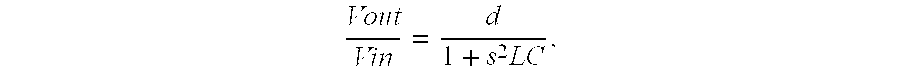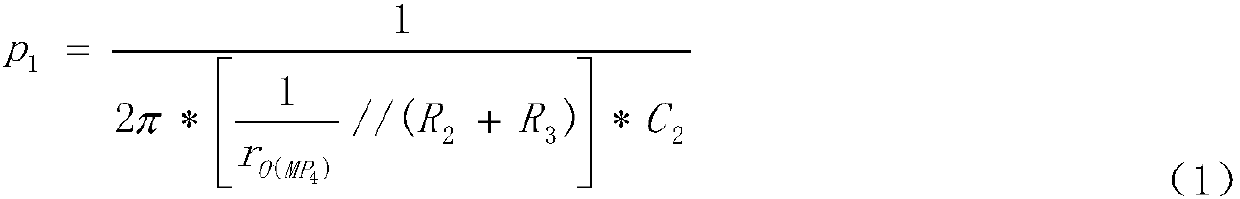Patents
Literature
581 results about "Power supply rejection ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
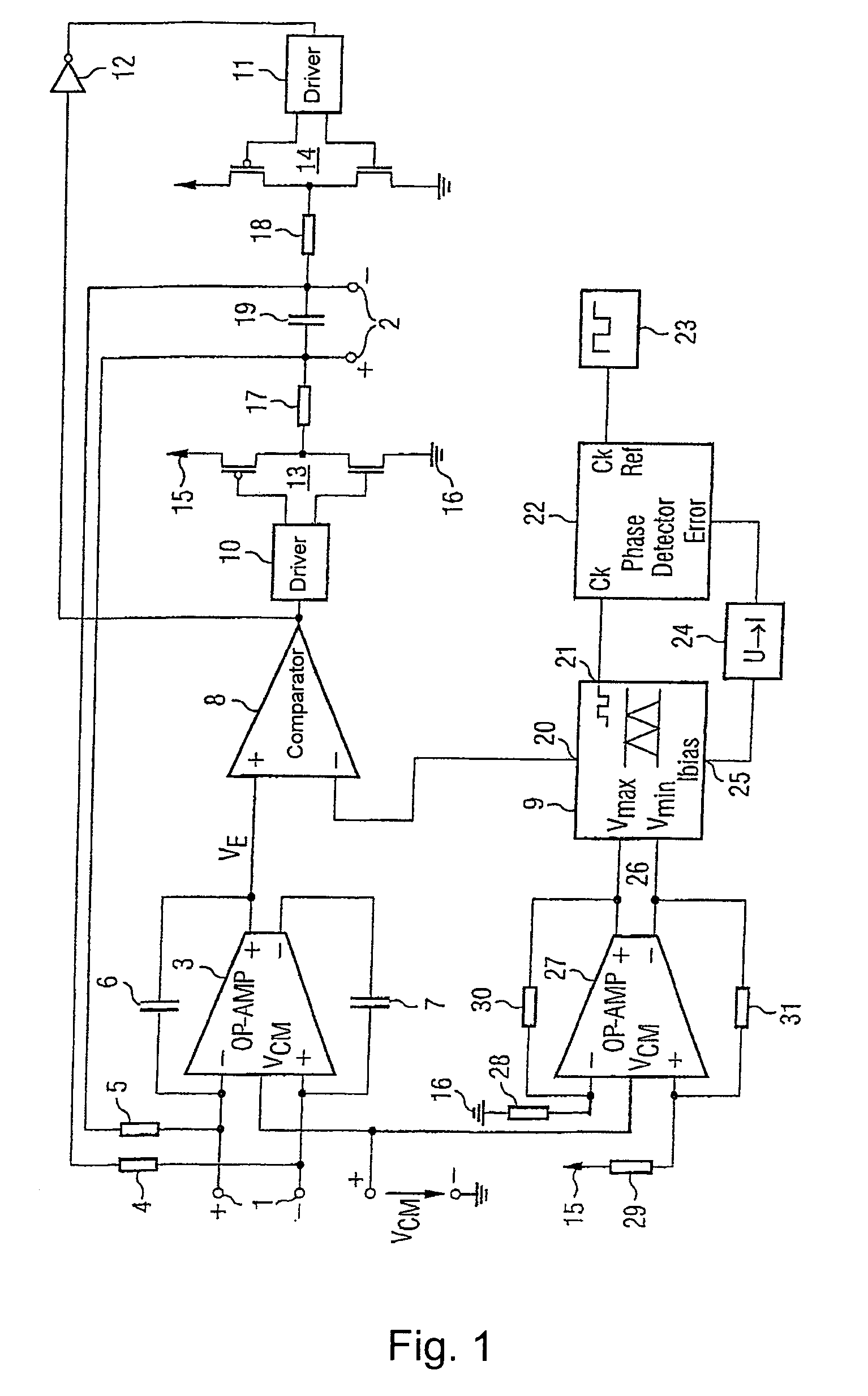
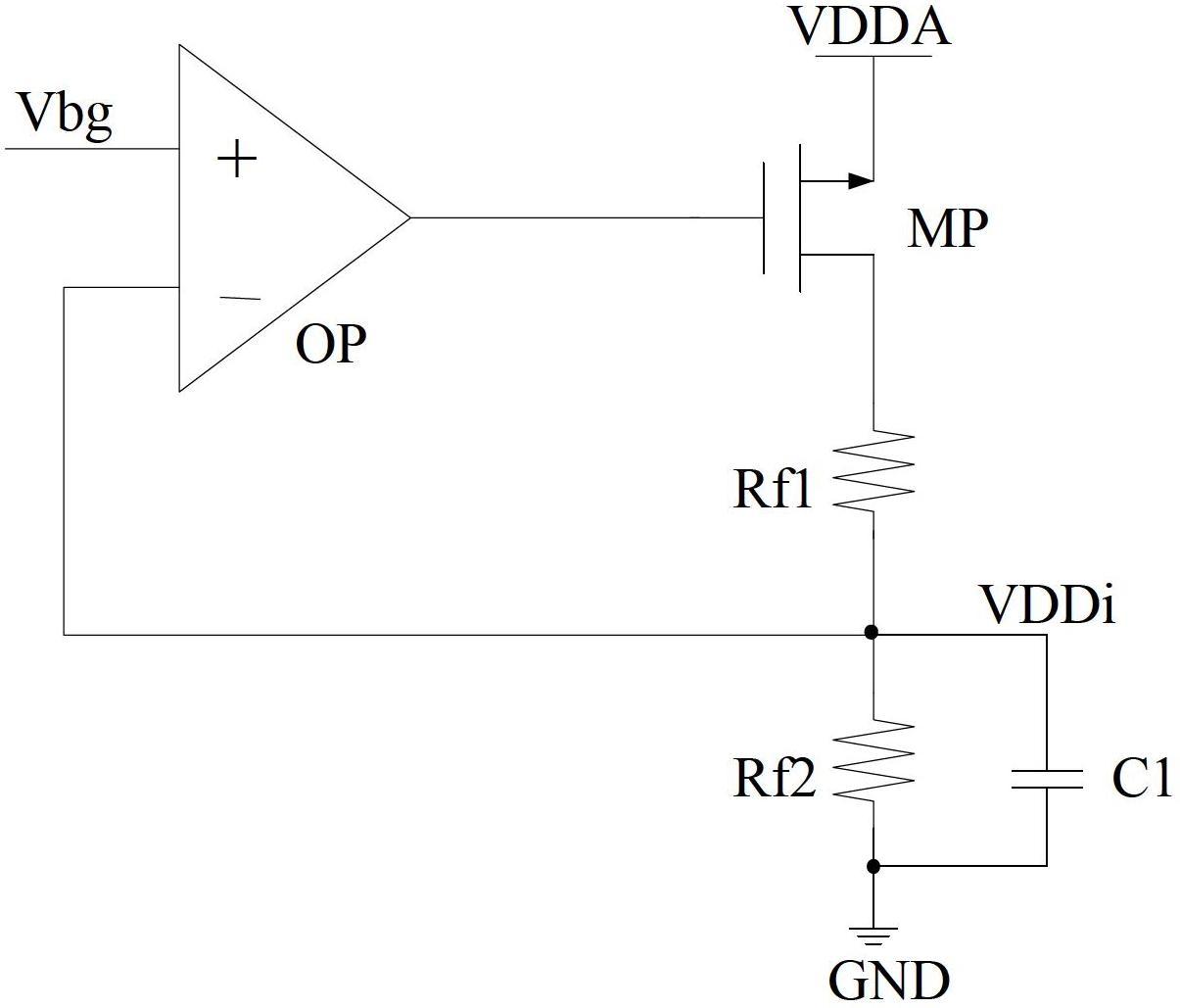
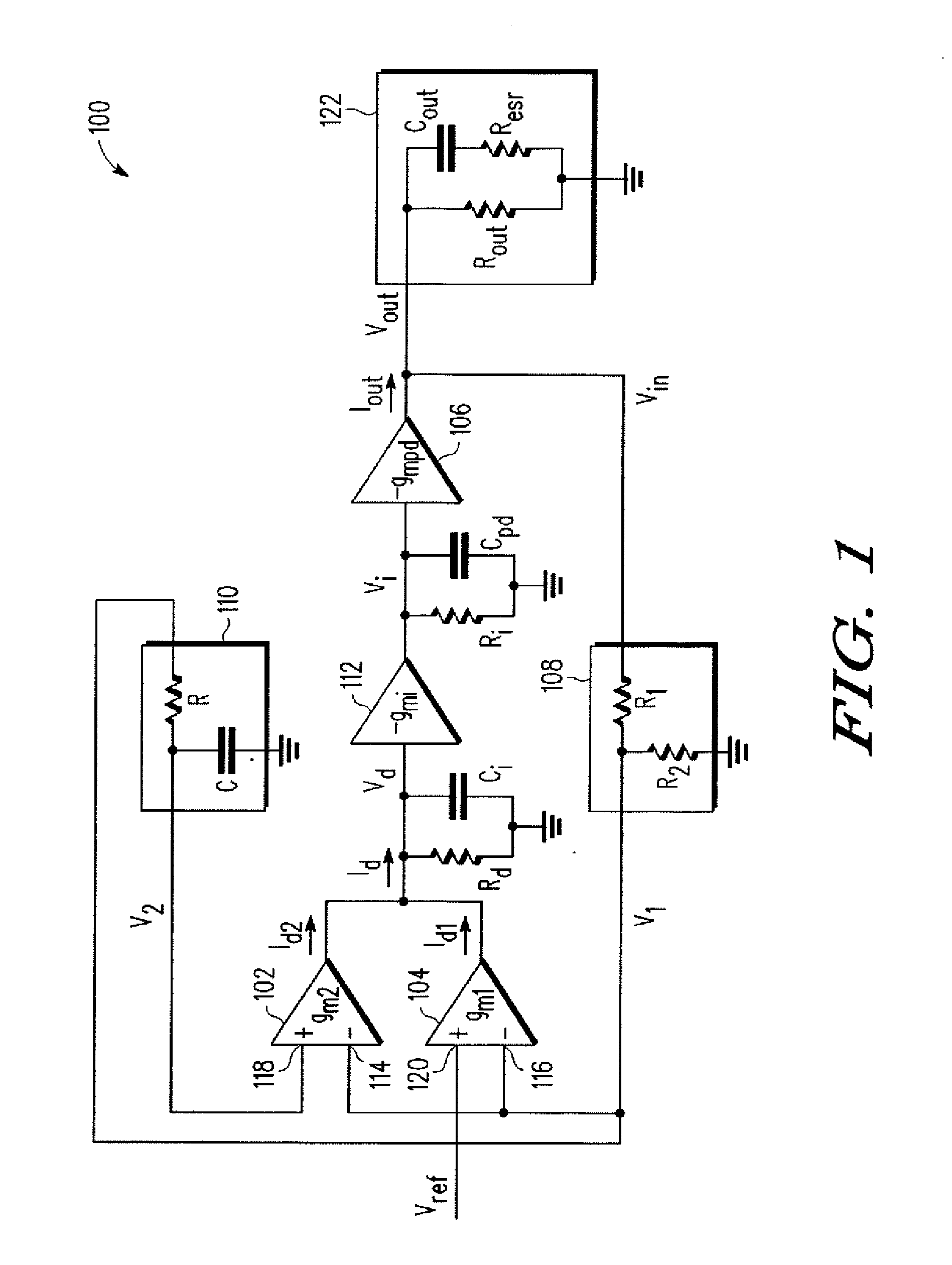
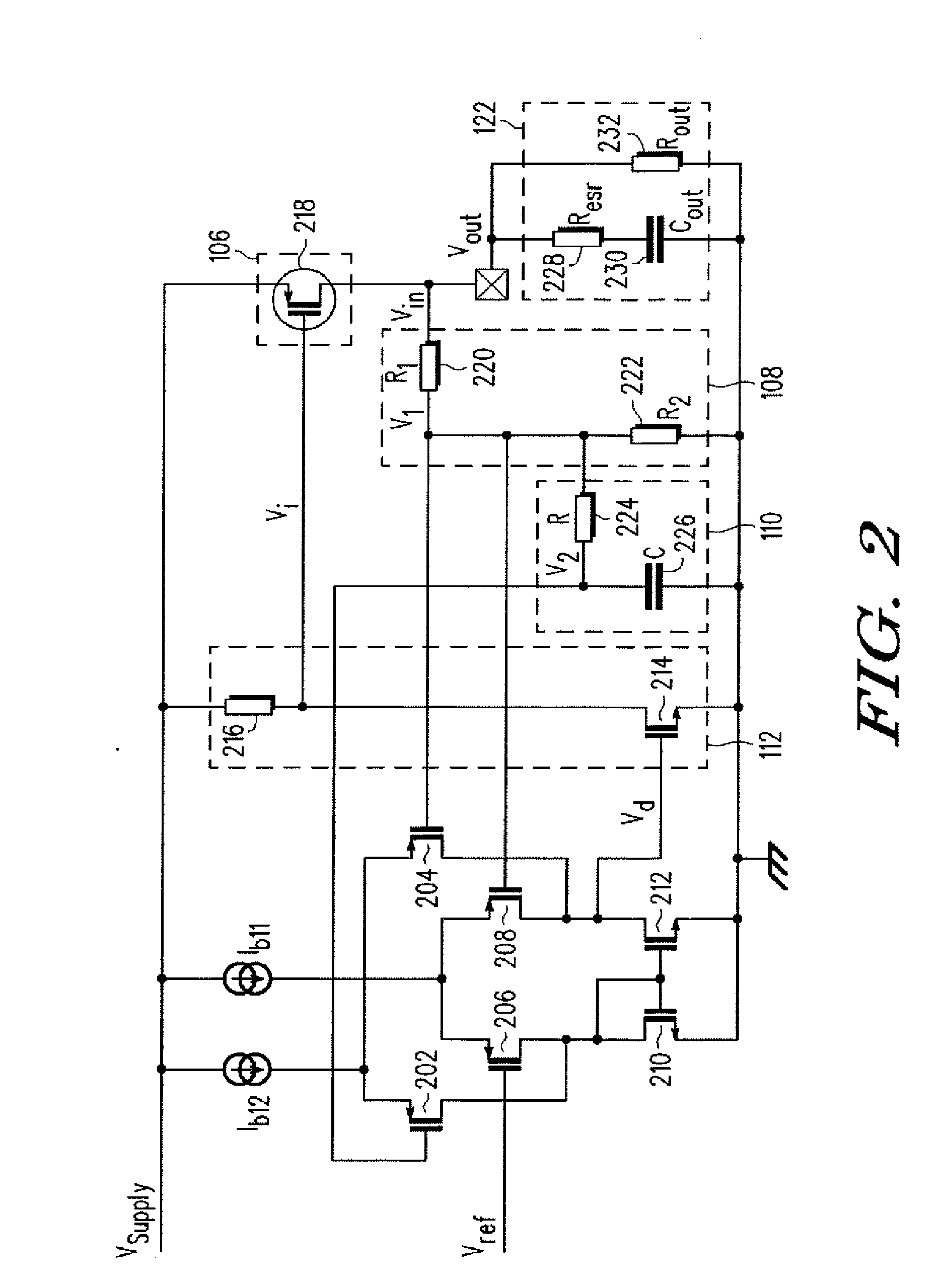
In electronic systems, power supply rejection ratio (PSRR), also supply-voltage rejection ratio (kSVR; SVR), is a term widely used to describe the capability of an electronic circuit to suppress any power supply variations to its output signal. In the specifications of operational amplifiers, the PSRR is defined as the ratio of the change in supply voltage to the equivalent (differential) output voltage it produces, often expressed in decibels.
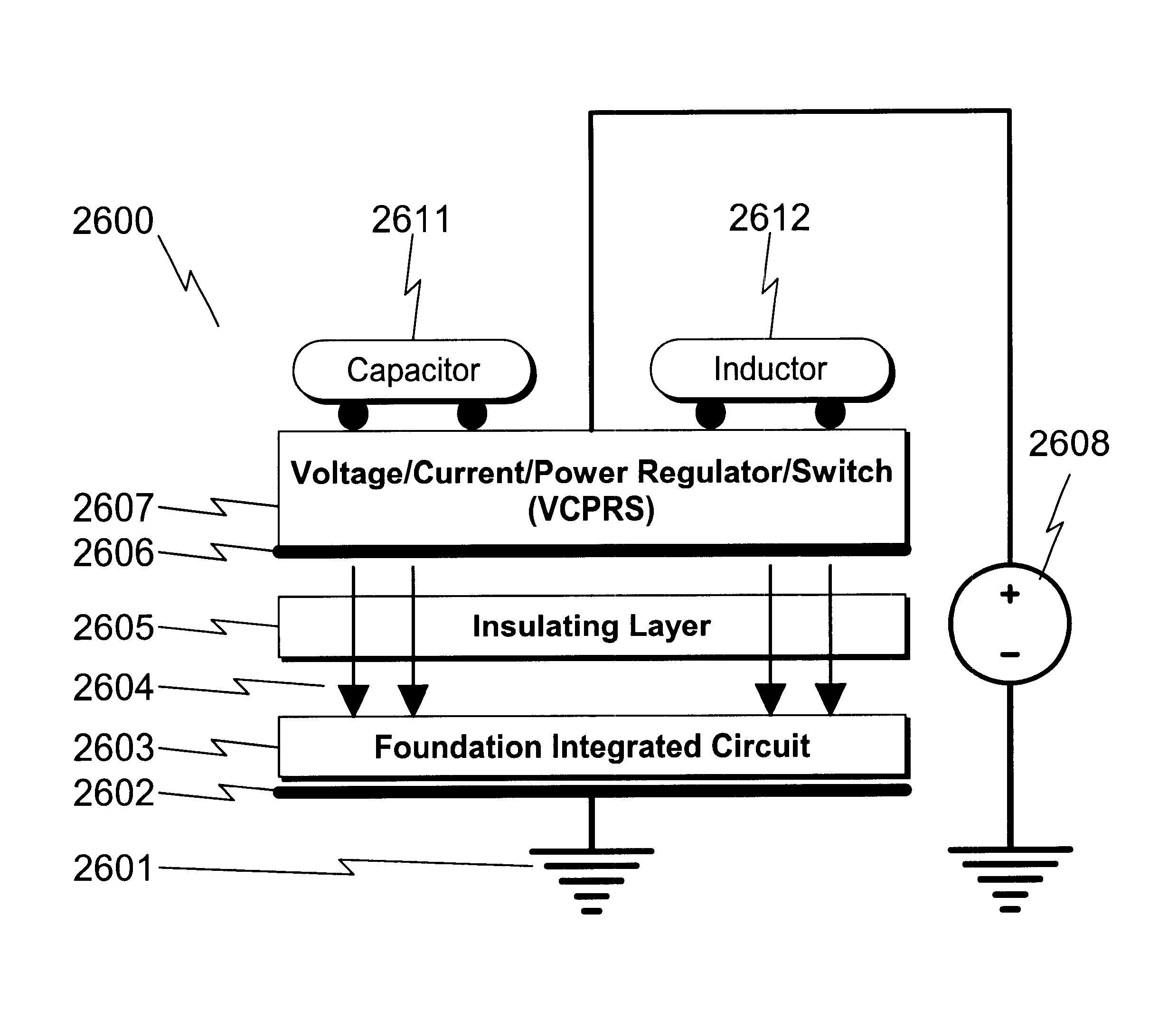
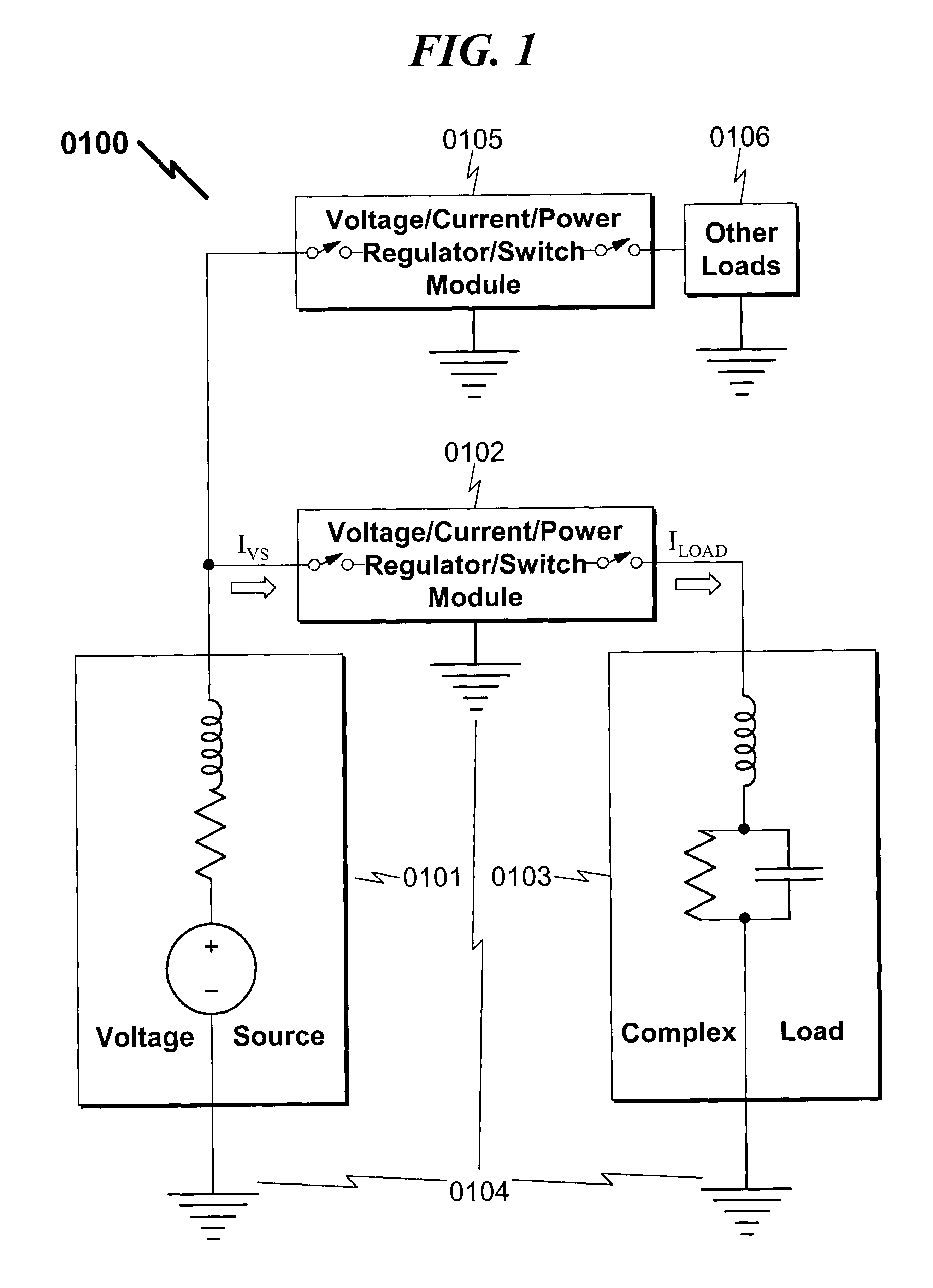
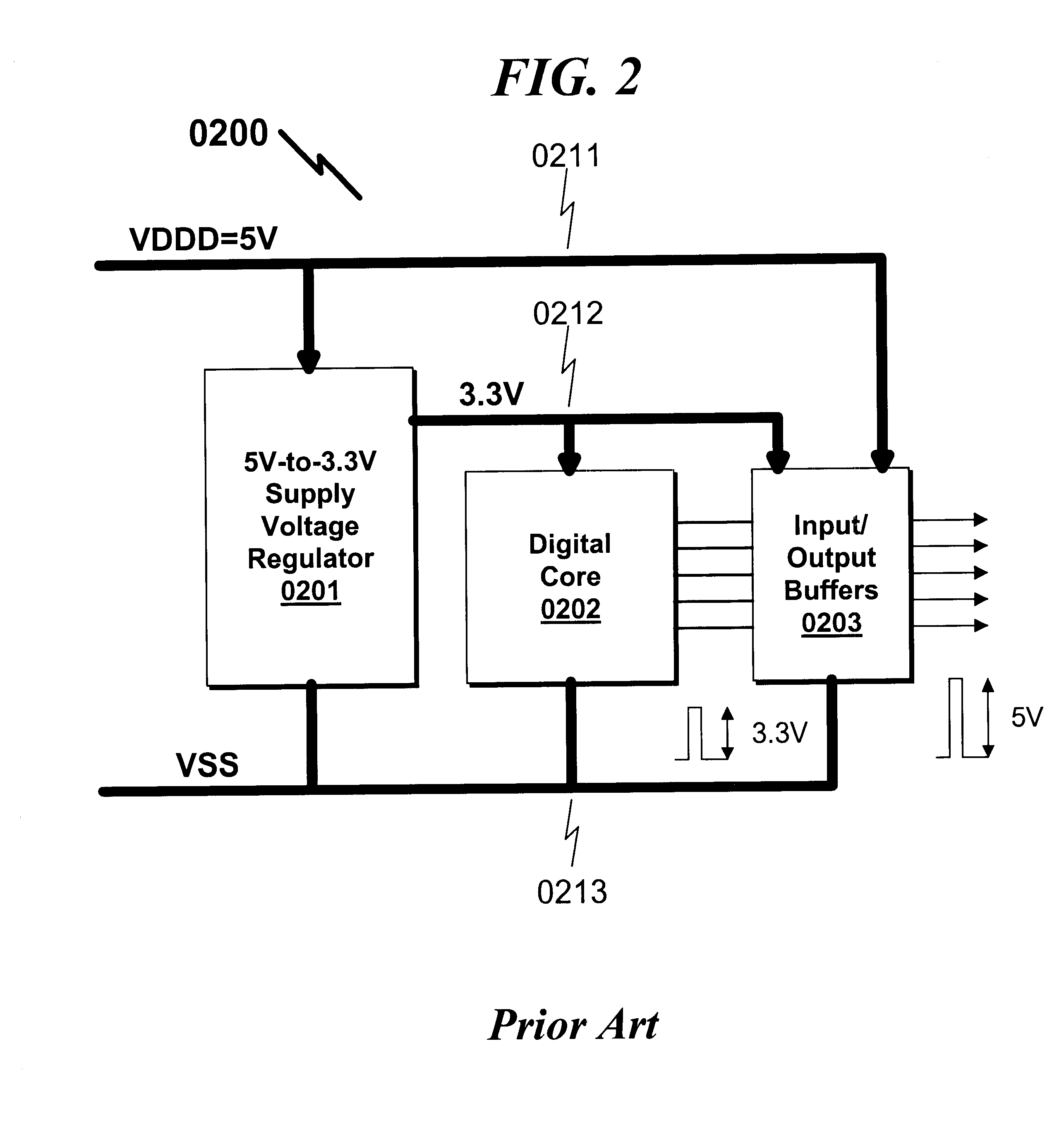
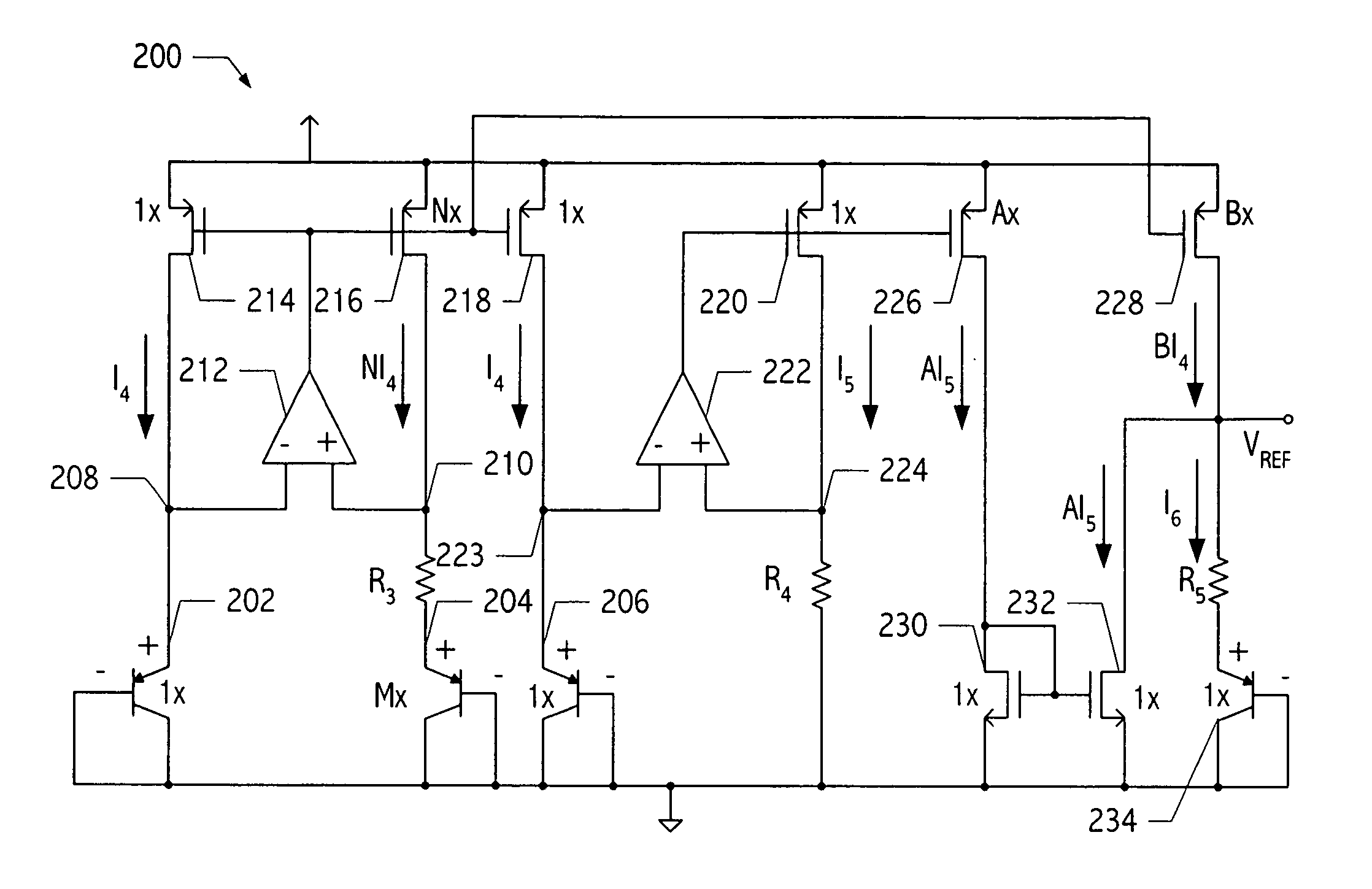
Integrated voltage/current/power regulator/switch system and method
InactiveUS6396137B1Minimal noiseGood PSRRSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDc-dc conversionPower applicationPower capability
An integrated voltage / current / power regulator / switch (VCPRS) system and method are disclosed in which regulator / switch circuitry is vertically integrated on top of an existing integrated circuit. The present invention does not require additional integrated circuit chip area for the regulator pass device as is required in the prior art, and by virtue of its construction provides a significantly reduced on-resistance as compared to all prior art implementations. The present invention both stabilizes the power supply for large area integrated circuits and permits individual areas of the integrated circuit to have switched power capability, a highly desirable feature in low power and battery power applications. The present invention permits an increase in the power supply rejection ratio (PSRR) for digital, analog, and especially mixed-signal integrated circuit designs by permitting various circuit blocks to have localized power regulation that is obtained from a common power supply plane within the integrated circuit framework. Finally, the present invention appears to be the only economically practical method of addressing the power supply regulation requirements of modern and future integrated microprocessor designs.
Owner:KLUGHART KEVIN MARK
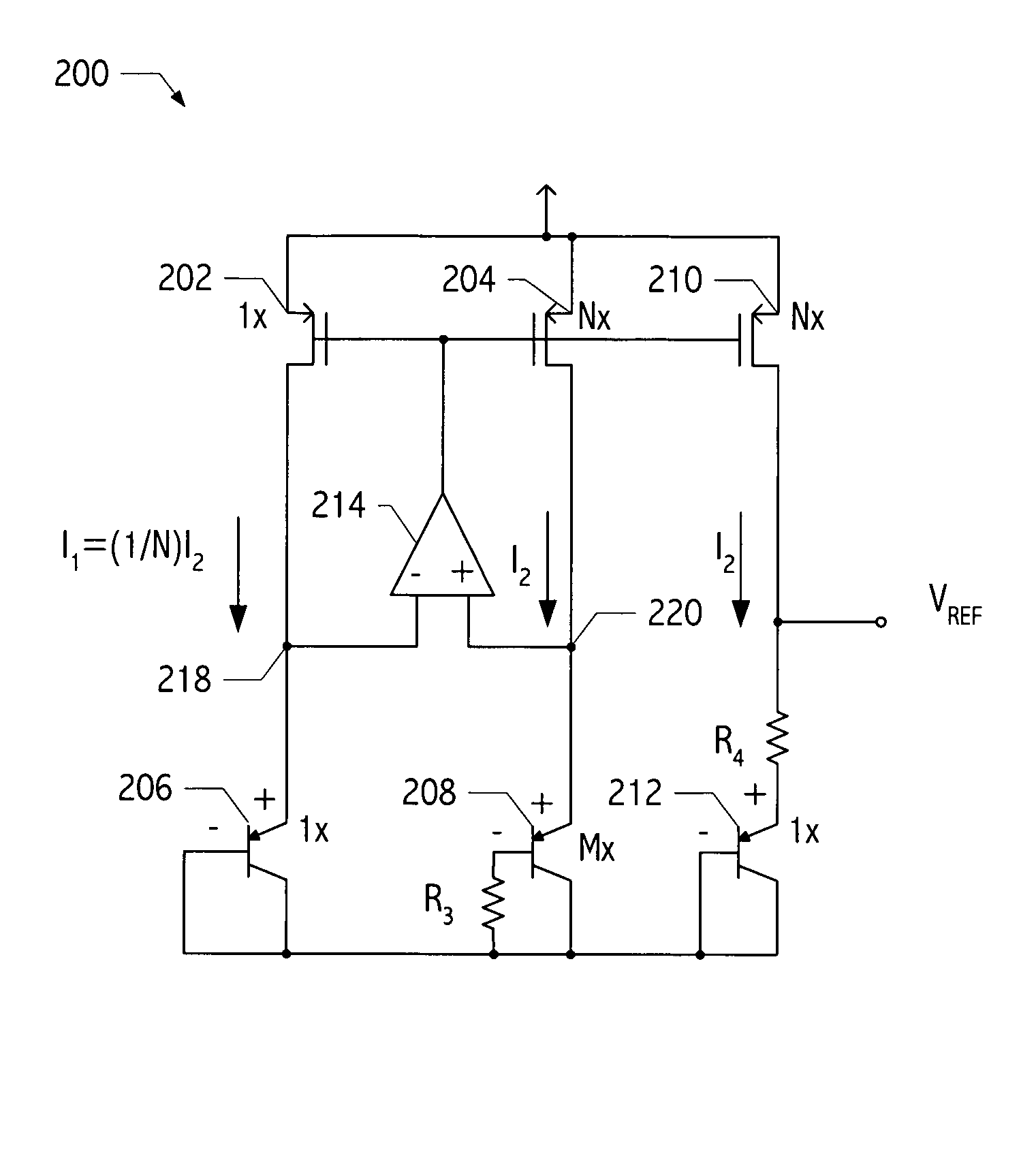
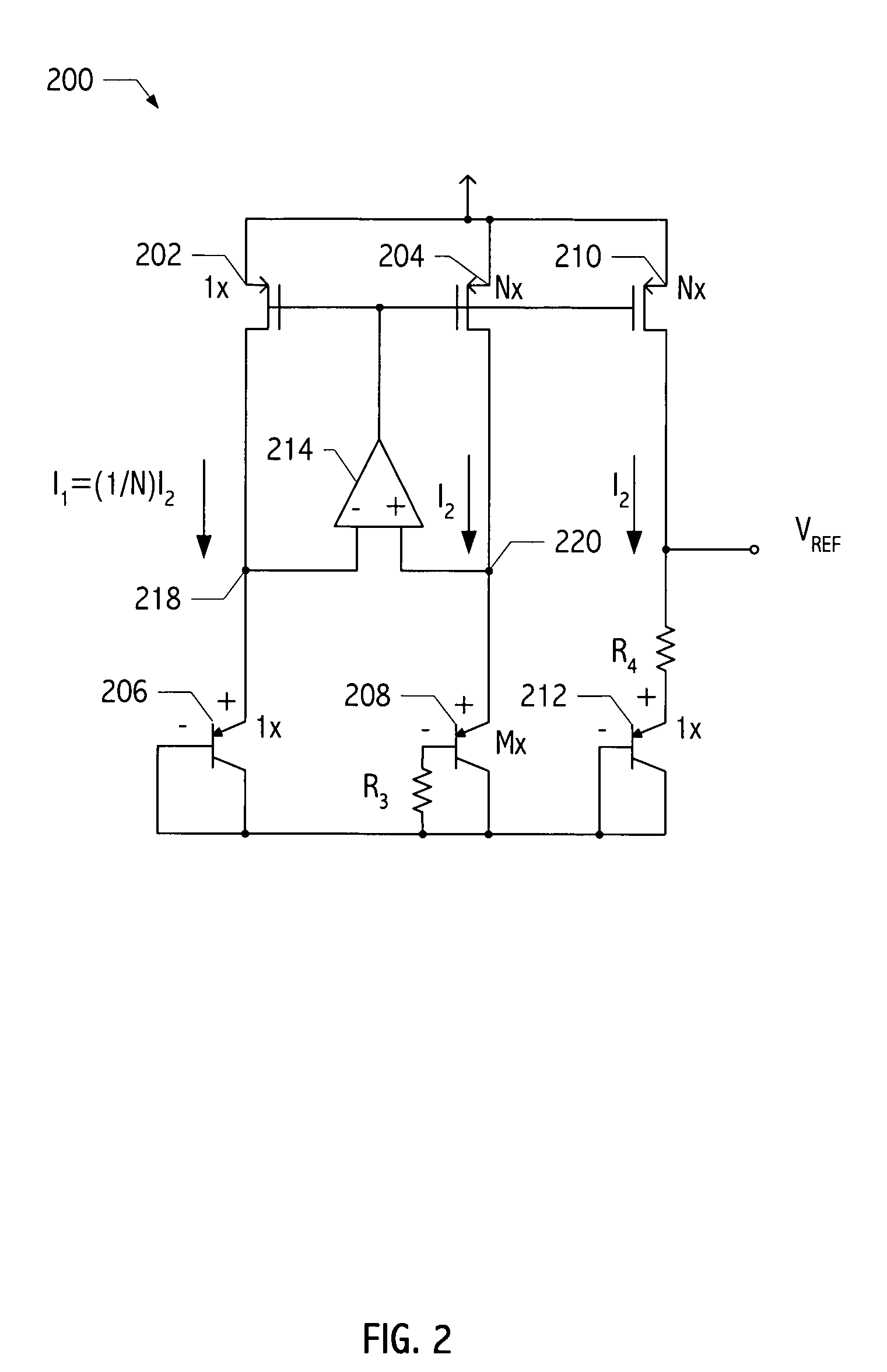
Voltage reference generator circuit subtracting CTAT current from PTAT current
ActiveUS7224210B2Dc network circuit arrangementsElectric variable regulationEngineeringVoltage reference
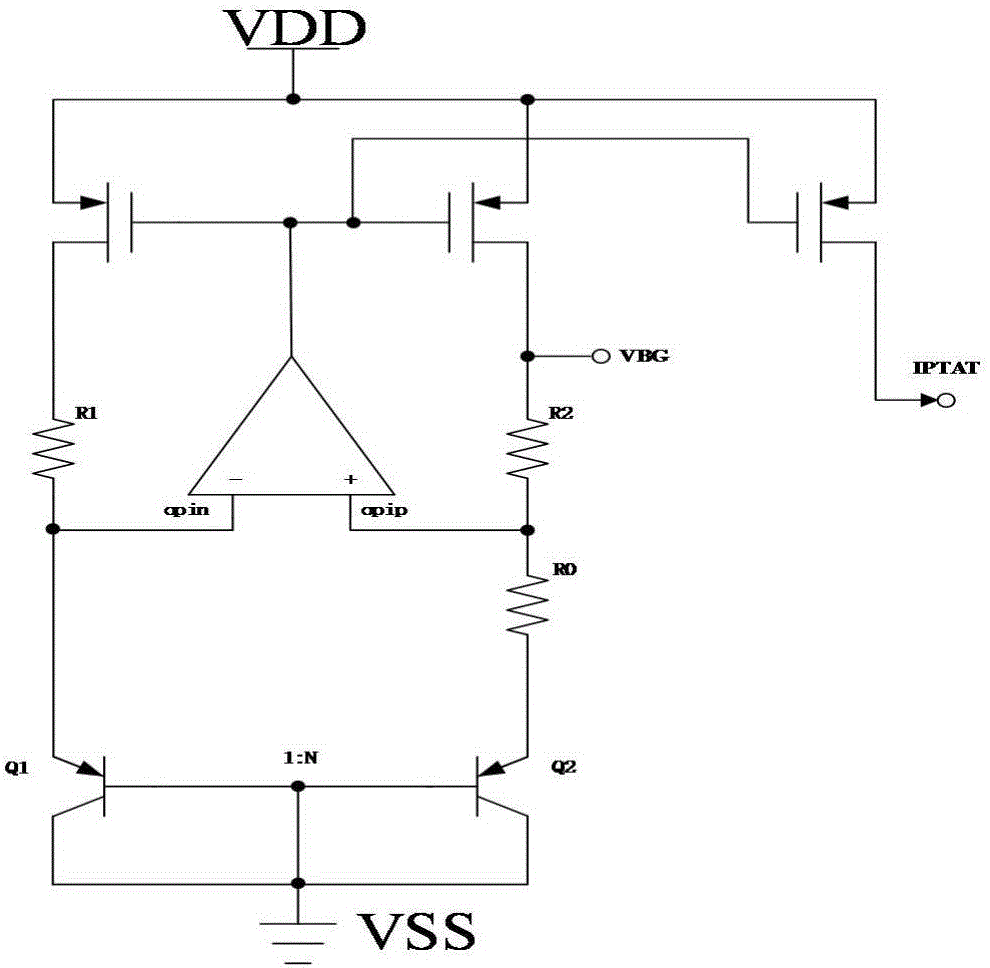
A voltage reference generator generates a stable reference voltage that is less than the bandgap voltage of silicon for power supply voltages less than 2V, yet provides sufficient voltage headroom to operate a current mirror. In one embodiment, the voltage reference generator has a power supply rejection ratio of at least 60 dB and has comparable noise performance as compared to traditional bandgap cirucits. These advantages are achieved by subtracting a current proportional to a complement of an absolute temperature from a current proportional to the absolute temperature to generate a voltage having a positive temperature coefficient, which is then added to a voltage that is a complement of the absolute temperature to achieve a voltage that has a low temperature coefficient.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Low dropout regulator capable of on-chip implementation
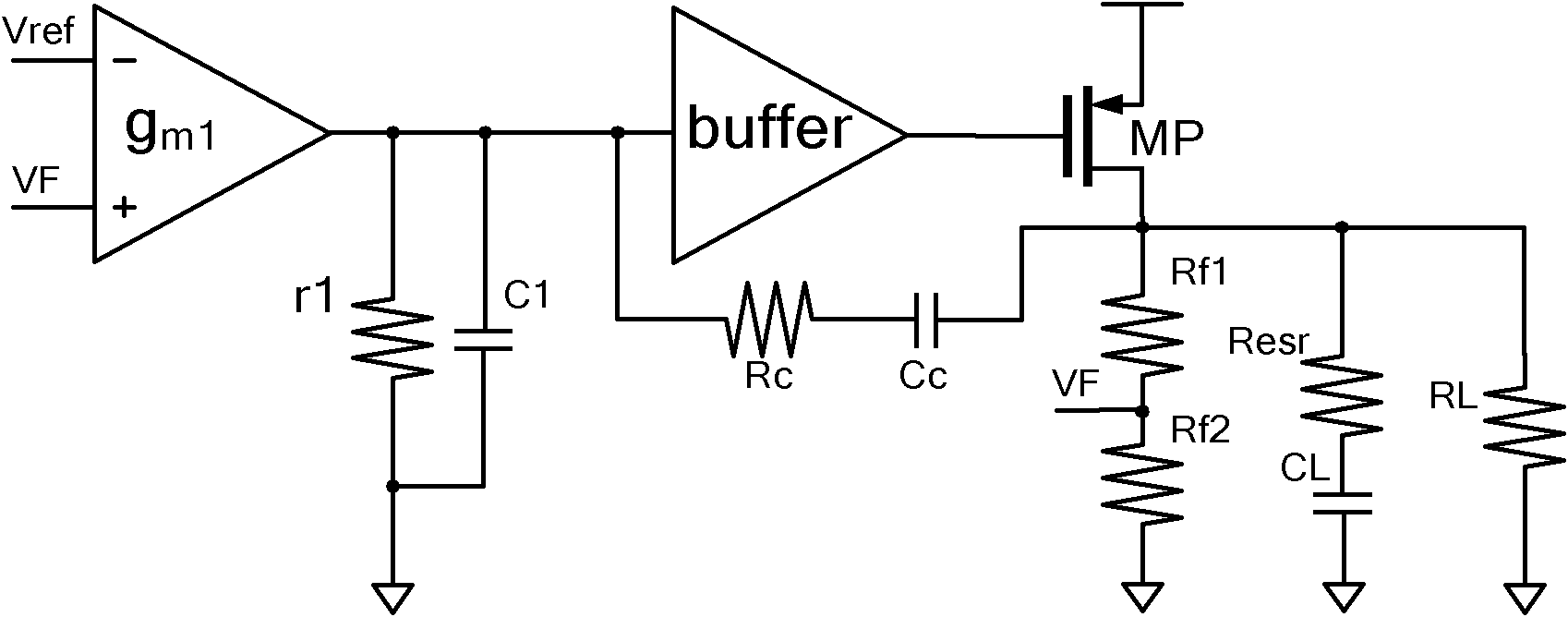
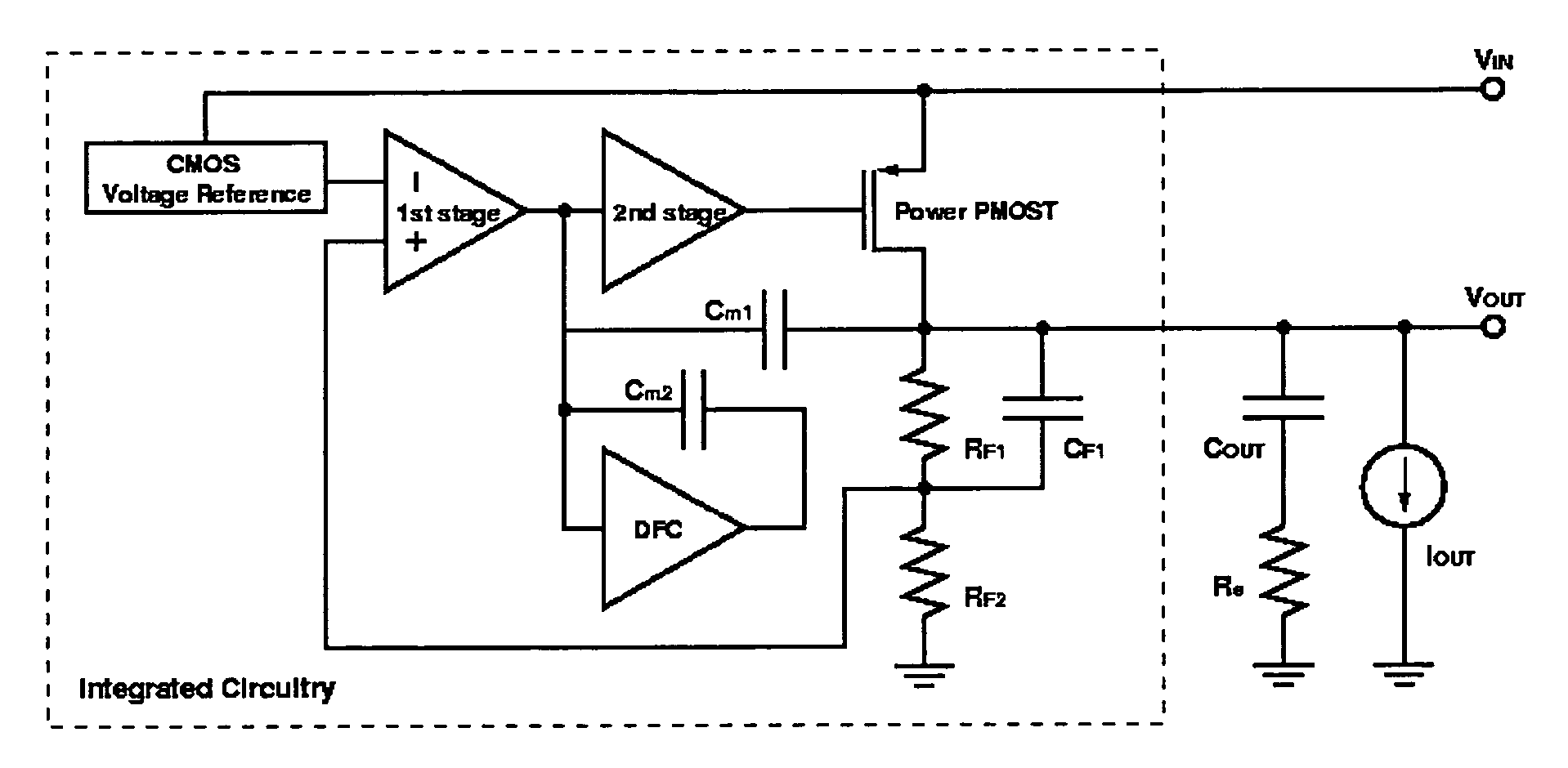
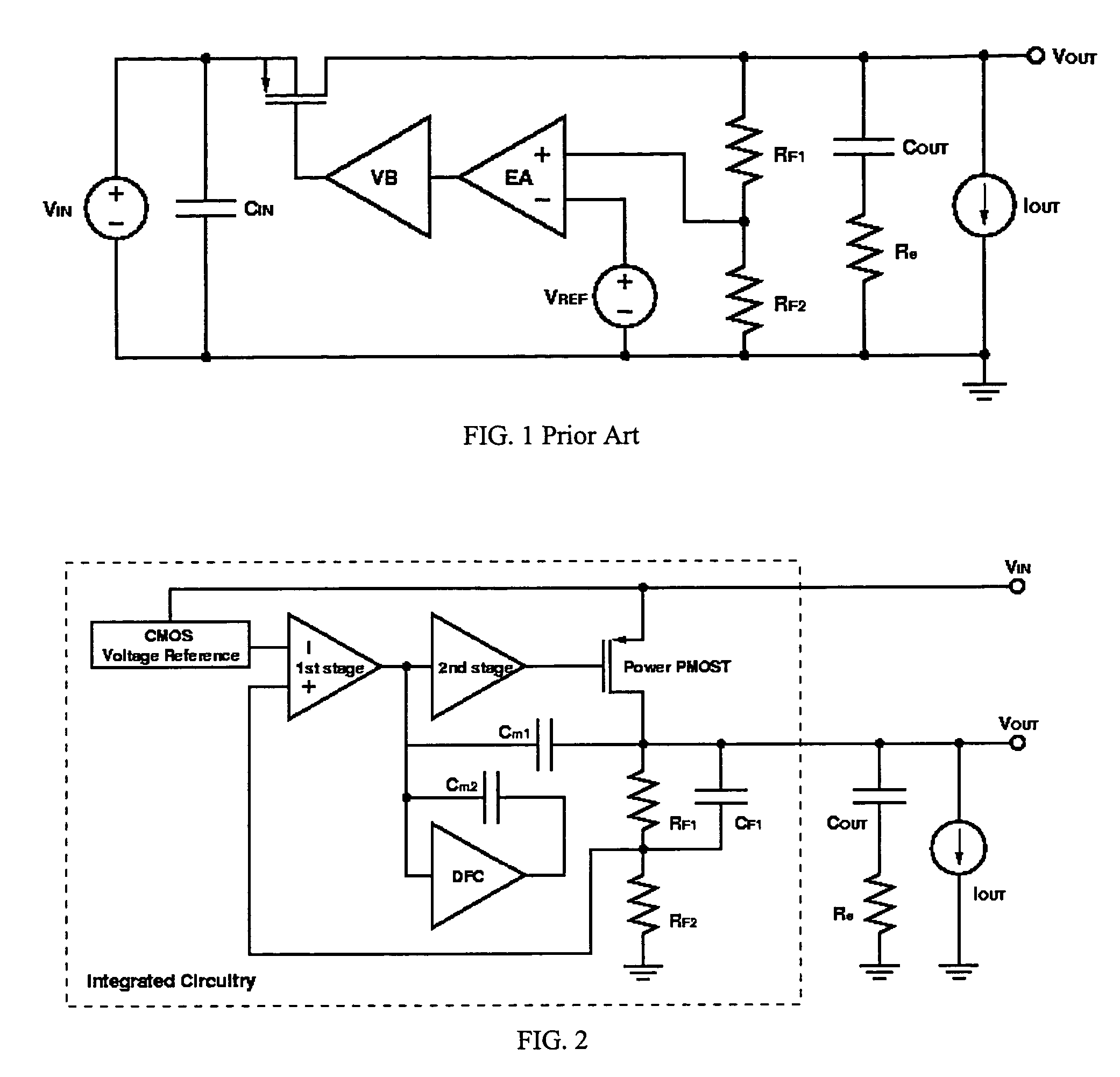
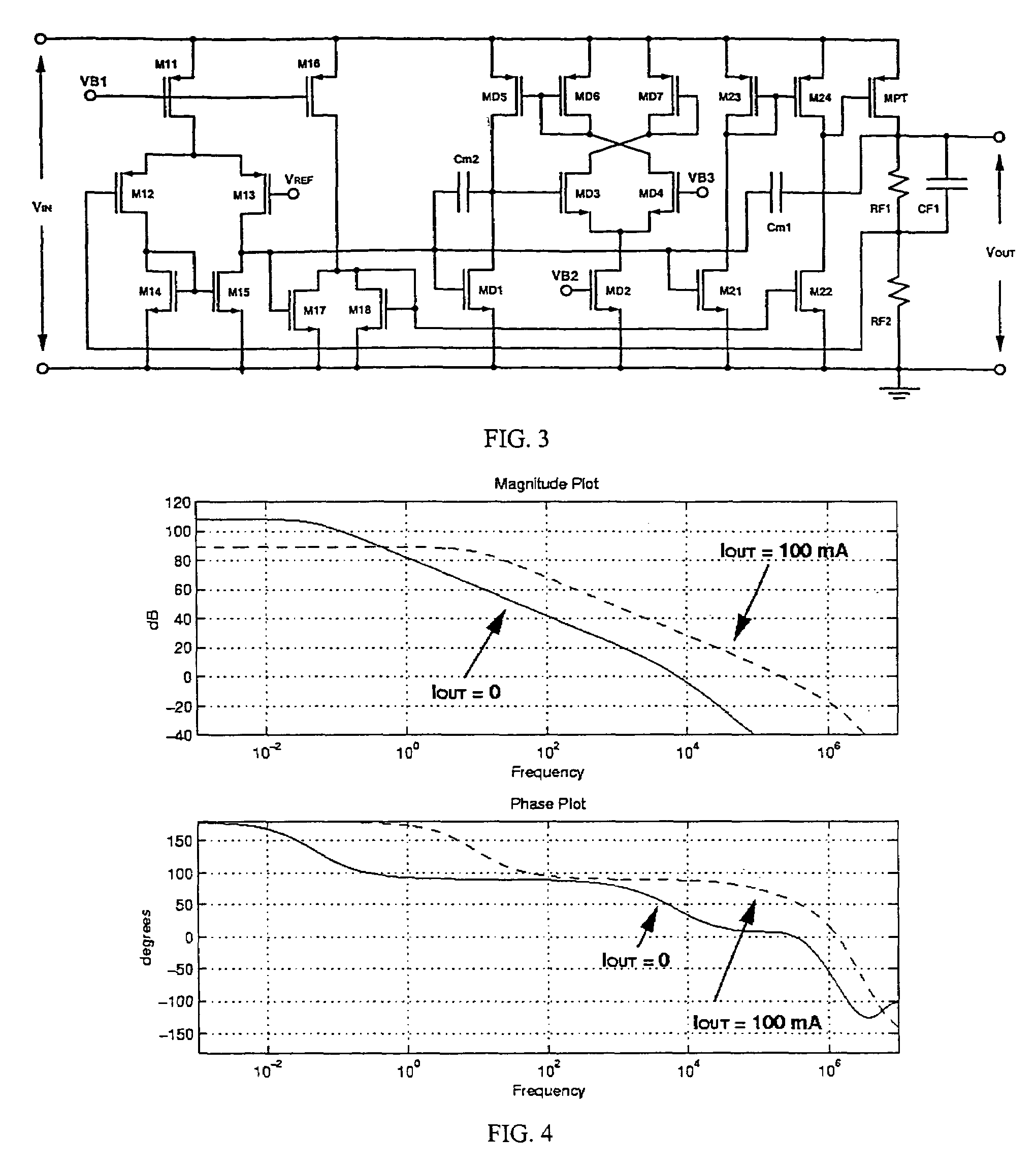
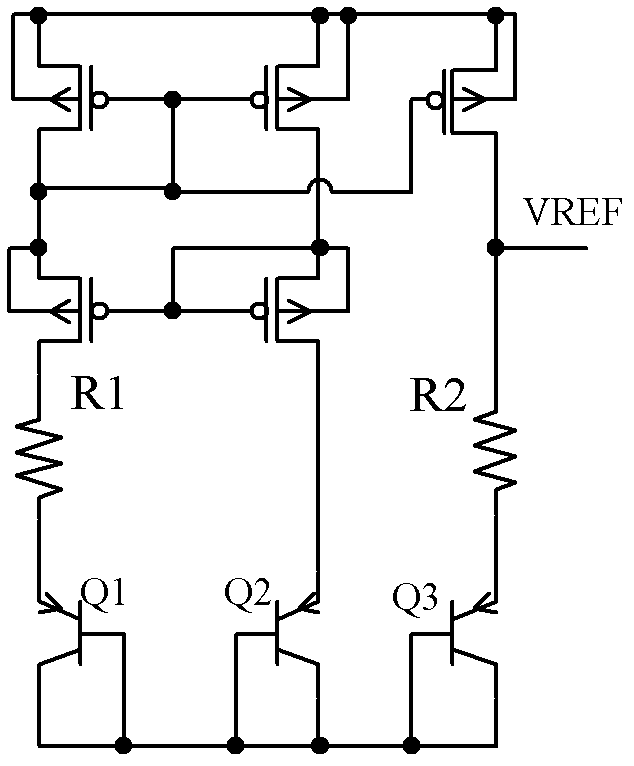
A low-dropout regulator comprises a high-gain error amplifier having a differential input stage and a single-ended output, a high-swing high-positive-gain second stage with input connecting to the output of the error amplifier and a single-ended output, a p-type MOS transistor with gate terminal connecting to the output of the second stage, source terminal connecting to the supply voltage, and drain terminal to the output of the low-dropout regulator. A first-order high-pass feedback network connects the output of the low-dropout regulator and the positive input of the error amplifier, and a damping-factor-control means comprising a negative gain stage with a feedback capacitor connects the input and output of this gain stage. A capacitor is connected between the output of the error amplifier and the output of the low-dropout regulator, while a voltage reference connects to the negative input of the error amplifier. The regulator does not require an off-chip capacitor for stability and has improved load transient response and power supply rejection ratio.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Voltage reference generator circuit subtracting CTAT current from PTAT current
ActiveUS20050285666A1Dc network circuit arrangementsElectric variable regulationEngineeringVoltage reference
A voltage reference generator generates a stable reference voltage that is less than the bandgap voltage of silicon for power supply voltages less than 2V, yet provides sufficient voltage headroom to operate a current mirror. In one embodiment, the voltage reference generator has a power supply rejection ratio of at least 60 dB and has comparable noise performance as compared to traditional bandgap cirucits. These advantages are achieved by subtracting a current proportional to a complement of an absolute temperature from a current proportional to the absolute temperature to generate a voltage having a positive temperature coefficient, which is then added to a voltage that is a complement of the absolute temperature to achieve a voltage that has a low temperature coefficient.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
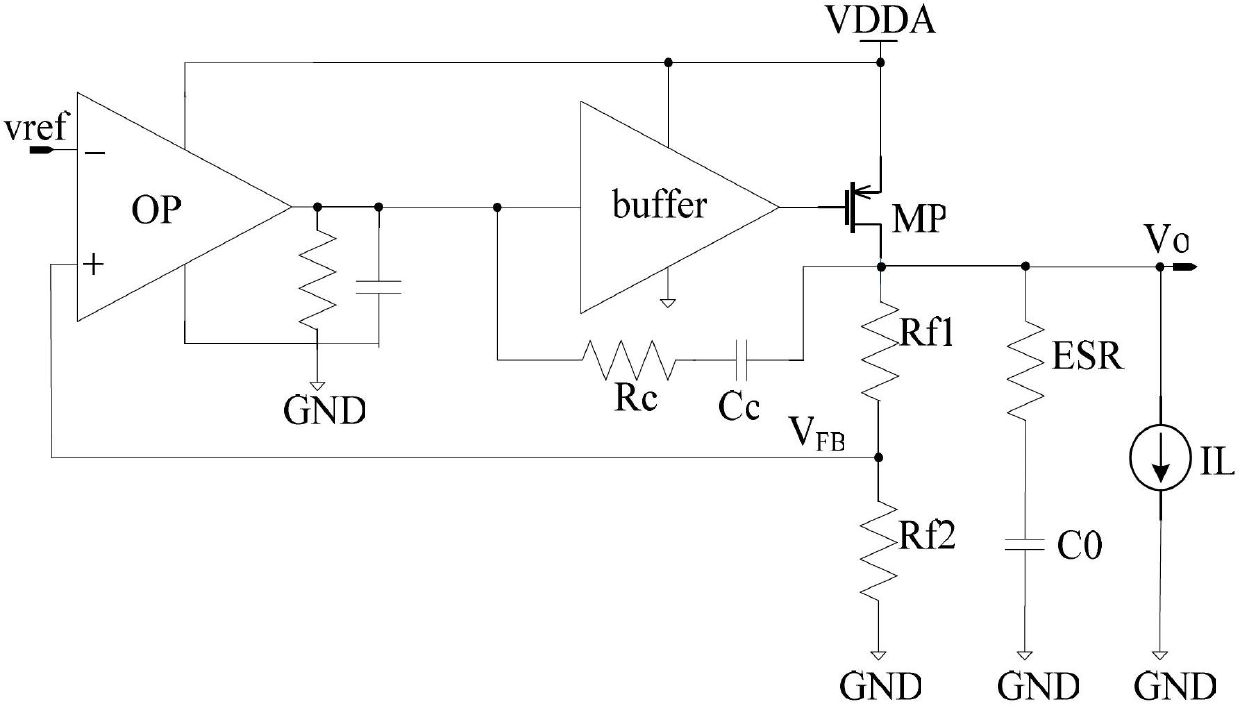
Linear voltage stabilizing circuit with low voltage difference
InactiveCN102681582ALower resistanceHigh inhibition ratioElectric variable regulationLow voltageHemt circuits
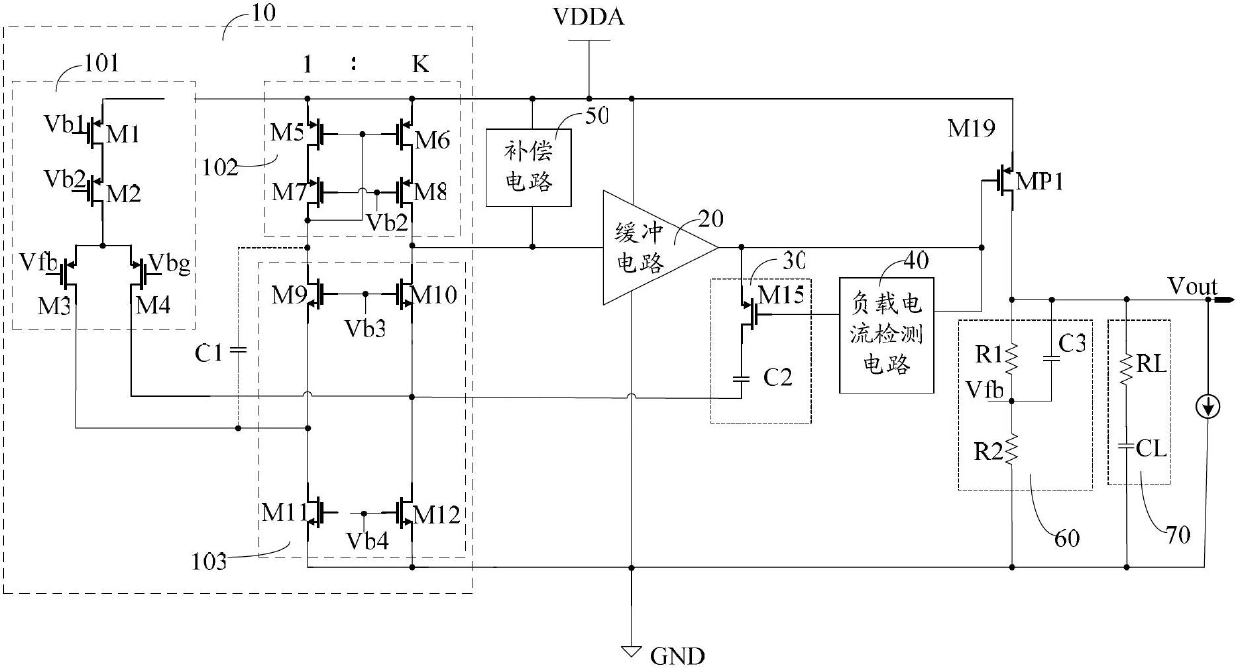
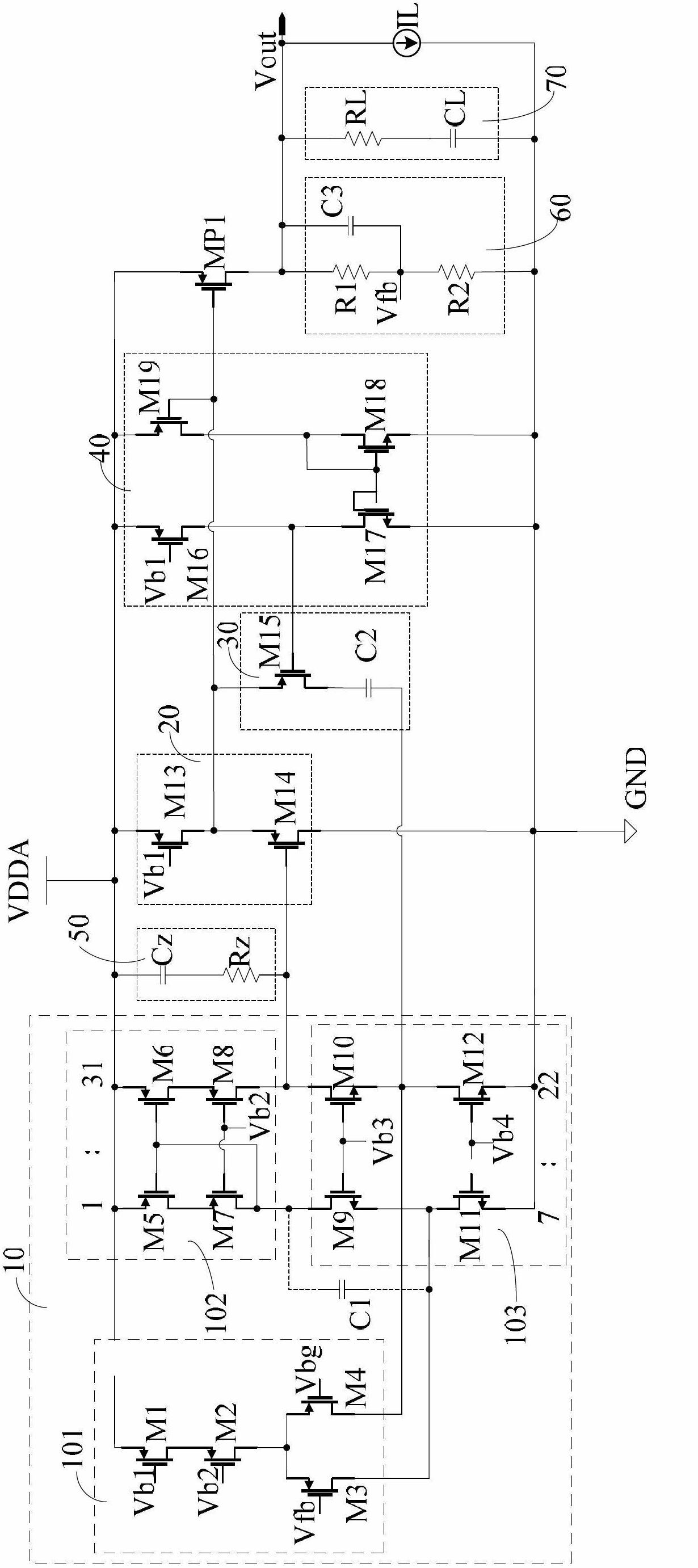
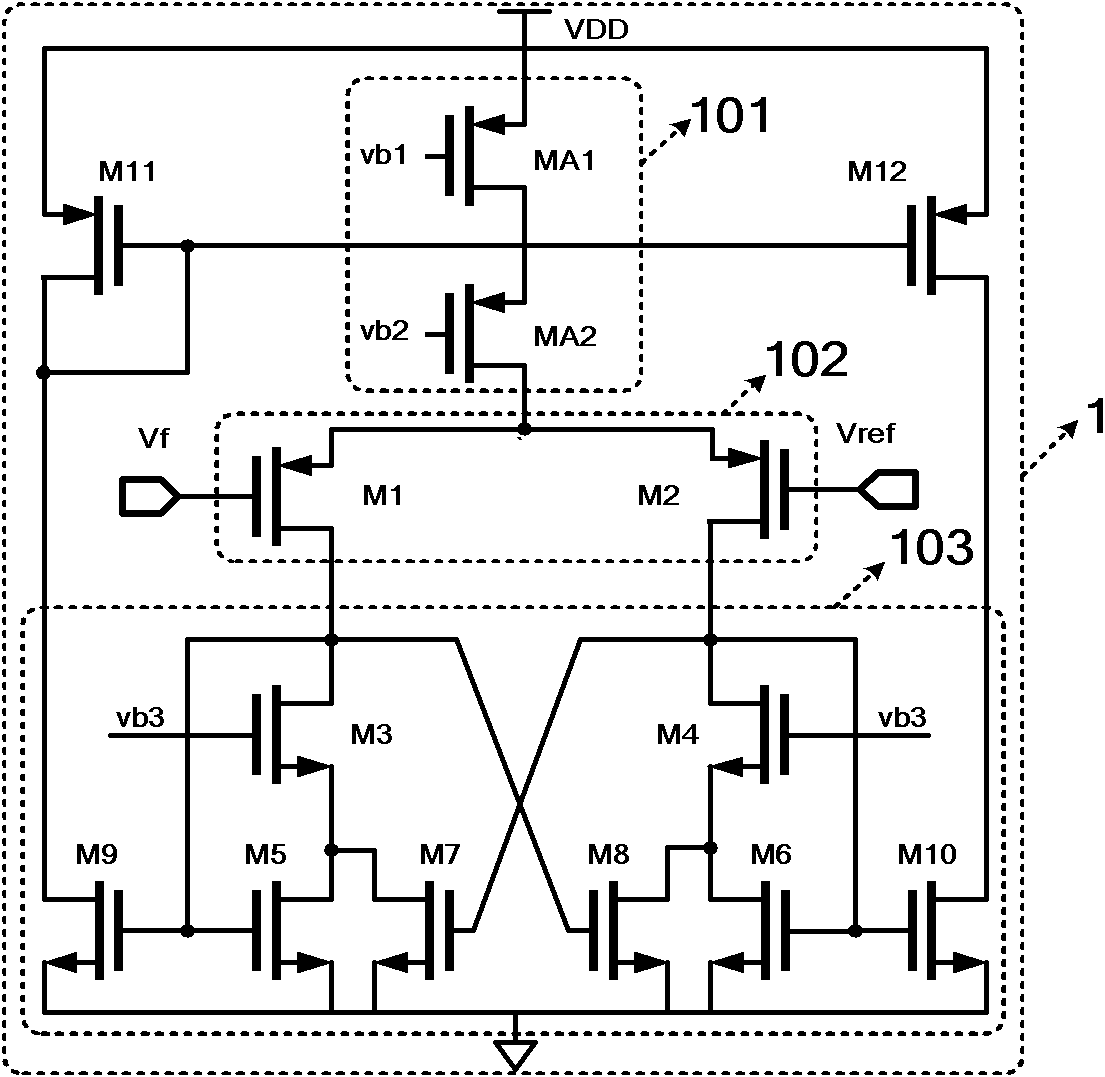
The invention provides a linear voltage stabilizing circuit with low voltage difference. The linear voltage stabilizing circuit with the low voltage difference is provided with high power supply rejection ratio and comprises an error amplifier, a buffer circuit, a P-channel metal oxide semiconductor (PMOS) regulating transistor, a compensation circuit, a voltage division feedback circuit and an output circuit. The error amplifier is a novel error amplifier. Ratio of width to length ratio of a fifth PMOS tube and a sixth PMOS tube, ratio of width to length ratio of a seventh PMOS tube and an eighth PMOS tube and ratio of width to length ratio of a ninth N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) tube and a tenth NMOS tube are all 1: K, and K is an integer greater than 1. The ratio of width to length ratio of the metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) tubes is changed, resistance of an output node of the error amplifier to a power supply is reduced, power interference enters from a current mirror low resistance point is amplified through current amplification technology, and power supply high frequency small signal interference in output signals of the error amplifier cannot be attenuated excessively. Therefore, the linear voltage stabilizing circuit with the low voltage difference enables power supply interference signals arriving at a PMOS regulating transistor grid to be varied according to variation of power supply voltage well, and improves the power supply rejection ratio of circuits.
Owner:BRIGATES MICROELECTRONICS KUNSHAN
Amplifier circuit
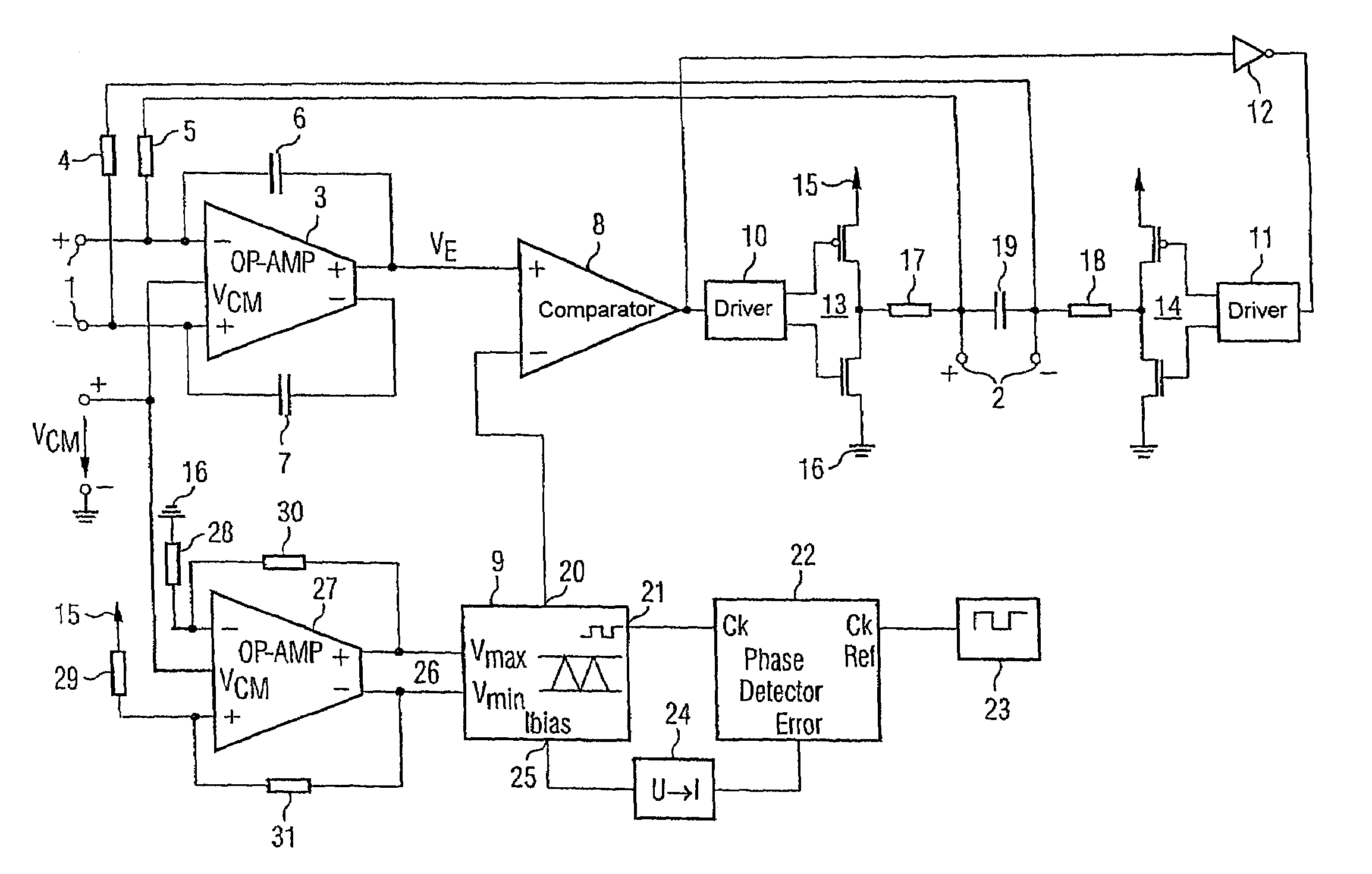
InactiveUS7068095B2Improve power supply rejection ratioNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierAmplitude control
The invention is directed to an amplifier circuit based on the principle of a class D amplifier. To avoid unwanted convolution effects and to improve the power supply rejection ratio, provision is made for the amplitude of the ramp signal used for pulse width modulation to track proportionally the supply voltage for the amplifier circuit. For this purpose, the ramp signal generator has an amplitude control input suitably connected to supply and reference potentials. This ensures a constant duty ratio which is independent of the supply voltage. The present circuit may be used, for example, as a DC / DC converter or as an audio amplifier.
Owner:INTEL MOBILE COMM GMBH
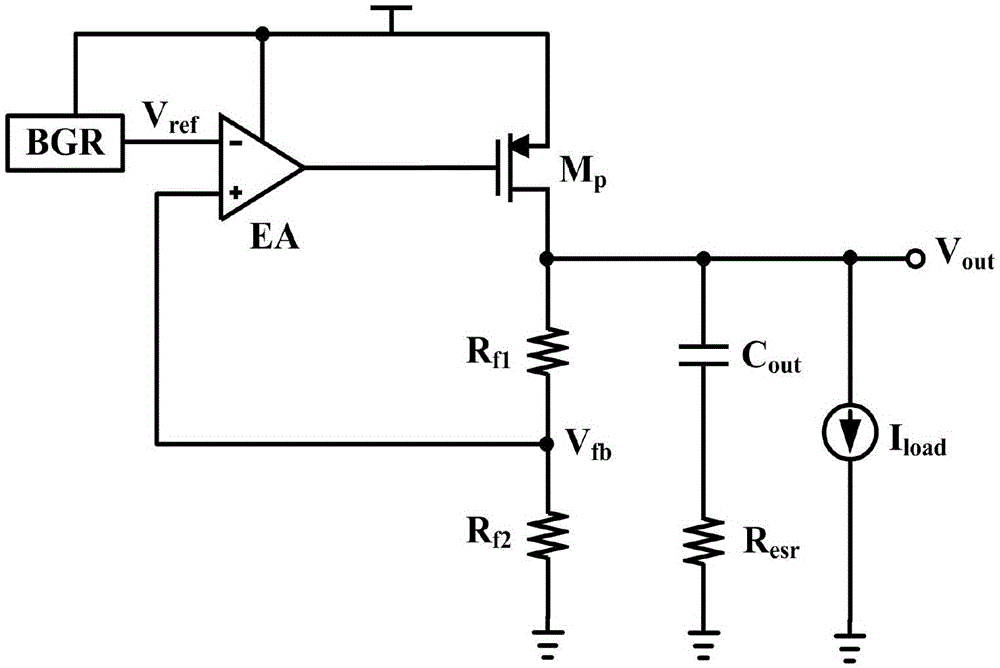
High-slew-rate error amplifier-based high-accuracy and high-speed low dropout (LDO) regulator circuit
InactiveCN102096434AGuaranteed stabilityReduce precisionElectric variable regulationLoad circuitPush–pull output
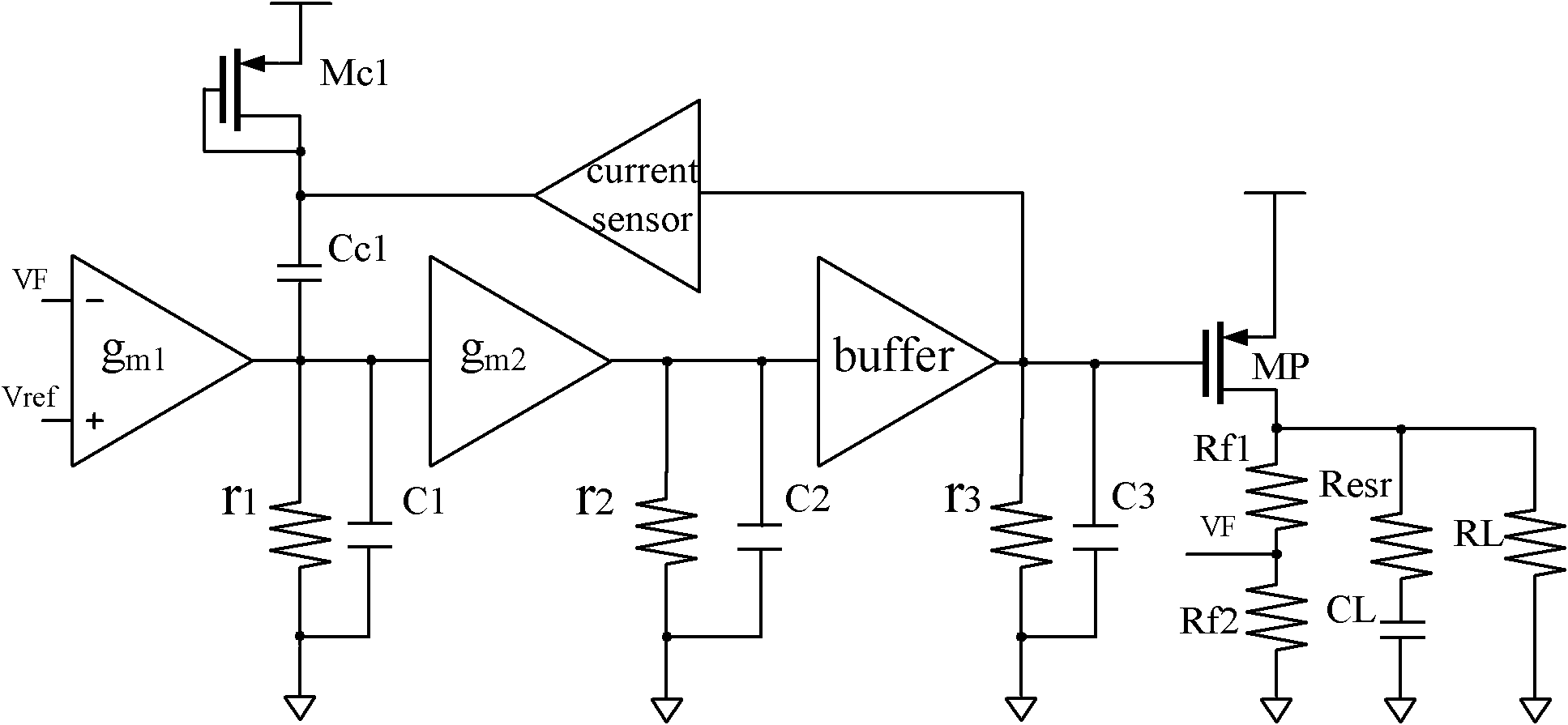
The invention discloses a high-slew-rate error amplifier-based high-accuracy and high-speed low dropout (LDO) regulator circuit, which comprises an over-the-air (OTA) circuit, a second-stage push-pull output circuit, a Miller compensation and dynamic zero compensation circuit, a load current detection circuit, a super source-level follower, a dynamic offset pipe, a feedback network and an output and load circuit. By the LDO circuit, the problems of low gain, low accuracy, low power supply suppression ratio and low response speed of the conventional LDO are solved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
High mains rejection ratio low dropout voltage linear voltage regulator with feedforward transconductance
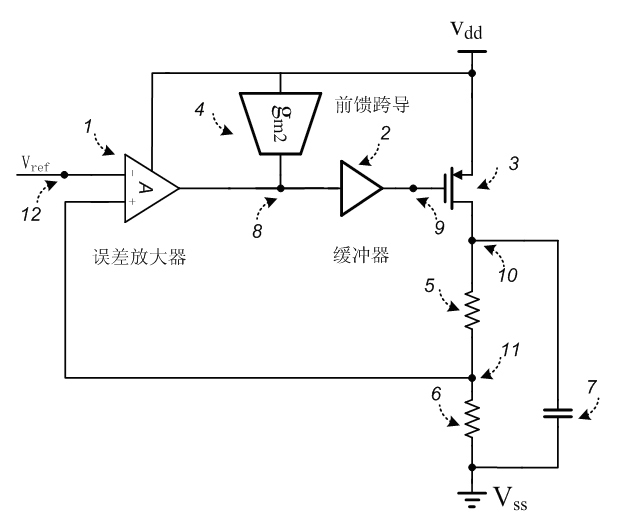
InactiveCN101853040AHigh rejection ratioSuppression Ratio OptimizationElectric variable regulationCapacitanceDropout voltage
The invention belongs to the technical field of integrated circuits and specifically relates to a high mains rejection ratio low dropout voltage linear voltage regulator with a feedforward transconductance, which consists of an error amplifier, a buffer, a PMOS pass transistor, a feedforward transconductance, two feedback resistors and a filter capacitor, wherein the error amplifier is a current mirror amplifier consisting of a tail current source, a PMOS input differential pair and three groups of current mirrors. The mains voltage fluctuation influences the output mainly via two paths of the PMOS pass transistor and the parasitic resistor of and PMOS pass transistor. The feedforward transconductance transforms the perturbation of the mains voltage into the perturbation of the current, and then the perturbation of the current is transformed into the in-phase voltage perturbation of the grid of the pass transistor via the parasitic resistor of the error amplifier. The influence of the mains voltage perturbation on the output can be eliminated by the control of the gain of the feedforward transconductance so as to realize high mains rejection ratio. The invention can optimize the mains rejection ratio within a wider range of load current and does not reduce the efficiency of the low dropout voltage linear voltage regulator.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
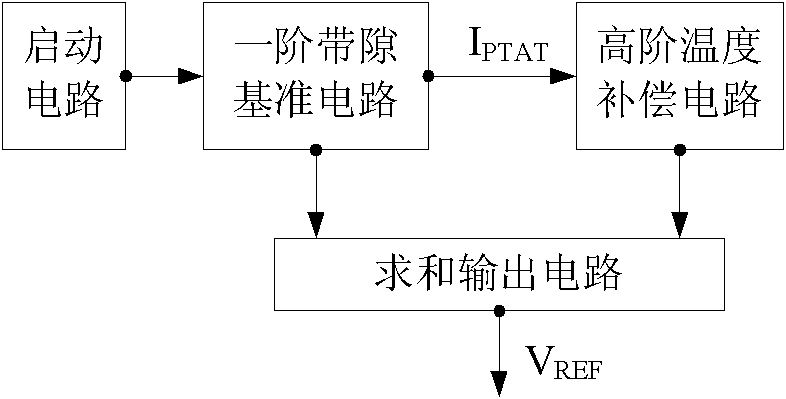
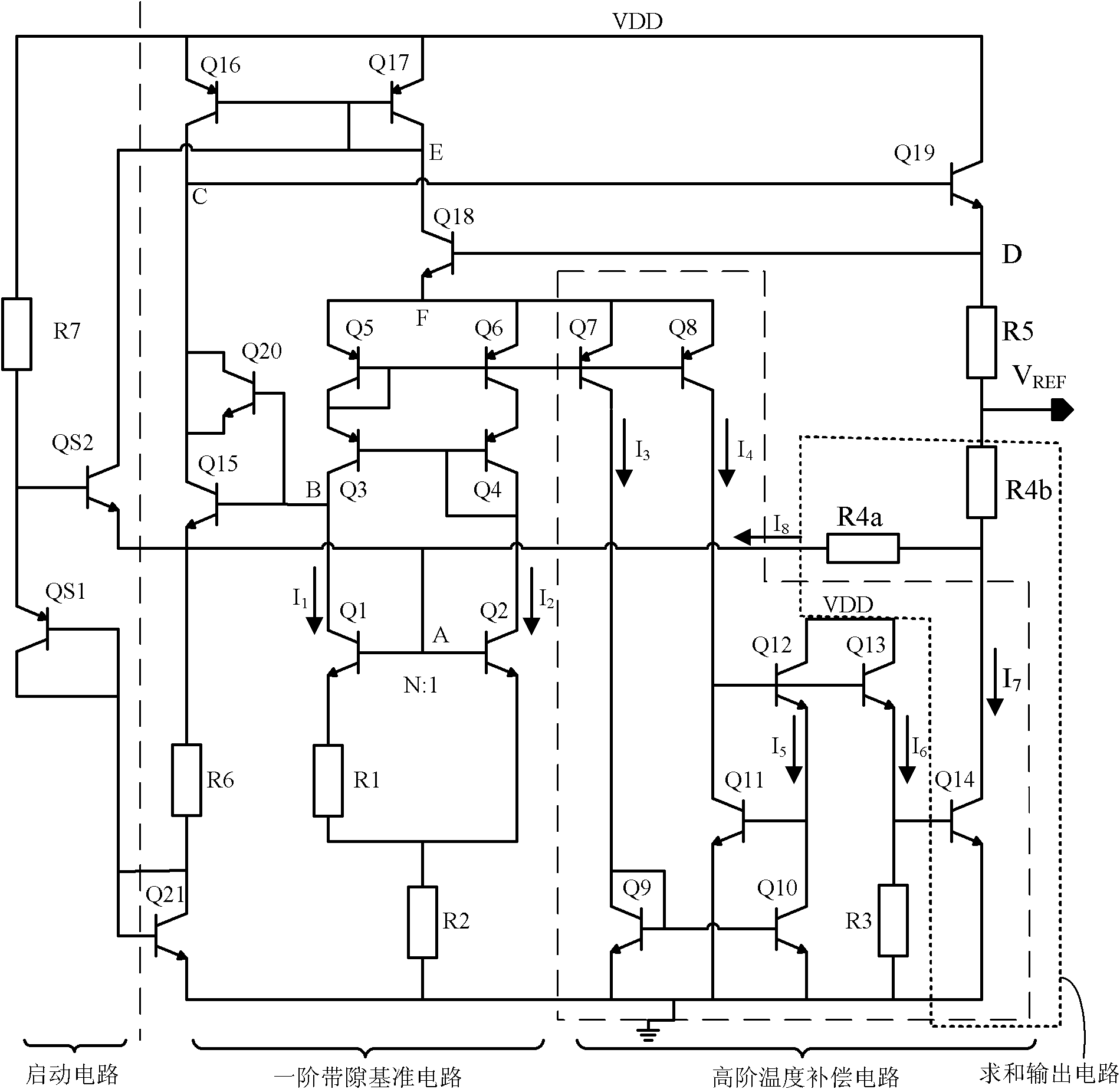
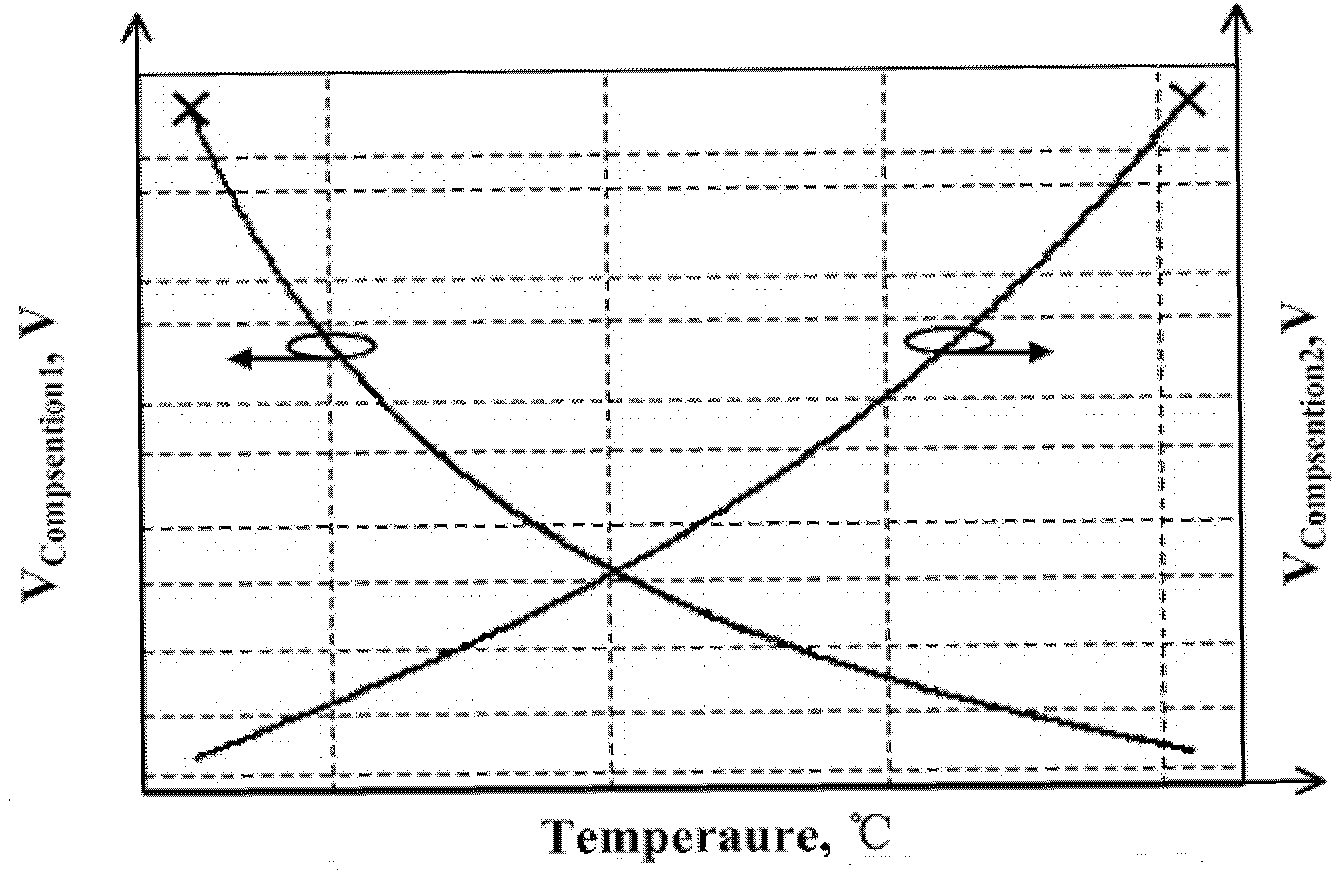
Band-gap voltage reference source for high-order temperature compensation
InactiveCN102323842AEnhanced inhibitory effectEasy to adjustElectric variable regulationLow voltageEngineering
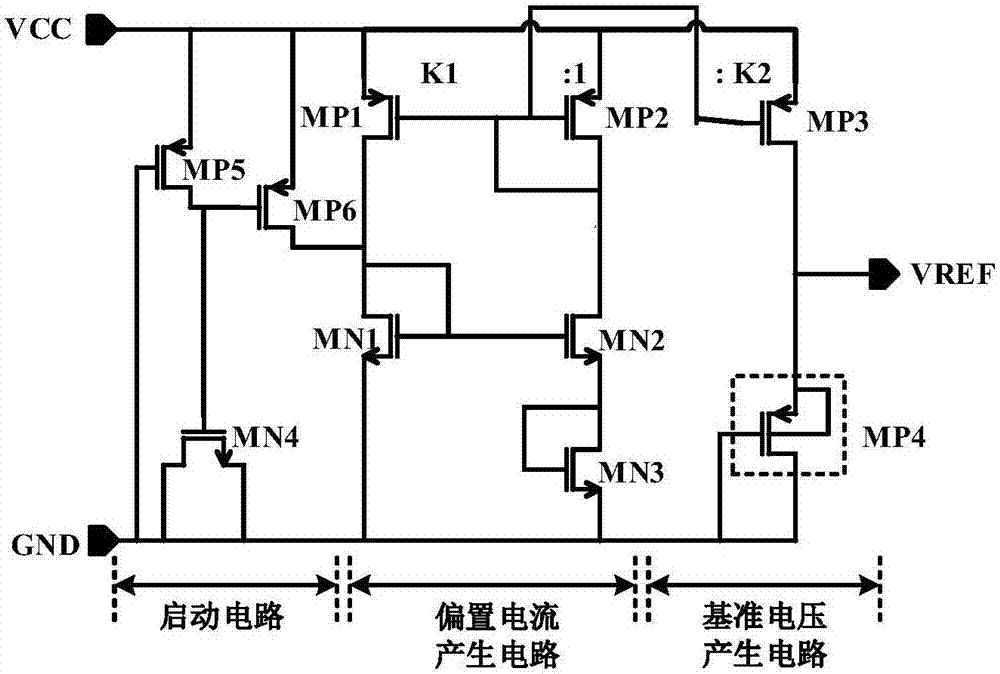
The invention belongs to the technical field of power supplies, and discloses a band-gap voltage reference source for high-order temperature compensation, which specifically comprises a starting circuit, a first-order band-gap reference circuit, a high-order temperature compensation circuit and a summation output circuit. The band-gap voltage reference source works out the reference voltage by summating the first-order band-gap reference voltage which is generated by the first-order band-gap reference circuit and the voltage which is converted from the high-order temperature compensation current which is generated by the high-order temperature compensation circuit, and improves the temperature coefficient of the band-gap reference voltage source by introducing index compensation; the designed circuit simultaneously adopts two feedback loops, so that the power supply rejection ratio (PSRR) and the linear adjustability are improved; and simultaneously, because the low-voltage working requirement is met, the voltage reference source has a very wide scope of application.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Low dropout linear voltage regulator (LDO) without off-chip capacitor for improving transient response and increasing power supply rejection ratio (PSRR)
InactiveCN105045329AHighly integratedReduce areaElectric variable regulationLinear regulatorCapacitance
The invention relates to a low dropout linear voltage regulator (LDO) without an off-chip capacitor for improving transient response and increasing power supply rejection ratio (PSRR). The LDO without the off-chip capacitor comprises an error amplifier, a reference voltage source module, a power adjusting tube, an NMC Miller's compensating circuit, a PSRR enhanced network and a transient response intensifier circuit. According to the LDO without the off-chip capacitor, the NMC compensation technique is used for meeting the system stability requirement; a second-stage gm improved circuit of the amplifier is used for increasing the charging and discharging currents to the grid of the power tube; a slew rate intensifier circuit is introduced, needed currents can be provided for a load when the load of the LDO is subjected to step hopping from small to large, and thus the transient response capacity of the LDO is improved under the double actions. In addition, the PSRR enhanced network is additionally arranged to be used for controlling the PSRR feedback factors beta of the system, an original zero point is pushed to the position with higher frequency, and therefore the PSRR characteristic of the system is improved. The LDO without the off-chip capacitor is improved on the aspect of transient response and the aspect of PSRR.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Low noise bandgap reference circuit and reference source generation system
The invention discloses a low noise bandgap reference circuit and a reference source generation system. The reference source generation system comprises a bandgap reference generation circuit, a low dropout linear voltage stabilizing circuit and the low noise bandgap reference circuit. The low noise bandgap reference circuit comprises a starting circuit, a clamping circuit, a temperature coefficient compensation circuit and an output circuit, wherein the starting circuit is used for supplying starting voltage to other circuits and is turned off after other circuits are started; the clamping circuit comprises four metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) tubes which are connected by a current mirror structure to realize a clamping function; the temperature coefficient compensation circuit is used for performing temperature coefficient compensation on voltage which is output by the clamping circuit and generating reference voltage which is irrelevant to temperature; and the output circuit is used for outputting second reference voltage. The reference source generation system generates extremely low noise and has high power rejection ratios.
Owner:BRIGATES MICROELECTRONICS KUNSHAN
Amplifier circuit
InactiveUS20050200404A1Improve power supply rejection ratioAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierAmplitude control
The invention is directed to an amplifier circuit based on the principle of a class D amplifier. To avoid unwanted convolution effects and to improve the power supply rejection ratio, provision is made for the amplitude of the ramp signal used for pulse width modulation to track proportionally the supply voltage for the amplifier circuit. For this purpose, the ramp signal generator has an amplitude control input suitably connected to supply and reference potentials. This ensures a constant duty ratio which is independent of the supply voltage. The present circuit may be used, for example, as a DC / DC converter or as an audio amplifier.
Owner:INTEL MOBILE COMM GMBH
Wide-input voltage high-power supply rejection ratio reference voltage source
InactiveCN102053645AIncrease loading capacityOp amp reductionElectric variable regulationEngineeringFeedback circuits
The invention discloses a wide-input voltage high-power supply rejection ratio reference voltage source. The reference voltage source comprises a self-bias circuit (1), a primary presetting circuit (2), a secondary presetting circuit (3), a bandgap reference core circuit (4) and a signal feedback circuit (5) which are sequentially connected. By using the self-bias circuit in a self-bias current mirror structure, the circuit can be started independently without using additional start circuits; by directly using the output of the secondary presetting circuit as the output of the reference voltage and simultaneously supplying power to the bandgap reference core circuit, the connection mode can improve the loading capacity of the reference voltage; by using the operational amplifier-free feedback loop for regulation, one clamping operational amplifier is removed from the traditional reference voltage source circuit, thereby saving the area and reducing the quiescent power dissipation; andcompared with the traditional bandgap reference voltage source circuit, the power supply rejection ratio of the output reference voltage, especially the performance under a high-frequency condition, is greatly improved.
Owner:CHENGDU PROMISING CHIP ELECTRONICS
Voltage regulator with improved power supply rejection ratio characteristics and narrow response band
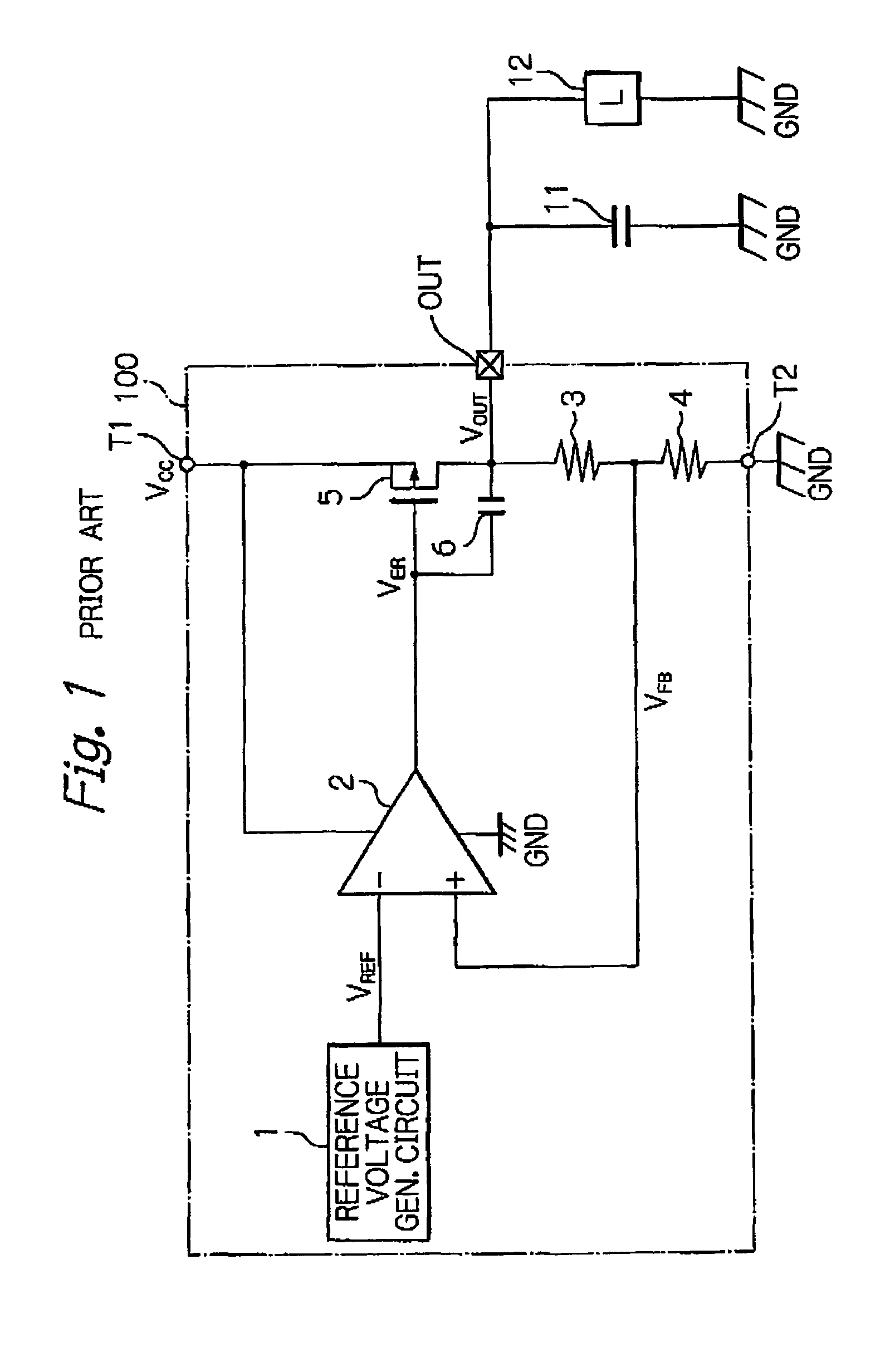
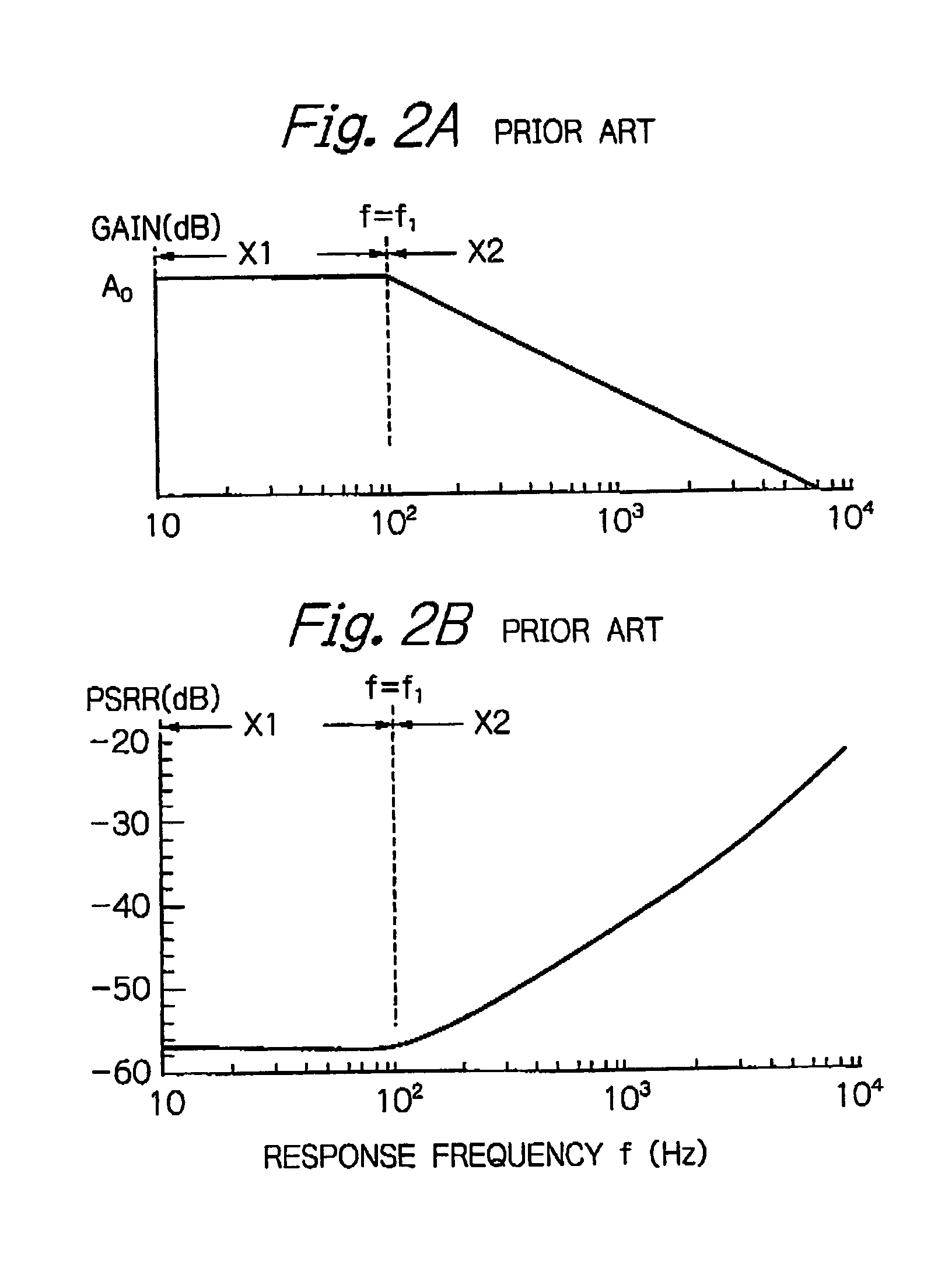
InactiveUS7248025B2Improved PSRR characteristicSolve the large power consumptionTelephone set constructionsElectric variable regulationVoltage regulationVoltage reference
In a voltage regulator, a reference voltage generating circuit generates a reference voltage. A drive transistor is connected between a first power supply terminal and an output terminal and has a control terminal. A voltage divider generates a feedback voltage which is an intermediate voltage between voltages at the output terminal and a first power supply terminal. A differential amplifier generates an error voltage in accordance with the feedback voltage of the voltage divider and the reference voltage, and transmits it to the control terminal of the drive transistor. An oscillation preventing capacitor is connected between the control of the drive transistor and the output terminal. A capacitor is connected between the first power supply terminal and the first input of the differential amplifier.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
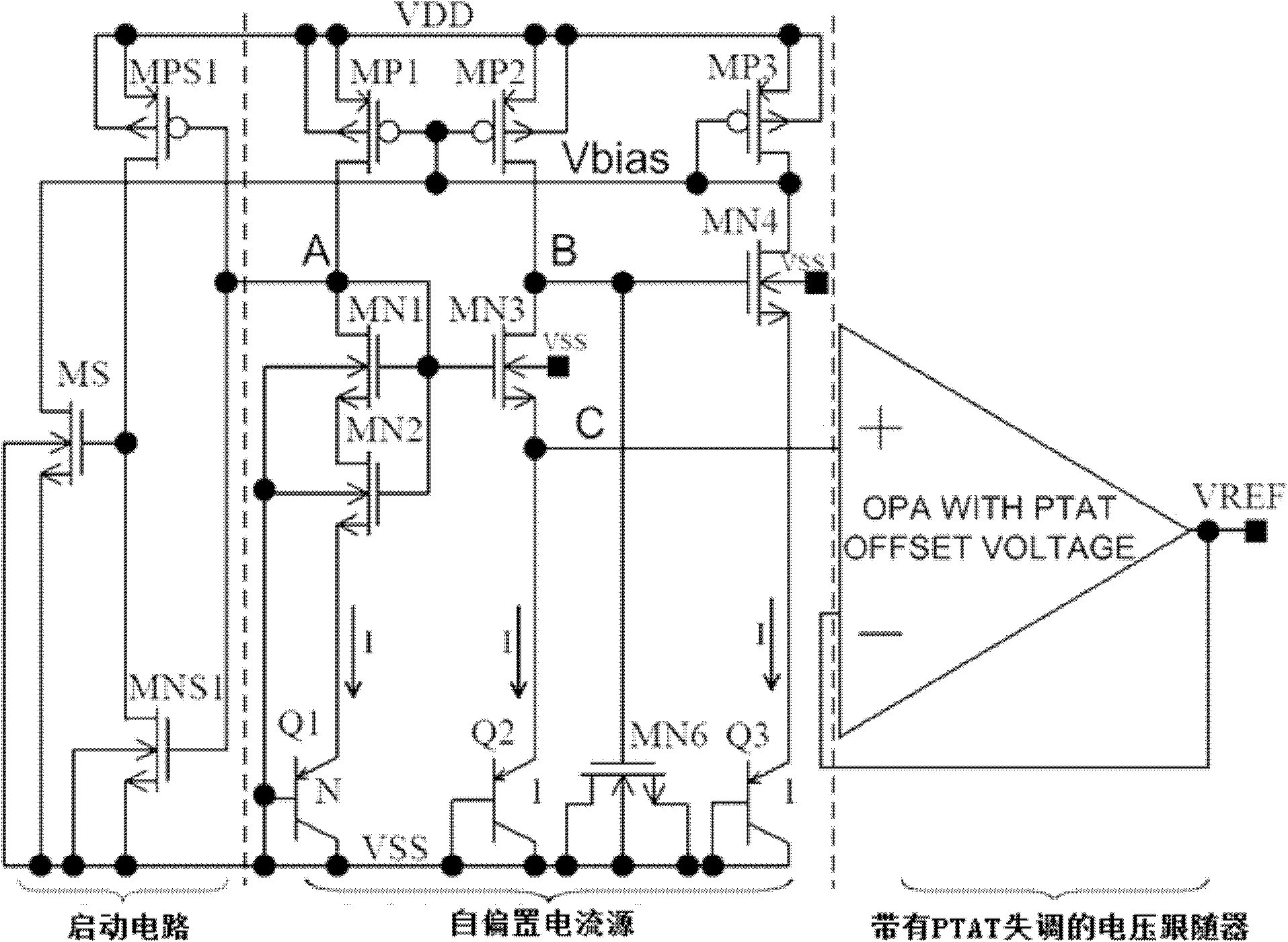
Resistance-free bandgap voltage reference source
InactiveCN102147632AHigh inhibition ratioSmall temperature coefficientElectric variable regulationCMOSVoltage reference
The invention discloses a resistance-free bandgap voltage reference source, specifically comprising a start-up circuit, a self-biasing current source circuit and a voltage follower with PTAT (Proportional To Absolute Temperature) offset, wherein the start-up circuit is connected with the self-biasing current source circuit; and the voltage follower with PTAT offset is connected with the self-biasing current source circuit. Without using a resistor in the circuit structure, the resistance-free bandgap voltage reference source provided by the invention can be compatible with a CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Transistor) process, so that the designing complexity is reduced and the area of a chip is reduced; in addition, due to the adoption of the self-biasing current source circuit and the voltage follower with PTAT offset in the voltage reference source disclosed by the invention, the reference voltage has lower temperature coefficient, and meanwhile, the power supply rejection ratio of a bandgap voltage reference source is increased.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Pure metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) structure voltage reference source with high power supply rejection ratio
ActiveCN103529897AImprove voltage suppression performanceReduce design difficultyElectric variable regulationVoltage referenceFeedback circuits
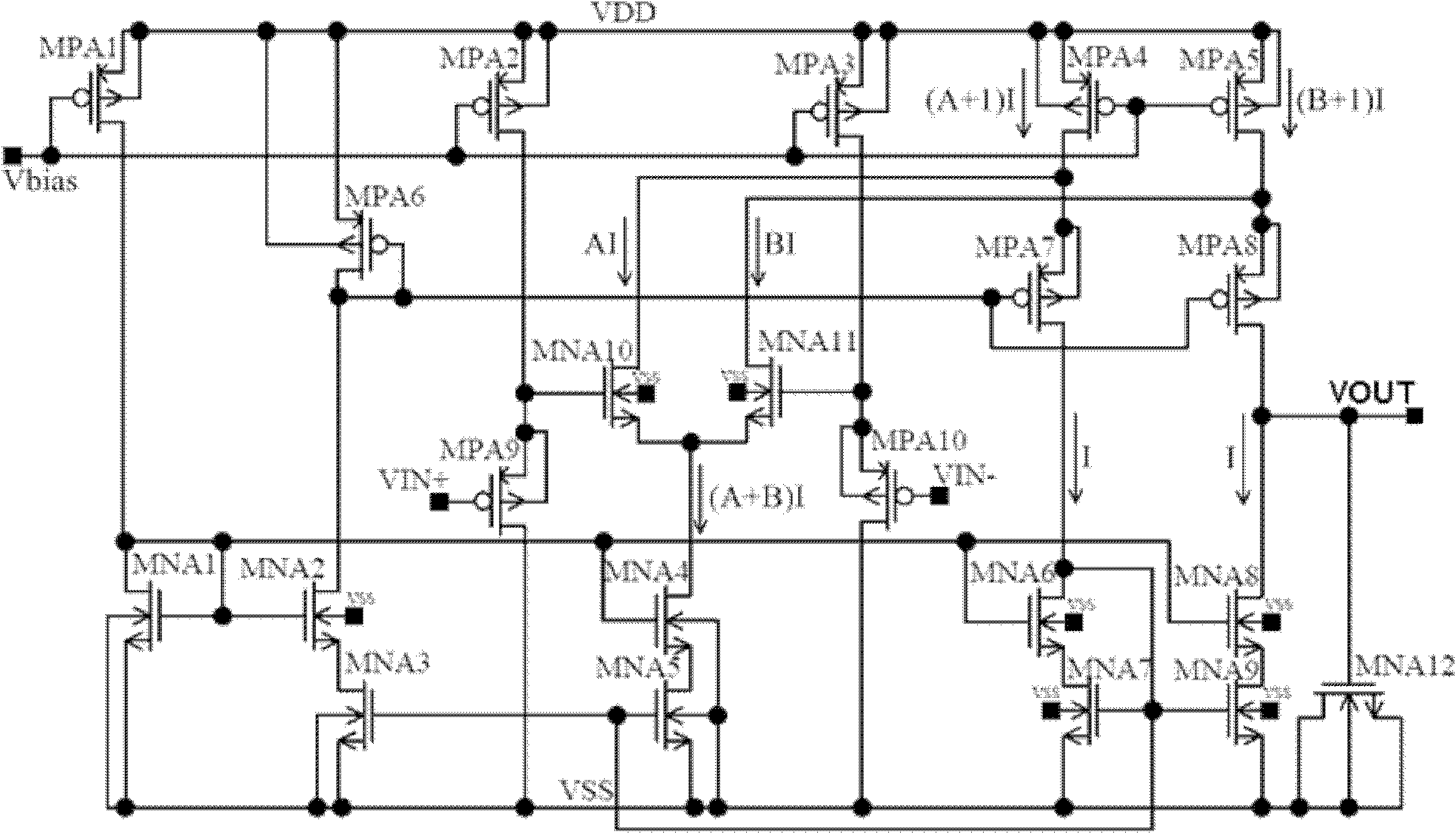
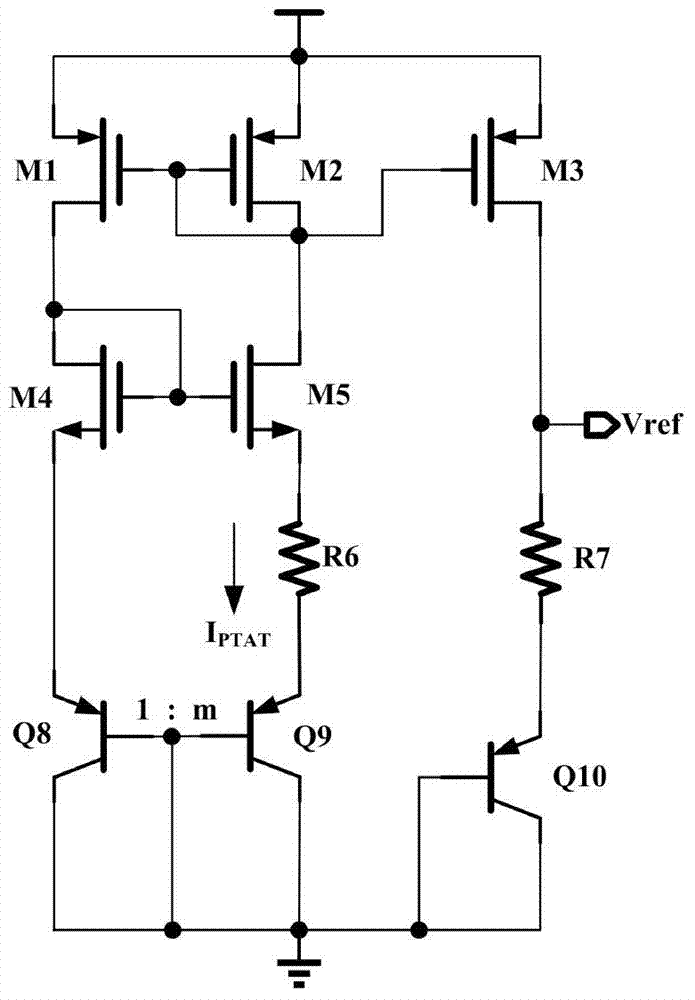
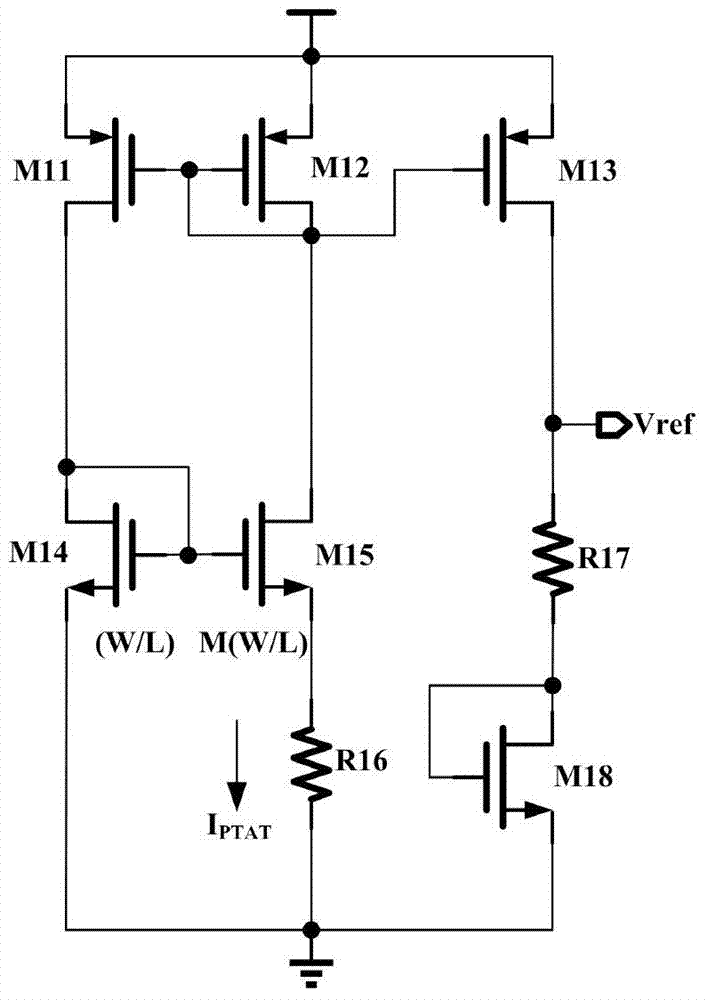
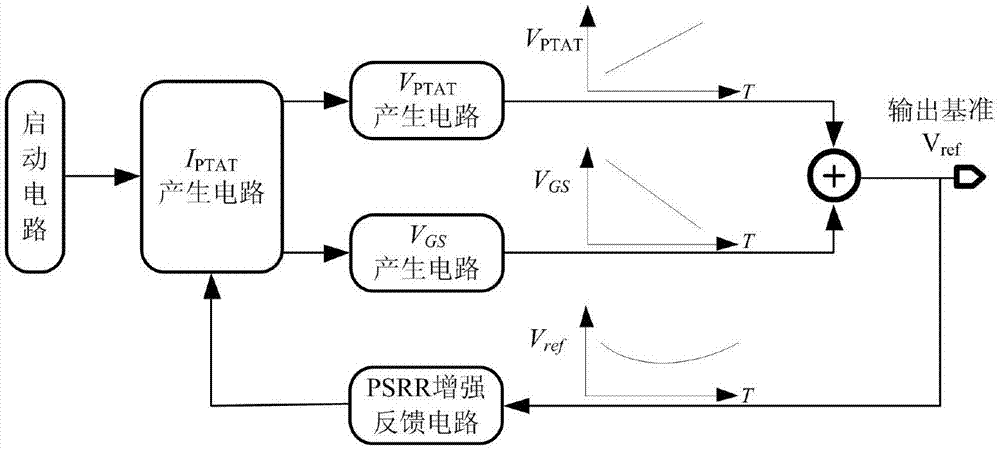
A pure metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) structure voltage reference source with high power supply rejection ratio (PSRR) comprises a starting circuit, an IPTAT generation circuit, a VPTAT generation circuit, a VGS generation circuit and a PSRR reinforcing feedback circuit. The starting circuit is connected with the IPTAT generation circuit, the output of the IPTAT generation circuit is connected with the VPTAT generation circuit and the VGS generation circuit, the output of the VPTAT generation circuit and the output of the VGS generation circuit are overlapped to form Vref reference voltage output, and the output reference voltage is fed back to the IPTAT generation circuit through the PSRR reinforcing feedback circuit to generate a circuit to form a closed feedback loop.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
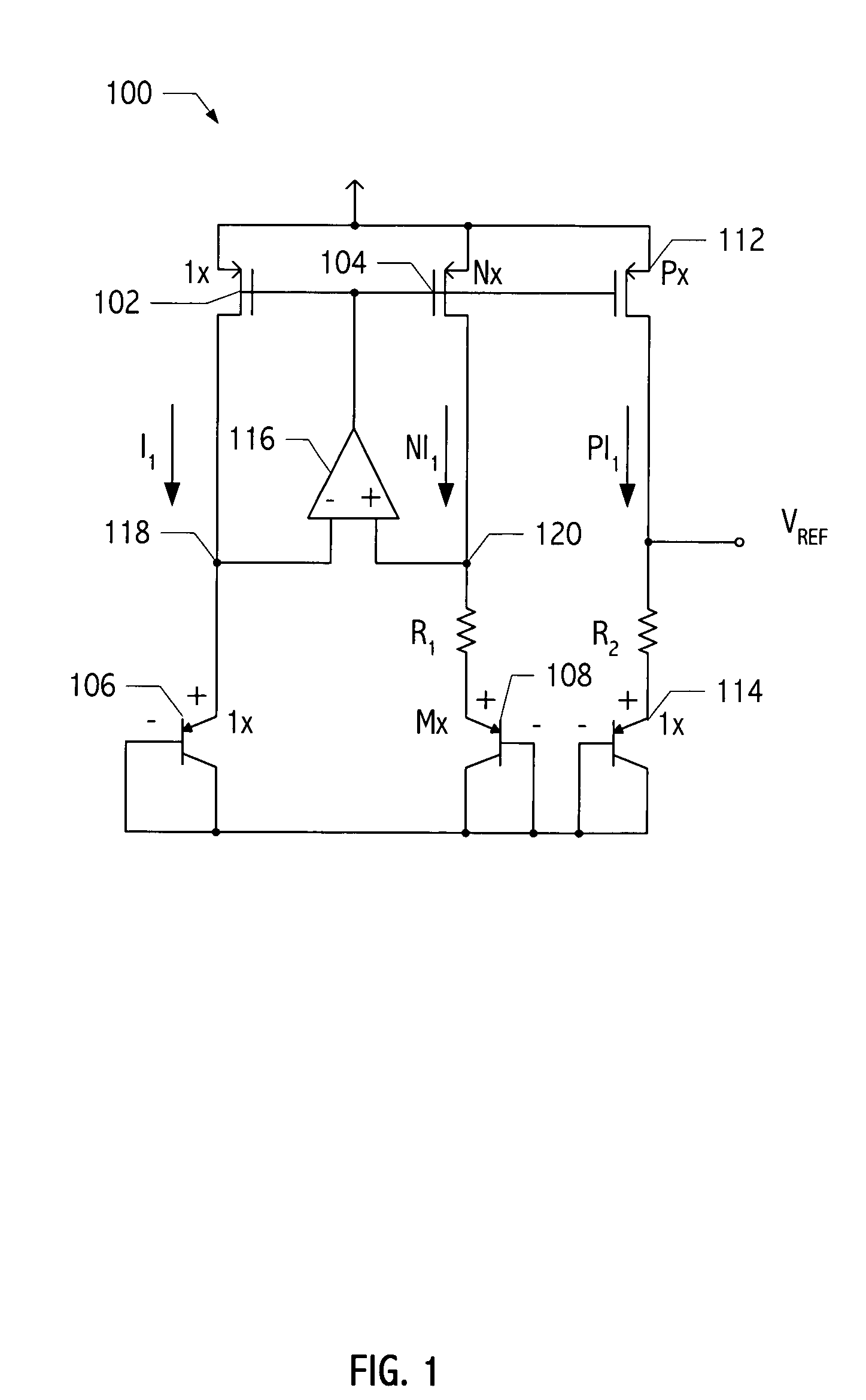
Voltage reference generator circuit using low-beta effect of a CMOS bipolar transistor
A voltage reference generator has been discovered that generates a stable reference voltage that is less than the bandgap voltage of silicon for power supply voltages less than 2V, yet provides sufficient voltage headroom to operate a cascaded current mirror. In one embodiment, the voltage reference generator has a power supply rejection ratio of at least 60 dB and has improved noise performance as compared to traditional bandgap circuits. These advantages are achieved by leveraging the low-beta effect of a CMOS bipolar transistor to generate a current proportional to an absolute temperature.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
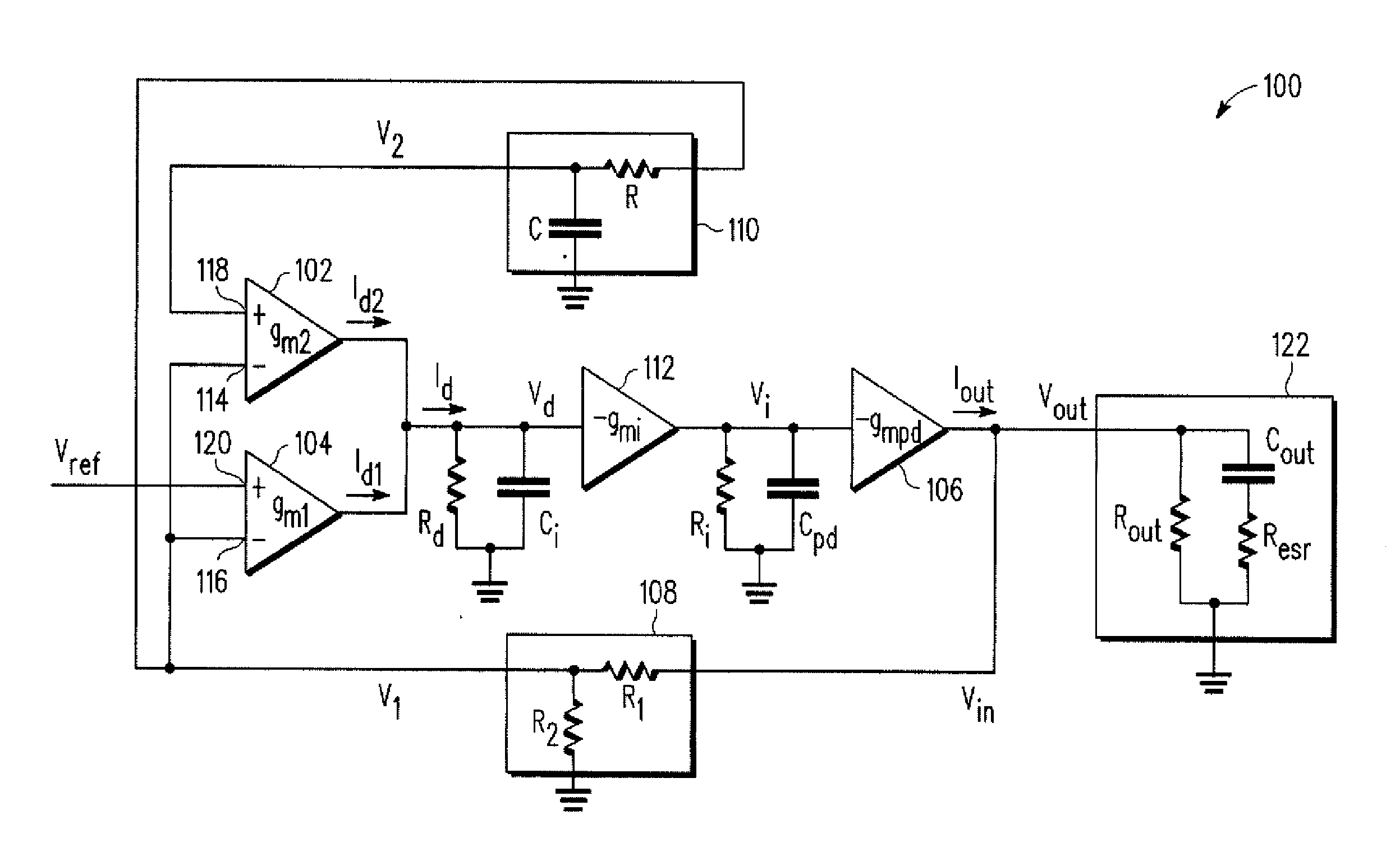
Low Pass Filter Low Drop-out Voltage Regulator
A low dropout voltage regulator is described having a pass device, differential amplifiers, and a feedback loop including a low pass filter. Two differential amplifiers arranged in parallel coupled to the low pass filter in the feedback loop provide a specified and stable DC voltage whose input-to-output voltage difference is low. Improved stability, reduced die area, improved power supply rejection ratio, increased bandwidth, decreased power consumption, and better electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection may result.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Ultralow temperature drift high power supply rejection ratio band-gap reference voltage source
InactiveCN106125811ASmall temperature coefficientHigh inhibition ratioElectric variable regulationEngineeringVoltage source
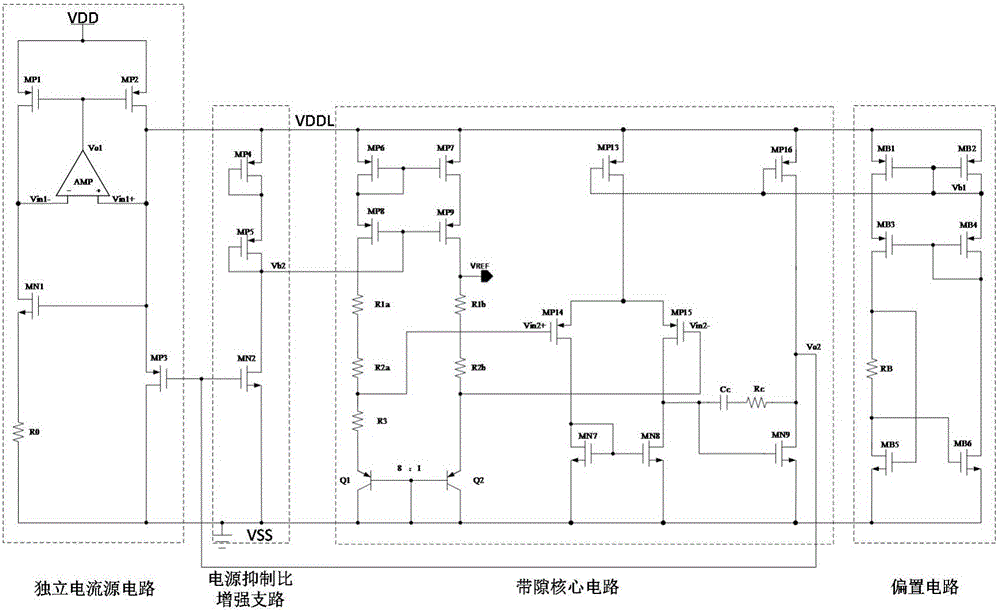
The invention provides an ultralow temperature drift high power supply rejection ratio band-gap reference voltage source, and relates to the field of analog integrated circuit design. Mainly aimed at problems of temperature drift and power supply rejection ratio of an existing reference source, a comprehensive solution is provided. The band-gap reference voltage source comprises an independent current source circuit, a biasing circuit, a band-gap core circuit, and a PSRR enhancing circuit. The independent current source circuit is used to generate current which is basically independent of supply voltage to supply power. The bias circuit generates bias voltage used for operational amplification of the band-gap core circuit. The band-gap core circuit uses temperature compensation to obtain reference voltage. The power supply rejection ratio (PSRR) enhancing circuit provides grid bias voltage of the band-gap core circuit and improves power supply rejection ratio. Beneficial effects of the band-gap reference voltage source are that temperature coefficient of band-gap reference is greatly reduced, and power supply rejection ratio is improved. The band-gap reference voltage source is suitable to be used for a radio frequency identification power management module.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
High-power supply rejection ratio, low-noise low-voltage difference linear voltage stabilizer
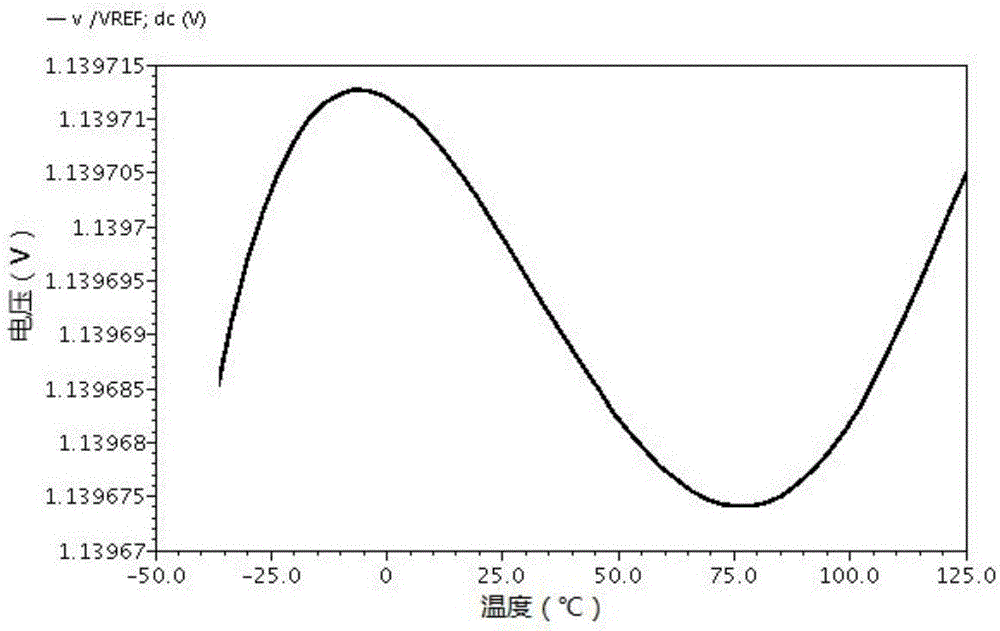
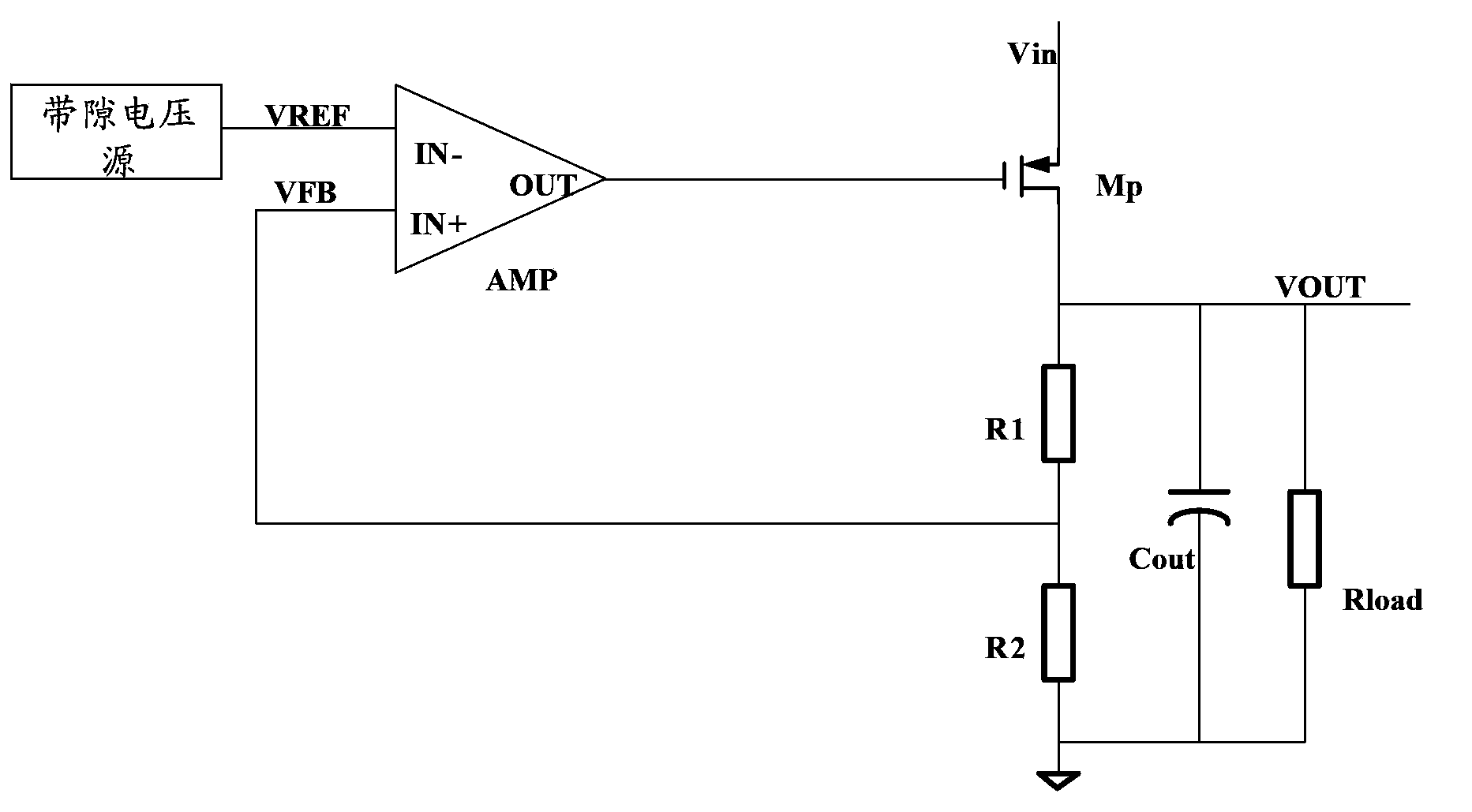
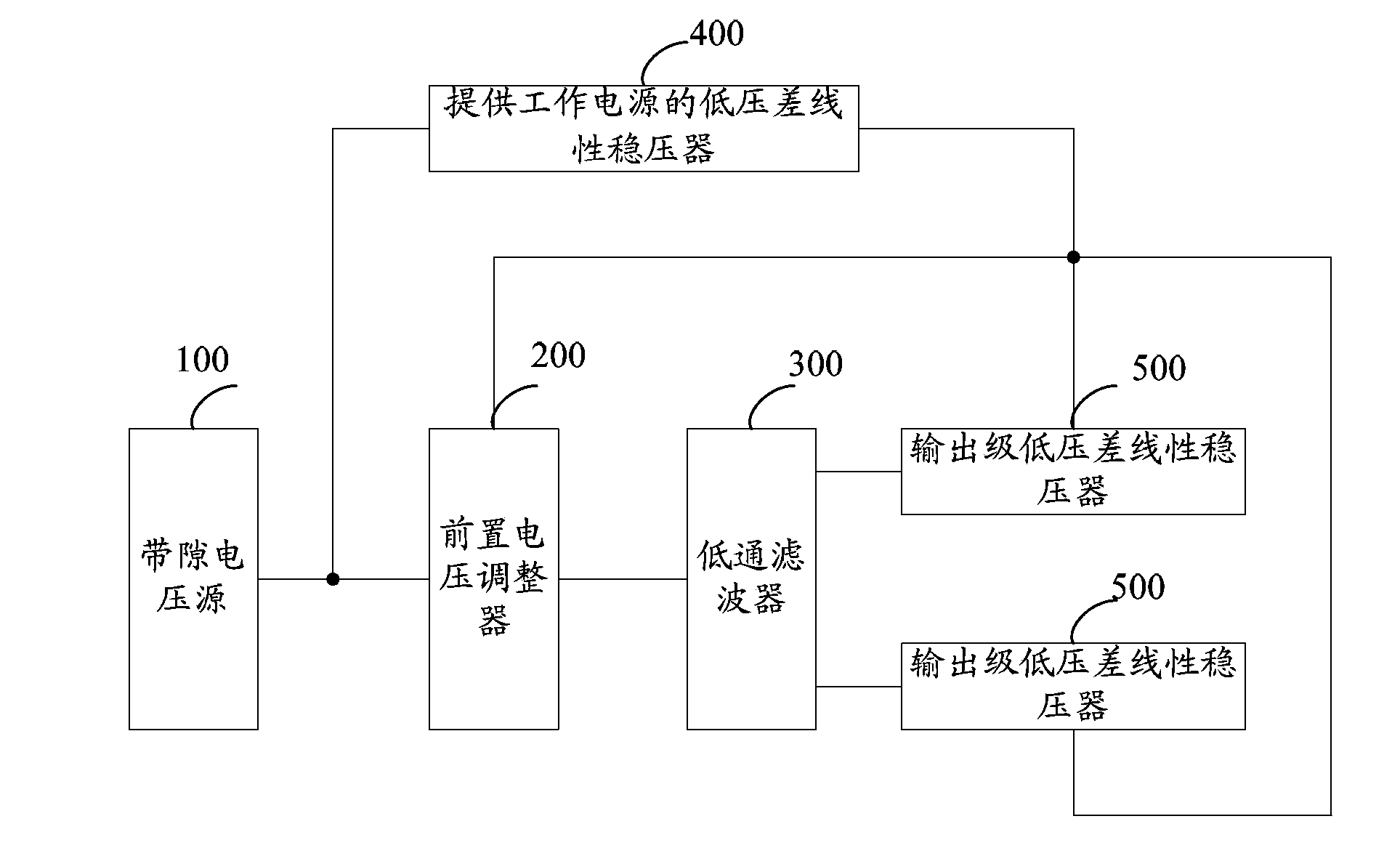
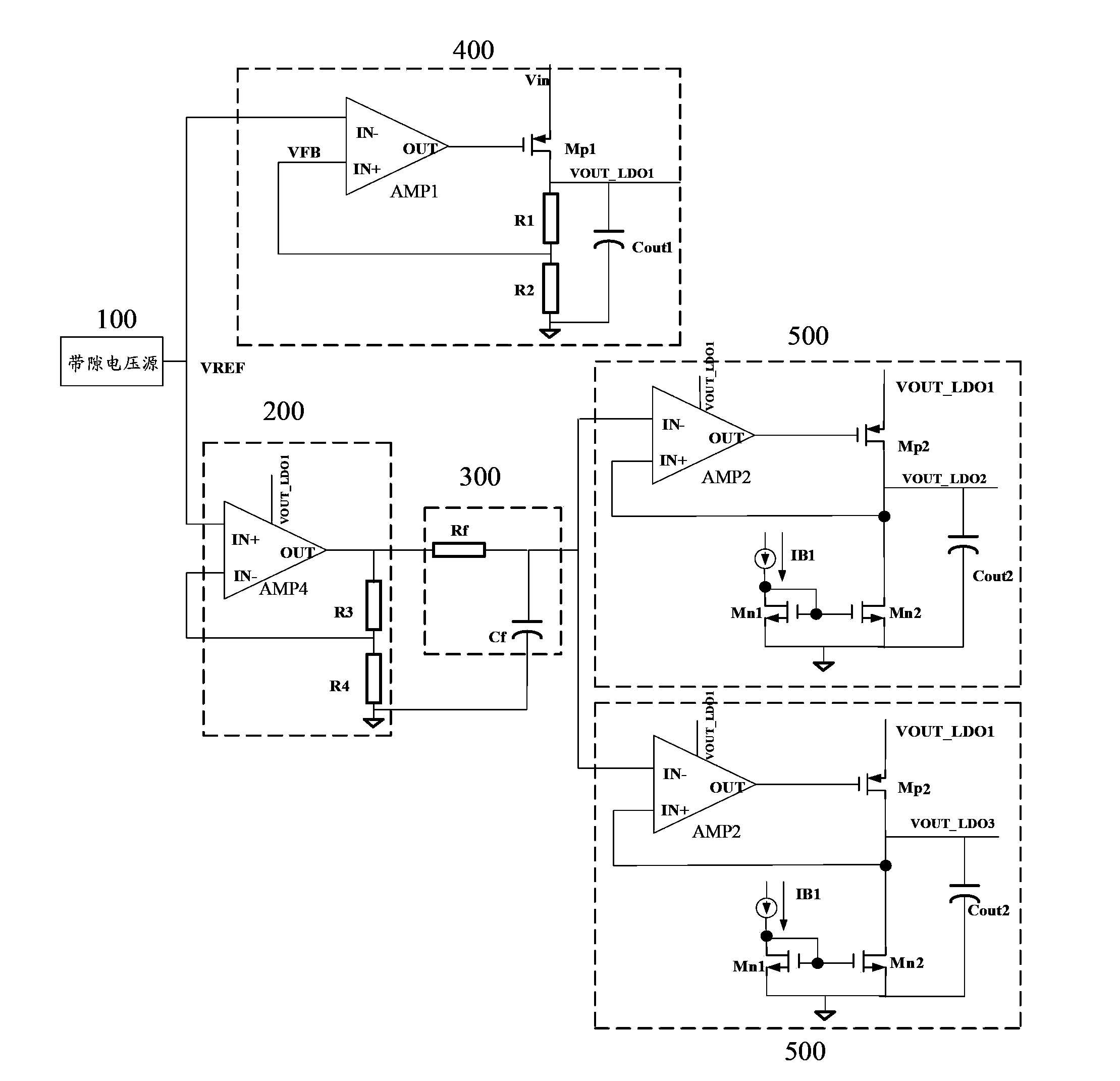
The invention provides a high-power supply rejection ratio, low-noise low-voltage difference linear voltage stabilizer, comprising a bandgap reference voltage source, a front positioned voltage regulator, a lowpass filter, a low-voltage difference linear voltage stabilizer for providing a work power supply and an output level low-voltage difference linear voltage stabilizer; the bandgap voltage source provides a reference voltage for the front positioned voltage regulator and the low-voltage difference linear voltage stabilizer for providing the work power supply; the output voltage of the low-voltage difference linear voltage stabilizer for providing the work power supply is used as the work voltage of the front positioned voltage regulator and an output level low-voltage linear voltage stabilizer; the reference voltage generated by the bandgap voltage source passes by the front positioned voltage regulator and the lowbass filter to provide the reference voltage for the output level low-voltage linear voltage stabilizer; the output level low-voltage linear voltage stabilizer comprises at least two same second level low-voltage difference linear voltage stabilizers; outputs of all second level low-voltage difference linear voltage stabilizer are independent. The low-voltage difference linear voltage stabilizer has the performance of low noise and can independently output in a multipath mode.
Owner:ANYKA (GUANGZHOU) MICROELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Low dropout regulator capable of on-chip implementation
A low-dropout regulator comprises a high-gain error amplifier having a differential input stage and a single-ended output, a high-swing high-positive-gain second stage with input connecting to the output of the error amplifier and a single-ended output, a p-type MOS transistor with gate terminal connecting to the output of the second stage, source terminal connecting to the supply voltage, and drain terminal to the output of the low-dropout regulator. A first-order high-pass feedback network connects the output of the low-dropout regulator and the positive input of the error amplifier, and a damping-factor-control means comprising a negative gain stage with a feedback capacitor connects the input and output of this gain stage. A capacitor is connected between the output of the error amplifier and the output of the low-dropout regulator, while a voltage reference connects to the negative input of the error amplifier. The regulator does not require an off-chip capacitor for stability and has improved load transient response and power supply rejection ratio.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Bandgap reference voltage source
ActiveCN102591394ASmall temperature coefficientImprove power supply rejection ratioElectric variable regulationEngineeringVoltage source
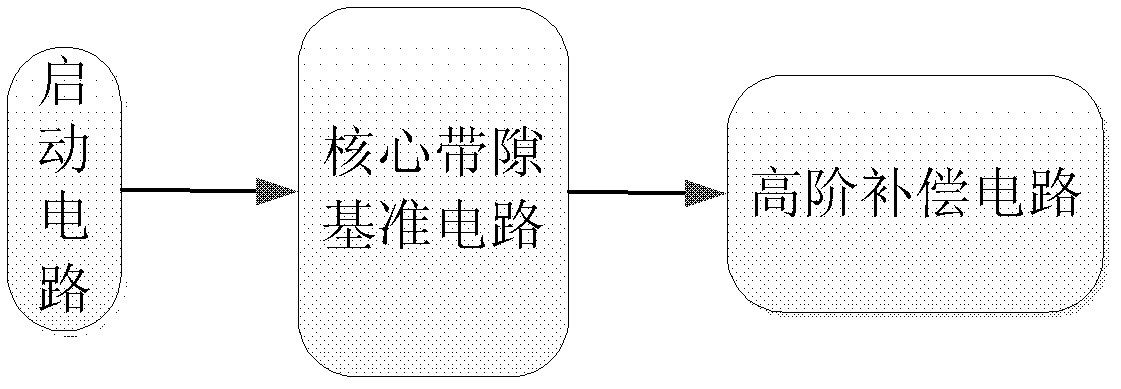
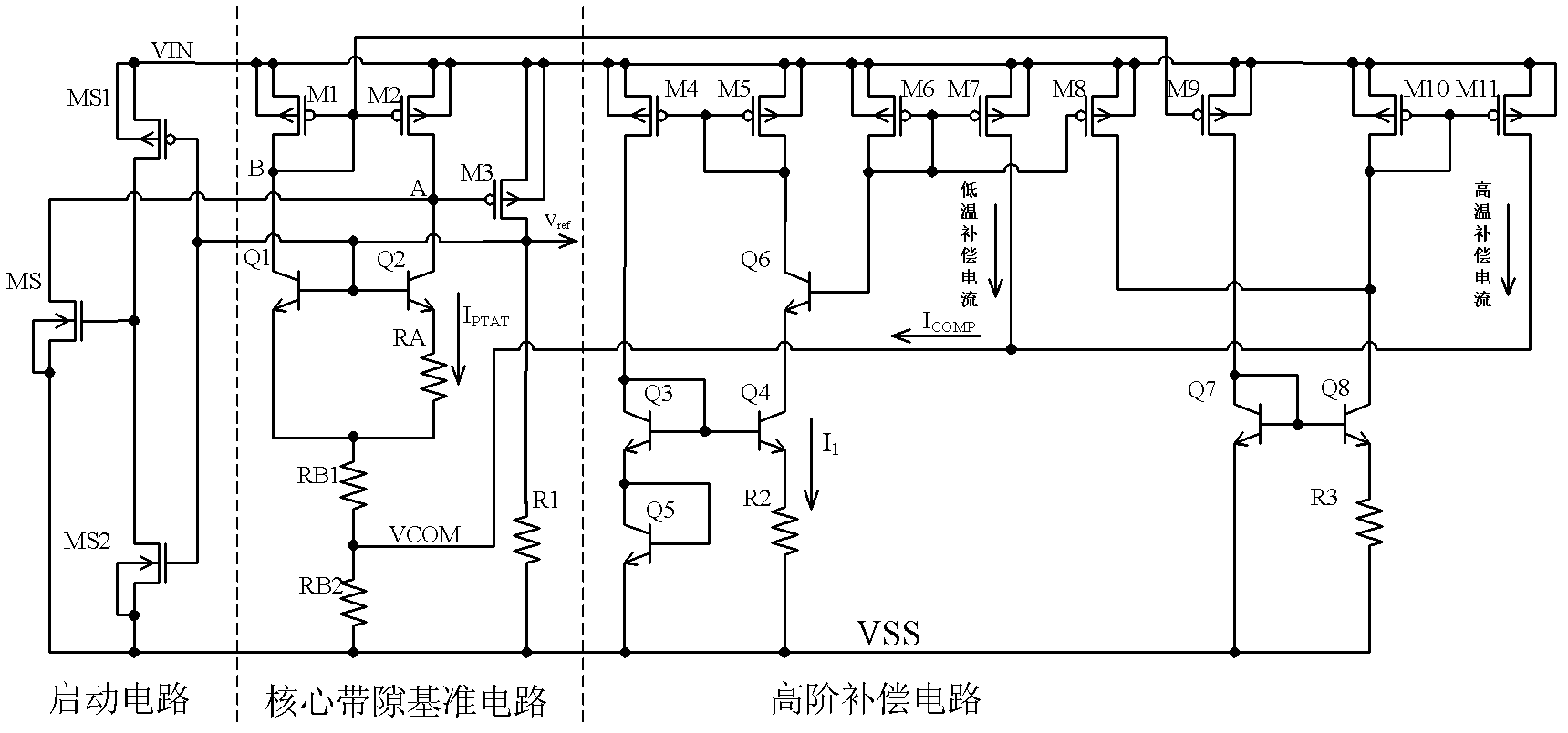
The invention discloses a bandgap reference voltage source which comprises a starting circuit, a core bandgap reference circuit and a high-order compensation circuit. The core bandgap reference circuit comprises PMOS tubes M1, M2 and M3, NPN triodes Q1 and Q2 and resistance units R1, RB1, RB2 and RA; and the high-order compensation circuit comprises PMOS tubes M4, M5, M6, M7, M8, M9, M10 and M11, NPN triodes Q3, Q4, Q5, Q6, Q7 and Q8 and resistance units R2 and R3. The bandgap reference voltage source disclosed by the invention adopts the high-order compensation circuit, thereby the temperature coefficient is reduced greatly; the circuits adopt the resistance ratio, thus the circuits can not be affected by the absolute value of the resistance, and the influence of the temperature coefficient of the resistance to the output quantity can be reduced. The bandgap reference voltage source has high power supply rejection ratio and can ensure that the circuits can resist the interference of a power supply.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
High-order temperature compensation band-gap reference circuit free of bipolar transistors
ActiveCN106774592AHigh inhibition ratioHigh precisionElectric variable regulationSub thresholdNegative temperature
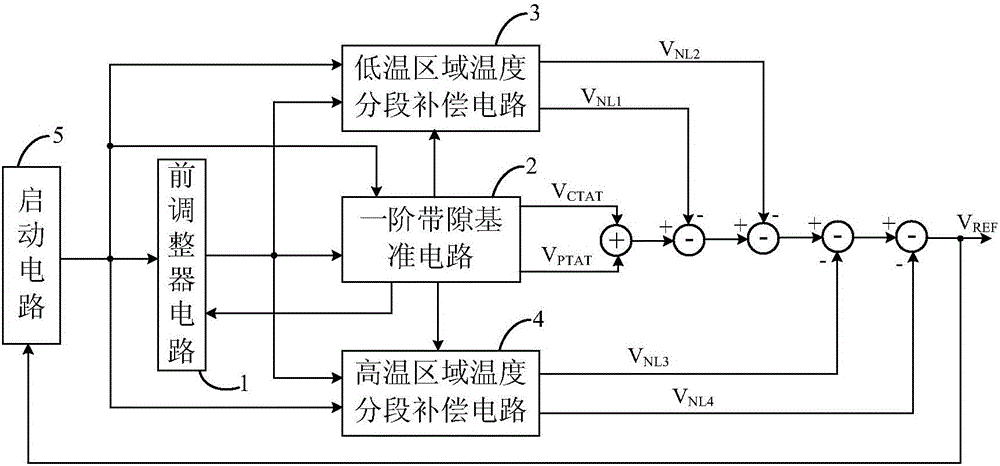
The invention provides a high-order temperature compensation band-gap reference circuit free of bipolar transistors. The high-order temperature compensation band-gap reference circuit free of the bipolar transistors comprises a front adjuster circuit, a first-order band-gap reference circuit, a low-temperature zone temperature sectional compensation circuit, a high-temperature zone temperature sectional compensation circuit and a starting circuit; a first-order band-gap reference voltage is obtained by adopting a negative-temperature-coefficient voltage VCTAT produced by a grid-source voltage of a sub-threshold NMOS (N-channel metal oxide semiconductor) transistor and a positive-temperature-coefficient voltage VPTAT produced by difference between grid-source voltages of two sub-threshold NMOS transistors, low-temperature zone temperature sectional compensation voltages (VNL1 and VNL2) and high-temperature zone temperature sectional compensation voltages (VNL3 and VNL4) are introduced into the first-order band-gap reference voltage produced by the first-order band-gap reference circuit, a band-gap reference voltage with low temperature coefficient is obtained, and a power supply rejection ratio of band-gap reference is increased with a front adjuster technology, so that the high-order temperature compensation band-gap reference circuit free of the bipolar transistors is obtained.
Owner:重庆医之舟信息科技有限公司
Bandgap reference with high power supply rejection ratio
ActiveCN108958348AHigh ability to suppress PSRThe voltage value is stableElectric variable regulationNegative temperatureLow voltage
The invention discloses a bandgap reference with a high power supply rejection ratio, and belongs to the technical field of electronic circuits. The bandgap reference comprises a power automatic biasing module, a starting module, a bandgap reference core module and a biasing module, power voltage is converted into a first power rail signal by the power automatic biasing module through a seventh NMOS tube to serve as a power rail of the biasing module, biasing is established for the biasing module by the starting module and the power automatic biasing module, and biasing is provided for the bandgap reference core module by the biasing module; second and third switch tubes of the starting circuit operate to prevent a whole circuit from being maintained in a zero state when power is established, and the second and third switch tubes of the starting circuit stop operating after the circuit enters a normal working condition; a resistance network in the starting circuit is used for adjustingthe negative temperature coefficient voltage of the bandgap reference core module, and the adjusted negative temperature coefficient voltage and positive temperature coefficient voltage generated bythe bandgap reference core module overlap to generate a reference voltage. The bandgap reference with the high power supply rejection ratio has the advantages of higher power rejection capability, simple structure, high accuracy and high stability.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Reference voltage generator and method for providing multiple reference voltages
ActiveCN101329586ALarge voltage marginElectric variable regulationElectrical resistance and conductanceVoltage generator
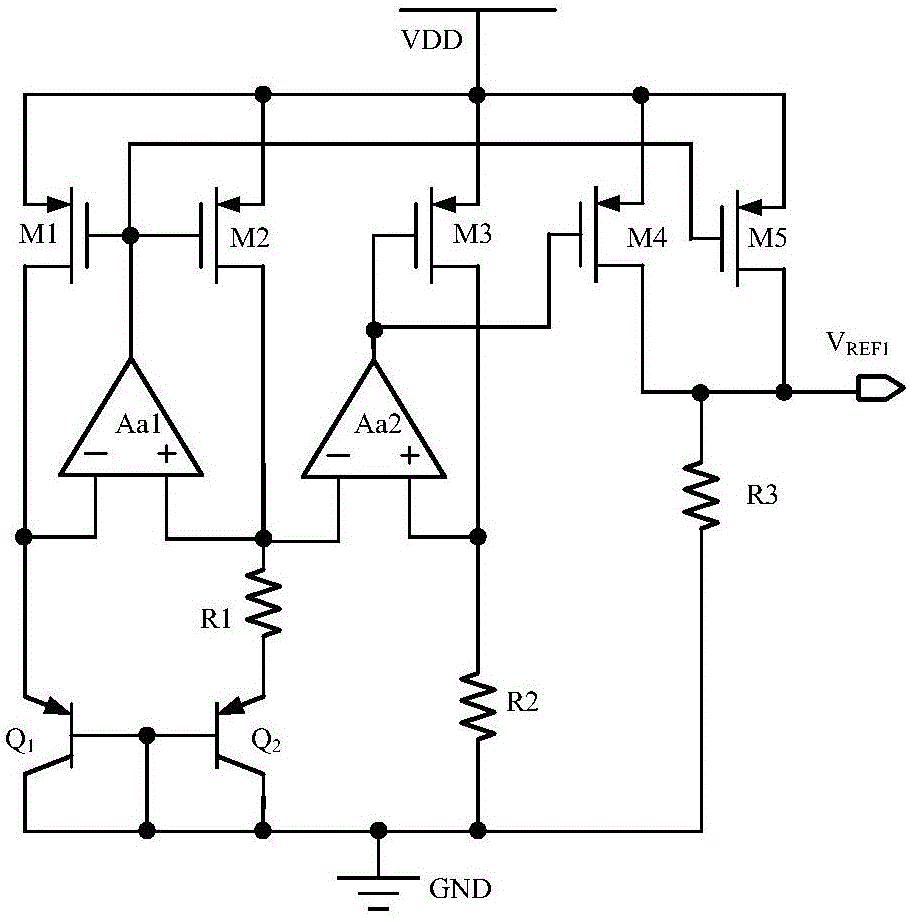
The present invention relates to a reference voltage generator and a method for providing a plurality of reference voltages. The reference voltage generator comprises a voltage regulator, a band-voltage circuit and an amplifying circuit. The voltage regulator with an input node is coupled to an external power supply for generating a regulated voltage source. The band-gap voltage circuit includes a first resistor and a second resistor and a first transistor and a second transistor to generate a voltage difference between the base-to-emitter voltages of the first and the second transistors. The first resistor is coupled to the first transistor. The second resistor is coupled to the first resistor, the first transistor and a regulated voltage source, the second resistor is coupled to the first resistor and a first transistor for generating the first predetermined voltage in response to the voltage difference. The amplifier circuit is coupled to the first transistor of the band-gap voltage circuit for receiving a first amplifying signal and generating an amplified signal so as to regulate the regulated voltage source. The present invention can generate an input reference voltages according under the more supply source and can improve more voltage sources.
Owner:AOTU ELECTRONICS WUHAN
CMOS subthreshold high-order temperature compensation bandgap reference circuit
InactiveCN101609344AHigh rejection ratioSmall temperature coefficientElectric variable regulationCMOSElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention discloses a CMOS subthreshold high-order temperature compensation bandgap reference circuit comprising a current mould bandgap reference circuit and a feedback control loop, wherein the current mould bandgap reference circuit comprises six PMOS pipes, four NMOS pipes and five resistors, and the feedback control loop comprises two PMOS pipes and four NMOS pipes. The invention has lower temperature coefficient and higher power supply suppression ratio. By adopting a CMOS technology library with a CSMC0.5mum standard, the obtained temperature coefficient temperature coefficient is after simulation only 0.42ppm / DEG C, and the PSRR under low frequency reaches more than 78dB.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
High-fidelity D type voice frequency amplifier
InactiveCN102832887AReduce power consumptionImprove efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionEnergy efficient ICTTotal harmonic distortionPerformance index
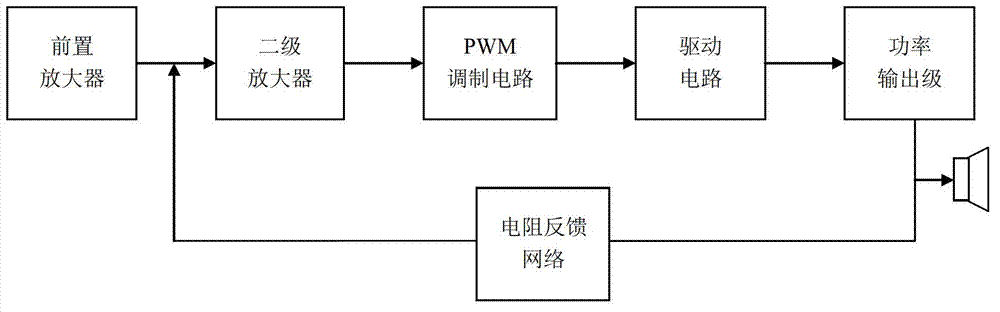
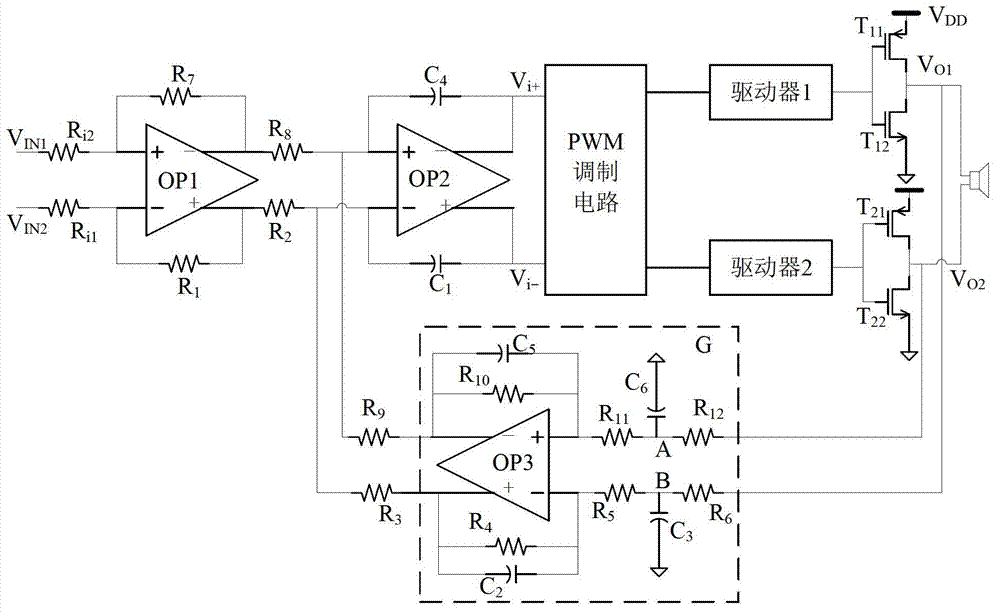
The invention relates to a voice frequency power amplifier, and discloses a high-fidelity D type voice frequency amplifier aiming at the shortcoming of a filter-free D type voice frequency amplifier in the prior art, which improves the performance index of the filter-free D type voice frequency amplifier by improvement of a feedback network and optimum design of a circuit. The high-fidelity D type voice frequency amplifier comprises a preamplifier, a two-stage amplifier, a PWM (pulse width modulation) circuit, a driving circuit, a power amplifier and a feedback network, wherein the feedback network adopts an active RC (resistance-capacitance) filter network, effectively inhibits the errors of PWM signal phase and duty ratio in the modulation process, realizes superior total harmonic distortion (THD) and noise performance index and has lower intermodulation distortion (IMD) as compared with the traditional resistance feedback network. The voice frequency power amplifier has the characteristics of high efficiency, low power consumption and high PSRR (power supply rejection ratio), guarantees the stability of the whole amplifier and is very suitable for the requirements of mobile communication equipment and other portable type systems.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
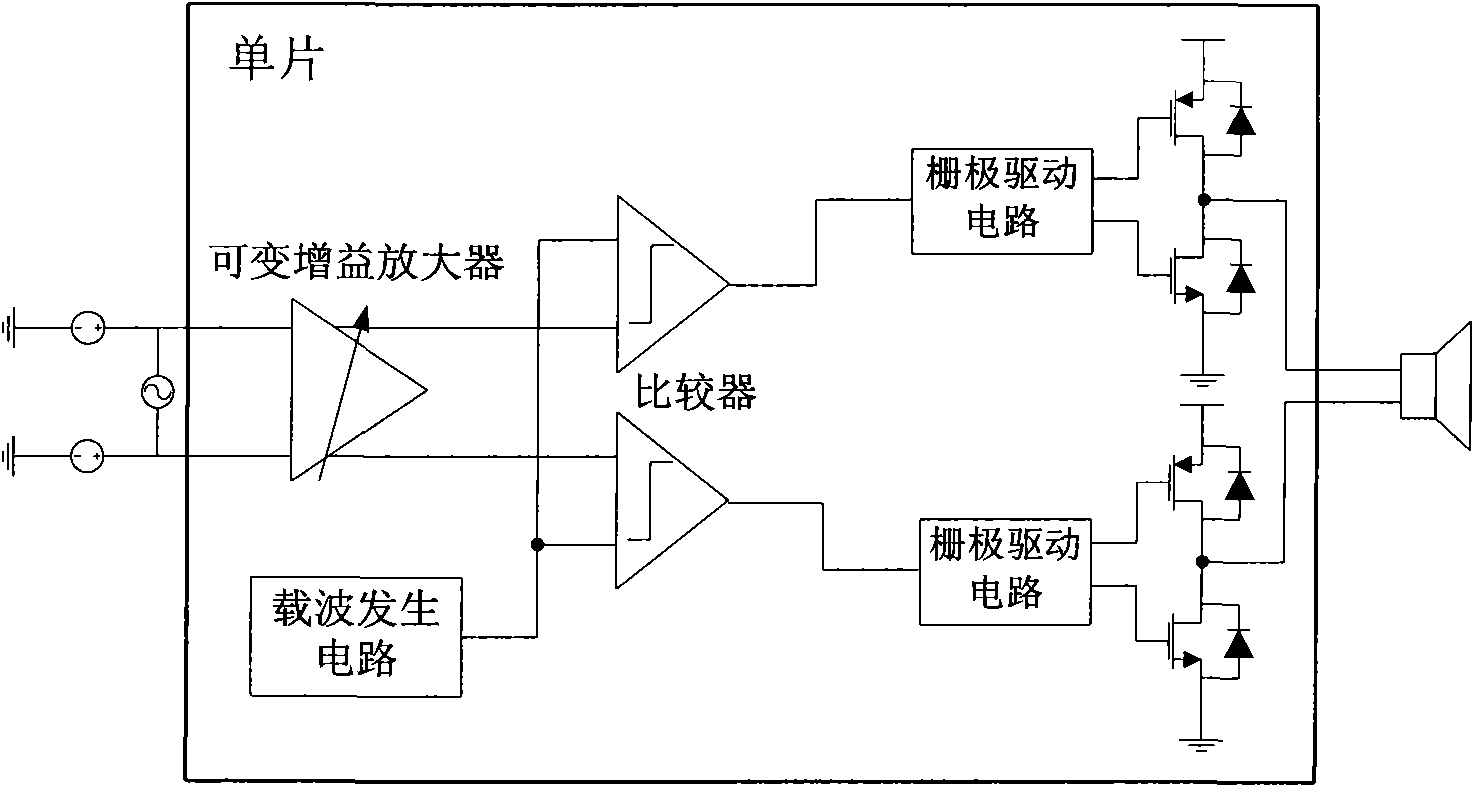
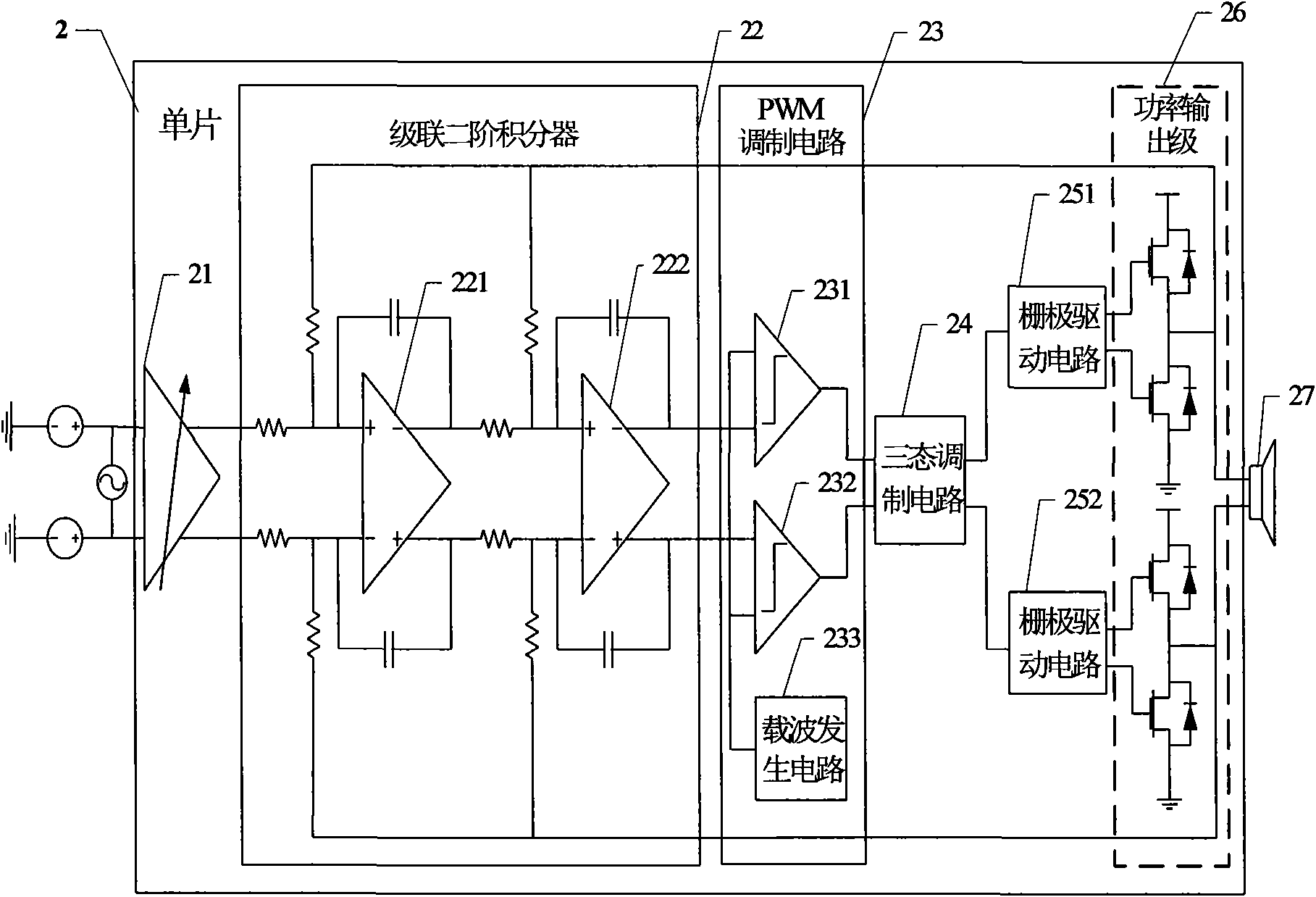
High-performance D type audio power amplifier with high-order multipath feedback structure
InactiveCN101847968AAvoid inability to guarantee stabilityImprove performanceAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceIntegratorTotal harmonic distortion
The invention discloses a high-performance D type audio power amplifier adopting high-order multipath feedback structure, which comprises a prepositive variable gain amplifier, an integrator, a pulse width modulation (PWM) circuit, a three-state regulating circuit, a grid driving circuit and a power output stage. The integrator is in a two-order structure formed by cascade connection of two stages of integrators, and two paths of feedback are introduced to form a higher-order double-feedback loop, thereby effectively increasing the loop gain and the out-off-band attenuation, and obviously improving the suppression ratio of total harmonic distortion and noise to power sources and other main properties in the range of audio frequency band (22Hz-22KHz). By introducing two paths of voltage negative feedback and comprehensively considering the input dynamic range, the signal-to-noise ratio and stability factors, the ratio of two stages of feedback coefficients can be regulated by regulating the ratio of the input resistance and the feedback resistance of two stages of integrators, thereby ensuring the stability of a system. The D type audio power amplifier with the structure has the characteristics of high integration level and high performance and can be widely applied to the fields of portable equipment, consumer electronics and the like.
Owner:杭州中科微电子有限公司
LDO circuit with dynamic compensation and rapid transient response
ActiveCN107797599AGuaranteed stabilityImprove power supply rejection ratioElectric variable regulationEngineeringHeavy load
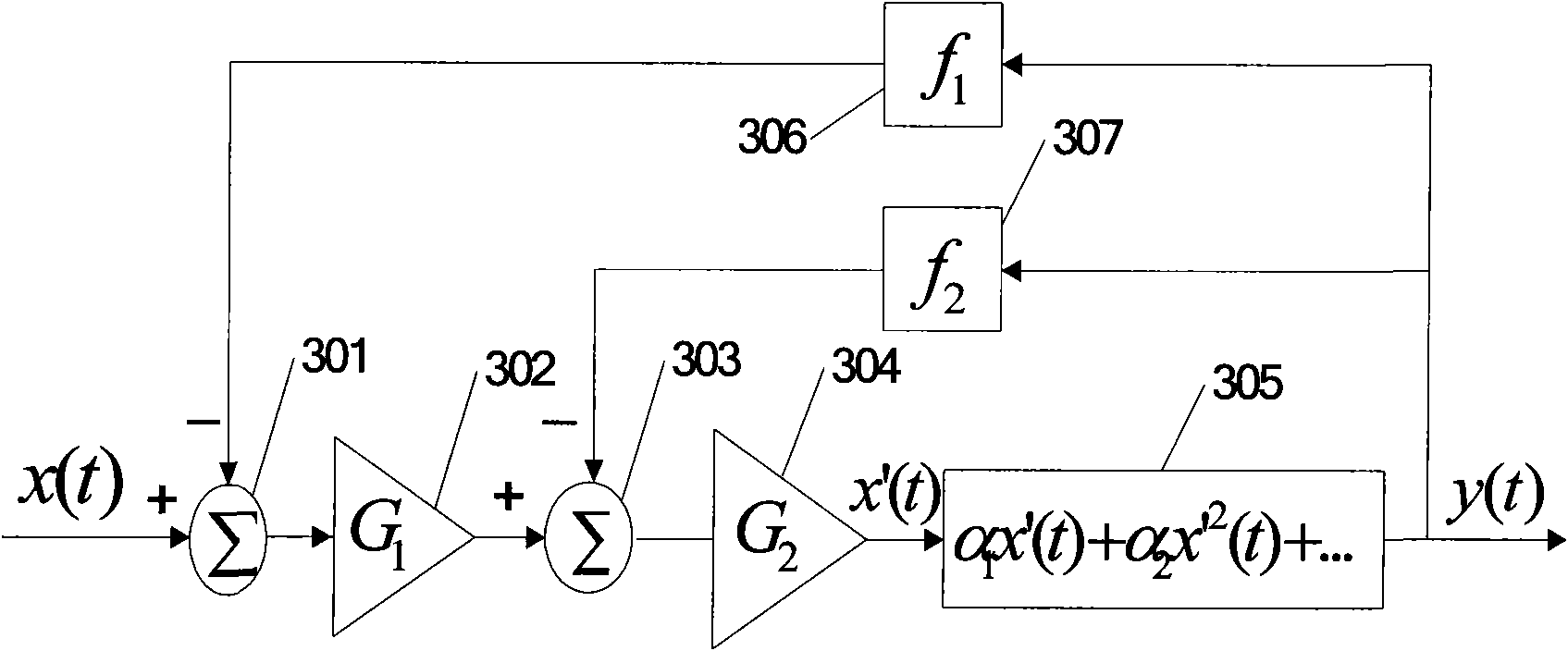
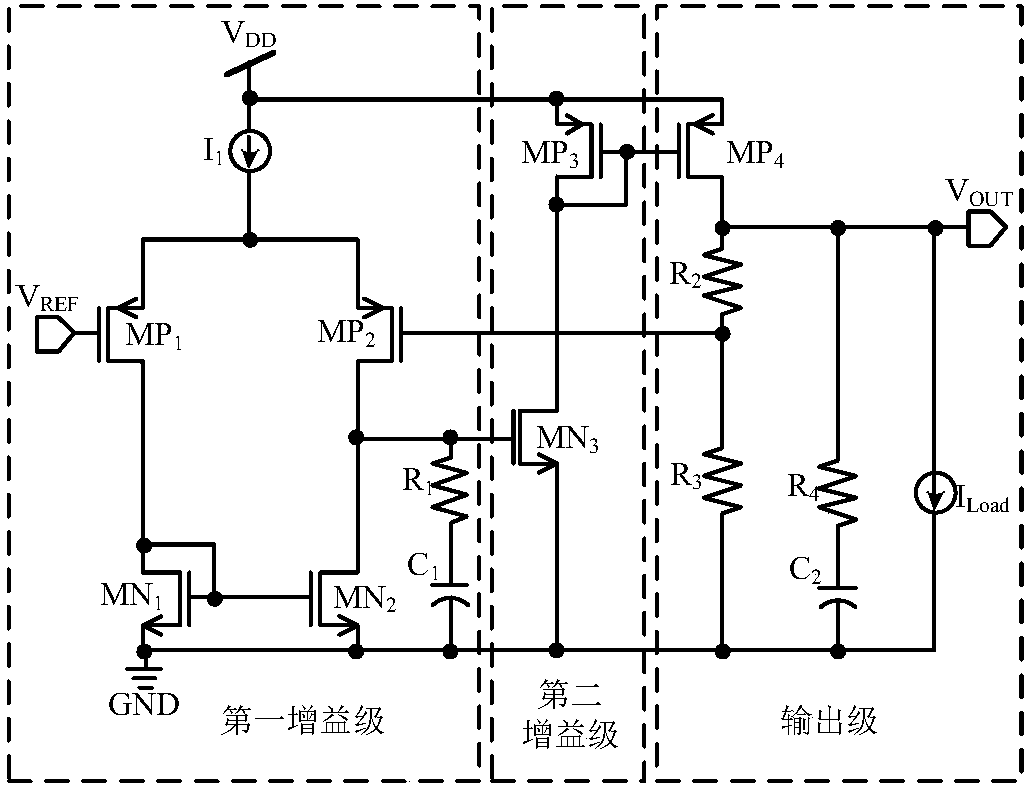
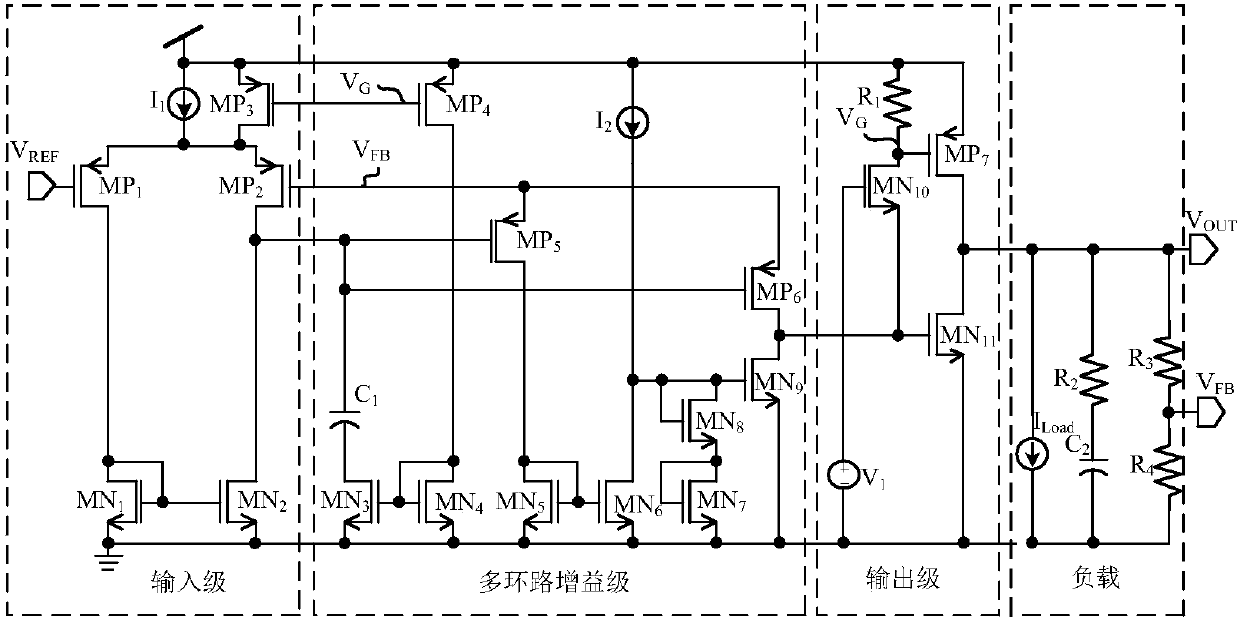
The embodiment of the invention relates to the technical field of analog integrated circuits, in particular to an LDO circuit with dynamic compensation and rapid transient response. The circuit comprises an input stage, a multi-loop gain stage, an output stage and a load stage. By introducing the dynamic bias mode, gain of the input stage, C1 in the multi-loop gain stage and a pole-zero doublet introduced by an MOS resistor RMN3 working in a deep linear region are related to load current ILoad, and the stability of loops within the whole load range is ensured. Meanwhile, due to the dynamic bias mode, the unity-gain bandwidth of the input stage becomes larger, and the power supply rejection ratio of the circuit is increased. In addition, MP6 and MN11 adopted in the multi-loop gain stage, sothat discharging of charges on an output cavity can be accelerated, and the circuit response speed during hopping from heavy load to light load is increased. Due to the MN9, discharging of charges ona power tube MP7 grid stray capacitor can be accelerated, and the response speed of the circuit during hopping from light load to heavy load is increased.
Owner:58TH RES INST OF CETC
Non-resistance type reference source
InactiveCN107256062AGood temperature characteristicsReduce power consumptionElectric variable regulationReference circuitPositive temperature
The invention discloses a non-resistance type reference source, and belongs to the technical field of power supply management. The non-resistance type reference source comprises a starting circuit, a reference voltage generation circuit and a bias current generation circuit, wherein when a power supply is constructed, the starting circuit makes the reference source disengaged from a zero state and then retreats after starting is completed; a PMOS pipe with large threshold voltage negative temperature coefficient and an NMOS pipe with small negative temperature coefficient are selected, the negative temperature voltage in reference voltage is obtained through the threshold voltage difference of the PMOS pipe and the NMOS pipe, the positive temperature voltage is determined according to the thermal voltage, the sub-threshold slope factor and the related width-to-length ratio of the MOS pipe, and then the reference voltage VREF with good temperature characteristics can be obtained; bias currents with positive temperature characteristics are generated through the NMOS pope working in a sub-region, and the positive temperature characteristics of the currents can be enhanced when temperature rises. On the basis of traditional threshold reference, reference circuit branches are reduced, so power consumption of a reference circuit is reduced, and the power supply rejection ratio of the reference voltage is increased.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com