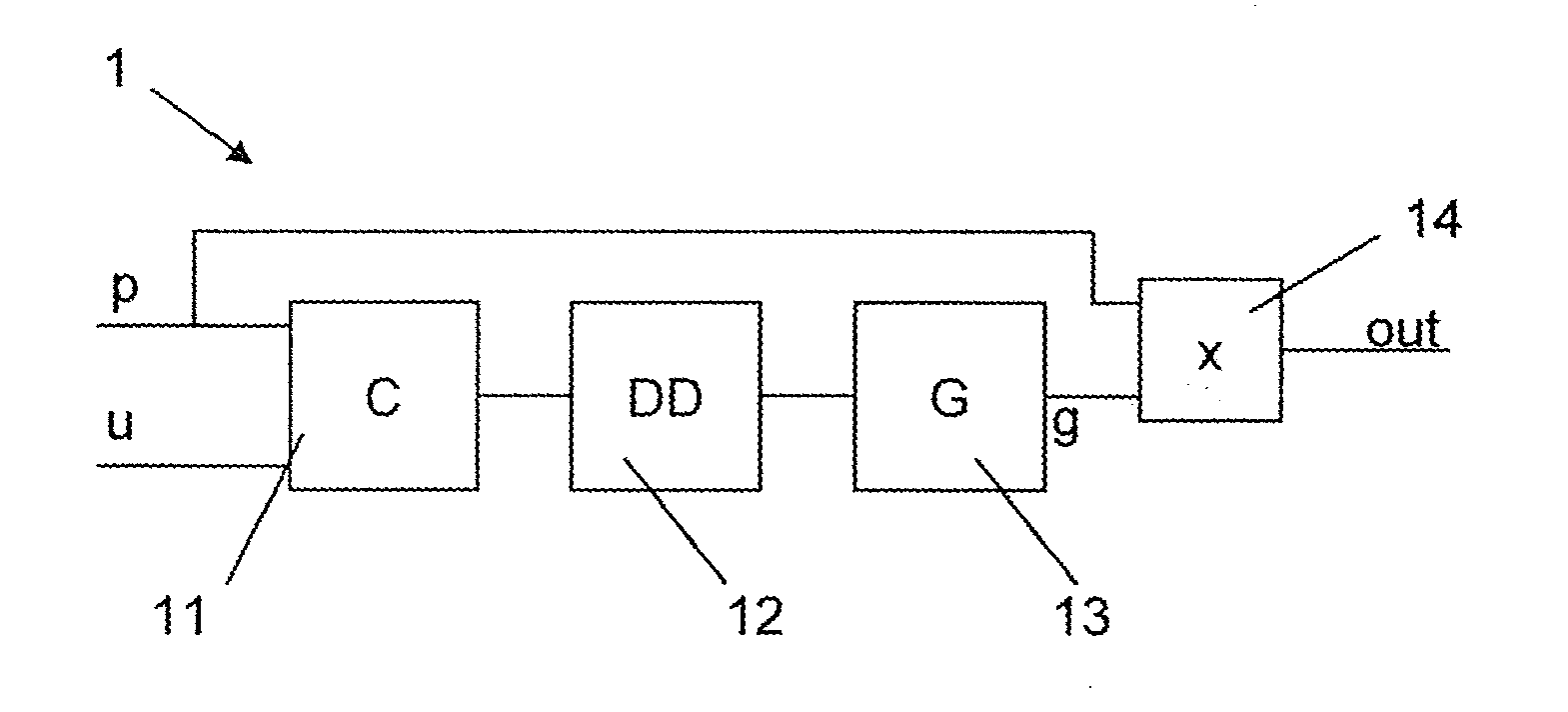
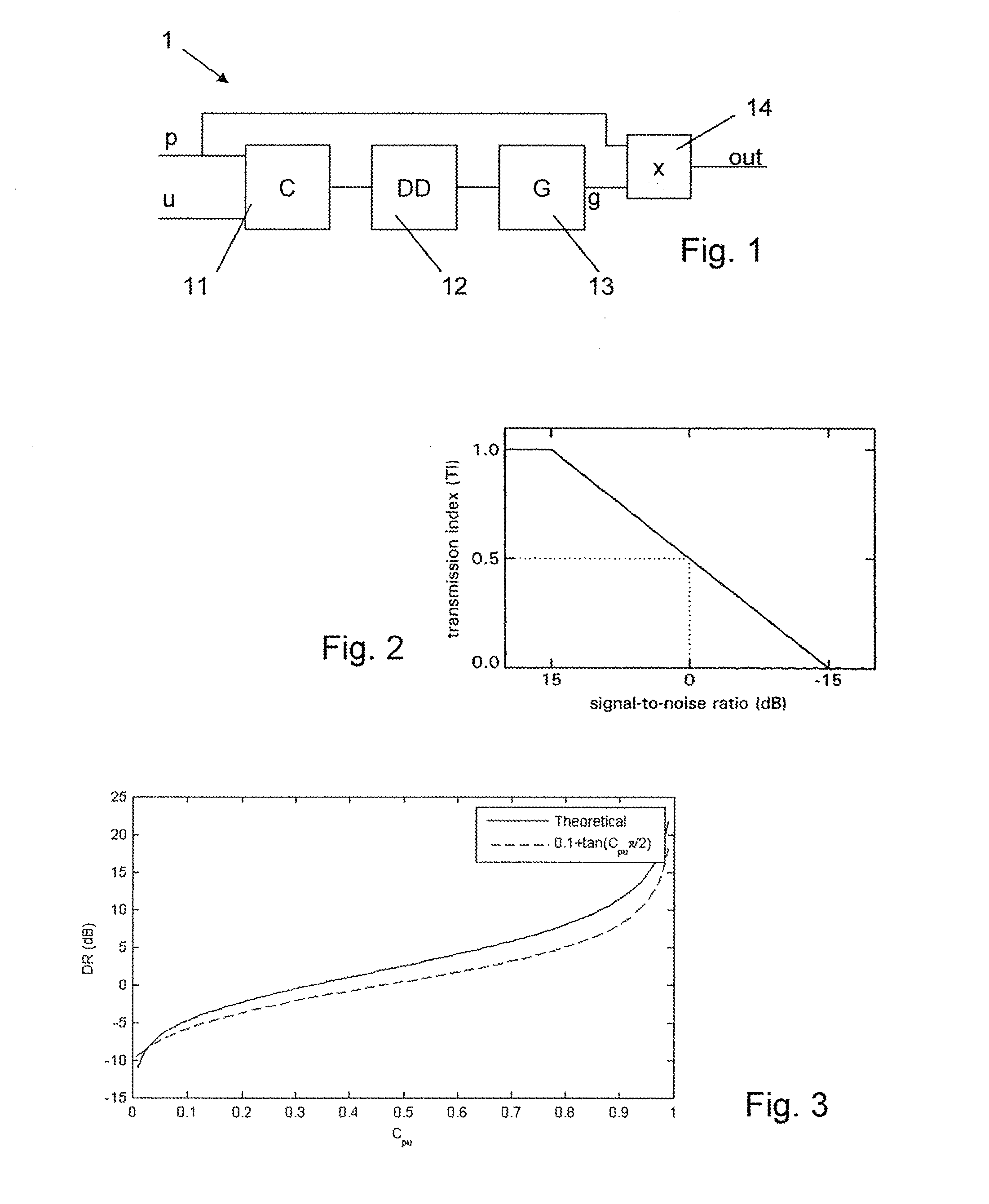
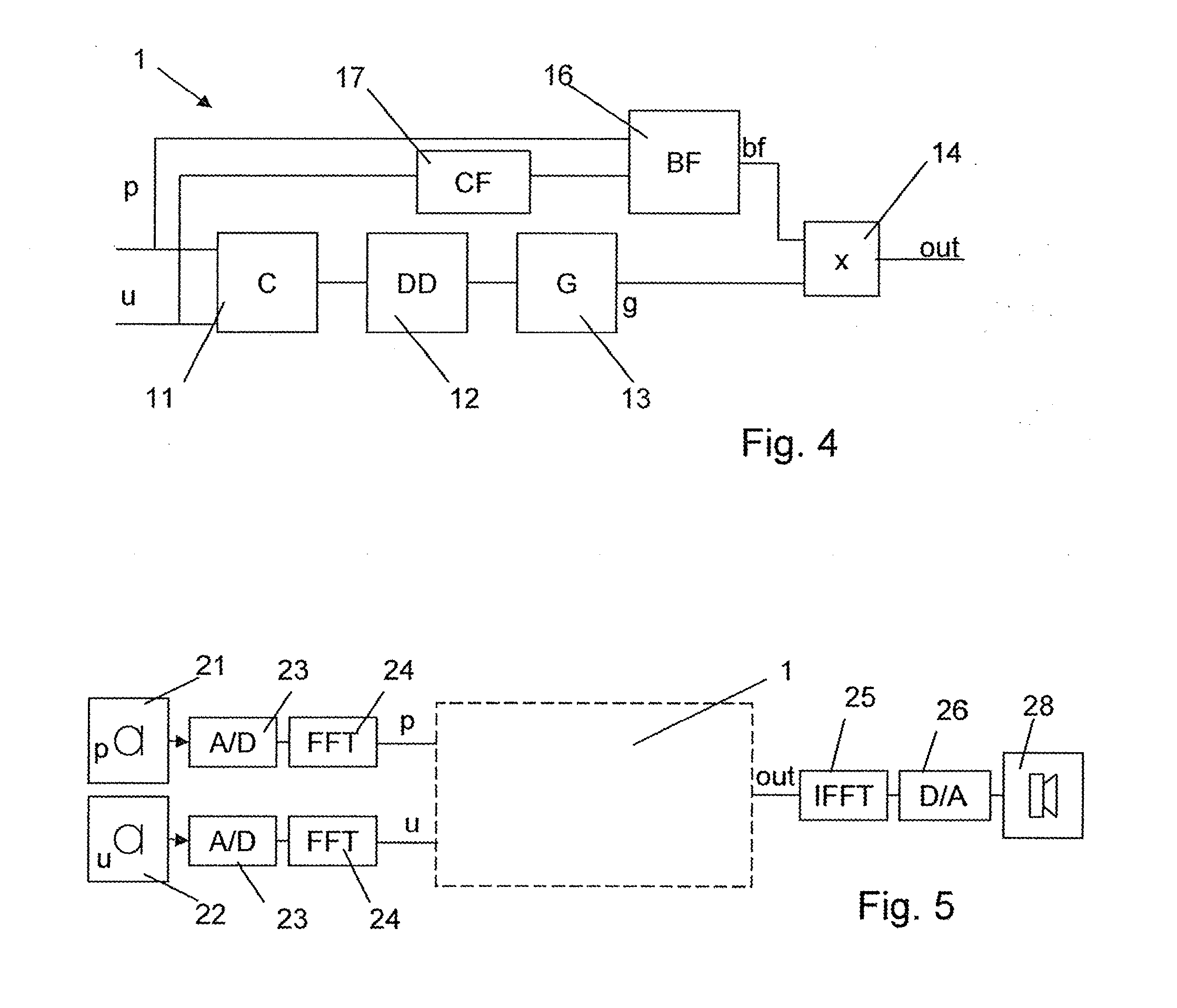
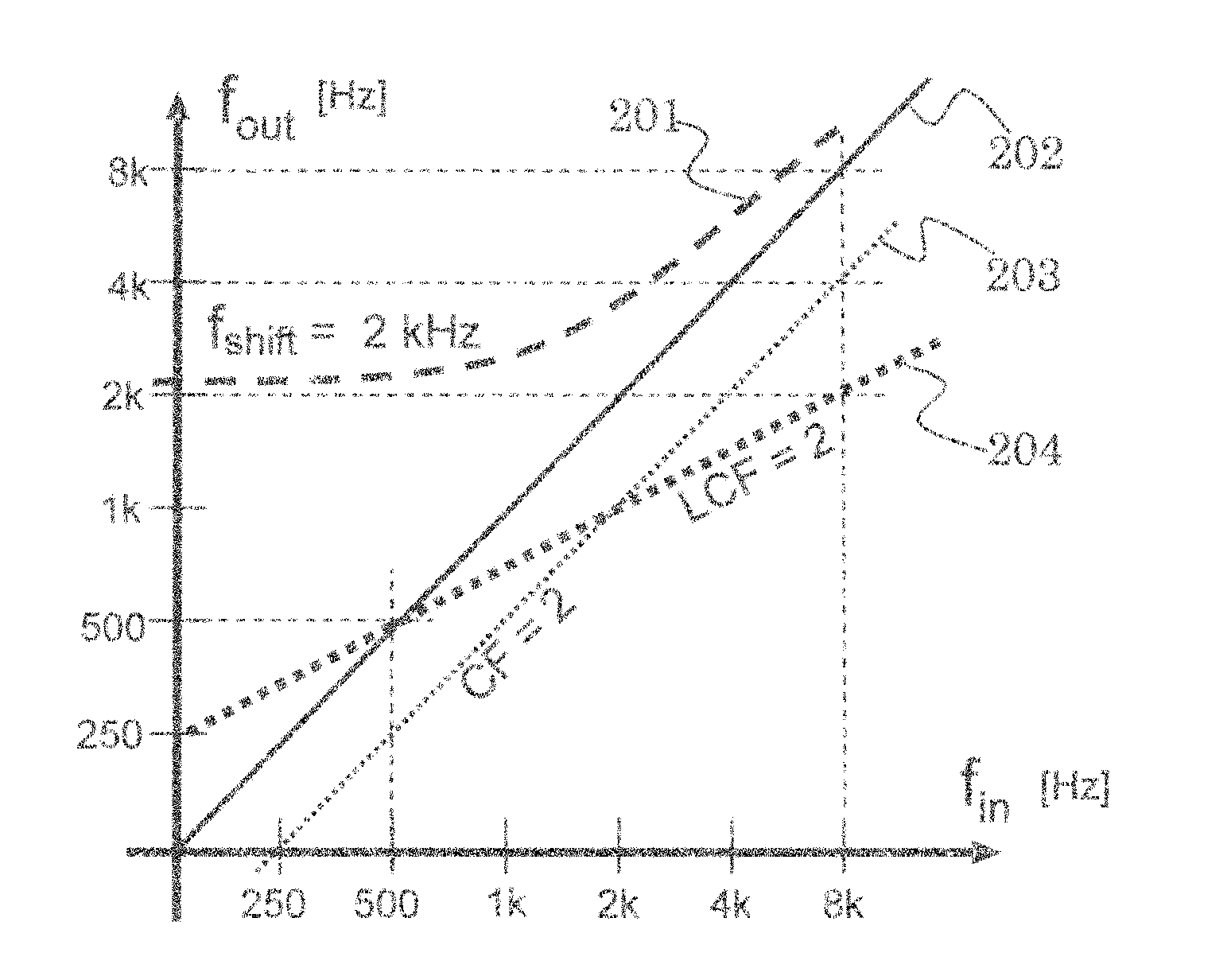
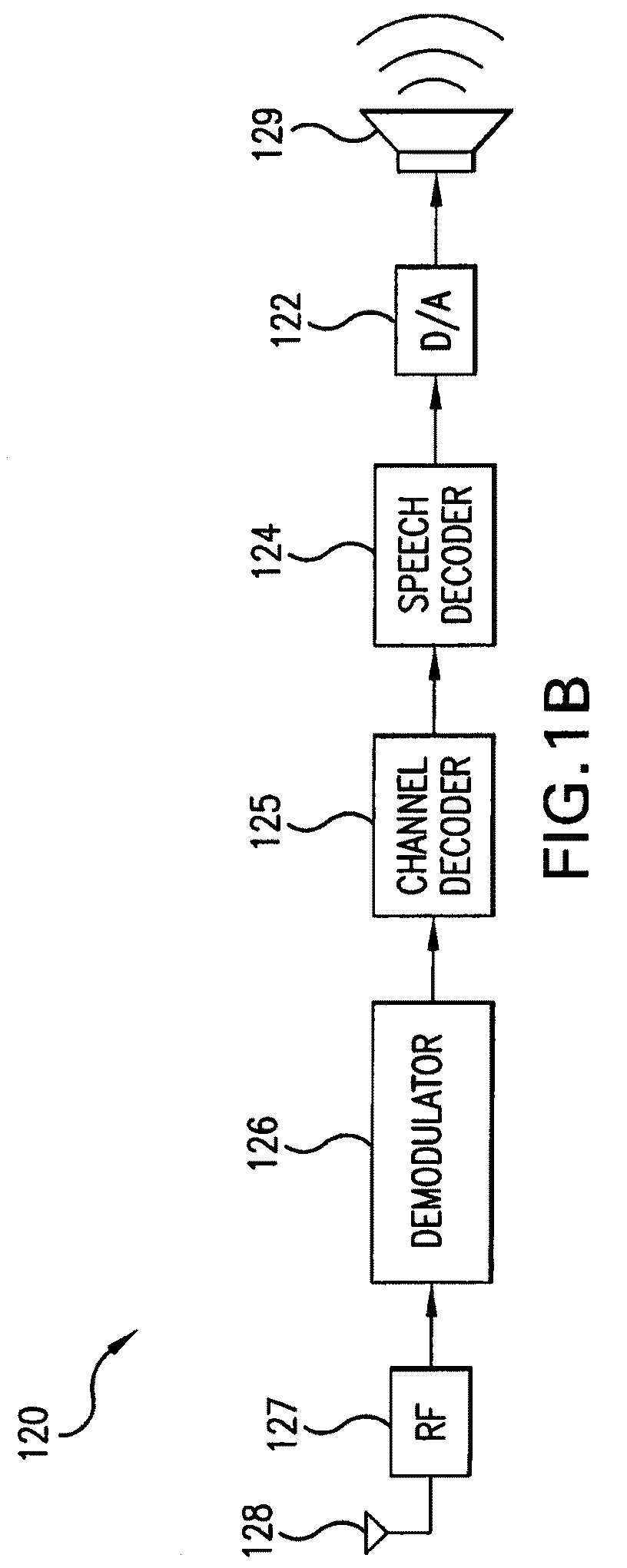
Patents
Literature
126results about How to "Improve speech clarity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Enhancing speech intelligibility using variable-rate time-scale modification
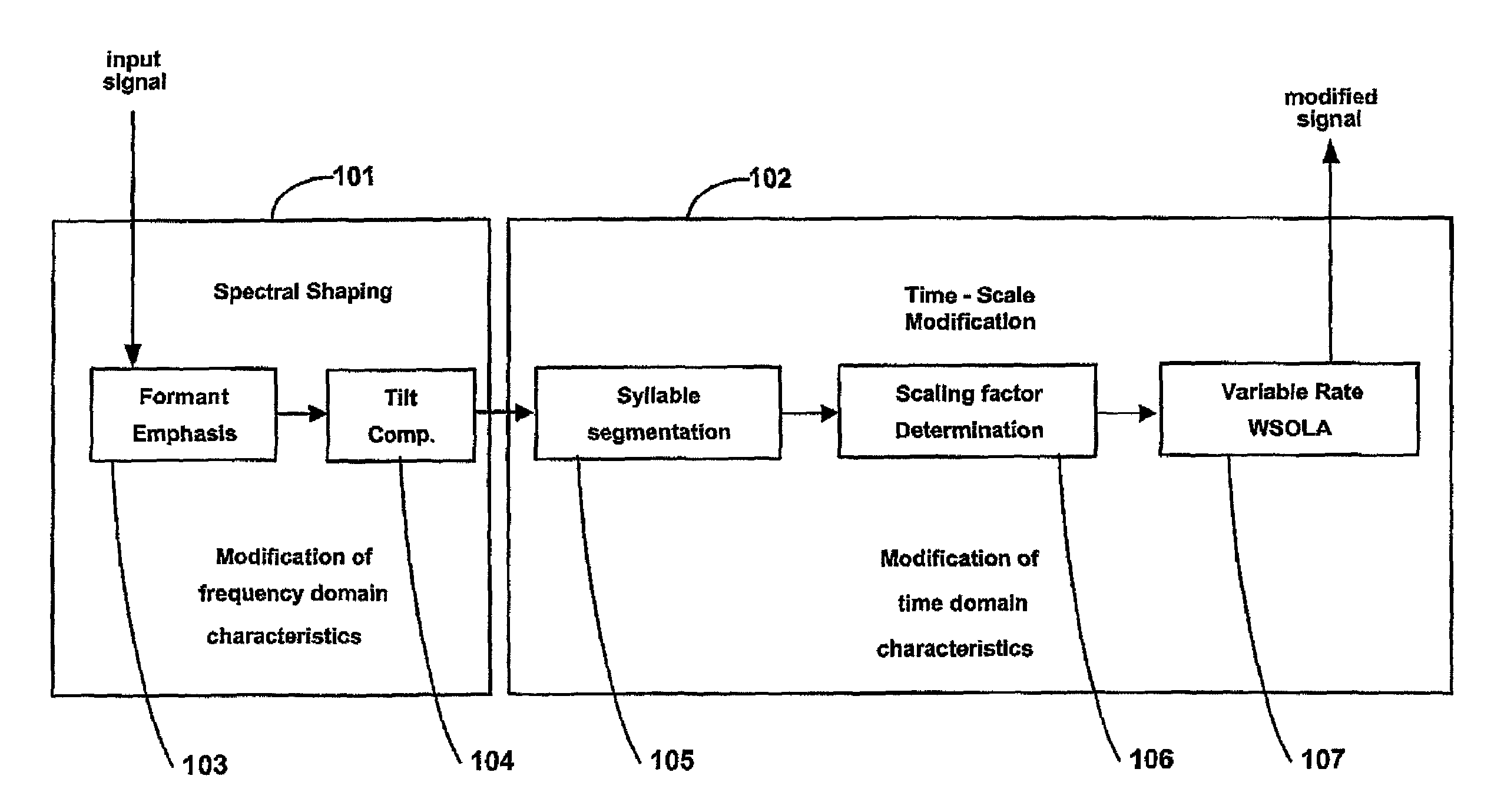
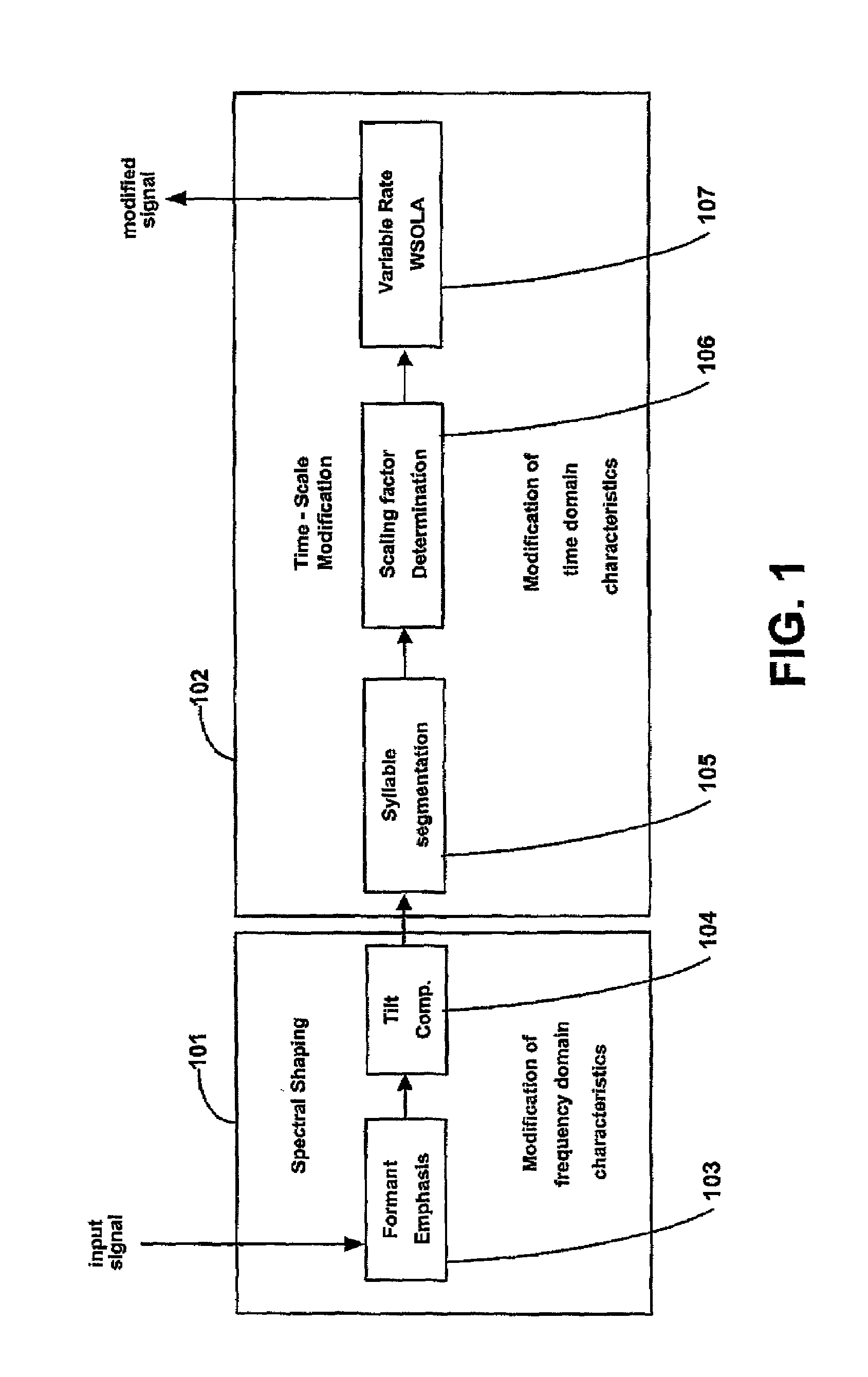
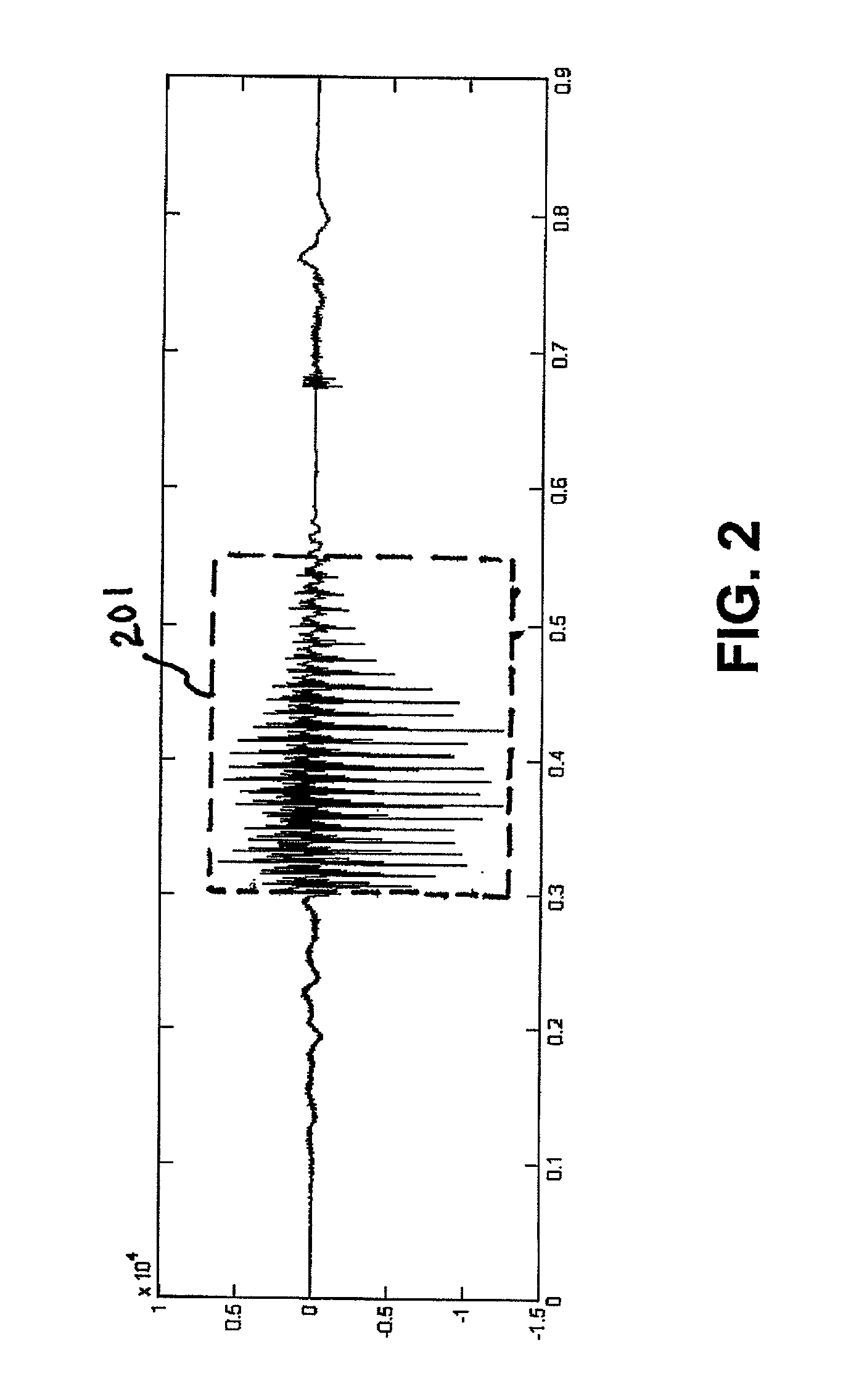
The method and preprocessor enhances the intelligibility of narrowband speech without essentially lengthening the overall time duration of the signal. Both spectral enhancements and variable-rate time-scaling procedures are implemented to improve the salience of initial consonants, particularly the perceptually important formant transitions. Emphasis is transferred from the dominating vowel to the preceding consonant through adaptation of the phoneme timing structure. In a further embodiment, the technique is applied as a preprocessor to a speech coder.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
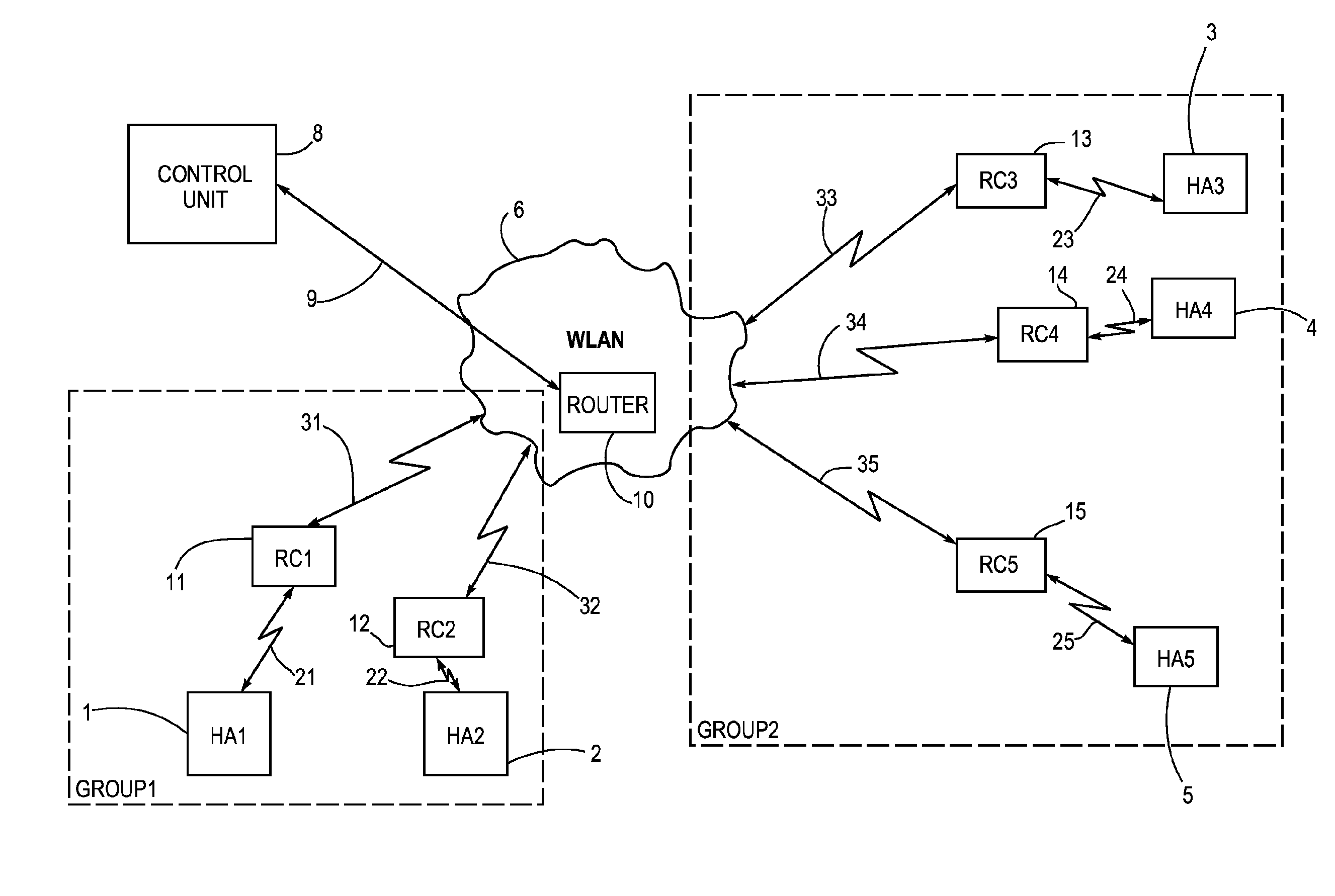
Hearing aid system for establishing a conversation group
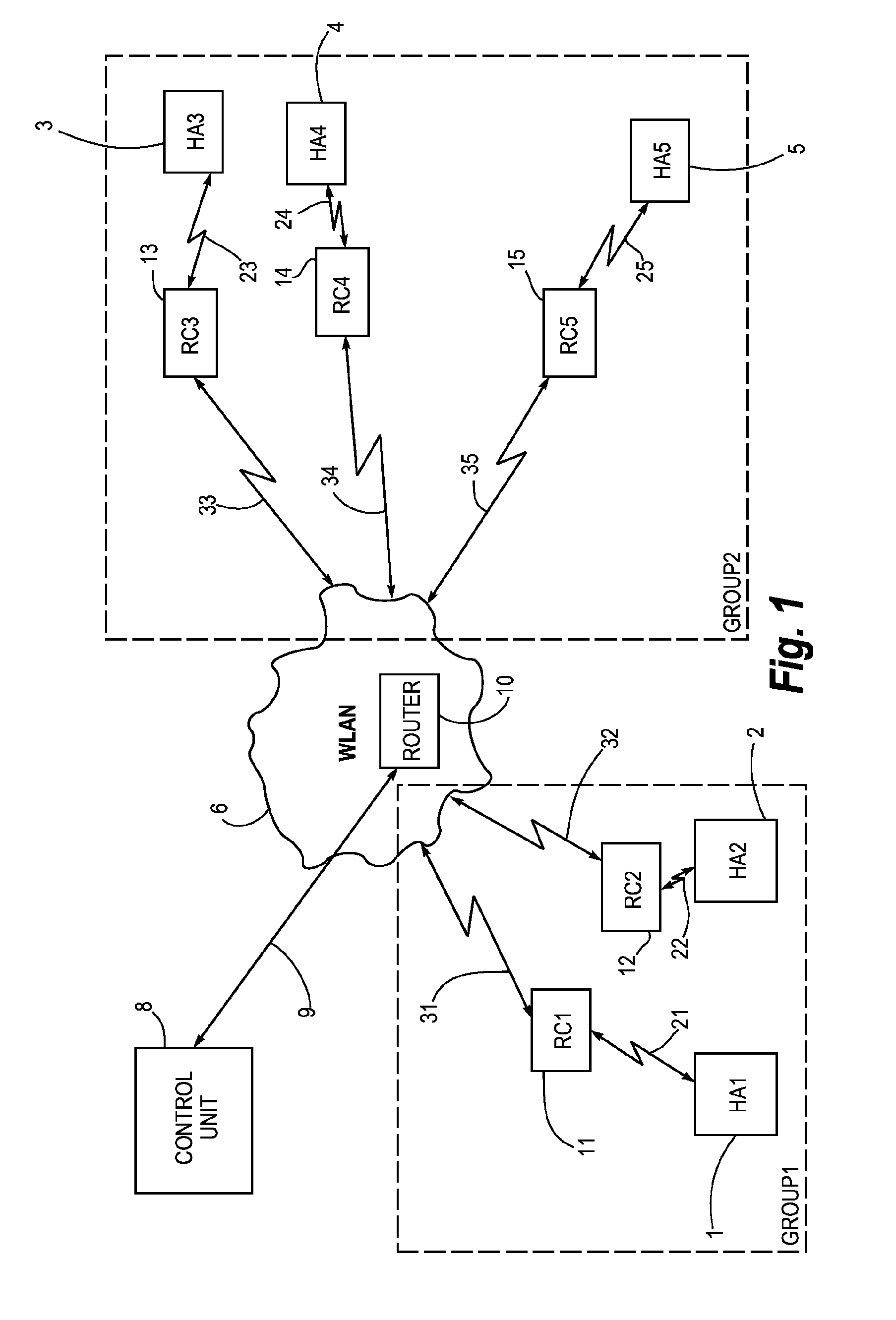
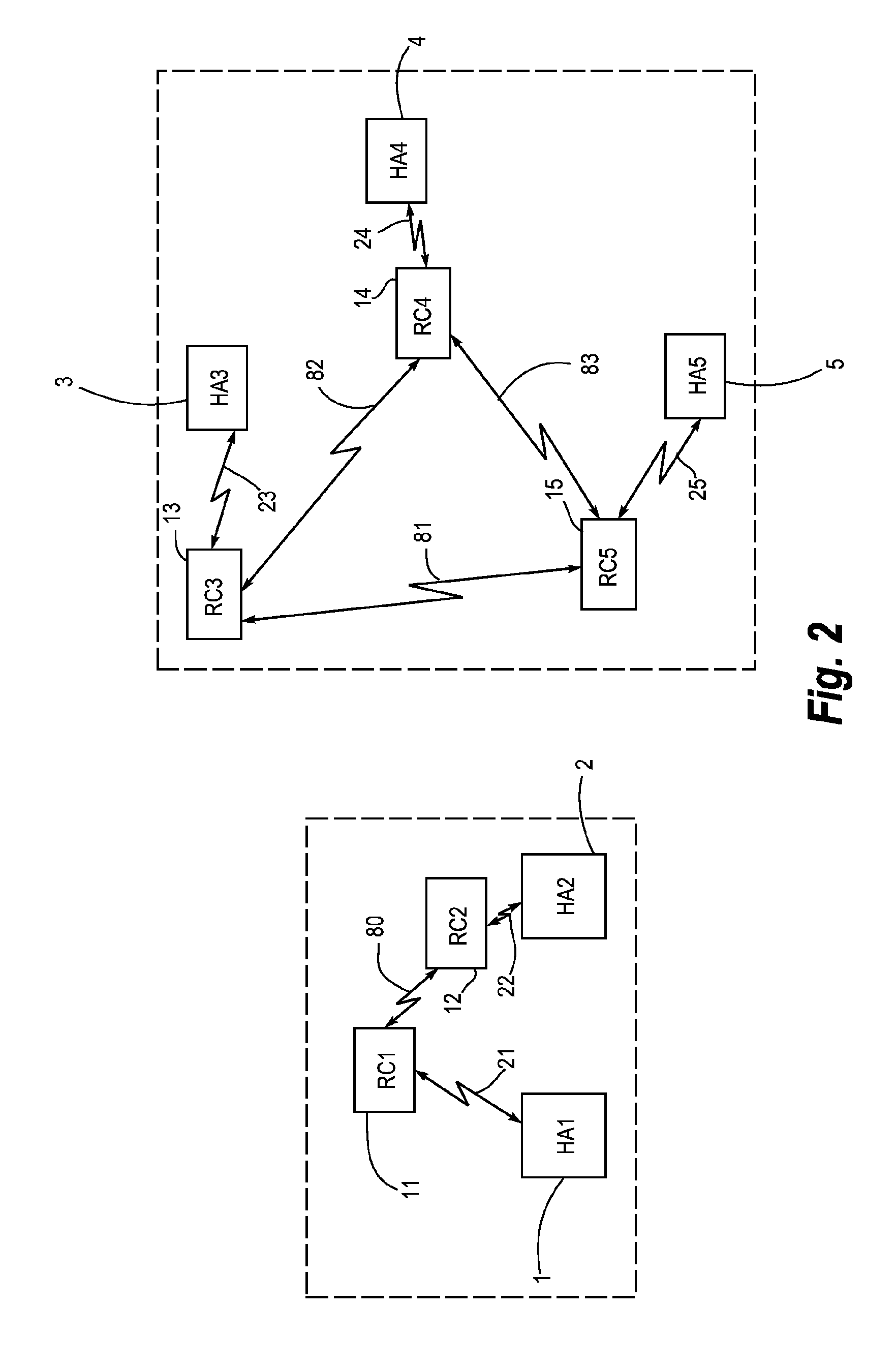
ActiveUS20100086152A1Small sizePower transmissionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexEngineeringHearing aid
A hearing aid system adapted for establishing a conversation group with other hearing aid systems used by different users, comprises a hearing aid (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) with an associated relay device (11, 12, 13, 14, 15). The relay device is (11, 12, 13, 14, 15) adapted for wireless communication (21, 22, 23, 24, 25) with said hearing aid and for wireless communication (31, 32, 33, 34, 35) with a second hearing aid system. The relay device (11, 12, 13, 14, 15) is also adapted for receiving and displaying information about said second hearing aid systems being available for participation in said conversation group, and it comprises means for selection of said other hearing aid systems for inclusion into the conversation group. The invention further provides a method for establishing a conversation group among hearing aid users.
Owner:WIDEX AS
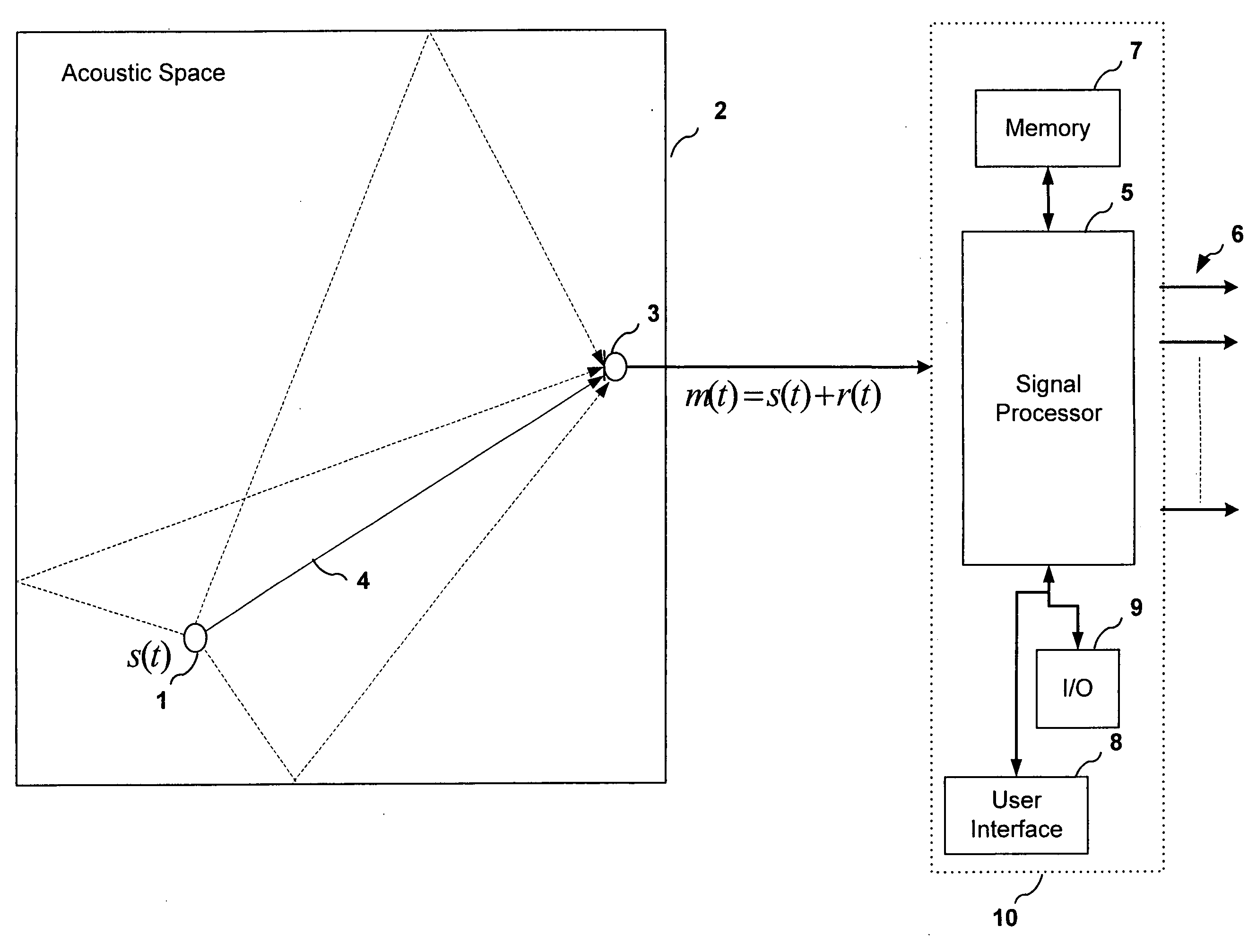
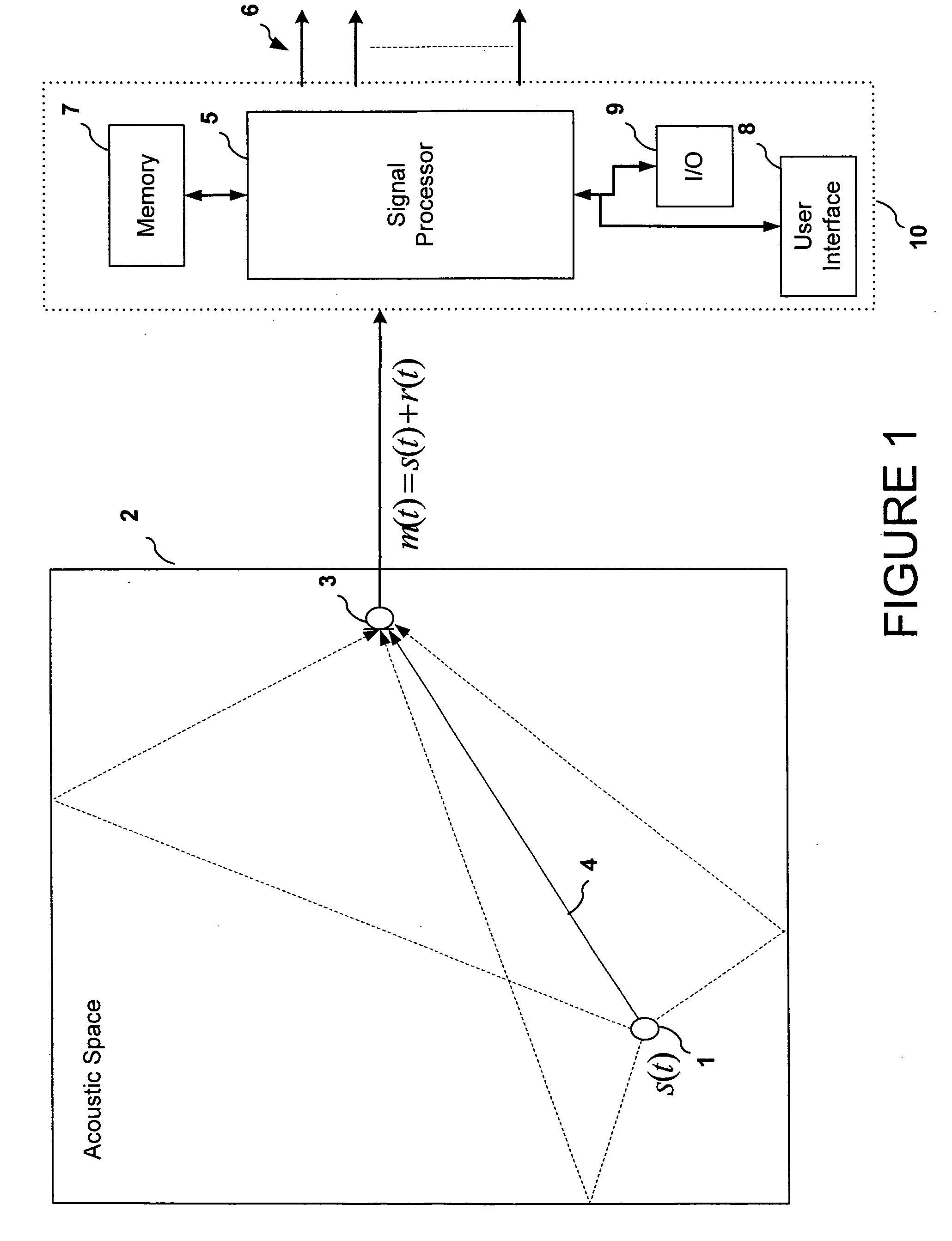
System for modifying an acoustic space with audio source content
An audio signal processing system is configured to separate an audio signal into a dry signal component and one or more reverberant signal components. The dry signal component and the reverberant signal components can be separately modified and then recombined to form a processed audio signal. Alternatively, the dry signal component may be combined with an artificial reverberation component to form the processed audio signal. Modification of the reverberation signal component and generation of the artificial reverberation component may be performed in order to modify the acoustic characteristics of an acoustic space in which the audio signal is driving loudspeakers. The audio signal may be a pre-recorded audio signal or a live audio signal generated inside or outside the acoustic space.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
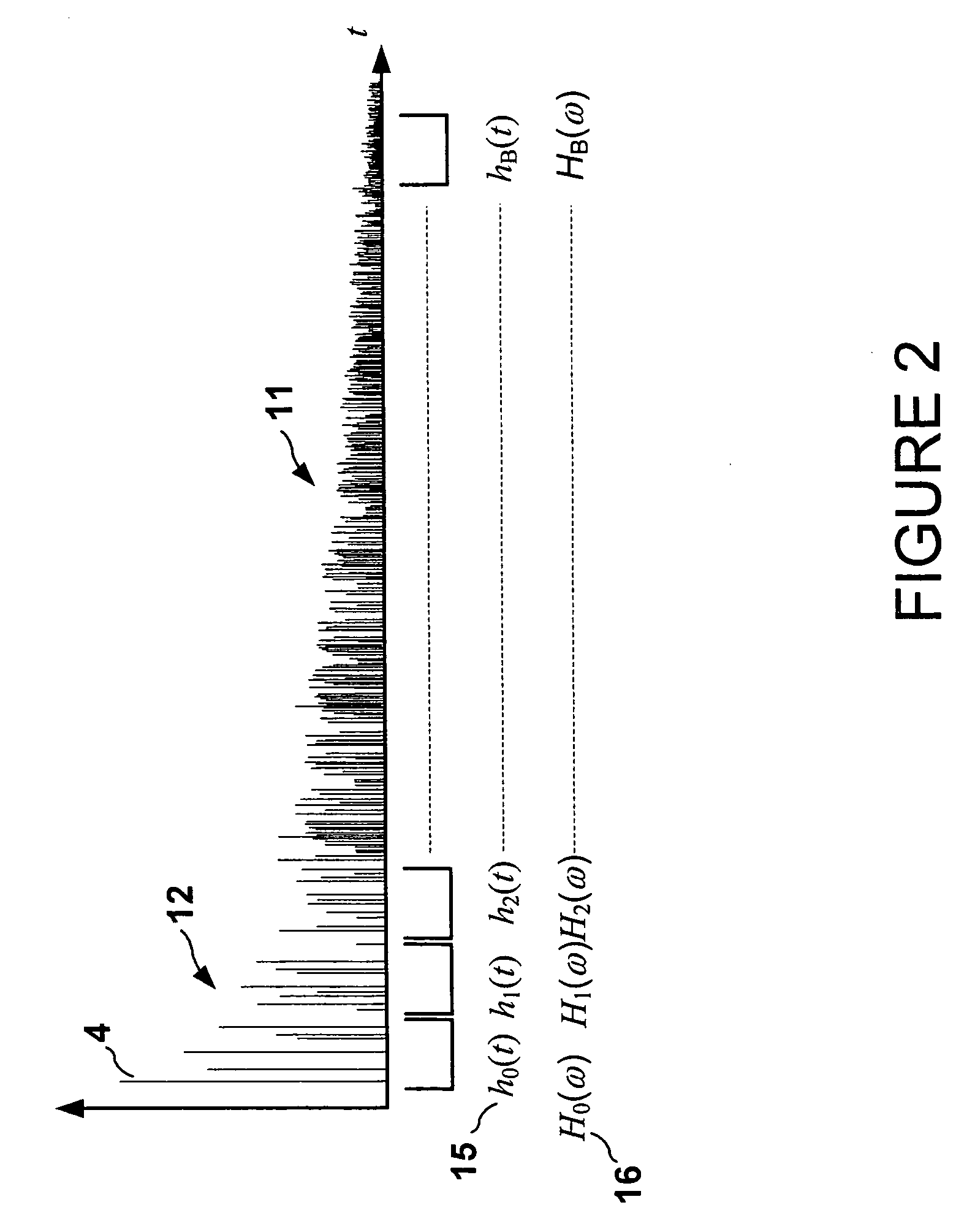
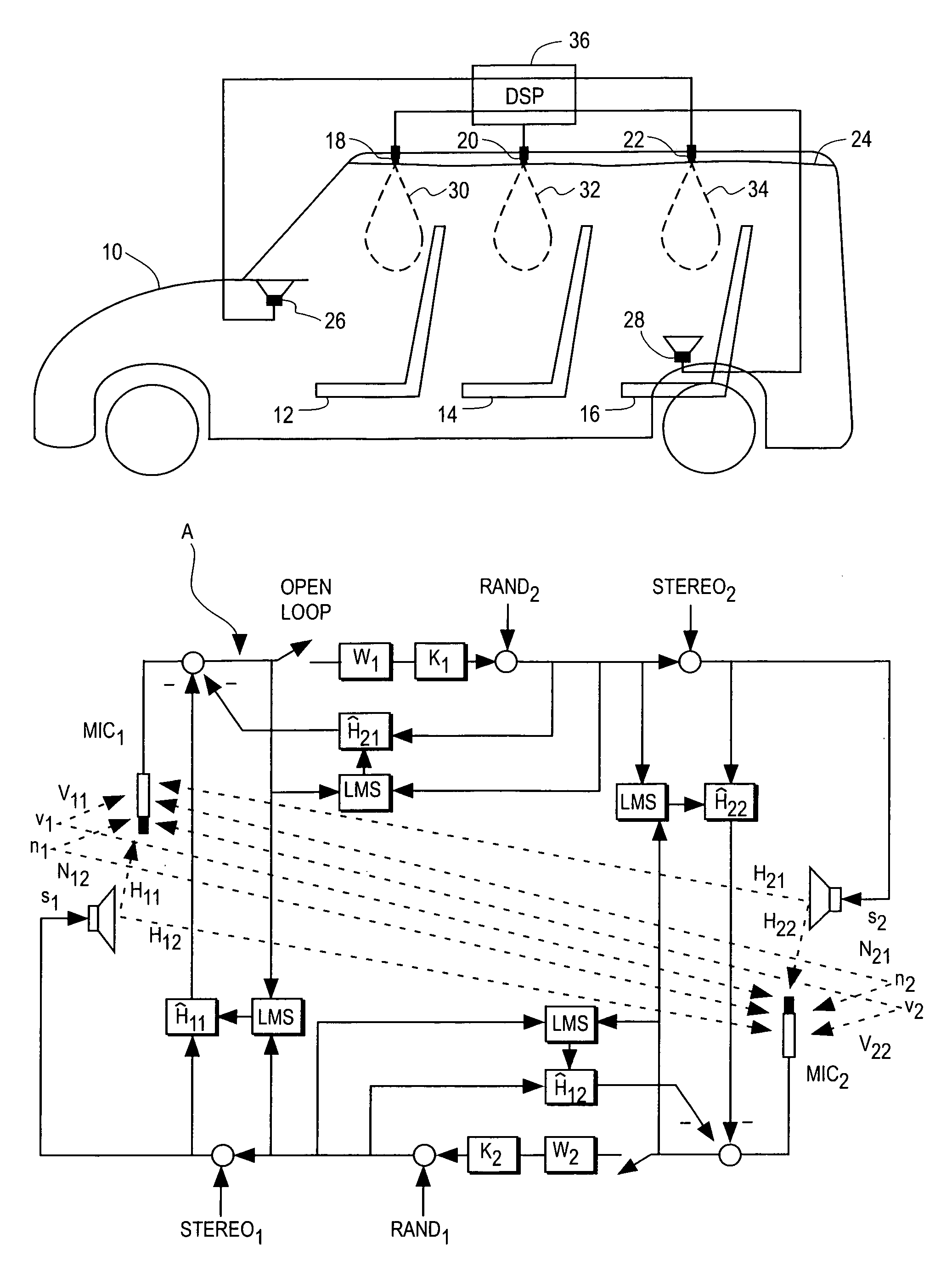
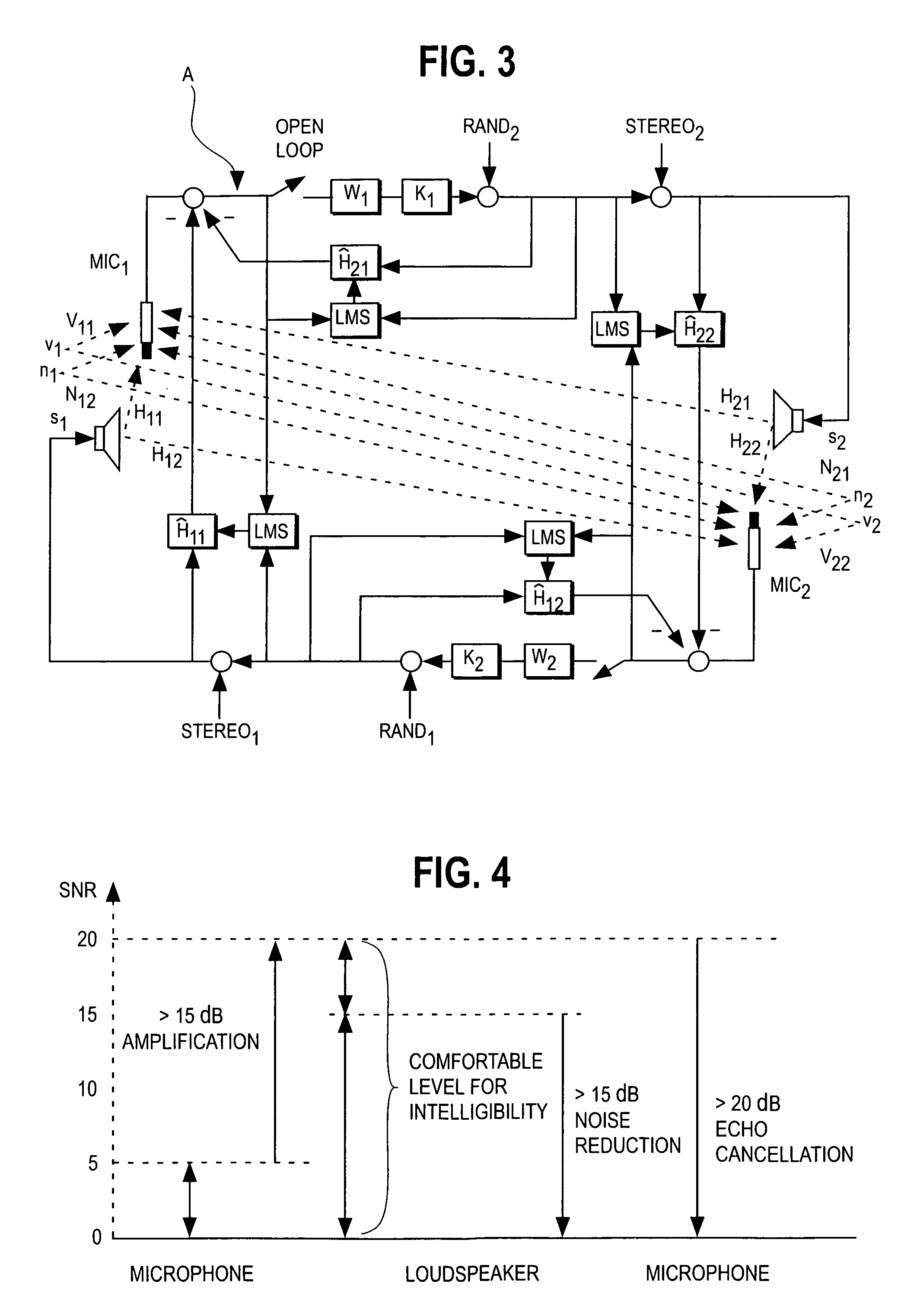
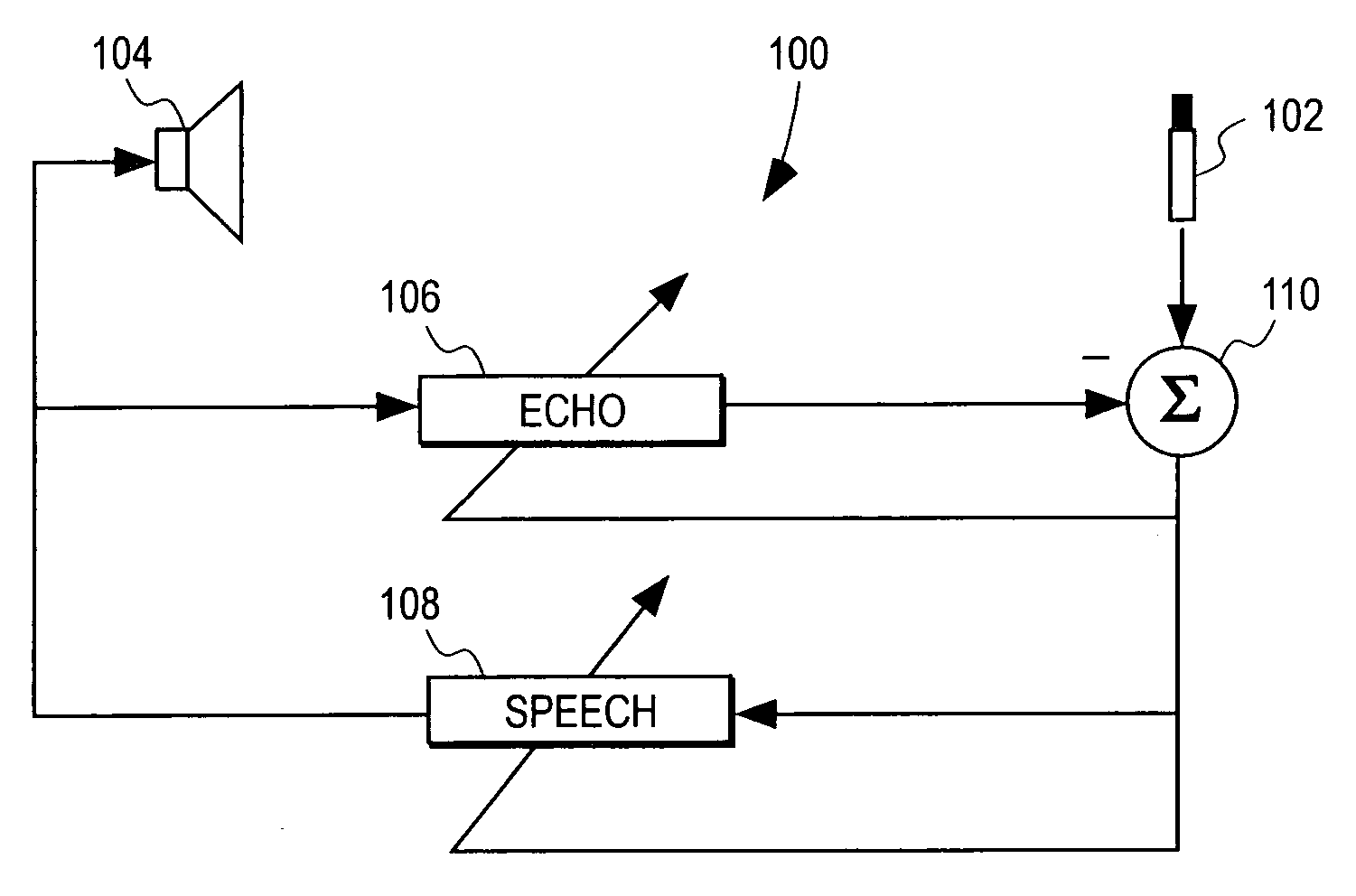
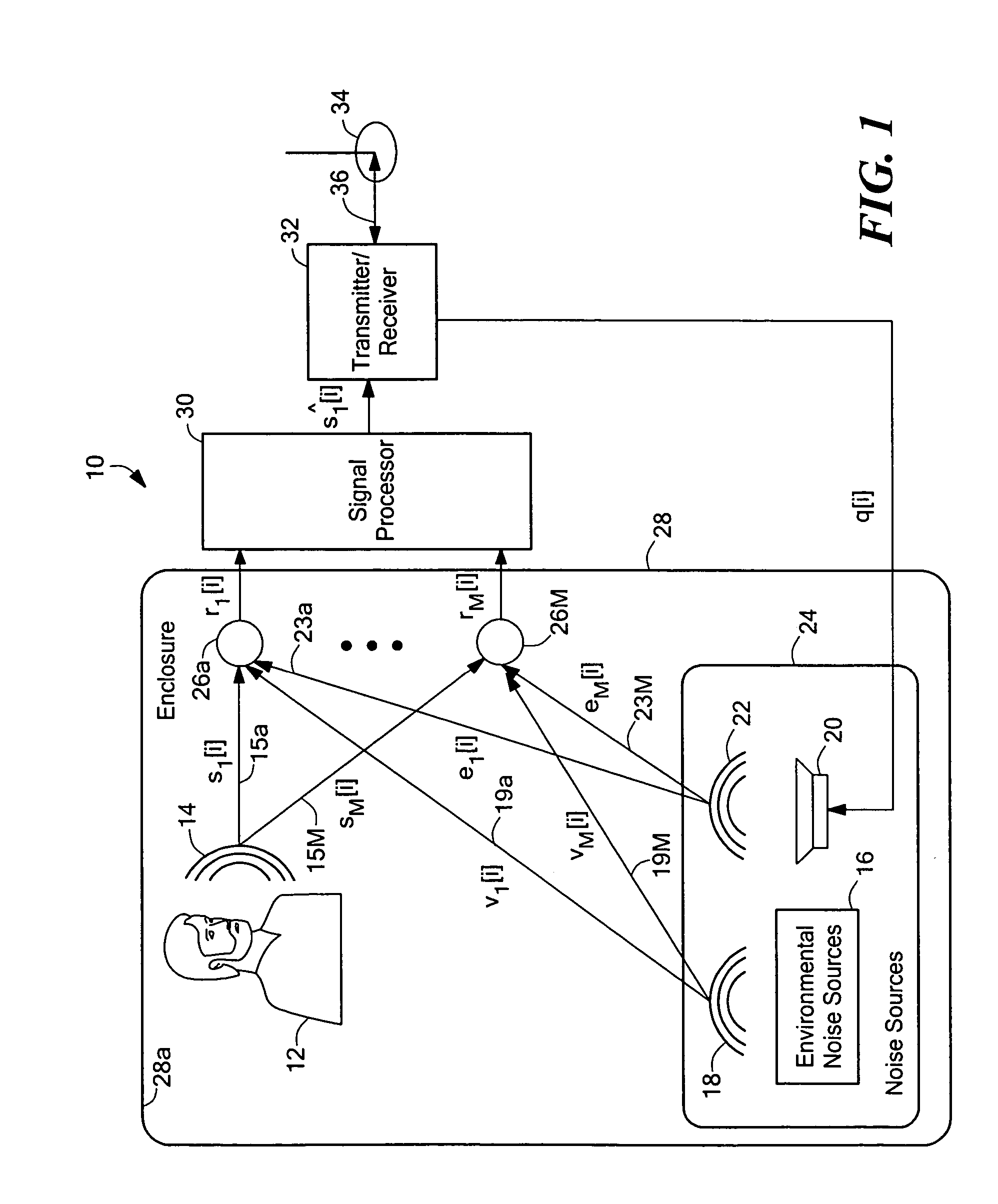
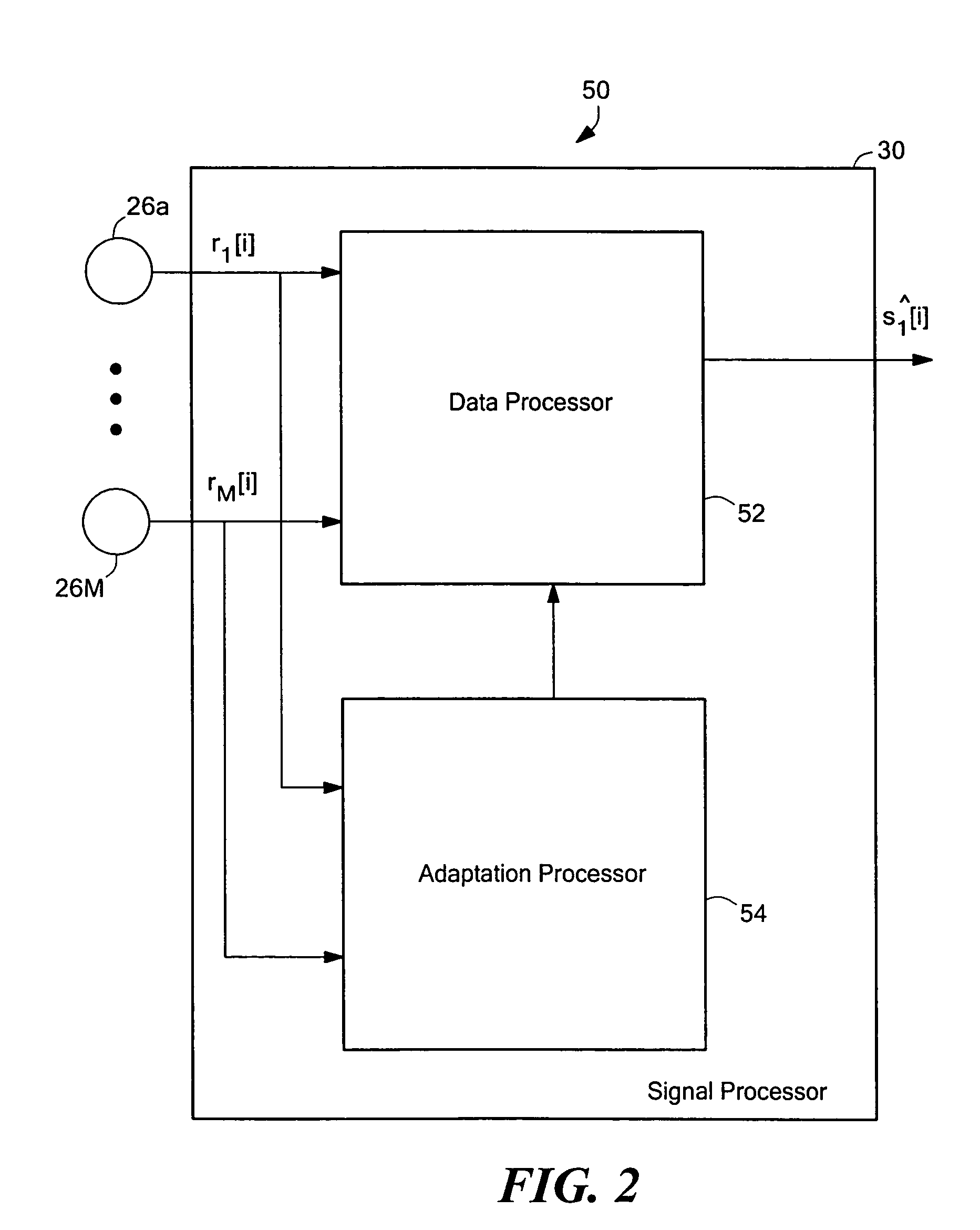
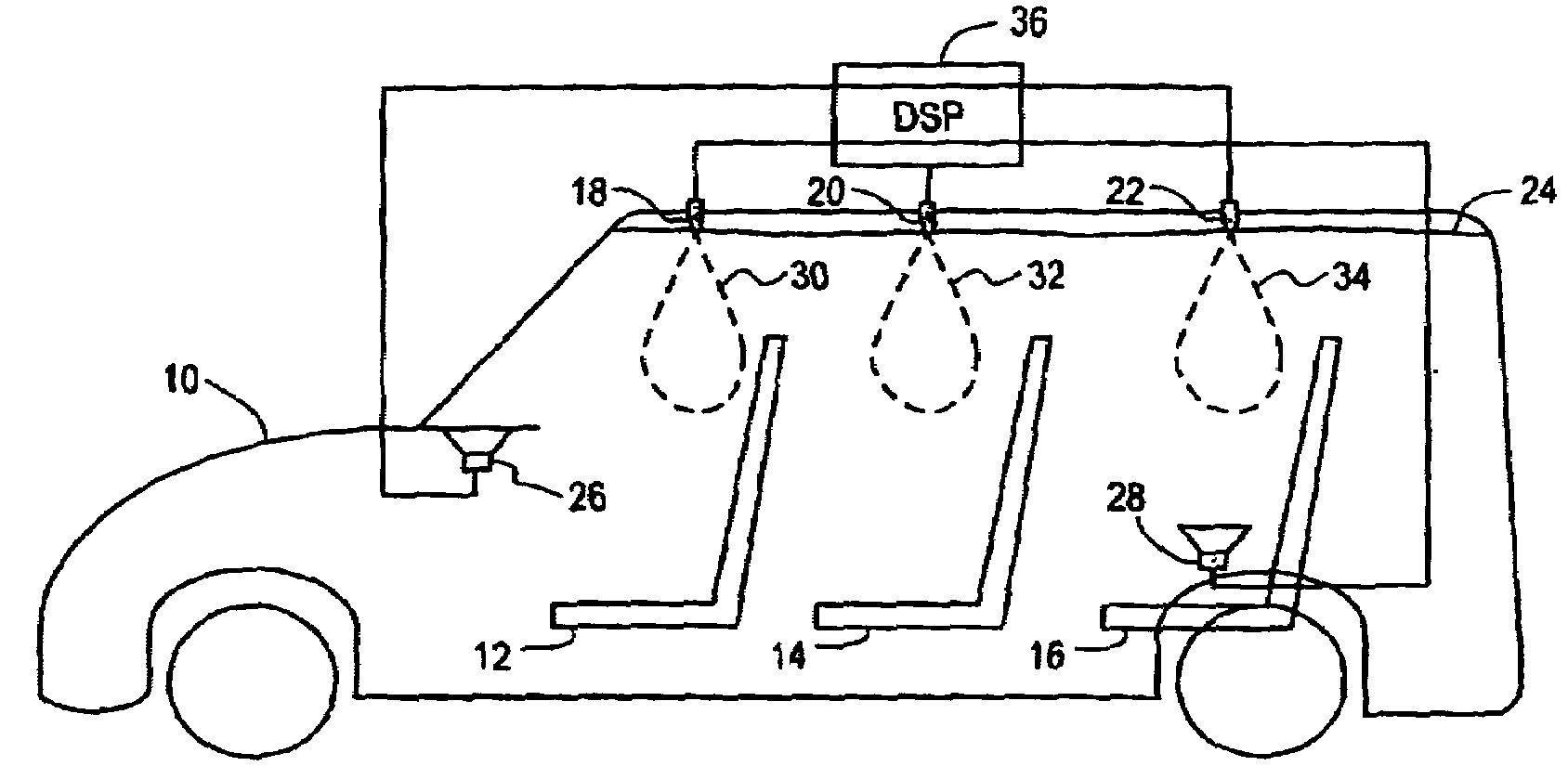
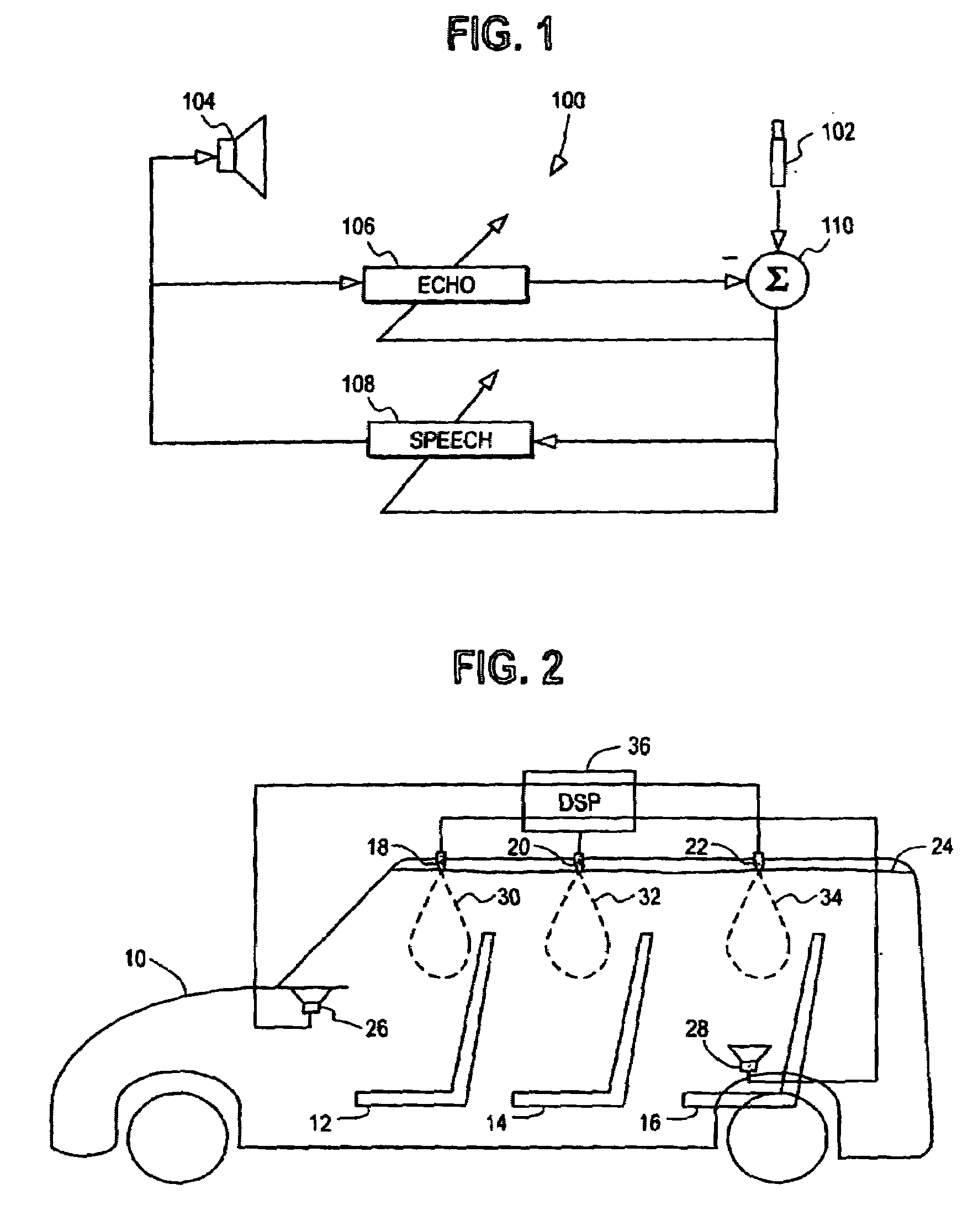
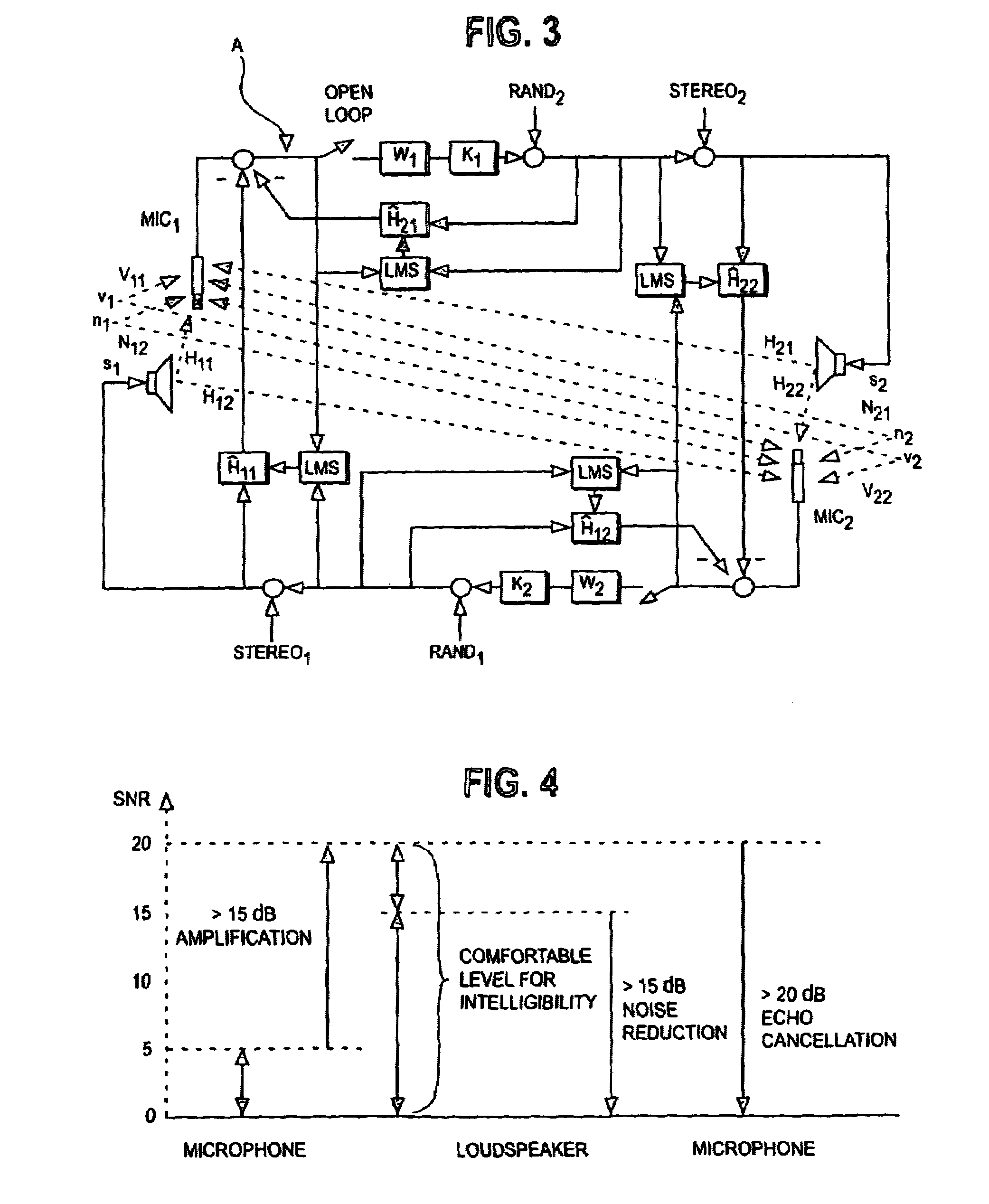
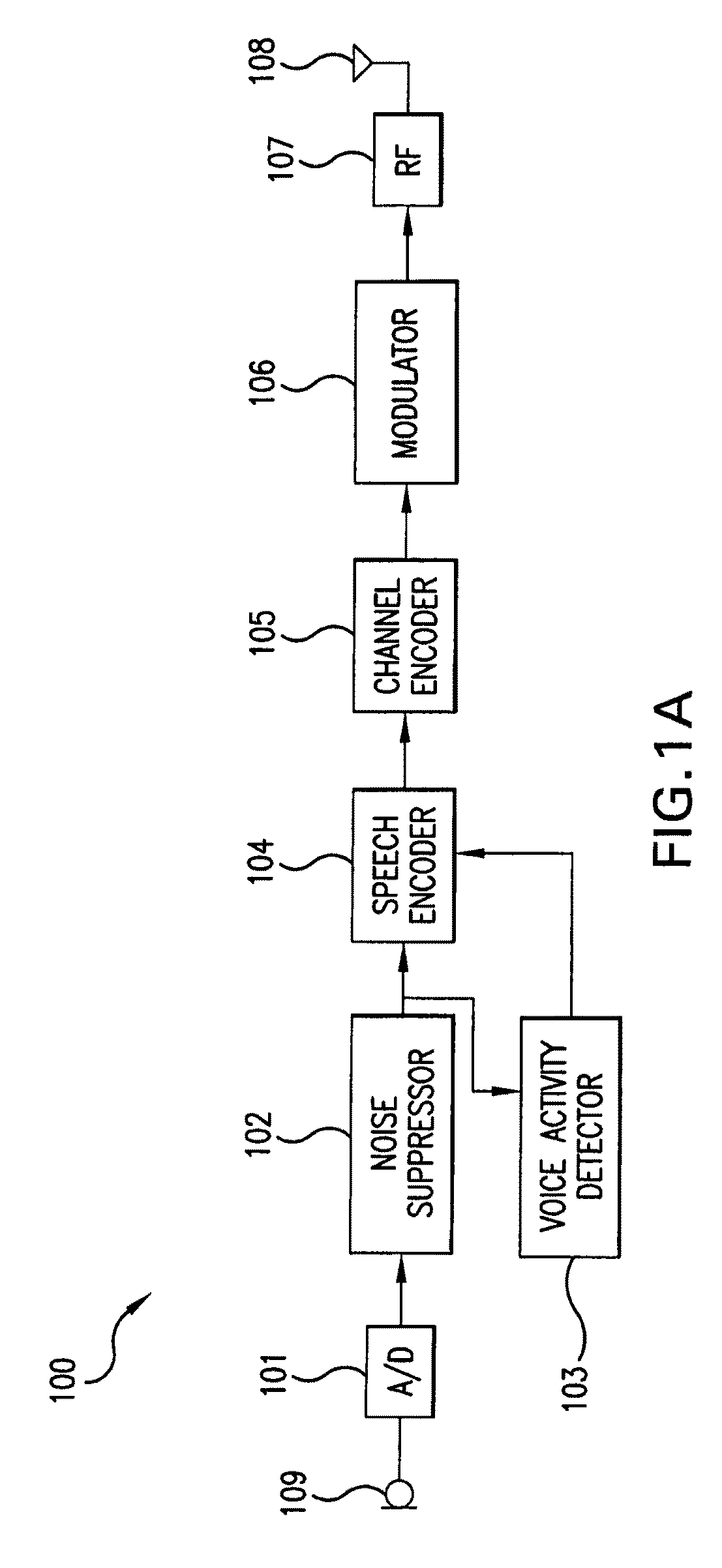
Robust and reliable acoustic echo and noise cancellation system for cabin communication
InactiveUS7171003B1Improve speech clarityImproving ease and flexibilityTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsGain controlEnvironmental noiseCommunications system
A cabin communication system for improving clarity of a voice spoken within an interior cabin having ambient noise includes an adaptive speech enhancement filter for receiving an audio signal that includes a first component indicative of the spoken voice, a second component indicative of a feedback echo of the spoken voice and a third component indicative of the ambient noise, the speech enhancement filter filtering the audio signal by removing the third component to provide a filtered audio signal, the speech enhancement filter adapting to the audio signal at a first adaptation rate, and an adaptive acoustic echo cancellation system for receiving the filtered audio signal and removing the second component in the filtered audio signal to provide an echo-cancelled audio signal, the echo cancellation signal adapting to the filtered audio signal at a second adaption rate, wherein the first adaptation rate and the second adaptation rate are different from each other so that the speech enhancement filter does not adapt in response to operation of the echo-cancellation system and the echo-cancellation system does not adapt in response to operation of the speech enhancement filter.
Owner:LEAR CORP
Adaptive filter for speech enhancement in a noisy environment
InactiveUS7117145B1Improve clarityImprove easeSpeech analysisDigital computer detailsEnvironmental noiseAdaptive filter
A cabin communication system for improving clarity of a voice spoken within an interior cabin having ambient noise includes a microphone for receiving the spoken voice and the ambient noise and for converting the spoken voice and the ambient noise into an audio signal, the audio signal having a first component corresponding to the spoken voice and a second component corresponding to the ambient noise, a speech enhancement filter for removing the second component from the audio signal to provide a filtered audio signal, the speech enhancement filter removing the second component by processing the audio signal by a method taking into account elements of psycho-acoustics of a human ear, and a loudspeaker for outputting a clarified voice in response to the filtered audio signal.
Owner:LEAR CORP
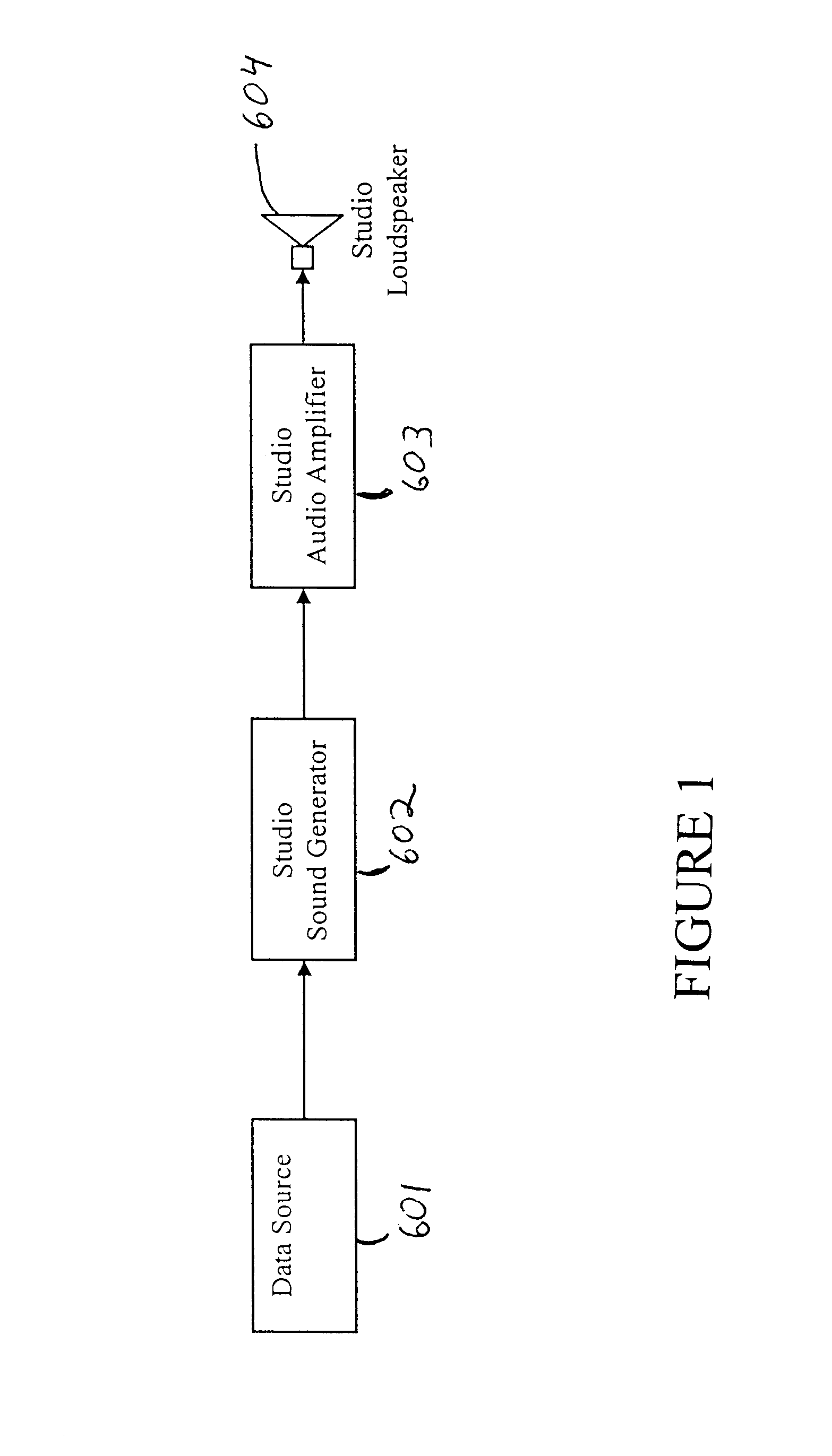
Method and apparatus for audio broadcast of enhanced musical instrument digital interface (MIDI) data formats for control of a sound generator to create music, lyrics, and speech
InactiveUS6462264B1Inhibit outputImprove speech clarityElectrophonic musical instrumentsCode conversionCarrier signalData format
A method and apparatus for the transmission and reception of broadcasted instrumental music, vocal music, and speech using digital techniques. The data is structured in a manner similar to the current standards for MIDI data. Transmitters broadcast the data to receivers which contain internal sound generators or an interface to external sound generators that create sounds in response to the data. The invention includes transmission of multiple audio data signals for several languages on a conventional radio and television carrier through the use of low bandwidth data. Error detection and correction data is included within the transmitted data. The receiver has various error compensating mechanisms to overcome errors in data that cannot be corrected using the error correcting data that the transmitter sent. The data encodes for elemental vocal sounds and music.
Owner:ELAM CARL
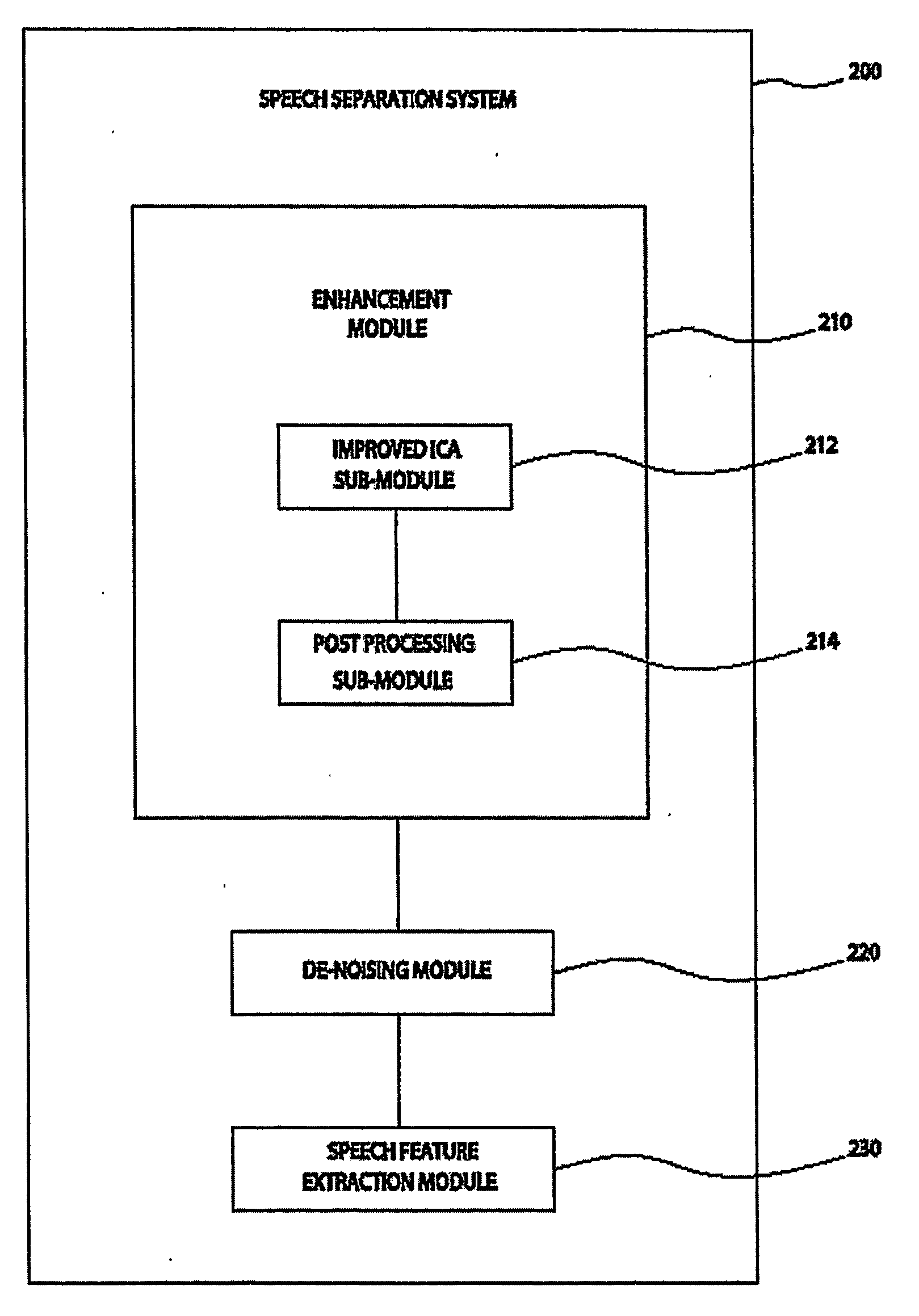
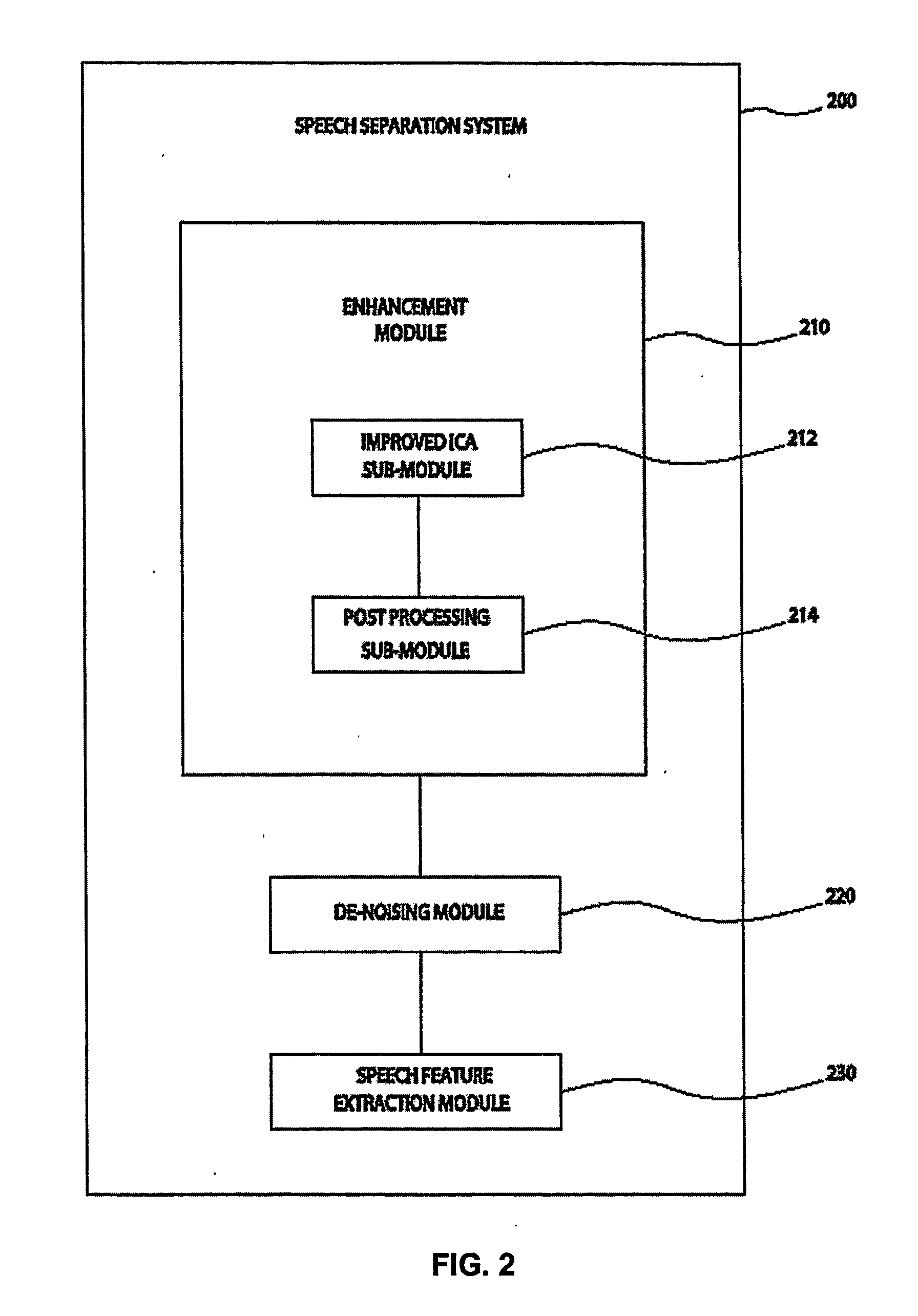
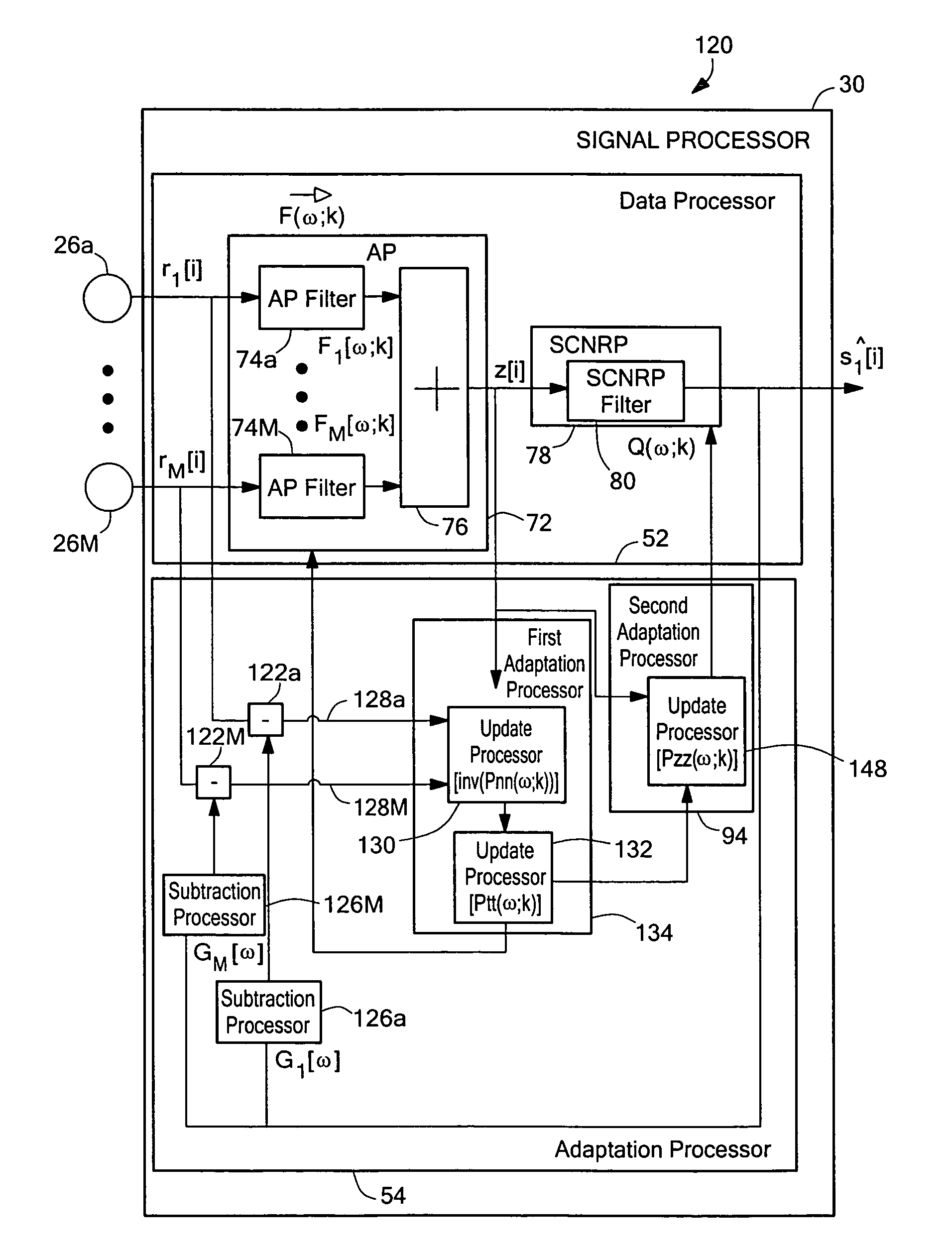
System and method for speech processing using independent component analysis under stability restraints
ActiveUS20060053002A1Constrain filter weight adaptation speedAvoid reverberation effectAdaptive networkSpeech analysisLearning ruleIndependent component analysis
A system and method for separating a mixture of audio signal into desired audio signals (430) (e.g., speech) and a noise sign (440) is disclosed. Microphones (310, 320) are positioned to receive the mixed audio signals, and an independent component analysis (ICA) processes (212) the sound mixture using stability constraints. The ICA process (508) uses predefined characteristics of the desired speech signal to identify and isolate a target sound signal (430). Filter coefficients are adapted with a learning rule and filter weight update dynamics are stabilized to assist convergence to a stable separated ICA signal result. The separated signals may be peripherally-processed to further reduce noise effects using post-processing (214) and pre-processing (220, 230) techniques and information. The proposed system is designed and easily adaptable for implementation on DSP units or CPUs in audio communication hardware environments.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
System and method for noise reduction having first and second adaptive filters responsive to a stored vector
InactiveUS7099822B2Improve speech clarityReduce processing timeMultiple-port networksEar treatmentAdaptive filterAcoustic transfer function
A system for microphone noise reduction includes first and second filter portions and a control processor adapted to adapt the first and second filter portions in response to a one of a plurality of stored vectors. Each stored vector is representative of acoustic transfer functions in accordance with a model of a vehicle and a respective position within the vehicle. A method for processing microphone signals includes selecting a vehicle model, selecting positions within the vehicle model, measuring acoustic response vectors at the positions, storing the response vectors, selecting one of the response vectors, and adapting first and second filter portions in accordance with the selected response vector.
Owner:F POSZAT HU
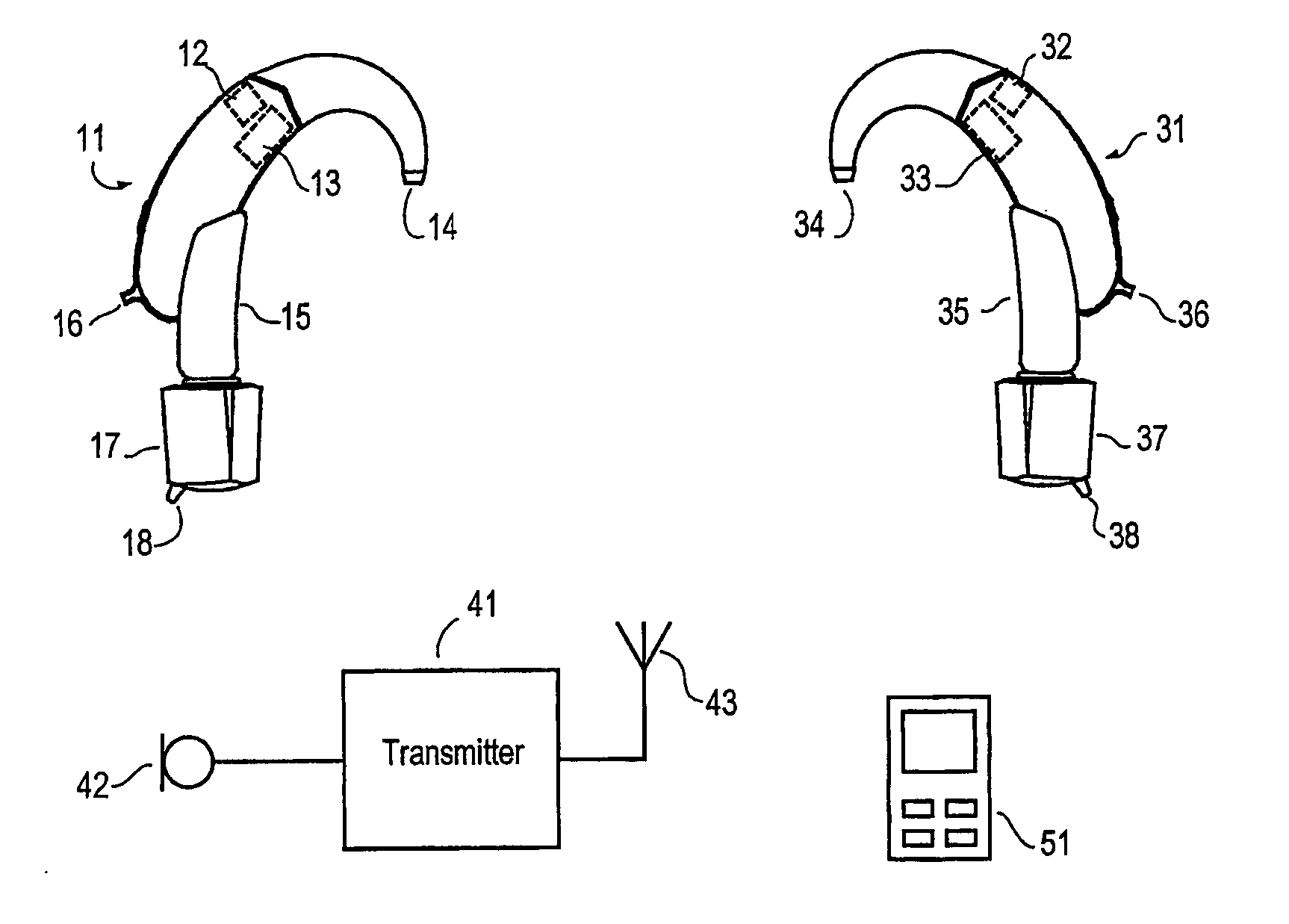
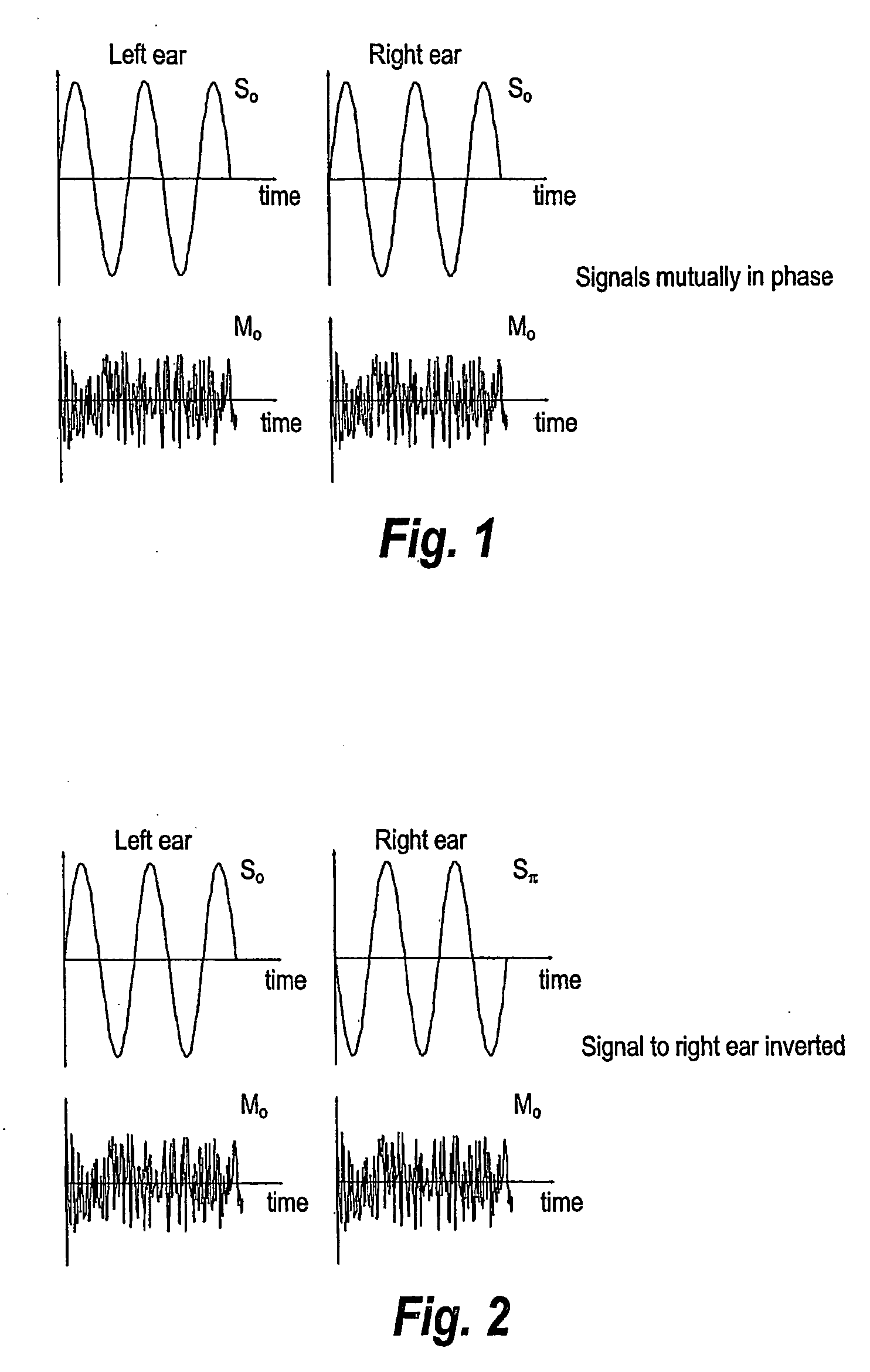
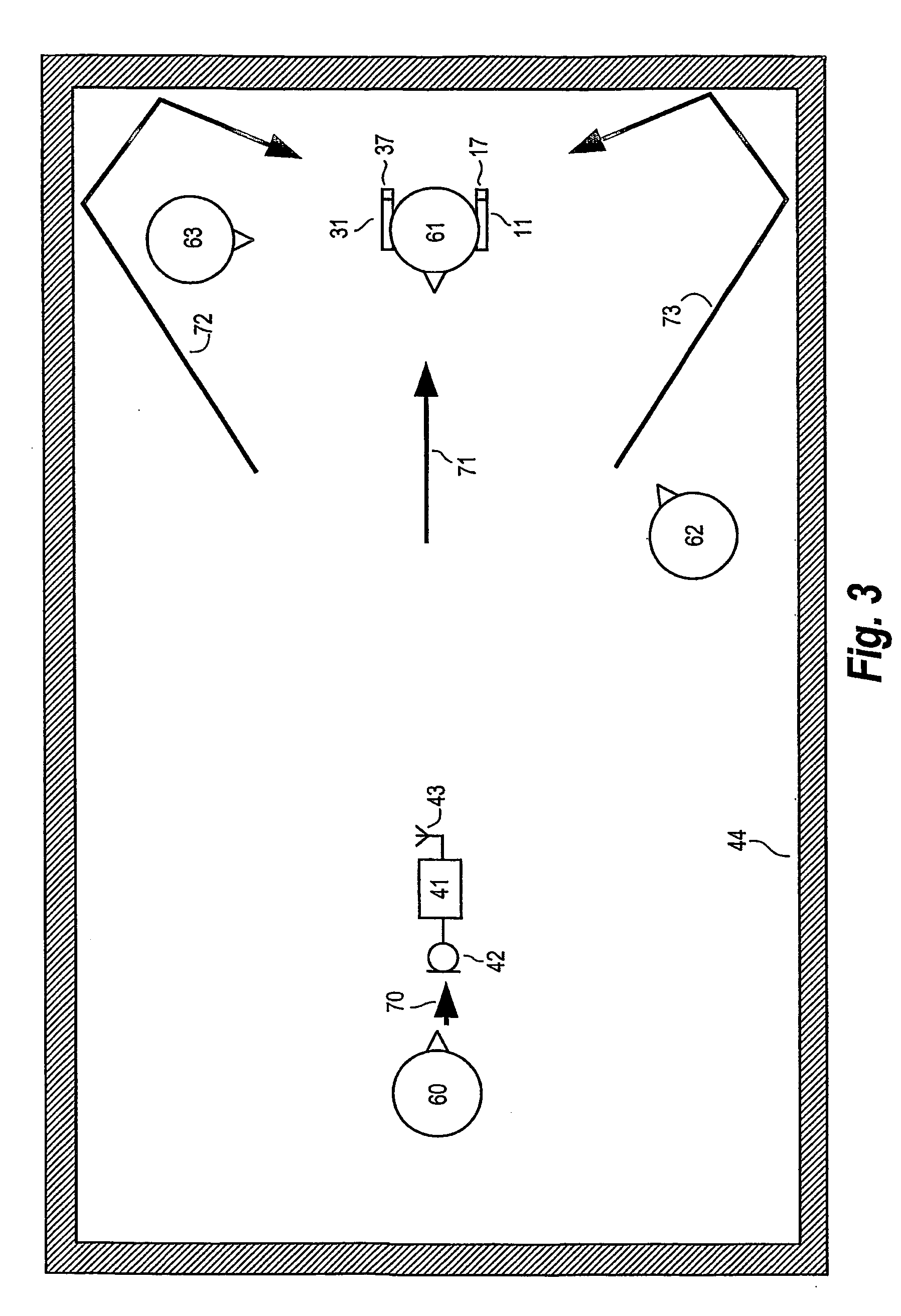
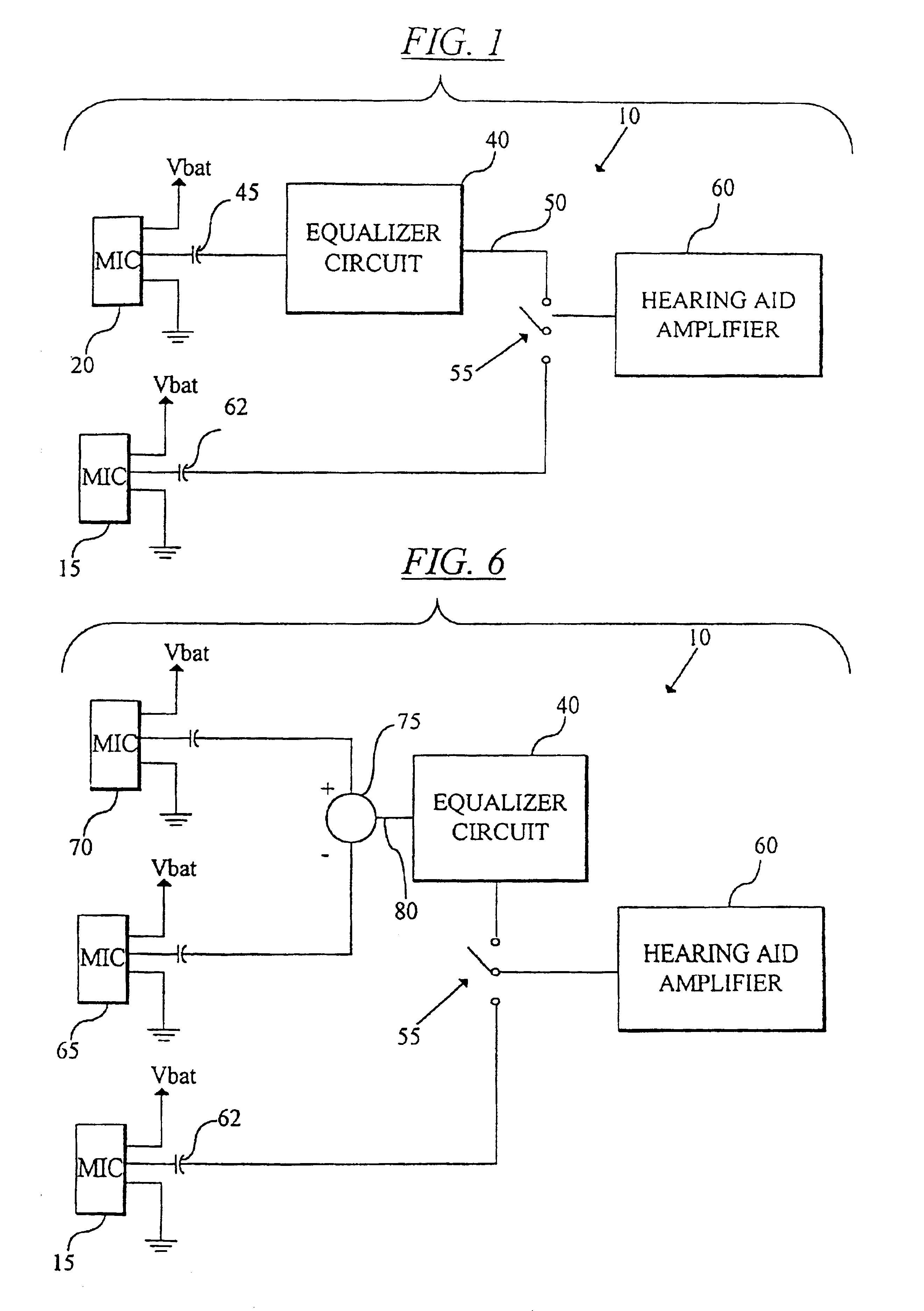
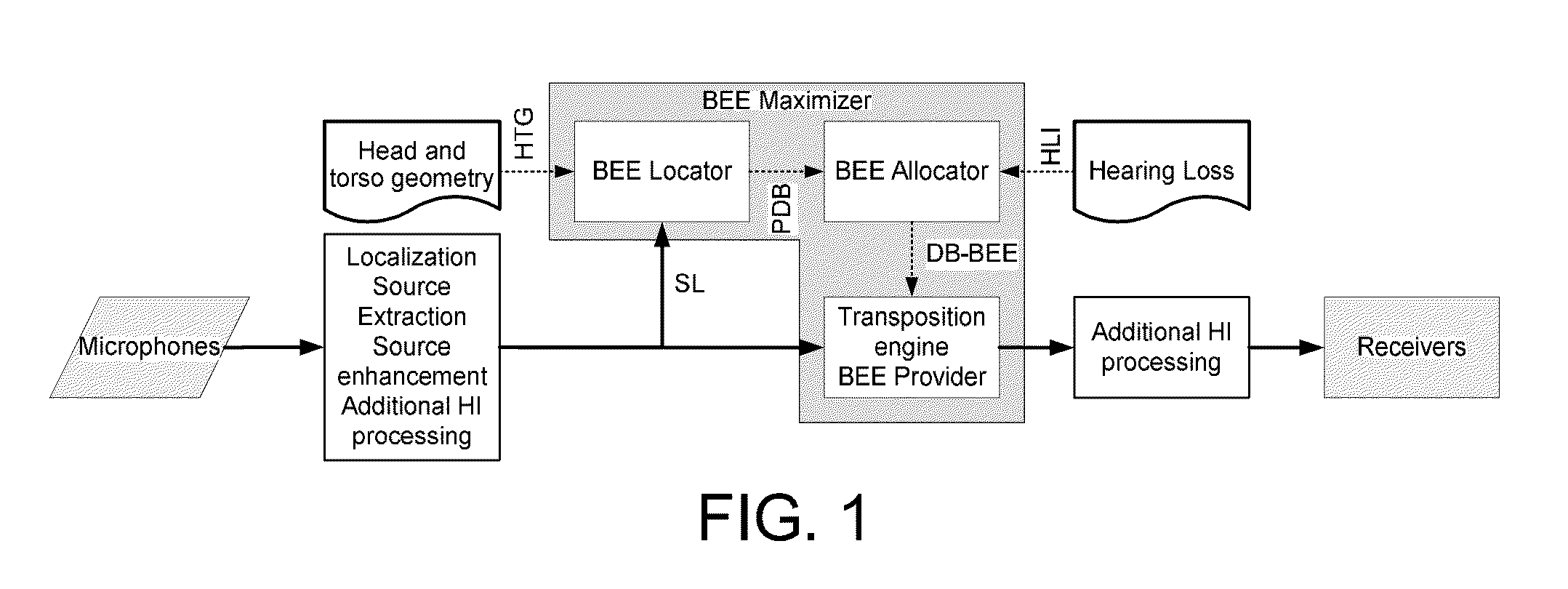
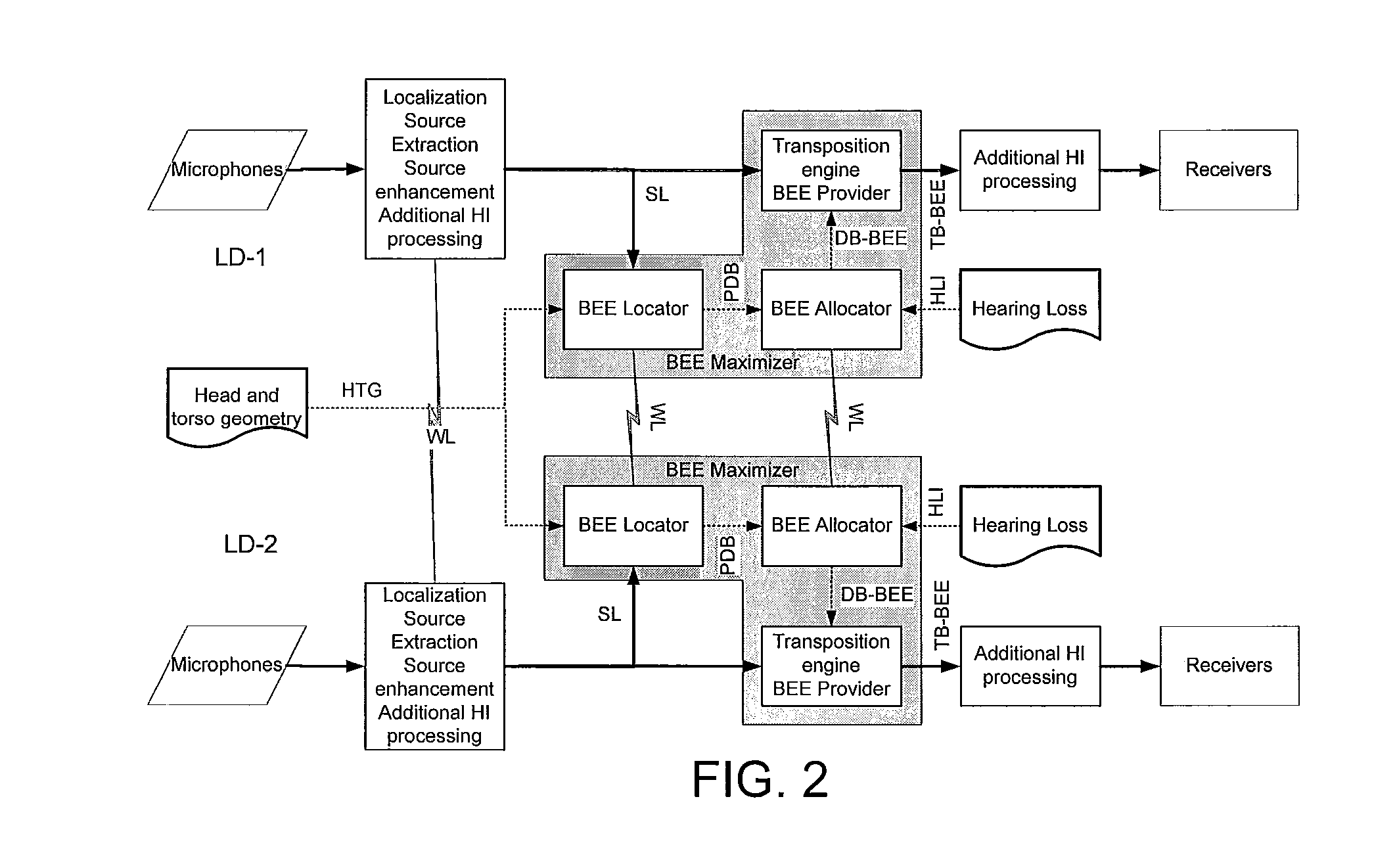
Hearing aid system, a hearing aid and a method for processing audio signals
ActiveUS20060093172A1Improve speech intelligibilityRaise the ratioDeaf aid adaptationMicrophoneEngineering
A composite hearing aid system comprises two hearing aids (11, 31) with respective microphones (12, 32) and electronic receivers (17, 37), a microphone (42) and a transmitter (41) adapted to transmit the signal from the microphone (42) to the electronic receivers. At least one of the hearing aids (11, 31) comprises means for inverting the phase of the signal received by the electronic receivers (17, 37). When the phase of the received signal is inverted in one of the hearing aids (11, 31), a release from masking is obtained, and the perceived signal-to-noise ratio is improved. The invention provides a composite hearing aid system, a hearing aid and a method for processing audio signals.
Owner:WIDEX AS
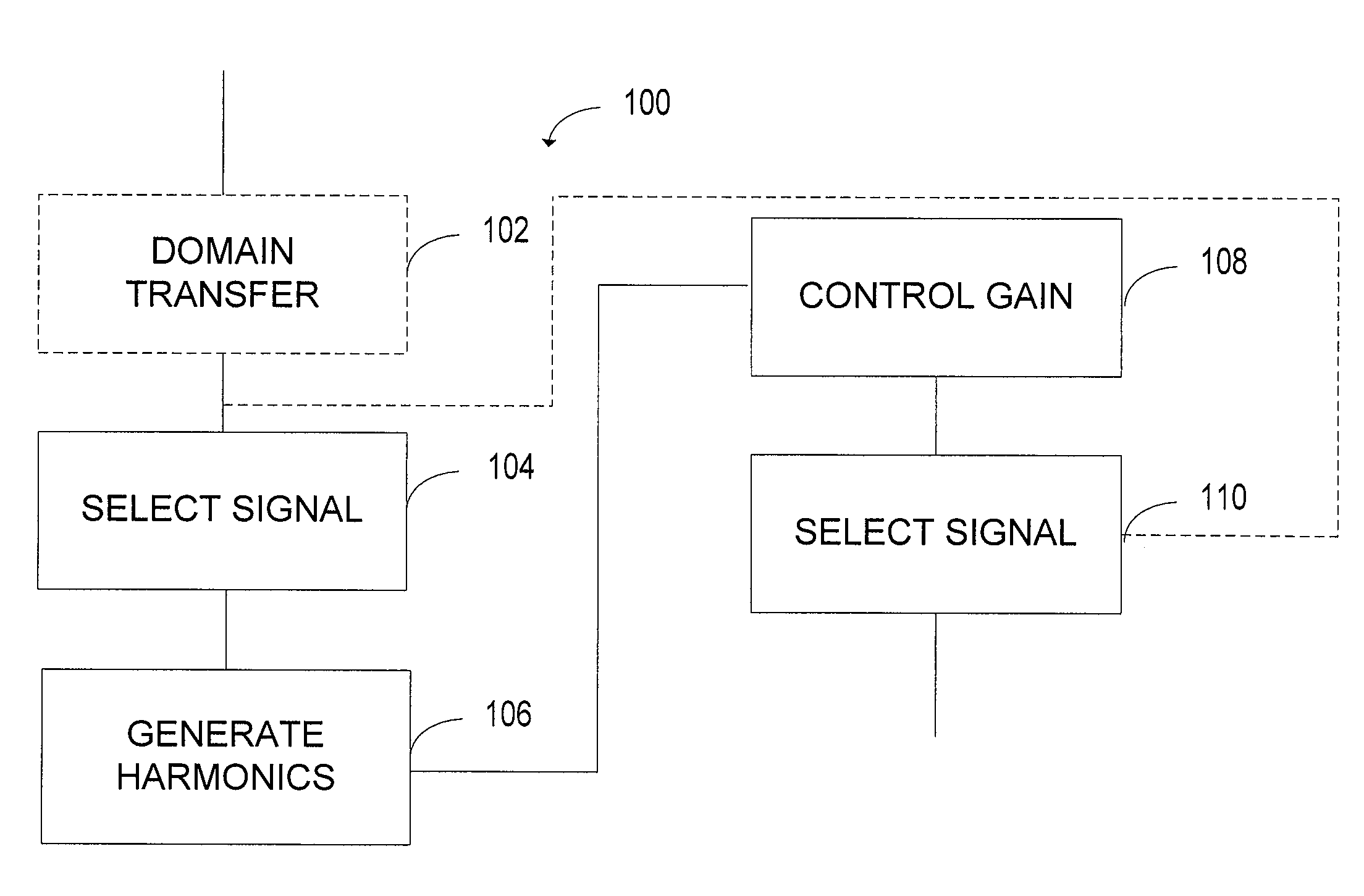
Speech enhancement through partial speech reconstruction
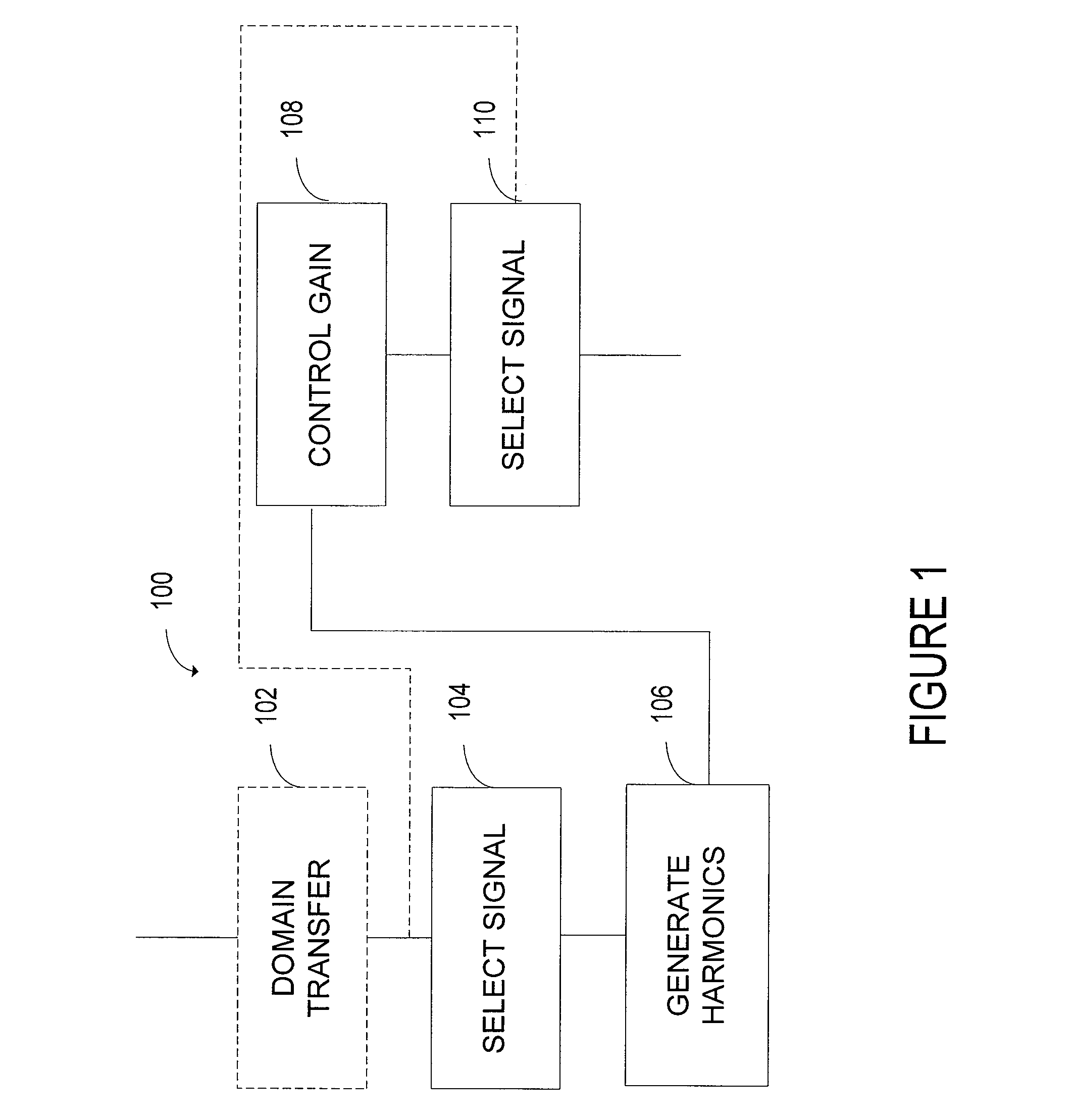
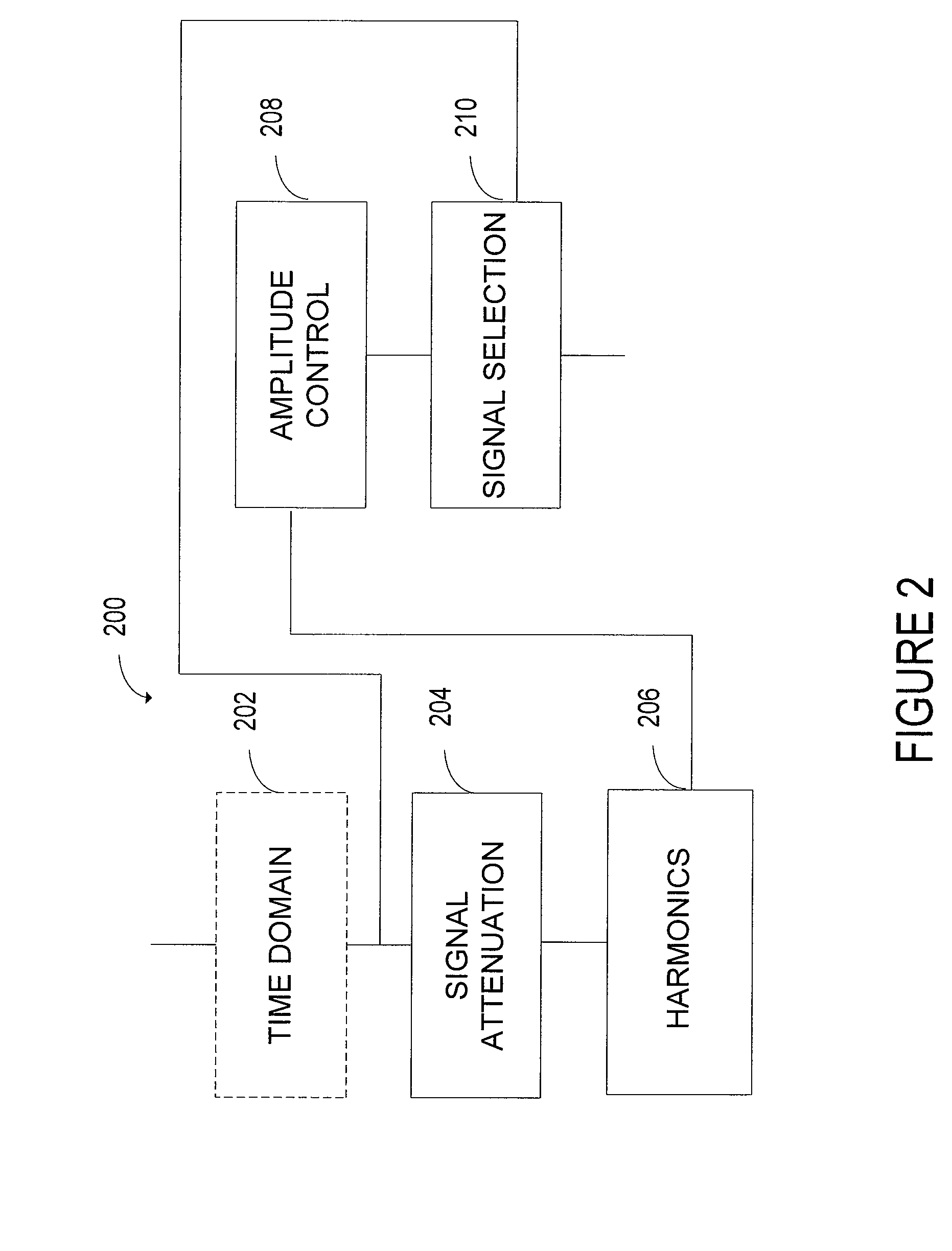
ActiveUS20090112579A1Improve speech intelligibilityImprove speech clarityTransmission noise suppressionTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsBackground noiseSpeech reconstruction
A system improves speech intelligibility by reconstructing speech segments. The system includes a low-frequency reconstruction controller programmed to select a predetermined portion of a time domain signal. The low-frequency reconstruction controller substantially blocks signals above and below the selected predetermined portion. A harmonic generator generates low-frequency harmonics in the time domain that lie within a frequency range controlled by a background noise modeler. A gain controller adjusts the low-frequency harmonics to substantially match the signal strength to the time domain original input signal.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
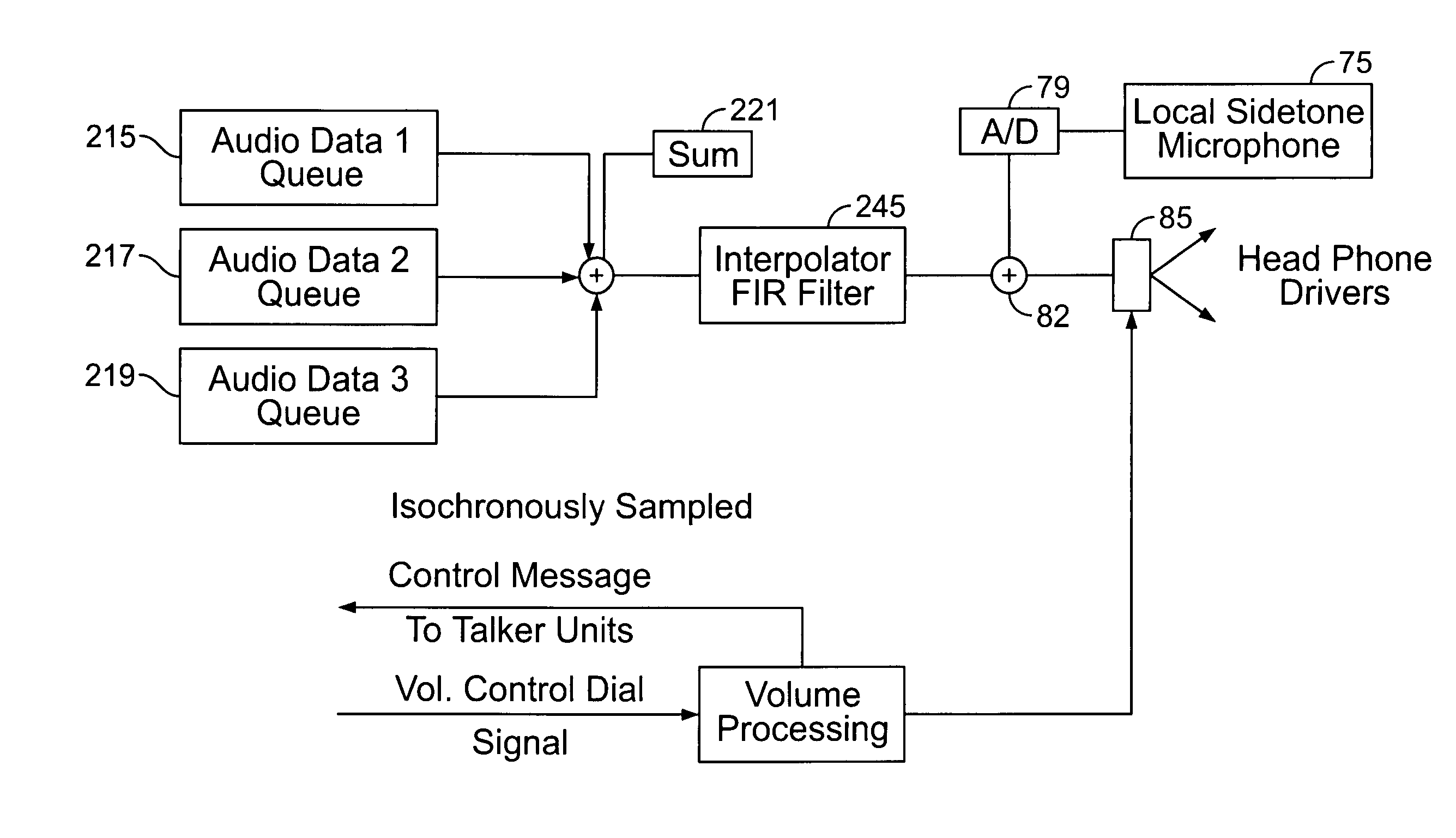
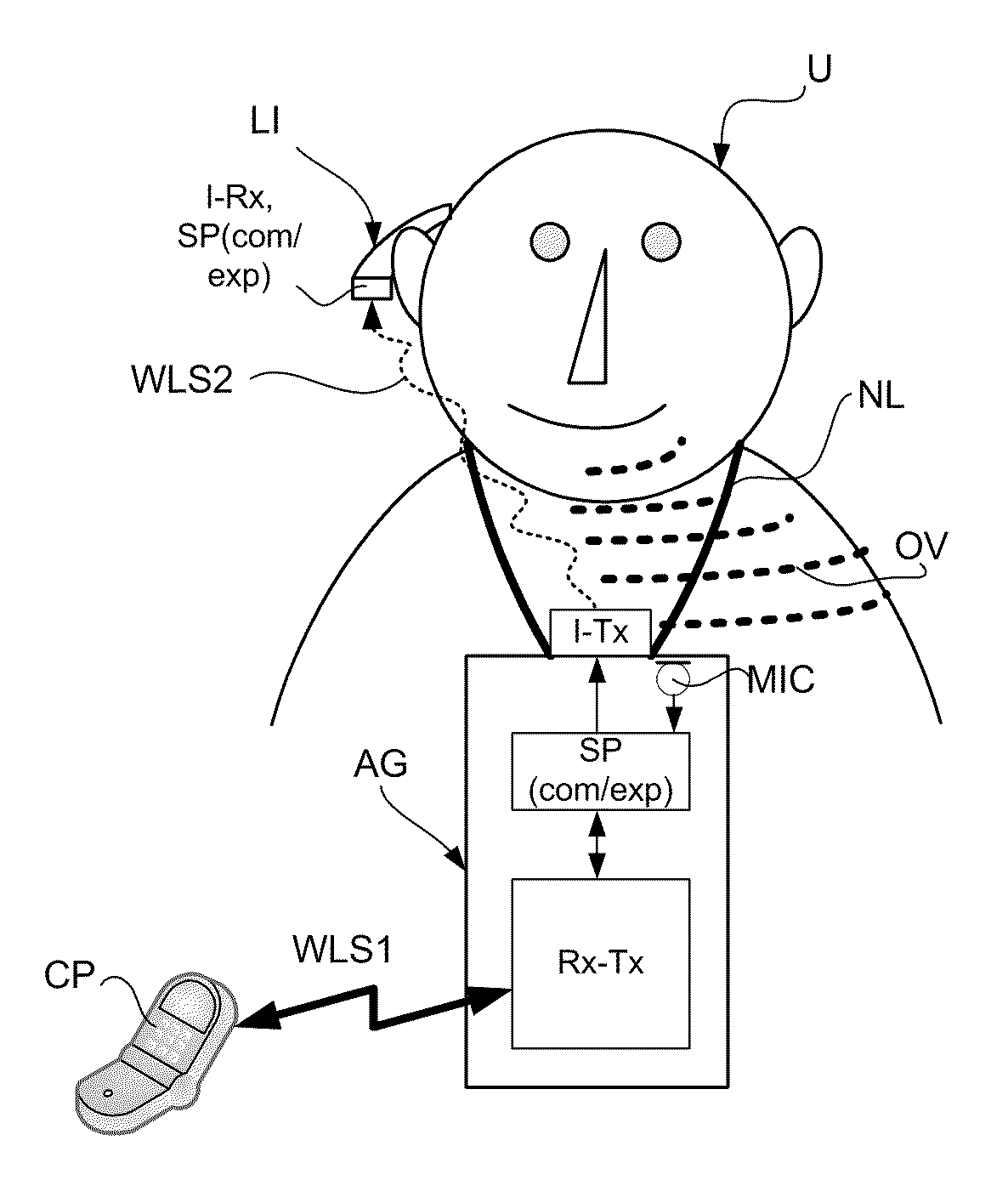
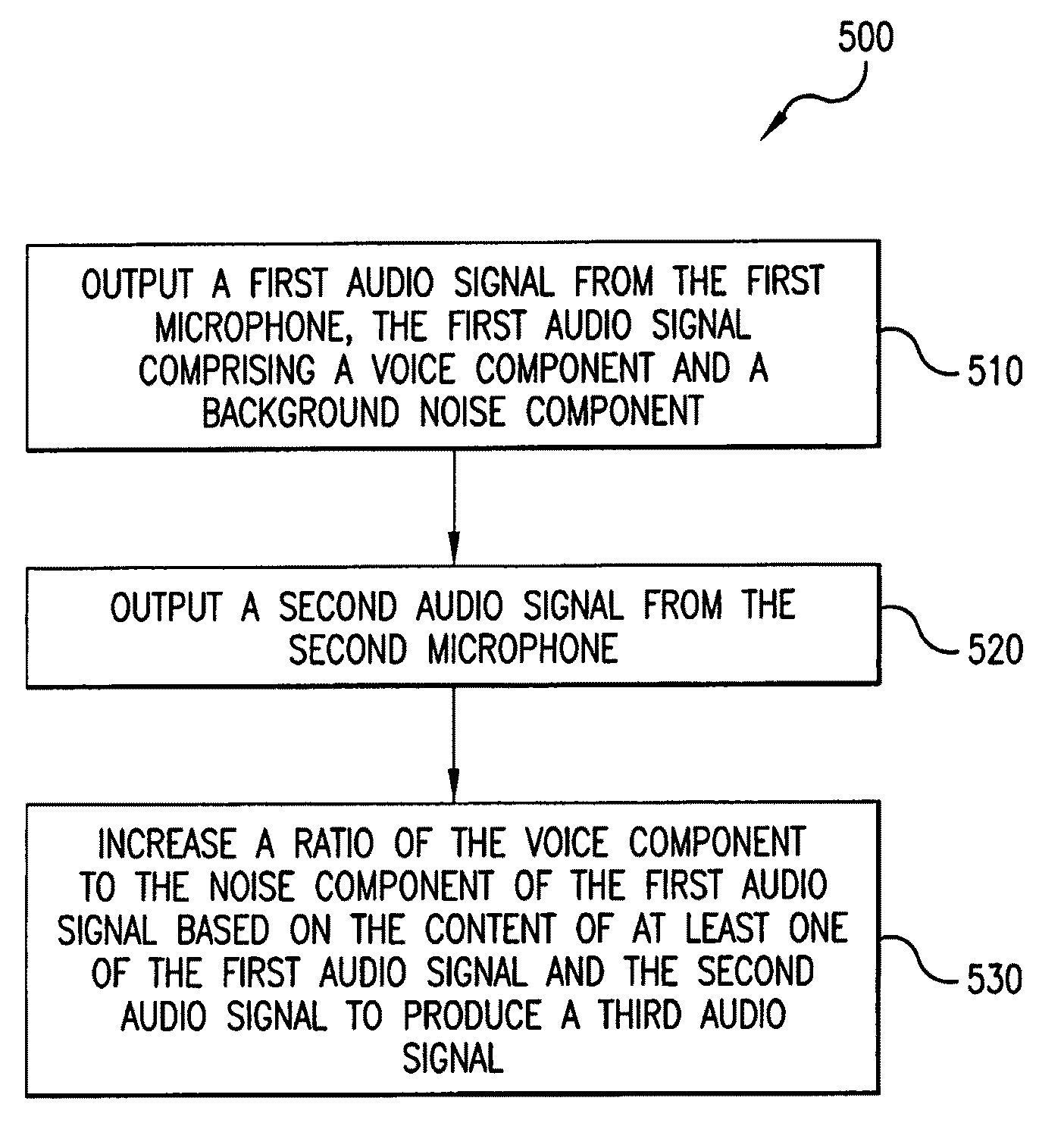
Companion microphone system and method
ActiveUS20050195996A1Improve speech clarityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesSpatial transmit diversityEngineeringAudio signal
A method and system for enhancing speech intelligibility using wireless communication in portable, battery-powered and entirely user-supportable devices. The devices may be talker devices and receiver devices, where the audio signals input into the talker devices may be transmitted to the receiver devices to provide better quality audio to person using the receiver devices. The receiver devices may initiate and terminate communications with the talker devices. Additionally, the receiver devices may indicate to the talker devices the gain level the talker devices need to apply to the audio signals before sending them to the receiver devices.
Owner:MCK AUDIO INC
User interface for communication system
InactiveUS7039197B1Improve clarityImprove easeMicrophones signal combinationTransmissionCommunications systemEngineering
An improved user interface is installed in the cabin of a vehicle incorporating a cabin communication system using acoustic echo cancellation for improving the ease and flexibility of the cabin communication. Separate controls at each seat location enable the person occupying that seat to selectively converse with other occupants in the vehicle, create a recorded message and / or place a telephone call.
Owner:LEAR CORP
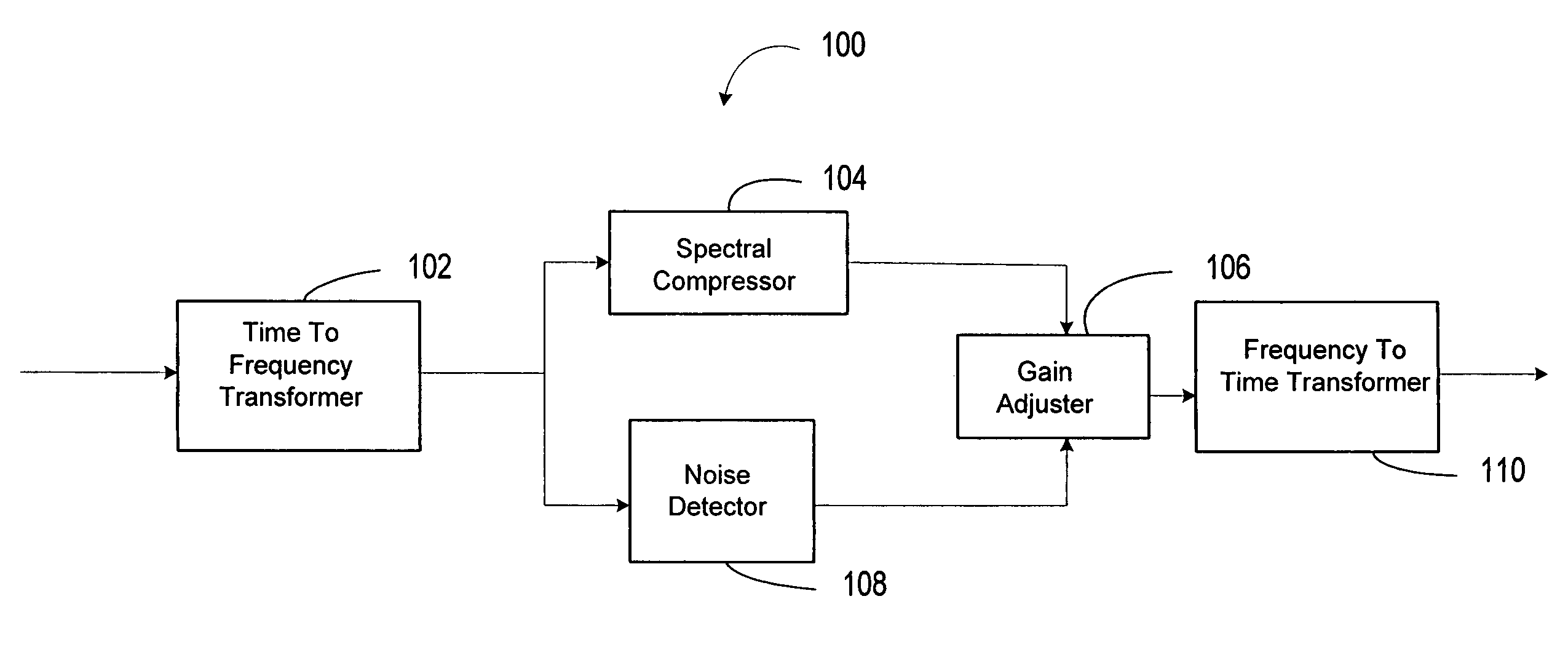
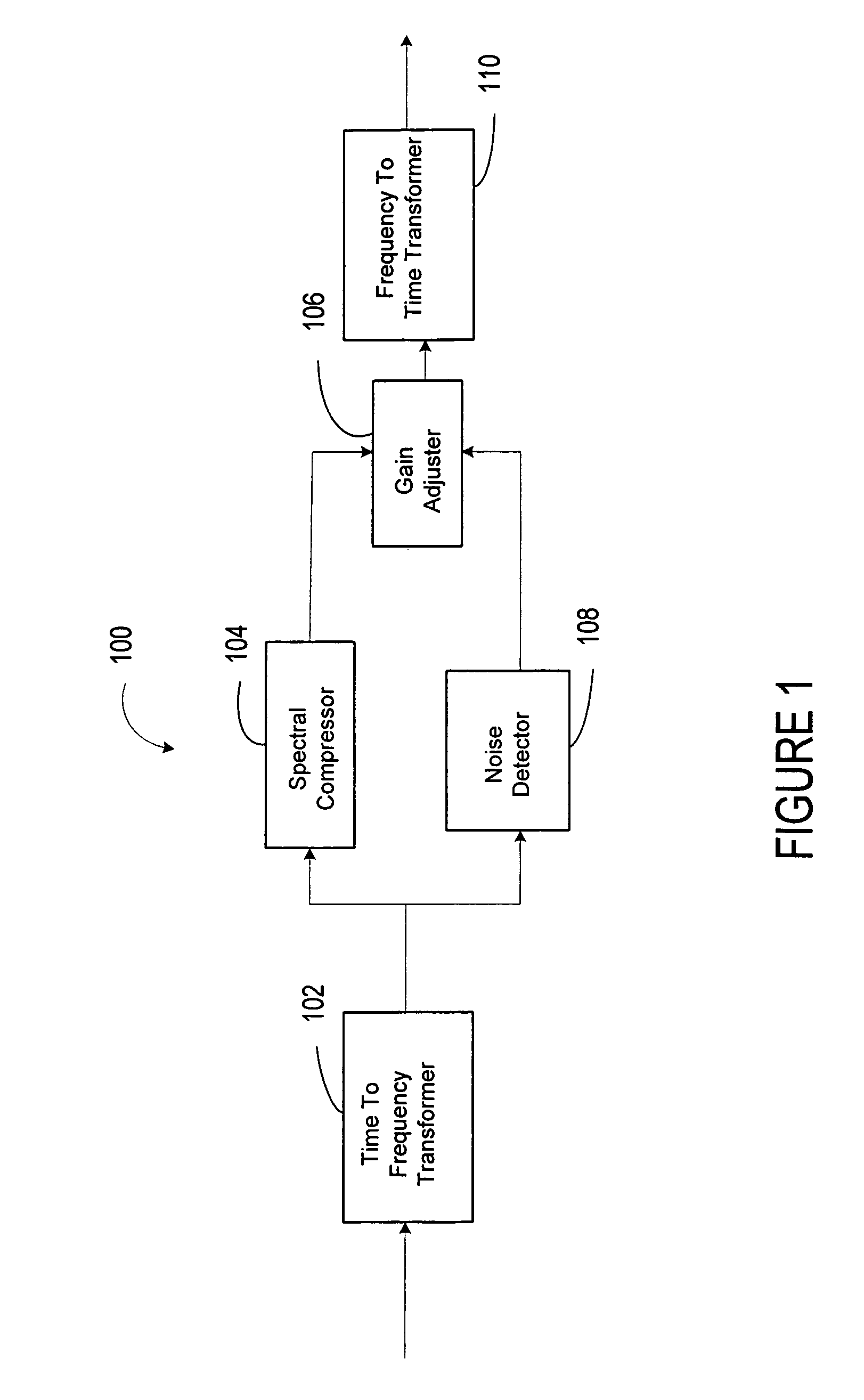
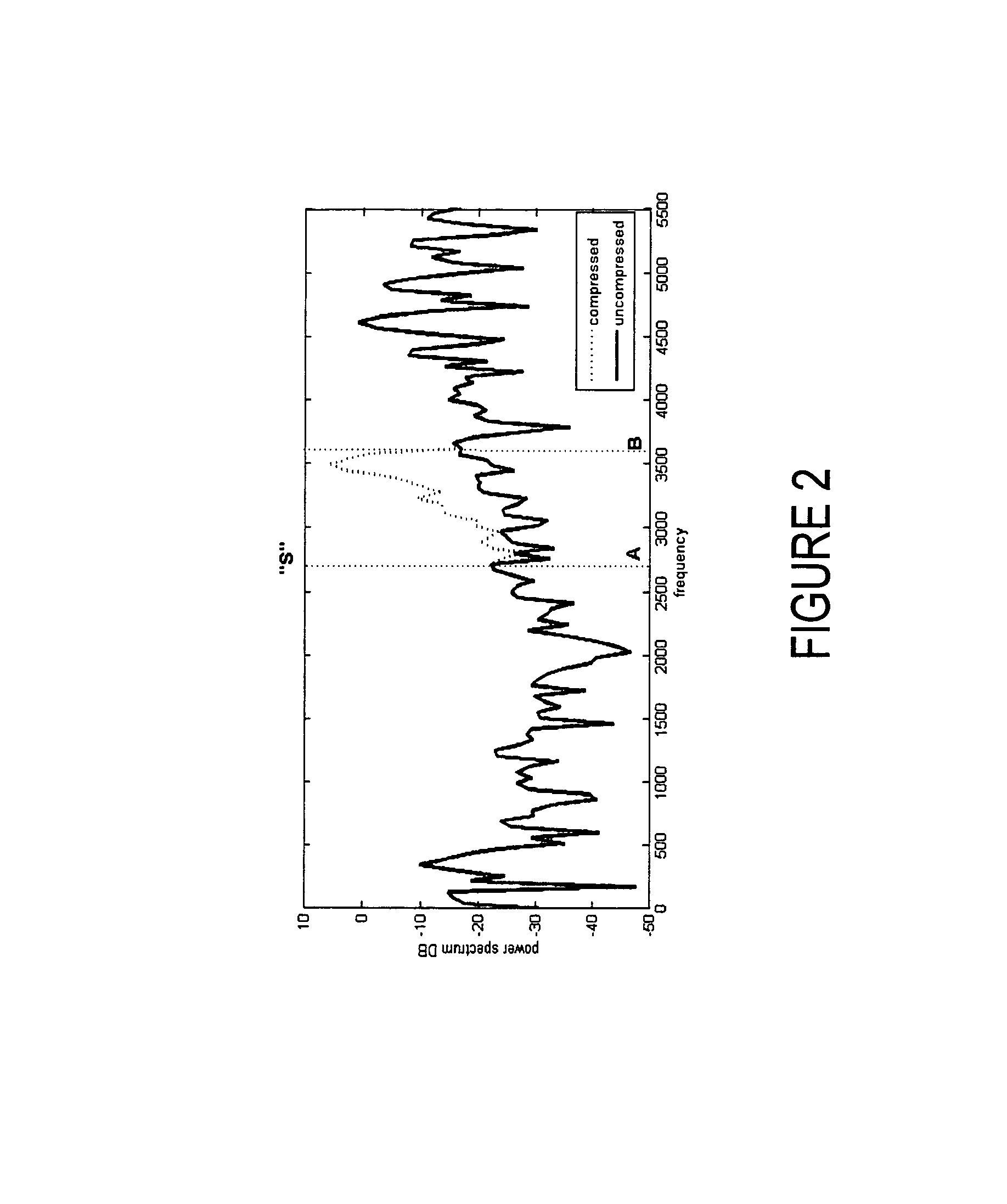
System for improving speech quality and intelligibility
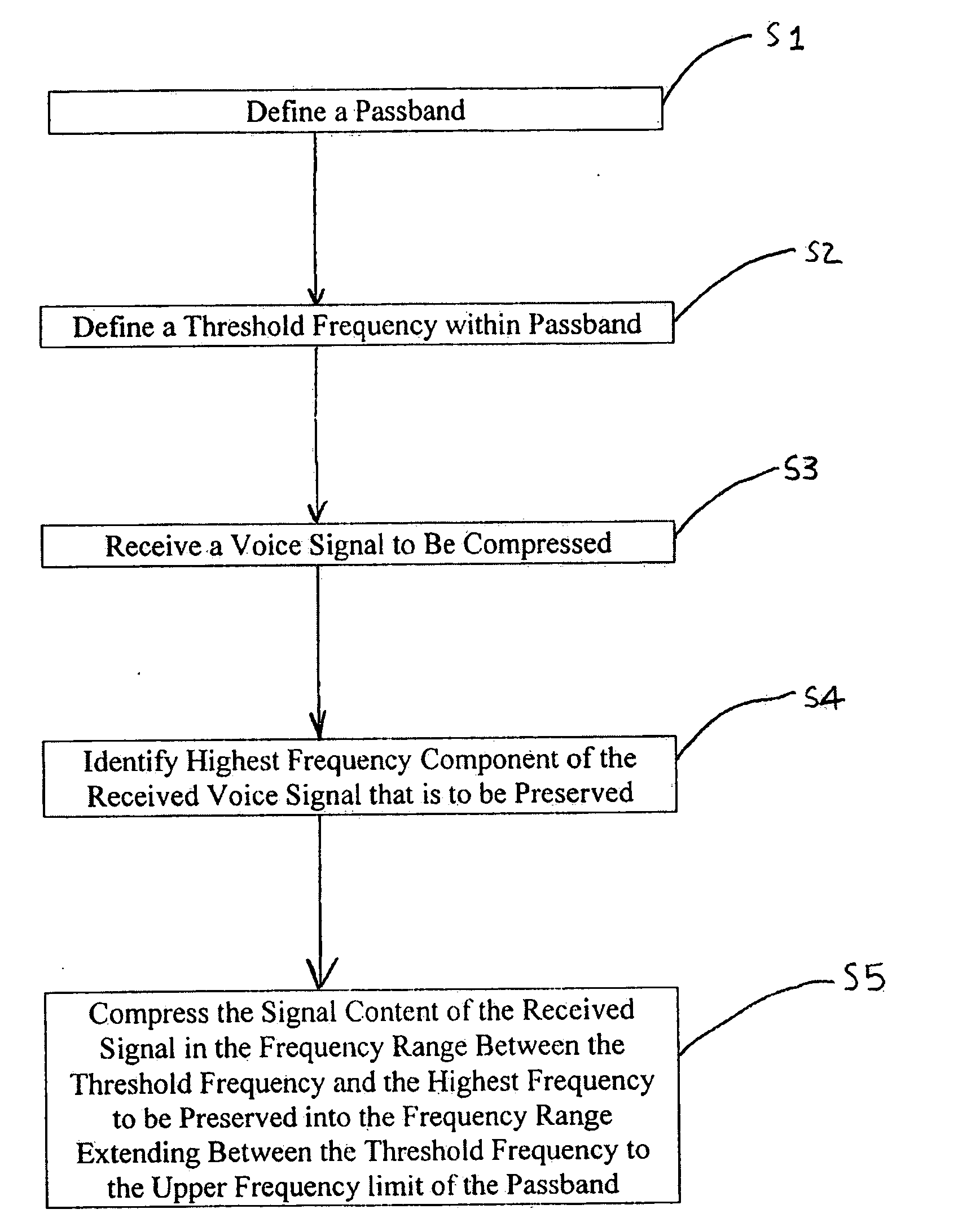
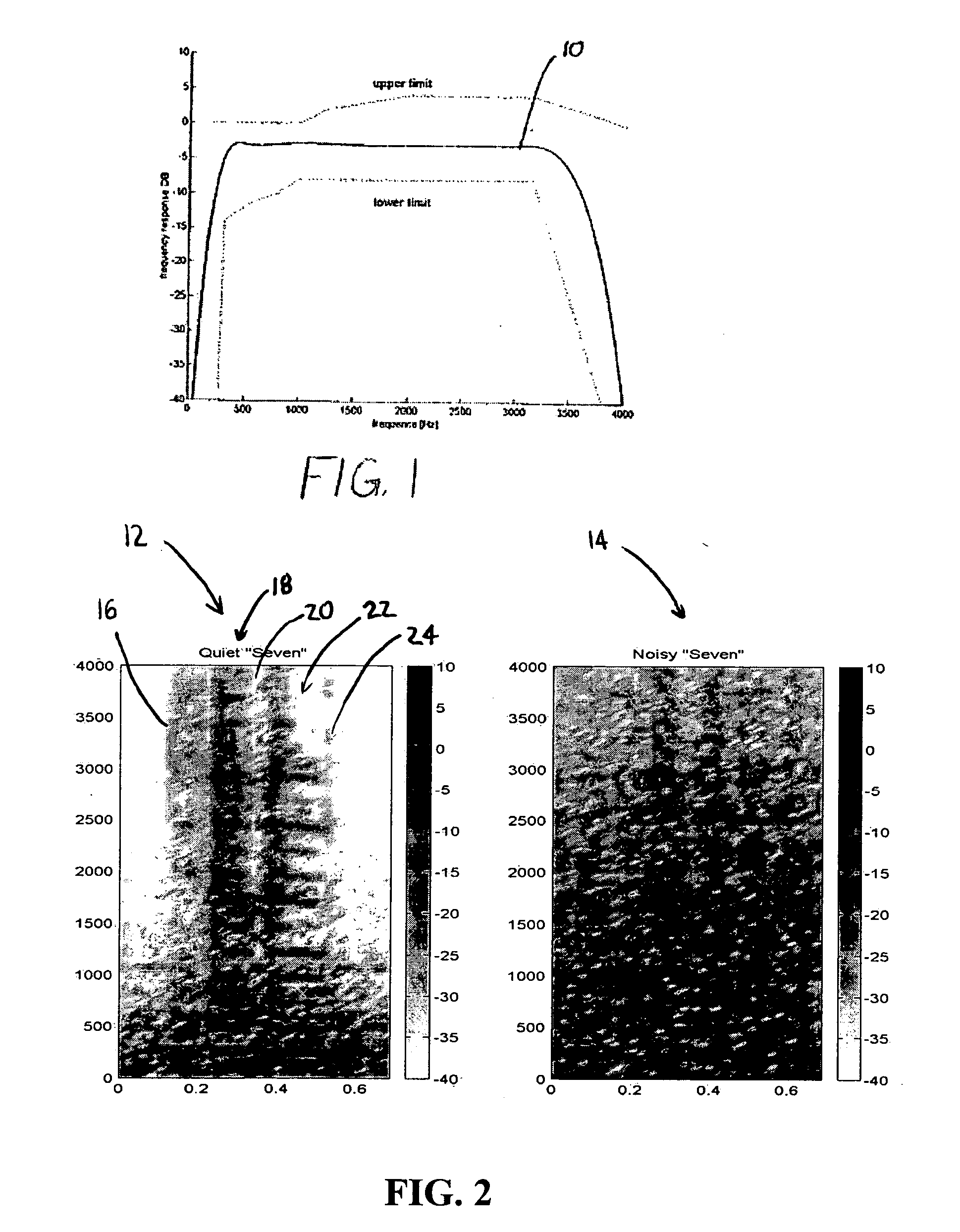
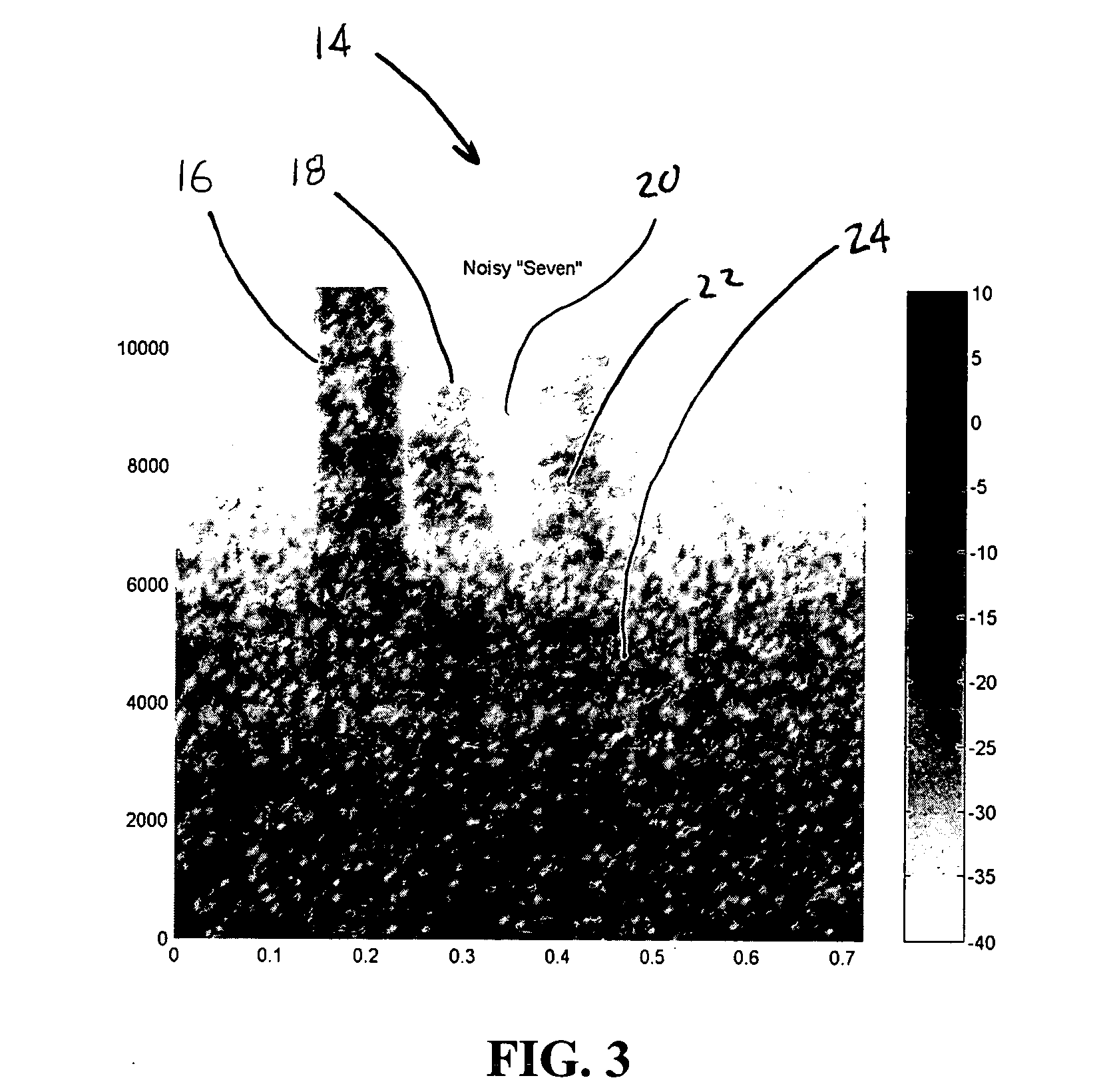
ActiveUS20060247922A1Improve speech clarityIncrease probabilitySpeech analysisFrequency compressionSound quality
A system and method are provided for improving the quality and intelligibility of speech signals. The system and method apply frequency compression to the higher frequency components of speech signals while leaving lower frequency components substantially unchanged. This preserves higher frequency information related to consonants which is typically lost to filtering and bandpass constraints. This information is preserved without significantly altering the fundamental pitch of the speech signal so that when the speech signal is reproduced its overall tone qualities are preserved. The system and method further apply frequency expansion to speech signals. Like the compression, only the upper frequencies of a received speech signal are expanded. When the frequency expansion is applied to a speech signal that has been compressed according to the invention, the speech signal is substantially returned to its pre-compressed state. However, frequency compression according to the invention provides improved intelligibility even when the speech signal is not subsequently re-expanded. Likewise, speech signals may be expanded even though the original signal was not compressed, without significant degradation of the speech signal quality. Thus, a transmitter may include the system for applying high frequency compression without regard to whether a receiver will be capable of re-expanding the signal. Likewise, a receiver may expand a received speech signal without regard to whether the signal was previously compressed.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
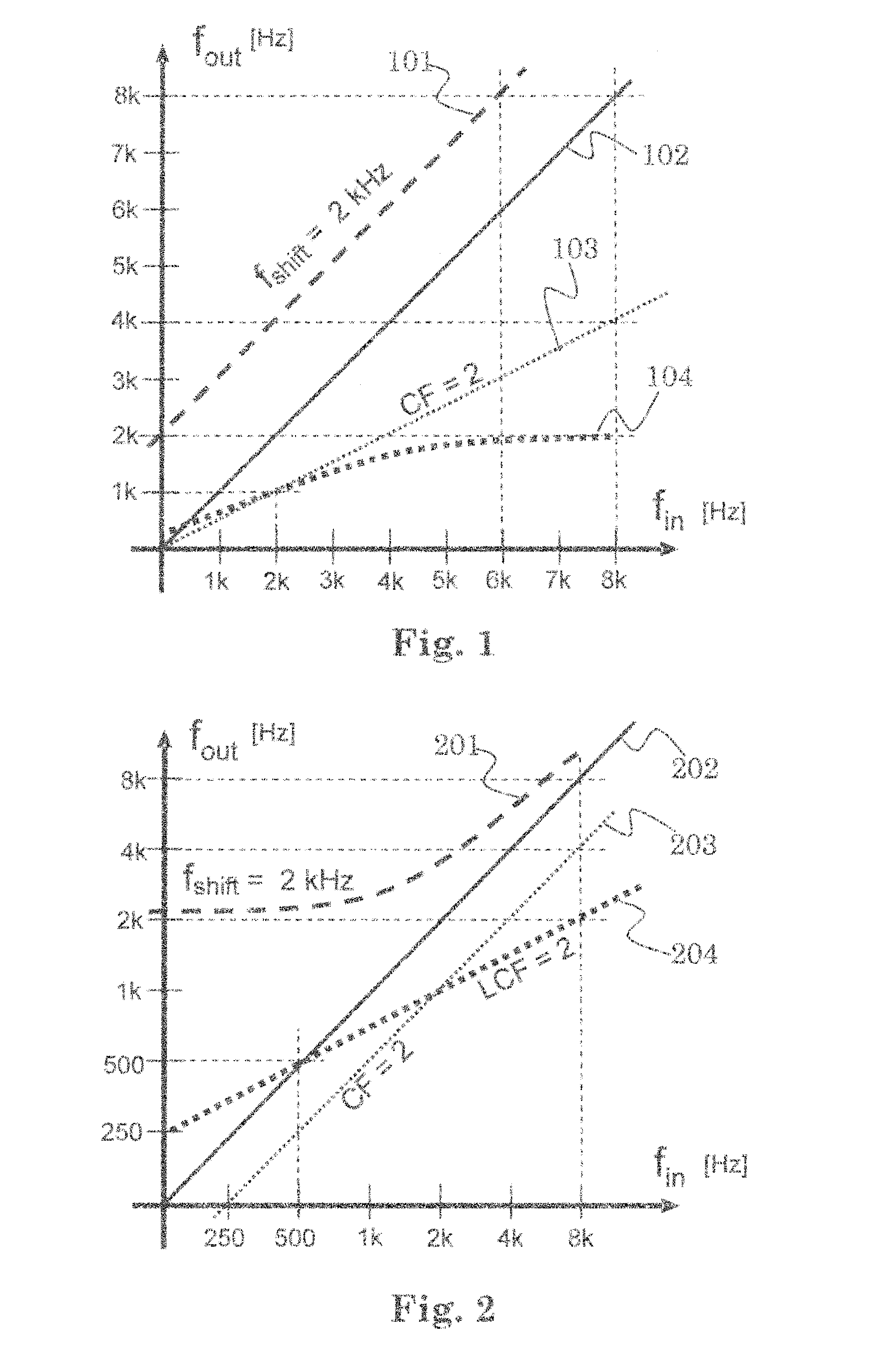
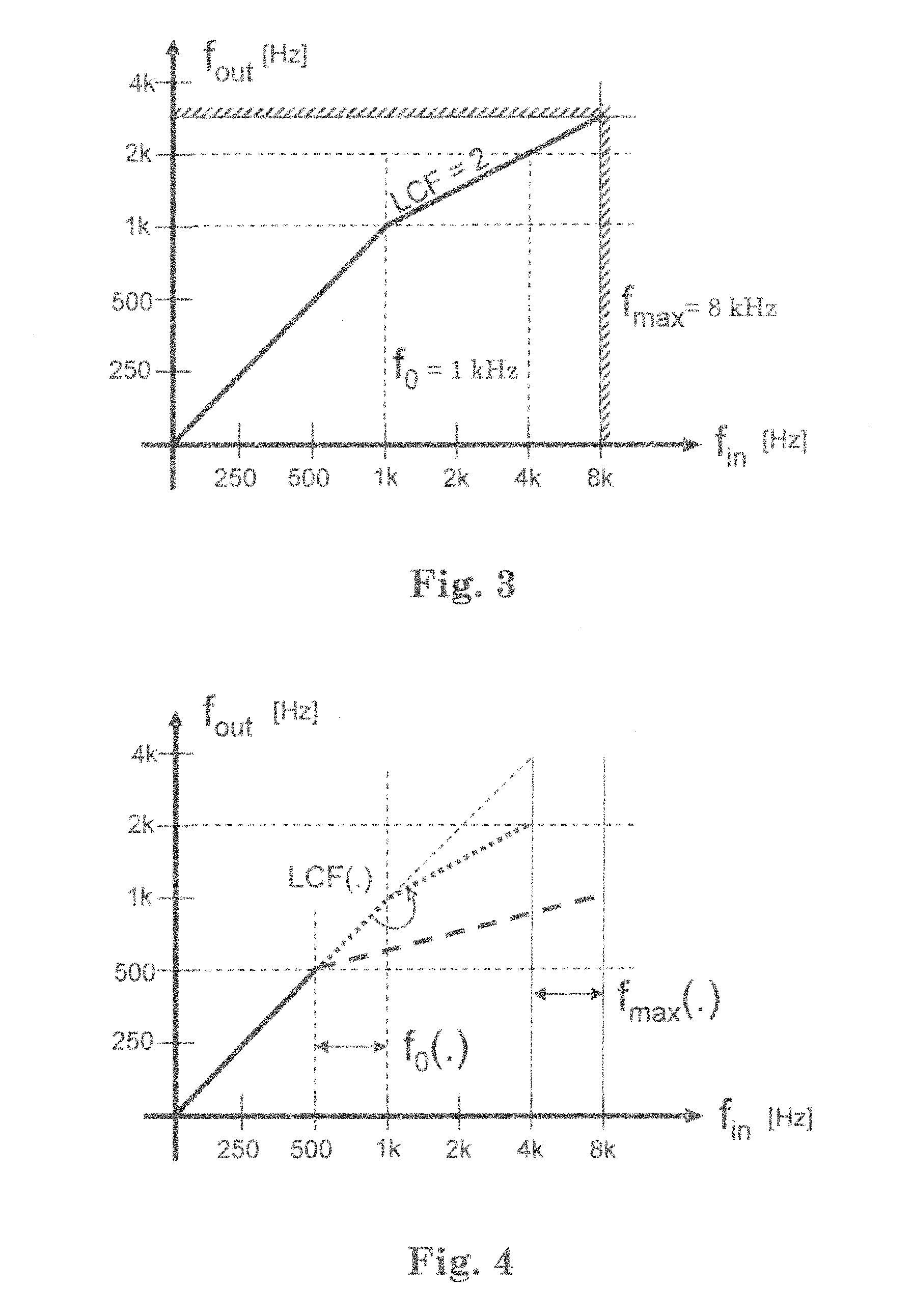
Sound perception using frequency transposition by moving the envelope
ActiveUS20110249843A1Facilitate cognitionImprove sound qualityHearing aids signal processingTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsSound perceptionSound quality
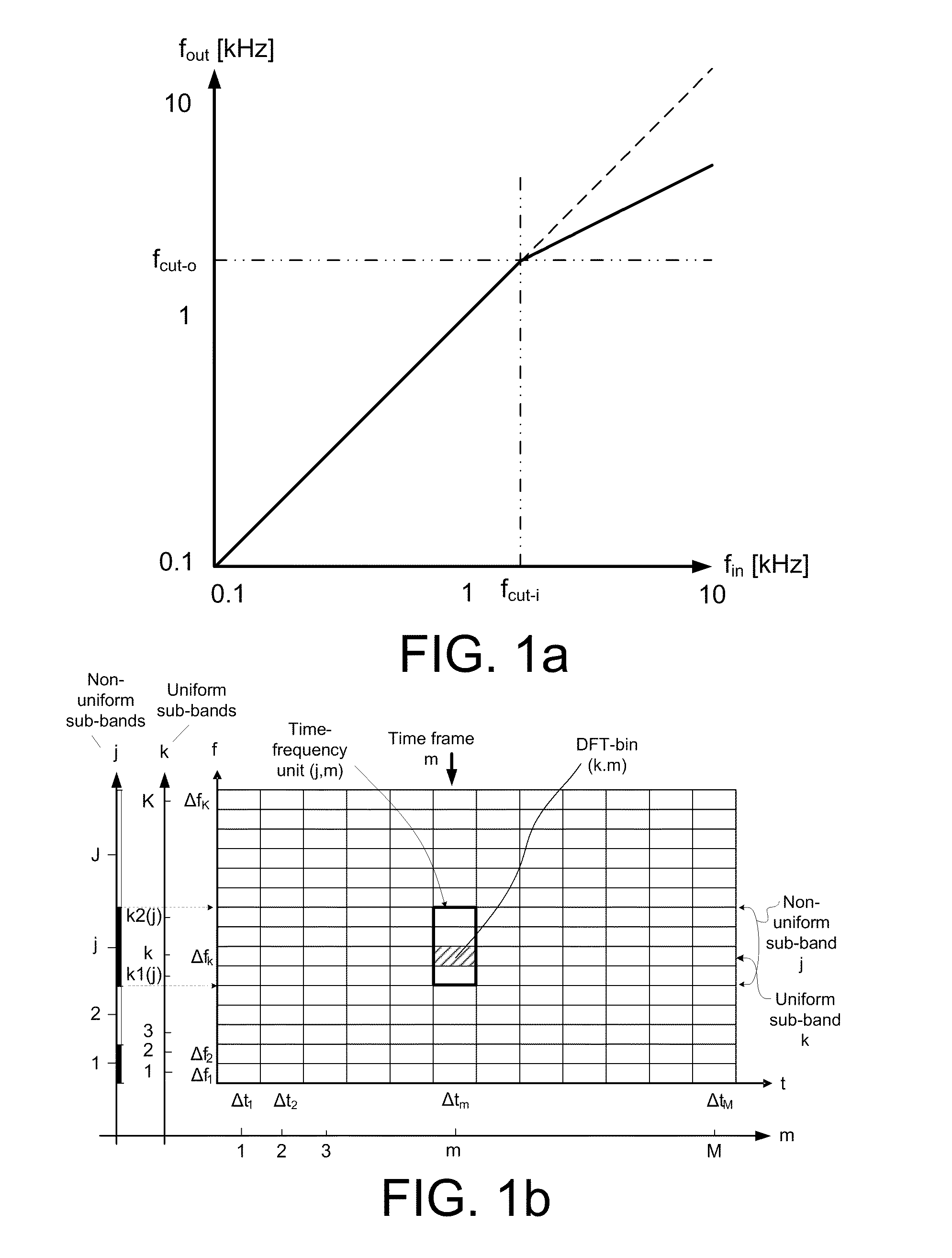
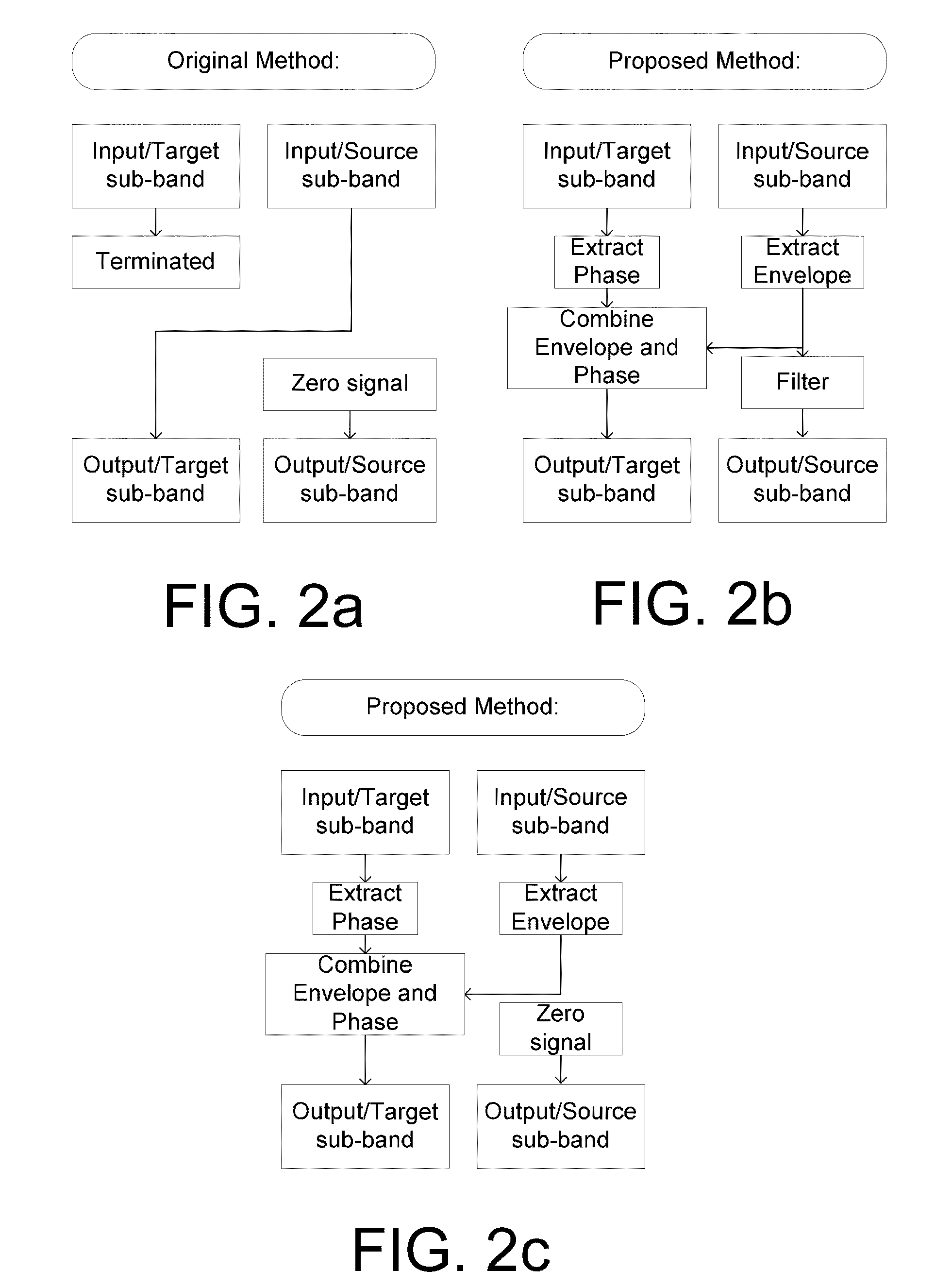
The application relates to a method of improving a user's perception of an input sound. The application further relates to an audio processing device and to its use. The object of the present application is to increase the sound quality of a sound signal as perceived by a user, e.g. a hearing impaired user. The method comprises a) Defining a critical frequency fcrit between a low frequency range and a high frequency range; b) Analyzing an input sound in a number of frequency bands below and above said critical frequency; c) Defining a cut-off frequency fcut below said critical frequency fcrit; d) Identifying a source frequency band above said cut-off frequency fcut; e) Extracting the envelope of said source band; f) Identifying a corresponding target band below said critical frequency fcrit; g) Extracting the phase of said target band; h) Combining the envelope of said source band with the phase of said target band. This has the advantage of increasing the sound quality, and the potential to further improve speech intelligibility in frequency transposition, e.g. frequency lowering systems. The invention may e.g. be used in communication devices, such as telephones, or listening devices, e.g. hearing instruments, headsets, head phones, active ear protection devices or combinations thereof.
Owner:OTICON
Voice enhancement method and device using same
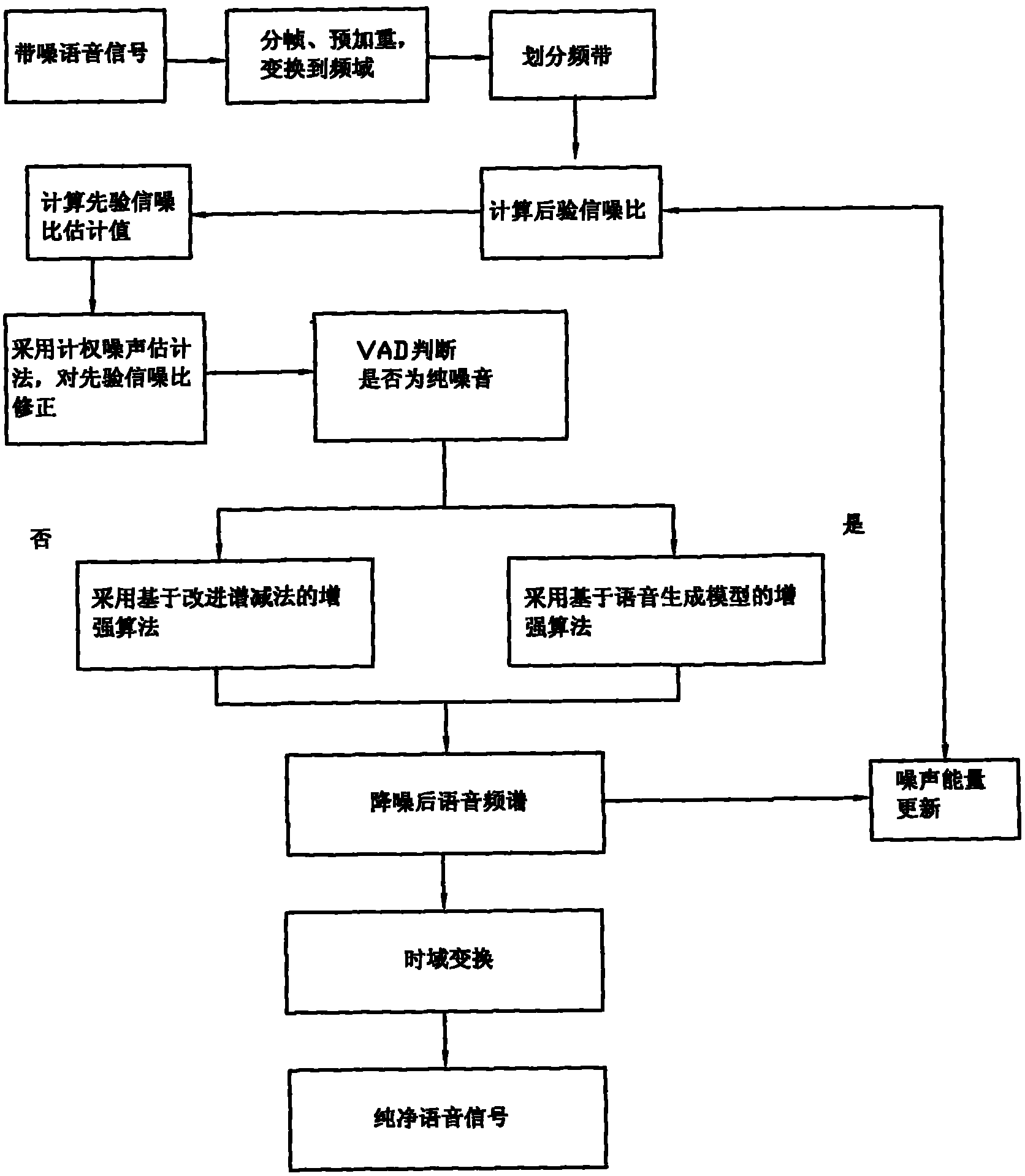
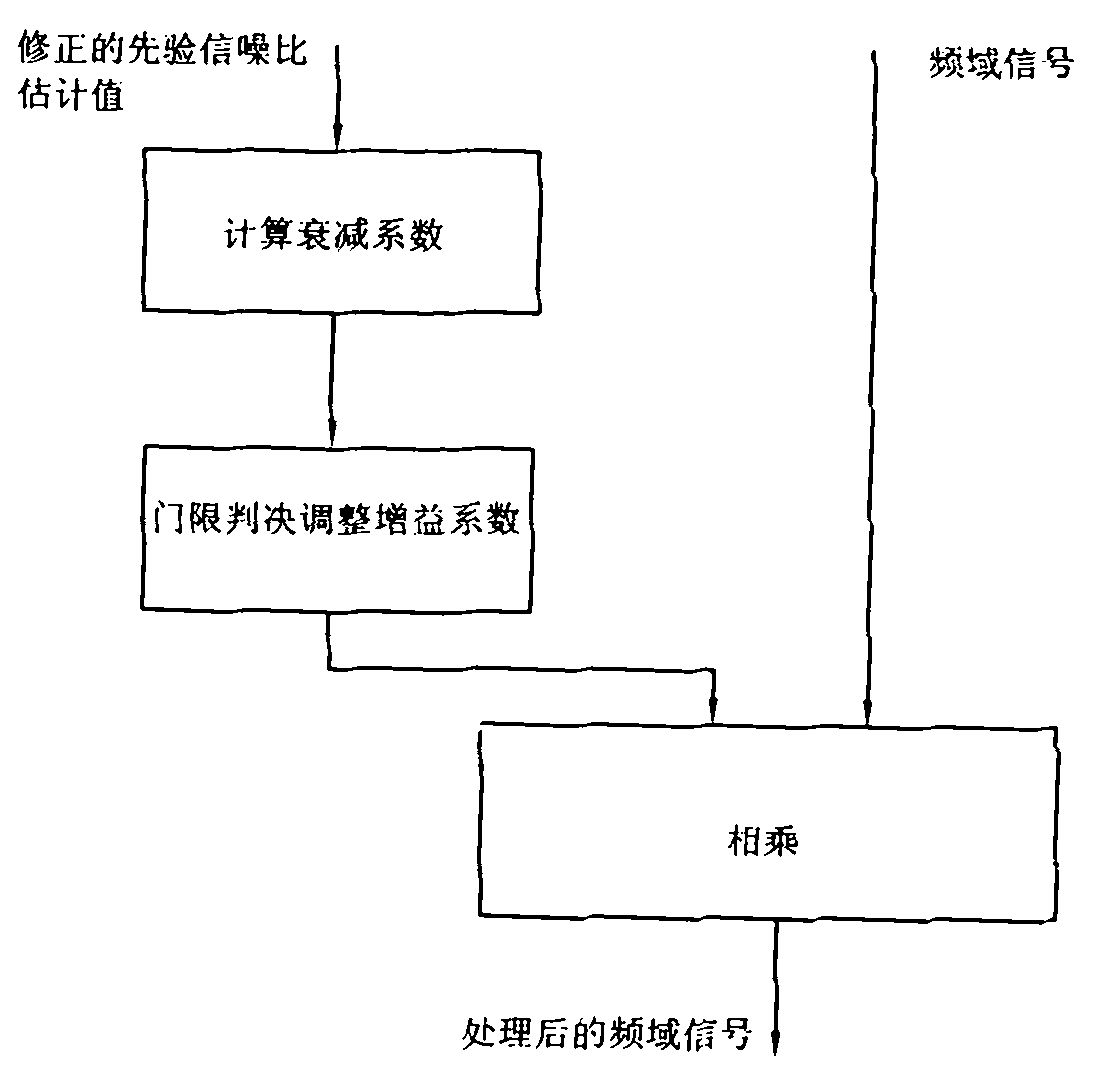
ActiveCN101976566AGuaranteed intelligibilitySuppress background noiseSpeech analysisTime domainUltrasound attenuation
The invention provides a voice enhancement method. The method comprises the following steps of: judging whether the current frame has pure noise by using a judgment device; if the current frame has pure noise and a plurality of previous frames of the current frame have pure noise, improving frequency domain signals by using a voice enhancement algorithm of an improved spectral subtraction method, otherwise, improving the frequency domain signals by using an enhancement algorithm of a voice generating model; and transforming the processed frequency domain signals to a time domain, performing de-emphasis processing and acquiring output signals. The invention also provides a device using the method. The voice enhancement method greatly improves the attenuation of residual noise, and ensures the voice intelligibility.
Owner:AAC TECH PTE LTD
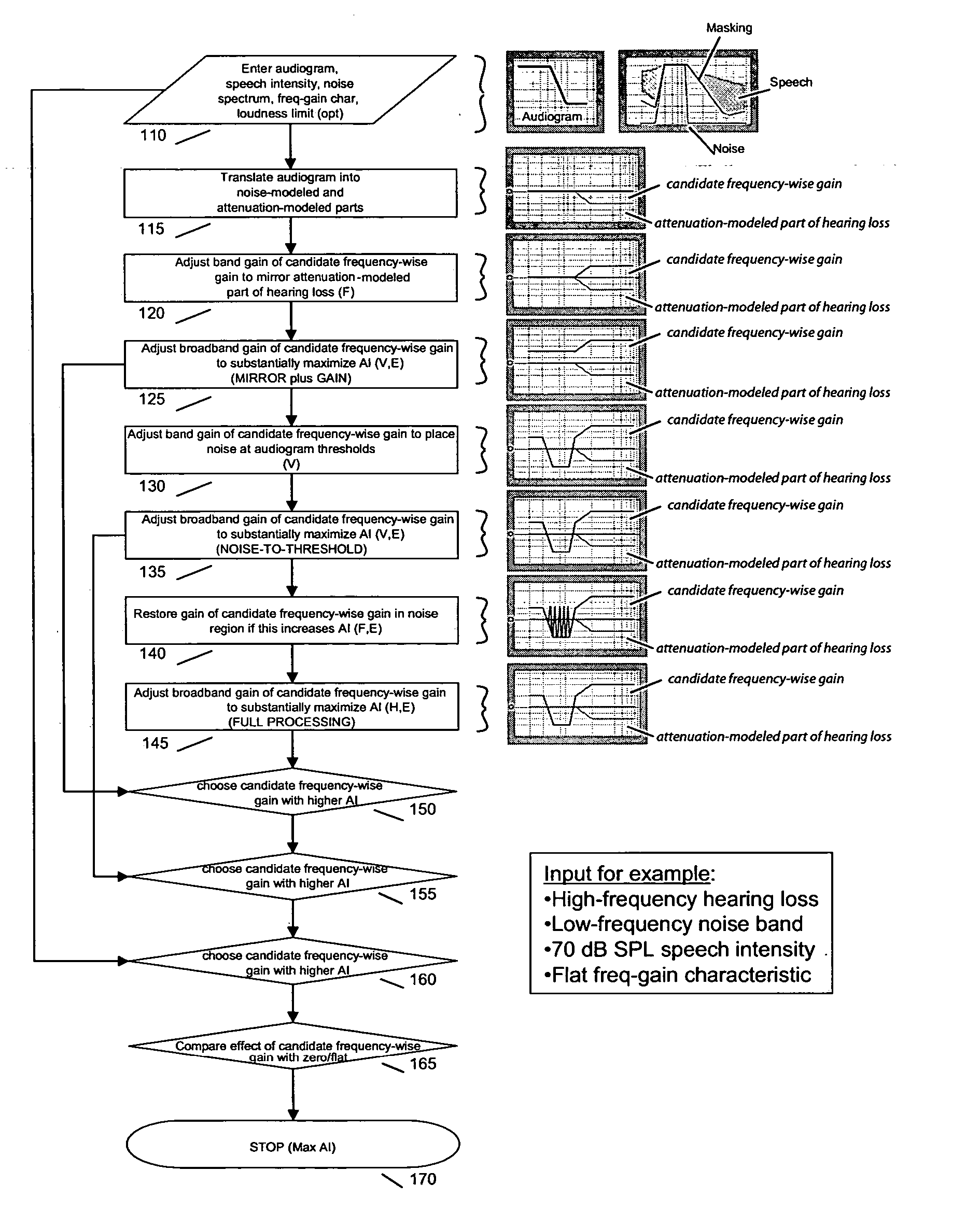
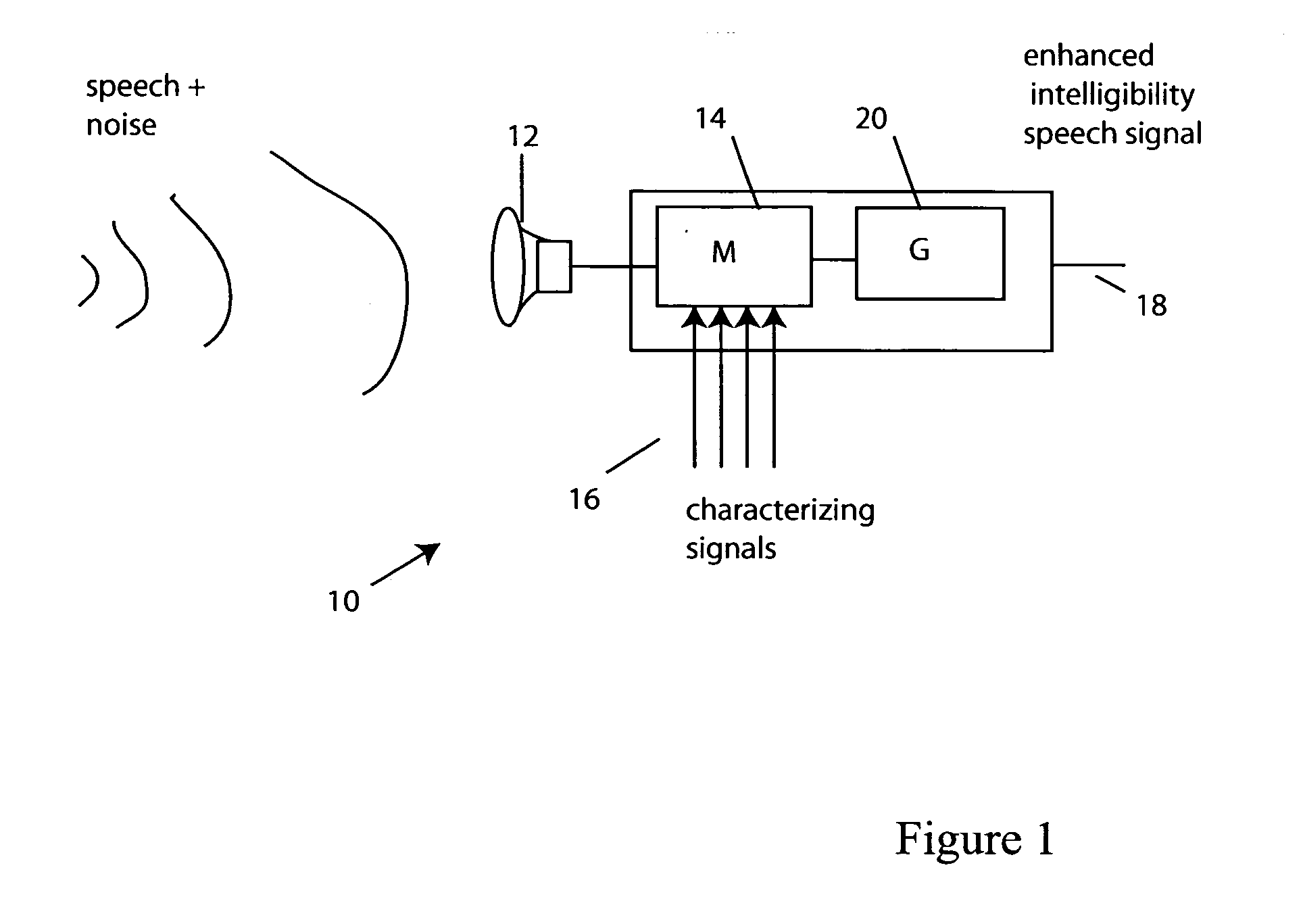
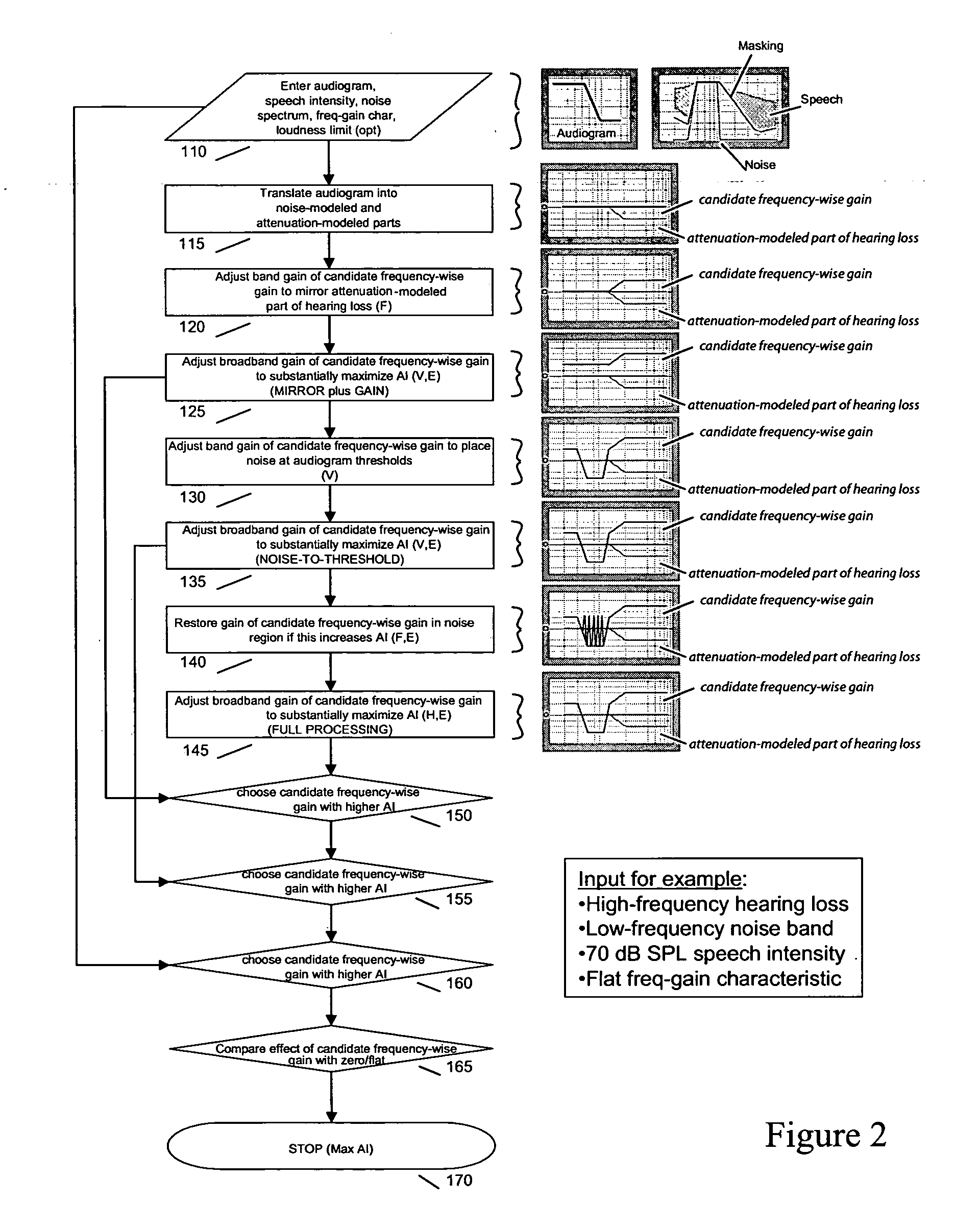
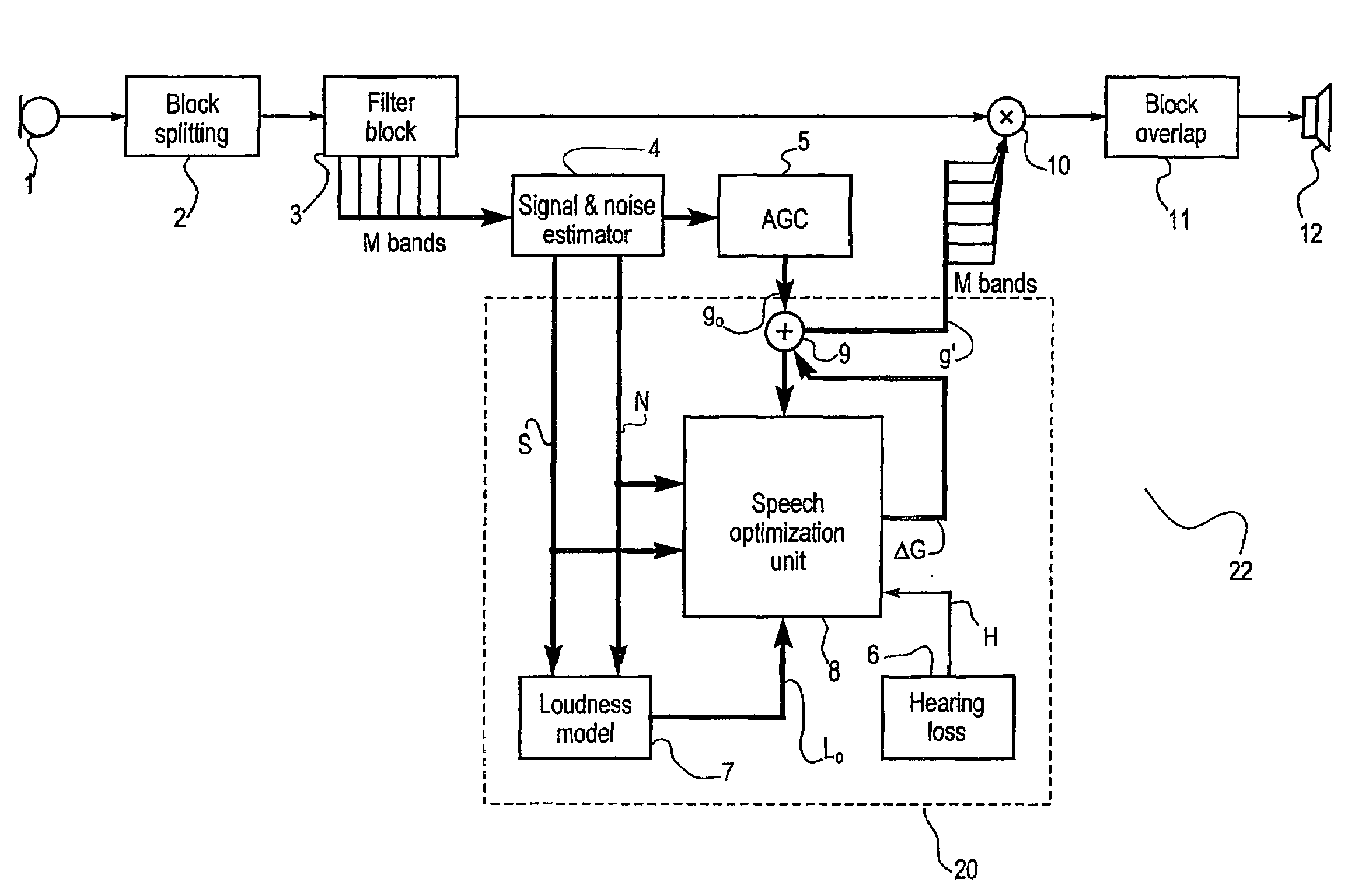
Methods and apparatus for maximizing speech intelligibility in quiet or noisy backgrounds
ActiveUS20050114127A1Improve speech clarityMaximize intelligibility metricSpeech recognitionPublic address systemHearing test
Methods and apparatus for maximizing speech intelligibility use psycho-acoustic variables of a model of speech perception to control the determination of optimal frequency-band specific gain adjustments. Speech signals (or other audio input) whose intelligibility is to be improved are characterized by parameters which are applied to the model. These include measurements or estimates of speech intensity level, average noise spectrum of the incoming audio signal, and / or the current frequency-gain characteristic of the hearing compensation device. Characterizations of listeners based on hearing test results, for example, may also be applied to the model. Frequency-band specific gain adjustments generated by use of the model can be used for hearing aids, assistive listening devices, telephones, cellular telephones, or other speech delivery systems, personal music delivery systems, public-address systems, sound systems, speech generating systems, or other devices or mediums which project, transfer or assist in the detection or recognition of speech.
Owner:ARTICULATION
Method of processing a signal in a hearing instrument, and hearing instrument
ActiveUS20140177857A1Improve speech claritySatisfied with the resultHearing aids signal processingElectronic input selection/mixingUltrasound attenuationEngineering
A method of processing a signal in a hearing instrument includes the steps of calculating a coherence between two microphone signals or microphone combination signals having different directional characteristics, determining an attenuation from the coherence, and applying the attenuation to the signal.
Owner:SONOVA AG
Method for adapting sound in a hearing aid device by frequency modification and such a device
InactiveUS20110150256A1Reduce presenceLess distortionOcclusion effect electronic compensationHearing device energy consumption reductionDistortionDigital hearing aid
In a digital hearing aid device (1) frequency modification is employed above a lower spectral bound and in accordance with a compression factor. The frequency modification is dynamically adjusted in dependence on a sound environment analysis (10) or an end-user input (30), by modifying the frequency modification parameters such as a lower spectral bound and a compression factor. The adjustment can be based on an interpolation between predefined parameters. In certain sound environments, such as loud noise, own-voice and telephone conversations, frequency modification is reduced or switched off. The proposed solutions have the advantage that the occurrence of disturbing noise and of distortions of harmonic relationships at the end-user's ear is reduced and signal processing resources as well as battery resources are saved.
Owner:SONOVA AG
Hearing aid having second order directional response
InactiveUS7103191B1Improve speech clarityMicrophones signal combinationElectronic input selection/mixingAudio power amplifierIntermediate frequency
A hearing aid apparatus is disclosed that employs both an omnidirectional microphone and at least one directional microphone of at least the first order. The electrical signals output from the directional microphone are supplied to an equalization amplifier which at least partially equalizes the amplitude of the low frequency electrical signal components of the electrical signal with the amplitude of the mid and high frequency electrical signal components of the electrical signals of the directional microphone. A switching circuit accepts the signals output from both the omnidirectional microphone and the directional microphone. The switching circuit connects the signal from the omnidirectional microphone to an input of a hearing aid amplifier when the switching circuit is in a first switching state, and connects the output of the equalization circuit to the hearing aid amplifier input when the switching circuit is in a second switching state. The switching circuit may be automatically switched in response to sensed ambient noise levels.
Owner:ETYMOTIC RES
Method for sound processing in a hearing aid and a hearing aid
ActiveUS20110013794A1Control propertiesQuality improvementSignal processingHearing aids signal processingControl signalEngineering
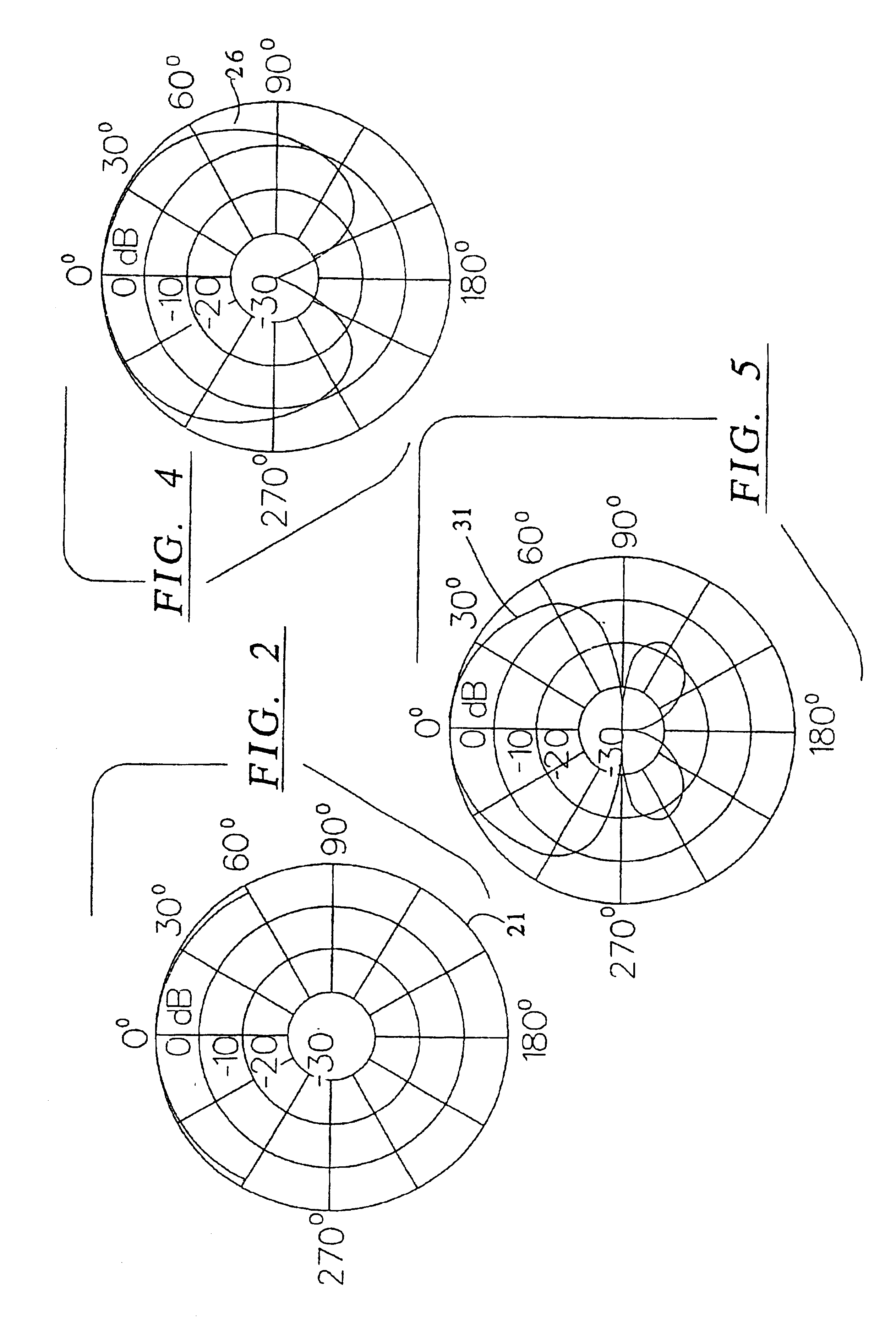
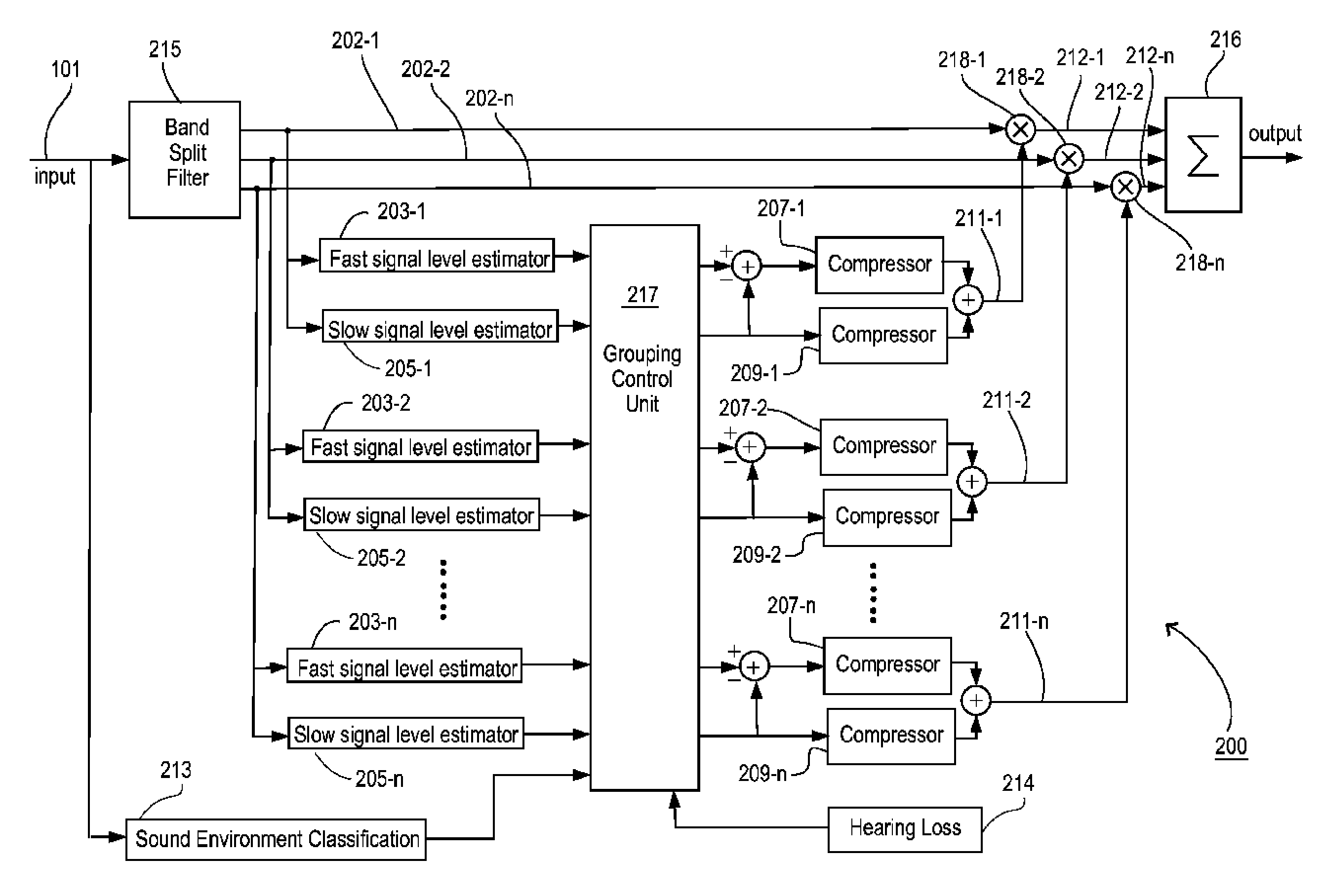
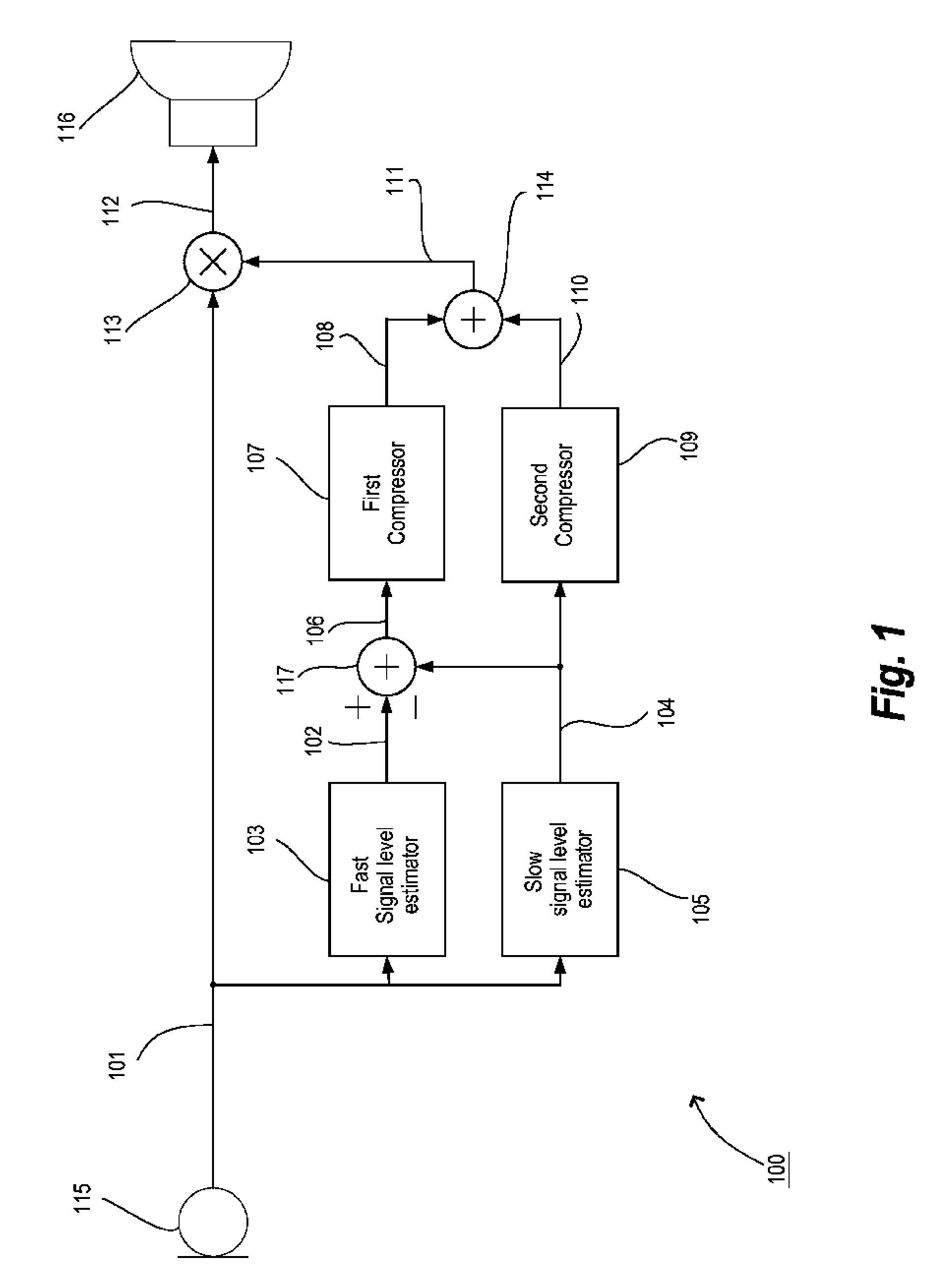
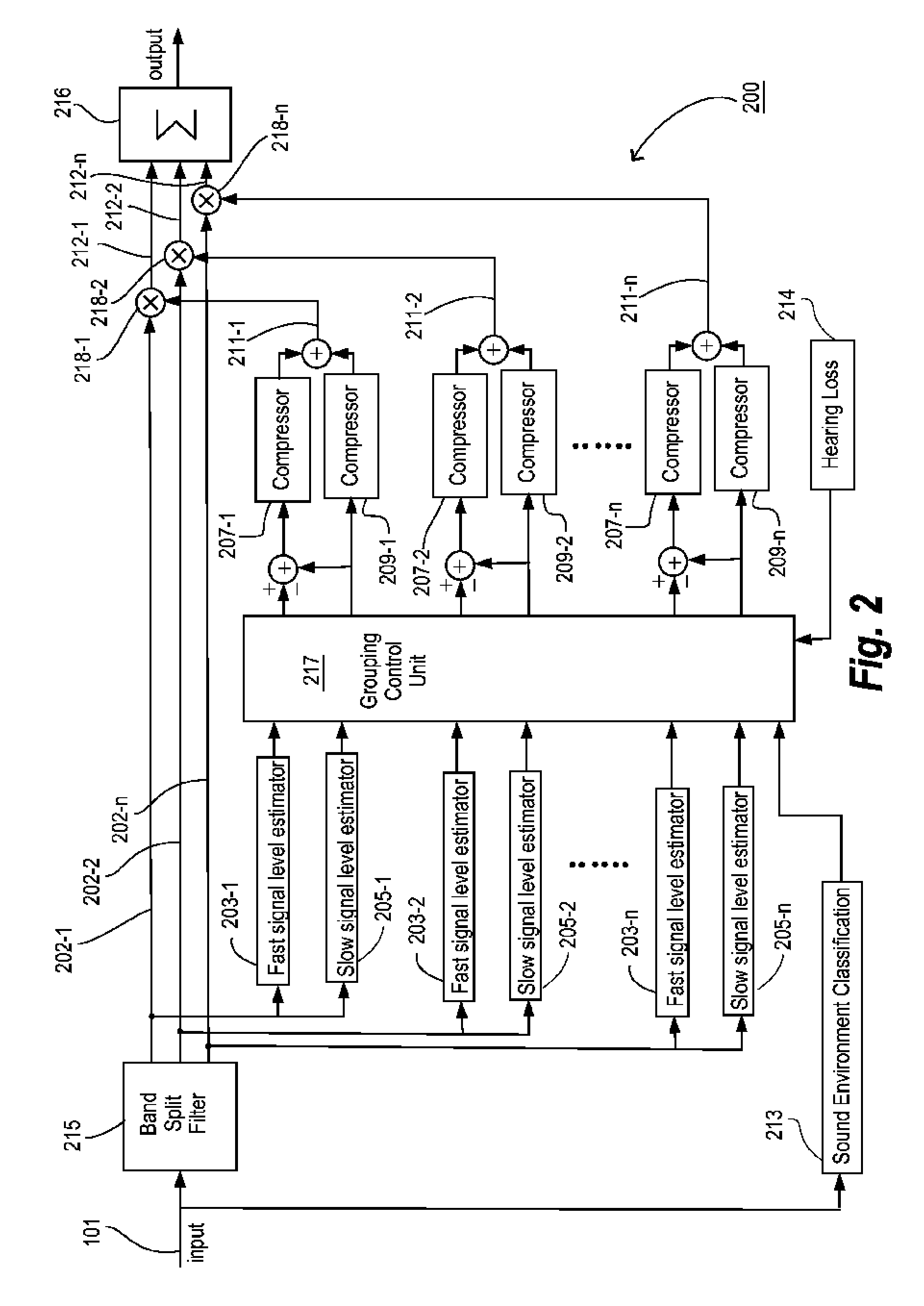
A method for processing and controlling sound signals in a hearing aid is provided. The method comprises estimating a first (102) and a second (104) signal level of an electric input signal (101) based on a first (103) and a second (105) signal level estimator adapted for responding according to a first and a second speed respectively, where the second speed is lower than the first speed and where the estimated second signal level is subtracted from the estimated first signal level, thereby forming a third signal level (106). Subsequently a first and a second compressor gain control output are determined in a first (107) and second (109) compressor based on said third and second signal level respectively. Then the first and second compressor gain control outputs are summed and hereby a net gain control signal (111) is created. Finally the electric input signal is amplified in accordance with the net gain control signal and thereby creating an electric output signal (112). The invention also relates to a hearing aid operating according to said method.
Owner:WIDEX AS
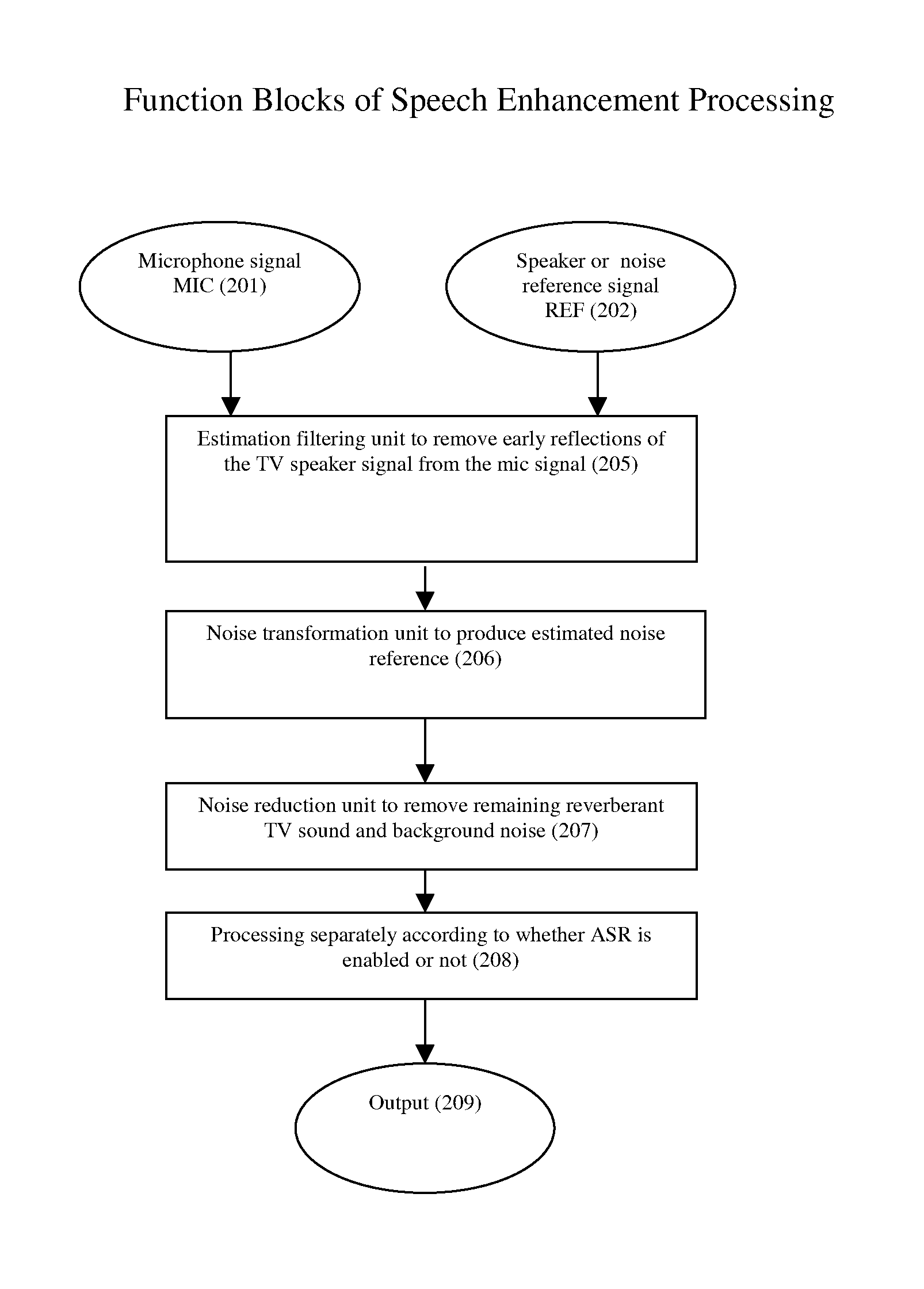
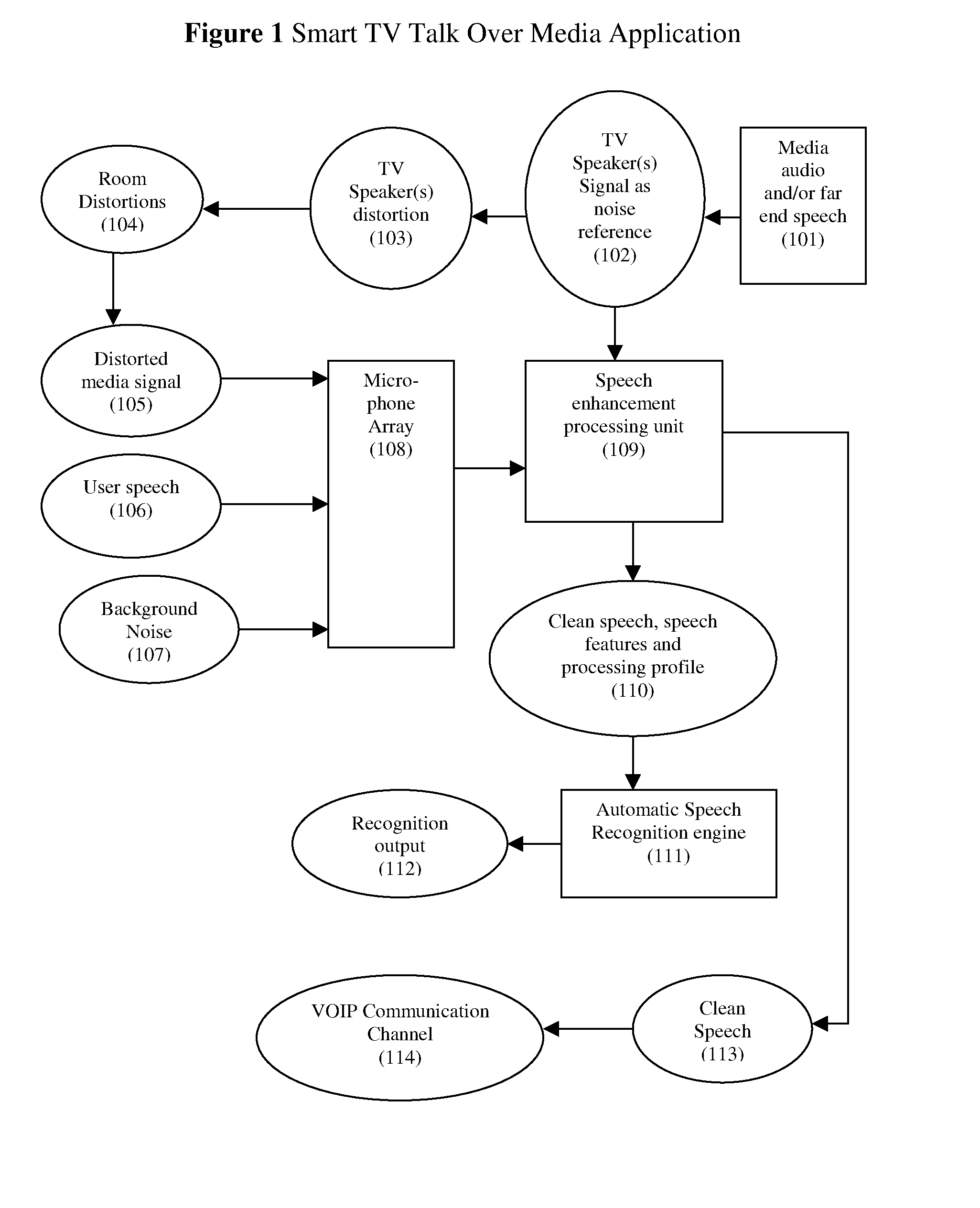
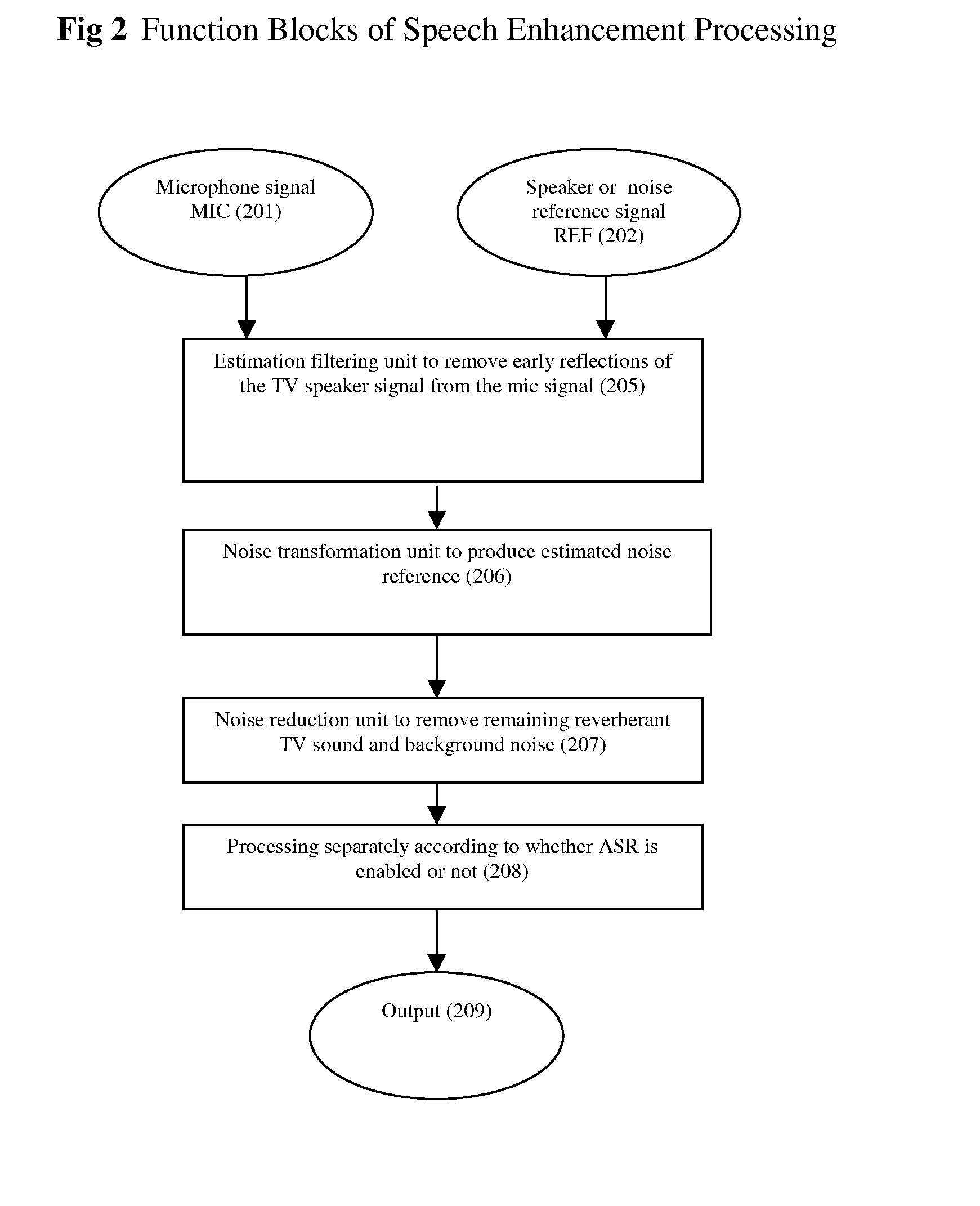
Speech enhancement to improve speech intelligibility and automatic speech recognition
InactiveUS20140025374A1Improve speech clarityImprove the detection rateSpeech recognitionFrequency spectrumSystem configuration
The present invention provides a system and method to enhance speech intelligibility and improve the detection rate of automatic speech recognizer in noisy environments. The present invention reduces an acoustically coupled loudspeaker signal from a plurality of microphone signals to enhance a near end user speech signal. A decision unit checks a system configuration parameter to determine if the cleaned speech is intended for human communication and / or Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR). A formant emphasis filer and a spectrum band reconstruction unit are used to further enhance the speech quality and improve the ASR recognition rate. The present invention can also apply to devices which has a foreground microphone(s) and a background microphone(s).
Owner:LOU XIA
Method and a binaural listening system for maximizing a better ear effect
InactiveUS20130051566A1Good effectImprove sound positioningHearing aids signal processingStereophonic systemsElectricityEngineering
The present invention relates to a listening device for a hearing impaired person. The present invention furthermore relates to a corresponding operating method of operating a listening device and to a corresponding computer program. In particular, the present invention relates to a listening device that comprises a signal processing unit that is controlled by a controller configured to implement a combined feed-forward and feed-back control in order to ensure that both an electric input signal and a processed electric output signal have at least almost identical modulation index values. Thereby, speech intelligibility is increased, in particular for a hearing impaired person being capable of perceiving sound pressure levels in a substantially decreased dynamic range.
Owner:OTICON
Speech intelligibility in telephones with multiple microphones
ActiveUS8428661B2Improve speech clarityMicrophones signal combinationSubstation equipmentVoice activityBackground noise
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
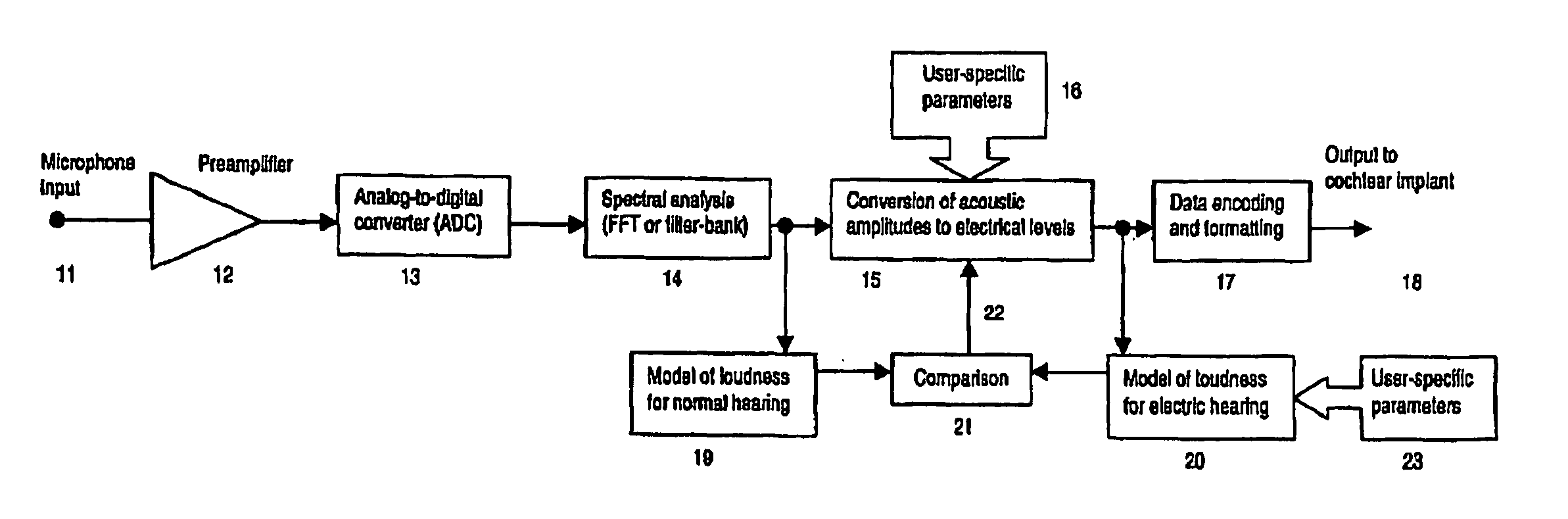
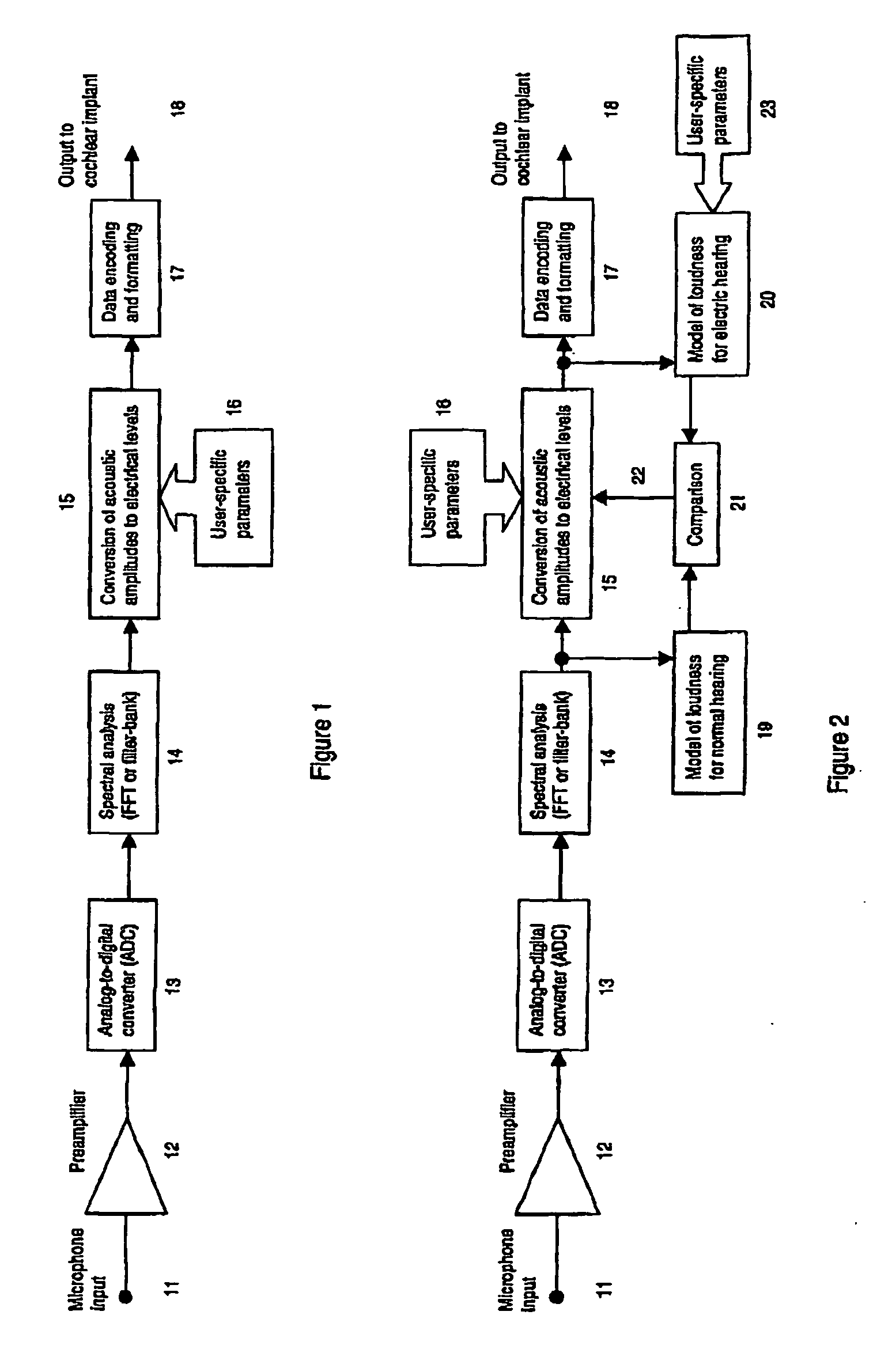
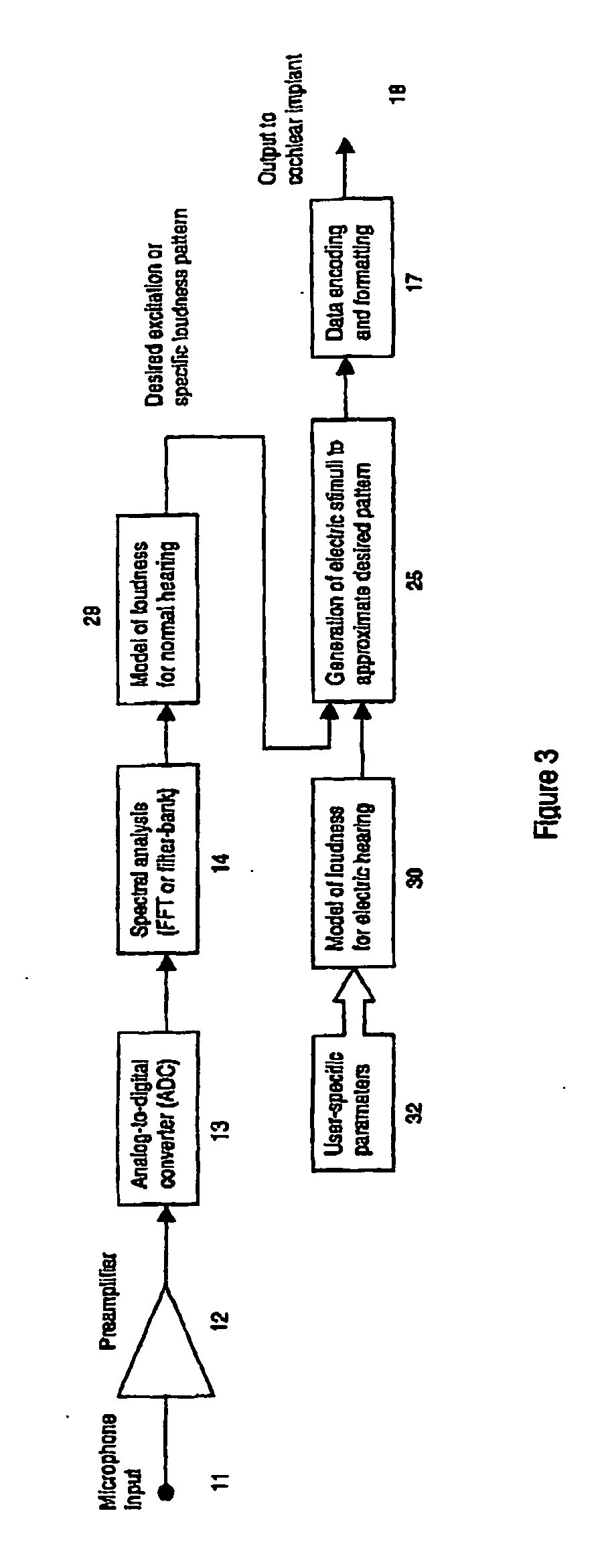
Sound-processing strategy for cochlear implants
InactiveUS20070043403A1Reduce impactNormalising overall loudnessElectrotherapyEar treatmentCochlear implantationProsthesis
A sound processing method for auditory prostheses, such as cochlear implants, which is adapted to improve the perception of loudness by users, and to improve speech perception. The overall contribution of stimuli to simulated loudness is compared with an estimate of acoustic loudness for a normally hearing listener based on the input sound signal. A weighting is applied to the filter channels to emphasize those frequencies which are most important to speech perception for normal hearing listeners when selecting channels as a basis for stimulation.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE
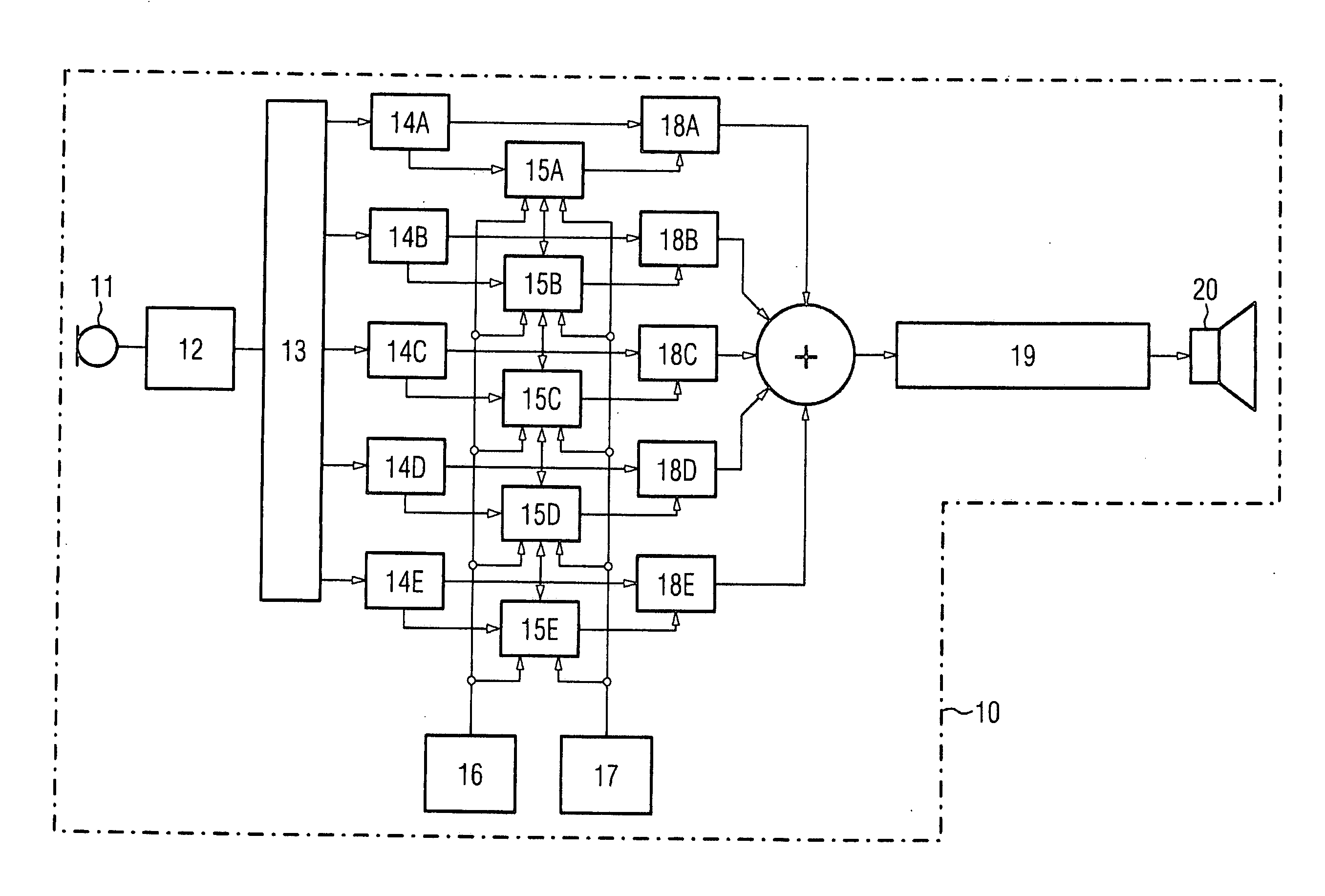
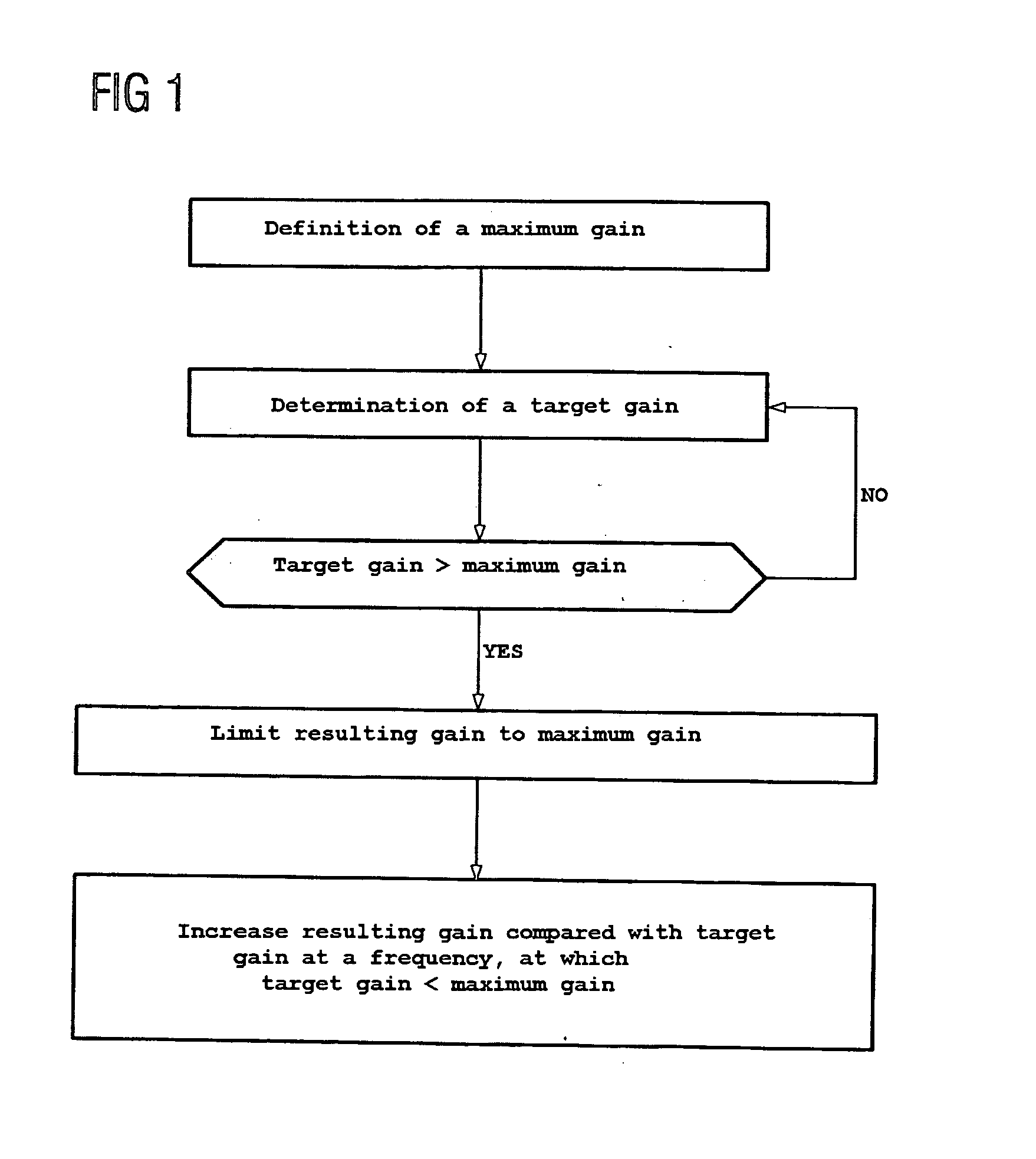
Automatic gain adjustment for a hearing aid device
InactiveUS20060245610A1Improve speech clarityHearing aids signal processingDeaf aid adaptationEngineeringHearing aid
The object of the claimed hearing aid device is to improve the speech intelligibility of a speech signal transmitted by the hearing aid device. To this end provision is made to define a maximum gain of the input signal and to determine a target gain at least at a first and second frequency of an input signal. A resulting gain is set in the hearing aid device, which does not exceed the maximum gain. A reduction of the resulting gain compared with the target gain at the first frequency is compensated for according to the invention by an automatic increase in the set resulting gain compared with the target gain at the second frequency, with compensation preferably being achieved by improving the speech intelligibility of a speech signal transmitted with the aid of the hearing aid device.
Owner:SIEMENS AUDIOLOGISCHE TECHN
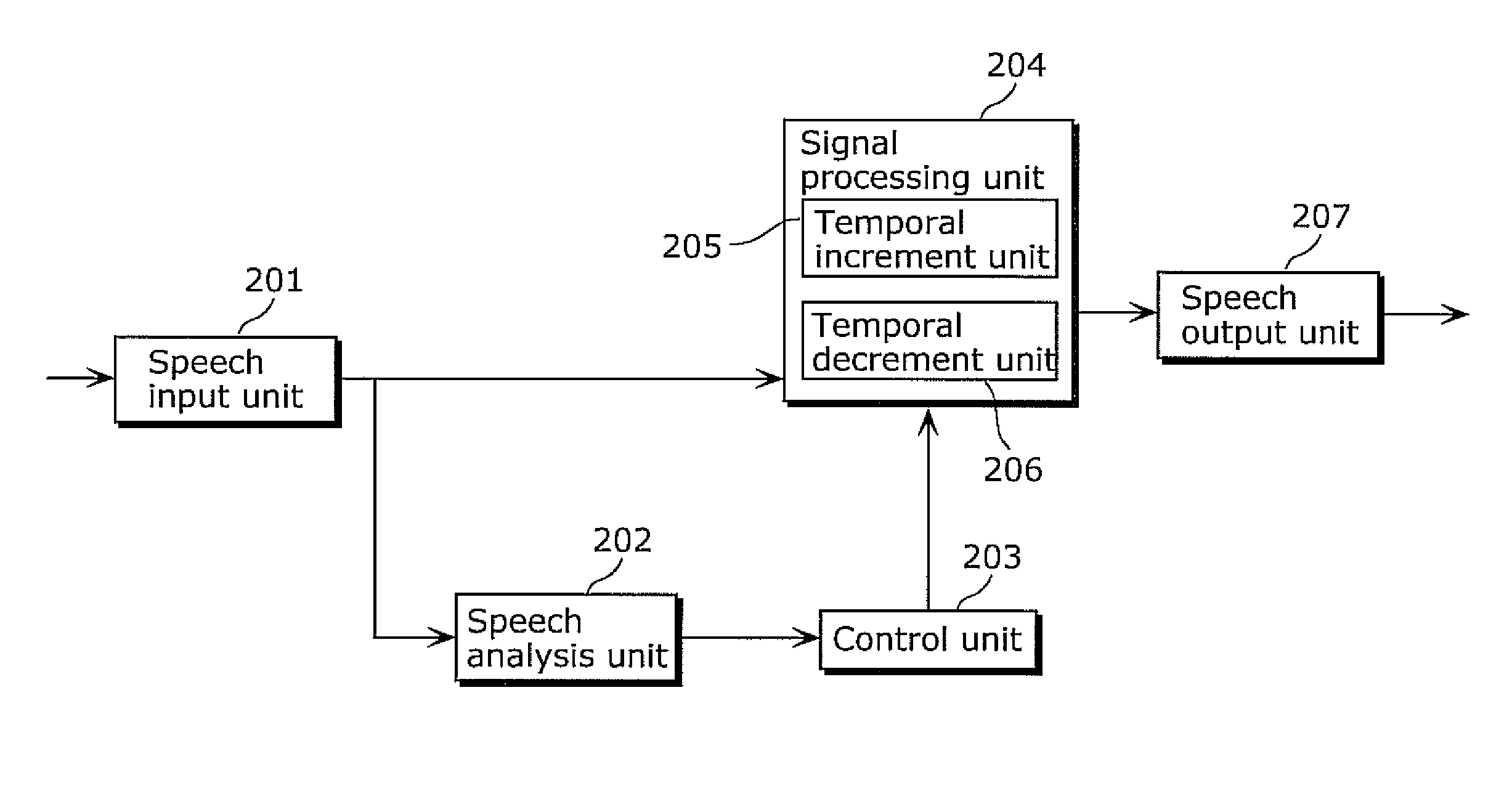
Hearing aid and hearing-aid processing method
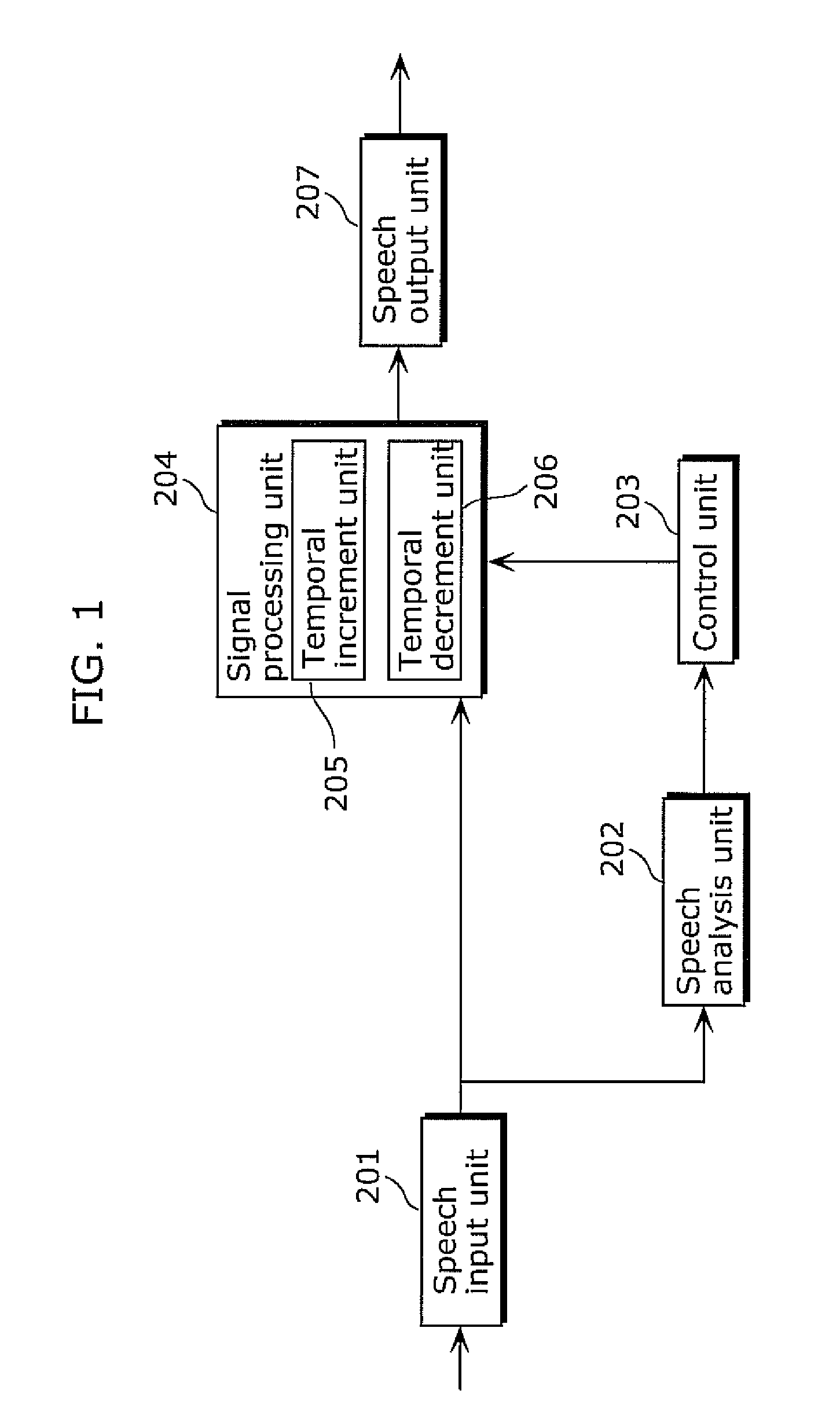
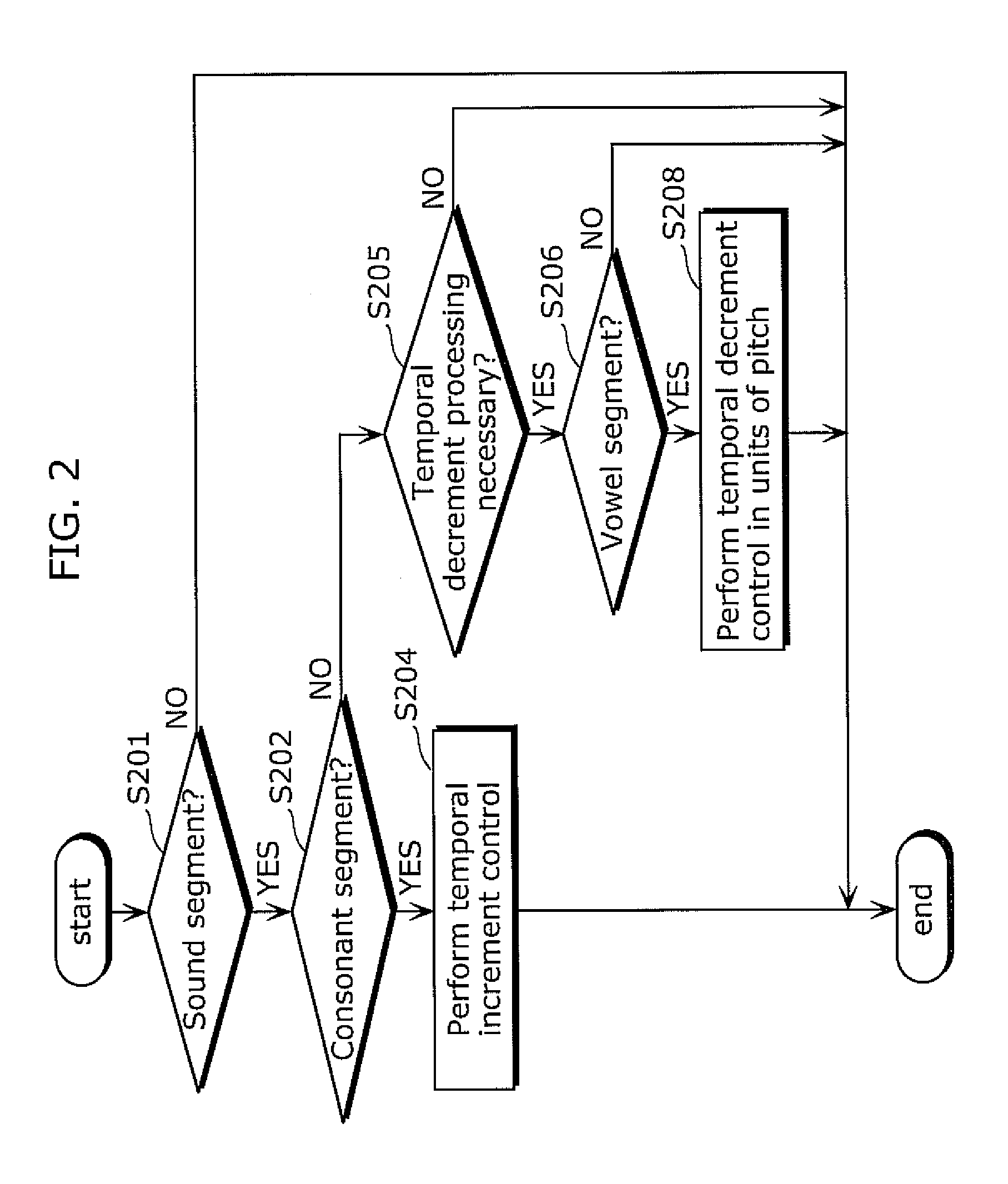
ActiveUS20110004468A1Improve recognition rateImprove speech clarityBone conduction transducer hearing devicesSpeech analysisTemporal resolutionImage resolution
A hearing aid for improving diminished hearing caused by reduced temporal resolution includes: a speech input unit (201) which receives a speech signal from outside; a speech analysis unit (202) which detects a sound segment and a segment acoustically regarded as soundless from the speech signal received by the speech input unit and detects a consonant segment and a vowel segment within the detected sound segment; and a signal processing unit (204) which temporally increments the consonant segment detected by the speech analysis unit (204) and temporally decrements at least one of the vowel segment and the segment acoustically regarded as soundless detected by the speech analysis unit (204).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Hearing aid and a method for improving speech intelligibility of an audio signal
ActiveUS20150199977A1Improve speech clarityControl delayHearing aids signal processingSpeech recognitionWireless dataPeripheral
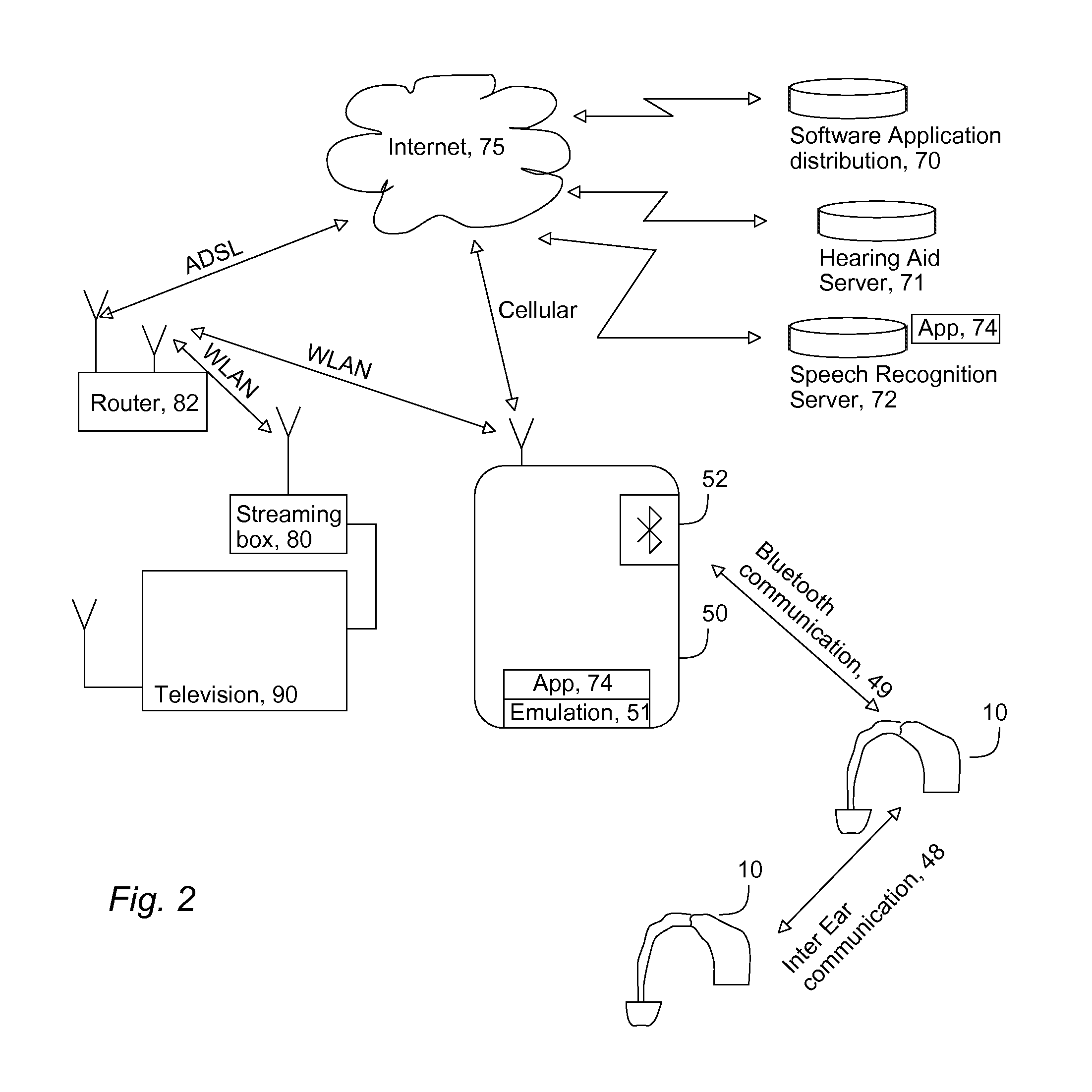
A system for improving speech intelligibility of an audio signal, comprises a hearing aid (10), a server (71), and an external device (50)—such as a smartphone or a tablet computer. The hearing aid has a short range transceiver. The server is accessible via the Internet, and has a Speech Recognition Engine converting speech into text. The external device has a short range transceiver for communication with said hearing aid, a second transceiver for providing a wireless data connection to said server via the Internet, means for handling a speech stream intended for the hearing aid, and a Text-To-Speech engine adapted to synthesize speech based on a string of text. The invention also provides a method of improving speech intelligibility of an audio signal.
Owner:WIDEX AS
Optical sensing in a directional MEMS microphone
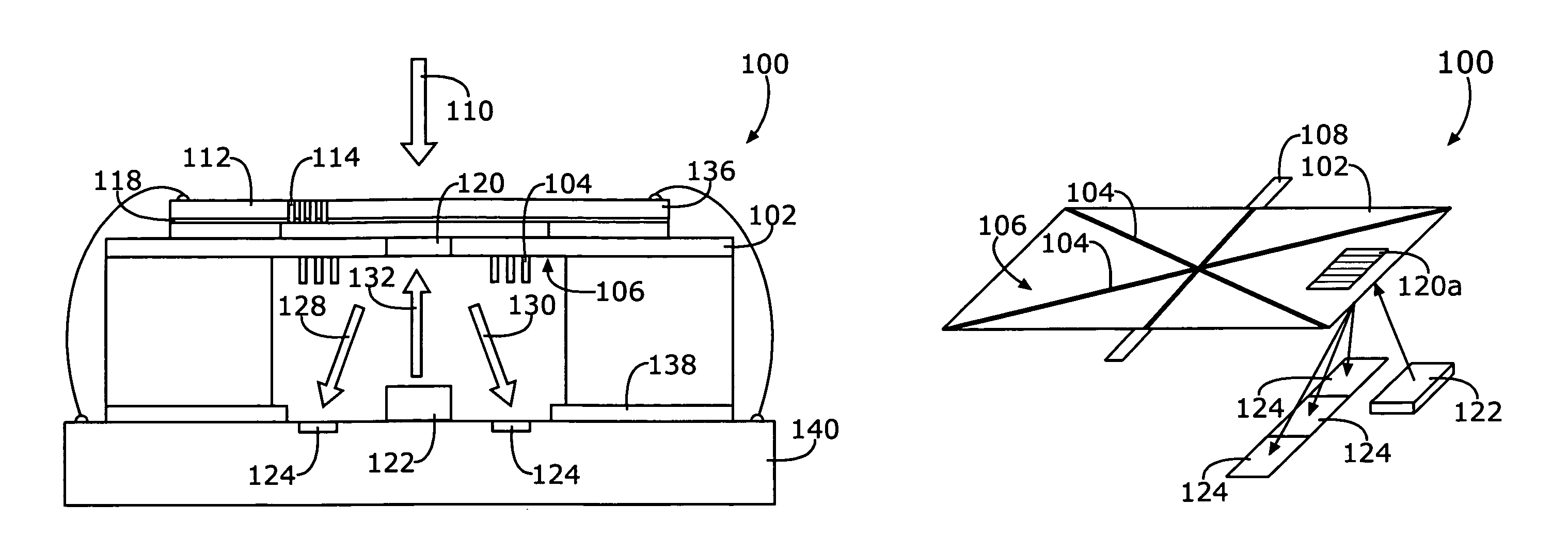
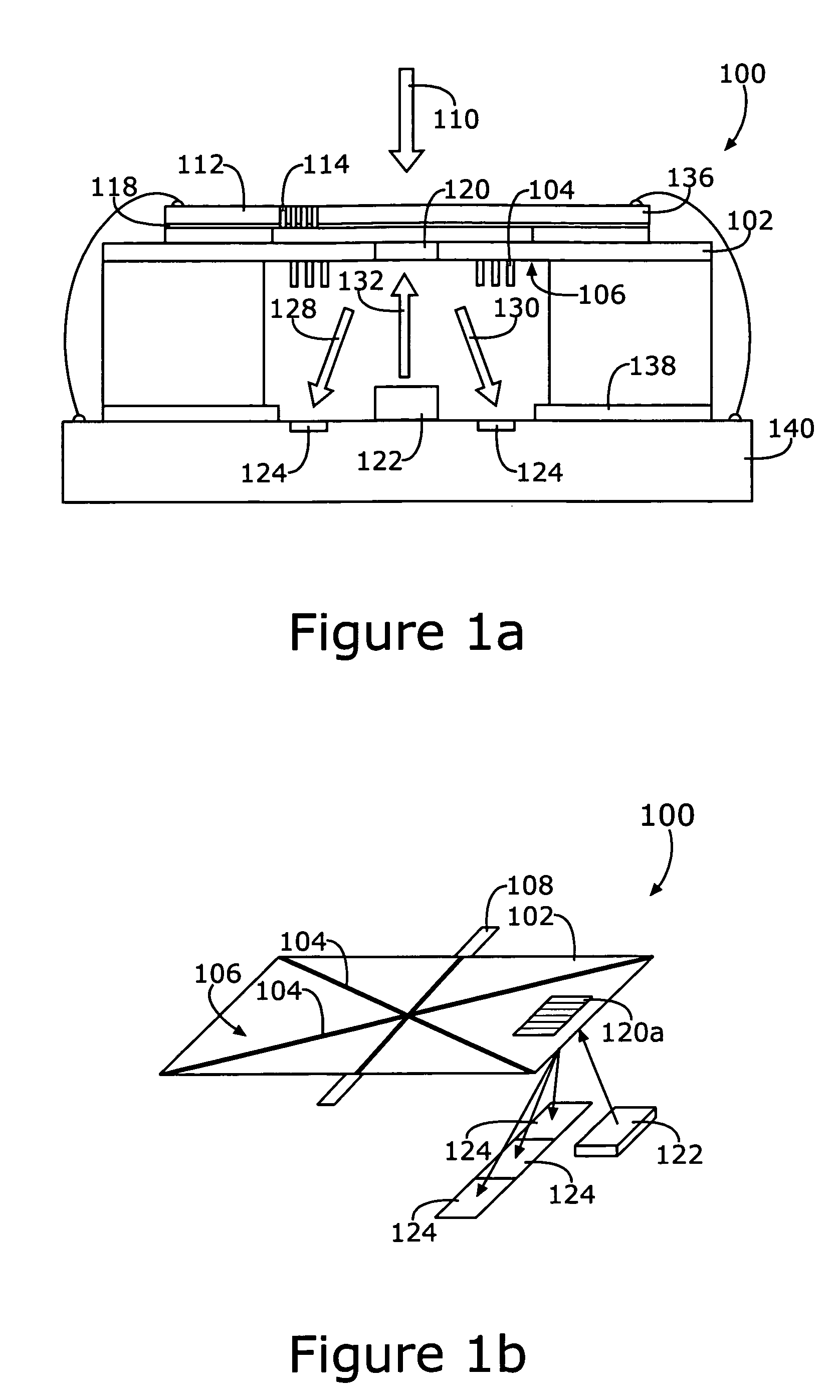
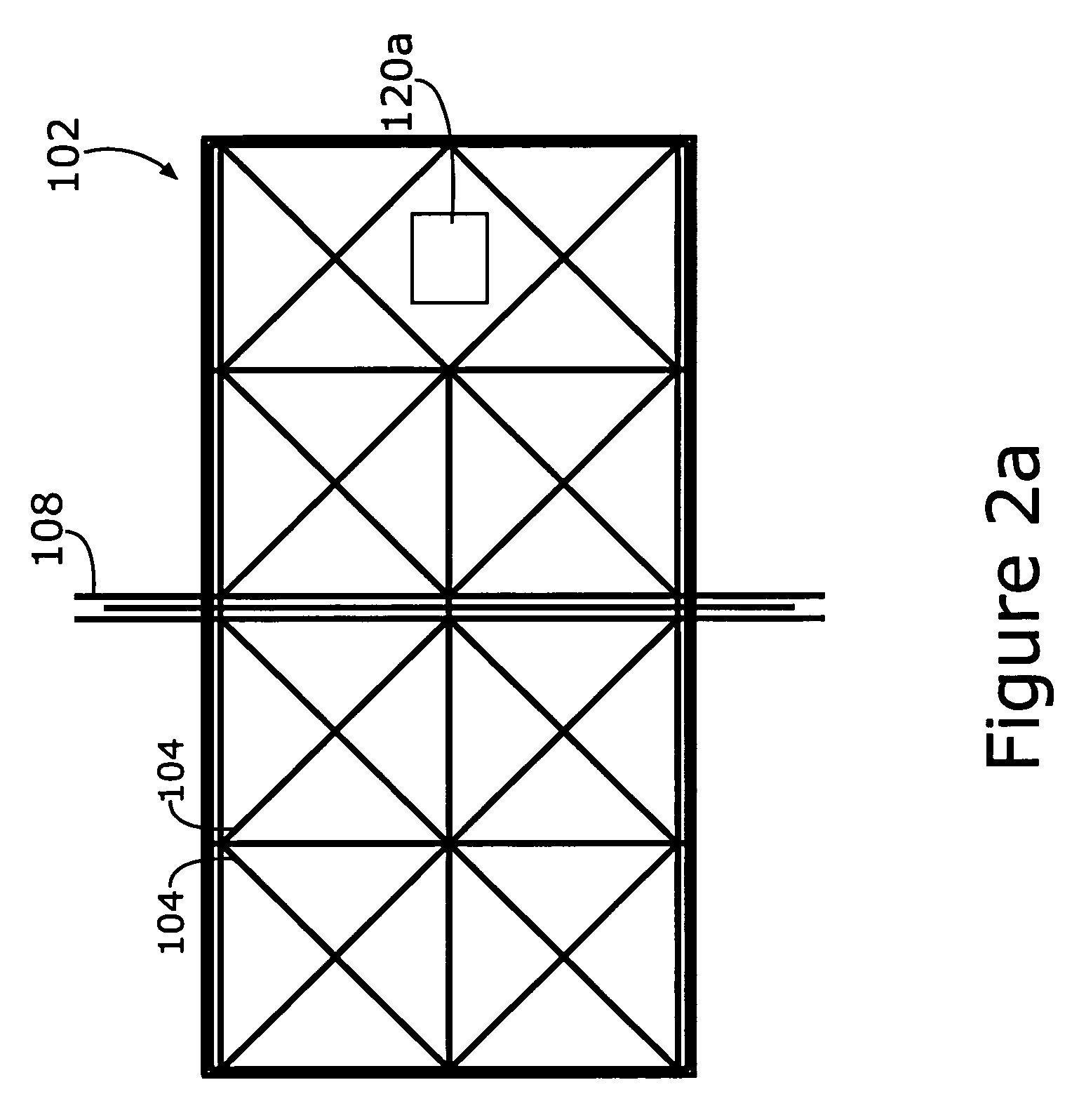
InactiveUS7826629B2Bulky and heavyReduce noiseVibration measurement in solidsSolid state device transducersEngineeringMems microphone
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
High frequency compression integration
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Hearing aid and a method for enhancing speech intelligibility
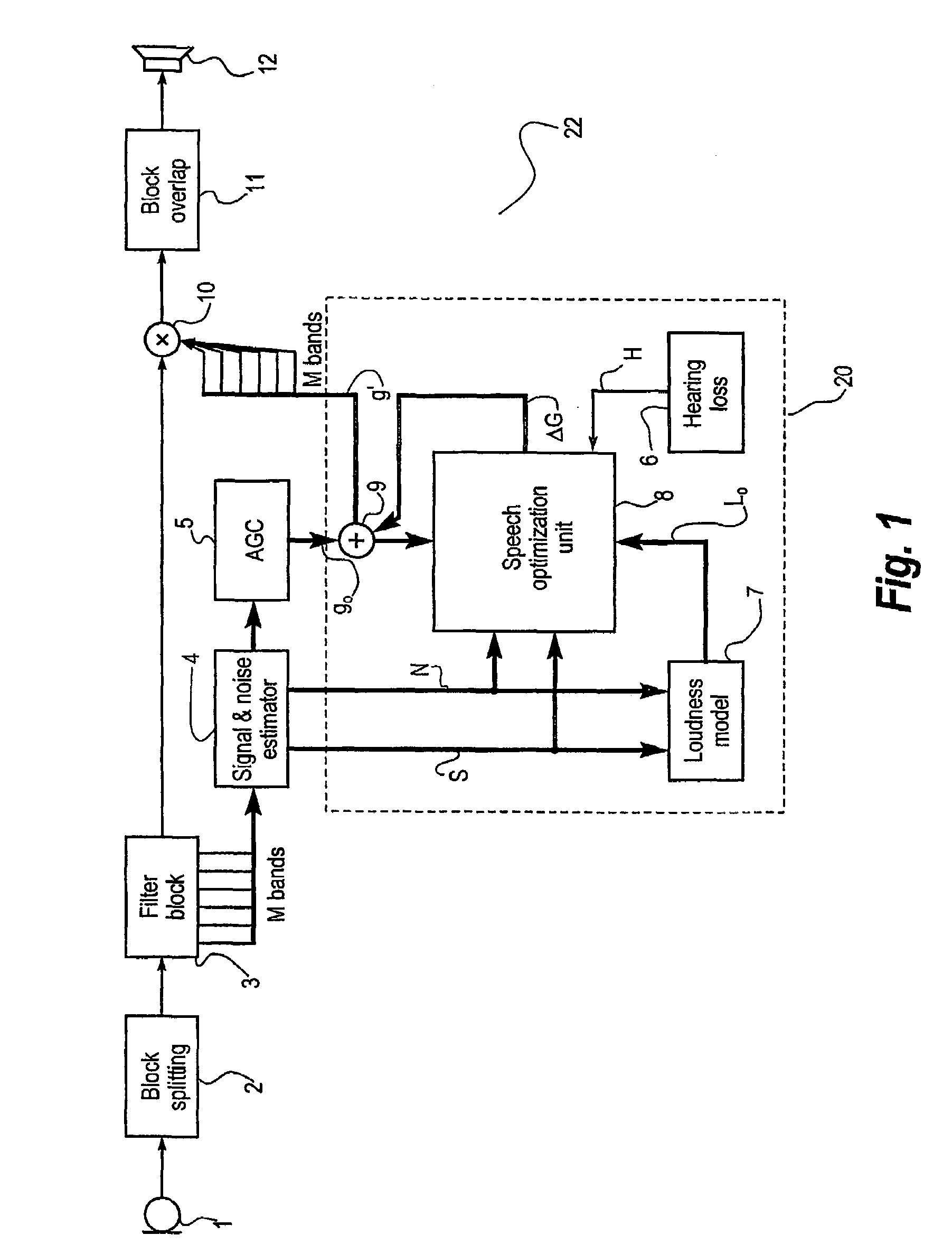
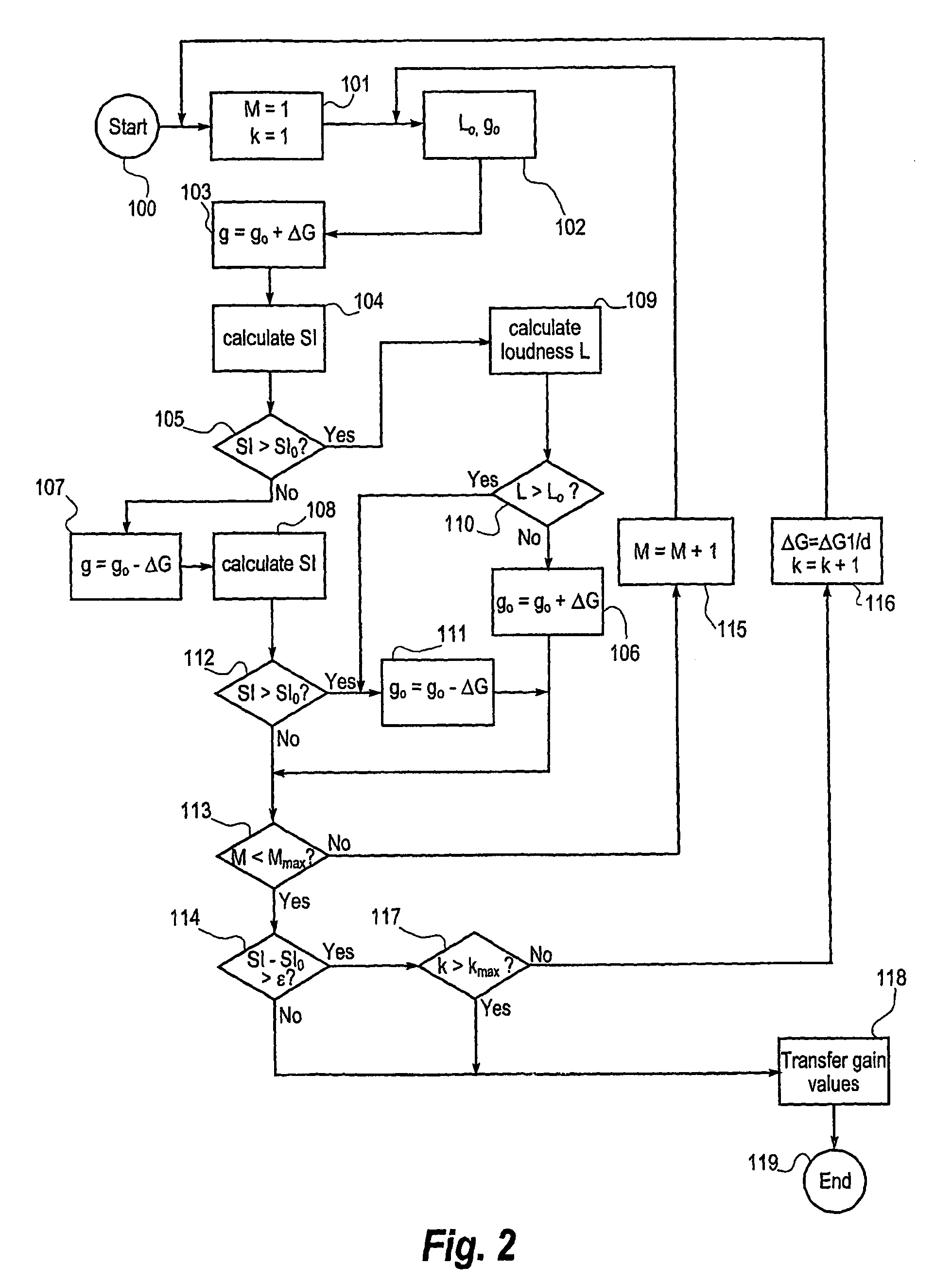
ActiveUS7599507B2Improve speech claritySpeech analysisHearing aids signal processingTransducerSpeech sound
A hearing aid (22) having a microphone (1), a processor (53) and an output transducer (12), is adapted for obtaining an estimate of a sound environment, determining an estimate of the speech intelligibility according to the sound environment estimate, and for adapting the transfer function of the hearing aid processor in order to enhance the speech intelligibility estimate. The method according to the invention achieves an adaptation of the processor transfer function suitable for optimizing the speech intelligibility in a particular sound environment. Means for obtaining the sound environment estimate and for determining the speech intelligibility estimate may be incorporated in the hearing aid processor, or they may be wholly or partially implemented in an external processing means (56), adapted for communicating data to the hearing aid processor via an appropriate link.
Owner:WIDEX AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com