Patents
Literature
694results about How to "Reduce static power consumption" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
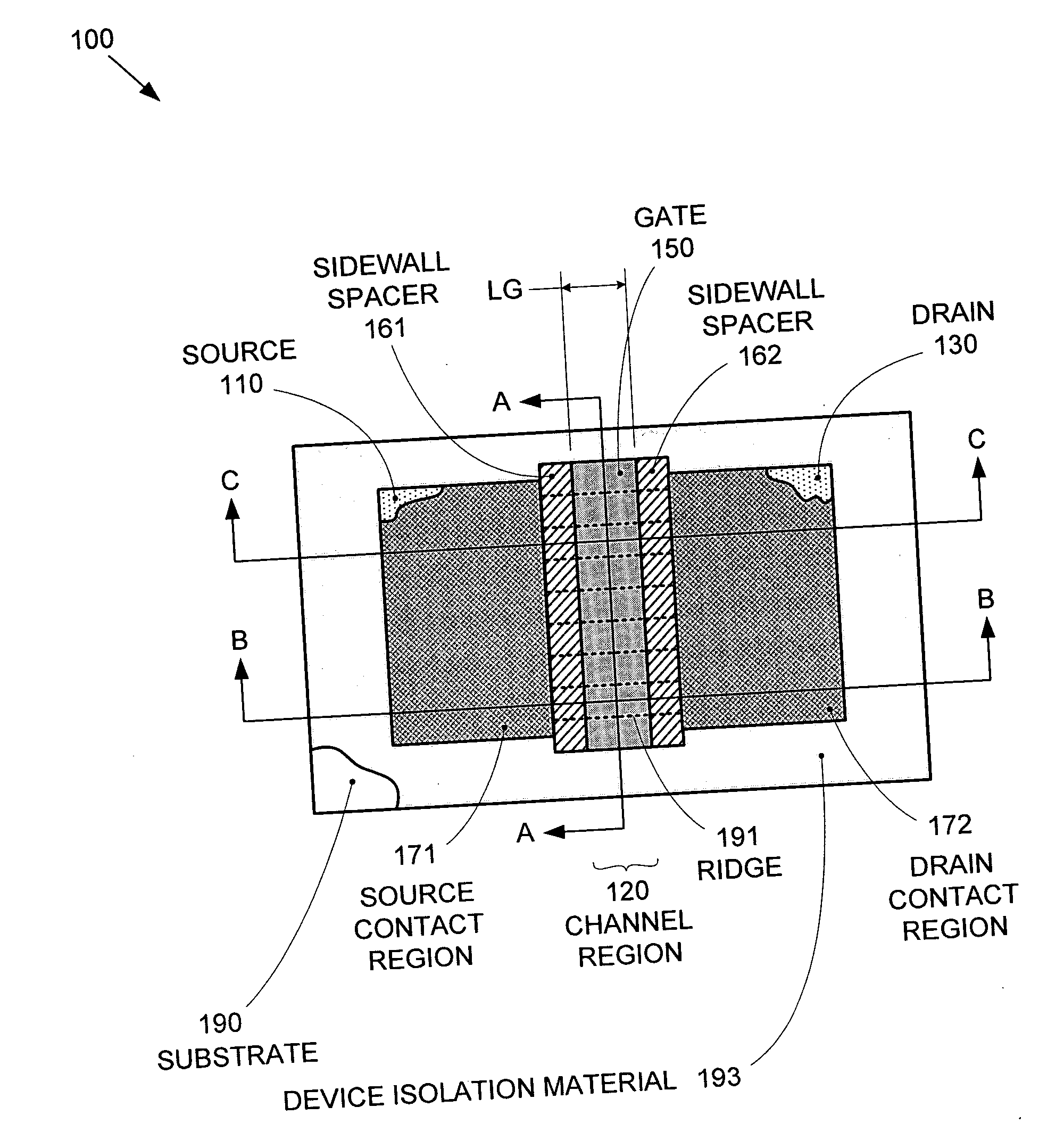
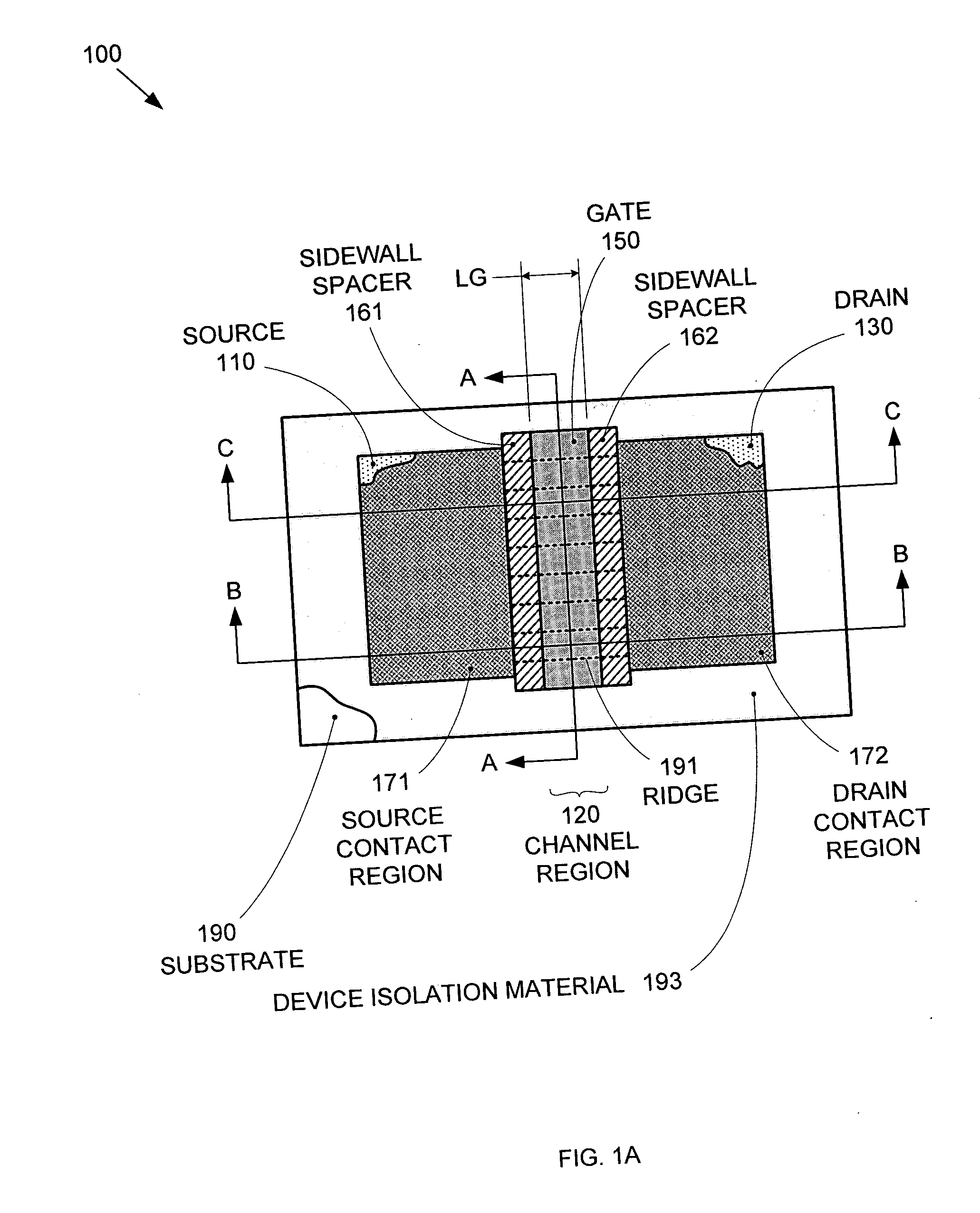
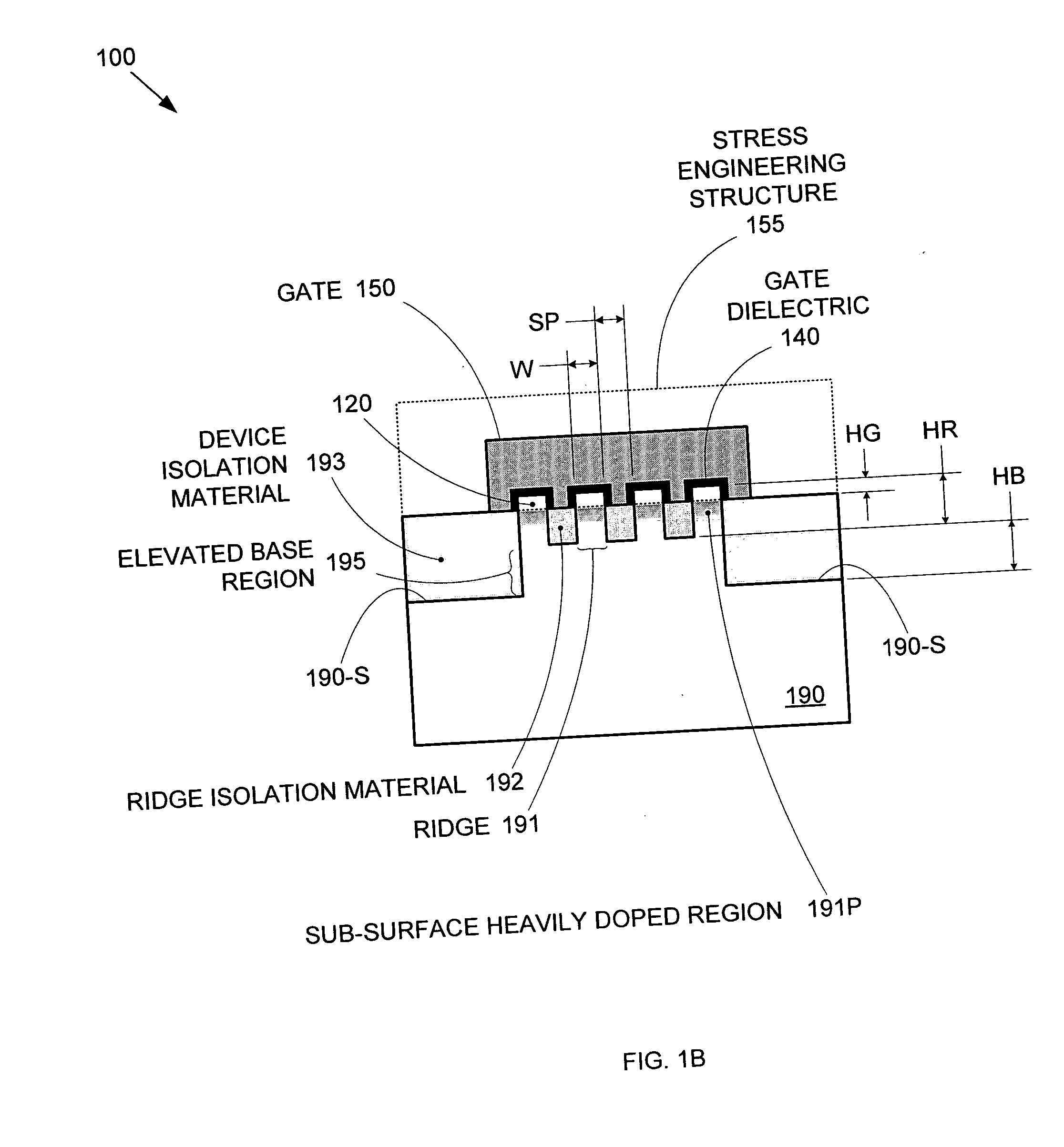
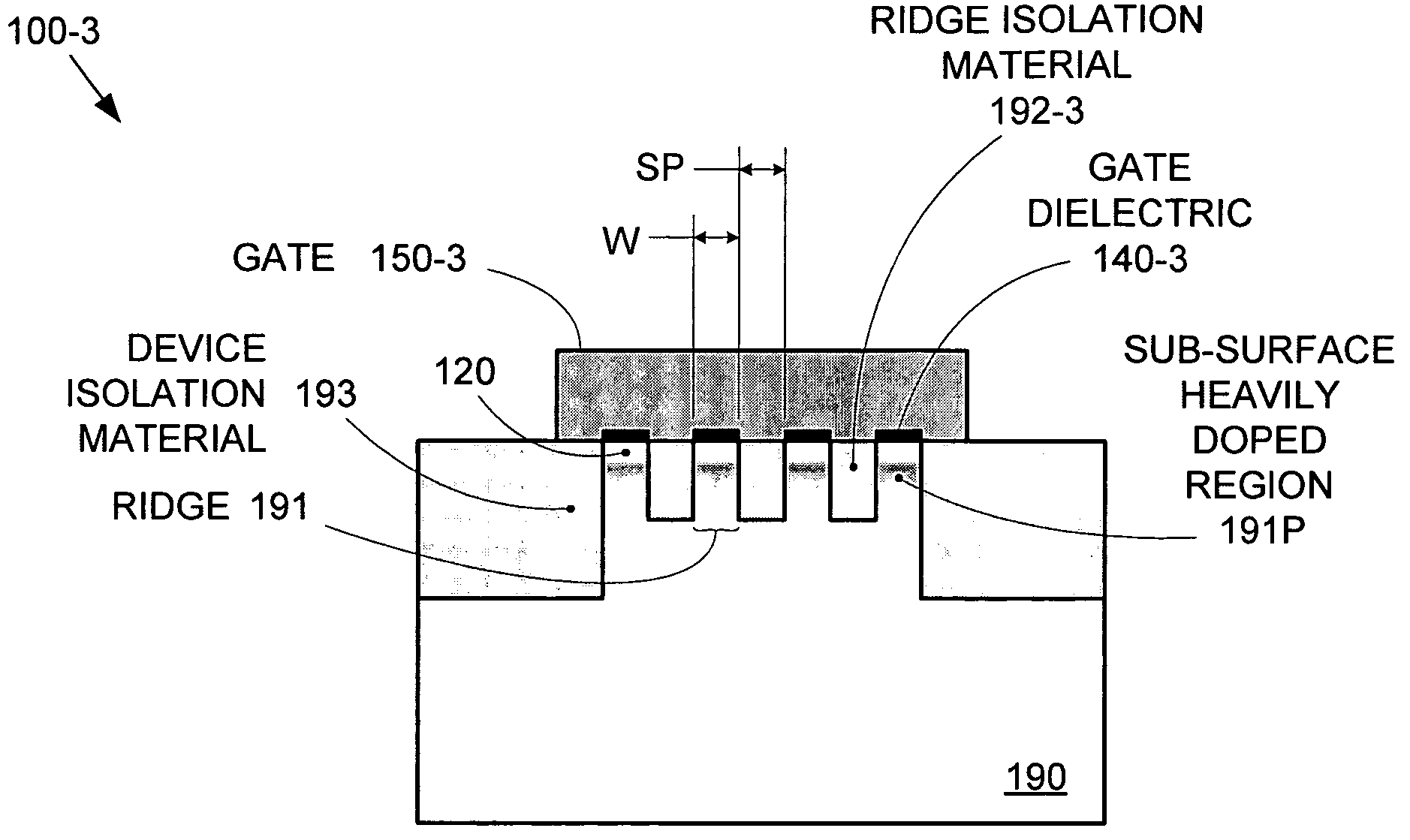
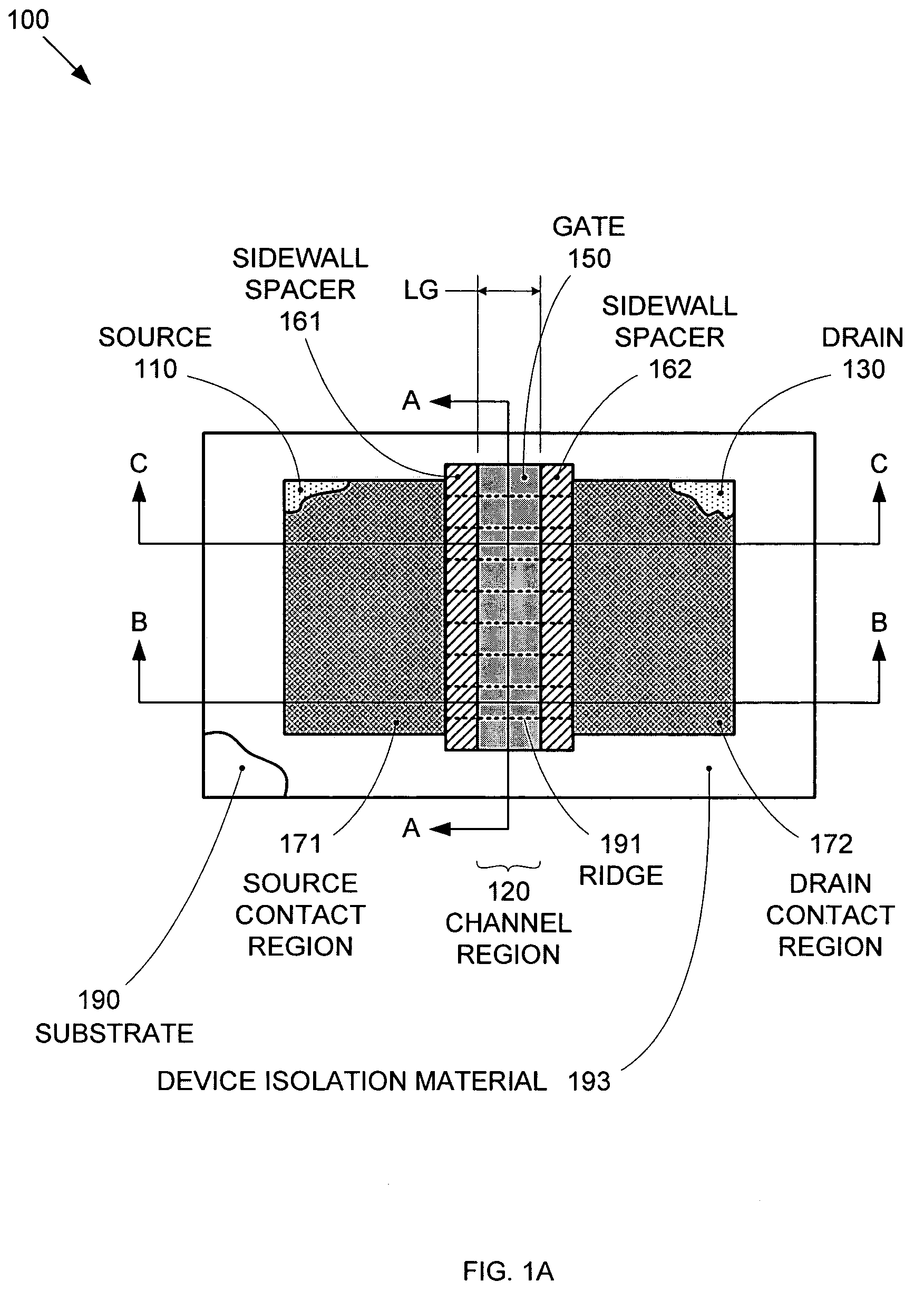
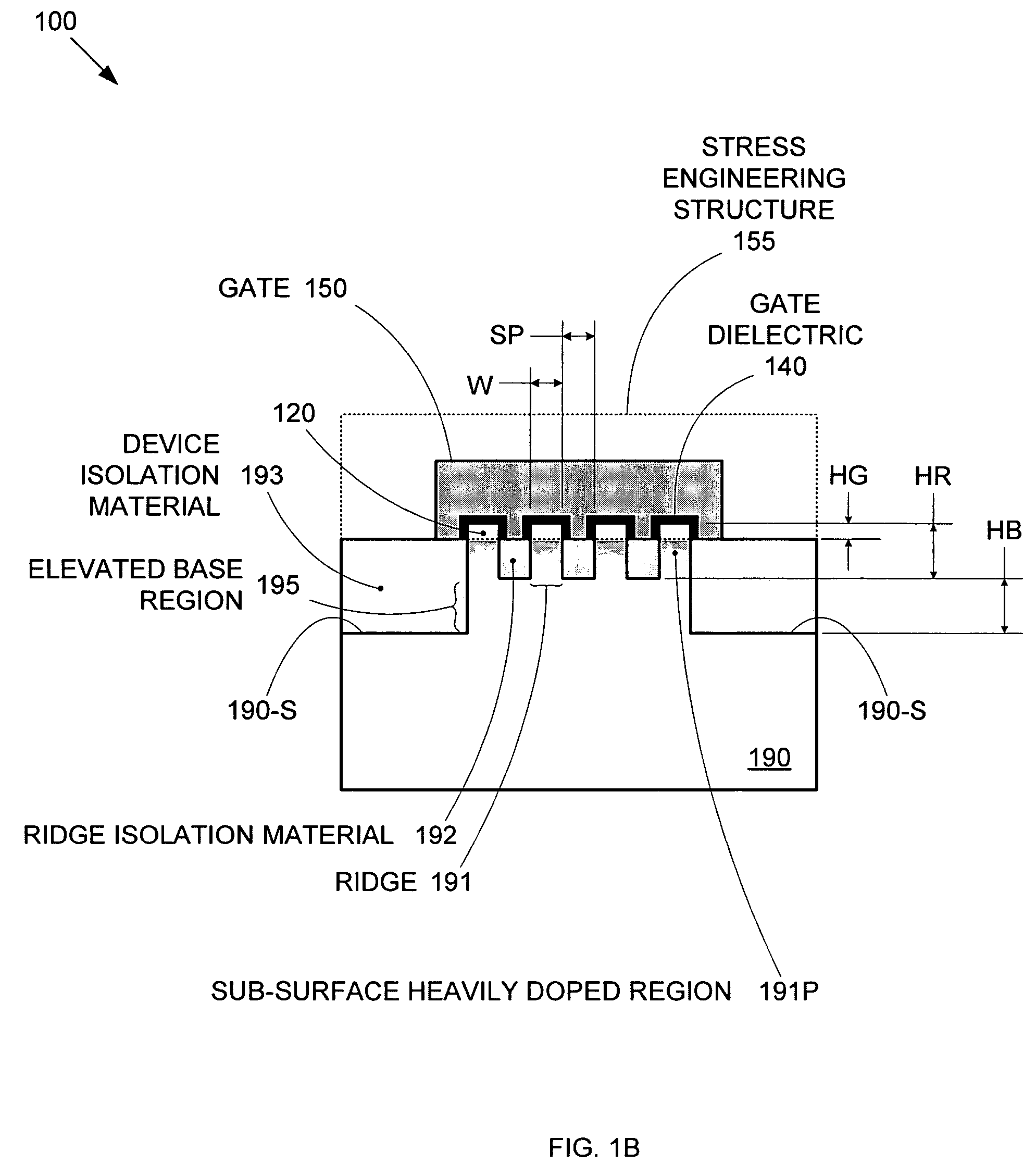
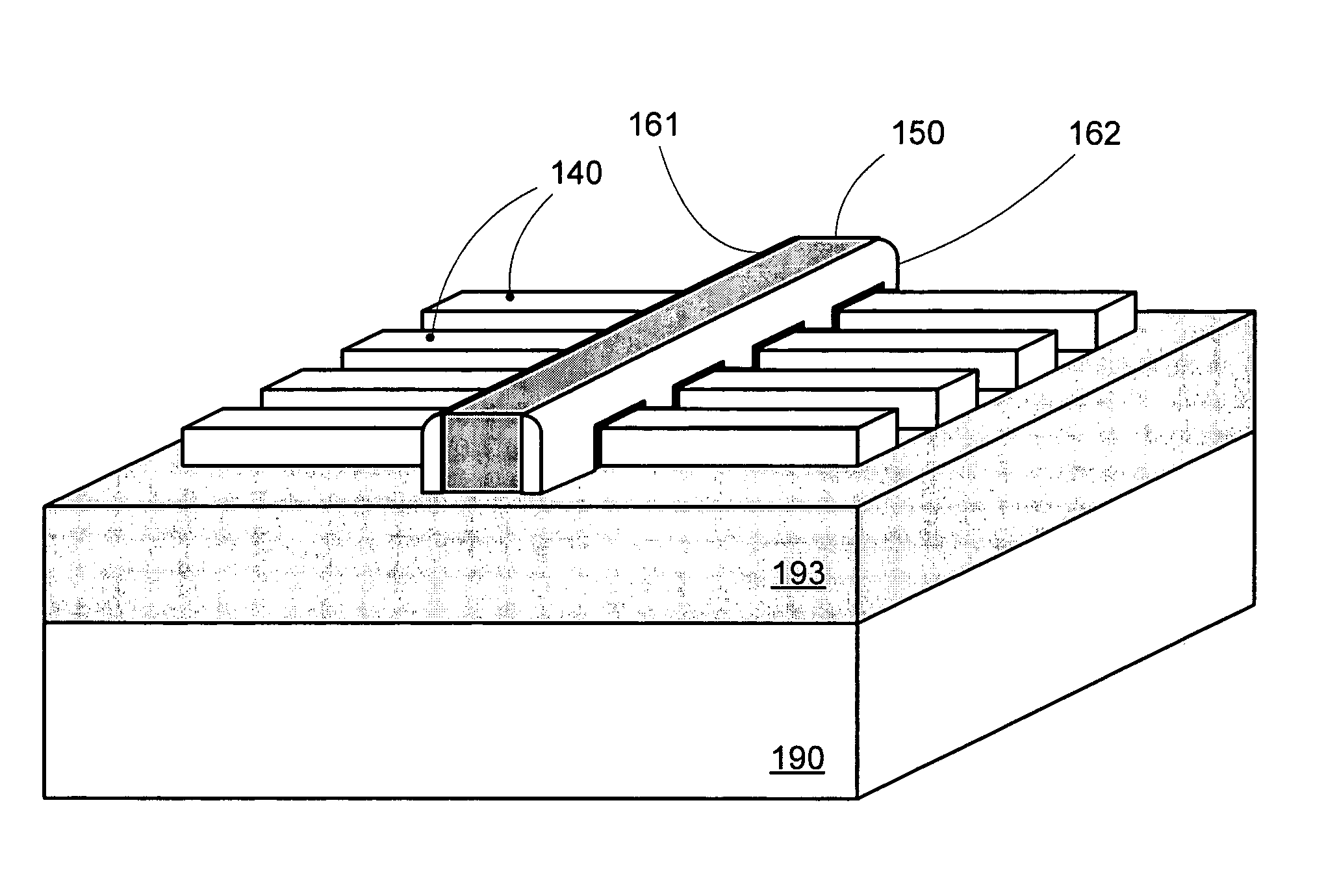
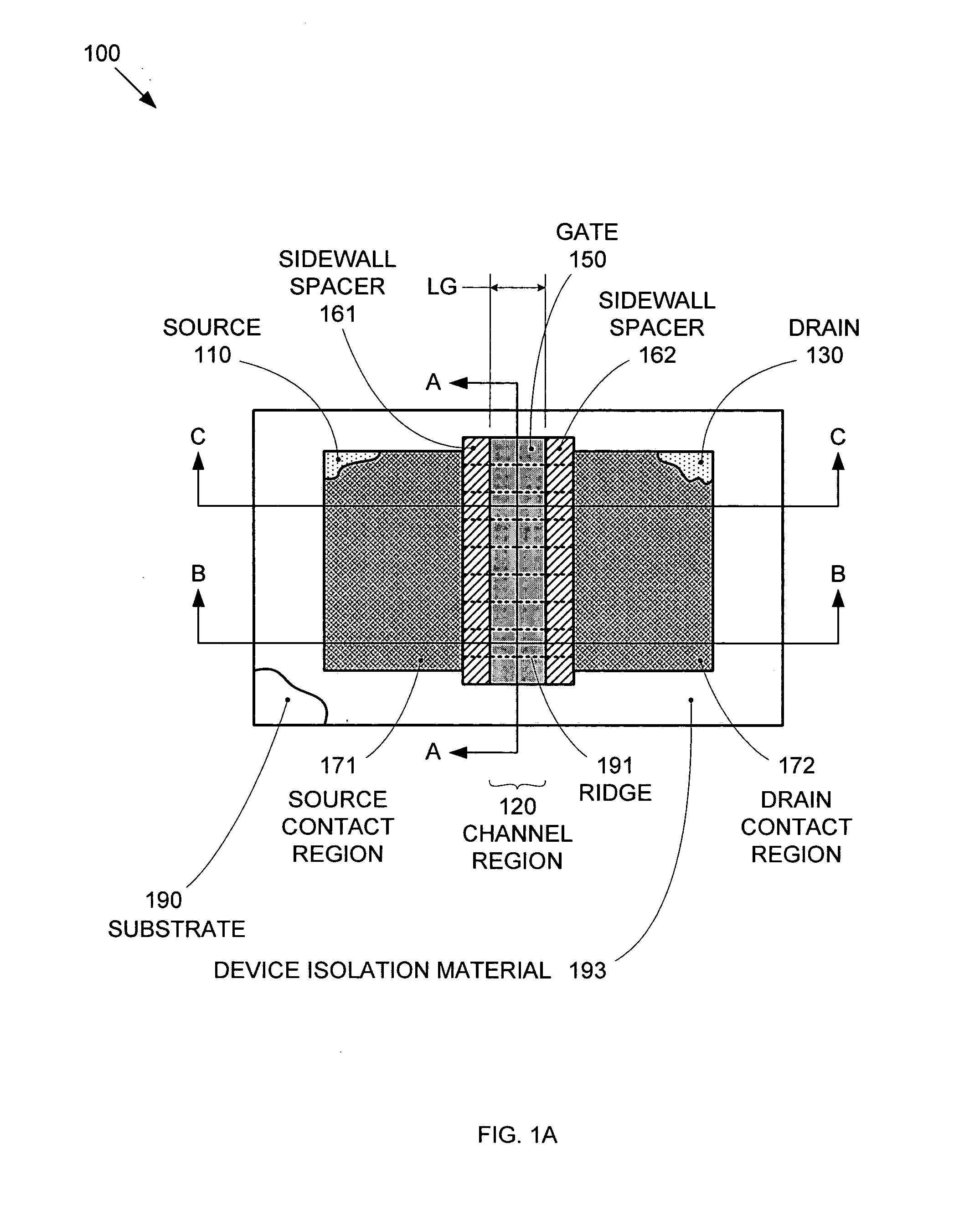
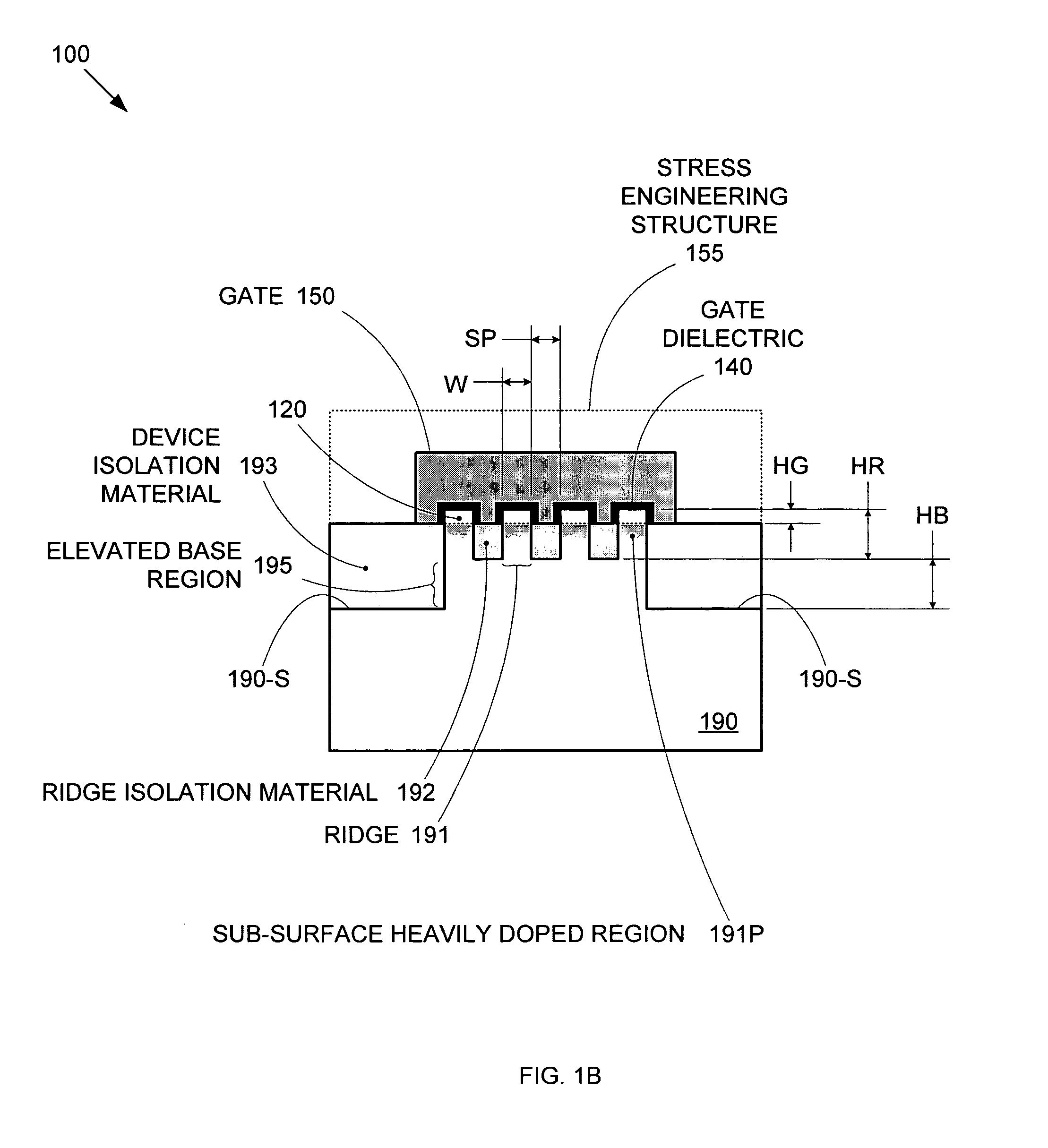
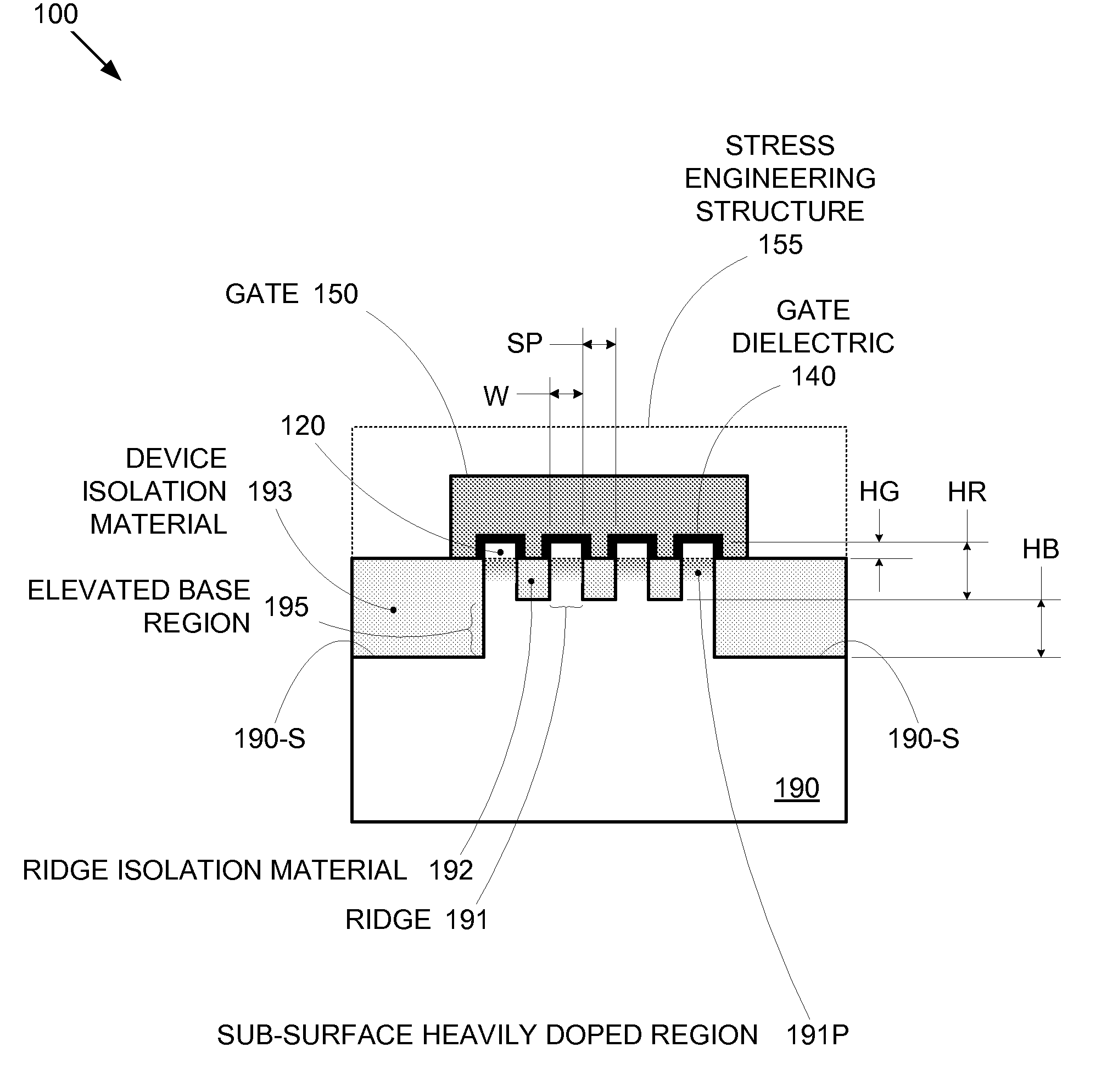
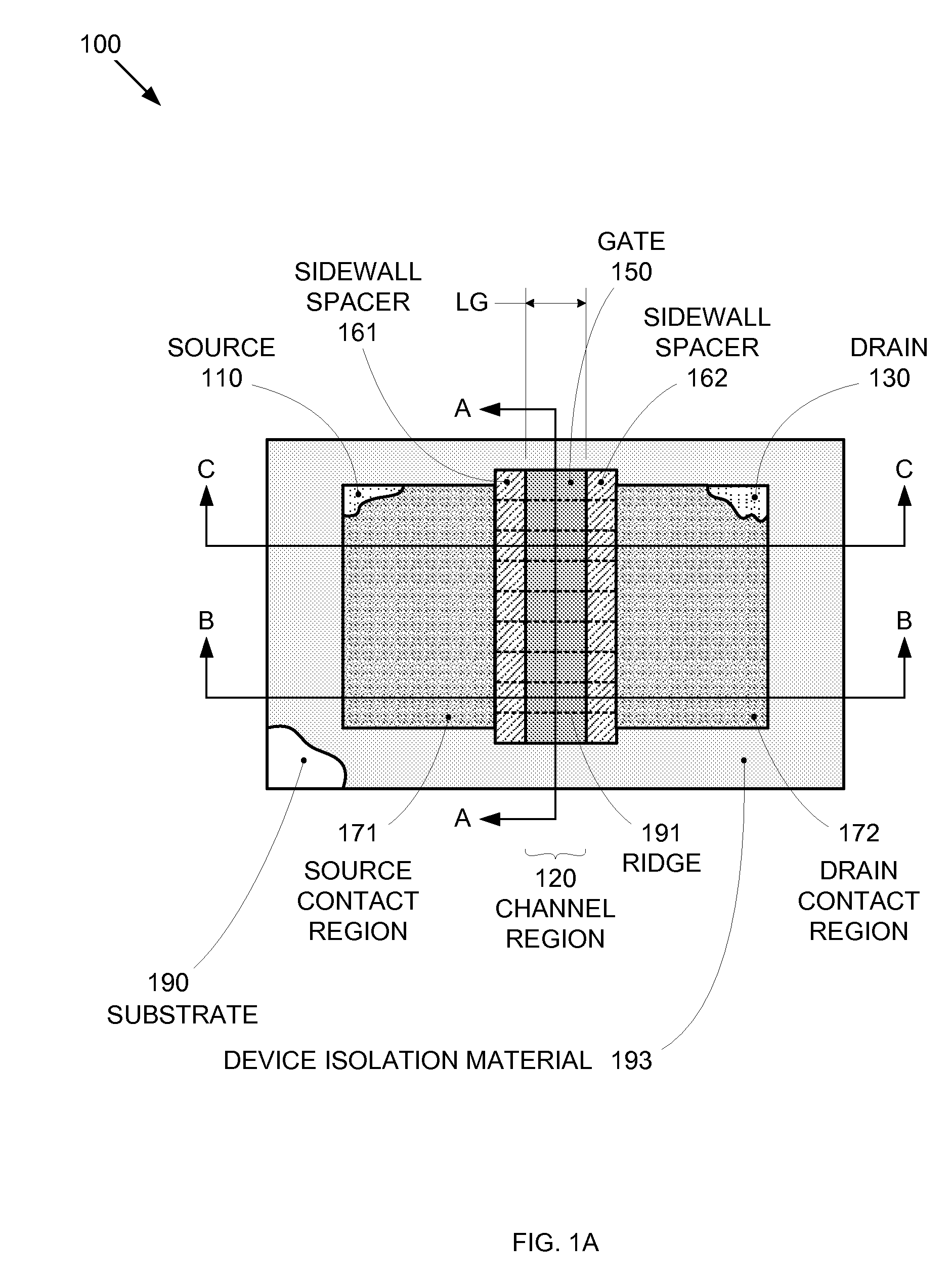
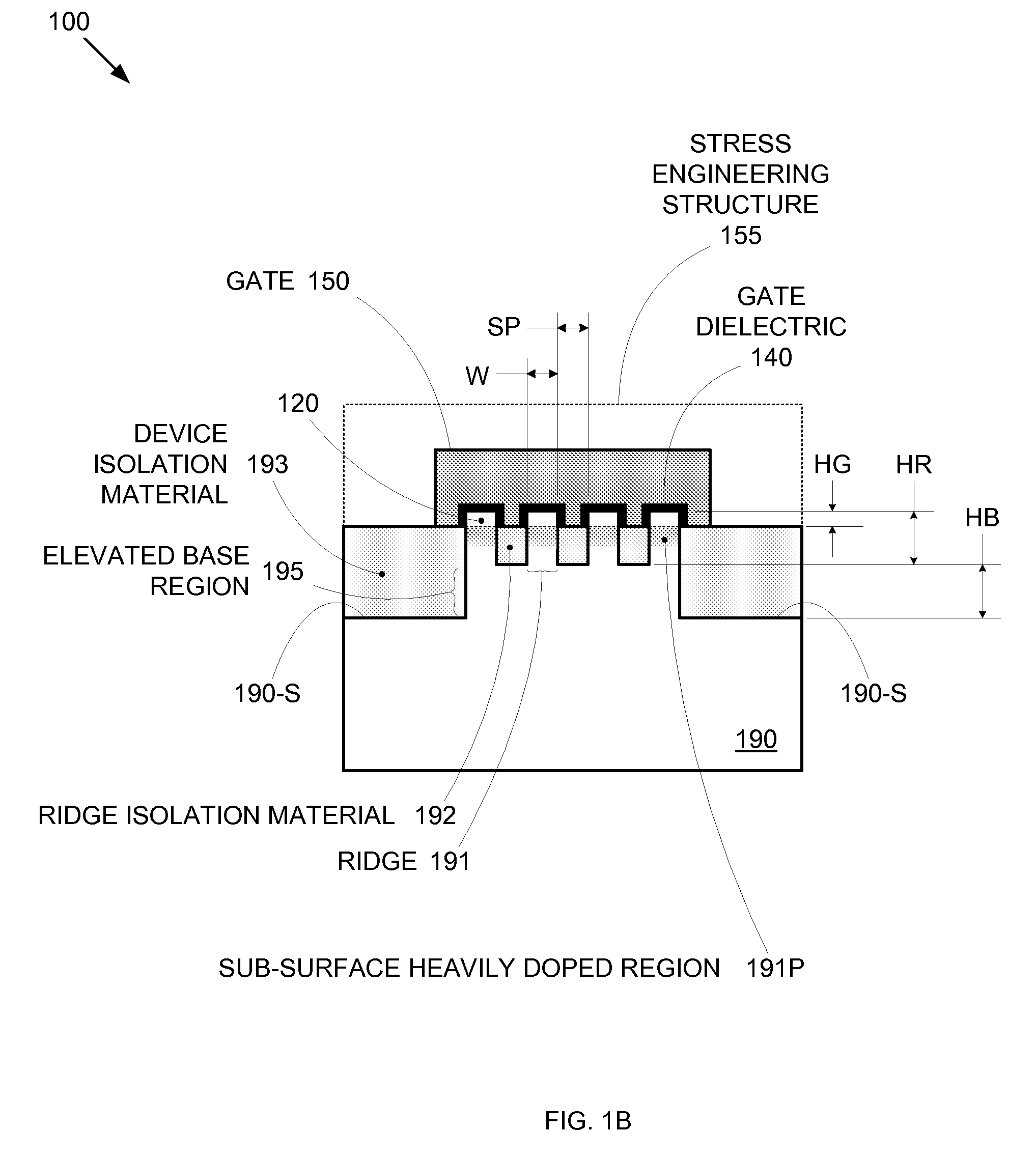
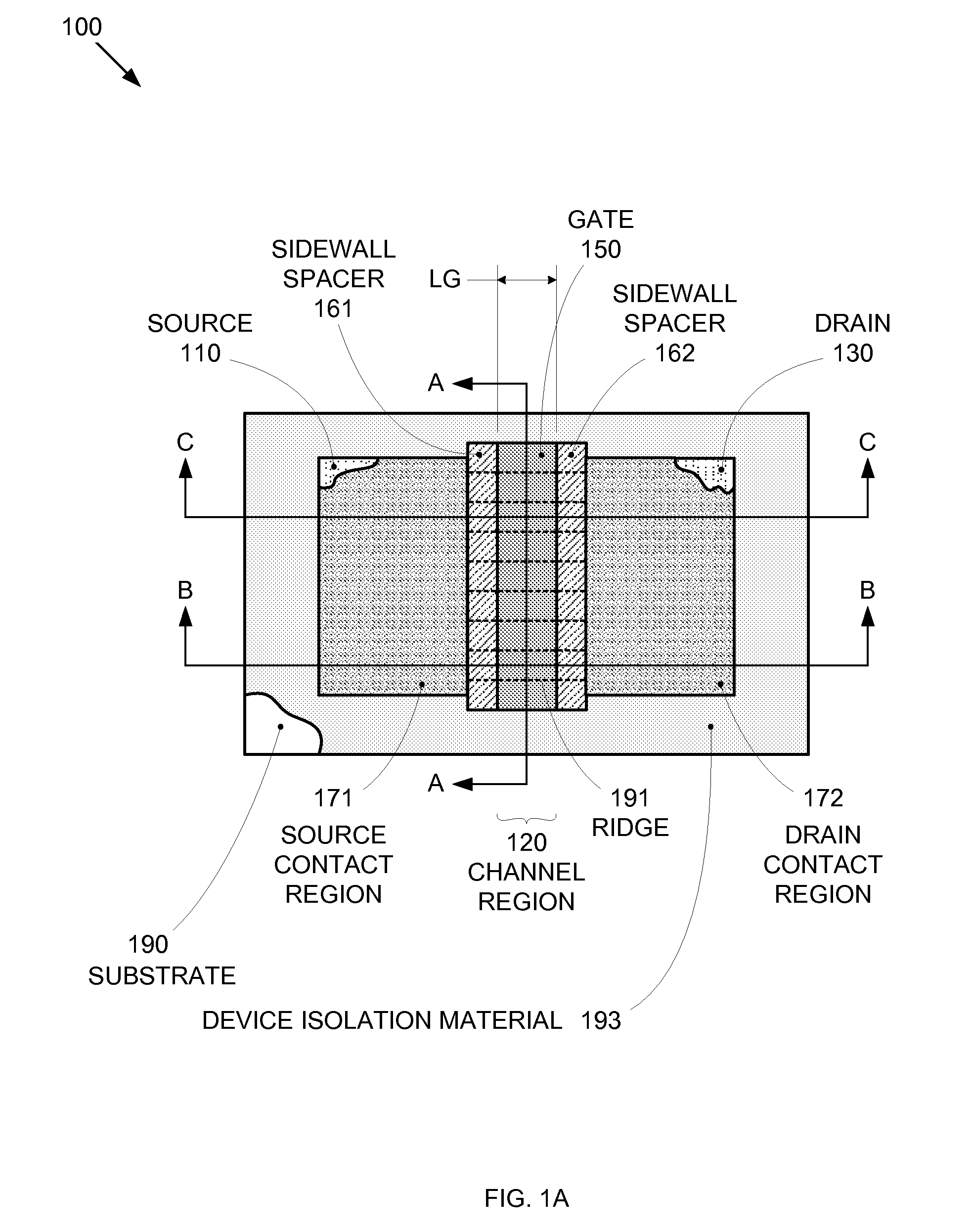
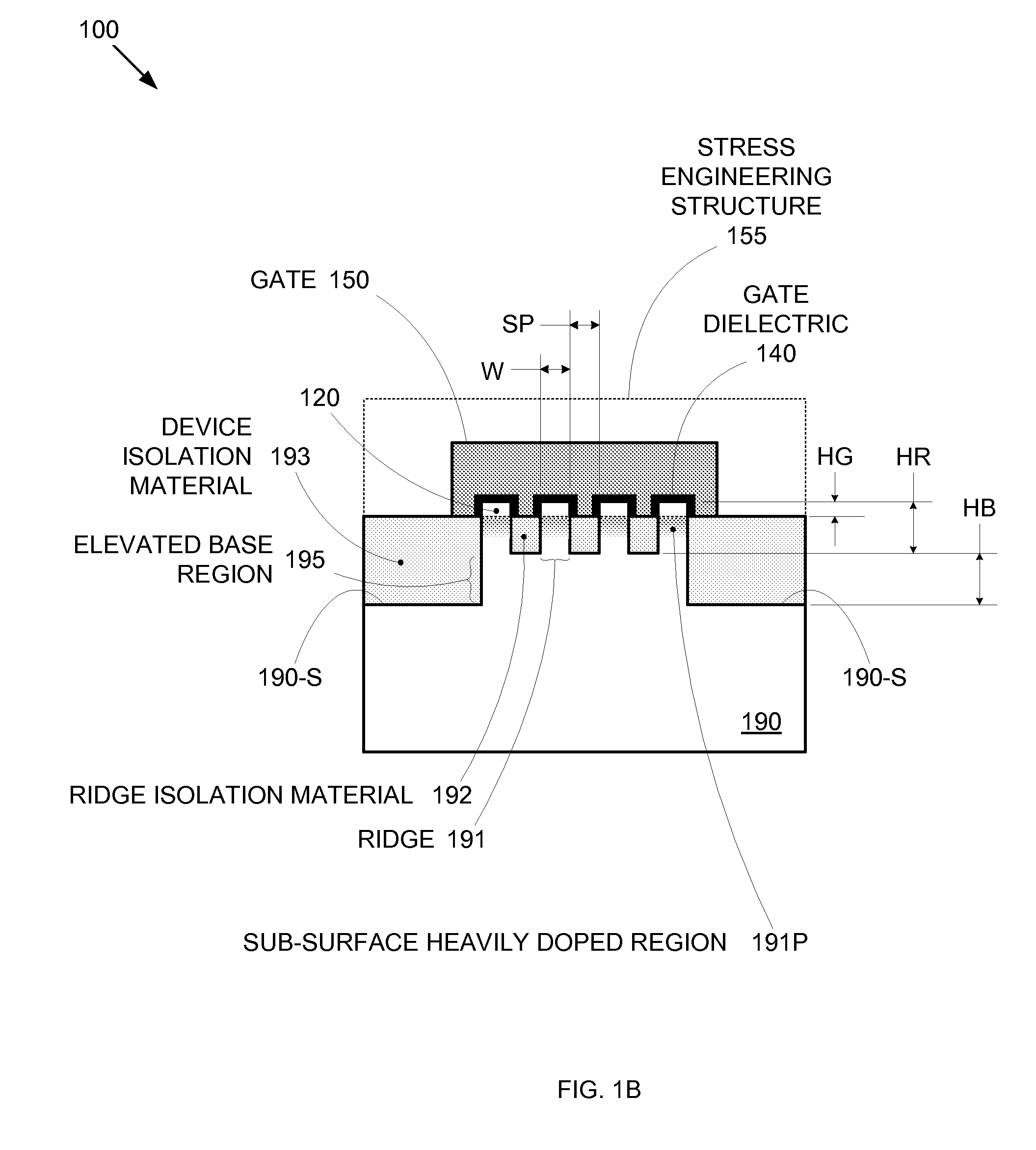
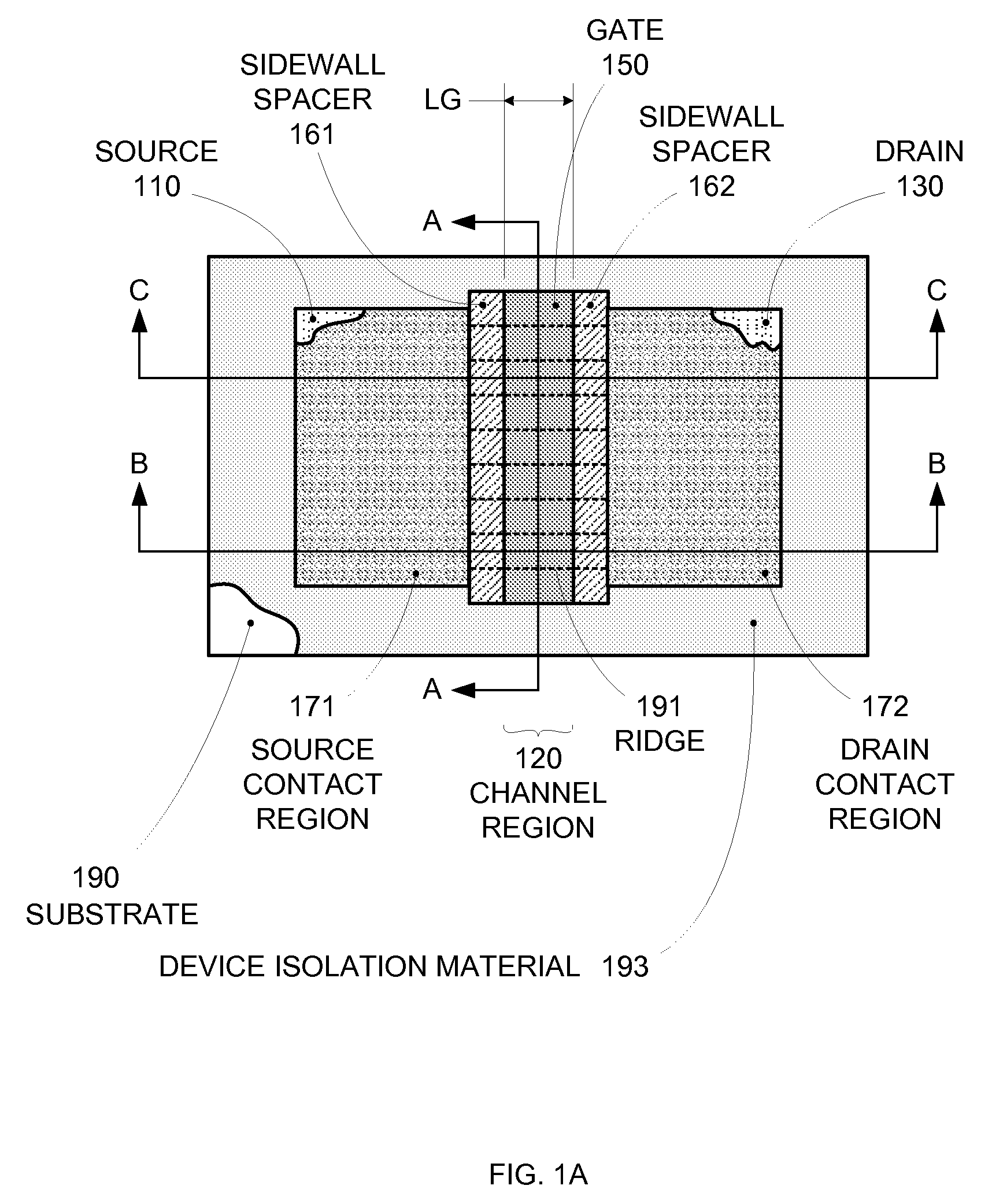
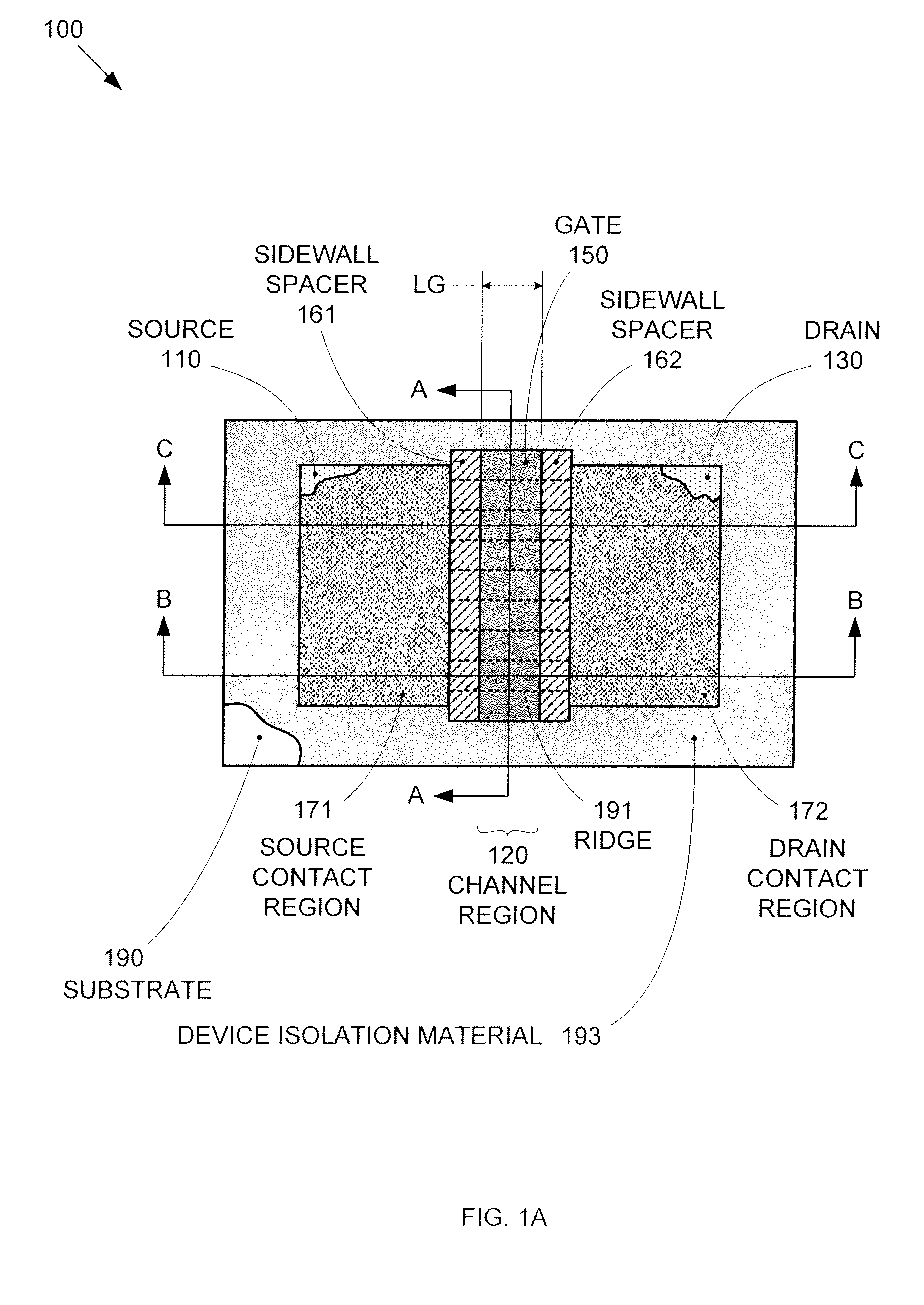
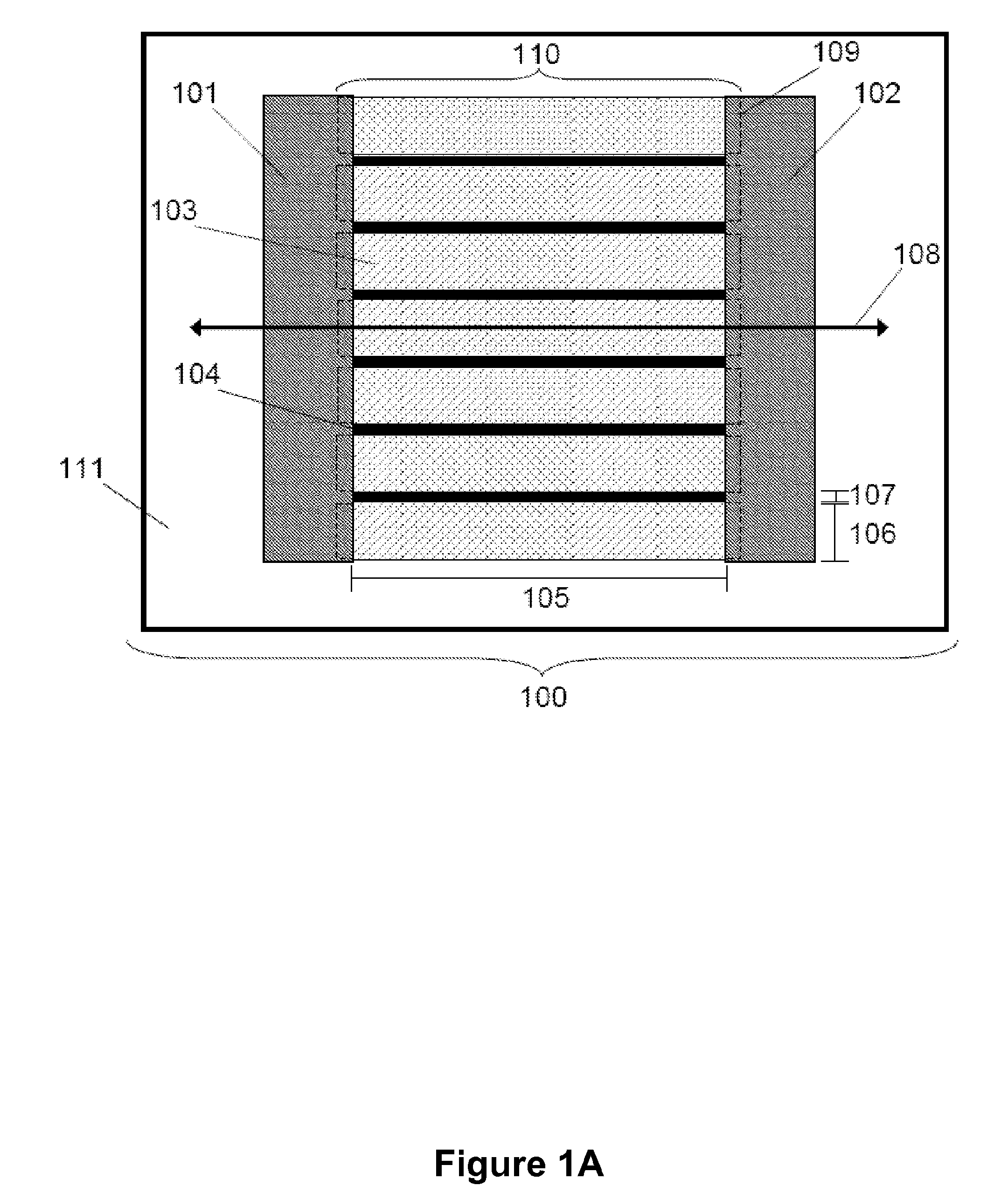
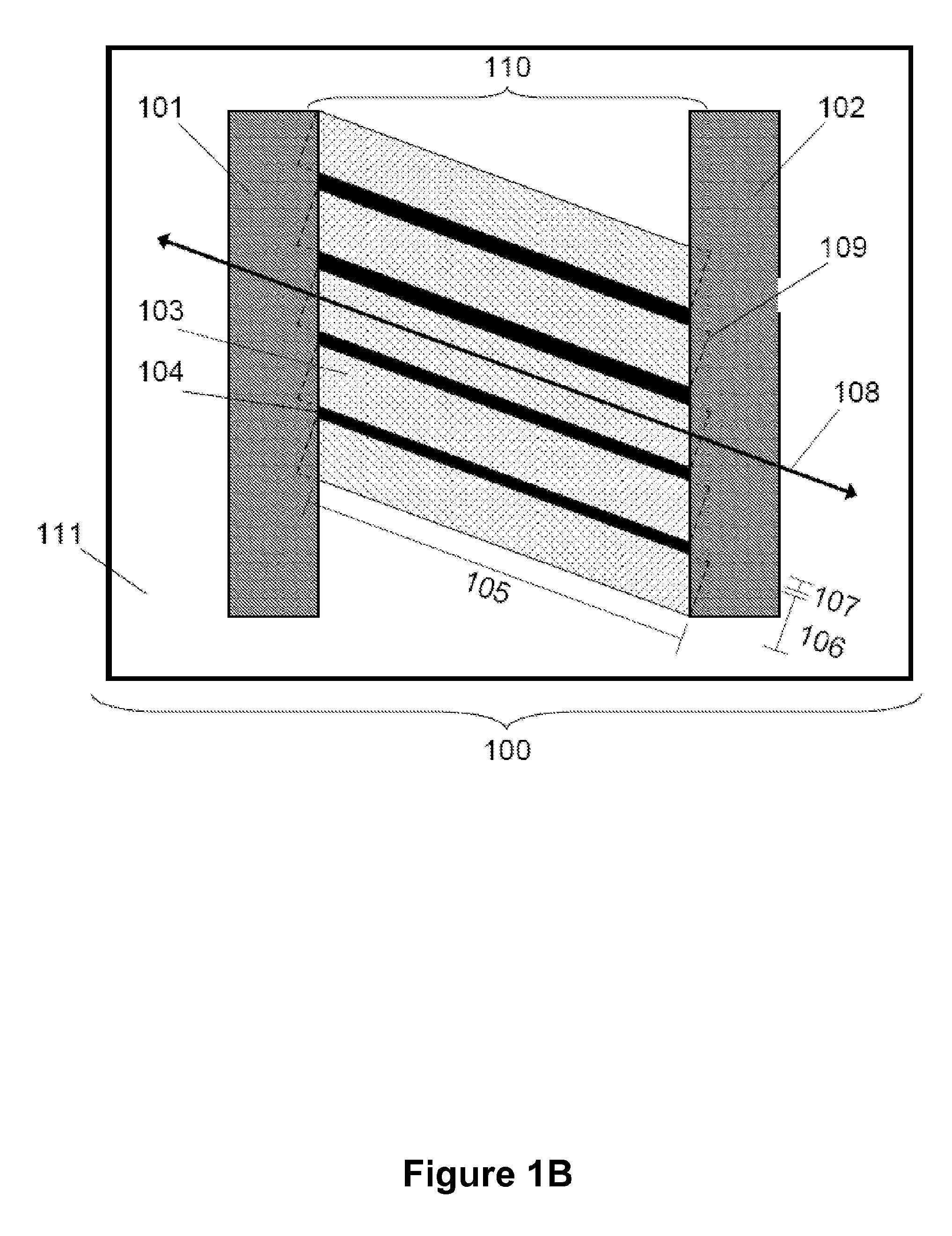
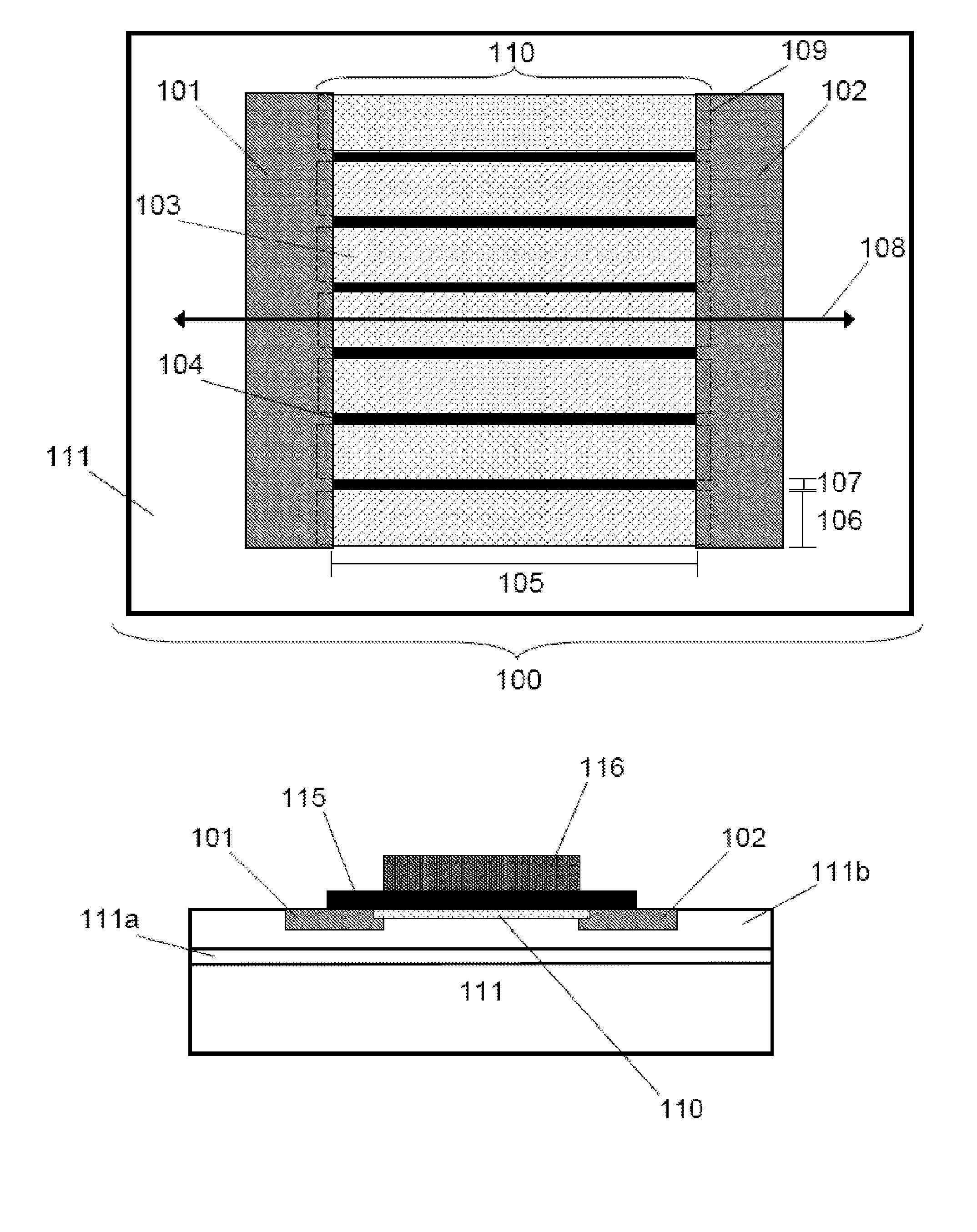
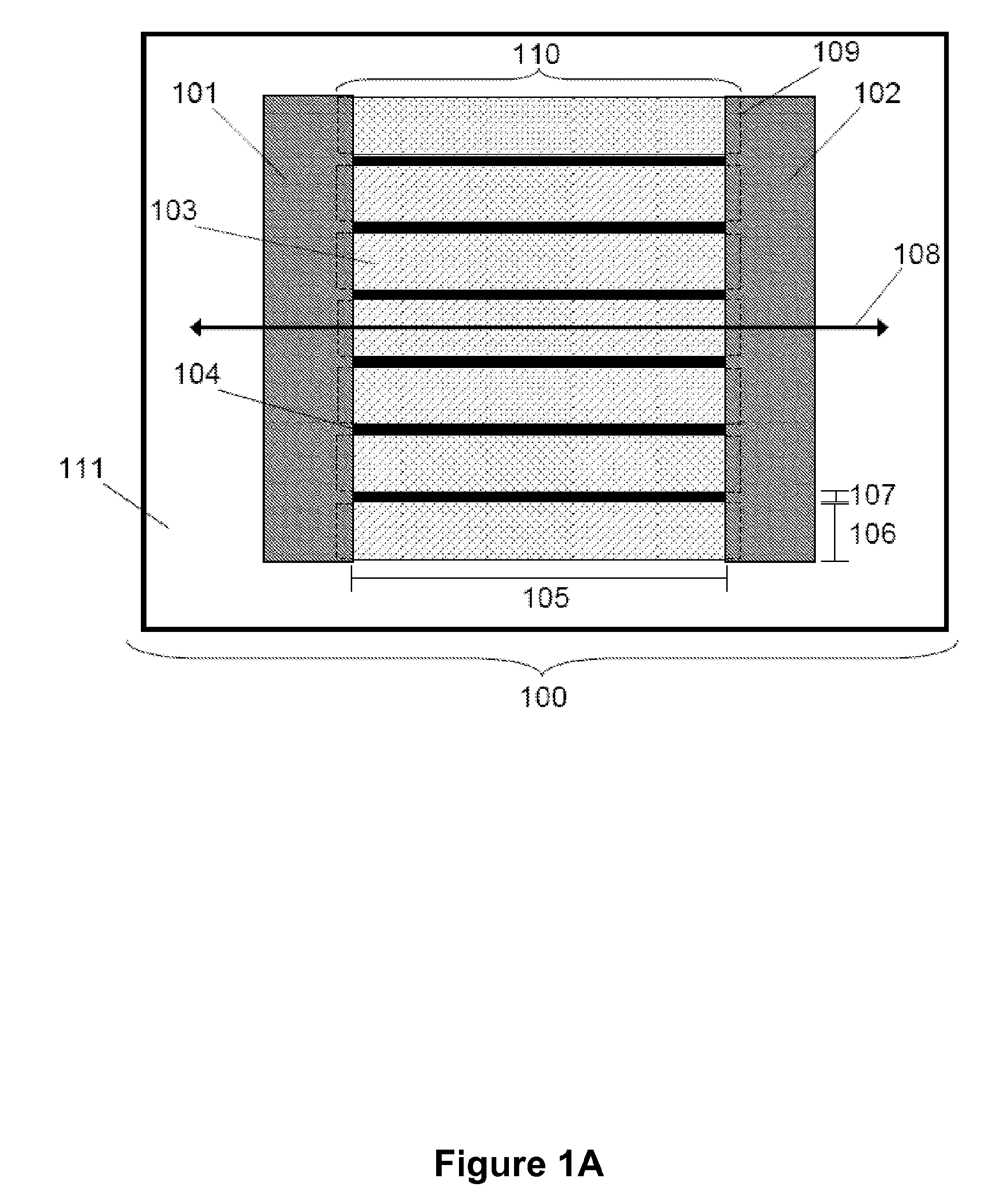
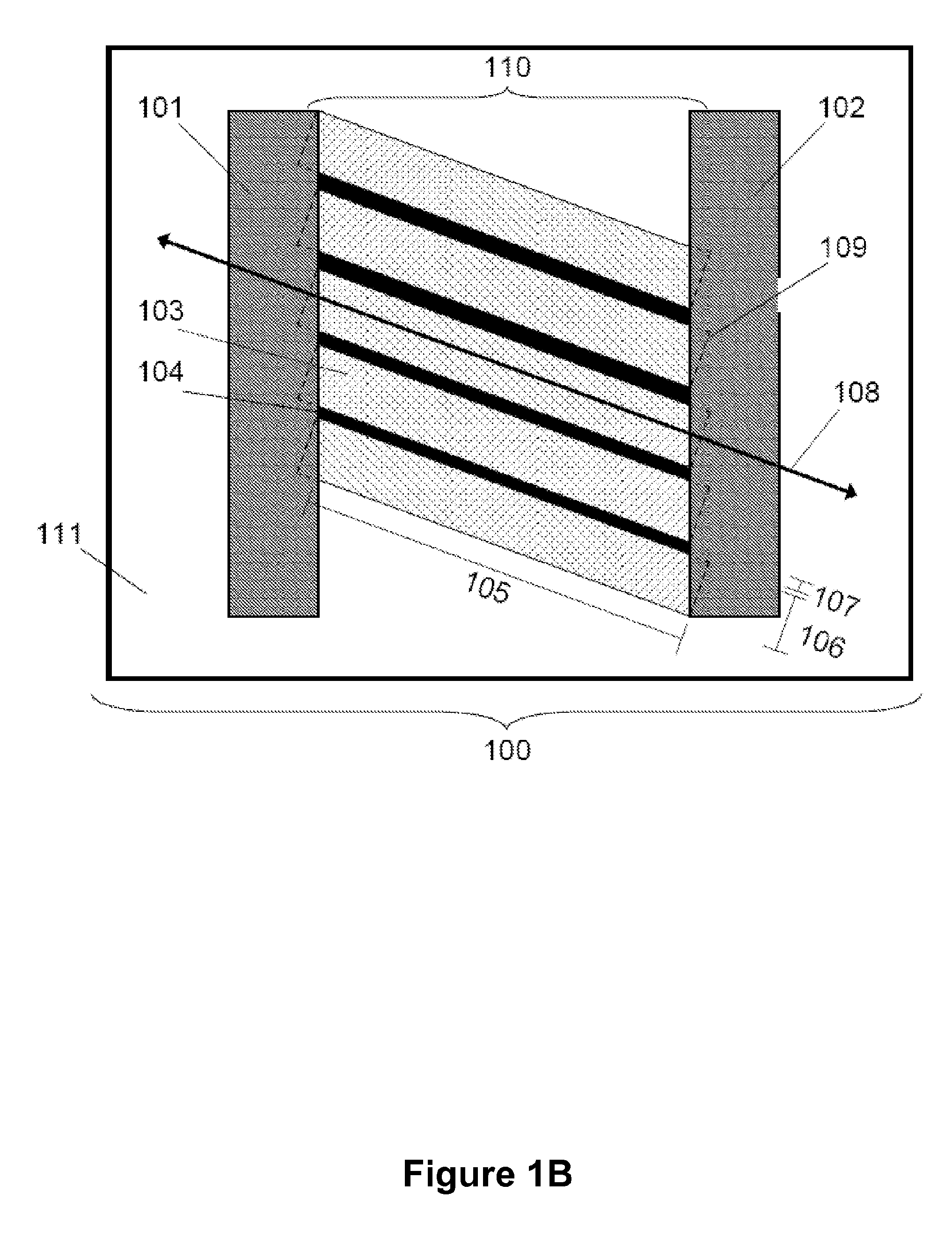
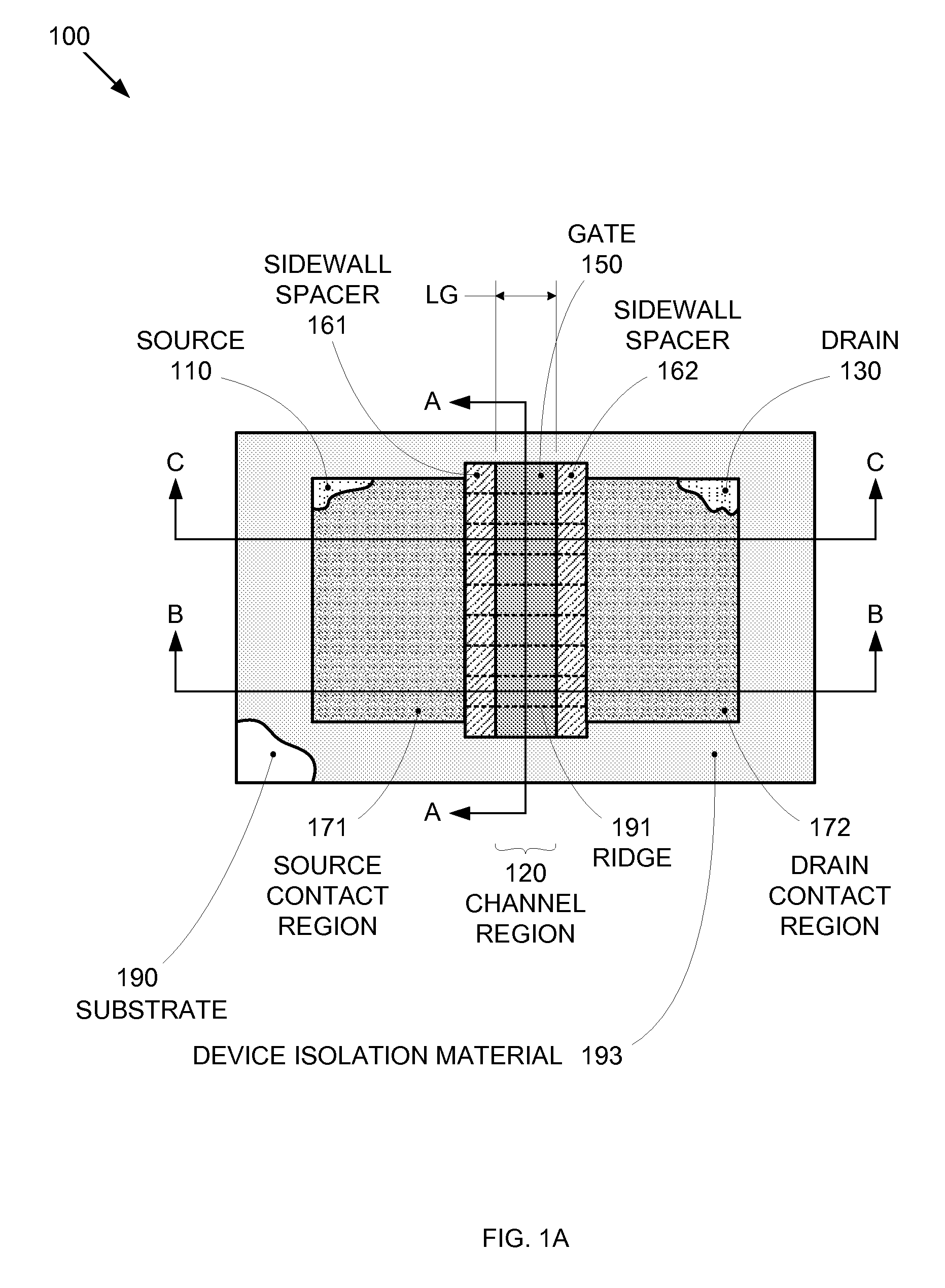
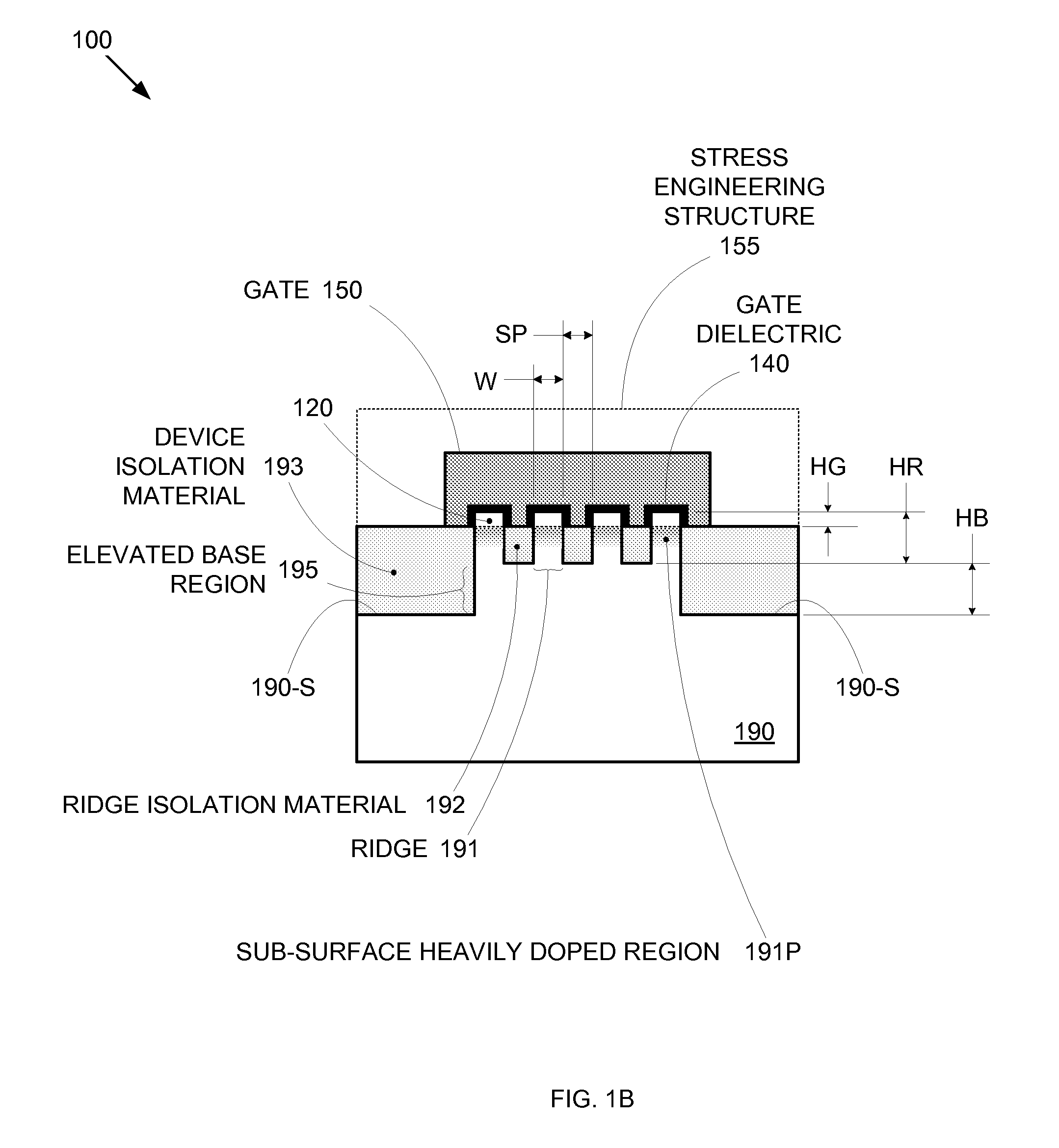
Segmented channel MOS transistor
ActiveUS7247887B2Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETLithographic artist
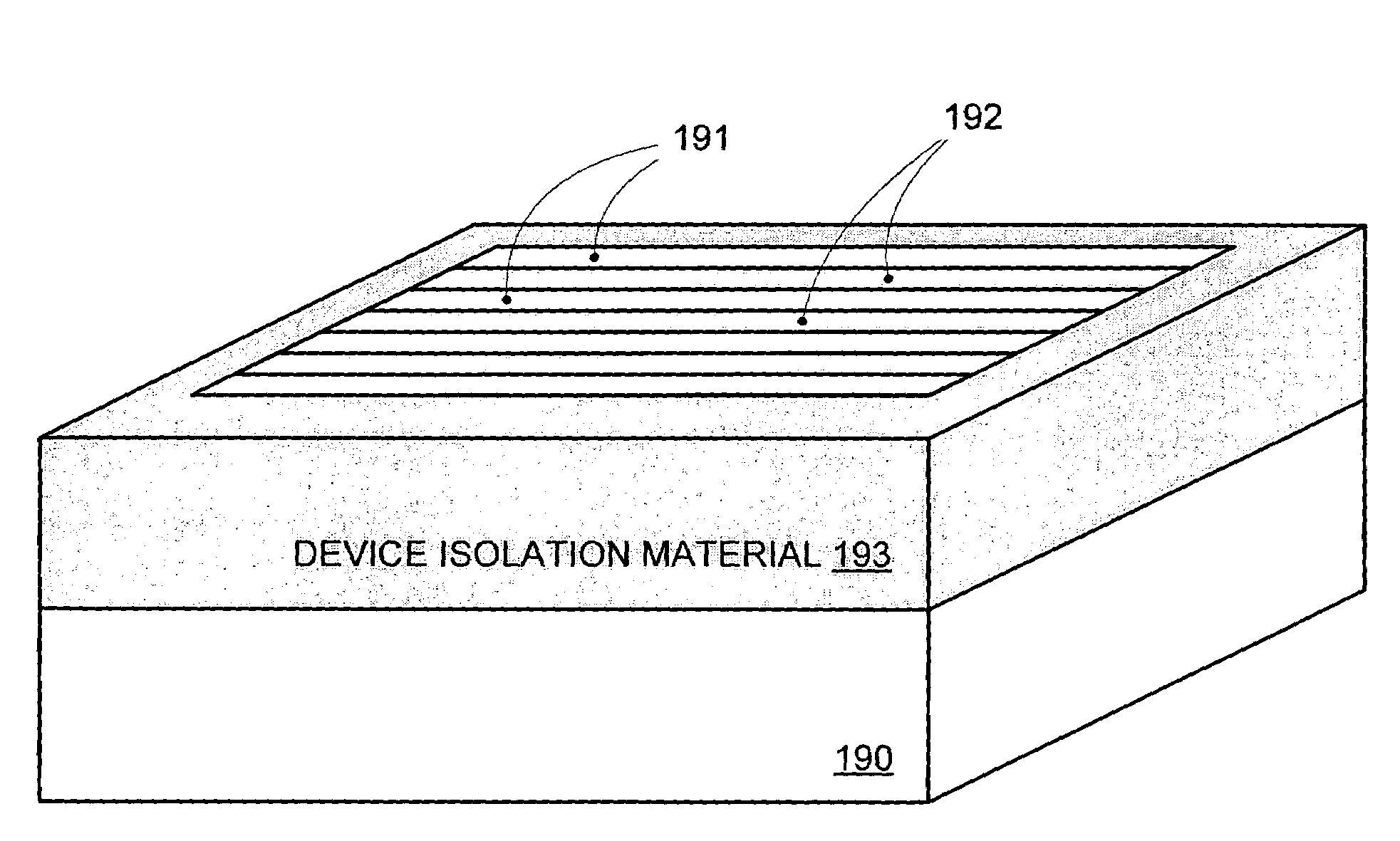
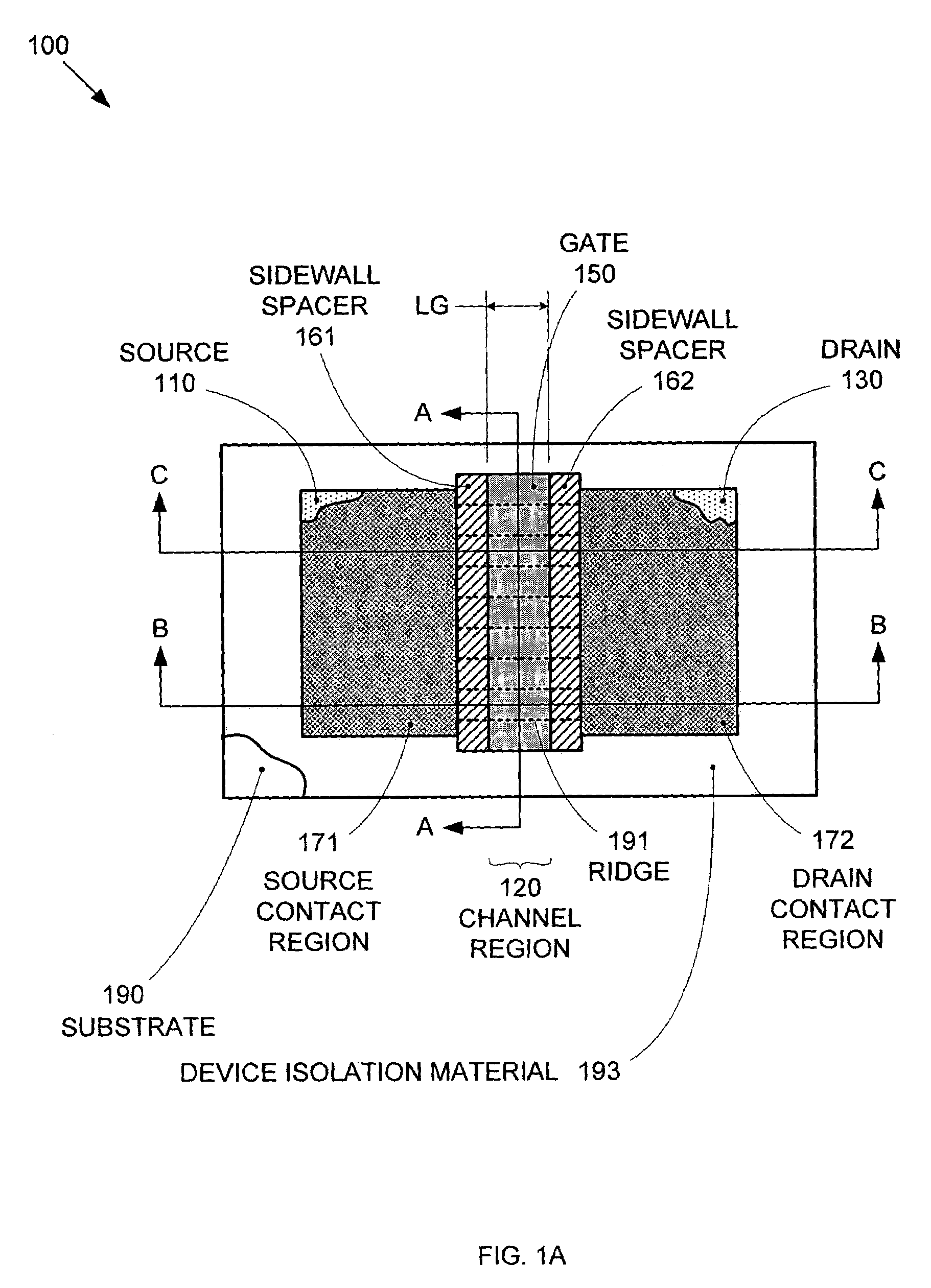
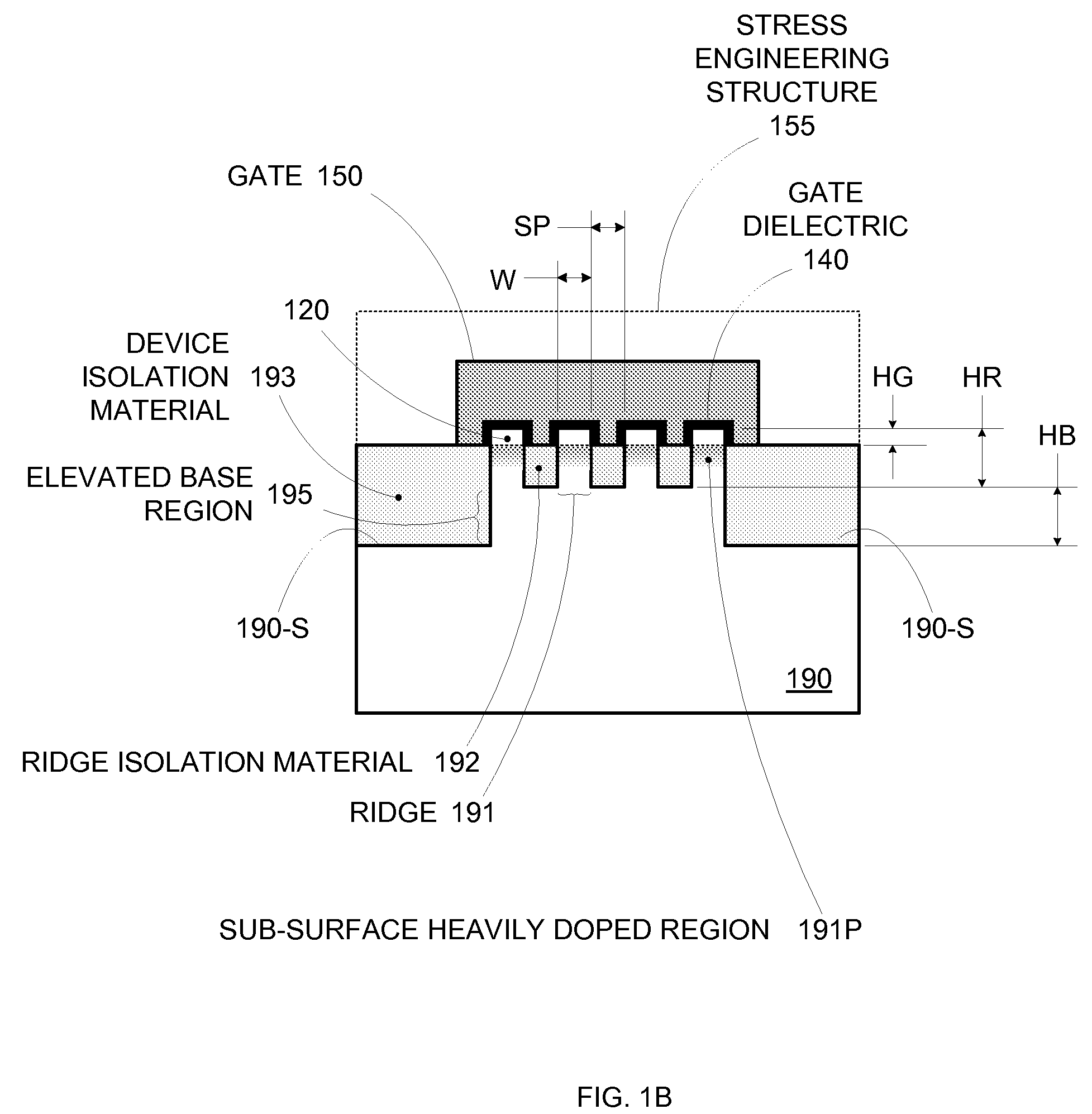
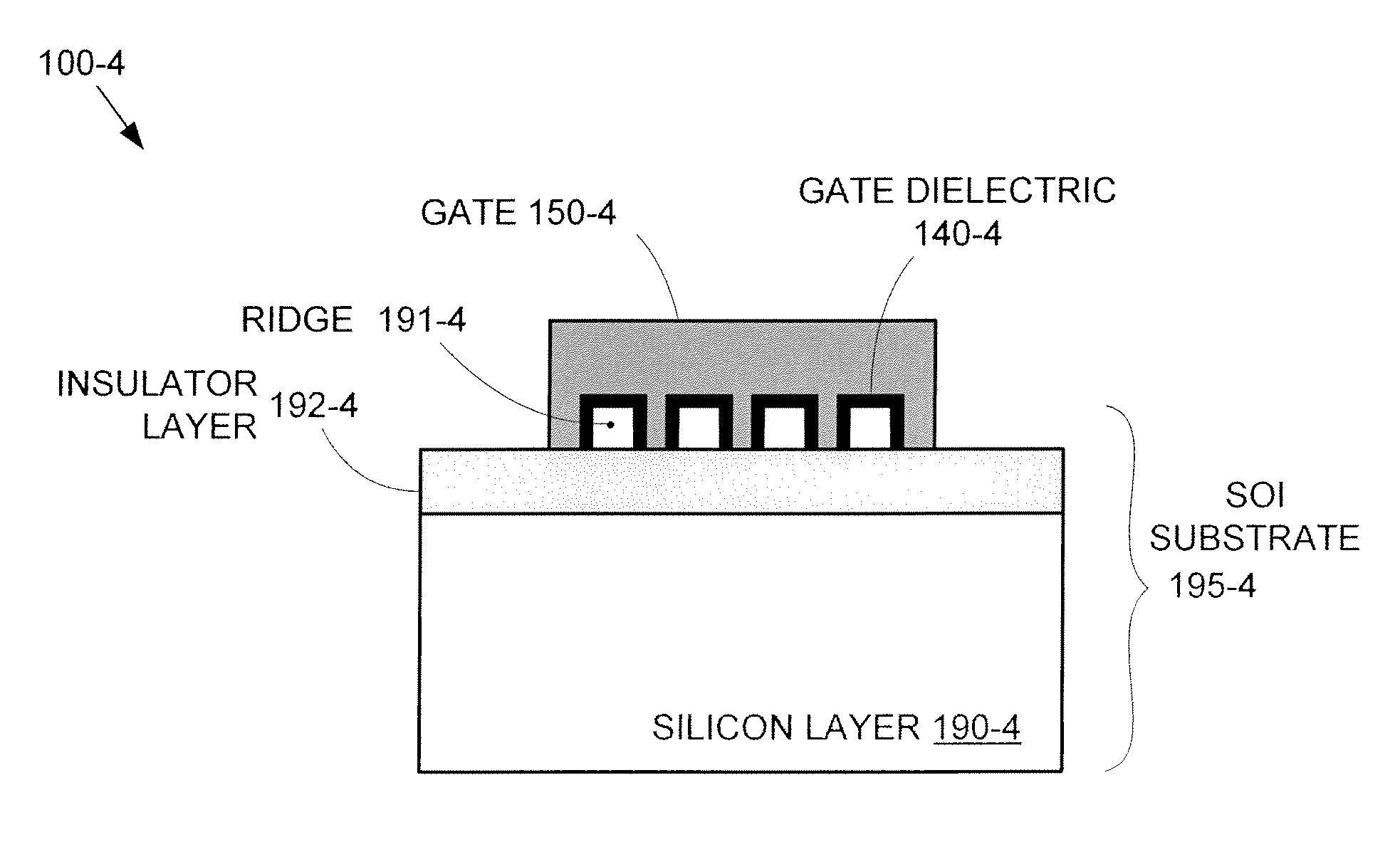
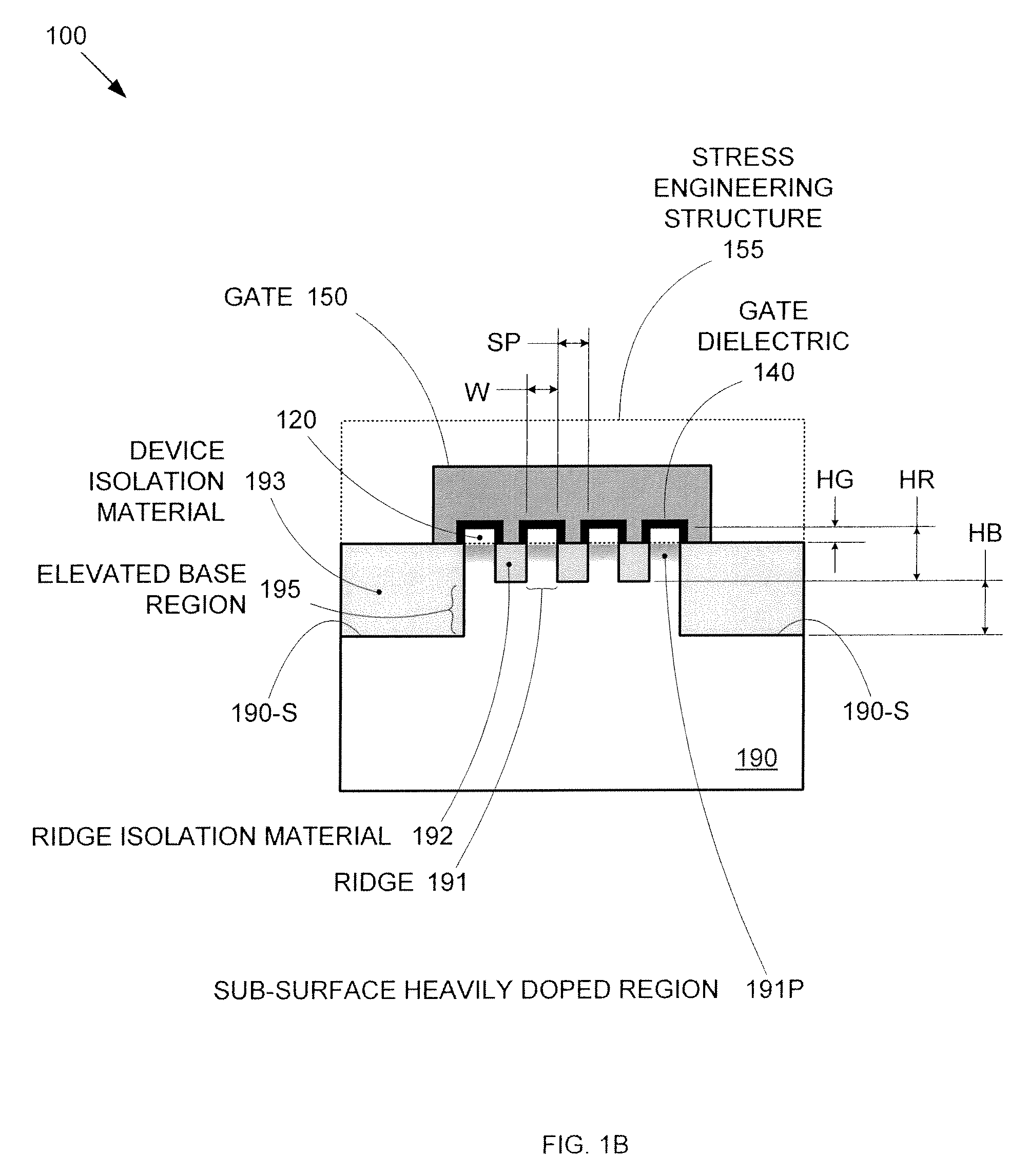
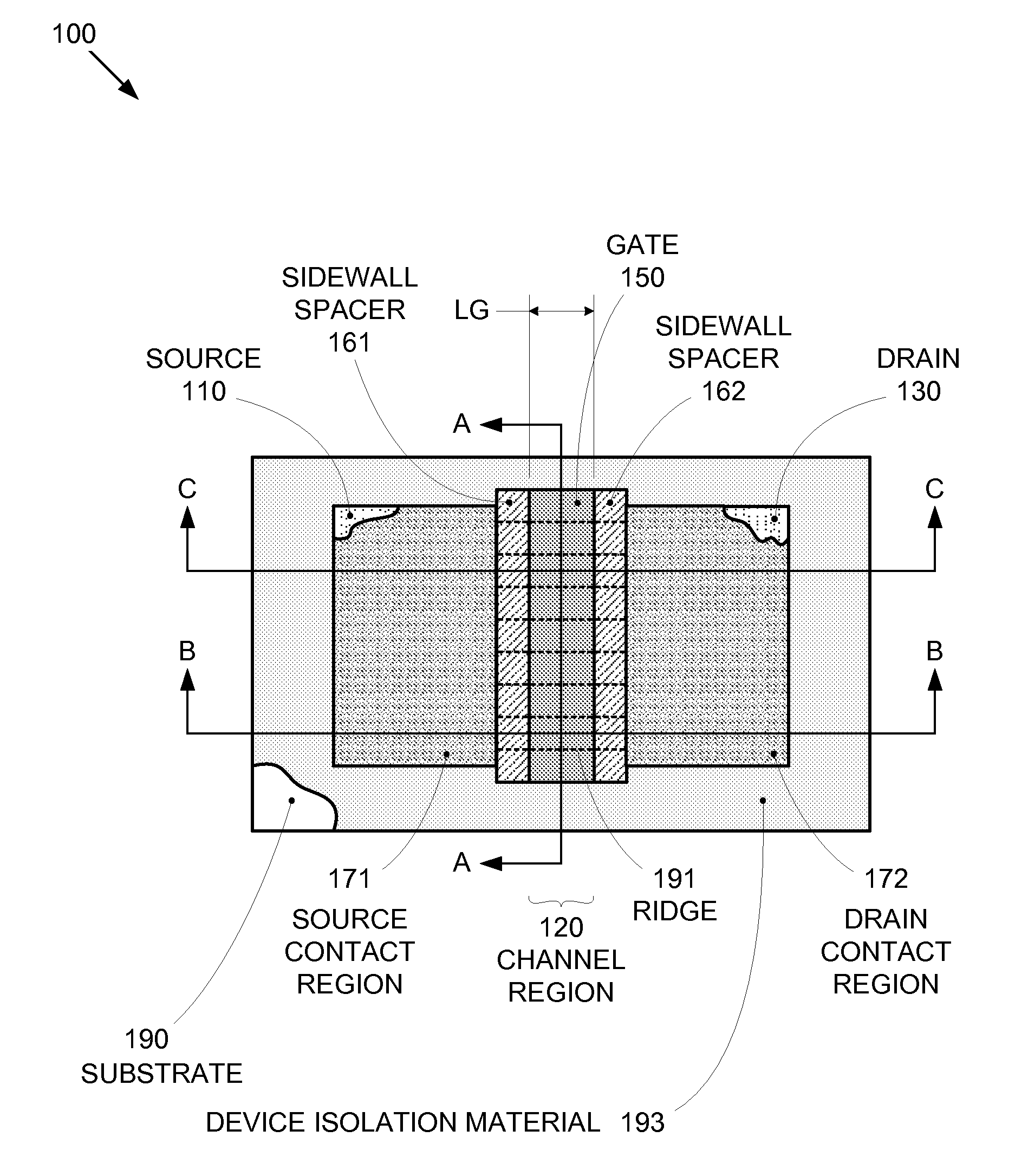
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping and “wrapped” gates can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Integrated circuit on corrugated substrate
ActiveUS7190050B2Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMOSFETPerformance enhancement
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping and “wrapped” gates can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
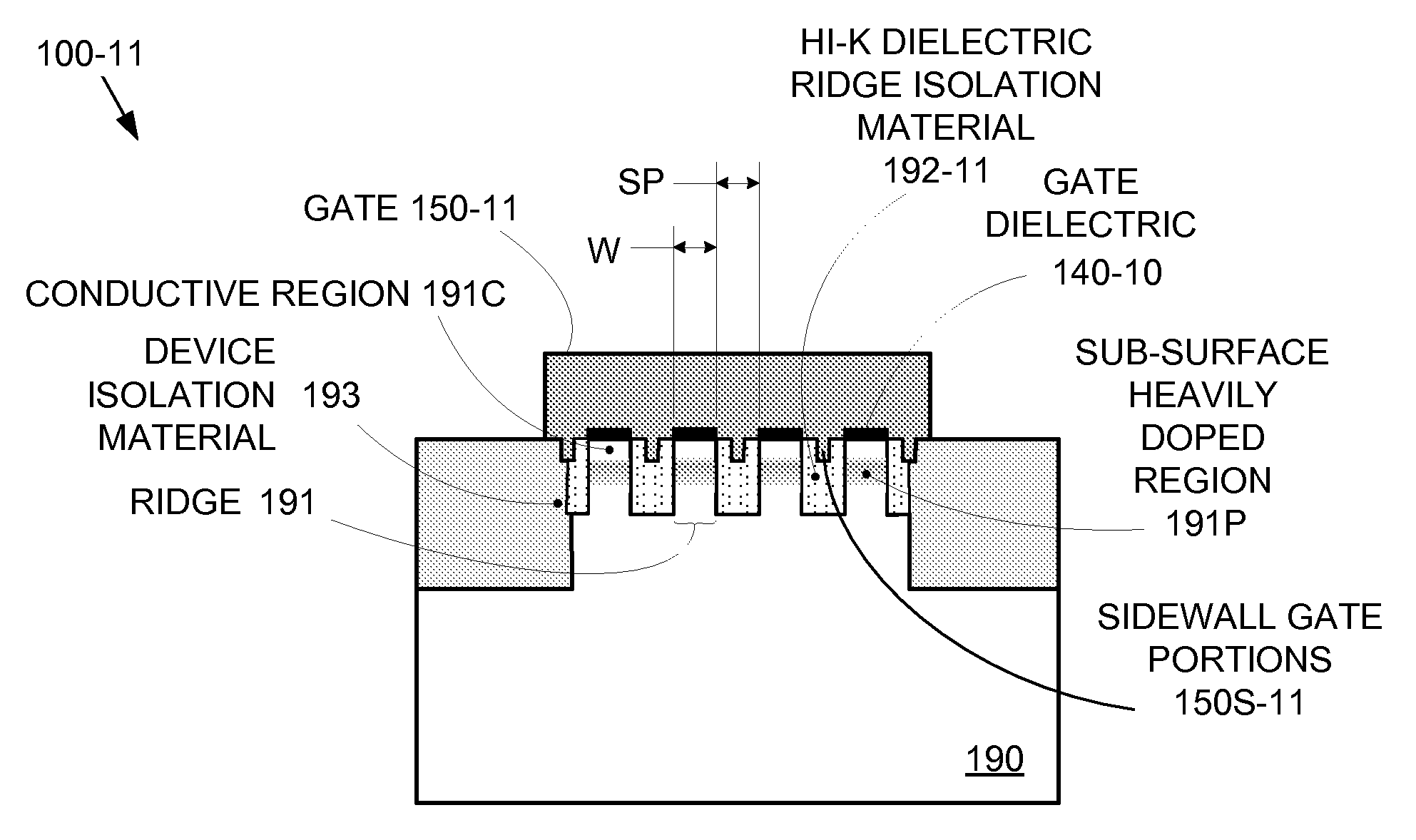
Enhanced Segmented Channel MOS Transistor with Multi Layer Regions
ActiveUS20070120156A1Increase costImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETPerformance enhancement
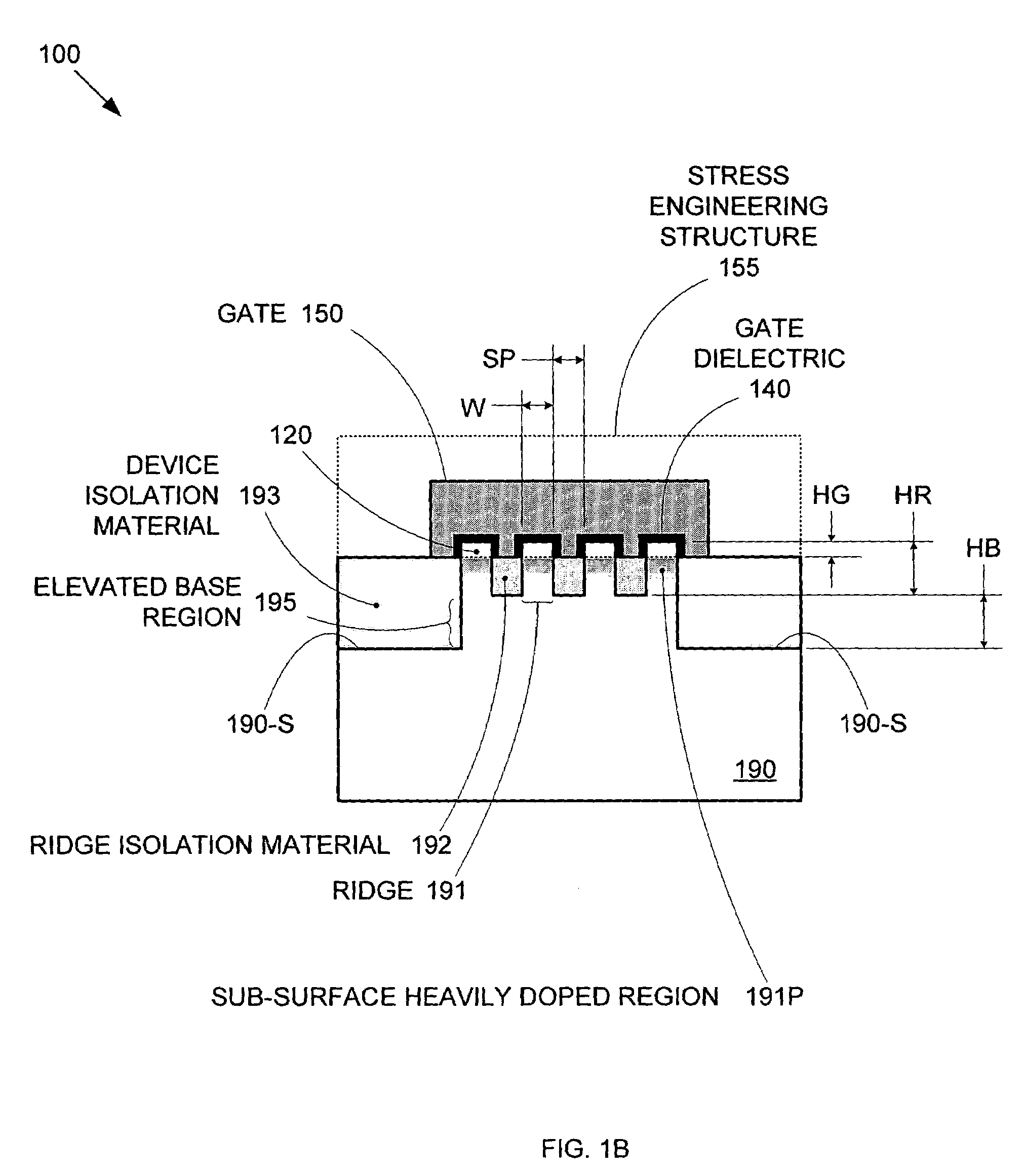
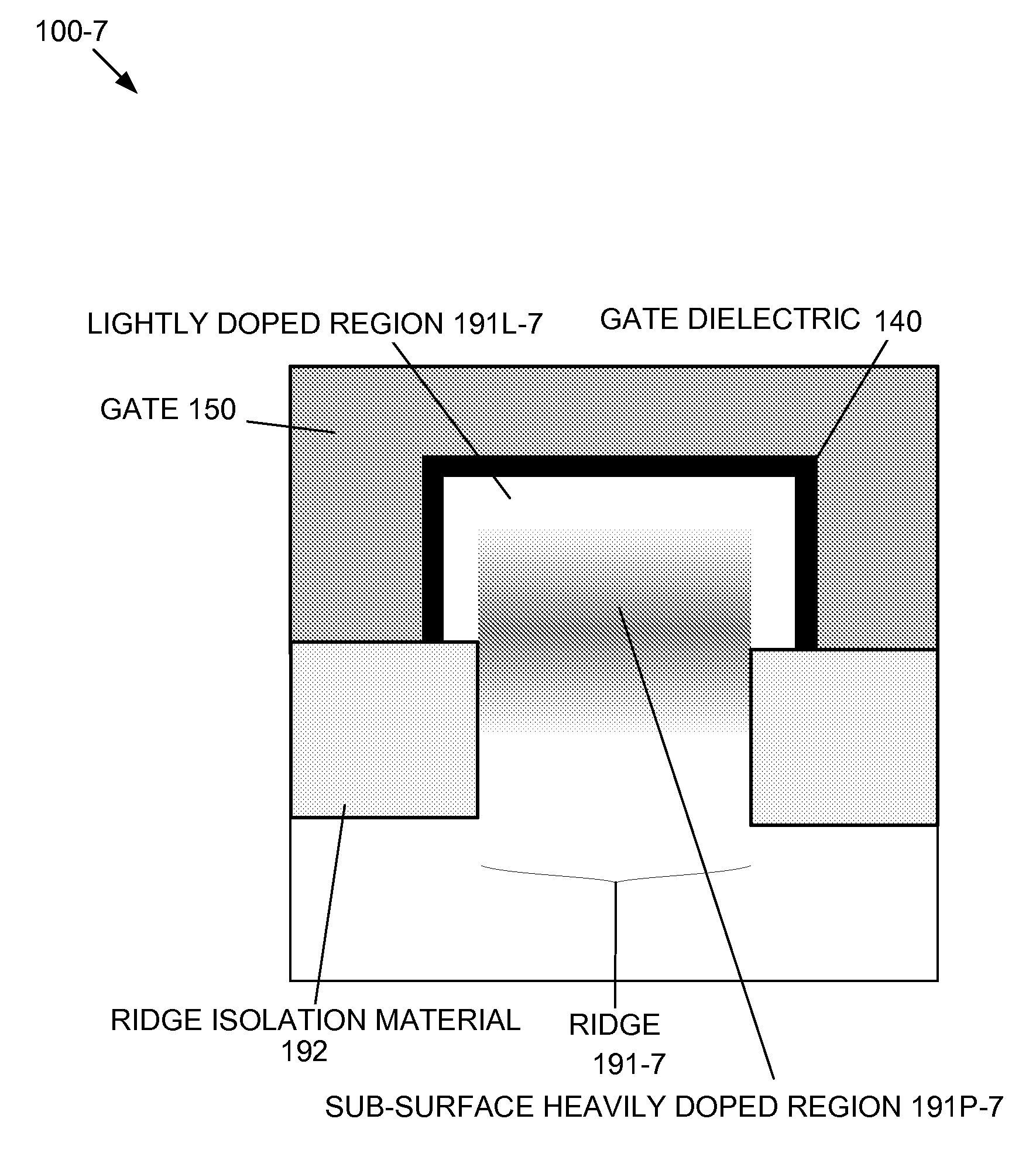
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping, “wrapped” gates, epitaxially grown conductive regions, epitaxially grown high mobility semiconductor materials (e.g. silicon-germanium, germanium, gallium arsenide, etc.), high-permittivity ridge isolation material, and narrowed base regions can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Method of IC production using corrugated substrate
ActiveUS7265008B2Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceLaser detailsSolid-state devicesMOSFETPerformance enhancement
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping and “wrapped” gates can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Enhanced segmented channel MOS transistor with narrowed base regions
ActiveUS7508031B2Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETPerformance enhancement
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably produced. Ridges on the corrugated substrate can be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping, “wrapped” gates, epitaxially grown conductive regions, epitaxially grown high mobility semiconductor materials, high-permittivity ridge isolation material, and narrowed base regions can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Enhanced segmented channel MOS transistor with high-permittivity dielectric isolation material
ActiveUS7605449B2Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETPerformance enhancement
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping, “wrapped” gates, epitaxially grown conductive regions, epitaxially grown high mobility semiconductor materials (e.g. silicon-germanium, germanium, gallium arsenide, etc.), high-permittivity ridge isolation material, and narrowed base regions can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Integrated Circuit On Corrugated Substrate
ActiveUS20070132053A1Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMOSFETSemiconductor materials
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping and “wrapped” gates can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Dual-polarized optically controlled microwave antenna
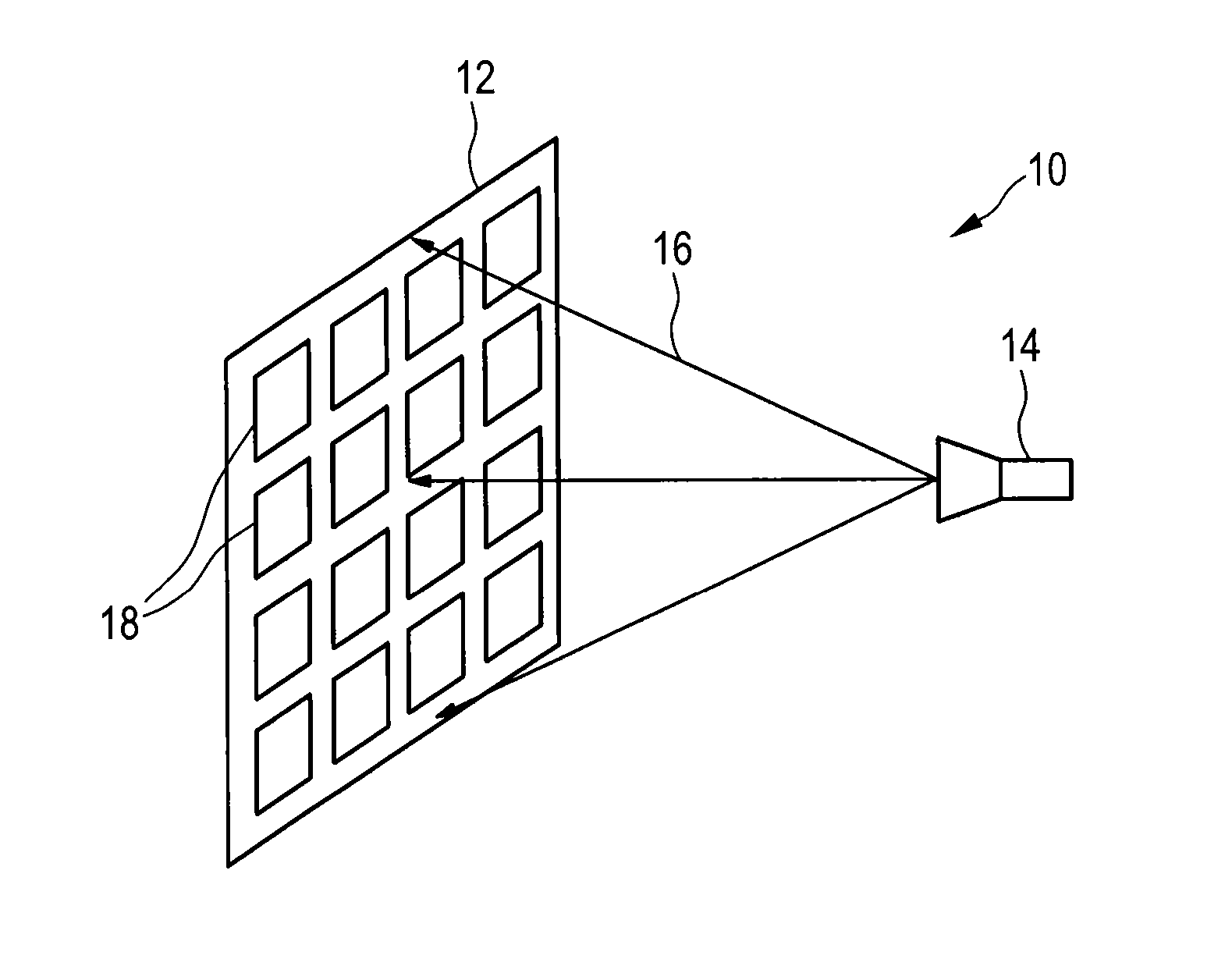
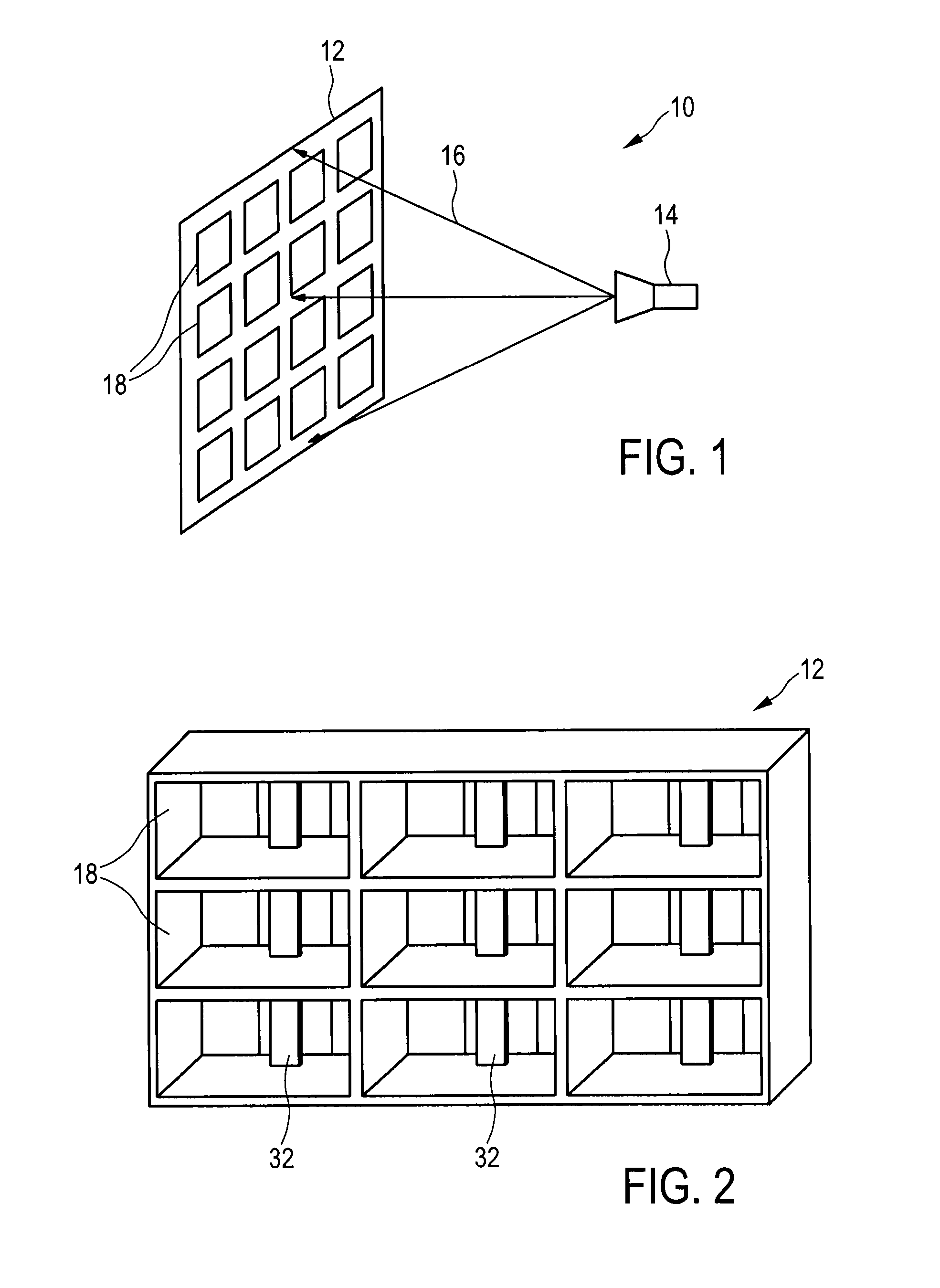
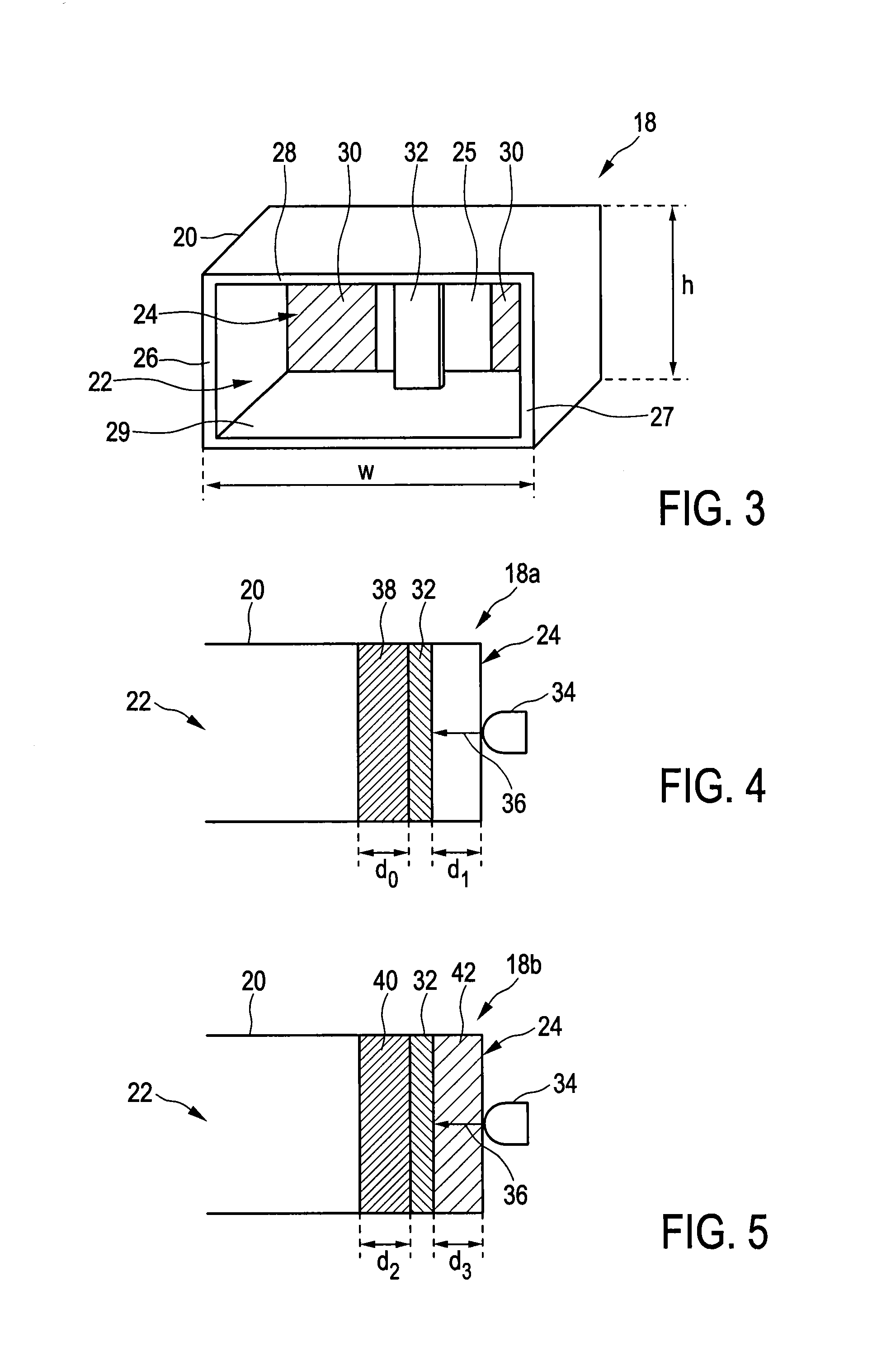
An optically controlled microwave antenna that reduces the optical power consumed by the antenna and to enable polarimetric detection an optically controlled microwave antenna comprises an antenna array and a feed for illuminating said antenna array with and / or receiving microwave radiation. The antenna array comprises a plurality of antenna elements each including a waveguide, two optically controllable semiconductor elements arranged within the waveguide in front of the light transmissive portion of the second end portion, a controllable light source arranged at or close to the light transmissive portion of the second end portion for projecting a controlled light beam onto said semiconductor element for controlling its material properties, and a septum arranged within the waveguide in front of the light transmissive portion of the second end portion and separating said waveguide into two waveguide portions.
Owner:SONY CORP
Medium Scale Carbon Nanotube Thin Film Integrated Circuits on Flexible Plastic Substrates
InactiveUS20110147715A1Improve electronic propertyImprove electronic performanceNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesIntegrated circuitElectronic properties
The present invention provides device components geometries and fabrication strategies for enhancing the electronic performance of electronic devices based on thin films of randomly oriented or partially aligned semiconducting nanotubes. In certain aspects, devices and methods of the present invention incorporate a patterned layer of randomly oriented or partially aligned carbon nanotubes, such as one or more interconnected SWNT networks, providing a semiconductor channel exhibiting improved electronic properties relative to conventional nanotubes-based electronic systems.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC +1
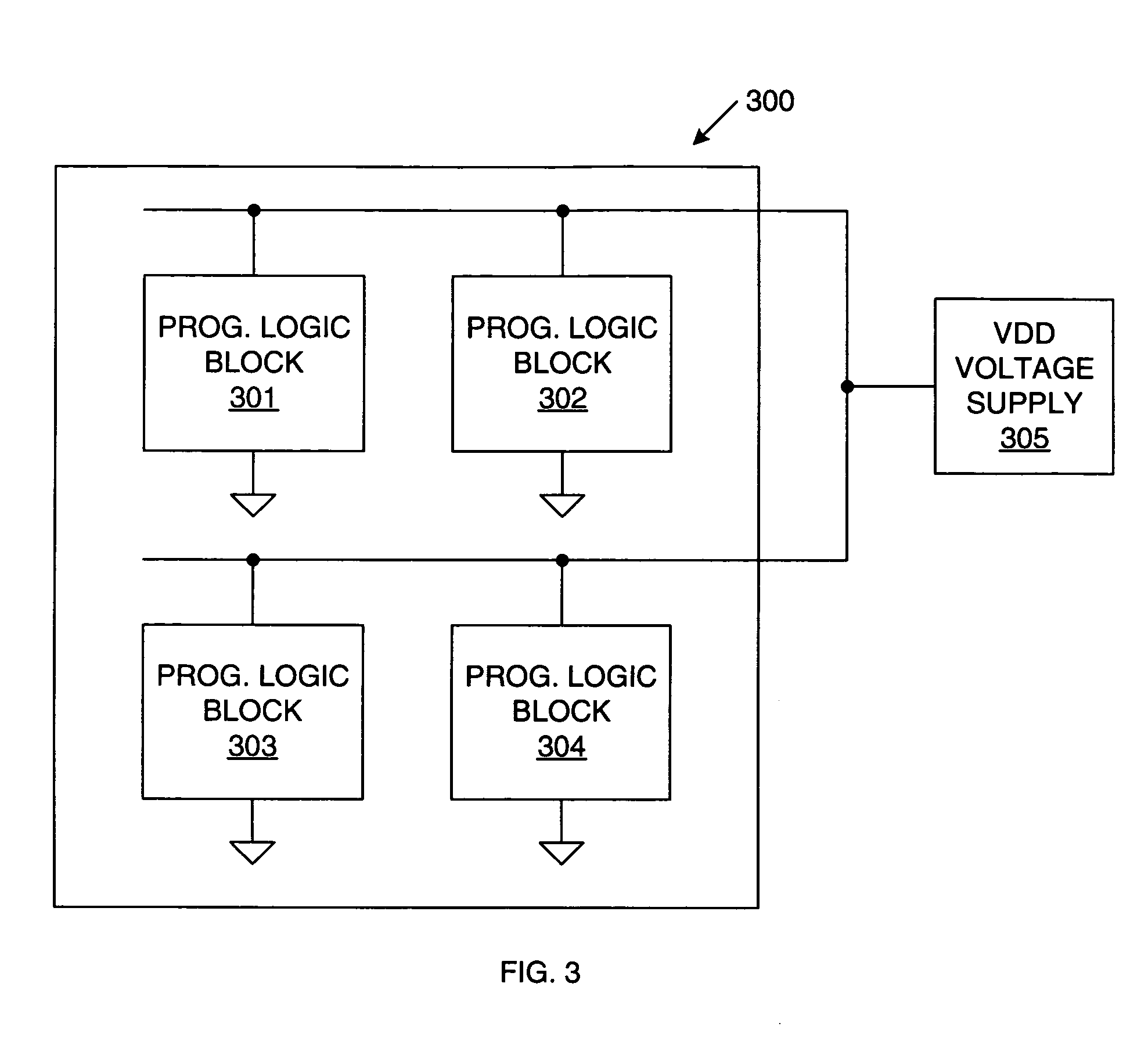
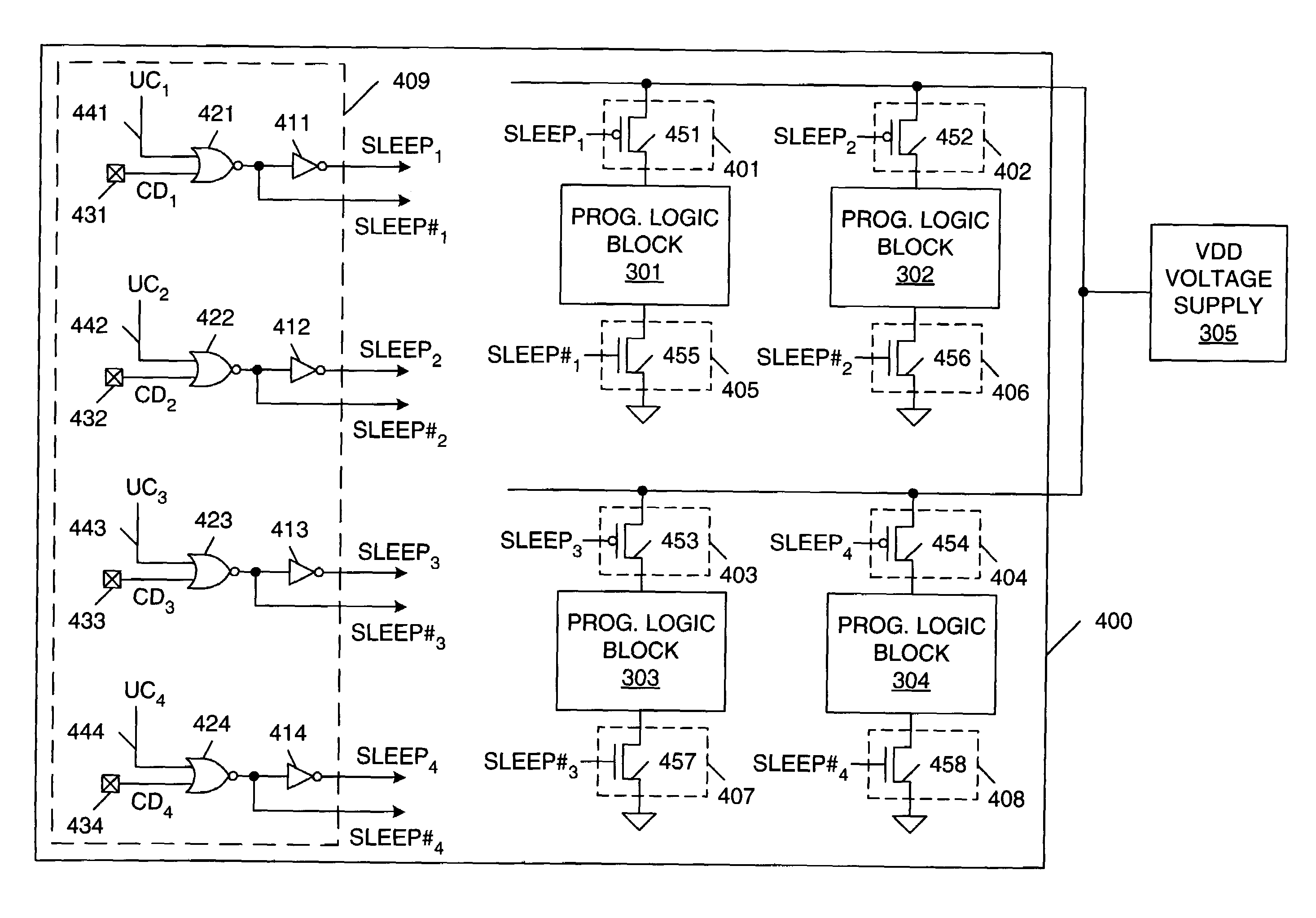
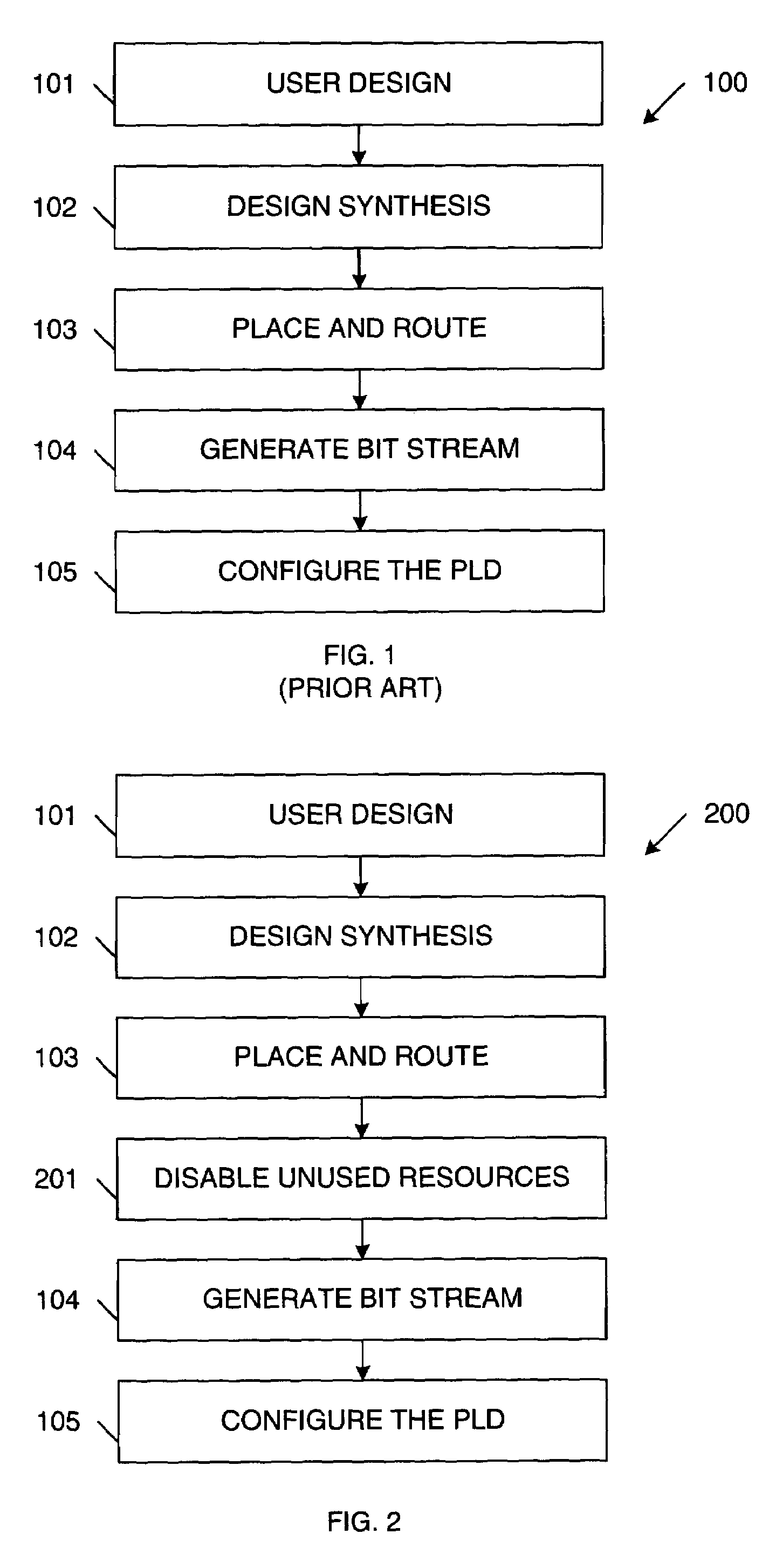
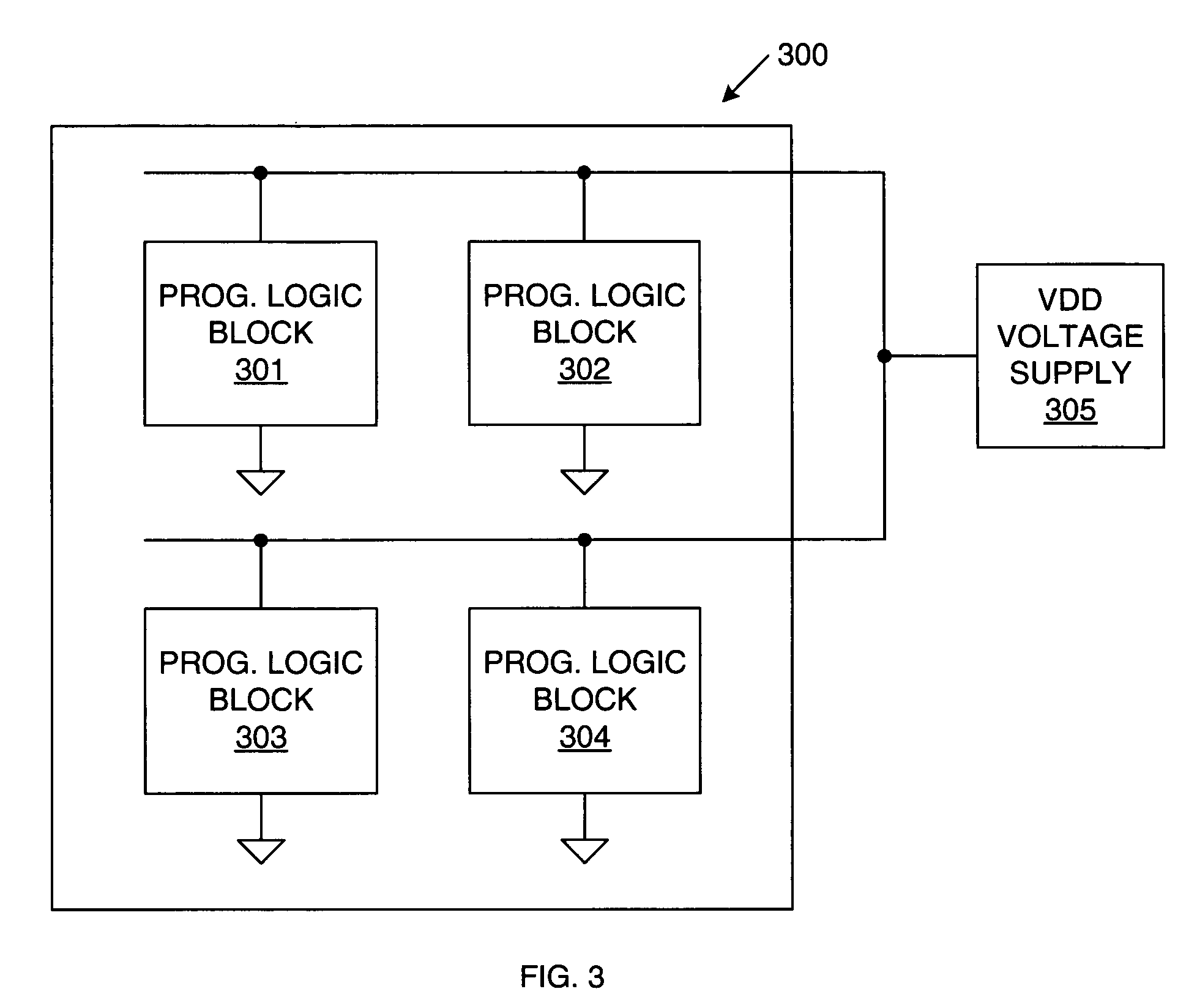
Disabling unused/inactive resources in programmable logic devices for static power reduction
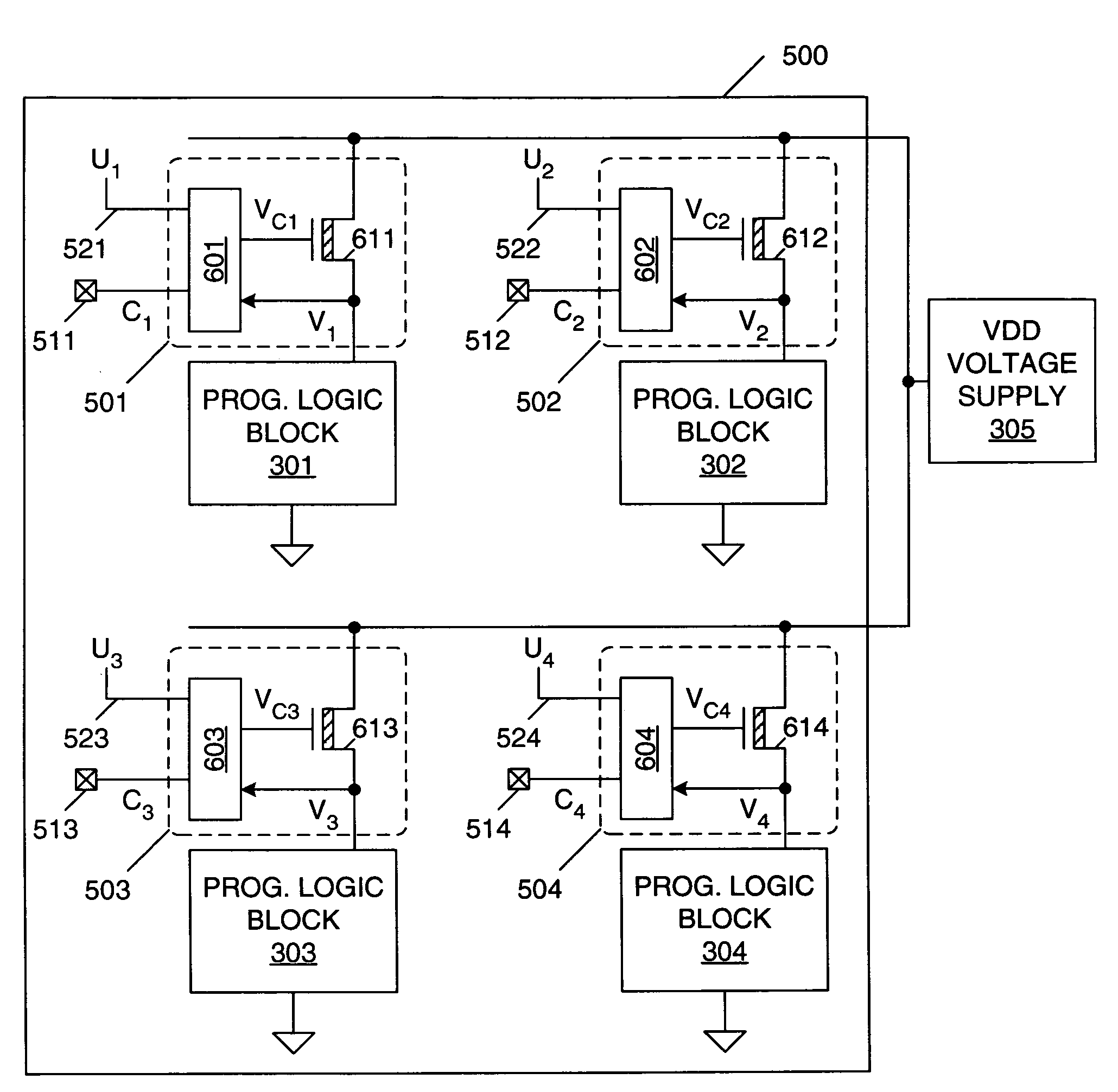
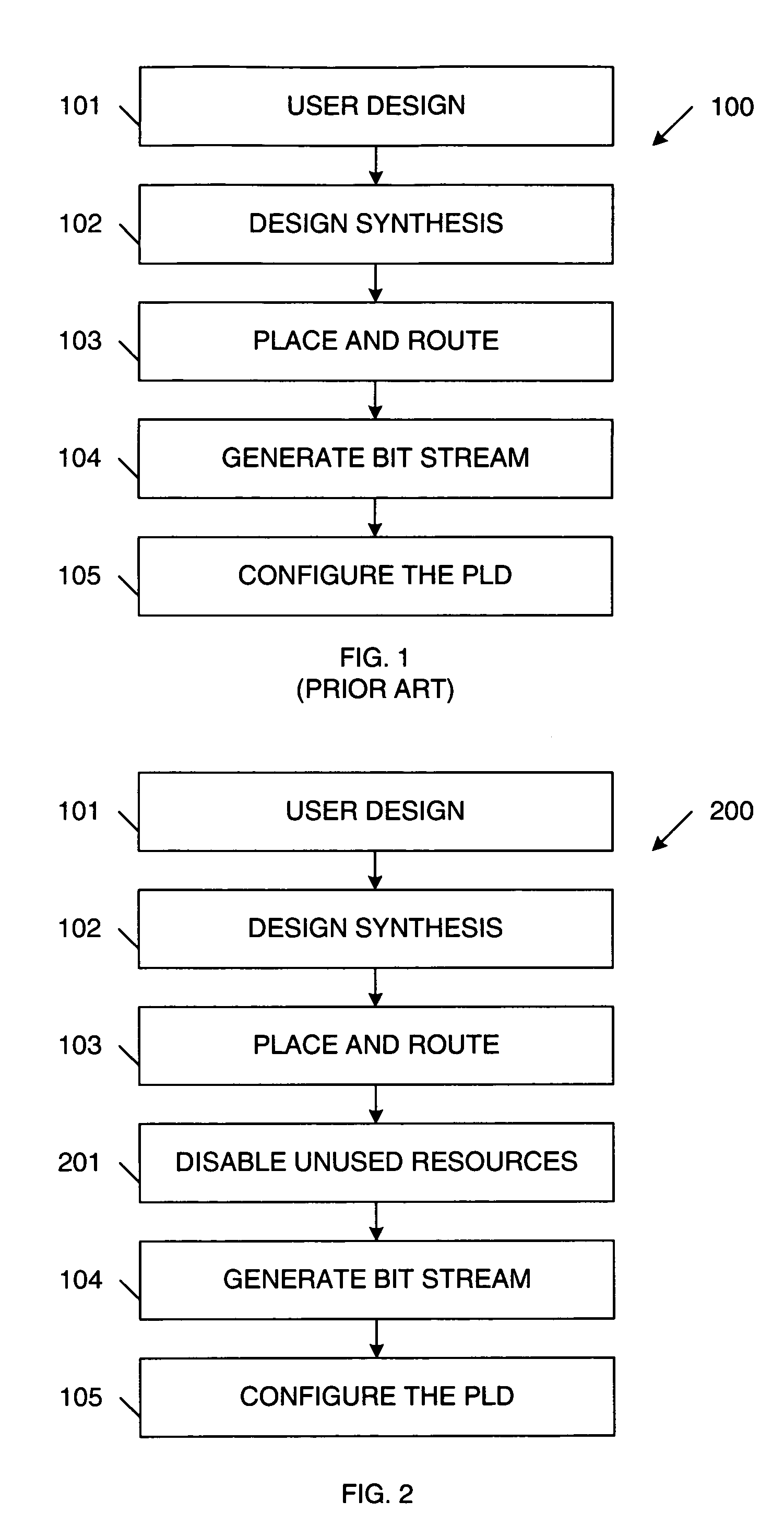
ActiveUS7098689B1Reduce static power consumptionStatic storageLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsProgrammable logic deviceErasable programmable logic device
A method of operating a programmable logic device, including the steps of enabling resources of the programmable logic device being used in a circuit design implemented by the programmable logic device, and disabling unused or inactive resources of the programmable logic device that are not being used in the circuit design. The step of disabling can include de-coupling the unused or inactive resources from one or more power supply terminals. Alternatively, the step of disabling can include regulating a supply voltage applied to the unused or inactive resources. The step of disabling can be performed in response to configuration data bits stored by the programmable logic device and / or in response to user controlled signals. The step of disabling can be initiated during design time and / or run time of the programmable logic device.
Owner:XILINX INC
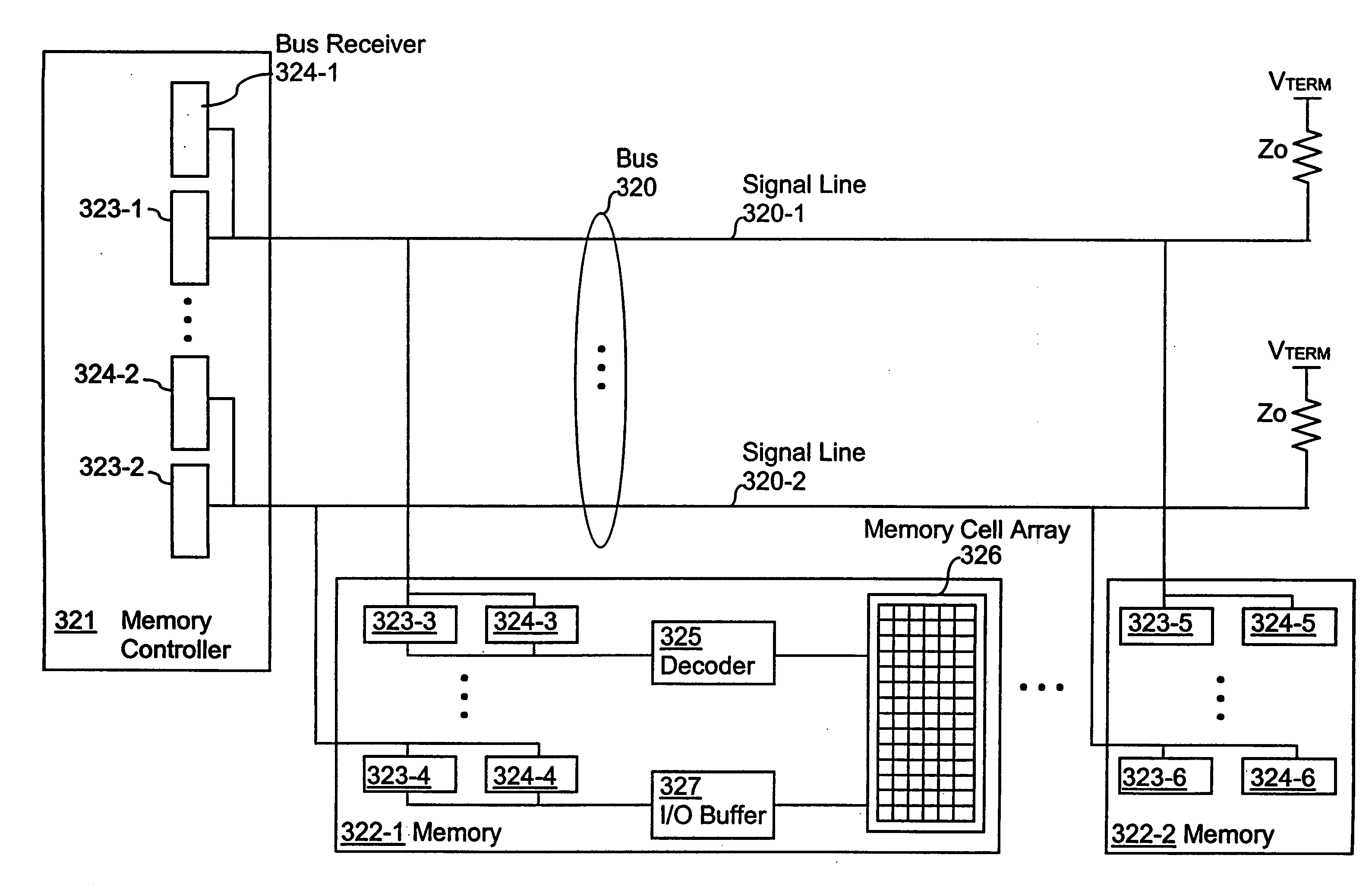
Low latency multi-level communication interface
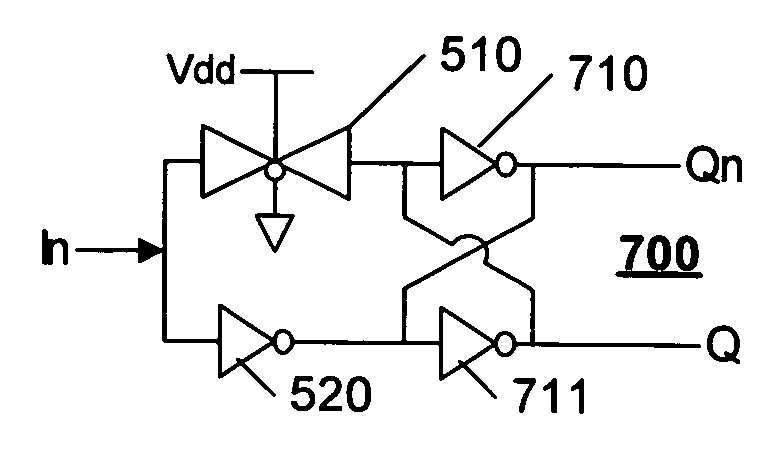
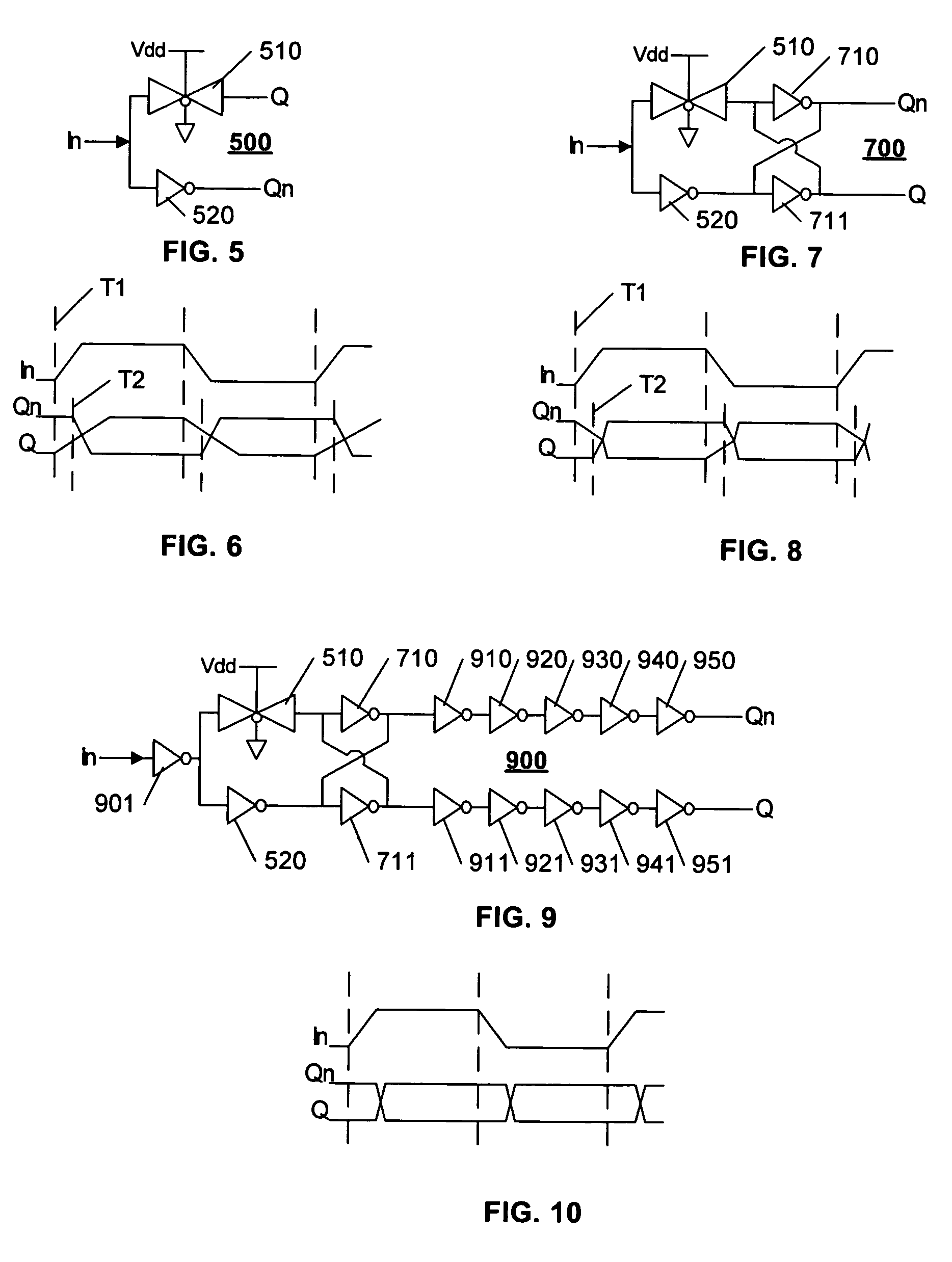
InactiveUS20060170453A1Low static power consumptionWider rangeComputing operations for integral formationComputing operations for integration/differentiationCommunication interfaceMultiple pulse
A memory system uses multiple pulse amplitude modulation (multi-PAM) output drivers and receivers to send and receive multi-PAM signals. A multi-PAM signal has more than two voltage levels, with each data interval now transmitting a “symbol” at one of the valid voltage levels. In one embodiment, a symbol represents two or more bits. The multi-PAM output driver drives an output symbol onto a signal line. The output symbol represents at least two bits that include a most significant bit (MSB) and a least significant bit (LSB). The multi-PAM receiver receives the output symbol from the signal line and determines the MSB and the LSB.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
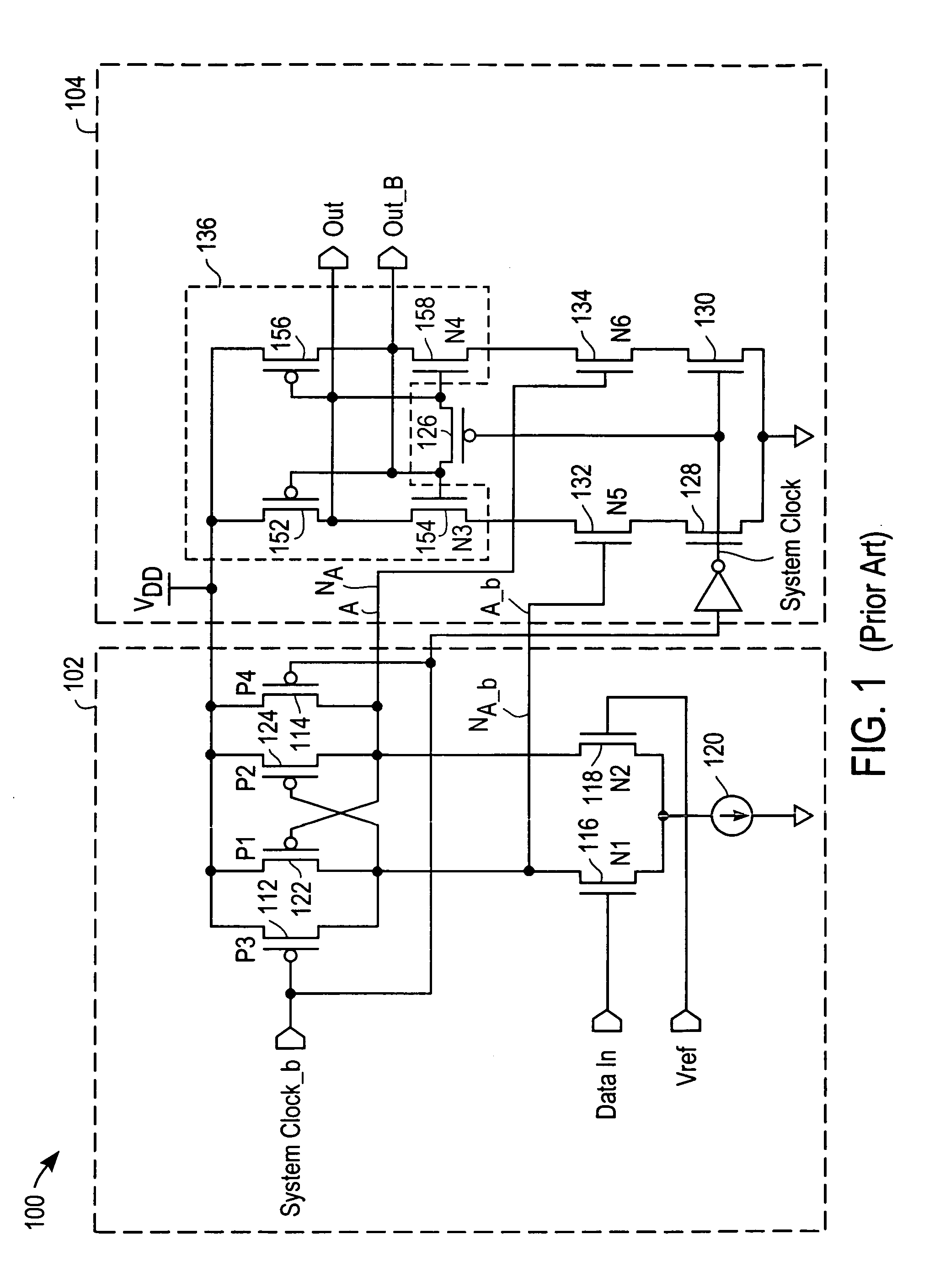
Low-skew single-ended to differential converter
InactiveUS7119602B2Reduce offsetReduce static power consumptionTransistorSingle output arrangementsTransmission gateEngineering
A single-ended to differential converter uses a cross-coupled latch that maximizes the output zero-crossing symmetry and is self compensating over PVT variations. An in-phase driving signal is provided by an always-on transmission gate coupled to the input. An out-of-phase driving signal is provided by an inverter coupled to the input. The in-phase and out-of-phase driving signals each drive an input of the cross-coupled latch. The in-phase driving signal from the always-on transmission gate starts to bring the cross-coupled latch into conduction, and when the out-of-phase driving signal arrives, the simultaneous driving of the cross-coupled latch causes a rapid and symmetric transition of both outputs of the cross-coupled latch.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Low latency multi-level communication interface
InactiveUS7124221B1Reduce static power consumptionWide input common mode rangePulse modulation television signal transmissionElectric analogue storesCommunication interfaceLeast significant bit
A memory system uses multiple pulse amplitude modulation (multi-PAM) output drivers and receivers to send and receive multi-PAM sigsnals. A multi-PAM signal has more than two voltage levels, with each data interval now transmitting a “symbol” at one of the valid voltage levels. In one embodiment, a symbol represents two or more bits. The multi-PAM output driver drives an output symbol onto a signal line. The output symbol represents at least two bits that include a most significant bit (MSB) and a least significant bit (LSB). The multi-PAM receiver receives the output symbol from the signal line and determines the MSB and the LSB.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
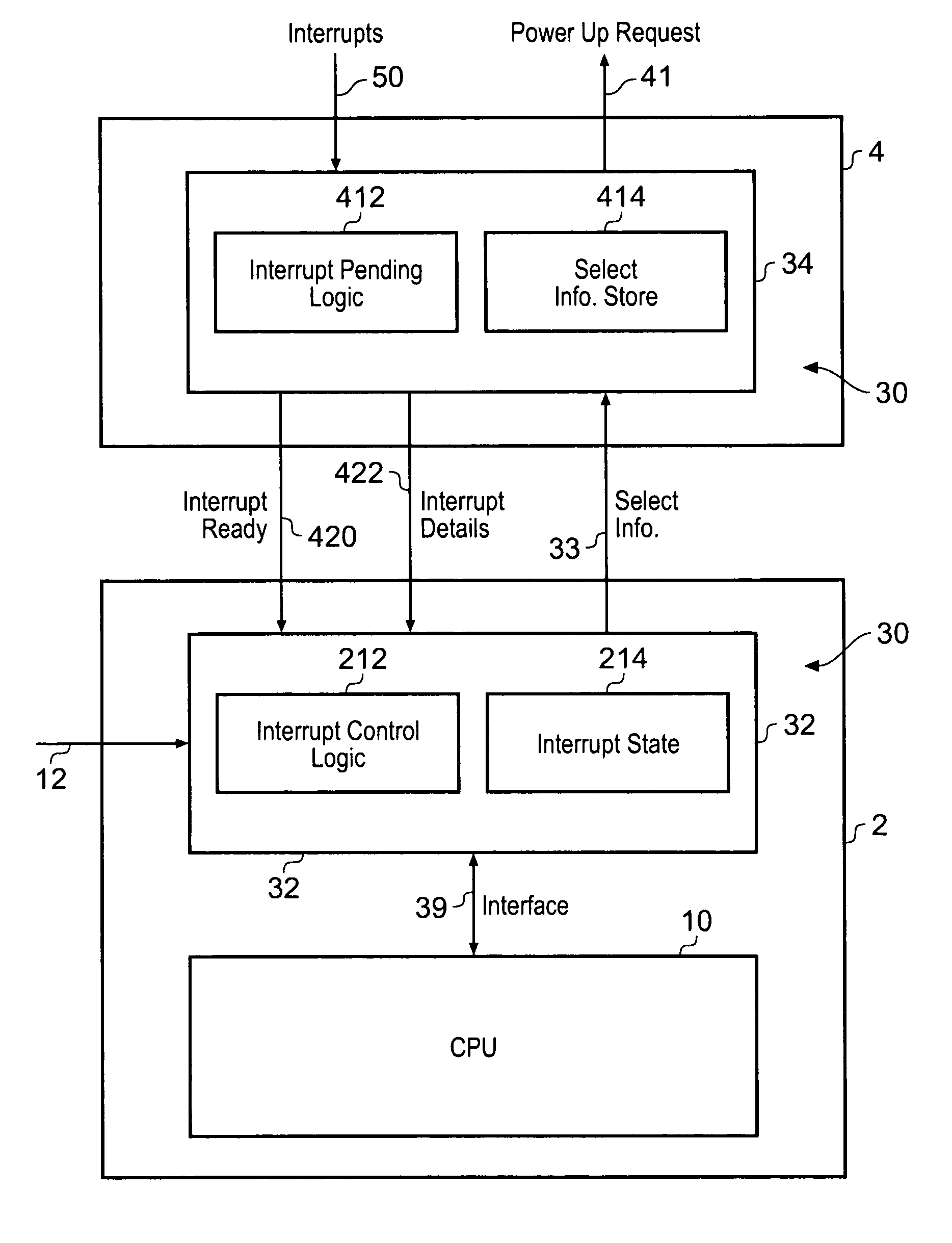
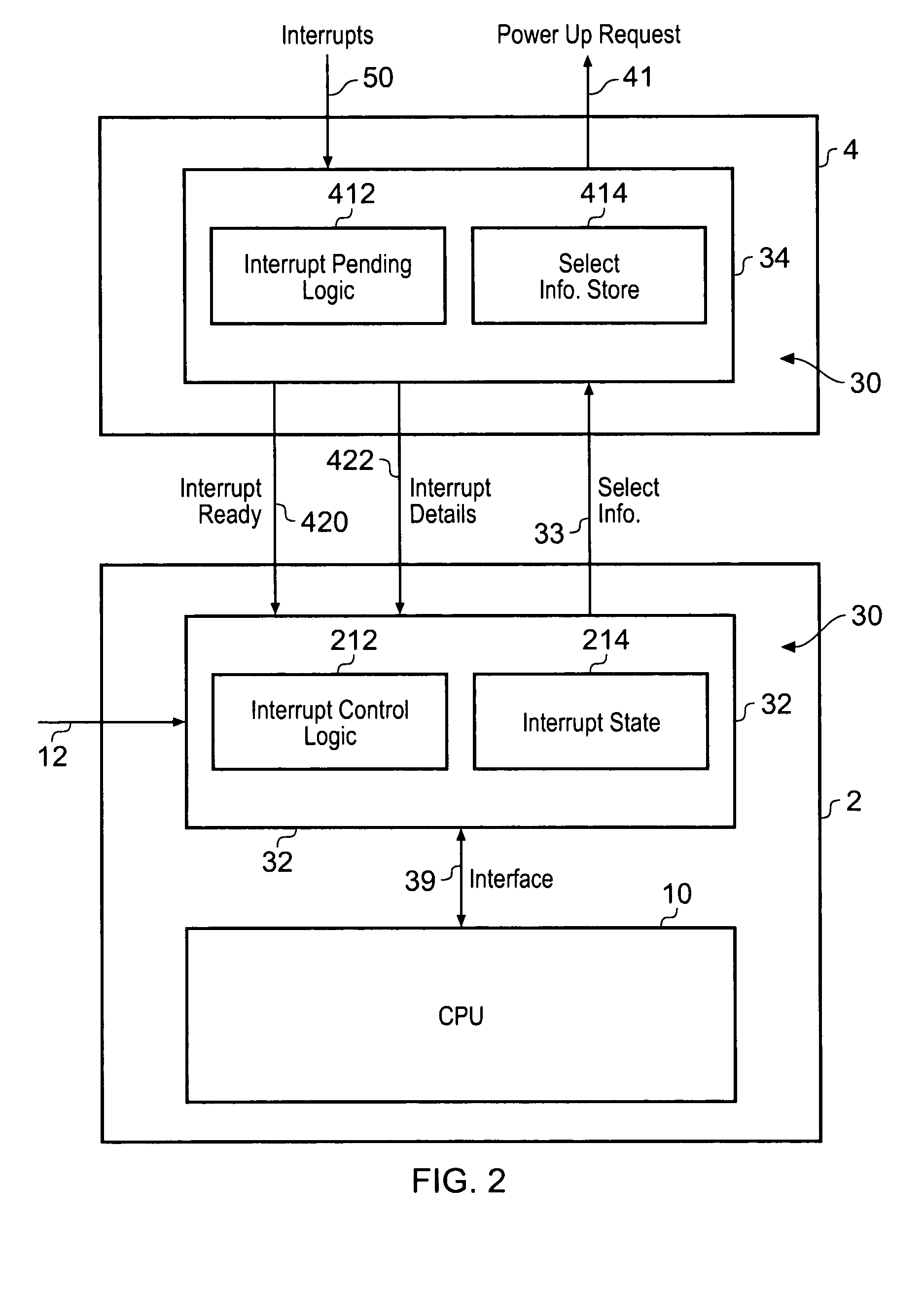
Interrupt controller
ActiveUS7624215B2Increase powerStatic power consumption of the interrupt controller can be reducedEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementPower modeControl circuit
Owner:ARM LTD
Medium scale carbon nanotube thin film integrated circuits on flexible plastic substrates
InactiveUS8946683B2Improve electronic performanceImprove electronic propertiesNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesElectronic systemsElectronic properties
The present invention provides device components geometries and fabrication strategies for enhancing the electronic performance of electronic devices based on thin films of randomly oriented or partially aligned semiconducting nanotubes. In certain aspects, devices and methods of the present invention incorporate a patterned layer of randomly oriented or partially aligned carbon nanotubes, such as one or more interconnected SWNT networks, providing a semiconductor channel exhibiting improved electronic properties relative to conventional nanotubes-based electronic systems.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC +1
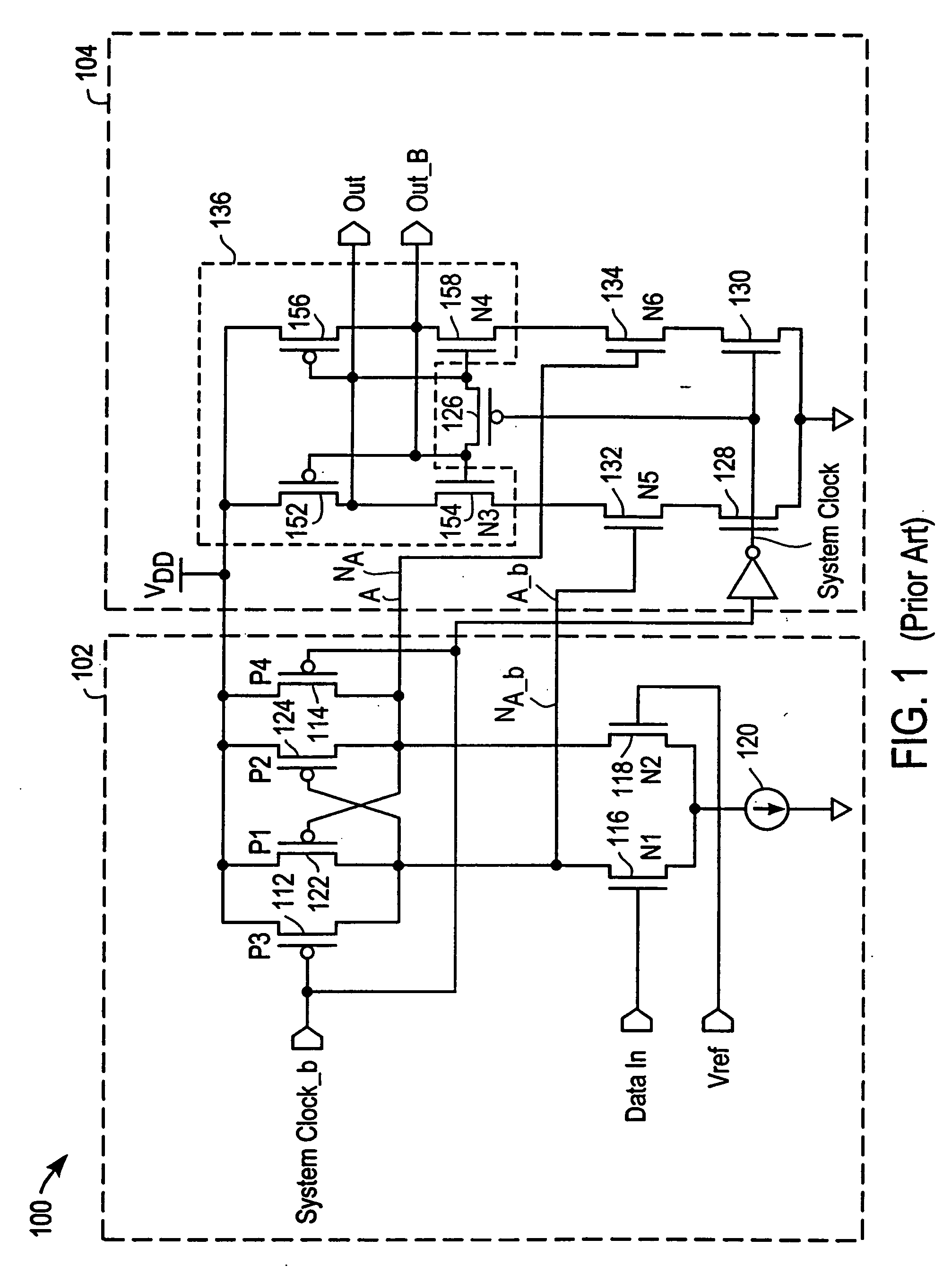
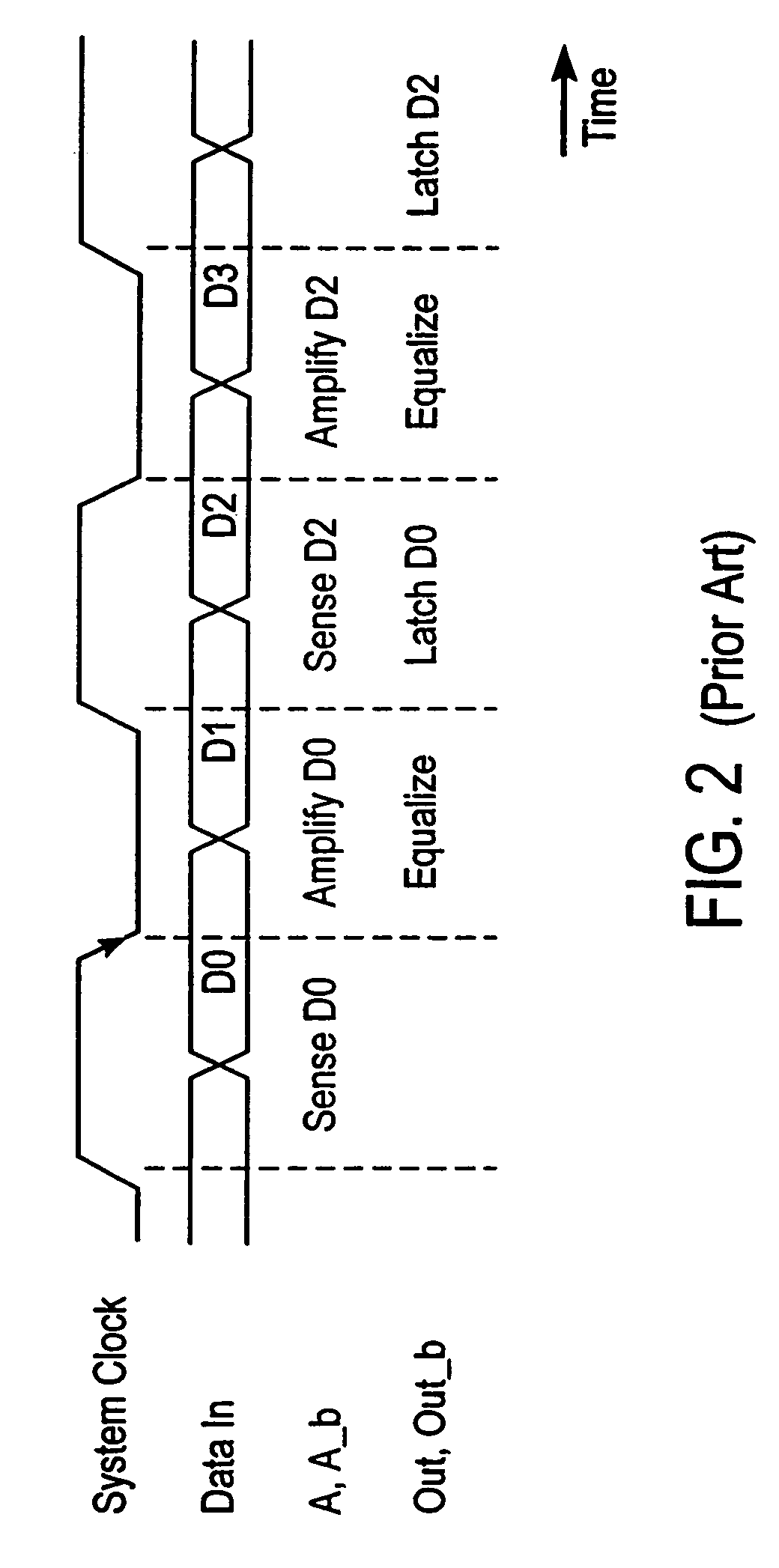
Data processor memory circuit
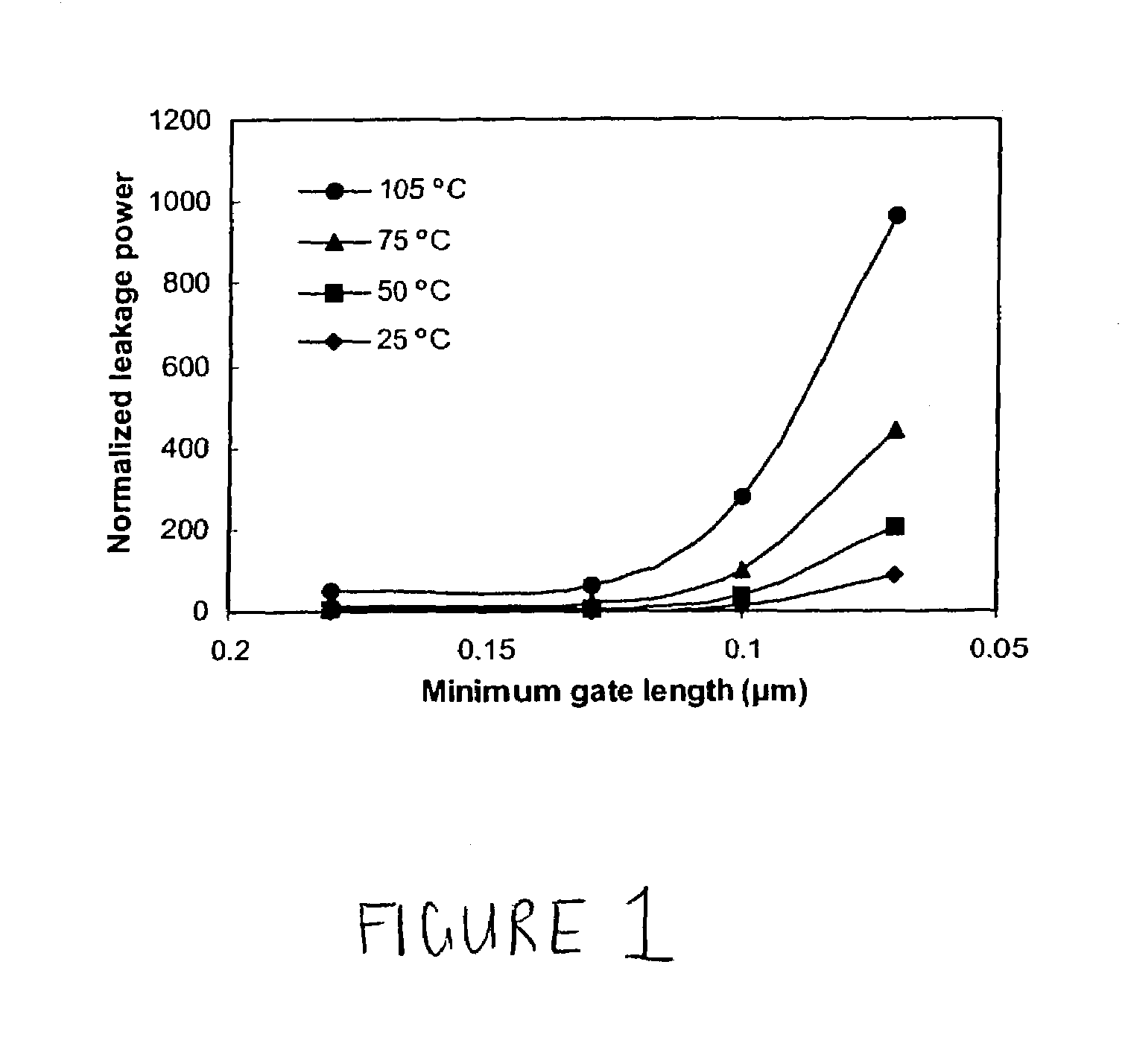
ActiveUS7055007B2Reduce leakageRaise the threshold voltageMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTMemory circuitsComputer science
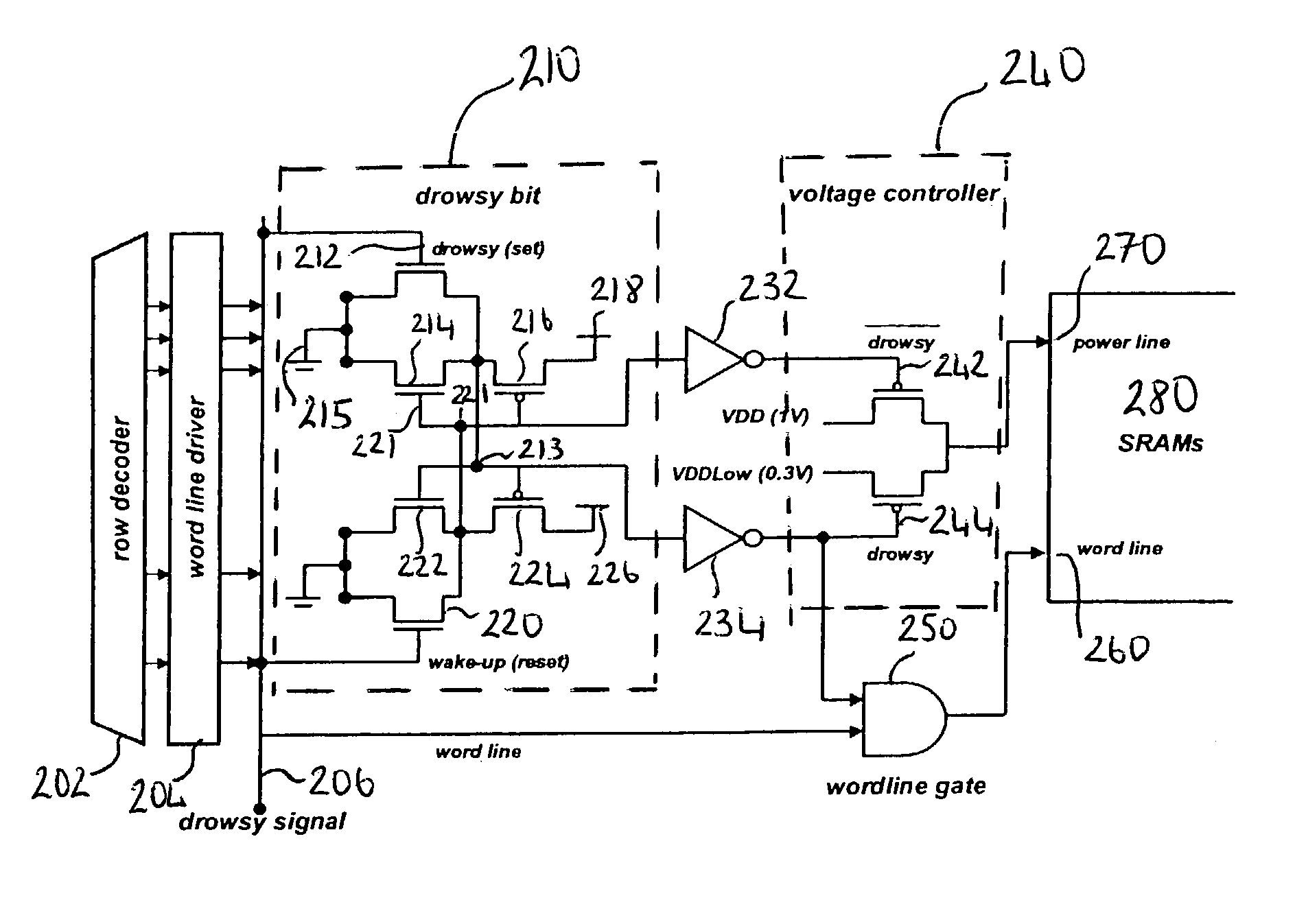
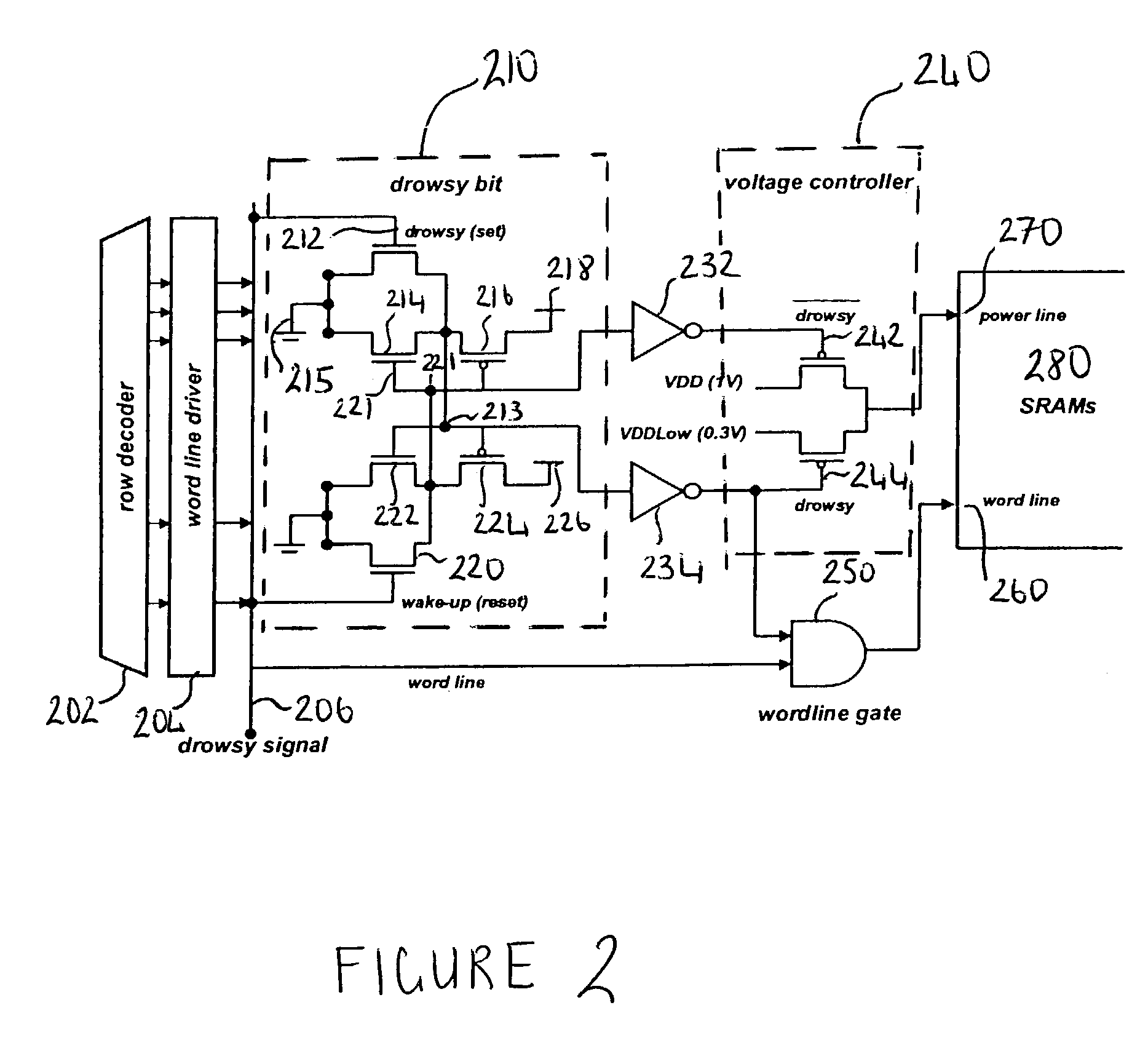
A memory circuit for use in a data processing circuit is described, in which memory cells have at least two states, each state being determined by both a first voltage level corresponding to a first supply line and a second voltage level corresponding to a second supply line. The memory circuit comprises a readable state in which information stored in a memory cell is readable and an unreadable state in which information stored in said memory cell is reliably retained but unreadable. Changing the first voltage level but keeping the second voltage level substantially constant effects a transition between the readable state and the unreadable state. In use, the static power consumption of the memory cell in the unreadable state is less than static power consumption of the memory cell in the readable state.
Owner:ARM LTD +1
Sequential selective epitaxial growth
ActiveUS7807523B2Improve performance consistencyImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETCMOS
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. A multi step epitaxial process can be used to extend the ridges with different dopant types, high mobility semiconductor, and or advanced multi-layer strutures. For CMOS integrated circuits a capping layer is formed over the a first region. Epitaxial layers are formed in a second region. Then the capping layer is removed from the first region and a capping layer is formed over the second region. Epitaxial layers can than be formed in the first region.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Wide-input voltage high-power supply rejection ratio reference voltage source
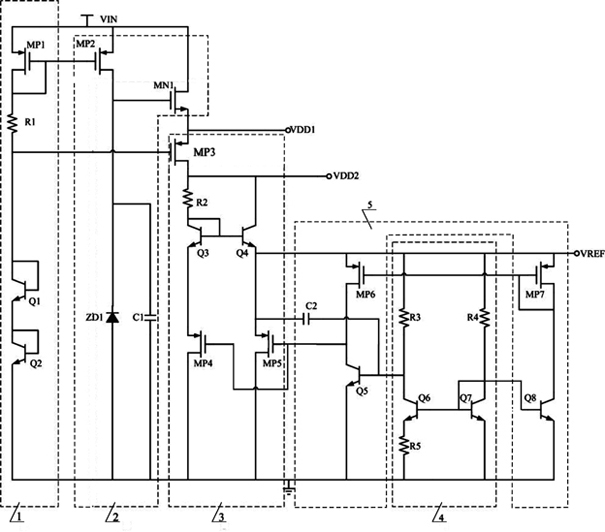
InactiveCN102053645AIncrease loading capacityOp amp reductionElectric variable regulationEngineeringFeedback circuits
The invention discloses a wide-input voltage high-power supply rejection ratio reference voltage source. The reference voltage source comprises a self-bias circuit (1), a primary presetting circuit (2), a secondary presetting circuit (3), a bandgap reference core circuit (4) and a signal feedback circuit (5) which are sequentially connected. By using the self-bias circuit in a self-bias current mirror structure, the circuit can be started independently without using additional start circuits; by directly using the output of the secondary presetting circuit as the output of the reference voltage and simultaneously supplying power to the bandgap reference core circuit, the connection mode can improve the loading capacity of the reference voltage; by using the operational amplifier-free feedback loop for regulation, one clamping operational amplifier is removed from the traditional reference voltage source circuit, thereby saving the area and reducing the quiescent power dissipation; andcompared with the traditional bandgap reference voltage source circuit, the power supply rejection ratio of the output reference voltage, especially the performance under a high-frequency condition, is greatly improved.
Owner:CHENGDU PROMISING CHIP ELECTRONICS
Integrated circuit and standby controlling method thereof
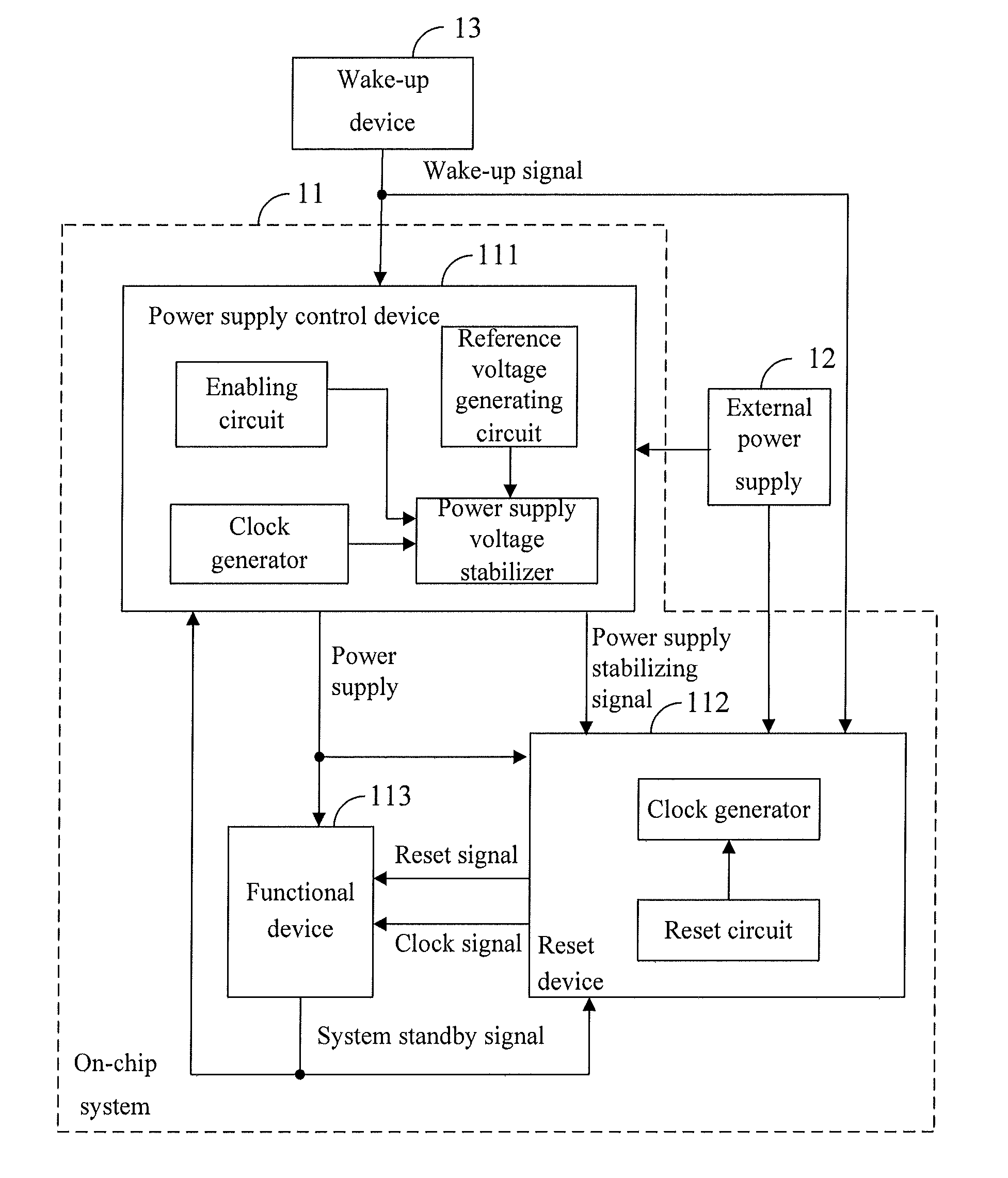
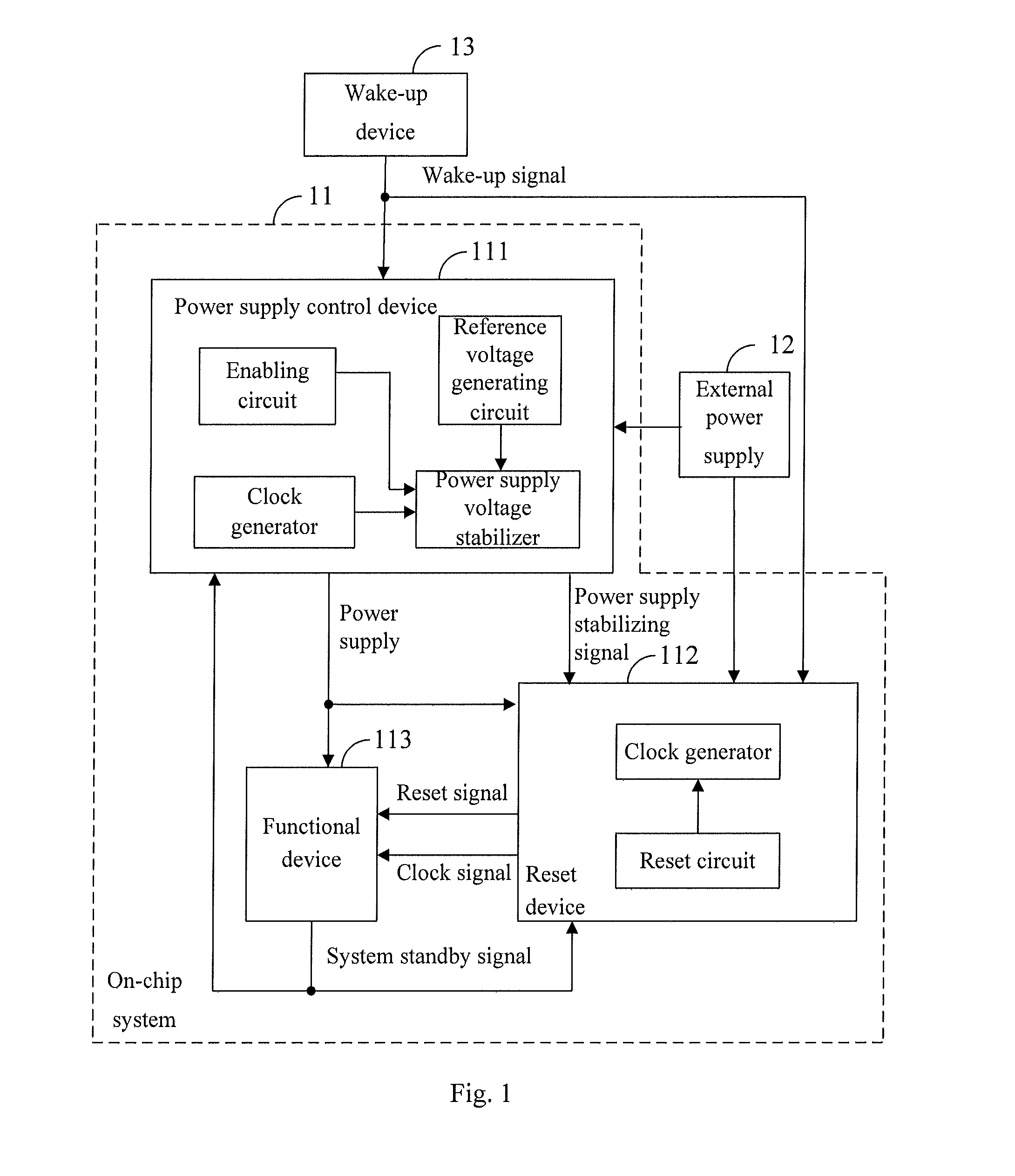
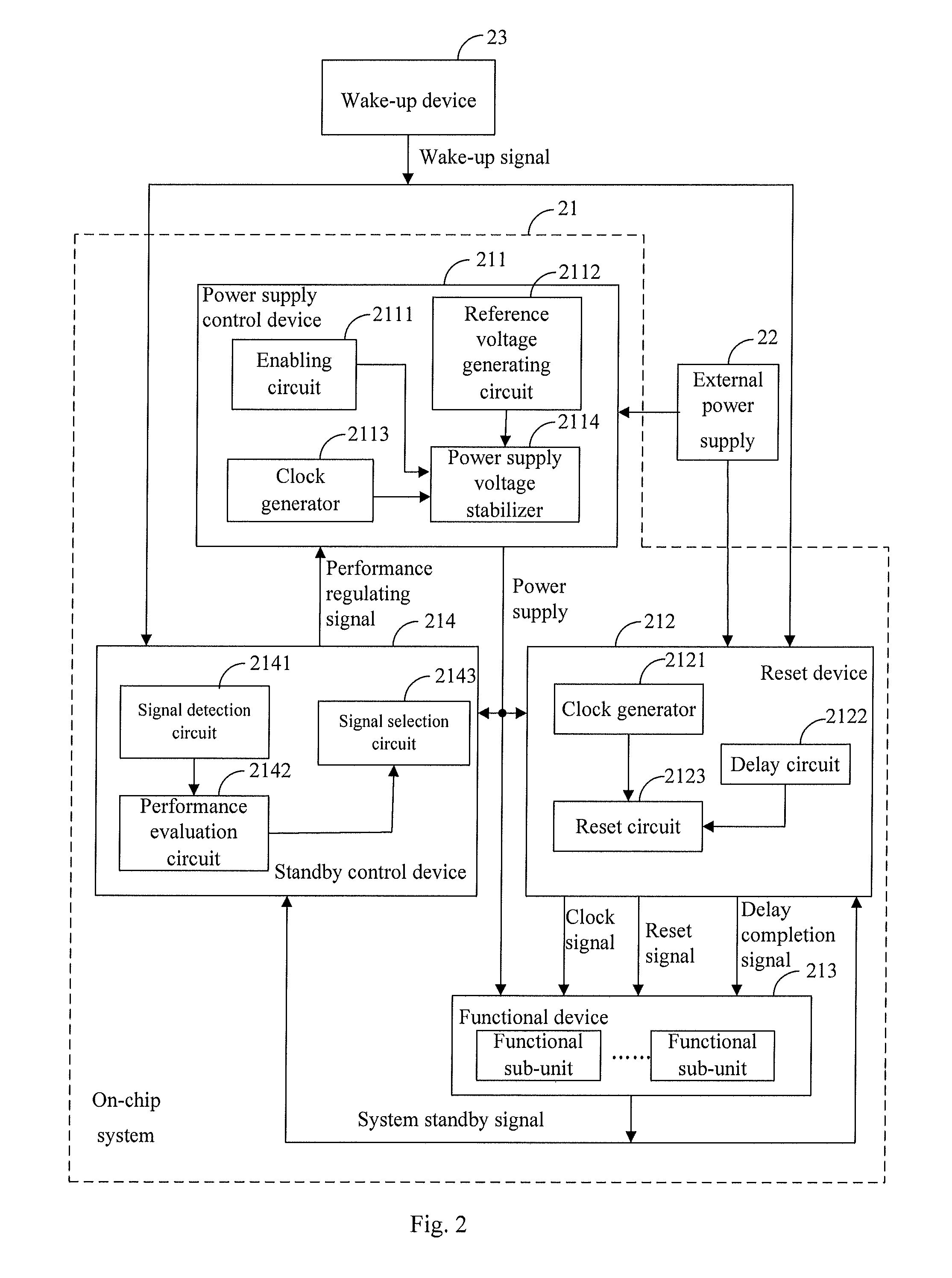
ActiveUS20110221483A1Rapid wake-upReduce standby power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTPulse automatic controlEngineeringControl equipment
The present invention is applicable to the field of electrics and provides an integrated circuit (IC) and a standby controlling method thereof. The IC comprises a reset device, a standby control device, a functional device and a power supply control device. The functional device at least comprises a functional unit that does not operate in a standby mode. The power supply control device is configured to supply power to the functional device, the standby control device and the reset device. The standby control device is configured to control the power supply control device to control a power supply voltage of the functional unit to be within a preset range below a normal operating voltage when a standby status signal is detected, and restore the power supply voltage into the normal operating voltage when a wake-up signal is detected; and the reset device is configured to reset the functional device when the system standby status signal is detected and release the resetting of the functional device when the wake-up signal is detected. The IC of the present invention reduces the time required by the IC to wake up from the standby mode while ensuring that the whole functional device has low static power consumption.
Owner:ARTEK MICROELECTRONICS
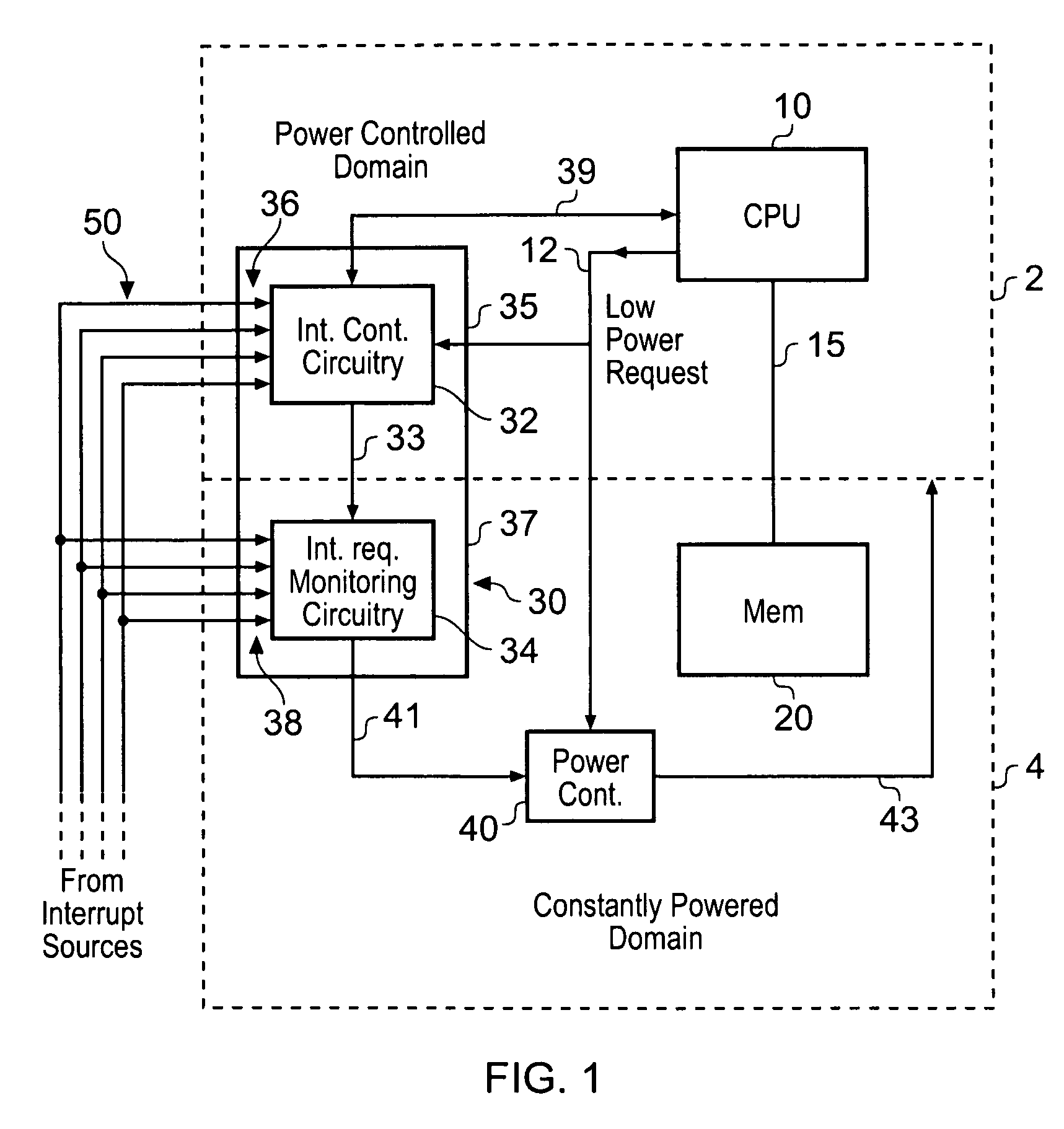
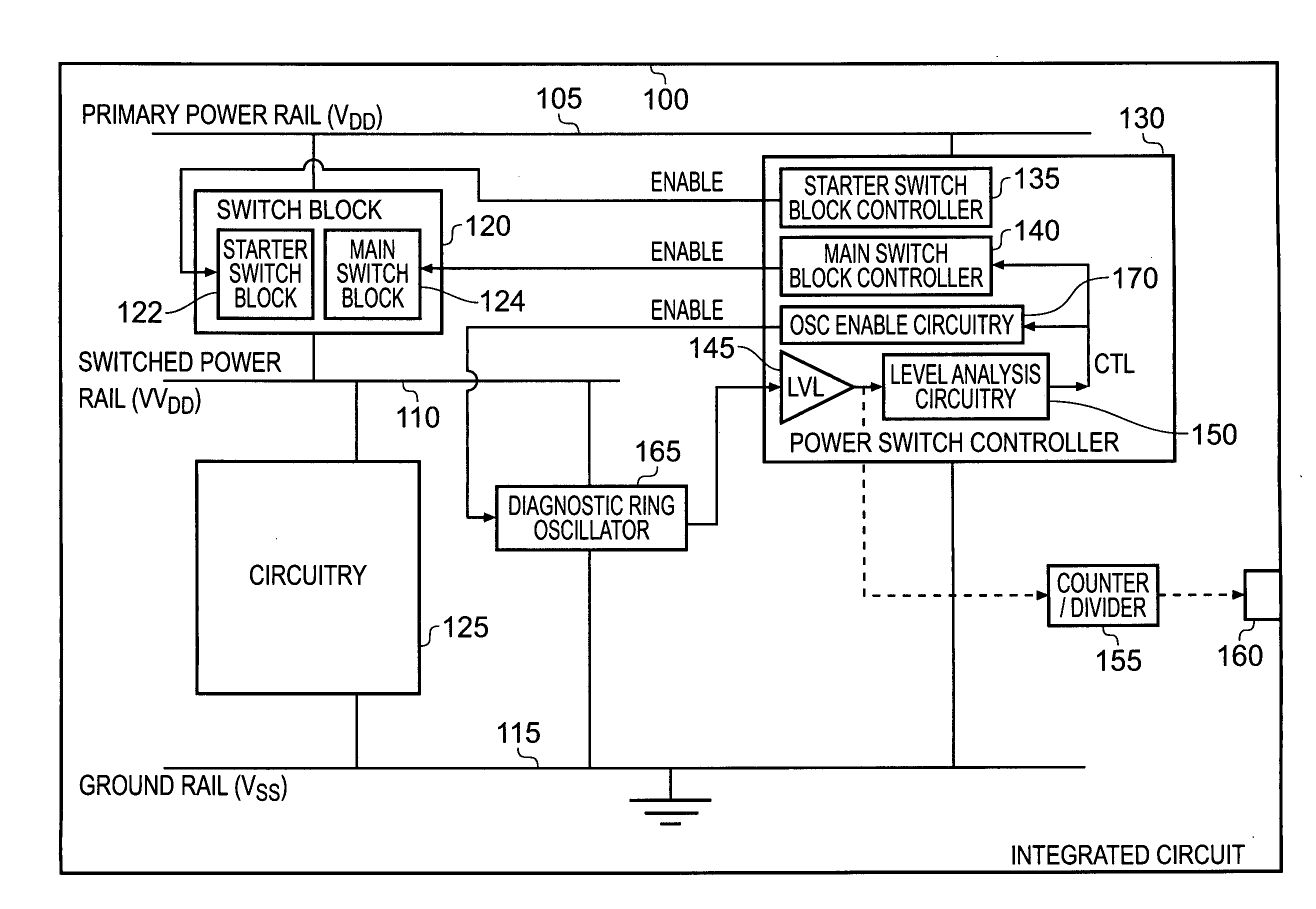
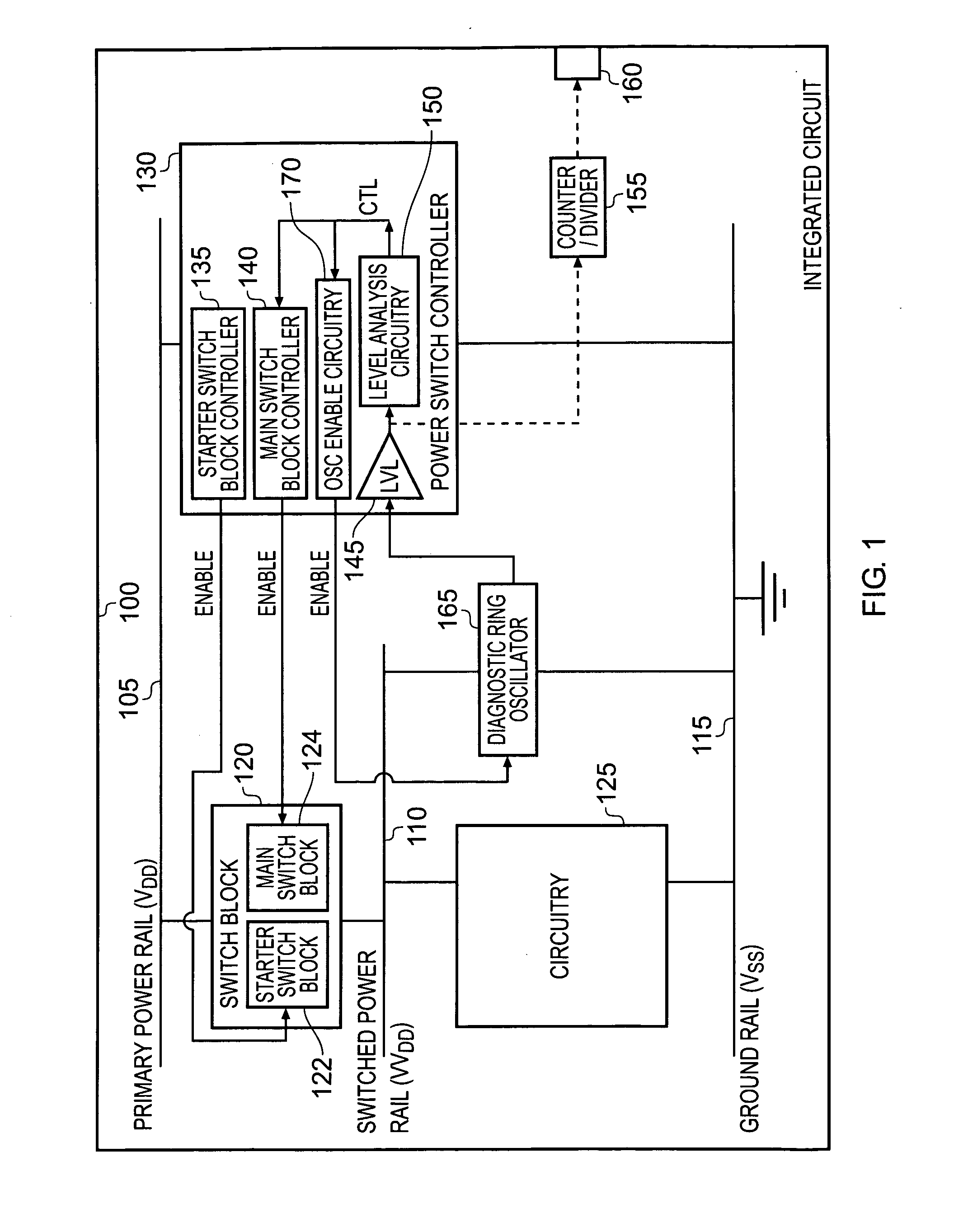
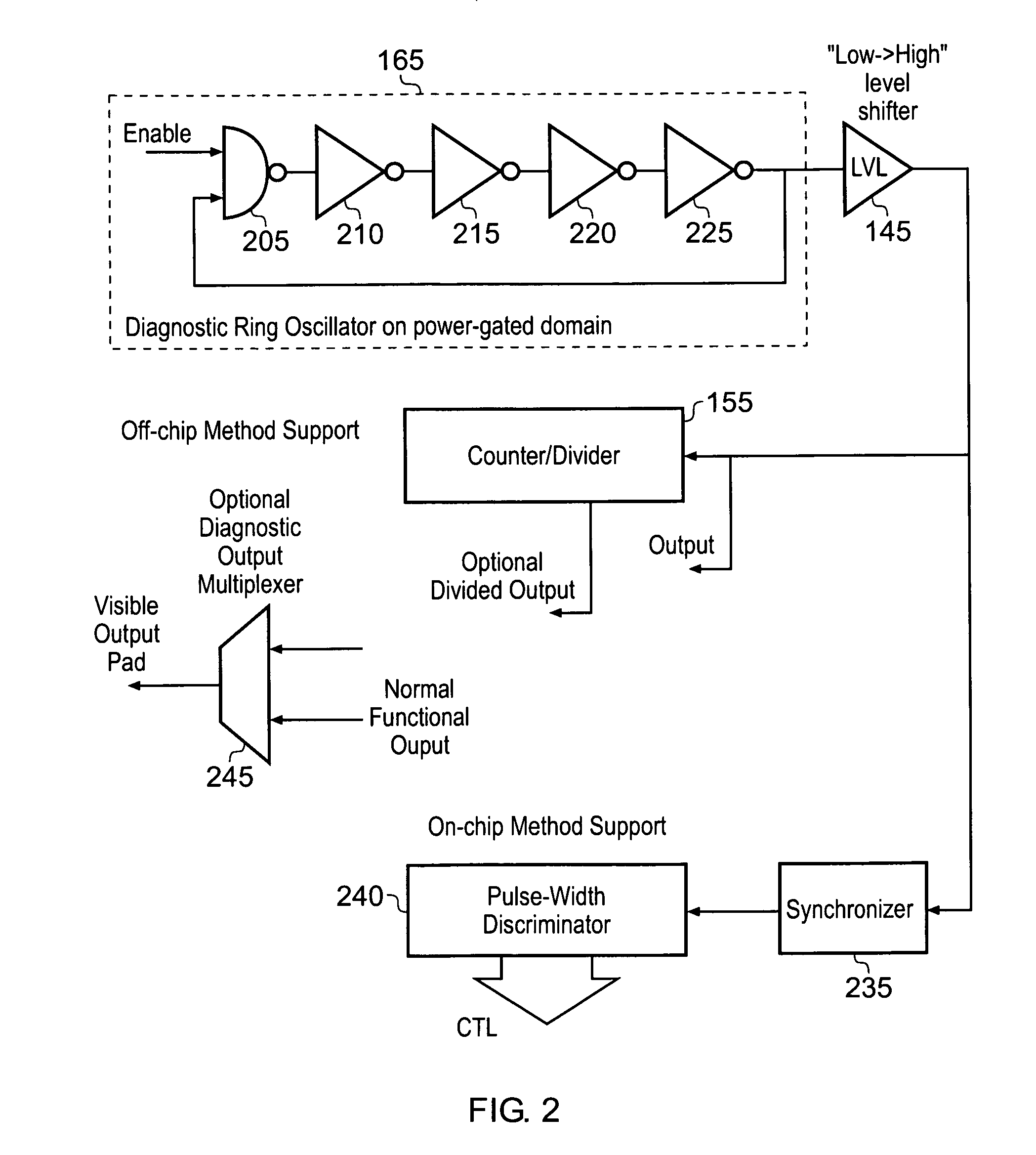
Power control circuitry, circuitry for analysing a switched power rail, and method of controlling connection of a power source to a switched power rail
ActiveUS20090115258A1Improve toleranceReduce power consumptionPower reduction by control/clock signalBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsVoltage variationControl circuit
Power control circuitry is provided for controlling connection of a power source having a source voltage level to a switched power rail to provide power to an associated circuit block. The power control circuitry comprises a switch block for selectively connecting the switched power rail to the power source, and a switch controller for controlling operation of the switch block. A ring oscillator circuit is powered from the switched power rail and produces an oscillating output signal, and analysis circuitry is then used to analyse change in frequency of the oscillating output signal produced by the ring oscillator circuit during a period of time when the switched power rail is not at the source voltage level. The switch controller is then arranged to control at least one aspect of the operation of the switch block in dependence on the analysis. This technique provides a simple and effective digital technique for observing voltage changes on the switched power rail.
Owner:ARM LTD
Equalizing charge method and equalizing charger
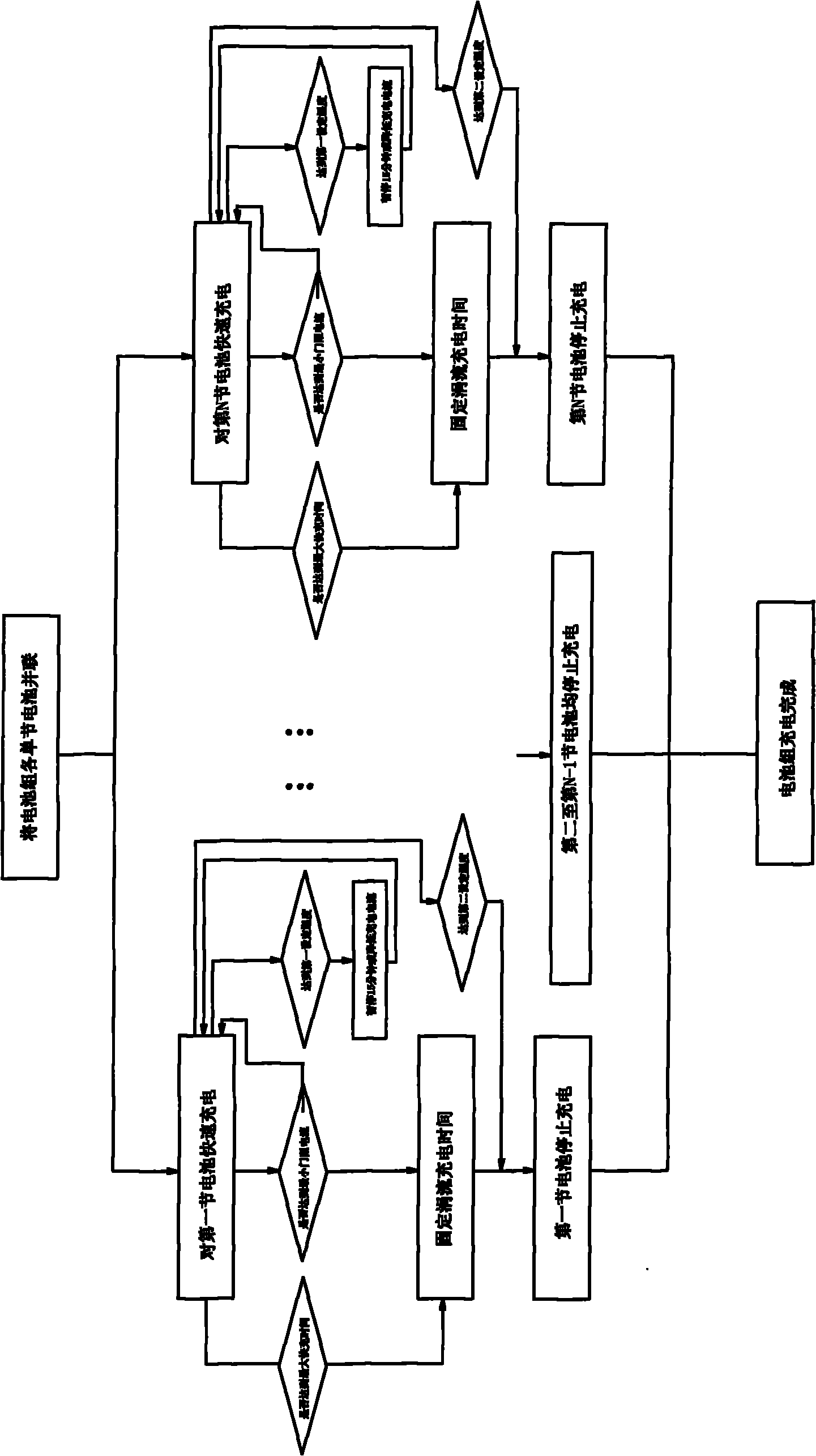
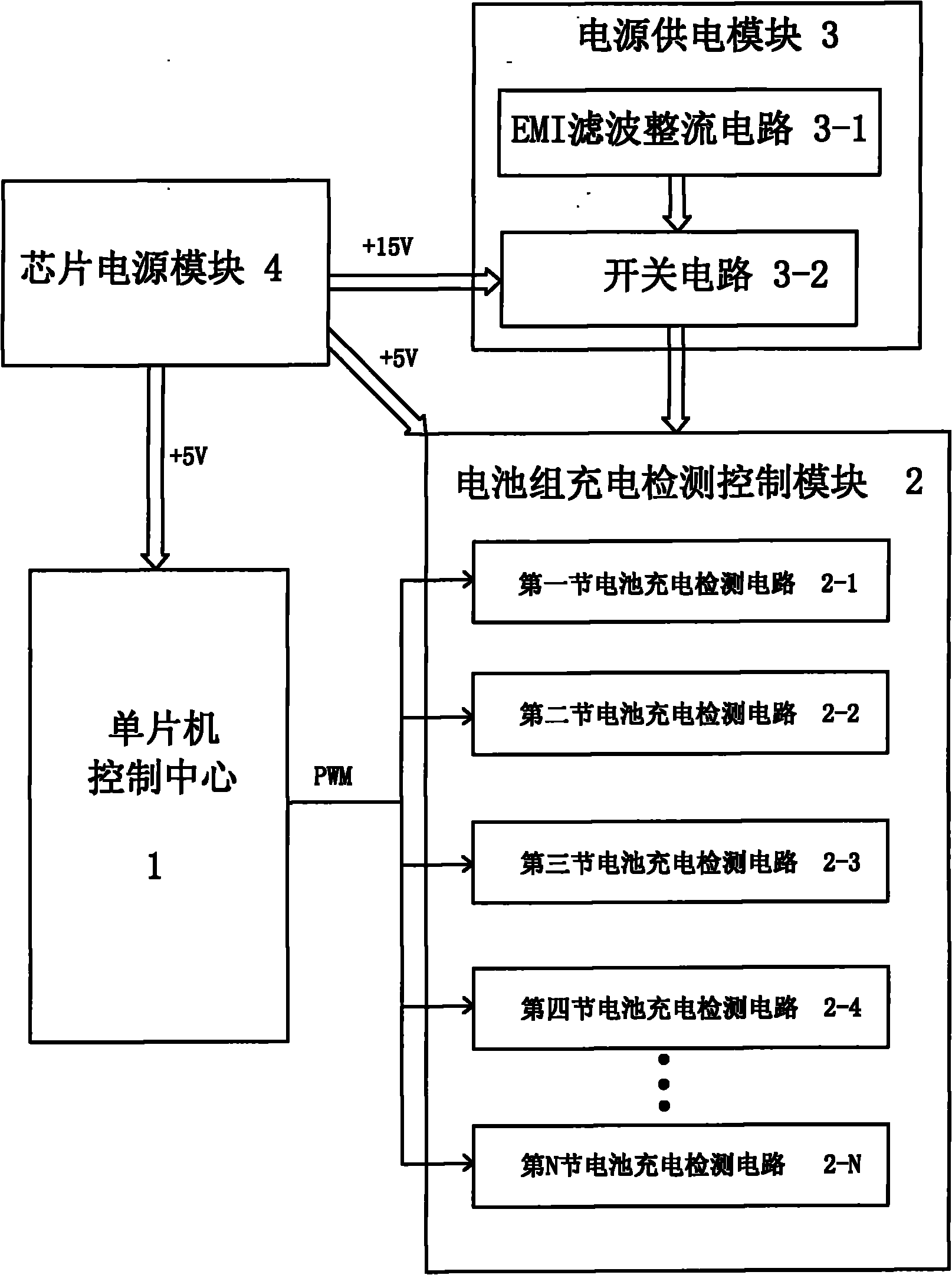
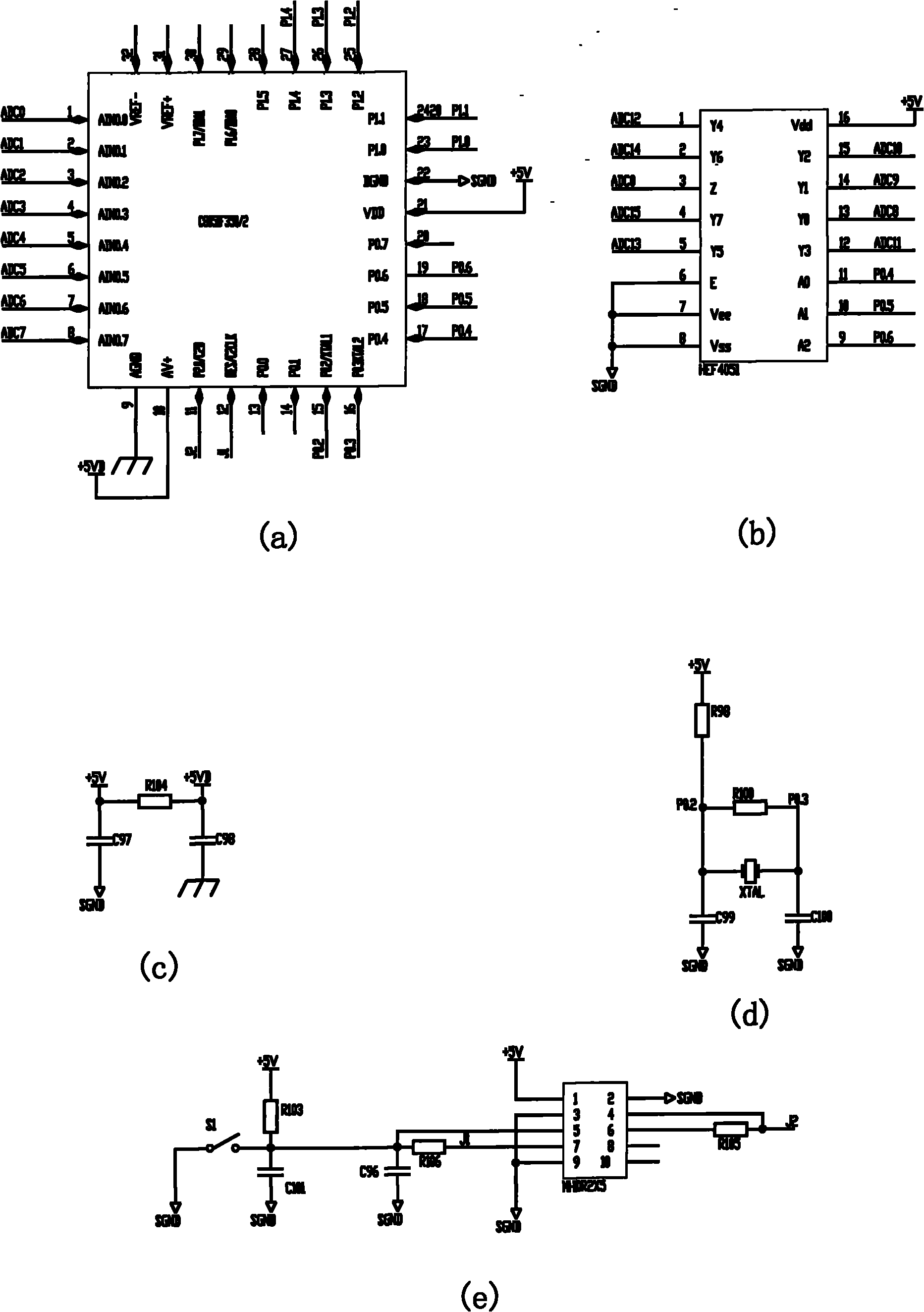
InactiveCN101777675ABalanced chargingEnsure consistencyBatteries circuit arrangementsSecondary cells charging/dischargingSingle chipBattery charger
The invention discloses an equalizing charge method and an equalizing charger. The equalizing charge method comprises the following steps: (1) connecting N (N is integer and is more than or equal to 2) single batteries in a battery pack in parallel; (2) independently and quickly charging the N single batteries at the same time; and (3) after the single batteries meet the charge requirement, finishing charging the battery pack. The equalizing charge method of the invention changes the series discharge mode of the single batteries of the battery pack into a parallel mode to independently charge the batteries of the battery pack, thus independently controlling the charge process of the single batteries to ensure equalizing charge for the single batteries. The charger of the invention uses a single chip control center as the core, and simply and precisely realizes independent charge and independent control of the single batteries.
Owner:常州黄海麦科卡电动汽车有限公司
[source driver and liquid crystal display using the same]
InactiveUS20050206629A1Reduce the amplitudeReduce dynamic power consumptionPulse automatic controlCathode-ray tube indicatorsVoltage amplitudeLiquid-crystal display
A low-power-consumption source driver for a liquid crystal display is provided. Morethan one middle voltage level for the level shifter and the output buffer is provided, in addition to the power supply voltage level VDD and the ground level GND, to provide different voltage levels for image data of different polarities. Hence, amplitude of the operational voltage of the level shifters and the analog circuits with different polarities can be reduced. It also can reduce the amplitude of the operational voltage of the level shifter and can reduce significantly the dynamic power consumption of the level shifter and the DAC. Because the voltage amplitude of the circuit is reduced and a low-voltage tolerated device can be used, so that the present invention can further reduce the cost of the circuit.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
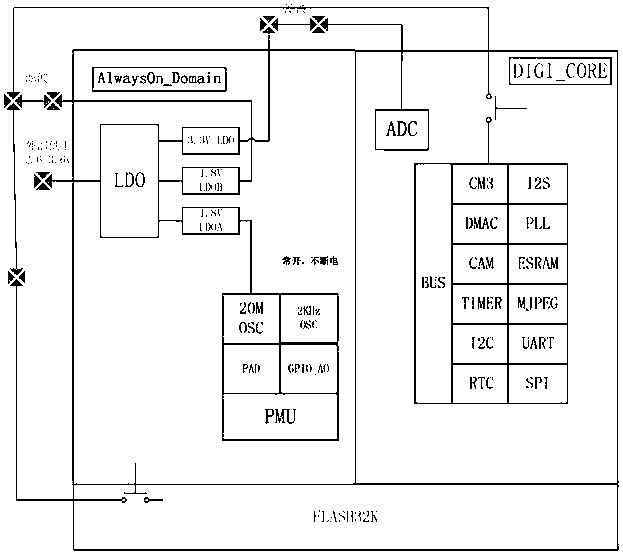
Integrated circuit SoC chip circuit structure capable of realizing power reduction and method thereof
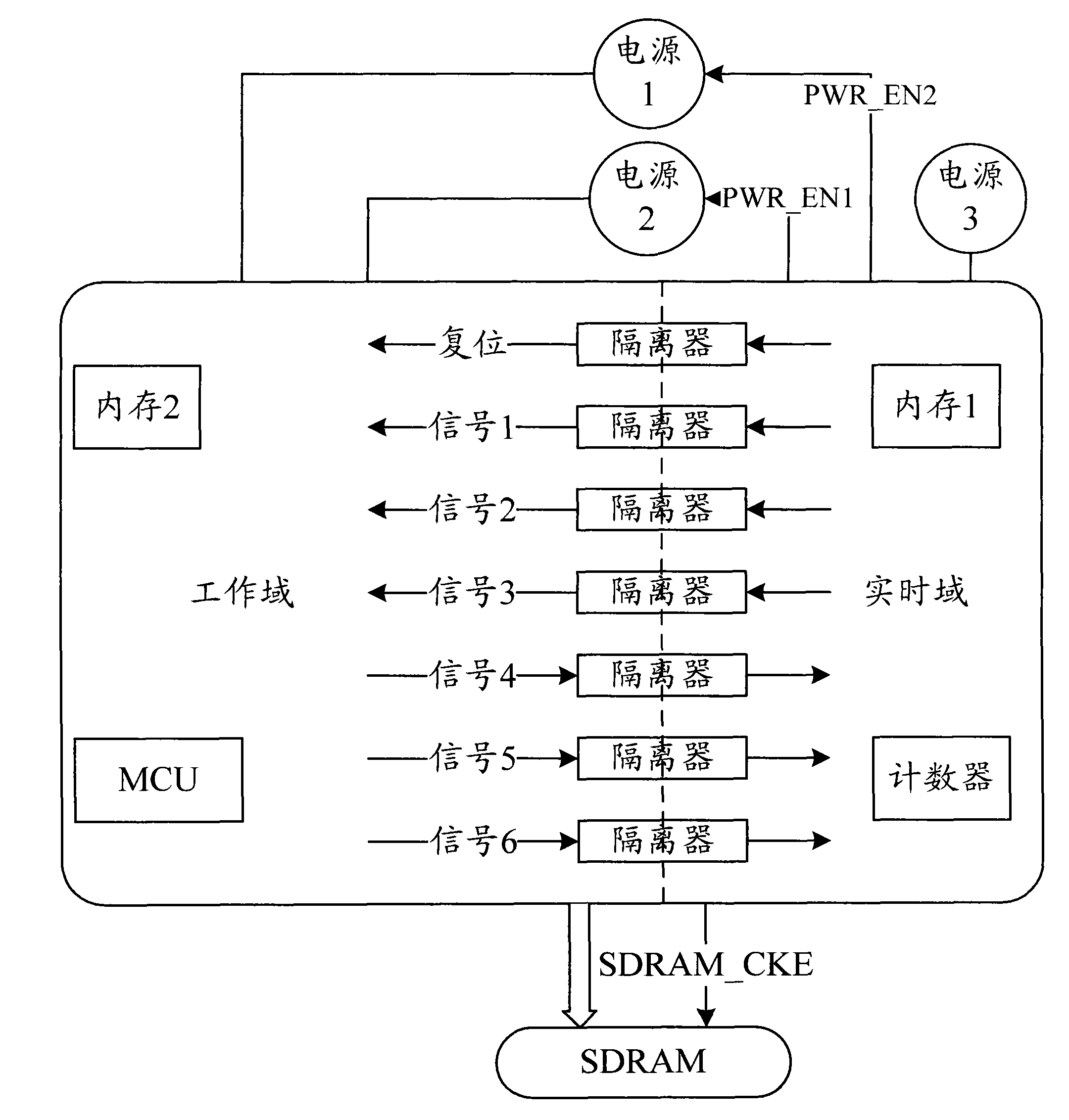
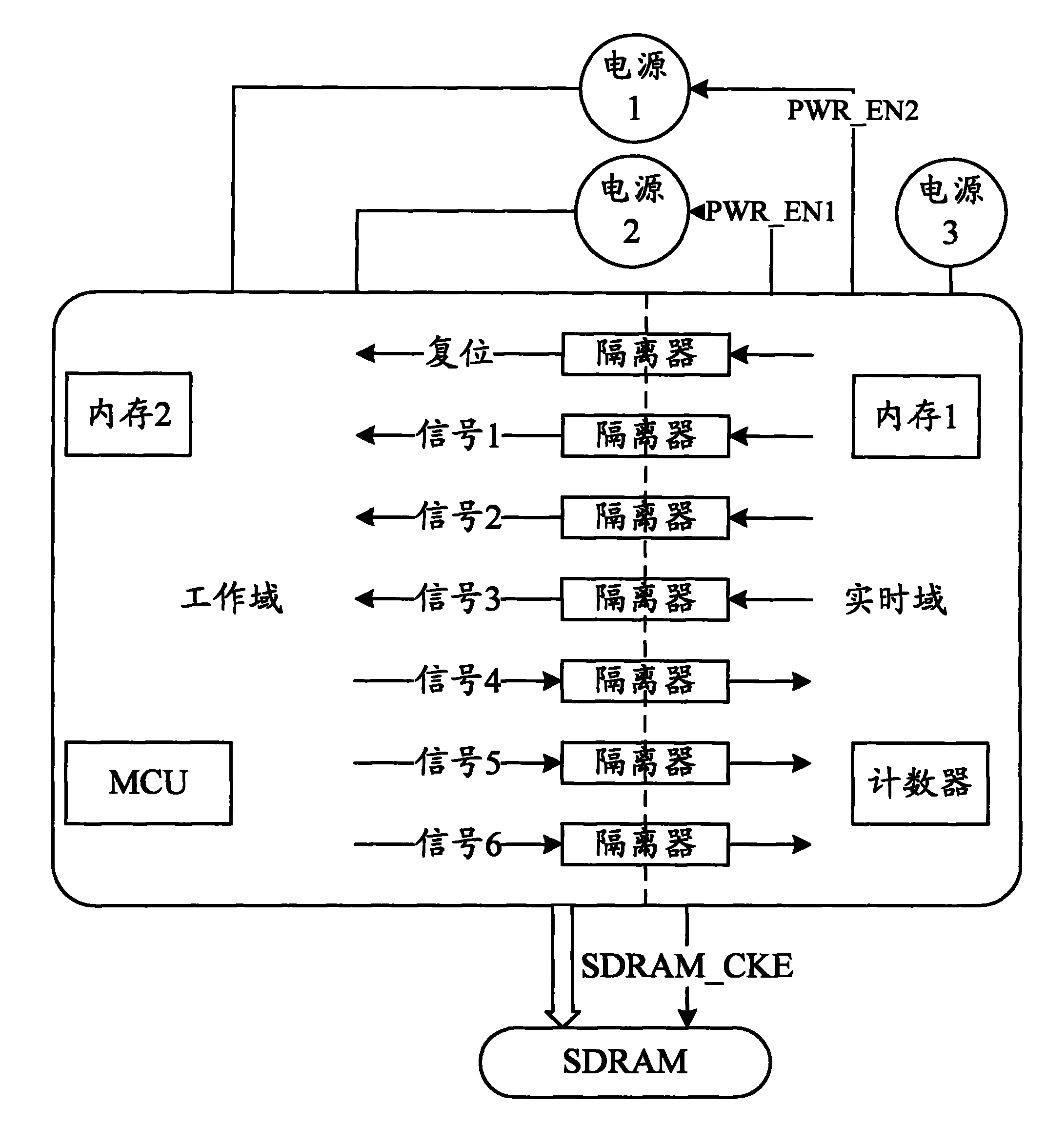
ActiveCN101859172AReduce power consumptionReduce static power consumptionPower supply for data processingTime domainTerra firma
The invention relates to an integrated circuit SoC chip circuit structure capable of realizing power reduction and a method thereof. The SoC chip contains at least one working domain which powers off when idle and at least one real-time-domain which continuously powers on, wherein an isolator is arranged between the working domain and the real-time-domain, and the working domain and the real-time-domain are separately connected with an external power supply source. The method of the invention comprises the processes of working domain power-off treatment and working domain wakeup power-on treatment. By adopting the integrated circuit SoC chip circuit structure capable of realizing power reduction and the method thereof, when the chip is idle, the working domain is in power-off state and the real-time-domain generates quiescent power drain; if the leakage of the real-time-domain is ensured to be as low as possible, the quiescent power drain of the chip can be reduced to be as low as possible and the quiescent power drain of the SoC chip can be effectively reduced; the structure is simple and practical, the control process is fast and convenient, the work performance is stable and reliable and the range of application is wide, thus the structure lays a solid foundation for the application of higher precision integrated circuit process technology in portable devices and the further development of portable devices.
Owner:SPREADTRUM COMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Regulating unused/inactive resources in programmable logic devices for static power reduction
ActiveUS7504854B1Reduce static power consumptionStatic storageLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsProgrammable logic deviceComputer module
A method of operating a programmable logic device, including the steps of using a full VDD supply voltage to operate one or more active blocks of the programmable logic device, and using a reduced supply voltage (e.g., ½ VDD) to operate one or more inactive blocks of the programmable logic device. The full VDD supply voltage and reduced supply voltage can be provided to the blocks of the programmable logic device through high-voltage n-channel transistors. A boosted voltage, greater than VDD, is applied to the gate of an n-channel transistor to provide the full VDD supply voltage to an active block. A standby voltage, less than VDD, is applied to the gate of an n-channel transistor to provide the reduced supply voltage to an inactive block. The inactive blocks can be determined during run time and / or design time of the programmable logic device.
Owner:XILINX INC
Method of IC production using corrugated substrate
ActiveUS20070004113A1Enhance their performance and costReduce static power consumptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETPre-existing
By forming MOSFETs on a substrate having pre-existing ridges of semiconductor material (i.e., a “corrugated substrate”), the resolution limitations associated with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes can be overcome, and high-performance, low-power transistors can be reliably and repeatably produced. Forming a corrugated substrate prior to actual device formation allows the ridges on the corrugated substrate to be created using high precision techniques that are not ordinarily suitable for device production. MOSFETs that subsequently incorporate the high-precision ridges into their channel regions will typically exhibit much more precise and less variable performance than similar MOSFETs formed using optical lithography-based techniques that cannot provide the same degree of patterning accuracy. Additional performance enhancement techniques such as pulse-shaped doping and “wrapped” gates can be used in conjunction with the segmented channel regions to further enhance device performance.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
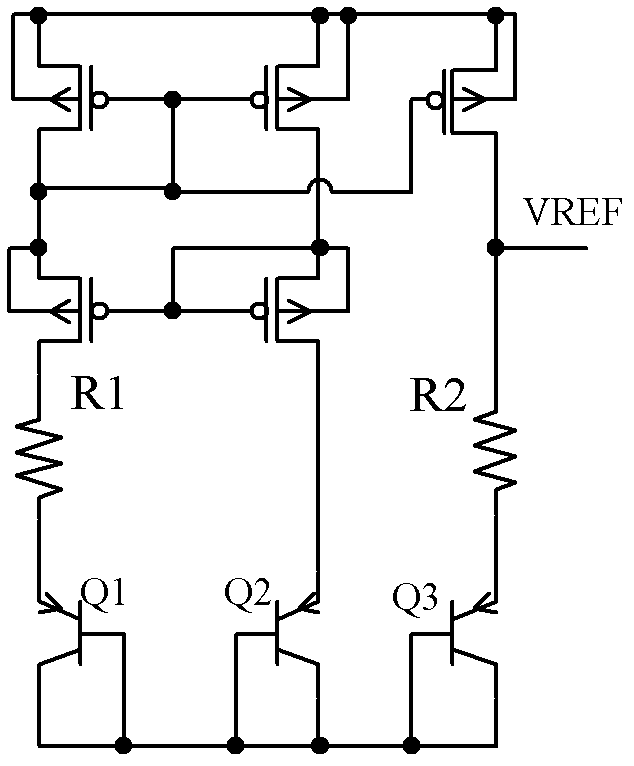
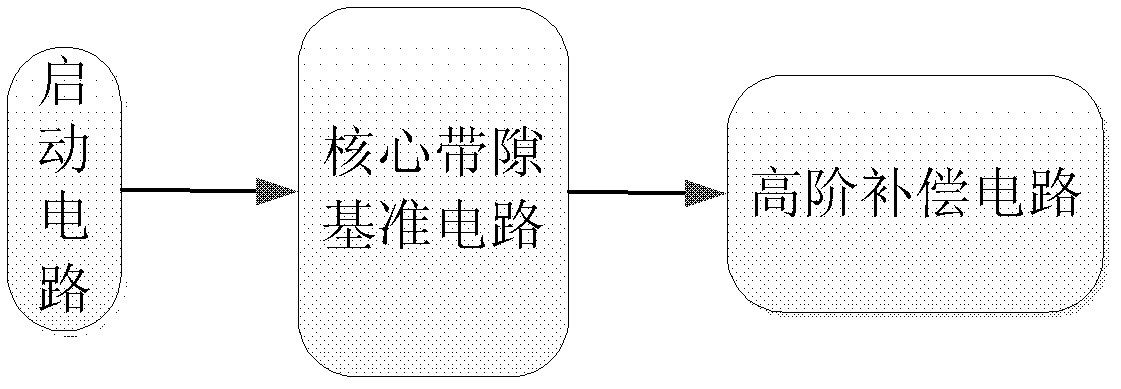
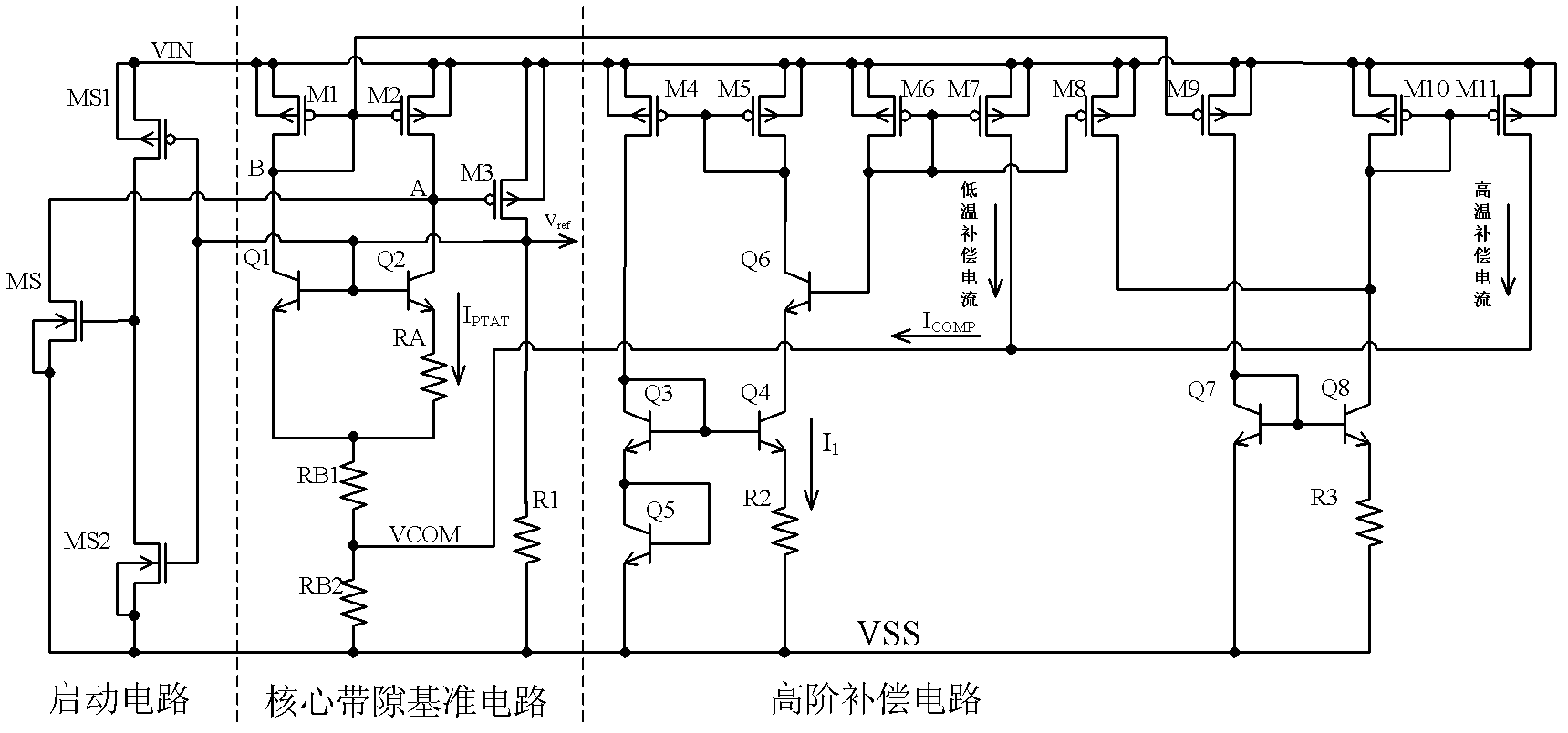
Bandgap reference voltage source
ActiveCN102591394ASmall temperature coefficientImprove power supply rejection ratioElectric variable regulationEngineeringVoltage source
The invention discloses a bandgap reference voltage source which comprises a starting circuit, a core bandgap reference circuit and a high-order compensation circuit. The core bandgap reference circuit comprises PMOS tubes M1, M2 and M3, NPN triodes Q1 and Q2 and resistance units R1, RB1, RB2 and RA; and the high-order compensation circuit comprises PMOS tubes M4, M5, M6, M7, M8, M9, M10 and M11, NPN triodes Q3, Q4, Q5, Q6, Q7 and Q8 and resistance units R2 and R3. The bandgap reference voltage source disclosed by the invention adopts the high-order compensation circuit, thereby the temperature coefficient is reduced greatly; the circuits adopt the resistance ratio, thus the circuits can not be affected by the absolute value of the resistance, and the influence of the temperature coefficient of the resistance to the output quantity can be reduced. The bandgap reference voltage source has high power supply rejection ratio and can ensure that the circuits can resist the interference of a power supply.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
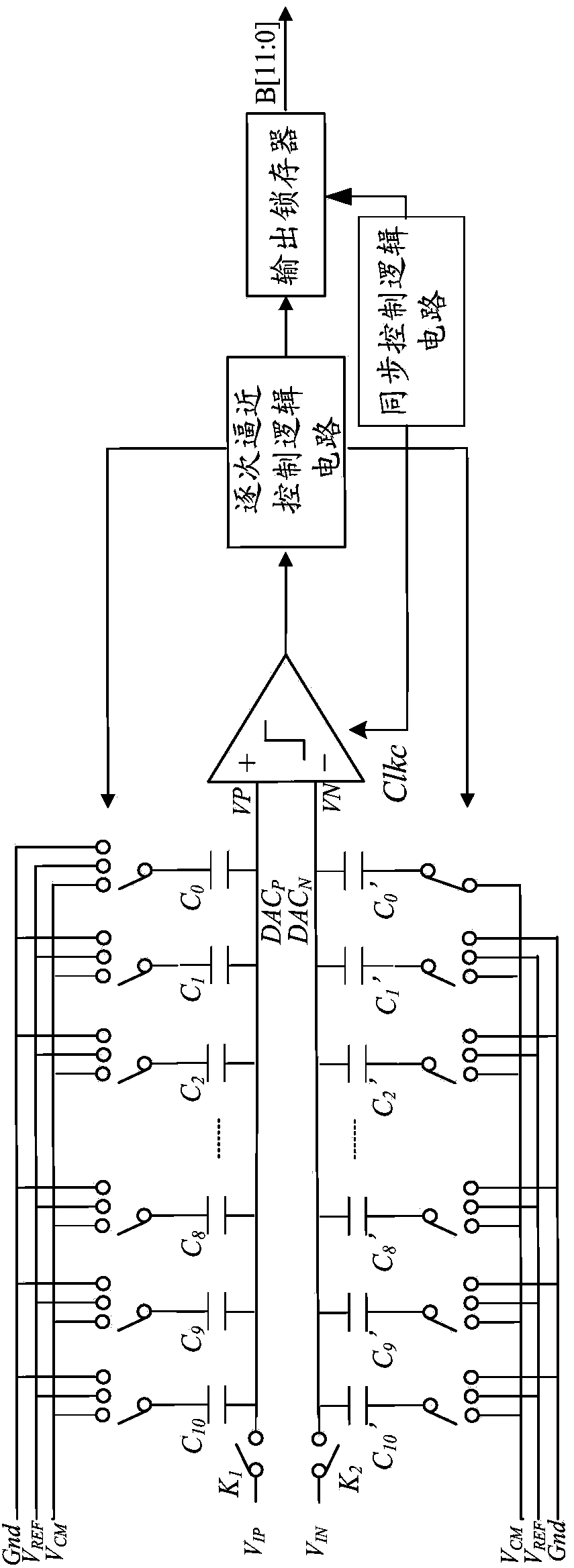
12-bit intermediate-rate successive approximation type analog-digital converter
ActiveCN104113341AArea halvedReduce static power consumptionAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsCapacitanceNegative phase
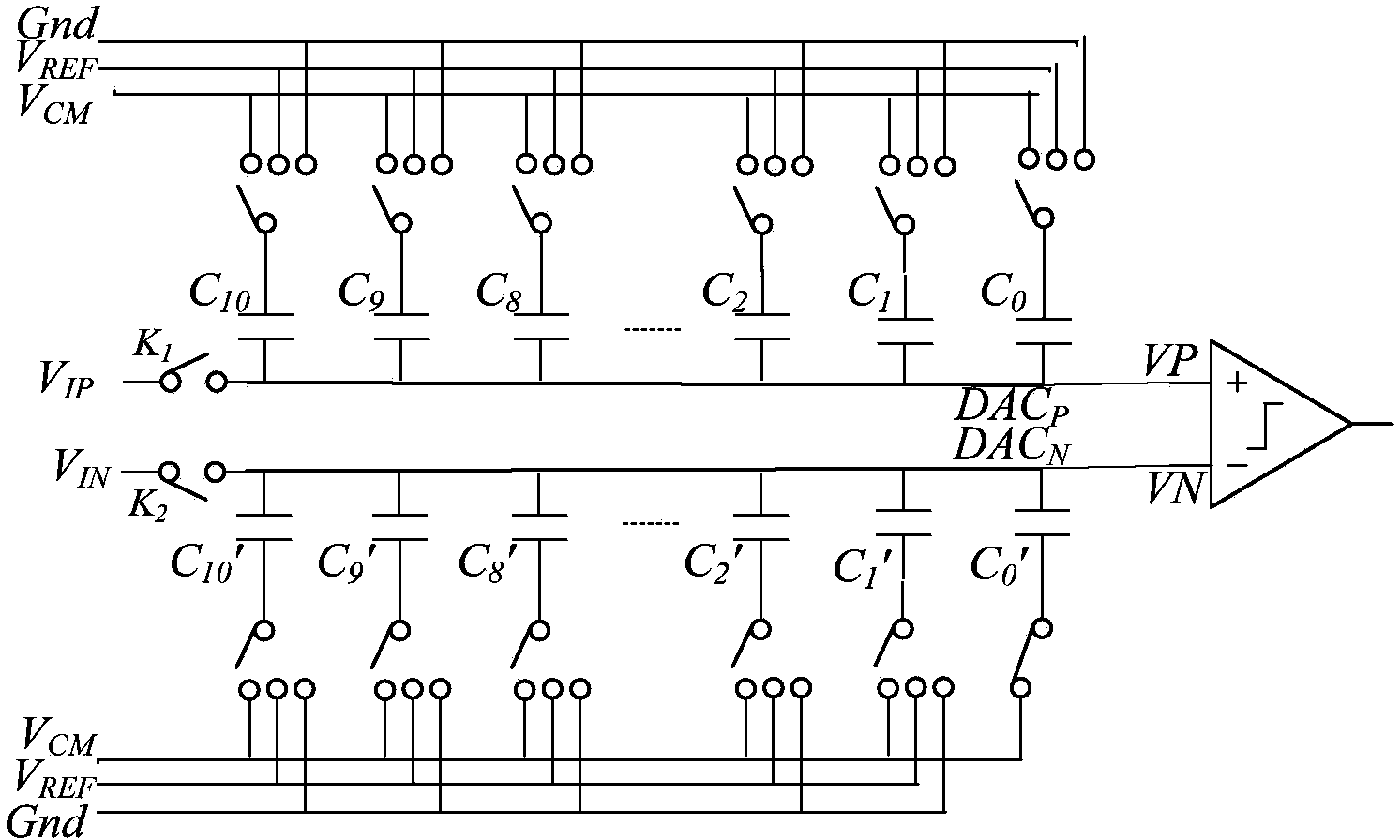
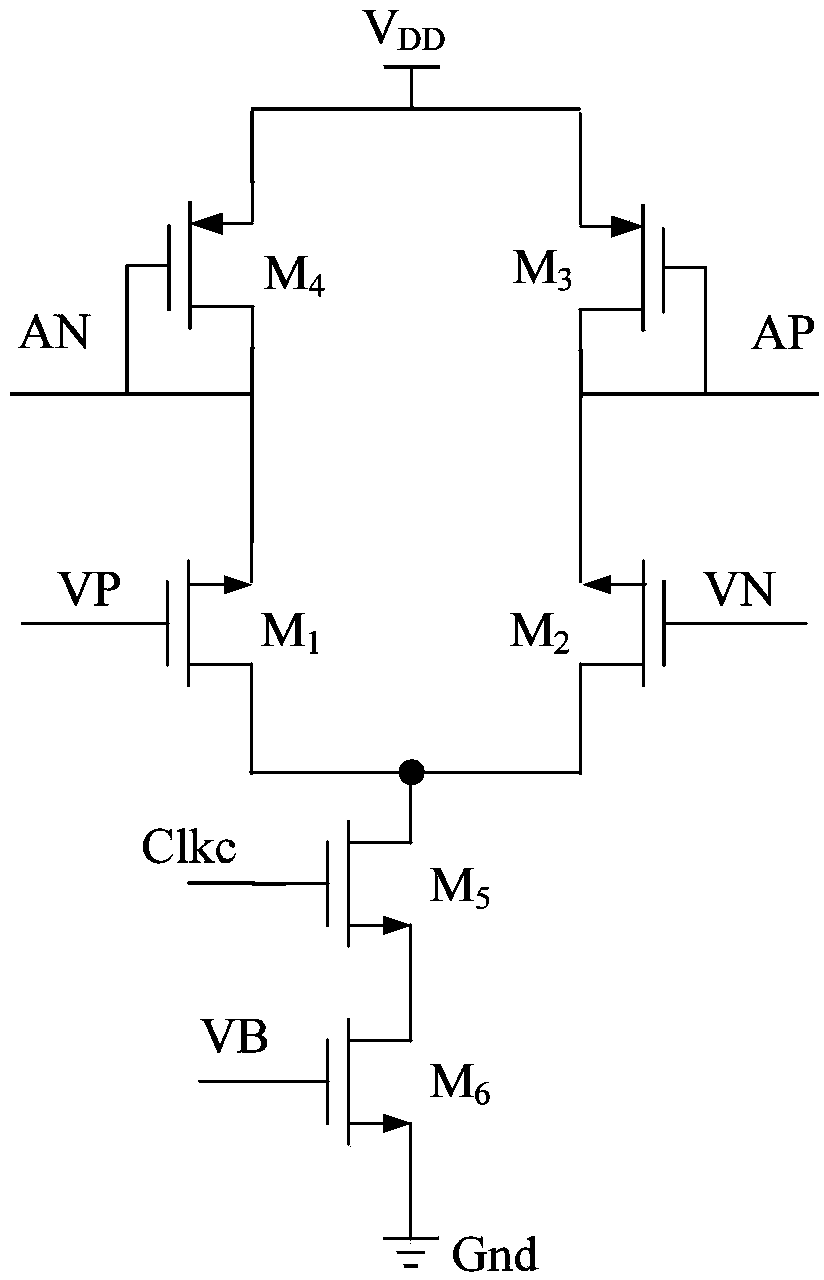
The invention provides a 12-bit intermediate-rate successive approximation type analog-digital converter and relates to the field of analog-digital converters. The 12-bit intermediate-rate successive approximation type analog-digital converter comprises a sampling network, a differential capacitor array connected with the sampling network, and a comparator circuit connected with the differential capacitor array, wherein the differential capacitor array comprises a first capacitor array connected with the positive-phase input end of the comparator circuit, and a second capacitor array connected with the negative-phase input end of the comparator circuit; both the first capacitor array and the second capacitor array are composed of 11 groups of binary-structured bit capacitors, and the bottom plates of the redundant capacitors of the second capacitor array are constantly connected with a common-mode voltage VCM. The 12-bit intermediate-rate successive approximation type analog-digital converter solves the problems of large capacitor area and high power consumption of a traditional binary capacitor type structure.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Piezoelectric energy collection system and control method thereof
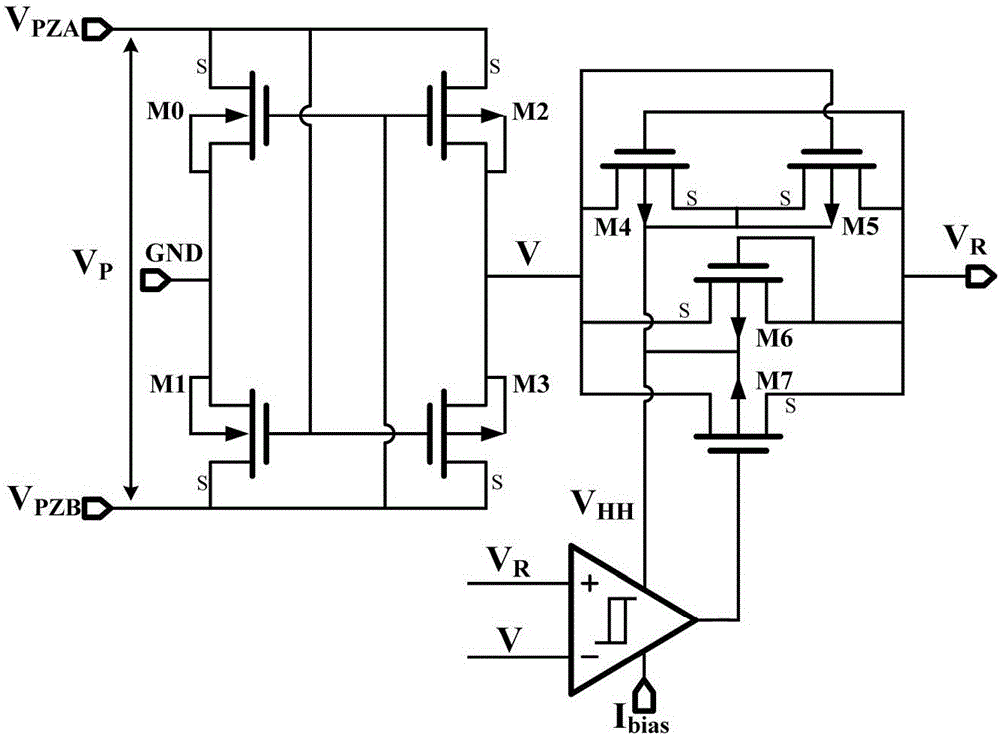
ActiveCN106301072ARealize the function of self-startingReduce static power consumptionPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesUltra low powerCollection system
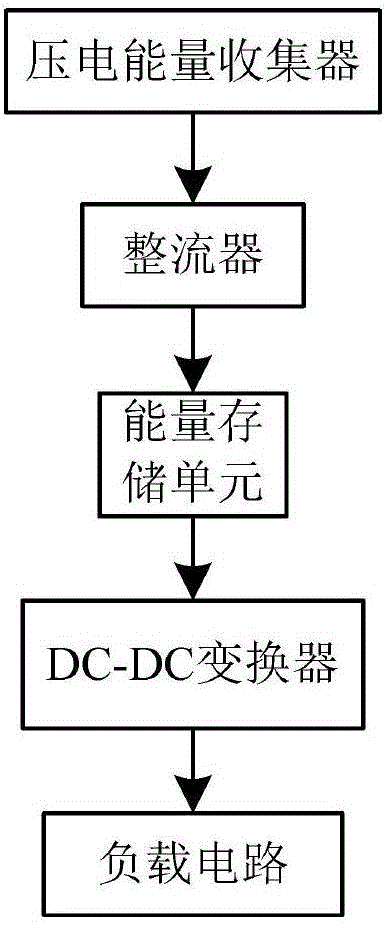
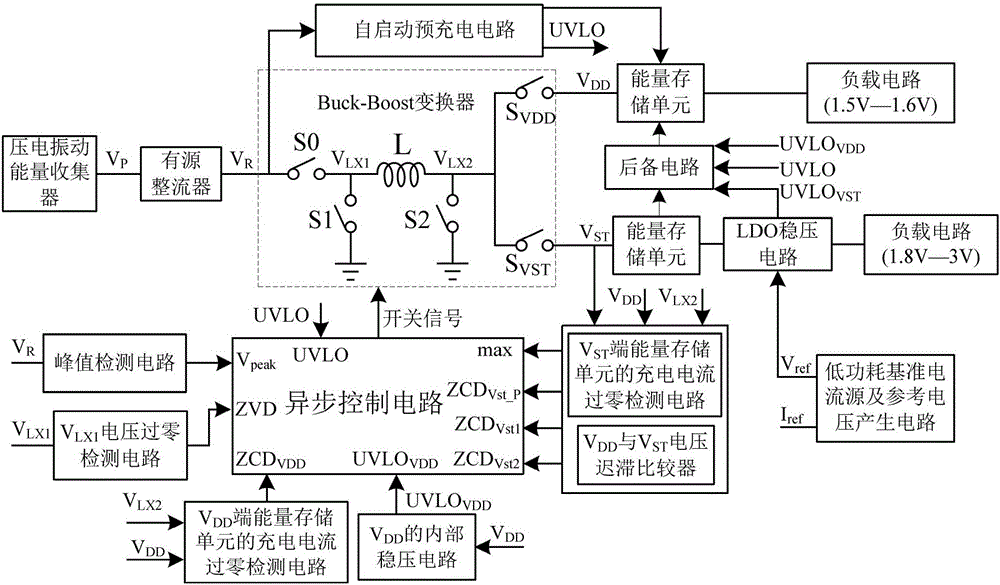
The invention discloses a piezoelectric energy collection system and a control method thereof. The piezoelectric energy collection system comprises a piezoelectric energy collector, an active rectifier, a Buck-boost converter, an asynchronous control circuit, a self-startup precharge circuit, a peak detection circuit, an inductance input-end voltage zero-crossing detection circuit, a VDD-end energy storage unit, a charge current zero-crossing detection circuit of the VDD-end energy storage unit, a VST-end energy storage unit, a charge current zero-crossing detection circuit of the VST-end energy storage unit, an inter-storage-unit energy conversion circuit, an LDO voltage-stabilizing circuit, a VDD internal voltage-stabilizing circuit and a low-power reference current source and reference voltage generation circuit. According to the invention, an ultralow-power design technology is introduced, a conventional circuit structure is improved, performance optimization and structural innovation are performed on each circuit module, static power consumption of the whole circuit system is reduced to 111.1nW, and the energy conversion efficiency is as high as 89.4%. Besides, the system also has the advantages of small chip area, high integration, complete automation, high adaptive capacity to environment and the like.
Owner:NANJING LOW POWER IC TECH INST CO LTD
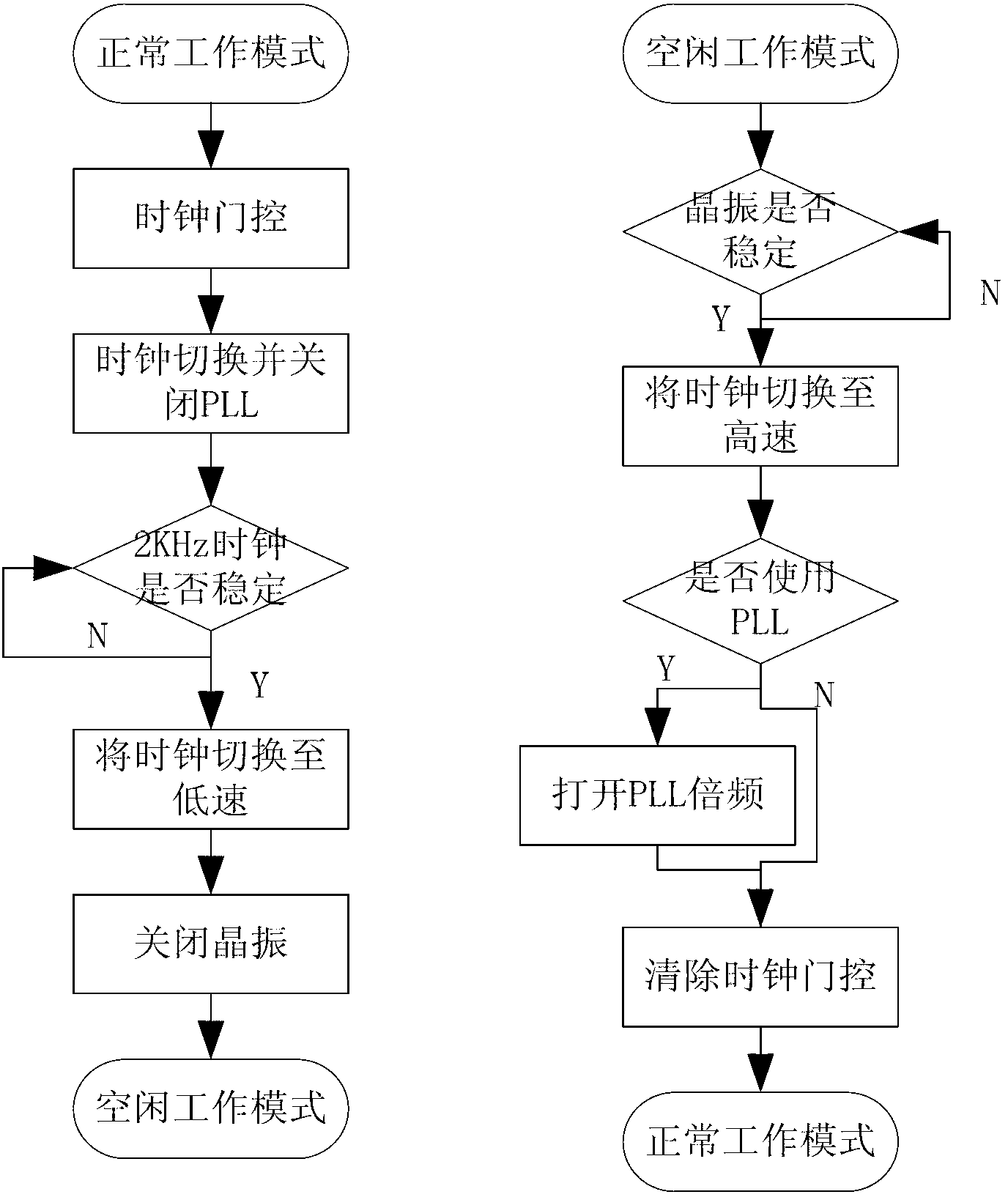
Low-power design method for wireless sensor network core chip
InactiveCN103324268AReduce dynamic power consumptionReduce power consumptionPower supply for data processingLine sensorLow-power electronics
The invention discloses a low-power design method for a wireless sensor network core chip. According to the low-power design method for the wireless sensor network core chip, the working mode of the chip is divided into a normal working mode and a low-power working mode, when the chip works in the normal working mode, the working frequency of the chip can be configured according to requirements of a specific application, and the clock frequency is reduced to save most dynamic power consumption due to unnecessary flipping of a clock; when the chip does not need to process tasks, the chip chooses to work in the low-power working mode, in the low-power working mode, the clock or power supplies in certain regions inside the chip can automatically turn off, and further the dynamic power consumption and the static power consumption are saved. According to the low-power design method for the wireless sensor network core chip, unnecessary power consumption can be reduced substantially whenever the chip works or sleeps, the service life of batteries is prolonged for wireless sensor network nodes, very important significance for power consumption reduction under the condition that the correct working of the wireless sensor network nodes is guaranteed is achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
First-stage circuit structure of pipelined analog-to-digital converter
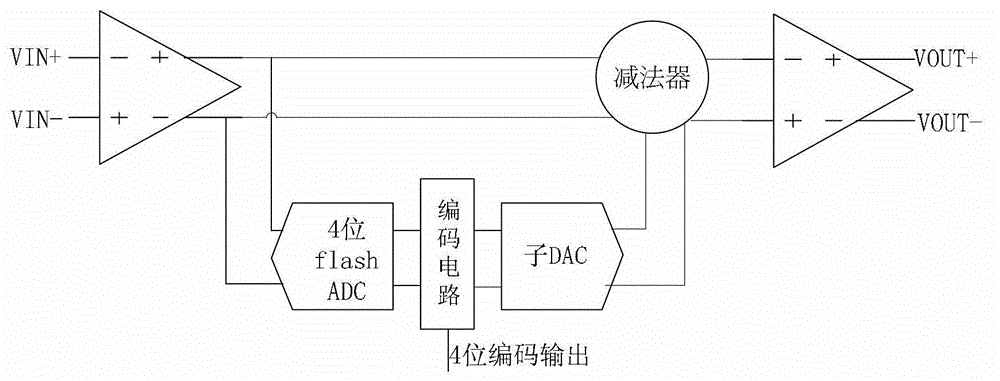
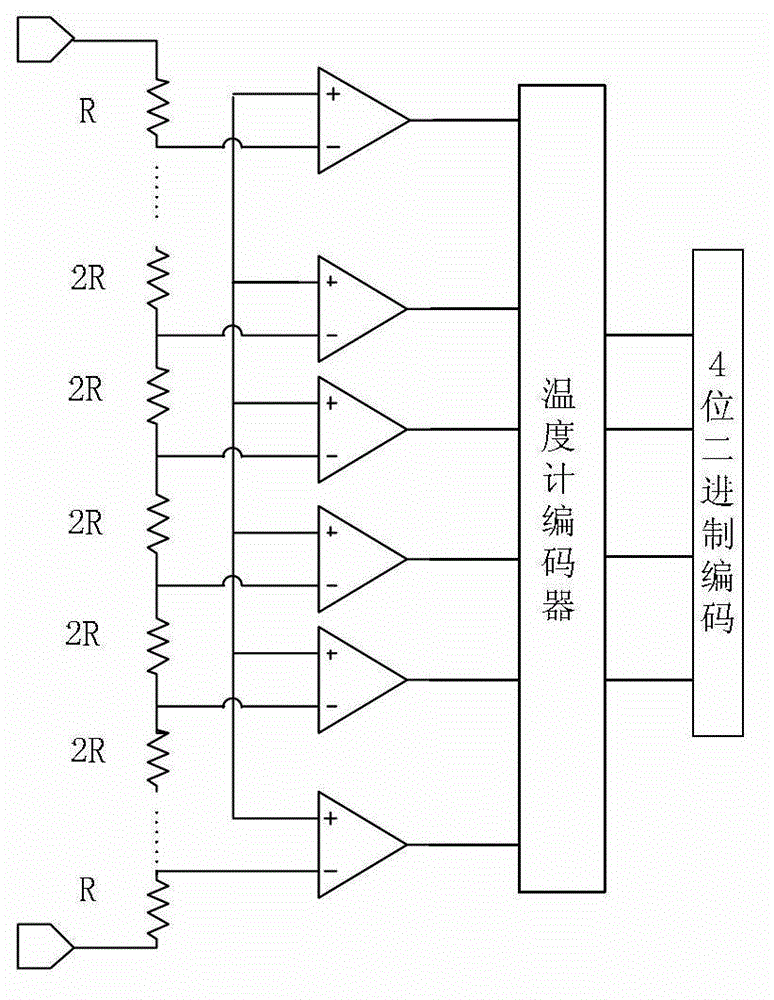
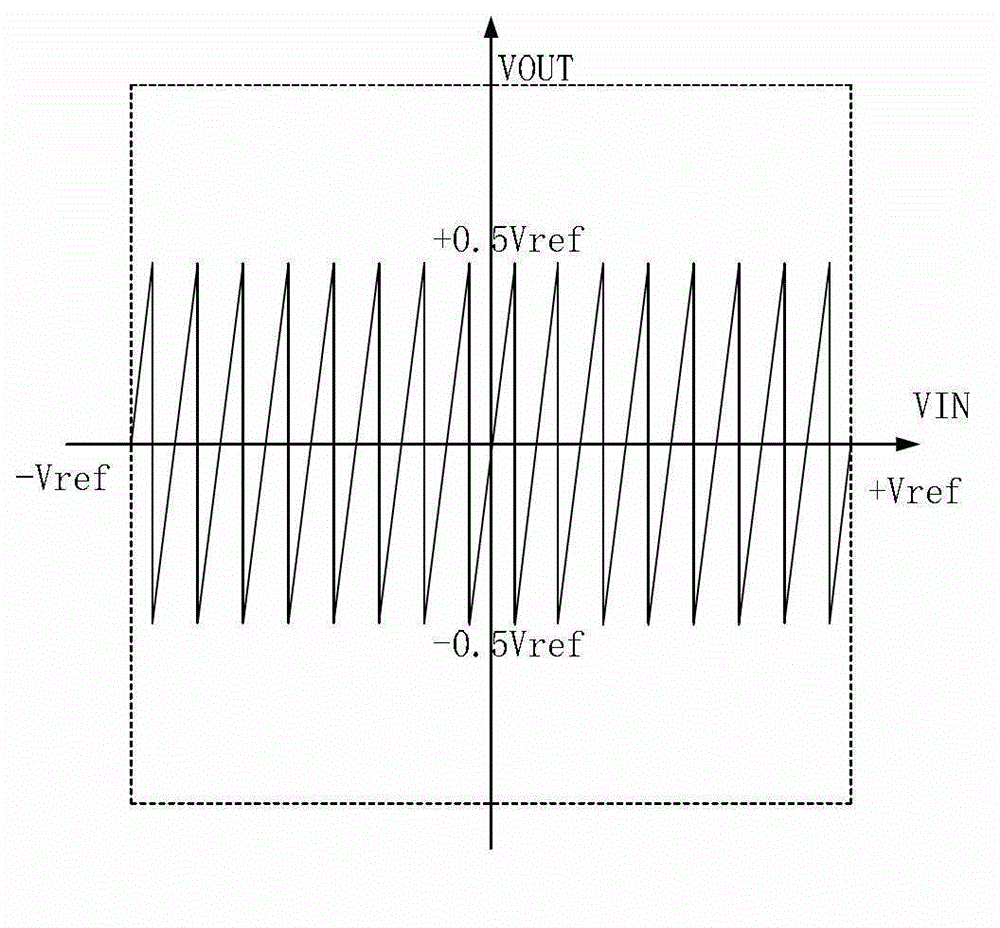
InactiveCN102983863AGuaranteed accuracyReduce design pressureAnalogue-digital convertersCapacitanceDigital down converter
The invention discloses a first-stage circuit structure of a pipelined analog-to-digital converter, which comprises a 4-digit fully parallel analog-to-digital converter, a code circuit and a residue gain analog-to-digital converter. A two-phase non-overlapping clock is adopted, a sampling phase samples input voltage, and a maintaining phase amplifies residual voltage. The residue gain analog-to-digital converter consists of a sub analog-to-digital converter, a subtracter and a residue amplifier. During sampling, the 4-digit fully parallel analog-to-digital converter conducts comparison and quantification on the input voltage and generates a 16-digit thermometer code which is converted to a 4-digit binary output code by the encoder. A lower pole plate of a sampling capacitor array is connected with the input voltage, and an upper pole plate thereof is connected with a common mode level for sampling an input. During maintaining, the sub analog-to-digital converter outputs different voltages to the sampling capacitor array according to a control of the thermometer code; subtraction from the input voltage is accomplished according to twice charge conservation; and a feedback capacitor is in bridge connection with the two ends of the residue amplifier to amplify the residual voltage by 8 times for use by a backward-stage circuit.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![[source driver and liquid crystal display using the same] [source driver and liquid crystal display using the same]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e88e2294-b4cf-4ae2-a43e-a258af6a2325/US20050206629A1-20050922-D00000.png)
![[source driver and liquid crystal display using the same] [source driver and liquid crystal display using the same]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e88e2294-b4cf-4ae2-a43e-a258af6a2325/US20050206629A1-20050922-D00001.png)
![[source driver and liquid crystal display using the same] [source driver and liquid crystal display using the same]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e88e2294-b4cf-4ae2-a43e-a258af6a2325/US20050206629A1-20050922-D00002.png)