Patents
Literature
5614results about "Stereophonic systems" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
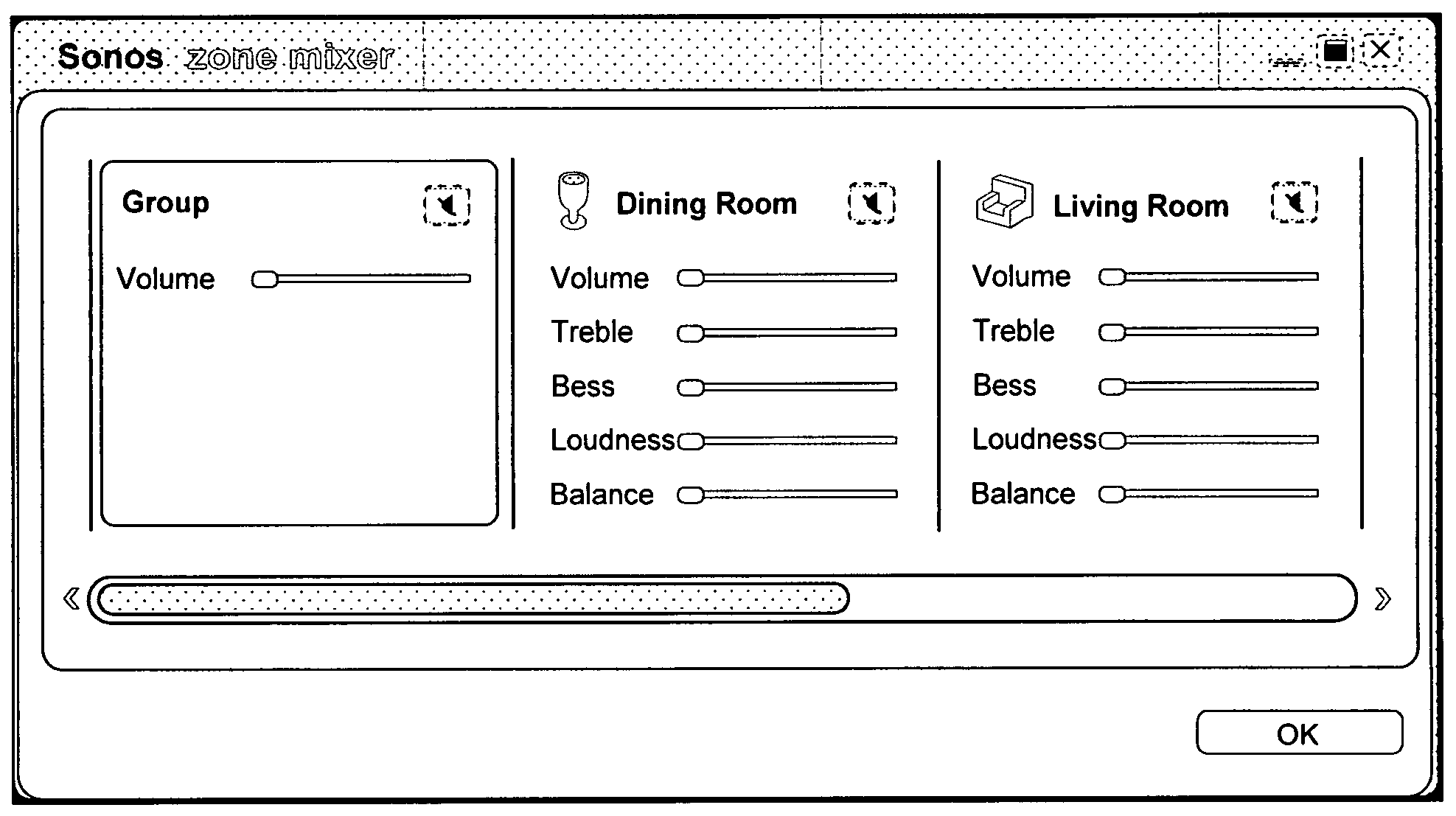
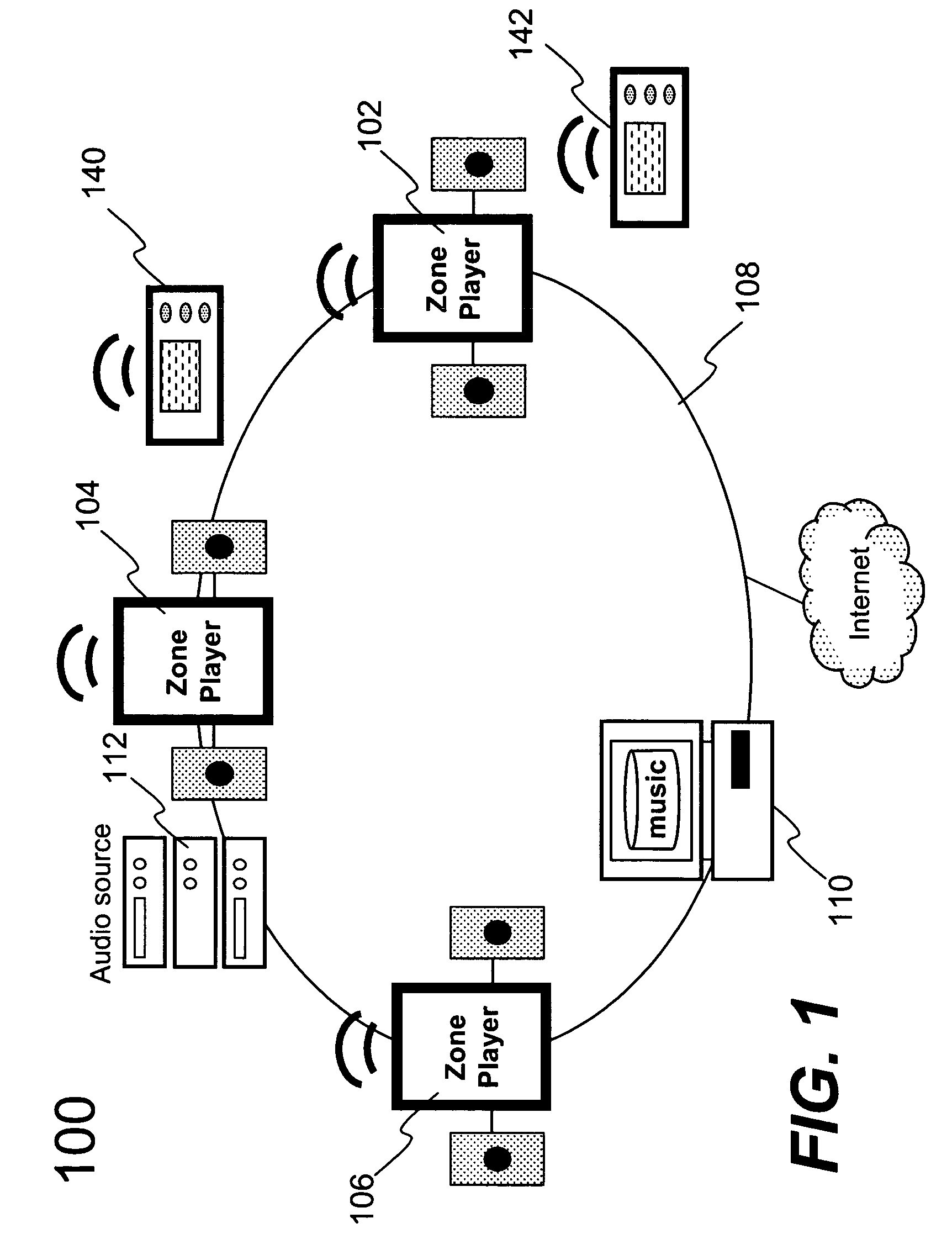
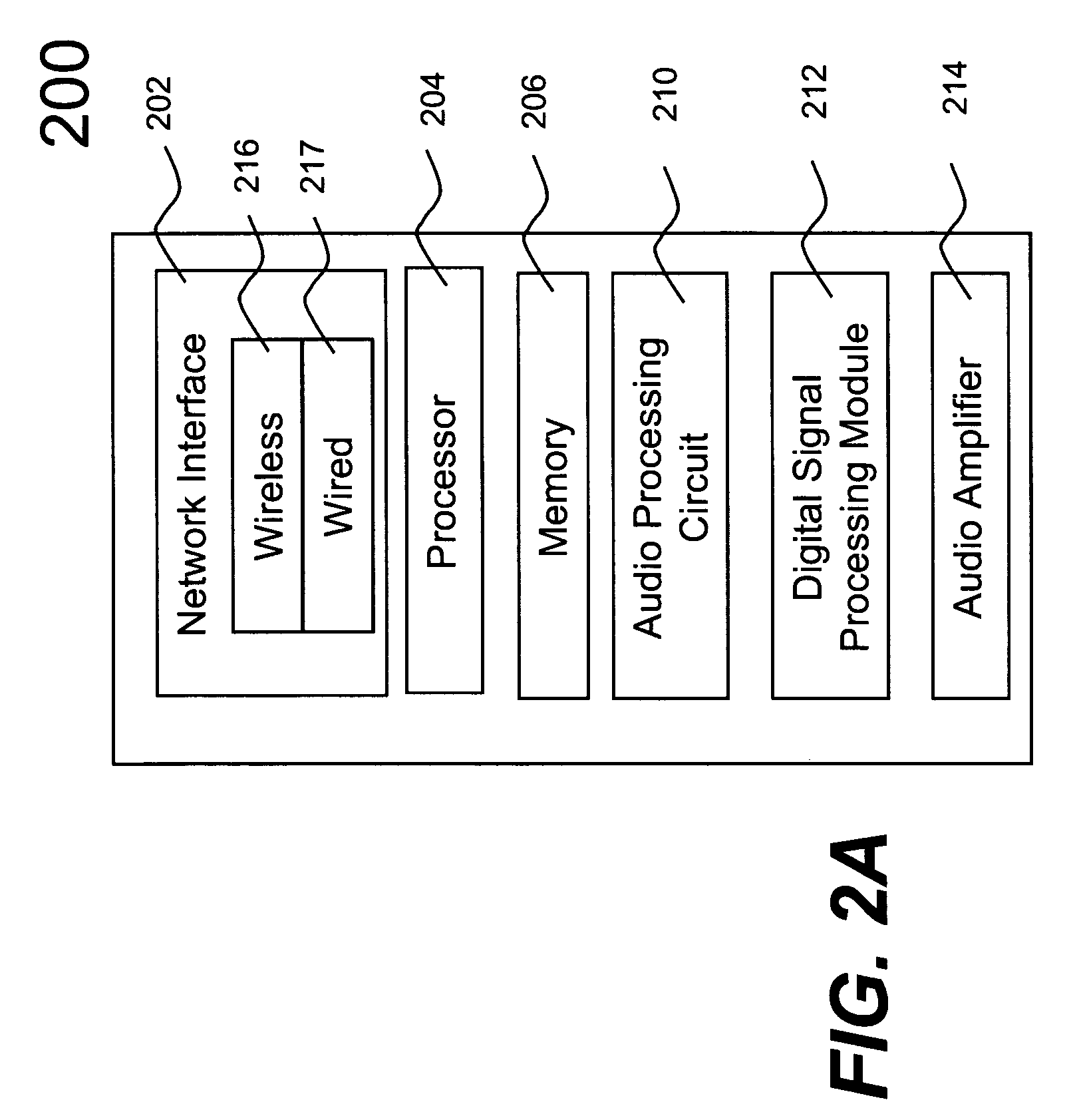
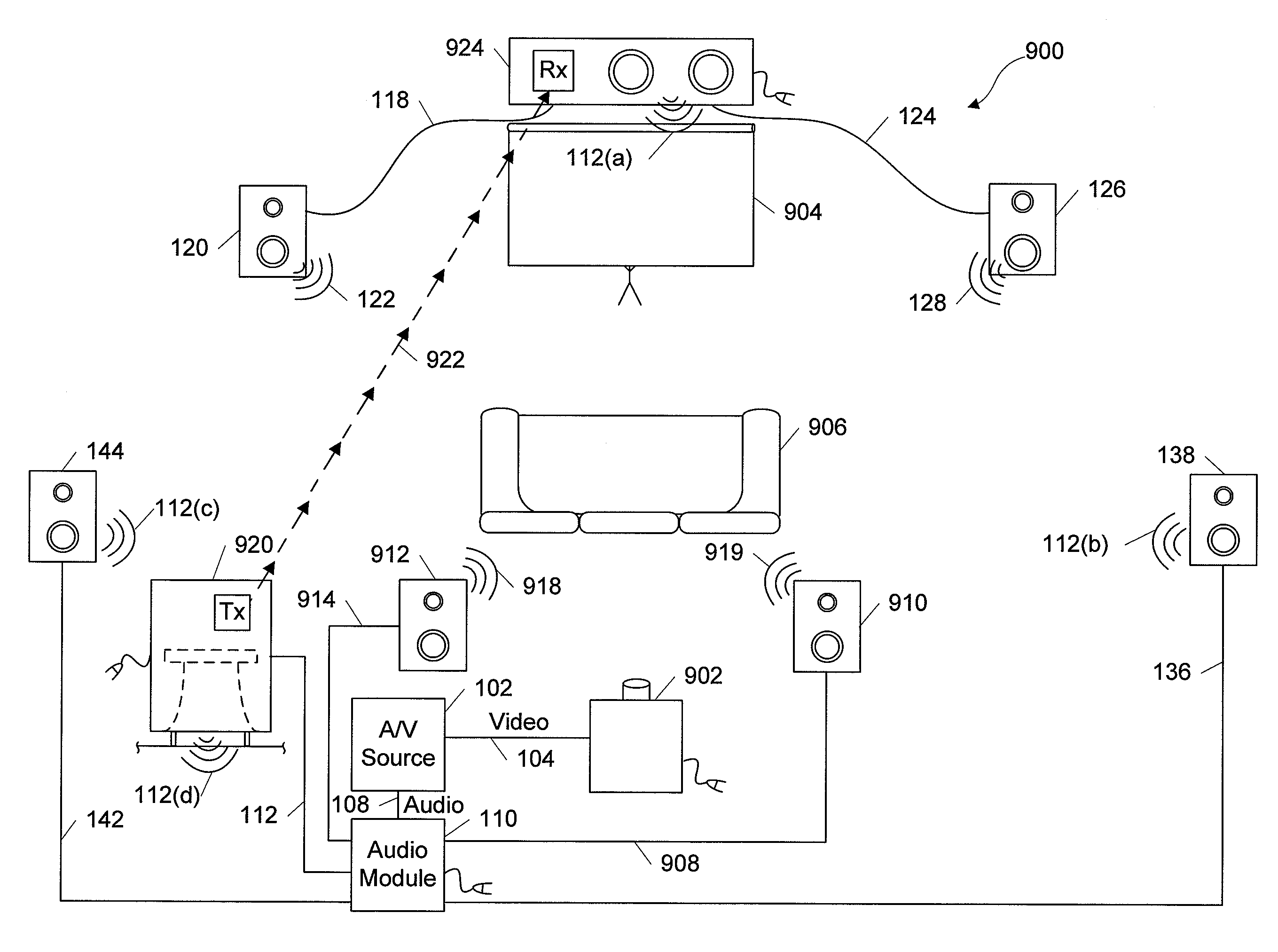
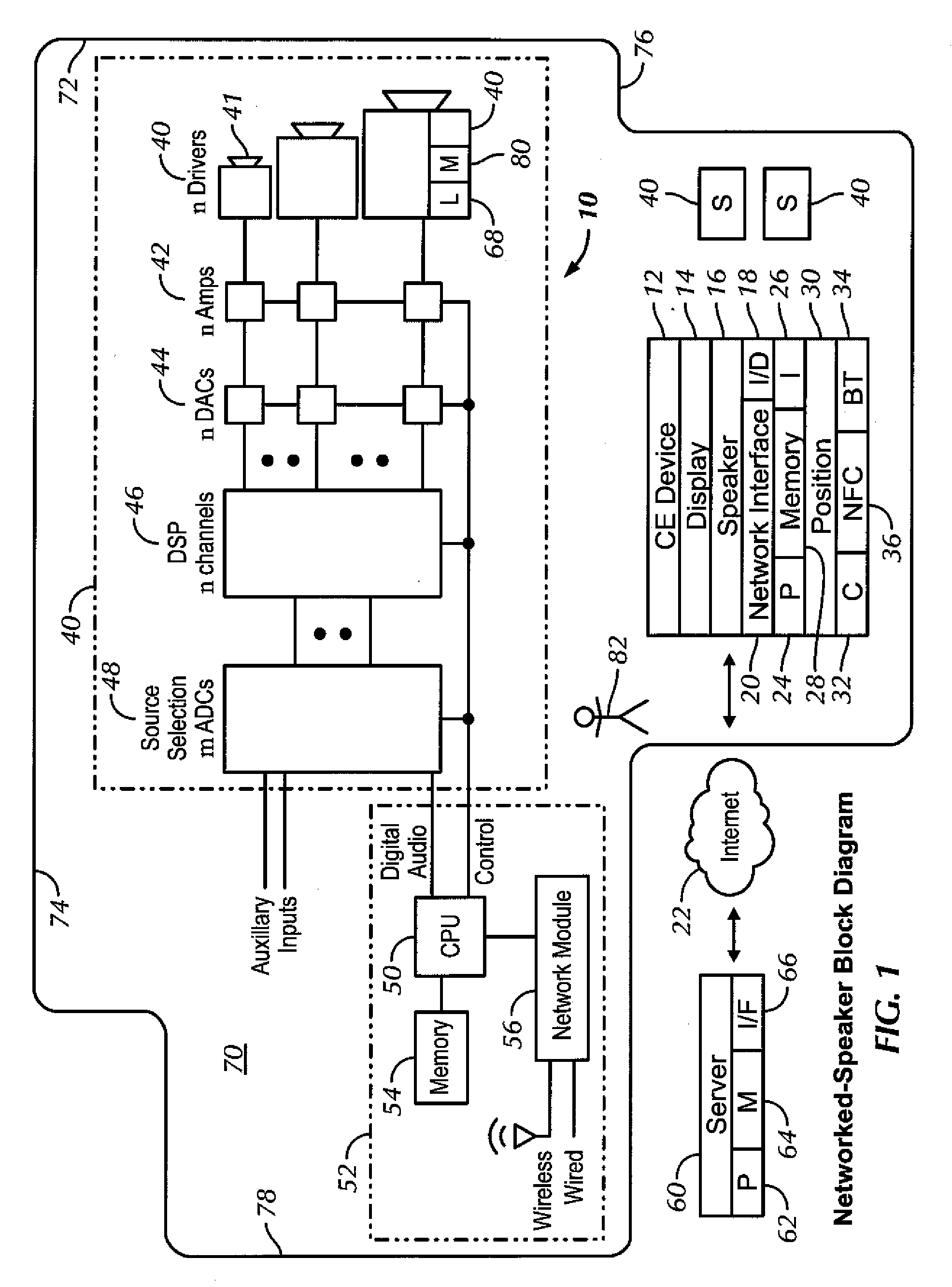
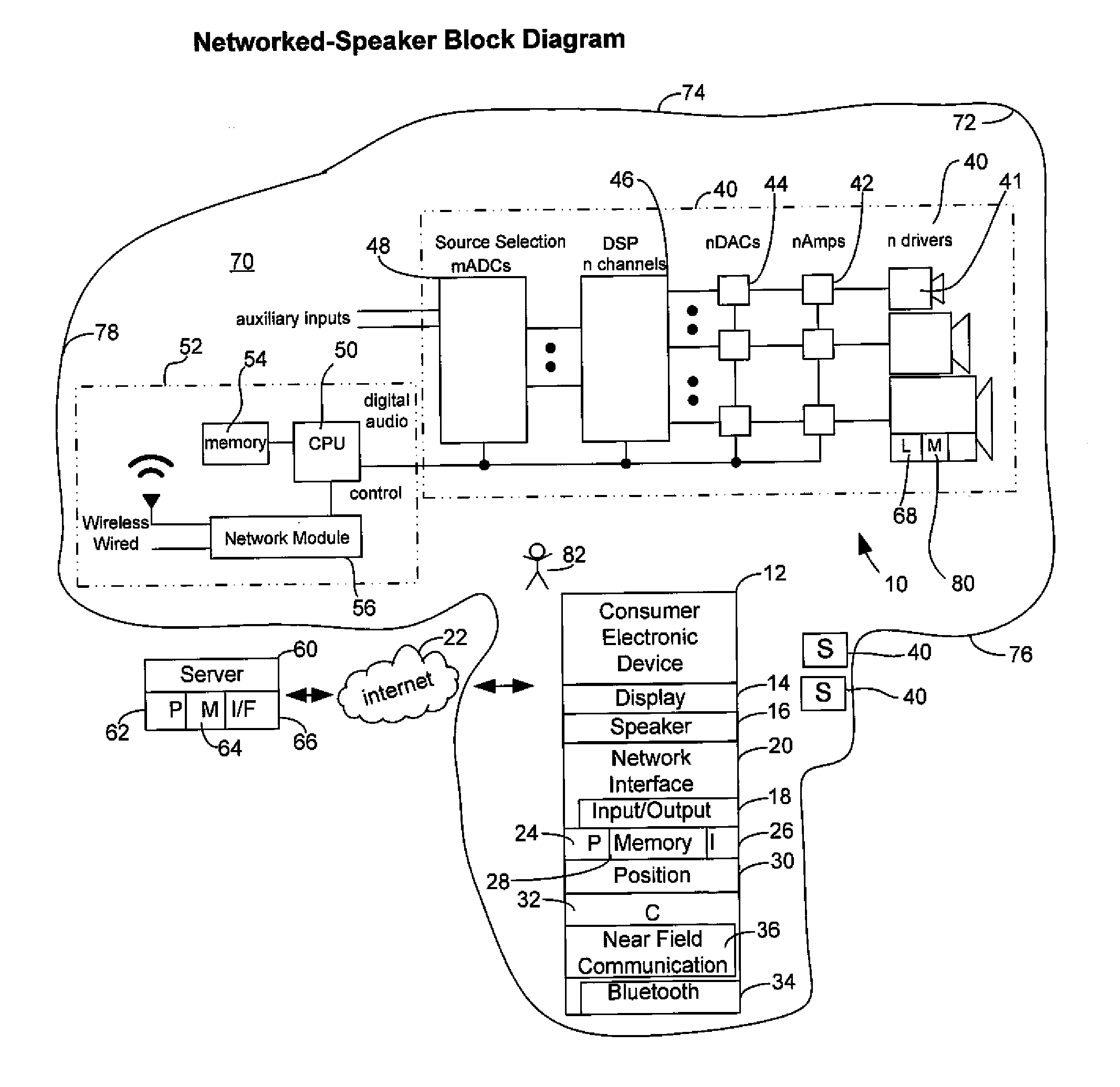
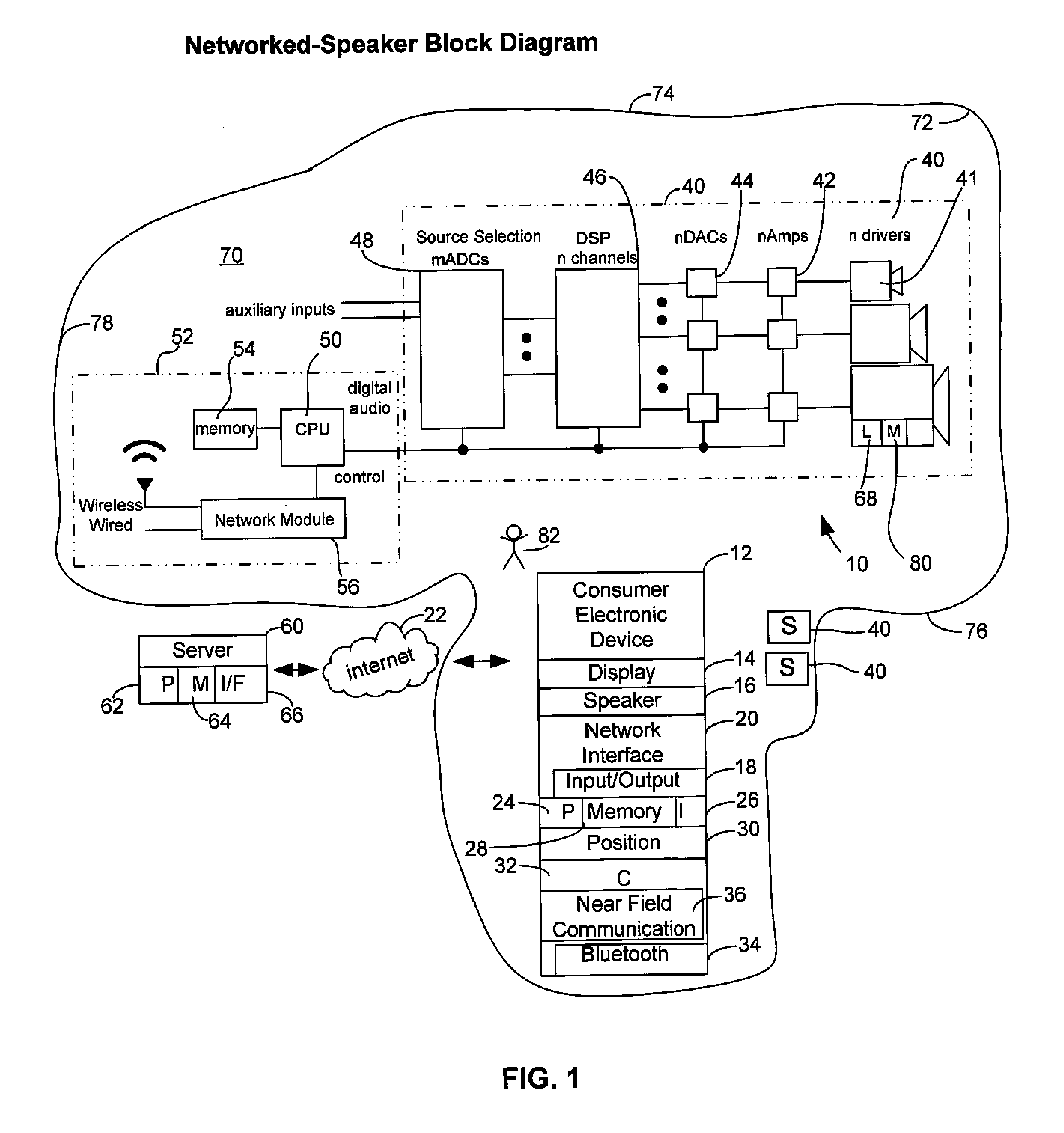
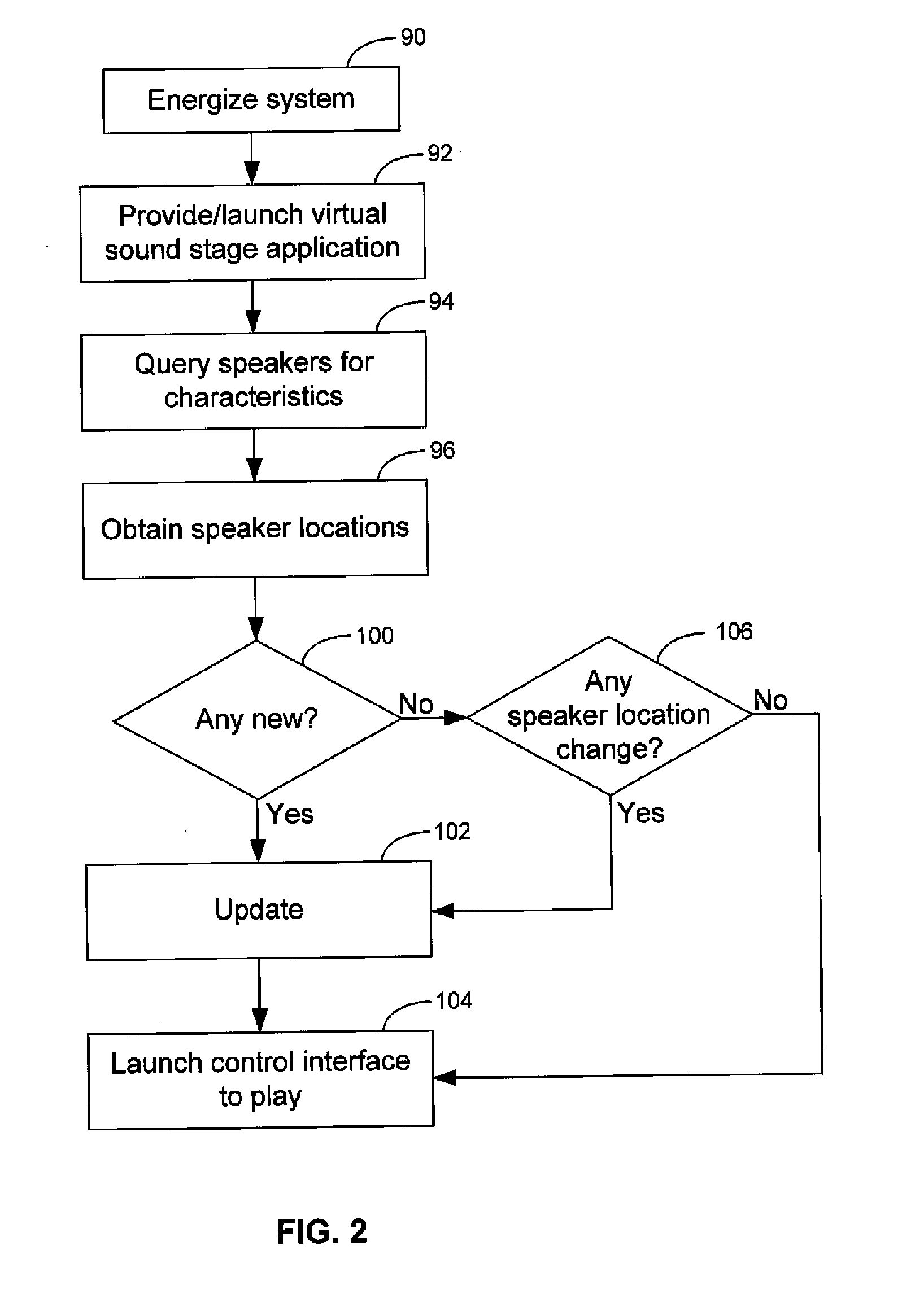
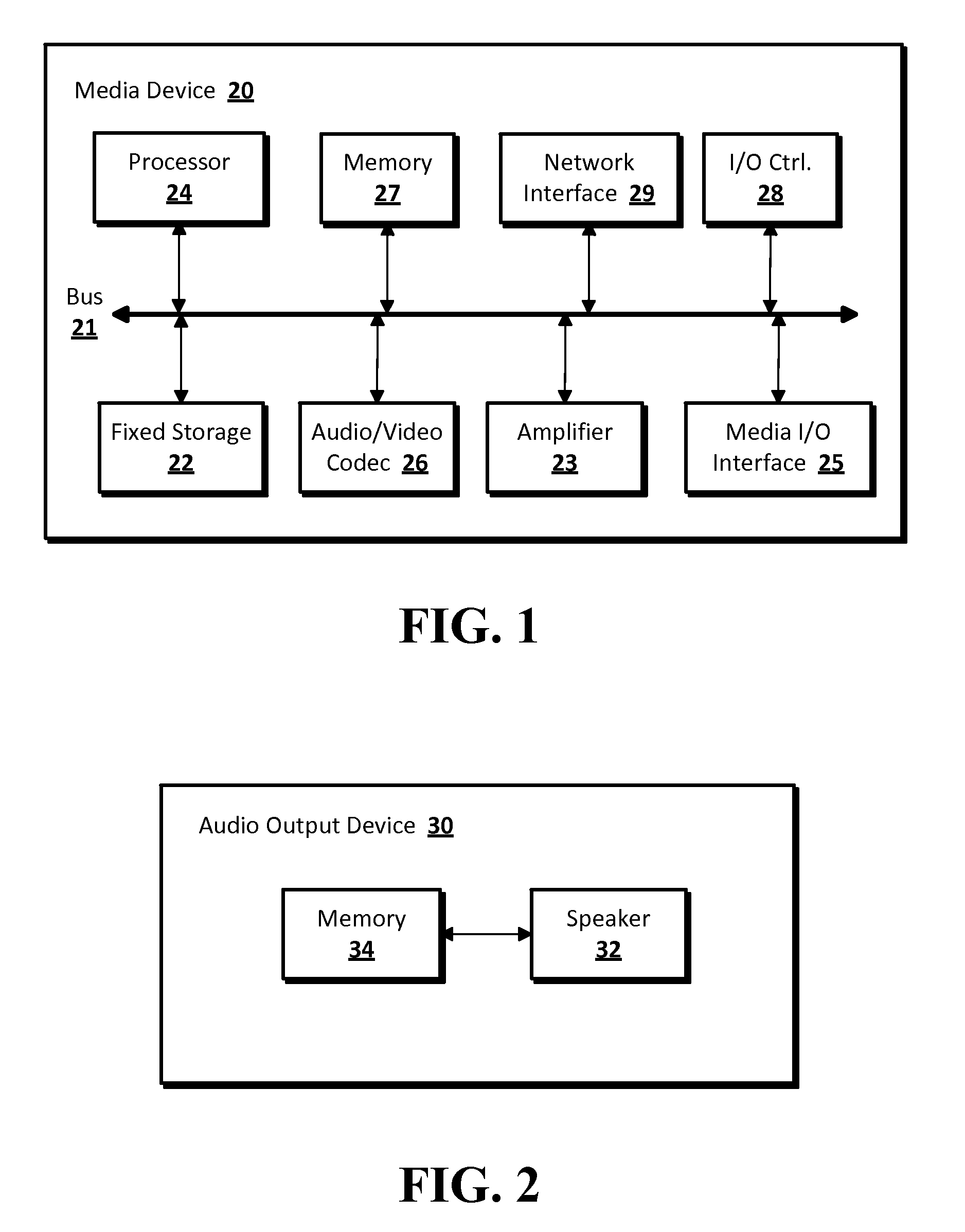
Method and apparatus for controlling multimedia players in a multi-zone system
Techniques for controlling zone group and zone group characteristics such as audio volume in a multi-zone system are disclosed. The multi-zone system includes a number of multimedia players, each preferably located in a zone. A controller may control the operations of all of the zone players remotely from any one of the zones. Two or more zone players may be dynamically grouped as a zone group for synchronized operations. According to one aspect of the techniques, a zone group configuration can be managed, updated, modified via an interactive user interface provided in a controlling device. The zone group configuration may be saved in one of zone players. According to another aspect of the techniques, the audio volume control of a zone group can be performed individually or synchronously as a group.
Owner:SONOS
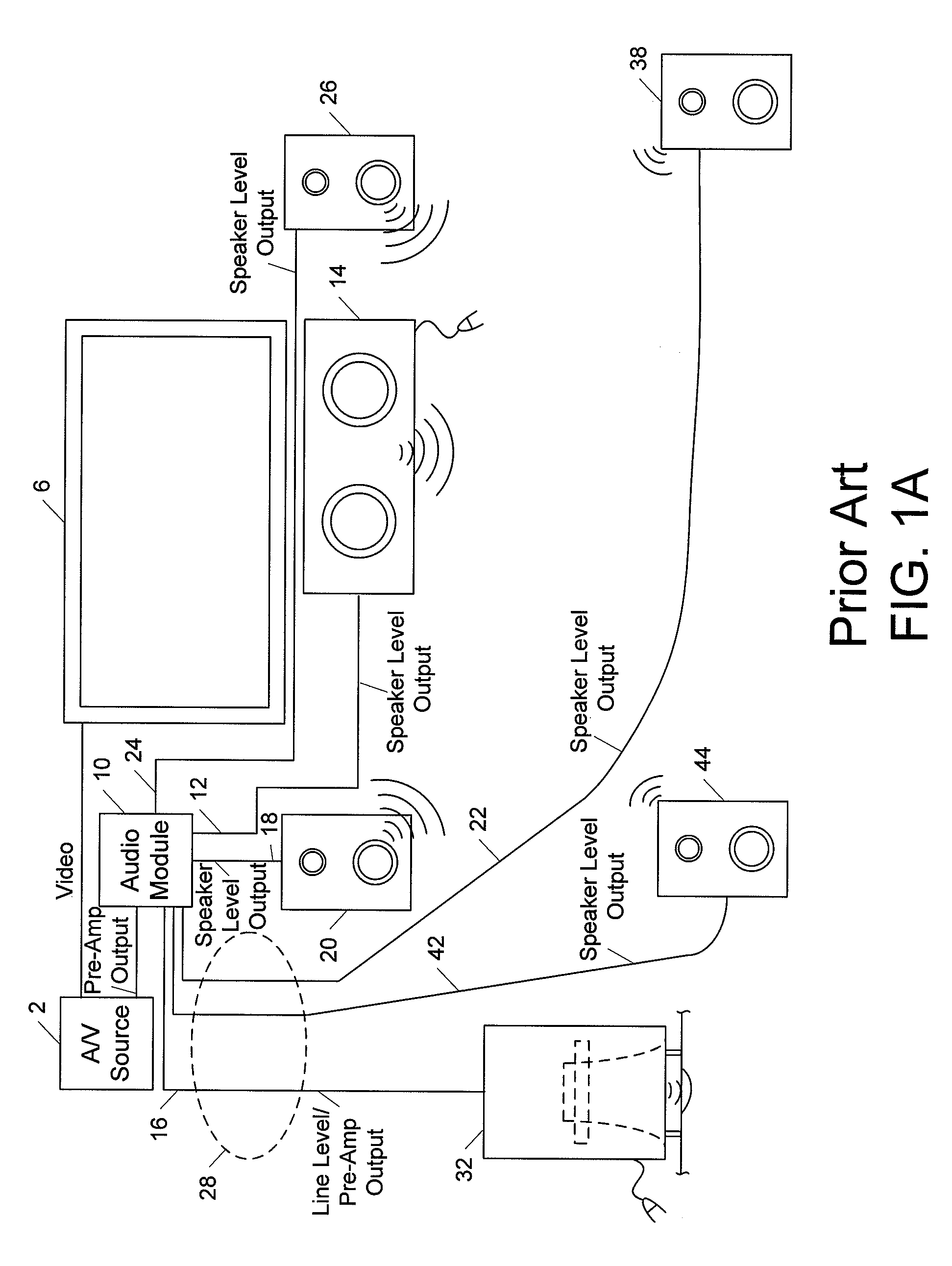
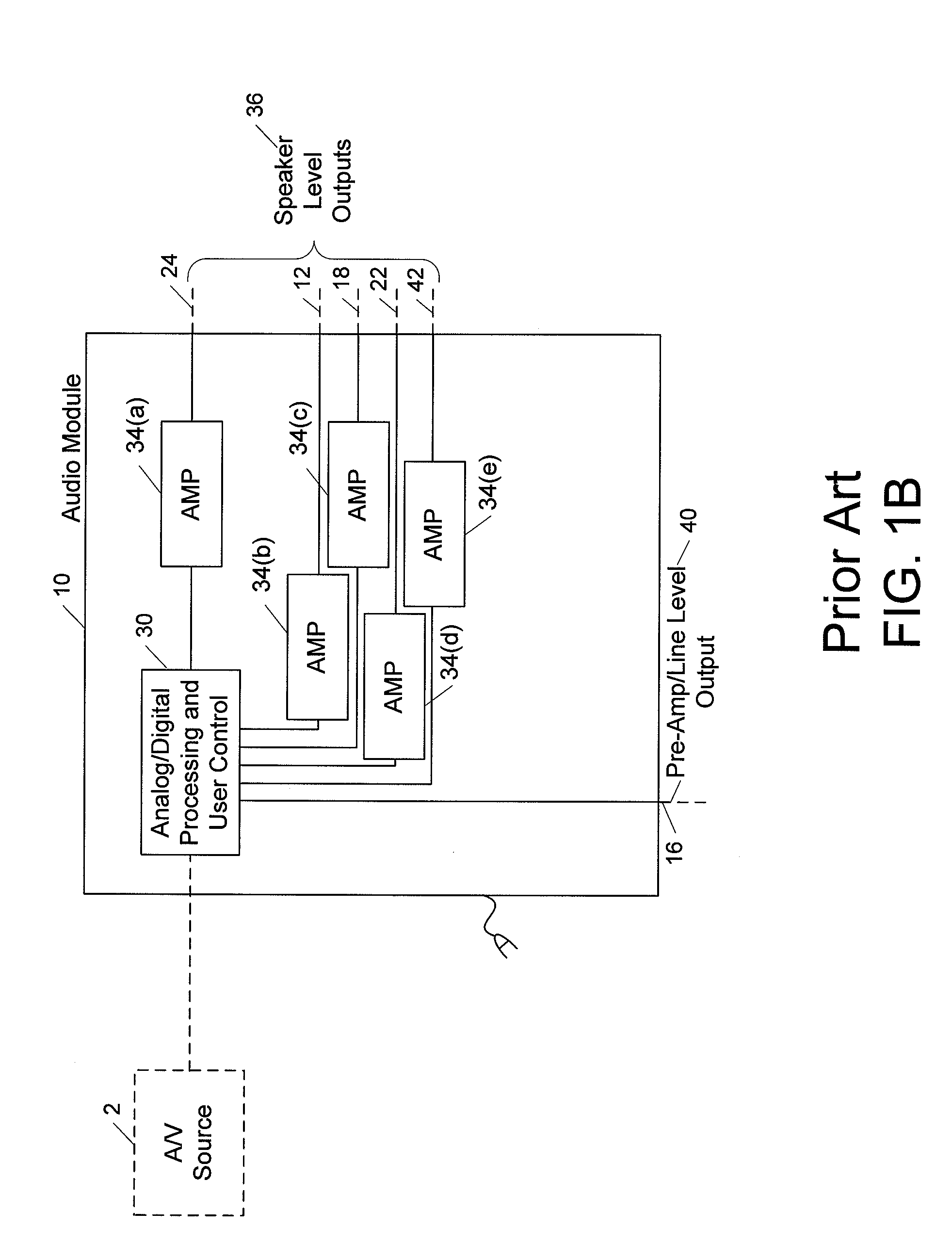
Wireless and wired speaker hub for a home theater system
Owner:APPLE INC
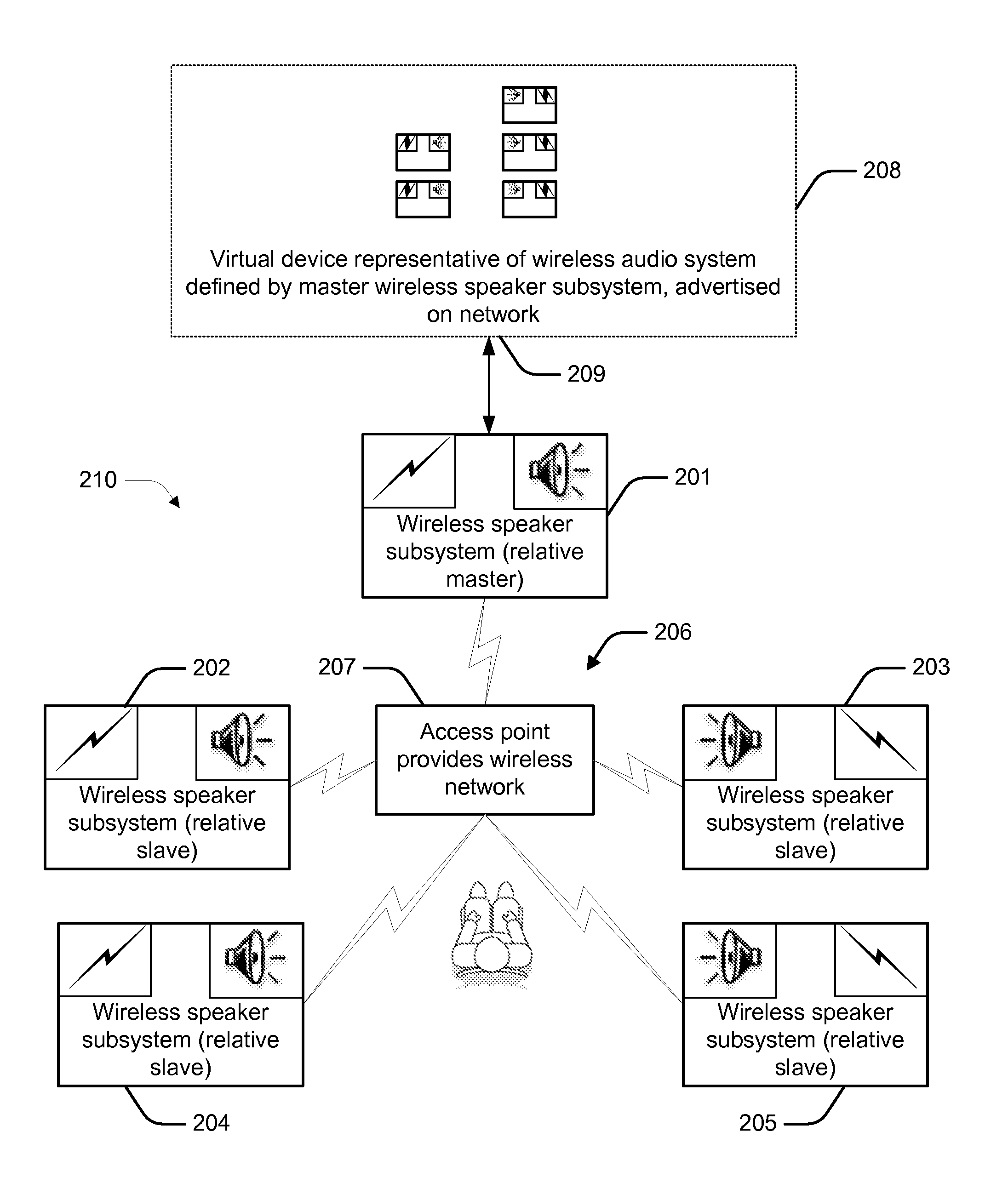
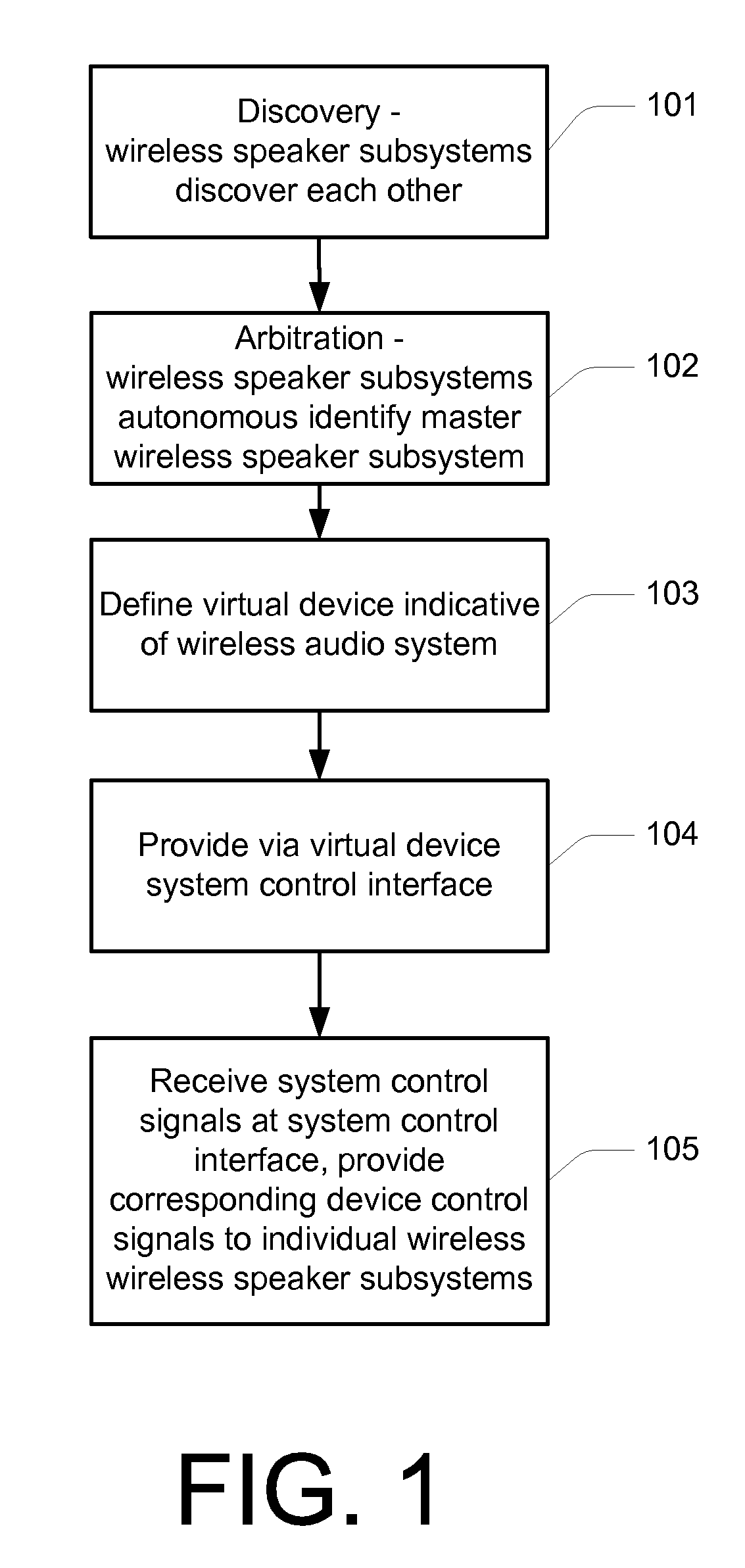
Unification of multimedia devices
ActiveUS7987294B2Multiple digital computer combinationsLoudspeaker signals distributionComputer scienceMultimedia device
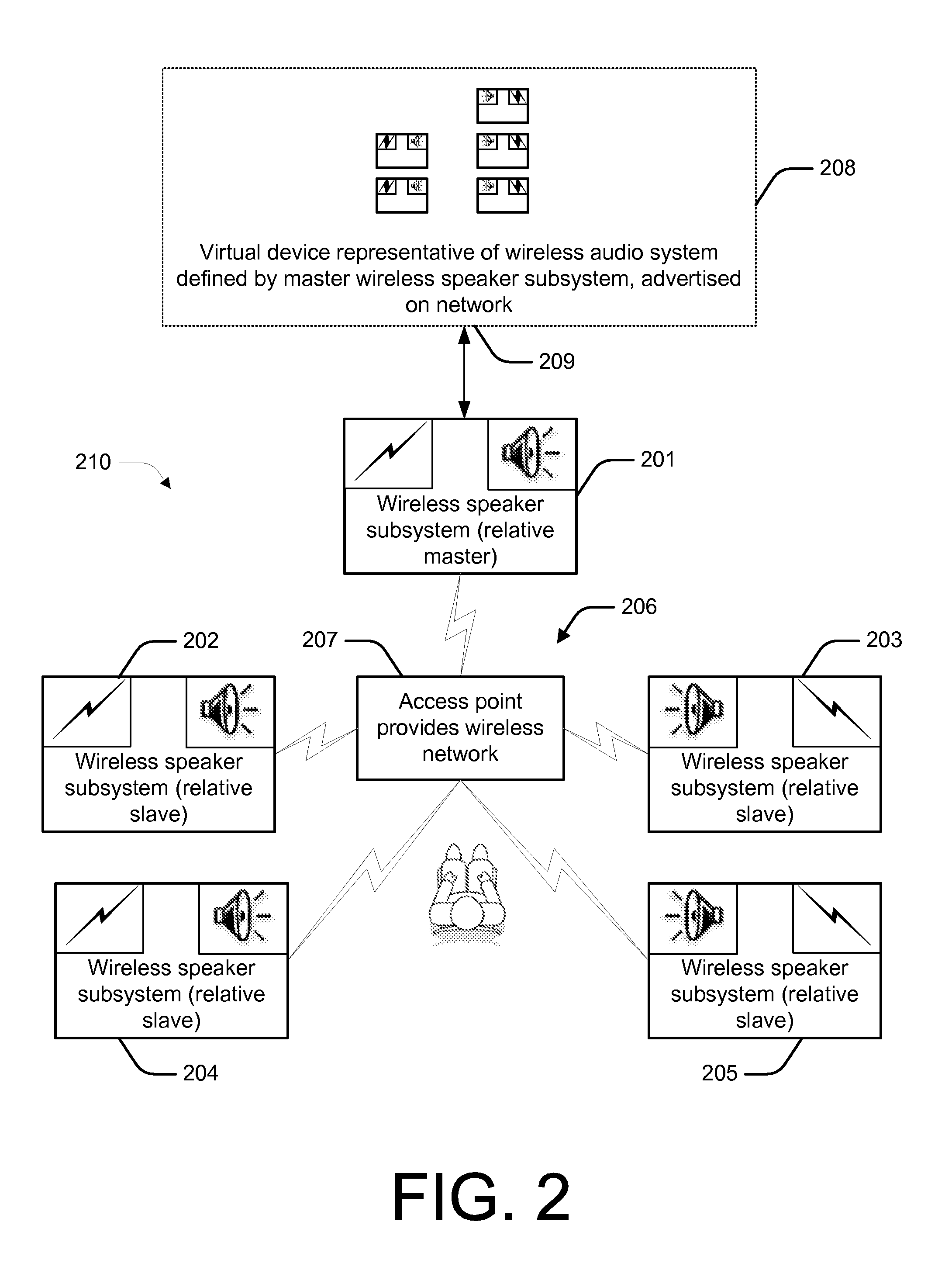
Described herein are various methods and systems relating to the unification of media devices, and more specifically to the provision of wireless audio systems. In overview, two or more wireless speaker subsystem units substantially autonomously form a single wireless audio system having its own control interface. This control interface is used to apply operational changes across the wireless audio system, such as volume adjustment. That is, an operational change may be applied to the system as a whole, and this change is subsequently implemented by each of the individual wireless speaker subsystem units.
Owner:D & M HOLDINGS INC
System and method for calibration of an acoustic system
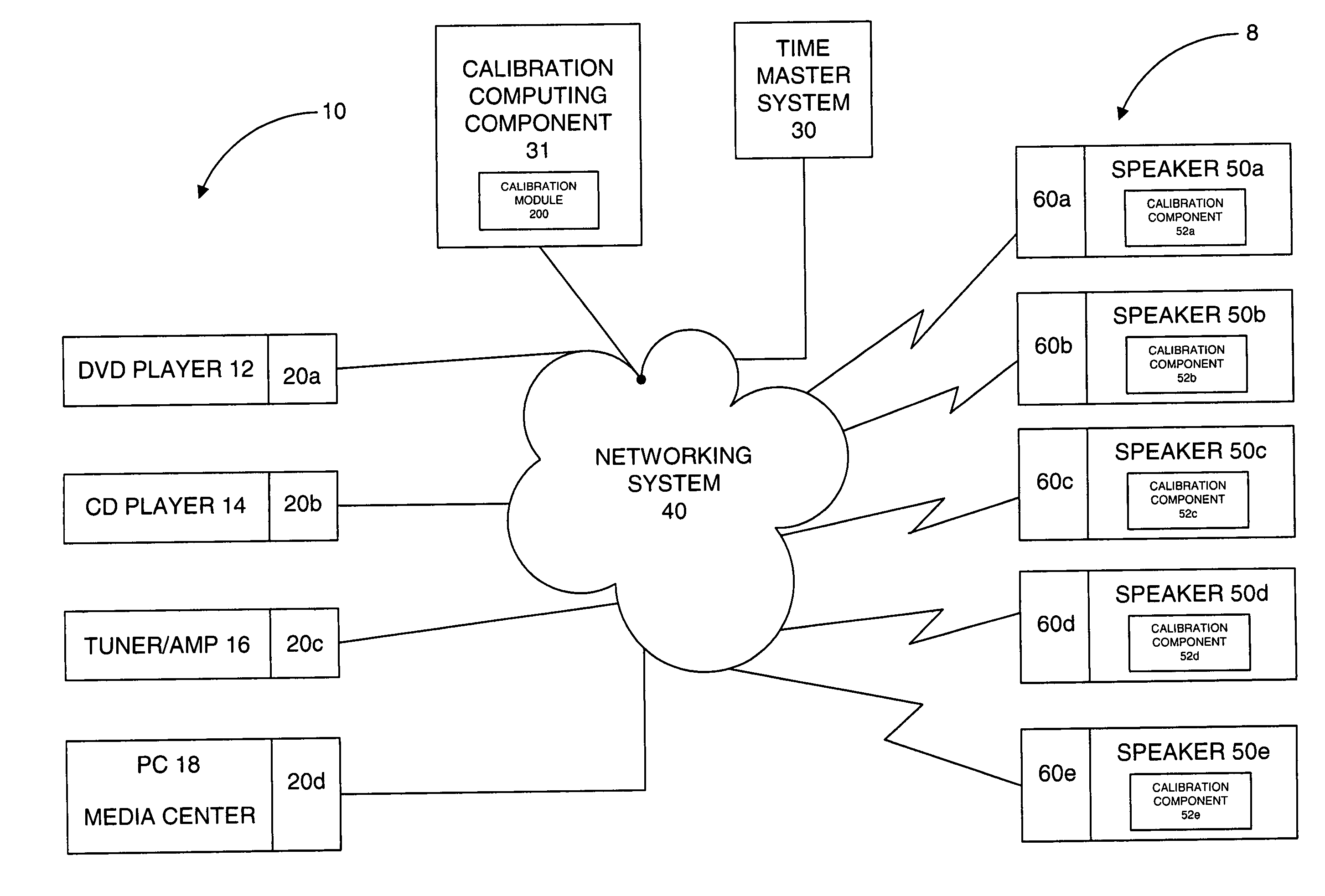
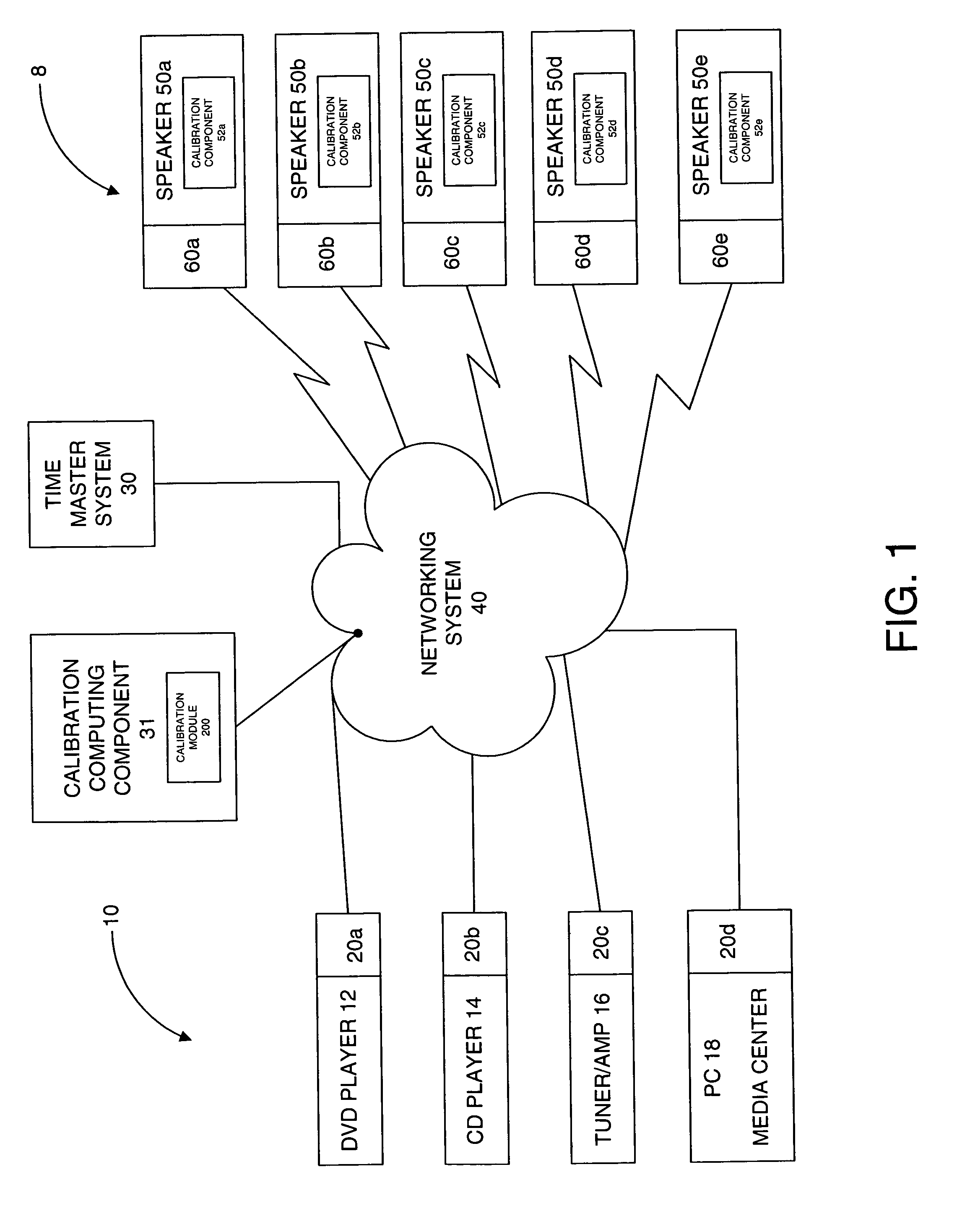
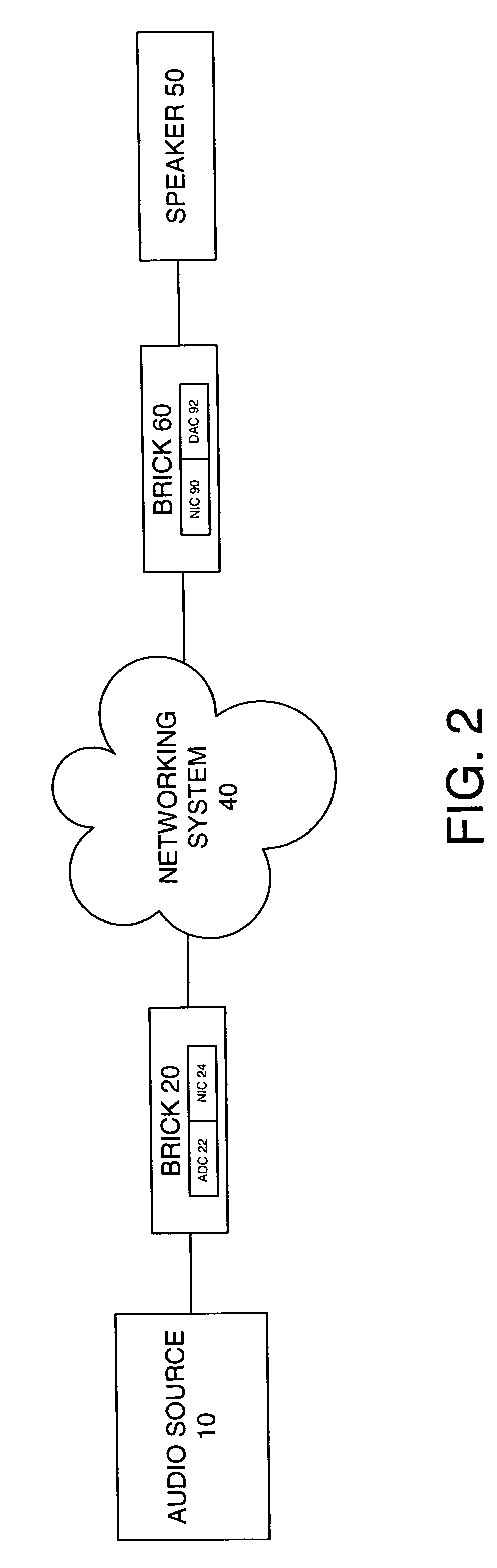
The present invention is directed to a method and system for automatic calibration of an acoustic system. The acoustic system may include a source A / V device, calibration computing device, and multiple rendering devices. The calibration system may include a calibration component attached to each rendering device and a source calibration module. The calibration component on each rendering device includes a microphone. The source calibration module includes distance and optional angle calculation tools for automatically determining a distance between the rendering device and a specified reference point upon return of the test signal from the calibration component.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
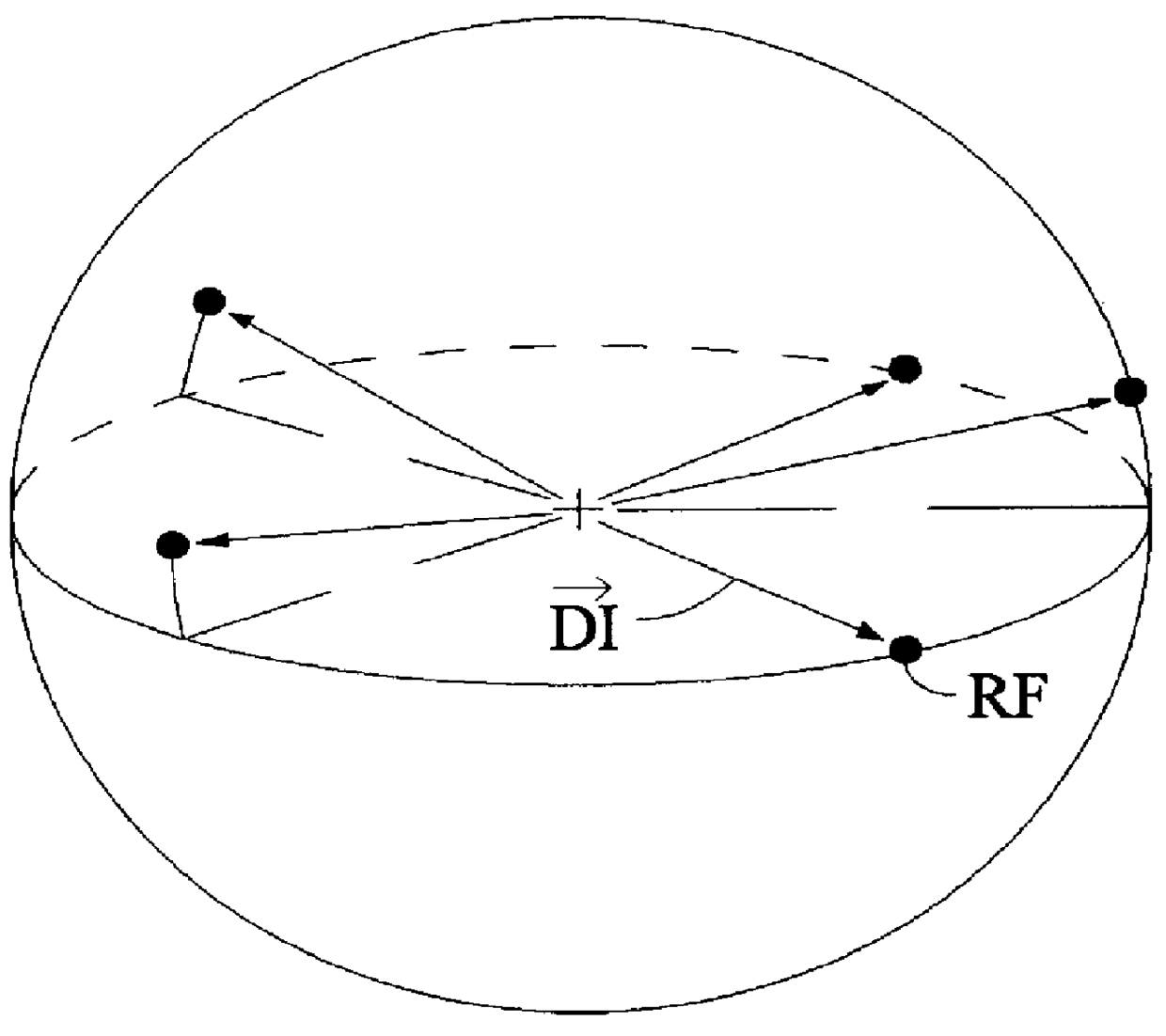
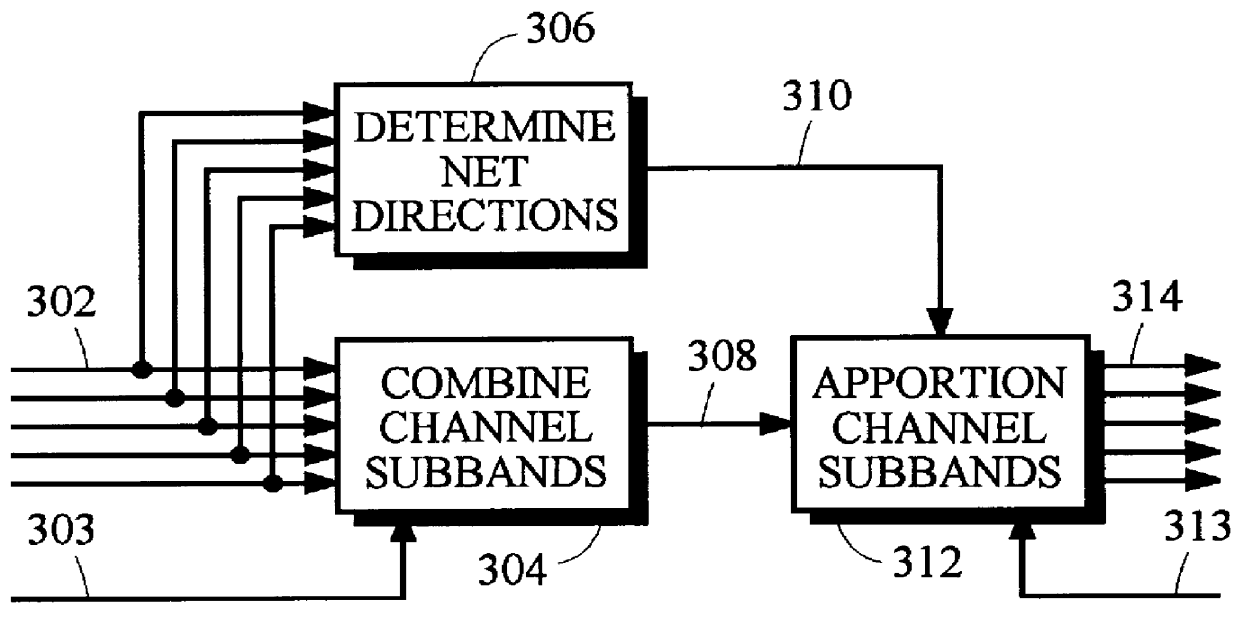
Coding method and apparatus for multiple channels of audio information representing three-dimensional sound fields
InactiveUS6021386AConserve substantial bandwidthConveniently implementedBroadcast information characterisationSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumBit allocation
In an encoder, multiple channels of audio information representing multidimensional sound fields are split into subband signals and the subband signals in one or more subbands are combined to form composite signals. The composite signals, the subband signals not combined into a composite signal and information describing the spectral levels of subband signals combined into composite signals are assembled into an encoded output signal. The spectral level information conveys either the amplitude or power of the combined subband signals or the apparent direction of the sound field represented by the combined subband signals. In digital implementations, adaptive bit allocation may be used to reduce the informational requirements of the encoded signal.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
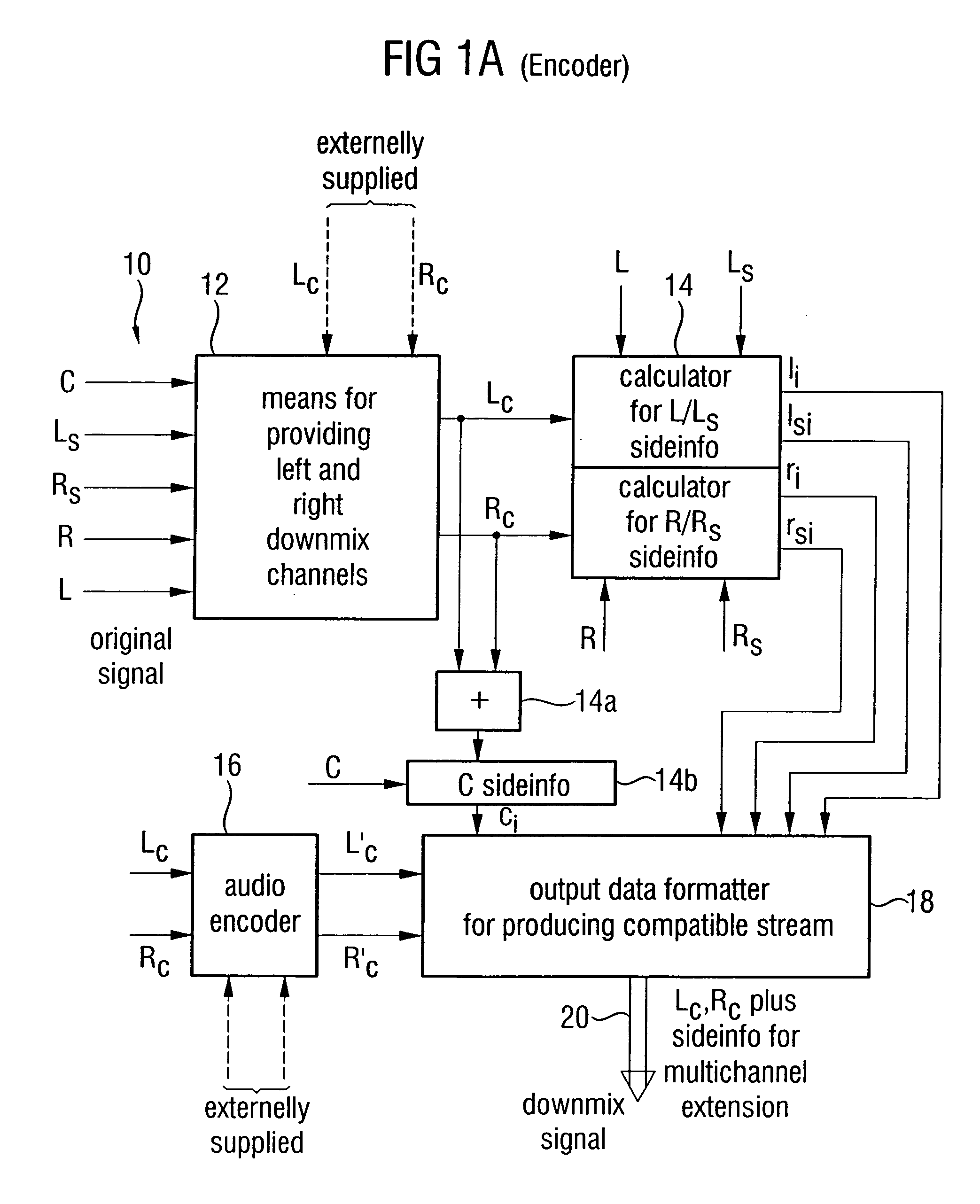
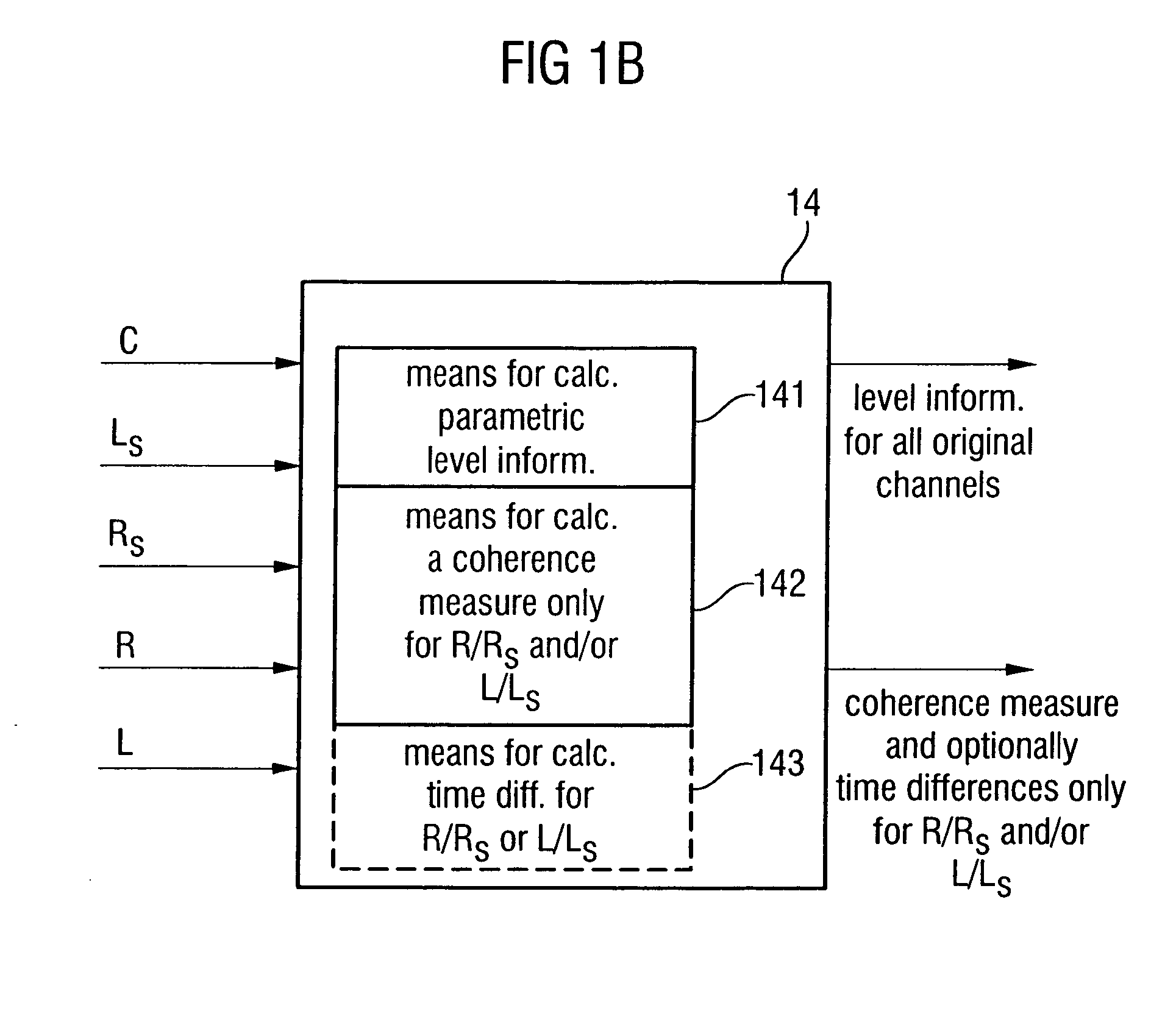
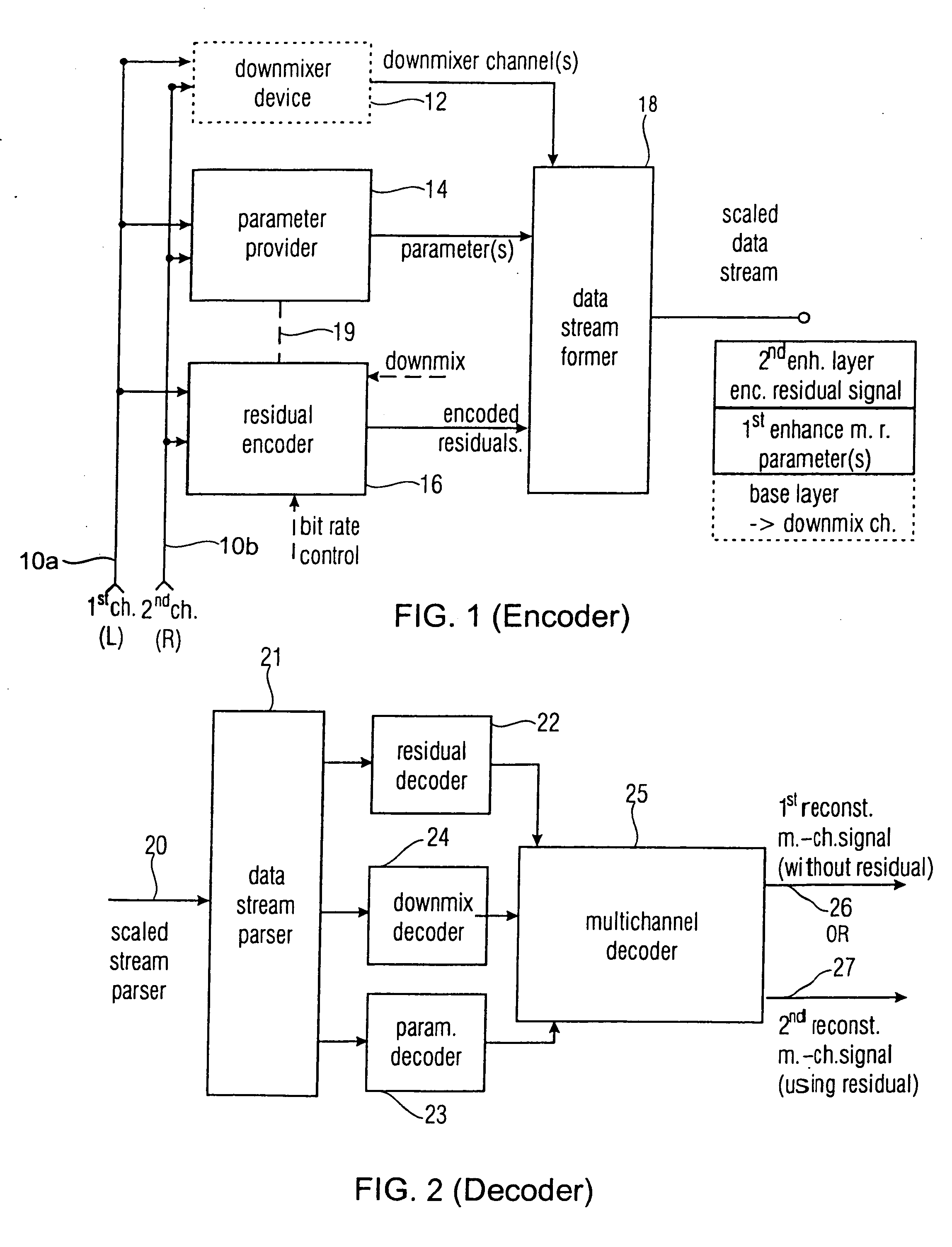
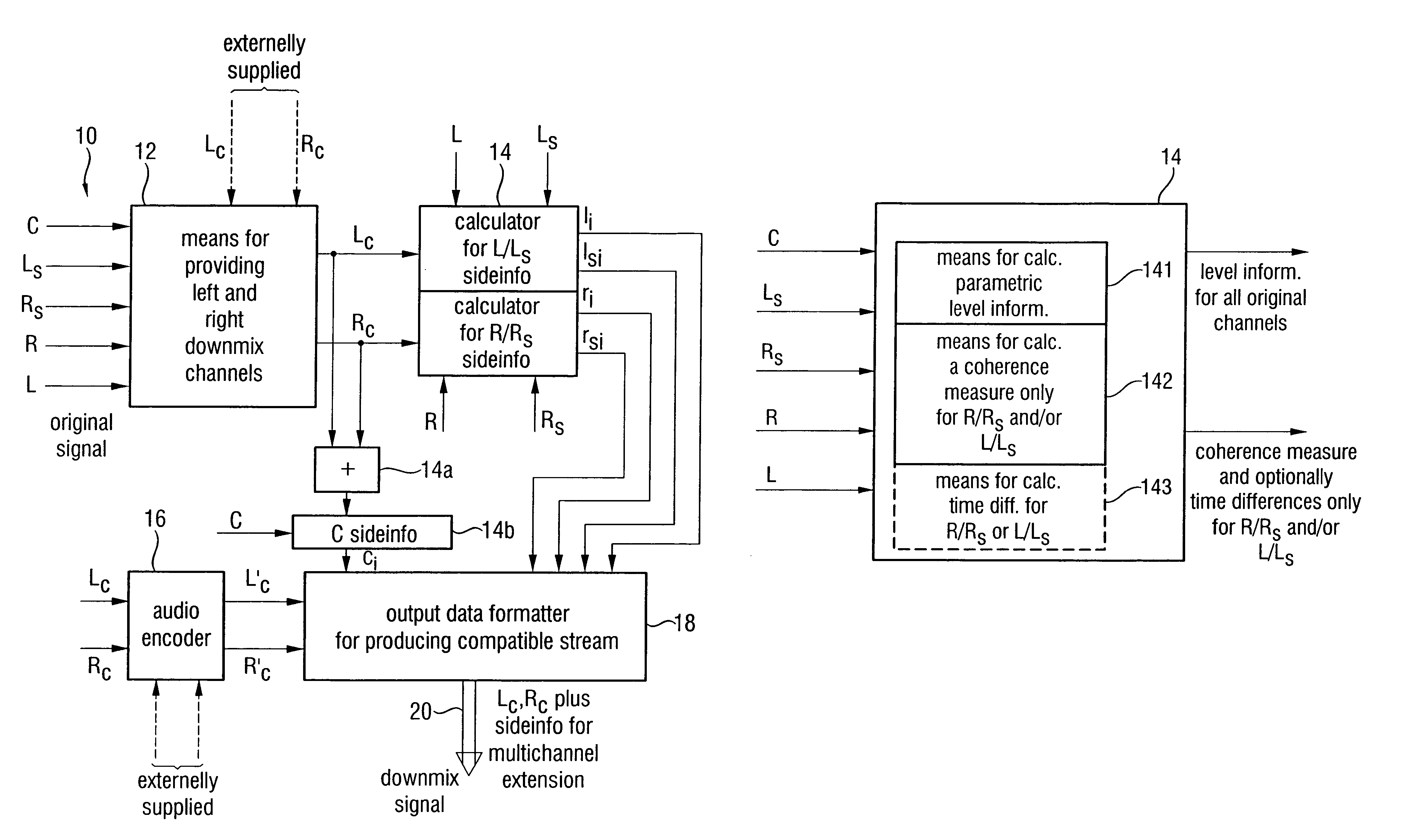
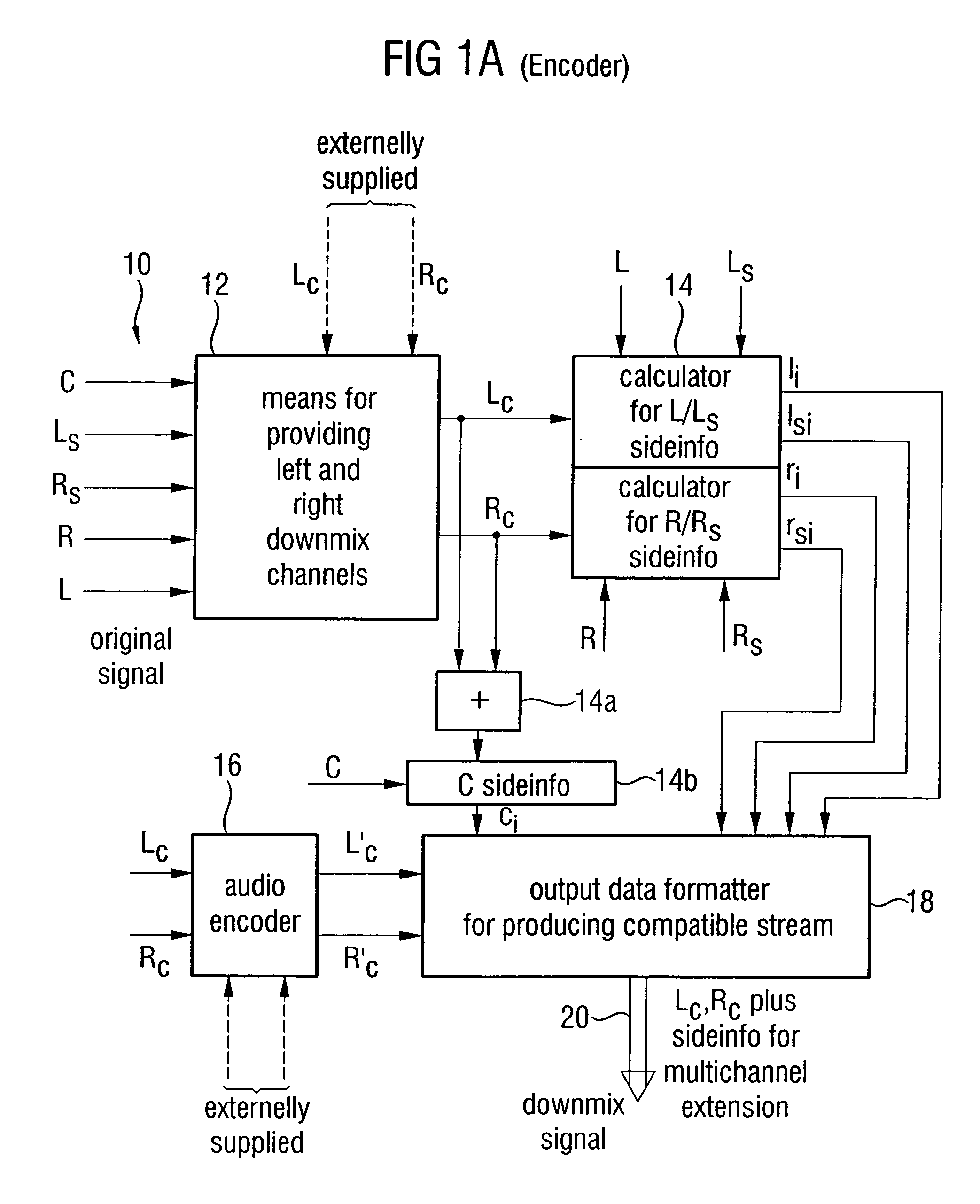
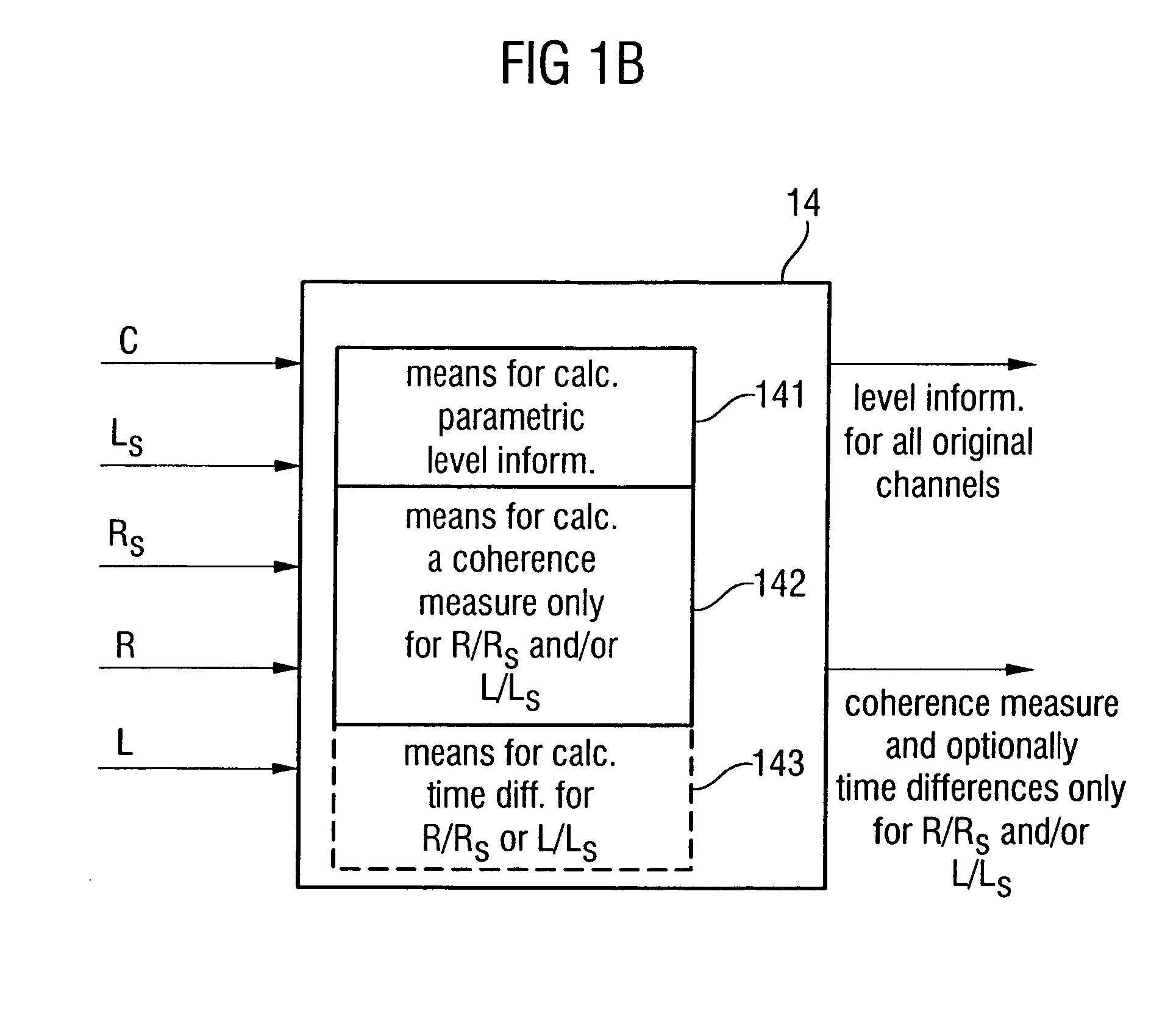
Apparatus and method for constructing a multi-channel output signal or for generating a downmix signal
ActiveUS20050157883A1High scaleReduce processing loadSpeech analysisTransmissionSide informationEngineering
The apparatus for constructing a multi-channel output signal using an input signal and parametric side information, the input signal including the first input channel and the second input channel derived from an original multi-channel signal, and the parametric side information describing interrelations between channels of the multi-channel original signal uses base channels for synthesizing first and second output channels on one side of an assumed listener position, which are different from each other. The base channels are different from each other because of a coherence measure. Coherence between the base channels (for example the left and the left surround reconstructed channel) is reduced by calculating a base channel for one of those channels by a combination of the input channels, the combination being determined by the coherence measure. Thus, a high subjective quality of the reconstruction can be obtained because of an approximated original front / back coherence.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV +1
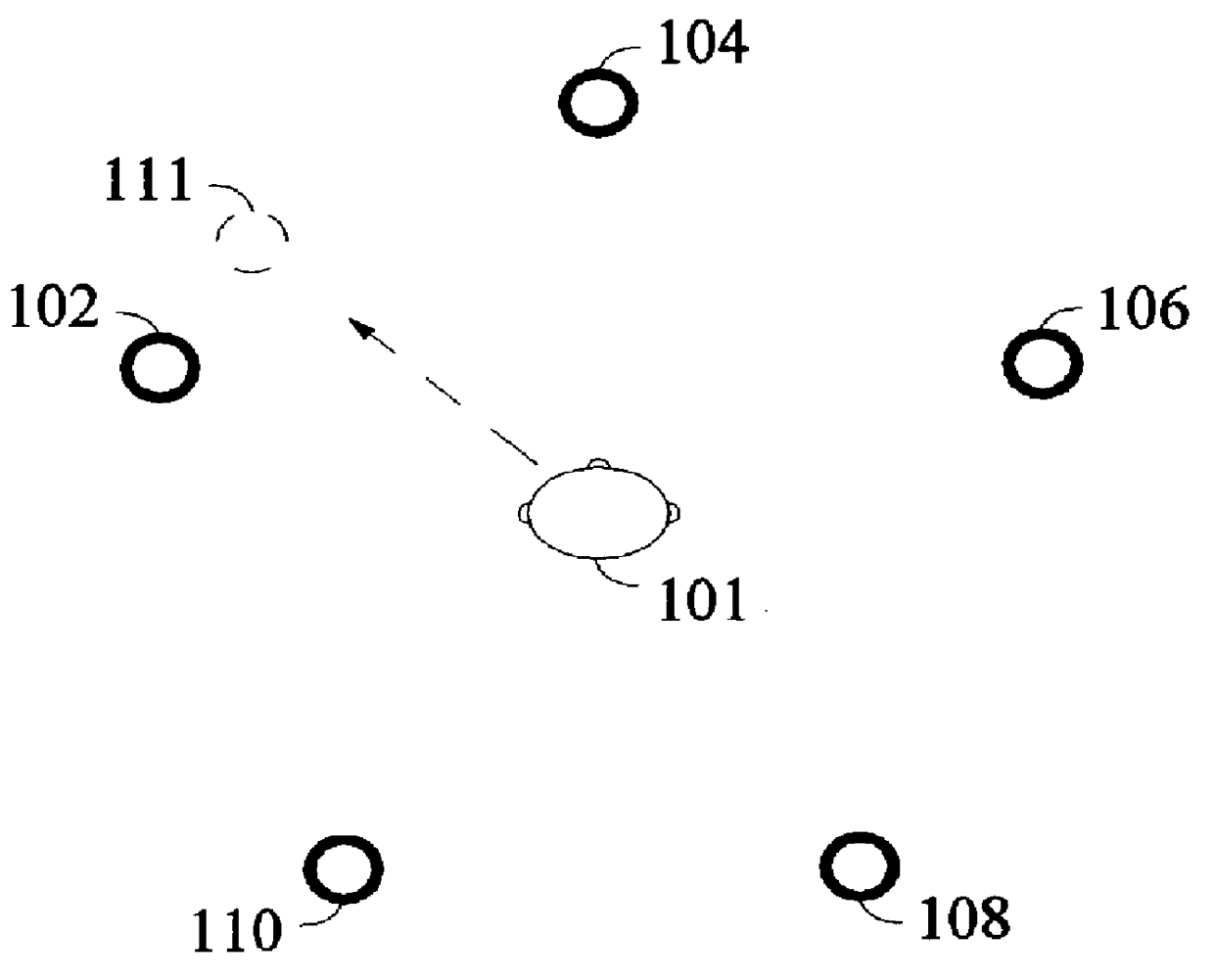
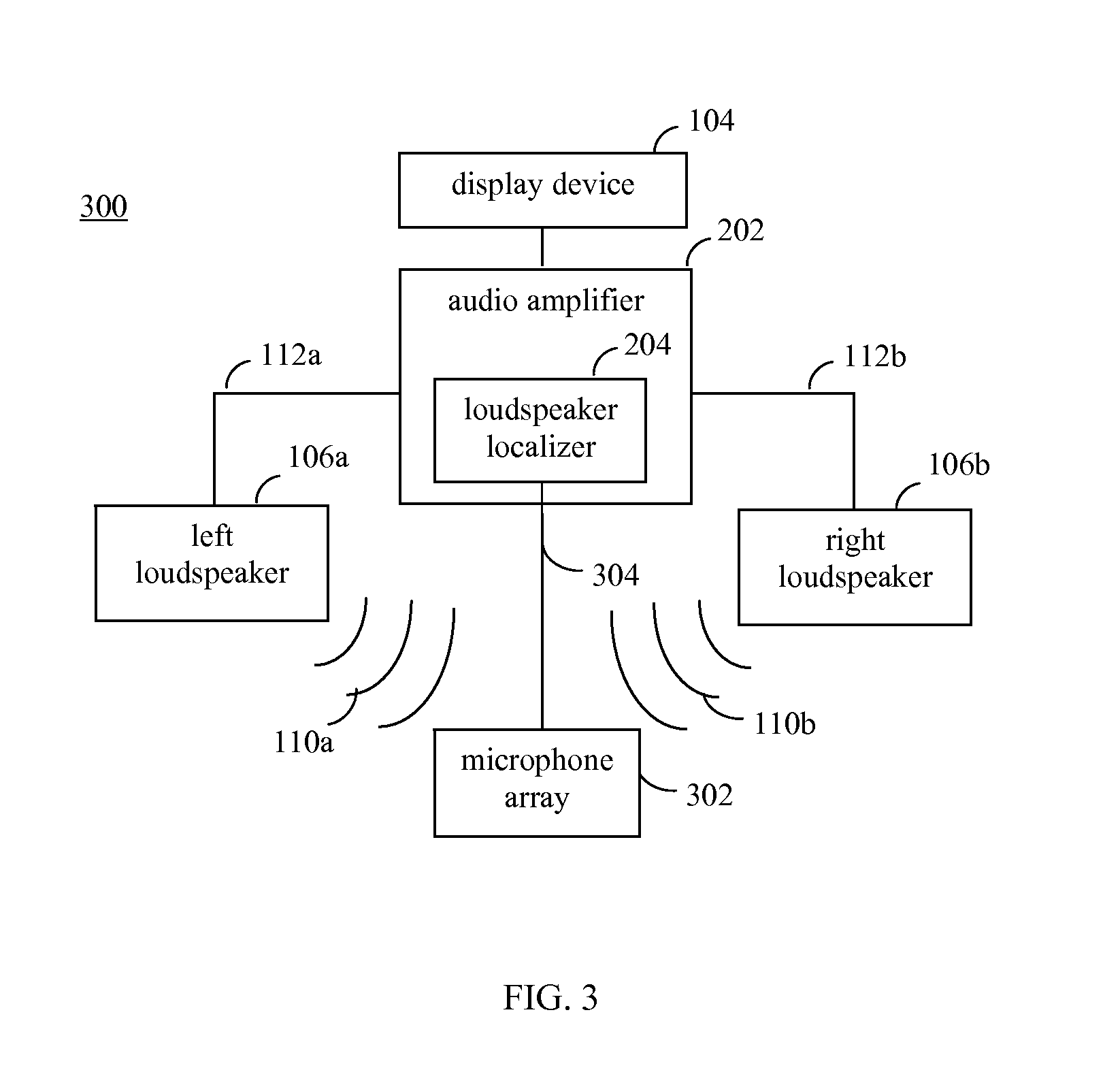
Loudspeaker localization techniques
Techniques for loudspeaker localization are provided. Sound is received from a loudspeaker at a plurality of microphone locations. A plurality of audio signals is generated based on the sound received at the plurality of microphone locations. Location information is generated that indicates a loudspeaker location for the loudspeaker based on the plurality of audio signals. Whether the generated location information matches a predetermined desired loudspeaker location for the loudspeaker is determined. A corrective action with regard to the loudspeaker is enabled to be performed if the generated location information is determined to not match the predetermined desired loudspeaker location for the loudspeaker.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
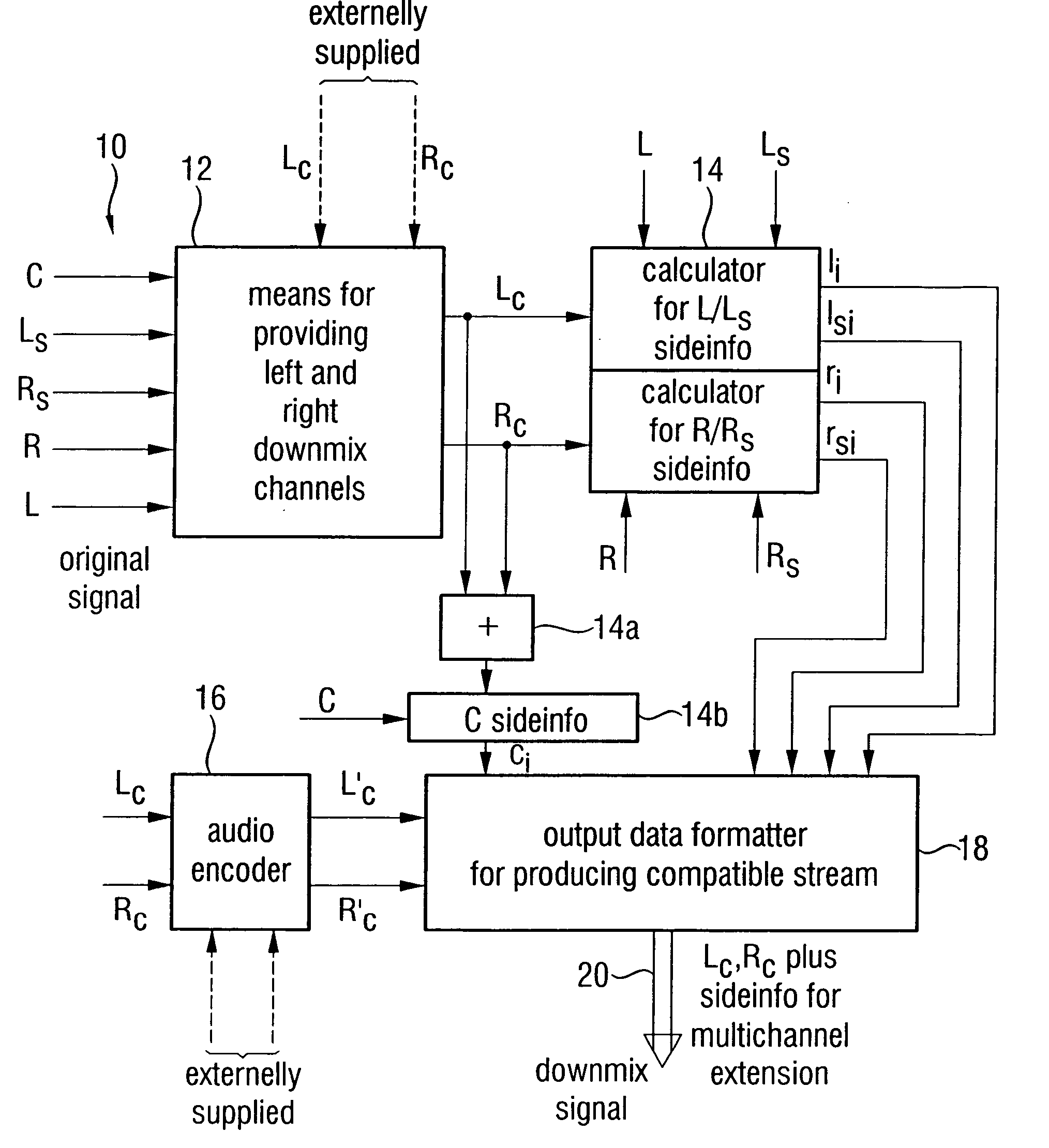
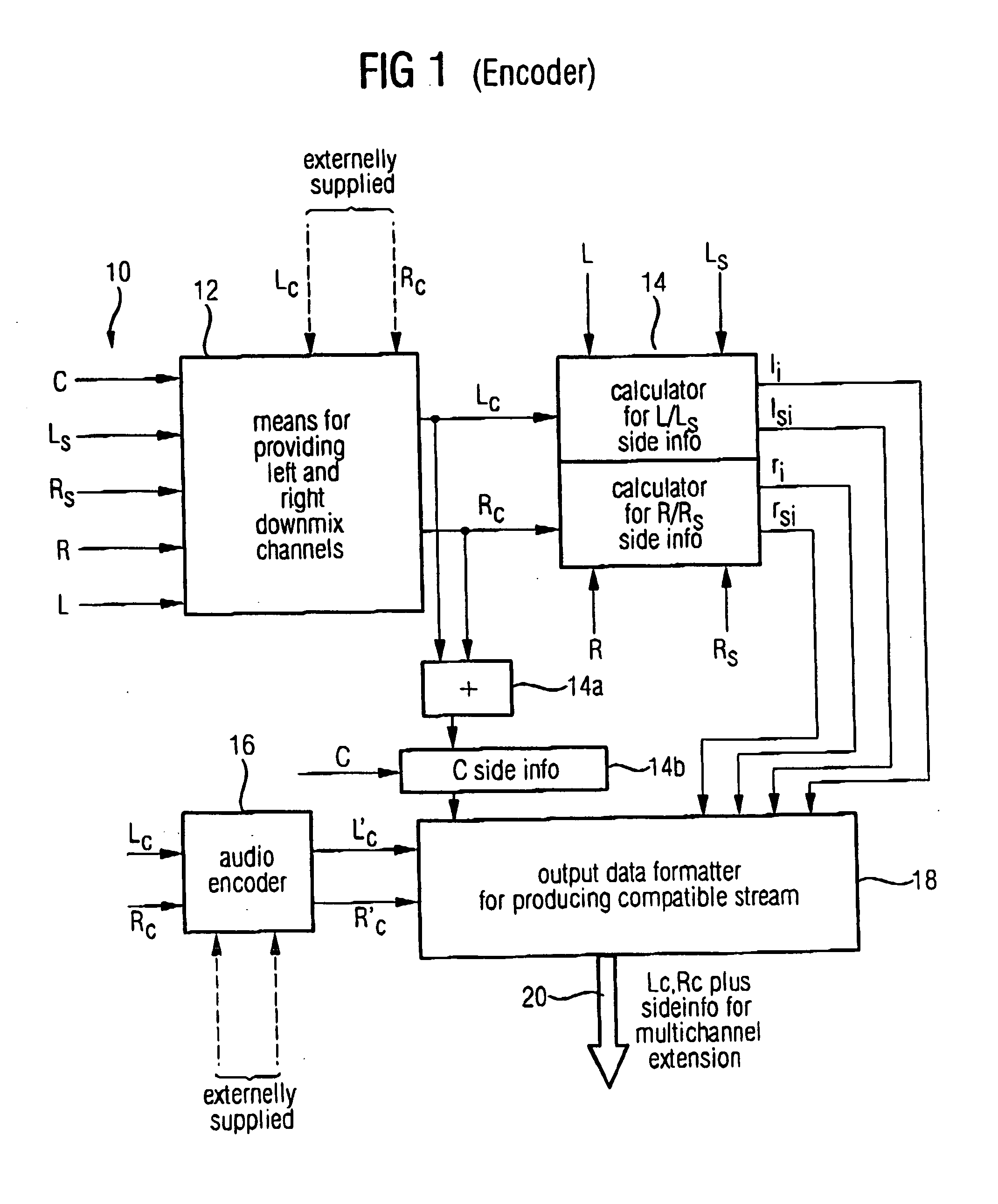
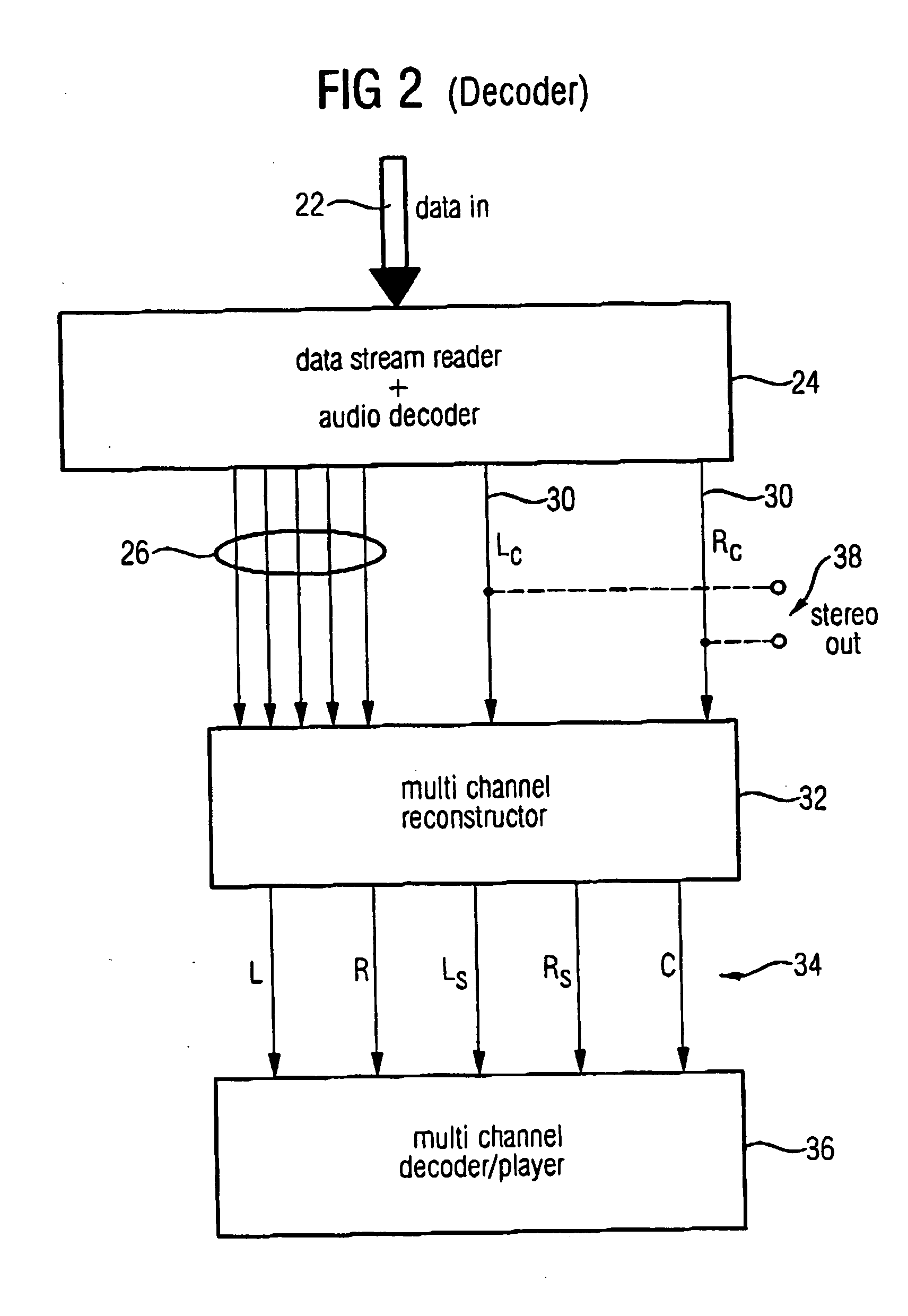
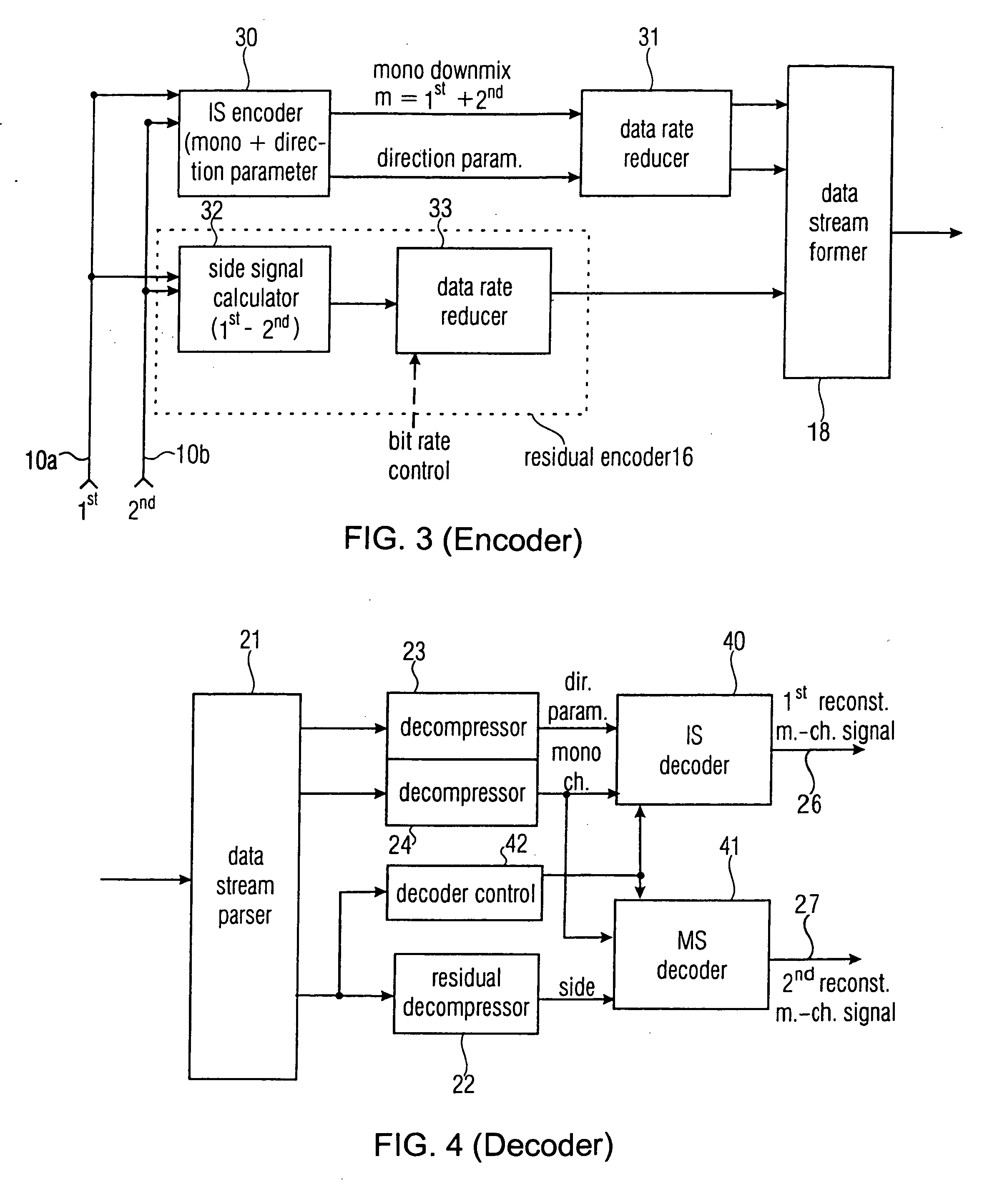
Compatible multi-channel coding/decoding
ActiveUS20050074127A1Suitable for processingEfficient and artifact-reduced encodingSpeech analysisStereophonic systemsSide informationComputer science
In processing a multi-channel audio signal having at least three original channels, a first downmix channel and a second downmix channel are provided, which are derived from the original channels. For a selected original channel of the original channels, channel side information are calculated such that a downmix channel or a combined downmix channel including the first and the second downmix channels, when weighted using the channel side information, results in an approximation of the selected original channel. The channel side information and the first and second downmix channels form output data to be transmitted to a decoder, which, in case of a low level decoder only decodes the first and second downmix channels or, in case of a high level decoder provides a full multi-channel audio signal based on the downmix channels and the channel side information. Since the channel side information only occupy a low number of bits, and since the decoder does not use dematrixing, an efficient and high quality multi-channel extension for stereo players and enhanced multi-channel players is obtained.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV +1
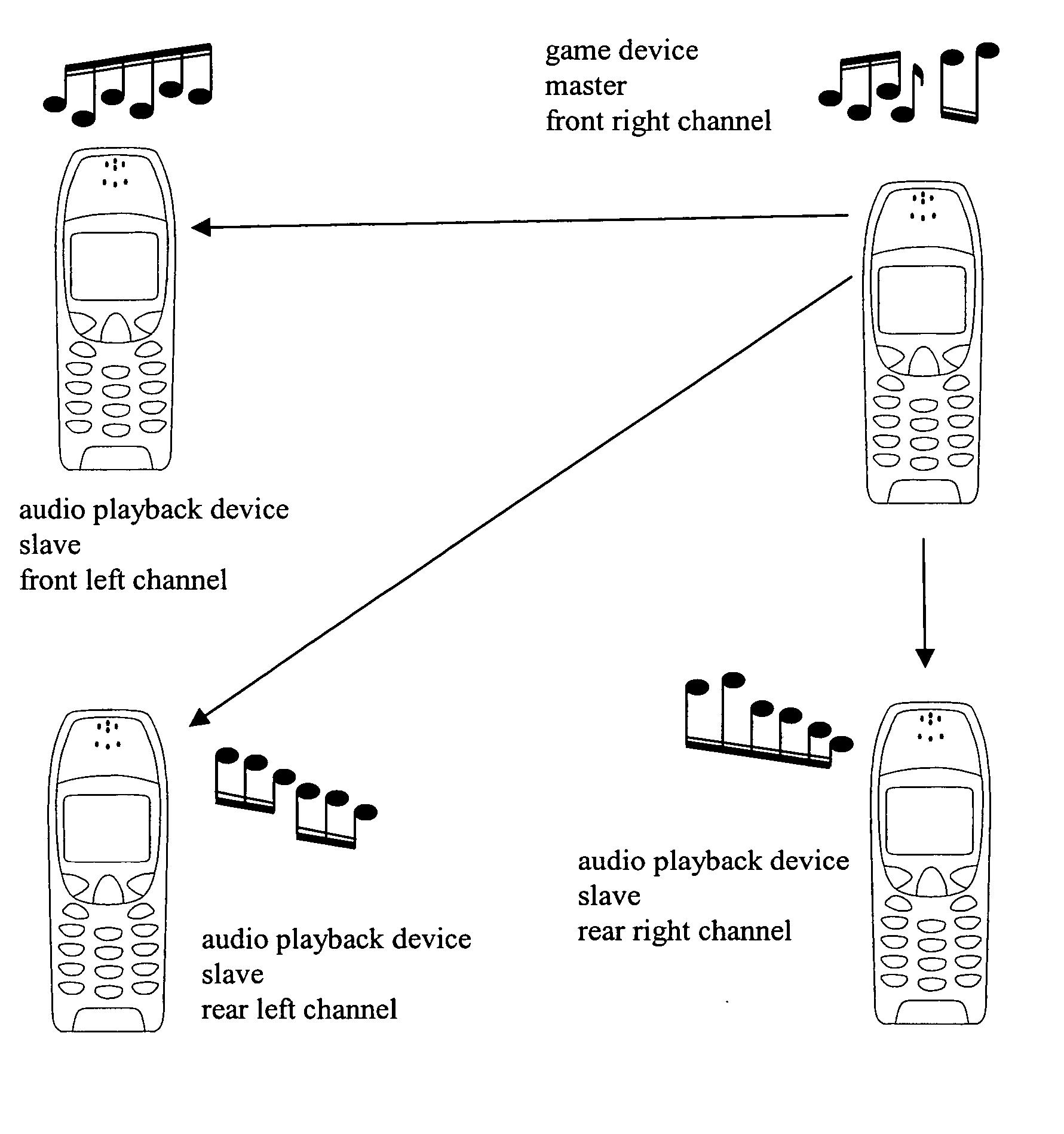
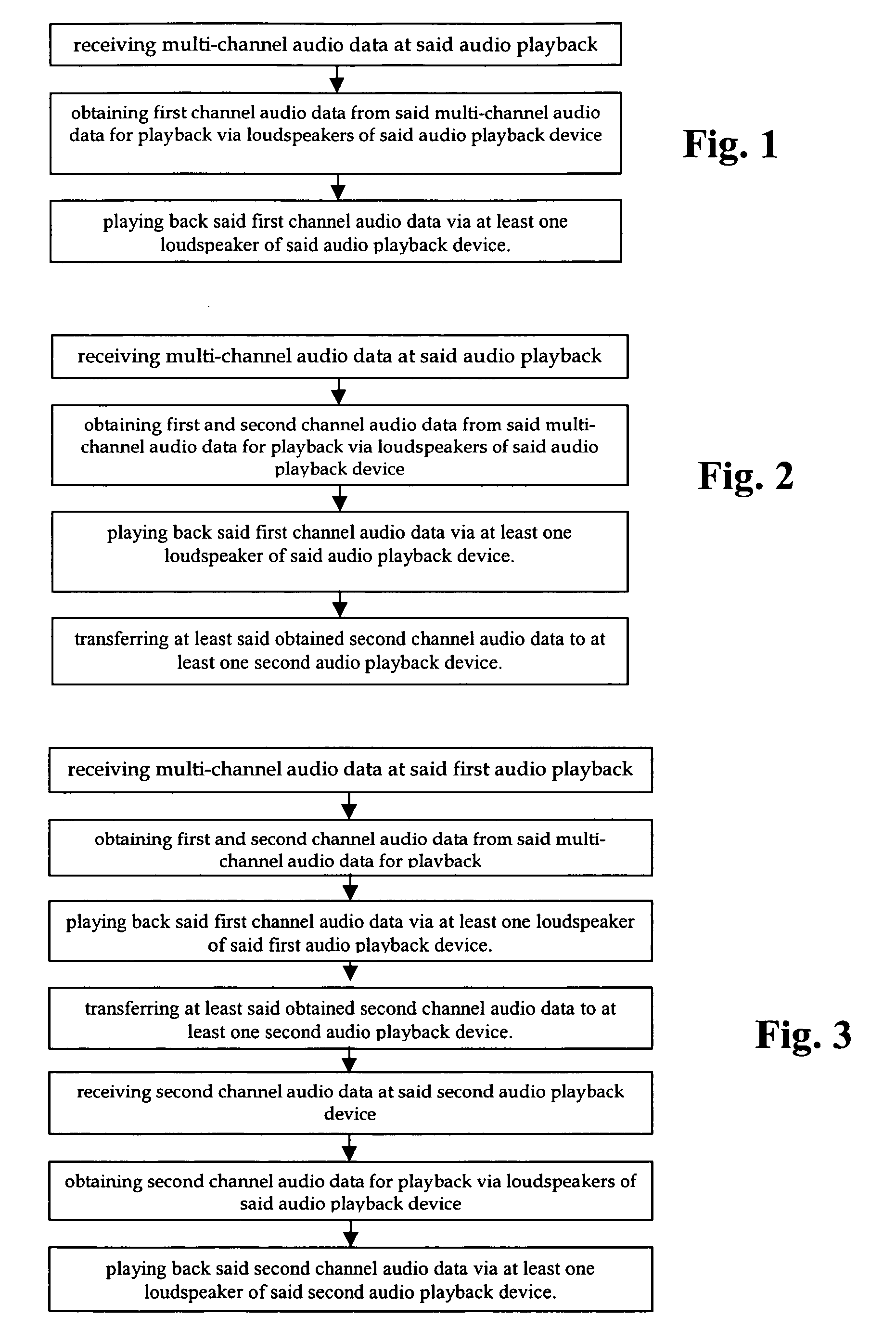
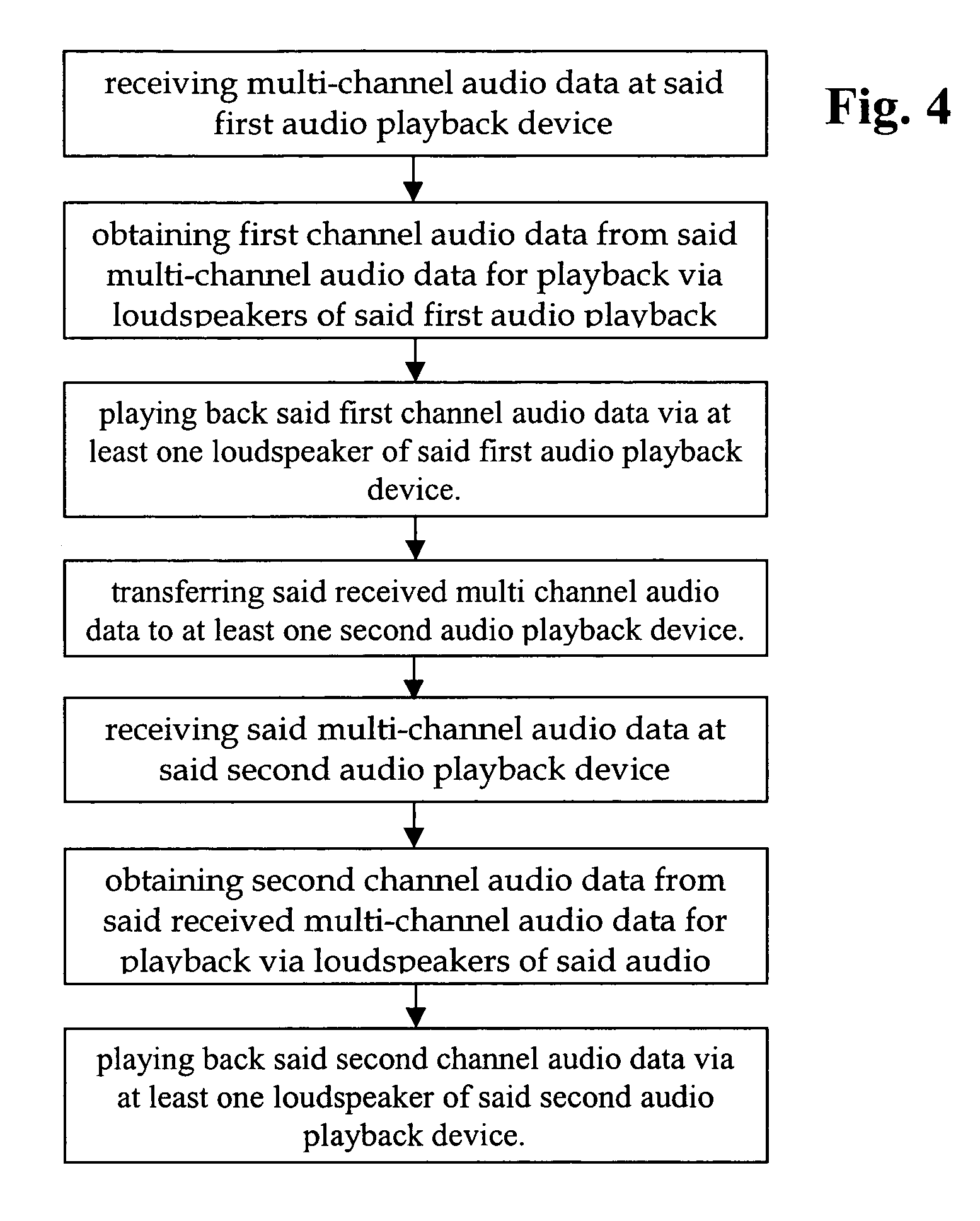
Audio playback device and method of its operation
InactiveUS20070087686A1Surround sound field/effectImproved audio playbackLoudspeaker enclosure positioningStereophonic systemsMobile deviceLoudspeaker
The invention relates to mobile audio playback devices and methods of its operation for enhanced music and sound experience for mobile devices. To provide stereo and surround sound, the present invention provides an audio playback device with a receiving means for receiving multi-channel audio data, obtaining means connected to the receiving means, for obtaining first channel audio data from the multi-channel audio data for playback on the audio playback device, and playback means having at least one loudspeaker, and being connected to the obtaining means for outputting the first channel audio data. The other not selected audio channels or all received audio data may be transferred to other terminals for playback or may be discarded.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
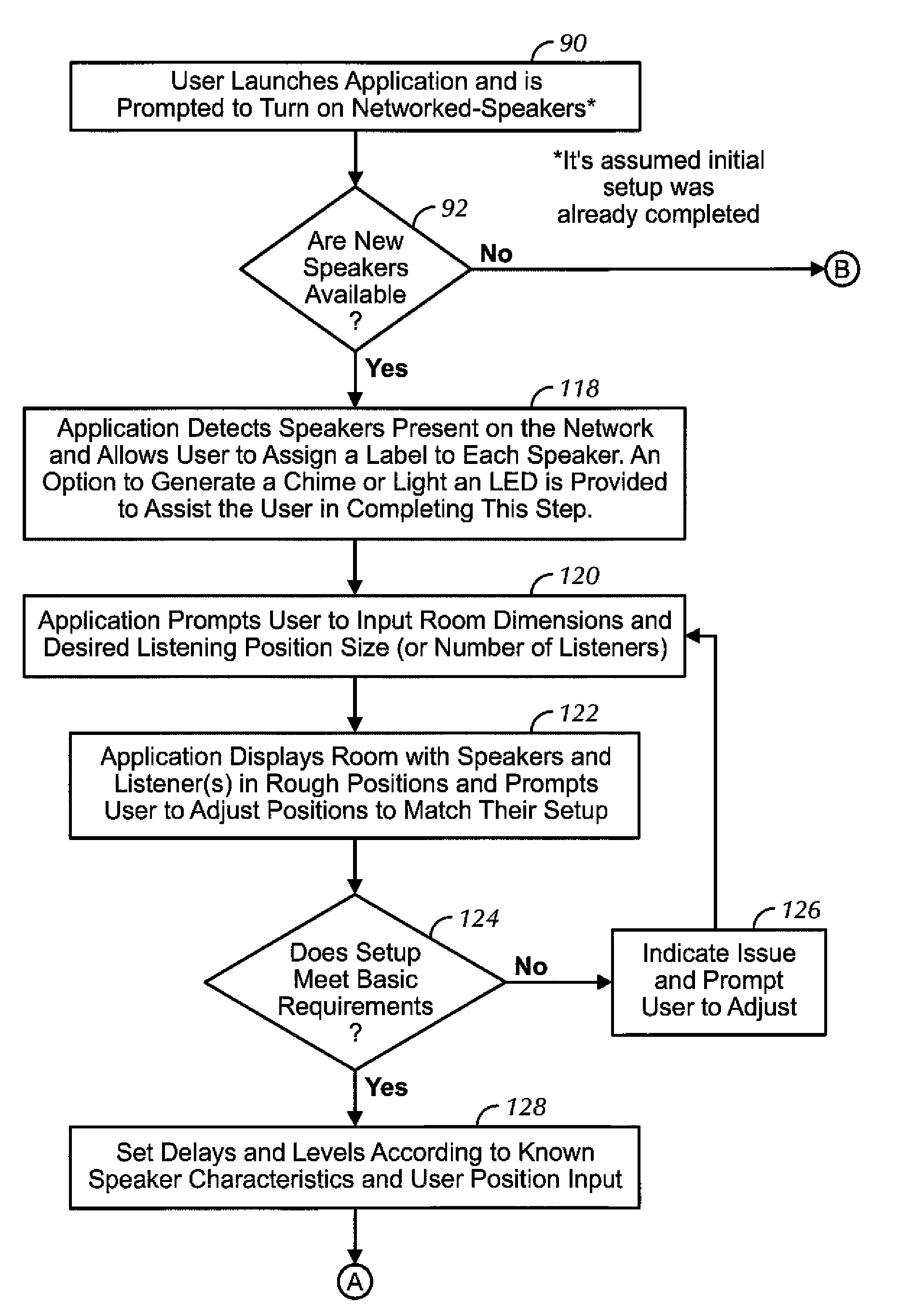
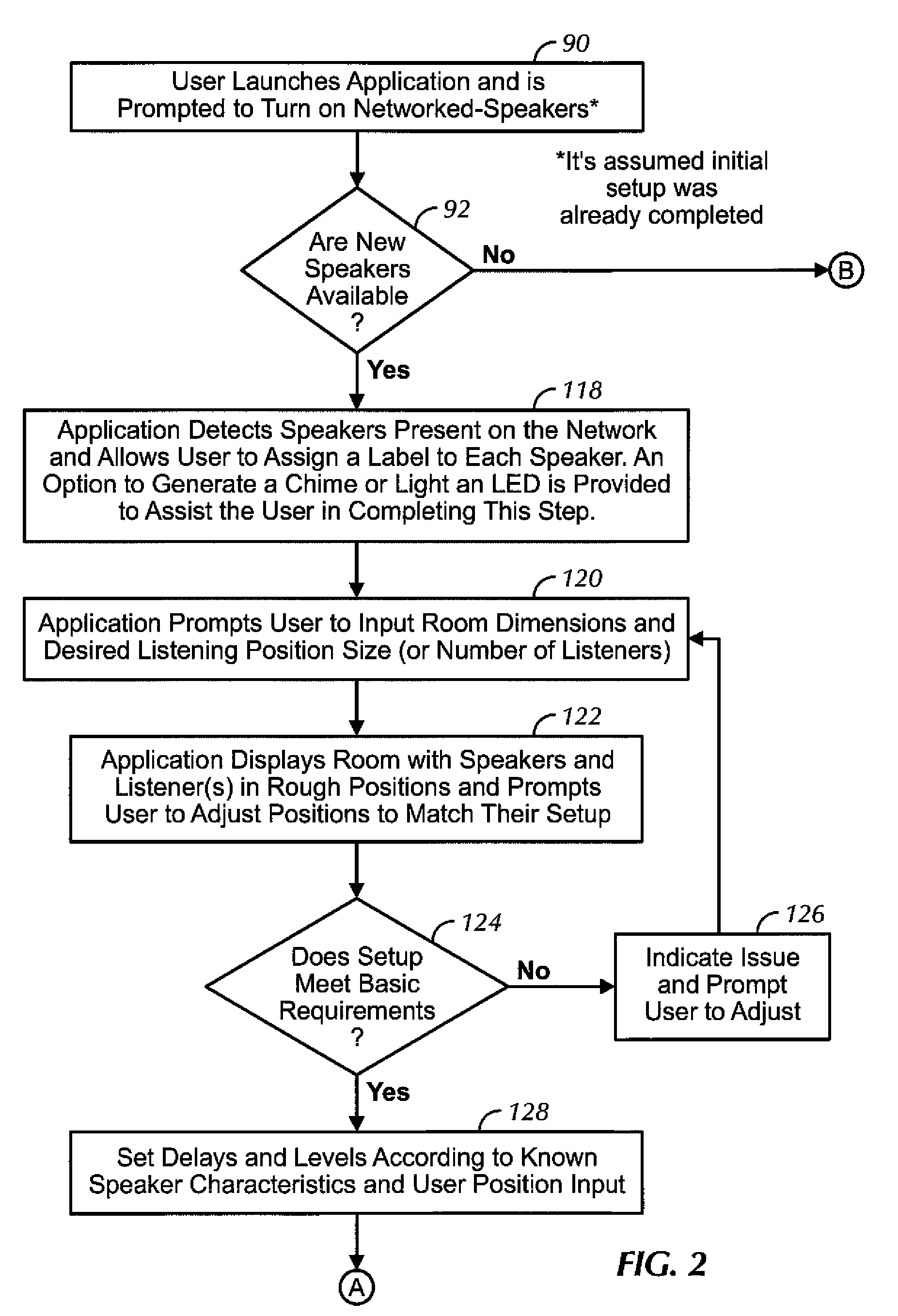
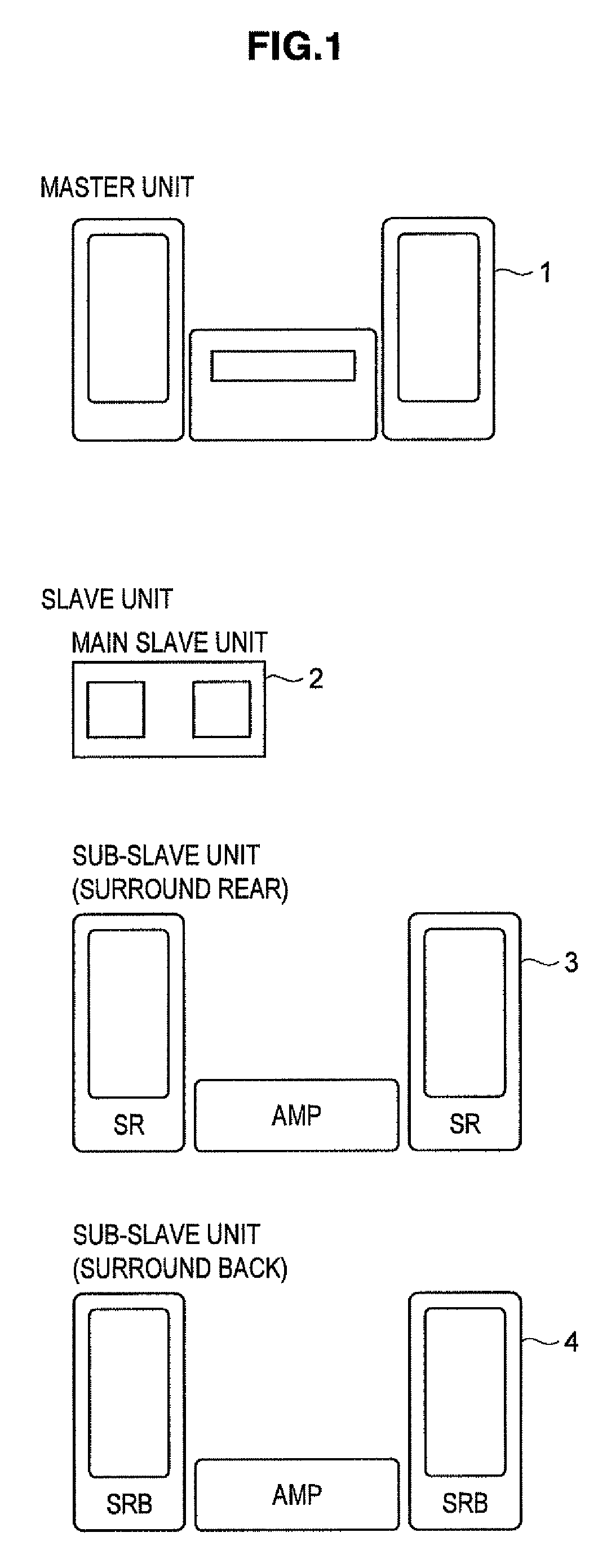
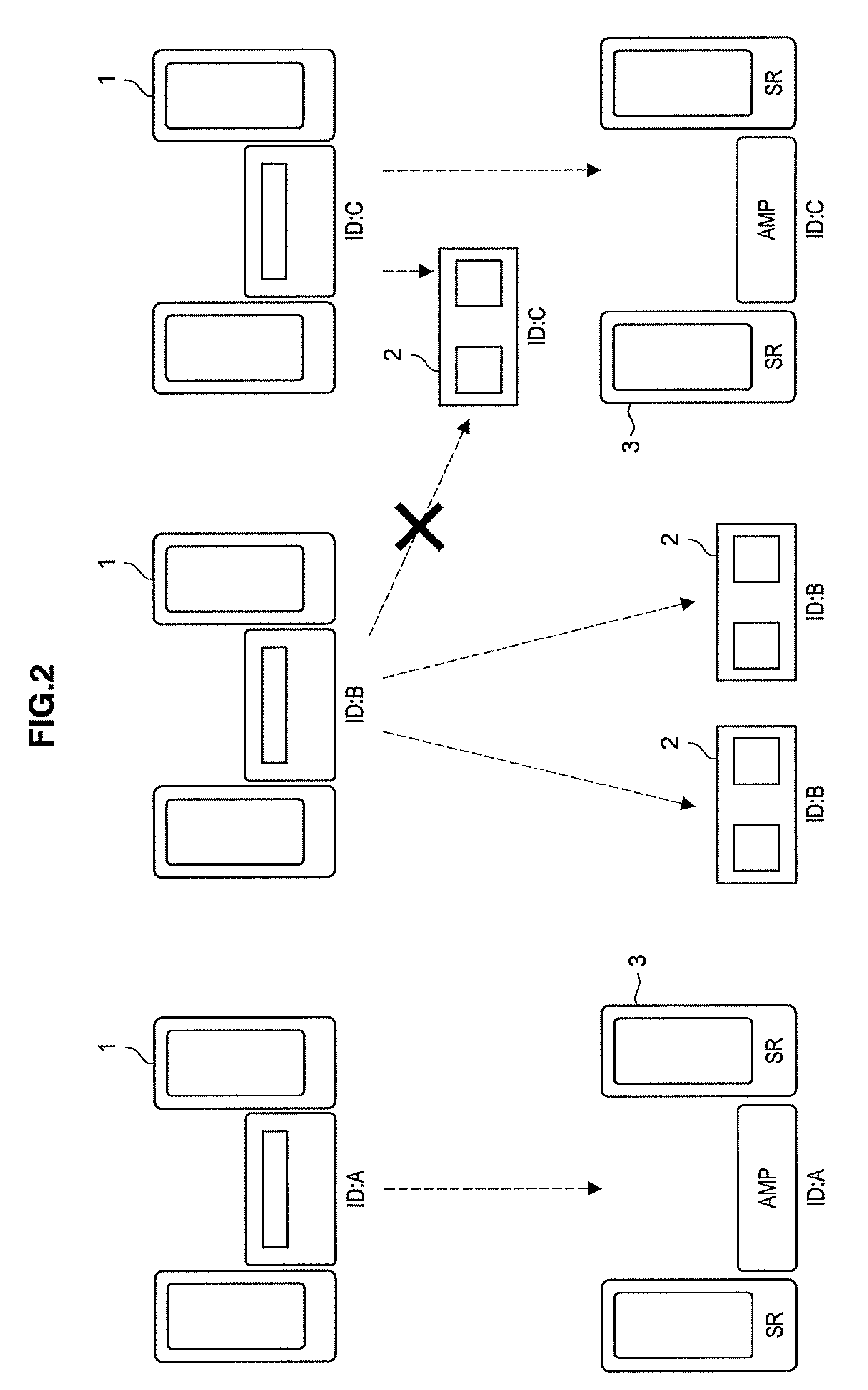
Distributed wireless speaker system with automatic configuration determination when new speakers are added
ActiveUS9288597B2Facilitate easier setupIncrease experienceTransducer detailsPublic address systemsAuto-configurationUser input
Owner:SONY CORP
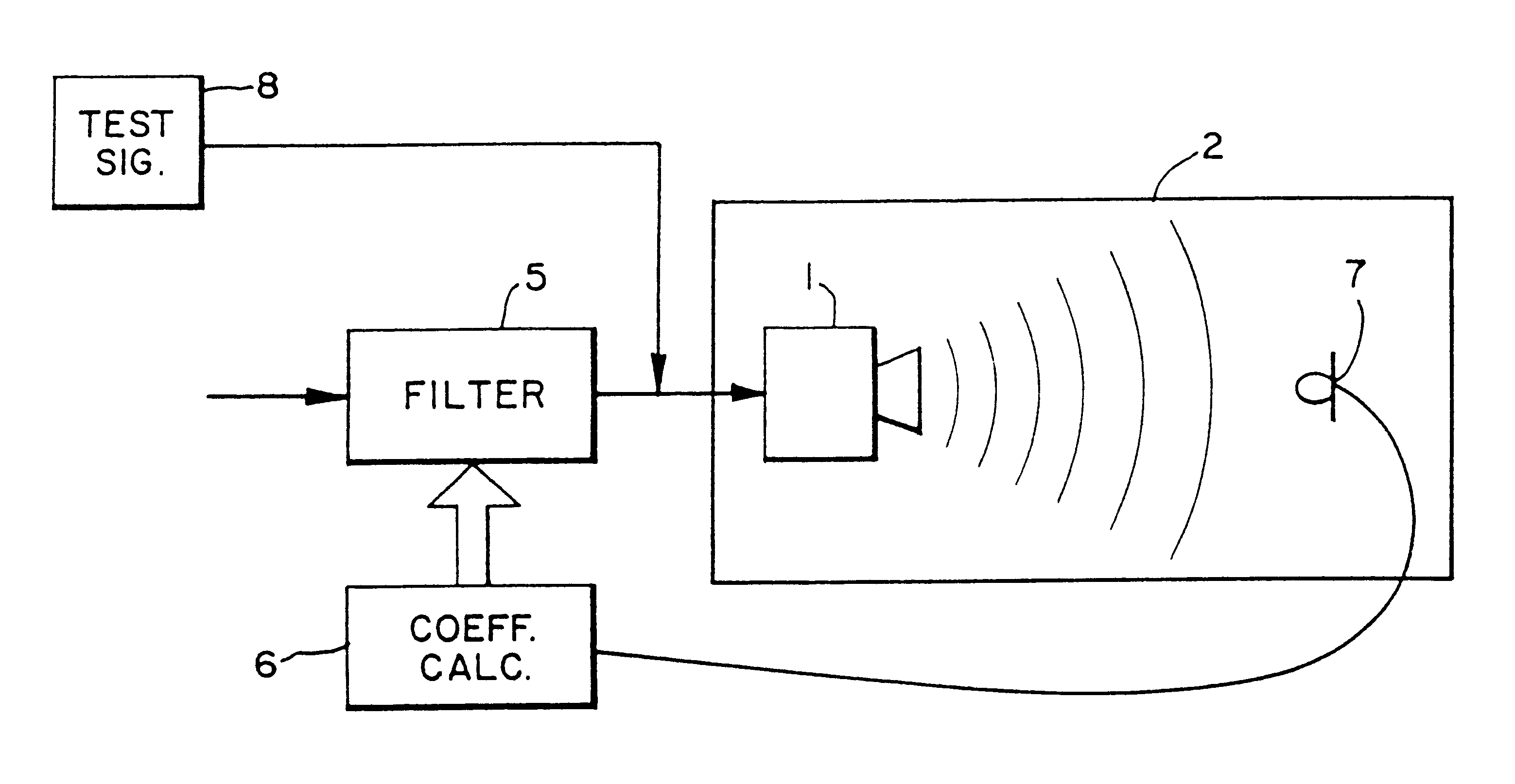
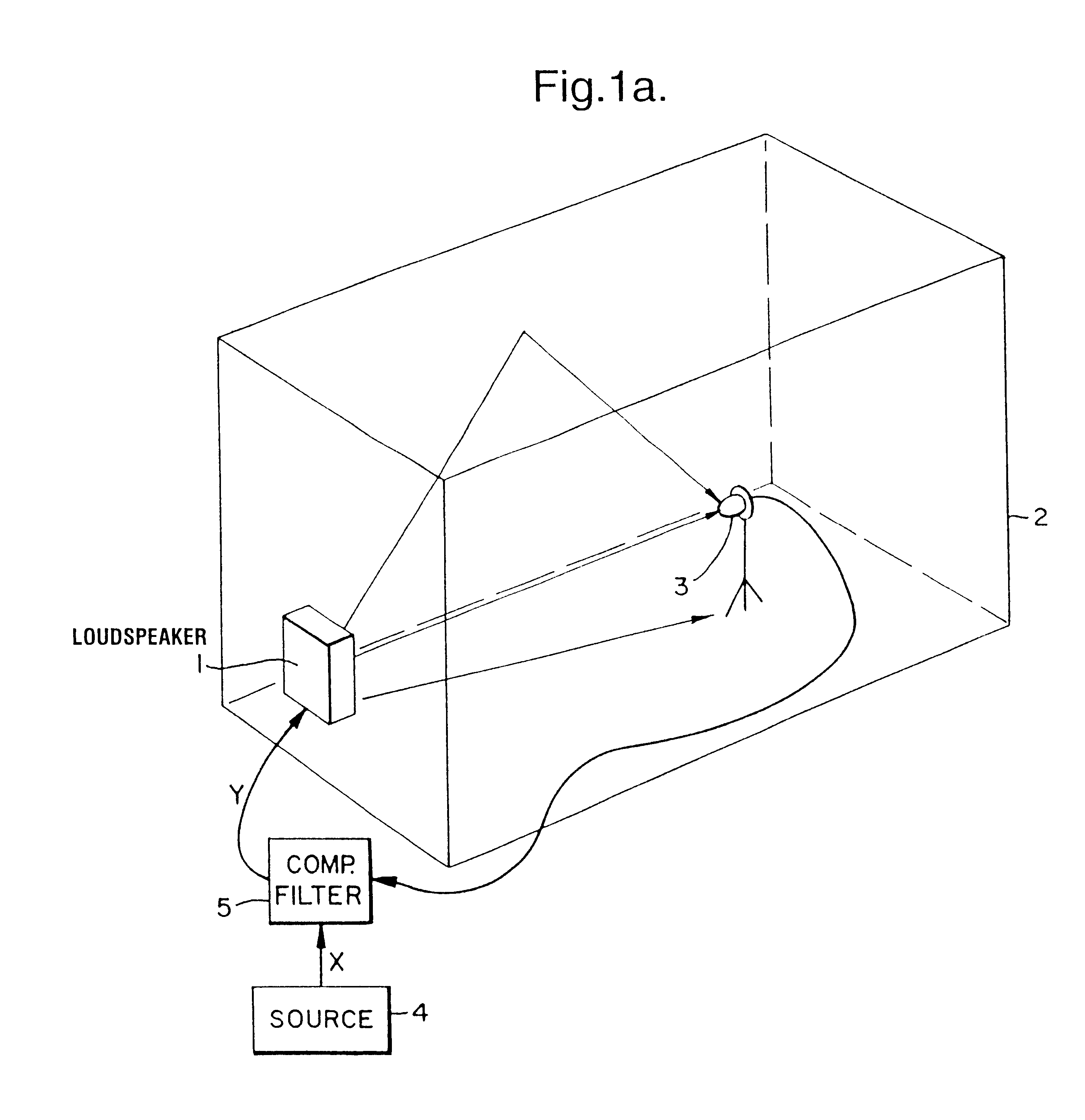
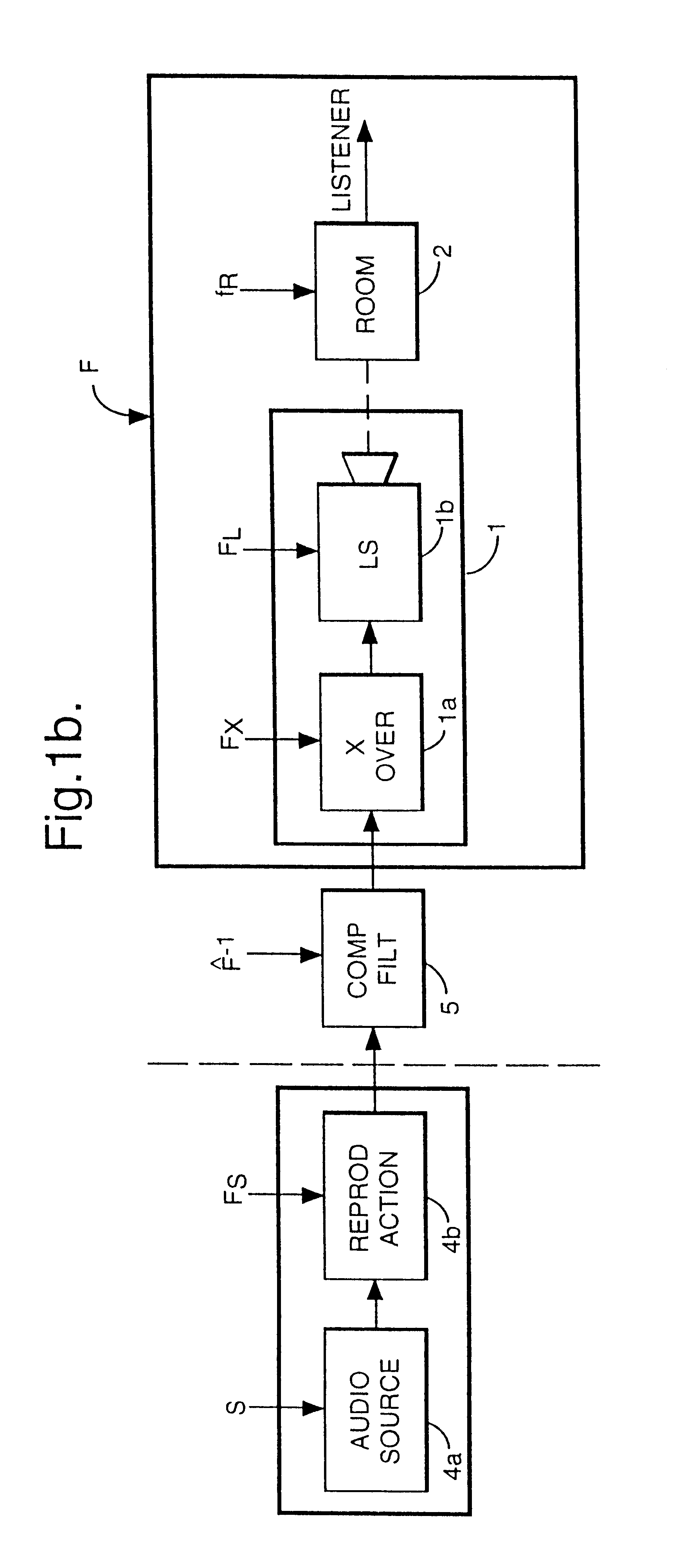
Compensating filters
InactiveUS6760451B1Eliminate phase distortionAdaptive networkAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlDigital signal processingAmplitude response
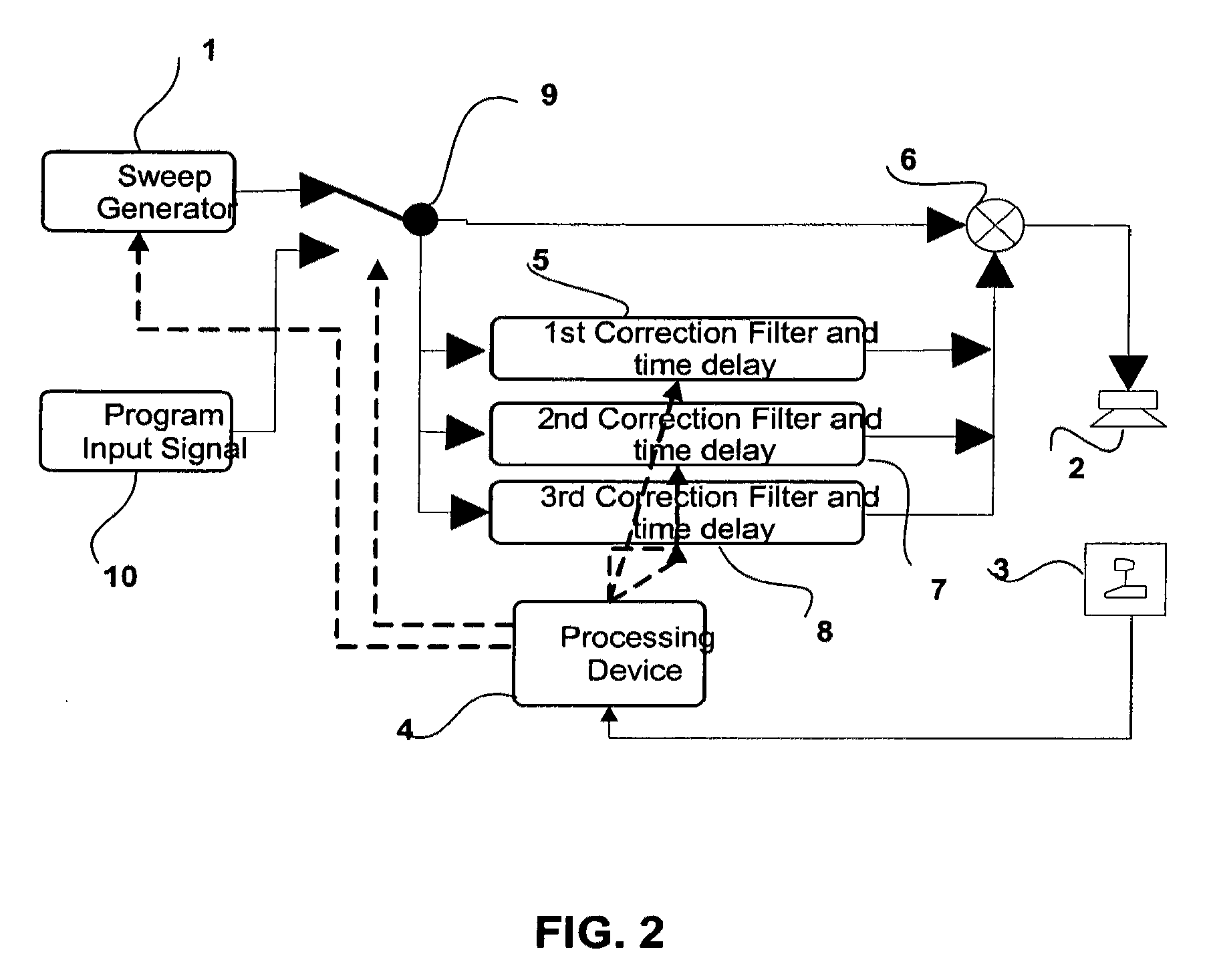
A prefilter (5) for an audio system comprising a loudspeaker (1) in a room (2), which corrects both amplitude and phase errors due to the loudspeaker (1) by a linear phase correction filter response and corrects the amplitude response of the room (2) whilst introducing the minimum possible amount of extra phase distortion by employing a minimum phase correction filter stage. A test signal generator (8) generates a signal comprising a periodic frequency sweep with a greater phase repetition period than the frequency repetition period. A microphone (7) positioned at various points in the room (2) measures the audio signal processed by the room (2) and loudspeaker (1), and a coefficient calculator (6) (e.g. a digital signal processor device) derives the signal response of the room and thereby a requisite minimum phase correction to be cascaded with the linear phase correction already calculated for the loudspeaker (1). Filter (5) may comprise the same digital signal processor as the coefficient calculator (6). Applications in high fidelity audio reproduction, and in car stereo reproduction.
Owner:CRAVEN PETER GRAHAM +1
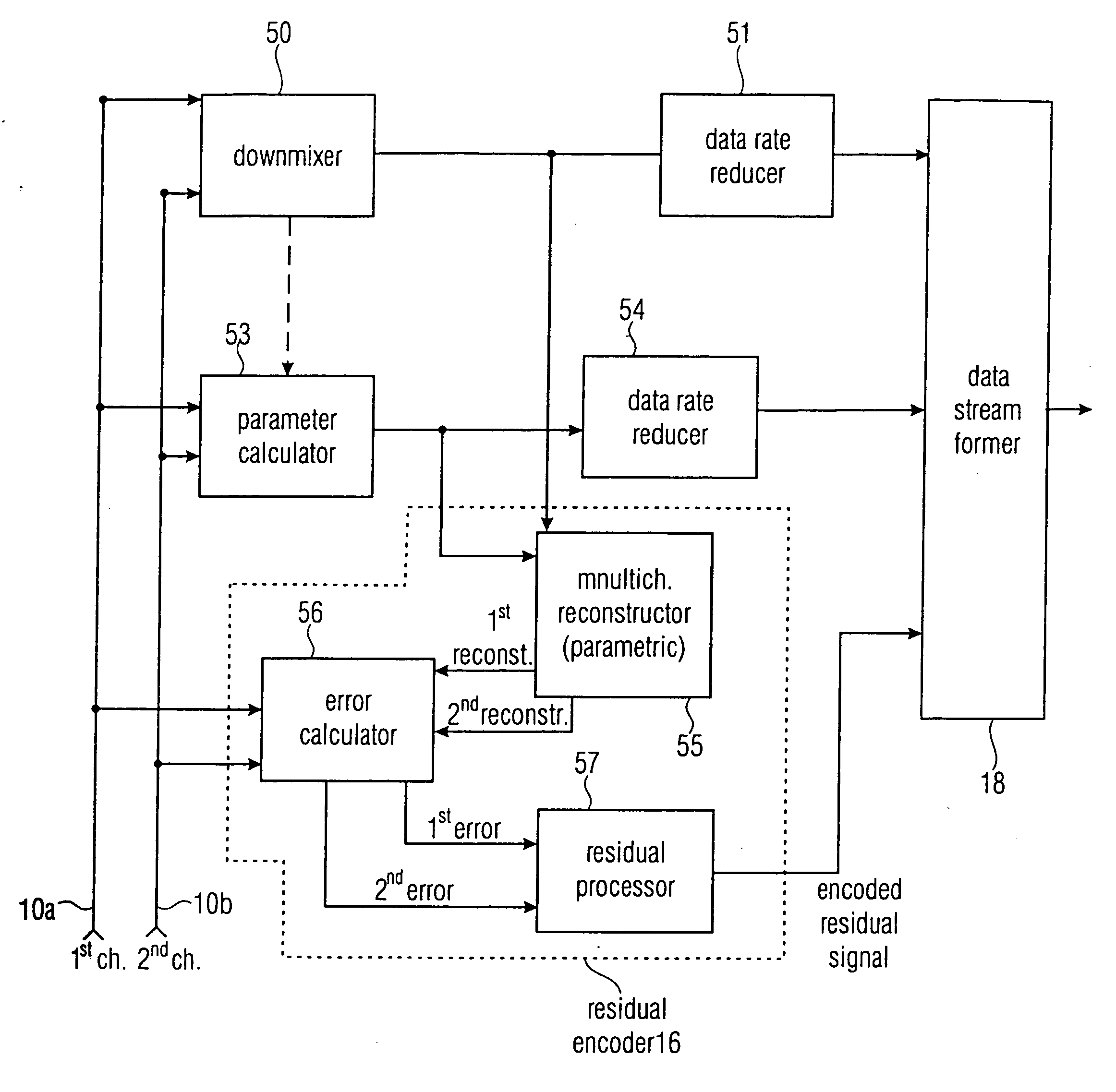
Near-transparent or transparent multi-channel encoder/decoder scheme
ActiveUS20060190247A1Quality improvementReduce bitrateError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsChannel decoderComputer science
A multi-channel encoder / decoder scheme additionally preferably generates a waveform-type residual signal. This residual signal is transmitted together with one or more multi-channel parameters to a decoder. In contrast to a purely parametric multi-channel decoder, the enhanced decoder generates a multi-channel output signal having an improved output quality because of the additional residual signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Apparatus and method for constructing a multi-channel output signal or for generating a downmix signal
ActiveUS7394903B2Decoder-side computing workload can be reducedHigh scaleSpeech analysisSpecial data processing applicationsSide informationEngineering
The apparatus for constructing a multi-channel output signal using an input signal and parametric side information, the input signal including the first input channel and the second input channel derived from an original multi-channel signal, and the parametric side information describing interrelations between channels of the multi-channel original signal uses base channels for synthesizing first and second output channels on one side of an assumed listener position, which are different from each other. The base channels are different from each other because of a coherence measure. Coherence between the base channels (for example the left and the left surround reconstructed channel) is reduced by calculating a base channel for one of those channels by a combination of the input channels, the combination being determined by the coherence measure. Thus, a high subjective quality of the reconstruction can be obtained because of an approximated original front / back coherence.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV +1
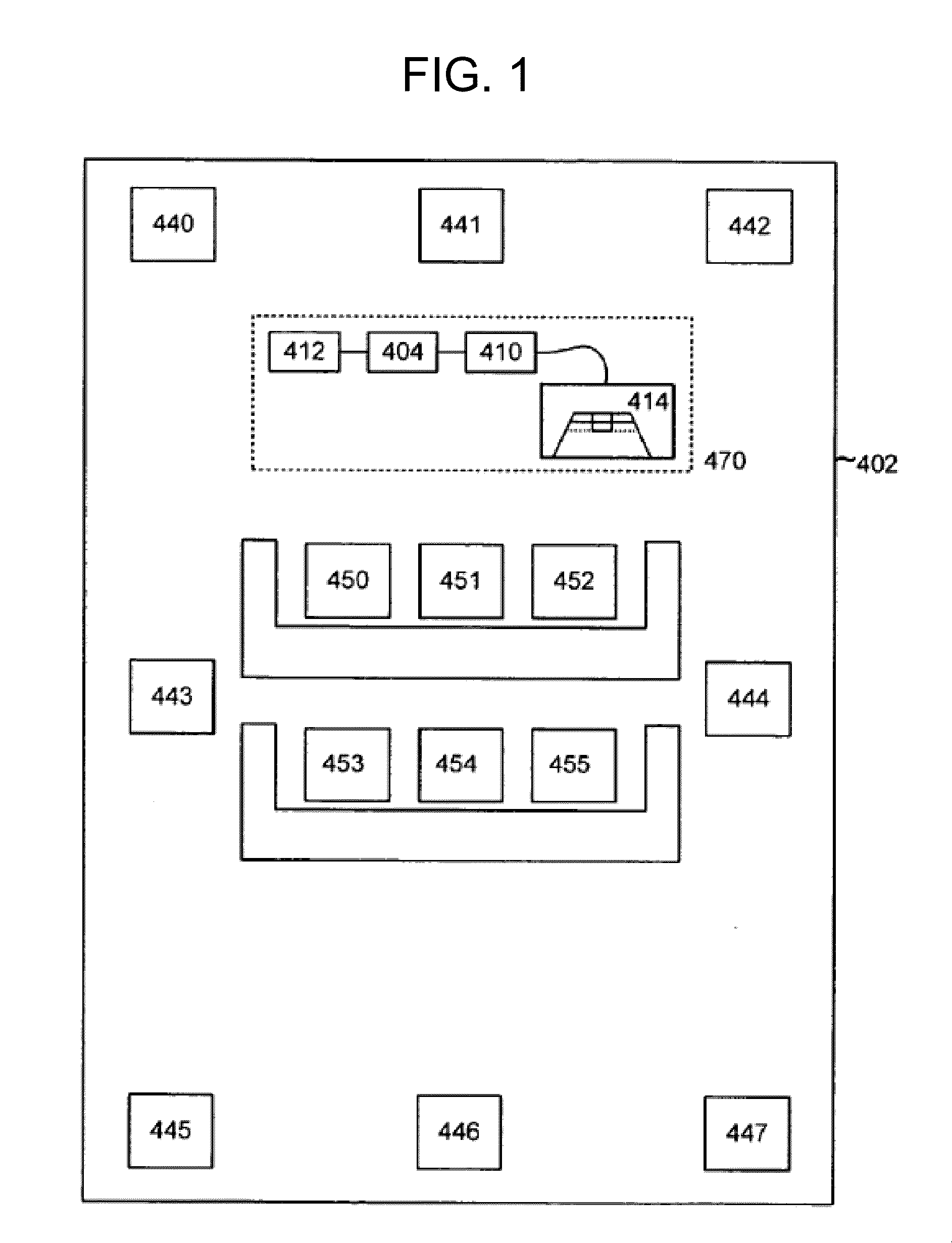
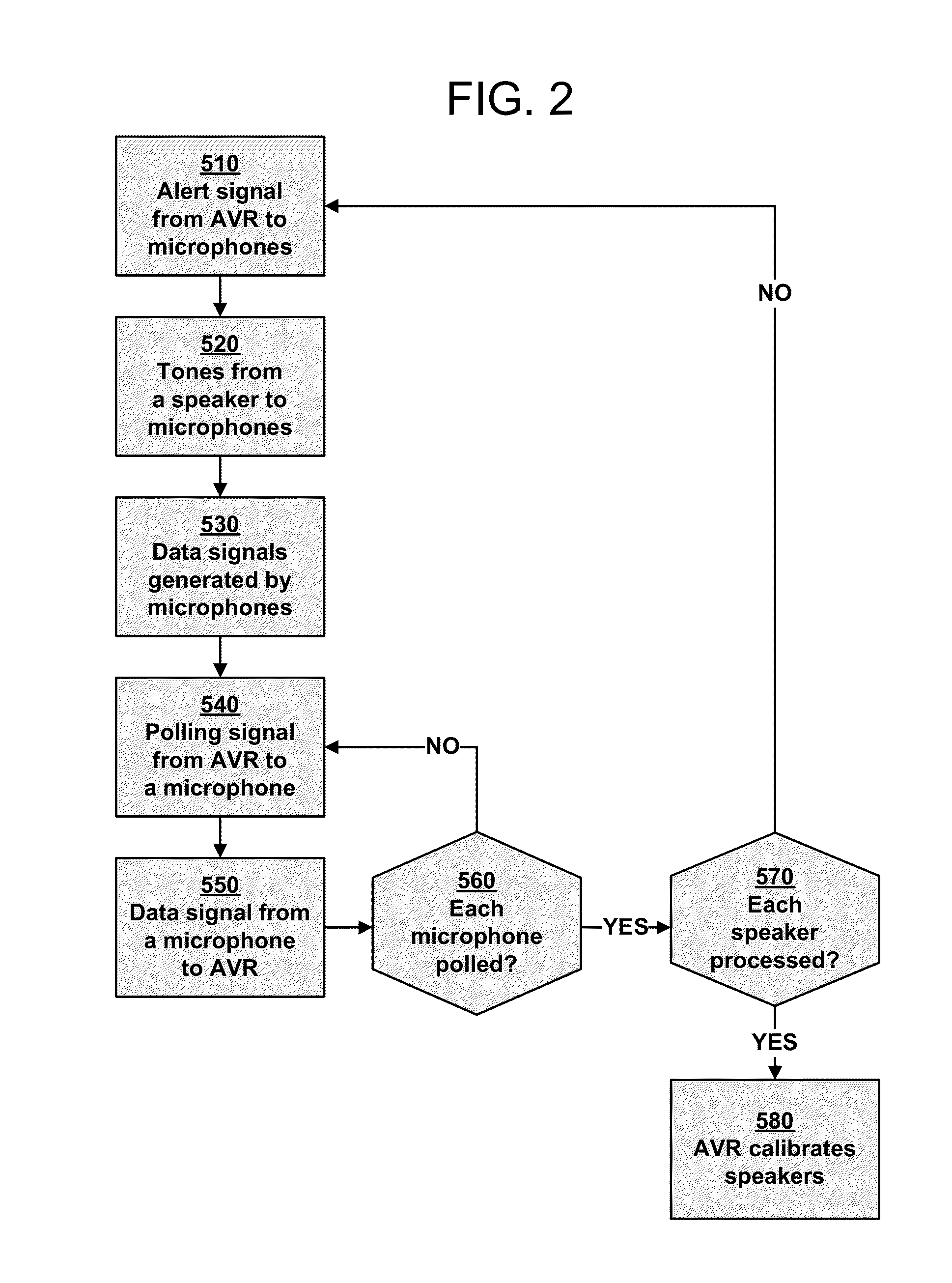
Loudspeaker Calibration Using Multiple Wireless Microphones
An illustrative embodiment includes a method for use in performing acoustic calibration of at least one audio output device for a plurality of listening locations. An audio input device generates a data signal based on a series of one or more tones output by the at least one audio output device. The audio input device wirelessly transmits the data signal to a calibration device. The audio input device is one of a plurality of audio input devices deployed at respective ones of the plurality of listening locations. The data signal is one of a plurality of data signals generated by respective ones of the plurality of audio input devices based on the series of one or more tones output by the at least one audio output device. The plurality of data signals are wirelessly transmitted by the respective ones of the plurality of audio input devices to the calibration device.
Owner:CRESTRON ELECTRONICS
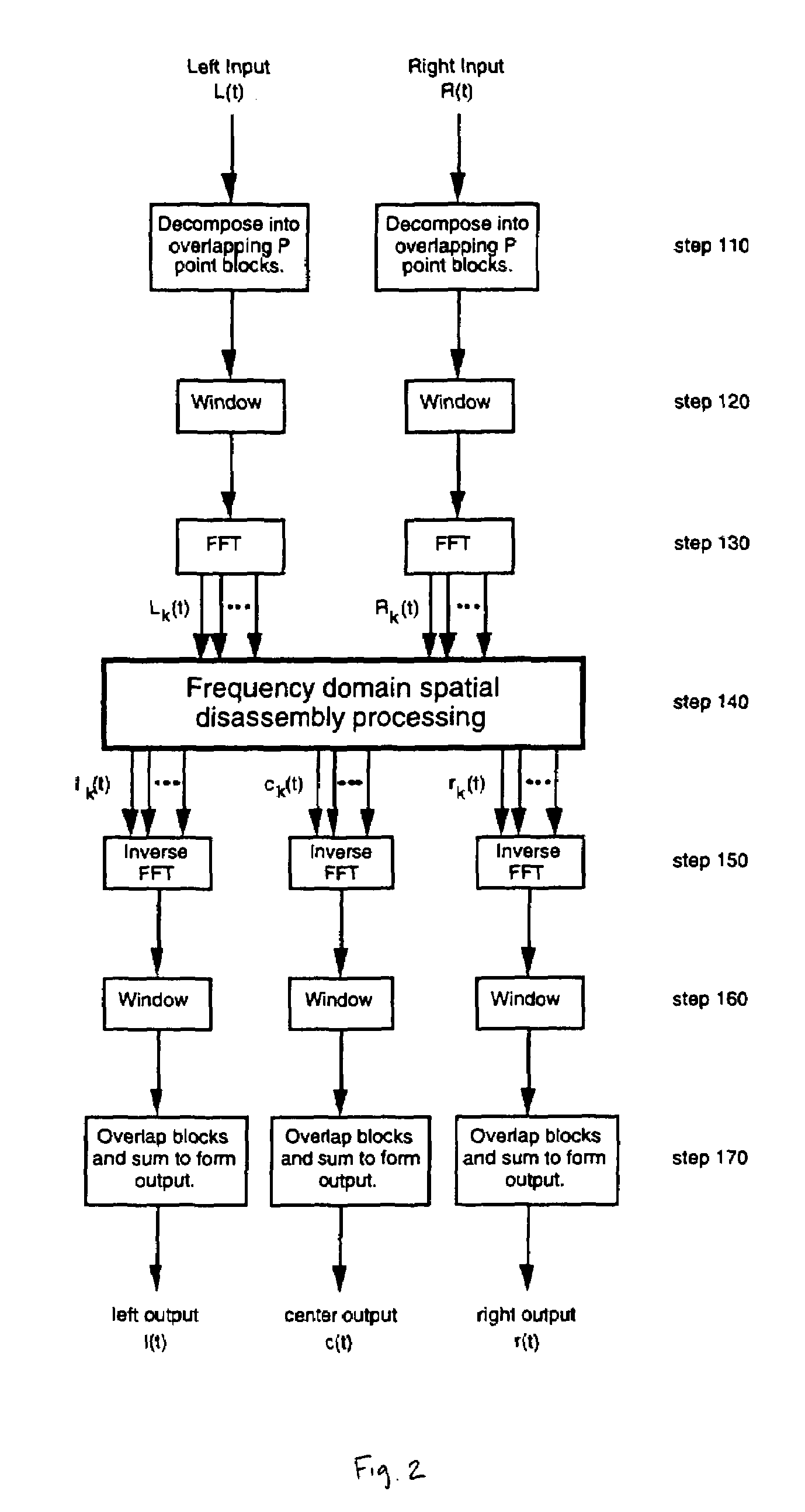
Spatial disassembly processor
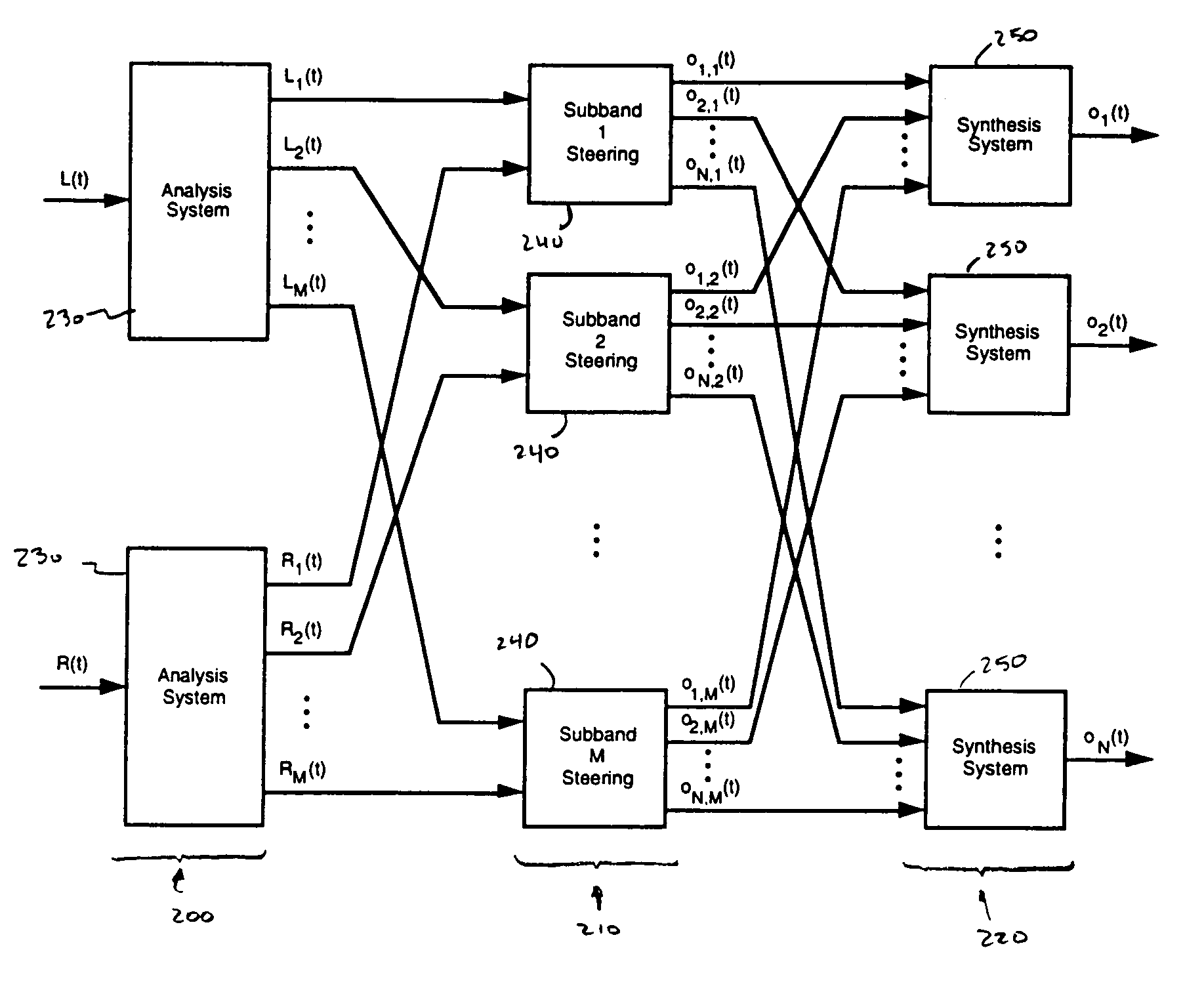
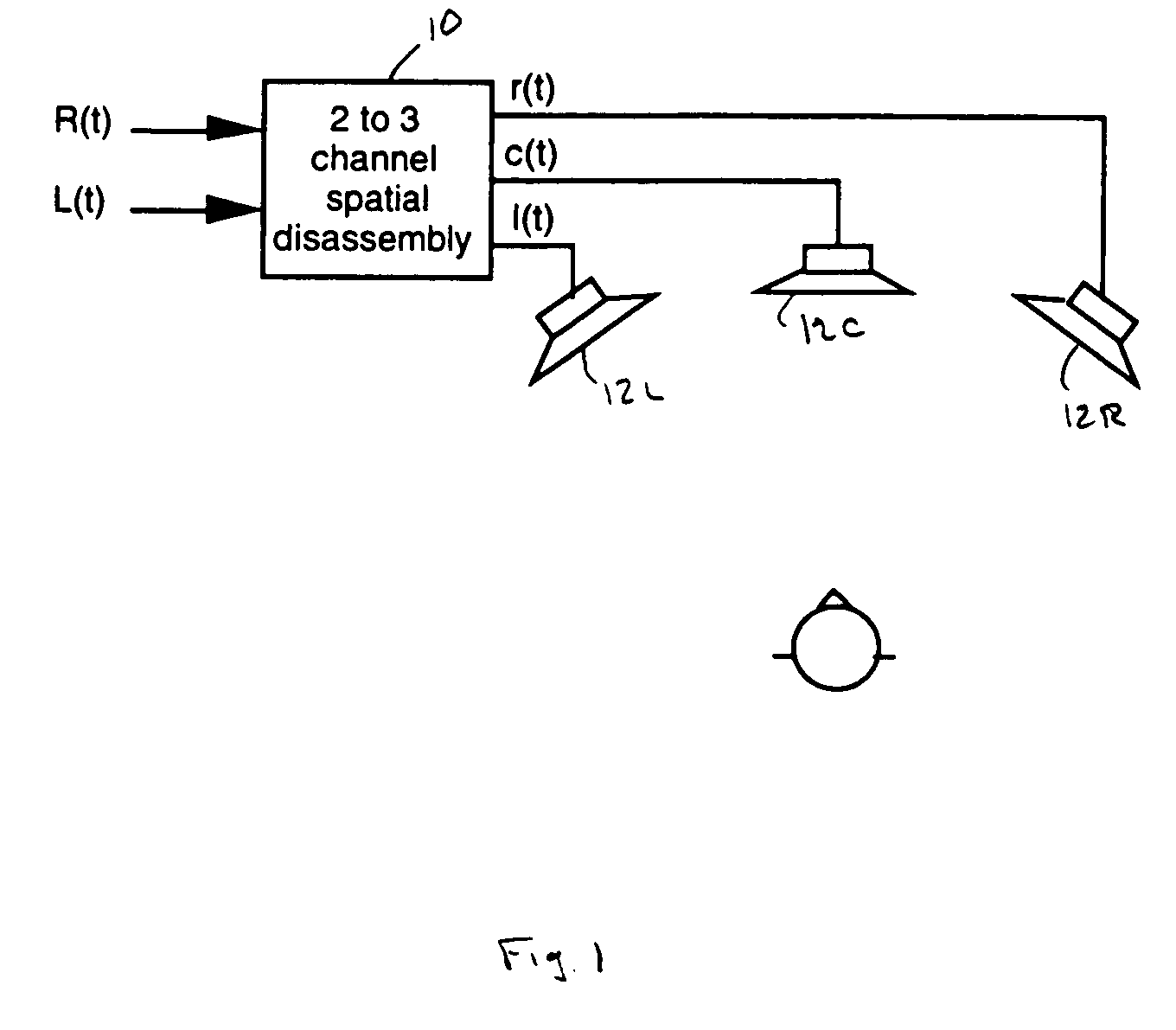
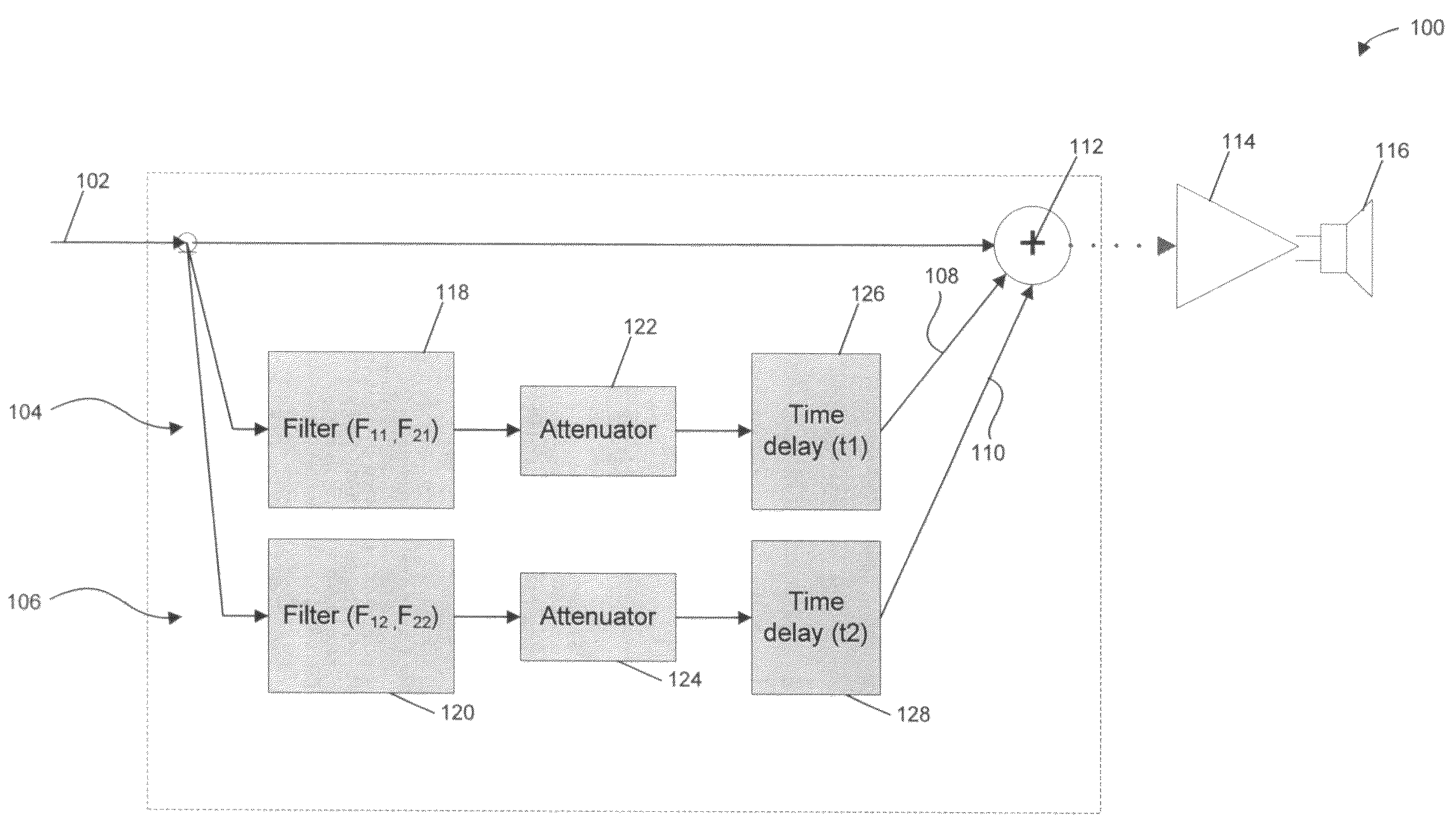
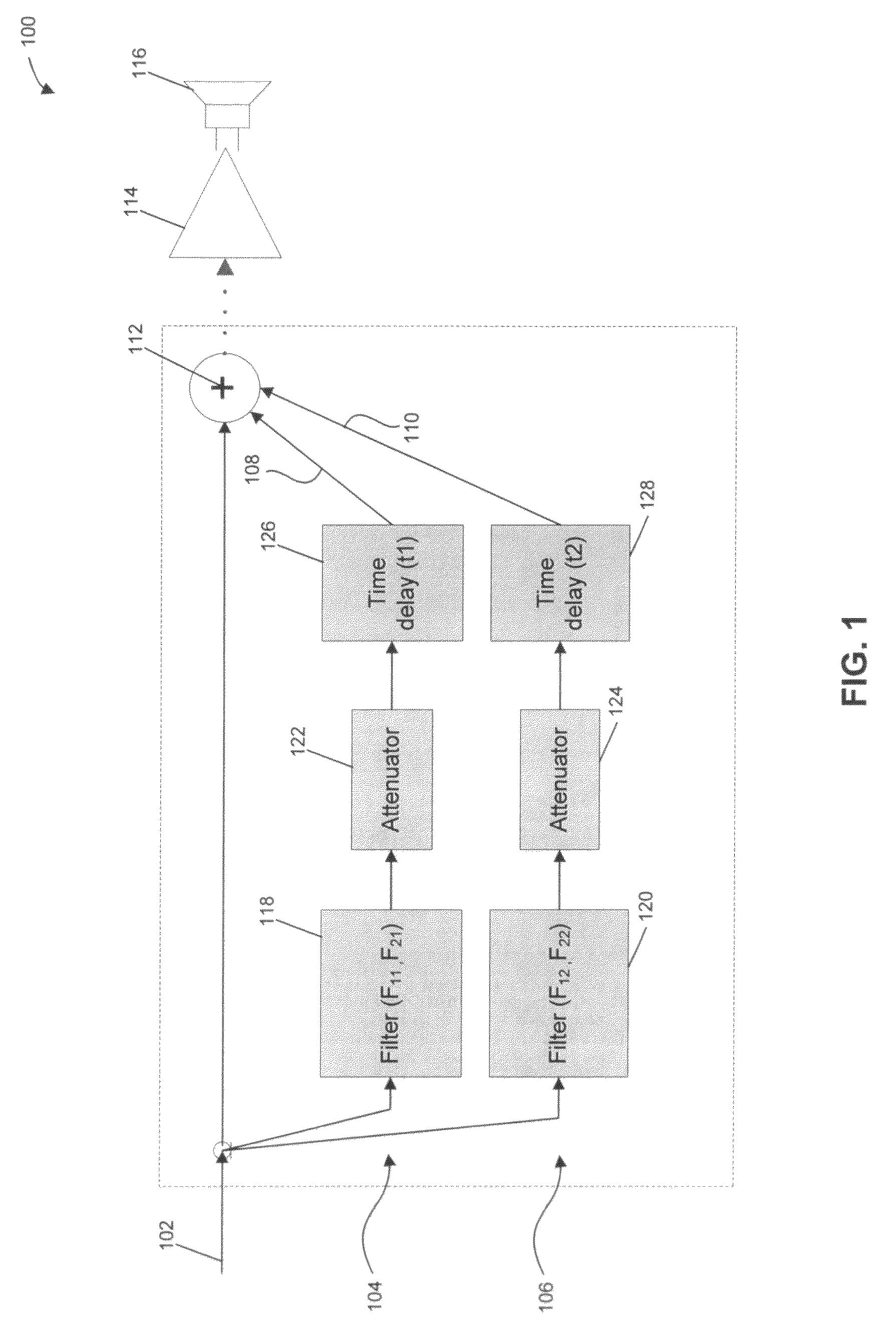
ActiveUS7630500B1Easy to mergeImprove stabilityStereophonic systemsStereophonic arrangmentsComputer science
A method of disassembling a pair of input signals L(t) and R(t) to form subband representations of N output channel signals o1(t), o2(t), . . . , oN(t), wherein t is time. The method includes the steps of generating a subband representation of the signal L(t) containing a plurality of subband components Lk(t) where k is an integer ranging from 1 to M; generating a subband representation of the signal R(t) containing a plurality of subband components Rk(t); and constructing the subband representation for each of the plurality of output channel signals, each of those subband representations containing a plurality of subband components oj,k(t), wherein oj,k(t) represents the kth subband of the jth output channel signal and is constructed by combining components of the input signals L(t) and R(t) according to an output construction rule: oj,k(t)=f(Lk(t),Rk(t)) for k=1, 2, . . . , M and j=1, 2, . . . , N.
Owner:BOSE CORP
System for Rendering and Playback of Object Based Audio in Various Listening Environments
ActiveUS20150223002A1Transducers for sound channels pluralityPublic address systemsObject basedData set
Embodiments are described for a system of rendering object-based audio content through a system that includes individually addressable drivers, including at least one driver that is configured to project sound waves toward one or more surfaces within a listening environment for reflection to a listening area within the listening environment; a renderer configured to receive and process audio streams and one or more metadata sets associated with each of the audio streams and specifying a playback location of a respective audio stream; and a playback system coupled to the renderer and configured to render the audio streams to a plurality of audio feeds corresponding to the array of audio drivers in accordance with the one or more metadata sets.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
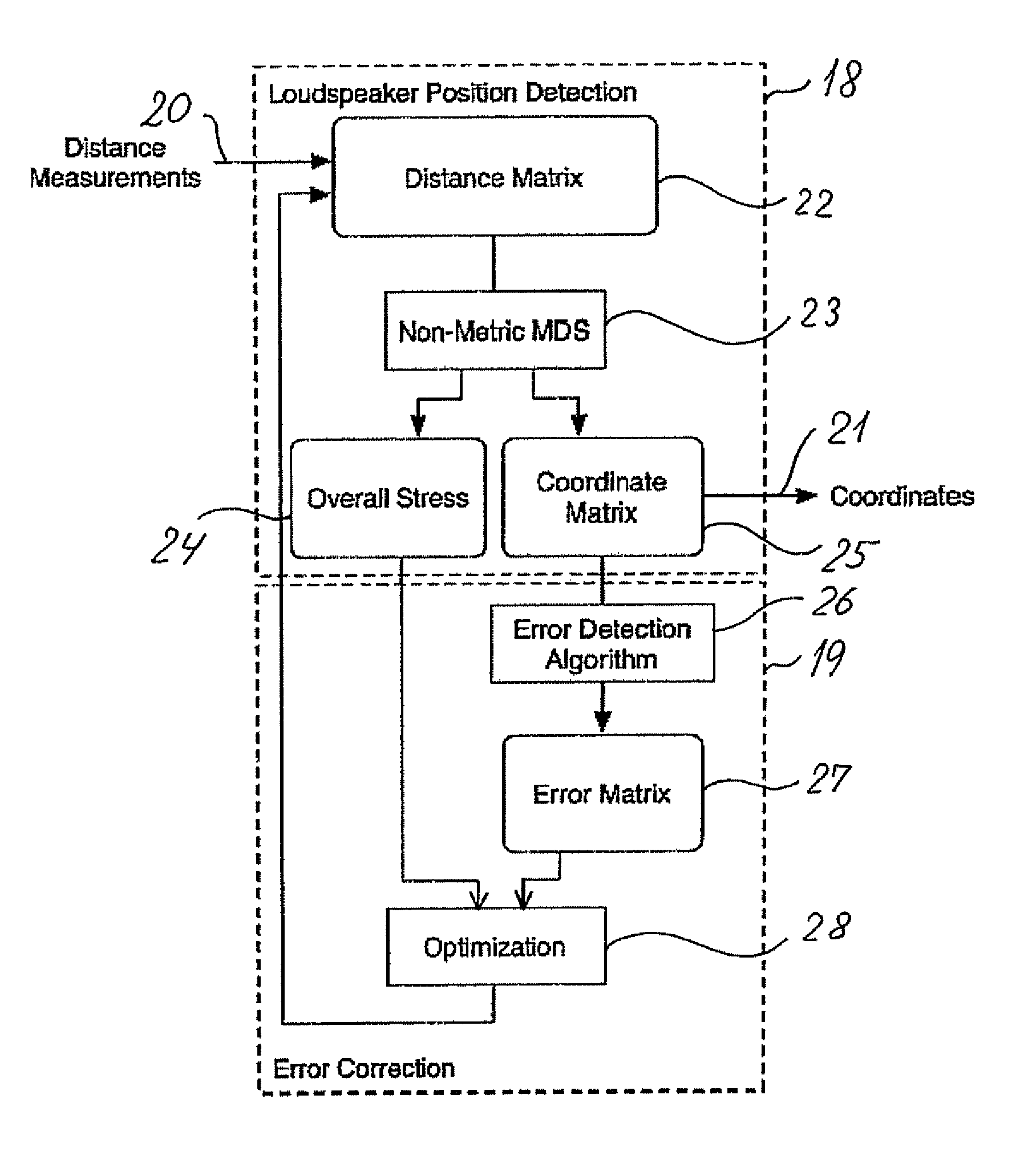
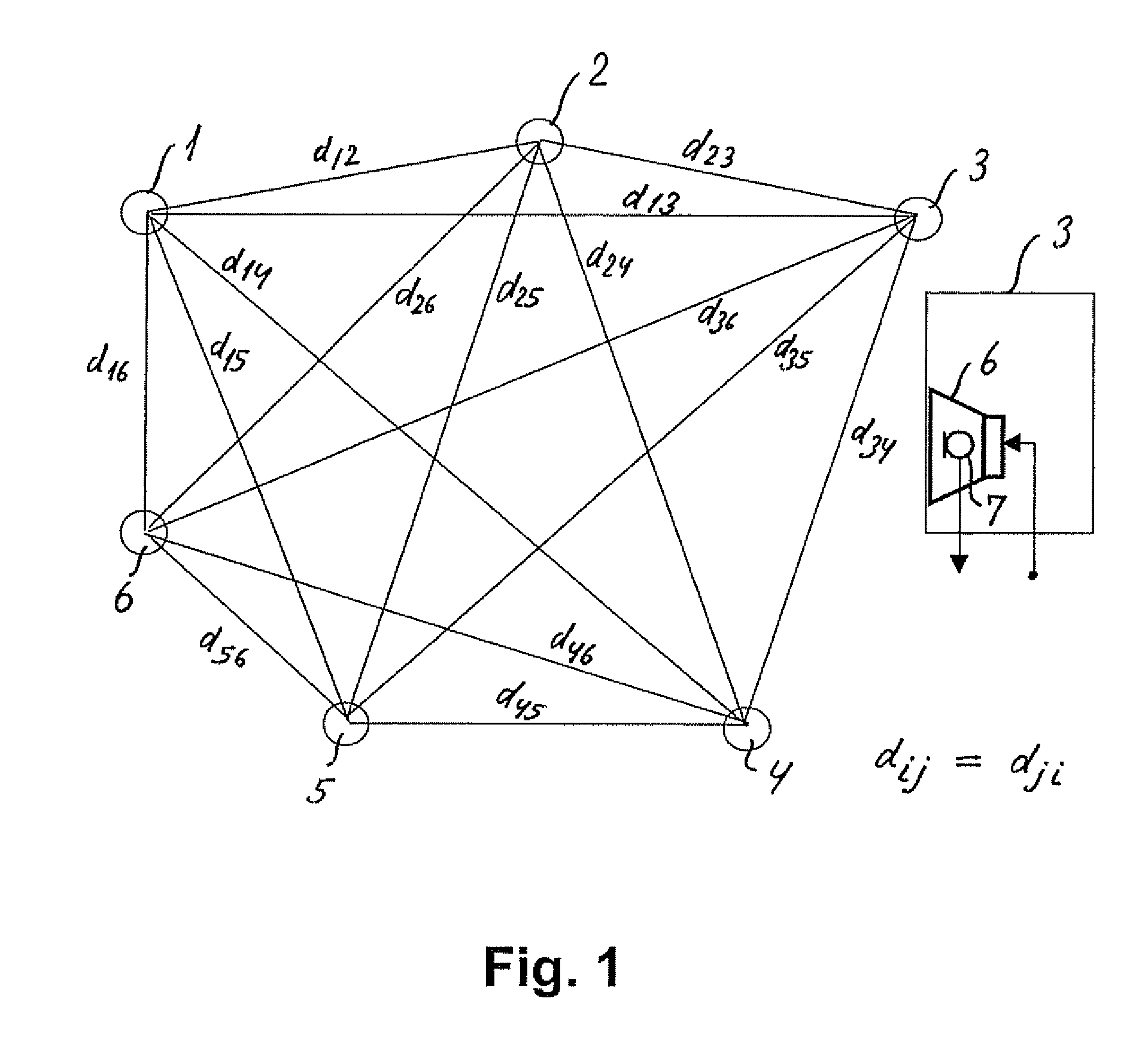
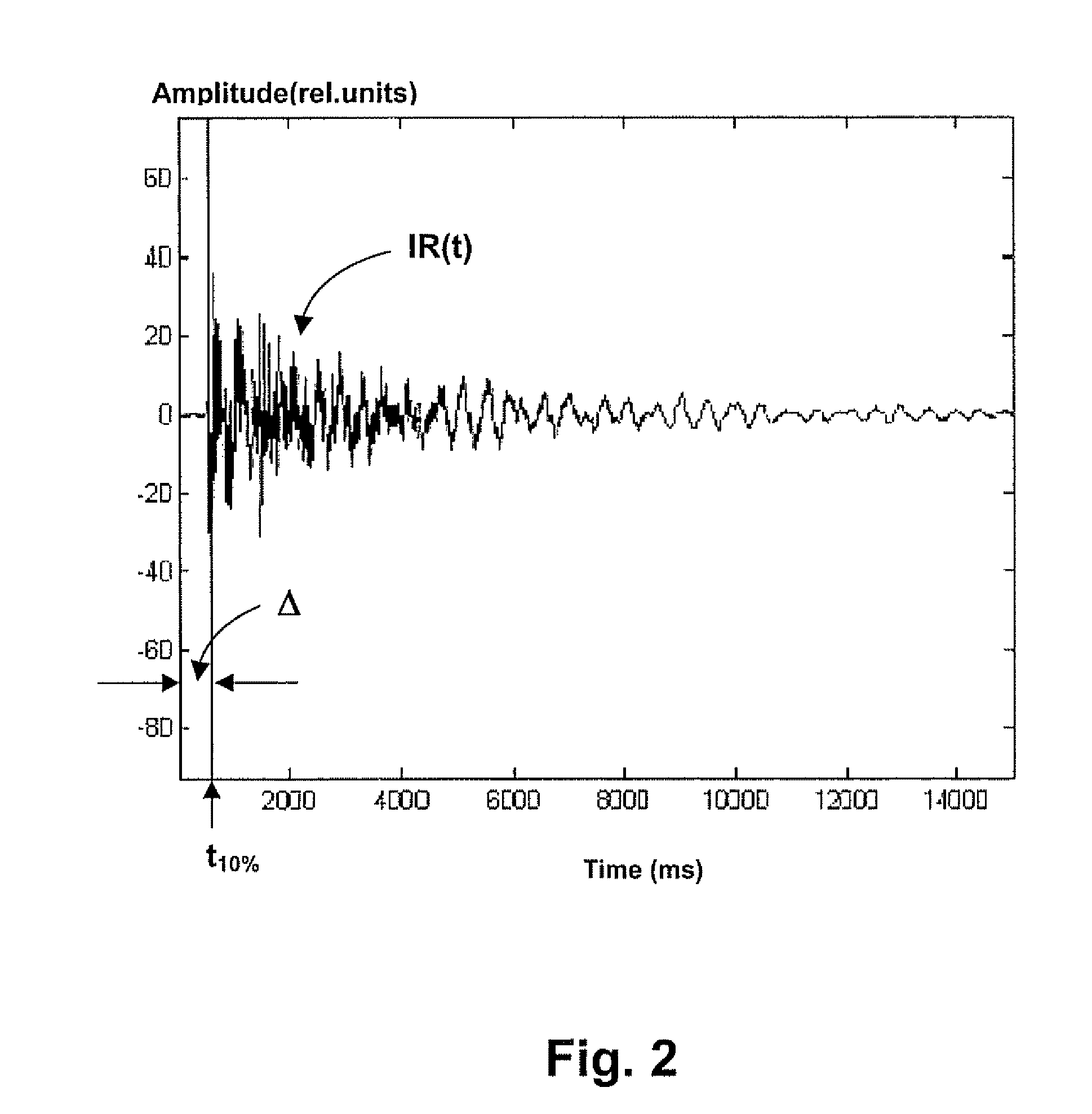
Loudspeaker position estimation
ActiveUS8279709B2Direction finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesLoudspeakersMultidimensional scalingDistance matrix
The invention relates to an automated estimation of the position (co-ordinates) of a set of loudspeakers in a ioom Based on measured impulse responses the distances between each pair of loudspeakers are estimated, thereby forming a distance matrix, and the resultant distance matrix is used by a multidimensional scaling (MDS) algorithm to estimate the co-ordinates of each individual loudspeaker An improved co-ordinate estimation can, if desired, be derived by utilizing the stress values provided by the MDS algorithm.
Owner:BANG & OLUFSEN
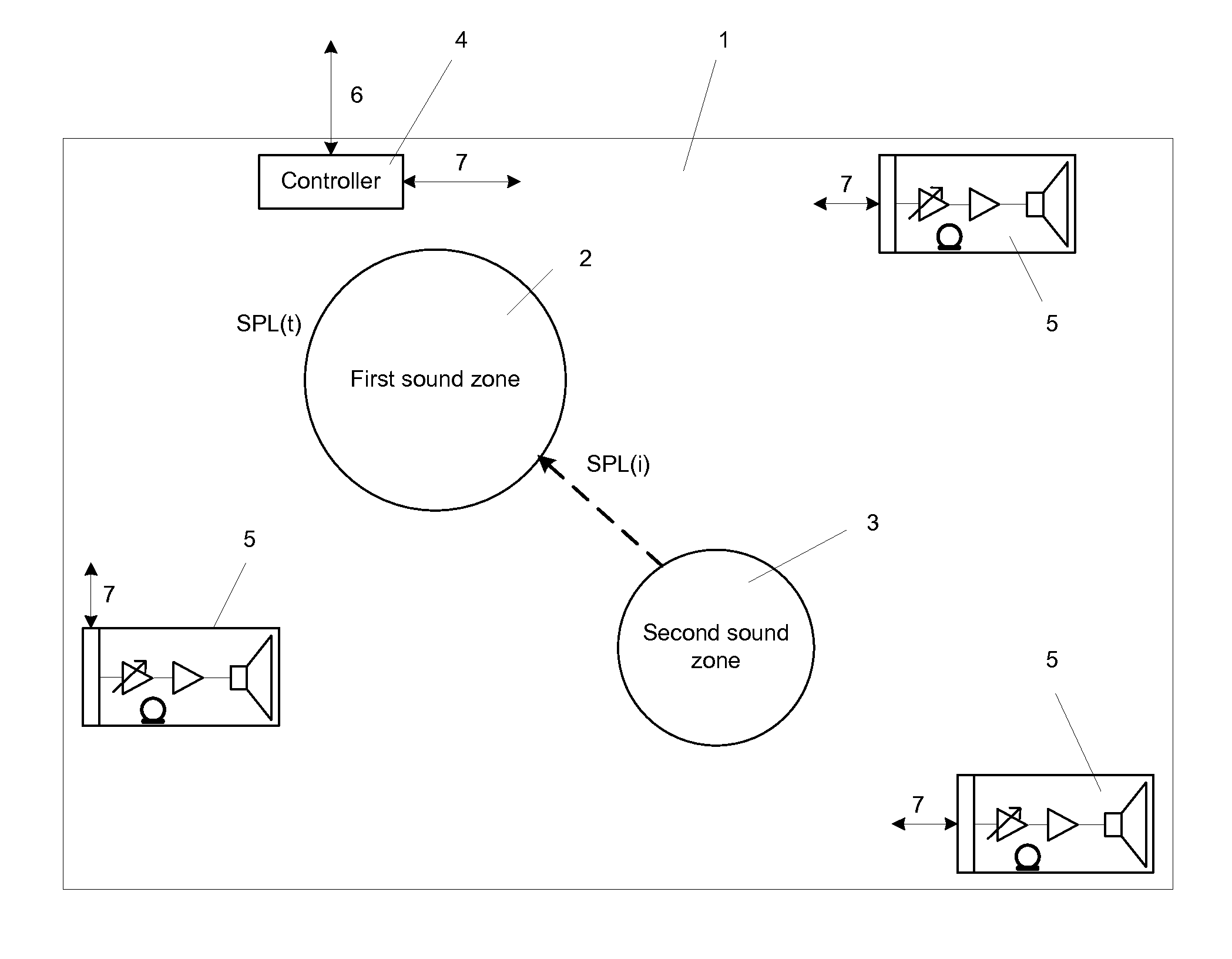
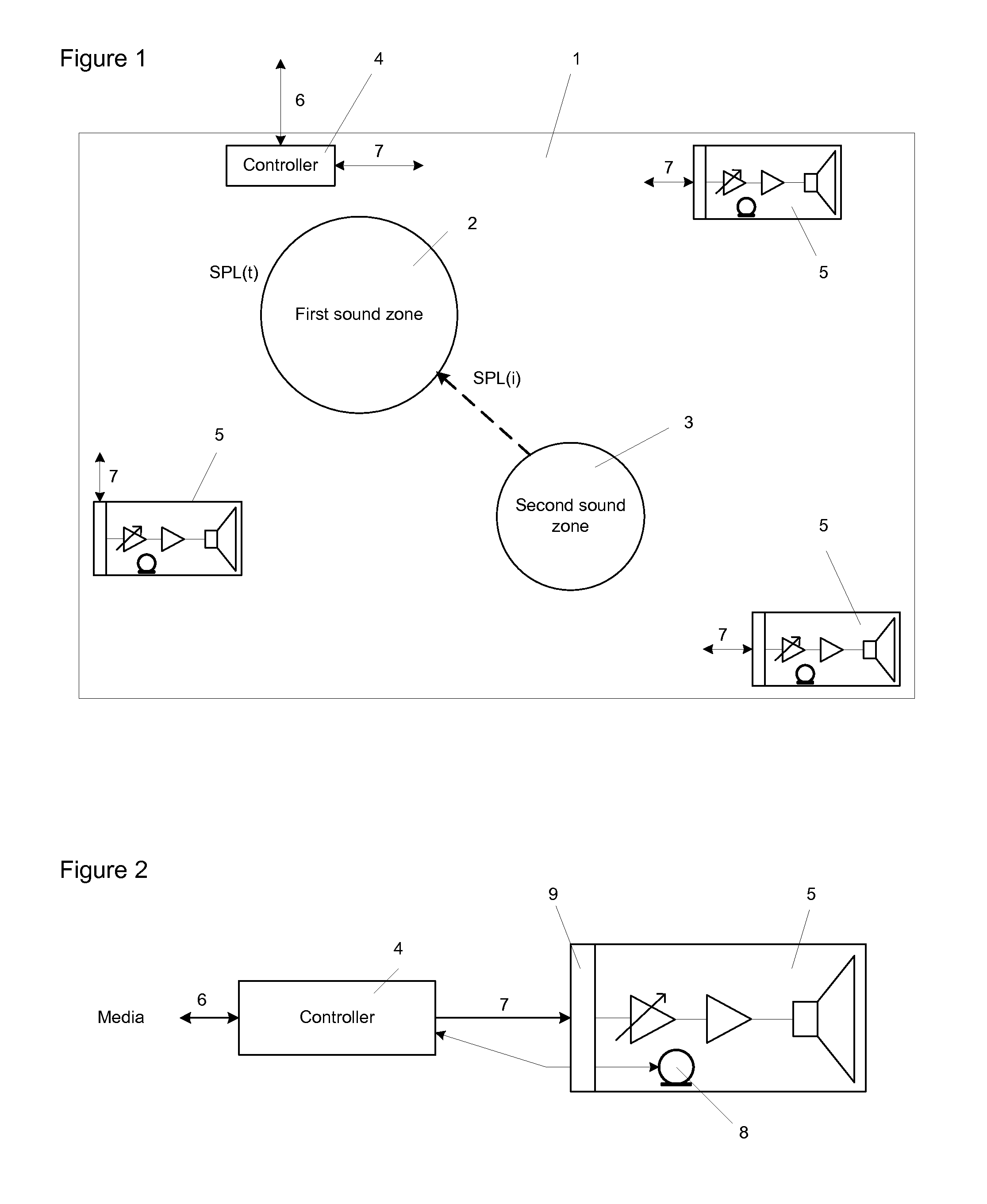
System for optimizing the perceived sound quality in virtual sound zones
ActiveUS20130230175A1Stereophonic circuit arrangementsStereophonic systemsOperation modeSound quality
The invention discloses a system applied to optimize the perceived sound quality in virtual sound zones. The system includes a method to establish a threshold of acceptability for an interfering audio programme on a target audio programme. The method includes physical parameters like target programme and interferer programme which combined with the scenarios: information gathering, entertainment and reading and / or working, constitutes modes of operations that may be processed and controlled by a system controller.
Owner:BANG & OLUFSEN
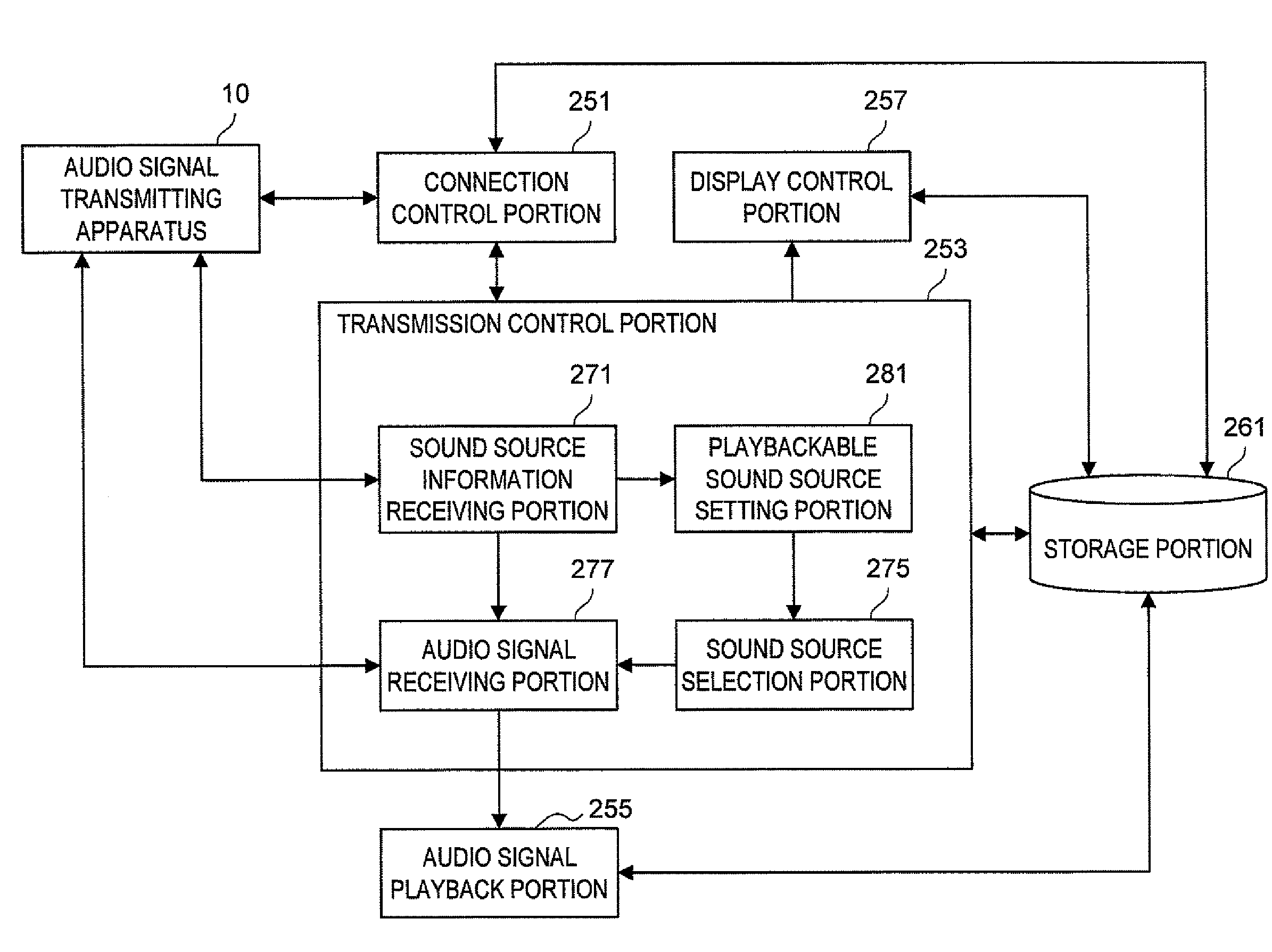
Audio signal receiving apparatus, audio signal receiving method and audio signal transmission system
InactiveUS8116476B2Filamentary/web record carriersPublic address systemsSound sourcesAudio frequency
Owner:SONY CORP
Networked speaker system with follow me
ActiveUS20150256954A1Save powerPublic address systemsSelective content distributionEngineeringLoudspeaker
In a multi-speaker audio system for, e.g., a home entertainment system or other entertainment system, each networked-speaker (wired or wireless) is activated or deactivated as appropriate such that audio play follows a user as the user moves around the home.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method and system for adapting a loudspeaker to a listening position in a room
ActiveUS8144883B2Loudspeaker enclosure positioningFrequency response correctionEngineeringLoudspeaker
The invention relates to a method and a system for adapting a loudspeaker to a specific listening position relative to the loudspeaker according to which method and system the acoustic power radiated by the loudspeaker is corrected by means of a correction filter inserted in the signal path through the loudspeaker, the response of said correction filter being determined by comparison between the a quantity characterising the radiated acoustic power measured at an actual listening position and a similar quantity measured at a reference listening position. According to a specific embodiment of the invention said characterising quantities are the radiation resistances measured at the actual listening position and the reference listening position respectively.
Owner:BANG & OLUFSEN
In-room acoustic magnitude response smoothing via summation of correction signals
A system and method are provided for smoothing the in-room acoustic magnitude response of an audio reproduction system. An in-room acoustic magnitude response analysis is performed to determine a room resonance induced peak associated with an audio signal. A replica of the audio signal is filtered at the room resonance induced peak. The filtered replica signal is added with the audio signal. Through this, smoothing of the room resonance induced peak may be achieved, such that a subjective impression of transient response and dynamics of the audio signal are preserved.
Owner:POLK AUDIO LLC +1
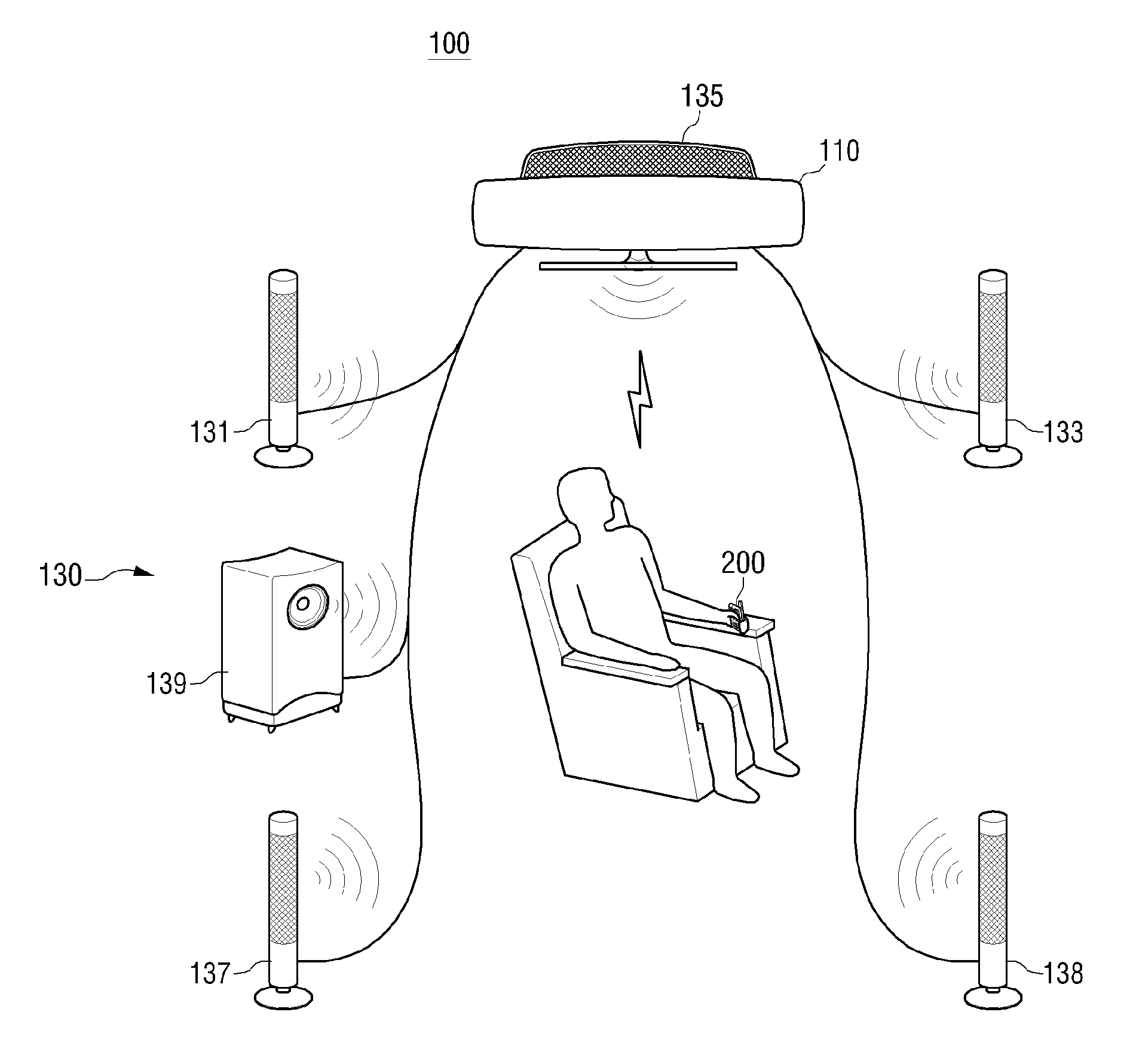
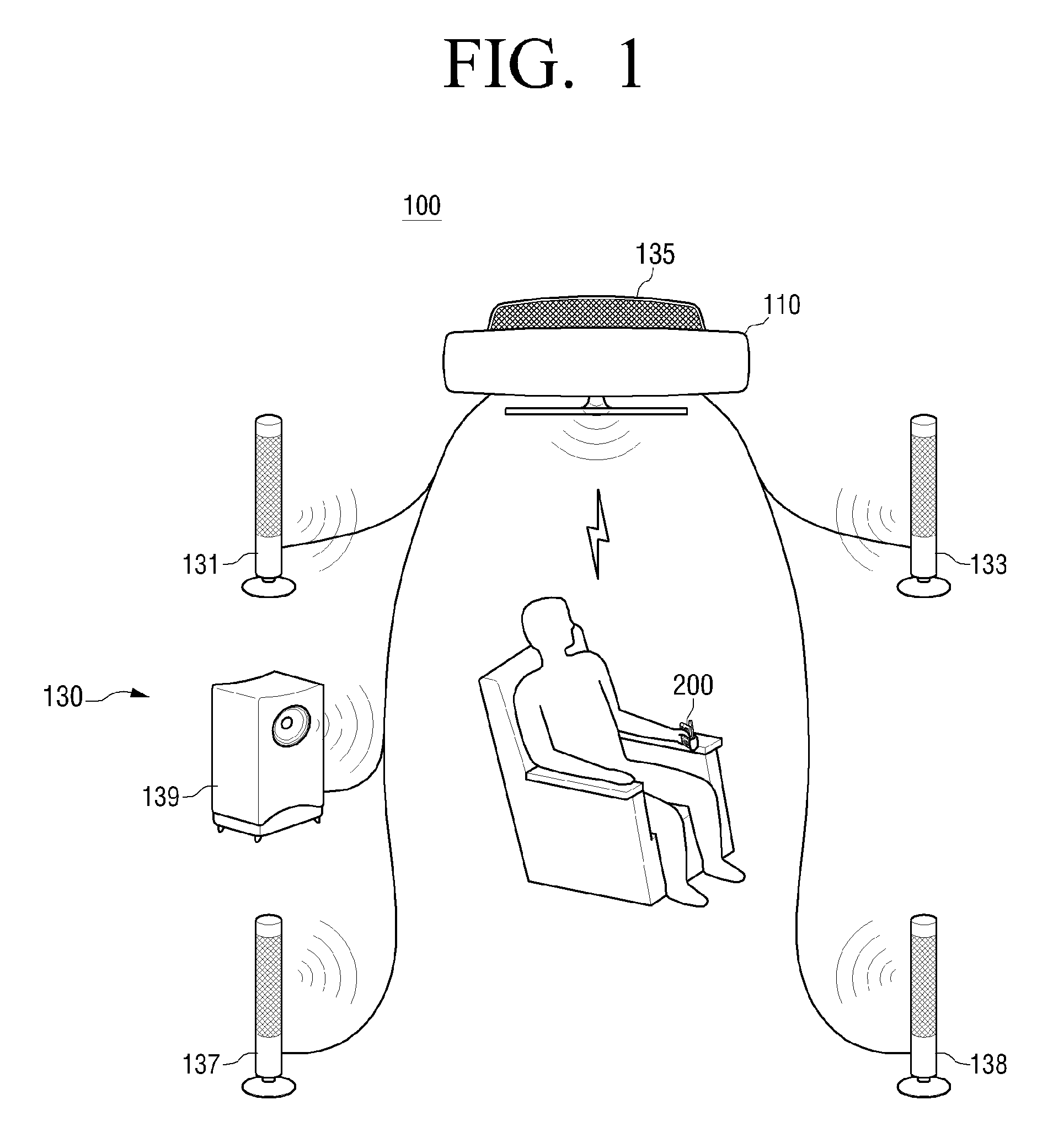
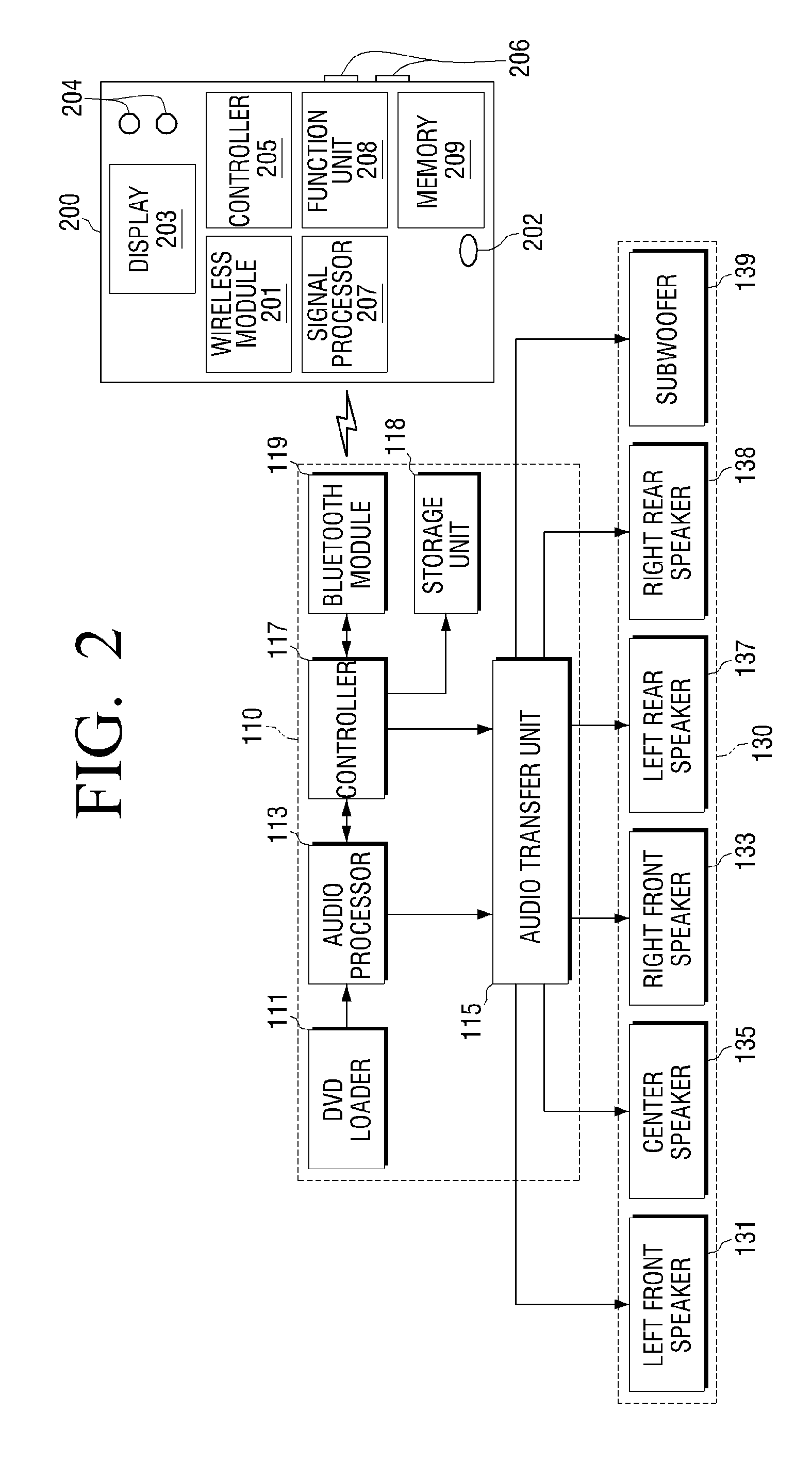
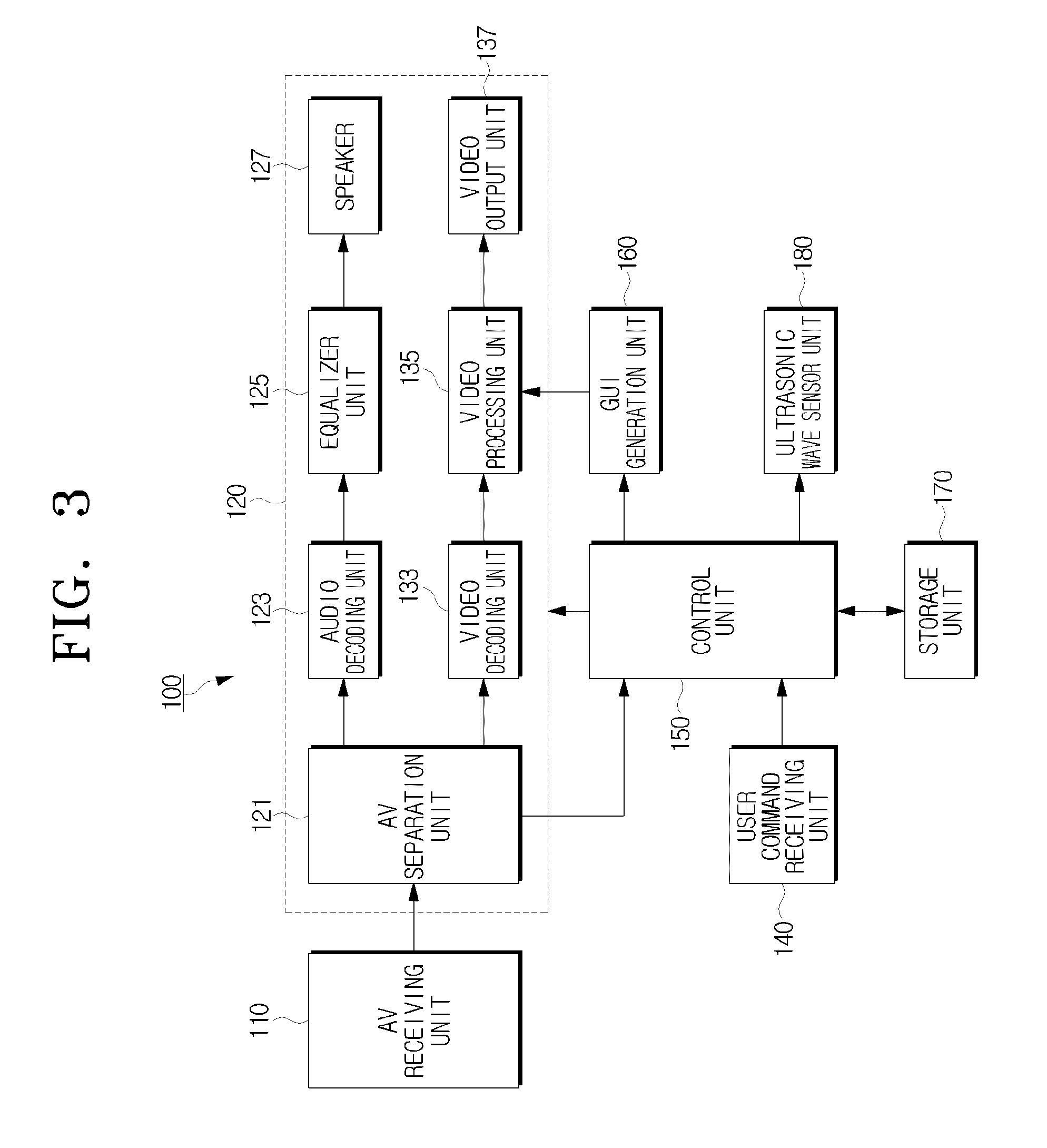
Audio apparatus and signal calibration method thereof
An audio system to calibrate an audio signal based on a wirelessly received signal, and a signal calibration method are provided. The audio system includes a sound output unit to output a sound corresponding to a received audio signal. A transceiver is connected to an external device to enable wireless communication between a main unit and the external device. The external device converts the sound output from the sound output unit into an electric signal to generate a calibration audio signal. The main unit performs calibration on an audio signal to be played back through the sound output unit using the calibration audio signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
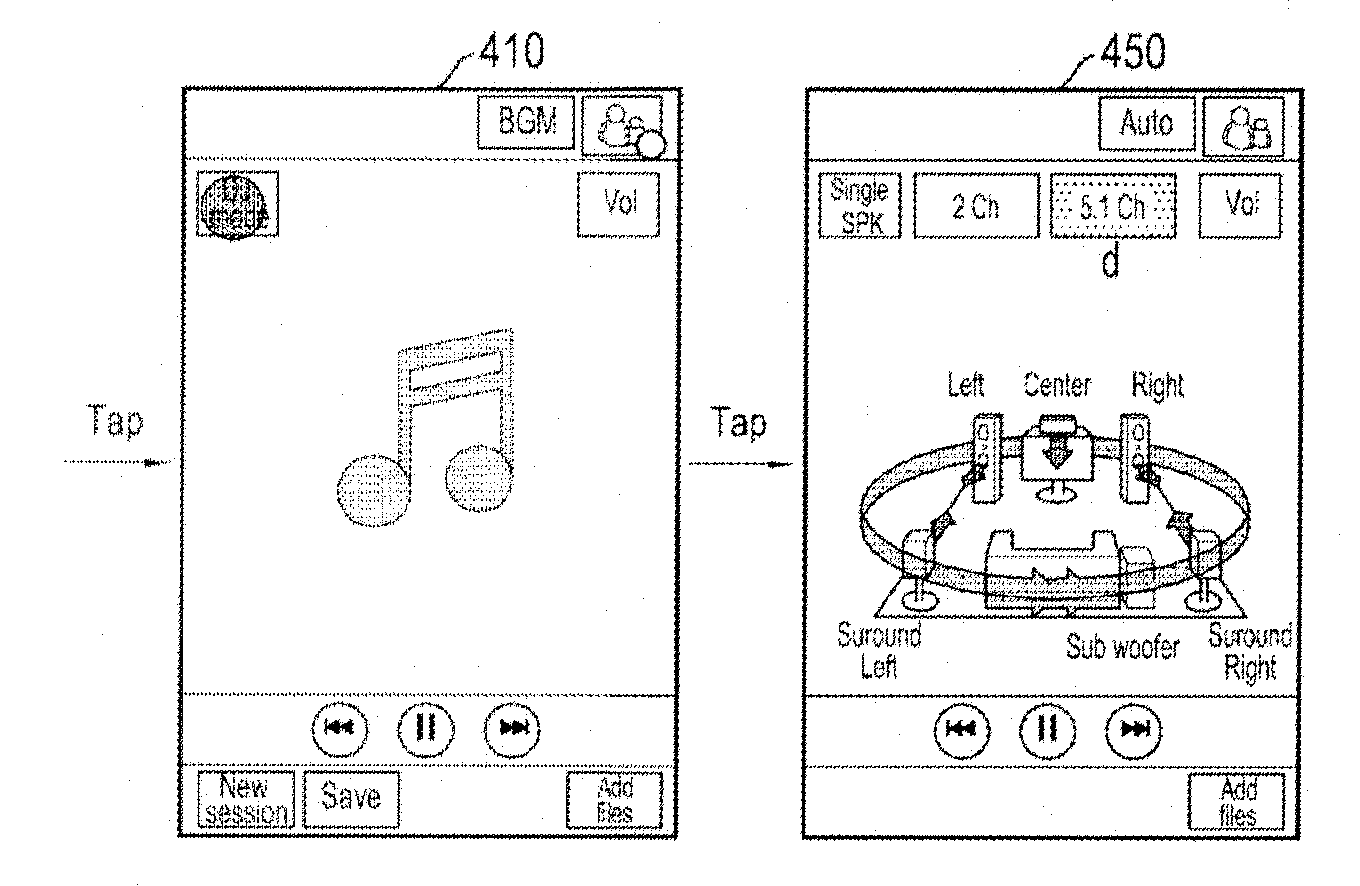
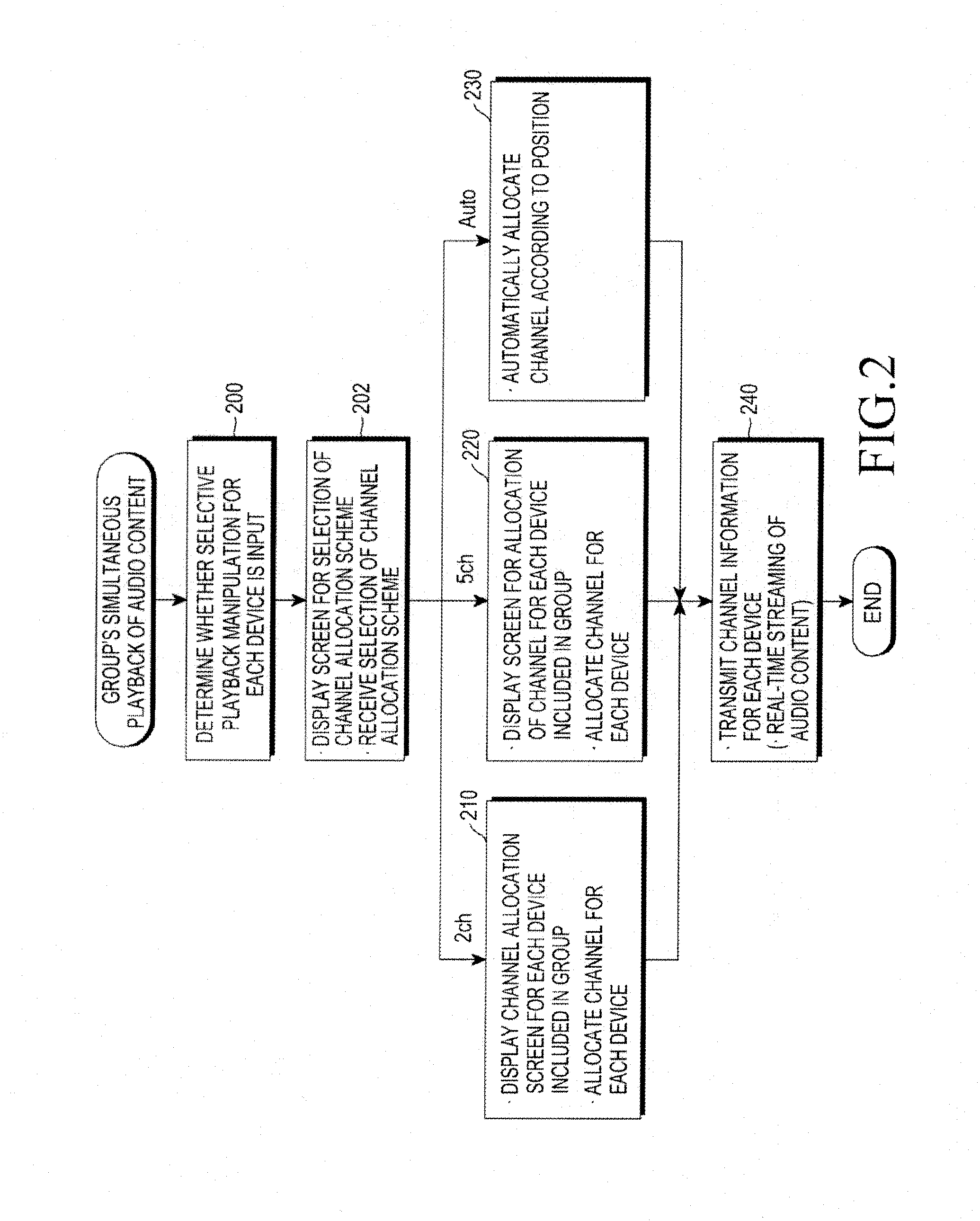
Audio content playback method and apparatus for portable terminal
An audio content playback method for a portable terminal The audio content playback method includes checking a channel that is supportable by audio content that is currently engaged in group's simultaneous playback, in group's simultaneous playback of the audio content. The method includes allocating a channel to each of devices included in a group based on position information of each device included in the group or based on an input state in a user interface environment that is preset for channel allocation for each device included in the group, and transmitting the allocated channel information to each device included in the group to allow the device to select its allocated channel and play the audio content.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Automatic detection of loudspeaker characteristics
Disclosed is subject matter that proposes a system and method for a media device to automatically detect the characteristics of an attached speaker. Speakers have many different characteristics, for example, power, impedance, frequency response, etc. With knowledge of the speaker characteristics, audio output can be equalized appropriately, and an amplifier of the media device, for example, can prevent exceeding the maximum power handling capability of the speaker. Described is a device and method for retrieving information about the speaker from a memory that is coupled to the speaker. A media device can read the data from the memory over existing speaker wires. Software and / or hardware in the media device can optimize the output to the attached speaker. Accordingly, the media device can interrogate the speaker directly over speaker wire to obtain the characteristics of the speaker.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
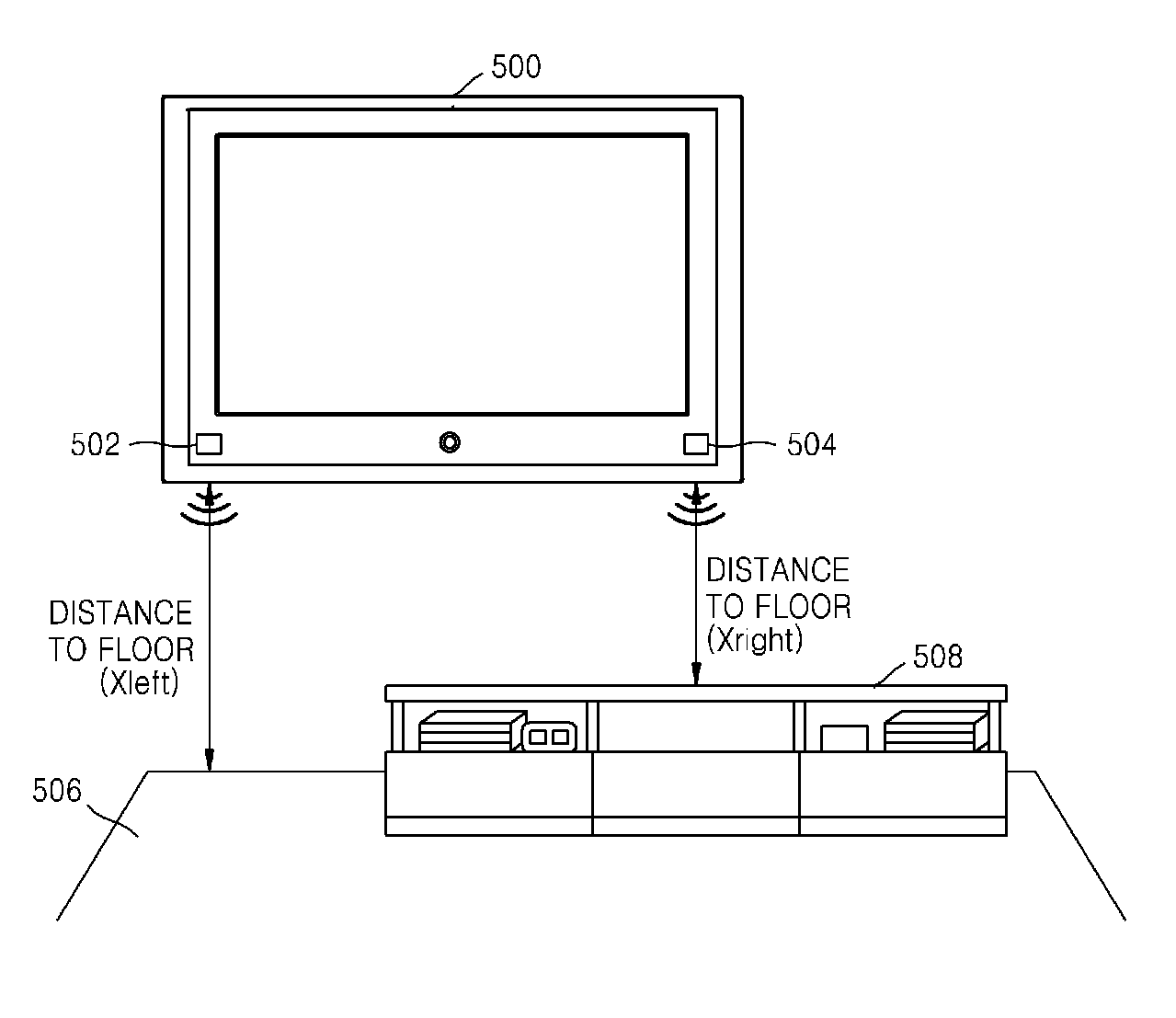
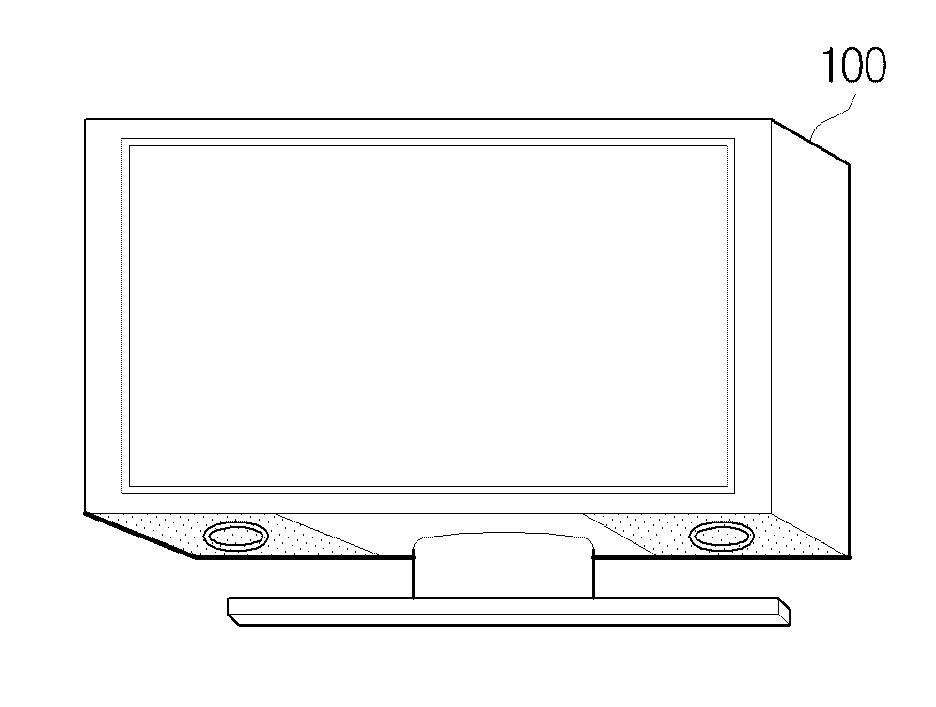
Method of compensating for audio frequency characteristics and audio/video apparatus using the method
A method of compensating for spatial audio frequency characteristics that varies in accordance with a mounting condition of a down firing speaker of an audio / video (AV) apparatus includes calculating a listening distance between the AV apparatus and a listener, calculating a distance between a speaker mounted on the AV apparatus and a neighboring reflective surface, setting a spatial frequency compensation filter value and a speaker frequency characteristic compensation filter value based on the calculated distances, and compensating for frequency characteristics of an audio signal by combining the spatial frequency compensation filter value and the speaker frequency characteristic compensation filter value.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
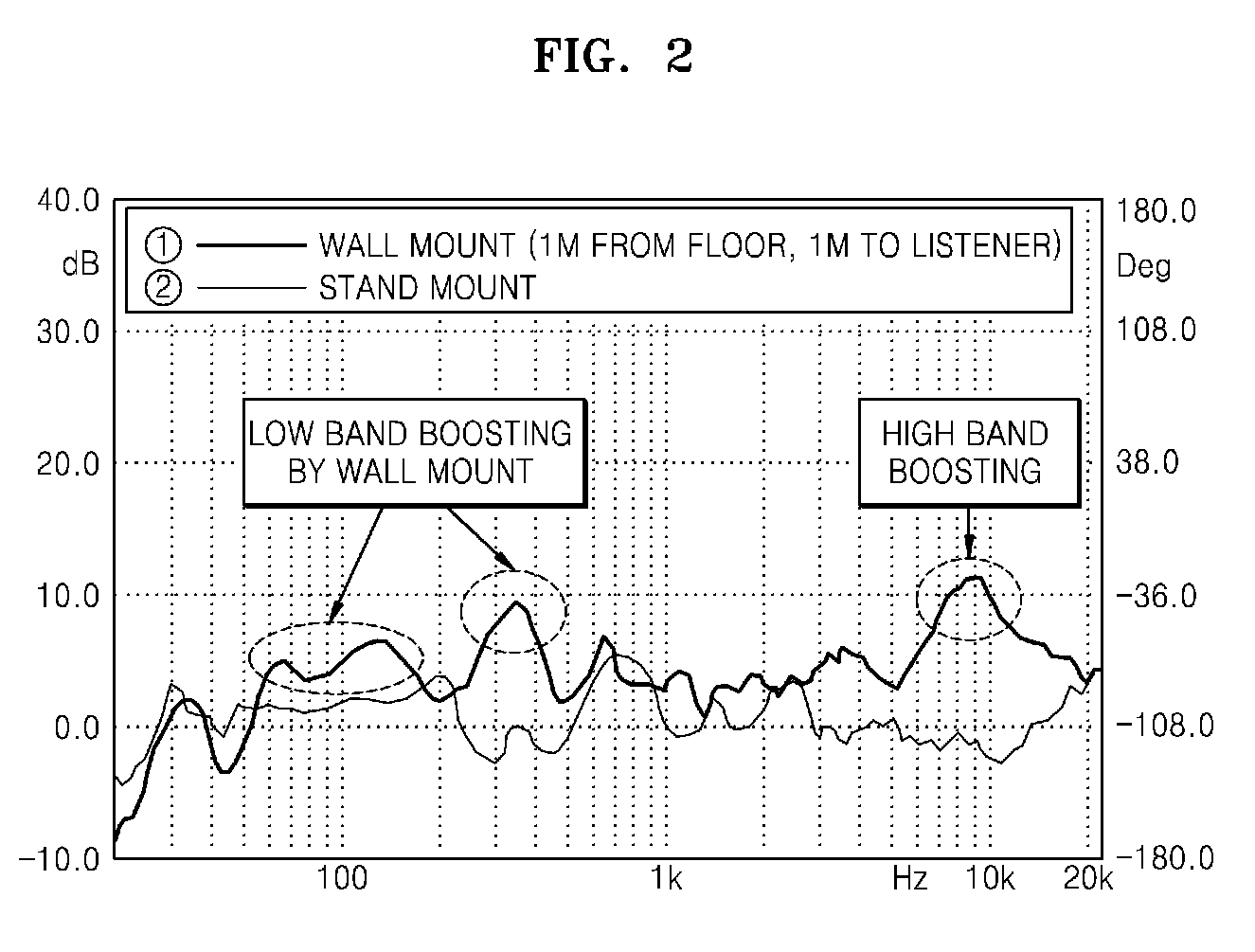
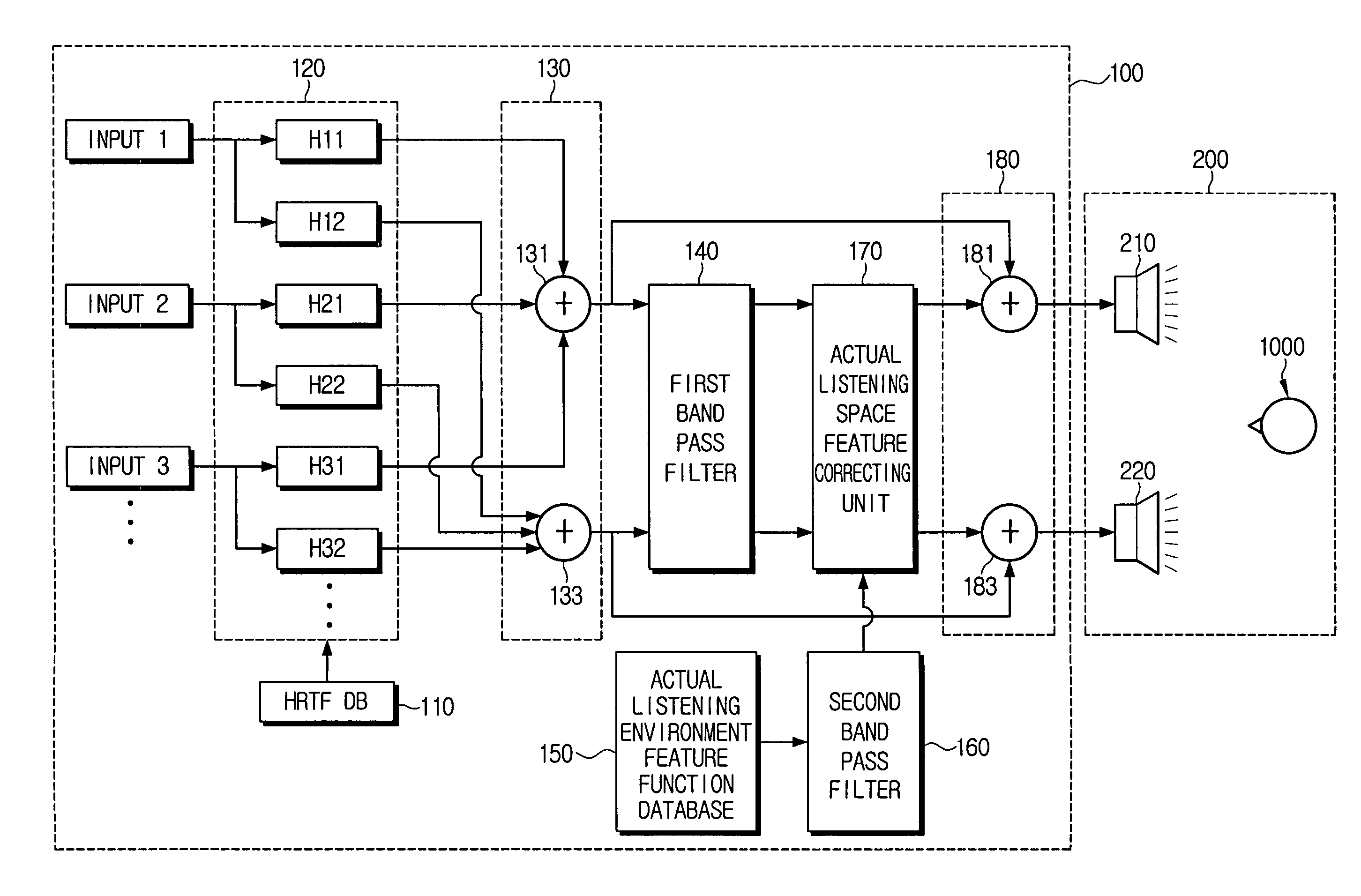
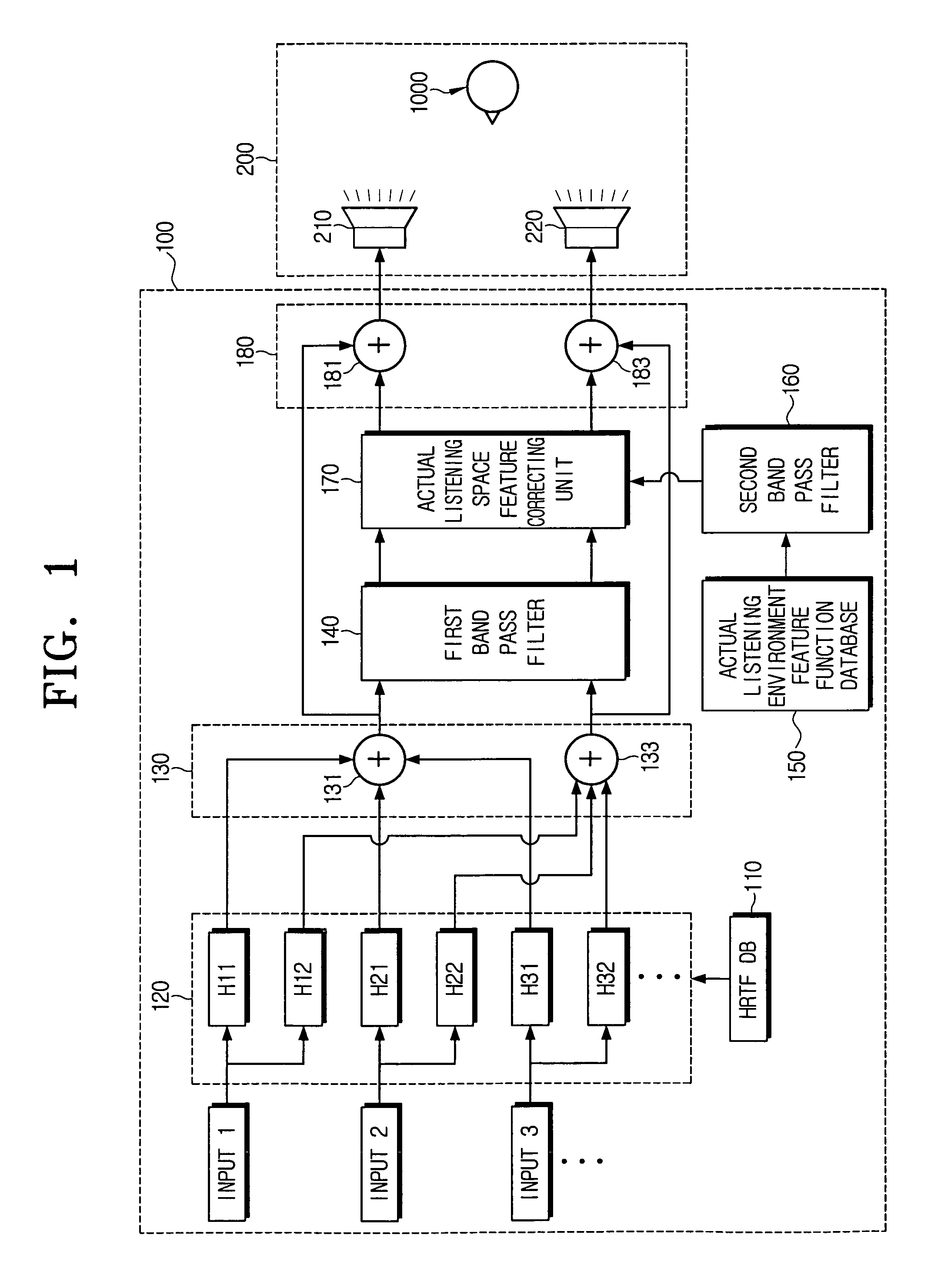
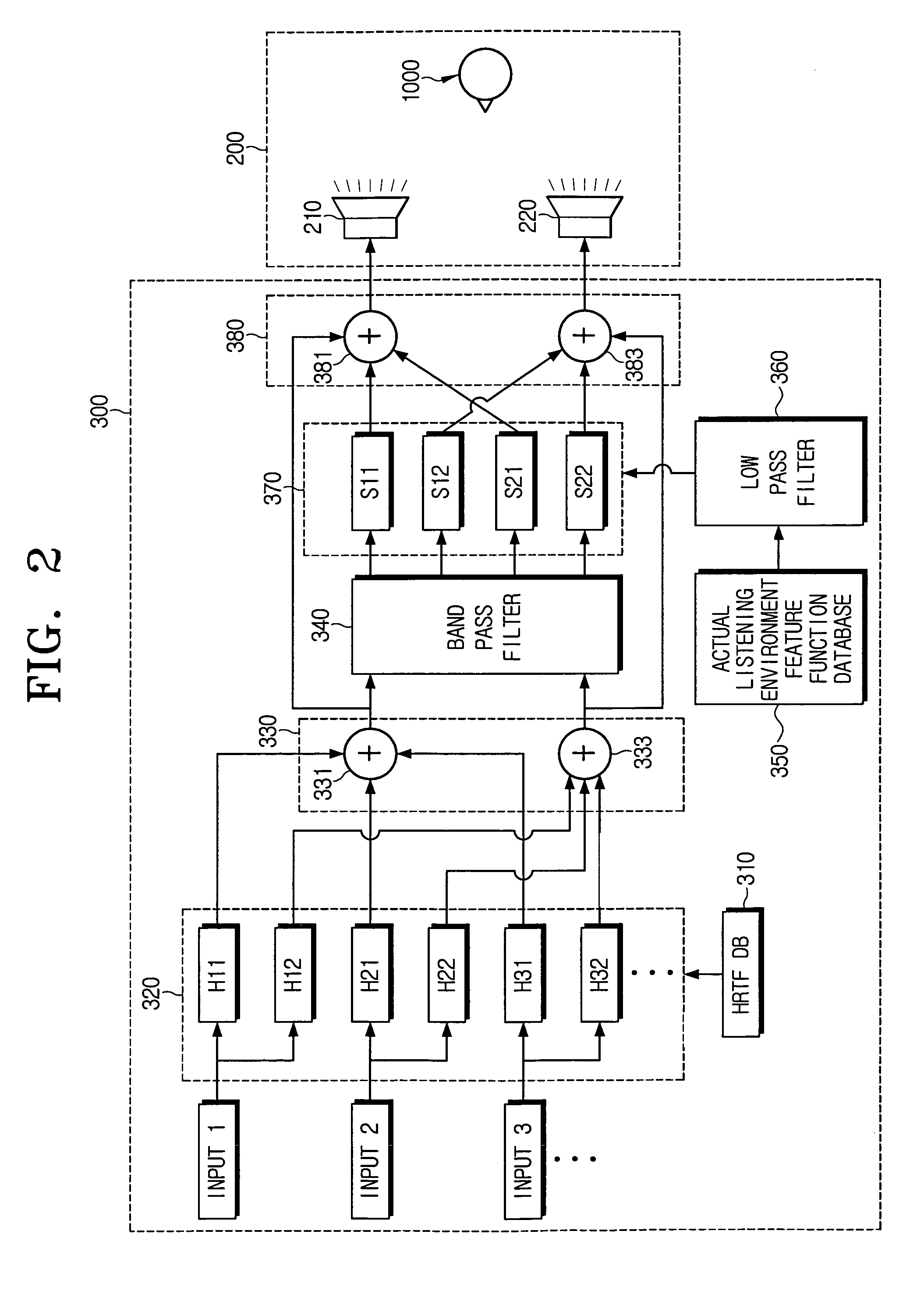
Sound reproducing apparatus and sound reproducing method
InactiveUS8160281B2Accurate featuresLarge spacingTransducer acoustic reaction preventionLoudspeaker spatial/constructional arrangementsComputer scienceDistortion
A sound reproducing apparatus and a sound reproducing method. The sound reproducing apparatus includes an actual listening environment feature function database where an actual listening space feature function is stored for correcting the virtual source in response to a feature of an actual listening space provided at the time of listening; and an actual listening space feature correcting unit of reading out the actual listening space feature function stored in the actual listening environment feature function database, and correcting the virtual source based on the reading result. Accordingly, causes of each distortion may be removed to provide sounds having the best quality.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
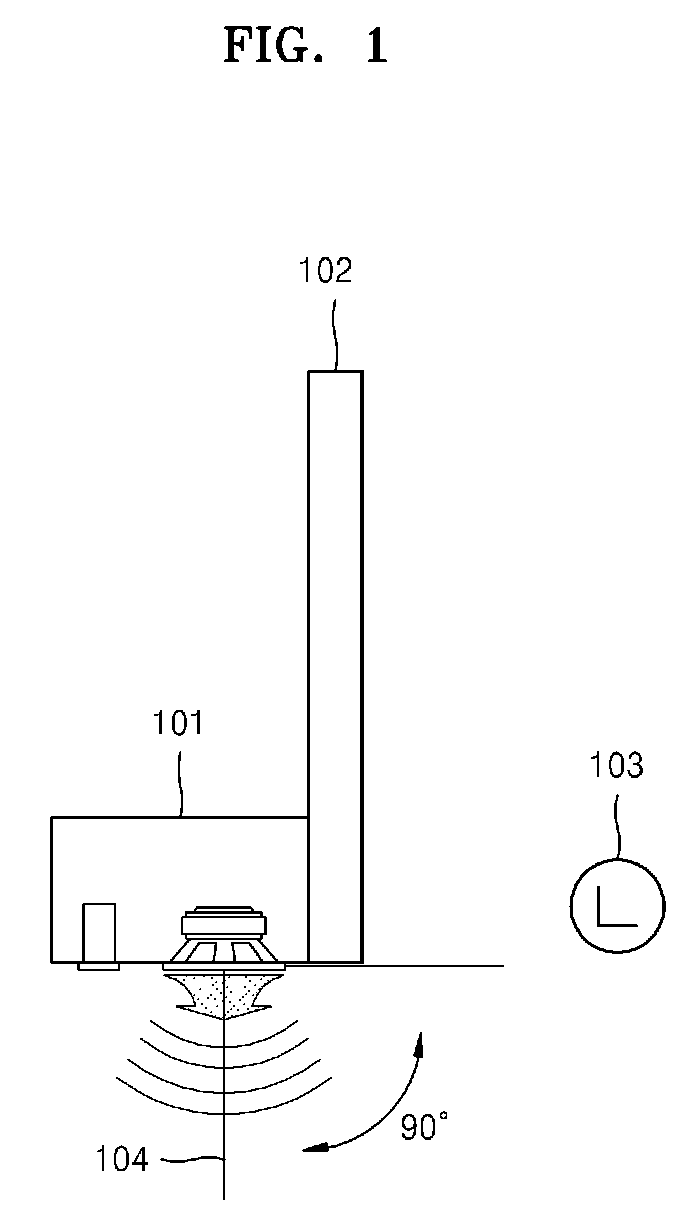
Method for equalizing audio, and video apparatus using the same
InactiveUS8600075B2Prevent audio attenuationDesign moreTelevision system detailsStereophonic systemsUltrasound attenuationLoudspeaker
A method for equalizing audio and a video apparatus using the audio equalizing method are provided. The method for equalizing audio includes detecting the distance between a speaker mounted in a video apparatus and a reflective surface, and equalizing an audio signal to be output from the speaker based on the detected distance. Accordingly, attenuation of audio output is reduced, so audio output is optimized.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
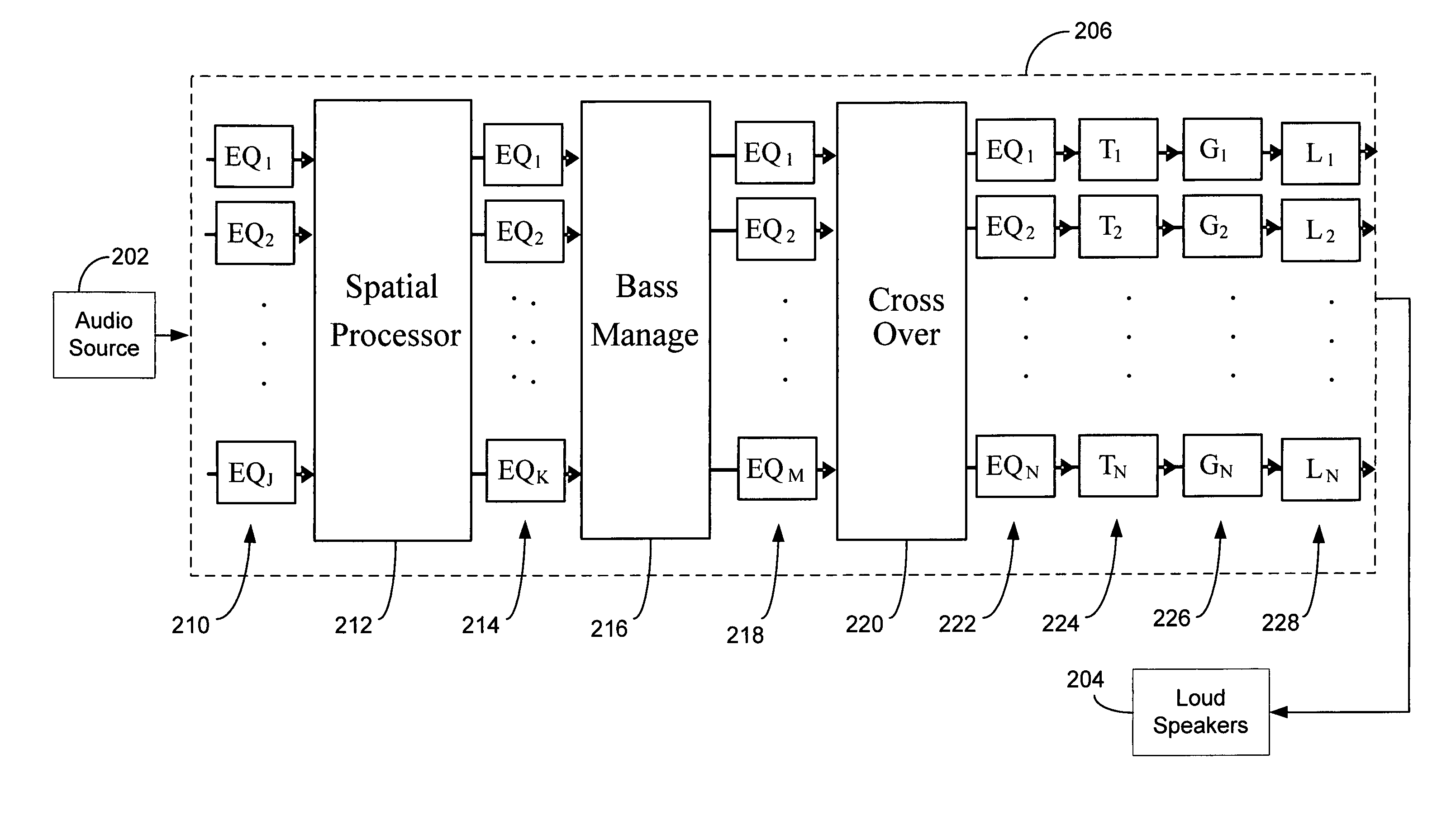
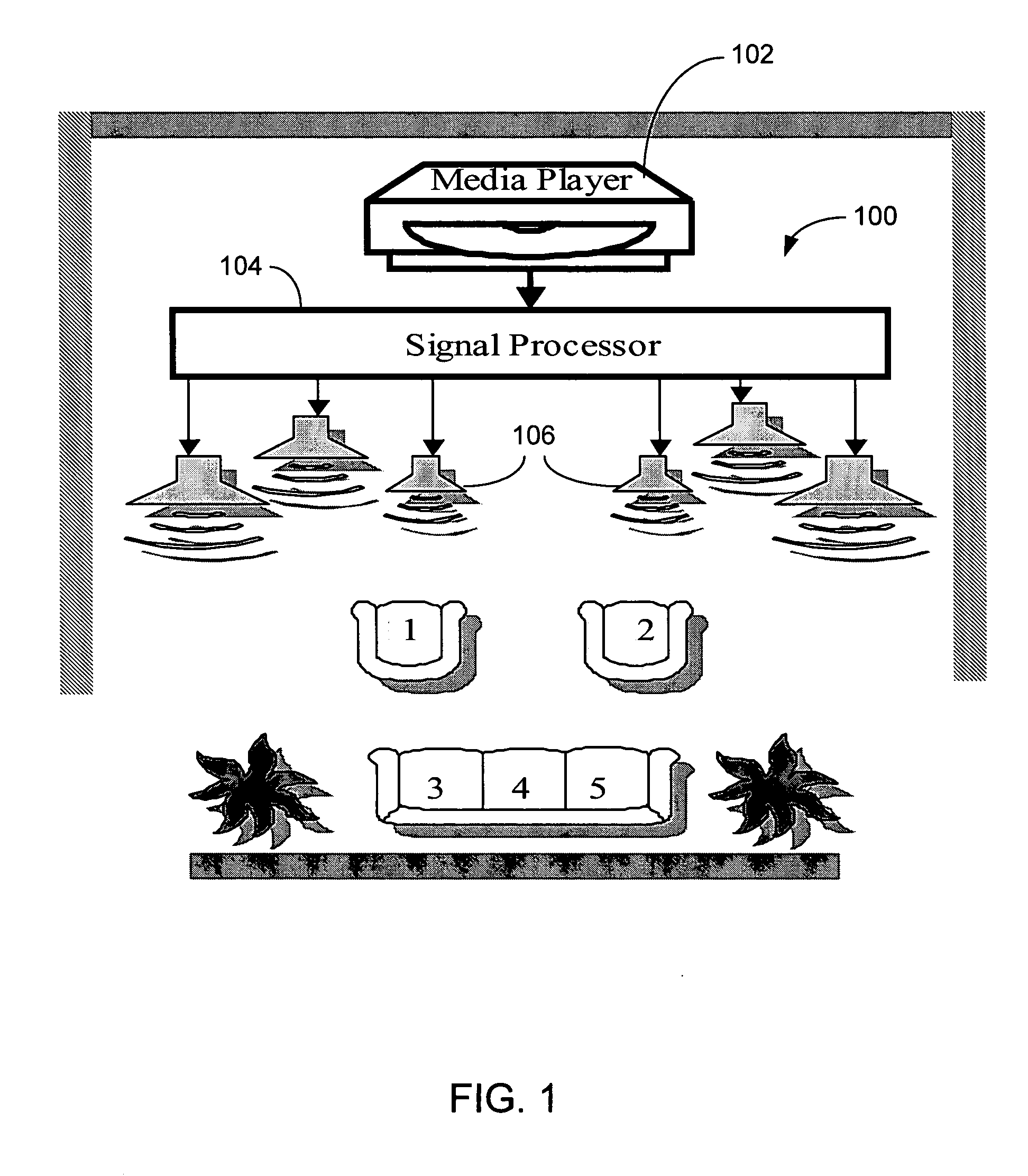
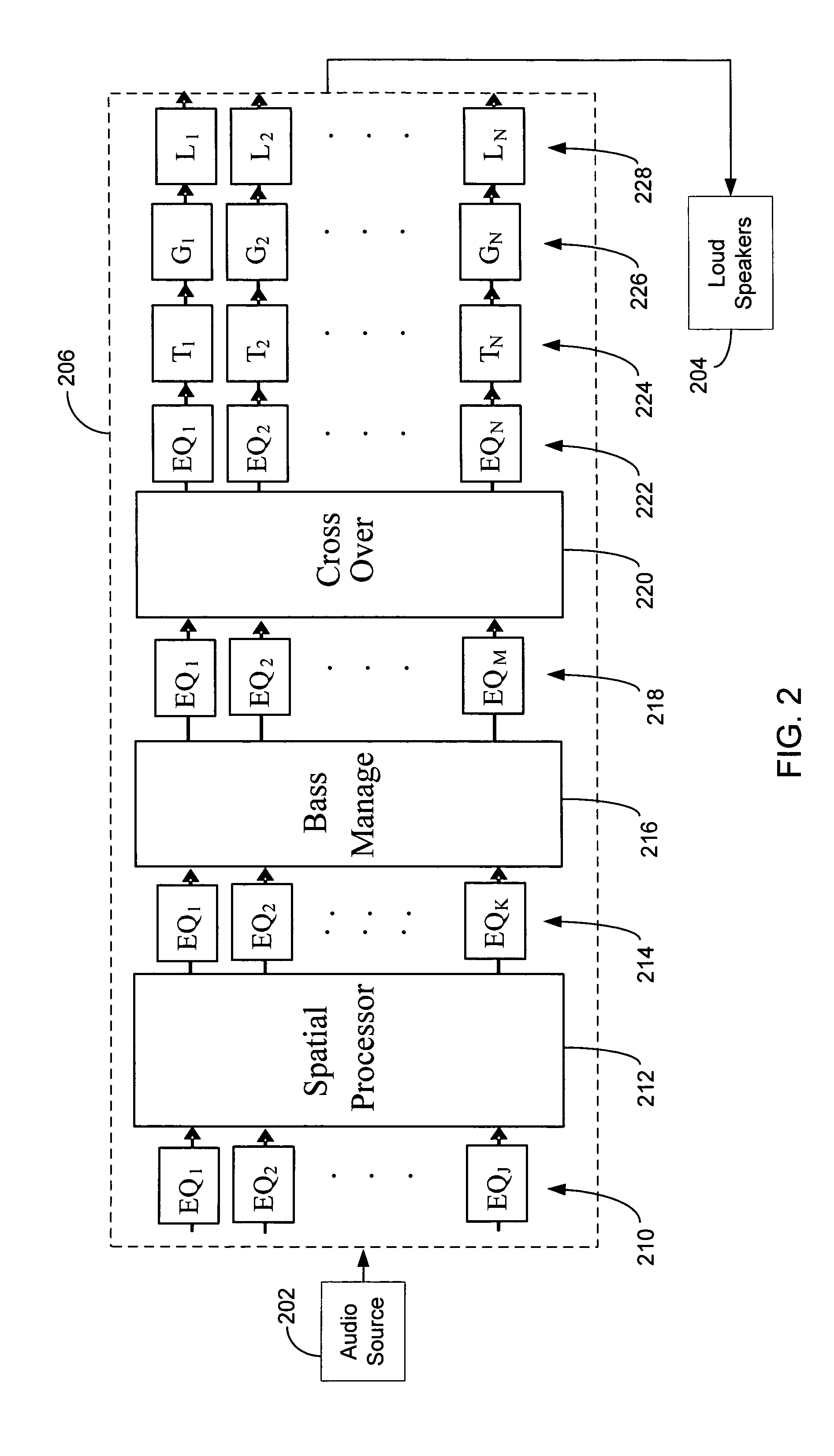
Audio tuning system
An audio system installed in a listening space may include a signal processor and a plurality of loudspeakers. The audio system may be tuned with an automated audio tuning system to optimize the sound output of the loudspeakers within the listening space. The automated audio tuning system may provide automated processing to determine at least one of a plurality of settings, such as channel equalization settings, delay settings, gain settings, crossover settings, bass optimization settings and group equalization settings. The settings may be generated by the automated audio tuning system based on an audio response produced by the loudspeakers in the audio system. The automated tuning system may generate simulations of the application of settings to the audio response to optimize tuning.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
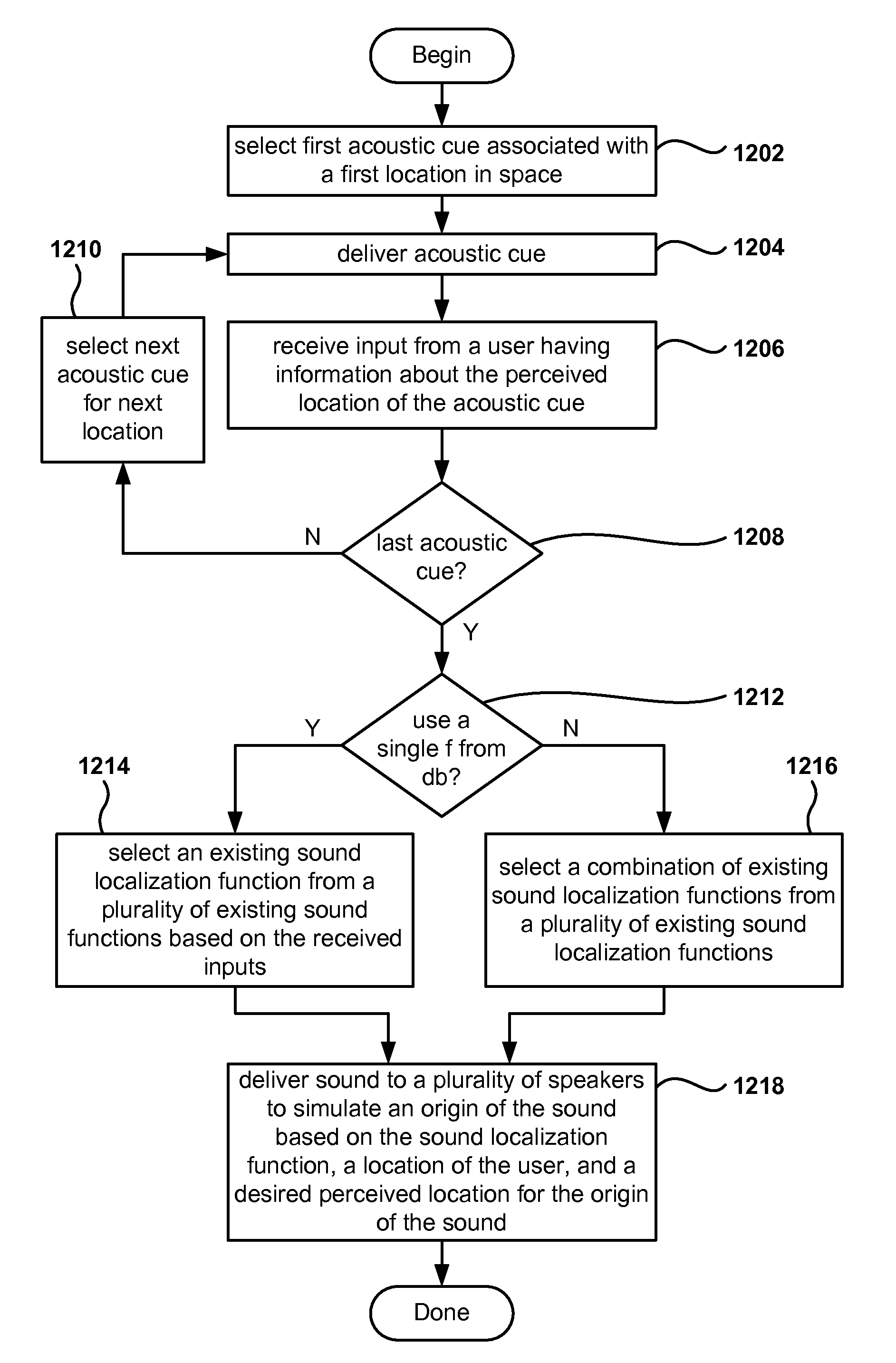
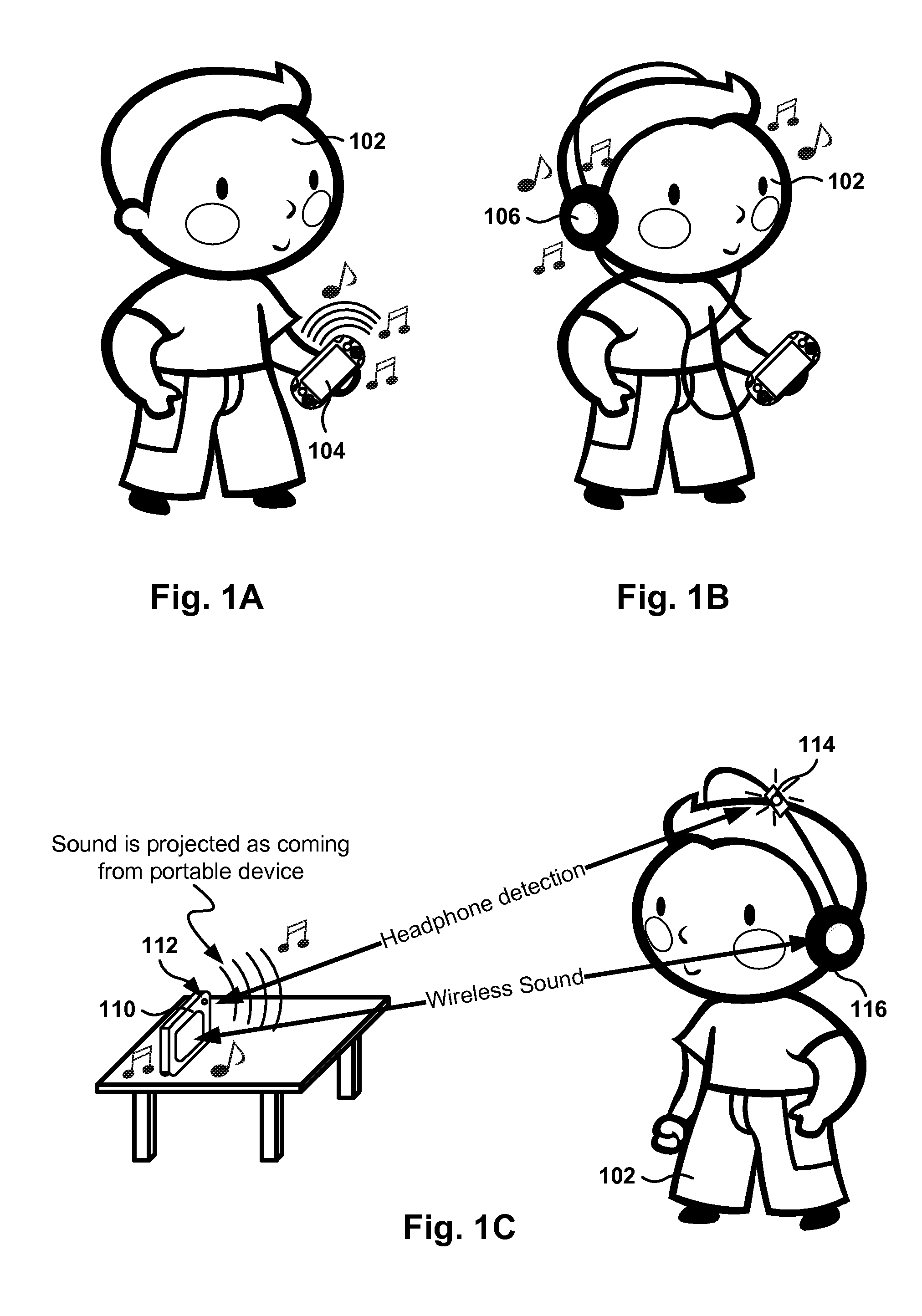
Sound localization for user in motion
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com