Patents
Literature
13427results about "Transducer casings/cabinets/supports" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
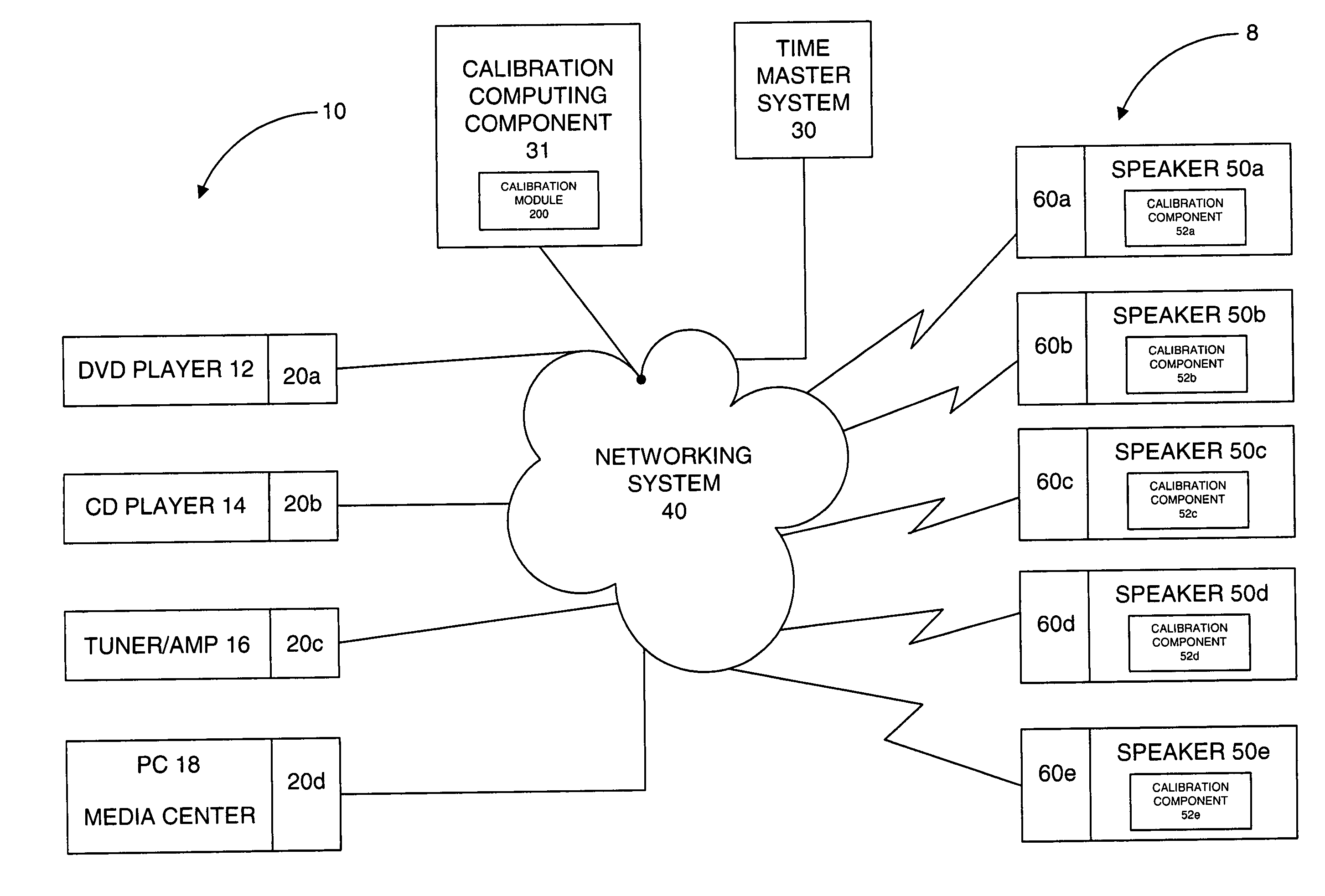
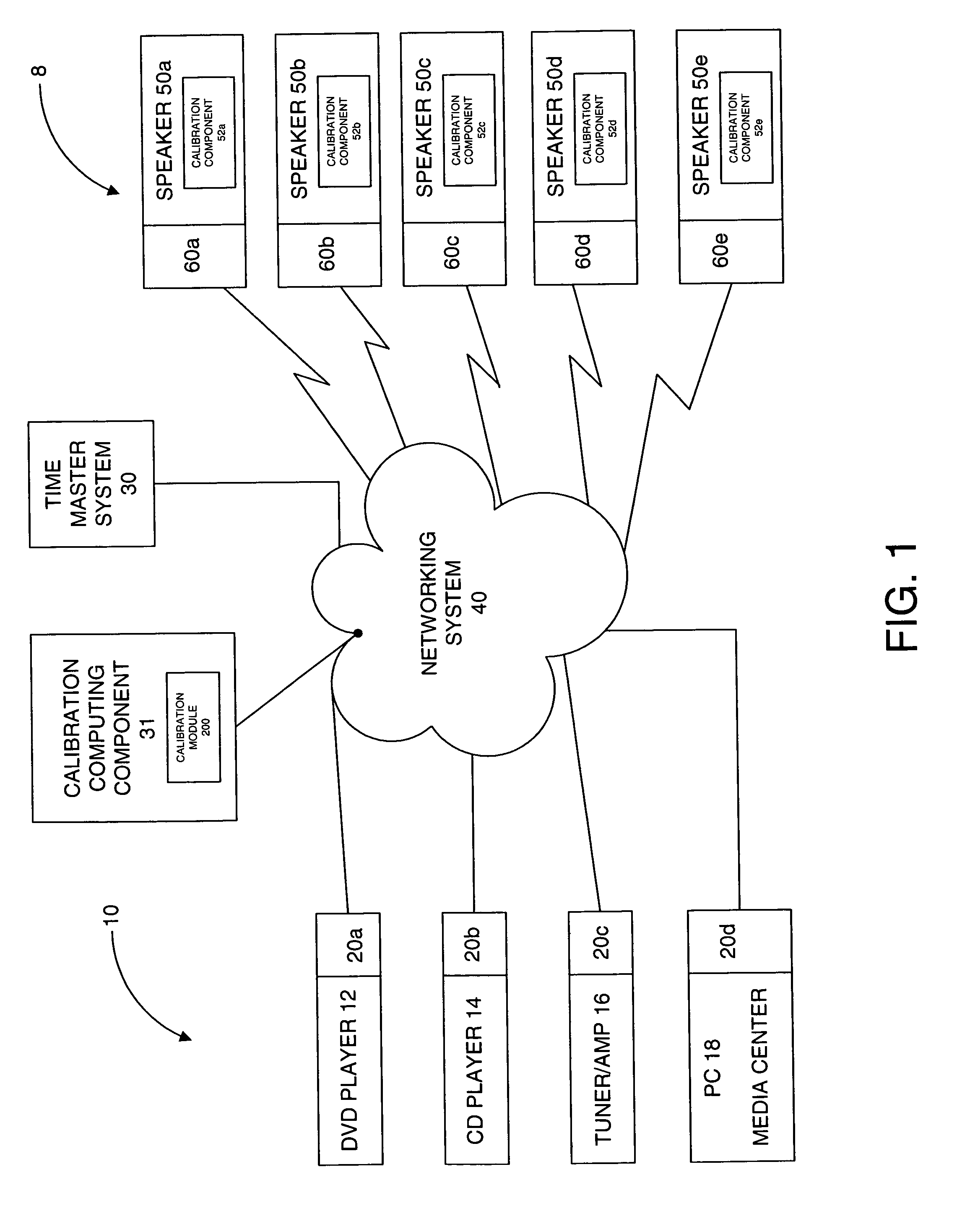
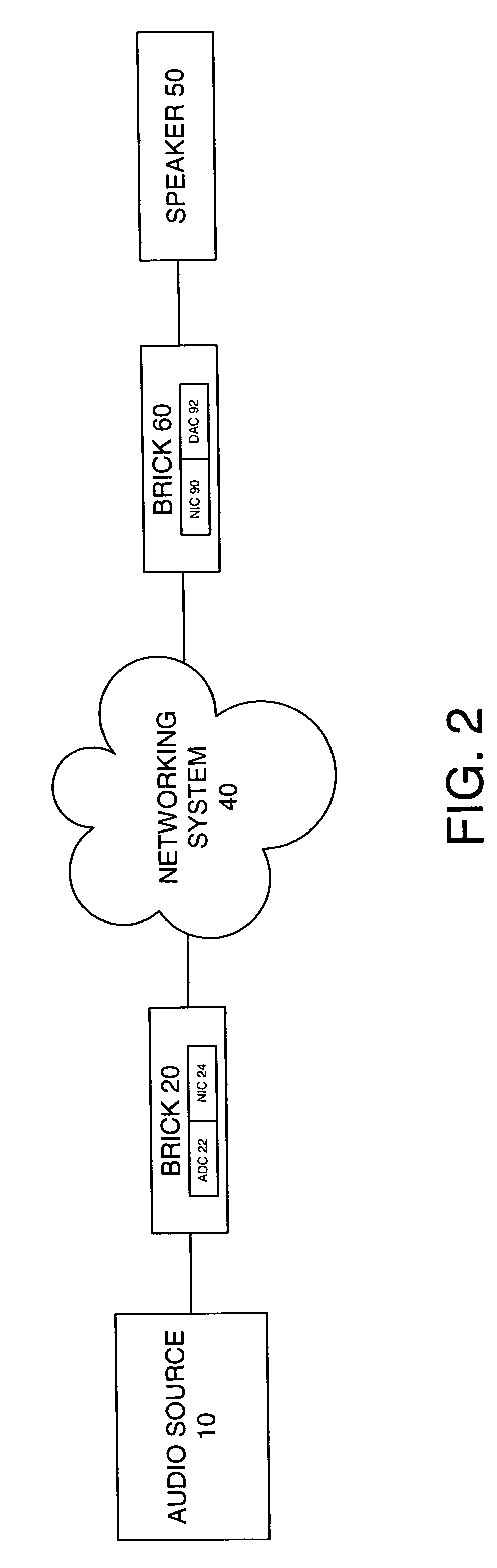
System and method for calibration of an acoustic system
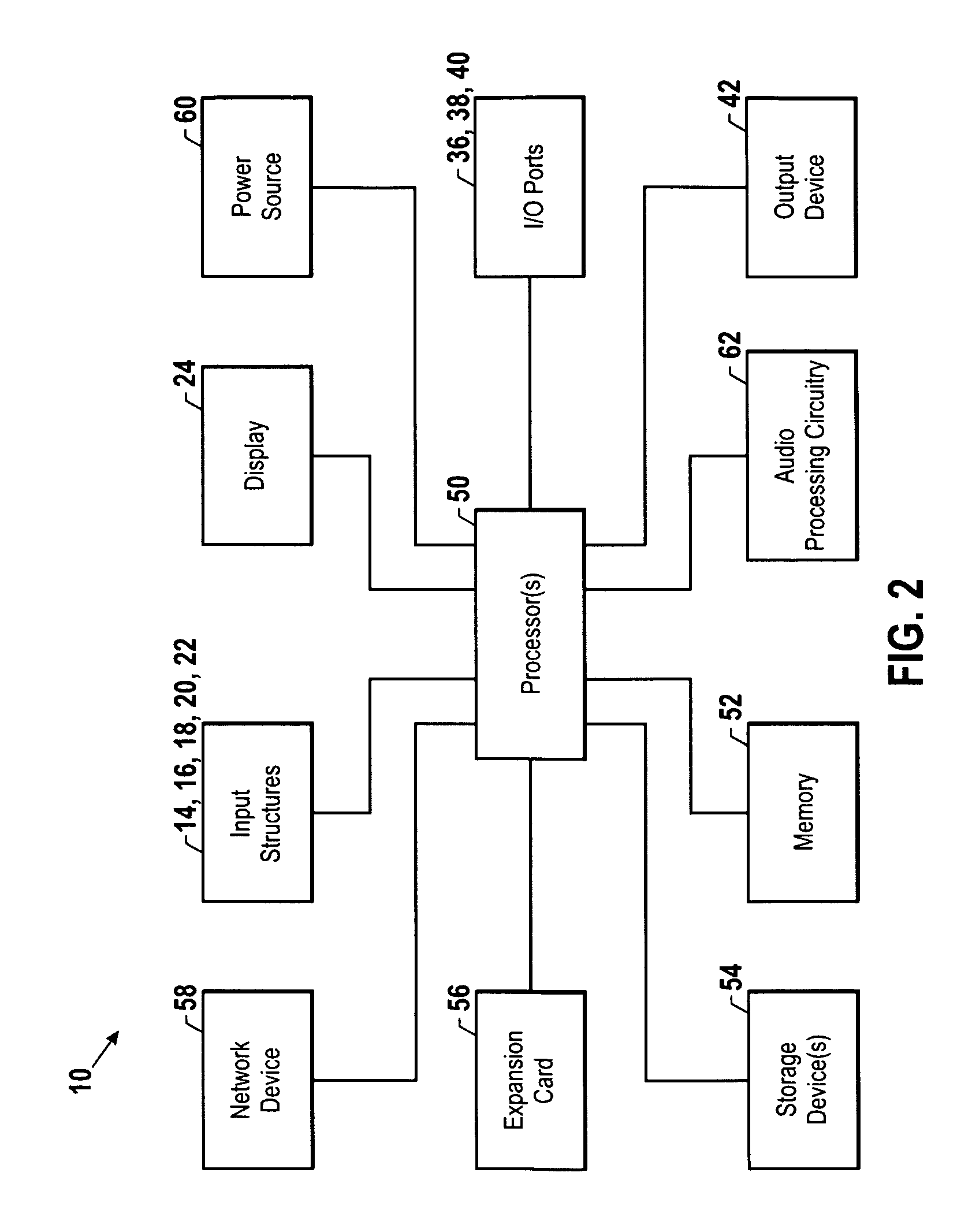
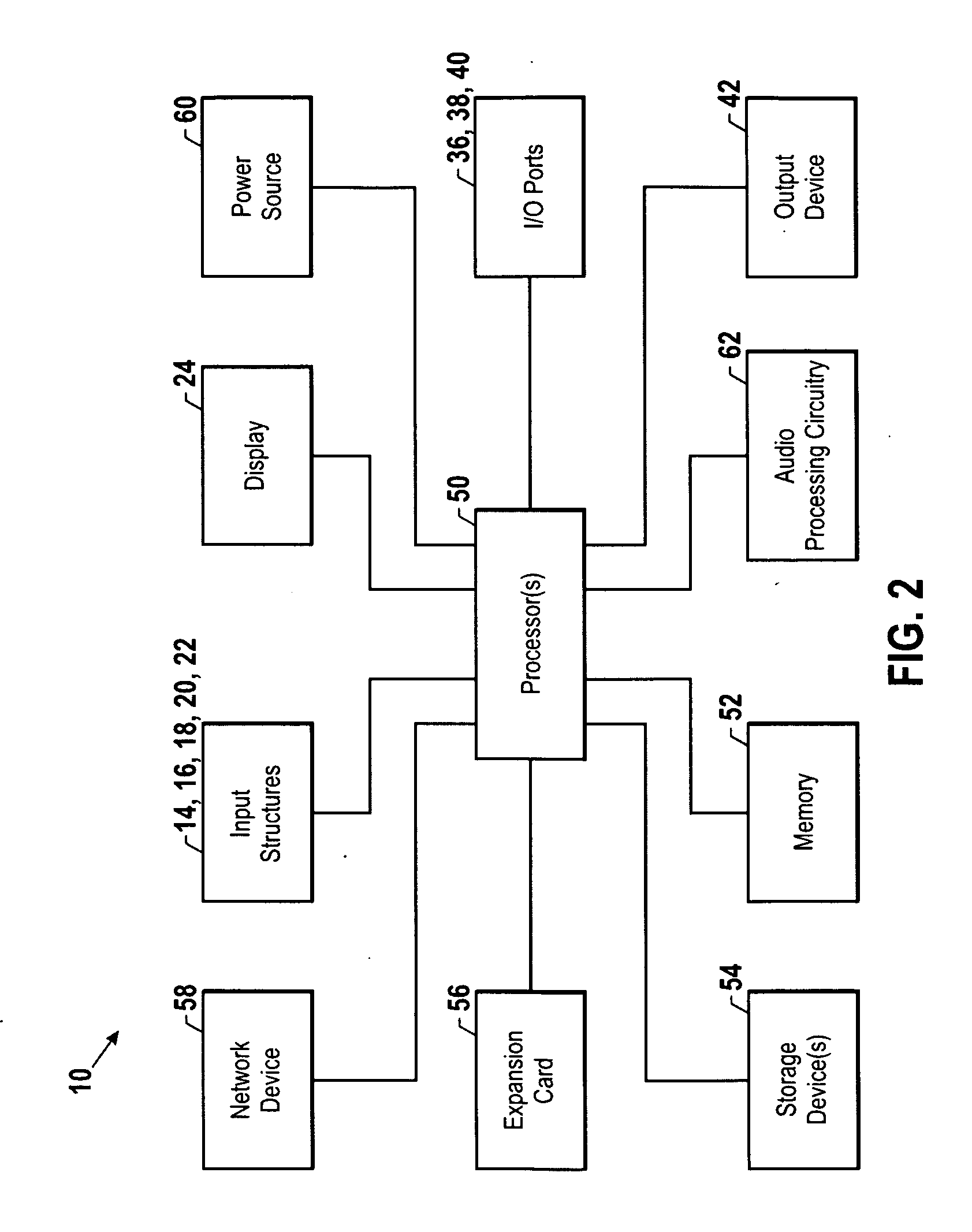
The present invention is directed to a method and system for automatic calibration of an acoustic system. The acoustic system may include a source A / V device, calibration computing device, and multiple rendering devices. The calibration system may include a calibration component attached to each rendering device and a source calibration module. The calibration component on each rendering device includes a microphone. The source calibration module includes distance and optional angle calculation tools for automatically determining a distance between the rendering device and a specified reference point upon return of the test signal from the calibration component.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
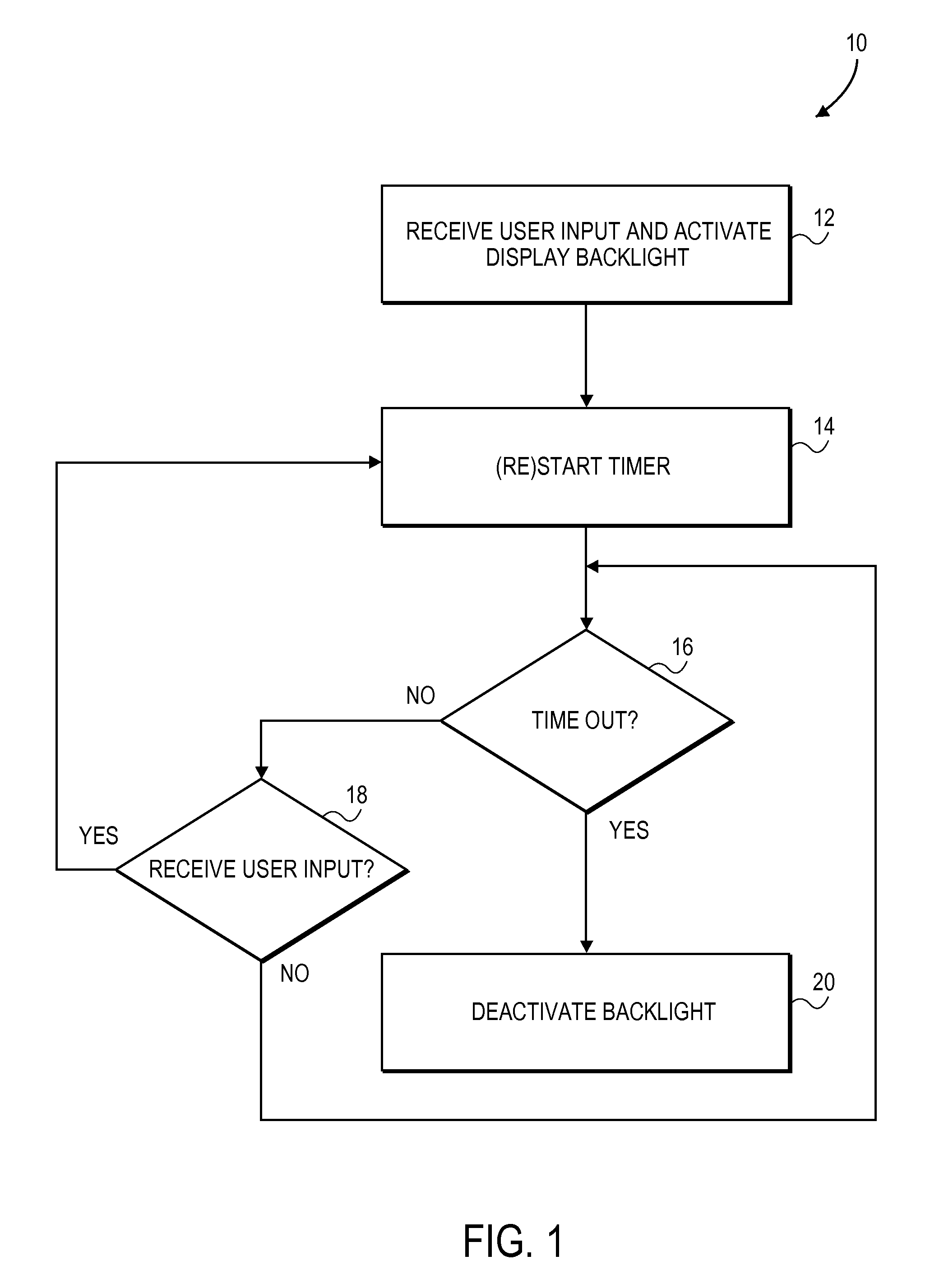
Automated response to and sensing of user activity in portable devices
ActiveUS7633076B2Input/output for user-computer interactionGain controlComputer scienceEquipment state
Owner:APPLE INC
Self calibrating multi-element dipole microphone
ActiveUS8824692B2Maintain performancePiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesElectrostatic transducer microphonesSound sourcesDigital filter
Owner:VOCOLLECT
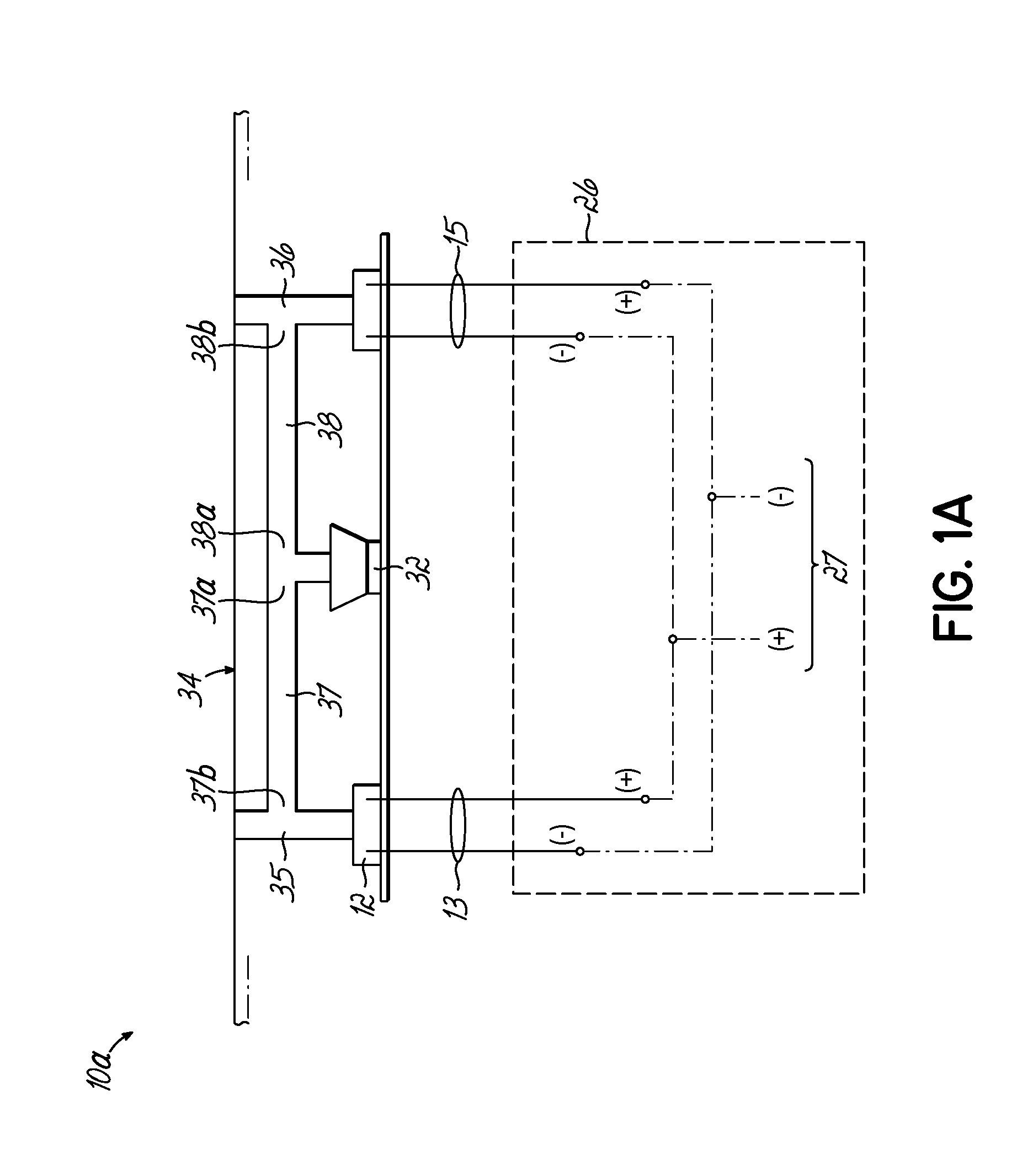
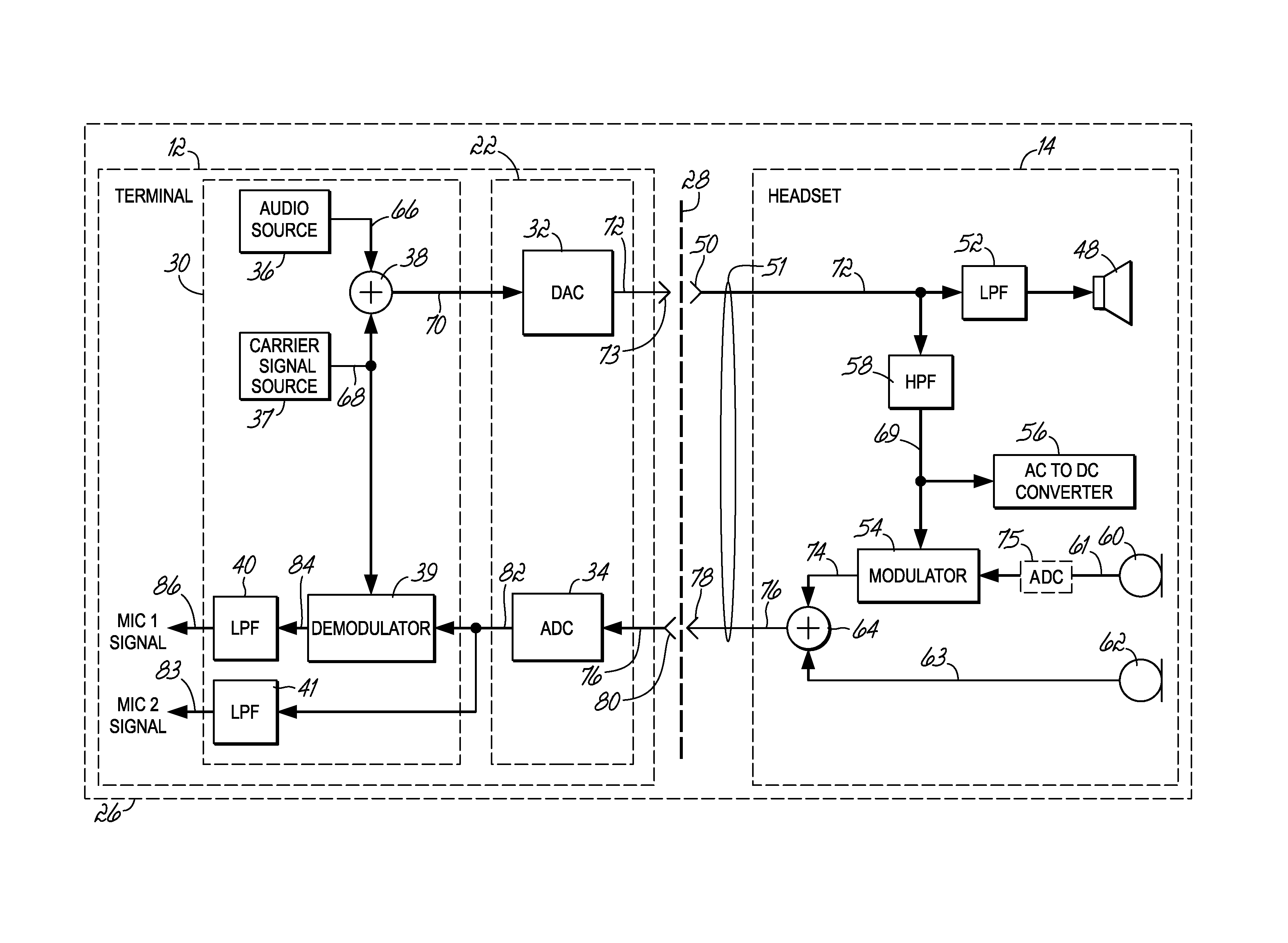
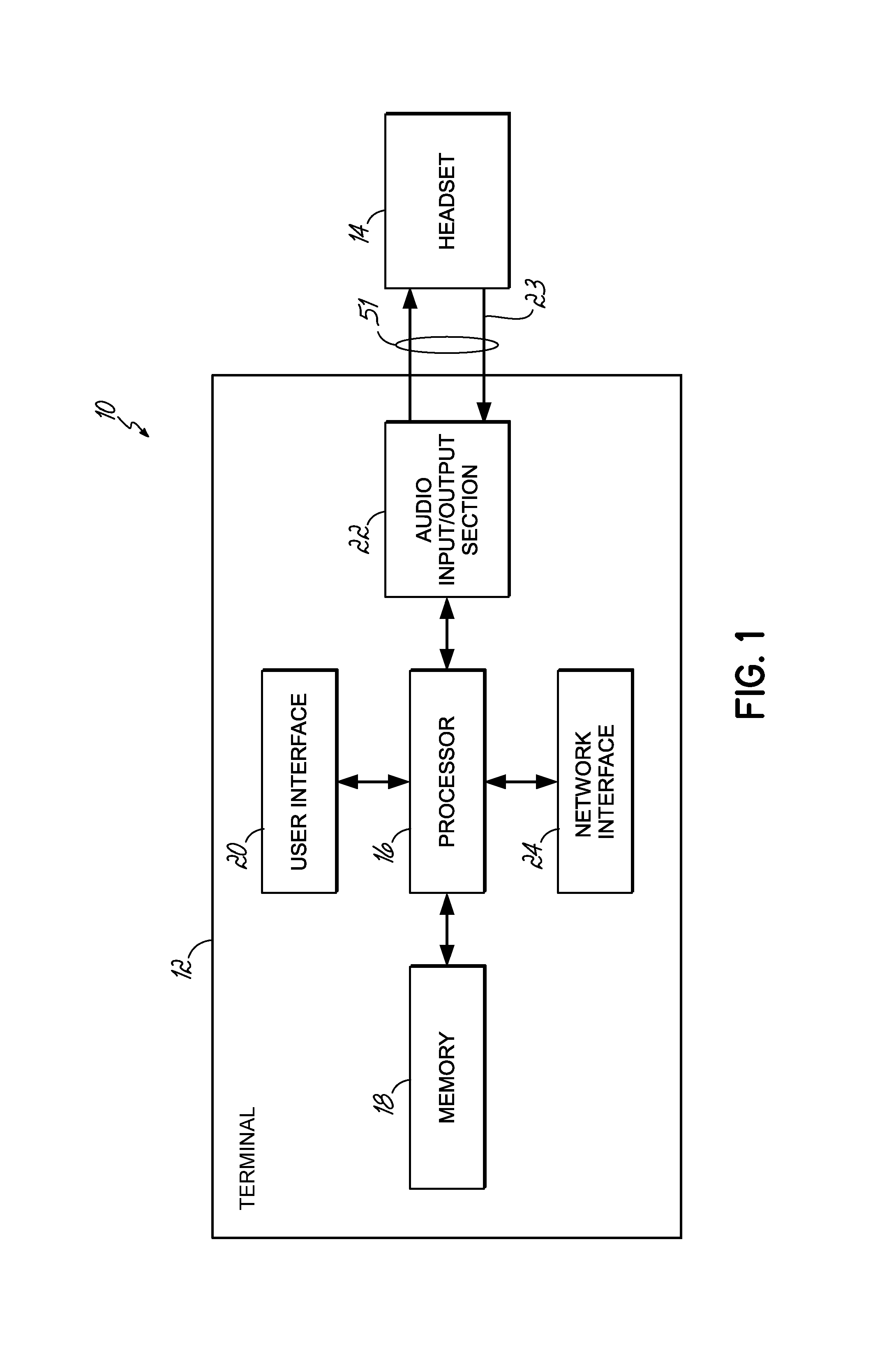
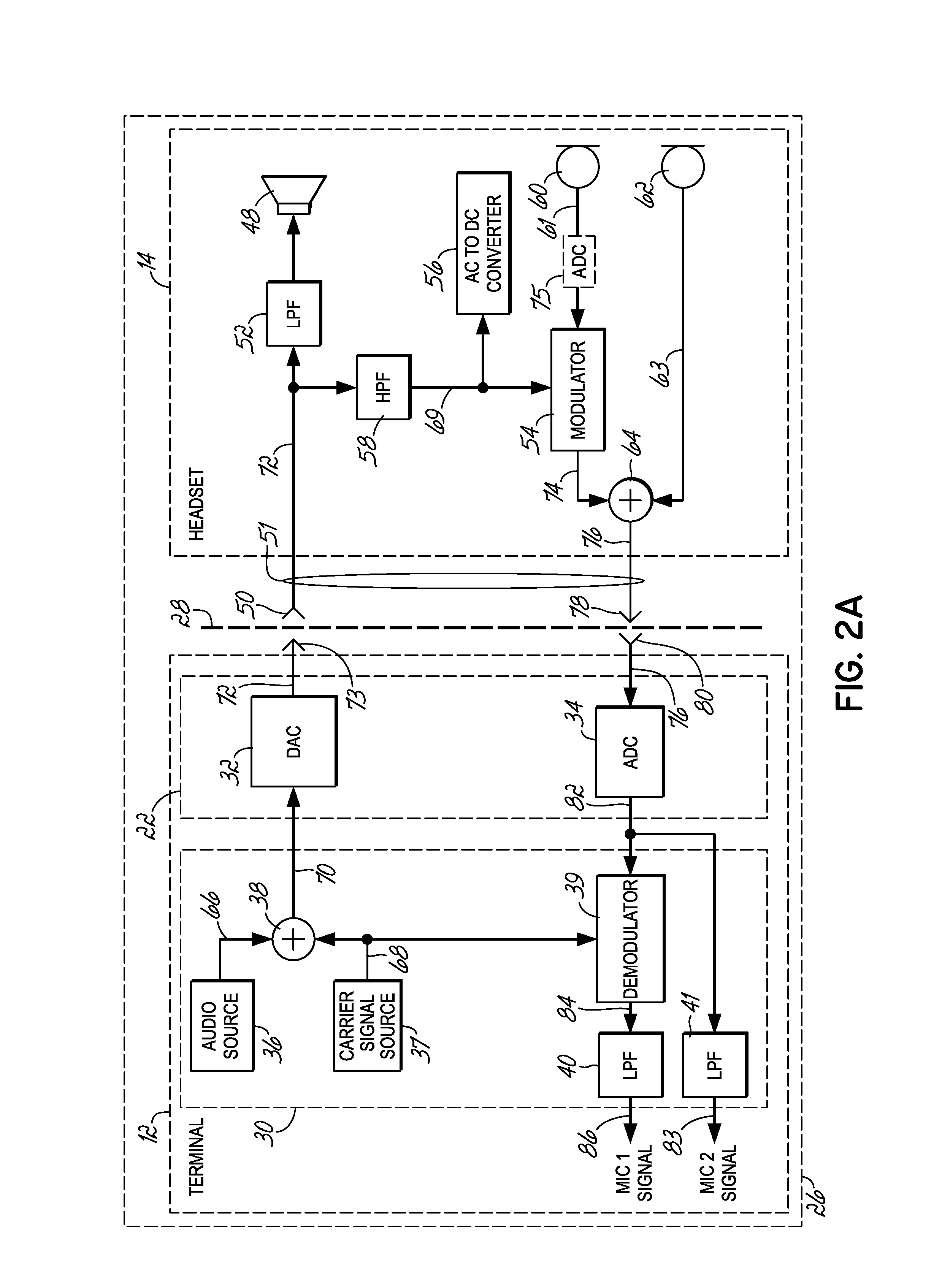
Headset signal multiplexing system and method
Owner:VOCOLLECT
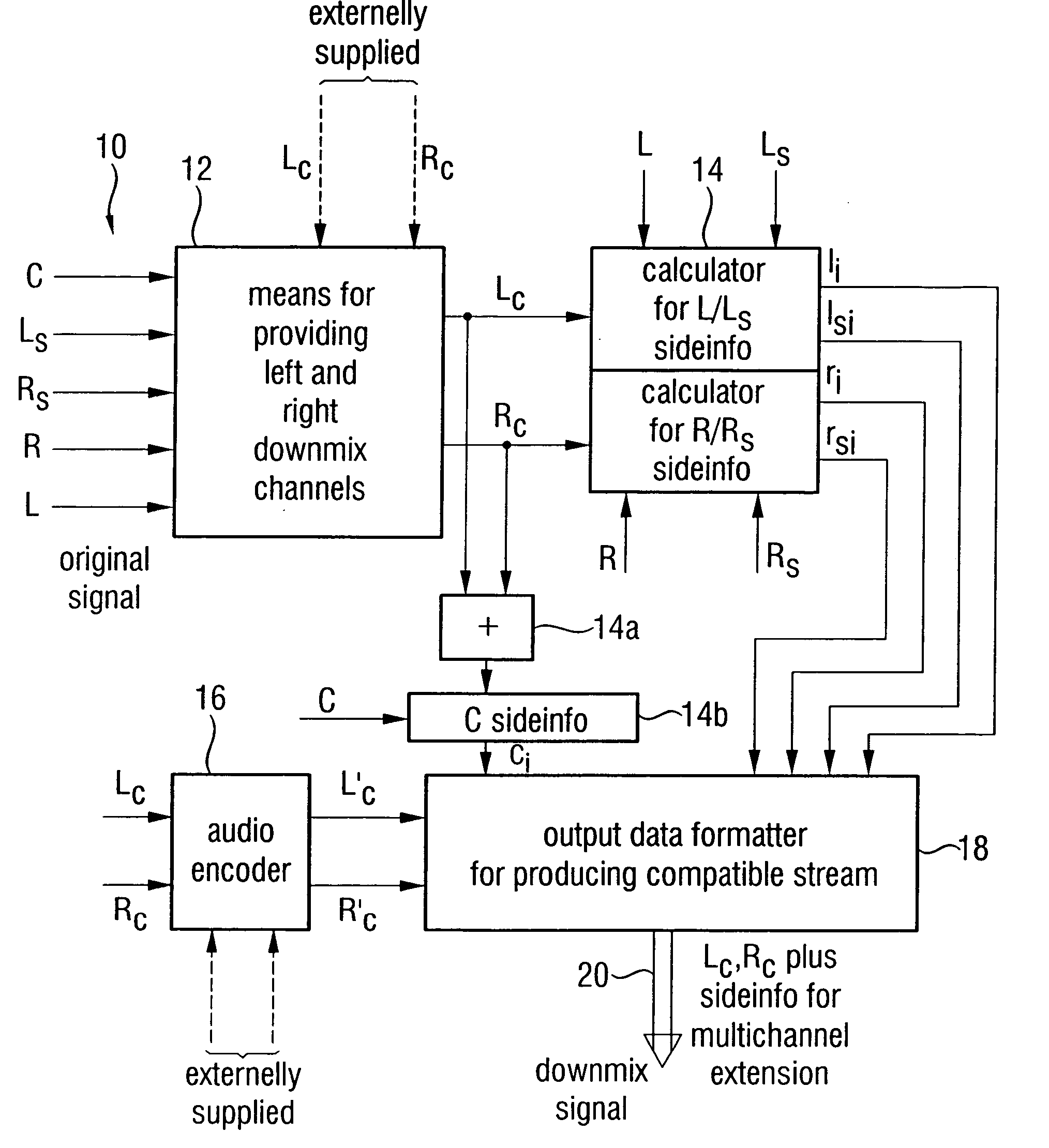
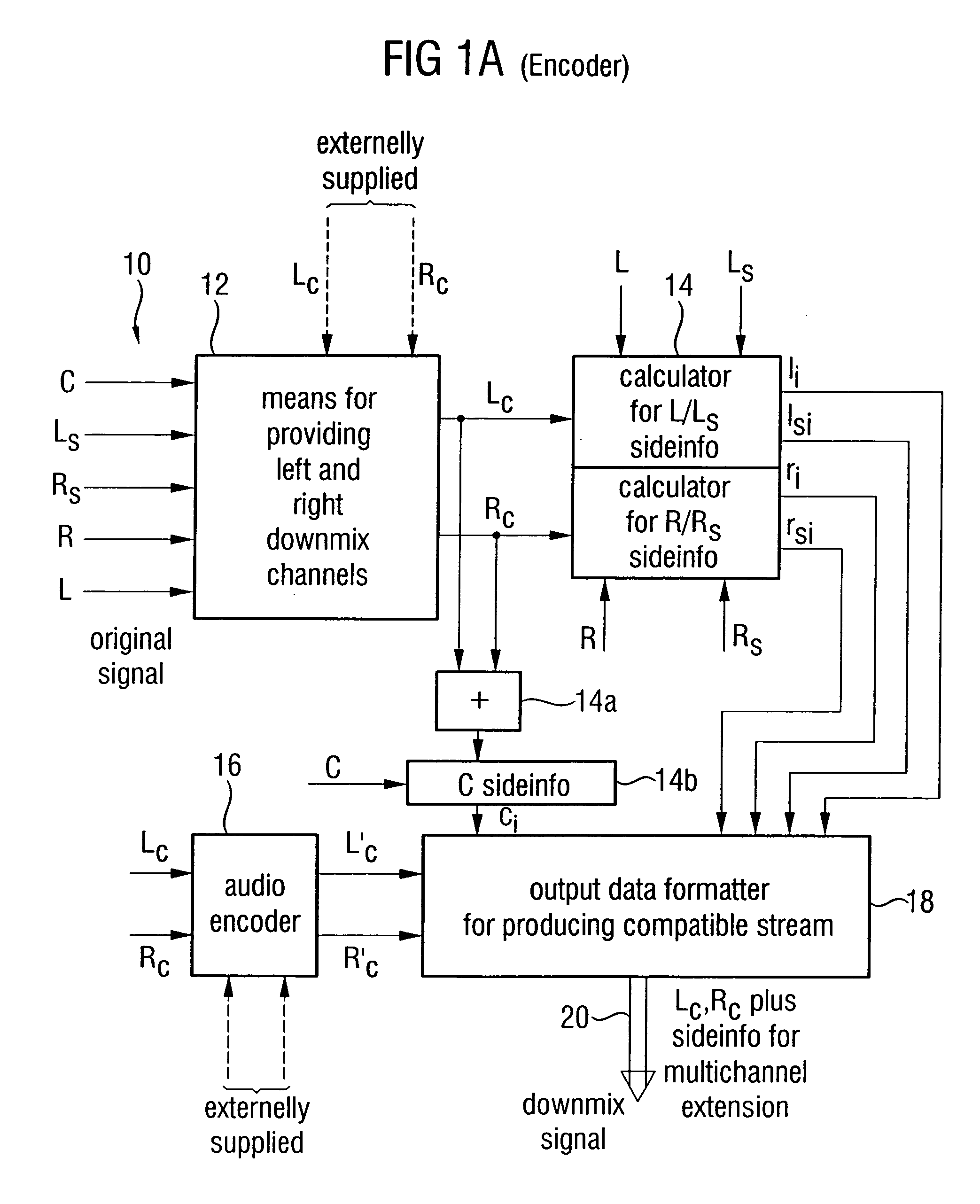
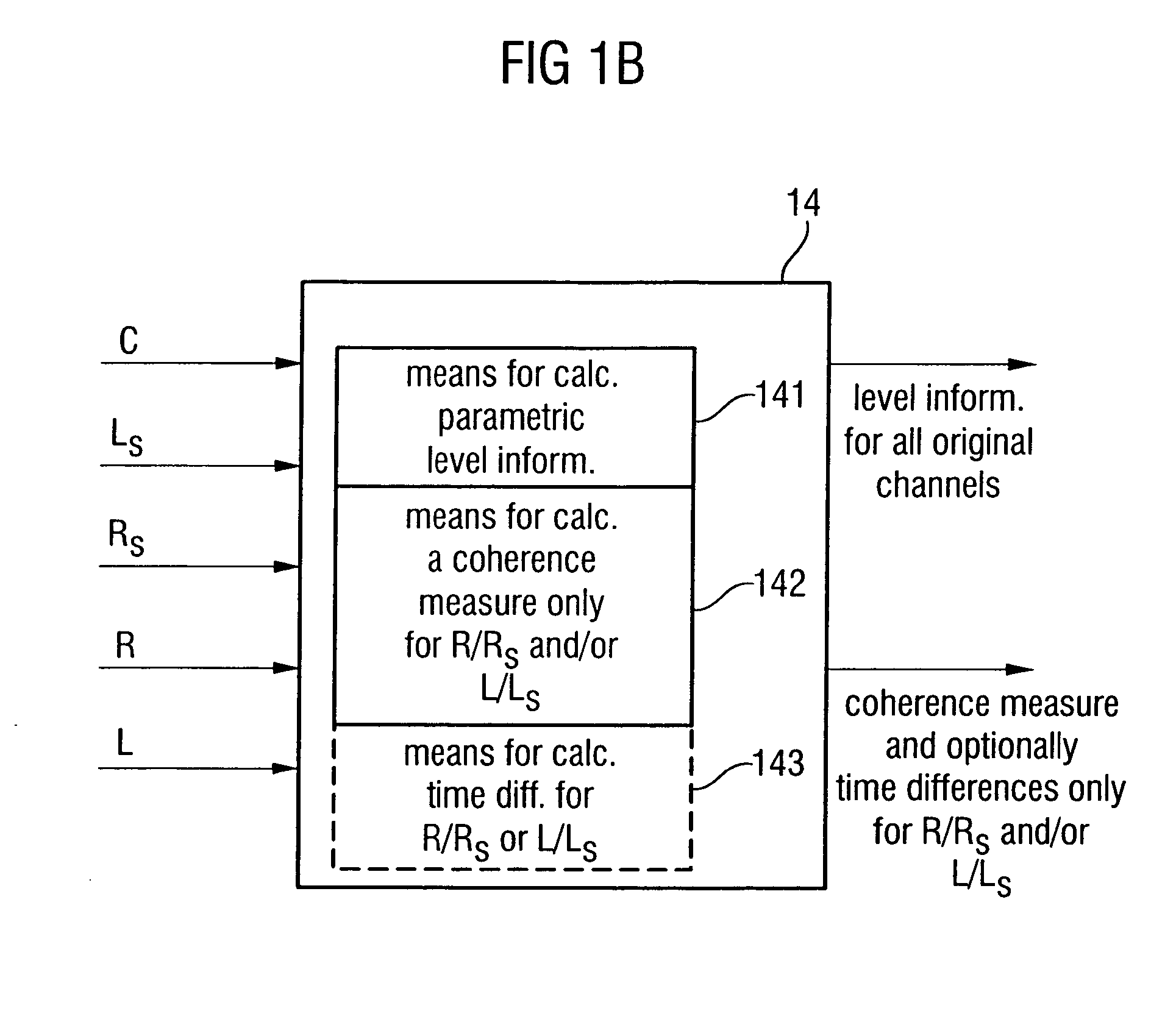
Apparatus and method for constructing a multi-channel output signal or for generating a downmix signal
ActiveUS20050157883A1High scaleReduce processing loadSpeech analysisTransmissionSide informationEngineering
The apparatus for constructing a multi-channel output signal using an input signal and parametric side information, the input signal including the first input channel and the second input channel derived from an original multi-channel signal, and the parametric side information describing interrelations between channels of the multi-channel original signal uses base channels for synthesizing first and second output channels on one side of an assumed listener position, which are different from each other. The base channels are different from each other because of a coherence measure. Coherence between the base channels (for example the left and the left surround reconstructed channel) is reduced by calculating a base channel for one of those channels by a combination of the input channels, the combination being determined by the coherence measure. Thus, a high subjective quality of the reconstruction can be obtained because of an approximated original front / back coherence.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV +1
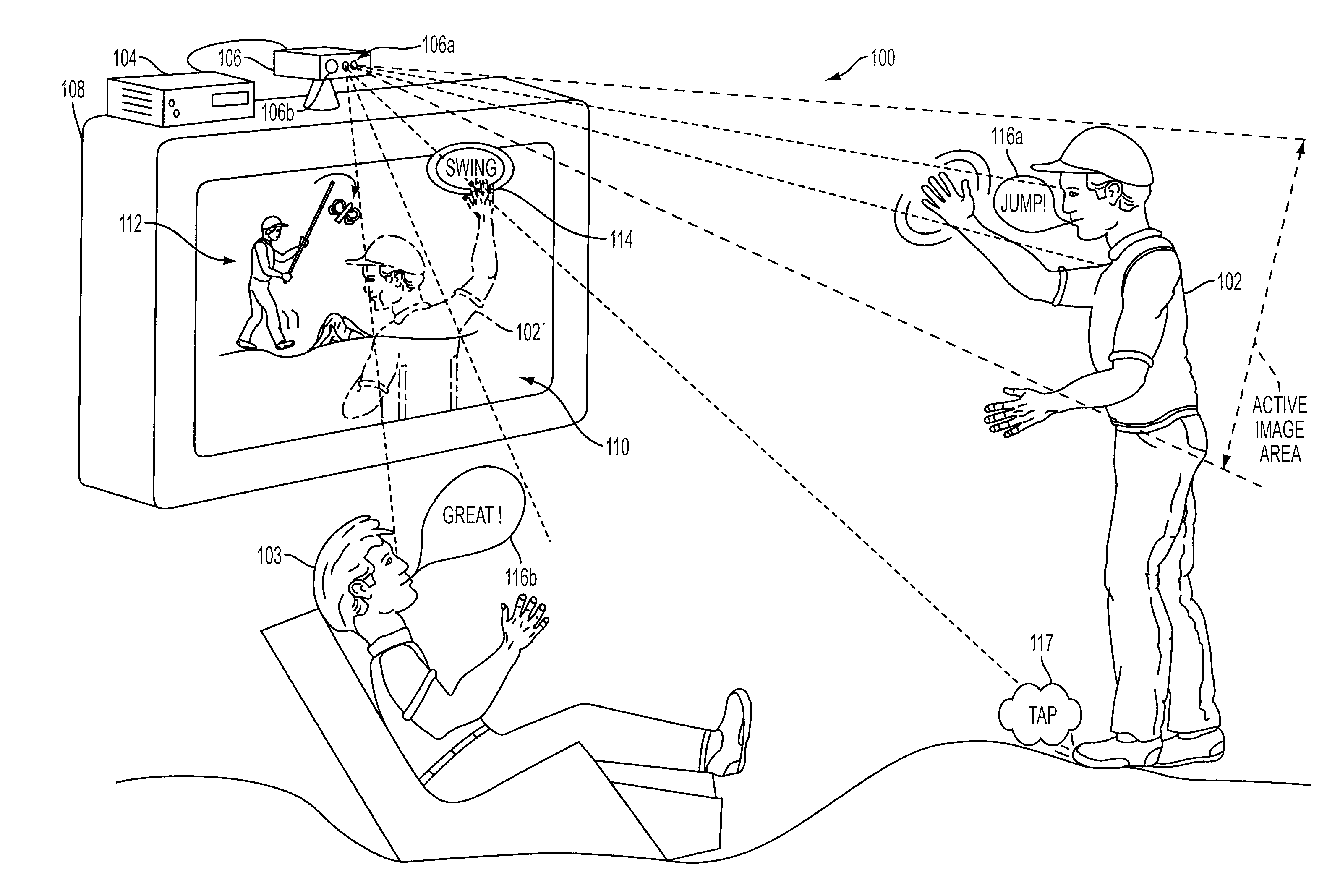
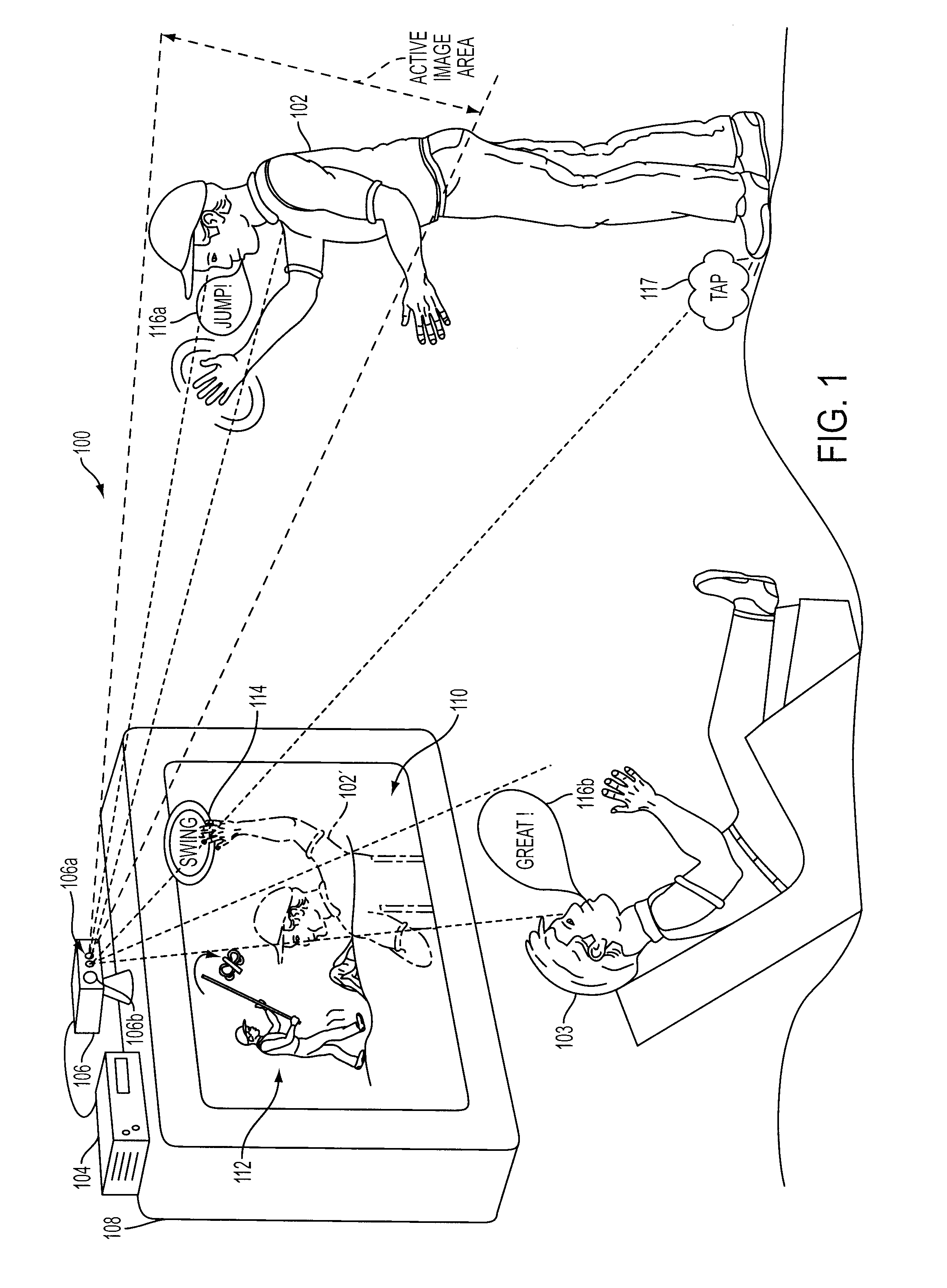
Methods and apparatus for targeted sound detection and characterization
ActiveUS20060239471A1Enhanced interactionRespondMicrophonesSignal processingSound detectionSound sources
Sound processing methods and apparatus are provided. A sound capture unit is configured to identify one or more sound sources. The sound capture unit generates data capable of being analyzed to determine a listening zone at which to process sound to the substantial exclusion of sounds outside the listening zone. Sound captured and processed for the listening zone may be used for interactivity with the computer program. The listening zone may be adjusted based on the location of a sound source. One or more listening zones may be pre-calibrated. The apparatus may optionally include an image capture unit configured to capture one or more image frames. The listening zone may be adjusted based on the image. A video game unit may be controlled by generating inertial, optical and / or acoustic signals with a controller and tracking a position and / or orientation of the controller using the inertial, acoustic and / or optical signal.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
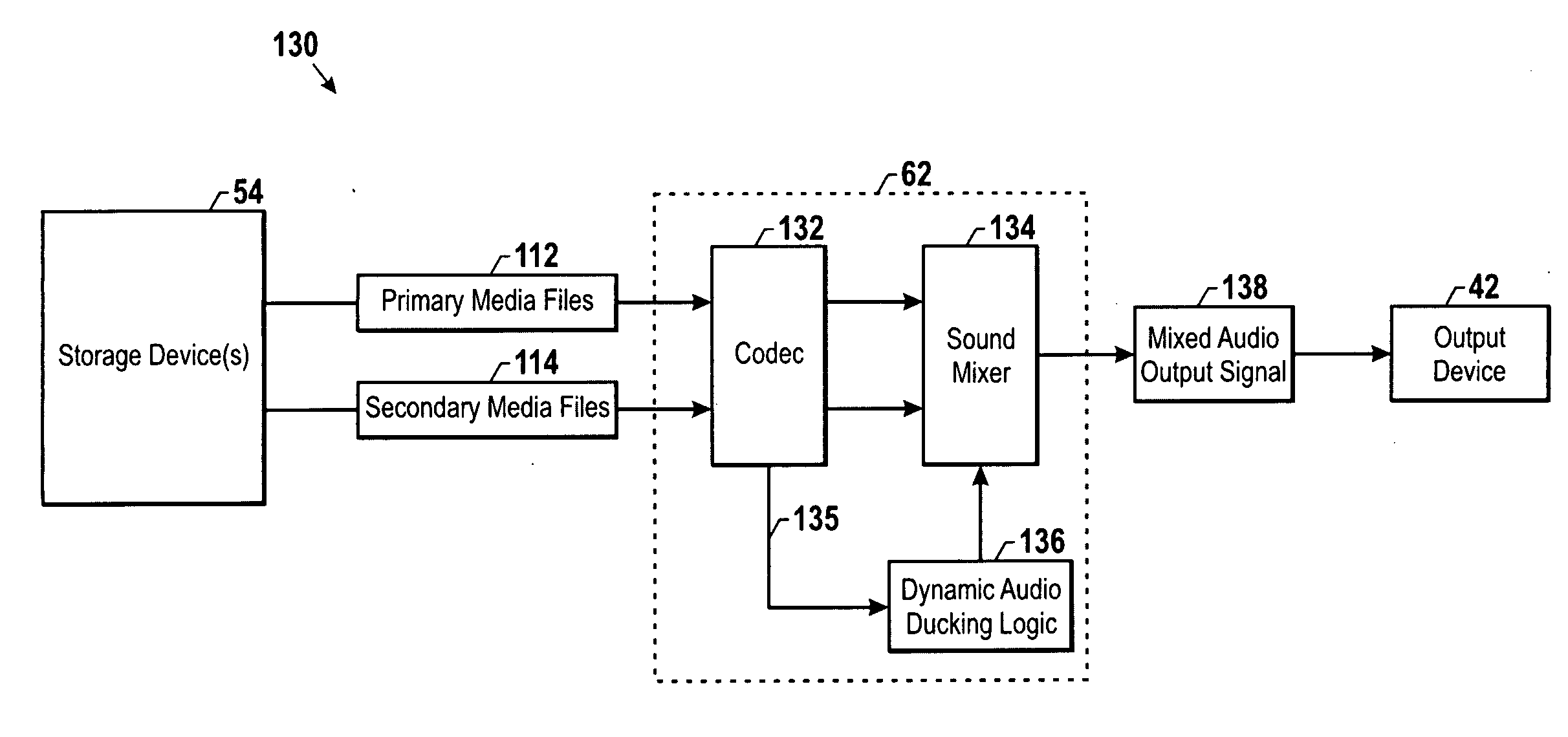
Dynamic audio ducking
Various dynamic audio ducking techniques are provided that may be applied where multiple audio streams, such as a primary audio stream and a secondary audio stream, are being played back simultaneously. For example, a secondary audio stream may include a voice announcement of one or more pieces of information pertaining to the primary audio stream, such as the name of the track or the name of the artist. In one embodiment, the primary audio data and the voice feedback data are initially analyzed to determine a loudness value. Based on their respective loudness values, the primary audio stream may be ducked during the period of simultaneous playback such that a relative loudness difference is generally maintained with respect to the loudness of the primary and secondary audio streams. Accordingly, the amount of ducking applied may be customized for each piece of audio data depending on its loudness characteristics.
Owner:APPLE INC
Dynamic audio ducking
Various dynamic audio ducking techniques are provided that may be applied where multiple audio streams, such as a primary audio stream and a secondary audio stream, are being played back simultaneously. For example, a secondary audio stream may include a voice announcement of one or more pieces of information pertaining to the primary audio stream, such as the name of the track or the name of the artist. In one embodiment, the primary audio data and the voice feedback data are initially analyzed to determine a loudness value. Based on their respective loudness values, the primary audio stream may be ducked during the period of simultaneous playback such that a relative loudness difference is generally maintained with respect to the loudness of the primary and secondary audio streams. Accordingly, the amount of ducking applied may be customized for each piece of audio data depending on its loudness characteristics.
Owner:APPLE INC
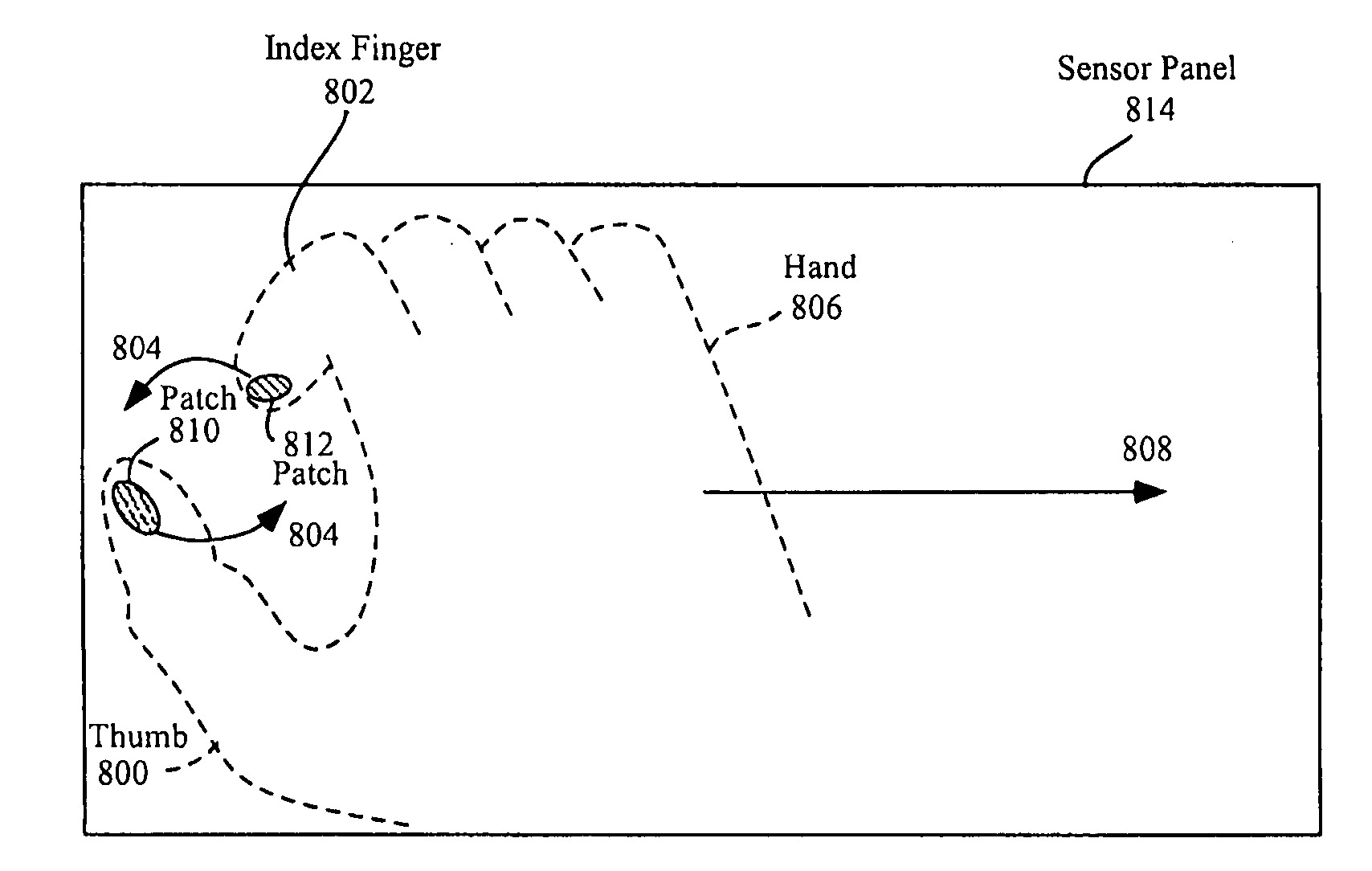
Pinch-throw and translation gestures
ActiveUS20080309632A1Efficiently and accurately effectCharacter and pattern recognitionWireless commuication servicesComputer scienceVelocity vector
Owner:APPLE INC
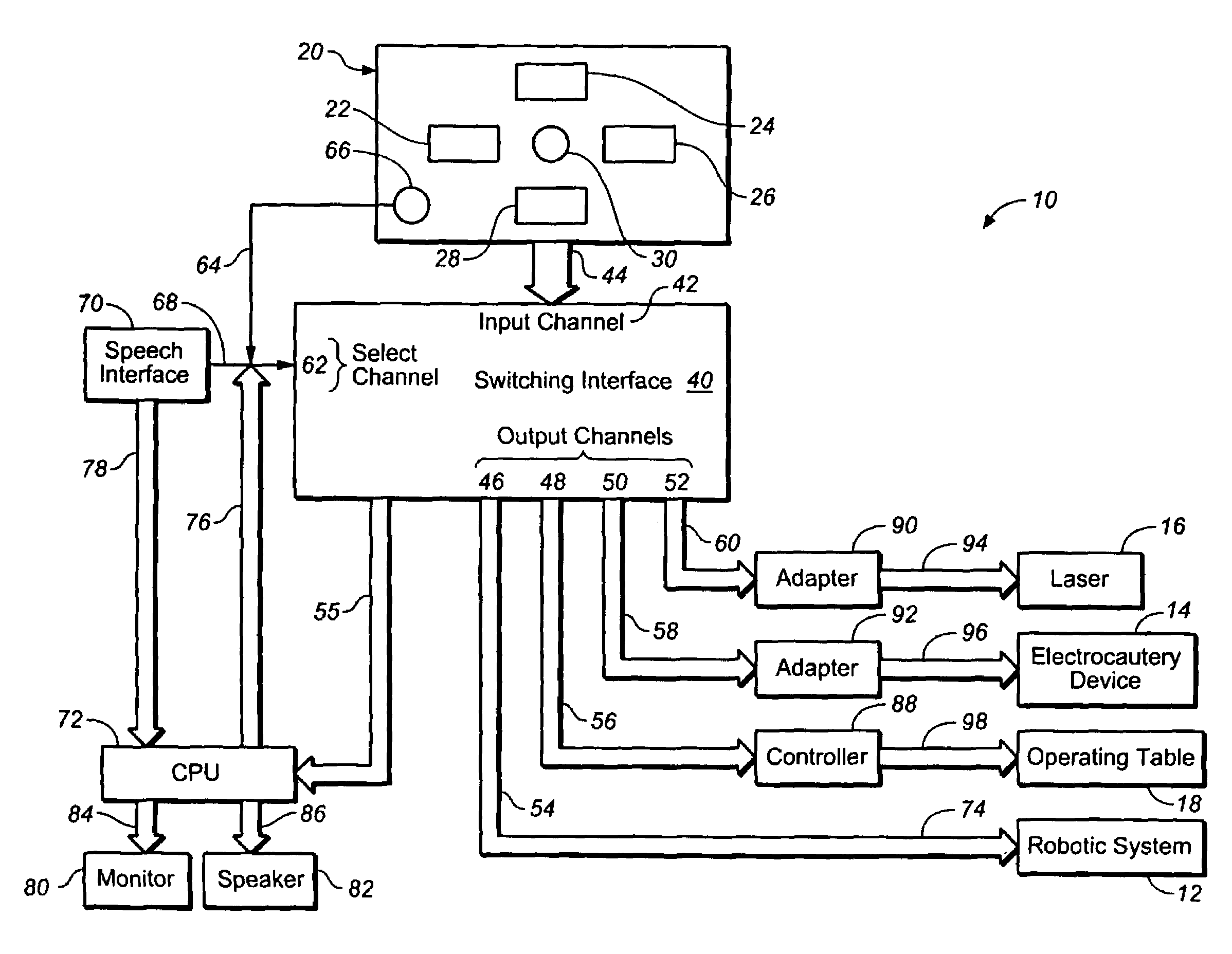
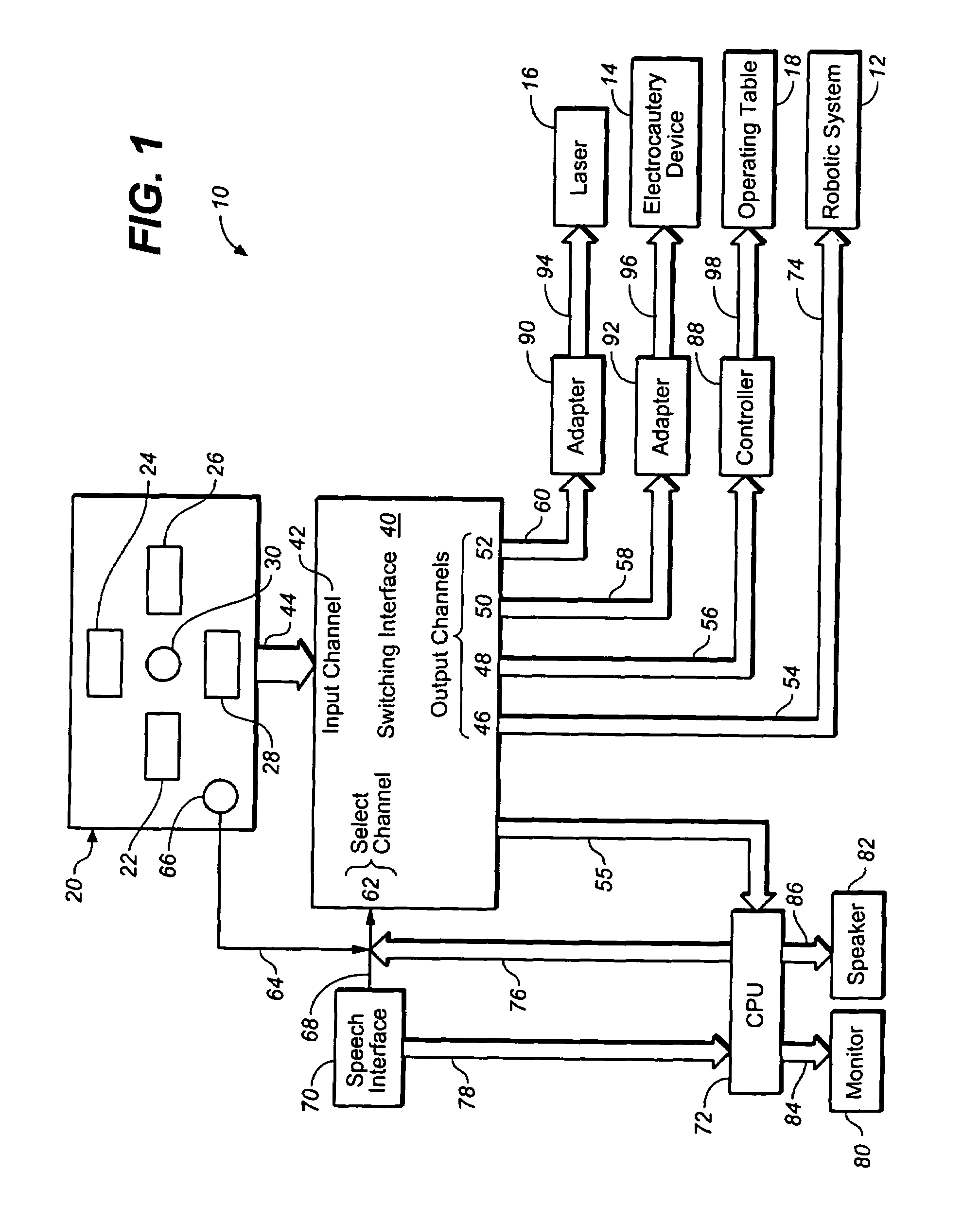
Multi-functional surgical control system and switching interface
An interface which allows a surgeon to operate multiple surgical devices from a single input device. The input device may be a foot pedal that provides output signals to actuate a number of different surgical devices. The surgical devices may include a robotic arm, a laser, an electrocautery device, or an operating table. The interface has an input channel that is coupled to the input device and a plurality of output channels that are coupled to the surgical devices. The interface also has a select input channel which can receive input commands to switch the input channel to one of the output channels. The select channel may be coupled to a speech interface that allows the surgeon to select one of the surgical devices with a voice command. The surgeon can operate any device by providing an input command which switches the input channel to the desired output channel.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Variable gain active noise canceling system with improved residual noise sensing
InactiveUS6118878AReduce the possibilityCancellation system retains its effectiveness across its bandwidthNoise generationSound producing devicesInstabilityEngineering
An active noise cancellation system includes a series of features for more effective cancellation, greater reliability, and improved stability. A particular feature adapted for headset systems includes locating a residual microphone radially offset from the center of a sound generator to detect a signal more similar to that incident upon the eardrum of the user. In addition, an open back headset design includes perforations on the side of the headset instead of the back, so that the perforations are less susceptible to inadvertent blockage. The system also includes a mechanism for detecting changes in the acoustic characteristics of the environment that may be caused, for example, by pressure exerted upon the earpieces, and that may destabilize the cancellation system. The system automatically responds to such changes, for example, by reducing the gain or the frequency response of the system to preserve stability. The system further includes other methods for detecting imminent instability and compensating, such as detecting the onset of signals within enhancement frequencies characteristic of the onset of instability, and adjusting the gain or frequency response of the system or suppressing the enhanced signals. The system further includes a mechanism for conserving battery life by turning the system off when sound levels are low, or adjusting the power supply to the system to correspond to the current power requirements of the system.
Owner:NOISE CANCELLATION TECH
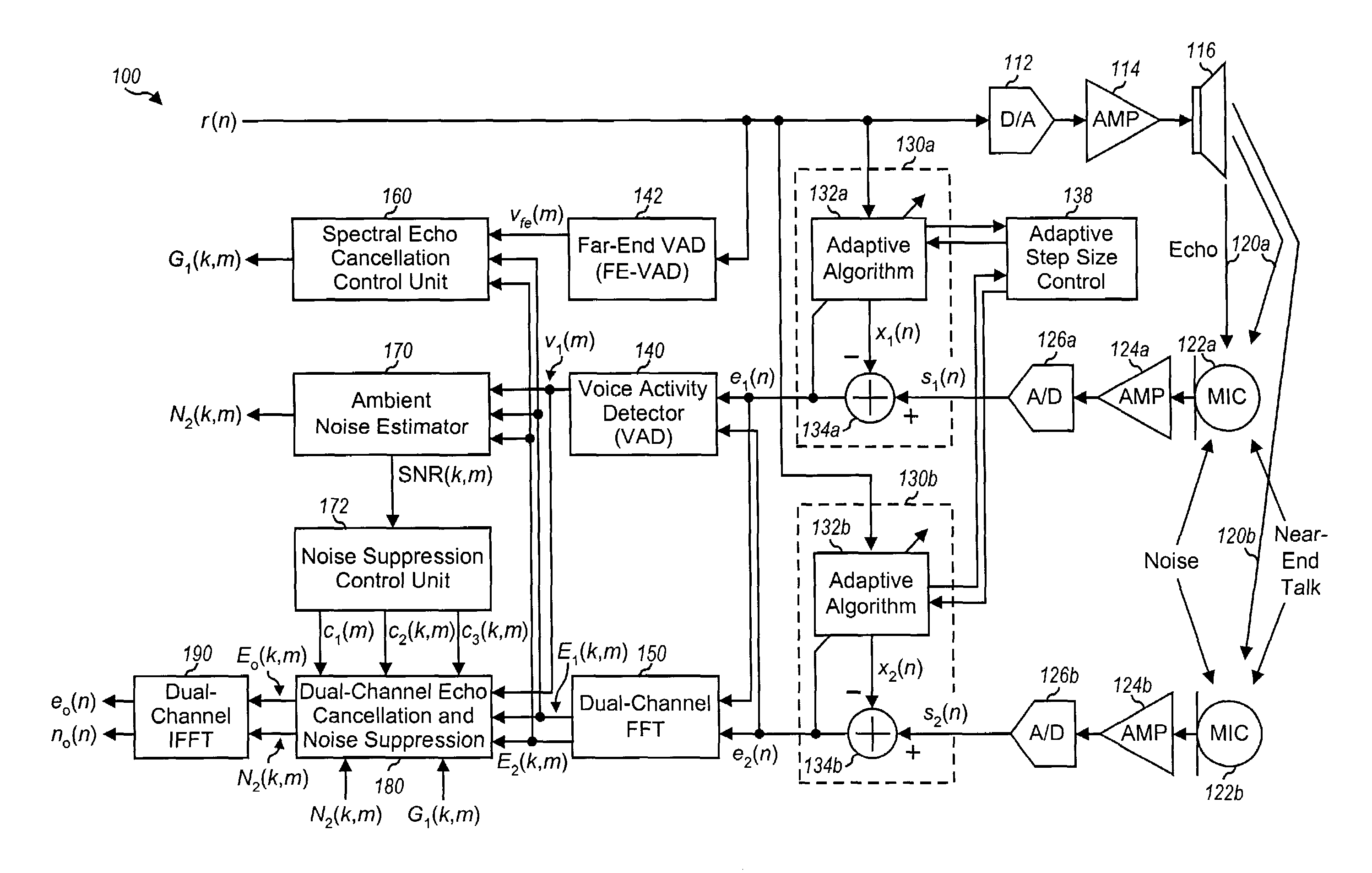
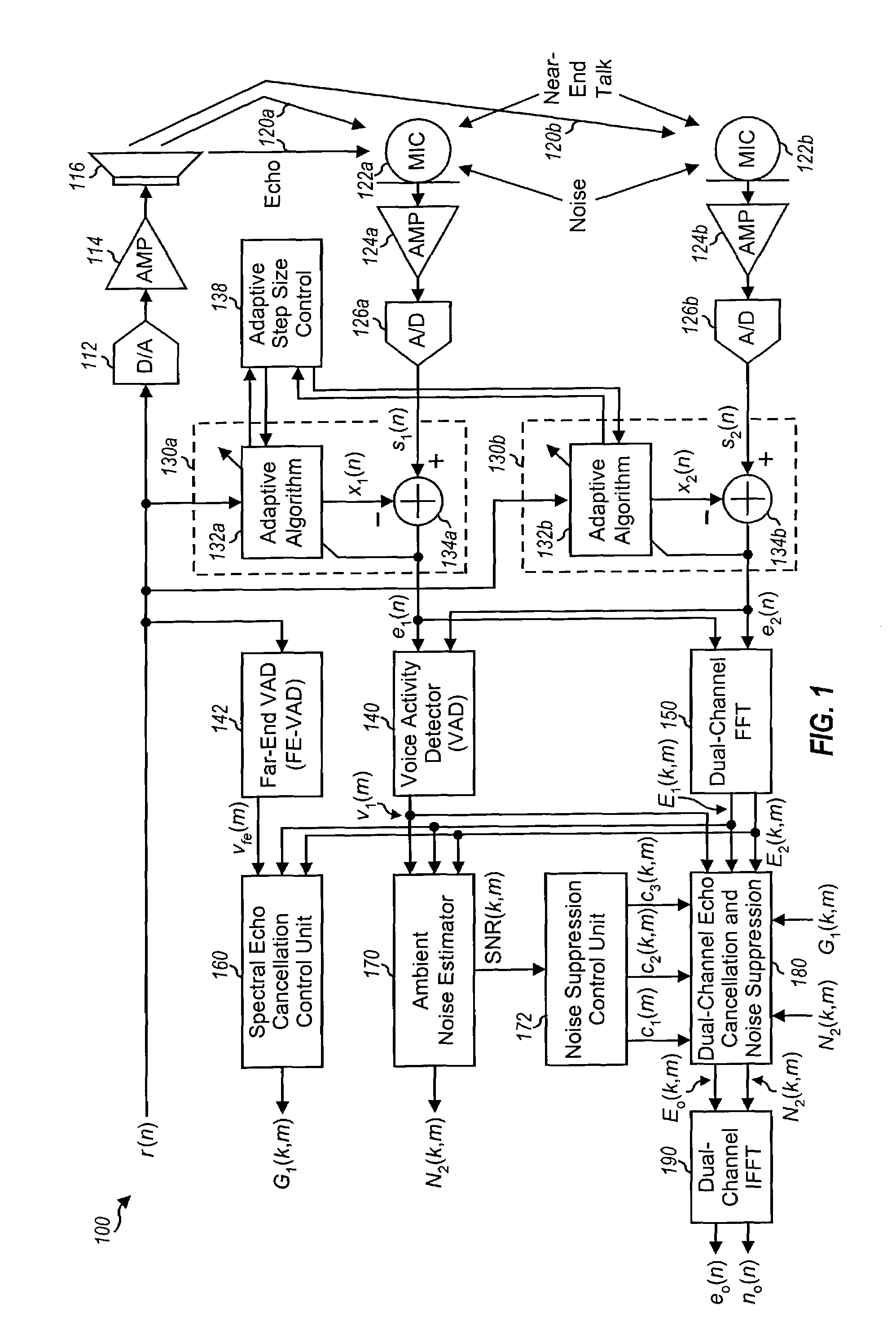
Small array microphone for acoustic echo cancellation and noise suppression
ActiveUS7003099B1Suppress noiseReducing non-stationary ambient noiseTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSubstation equipmentControl signalEngineering
Techniques for canceling echo and suppressing noise using an array microphone and signal processing. In one system, at least two microphones form an array microphone and provide at least two microphone input signals. Each input signal may be processed by an echo canceller unit to provide a corresponding intermediate signal having some echo removed. An echo cancellation control unit receives the intermediate signals and derives a first gain used for echo cancellation. A noise suppression control unit provides at least one control signal used for noise suppression based on background noise detected in the intermediate signals. An echo cancellation and noise suppression unit derives a second gain based on the control signal(s), cancels echo in a designated intermediate signal based on the first gain, and suppresses noise in this intermediate signal based on the second gain. The signal processing may be performed in the frequency domain.
Owner:FORTEMEDIA
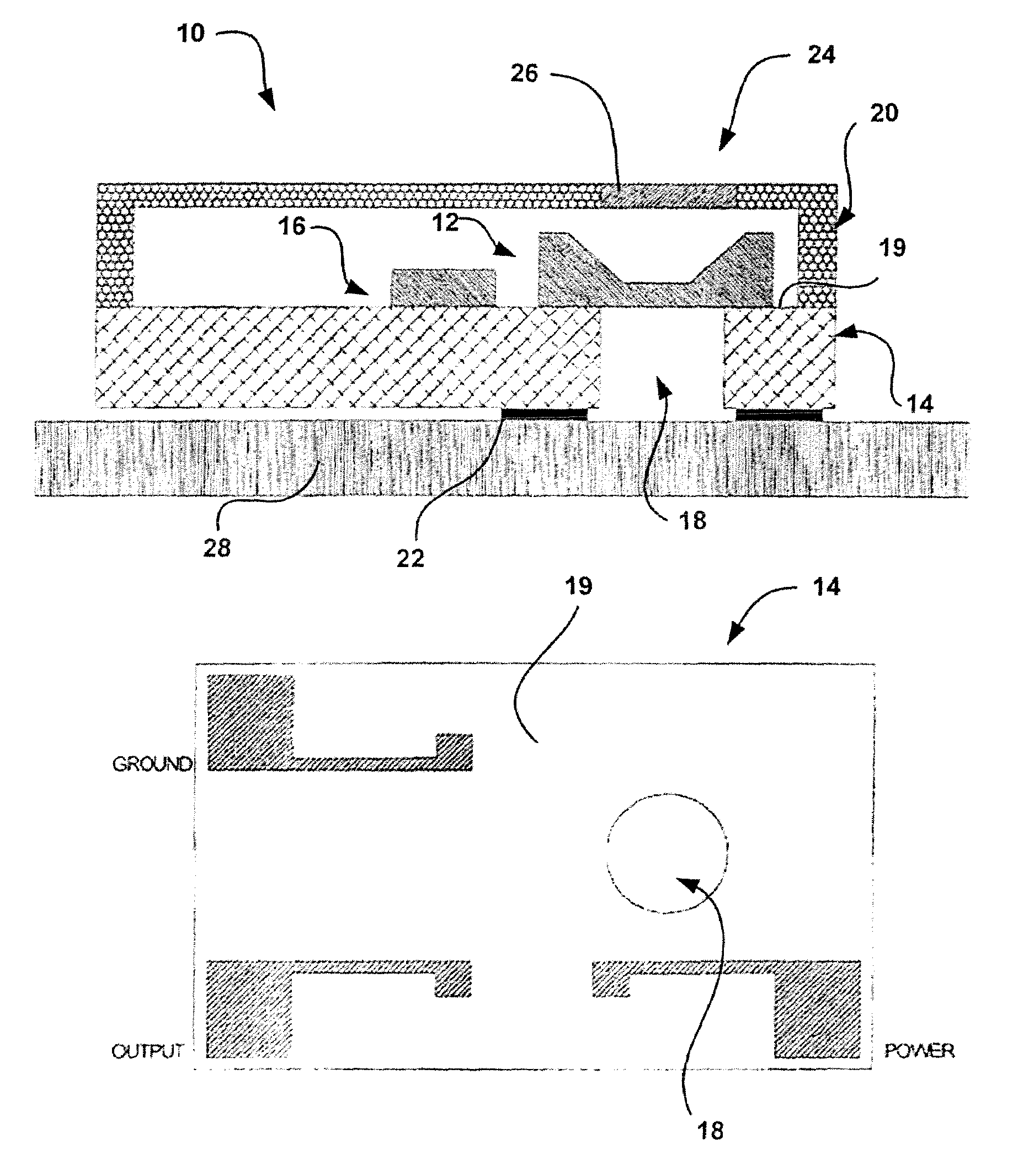
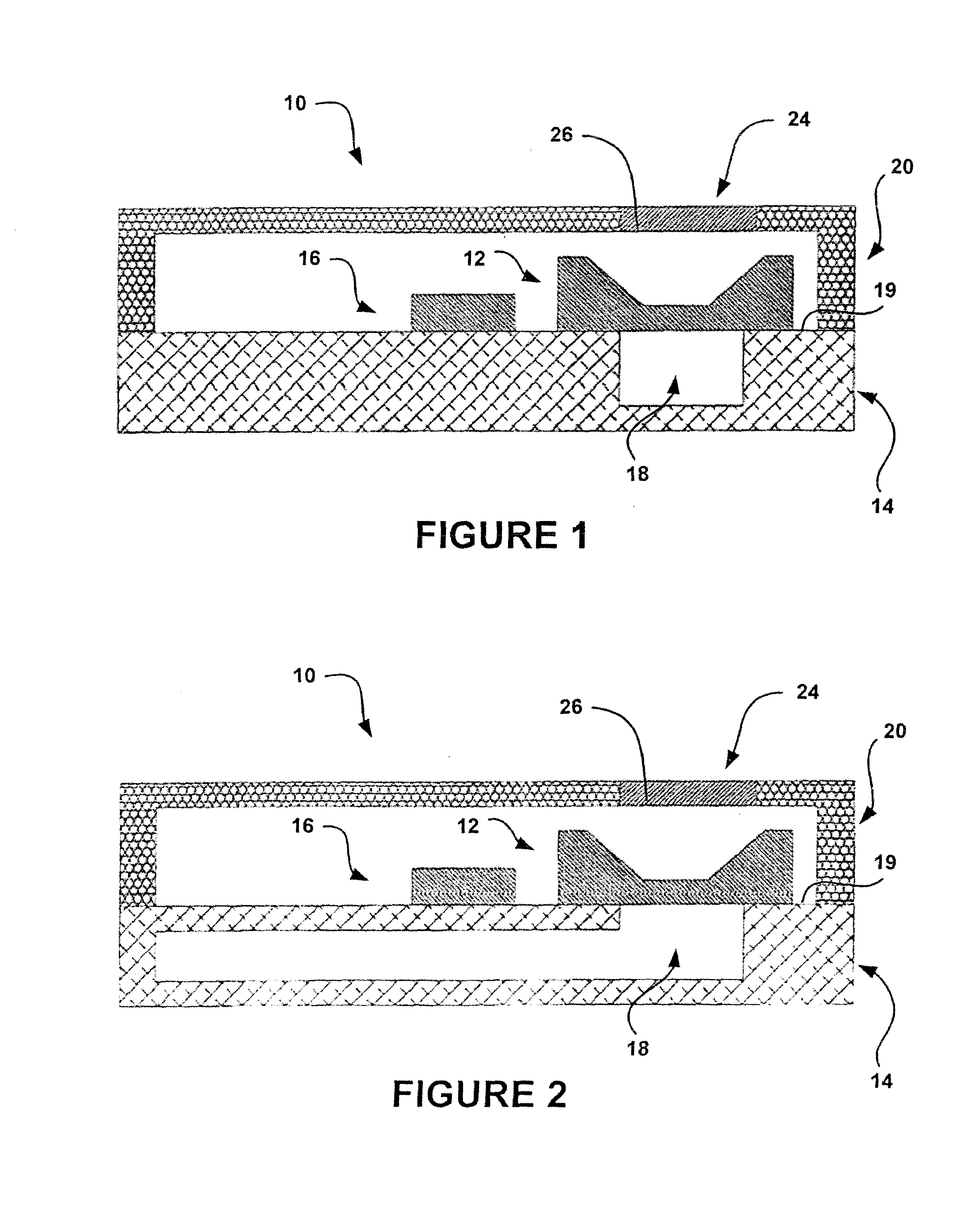
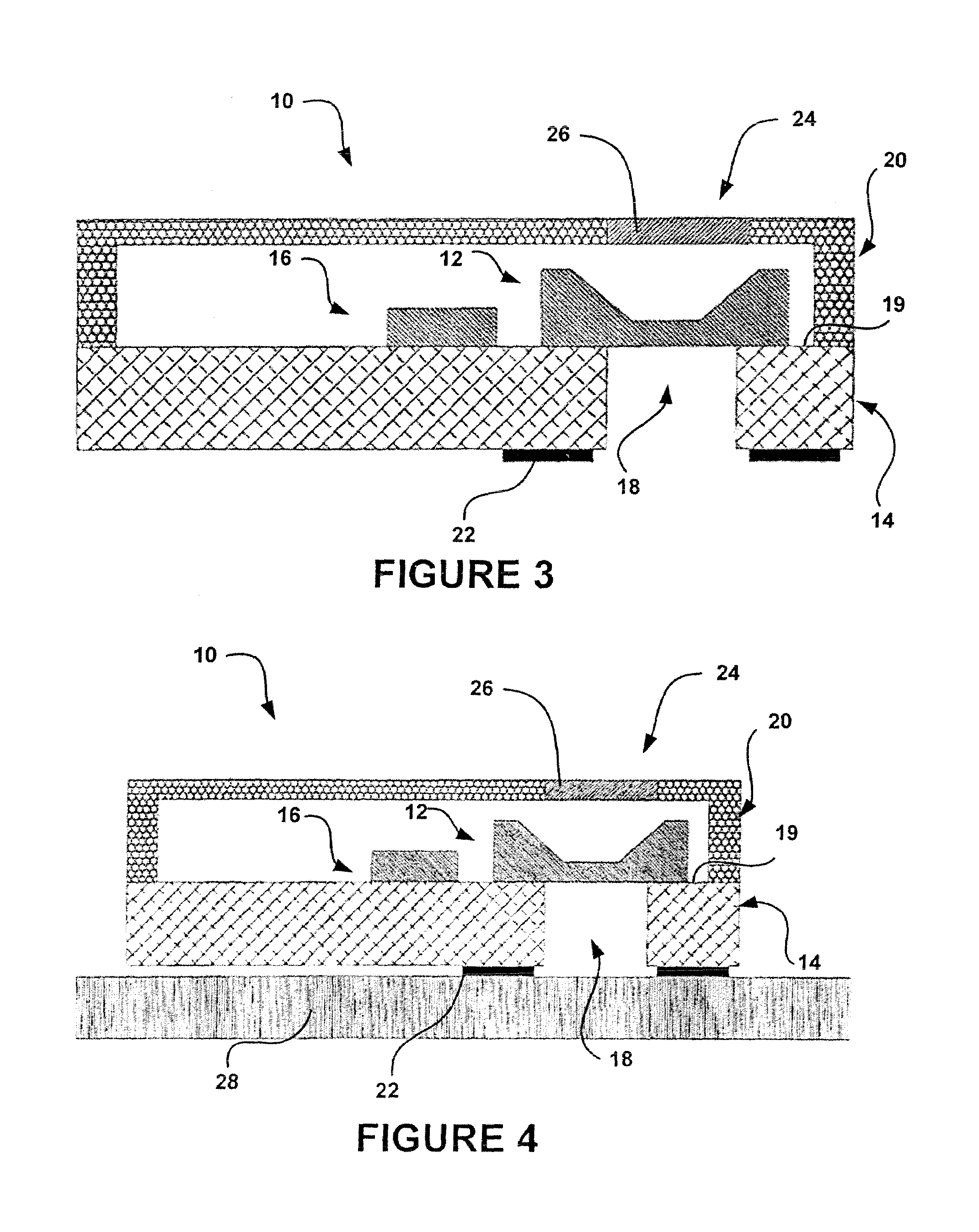
Acoustic device
InactiveUS6332029B1Spread fastGood effectTelevision system detailsElectrophonic musical instrumentsEngineeringBending stiffness
Acoustic device including a member extending transversely of its thickness and capable of sustaining bending waves at least over an intendedly consequentially acoustically active area of the transverse extent of said member, the member having, by reason of orderly design methodology disclosed and claimed, a distribution of resonant modes of its natural bending wave vibration at least over said area that is dependent on values of particular parameters of said members, including geometrical configuration and directional bending stiffness(es), which values have been selected to predetermine said distribution of natural resonant modes being consonant with required achievable acoustic action of said member for operation of said device over a desired operative acoustic frequency range.
Owner:NEW TRANSDUCERS LTD
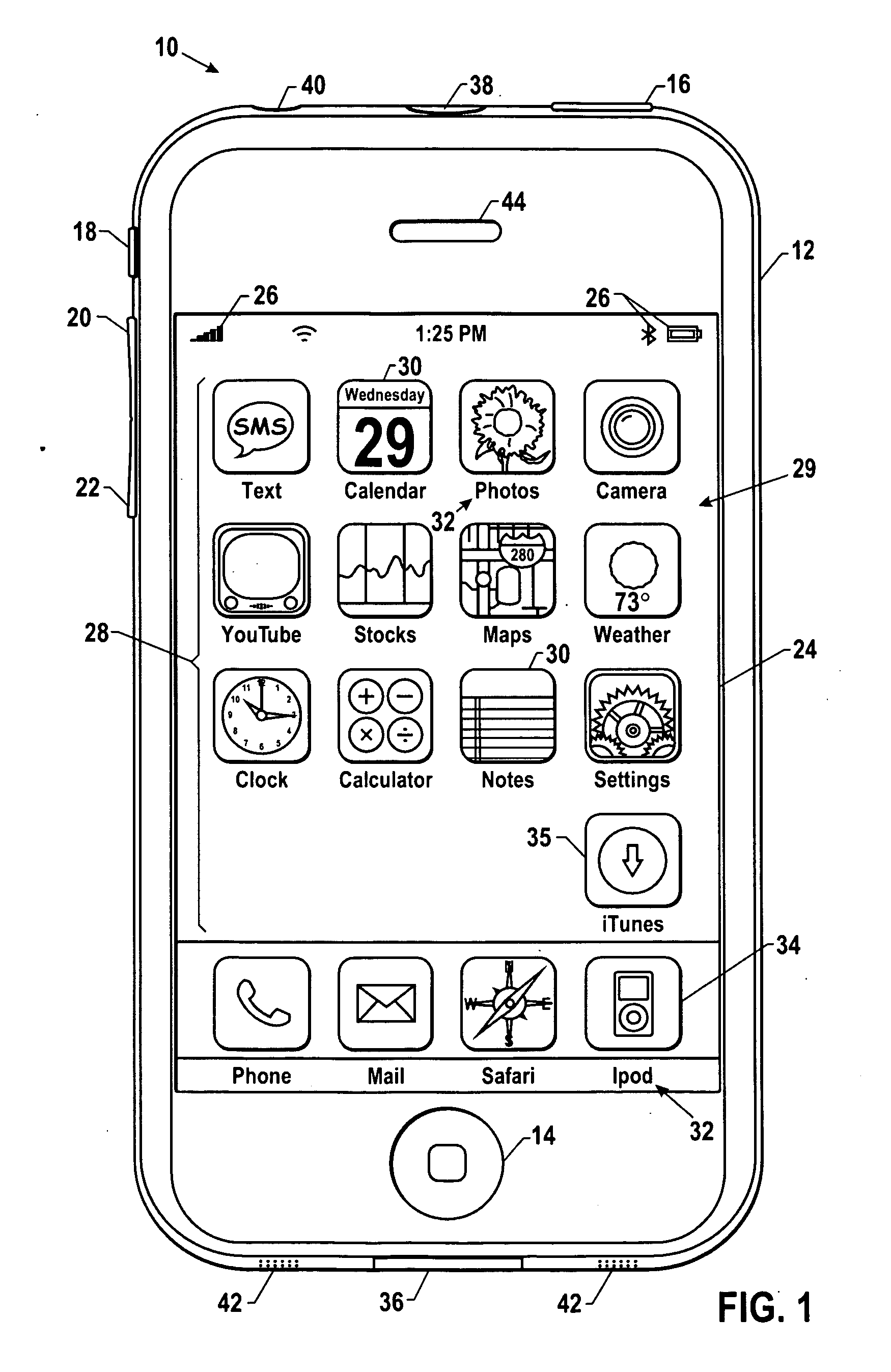
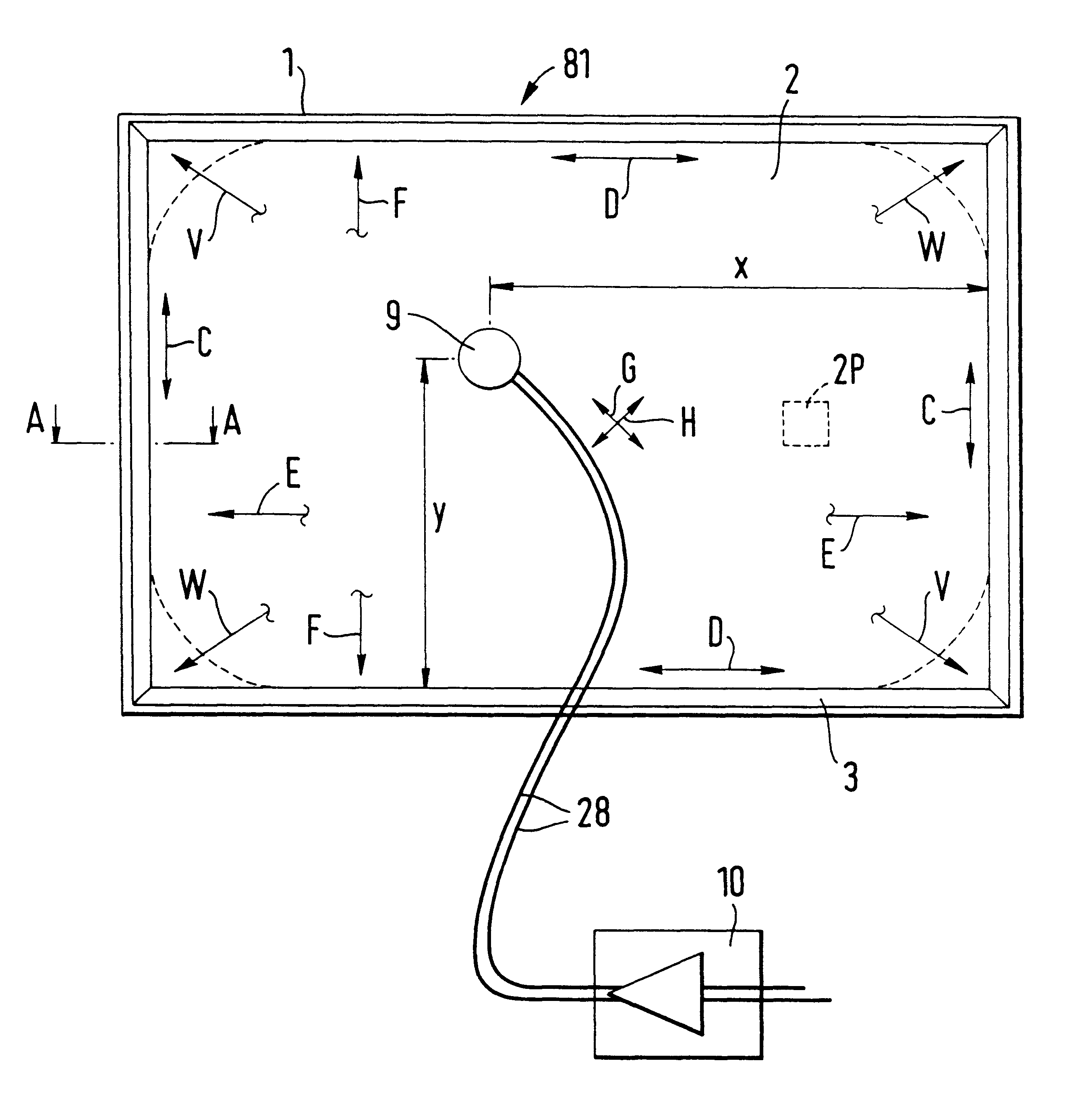
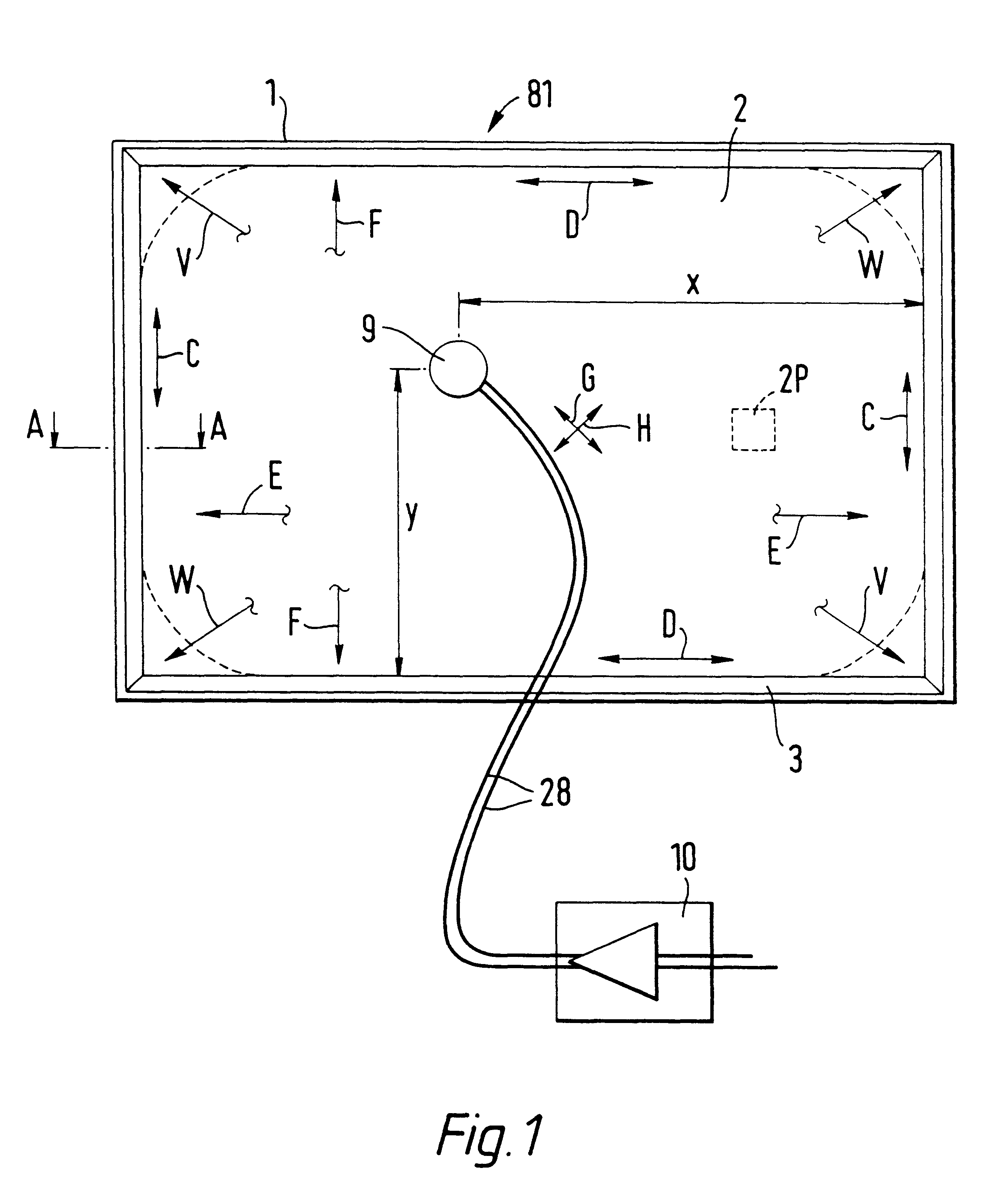
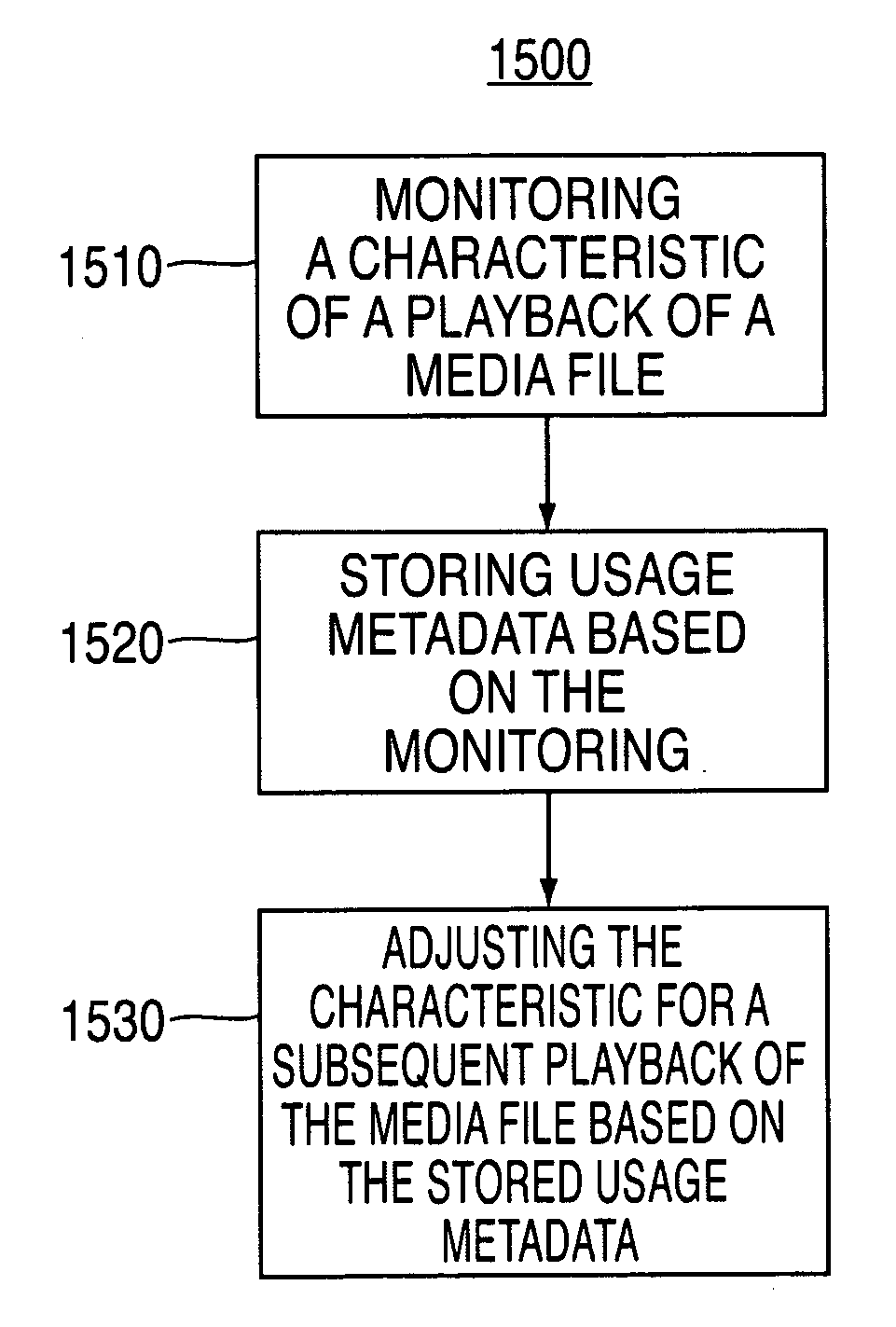
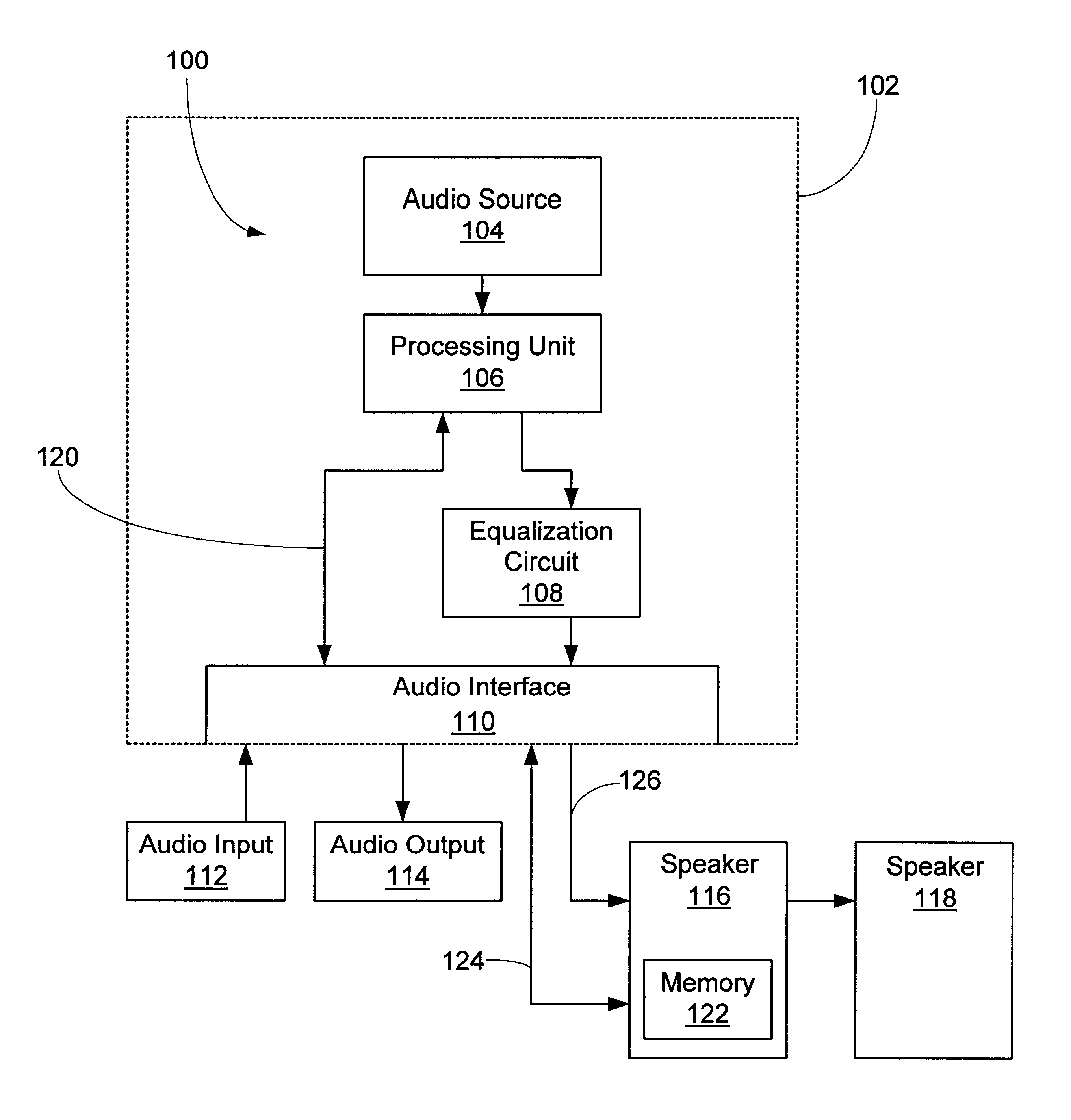
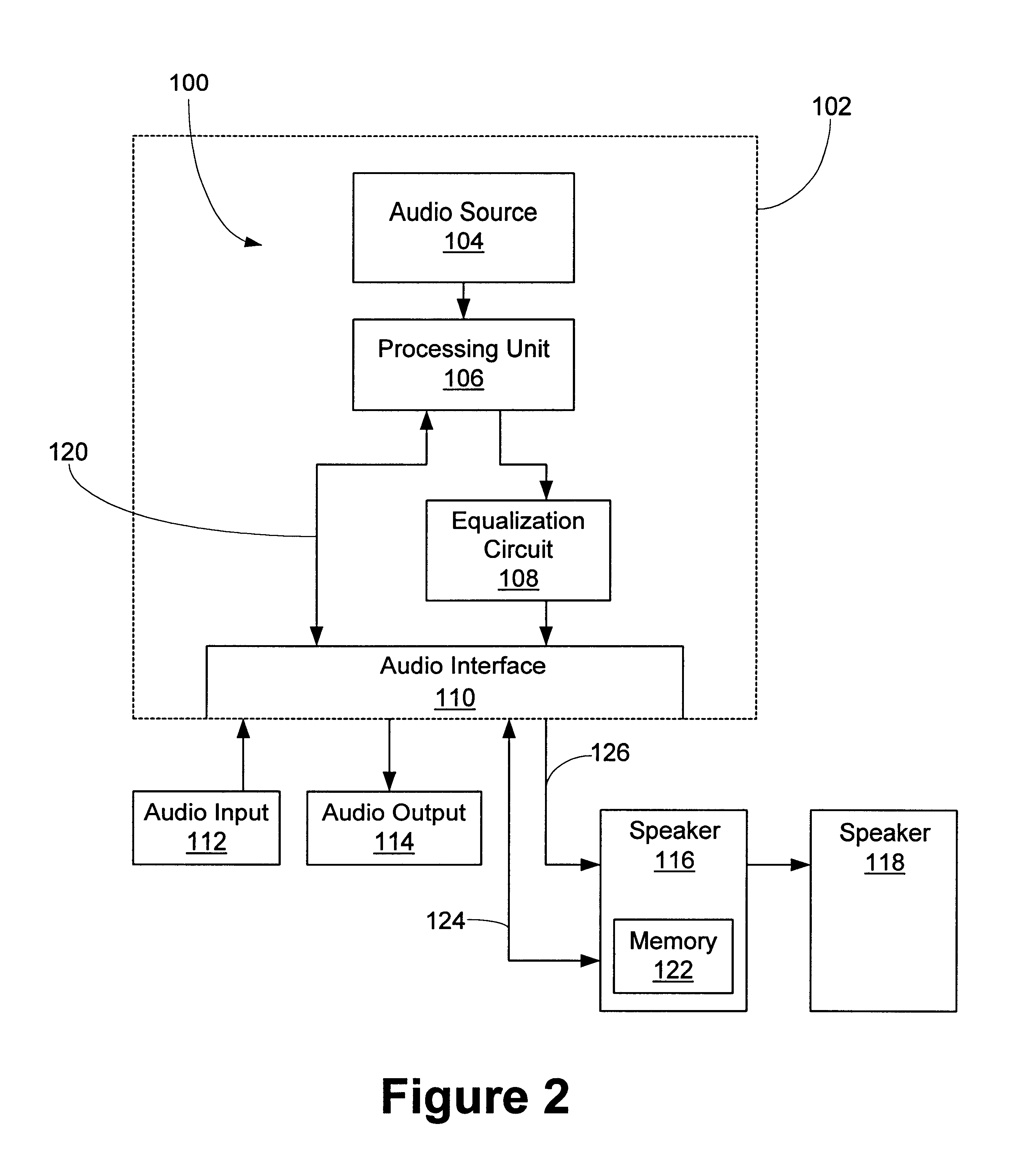
System and methods for adjusting graphical representations of media files based on previous usage
Systems and methods for adjusting playback and graphical representations of media files are provided. The systems and methods can monitor playback and access of media files to create usage metadata. The usage metadata can then be used to adjust the playback of the media file. For example, the usage metadata may indicate that a user skips, on average, the first 22 seconds of a particular song so the next time that song is played, the first 22 seconds will automatically be skipped. The usage metadata can additionally or alternatively be used to adjust a graphical representation of the media file. For example, the usage metadata may indicate that a user rarely accesses a particular song so the graphical representation of that song will be small and faded. This change in graphical representation can help a user find more commonly used media files.
Owner:APPLE INC
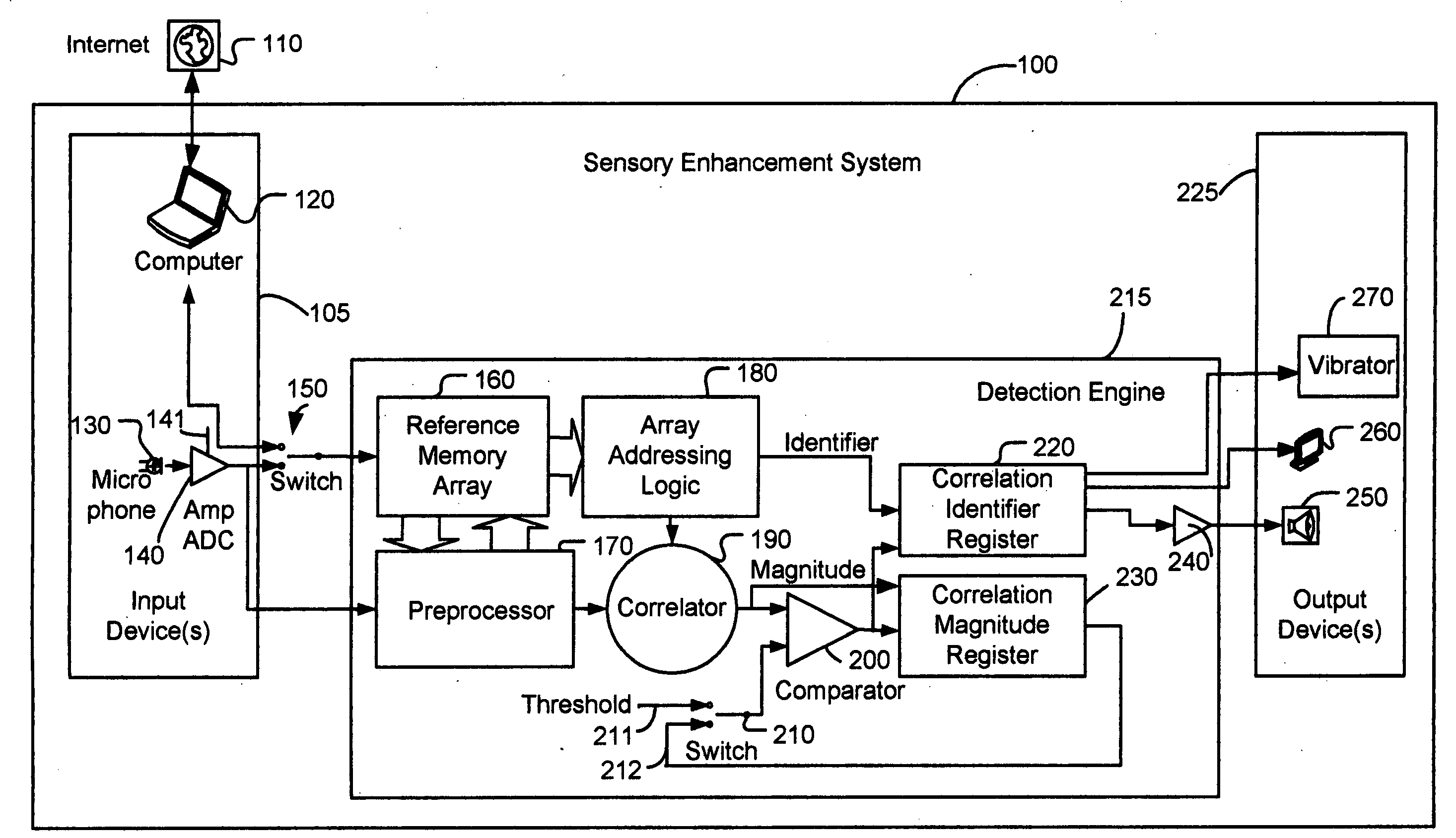
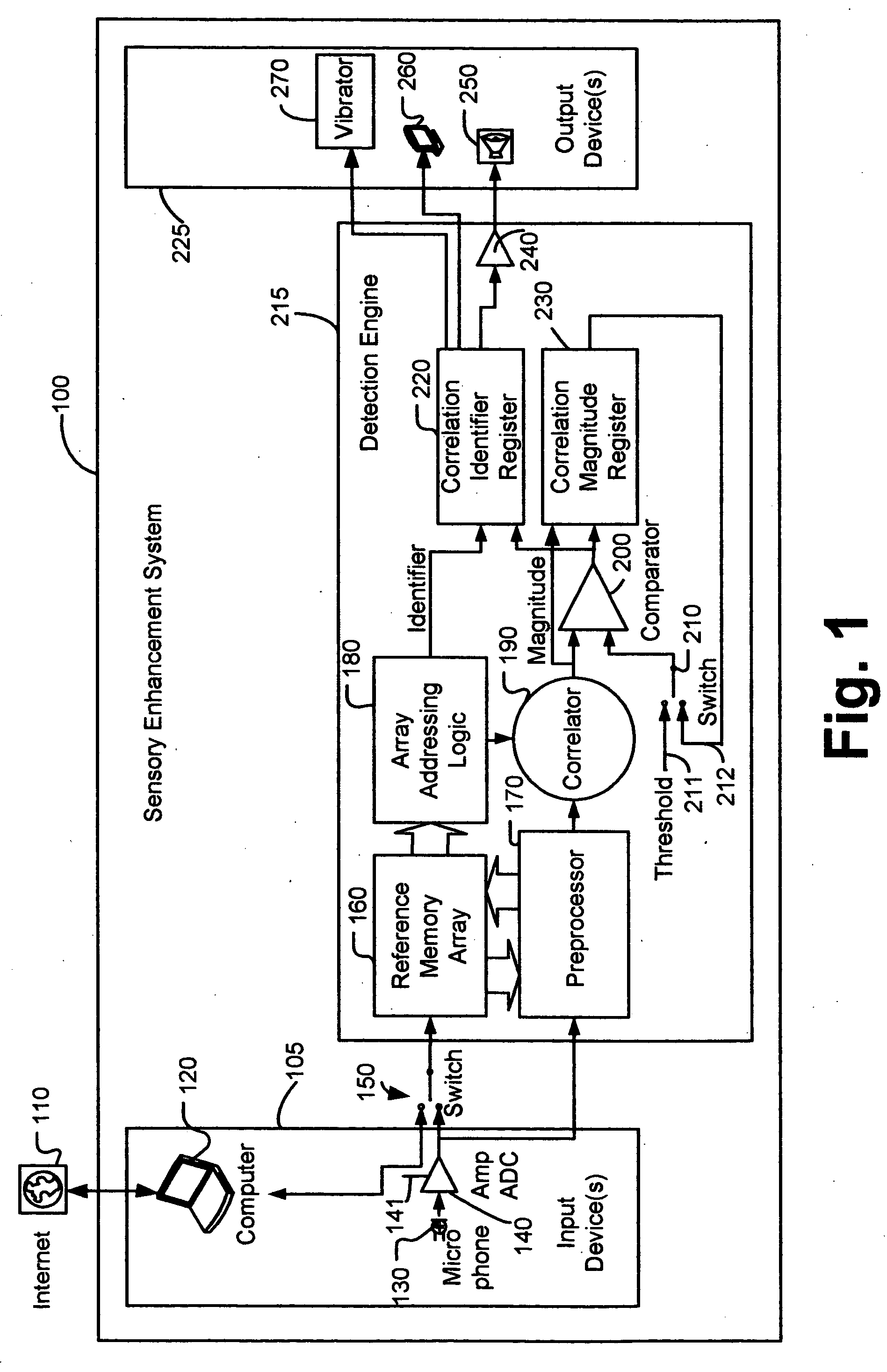
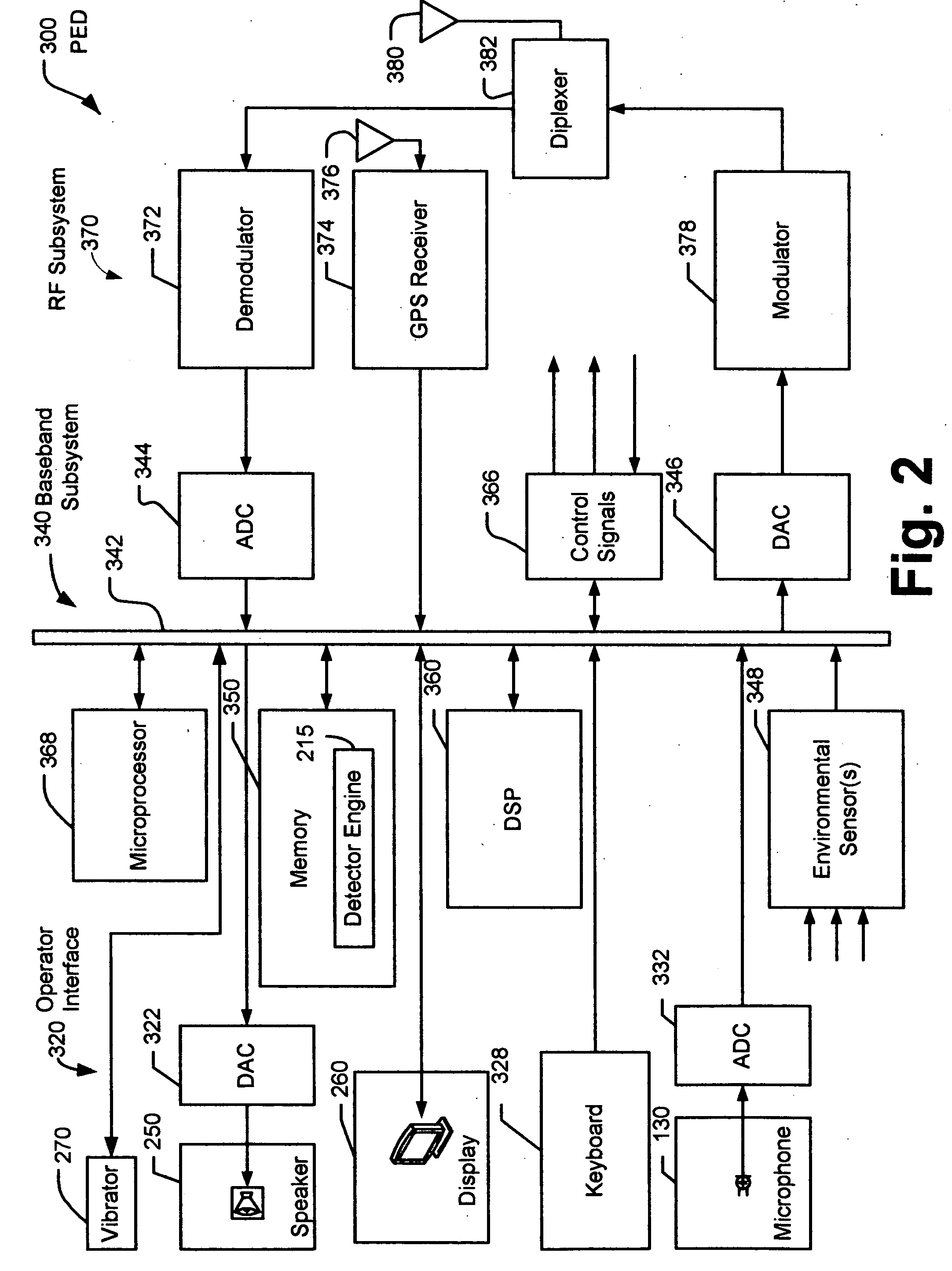
Sensory enhancement systems and methods in personal electronic devices
InactiveUS20090085873A1Input/output for user-computer interactionDevices with GPS signal receiverComputer science
Disclosed are personal electronic devices (PEDs) having a sensory enhancement (SE) system for monitoring environmental conditions and detecting environmental events, for example but not limited to, changes in acoustic, thermal, optical, electromagnetic, chemical, dynamic, wireless, atmospheric, or biometric conditions. The detection of such events can be used to invoke a notification, an alert, a corrective action, or some other action, depending upon the implementation to the PED user or another party.
Owner:INNOVATION SPECIALISTS
Plug and play compatible speakers
InactiveUS6859538B1Stereophonic circuit arrangementsFrequency response correctionTransducerLoudspeaker
A speaker includes at least one transducer and at least one memory device. The at least one transducer is adapted to receive an audio signal. The at least one memory device is adapted to store data related to the speaker. A method includes reading data from a memory device of at least one speaker. An audio signal is provided from an audio system.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Personal audio assistant device and method
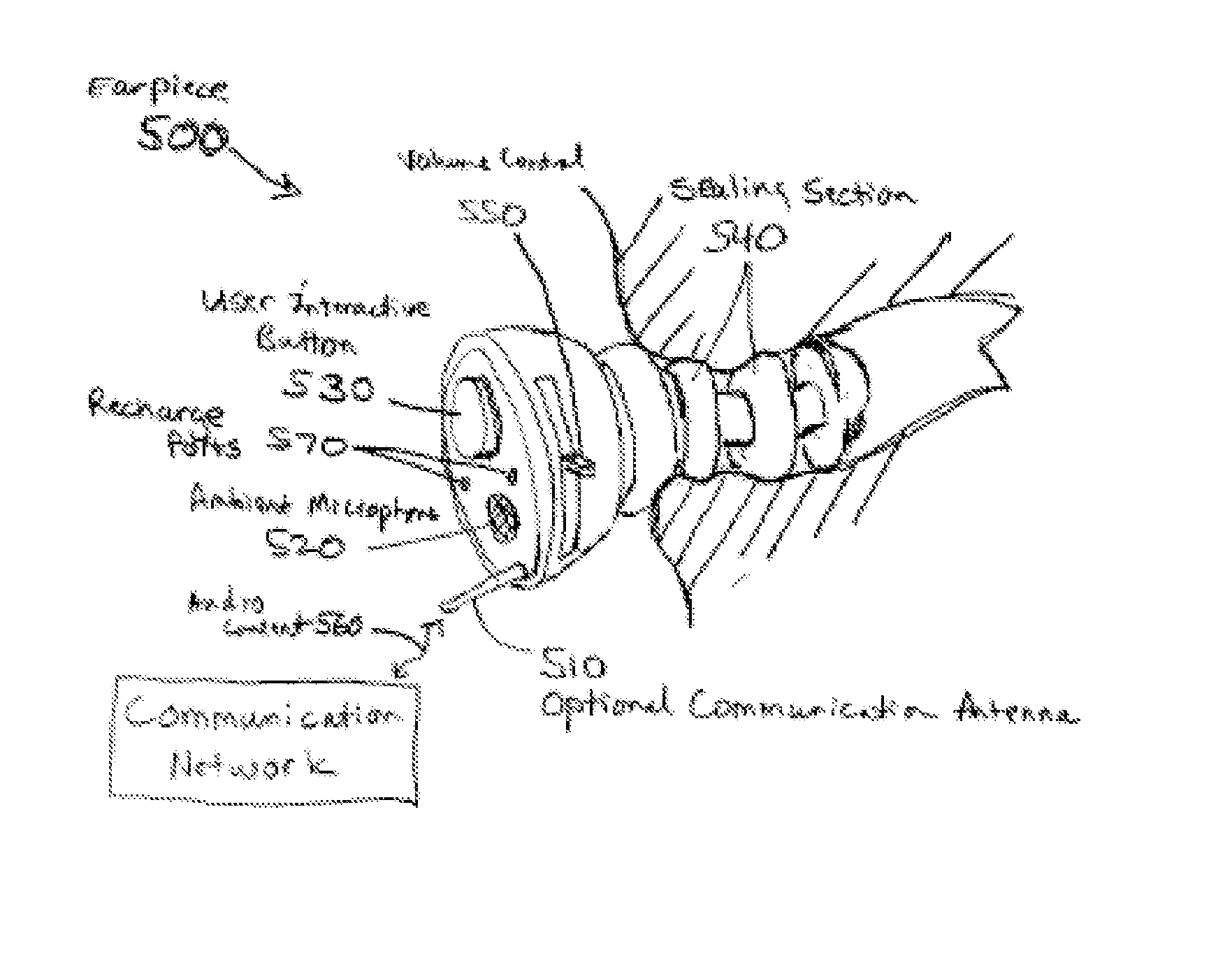
At least one exemplary embodiment is directed to an earpiece comprising: an ambient microphone; an ear canal microphone; an ear canal receiver; a sealing section; a logic circuit; a communication module; a memory storage unit,; and a user interaction element, where the user interaction element is configured to send a play command to the logic circuit when activated by a user where the logic circuit reads registration parameters stored on the memory storage unit and sends audio content to the ear canal receiver according to the registration parameters.
Owner:STATON TECHIYA LLC
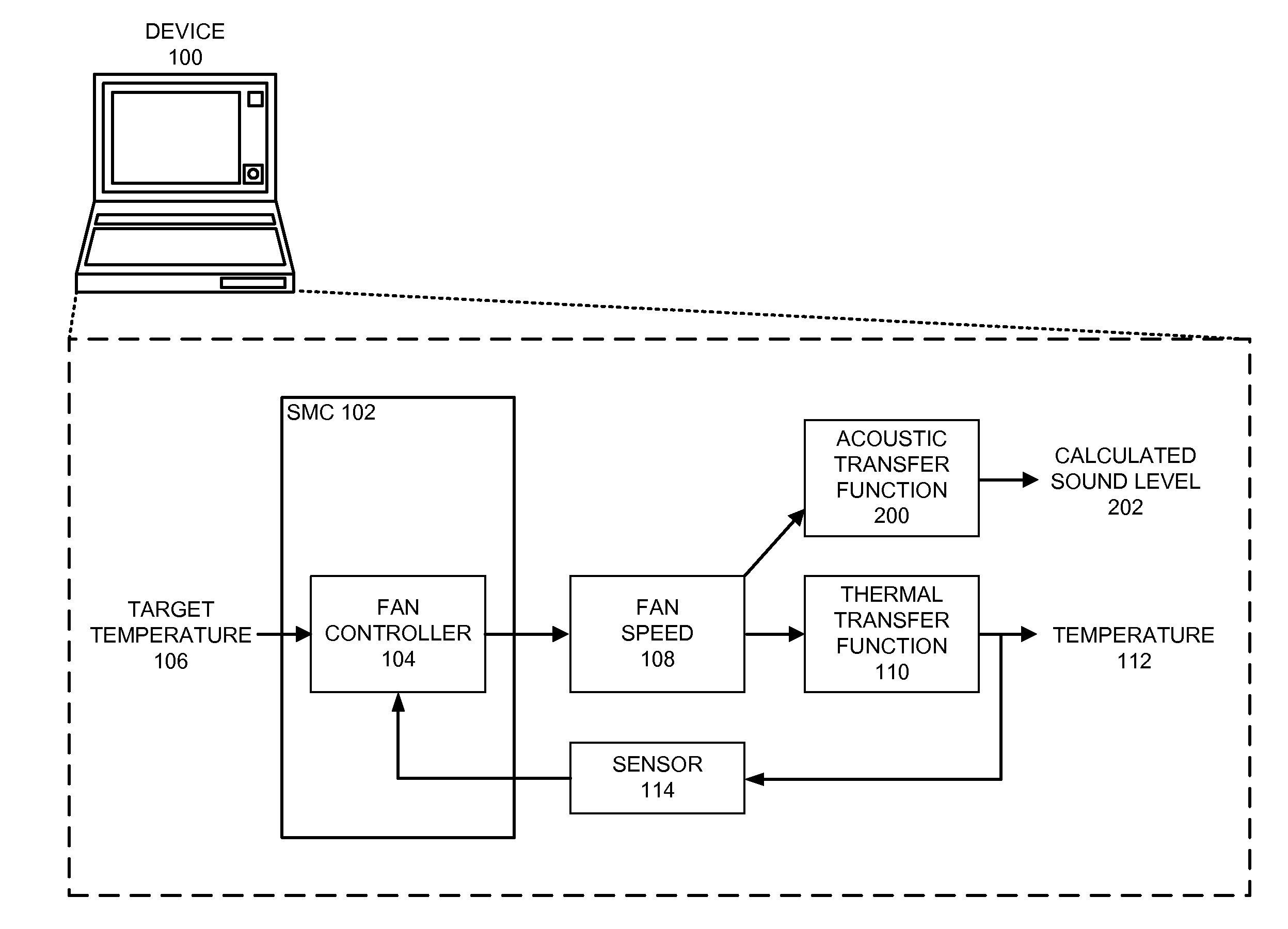
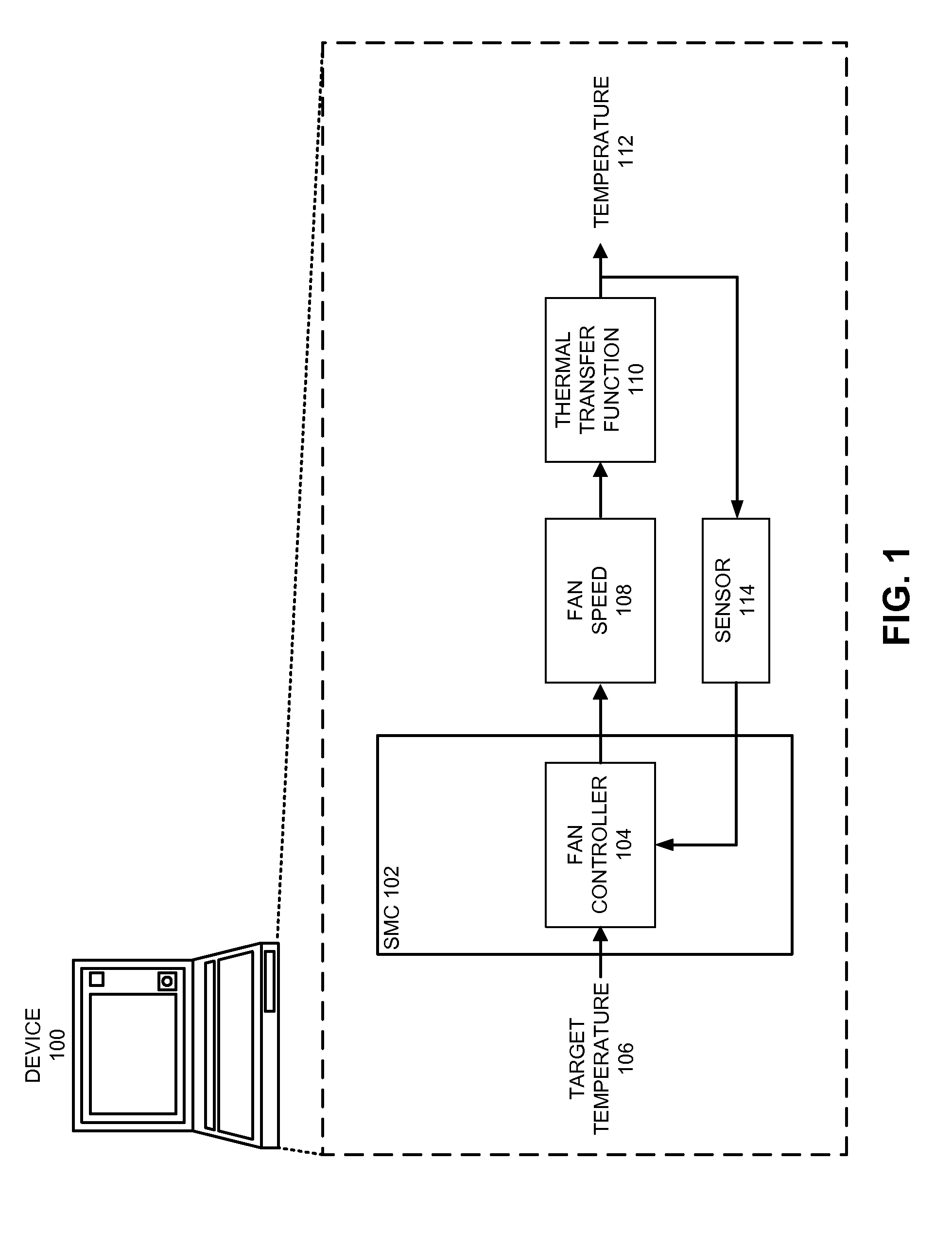
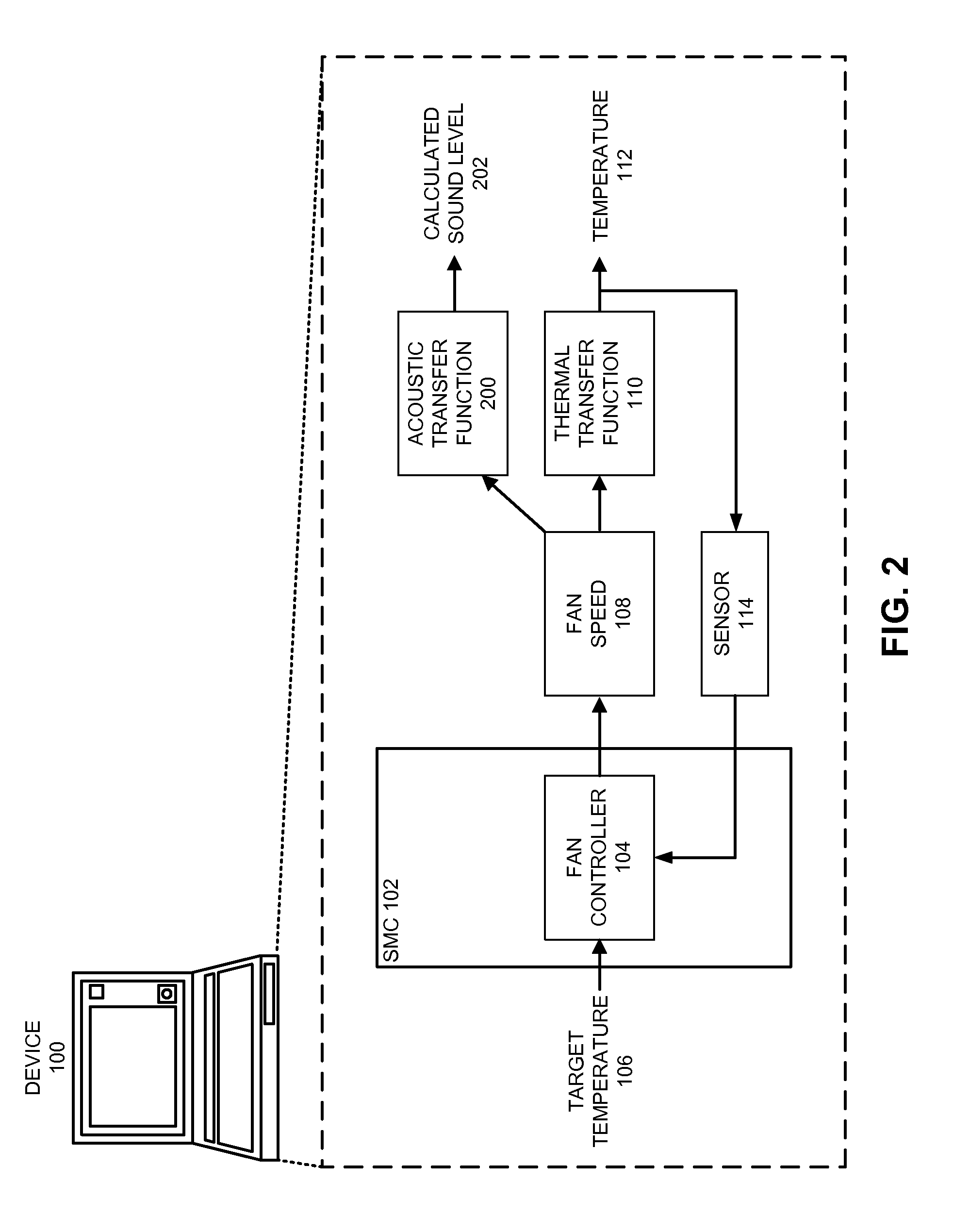
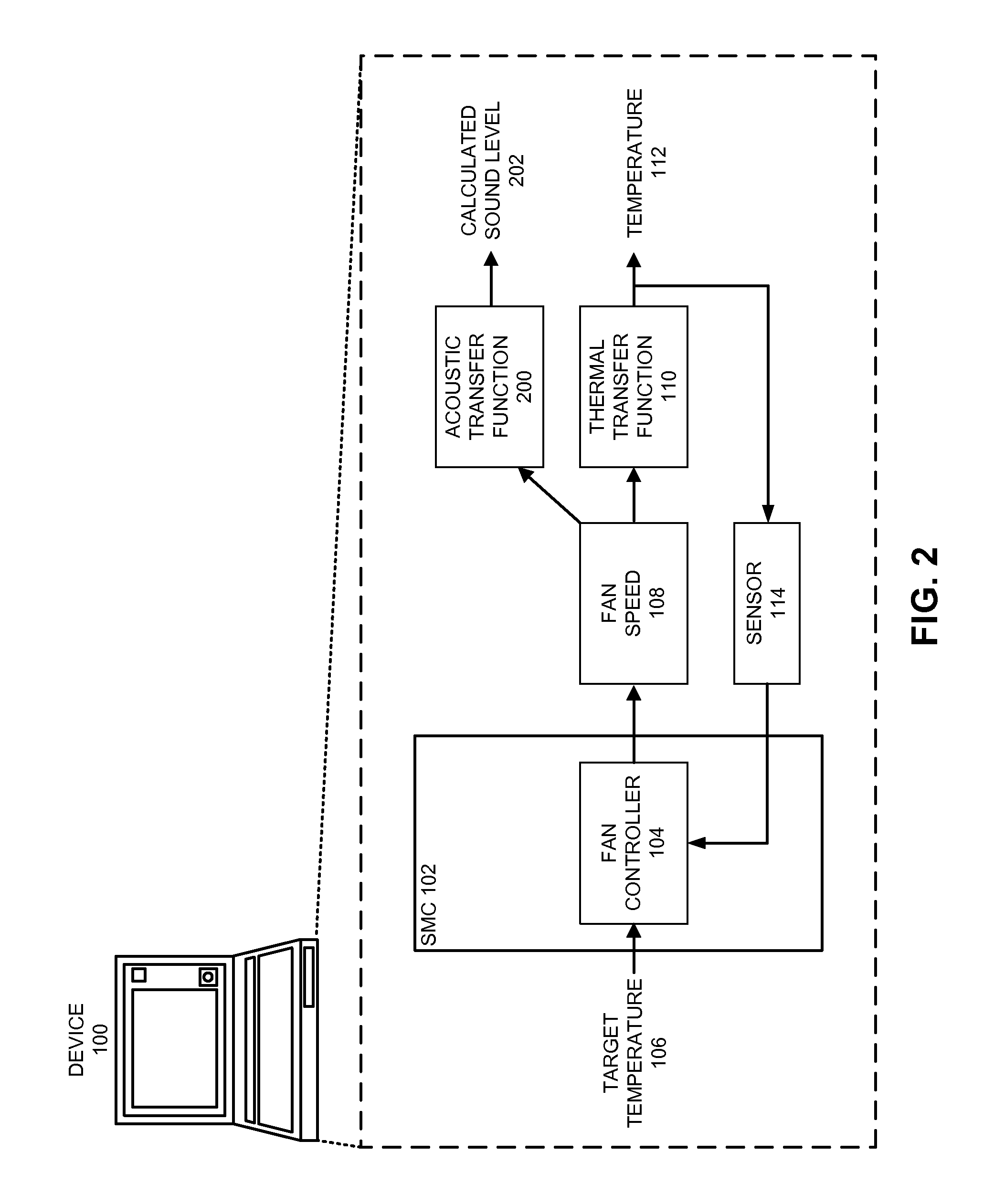
Reducing annoyance by managing the acoustic noise produced by a device
ActiveUS20090092261A1Less worryReduce user annoyanceEnergy efficient ICTEar treatmentAcousticsNoise estimation
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that reduces annoyance by managing the acoustic noise produced by a device. During operation, the system receives a set of acoustic characteristics for noise-producing components within the device. The system then uses these acoustic characteristics to estimate the acoustic noise being generated by each of these noise-producing components. Next, the system aggregates this set of acoustic noise estimates to produce an aggregate estimate for the acoustic noise produced by the device. The system then analyzes this aggregate estimate using an acoustic annoyance model to determine the acoustic annoyance level. The system then adjusts a setting in the device to manage the acoustic annoyance level produced by the device.
Owner:APPLE INC
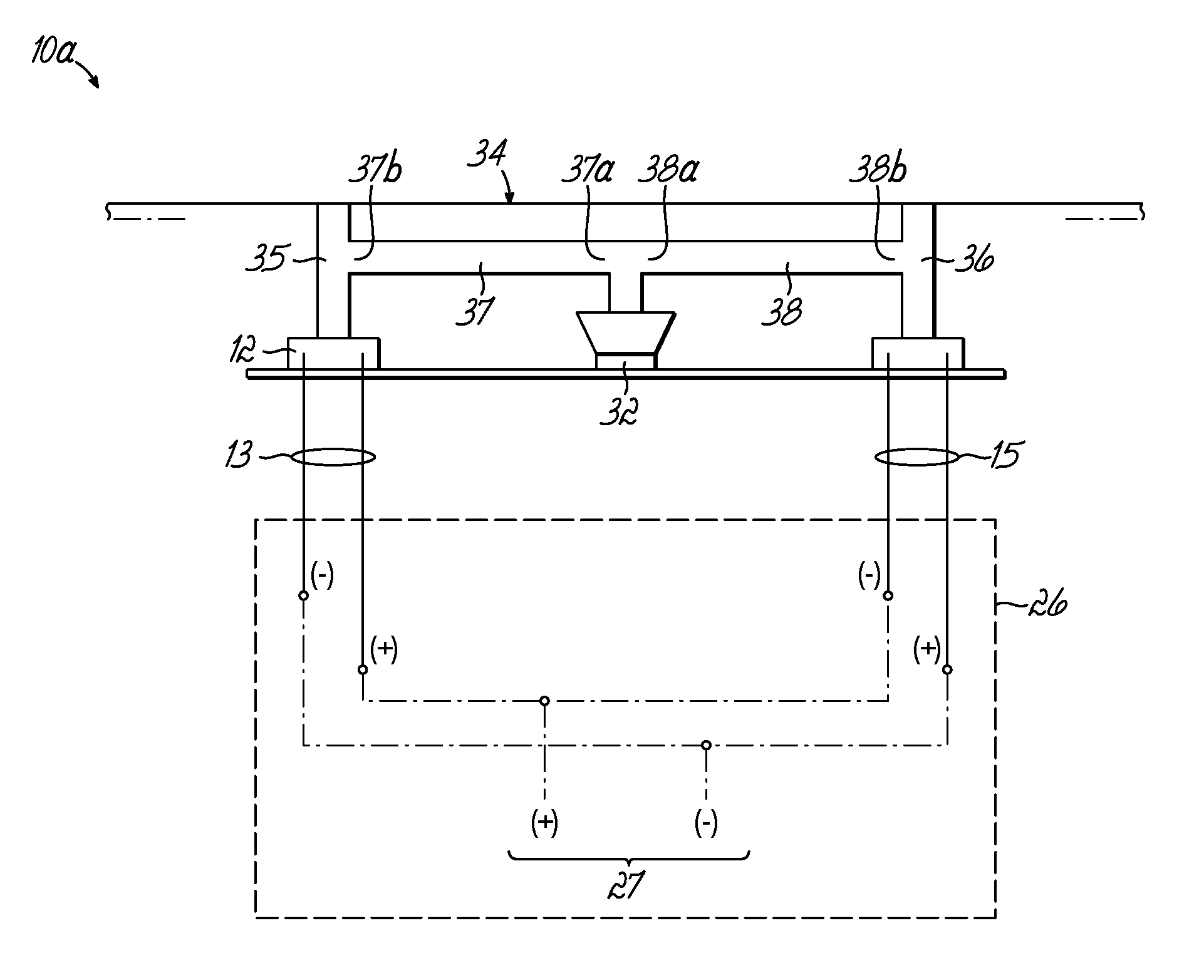
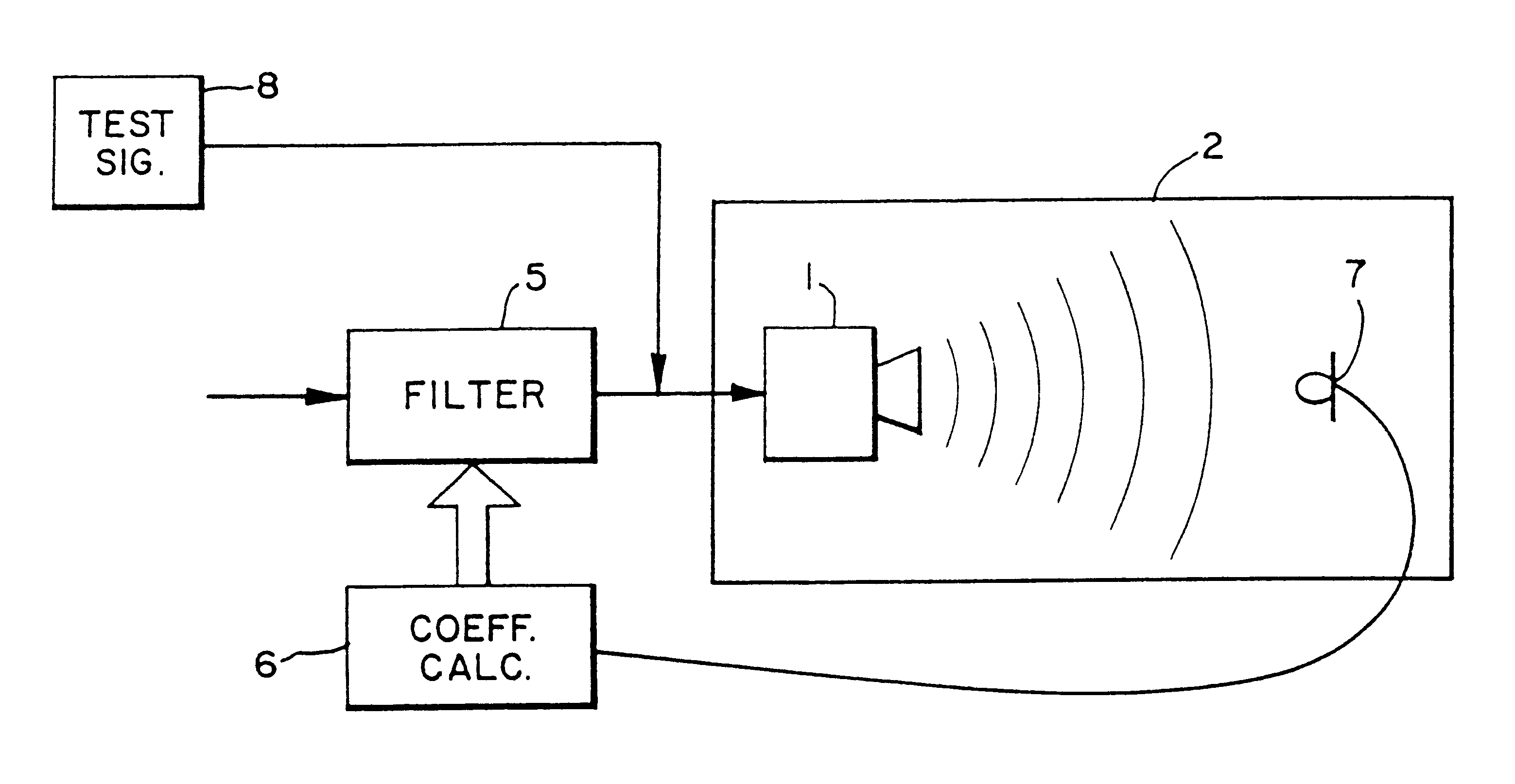
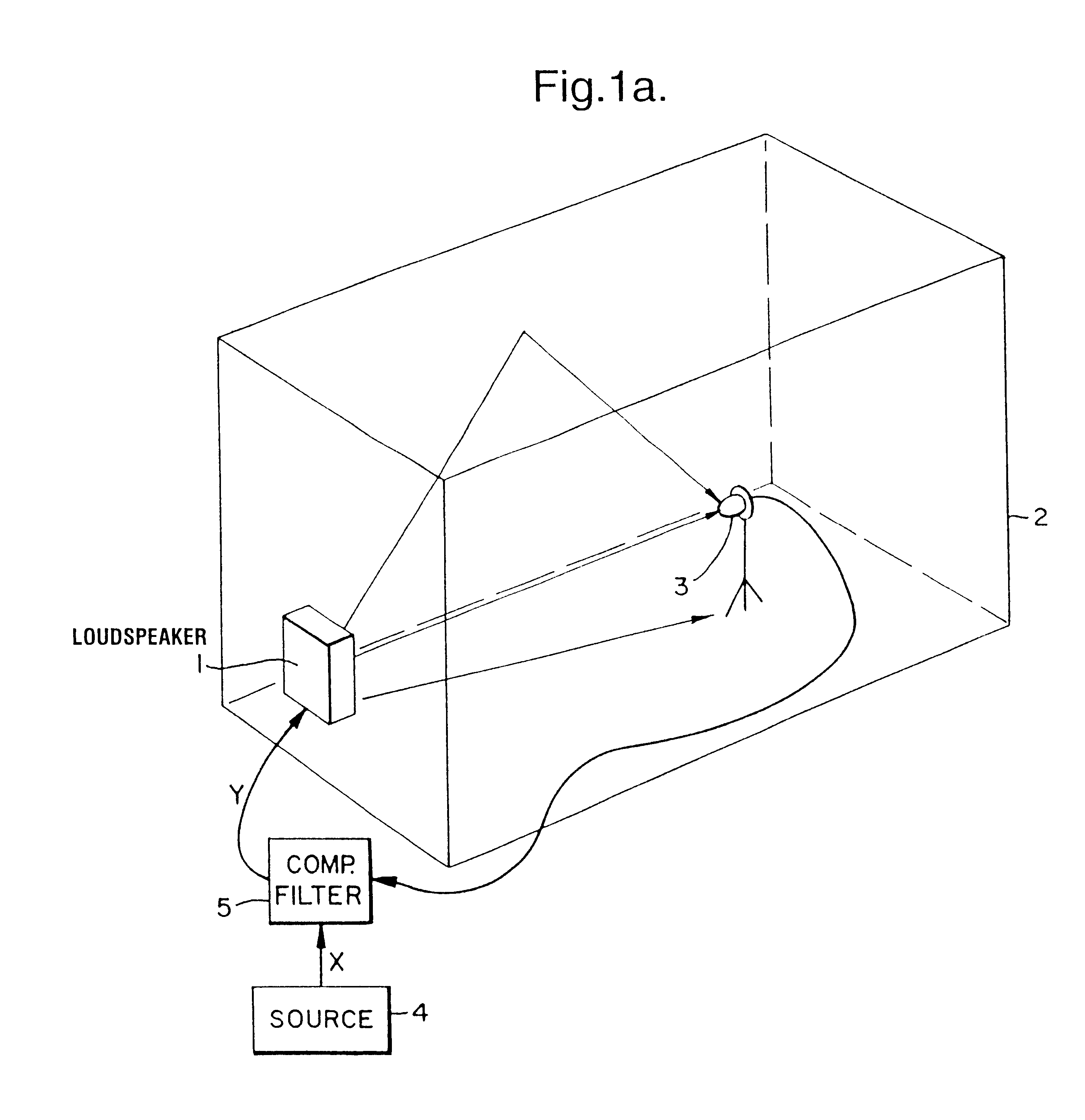
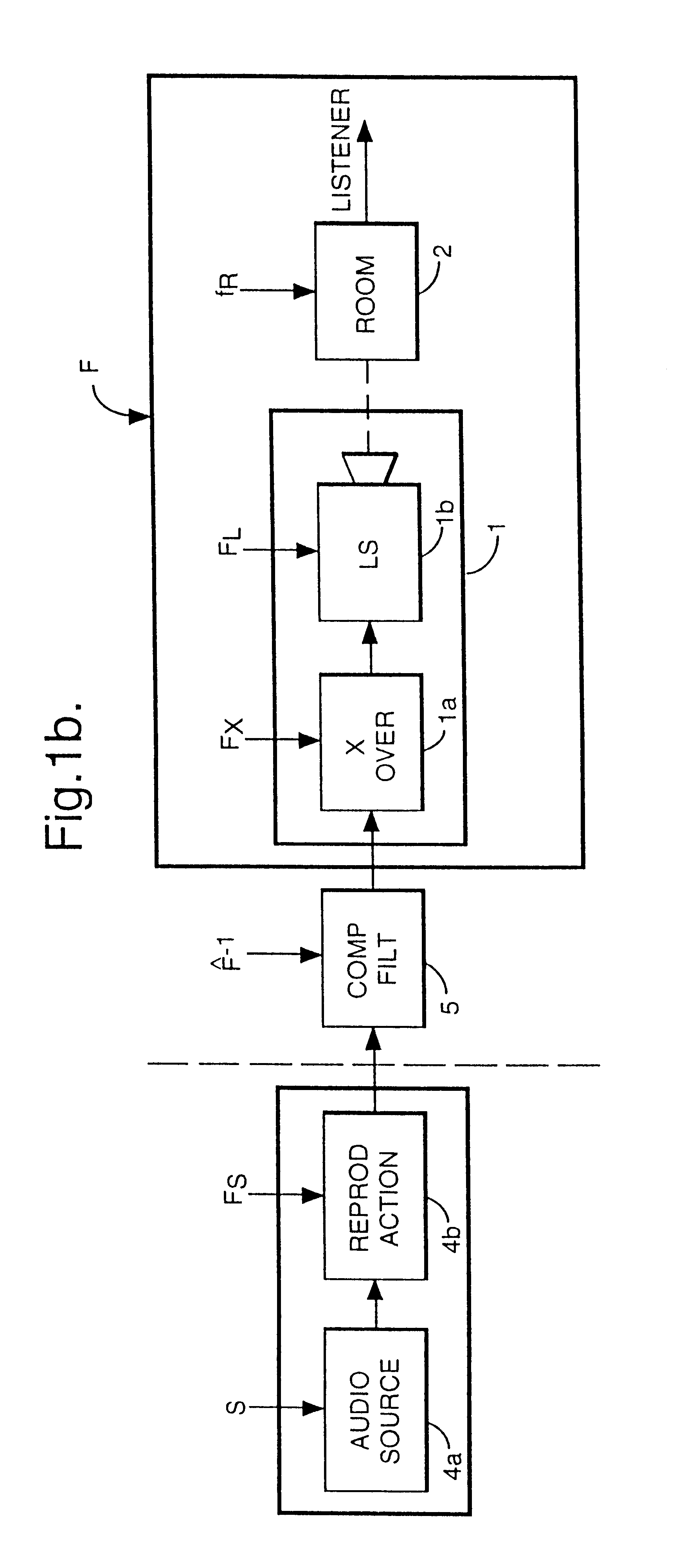
Compensating filters
InactiveUS6760451B1Eliminate phase distortionAdaptive networkAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlDigital signal processingAmplitude response
A prefilter (5) for an audio system comprising a loudspeaker (1) in a room (2), which corrects both amplitude and phase errors due to the loudspeaker (1) by a linear phase correction filter response and corrects the amplitude response of the room (2) whilst introducing the minimum possible amount of extra phase distortion by employing a minimum phase correction filter stage. A test signal generator (8) generates a signal comprising a periodic frequency sweep with a greater phase repetition period than the frequency repetition period. A microphone (7) positioned at various points in the room (2) measures the audio signal processed by the room (2) and loudspeaker (1), and a coefficient calculator (6) (e.g. a digital signal processor device) derives the signal response of the room and thereby a requisite minimum phase correction to be cascaded with the linear phase correction already calculated for the loudspeaker (1). Filter (5) may comprise the same digital signal processor as the coefficient calculator (6). Applications in high fidelity audio reproduction, and in car stereo reproduction.
Owner:CRAVEN PETER GRAHAM +1
Data-driven media management within an electronic device
Owner:APPLE INC
Miniature silicon condenser microphone
InactiveUS7166910B2Piezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceTransducer
Owner:KNOWLES ELECTRONICS INC
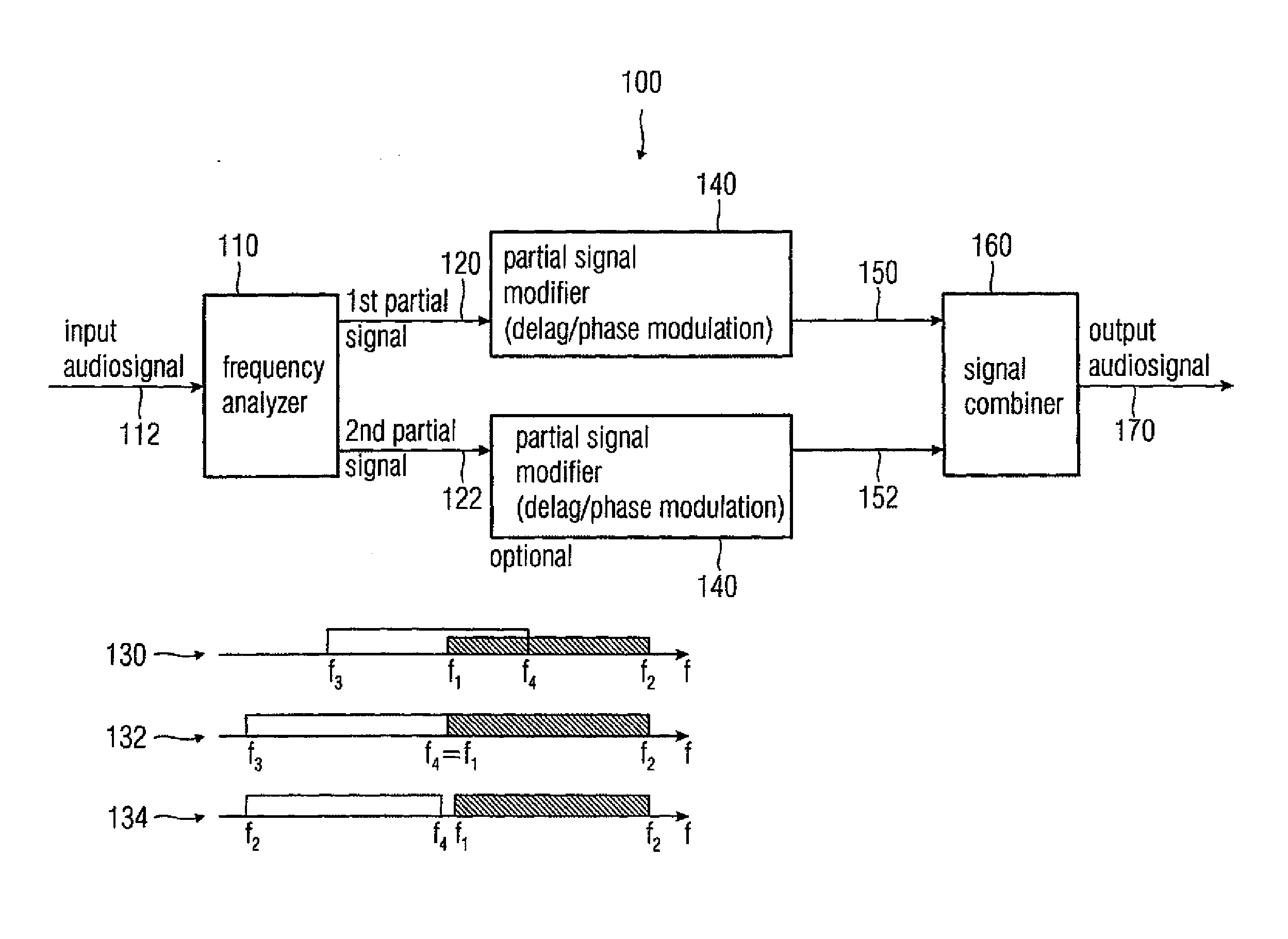
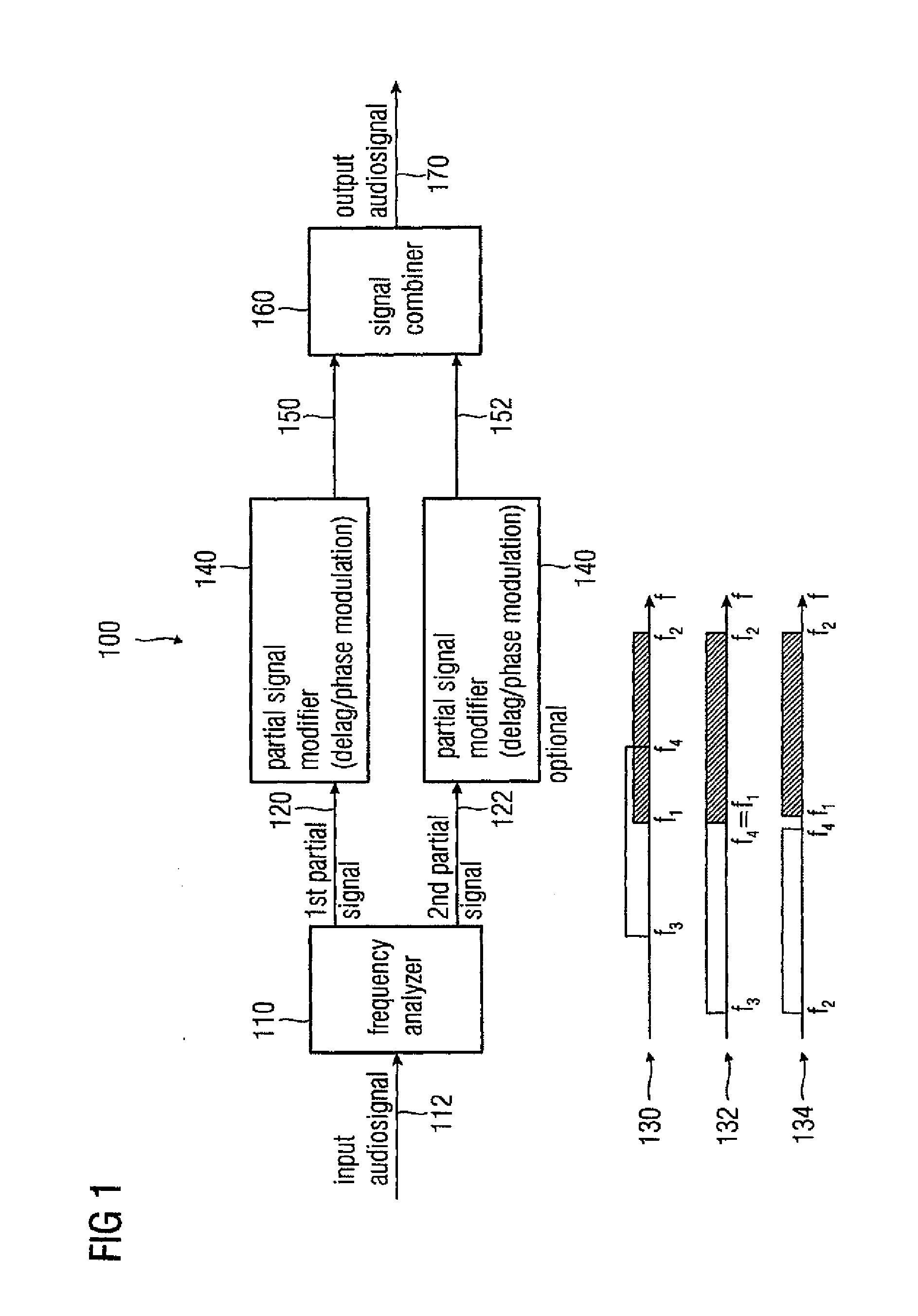
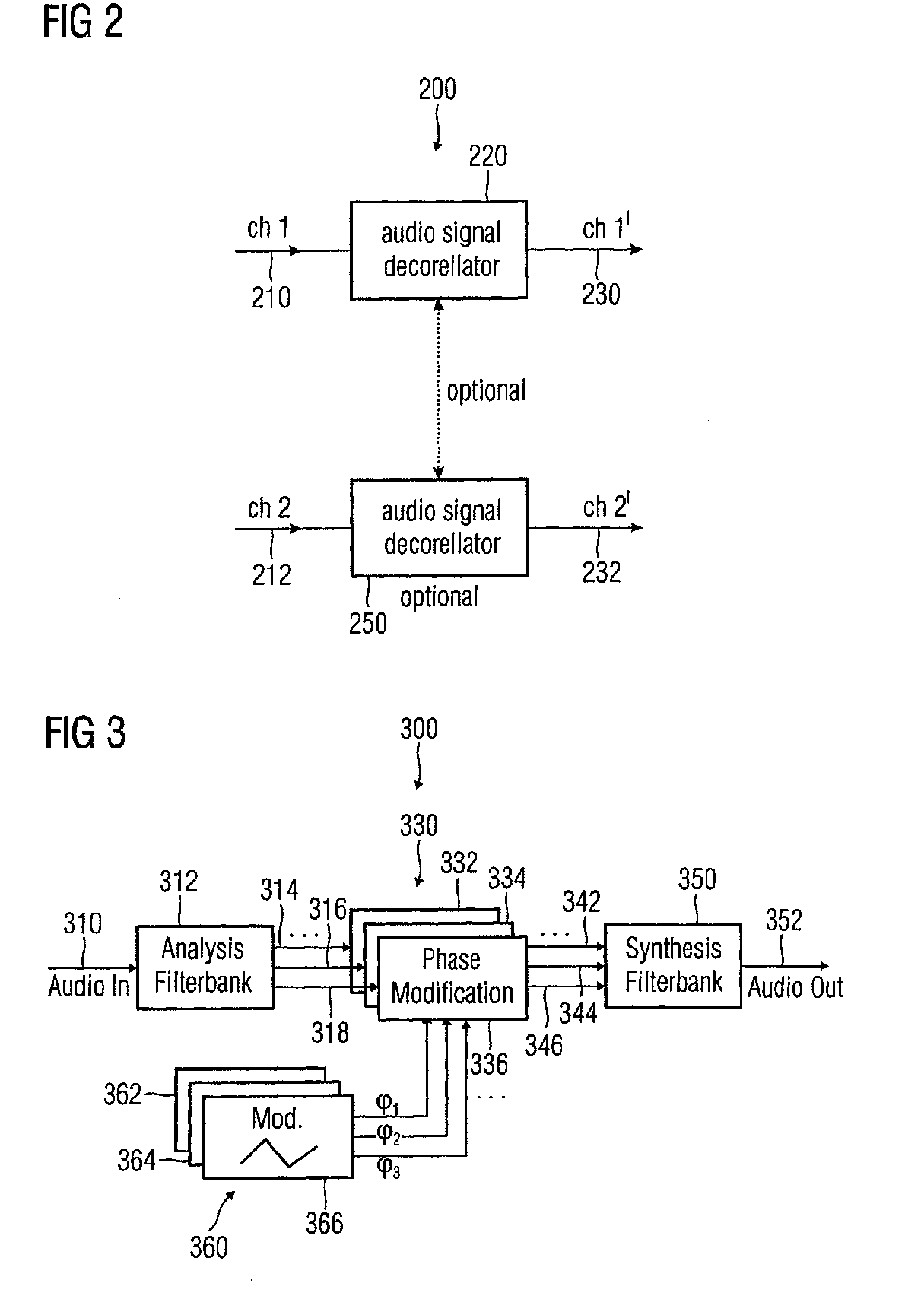
Audio signal decorrelator, multi channel audio signal processor, audio signal processor, method for deriving an output audio signal from an input audio signal and computer program
ActiveUS20090304198A1Simple designReducing and removing audio contentTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSpeech analysisVIT signalsAudio signal
An audio signal decorrelator for deriving an output audio signal from an input audio signal has a frequency analyzer for extracting from the input audio signal a first partial signal descriptive of an audio content in a first audio frequency range and a second partial signal descriptive of an audio content in a second audio frequency range having higher frequencies compared to the second audio frequency range. A partial signal modifier for modifies the first and second partial signals, to obtain first and second processed partial signals, so that a modulation amplitude of a time variant phase shift or time variant delay applied to the first partial signal is higher than that applied to the second partial signal, or for modifying only the first partial signal. A signal combiner combines the first and second processed partial signals, or combines the first processed partial signal and the second partial signal, to obtain an output audio signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
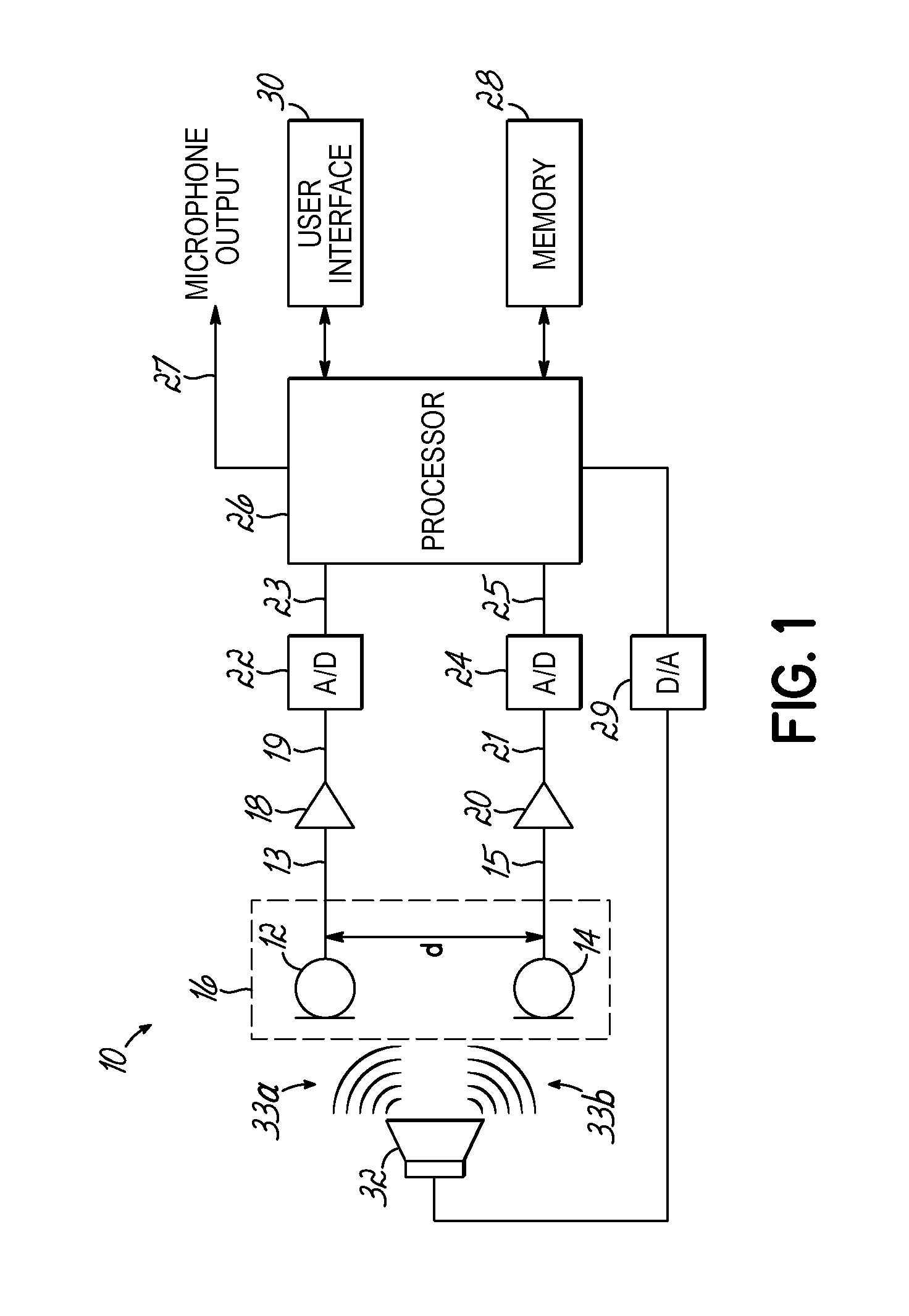
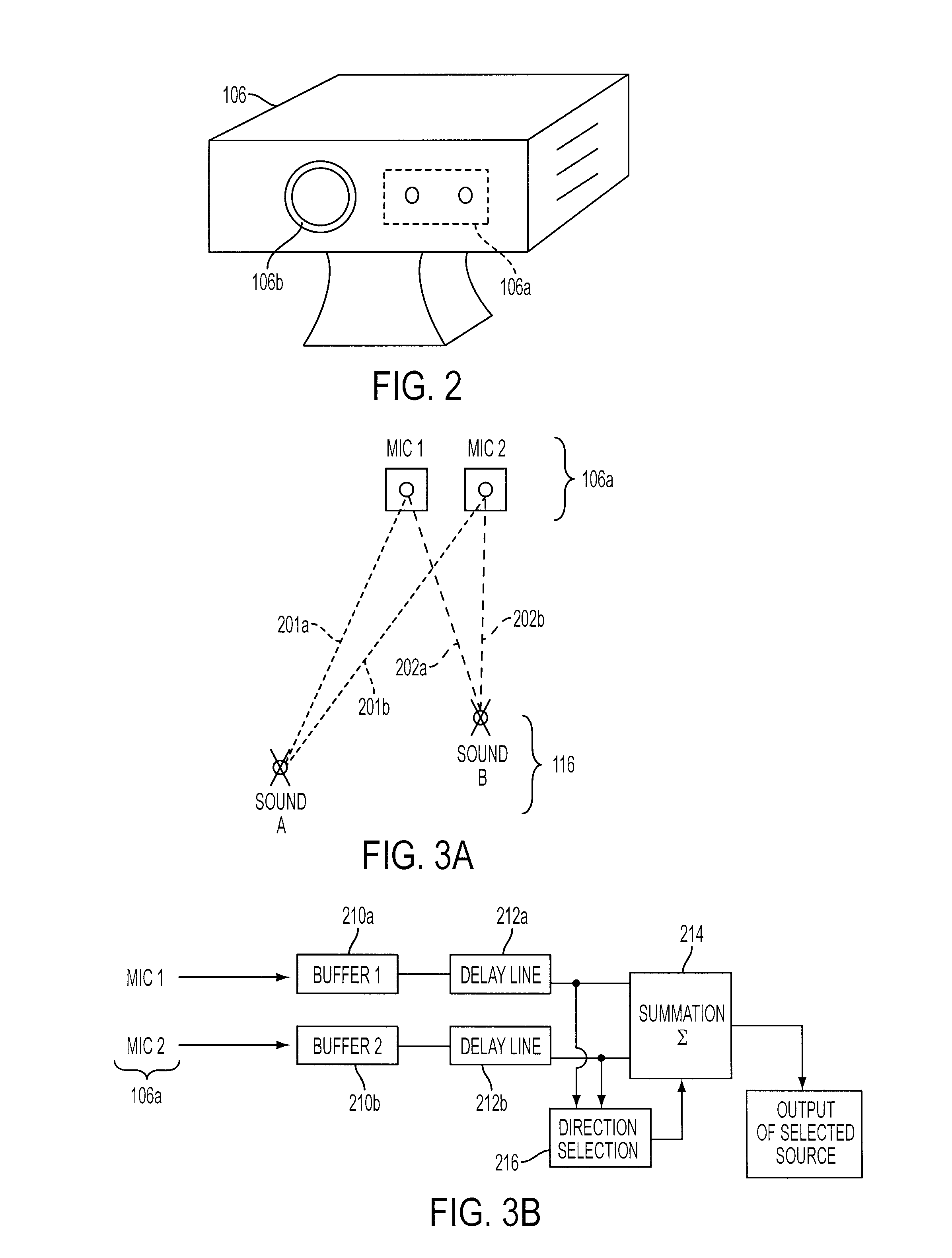
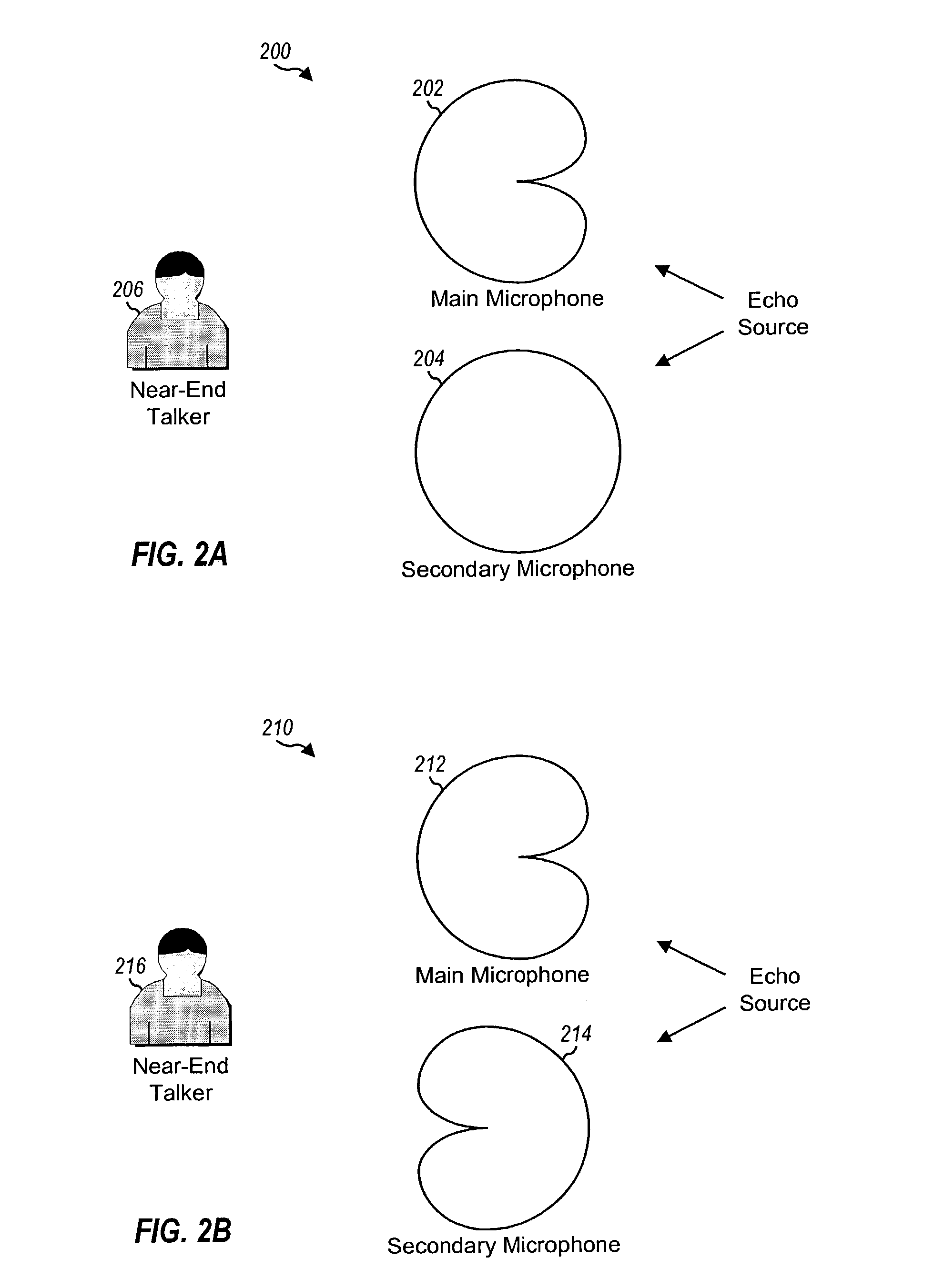
System and method for beamforming using a microphone array
InactiveUS20050195988A1Maximal noise suppressionIncrease widthPosition fixationMicrophones signal combinationEnvironmental noiseSound sources
The ability to combine multiple audio signals captured from the microphones in a microphone array is frequently used in beamforming systems. Typically, beamforming involves processing the output audio signals of the microphone array in such a way as to make the microphone array act as a highly directional microphone. In other words, beamforming provides a “listening beam” which points to a particular sound source while often filtering out other sounds. A “generic beamformer,” as described herein automatically designs a set of beams (i.e., beamforming) that cover a desired angular space range within a prescribed search area. Beam design is a function of microphone geometry and operational characteristics, and also of noise models of the environment around the microphone array. One advantage of the generic beamformer is that it is applicable to any microphone array geometry and microphone type.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
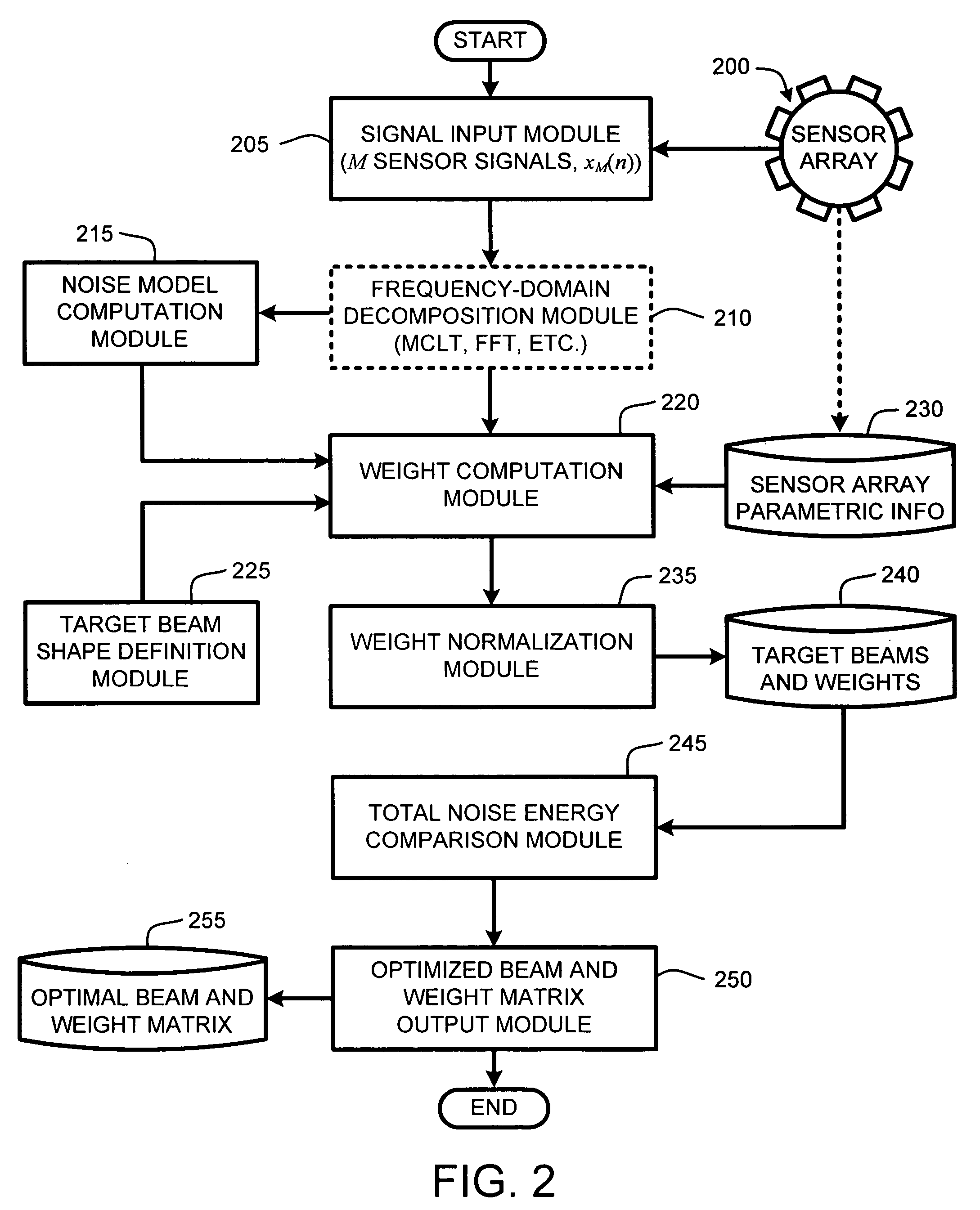
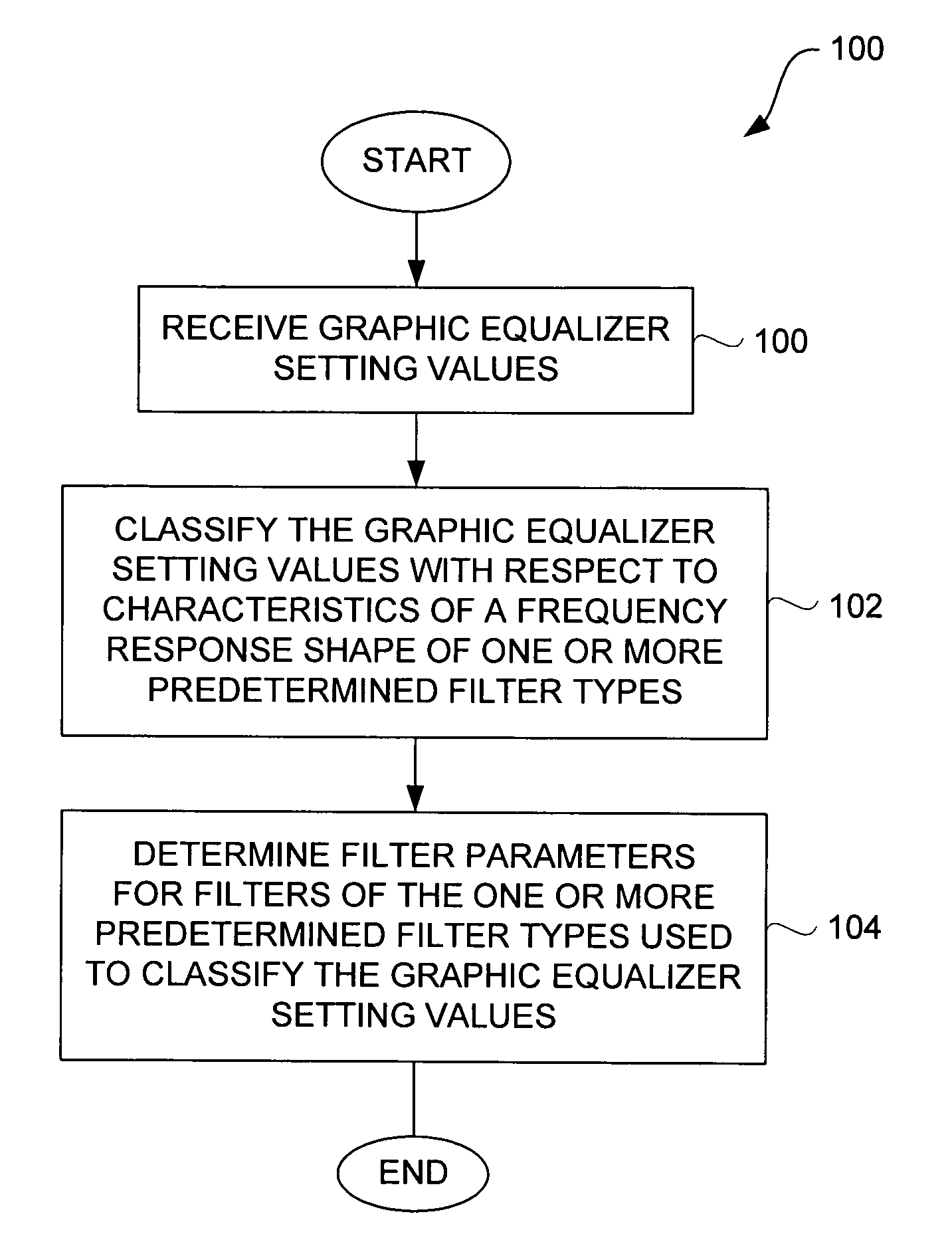
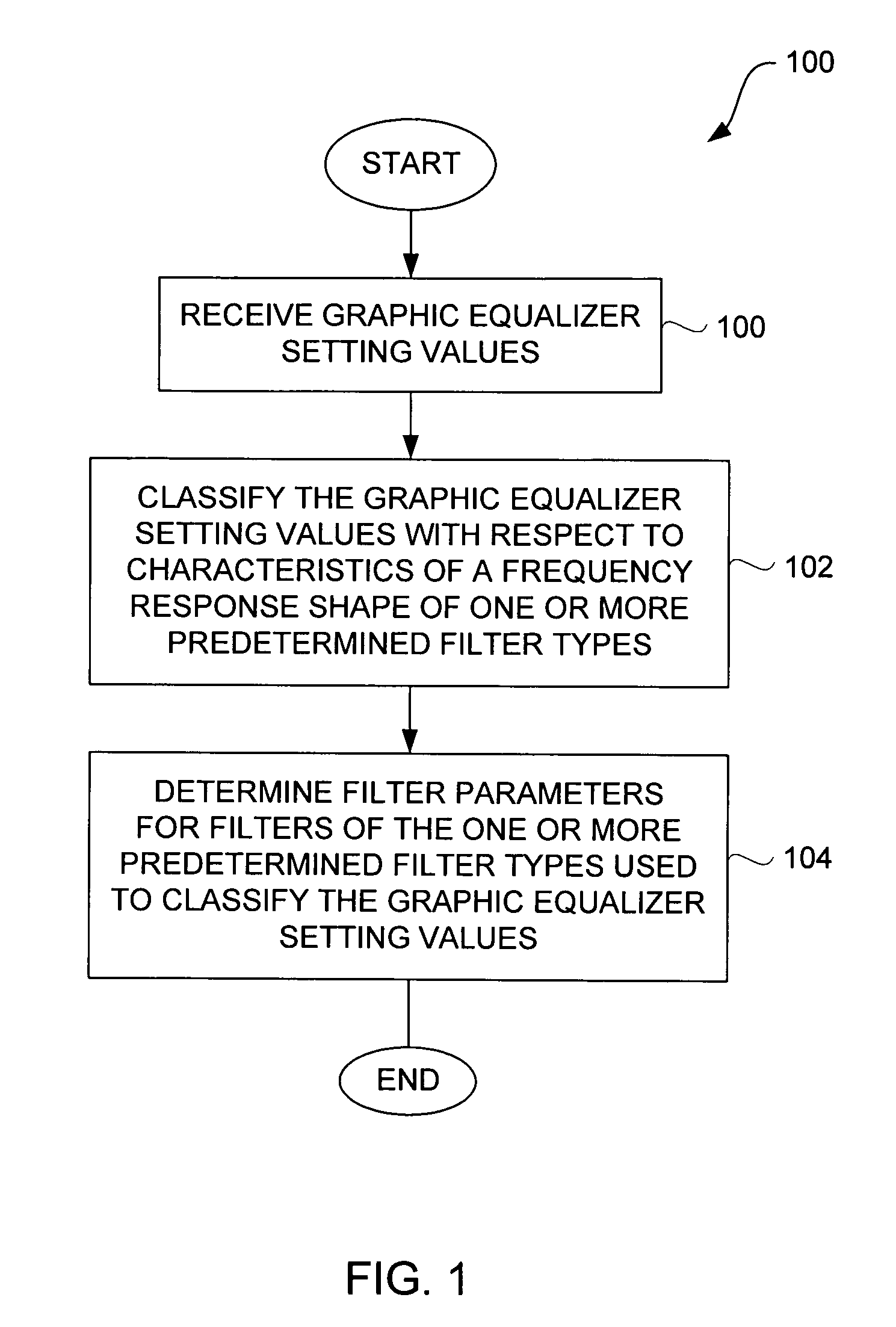
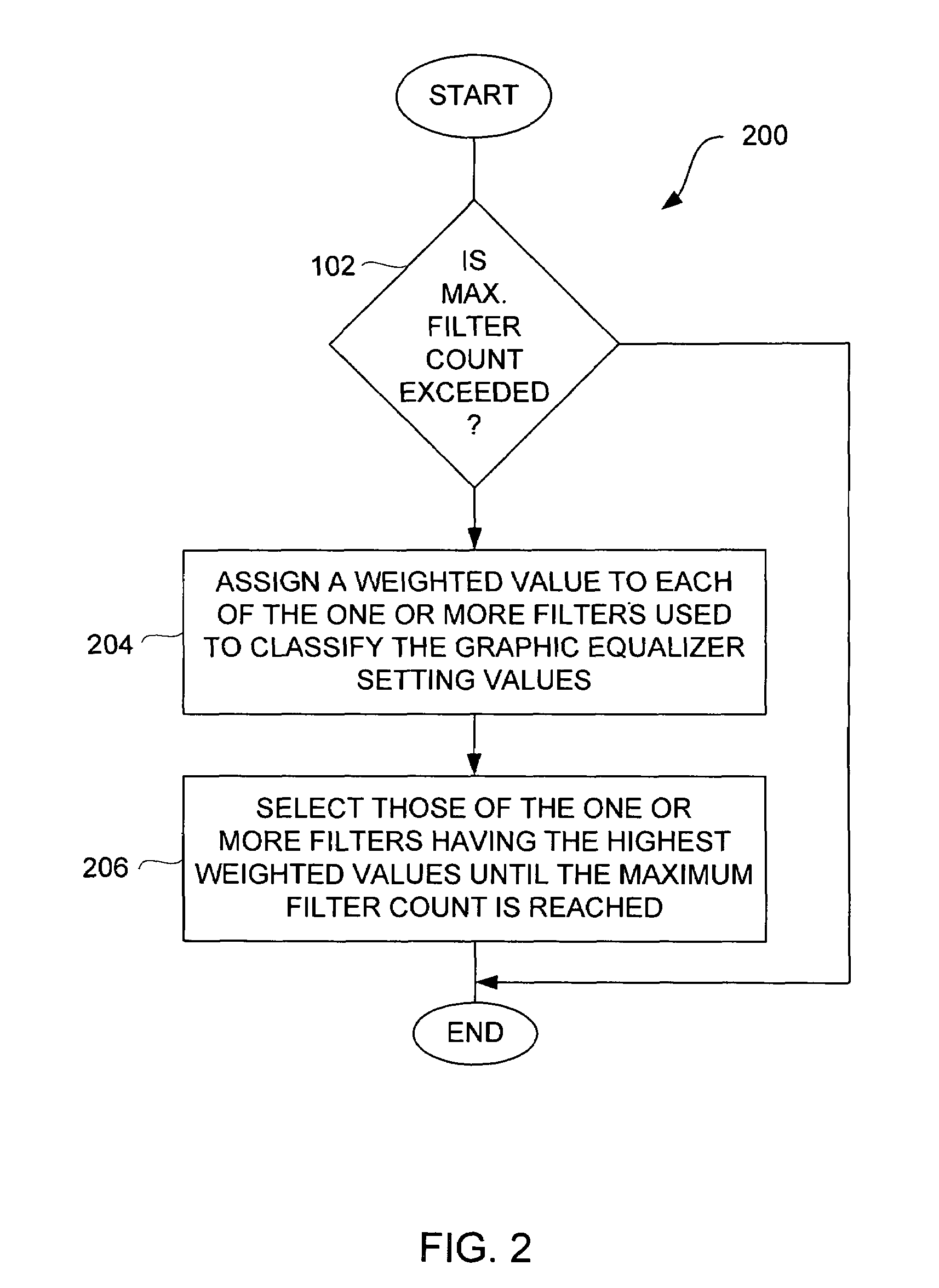
Method and system for approximating graphic equalizers using dynamic filter order reduction
InactiveUS7711129B2Limited computing resourceImprove approachSpecial data processing applicationsTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsGraphicsMulti band
Improved approaches to flexibly implementing graphic equalizers on media players are disclosed. These approaches provide dynamic order reduction of a multi-band graphic equalizer so that equalizer effects can be timely performed with only limited computational resources. In one embodiment, a media player receives a media item and associated equalizer settings for a multi-band graphic equalizer. The media player can then automatically (i.e., without user action) approximate the multi-band graphic equalizer with the equalizer settings for the media item using a fewer number of filters. Fewer filters means order reduction, and thus reduction in computational requirements. After the multi-band graphic equalizer is approximated, the media player can present the media item to its user in accordance with the reduced complexity, approximated equalizer.
Owner:APPLE INC
Multiple simultaneous frequency detection
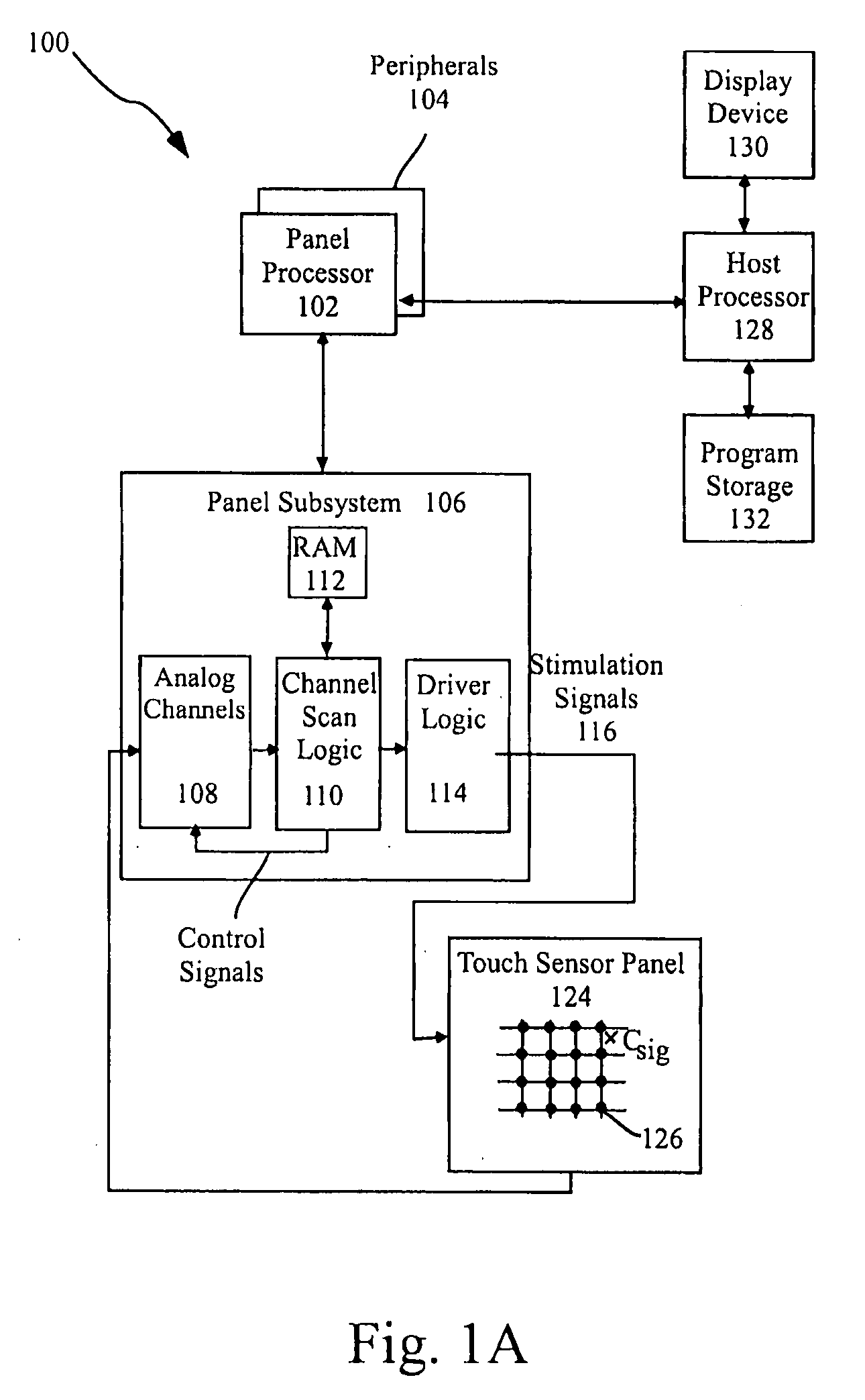
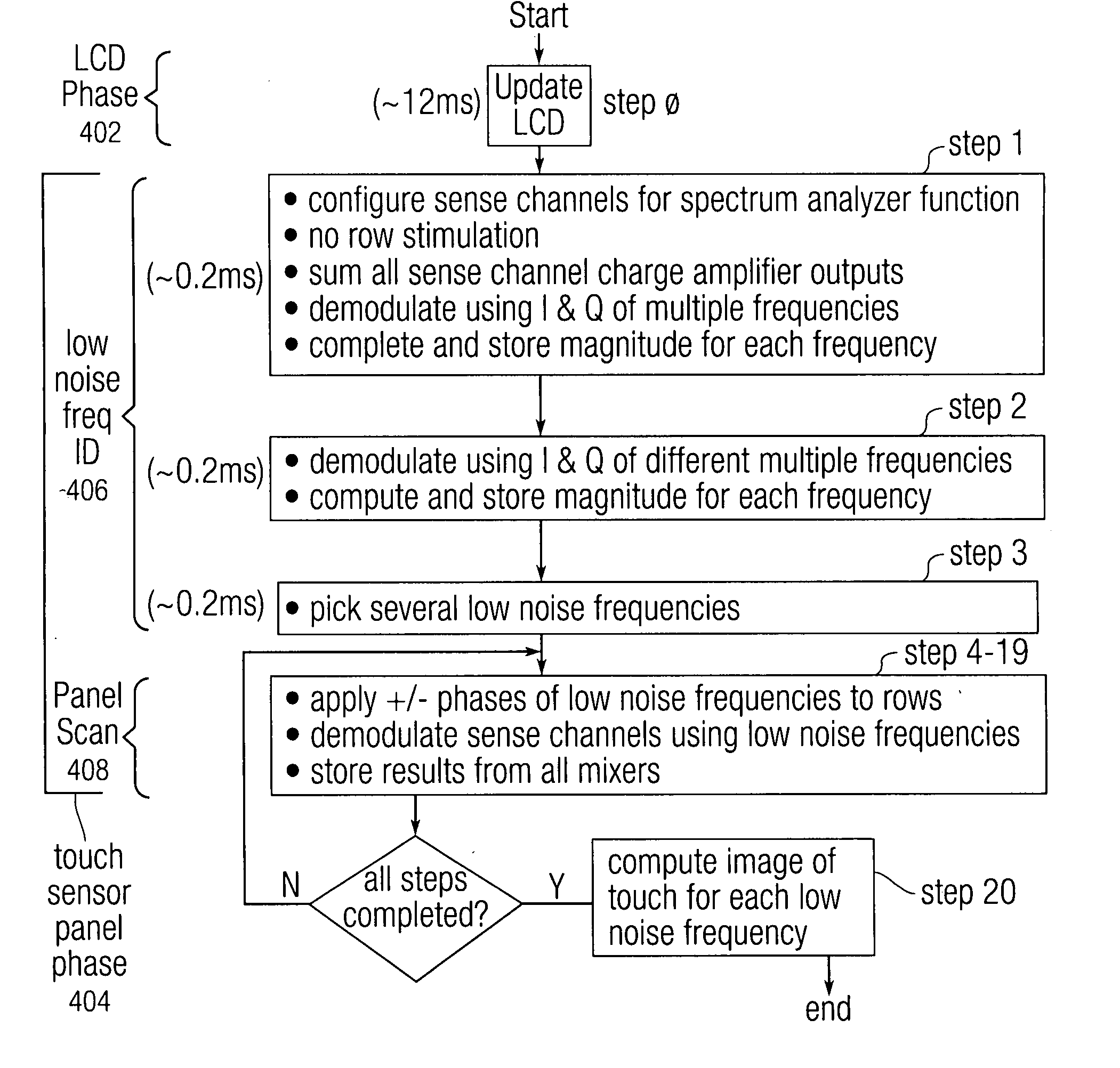
ActiveUS20080309625A1Wireless commuication servicesTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsFrequency mixerFrequency detection
The use of multiple stimulation frequencies and phases to generate an image of touch on a touch sensor panel is disclosed. Each of a plurality of sense channels can be coupled to a column in a touch sensor panel and can have multiple mixers. Each mixer in the sense channel can utilize a circuit capable generating a demodulation frequency of a particular frequency. At each of multiple steps, various phases of selected frequencies can be used to simultaneously stimulate the rows of the touch sensor panel, and the multiple mixers in each sense channel can be configured to demodulate the signal received from the column connected to each sense channel using the selected frequencies. After all steps have been completed, the demodulated signals from the multiple mixers can be used in calculations to determine an image of touch for the touch sensor panel at each frequency.
Owner:APPLE INC
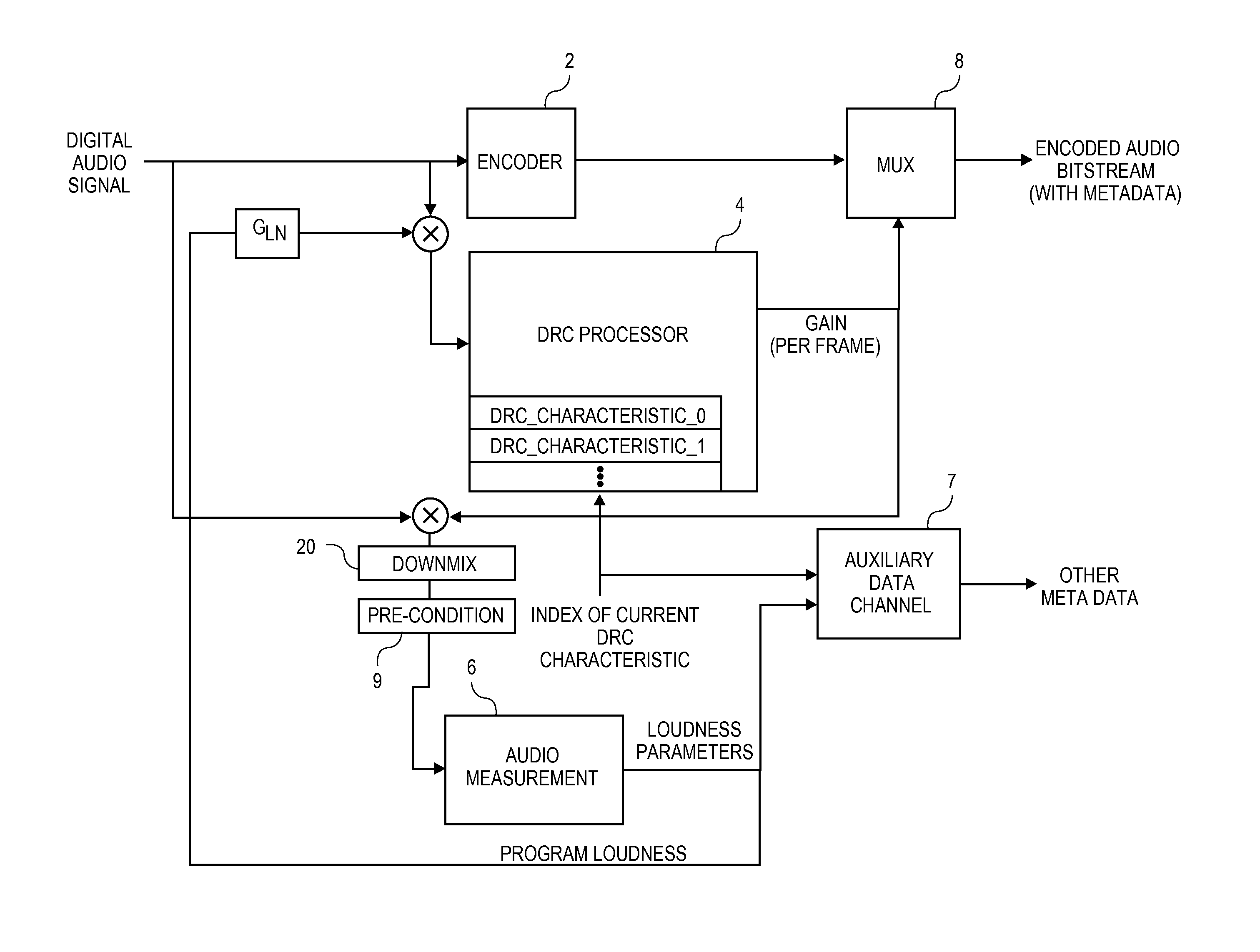
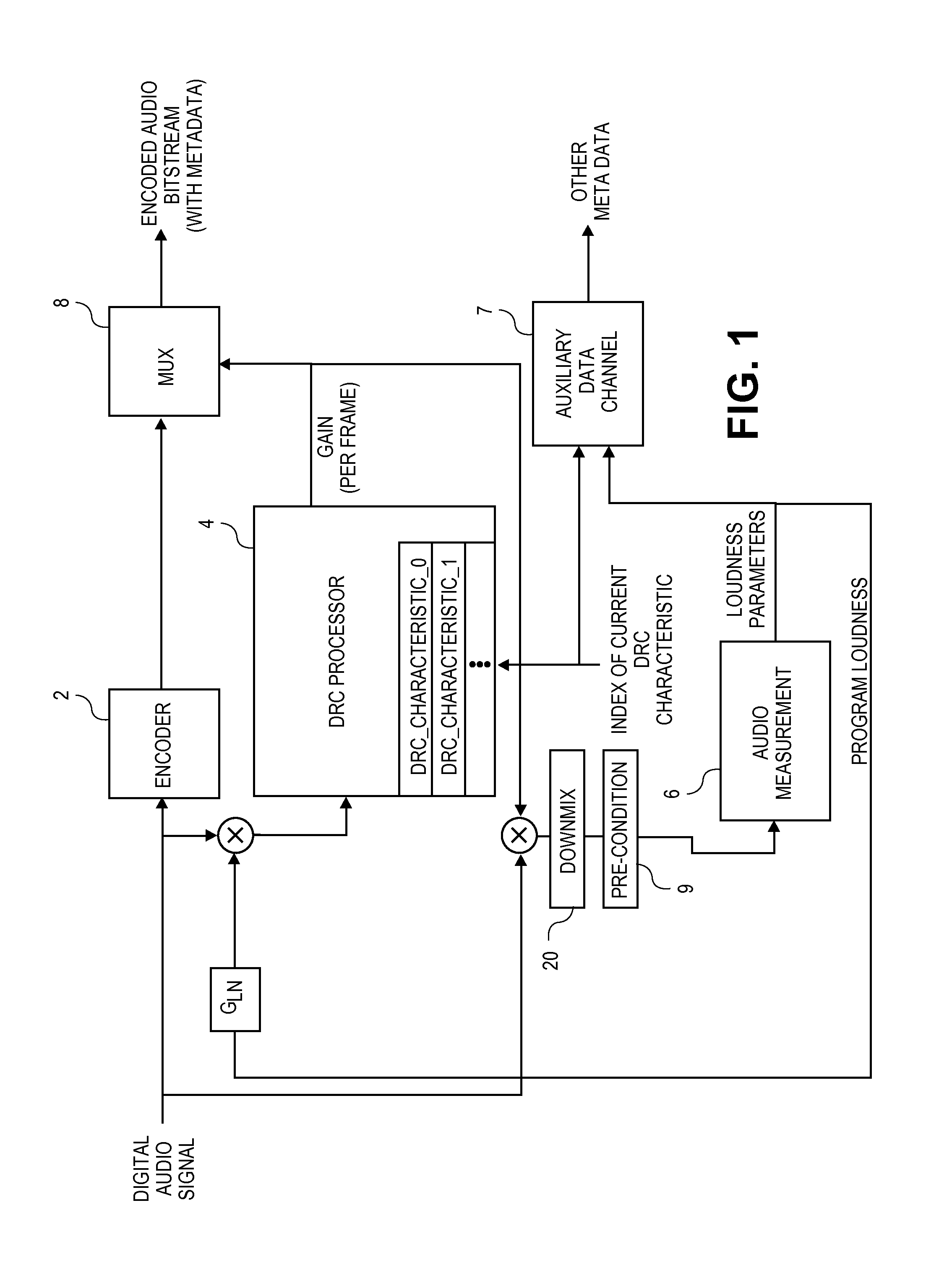
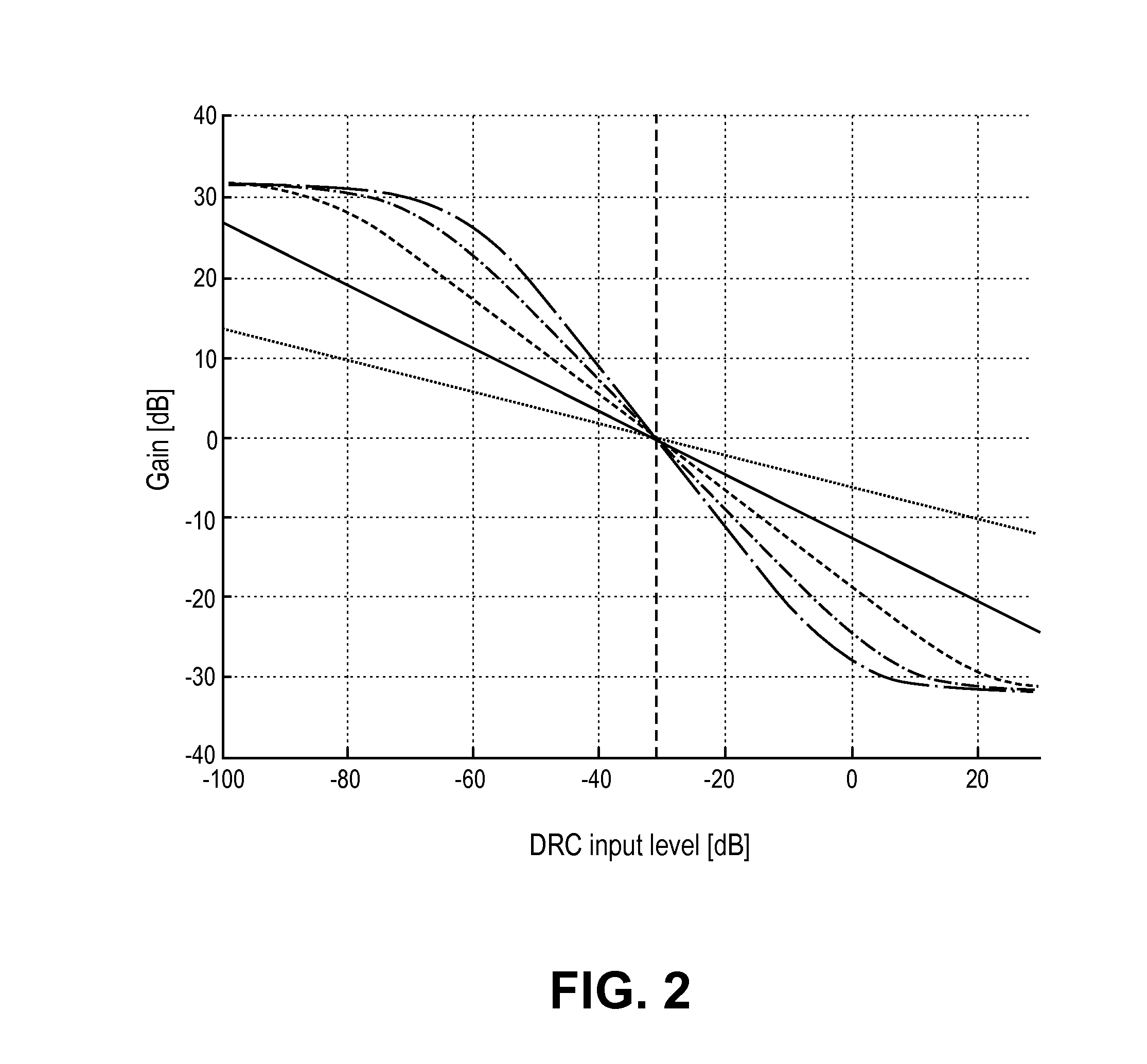
Metadata for loudness and dynamic range control
ActiveUS20140294200A1Improve the user's experience of playbackImprove experienceGain controlSpeech analysisAudio normalizationLoudness
An audio normalization gain value is applied to an audio signal to produce a normalized signal. The normalized signal is processed to compute dynamic range control (DRC) gain values in accordance with a selected one of several pre-defined DRC characteristics. The audio signal is encoded, and the DRC gain values are provided as metadata associated with the encoded audio signal. Several other embodiments are also described and claimed.
Owner:APPLE INC
Managing acoustic noise produced by a device
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that manages the acoustic noise produced by a device. During operation, the system receives a set of acoustic characteristics for the device. The system then uses these acoustic characteristics to estimate the acoustic noise being generated by the device. Next, the system uses the estimated acoustic noise to adjust a setting in the device to manage the acoustic noise produced by the device.
Owner:APPLE INC
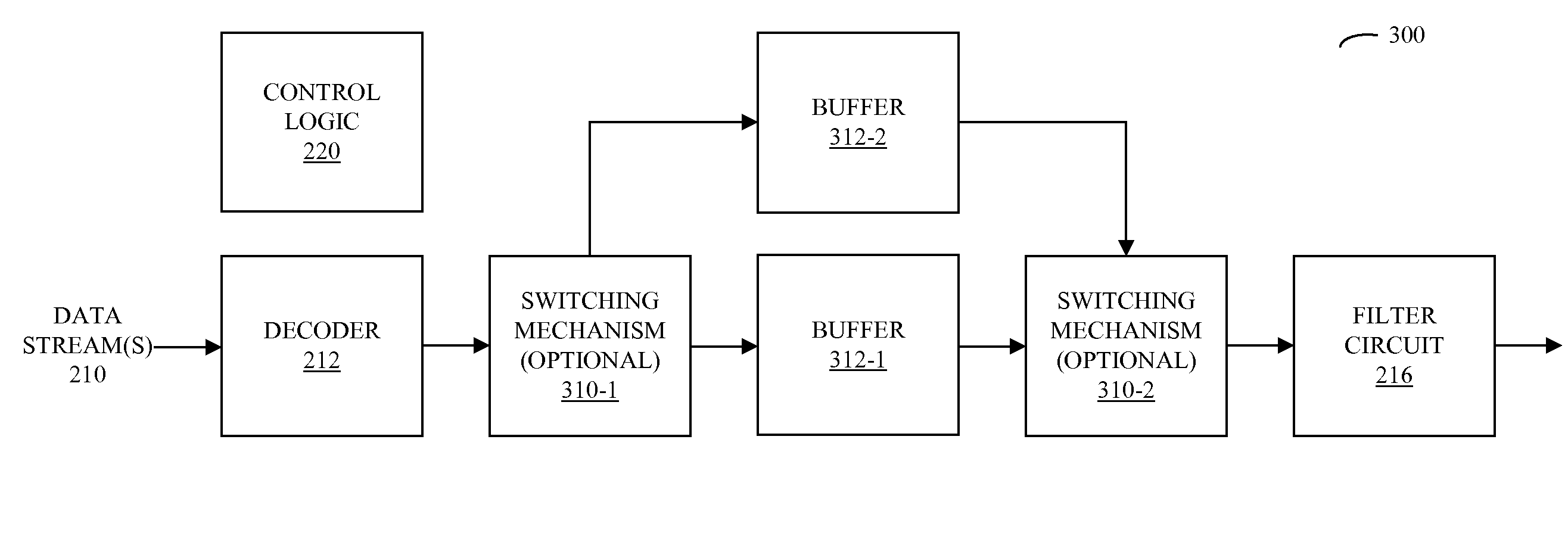
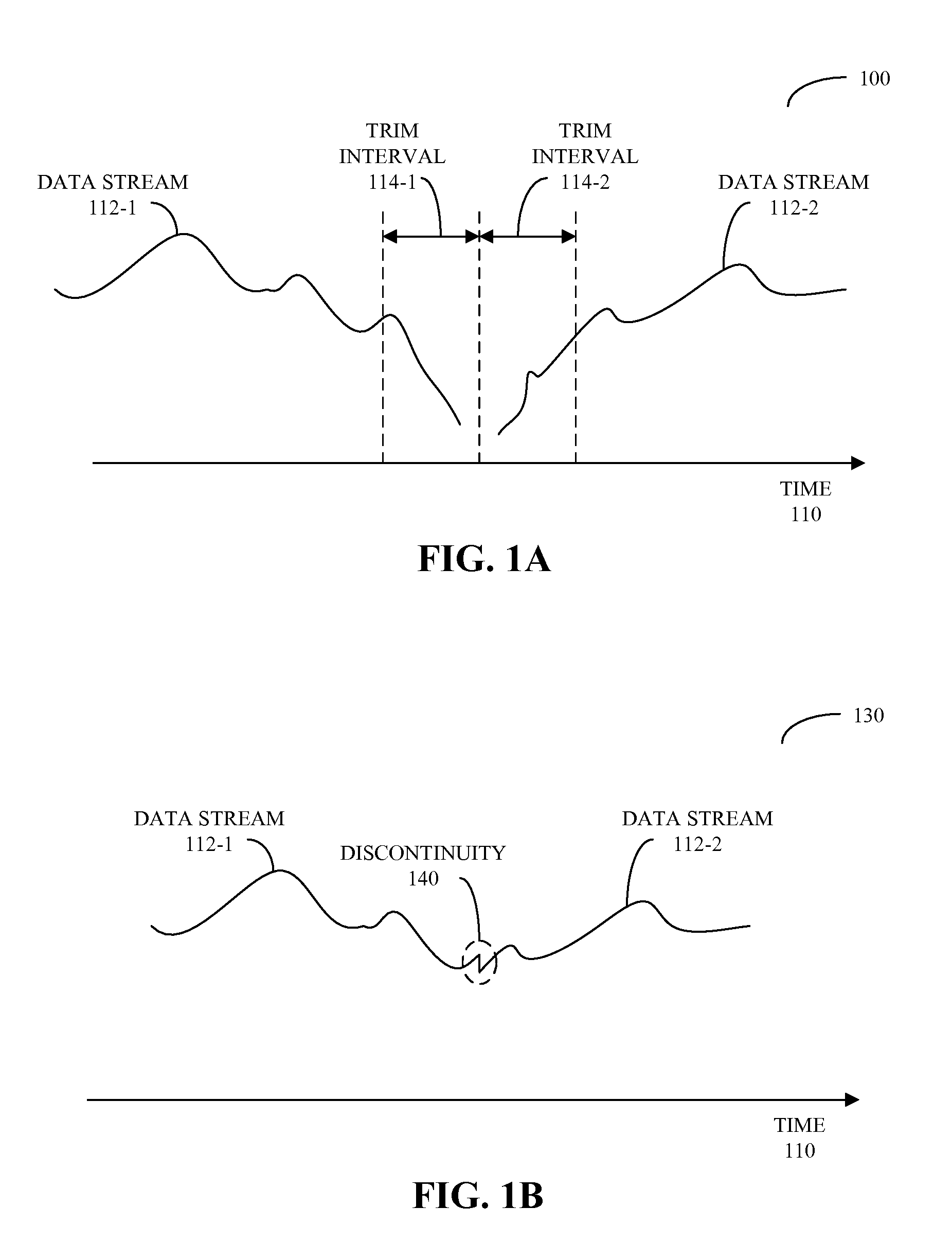
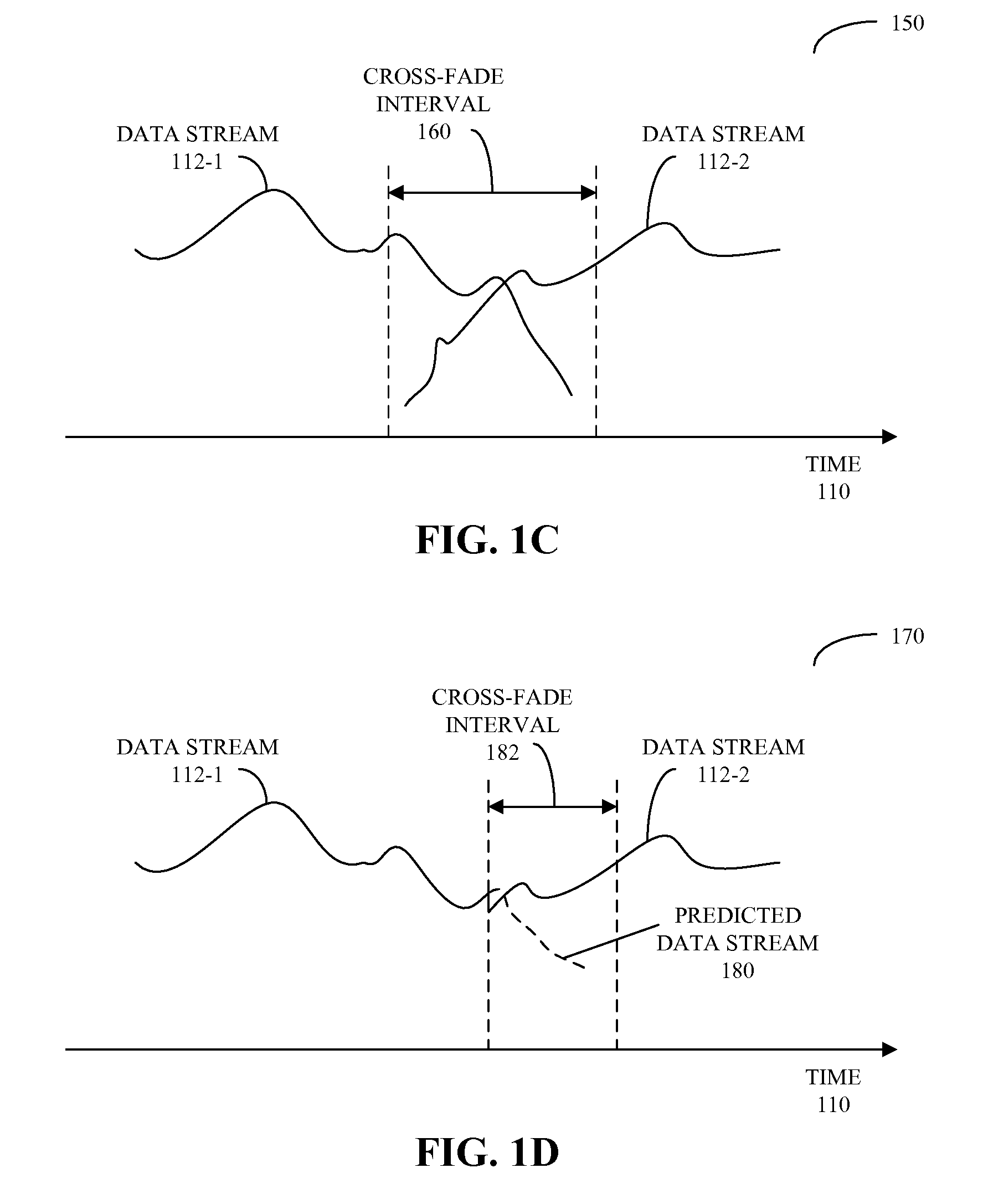
Zero-gap playback using predictive mixing
ActiveUS20090083047A1Reducing and eliminating gapReduce discontinuityElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsSpeech analysisElectricityData stream
Circuits and methods for providing zero-gap playback of consecutive data streams in portable electronic devices, such as media players, are described. In some embodiments, a circuit includes a decoder circuit configured to receive encoded audio data and to output decoded audio data including data streams associated with a data file and a subsequent data file. Moreover, a predictive circuit, which is electrically coupled to the decoder circuit, is configured to selectively generate additional samples based on samples in the data file, where the additional samples correspond to times after the end of a data stream associated with the data file. Additionally, a filter circuit, which is electrically coupled to the decoder circuit and selectively electrically coupled to the predictive circuit, is configured to selectively combine or blend samples at a beginning of the subsequent data file with the additional samples. Note that the circuit may be included in an integrated circuit.
Owner:APPLE INC
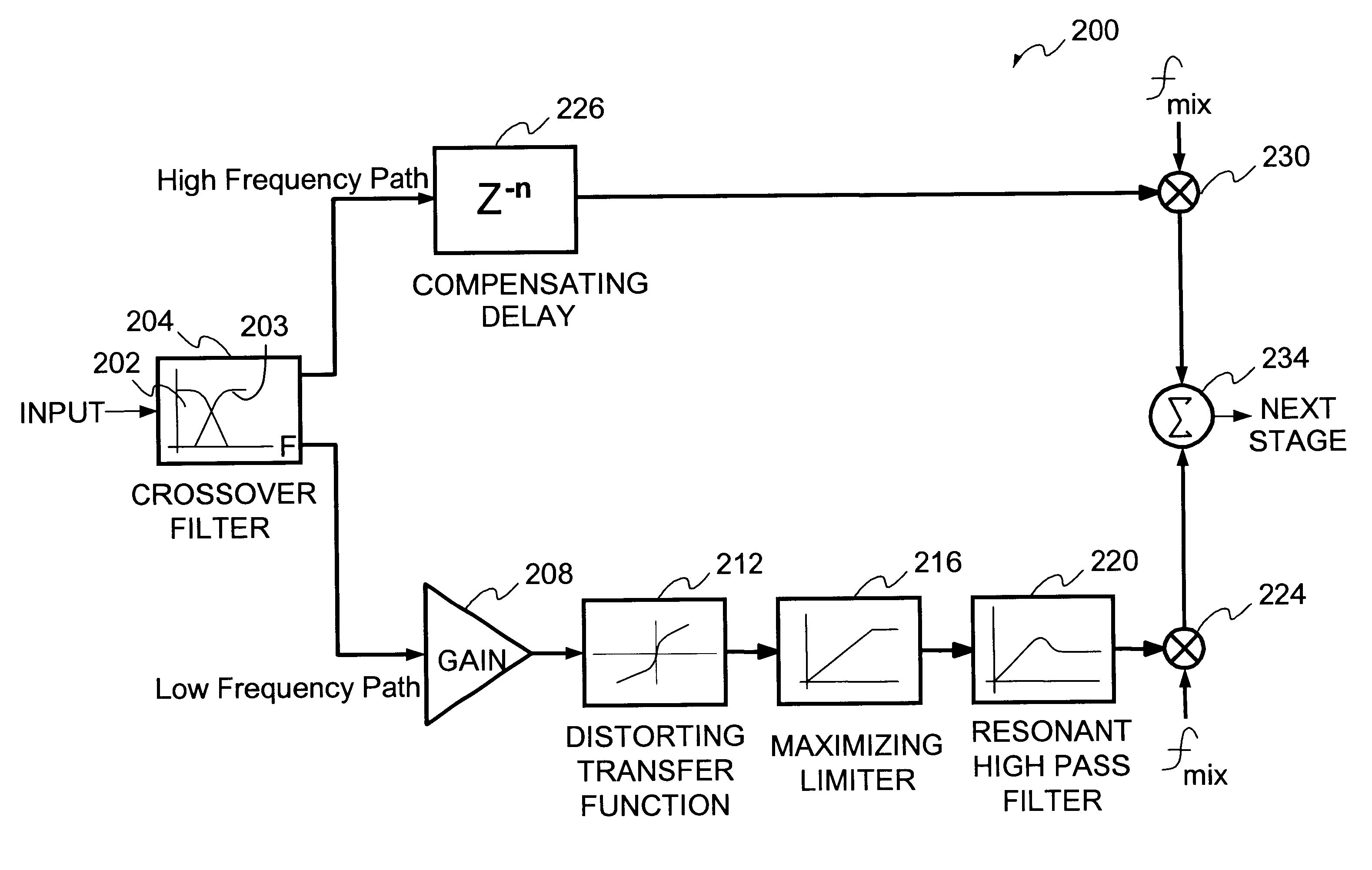
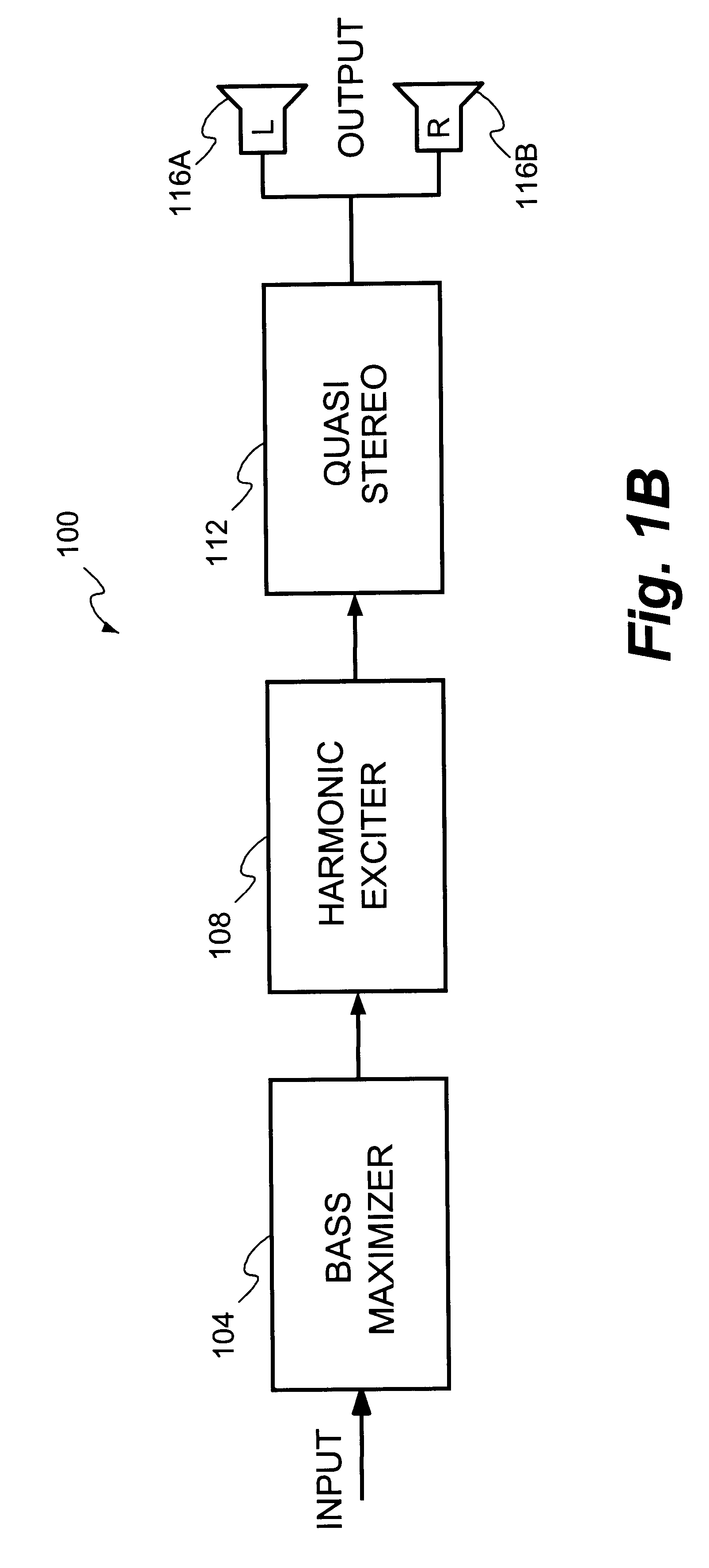
Method and system for enhancing audio signals
InactiveUS6606388B1Facilitates separate modificationFacilitates enhancementElectrophonic musical instrumentsGain controlHarmonicComputer module
A technique for enhancing audio signals generated from compressed digital audio files is described. The technique uses a Bass Maximizer module, a Harmonic Exciter module and a Quasi Stereo module. The Bass Exciter module enhances the intensity, depth and punch of the bass audio content by creating harmonic sequences from low frequency components contained in the original input signal. The Harmonic Exciter module adds to the treble audio content of the original input signal by generating harmonic series from the high frequency components contained in the input signal. The Quasi Stereo Module creates a stereo image of the enhanced input signal by adding and subtracting delayed and filtered versions of the enhanced input signal with itself to create left and right channeled stereo-like outputs. The technique provides a useful tool to regenerate from an audio signal more pleasant and joyful sounds.
Owner:ARBORETUM SYST
Adjustment of acoustic properties based on proximity detection
One or more acoustic transducers of a device may be adjusted based on automatic detection of device proximity to the user. In a mobile telephone, when the user is using the receiver and holding the telephone against his / her ear, if the telephone detects that the user has moved the telephone further from his / her ear, the telephone will raise the receiver volume. Similarly, if the user is using the speaker, the telephone will adjust the speaker volume as user distance from the telephone changes. In another embodiment the telephone may fade between the receiver and the speaker. Volume is not the only acoustic property that could be adjusted according to user proximity. Frequency response is another property that could be adjusted, such as using appropriate electronic filtering, or by turning on another transducer that is not otherwise being used.
Owner:APPLE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com