Patents
Literature
2295 results about "Filter bank" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
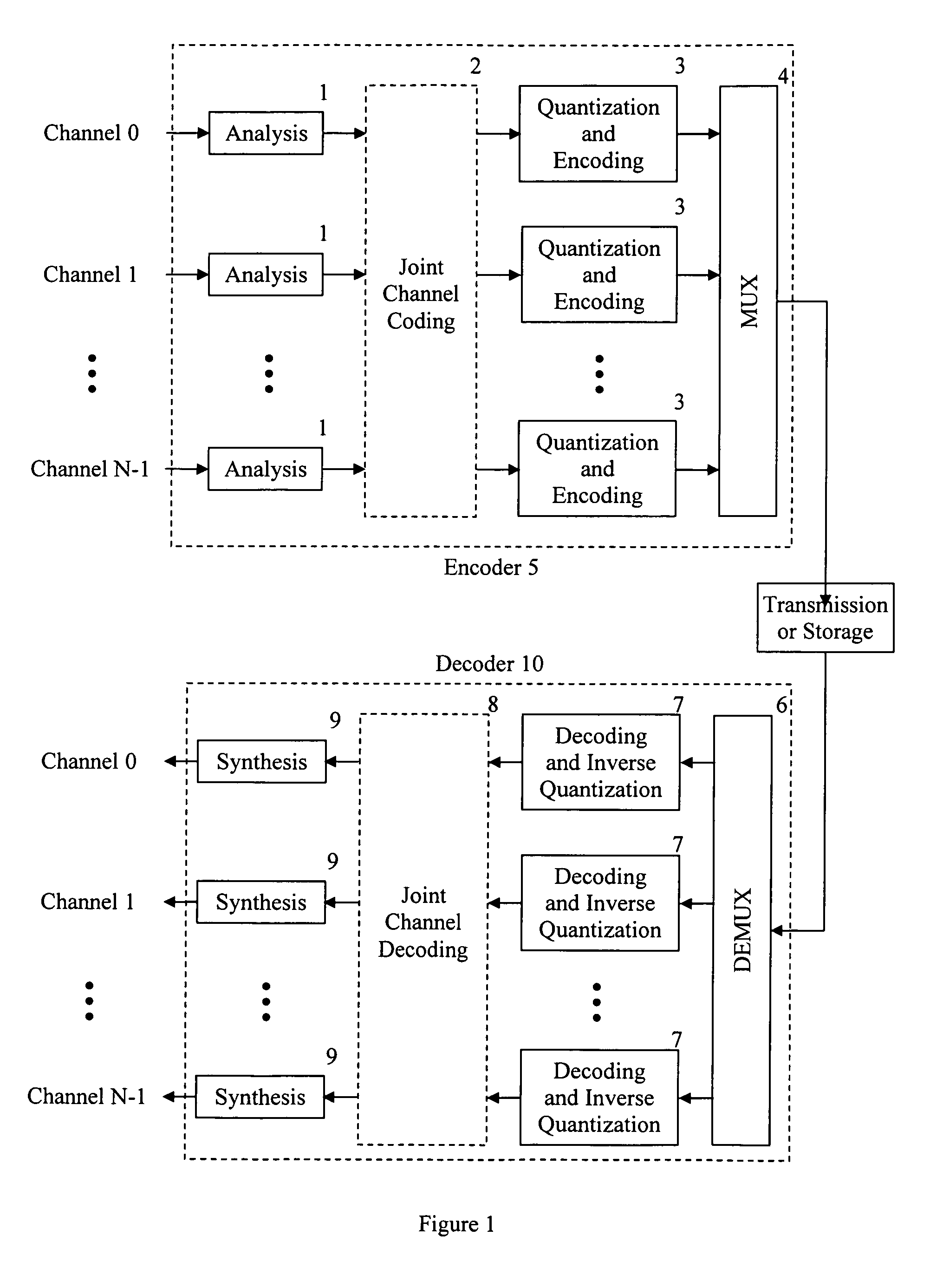
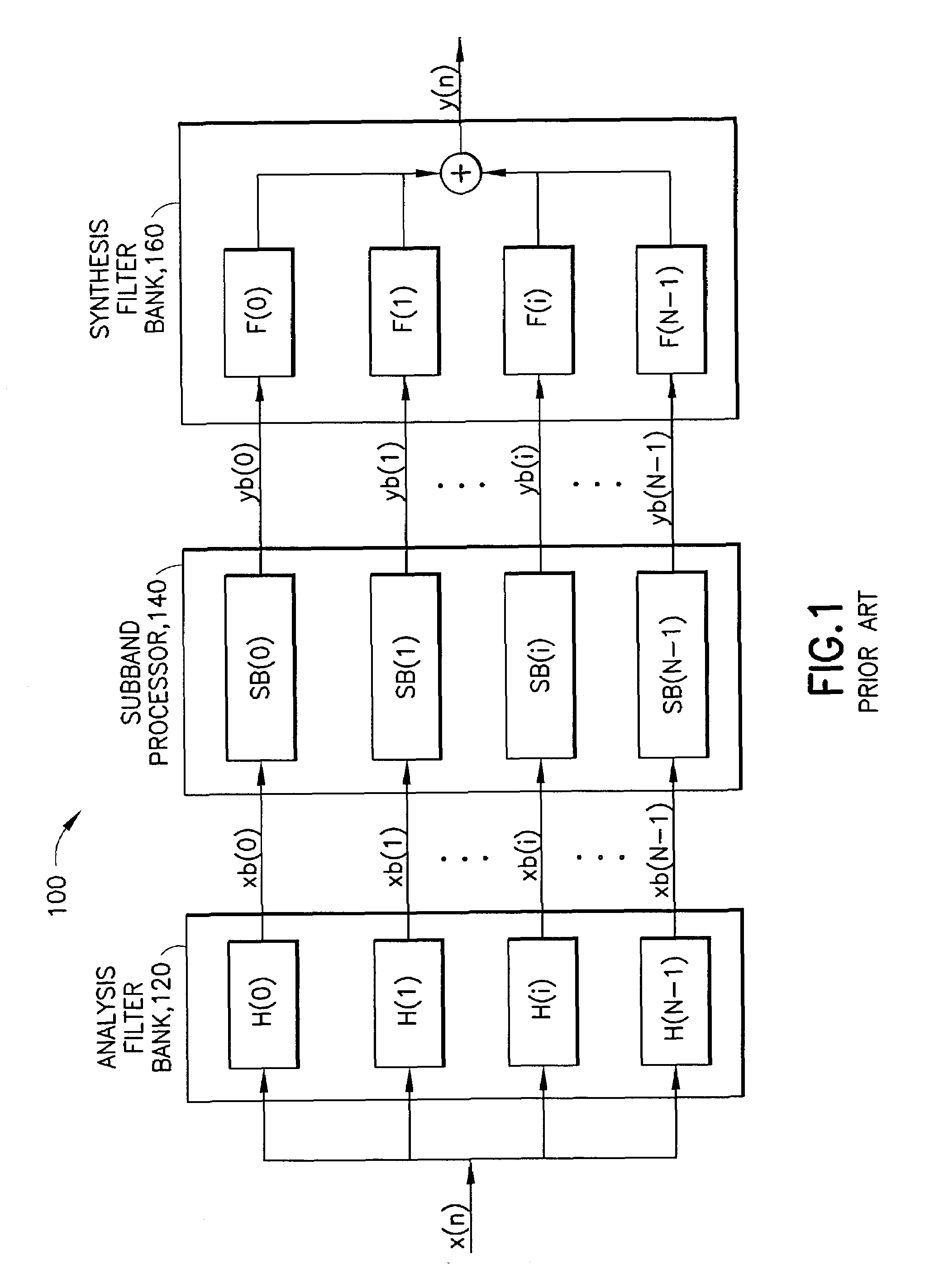
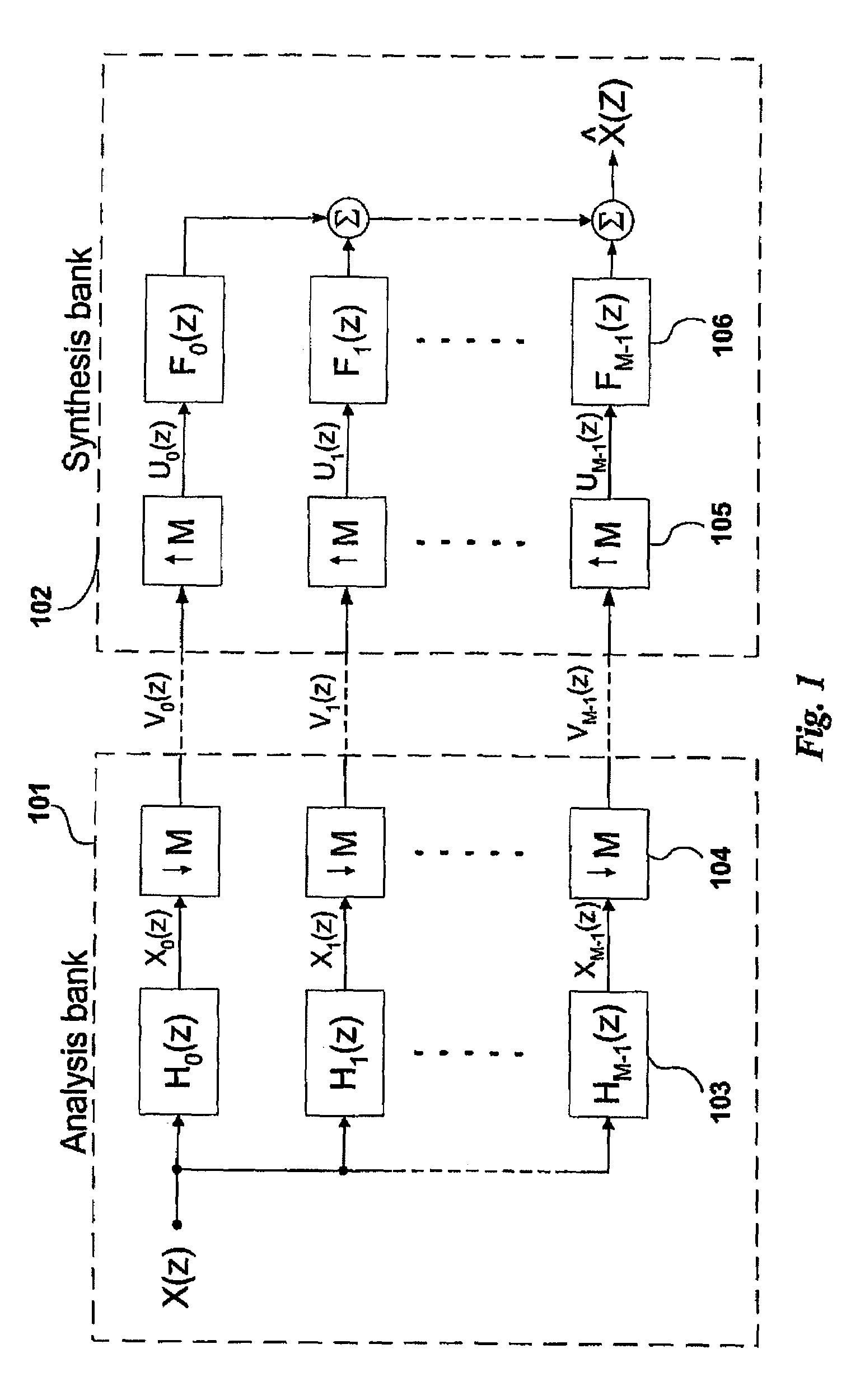
In signal processing, a filter bank is an array of band-pass filters that separates the input signal into multiple components, each one carrying a single frequency sub-band of the original signal. One application of a filter bank is a graphic equalizer, which can attenuate the components differently and recombine them into a modified version of the original signal. The process of decomposition performed by the filter bank is called analysis (meaning analysis of the signal in terms of its components in each sub-band); the output of analysis is referred to as a subband signal with as many subbands as there are filters in the filter bank. The reconstruction process is called synthesis, meaning reconstitution of a complete signal resulting from the filtering process.
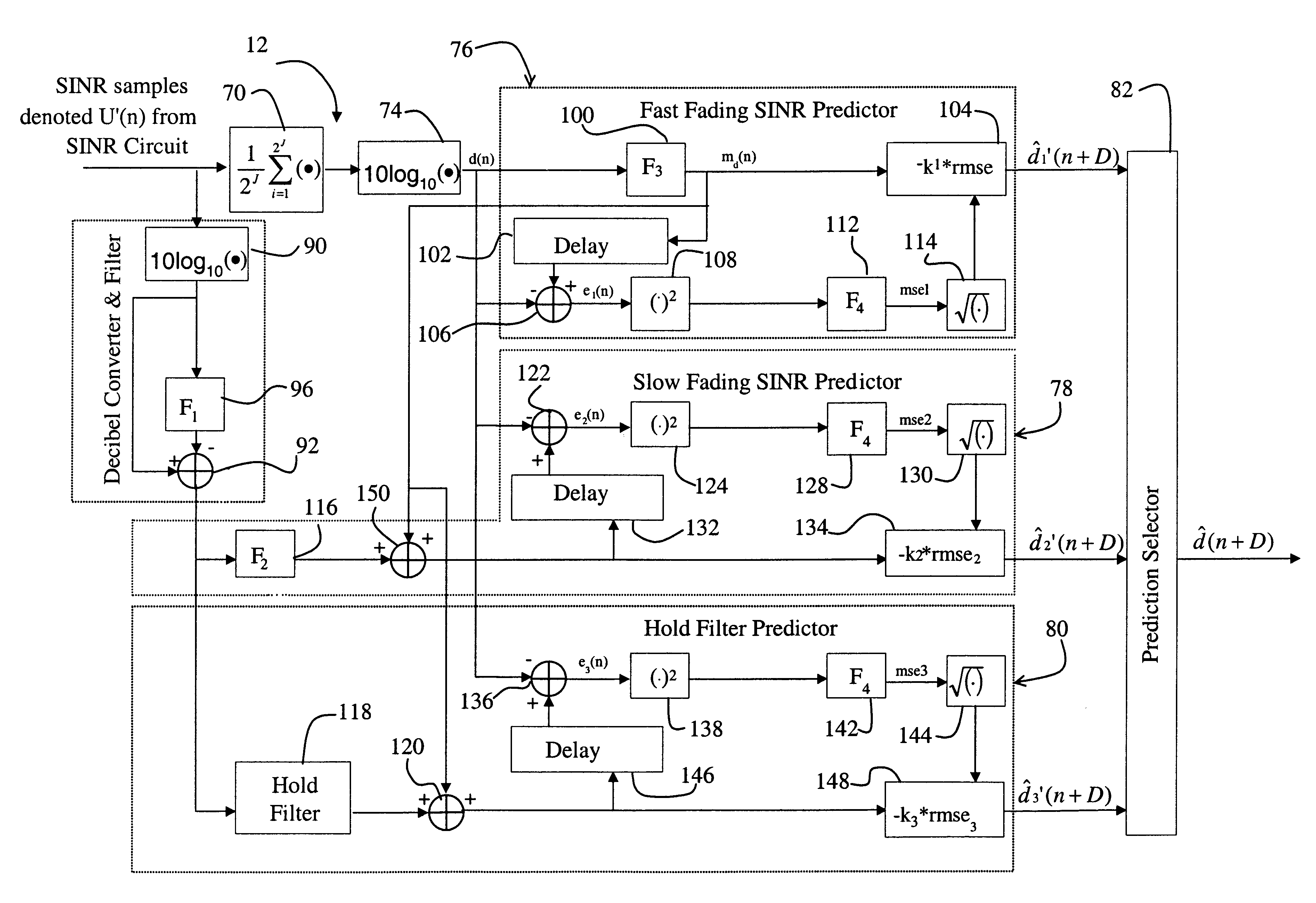
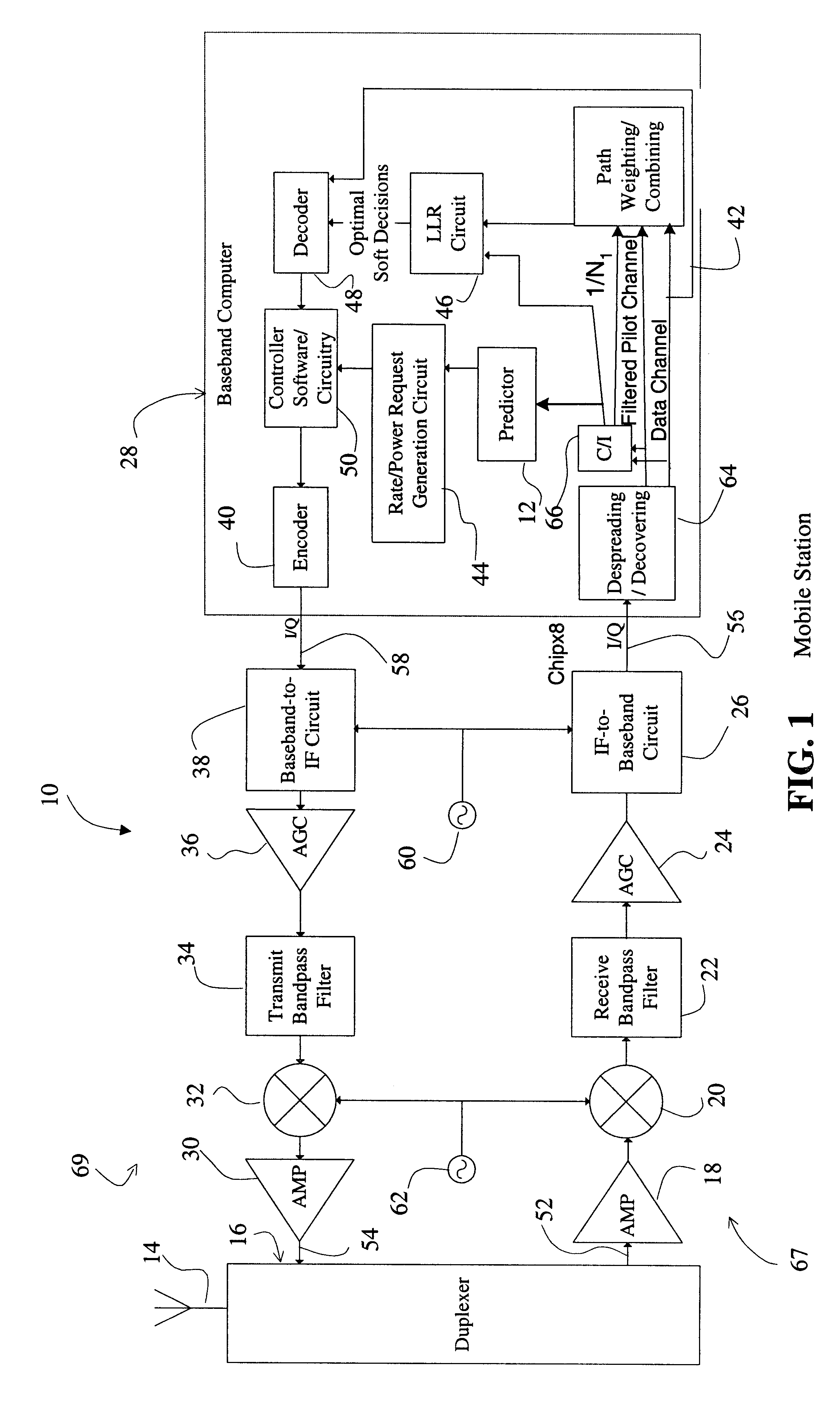
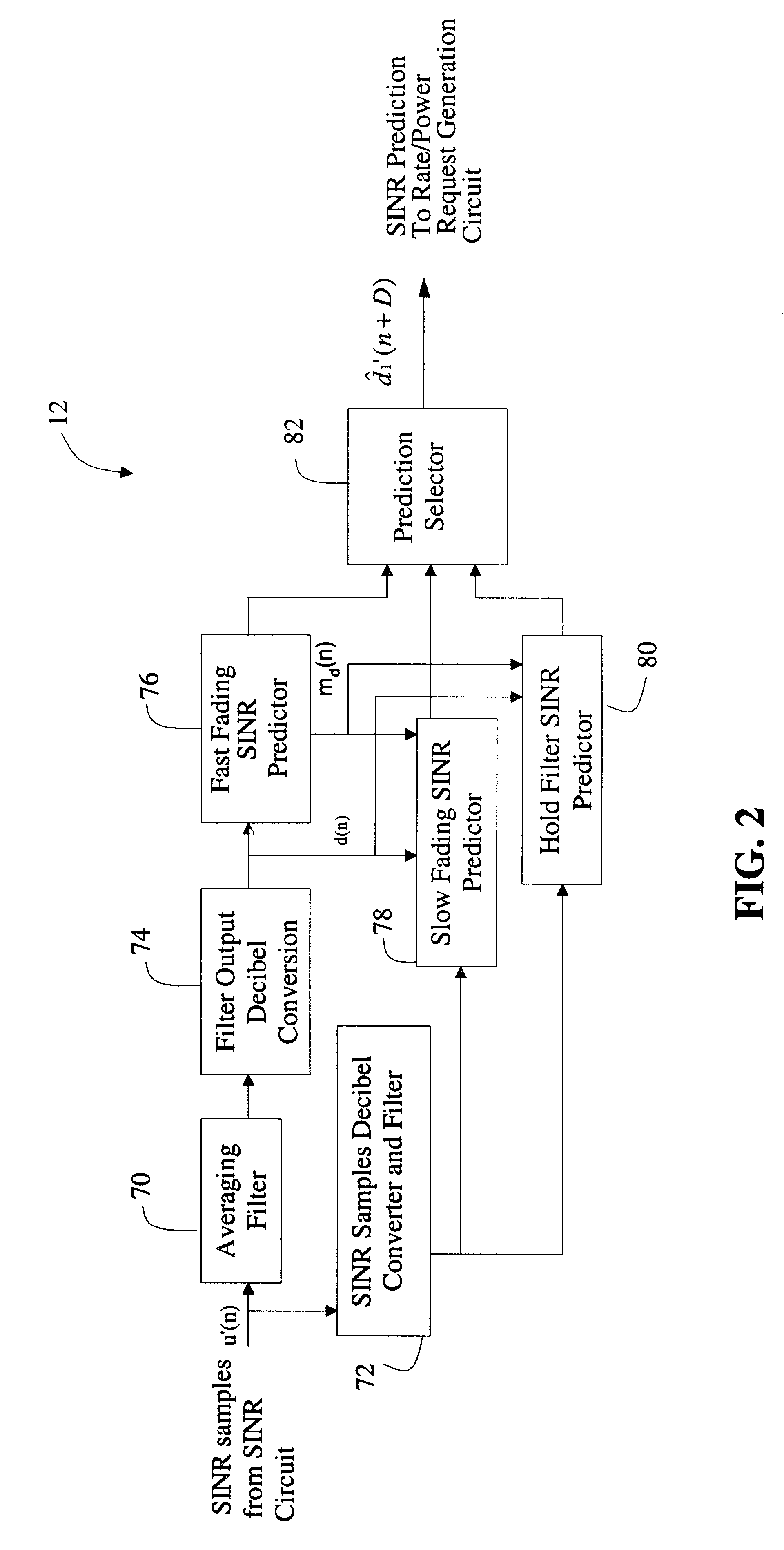
System and method for accurately predicting signal to interference and noise ratio to improve communications system performance
InactiveUS6426971B1Energy efficient ICTError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorFinite impulse responseEngineering
A system for providing an accurate prediction of a signal-to-interference noise ratio is described. The system includes a first circuit for receiving a signal transmitted across a channel via an external transmitter. A second circuit generates a sequence of estimates of signal-to-interference noise ratio based on the received signal. A third circuit determines a relationship between elements of the sequence of estimates. A fourth circuit employs the relationship to provide a signal-to-interference noise ratio prediction for a subsequently received signal. In the illustrative embodiment, the inventive system further includes a circuit for generating a data rate request message based on the signal-to-noise ratio prediction. A special transmitter transmits the data rate request message to the external transmitter. In the specific embodiment, the relationship between elements of the sequence of estimates is based on an average of the elements of the sequence of estimates. The third circuit includes a bank of filters for computing the average. The bank of filters includes finite impulse response filters. Coefficients of the transfer functions associated with each filter in the bank of filters are tailored for different fading environments. The different fading environments include different Rayleigh fading environments, one environment associated with a rapidly moving system, a second environment associated with a slow moving system, and a third system associated with a system moving at a medium velocity. A selection circuit is connected to each of the filter banks and selects an output from one of the filters in the filter bank. The selected output is associated with a filter having a transfer function most suitable to a current fading environment.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Frame-based audio coding with video/audio data synchronization by dynamic audio frame alignment
InactiveUS6124895AQuality improvementPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionUltrasound attenuationData synchronization
Several audio signal processing techniques may be used in various combinations to improve the quality of audio represented by an information stream formed by splice editing two or more other information streams. The techniques are particularly useful in applications that bundle audio information with video information. In one technique, gain-control words conveyed with the audio information stream are used to interpolate playback sound levels across a splice. In another technique, special filterbanks or forms of TDAC transforms are used to suppress aliasing artifacts on either side of a splice. In yet another technique, special filterbanks or crossfade window functions are used to optimize the attenuation of spectral splatter created at a splice. In a further technique, audio sample rates are converted according to frame lengths and rates to allow audio information to be bundled with, for example, video information. In yet a further technique, audio blocks are dynamically aligned so that proper synchronization can be maintained across a splice. An example for 48 kHz audio with NTSC video is discussed.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
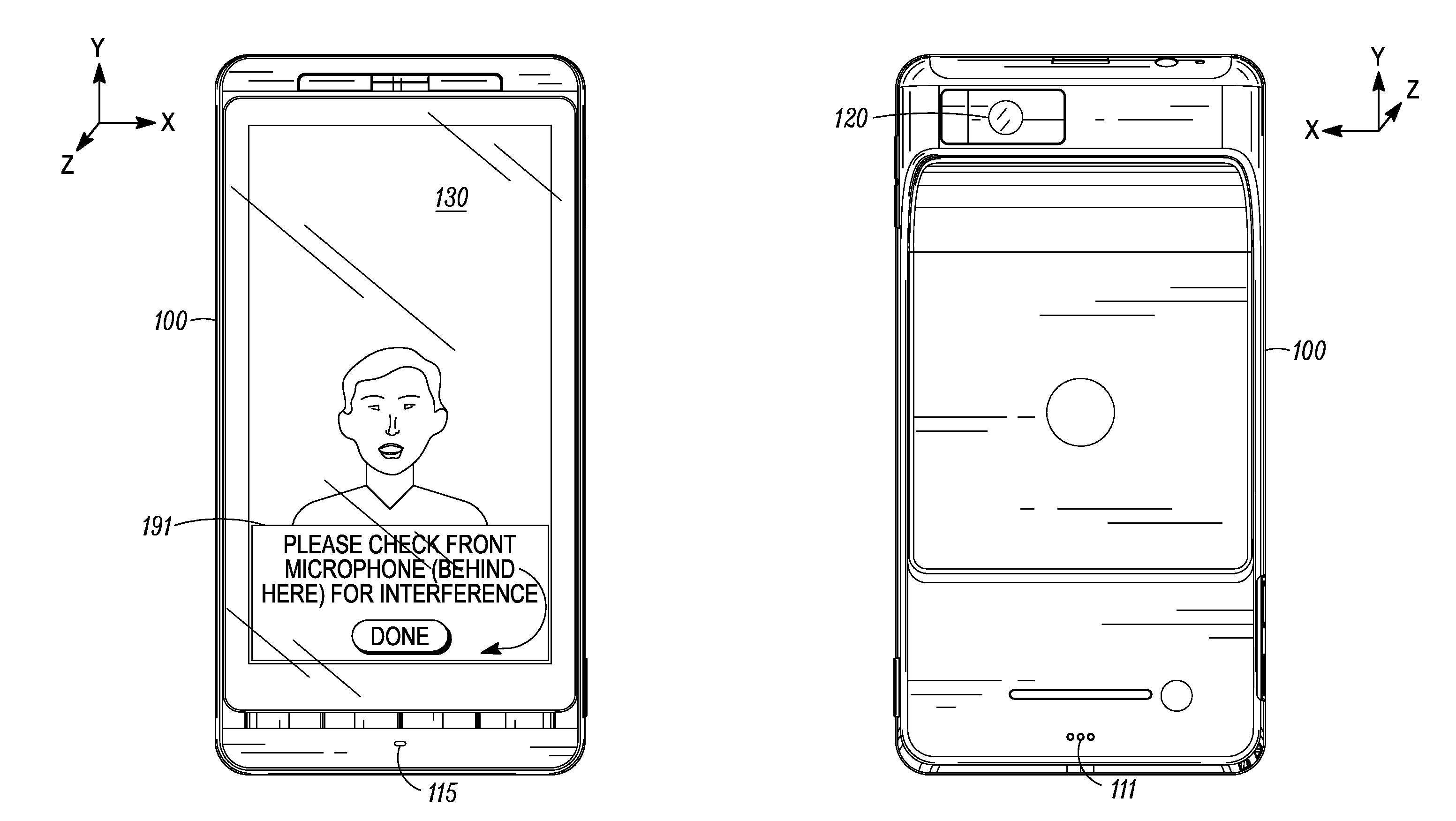
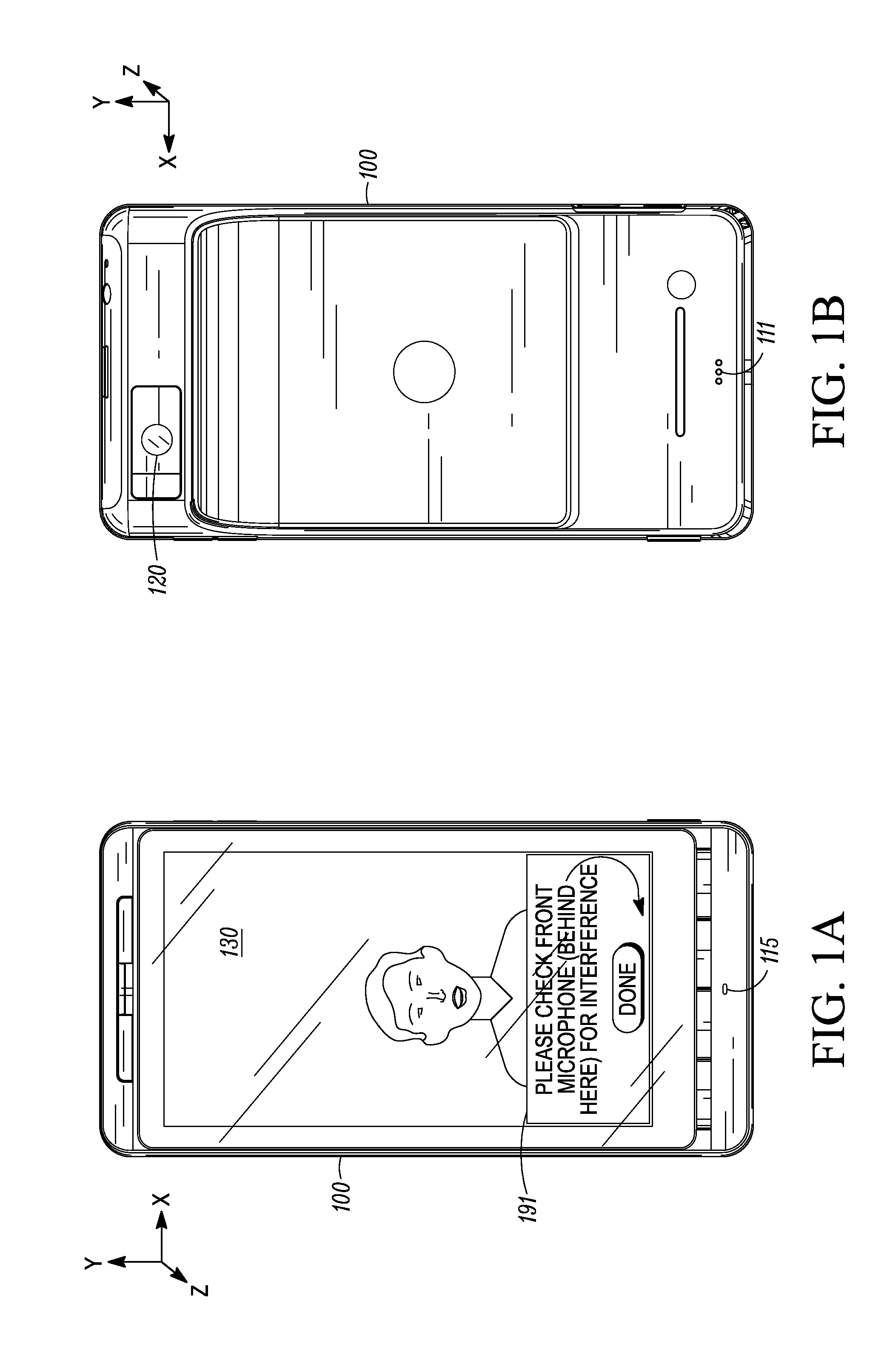
Microphone Interference Detection Method and Apparatus
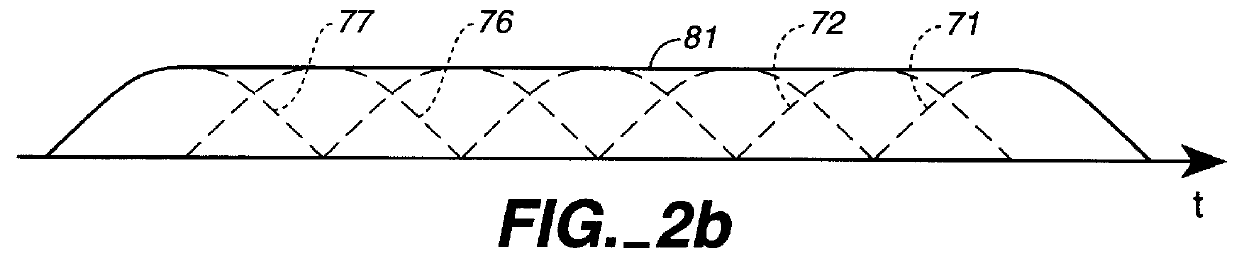
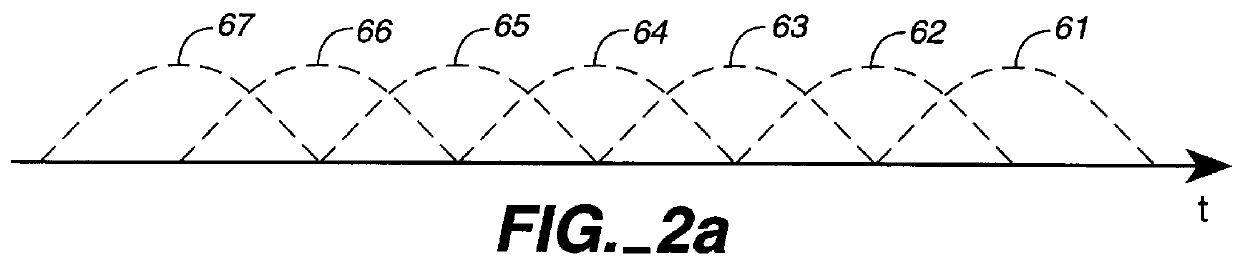
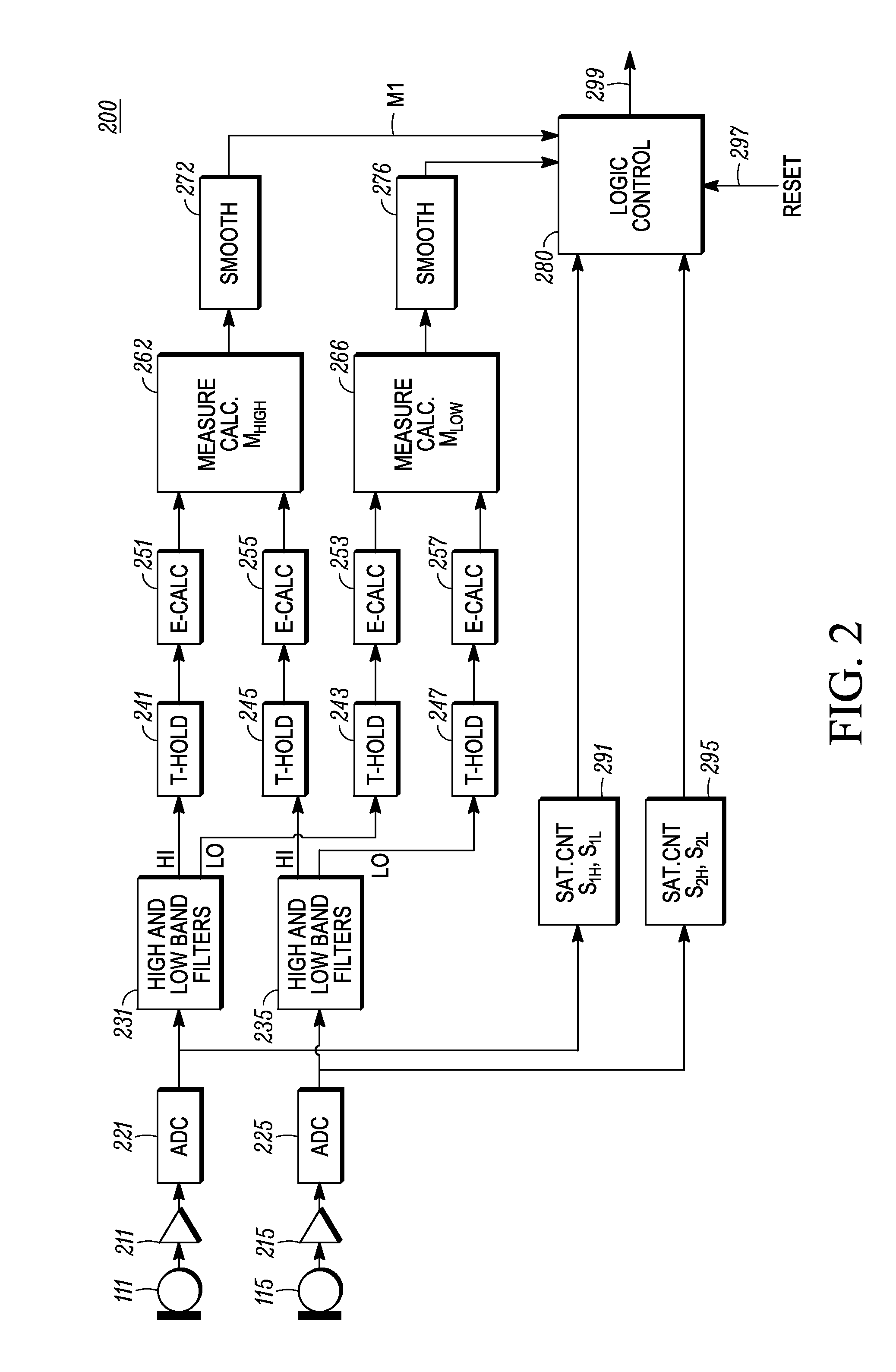
A method and apparatus for detecting microphone interference includes first and second built-in microphones producing first and second microphone signals. A first filter bank creates first high-frequency-band and first low-frequency-band signals from the first microphone signal. A second filter bank creates second high-frequency-band and second low-frequency-band signals from the second microphone signal. A first measurement calculator determines a high-frequency-band energy value from the first high-frequency-band signal and the second high-frequency-band signal when the first and second high-frequency-band signals' magnitudes exceeds predetermined thresholds. A second measurement calculator calculates a low-frequency-band energy value from the first low-frequency-band signal and the second low-frequency-band signal when the first and second low-frequency-band signals' magnitudes exceed predetermined thresholds. A logic control block, coupled to the first measurement calculator and the second measurement calculator, detects microphone interference and produces an output signal indicating microphone occlusion or wind noise.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Method and apparatus for highly scalable intraframe video coding
ActiveUS20090175333A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureInter layer
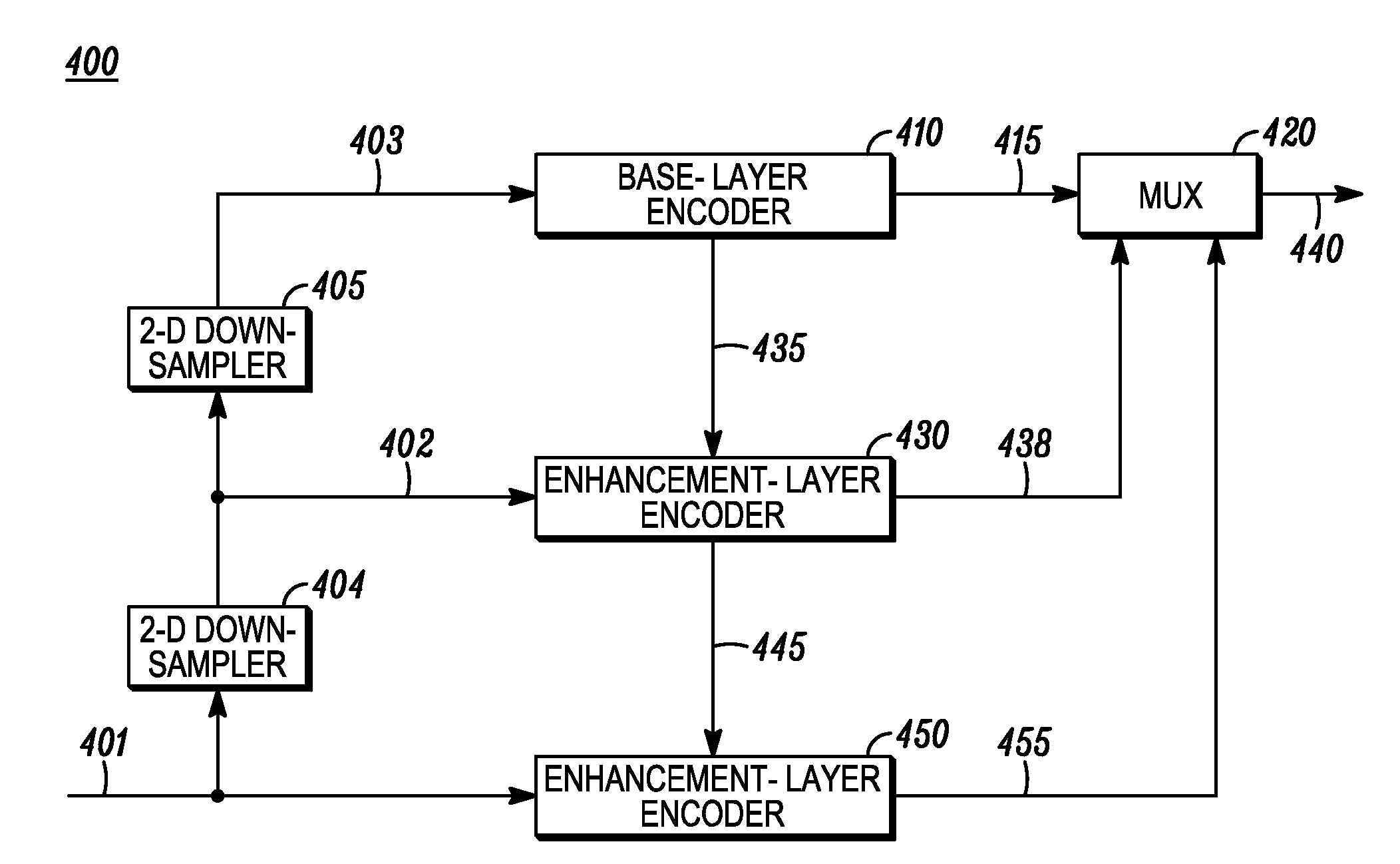
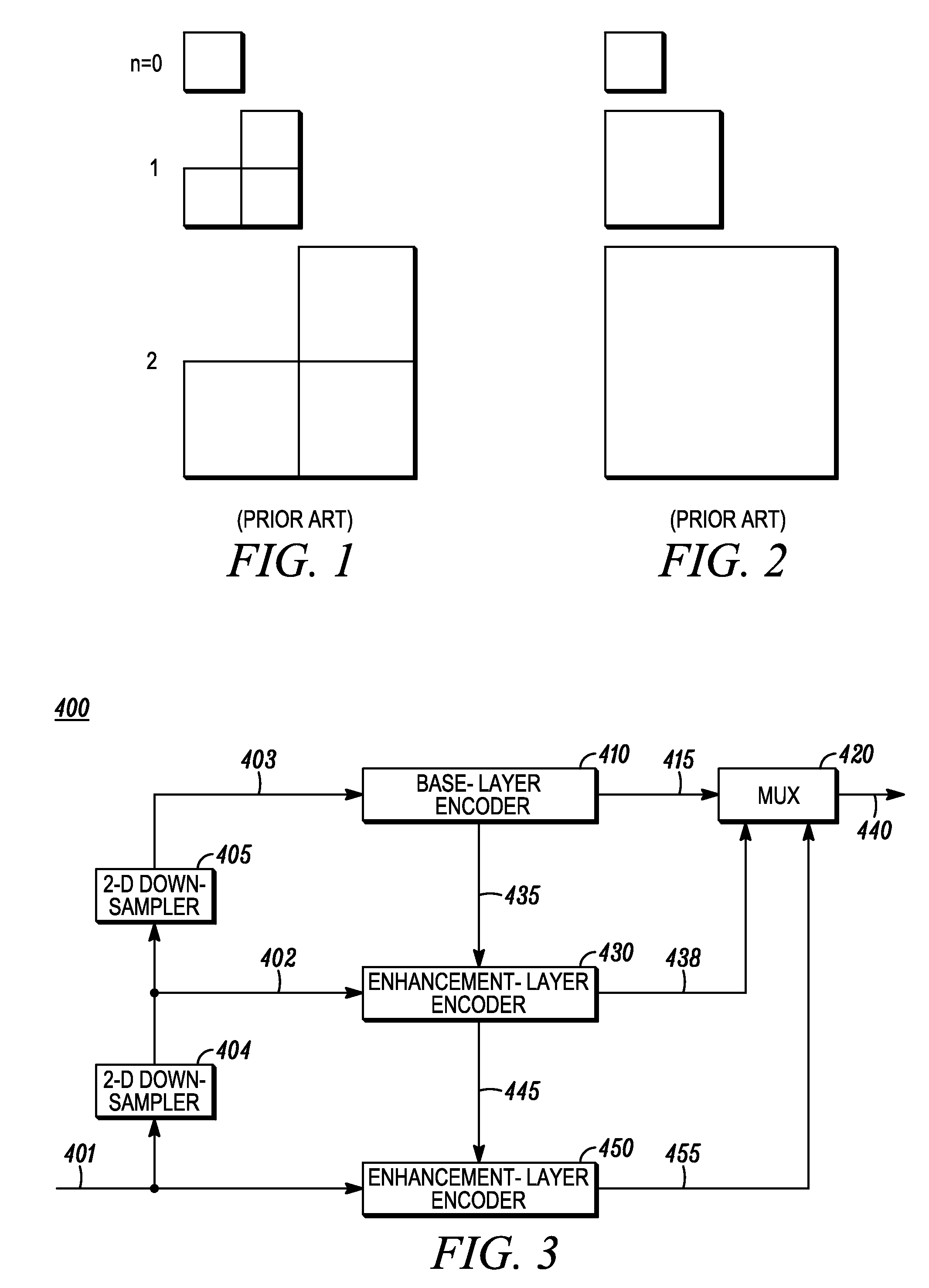
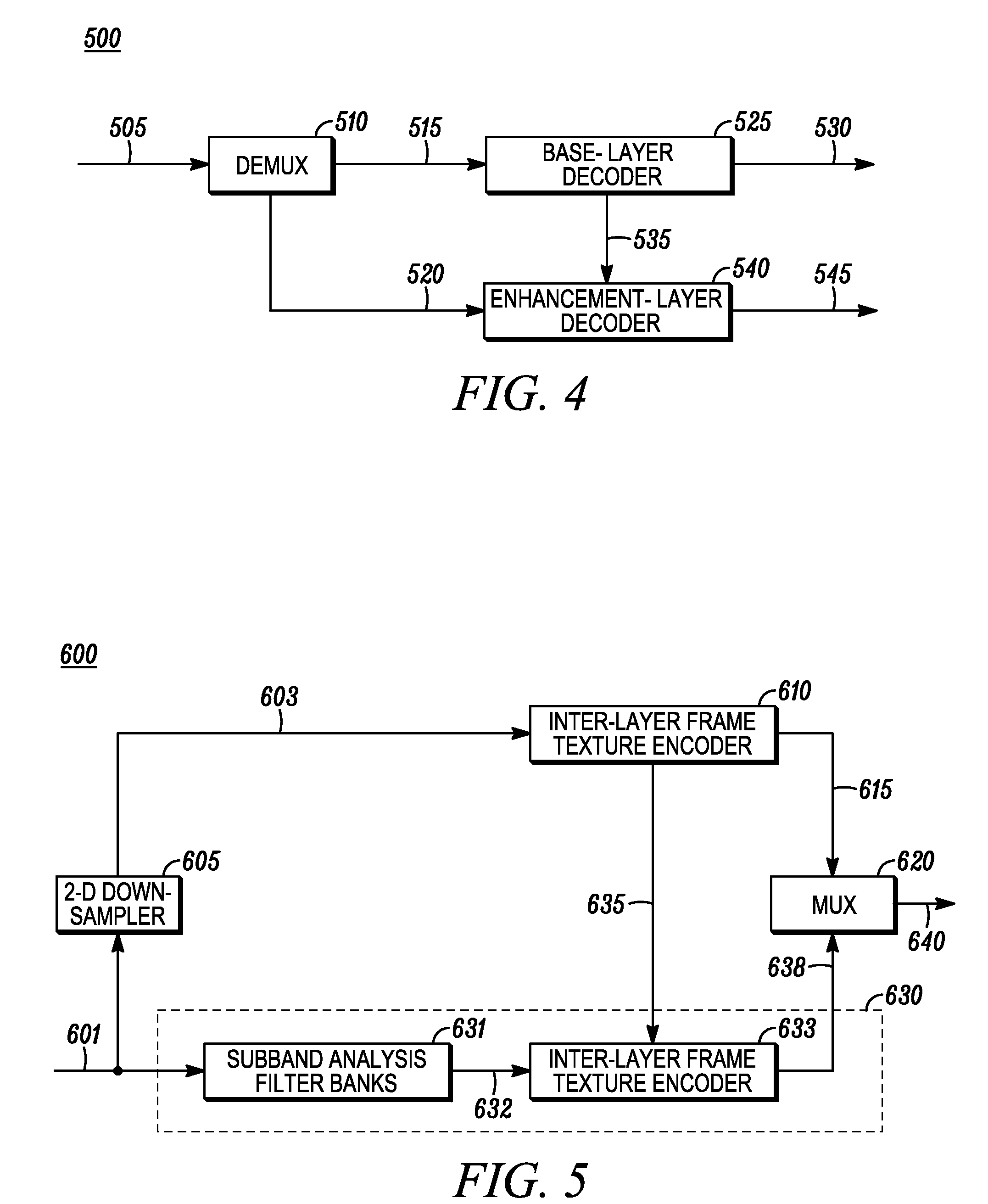
An apparatus and method is provided for highly scalable intraframe video coding. The conventional macroblock DCT tools are integrated with the subband filter banks for the improved efficiency of scalable compression. The enhancement layers are represented in a subband domain and coded by an inter-layer frame texture coder utilizing inter-layer prediction signal formed by the decoded previous layer. Each quality enhancement layer is additionally scalable in resolution.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
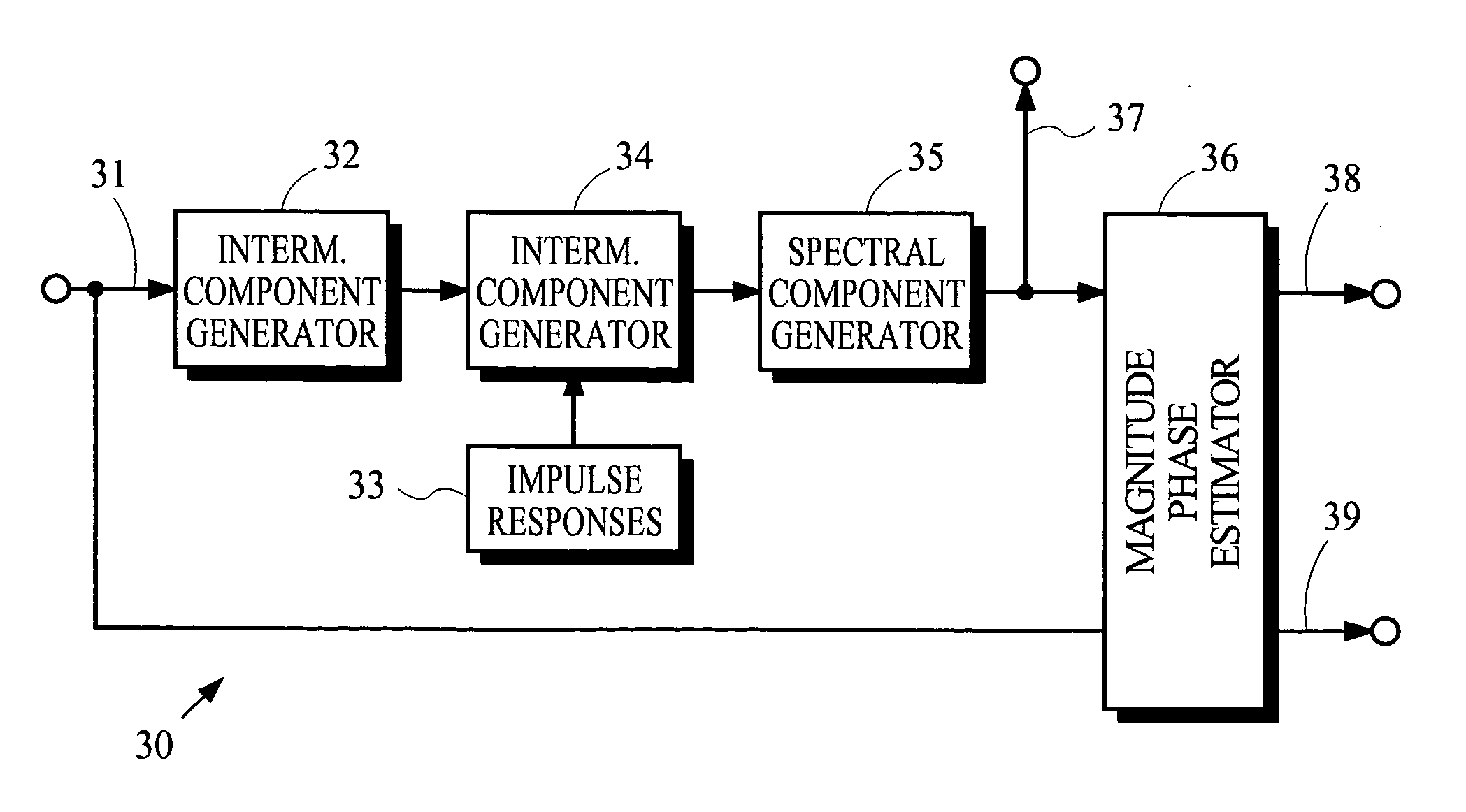
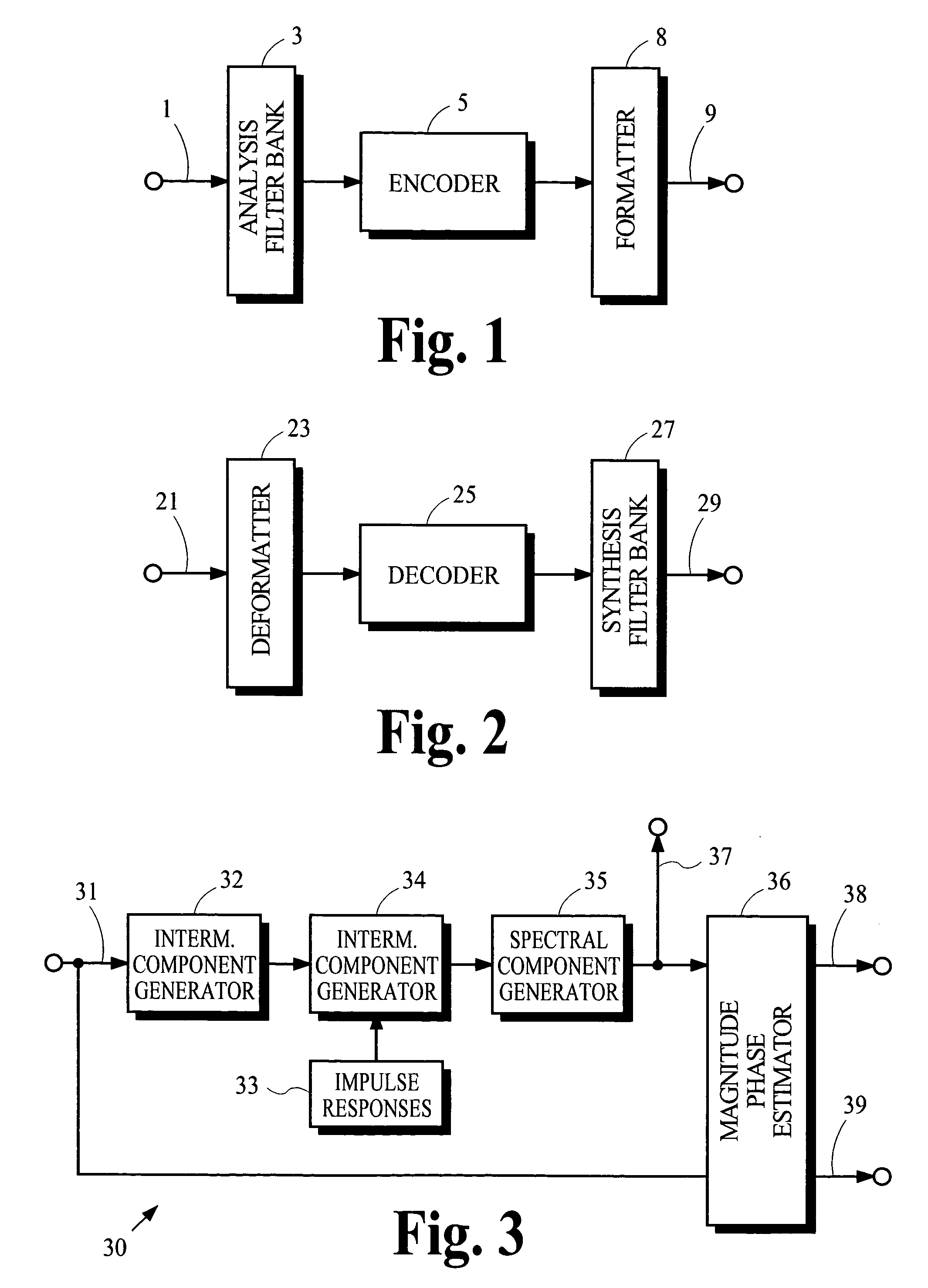
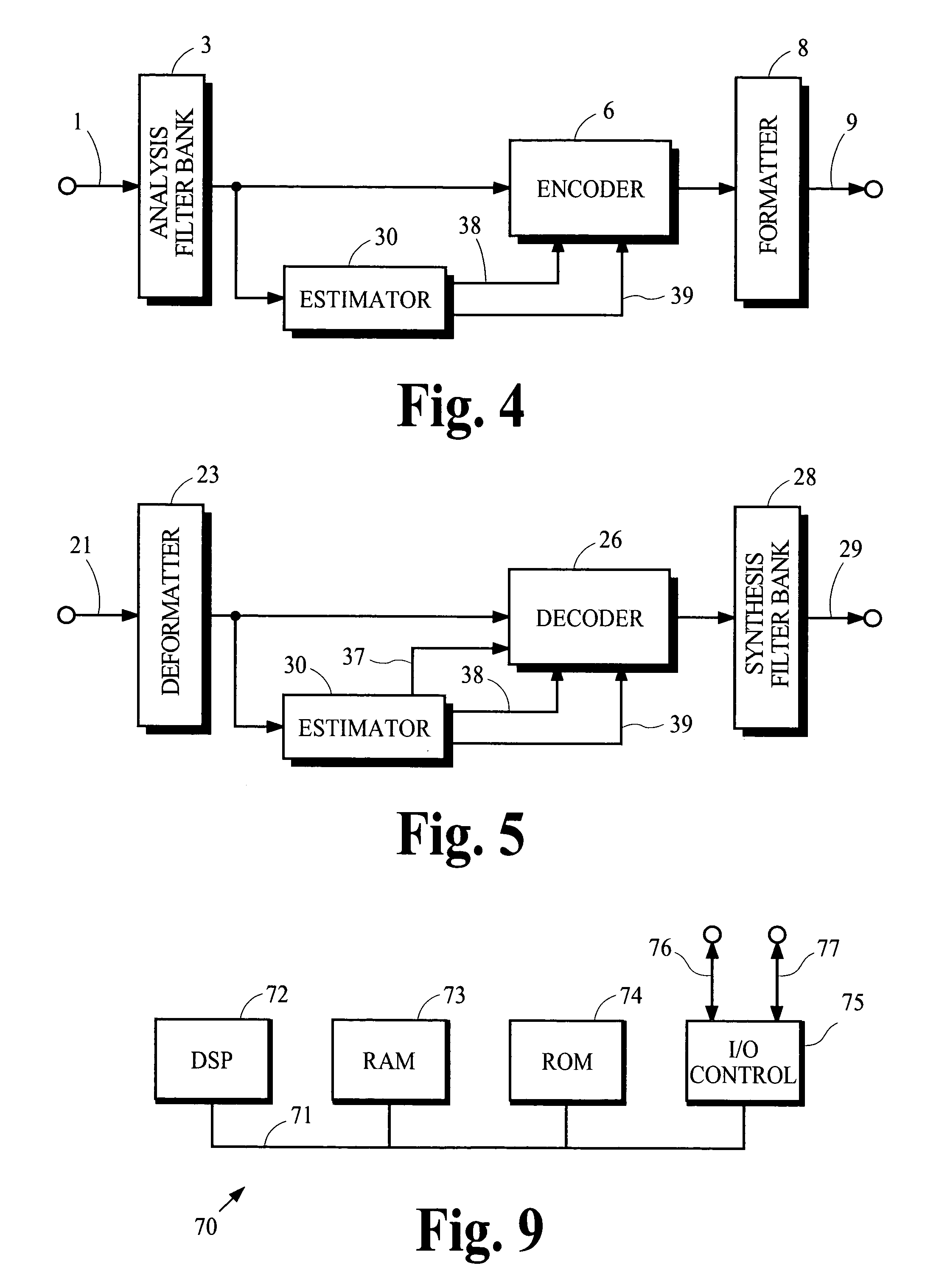
Coding techniques using estimated spectral magnitude and phase derived from MDCT coefficients
ActiveUS6980933B2Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceSpeech analysisComputation complexityFrequency spectrum
Estimates of spectral magnitude and phase are obtained by an estimation process using spectral information from analysis filter banks such as the Modified Discrete Cosine Transform. The estimation process may be implemented by convolution-like operations with impulse responses. Portions of the impulse responses may be selected for use in the convolution-like operations to trade off between computational complexity and estimation accuracy. Mathematical derivations of analytical expressions for filter structures and impulse responses are disclosed.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
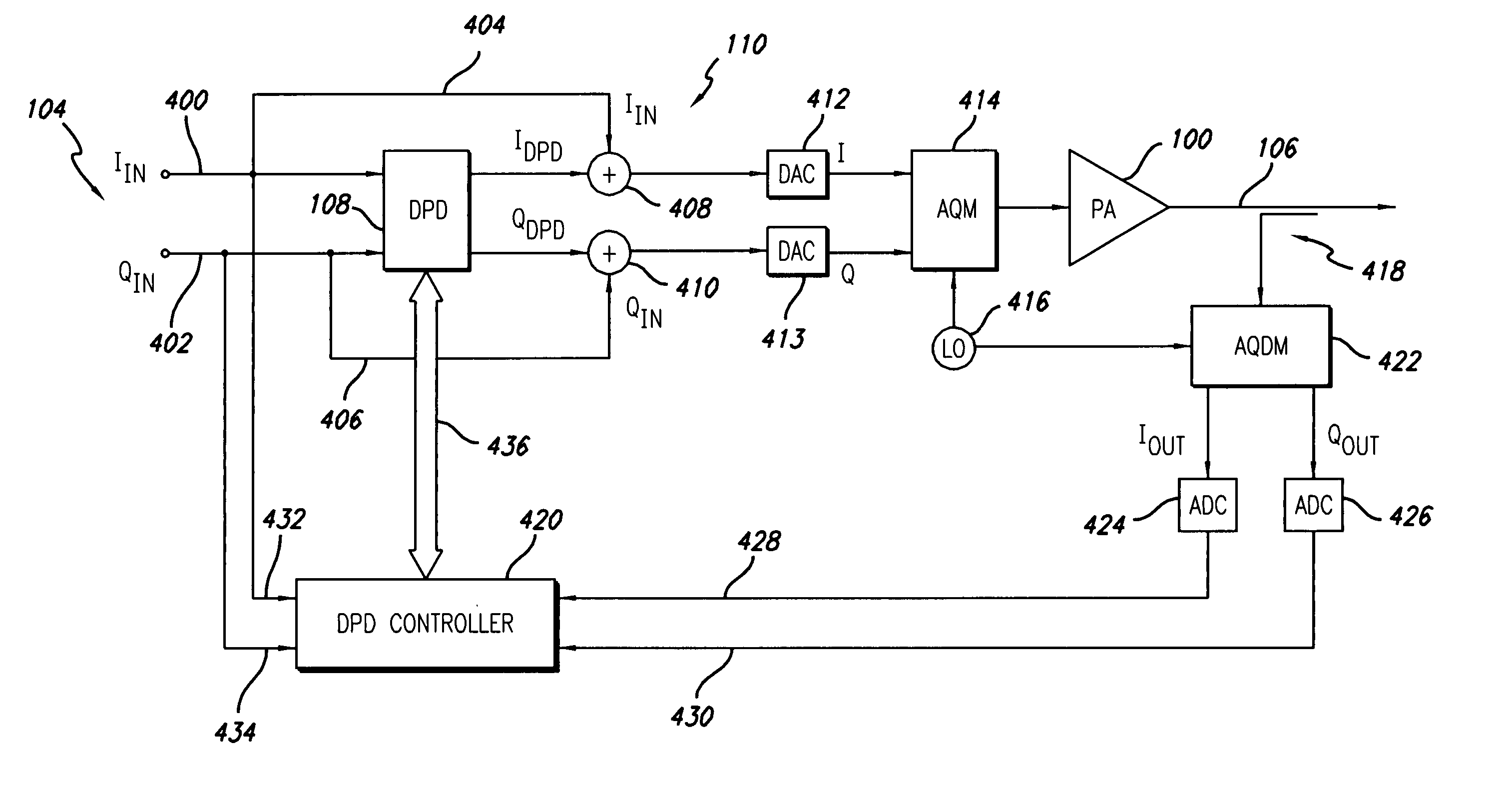
Digital predistortion system and method for high efficiency transmitters
ActiveUS20050195919A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifiers with memory effect compensationNon linear dynamicEngineering
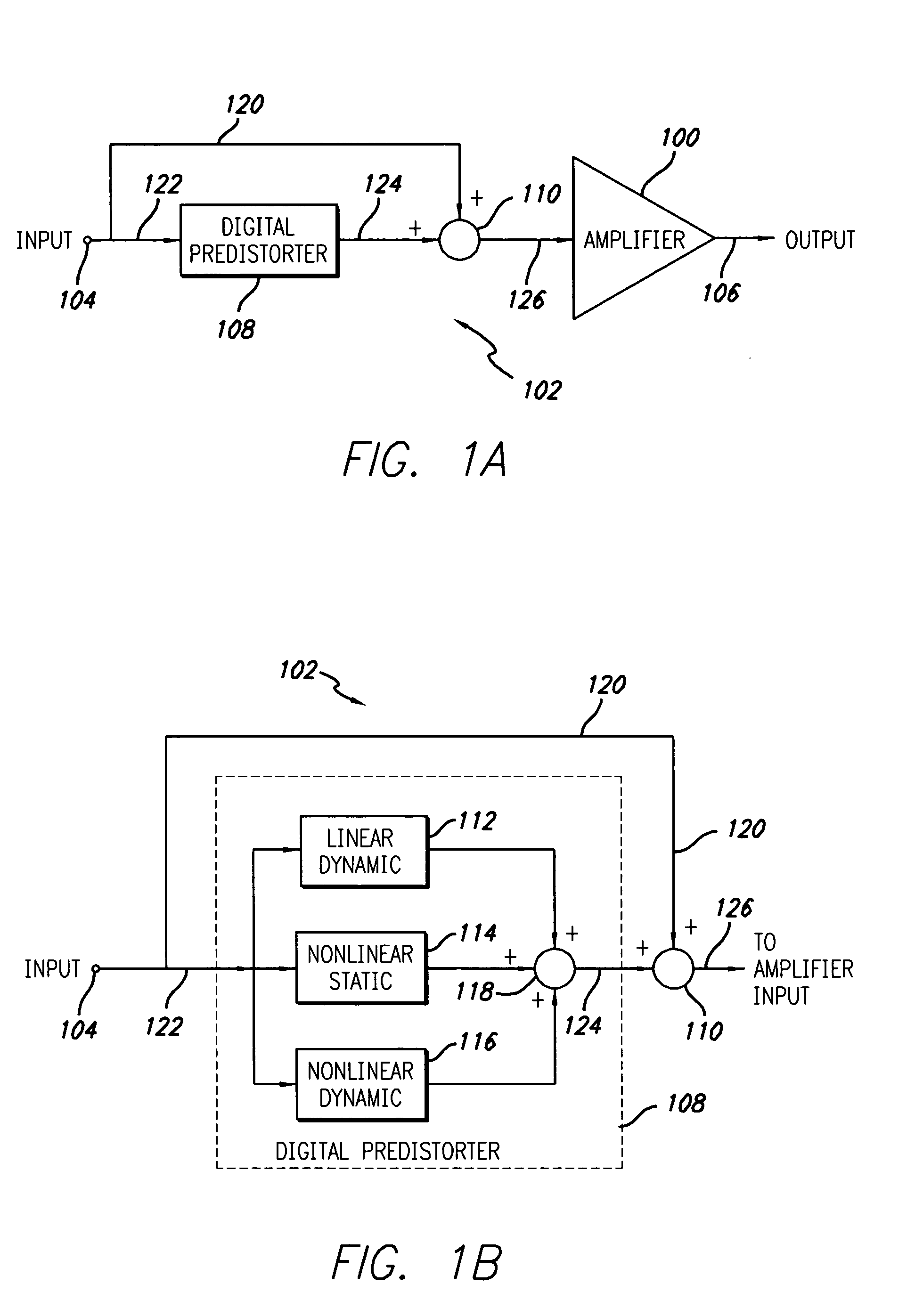
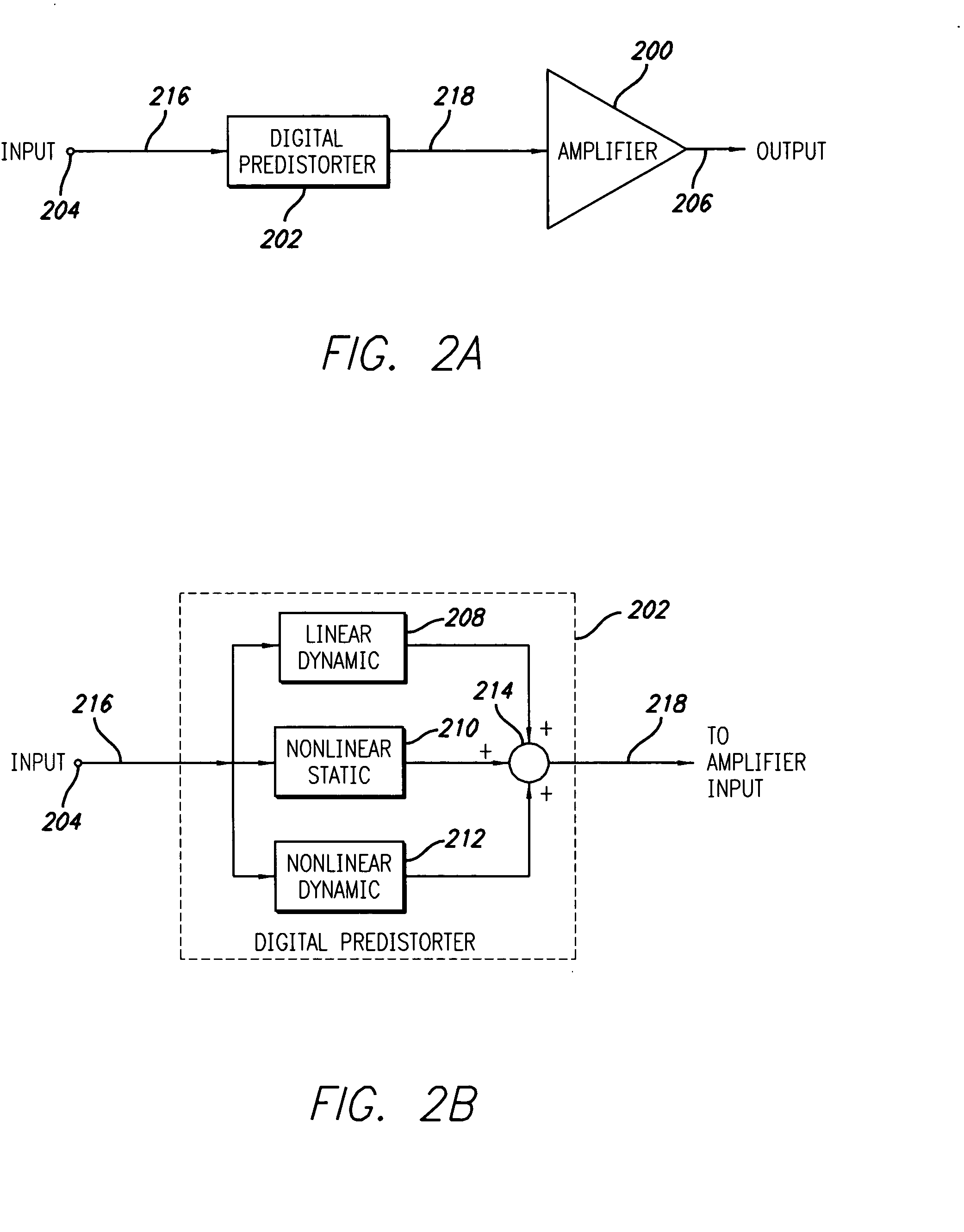
A system for digitally linearizing the nonlinear behaviour of RF high efficiency amplifiers employing baseband predistortion techniques is disclosed. The system provides additive or multiplicative predistortion of the digital quadrature (I / Q) input signal in order to minimize distortion at the output of the amplifier. The predistorter uses a discrete-time polynomial kernel to model the inverse transfer characteristic of the amplifier, providing separate and simultaneous compensation for nonlinear static distortion, linear dynamic distortion and nonlinear dynamic effects including reactive electrical memory effects. Compensation for higher order reactive and thermal memory effects is embedded in the nonlinear dynamic compensation operation of the predistorter in an IIR filter bank. A predistortion controller periodically monitors the output of the amplifier and compares it to the quadrature input signal to compute estimates of the residual output distortion of the amplifier. Output distortion estimates are used to adaptively compute the values of the parameters of the predistorter in response to changes in the amplifier's operating conditions (temperature drifts, changes in modulation input bandwidth, variations in drive level, aging, etc). The predistortion parameter values computed by the predistortion controller are stored in non-volatile memory and used in the polynomial digital predistorter. The digital predistortion system of the invention may provide broadband linearization of highly nonlinear and highly efficient RF amplification circuits including, but not limited to, dynamic load modulation amplifiers.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
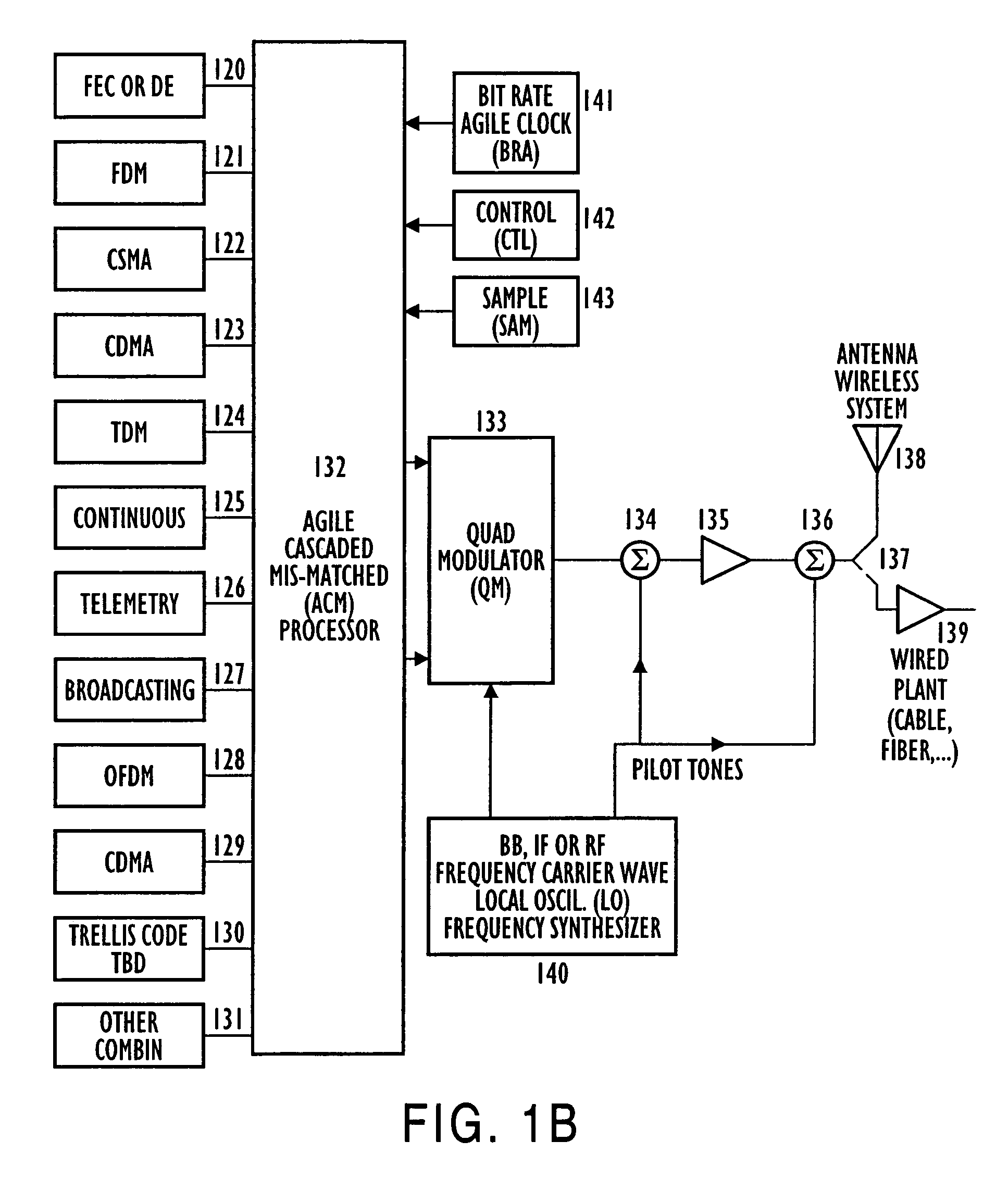
Adaptive receivers for bit rate agile (BRA) and modulation demodulation (modem) format selectable (MFS) signals
InactiveUS7376180B2Improve performanceSignificant spectral saving advantageMultiple-port networksSecret communicationModem deviceThird generation
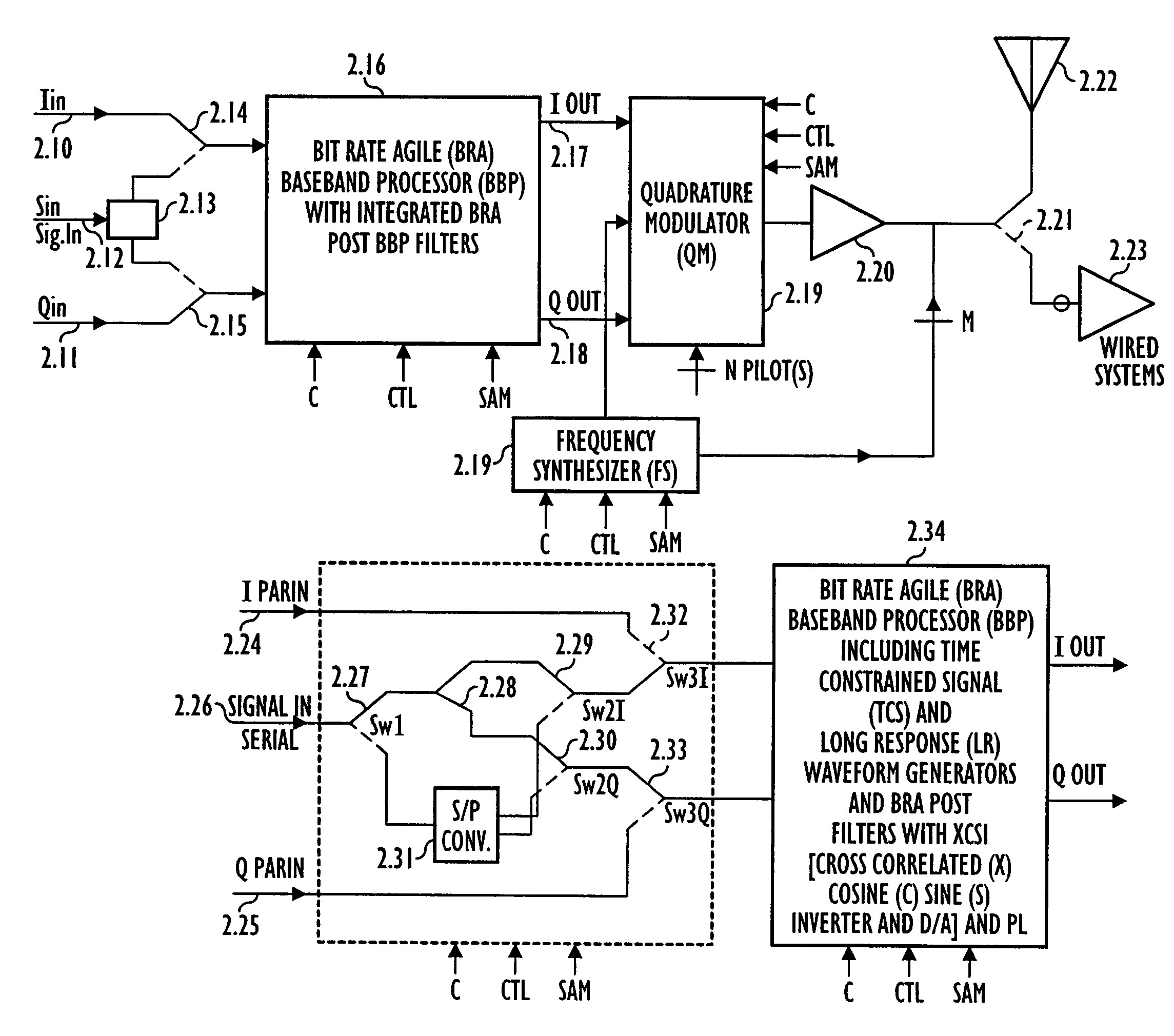
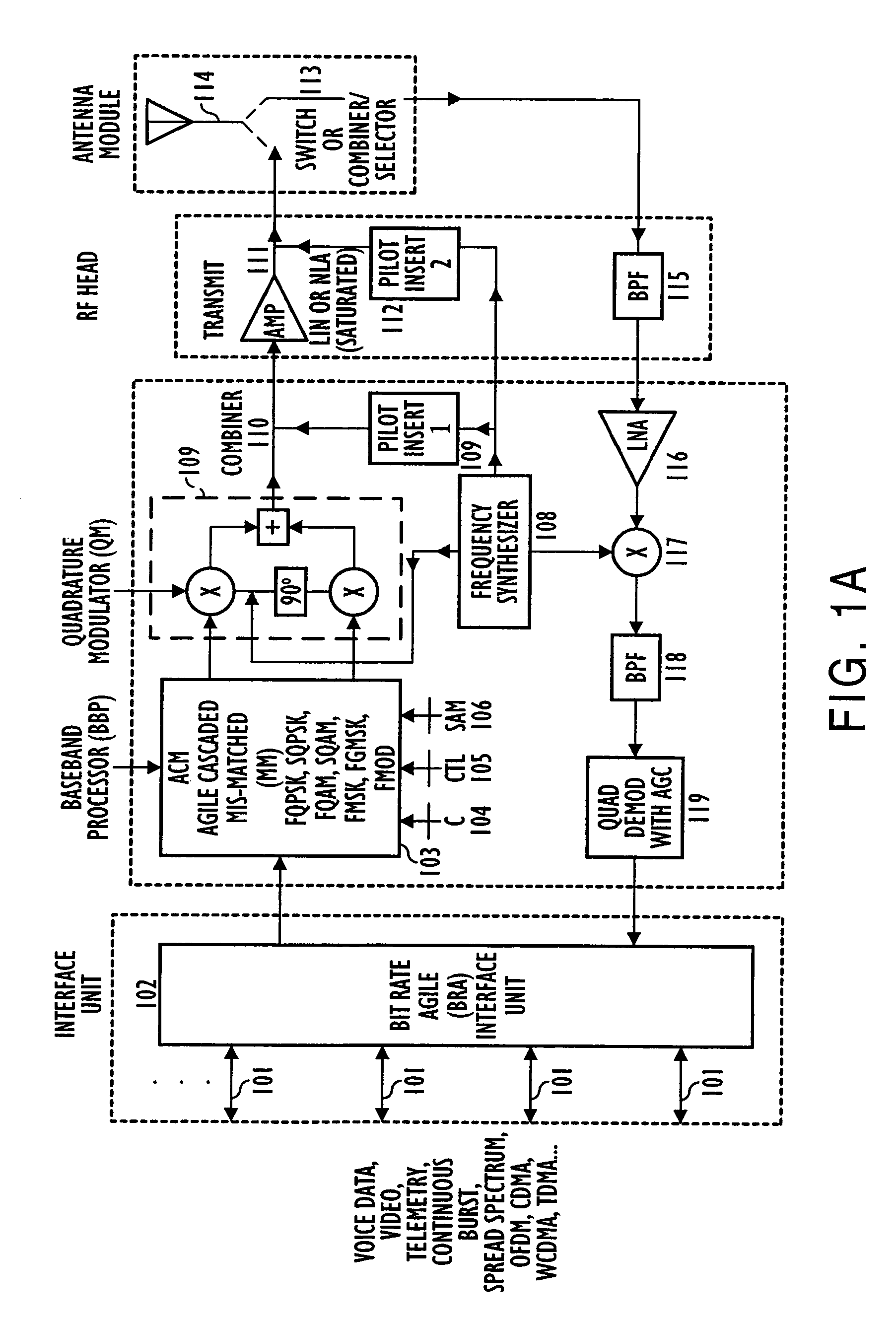
Systems, apparatus, and methods for new generations of wireless systems, including multiple standard, interoperable Third-Generation (3G) and Second-Generation (2G), Spread Spectrum CDMA, WCDMA, GSM, Enhanced GSM systems and CSMA, TDMA and OFDM. Bit Rate Agile (BRA), Modulation and Code Selectable processing techniques of Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying (GMSK), Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK), Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM), and of Mis-Matched demodulator filters in which the demodulator filter set is mismatched to the filter set of the signal modulator.
Owner:FEHER KAMILO
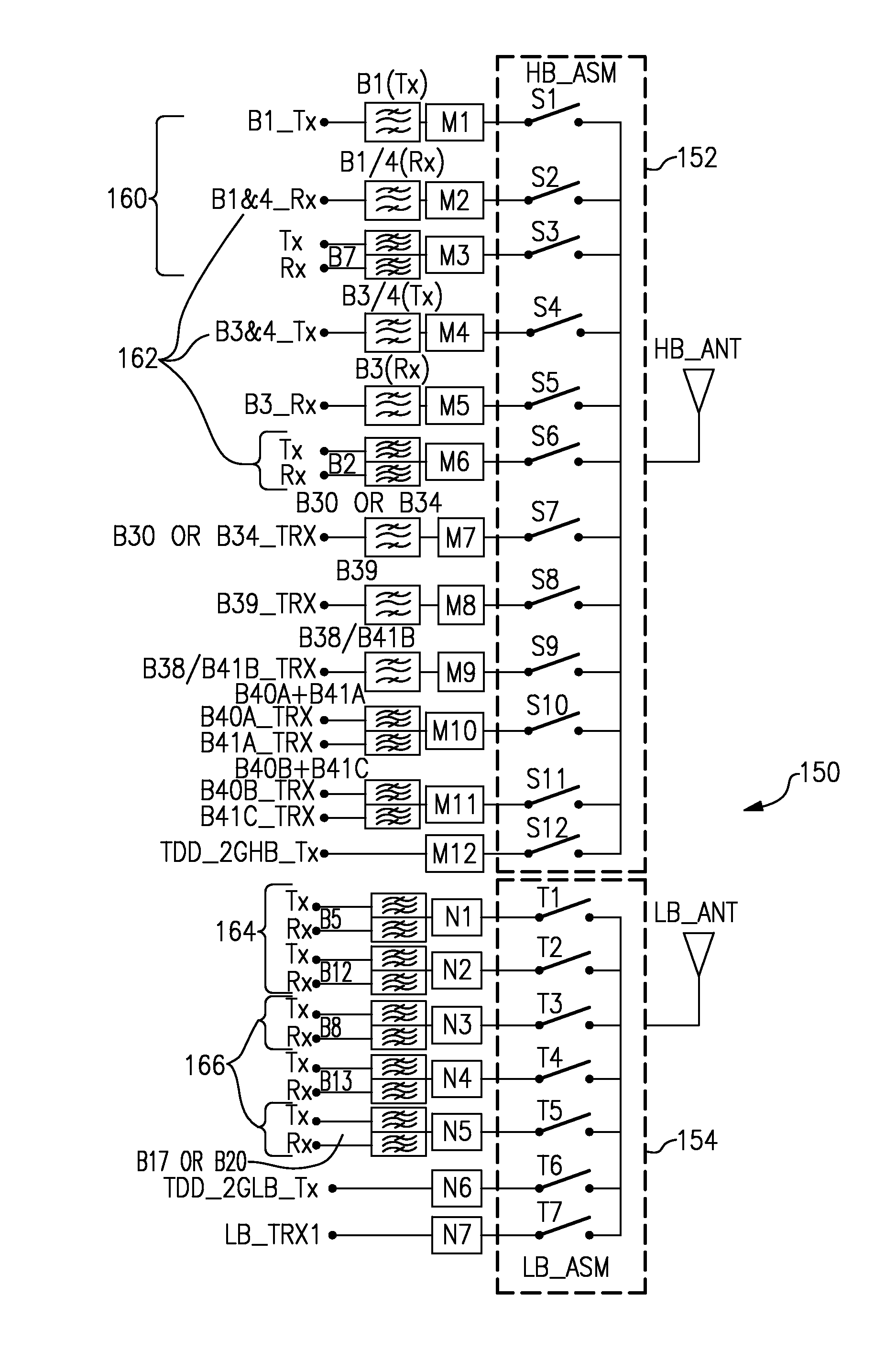
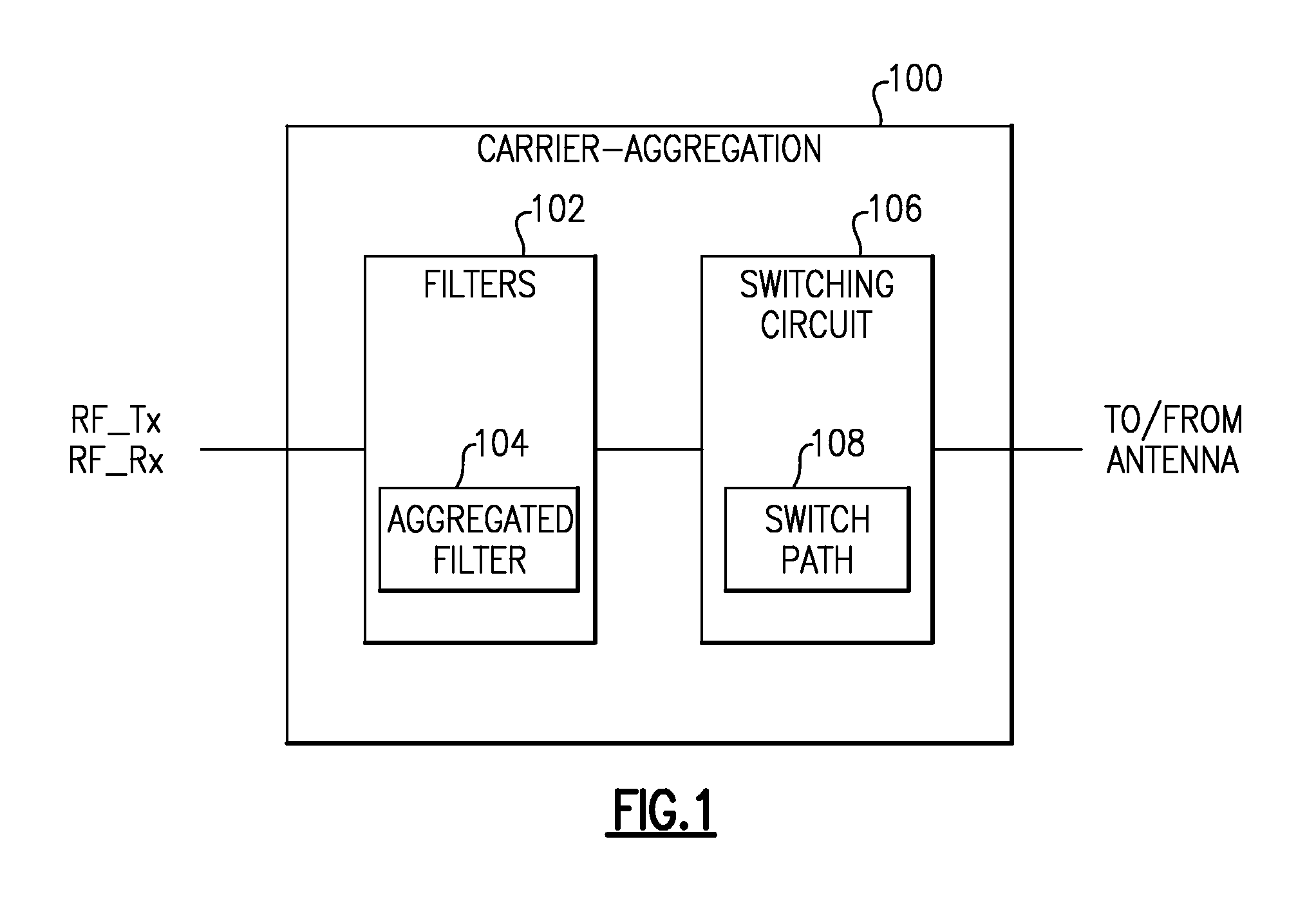
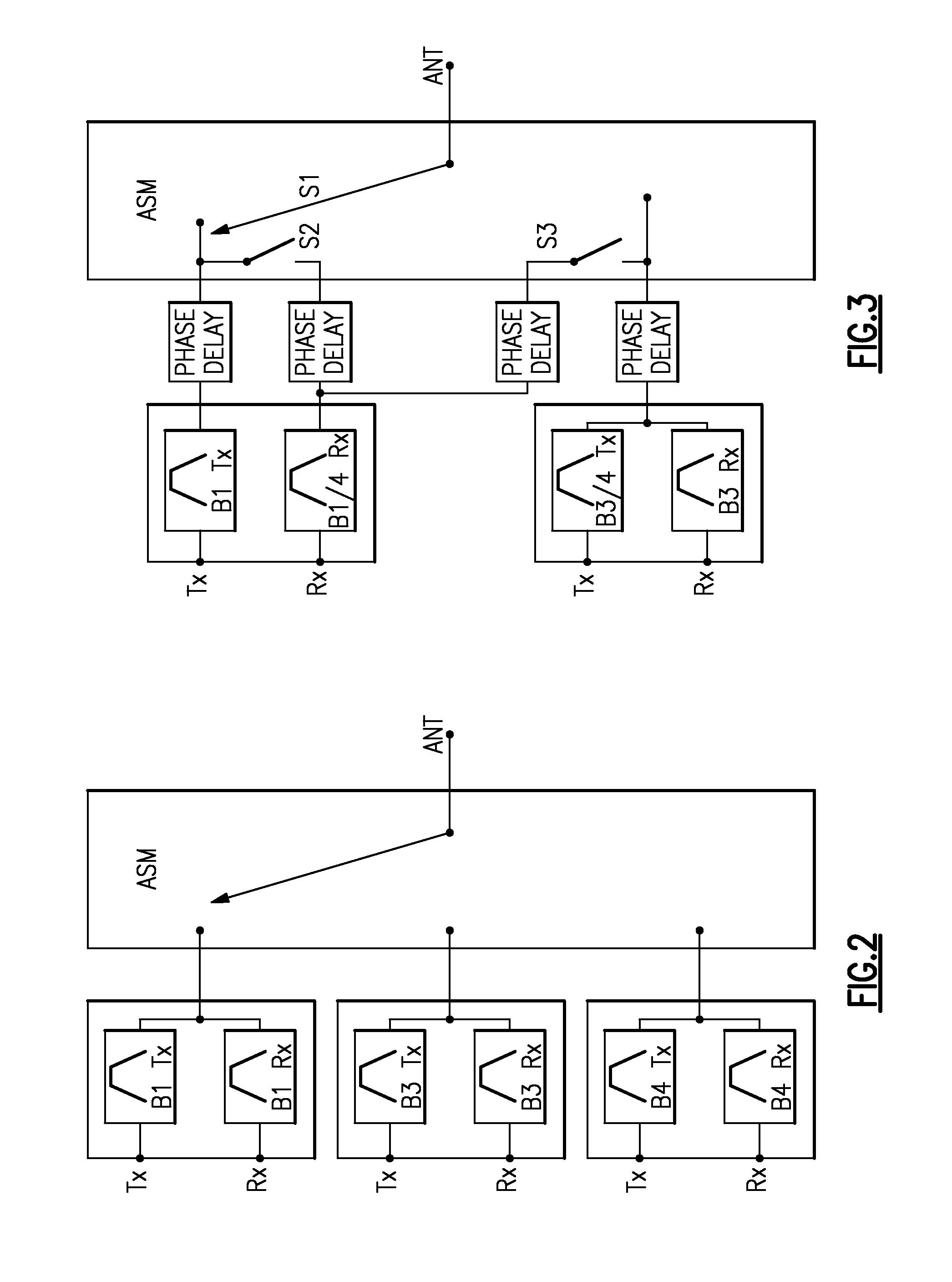
Systems and methods related to carrier aggregation front-end module applications
Improved switched multiplexer architecture for supporting carrier aggregation in front-end applications. In some embodiments, an N-plexing system can include an assembly of filters configured to provide N filtered paths, and a switching circuit in communication with the assembly of filters. The switching circuit can be configured to provide a plurality of switchable paths between the assembly of filters and an antenna port to allow simultaneous operation between the N filtered paths and the antenna port. In some embodiments, N can be 4 for a quadruplexing system or 2 for a duplexing system, and such a system can be implemented in a front-end module (FEM) for wireless devices.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Apparatus and methods for multichannel digital audio coding
ActiveUS20060074642A1Low bit-rate codingSame level of compressionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningImage resolutionVocal tract
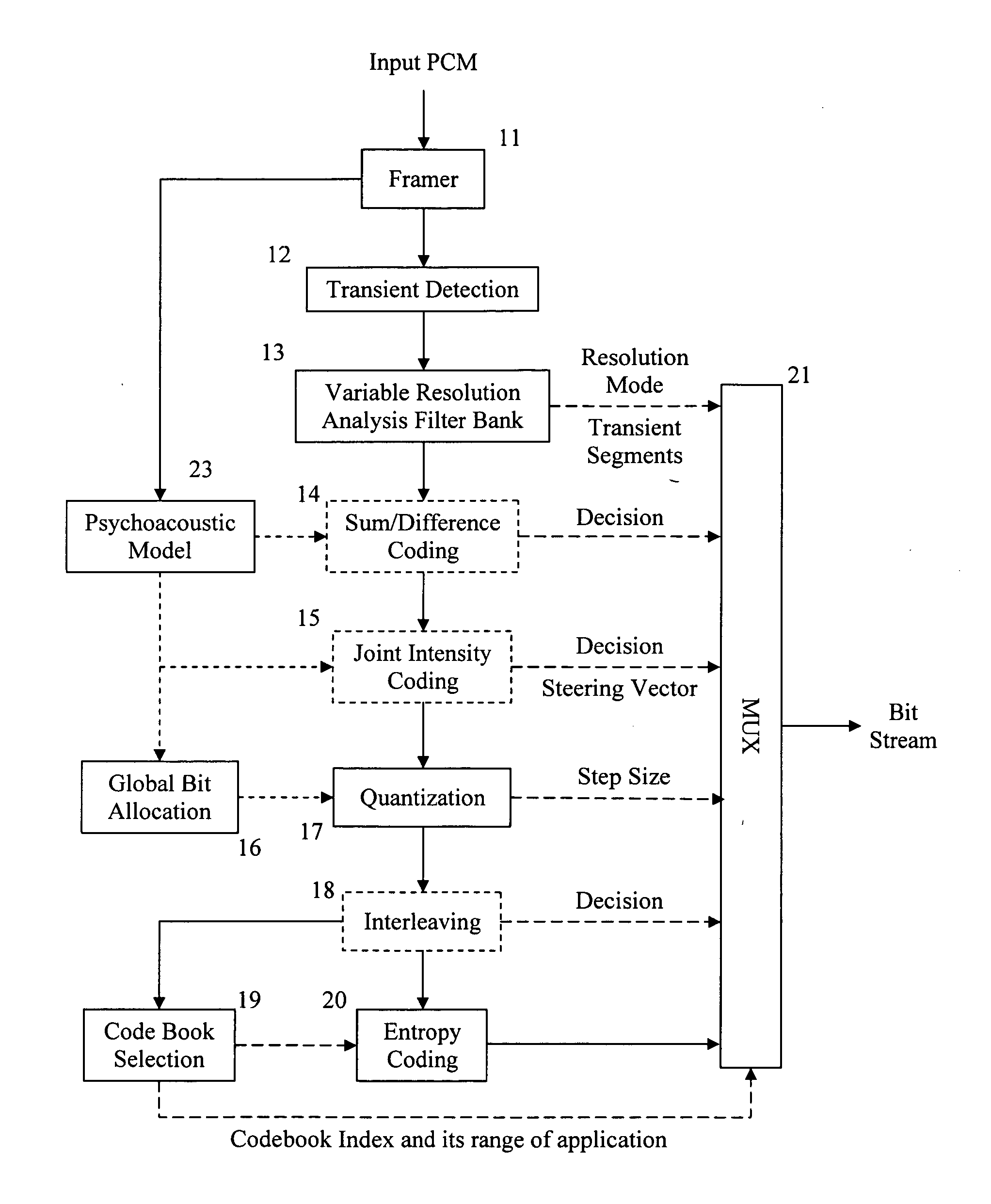
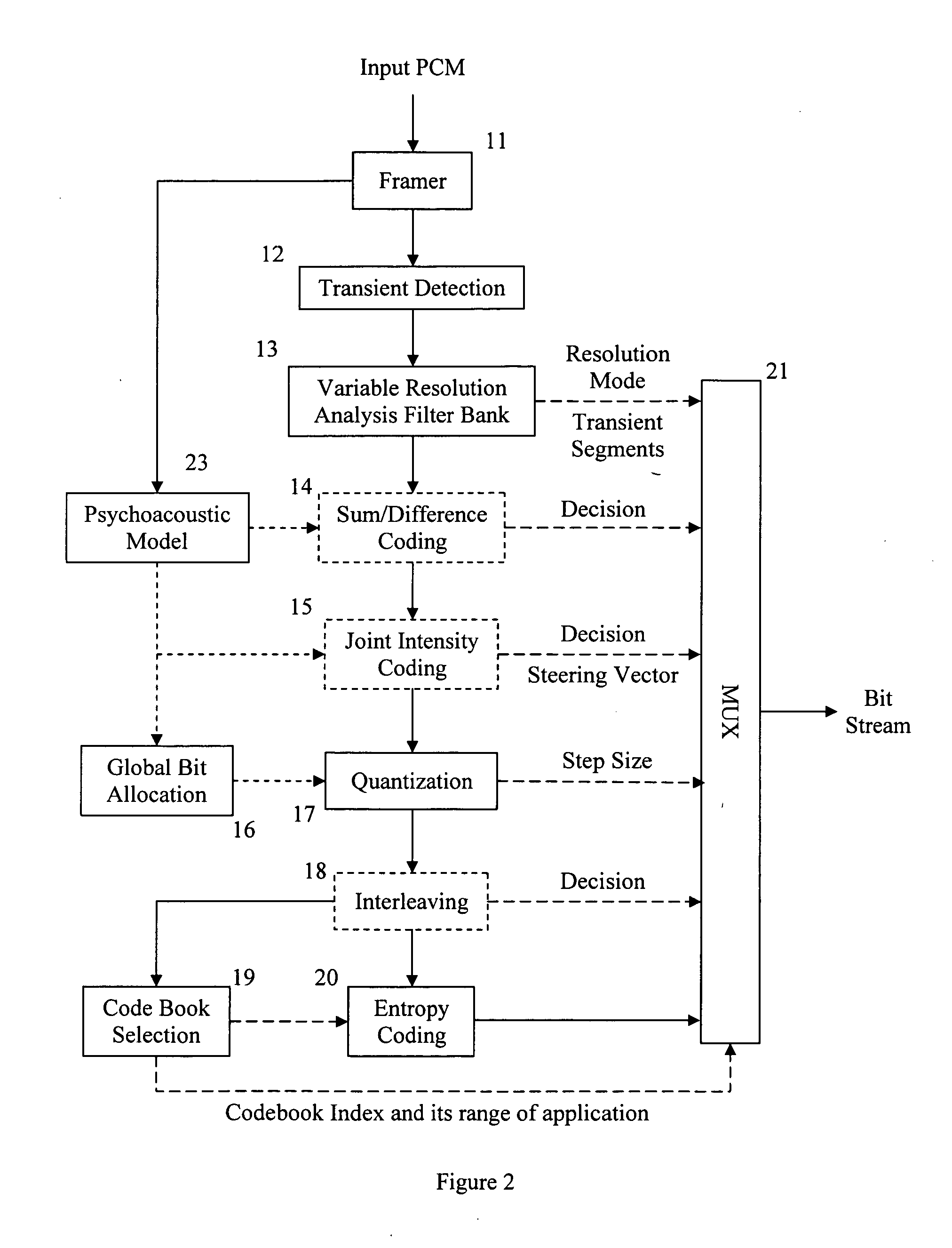
A low bit rate digital audio coding system includes an encoder which assigns codebooks to groups of quantization indexes based on their local properties resulting in codebook application ranges that are independent of block quantization boundaries. The invention also incorporates a resolution filter bank, or a tri-mode resolution filter bank, which is selectively switchable between high and low frequency resolution modes or high, low and intermediate modes such as when detecting transient in a frame. The result is a multichannel audio signal having a significantly lower bit rate for efficient transmission or storage. The decoder is essentially an inverse of the structure and methods of the encoder, and results in a reproduced audio signal that cannot be audibly distinguished from the original signal.
Owner:DIGITAL RISE TECH CO LTD
Device and method for converting spatial audio signal
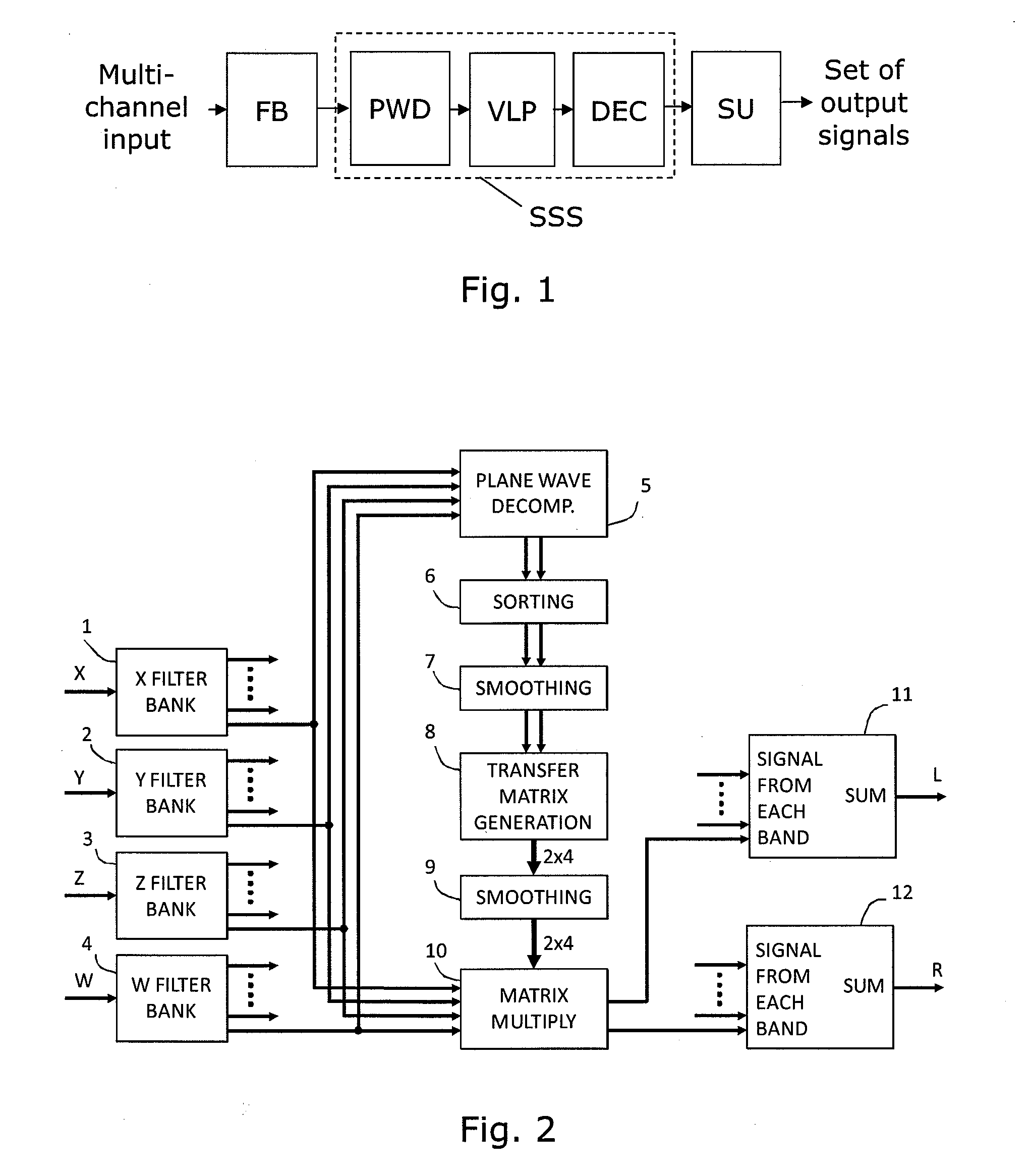
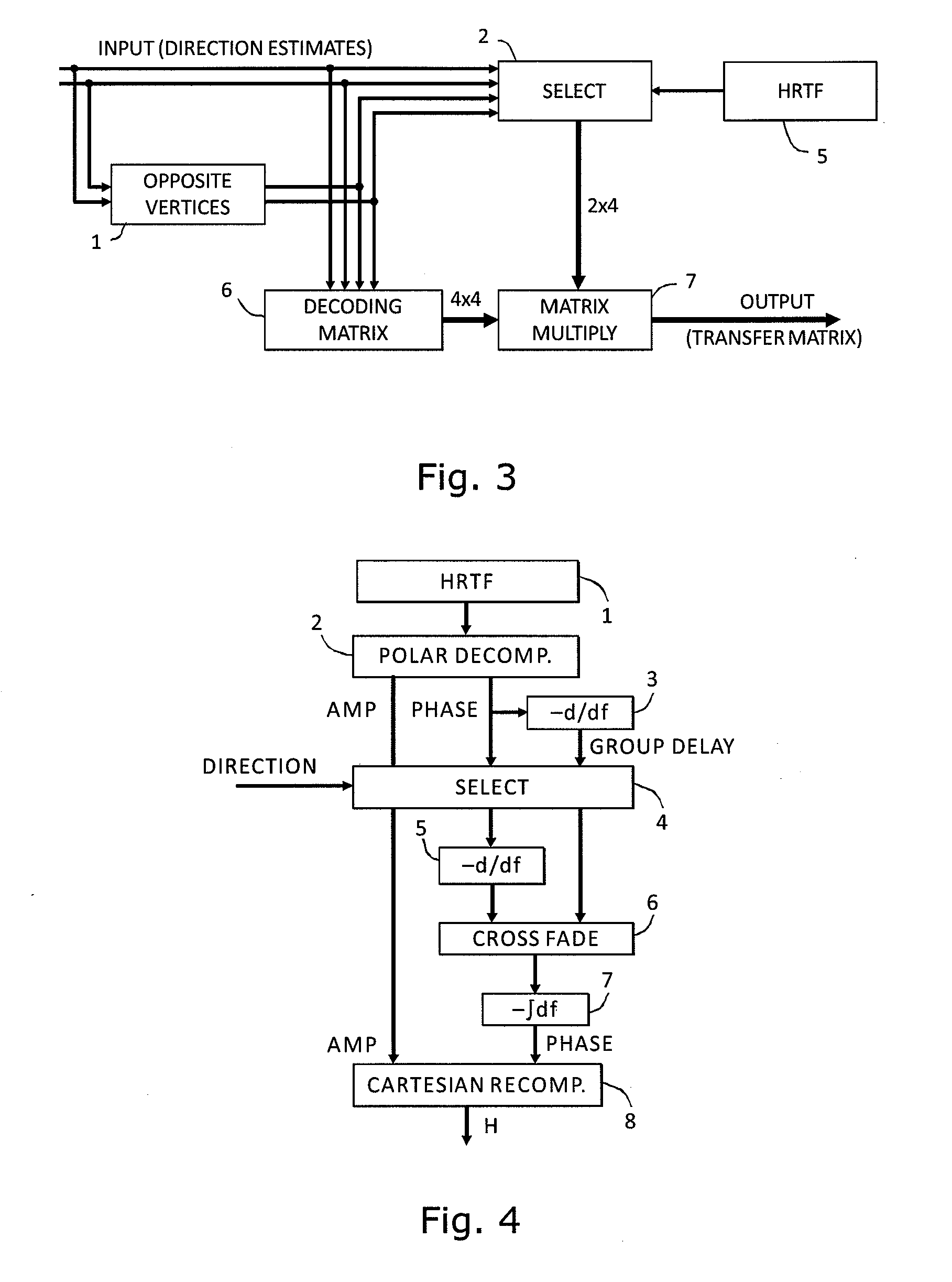
ActiveUS20100329466A1Promote reproductionPromote conversionSignal processingLoudspeaker signals distributionSound sourcesHeadphones
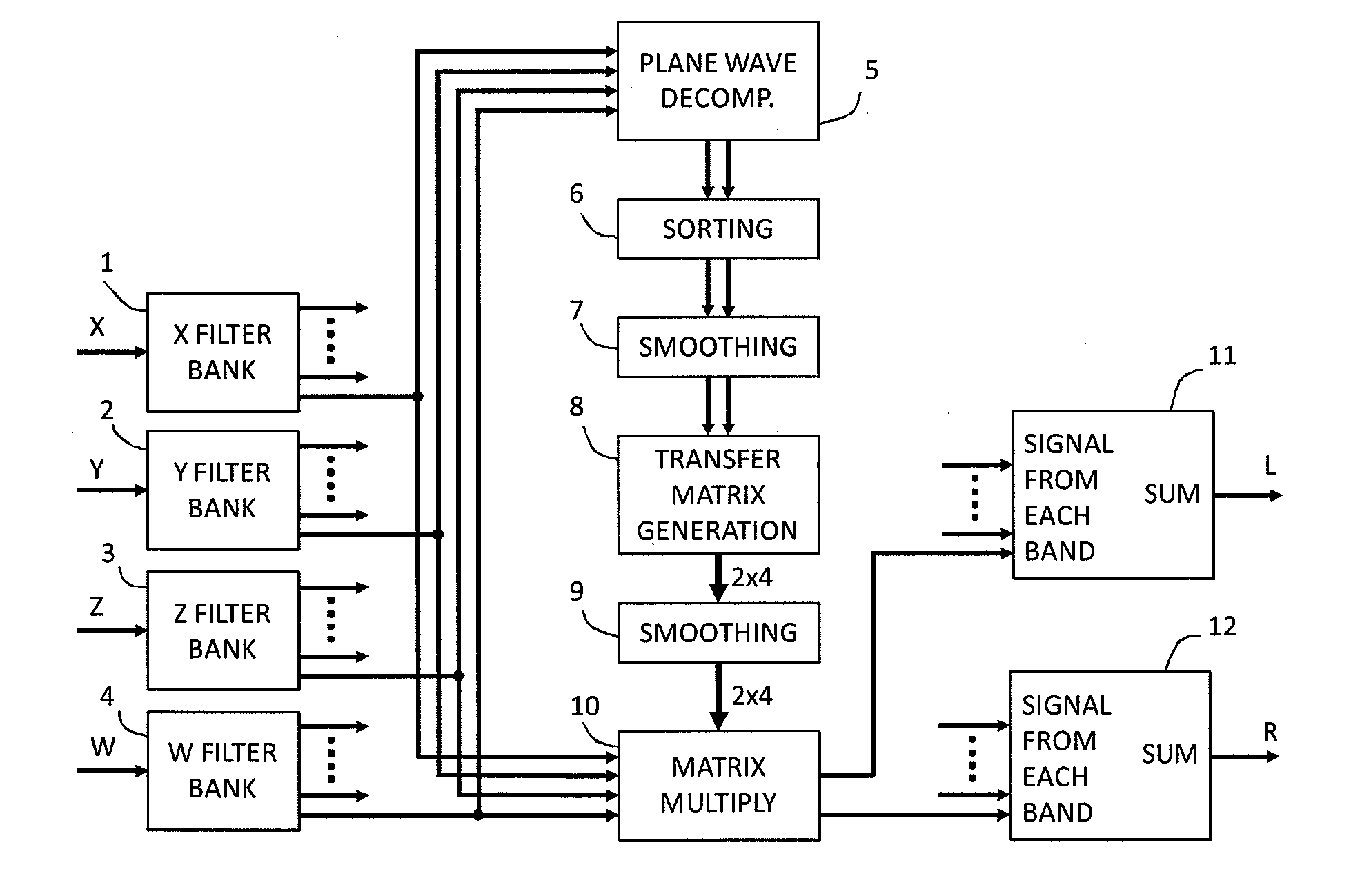
An audio processor for converting a multi-channel audio input signal, such as a B-format sound field signal, into a set of audio output signals, such as a set of two or more audio output signals arranged for headphone reproduction or for playback over an array of loudspeakers. A filter bank splits each of the input channels into frequency bands. The input signal is decomposed into plane waves to determine one or two dominant sound source directions. The(se) are used to determine a set of virtual loudspeaker positions selected such that the dominant direction(s) coincide(s) with virtual loudspeaker positions. The input signal is decoded into virtual loudspeaker signals corresponding to each of the virtual loudspeaker positions, and the virtual loudspeaker signals are processed with transfer functions suitable to create the illusion of sound emanating from the directions of the virtual loudspeakers. A high spatial fidelity is obtained due to the coincidence of virtual loudspeaker positions and the determined dominant sound source direction(s). Improved performance can be obtained in the case where Head-Related Transfer Functions are used by differentiating the phase of a high frequency part of the HRTFs with respect to frequency, followed by a corresponding integration of this part with respect to frequency after combining the components of HRTFs from different directions.
Owner:HARPEX LTD
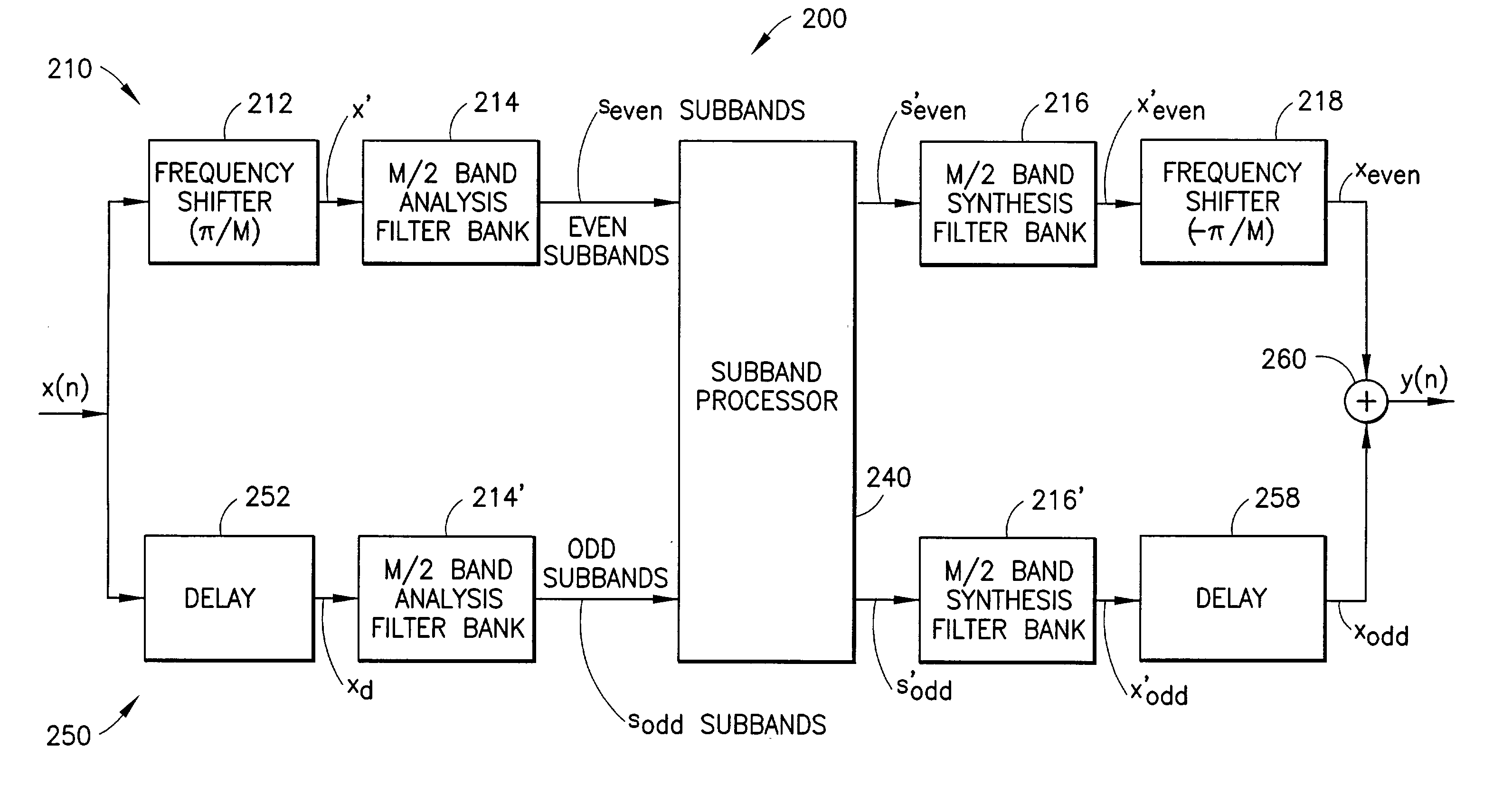
Oversampled filter bank for subband processing
InactiveUS6947509B1Aliasing between subbands is substantially reducedLower prototype filter orderDigital technique networkTransmissionEngineeringFrequency shift
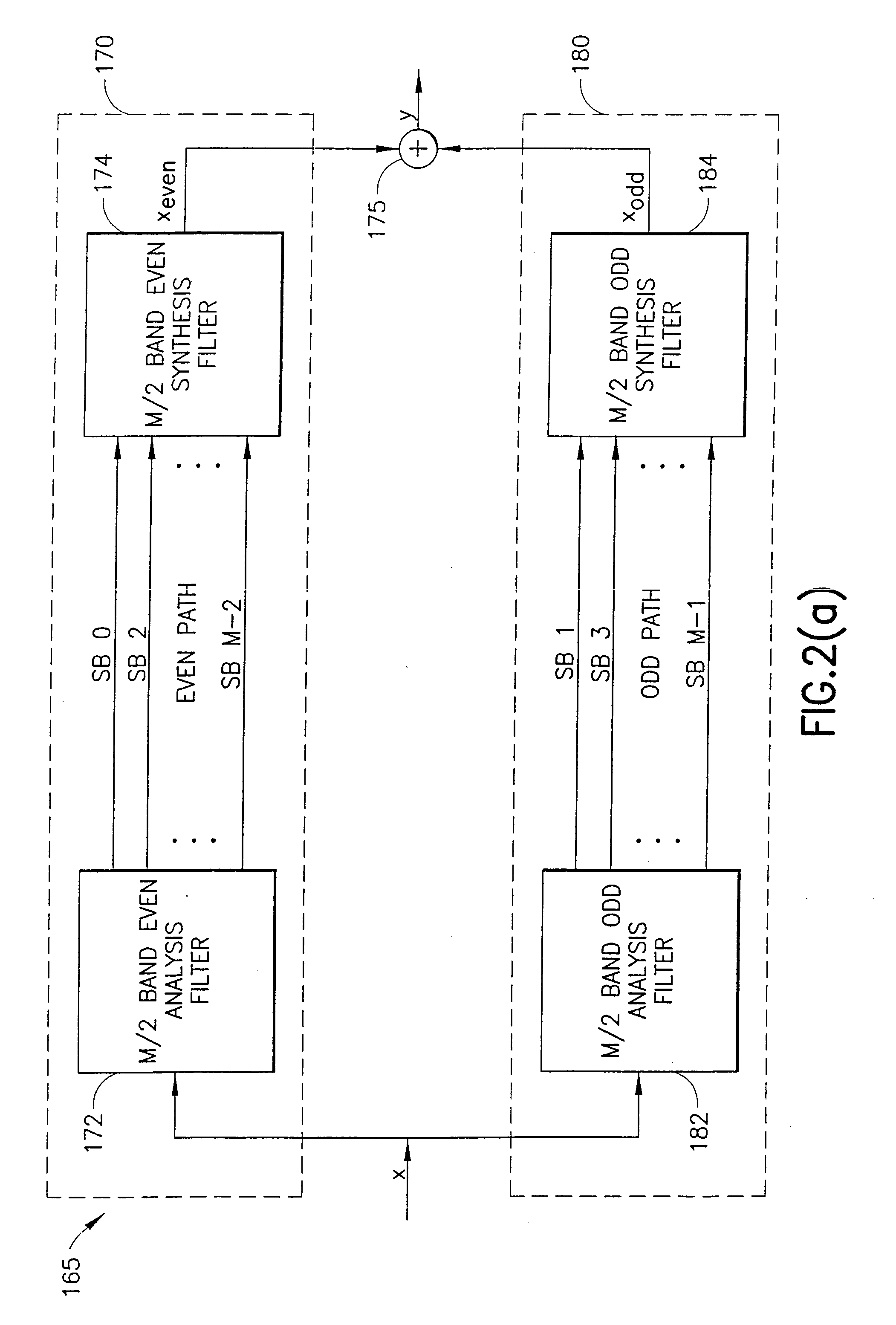
An oversampled filter bank structure that can be implemented using popular and efficient fast filter banks to allow subband processing of an input signal with substantially reduced aliasing between subbands. Even subbands (SB0, SB2, SB4, . . . ) of an input signal (x(n)) are frequency-shifted (212, 1012, 1012′, 1012″) prior to analysis filtering (214, 214′, 214″) at a 2× oversampled filter bank, subband processing (240, 240′, 240″), and synthesis filtering (216, 216′, 216″). A subsequent frequency-shift (218, 218′) returns the even subbands to their original band positions. The odd subbands (SB1, SB3, SB5, . . . ) are delayed (252) to compensate for the processing time of the frequency shifting. Separate analysis (214, 214′) and synthesis (216, 216′) filter banks may be provided for the even and odd subbands, or common complex analysis (284) and synthesis (286) filter banks may be used. In another embodiment, the subbands are processed in four subband paths (Paths 0, 1, 2, 3), and 4× oversampling is used. A filter bank structure (1400) for 2-D data is also provided.
Owner:VERANCE
Matched filter bank
InactiveUS6512785B1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsRadio transmissionCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
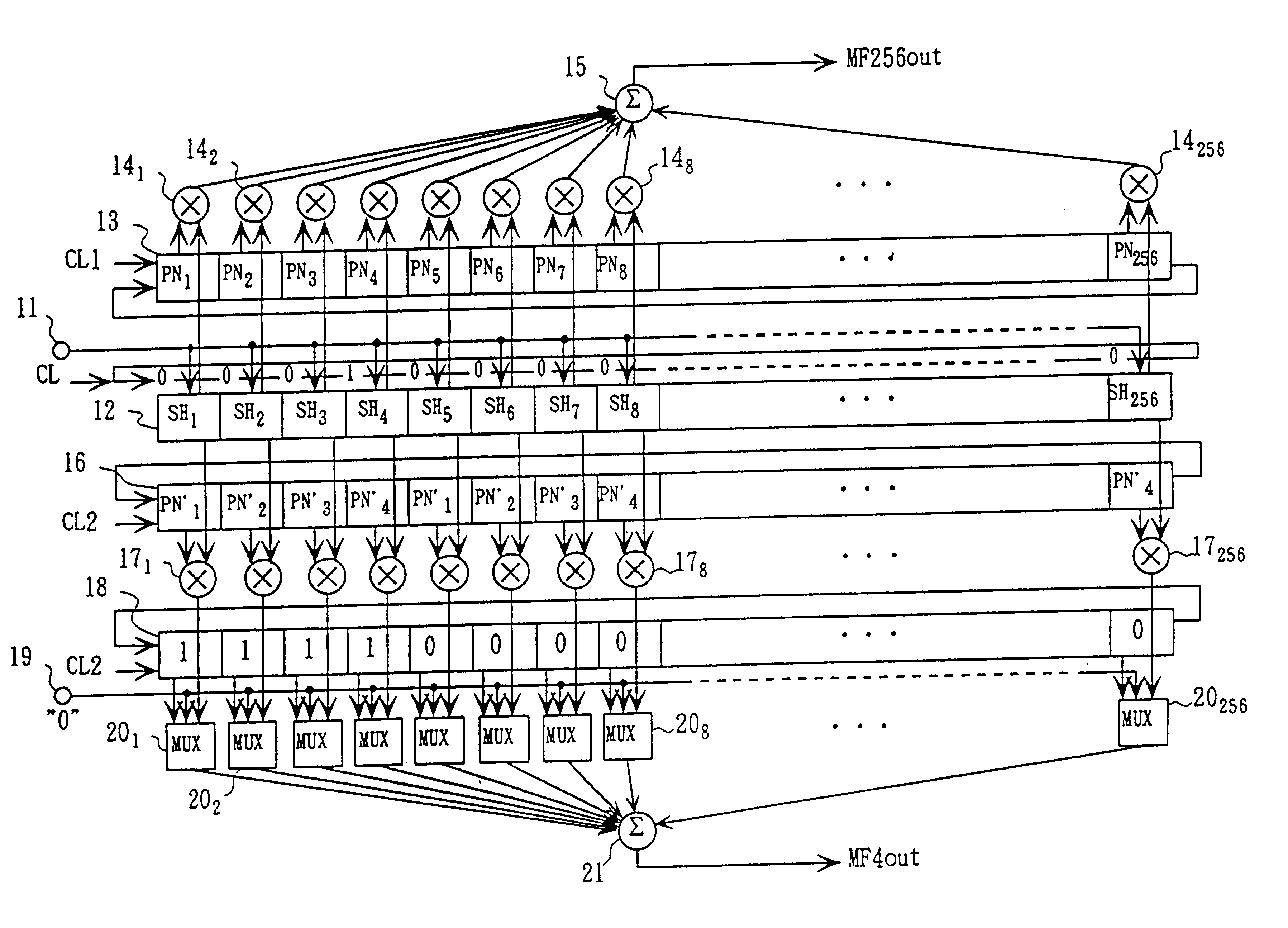
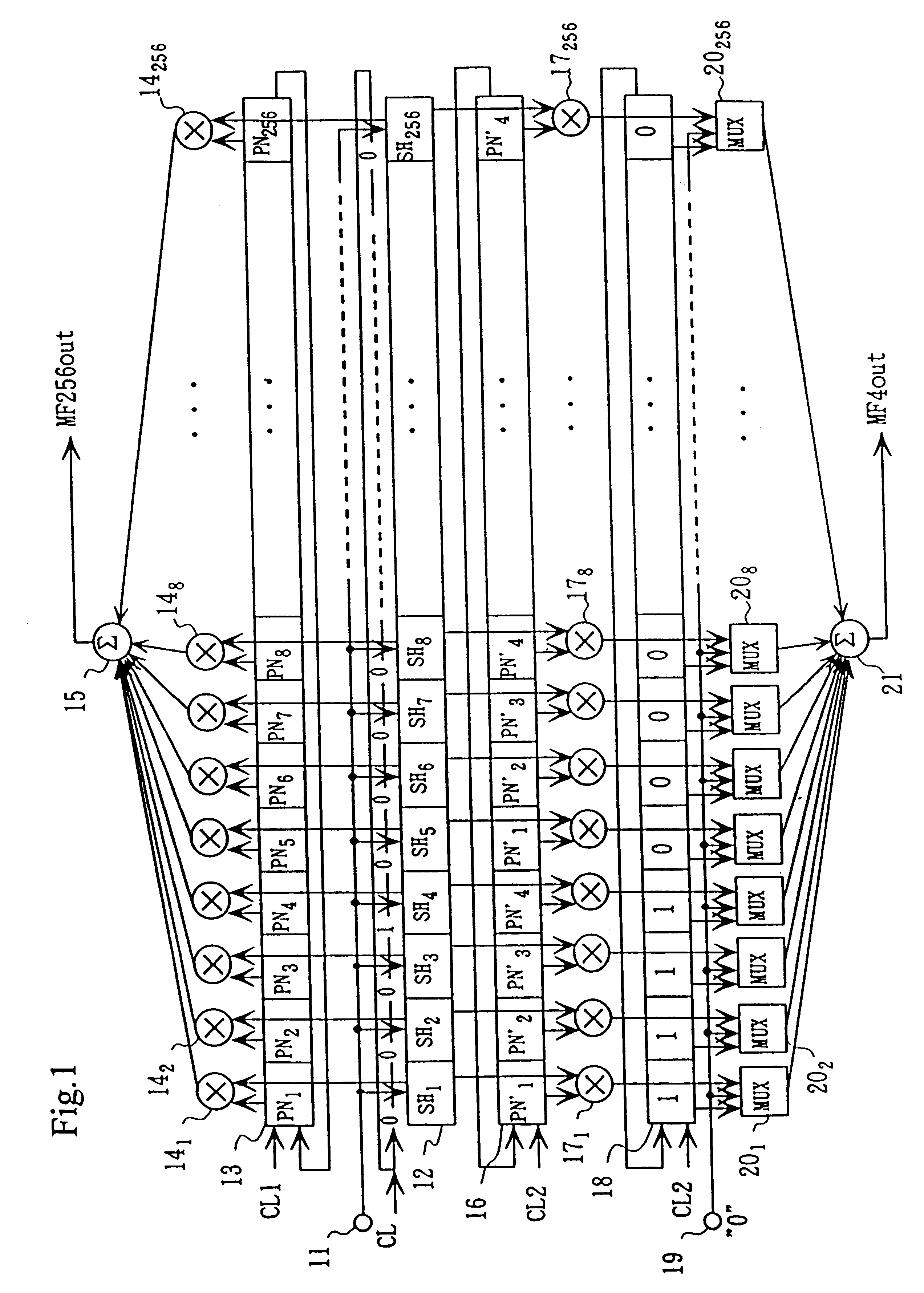
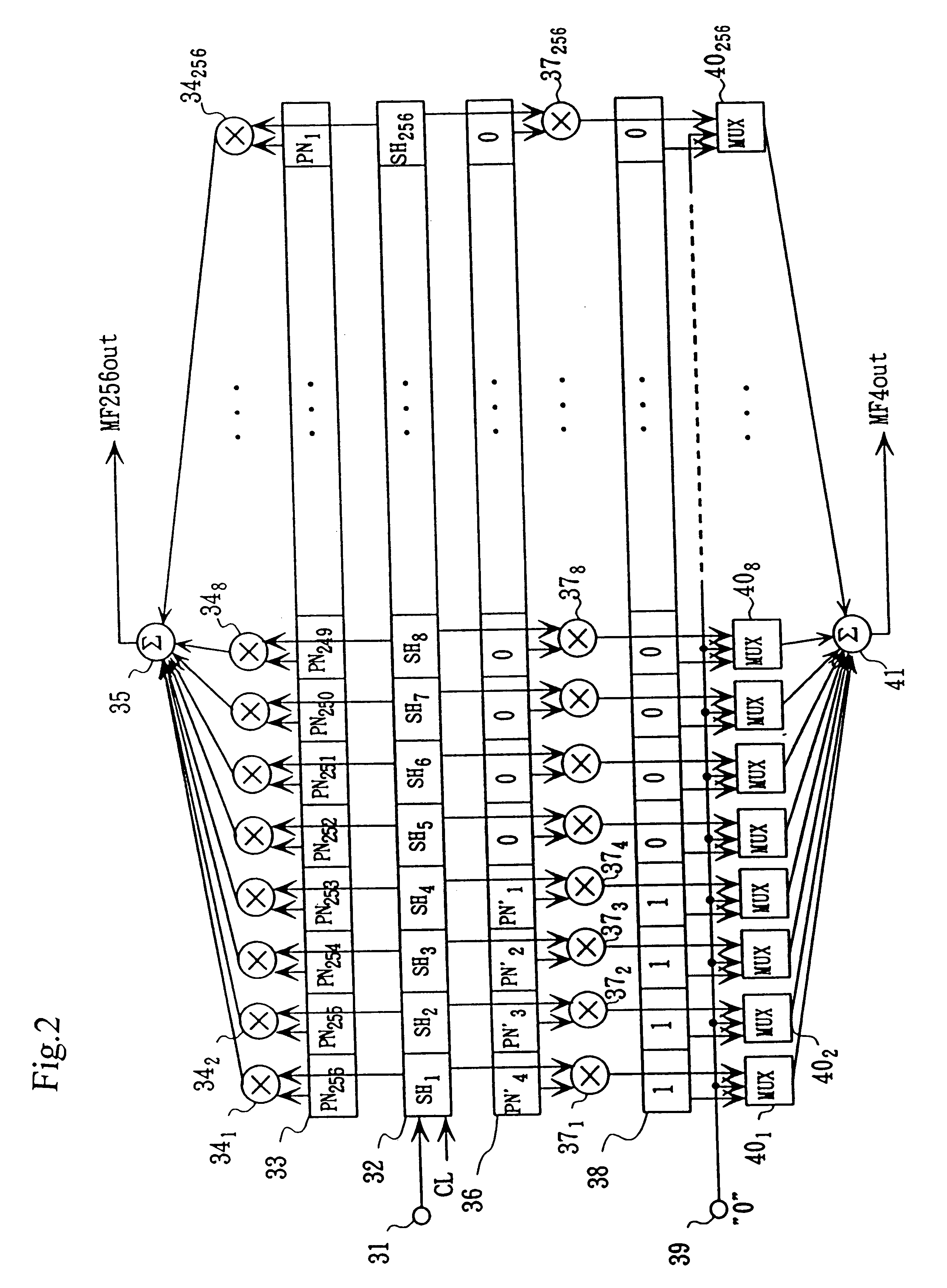
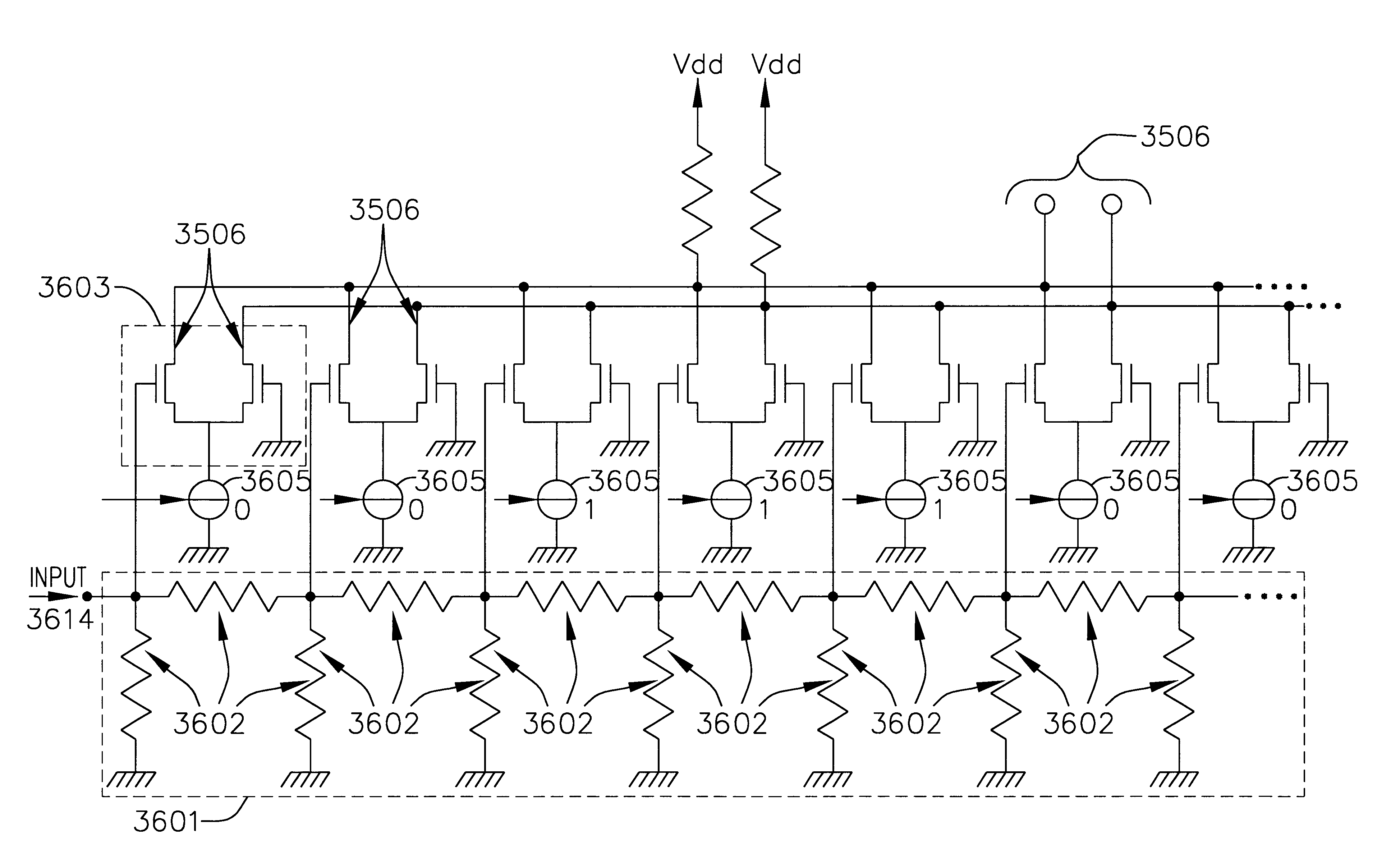
A matched filter bank including a plurality of matched filters and a sampling and holding units commonly used by the total matched filters. Therefore, the circuit size is diminished.An inverting amplifier for the matched filter with a variable gain includes an input capacitance, an inverting amplifier connected to an output of the input capacitance, and a plurality of feedback capacitances connected between an input and output of the inverting amplifier. A plurality of switches are connected to input side of the feedback capacitances for alternatively connecting the feedback capcitanec to the input of the inverting amplifier or a reference voltage. The feedback capacitances connected to the reference voltage are invalid with respect to a composite capacitance of the feedback capacitance and have no influence to the amplifier.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC
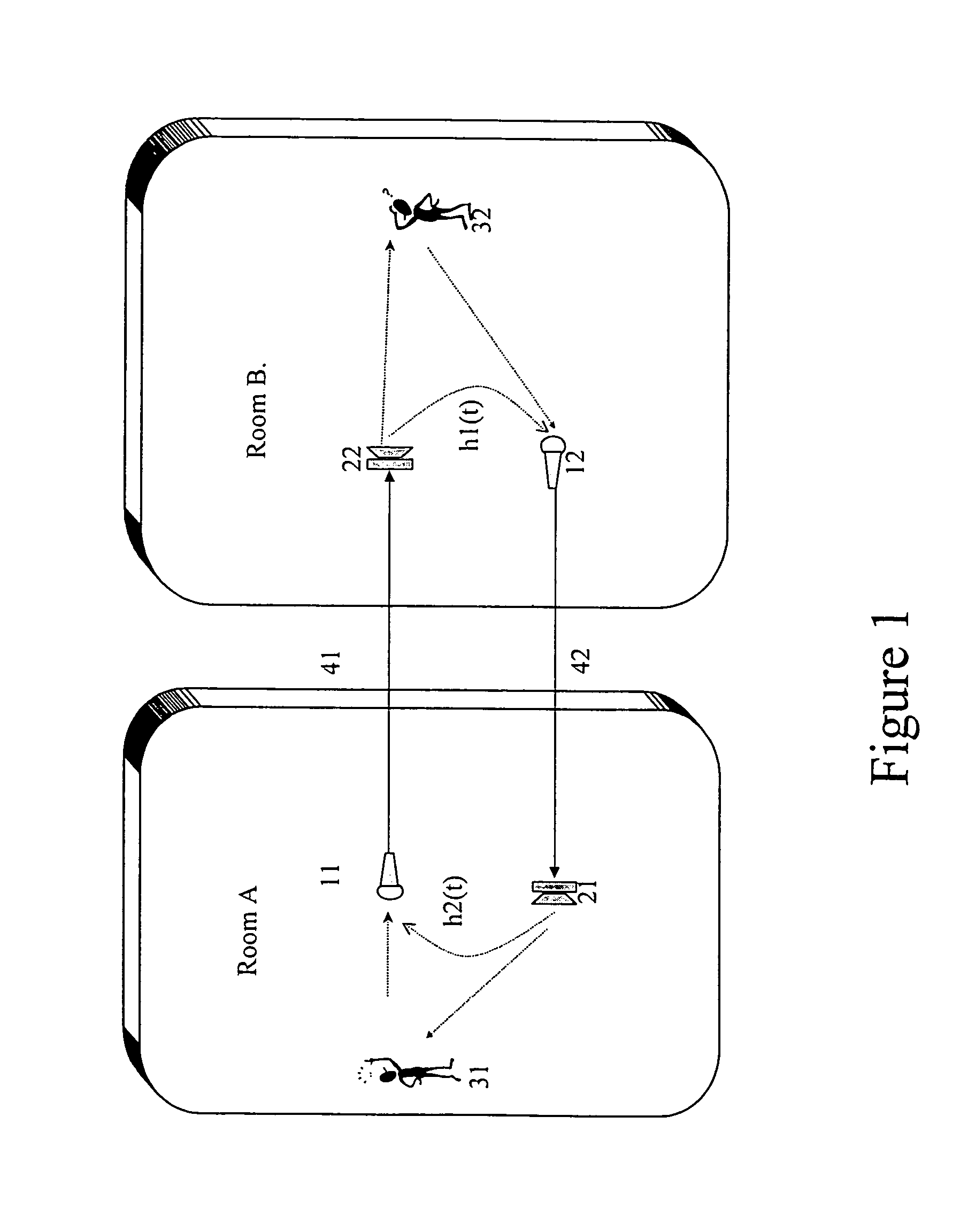
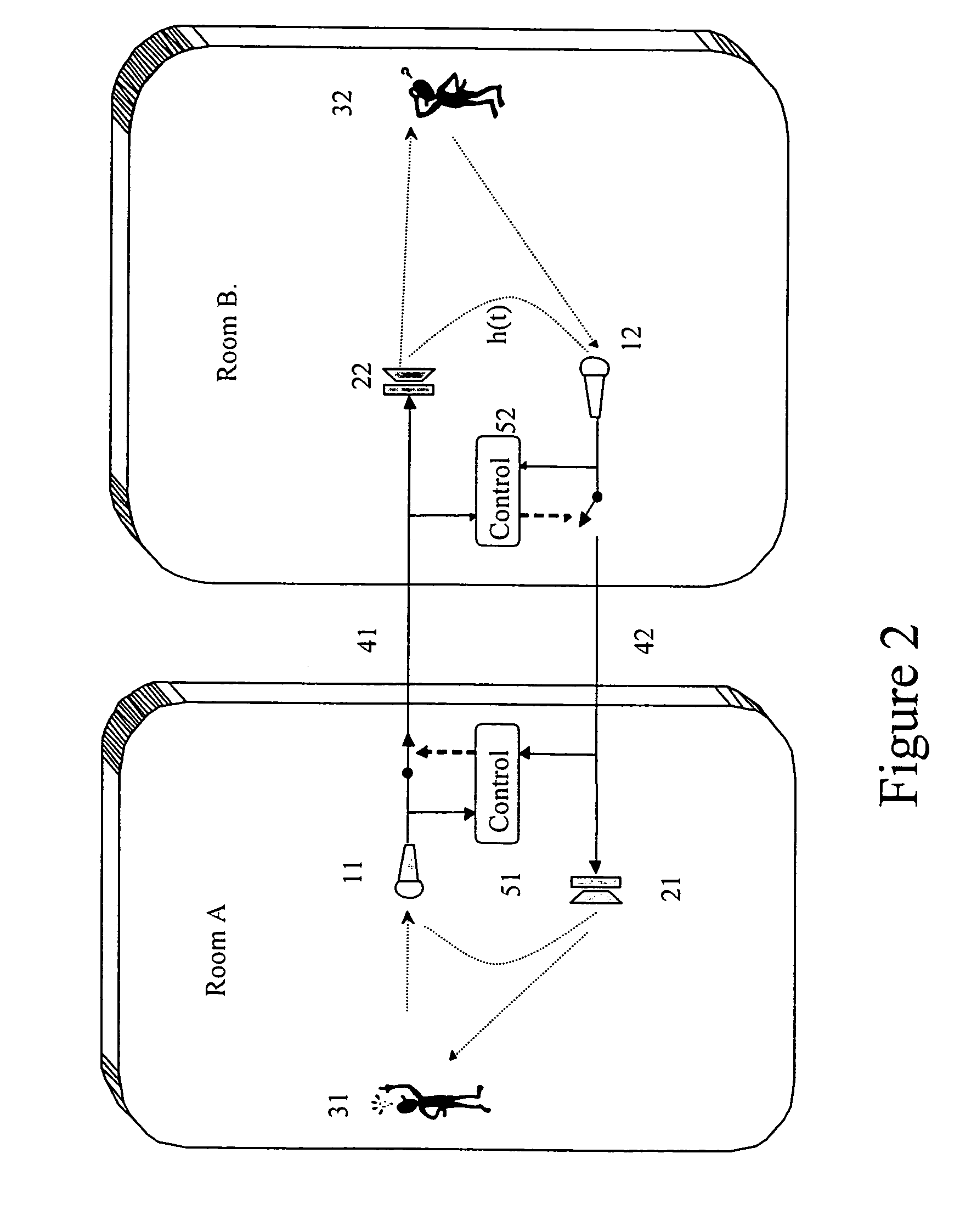
Separation of a mixture of acoustic sources into its components
InactiveUS6317703B1MicrophonesAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceSound sourcesEngineering
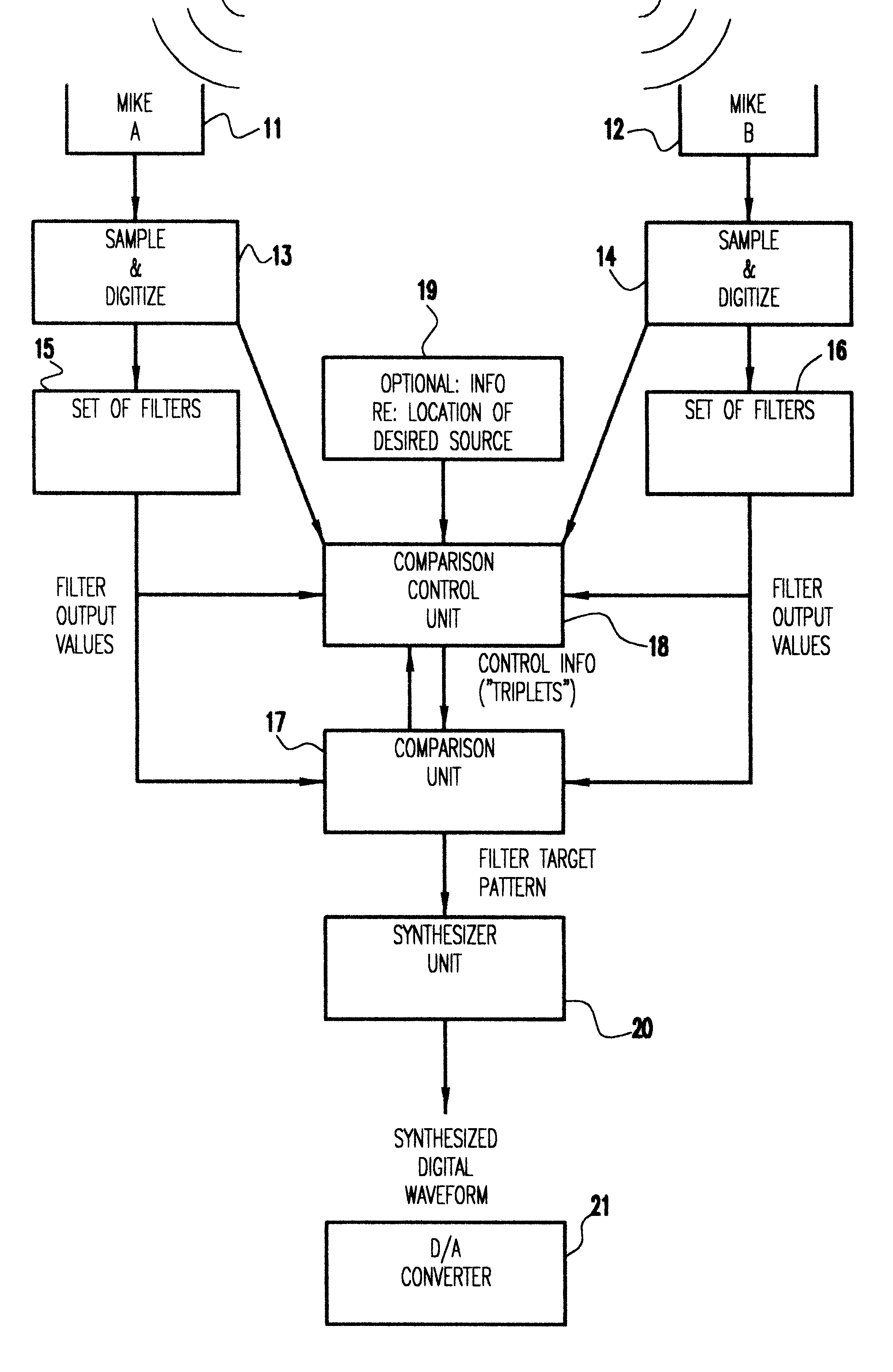
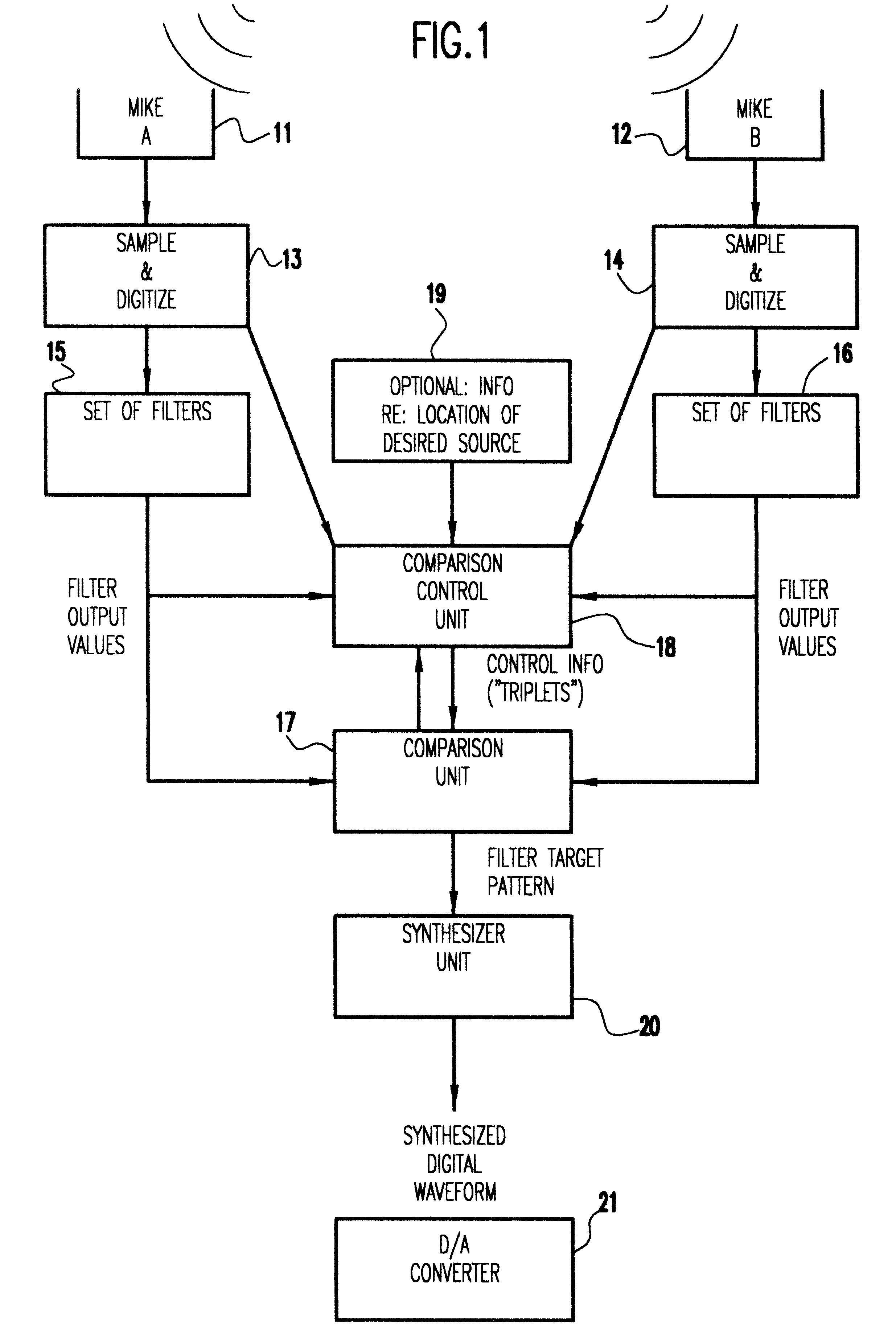
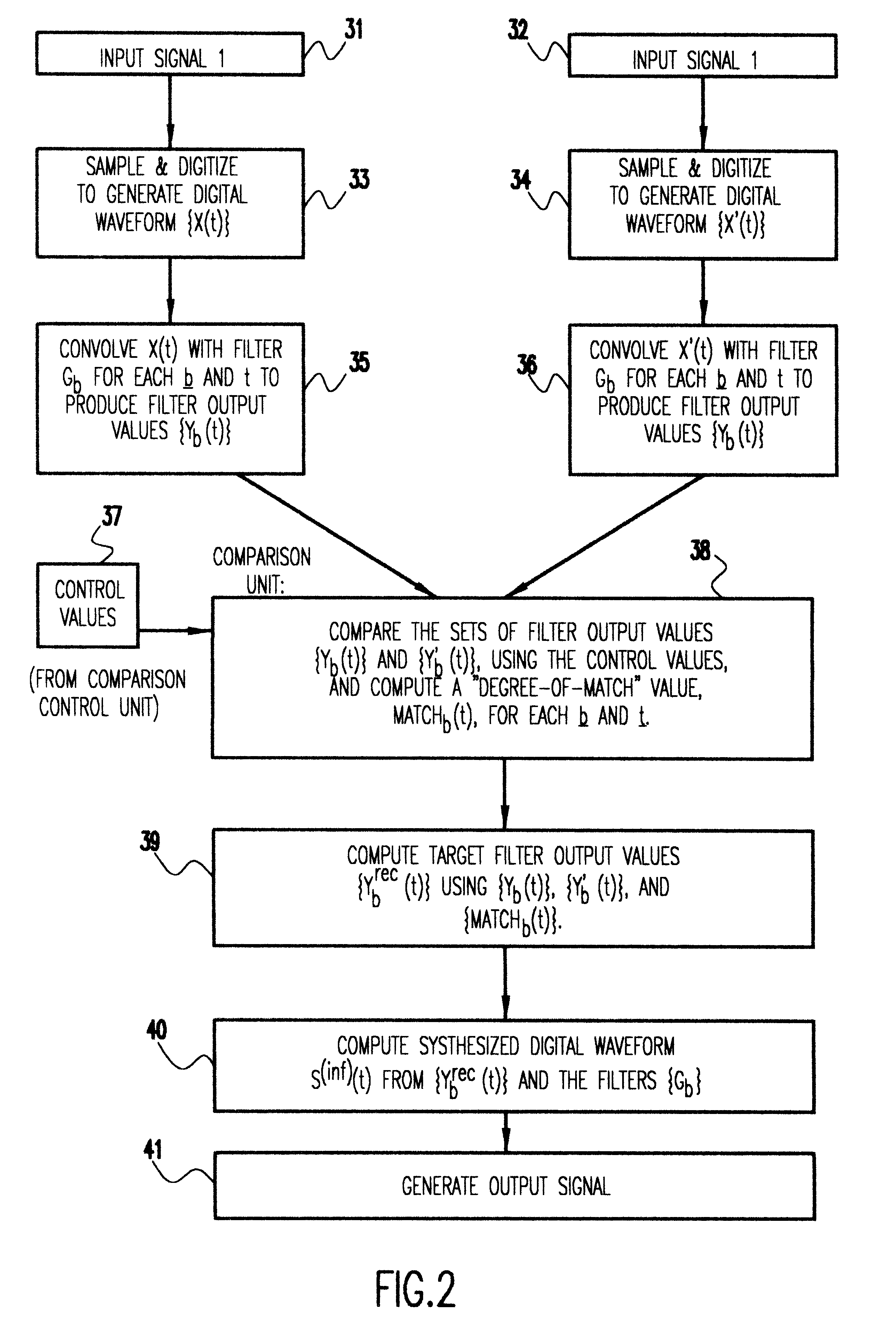
A method and apparatus for processing a composite acoustic signal to reconstruct an acoustic signal that substantially matches a selected one of a plurality of sources. A plurality of microphones positioned at different spatial locations detect. variations in sound pressure level resulting from the activity of a plurality of acoustic sources at different locations. The outputs of the microphones are sampled and digitized, and the resulting digital waveform from each microphone is provided as an input to a corresponding filter bank. The outputs of the filter banks are input to a comparison unit. A comparison control unit generates "signature" information that characterizes each source with respect to the microphones. The comparison unit receives "signature" information of a selected source from the comparison control unit and provides an output to a synthesizer unit which produces a synthesized digital waveform for the selected source. Optionally, the synthesized digital waveform is input to a digital-to-analog (D / A) converter to generate an analog signal of the reconstructed source.
Owner:IBM CORP
Keyed filter assembly
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Signal encoding
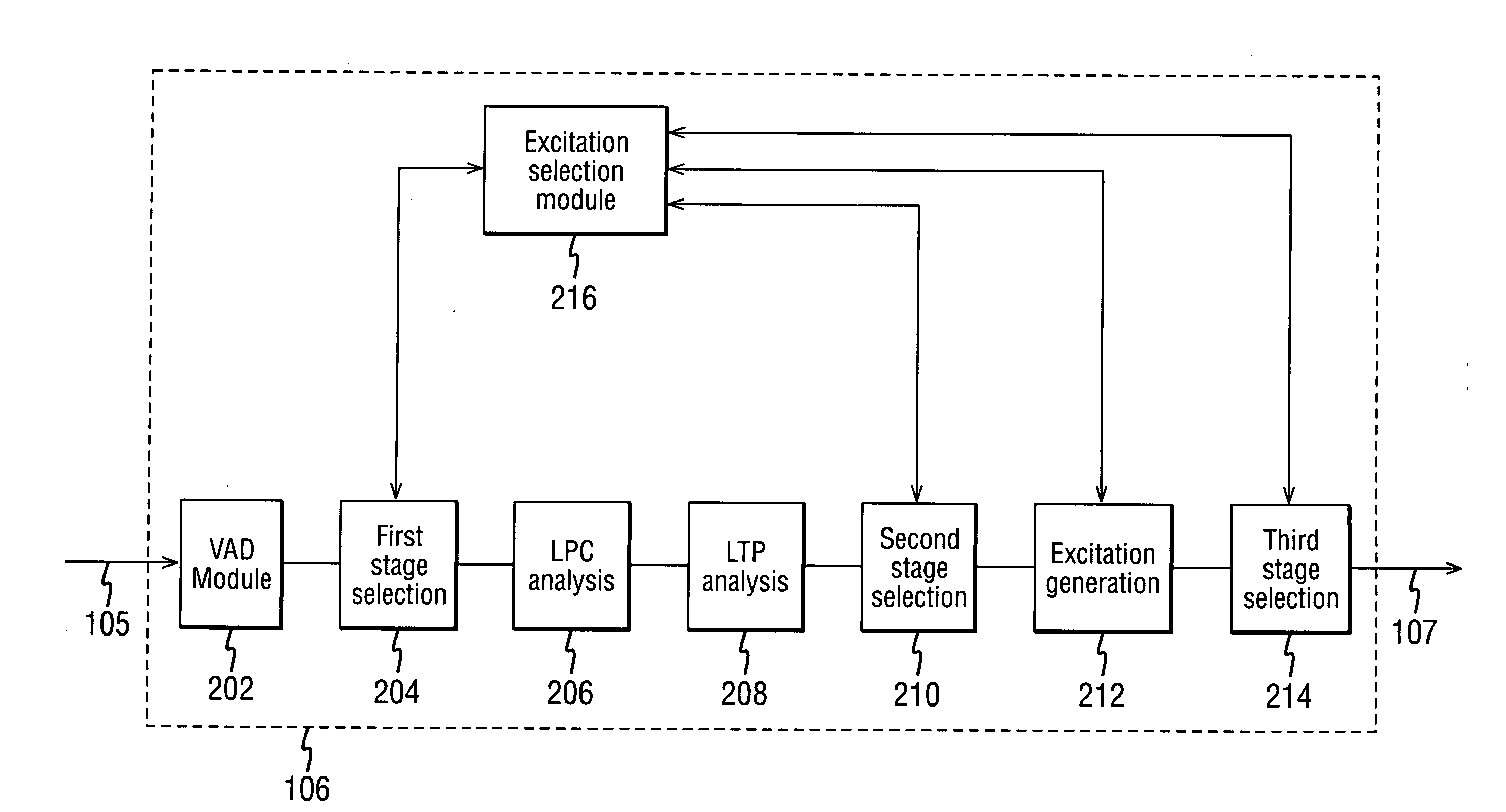
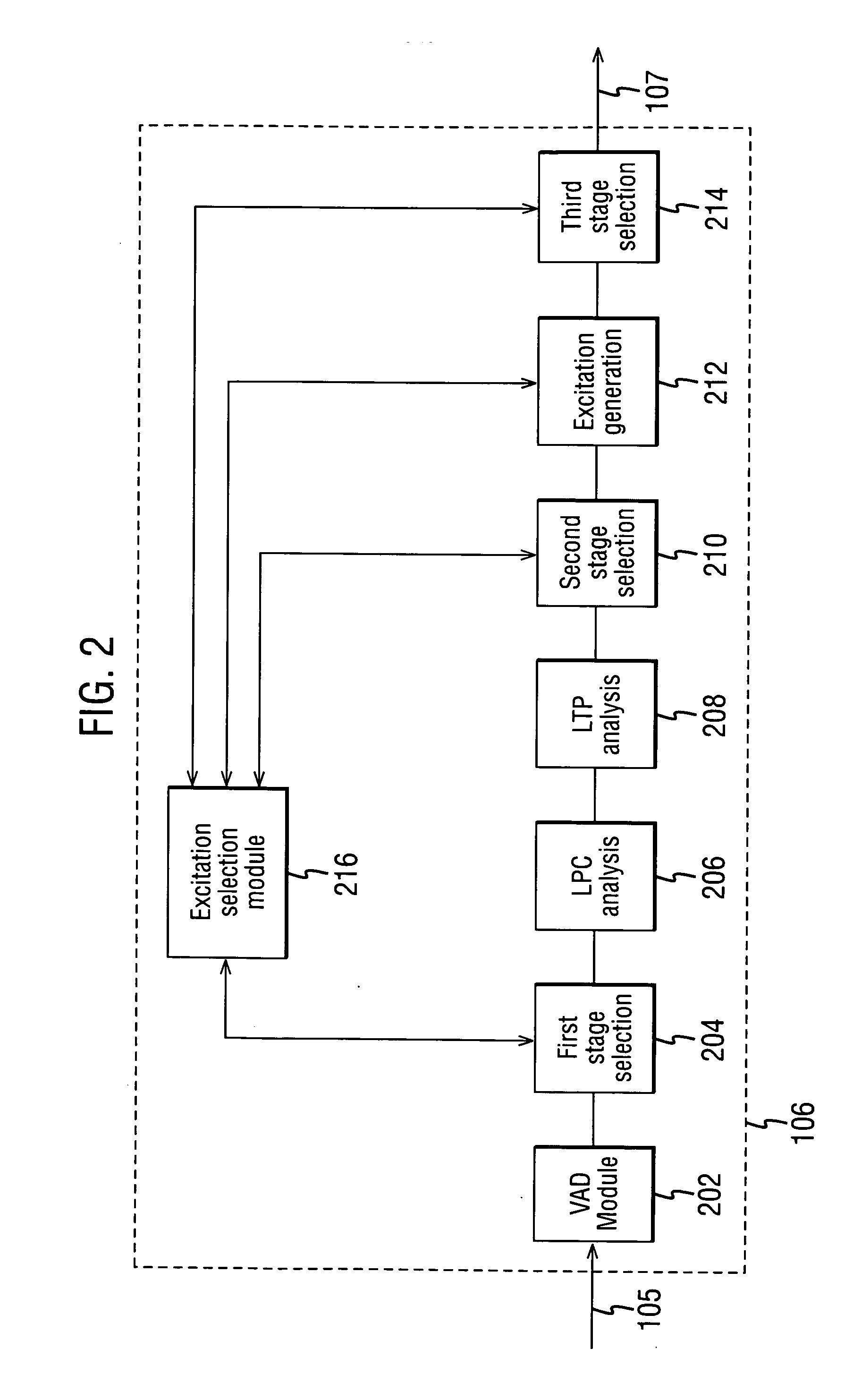
A method for encoding a frame in an encoder of a communication system, said method comprising the steps of: calculating a first set of parameters associated with the frame, wherein said first set of parameters comprises filter bank parameters; selecting, in a first stage, one of a plurality of encoding methods based on the first set of parameters one of modes for encoding; calculating a second set of parameters associated with the frame; selecting, in a second stage, one of the plurality of encoding methods based on the result of the first stage selection and the second set of parameters one of modes for encoding; and encoding the frame using the selected encoding excitation method from the second stage.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
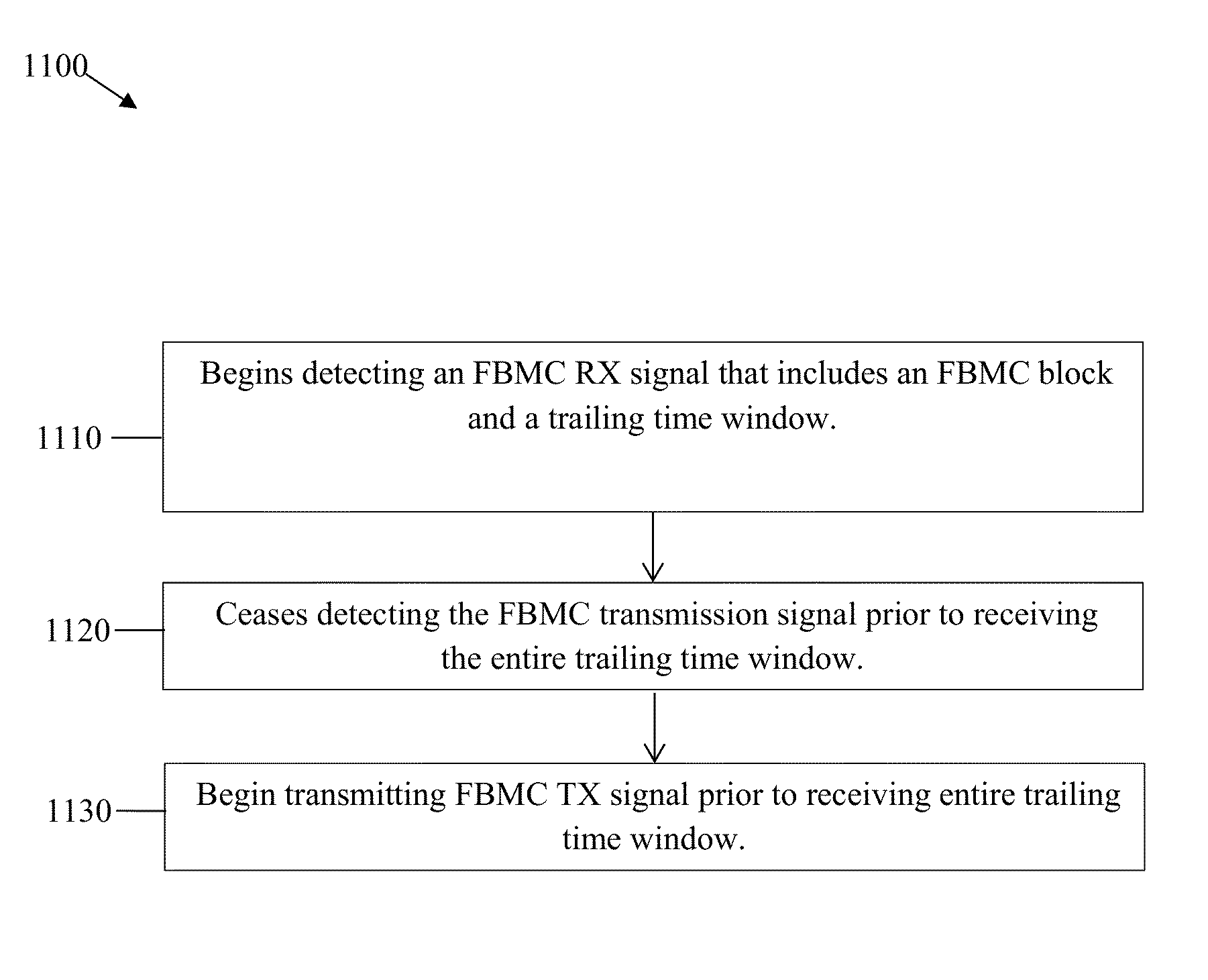
Frame Structure for Filter Bank Multi-Carrier (FBMC) Waveforms
ActiveUS20140233437A1Reduce overhead timeSynchronisation arrangementModulated-carrier systemsTime domainTelecommunications
A unified frame structure for filter bank multi-carrier (FBMC) and orthogonal frequency division multiplexed (OFDM) waveforms may allow FBMC and OFDM frames to be communicated over a common channel without significant inter-frame gaps. The unified frame structure may set an FBMC frame duration to an integer multiple of an OFDM frame element duration to enable alignment of FBMC frames and OFDM frames in the time domain. The unified frame structure may also map control channels in the FBMC and OFDM frames to common resource locations so that the respective control channels are aligned in the time and / or frequency domains. The unified frame structure may also share synchronization channels between FBMC and OFDM frames. Additionally, overhead in an FBMC time division duplexed (TDD) communications channel can be reduced by overlapping time windows appended to FBMC blocks.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
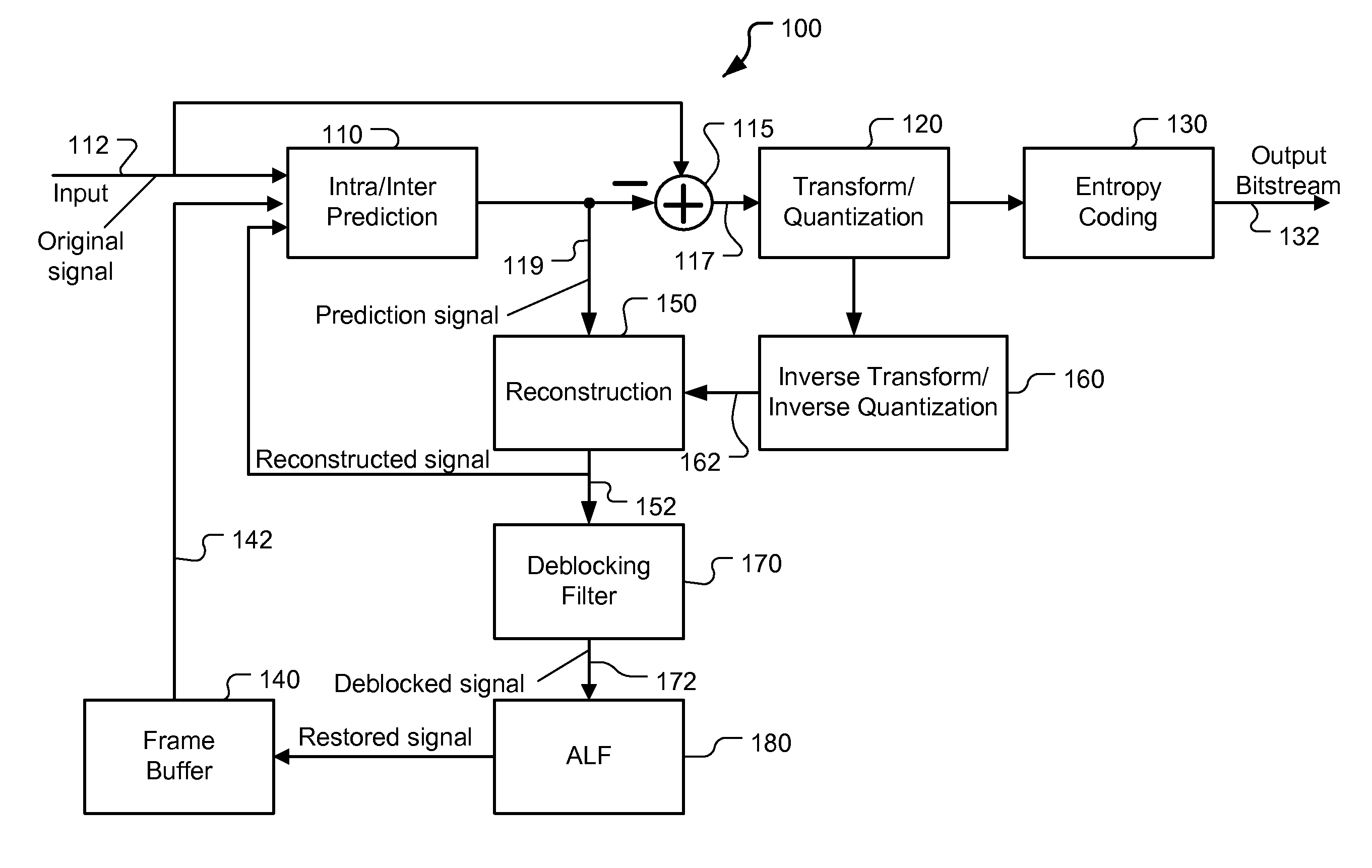
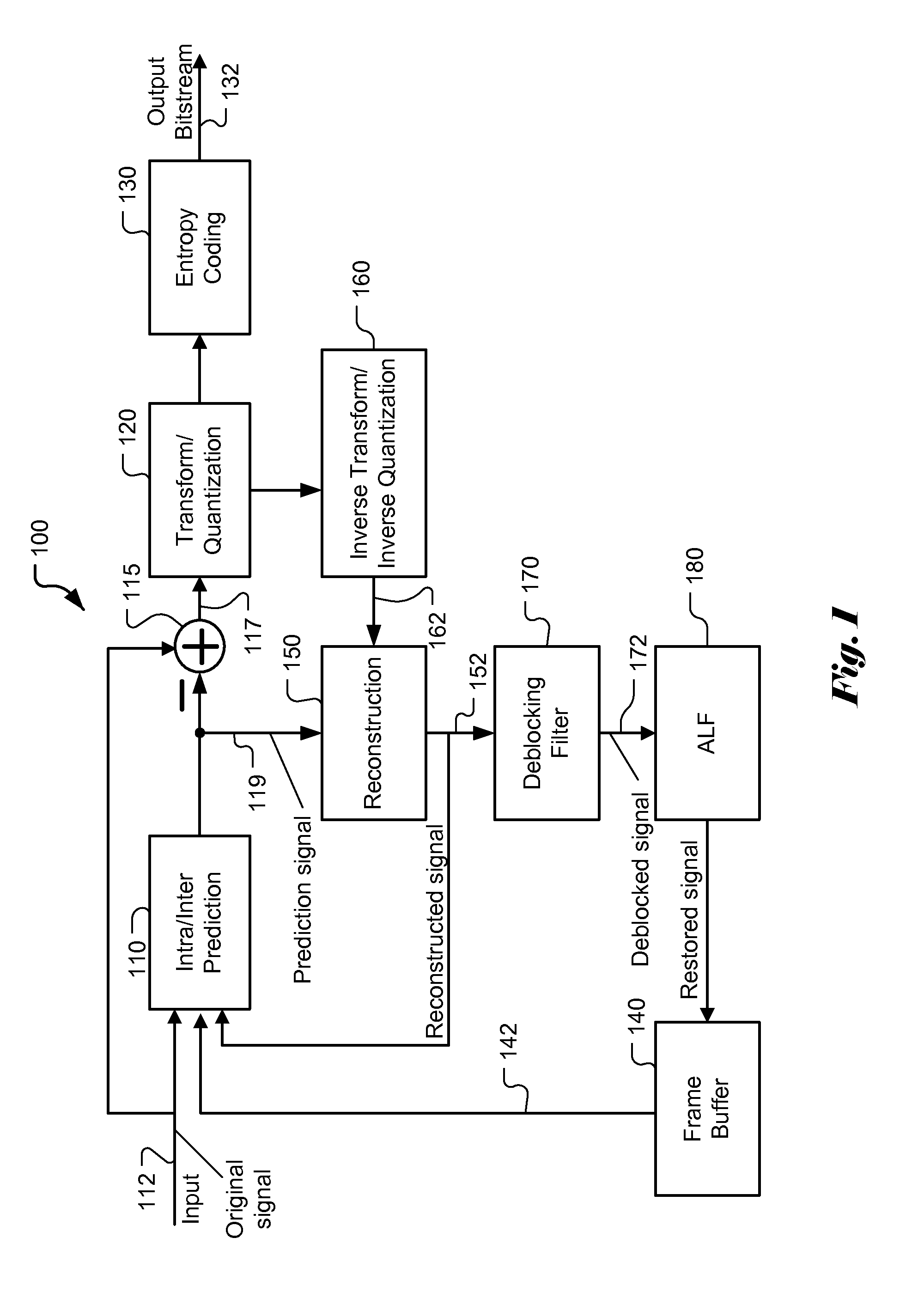
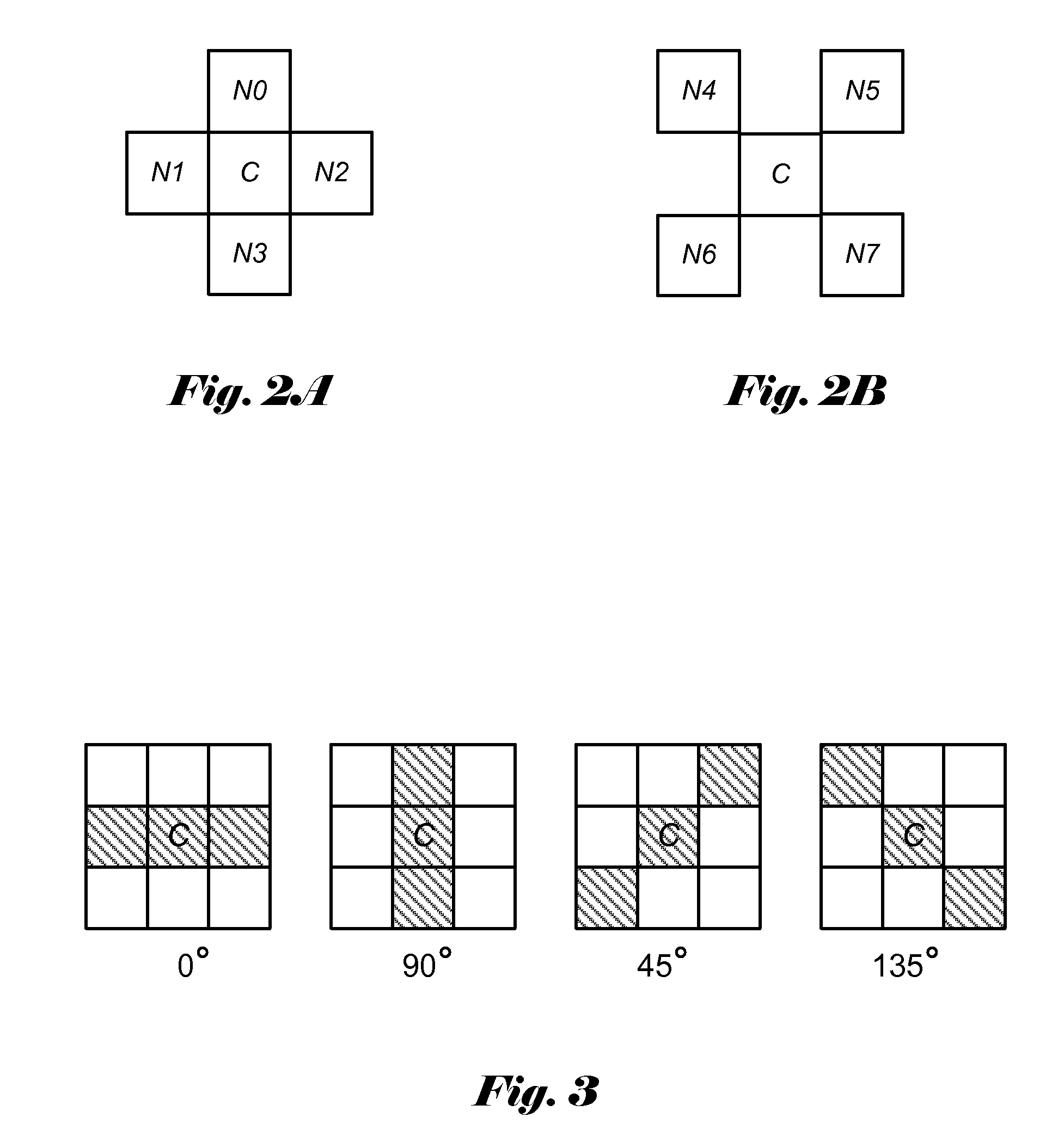
Method and Apparatus of Adaptive Loop Filtering
ActiveUS20120082241A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionRate distortionSelf adaptive
A method and apparatus for processing in-loop reconstructed video using an in-loop filter is disclosed. In the recent HEVC development, adaptive loop filtering (ALF) is being adopted to process in-loop reconstruction video data, where ALF can be selectively turned ON or OFF for each block in a frame or a slice. An advanced ALF is disclosed later that allows a choice of multiple filter sets that can be applied to the reconstructed video data adaptively. In the present disclosure, pixels of the in-loop reconstructed video data are divided into a plurality of to-be-filtered regions, and an in-loop filter from a filter set is determined for each to-be-filtered region based on a rate-distortion optimization procedure. According to one embodiment of the present invention, computation of cost function associated with the rate-distortion optimization procedure is related to correlation values associated with original video data and the in-loop reconstructed video data. Furthermore, the correlation values can be shared by the multiple candidate filters during the rate-distortion optimization procedure for said each to-be-filtered region. In another embodiment, the correlation values can be shared by multiple candidate to-be-filtered regions of an area of the in-loop reconstructed video data during the rate-distortion optimization procedure for the area of the in-loop reconstructed video data.
Owner:HFI INNOVATION INC
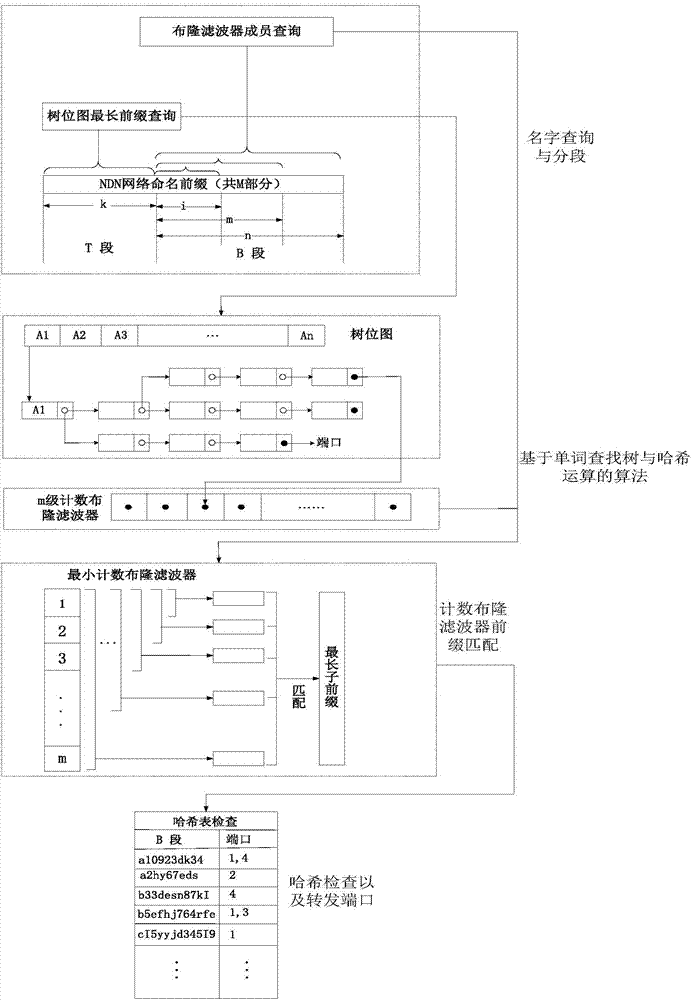
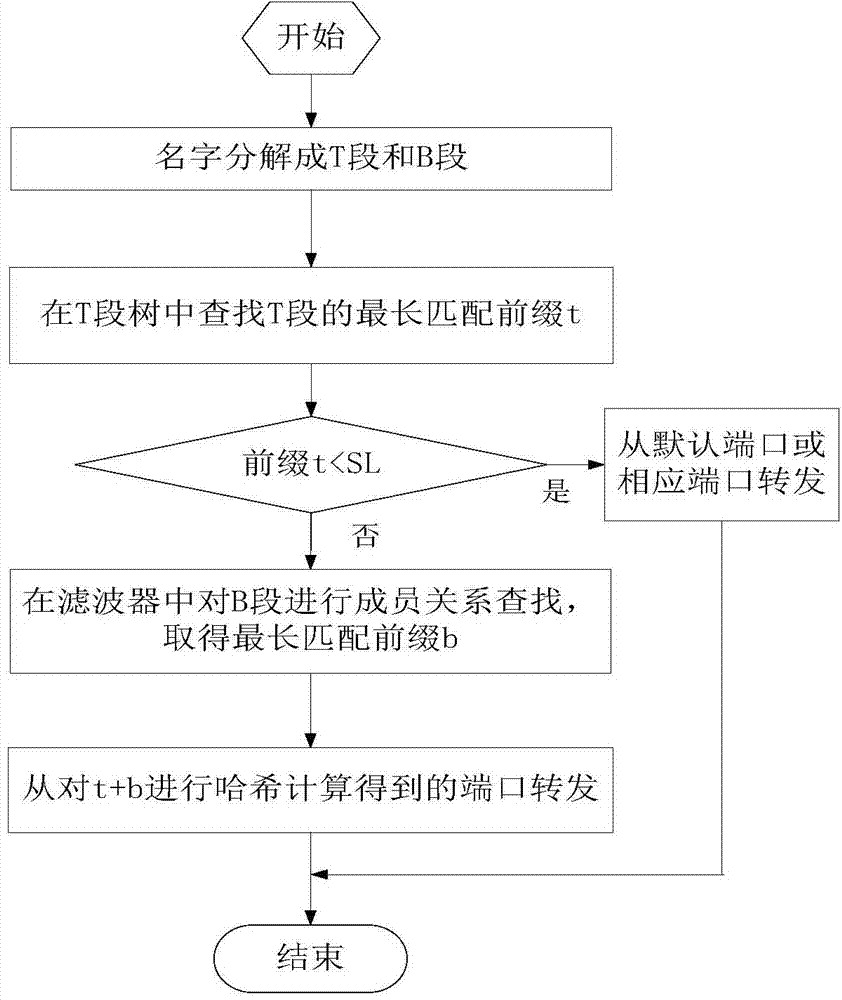
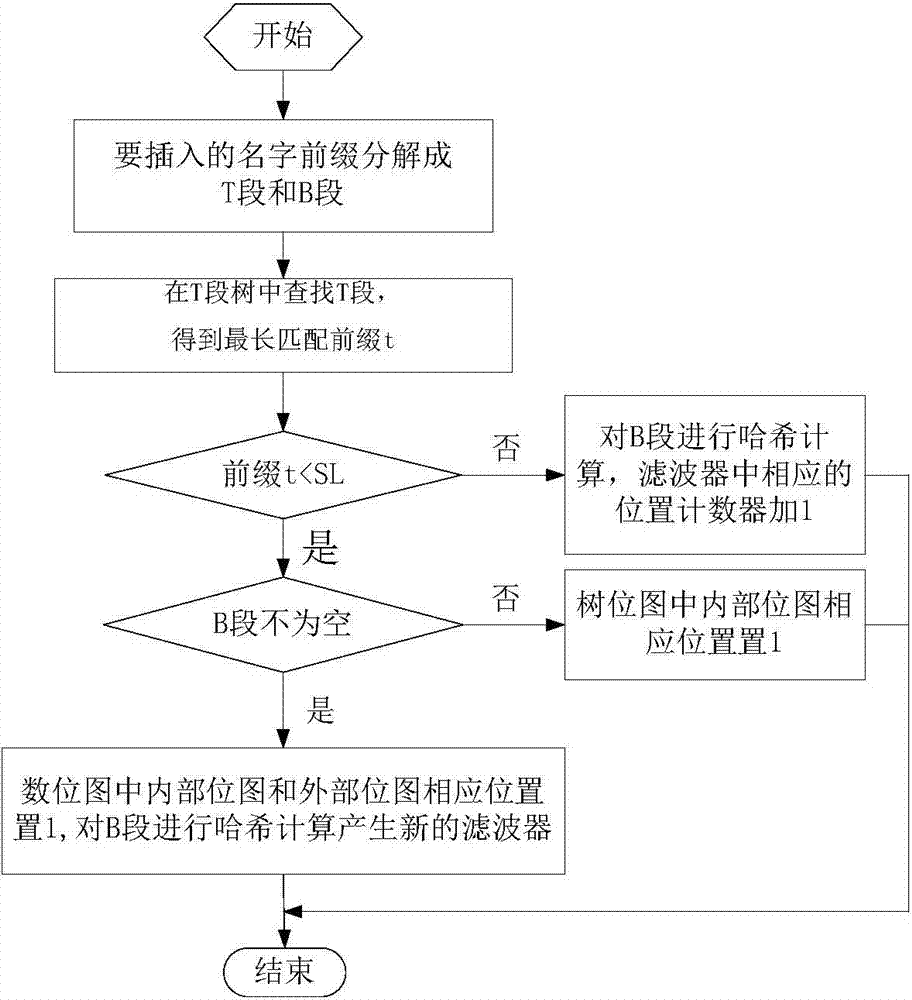
Name routing fast matching search method and device
ActiveCN103873371AControl depthReduce the numberData switching networksSpecial data processing applicationsLongest prefix matchBitmap
The invention discloses a name routing fast matching search method and device. The device mainly comprises a tree-bitmap and a Blond filter. The tree-bitmap is used for storing the first m layers of name routing, and performing fast longest prefix matching on the first m layers of request content name reaching a router; the Blond filter is used for storing the rest of the prefix of the name routing, and performing longest prefix matching on the rest of the request content name reaching the router. According to the different prefix length of the name routing to be updated, the tree-bitmap and the Blond filter can be updated respectively or simultaneously by the method. According to the invention, the characteristics of fast searching, little required storing of the tree-bitmap and the characteristics of high time efficiency and spatial efficiency are utilized, the routing addressing problem based on the content name in the novel network system is solved, and the requirements of little occupied memory, fast matching speed and fast updating speed of the future network routing are met.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
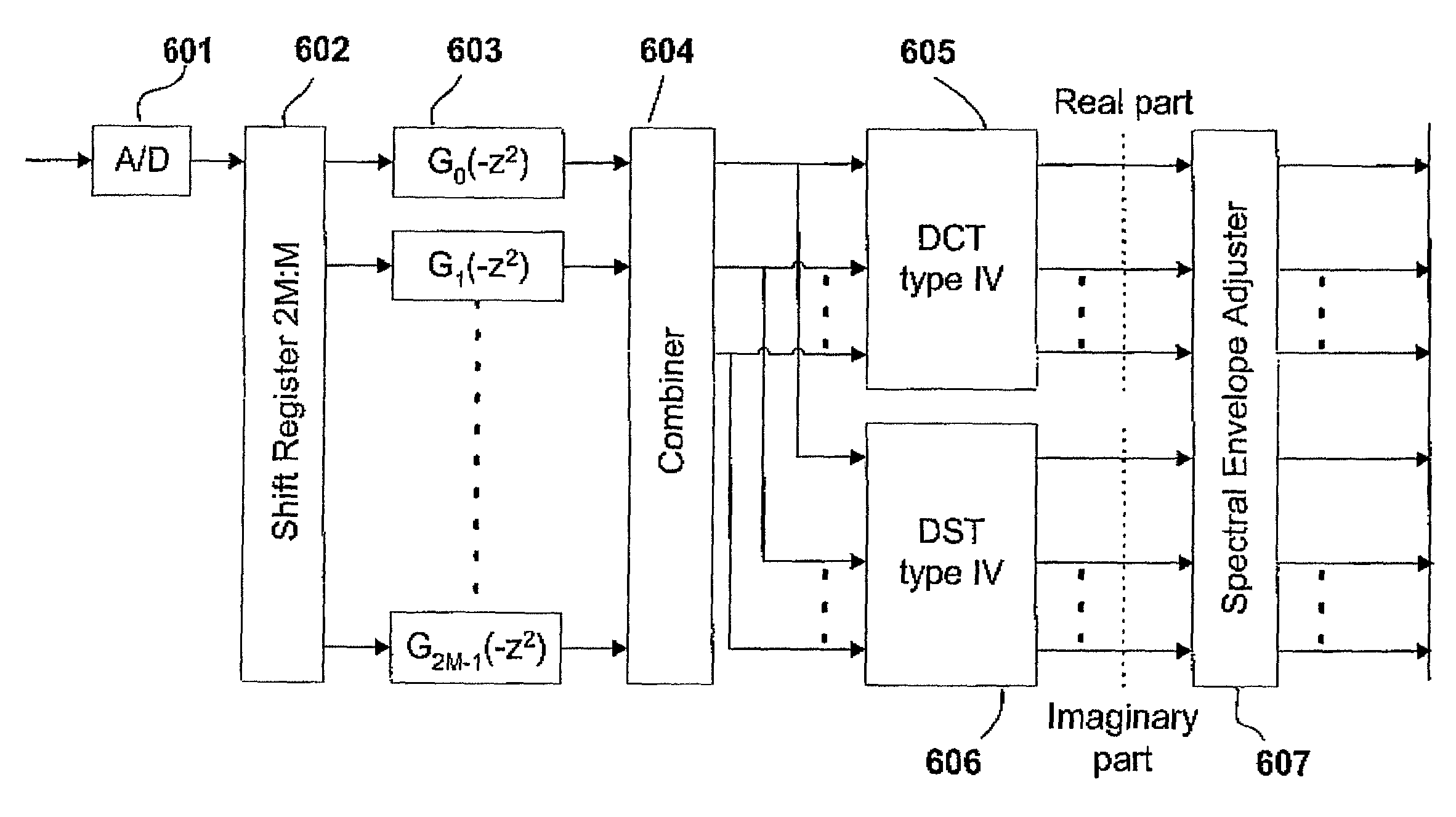
Aliasing reduction using complex-exponential modulated filterbanks
ActiveUS7242710B2Signal can be impairedMitigation of impairmentMultiple-port networksAdaptive networkFrequency spectrumComputer science
The present invention proposes a new method and apparatus for the improvement of digital filterbanks, by a complex extension of cosine modulated digital filterbanks. The invention employs complex-exponential modulation of a low-pass prototype filter and a new method for optimizing the characteristics of this filter. The invention substantially reduces artifacts due to aliasing emerging from independent modifications of subband signals, for example when using a filterbank as an spectral equalizer. The invention is preferably implemented in software, running on a standard PC or a digital signal processor (DSP), but can also be hardcoded on a custom chip. The invention offers essential improvements for various types of digital equalizers, adaptive filters, multiband companders and spectral envelope adjusting filterbanks used in high frequency reconstruction (HFR) systems.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Electronic Signal Filtering System Suitable for Medical Device and Other Usage
InactiveUS20080154105A1Reduce power consumptionLower component costsMultiple-port networksDiagnostic recording/measuringMultiplexingFilter (signal processing)
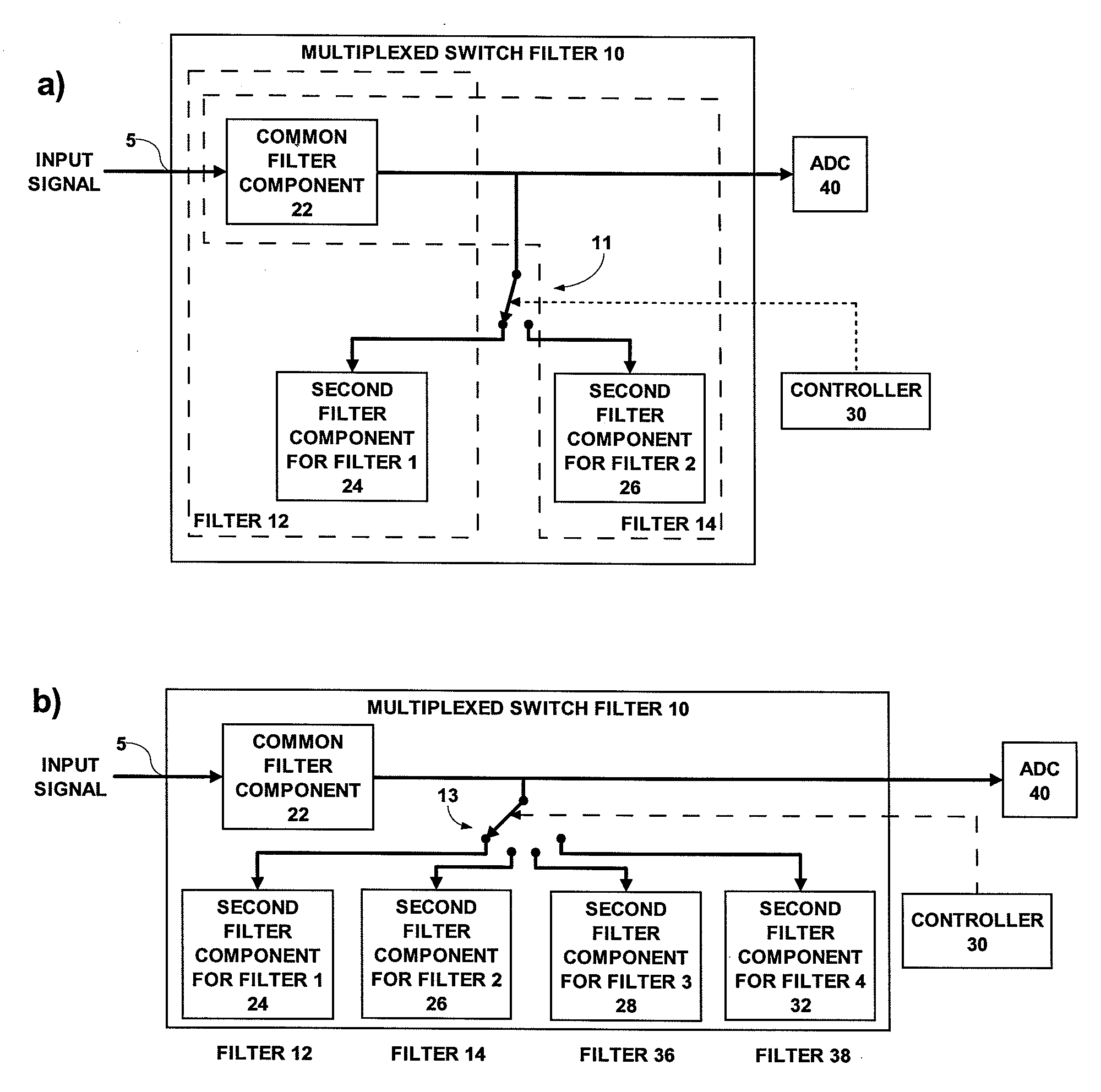
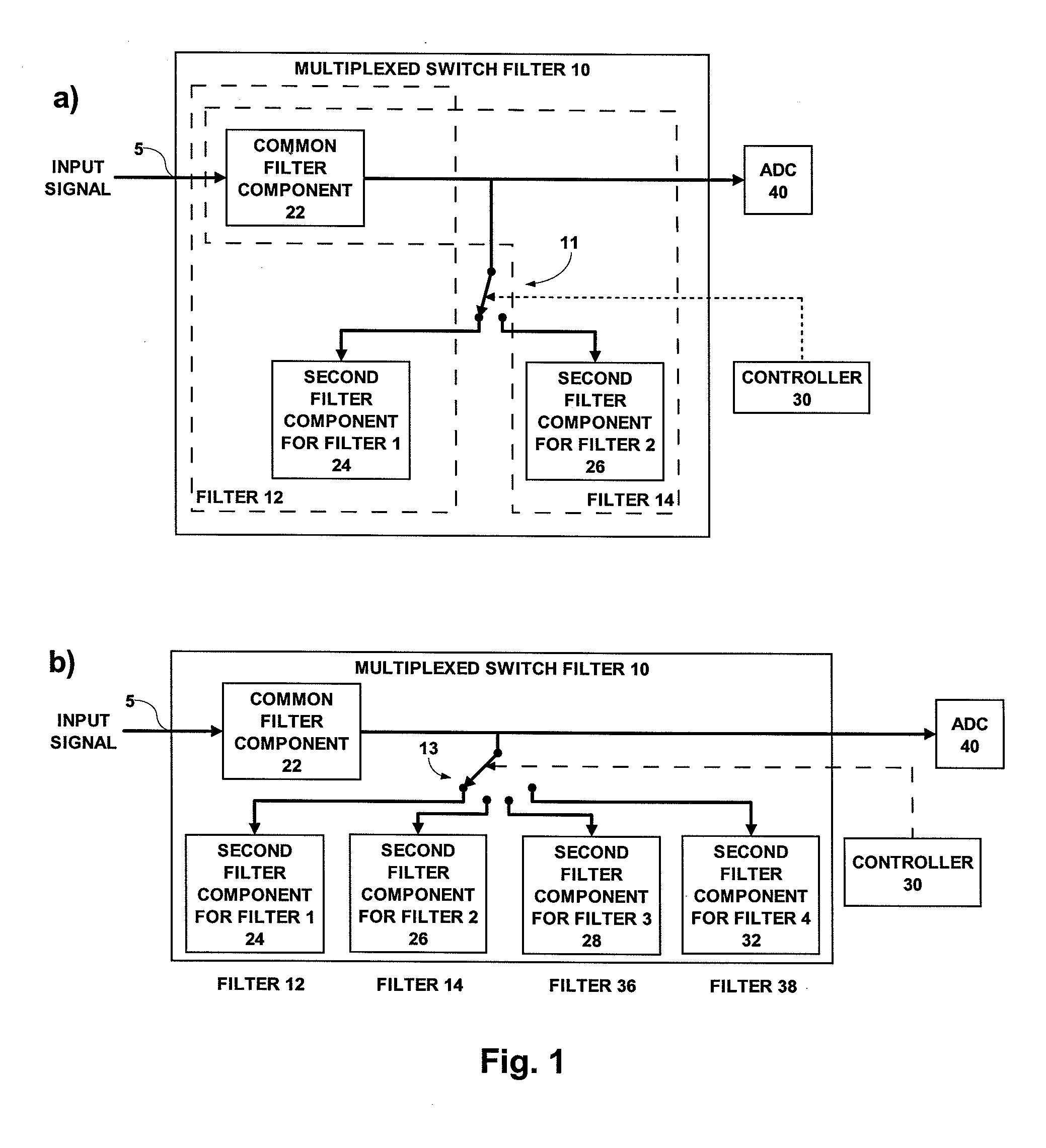
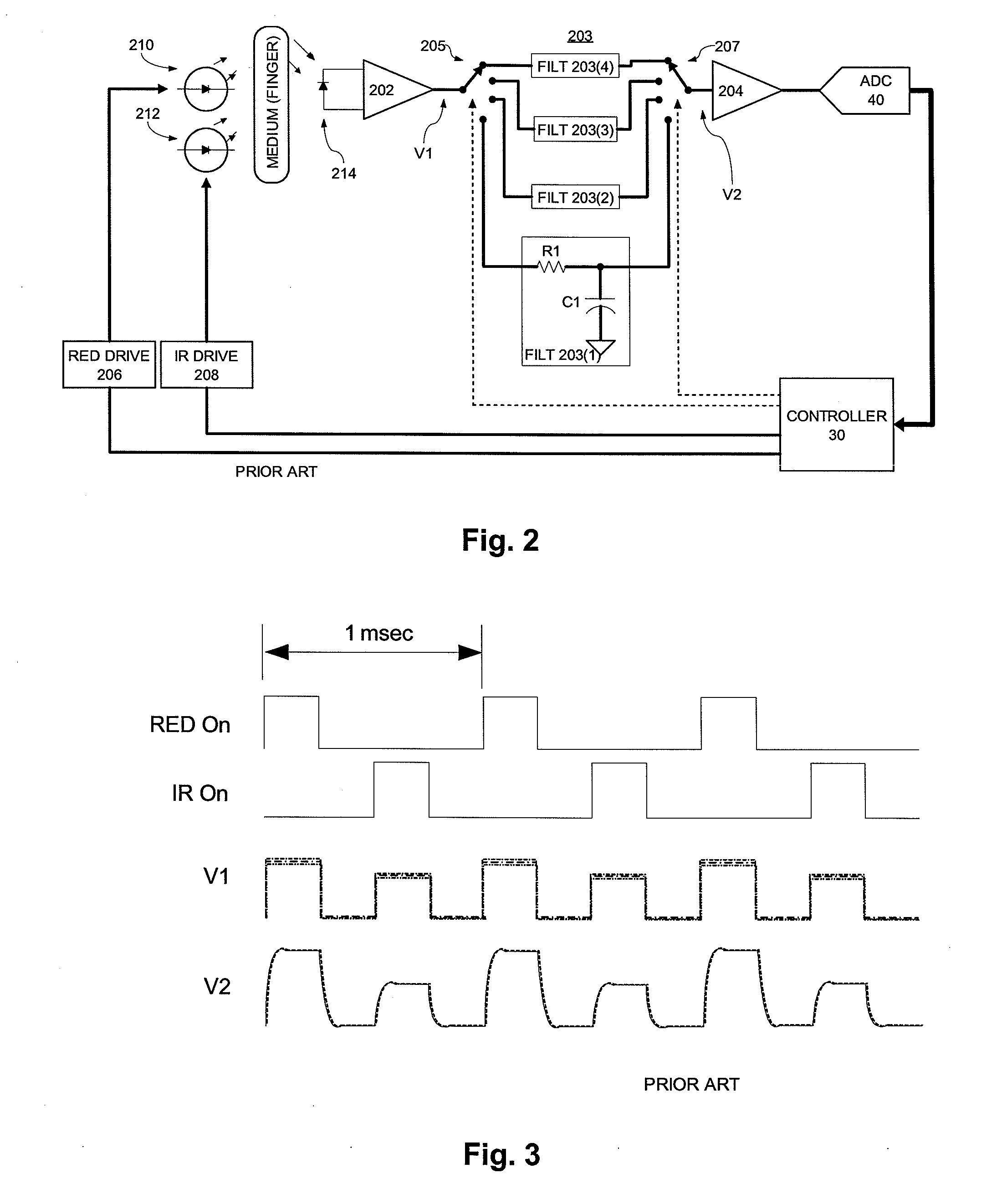
A switched filter signal processing system includes an input terminal for receiving an input signal conveying first signal information in a first time phase and second signal information in a different second time phase. Desired information represents the difference between the first and second signal information. A multiplexed switch filter filters the input signal in the first phase with a first filter to obtain the first signal information and filters the input signal in the different second time phase with a second filter to obtain the second signal information. The system also includes a common filter component, which is shared by the first and second filter, and respective second filter components for the first and second filters. A controller controls the multiplexed switch filter to couple the common filter component to the second filter component of said first filter in said first time phase and to couple the common filter component to the second filter component of the second filter in the second time phase.
Owner:DRAEGER MEDICAL SYST INC
Device and method for generating a complex spectral representation of a discrete-time signal
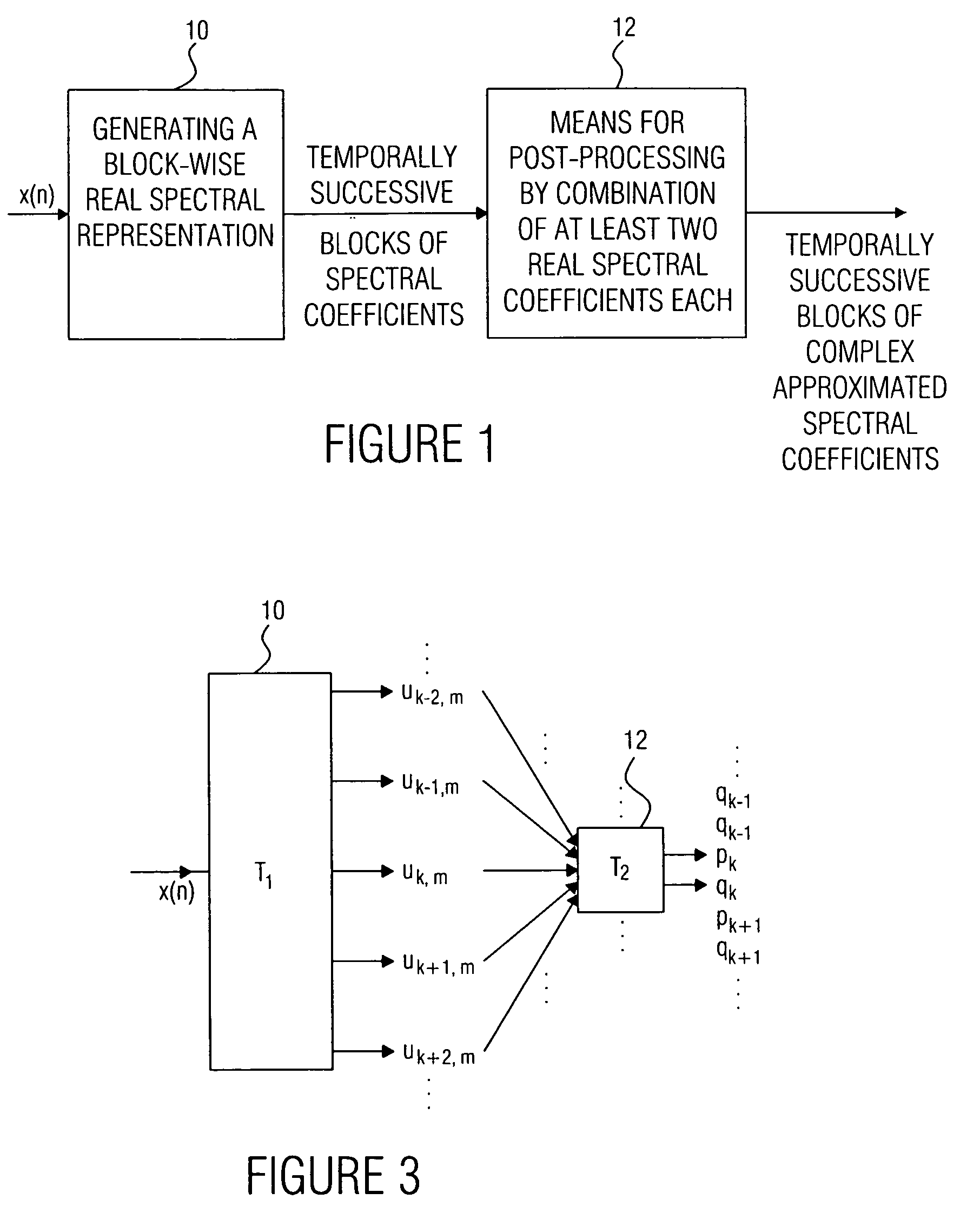
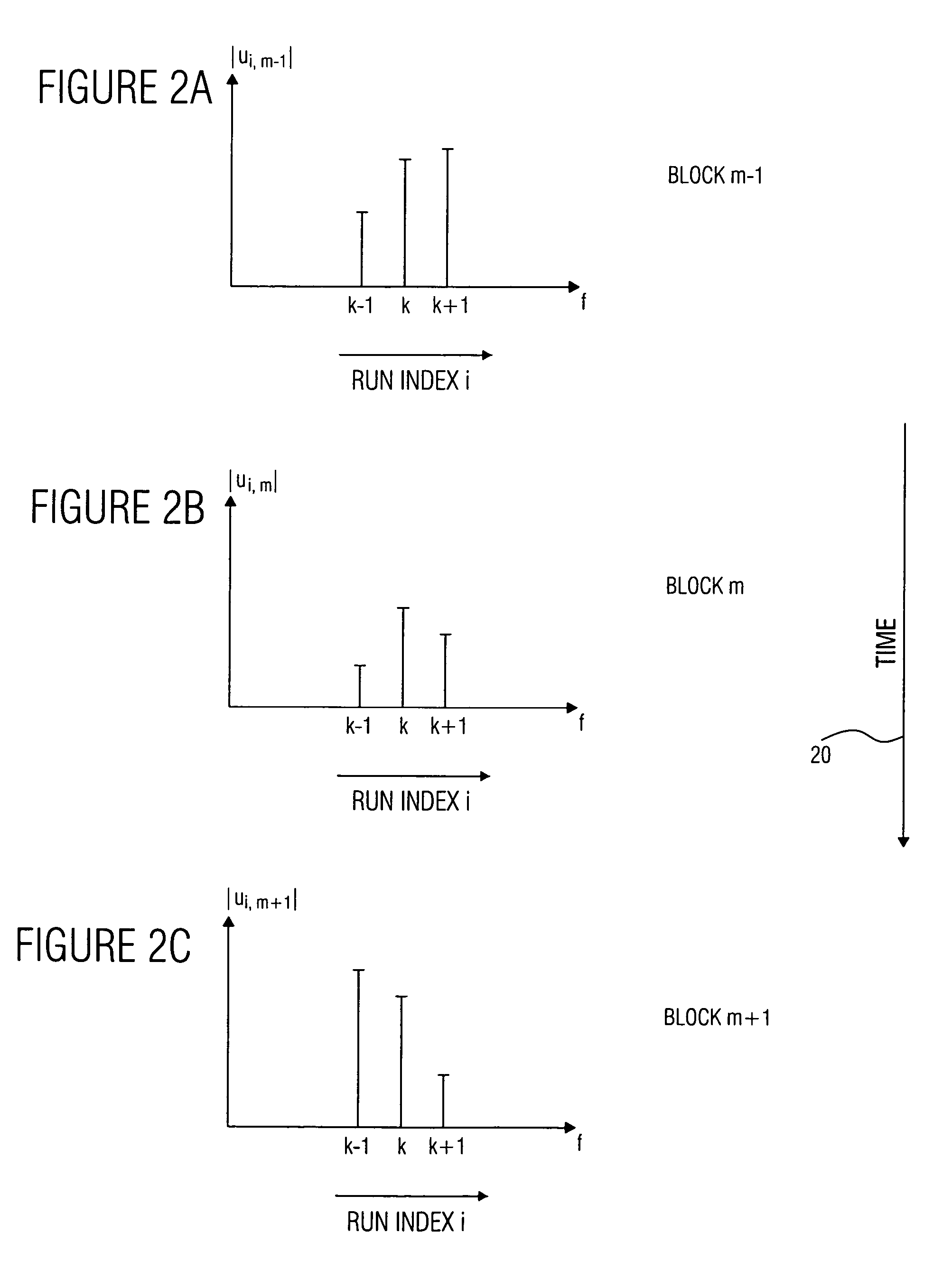
ActiveUS20050197831A1Improve approximationSpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumPost processor
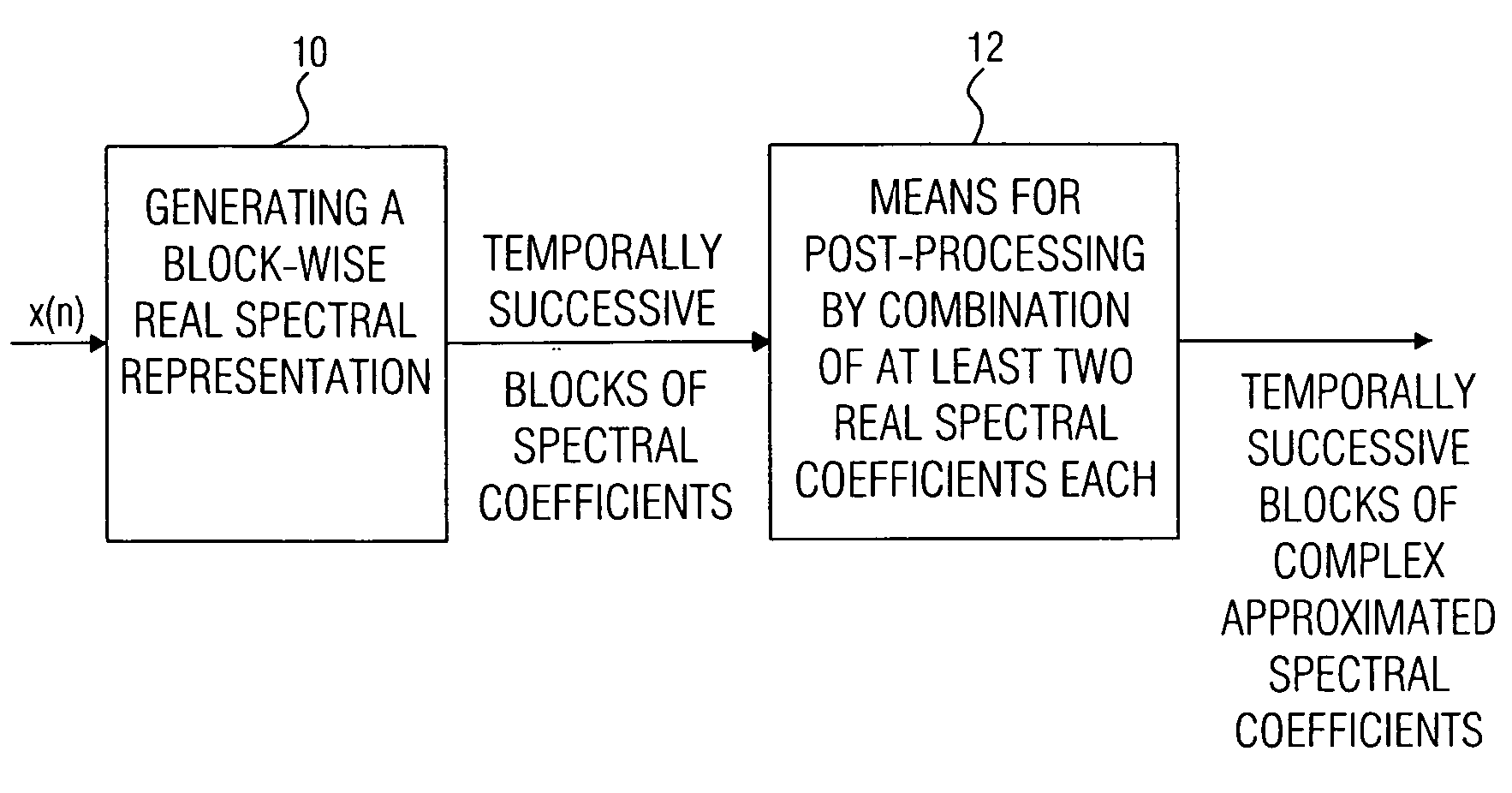
A filter bank device for generating a complex spectral representation of a discrete-time signal includes a generator for generating a block-wise real spectral representation, which, for example, implements an MDCT, to obtain temporally successive blocks of real spectral coefficients. The output values of this spectral conversion device are fed to a post-processor for post-processing the block-wise real spectral representation to obtain an approximated complex spectral representation having successive blocks, each block having a set of complex approximated spectral coefficients, wherein a complex approximated spectral coefficient can be represented by a first partial spectral coefficient and by a second partial spectral coefficient, wherein at least one of the first and second partial spectral coefficients is determined by combining at least two real spectral coefficients. A good approximation for a complex spectral representation of the discrete-time signal is obtained by combining two real spectral coefficients, preferably by a weighted linear combination, wherein additionally more degrees of freedom for optimizing the entire system are available.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Method for extracting features of irises in images using difference of sum filters
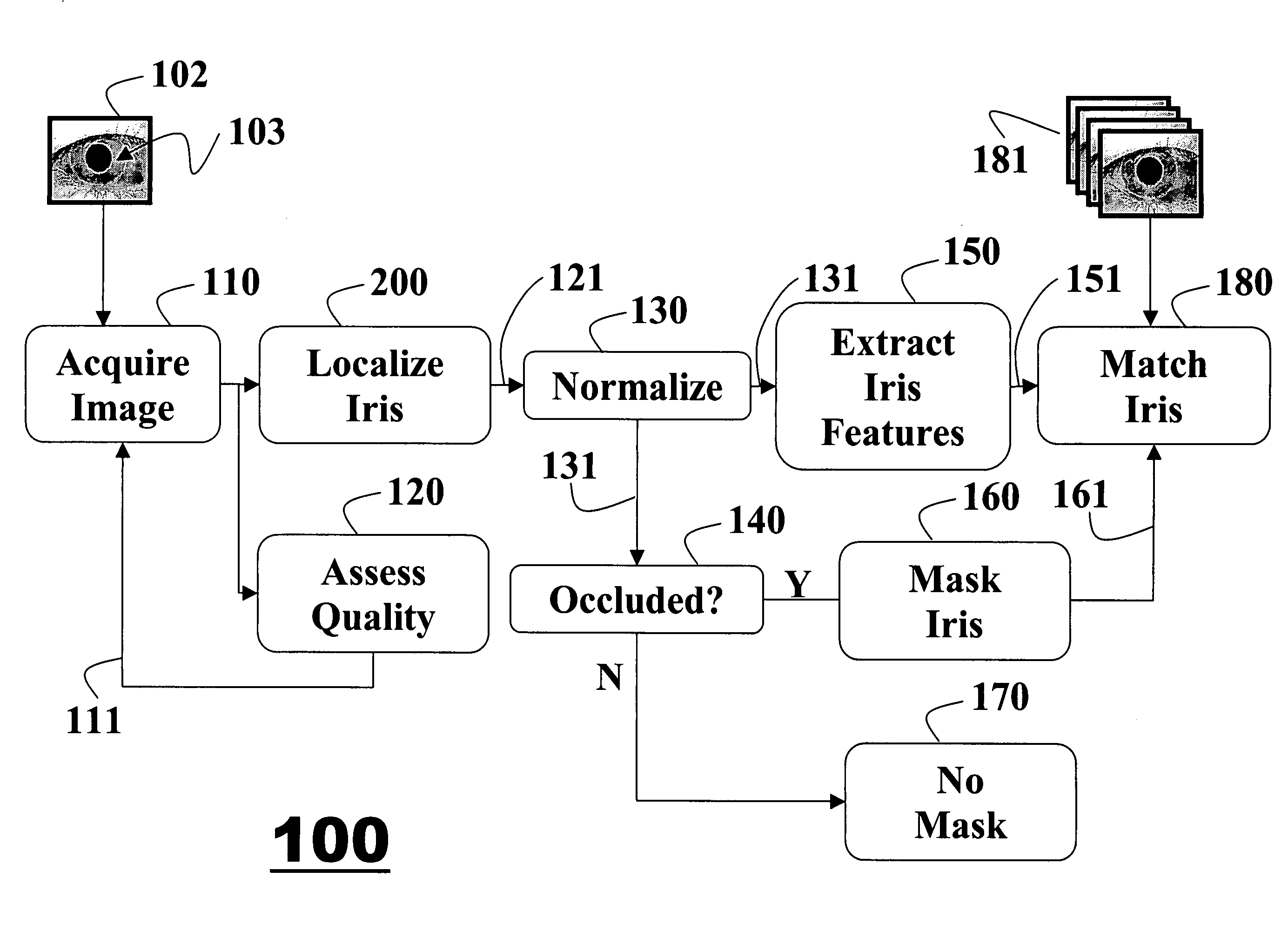
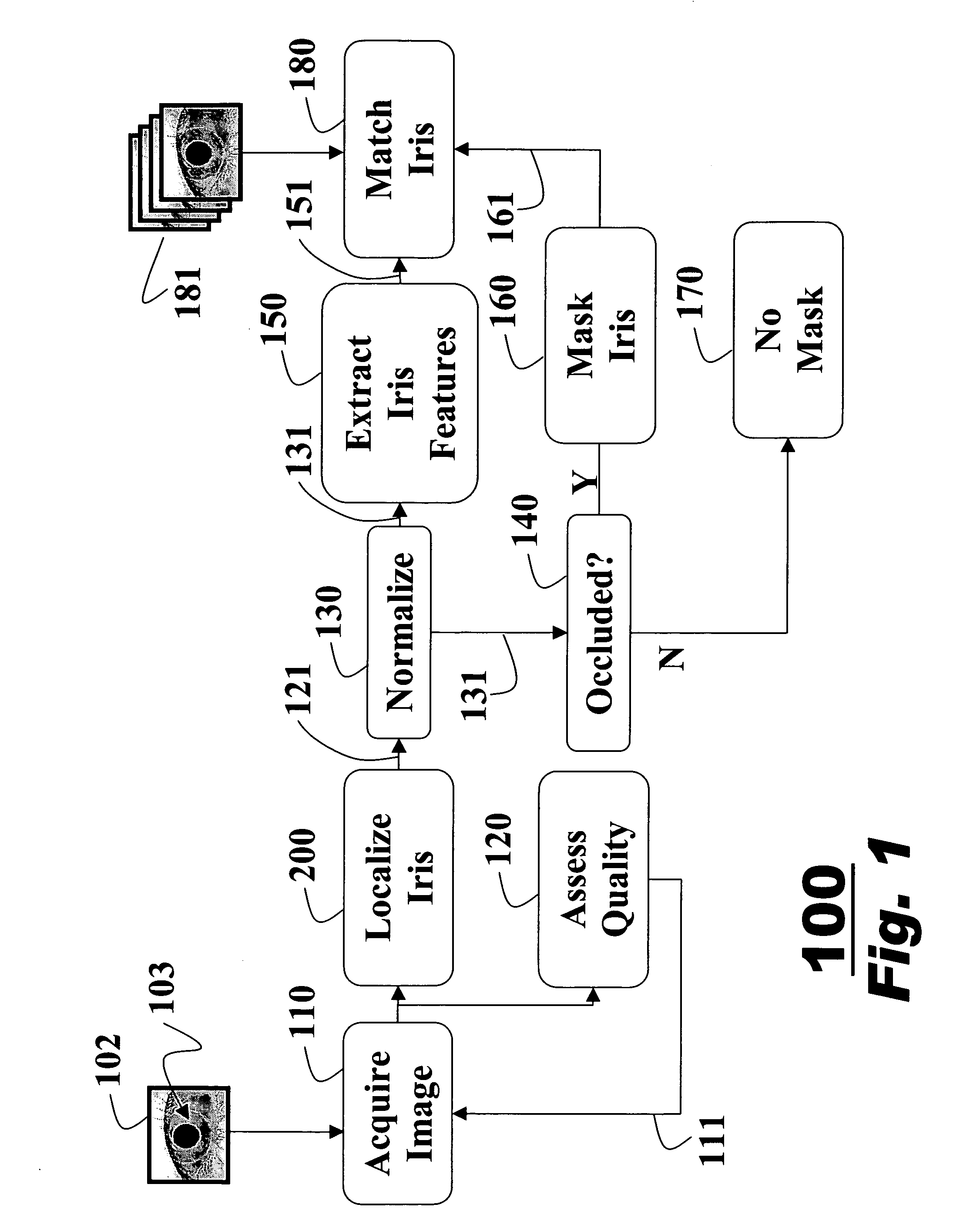
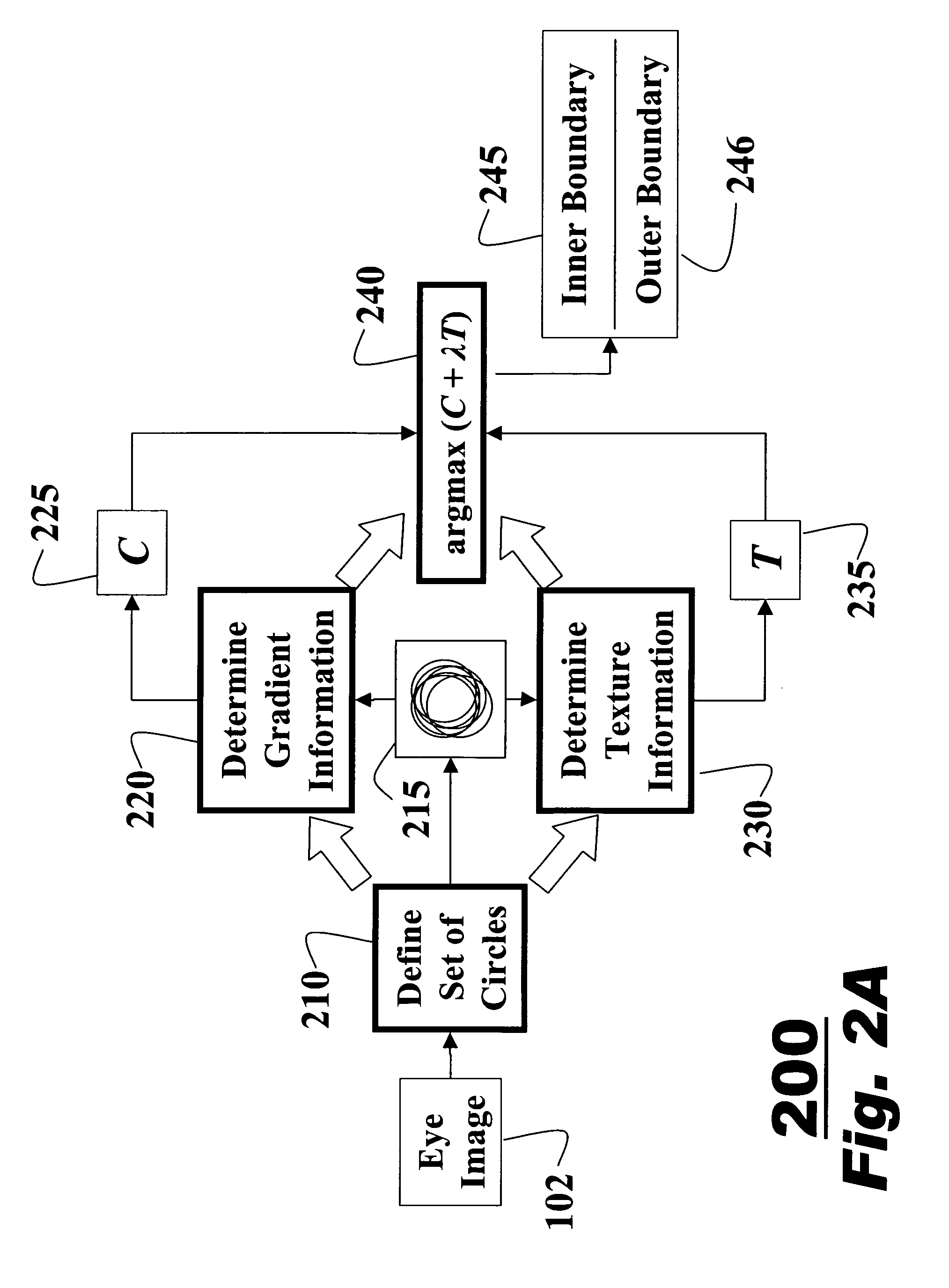
InactiveUS20070160266A1Improve accuracyAcquiring/recognising eyesPerson identificationFeature vectorIris image
A method for extracting features of an iris in an image is described. An unwrapped iris image is converted to an integral image by summations of pixel intensities. A novel bank of difference of sum filters is used to filter the integral image. The filtered output is binarized to produce an iris feature vector. The iris feature vector is used for iris matching.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Dynamic digital pre-distortion system
ActiveUS20080260066A1Simplify reduce numberImprove efficiencyTransmitters monitoringPower managementAudio power amplifierLinear filter
A Dynamic Digital Pre-Distortion (DDPD) system is disclosed to rapidly correct power amplifier (PA) non-linearity and memory effects. To perform pre-distortion, a DDPD engine predistorts an input signal in order to cancel PA nonlinearities as the signal is amplified by the PA. The DDPD engine is implemented as a composite of one linear filter and N-1 high order term linear filters. The bank of linear filters have programmable complex coefficients. To compute the coefficients, samples from the transmit path and a feedback path are captured, and covariance matrices A and B are computed using optimized hardware. After the covariance matrices are computed, Gaussian elimination processing may be employed to compute the coefficients. Mathematical and hardware optimizations may be employed to simplify and reduce the number of multiplication operands and other operations, which can enable the DDPD system to fit within a single chip.
Owner:MICROELECTRONICS TECH INC
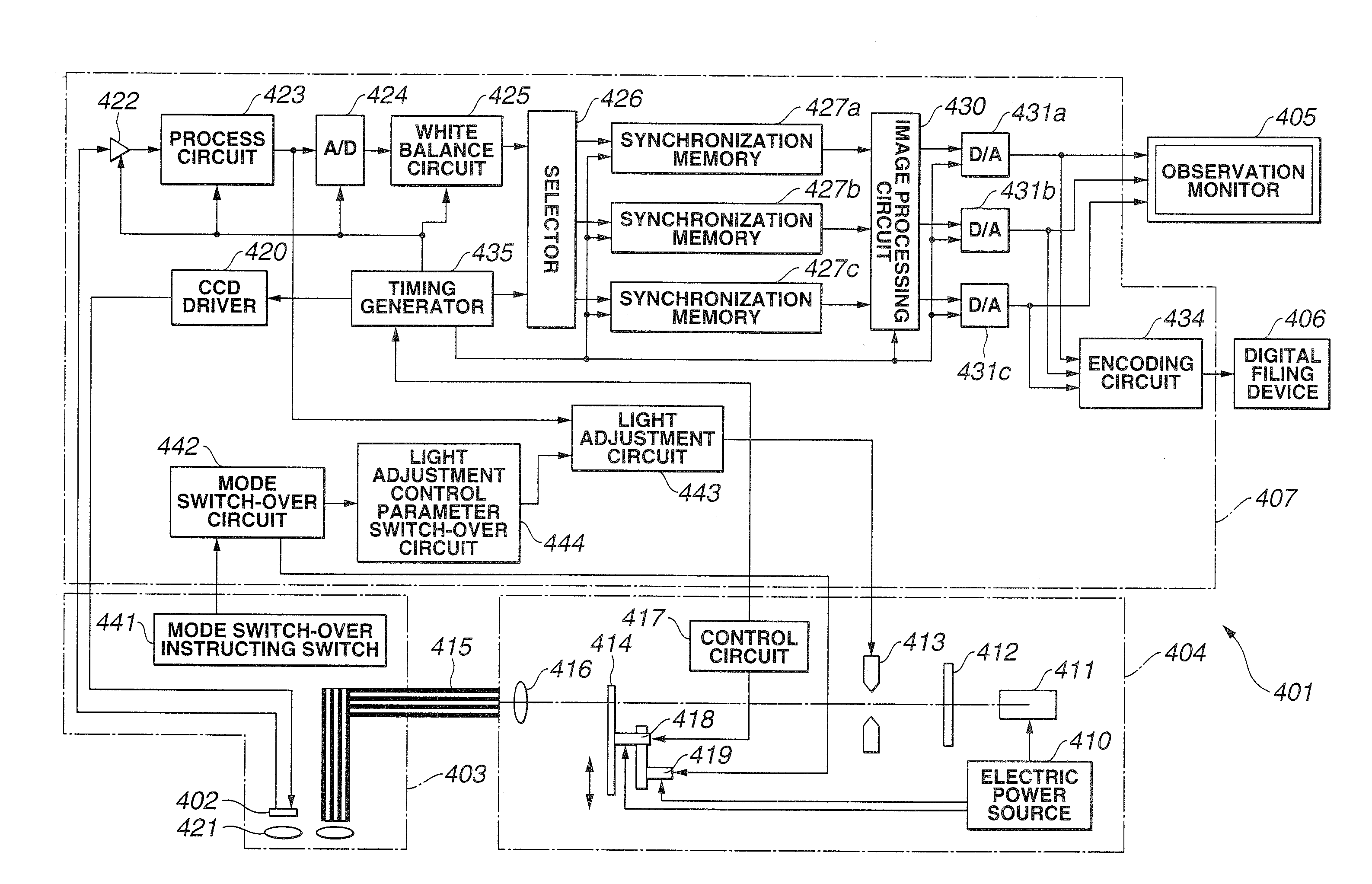
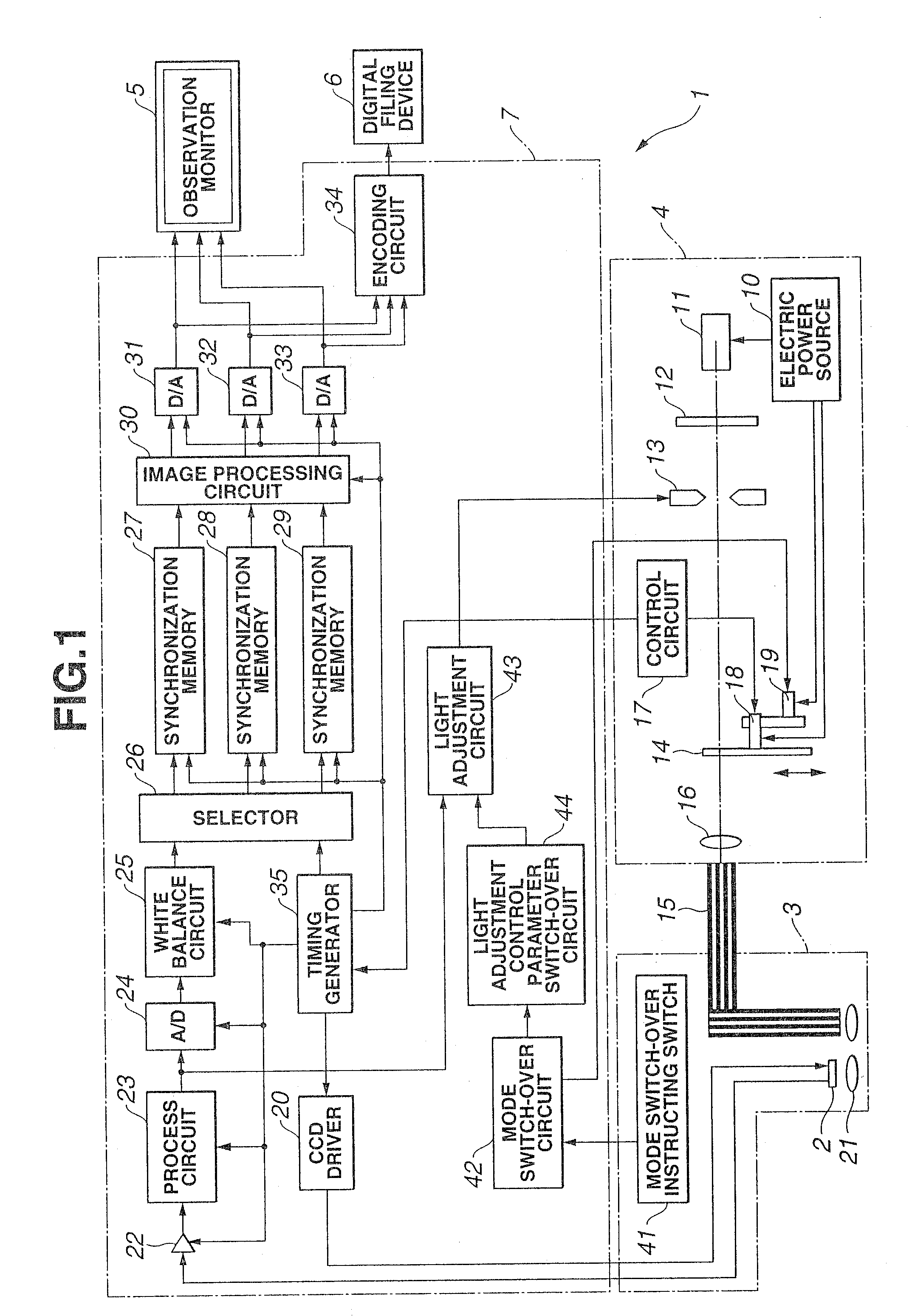
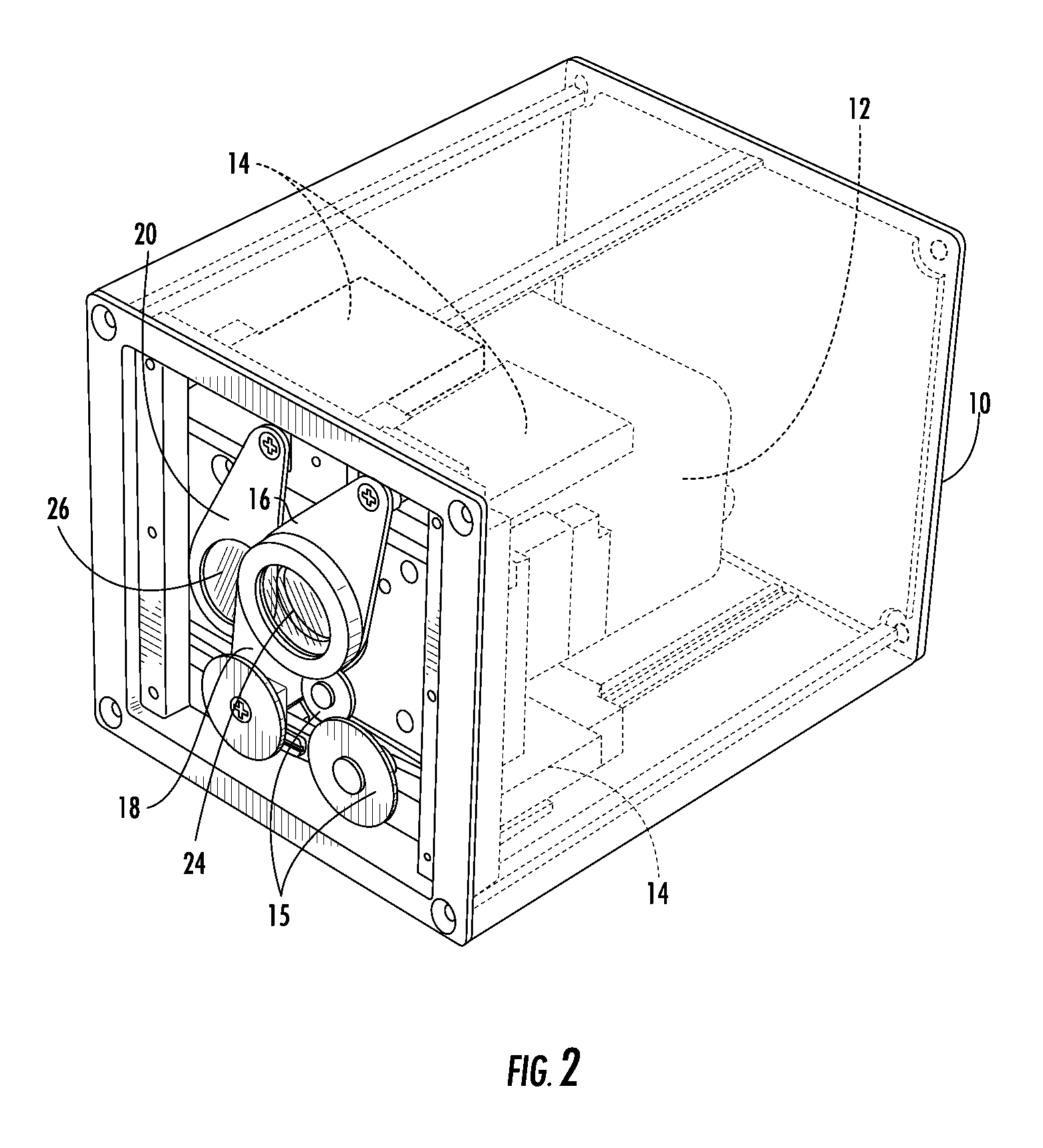
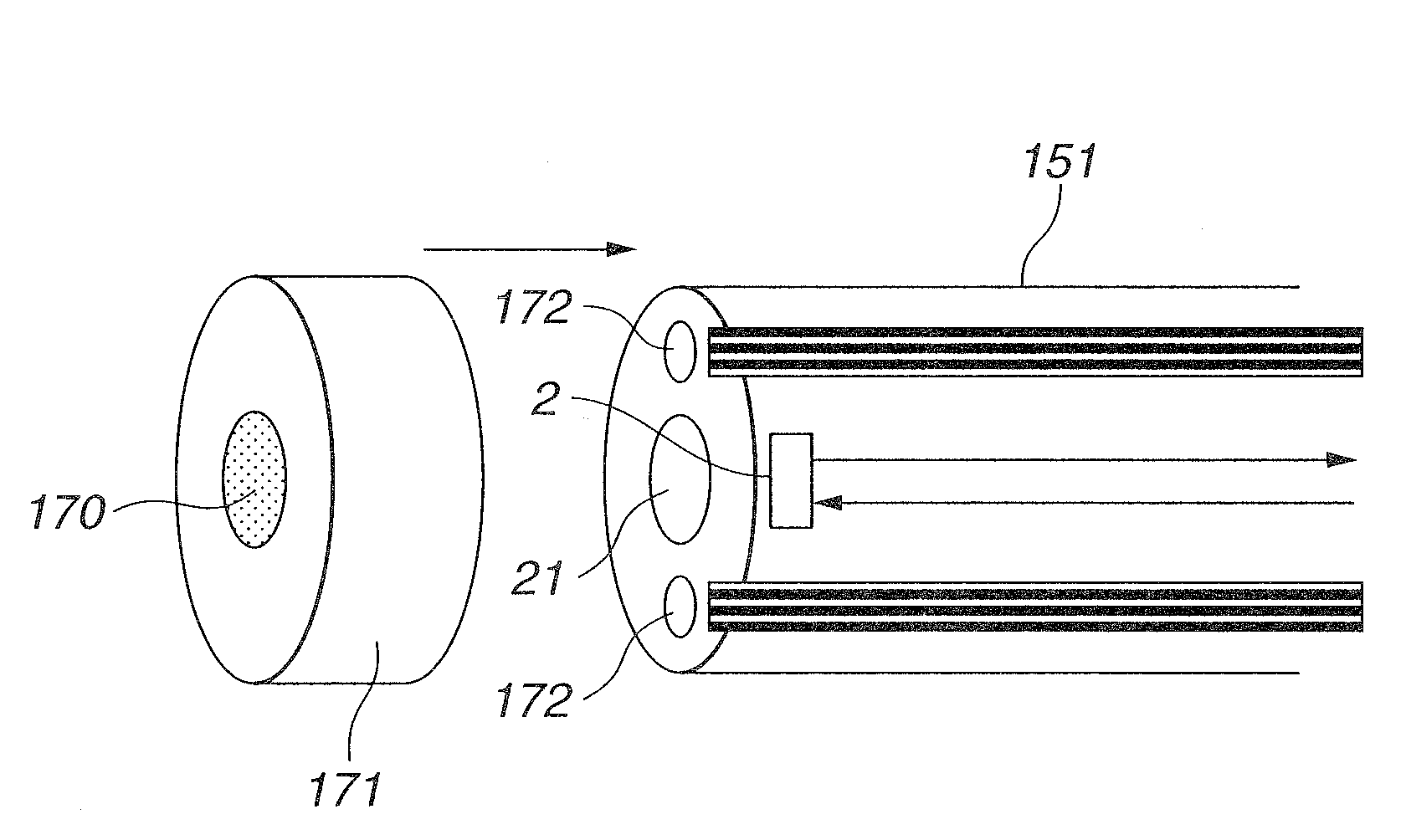
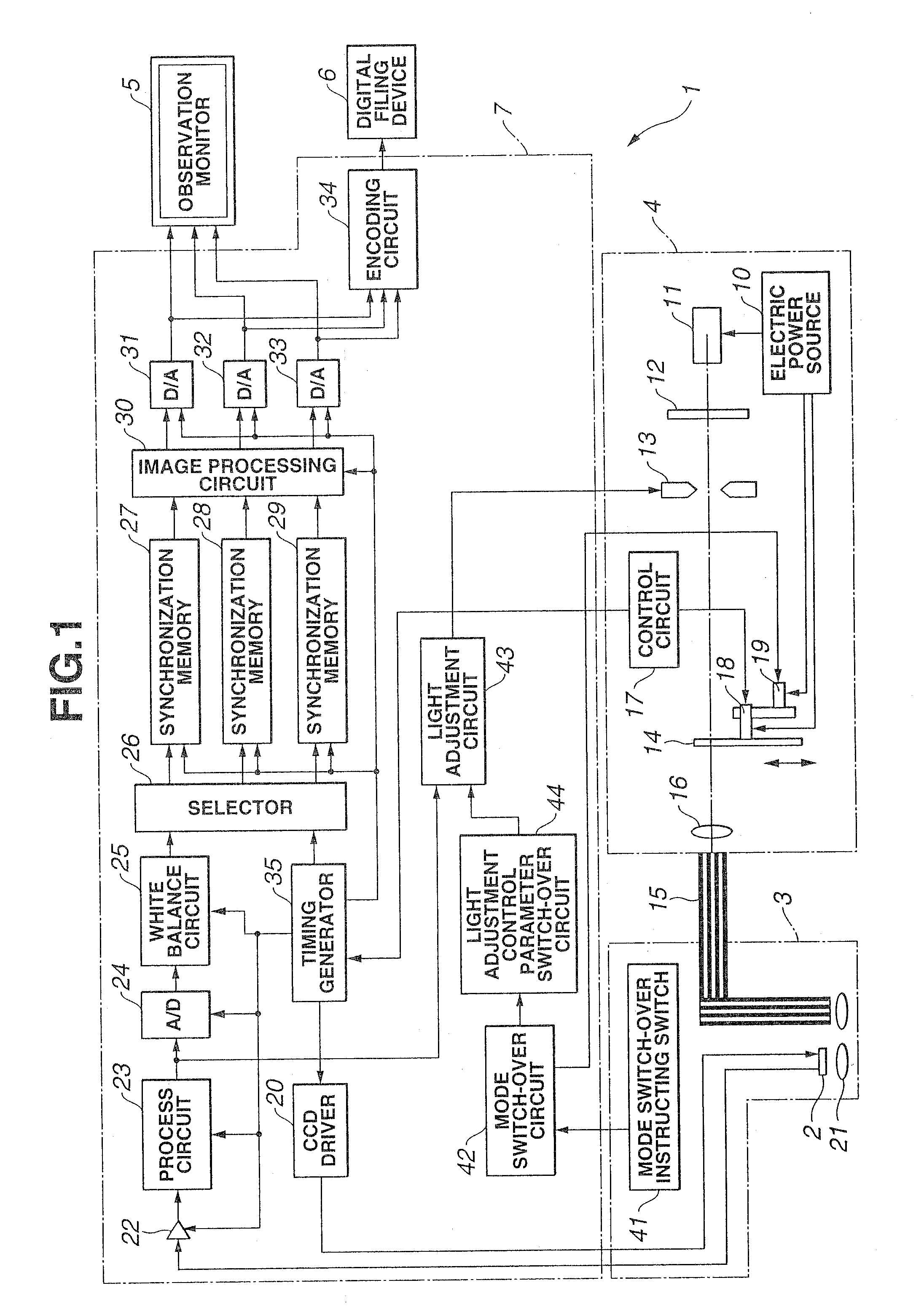
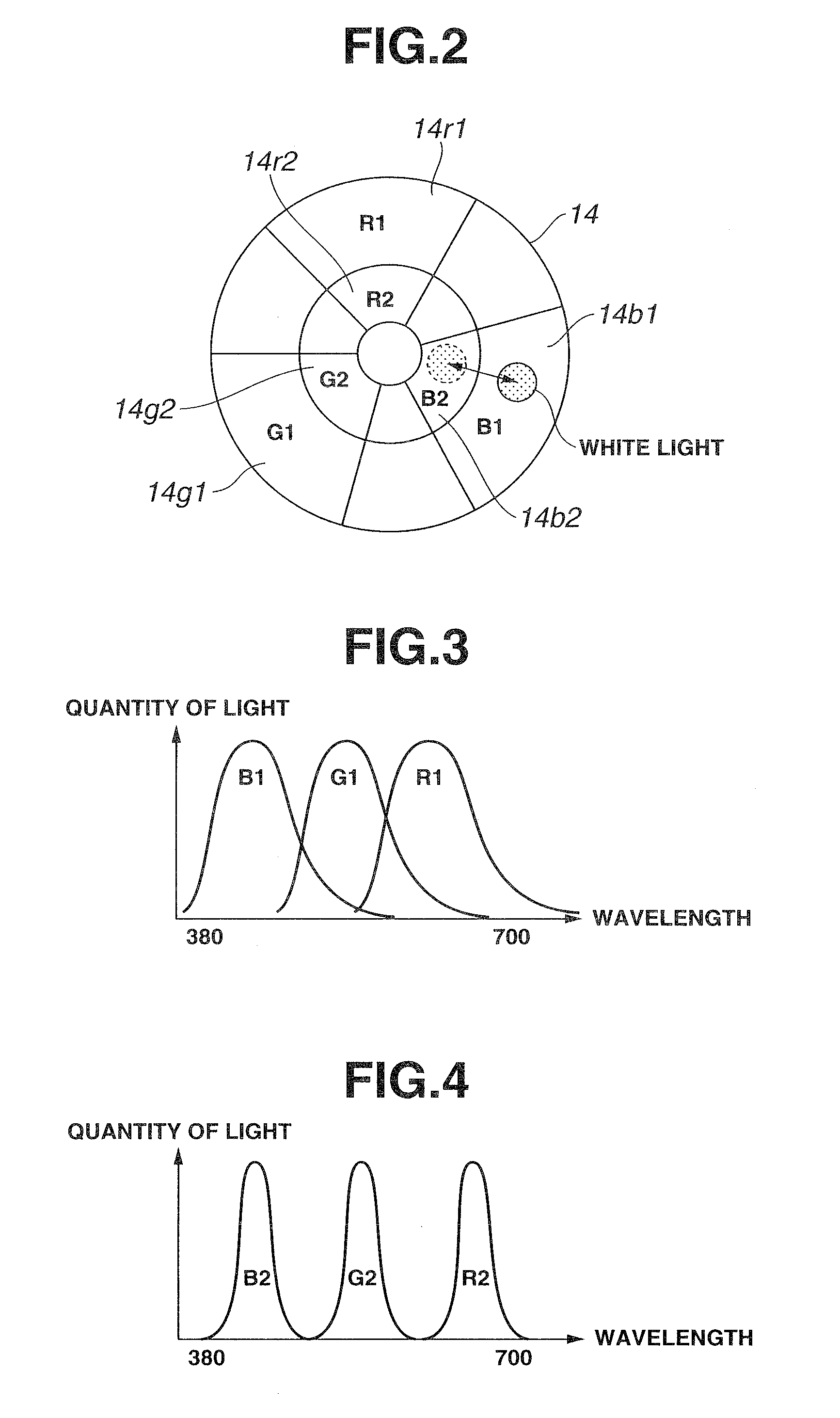
Endoscope device
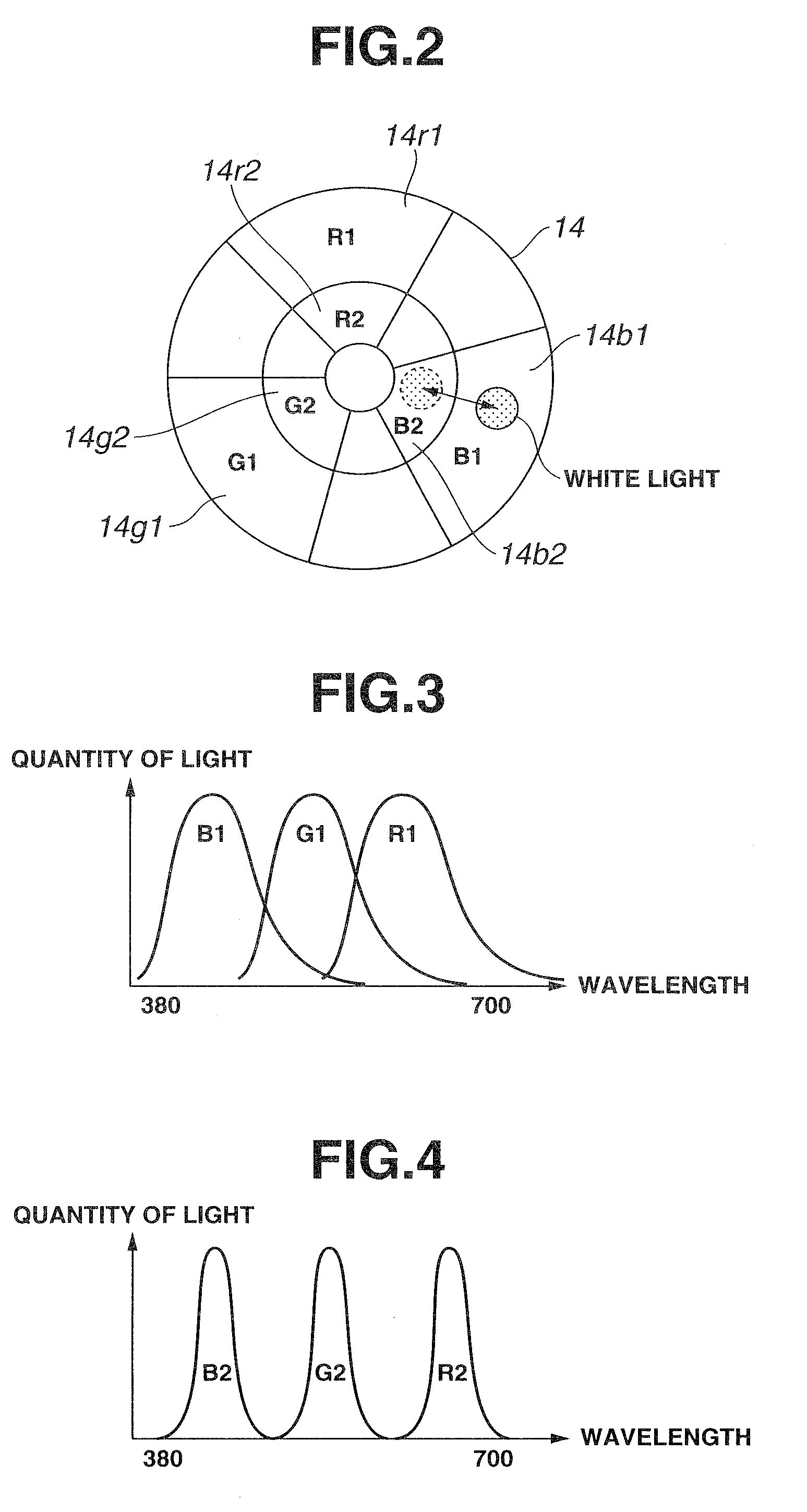
An endoscope device obtains tissue information of a desired depth near the tissue surface. A xenon lamp (11) in a light source (4) emits illumination light. A diaphragm (13) controls a quantity of the light that reaches a rotating filter. The rotating filter has an outer sector with a first filter set, and an inner sector with a second filter set. The first filter set outputs frame sequence light having overlapping spectral properties suitable for color reproduction, while the second filter set outputs narrow-band frame sequence light having discrete spectral properties enabling extraction of desired deep tissue information. A condenser lens (16) collects the frame sequence light coming through the rotating filter onto the incident face of a light guide (15). The diaphragm controls the amount of the light reaching the filter depending on which filter set is selected.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
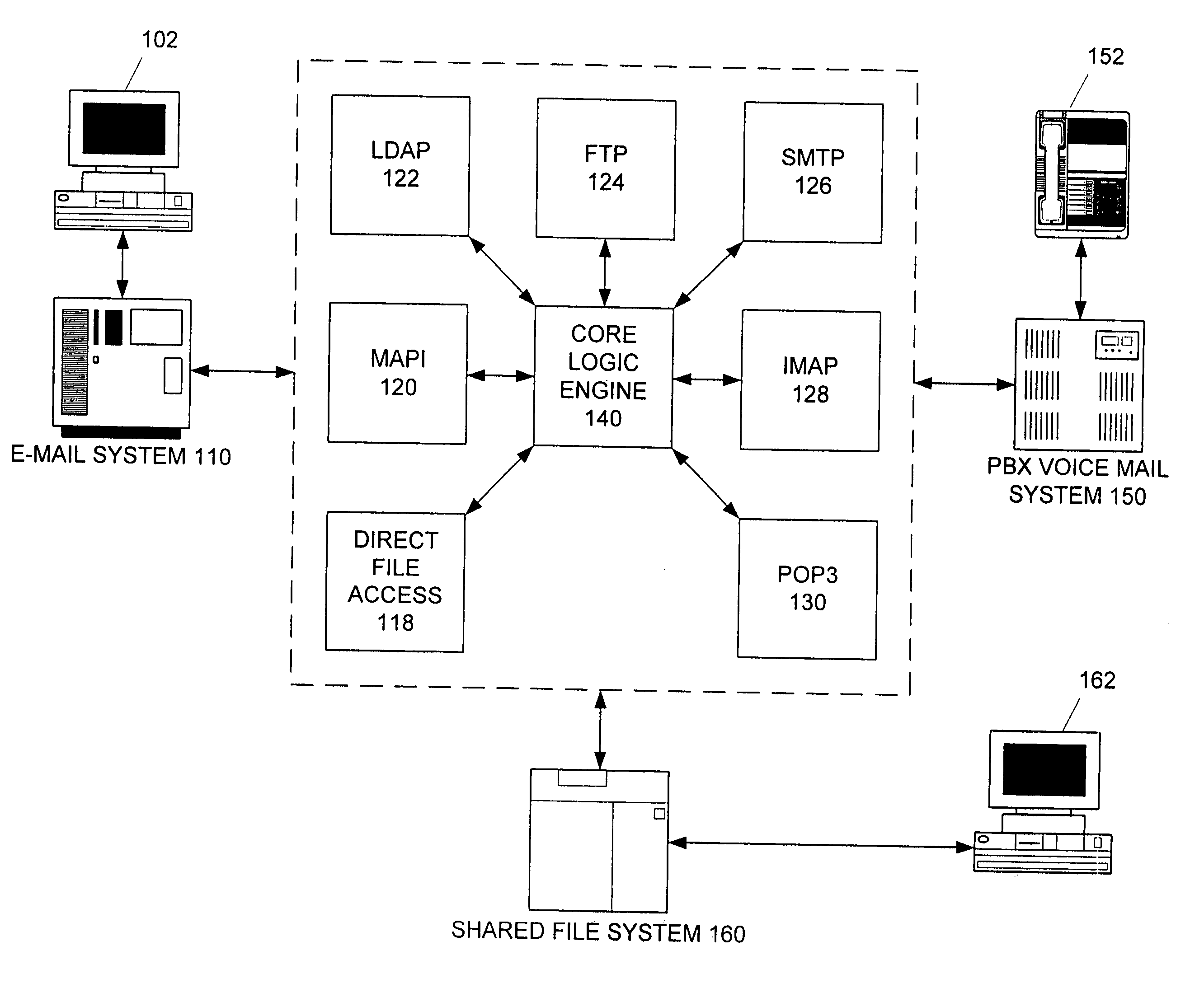
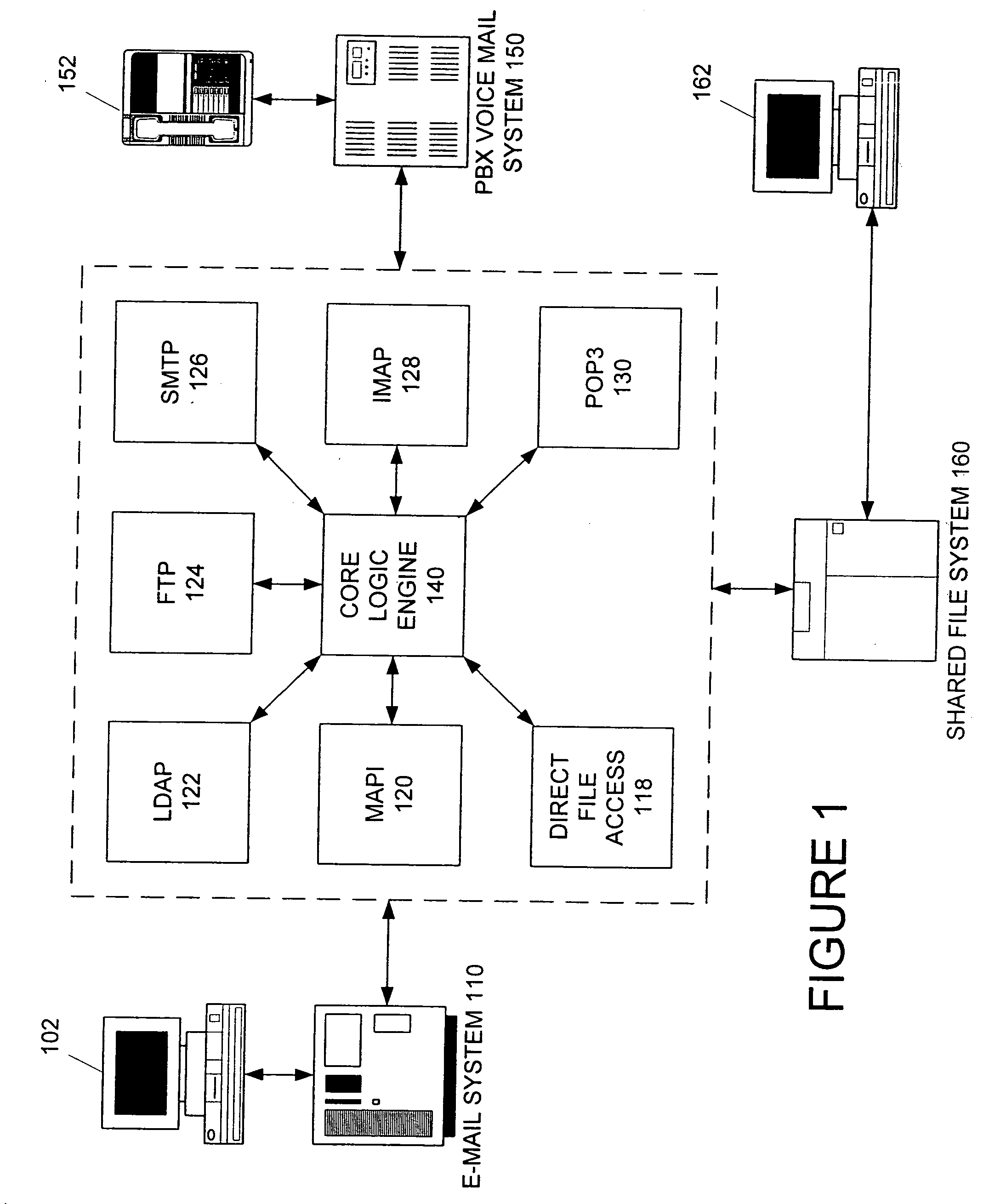
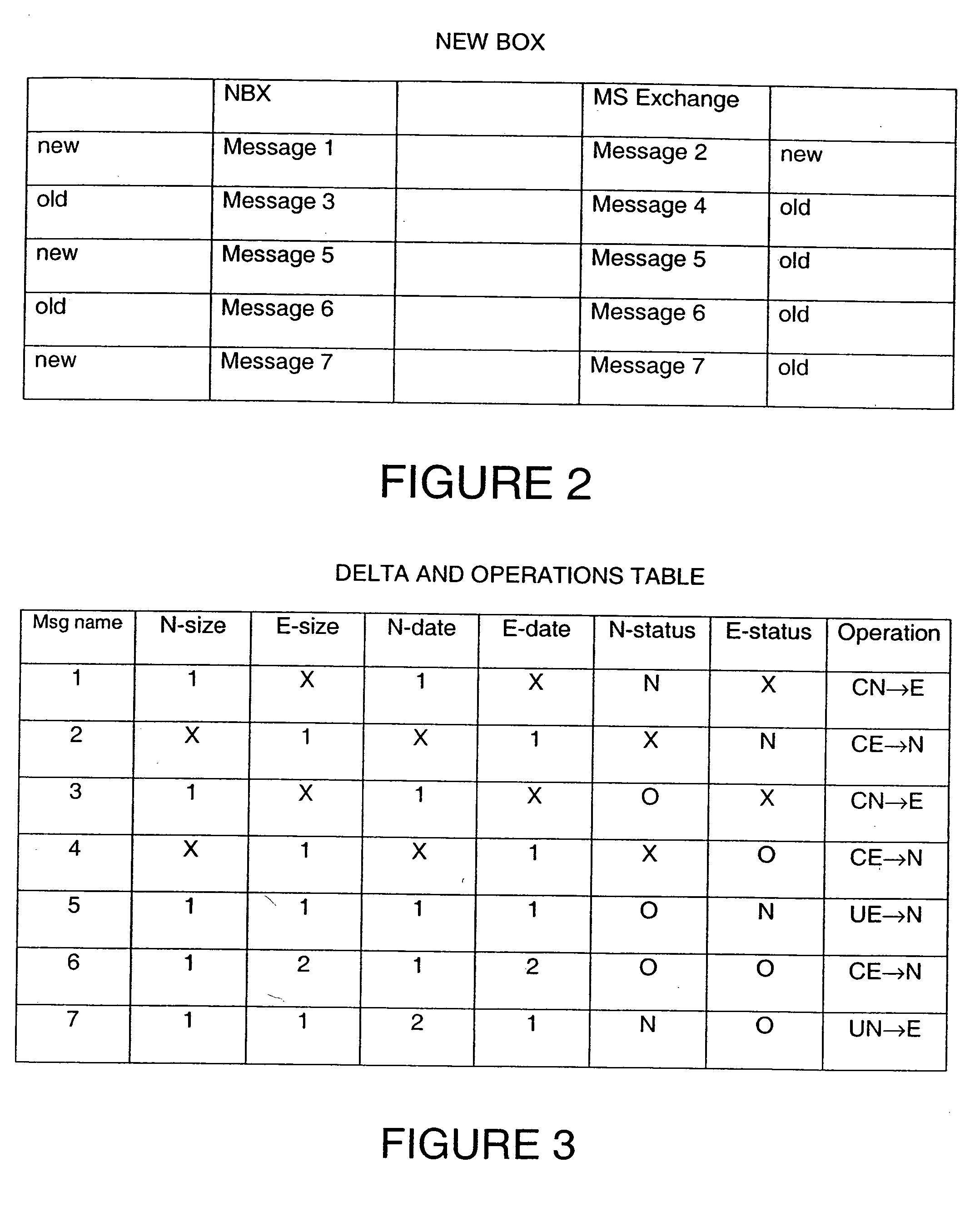
Apparatus and method for providing a unified messaging integration tool
InactiveUS20060013368A1Eliminate duplicationKeep in syncSpecial service for subscribersData switching networksFilter bankElectronic mail
The software tool of the present invention operates on a network connected to plural messaging systems and is a synchronization engine to provide a unified messaging system. It consists of a series of intelligent logic functions and filters. The engine periodically polls the various messaging systems and is able to accept lists of messages from any messaging system (voice, e-mail, fax, or otherwise), correlate changes to the messages based on definable parameters (such as: size, date, type, status), and then replicate and synchronize the messages between all of the messaging systems in appropriate formats. By doing this, each messaging system can contain identical content using the most recent version so that any of the messaging systems can be accessed and the exact same data can be independently accessed and modified. The present invention's logic functions are optimized to eliminate copying of unchanged messages.
Owner:LABAW CHRISTOPHER D
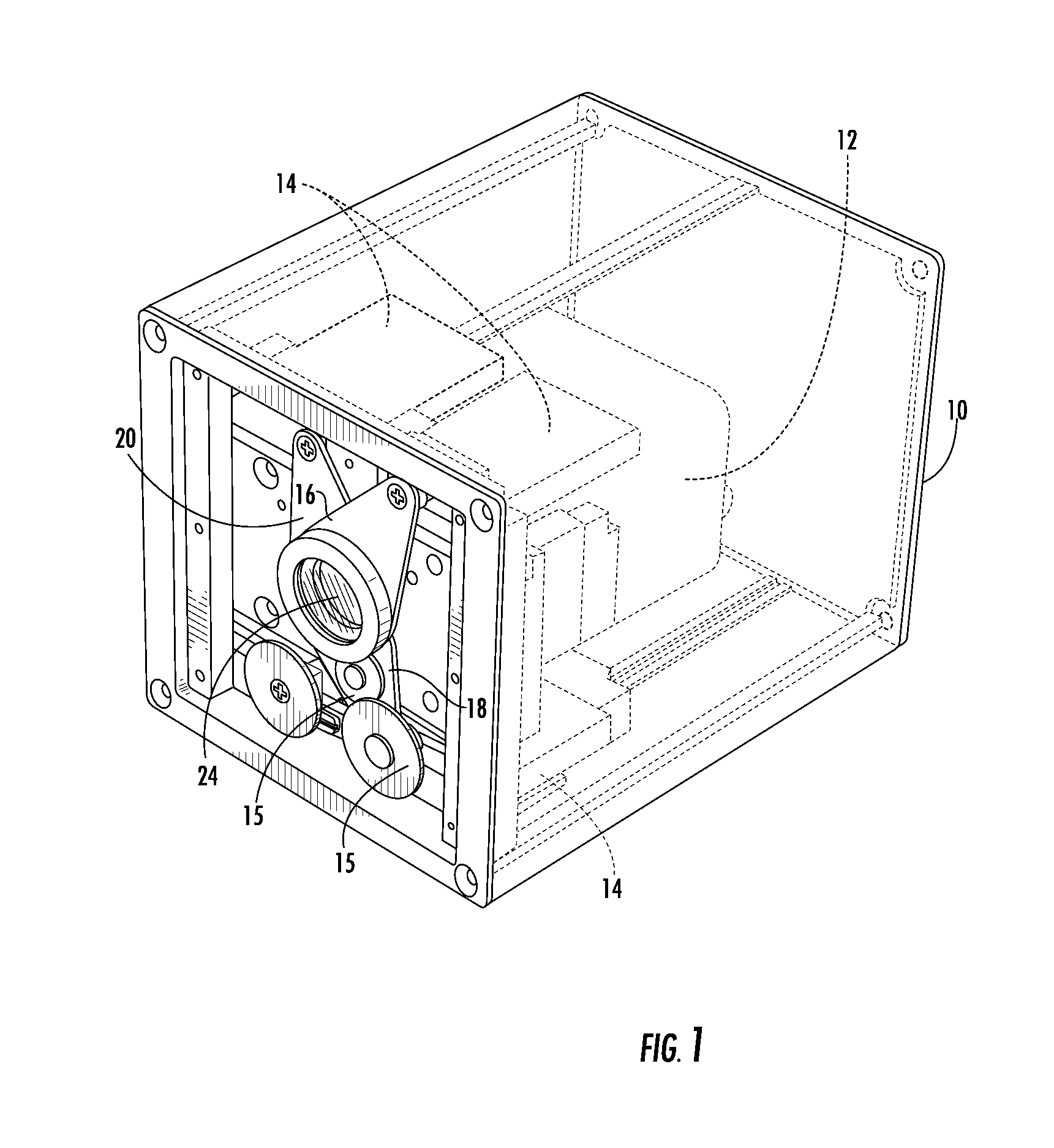
Filter assembly and image enhancement system for a surveillance camera and method of using the same
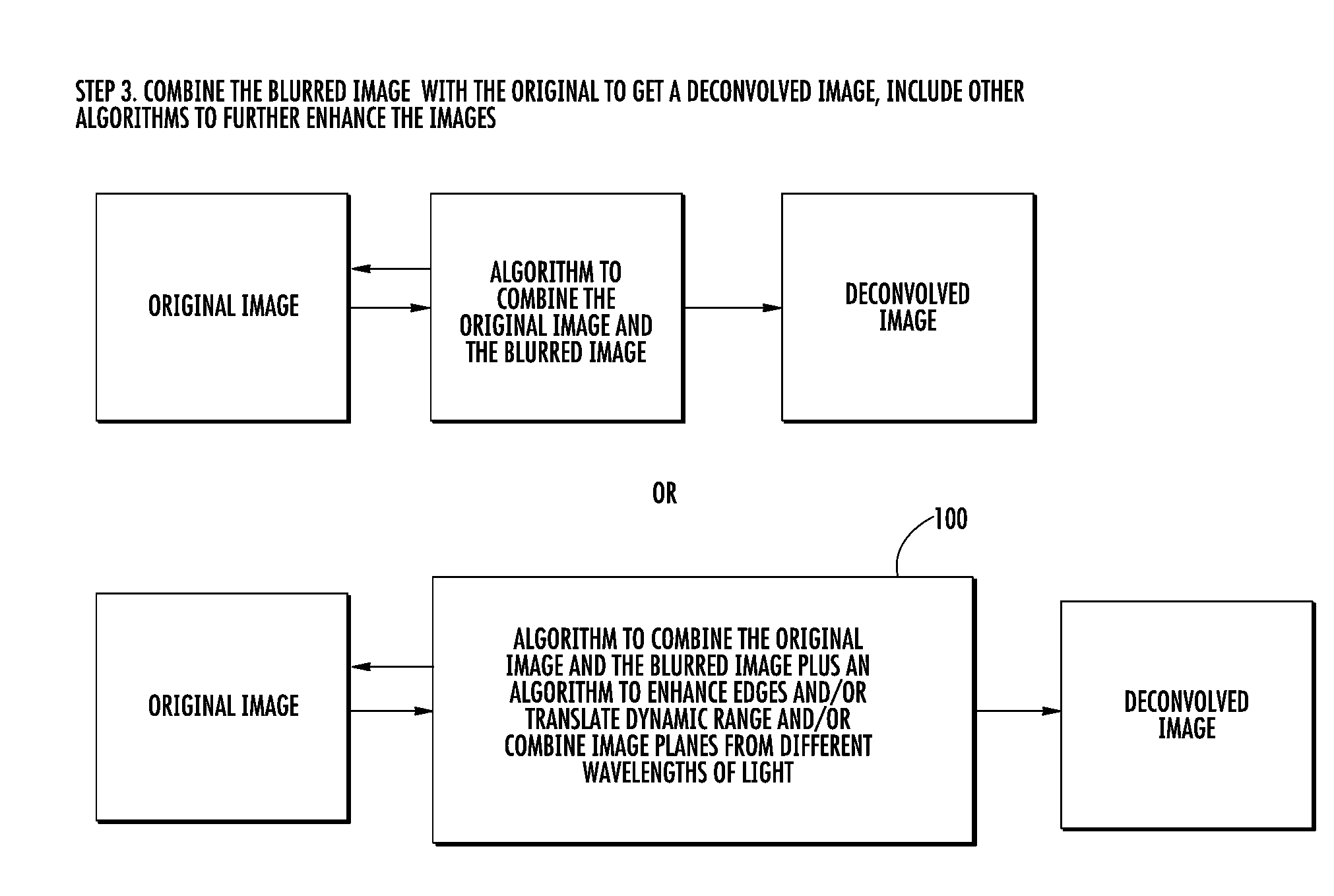
InactiveUS20080252882A1Reduce glareReduce the amount requiredTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometrySurveillance cameraDeconvolution
A filter assembly adapted to be used with a camera for selectively controlling the light that reaches the camera's aperture. In one embodiment, the filter assembly comprises three filters adapted to be independently moved between a first position wherein they are not in front of the camera's aperture and a second position wherein they are in front of the camera's aperture. The first and second filters are polarizing filters adapted to block portions of visible light. The third filter is an infrared filter adapted to block infrared light. In addition to moving between its first position and its second position, the second filter is also adapted to rotate up to 360 degrees. The image captured by the camera may be improved using a computer implemented image enhancement system that uses one or more of multi-spectral imaging, deconvolution, edge enhancement, and dynamic range translation.
Owner:KESTERSON JOHN
Endoscope device
An endoscope device obtains tissue information of a desired depth near the tissue surface. A xenon lamp (11) in a light source (4) emits illumination light. A diaphragm (13) controls a quantity of the light that reaches a rotating filter. The rotating filter has an outer sector with a first filter set, and an inner sector with a second filter set. The first filter set outputs frame sequence light having overlapping spectral properties suitable for color reproduction, while the second filter set outputs narrow-band frame sequence light having discrete spectral properties enabling extraction of desired deep tissue information. A condenser lens (16) collects the frame sequence light coming through the rotating filter onto the incident face of a light guide (15). The diaphragm controls the amount of the light reaching the filter depending on which filter set is selected.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Integrated switchless programmable attenuator and low noise amplifier
InactiveUS6879816B2Multiple-port active networksSwitched capacitor networksCapacitanceLocal oscillator signal
An integrated receiver with channel selection and image rejection substantially implemented on a single CMOS integrated circuit is described. A receiver front end provides programmable attenuation and a programmable gain low noise amplifier. Frequency conversion circuitry advantageously uses LC filters integrated onto the substrate in conjunction with image reject mixers to provide sufficient image frequency rejection. Filter tuning and inductor Q compensation over temperature are performed on chip. The filters utilize multi track spiral inductors. The filters are tuned using local oscillators to tune a substitute filter, and frequency scaling during filter component values to those of the filter being tuned. In conjunction with filtering, frequency planning provides additional image rejection. The advantageous choice of local oscillator signal generation methods on chip is by PLL out of band local oscillation and by direct synthesis for in band local oscillator. The VCOs in the PLLs are centered using a control circuit to center the tuning capacitance range. A differential crystal oscillator is advantageously used as a frequency reference. Differential signal transmission is advantageously used throughout the receiver.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Echo cancellation
InactiveUS6931123B1Two-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSubstations coupling interface circuitsAdaptive filterVocal tract
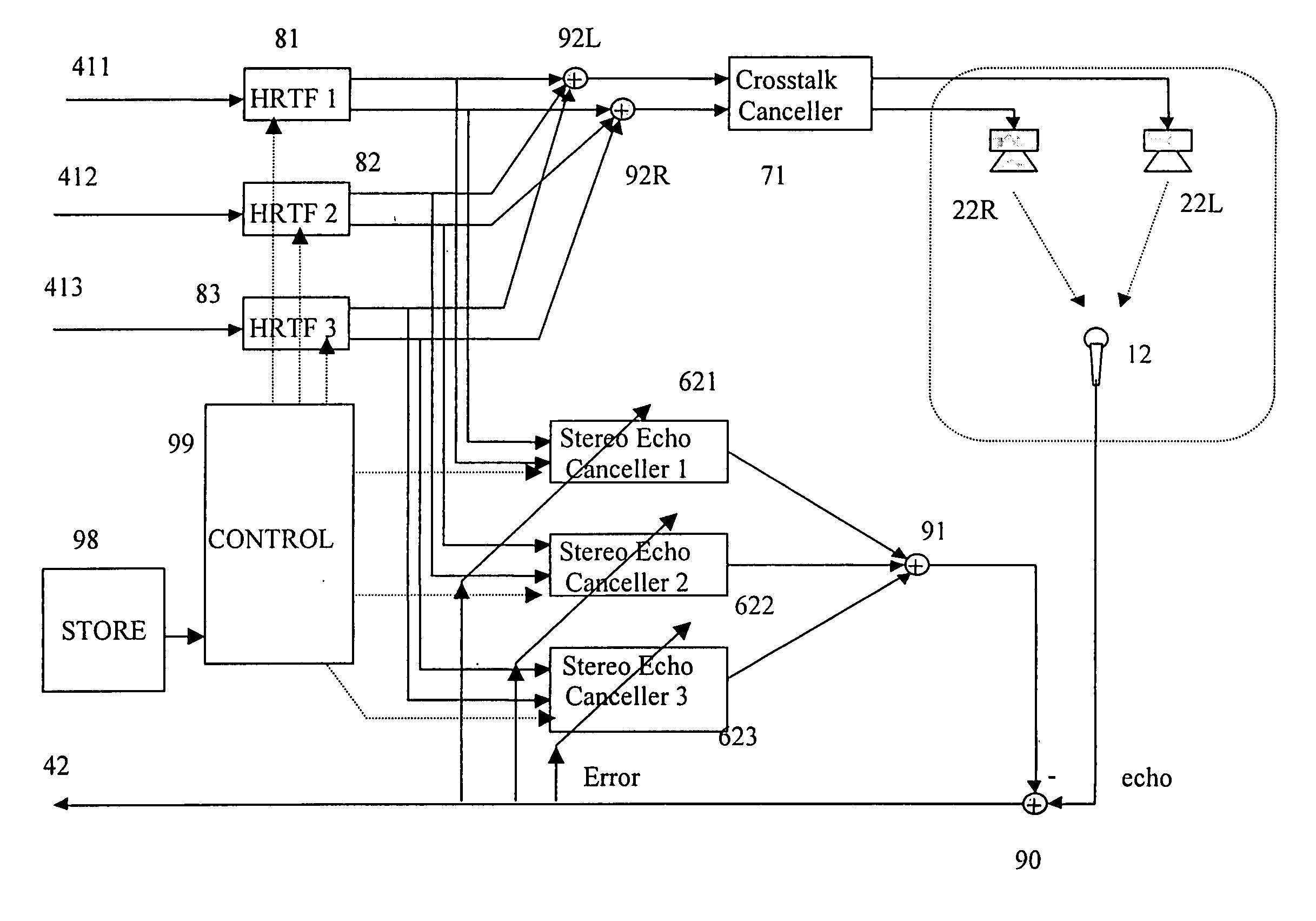
An audio conferencing system in which each participant in the conference generates a monaural signal for transmission on an output channel to the other participants, and receives a plurality of input channels from the other participants. The input channels are individually converted to stereophonic signal pairs by respective filter banks having selected predetermined transfer functions. The stereo channels are combined linearly to provide a stereophonic audio output. The system has an echo cancellation system in which an adaptive filter process is applied to the input channels to generate a combined echo cancellation signal for applying to the output channel.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com