Patents
Literature
193 results about "Push–pull output" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
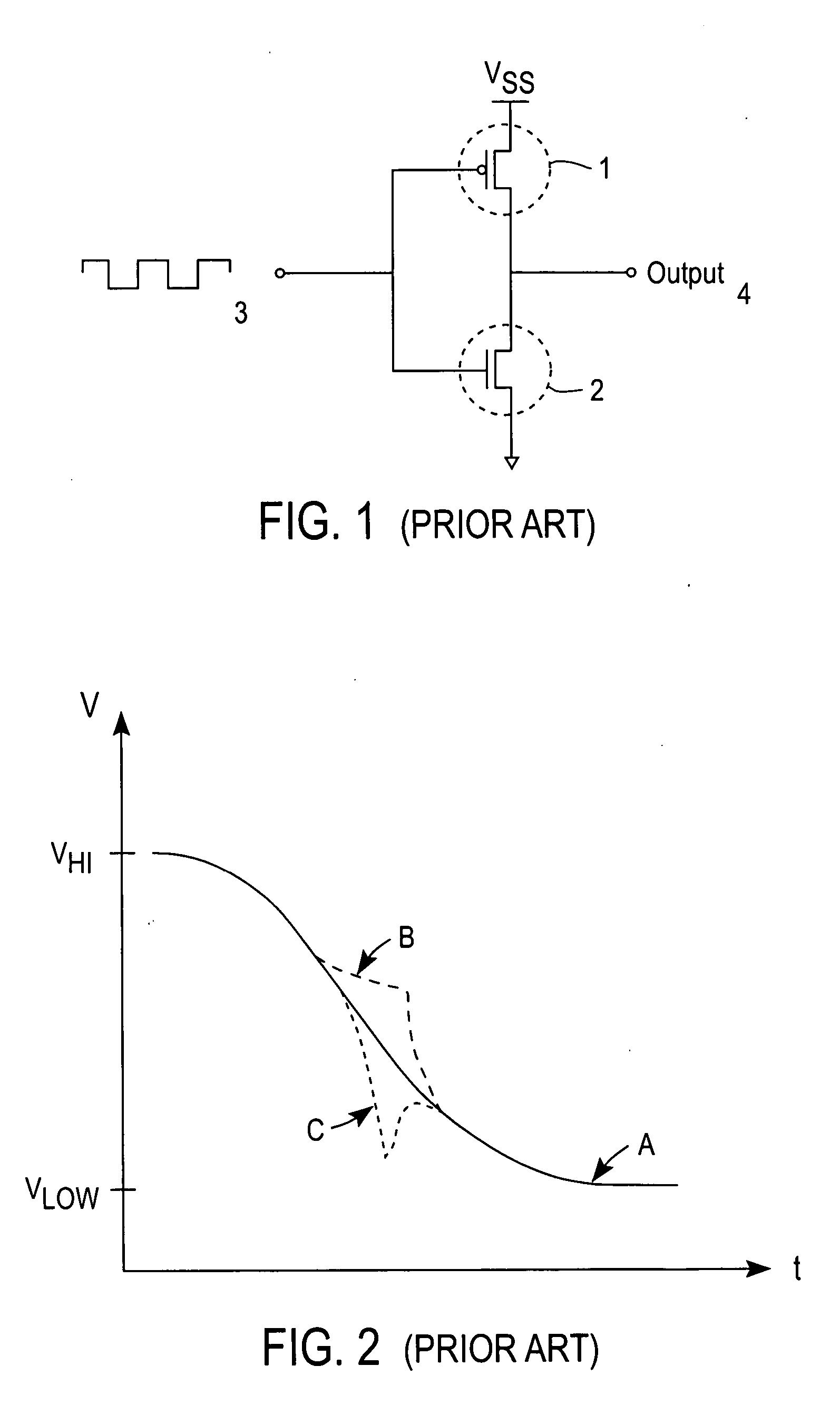
A push–pull amplifier is a type of electronic circuit that uses a pair of active devices that alternately supply current to, or absorb current from, a connected load. Push–pull outputs are present in TTL and CMOS digital logic circuits and in some types of amplifiers, and are usually realized as a complementary pair of transistors, one dissipating or sinking current from the load to ground or a negative power supply, and the other supplying or sourcing current to the load from a positive power supply.
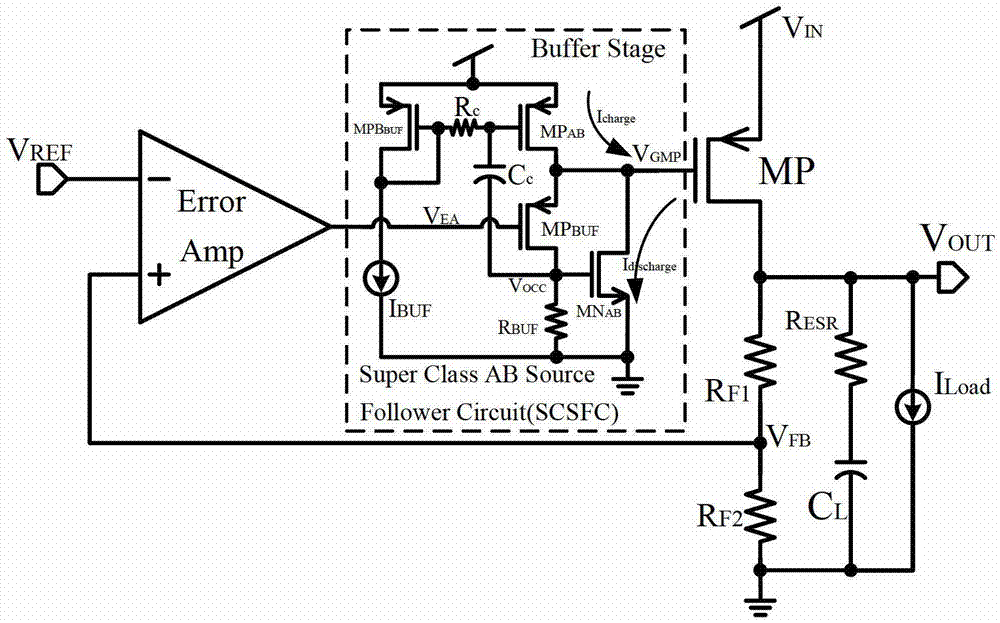
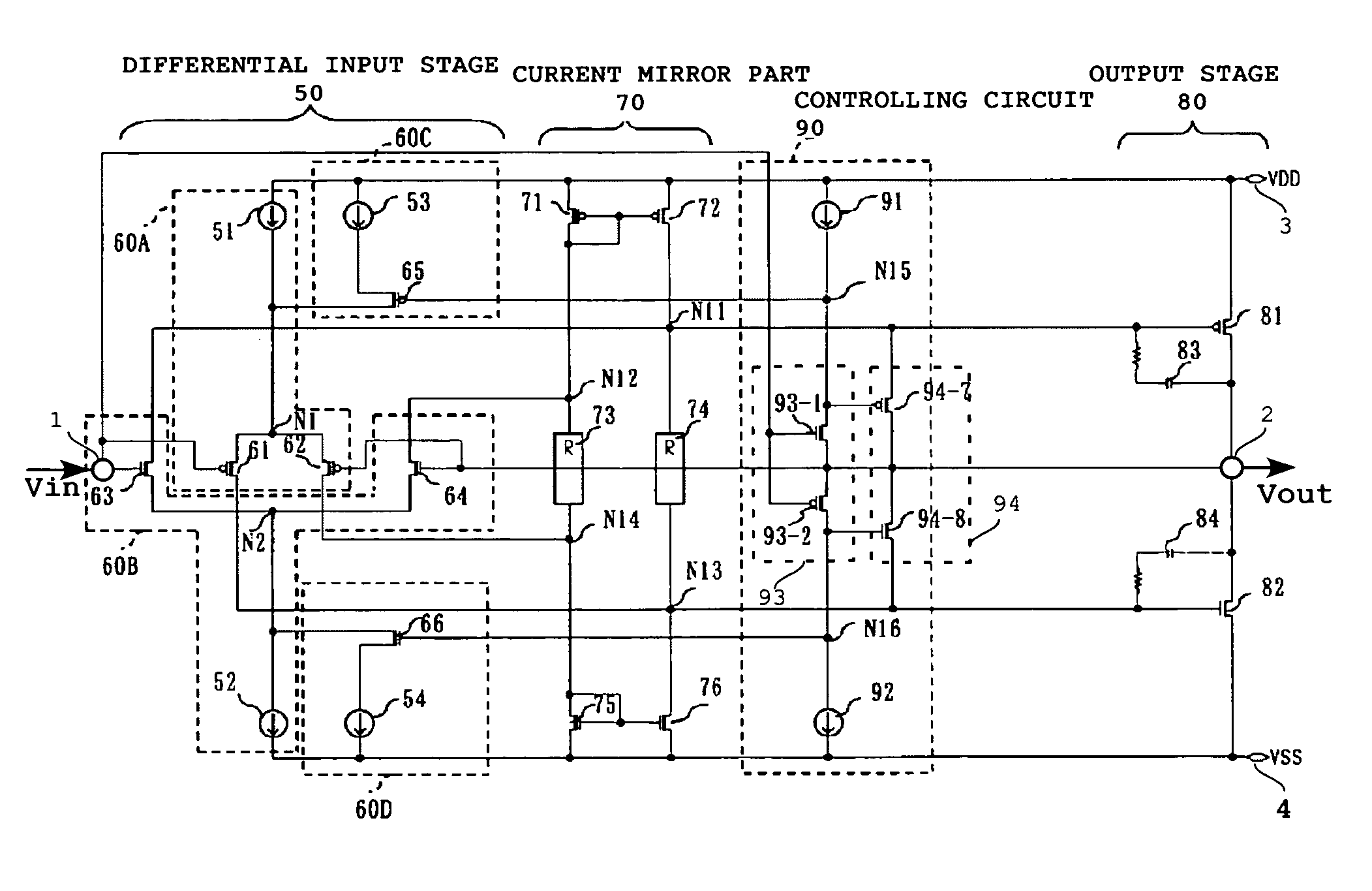
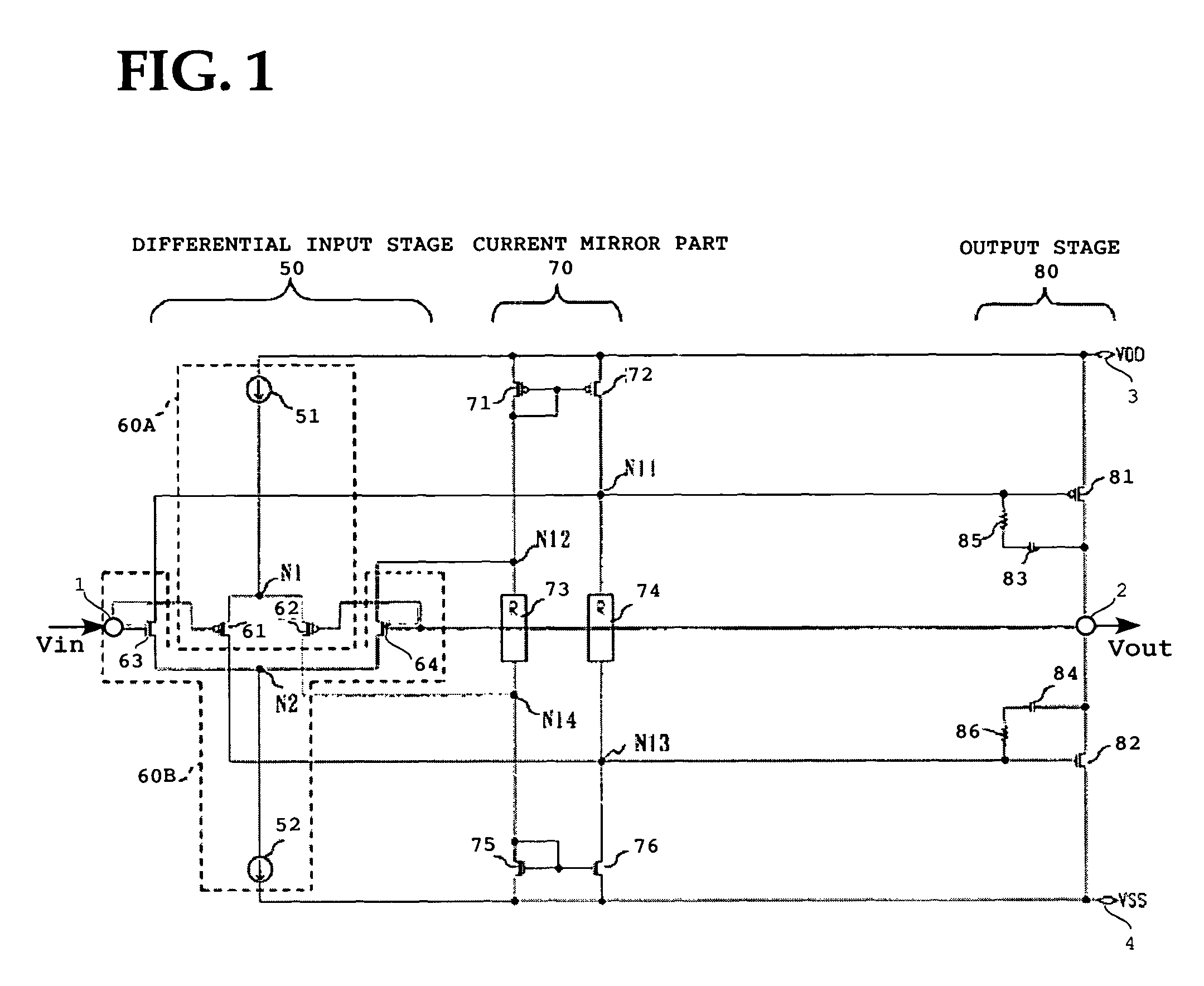
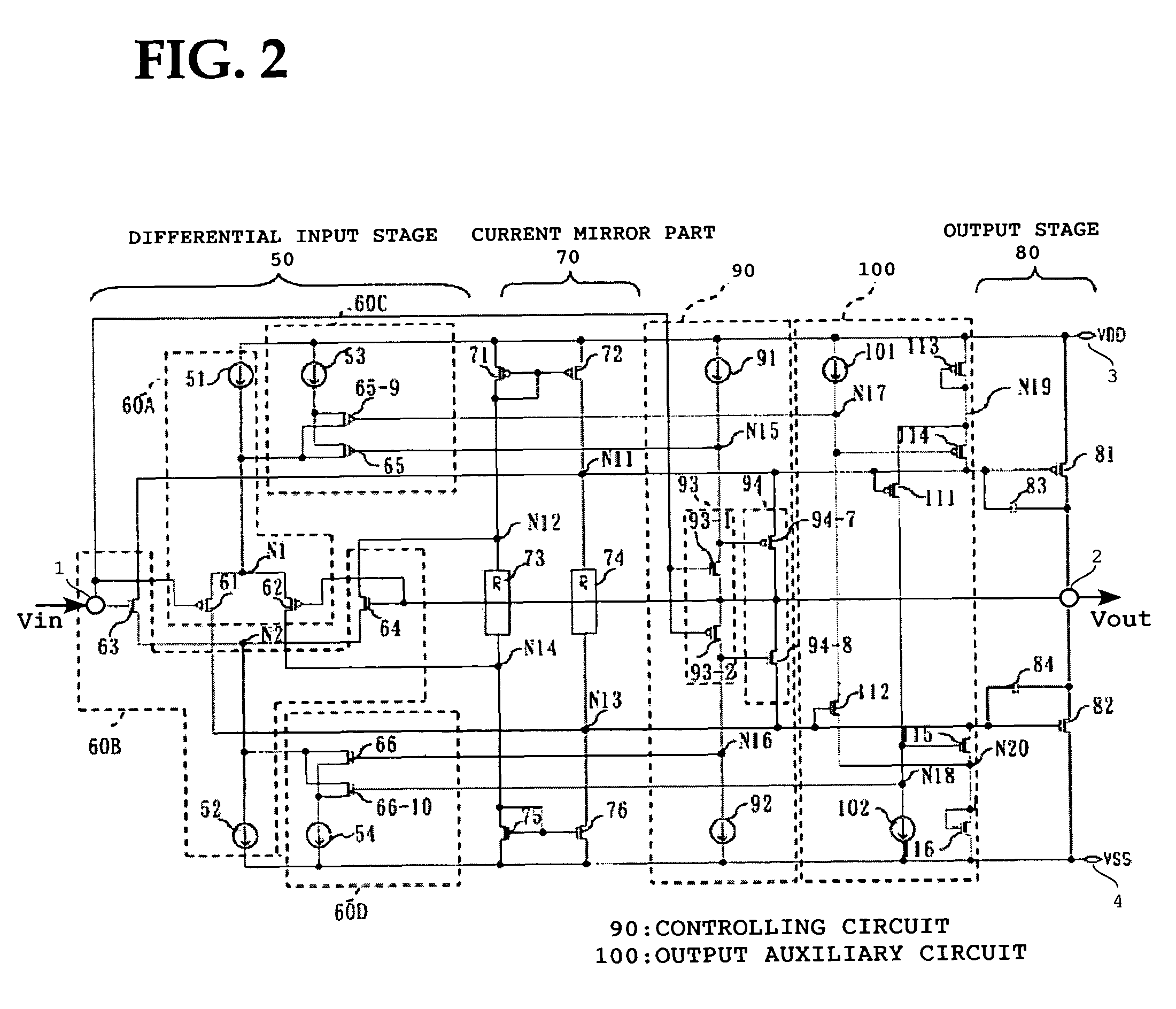
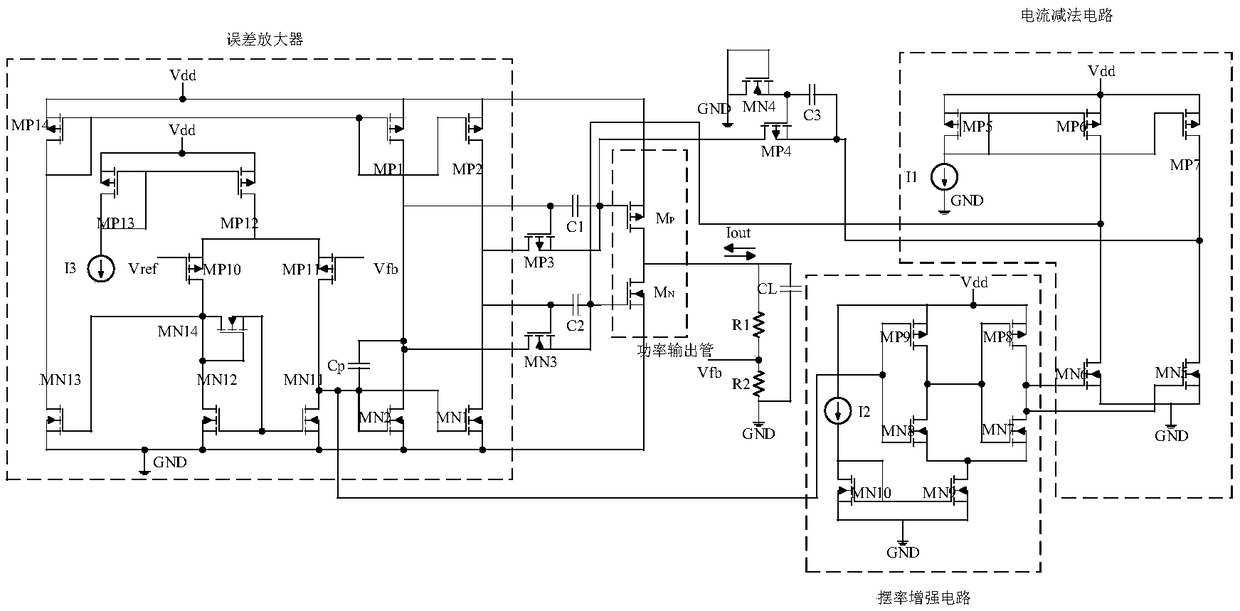
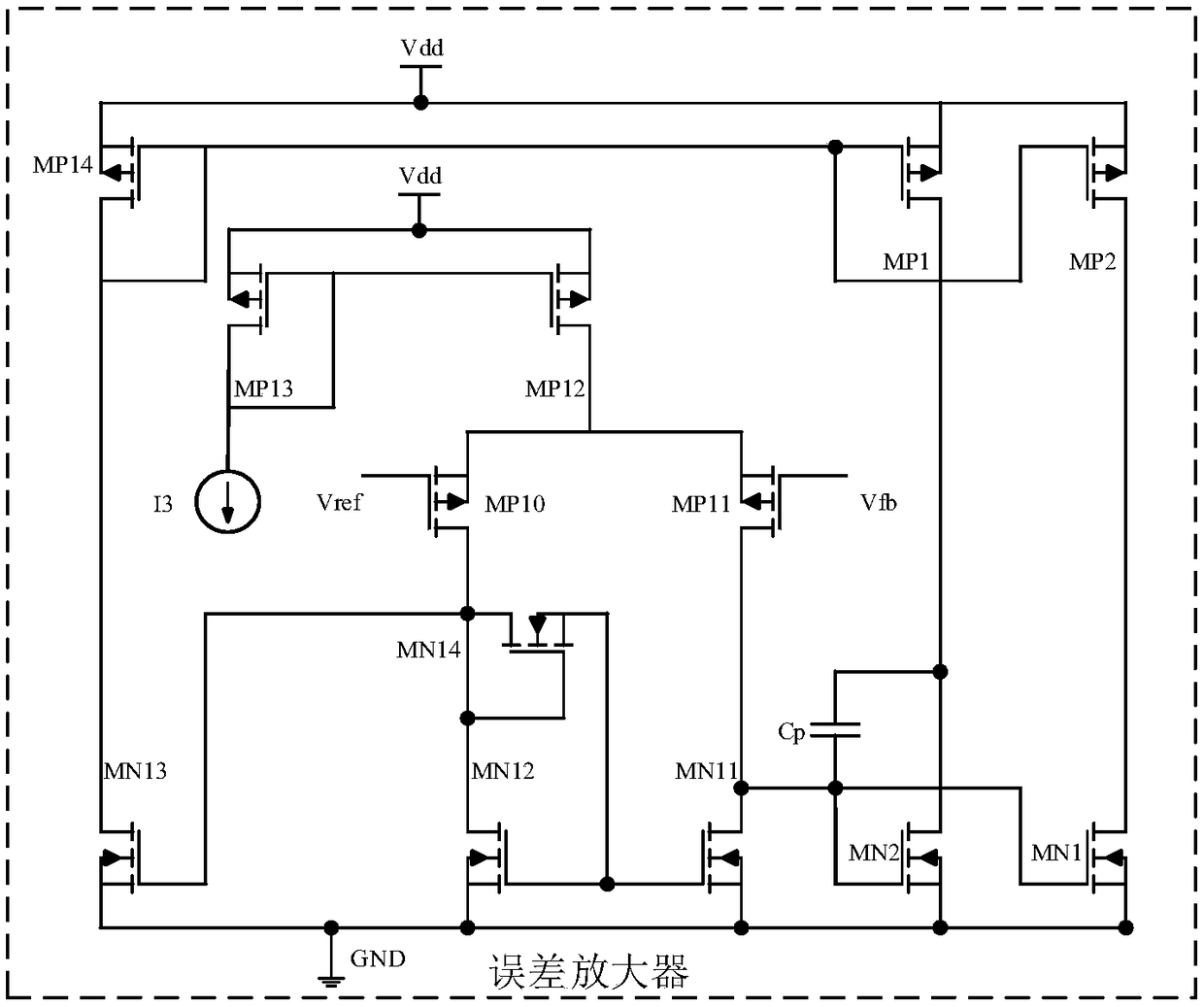
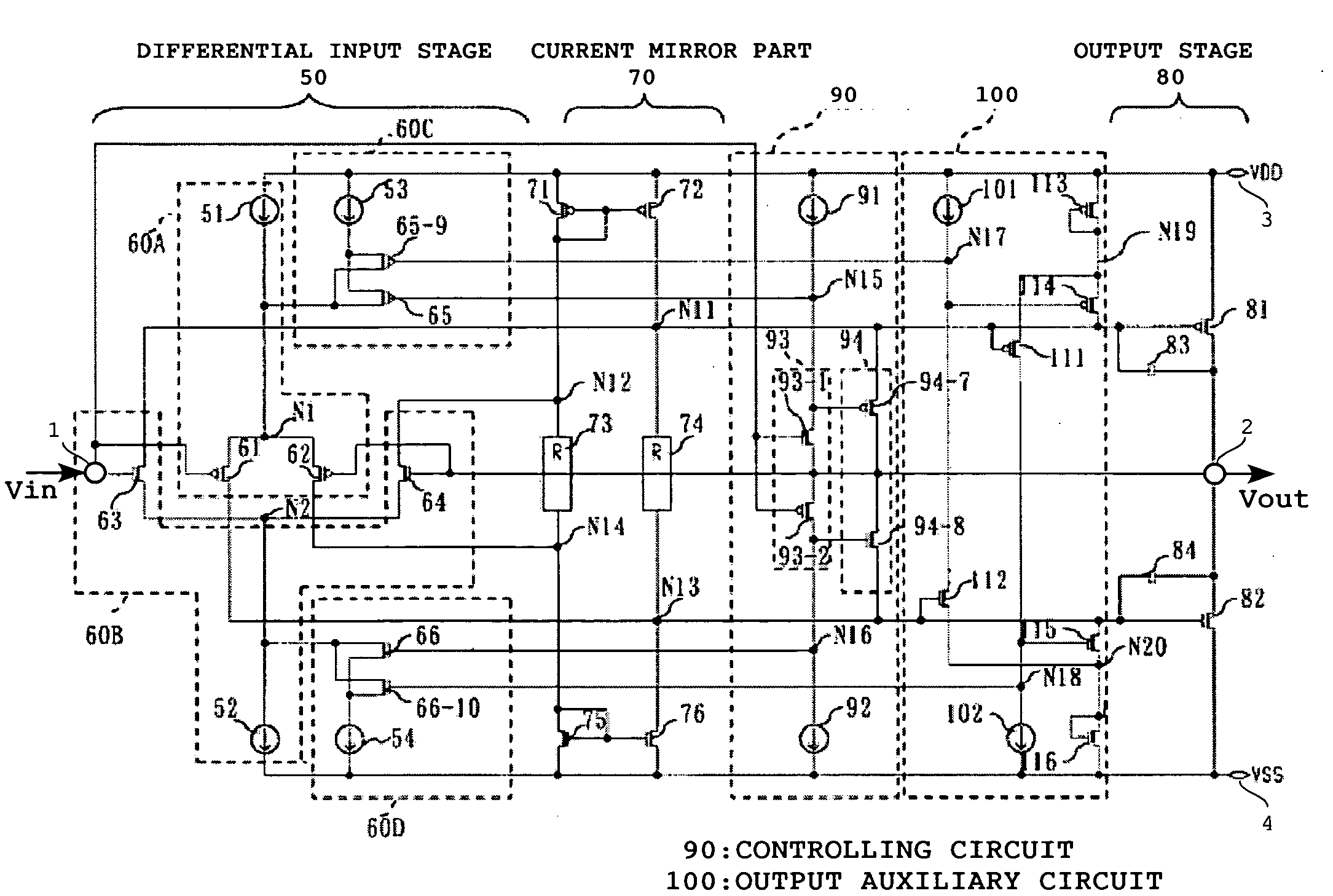
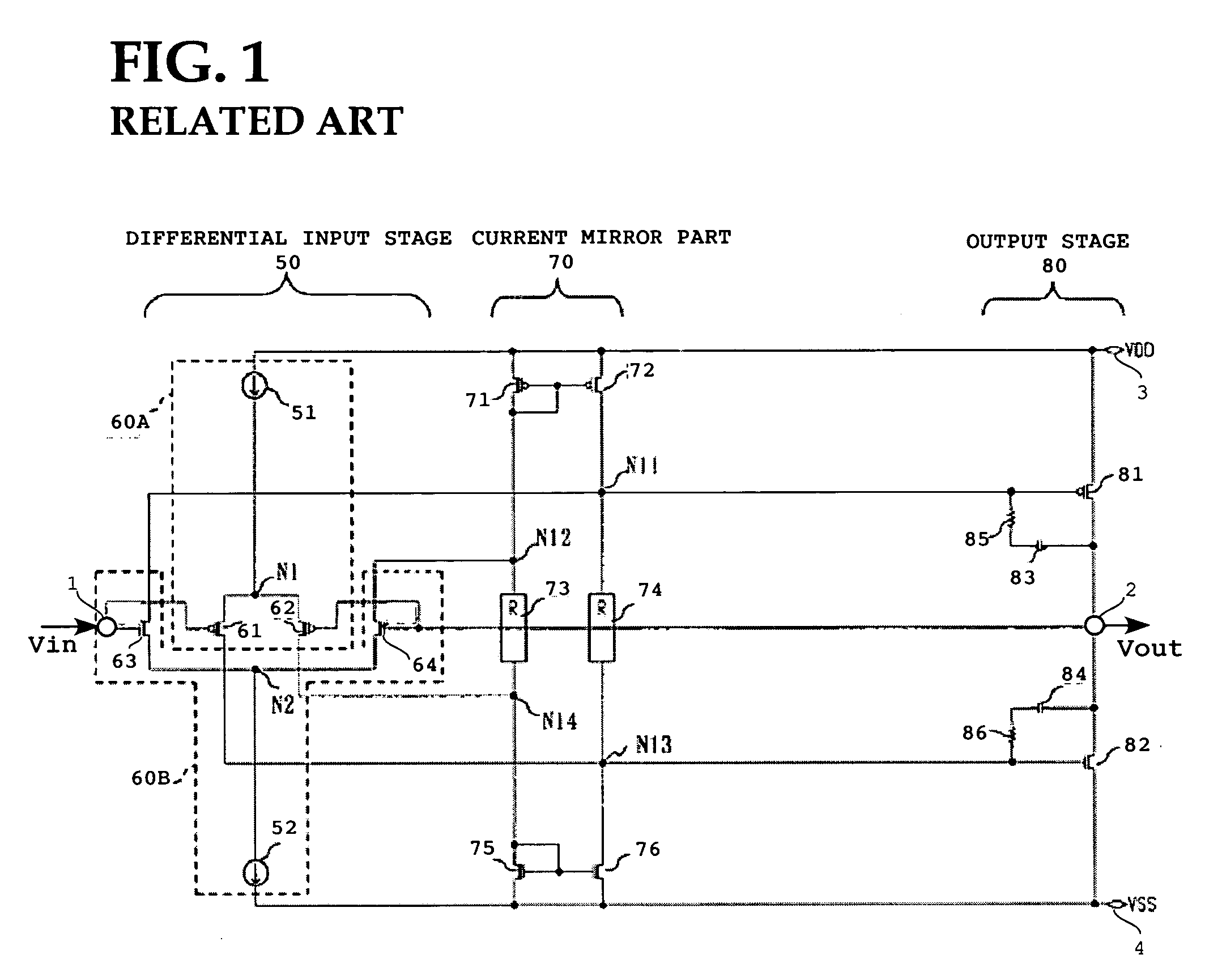
High-slew-rate error amplifier-based high-accuracy and high-speed low dropout (LDO) regulator circuit
InactiveCN102096434AGuaranteed stabilityReduce precisionElectric variable regulationLoad circuitPush–pull output
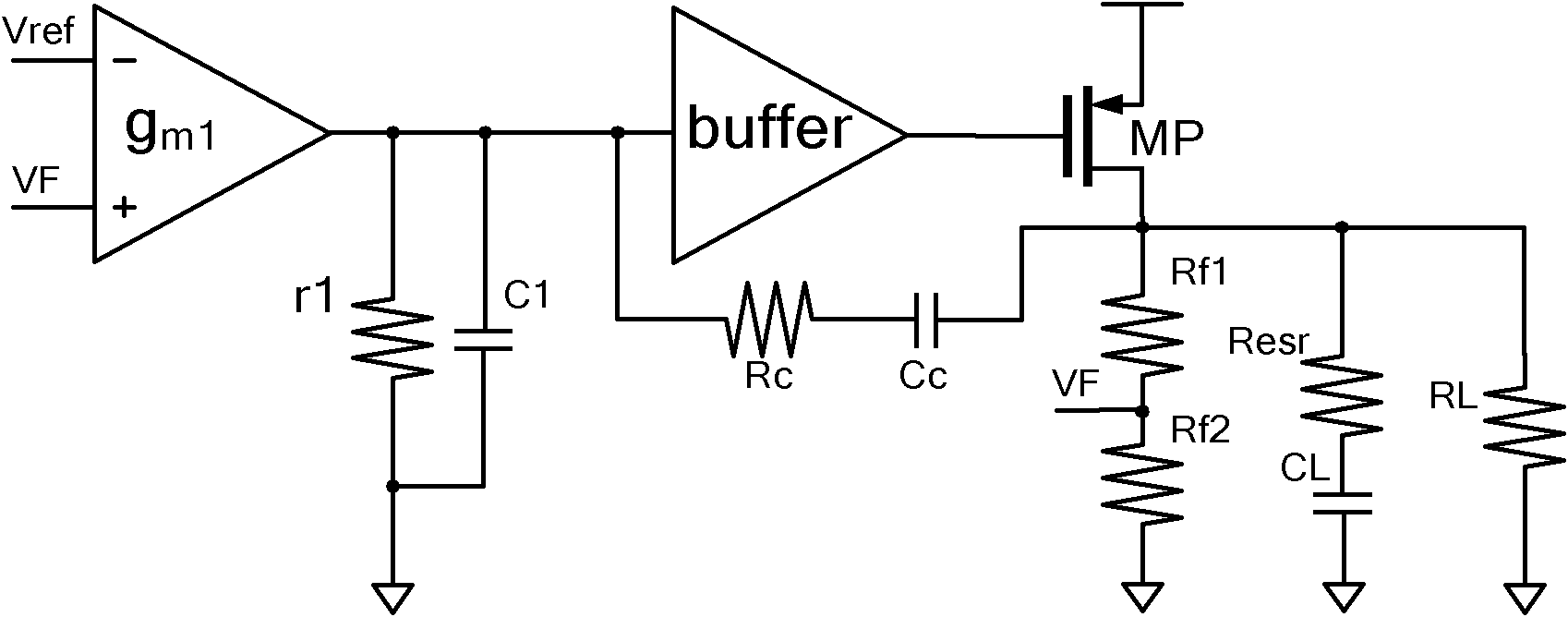
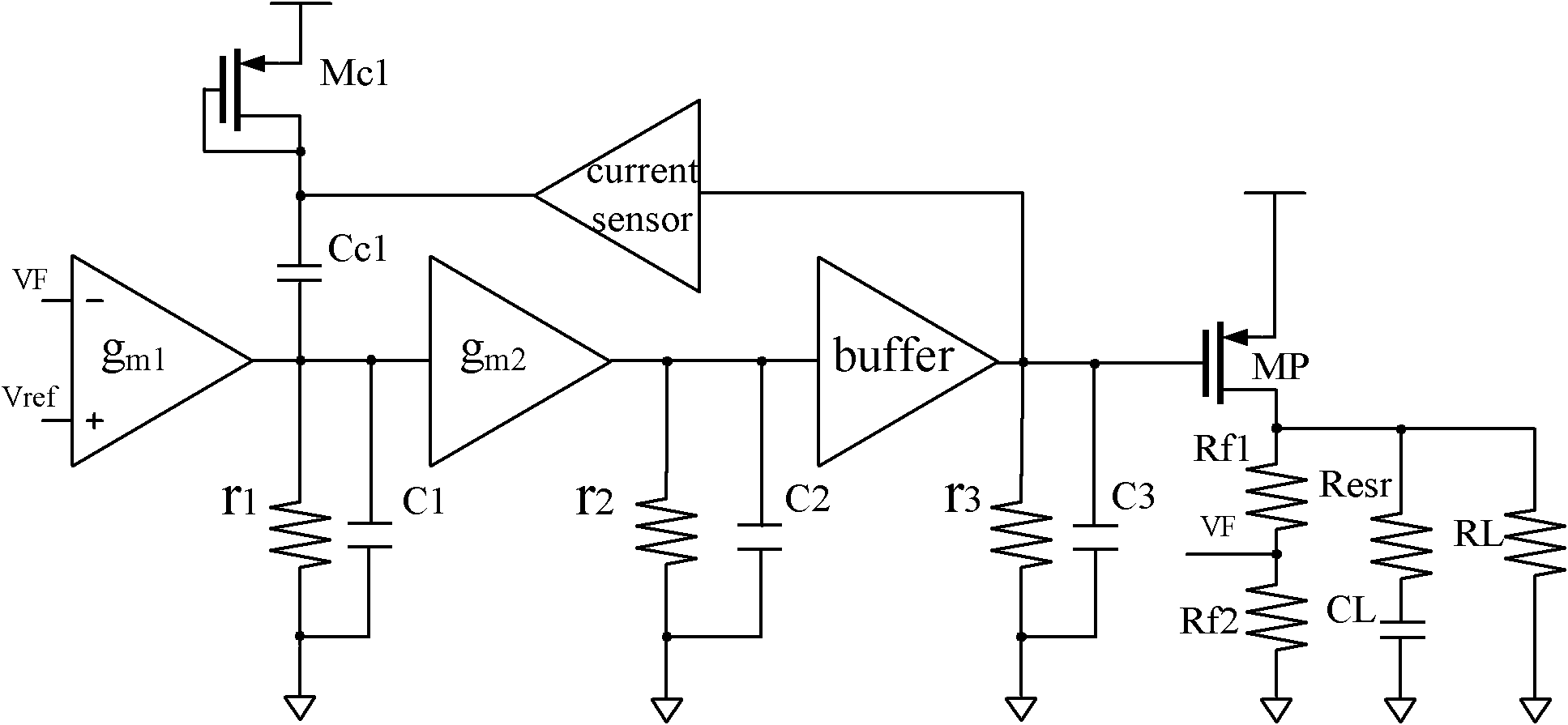
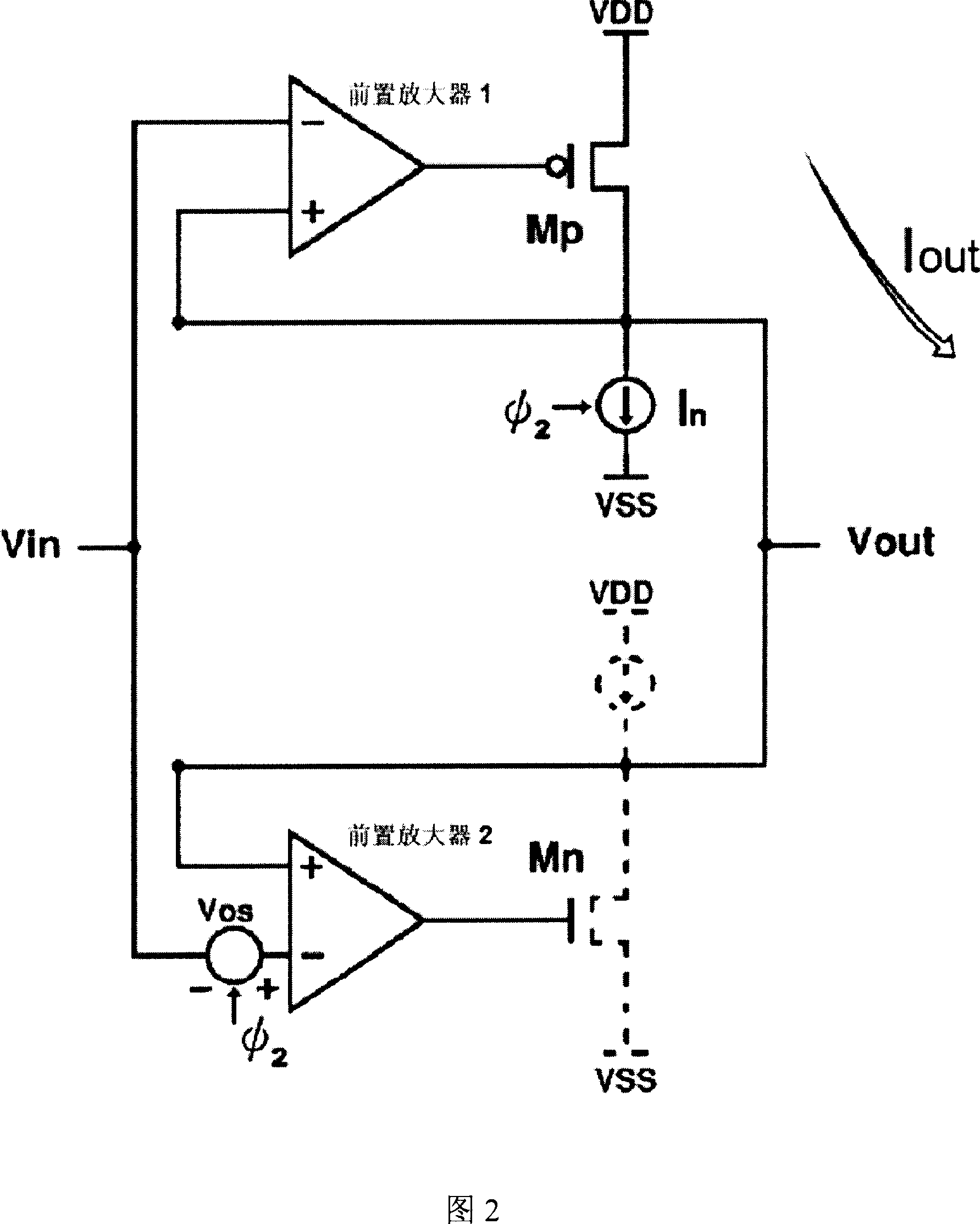
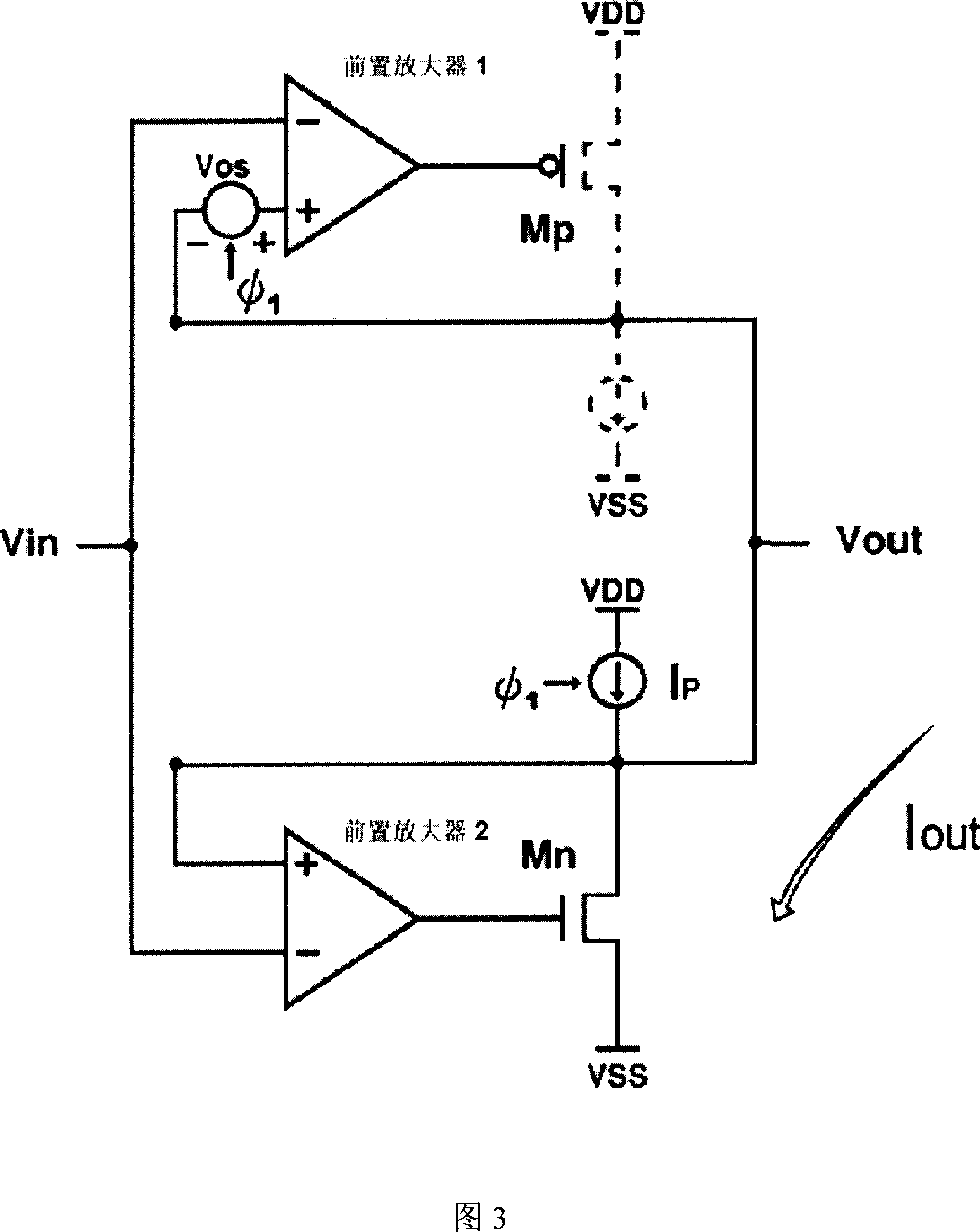
The invention discloses a high-slew-rate error amplifier-based high-accuracy and high-speed low dropout (LDO) regulator circuit, which comprises an over-the-air (OTA) circuit, a second-stage push-pull output circuit, a Miller compensation and dynamic zero compensation circuit, a load current detection circuit, a super source-level follower, a dynamic offset pipe, a feedback network and an output and load circuit. By the LDO circuit, the problems of low gain, low accuracy, low power supply suppression ratio and low response speed of the conventional LDO are solved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
DC solid-state power switch circuit
ActiveCN1667951APrecise inverse time overcurrent protection functionLimit current surgeElectronic switchingDriver circuitPush and pull
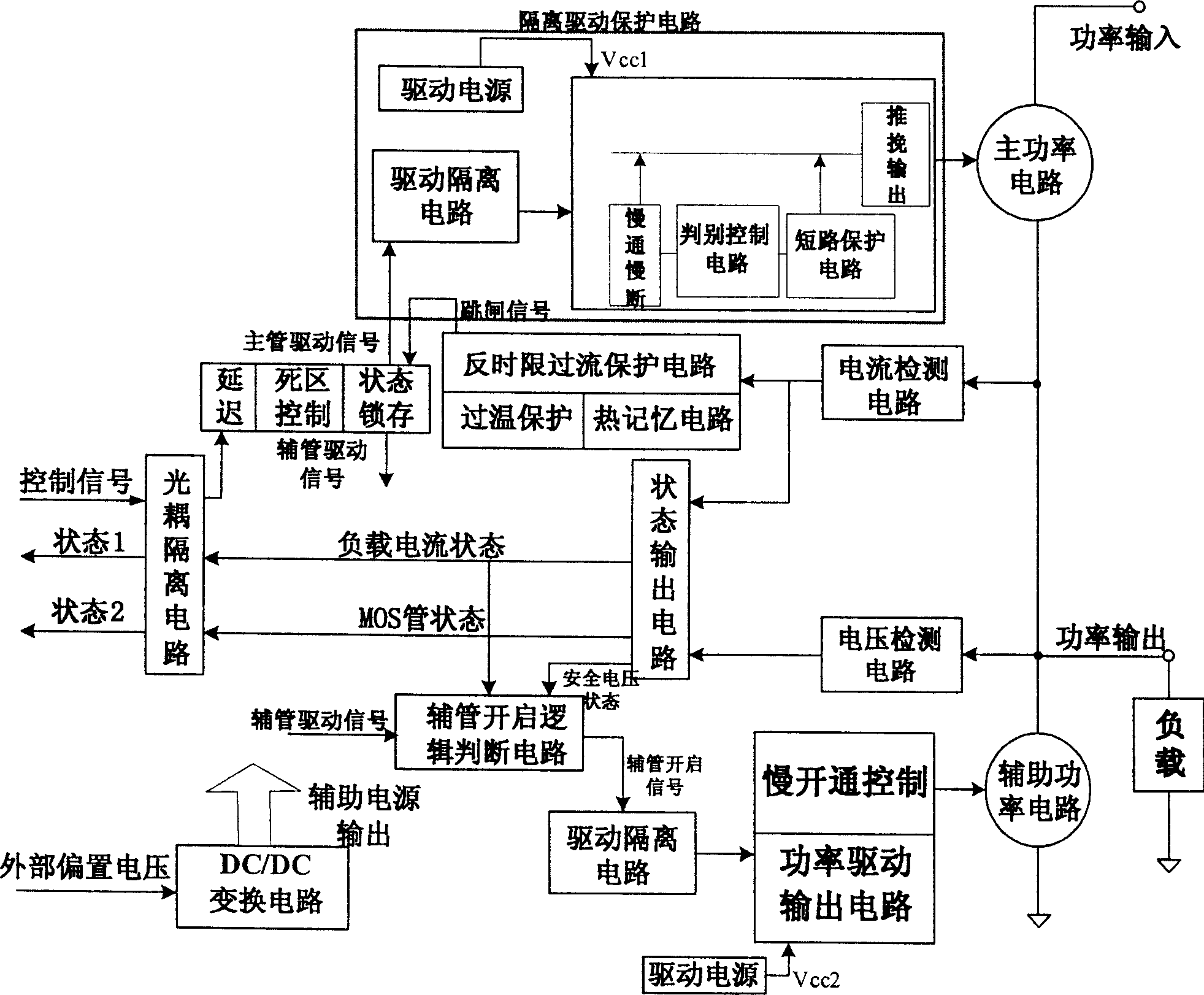
A DC solid power switch circuit includes a main power circuit, a subsidiary power circuit parallel to the load, an isolated drive protection circuit composed of a drive supply, a drive isolation circuit, a slow turned-on-off control circuit, a discriminating control circuit, a short circuit protection circuit and a push and pull output circuit, a current detection circuit, a voltage detection circuit, a main power valve drive circuit, a light-coupled isolating circuit, an assistant power valve switch-on logic circuit and a power drive output circuit, which can limit the current impulse in the period of switching on capacitive load, and suppress the peak voltage in turning off the inductive load.
Owner:SHANGHAI AVIATION ELECTRIC
Voltage buffer circuit and low dropout regulator (LDO) integrated with voltage buffer circuit
InactiveCN102778911AGuaranteed stabilityReduce undershoot spikesElectric variable regulationEngineeringHeavy load
The invention discloses a voltage buffer circuit and a low dropout regulator (LDO) integrated with the voltage buffer circuit. The buffer circuit comprises a first metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) transistor, a second MOS transistor, a third MOS transistor, a fourth MOS transistor, a first resistor unit, a second resistor unit, a capacitor element and a current source. The LDO of the voltage buffer circuit is integrated, the circuit stability is ensured at high-power tube gate parasitic poles, the current pull-down capacity of the power tube gate is improved, and the undershoot peak from light load to heavy load is reduced; due to the action of an RC high-pass coupling circuit in the buffer circuit, when the operating frequency of the circuit is near the filter cut-off frequency, the charging current of the power tube gate is increased, the overshoot peak from heavy load to light load is reduced, push-pull output is formed under the condition that the quiescent dissipation is not obviously increased, and the transient response of the LDO circuit is improved; and meanwhile, the LDO integrated with the voltage buffer circuit is simple in structure, and the chip area is saved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
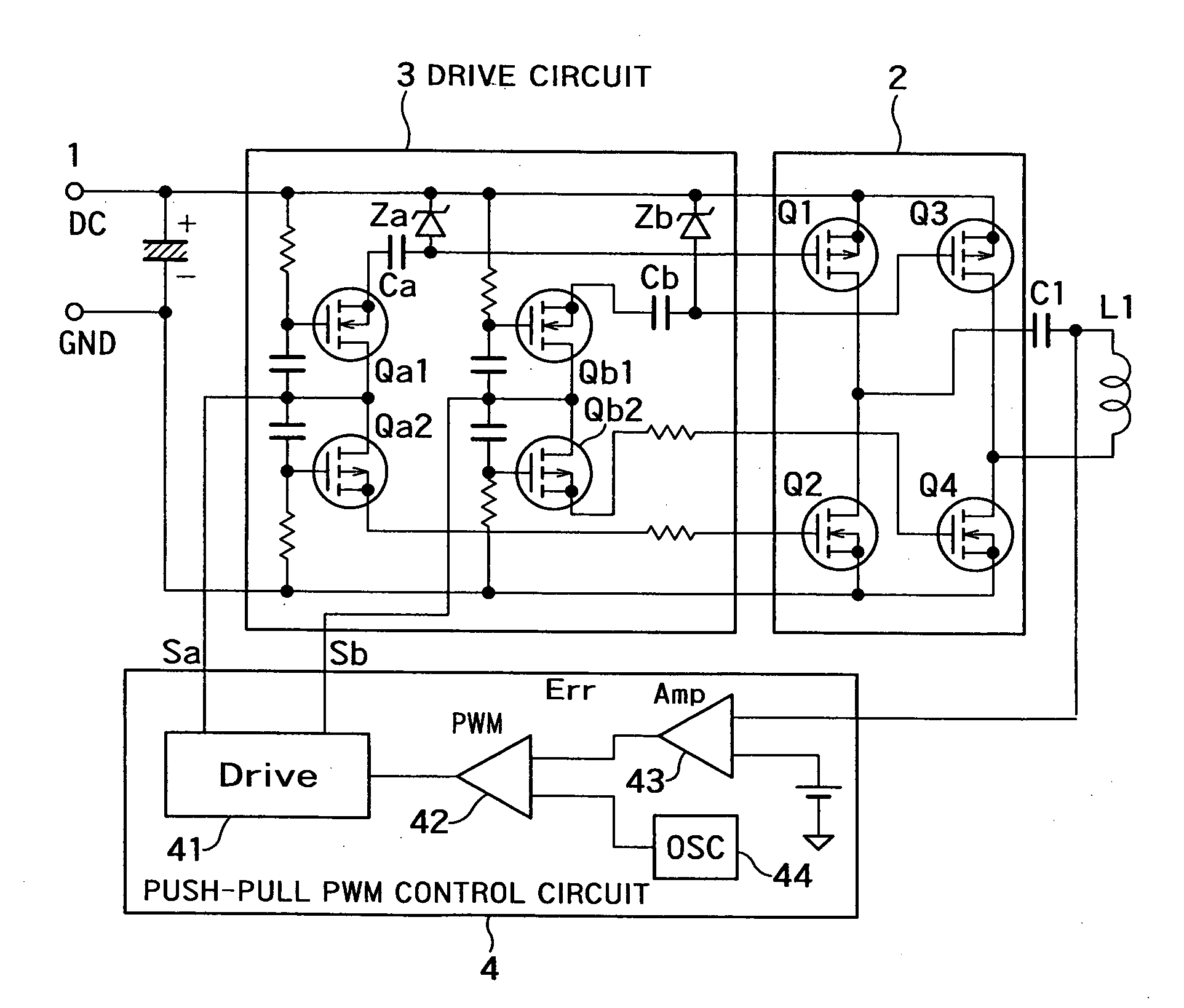
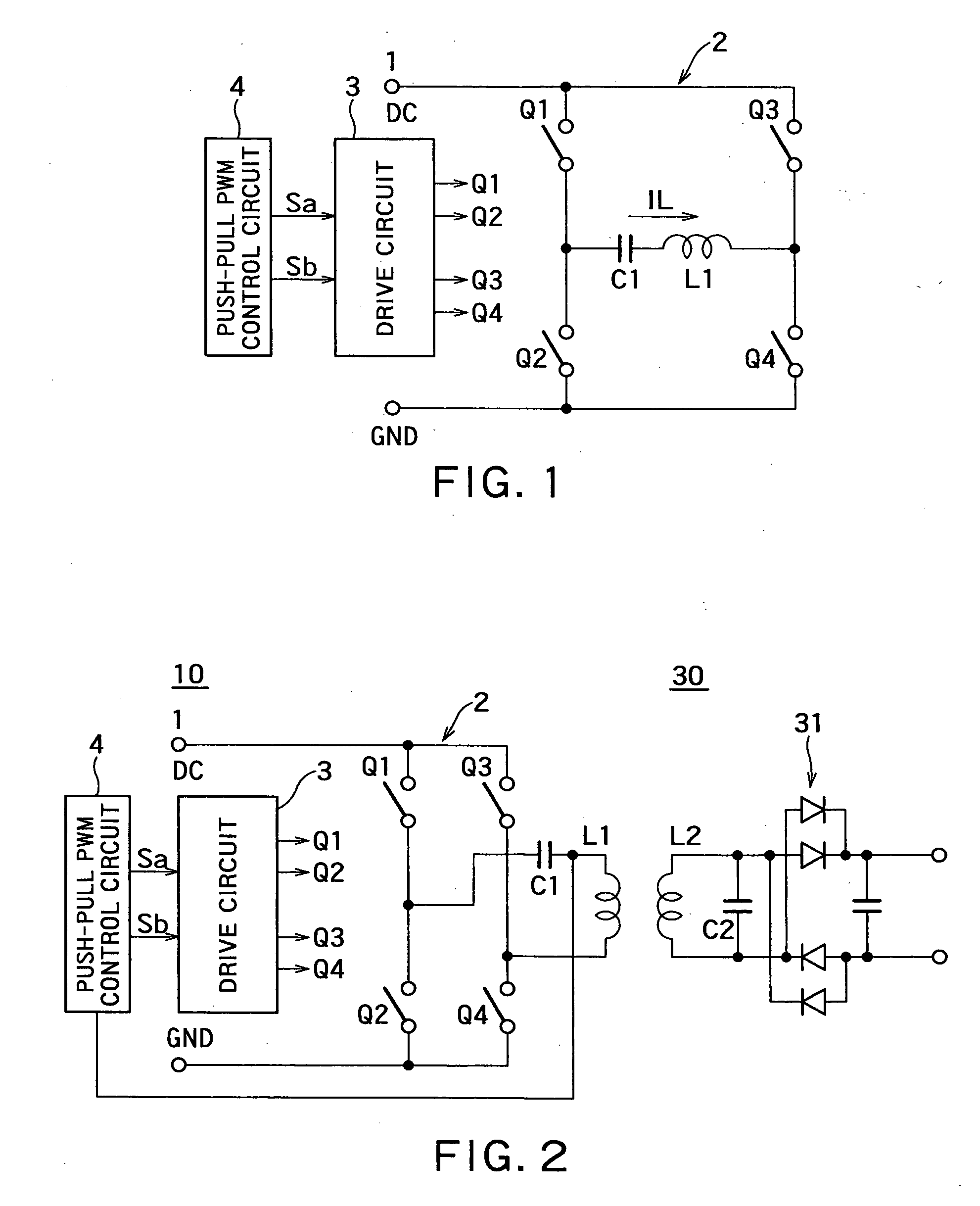
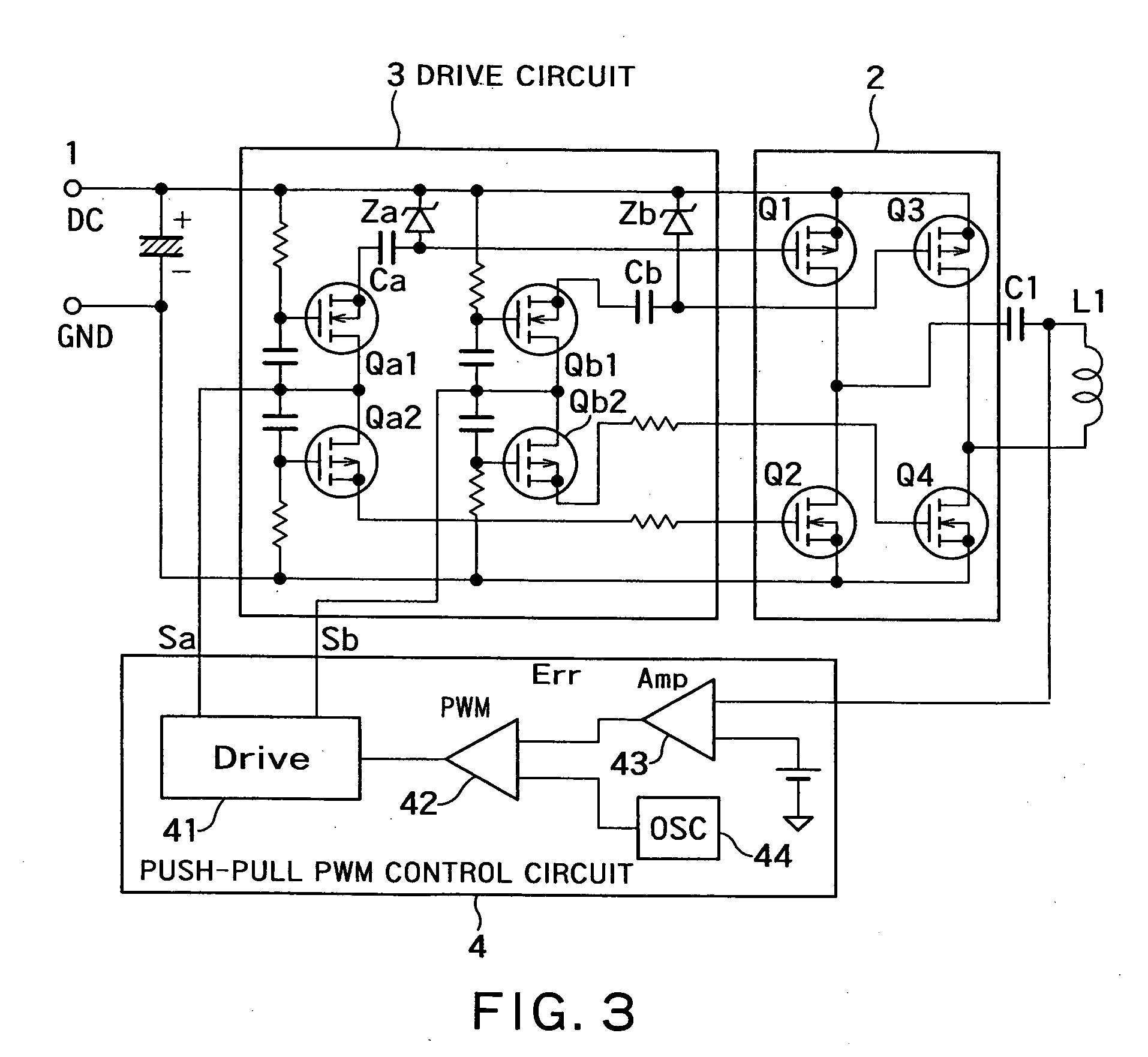
Non-contact electric power transmission circuit
InactiveUS20100148590A1Easy to implementImprove efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsElectromagnetic wave systemElectric power transmissionElectromagnetic coupling
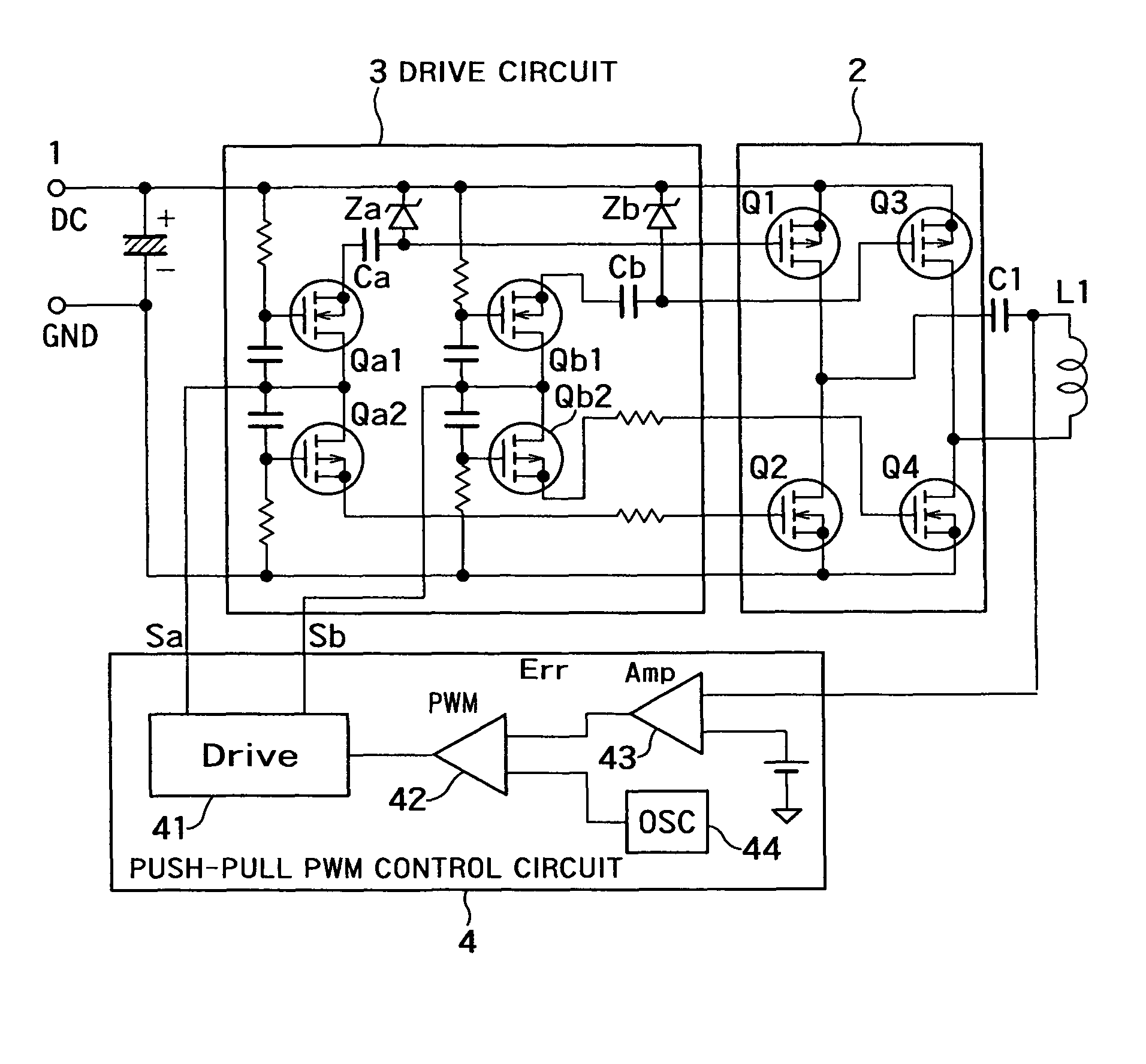
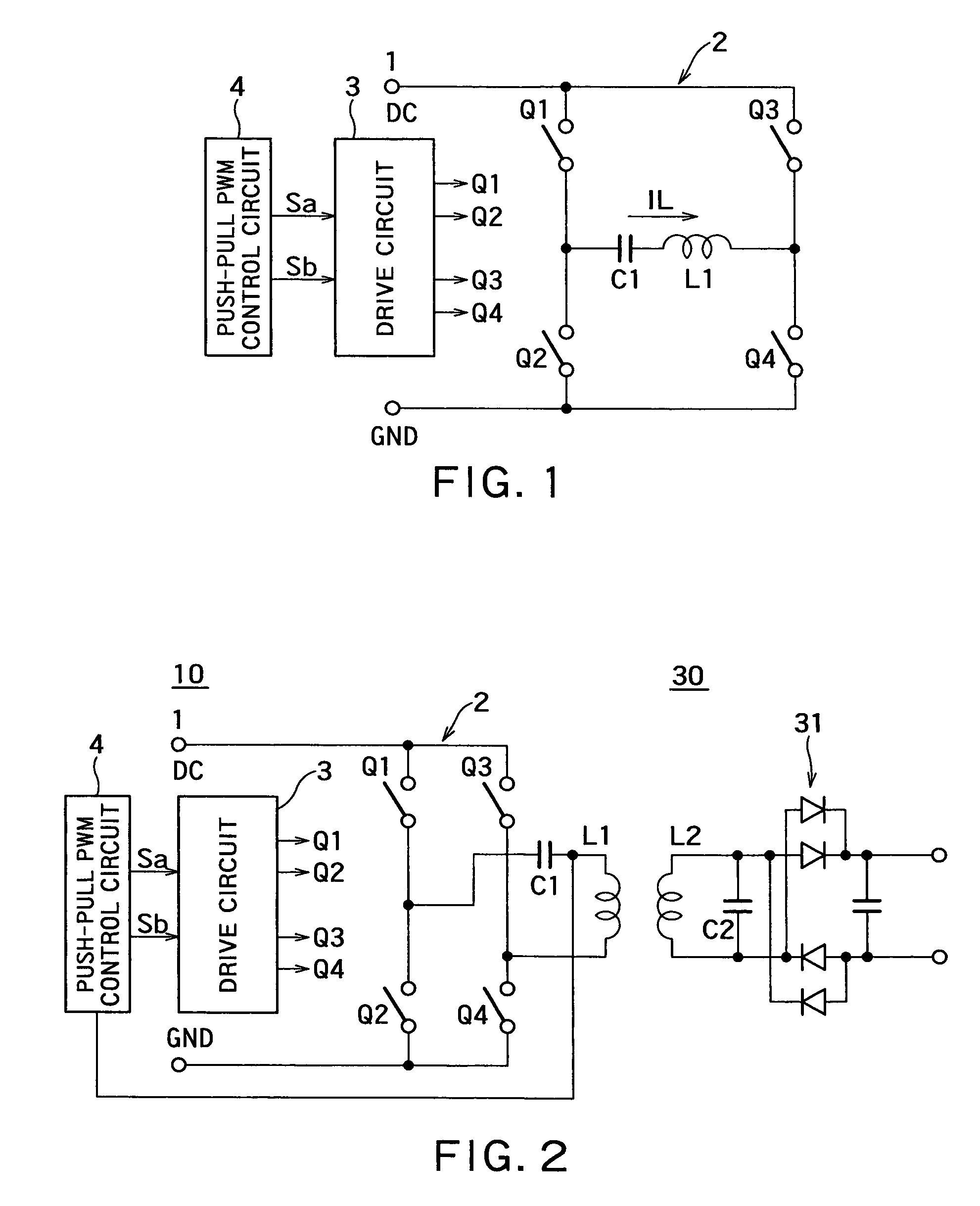
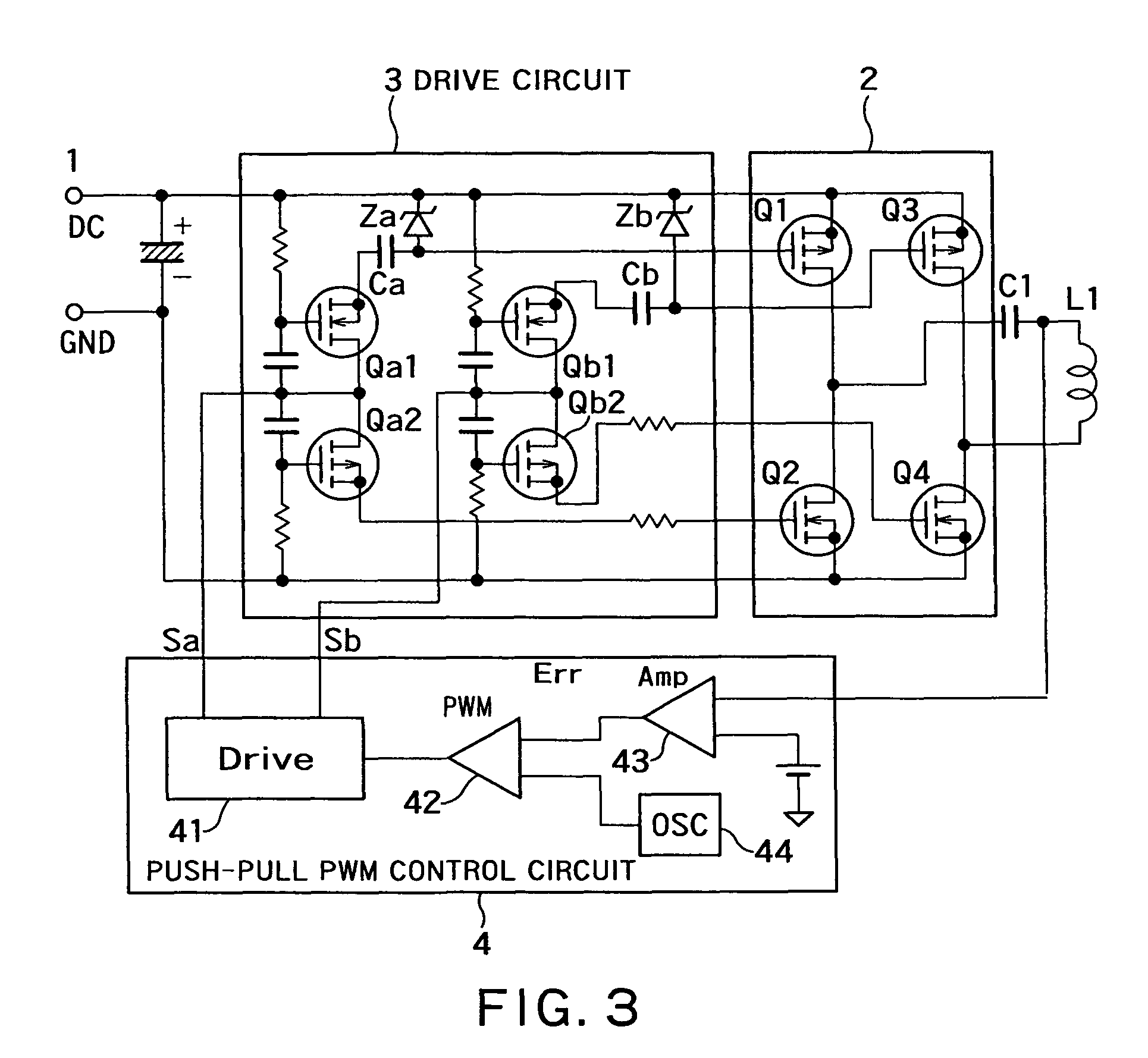
A non-contact electric power transmission circuit according to an embodiment of the invention includes an electric power transmission circuit and an electric power receiving circuit. The electric power transmission circuit includes a full bridge circuit and a resonant type full bridge circuit. A direct-current power supply is used as an input of the full bridge circuit, the full bridge circuit includes two sets of switching elements, two switching elements being connected in series in each set of the switching elements, a drive circuit alternately feeds a pulse signal to gates of the switching elements to perform switching of the direct-current input in the full bridge circuit, and a serial resonant circuit of a resonant capacitor and an electric power transmission coil is connected to an output of the full bridge circuit in the resonant type full bridge circuit. The electric power receiving circuit includes an electric power receiving coil and a rectifying and smoothing circuit. The electric power receiving coil is electromagnetically coupled to the electric power transmission coil, and the rectifying and smoothing circuit rectifies an output of the electric power receiving coil. In the non-contact electric power transmission circuit, a push-pull output PWM control circuit is provided in the drive circuit that controls the full bridge circuit, and only one of the switching elements in each set of switching elements performs a regenerative operation. Therefore, a non-contact electric power transmission circuit in which the resonant type full bridge circuit can be controlled by PWM control at a level similar to that of a phase shift operation can be provided.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
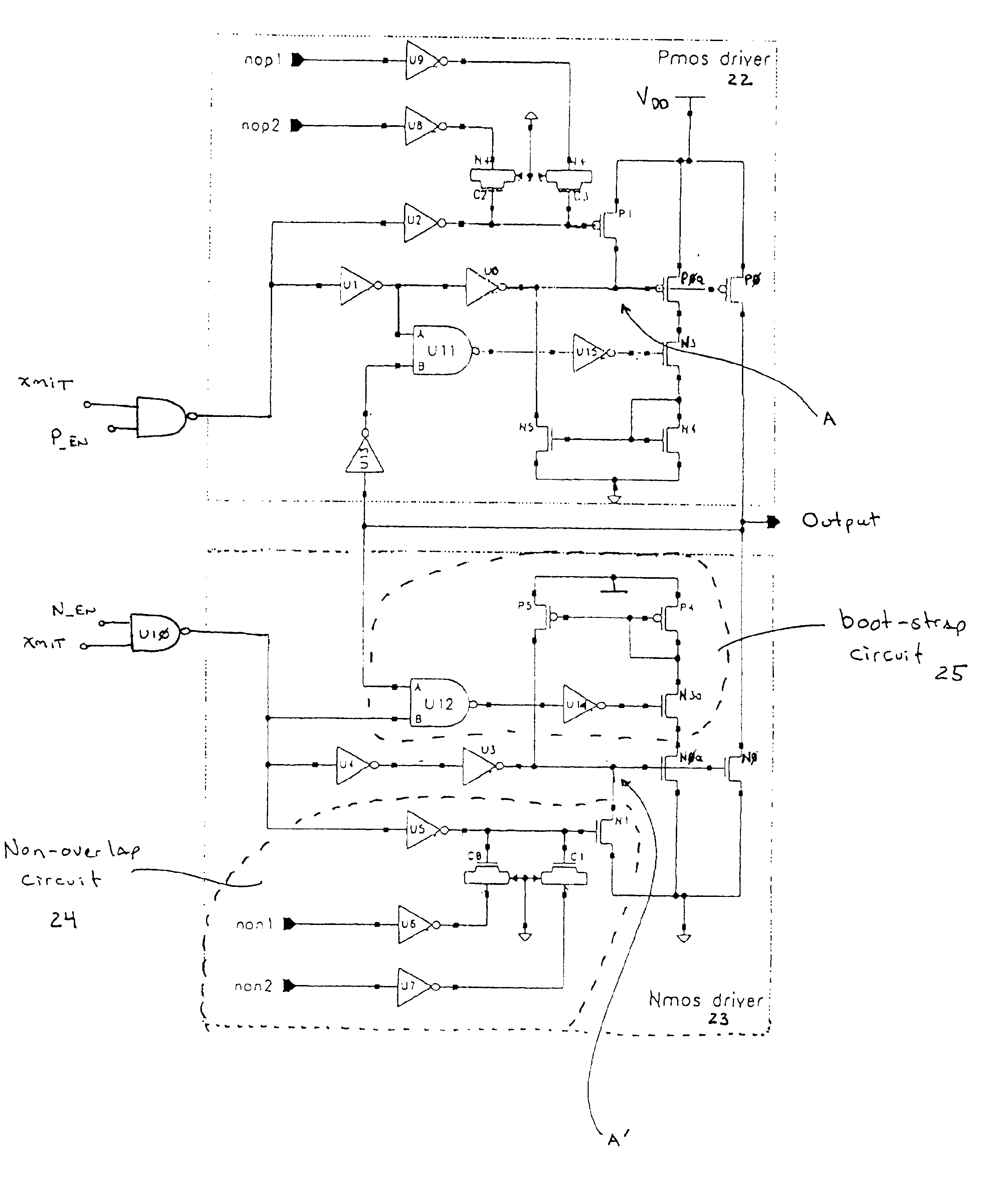
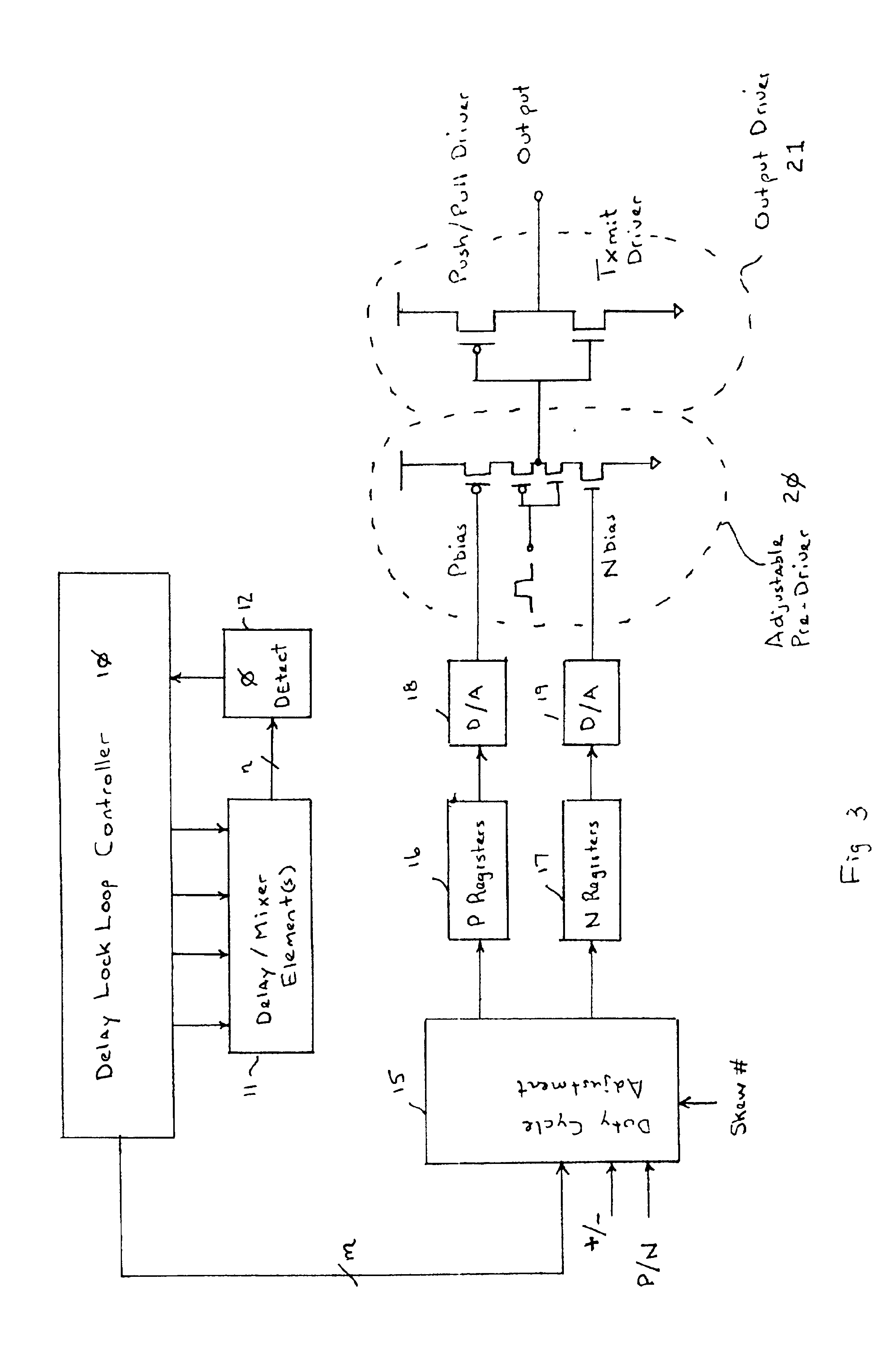
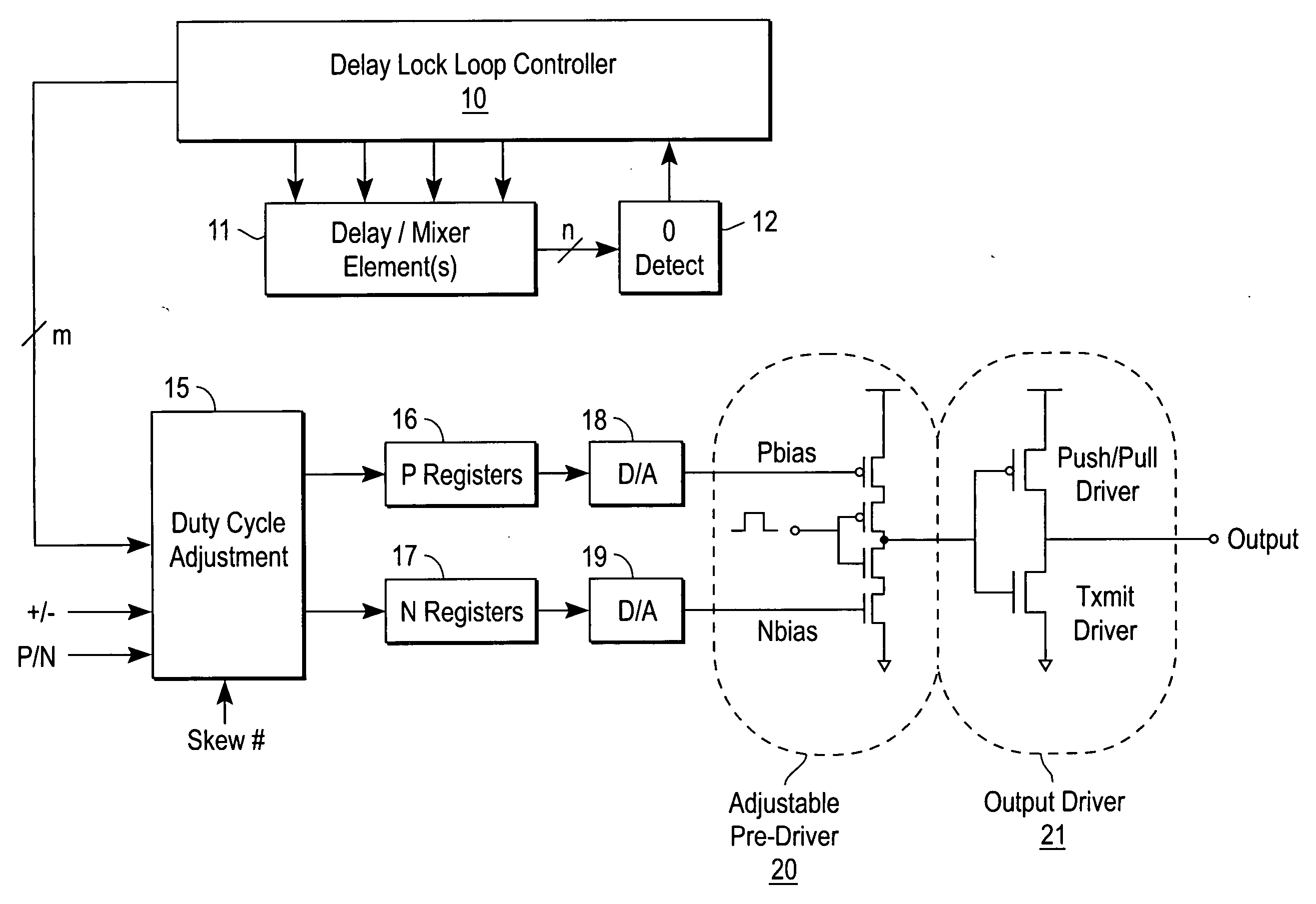
Push-pull output driver
InactiveUS6781416B1Power reduction in field effect transistorsReliability increasing modificationsDriver circuitPush–pull output
An improved, open-loop push-pull driver is described. Closed-loop feedback loop techniques for control of the push-pull driver are described. These techniques are particularly well adapted to control shoot-through current in a push-pull driver circuit.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Push-pull output driver
InactiveUS20050057278A1Improve performanceImprove protectionPower reduction in field effect transistorsElectronic switchingDriver circuitPush–pull output
An improved, open-loop push-pull driver is described. Closed-loop feedback loop techniques for control of the push-pull driver are described. These techniques are particularly well adapted to control shoot-through current in a push-pull driver circuit.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Plate voltage generation circuit capable controlling dead band
Owner:LONGITUDE SEMICON S A R L
Wobble signal reproducing circuit
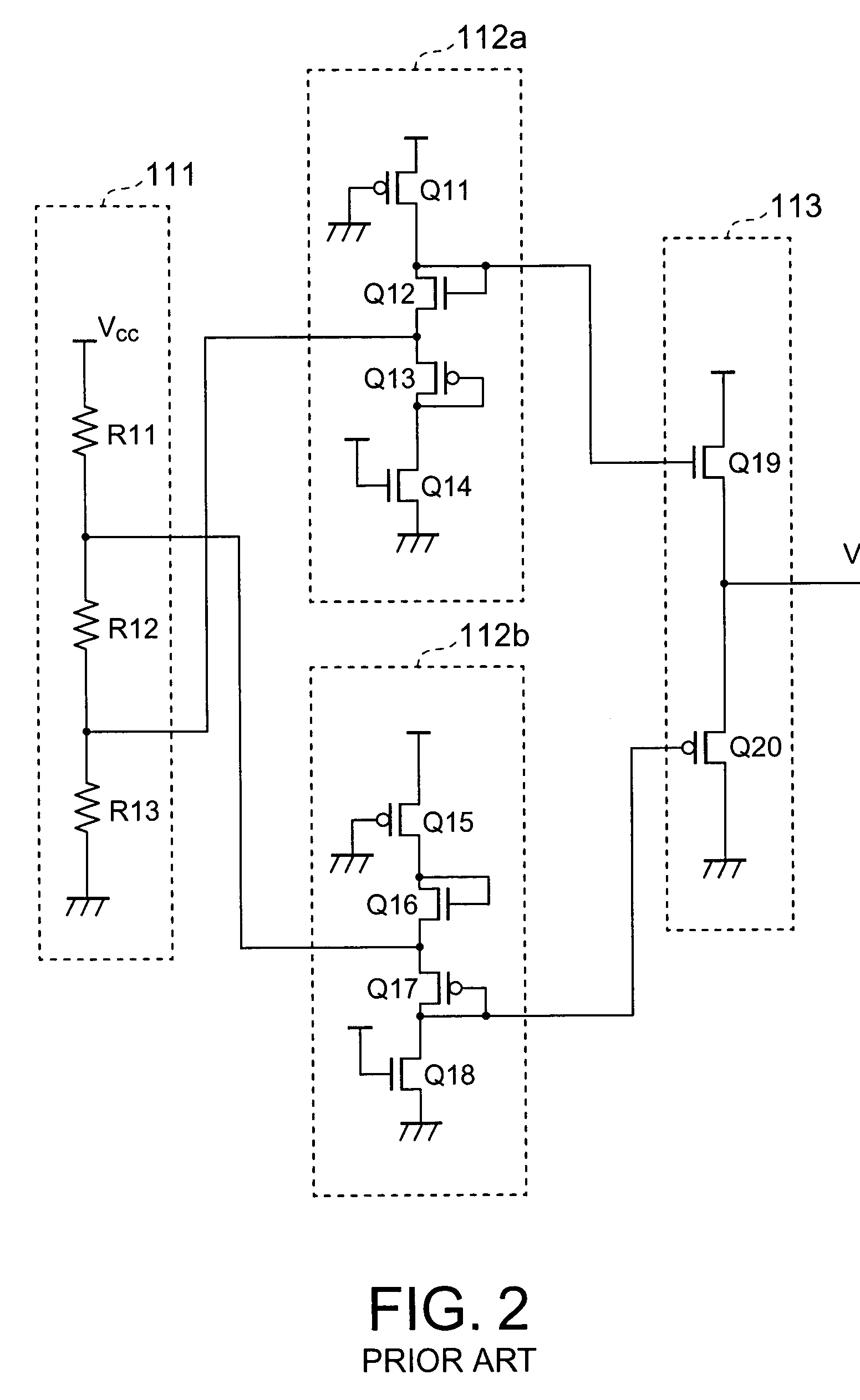
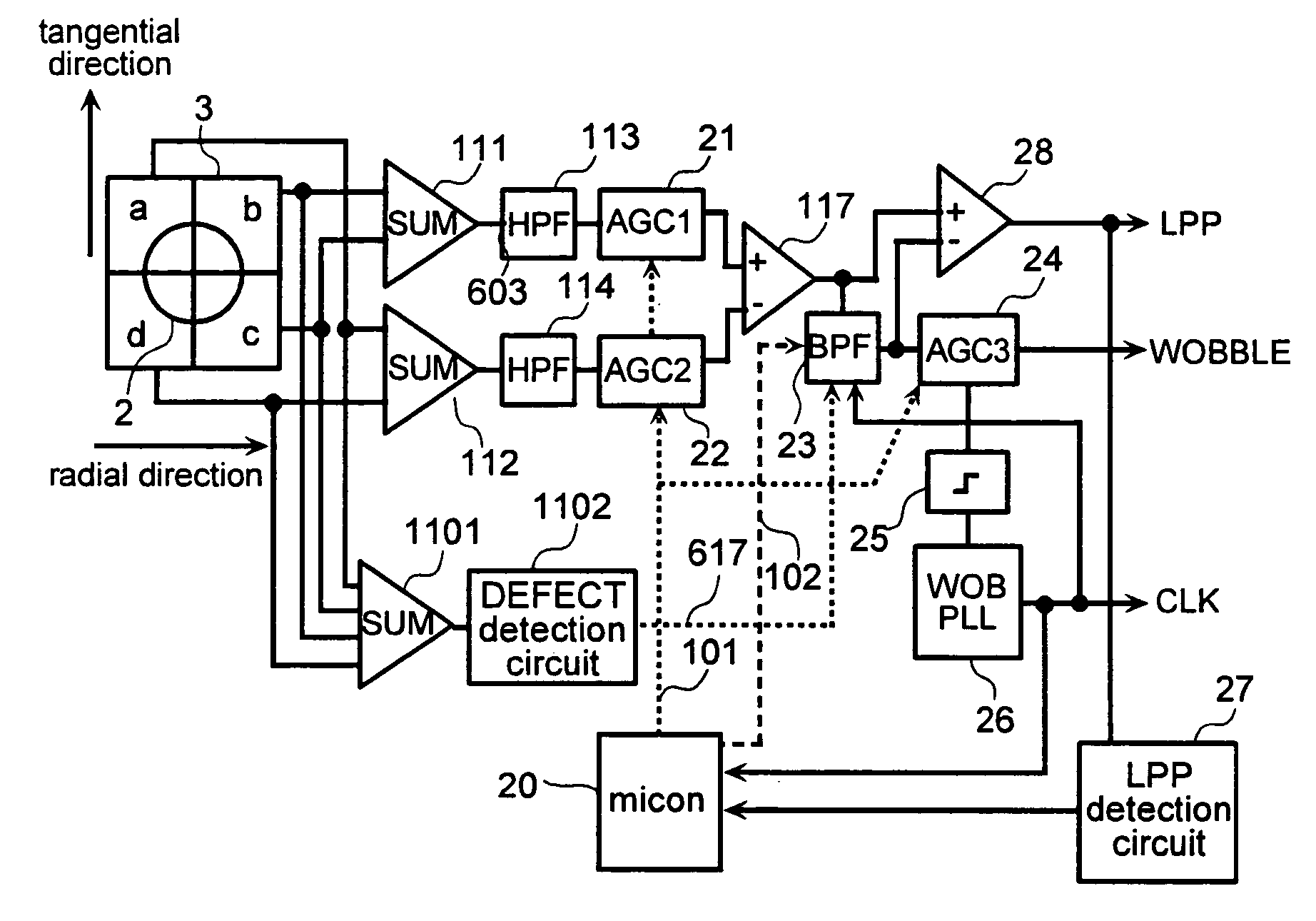
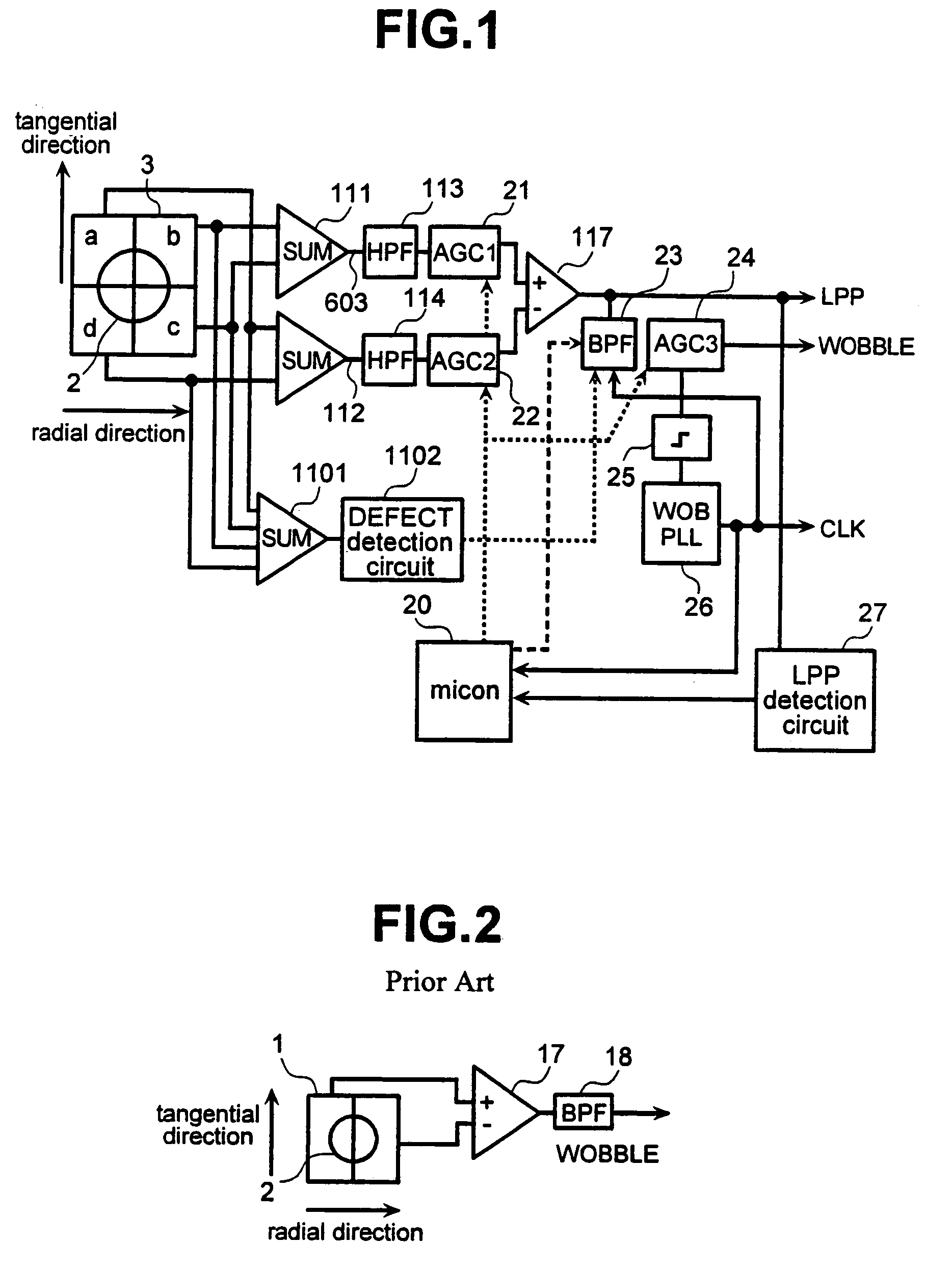
InactiveUS7133335B2Reduce offsetImprove accuracyCombination recordingFilamentary/web record carriersDVD-RAMPush–pull output
The present invention has an object to stably reproduce wobble signals of all disks of CD-R / RW, DVD-R / RW and DVD-RAM by one wobble signal reproducing circuit. In the wobble signal reproducing circuit, an AGC (AUTOMATIC GAIN CONTROL) circuit for equating a push-pull circuit output of a wide range and an RF amplitude of an optical detector output of two systems obtained by push-pull, and an AGC (AUTOMATIC GAIN CONTROL) circuit for making a wobble amplitude uniform are provided with a function to hold a gain or to change over a response time constant, and at the time of reproduction of the DVD-R / RW, a land pre-pit region is detected by the push-pull output to hold AGC (AUTOMATIC GAIN CONTROL) or change over a response time constant. Besides, in an address information recording region (PID region) at the time of reproduction of the DVD-RAM, the AGC (AUTOMATIC GAIN CONTROL) is held or the response time constant is changed over.
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP
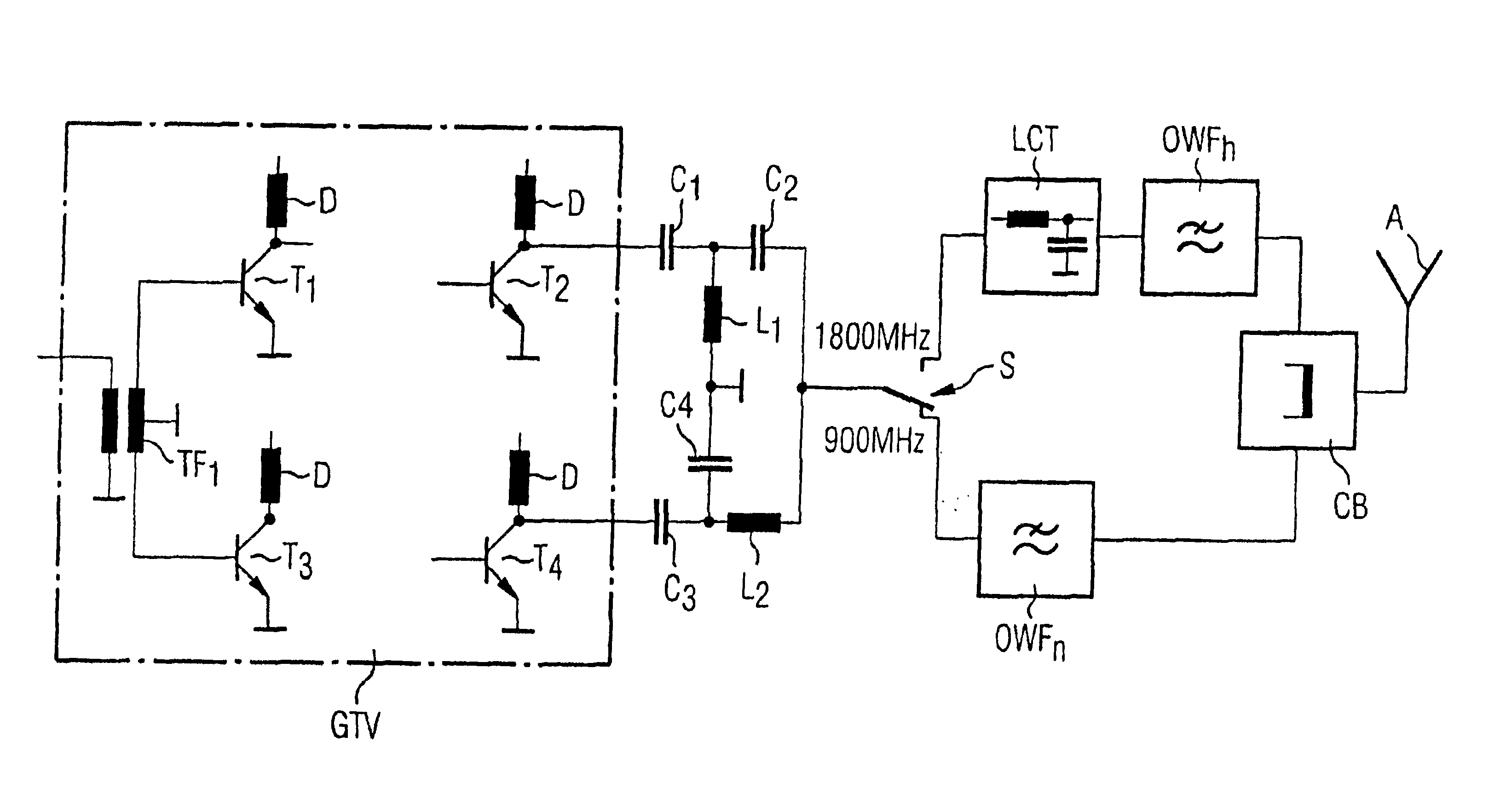
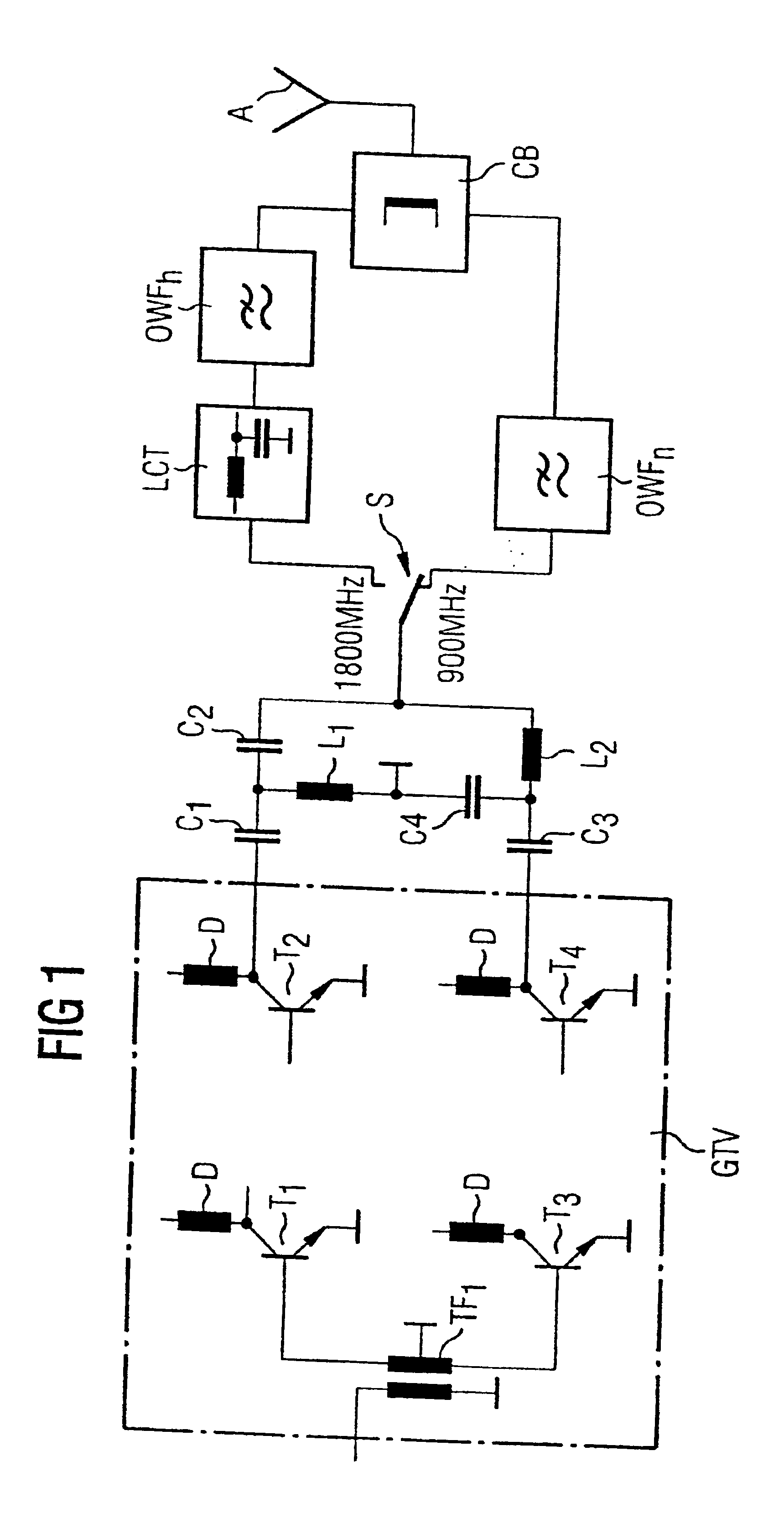
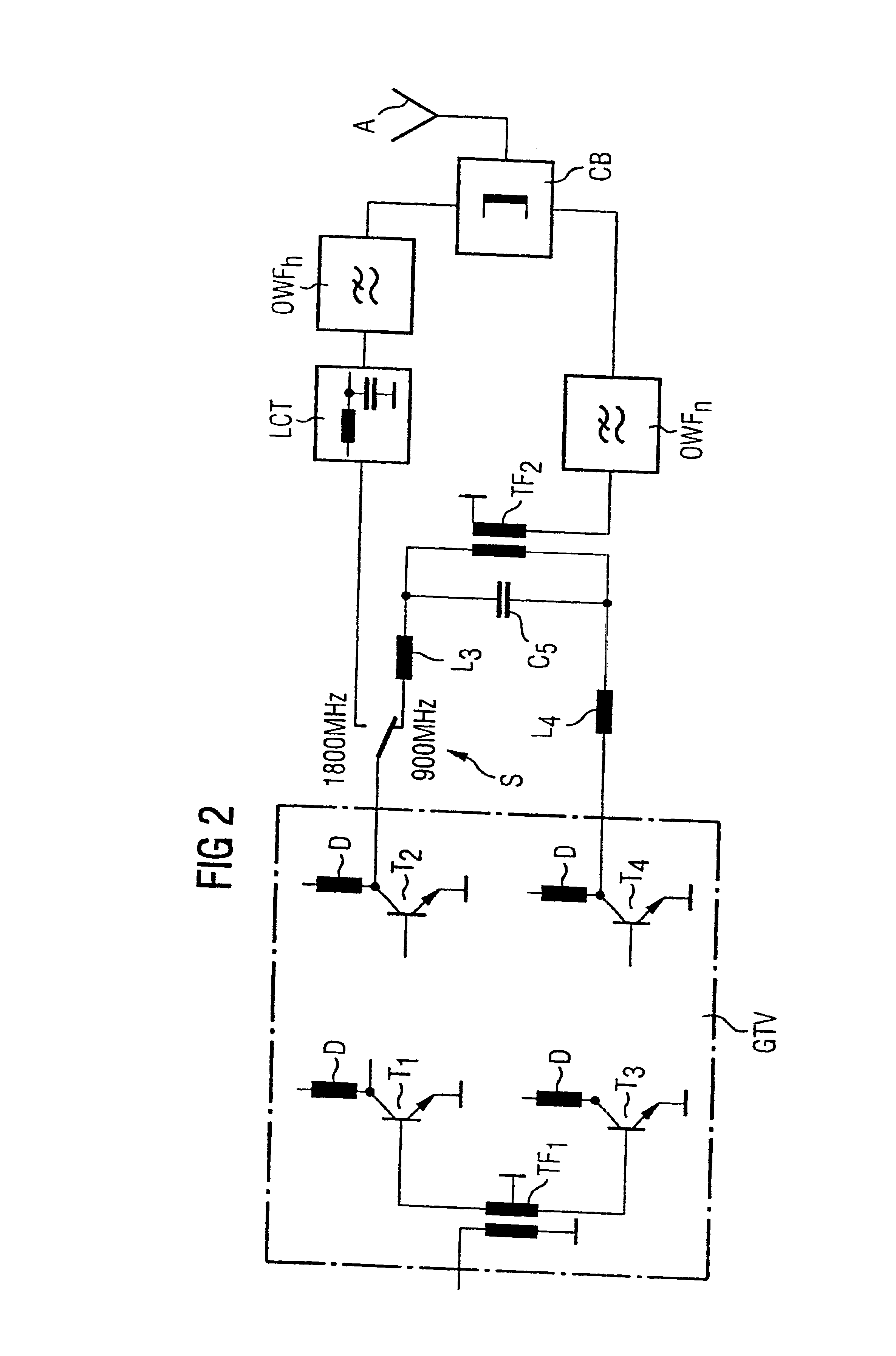
Transmission output stage for a mobile telephone
InactiveUS6895227B1Reduce expenditureReduces circuit expenditurePush-pull amplifiersPhase-splittersPush–pull outputMobile phone
In a transmission output stage for a multifrequency mobile telephone, the transmit signal of operation at the low frequency is generated by a push-pull output stage which is operated in single-ended mode for generating the transmit signal at the higher frequency.
Owner:CINTERION WIRELESS MODULES
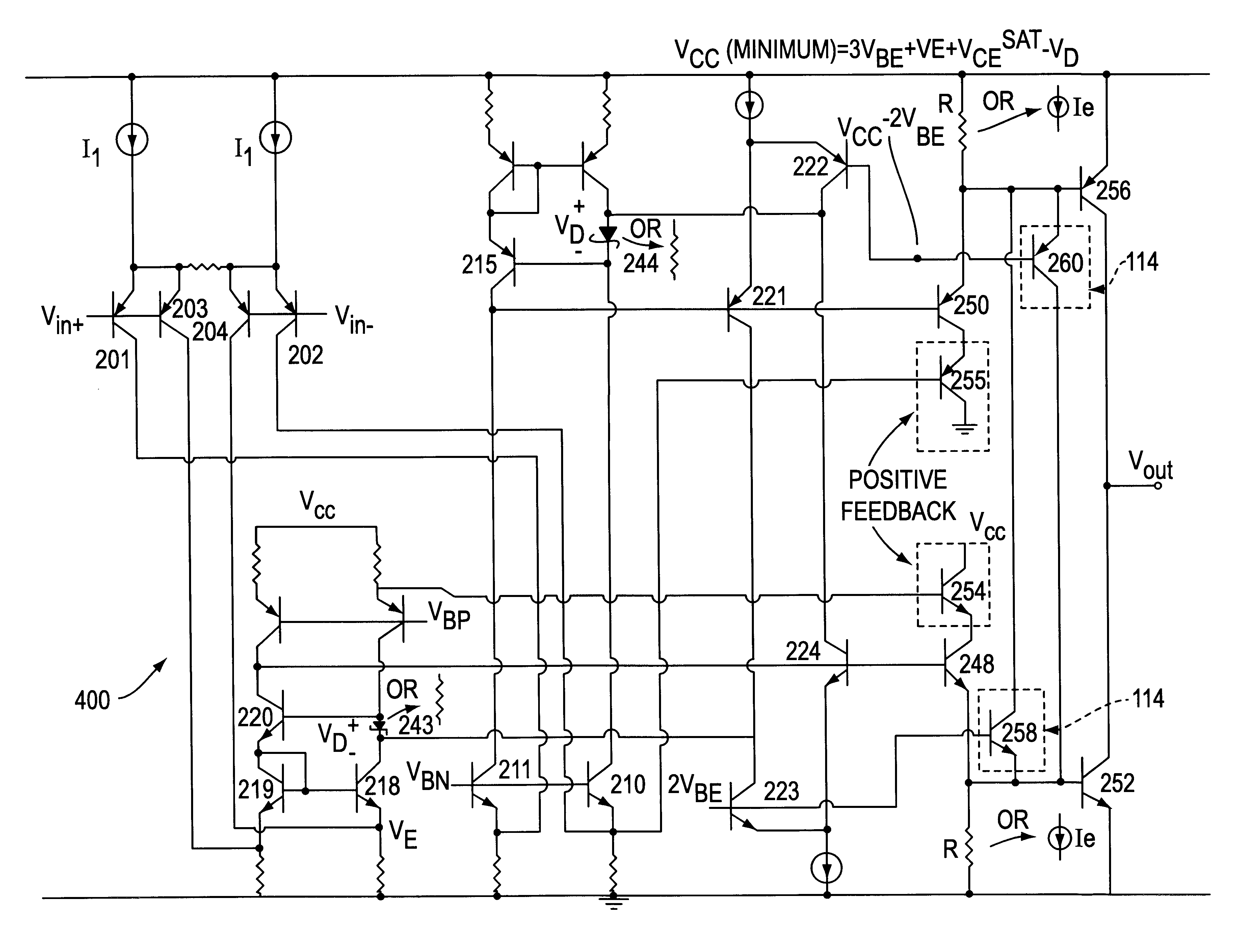
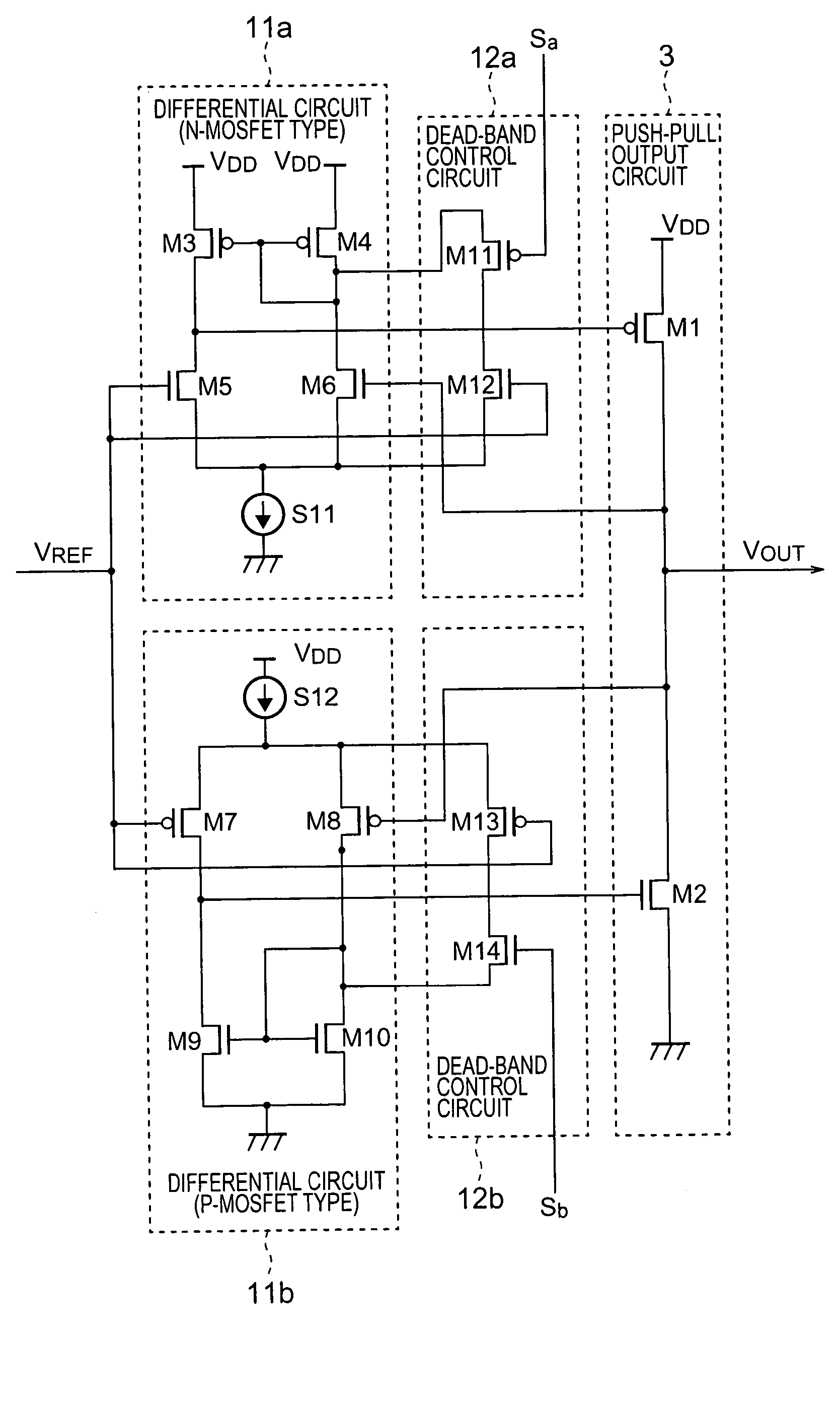
Control circuit driven by a differential input voltage and method for controlling same
The present invention teaches a variety of output stages for amplifying high speed signals while keeping distortion low and using a low supply voltage. The invention includes the use of dual complementary signal paths that include a complementary push-pull output stage. Bias circuits are used to keep the paths symmetrical and positive feedback is used to oppose output loading effects.
Owner:GAINTECH
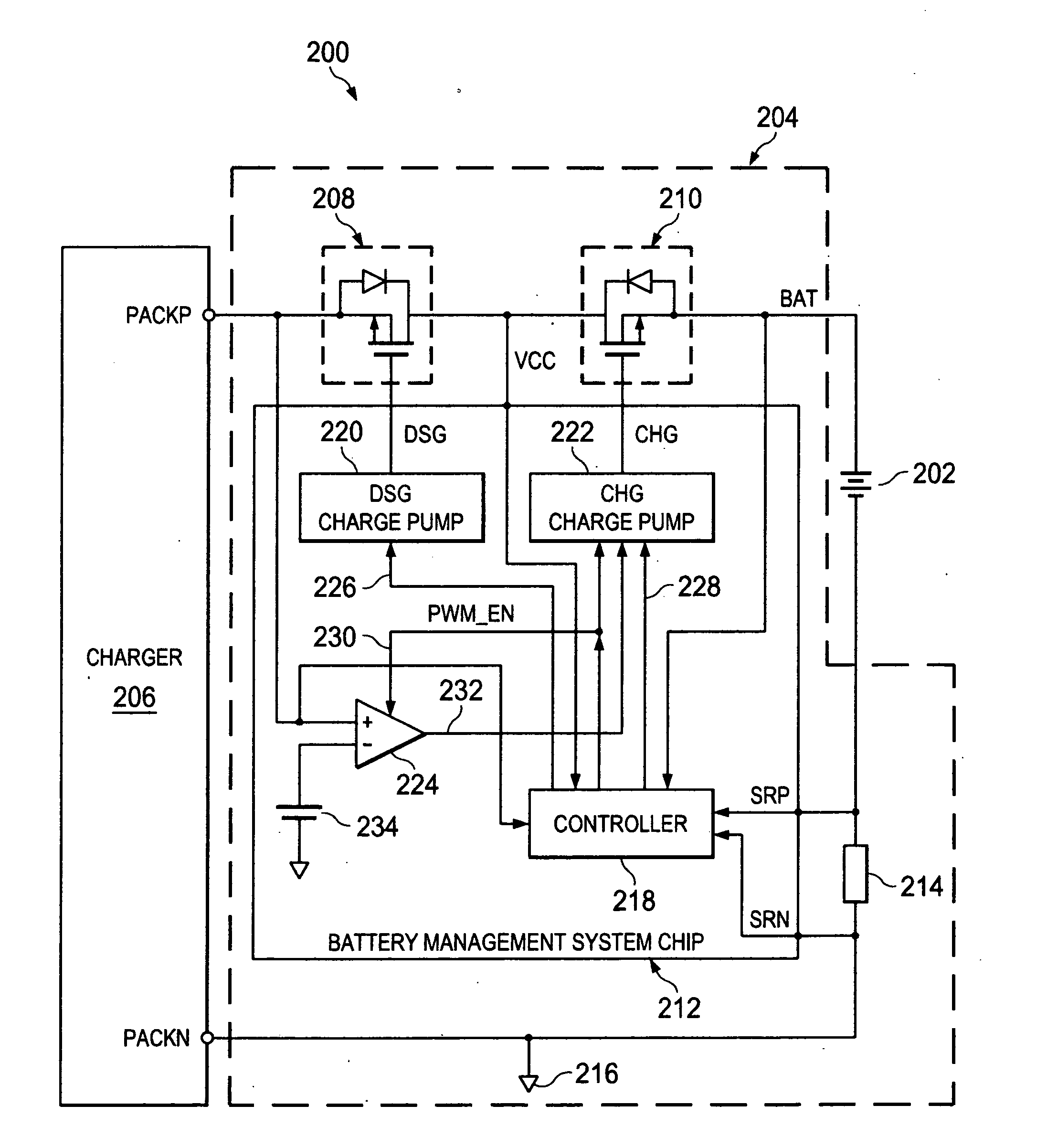
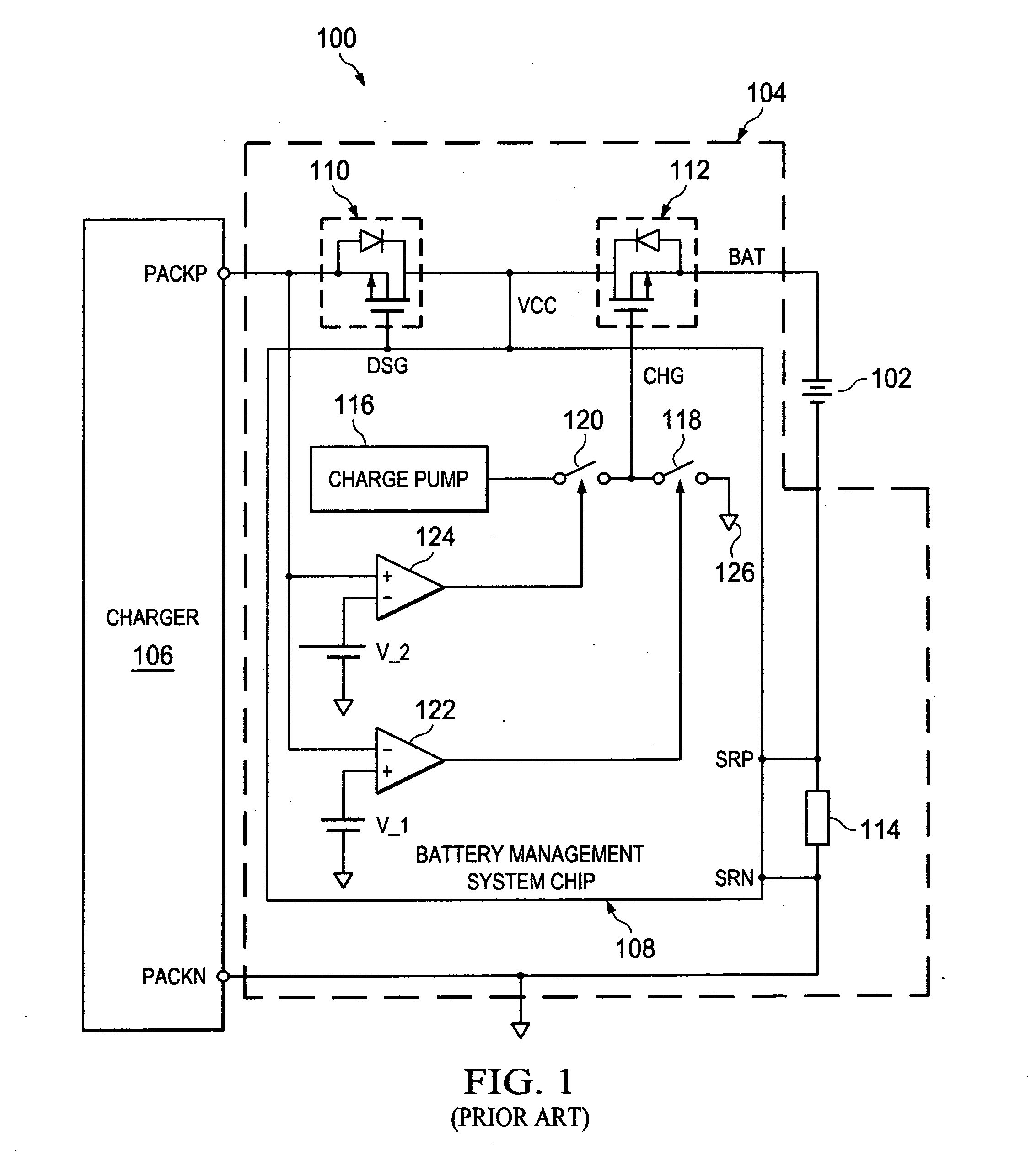
Pulse width modulated battery charging
InactiveUS20110140673A1Electric powerBattery overcharge protectionElectrical batteryElectrical connection
A battery management system for charging a battery by a charger includes a transistor and either a charge pump or a push-pull output driver. The transistor increases and decreases an electrical connection between the battery and a voltage from the charger and transmits a charge current from the charger to the battery by turning on and off in response to a pulse width modulated drive signal generated by the charge pump or the push-pull output driver. The charge pump or the push-pull output driver increases the drive signal when the voltage from the charger is above a pre-charge threshold voltage and decreases the drive signal when the voltage from the charger is below the pre-charge threshold voltage.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Zero dead area grid driving circuit
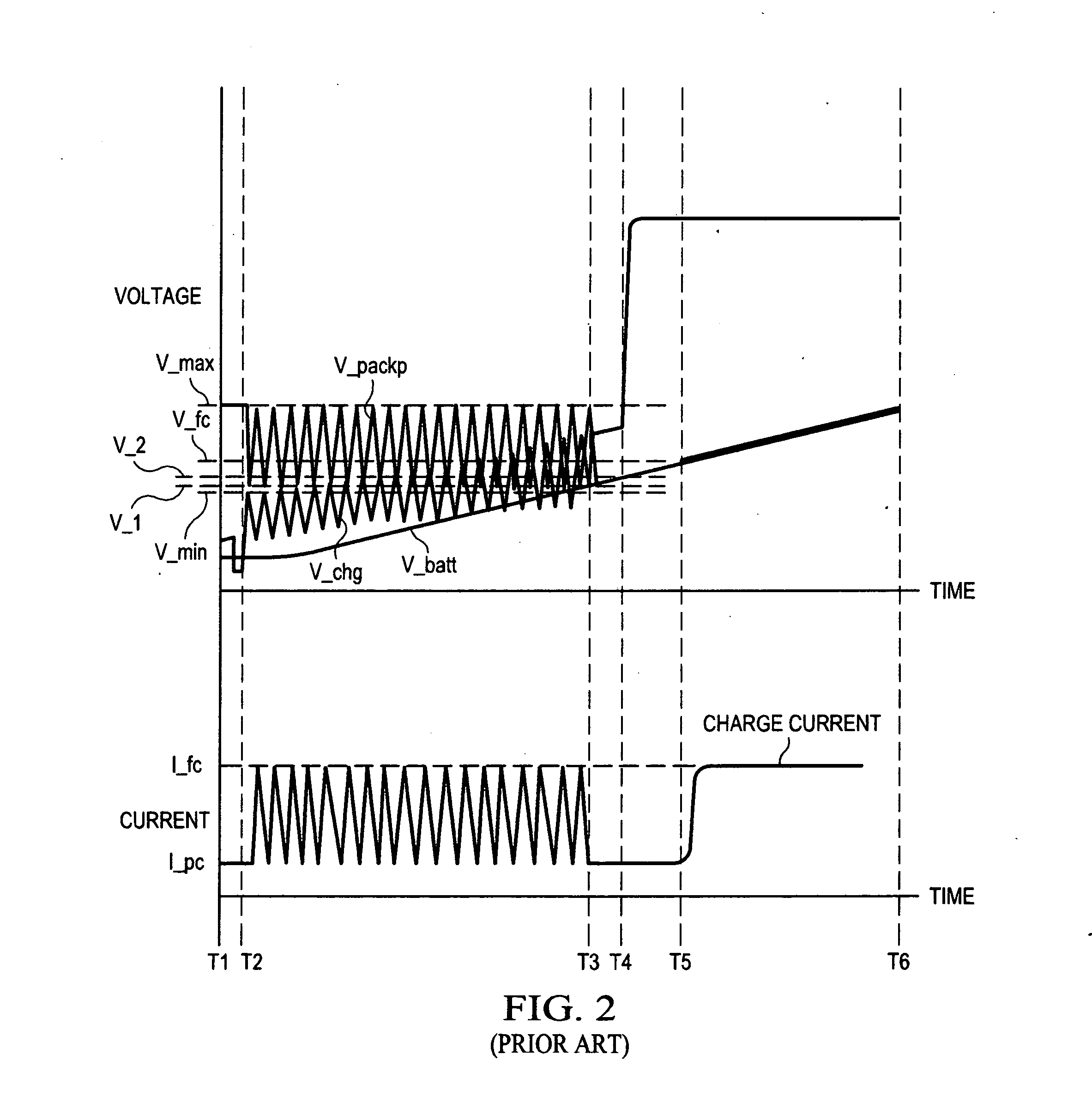
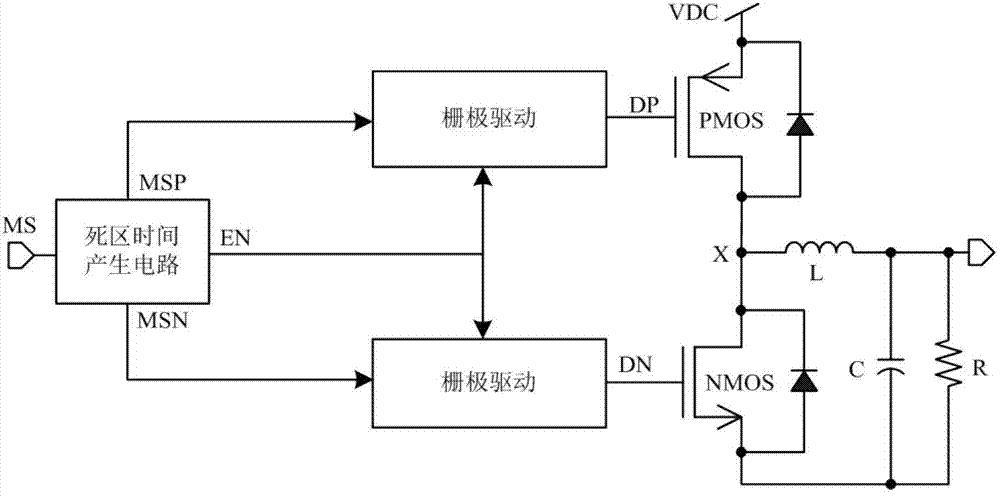
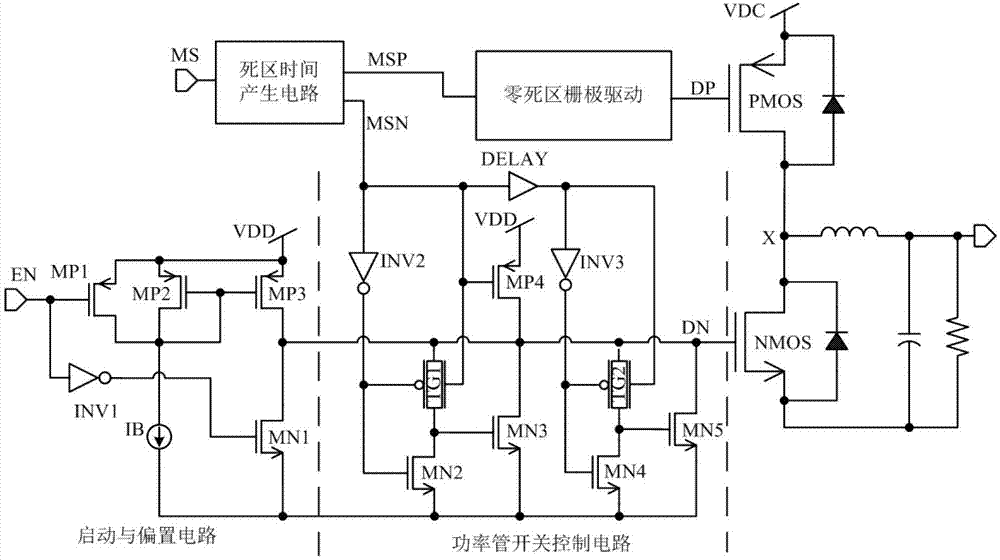
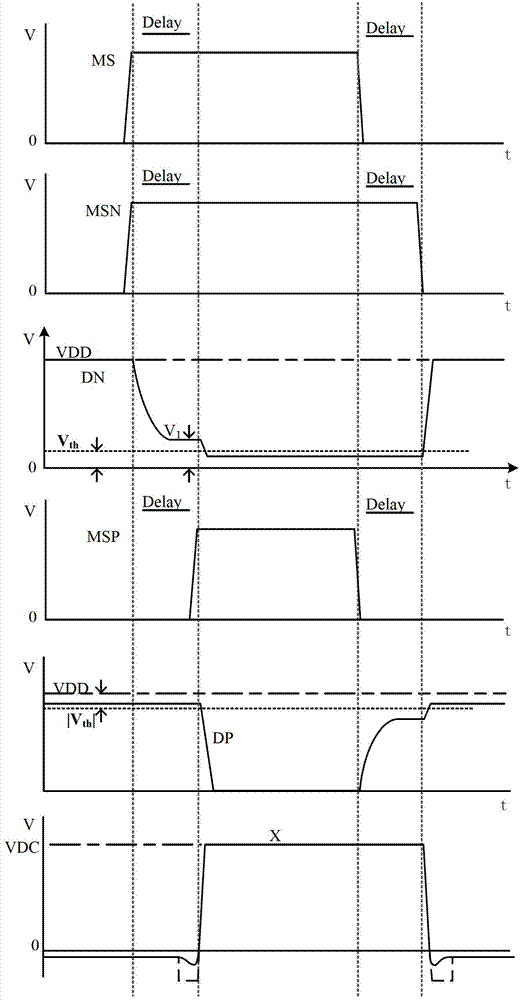
The invention relates to a grid driving circuit which aims at solving the starting problem of a parasitic diode generated by a grid driving circuit in the prior art. The zero dead area grid driving circuit comprises a starting and current offset circuit and a power tube switch control circuit, wherein the starting and current offset circuit comprises three P-channel metal oxide semiconductor (PMOS) tubes (an MP1, an MP2 and an MP3), an N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) tube MN1 and an inverter INV1; and the power tube switch control circuit comprises a PMOS tube (an MP4), four NMOS tubes (an MN2, an MN3, an MN4 and an MN5), two inverters (an INV2 and an INV3), two transmission gates (a TG1 and TG2) and a delay unit (DELAY). The grid driving circuit avoids starting of the parasitic diode and avoids loss and electromagnetic interface caused by the parasitic diode. The grid driving circuit is mainly used in direct current / direct current (DC / DC) converters and various push-pull output circuits adopting PMOS power tubes and NMOS power tubes.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Reduction of dead-time distortion in class D amplifiers
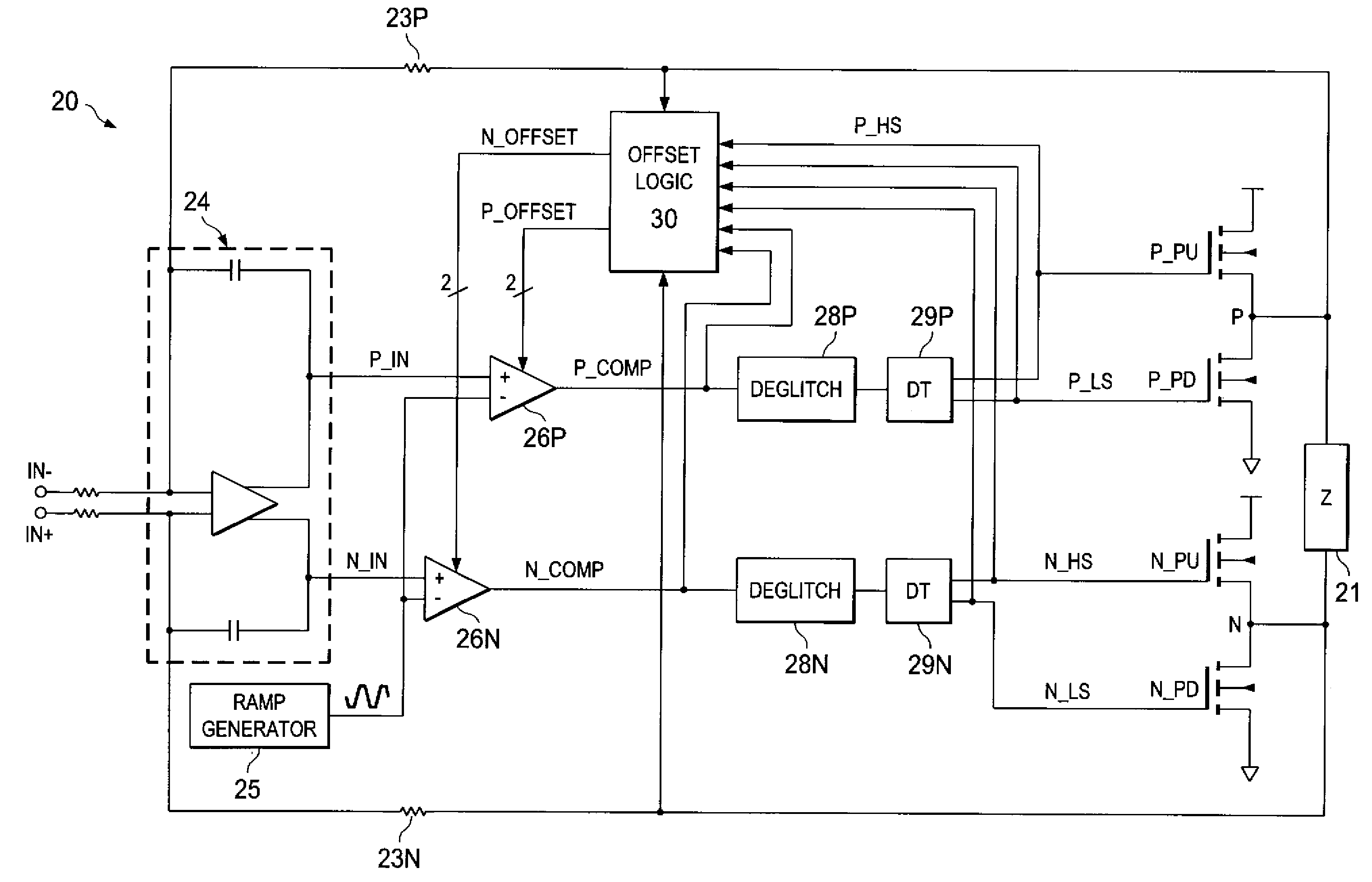
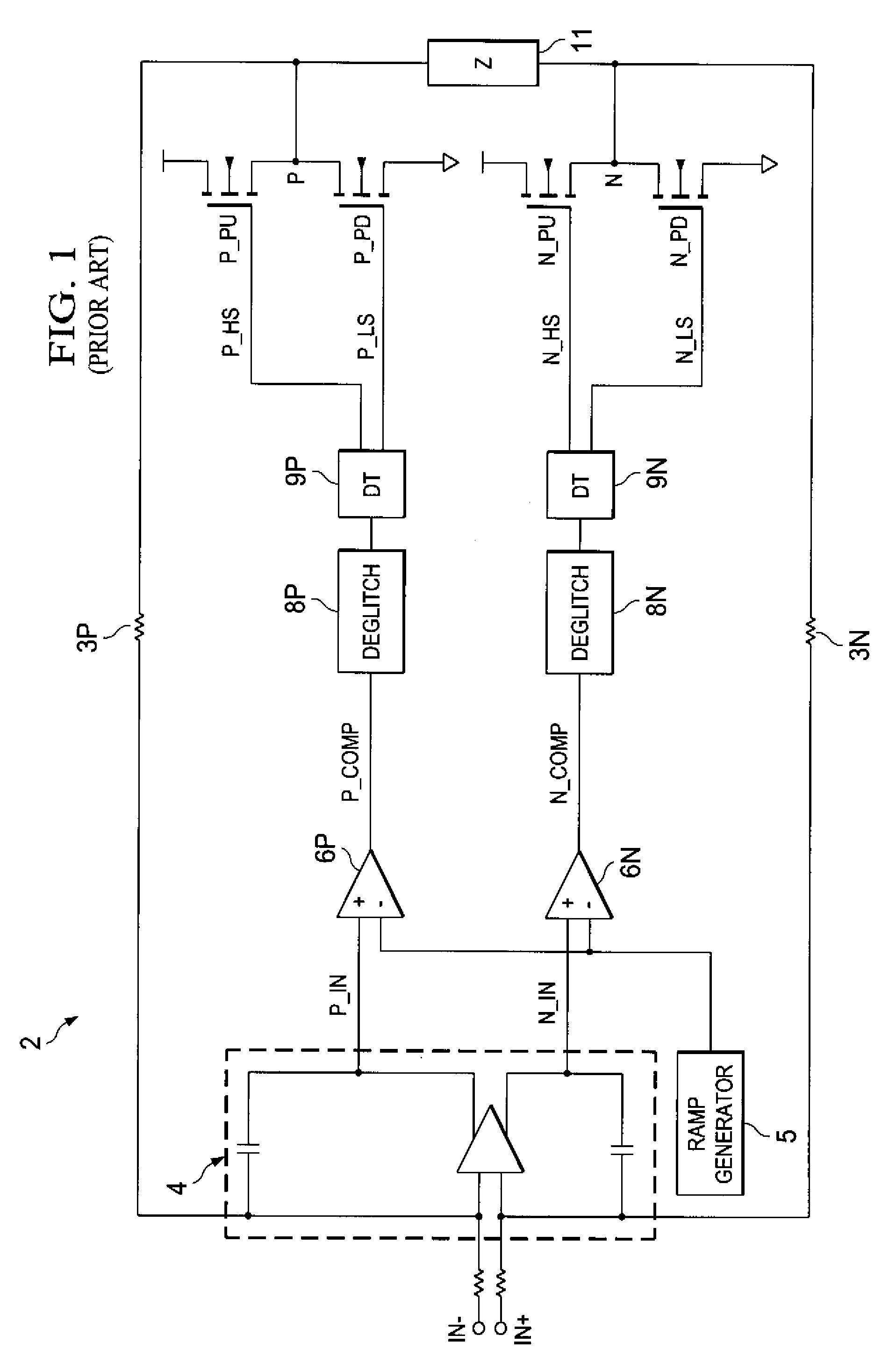
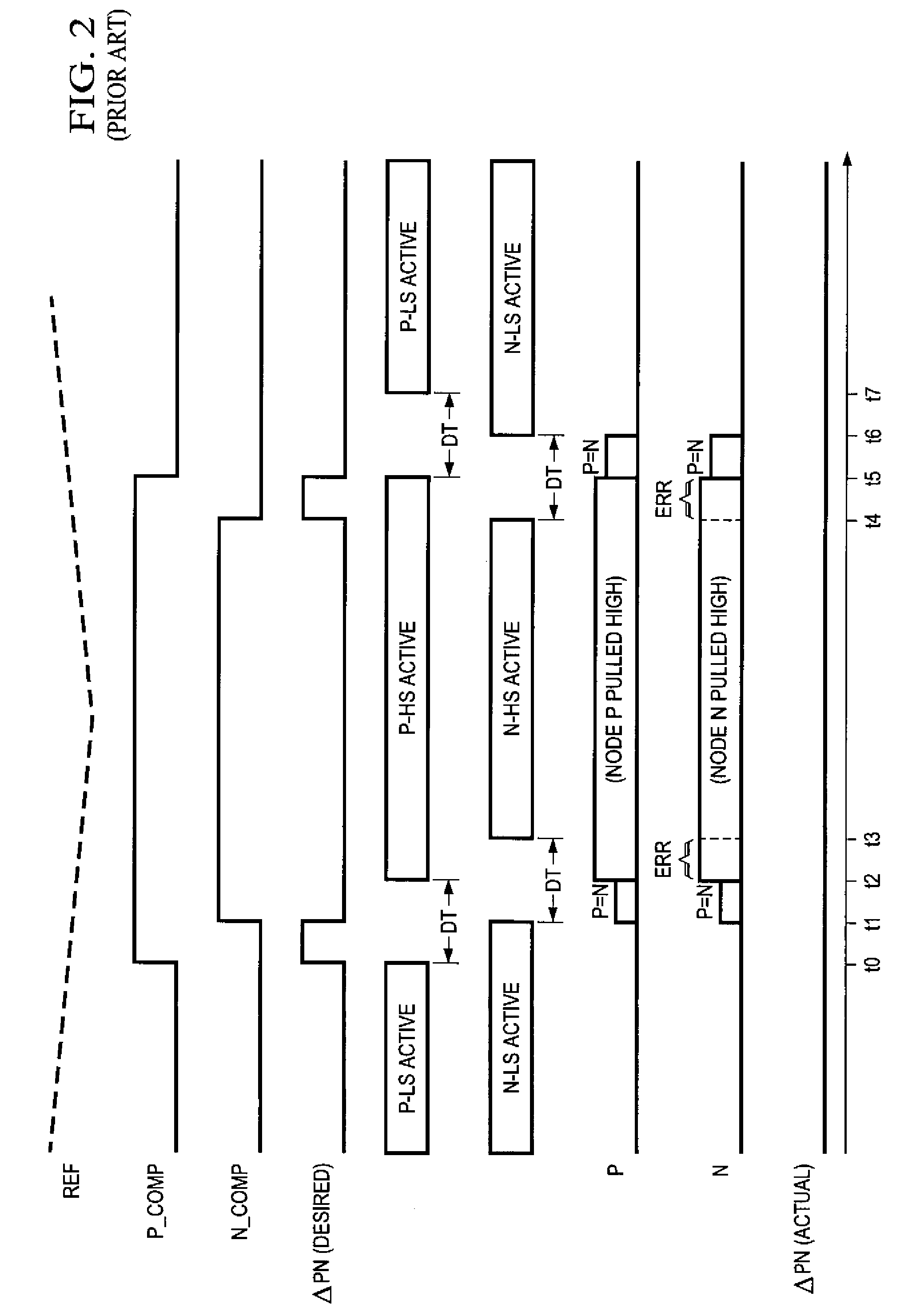
ActiveUS7795970B2Reduce Harmonic DistortionLower levelNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyCircuit complexityDead time
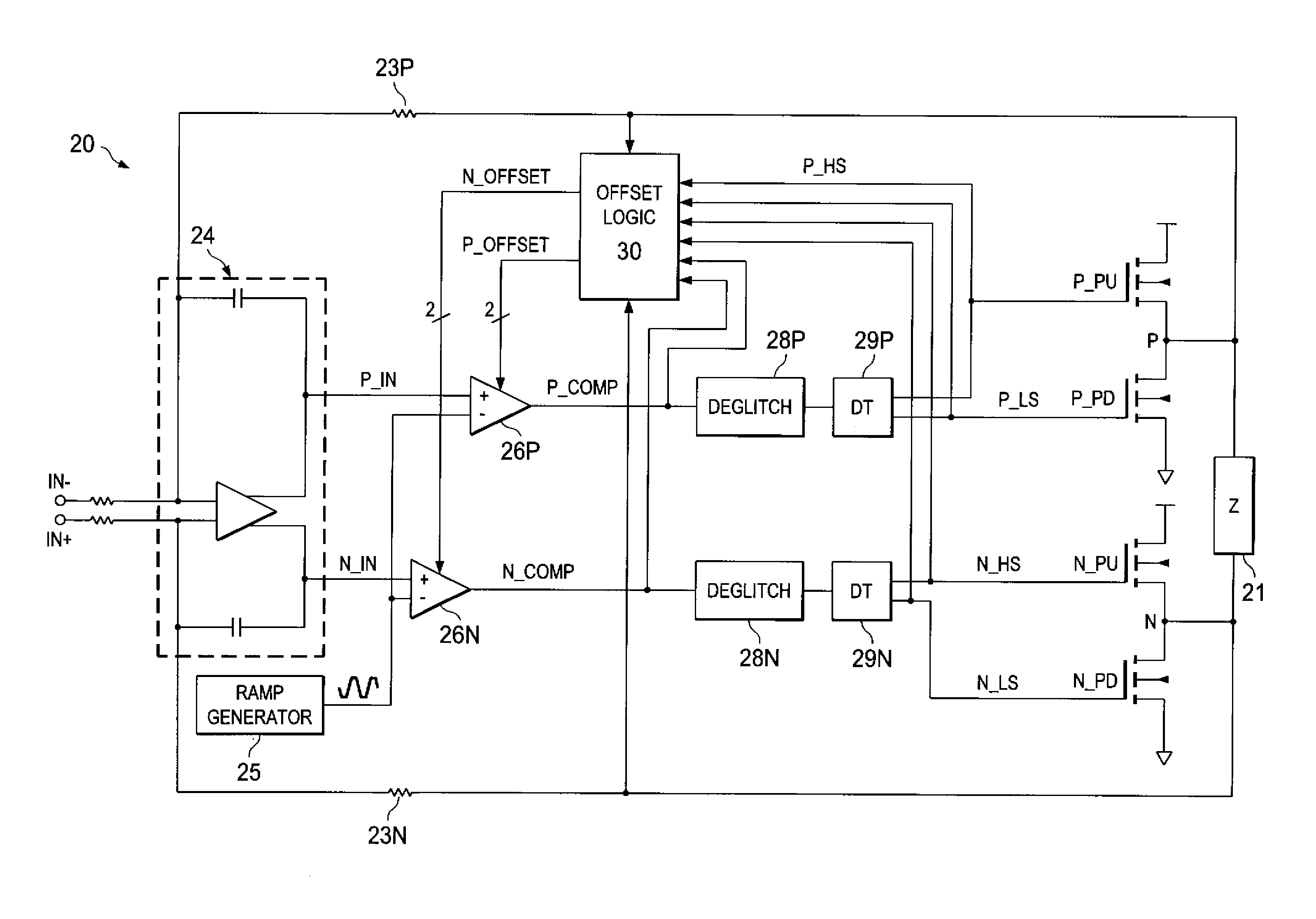
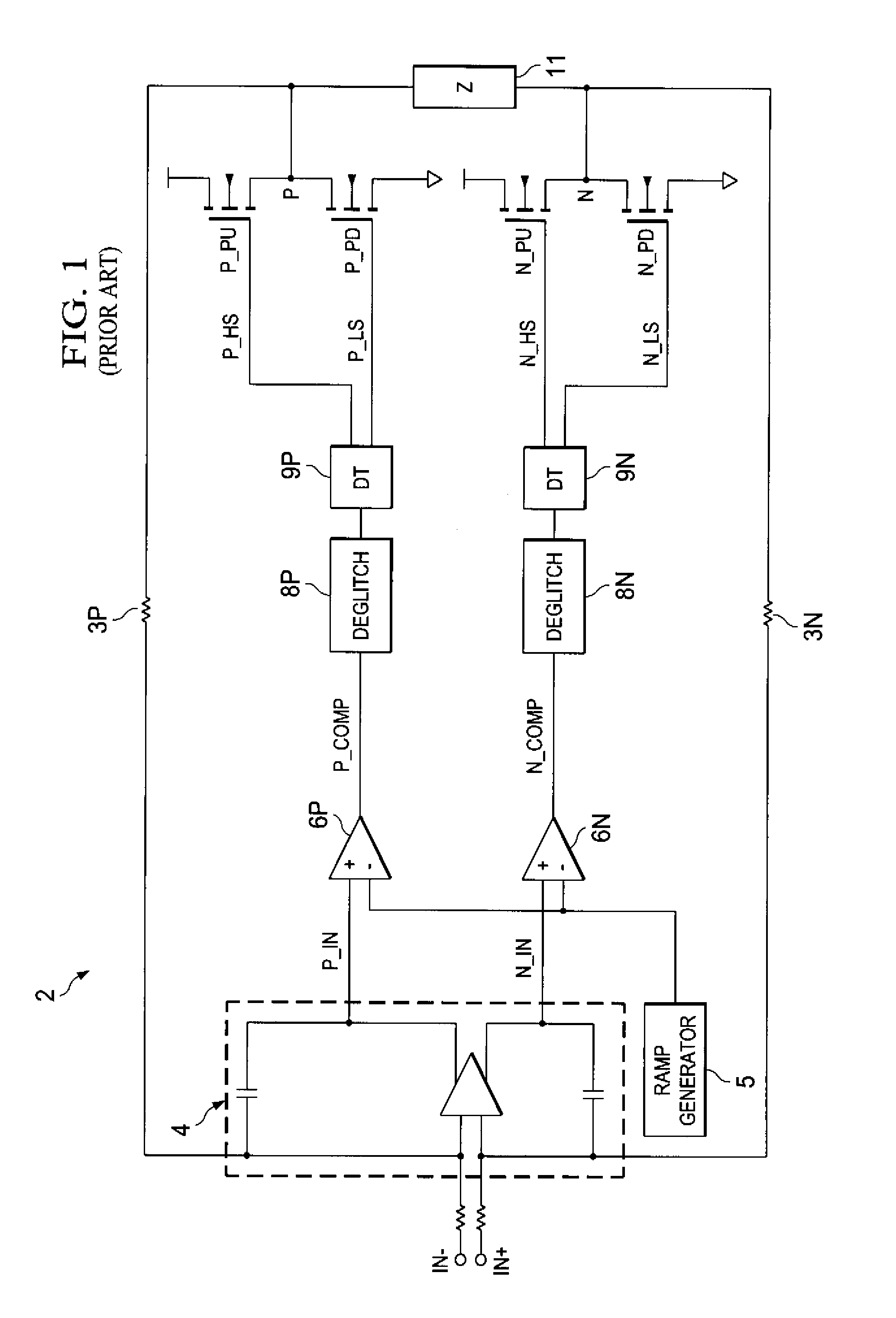
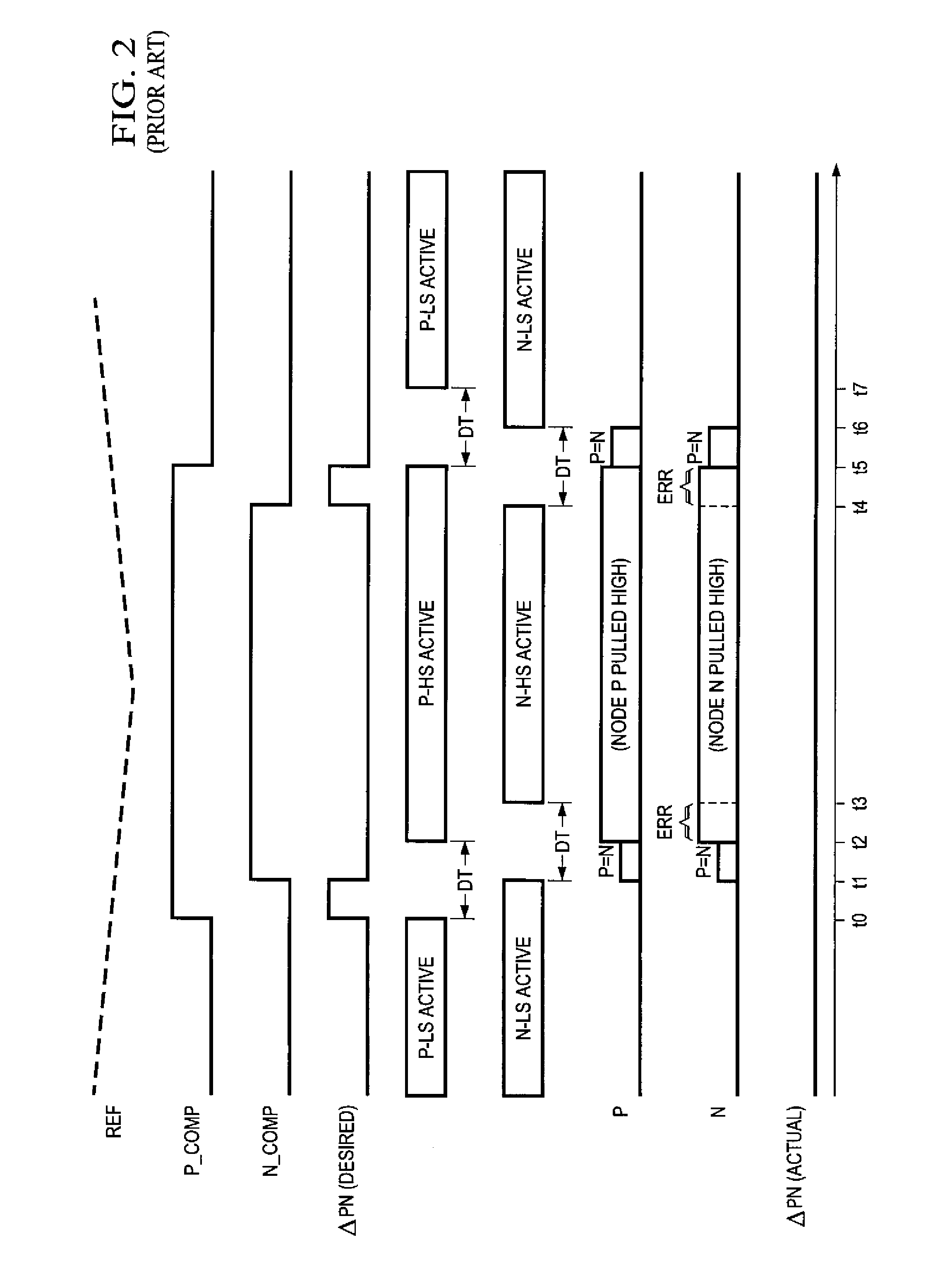
Pulse-width-modulating class D amplifier with an H-bridge output stage, and method of operating the same. in which output stage dead-time is compensated. Offset logic circuitry detects various dead-time-related conditions at push-pull output drivers, and generates an offset signal applied to the amplified differential input signal, to adjust the time at which the voltage at differential signal lines crosses a ramp reference waveform. The offset signal can correspond to the duration of a disturbance (dead-time at one driver in combination with an active signal at the active driver), or the sum of that disturbance duration with a dead-time at the active driver. The offset signal is generated by charging a capacitor for the duration of this disturbance, or disturbance plus dead-time. According to another approach, error is reduced by charging a capacitor for each transition of the signal for a duration of the dead-time of the active driver. Total harmonic distortion is reduced without requiring increased circuit complexity and without shortening the dead-time to unsafe margins.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Drive method and circuit for Polymer Dispersed Liquid Crystal (PDLC)
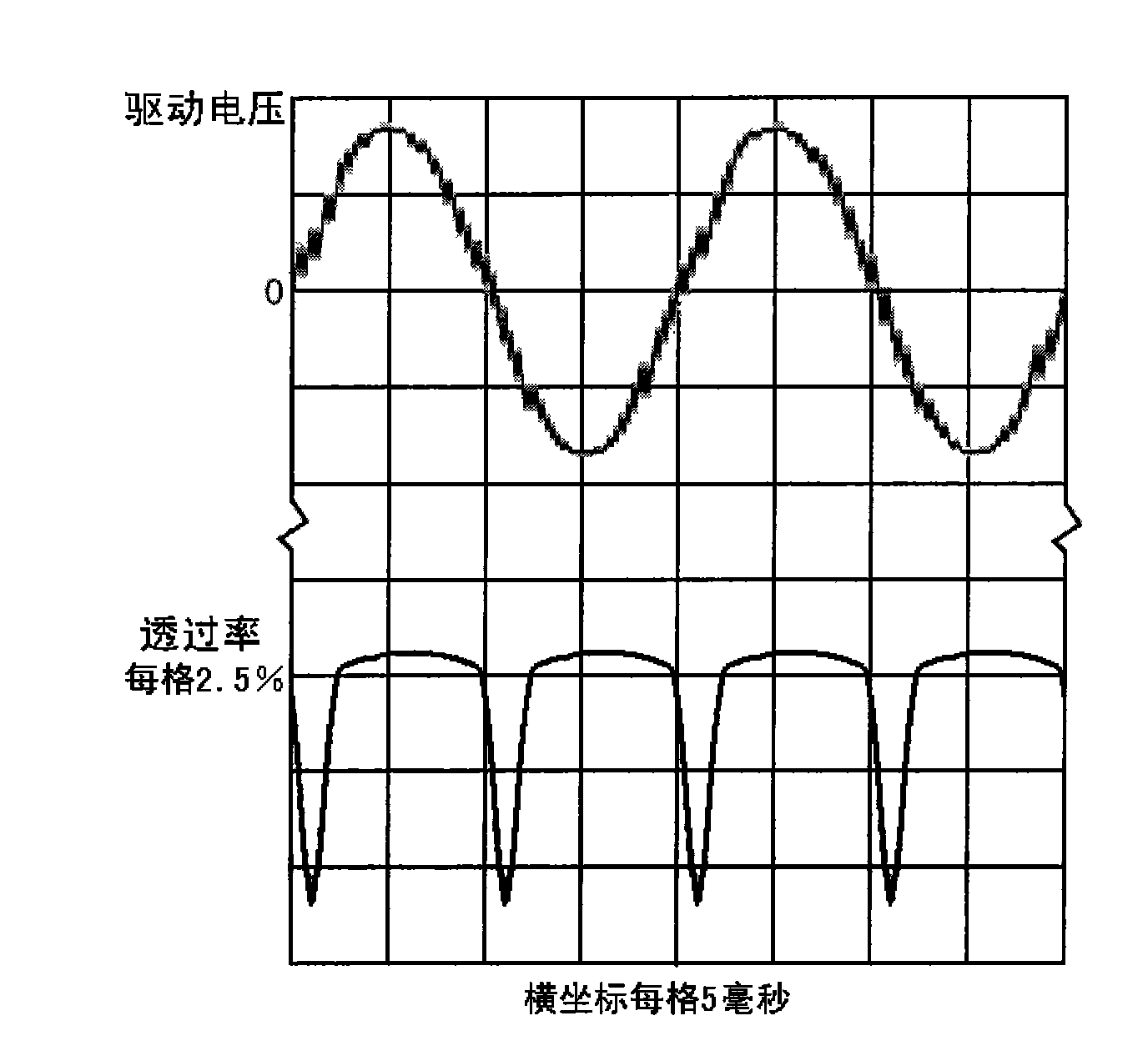
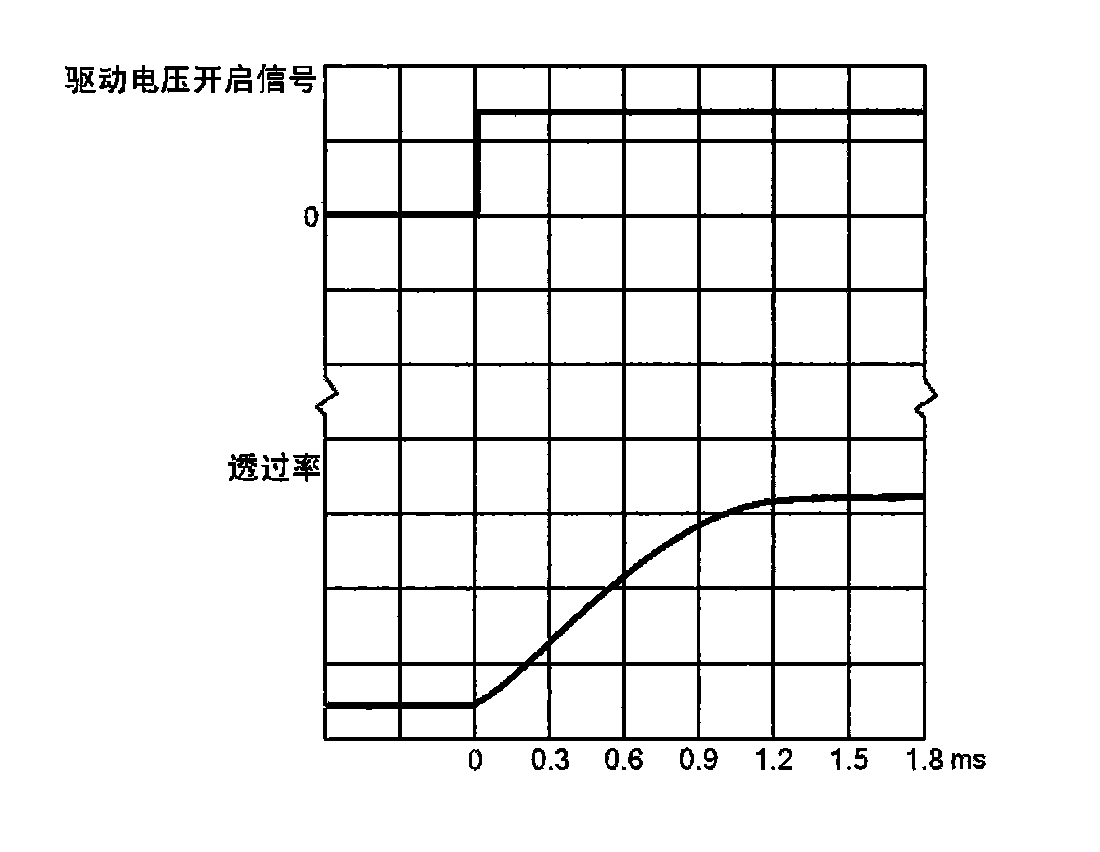
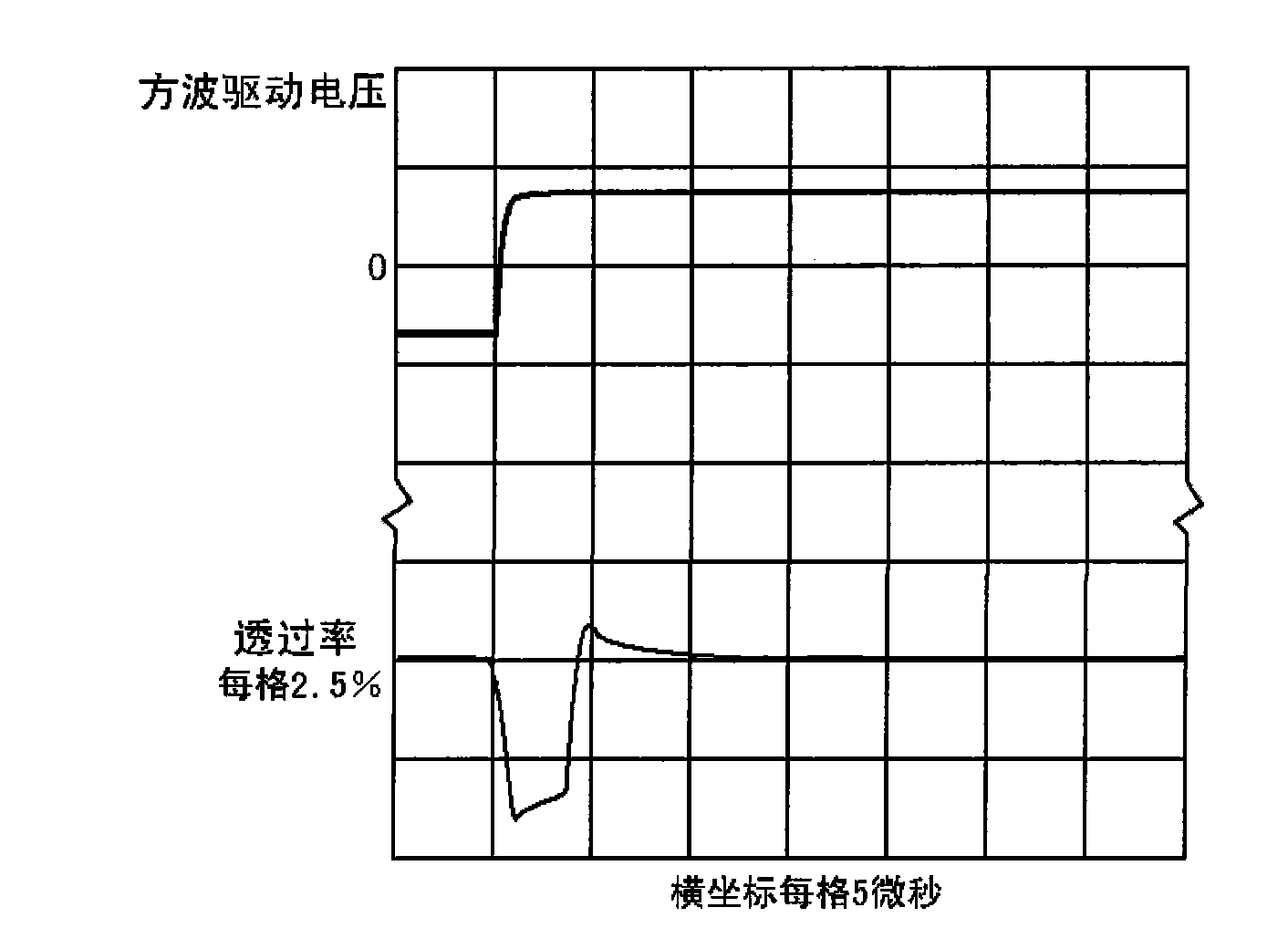
InactiveCN101930135AEliminate screen flickerImprove transmittanceStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsElectricityPush–pull output
The invention relates to a drive method and circuit for Polymer Dispersed Liquid Crystal (PDLC). A drive power supply is electrically connected with two input electrodes of the polymer dispersed liquid crystal film; the waveform of voltage applied to the input electrodes of the polymer dispersed liquid crystal film by the drive power supply is rectangular wave; and the front and rear edges of the rectangular wave are quickly changed, and the ascending and descending time of the rectangular wave is far less than the opening and closing response time of the polymer dispersed liquid crystal film. The drive power supply comprises a rectangular wave generating circuit, a drive stage and a double-arm bridge type pull output circuit, wherein the double-arm bridge type pull output circuit comprises four field effect transistors. The method effectively eliminates the screen splash phenomenon, does not need to drive the frequency of the alternating voltage of the PDLC film to synchronize with the frame frequency of a display observed through the PDLC film by adopting a scanning mode, improves the transmittance of the transparent state of the PDLC film and reduces the haze.
Owner:北京众智同辉科技有限公司
Non-contact electric power transmission circuit
InactiveUS8461723B2Improve efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsTransformersElectric power transmissionFull bridge
A non-contact electric power transmission circuit according to an embodiment of the invention includes an electric power transmission circuit and an electric power receiving circuit. The electric power transmission circuit includes a full bridge circuit and a resonant type full bridge circuit. A direct-current power supply is used as an input of the full bridge circuit, the full bridge circuit includes two sets of switching elements, two switching elements being connected in series in each set of the switching elements, a drive circuit alternately feeds a pulse signal to gates of the switching elements to perform switching of the direct-current input in the full bridge circuit, and a serial resonant circuit of a resonant capacitor and an electric power transmission coil is connected to an output of the full bridge circuit in the resonant type full bridge circuit. The electric power receiving circuit includes an electric power receiving coil and a rectifying and smoothing circuit. The electric power receiving coil is electromagnetically coupled to the electric power transmission coil, and the rectifying and smoothing circuit rectifies an output of the electric power receiving coil. In the non-contact electric power transmission circuit, a push-pull output PWM control circuit is provided in the drive circuit that controls the full bridge circuit, and only one of the switching elements in each set of switching elements performs a regenerative operation. Therefore, a non-contact electric power transmission circuit in which the resonant type full bridge circuit can be controlled by PWM control at a level similar to that of a phase shift operation can be provided.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Buffer amplifier for source driver
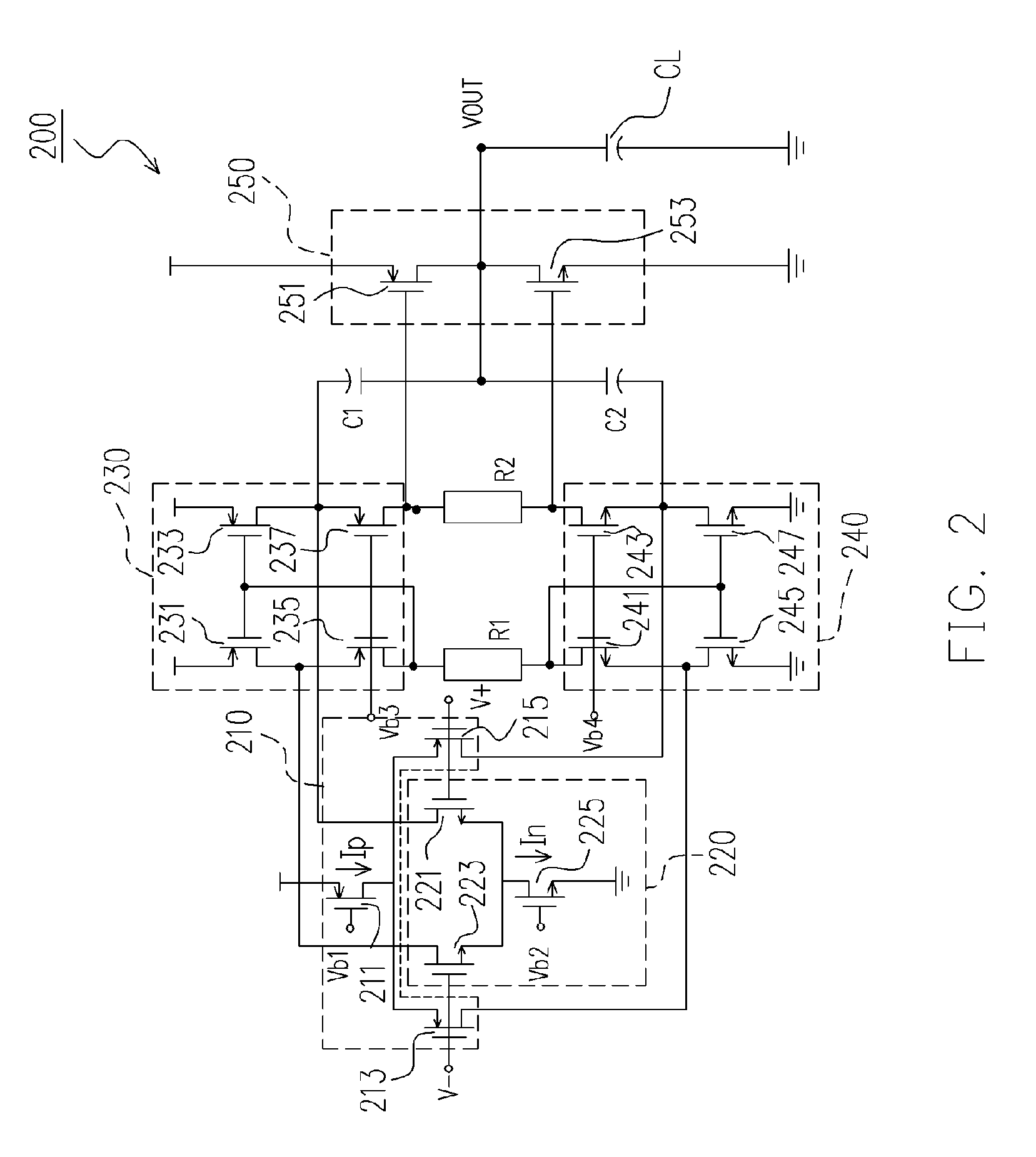
InactiveUS7348848B2Reduce power consumptionHigh speedDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesAudio power amplifierPush–pull output
A buffer amplifier for source driver is disclosed. The buffer amplifier has an N-channel differential amplifier and a P-channel differential amplifier as its input stages so as to achieve rail-to-rail input, and a class AB amplifier to push-pull the output stage so as to achieve rail-to-rail output. The output stage of the buffer amplifier is capable of larger charge / discharge, is faster, and has equal charge / discharge time. More importantly, the buffer amplifier has advantages such as lower power consumption, higher slew rate, and a more stable output.
Owner:DENMOS TECH
Reduction of dead-time distortion in class d amplifiers
ActiveUS20100201443A1Reduce Harmonic DistortionLower levelAmplififers with field-effect devicesCircuit complexityDead time
Pulse-width-modulating class D amplifier with an H-bridge output stage, and method of operating the same. in which output stage dead-time is compensated. Offset logic circuitry detects various dead-time-related conditions at push-pull output drivers, and generates an offset signal applied to the amplified differential input signal, to adjust the time at which the voltage at differential signal lines crosses a ramp reference waveform. The offset signal can correspond to the duration of a disturbance (dead-time at one driver in combination with an active signal at the active driver), or the sum of that disturbance duration with a dead-time at the active driver. The offset signal is generated by charging a capacitor for the duration of this disturbance, or disturbance plus dead-time. According to another approach, error is reduced by charging a capacitor for each transition of the signal for a duration of the dead-time of the active driver. Total harmonic distortion is reduced without requiring increased circuit complexity and without shortening the dead-time to unsafe margins.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
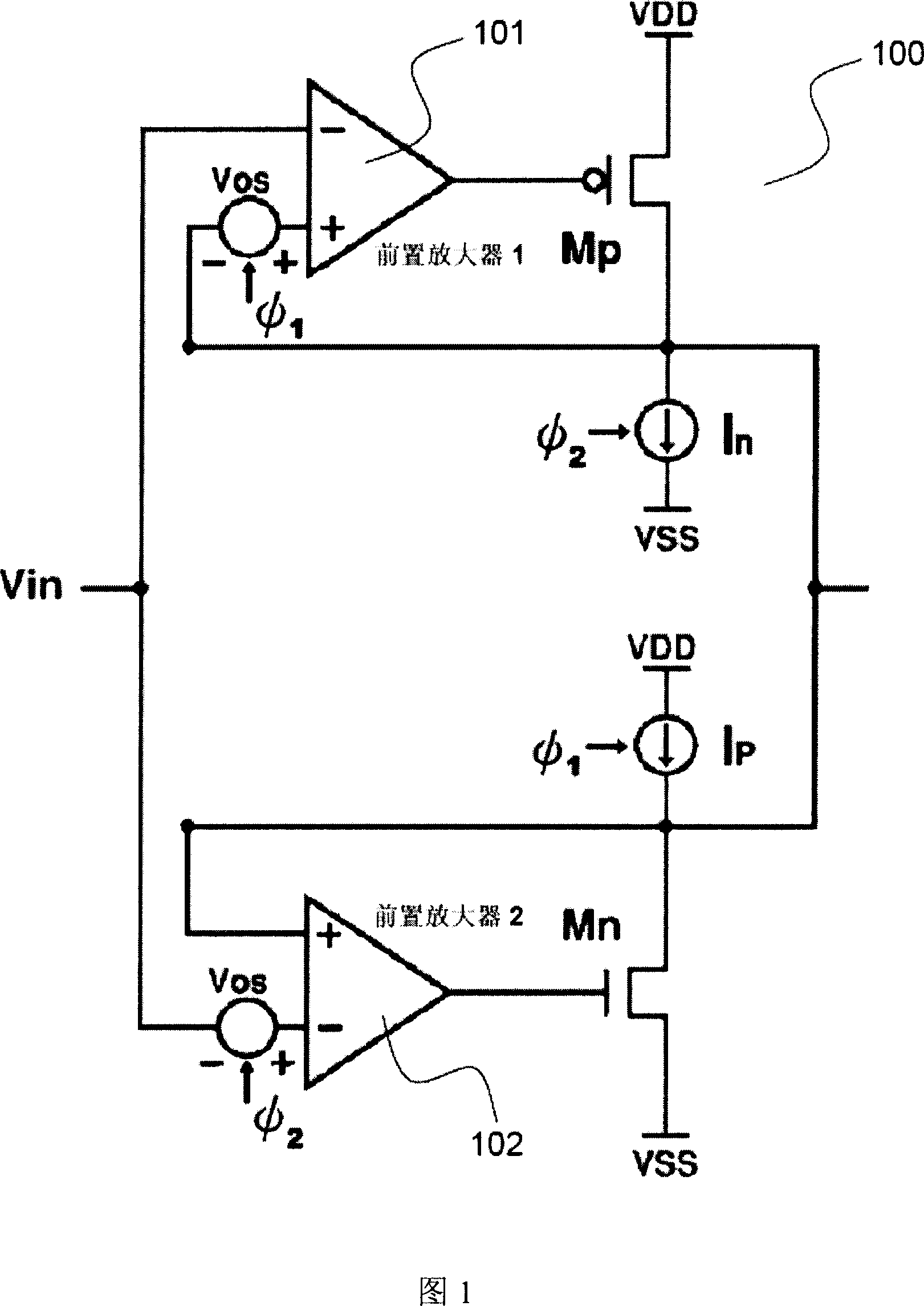
Apparatus and method for increasing a slew rate of an operational amplifier
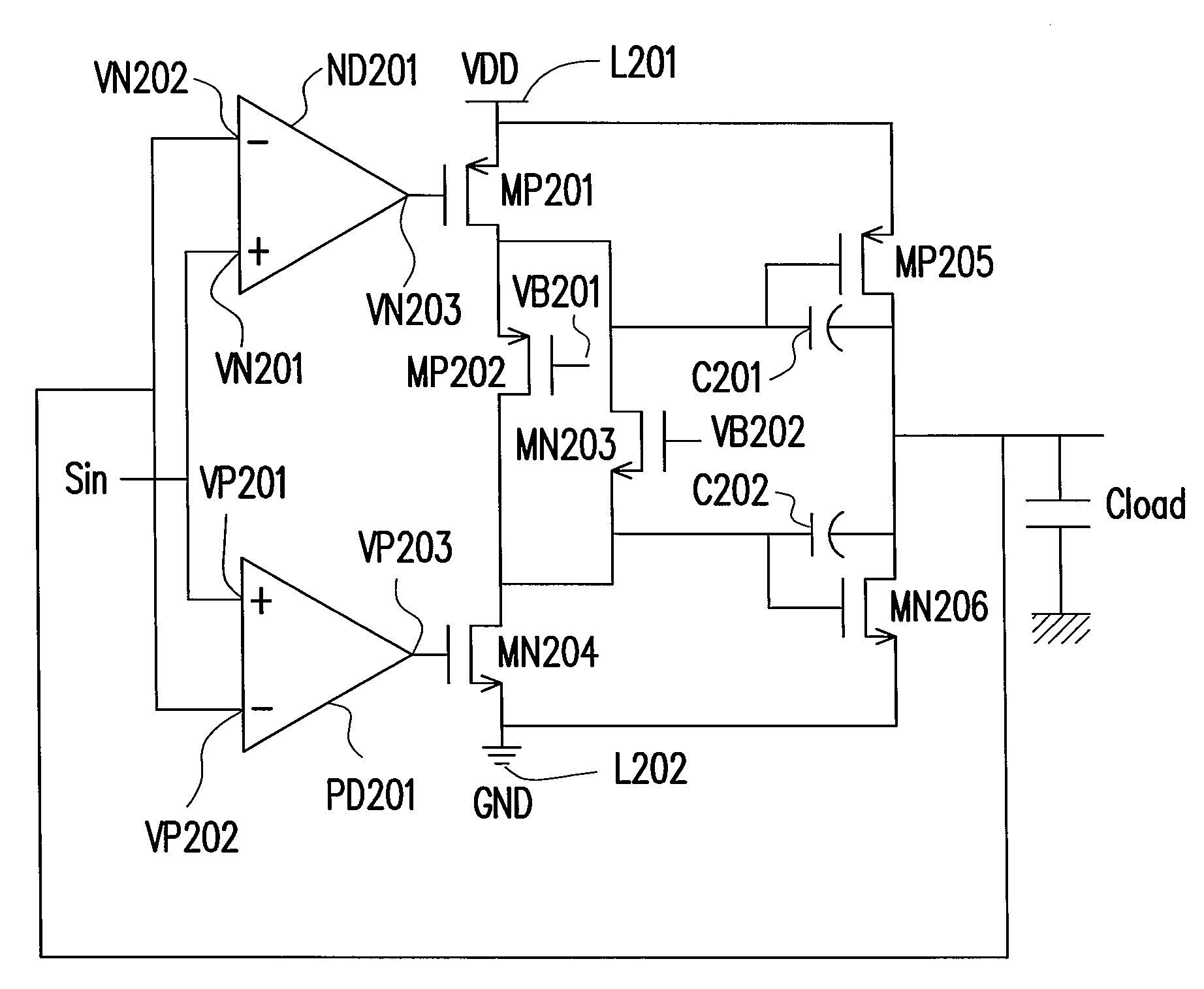
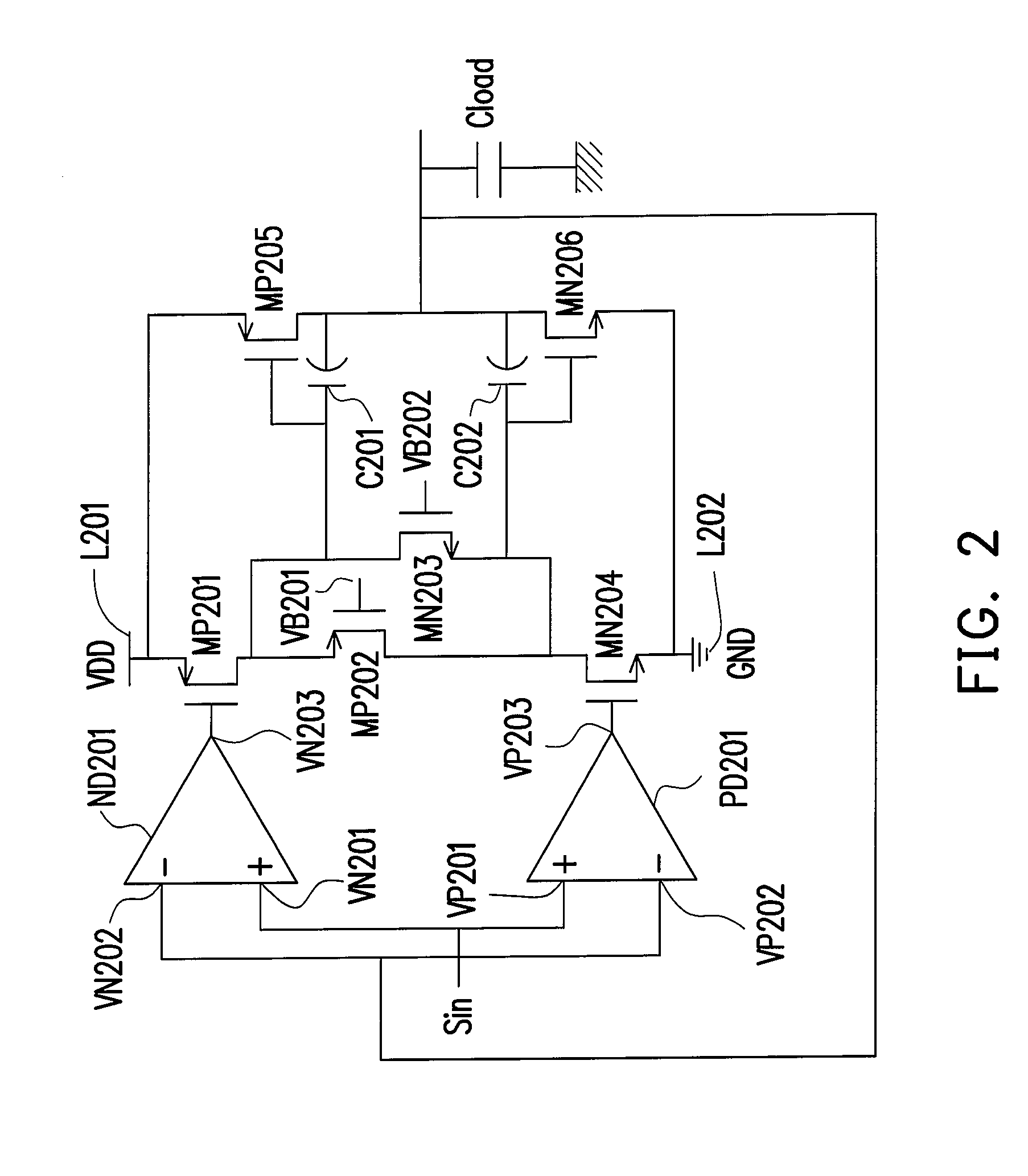
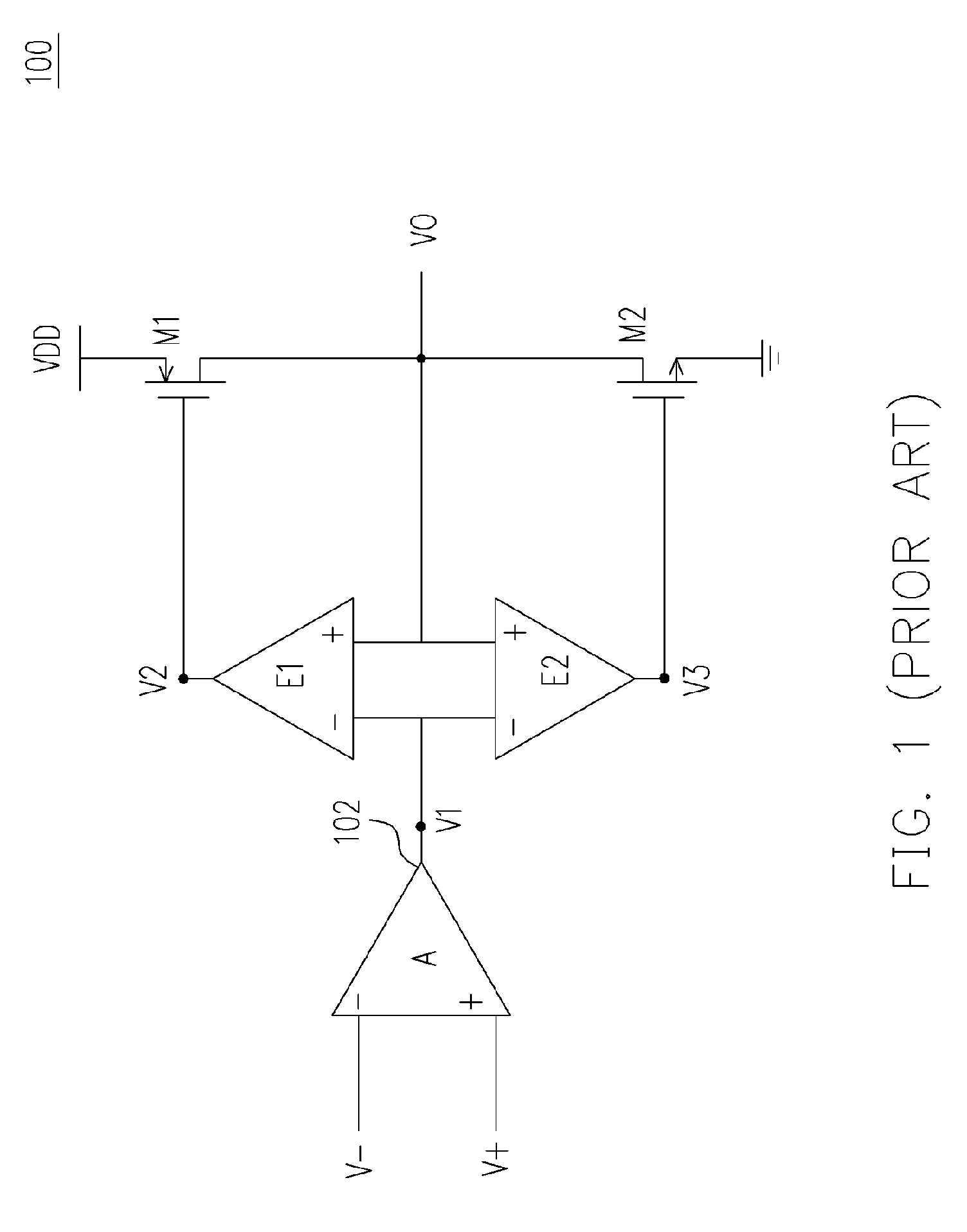
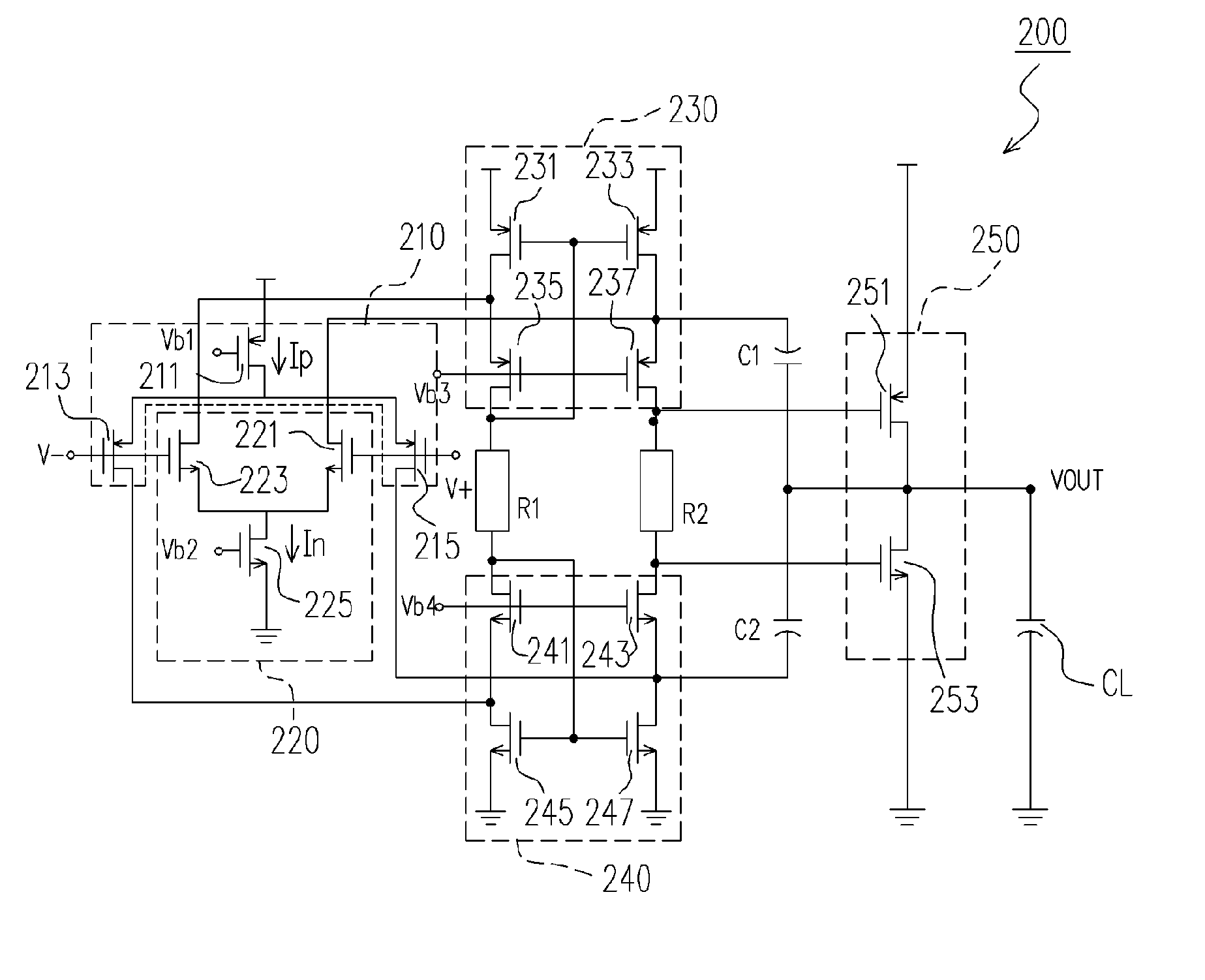
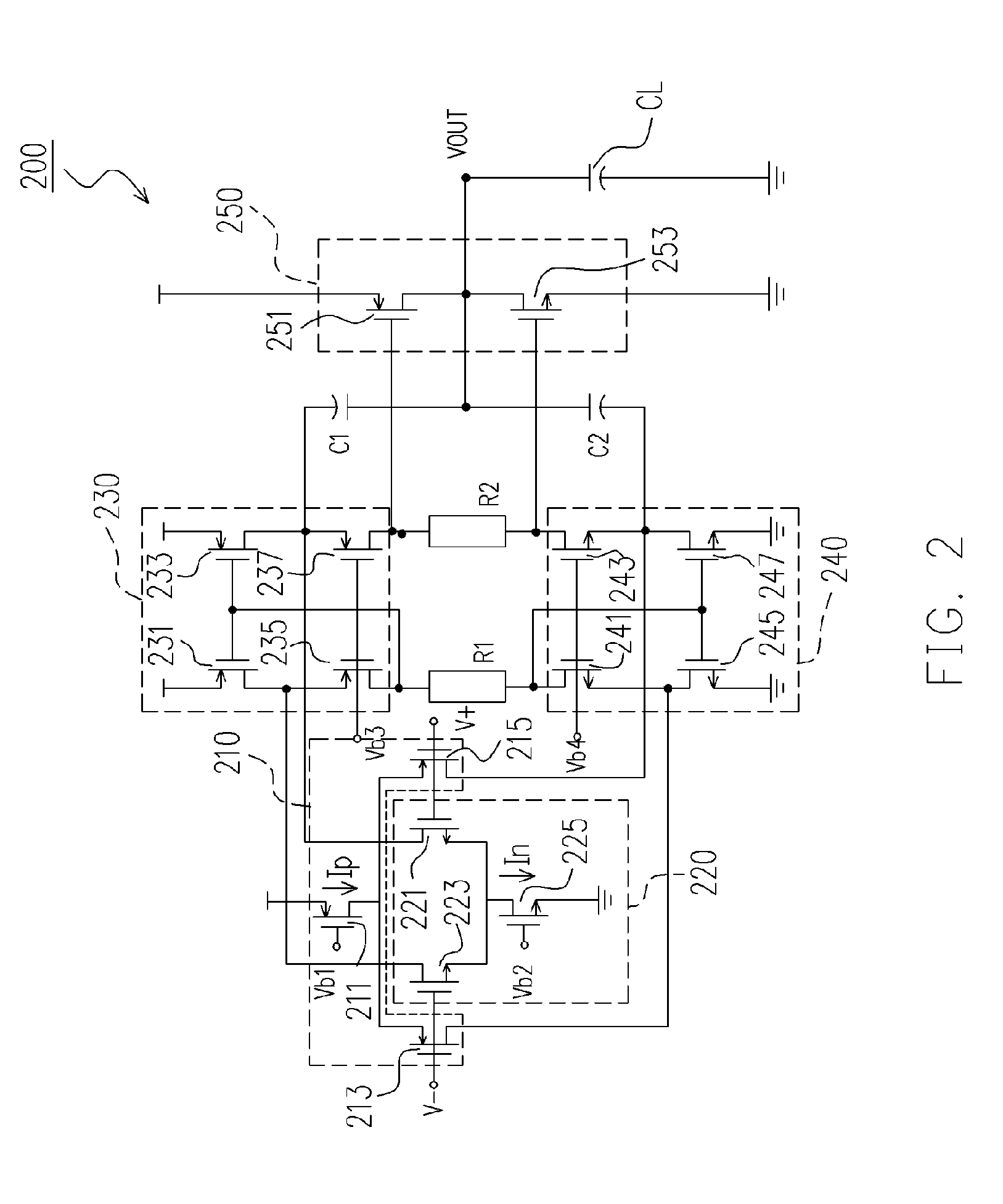
InactiveUS7102436B2Increase conversion rateLower average currentDifferential amplifiersSingle-ended push-pull amplifiersPush–pull outputAudio power amplifier
An apparatus and method for increasing a slew rate of an operational amplifier are provided. It only requires an operational amplifier, a monitoring control device, a push-pull output device, and a second input current source pair. It uses a monitoring control device controlled by the output stage to control the supplementary device and the second input current source pair in order to increase a slew rate of an operational amplifier. This operational amplifier also provides the rail-to-rail output function. In addition, because it does not require additional circuit to increase the slew rate, the chip size is smaller. With respect to the circuit structure, it is very simple and can be applied to the pre-existing operational amplifier without re-designing the operational amplifier and thus can keep the original characteristics of the operational amplifier.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
High-precision output voltage-adjustable reference voltage generating circuit
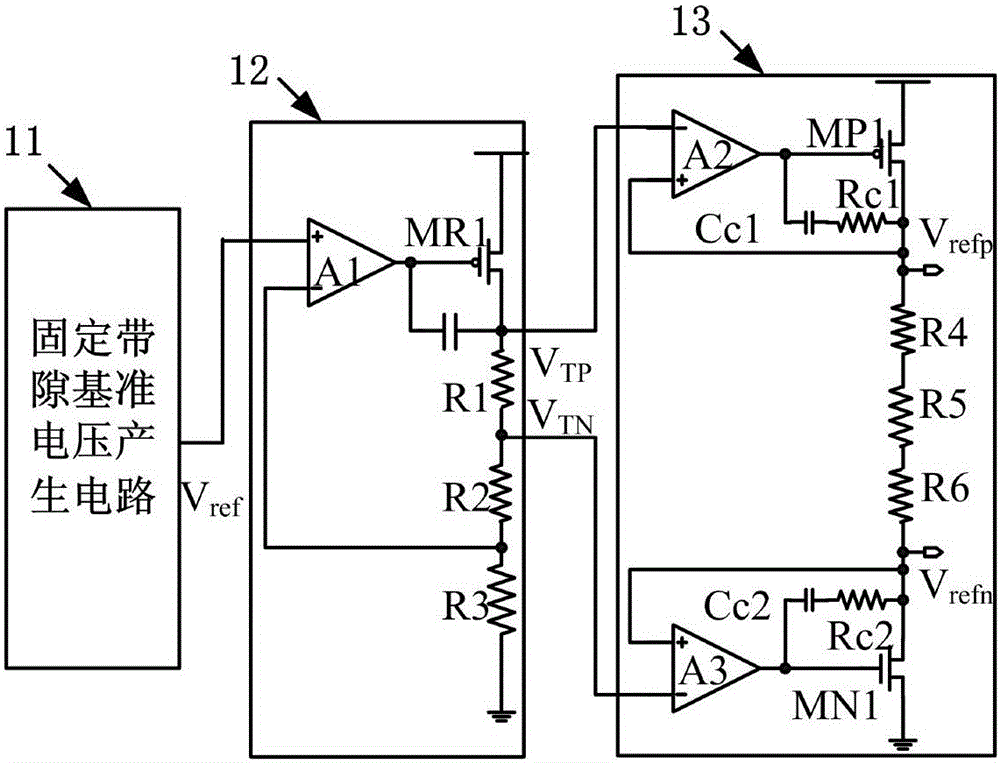
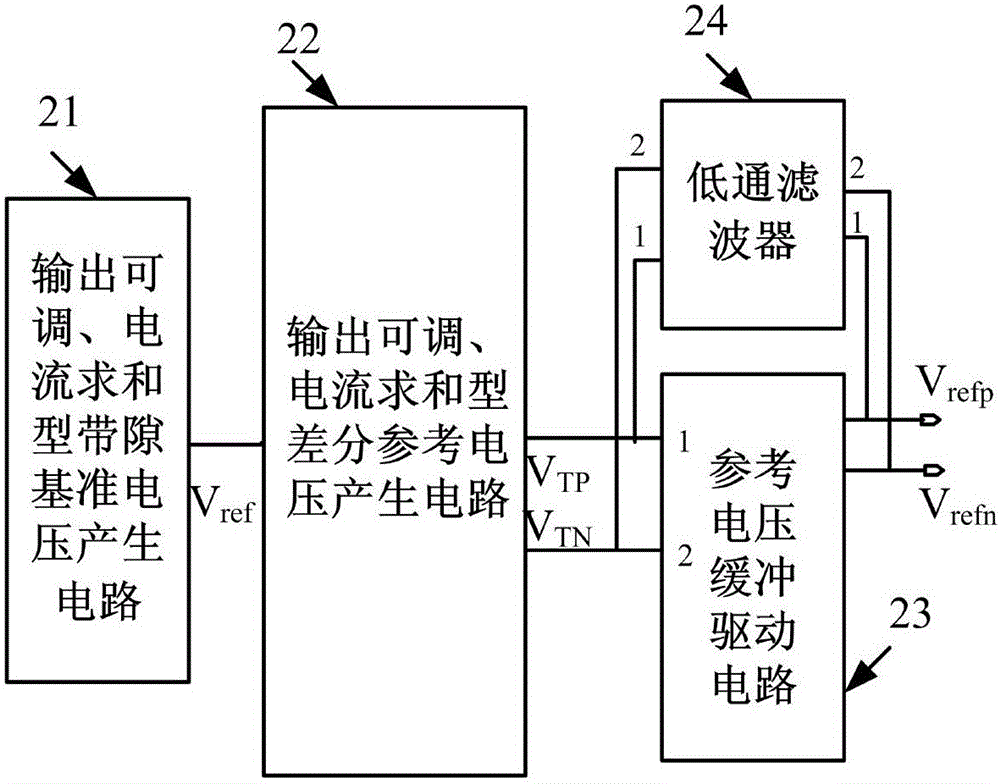
ActiveCN105867517AImprove PSRRIncrease power consumptionElectric variable regulationNegative feedbackPush–pull output
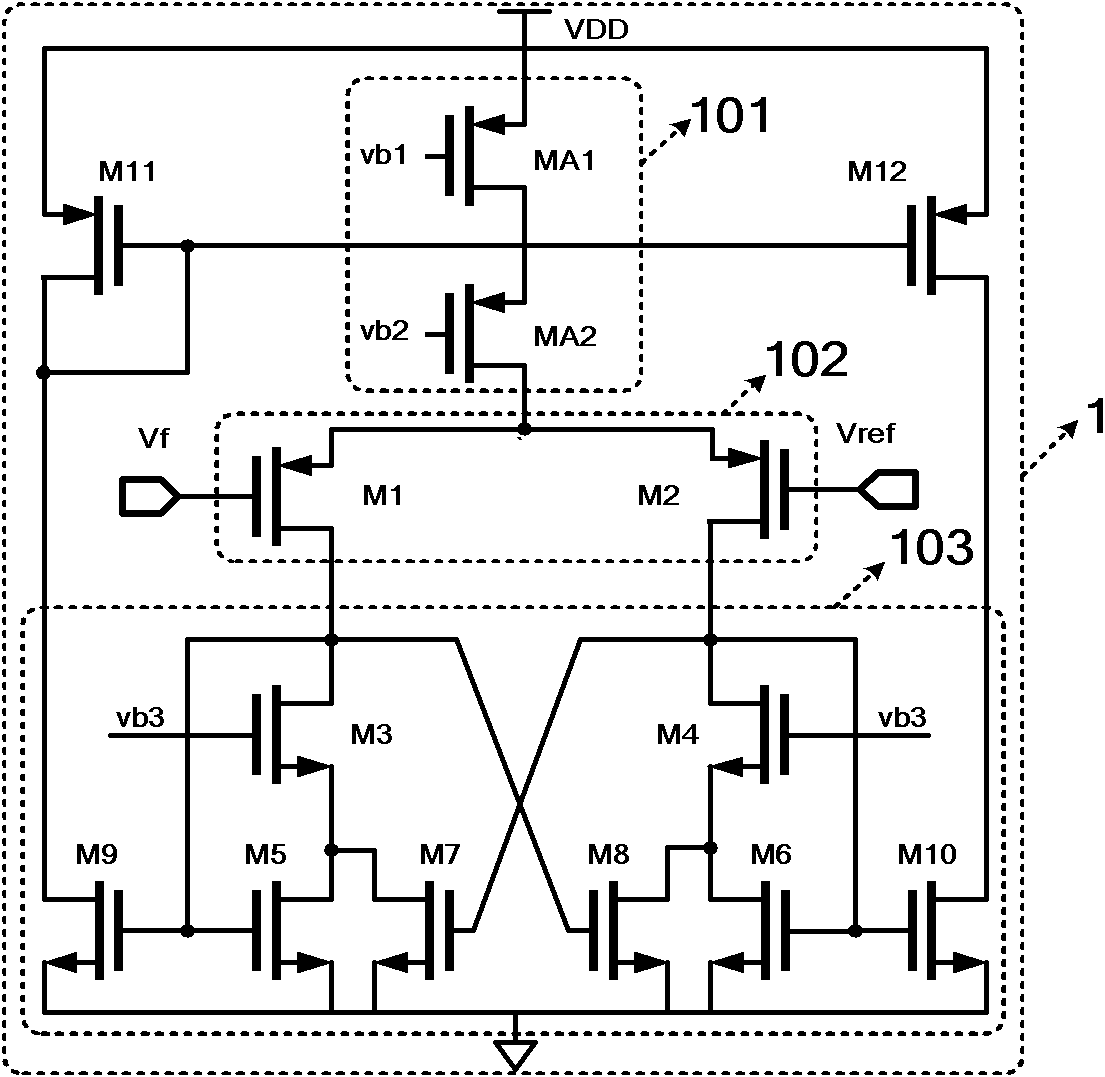
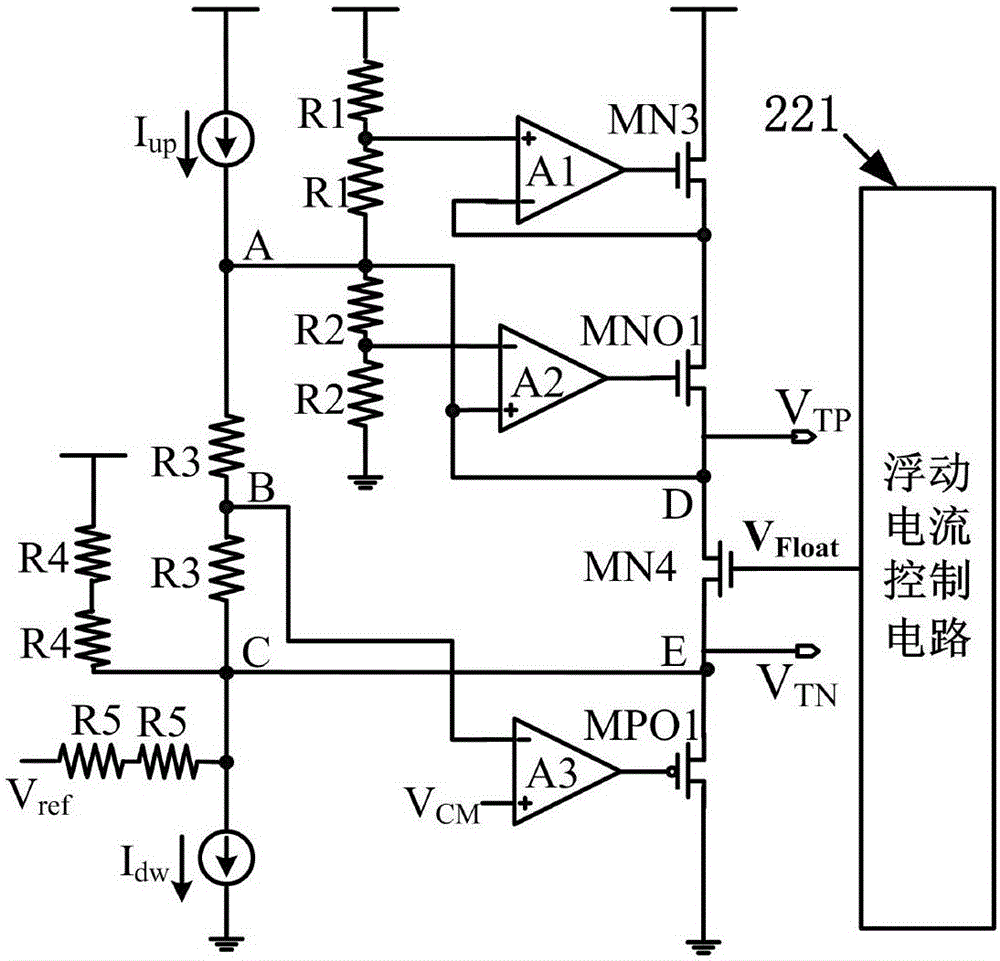
The invention relates to a high-precision output voltage-adjustable reference voltage generating circuit which comprises an output-adjustable current summation type bandgap reference voltage generating circuit, an output-adjustable current summation type difference reference voltage generating circuit and a reference voltage buffer driving circuit. The output-adjustable current summation type bandgap reference voltage generating circuit generates a bandgap reference voltage Vref for output; through the output-adjustable current summation type difference reference voltage generating circuit, difference reference voltages VTP and VTN are generated for output; and through the reference voltage buffer driving circuit, reference voltages Vrefp and Vrefn are output. Through current summation and a floating current source negative feedback control technology, the output voltage-adjustable fully differential reference voltage buffer driving circuit is designed. The buffer driving circuit is further of a structure with a source electrode push-pull output and duplicate circuit, a smaller output impedance is obtained while the power supply rejection ratio (PSRR) of the reference voltage is further improved, and the high-precision output voltage-adjustable reference voltage generating circuit has better driving capability.
Owner:58TH RES INST OF CETC
Bidding purchasing information calibration circuits
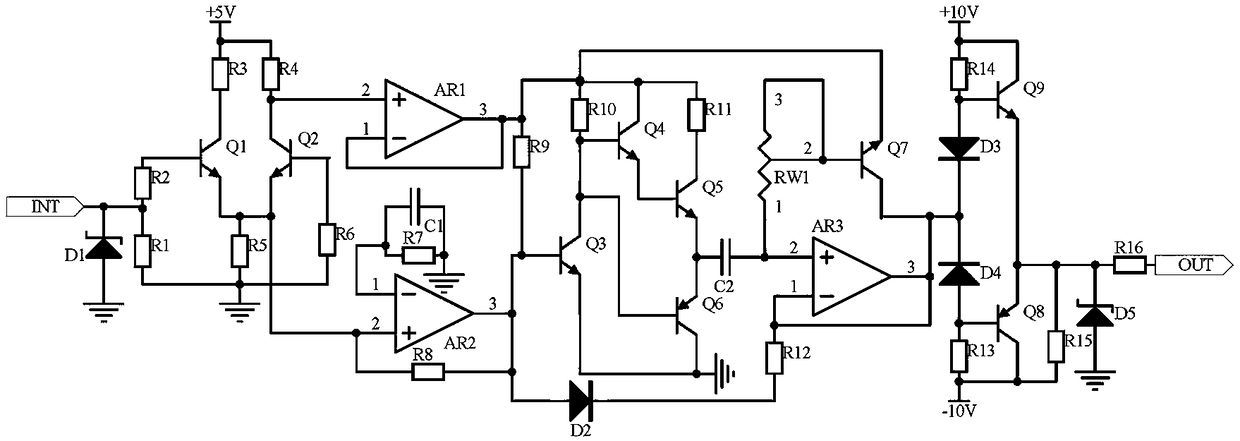
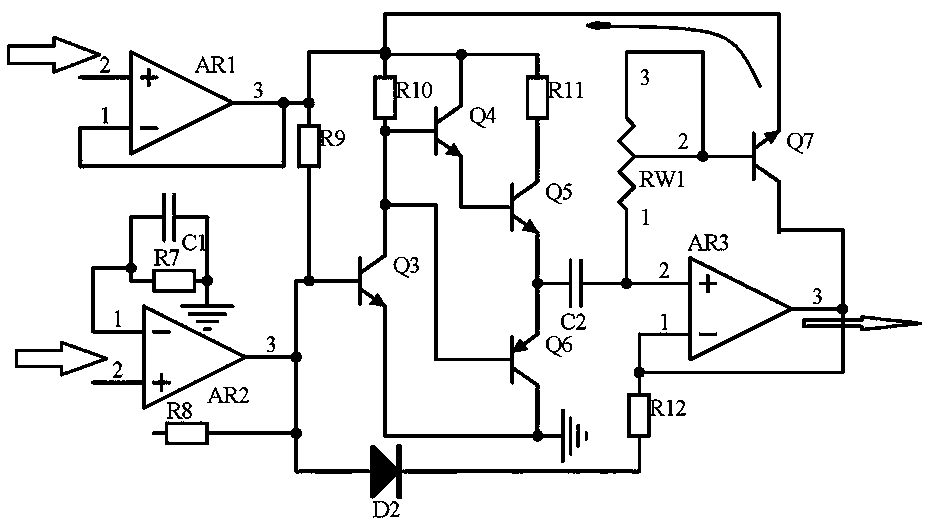
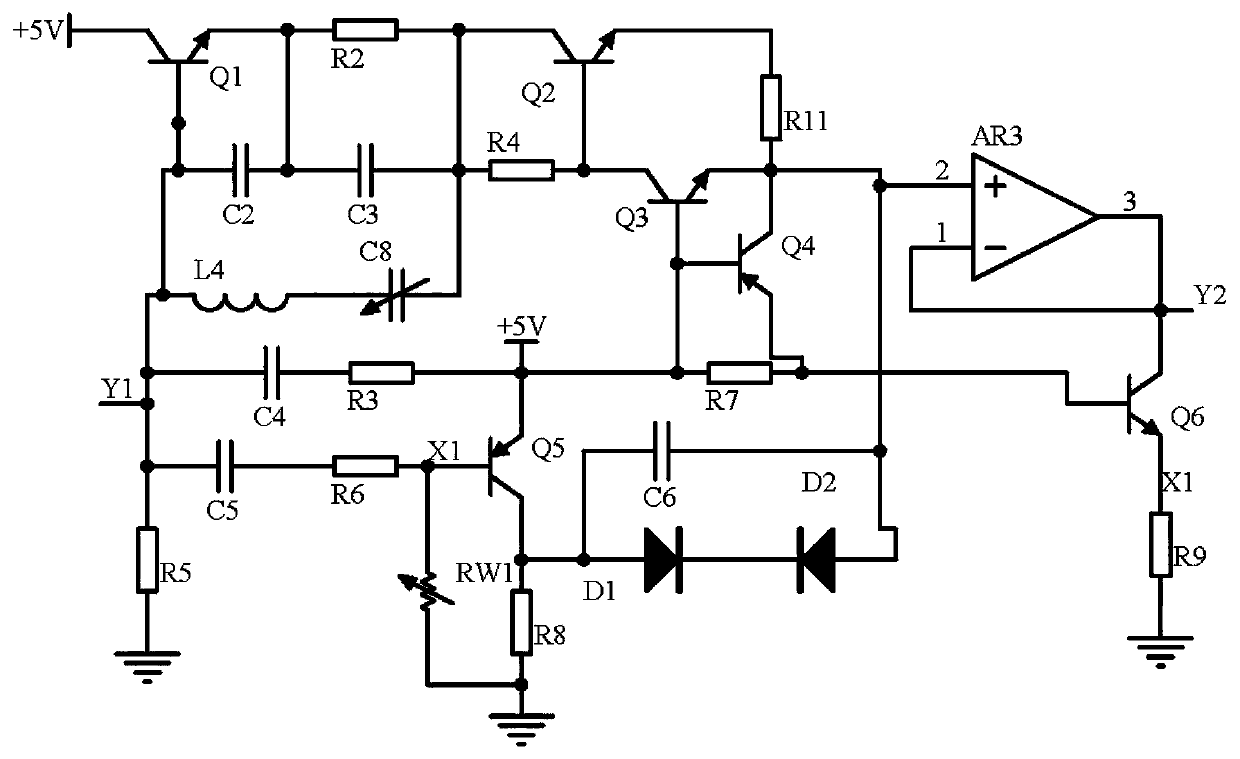
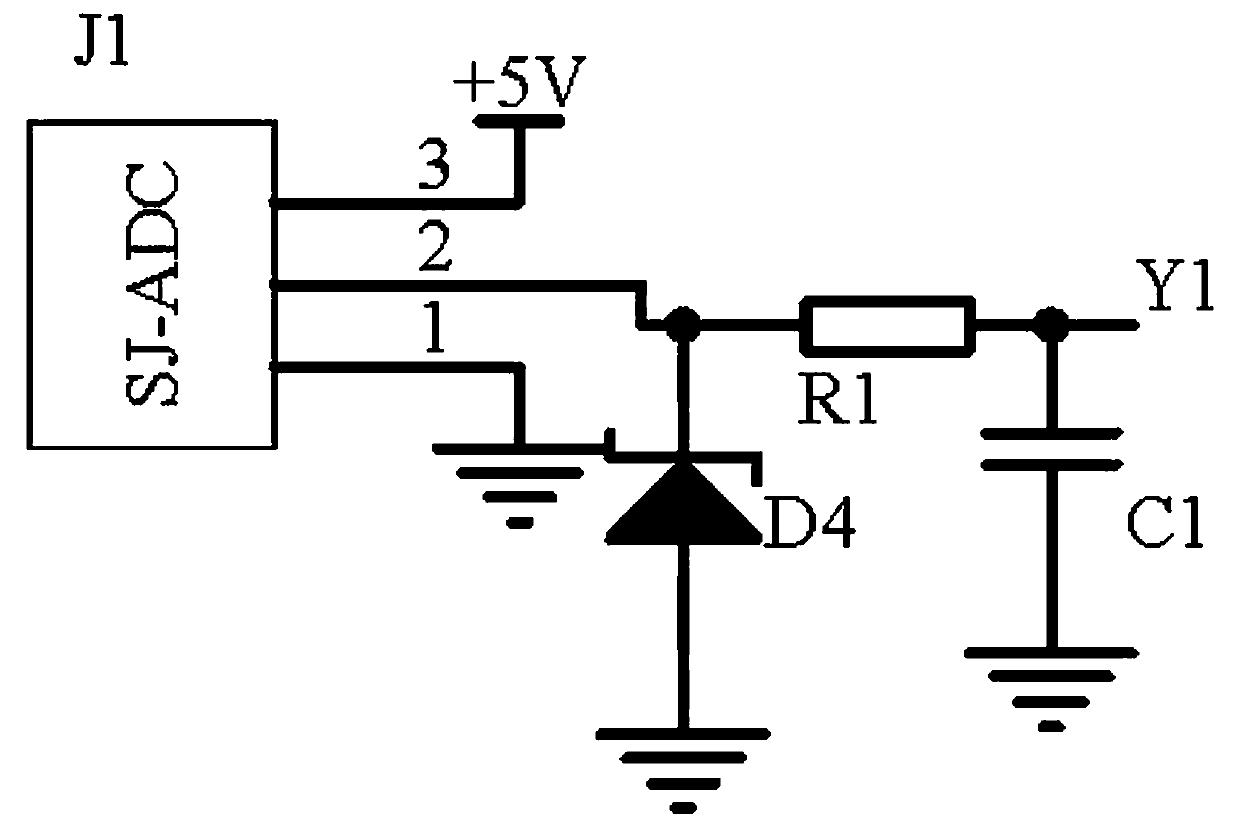
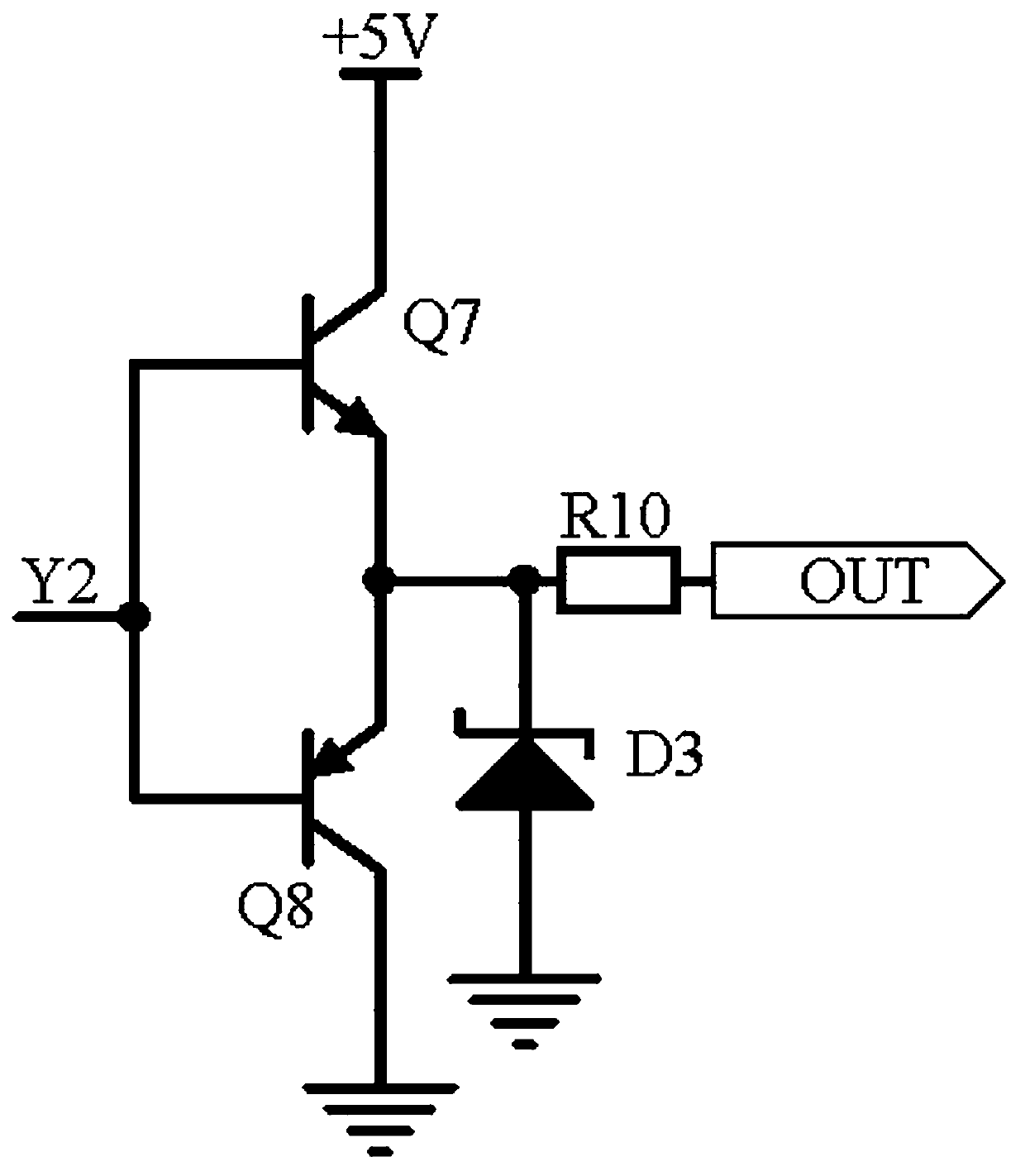
The invention discloses bidding purchasing information calibration circuits. A bidding purchasing information calibration circuit comprising a signal input circuit, a rectification and comparison circuit and a push-pull output circuit. The signal input circuit receives a signal at an input end of a signal transmission channel for a control terminal to receive a data signal, in a bidding purchasinginformation management system. The rectification and comparison circuit receives signals output by the signal input circuit, rectifies the signals through application of a rectification circuit composed of an operational amplifier AR1, an operational amplifier AR2, a resistor R7 and a capacitor C1, carries out frequency modulation on the signals through application of a frequency modulation circuit composed of a triode Q3, a triode Q4, a triode Q5 and a triode Q6, and compares and processes the signals output by the frequency modulation circuit and the rectification circuit through application of a comparer AR3, thereby stabilizing a signal static working point. Signal potential output by the frequency modulation circuit is fed back and adjusted through application of a variable resistorRW1 and a triode Q7. The push-pull output circuit carries out voltage stabilization on the signals and outputs the signals. Automatic signal calibration is realized, signal stability is improved, andsignal frequency modulation and distortion are prevented.
Owner:PINGDINGSHAN UNIVERSITY
Electronic equipment analog signal calibration circuit
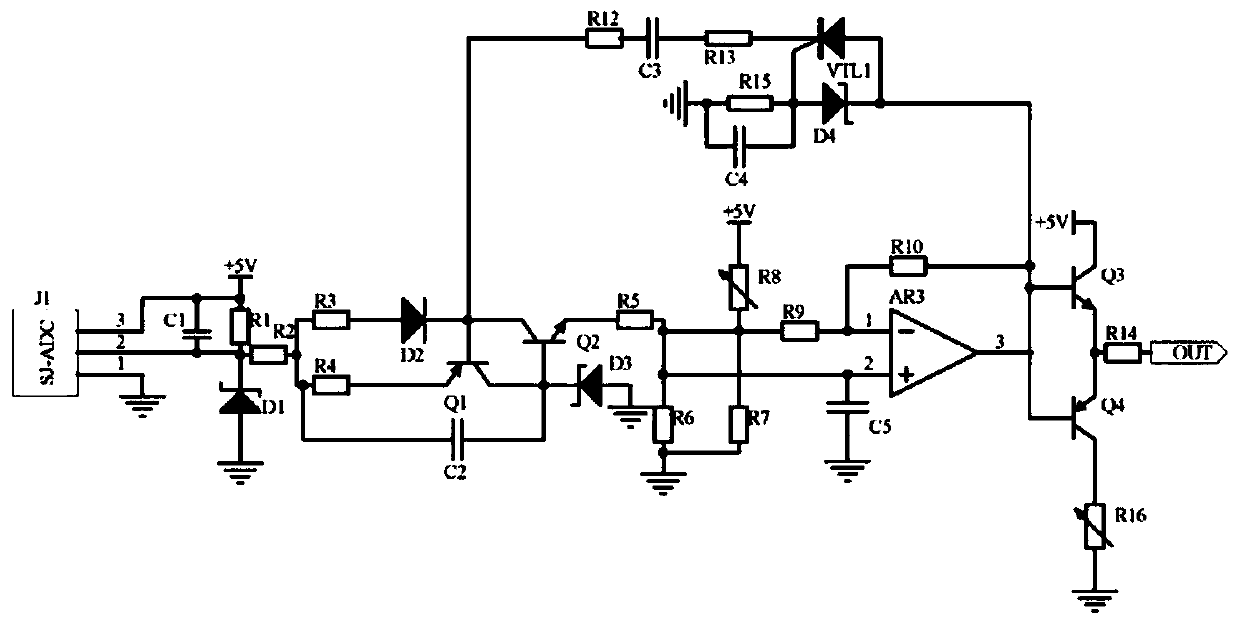
PendingCN110022146ARealize automatic calibrationReliability increase in bipolar transistorsSilicon-controlled rectifierLow voltage
The invention discloses an electronic equipment analog signal calibration circuit. The circuit comprises a frequency acquisition circuit, a feedback constant current circuit and a push-pull output circuit. The frequency acquisition circuit acquires signal frequency in an analog signal channel in the low-voltage electronic equipment control terminal; the feedback constant current circuit utilizes atriode Q1, a triode Q2 and a voltage stabilizing tube D3 to form a constant current source circuit stable signal potential. Meanwhile, a current-voltage conversion circuit composed of a variable resistor R8 and an operational amplifier AR3 is used for converting a current signal into a voltage signal and inputting the voltage signal into a push-pull output circuit; an abnormal signal detection circuit is composed of a silicon controlled rectifier VTL1 and a voltage-regulator tube D4 and feeds back abnormal signals to the collector electrode of a triode Q2. and finally, the push-pull output circuit uses a triode Q3, a triode Q4 and a variable resistor R16 to form a push-pull circuit to reduce signal conduction loss and then output the signal, so that the signal frequency can be converted into a compensation signal of a signal in an analog signal channel in a remote intelligent equipment control terminal.
Owner:WUXI CITY COLLEGE OF VOCATIONAL TECH
Driver circuit usable for display panel
ActiveUS8044950B2Increase conversion rateAvoid elevationPulse automatic controlElectric analogue storesDriver circuitPower flow
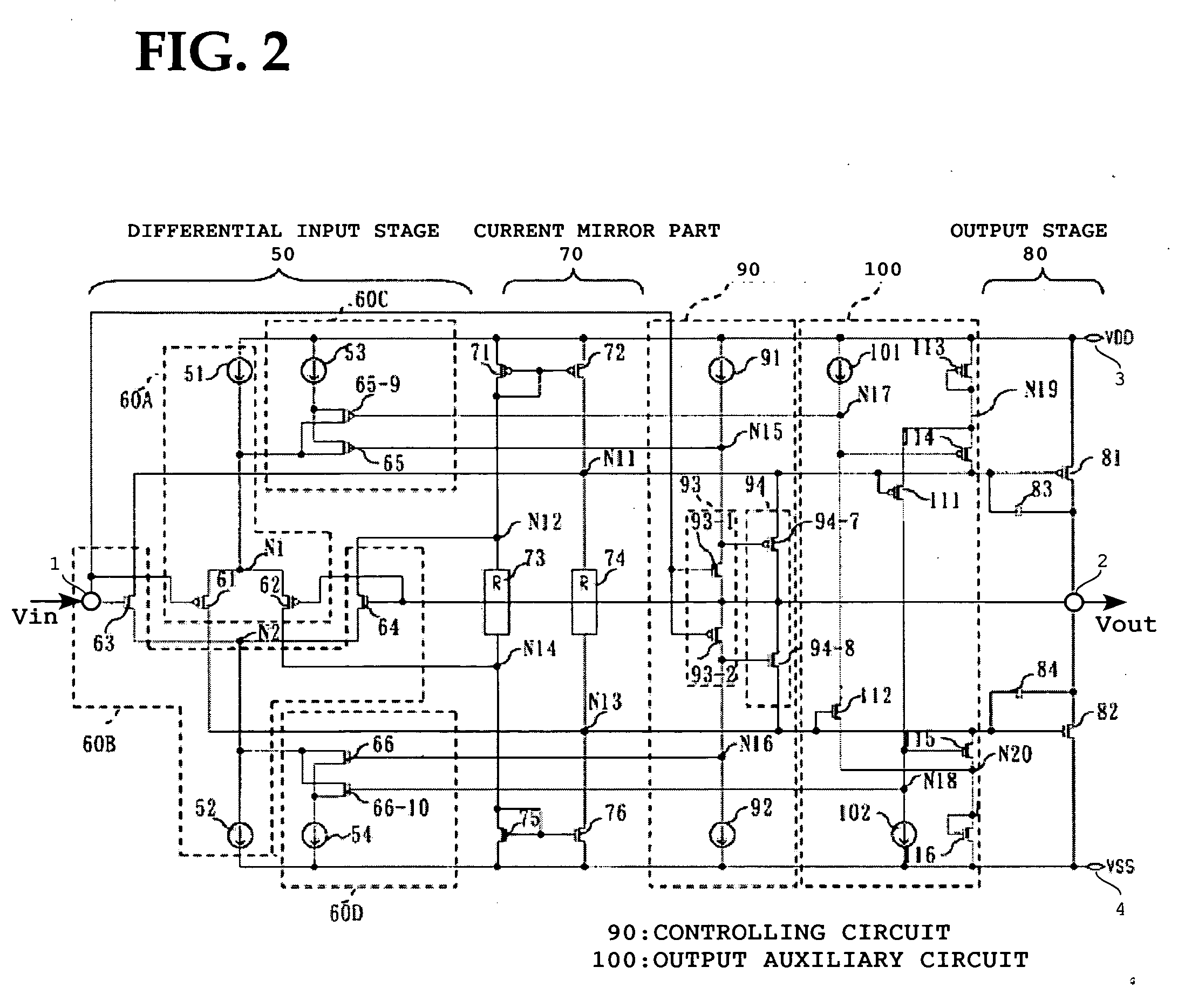
A driver circuit usable for a display panel can generate an output signal in response to an input pulse signal supplied to only one input signal terminal thereof. The driver circuit includes a pulse generating circuit for generating an output signal at the output terminal. The pulse generating circuit has a first and second differential input stage for respectively driving a push-pull construction of output transistors in response to the input pulse signal supplied through the input signal terminal with respect to the push-pull output, whereby to simplify the circuitry, operate at a high slew rate, and decrease electric current consumption.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Source drive amplifier for flat panel display
ActiveCN101089937AReduce areaReduce static power consumptionStatic indicating devicesDriving currentAudio power amplifier
Owner:SOLOMON SYSTECH CHINA LTD
Push-pull output stage LDO (low dropout regulator) circuit
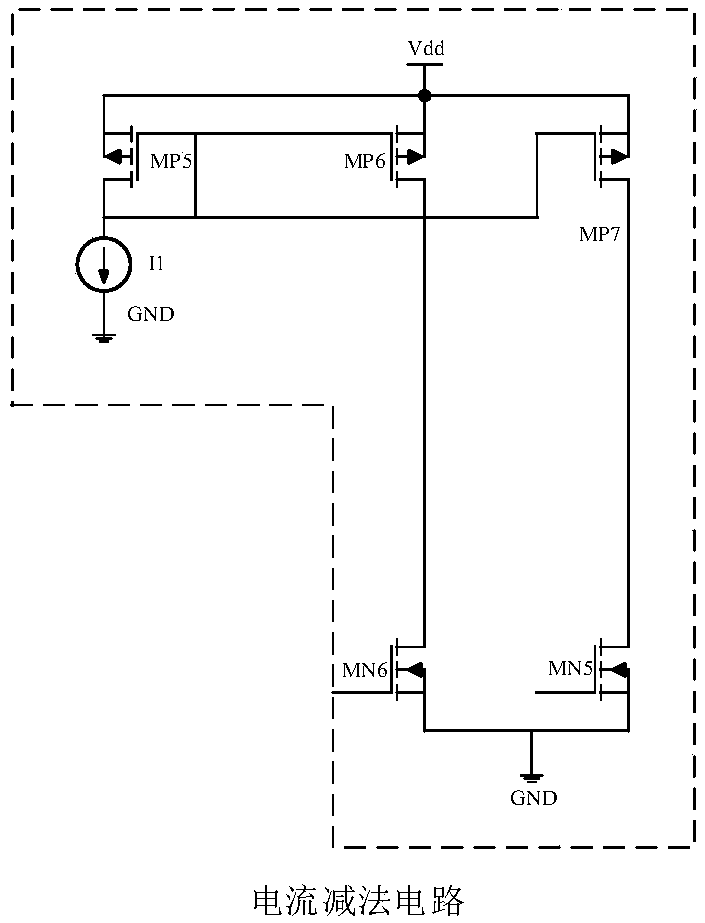
ActiveCN108762363AStable outputStrong control abilityElectric variable regulationCapacitancePush–pull output
The invention discloses a push-pull output stage LDO (low dropout regulator) circuit and belongs to the technical field of electronic circuit. The push-pull output stage LDO circuit utilizes CLASS-ABoutput staged error amplifier to drive a NMOS power tube and a PMOS power tube at the same time to form push-pull output stage LDO circuit, excessive current can be loaded into or absorbed, the control and adjustment ability to the output voltage is enhanced, and the output is stabler. A third NMOS tube, a third PMOS tube, a first capacitance and a second capacitance form a transmission door to enables the transient response of the system to be faster. A current subtraction circuit is used to reduce the power dissipation of the LDO circuit, and a slew-rate enhancement circuit in practical cases enables the transient response of the whole circuit to be faster. In different working status, the conducting of the NMOS power tube and the PMOS power tube of push-pull output stage LDO circuit isdifferent, only one conducting exists in the both power tubes, and the both are shut off at the time of on-load, and then the output and the static power consumption are extremely low. The push-pulloutput stage LDO circuit has the advantages of strong ability in controlling the output power, stable output, fast transient response and low power dissipation.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Output buffer circuit for drive voltage in liquid crystal display drive control chip
InactiveCN1804688AReduce static power consumptionSimple structureStatic indicating devicesPush–pull outputLiquid-crystal display
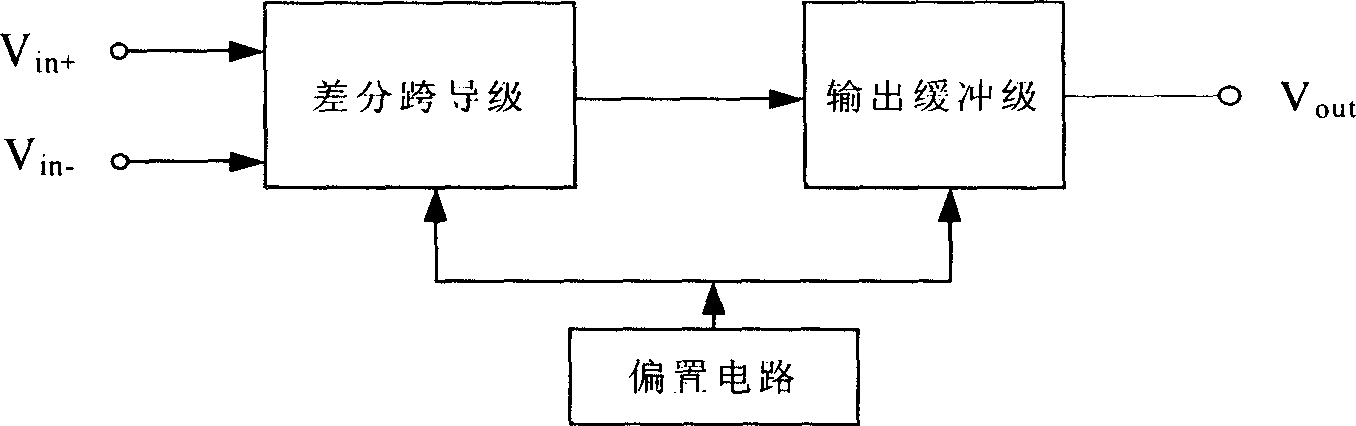
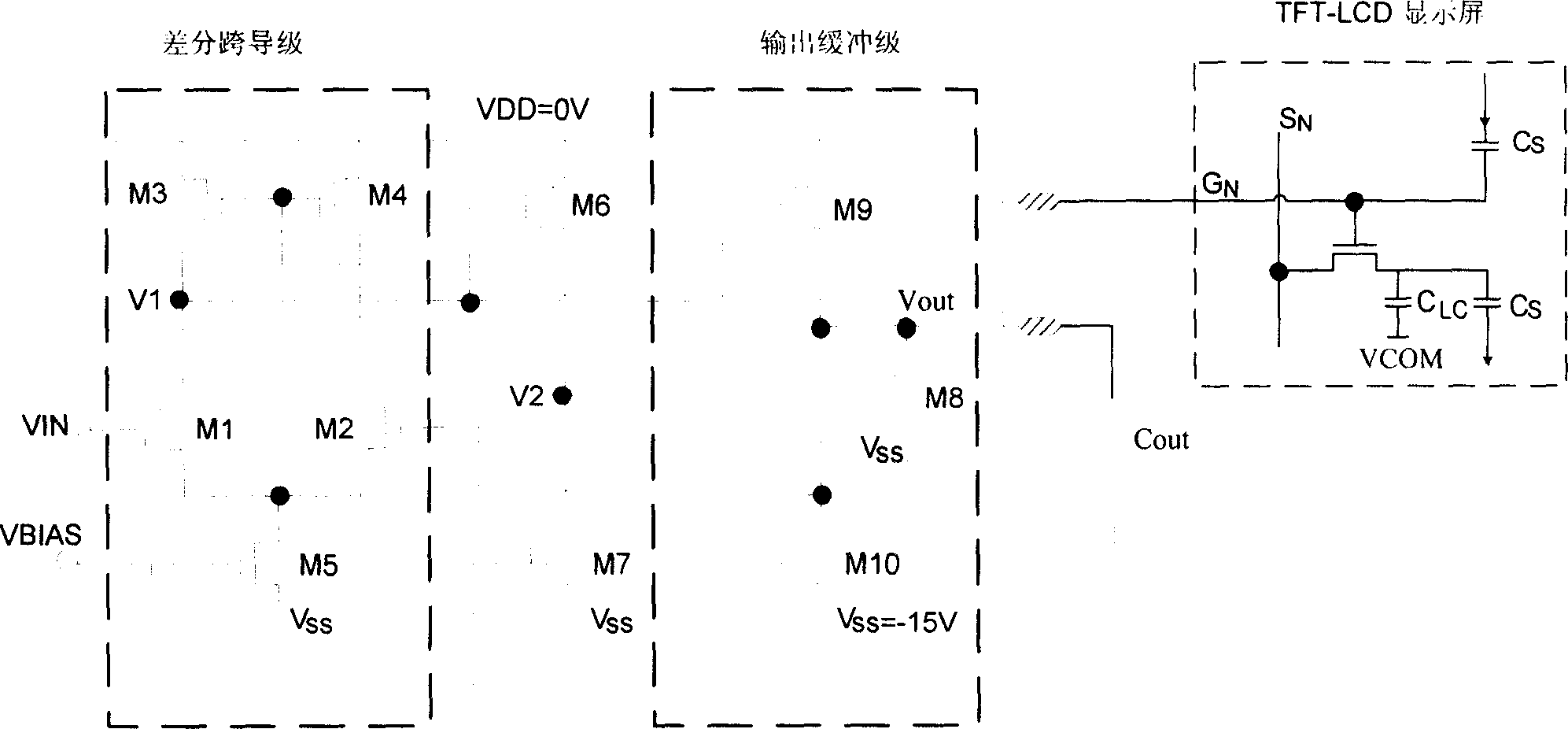
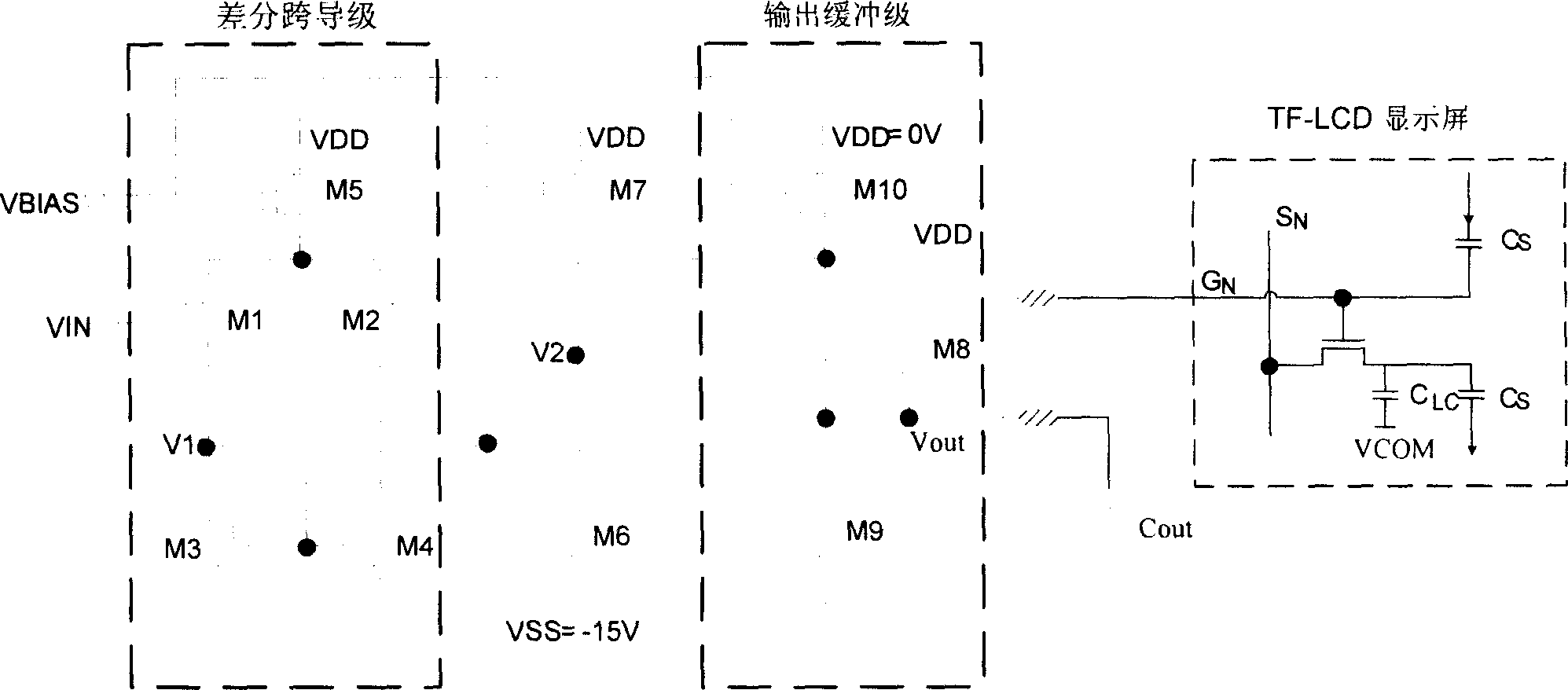
The invention discloses an output buffer circuit which uses liquid crystal display to drive the driving voltage of the control chip. The first level amplifier is a difference mutual admittance circuit which is formed by MOS pipes (M1-M5); the second level amplifier is a common source stage amplifier circuit which is formed by MOS pipes (M9-M10); it adds source electrode follower of MOS pipe (M8) on the output end. It adopts complementary push-pull output circuit, one pipe works at any time, when one pipe stops, 1) when the output voltage stabilizes, MOS pipe (M8) stops, the static deflexed current doesn't follow to the MOS pipe (M8) and the static deflexed current of MOS pipe (M9) is 0.2úÑ of the current technology static deflexed current which can reduce the static power of the circuit; 2) When the MOS pipe (M8) stops, the output buffer circuit is formed by two level amplifiers.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Industrial equipment operation monitoring signal adjusting circuit
ActiveCN110460796AEnsure consistencyPrevent Crossover DistortionElectrical cable transmission adaptationIndustrial equipmentPush pull
The invention discloses an industrial equipment operation monitoring signal adjusting circuit. The circuit comprises a frequency acquisition circuit, a separation switch circuit and a push-pull outputcircuit. The frequency acquisition circuit acquires analog signal frequency received by the industrial equipment operation monitoring control terminal. According to the separation switch circuit, a triode Q5, a variable resistor RW1, a capacitor C4 and a capacitor C5 form a synchronous separation circuit to divide a signal into two paths of signals with the same frequency and different amplitudes; a capacitor C2, a capacitor C3, an inductor L4 and a triode Q1 are used in one parth to form a frequency modulation circuit to adjust the signal frequency; in the second path, a diode D1, a diode D2and a capacitor C6 form a noise reduction circuit to reduce the signal-to-noise ratio; and finally, the push-pull output circuit uses a triode Q7 and a triode Q8 to form a push-pull circuit to prevent signal crossover distortion, and the signal is output after being stabilized by a voltage stabilizing tube D3, i.e., a compensation signal of an analog signal received by the industrial equipment operation monitoring control terminal, so that high-frequency component attenuation is overcome.
Owner:中瑞恒(北京)科技有限公司
Stringed instrument with simulator preamplifier
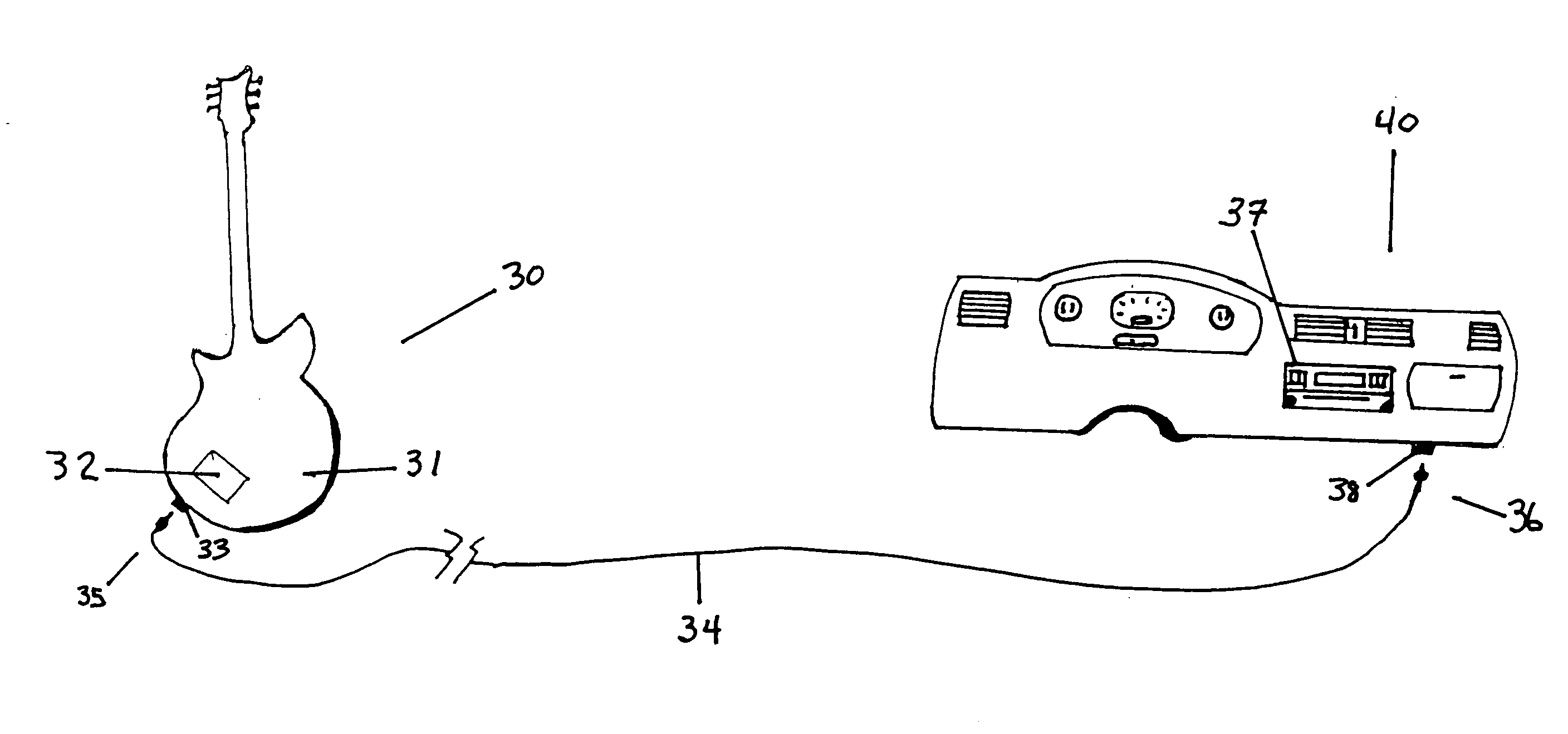
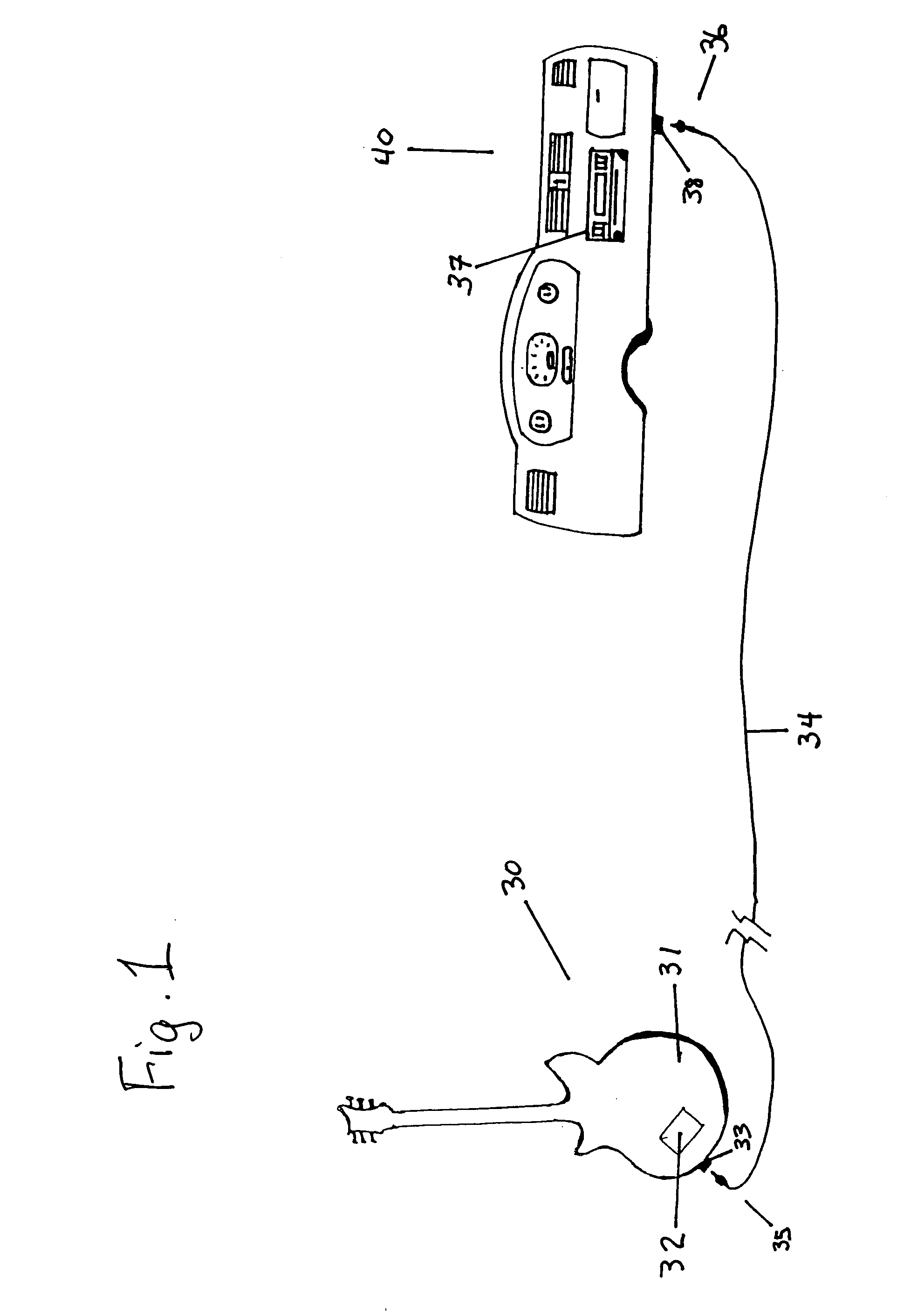
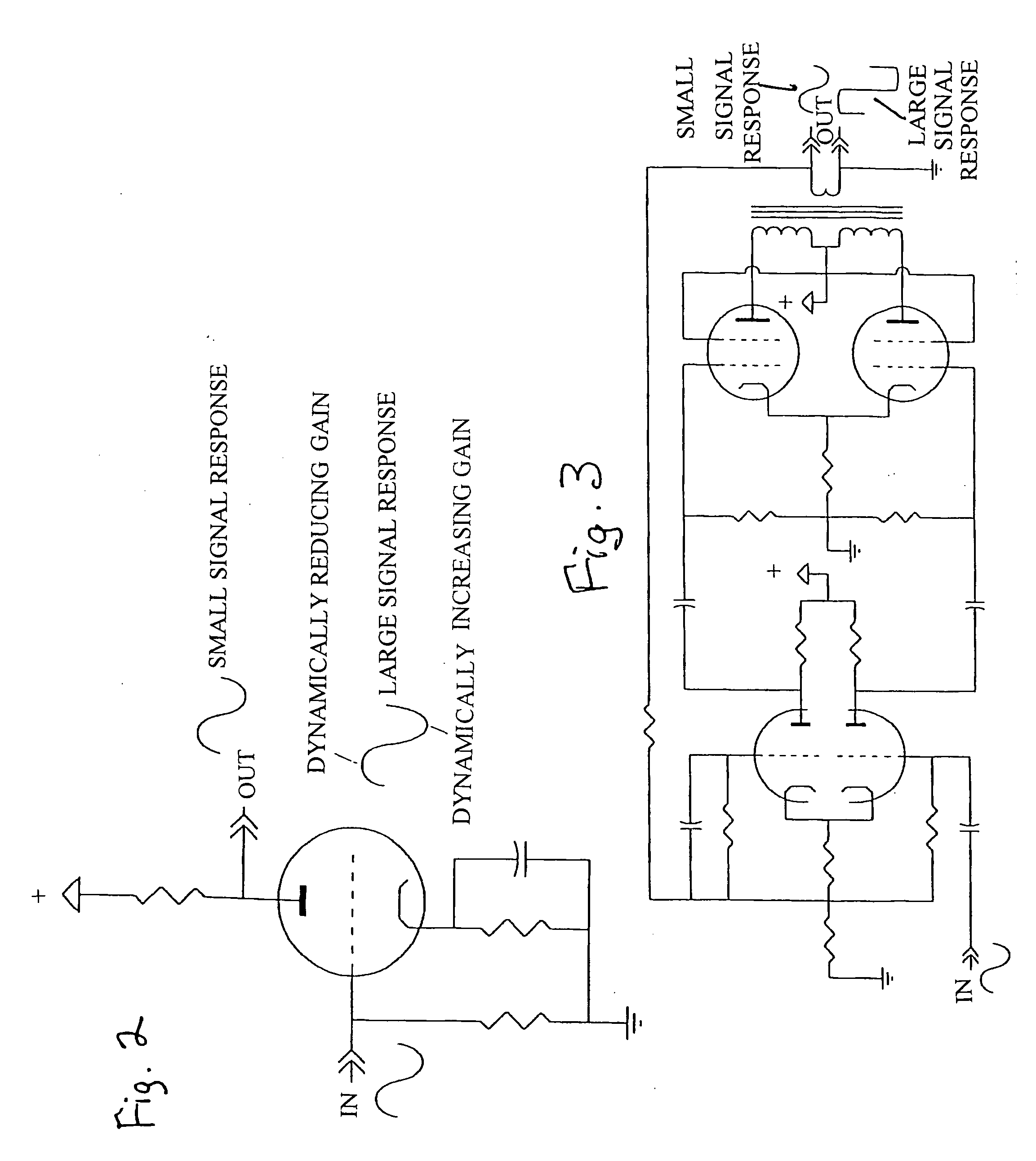
InactiveUS20090080677A1Improves approximation of amplification characteristicSmall and large signalElectrophonic musical instrumentsTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsEngineeringResistor
A stringed instrument and preamplifier combination where the preamplifier simulates the sound of analog tube amplifiers, and contains only solid state active devices. The preamplifier uses a diode branch with the diode biased into its forward active region and as a non-linear resistive element to provide signal-modulated gain on the operational amplifier gain stage. An alternative embodiment supplements the diode branch with series and parallel resistors as additional design optimization parameters. Another alternative embodiment adds symmetrical output clipping diodes to simulate a vacuum tube push-pull output independently of the diode branch.
Owner:FIRST ACT
Driver circuit usable for display panel
ActiveUS20070176913A1Increase conversion rateAvoid elevationPulse automatic controlElectric analogue storesDriver circuitPush–pull output
A driver circuit usable for a display panel can generate an output signal in response to an input pulse signal supplied to only one input signal terminal thereof. The driver circuit includes a pulse generating circuit for generating an output signal at the output terminal. The pulse generating circuit has a first and second differential input stage for respectively driving a push-pull construction of output transistors in response to the input pulse signal supplied through the input signal terminal with respect to the push-pull output, whereby to simplify the circuitry, operate at a high slew rate, and decrease electric current consumption.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Plate voltage generation circuit capable controlling dead band
Owner:LONGITUDE SEMICON S A R L
Apparatus and method for increasing a slew rate of an operational amplifier
InactiveUS20050179495A1Increase conversion rateLower average currentDifferential amplifiersSingle-ended push-pull amplifiersAudio power amplifierPush–pull output
An apparatus and method for increasing a slew rate of an operational amplifier are provided. It only requires an operational amplifier, a monitoring control device, a push-pull output device, and a second input current source pair. It uses a monitoring control device controlled by the output stage to control the supplementary device and the second input current source pair in order to increase a slew rate of an operational amplifier. This operational amplifier also provides the rail-to-rail output function. In addition, because it does not require additional circuit to increase the slew rate, the chip size is smaller. With respect to the circuit structure, it is very simple and can be applied to the pre-existing operational amplifier without re-designing the operational amplifier and thus can keep the original characteristics of the operational amplifier.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com