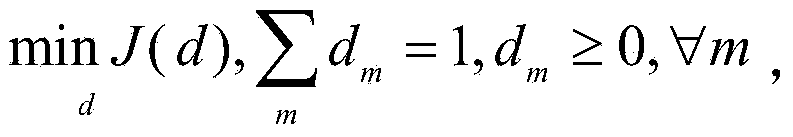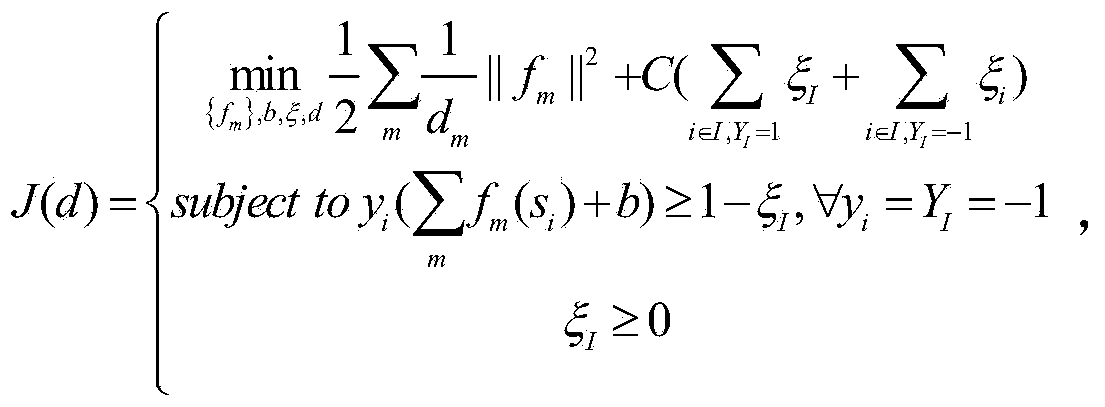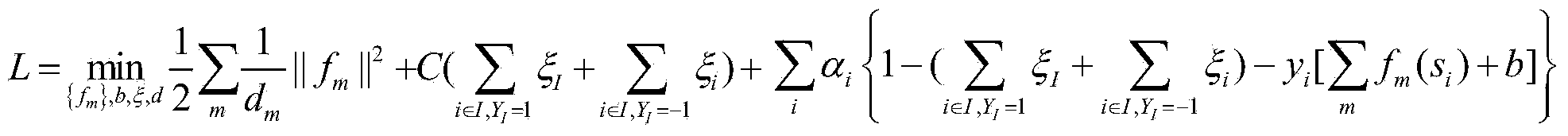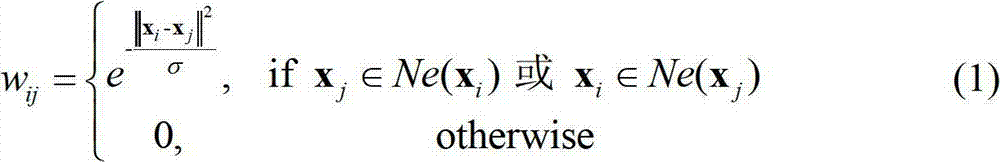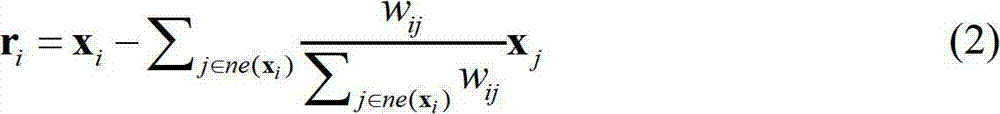Patents
Literature
273 results about "Difference vector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Vector Difference. A vector difference is the result of subtracting one vector from another. A vector difference is denoted using the normal minus sign, i.e., the vector difference of vectors and is written . A vector difference is equivalent to a vector sum with the orientation of the second vector reversed, i.e.,
Video encoding method and video decoding method
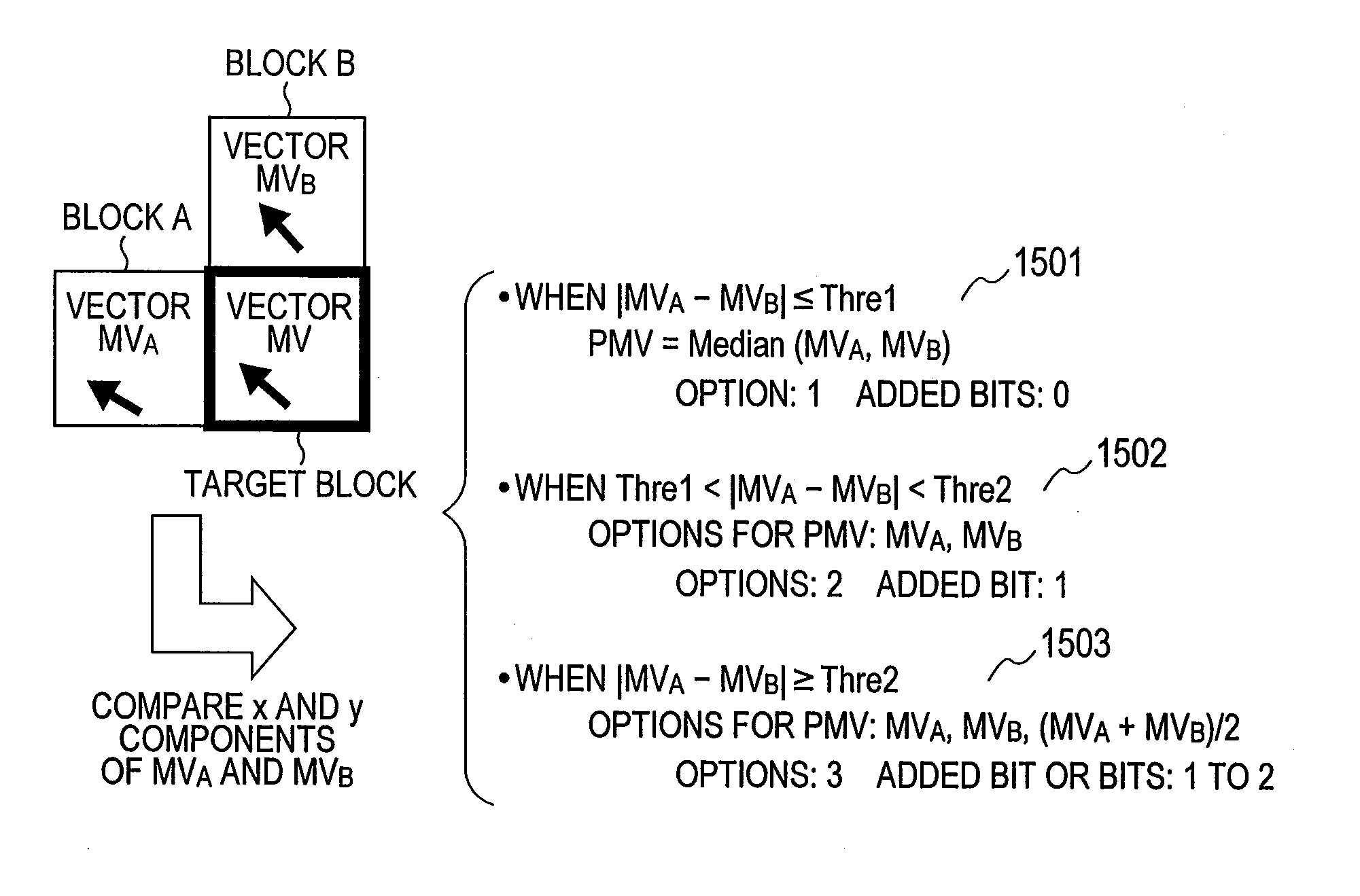
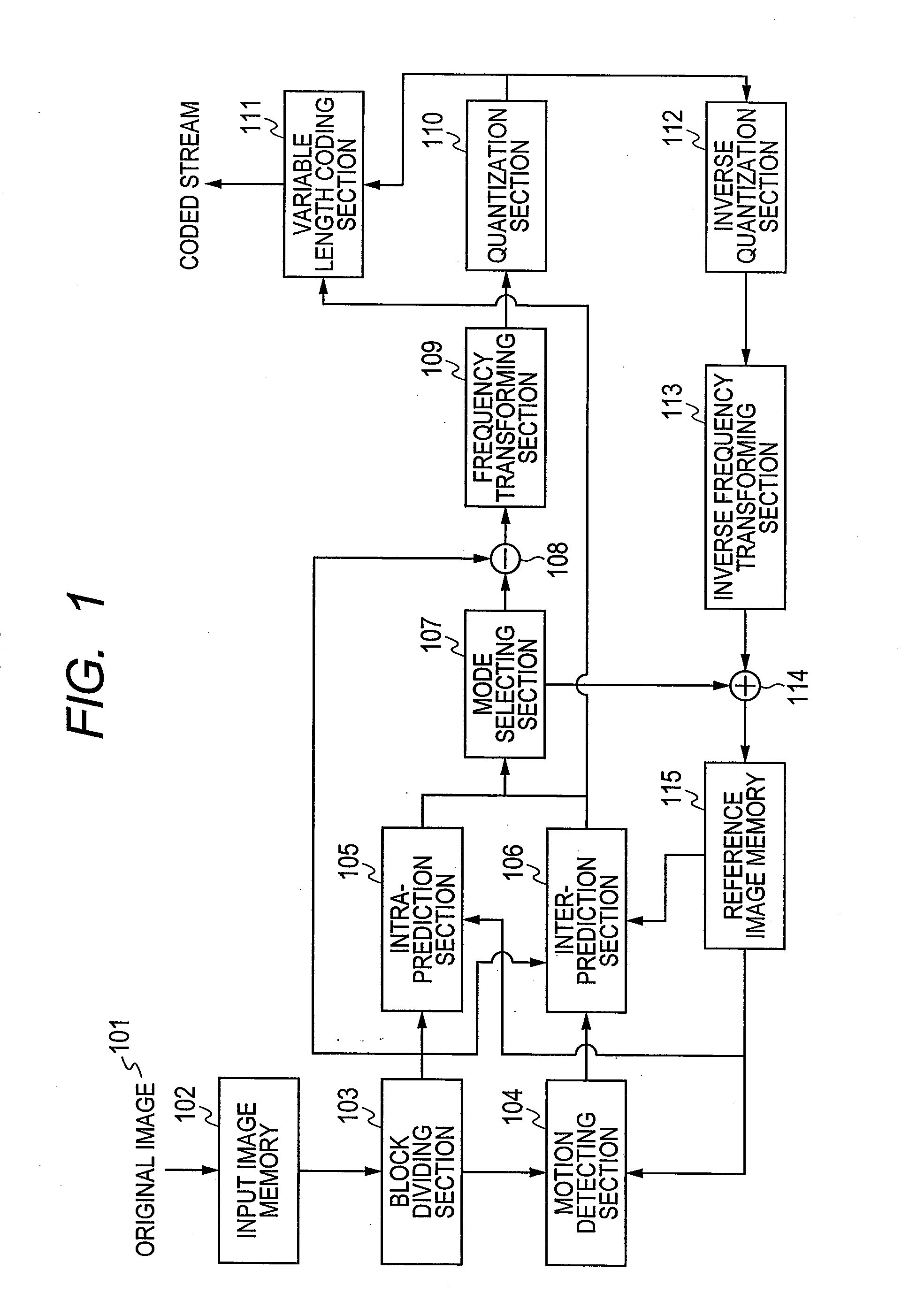
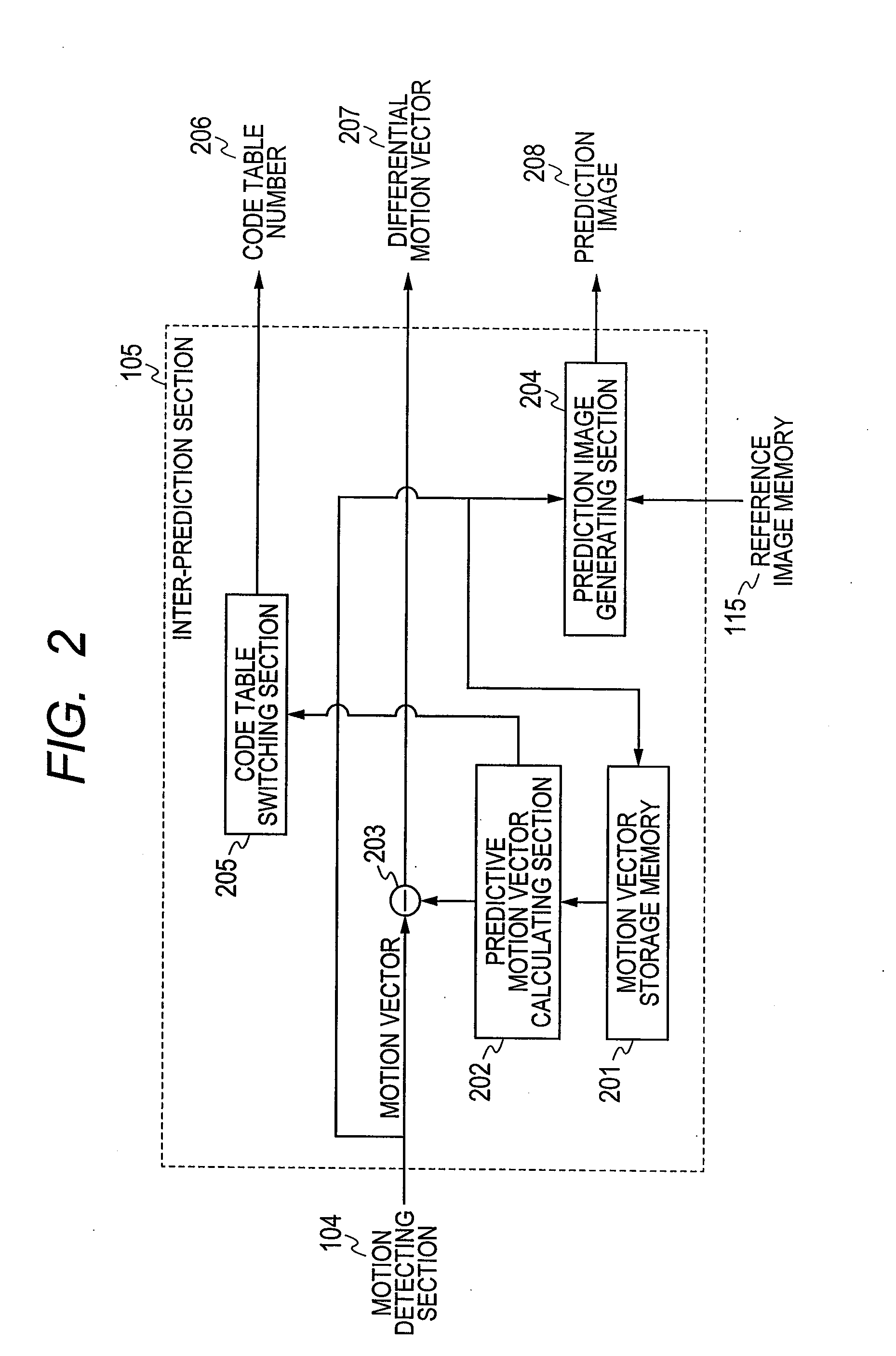
ActiveUS20110142133A1Reduce the amount requiredImprove compression efficiencyPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningVideo encodingMotion vector
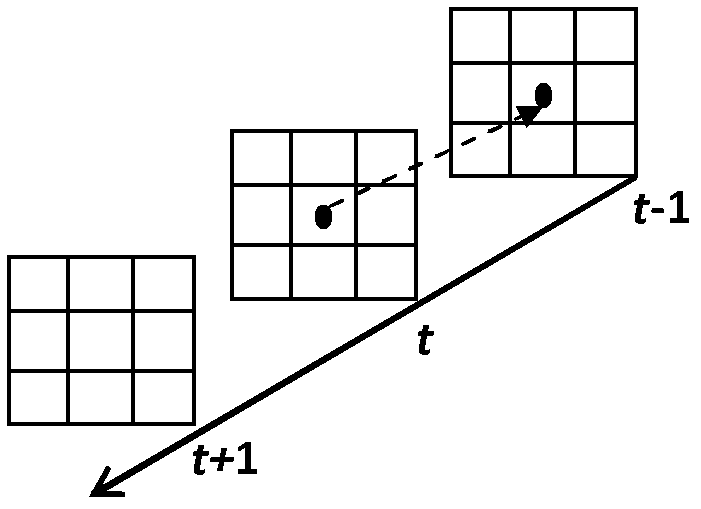
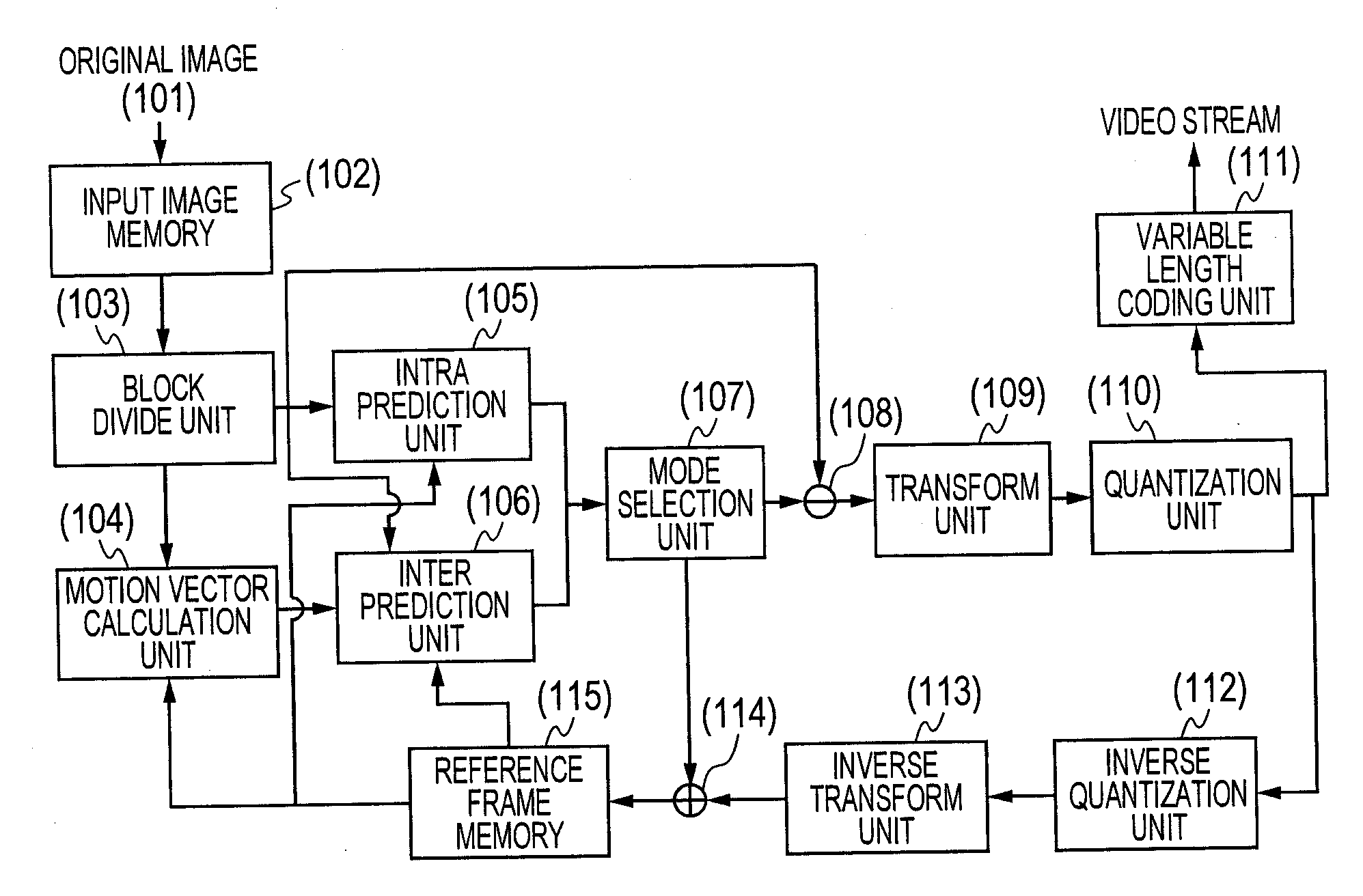
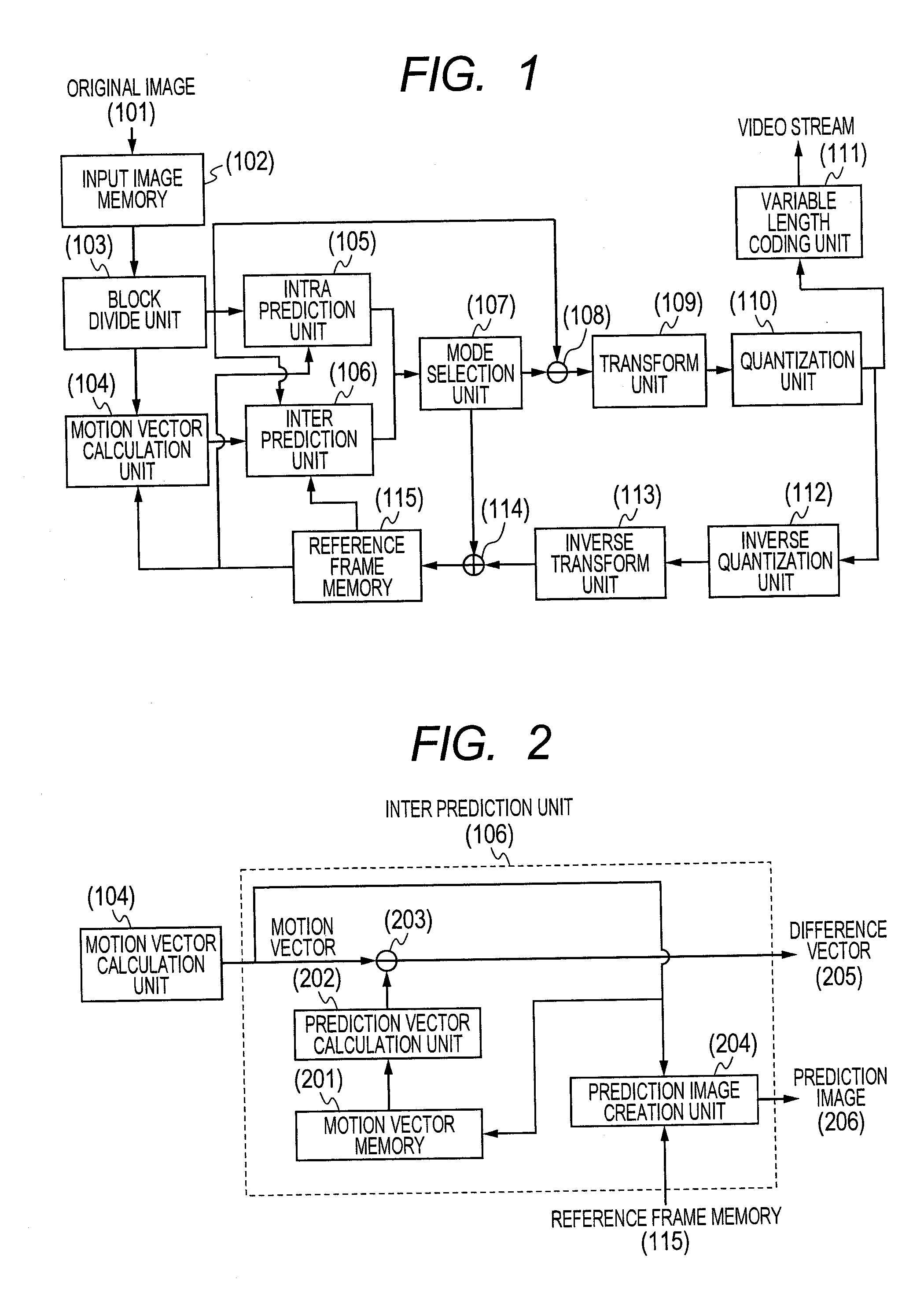
Provided is a video encoding / decoding technique for improving the compression efficiency by reducing the motion vector code amount. In a video decoding process, the prediction vector calculation method is switched from one to another in accordance with a difference between predetermined motion vectors among a plurality of motion vectors of a peripheral block of a block to be decoded and already decoded. The calculated prediction vector is added to a difference vector decoded from an encoded stream so as to calculate a motion vector. By using the calculated motion vector, the inter-image prediction process is executed.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
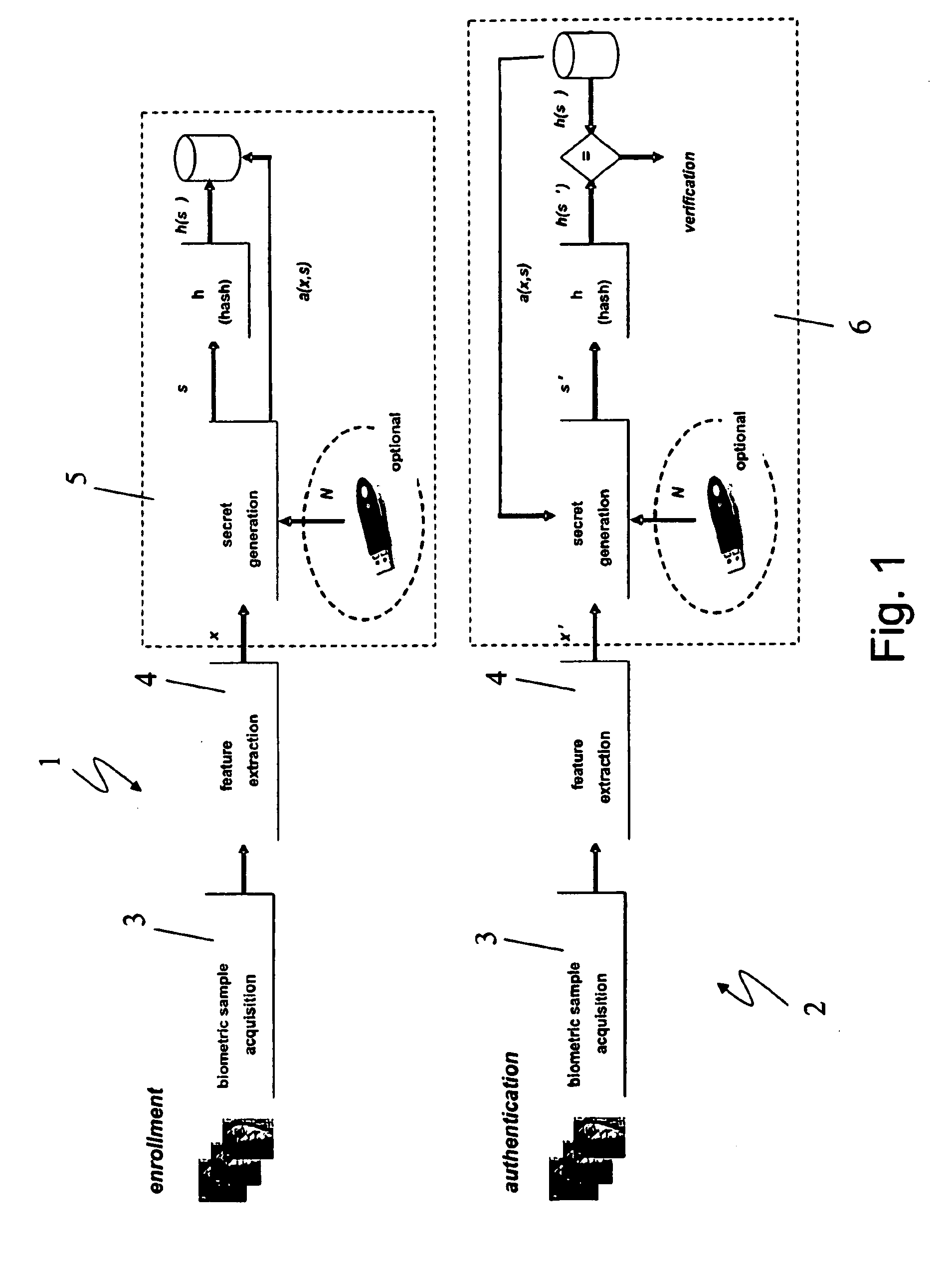
Method and system for biometric authentication and encryption
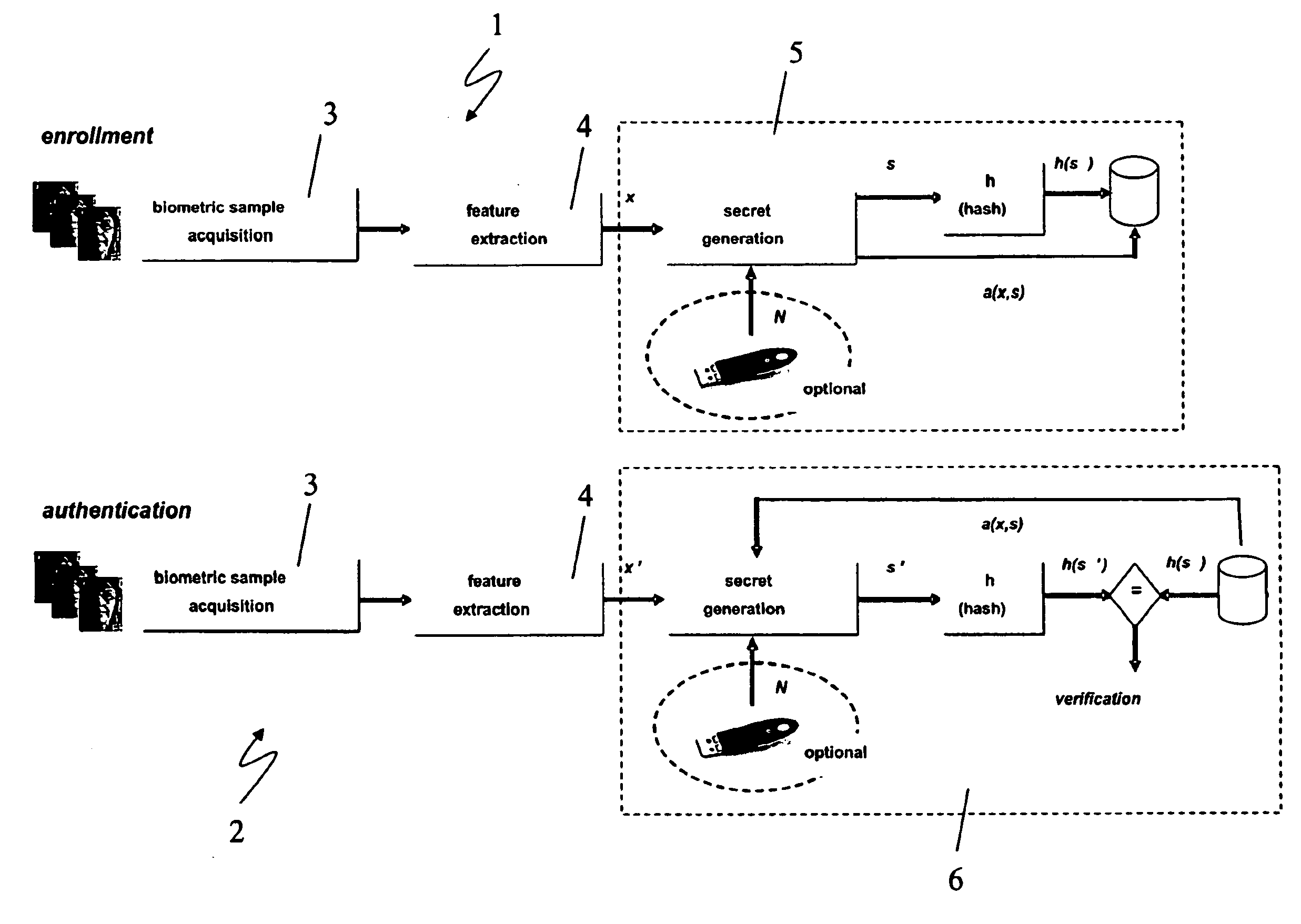
ActiveUS20100017618A1Privacy protectionAddress privacy concernsDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationFeature vectorMean vector
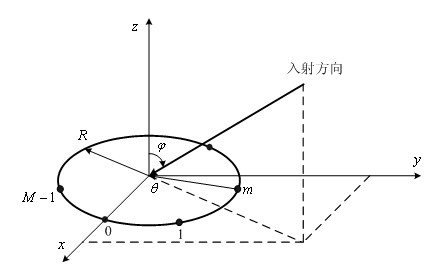
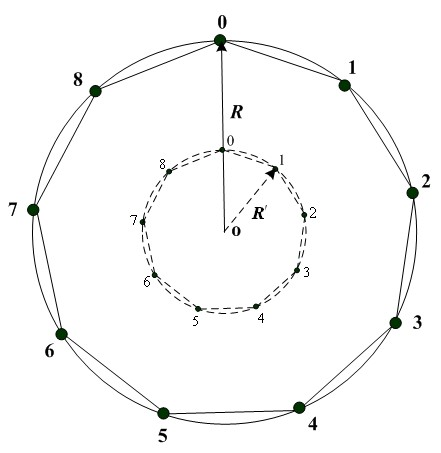
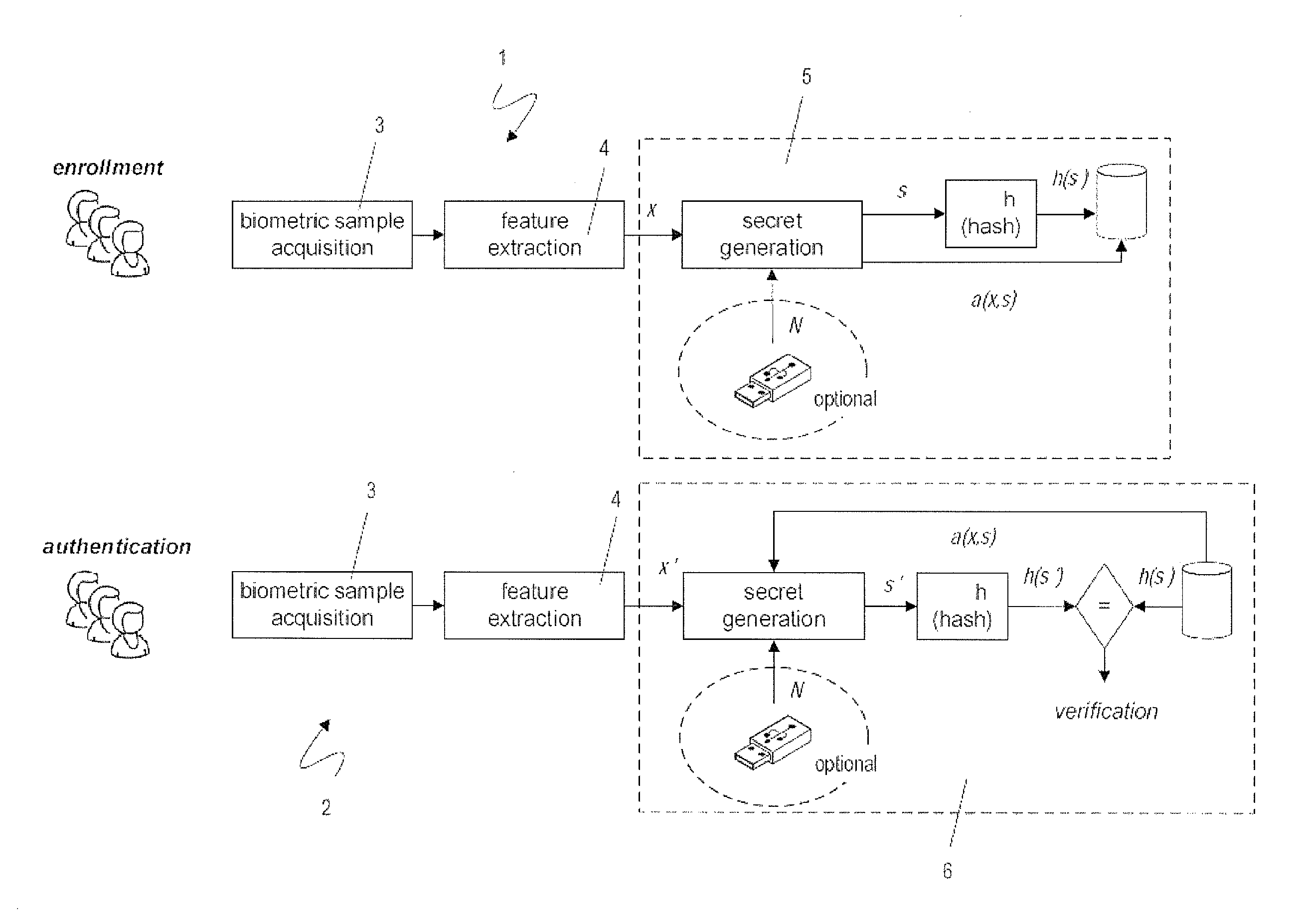
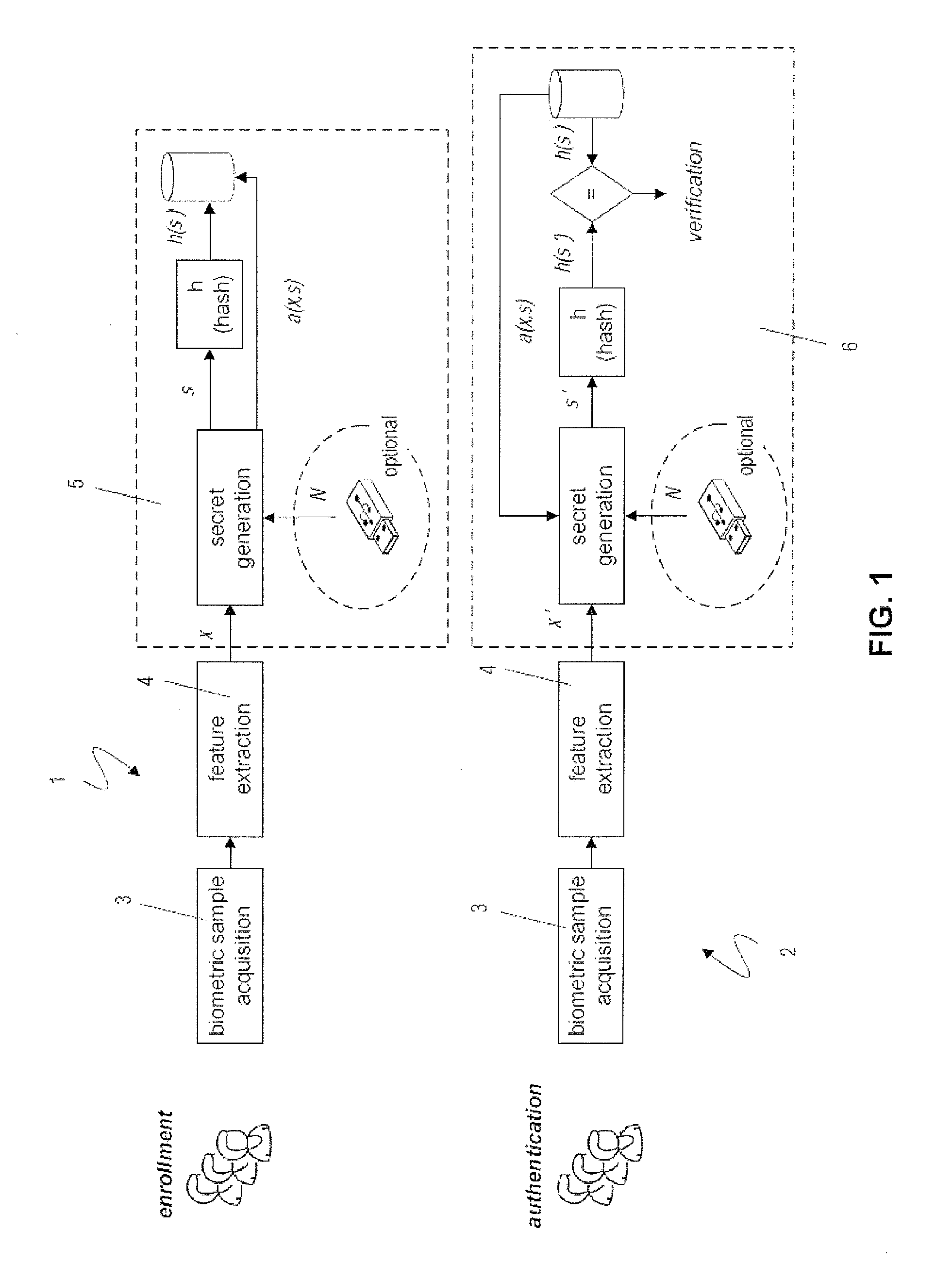
A biometric user authentication method, includes enrolling a user based on user's biometric samples to generate user's reference data; and authenticating the user based on a user's live biometric sample and the user's reference data; wherein enrolling a user includes acquiring the user's biometric samples; extracting an enrollment feature vector from each user's biometric sample; computing a biometric reference template vector as a mean vector based on the enrollment feature vectors; computing a variation vector based on the enrollment feature vectors and the mean vector; randomly generating an enrollment secret vector; computing an enrollment code vector based on the enrollment secret vector and the variation vector; computing a difference vector as a wrap-around difference between the enrollment code vector and the mean vector; computing an error correction vector based on the enrollment secret vector to enable error correction during the user authentication phase according to a given error tolerance level, wherein the error correction vector is not computed if the error tolerance level is equal to zero; and storing the variation vector, the difference vector, and the error correction vector as a part of the user's reference data to be used during the user authentication phase.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
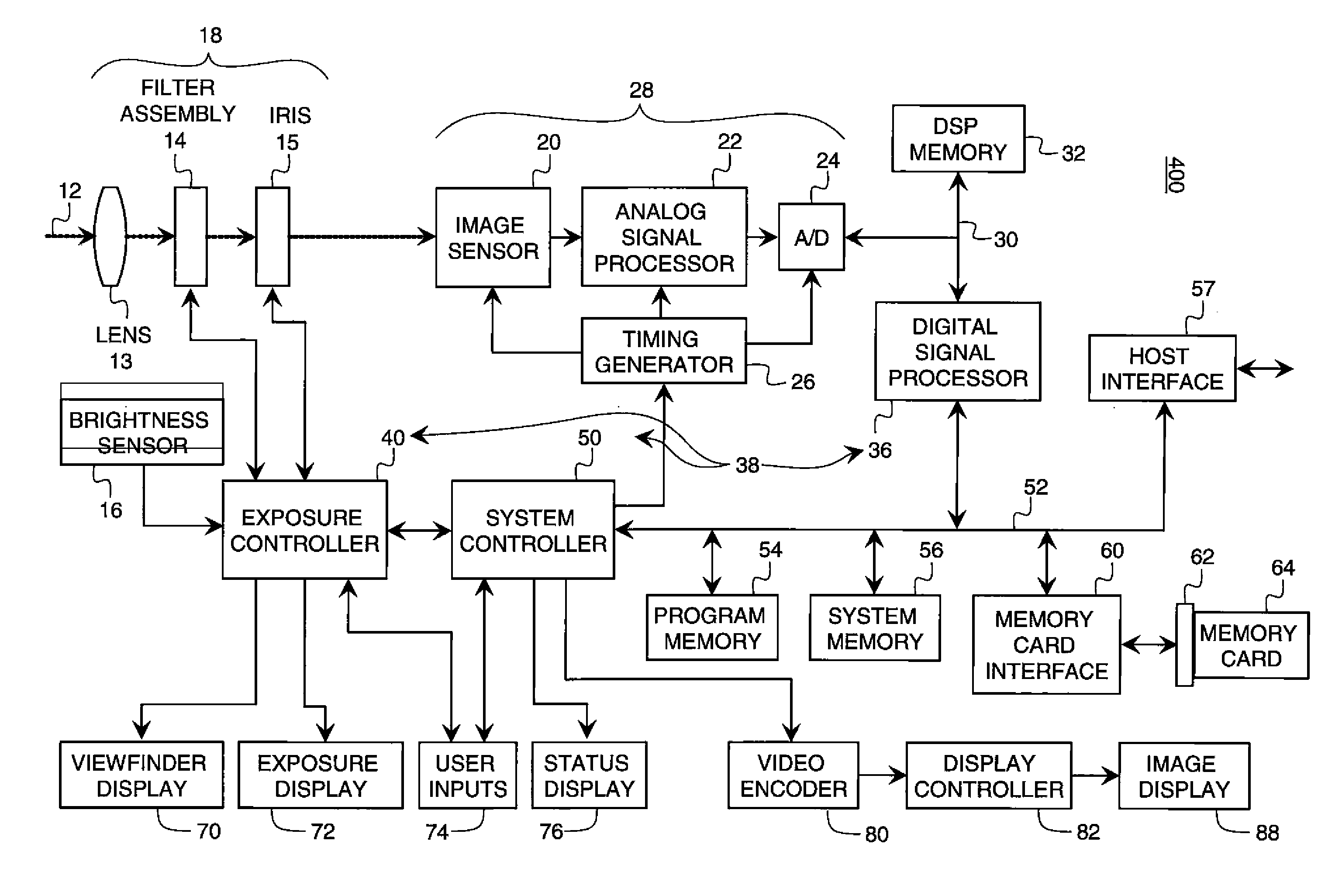
Image processing apparatus, imaging apparatus, image processing method, and program
An image processing apparatus includes an image evaluation unit evaluating properness of synthesized images as the 3-dimensional images. The image evaluation unit performs the process of evaluating the properness through analysis of a block correspondence difference vector calculated by subtracting a global motion vector indicating movement of an entire image from a block motion vector which is a motion vector of a block unit of the synthesized images, compares a predetermined threshold value to one of a block area of a block having the block correspondence difference vector and a movement amount additional value, and performs a process of determining that the synthesized images are not proper as the 3-dimensional images, when the block area is equal to or greater than a predetermined area threshold value or when the movement amount addition value is equal to or greater than a predetermined movement amount threshold value.
Owner:SONY CORP
Compressed sensing wireless communication channel estimation method based on sparsity self-adapting
InactiveCN102497337AImprove spectrum utilizationReduce the number of pilotsBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsChannel impulse responseEstimation methods
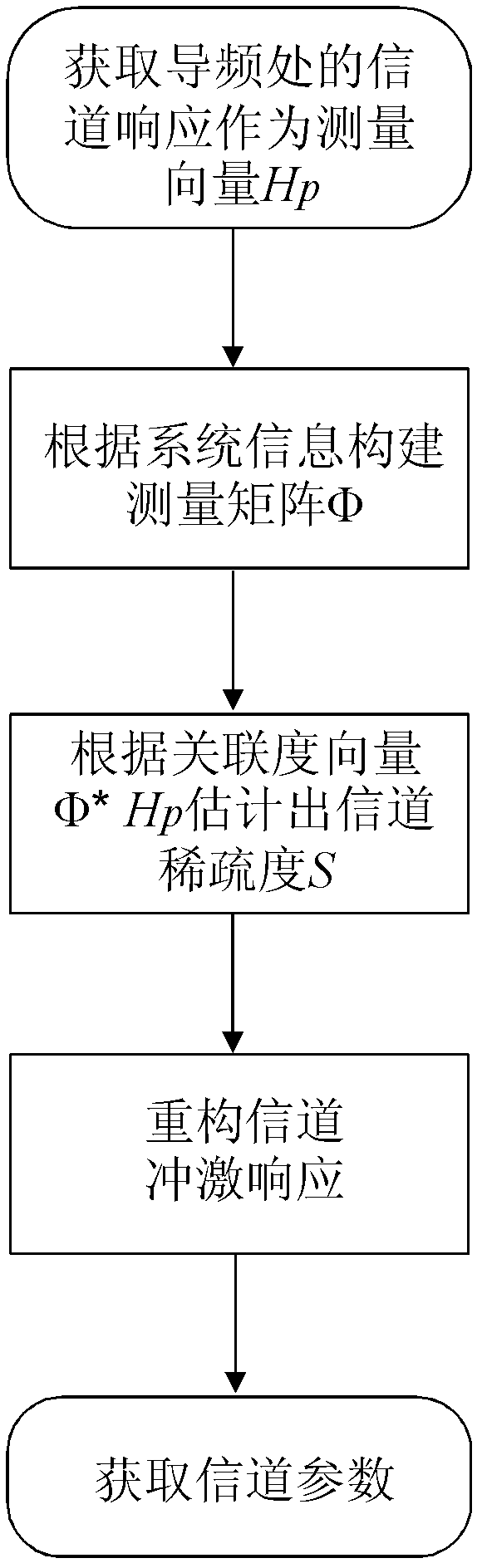
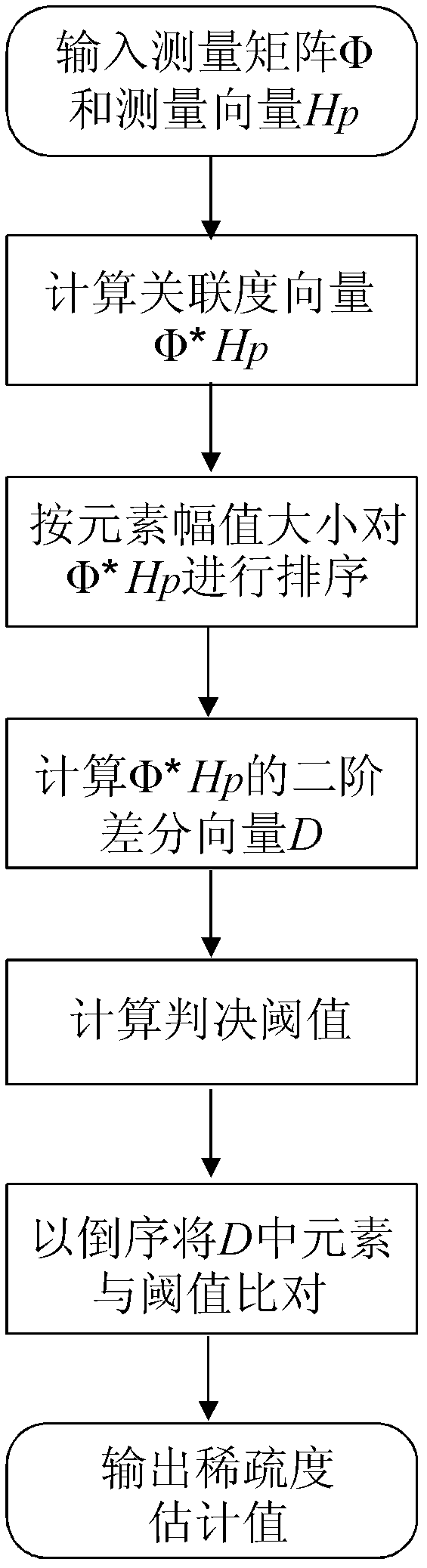
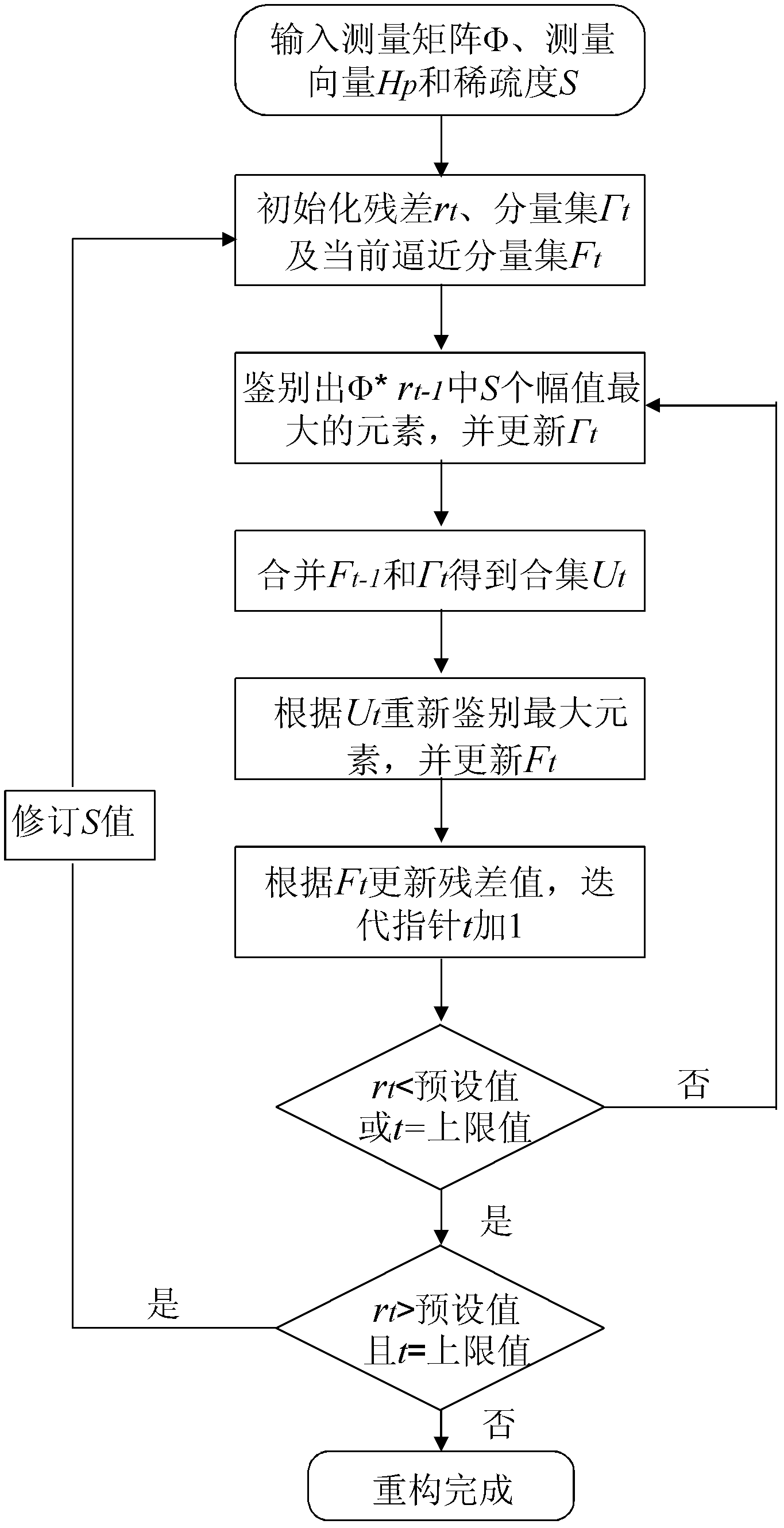
The invention belongs to the field of wireless communication channel estimation, particularly relates to a compressed sensing wireless communication channel estimation method based on sparsity self-adapting, which includes the ssteps: (1) collecting demodulated receiving signals and calculating channel response of a pilot frequency position; (2) constructing a measurement matrix phi required by signal reconstruction; (3) calculating an association degree vector and sequencing elements of the vector; (4) calculating second difference vector of a novel association degree vector after sequencing and setting a threshold value I for judging sparsity of signals; (5) estimating sparsity S of channel impulse response; (6) comparing the threshold value I with the last element of a vector D sequentially, and a coefficient value corresponding to the first element larger than the threshold value is the estimated sparsity S of the signals; and (7) reconstructing the signals. The channel estimation method breaks a bottleneck of a traditional compressed sensing algorithm that the sparsity of the signals must be known, and signal reconstruction of sparsity self-adapting is achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
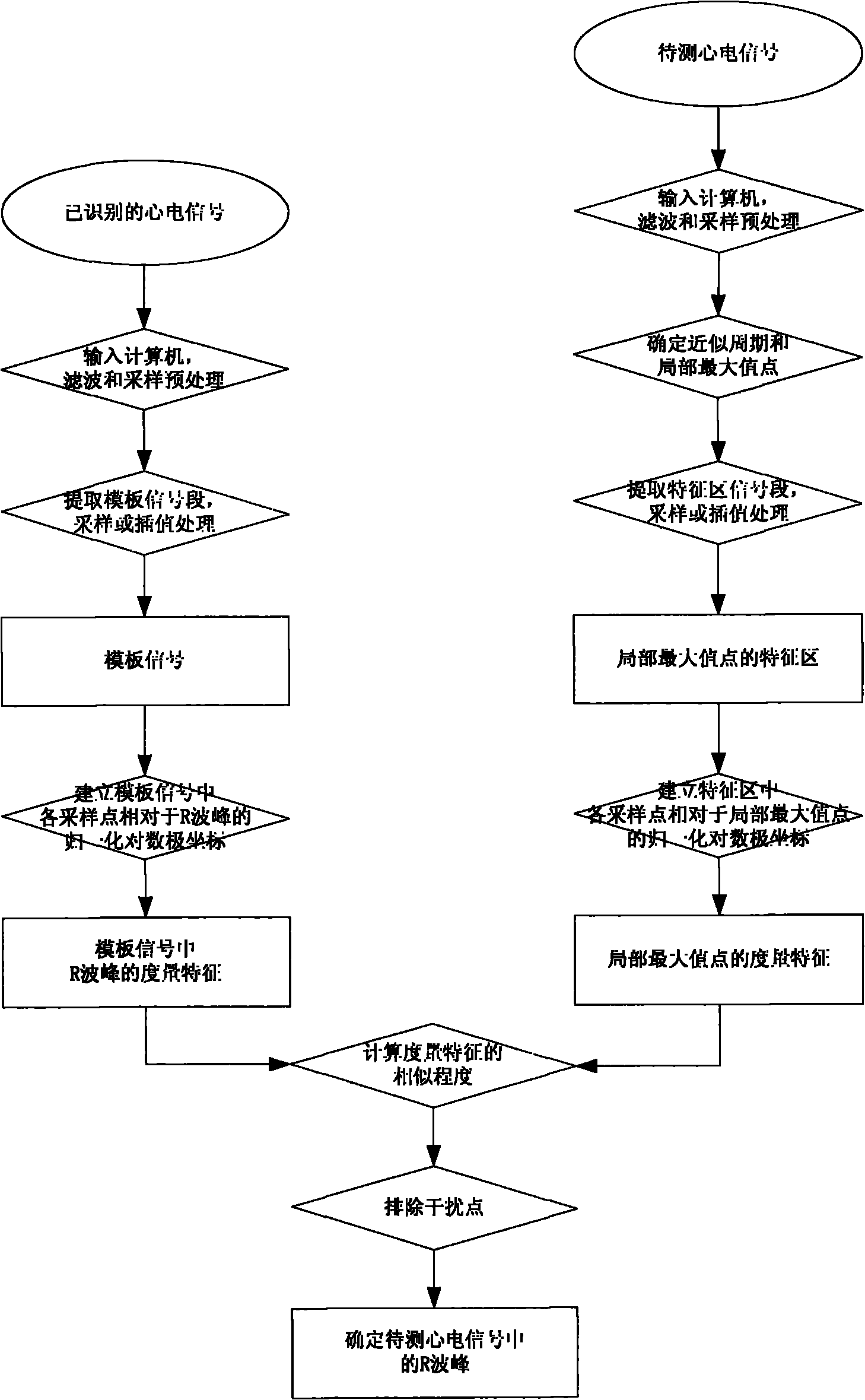
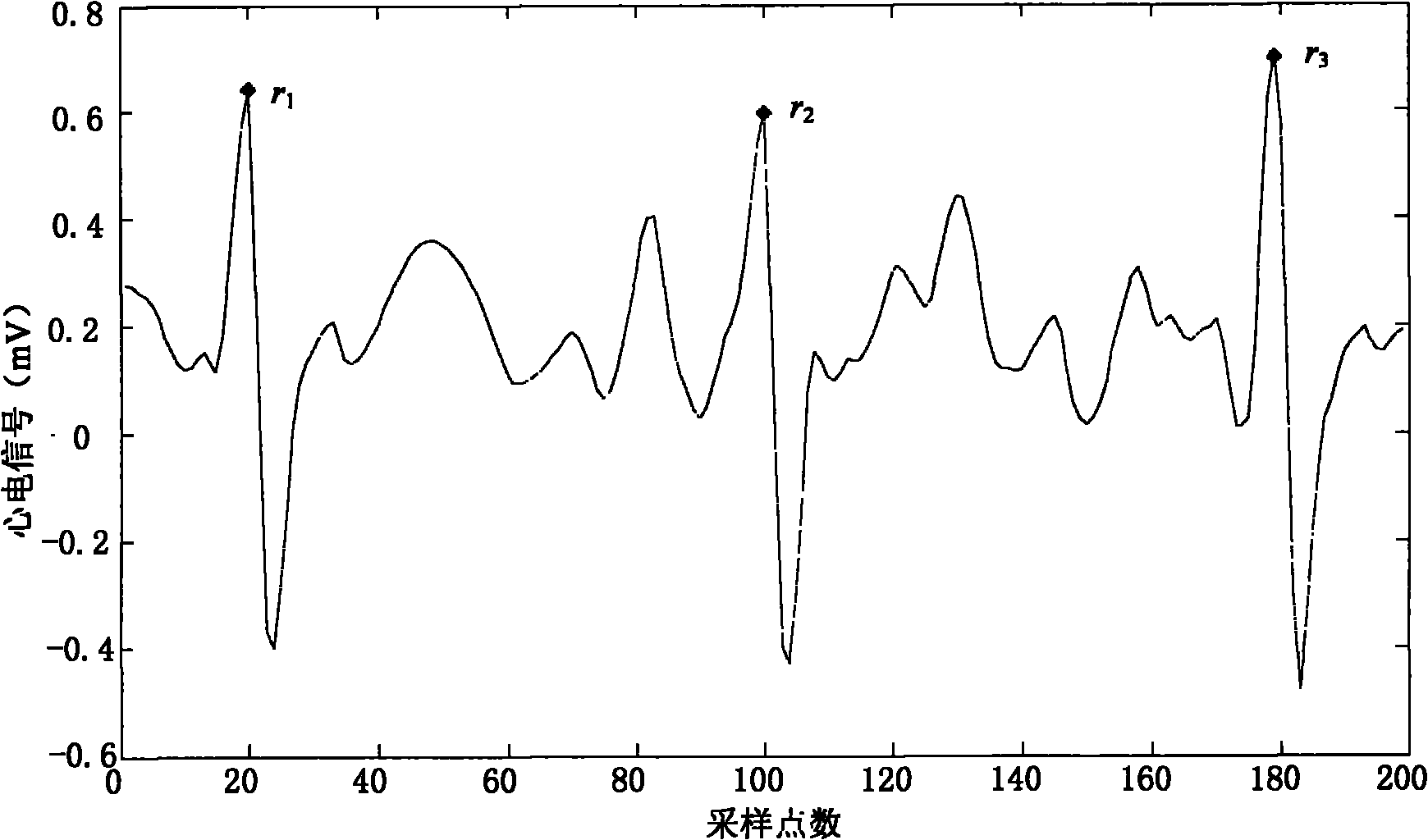
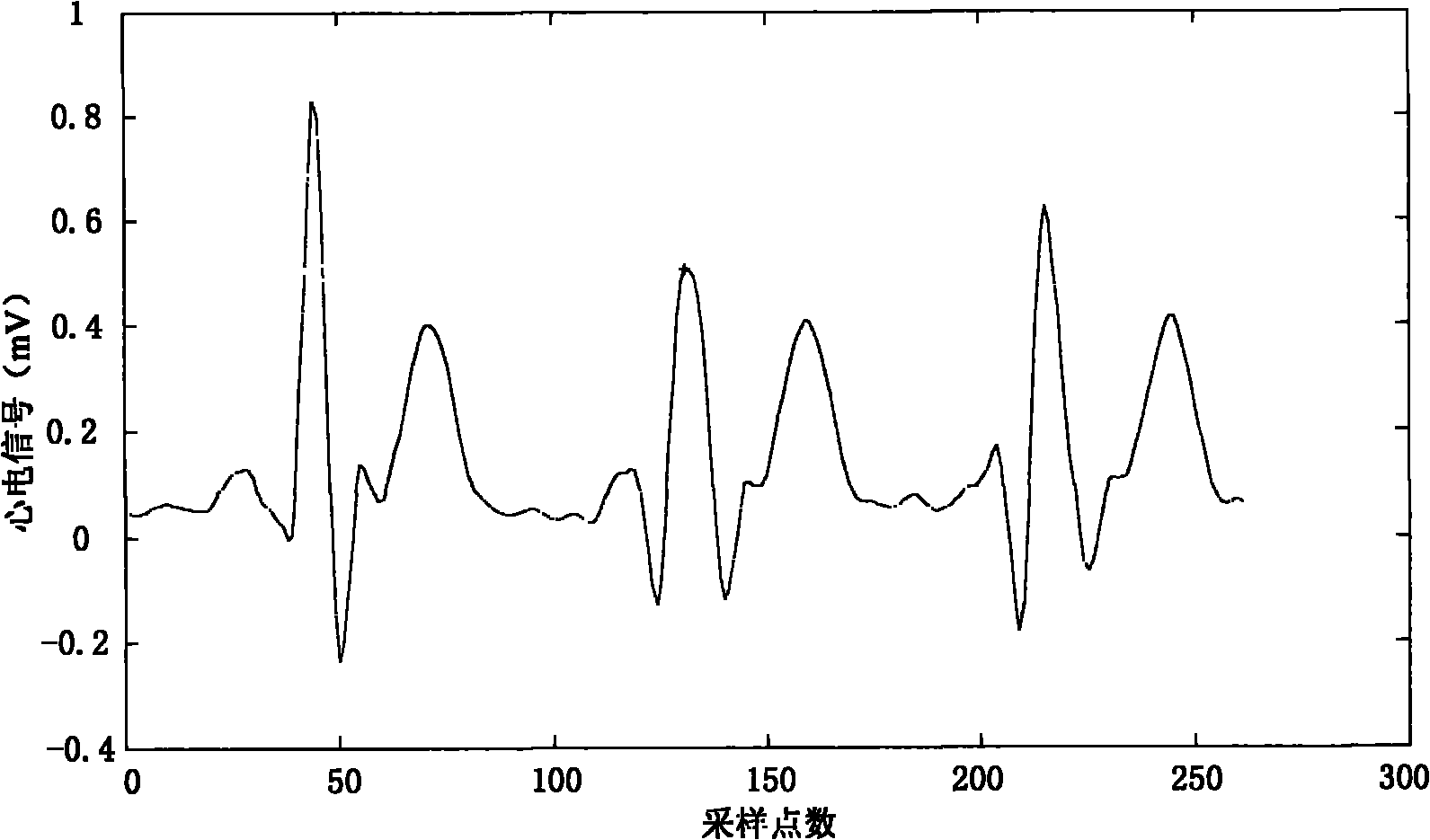
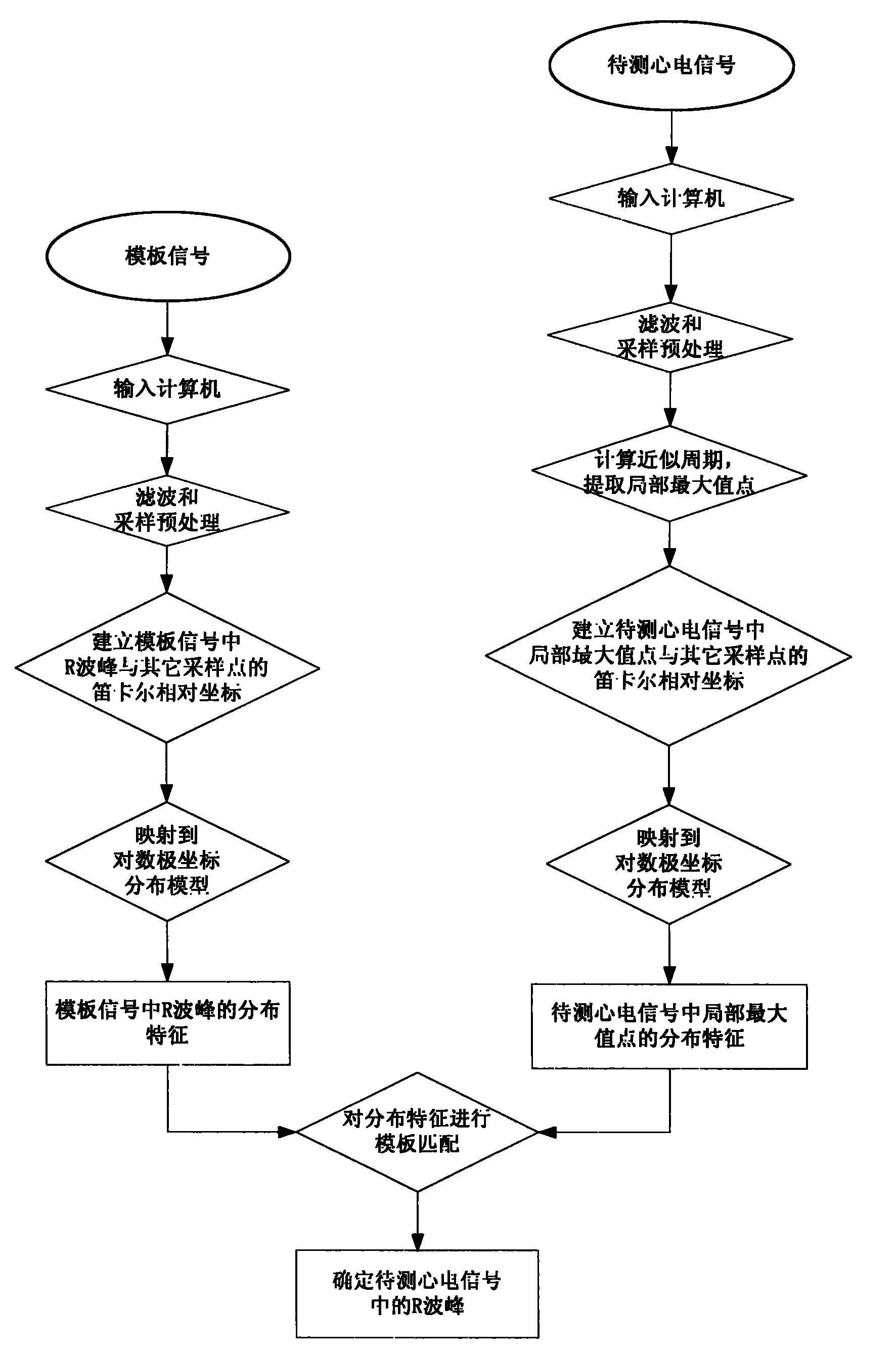
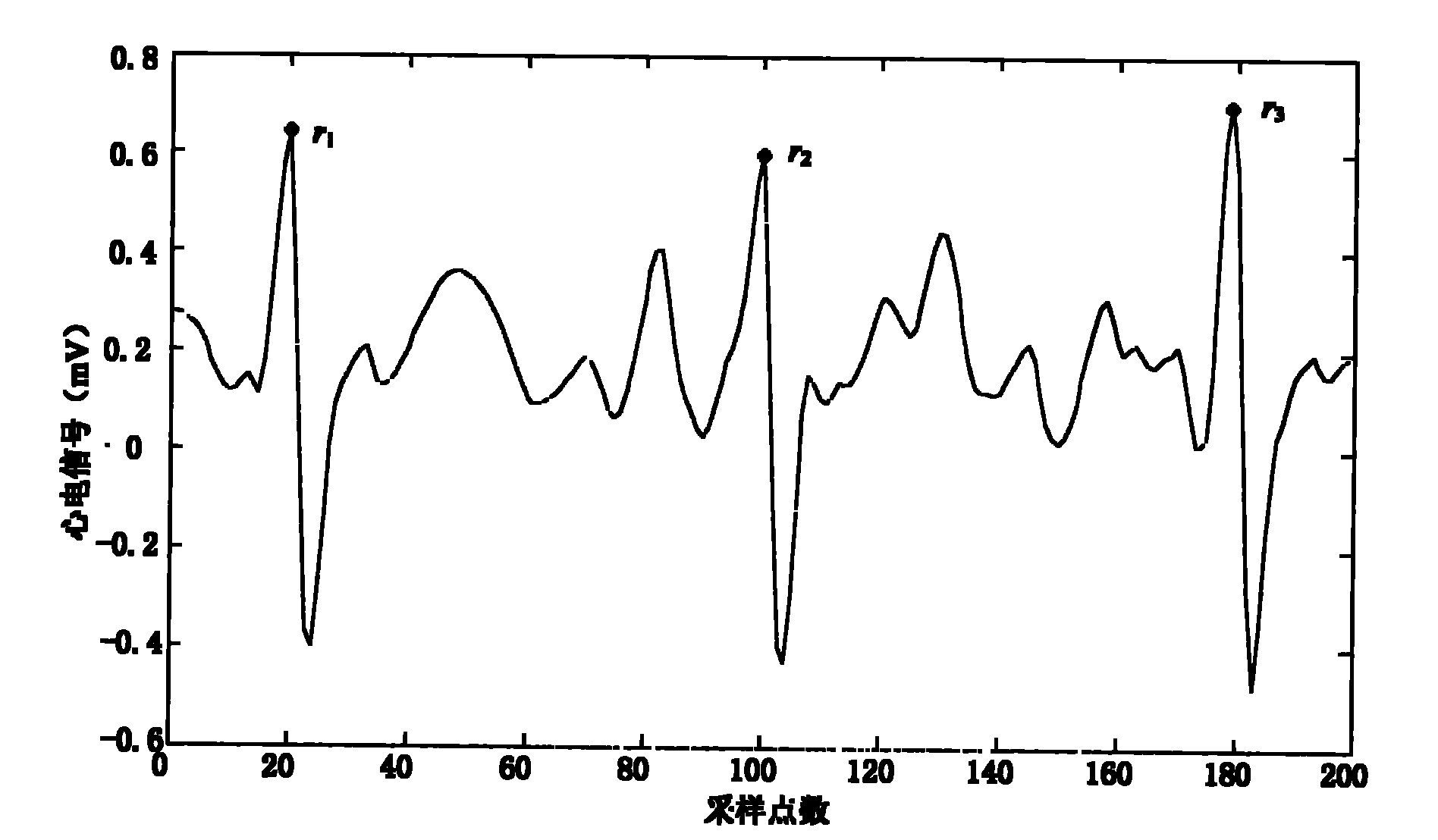
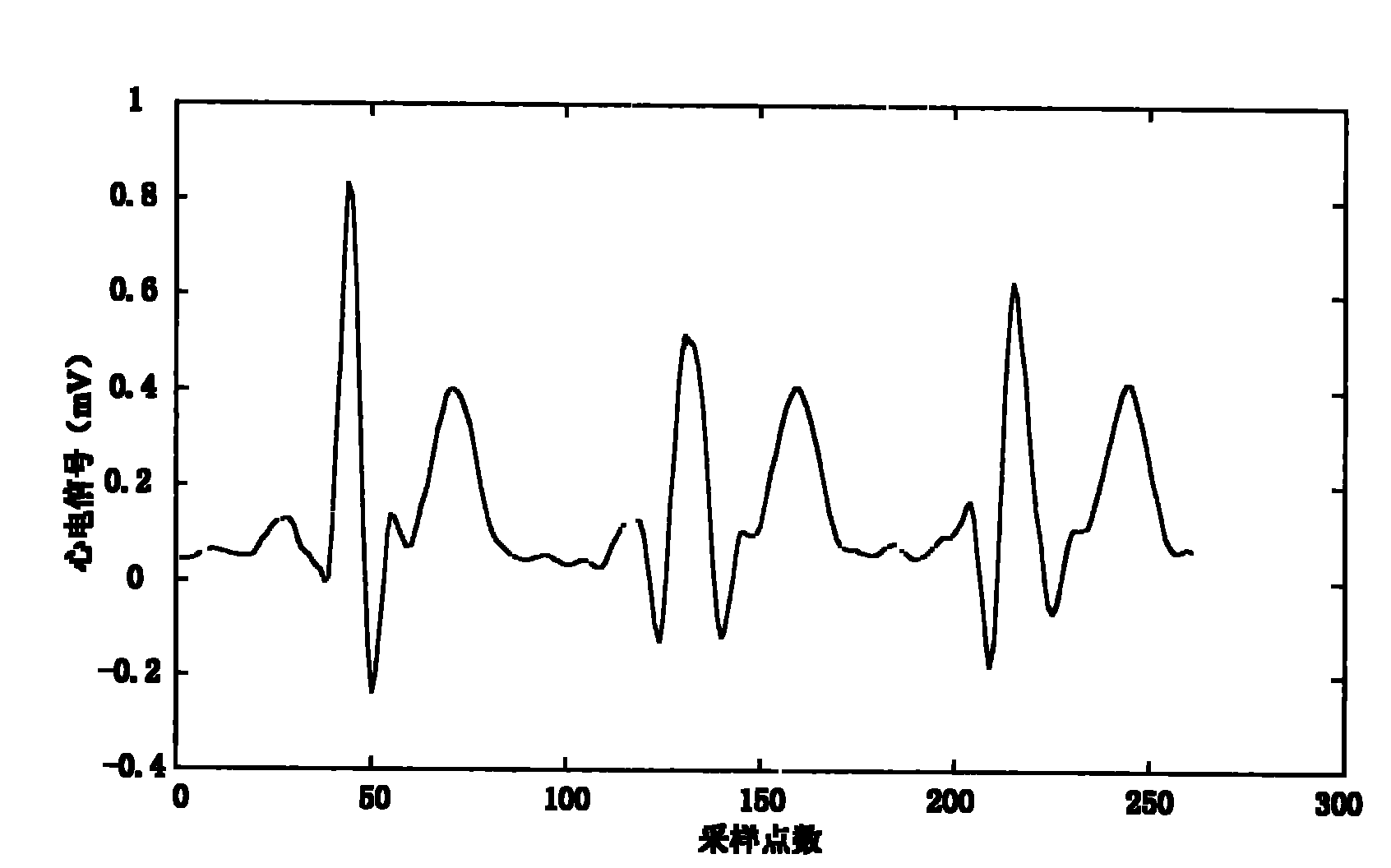
Method for detecting R wave crest of electrocardiosignal
InactiveCN101856225AOvercoming the Effects of DriftRobustDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalComputer science
The invention provides a method for detecting an R wave crest of an electrocardiosignal. The method takes point to point difference vector as a base characteristic. The base characteristic has translational and rotational invariance and can overcome influences of baseline drift of the electrocardiosignal. Meanwhile, logarithm polar coordinate conversion is carried out on the difference vector to measure similarity of waveforms. The measurement is sensitive to morphological characteristics of the adjacent waveforms, can capture the whole contour information of the waveforms at the same time, and has robustness on waveform swing. In addition, the method can effectively eliminate influences of interference signals by setting appropriate thresholds. The method for converting the point to point similarity measurement into measurement of waveforms of the points accurately identifies and detects the R wave crest of the electrocardiosignal. The method is applied to related electrocardiogram analytical instruments, can accurately identify the R wave crest in the electrocardiosignal, and is favorable for improving detection and analysis capabilities of electrocardiogram analytical equipment.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
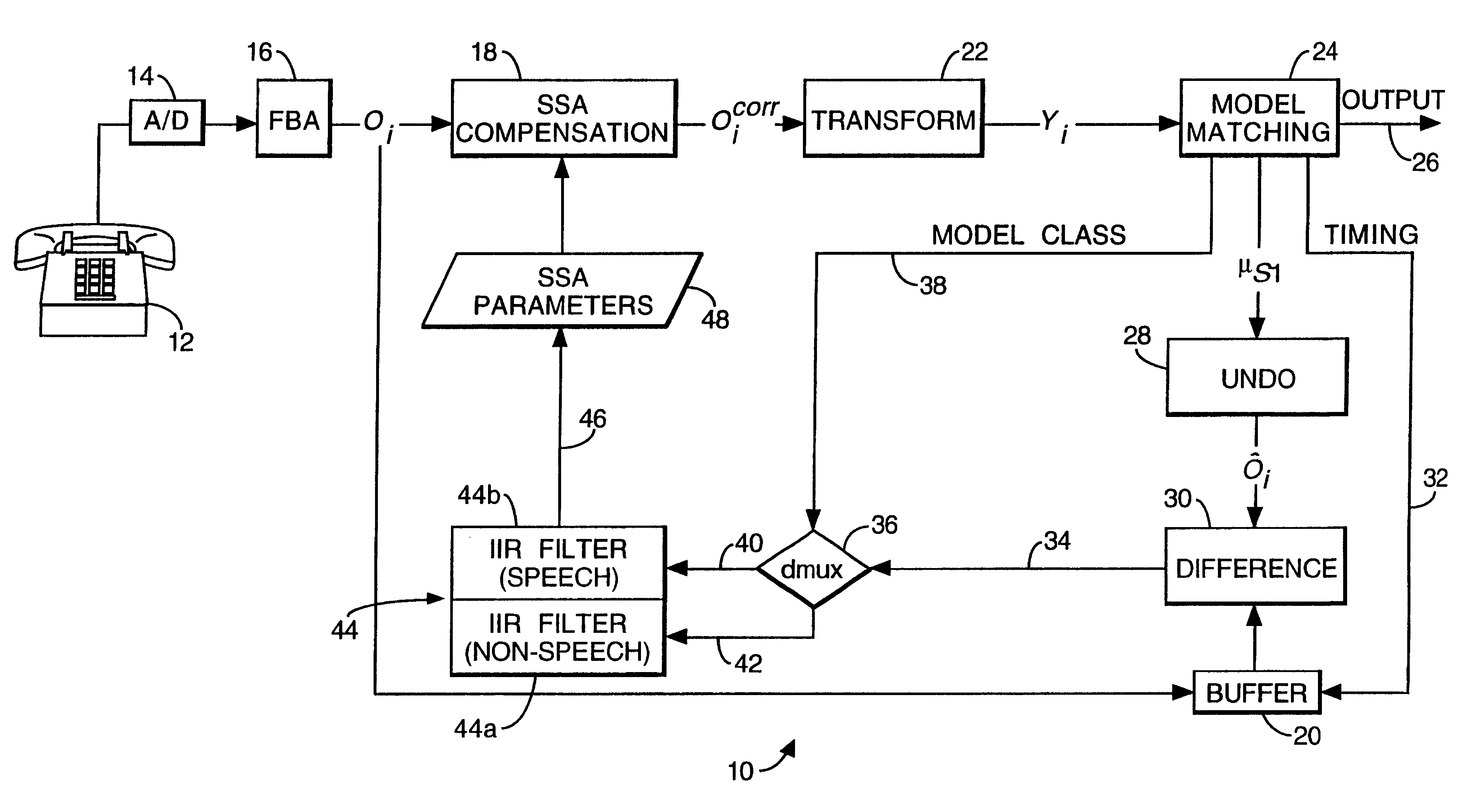
Recognition system
InactiveUS6671666B1Reduce dimensionalityAdd dimensionImage analysisDigital technique networkFrequency spectrumFilter bank
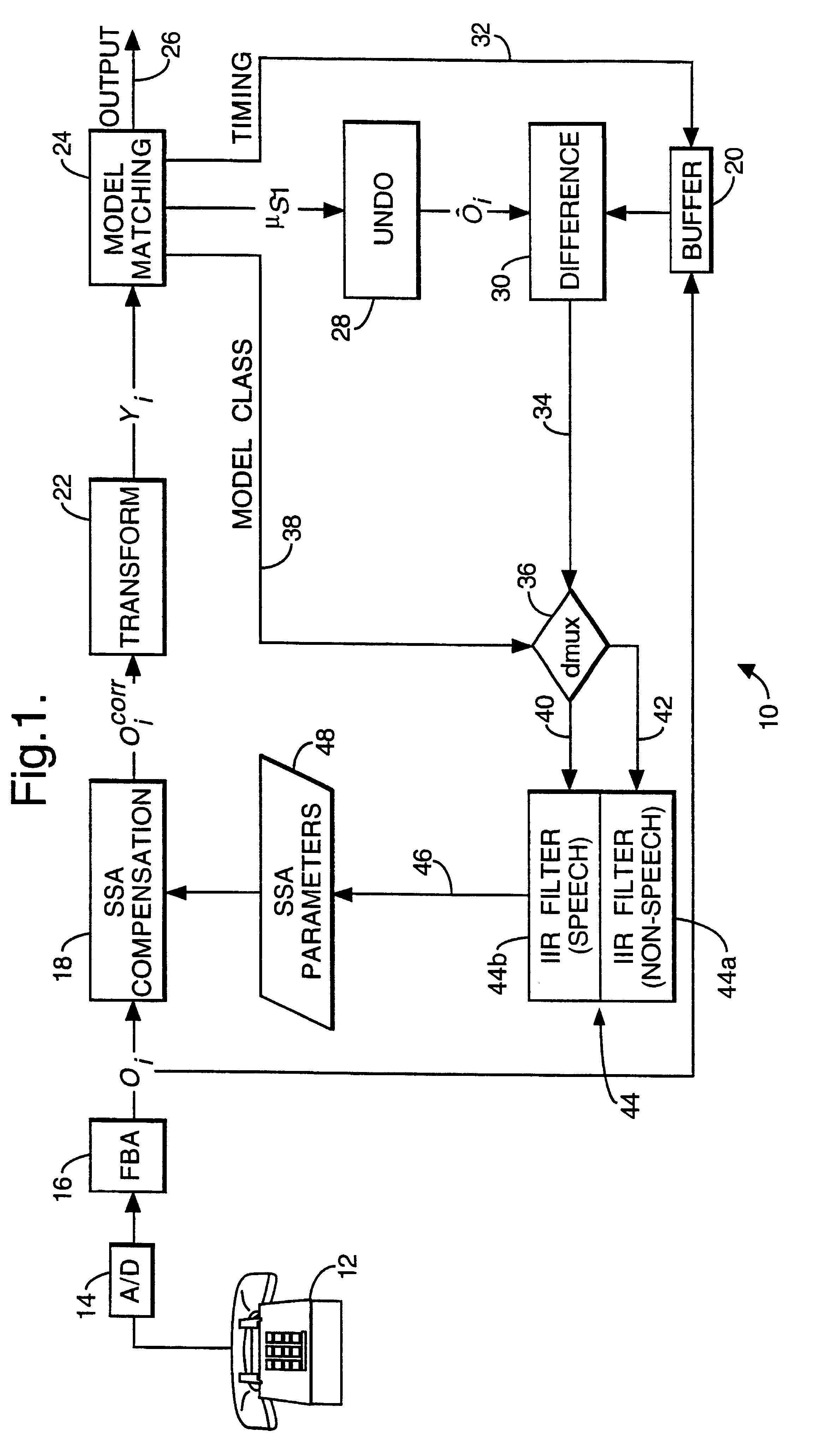
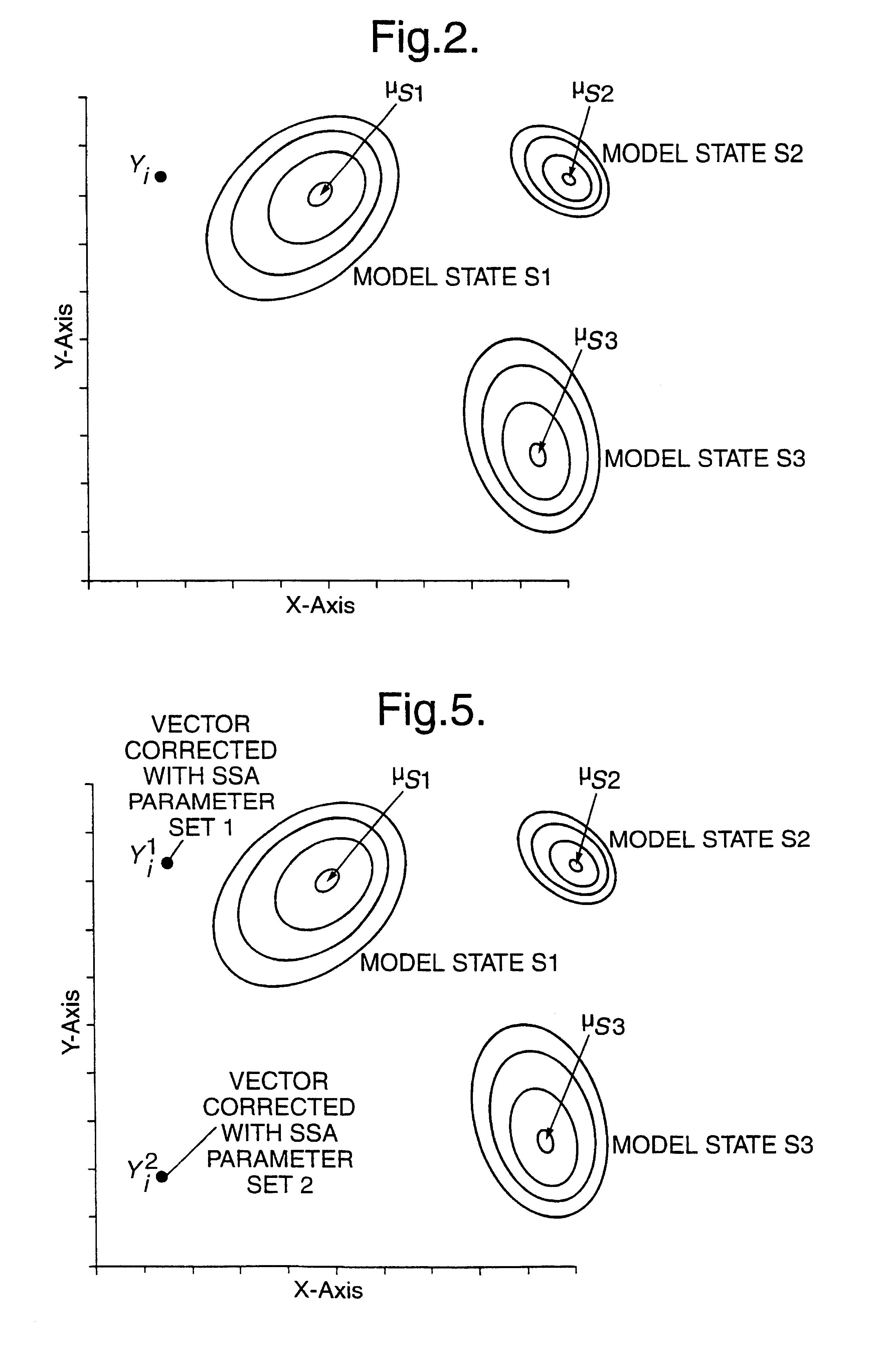
A recognition system (10) incorporates a filterbank analyser (16) producing successive data vectors of energy values for twenty-six frequency intervals in a speech signal. A unit (18) compensates for spectral distortion in each vector. Compensated vectors undergo a transformation into feature vectors with twelve dimensions and are matched with hidden Markov model states in a computer (24). Each matched model state has a mean value which is an estimate of the speech feature vector. A match inverter (28) produces an estimate of the speech data vector in frequency space by a pseudo-inverse transformation. It includes information which will be lost in a later transformation to frequency space. The estimated data vector is compared with its associated speech signal data vector, and infinite impulse response filters (44) average their difference with others. Averaged difference vectors so produced are used by the unit (18) in compensation of speech signal data vectors.
Owner:AURIX
Inertial sensor and electrical or electronic device
InactiveUS20080245148A1Simple structureSimple harmonic motionAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsAngular velocityMechanics
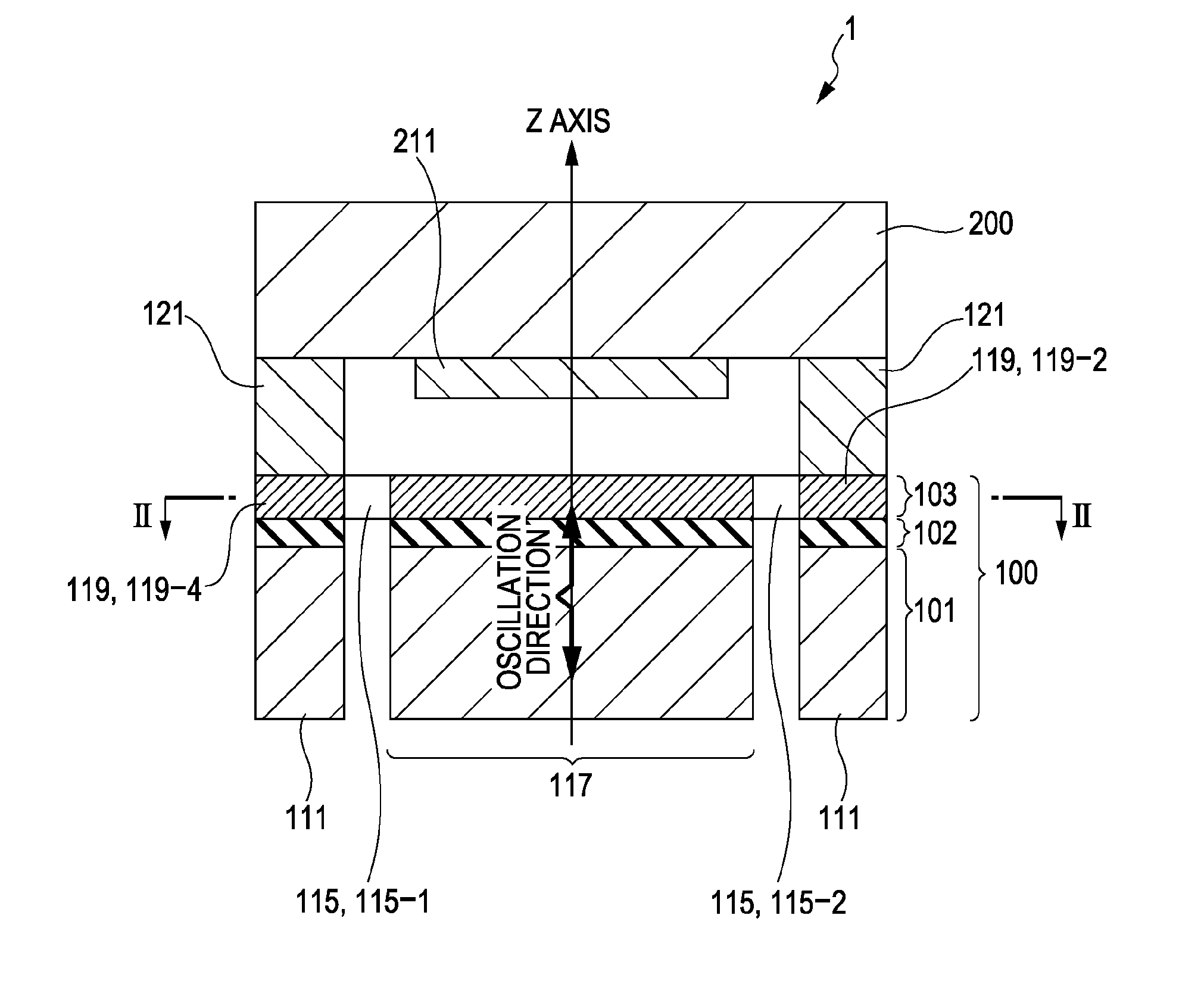
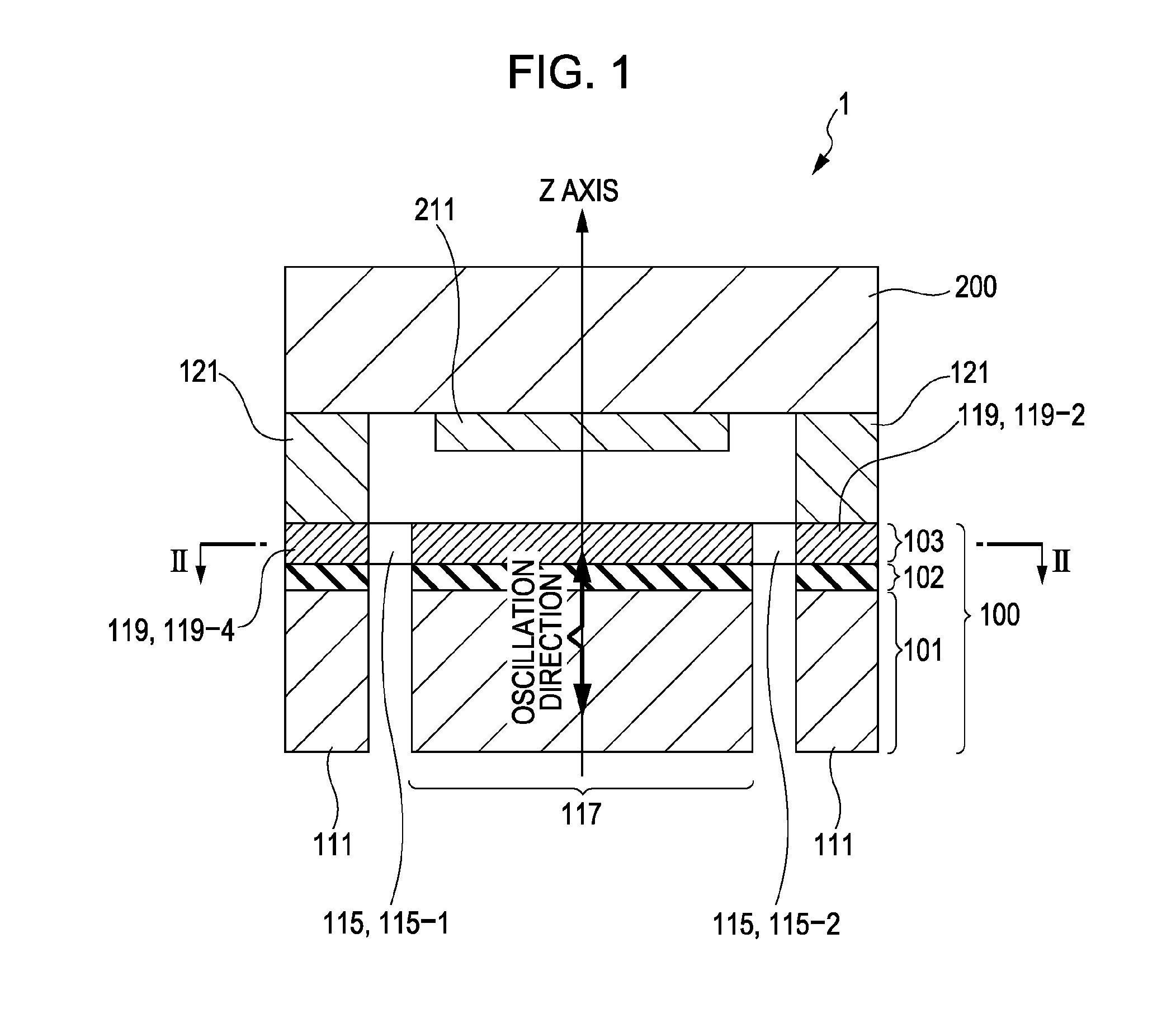
An inertial sensor includes an oscillator that is supported by an elastic supporting member such that the oscillator is floating relative to a base and the oscillator is displaceable along a single axis, and a displacement detection unit detecting a displacement of the oscillator. The oscillation of the oscillator is a simple harmonic motion along a Z axis. An X axis, a Y axis, and the Z axis, serving as reference axes of an oscillation coordinate system for the oscillator, are shifted to provide x, y, and z axes, serving as new reference axes. Position coordinates of the oscillator of the x, y, and z axes are determined in at least two points during one period of the oscillator. A difference vector (Δx, Δy, Δz) is calculated on the basis of the determined position coordinates. An angular velocity or an acceleration is obtained using the difference vector.
Owner:SONY CORP
Image processing apparatus and method, recording medium, and program
InactiveUS20050265453A1Accurate extractionImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingObject based
An image processing apparatus that performs image processing on a first image and a second image includes a dividing unit dividing the first image into a plurality of blocks; a first motion-vector calculator calculating first motion vectors representing movements from the blocks of the first image to corresponding regions of the second image; a second motion-vector calculator calculating second motion vectors representing movements of the blocks that occur when the blocks are transformed based on a first positional-relationship parameter representing positional relationship between the first image and the second image; a difference-vector calculator calculating difference vectors representing differences between the first motion vectors and the second motion vectors; and an extracting unit extracting blocks including a moving object or blocks including a non-moving object based on distribution density of end points of the difference vectors.
Owner:SONY CORP
Detecting illuminant flicker
InactiveUS20100045819A1Improve abilitiesImprove dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsComputer graphics (images)Time–frequency analysis
A method of determining when an image capture device with a rolling shutter is in an environment having a flickering illuminant by using autocorrelation or frequency analysis of difference vectors produced from first and second captured images.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES FUND 83 LLC
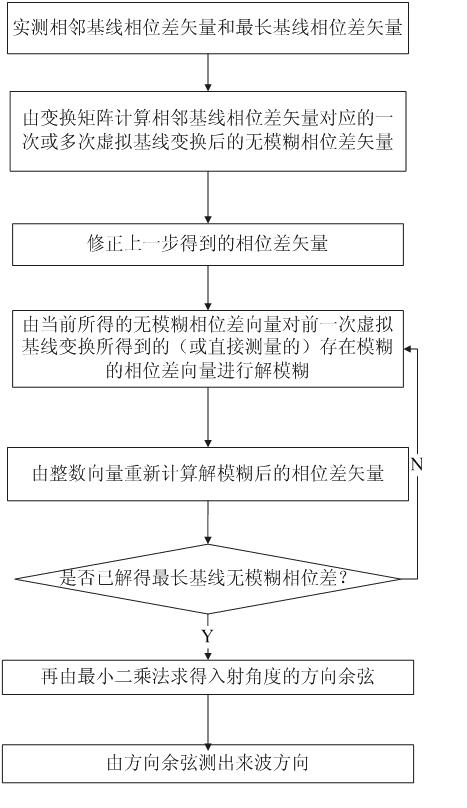
Round array phase interferometer two-dimensional (2D) direction-finding method based on virtual base line
The invention belongs to the technical field of communication radar, in particular relates to a broadband phase interferometer two-dimensional (2D) direction-finding method in radio monitoring. The invention provides a least square phase interferometer 2D direction-finding method based on a virtual base line defuzzification. The method comprises the following steps: firstly performing the virtualbase line conversion on a phase difference vector that is really measured on a short base line and has phase ambiguity once or several times so as to obtain a non-ambiguity virtual phase difference vector corresponding to the short base line; then orderly performing the defuzzification on the virtual phase difference vector, an adjacent base line phase difference vector and the longest base line phase difference vector, which all have ambiguity, according to the virtual phase difference vector, and finally estimating an incident direction by using the least square method according to the non-ambiguity longest base line difference vector. The defuzzification based on the virtual base line conversion provided by the invention can be used for obtaining a high-accuracy and non-ambiguity 2D direction-finding result in existence of angle-measuring ambiguity, and is an efficient 2D angle-measuring algorithm.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method and system for biometric authentication and encryption
ActiveUS8312291B2Address privacy concernsEasily changeableDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationFeature vectorMean vector
A biometric user authentication method, includes enrolling a user based on user's biometric samples to generate user's reference data; and authenticating the user based on a user's live biometric sample and the user's reference data; wherein enrolling a user includes acquiring the user's biometric samples; extracting an enrollment feature vector from each user's biometric sample; computing a biometric reference template vector as a mean vector based on the enrollment feature vectors; computing a variation vector based on the enrollment feature vectors and the mean vector; randomly generating an enrollment secret vector; computing an enrollment code vector based on the enrollment secret vector and the variation vector; computing a difference vector as a wrap-around difference between the enrollment code vector and the mean vector; computing an error correction vector based on the enrollment secret vector to enable error correction during the user authentication phase according to a given error tolerance level, wherein the error correction vector is not computed if the error tolerance level is equal to zero; and storing the variation vector, the difference vector, and the error correction vector as a part of the user's reference data to be used during the user authentication phase.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
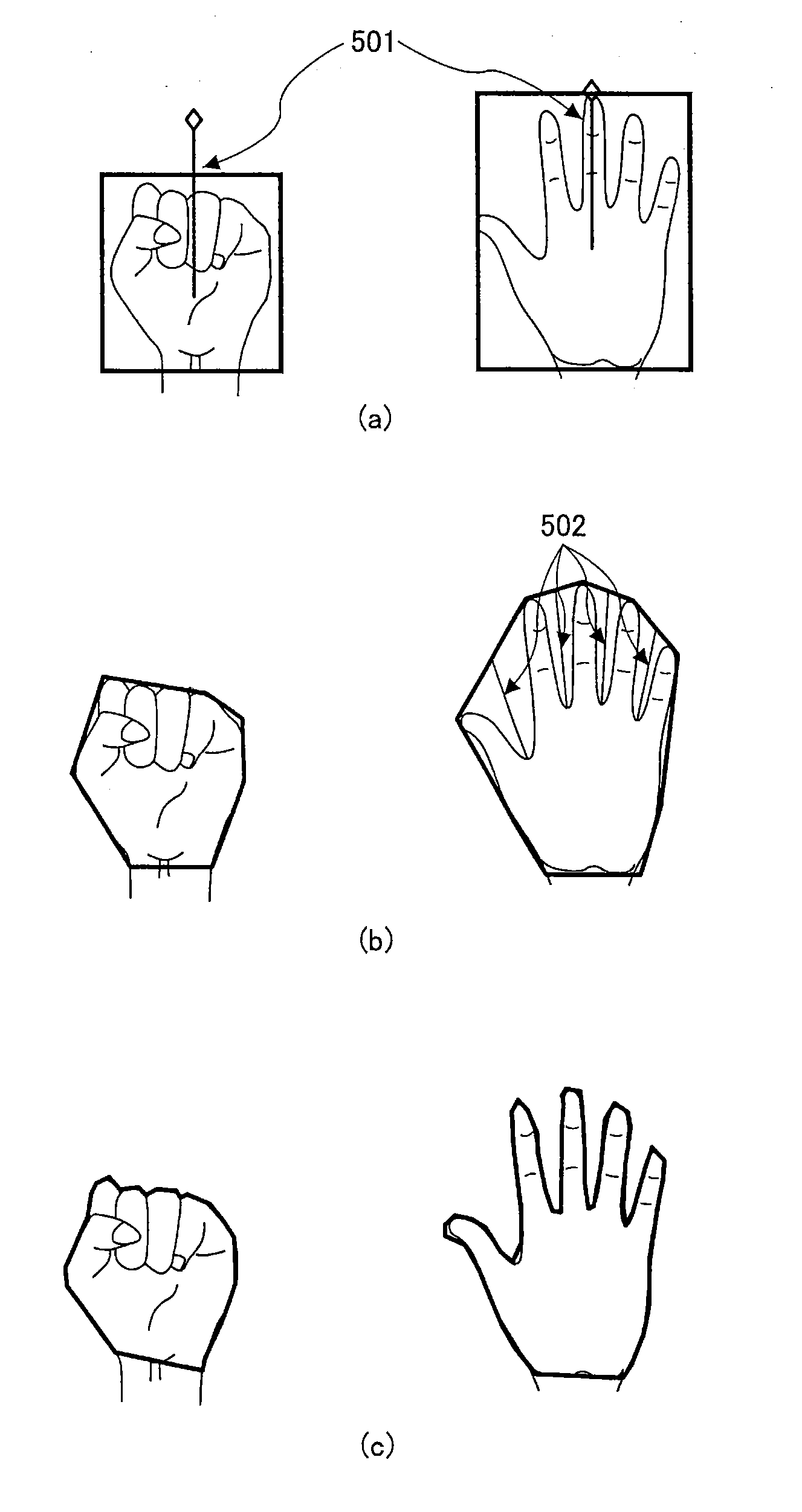
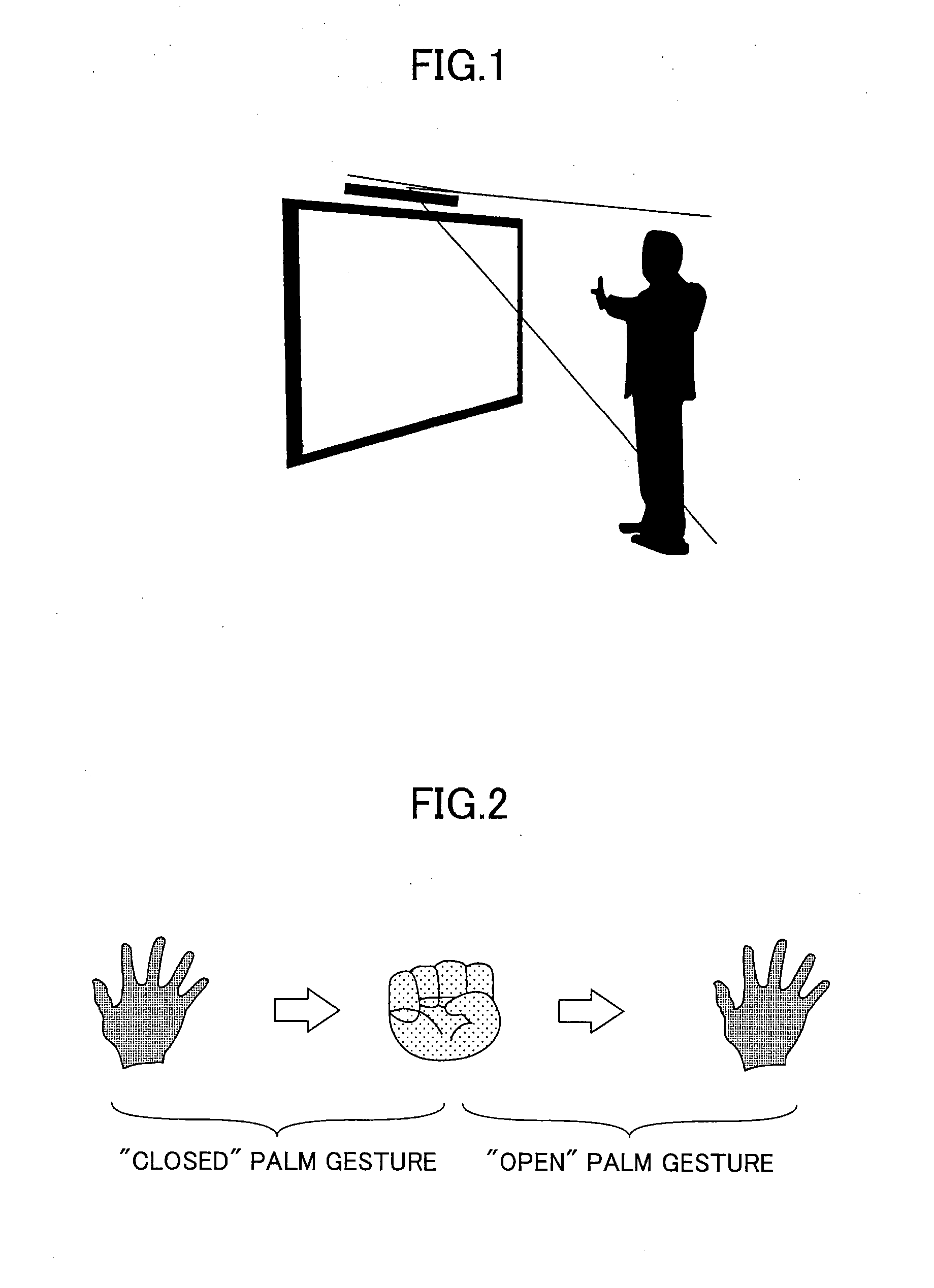
Palm gesture recognition method and device as well as human-machine interaction method and apparatus
ActiveUS20140198031A1Recognition errorGuaranteed recognitionInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionMaximum differenceHuman–computer interaction
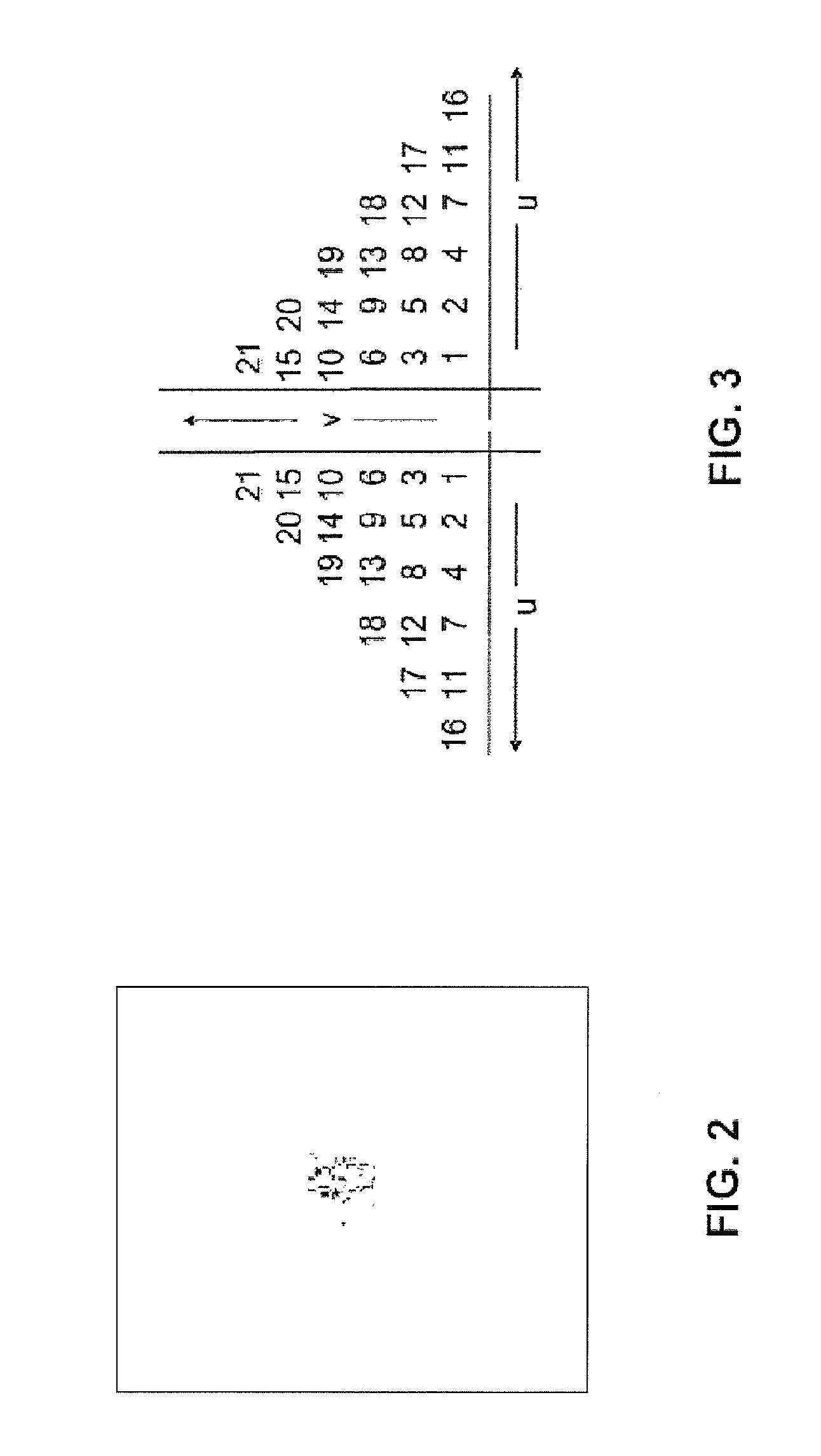
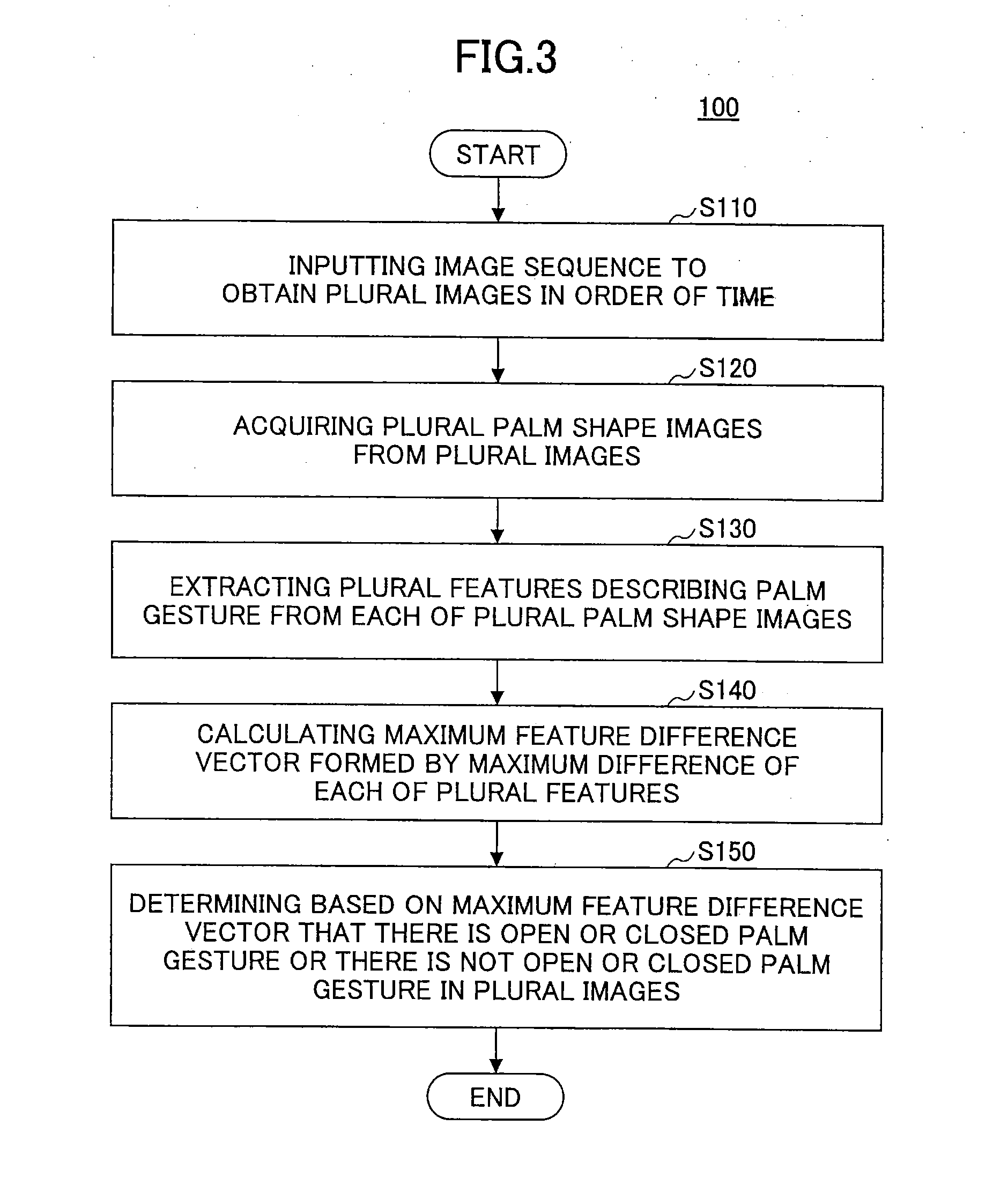
Disclosed is a palm gesture recognition method comprising a step of obtaining plural images according to an order of time; a step of acquiring plural palm shaped images from the plural images; a step of extracting plural features describing an open or closed palm gesture from each of the plural palm shaped images; a step of calculating a maximum feature difference vector formed by a maximum difference of each of the plural features; and a step of determining, on the basis of the maximum feature difference vector, that there is the open or closed palm gesture or there isn't the open or closed palm gesture in the plural images.
Owner:RICOH KK
Apparatus and method for detecting defects in periodic pattern on object
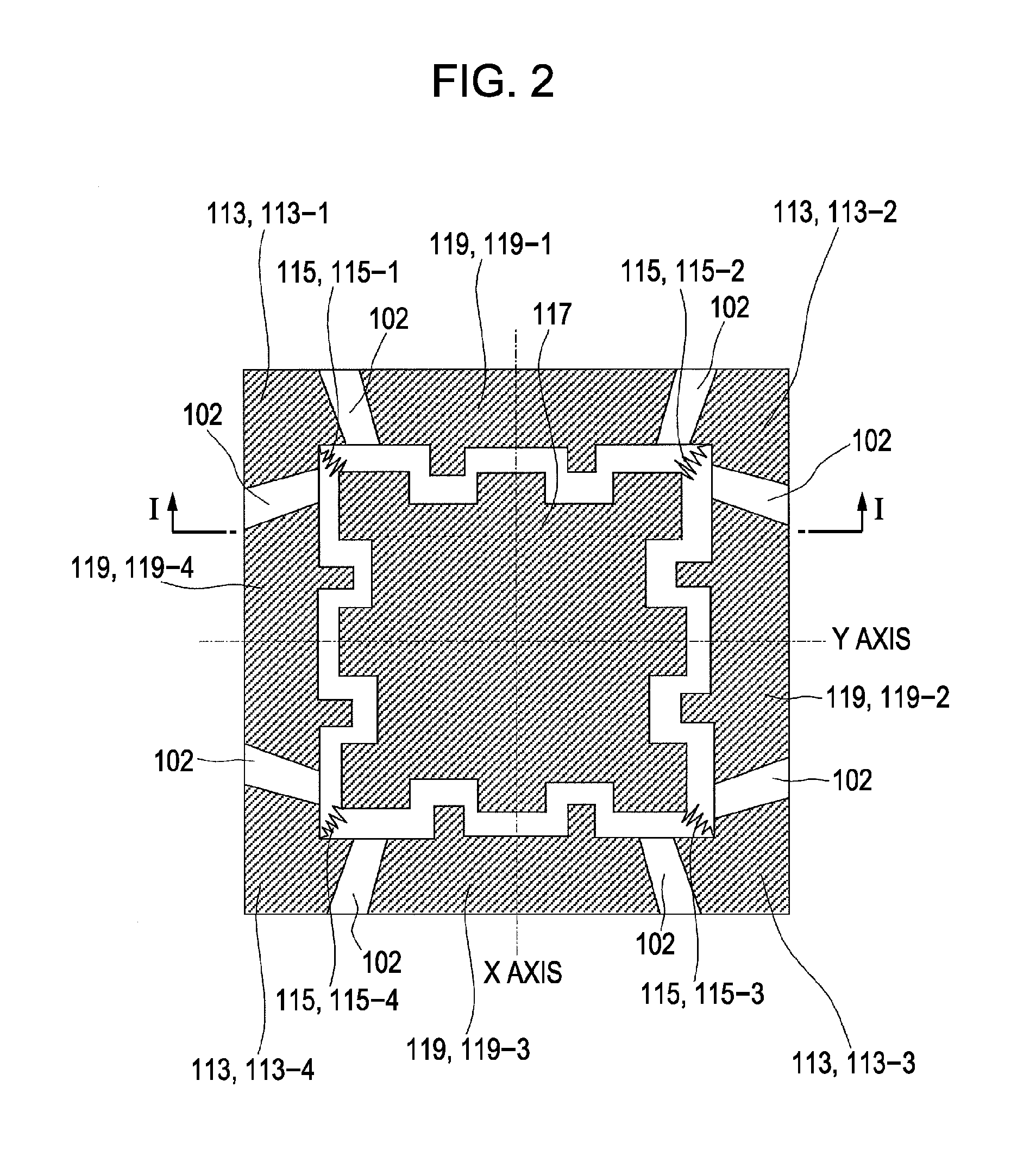
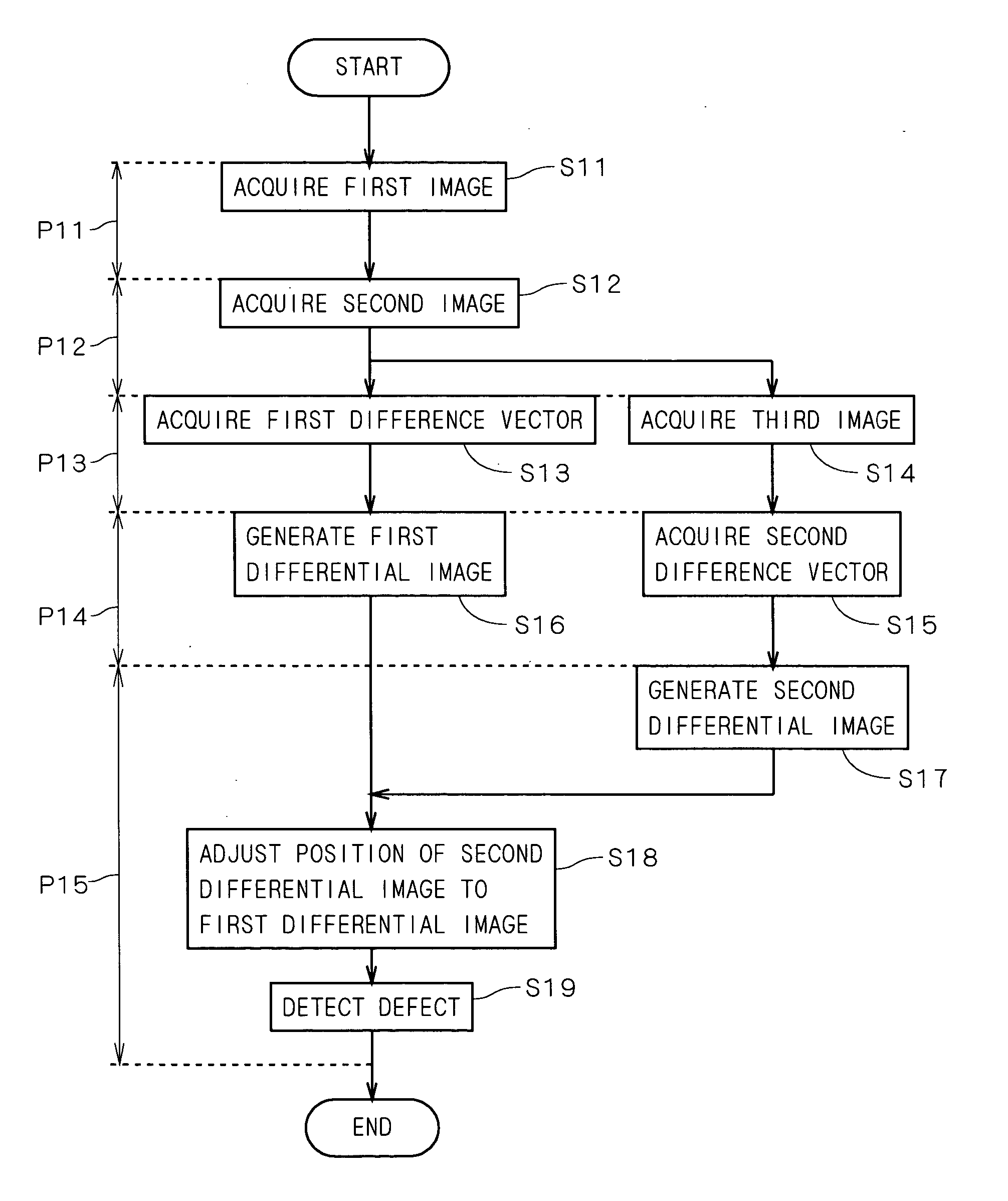
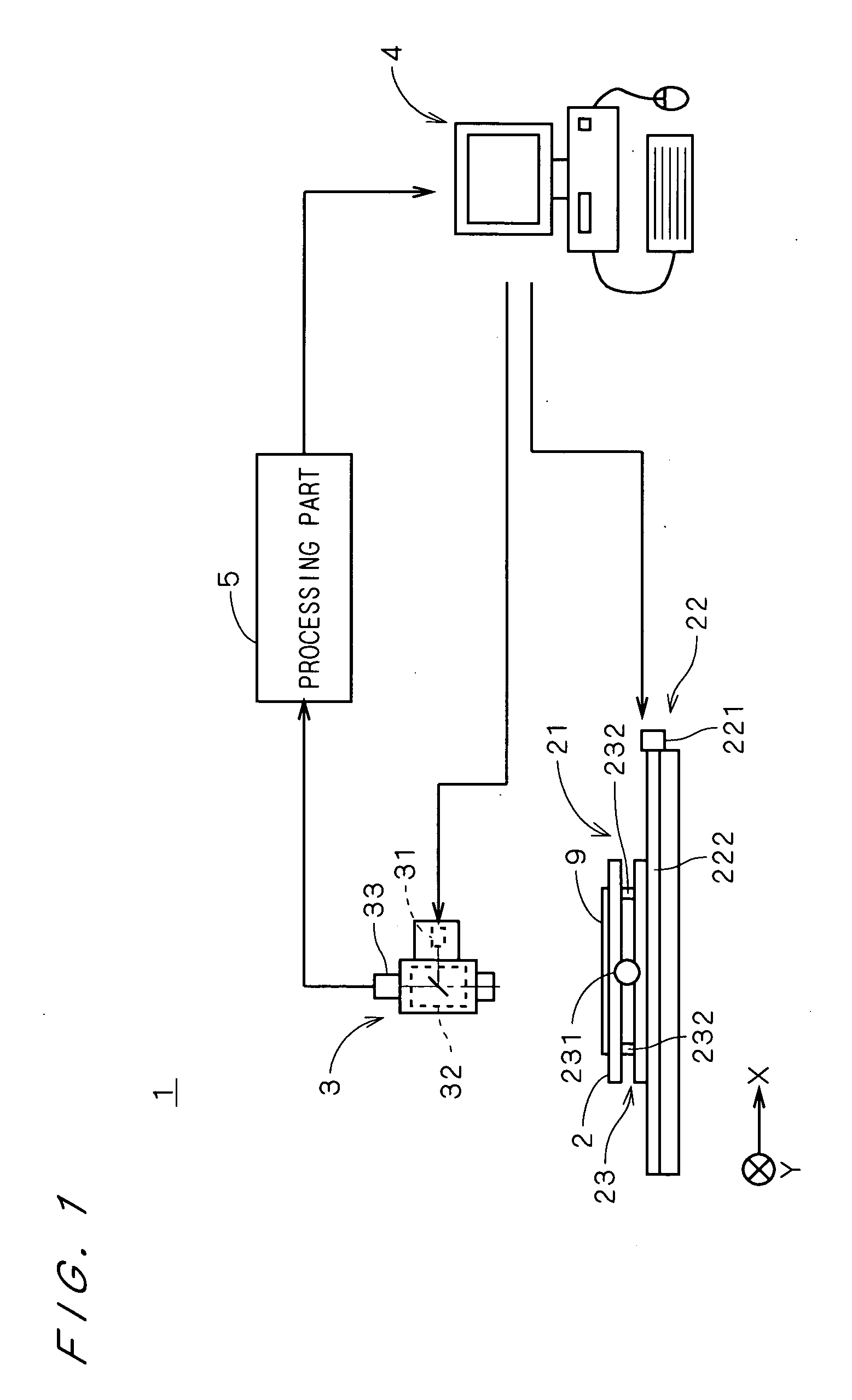
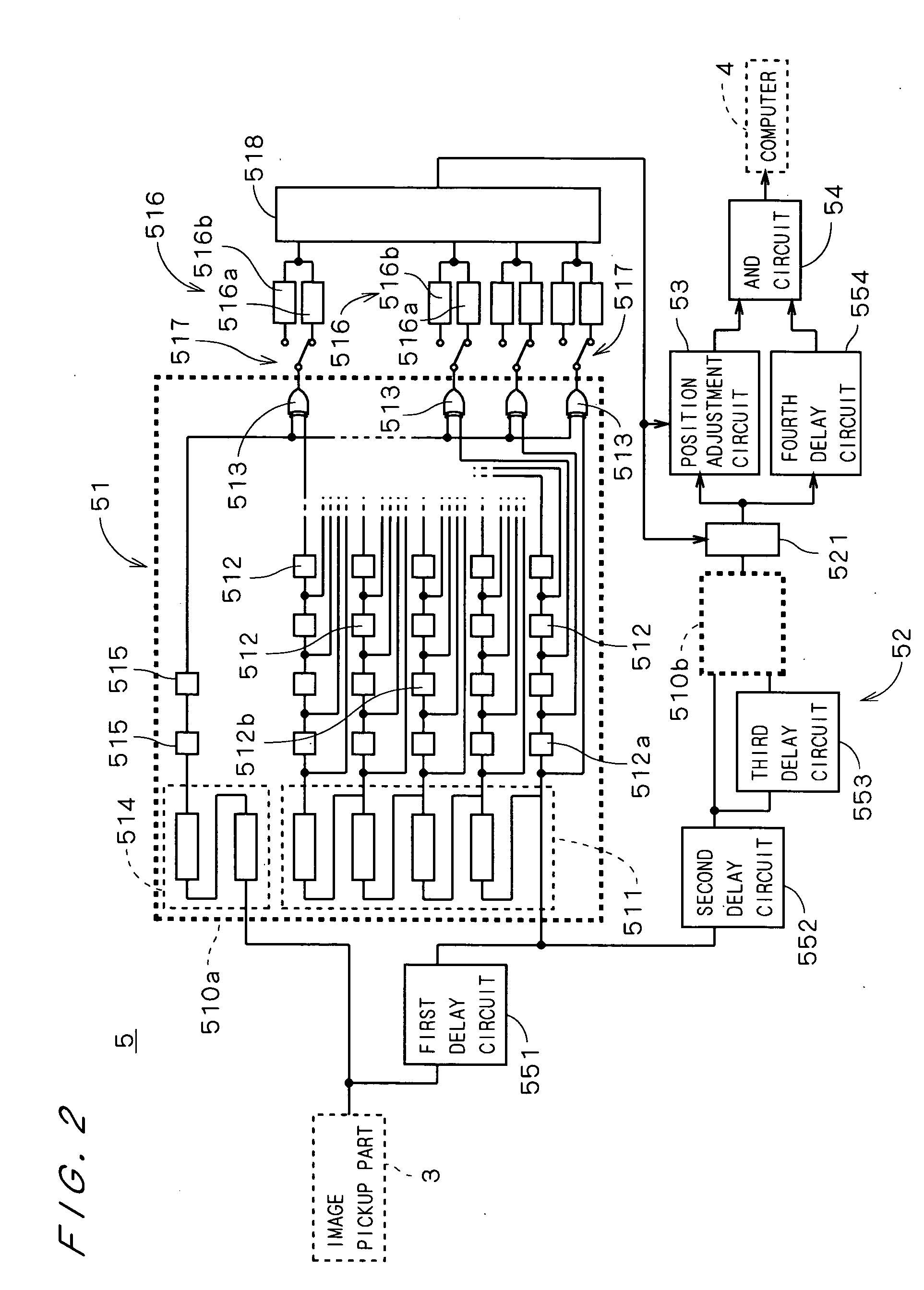
InactiveUS20050232478A1Improve accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisImage generationDifference vector
In a defect detection apparatus, images of first to third inspection areas on a substrate are picked up to acquire first to third images. A positional difference acquisition part (51) acquires a first difference vector between the first image and the second image and a second difference vector between the second image and the third image. A differential image generation part (52) generates a first differential image between the first image and the second image while adjusting a position of the first image to the second image on the basis of the first difference vector and a second differential image between the second image and the third image while adjusting a position of the second image to the third image on the basis of the second difference vector. Then, a position of the second differential image is adjusted to the first differential image on the basis of the second difference vector and the second differential image after position adjustment and the first differential image are compared with each other, to detect a defect in a periodic pattern on the substrate with high accuracy.
Owner:DAINIPPON SCREEN MTG CO LTD
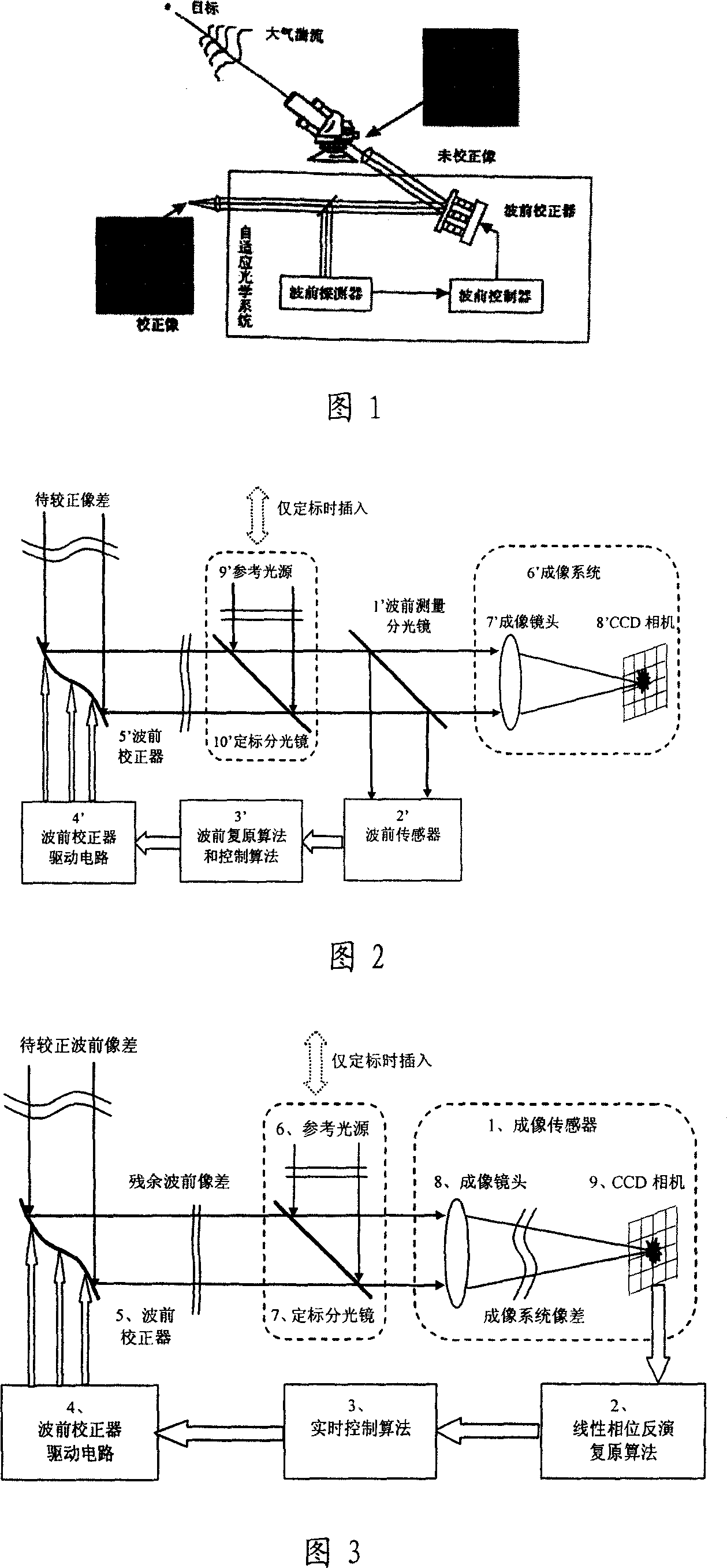
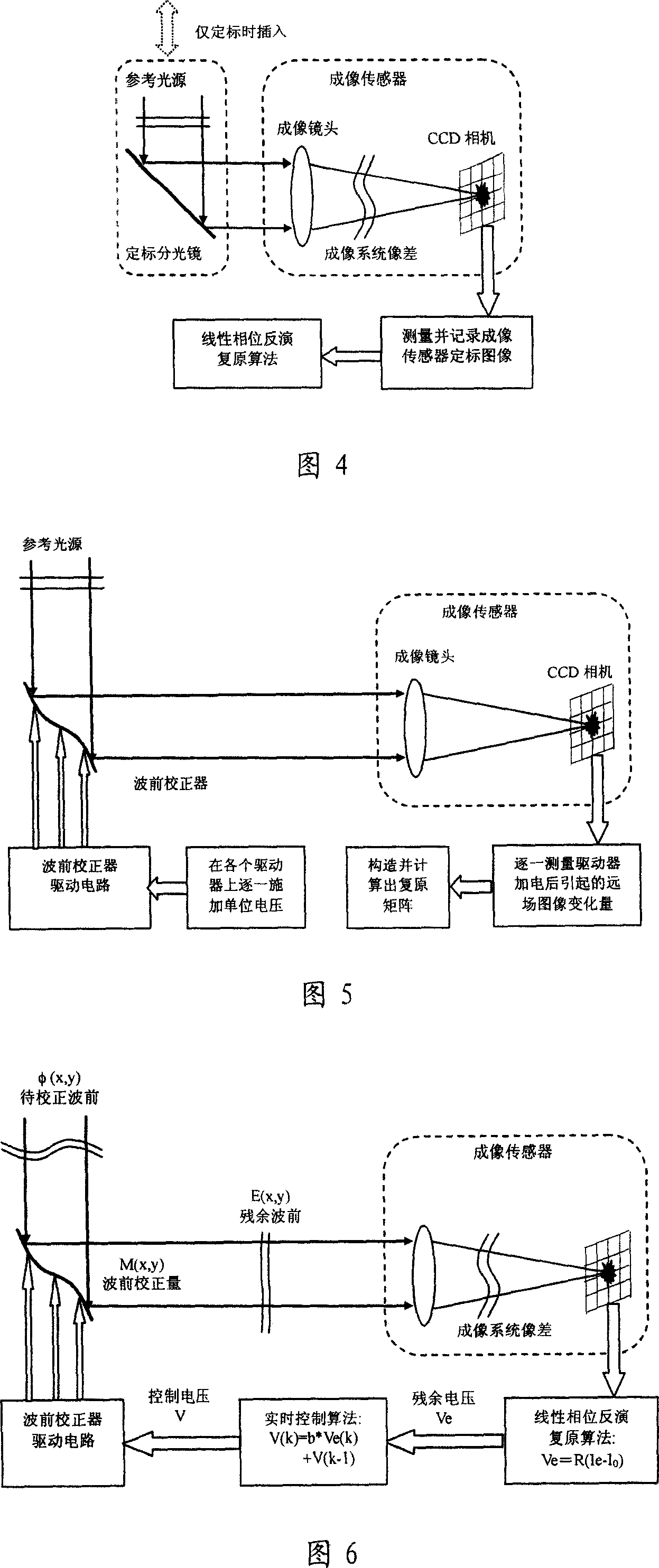
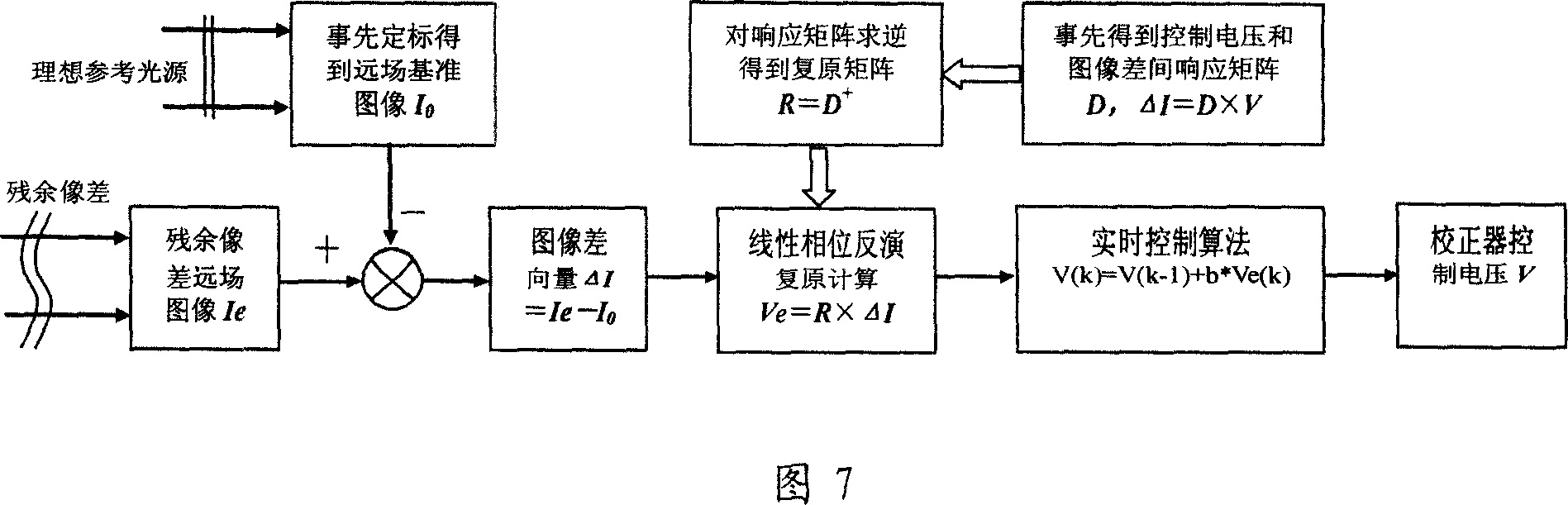
Self-adaptive optical system based on linear phase inversion restoration technology
InactiveCN101013195ASimple structureImprove light energy utilizationOptical measurementsOptical elementsInversion recoveryTime control
It is an adaptive optics system based on the linear phase inversion recovery technique, comprising the imaging sensor, the linear phase inversion recovery algorithm, the real-time control algorithm, the wave-front correction and drive circuit, and the reference light source. During the system running, the imaging sensor measures the residual aberration far-field image after the compensation of the wave-front correction device, and subtracting with the benchmark image to obtain the image difference vector. In advance, using the reference light source to calibrate the imaging sensor to obtain the benchmark image, and according to the corresponding relations between the wave-front correction device and the imaging sensor, obtaining the recovery matrix between the image difference vector and control voltage. Multiply the image difference vector and the recovery matrix to obtain the corresponding control voltage of the residual wave-front, and use real-time control algorithms, such as proportional integral, to obtain the control voltage of the wave-front correction device, making the wave-front aberration to be corrected. Compared the adaptive optics system based on the linear phase inversion recovery technique and the conventional adaptive optical technology, it has simple structure, high optical energy efficiency, and other advantages.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
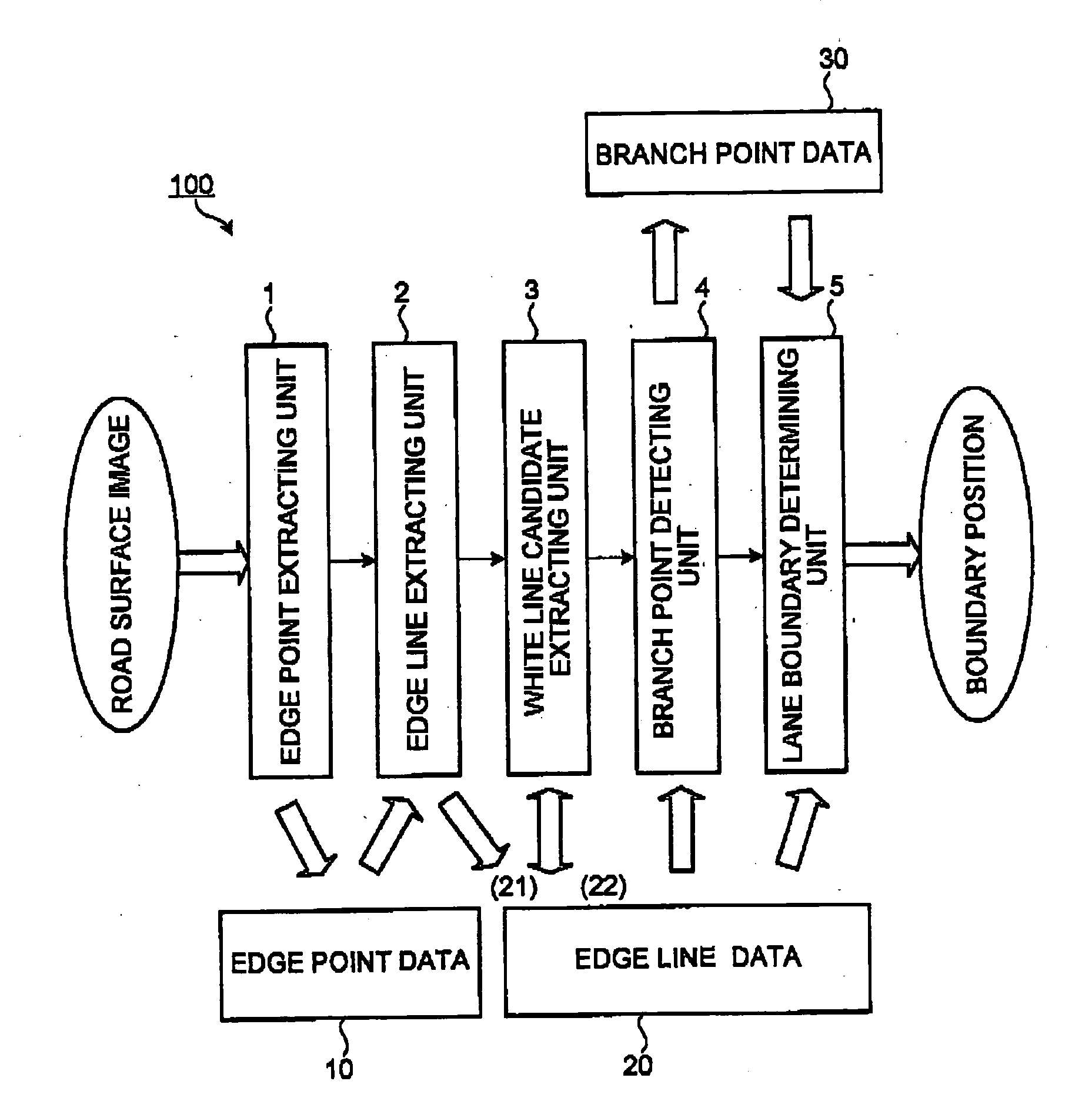
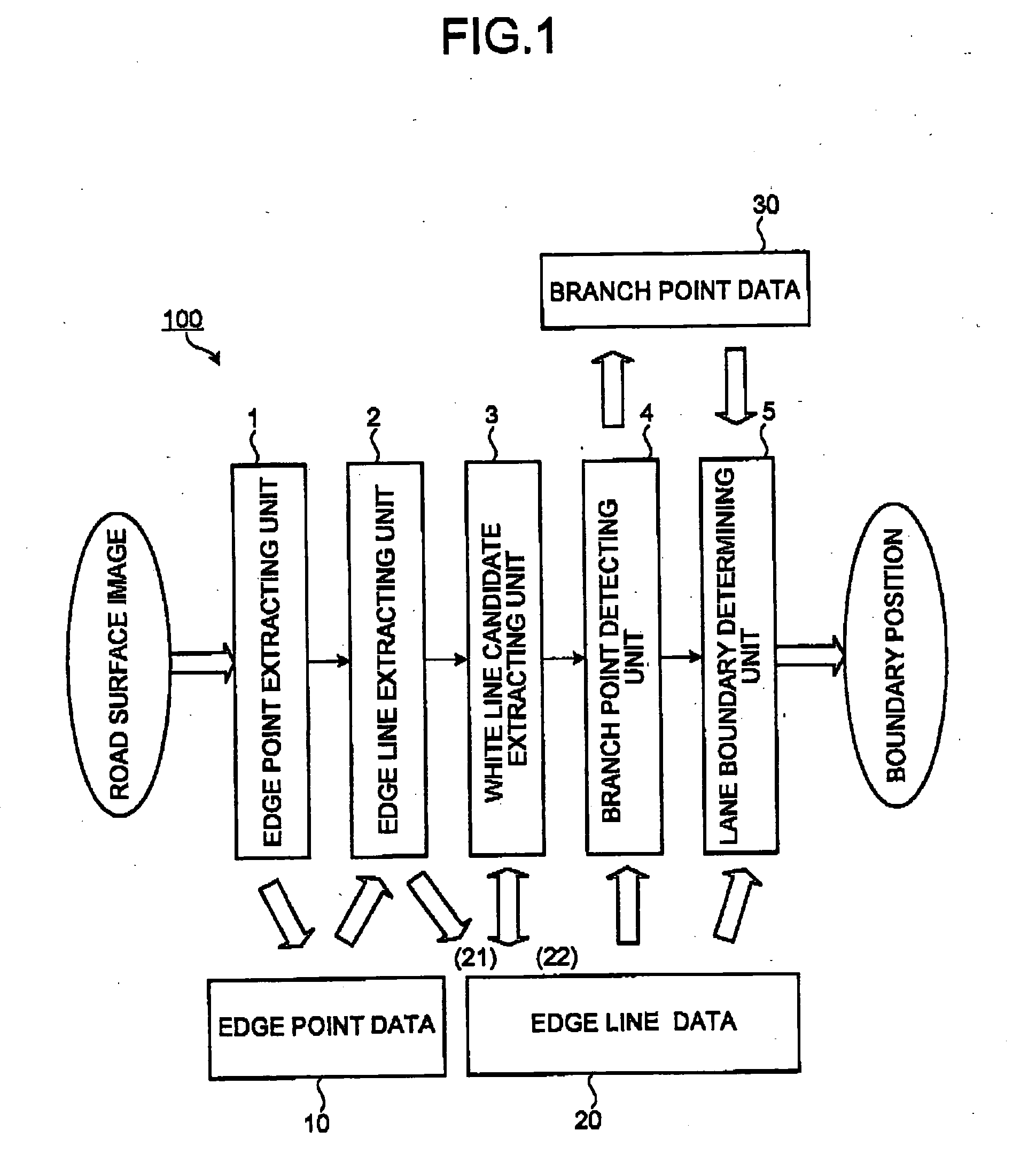
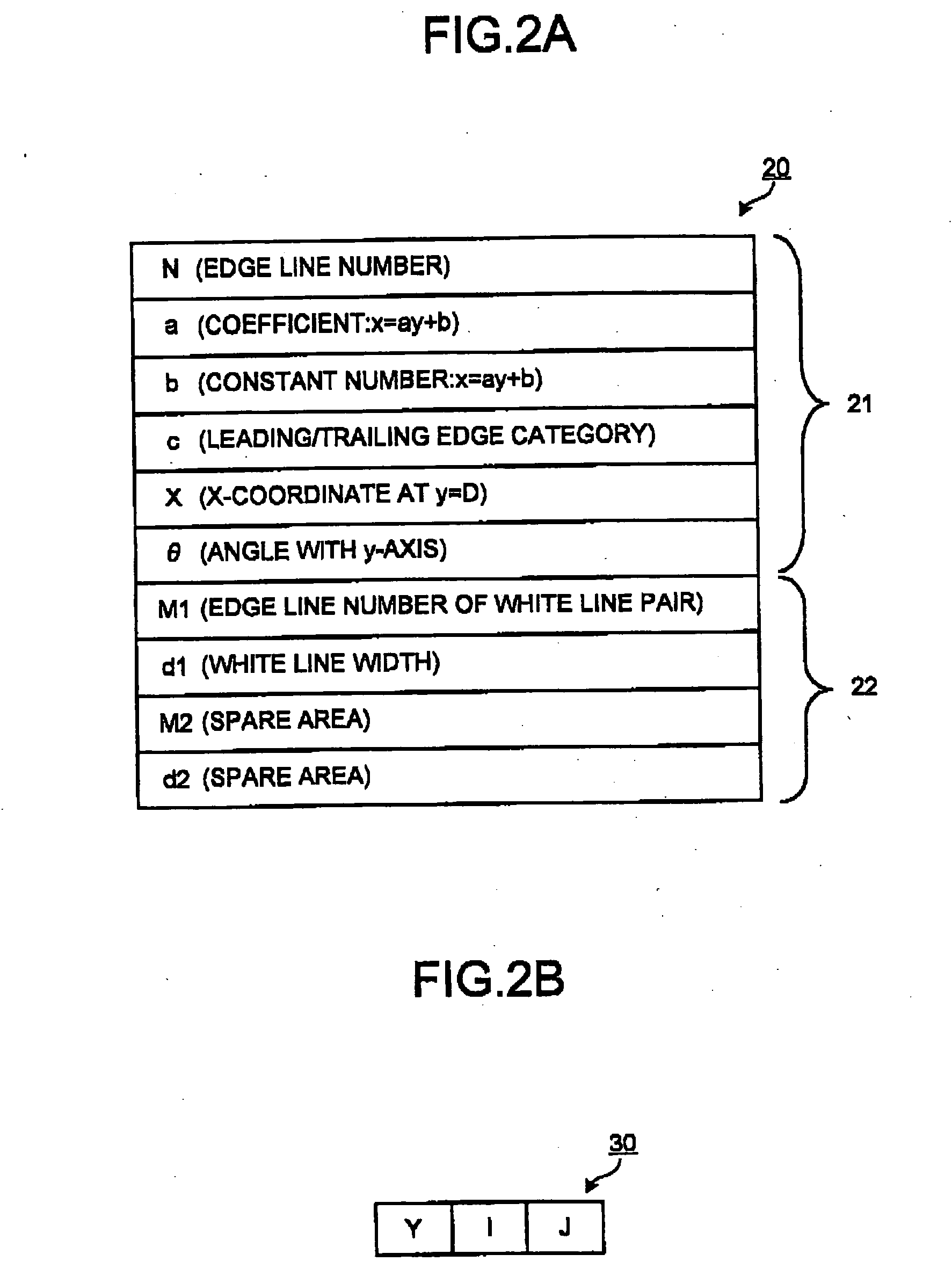
Lane boundary detector
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Multi-kernel support vector machine multi-instance learning algorithm applied to pedestrian re-identification
ActiveCN103839084AImprove recognition rateCharacter and pattern recognitionRe identificationPedestrian
The invention discloses a multi-kernel support vector machine multi-instance learning algorithm applied to pedestrian re-identification. The algorithm includes two main steps, namely multi-feature description and a multi-kernel SVM model multi-instance learning algorithm. According to the algorithm, HSV color features and SIFT local features of two pictures, taken under a camera A and a camera B, of the same pedestrian are extracted to construct a word bag, and difference vectors of the two kinds of the features represent the conversion relation under the two cameras to serve as two instance samples and are encapsulated as a bag; then a multi-kernel support vector machine model is optimized, the bag is trained by means of linear fusion of the Gaussian kernel and a polynomial kernel, optimal parameters are obtained through multi-instance learning, and a high identification rate is achieved.
Owner:HUZHOU TEACHERS COLLEGE
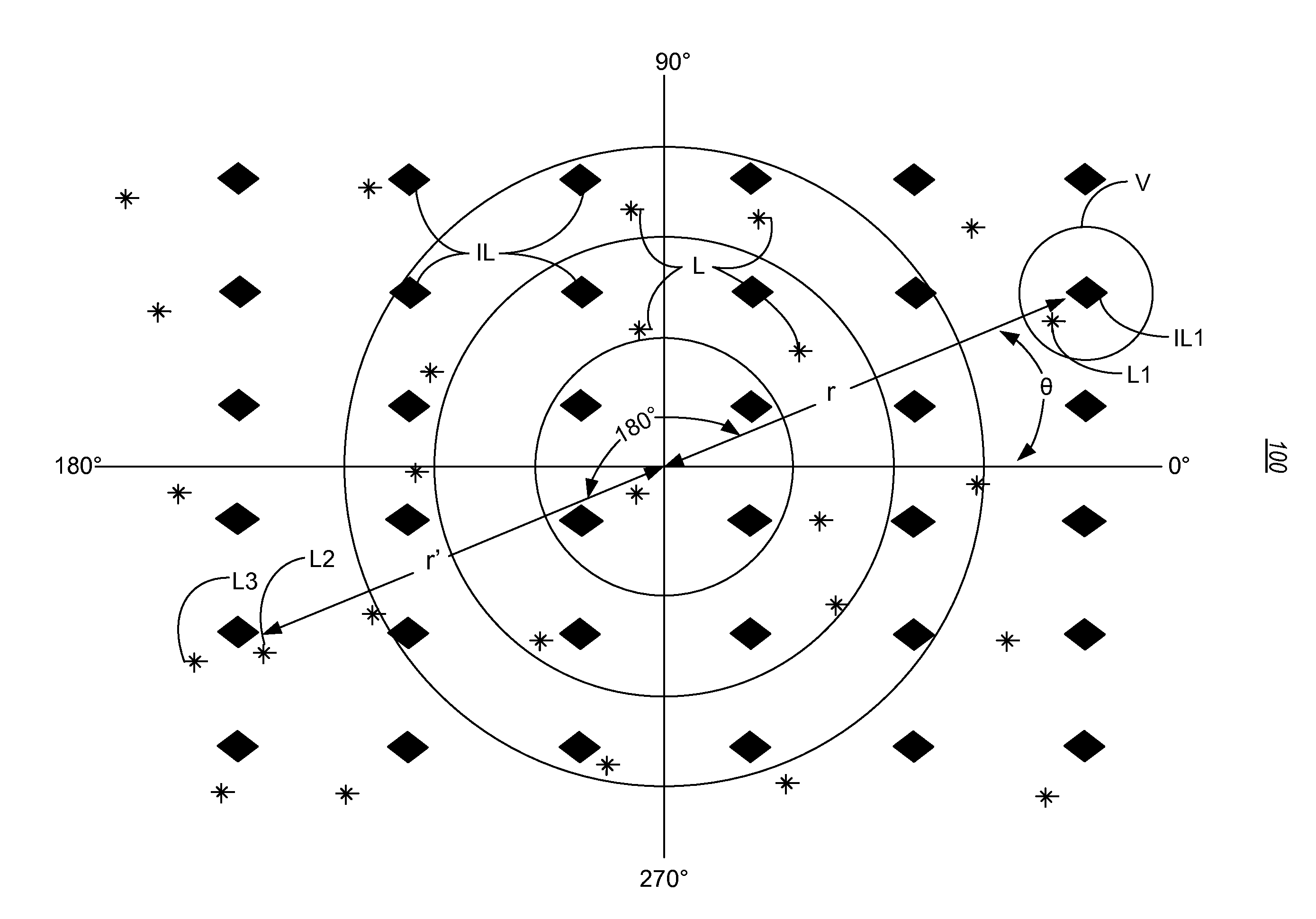
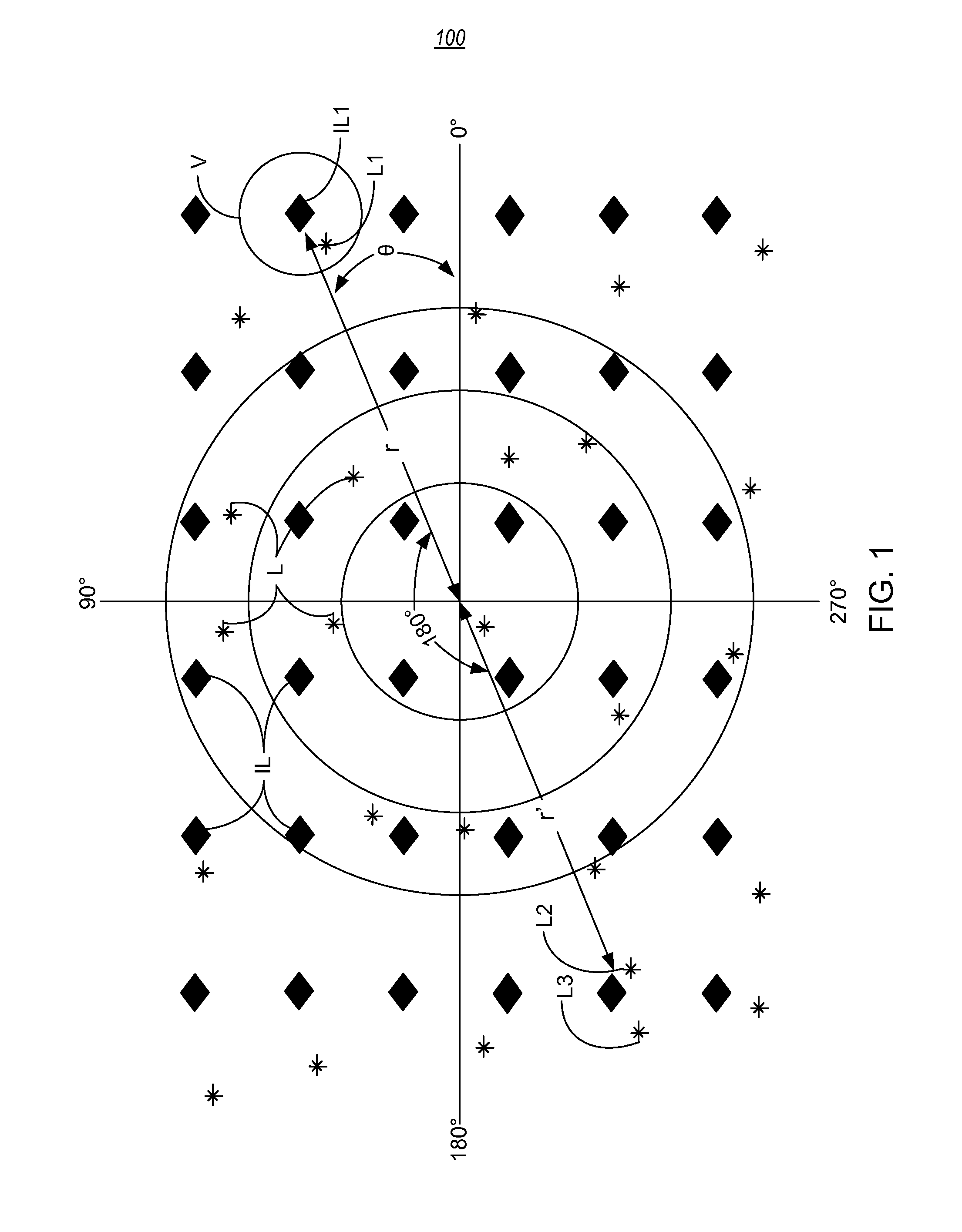
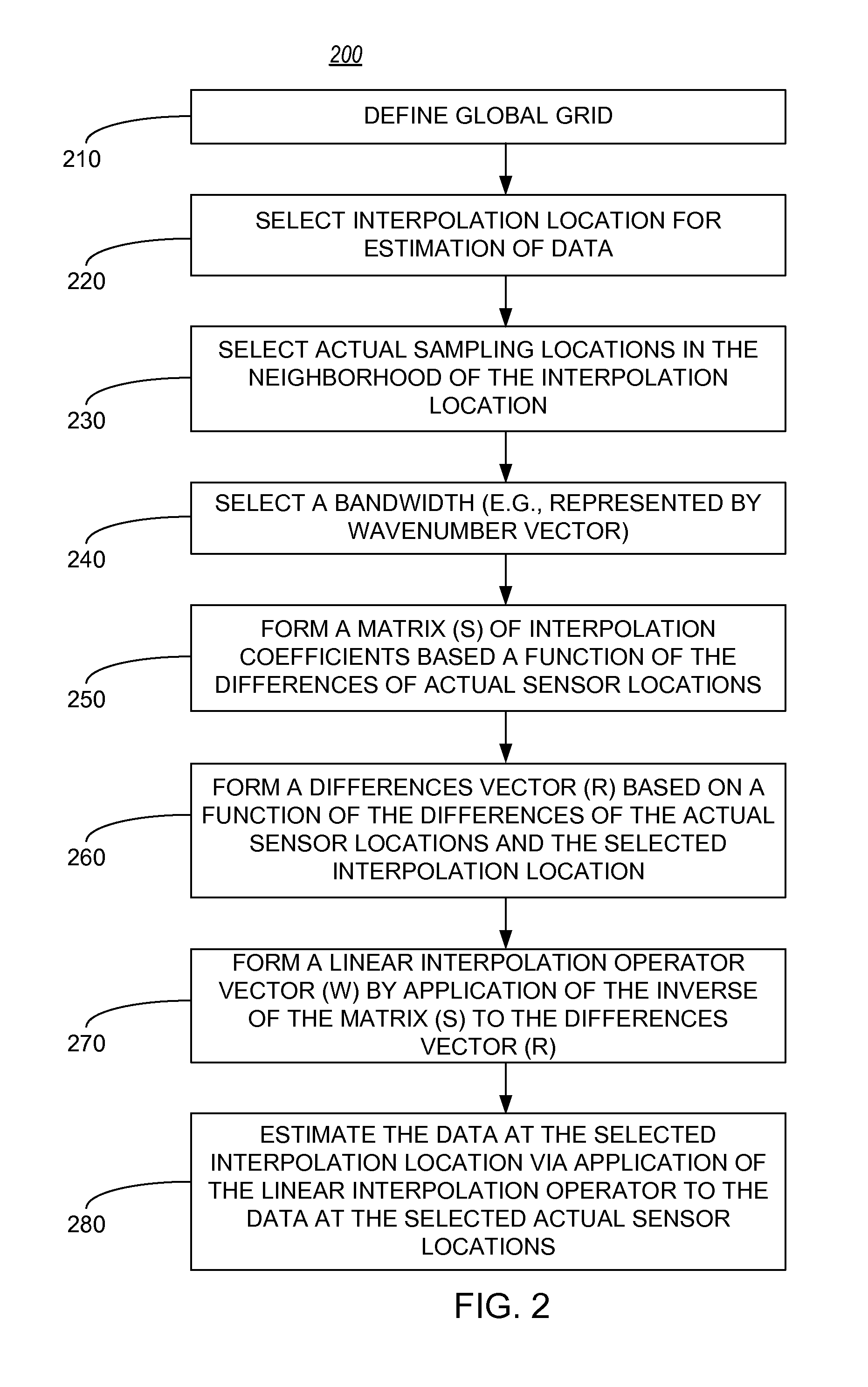
Interpolation of periodic data
InactiveUS20110191032A1Well formedDigital computer detailsSeismic signal processingData valueCoefficient matrix
A method for interpolating data. The method includes receiving data acquired at one or more locations where the data represents subterranean formations in the earth. The method also includes selecting one or more of the locations such that the selected locations are within a vicinity of an interpolation location. Next, the method includes forming a matrix of interpolation coefficients based on a first function having one or more interpolation variables, a bandwidth for an interpolation operator and one or more differences between the selected locations, wherein at least one of the interpolation variables is periodic. The method then includes forming a differences vector based on a second function having the interpolation variables, the bandwidth and one or more differences between the selected locations and the interpolation location. Using the matrix of interpolation coefficients and the differences vector, the method then forms an interpolation operator vector by applying an inverse of the matrix of interpolation coefficients to the differences vector. The method then estimates a data value for the interpolation location using the interpolation operator vector.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Electrocardiosignal R peak detection method based on waveform characteristic matching
InactiveCN101828918AOvercoming the Effects of DriftWith translationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalWave form
The invention provides an electrocardiosignal R peak detection method based on waveform characteristic matching. The method utilizes waveform characteristic matching to identify R peak of electrocardiosignal, the characteristic matching method takes difference vector between points as basic characteristic, the basic characteristic has translational invariance and rotational invariance and can overcome influence of baseline drift of electrocardiosignal signal; meanwhile, logarithm polar coordinate transformation is carried out on the difference vector and partition is carried out to measure similarity of wave form, the measurement is sensitive to the adjacent morphological characteristic, can capture global outline information of wave form and has robustness to wave form ripple; besides, influence of interference signal can be eliminated by setting proper threshold, and further accurate identification and detection on R peak of electrocardiosignal are realized. The invention is applied to related electrocardiogram analyser, accurate identification on R peak of electrocardiosignal can be realized, thus being beneficial to improving detection and analysis capability of electrocardiogram analysis equipment.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
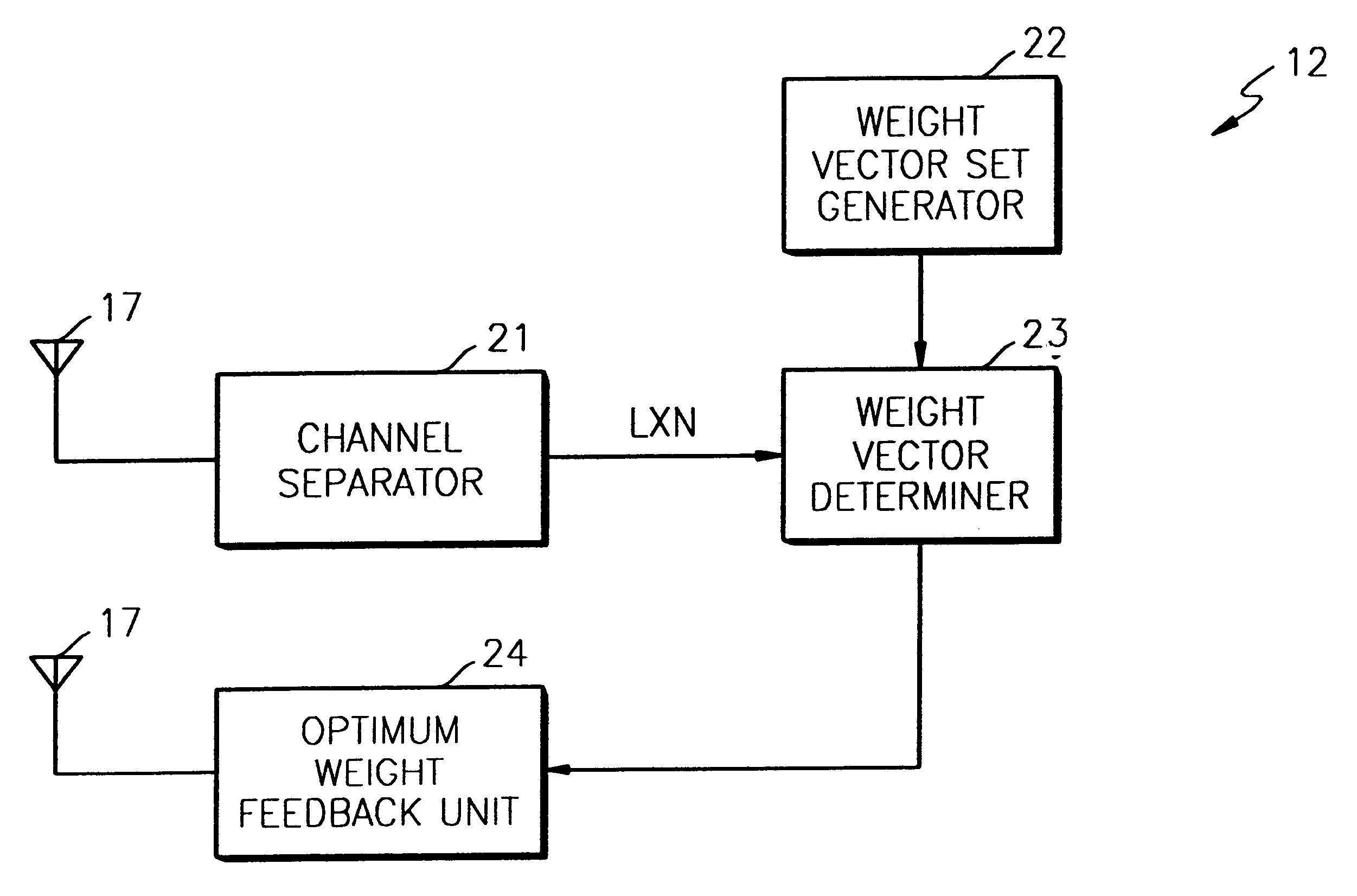
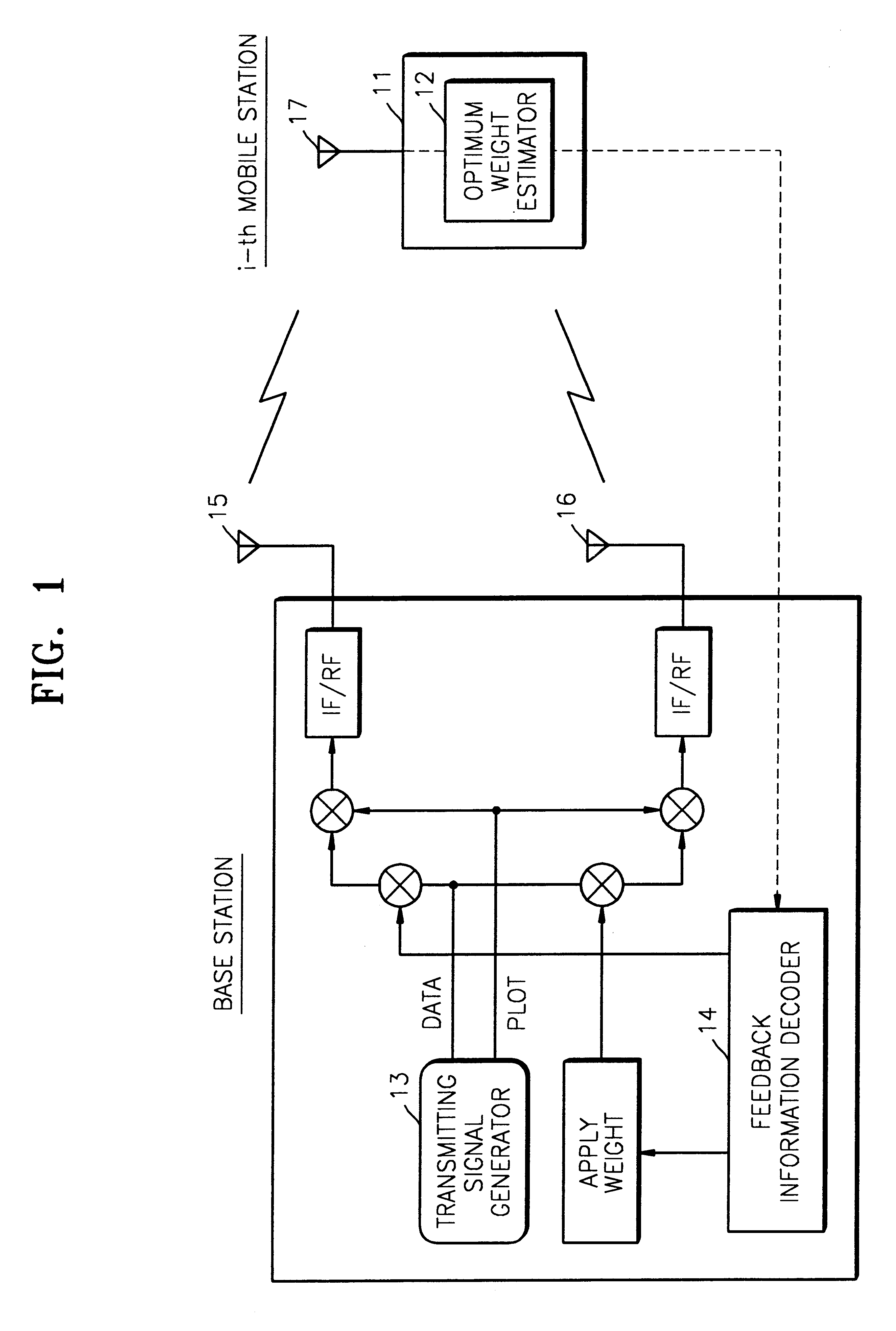
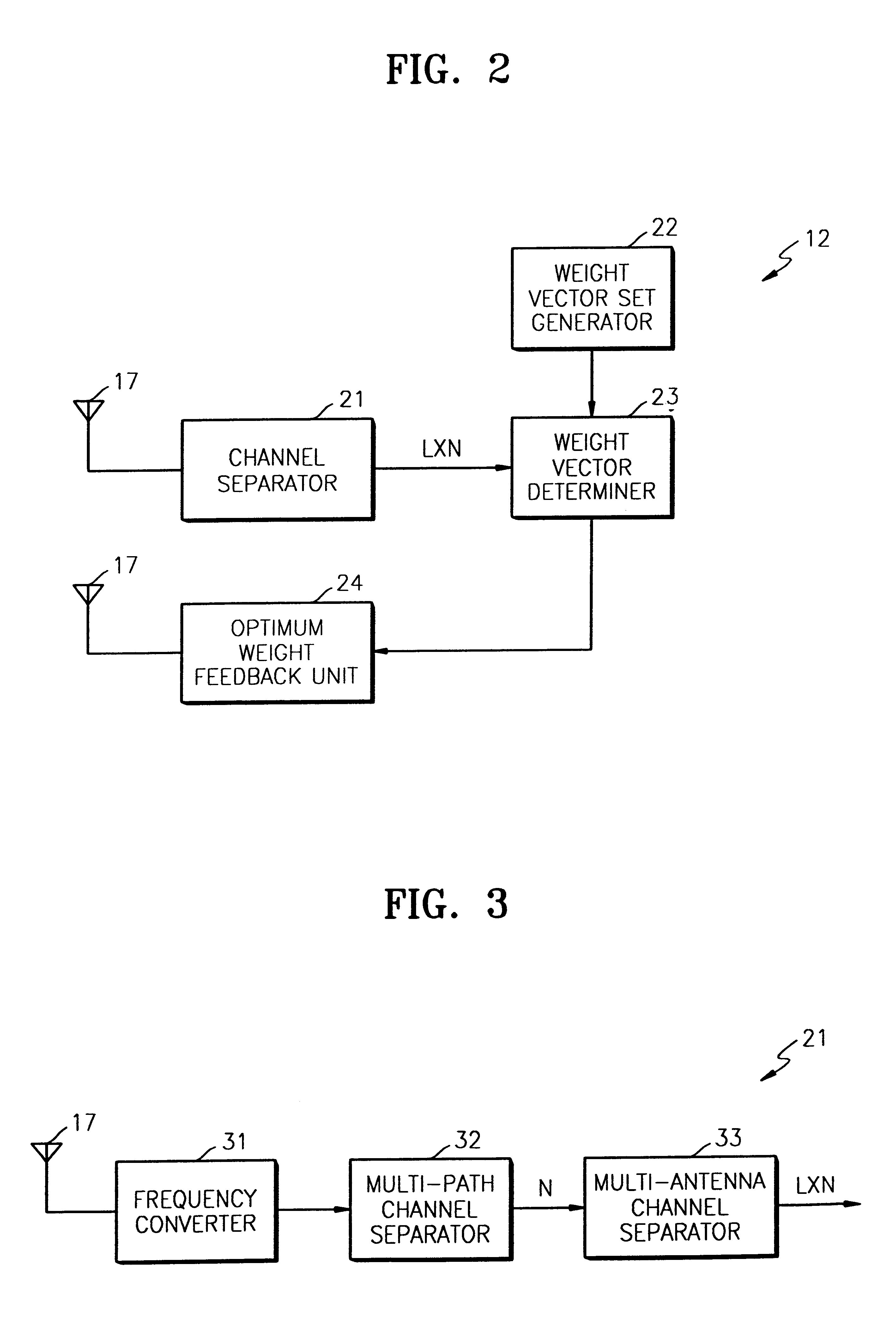
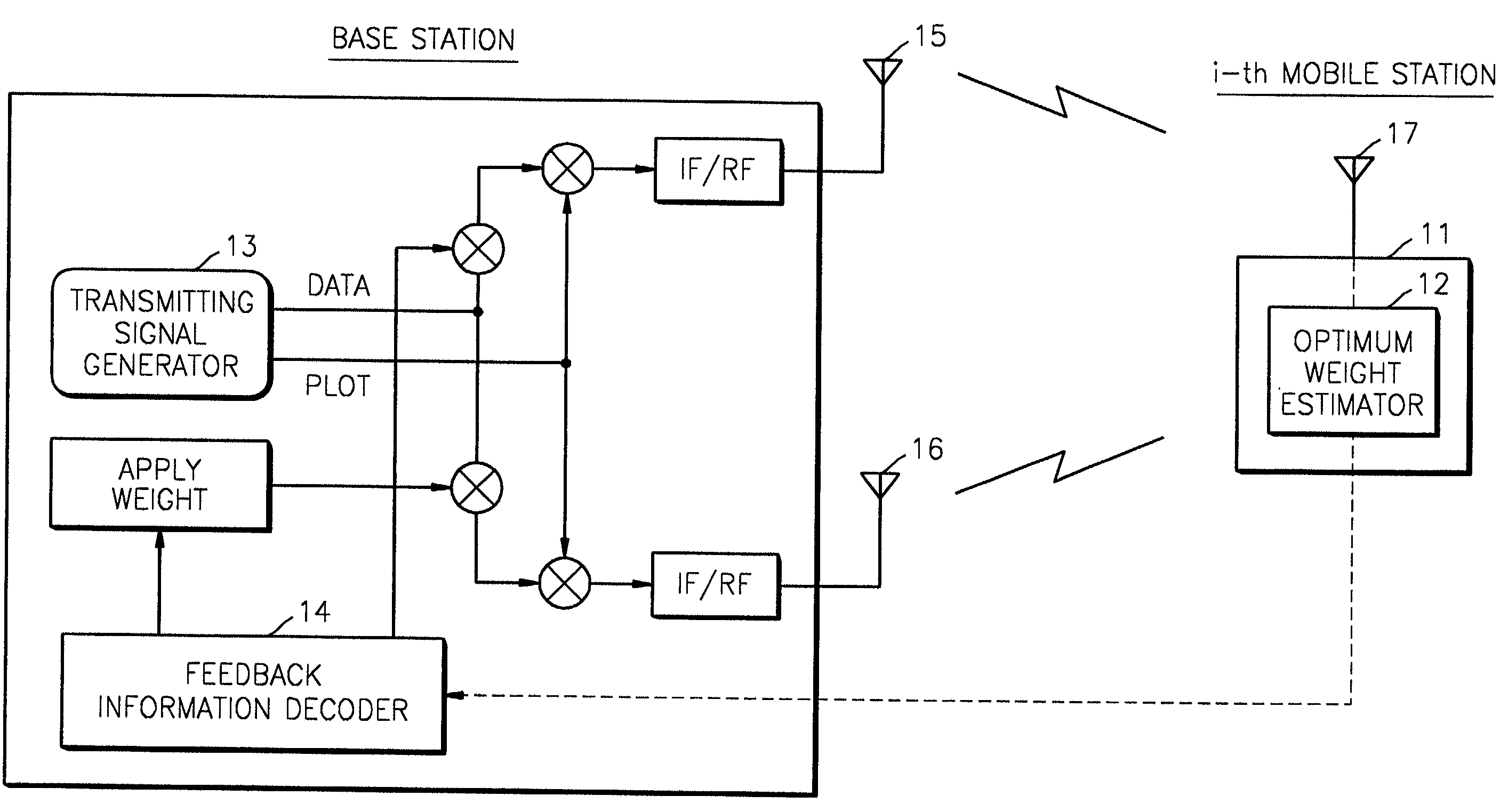
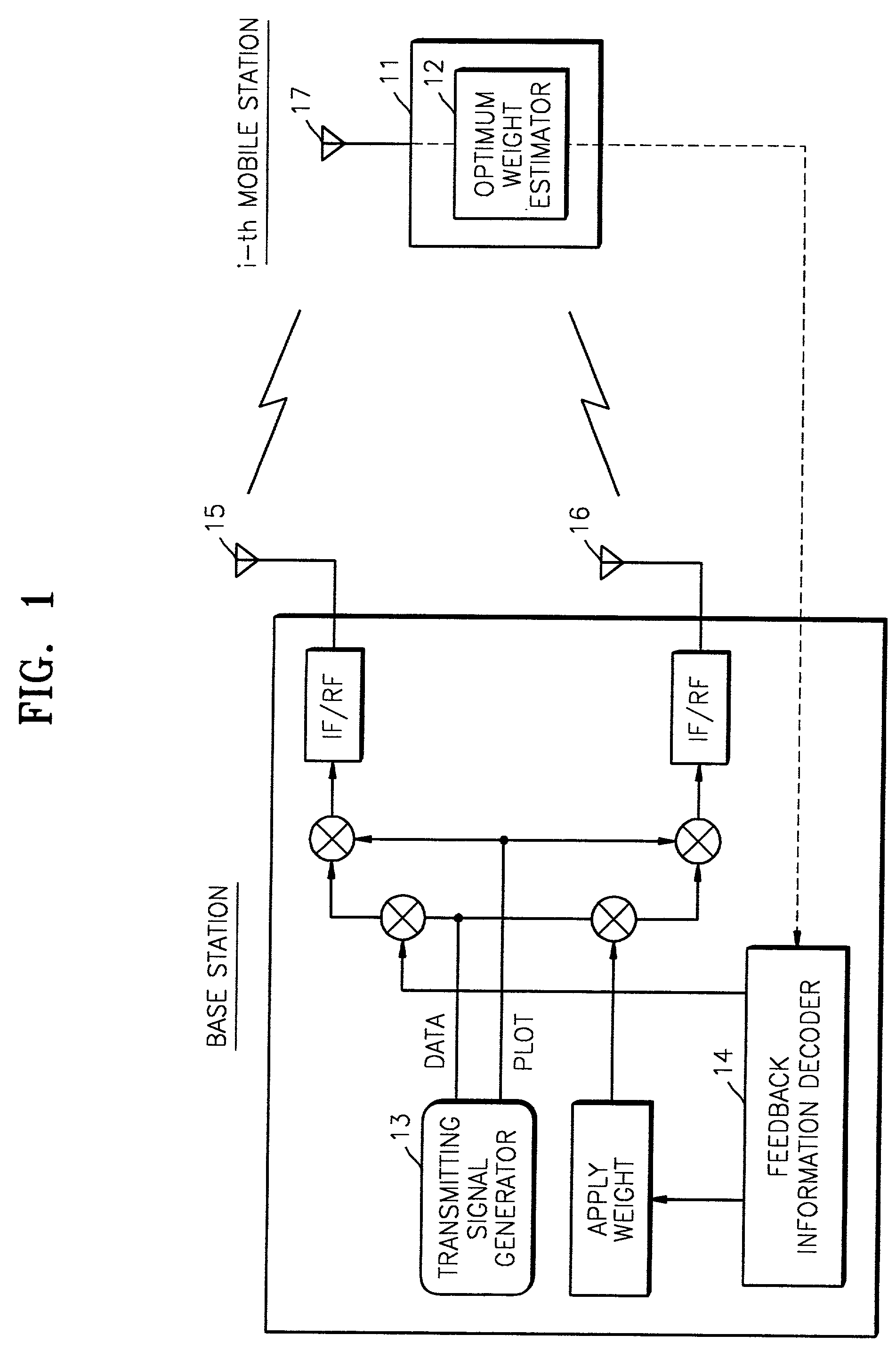
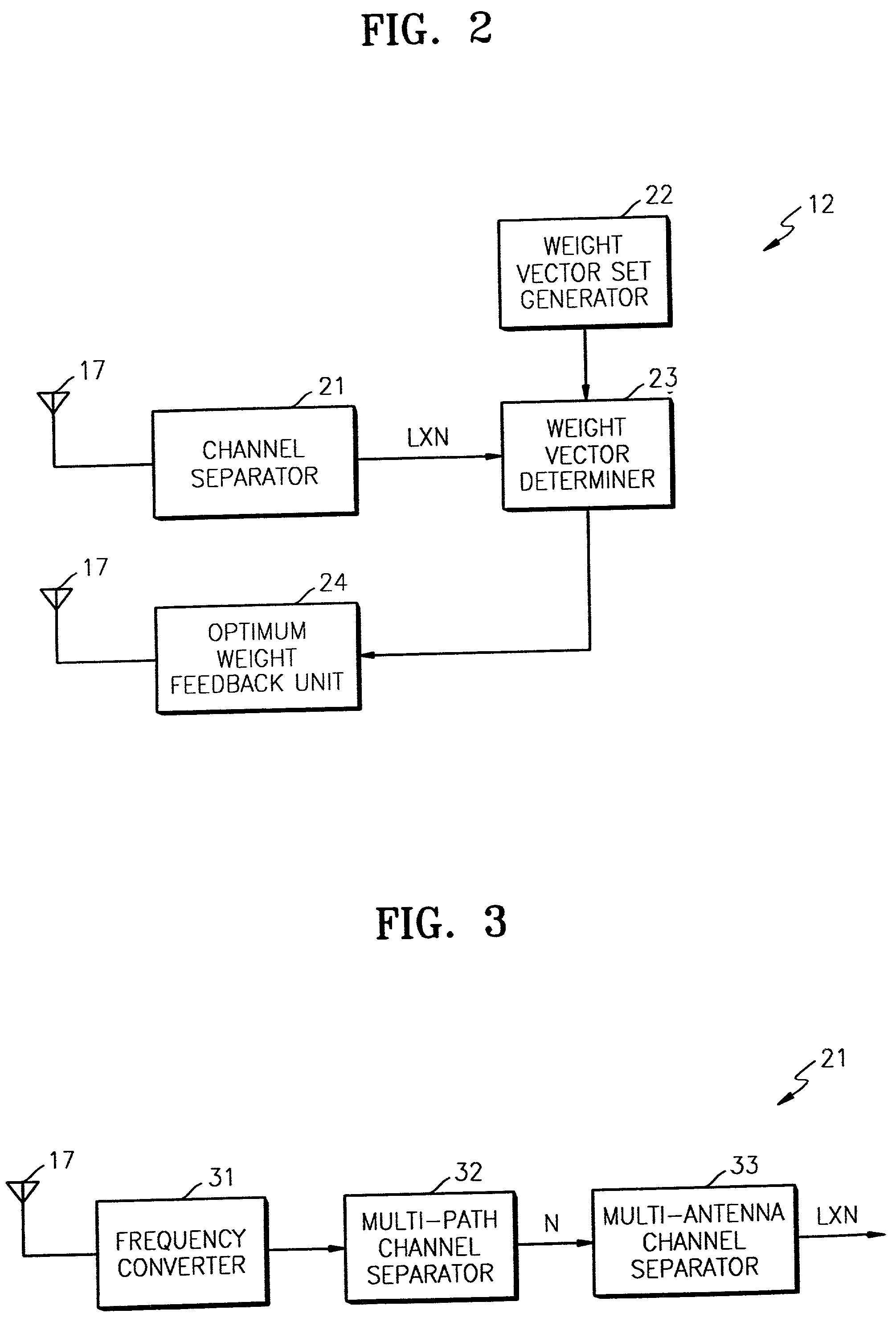
Method and apparatus for estimating optimum weight of closed loop transmit deversity for mobile communication
InactiveUS6766144B2Power Loss MinimizationImprove performanceEnergy efficient ICTSpatial transmit diversityClosed loopEngineering
An optimum weight estimating apparatus and method of a mobile station for a mobile communication system in which a base station uses closed transmit diversity technology. Conventionally, all weight vectors stored in a lookup table should be applied to an optimum weight estimator to calculate receiving power, so that the amount of calculation considerably increases when there are many antennas. To overcome this problem, the weights of the lookup table are appropriately adjusted so that the variation of the differences between two adjacent vectors can be minimized. An optimum weight is obtained using the difference vector between weight vectors, thereby simplifying the calculation of receiving power. Therefore, the power loss of the mobile station can be minimized.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Image processing device and image processing method
ActiveUS20140126642A1Reduced inhibition efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionParallaxImaging processing
The present technique relates to an image processing device and method capable of suppressing a decrease in encoding efficiency. The image processing device includes: a predictive vector generating unit that generates a predictive vector of a current parallax vector of a current block used in prediction using correlation in a parallax direction using a reference parallax vector referred when generating a predictive motion vector, when encoding the current parallax vector; and a difference vector generating unit that generates a difference vector between the current parallax vector and the predictive vector generated by the predictive vector generating unit. The present disclosure can be applied to an image processing device.
Owner:SONY CORP
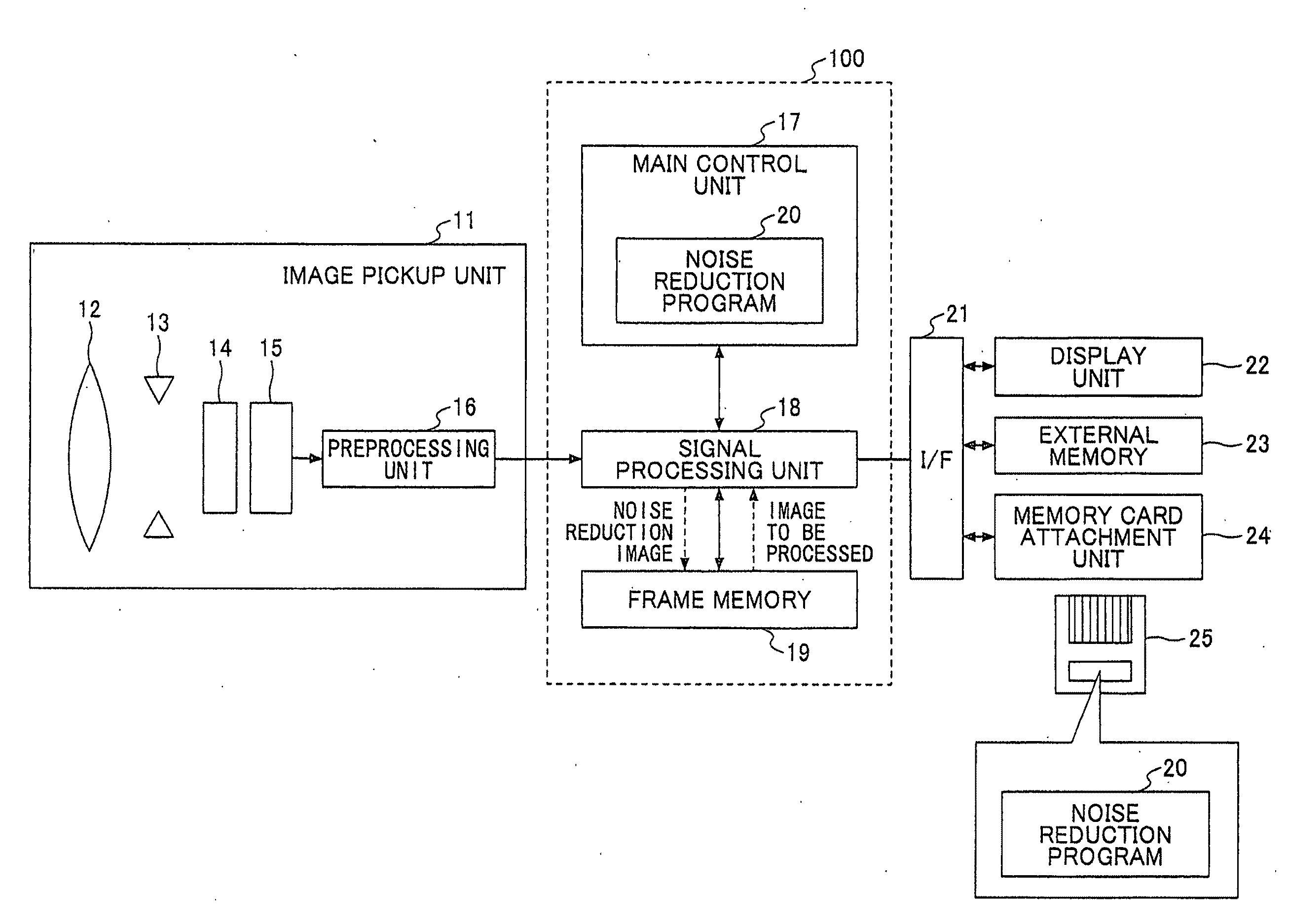
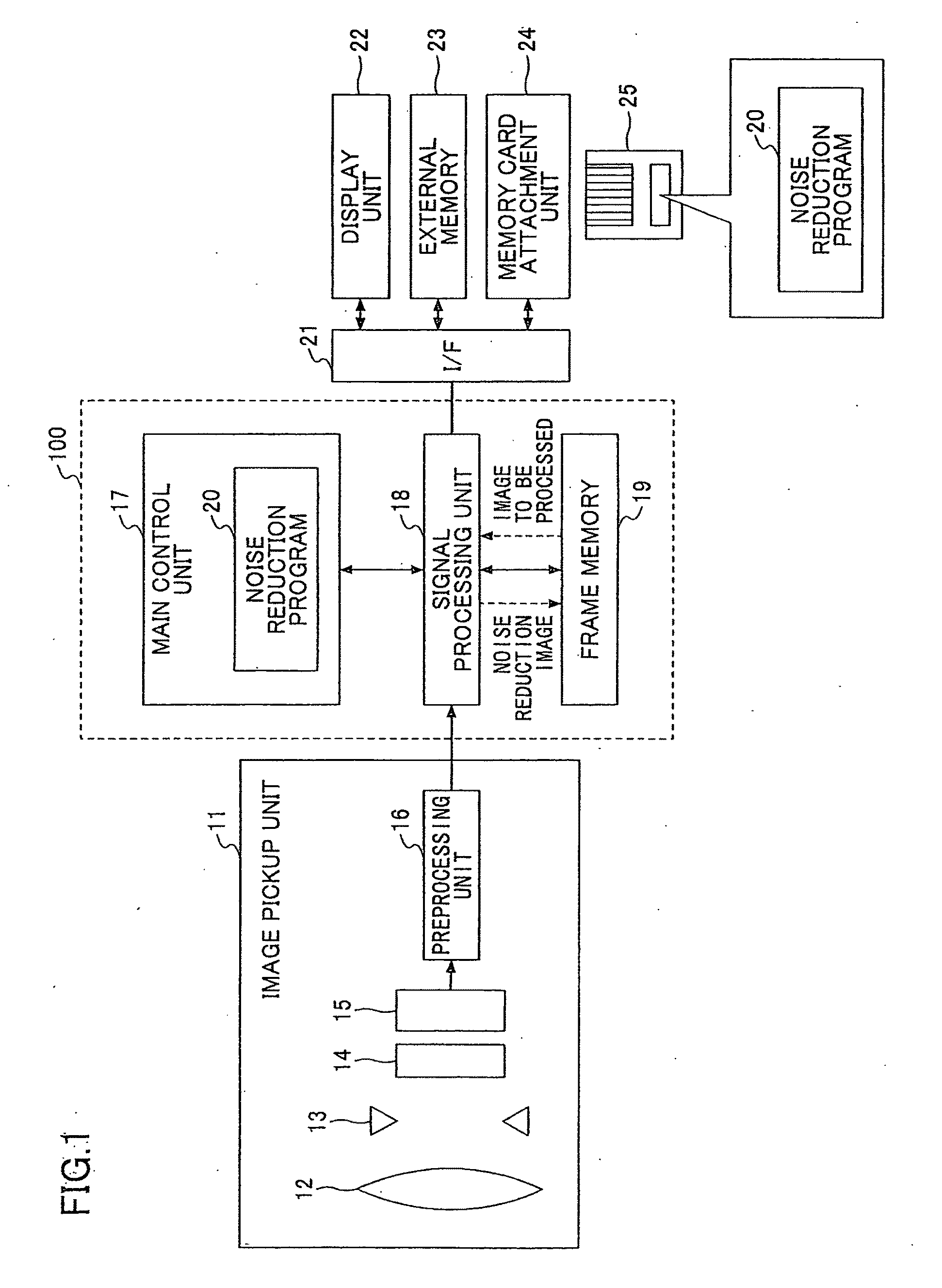
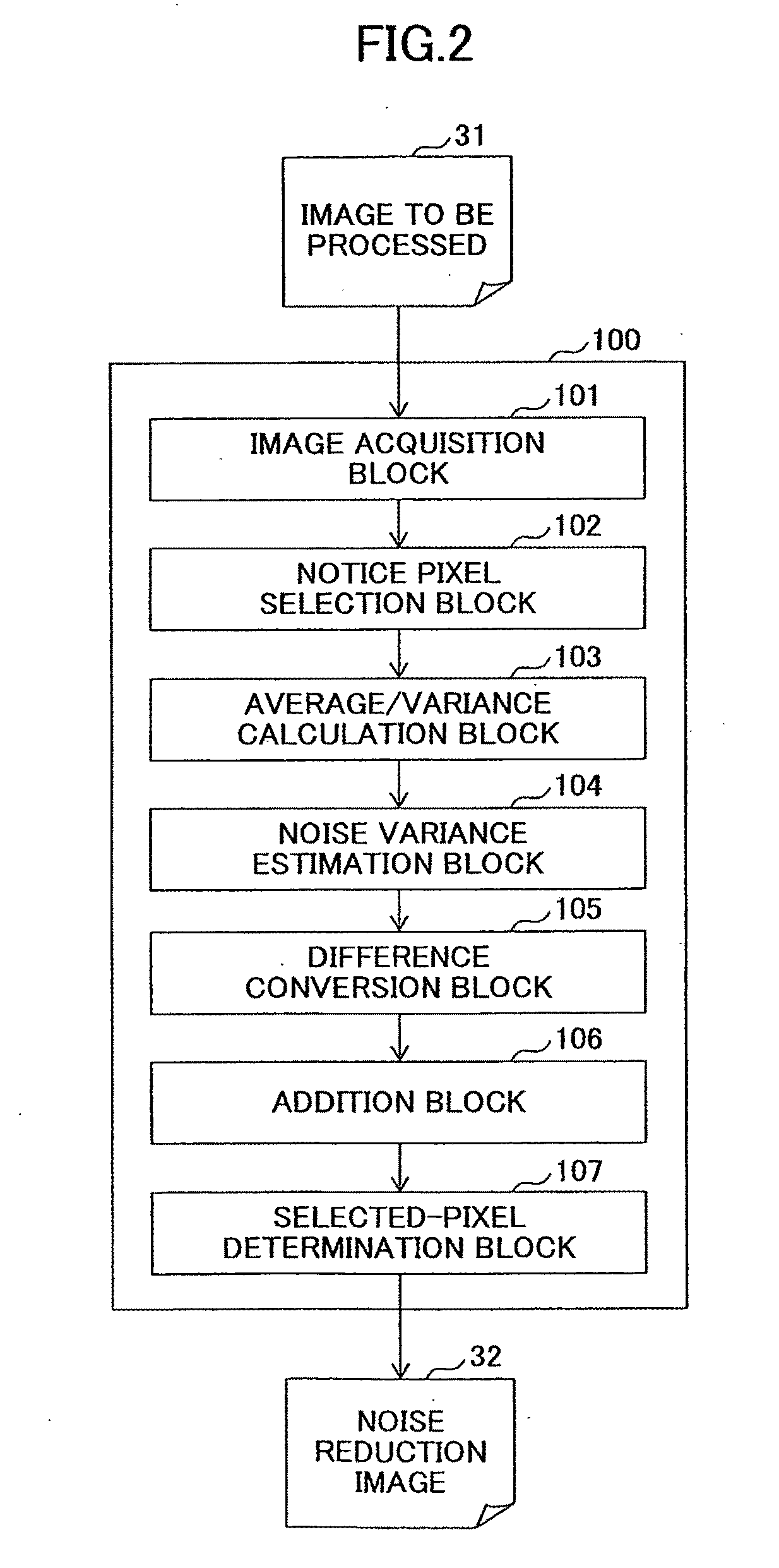
Noise reduction device, noise reduction method, noise reduction program, and recording medium
ActiveUS20110274350A1Reducing noiseImprove accuracyImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionNoise reduction
Disclosed is a noise reduction device that includes a representative-value vector calculation unit that extracts from the neighboring region the pixels of a similarity region having a degree of similarity, greater than or equal to a threshold, to the notice pixel in a predetermined color space and calculates a representative-value vector of the pixels of the similarity region; a difference projection unit that projects a difference vector between a notice-pixel vector of the notice pixel and the representative-value vector in a specific direction of the color space; and a pixel-value correction unit that replaces an element of a vector obtained by adding the difference vector projected in the specific direction to the representative-value vector with the pixel value of the notice pixel.
Owner:RICOH KK
A method and decoding and encoding method for capturing the video difference vector in the multi-video coding process
InactiveCN101056398AAccurate estimateImprove estimation accuracyPulse modulation television signal transmissionDigital video signal modificationParallaxSpace object
The invention relates to a disparity vector acquiring method during a multi-view encoding process, and an encoding and a decoding method thereof. The invention comprises confirming a disparity vector between two views during the multi-view image encoding process, calculating to obtain a disparity vector between other two views according to the preceding disparity vector between two views and known relative position information of views, then performing multi-view encoding and decoding operations by means of the disparity vectors. The method of the invention, on one hand, primely utilizes the correlation between the disparity vector and the space object deep information, and on the other hand, primely utilizes the direct relation between the disparity vector and the position of each camera. Experiments show that the disparity vector between views can be precisely calculated during the multi-view encoding process, thereby effectively improving the multi-view encoding performance.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
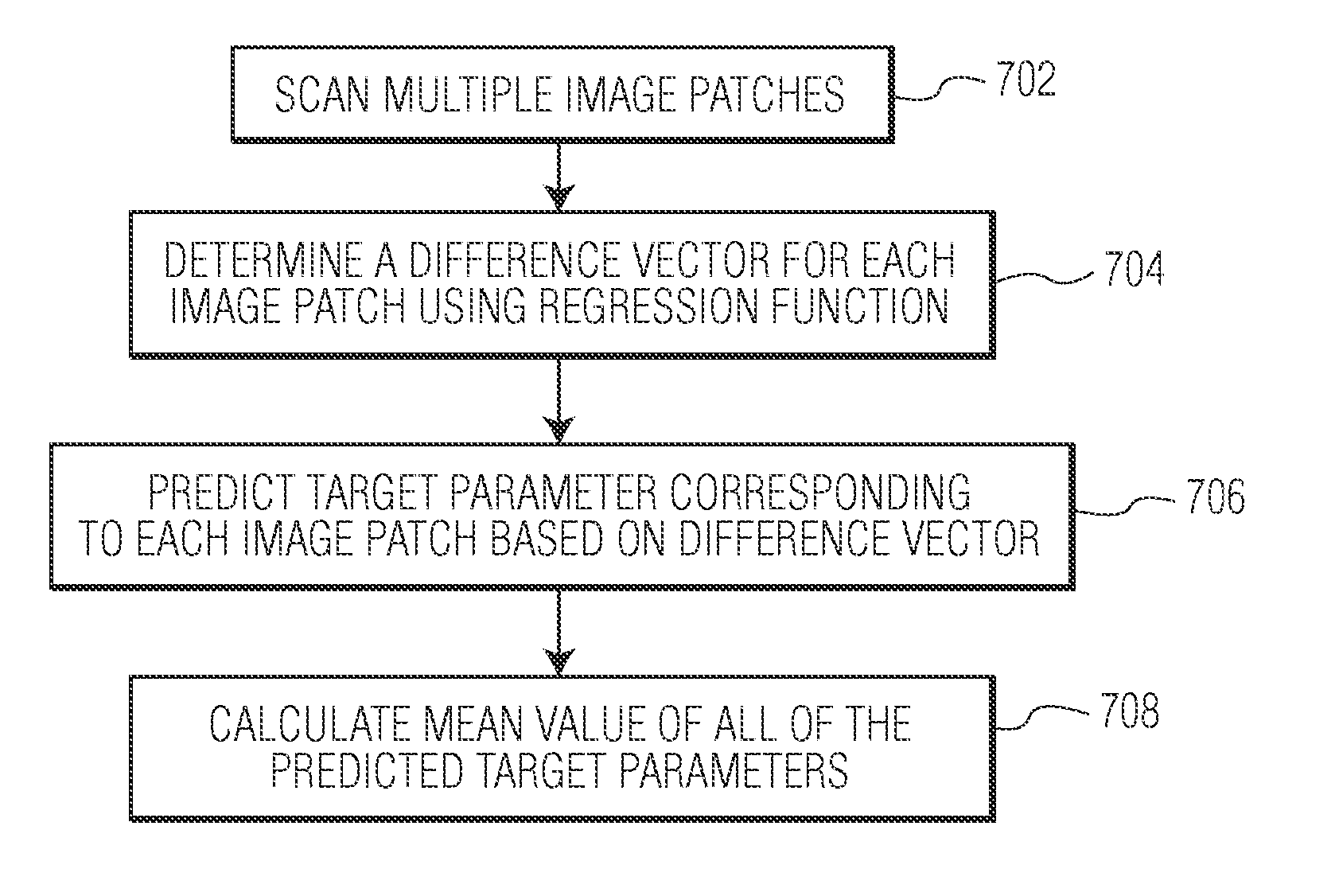
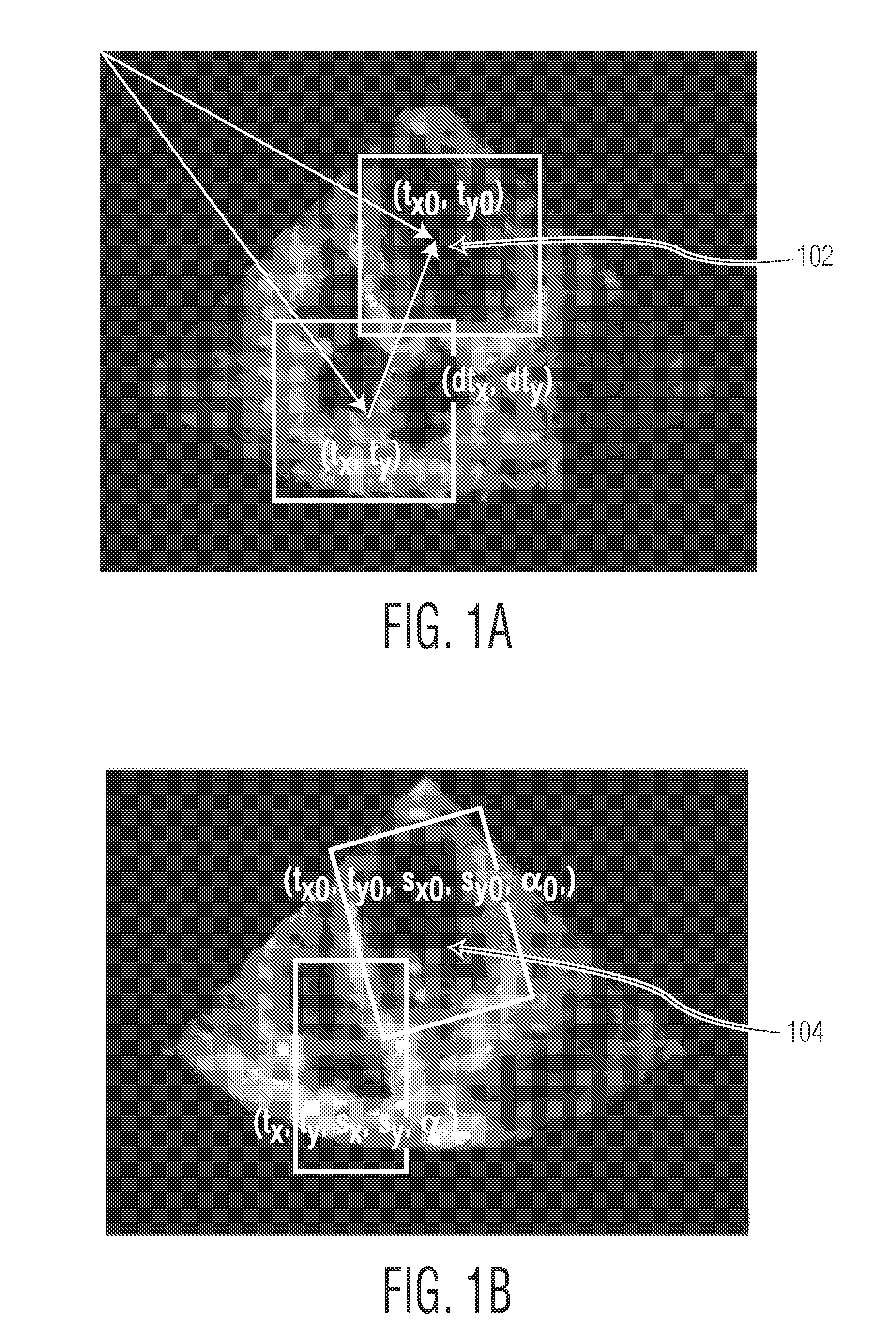
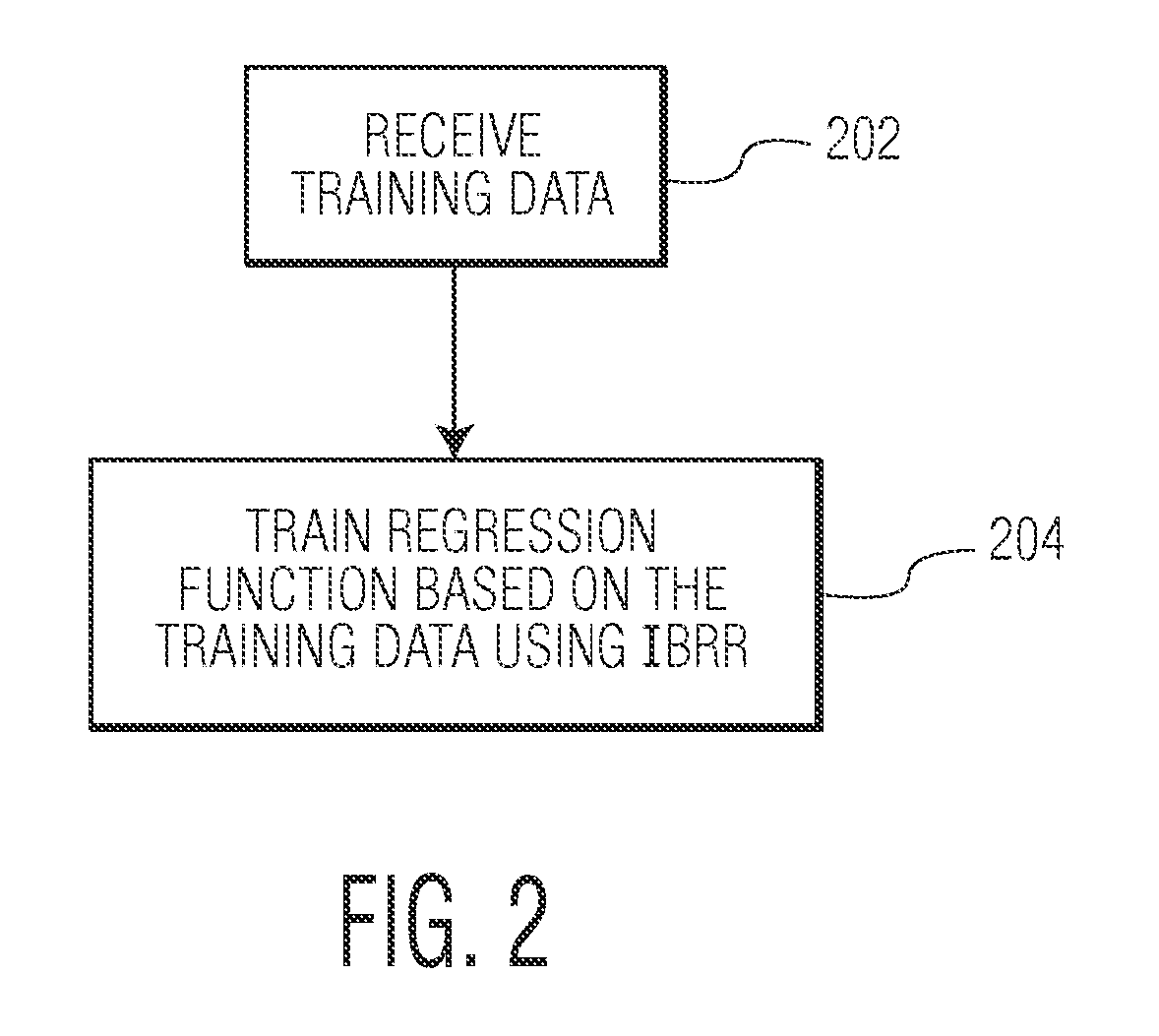
Method and System For Regression-Based Object Detection in Medical Images
A method and system for regression-based object detection in medical images is disclosed. A regression function for predicting a location of an object in a medical image based on an image patch is trained using image-based boosting ridge regression (IBRR). The trained regression function is used to determine a difference vector based on an image patch of a medical image. The difference vector represents the difference between the location of the image patch and the location of a target object. The location of the target object in the medical image is predicted based on the difference vector determined by the regression function.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
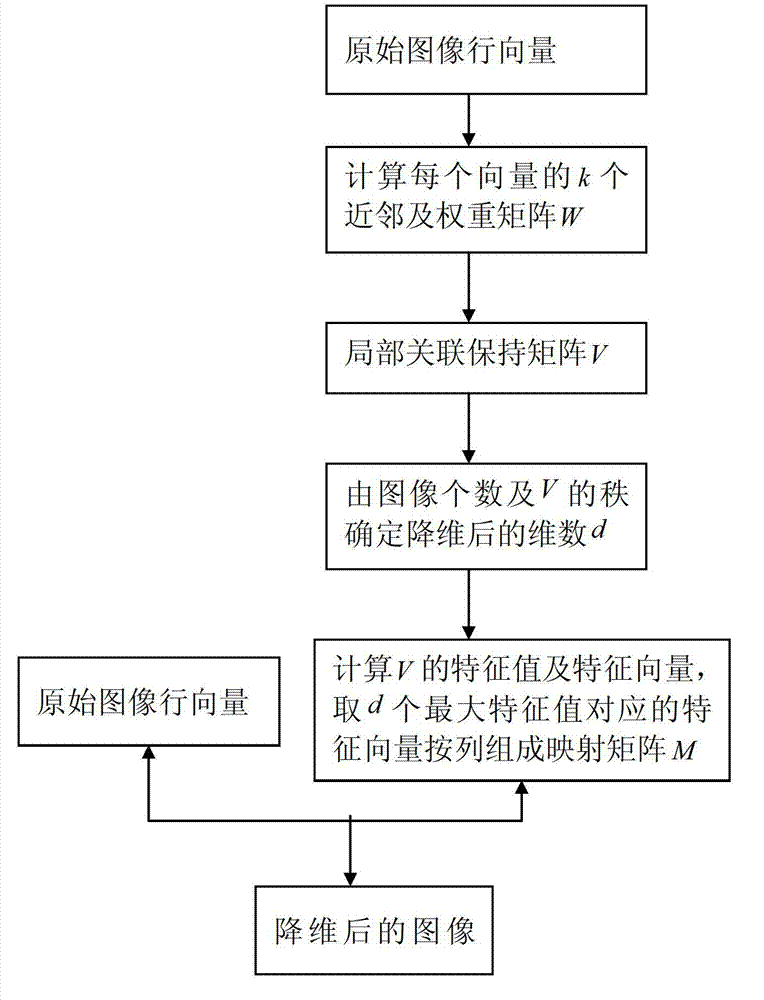
Face image dimension reducing method based on local correlation preserving
InactiveCN102737237AMaintain local relevanceFacilitate image recognitionCharacter and pattern recognitionHat matrixFeature vector
The invention discloses a face image dimension reducing method based on local correlation preserving. The method comprises the following steps of: expressing a face image by using multi-dimensional vectors, acquiring k neighbors of each vector according to the norm of two difference vectors, and calculating normalization weight of the k neighbors of each vector according to a radial basis function; calculating a difference vector of each vector and the sum of the weights of the k neighbors of each vector, acquiring a matrix by multiplying transposition of each difference vector by each difference vector, and adding the matrixes corresponding all the vectors to acquire a local correlation preserving matrix; and calculating characteristic values and characteristic vectors of the local correlation preserving matrix, and selecting the characteristic vectors corresponding to partial large characteristic values as basic vectors to form a projection matrix, and thus realizing dimension reduction. The dimension reduced face image well preserves local data association, the method is beneficial to image identification, and the classification effect after characteristics are extracted by the method is superior to those of primal component analysis (PCA) and locality preserving projection (LPP); and calculation complexity is reduced, and a relation among the new method, the PCA and the LPP is disclosed.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
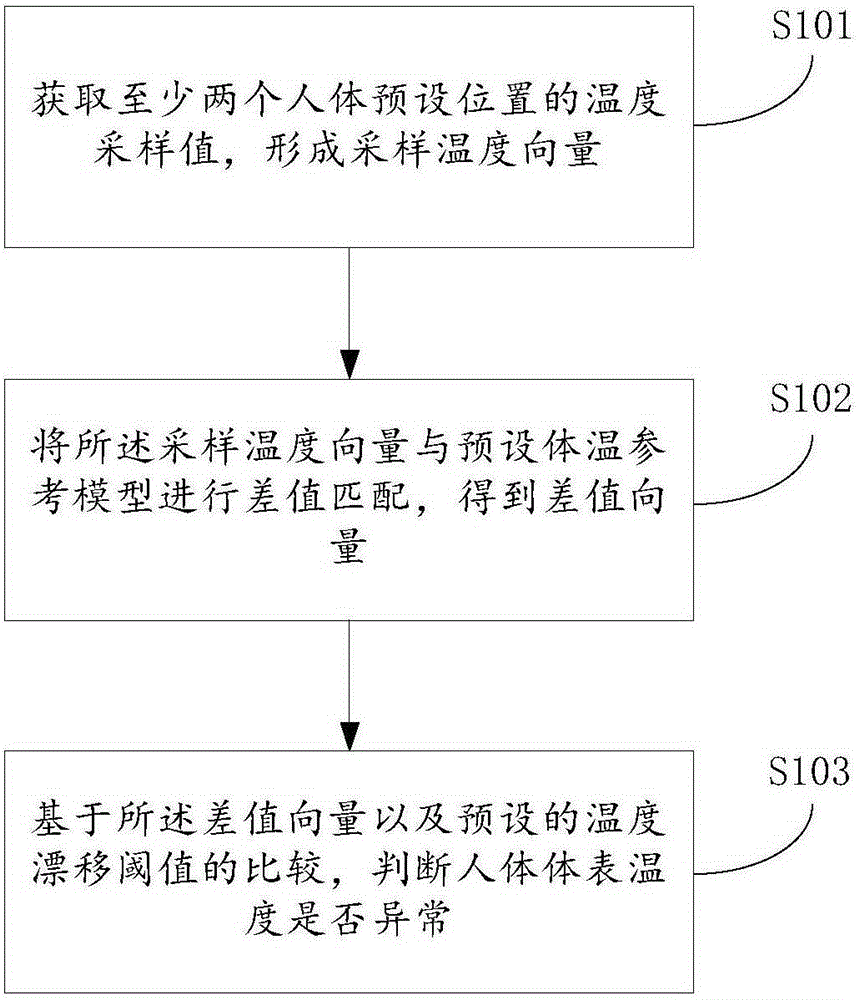
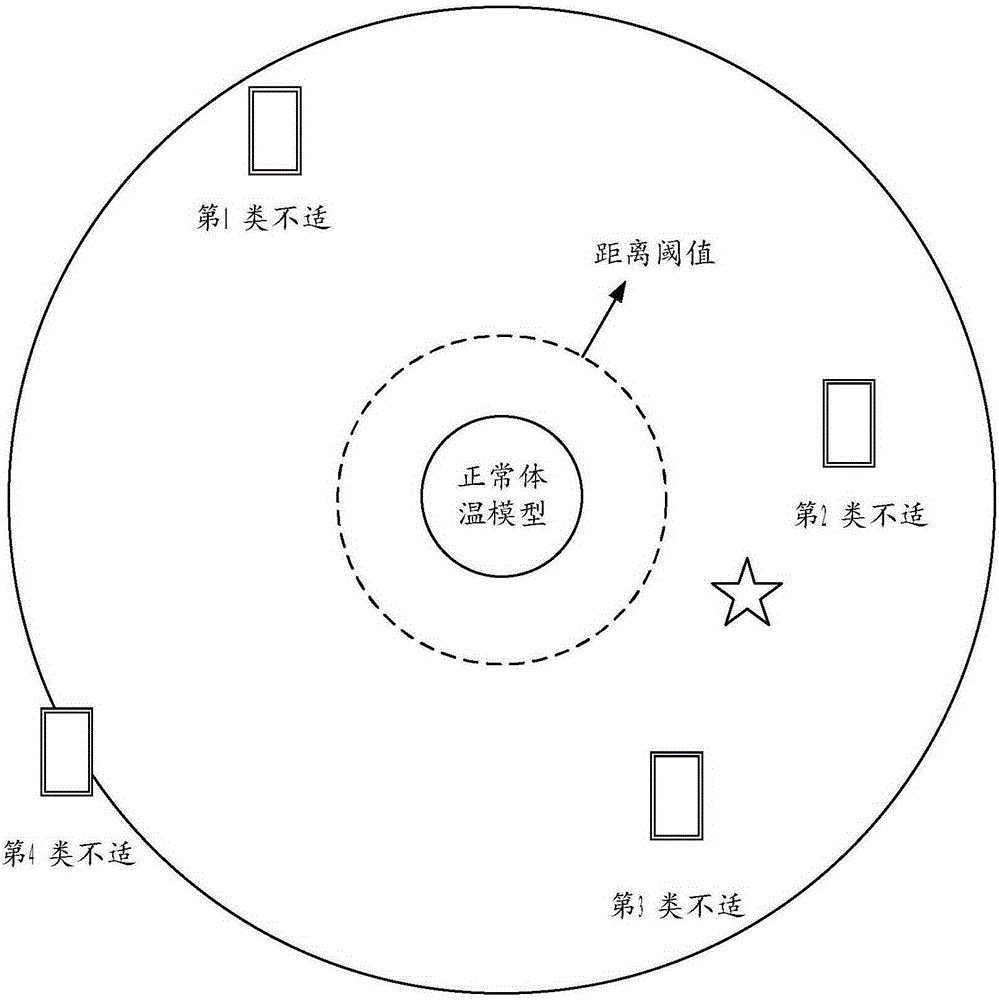
Health assessment method and expert system based on human body temperature modeling
ActiveCN105260620AThe judgment process is simpleMedical simulationMedical automated diagnosisReference modelSimulation
The invention provides a health assessment method and an expert system based on human body temperature modeling and an electronic device. The health assessment method based on human body temperature modeling comprises the steps of acquiring temperature sampling values of at least two preset human body positions to form a sampled temperature vector; performing difference matching to the sampled temperature vector and a preset body temperature reference model to obtain a difference vector; judging whether human body shell temperature is abnormal or not based on a comparison between the difference vector and a preset temperature drift threshold. By adopting the technical scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention, the abnormal state of human body temperature change can be easily recognized and a corresponding prompt in the aspect of physiological function can be given.
Owner:上海节律生物科技有限公司
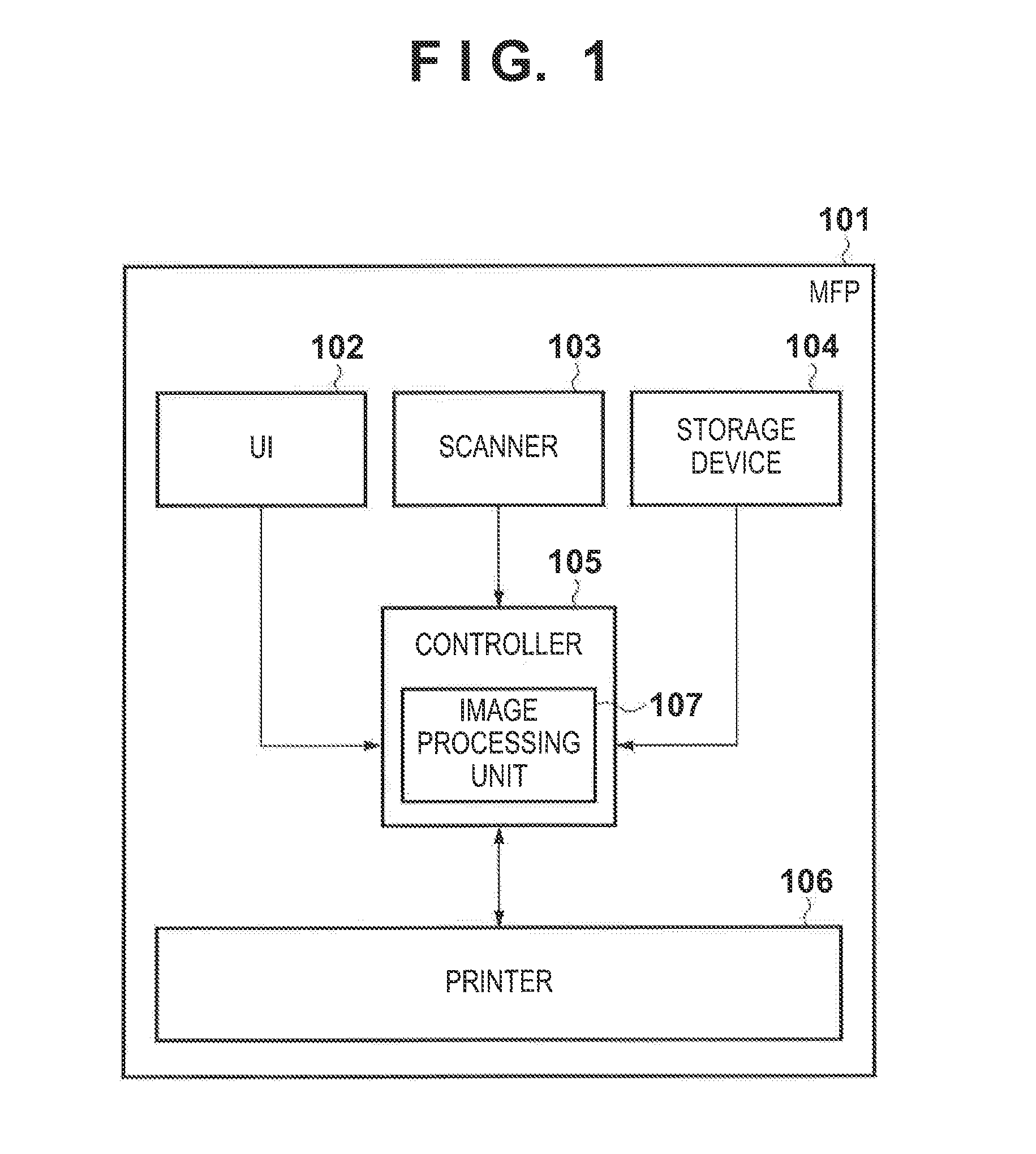
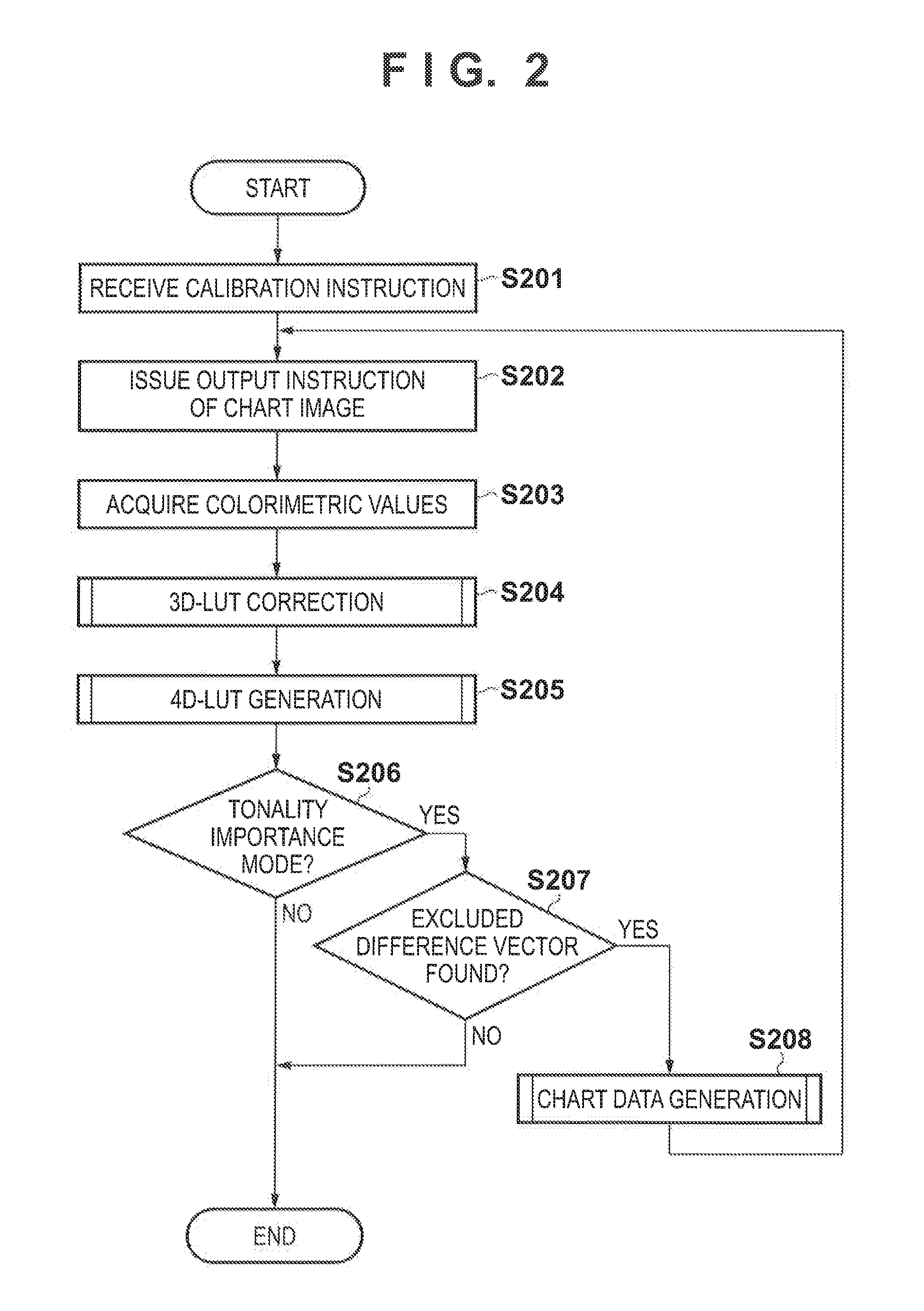
Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and storage medium
InactiveUS20120206744A1Suppress tonalityDigitally marking record carriersVisual presentation using printersPattern recognitionColor transformation
There is provided an image processing apparatus comprising a selection unit configured to select difference vectors to be used in correction processing of a first color conversion table from difference vectors between reference values and corresponding colorimetric values; a table correction unit configured to correct output values for respective grid points of the first color conversion table using the selected difference vectors; and a table generation unit configured to set conversion results of data which represent grid points of a third color conversion table as output values for the grid points, wherein the conversion results are obtained by performing conversion using a second color conversion table and the first color conversion table which is corrected by the table correction unit.
Owner:CANON KK
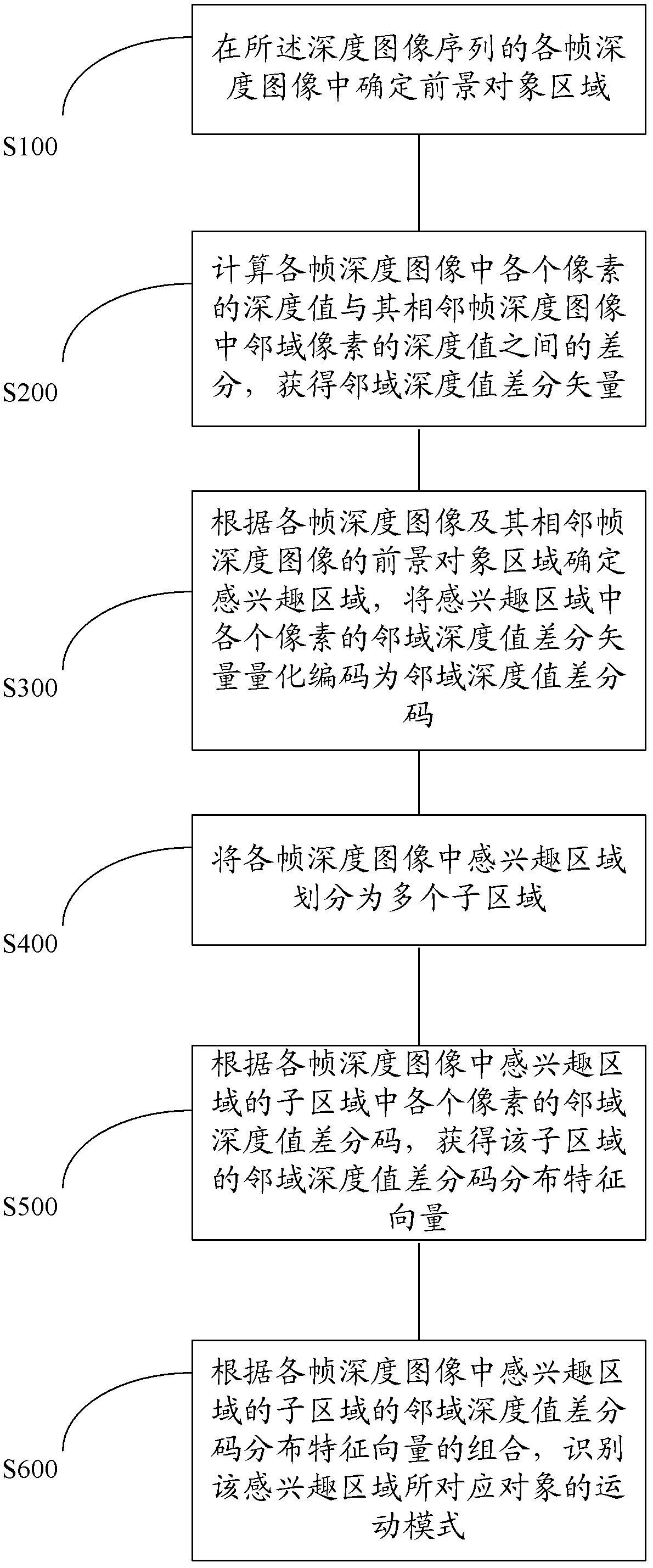
Object locomotion mode identification method and device based on depth image sequence
ActiveCN103208006ASmooth motionEasy to identifyCharacter and pattern recognitionCode distributionIdentification device
Provided is an object locomotion mode identification method based on a depth image sequence. The method comprises a foreground determining step of determining a foreground object area in every depth image frame; a difference step of calculating difference between depth values of every pixel in every depth image frame and depth values of neighborhood pixels of the pixel so as to obtain difference vectors of the neighborhood depth values; a quantization coding step of determining an area of interest according to the foreground object area and enabling the difference vectors of the neighborhood depth values of every pixel in the area of interest to undergo quantization coding to become neighborhood depth value differential codes; an area division step of dividing the area of interest into a plurality of subareas; a distribution description step of obtaining neighborhood depth value differential code distribution characteristic vectors of the subareas; and an identification step of identifying a locomotion mode of an object corresponding to the area of interest according to combination of the neighborhood depth value differential code distribution characteristic vectors. An object locomotion mode identification device based on the depth image sequence is further provided correspondingly.
Owner:RICOH KK
Moving Picture Decoding Method and Moving Picture Encoding Method
ActiveUS20110249749A1High-quality videoColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionDecoding methods
High-quality video is provided using a small amount of coded bits. The moving picture decoding method performs inter-frame prediction processing. With the aforementioned inter-frame prediction processing, blocks with similar motion vectors from among the motion vectors in multiple blocks that have already been decoded are combined and a combined area is computed. A predicted vector for a target block to be decoded is computed using the motion vector of the aforementioned combined area, and a motion vector for the aforementioned target block is computed based on the aforementioned predicted vector and a difference vector which is included in a coded stream that is input. A predicted image is generated using the aforementioned motion vector, and a difference image which is included in the aforementioned coded stream and the aforementioned predicted image are added to generate a decoded image.
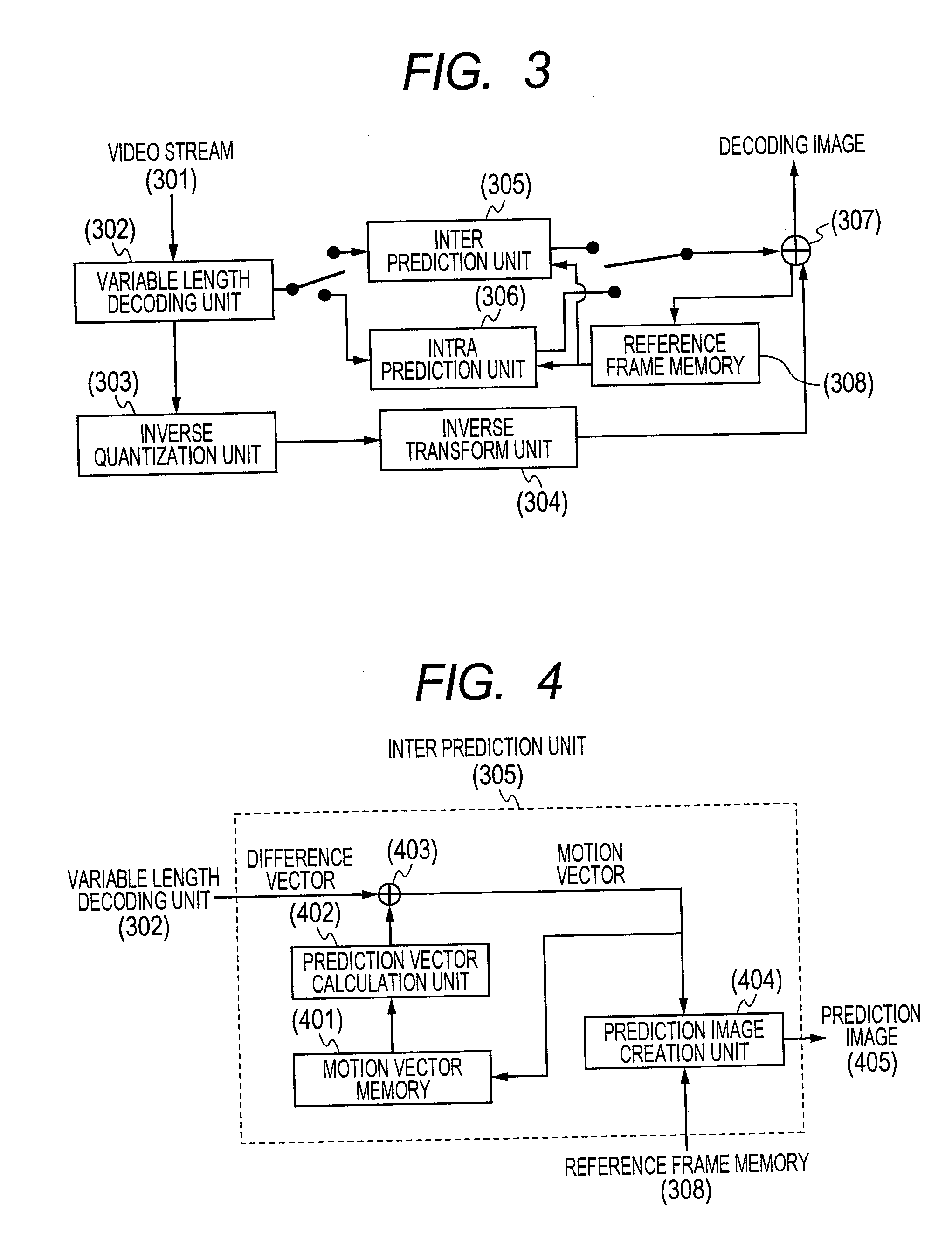
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
Image processing program and image processing device for moving display area
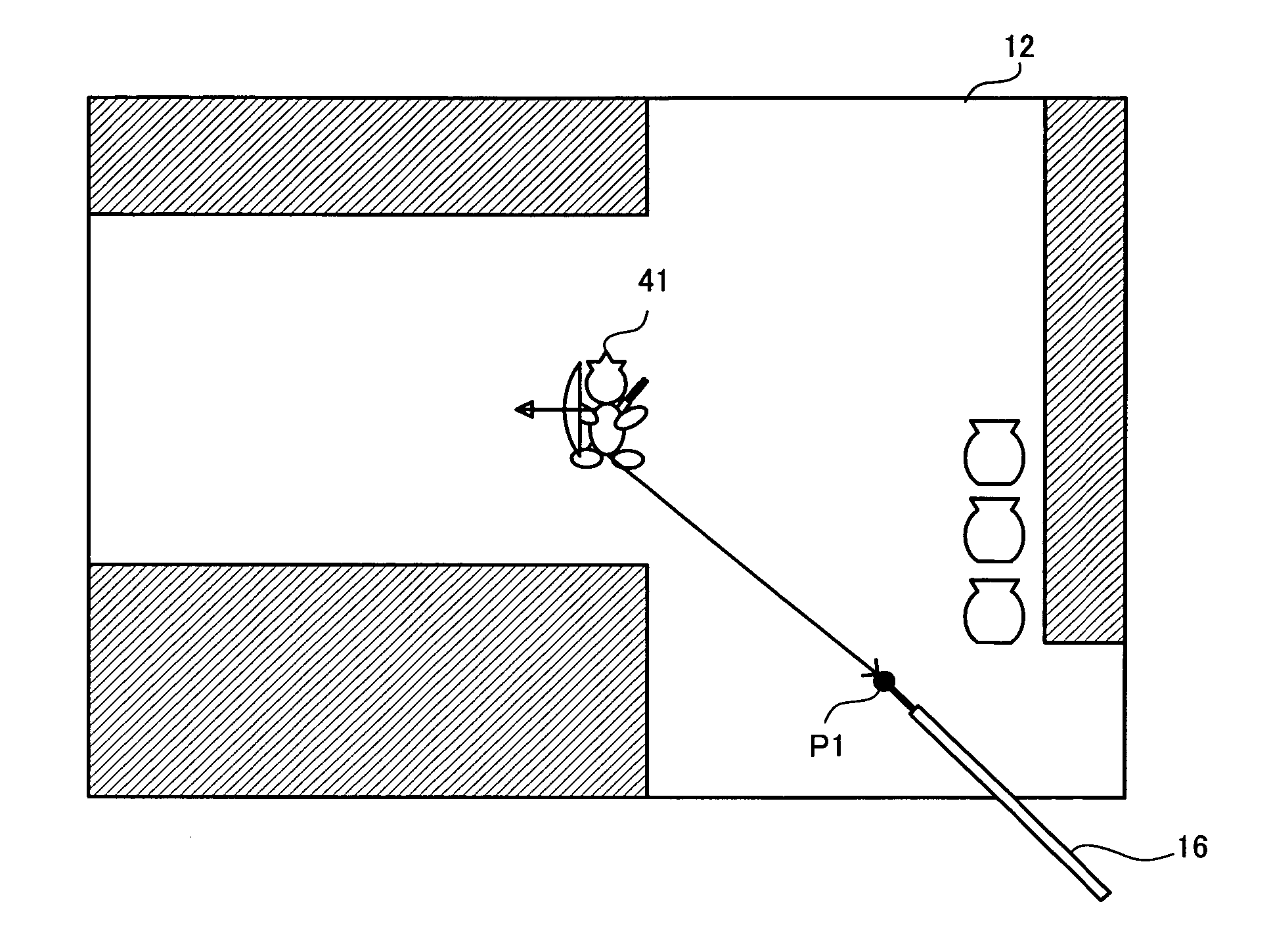
A video game device calculates a difference vector extending from a predetermined reference position on the screen to an input position. Moreover, the video game device calculates movement parameter data used for moving, with respect to a fixed point in the virtual space uniquely determined based on a position of the controlled object, the point of sight to a position that is determined by a direction in the virtual space based on a direction of the difference vector and a distance in the virtual space based on a magnitude of the difference vector. The point of sight is moved based on the movement parameter data. The video game device produces an image based on a virtual camera, which has been moved according to the movement of the point of sight, and displays the image on the screen of a display device.
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD
Method and apparatus for estimating optimum weight of closed loop transmit deversity for mobile communication
InactiveUS20020013130A1Power Loss MinimizationImprove performanceEnergy efficient ICTSpatial transmit diversityClosed loopEngineering
An optimum weight estimating apparatus and method of a mobile station for a mobile communication system in which a base station uses closed transmit diversity technology. Conventionally, all weight vectors stored in a lookup table should be applied to an optimum weight estimator to calculate receiving power, so that the amount of calculation considerably increases when there are many antennas. To overcome this problem, the weights of the lookup table are appropriately adjusted so that the variation of the differences between two adjacent vectors can be minimized. An optimum weight is obtained using the difference vector between weight vectors, thereby simplifying the calculation of receiving power. Therefore, the power loss of the mobile station can be minimized.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com