Patents
Literature
591 results about "Linear phase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Linear phase is a property of a filter, where the phase response of the filter is a linear function of frequency. The result is that all frequency components of the input signal are shifted in time (usually delayed) by the same constant amount (the slope of the linear function), which is referred to as the group delay. And consequently, there is no phase distortion due to the time delay of frequencies relative to one another.
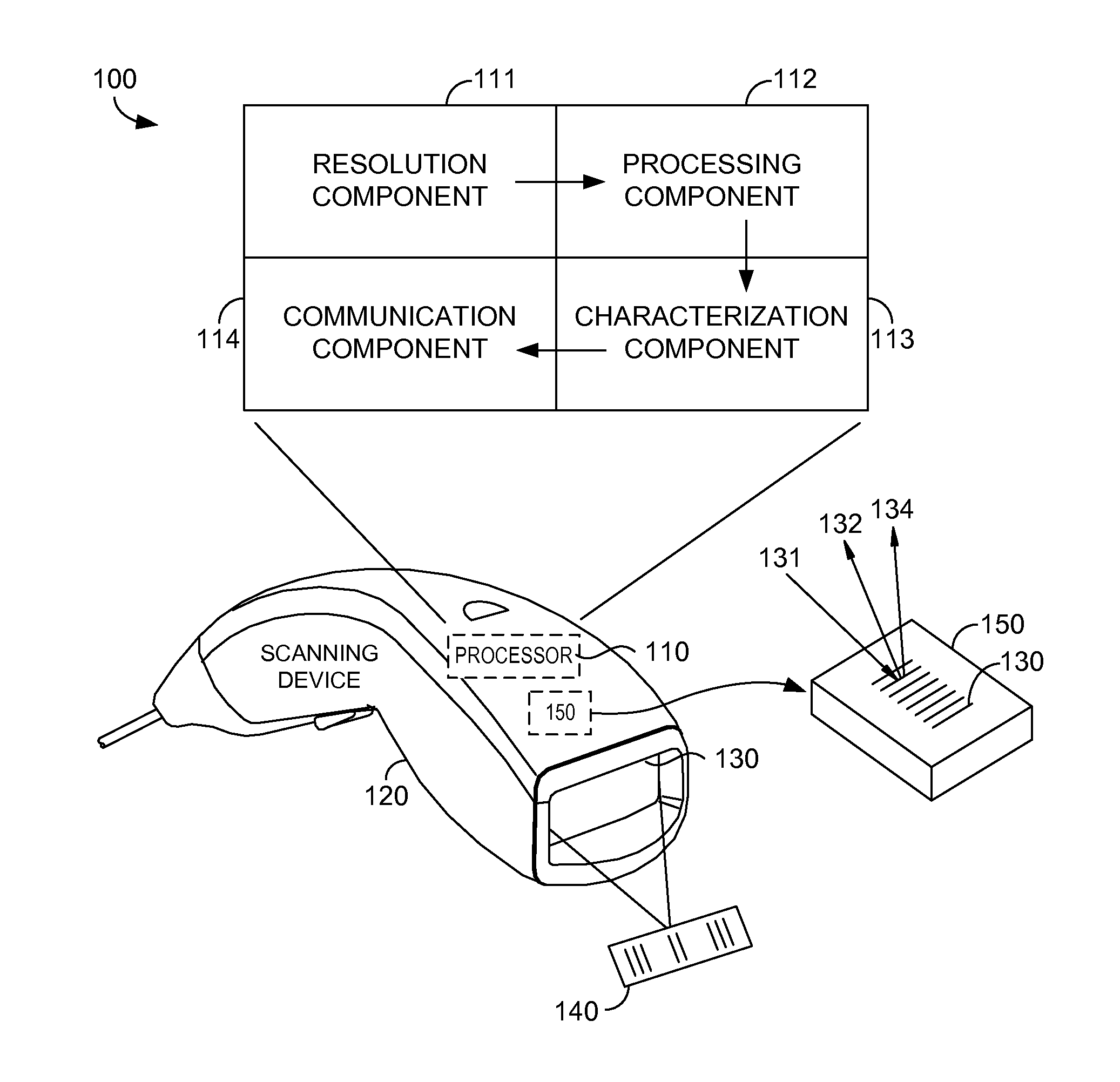
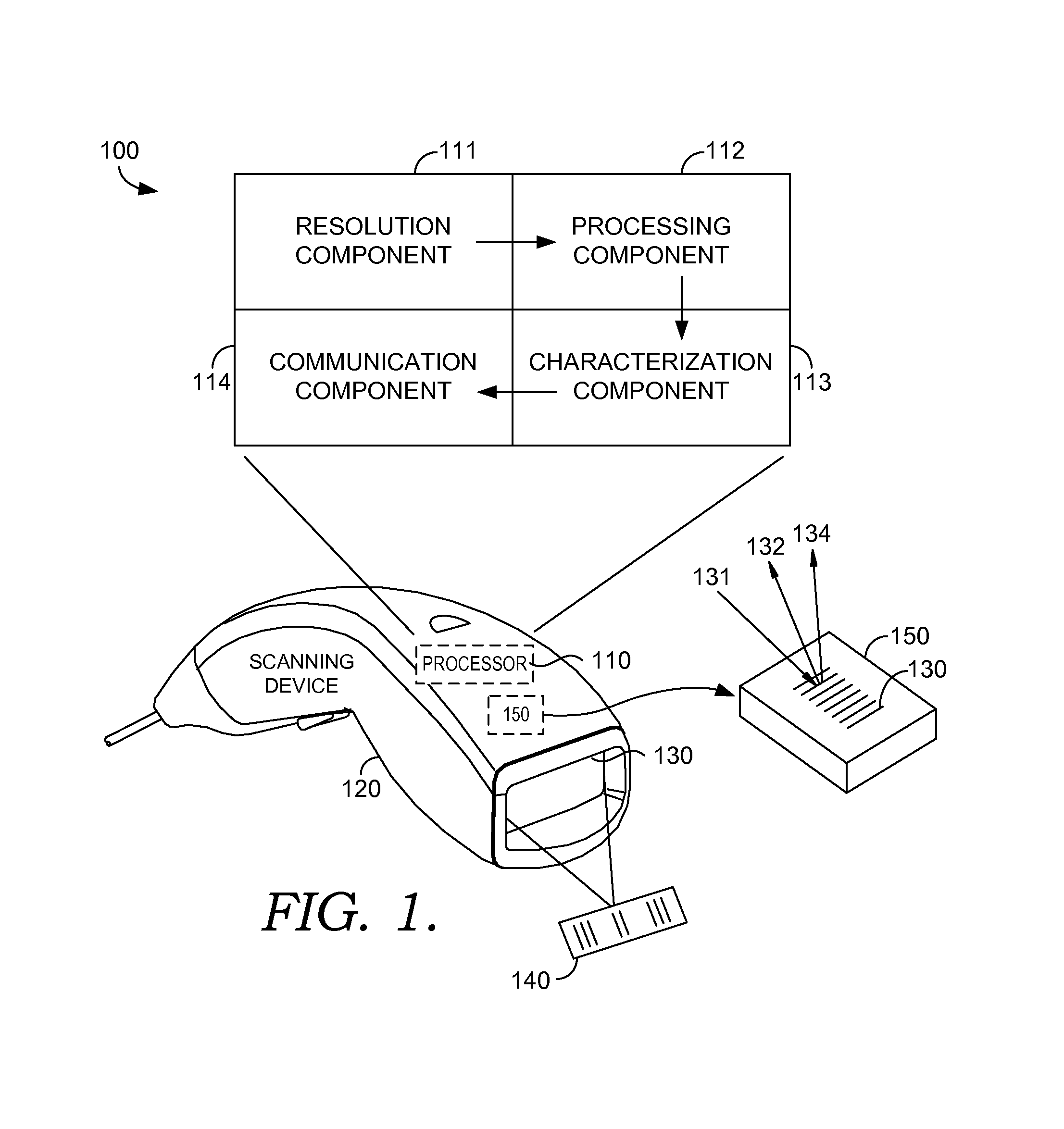
Optical grid enhancement for improved motor location
ActiveUS8976368B2Reduce spacingMinimal positional discrepancyUsing optical meansSensing record carriersGratingImage resolution
Methods for performing a scheme that results in a refined measurement pattern within an optical grid are provided. Physically adjusting spacing of elements within an optical grid to achieve enhanced resolution is historically unfeasible, as reduction of the spacing causes light sensors of the optical grid to pick up false signals when reading light beams. Technology introduced by the present invention generates a virtual reduced spacing of the elements within the optical grid by using two signals that are slightly different. These slightly different signals can accomplish, at least, quarter-grid spacing resolution within the optical grid. Additionally, the enhanced resolution derived from the virtual reduced spacing is employed to govern movement of a motor. The motor movement is in response to one or more changes of direction such that the motor is operating in its linear range. Advantageously, the virtual reduced spacing allows for substantial movement in a non-linear phase, while only limited movement in a linear phase is necessary to locate accurately a target within the optical grid.
Owner:INTERMEC IP CORP
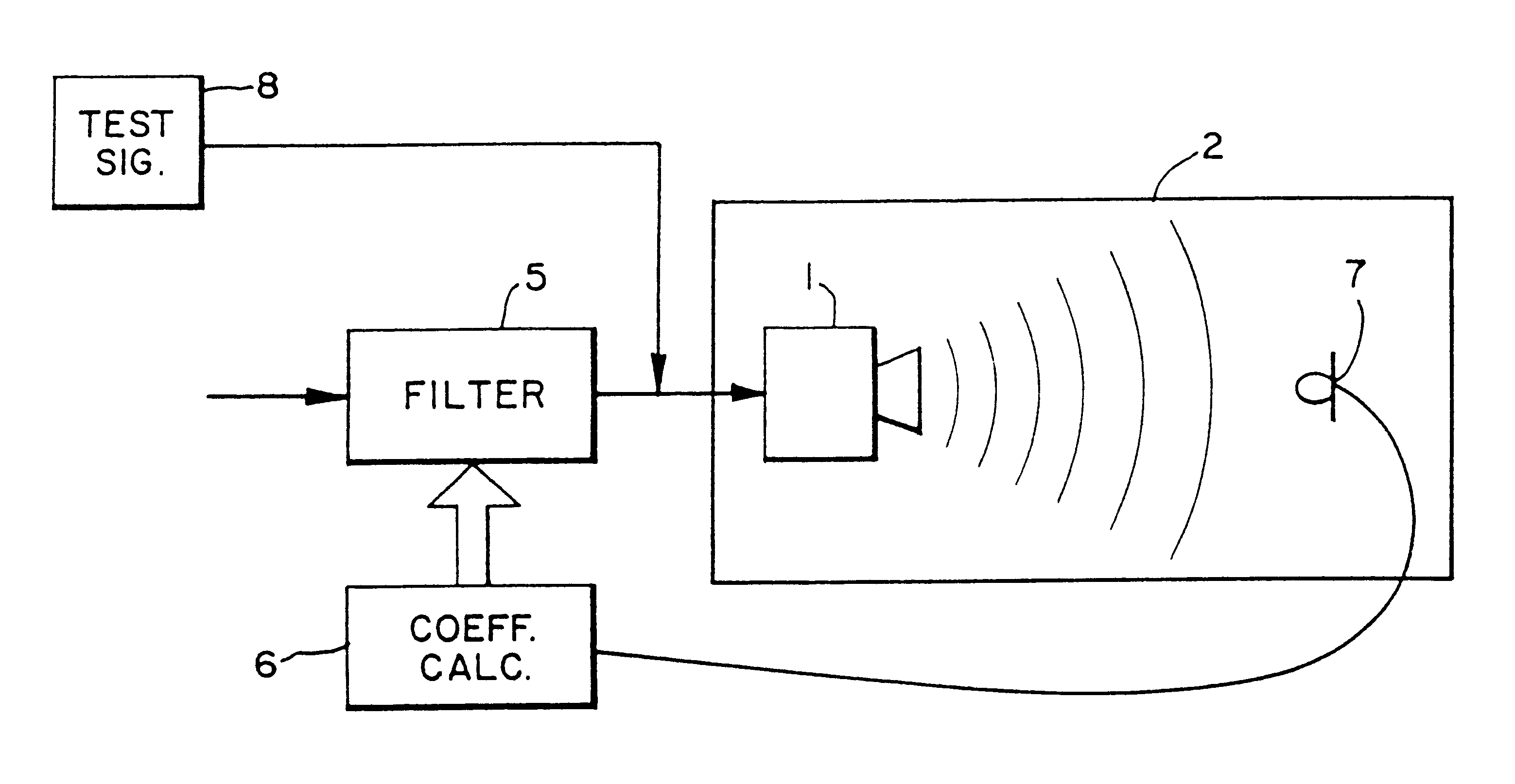
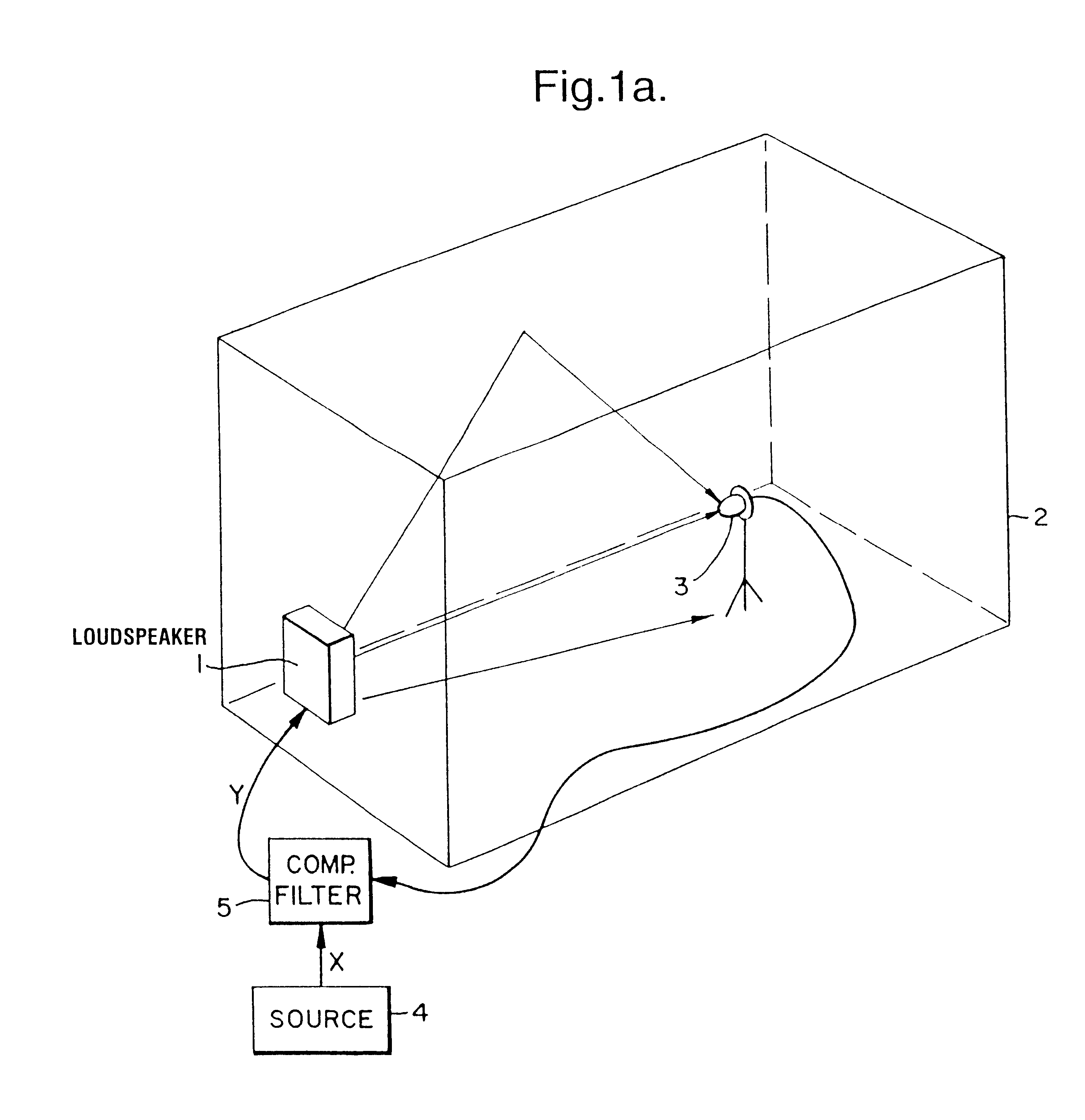
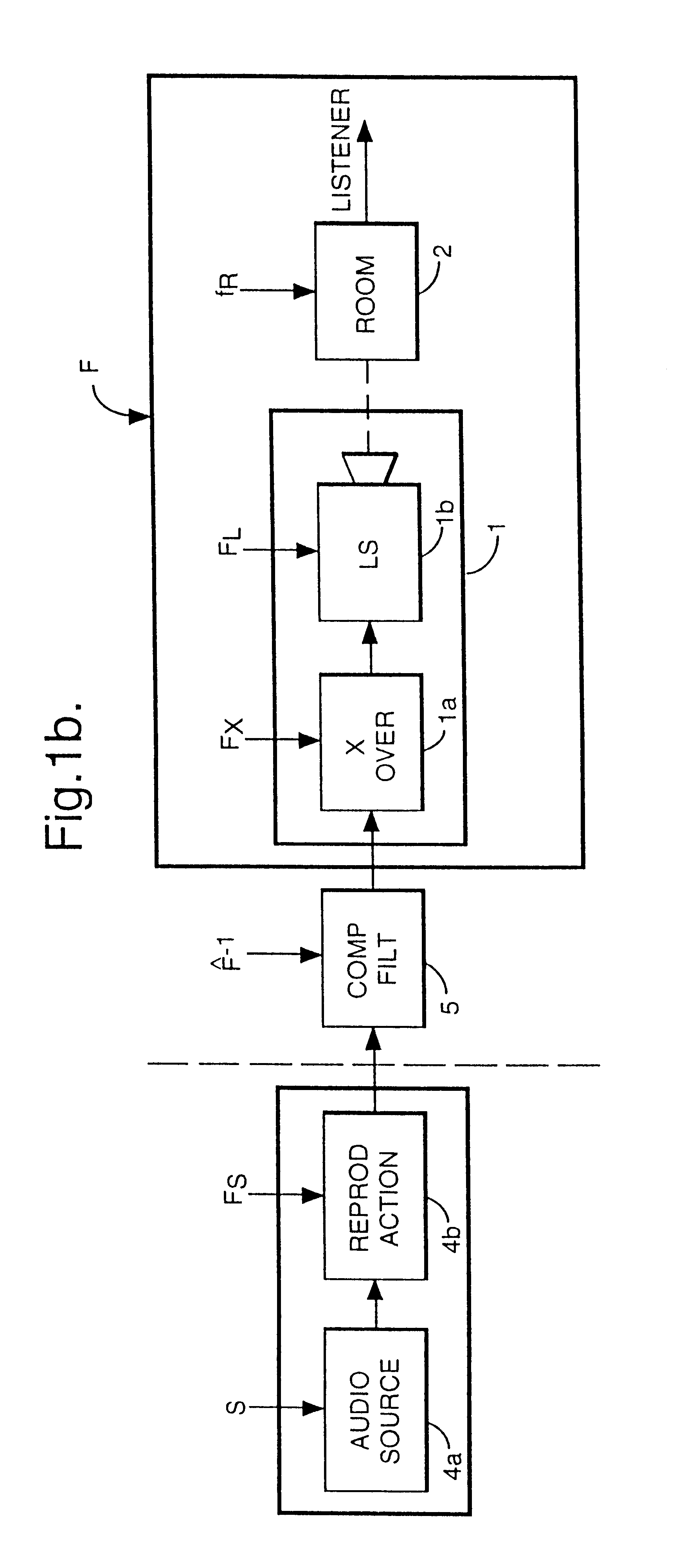
Compensating filters
InactiveUS6760451B1Eliminate phase distortionAdaptive networkAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlDigital signal processingAmplitude response
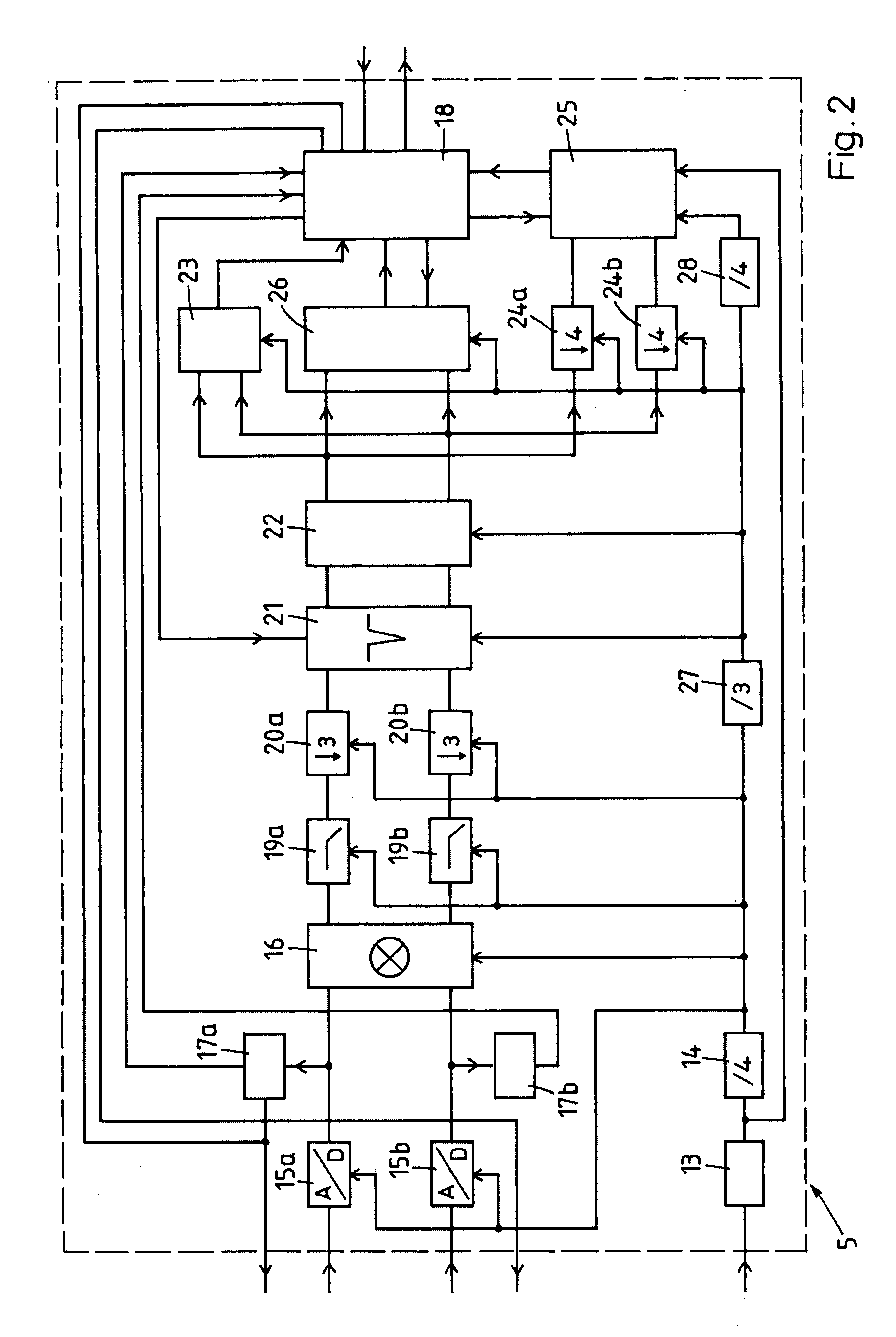
A prefilter (5) for an audio system comprising a loudspeaker (1) in a room (2), which corrects both amplitude and phase errors due to the loudspeaker (1) by a linear phase correction filter response and corrects the amplitude response of the room (2) whilst introducing the minimum possible amount of extra phase distortion by employing a minimum phase correction filter stage. A test signal generator (8) generates a signal comprising a periodic frequency sweep with a greater phase repetition period than the frequency repetition period. A microphone (7) positioned at various points in the room (2) measures the audio signal processed by the room (2) and loudspeaker (1), and a coefficient calculator (6) (e.g. a digital signal processor device) derives the signal response of the room and thereby a requisite minimum phase correction to be cascaded with the linear phase correction already calculated for the loudspeaker (1). Filter (5) may comprise the same digital signal processor as the coefficient calculator (6). Applications in high fidelity audio reproduction, and in car stereo reproduction.
Owner:CRAVEN PETER GRAHAM +1
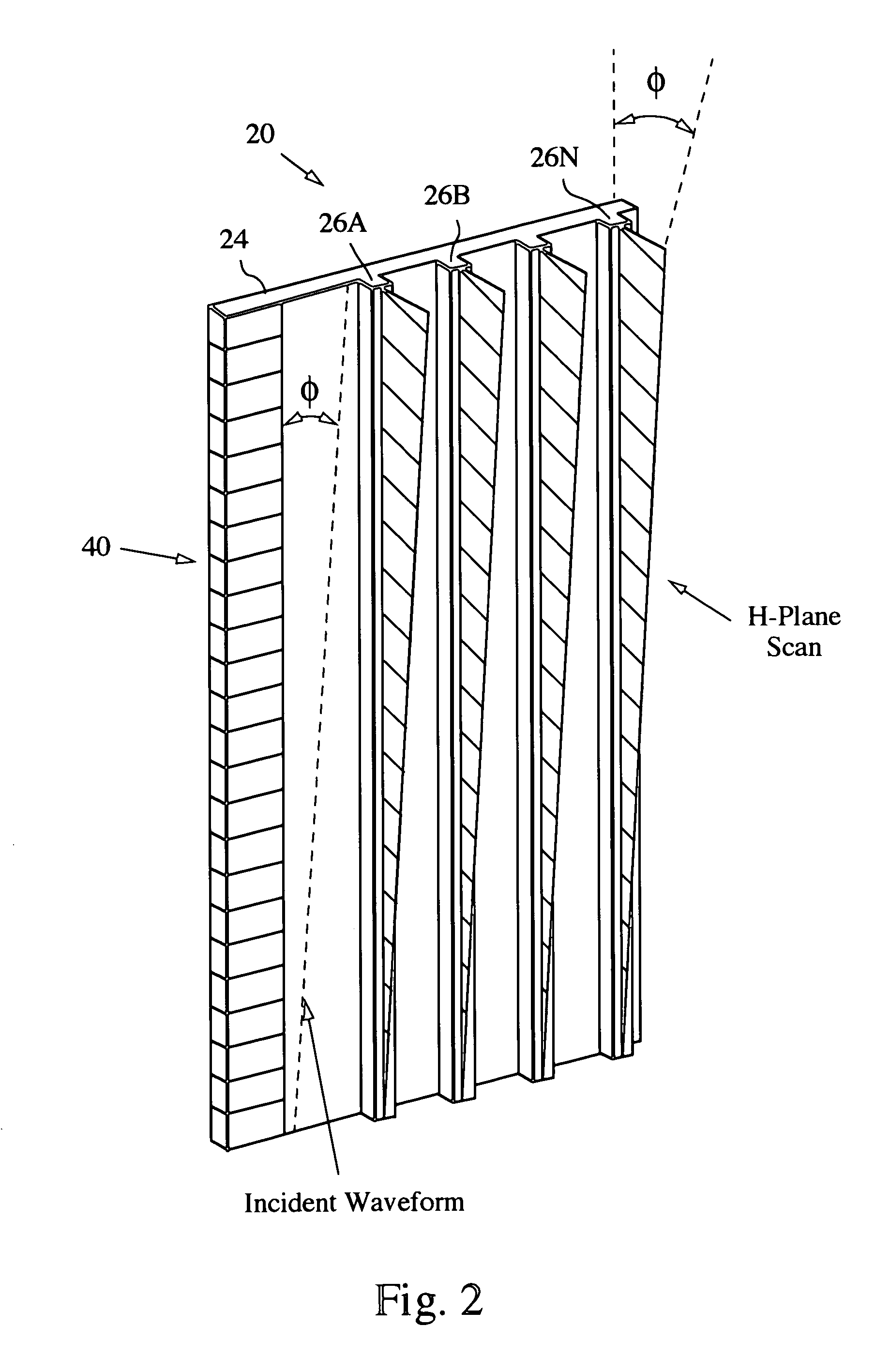
MMW electronically scanned antenna
A millimeter wave (MMW) antenna array includes a continuous transverse stub (CTS) radiating aperture comprising a set of spaced continuous transverse stubs, each having a longitudinal extent. A series feed system is coupled to an excitation source for exciting the stubs with MMW electromagnetic energy having a linear phase progression along the longitudinal extent of the stubs to produce an array beam which can be scanned over a beam scan range by changing the excitation frequency.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO +1
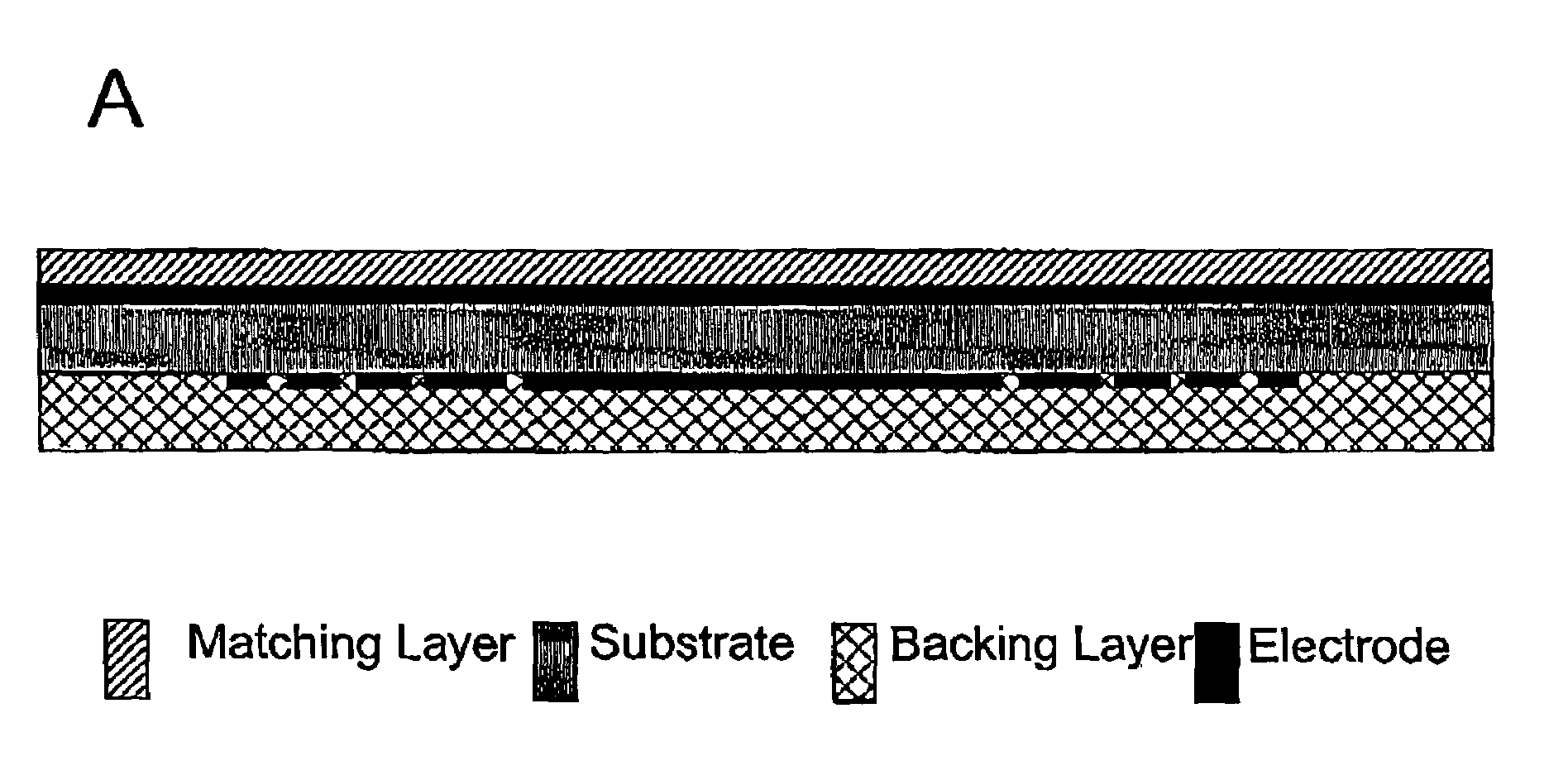
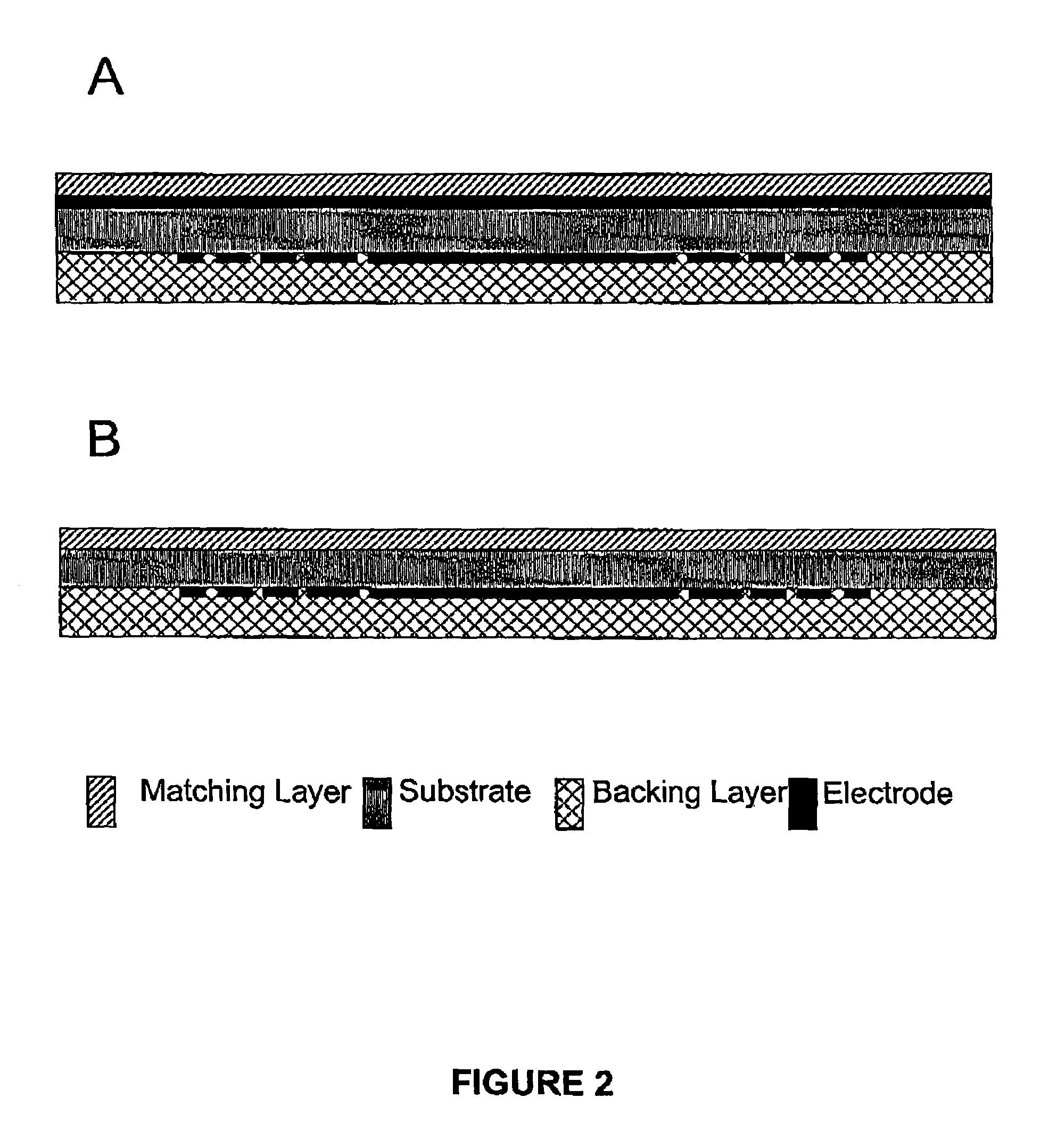
Ultrasound transducer array
InactiveUS6974417B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPhased arrayOperating frequency
This invention relates to an ultrasonic transducer array for non-destructive imaging and inspection of materials, suitable for applications such as bio-medical imaging. According to the invention, the transducer has at least one electrode comprising an array of electrode elements, wherein the elements are not separated by a grooves or kerfs. The grooveless transducer design simplifies transducer construction and permits very high operating frequencies, and hence very high resolution. In one embodiment suitable for producing real-time high resolution 3-dimension images, the invention provides a hybrid transducer comprising two opposed electrodes, one electrode being a grooveless linear array and the second electrode being a grooved linear phased array.
Owner:QUEENS UNIV OF KINGSTON
Linear phase interpolator and phase detector
ActiveUS20090103675A1Pulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionPhase detectorOperating point
A novel interpolating phase detector for use in a multiphase PLL is described comprising an array of individual phase comparators, all operating at essentially the same operating point which permits the circuits to be designed simultaneously for high speed and for low power consumption. Two adjacent phase outputs of a multi-phase VCO may be selected and interpolated in between, by selectively attaching a variable number of phase comparators to each phase output and summing their phase error outputs. By varying the number of phase comparators attached to each phase output, interpolation can be achieved with high linearity.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Dual frequency band ultrasound transducer arrays
ActiveUS7727156B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSonificationArray aperture
Owner:ANGELSEN BJORN A J +4
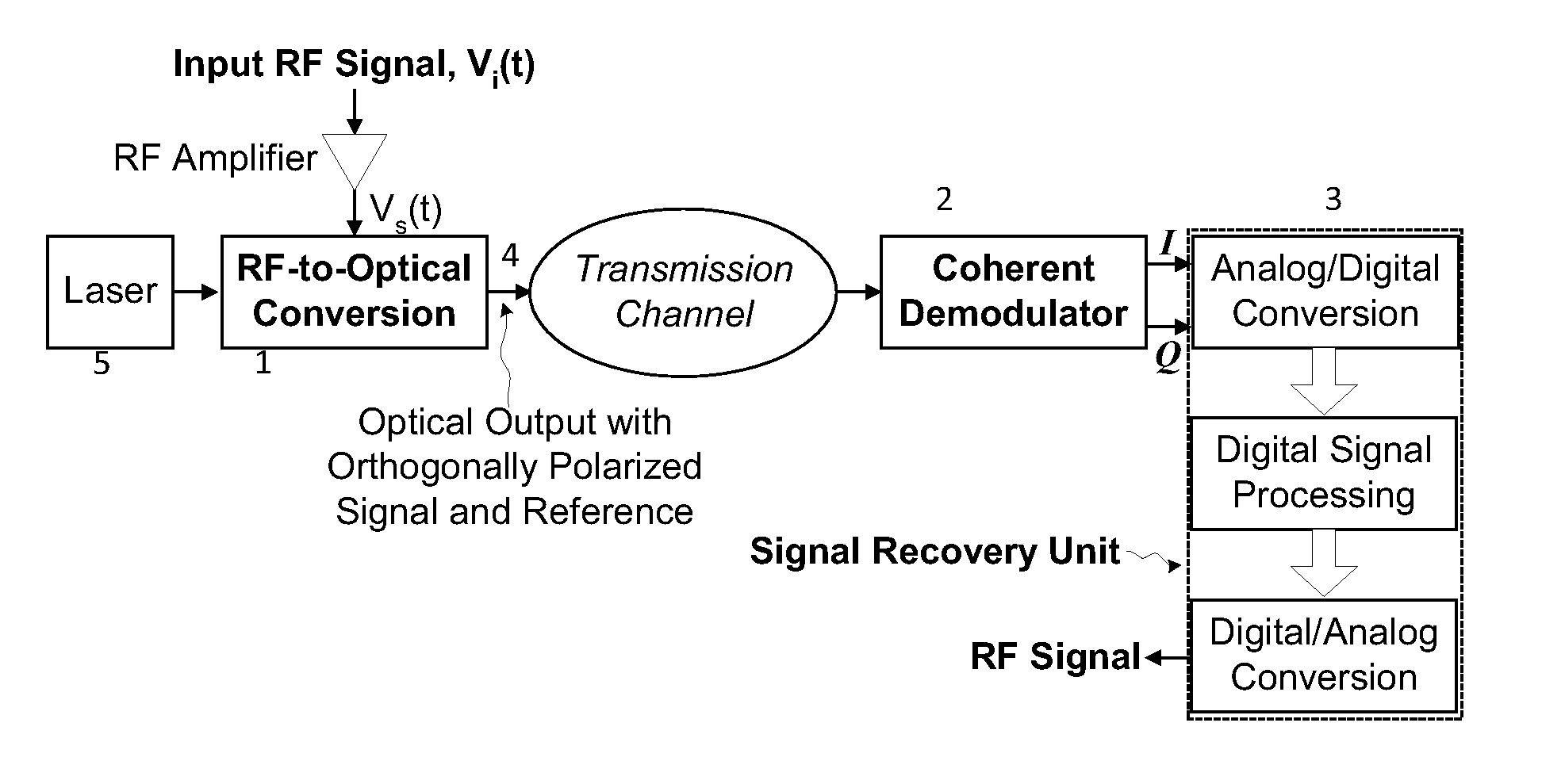
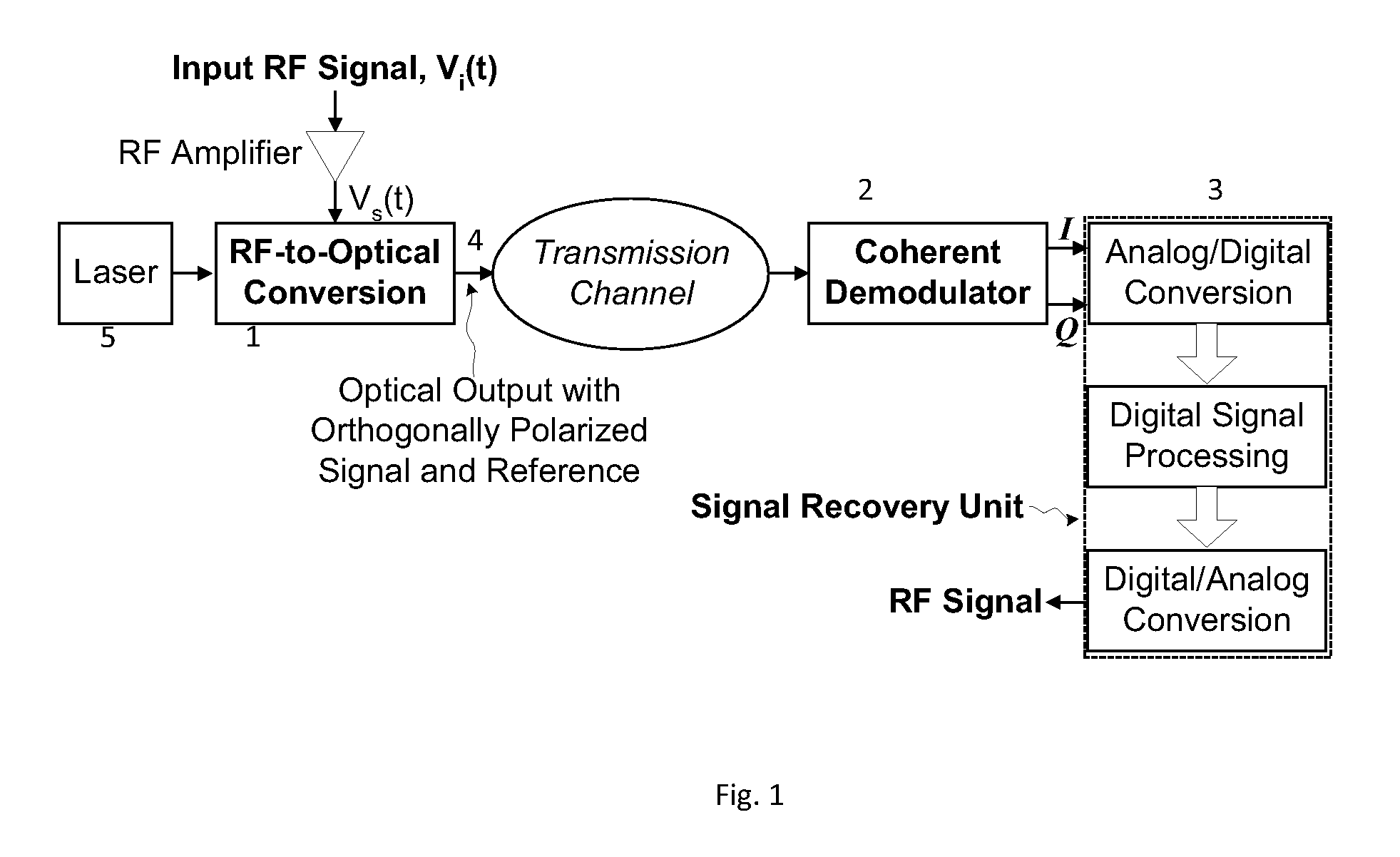
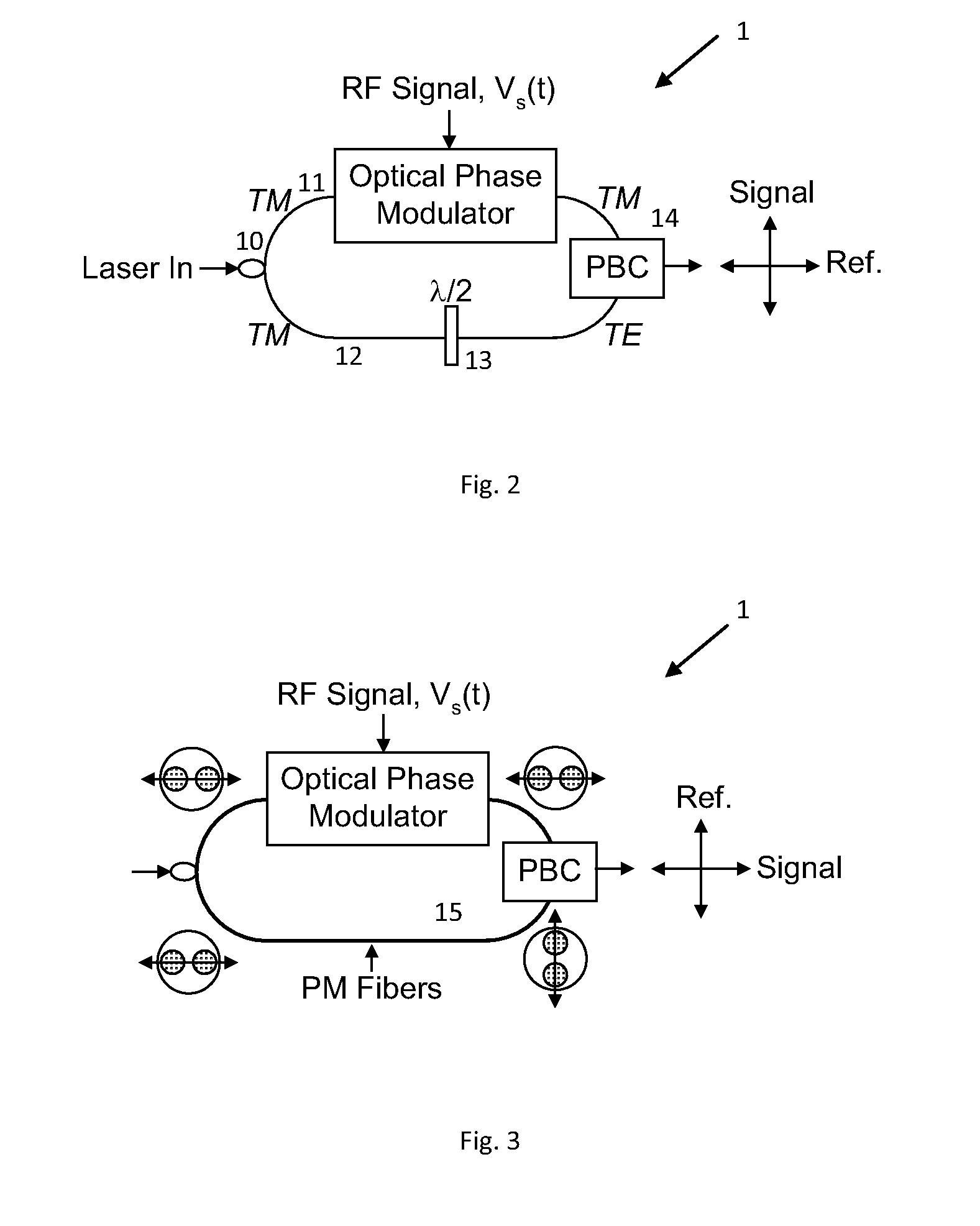
Method and apparatus for coherent analog RF photonic transmission
A system for high fidelity analog RF photonic communications is disclosed wherein linear phase modulation and linear coherent demodulation is included. A single optical beam with a phase-modulated signal optical carrier combined with an orthogonally polarized reference unmodulated optical carrier is transmitted simultaneously. At the receiver, the polarization of the reference carrier is transform to match that of the signal followed by coherent detection. An in-phase and quadrature-phase component of the homodyne signal is generated where they are digitized and processed to recover the original RF signal.
Owner:CELIGHT
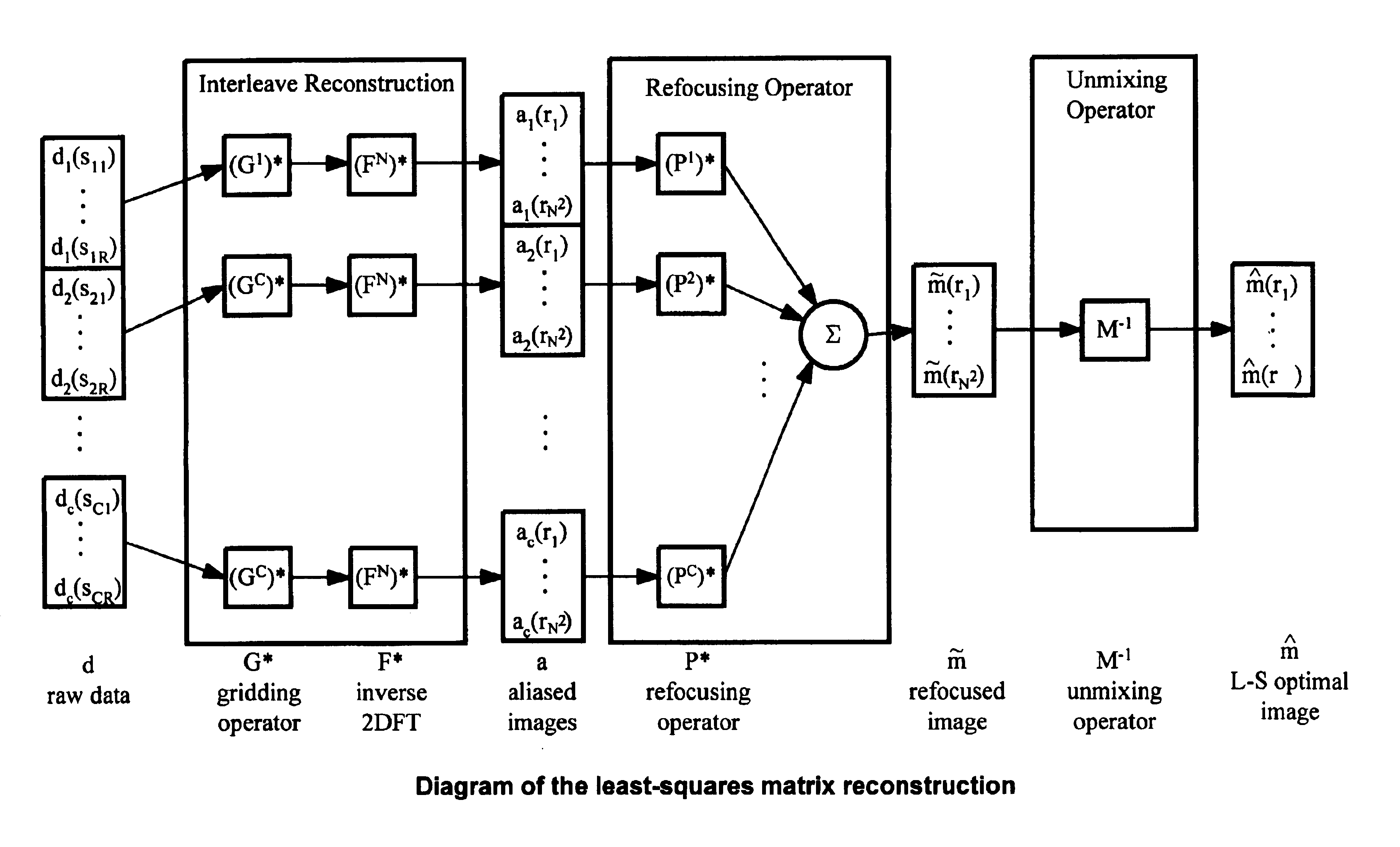
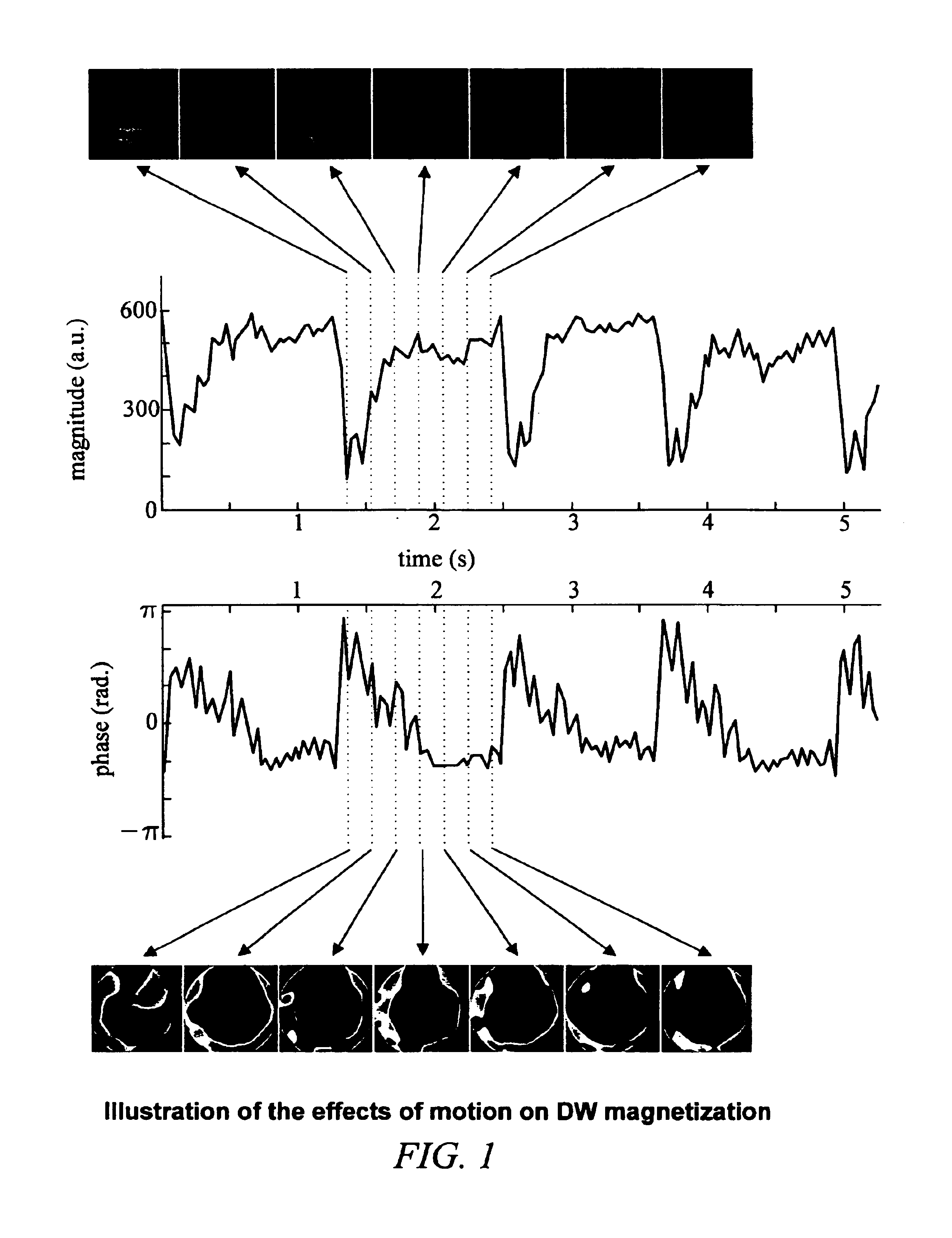
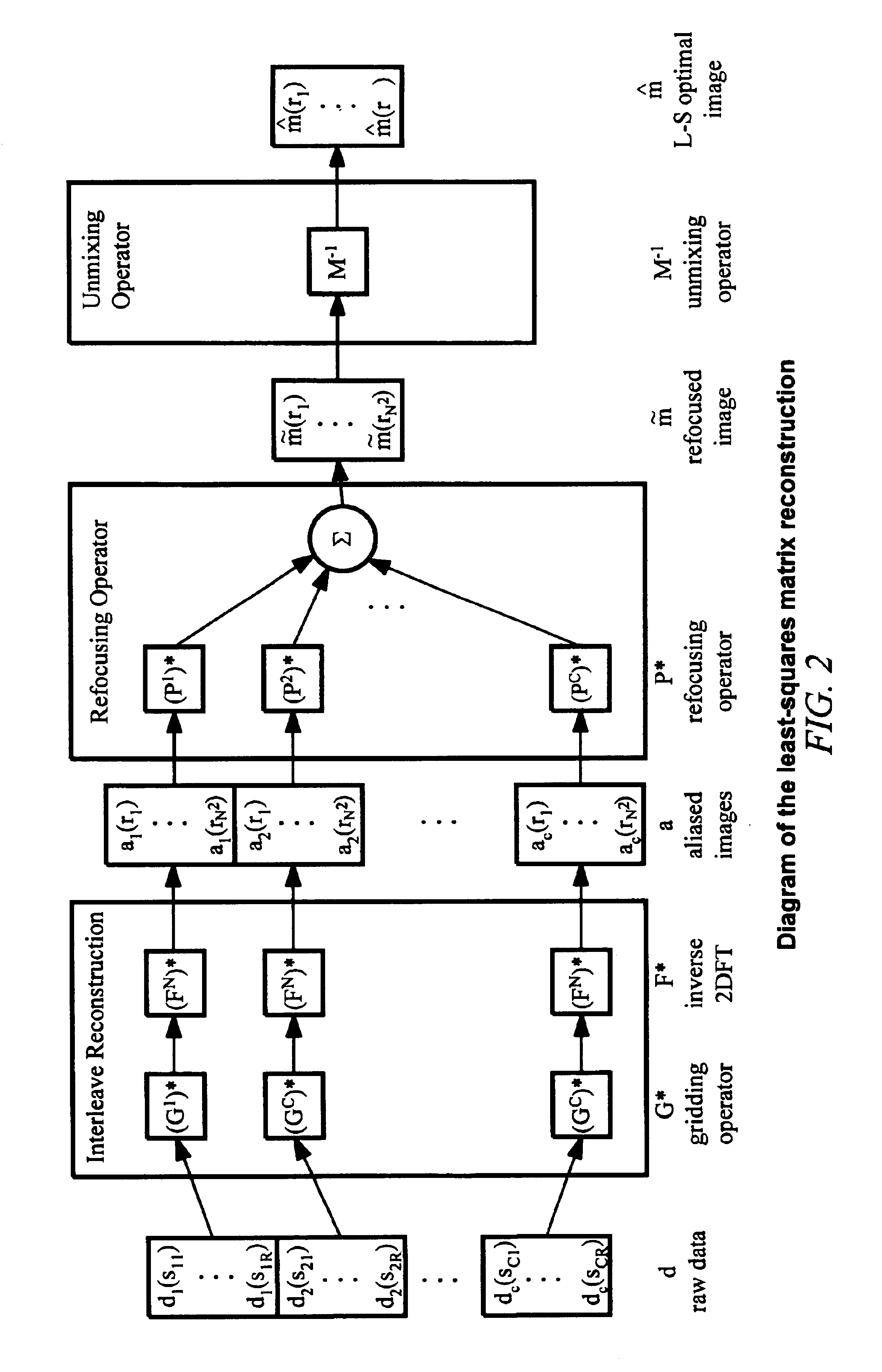
Method of removing dynamic nonlinear phase errors from MRI data
ActiveUS6853191B1Improve performanceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionReconstruction methodComputer science
Disclosed is a generalized reconstruction method that corrects for non-linear phase errors based on least-squares estimation. An approximation of the least squares estimate utilizes refocusing reconstruction in which high-resolution data is multiplied by the phase conjugate of a navigator in image-space. The multiplication rephases the unaliased signal in the high-resolution data. The high-resolution data can then be added together coherently. The multiplication can be effected in k-space as a convolution using a gridding reconstruction of the high-resolution data using the low resolution navigator.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Linear phase robust carrier recovery for QAM modems
InactiveUS6904098B1Large loop bandwidthLower latencyDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionAutomatic frequency control detailsQam modulationBlind equalization
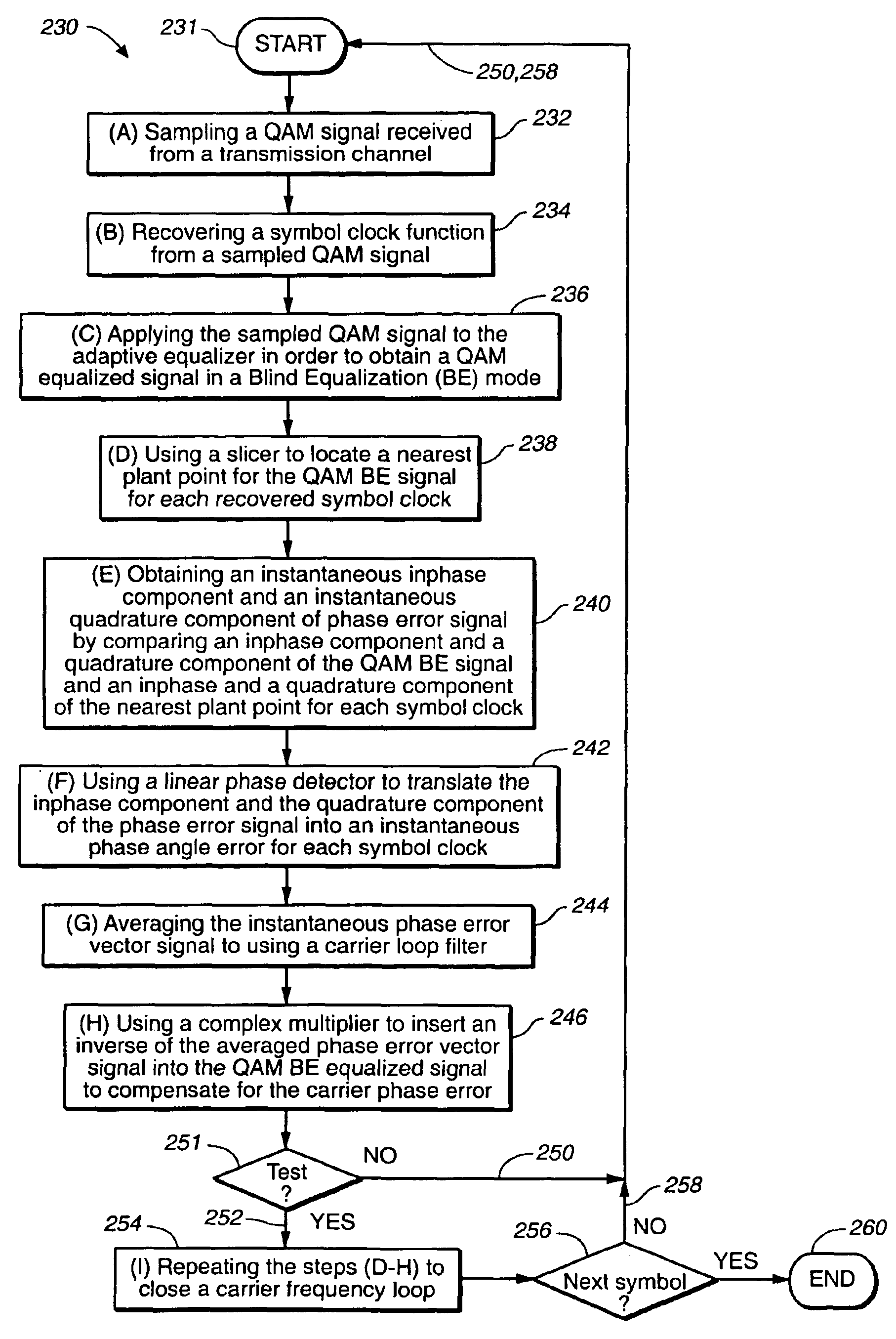
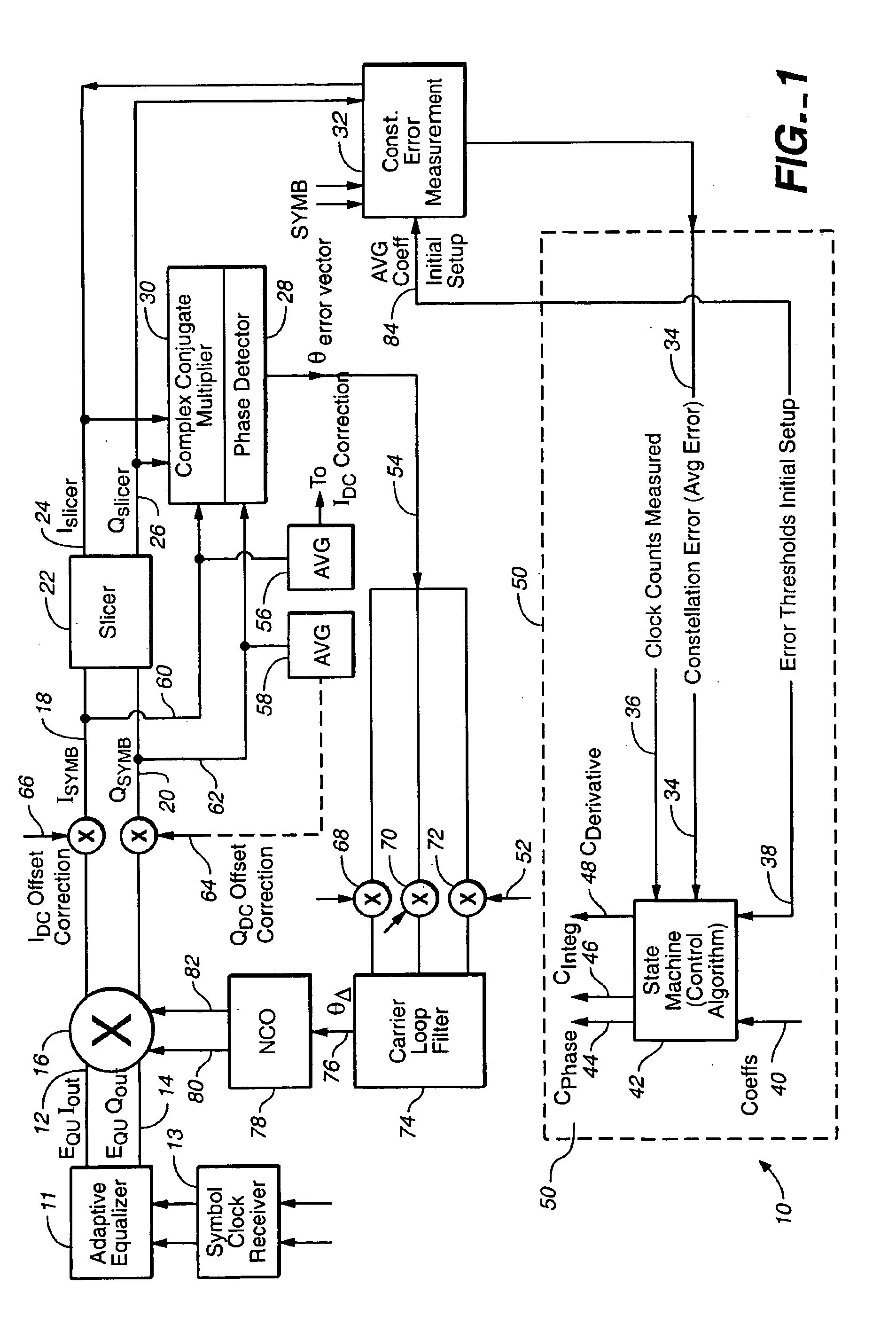
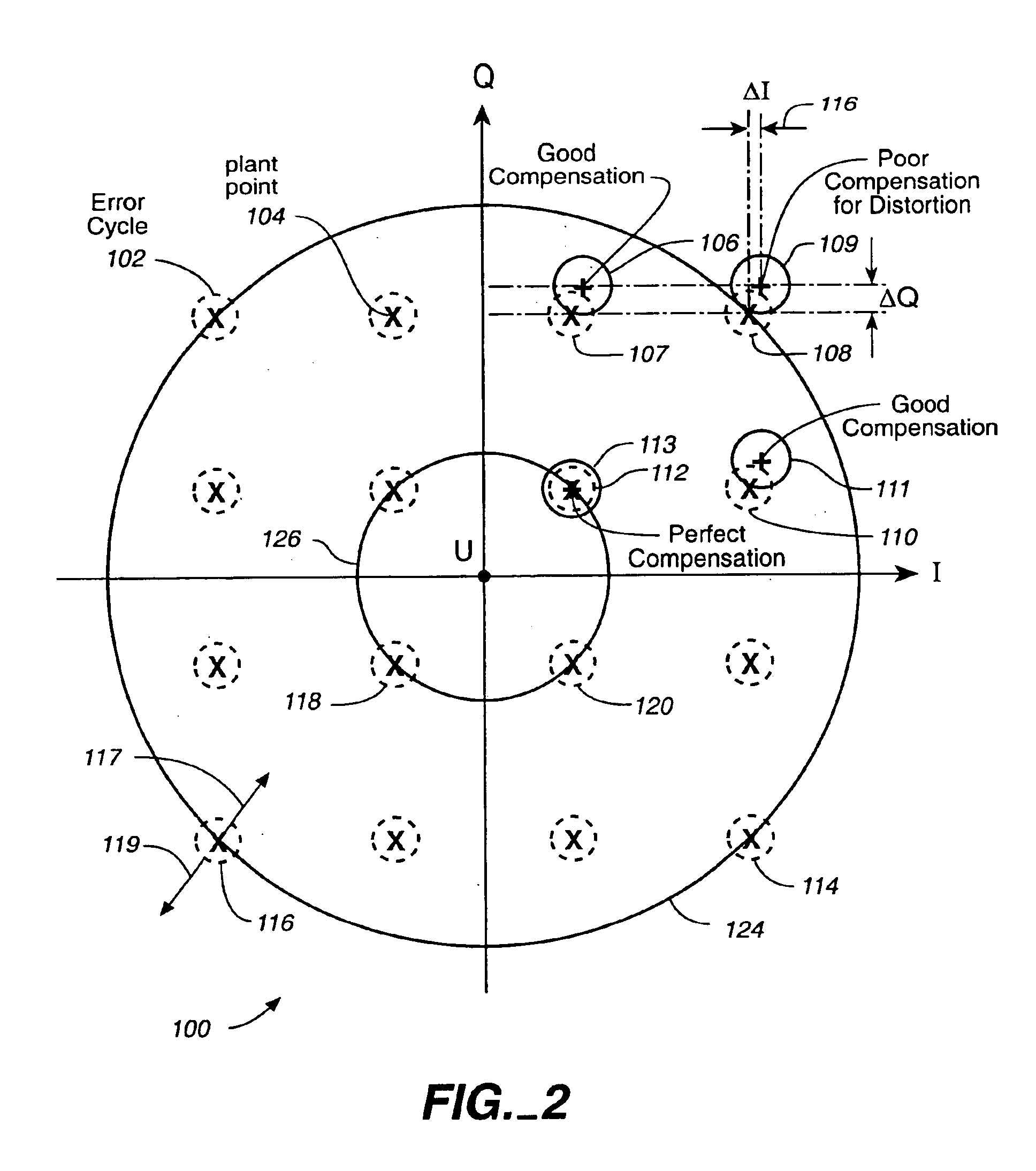
In a QAM demodulator including an adaptive equalizer, a method of carrier tracking comprising the following steps is disclosed: (A) sampling a QAM signal received from a transmission channel; (B) recovering a symbol clock function from the sampled QAM signal; (C) applying the sampled QAM signal to the adaptive equalizer in order to obtain a QAM equalized signal in a Blind Equalization (BE) mode; (D) using a slicer to locate a nearest plant point for the QAM Blind equalized signal for each recovered symbol clock; (E) using a complex conjugate multiplier to obtain an instantaneous inphase component and an instantaneous quadrature component of a phase angle error signal; (F) using a linear phase detector to obtain an instantaneous phase angle error for each symbol clock; (G) averaging the instantaneous phase angle error signal by using a carrier loop filter; (H) using a complex multiplier to insert an inverse of the averaged phase angle error signal into the QAM Blind equalized signal to compensate for the carrier phase angle error; and (I) repeating the steps (D-H) to close a carrier frequency loop.
Owner:REMEC BROADBAND WIRELESS NETWORKS LLC
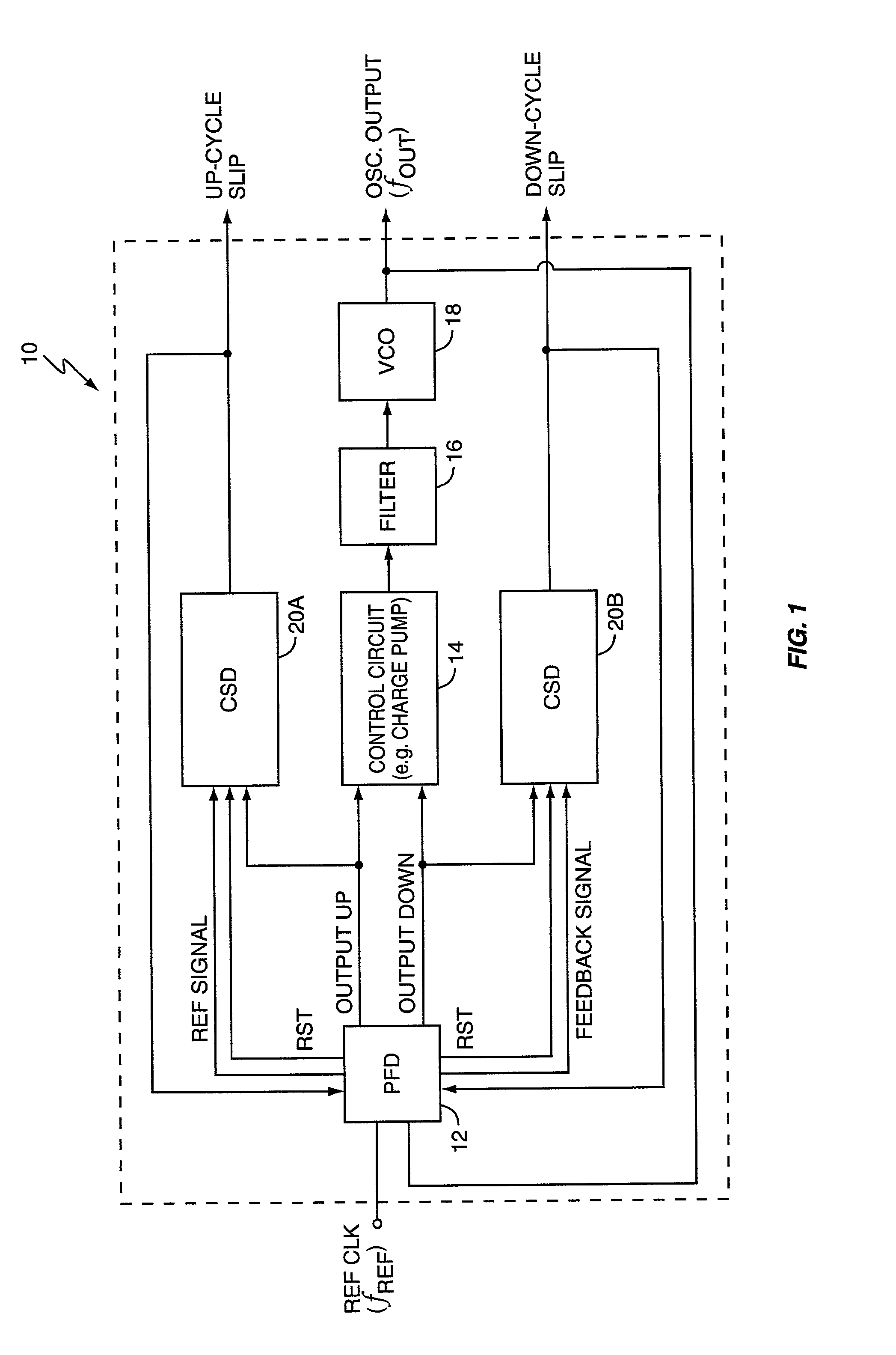
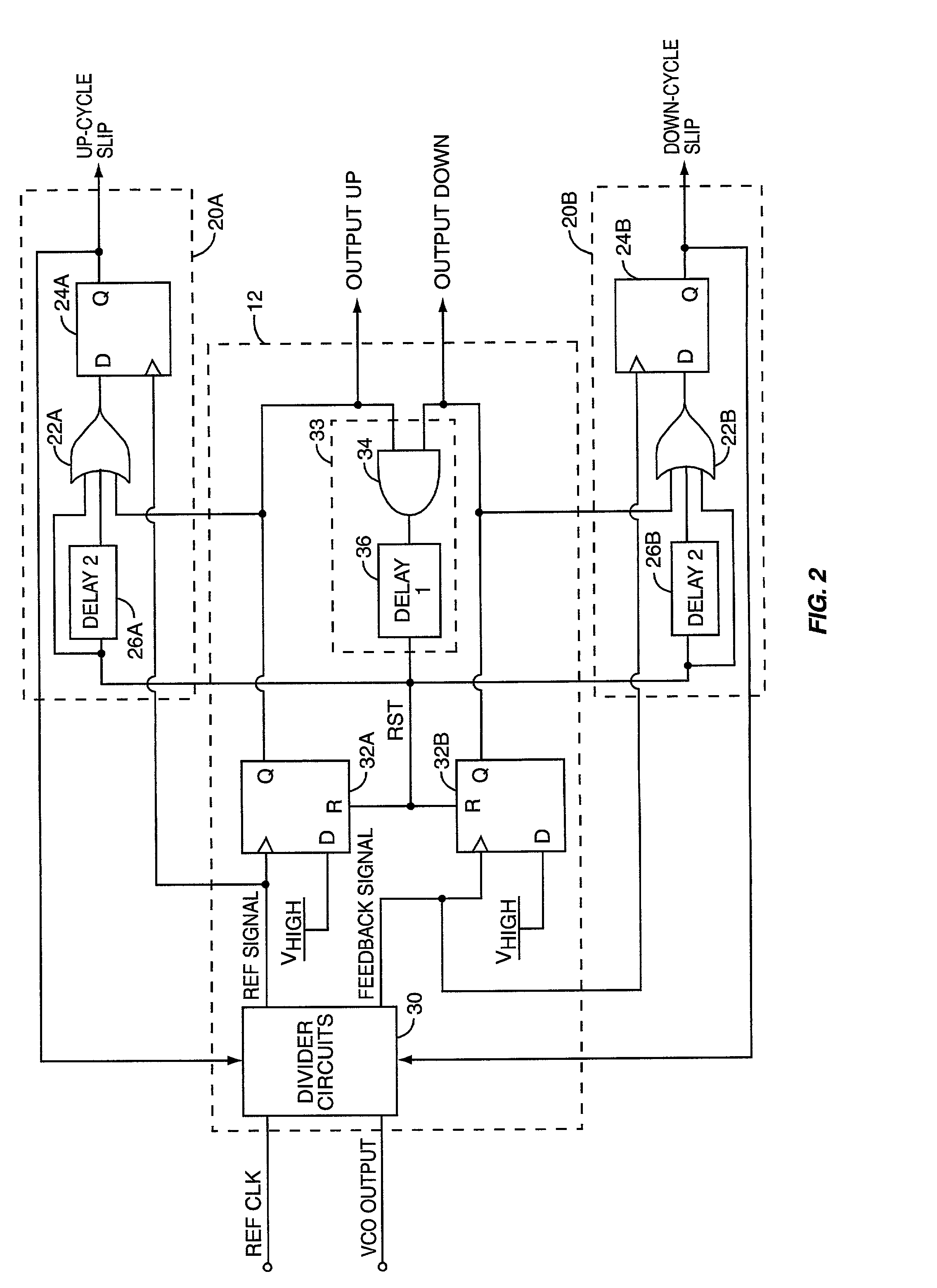
PLL cycle slip detection
InactiveUS7003065B2Pulse automatic controlVoltage-current phase angleControl signalPhase locked loop circuit
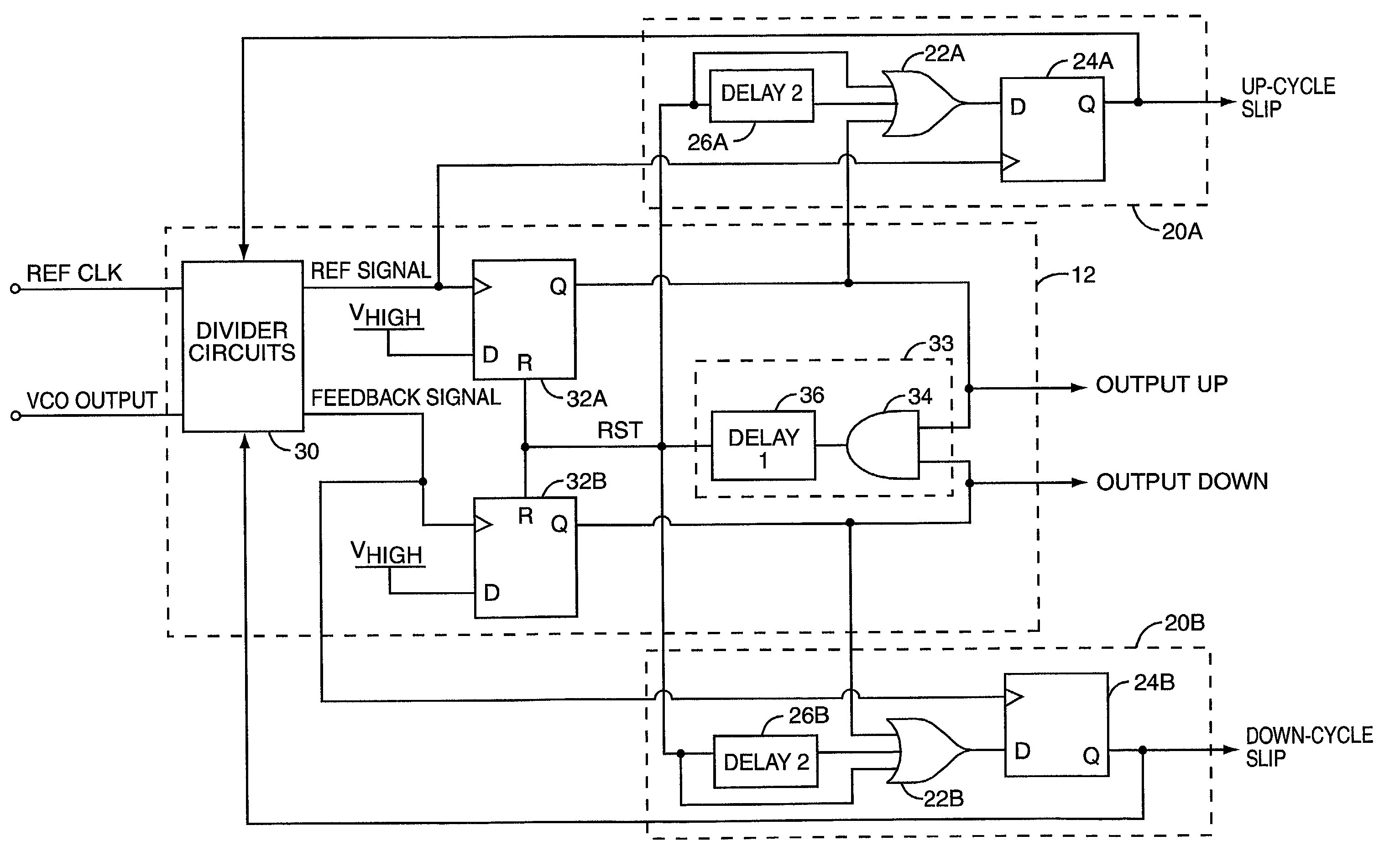
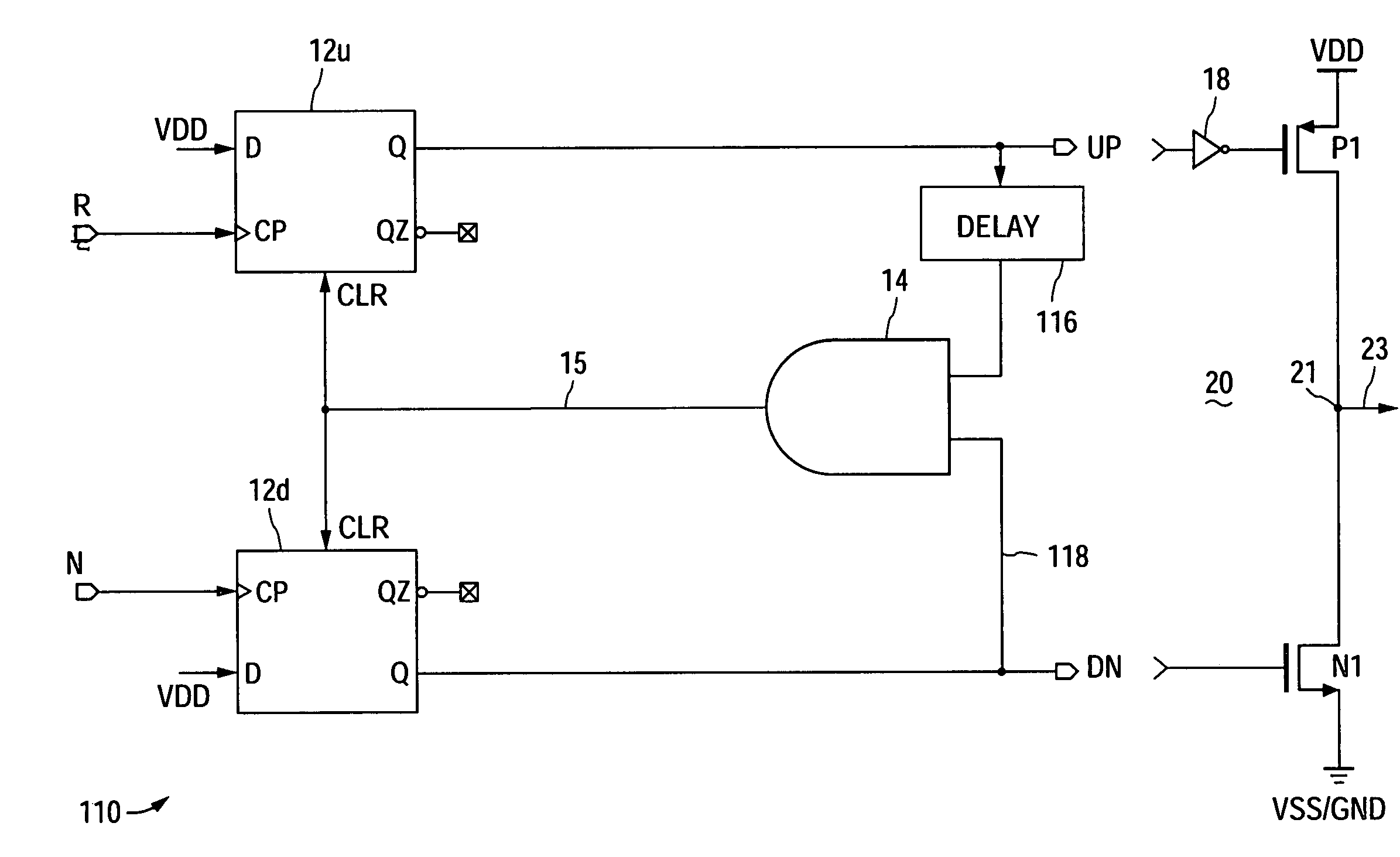
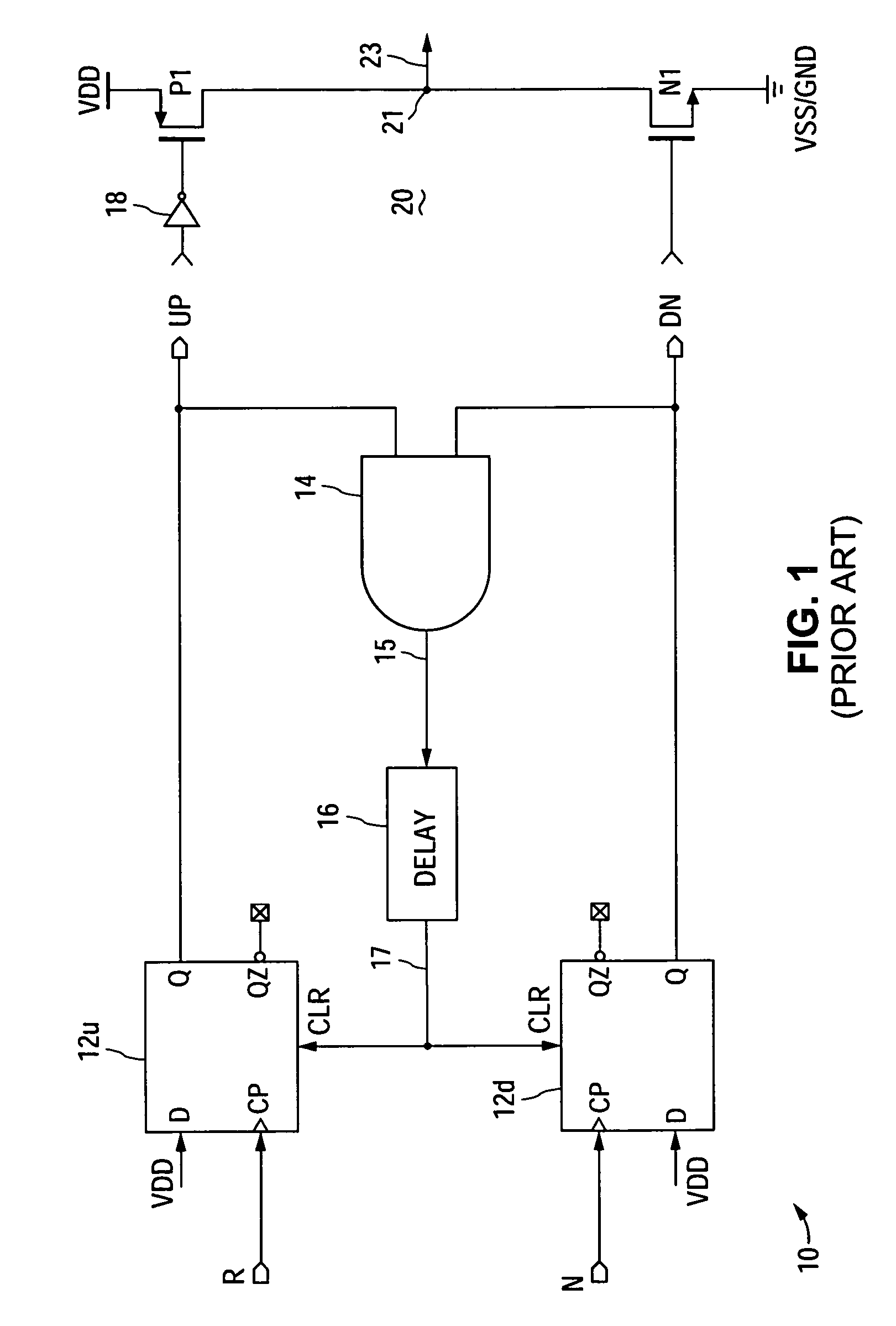
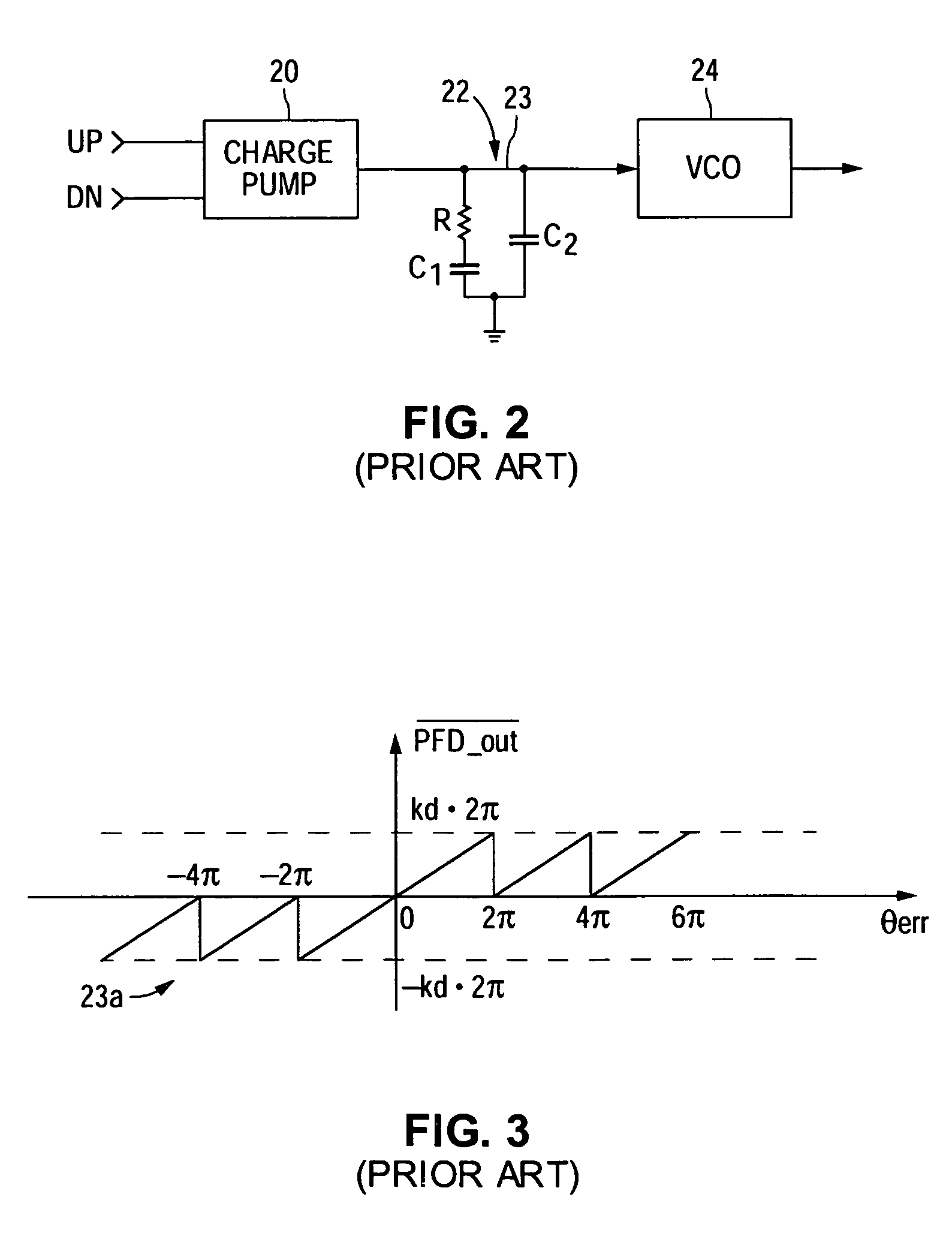
A cycle slip detector interfaces with a phase / frequency detector (PFD), such as might be used in a phase-locked loop circuit (PLL), and indicates when cycle slips occur in the PFD. Typically, the PFD generates output control signals as a function of the phase difference between first and second input signals, with the first input signal usually serving as a reference signal against which the PLL adjusts the second input signal. The PFD provides linear phase comparison between its input signals, provided their relative phase difference does not exceed ±2π radians. If one of the two signals leads or lags the other by more than that amount, a cycle slip occurs, and the PFD responds nonlinearly. The cycle slip detector provides logic for detecting and indicating leading and lagging cycle slips as they occur in the PDF, and is typically implemented as a minimal arrangement of logic gates and flip-flops.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
Nonlinear digital signal processor
InactiveUS20080080644A1Multiple-port networksAdaptive networkDigital signal processingPhase response
A digital signal processor (DSP) comprises an input terminal configured to receive an input, an adaptive nonlinear phase filter coupled to the input terminal, the adaptive nonlinear phase filter having a time-varying phase response, and an adaptive nonlinear amplitude filter coupled to the input terminal, the adaptive nonlinear amplitude filter having a time-varying amplitude response.A method of processing a signal comprises receiving the signal, sending the signal to an adaptive nonlinear phase filter, the adaptive nonlinear phase filter having a time-varying phase response, and sending the signal to an adaptive nonlinear amplitude filter, the adaptive nonlinear amplitude filter having a time-varying amplitude response.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method for data acquisition acceleration in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) using receiver coil arrays and non-linear phase distributions
InactiveUS20110148410A1Specifically designedIncrease freedomElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRTransverse magnetizationData acquisition
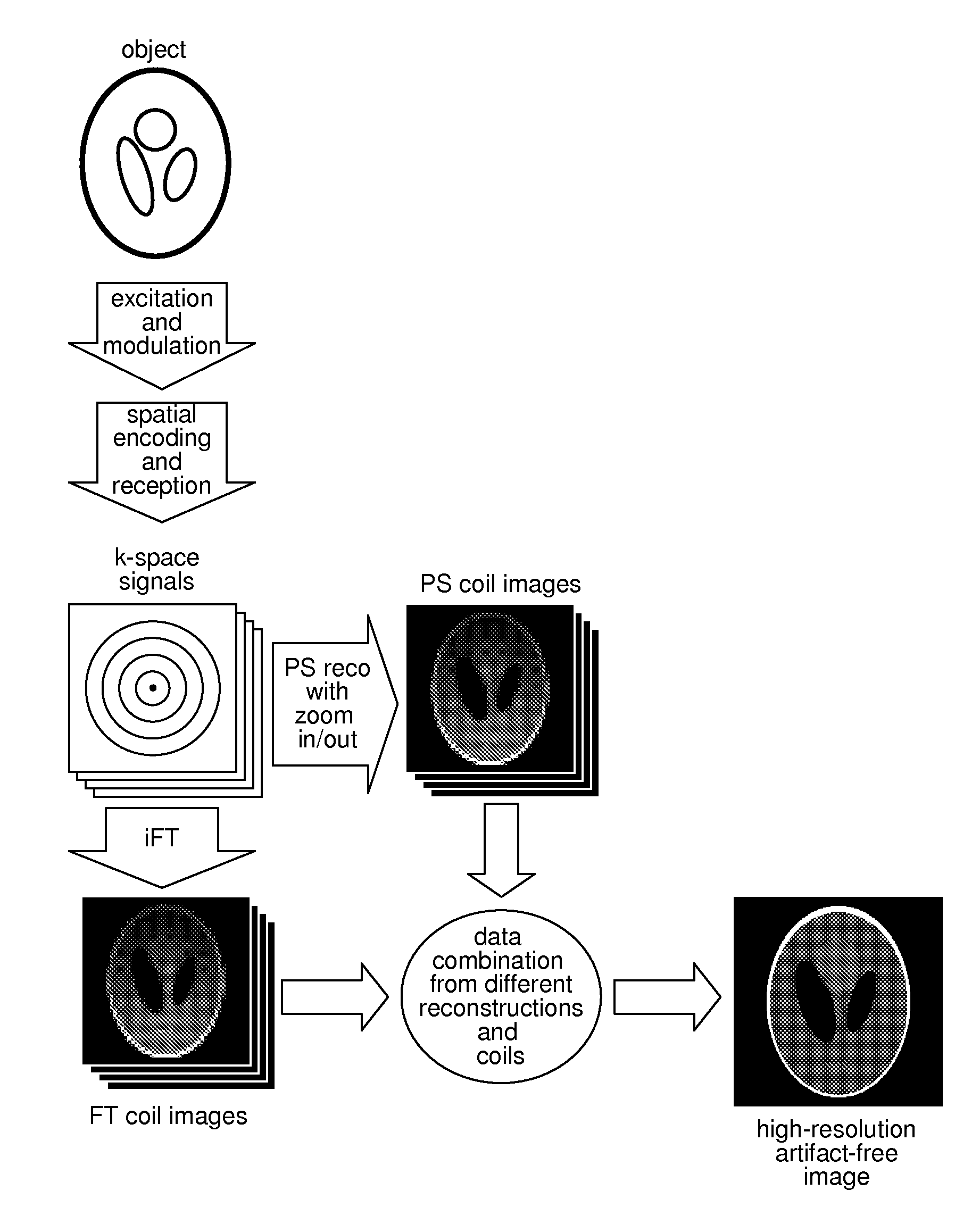
A method for accelerating data acquisition in MRI with N-dimensional spatial encoding has a first method step in which a transverse magnetization within an imaged object volume is prepared having a non-linear phase distribution. Primary spatial encoding is thereby effected through application of switched magnetic fields. Two or more RF receivers are used to simultaneously record MR signals originating from the imaged object volume, wherein, for each RF receiver, an N-dimensional data matrix is recorded which is undersampled by a factor Ri per selected k-space direction. Data points belonging to a k-space matrix which were not recoded by a selected acquisition schema are reconstructed using a parallel imaging method, wherein reference information concerning receiver coil sensitivities is extracted from a phase-scrambled reconstruction of the undersampled data matrix. The method generates a high-resolution image free of artifacts in a time-efficient manner by improving data sampling efficiency and thereby reducing overall data acquisition time.
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG
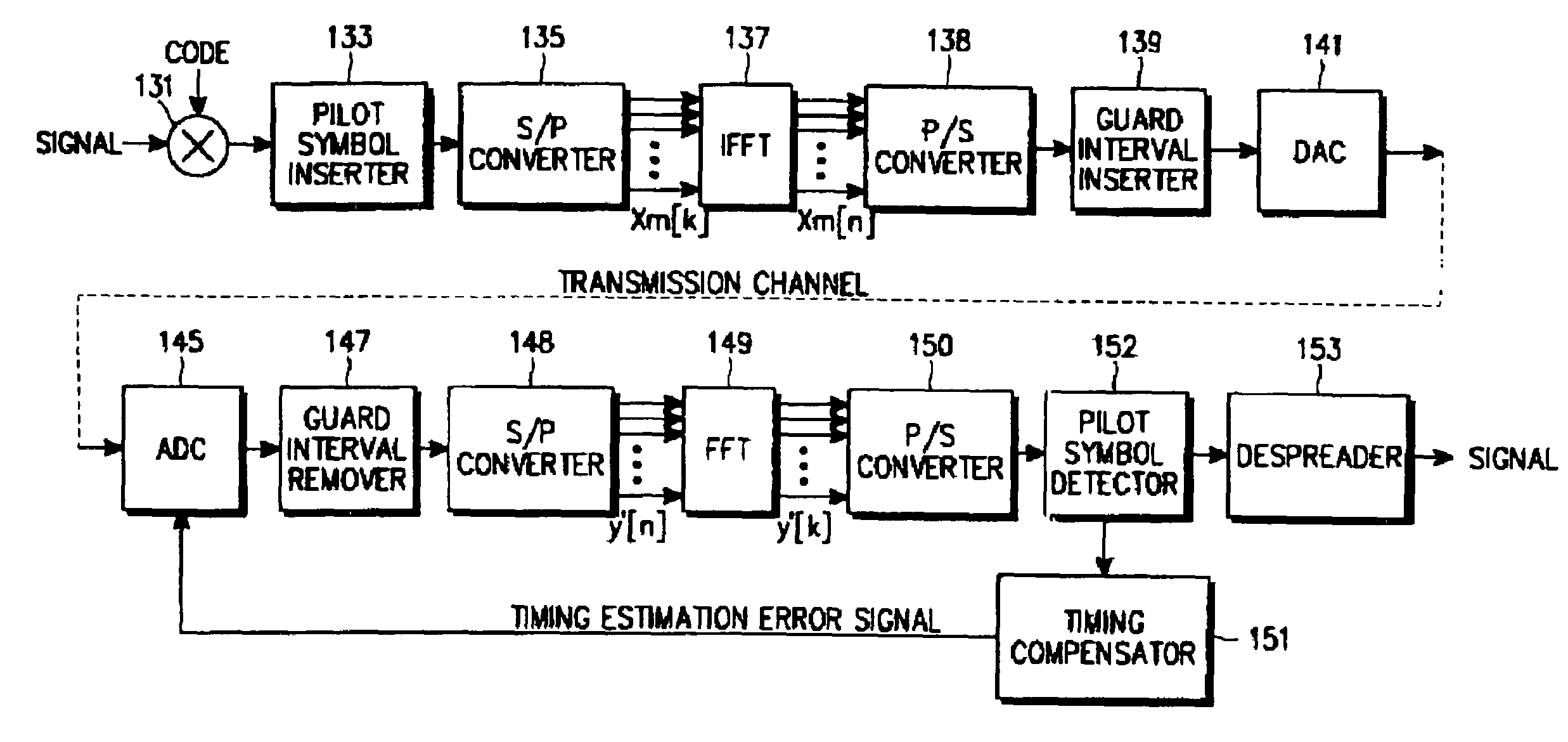
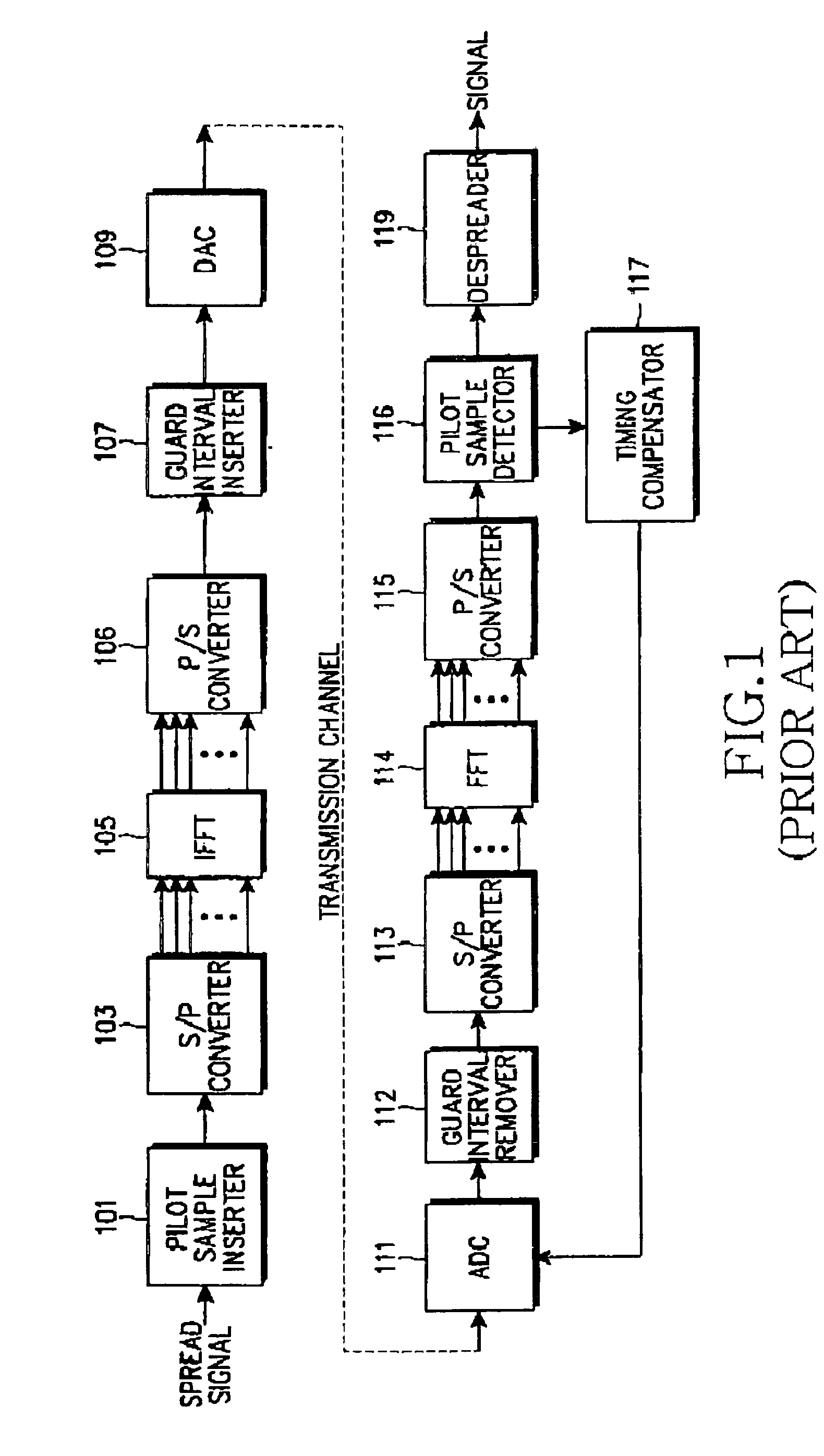
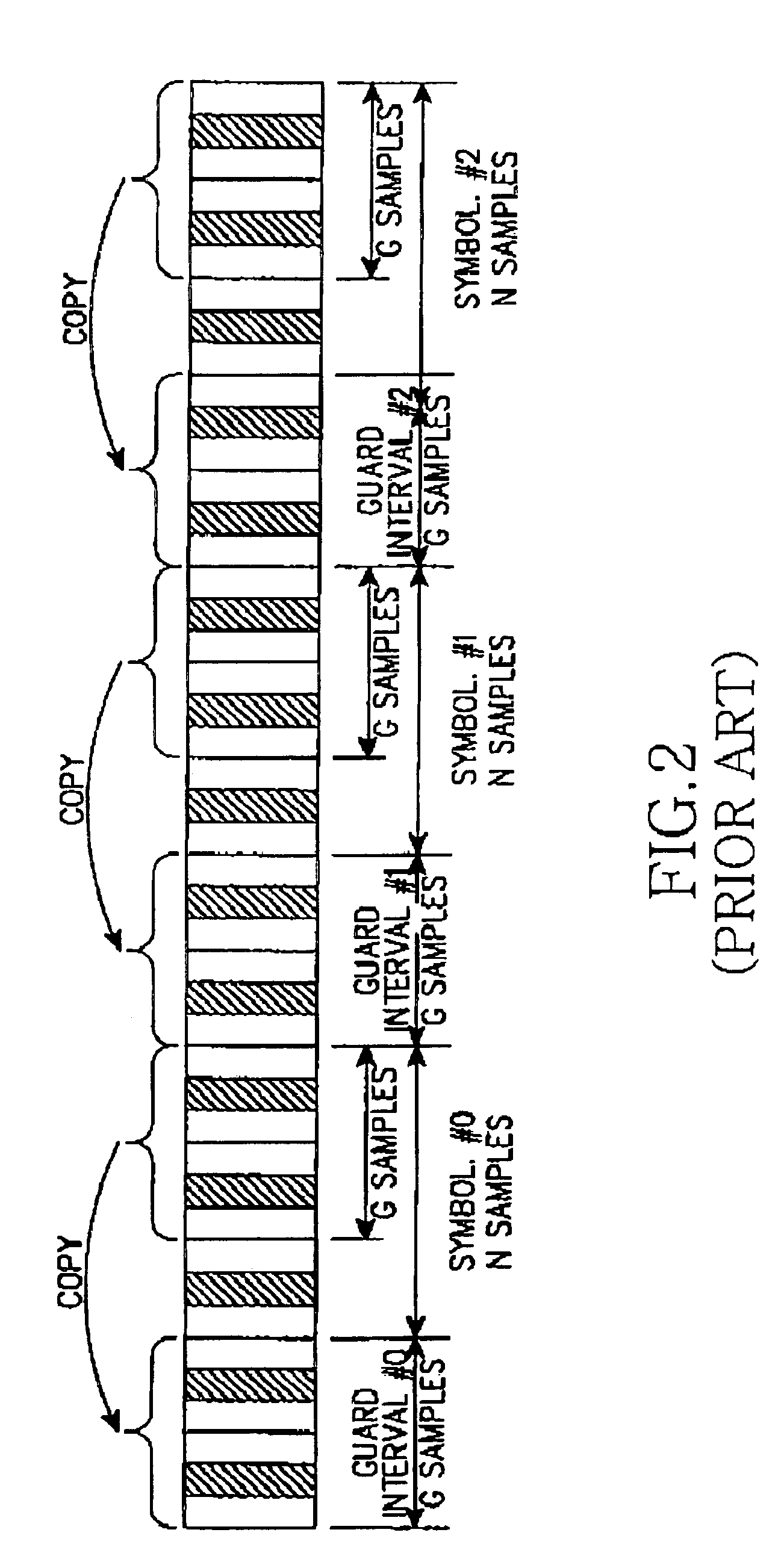
System and method for compensating timing error using pilot symbol in OFDM/CDMA communication system
InactiveUS7110387B1Frequency-division multiplexSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlTime errorAnalog-to-digital converter
A timing error compensation system in an OFMD / CDMA communication system includes an analog-to-digital converter for converting an OFDM signal, comprised of a data symbol stream in which a pilot symbol is inserted at intervals of a prescribed number of data symbols, received from a transmitter, to a digital OFDM symbol stream by prescribed sampling synchronization, a guard interval remover for removing a guard interval inserted in the OFDM symbol by prescribed frame synchronization, and a fast Fourier transform (FFT) device for performing fast Fourier transform on the guard interval-removed OFDM symbol and outputting a data symbol stream. In the time error compensation system, a pilot symbol detector receives the data symbol stream and detects the pilot symbols inserted in the data symbol stream at prescribed intervals. A timing compensator determines a linear phase difference line for the detected pilot symbol, generates a timing error estimation signal according to the determined linear phase difference line, and provides the timing error estimation signal to the analog-to-digital converter and the guard interval remover so as to determine the sampling synchronization and the frame synchronization.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
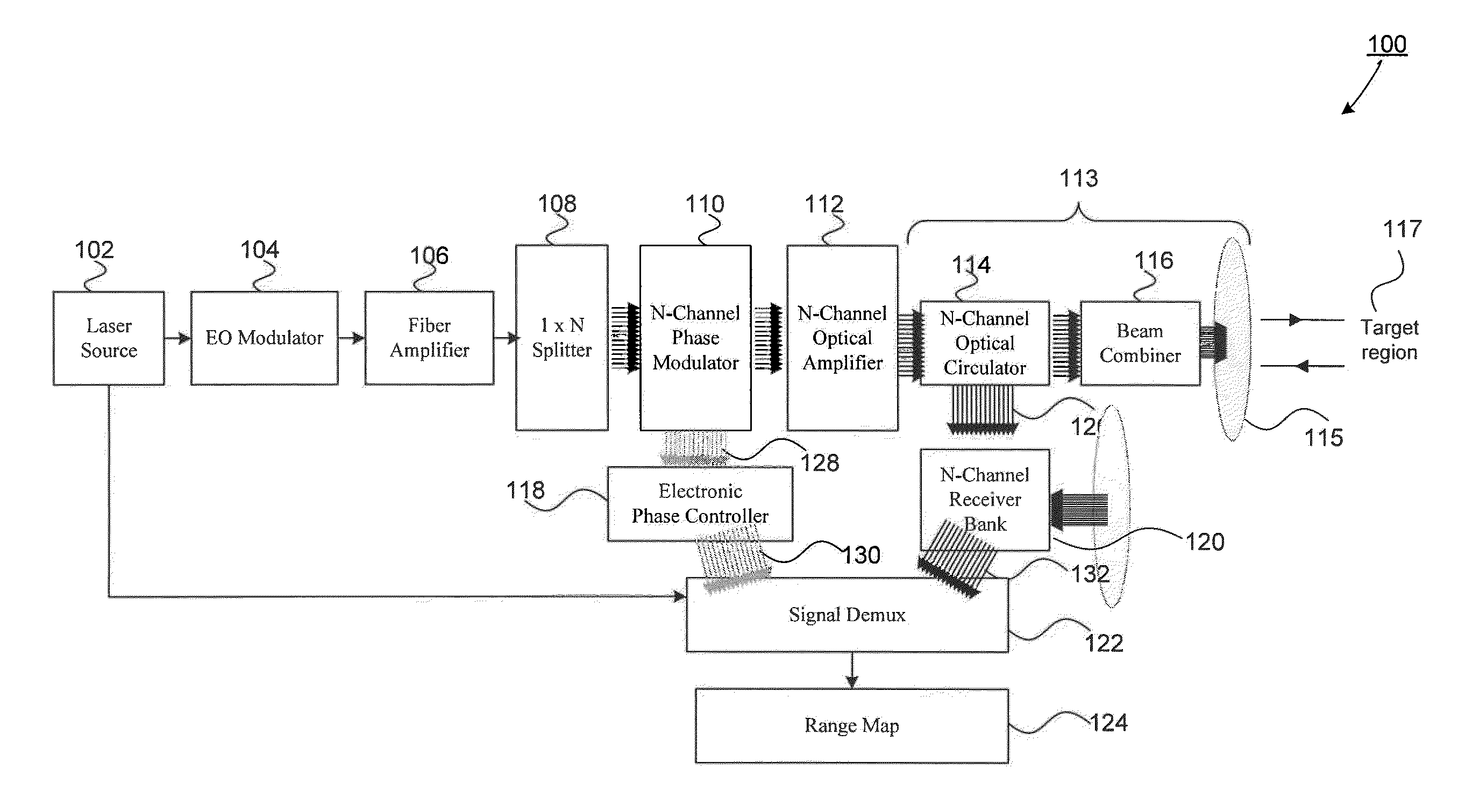
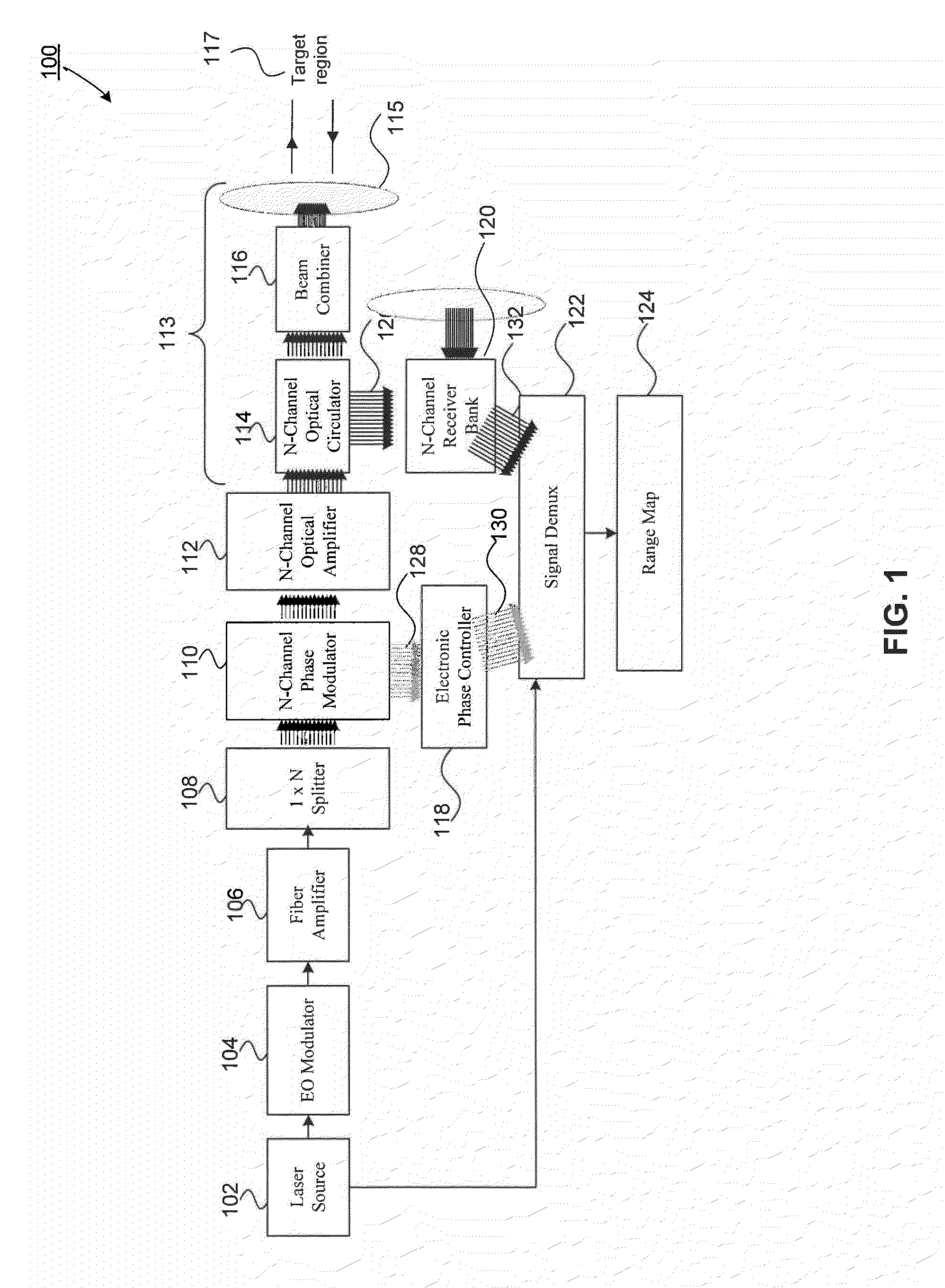
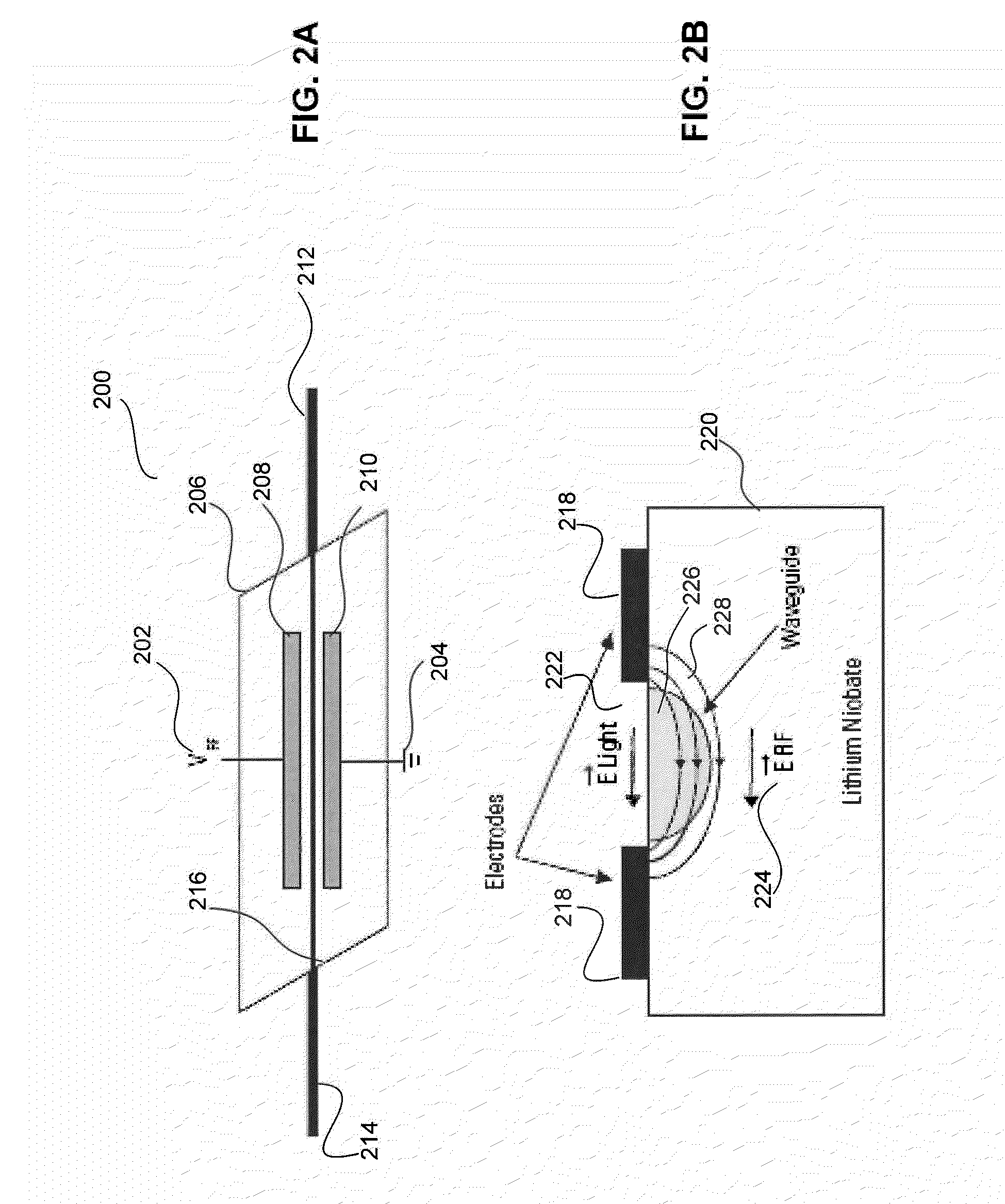
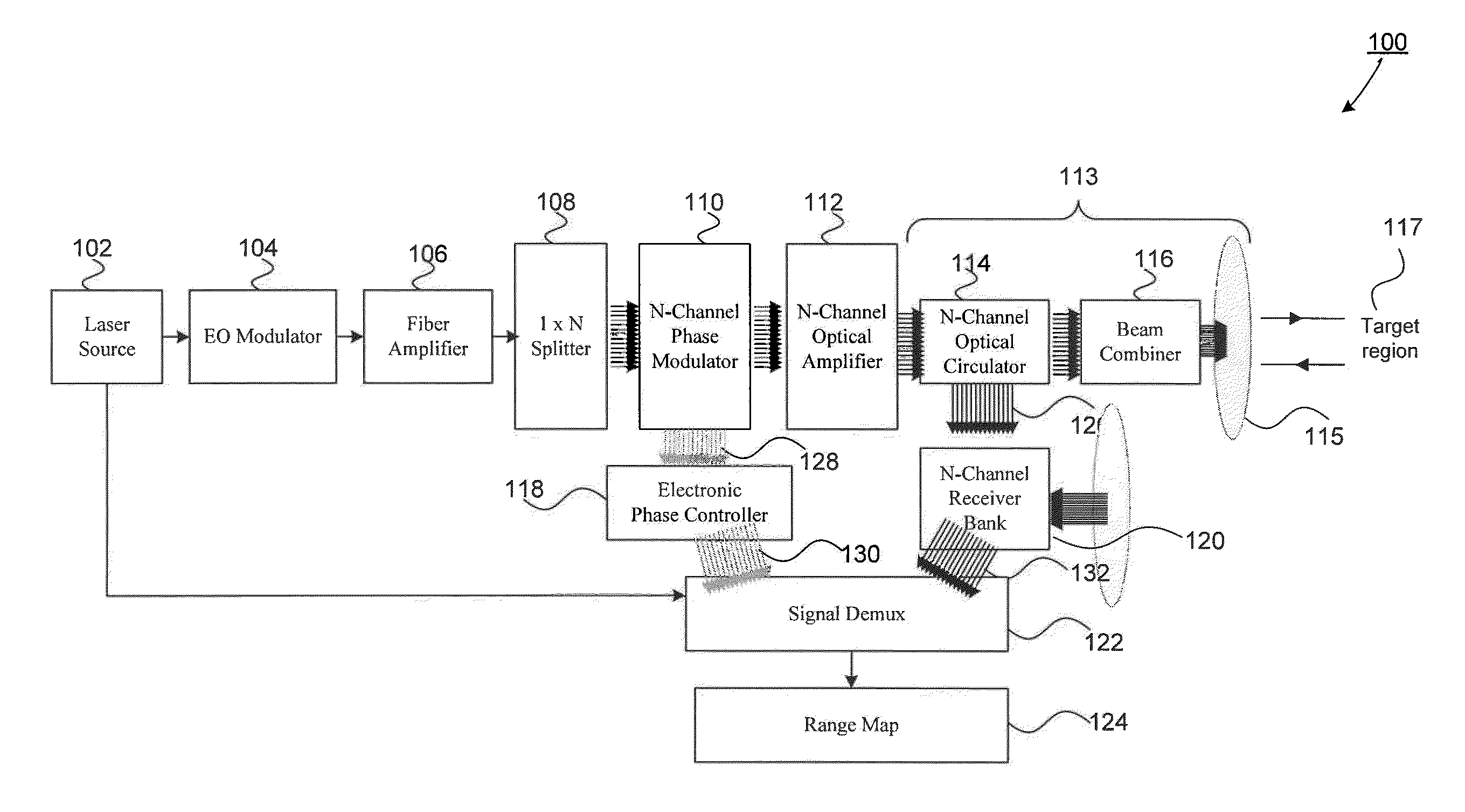
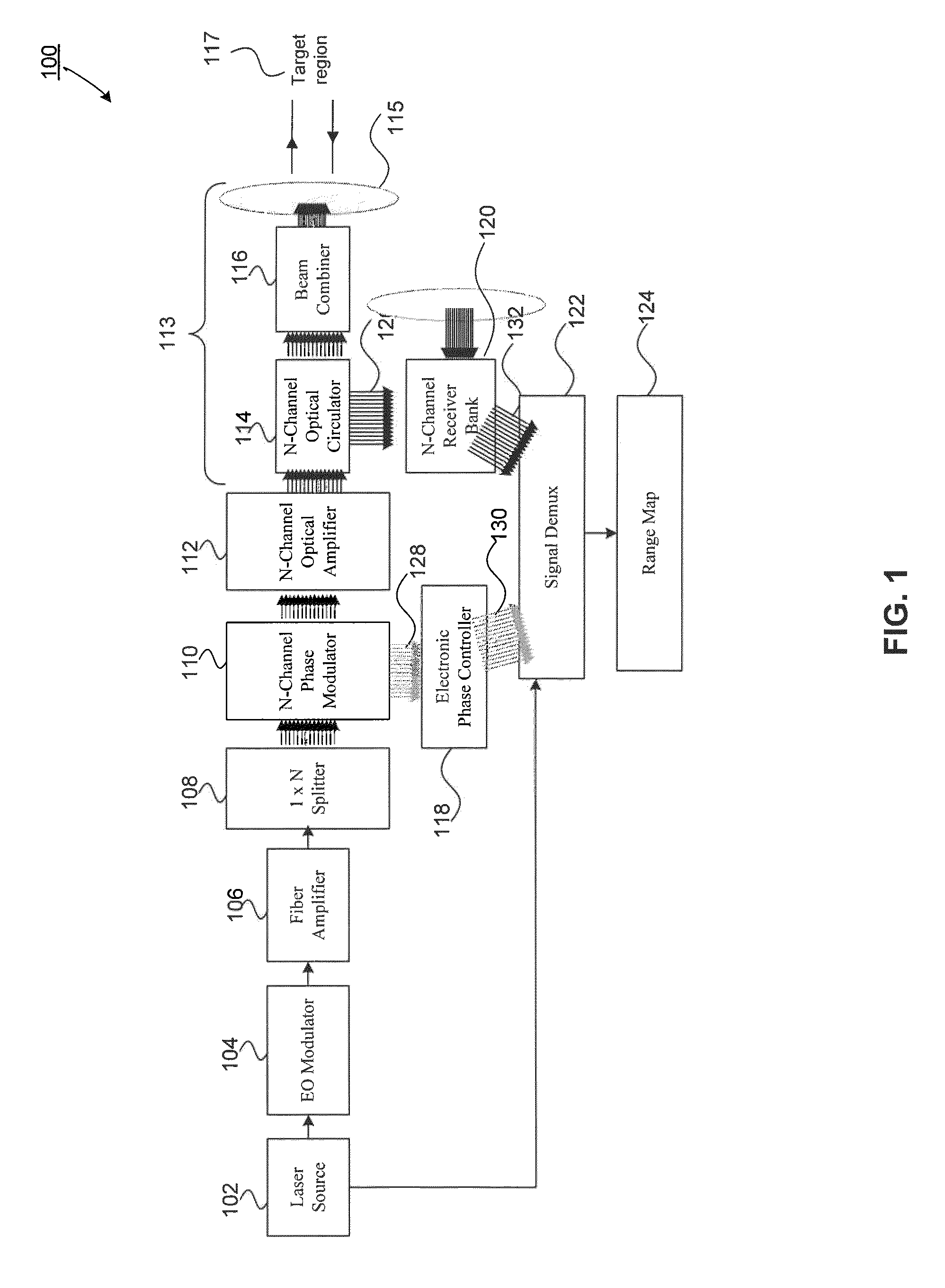
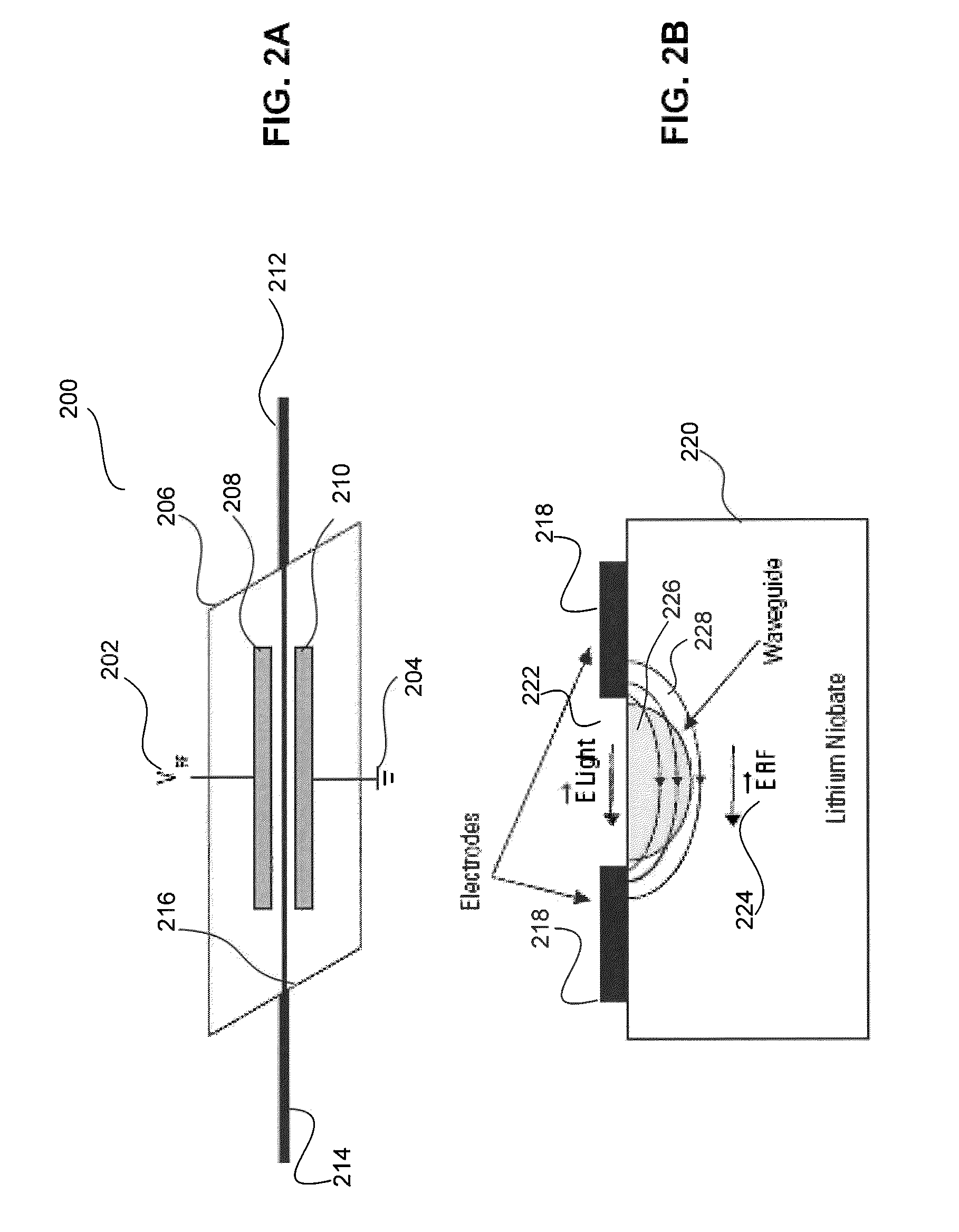
Scanning Non-Scanning LIDAR
ActiveUS20130044309A1Optical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationOptoelectronicsVisual perception
An all fiber optic laser based scanning system for real time terrain mapping under degraded visual conditions is disclosed. A laser output is modulated to achieve a desired pulse width and pulse repetition frequency (PRF) and the modulated signal is amplified. The amplified optical signals are split into N channels that correspond to N elements of an optically phased array that steers light by modulating the phase of light entering and exiting the optical system. By applying a linear phase shift across the beam's wave front, the light propagating along the system's optical axis is steered to an off-axis angle. A real time map of an underlying terrain is accomplished by sweeping the N channel array across the terrain while collecting range information from each scan grid.
Owner:RD2 LLC
Scanning non-scanning LIDAR
An all fiber optic laser based scanning system for real time terrain mapping under degraded visual conditions is disclosed. A laser output is modulated to achieve a desired pulse width and pulse repetition frequency (PRF) and the modulated signal is amplified. The amplified optical signals are split into N channels that correspond to N elements of an optically phased array that steers light by modulating the phase of light entering and exiting the optical system. By applying a linear phase shift across the beam's wave front, the light propagating along the system's optical axis is steered to an off-axis angle. A real time map of an underlying terrain is accomplished by sweeping the N channel array across the terrain while collecting range information from each scan grid.
Owner:RD2 LLC
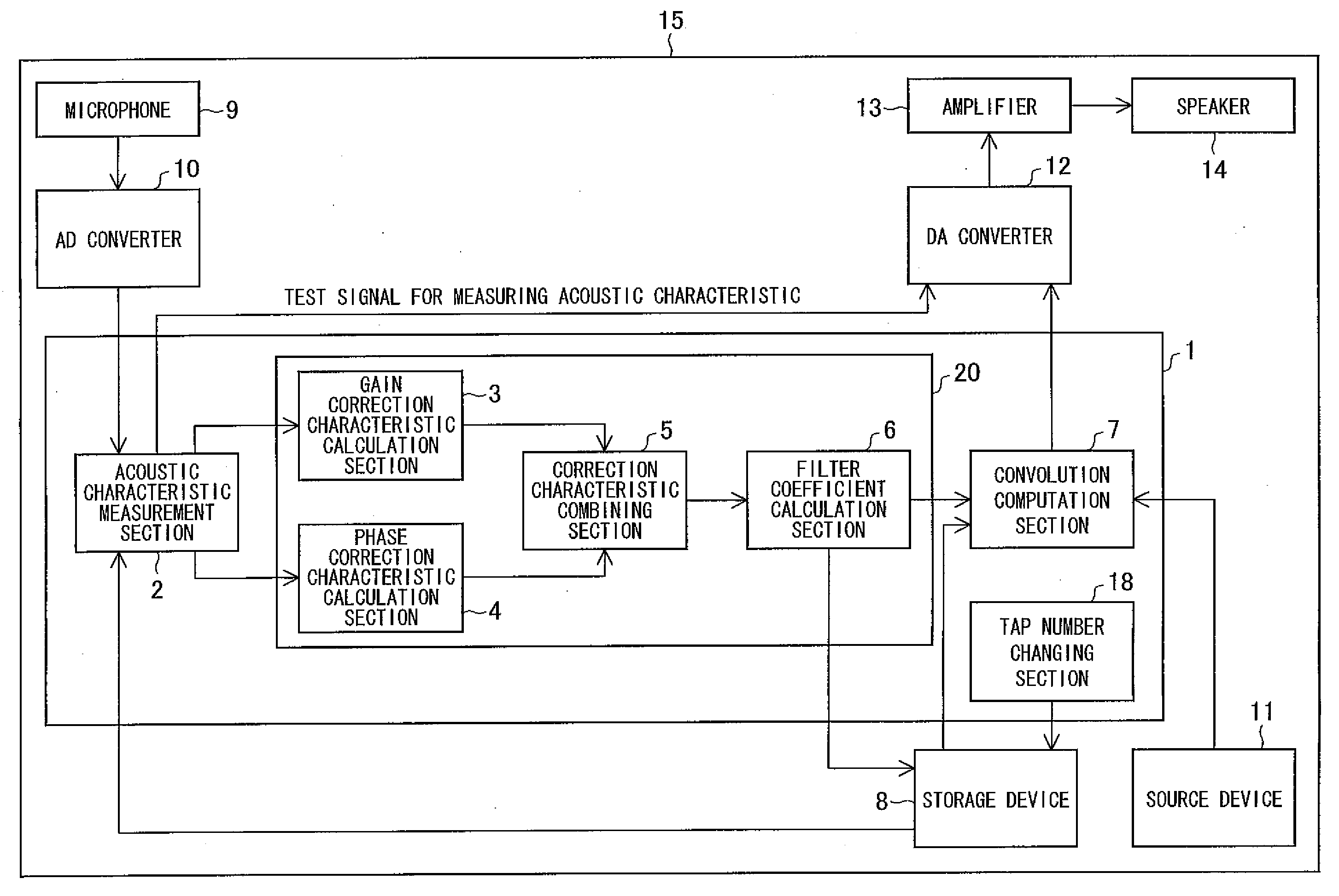
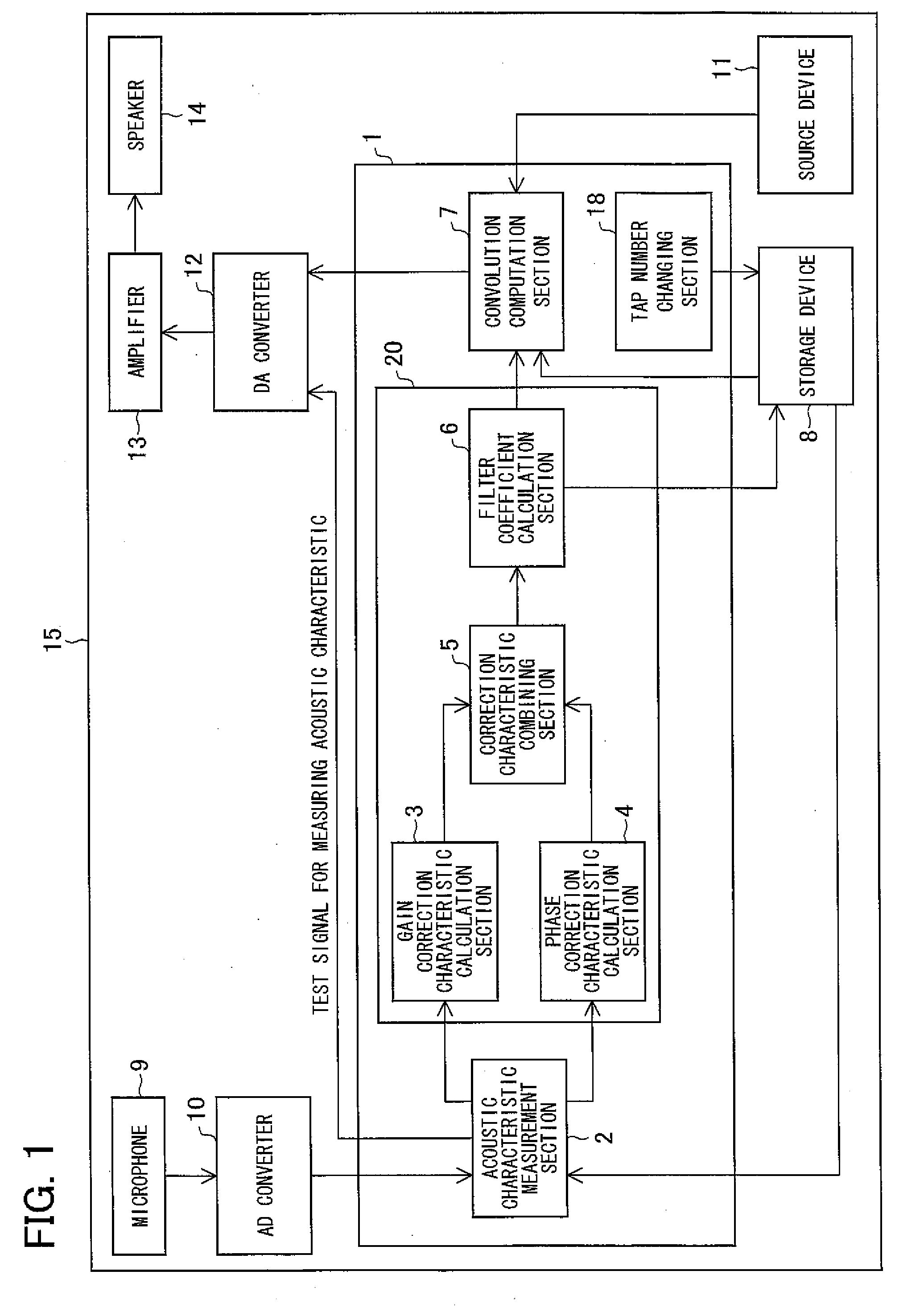
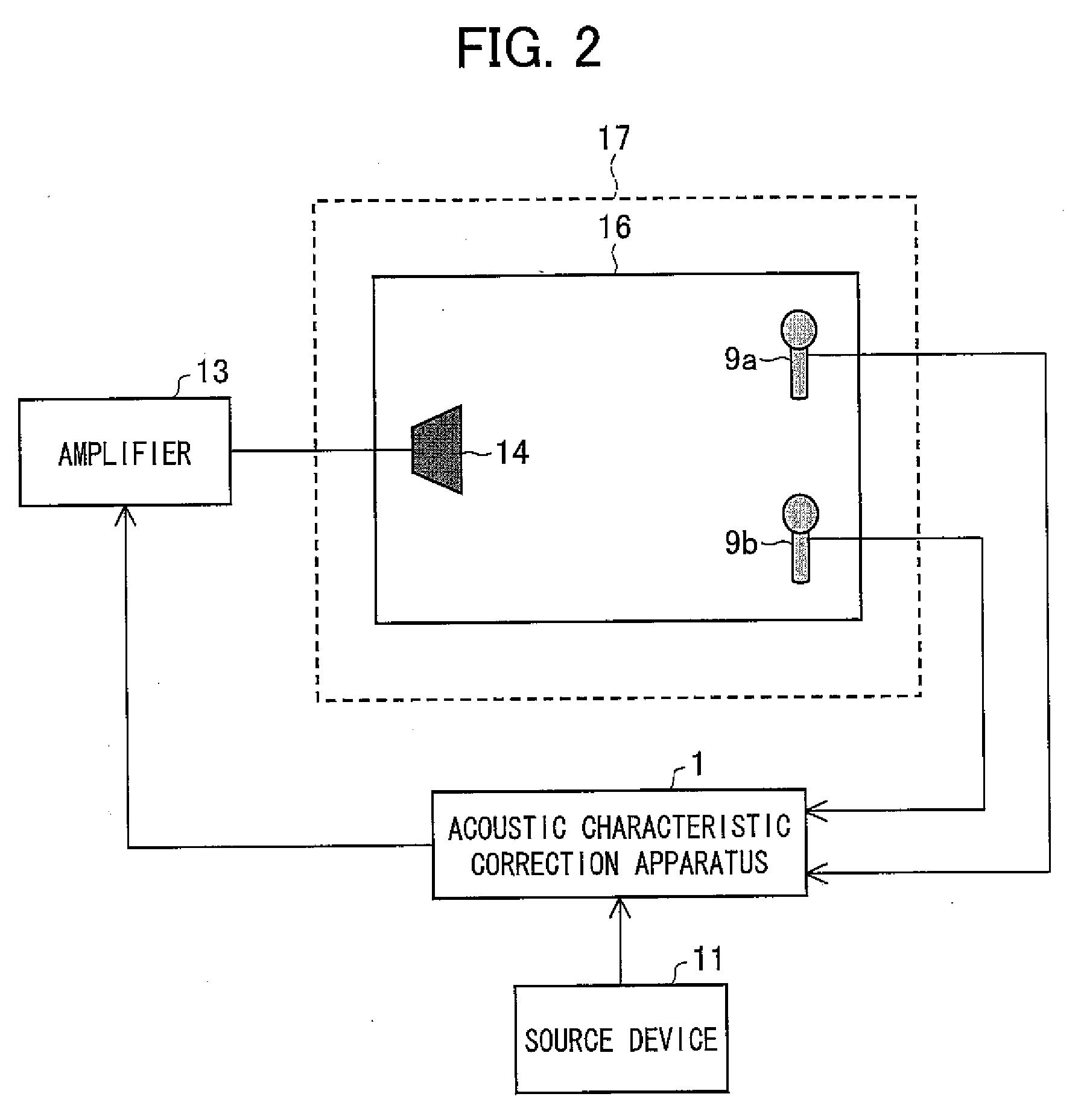
Filter coefficient calculation device, filter coefficient calculation method, control program, computer-readable storage medium, and audio signal processing apparatus
InactiveUS20080192957A1Makes it possibleReduce the amplitudeAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlFrequency response correctionPhase correctionPeak value
In a filter coefficient calculation device according to the present invention, a gain correction characteristic calculation section calculates impulse responses corresponding to a linear-phase filter having an inverse characteristic of a gain characteristic of a reproduction system, and calculates, as a gain correction characteristic, a frequency characteristic of continuous-time impulse responses that include a peak value, the continuous-time impulse responses being impulse responses, clipped from the calculated impulse responses, whose number is identical to the preset number of filter taps. Moreover, a phase correction characteristic calculation section calculates a phase correction characteristic by normalizing, from an inverse characteristic of a frequency characteristic of the reproduction system, a gain characteristic of the inverse characteristic, and a filter coefficient calculation section calculates, as filter coefficients of the reproduction characteristic correction filter, filter coefficients of a filter having a synthetic correction characteristic obtained by combining the gain correction characteristic with the phase correction characteristic. This makes it possible to correct acoustic characteristics with high accuracy even in cases where the number of taps is limited.
Owner:SHARP KK
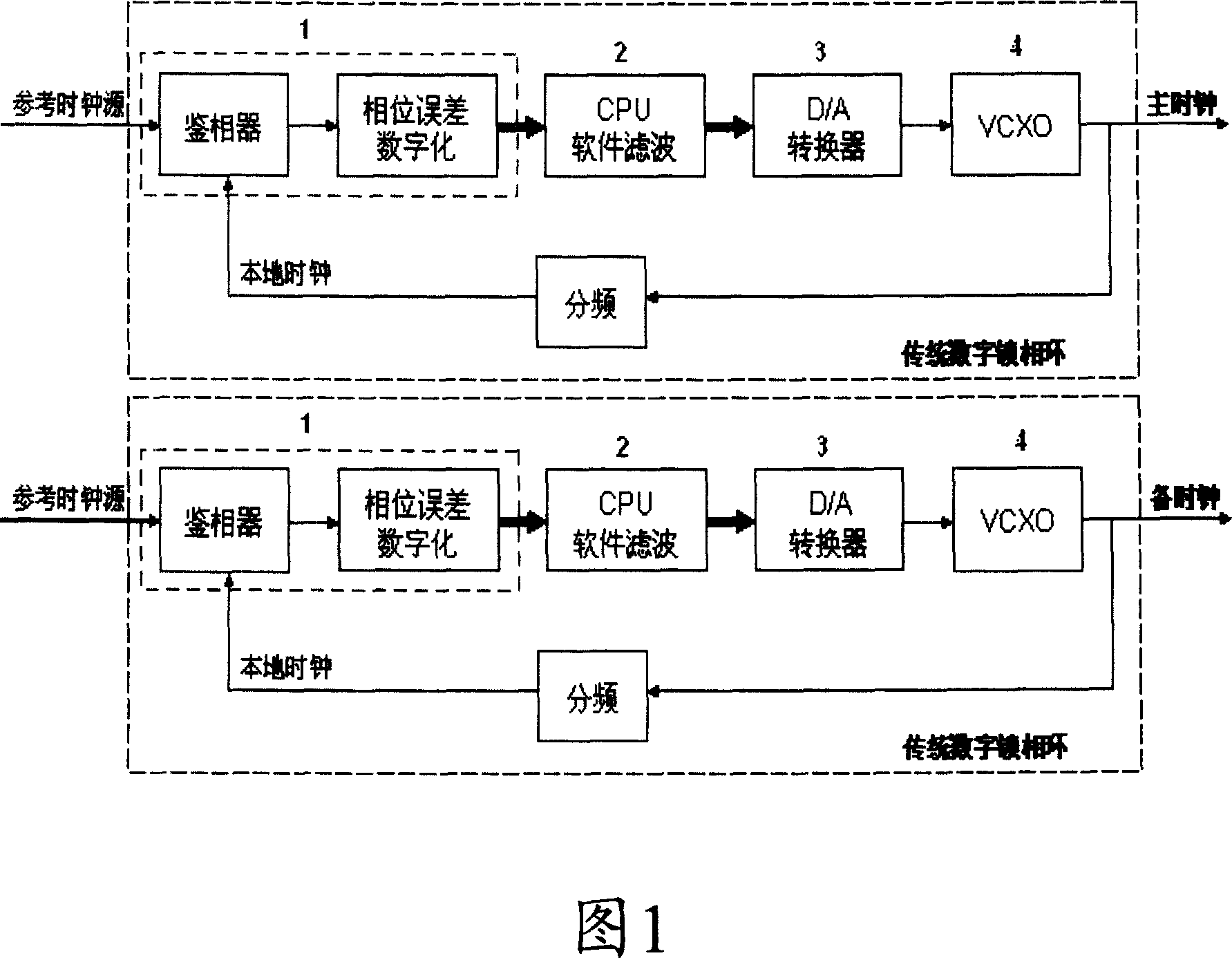
A digital phase lock loop device for smooth switching of clock phase and its method
InactiveCN101079630ASimple structureEasy to integratePulse automatic controlPhase differenceEngineering
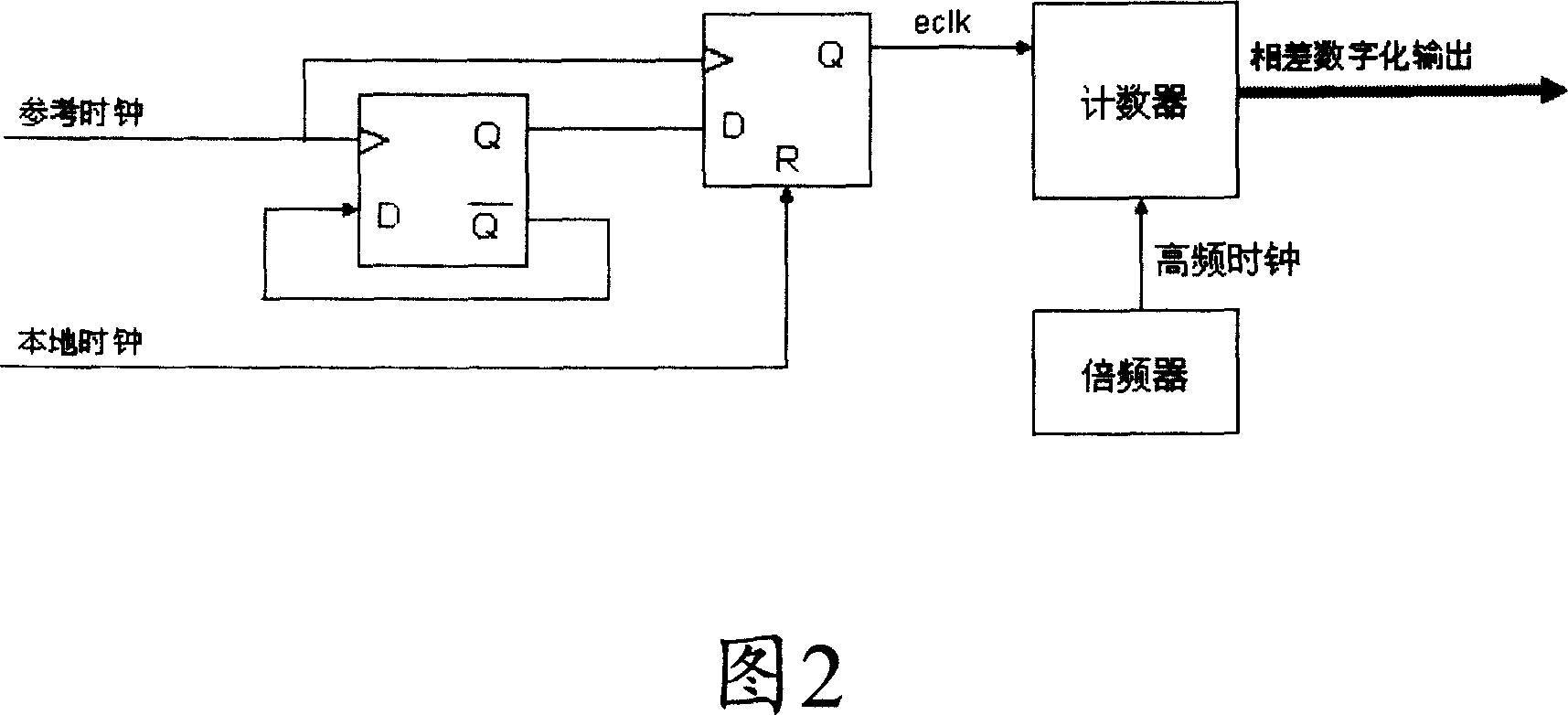
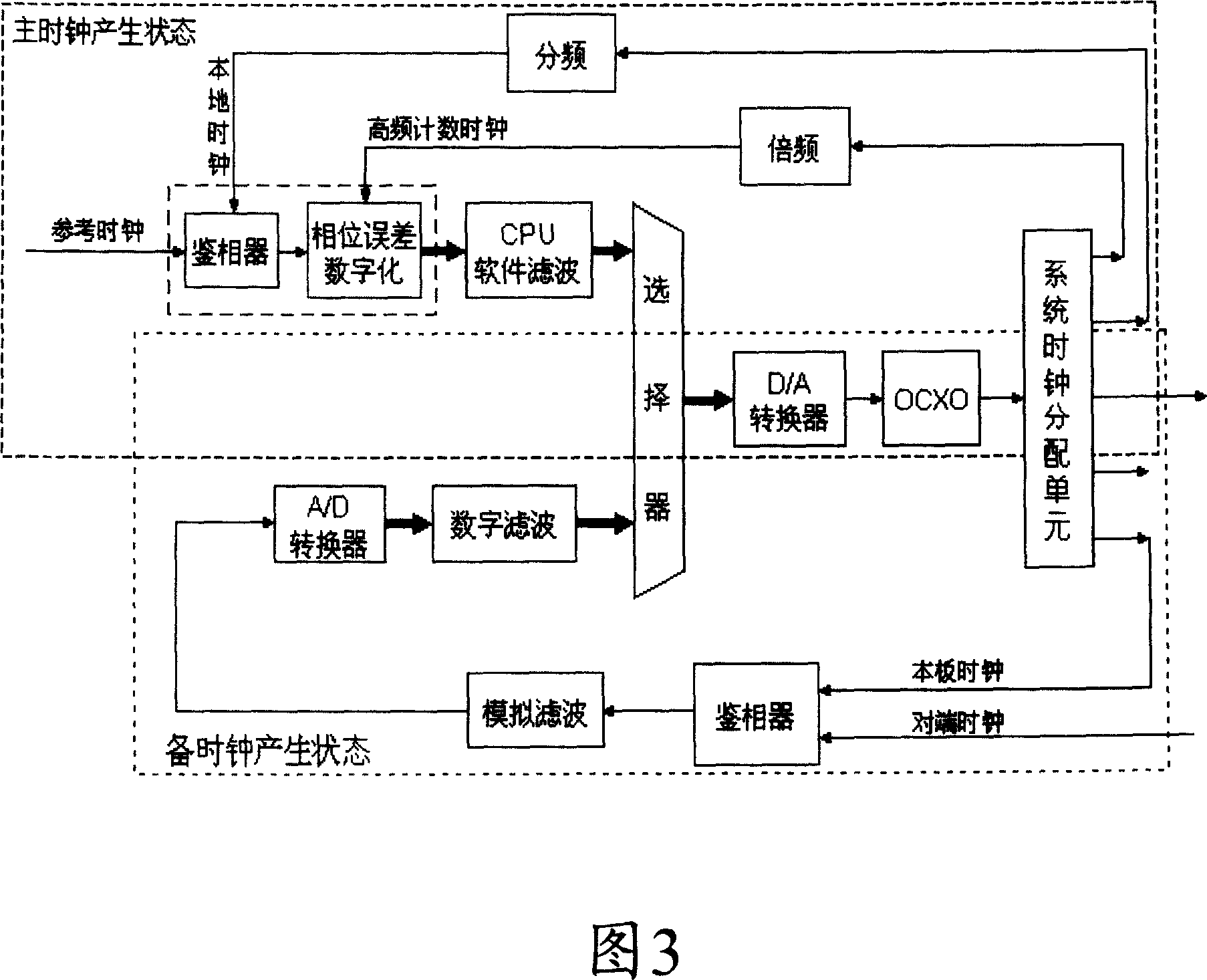
The invention discloses a digital locked ring device to realize clock phase smooth conversion, which is characterized by the following: the reference source processes the selected reference clock according to master spare pattern; the time digital converses the reference clock and phase difference from local clock of frequency divider into the corresponding coded digital code to realize phase demodulation and phase difference digitalization to be transmitted to CPU filter and locked processing unit the proceed linear phase disposal, low-pass digital filter disposal, locked disposal, which outputs the digital phased error signal to the digifax converser as corresponding analog voltage-controlled value, in order to control the corresponding vibrating frequency output by voltage-controlled crystal oscillator; the frequency is processed by frequency divider to transmit the local clock with the same frequency as reference frequency to time digital converter. The invention realizes high-precision error control of main spare systems, which is convenient to integrate chip with high reliability and integration level.
Owner:ZTE CORP
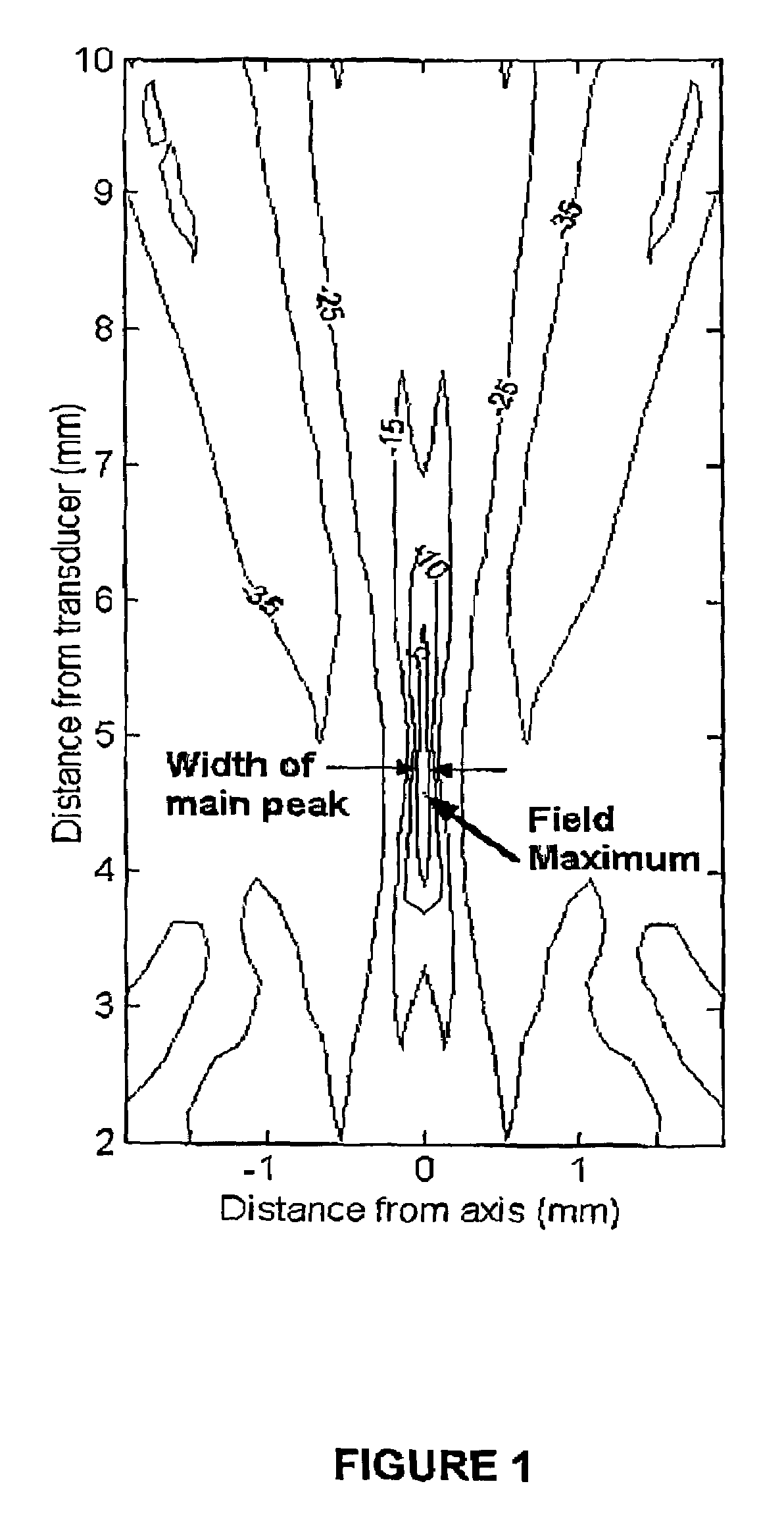
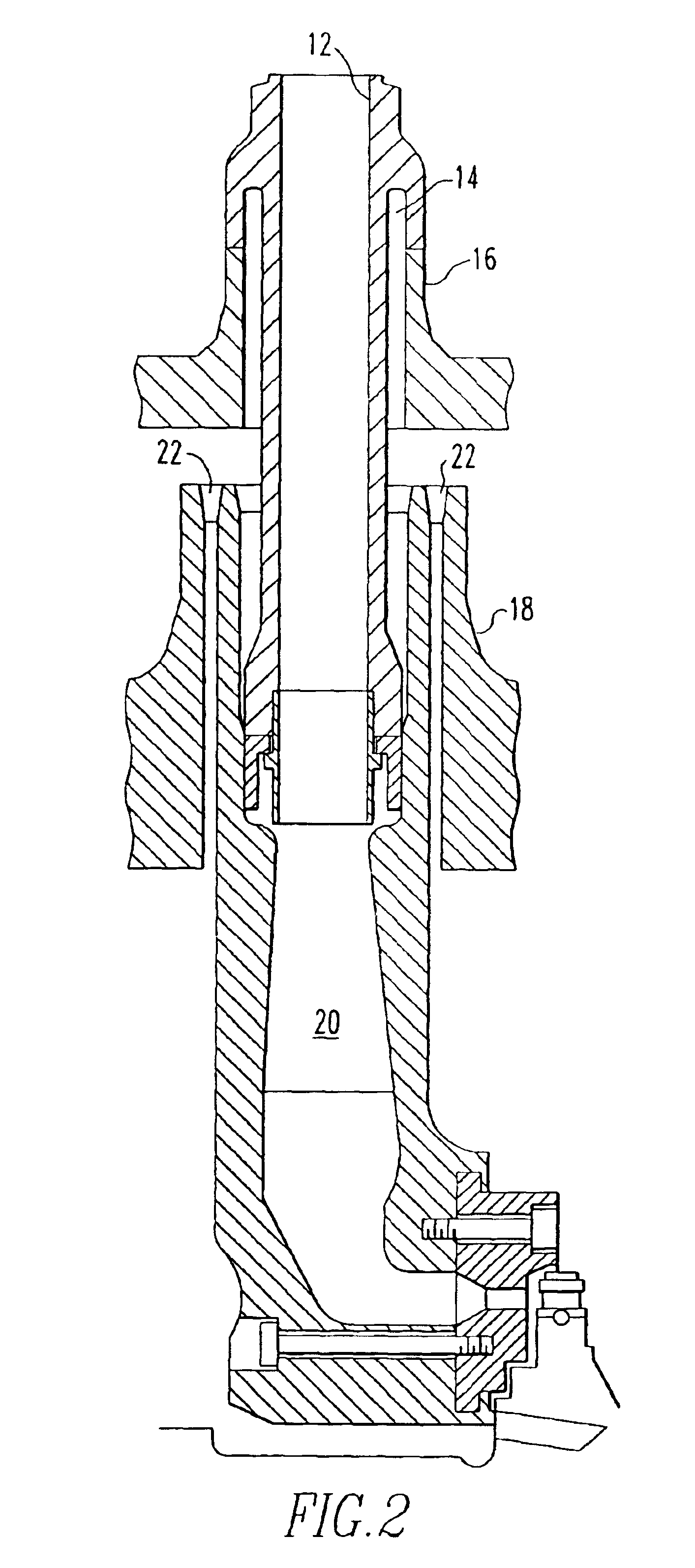
Nondestructive examination of high pressure turbine cylinders
ActiveUS6886407B1ConfidenceSave inspection timeMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSpecific gravity measurementEngineeringHigh pressure
A method of inspecting the steam inlet sleeves on high pressure outer cylinders and the nozzle chamber to cylinder welds on the high pressure steam turbines using linear phased array ultrasonic transducers. The transducers are supported on the surface of the component to be monitored. The transducers are then move axially while monitoring the transducer's output to identify the location to be monitored. The axial extent of the transducers are then fixed and the transducers are moved circumferentially around the surface of the component at least 360° while noting outputs of the transducers indicative of fatigue-induced flaws. The transducers are then routed to the location on the wall of the component where the most significant flaw was noted. Then the transducers are successively focused at different depths in the wall where the most significant flaw was identified to further characterize the depth and size of the flaw.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
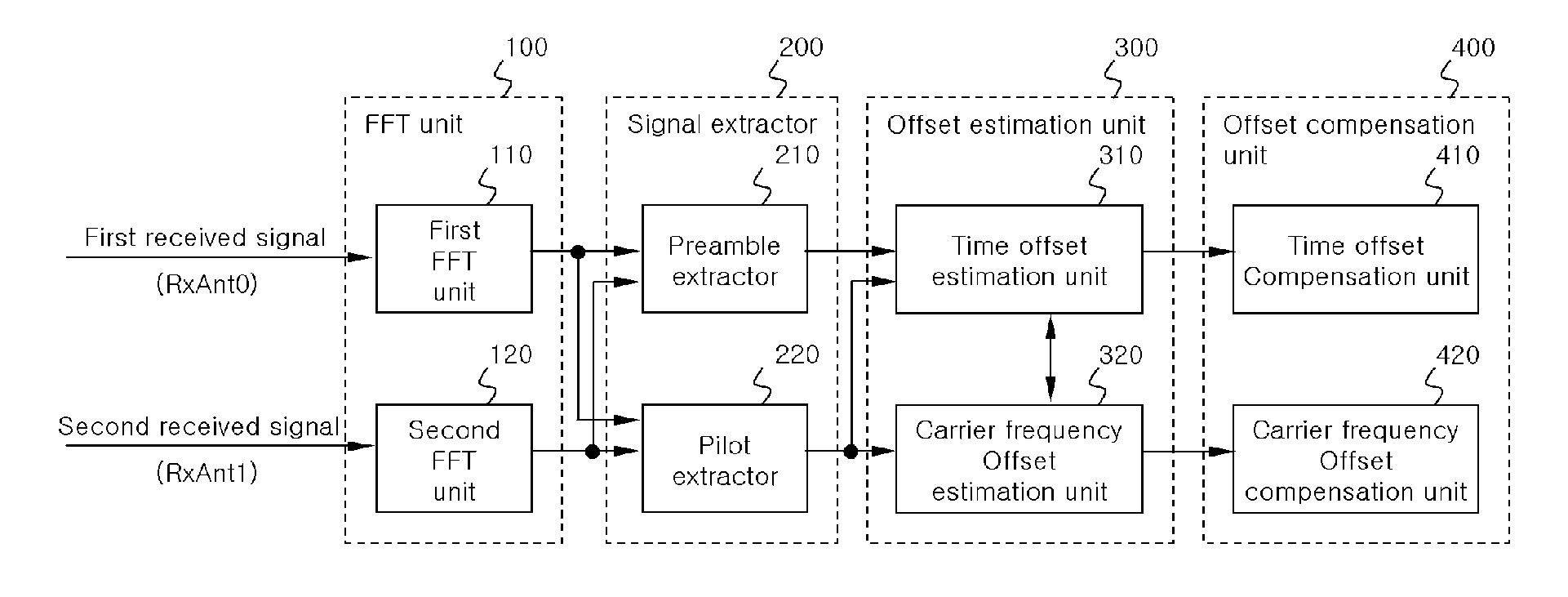
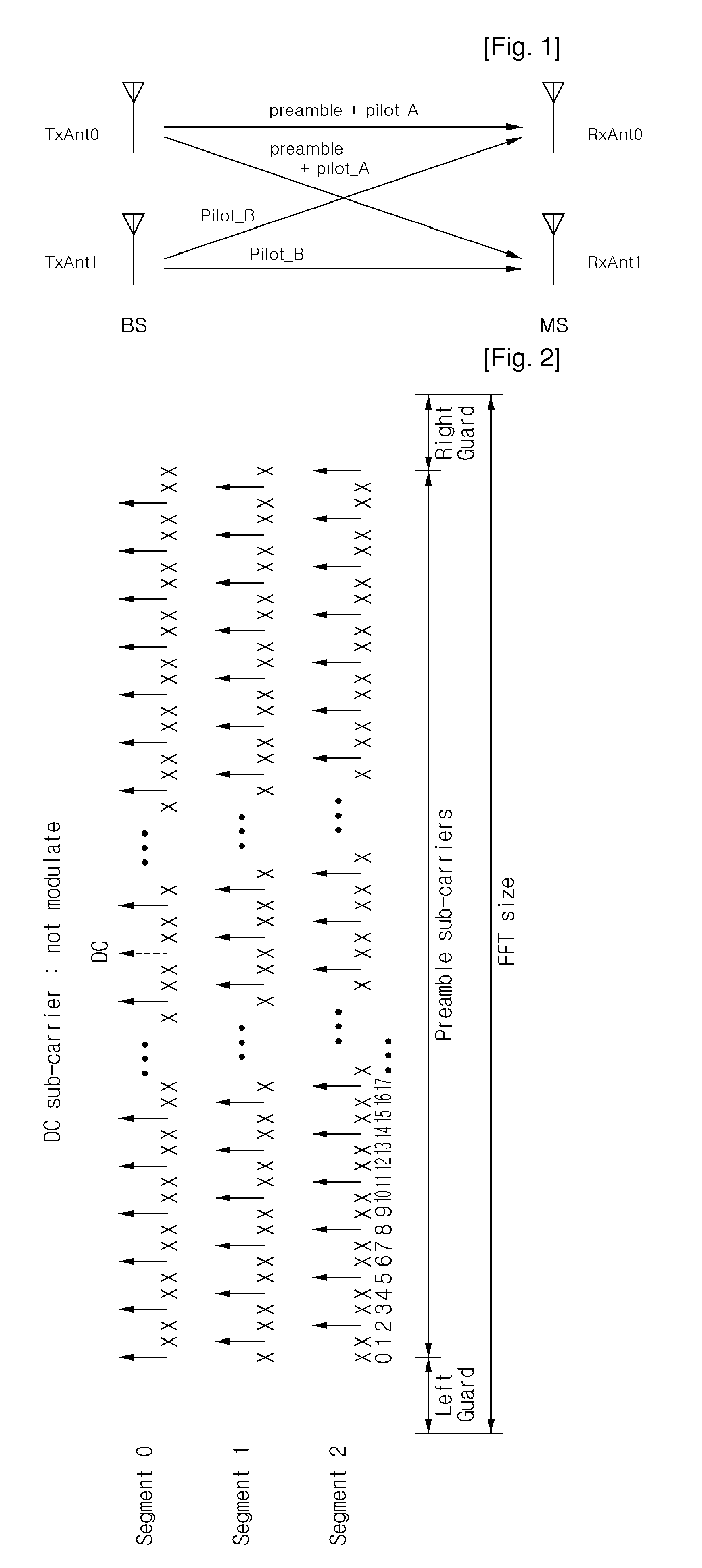
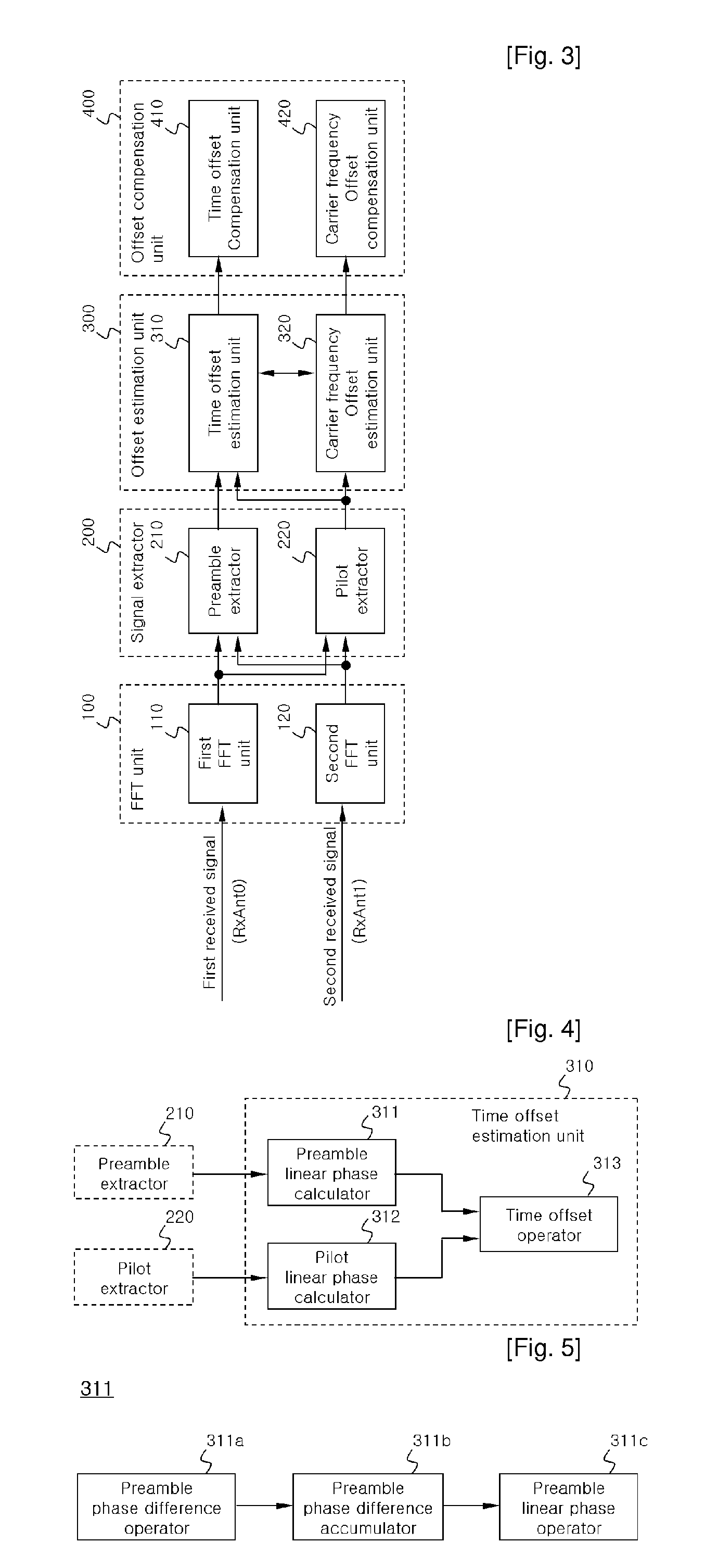
Apparatus and method for estimating and compensating time offset and/or carrier frequency offset in MIMO system based ofdm/ofdma
ActiveUS20100008216A1Improve reception performanceSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityCommunications systemPhase difference
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for estimating and compensating for a time offset and a carrier frequency offset in a Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) communication system that supports Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) or Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing Access (OFDMA). According to the present invention, a phase difference of pilot signals of the same transmitting antenna, which are received through receiving antennas, is calculated. An arc tangent operation is then carried out on the phase difference of the pilot signals to calculate a time offset linear phase and / or a carrier frequency offset linear phase. Further, a time offset compensation value and / or a carrier frequency offset compensation value are found by employing the time offset linear phase and / or the carrier frequency offset linear phase. A time offset and / or a carrier frequency offset with respect to pilots and data are compensated for by employing the time offset compensation value and / or the carrier frequency offset compensation value.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Apparatus for and method of measuring jitter
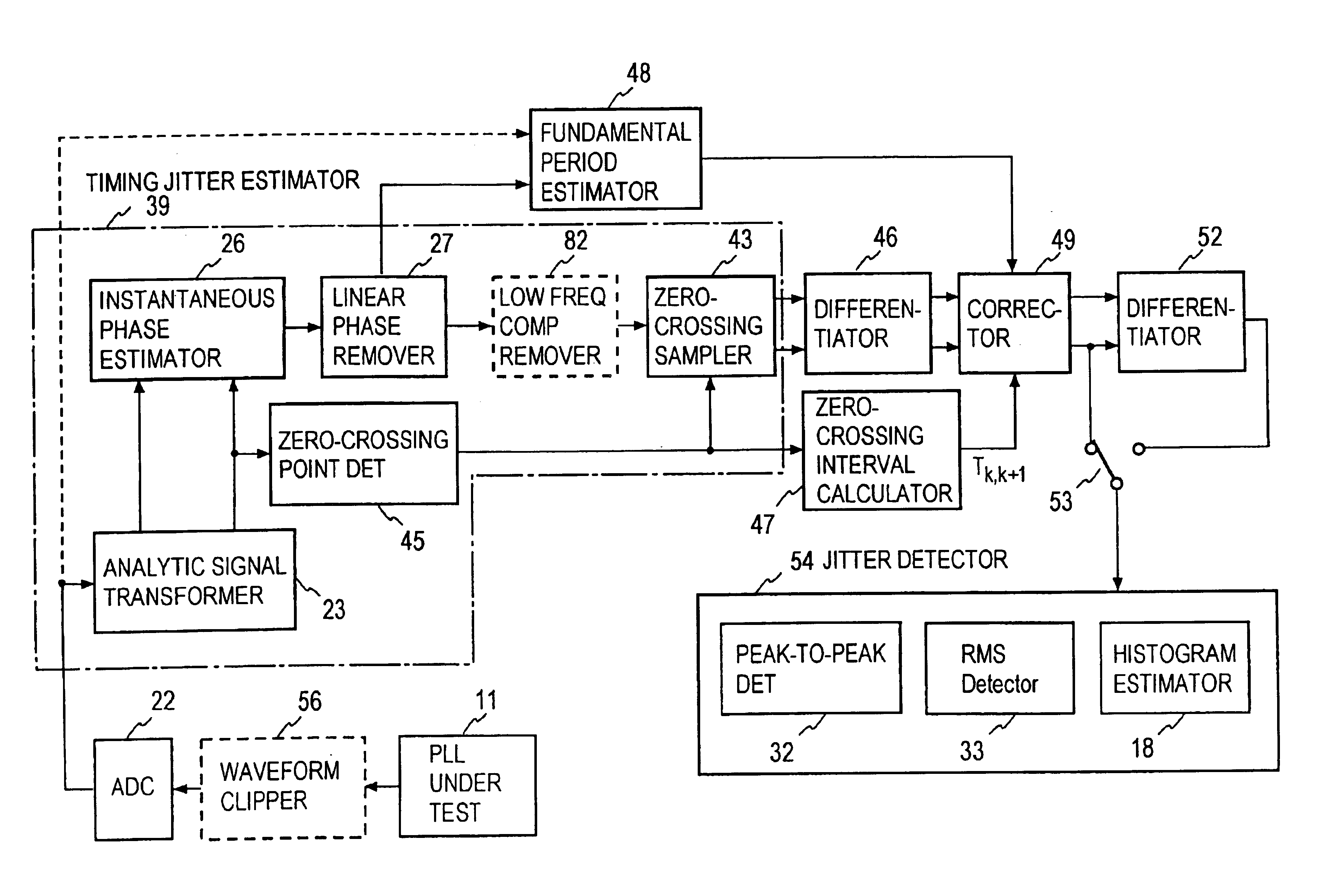
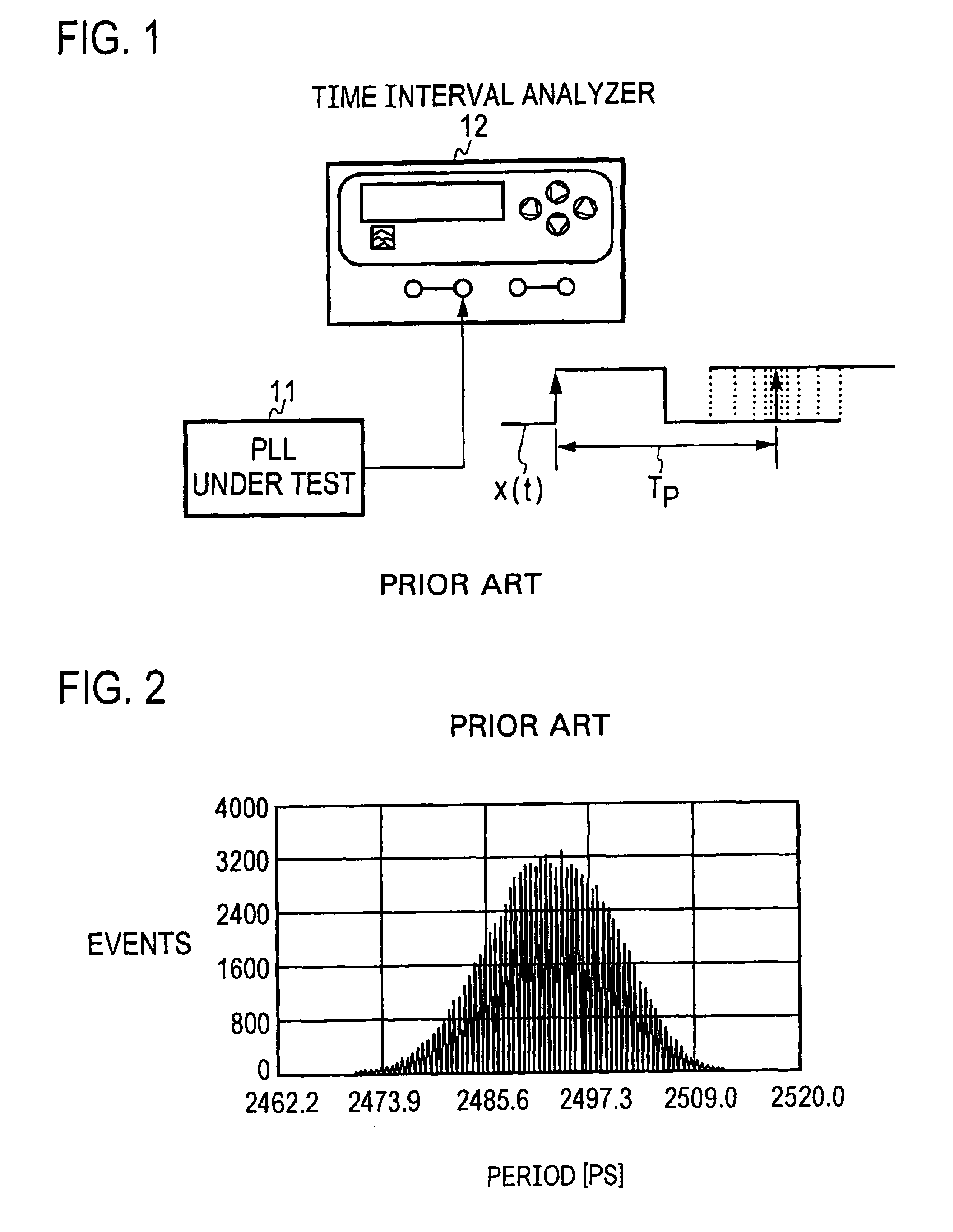
InactiveUS6922439B2Period jitter can beOver-sampling ratioMultiple input and output pulse circuitsError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorPhase noiseAnalytic signal
A signal under measurement x(t) is transformed into a complex analytic signal zc(t), and an instantaneous phase of the xc(t) is estimated using the zc(t). A linear phase is removed from the instantaneous phase to obtain a phase noise waveform Δφ(t) of the x(t), and the Δφ(t) is sampled at a timing close to a zero-crossing timing of the x(t) to obtain a timing jitter sequence. Then a difference sequence of the timing jitter sequence is calculated to obtain a period jitter sequence. The period jitter sequence is multiplied by a ratio T0 / Tk,k+1 of the fundamental period T0 of the x(t) and the sampling time interval Tk,k+1 to make a correction of the period jitter sequence. A period jitter value of the x(t) is obtained from the corrected period jitter sequence.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
Dual frequency band ultrasound transducer arrays
ActiveUS20070035204A1Eliminate the effects ofUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSonificationArray aperture
Ultrasound probes that transmits / receives ultrasound pulses with frequencies both in a low frequency (LF) and a high frequency (HF) band, where the radiation surfaces of said HF and LF bands at least have a common region. Several solutions for transmission (and reception) of LF and HF pulses through the same radiation surface are given. The arrays and elements can be of a general type, for example linear phased or switched arrays, or annular arrays or elements with division in both azimuth and elevation direction, like a 1.5D, a 1.75D and a full 2D array. The LF and HF element division and array apertures can also be different.
Owner:ANGELSEN BJORN A J +4
Method of processing a digital signal derived from an analog input signal of a GNSS receiver, a GNSS receiver base band circuit for carrying out the method and a GNSS receiver
ActiveUS20080240315A1Reliable suppressionAvoid distortionSatellite radio beaconingTransmissionContinuous wave interferenceEngineering
For suppression of continuous wave interferers at, e.g., up to four interferer frequencies (f1, f2, f3, f4) in a GNSS receiver base band circuit a raw digital signal is, in a band stop unit (21), shifted, by a first mixer (31a), by the negative of the first interferer frequency (f1) in the frequency domain whereupon the continuous wave interferer is suppressed by a band stop filter (30a), a linear phase FIR filter with a suppression band centered at zero, e.g., a filter subtracting a mean over previous subsequent signal values from the actual signal value. After further shifting of the shifted digital signal by the negative of the difference between the second interferer frequency (f2) and the first interferer frequency (f1) the shifted digital signal is again filtered by an identical band stop filter (30b) and so on. After the last filtering step the shifted digital signal is shifted back to its original position in the frequency domain to provide a filtered digital signal which corresponds to the raw digital signal with narrow interferer bands centered at the interferer frequencies (f1, f2, f3, f4) suppressed.
Owner:U-BLOX
Low profile quasi-optic phased array antenna
ActiveUS20080278394A1Amplitude weightingNon-resonant long antennasIndividually energised antenna arraysLight beamBeam steering
A phased array antenna device is described. The phased array antenna device includes at least one one-dimensional phased array of radiating elements arranged along an array direction, a lens, and a phase control element. The lens is arranged such that divergent beams from the radiating elements are collimated by the lens in a direction orthogonal to the array direction to produce a beam. The phase control element is configured to apply a linear phase gradient to the radiating elements thereby providing one-dimensional electronic beam steering for the antenna device. The antenna device may additionally include one or two mechanical positioners to mechanically move the at least one one-dimensional phased array in directions orthogonal to the array direction, where the phased array enables scanning along the array direction.
Owner:SMITHS INTERCONNECT INC
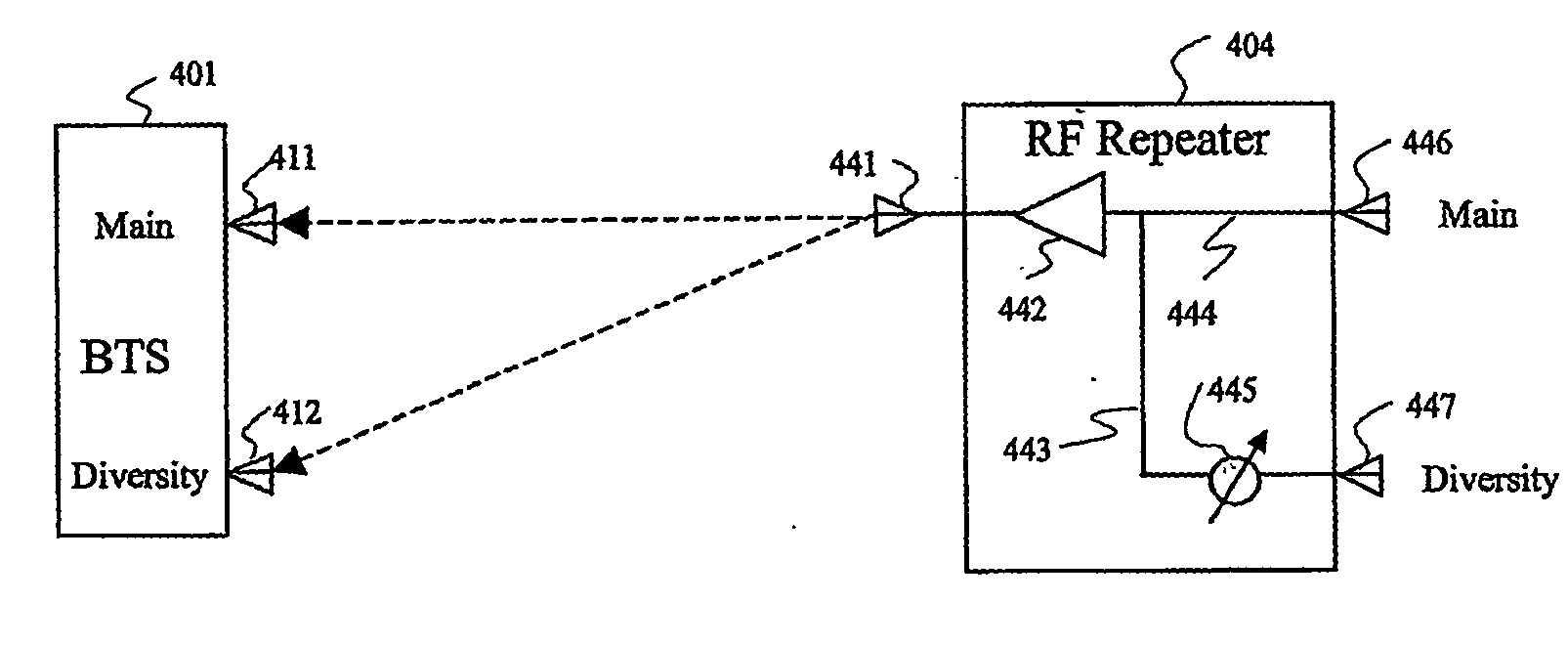
Phase sweeping methods for transmit diversity and diversity combining in bts sector extension and in wireless repeaters
InactiveUS20060172710A1Spatial transmit diversityElectromagnetic wave modulationEngineeringWireless repeater
Apparatus for inserting transmit diversity into an RF signal for transmission, comprises: an RF splitter for splitting the RF signal to be transmitted into two signal parts, and a non-linear phase modulator which applies a non-linear phase modulation to one of the two signal parts, thereby to provide transmit diversity between the first signal part and the second signal part. One of the ways of inserting a non-linear phase modulation into the RF signal is to use a spinning disc with tracks of different dielectric strength. The apparatus is useful in cellular telephony for supplying repeaters and base station extensions with diversity capability.
Owner:CELLETRA
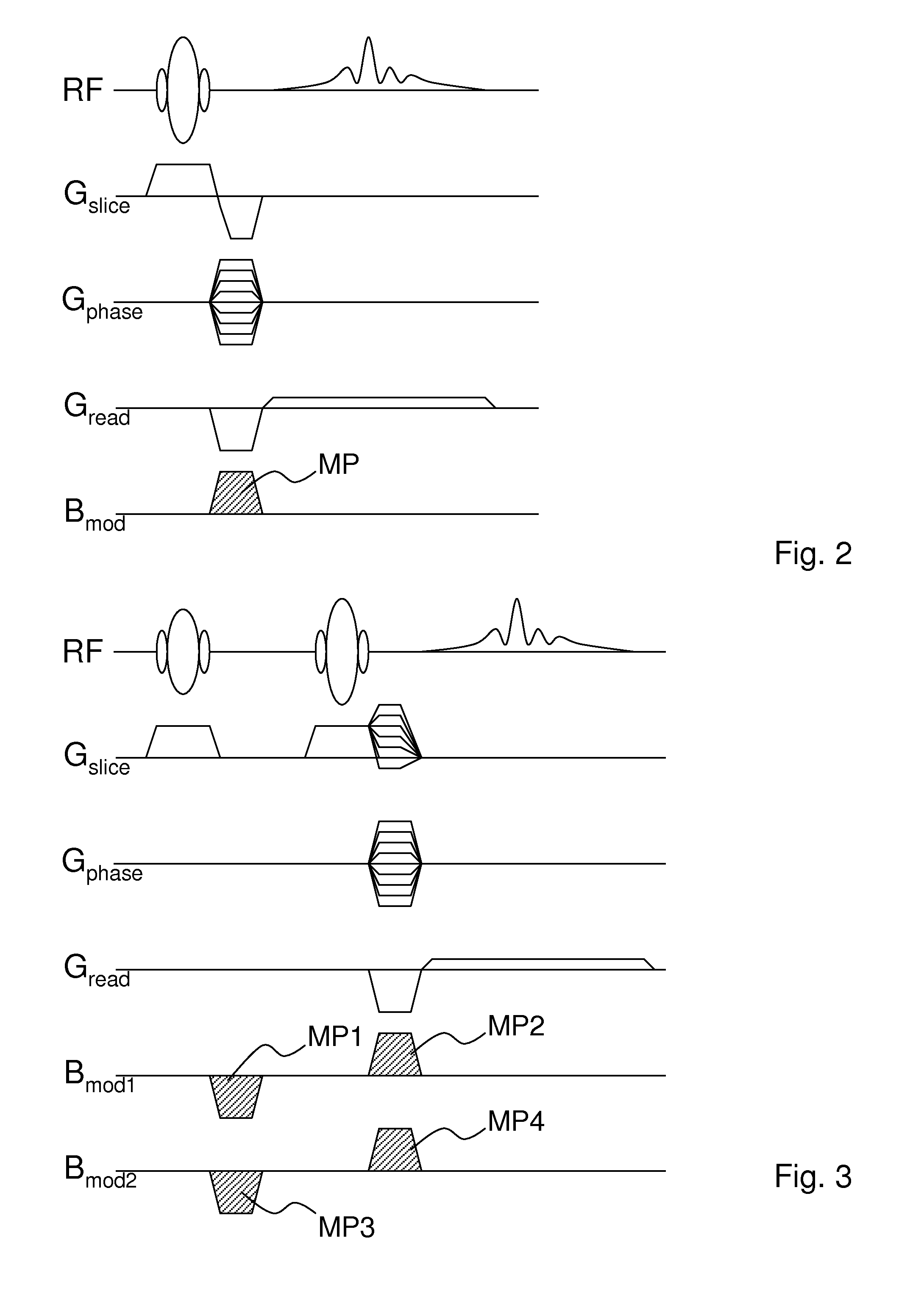
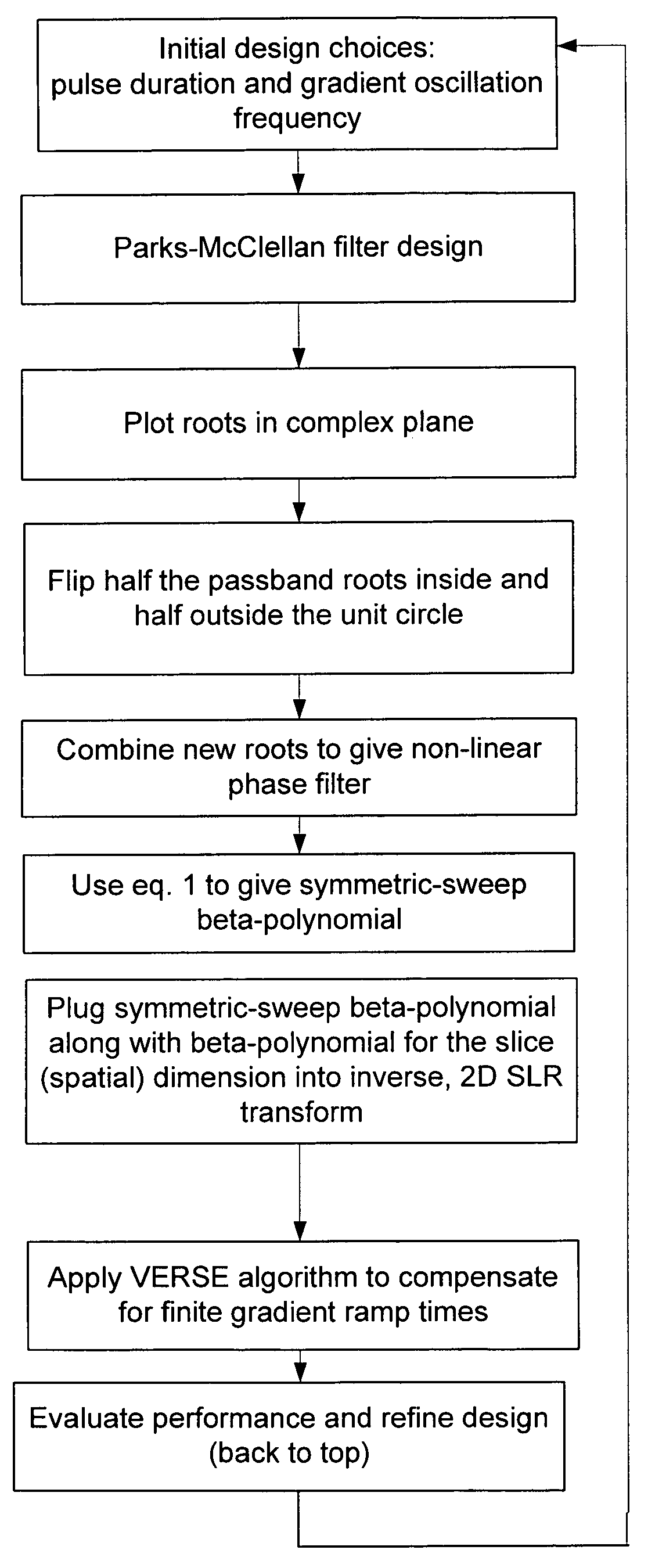
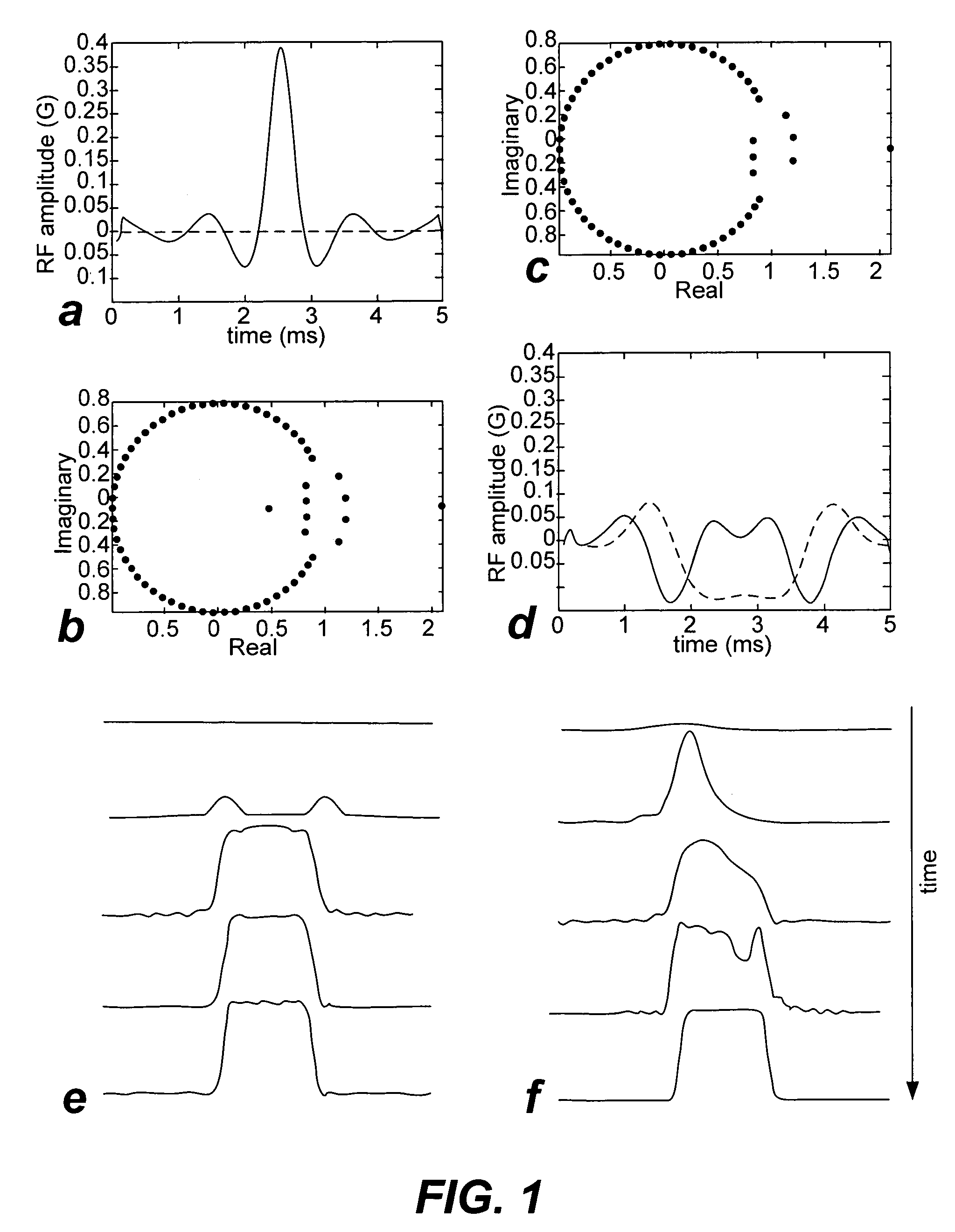
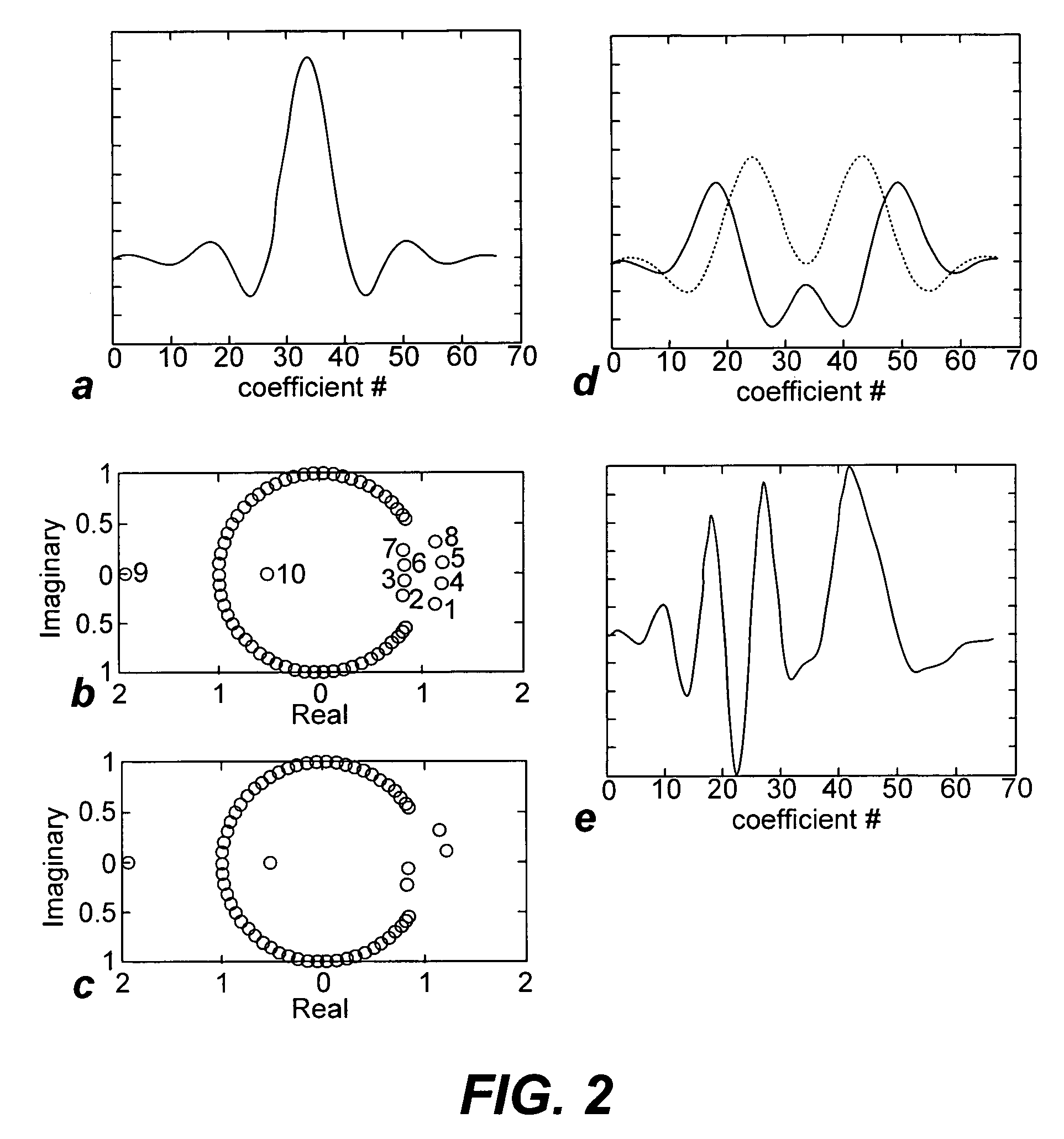
Non-linear symmetric sweep spectral-spatial RF pulses for MR spectroscopy
ActiveUS7042214B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionSpectroscopyRadio frequency
A method for designing non-linear phase 180° spectral-spatial radio frequency pulses that can be used for spectral editing in magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging. A novel feature of the pulse is a symmetric sweep developed by the spectral profile from the outside edges of the spectral window towards the middle whereby coupled components are tipped simultaneously and over a short interval. Pulses have been designed for lactate editing at 1.5T and 3T. The spectral and spatial spin-echo profiles of the RF pulses can be measured experimentally and altered in an iterative manner. Spectral-spatial radio frequency (SSRF) pulses allow simultaneous selection in both frequency and spatial domains. These pulses are particularly important for clinical and research magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) applications for suppression of large water and lipid resonances.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
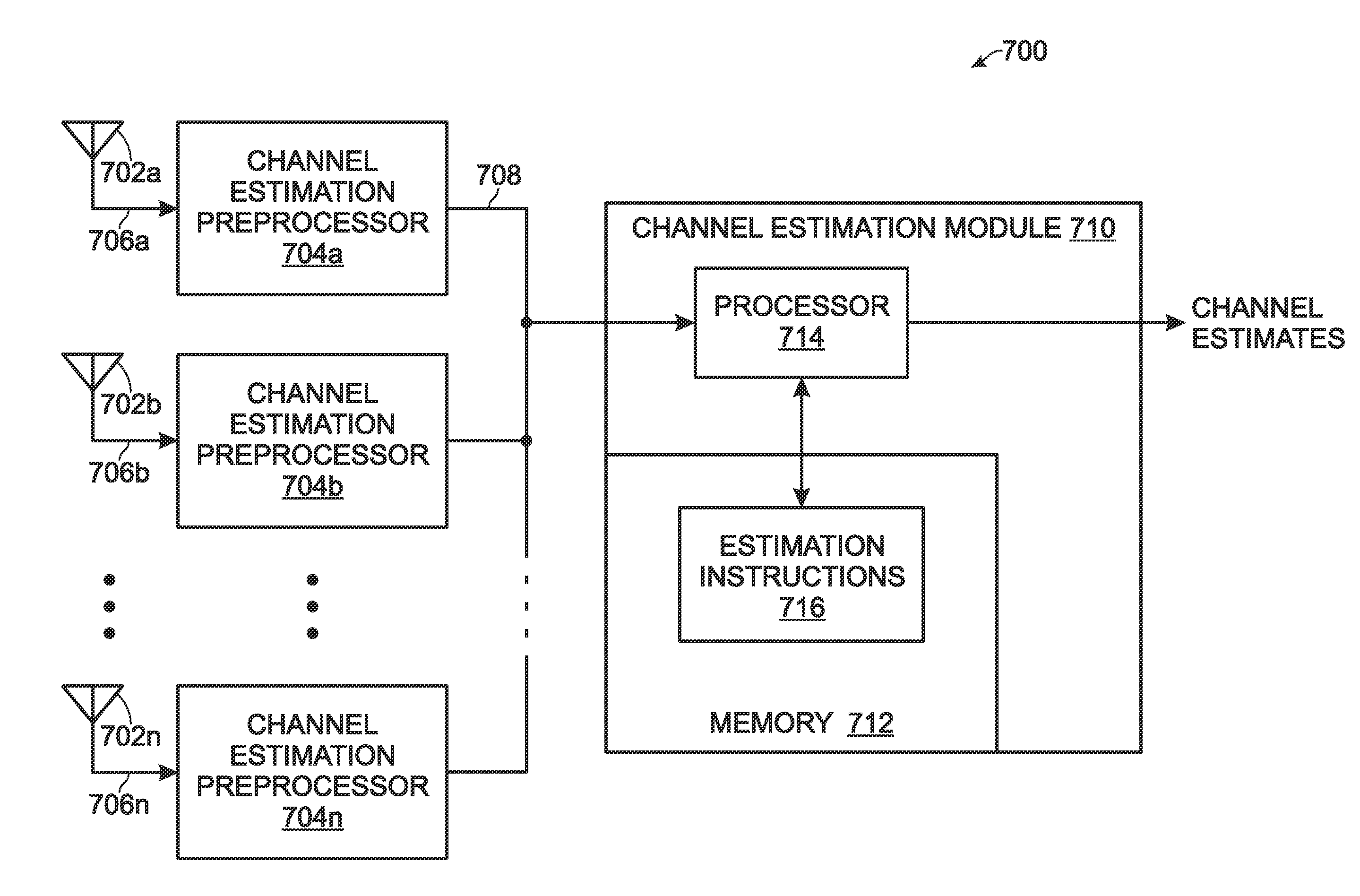
Multiuser multiple-input multiple-output (MU-MIMO) channel estimation for multicarrier communications
ActiveUS8238496B1Improve performanceReduce complexityMultiple-port networksError preventionCarrier signalMulti carrier
Provided are a system and method of estimating channels for a plurality of multicarrier signals in a wireless receiver. A receiver accepts a plurality of multicarrier signals, transmitted simultaneously from a plurality of transmitters, with overlapping carrier frequencies and nominally orthogonal reference signals. For each multicarrier signal, a reference signal is recovered including a plurality of adjacent subcarrier frequencies carrying predetermined symbols. A channel estimate is found across the plurality of adjacent subcarrier frequencies, for each multicarrier signal channel, by compensating for a loss of orthogonality between reference signals, in response to assuming a linear phase rotation for each channel across the plurality of adjacent reference signal subcarriers, and a constant amplitude for each channel across the plurality of adjacent reference signal subcarriers. More explicitly, the assumption of linear phase rotation and constant amplitude permits a Direction of Arrival (DoA) algorithm to be used.
Owner:MACOM CONNECTIVITY SOLUTIONS LLC
Self-adaptive optical system based on linear phase inversion restoration technology
InactiveCN101013195ASimple structureImprove light energy utilizationOptical measurementsOptical elementsInversion recoveryTime control
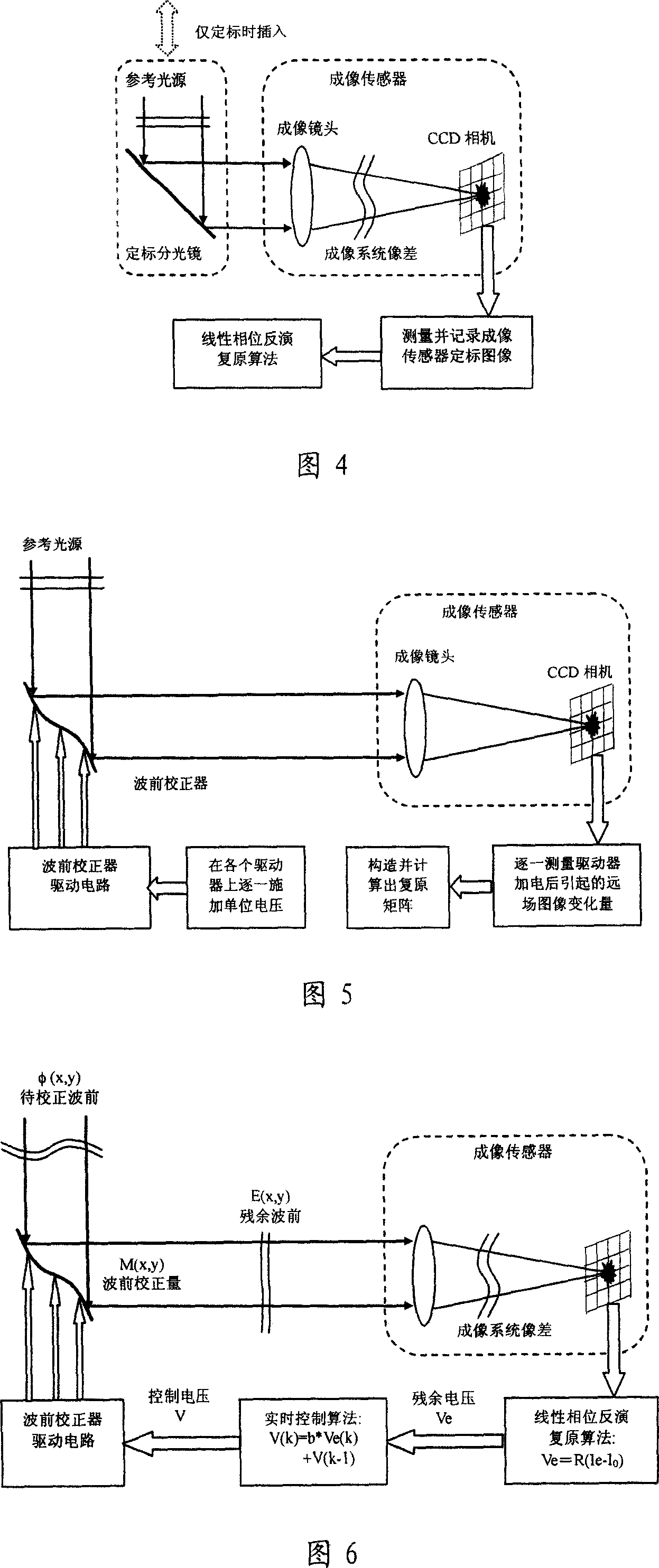
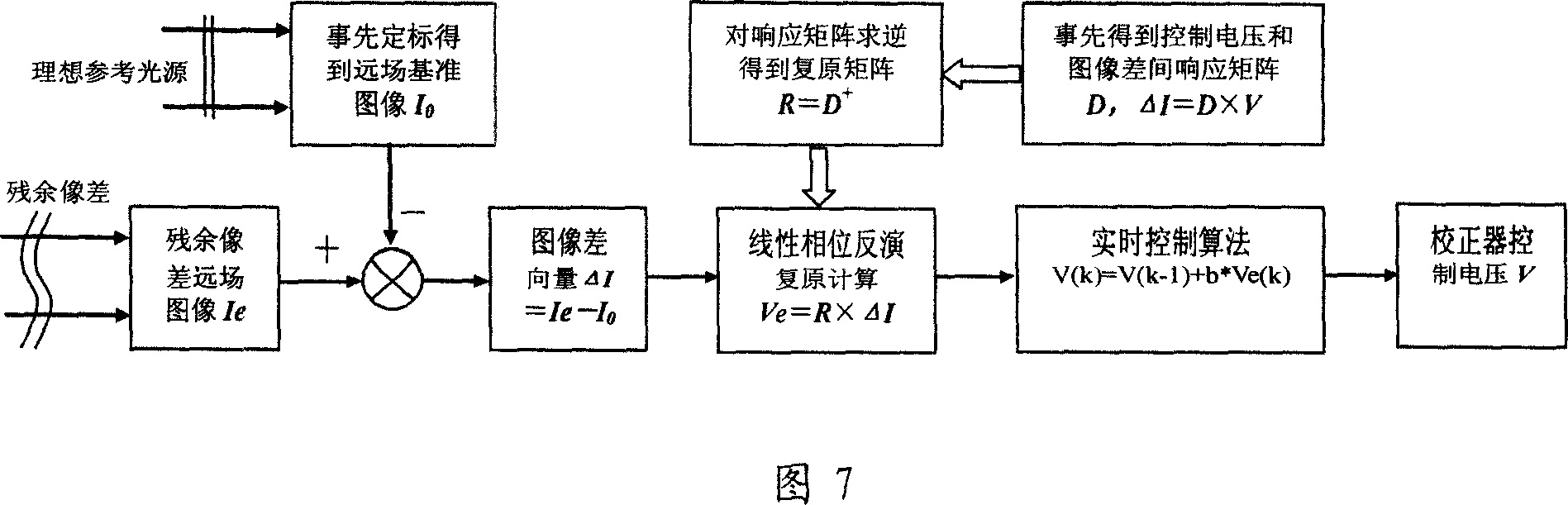
It is an adaptive optics system based on the linear phase inversion recovery technique, comprising the imaging sensor, the linear phase inversion recovery algorithm, the real-time control algorithm, the wave-front correction and drive circuit, and the reference light source. During the system running, the imaging sensor measures the residual aberration far-field image after the compensation of the wave-front correction device, and subtracting with the benchmark image to obtain the image difference vector. In advance, using the reference light source to calibrate the imaging sensor to obtain the benchmark image, and according to the corresponding relations between the wave-front correction device and the imaging sensor, obtaining the recovery matrix between the image difference vector and control voltage. Multiply the image difference vector and the recovery matrix to obtain the corresponding control voltage of the residual wave-front, and use real-time control algorithms, such as proportional integral, to obtain the control voltage of the wave-front correction device, making the wave-front aberration to be corrected. Compared the adaptive optics system based on the linear phase inversion recovery technique and the conventional adaptive optical technology, it has simple structure, high optical energy efficiency, and other advantages.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Phase-frequency detector with linear phase error gain near and during phase-lock in delta sigma phase-locked loop
ActiveUS7092475B1Pulse automatic controlOscillations comparator circuitsNon symmetricPhase difference
A phase-frequency detector (PFD) having substantially linear phase error gain within a predetermined phase error range centered about zero phase error when used in a delta sigma phase-locked loop (PLL). The output signals (e.g., charge pump control signals), which are also used to reset the input circuitry, are fed back with asymmetrical signal delays, thereby causing one of the output signals to remain in an asserted state for a substantially constant time duration at least during when a difference between the reference and feedback signal phases is within a predetermined phase difference range centered about zero phase difference.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Phase shifter, a phase shifter assembly, feed networks and antennas
A variable differential phase shifter including an isolation element providing good isolation between output ports, good return loss and reduced reflections. In one embodiment a Wilkinson divider is incorporated in the wiper arm of a wiper type variable differential phase shifter. In another embodiment a linear phase shifter incorporates a Wilkinson divider. Multistage embodiments are also disclosed. The variable differential phase shifter may be used in combination with a hybrid coupler to provide an isolated variable power divider. The variable differential phase shifter may be utilized in a variety of feed networks and antenna arrays to vary beam tilt, beam azimuth and beam width. Antennas incorporating the phase shifter exhibit low variation of half power beam width with frequency and reduced side lobes.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
PMD-insensitive method of chromatic dispersion estimation for a coherent receiver
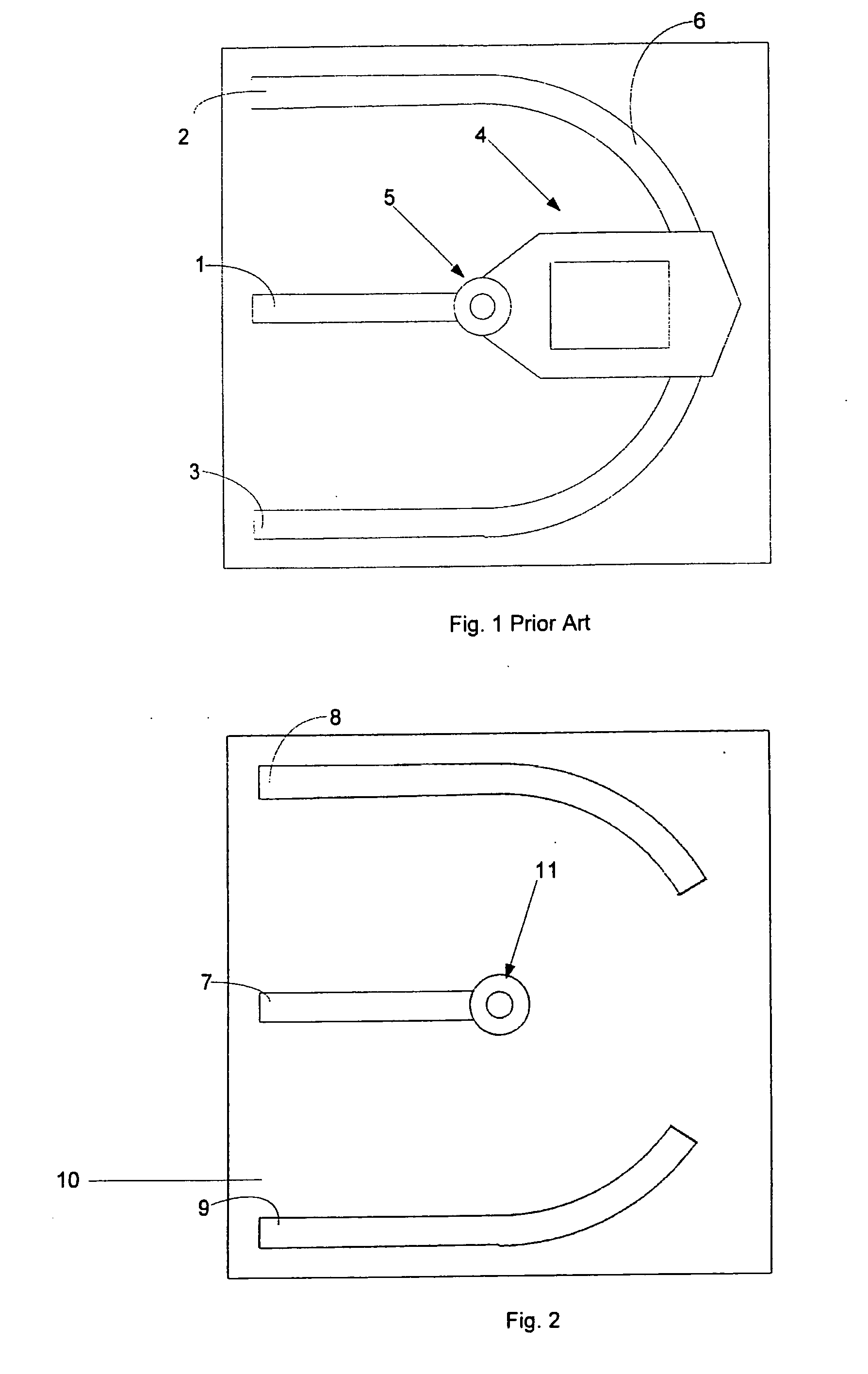
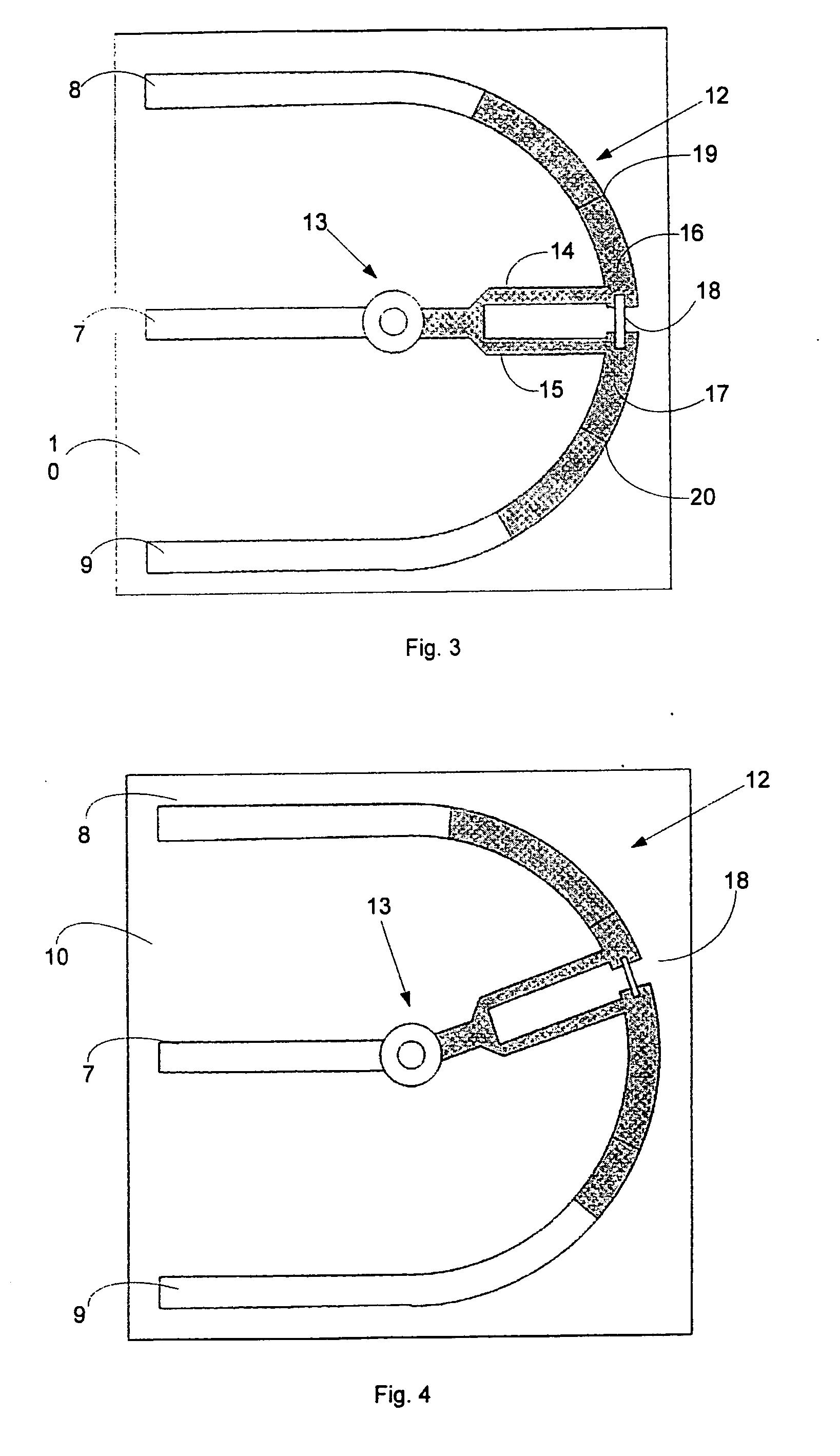
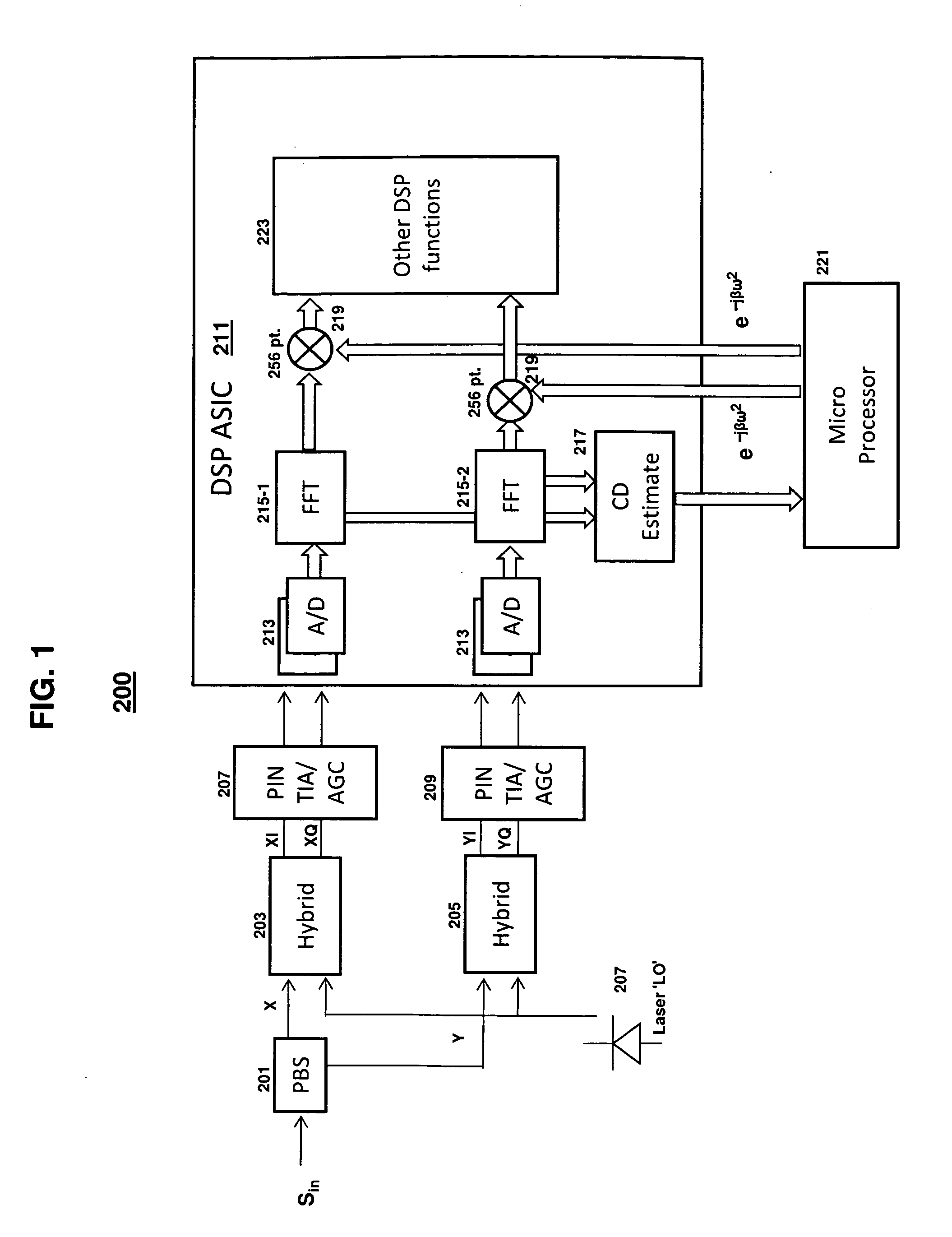
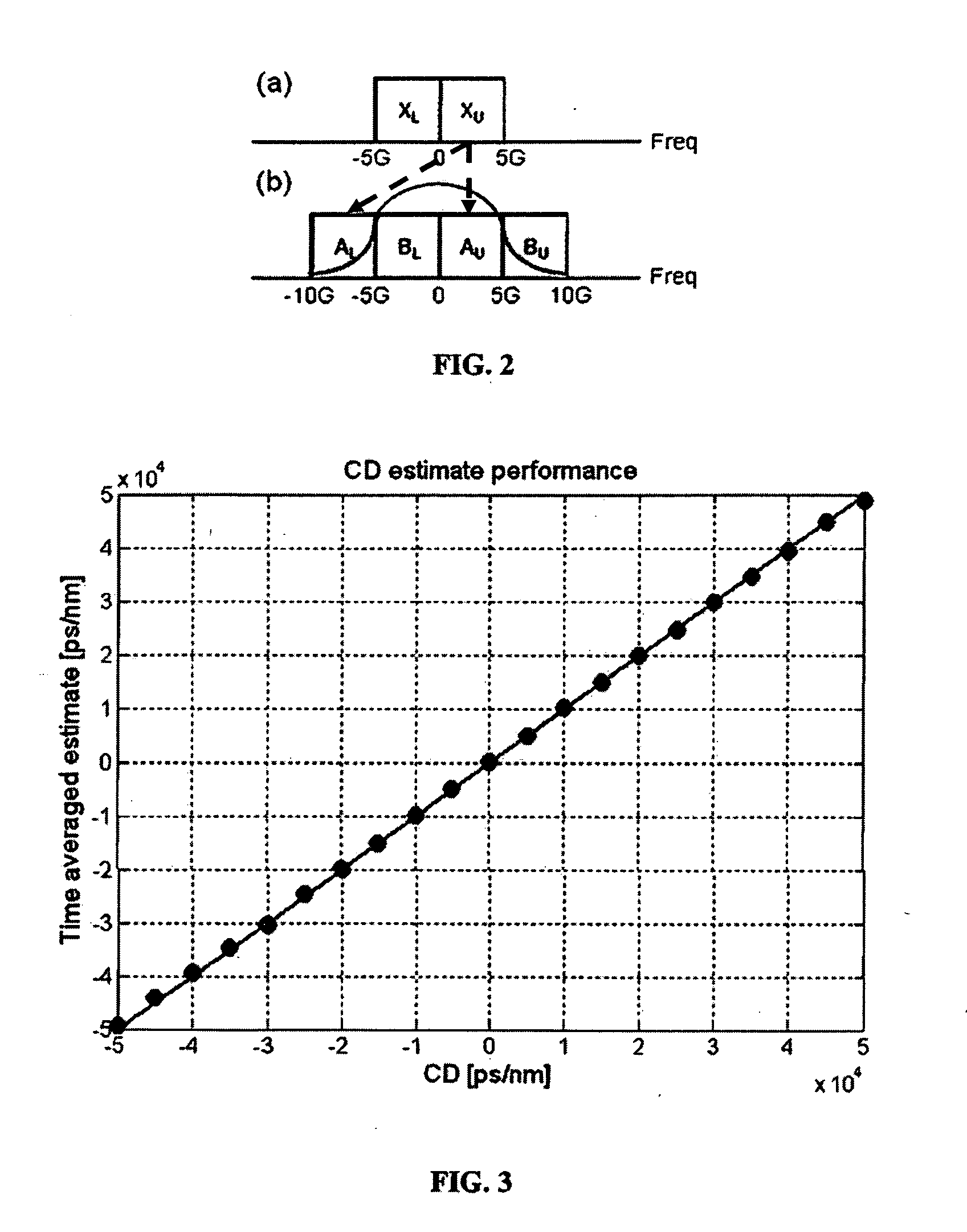
Consistent with the present disclosure, a method and system for estimating chromatic dispersion of an optical signal in a coherent receiver is provided that is insensitive to polarization mode dispersion (PMD) and other polarization effects in the optical communication system. The effects of chromatic dispersion in the optical system are estimated by first calculating a phase shift between a pair of related frequency domain data outputs of a Fourier transform circuit. The calculated phase shift includes a linear phase component that is proportional to the chromatic dispersion, a DC constant phase component, and a data spectrum component. The calculated phase shift is then averaged over a number of clock cycles to remove the data spectrum components. The time averaged result is used to normalize any effects of PMD from the received signal. A slope of the linear phase component as a function of frequency is then calculated and used to estimate the value for chromatic dispersion. The chromatic dispersion estimate is then used to determine a number of coefficients of an inverse frequency response of the chromatic dispersion in the system, and is used to compensate for the chromatic dispersion.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com