Patents
Literature
185 results about "Monaural" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Monaural or monophonic sound reproduction (often shortened to mono) is sound intended to be heard as if it were emanating from one position. This contrasts with stereophonic sound or stereo, which uses two separate audio channels to reproduce sound from two microphones on the right and left side, which is reproduced with two separate loudspeakers to give a sense of the direction of sound sources. In mono, only one loudspeaker is necessary, but, when played through multiple loudspeakers or headphones, identical signals are fed to each speaker, resulting in the perception of one-channel sound "imaging" in one sonic space between the speakers (provided that the speakers are set up in a proper symmetrical critical-listening placement). Monaural recordings, like stereo ones, typically use multiple microphones fed into multiple channels on a recording console, but each channel is "panned" to the center. In the final stage, the various center-panned signal paths are usually mixed down to two identical tracks, which, because they are identical, are perceived upon playback as representing a single unified signal at a single place in the soundstage. In some cases, multitrack sources are mixed to a one-track tape, thus becoming one signal. In the mastering stage, particularly in the days of mono records, the one- or two-track mono master tape was then transferred to a one-track lathe intended to be used in the pressing of a monophonic record. Today, however, monaural recordings are usually mastered to be played on stereo and multi-track formats, yet retain their center-panned mono soundstage characteristics.
Neural network classifier for separating audio sources from a monophonic audio signal
InactiveUS20070083365A1Improve robustnessEasy to separateSpeech recognitionNetwork outputAudio signal
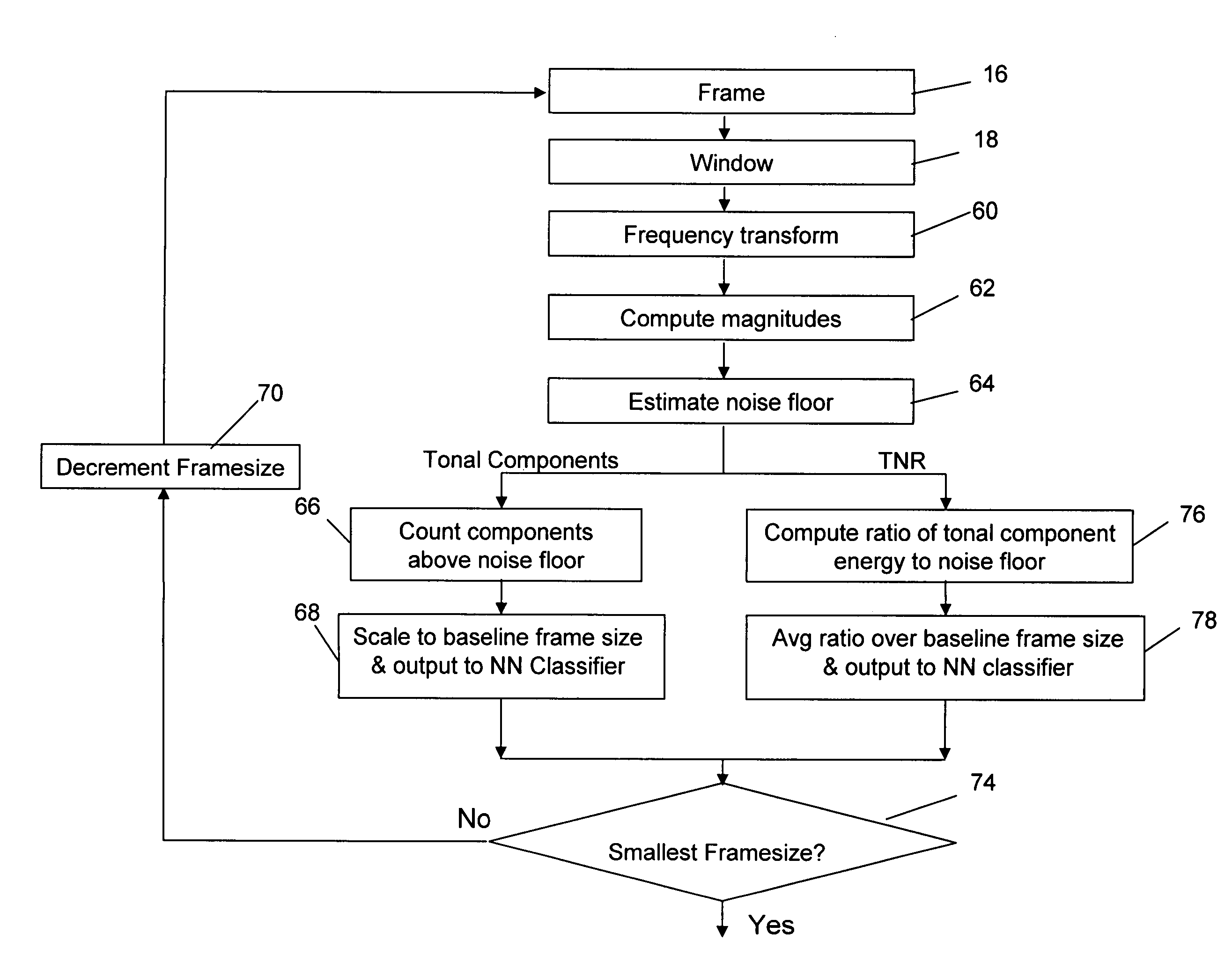
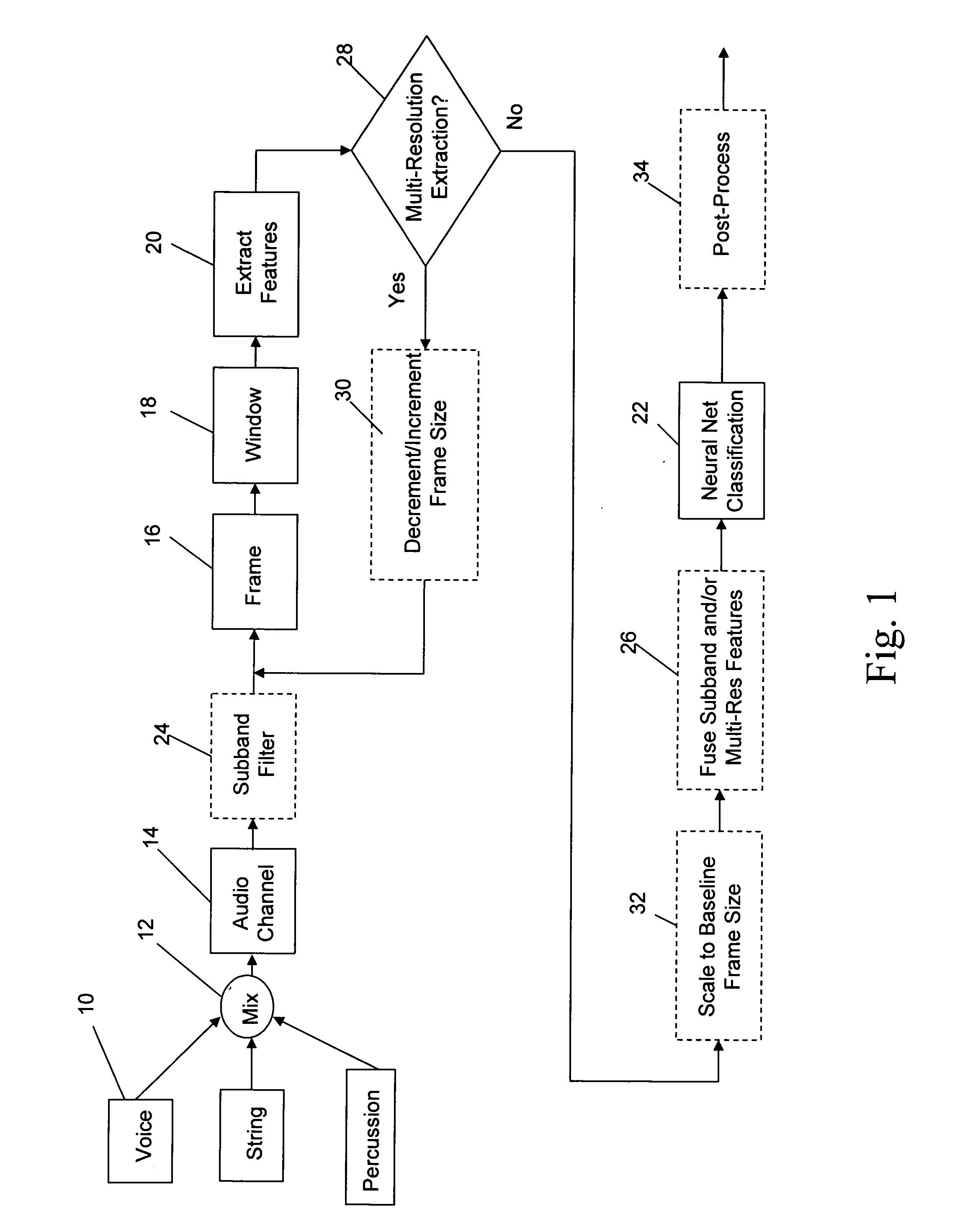
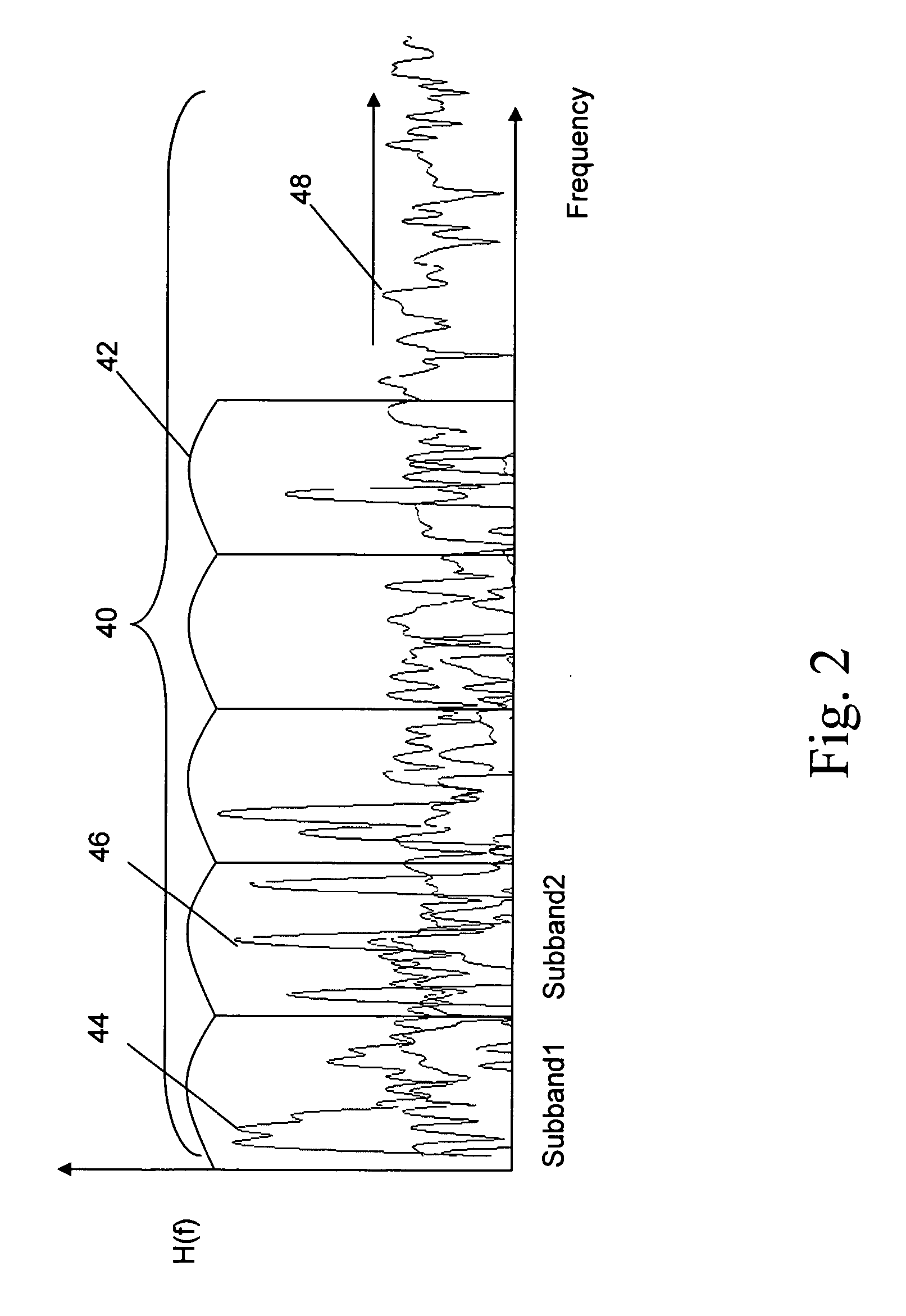
A neural network classifier provides the ability to separate and categorize multiple arbitrary and previously unknown audio sources down-mixed to a single monophonic audio signal. This is accomplished by breaking the monophonic audio signal into baseline frames (possibly overlapping), windowing the frames, extracting a number of descriptive features in each frame, and employing a pre-trained nonlinear neural network as a classifier. Each neural network output manifests the presence of a pre-determined type of audio source in each baseline frame of the monophonic audio signal. The neural network classifier is well suited to address widely changing parameters of the signal and sources, time and frequency domain overlapping of the sources, and reverberation and occlusions in real-life signals. The classifier outputs can be used as a front-end to create multiple audio channels for a source separation algorithm (e.g., ICA) or as parameters in a post-processing algorithm (e.g. categorize music, track sources, generate audio indexes for the purposes of navigation, re-mixing, security and surveillance, telephone and wireless communications, and teleconferencing).
Owner:DTS
Method and apparatus for three-dimensional acoustic field encoding and optimal reconstruction
ActiveUS20110305344A1Exact reproductionIncrease the areaSpeech analysisStereophonic systemsDecoding methodsVocal tract
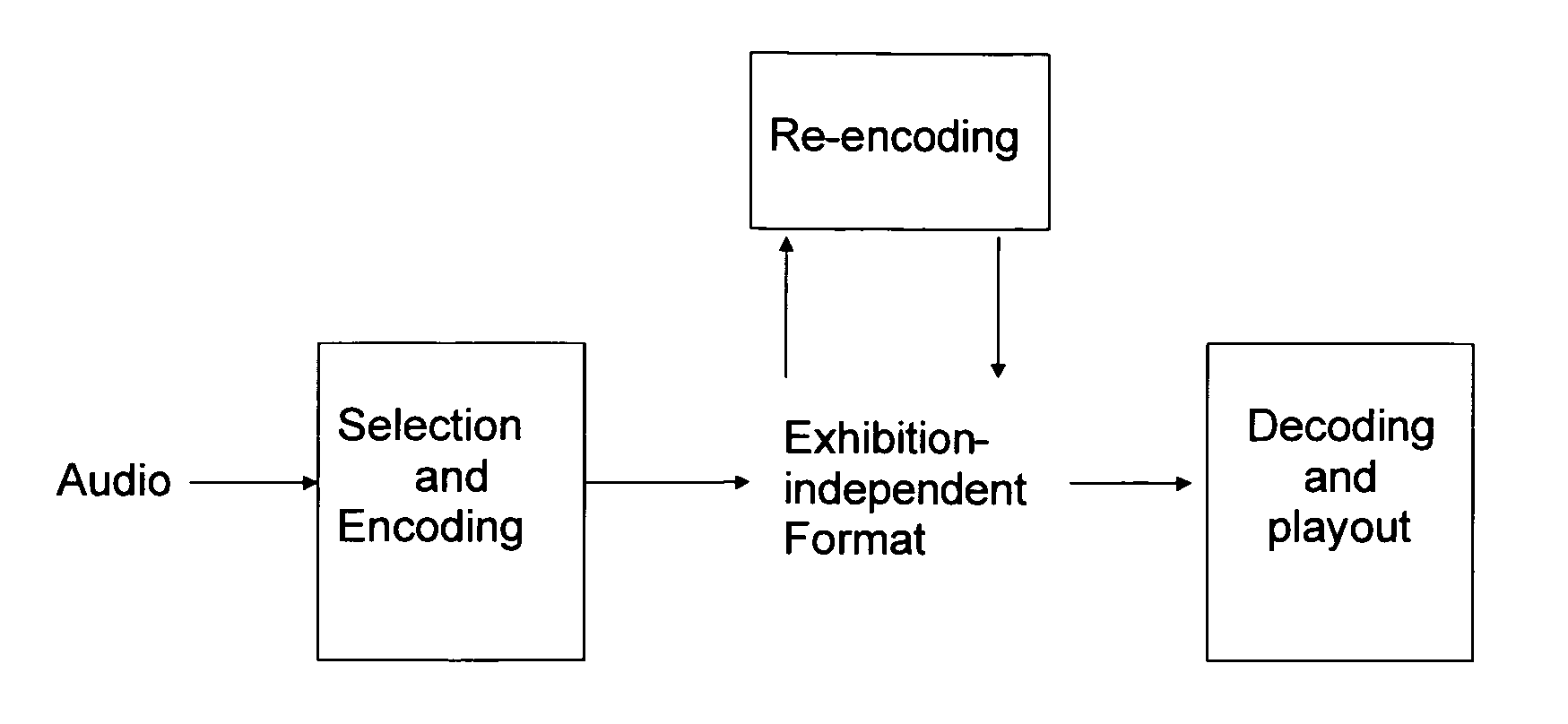
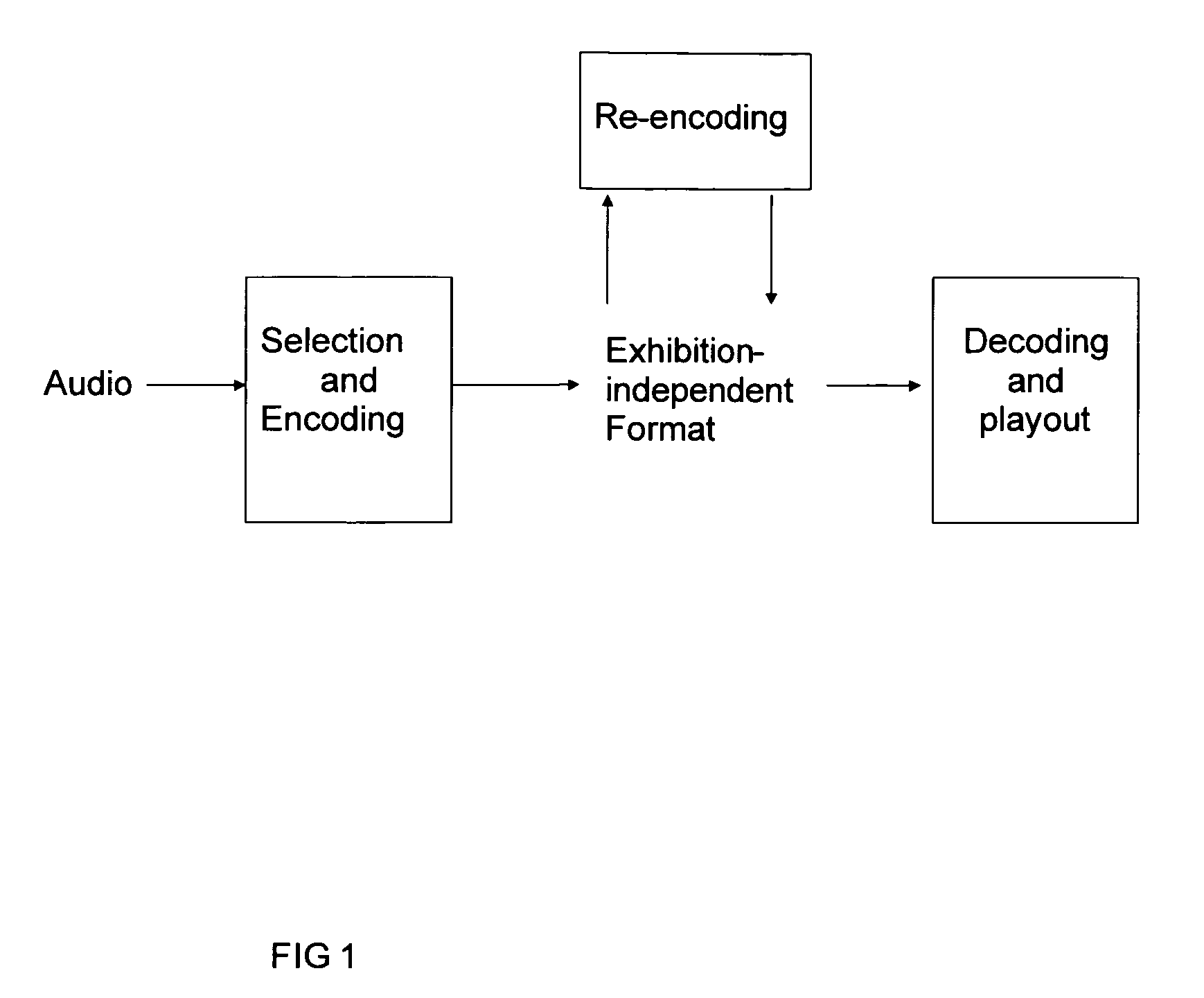
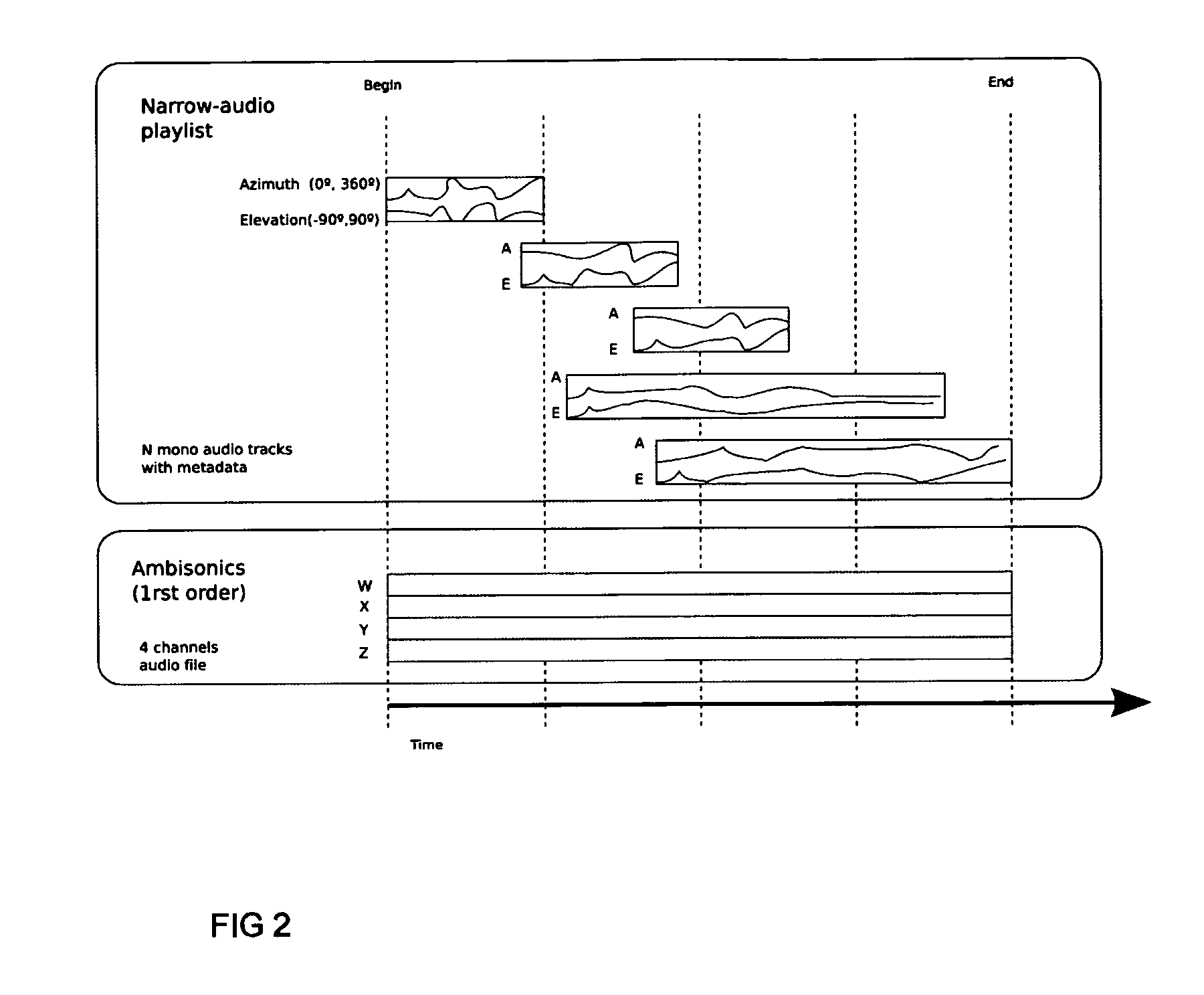
A method and apparatus to encode audio with spatial information in a manner that does not depend on the exhibition setup, and to decode and play out optimally for any given exhibition setup, maximizing the sweet-spot area, and including setups with loudspeakers at different heights, and headphones. The part of the audio that requires very precise localization is encoded into a set of mono tracks with associated directional parameters, whereas the remaining audio is encoded into a set of Ambisonics tracks of a chosen order and mixture. Upon specification of a given exhibition system, the exhibition-independent format is decoded adapting to the specified system, by using different decoding methods for each assigned group.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Audio coding
InactiveUS20050177360A1Reduce artifactsImprove performanceSpeech analysisCode conversionWindow switchingVocal tract
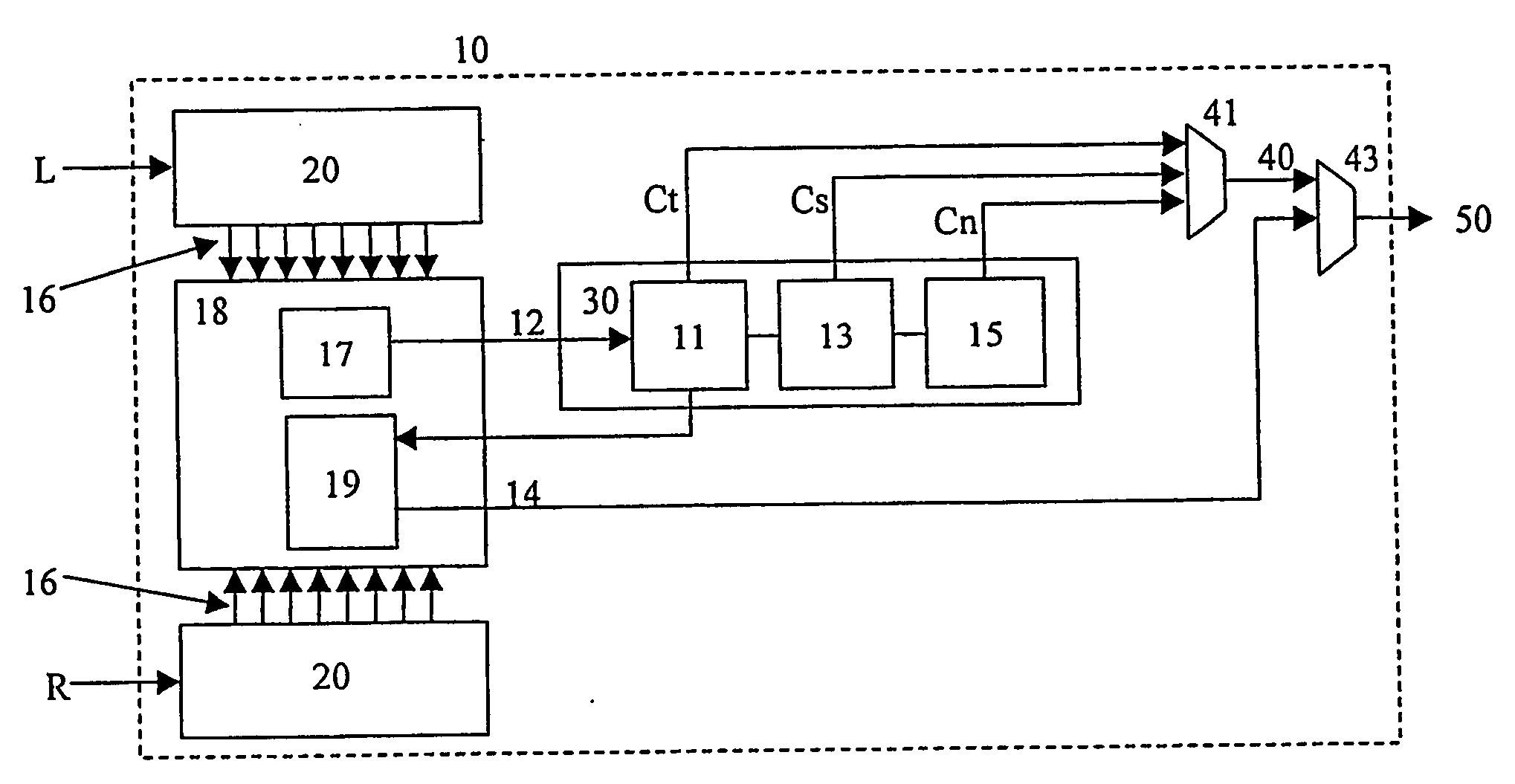
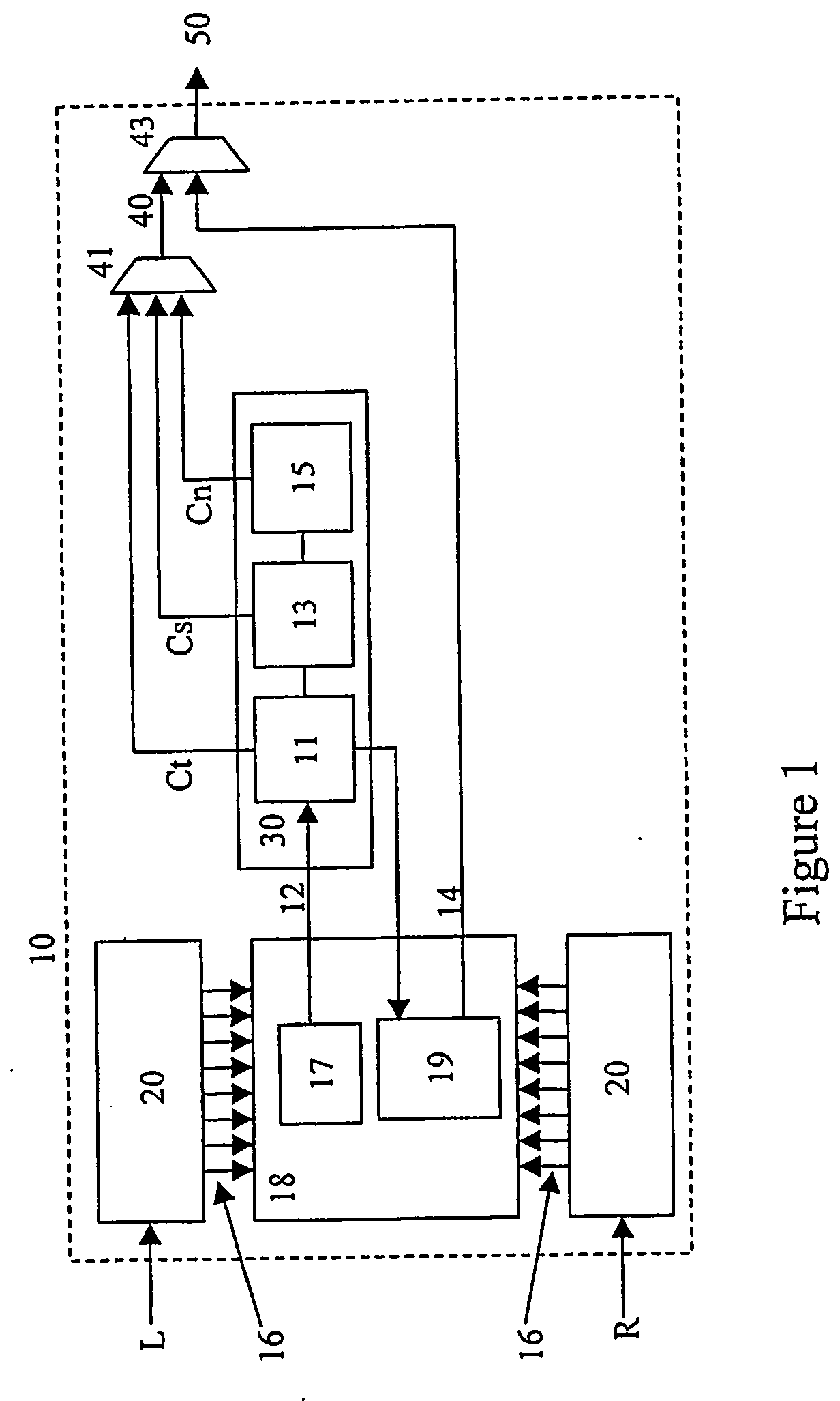
In binaural stereo coding, only one monaural channel is encoded. An additional layer holds the parameters to retrieve the left and right signal. An encoder is disclosed which links transient information extracted from the mono encoded signal to parametric multi-channel layers to provide increased performance. Transient positions can either be directly derived from the bit-stream or be estimated from other encoded parameters (e.g. window-switching flag in mp3).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Support of a multichannel audio extension
InactiveUS20070165869A1Efficient multichannel audio codingReduce computational complexitySpeech analysisTwo-channel systemsFrequency bandAudio signal
The invention relates to methods and units supporting a multichannel audio extension. In order to allow an efficient extension requiring a low computational complexity, it is proposed that at an encoding end, at least state information is provided as side information for a provided mono audio signal (M) generated out of a multichannel audio signal. The state information indicates for each of a plurality of frequency bands how a predetermined or equally provided gain value is to be applied in the frequency domain to the mono audio signal (M) for obtaining first and a second channel signals (L,R) of a reconstructed multichannel audio signal.
Owner:CORE WIRELESS LICENSING R L
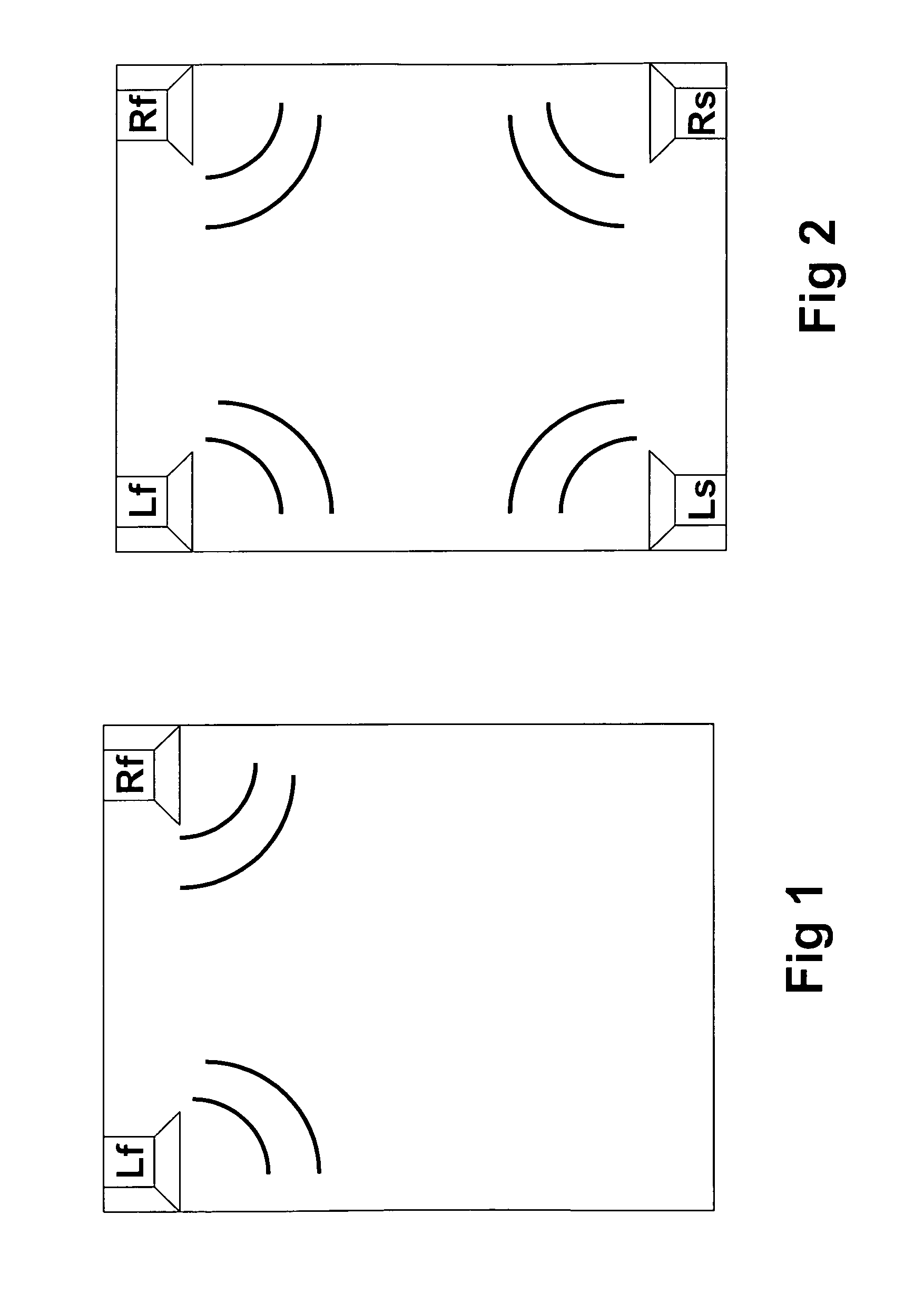
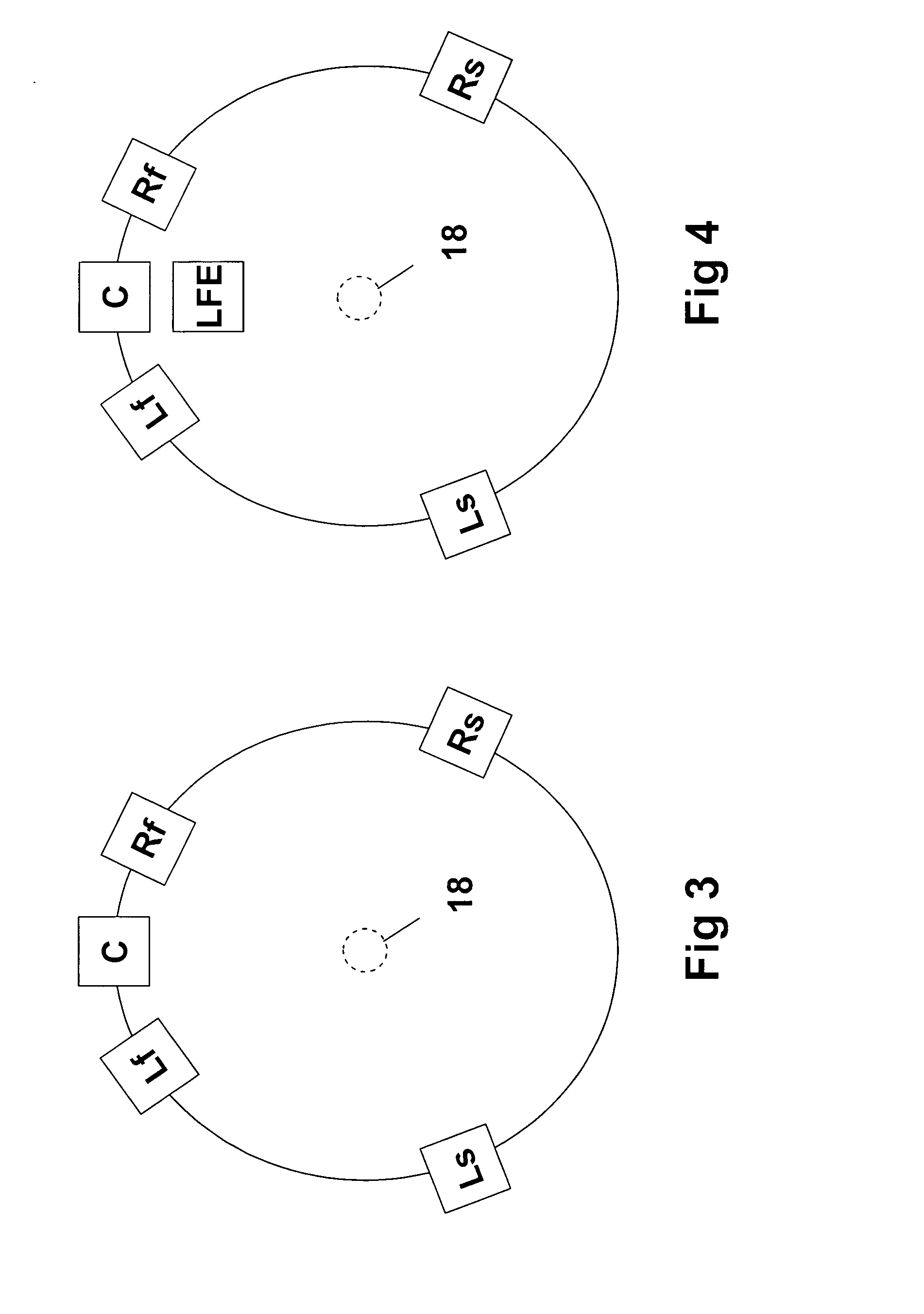
Multi-channel surround sound mastering and reproduction techniques that preserve spatial harmonics in three dimensions
InactiveUS6904152B1Improve realismExact reproductionGain controlPseudo-stereo systemsSound sourcesHarmonic
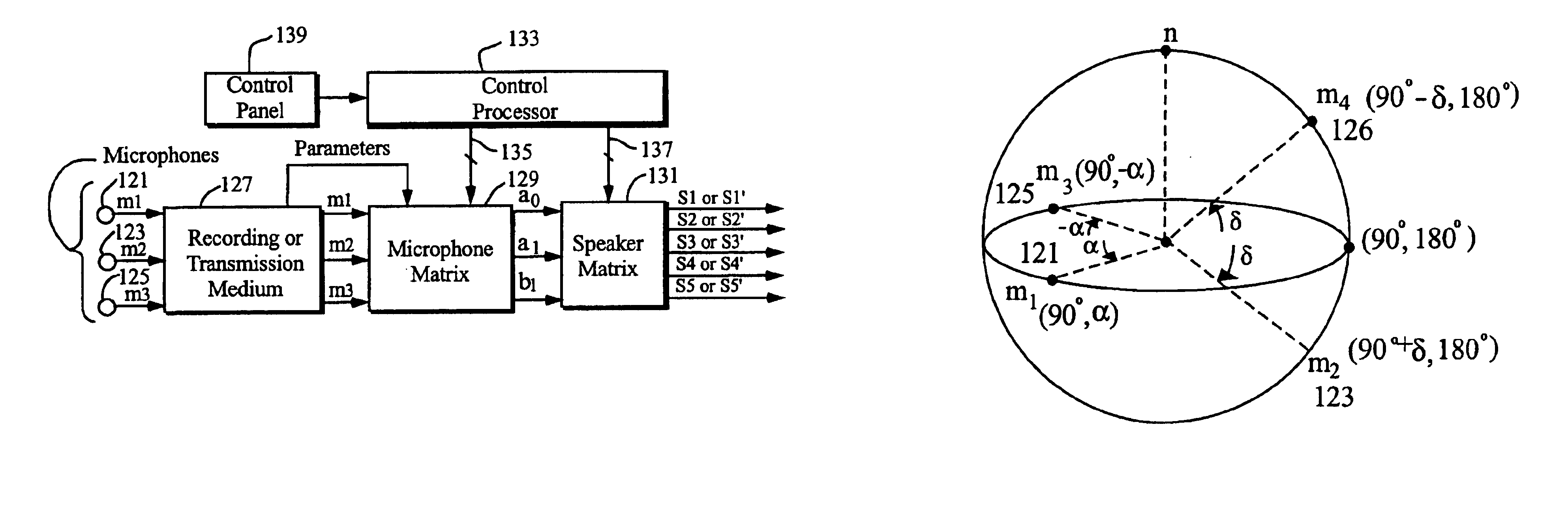
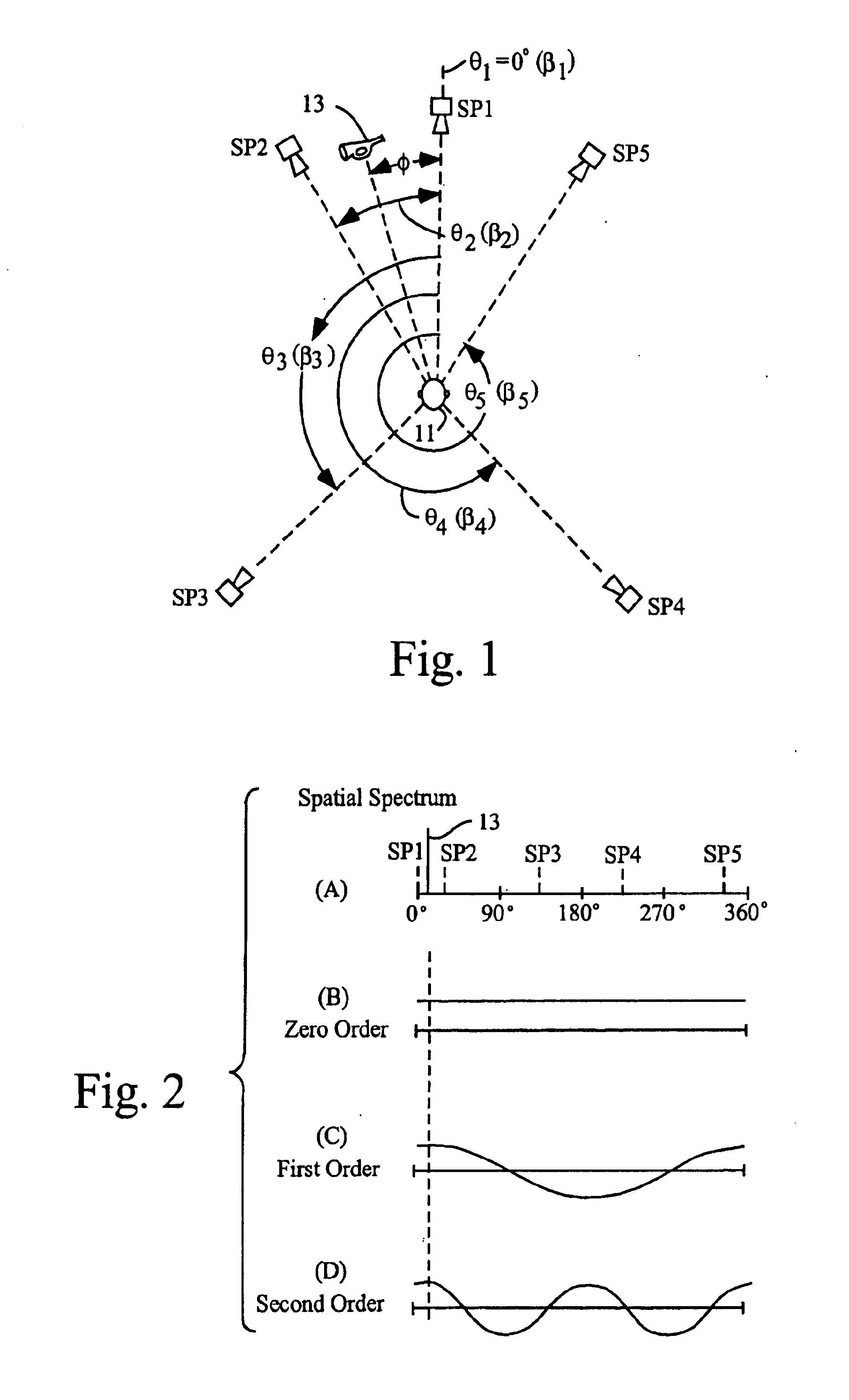
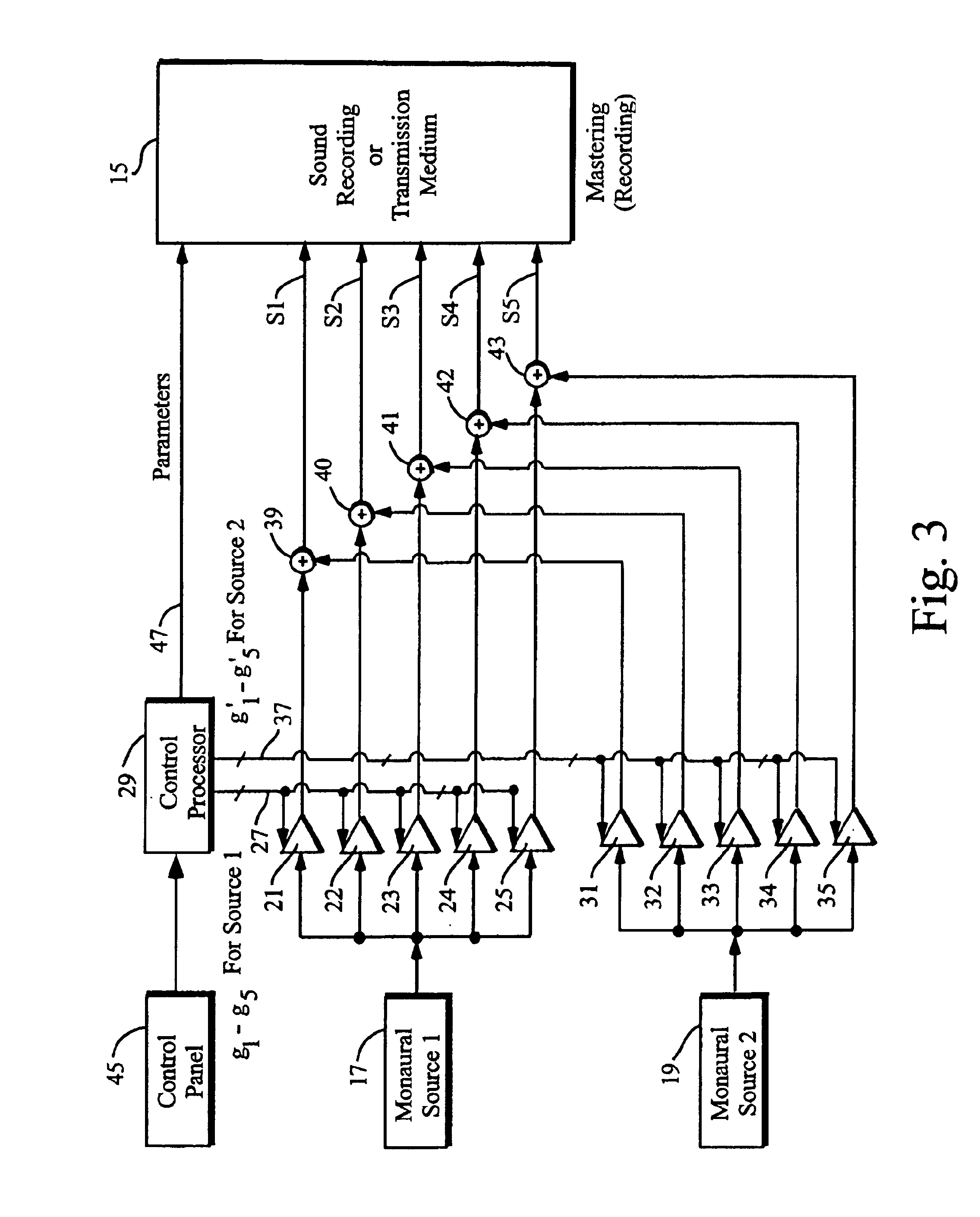
Techniques of making a recording of or transmitting a sound field from either multiple monaural or directional sound signals that reproduce through multiple discrete loud speakers a sound field with spatial harmonics that substantially exactly match those of the original sound field. Monaural sound sources are positioned during mastering to use contributions of all speaker channels in order to preserve the spatial harmonics. If a particular arrangement of speakers is different than what is assumed during mastering, the speaker signals are rematrixed at the home, theater or other sound reproduction location so that the spatial harmonics of the sound field reproduced by the different speaker arrangement match those of the original sound field. An alternative includes recording or transmitting directional microphone signals, or their spatial harmonic components, and then matrixing these signals at the sound reproduction location in a manner that takes into account the specific speaker arrangement. The techniques are described for both a two dimensional sound field and the more general three dimensional case, the latter based upon using spherical harmonics.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES FUND 83 LLC +1
Multi-channel hierarchical audio coding with compact side information
ActiveUS20060233380A1Small sizeMaintain good propertiesBroadcast information characterisationSpeech analysisSide informationComputer science
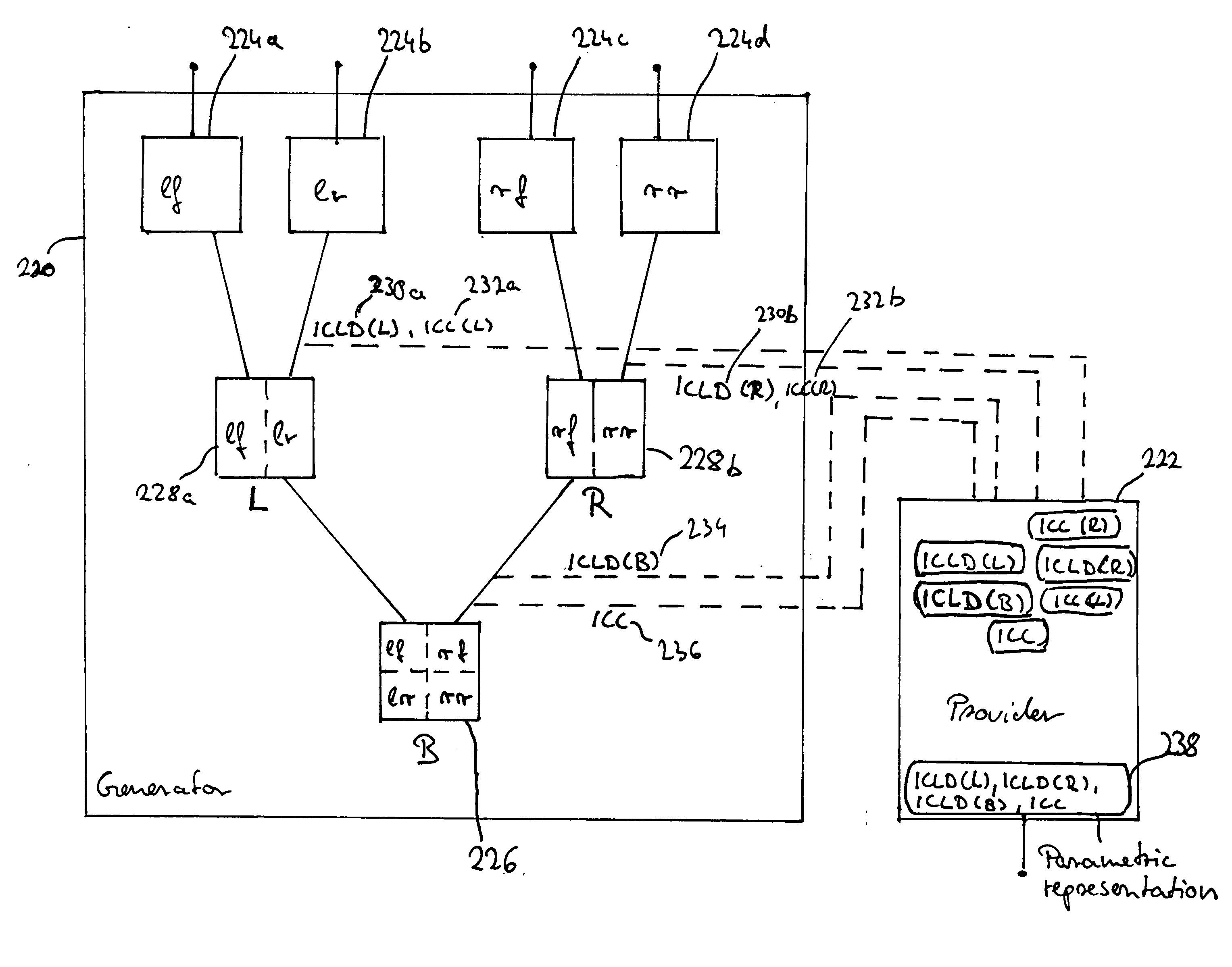
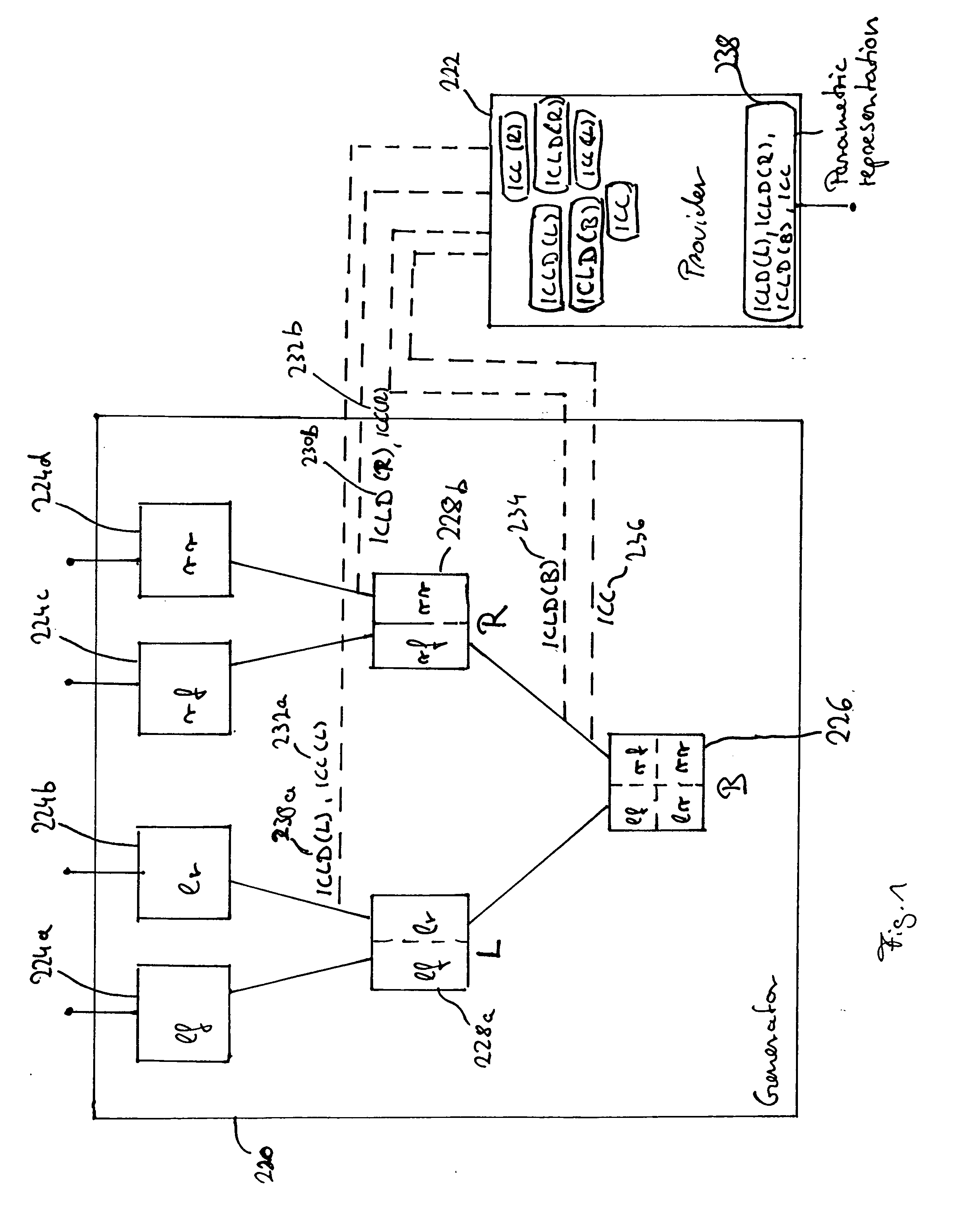
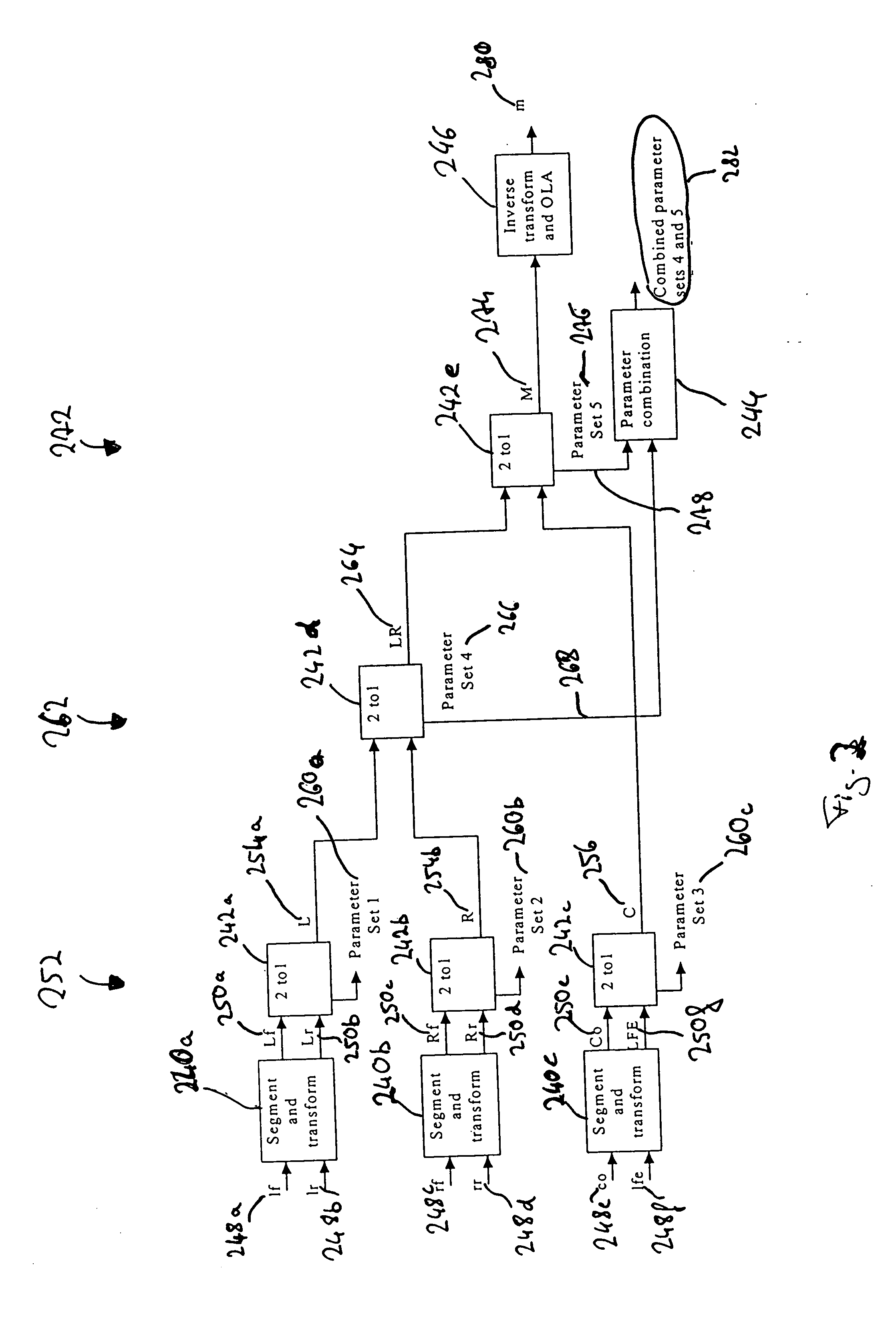
A parametric representation of a multi-channel audio signal describes the spatial properties of the audio signal well with compact side information when a coherence information, describing the coherence between a first and a second channel, is derived within a hierarchical encoding process only for channel pairs including a first channel having only information of a left side with respect to a listening position and including a second channel having only information from a right side with respect to a listening position. As within the hierarchical process the multiple audio channels of the audio signal are downmixed iteratively into monophonic channels, one can pick the relevant parameters from an encoding step involving only channel pairs carrying the information needed to describe the spatial properties of the multi-channel audio signal.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB +2
Systems and methods of spatial image enhancement of a sound source
ActiveUS20050129248A1Good audioAdditional componentBroadcast circuit arrangementsPseudo-stereo systemsSound sourcesVocal tract
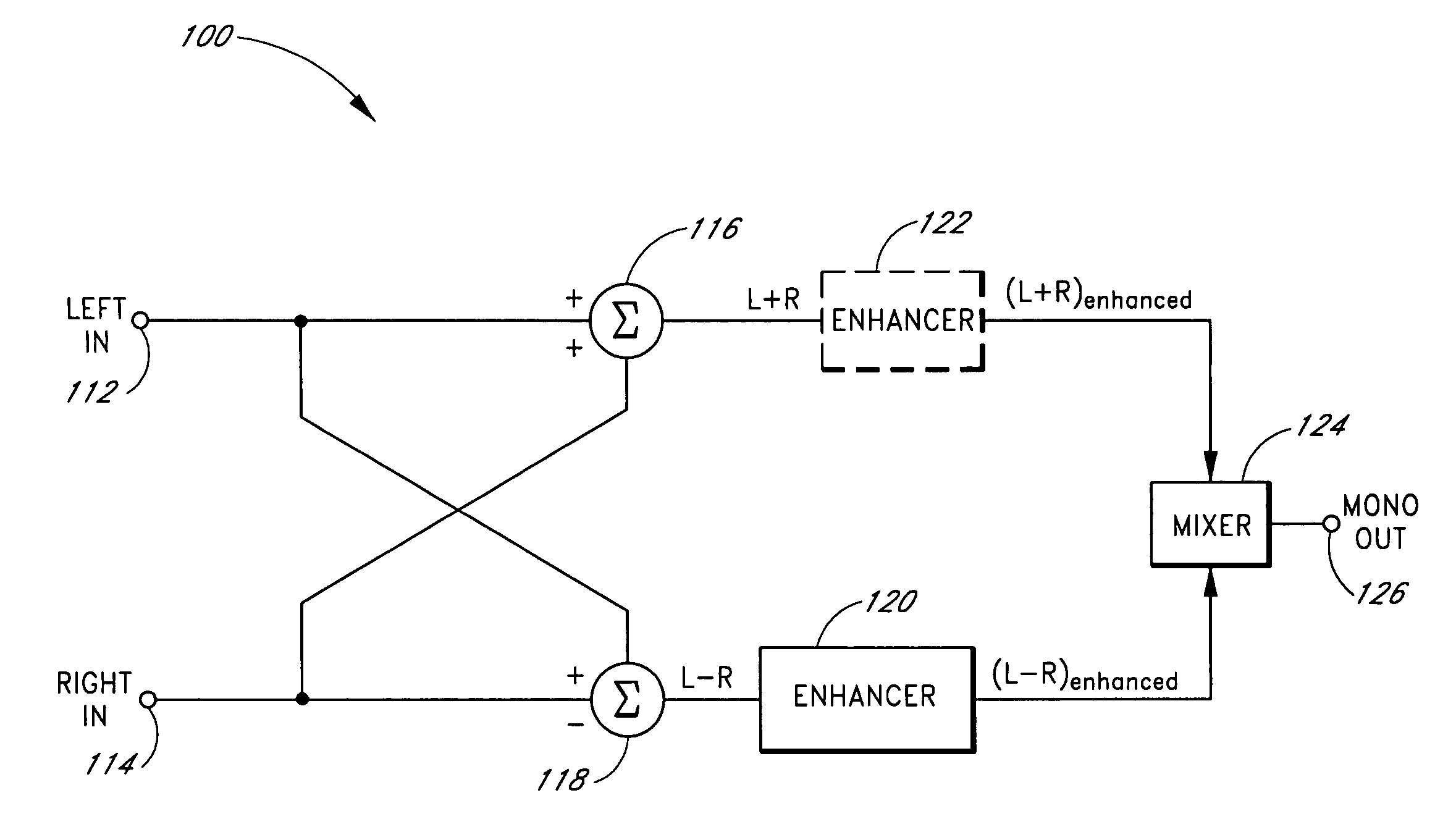
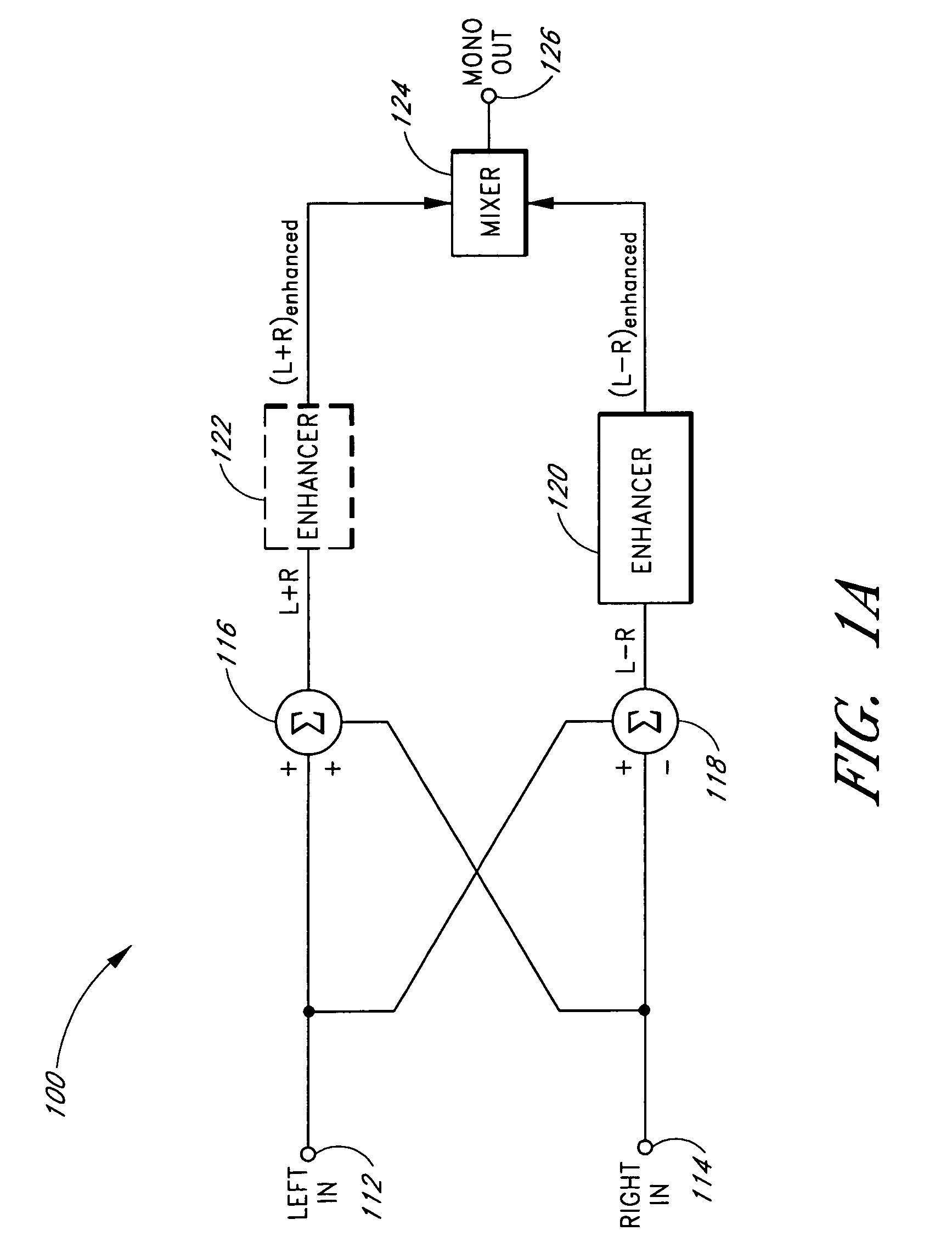
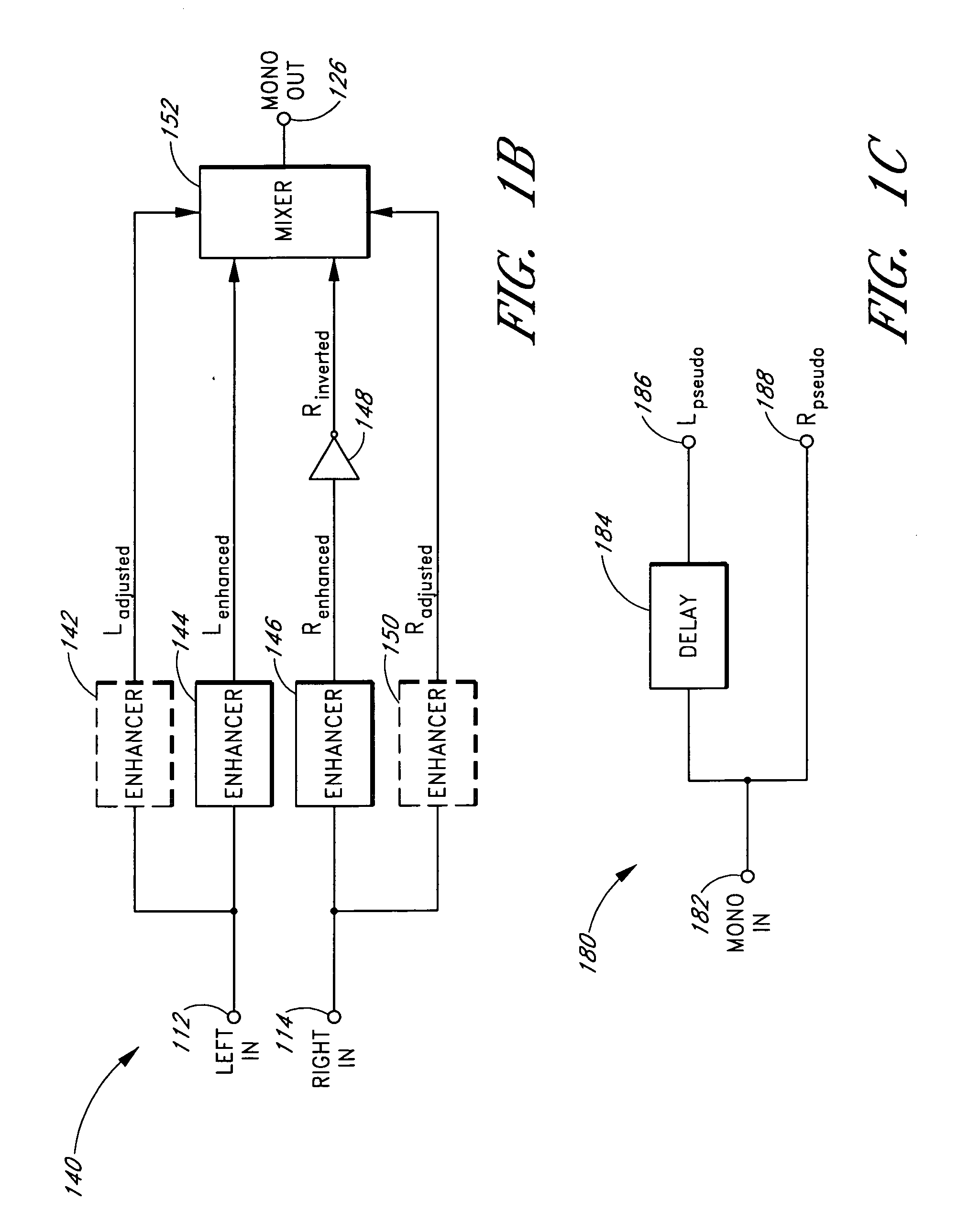
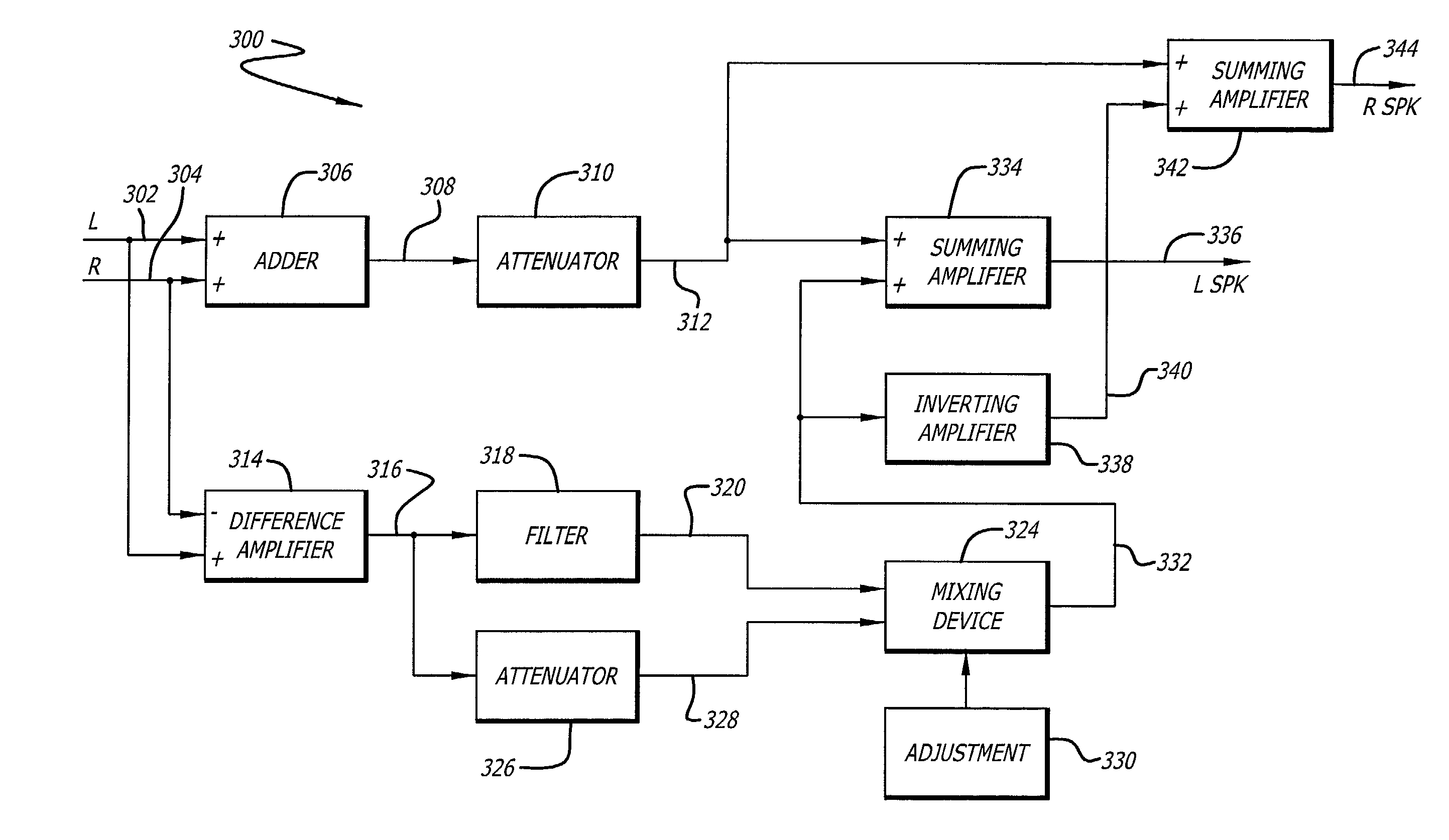
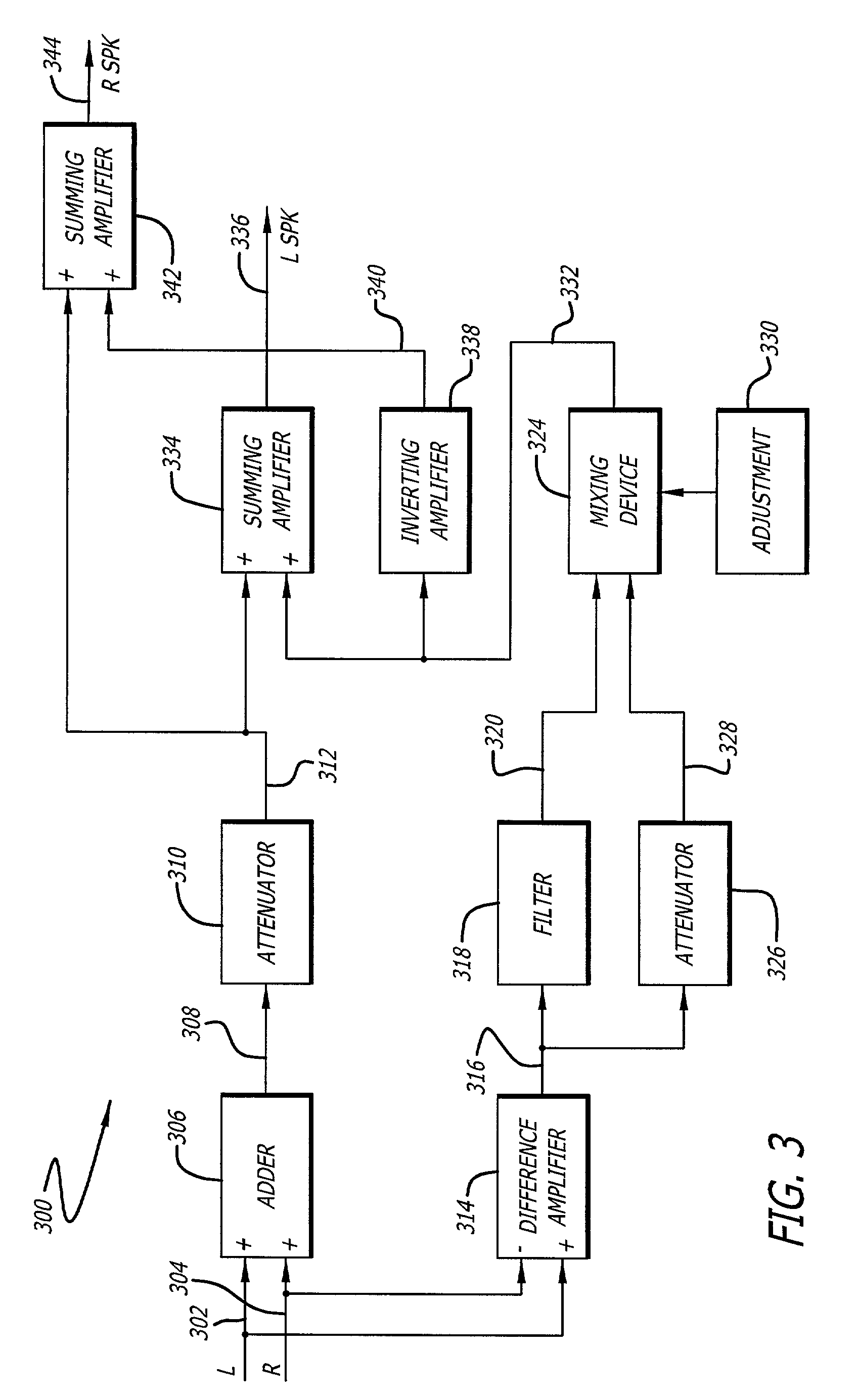
Reproduction of stereophonic audio information over a single speaker requires summing multiple stereo channels. When signals having approximately equal magnitudes and approximately opposite phases at a frequency are added together, the audio information at the frequency is lost. To preserve areas of potential cancellation and potential audio information loss, the audio enhancement system adjusts the phase relationship between the stereophonic channels. To avoid the loss of the spatial content of the stereo signal, the audio enhancement system determines the difference information that exists between different stereophonic channels. The audio enhancement system enhances the difference information and mixes the enhanced difference information with the phase adjusted signals to generate an enhanced monophonic output.
Owner:DTS
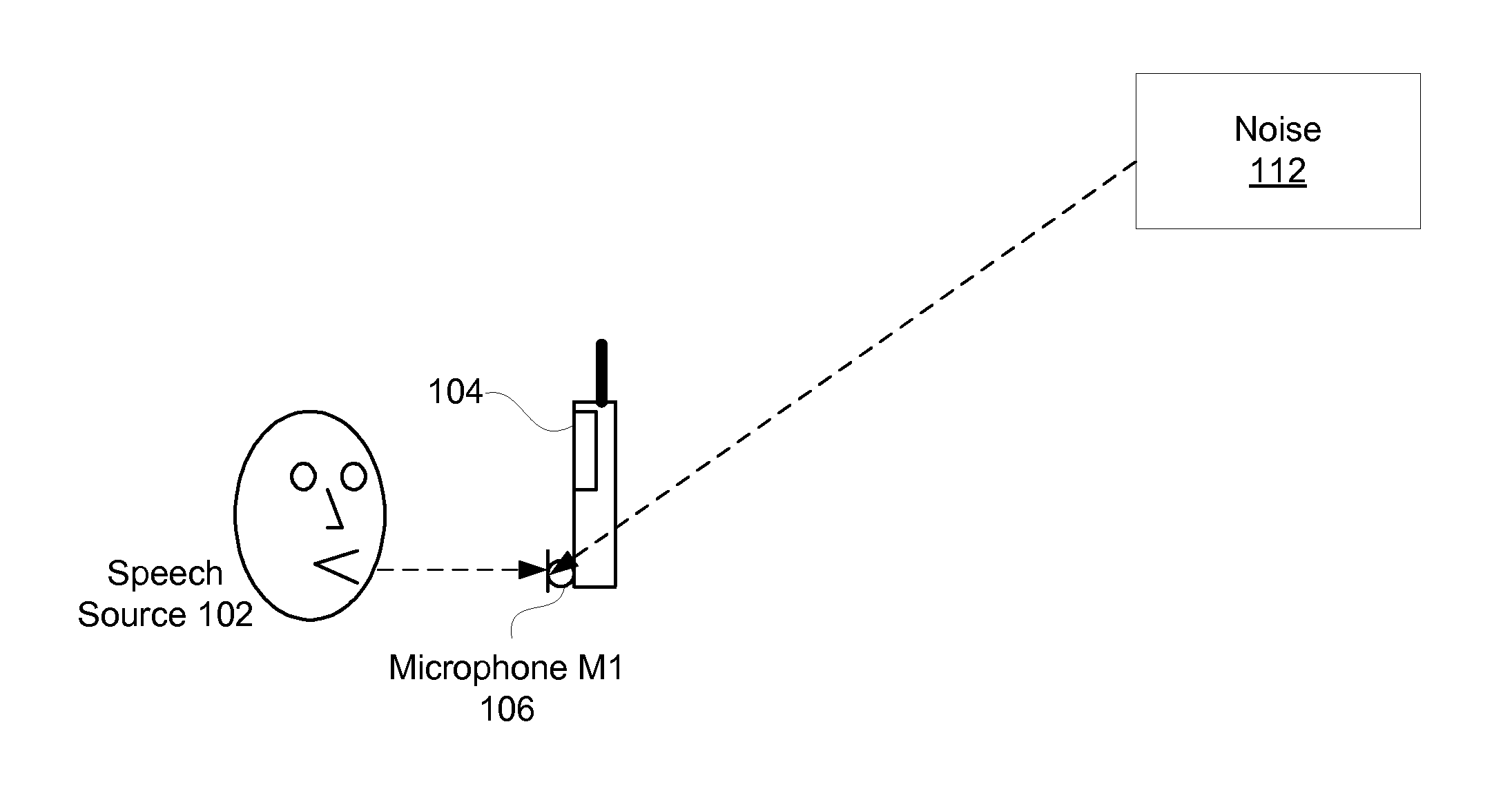
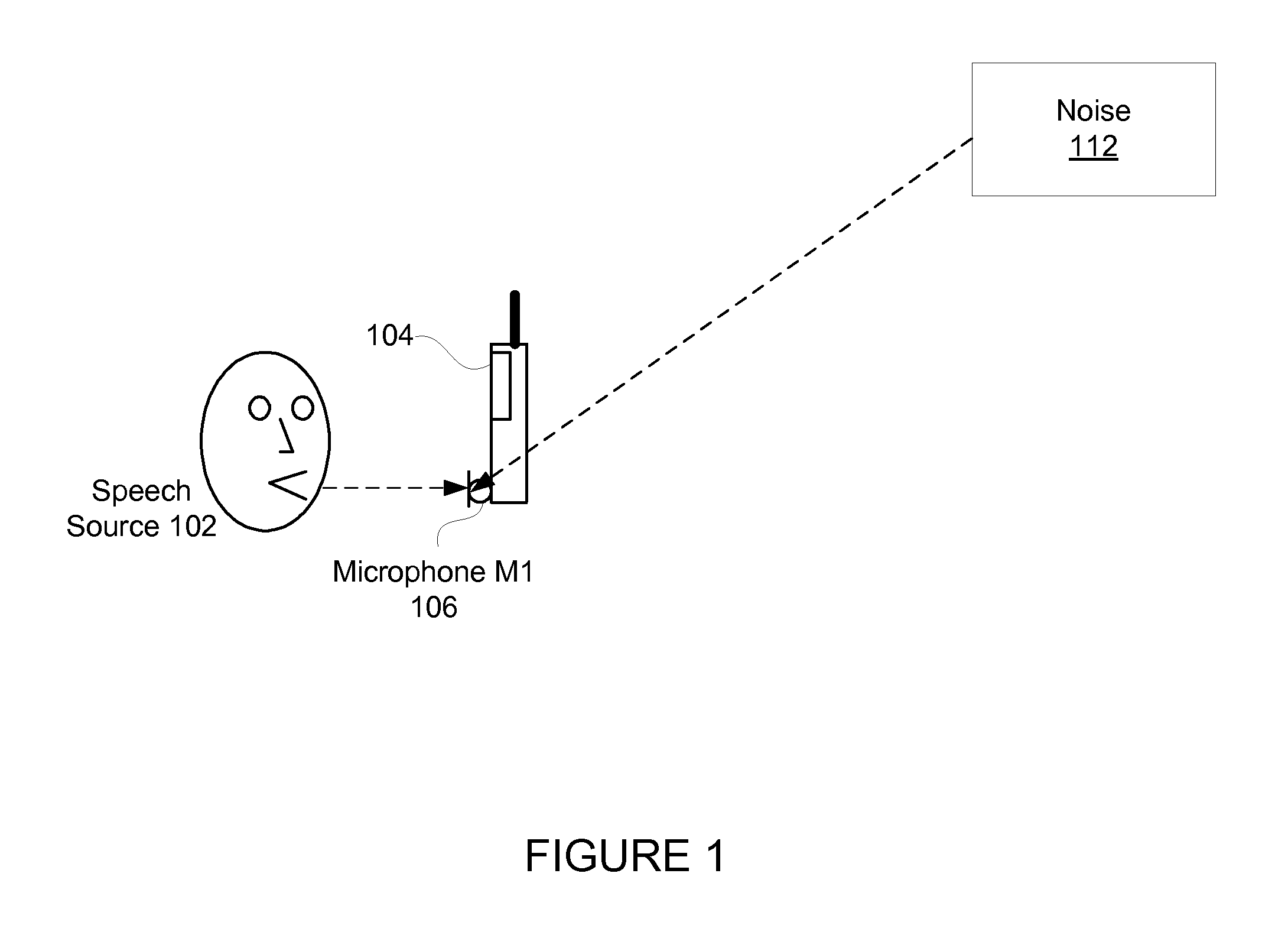
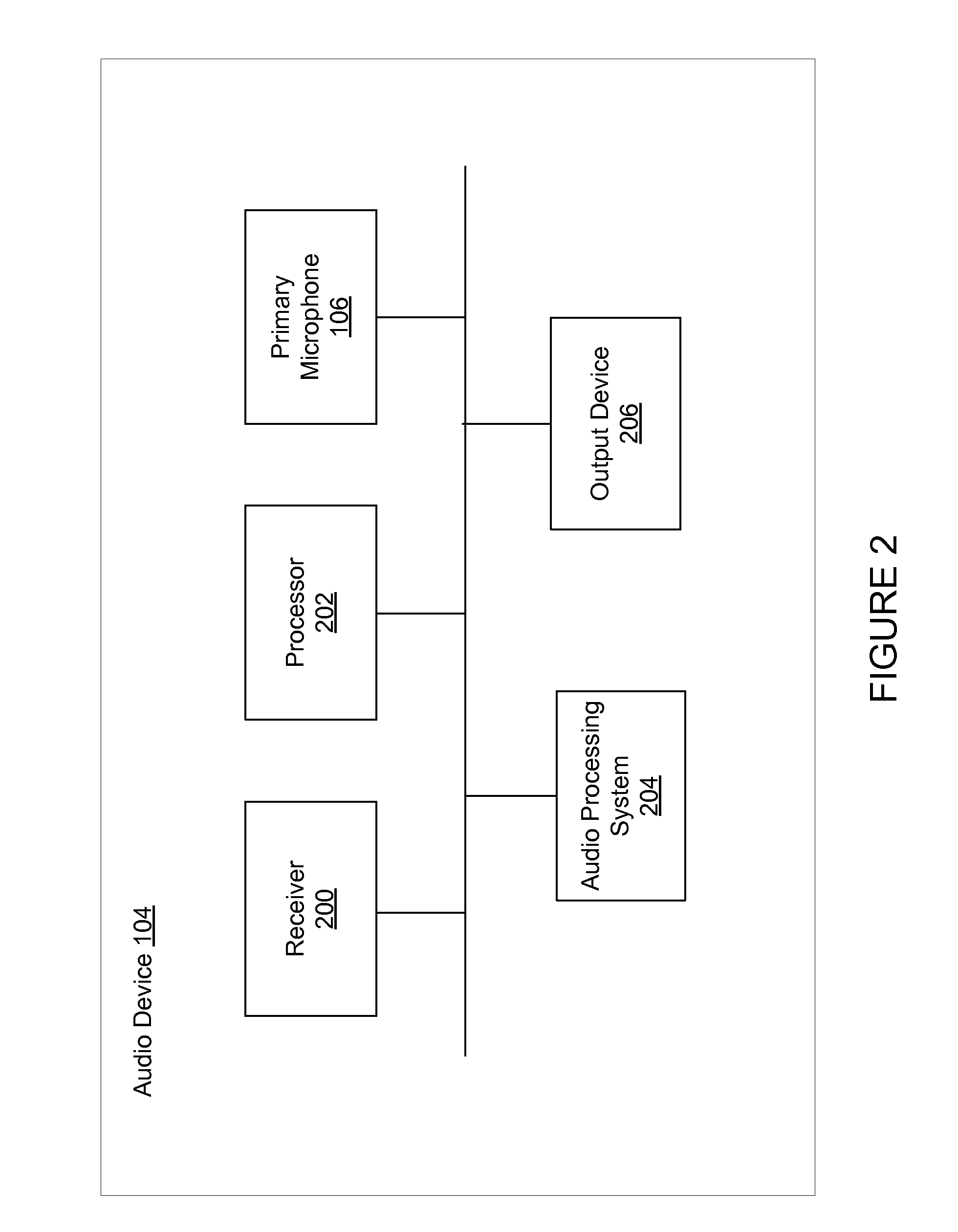
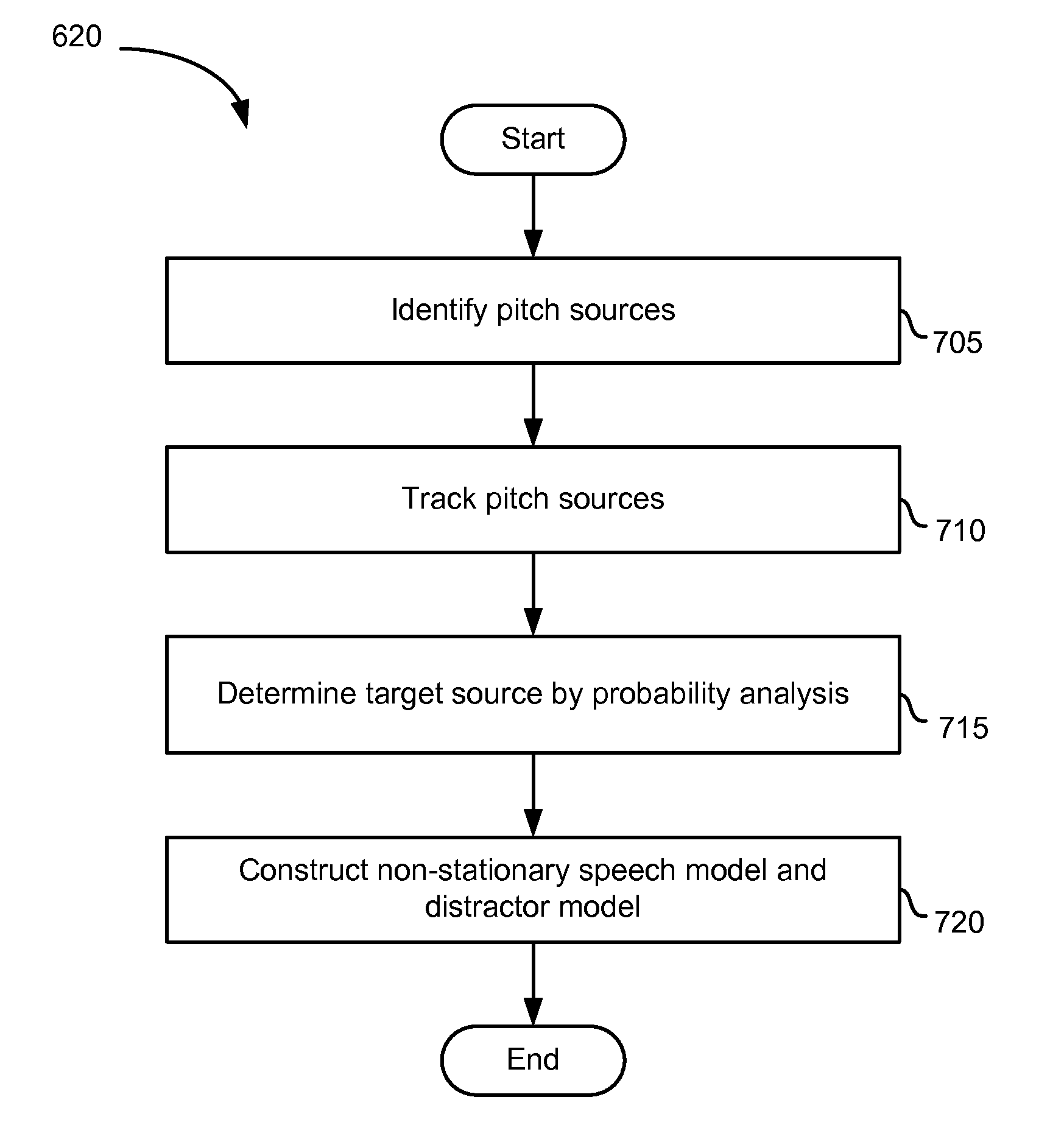
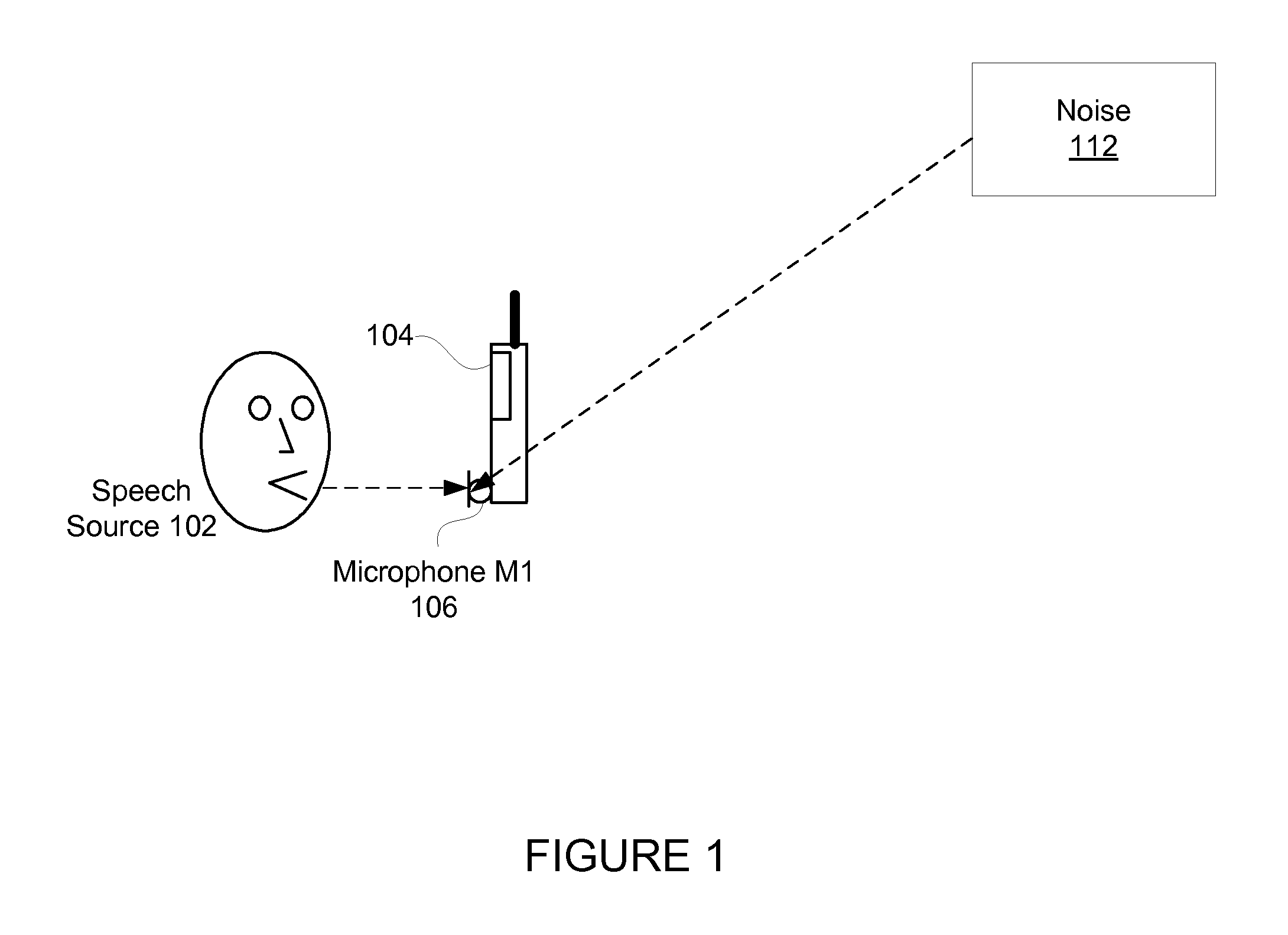
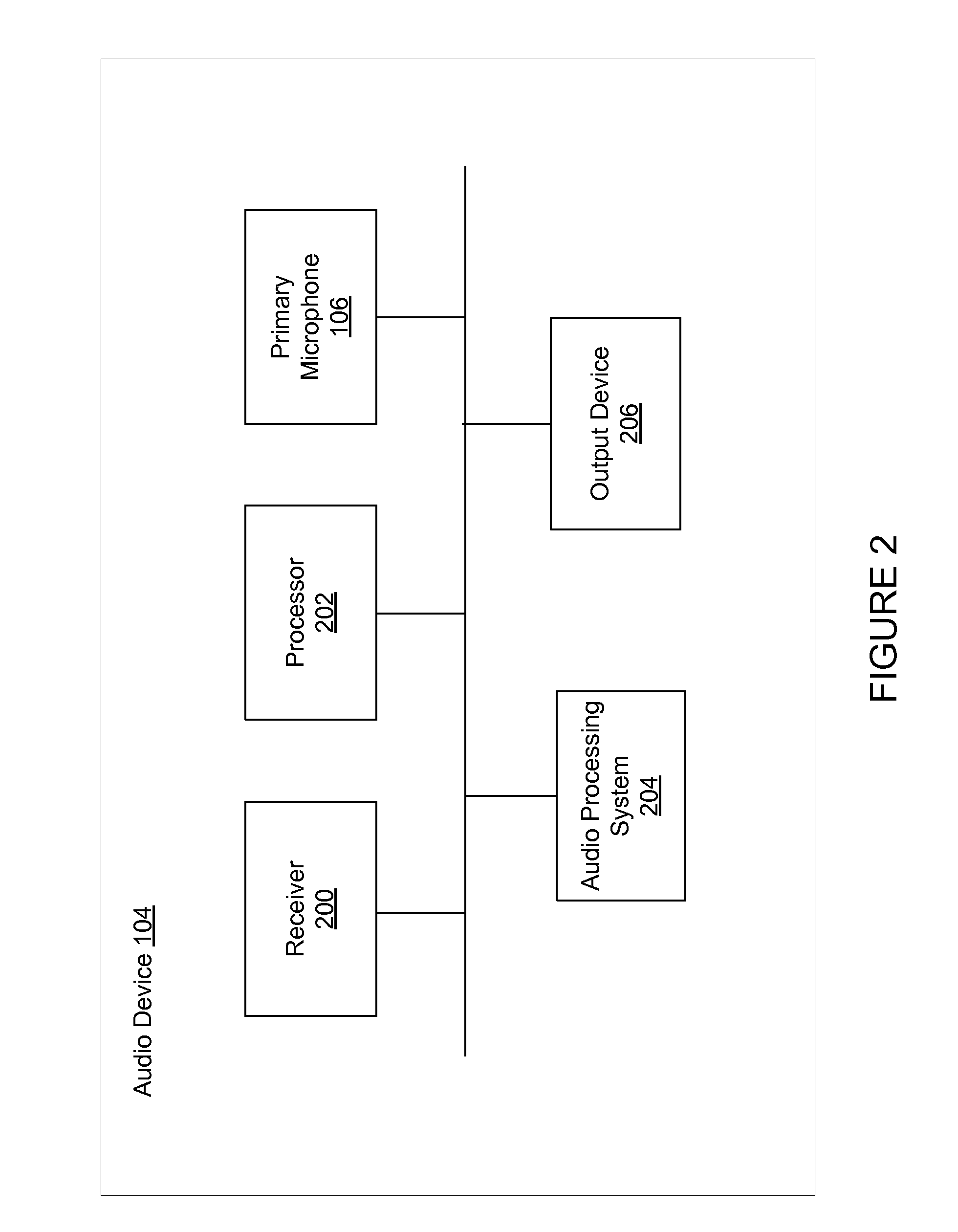
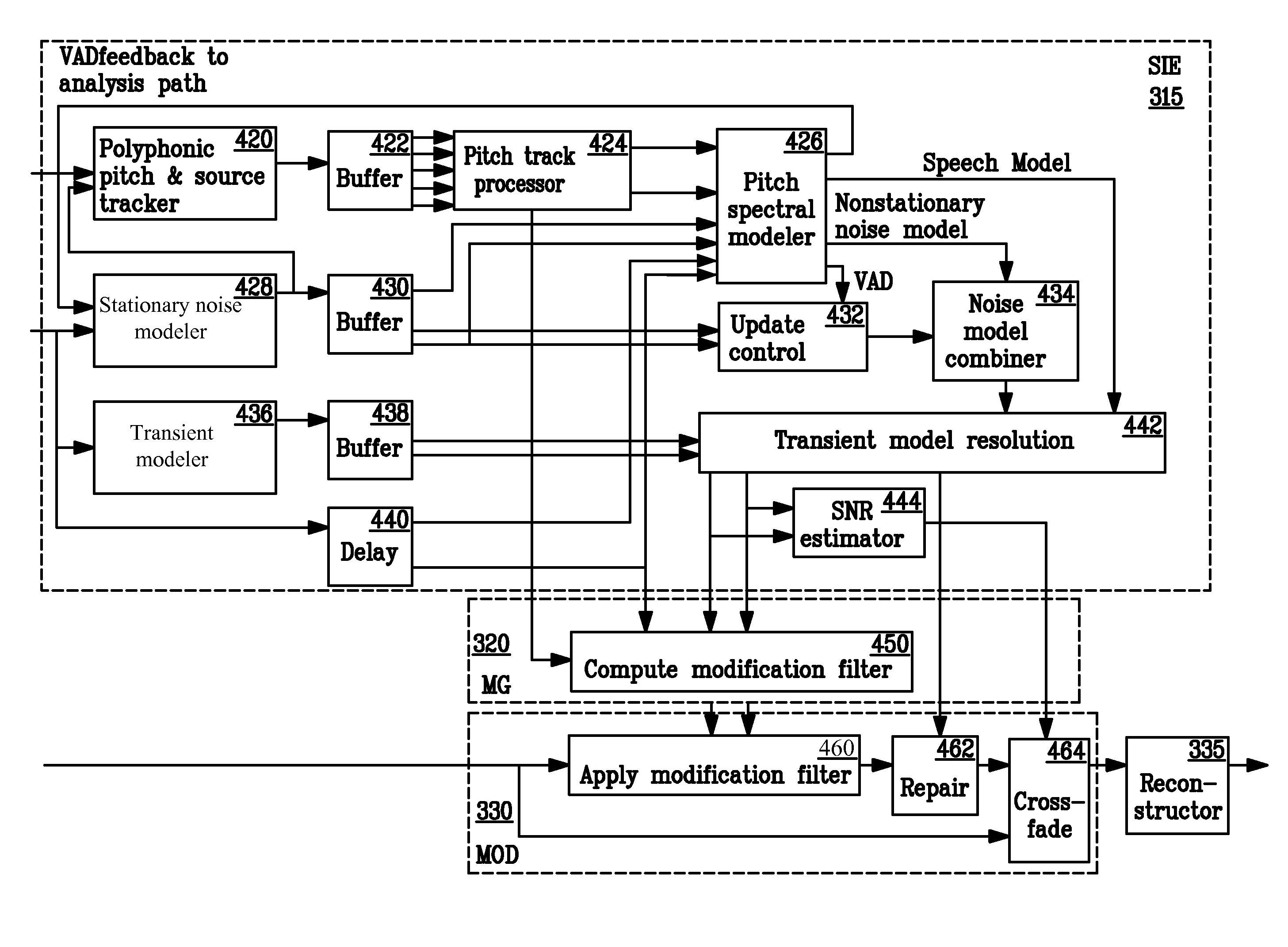
Monaural Noise Suppression Based on Computational Auditory Scene Analysis
The present technology provides a robust noise suppression system which may concurrently reduce noise and echo components in an acoustic signal while limiting the level of speech distortion. An acoustic signal may be received and transformed to cochlear domain sub-band signals. Features such as pitch may be identified and tracked within the sub-band signals. Initial speech and noise models may be then be estimated at least in part from a probability analysis based on the tracked pitch sources. Speech and noise models may be resolved from the initial speech and noise models and noise reduction may be performed on the sub-band signals and an acoustic signal may be reconstructed from the noise-reduced sub-band signals.
Owner:KNOWLES ELECTRONICS INC
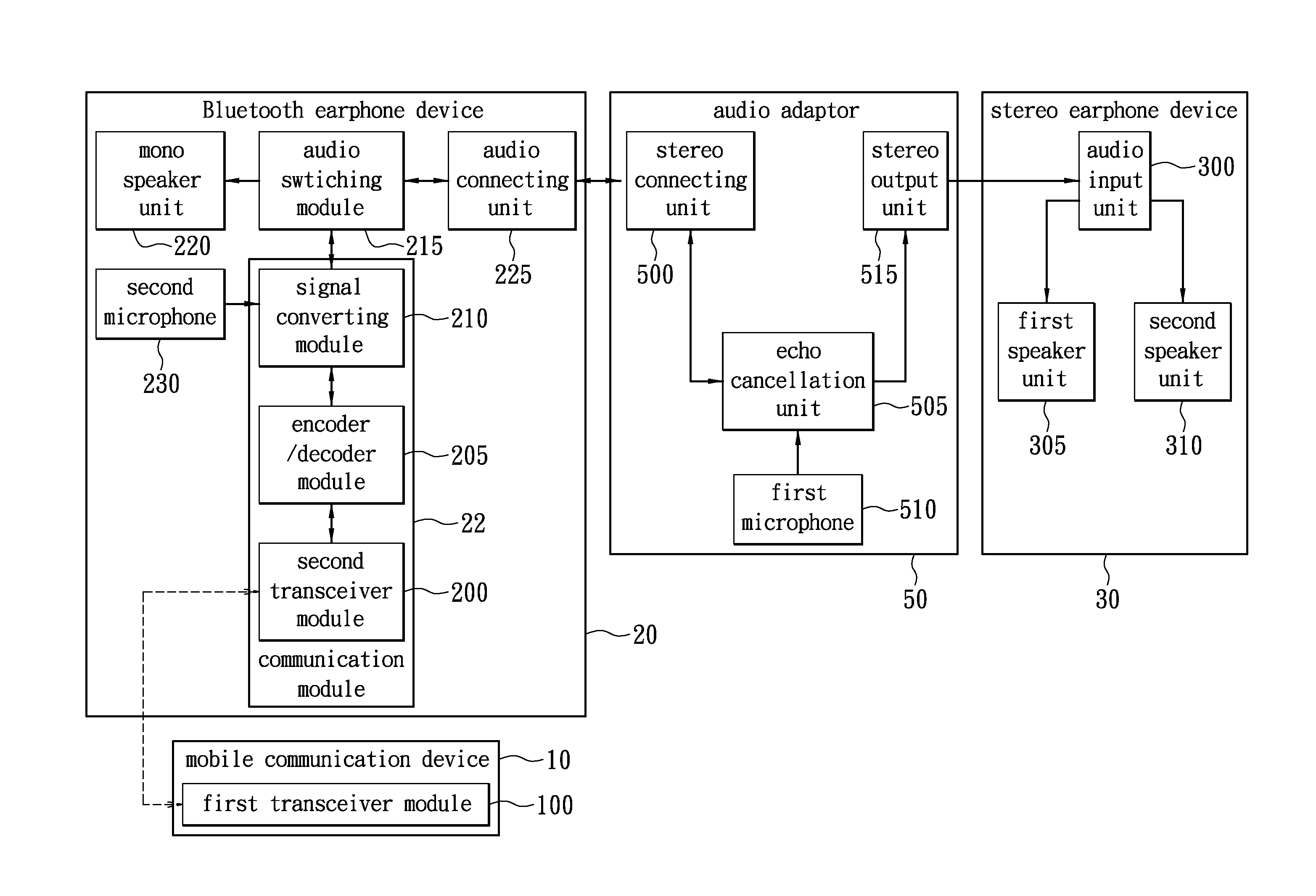
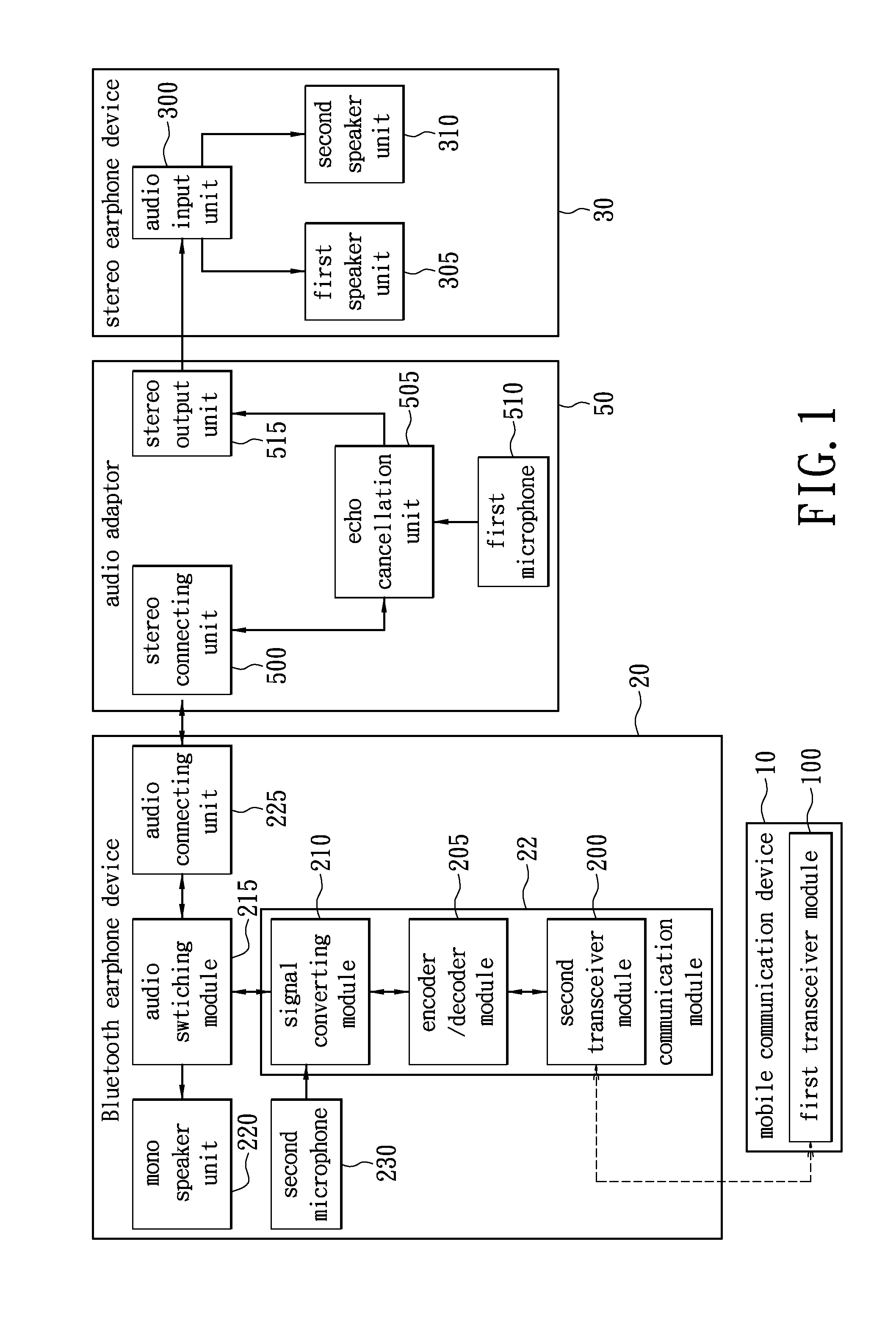
Wireless headset device capable of providing balanced stereo and method thereof
InactiveUS20120243691A1Headphones for stereophonic communicationStereophonic circuit arrangementsBluetoothHeadphones
A wireless earphone device capable of providing balanced stereo. The wireless headset includes a Bluetooth earphone device, an audio adaptor, and a stereo earphone device for giving balanced sounds on both left and right channels. When the Bluetooth earphone device and the stereo earphone device are connected with the audio adaptor respectively, an audio switching module of the Bluetooth earphone device determines to transmit stereo audio signal with first channel signal and second channel signal to the stereo earphone device through the audio adaptor. Otherwise, only one channel of the stereo audio signal is transmitted from the audio switching module to a mono speaker unit on the Bluetooth earphone device.
Owner:SURE BEST
Parametric stereo upmix apparatus, a parametric stereo decoder, a parametric stereo downmix apparatus, a parametric stereo encoder
ActiveUS20110096932A1Improve audio qualityQuality of left and rightSpeech analysisPseudo-stereo systemsPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
A parametric stereo upmix apparatus (300, 400) generating a left signal (206) and a right signal (207) from a mono downmix signal (204) based on spatial parameters (205). Said parametric stereo upmix being characterized in that it comprises a means (310) for predicting a difference signal (311) comprising a difference between the left signal (206) and the right signal (207) based on the mono downmix signal (204) scaled with a prediction coefficient (321). Said prediction coefficient is derived from the spatial parameters (205). Said parametric stereo upmix apparatus (300, 400) further comprises an arithmetic means (330) for deriving the left signal (206) and the right signal (207) based on a sum and a difference of the mono downmix signal (204) and said difference signal (311).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
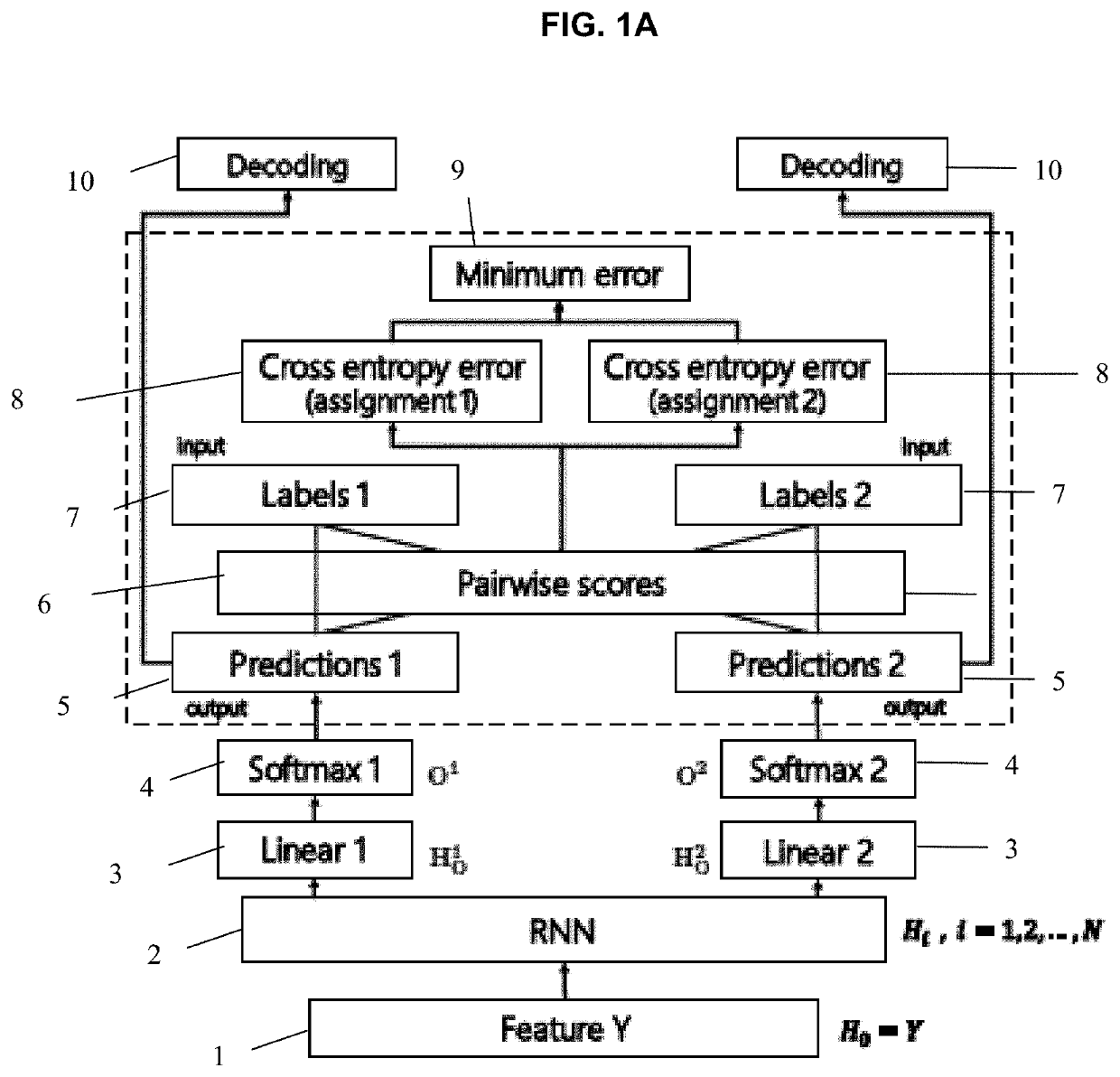
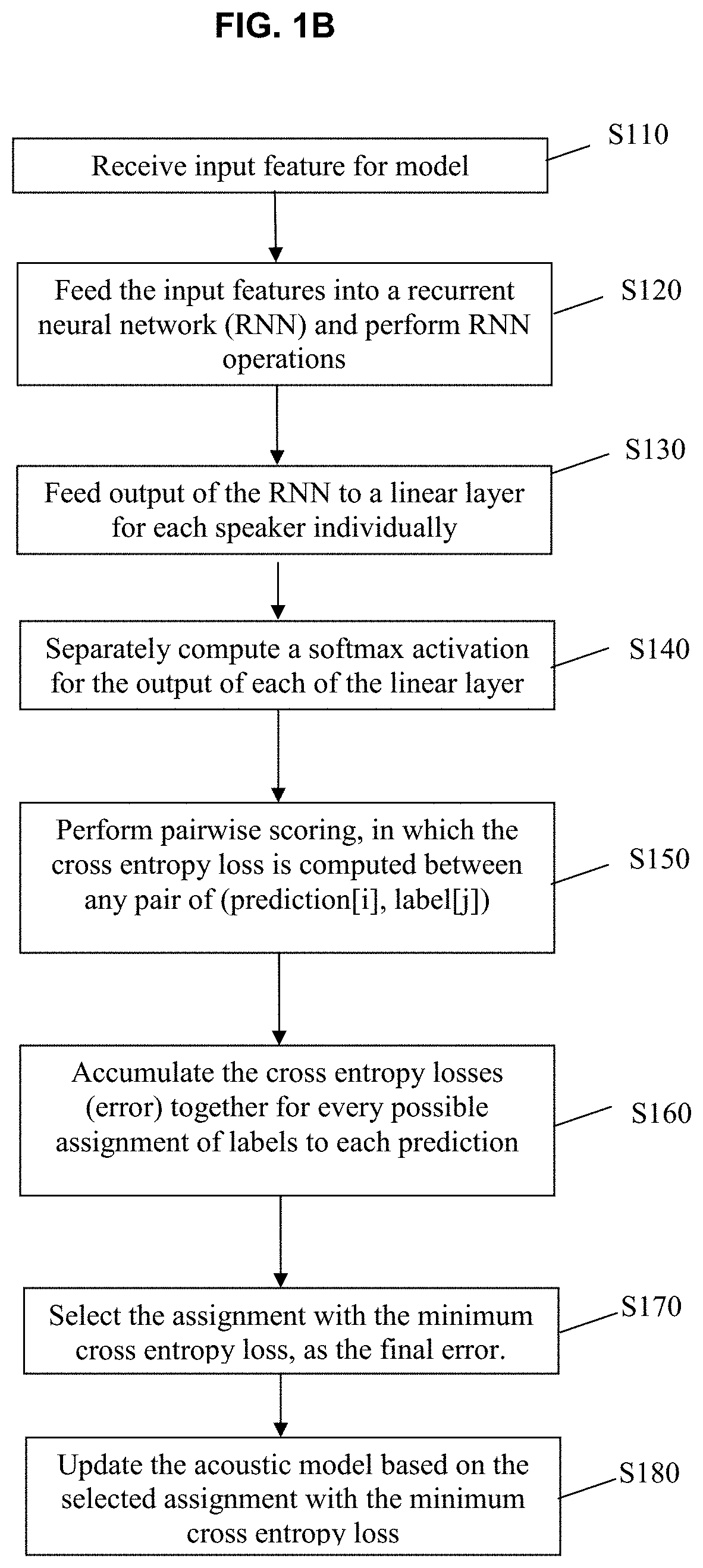
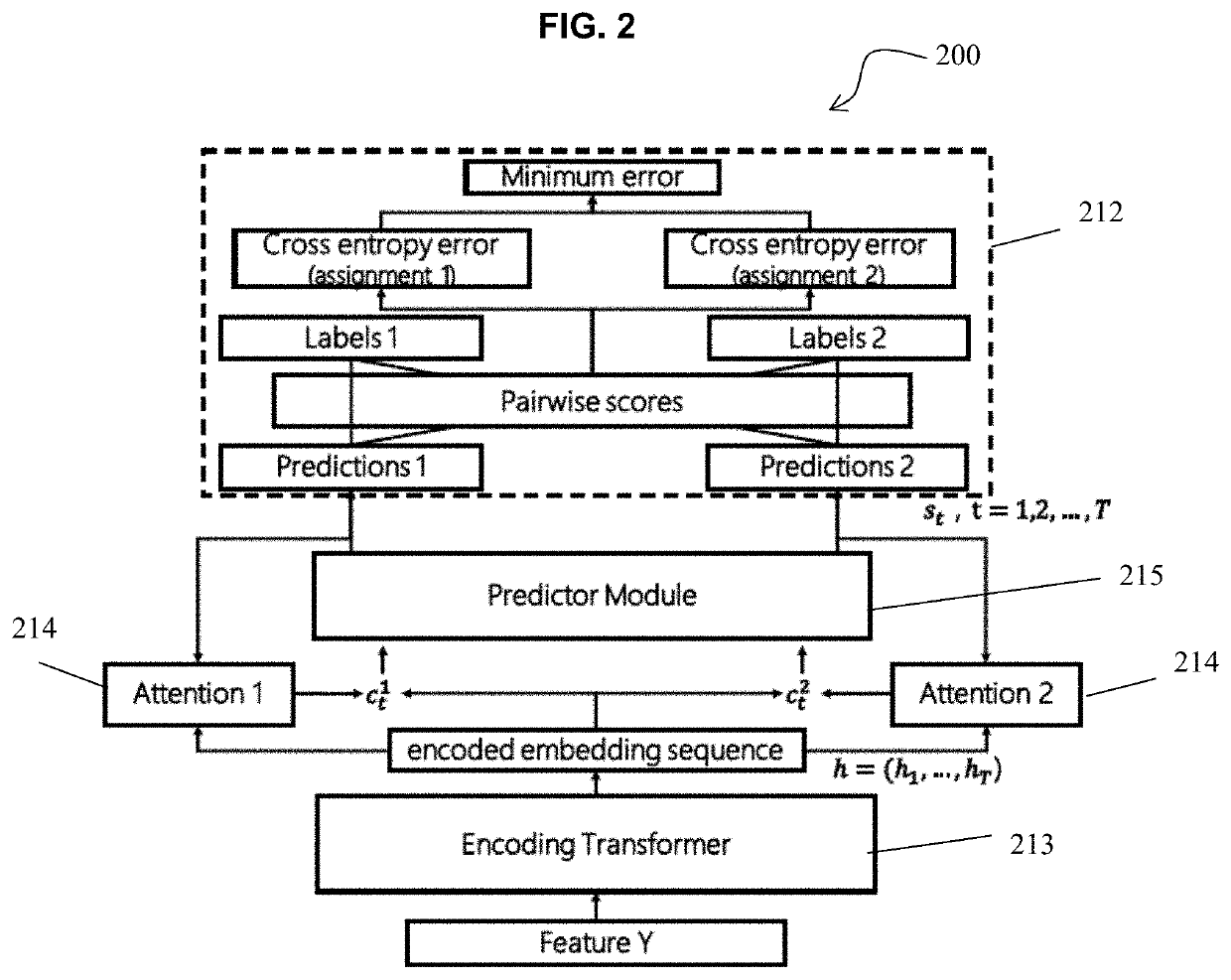
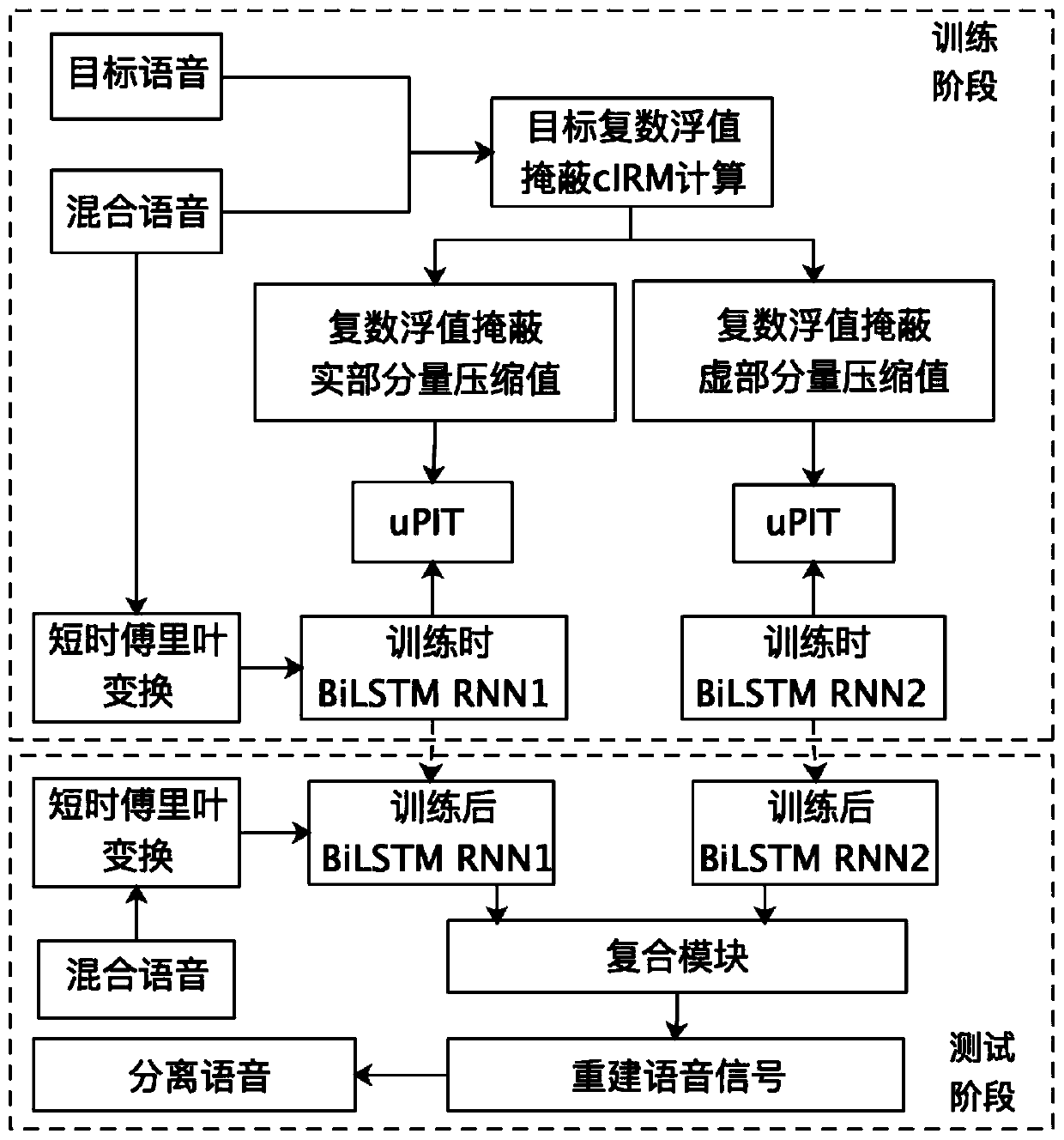
Monaural multi-talker speech recognition with attention mechanism and gated convolutional networks
Provided are a speech recognition training processing method and an apparatus including the same. The speech recognition training processing method includes acquiring multi-talker mixed speech sequence data corresponding to a plurality of speakers, encoding the multi-speaker mixed speech sequence data into an embedded sequence data, generating speaker specific context vectors at each frame based on the embedded sequence, generating senone posteriors for each of the speaker based on the speaker specific context vectors and updating an acoustic model by performing permutation invariant training (PIT) model training based on the senone posteriors.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Apparatus and method for producing sound
InactiveUS20060023898A1Improve soundLow costElectrophonic musical instrumentsBending wave transducersPianoVocal tract
A sound reproduction method and apparatus utilizes both distributed mode and pistonic loudspeakers which are simultaneously driven over frequency ranges which at least partially overlap, for enhancing the spaciousness of the sound produced. The disclosure includes monophonic, stereophonic and multi-channel sound reproduction systems and electronic musical instruments such as digital pianos.
Owner:KATZ SHELLEY
Monaural noise suppression based on computational auditory scene analysis
Owner:KNOWLES ELECTRONICS INC
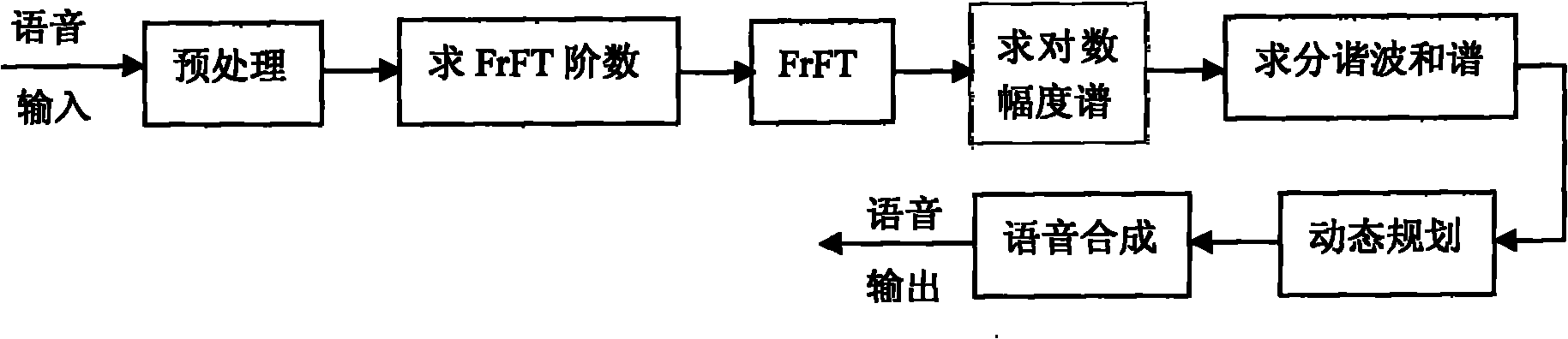
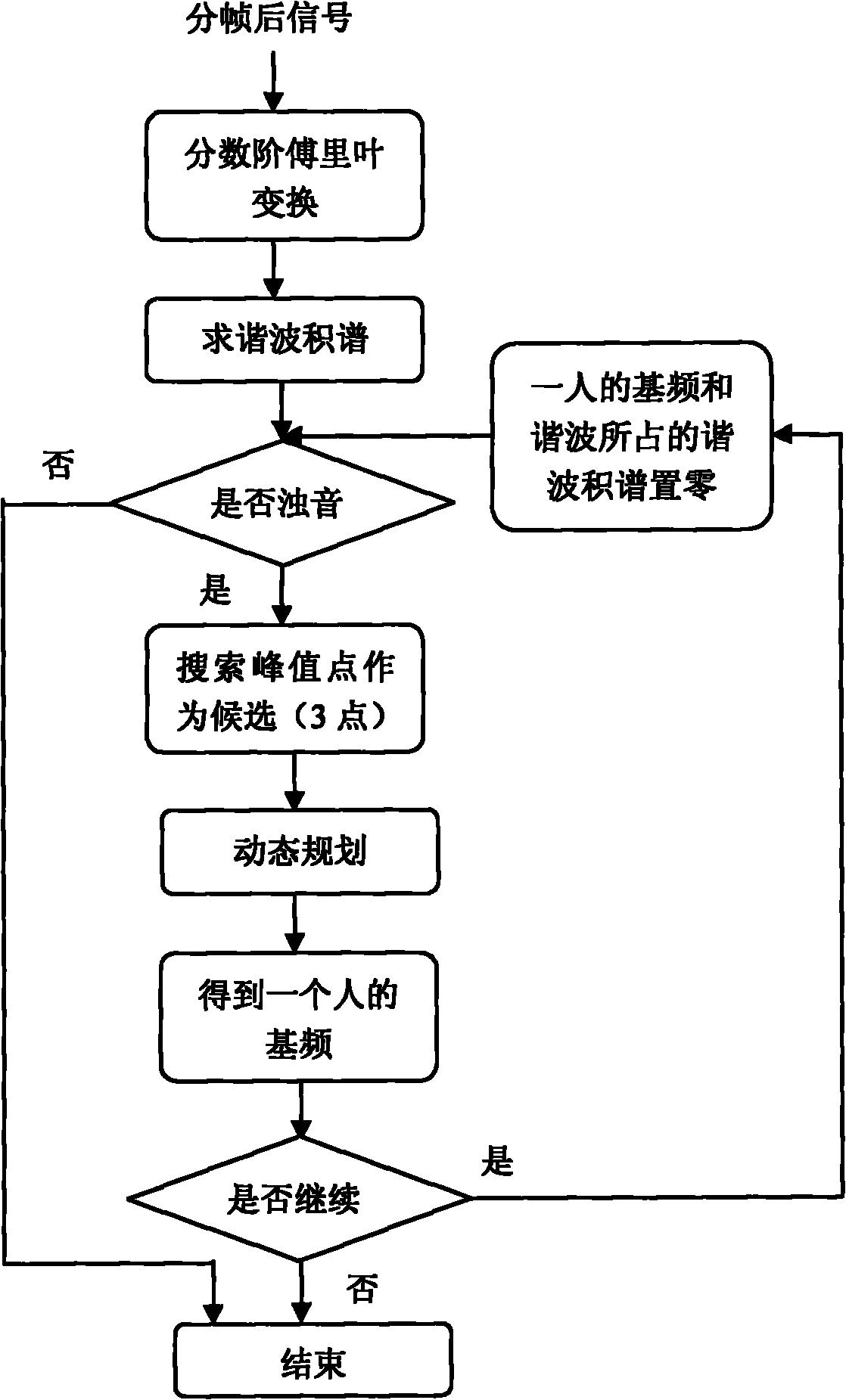
Method for separating monaural overlapping speeches based on fractional Fourier transform (FrFT)
The invention relates to a method for separating monaural overlapping speeches based on fractional Fourier transform (FrFT), which belongs to the technical field of audio signal processing. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, preprocessing overlapping speech signals so as to remove mute-section signals of the overlapping speech signals and find out sonant frames; then, carrying out pitch detection on sonant-frame signals based on FrFT so as to separate the fundamental frequencies of the overlapping speeches; and finally, integrating the fundamental frequencies with a sinusoidal model of speech signals so as to synthesize speeches, thereby obtaining each speech signal subjected to separation. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the fundamental frequencies of a plurality of overlapping speeches can be separated and extracted effectively, and finally, the effective separation of the overlapping speeches can be realized; and the pitch frequencies are extracted based on FrFT instead of traditional fast Fourier transform (FFT), thereby reducing the extension of a harmonic frequency spectrum and then obtaining more accurate fundamental frequencies of original signals. The method provided by the invention is especially suitable for the separation of monaural overlapping speeches containing speeches of two persons.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
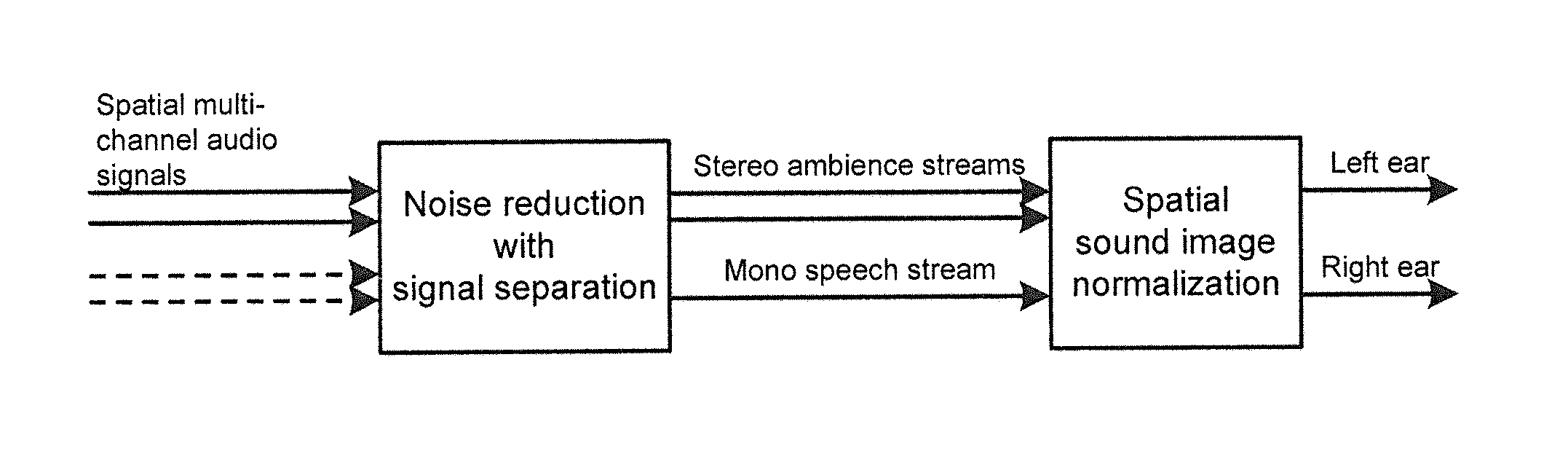
Method and apparatus for communicating with audio signals having corresponding spatial characteristics
ActiveUS20140247945A1Promotes its utilizationEasy to deployStereophonic circuit arrangementsSpeech analysisVirtual positionAudio signal flow
A method, apparatus computer program product are provided to facilitate the utilization of the spatial position of audio signals in order to improve voice quality. In the context of a method, a main mono signal is determined from one or more audio signals that were received. The method also includes determining one or more ambience signals from the one or more audio signals that were received, such as following removal of the main mono signal therefrom. The method also adjusts at least one of a virtual position of the main mono signal for provision to a recipient device or the one or more ambience signals for provision to the recipient device.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
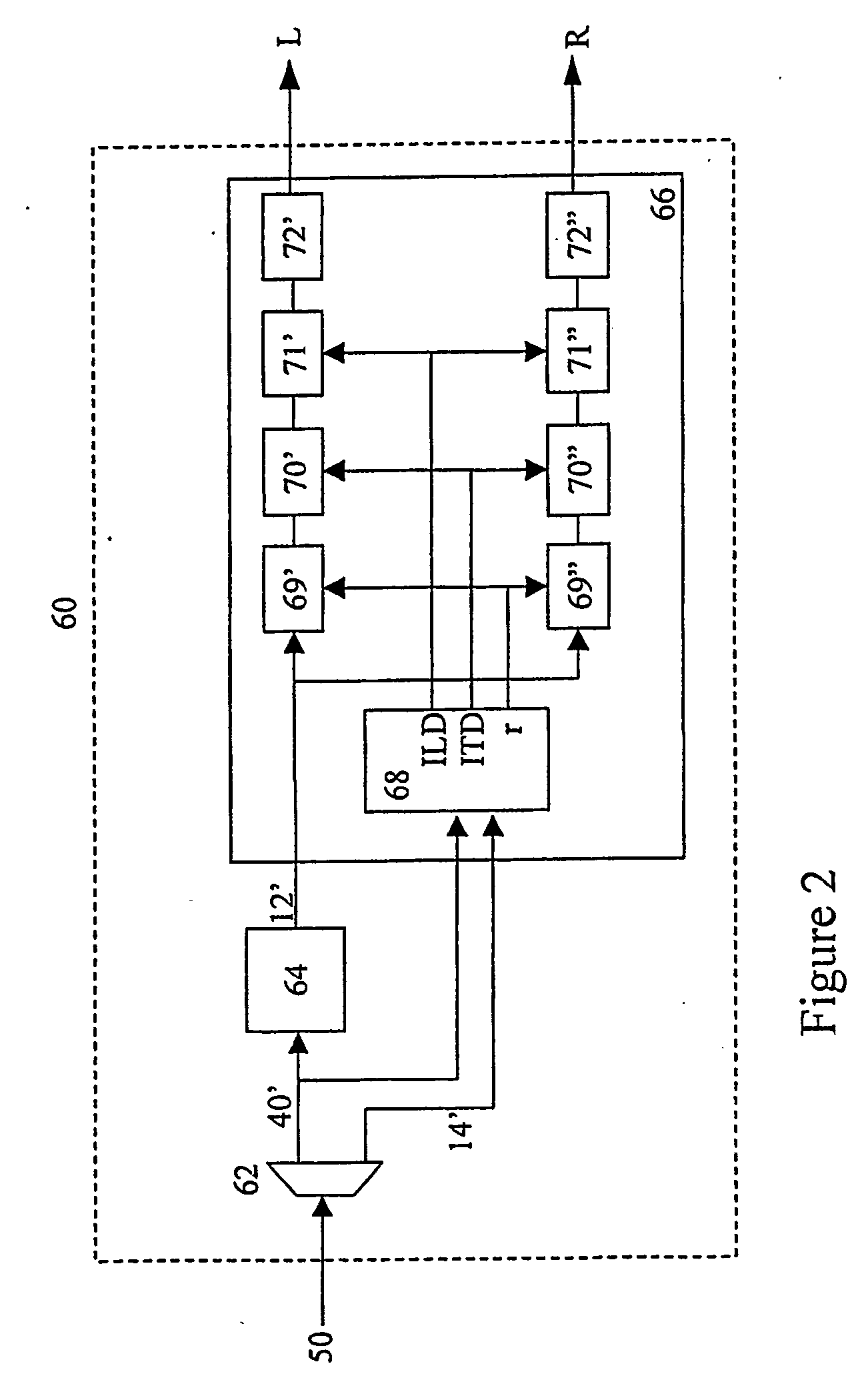
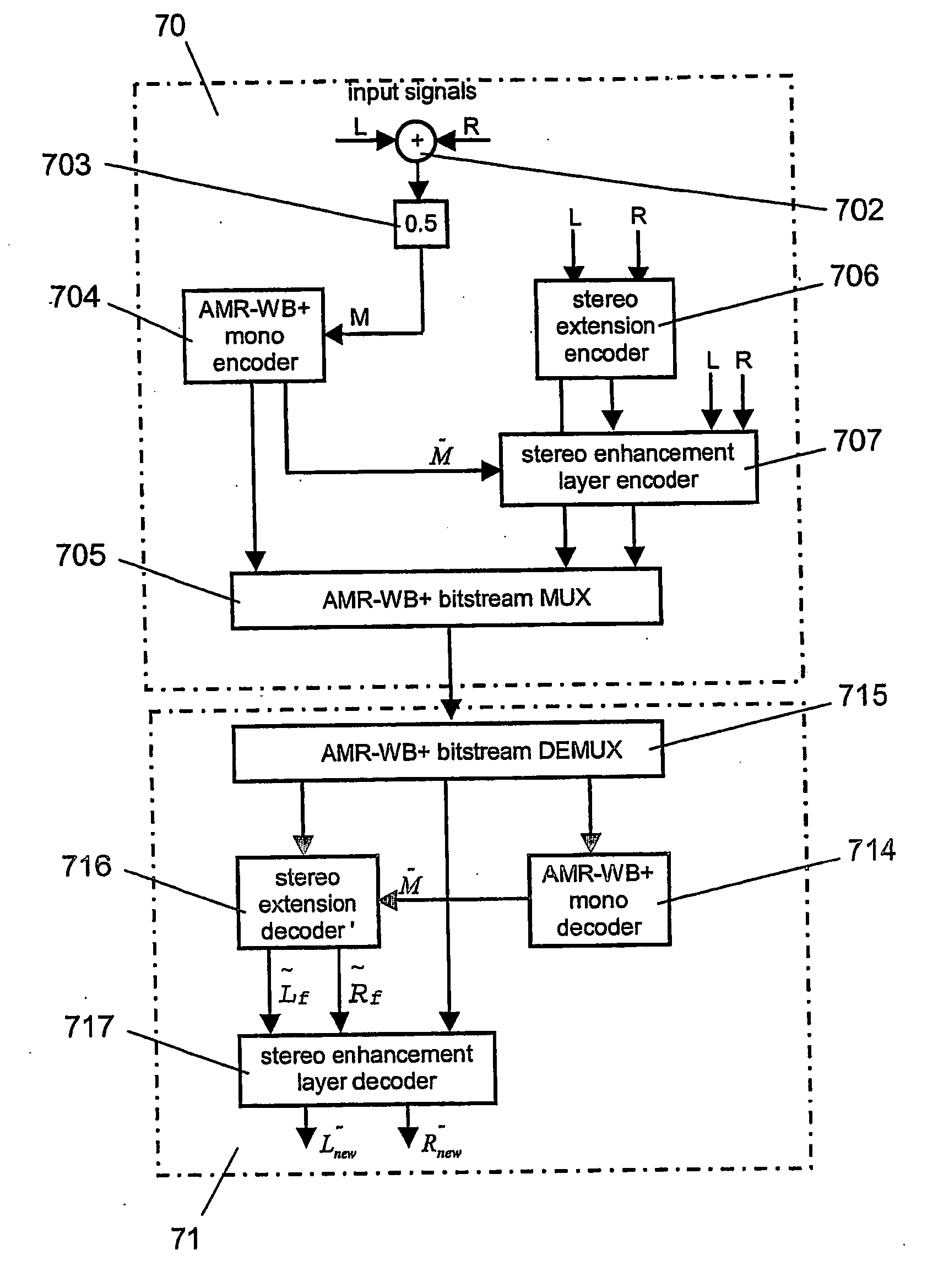
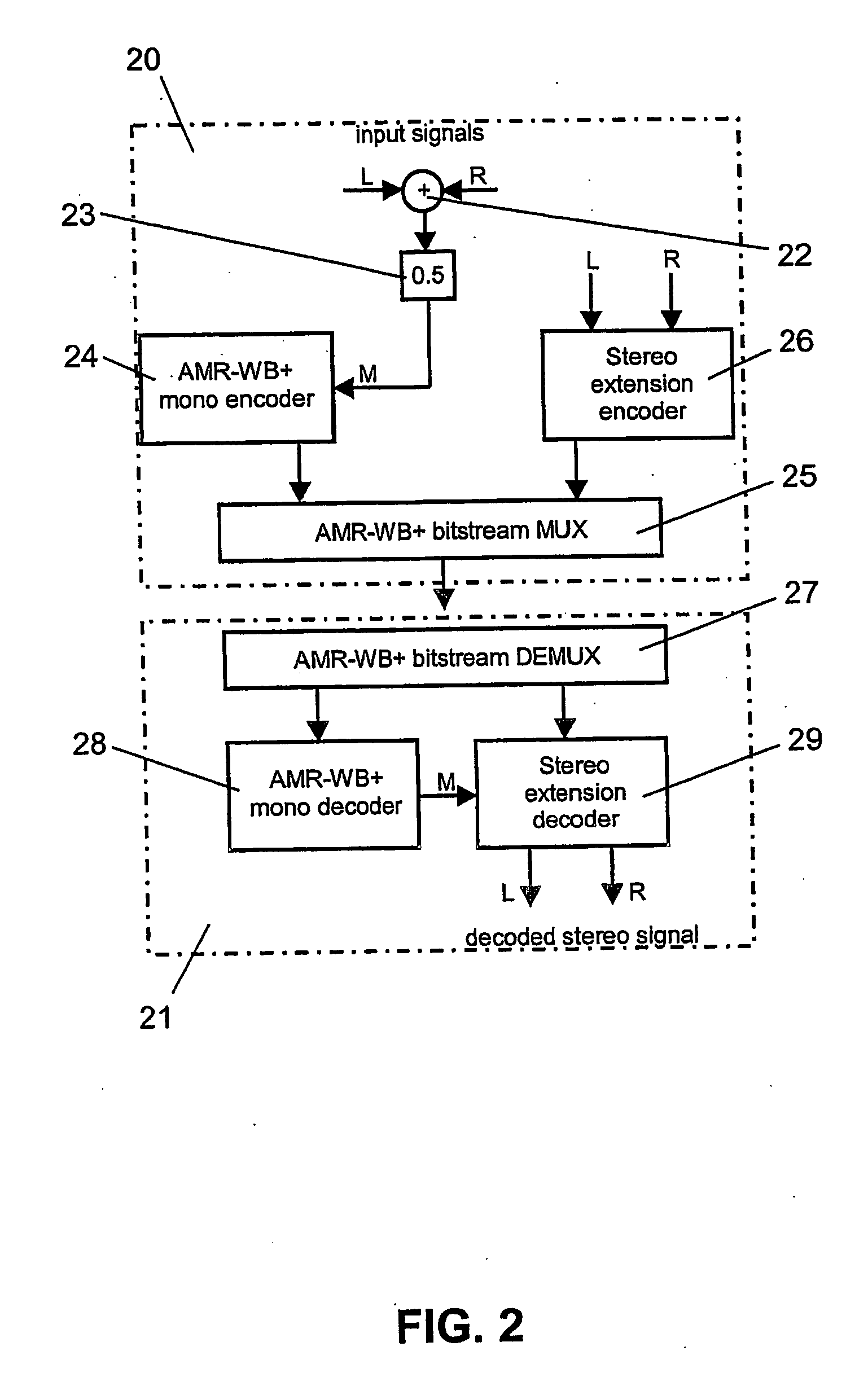
Method and encoder for combining digital data sets, a decoding method and decoder for such combined digital data sets and a record carrier for storing such combined digital data set
ActiveUS20100027819A1Precise positioningEasily hiddenSpeech analysisPseudo-stereo systemsDecoding methodsDigital data
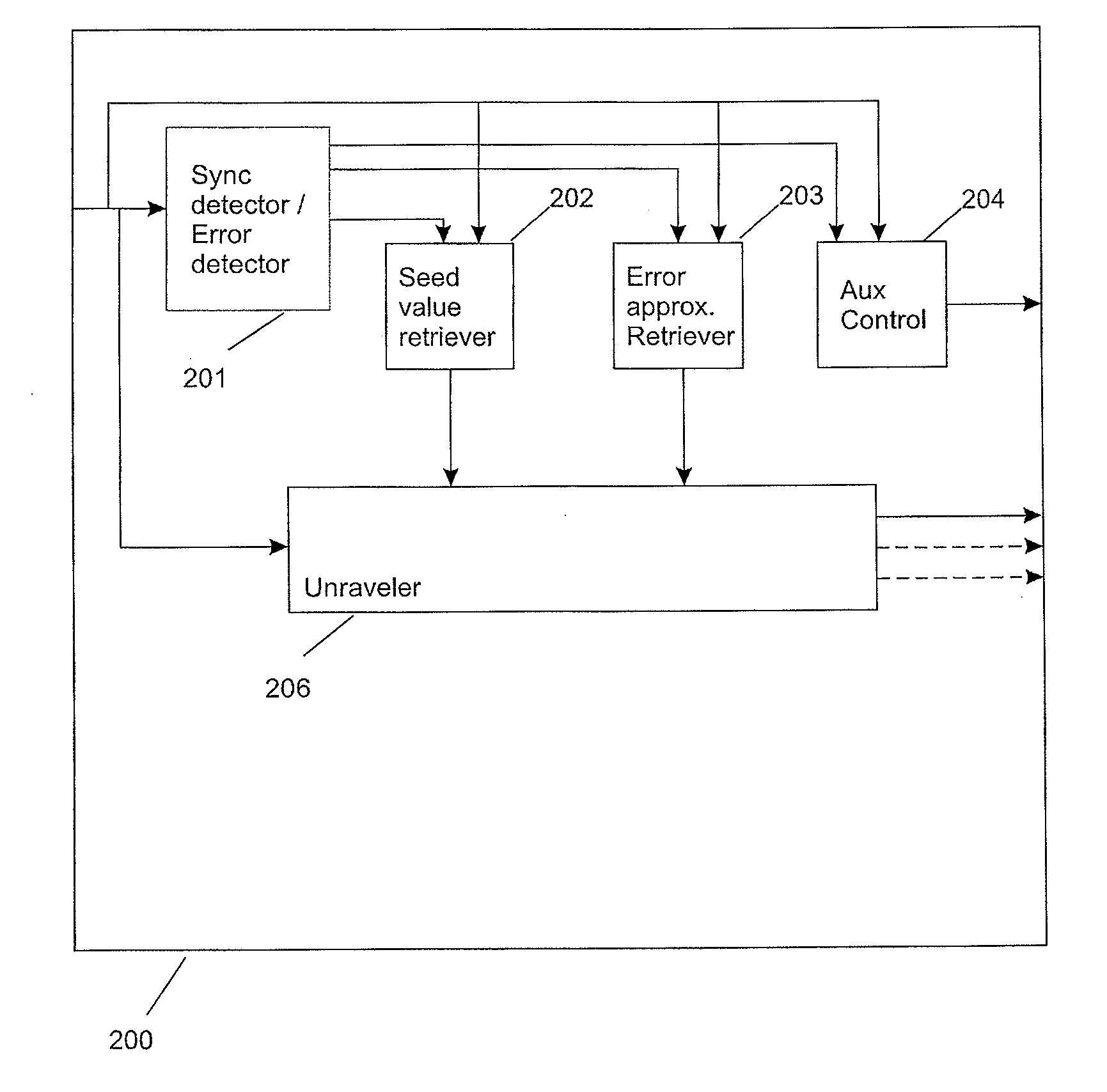
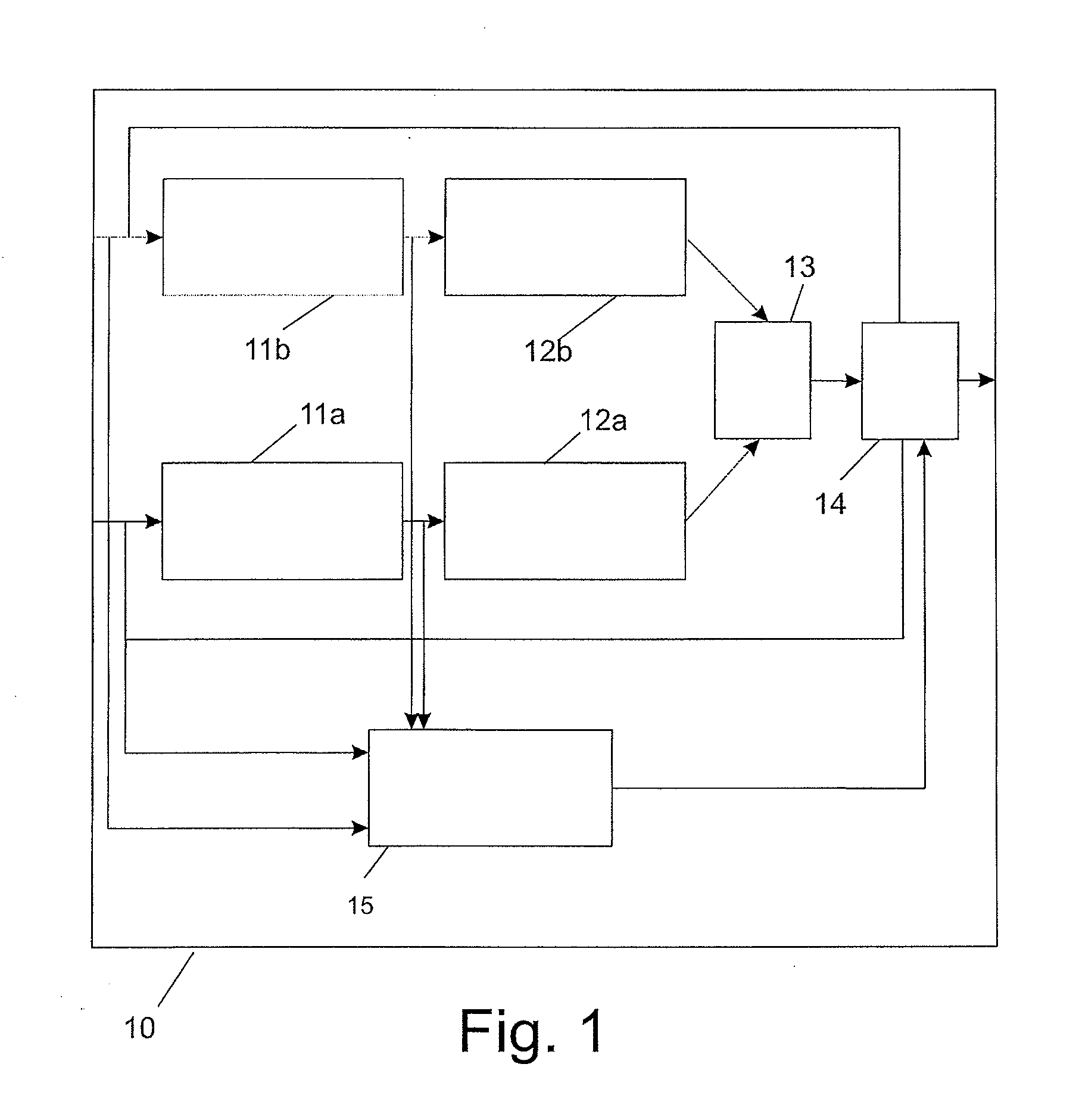
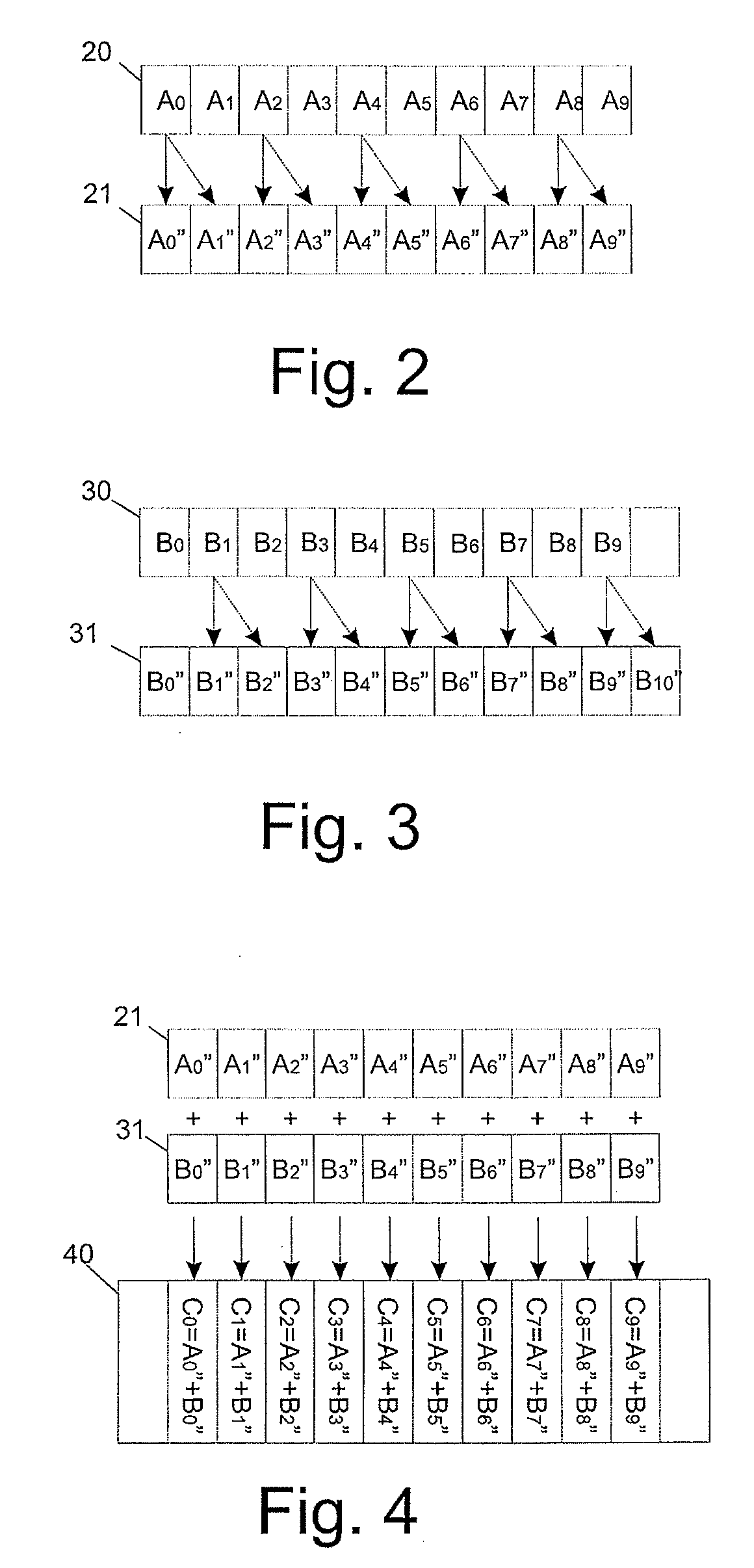
Two digital data sets are combined by equating a first subset of samples to neighboring samples from a second subset which is interleaved with the first subset of samples where the equated samples of the two digital data sets do not correspond in time, and by subsequently adding corresponding samples from both digital data sets. This results in a third digital data set that allows the unraveling of the two digital data sets. The third digital data set, when combining two digital audio streams into a single digital audio stream, is still a good mono representation of the two combined digital audio streams and can thus be reproduced on regular reproduction equipment, yet the use of a decoder according to the invention allows the unraveling of the two digital data sets from the third digital data set
Owner:AURO TECH
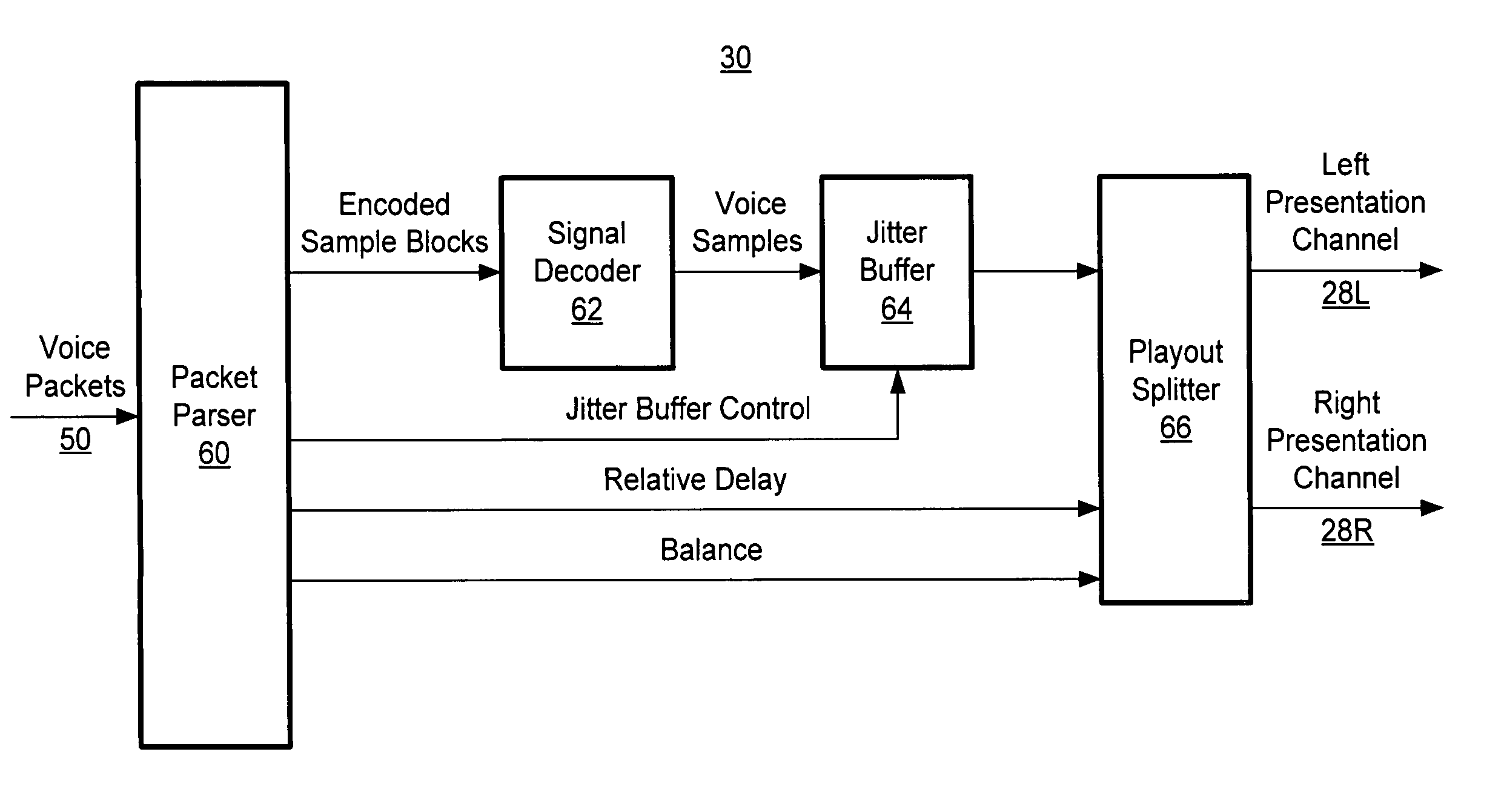
System and method for stereo conferencing over low-bandwidth links
InactiveUS20060023871A1High bandwidthSatisfactory sound qualityTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsPublic address systemsVocal tractComputer science
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Apparatus and method of out-of-head localization of sound image output from headpones
InactiveUS20080175396A1Reduction in tirednessReduce fatiguePseudo-stereo systemsTwo-channel systemsSound imageHeadphones
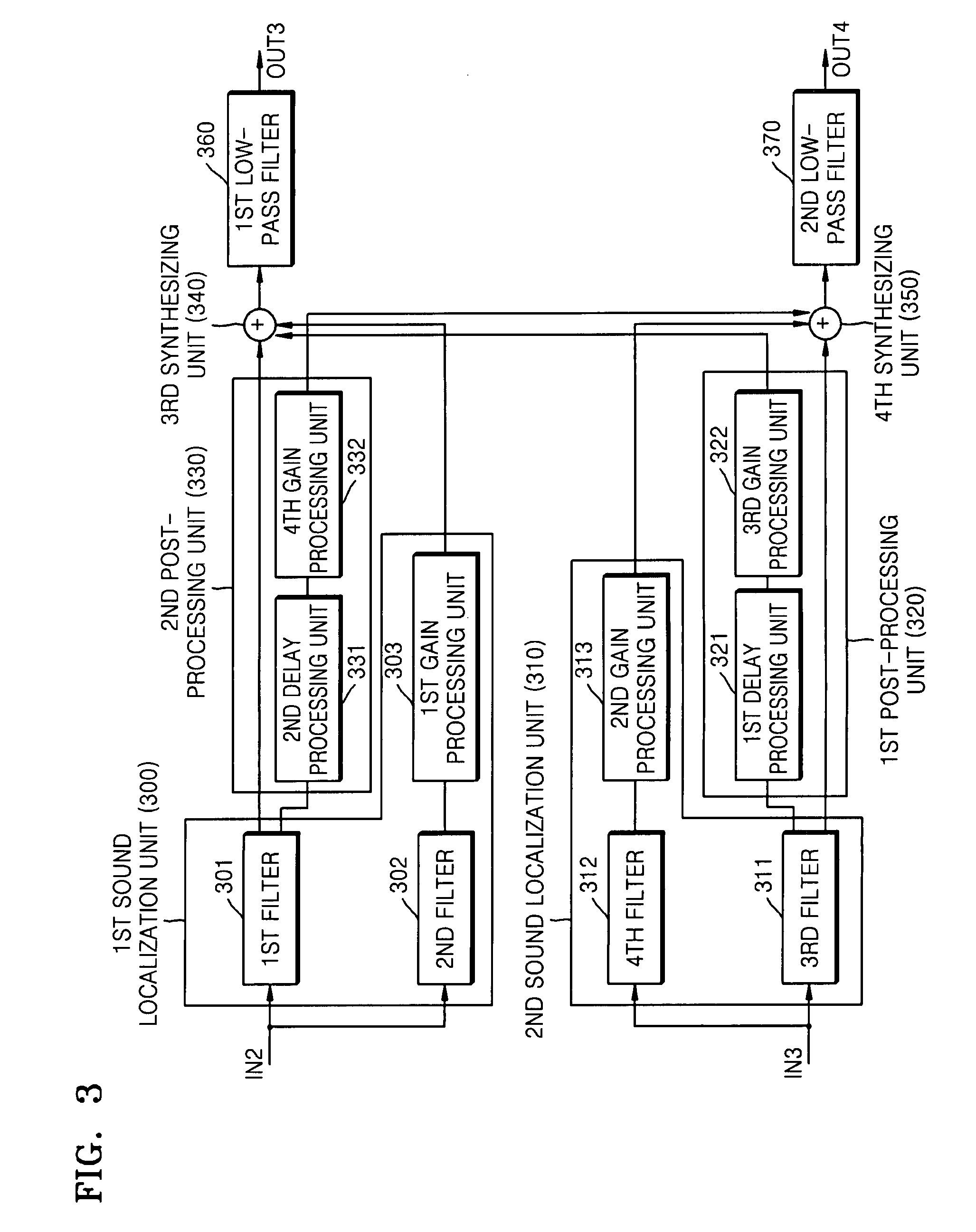
An apparatus for and method of externalizing a sound image output to headphones are provided. The method of externalizing a sound image output to headphones includes: localizing the sound image of an input signal to a predetermined area in front of a listener; and signal-processing a left signal component and a right signal component of the input signal with different delay values and gain values, respectively. According to the method and apparatus, the sound image output to the headphones can be localized to a virtual sound stage in front of the listener, thereby reducing tiredness occurring when listening through headphones, and even when a sound source includes many monophonic component, the sound image can be externalized.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System for transitioning from stereo to simulated surround sound
InactiveUS6996239B2Two-channel systemsLoudspeaker spatial/constructional arrangementsControl systemVocal tract
This invention provides a system capable of transitioning from surround sound effect to stereo sound effect, and then to a monophonic sound effect using front speakers. A user may control the amount of surround sound effect that is combined with stereo sound effect, and the amount of stereo sound effect that is combined with monophonic sound effect. The user may also control the system to hear pure surround sound effect, stereo sound effect, or monophonic sound effect. The system may allow a user to control the contribution of a particular sound effect by controlling the relative proportions of the filtered dipole signals and the attenuated unfiltered dipole signals. The signal processing may be also done through an analog device. The system may also process some audio channels in an inverted form and compensate for these inversions by reversing the polarity of that output to the speaker, as well as accept two-channel and four-channel audio inputs.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
Audio distribution system, an audio encoder, an audio decoder and methods of operation therefore
InactiveUS20070168183A1Efficient and high quality multi channel encodingQuality improvementSpeech analysisCode conversionDistribution systemVocal tract
A stereo audio encoder (100) comprises a parametric stereo encoder (115) which generates a mono signal and parametric stereo parameters for at least a high frequency part of an input stereo signal. A stereo intensity encoder (117) generates stereo intensity data for the mono signal. The mono signal and intensity data are encoded in accordance with an encoding standard such as MPEG Layer II and the parametric stereo parameters are included in the ancillary data sections by an output processor (113). Thus, a legacy decoder (such as an MPEG Layer II decoder) may generate a stereo signal using the stereo intensity data whereas a higher complexity decoder may generate a high quality audio signal using the parametric stereo parameters. A stereo decoder (200) receives the encoded data from the encoder (100). An intensity decoder (203) generates a stereo signal using intensity data. This is fed to a parametric stereo decoder (207) which processes the stereo signal in accordance with extracted parametric stereo data.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method for Generating a Surround Audio Signal From a Mono/Stereo Audio Signal
InactiveUS20140185812A1Enhance the imagePseudo-stereo systemsStereophonic arrangmentsMonauralAudio frequency
Disclosed is a method for generating a surround-channel audio signal (Mout) from a mono / stereo audio signal (Min, Sin), comprising the steps of: a) generating a first multi-channel signal (M1) by surround panning the mono / stereo audio signal (Sin); b) generating a second multi-channel signal (M2) by effect processing the mono / stereo input signal (Min, Sin) so that the rear signals comprise at least reverberation of the mono / stereo audio signals; and c) mixing the corresponding signals of the first multi-channel signal (M1) and the second multi-channel signal (M2), thereby forming the surround-channel audio signal (Mout).
Owner:VAN ACHTE TOM +2
Automatic stereo/monaural headphone
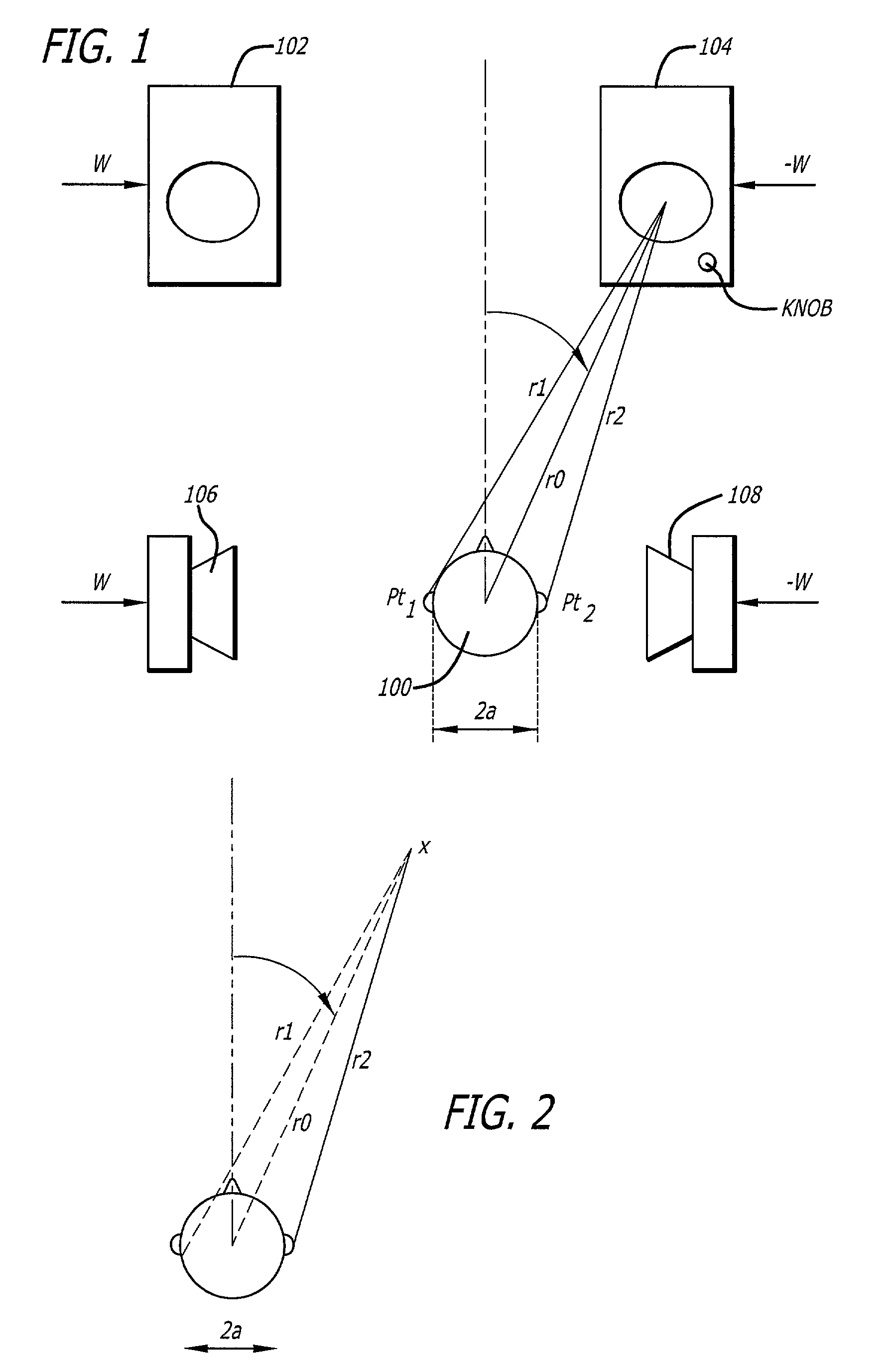
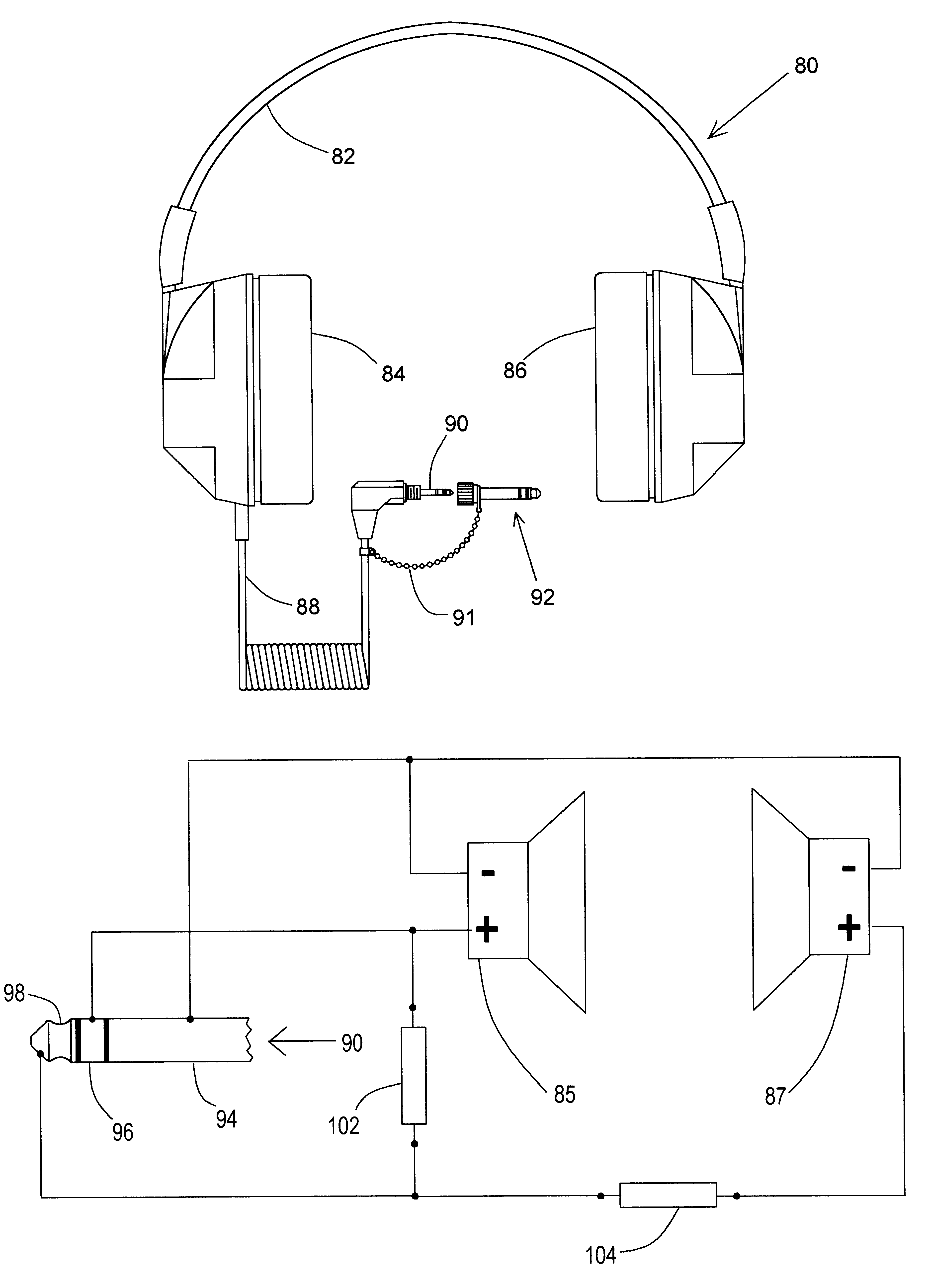
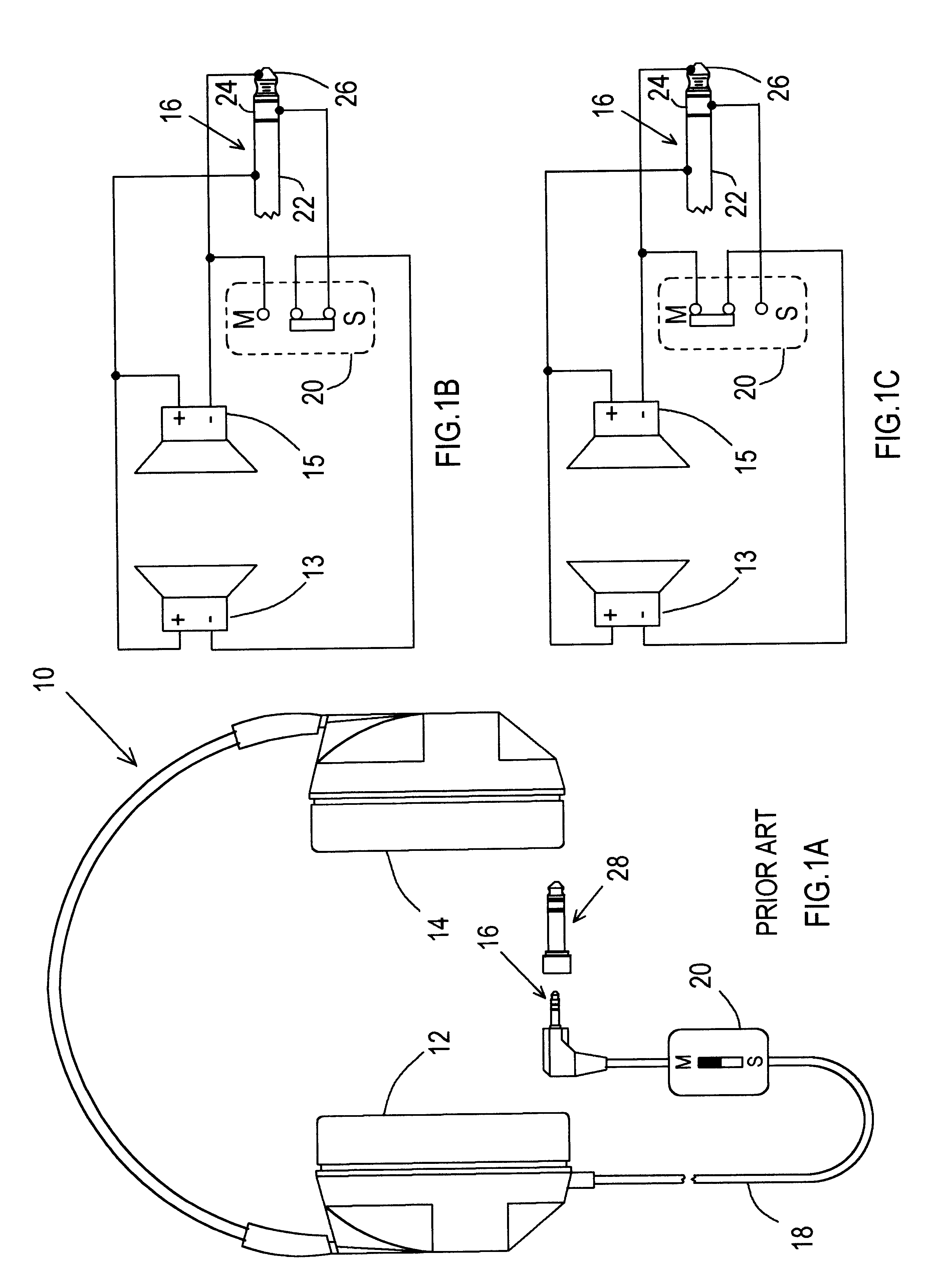
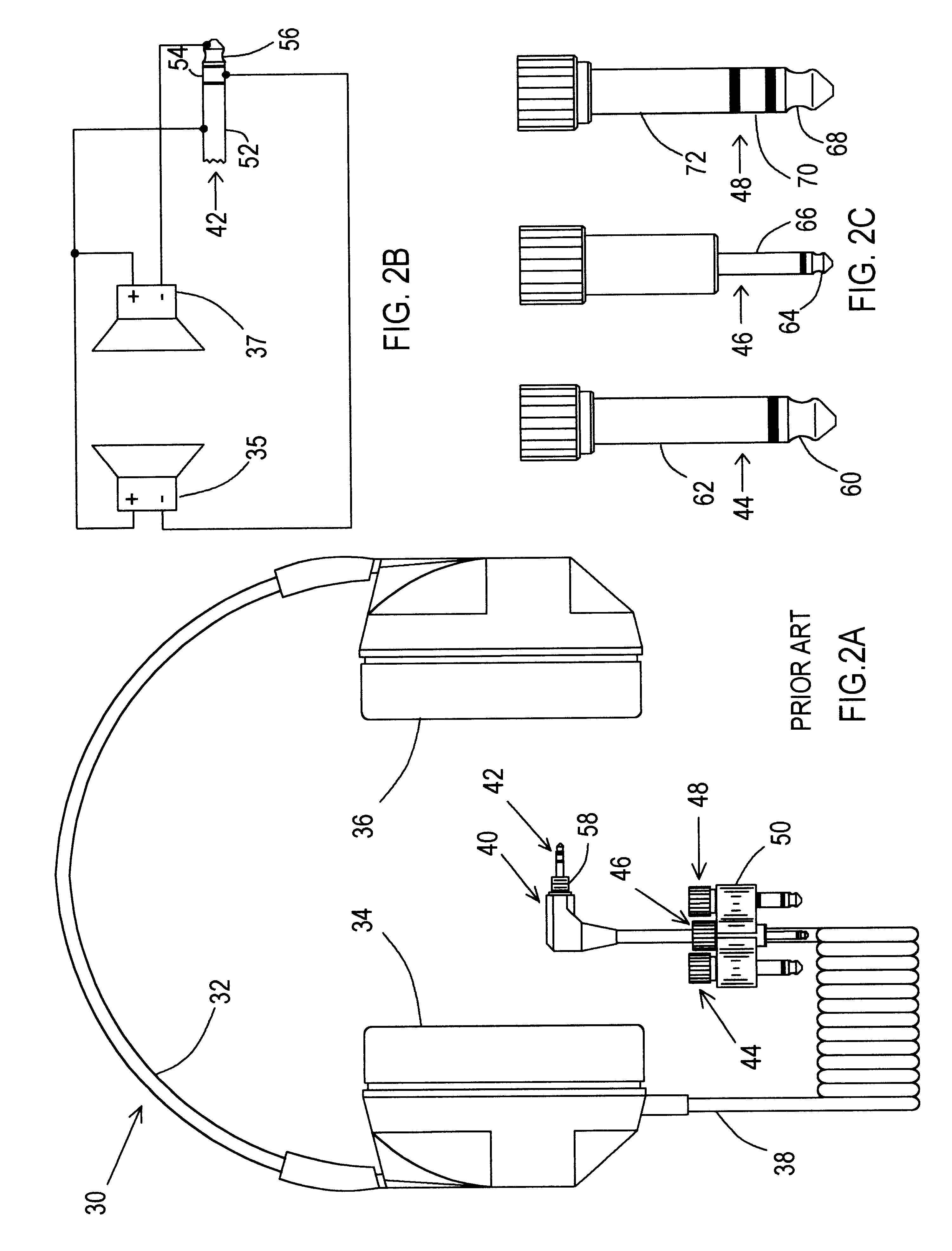
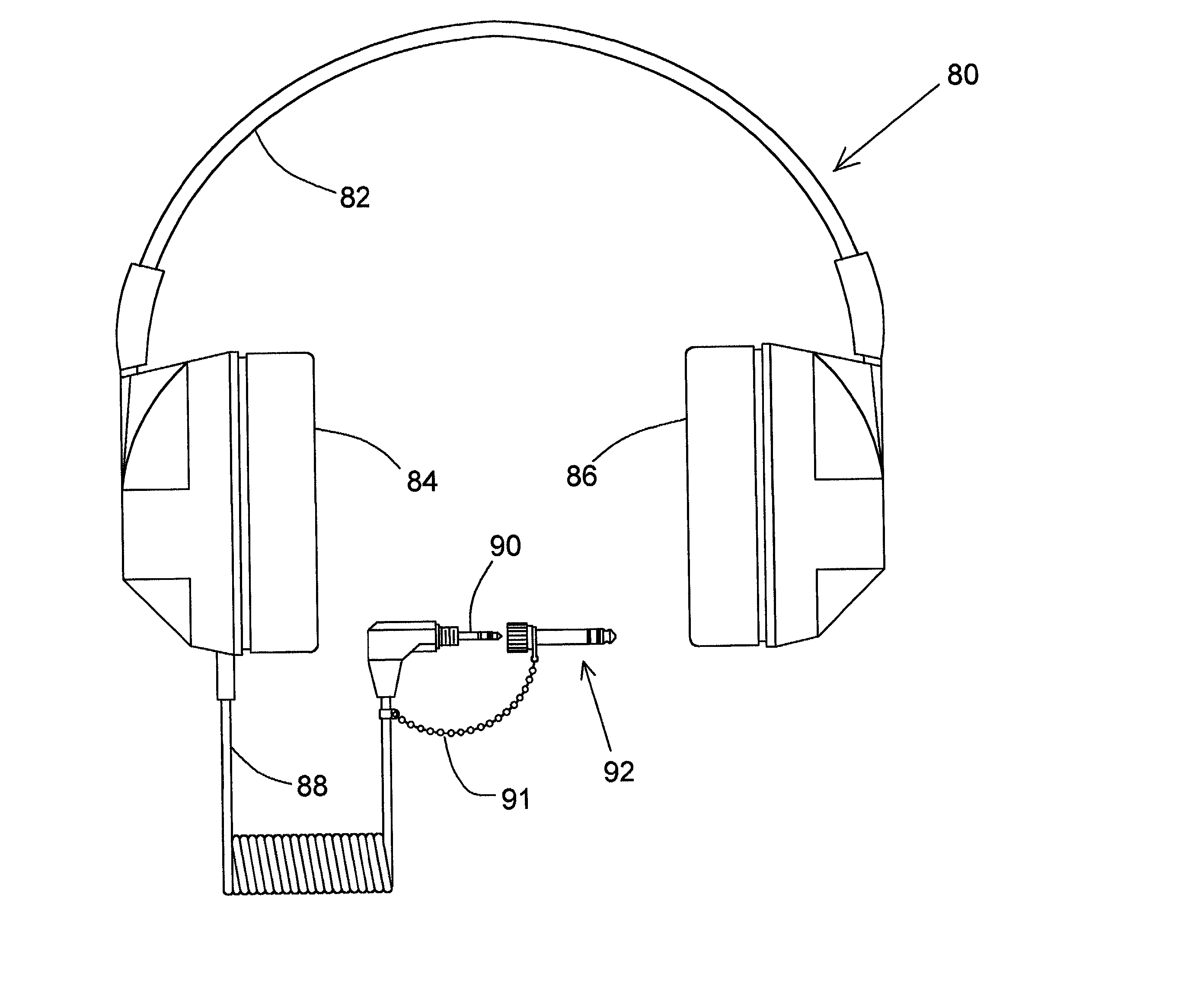
InactiveUS6711268B2Headphones for stereophonic communicationTwo-part coupling devicesSound sourcesMonaural
A stereo headphone employing a standard stereo headphone plug is adapted for automatically hearing a monaural signal at both earpieces, when accessing a typical monaural source. In the first embodiment of the invention, an impedance element couples the signal from a first acoustical driver that receives the monaural signal from the stereo plug tip, to a second acoustical driver that is connected to the stereo plug ring and normally receives no signal when plugged into a conventional monaural audio source output jack. The magnitude of the coupling impedance is selected with respect to the impedance of the acoustical driver so that the reduction in loudness at the second earpiece due to the signal voltage drop across the coupling impedance is not perceptible to the listener. This will occur when the reduction in loudness at the second earpiece is less than the threshold of perceivable loudness reduction at one ear when there is no reduction in loudness at the other ear. The effect of the coupling impedance, when listening to a stereo audio source is insignificant, firstly, because the two stereo channel signals appear at their respective drivers with virtually no attenuation due to the coupling impedance. Secondly, although the coupling impedance does contribute a slight amount of additional crosstalk between the stereo channels, the magnitude of the increase in crosstalk is dependent upon the ratio of the coupling impedance to the output impedance of the stereo source. A typical stereo source for which the use of this headphone is intended has an output impedance so low compared to the coupling impedance that the increase in crosstalk is too small to be perceptible as affecting the stereo separation or the stereo imaging afforded by the stereo source. In the second embodiment of the invention two equal impedance elements couple the monaural signal from the stereo plug tip to each acoustical driver. This equalizes the loudness of the monaural signal heard at each earpiece and slightly reduces the level of one stereo channel with respect to the other. Crosstalk and stereo imaging are virtually unaffected, as with the first embodiment.
Owner:ENZTEC LTD
Dual mono center channel
A pair of matched monaural speakers are added inside conventional left and right stereo speaker housings so that the left, right and flat panel monitor appear joined in a seamless aesthetic effect. The added speakers are provided with center channel monaural sound, making it appear as though such sound emanates from the center of the monitor, thereby enhancing home theater impact to provide stereo and center channel sound from each left and right speaker housing.
Owner:ARTISON LLC
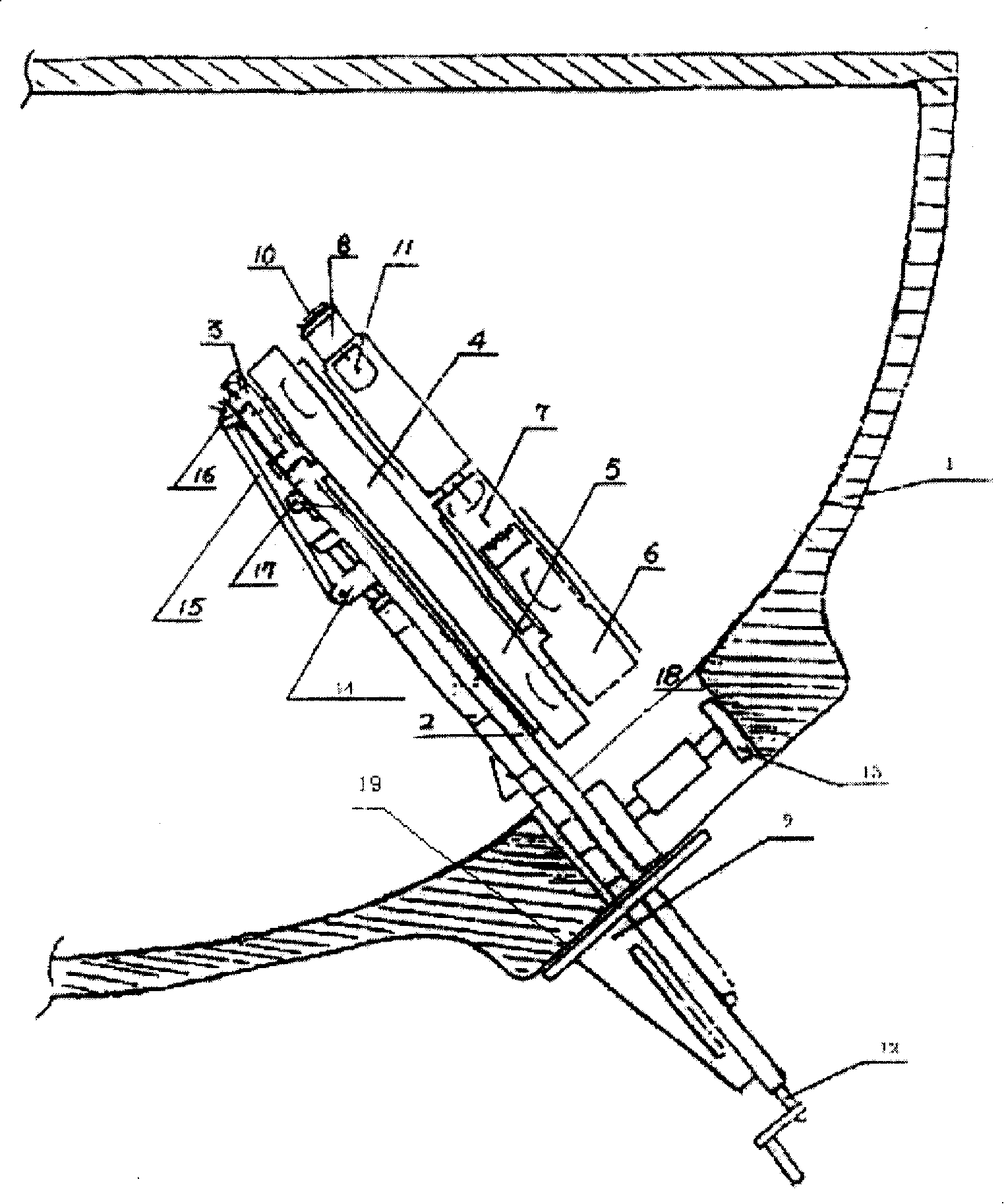
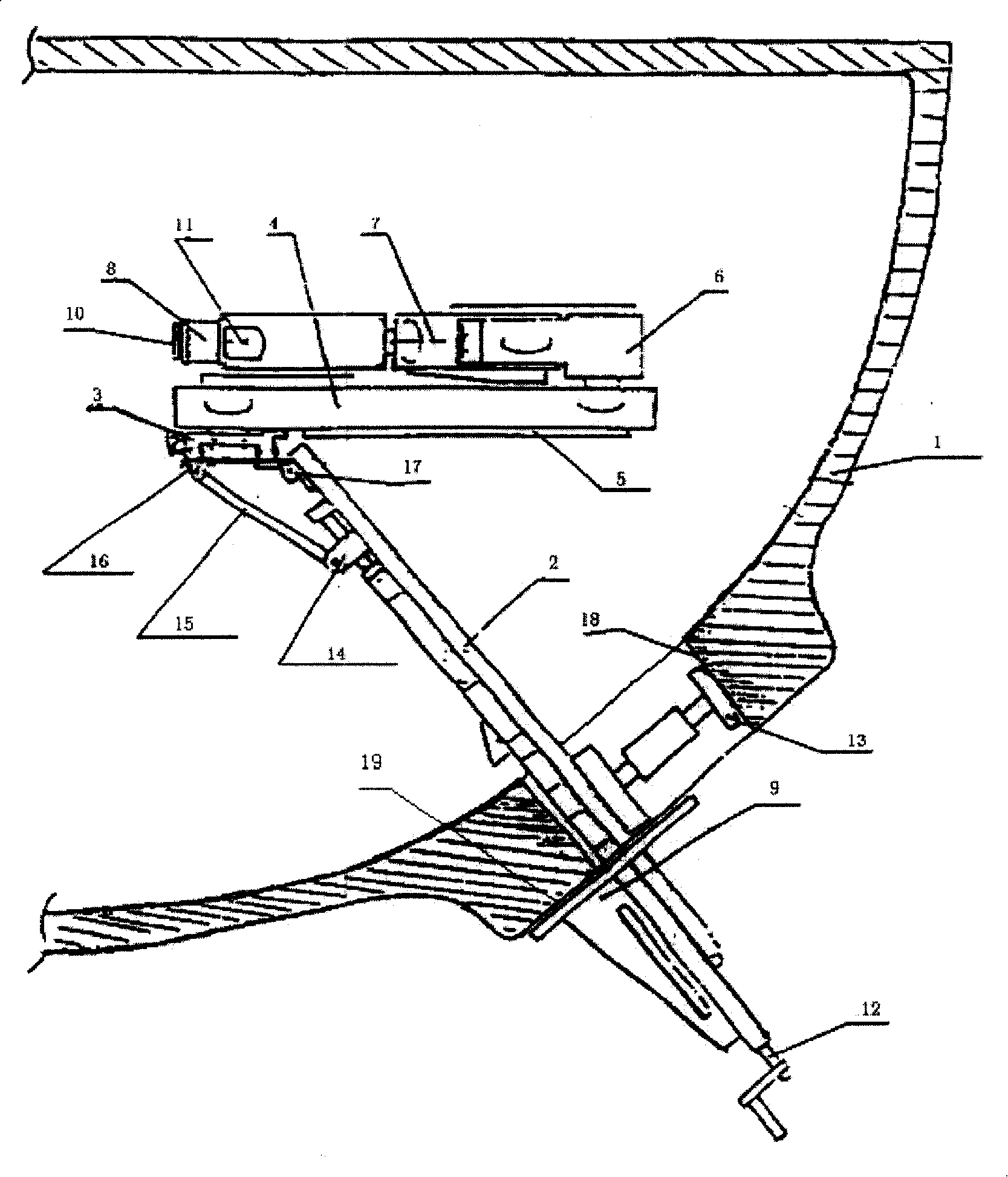
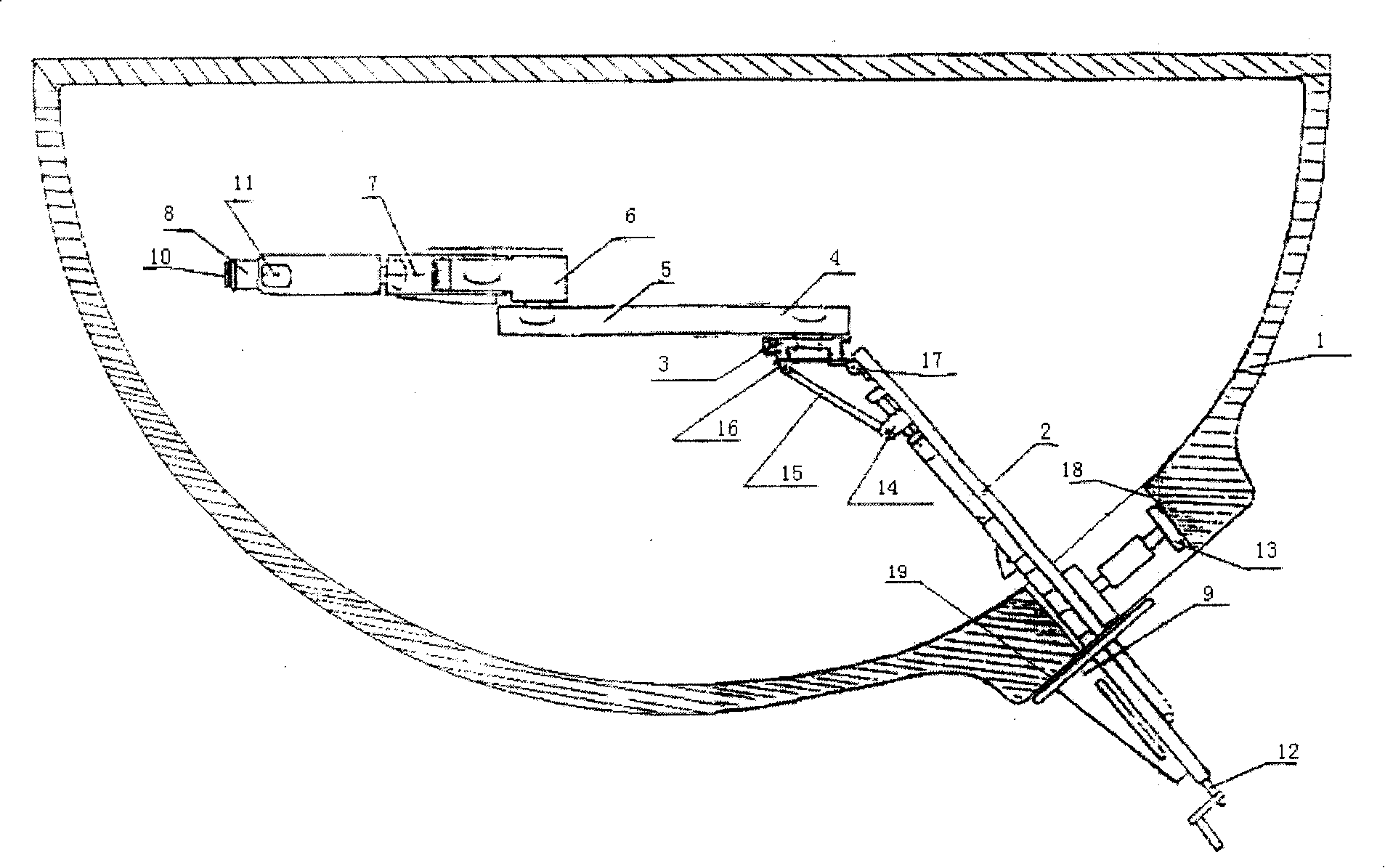
Nuclear boiler water indoor surface television set automatic checking device
ActiveCN101162617AGuaranteed repeat positioning accuracyAdjustable lengthNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringSheet steelMonaural
The invention provides an TV automatic checkout equipment for the water chamber inner surface of a nuclear steam generator, comprising a guide rail, a support platform, a large arm, a telescopic boom, a forearm, a rotating arm, a yawing arm, a ribbed slab, a support and a steel plate; two ends of the support are supported on the surface of the guide rail and the inner surface of a manhole respectively; the guide rail is connected with a flange; one end of the guide rail is arranged on the ribbed slab; a monaural on the side wall of the other end of the guide rail is connected with one end of the steel plate; the other end of the steel plate is connected with a monaural on the other location of the corresponding side of the support platform; the other side of the support platform is connected with one end of the large arm, the other end of the large arm is connected with the telescopic boom, the forearm, the rotating arm and the yawing arm in sequence. The device of the invention can have an overall inspection on the stainless overlaying layer of the water chamber surface of the steam generator so as to find if crackles, collision tracks, scratches, corrosive defects, abnormal indication or foreign objects exist.
Owner:RES INST OF NUCLEAR POWER OPERATION
USB communication equipment and method using mobile communication terminal earphone jack
InactiveCN1496166ARadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTelephone set constructionsMonauralExternal camera
A USB communication device using an earphone jack of a mobile communication terminal and a method for judging the type of the external device when the external device is connected to the earphone jack of the mobile communication terminal. When the external device is a USB external camera, the mobile communication terminal receives the converted image from the USB external camera through the earphone jack; The headphone earpiece of the headphone microphone chain, and receive mono sound from the microphone of the headphone microphone chain through the microphone signal line of the headphone jack. Therefore, in the present invention, the functions of USB communication between the mobile communication terminal and the external device, stereo output and monaural output can be selectively performed according to the kind of the external device connected to the earphone jack.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
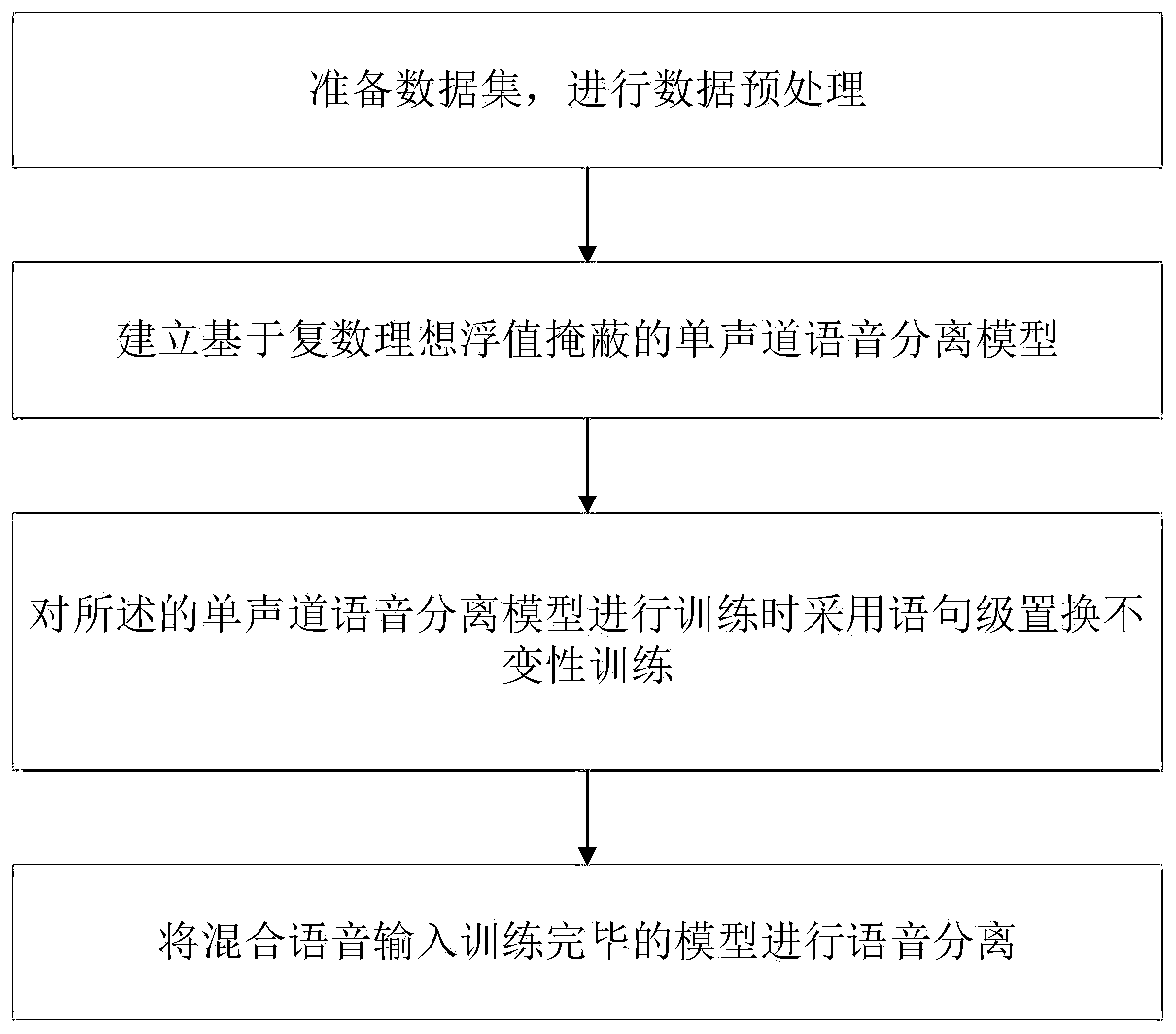
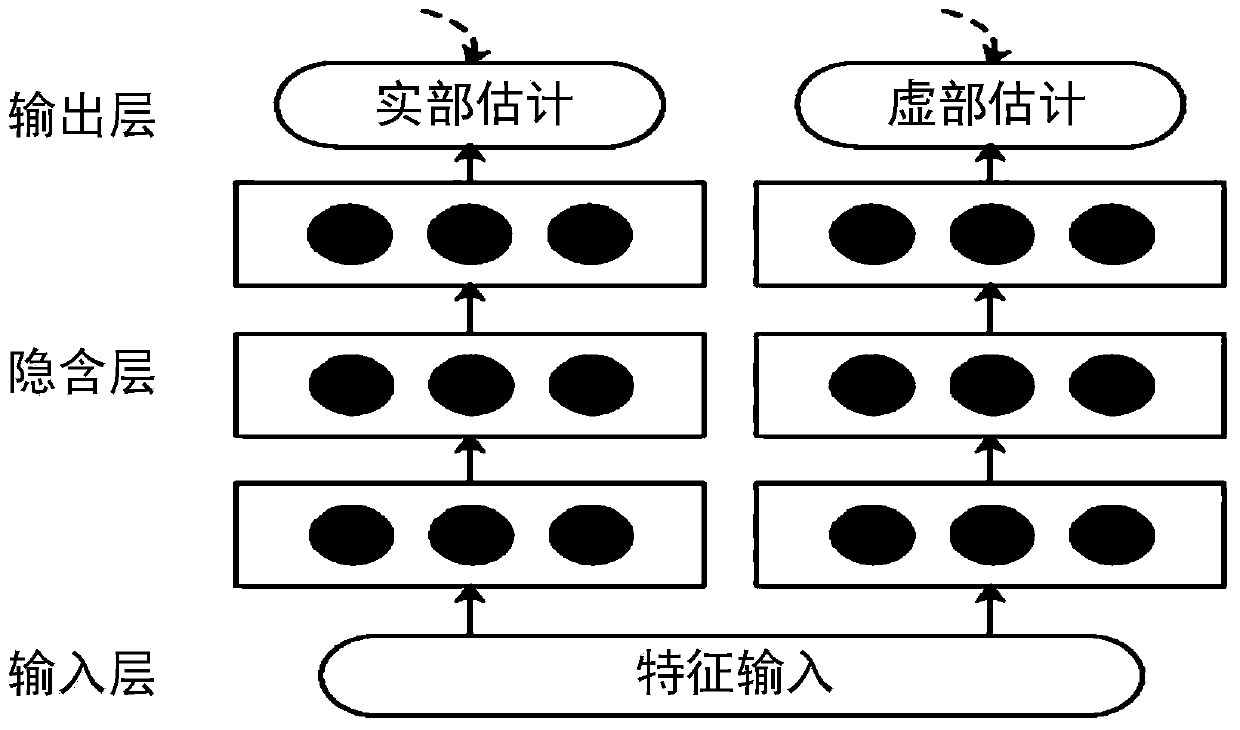
Speaker-independent single-channel voice separation method
ActiveCN111583954ASolve the problem of ambiguityThe estimate is accurateSpeech analysisMonauralNetwork structure
The invention discloses a speaker-independent single-channel voice separation method, which comprises the following steps: preparing a data set, and carrying out data preprocessing; establishing a single-channel voice separation model based on complex ideal floating value masking; when the single-channel voice separation model is trained, adopting statement-level replacement invariance training; and inputting the mixed voice data into the trained model for voice separation. According to the speaker-independent single-channel voice separation method based on statement-level replacement invariance training and complex ideal floating value masking, complex ideal floating value masking estimation is effectively and accurately realized through statement-level replacement invariant training; inthe method, a bidirectional long-short-term memory neural network structure is adopted to estimate complex number ideal floating value masking, and a statement-level replacement invariant training standard is further utilized to solve the problem of label blurring, so that single-channel voice separation has a good effect.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method and apparatus for virtual auditorium usable for a conference call or remote live presentation with audience response thereto
InactiveUS9131016B2Reduce needAmplifying effect behaviorSpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsAudience responseVocal tract
A method and apparatus are disclosed for providing a virtual auditorium for a remote, live performance to a remote, distributed audience, wherein the performers receive the reaction of the audience members in substantially real time. The live performance can itself be distributed geographically, as taught in the prior art, and may be multimedia in nature, for example audio (monophonic, stereo, or multi-channel) can be augmented by images, video, MIDI, text (e.g., commentary, lyrics), etc. Further, the distributed audience members can receive each other's reaction, also in substantially real time, whereby the virtual auditorium is created wherein the distributed audience members constitute a virtual assembly.The same virtual auditorium, sans performers, can be used as a venue to conduct a conference call of arbitrary size without the expense of a central voice bridge.
Owner:EJAMMING
Automatic stereo/monaural headphone
InactiveUS20020012435A1Headphones for stereophonic communicationTwo-part coupling devicesSound sourcesMonaural
A stereo headphone employing a standard stereo headphone plug is adapted for automatically hearing a monaural signal at both earpieces, when accessing a typical monaural source. In the first embodiment of the invention, an impedance element couples the signal from a first acoustical driver that receives the monaural signal from the stereo plug tip, to a second acoustical driver that is connected to the stereo plug ring and normally receives no signal when plugged into a conventional monaural audio source output jack. The magnitude of the coupling impedance is selected with respect to the impedance of the acoustical driver so that the reduction in loudness at the second earpiece due to the signal voltage drop across the coupling impedance is not perceptible to the listener. This will occur when the reduction in loudness at the second earpiece is less than the threshold of perceivable loudness reduction at one ear when there is no reduction in loudness at the other ear. The effect of the coupling impedance, when listening to a stereo audio source is insignificant, firstly, because the two stereo channel signals appear at their respective drivers with virtually no attenuation due to the coupling impedance. Secondly, although the coupling impedance does contribute a slight amount of additional crosstalk between the stereo channels, the magnitude of the increase in crosstalk is dependent upon the ratio of the coupling impedance to the output impedance of the stereo source. A typical stereo source for which the use of this headphone is intended has an output impedance so low compared to the coupling impedance that the increase in crosstalk is too small to be perceptible as affecting the stereo separation or the stereo imaging afforded by the stereo source. In the second embodiment of the invention two equal impedance elements couple the monaural signal from the stereo plug tip to each acoustical driver. This equalizes the loudness of the monaural signal heard at each earpiece and slightly reduces the level of one stereo channel with respect to the other. Crosstalk and stereo imaging are virtually unaffected, as with the first embodiment.
Owner:ENZTEC LTD
Monaural Noise Suppression Based on Computational Auditory Scene Analysis
ActiveUS20130231925A1Reduce noise and echo componentRestrict levelSpeech analysisTime domainMonaural
The present technology provides a robust noise suppression system that may concurrently reduce noise and echo components in an acoustic signal while limiting the level of speech distortion. A time-domain acoustic signal may be received and be transformed to frequency-domain sub-band signals. Features, such as pitch, may be identified and tracked within the sub-band signals. Initial speech and noise models may be then be estimated at least in part from a probability analysis based on the tracked pitch sources. Speech and noise models may be resolved from the initial speech and noise models and noise reduction may be performed on the sub-band signals. An acoustic signal may be reconstructed from the noise-reduced sub-band signals.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Teleconferencing using monophonic audio mixed with positional metadata
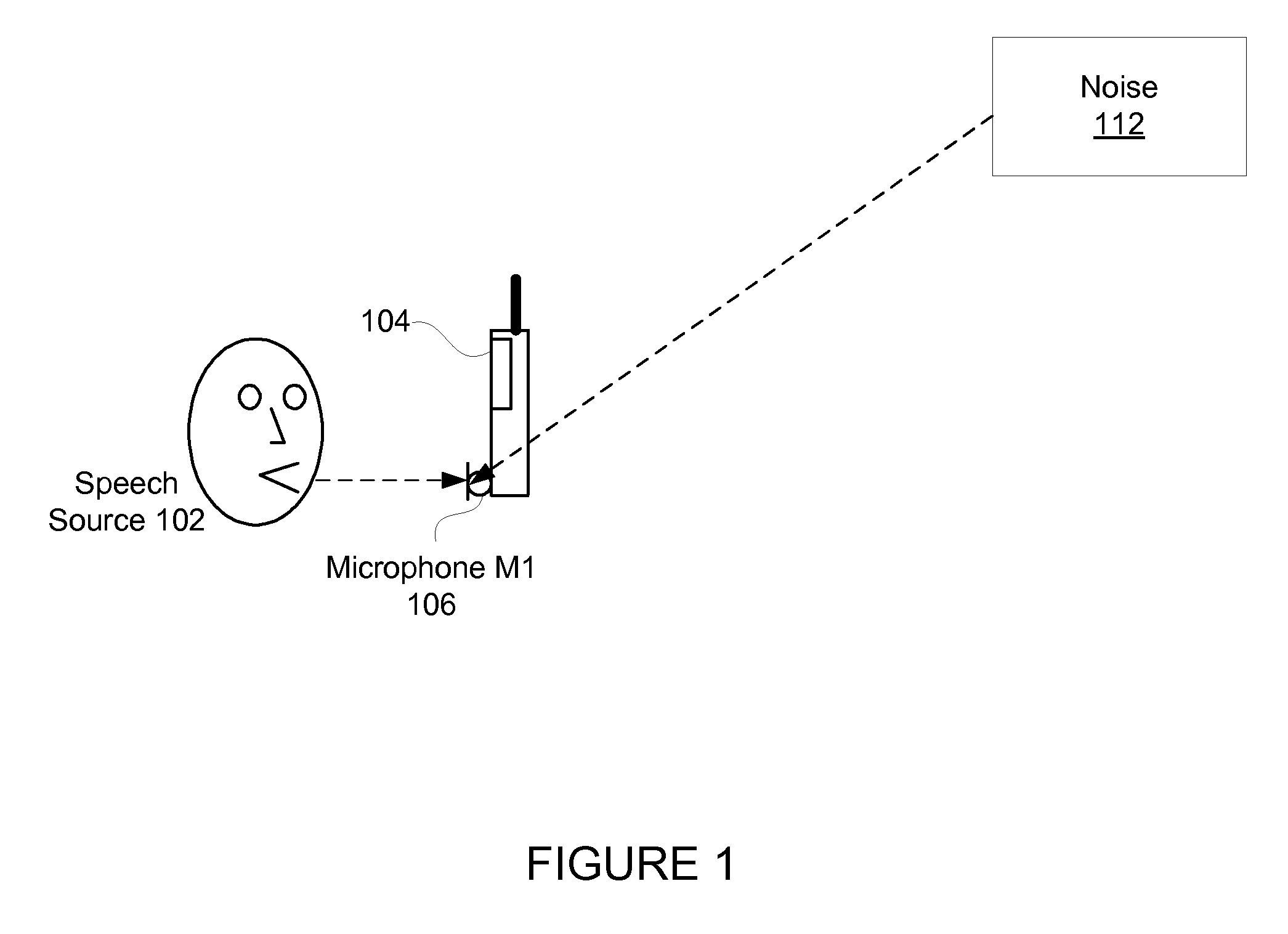
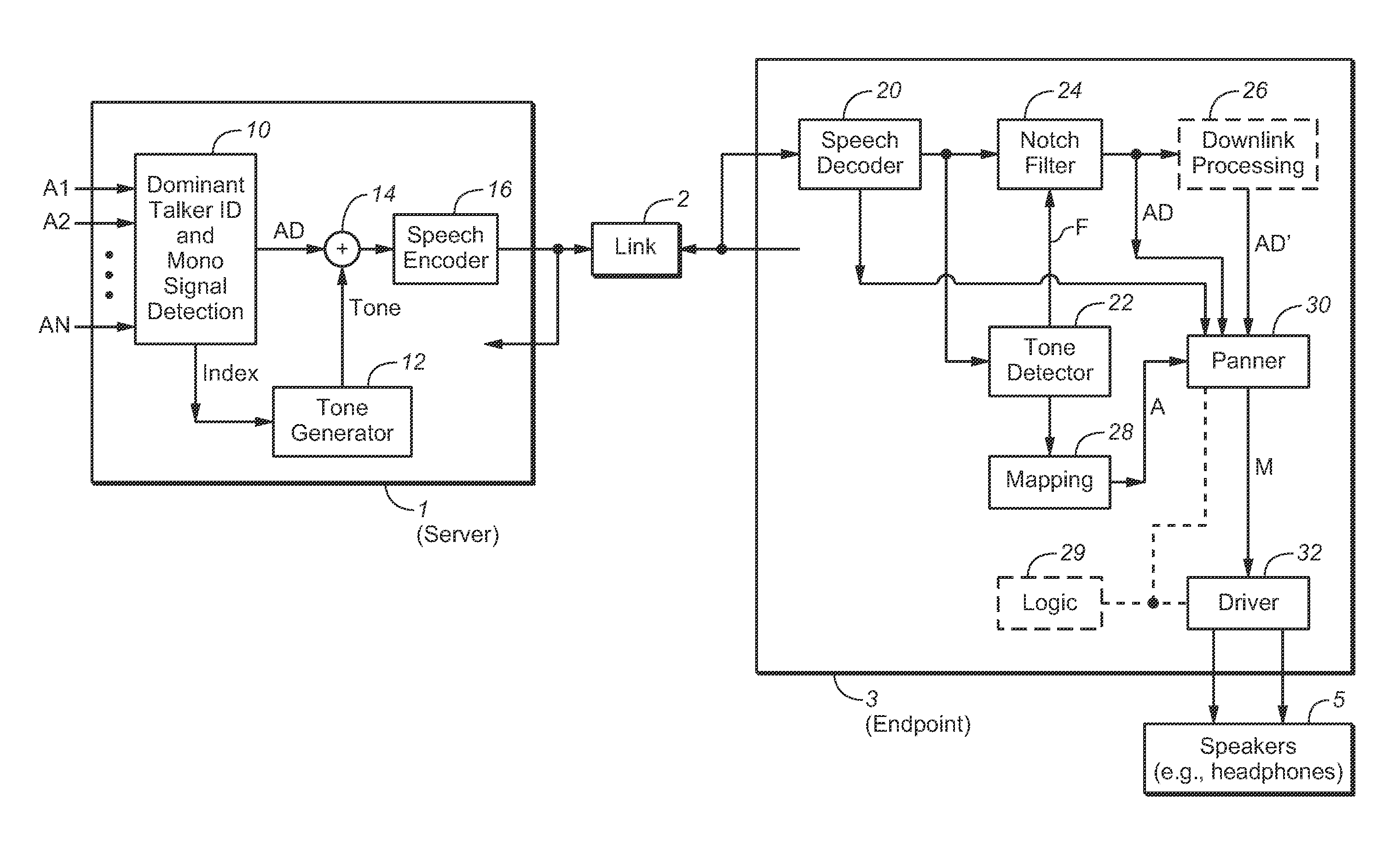
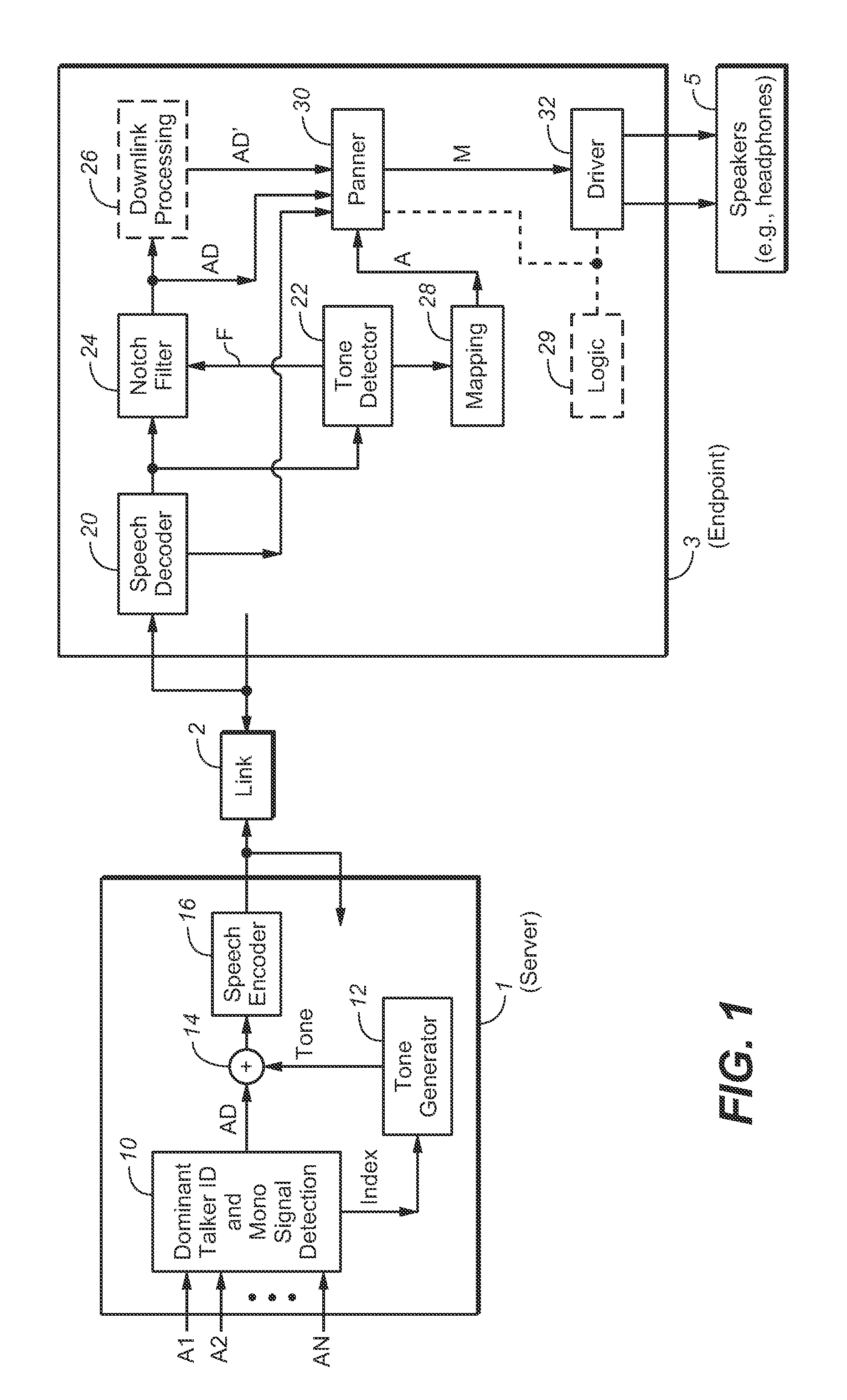
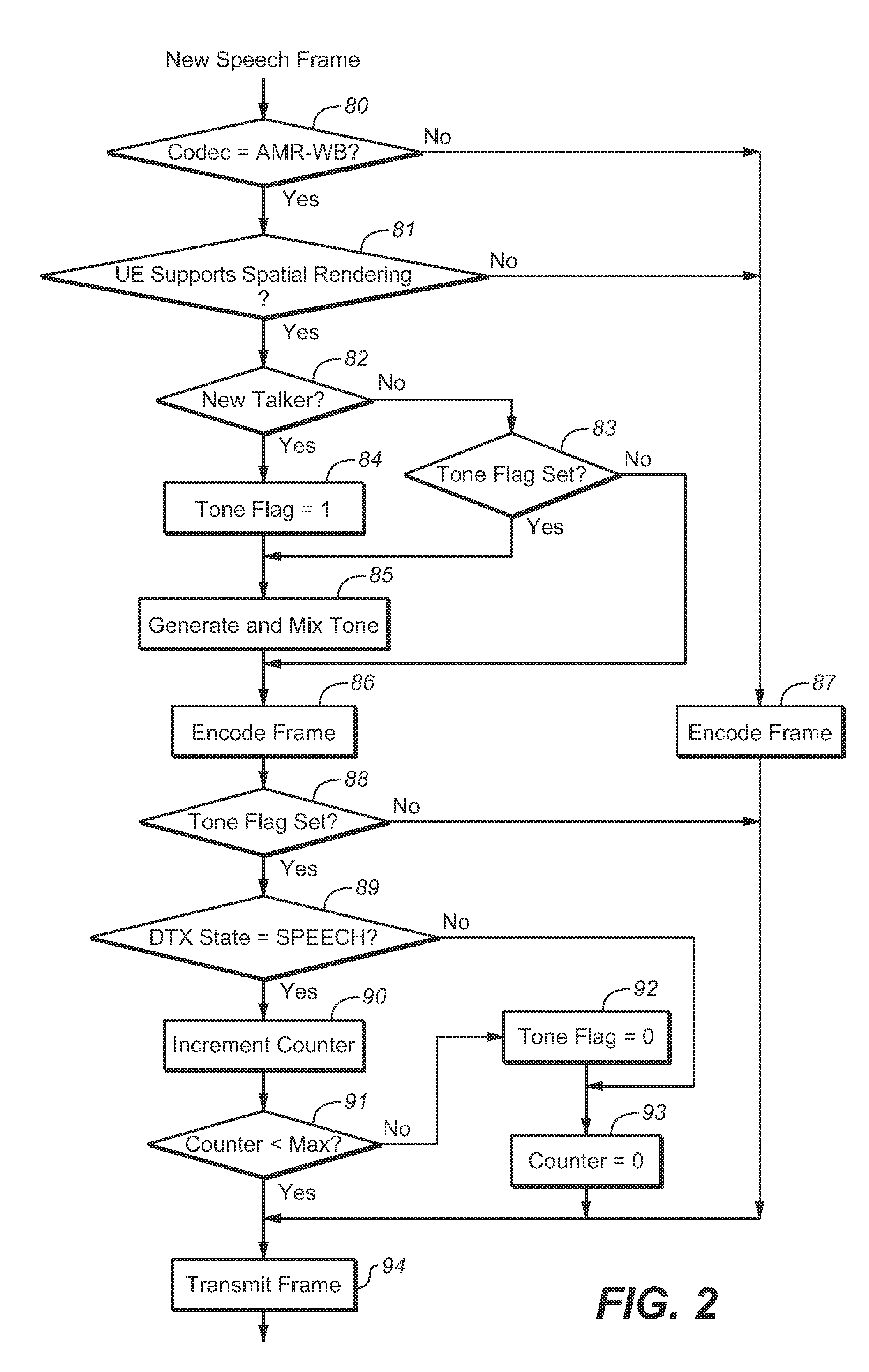
ActiveUS20150288824A1Improve user experienceMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationMonauralData signal
In some embodiments, a method for preparing monophonic audio for transmission to a node of a teleconferencing system, including steps of generating a monophonic mixed audio signal, including by a mixing a metadata signal (e.g., a tone) with monophonic audio indicative of speech by a currently dominant participant in a teleconference, and encoding the mixed audio signal for transmission, where the metadata signal is indicative of an apparent source position for the currently dominant conference participant. Other embodiments include steps of decoding such a transmitted encoded signal to determine the monophonic mixed audio signal, identifying the metadata signal, and determining the apparent source position corresponding to the currently dominant participant from the metadata signal. Other aspects are systems configured to perform any embodiment of the method or steps thereof.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com