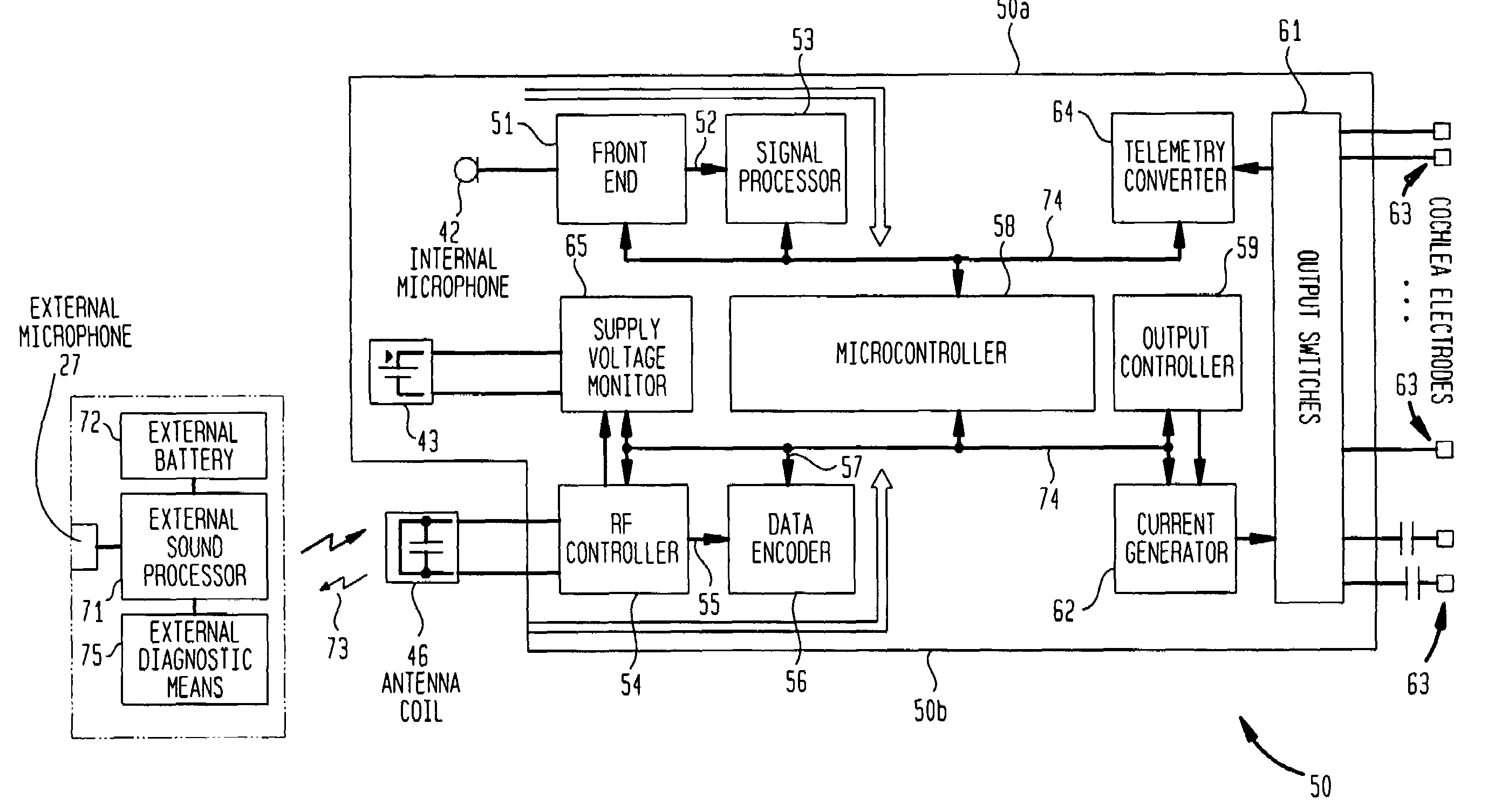
At least partially implantable system for rehabilitation of hearing disorder
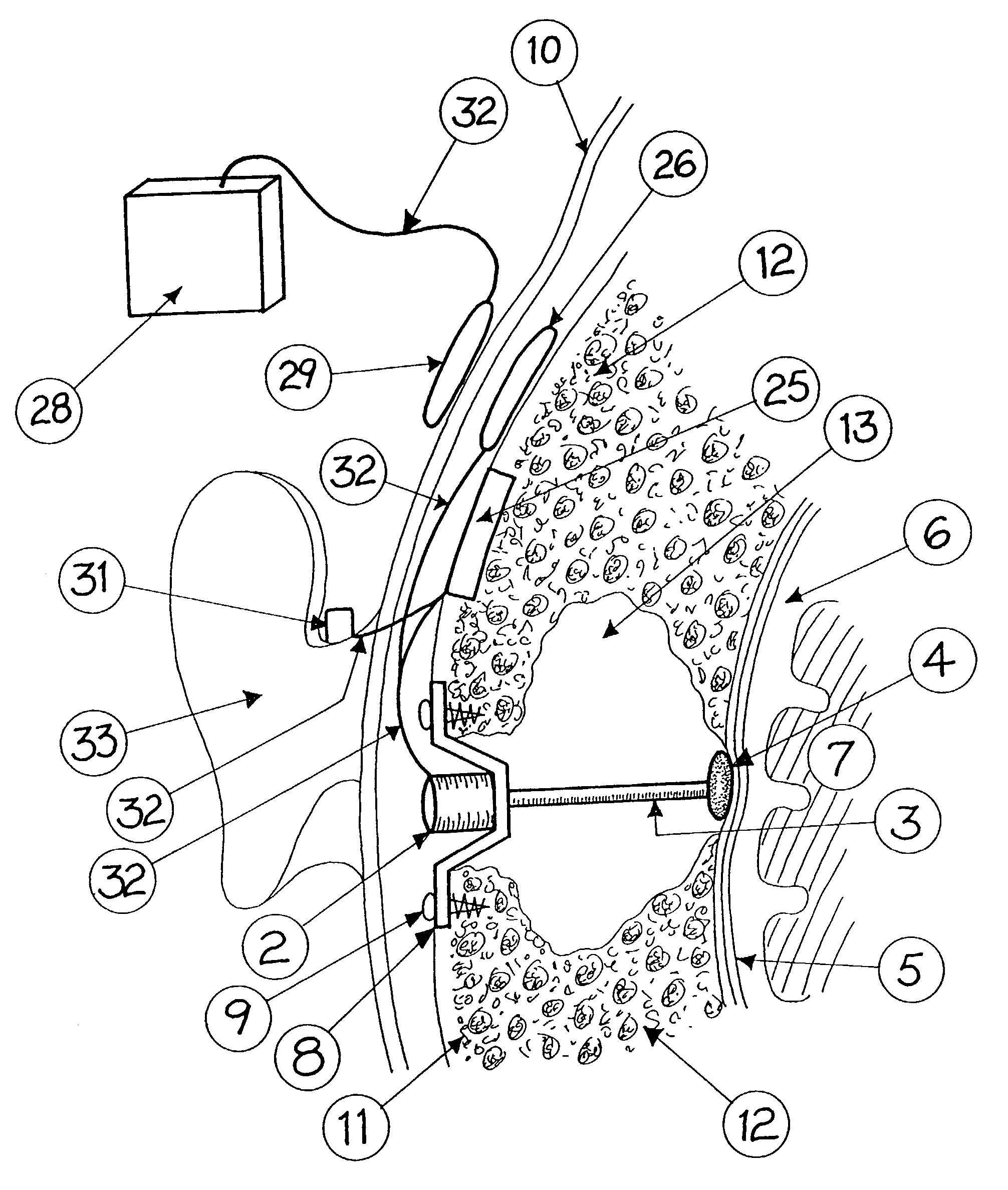
InactiveUS20010049466A1Long and longer service lifeExtended stayHead electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringEngineeringActuator
An at least partially implantable system for rehabilitation of a hearing disorder with at least one acoustic sensor (microphone) for picking up an acoustic sensor signal and converting the acoustic sensor signal into corresponding electrical signals, an electronic signal processing unit for audio signal processing and amplification, an electrical power supply unit which supplies individual components of the system with energy, and an output-side actuator stimulation arrangement, the actuator stimulation arrangement has a dual intracochlear arrangement in combination with a stimulator arrangement with at least one stimulator element for at least indirect mechanical stimulation of a damaged inner ear and one electrically acting stimulation electrode arrangement with at least one cochlear implant electrode for electrical stimulation of the inner ear.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Surgically implantable hearing aid
InactiveUS7033313B2Negligible riskSurgery is simpleEar treatmentDeaf-aid setsDura materCochlear implantation
The invention comprises a surgically implantable hearing aid for hearing impaired persons. The hearing aid includes a vibrational element which is vibrated by sound waves and attached to the skull of the person, and a connector which crosses the mastoid cavity and delivers the sound waves to the dura mater of the patient thereby vibrating the dura mater, the cerebrospinal fluids, and the brain to create a hearing percept. The invention can also be adapted to act as a tinnitus masker or used in conjunction with a cochlear implant. It can also be used in a modified form to connect directly through the skull of the person.
Owner:ALAN J LUPIN
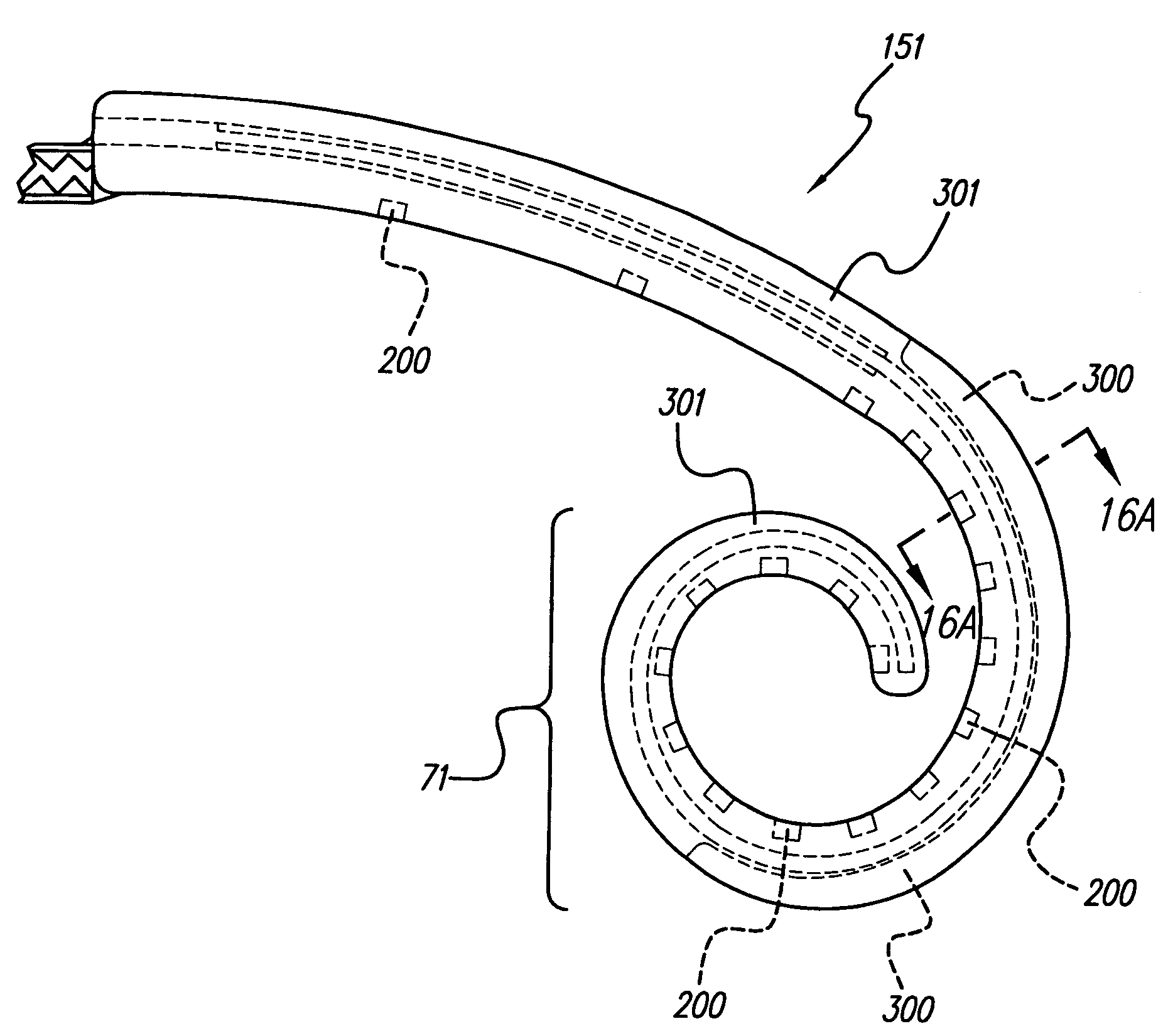
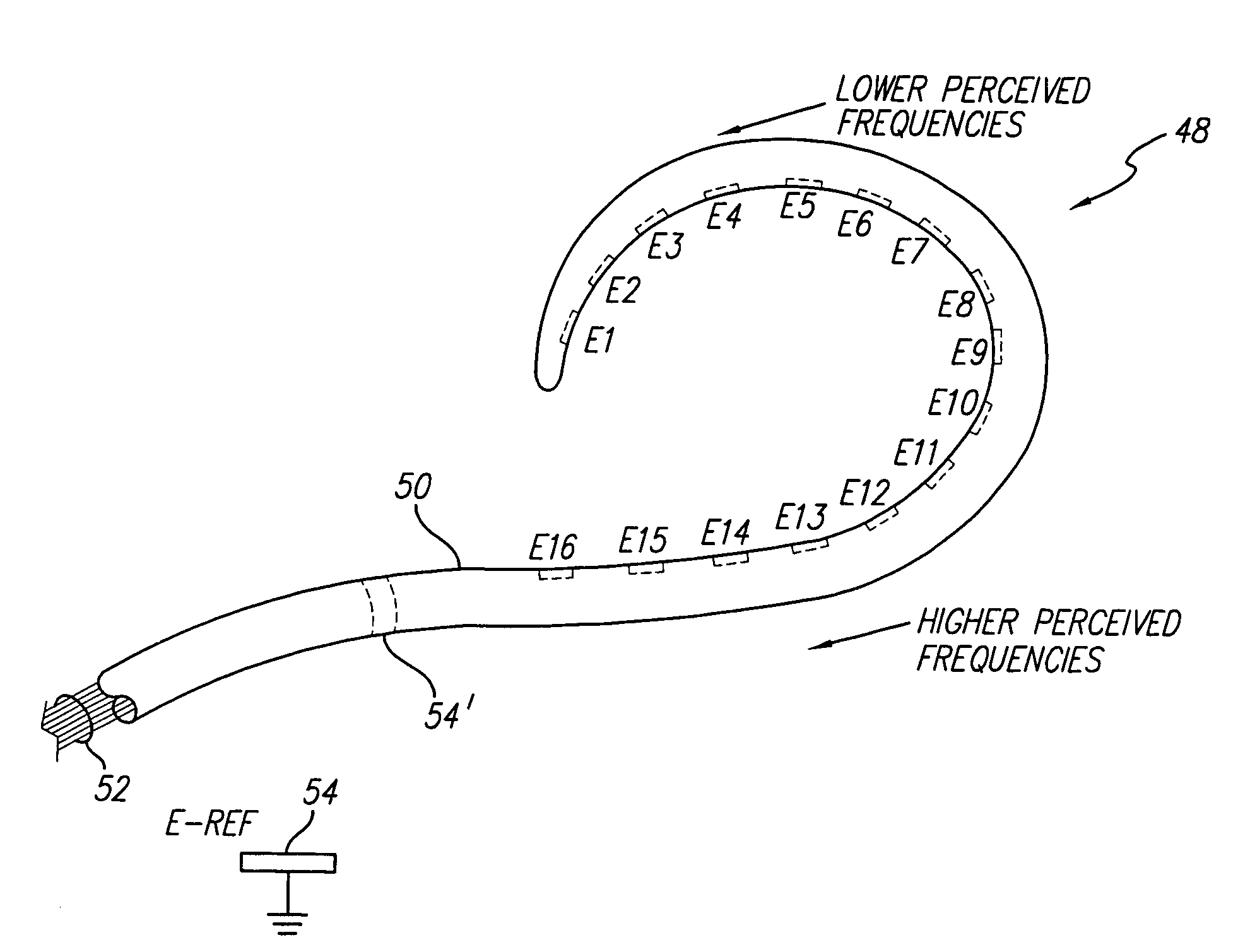
Spatial decimation stimulation in an implantable neural stimulator, such as a cochlear implant
ActiveUS7039466B1High rate stimulationReduce power levelElectrotherapyArtificial respirationCochlear implantationElectrode array
A cochlear implant system, or other neural stimulation system, has the capability to stimulate fast enough to induce stochastic neural firing so as to restore “spontaneous” neural activity. The stimulation rate applied to the more distally-located electrodes of an electrode array connected to the implant system is reduced from the stimulation rate applied to the more proximally-located electrodes. Thus, in the case of a cochlear implant system, the apically-located regions within the cochlea are stimulated at a reduced rate in order to conserve power. Pulse widths of the reduced-rate pulses may further be increased, and amplitudes reduced, to further conserve power. As needed, a low-level random conditioner stimulation signal may be applied to the apical regions of the cochlea in order to ensure the occurrence of random neural firings.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONICS AG
Optimizing pitch and other speech stimuli allocation in a cochlear implant
ActiveUS7251530B1Easy to controlImprove sound qualityElectrotherapyAudiometeringOctaveCochlear implantation
Errors in pitch (frequency) allocation within a cochlear implant are corrected in order to provide a significant and profound improvement in the quality of sound perceived by the cochlear implant user. In one embodiment, the user is stimulated with a reference signal, e.g., the tone “A” (440 Hz) and then the user is stimulated with a probe signal, separated from the reference signal by an octave, e.g., high “A” (880 Hz). The user adjusts the location where the probe signal is applied, using current steering, until the pitch of the probe signal, as perceived by the user, matches the pitch of the reference signal, as perceived by the user. In this manner, the user maps frequencies to stimulation locations in order to tune his or her implant system to his or her unique cochlea.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONICS AG
Totally implantable hearing prosthesis
ActiveUS7442164B2Easy and safe to implantMinimize power consumptionElectrotherapyImplantable hearing aidsHermetic sealProsthesis
The invention comprises a totally implantable hearing prosthesis for hearing impaired persons. An inertial vibrational element is hermetically sealed and implanted in bone between the lateral and superior semicircular canals without breaching the integrity of the canals. The vibrational element is adapted to vibrate the walls of the canals and the fluids contained therein, thereby vibrating contiguous fluids within the cochlea thus stimulating hair cells and creating a hearing percept. The invention can also be adapted to be a tinnitus masking system, and / or used in combination with a cochlear implant hearing system.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
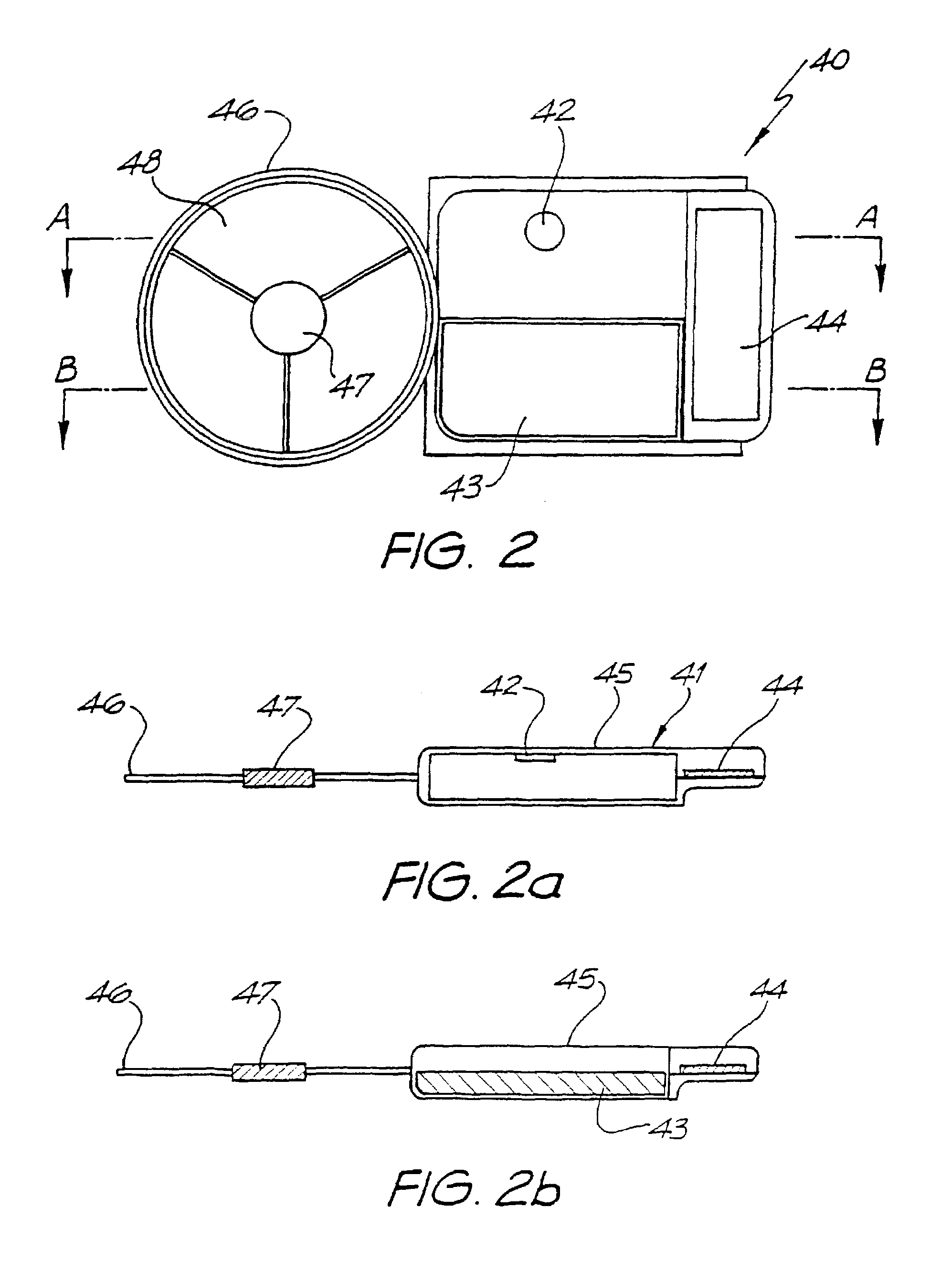
Atraumatic high-retention headpiece
A headpiece for a cochlear implant system includes a transcutaneous transmission coil that transfers power and / or data to an implantable device implanted under a user's skin. The headpiece includes a magnet for holding the transmission coil in close proximity to the receiver coil in the implanted device, which also contains a magnet, and provides the desired alignment between the coils so that inductive coupling may efficiently occur. The headpiece has a bottom surface for skin contact that includes a plurality of flexible bumps configured to distribute pressure over a large surface area while allowing blood flow throughout the area. This also provides friction contact with the skin to help secure the headpiece, reducing movement due to lateral loading, while reducing skin irritation and erosion.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONICS AG
System for generating a cochlear implant program using multi-electrode stimulation to elicit the electrically-evoked compound action potential
InactiveUS20070179565A1Increase amplitudeConvenient recordingHead electrodesArtificial respirationEvoked compound action potentialSequential stimulation
A multichannel cochlear implant system spatially spreads the excitation pattern in the target neural tissue by either: (1) rapid sequential stimulation of a small group of electrodes, or (2) simultaneously stimulating a small group of electrodes. Such multi-electrode stimulation stimulates a greater number of neurons in a synchronous manner, thereby increasing the amplitude of the extra-cellular voltage fluctuation and facilitating its recording. The electrical stimuli are applied simultaneously (or sequentially at a rapid rate) on selected small groups of electrodes while monitoring the evoked compound action potential (ECAP) on a nearby electrode. The presence of an observable ECAP not only validates operation of the implant device at a time when the patient may be unconscious or otherwise unable to provide subjective feedback, but also provides a way for the magnitude of the observed ECAP to be recorded as a function of the amplitude of the applied stimulus. From this data, a safe, efficacious and comfortable threshold level can be obtained which may be used thereafter as the initial setting of the stimulation parameters of the neurostimulation device, or to guide the setting of the stimulation parameters of the neurostimulation device.
Owner:ADVNACED BIONICS LLC
Dual microphone EAS system that prevents feedback
ActiveUS8233651B1Remove feedbackUndesirable feedbackElectrotherapyDeaf-aid setsCochlear implantationHearing aid
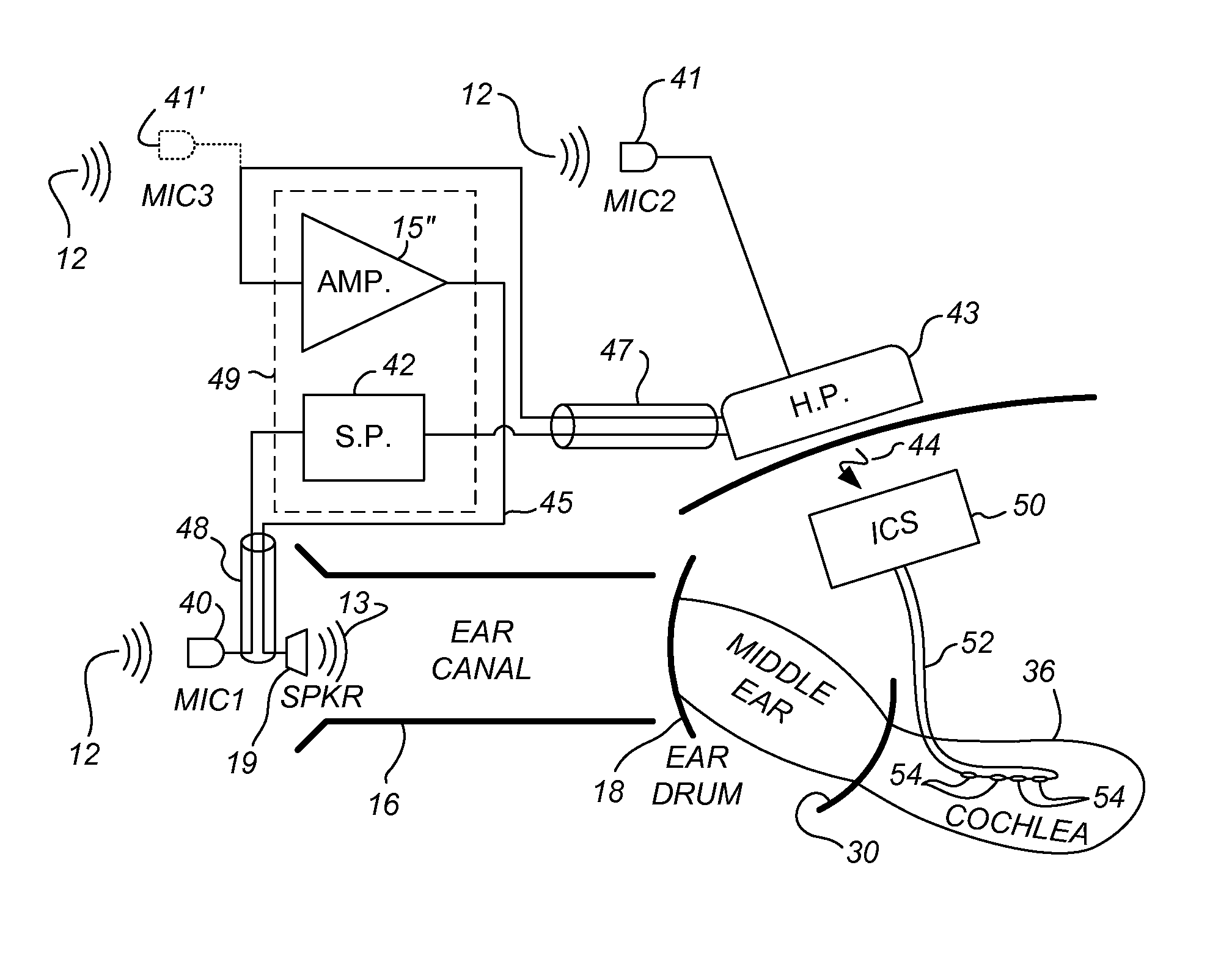
A hearing prosthesis includes both a hearing aid adapted to sense and amplify low frequency acoustic sound signals and a cochlear implant system adapted to sense high frequency acoustic sound signals. The hearing aid has a first microphone adapted to sense the low frequency acoustic sound signals, amplify these sensed low frequency acoustic sound signals, and present the resulting amplified low frequency acoustic sound signals in the ear canal of a user, thereby enabling the user to better hear these amplified sounds using his or her normal hearing processes. The cochlear implant system includes a second microphone adapted to sense the high frequency acoustic sound signals and selectively stimulate the inner ear with electrical stimulation that will be perceived as high frequency acoustic sound signals. Both the cochlear implant system and the hearing aid system are coupled to operate on the same ear of the user. Feedback within the hearing aid portion of the system is eliminated by positioning the first microphone at a location that is acoustically remote from the ear canal where the amplified low frequency acoustic sound signals are presented. High frequency acoustic sound signals are better sensed by placing the second microphone at a location that is in or near the ear canal where the amplified low frequency acoustic sound signals are presented.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONICS AG
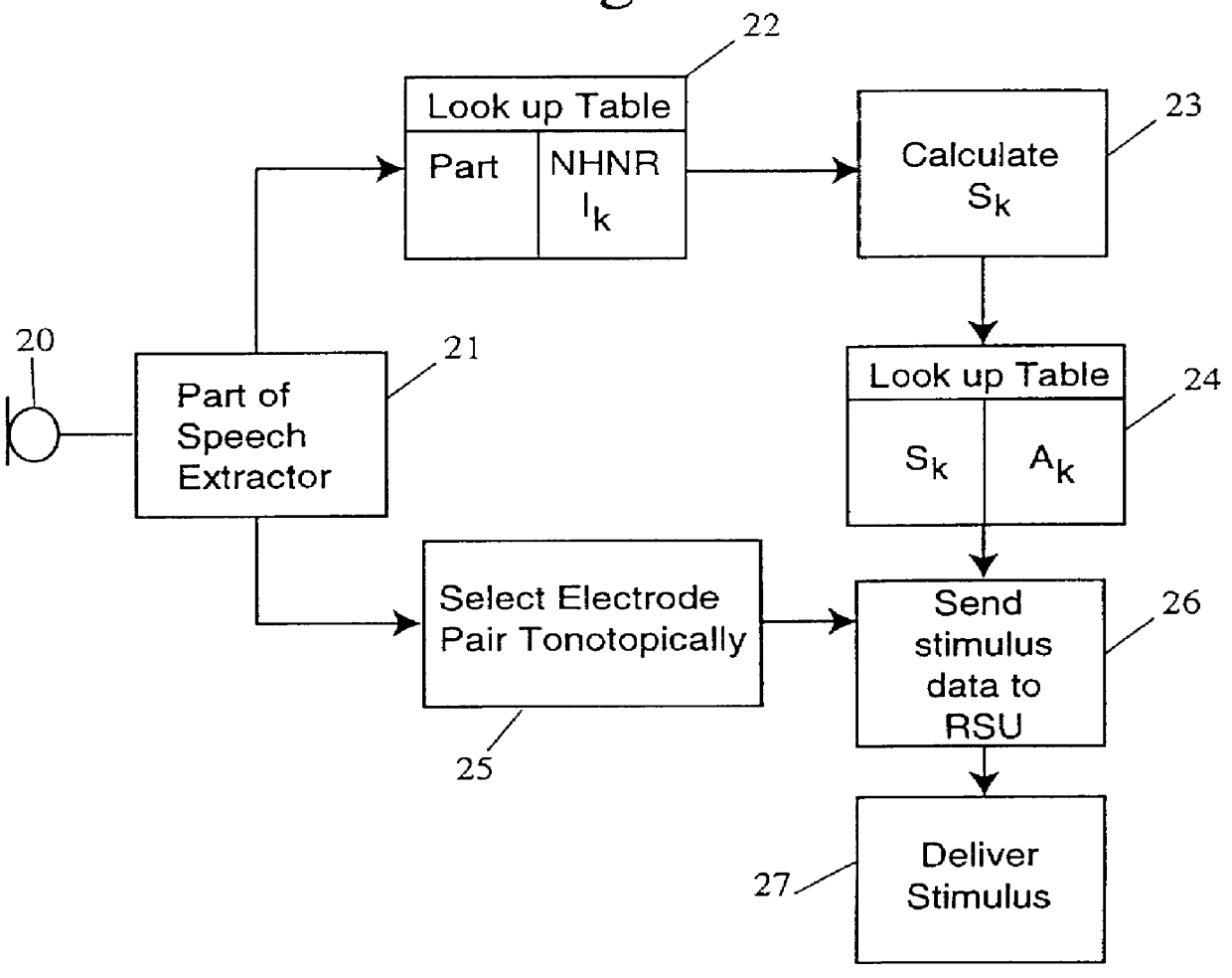
Sound processing method and system
Coding of received audio signals and the resulting application of electrical stimuli applied to electrodes used in a cochlear implant system are disclosed together with a method of fitting this new coding strategy. One of the aims is to place specific stimulation representing pitch by applying near threshold electrical stimuli with limited and focussed excitation fields. A range of stimulation rates and a minimal range of current levels above threshold are used for creation of a dynamic loudness percept for a cochlear implant recipient. Another aim is to disclose a coding scheme based on a model of physiological measures (i.e. refractoriness, adaptation, spread of activation field, spatiotemporal acoustical cochlear activation patterns and spontaneous activity) to estimate the proportions of available excitable auditory neurons close to the electrodes available for stimulation. The spectral bands formed from the pre-processing of incoming audio signals are weighted by these proportions of excitability to control place, timing, rate and current level of electrical stimuli applied to the electrodes available in the array.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
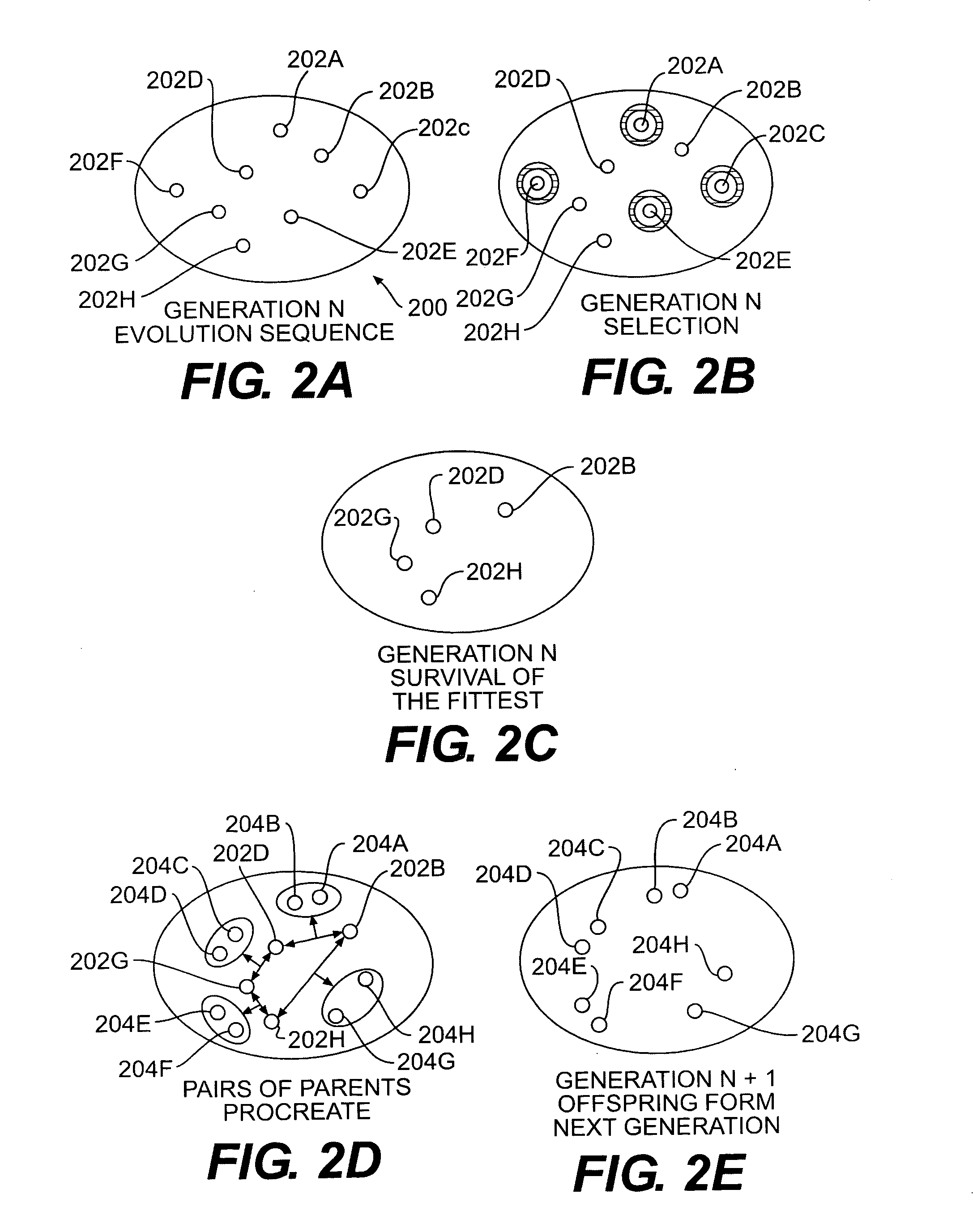
Using a genetic algorithm to fit a cochlear implant system to a patient
Apparatus and method for at least partially fitting a cochlear implant system to a patient is described, comprising: executing a genetic algorithm to select values for a subset of one or more parameters selected from a plurality of parameters for which values are to be selected to fit the implant, wherein said genetic algorithm is operable to generate one or more successive generations of values for said parameter subset; and determining, based on patient feedback, said values of said values for said parameter subset in each of said one or more successive generations.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
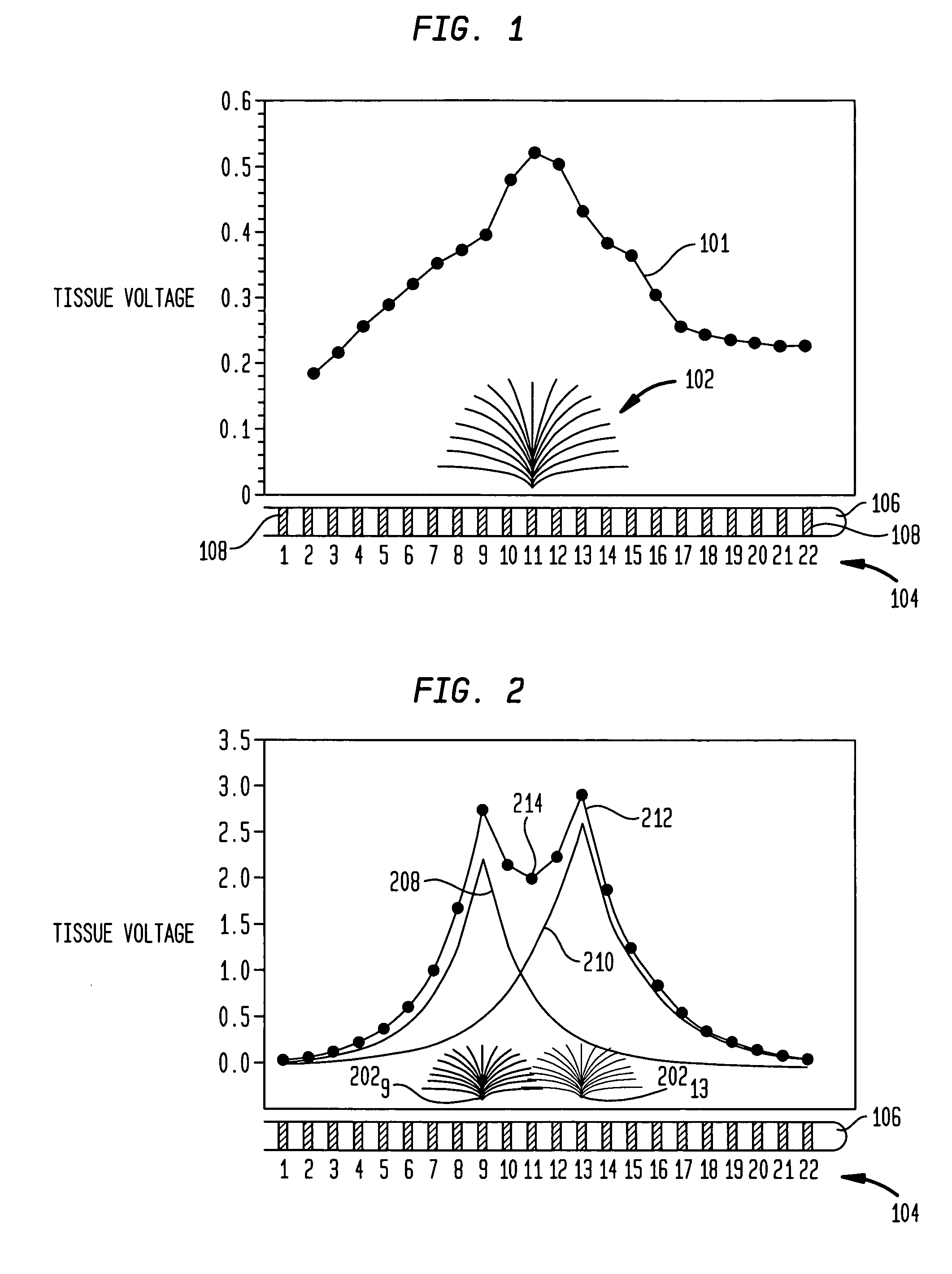
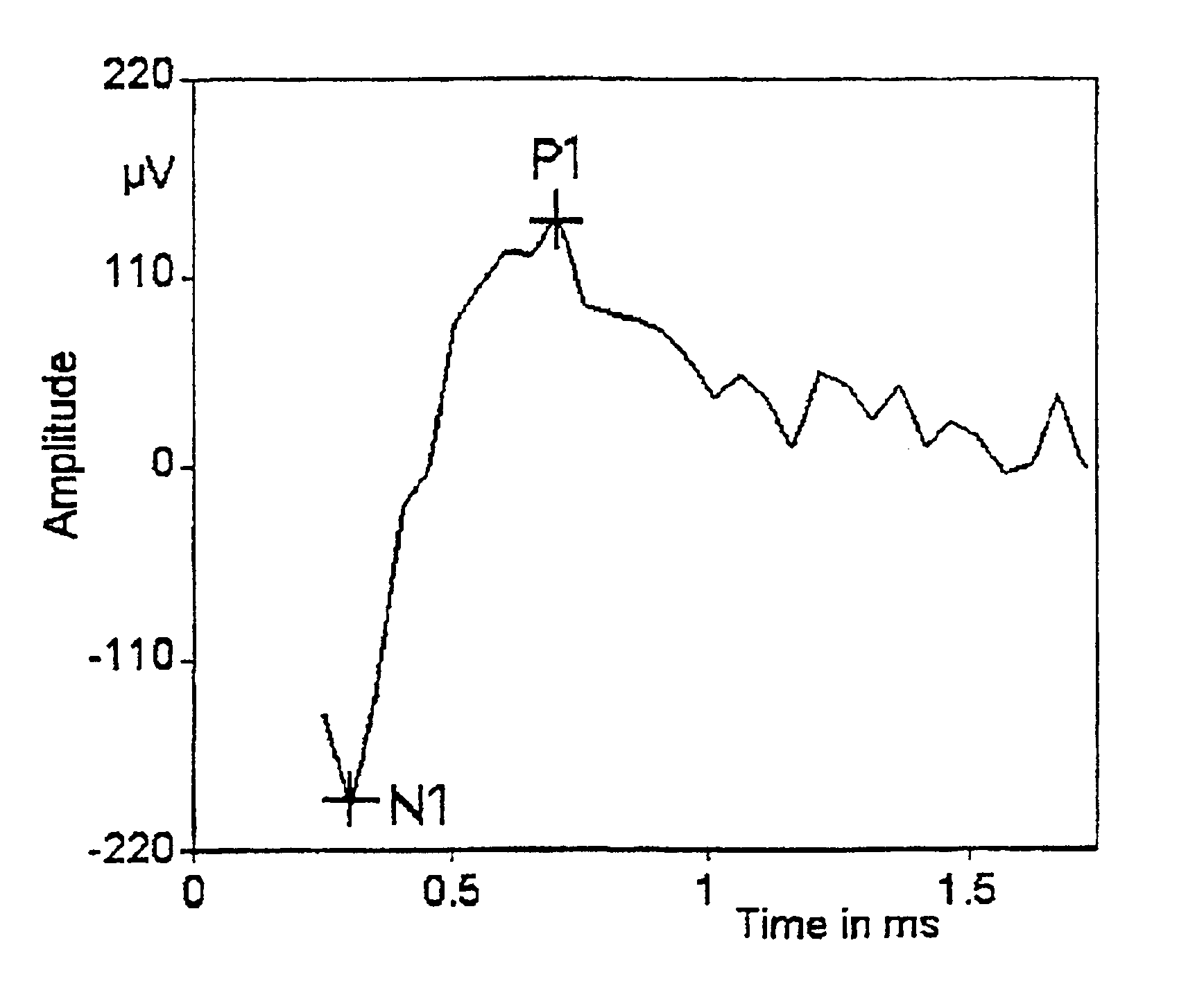
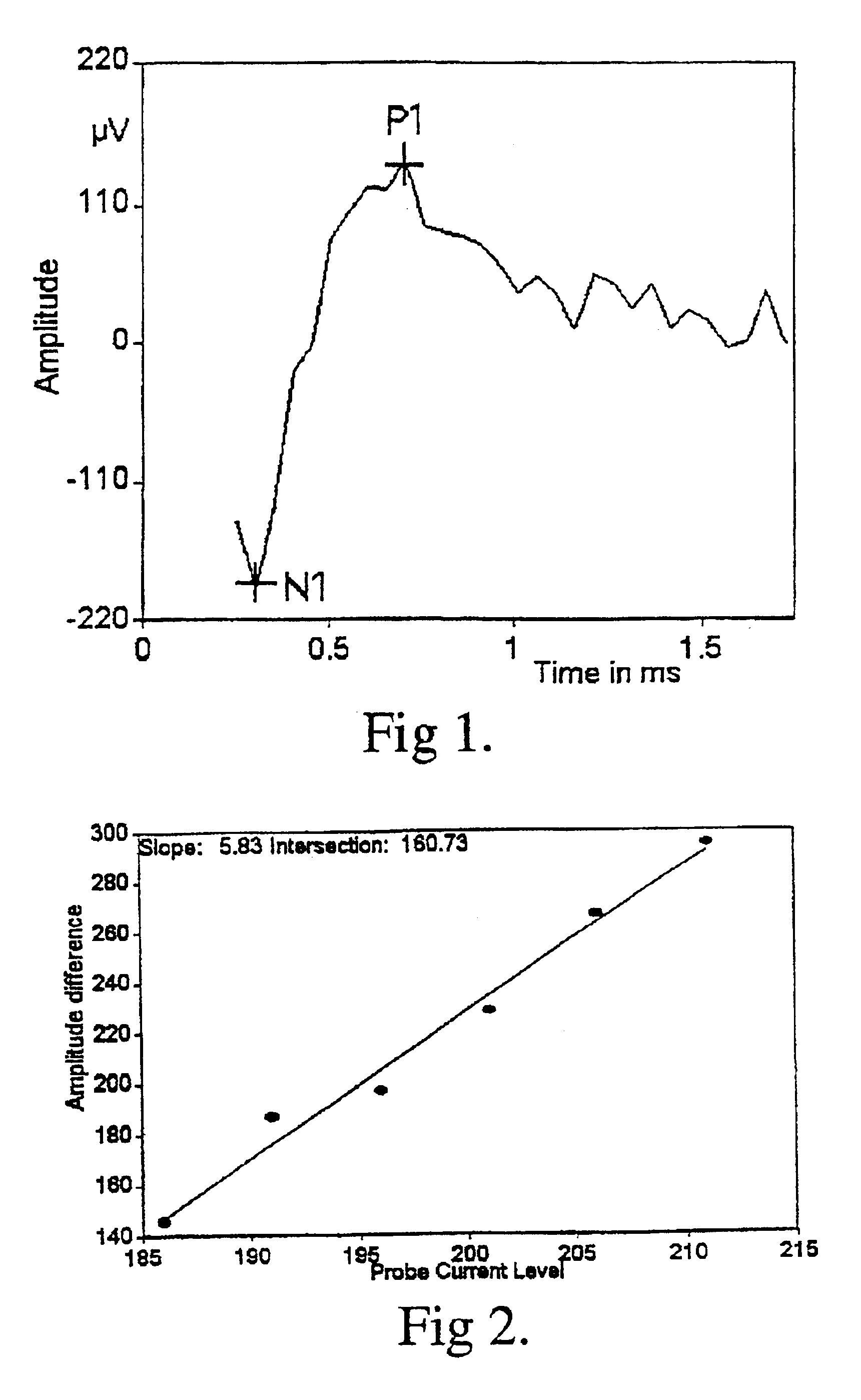
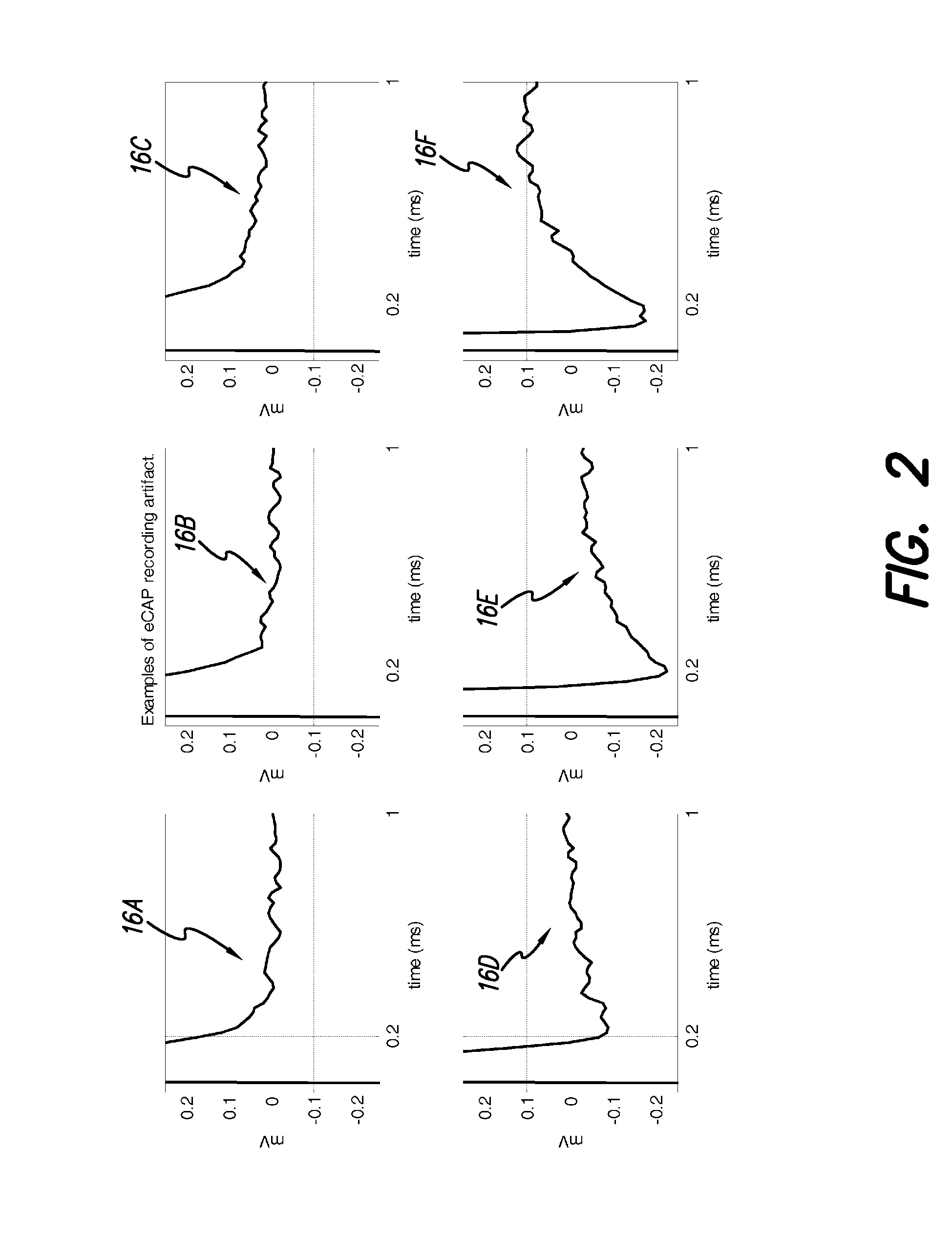
Removing Artifact in Evoked Compound Action Potential Recordings in Neural Stimulators
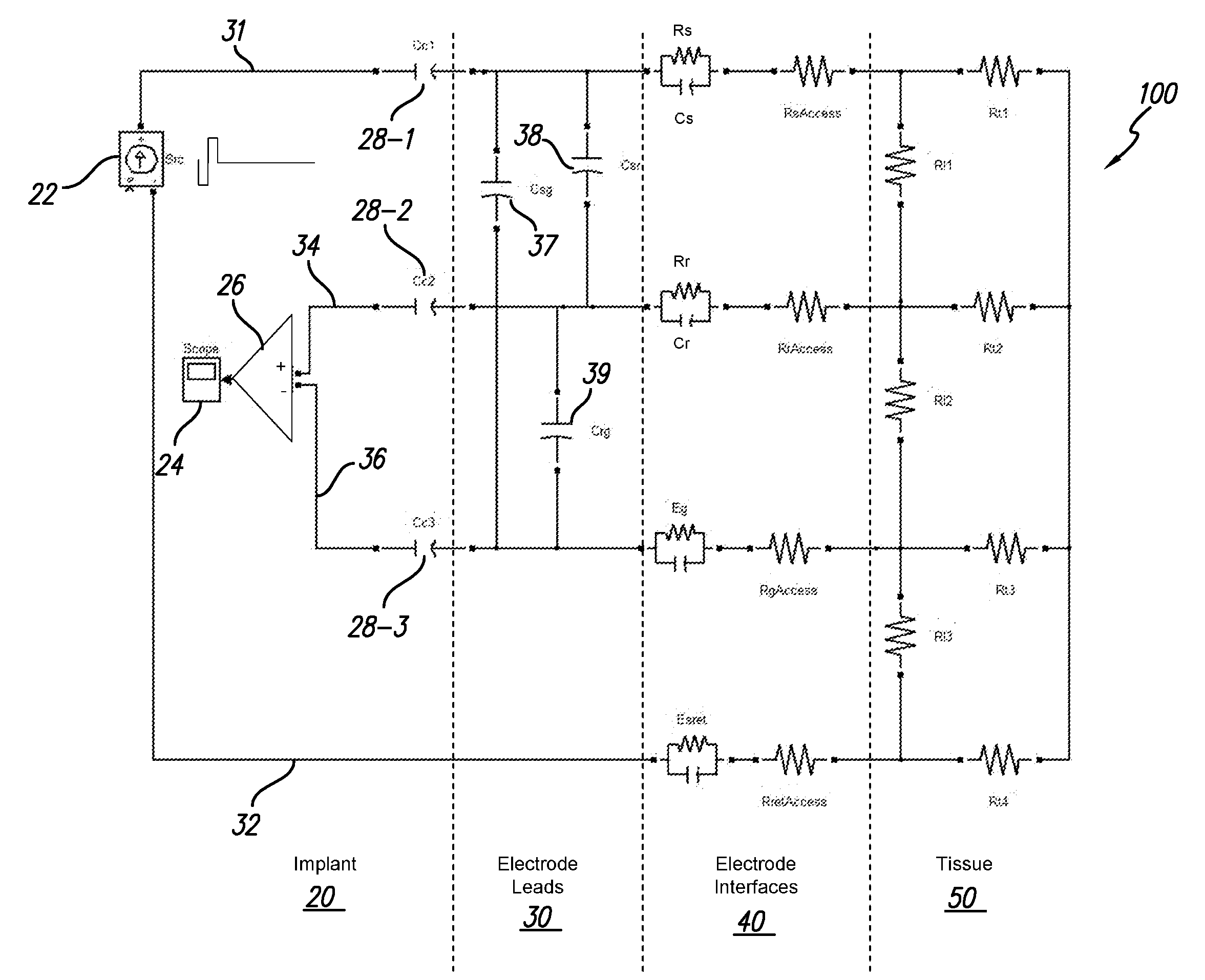
The accuracy of neural response recordings in neural stimulators, e.g., cochlear implants, is often degraded by a recording artifact. An idealized electrical-equivalent model of a neural stimulator is created to study, measure and compensate for artifact evoked compound action potential (eCAP). Using this model, the artifact is shown to occur even when the electrical components that make-up the neural stimulator are ideal. The model contains parasitic capacitances between the electrode wires. The model demonstrates that these small parasitic capacitances provide a current path during stimulation which can deposit charge on the electrode-tissue interfaces of the recording electrodes. The dissipation of this residual charge and the charge stored across the stimulating electrode is seen as the recording artifact. The proposed solution for eliminating the artifact problem is realized by utilizing a capacitive electrode material, e.g., TiO2, Ta2O5, or other dielectric coatings or films, instead of Faradaic electrode material, e.g., Platinum (Pt), Pt—Ir alloy or similar alloys, on the neural stimulator electrode lead.
Owner:ADVNACED BIONICS LLC
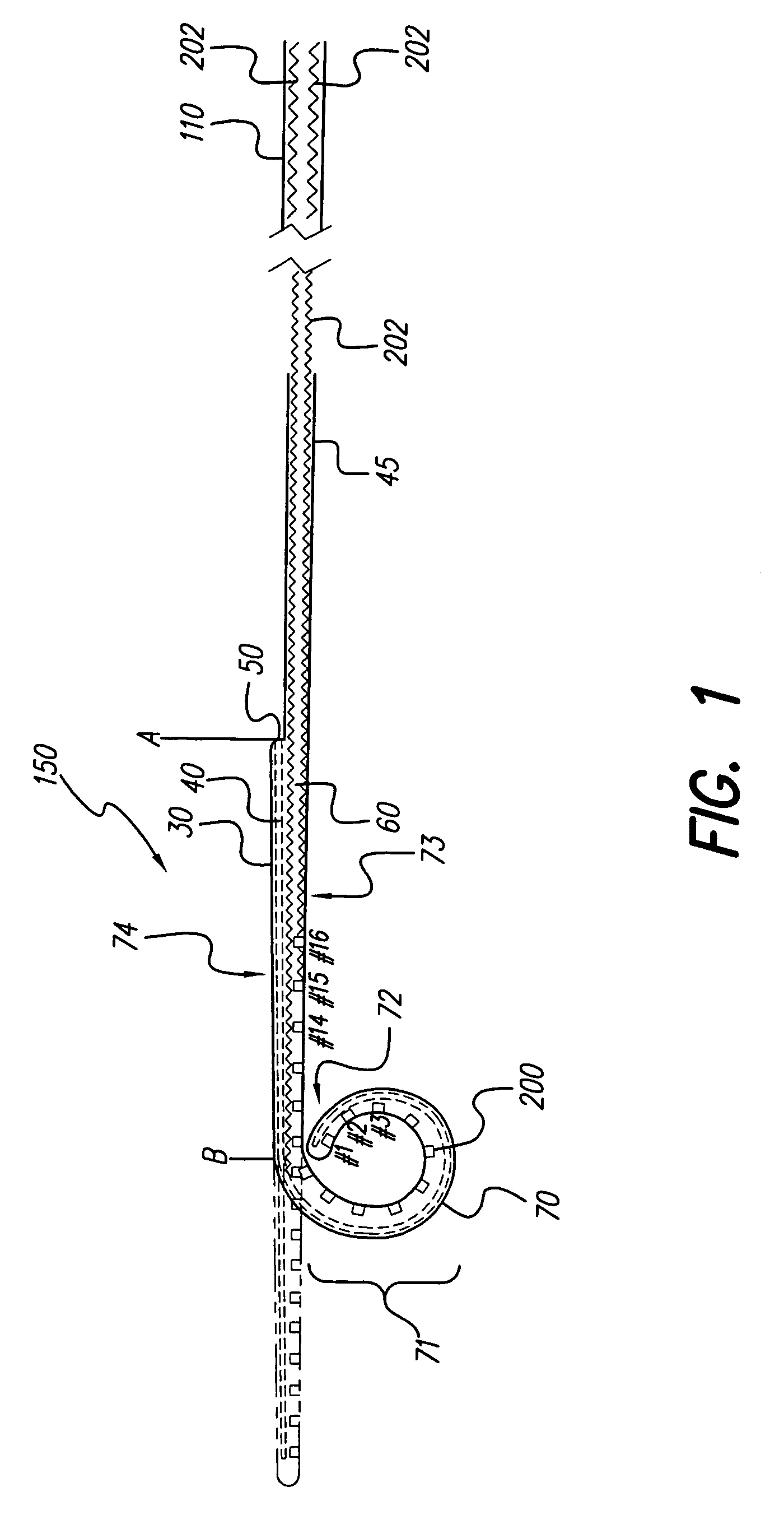
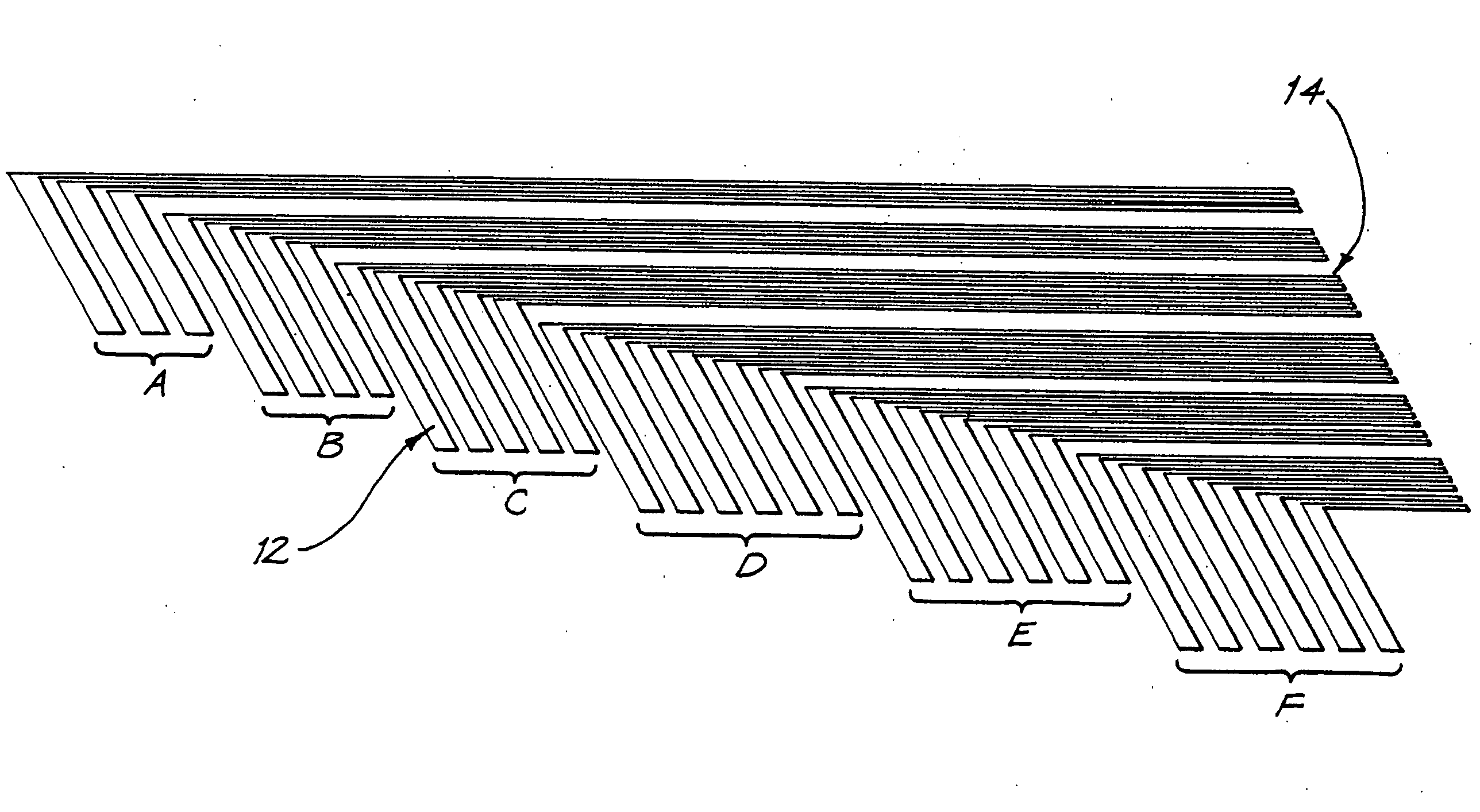
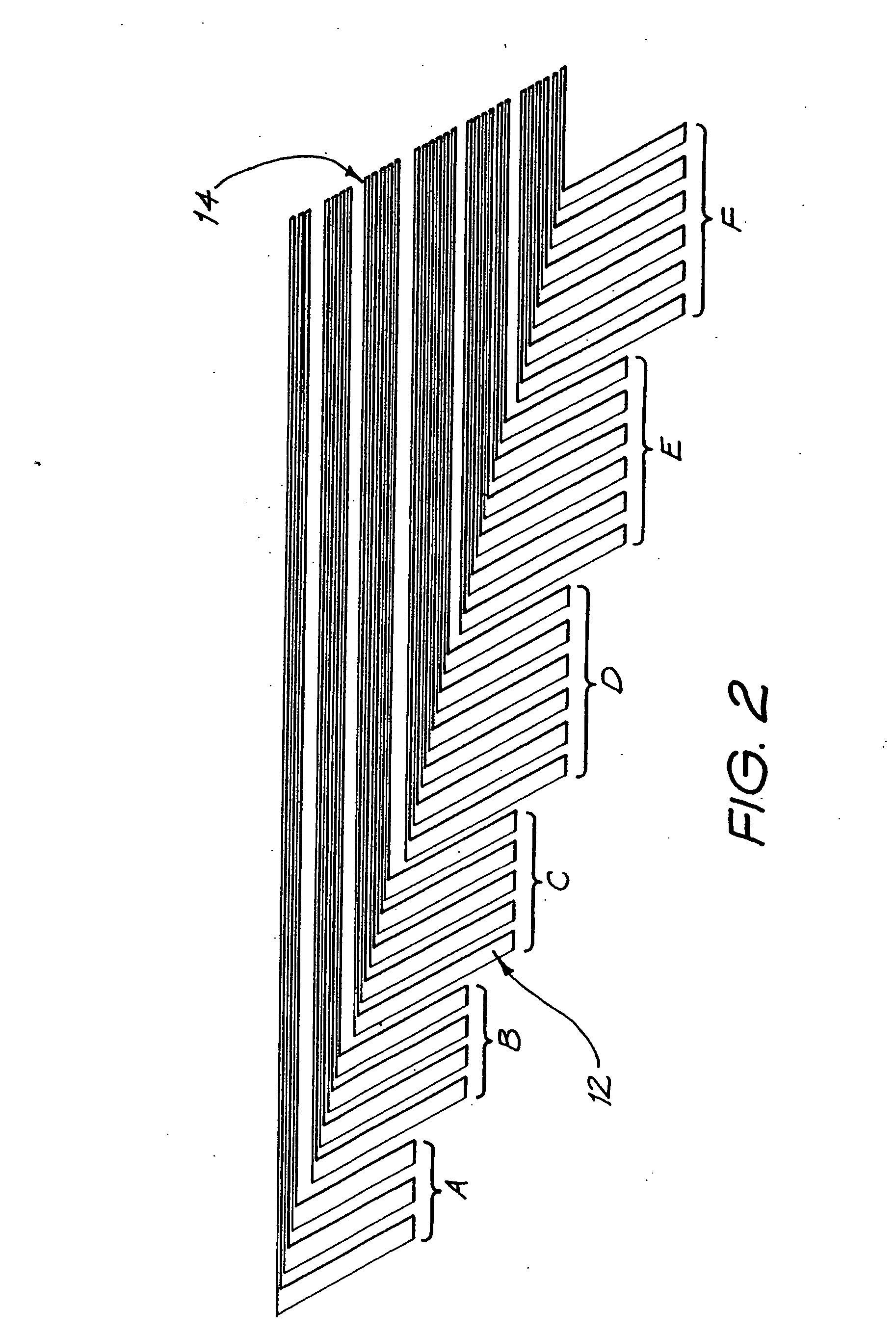
Combination stylet and straightening coating for a cochlear implant electrode array
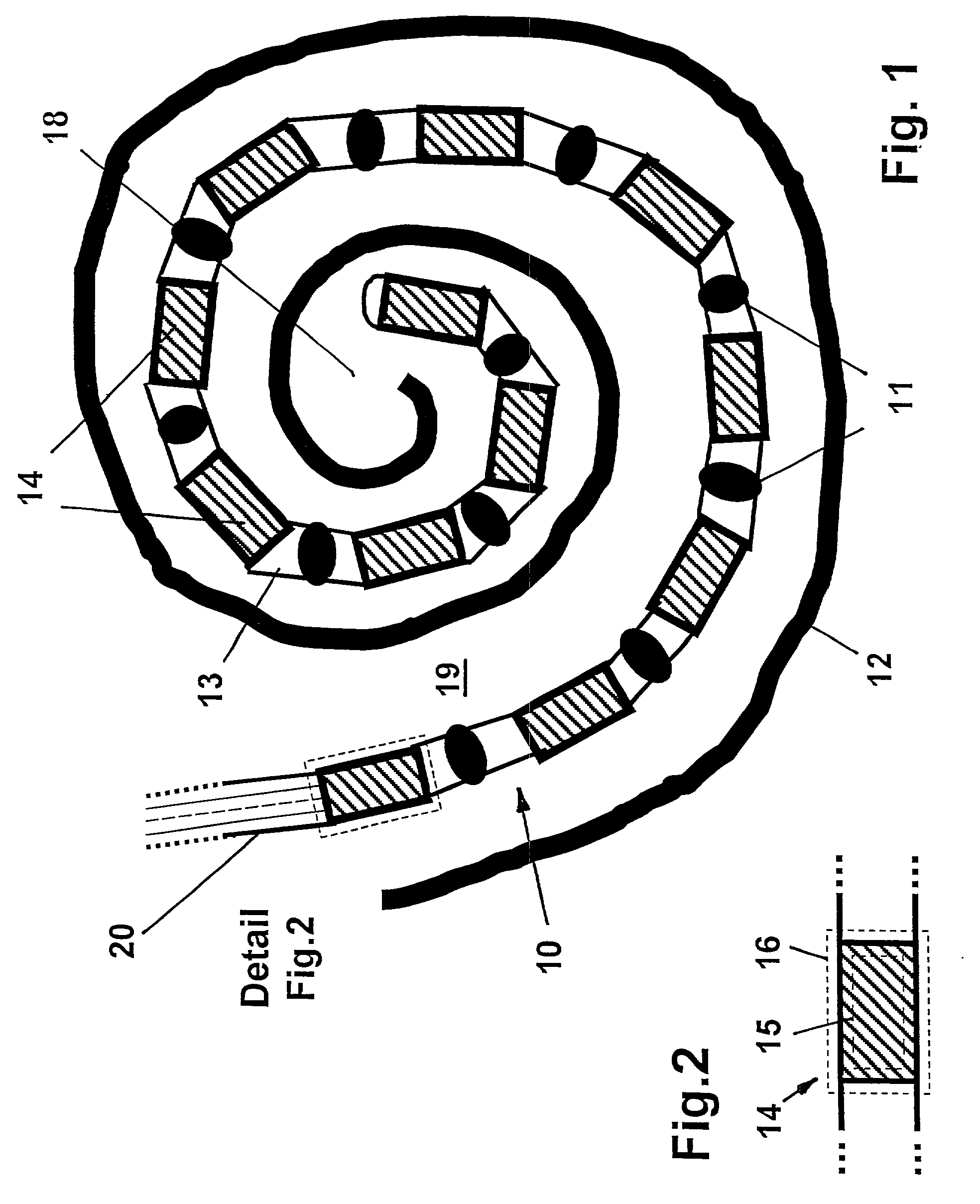
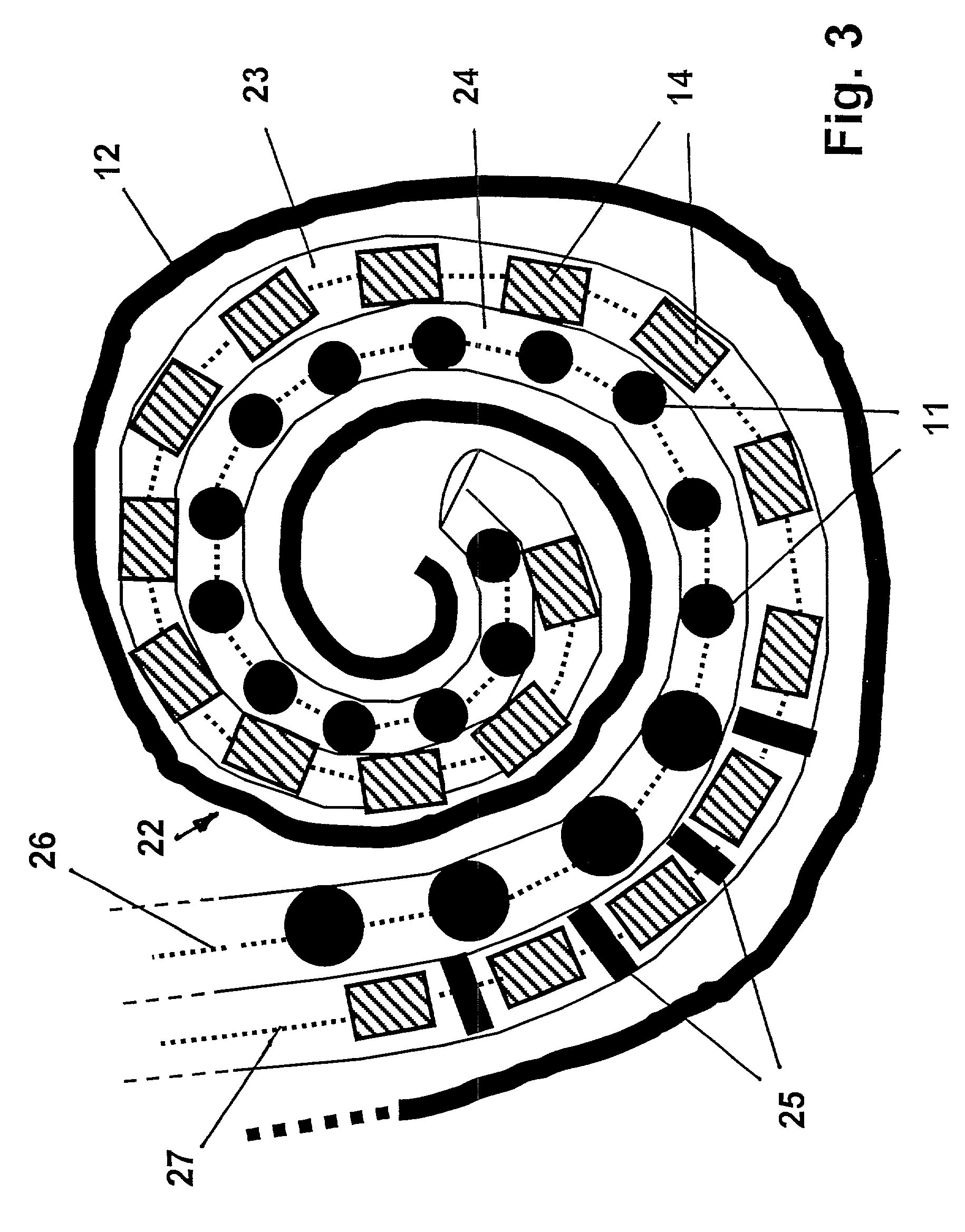
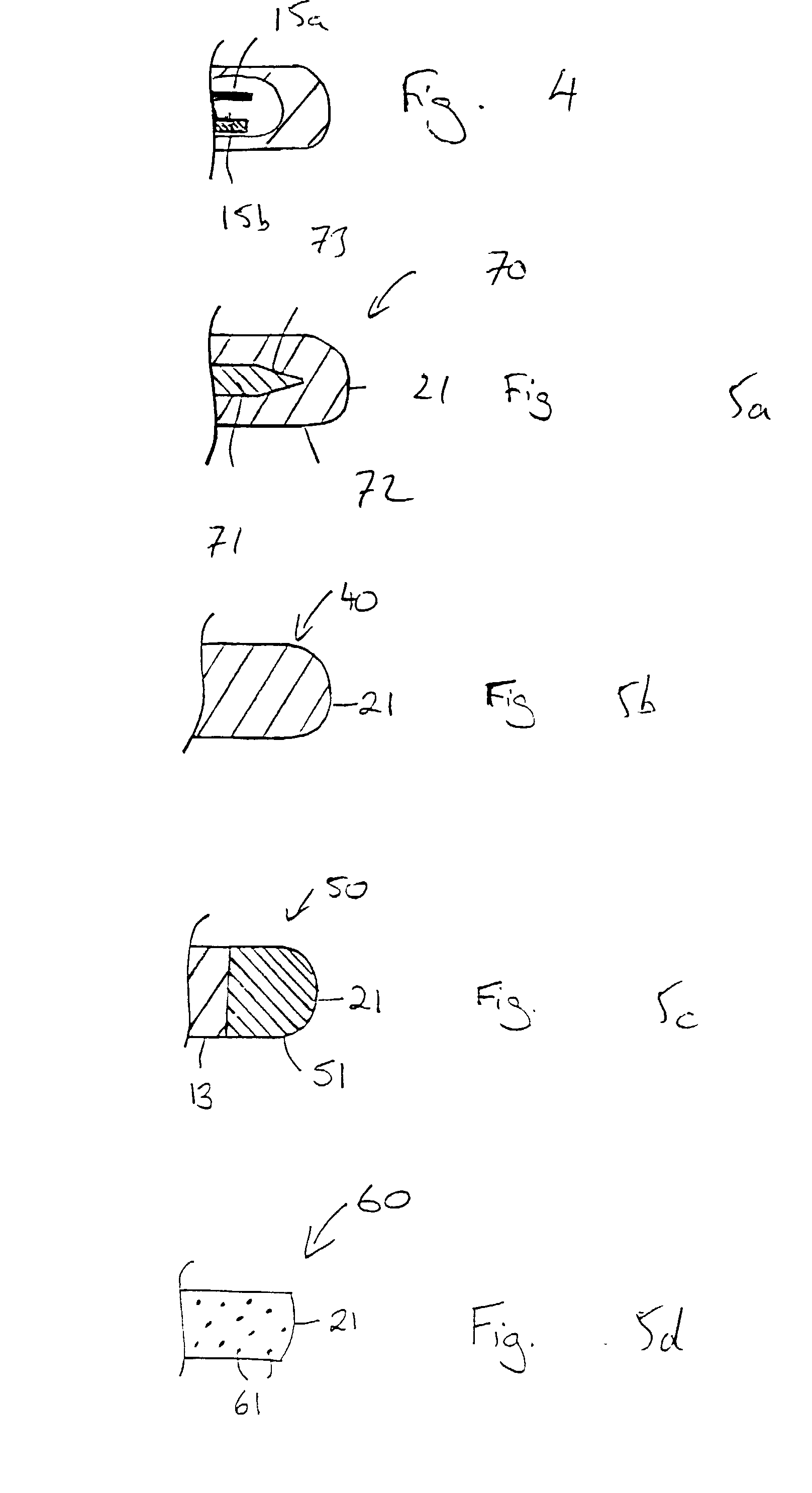
InactiveUS7146227B2Increase flexibilityIncrease in resilient flexibilityHead electrodesEar treatmentCochlear implantationElectrode array
A cochlear implant electrode assembly device (10) comprising an elongate electrode carrier member (11), a stiffening element (15), and a stiffening sheath (16) that at least partially envelops the elongate member (11). The member (11) is made of a resiliently flexible first material and has a plurality of electrodes (12) mounted thereon. The member (11) has a first configuration that allows it to be inserted into an implantee's cochlea (30). The member (11) also has a second configuration wherein the member is curved to match an inside surface of the cochlea (30), and at least one intermediate configuration between the first and second configurations. Both the stiffening element (15) and sheath (16) are made of a material that is relatively stiffer than the member (11). The stiffening element (15) and the stiffening sheath (16) in combination bias the elongate member (11) into the first configuration. If either the stiffening element (15) or the stiffening sheath (16) is removed or deactivated, the elongate member (11) adopts an intermediate configuration.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
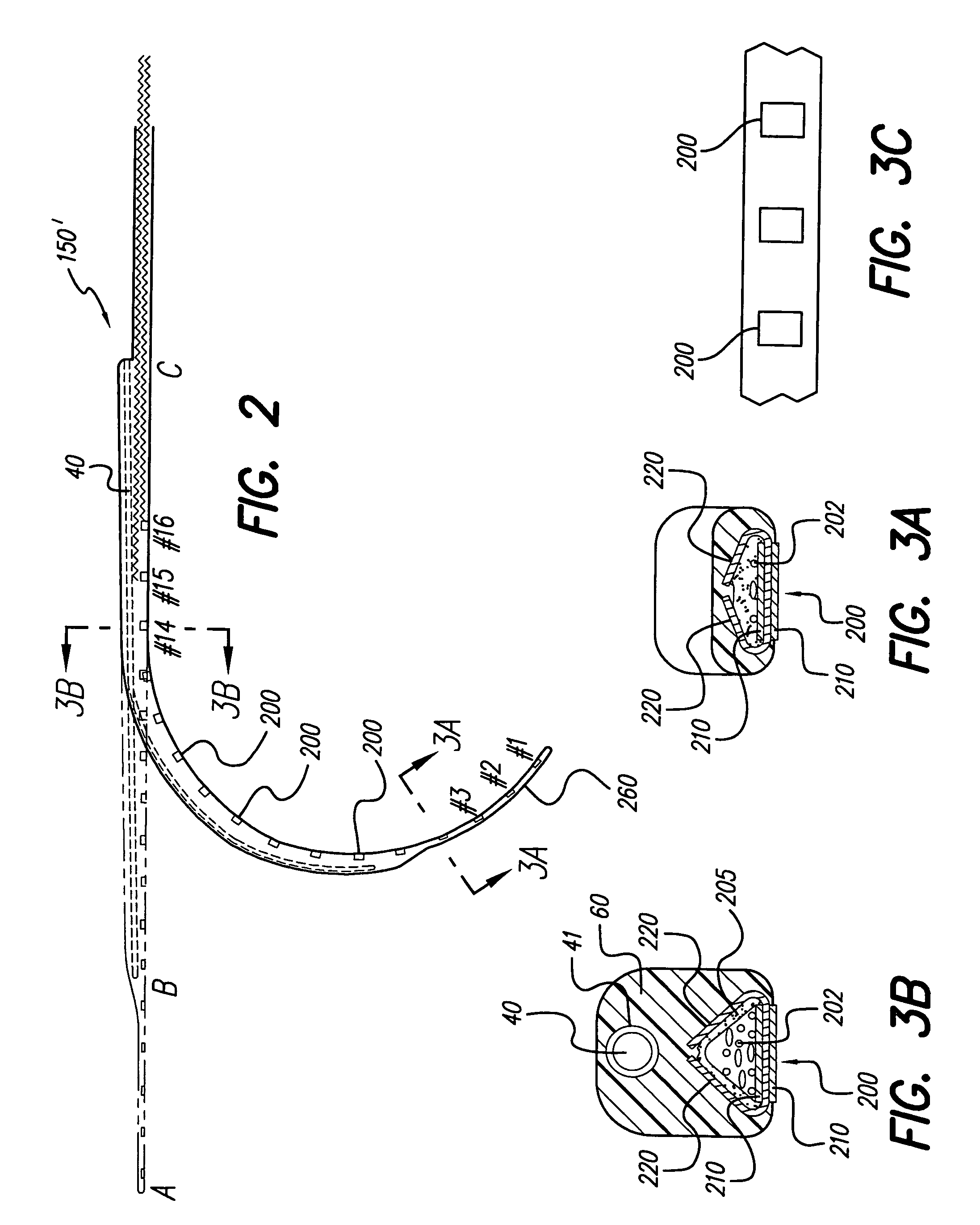
Double stylet insertion tool for a cochlear implant electrode array
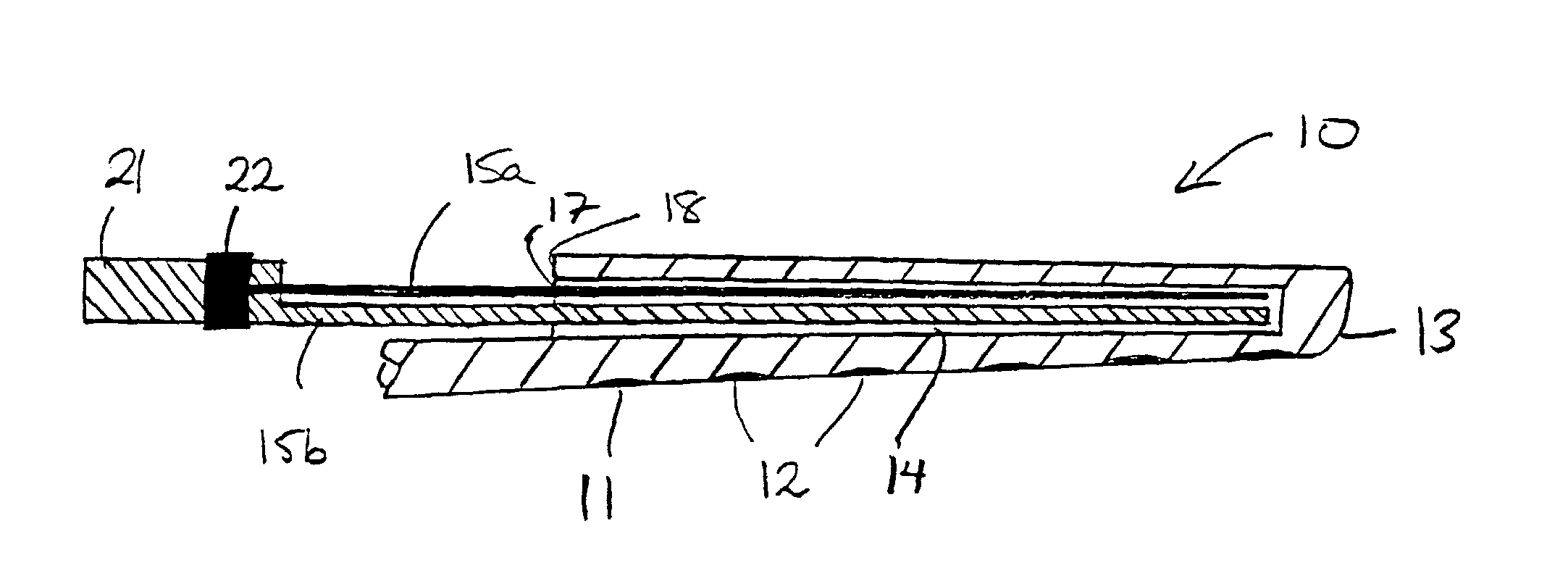
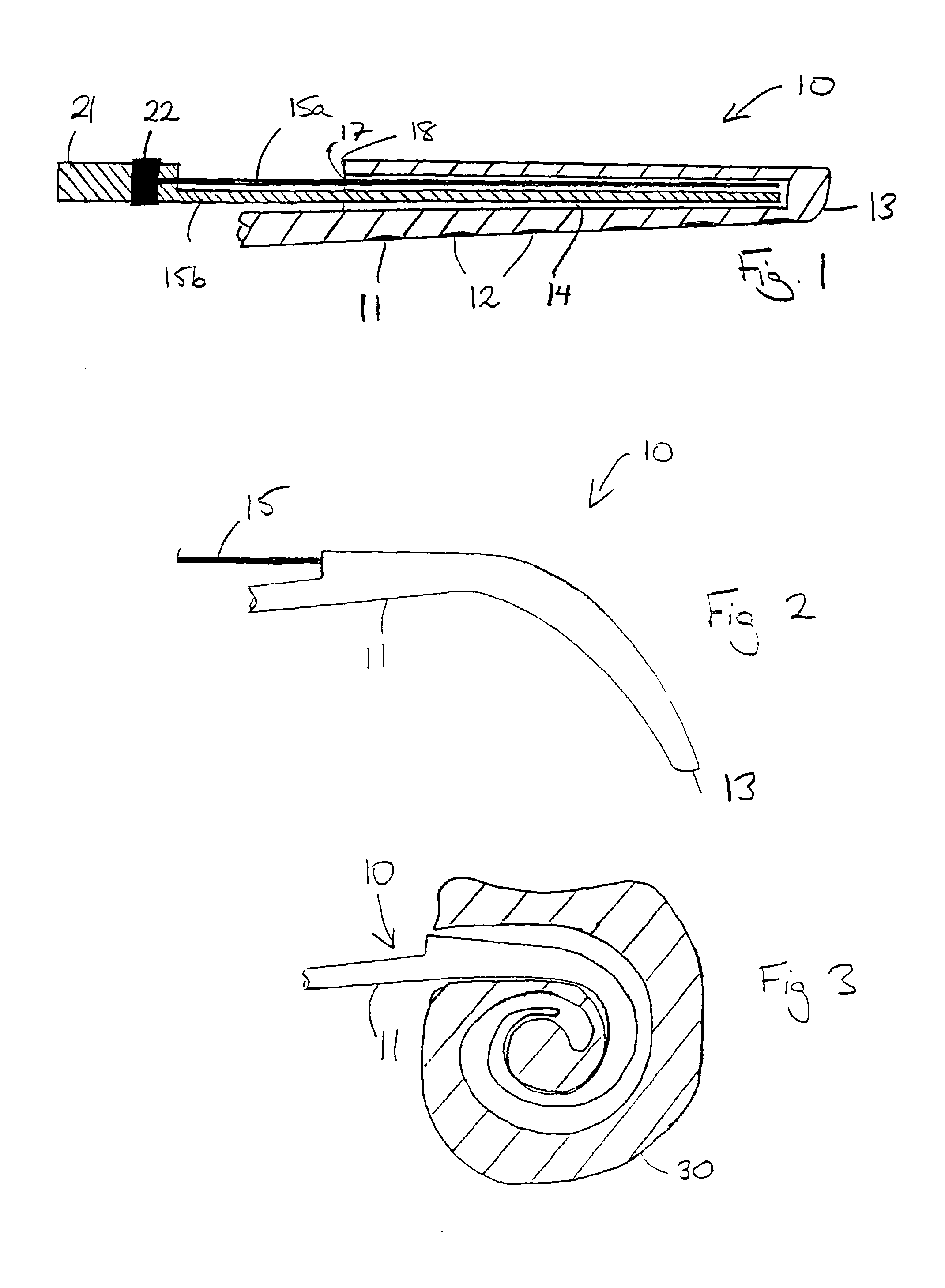
InactiveUS20030045921A1Increase flexibilityIncrease in resilient flexibilityHead electrodesEar treatmentCochlear implantationElectrode array
A cochlear implant electrode assembly device (10) comprising an elongate electrode carrier member (11), a first stiffening element (15a), and a second stiffening element (15b). The carrier member (11) is made of a resiliently flexible first material and has a plurality of electrodes (12) mounted thereon. The carrier member (11) has a first configuration selected to allow it to be inserted into an implantee's cochlea (30), a second configuration wherein it is curved in shape to match a surface of the cochlea (30), and at least one intermediate configuration between the first and second configurations. Both the first and second stiffening elements (15a, 15b) are made of a material relatively stiffer than said the material and in combination bias the elongate member into the first configuration. If either the first stiffening element (15a) or the second stiffening element (15b) are removed, the elongate member (11) adopts the at least one intermediate configuration.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
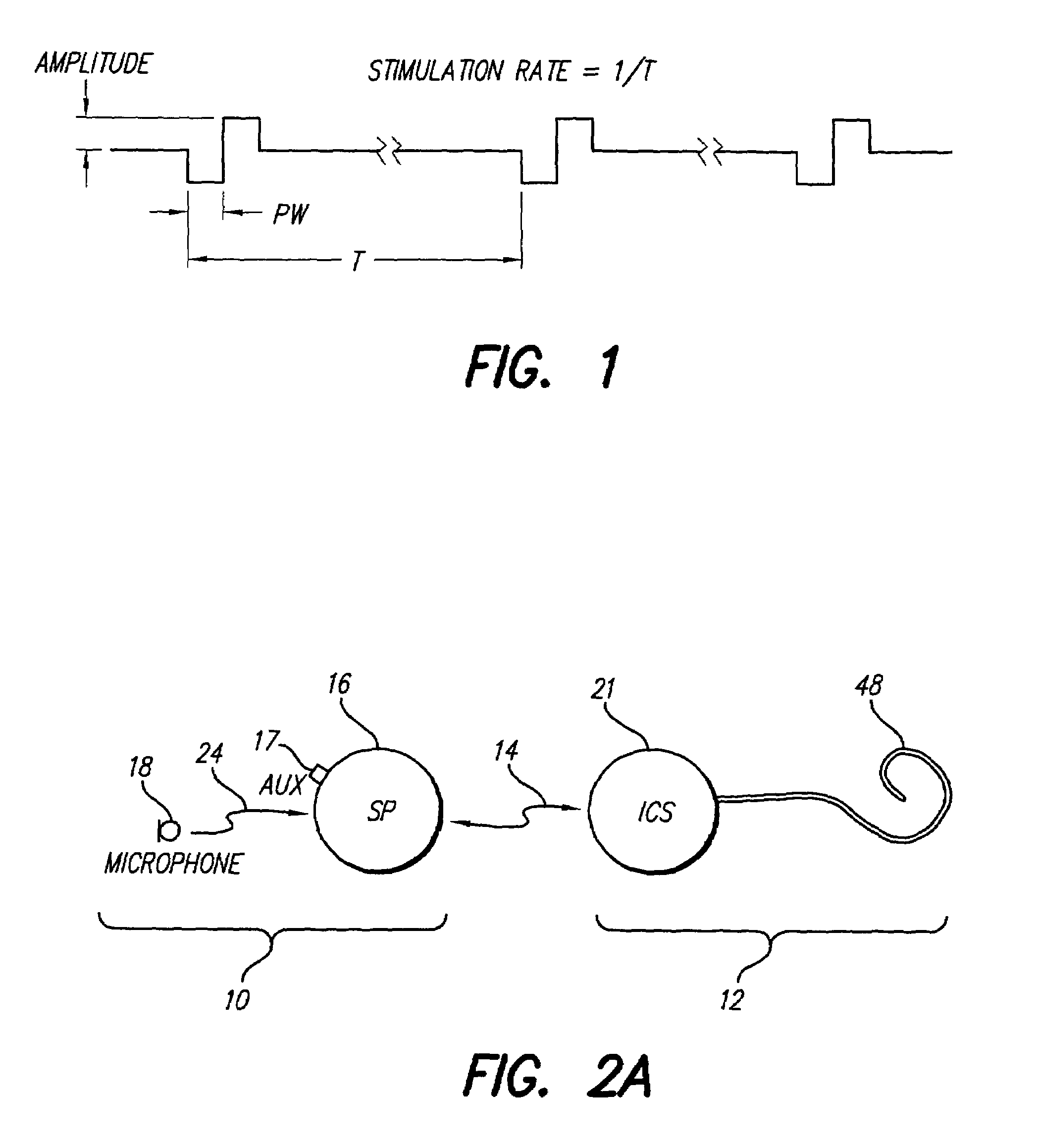
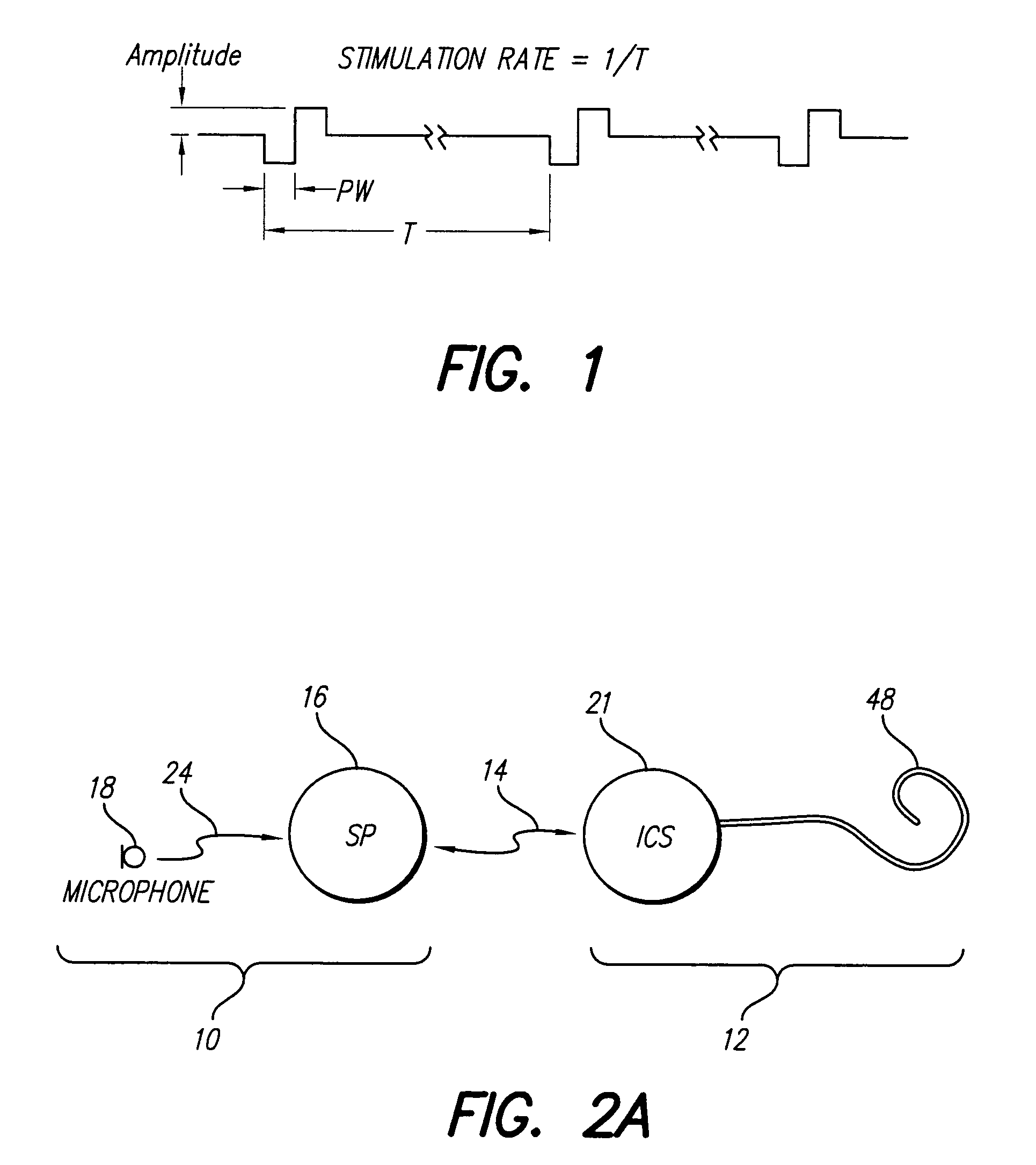
Multiple pulse stimulation
InactiveUS6064913AEasy to produceElectrotherapyArtificial respirationCochlear implantationTime domain response
A stimulation strategy for cochlear implants seeks to approximate the time domain response of a patient's neural system to electrical stimuli, to the time domain response of a normal hearing person to a corresponding acoustic stimulus. The strategy is designed to induce in the neurons of a patient a time domain response to an acoustic signal which is similar to, or approximates the time domain response induced by the normal processes in a healthy person. Various implementations are disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE
Peak-derived timing stimulation strategy for a multi-channel cochlear implant
ActiveUS7310558B2Improve time accuracyTemporal information can be goodElectrotherapyEar treatmentBand-pass filterCochlear implantation
A binaural cochlear implant system, including two intracochlear implants adapted for implantation in the cochleas of a user, each cochlear implant utilising a speech processing strategy wherein the electrical stimuli are matched to the relative timing of the relevant audio signals as detected at each ear, such that the interaural time delays between the audio signals at each ear are substantially preserved in electrical stimuli at each ear.The processing strategy comprises band pass filtering the audio signal, determining the peaks in, and intensity of, each band, prioritising and placing each peak in a buffer in time slots corresponding to the relative timing of each peak. The buffer output forms the basis for stimulus instructions.
Owner:HEAR WORKS PTY LTD
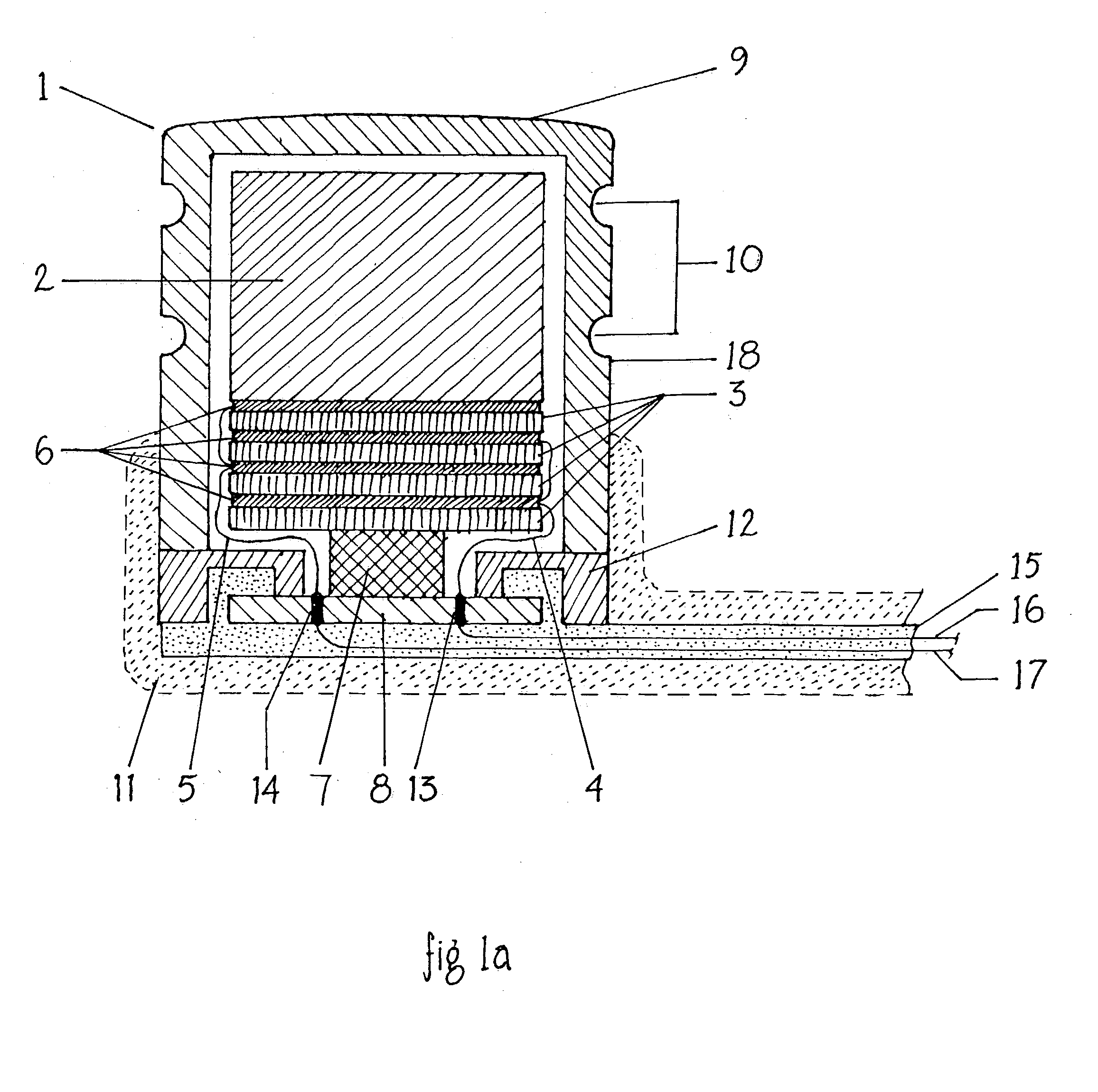
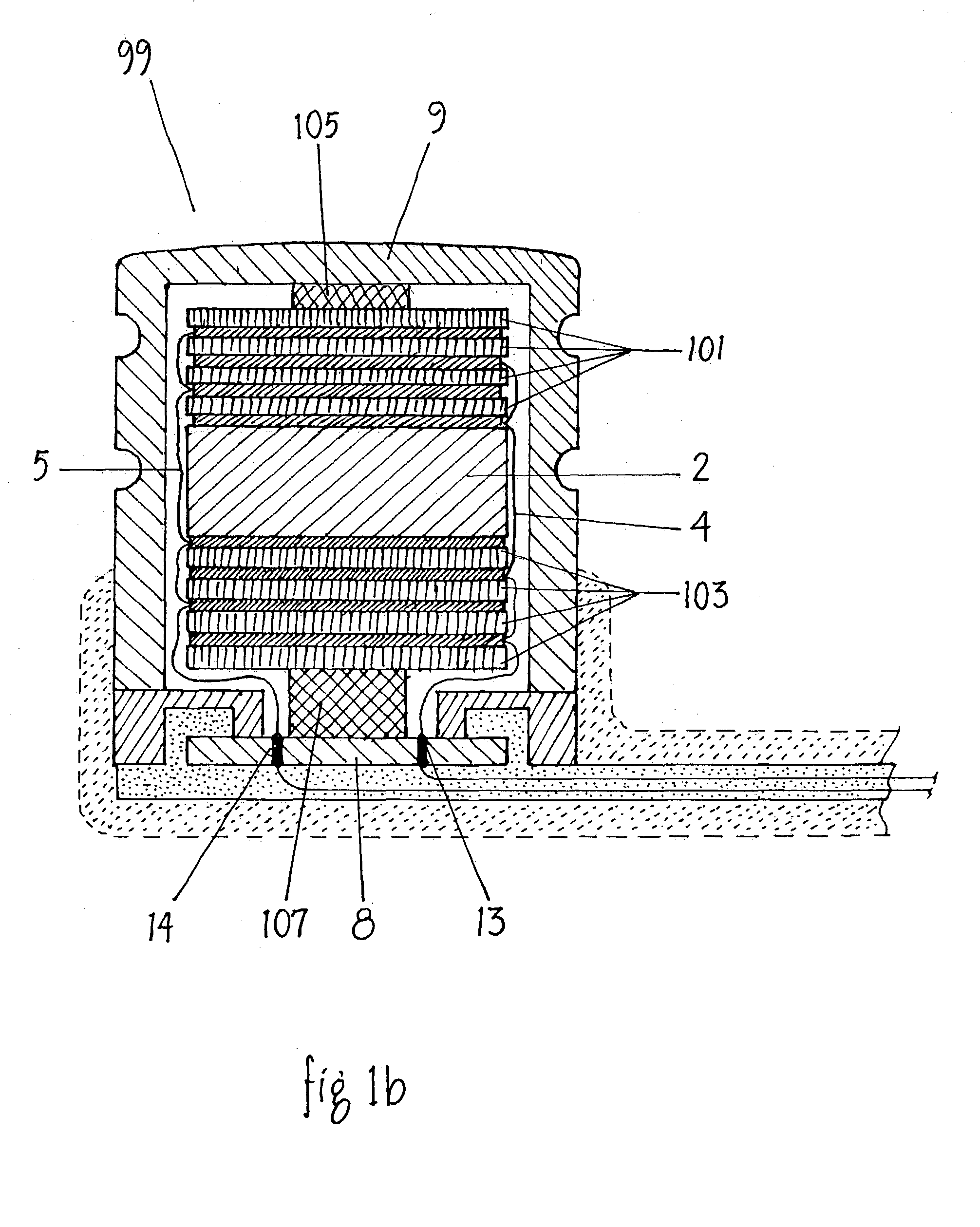
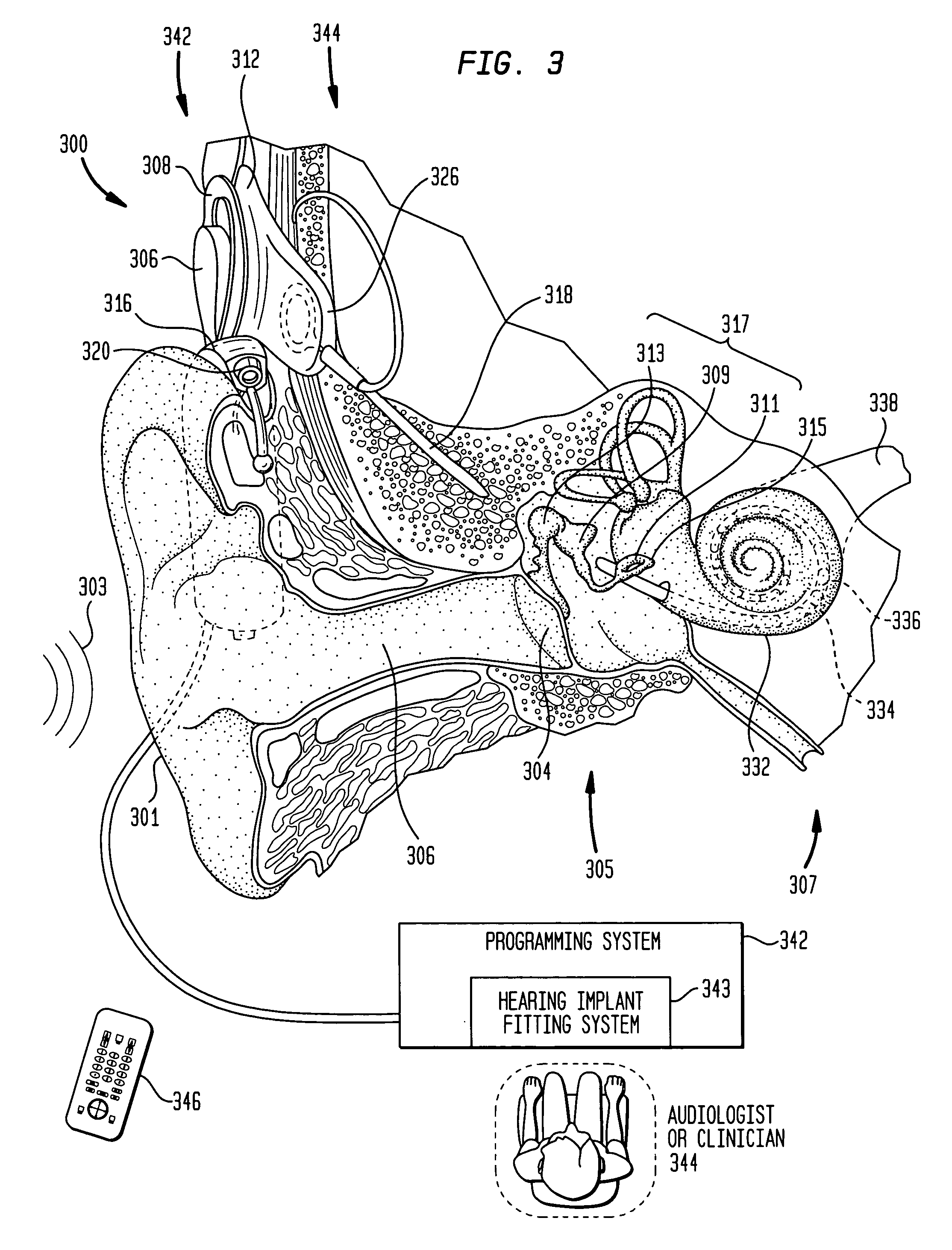
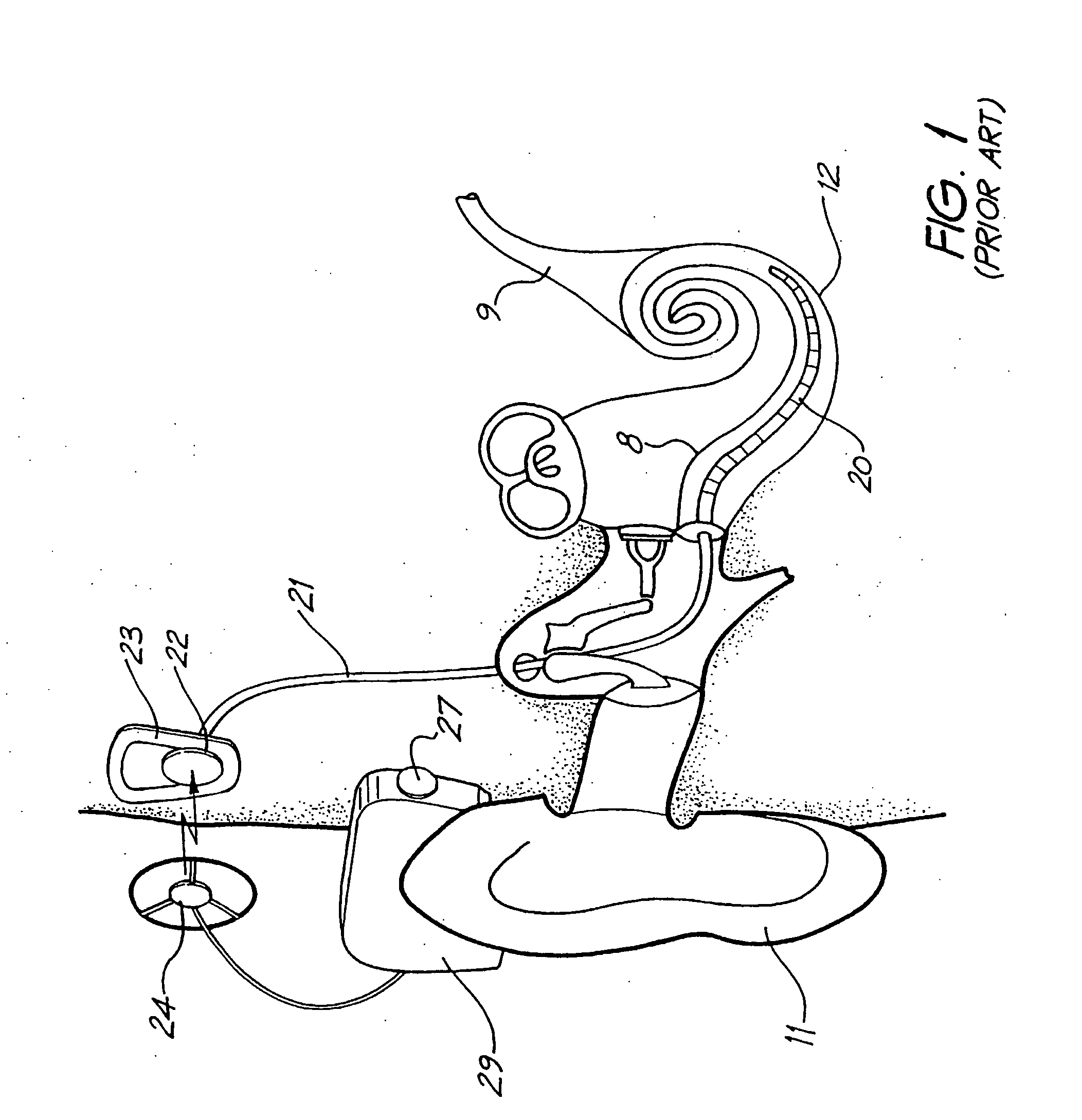
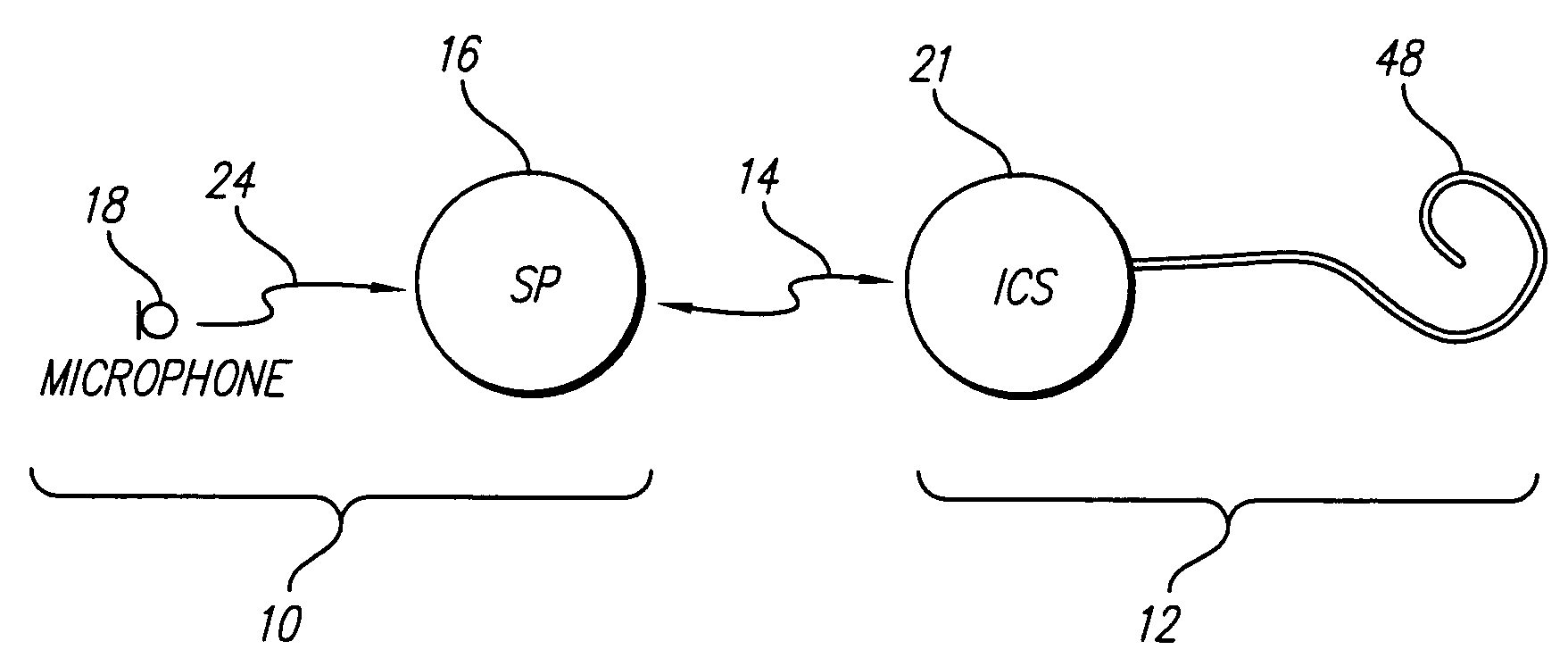
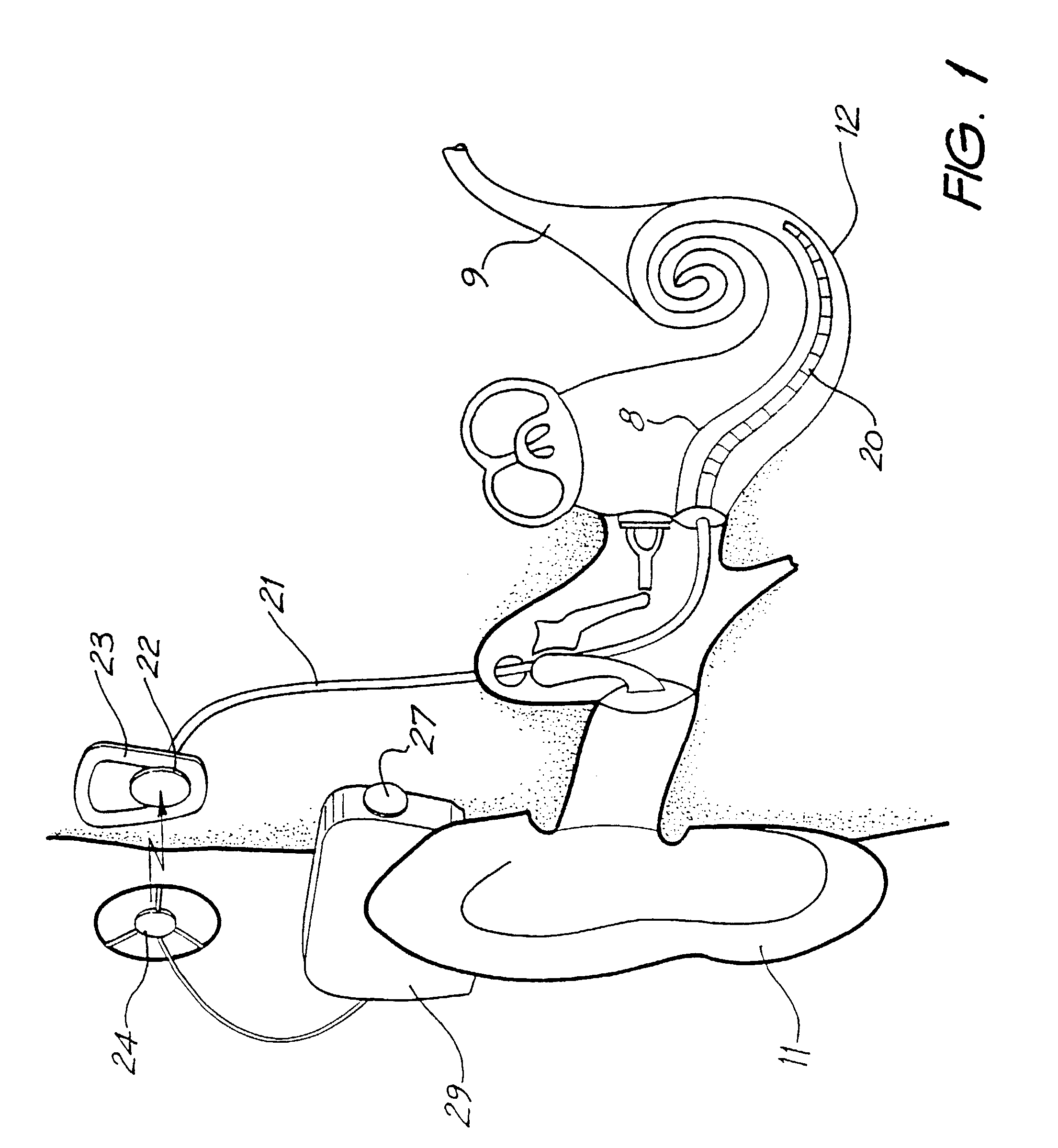
Cochlear implant
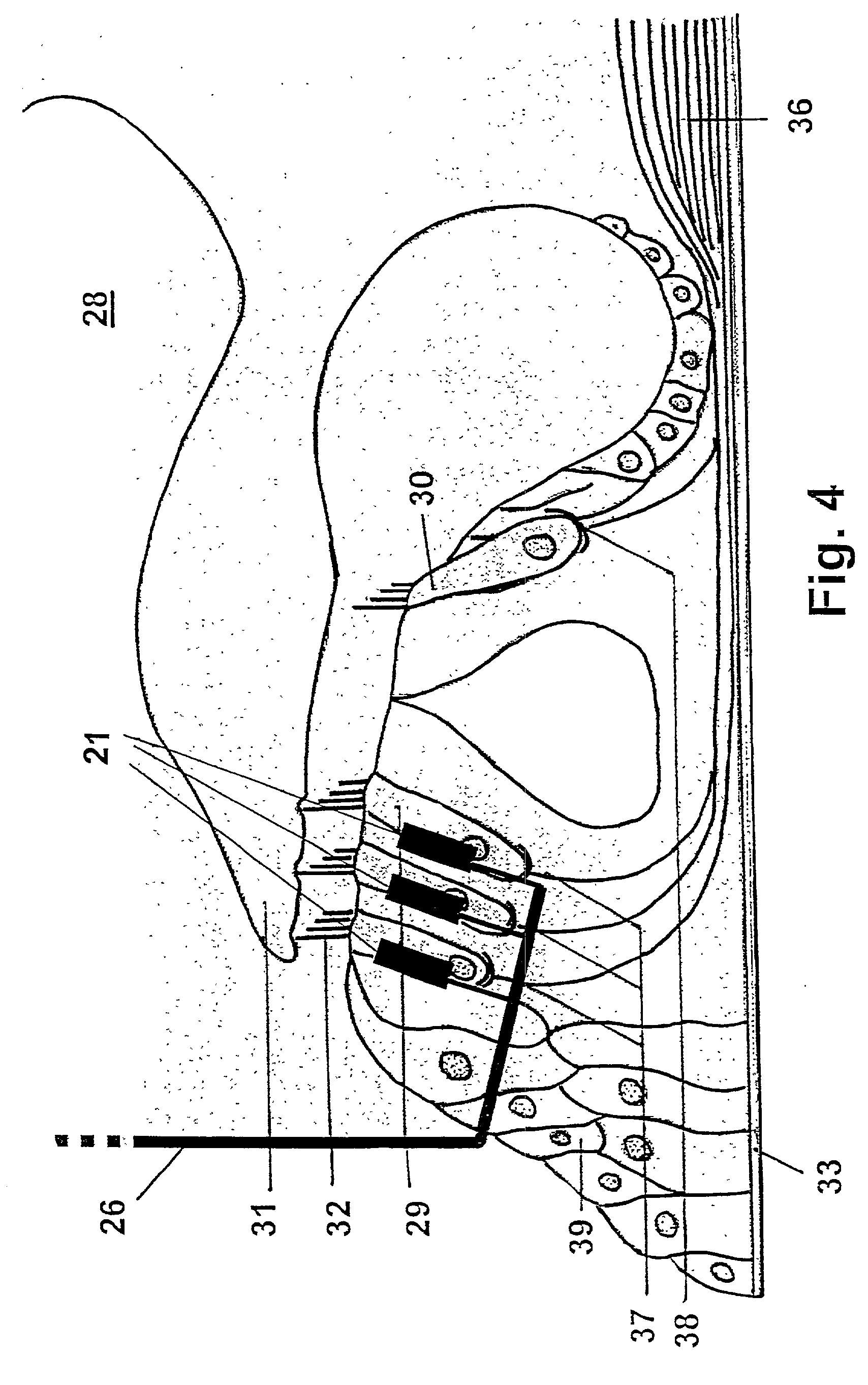
A totally implantable cochlear implant system forming a single implantable unit (40). The unit (40) has an implantable power source (43) that provides the power requirements of the implantable unit (40). The unit (40) also has an on-board microphone (42) that detects external sounds, such as speech, and outputs acoustic signals representative of the detected sounds. The unit further includes speech processor circuitry (44) that directly receives the acoustic signals from the microphone (42) and converts the signals into stimulation signals representative of the detected sounds. An electrode array (20) suitable for insertion of the cochlea (12) of an implantee receives the stimulation signals and transmits electrical stimulations to the implantee'auditory nerve (9).
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Implantable conducting lead
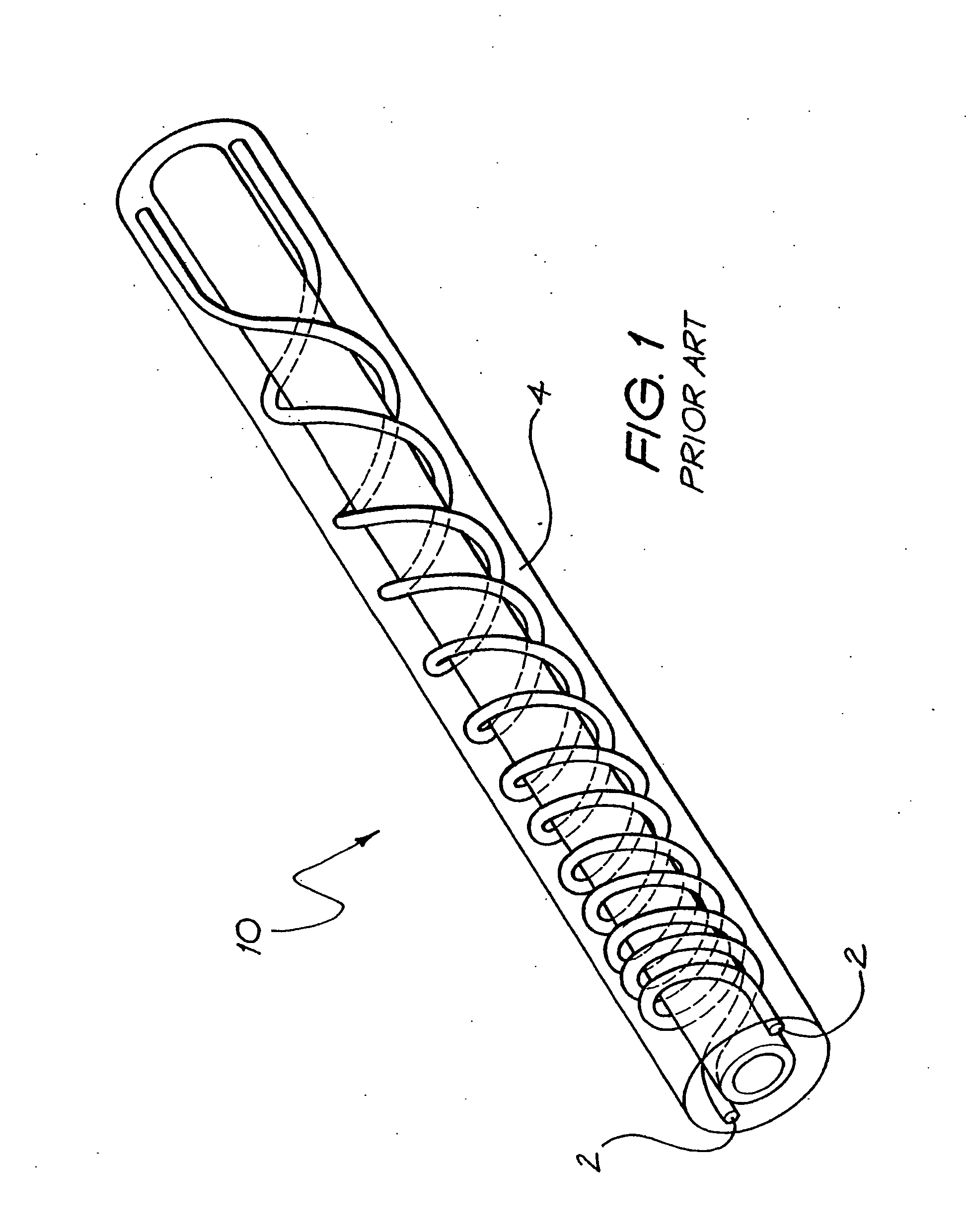
InactiveUS20060206185A1Increase flexibilityMinimize forceHead electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringElectrical conductorCochlear implantation
An electrically conducting lead (20) that can used in the body for electrical stimulations applications, such as a cochlear implant. The lead comprises a body of relatively electrically insulative material (41) having a relatively electrically conductive element (18) extending therethrough in a wound arrangement. The electrically conductive element (18) is comprised of a plurality of layers of electrical conductors (14). The conductive element (18) is disposed in the lead such that the longitudinal extent of each of the electrical conductors (14) is the same.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
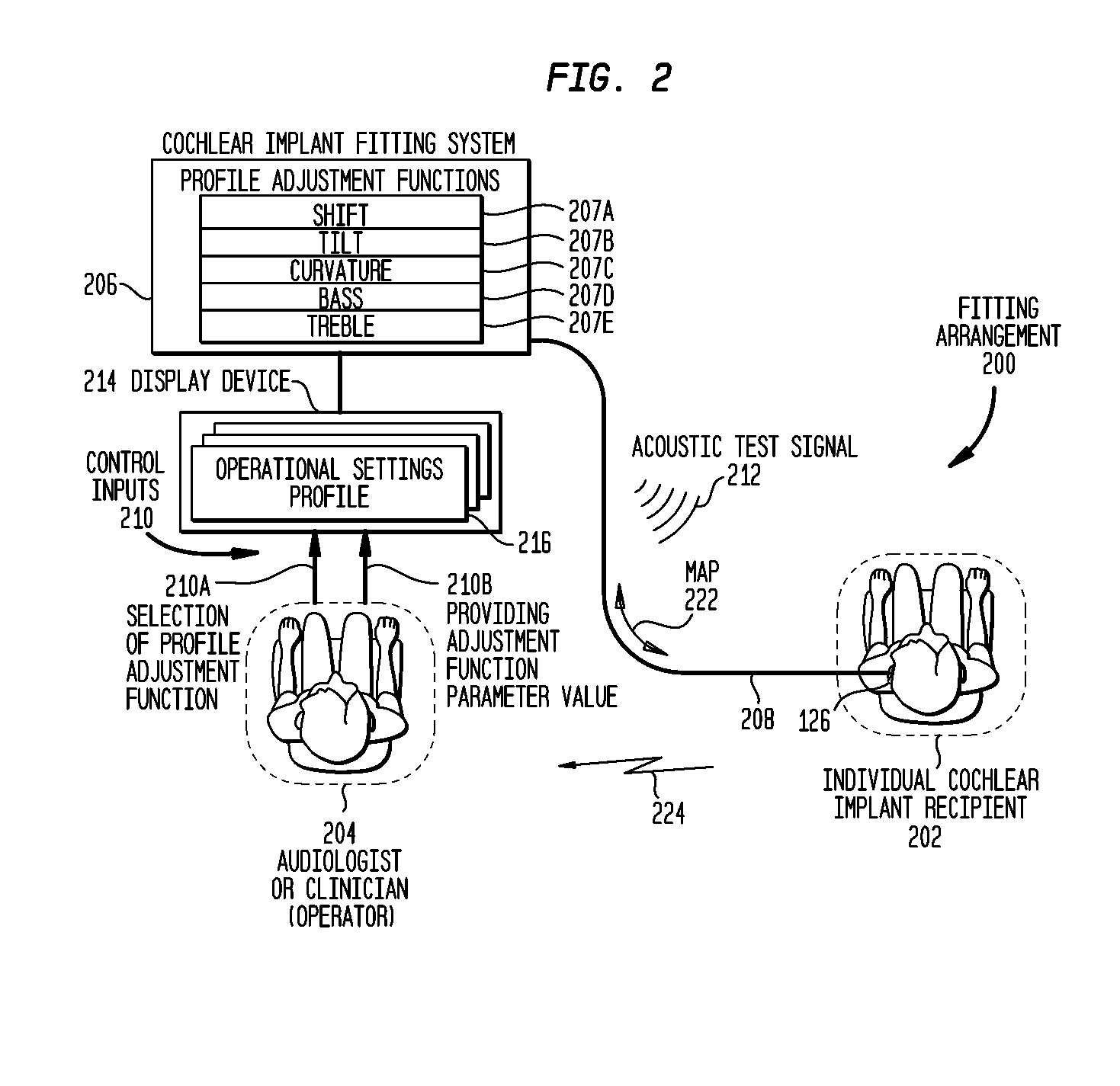
Perception-based parametric fitting of a prosthetic hearing device
According to one aspect of the present invention, there is provided a method of adjusting an established initial operational settings profile, the profile having two or more operational setting values for a speech processor of a recipient's cochlear implant, comprising: setting one or more profile adjustment functions with one or more function parameters; and modifying concurrently said two or more operational setting values in said operational settings profile using each of said set profile adjustment functions.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com