Patents
Literature
1614 results about "Transient response" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In electrical engineering and mechanical engineering, a transient response is the response of a system to a change from an equilibrium or a steady state. The transient response is not necessarily tied to abrupt events but to any event that affects the equilibrium of the system. The impulse response and step response are transient responses to a specific input (an impulse and a step, respectively).
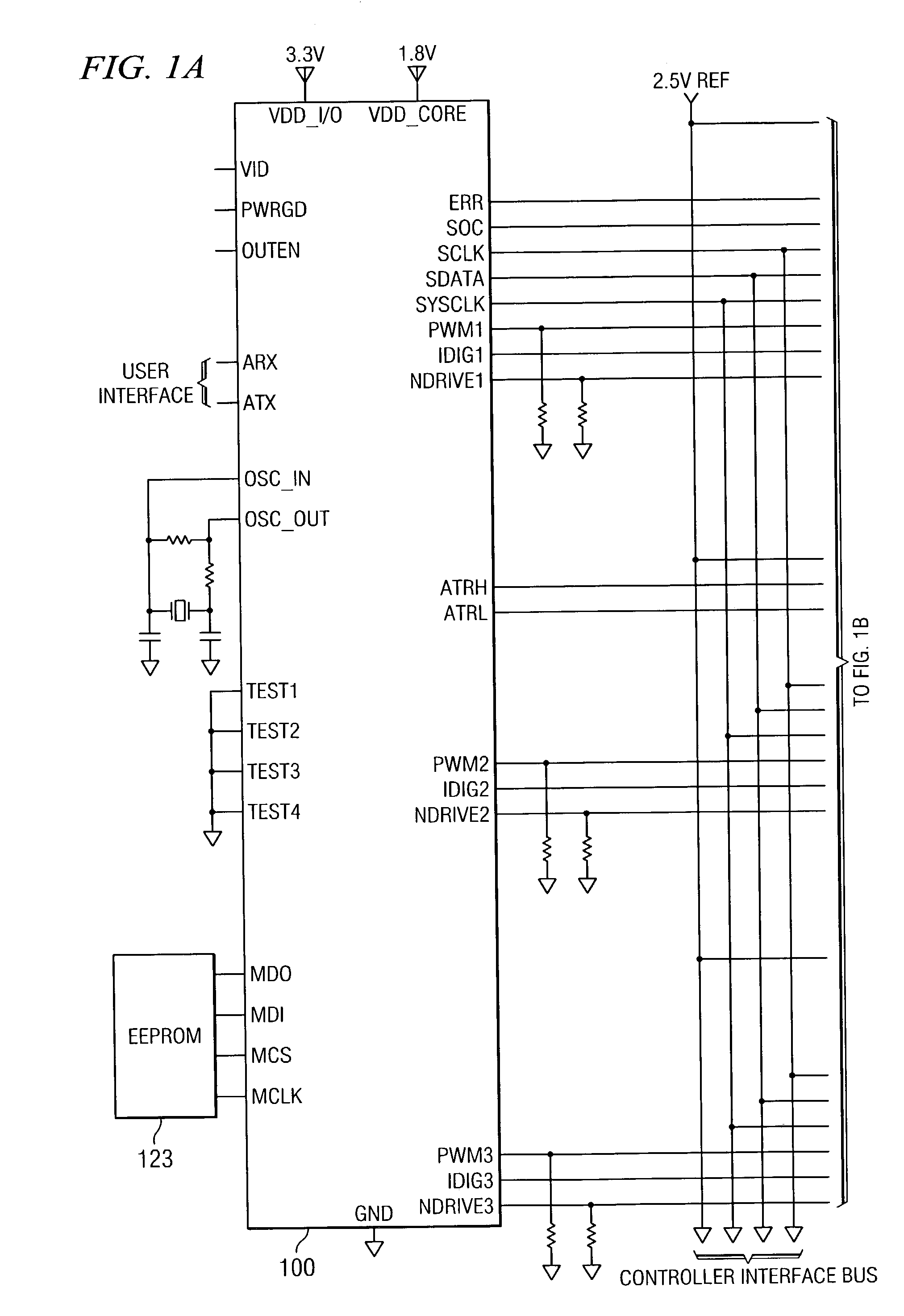
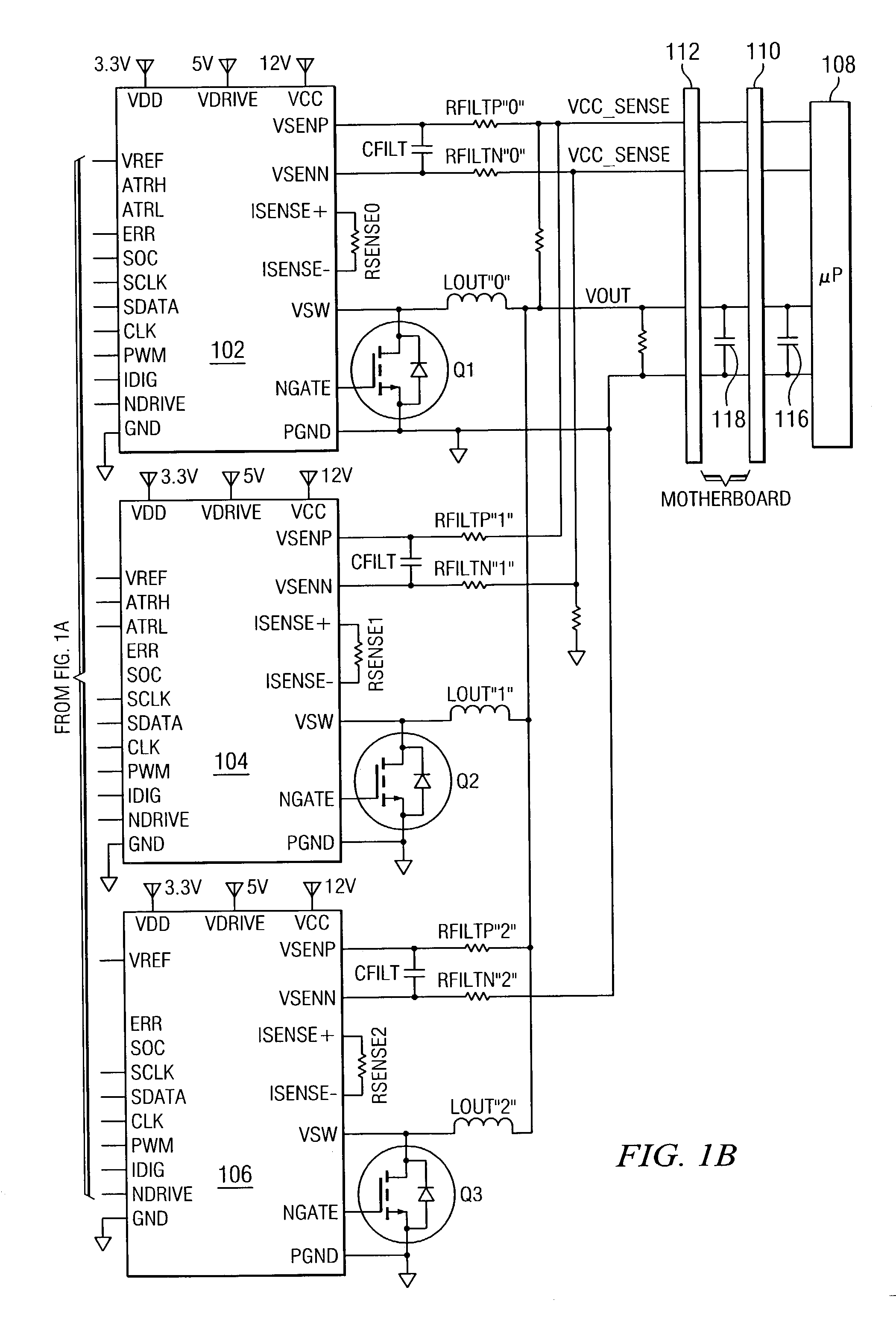
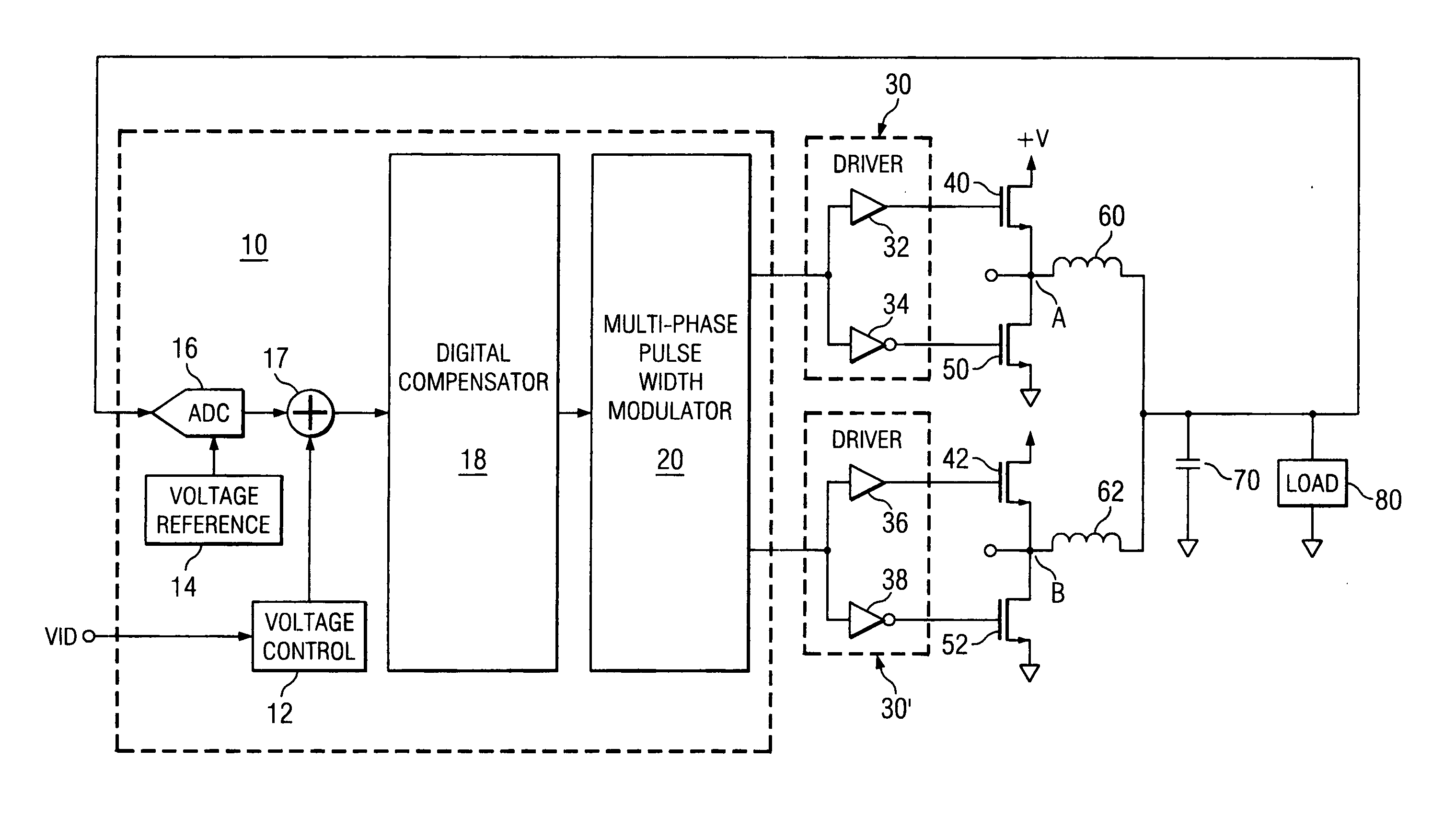
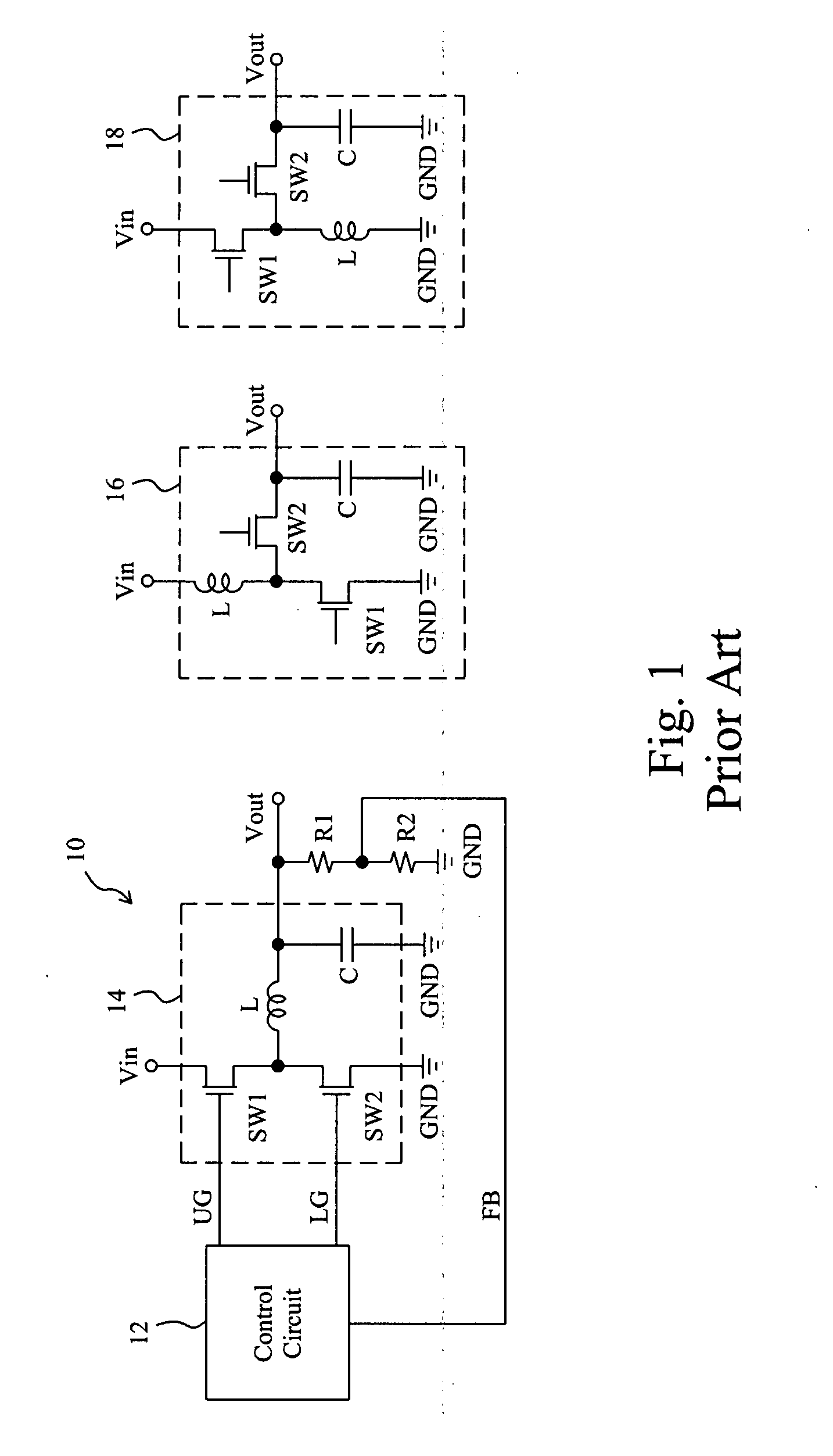
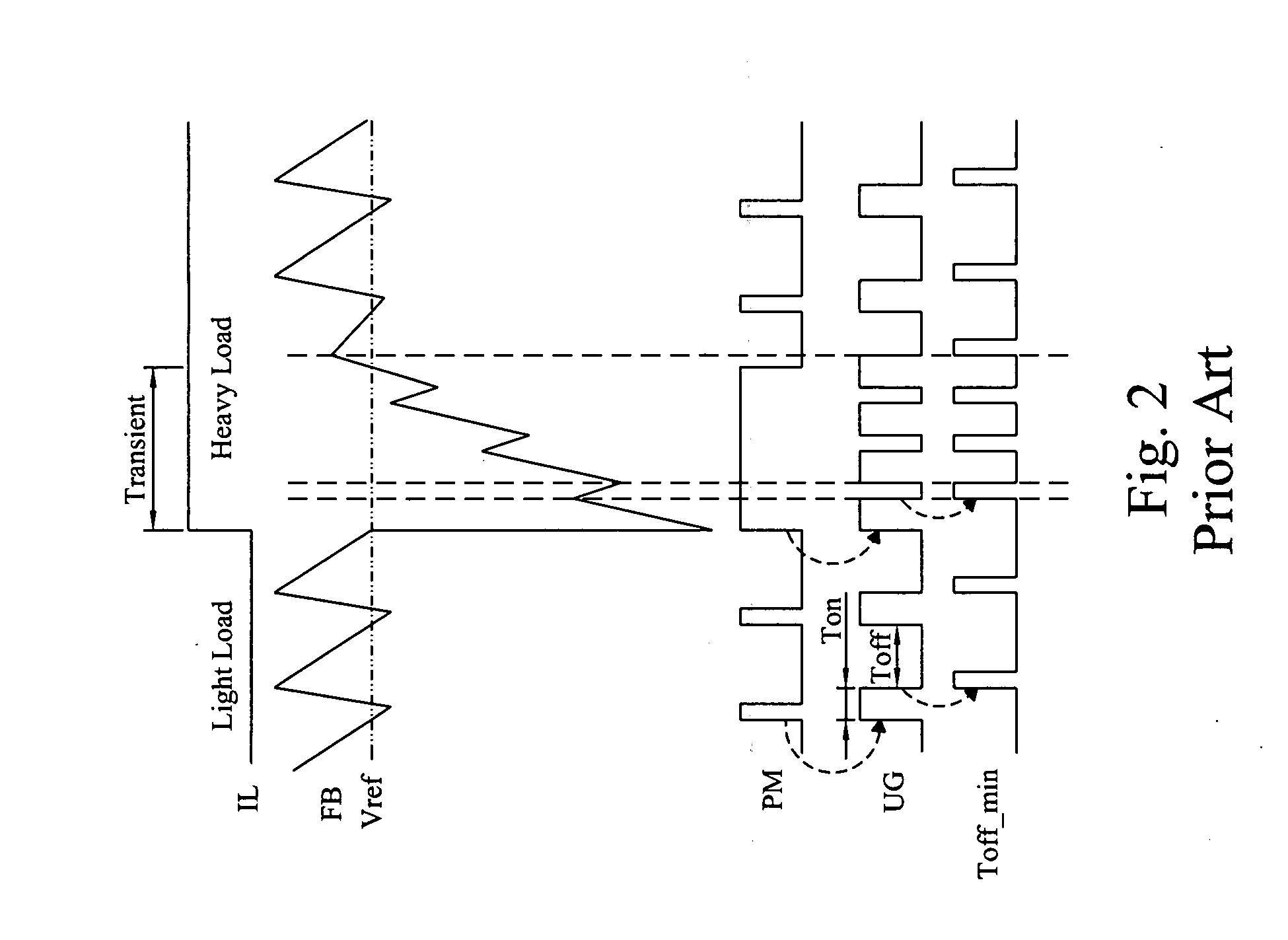
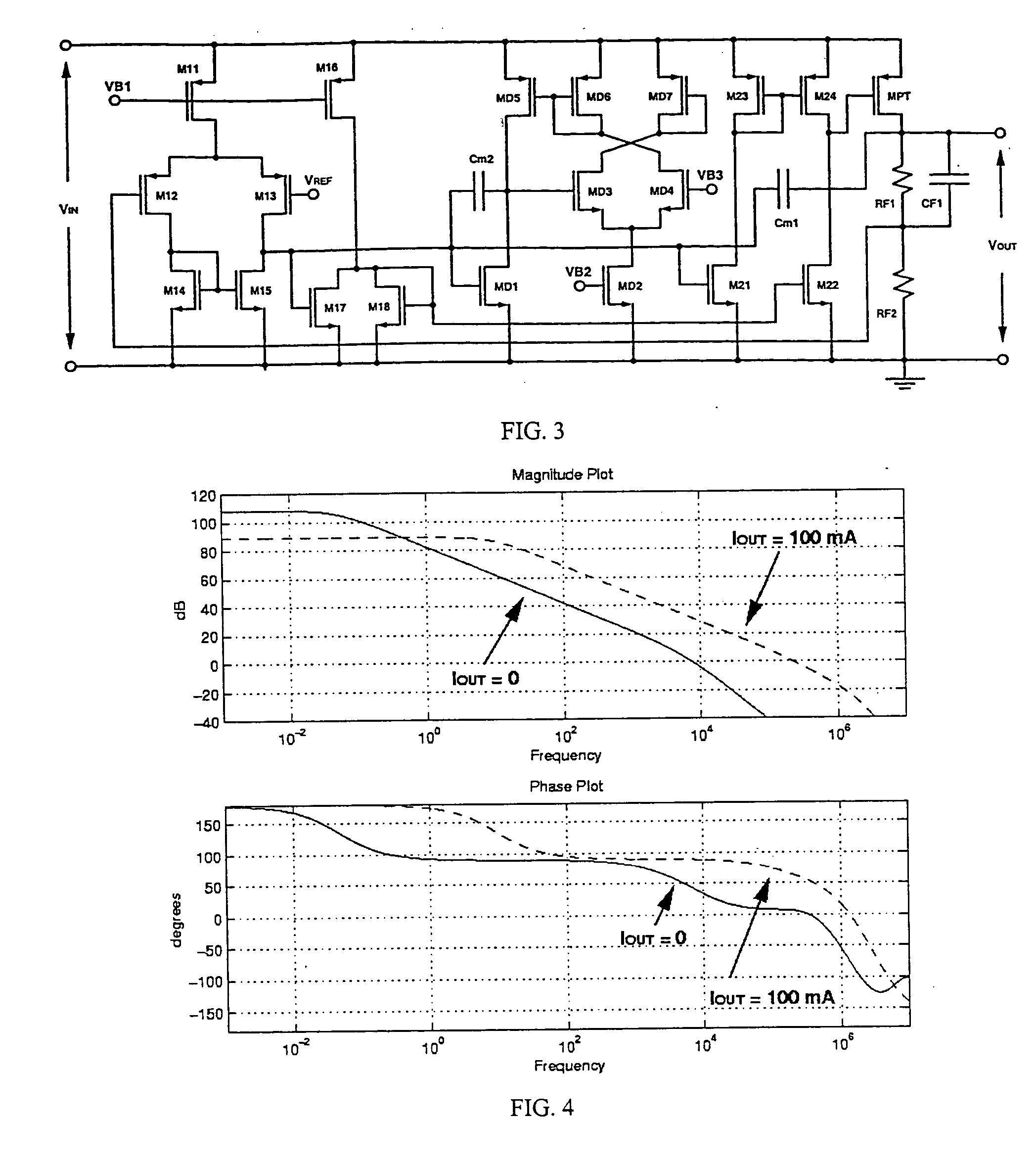
System and method for highly phased power regulation using adaptive compensation control
InactiveUS7007176B2Improved power regulation systemAdd control functionVolume/mass flow measurementDc-dc conversionComputer moduleEngineering
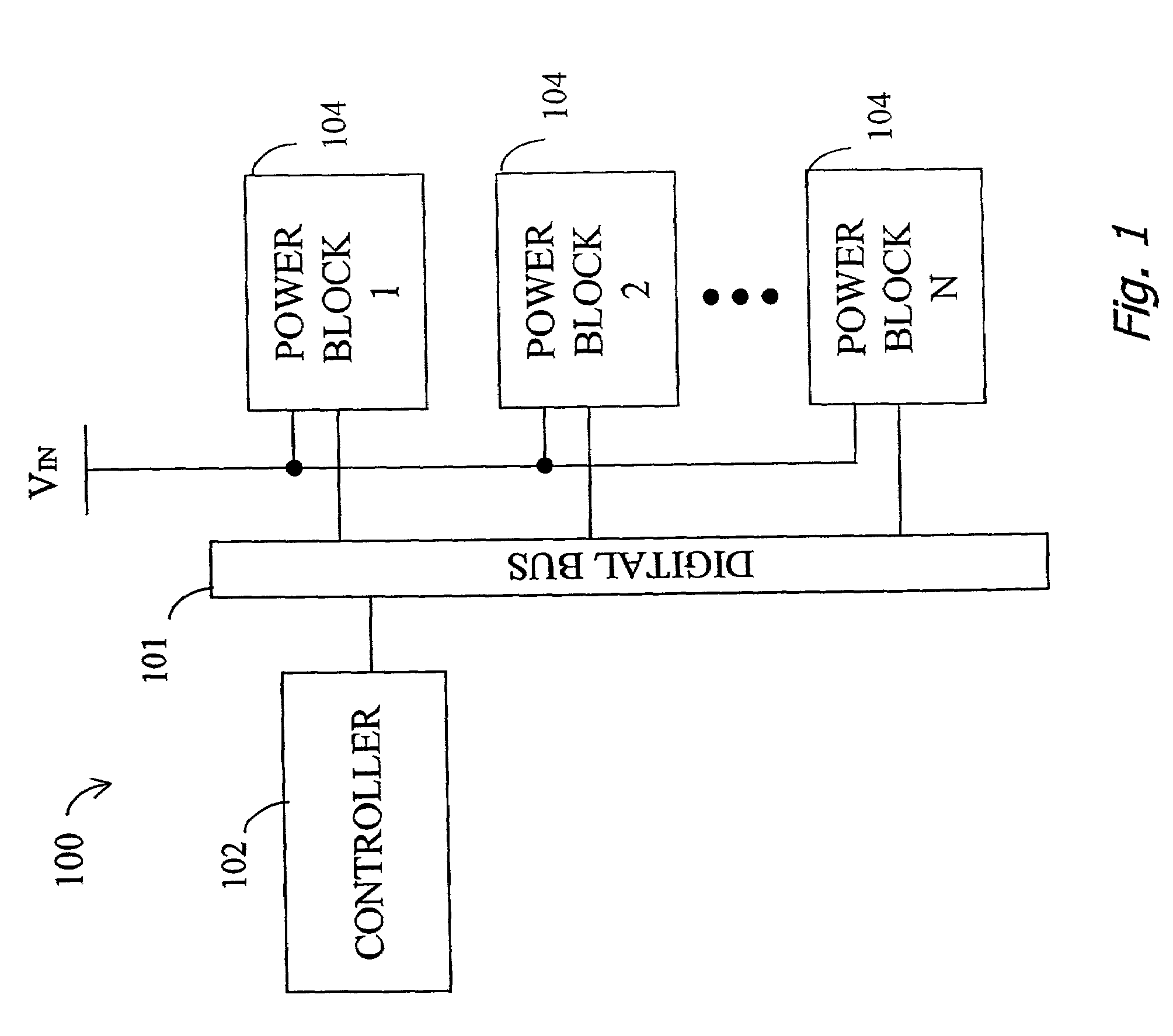
A highly phased power regulation (converter) system having an improved control feature is provided. A controller, such as a digital signal processor or microprocessor, receives digital information from a plurality of power conversion blocks and transmits control commands in response to the information. The controller is able to change the mode of operation of the system and / or re-phase the power blocks to accommodate a dynamic load requirement, occasions of high transient response or detection of a fault. A compensation block within the controller is used to regulate the output voltage and provide stability to the system. In one embodiment, the controller is implemented as a PID compensator controller. In another embodiment, a microprocessor is able to receive feedback on its own operation thus providing enabling the controller to anticipate and predict conditions by analyzing precursor data.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AUSTRIA AG
In-room acoustic magnitude response smoothing via summation of correction signals
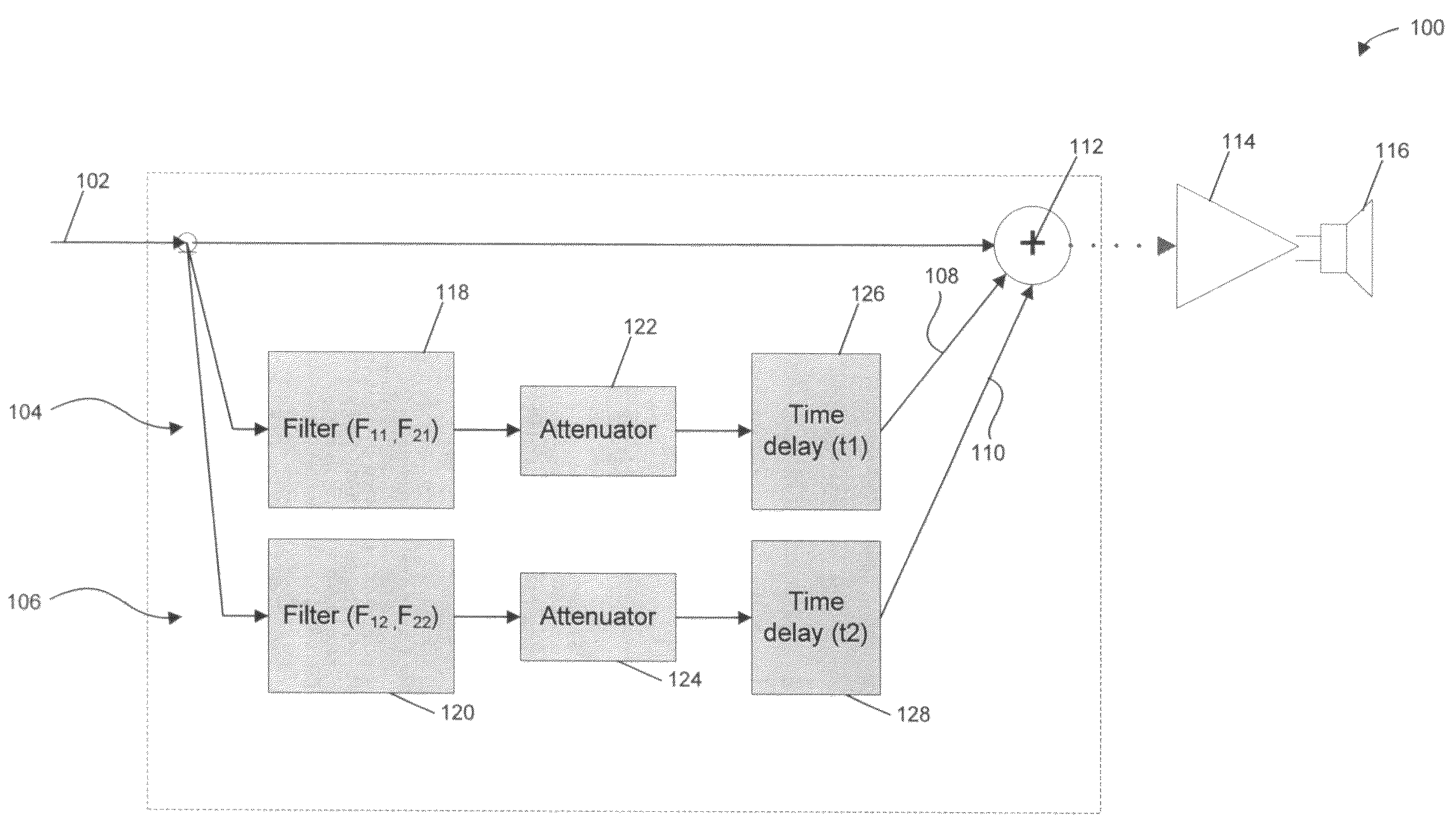
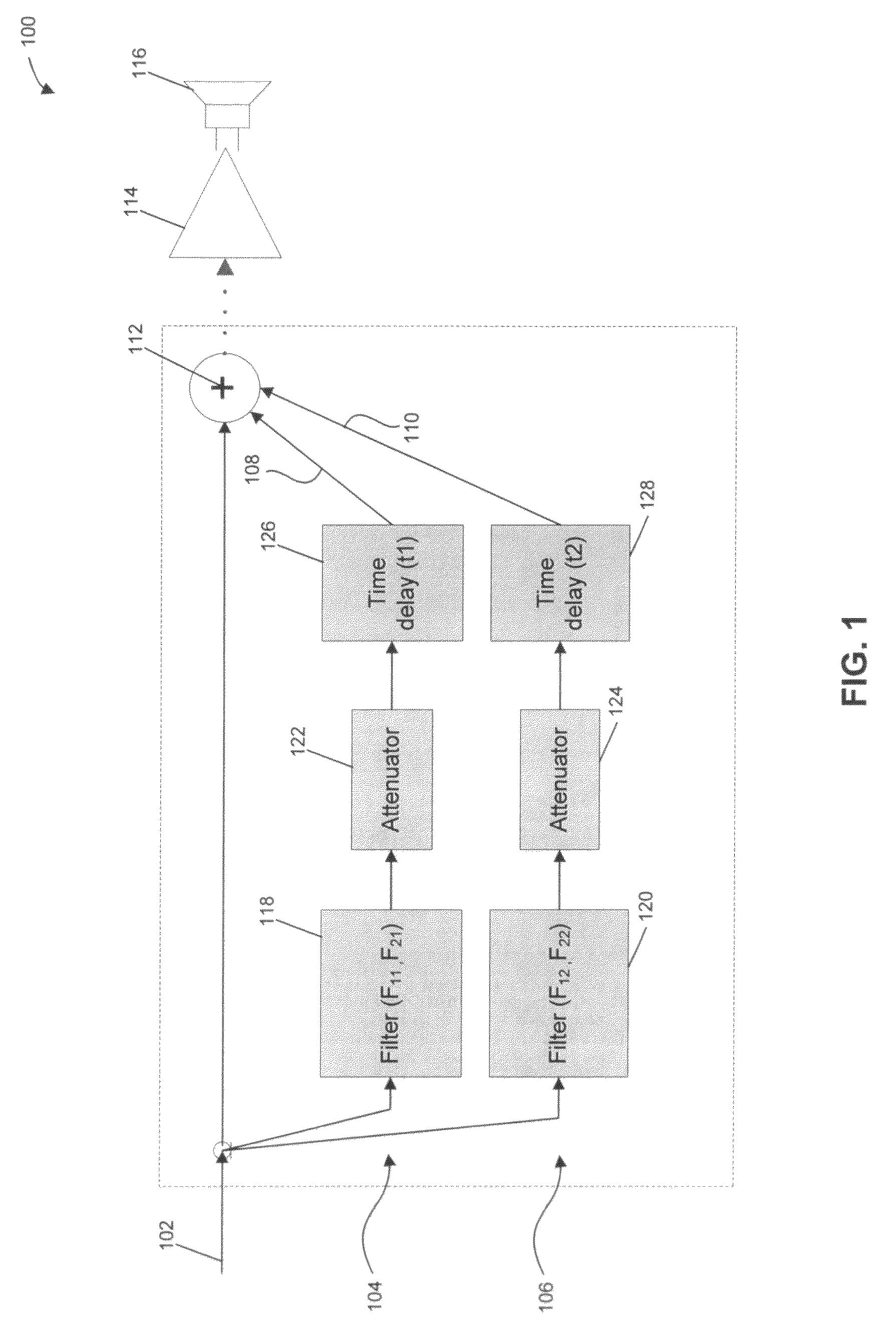
A system and method are provided for smoothing the in-room acoustic magnitude response of an audio reproduction system. An in-room acoustic magnitude response analysis is performed to determine a room resonance induced peak associated with an audio signal. A replica of the audio signal is filtered at the room resonance induced peak. The filtered replica signal is added with the audio signal. Through this, smoothing of the room resonance induced peak may be achieved, such that a subjective impression of transient response and dynamics of the audio signal are preserved.
Owner:POLK AUDIO LLC +1
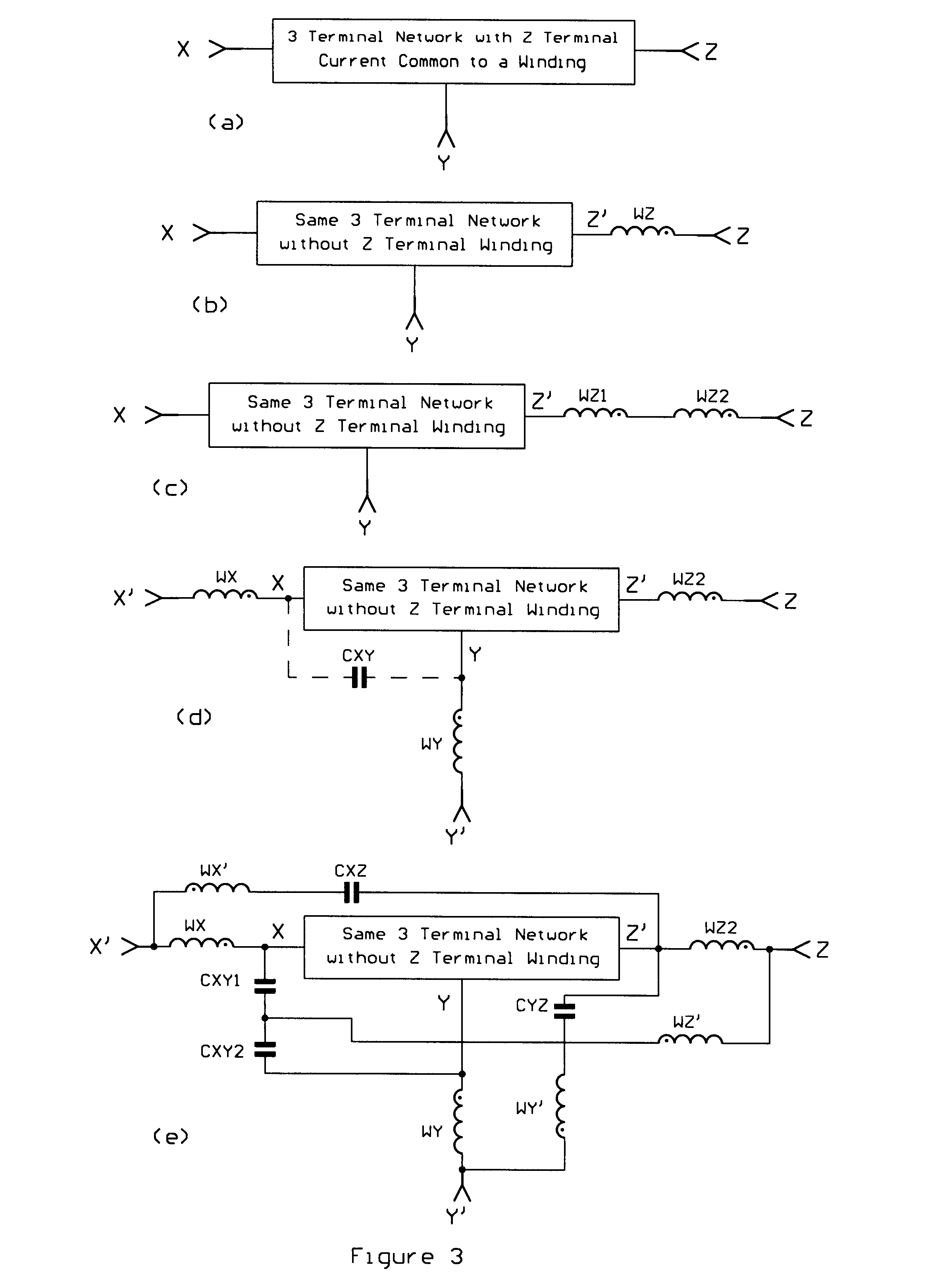
Synthesis methods for enhancing electromagnetic compatibility and AC performance of power conversion circuits
InactiveUS6507176B2Apparatus without intermediate ac conversionConversion using Cuk convertorsSynthesis methodsHemt circuits
Five circuit synthesis methods, for forming new power conversion circuits with enhanced electromagnetic compatibility and improved AC performance from old circuits with AC performance and / or electromagnetic compatibility deficiencies, are revealed. The new synthesis methods achieve performance improvements without requiring the addition of magnetic cores. In all cases a simple toroidal magnetic core structure is not precluded. In all cases splitting or adding magnetic windings is required, and, in many cases, additional capacitors are required. Many new circuits formed by applying the synthesis methods are revealed. The results achieved by application of the synthesis methods include zero ripple current at all terminals without adding magnetic cores or requiring a complex magnetic circuit element, cancellation of common mode currents, improved control loop bandwidth, and faster transient response.
Owner:TECHN WITTS
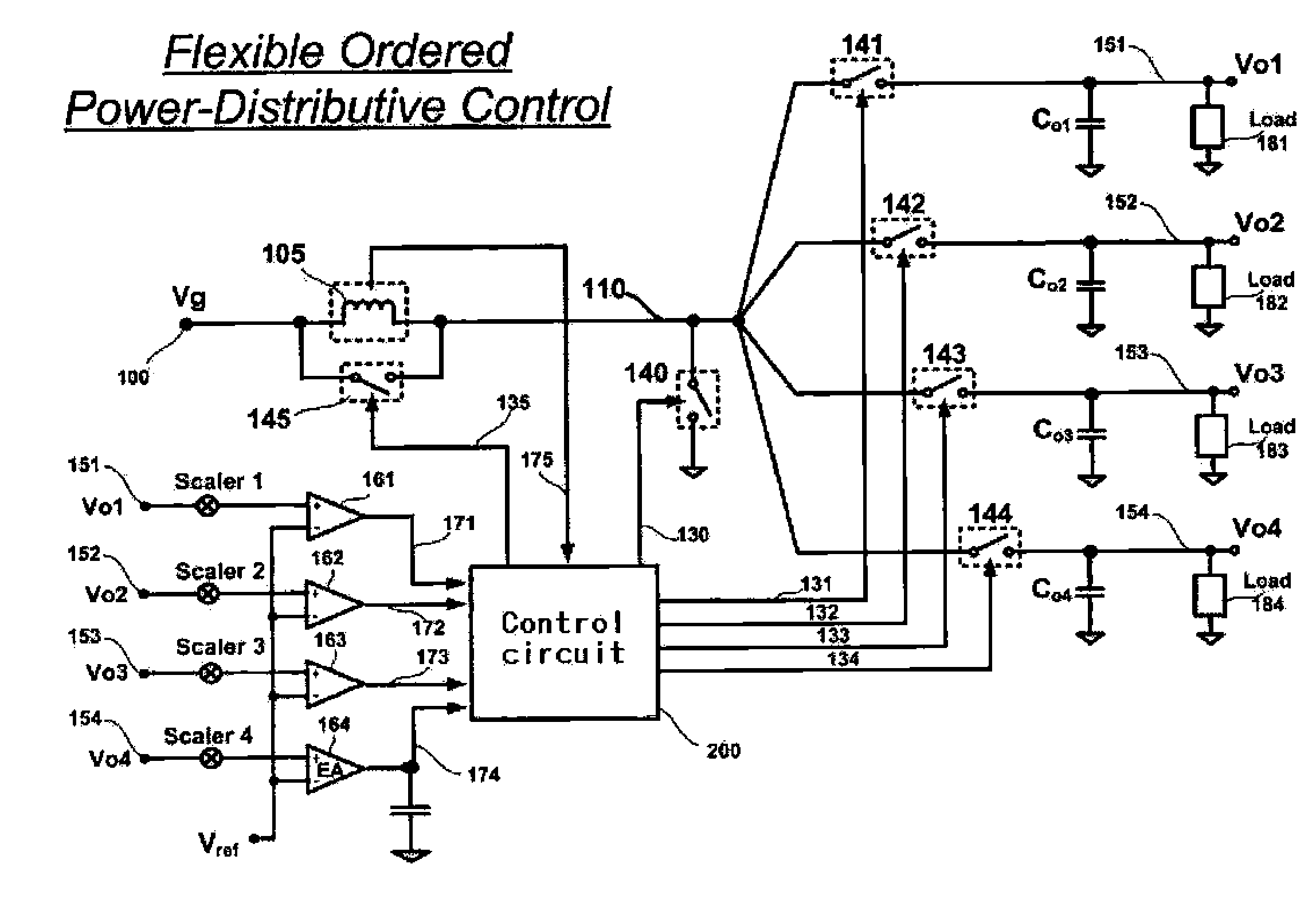
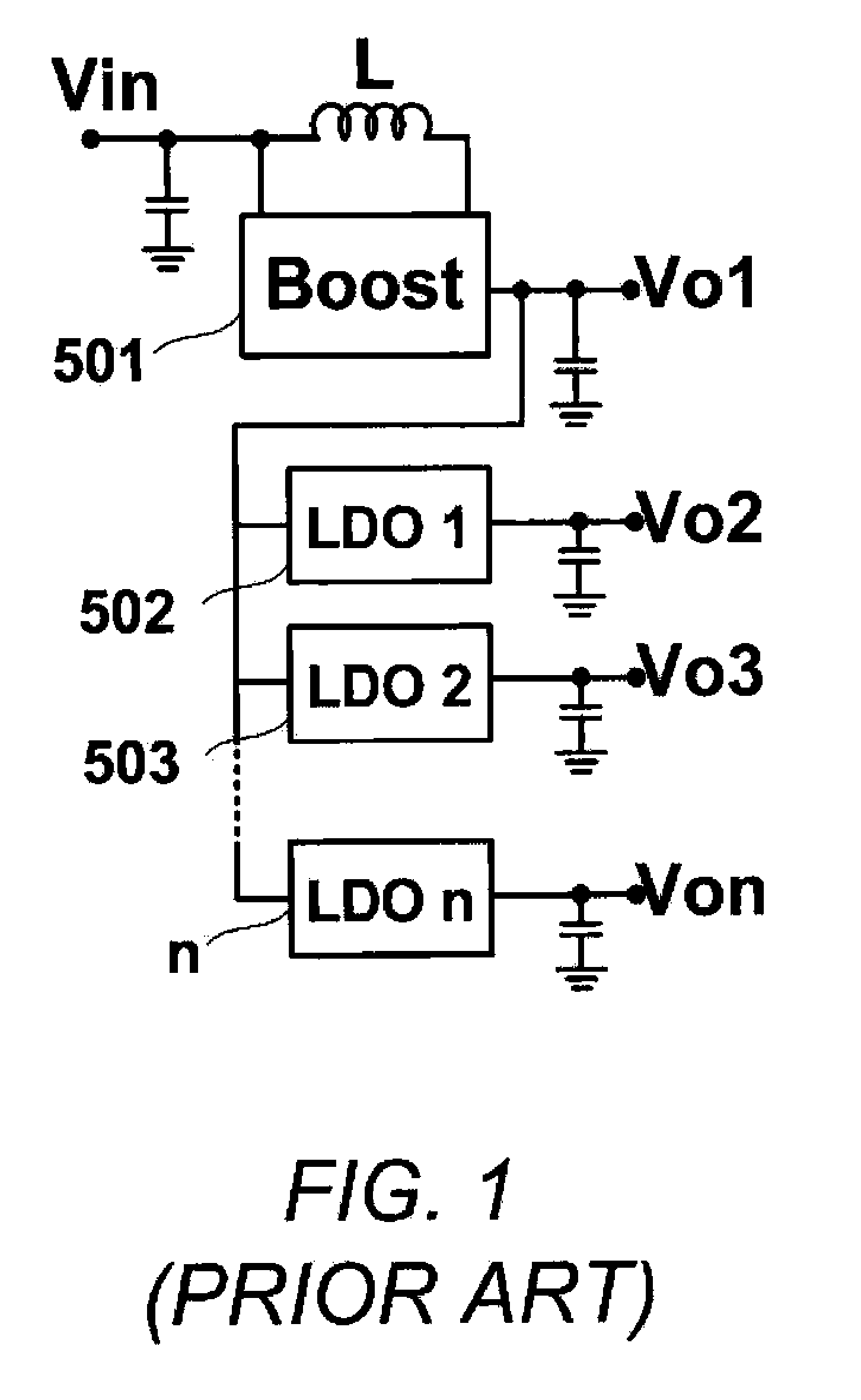
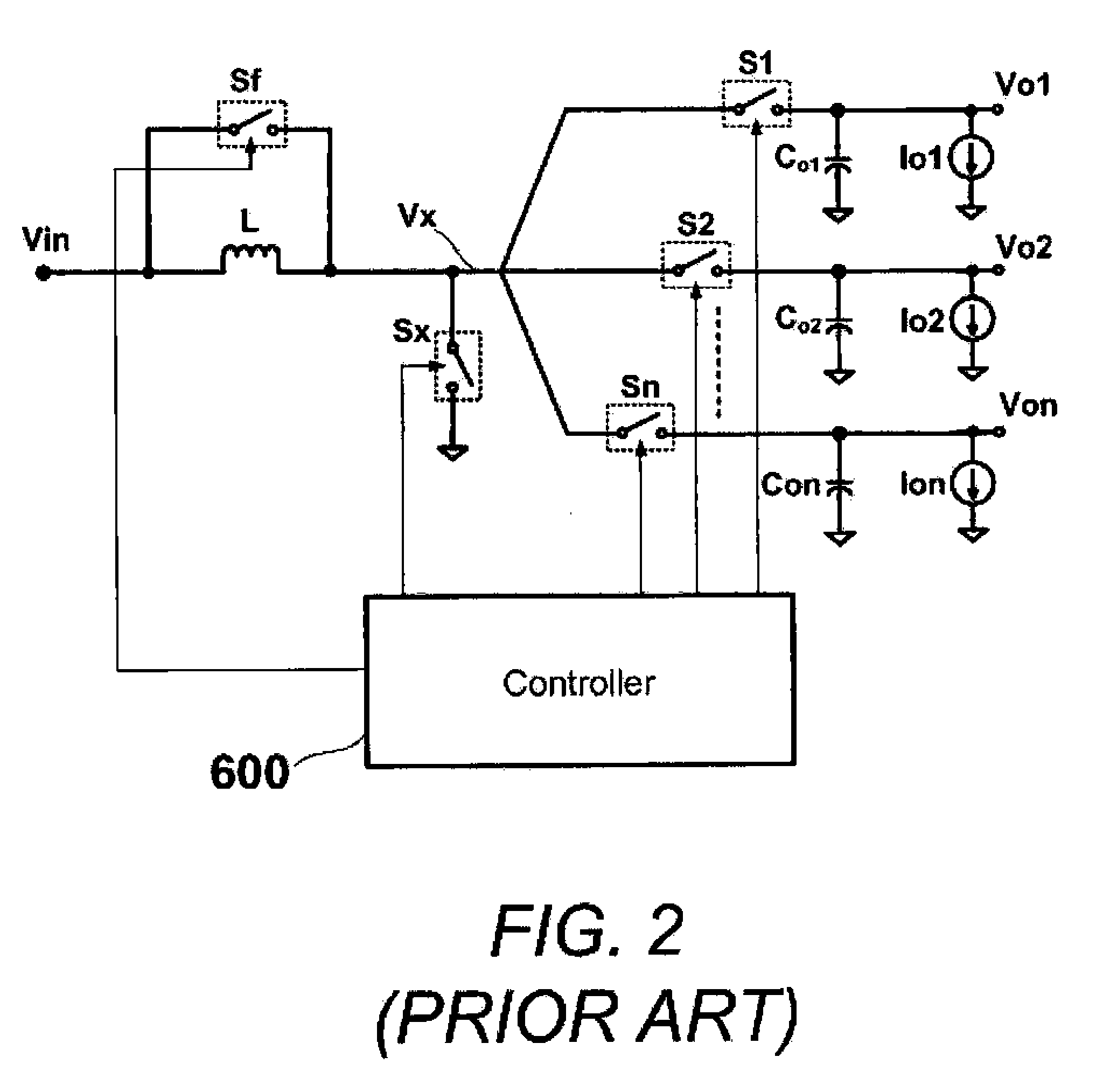
Multiple-Output DC-DC Converter
The invention relates to a DC / DC converter design. The converter requires only one single inductor to draw energy from one input source and distribute it to more than one outputs, employing Flexible-Order Power-Distributive Control (FOPDC). It include a single inductor, a number of power switches, comparators, only one error amplifier, a detecting circuit and a control block to regulate outputs. This converter can correctly regulate multiple outputs with fast transient response, low cross regulation, and effective switching frequency for each output. It can work in both discontinuous conduction mode (DCM) and continuous conduction mode (CCM). Moreover, with FOPDC, future output extension is simple, making a shorter time-to-market process for next versions of the converter. The design can be applied to different types of DC-DC converter.
Owner:JDA TECH
Multiphase clamp coupled-buck converter and magnetic integration
InactiveUS6784644B2Emergency protective circuit arrangementsApparatus without intermediate ac conversionVoltage regulator modulePush pull
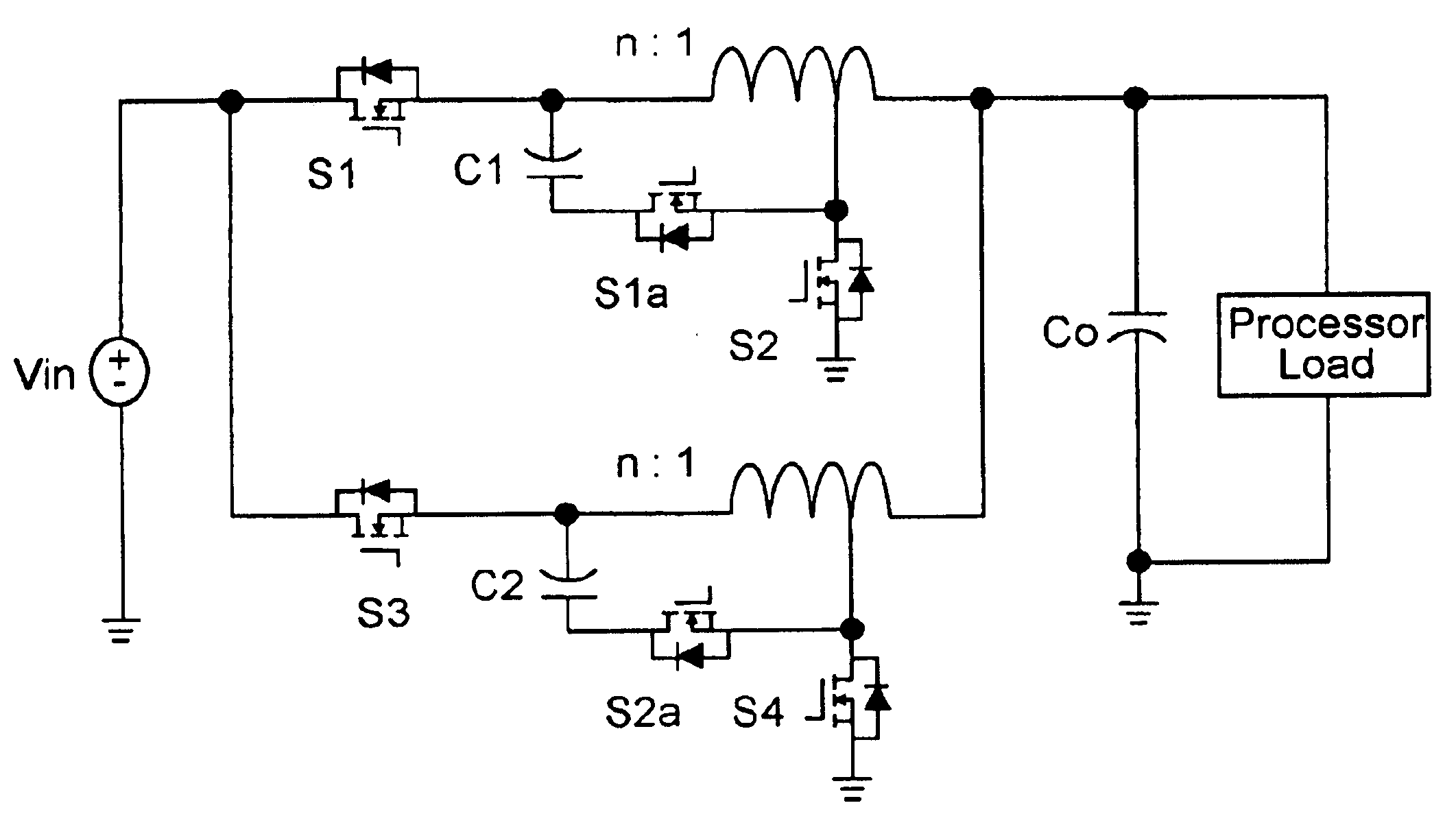
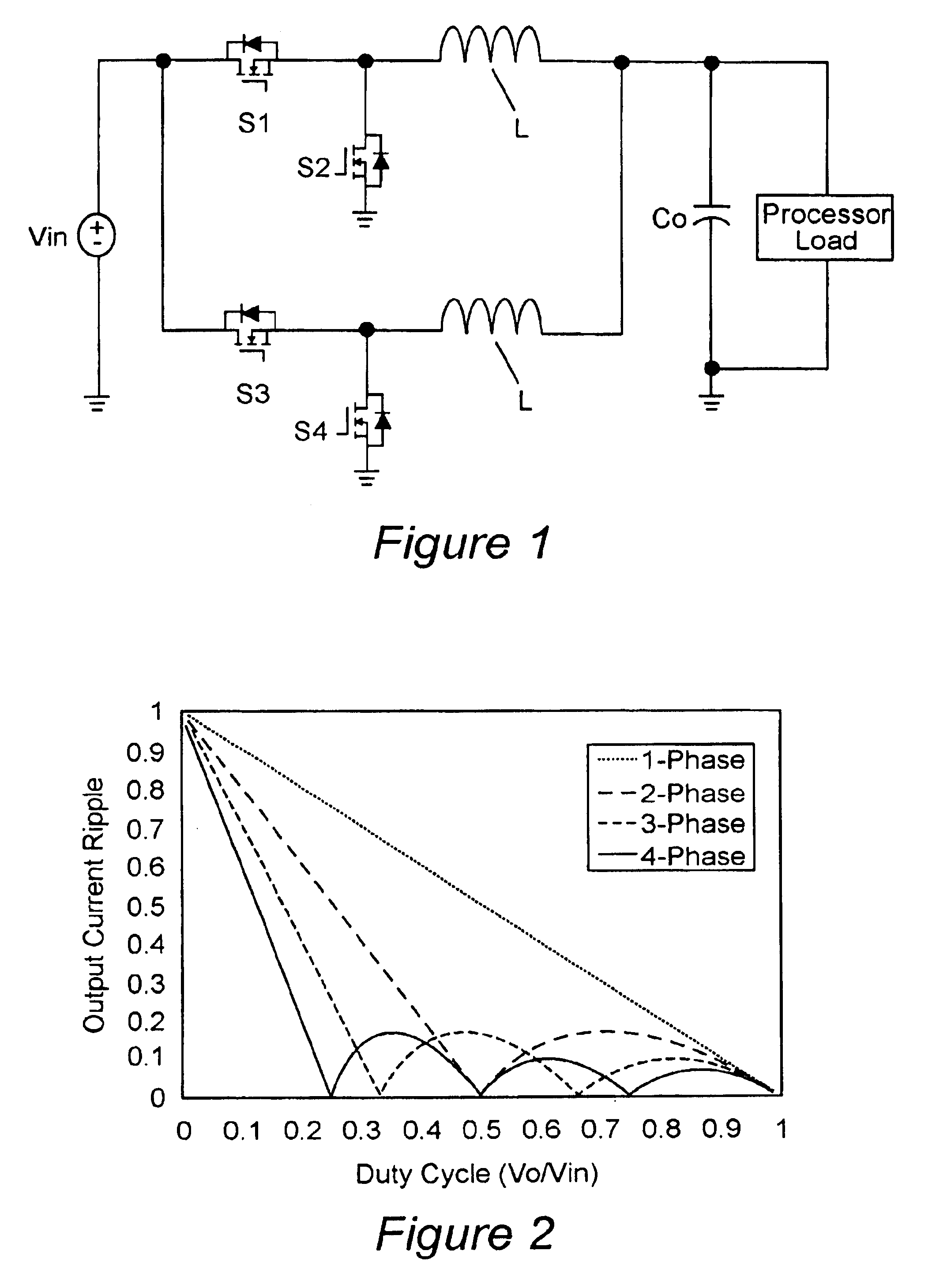
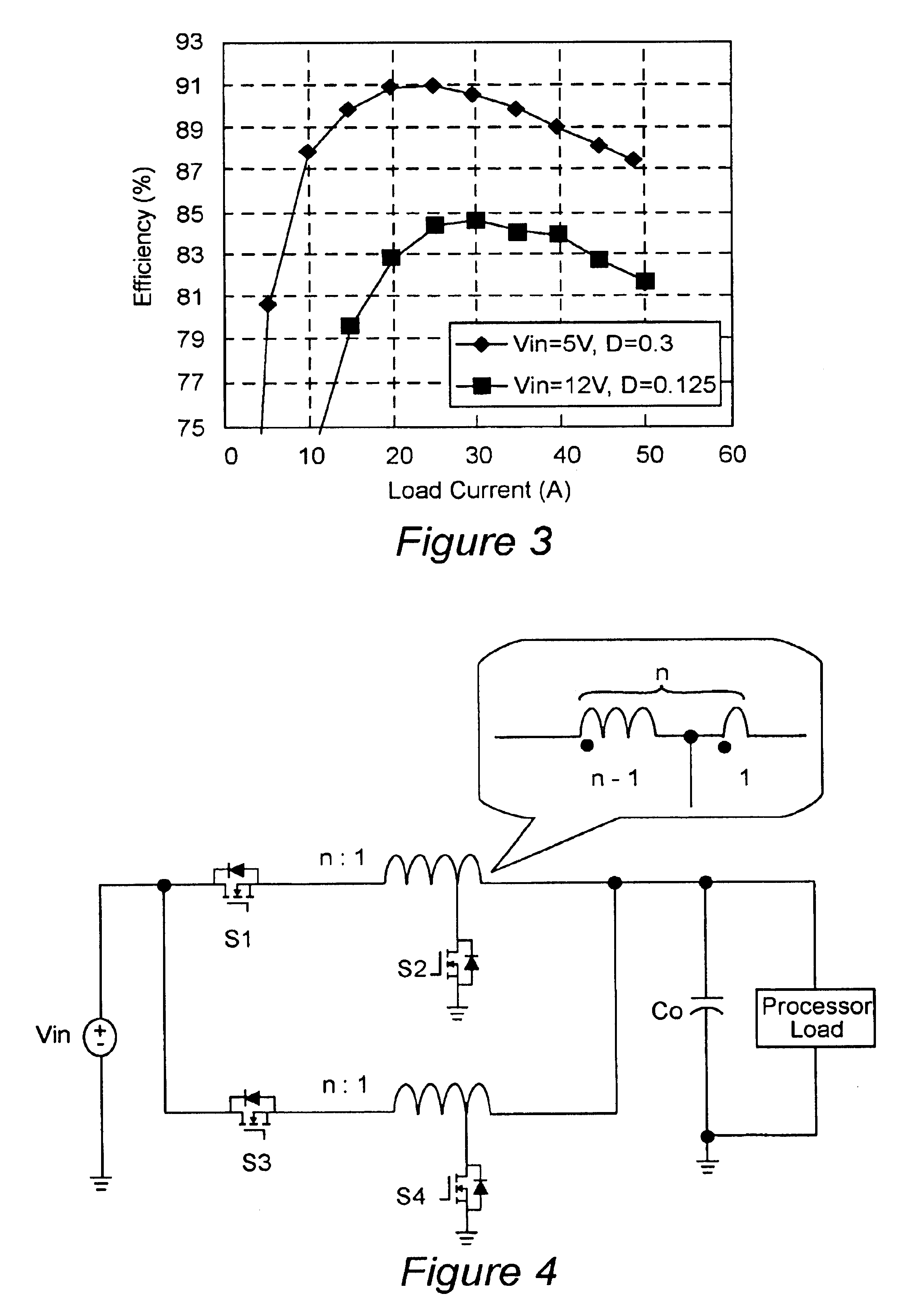
Voltage regulation, transient response and efficiency of a voltage regulator module (VRM) is improved where short duty cycles are necessitated by large differentials of input and output voltage by including at least one clamping of a tap of an inductance in series with an output of each of a plurality of parallel branches or phases which are switched in a complementary fashion or providing coupling between inductors of respective phases. Such coupling between inductors is achieved in a small module with an integrated magnetic structure. Reduced component counts are achieved while deriving built-in input and output filters. Principals of the invention can be extended to isolation applications and push-pull forward converts, in particular. A lossless clamping circuit is also provided allowing spike currents to be suppressed while returning power to the output of the VRM.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
System, device and method for providing voltage regulation to a microelectronic device
InactiveUS6965502B2High speed signal settlingAct quicklyPower supply for data processingArrangements responsive to excess currentEngineeringSteady state
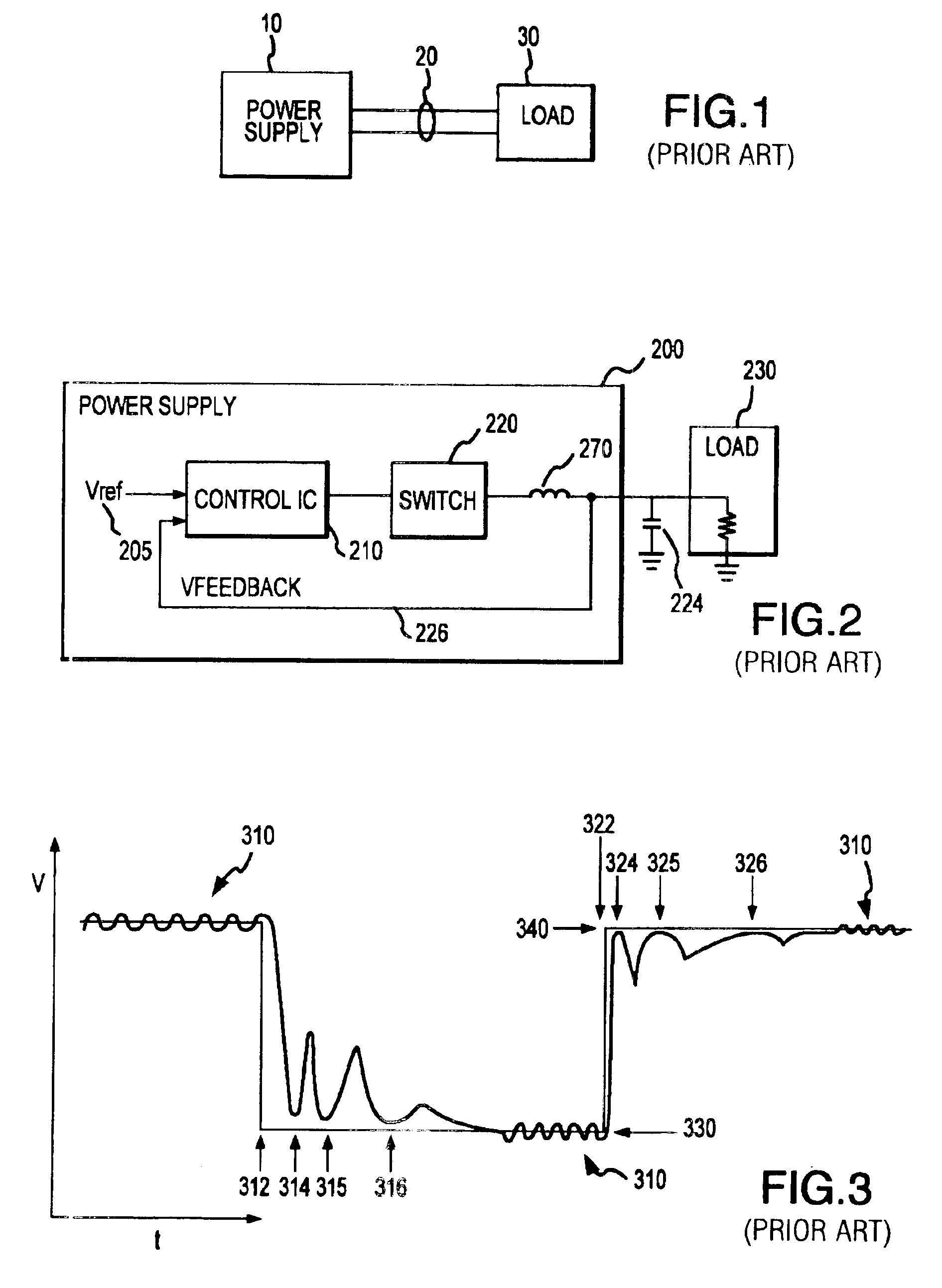
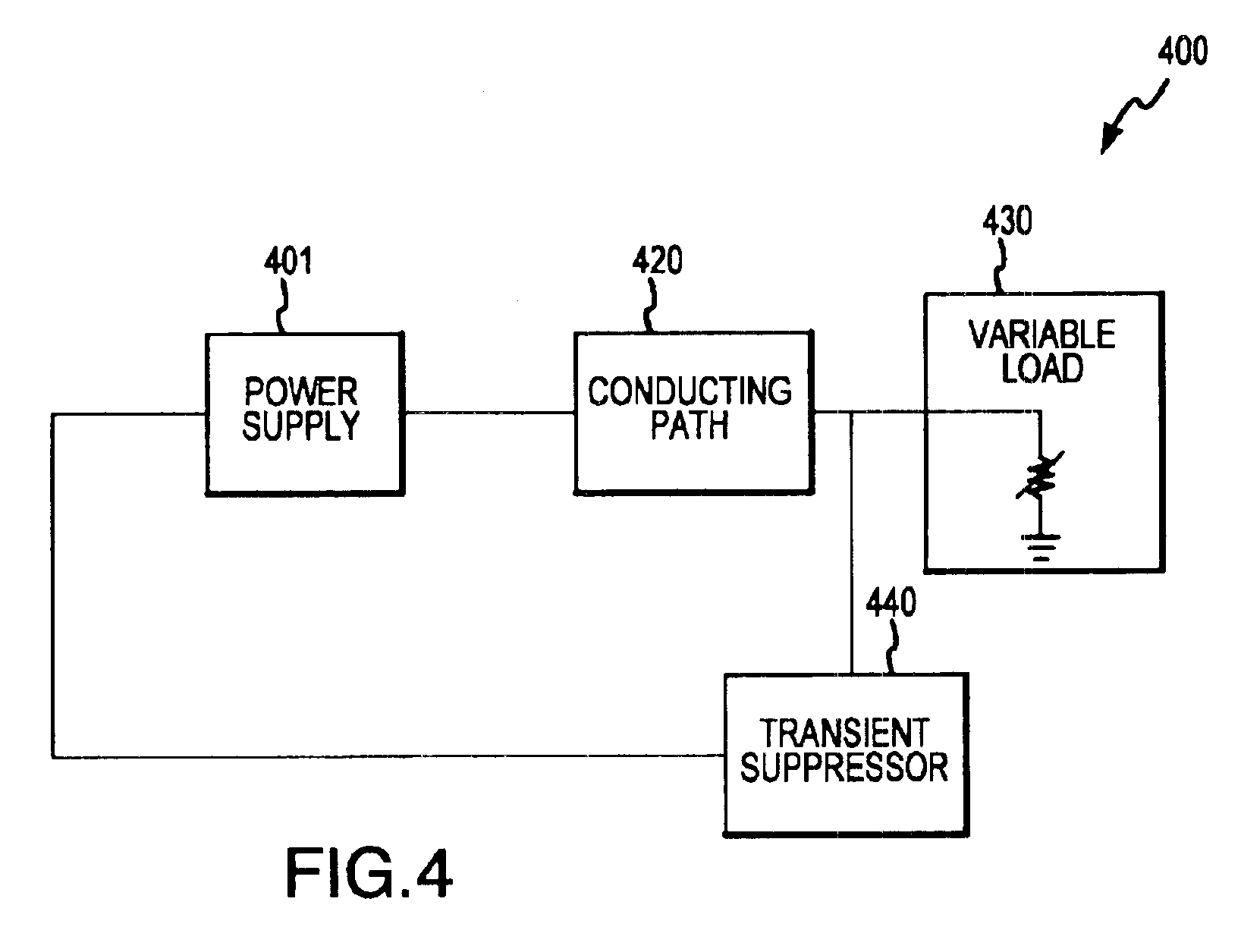
The present invention provides a power regulation system and method with high speed signal settling capabilities for providing rapid active transient response to a microelectronic device. An active transient response system includes a power supply configured to receive external and / or internal signals indicating the occurrence of transient load conditions and to respond to the transient load conditions based on one or more of these signals. The system may further include a transient suppressor configured for early detection of transients, assisting in transient suppression, and early signaling of transient activity to the power supply.The system provides rapid recovery to steady state operation from the active transient response mode by using a digital compensator to quickly modifying the duty cycle and provide a voltage offset proportional to the transient microprocessor load step. Recovery is further improved by current rephasing techniques.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AUSTRIA AG
Led-based illumination module on-board diagnostics
ActiveUS20110254554A1Light source combinationsElectrical apparatusLight-emitting diodeOperant conditioning
A light emitting diode (LED) based illumination module performs on-board diagnostics. For example, diagnostics may include estimating elapsed lifetime, degradation of phosphor, thermal failure, failure of LEDs, or LED current adjustment based on measured flux or temperature. The elapsed lifetime may be estimated by scaling accumulated elapsed time of operation by an acceleration factor derived from actual operating conditions, such as temperature, current and relative humidity. The degradation of phosphor may be estimated based on a measured response of the phosphor to pulsed light from the LEDs. A thermal failure may be diagnosed using a transient response of the module from a start up condition. The failure of LEDs may be diagnosed based on measured forward voltage. The current for LEDs may adjusted using measured flux values and current values and a desired ratio of flux values. Additionally, the LED current may be scaled based on a measured temperature.
Owner:SBC XICATO CORP
High-precision modeling filament
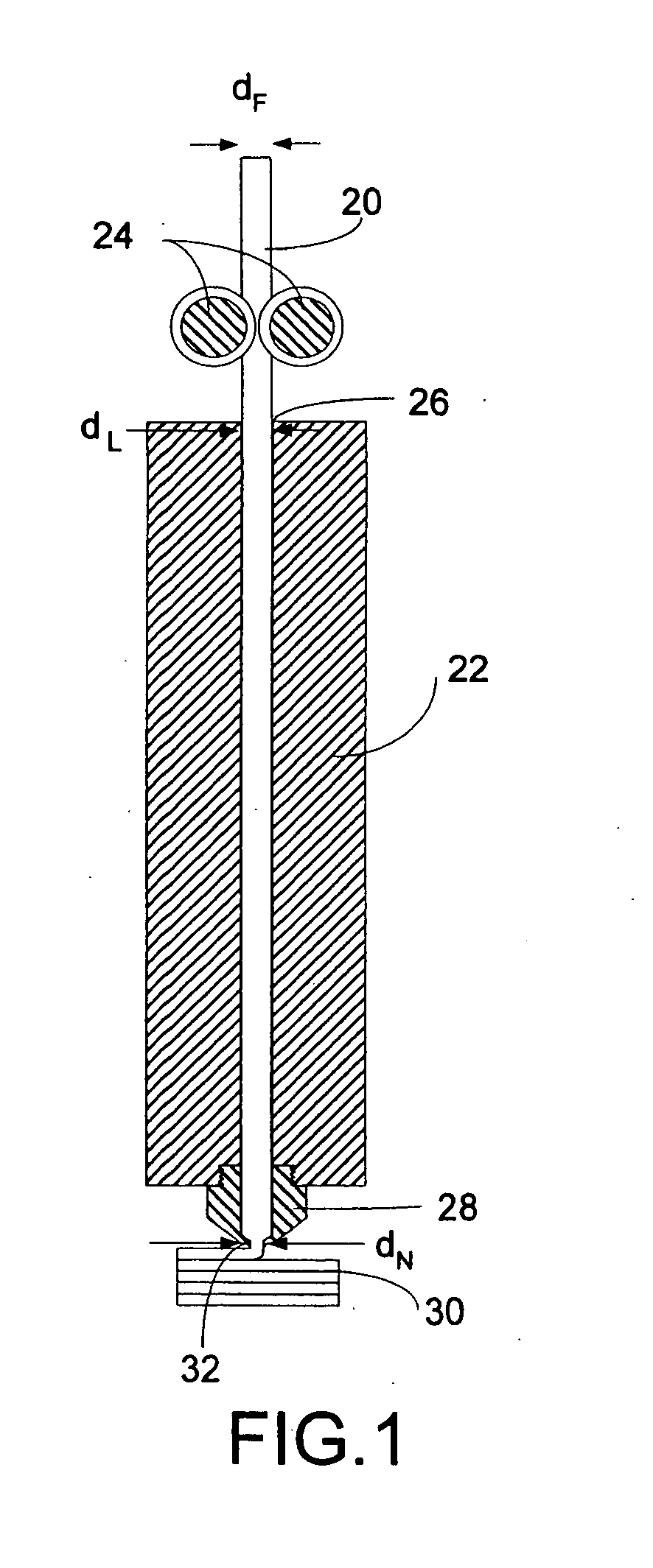
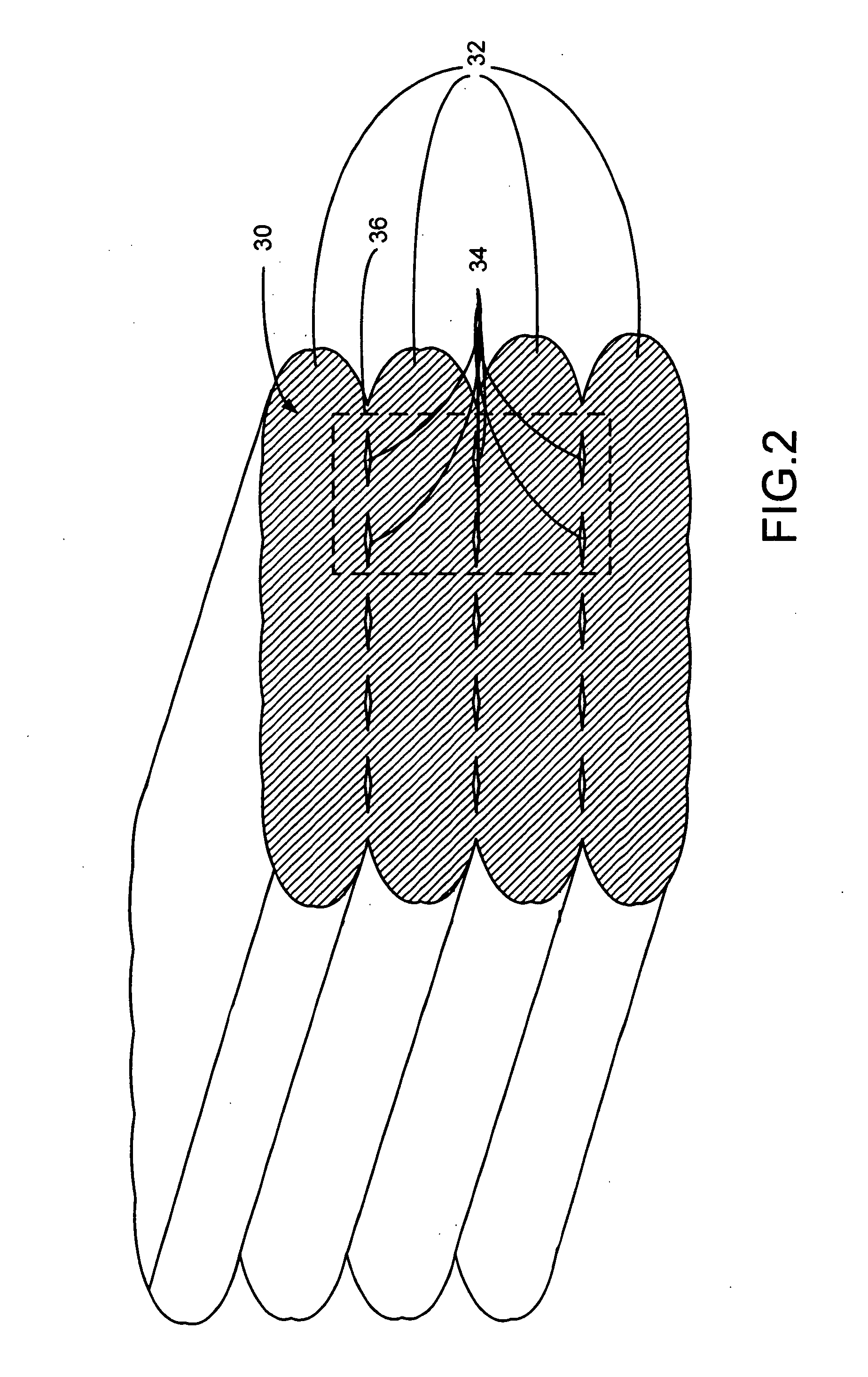
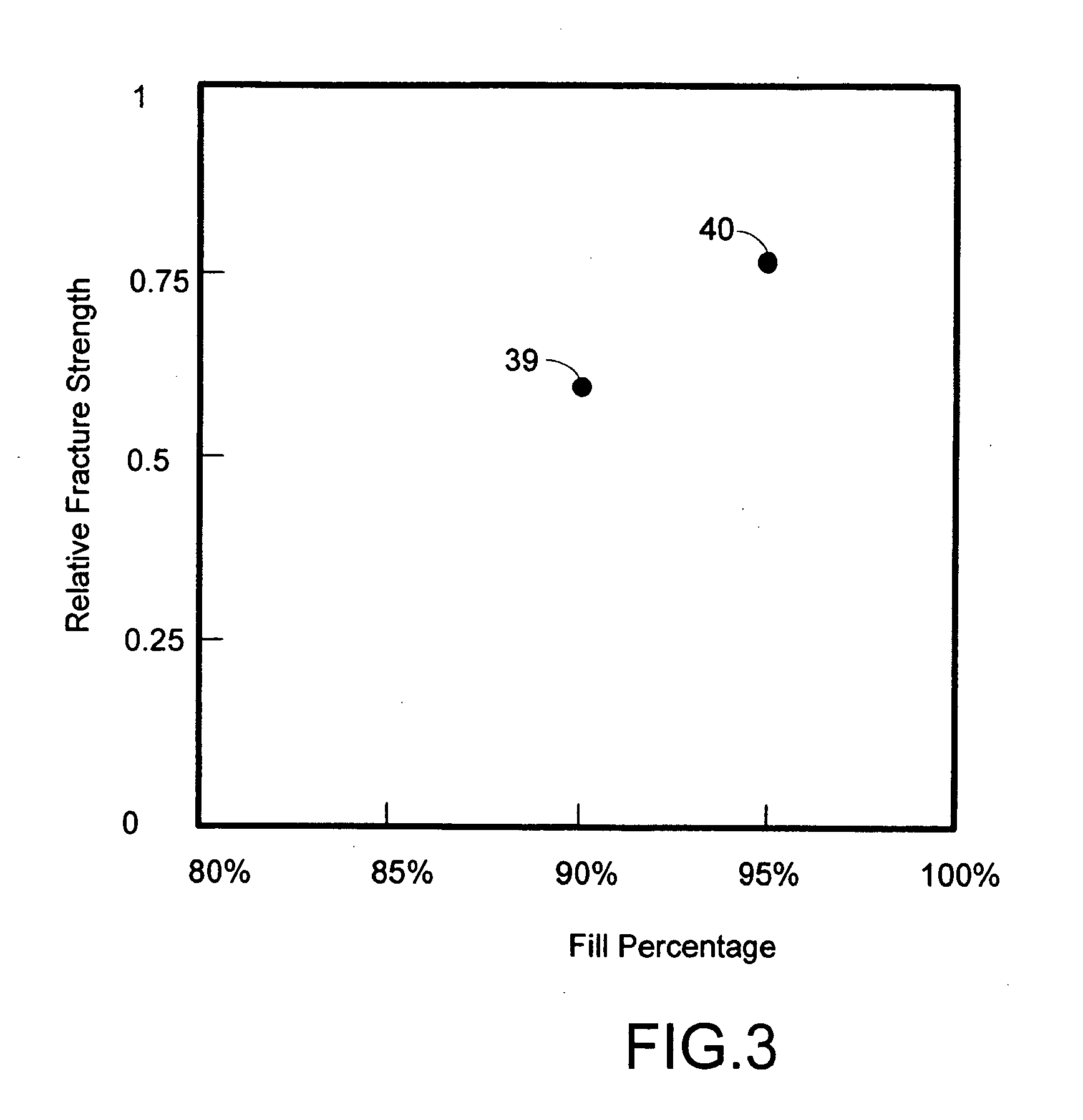
Disclosed is a modeling filament for use as feedstock in a fused deposition modeling liquifier, and a method for manufacturing the filament. The diameter and standard deviation of the filament are controlled to meet various tolerance requirements of jam resistance, slip resistance, model strength, liquifier overflow prevention and hysteresis-free transient response. Standard deviation of the filament diameter is matched to a filament target diameter. The resulting filament is used to form high-quality models.
Owner:STRATSYS INC
Hysteretic CL power converter
ActiveUS20120170334A1Reduce the valueSmall sizeEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionĆuk converterSwitching frequency
A novel switching hysteretic power converter is presented. The power converter combines the function of a capacitive charge pump with the function of an inductive step down converter to obtain a switching boost converter with a much simpler control method with respect to conventional inductive boost power converters. The hysteretic control provides stable operation in all conditions with excellent load transient response. Furthermore the hysteretic control allows high frequency switching reducing the size and cost of the passive components. The Discontinuous Conduction Mode of operation provides very high efficiency even at light loads. The presented power converter can be operated as a boost converter or as a buck converter simply by changing the switching phase of one switch. In both types of operation the efficiency of the hysteretic power converter can be quite high even at high switching frequencies.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
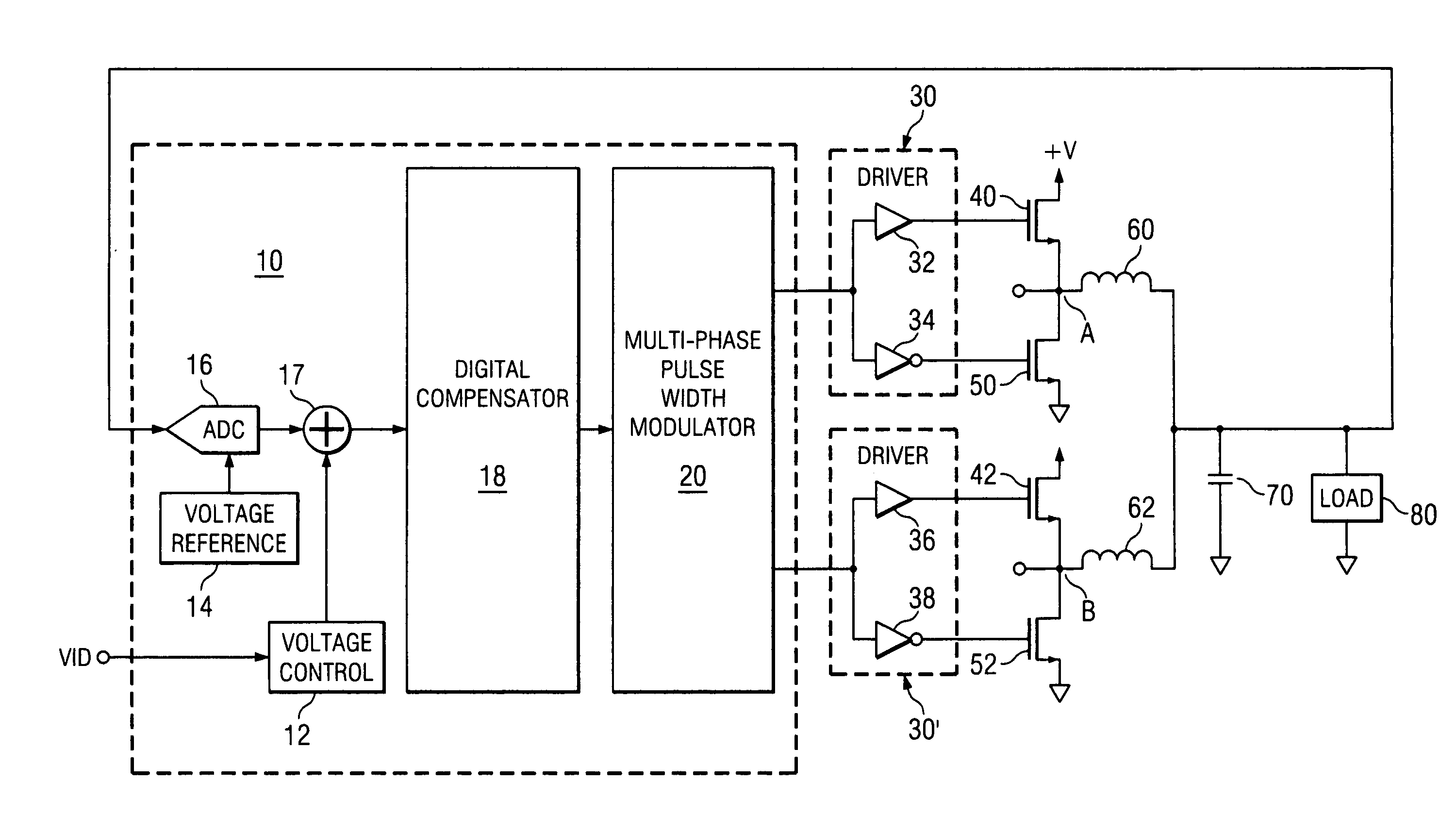
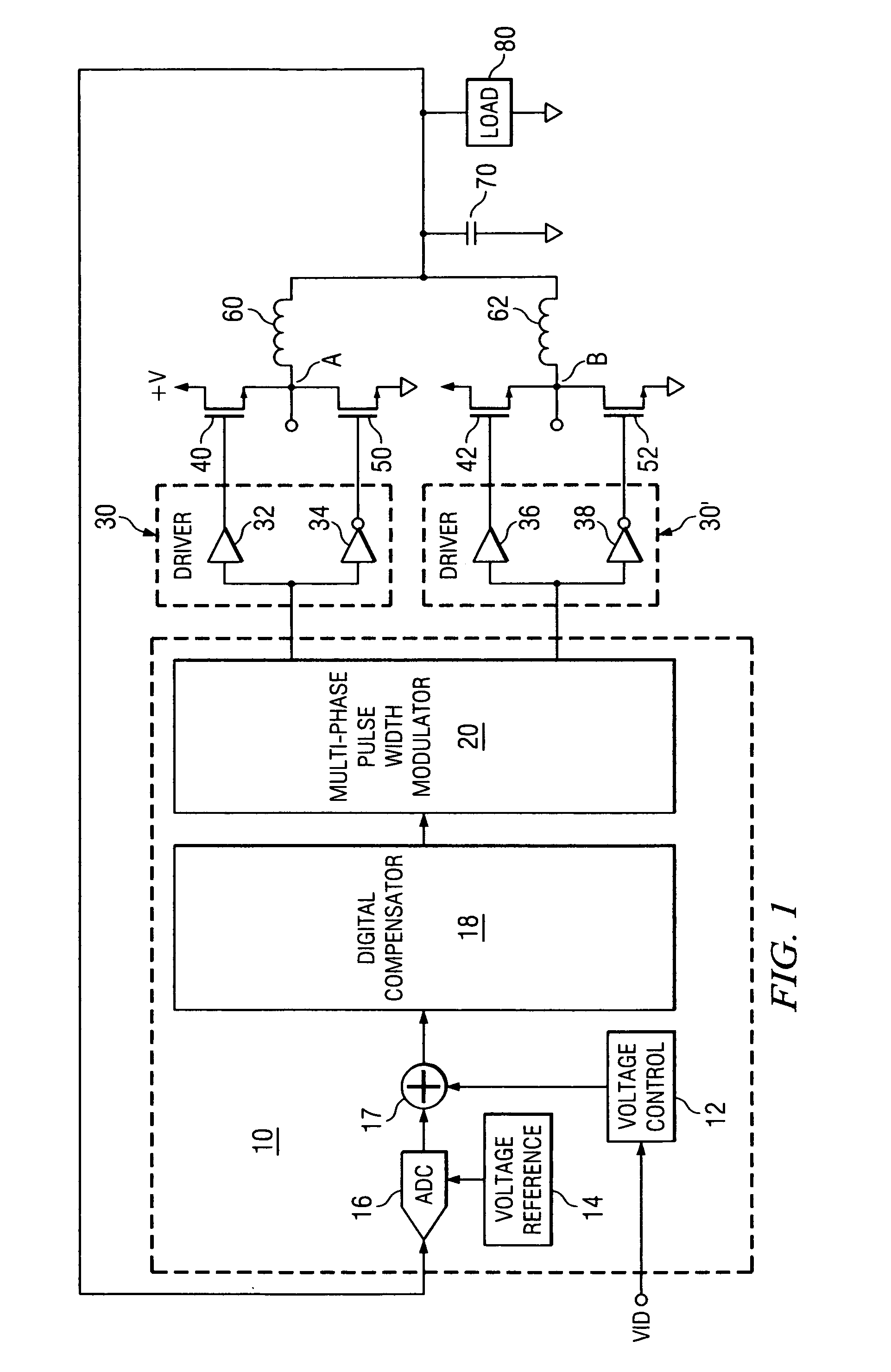
Digitally controlled voltage regulator
ActiveUS7023672B2Easy to customizePrecise power controlEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionControl signalOptimal control
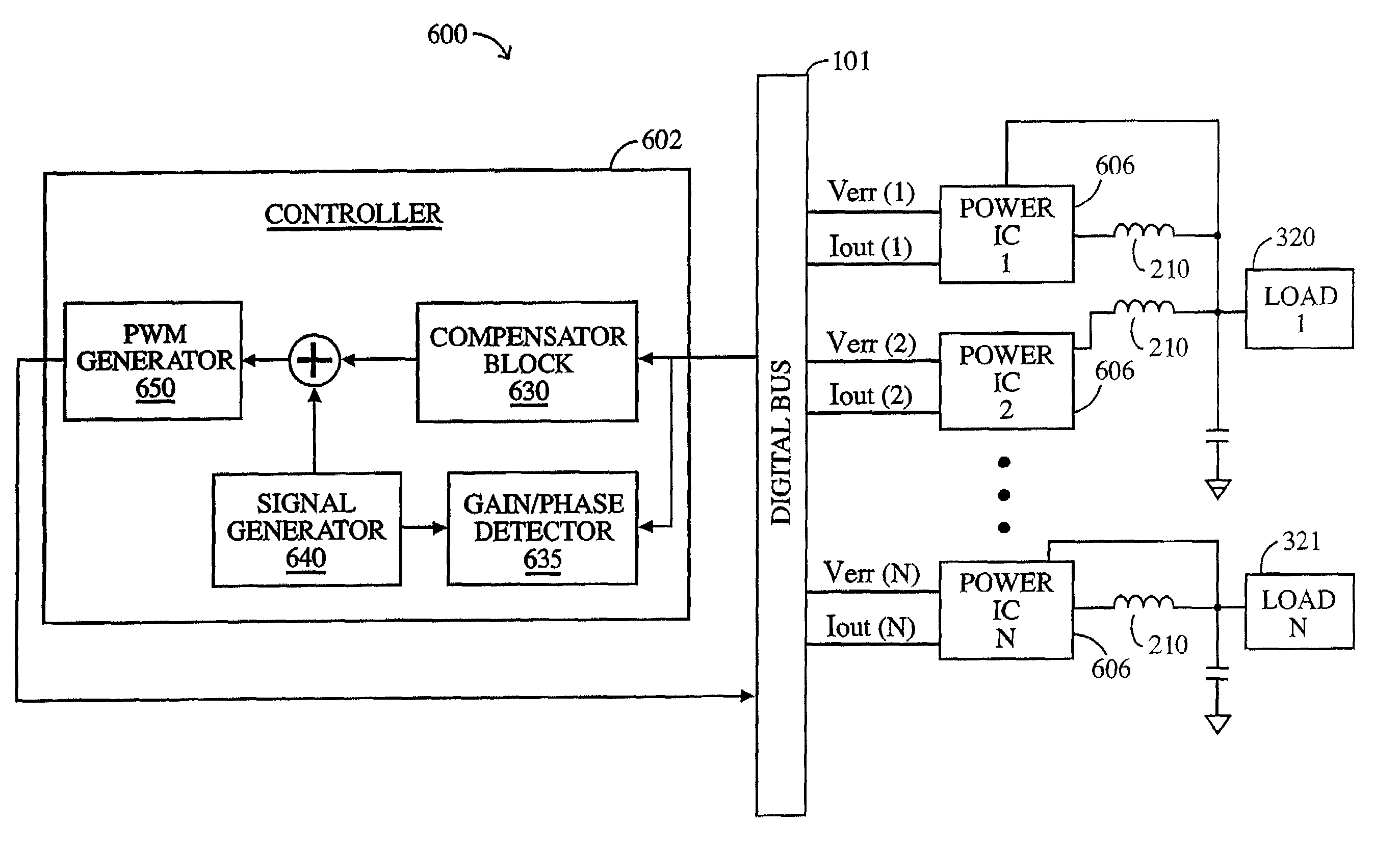
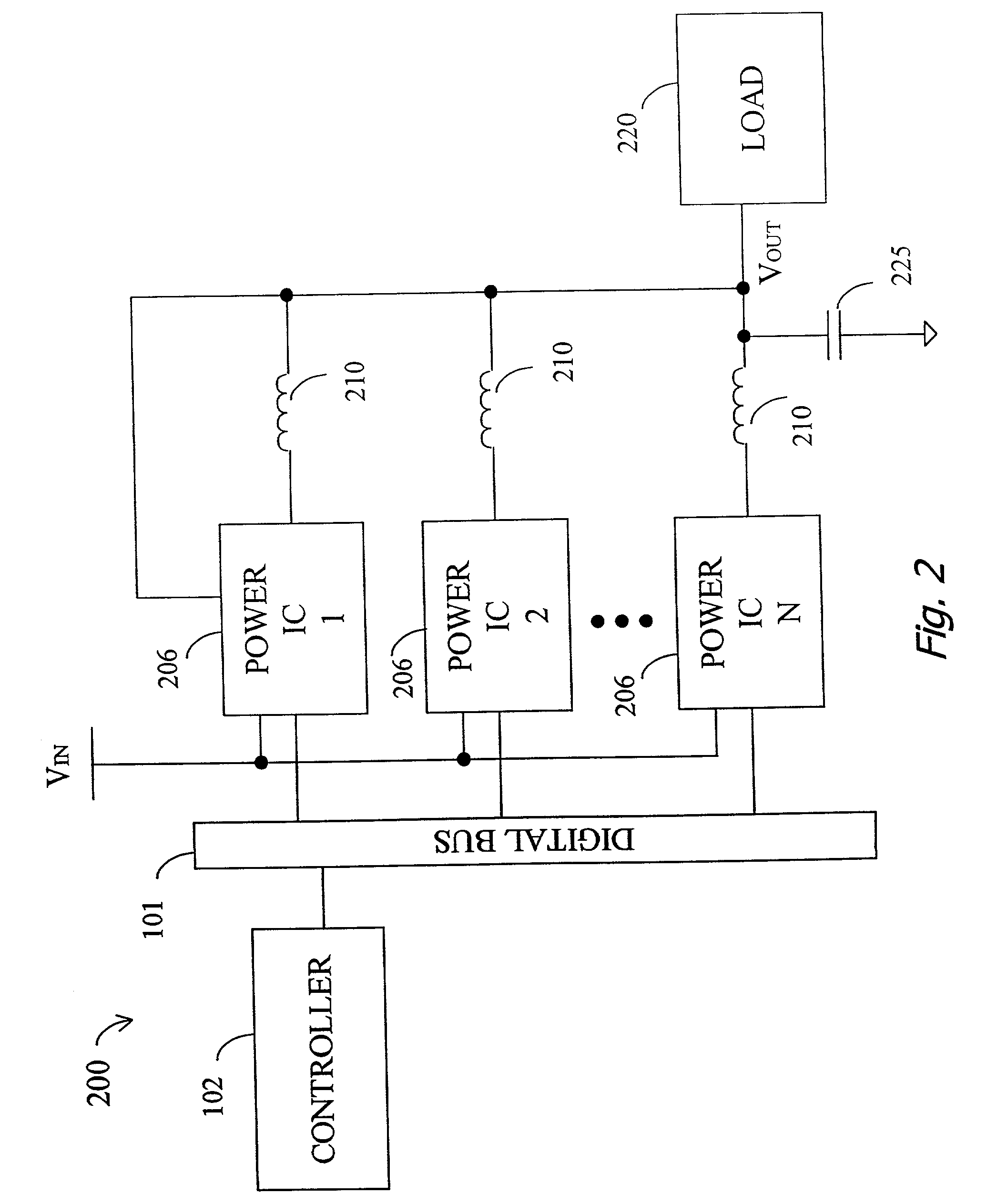
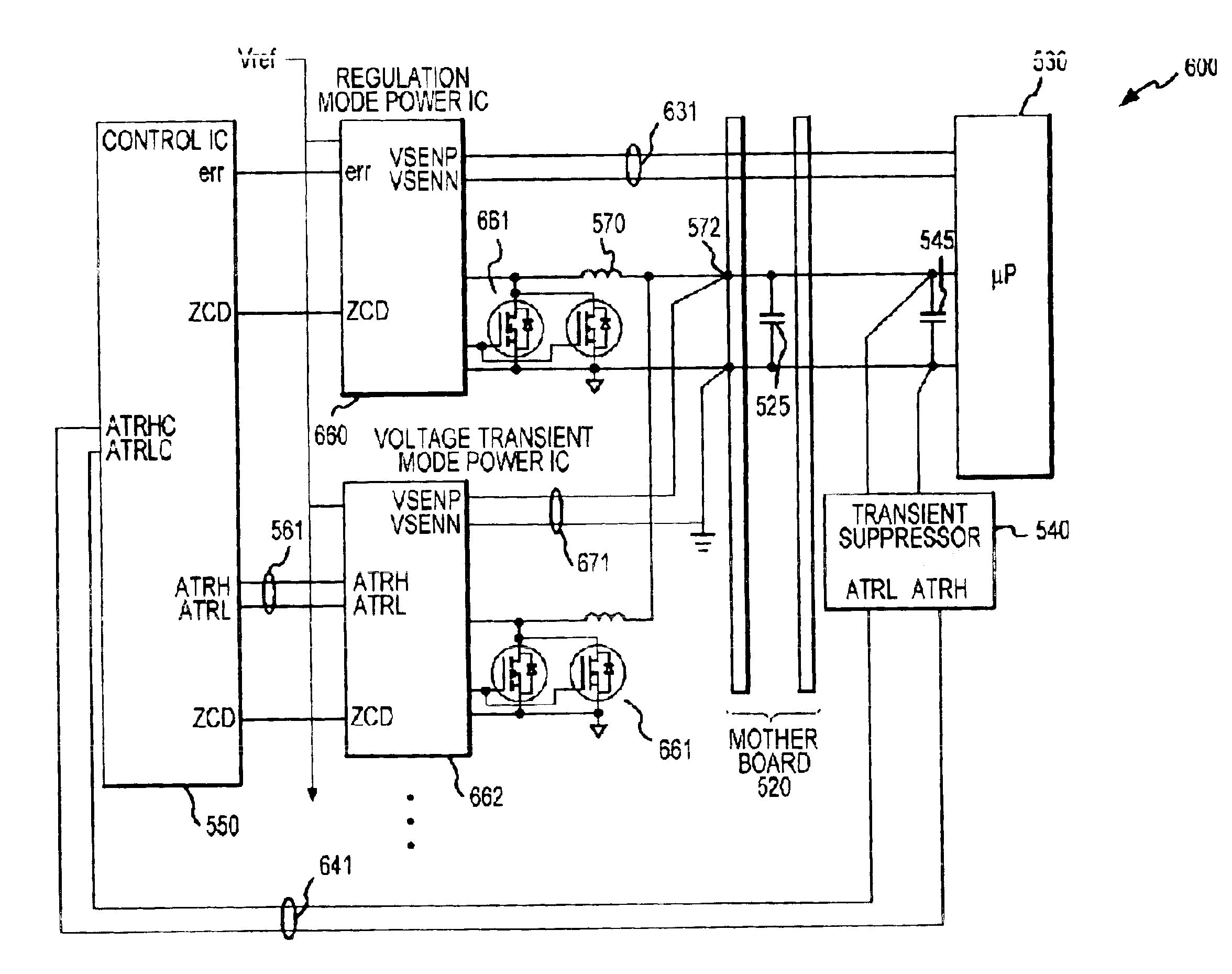
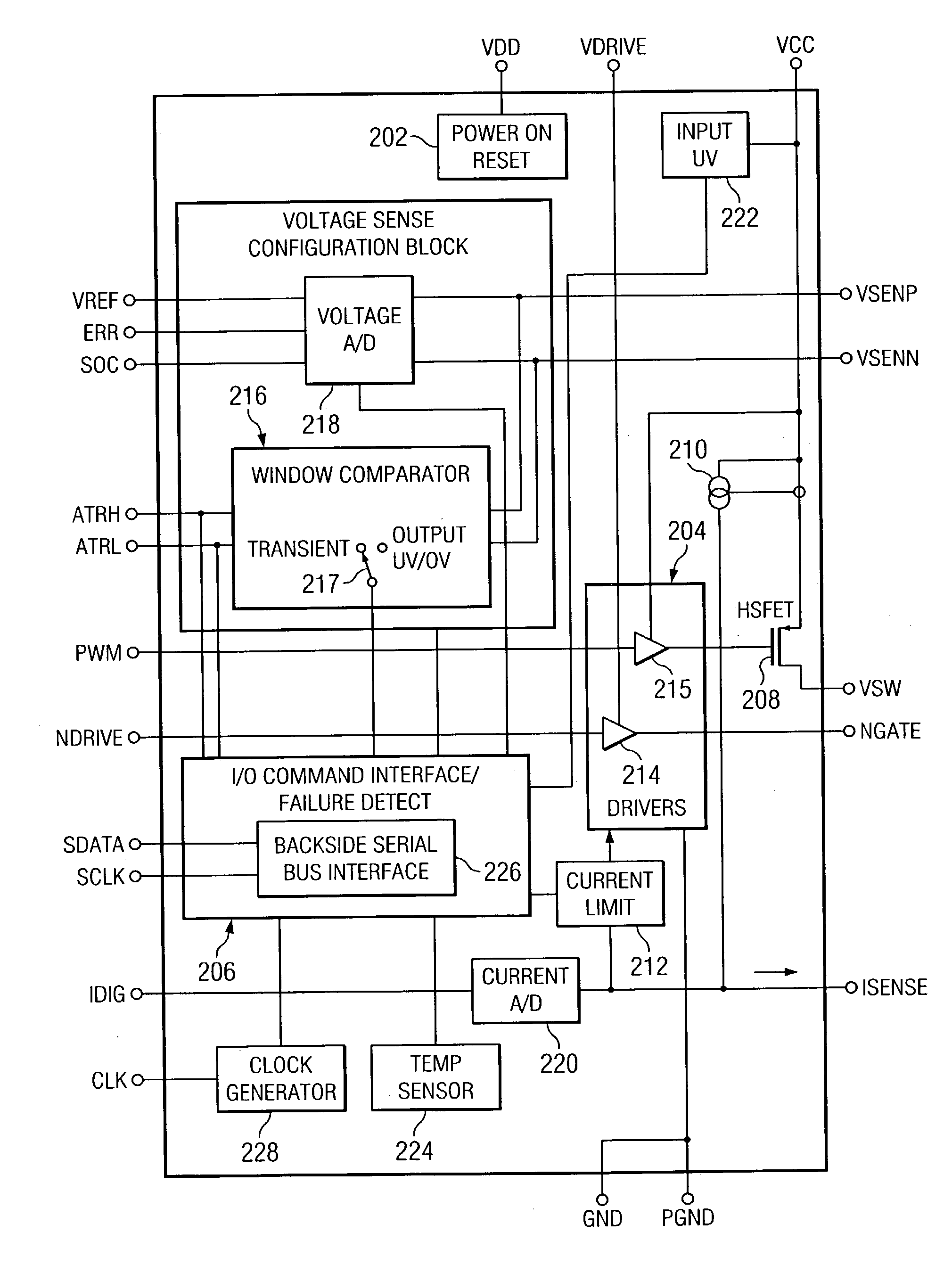
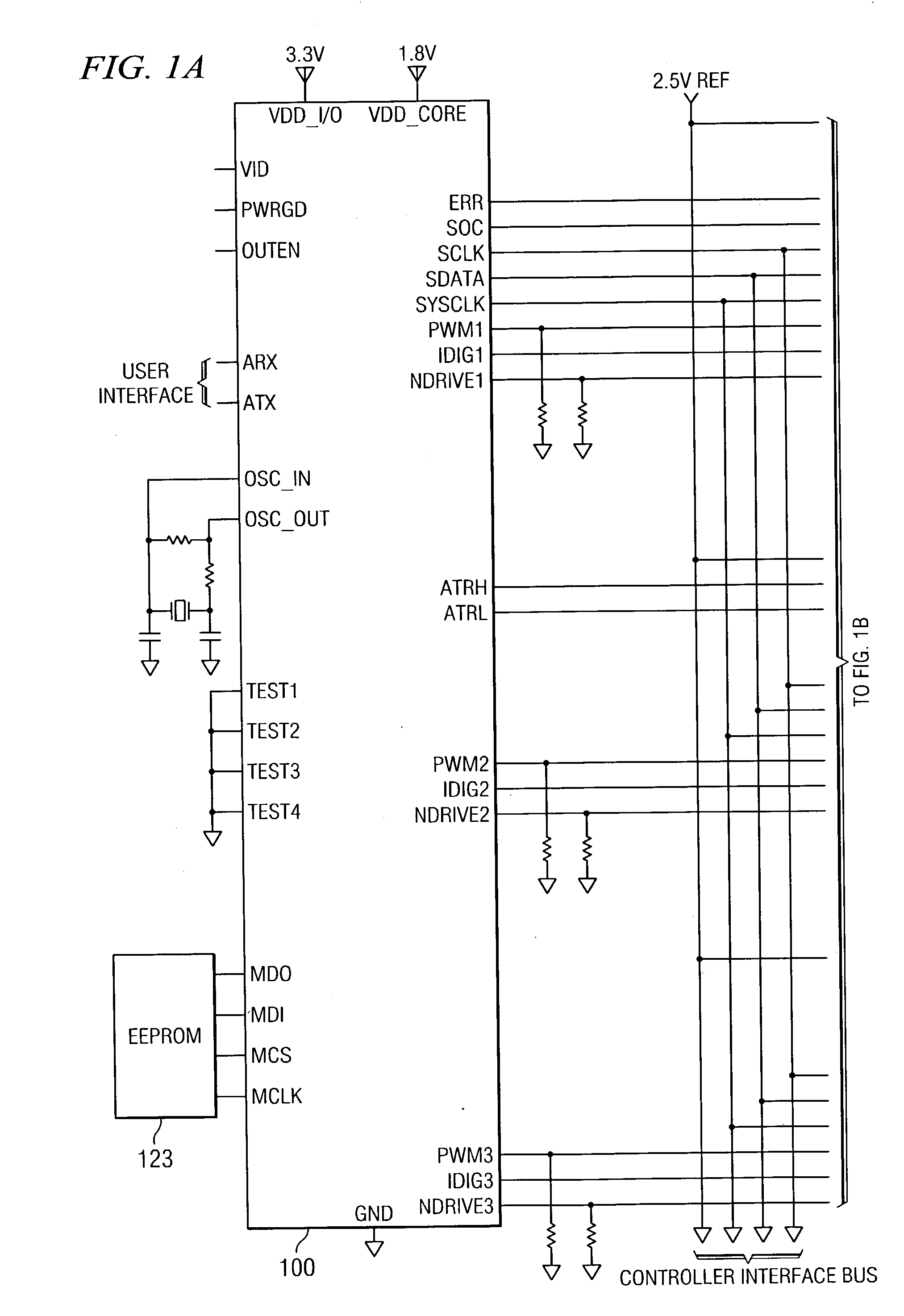
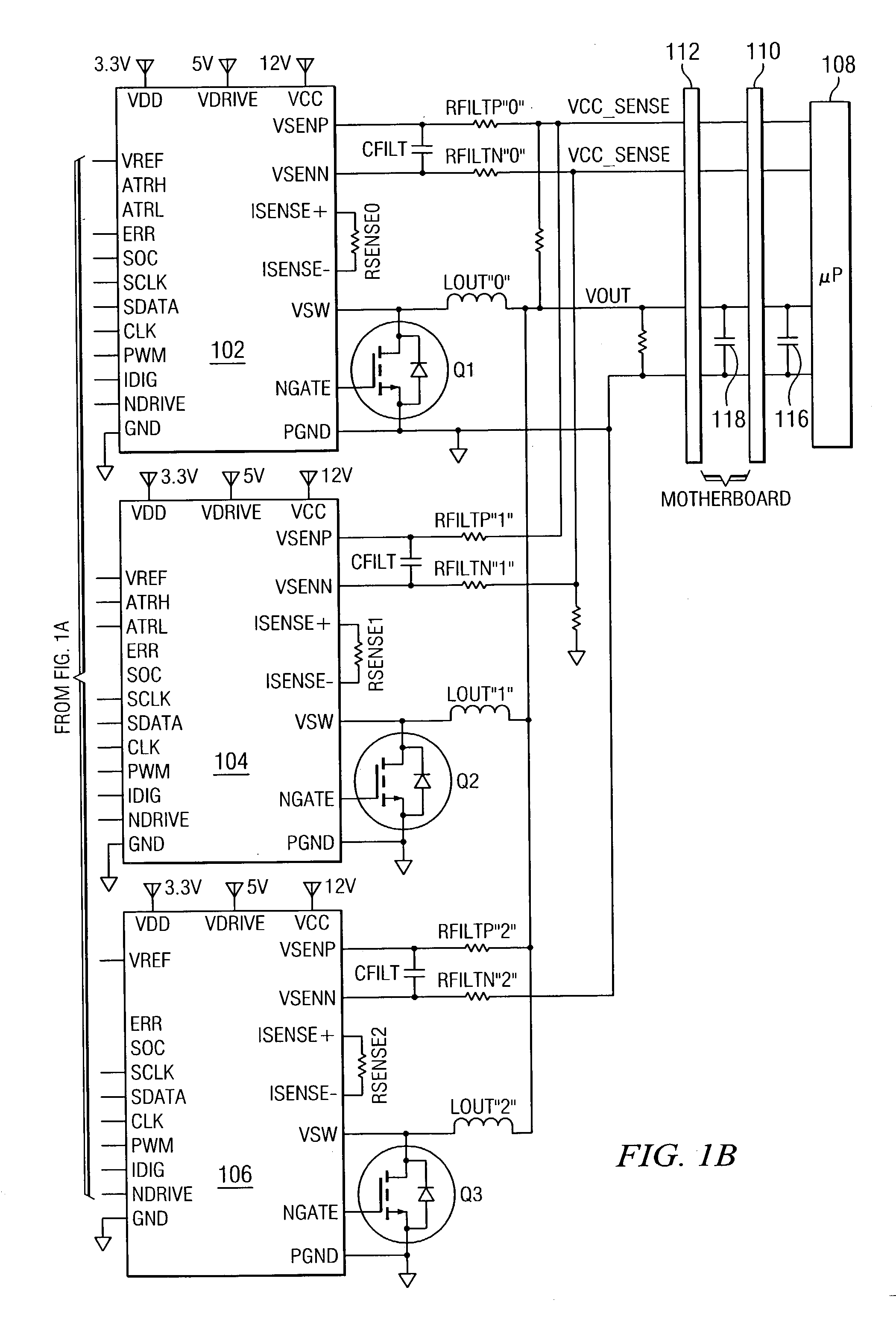
Disclosed is a digitally controlled multi-phase voltage regulator system providing regulated power to electronic components that have variable power requirements. Power is supplied by one or more power integrated circuits (IC) each having a high side power switch controlled by pulse width modulated signals and a low side power switch. The power IC senses voltage at the load and has an on-chip current mirror for generating a current that is a ratio of current delivered to the load. The power IC also has current limiting and on-chip temperature sensing components. The voltage and current information is digitized and provided to a control integrated circuit (IC). The control IC receives this digitized information as well as user provided parameters and, in the regulation mode of operation, provides digitized pulse width modulated control signals to the power IC. In an active transient response mode of operation, the control IC provides signals to turn either the high side switches or low side switches ON. Fault detection circuitry identifies over voltage, under voltage, and excessive temperatures. All communications between the control IC and the power IC are digital providing high bandwidth, optimal control frequency response, noise immunity and efficient active transient response.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AUSTRIA AG
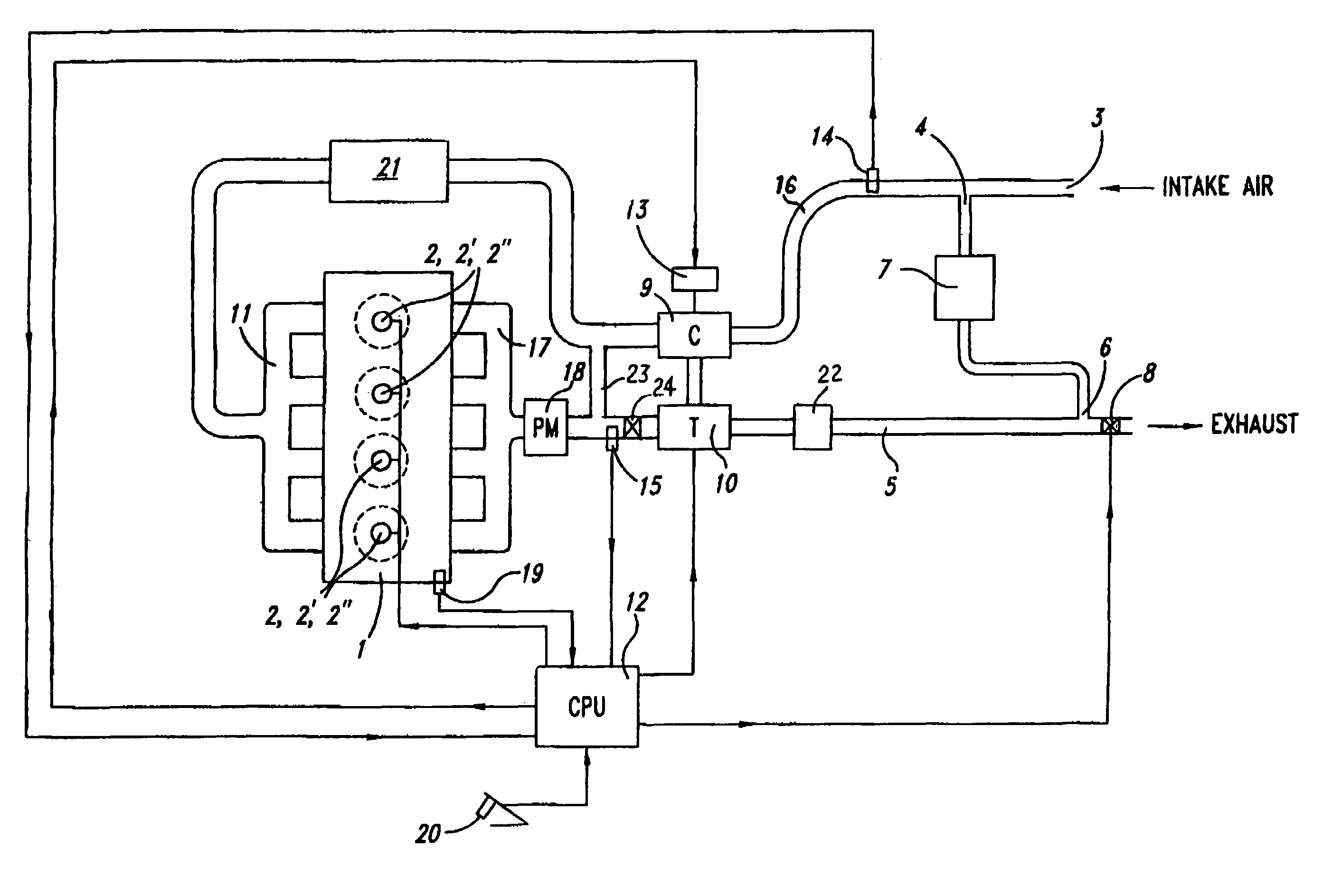
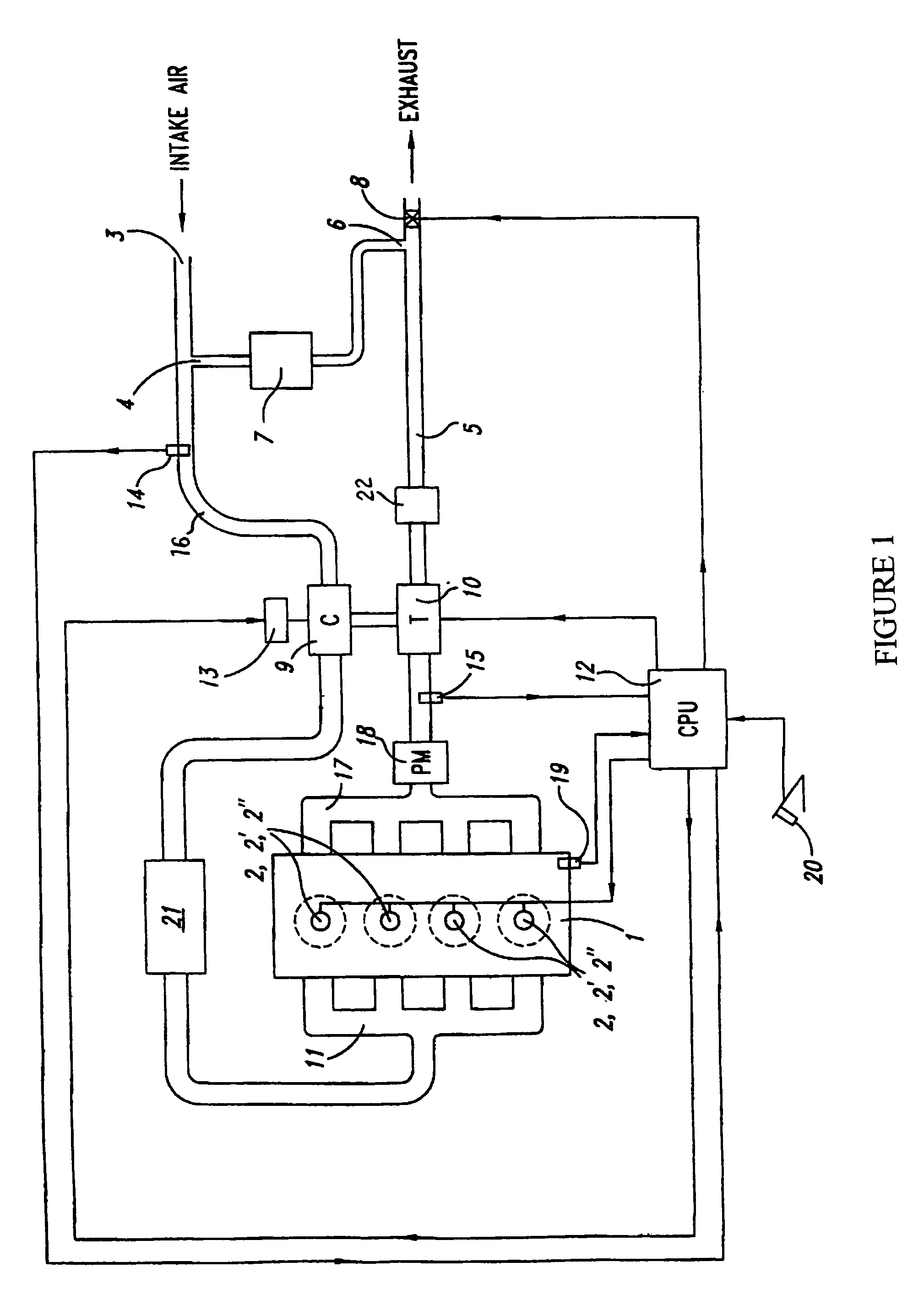
Control methods for low emission internal combustion system
InactiveUS7681394B2Cost-effectiveMaintaining NOx emissionsElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCombustion systemEngineering
Owner:US EPA OFFICE OF GENERAL COUNSEL UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE
Discrete time amplifier circuit and analog-digital converter
ActiveUS20090115523A1Simple circuit configurationShorten convergence timeElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersAudio power amplifierA d converter
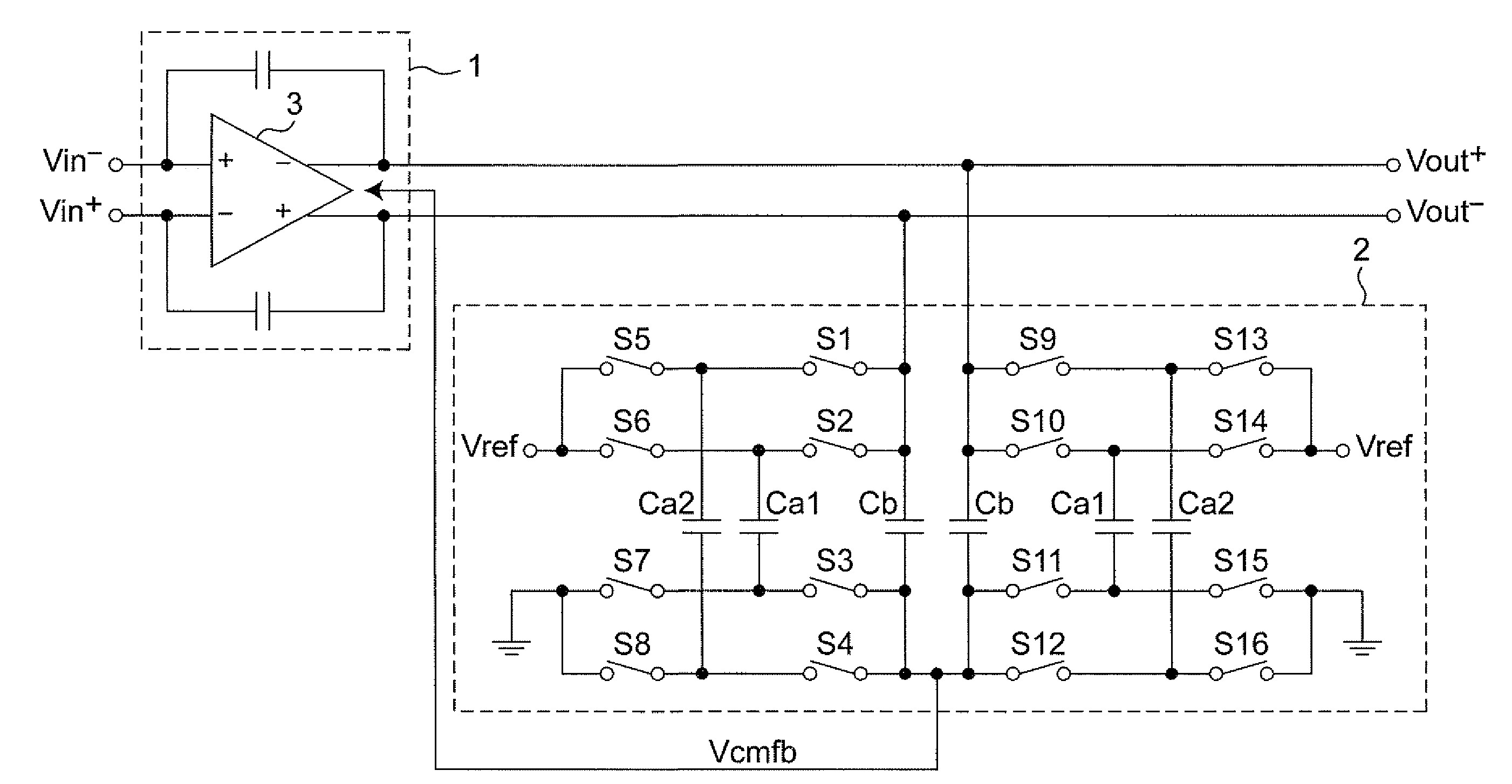
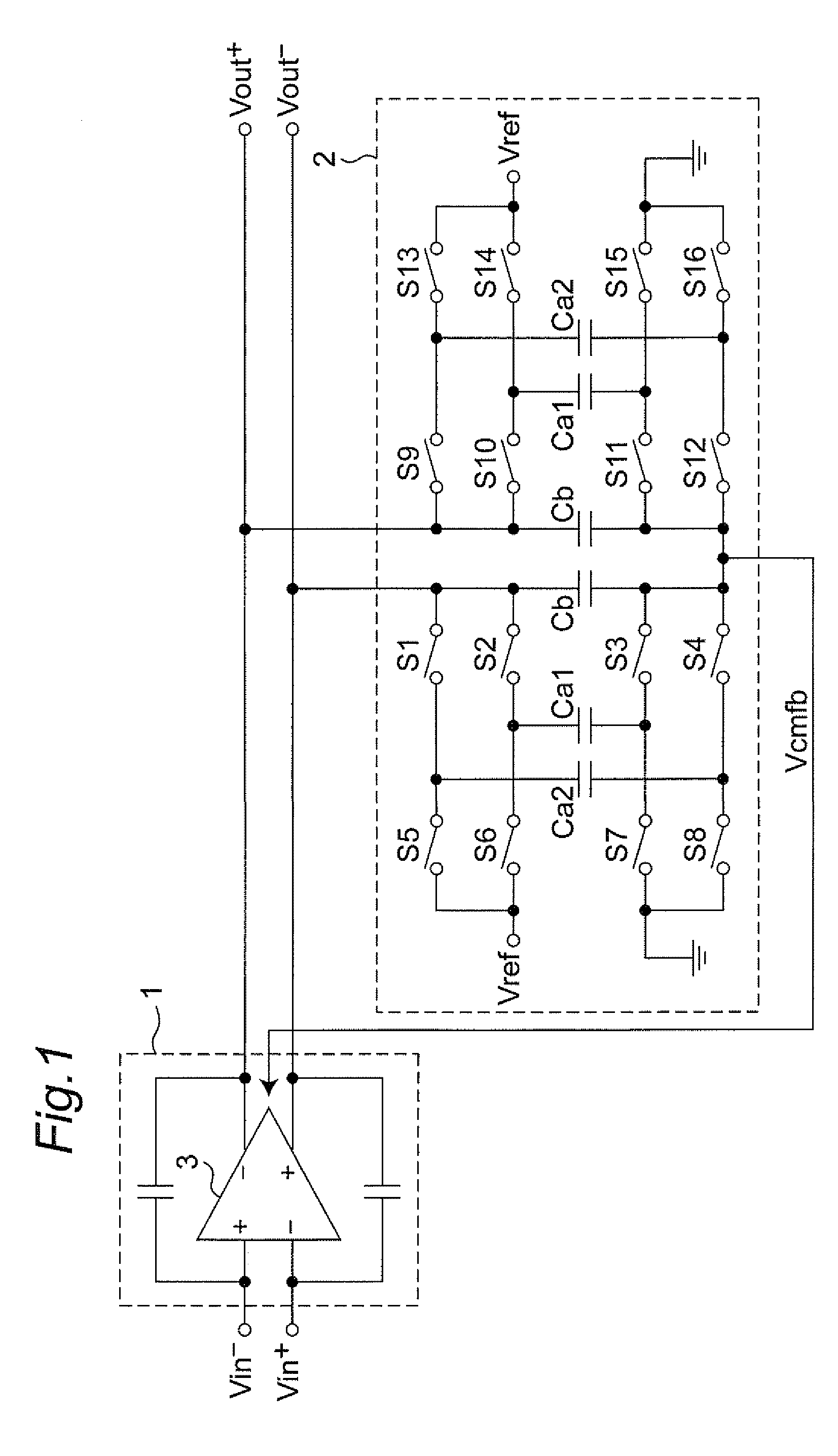
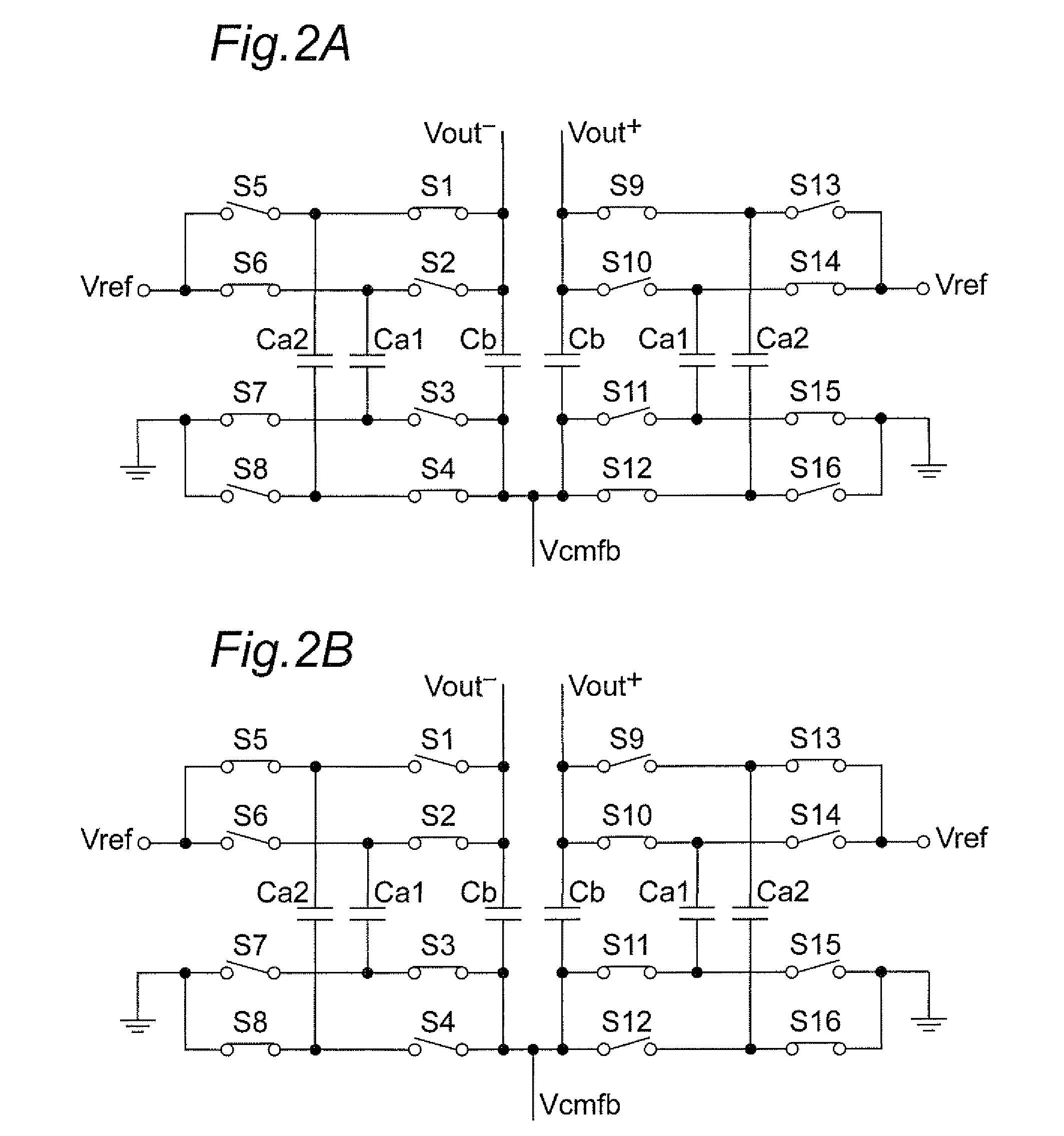
The present invention is intended to attain simplified circuit configuration and low current consumption in a discrete time amplifier circuit and an AD converter, to improve the convergence from the transient response state to the steady state of the amplifier circuit and to reduce noise and distortion owing to the variation in the output common-mode voltage. The discrete time amplifier circuit and the AD converter are provided with a switched-capacitor common-mode feedback (CMFB) circuit capable of detecting and feeding back the output common-mode voltage at every sampling timing in the case that the circuit operates at double sampling timing (every ½ cycle).
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
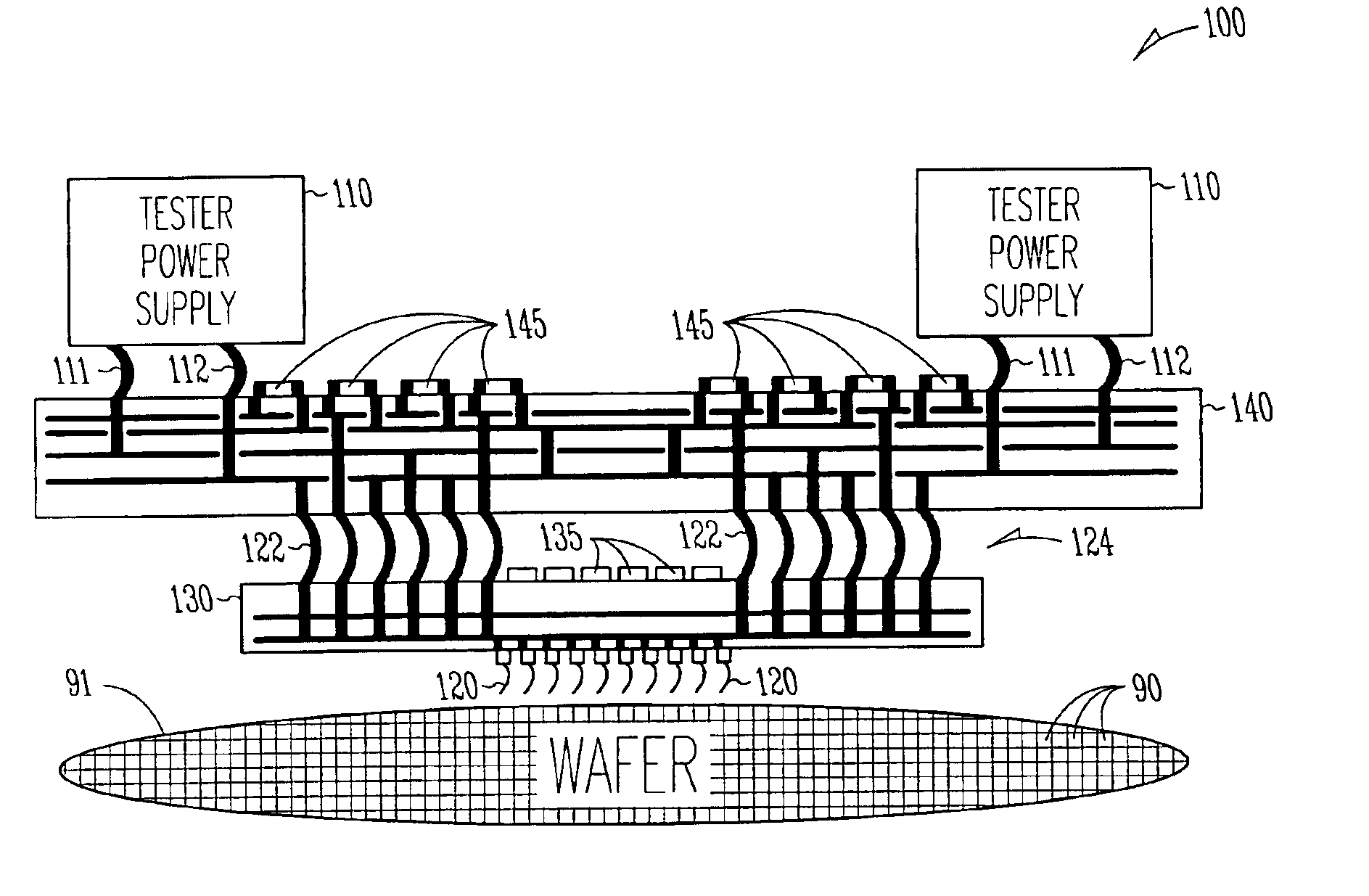
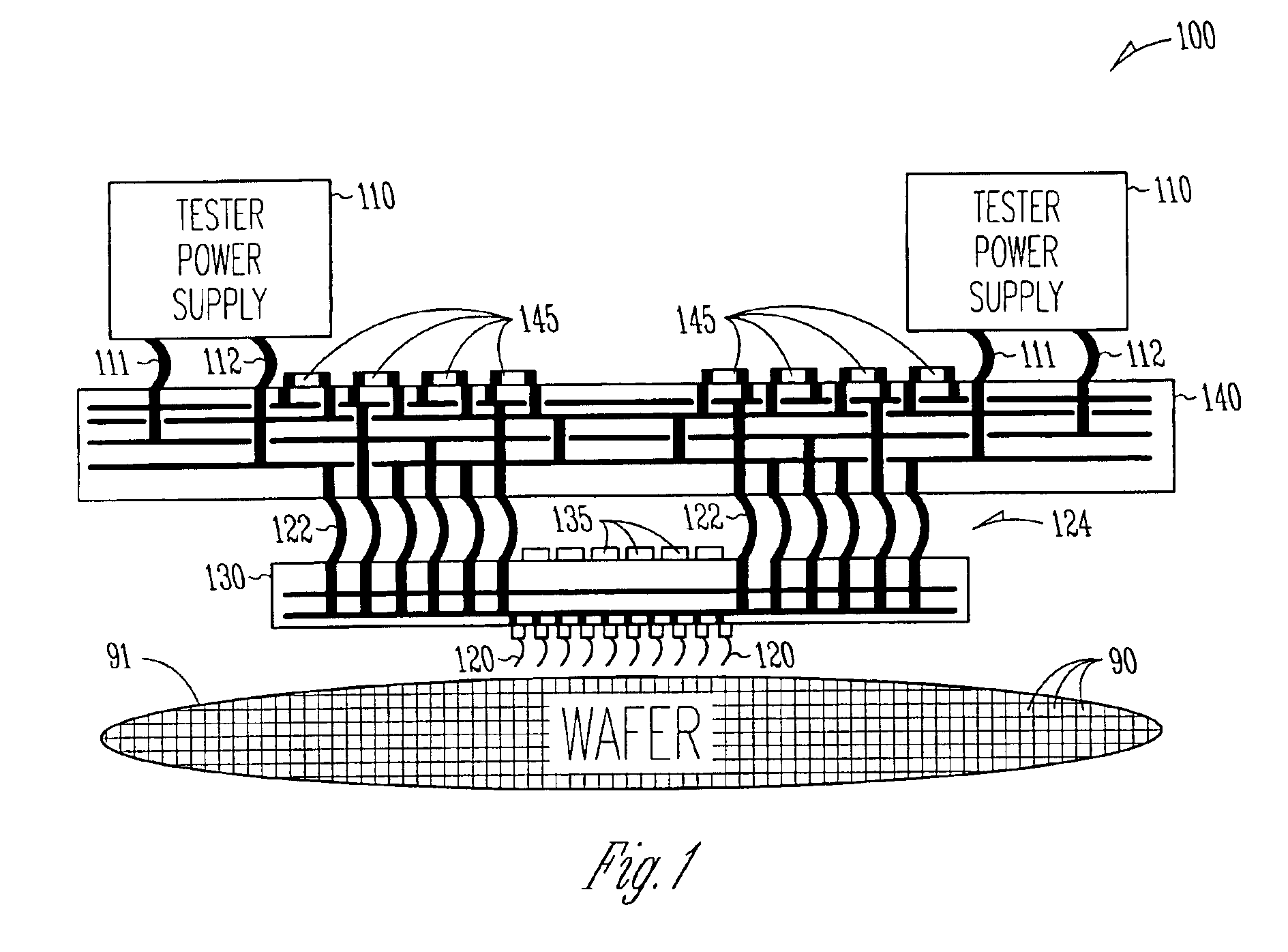
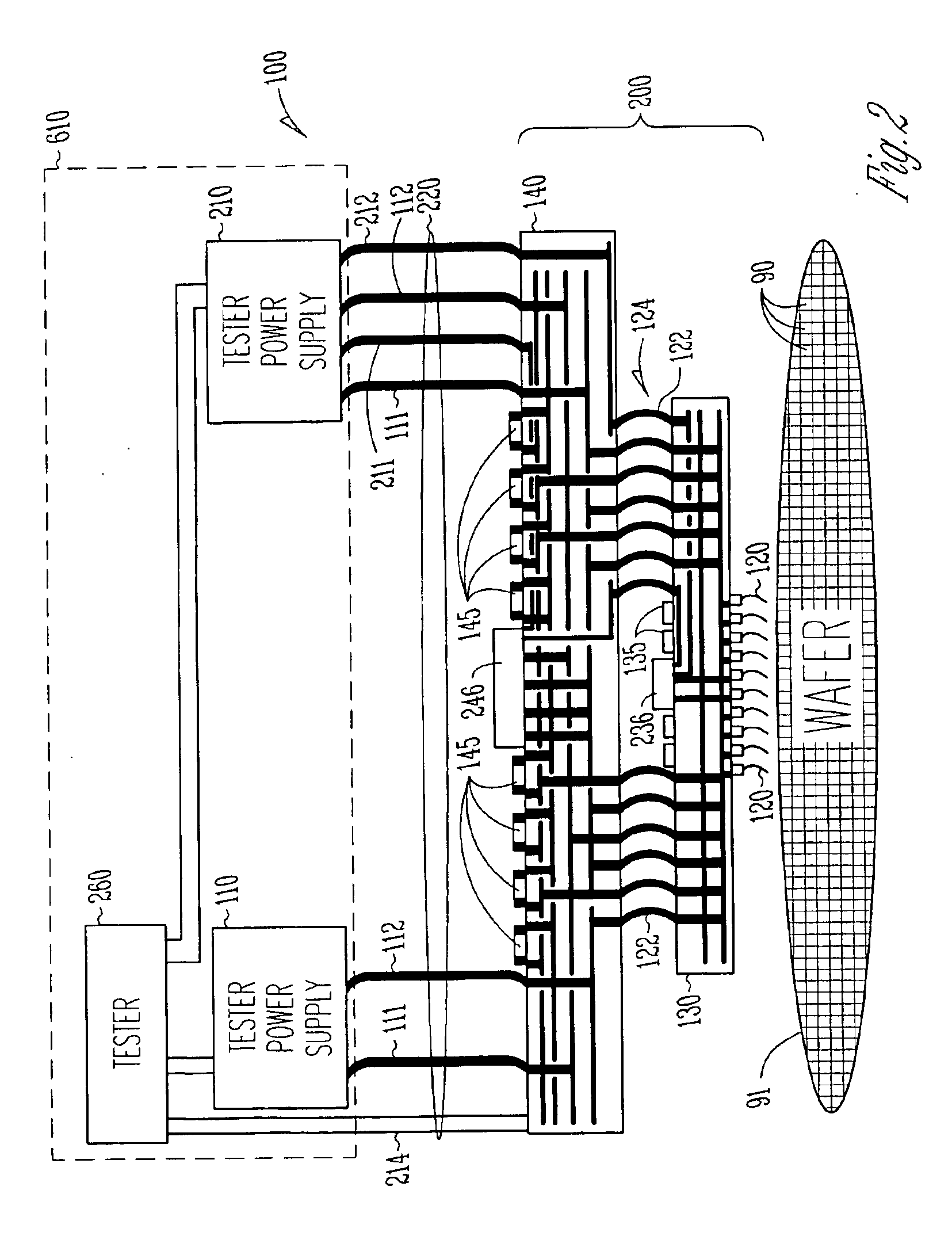
Embedded voltage regulator and active transient control device in probe head for improved power delivery and method
InactiveUS6897666B2Electrical measurement instrument detailsIndividual semiconductor device testingElectricityElectrical conductor
A method and apparatus for making a probe head that has reduced voltage droop and improved transient response. One embodiment a cable providing a plurality of signal conductors and a plurality of power conductors including a first power conductor and a second power conductor, a probe head wired to the cable, a plurality of electrical contacts including a first electrical contact and a second electrical contact, wherein each one of the plurality of electrical contacts is fixed to the probe head and wherein the first power conductor is connected to the first electrical contact, and a first regulatory device physically residing in the probe head and wired between the second power conductor and the first electrical contact. In some embodiments, the first regulatory device includes an active transient control device that senses an output voltage and sources or sinks an appropriate supplemental amount of current to improve transient response.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AUSTRIA AG +1
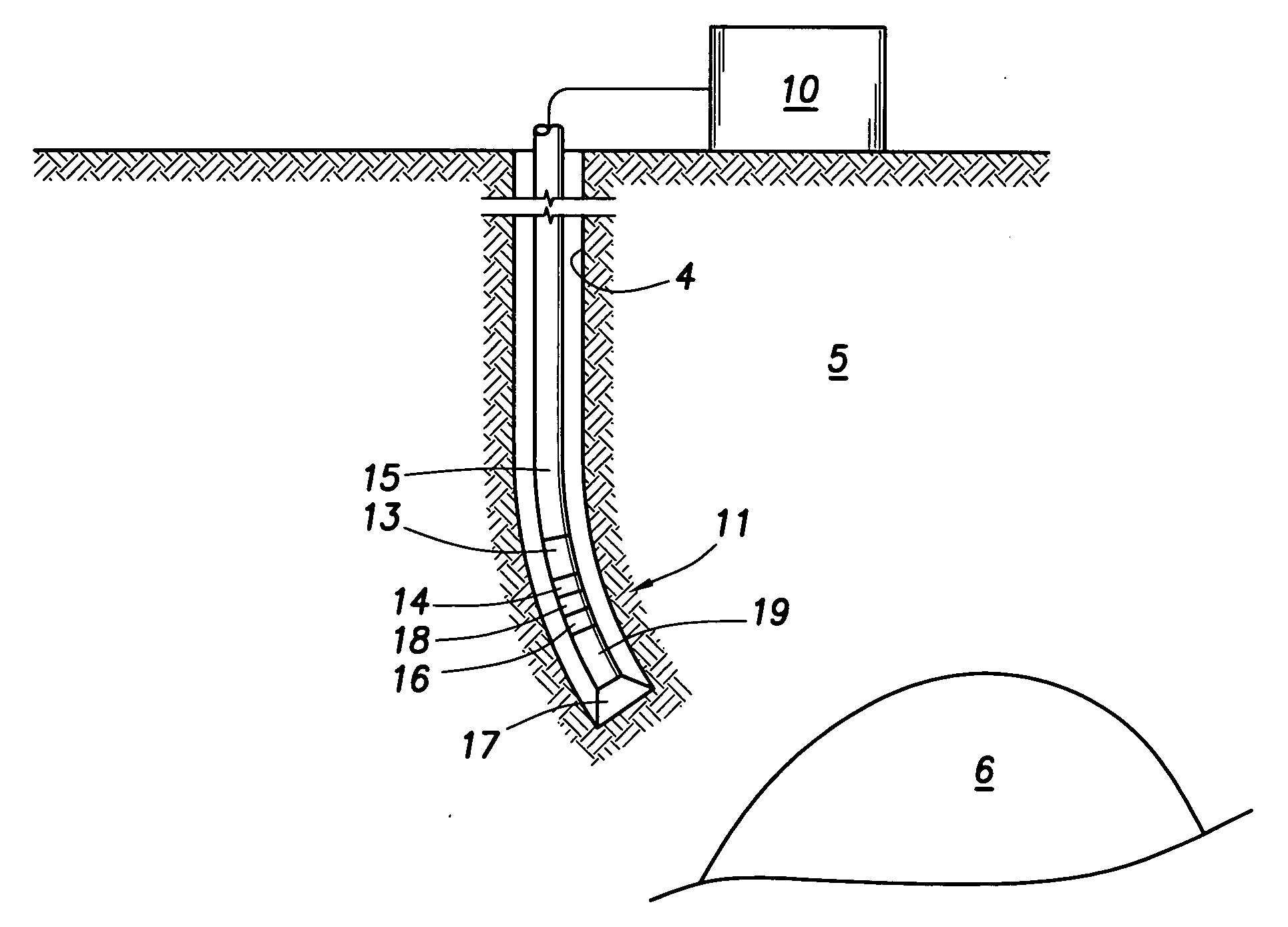
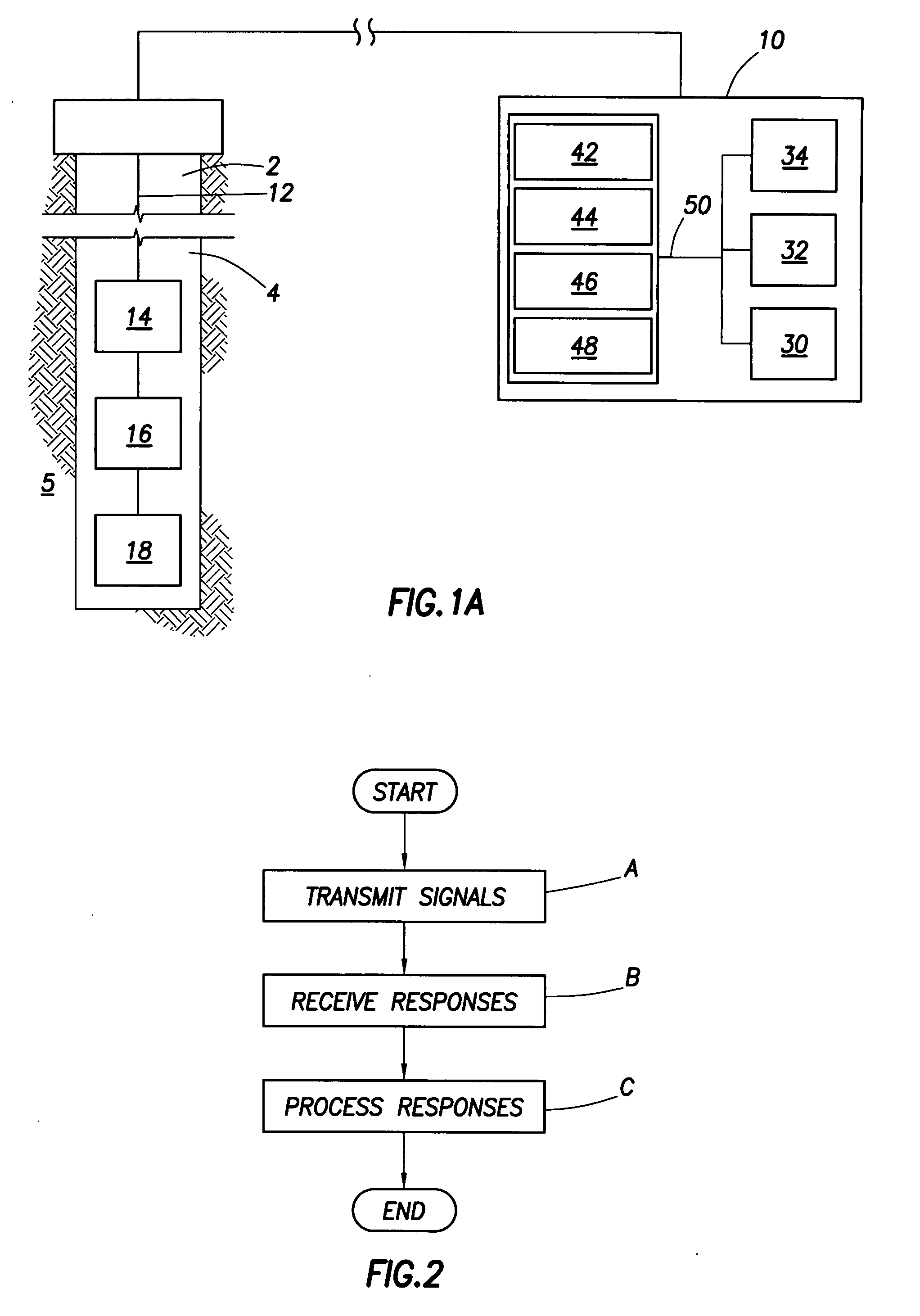
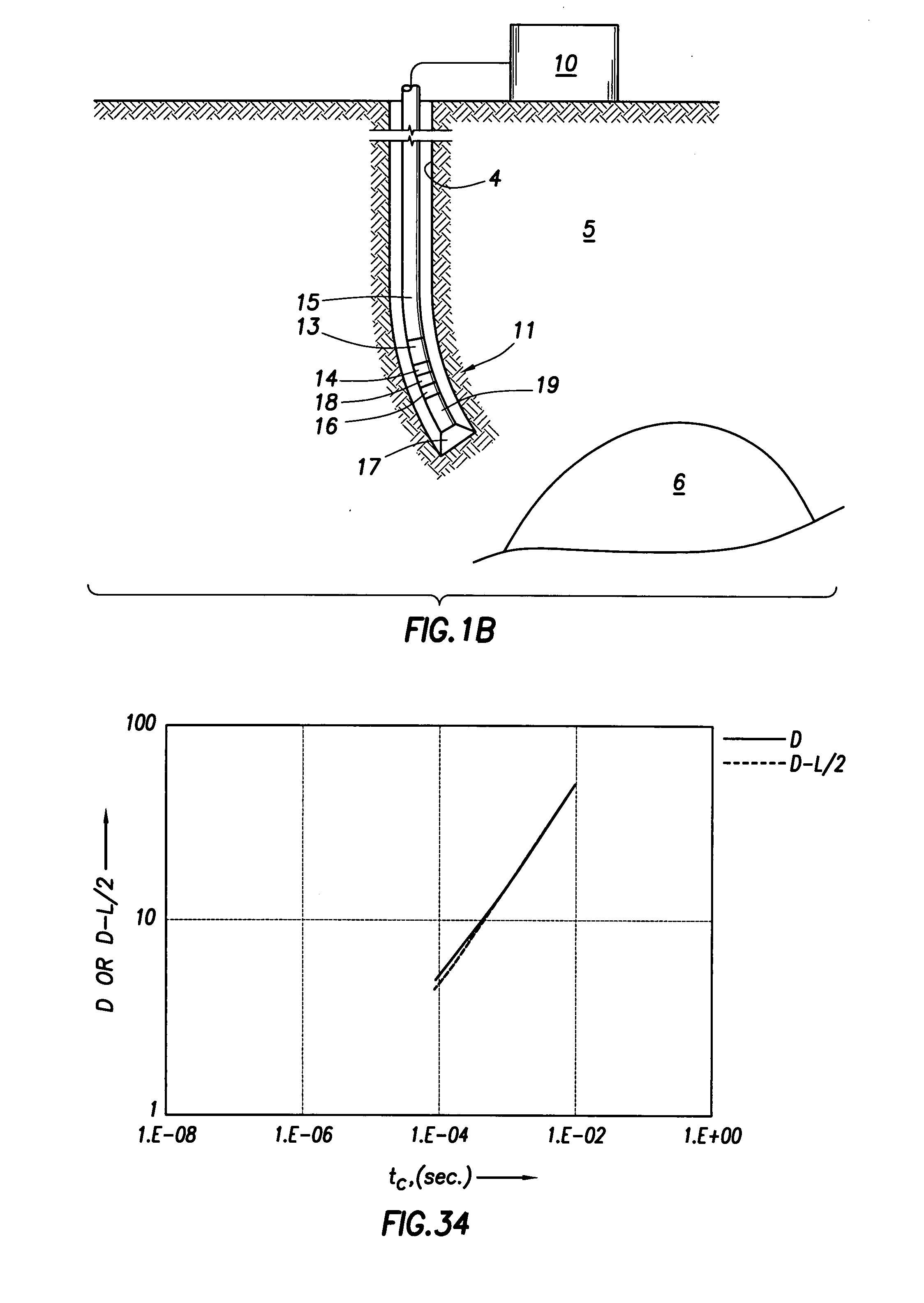
Method of analyzing a subterranean formation and method of producing a mineral hydrocarbon fluid from the formation
InactiveUS20070256832A1Accurate placementElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyGeosteeringTransmitter antenna
Method of analyzing a subterranean formation traversed by a wellbore. The method uses a tool comprising a transmitter antenna and a receiver antenna, the subterranean formation comprising one or more formation layers. The tool is suspended inside the wellbore, and one or more electromagnetic fields are induced in the formation. One or more time-dependent transient response signals are detected and analyzed. Electromagnetic anisotropy of at least one of the formation layers is detectable. Geosteering cues may be derived from the time-dependent transient response signals, for continued drilling of the well bore until a hydrocarbon reservoir is reached. The hydrocarbon may then be produced.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
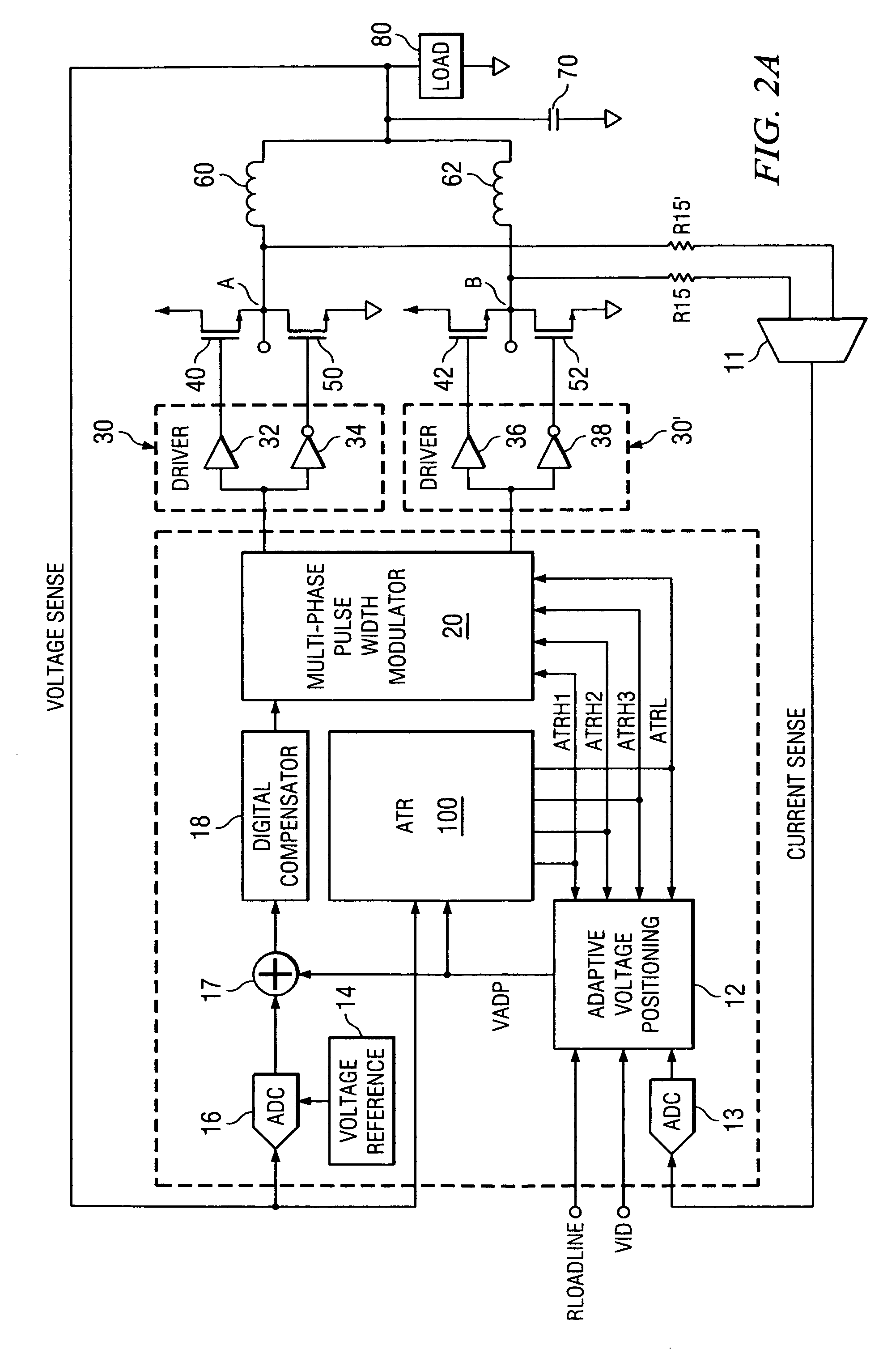
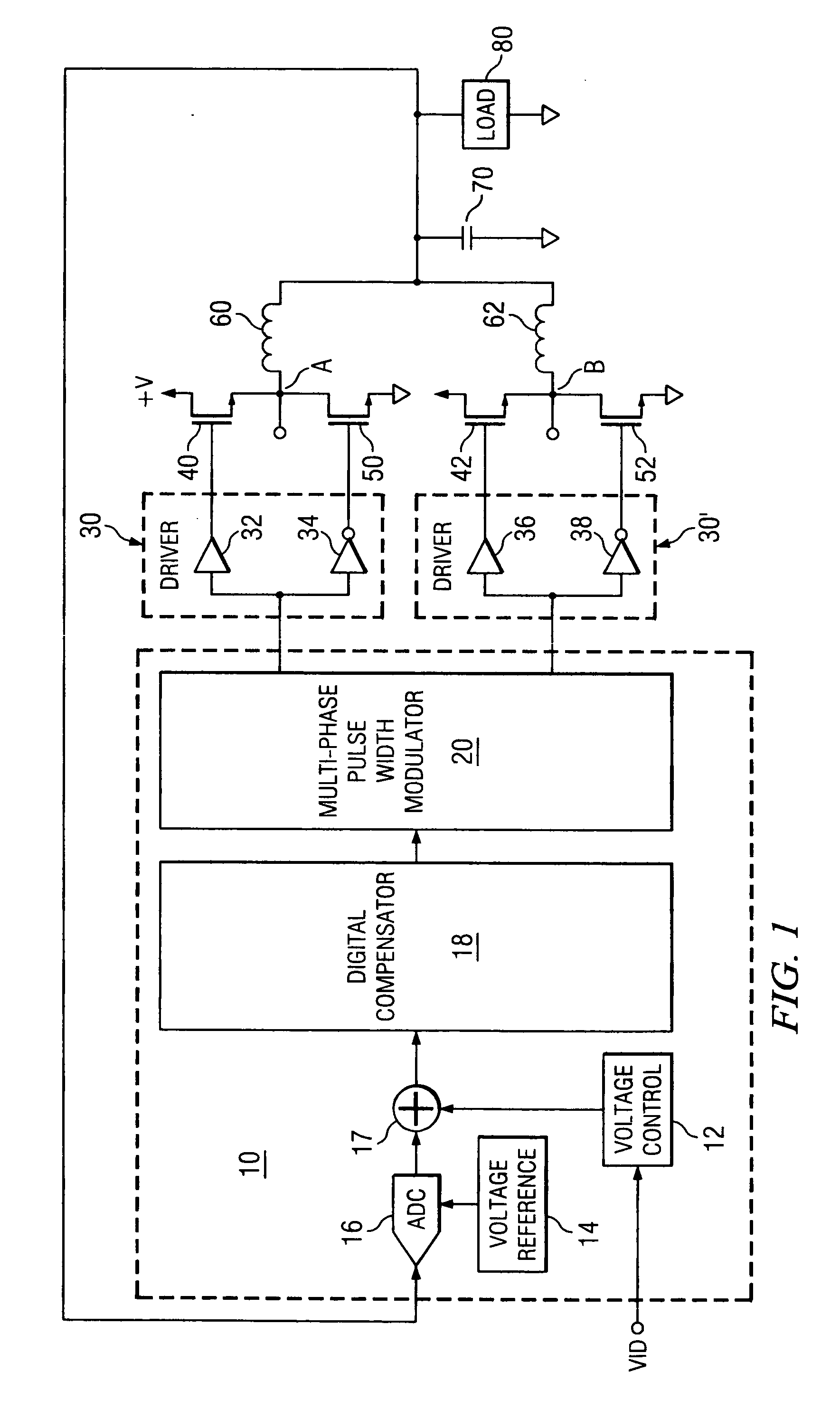
Active transient response circuits, system and method for digital multiphase pulse width modulated regulators
ActiveUS20060152205A1Accurately voltage excursionRapid enhanced responseDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationAdaptive filterEngineering
Disclosed is a multi-phase pulse width modulated voltage regulator and method in which transient voltage excursions or deviations that exceed the load line voltage by more than a pre-determined amount are detected by an ATR circuit and a correction signal is applied. The correction signal is in the form of asynchronous pulses and the number of such pulses is a function of the magnitude of the voltage excursion as determined by the number of thresholds that are exceeded. Also disclosed is an adaptive voltage positioning (AVP) circuit and method for early detection of a transient event by sensing voltage changes at the load and adjusting the target voltage with pre-determined current values prior to the time that ATR event changes in the current at the load are detected. The AVP load line is pre-positioned for more precise current control. Also disclosed is an adaptive filter with adjustable frequency characteristics in response to an ATR event. Also disclosed is a pulse limiting circuit. Also disclosed is a tri-state implementation. Response to transient events is further improved with an external ATR circuit coupled to the load.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AUSTRIA AG
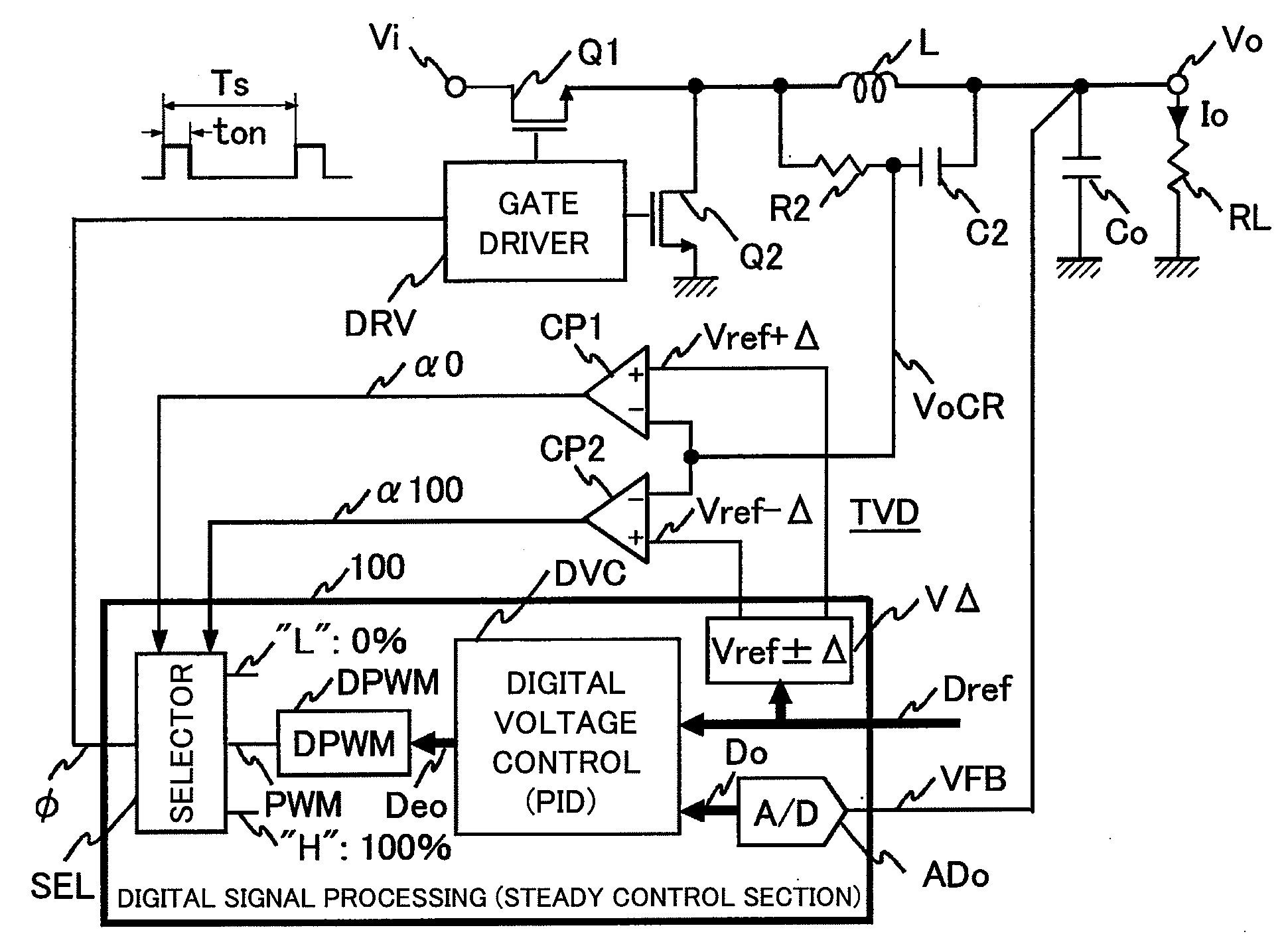
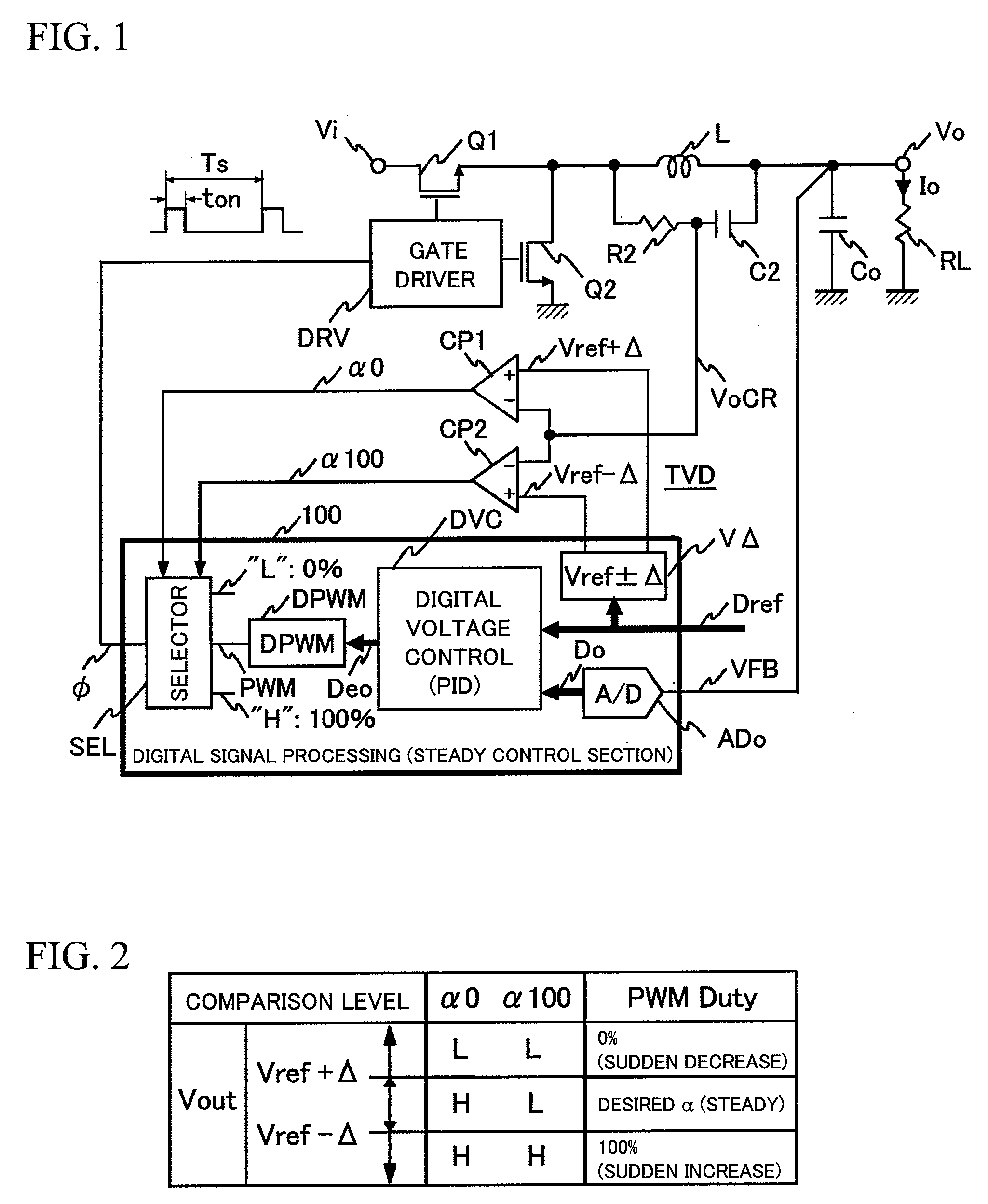
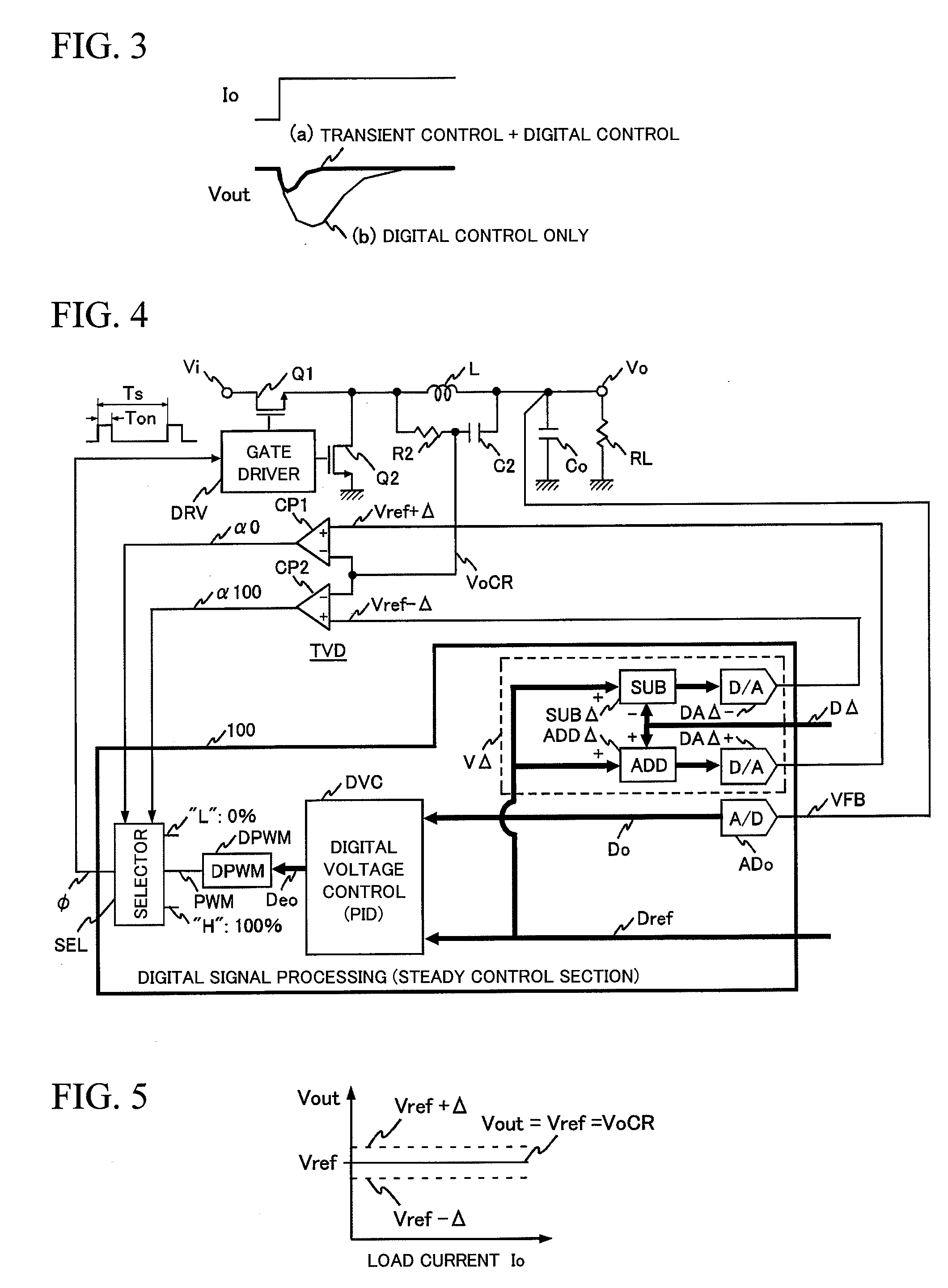
Digital control switching power-supply device and information processing equipment
ActiveUS20080252277A1Large capacitanceLow costDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationDigital signal processingInformation processing
To provide a digital control switching power-supply device capable of suitably achieving fast transient response at the time of a sudden load change. In parallel with normal digital signal processing means that outputs a PWM pulse signal having a desired duty, transient variation detection means composed of a CR filter provided across an output inductor and a window comparator is provided in preparation for a sudden load change. If a sudden decrease in load is detected, a PWM pulse signal having a duty of 0% is forcedly output, and if a sudden increase in load is detected, a PWM pulse signal having a duty of 100% is forcedly output.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Digitally controlled voltage regulator
ActiveUS20040150928A1Easy to customizePrecise power controlEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionControl signalOptimal control
Disclosed is a digitally controlled multi-phase voltage regulator system providing regulated power to electronic components that have variable power requirements. Power is supplied by one or more power integrated circuits (IC) each having a high side power switch controlled by pulse width modulated signals and a low side power switch. The power IC senses voltage at the load and has an on-chip current mirror for generating a current that is a ratio of current delivered to the load. The power IC also has current limiting and on-chip temperature sensing components. The voltage and current information is digitized and provided to a control integrated circuit (IC). The control IC receives this digitized information as well as user provided parameters and, in the regulation mode of operation, provides digitized pulse width modulated control signals to the power IC. In an active transient response mode of operation, the control IC provides signals to turn either the high side switches or low side switches ON. Fault detection circuitry identifies over voltage, under voltage, and excessive temperatures. All communications between the control IC and the power IC are digital providing high bandwidth, optimal control frequency response, noise immunity and efficient active transient response.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AUSTRIA AG
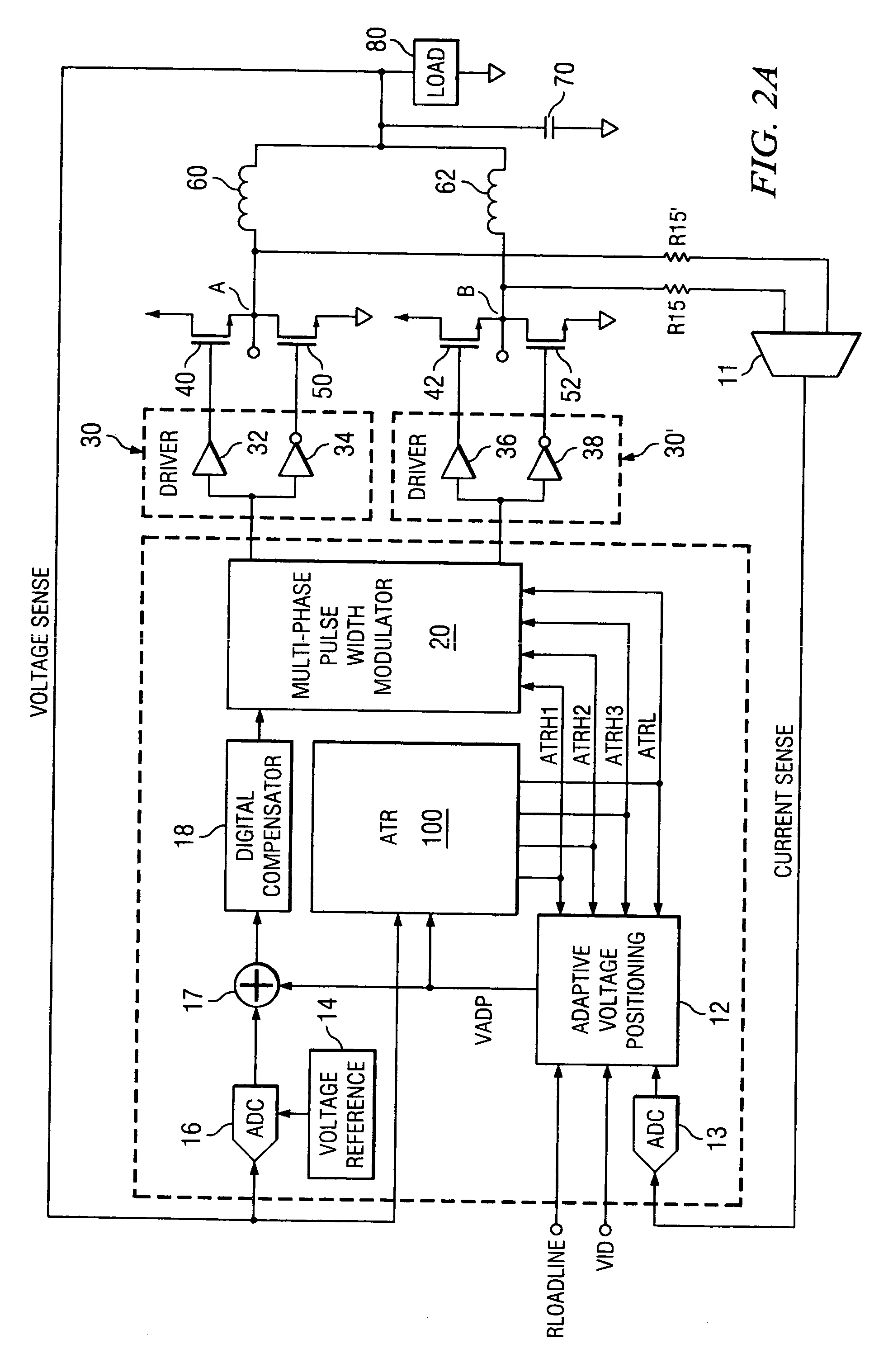
Multi-threshold multi-gain active transient response circuit and method for digital multiphase pulse width modulated regulators
ActiveUS20060055388A1Rapid enhanced responseEasy to adjustDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationVoltage shiftEngineering
Disclosed is a multi-phase pulse width modulated voltage regulator and method in which transient voltage excursions or deviations that exceed the load line voltage by more than a pre-determined amount are detected by an ATR circuit and a correction signal is applied. The correction signal is in the form of asynchronous pulses and the number of such pulses is a function of the magnitude of the voltage excursion as determined by the number of thresholds that are exceeded. Also disclosed is an adaptive voltage positioning (AVP) circuit and method for early detection of a transient event by sensing voltage changes at the load and adjusting the target voltage with pre-determined current values prior to the time that ATR event changes in the current at the load are detected.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AUSTRIA AG
Multiphase clamp coupled-buck converter and magnetic integration
InactiveUS20020118000A1Emergency protective circuit arrangementsDc-dc conversionVoltage regulator modulePush pull
Voltage regulation, transient response and efficiency of a voltage regulator module (VRM) is improved where short duty cycles are necessitated by large differentials of input and output voltage by including at least one clamping of a tap of an inductance in series with an output of each of a plurality of parallel branches or phases which are switched in a complementary fashion or providing coupling between inductors of respective phases. Such coupling between inductors is achieved in a small module with an integrated magnetic structure. Reduced component counts are achieved while deriving built-in input and output filters. Principals of the invention can be extended to isolation applications and push-pull forward converts, in particular. A lossless clamping circuit is also provided allowing spike currents to be suppressed while returning power to the output of the VRM.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
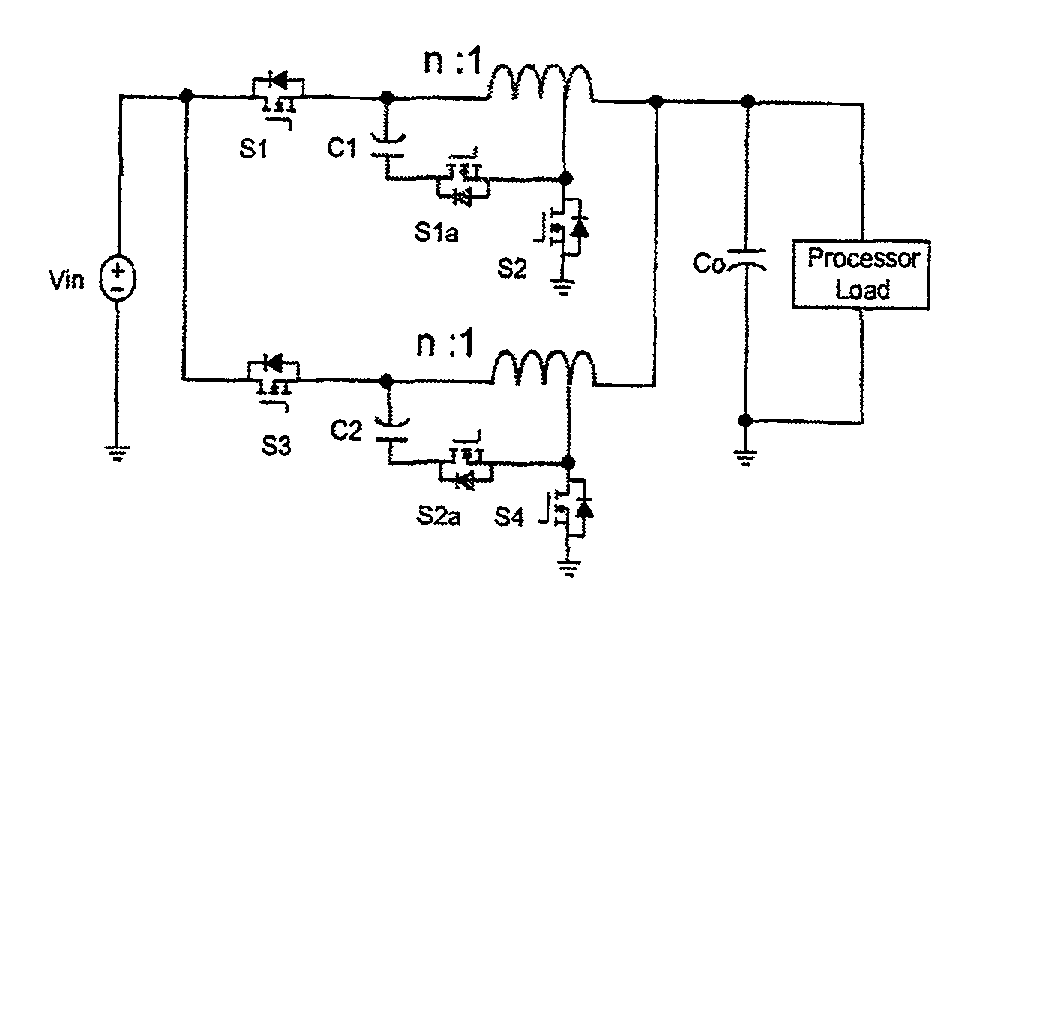
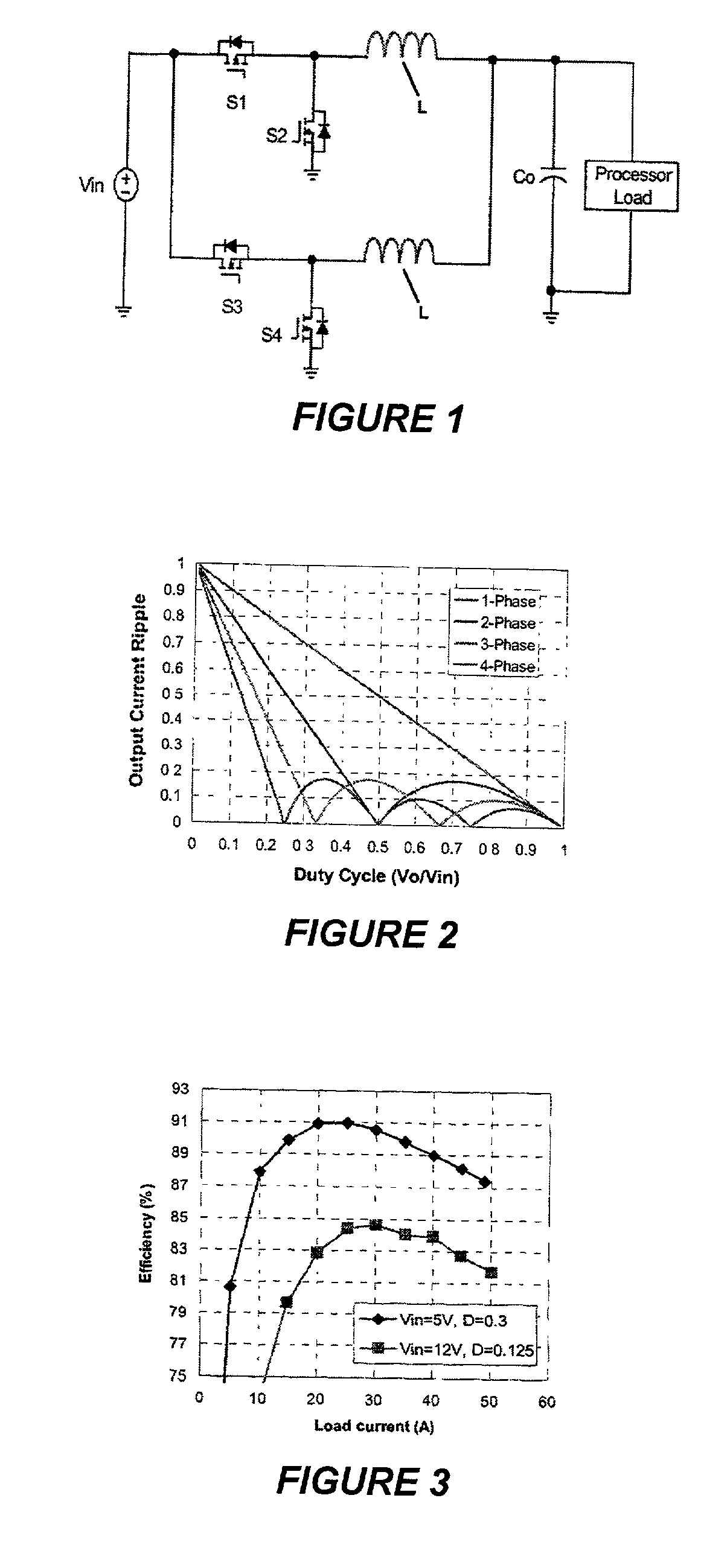
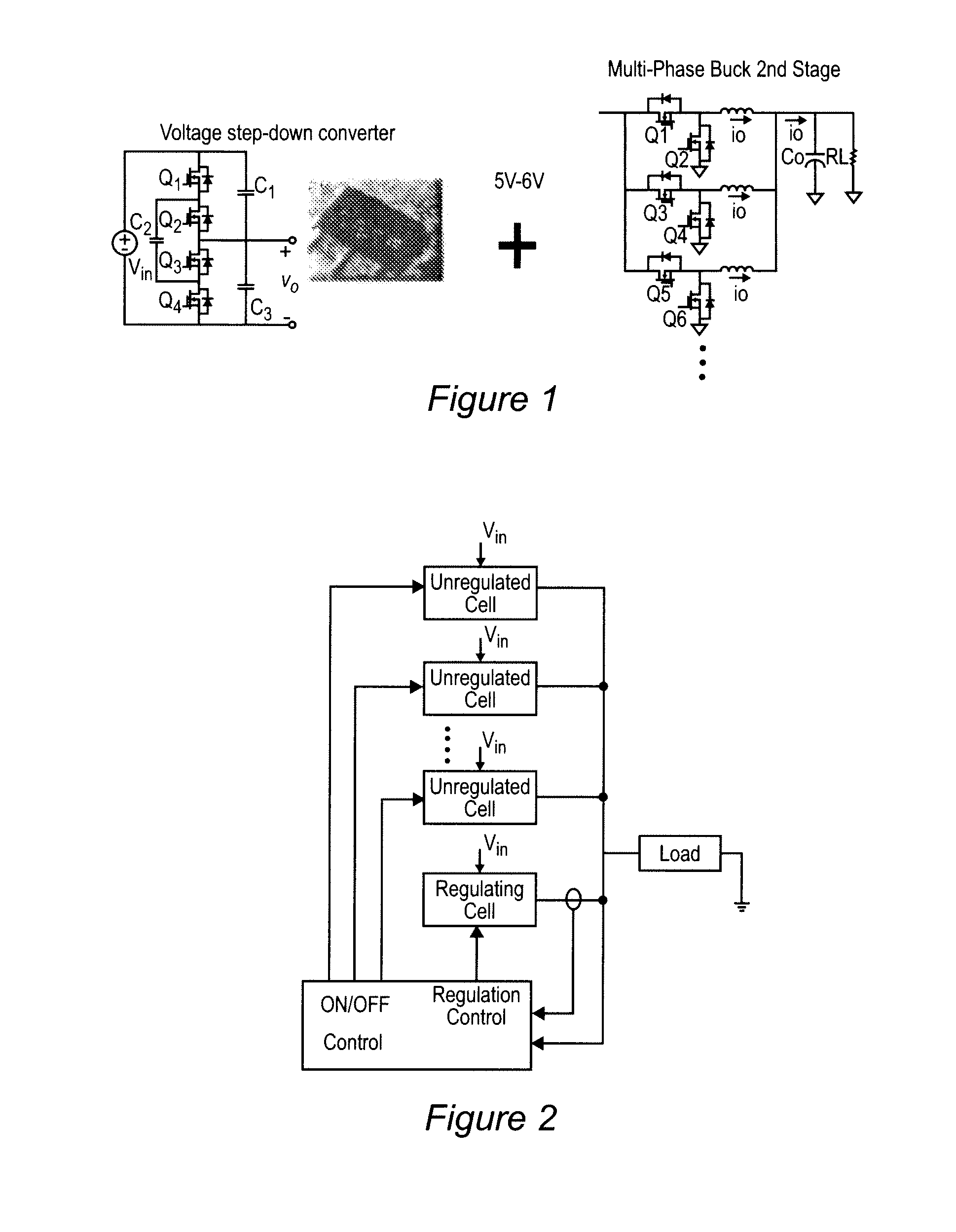
Coupled-Inductor Multi-Phase Buck Converters
InactiveUS20080205098A1Improved physical symmetryAvoid necessityDc-dc conversionFixed transformersTransformerConductor Coil
In a multi-phase power converter, efficiency is increased and ripple reduced while maintaining transient response and dynamic performance improved by electrically coupling secondary windings of transformers or provided for inductors of respective phases such that current to a load is induced in each phase by current in another phase. Magnetic coupling can also be provided between phases using a multi-aperture core of a configuration which minimizes primary winding length and copper losses. Efficiency at light load is enhanced by controlling current in the series connection of secondary windings in either binary or analog fashion.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
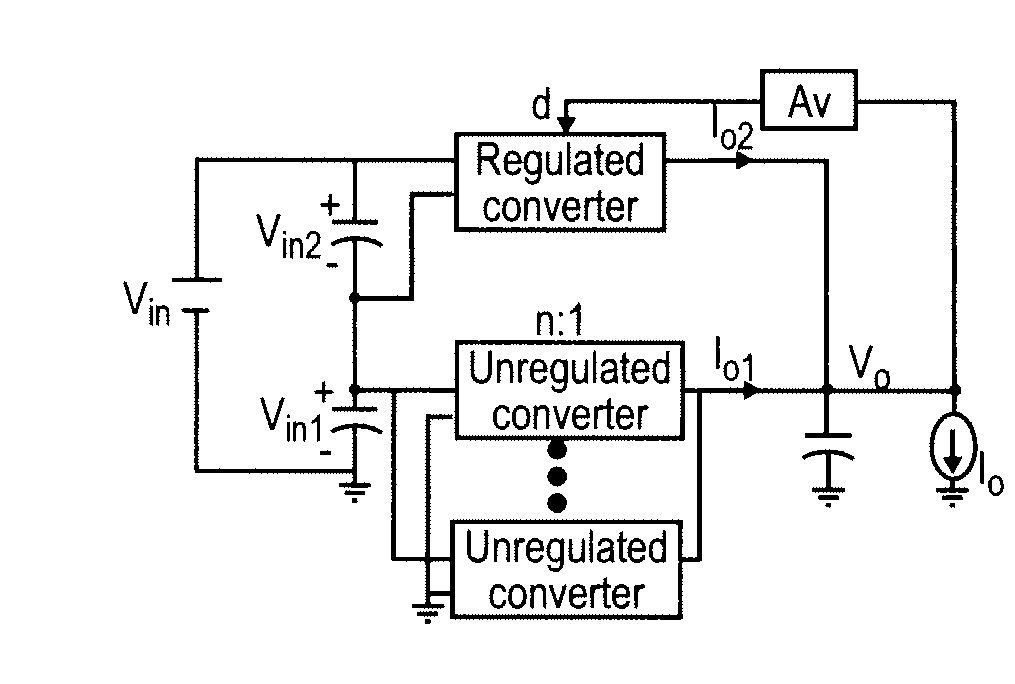
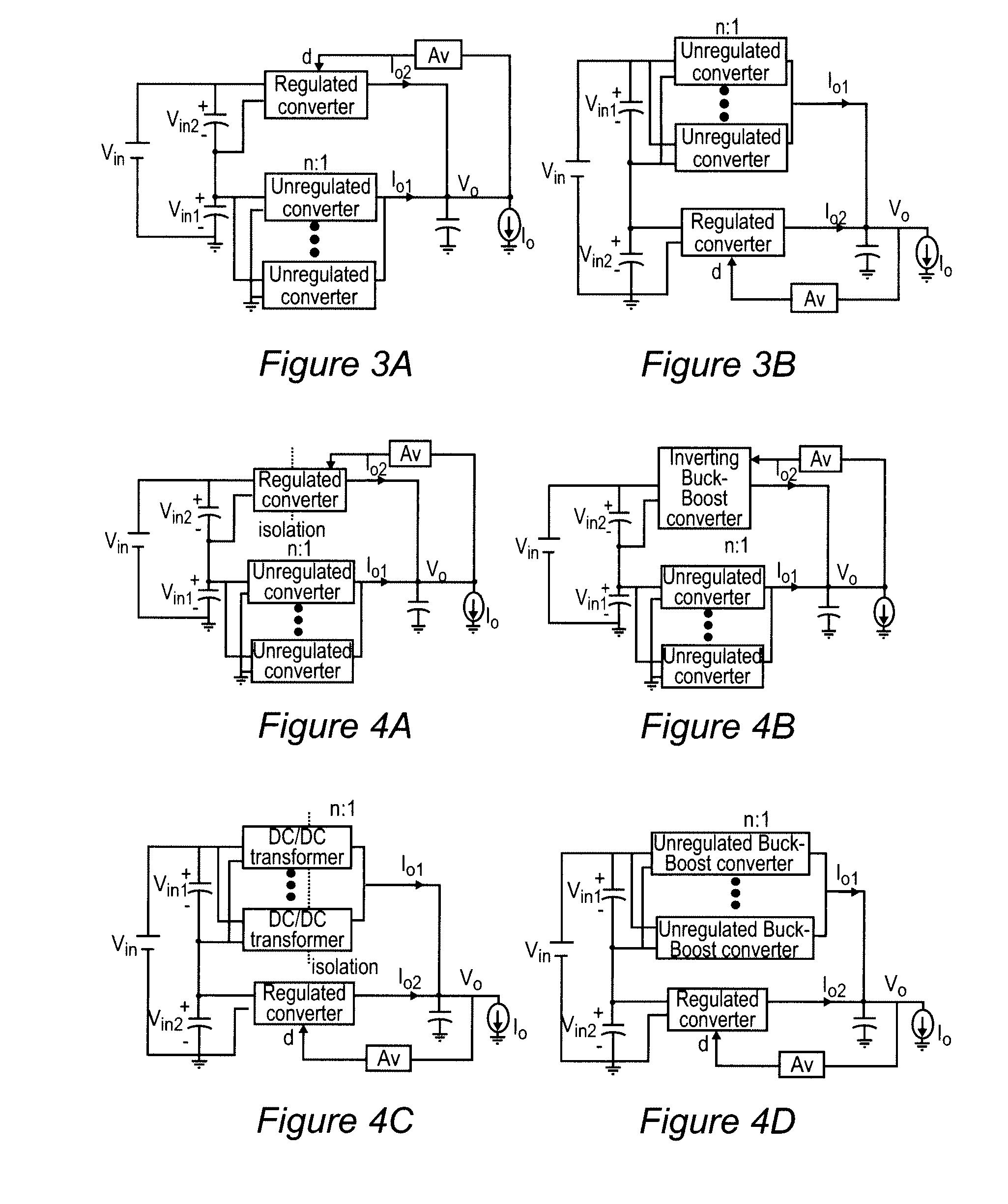
Quasi-Parallel Voltage Regulator
InactiveUS20090206804A1High currentSmall sizeEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionVoltage converterVoltage regulation
Improved regulation and transient response are provided by a power supply architecture providing both unregulated and regulated voltage converters in parallel but deriving input power from separate power supplies connected in series wherein regulated and unregulated branches each provide a substantially fixed and constant proportion of the output current. The series connection of input power sources may provide a further feedback mechanism in addition to feedback for regulation which enhances overall performance. As a perfecting feature of the invention, inductor-less resonant converters which are switched in an interleaved fashion may be used in the unregulated branch while substantially cancelling the characteristic large output voltage ripple thereof.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
High-precision modeling filament
InactiveUS6866807B2Improve accuracyQuality improvementAdditive manufacturing apparatusMouldsHysteresisEngineering
Disclosed is a modeling filament for use as feedstock in a fused deposition modeling liquifier, and a method for manufacturing the filament. The diameter and standard deviation of the filament are controlled to meet various tolerance requirements of jam resistance, slip resistance, model strength, liquifier overflow prevention and hysteresis-free transient response. Standard deviation of the filament diameter is matched to a filament target diameter. The resulting filament is used to form high-quality models.
Owner:STRATSYS INC
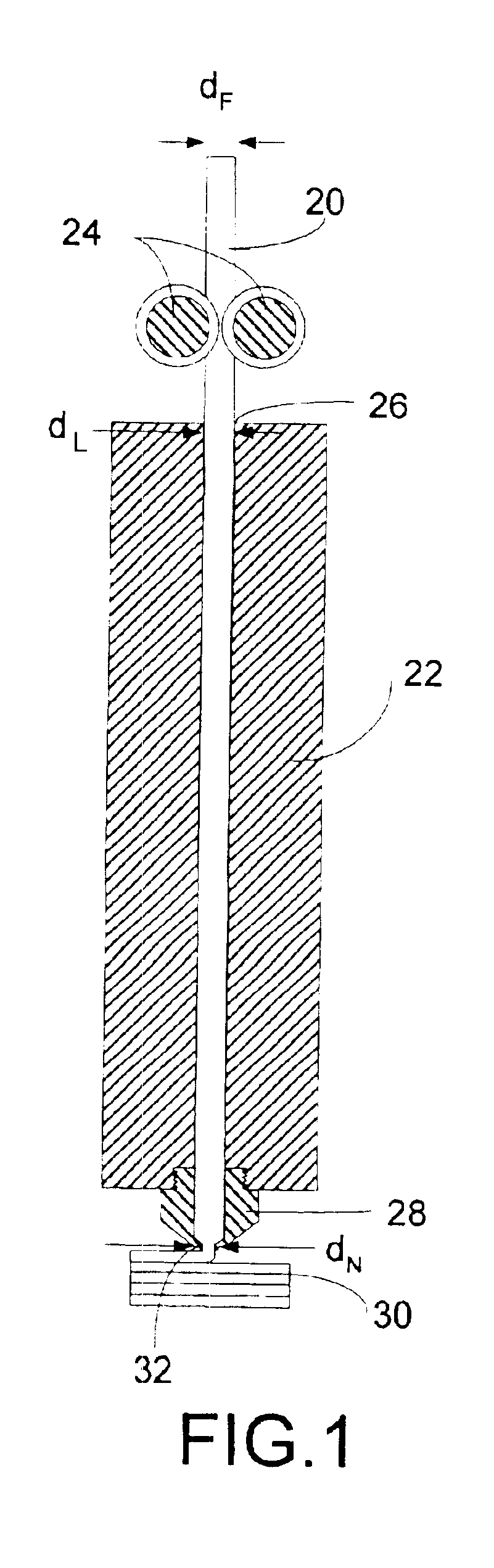
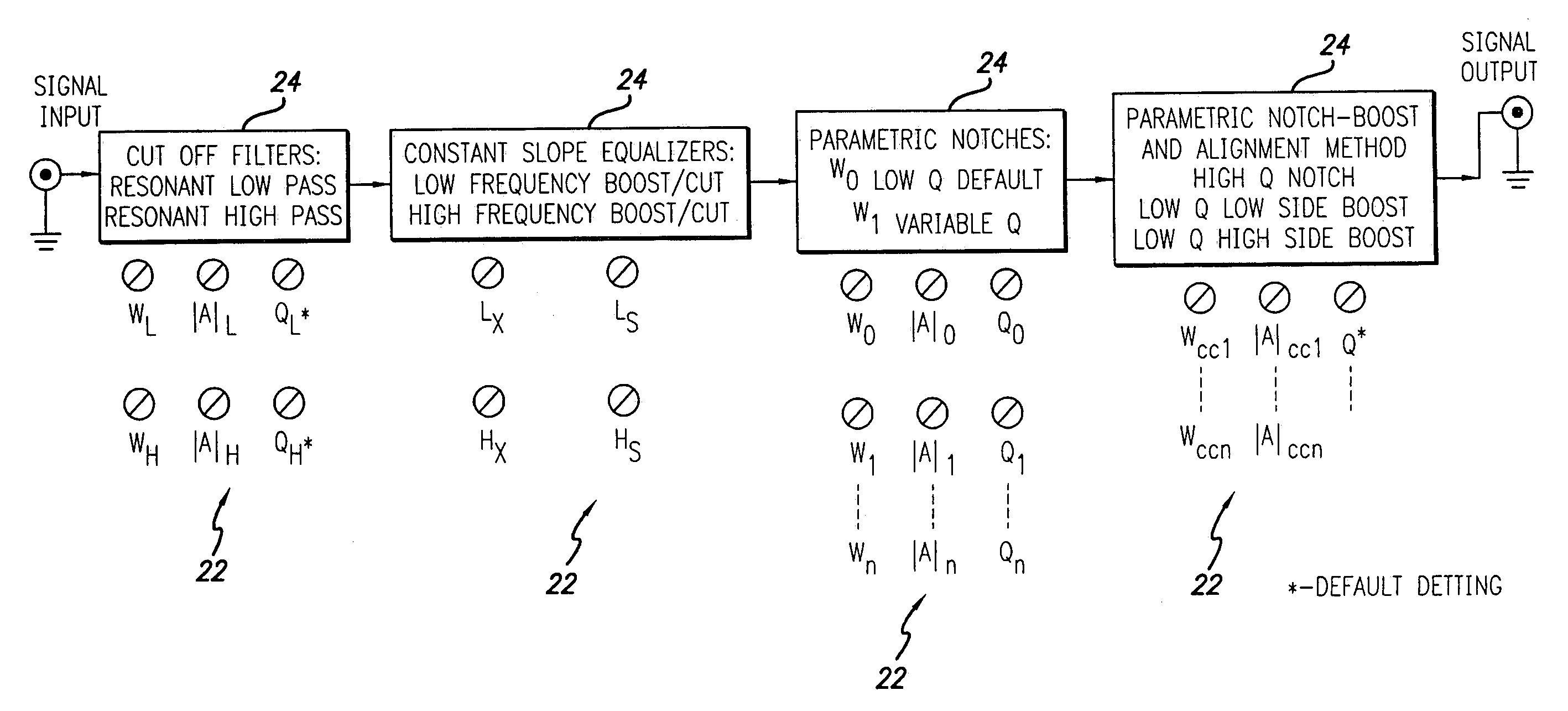
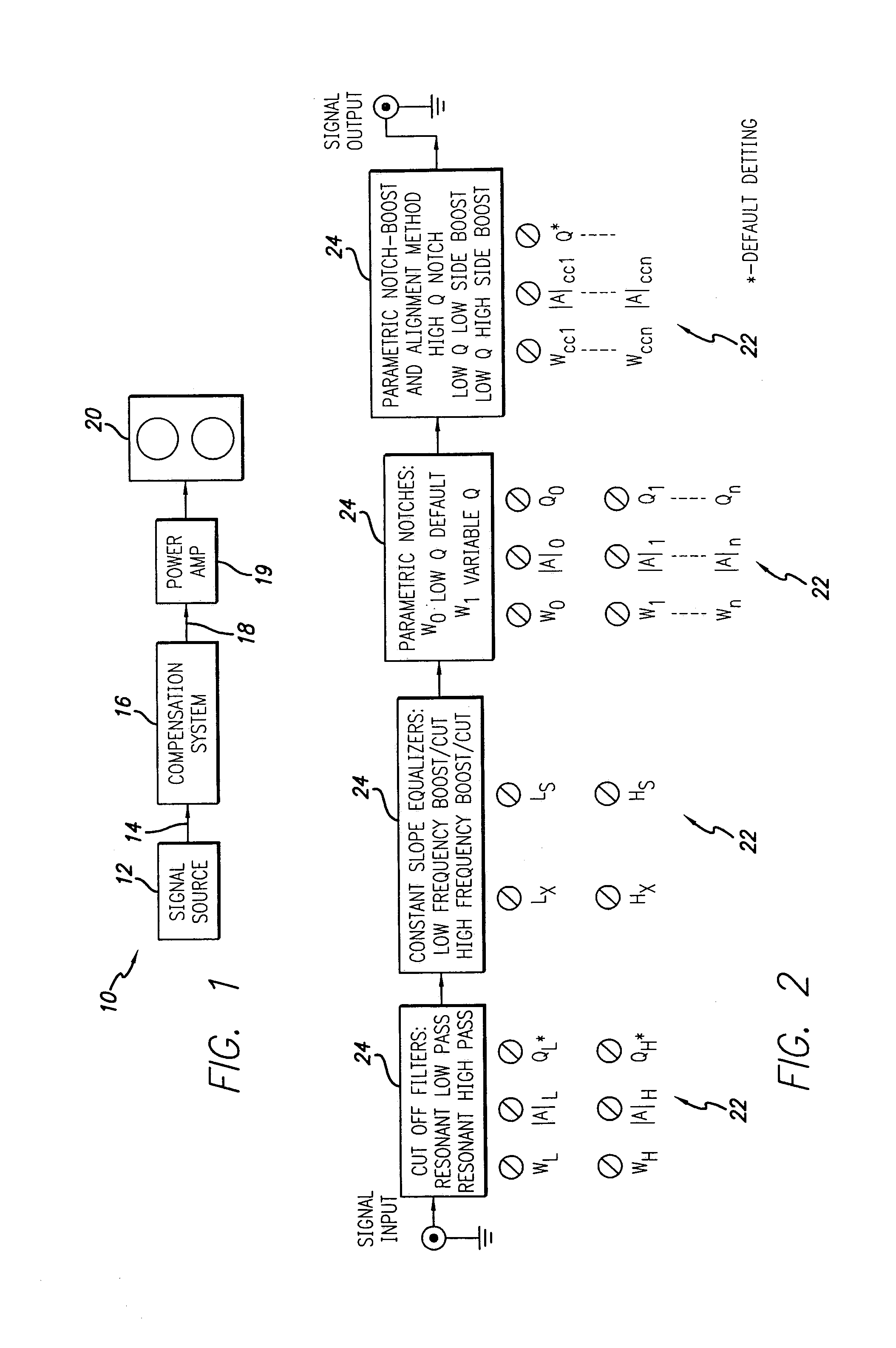
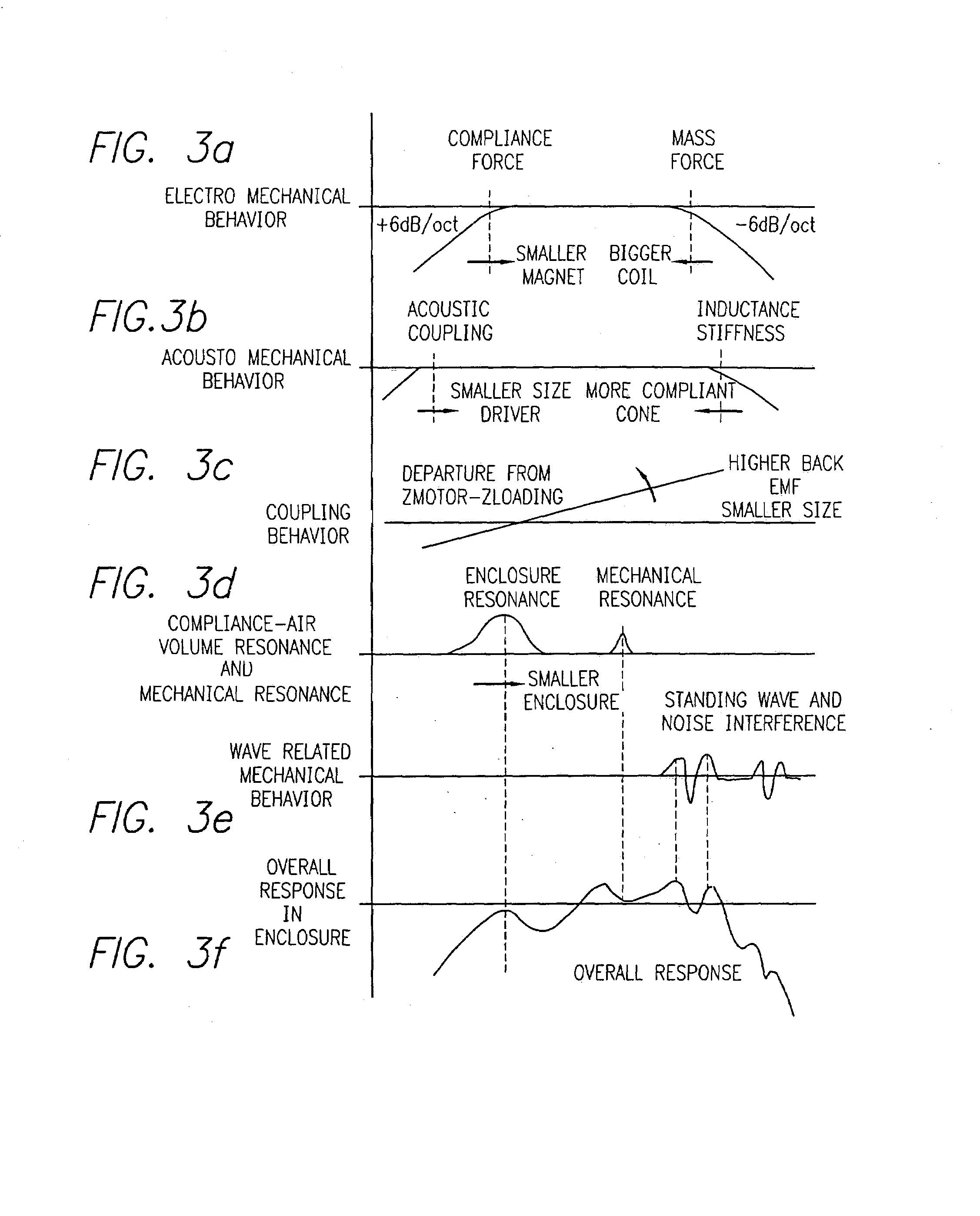
Compensation system and method for sound reproduction
InactiveUS7184556B1Reduce distortion problemsEnhance the imageGain controlDigital signal tone/bandwidth controlElectricityDigital signal processing
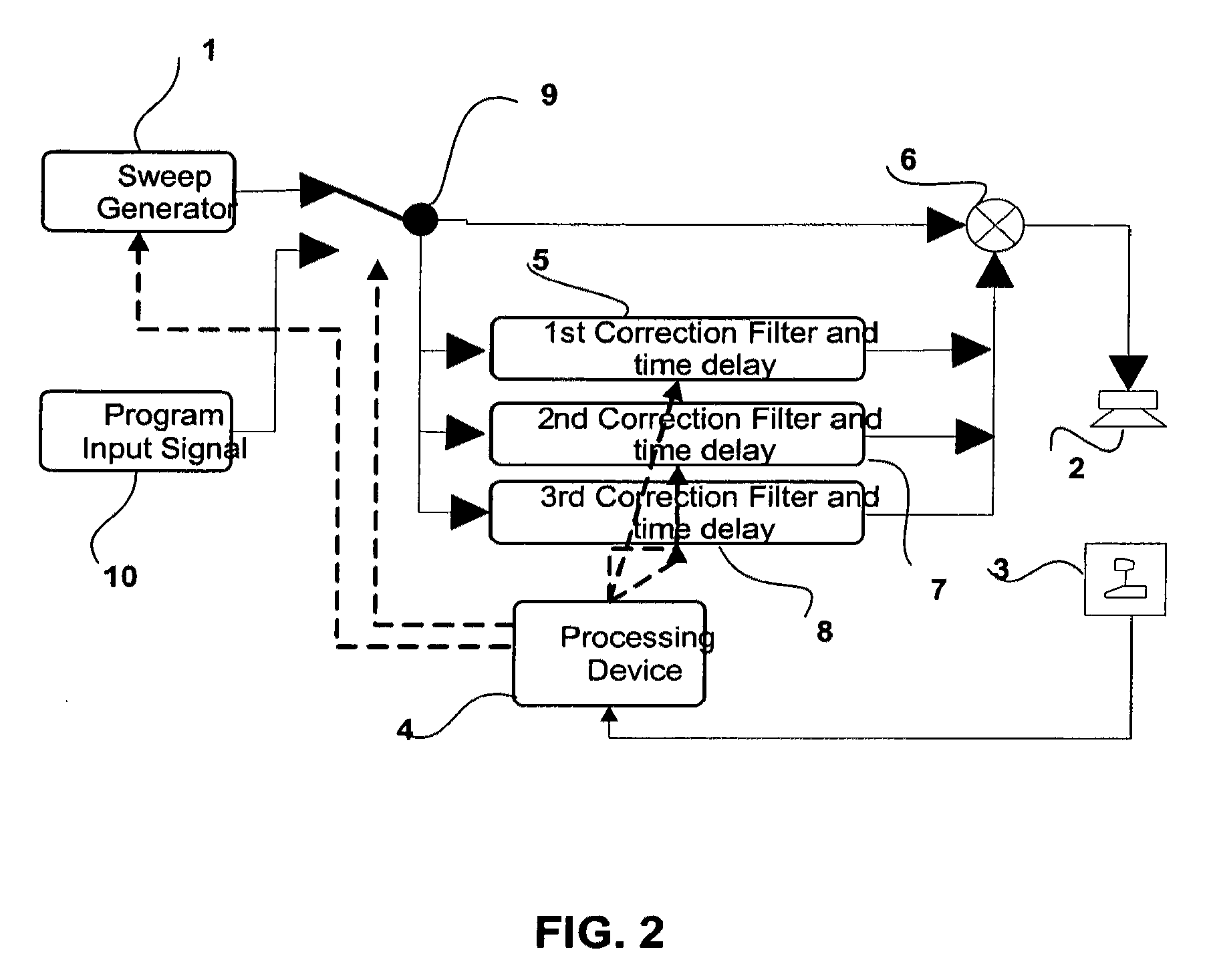
A sound compensation system alters an electrical audio signal for input to a sonic reproduction device having associated behavioral characteristics. The behavior characteristics of the device are defined by individual or groups of individual components of the sonic reproduction device and include mechanical, acoustic and electromagnetic behaviors. The model includes a plurality of filters that simulate at least one of the behavior characteristics of the sonic reproduction device. The filters are defined by digital signal processes or by analog circuits and are characterized by one or more of an associated frequency, time, phase and transient response. These responses combine to define an overall response for the model. The filters include adjustable parameters which are used to alter filter responses to produce responses that are conjugates to the responses of the unaltered filters and thus the sonic reproduction device. A controller modifies the parameters.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
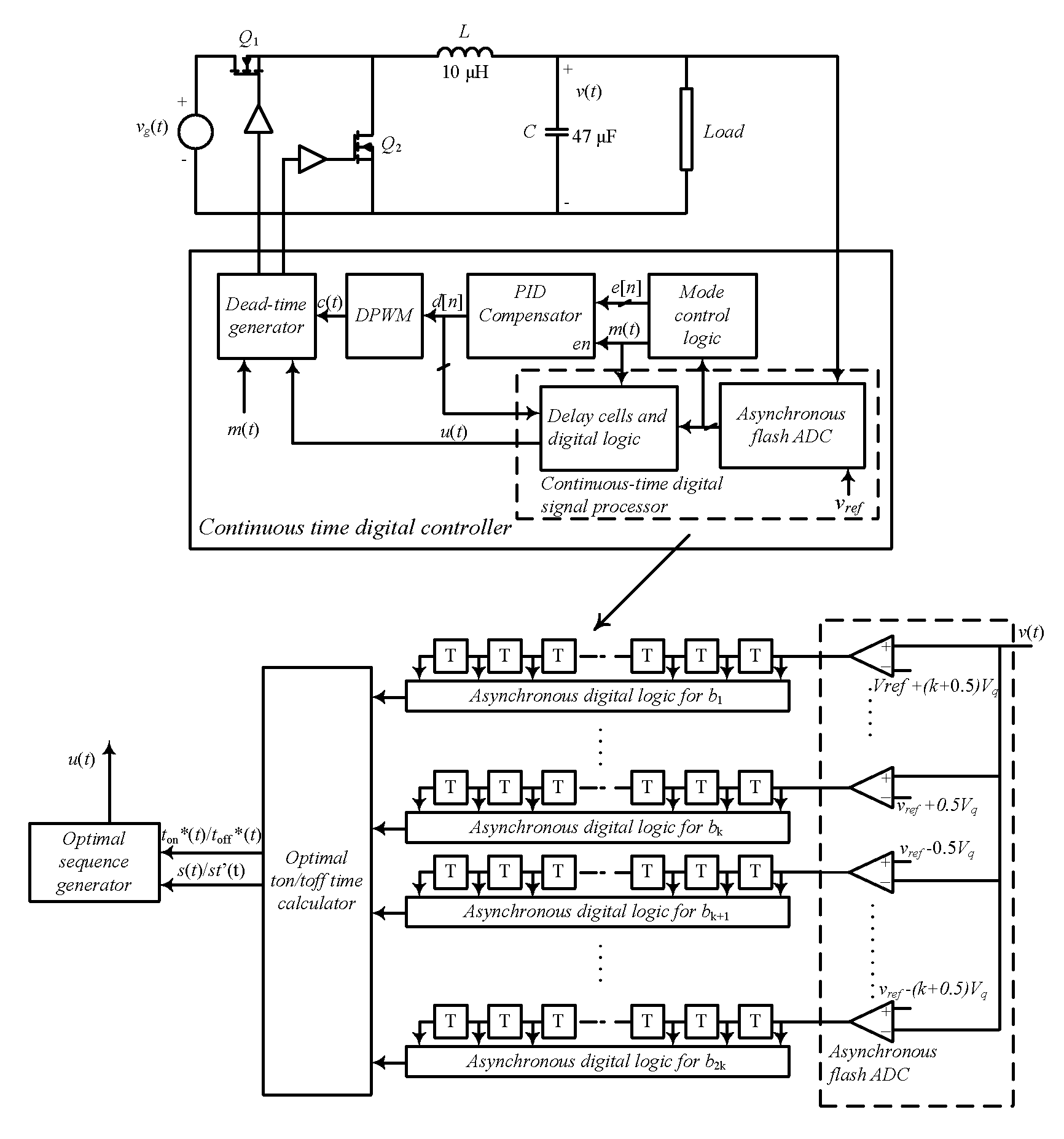
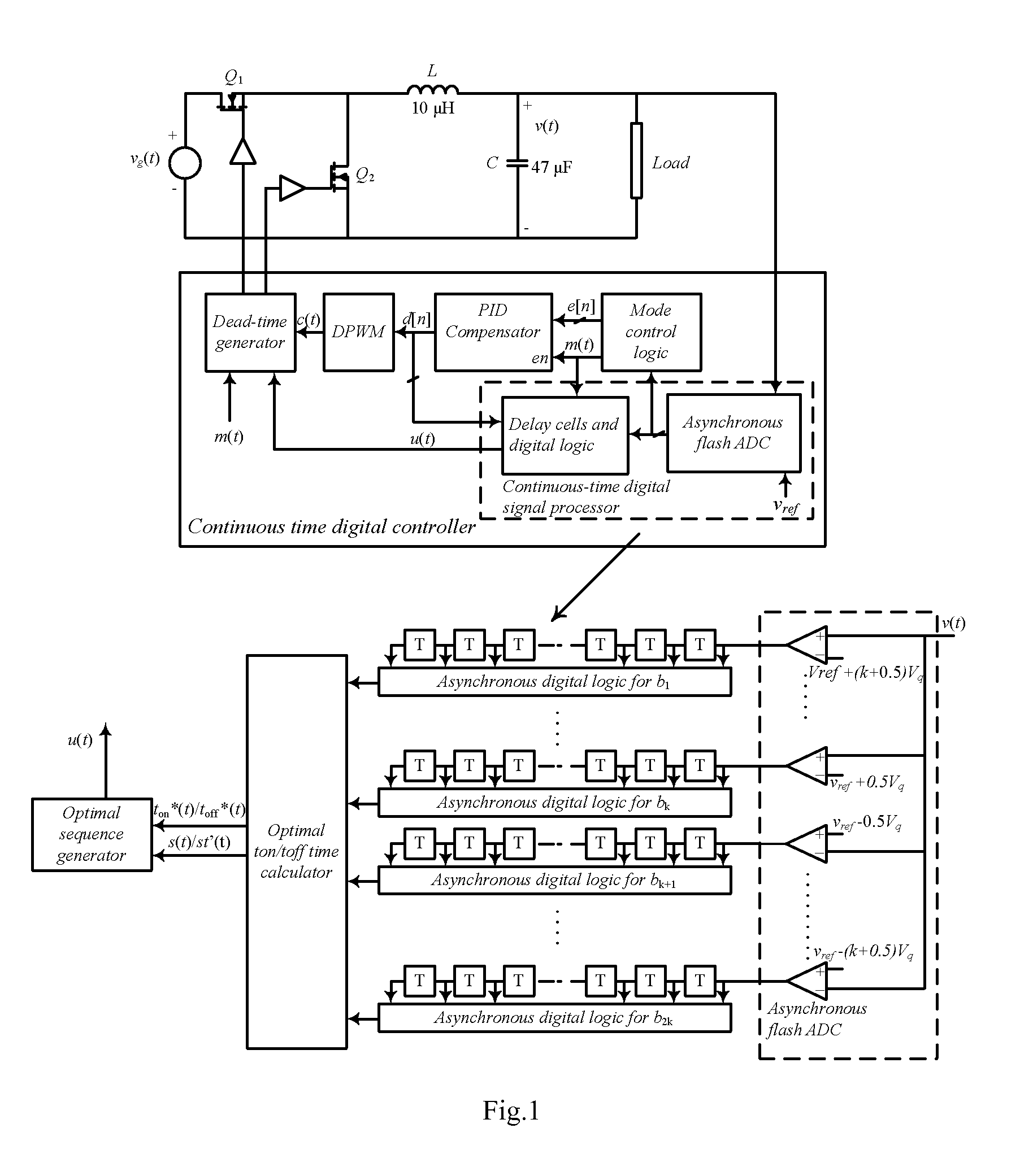
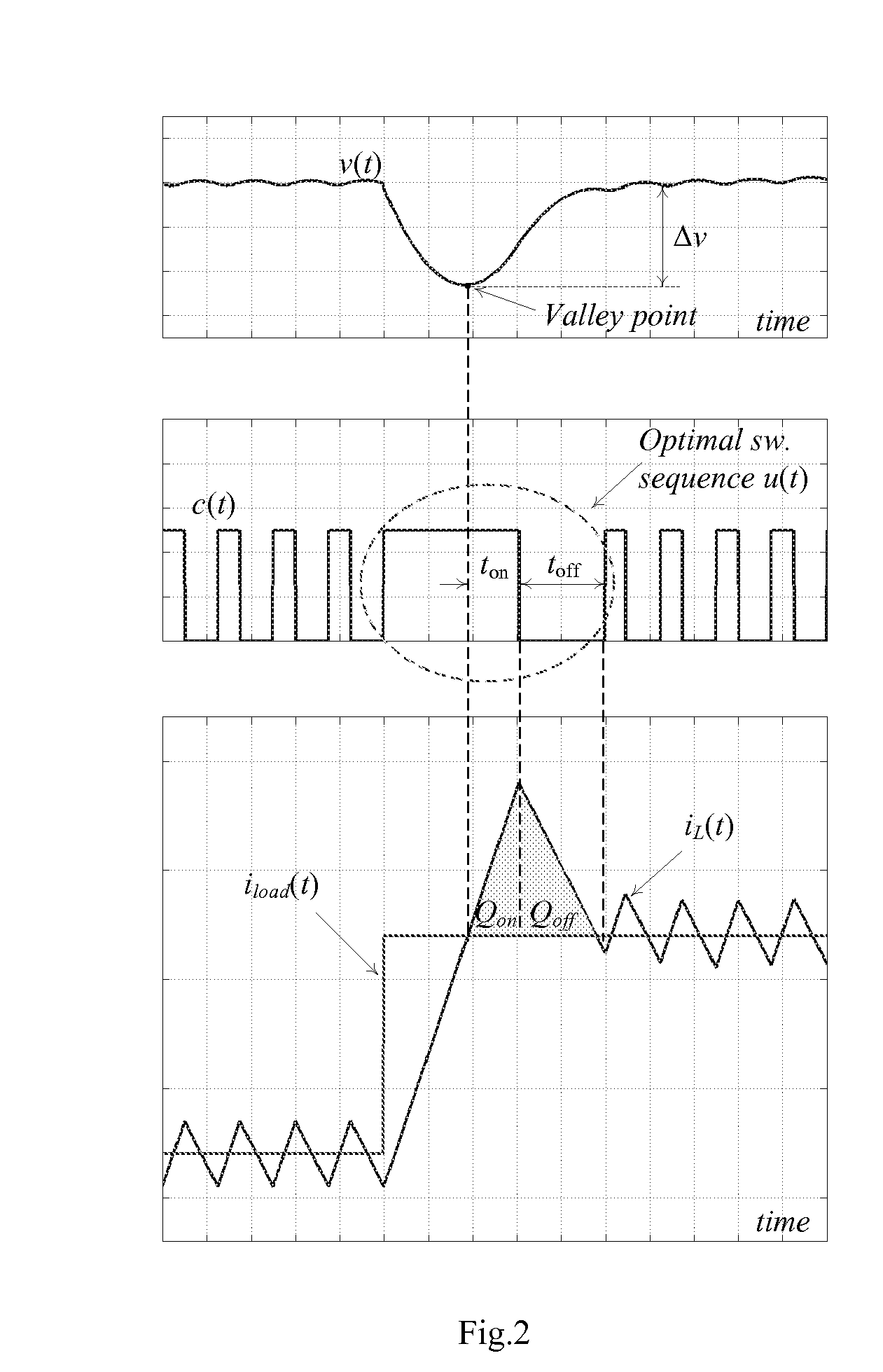
Continuous-time digital controller for high-frequency dc-dc converters
InactiveUS20080252280A1Analogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsMode controlEngineering
The present invention is a voltage mode digital controller for low-power high-frequency dc-dc converters that has recovery time approaching physical limitations of a given power stage. It consists of a digital controller with load transient response approaching physical limitations of a given power stage that is suitable for low-power SMPS. In one aspect the invention is a method of utilizing a continuous-time digital signal processor (CT-DSP) for regulation of the operation of switch-mode power supplies. A CT-DSP can be used to instantaneously detect changes of voltage or current during transition periods and immediately perform control action that results in the fastest possible response. The invention may include current program mode controllers for SMPS where the input current is sensed as well as power factor correction rectifiers (PFC), where often input voltage, input current and output voltage are sensed. Upon sensing a deviation in the input voltage the CT-DSP is utilized to apply a switch-mode power operation whereby the controller switches between continuous-time and digital function.
Owner:PRODIC ALEKSANDAR +1
DC to DC converter with high frequency zigzag transformer
ActiveUS7170268B2Total current dropEasy to controlDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationPhase shiftedSwitching frequency
A DC to DC converter including a zigzag transformer. The transformer operates at high frequency with integrated magnetics and does not provide isolation. The multiphase converter has gate inputs with PWM signals appropriately phase-shifted depending on the number of phases to make balanced phase voltages across the transformer windings. The switching frequency of the converter is relatively low but fast transient response can be achieved by adding an integrated zigzag transformer.
Owner:LITE ON TECH CORP
Control circuit and method for a constant on-time PWM switching converter
ActiveUS20080030181A1Reduce switching lossesImprove efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionControl signalSwitching frequency
A control circuit provides a control signal for a constant on-time PWM switching converter to produce an output voltage, such that the converter operates with a constant on-time at a first state and operates with a variable on-time at a second state, so as to decrease the switching frequency and thereby the switching loss, to increase the efficiency of the converter, to improve the transient response, and to reduce the recovery time of the output voltage.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
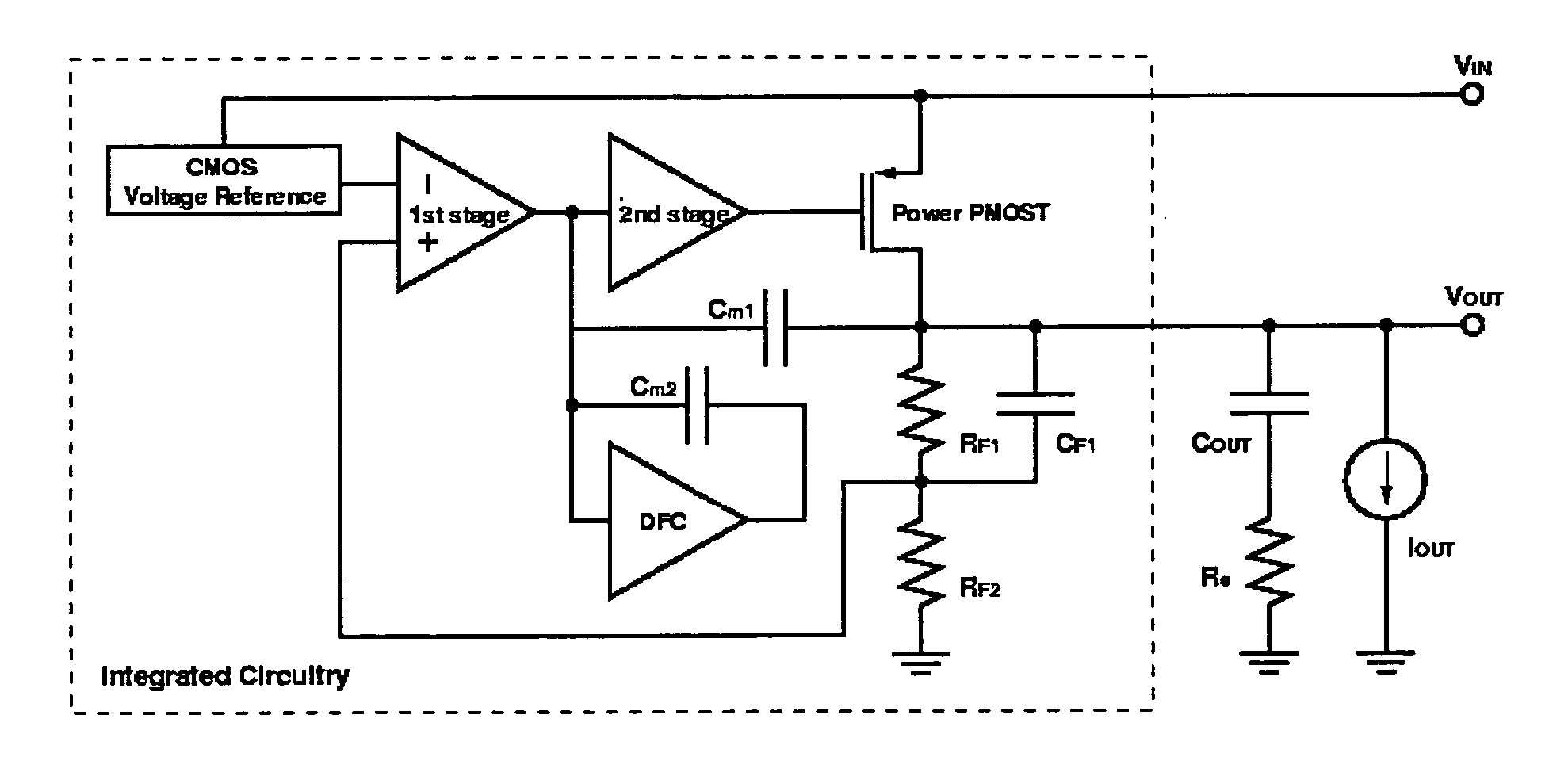
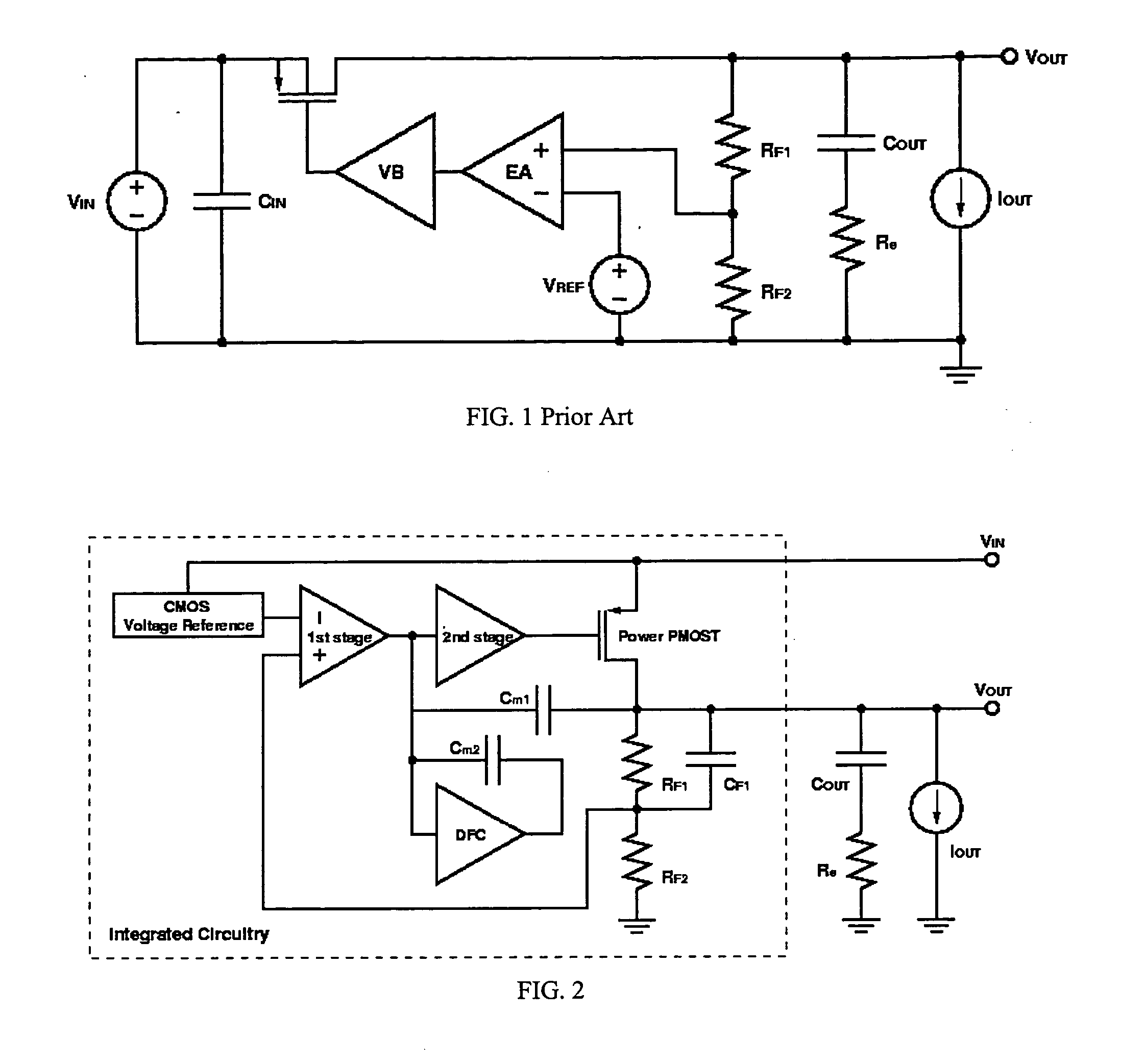
Low dropout regulator capable of on-chip implementation
A low-dropout regulator comprises a high-gain error amplifier having a differential input stage and a single-ended output, a high-swing high-positive-gain second stage with input connecting to the output of the error amplifier and a single-ended output, a p-type MOS transistor with gate terminal connecting to the output of the second stage, source terminal connecting to the supply voltage, and drain terminal to the output of the low-dropout regulator. A first-order high-pass feedback network connects the output of the low-dropout regulator and the positive input of the error amplifier, and a damping-factor-control means comprising a negative gain stage with a feedback capacitor connects the input and output of this gain stage. A capacitor is connected between the output of the error amplifier and the output of the low-dropout regulator, while a voltage reference connects to the negative input of the error amplifier. The regulator does not require an off-chip capacitor for stability and has improved load transient response and power supply rejection ratio.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
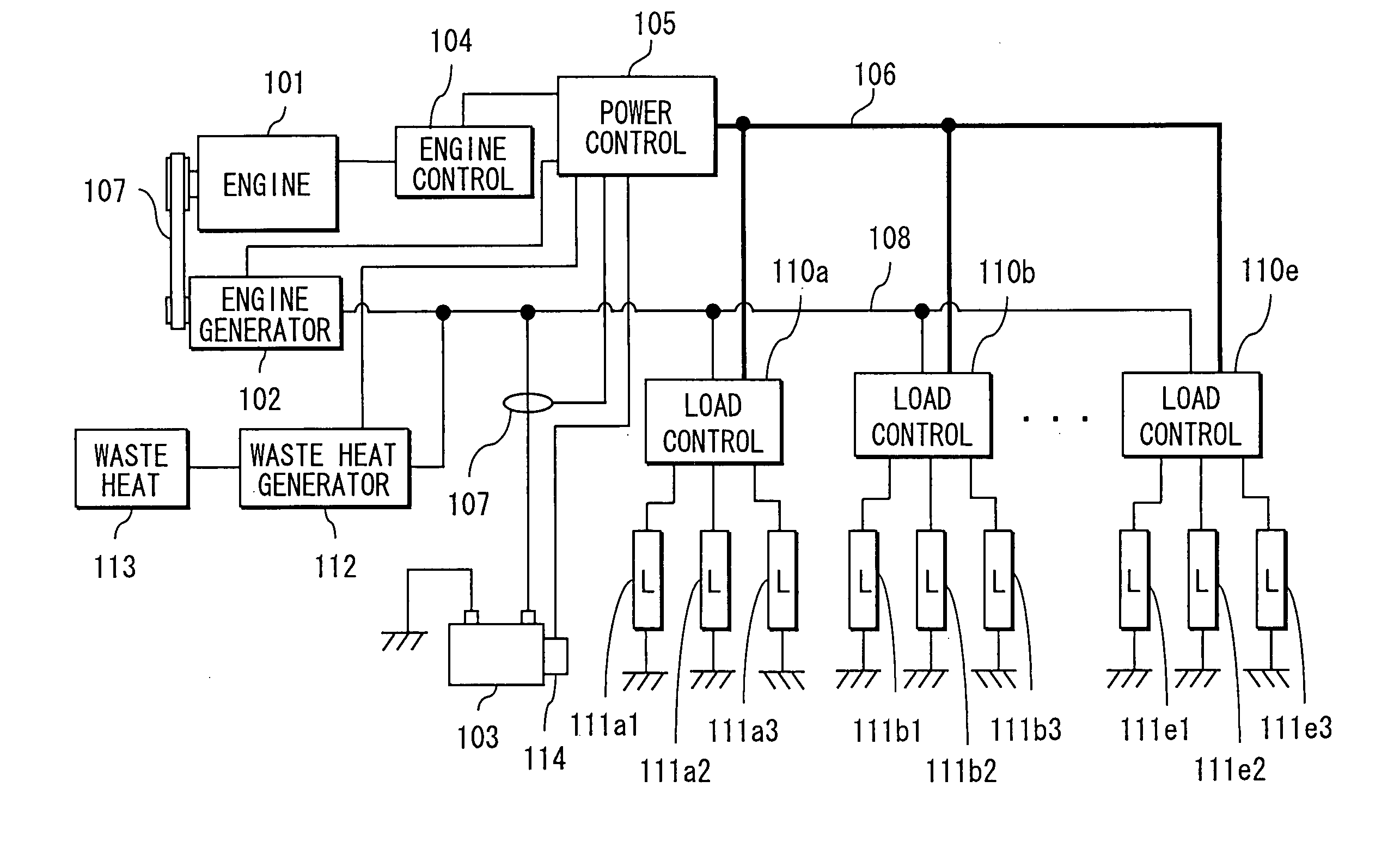
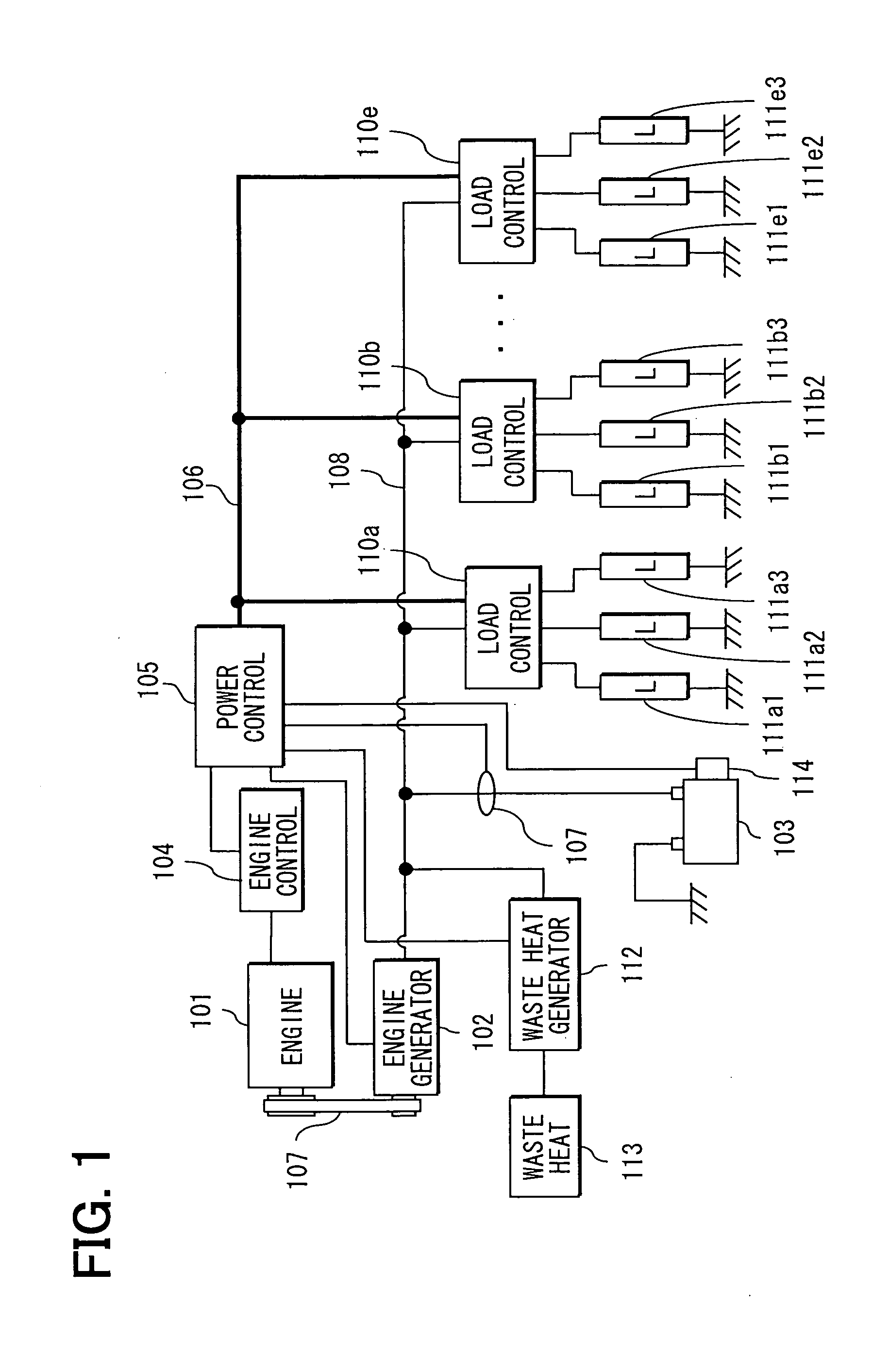
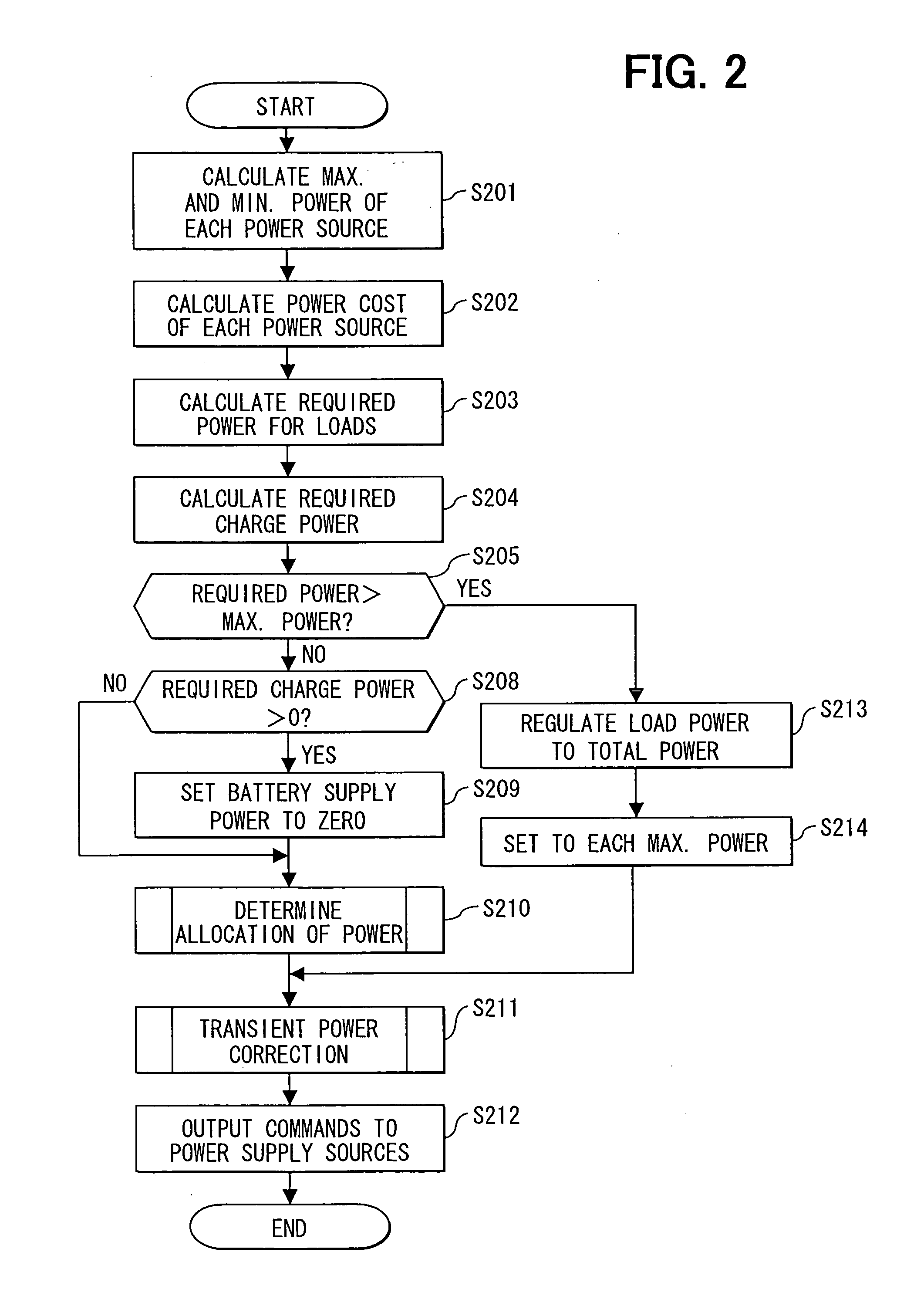
Power control apparatus and method for electrical system of vehicle
ActiveUS20060122737A1Increase fuel consumptionMinimize powerBatteries circuit arrangementsLevel controlEngineeringElectric power
A power control apparatus acquires a maximum supply amount of power, transient maximum supply amount of power, and transient minimum supply amount of power of each power supply source. The apparatus further acquires a power cost of respective power supply sources, a load-required power and a charge request power. The apparatus acquires a combination of power supply sources that minimizes specific fuel consumption and determines an allocation amount of power. Taking transient response of respective power supply sources into account, the allocation amount of power of each power supply sources is corrected to be greater than a transient minimum supply power and smaller than a transient maximum supply power.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Pulsed eddy current method for detection of corrosion in multilayer structures using the lift-off point of intersection
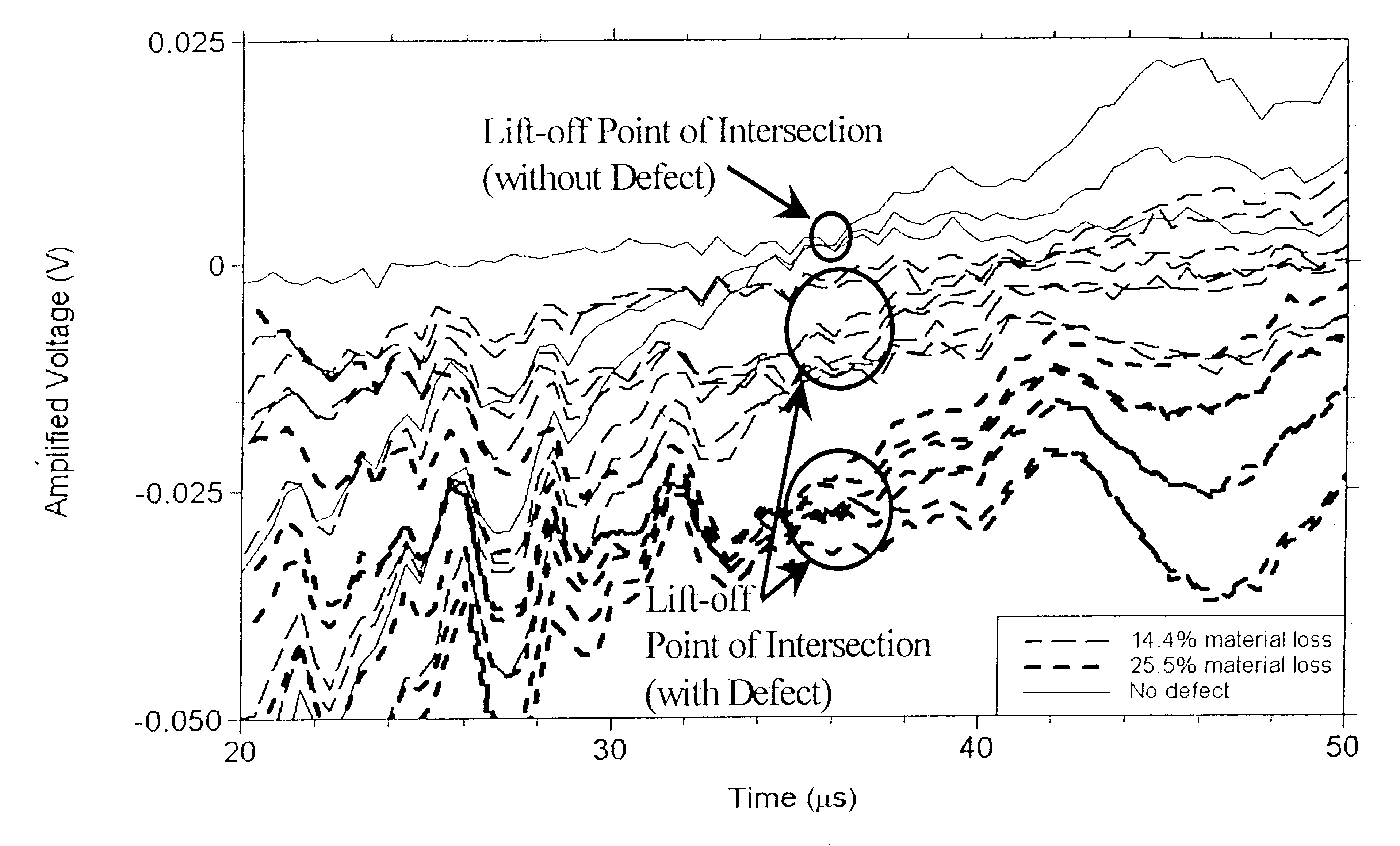
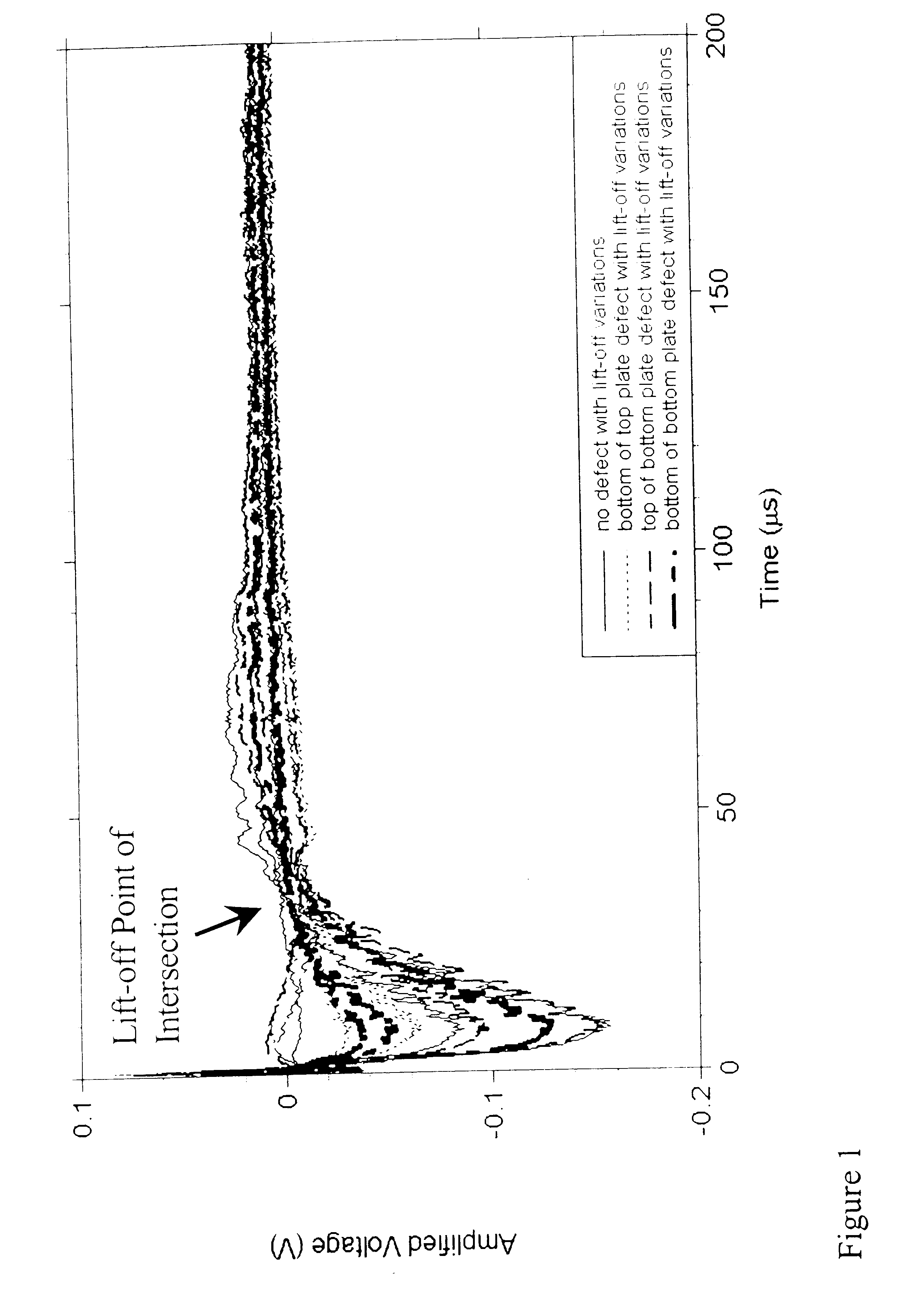
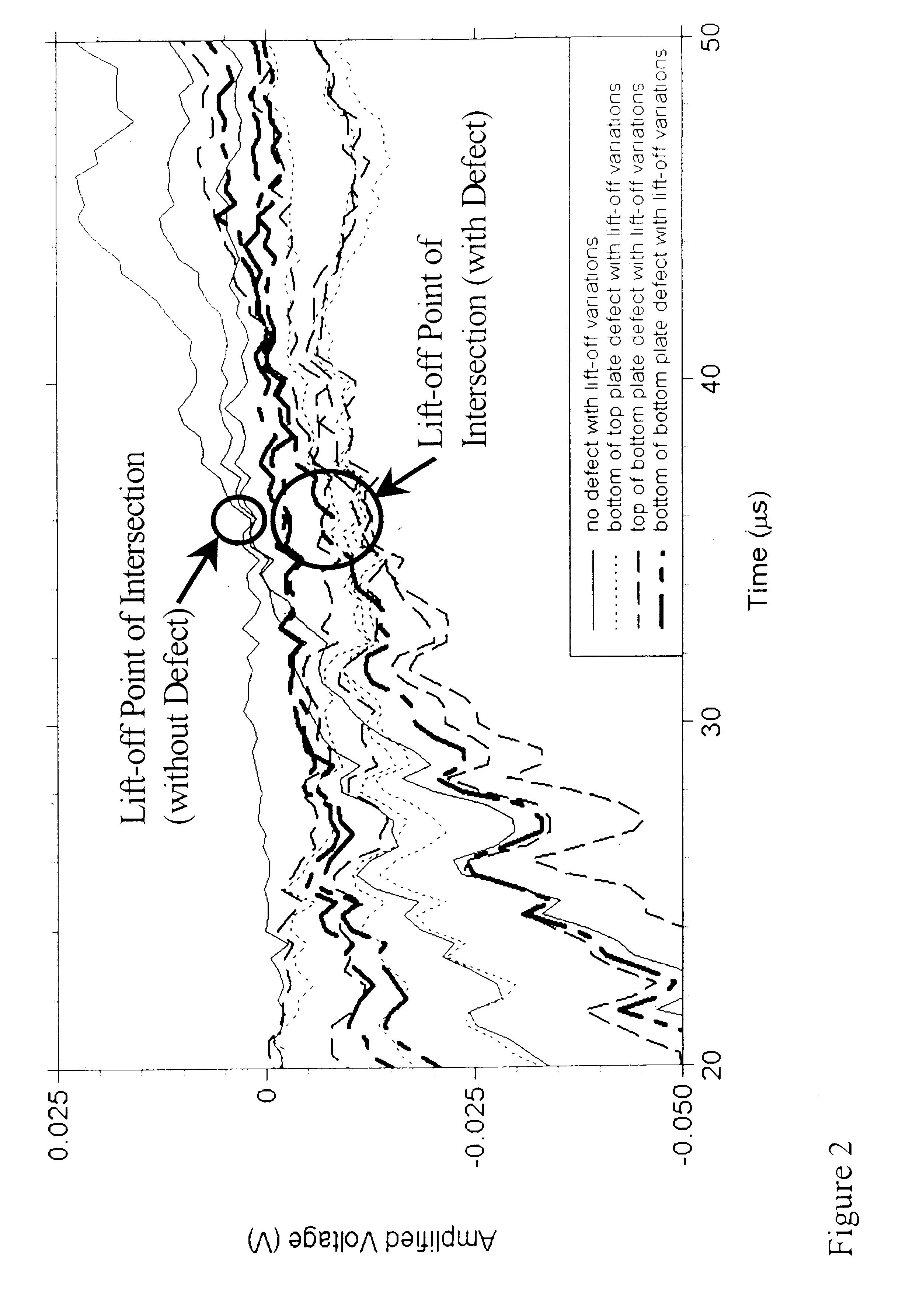
A method for the detection and the characterization of corrosion in multi-layer metallic structures using a pulsed eddy current technique. For this technique, a coil (or coils) is used both as field source (driven by a square wave voltage-controlled excitation), and / or as field sensor (measuring a transient response). The field sensor allows the capture of information about the condition of the area of the structure under inspection. The ability of this technique to detect corrosion hinges on the use of a transient response feature (i.e., Lift-off Point of Intersection) to infer the presence of material loss. With the help of a calibration standard, the Lift-off Point of Intersection provides the ability to quantify material loss in multi-layered structures. The results obtained with this method are independent of lift-off variations inherent to field inspections (i.e., changes in distance between the transducer and test object).
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN AS REPRESENTED BY THE MINIST OF NAT DEFENCE OF HER MAJESTYS CANADIAN GOVERNMENT
Low dropout regulator
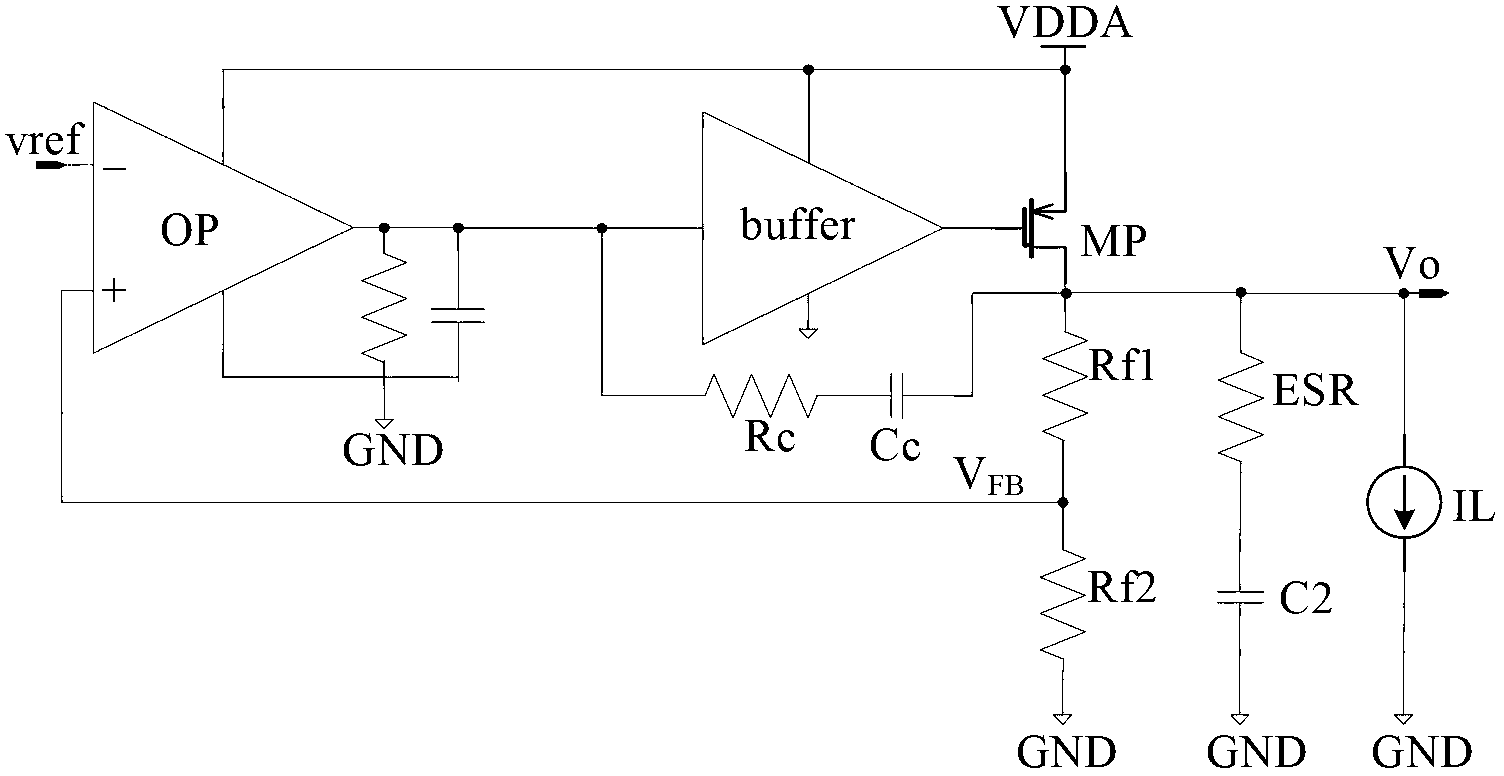
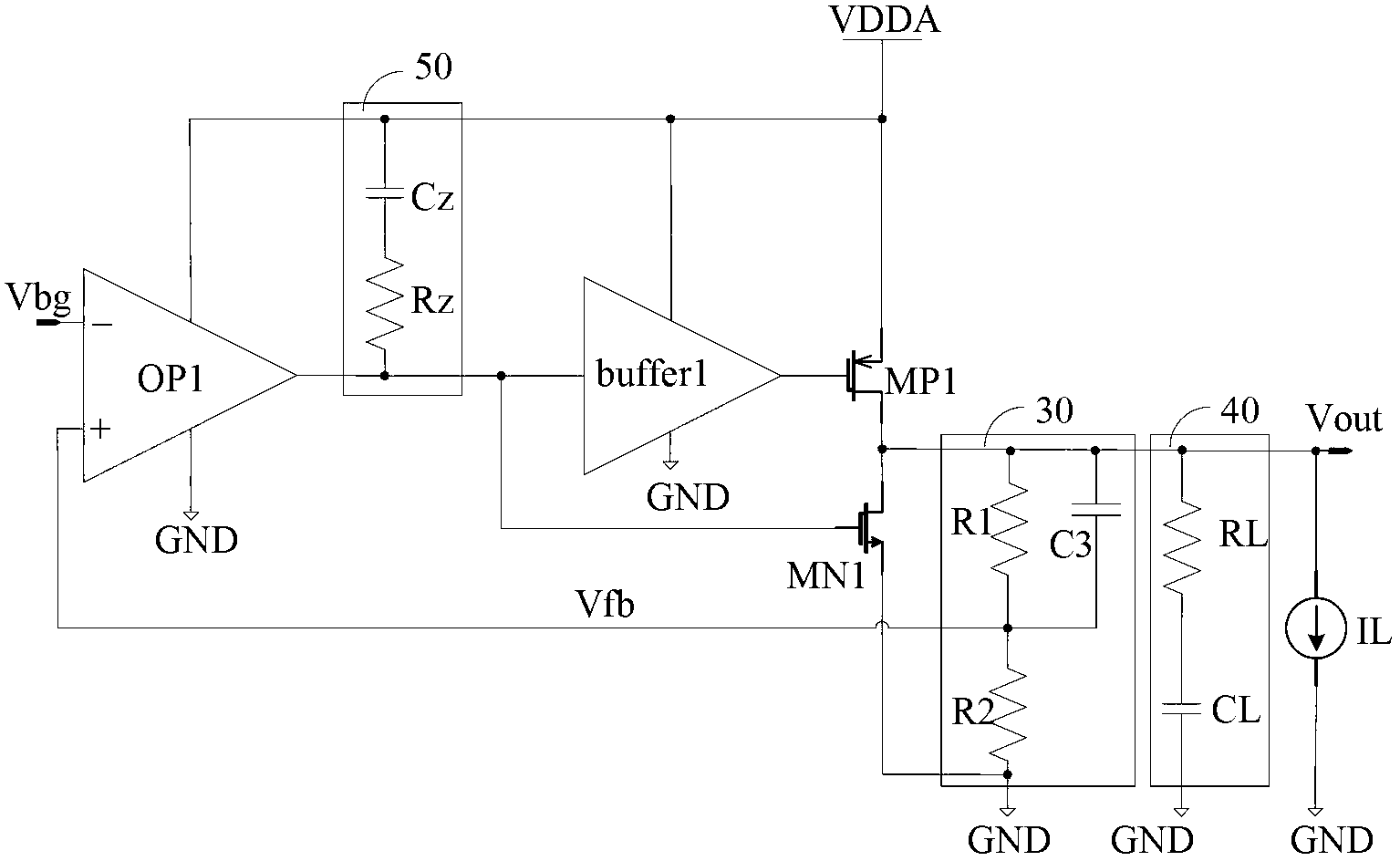
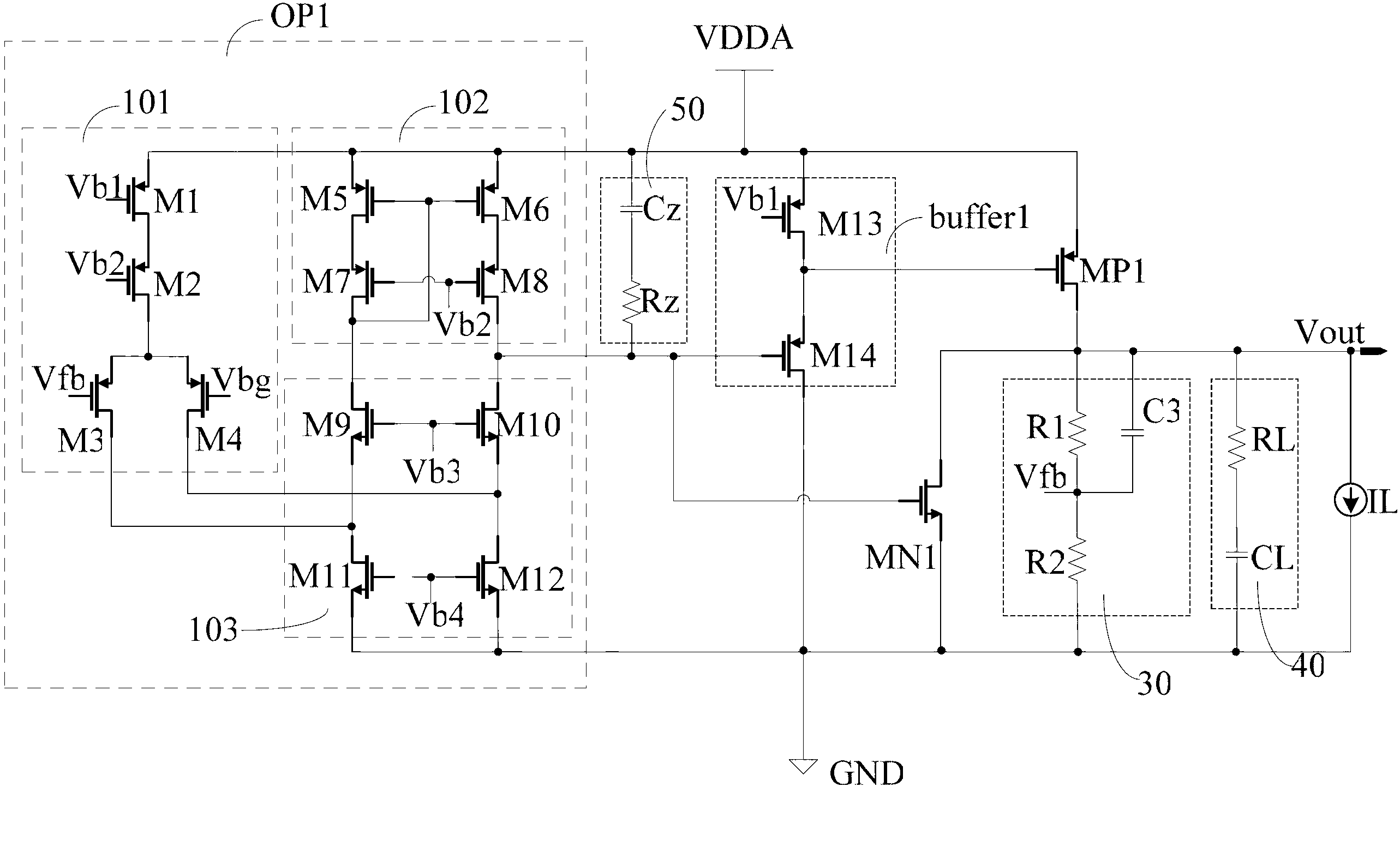
ActiveCN102707754AImprove transient response speedHigh precisionElectric variable regulationAudio power amplifierFeedback circuits
The invention discloses a low dropout regulator, which comprises an error amplifier, a buffer circuit, a P-channel metal oxide semiconductor (PMOS) regulation transistor, an N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) push-pull tube, a voltage division feedback circuit, a compensation circuit and an output circuit, wherein the gate of the PMOS regulation transistor is connected with the output end of the buffer circuit, the source of the PMOS regulation transistor is connected with power voltage, and the drain of the PMOS regulation transistor is used as the output end of the low dropout regulator; the gate of the NMOS push-pull tube is connected with the output end of the error amplifier, the drain of the NMOS push-pull tube is connected with the drain of the PMOS regulation transistor, and the source of the NMOS push-pull tube is grounded; and the error amplifier, the compensation circuit, the buffer circuit, the PMOS regulation transistor, the voltage division feedback circuit and an output circuit form a main control loop, and the error amplifier, the compensation circuit, the NMOS push-pull tube, the voltage division feedback circuit and the output circuit form an auxiliary control loop. According to the low dropout regulator, the transient response of the regulator can be quickened, and the accuracy of output voltage can be improved.
Owner:BRIGATES MICROELECTRONICS KUNSHAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com