Patents
Literature
2124 results about "Digital down converter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In digital signal processing, a digital down-converter (DDC) converts a digitized, band limited signal to a lower frequency signal at a lower sampling rate in order to simplify the subsequent radio stages. The process preserves all the information in the original signal less that which is lost to rounding errors in the mathematical processes. The input and output signals can be real or complex samples. Often the DDC converts from the raw radio frequency or intermediate frequency down to a complex baseband signal.
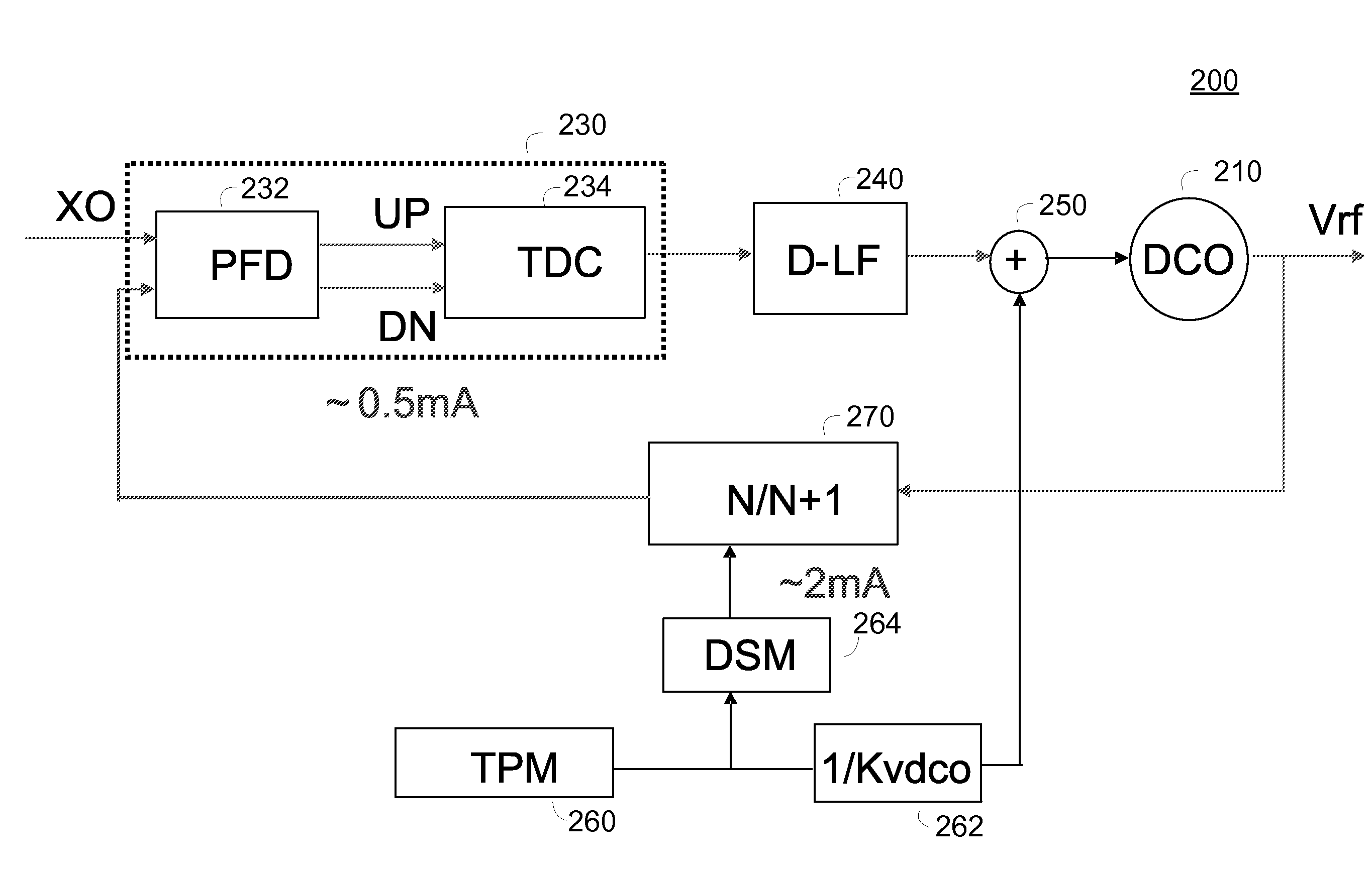
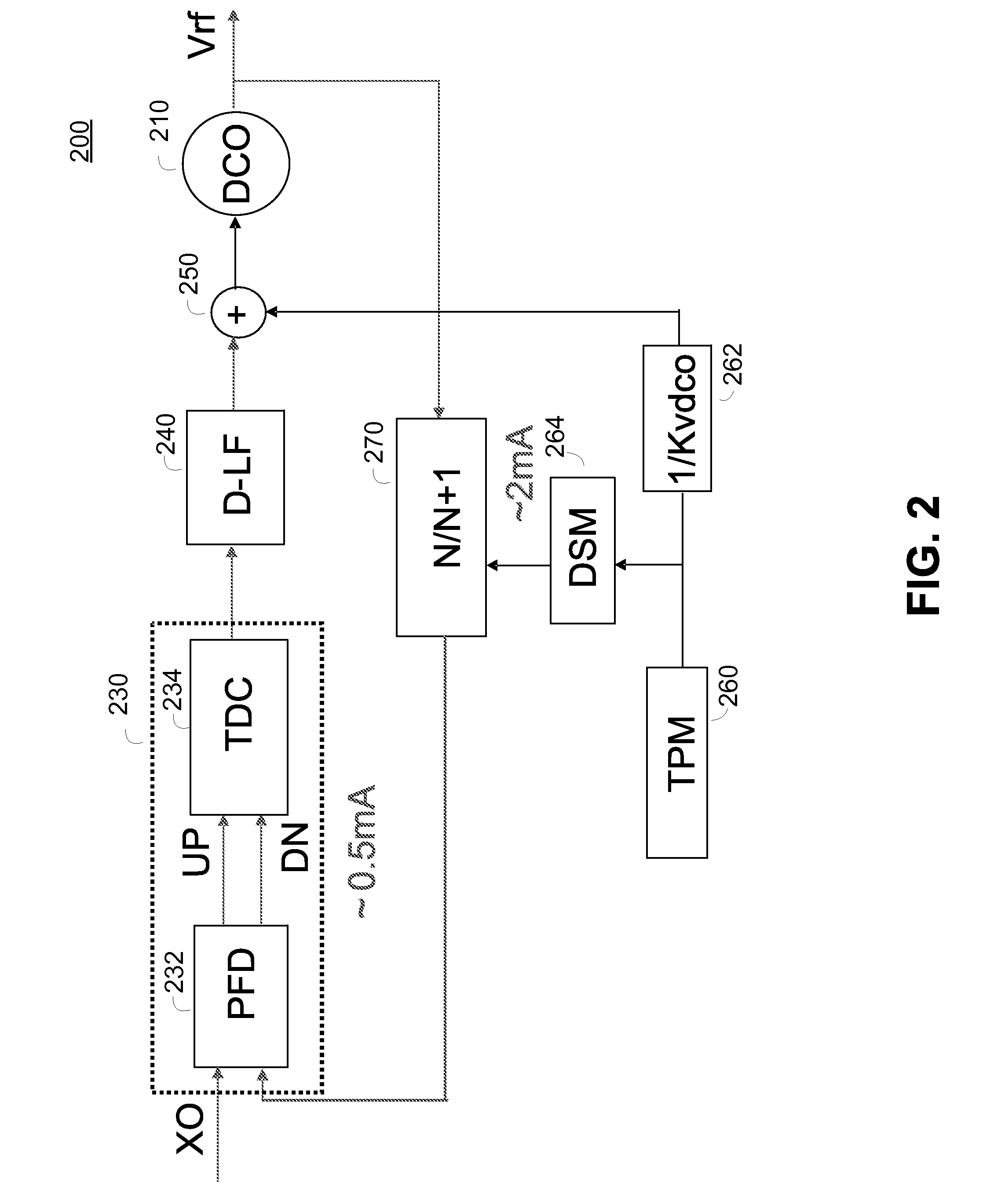
Phase to digital converter in all digital phase locked loop
ActiveUS20090256601A1Low power operationLower requirementElectric signal transmission systemsPulse automatic controlDigital down converterReference Period
A phase to digital converter, all digital phase locked loop, and apparatus having an all digital phase locked loop are described herein. The phase to digital converter includes a phase to frequency converter driving a time to digital converter. The time to digital converter determines a magnitude and sign of the phase differences output by the phase to frequency converter. The time to digital converter utilizes tapped delay lines and looped feedback counters to enable measurement of small timing differences typical of a loop tracking process and large timing differences typical of an loop acquisition process. The tapped delay lines permit the measurement of fractions of a reference period and enable lower power operation of the phase to digital converter by reducing requirements on the speed of the reference clock.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
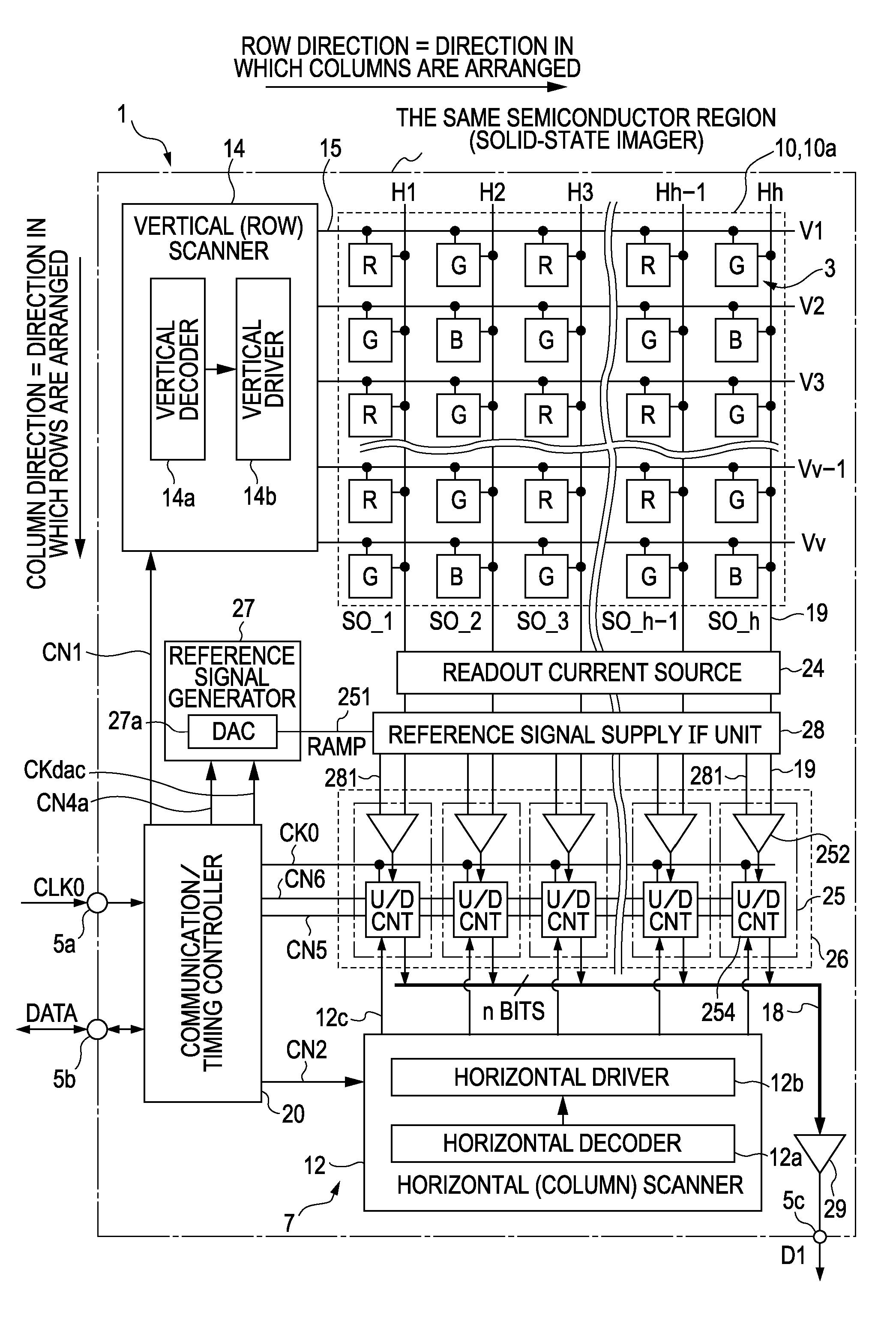
Analog-to-digital converter and semiconductor device
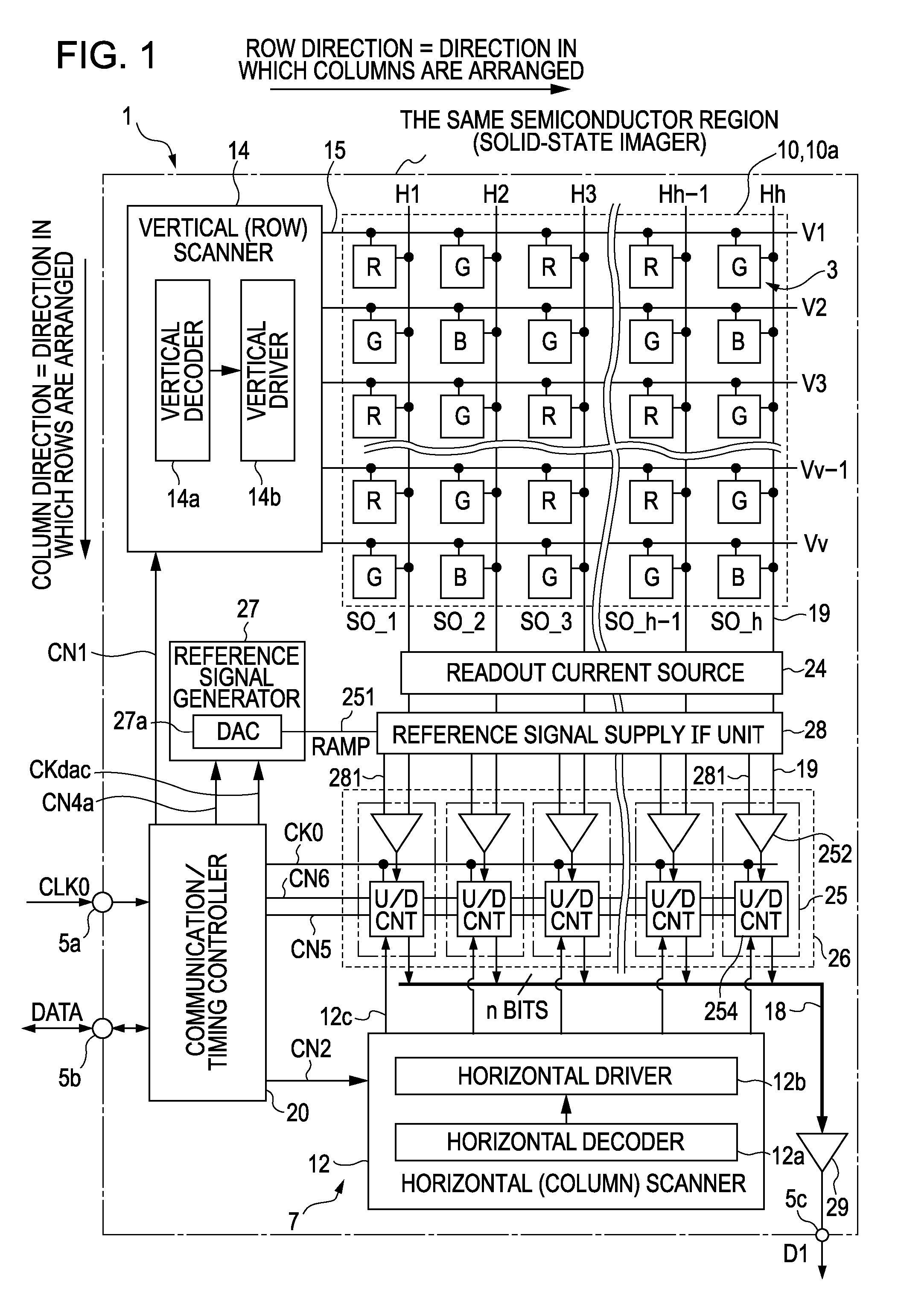
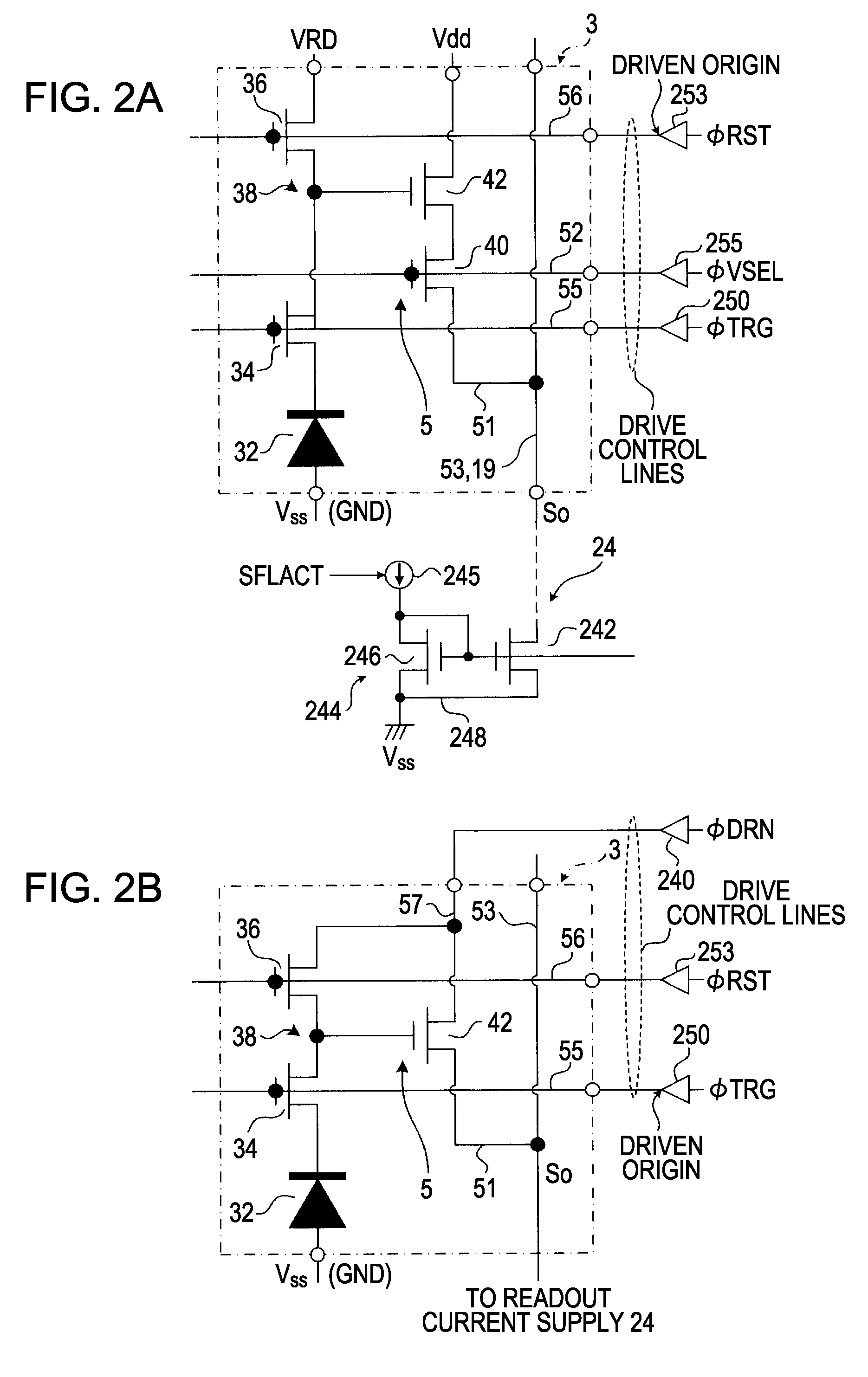
ActiveUS7321329B2Reduce adverse effectsTelevision system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsCMOSDigital down converter
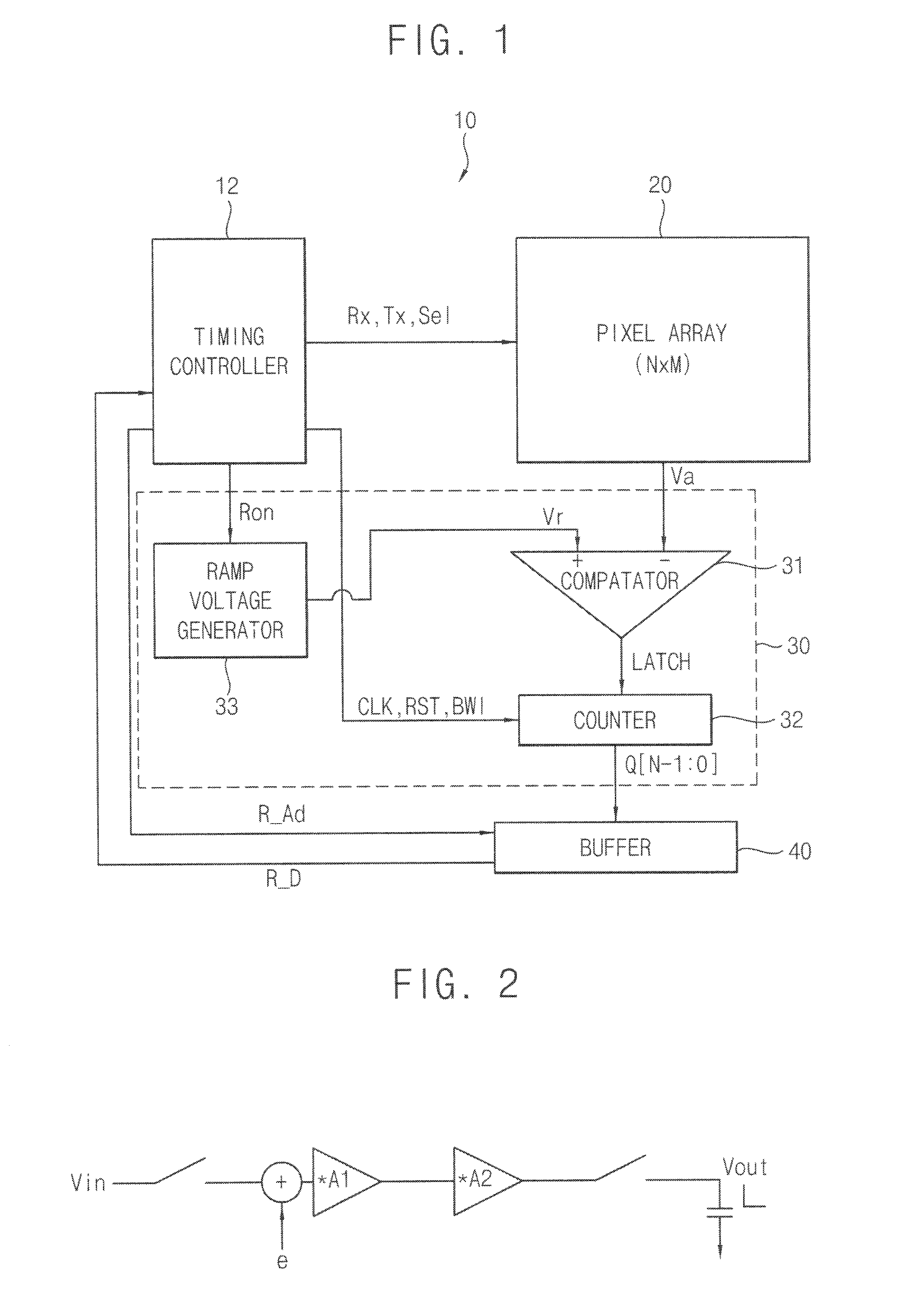
An electronic apparatus includes a CMOS image sensor and a signal processor operable to process an output signal from the CMOS image sensor. The CMOS image sensor includes the following elements: an imaging region; a reference signal generator operable to generate a reference signal; a comparator operable to compare the reference signal generated by the reference signal generator with a signal transmitted from the imaging region; a counter operable to count, in parallel with comparison performed by the comparator, a predetermined count clock and to hold a count value at the time of completion of comparison performed by the comparator; and a reference signal supply interface unit operable to supply the reference signal generated by the reference signal generator to a plurality of comparators via different signal lines, respectively.
Owner:SONY CORP
Apparatus for current-to-voltage integration for current-to-digital converter
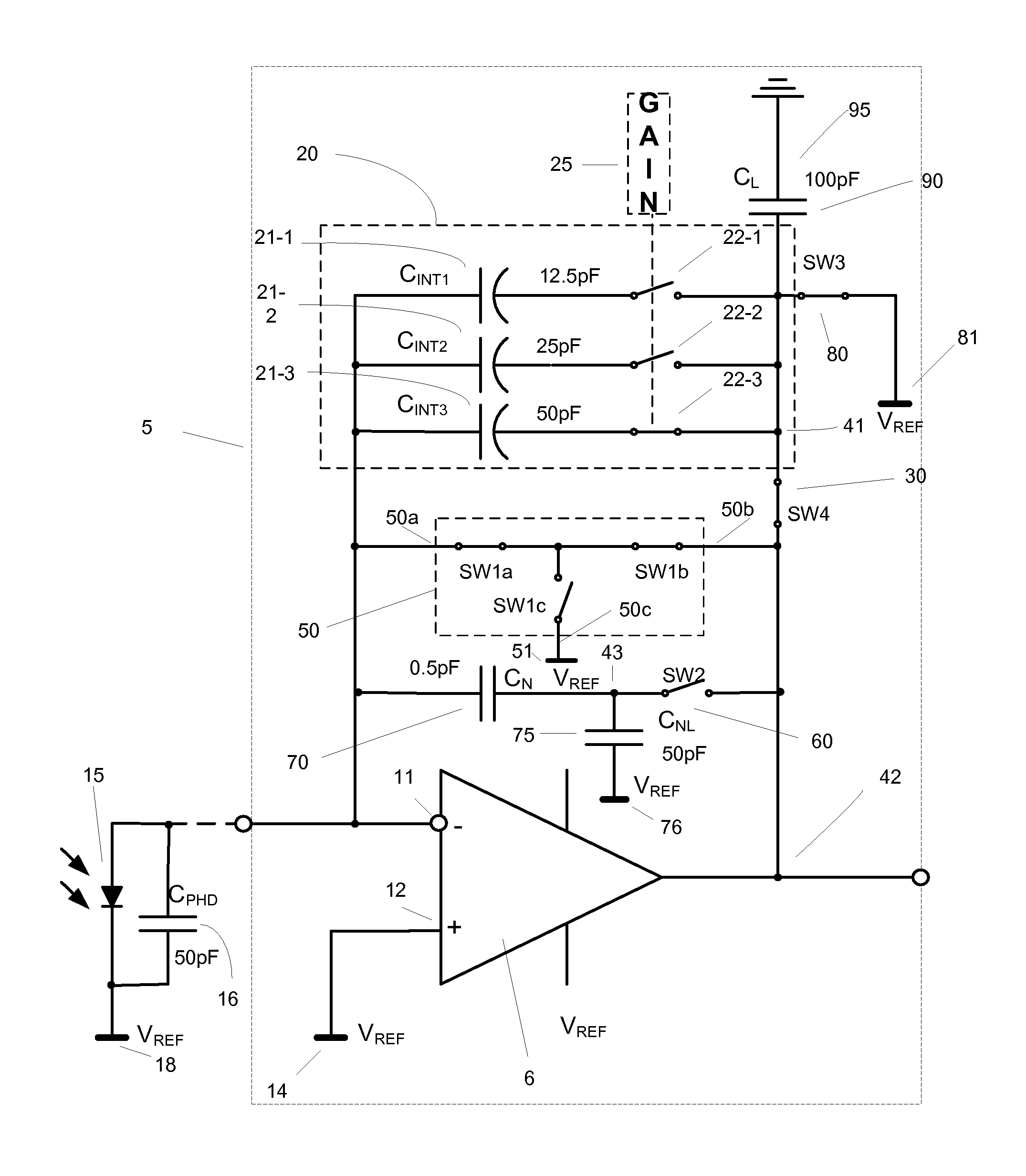
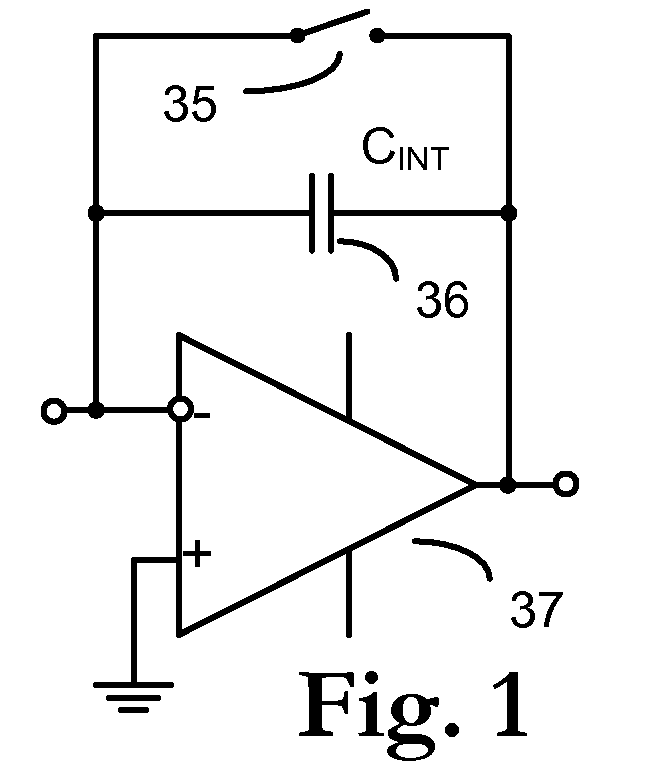
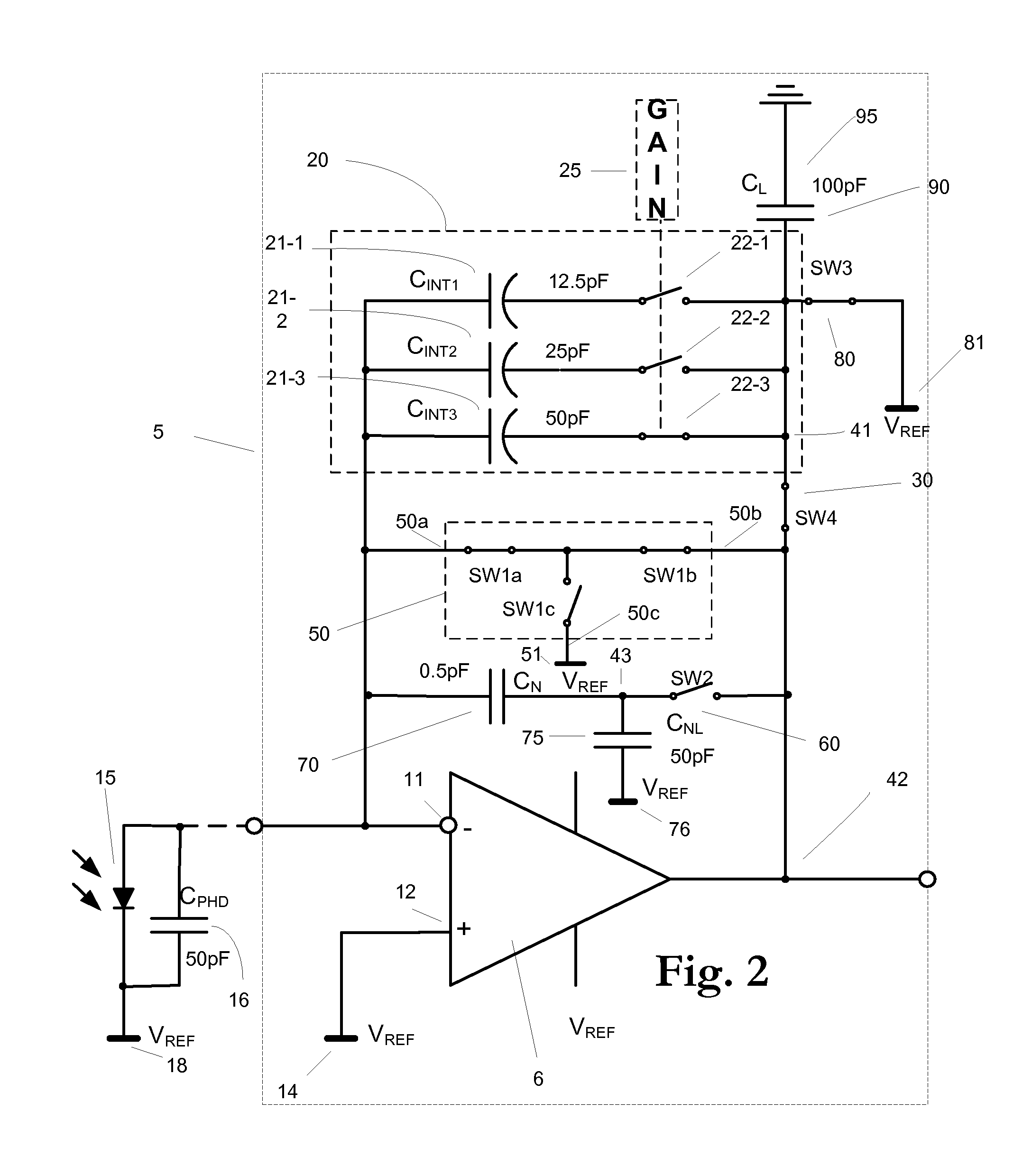
InactiveUS20090273386A1Reduce charge injectionReduce demandComputing operations for integral formationComputing operations for integration/differentiationDigital down converterIntegrator
Owner:CUSTOM ONE DESIGN
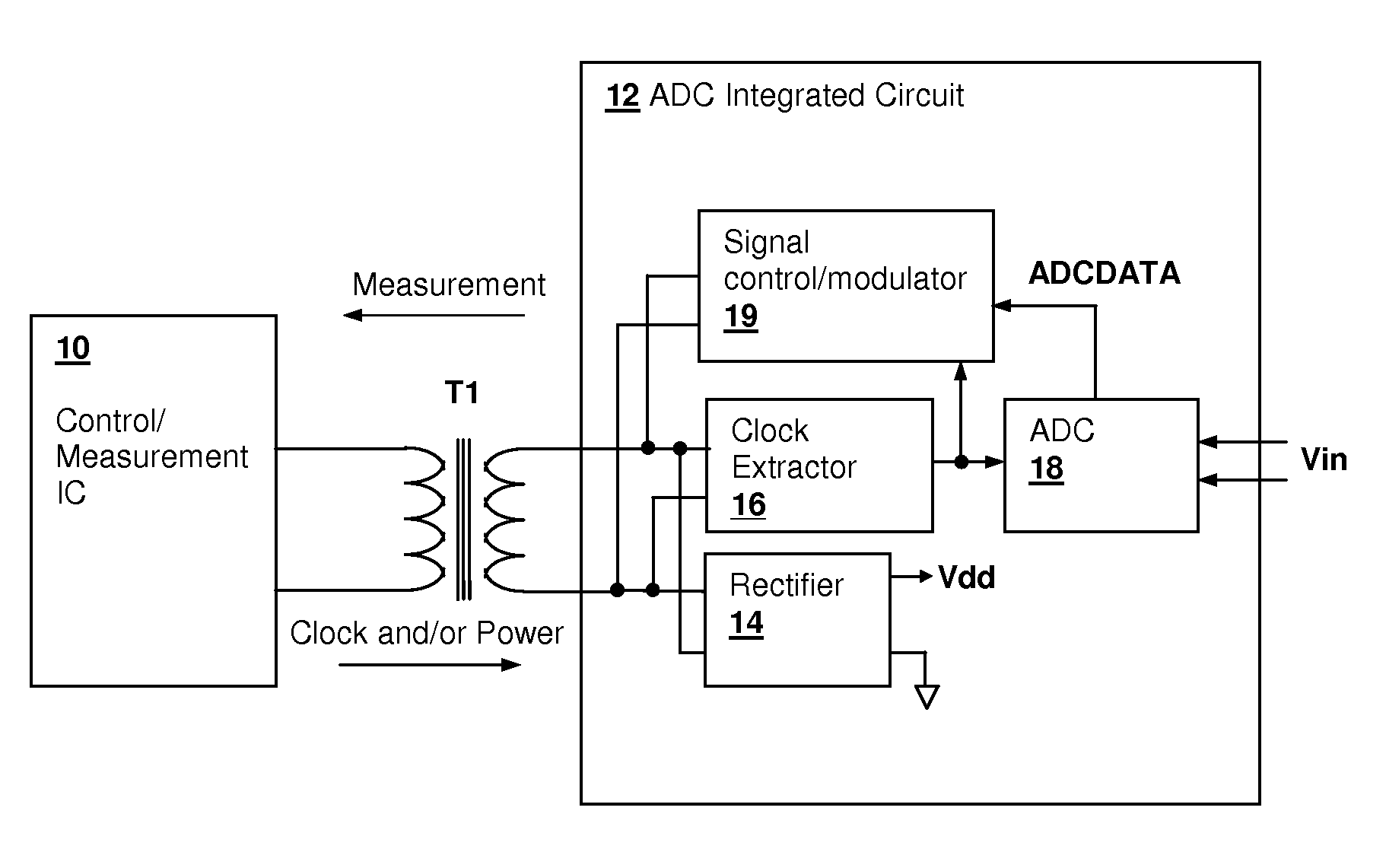
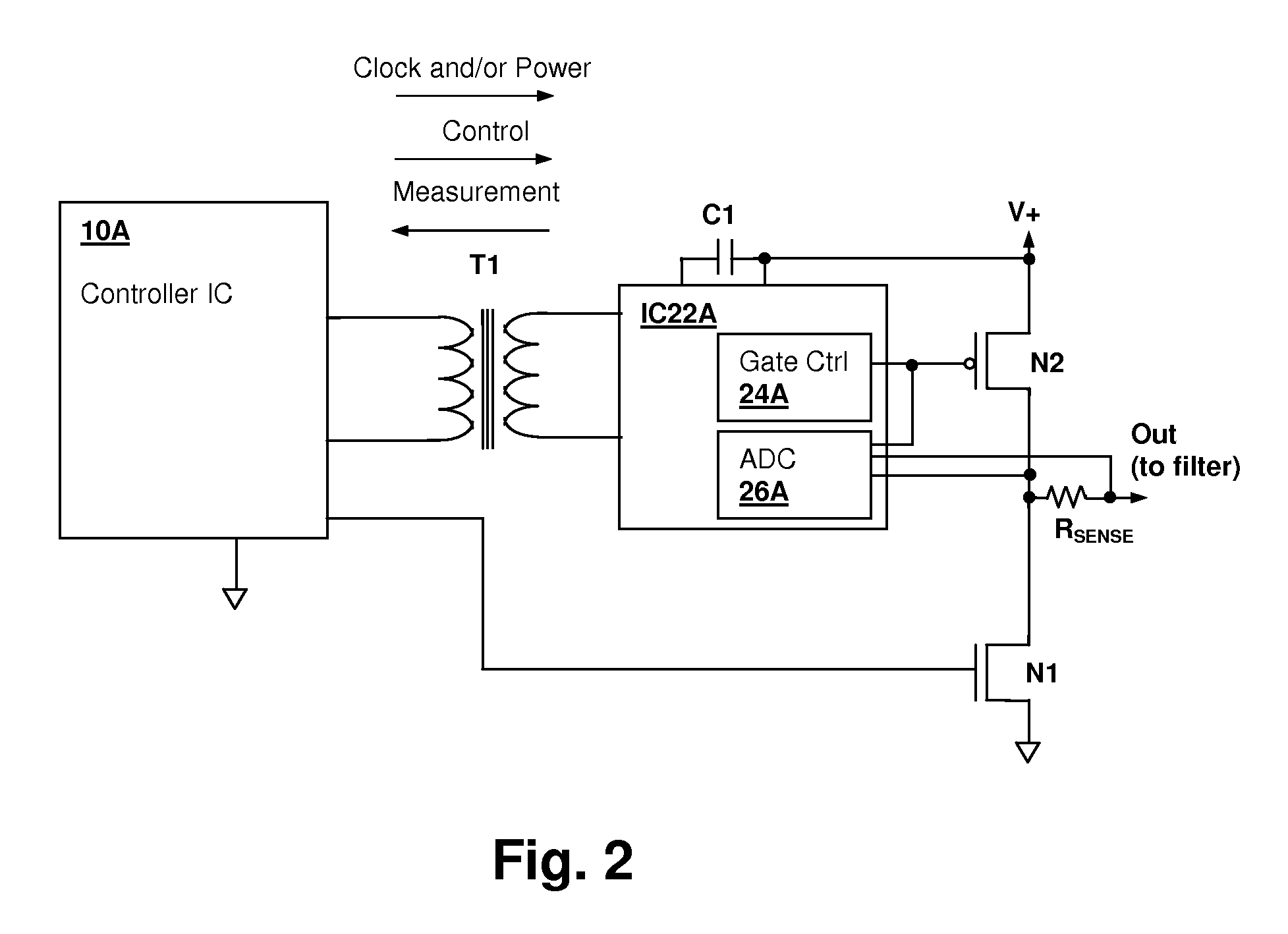
Transformer-isolated analog-to-digital converter (ADC) feedback apparatus and method
ActiveUS20090212759A1TransistorElectric signal transmission systemsCircuit complexityDigital down converter
A transformer-isolated analog-to-digital converter (ADC) feedback apparatus and method provides reduction of circuit complexity in high power / high voltage systems having a transformer-isolated sensing circuit. The feedback apparatus is a circuit including an ADC for receiving an analog input signal and a transformer having a first winding that receives a modulated output of the analog-to-digital converter. A second winding of the transformer provides an isolated data output of the ADC. A demodulator is coupled to the second winding of the transformer and demodulates the isolated output to generate a digital representation of the analog input signal. The ADC may be a delta-sigma converter and the demodulator may be the corresponding decimation filter. The circuit further includes an isolation circuit for introducing a clock signal and / or power supply waveform at the second winding of the transformer, so that the ADC circuit is supplied with an isolated clock and / or an isolated power supply.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Signaling dependent adaptive analog-to-digital converter (ADC) system and method of using same
InactiveUS6864817B1Maximize efficiencyReduce noiseElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionCapacitanceDigital down converter
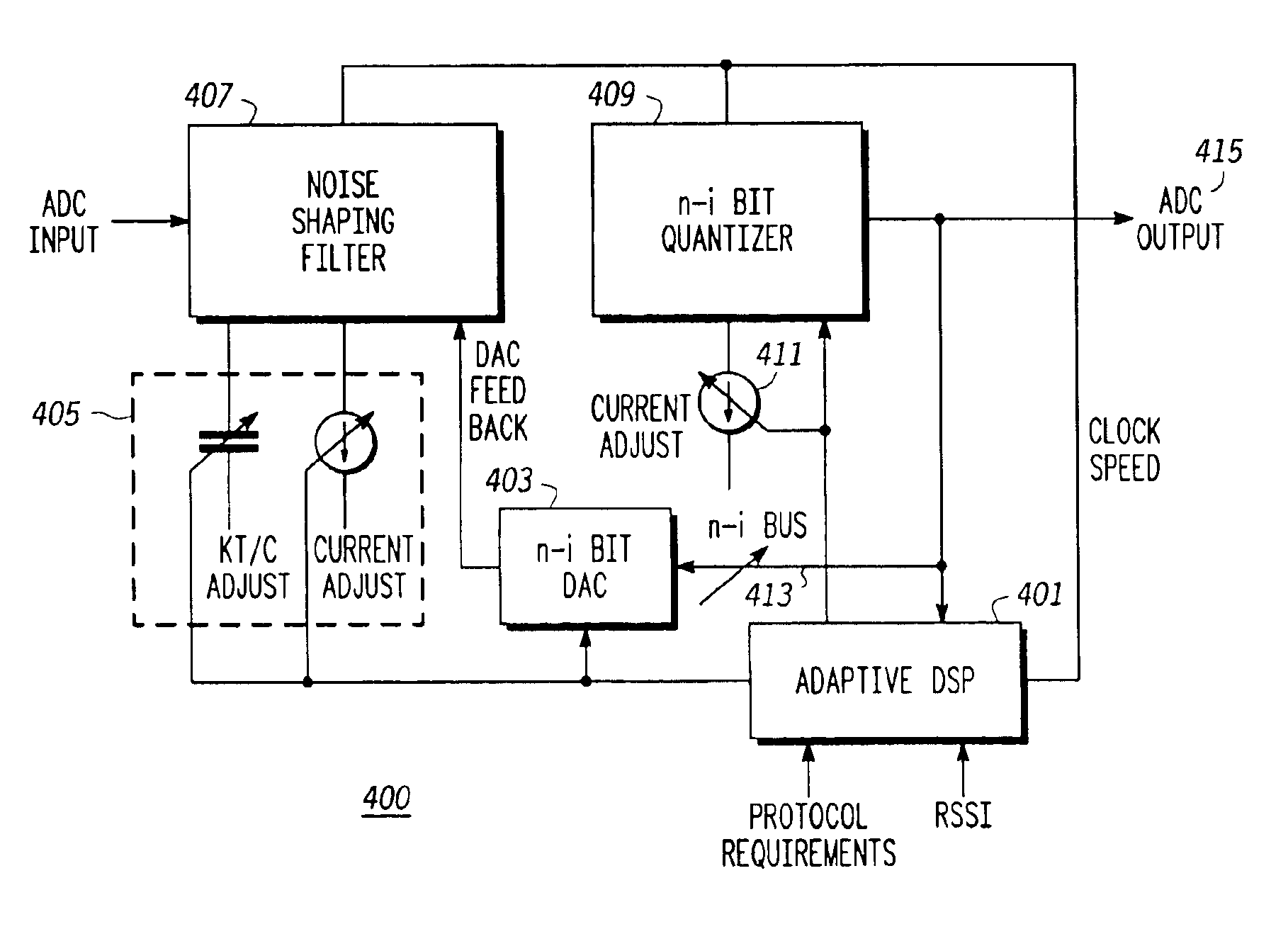
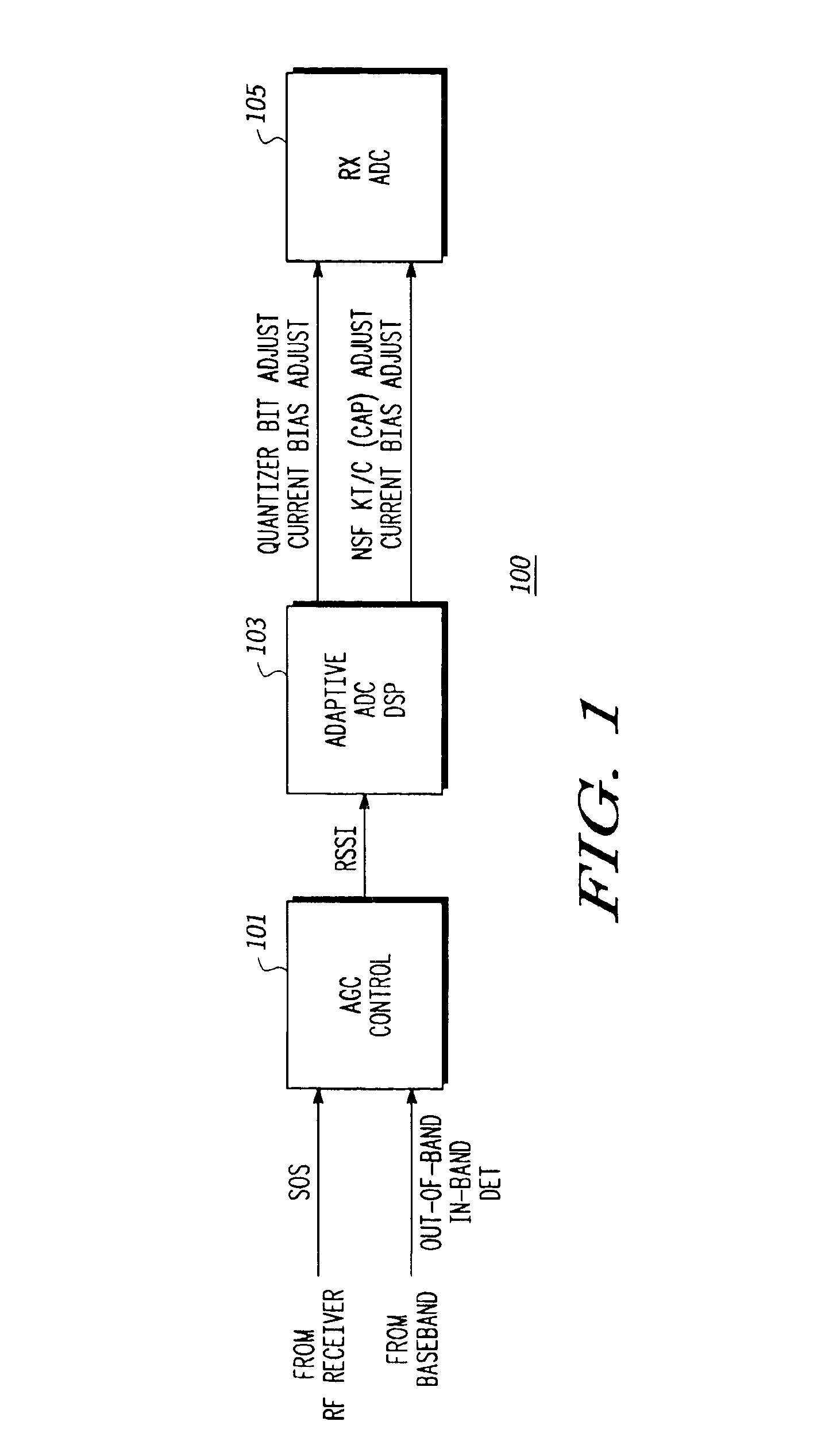
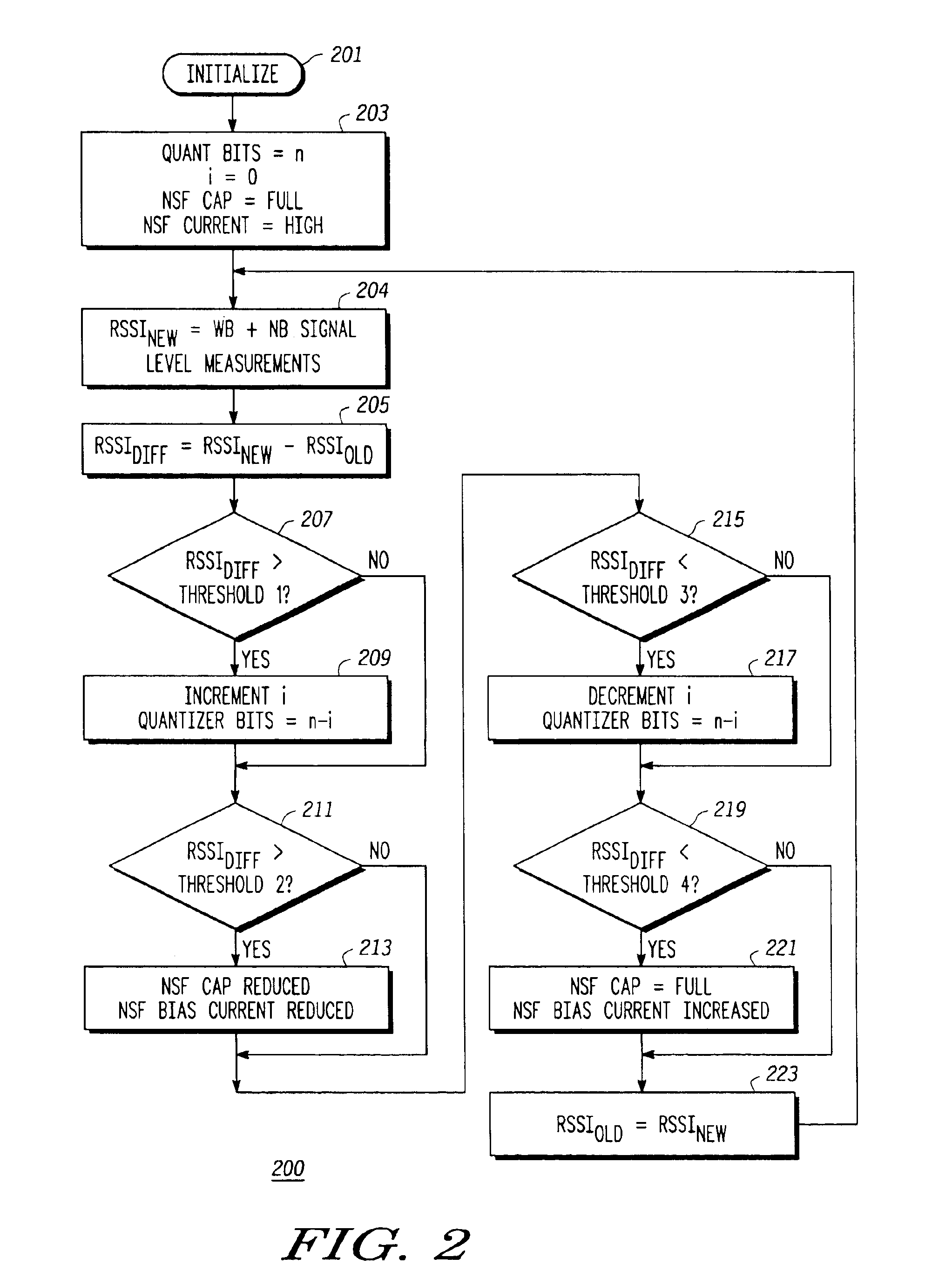
An adaptive analog-to-digital converter (ADC) system (100) includes an automatic gain control (AGC) controller (101) for receiving both in-band and out-of-band signals from a radio frequency (RF) receiver and producing an AGC control signal therefrom. A digital signal processor (DSP) (103) is then used for interpreting the AGC control signal and providing an adjustment signal to an ADC (105). The ADC (105) uses the adjustment signal to dynamically control efficiency of the ADC system 100 by adjusting bit resolution, reference capacitance and bias based upon the RF signal received and desired protocol requirements presented to the AGC controller (101).
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS +1
Ambient light sensing using a color sensor
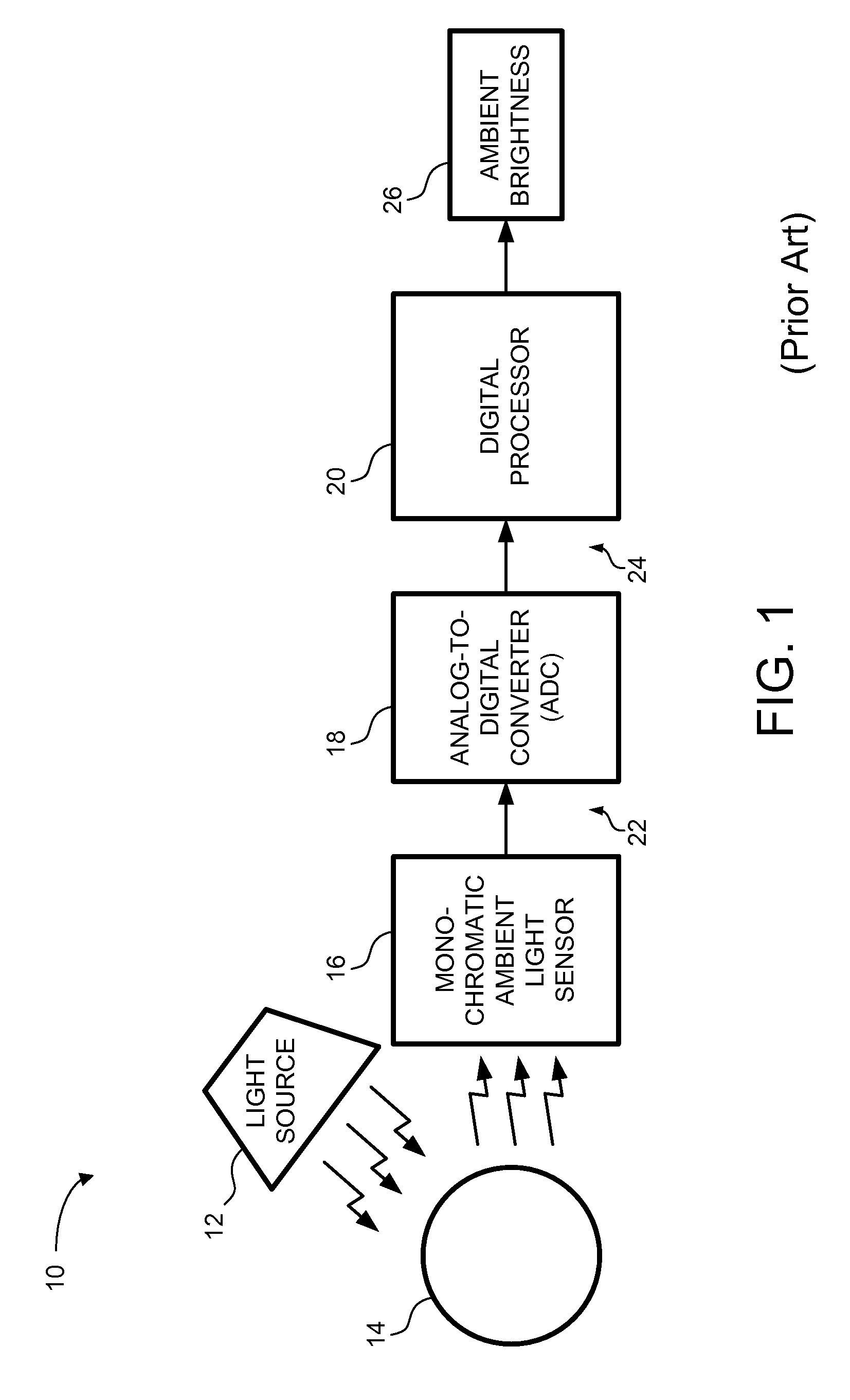
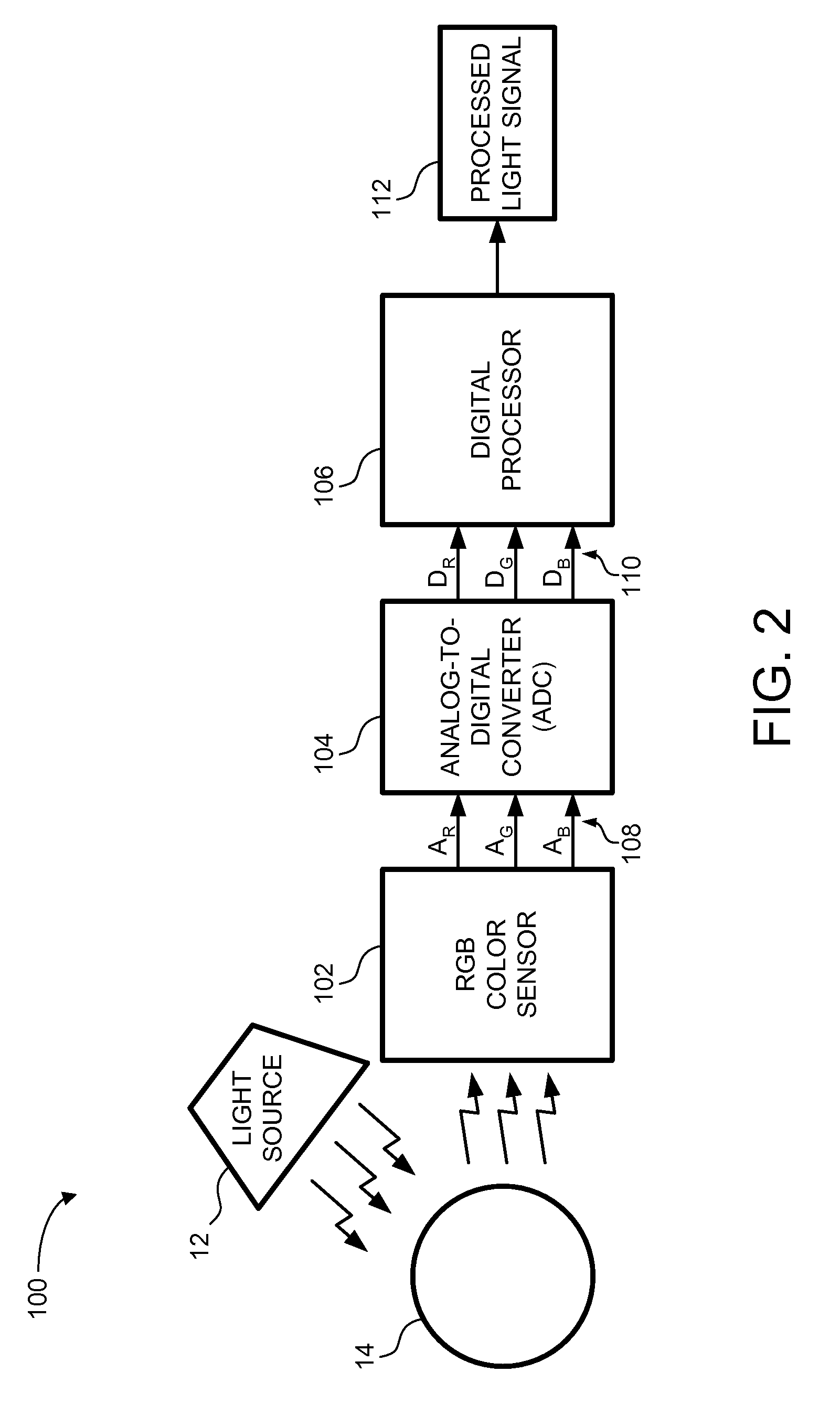
ActiveUS7446303B2Photometry using reference valueRadiation pyrometryDigital down converterLight sensing
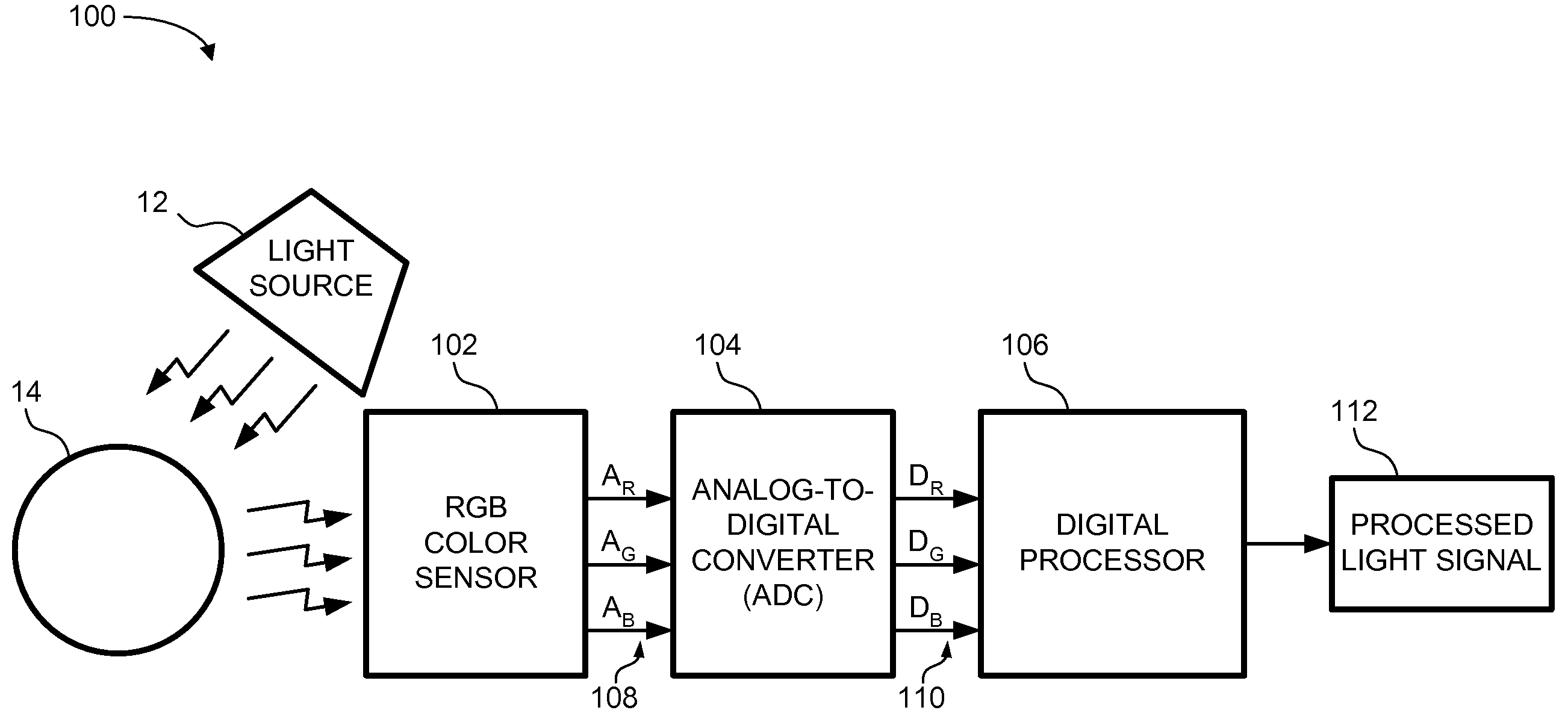
An ambient light sensor (ALS) system is described. The ALS system includes a polychromatic color sensor, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC), and a digital processor. The polychromatic color sensor generates a plurality of analog signals from a corresponding plurality of color channels based on a detected ambient light signal. The ADC is coupled to the polychromatic color sensor. The ADC converts the plurality of analog signals to a plurality of digital signals. The digital processor is coupled to the ADC. The digital processor generates a processed light signal. The processed light signal describes a characteristic of the detected ambient light signal. Embodiments of the ALS system provide a more comprehensive characterization of the ambient light, and facilitate control of a device based on the characterization of the ambient light.
Owner:WISTRON CORP
Image pickup device and signal processing method thereof
InactiveUS20090244328A1Television system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsDigital down converterDigital converter
Owner:CANON KK
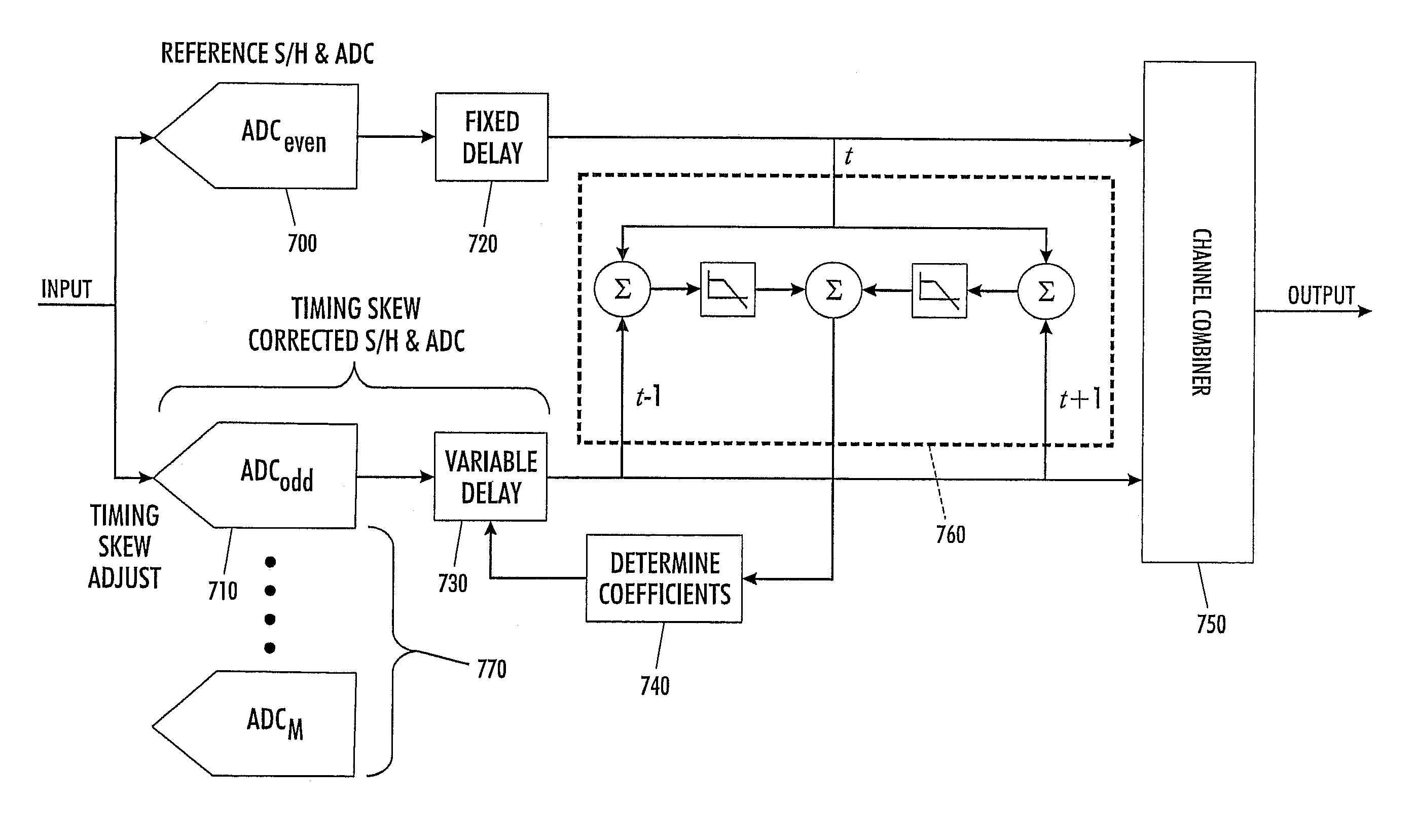
System and method for using timing skew estimation with a non-sequential time-interleaved analog-to-digital converter
ActiveUS7250885B1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersDigital down converterTime interleaved
A multi-channel analog-to-digital converter system includes an array of sub-analog-to-digital converters wherein within the array of sub-analog-to-digital converters, there is at least one designated reference analog-to-digital converter. The analog-to-digital converter system also includes a non-sequential channel select circuit to control a selection of the analog-to-digital converters and the reference analog-to-digital converter to non-sequentially interleave the outputs of said analog-to-digital converters and said reference analog-to-digital converter. Each channel of the plurality of sub-analog-to-digital converters includes a timing skew estimation circuit. Each timing skew estimation circuit receives an output signal from the reference analog-to-digital converter and receives the output signal from the associated analog-to-digital converter. Each timing skew estimation circuit generates a timing signal to be used in shifting or adjusting the actual or apparent sample times for the appropriate analog-to-digital converter.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
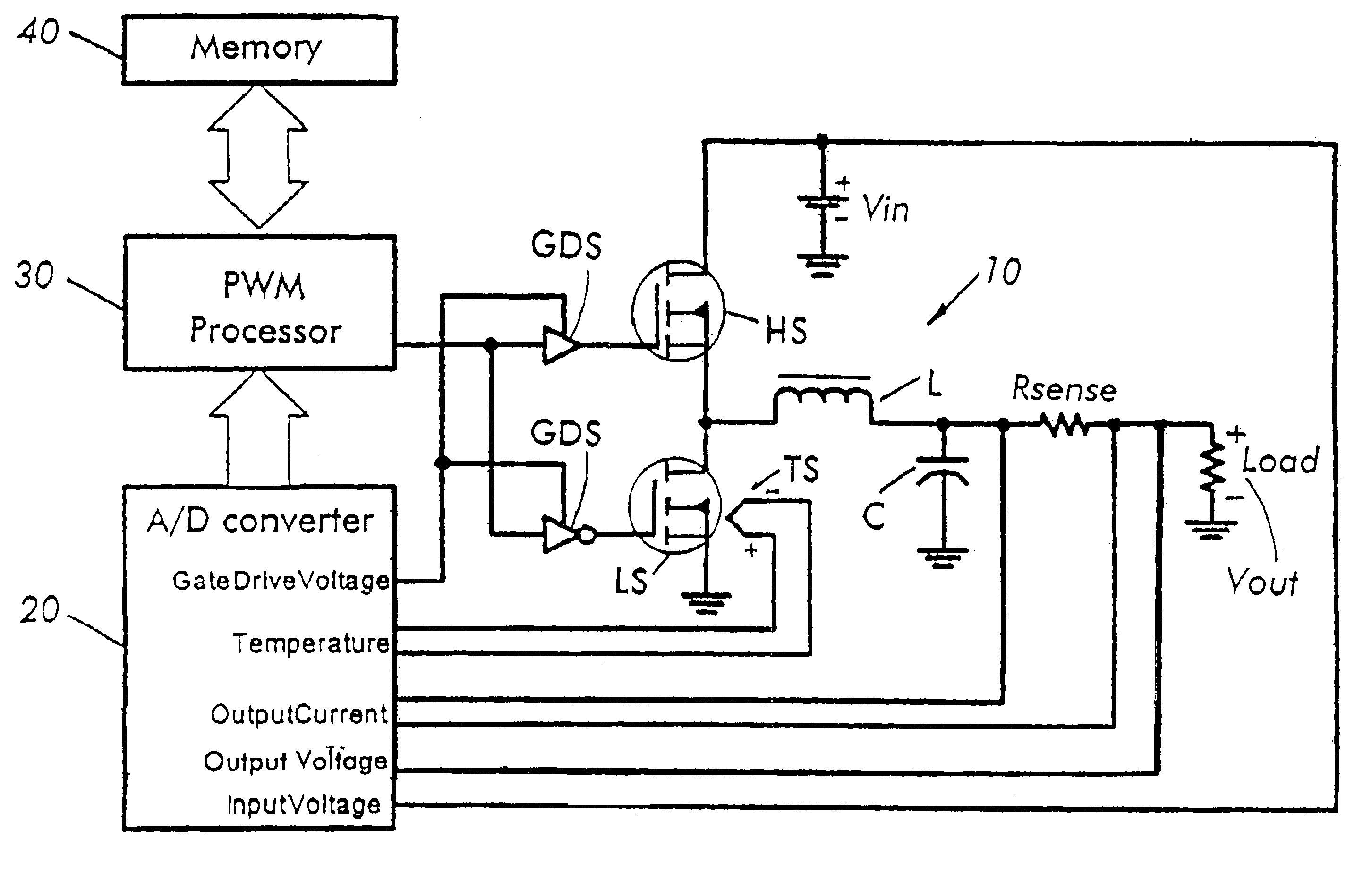
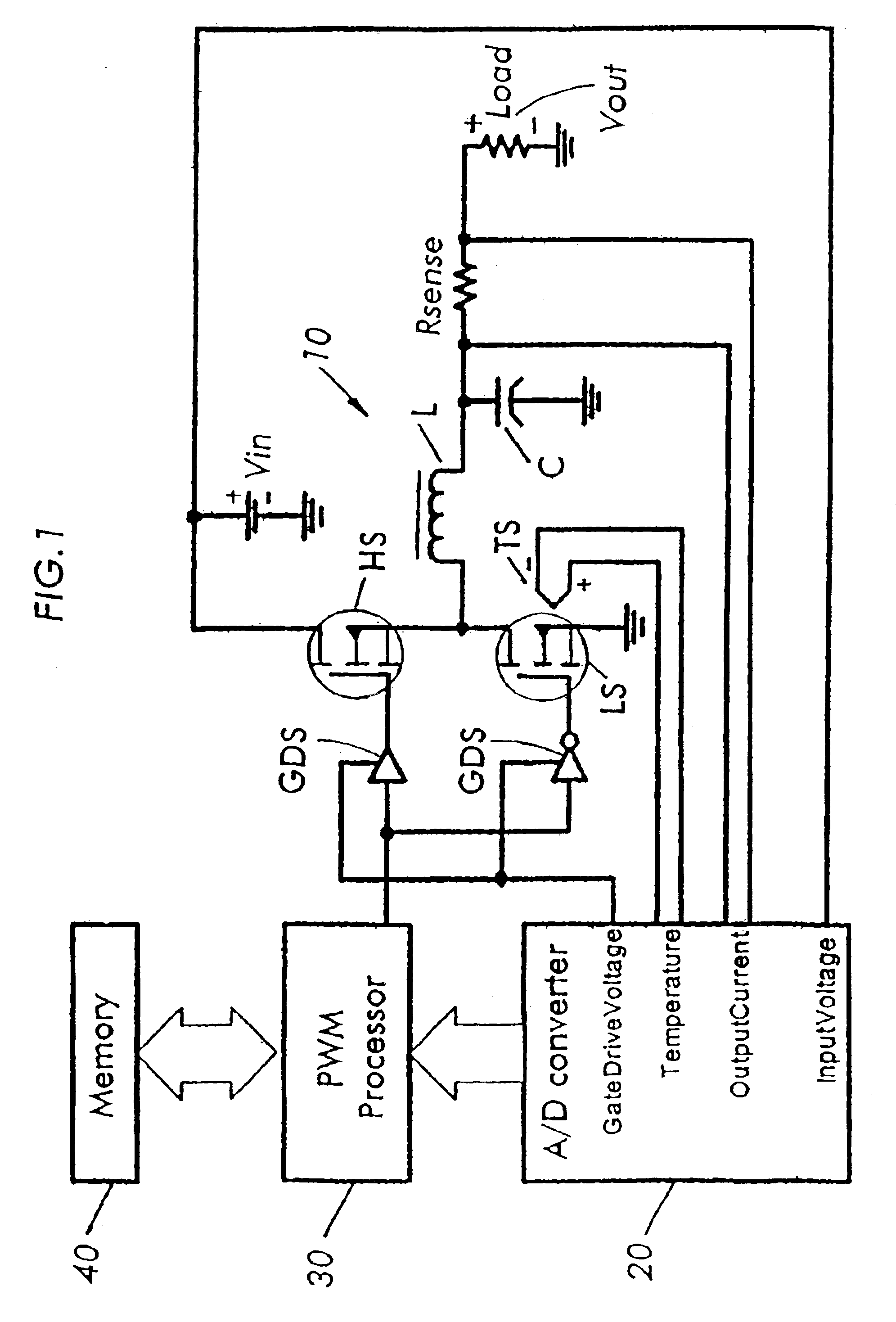
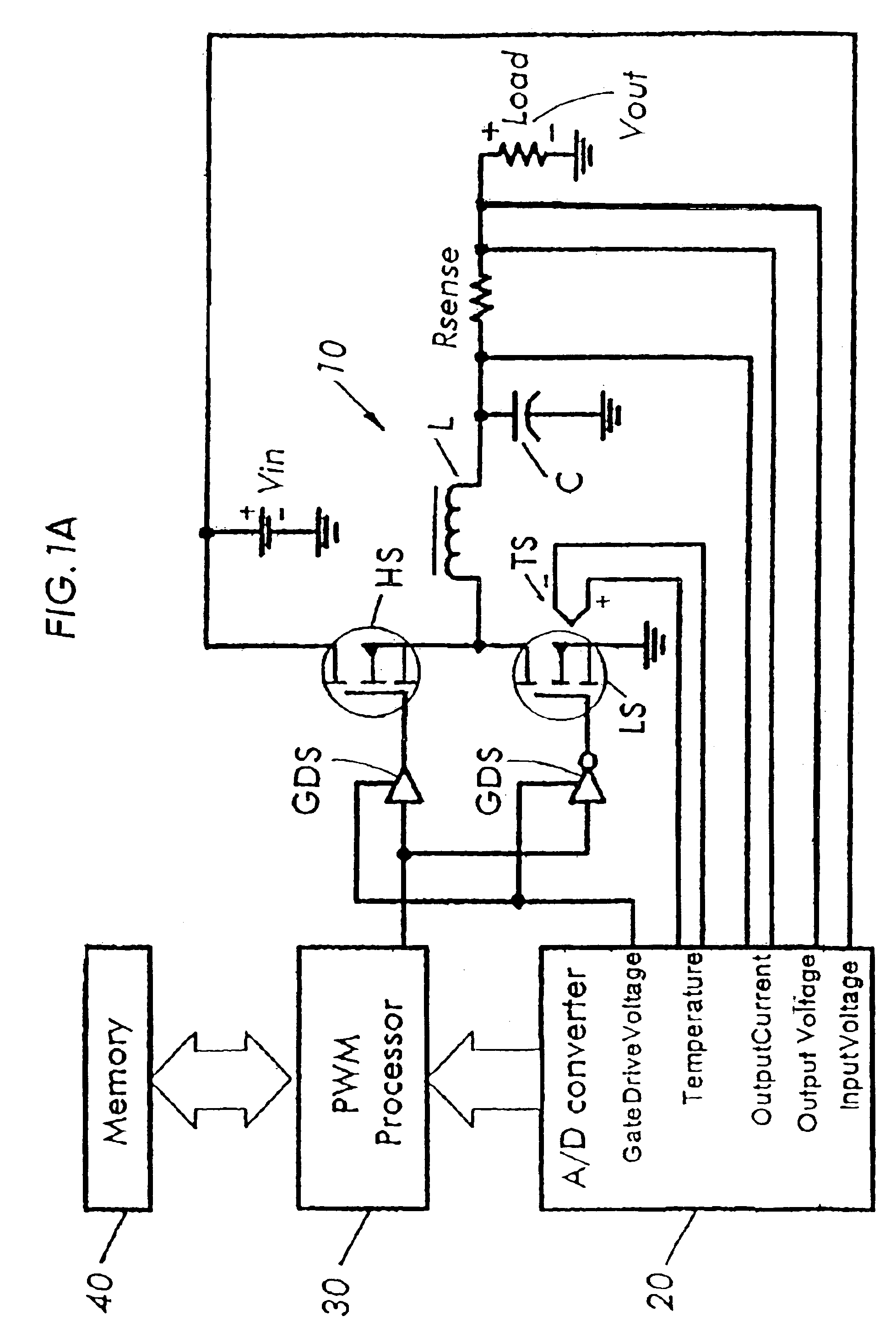
Total feed forward switching power supply control
ActiveUS6954054B2Easy to controlDc network circuit arrangementsDc-dc conversionDigital down converterControl signal
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
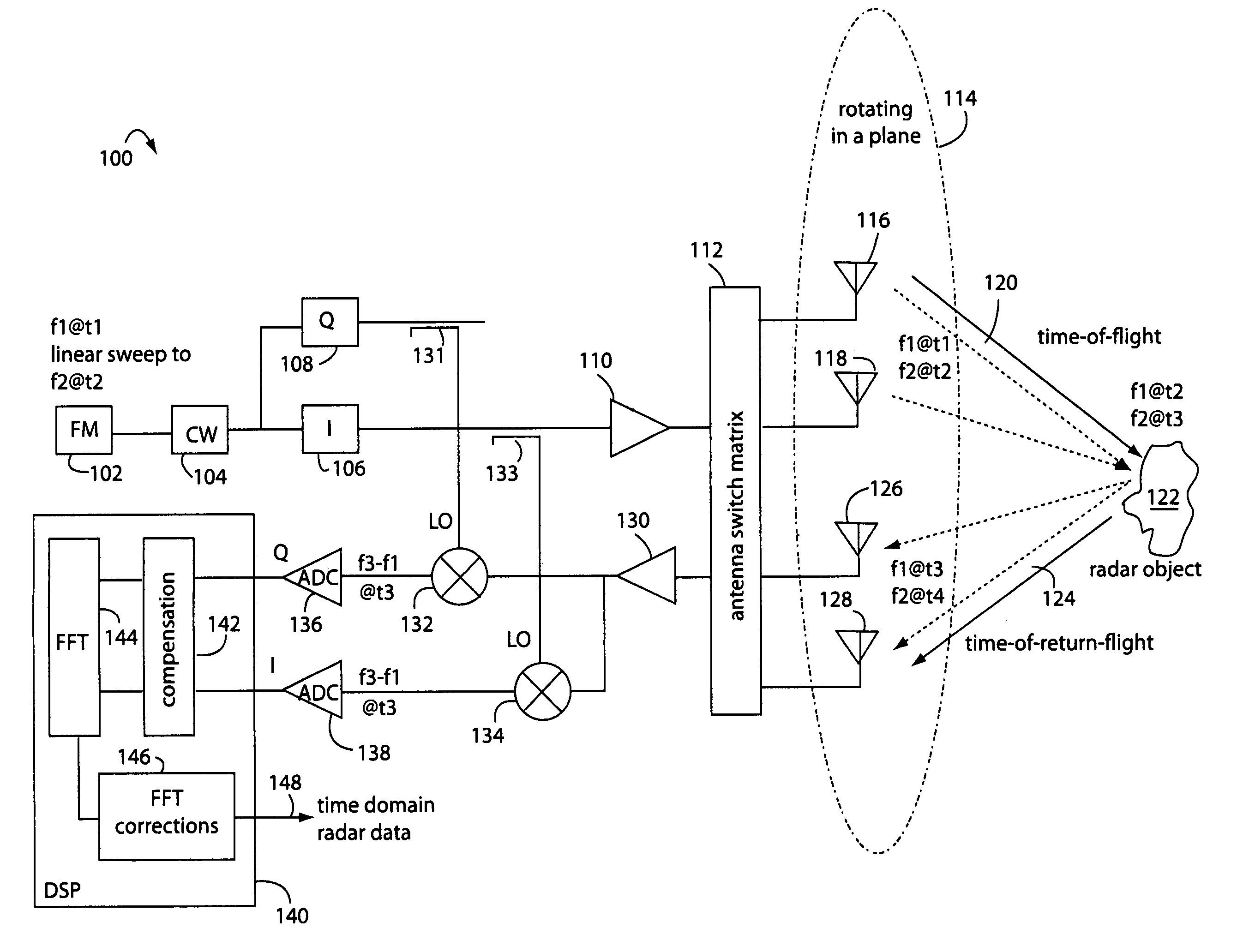
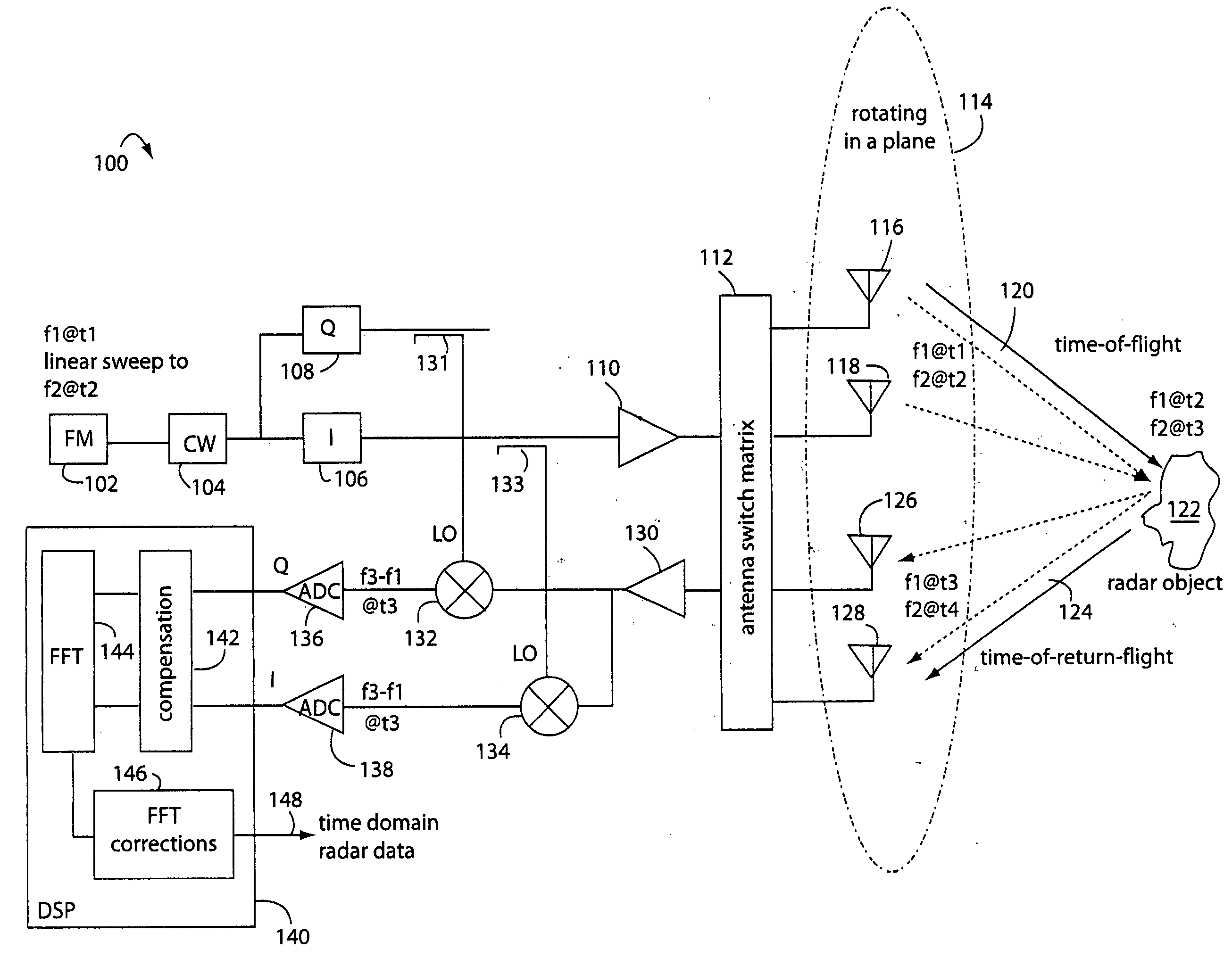
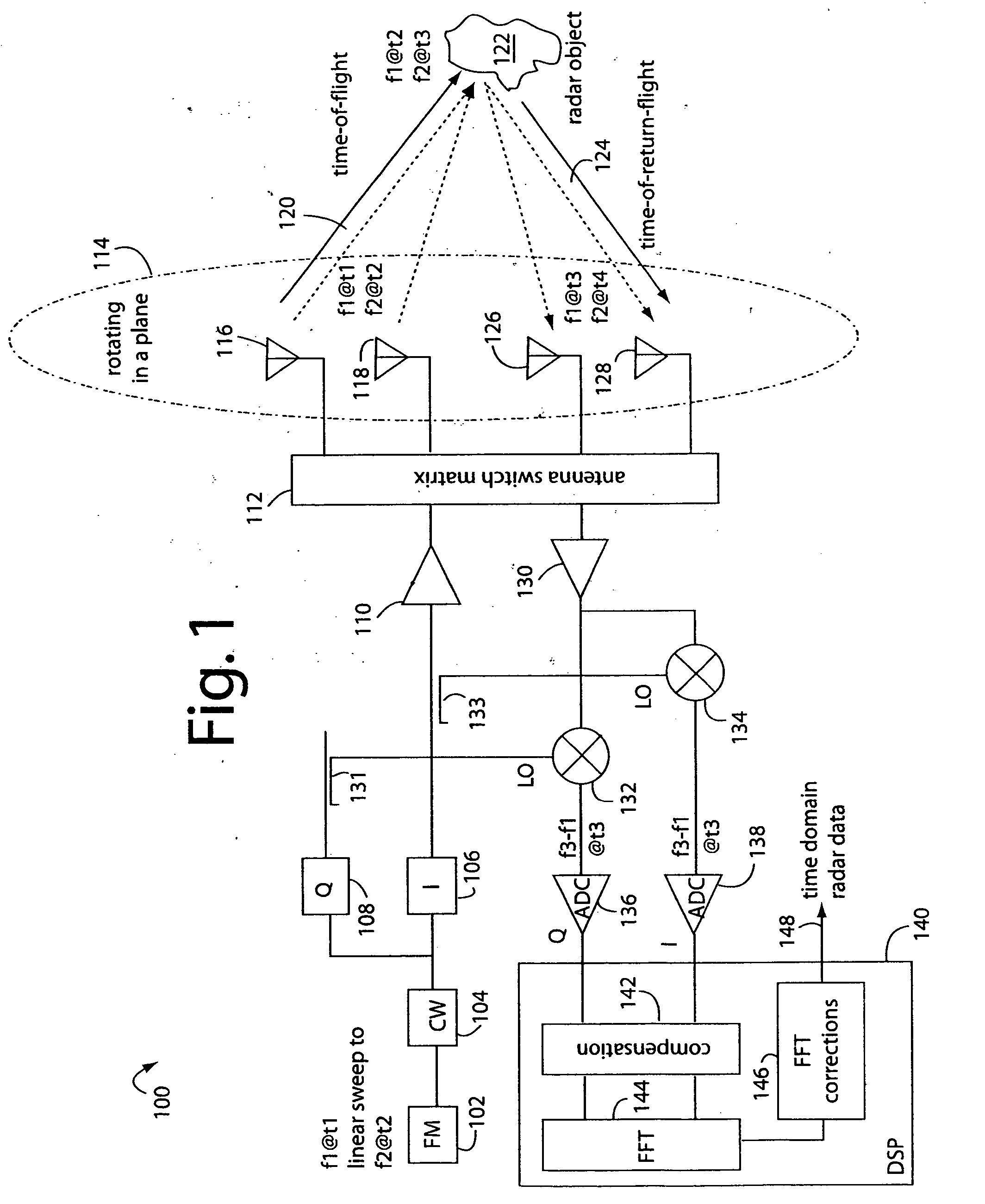
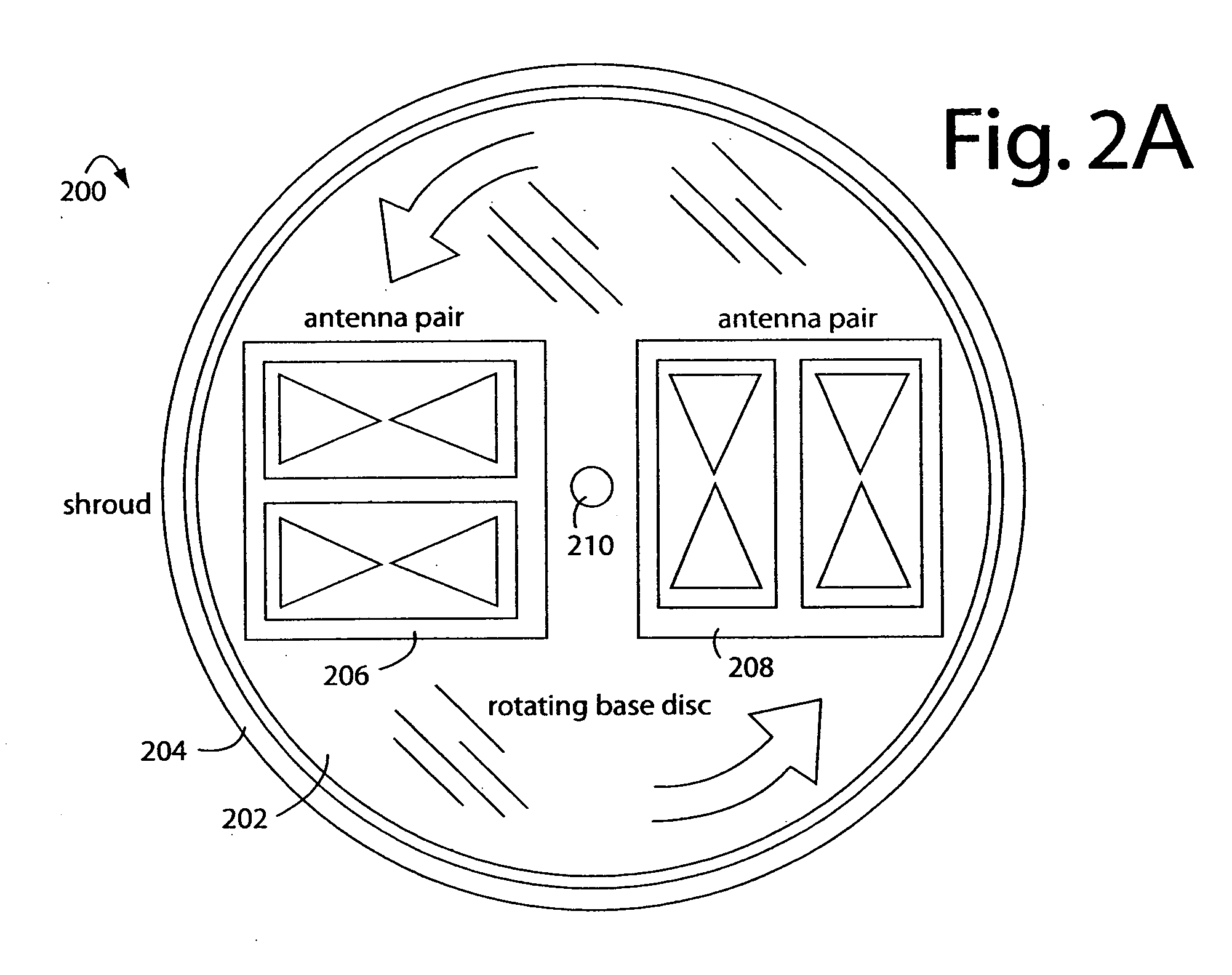
Linear FM radar
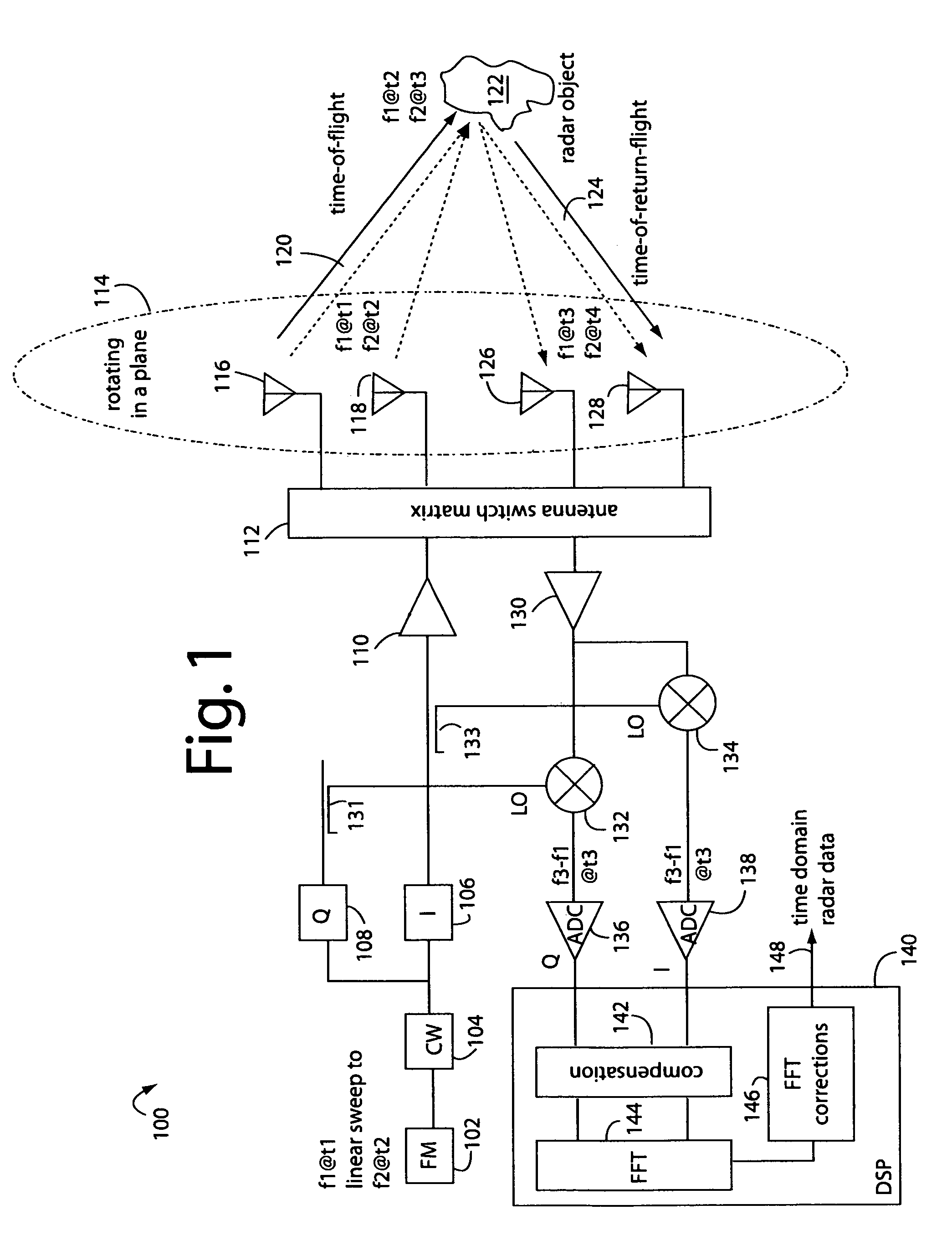
ActiveUS7170440B1Small volumeEasy to operateComputerised tomographsTomographyRadar systemsDigital down converter
A FM-CW radar system comprises a frequency modulated continuous wave digital generator that produces both in-phase (I) and quadrature-phase (Q) outputs to orthogonally oriented transmitter antennas. A linearly polarized beam is output from a switched antenna array that allows a variety of I-and-Q pairs of bowtie antennas to be alternately connected to the transmitter and receiver. The receiver inputs I-and-Q signals from another bowtie antenna in the array and mixes these with samples from the transmitter. Such synchronous detection produces I-and-Q beat frequency products that are sampled by dual analog-to-digital converters (ADC's). The digital samples receive four kinds of compensation, including frequency-and-phase, wiring delay, and fast Fourier transform (FFT). The compensated samples are then digitally converted by an FFT-unit into time-domain signals. Such can then be processed conventionally for range information to the target that has returned the FM-CW echo signal.
Owner:LANDRAY TECH
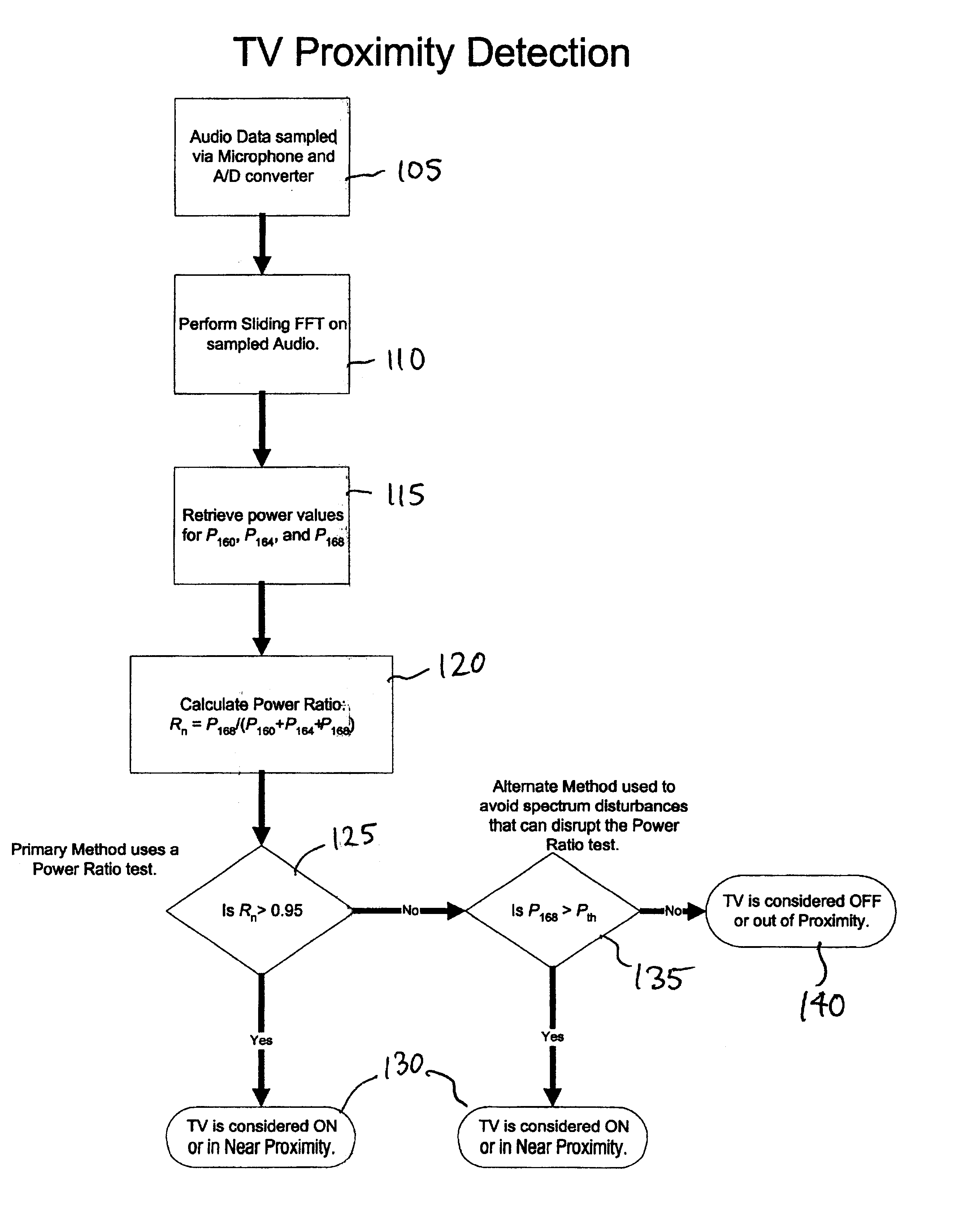
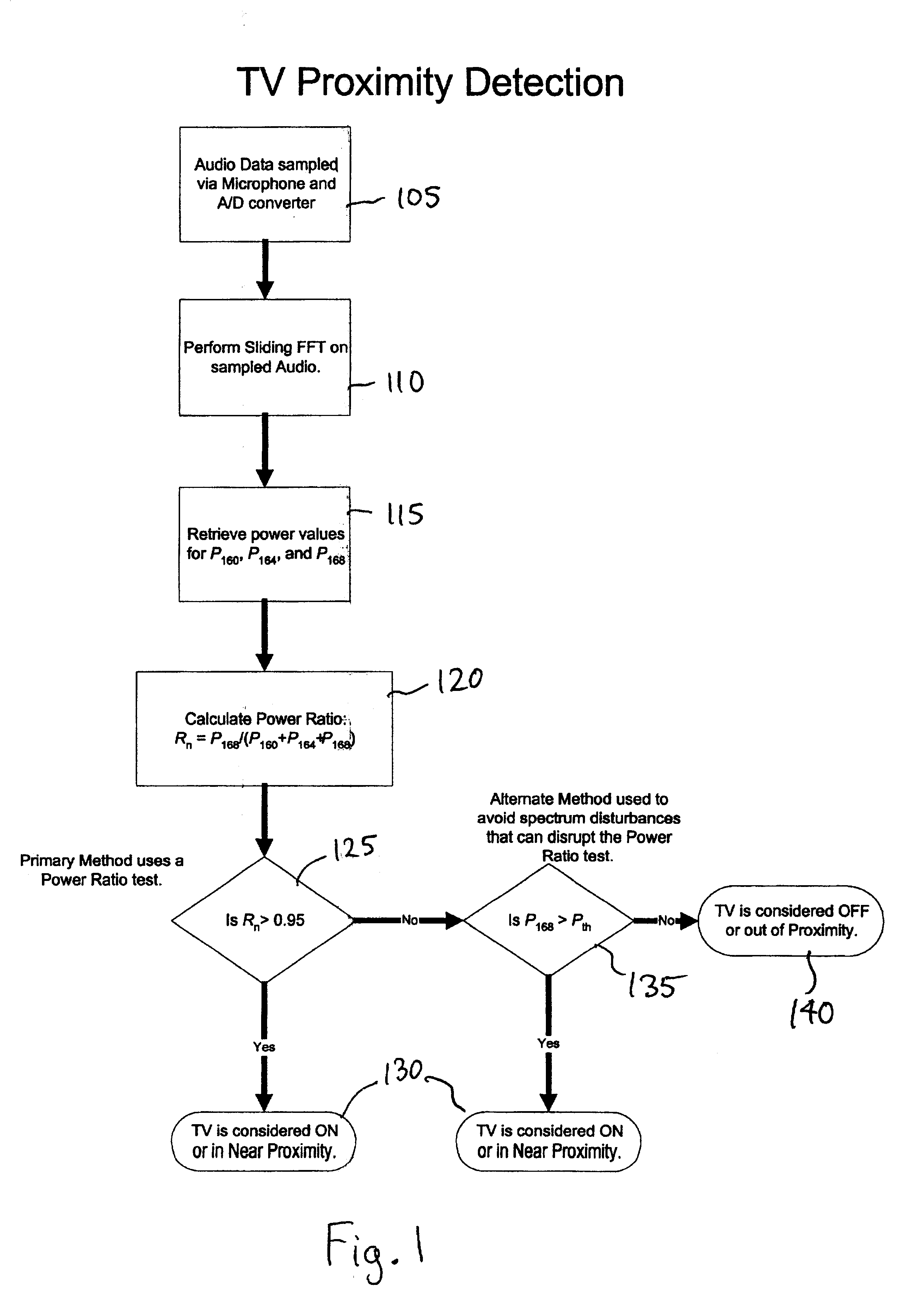
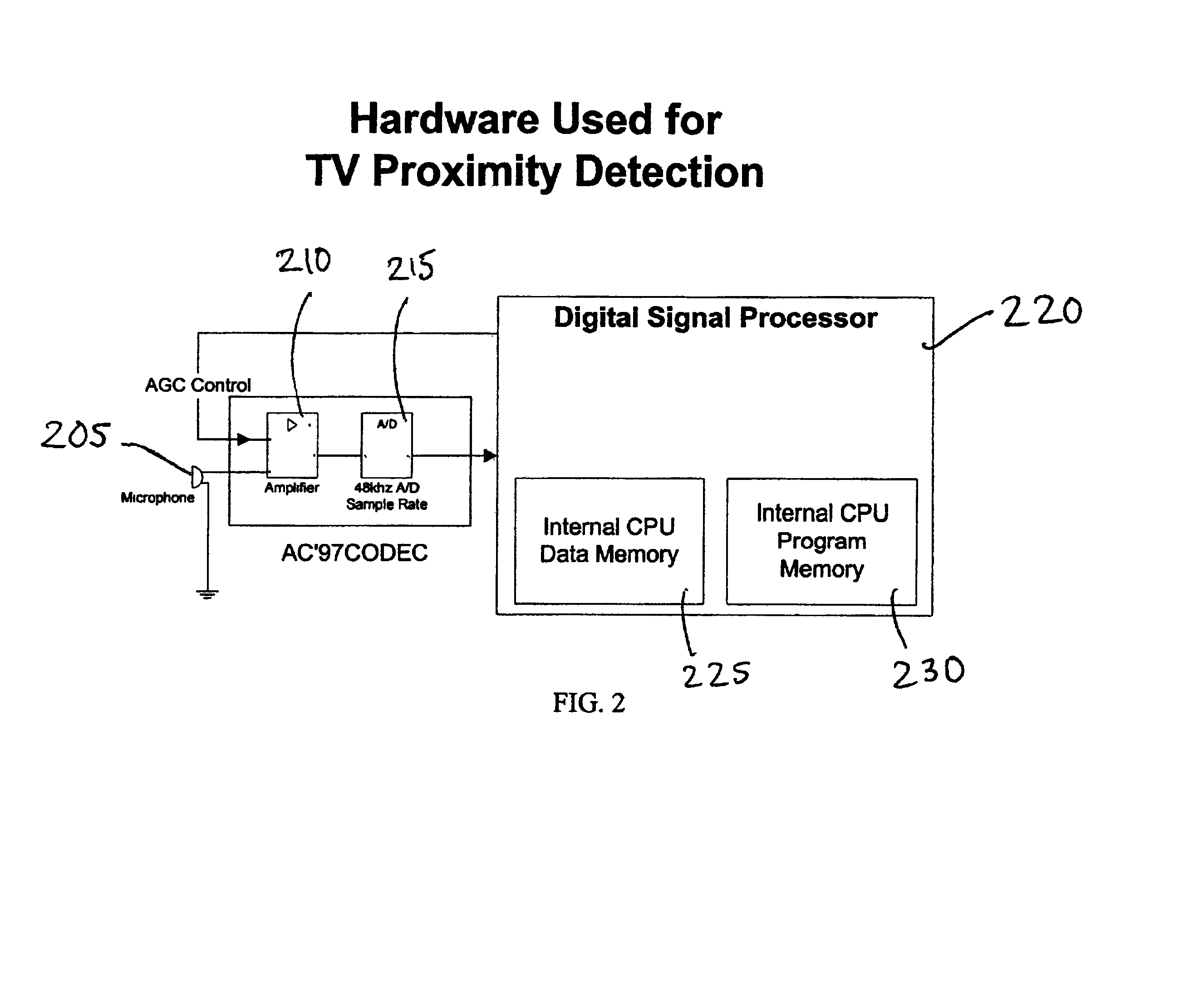
Television proximity sensor
ActiveUS7100181B2Analogue secracy/subscription systemsBroadcast components for monitoring/identification/recognitionProximity sensorDigital down converter
Systems and methods for determining whether a television is on and in as near proximity are provided. An example system includes a sensor, an analog-to-digital converter, and a digital signal processor. The digital signal processor processes a set of digital audio samples detected by the sensor to determine if the sensor is in near proximity to a television in an on state.
Owner:NIELSEN COMPANY US LLC THE A DELAWARE LIMITED LIABILITY
Linear FM radar
ActiveUS20070132630A1Small volumeEasy to operateAntenna feed intermediatesAntenna detailsRadar systemsDigital down converter
A FM-CW radar system comprises a frequency modulated continuous wave digital generator that produces both in-phase (I) and quadrature-phase (Q) outputs to orthogonally oriented transmitter antennas. A linearly polarized beam is output from a switched antenna array that allows a variety of I-and-Q pairs of bowtie antennas to be alternately connected to the transmitter and receiver. The receiver inputs I-and-Q signals from another bowtie antenna in the array and mixes these with samples from the transmitter. Such synchronous detection produces I-and-Q beat frequency products that are sampled by dual analog-to-digital converters (ADC's). The digital samples receive four kinds of compensation, including frequency-and-phase, wiring delay, and fast Fourier transform (FFT). The compensated samples are then digitally converted by an FFT-unit into time-domain signals. Such can then be processed conventionally for range information to the target that has returned the FM-CW echo signal.
Owner:LANDRAY TECH
Analog to digital converter using subranging and interpolation
InactiveUS6570523B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioAccurate representationElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersDigital down converterEngineering
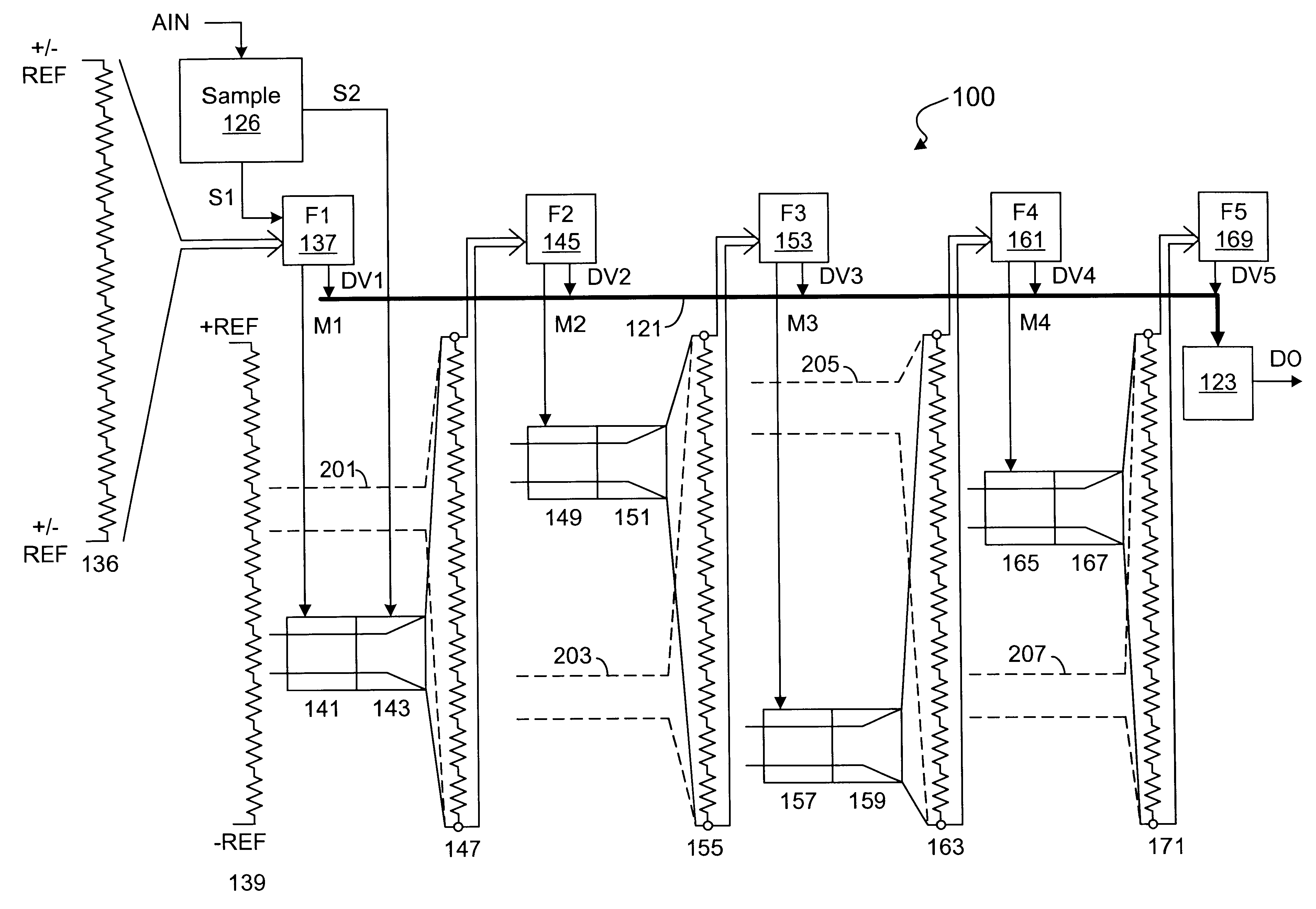
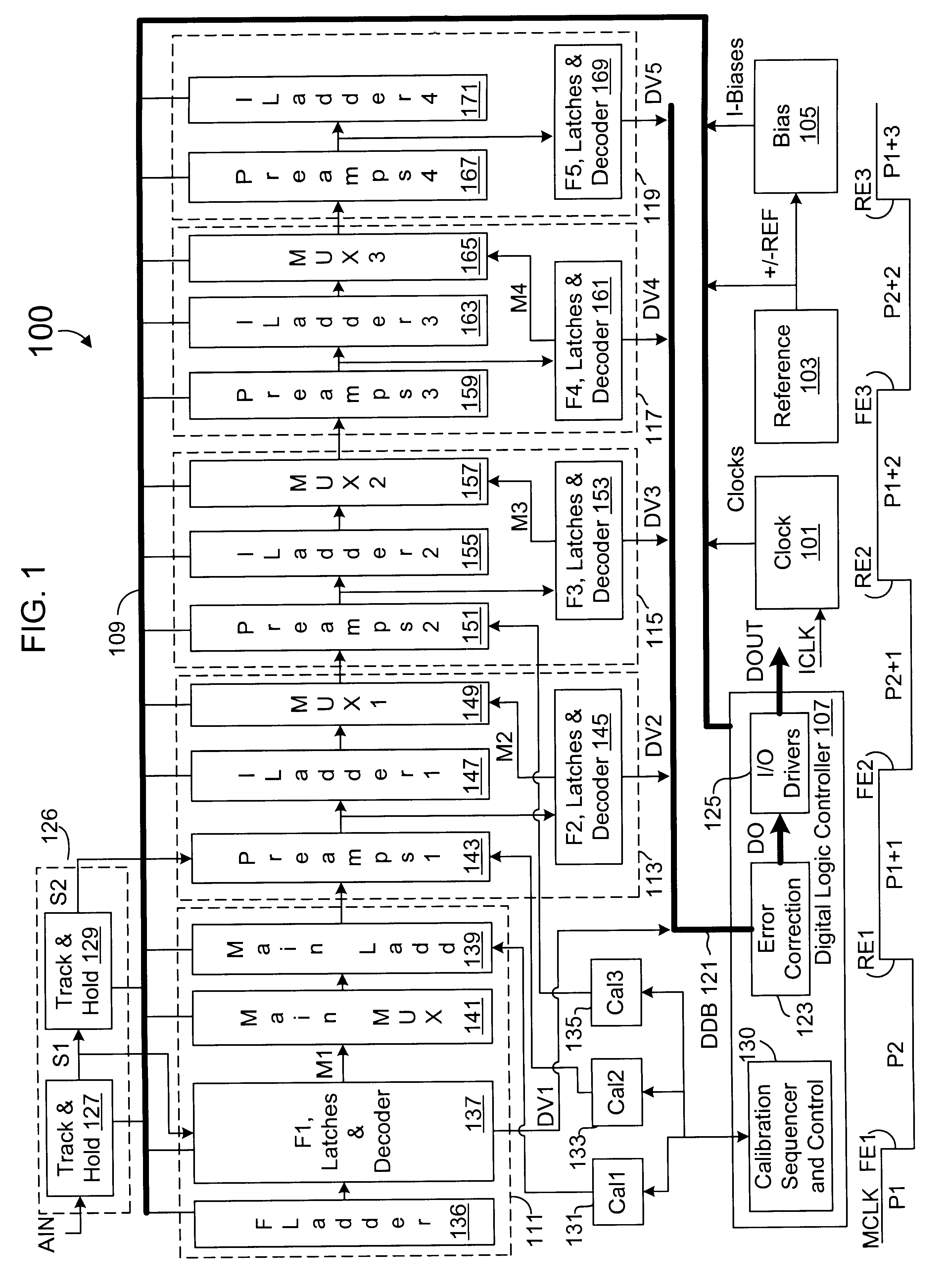
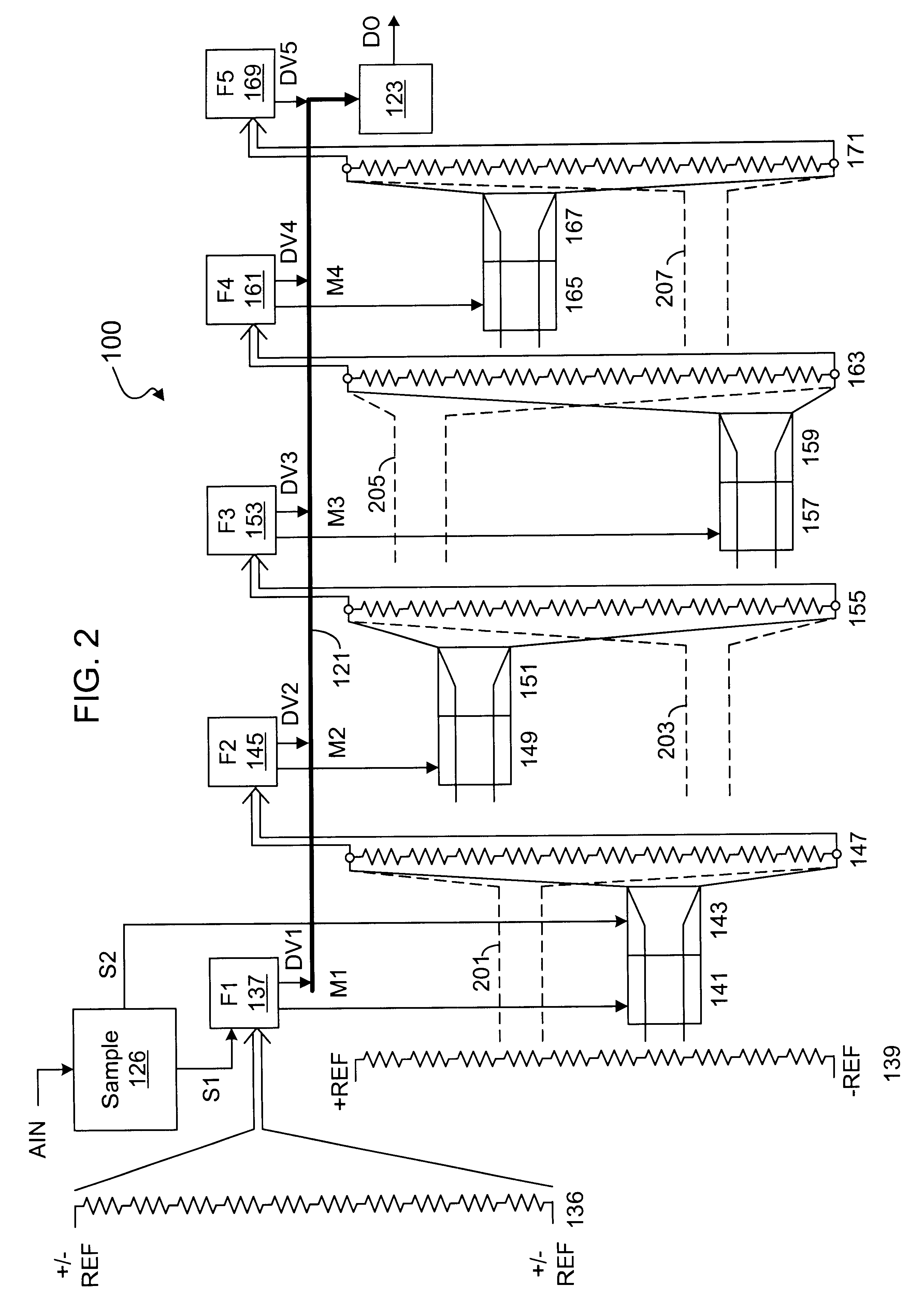
A multistage ADC that subranges and interpolates, and that amplifies selected subranges to convert an analog signal to a stream of digital values. The ADC samples the analog signal and provides a stream of sample signals. A first stage flash converts each sample signal into a first multiple bit value and subranges a reference ladder according to the first multiple bit value into selected reference signals. Each additional secondary stage amplifies a selected subrange of signals from a prior stage, flash converts the amplified residual signals to provide an additional multiple bit value, interpolates each set of amplified residual signals and subranges the interpolated signals according to the corresponding multiple bit value. A final stage amplifies and flash converts to determine a final multiple bit value. An error corrector combines each set of multiple bit values into a digital value.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
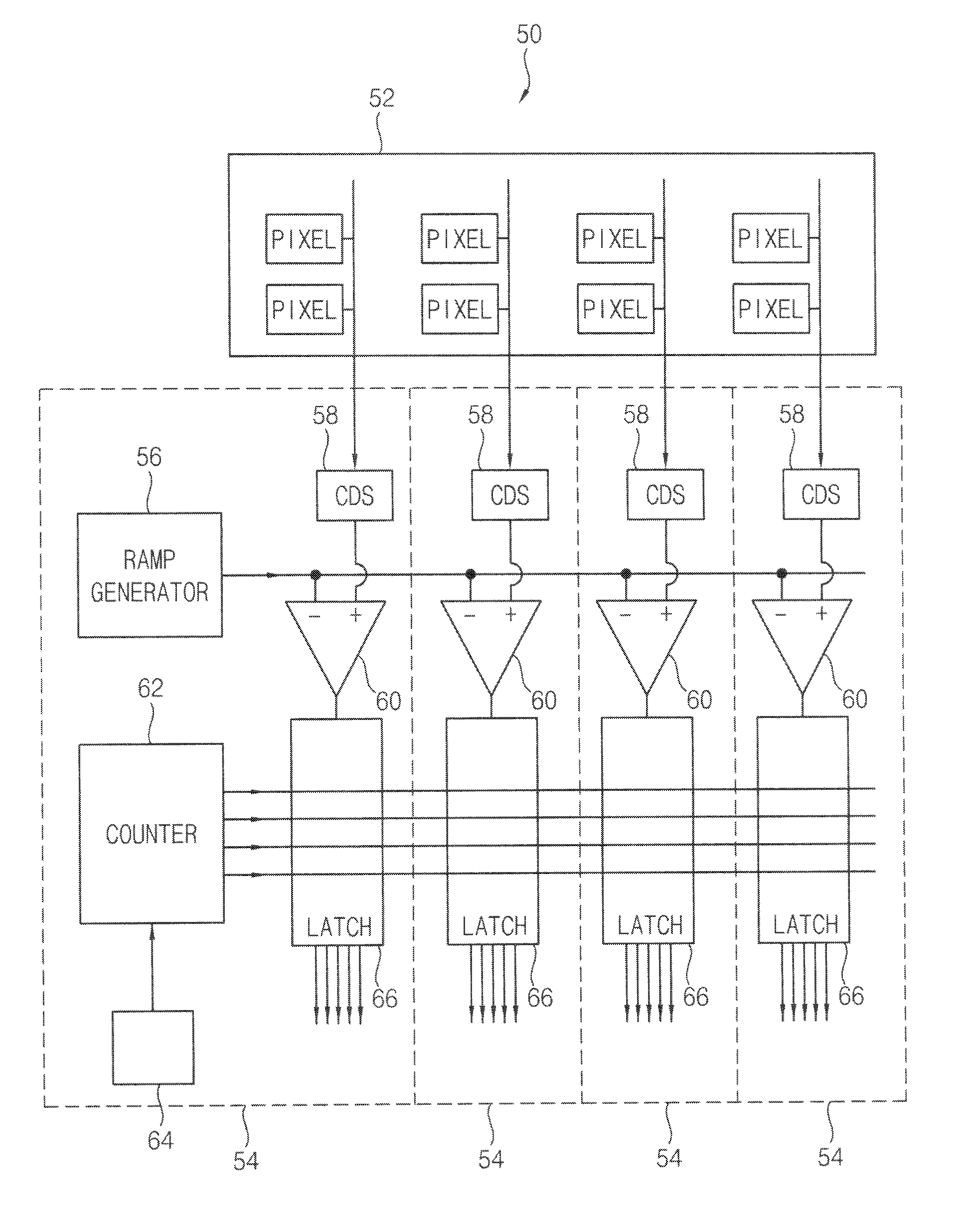
Double data rate (DDR) counter, analog-to-digital converter (ADC) using the same, CMOS image sensor using the same and methods in DDR counter, ADC and CMOS image sensor
InactiveUS20100225796A1Television system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsCMOSDouble data rate
In a double data rate (DDR) counter and counting method used in, for example, an analog-to-digital conversion in, for example, a CMOS image sensor and method, a first stage of the counter generates a least significant bit (LSB) of the value in the counter. The counter includes at least one second stage for generating another bit of the value in the counter. An input clock signal is applied to a data input of the first stage and a clock input of the second stage.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Time difference adders, time difference accumulators, sigma-delta time-to-digital converters, digital phase locked loops and temperature sensors
ActiveUS20120306553A1Computations using contact-making devicesPulse automatic controlDigital down converterProcessor register
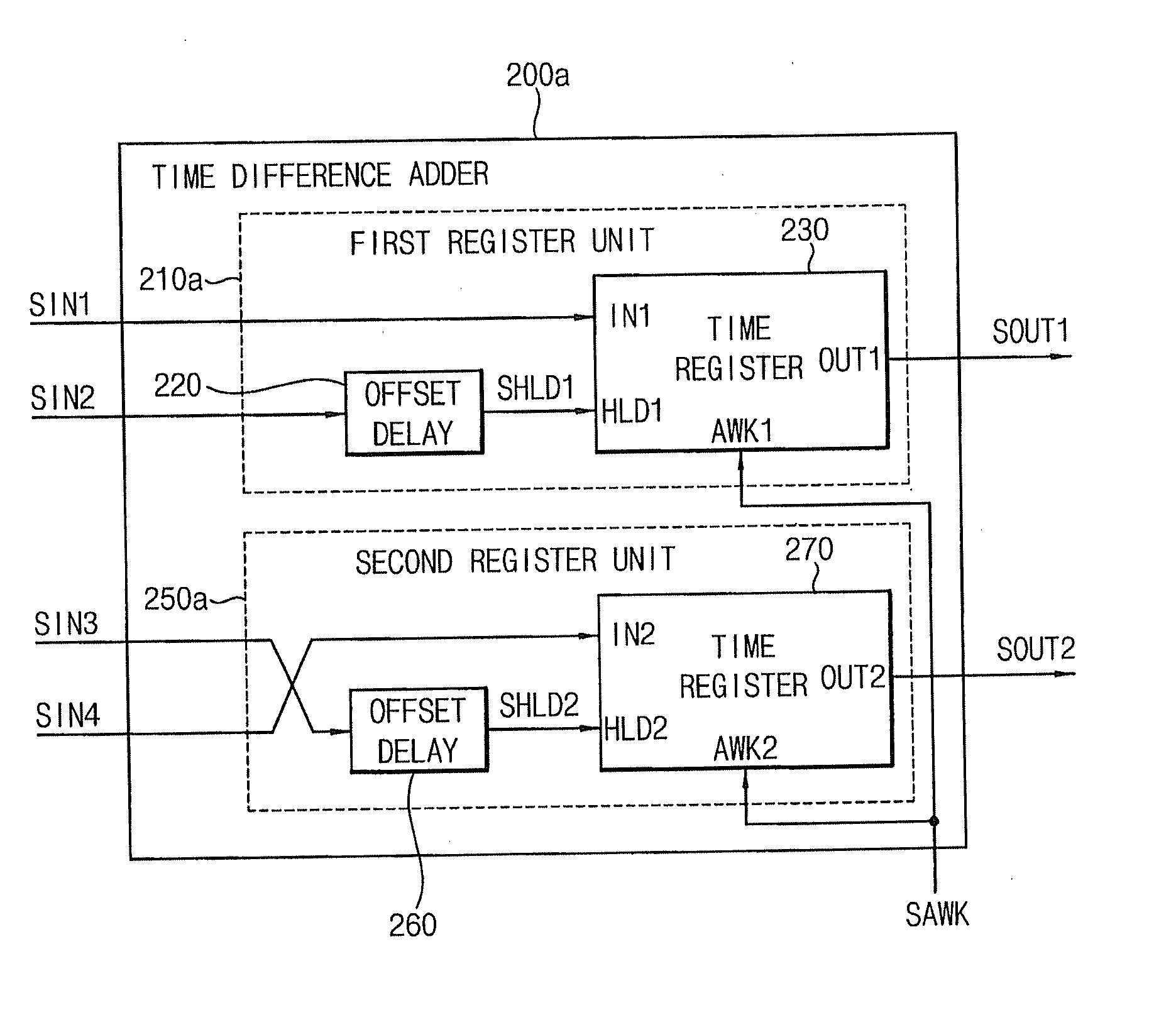
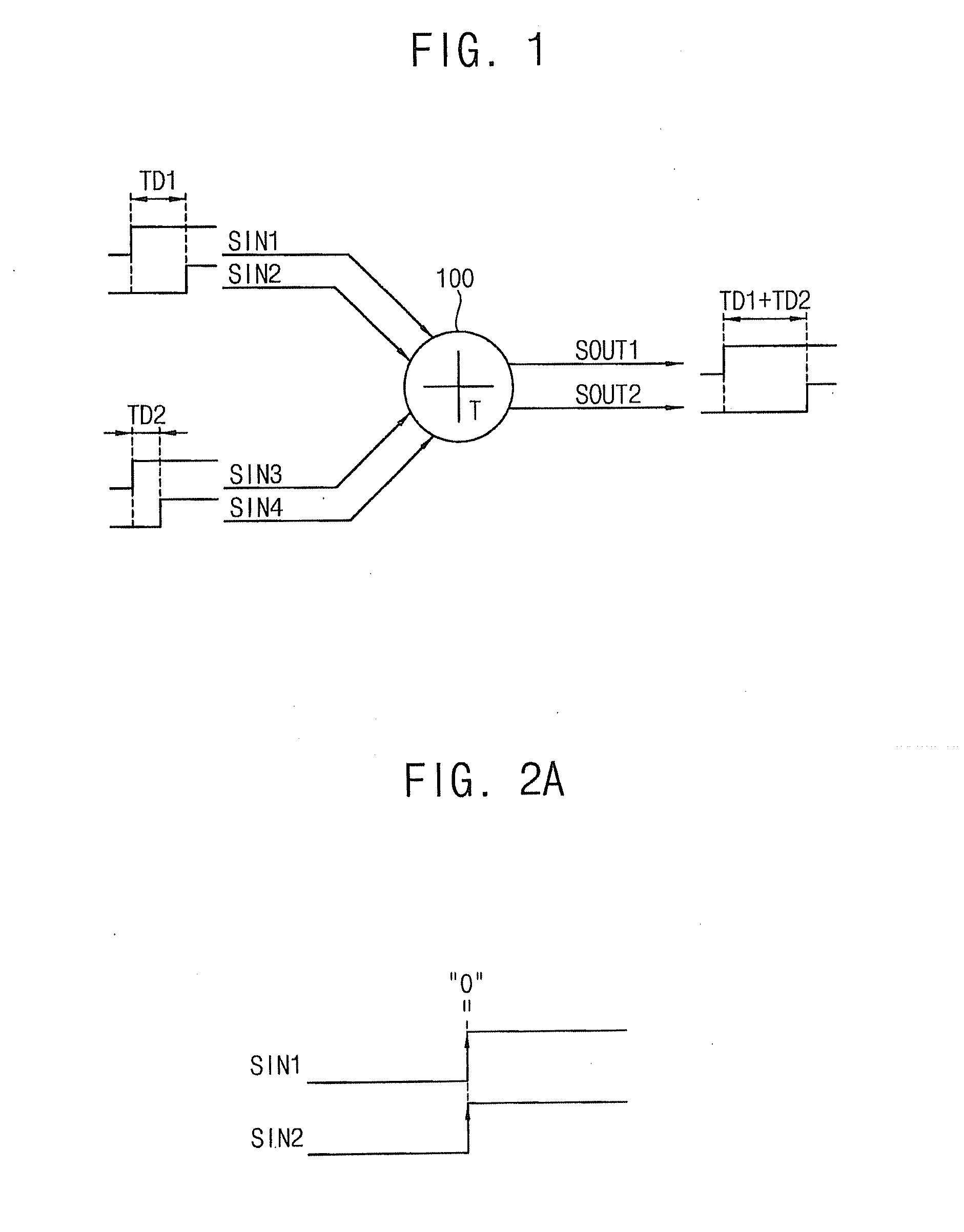
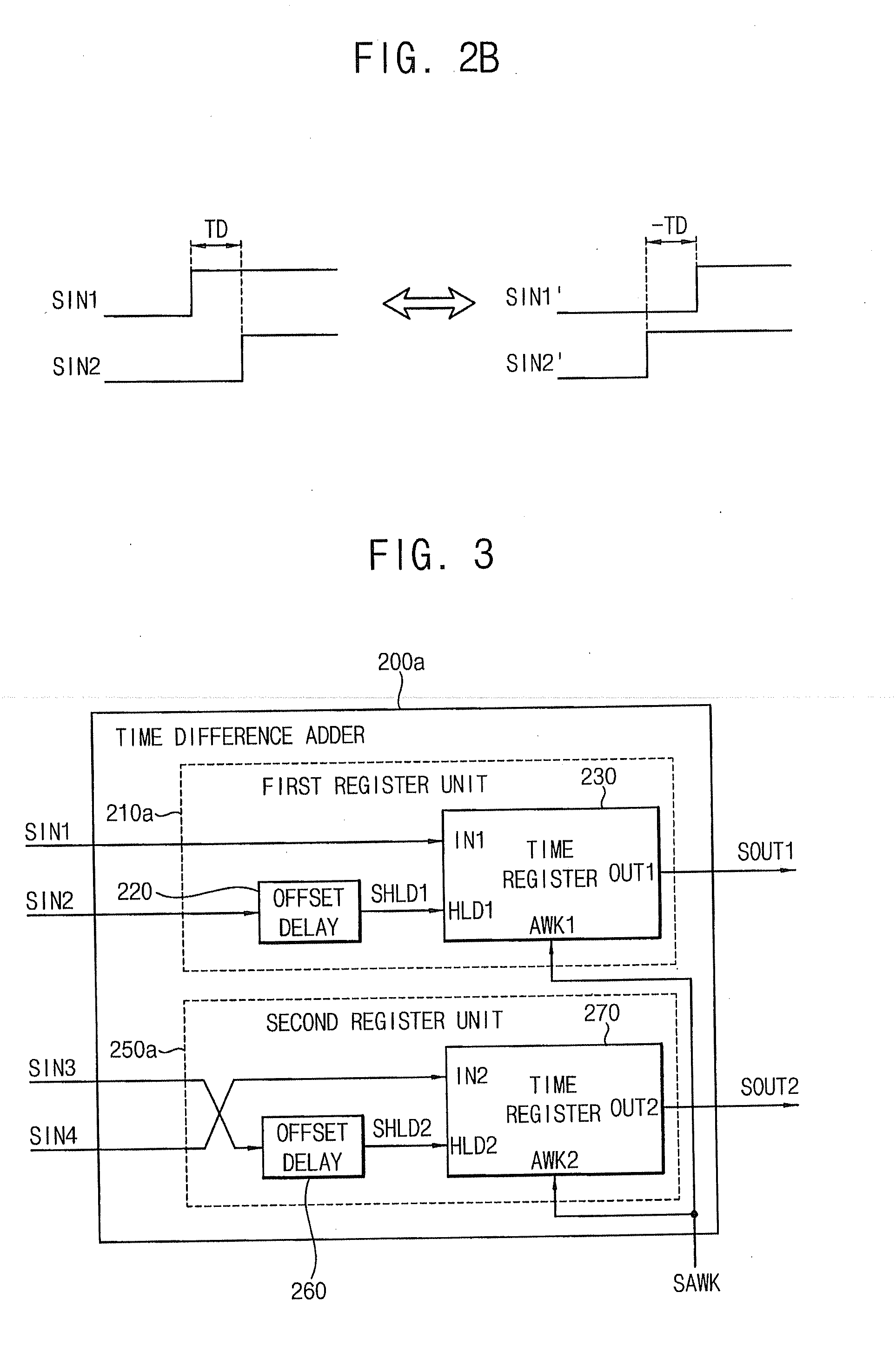
A time difference adder included in a system-on-chip (SOC) includes a first register unit and a second register unit. The first register unit is configured to receive first and second input signals having a first time difference, and generate a first output signal in response to a first signal. The second register unit is configured to receive third and fourth input signals having a second time difference, and generate a second output signal having a third time difference with respect to the first output signal in response to the first signal. The third time difference corresponds to a sum of the first time difference and the second time difference.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
One-chip microcomputer with analog-to-digital converter
InactiveUS6839014B2Reduce electric powerReduce power consumptionPower saving provisionsElectric signal transmission systemsMicrocontrollerDigital data
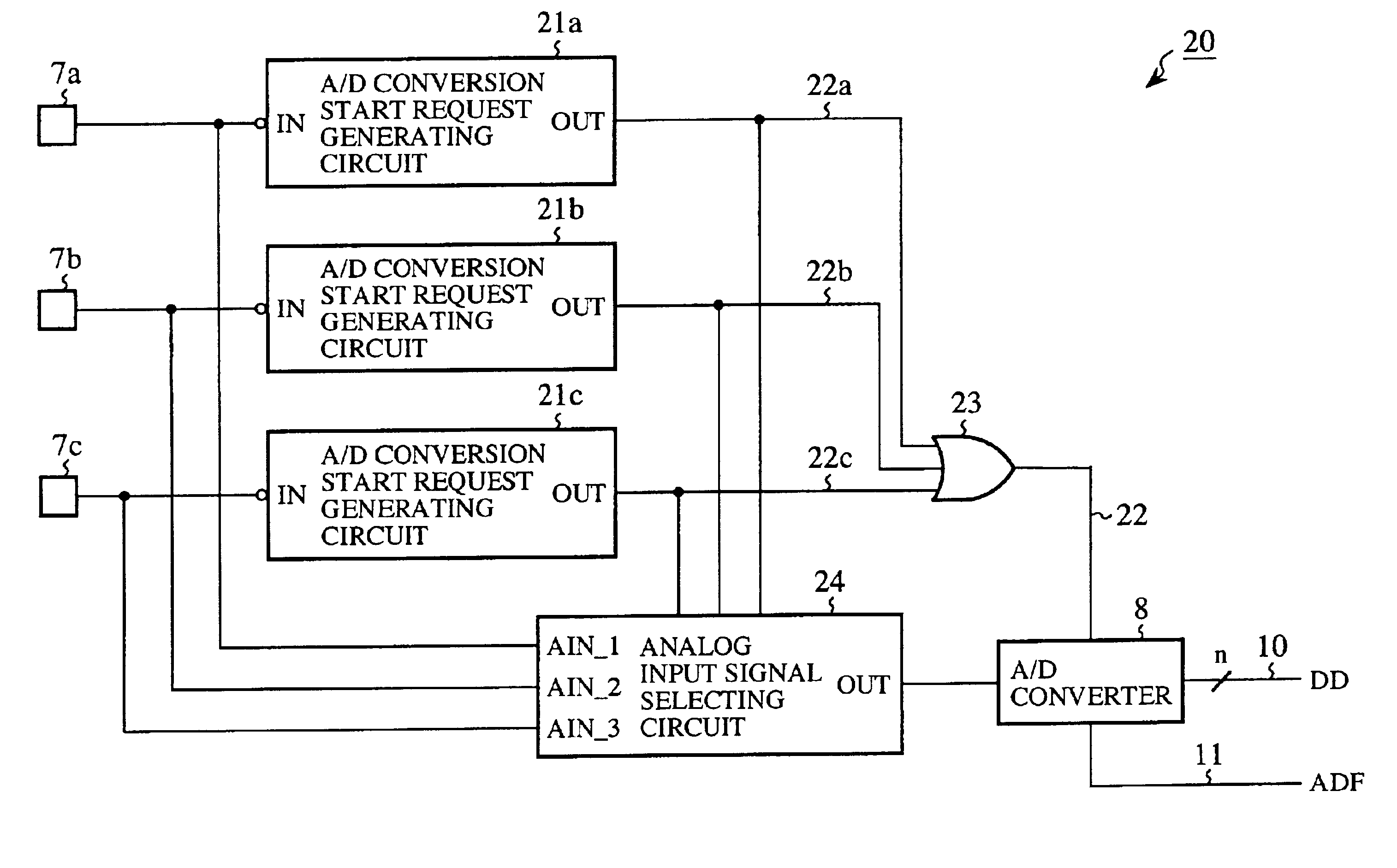
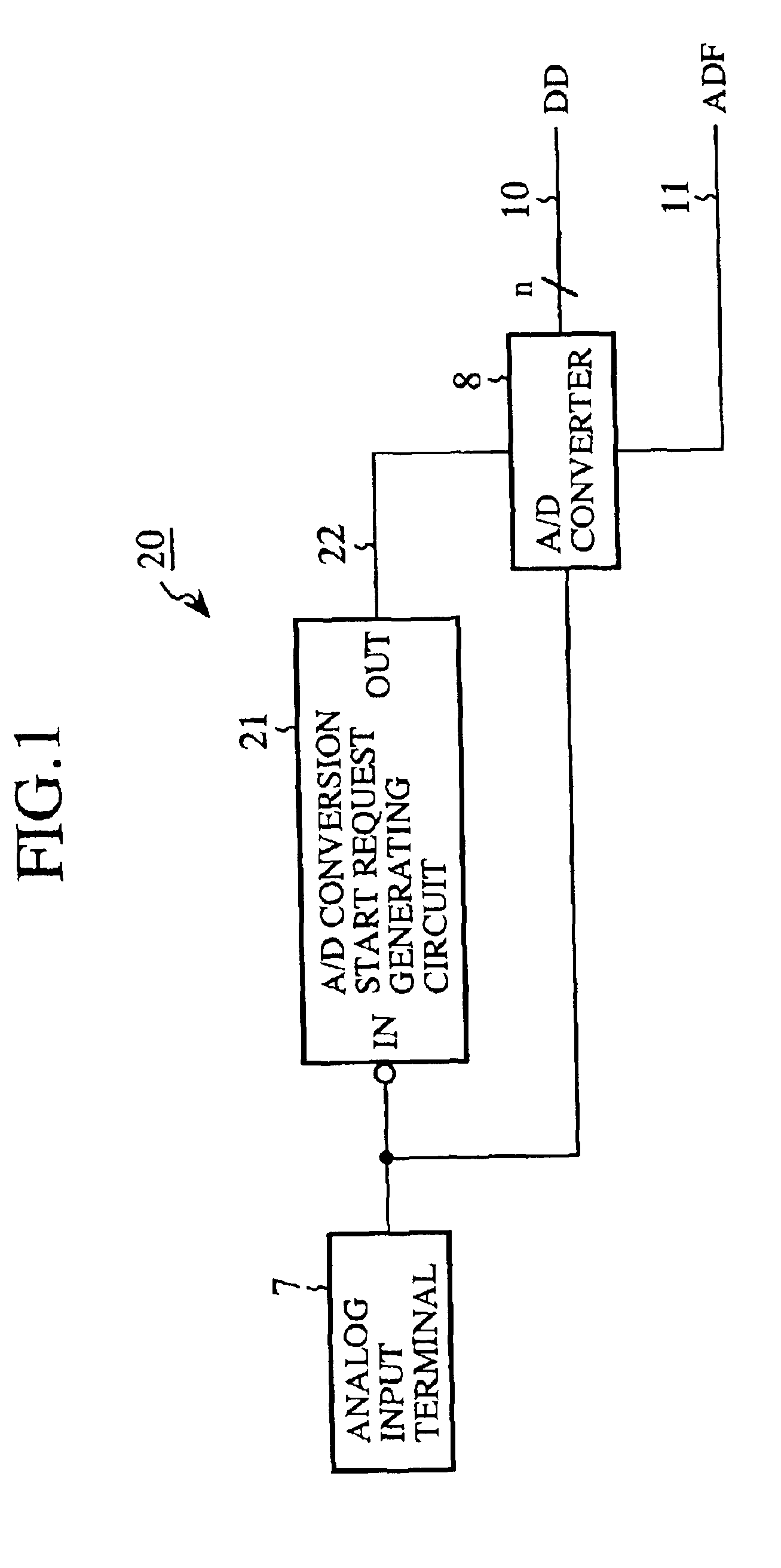
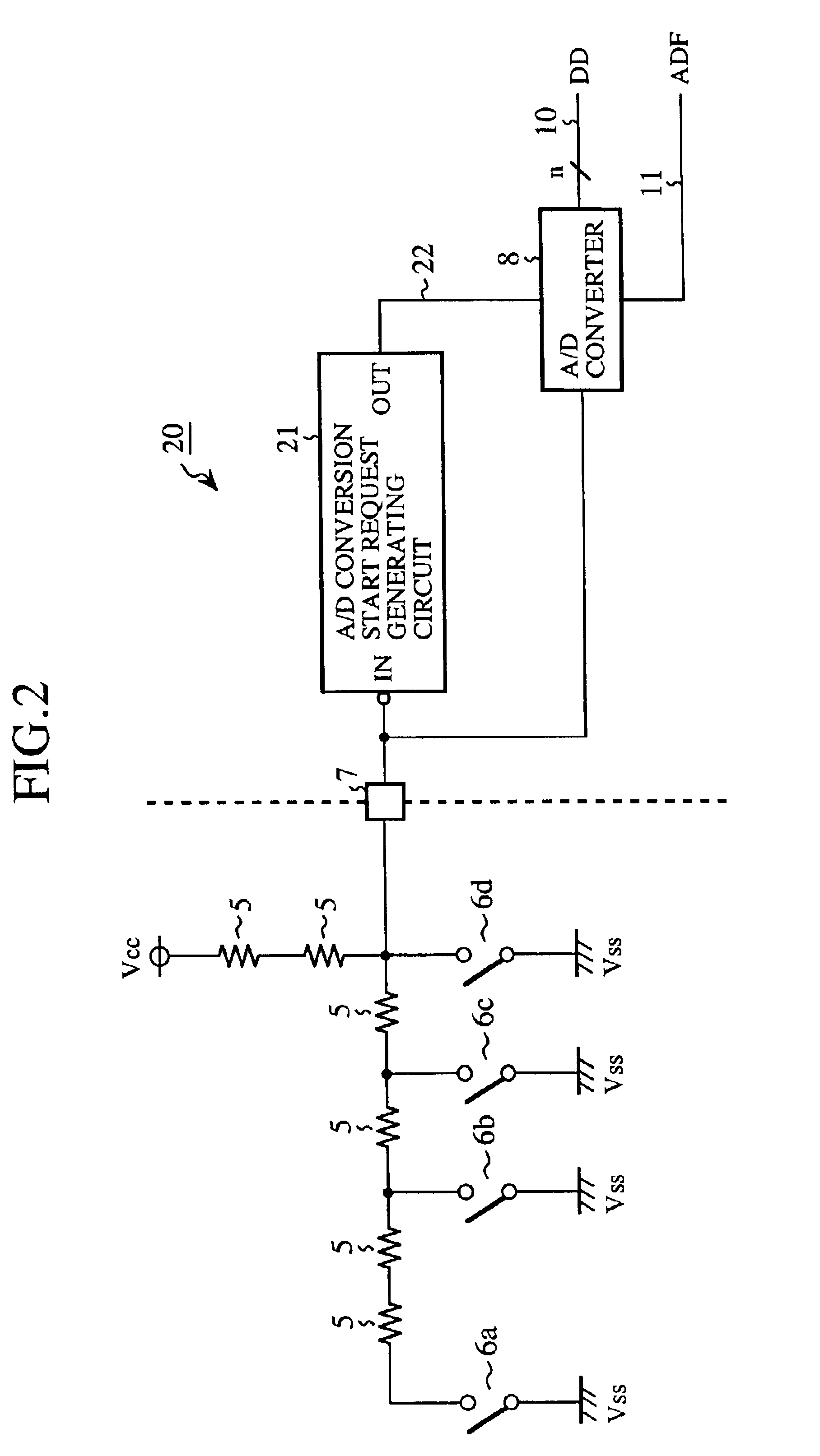
An input circuit of a one-chip microcomputer is connected to an external switching circuit. When an analog input signal of a significant level generated in the external switching circuit is received at an analog input terminal of the input circuit, an A / D conversion start request signal is generated in an A / D conversion start request generating circuit and is sent to an A / D converter. The operation of the A / D converter is started in response to the A / D conversion start request signal, the analog input signal received at the analog input terminal is converted into digital data, and an A / D conversion finish signal is sent from the A / D converter to a CPU of the one-chip microcomputer. The operation of the CPU is started in response to the A / D conversion finish signal, and the digital data is readout to the CPU. Therefore, the A / D converter, the CPU or a clock is not operated to wait for an analog input signal generated in the external switching circuit, but the A / D converter is operated for the A / D conversion, and the CPU is operated to read out the digital data. Accordingly, an electric power consumed in the A / D converter, the CPU and the clock can be reduced.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP +1
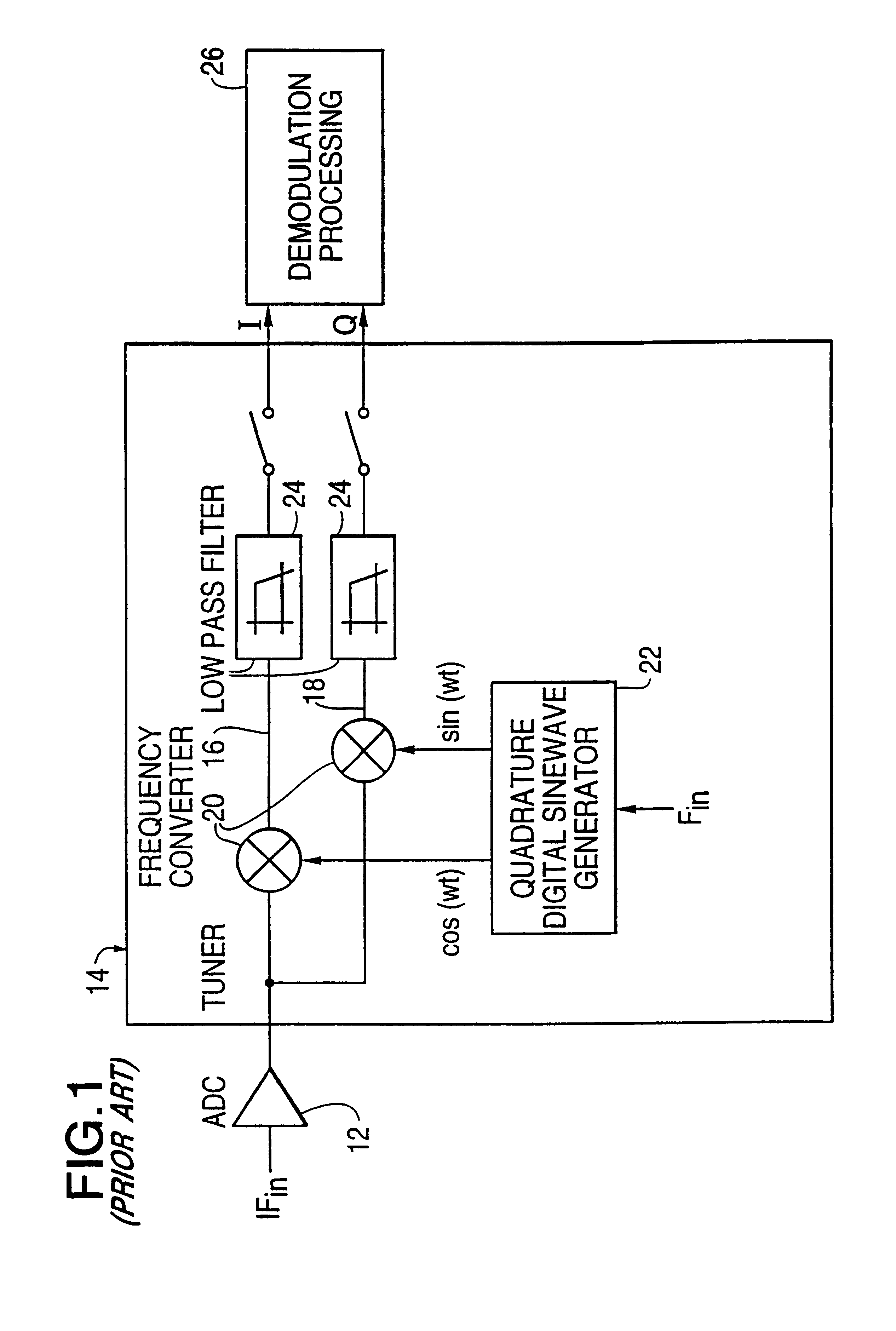
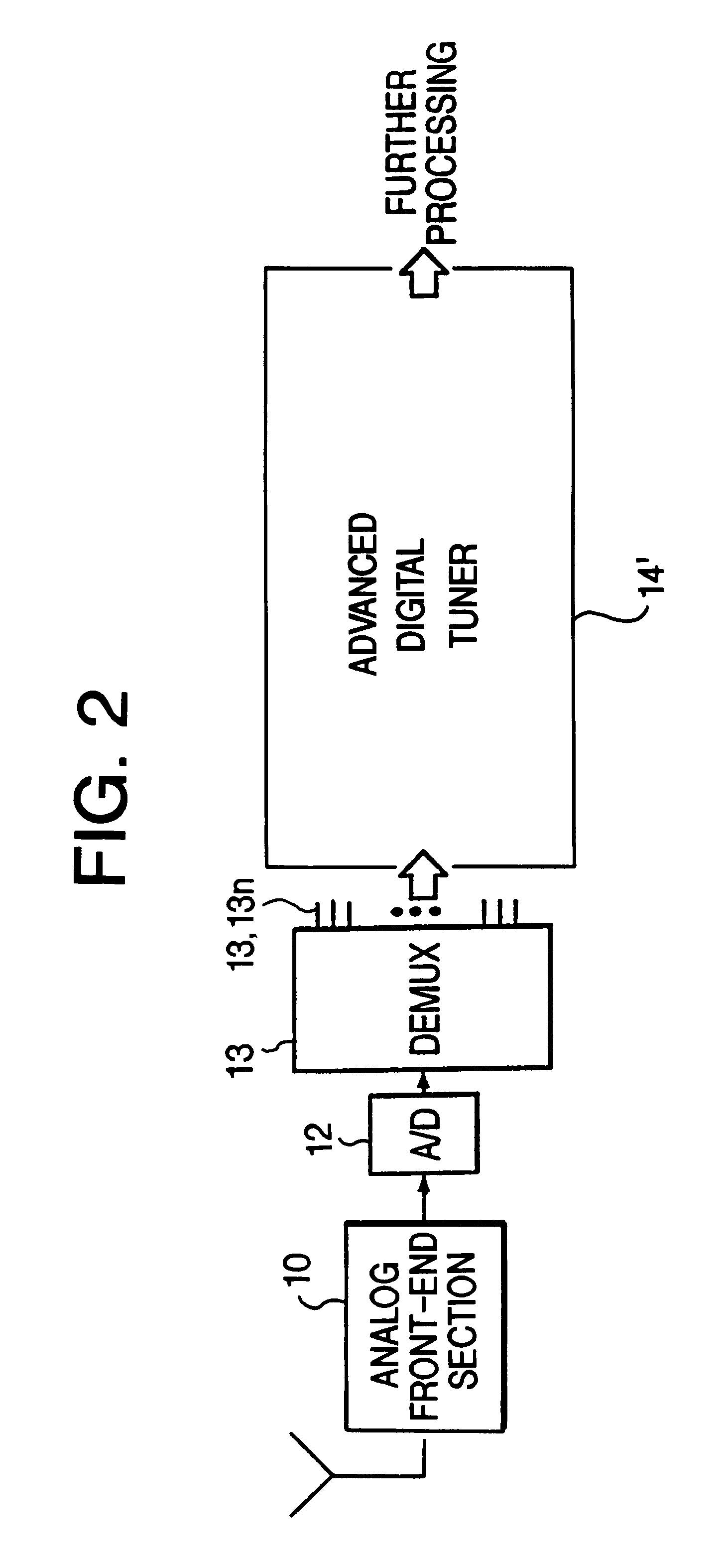
Wideband parallel processing digital tuner
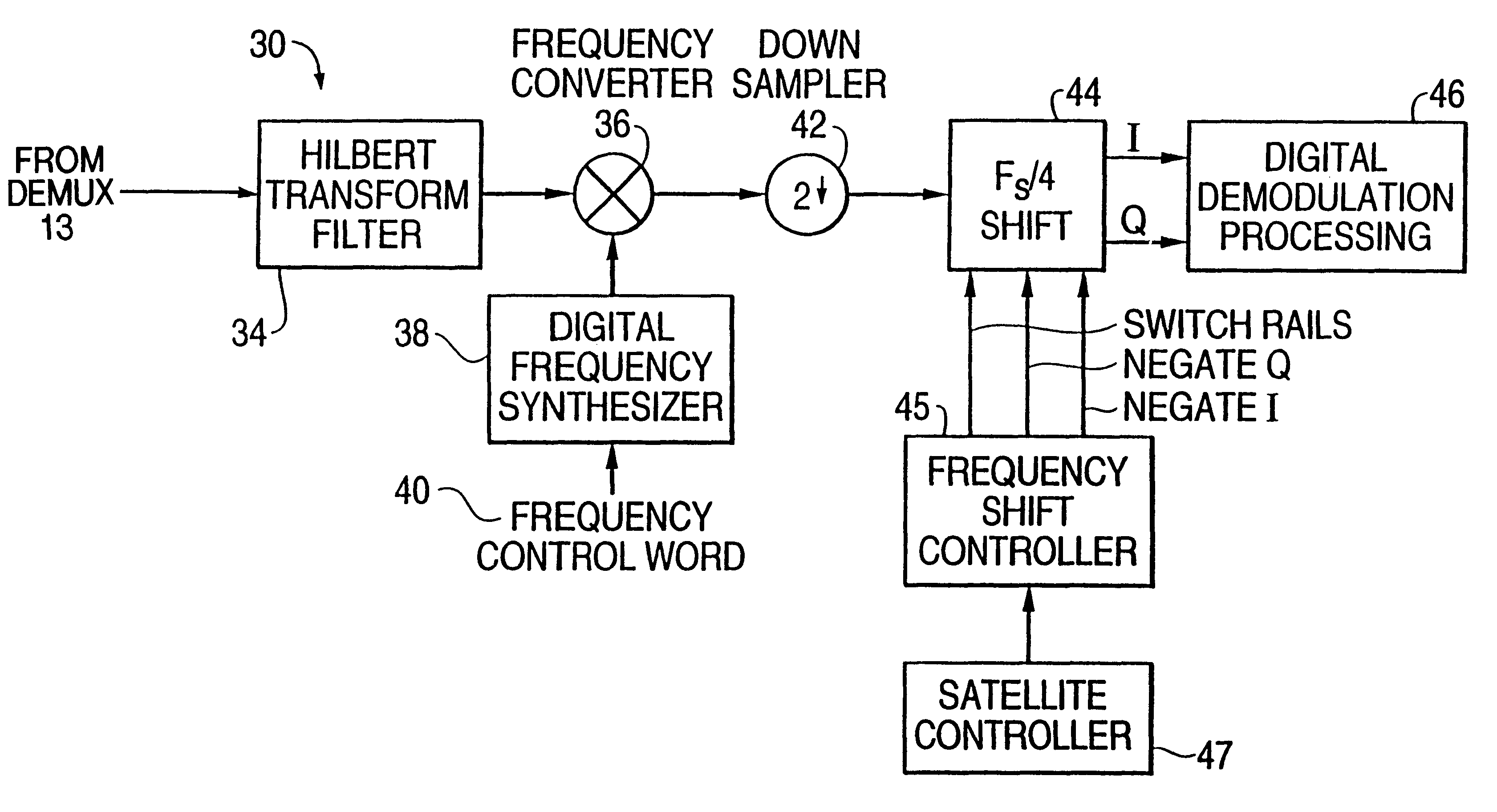
InactiveUS6263195B1High speed data rateAvoid disadvantagesPolarisation/directional diversityPhase-modulated carrier systemsDigital dataFrequency spectrum
A wideband digital tuner (14') has an analog front-end section (10), a high speed analog-to-digital converter (12), demultiplexer (13) and a plurality of filters (341-342) arranged in a parallel input architecture to process wideband digital data received at extremely high sampling rates, such as at 2 Gsps (giga-samples per second). The tuner greatly attenuates an undesired spectral half of the wide bandwidth digital spectrum of the incoming digital signal using a complex band-pass filter, such as a Hilbert Transform filter. The tuner places the remaining half of the wide bandwidth digital spectrum of the incoming digital signal at complex baseband and down samples by 2. The architecture of the tuner can be partitioned into two separate halves which are hardware copies of each other.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
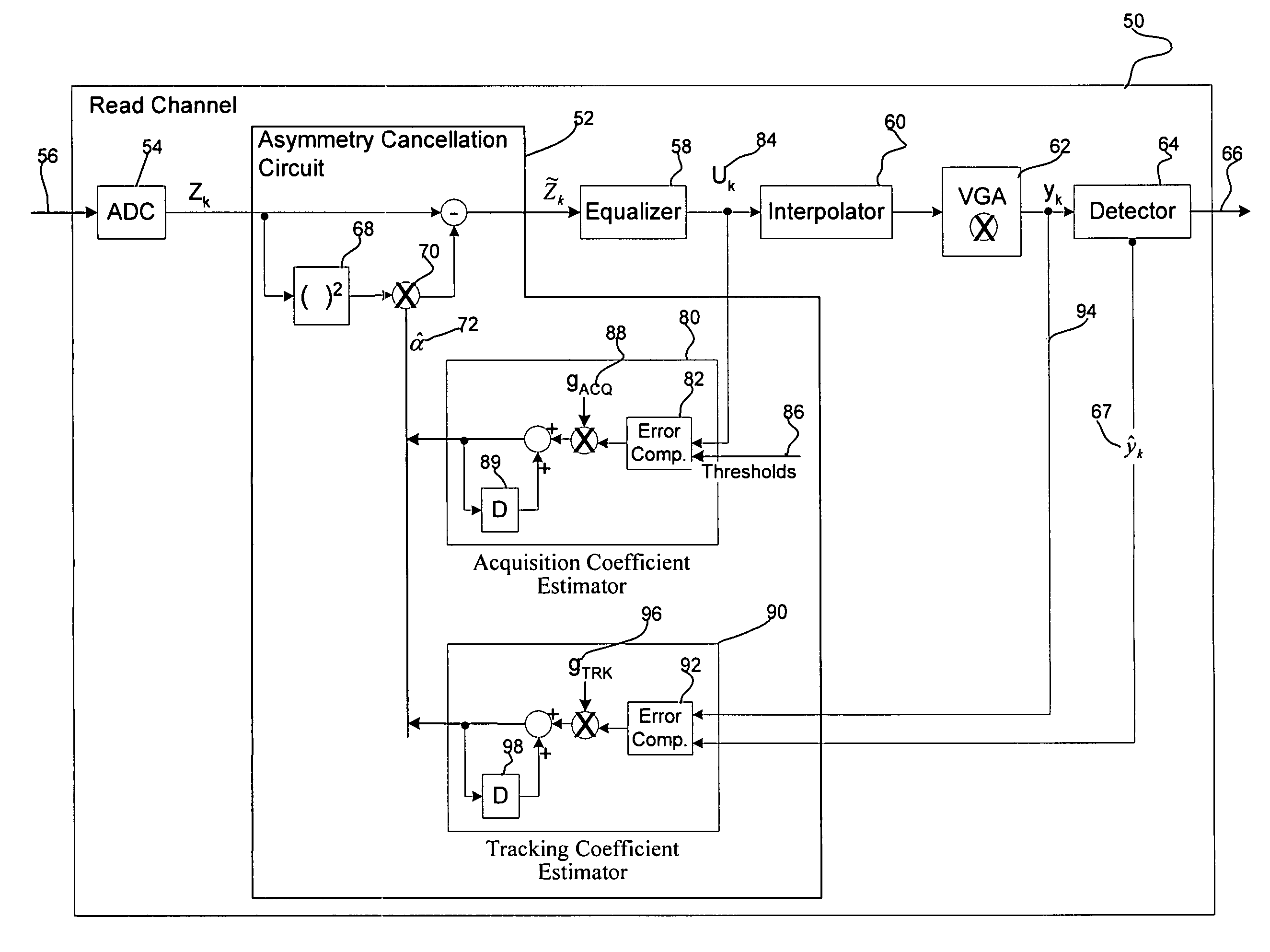
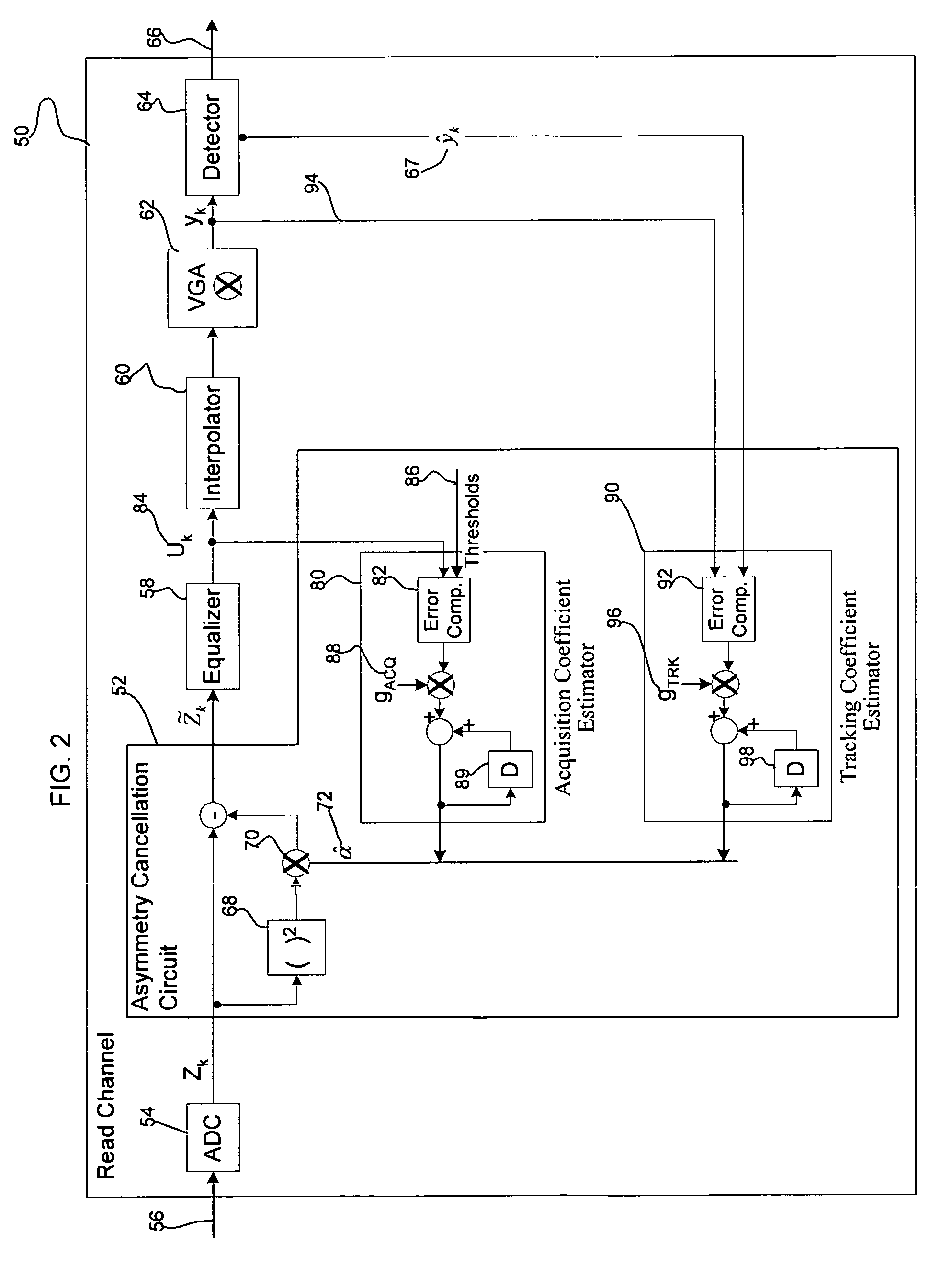
Dynamic method for asymmetry compensation in a storage read channel
Provided is a dynamic method for asymmetry compensation in a storage read channel. An asymmetry cancellation component in communication with an analog-to-digital converter receives an analog signal representing data read from a storage medium by a read head. The asymmetry cancellation component receives a digital signal from the analog-to-digital converter representing data read from the storage medium and computes an error signal indicating an asymmetry in the digital signal. The computed error signal is used to determine a coefficient. The digital signal is adjusted using the coefficient to produce a corrected digital signal.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
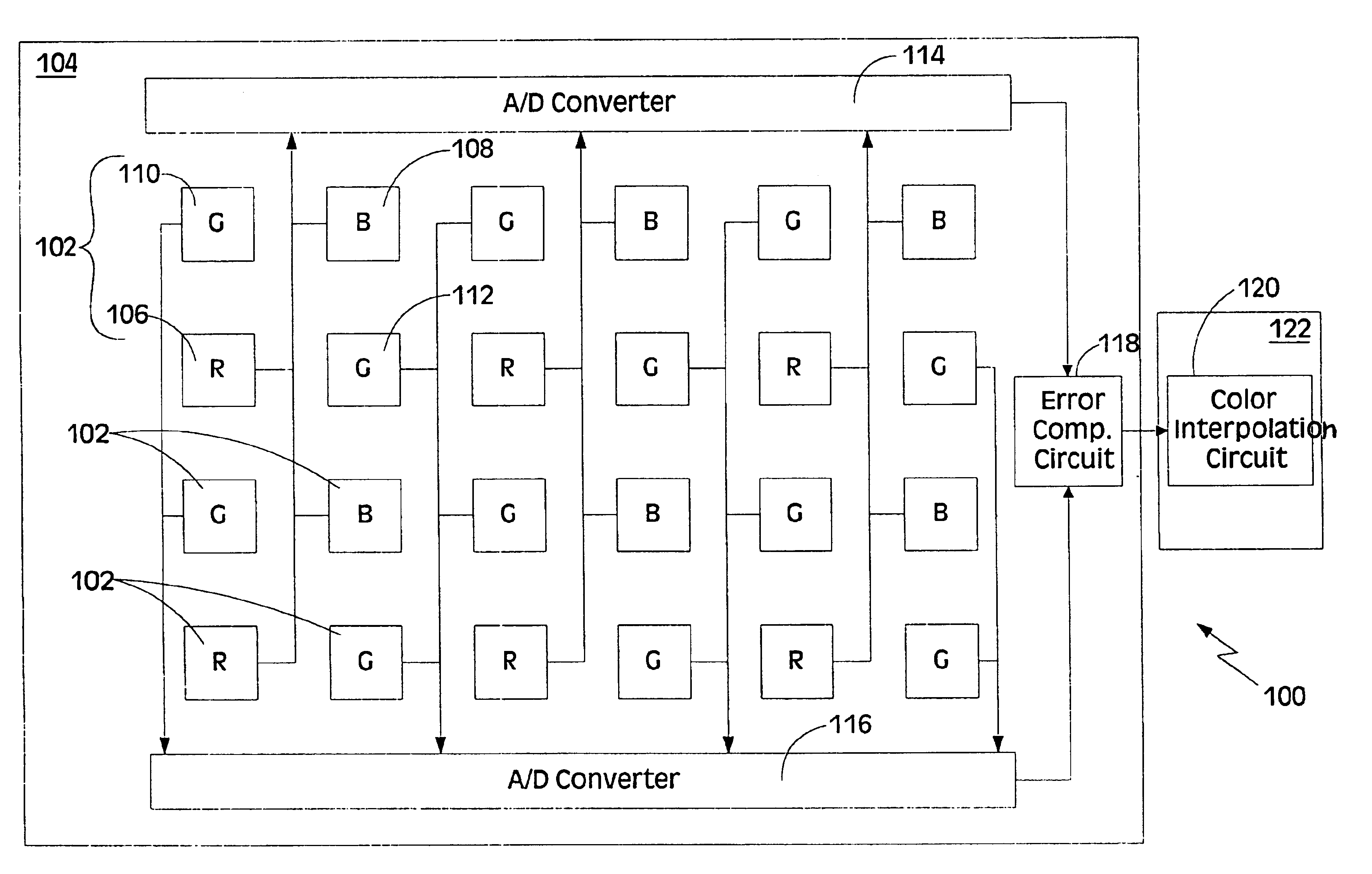
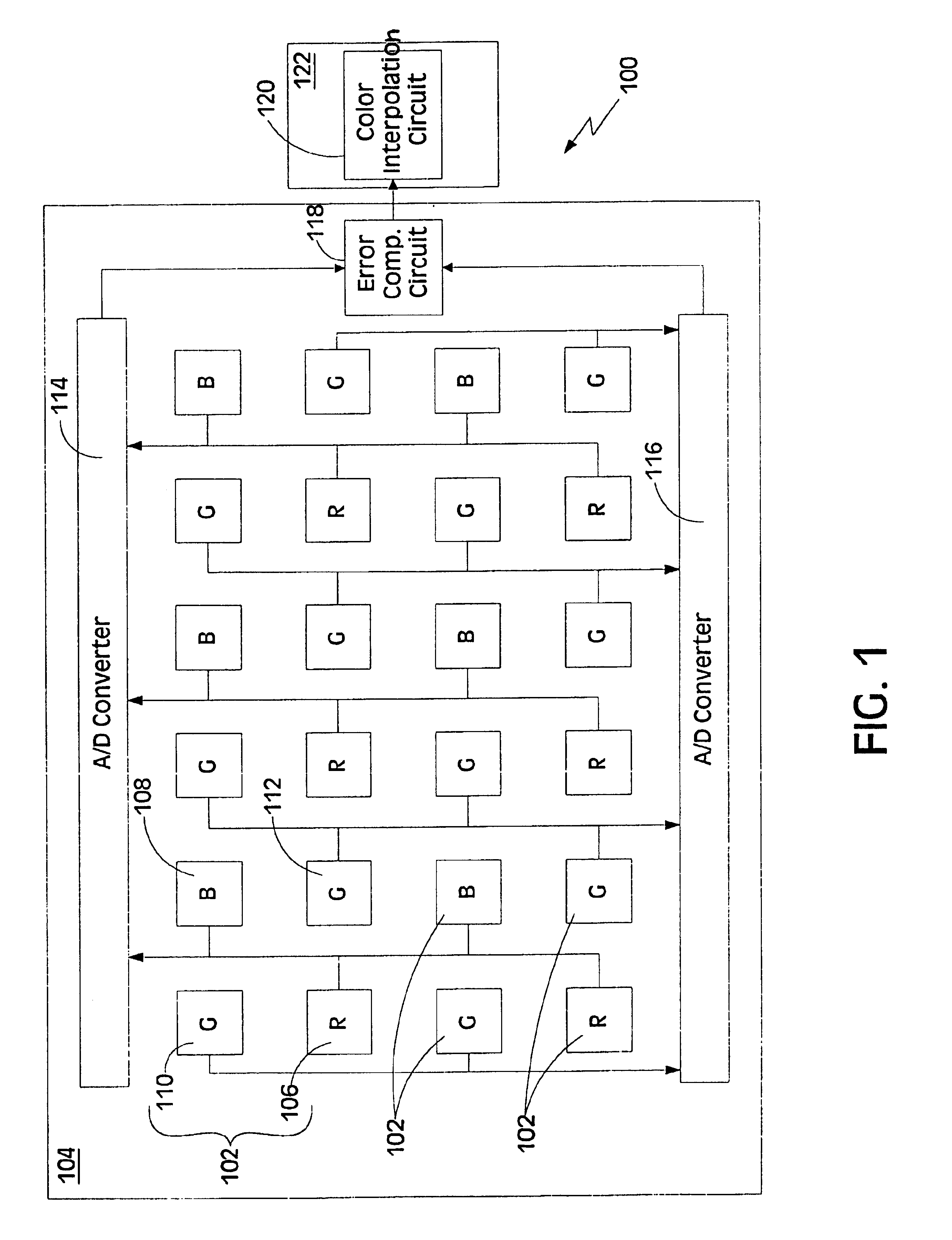
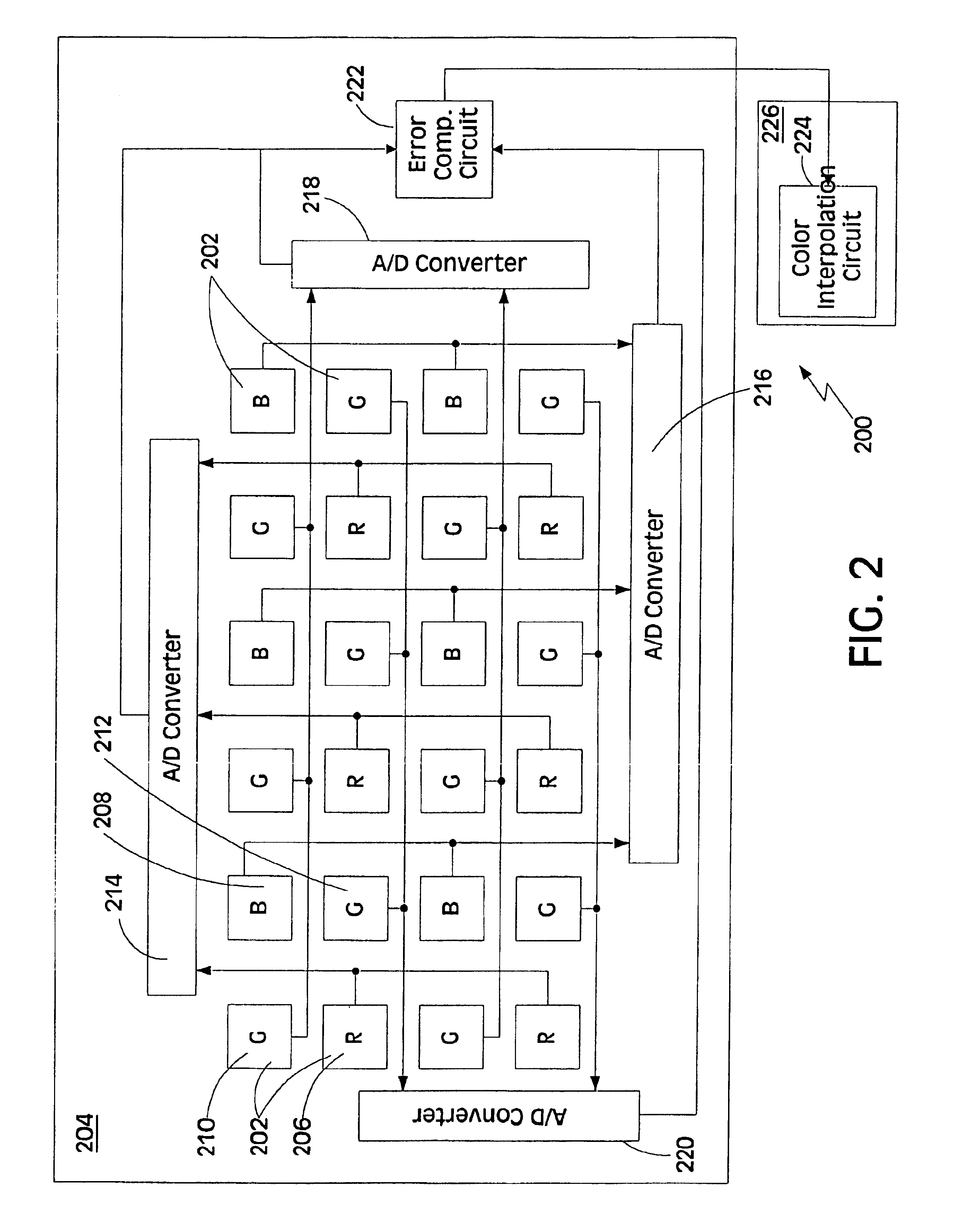
High sensitivity snap shot CMOS image sensor
InactiveUS6838651B1Save powerIncrease clock frequencyRadiation pyrometrySolid-state devicesCMOSDigital down converter
The present invention is directed to a solid state imaging device comprising a red pixel, a blue pixel, a first green pixel, a second green pixel, two analog-to-digital converters and a color interpolation circuit. The first analog-to-digital converter converts the output of the red pixel and output of the blue pixel into digital signals. The second analog-to-digital converter converts the output of the first green pixel and output of the second green pixel into digital signals. The color interpolation circuit combines the digital signals to determine the color of the pixel.The solid state imaging device may further comprise a third analog-to-digital converter, a fourth analog-to-digital converter, a programmable clock generator and a control. The third analog-to-digital converter converts the output of the blue pixel into a digital signal and the fourth analog-to-digital converter converts the output of the second green pixel into a digital signal. The programmable clock generator has a first clock frequency and a second clock frequency, where the first clock frequency is slower than the second clock frequency. The control is coupled to the programmable clock generator, the third analog-to-digital converter and the fourth analog-to-digital converter. The control deactivates the third and fourth analog-to-digital converters if the programmable clock generator is at the first clock frequency, and the control activates the third and fourth analog-to-digital converters if the programmable clock generator is at the second clock frequency.
Owner:ESS TECH INT INC +1
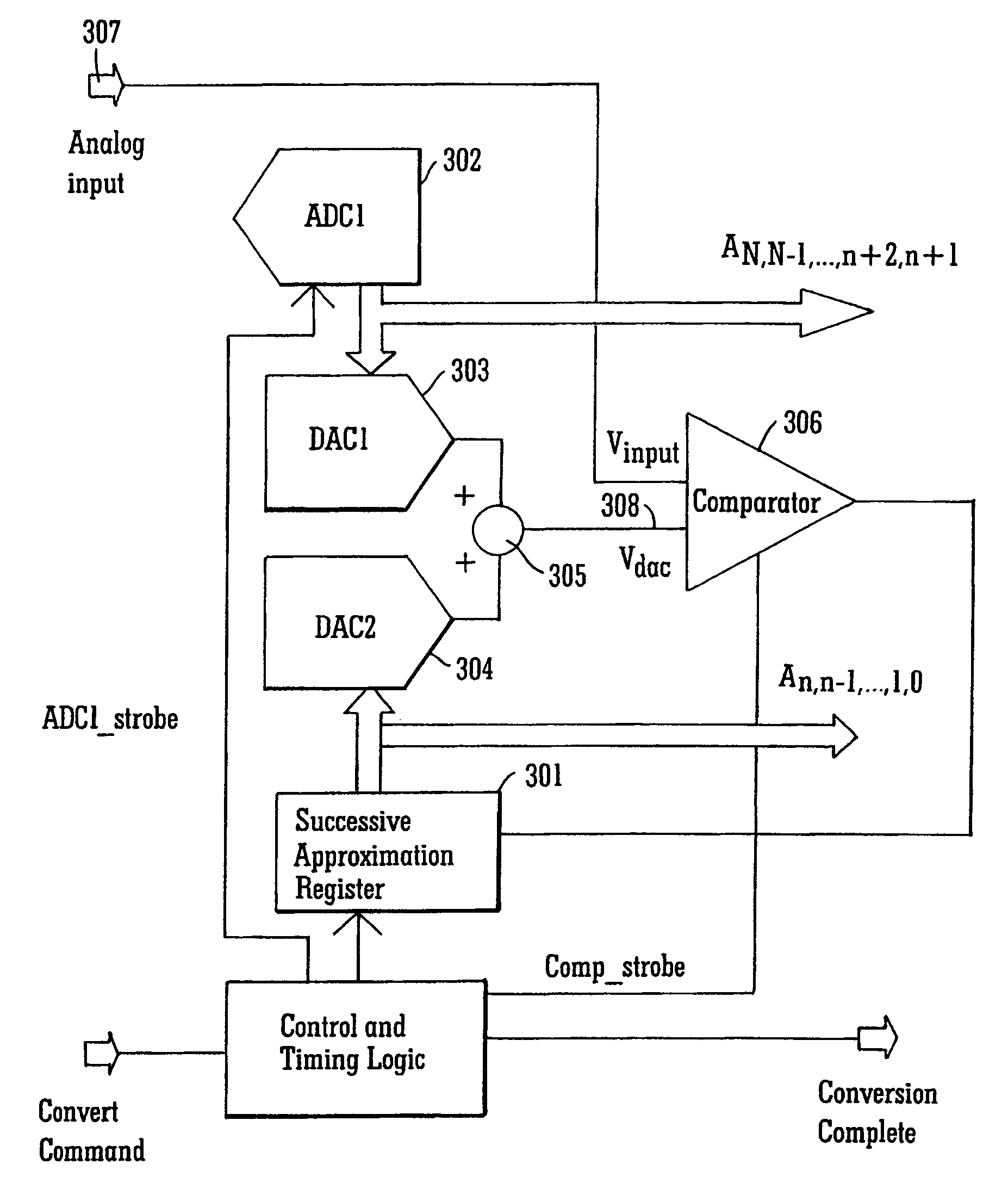
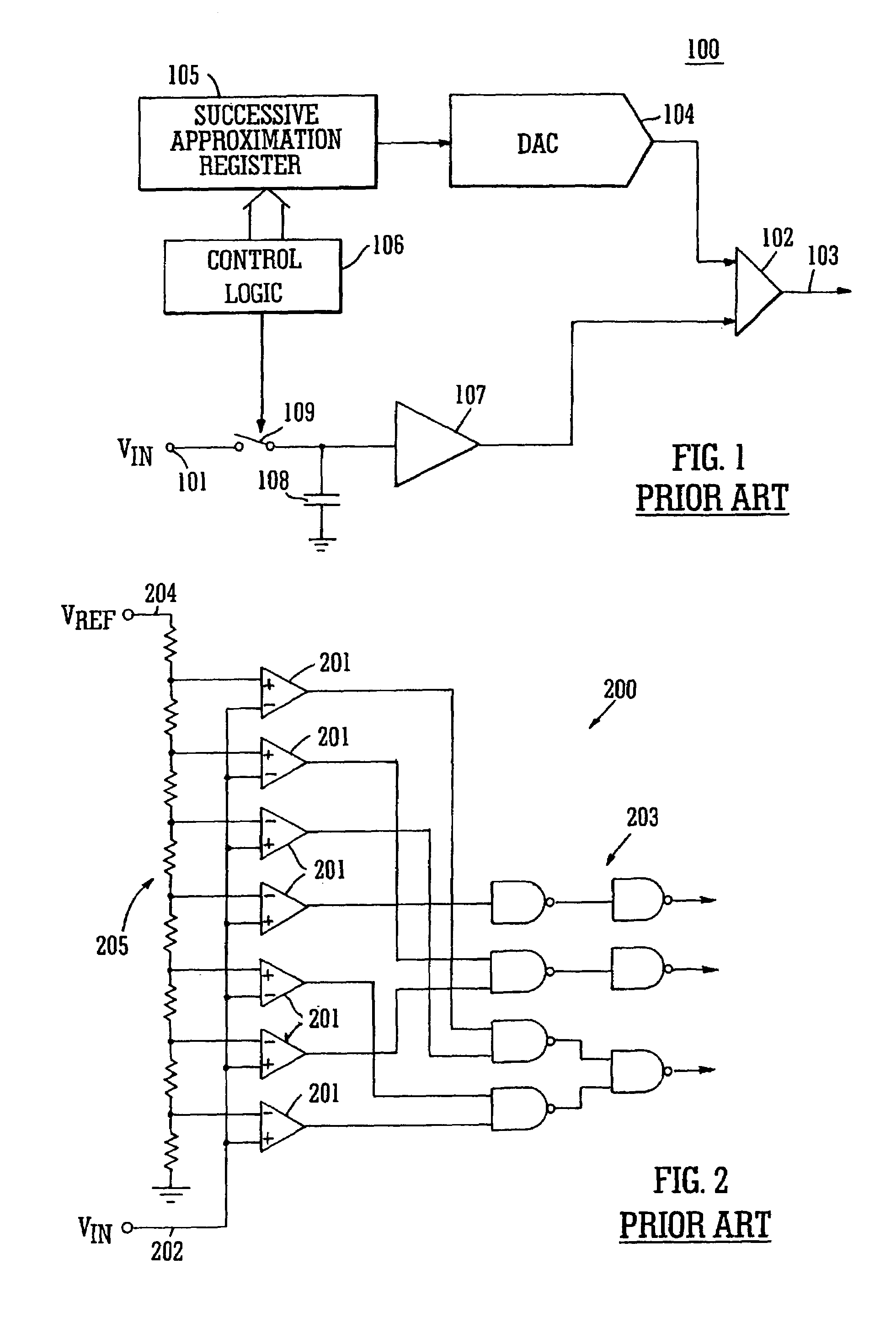
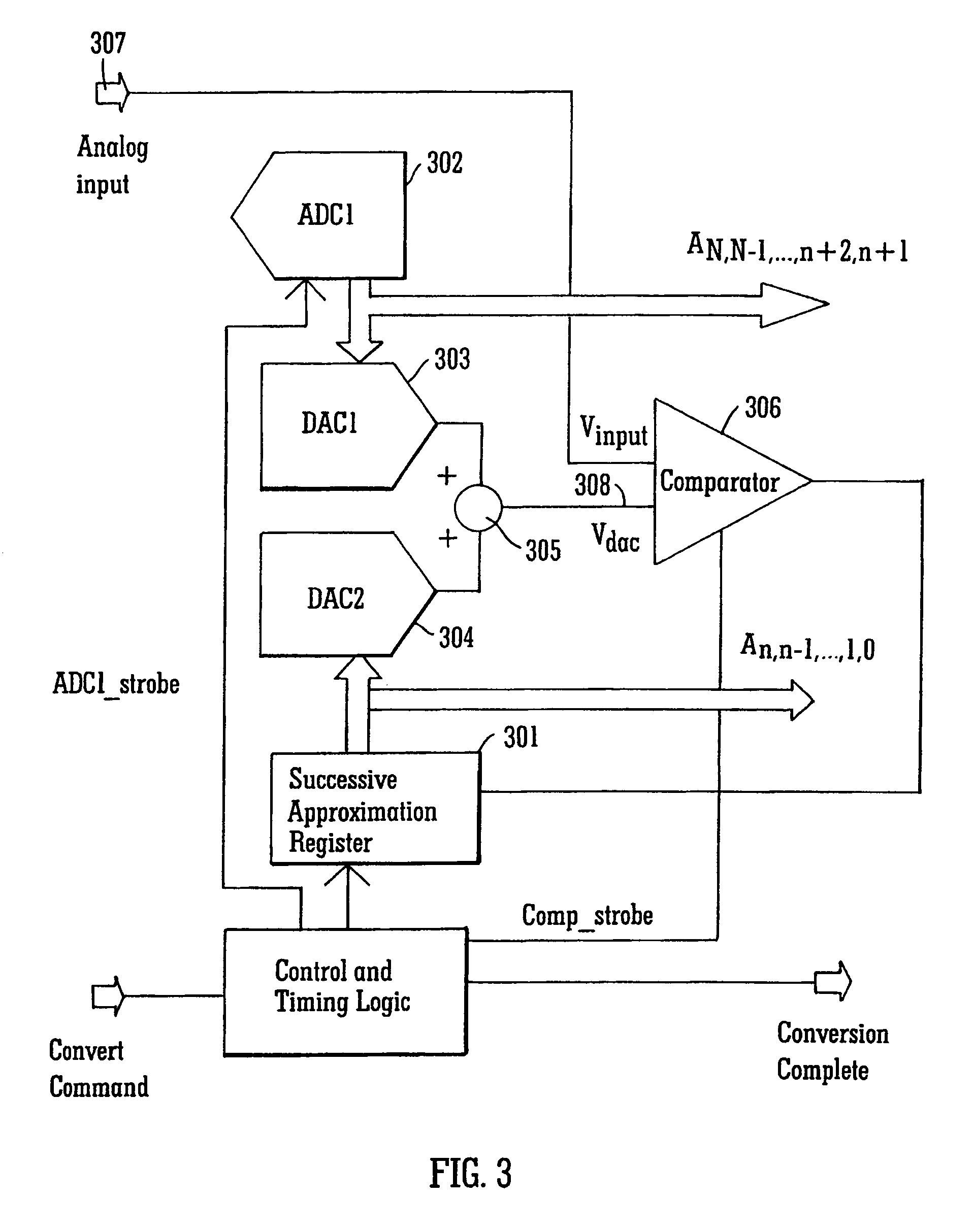
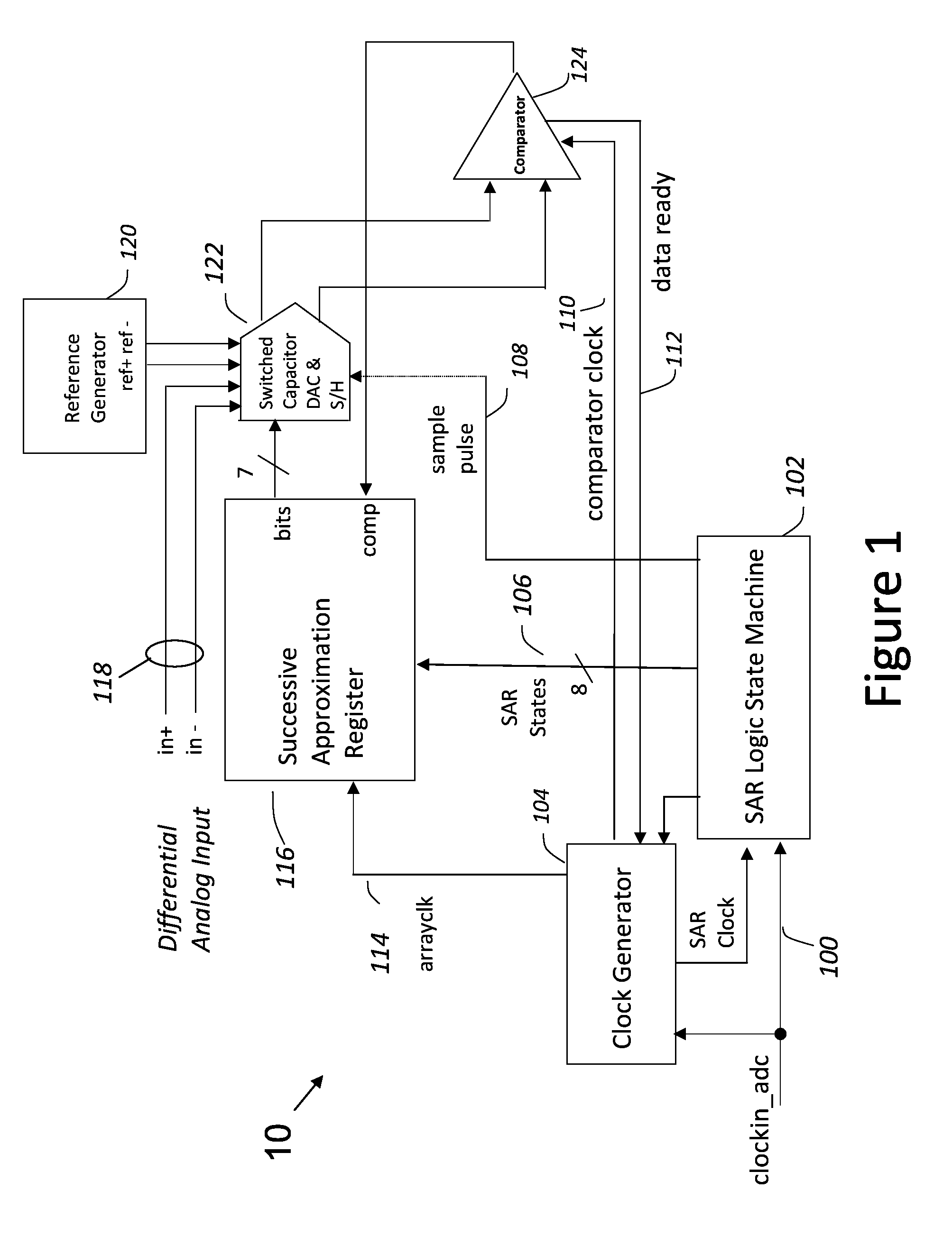
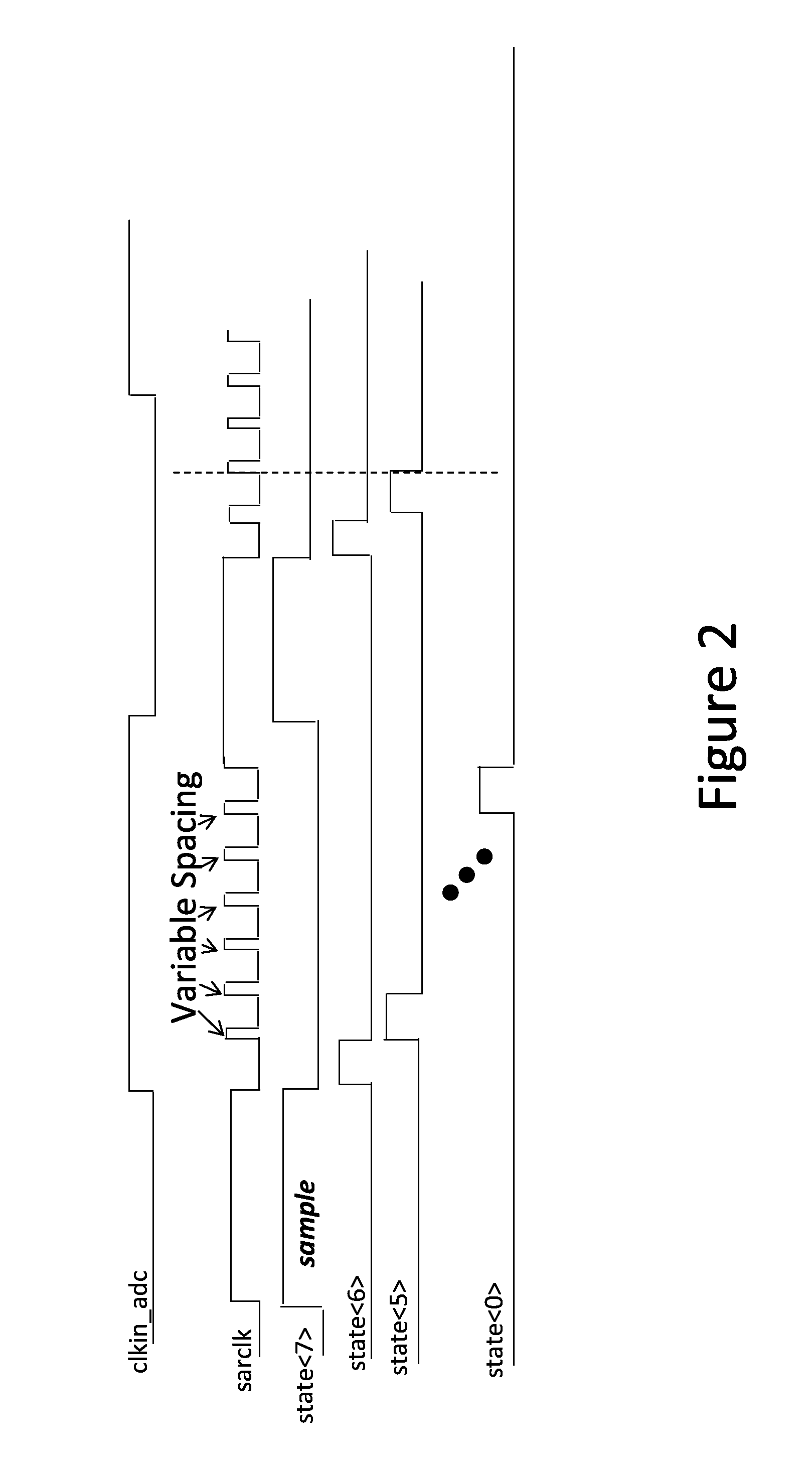
Successive approximation analog-to-digital converter with pre-loaded SAR registers
InactiveUS7038609B1Efficiently transitionEliminate effectiveElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersDigital down converterFlash ADC
A SAR converter having enhanced performance by virtue of effectively pre-loading the SAR's most significant bits with a value that makes the associated DAC output almost equal to the signal to be converted. A normal SAR conversion is then completed with the SAR bits that have not been pre-loaded. The value used to pre-load the most significant bits of the SAR is preferably obtained from a low-resolution, high-speed converter, such as a flash. The range of DAC bits used in the normal SAR part of the conversion may be increased such that errors up to a certain magnitude in the high-speed converter can be corrected. Reducing power consumption of a SAR system can be readily accomplished by reducing comparator supply voltage. For a SAR converter architecture using a CAPDAC array or CAPDAC (capacitor array DAC), fairly large variations in comparator input voltage can be expected under these circumstances. If the input voltage variation becomes too large, damage to the comparator input devices can occur, or inaccuracies may develop. In one embodiment of the invention, the most significant bits are provided by sampling the input signal through a flash ADC that does not suffer from the input voltage restriction described above.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
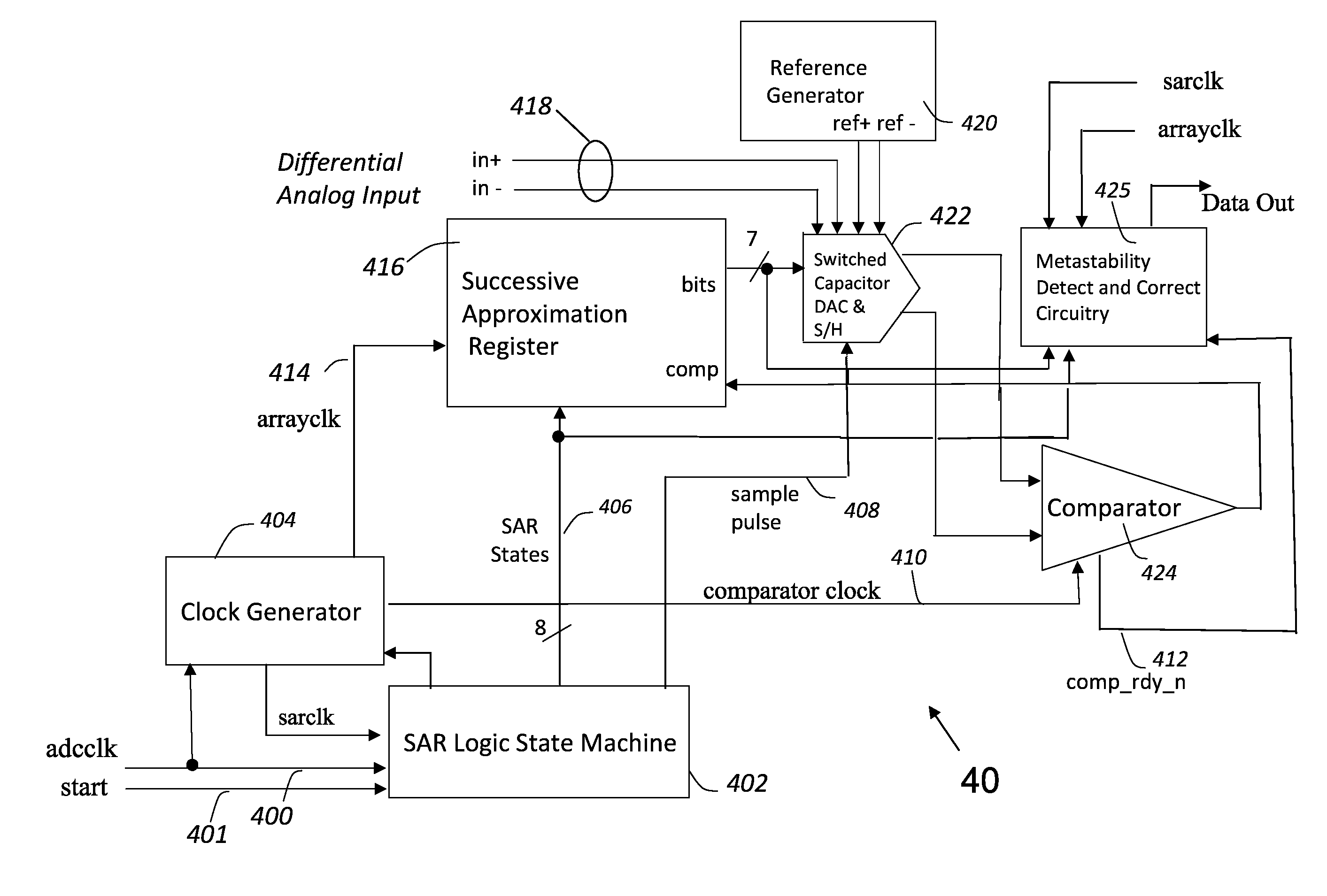
Metastability error detection and correction system and method for successive approximation analog-to-digital converters
ActiveUS8957802B1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersDigital down converterNAND gate
A system and method are provided for the detection and correction of metastability errors in a successive approximation analog to digital converter (ADC). The successive approximation ADC (40) includes a comparator unit (424) that includes a NAND gate circuit (550) that outputs a comp_rdy_n signal when the comparator (500) has latched a result. ADC (40) includes a metastability detection and correction circuit (425) that includes a first logic circuit (700) that monitors the comp_rdy_n signal and detects a metastable event if that signal is not received within a portion of a conversion time period of the ADC. Responsive to detection of a metastable event, a second logic circuit (750) generates a correct conversion code at the output of the ADC. If no metastable event is detected during a conversion cycle of the ADC, the second logic circuit (750) outputs the conversion codes determined by the comparator (500).
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
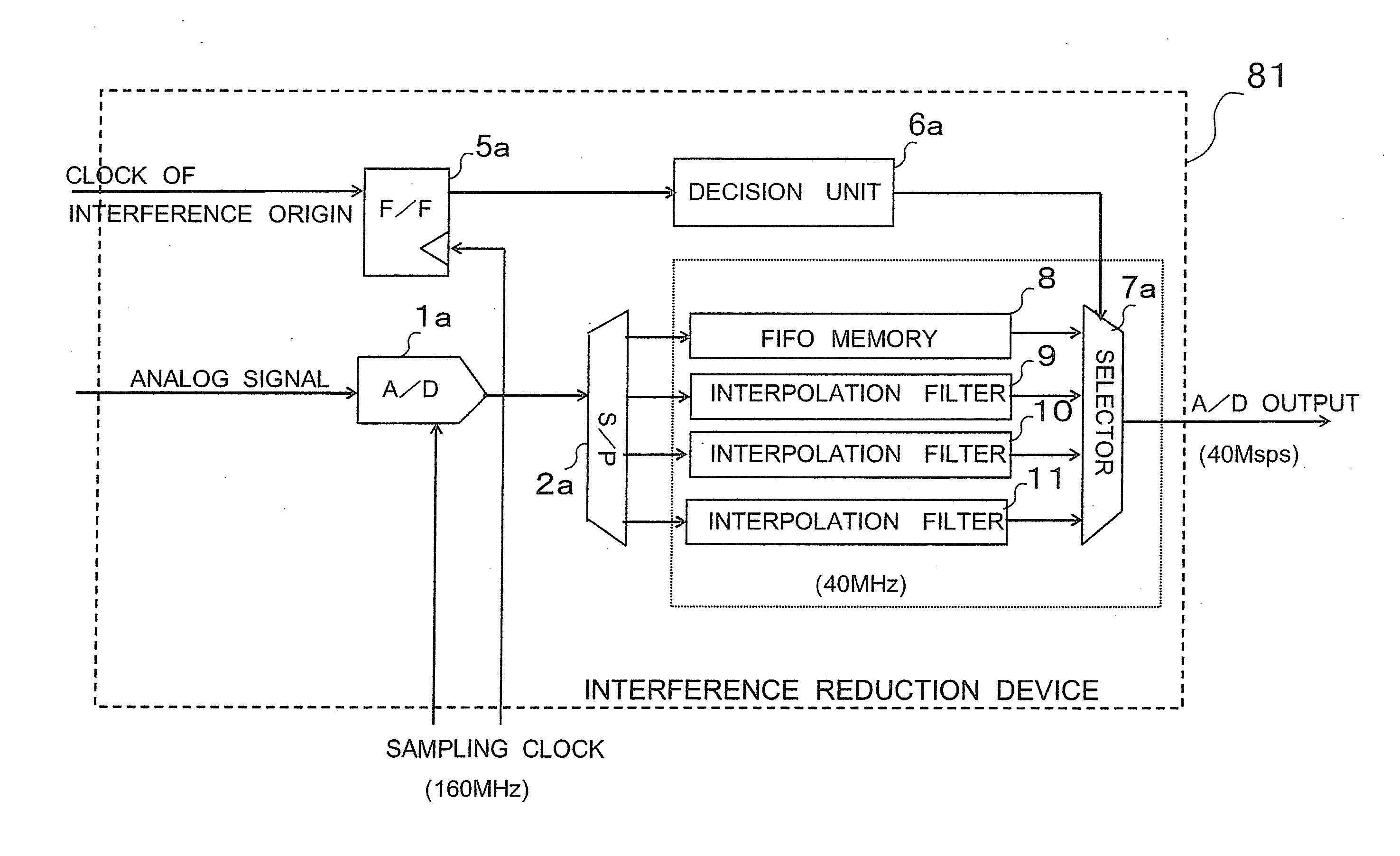
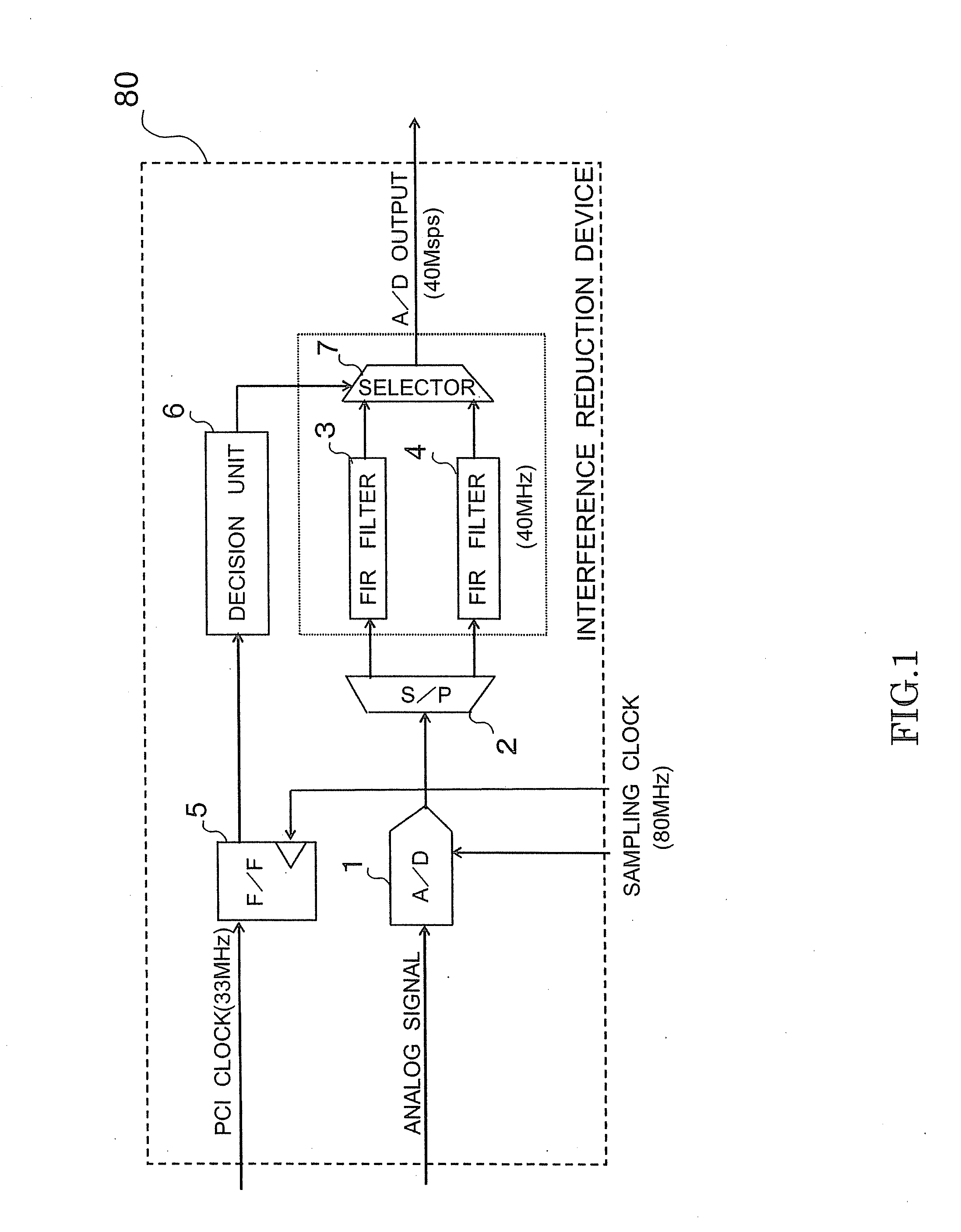
Interference reduction device
InactiveUS20100295716A1Little influenceElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersDigital down converterEngineering
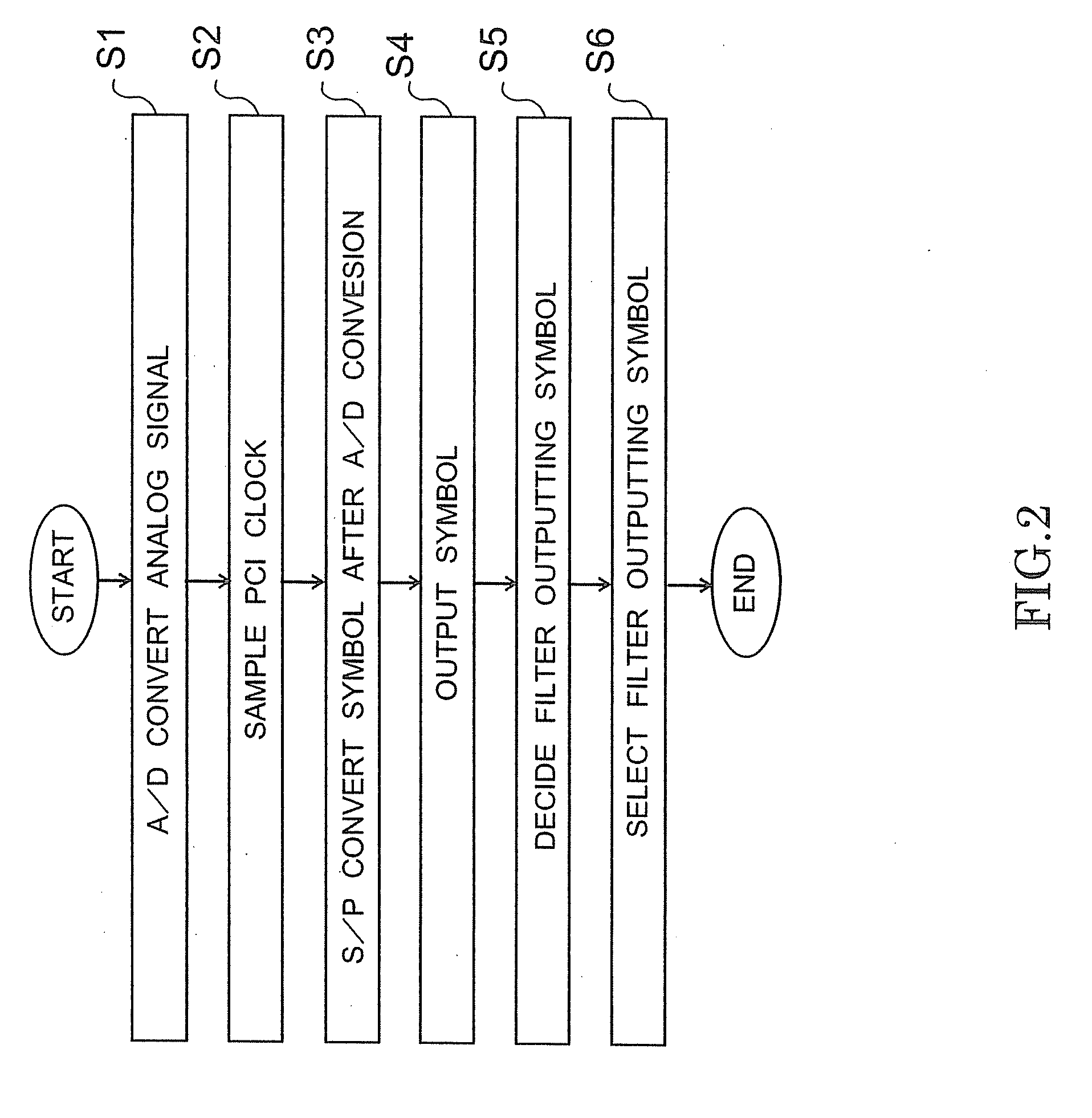
An interference reduction device includes an analog to digital converter, a serial to parallel converter, a first FIR filter, a second FIR filters, a flip-flop, a decision unit, and a selector. The analog to digital converter performs A / D conversion. The serial to parallel converter performs a session of distribution processing in which a digital signal obtained by the A / D conversion. The first FIR outputs the signal after a filer operation at the desired output frequency. The second FIR filters each perform a filter operation, also each output the generated signals at the desired output frequency. The flip-flop samples the inputted digital signal. The decision unit decides which one of the FIR filters has the smallest influence of interference of the input digital signal. The selector outputs one of the signals outputted by the FIR filters.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
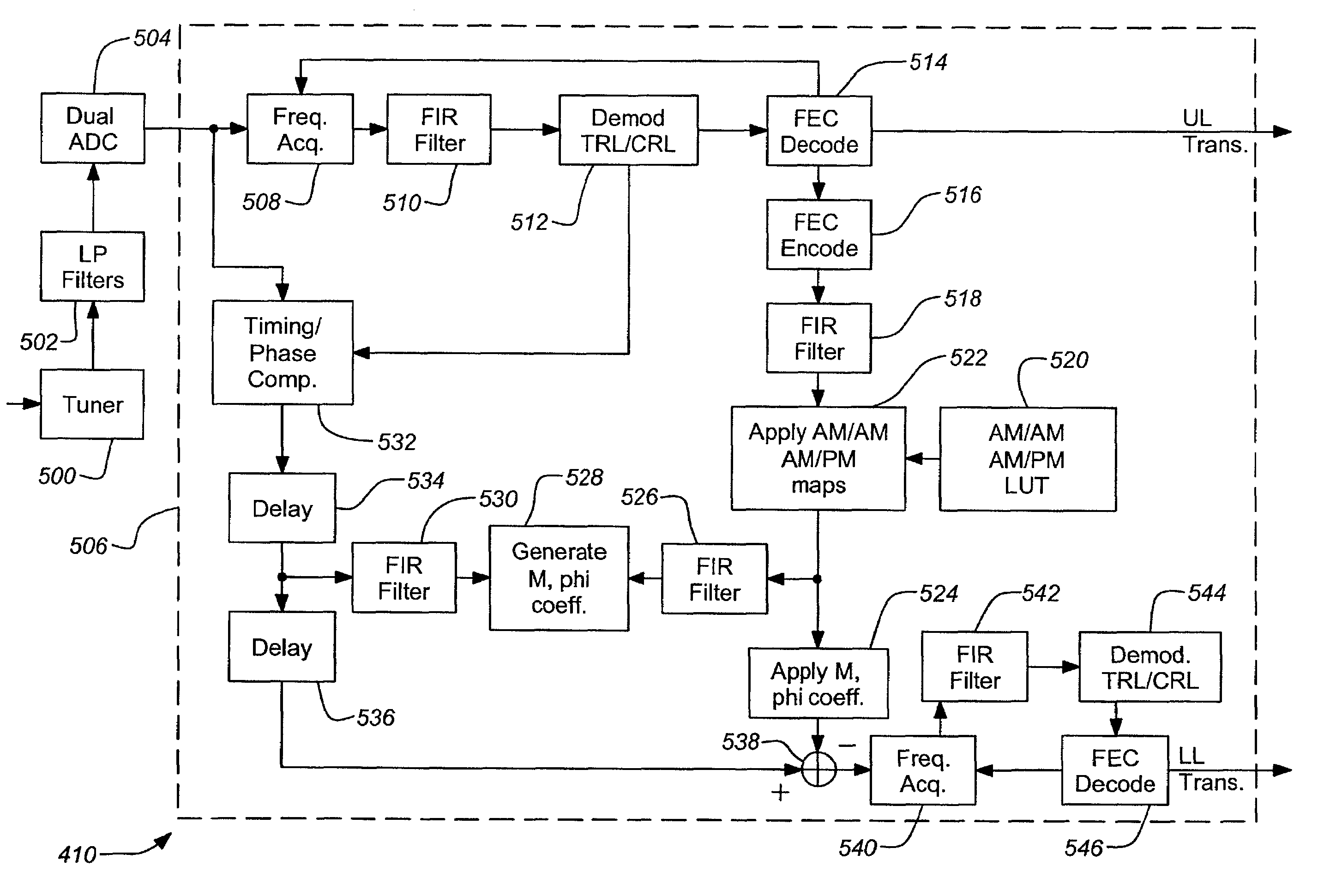
Dual layer signal processing in a layered modulation digital signal system
InactiveUS7173981B1Speed digital processingLow costTelevision system detailsFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationDigital down converterEngineering
Systems and methods for receiving layered modulation for digital signals are presented. An exemplary apparatus comprises a tuner for receiving a layered signal and producing a layered in-phase signal and a layered quadrature signal therefrom, an analog-to-digital converter for digitizing the layered in-phase signal and the layered quadrature signal and a processor for decoding the layered in-phase signal and the layered quadrature signal to produce one or more discrete layer signals.
Owner:HUGHES ELECTRONICS
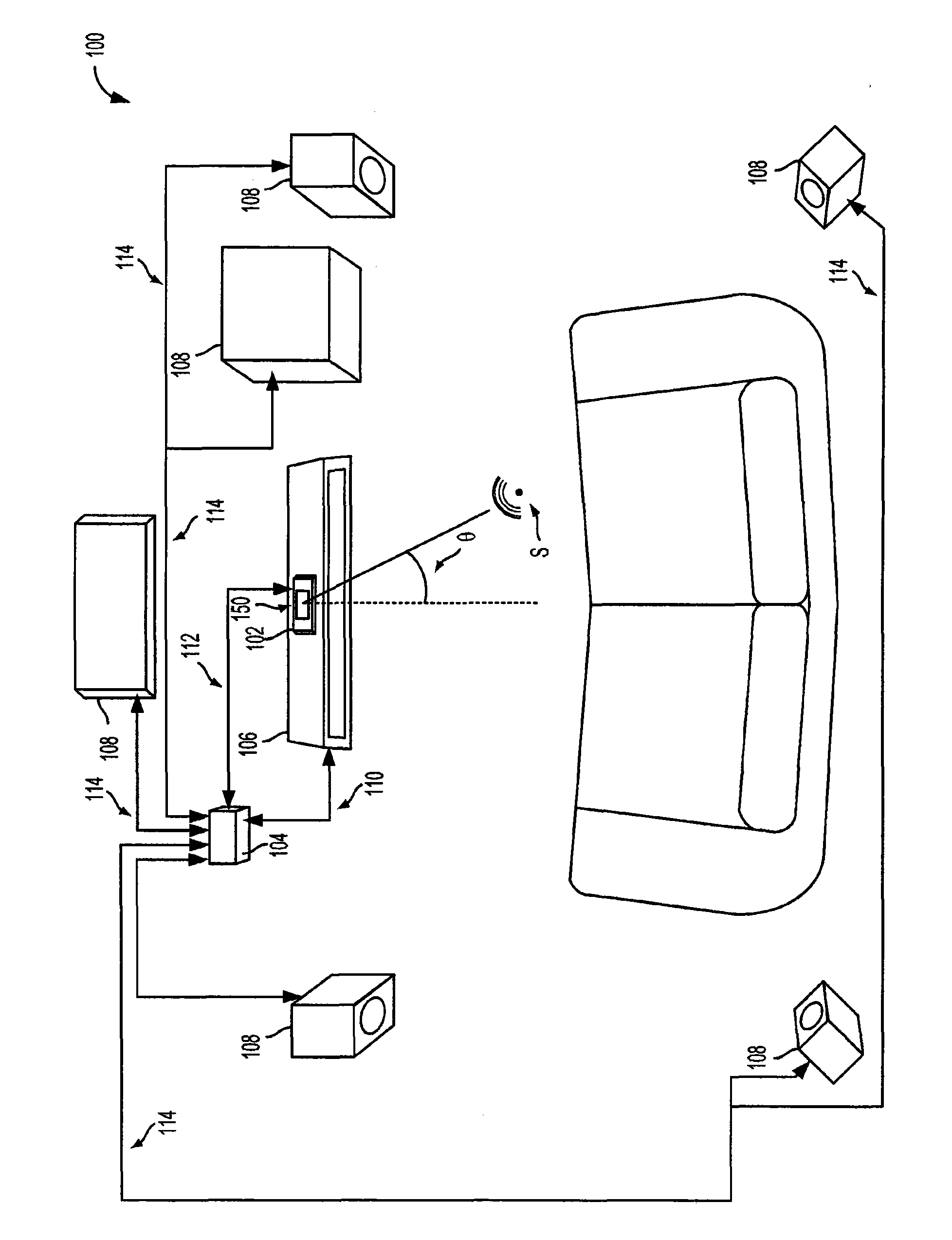
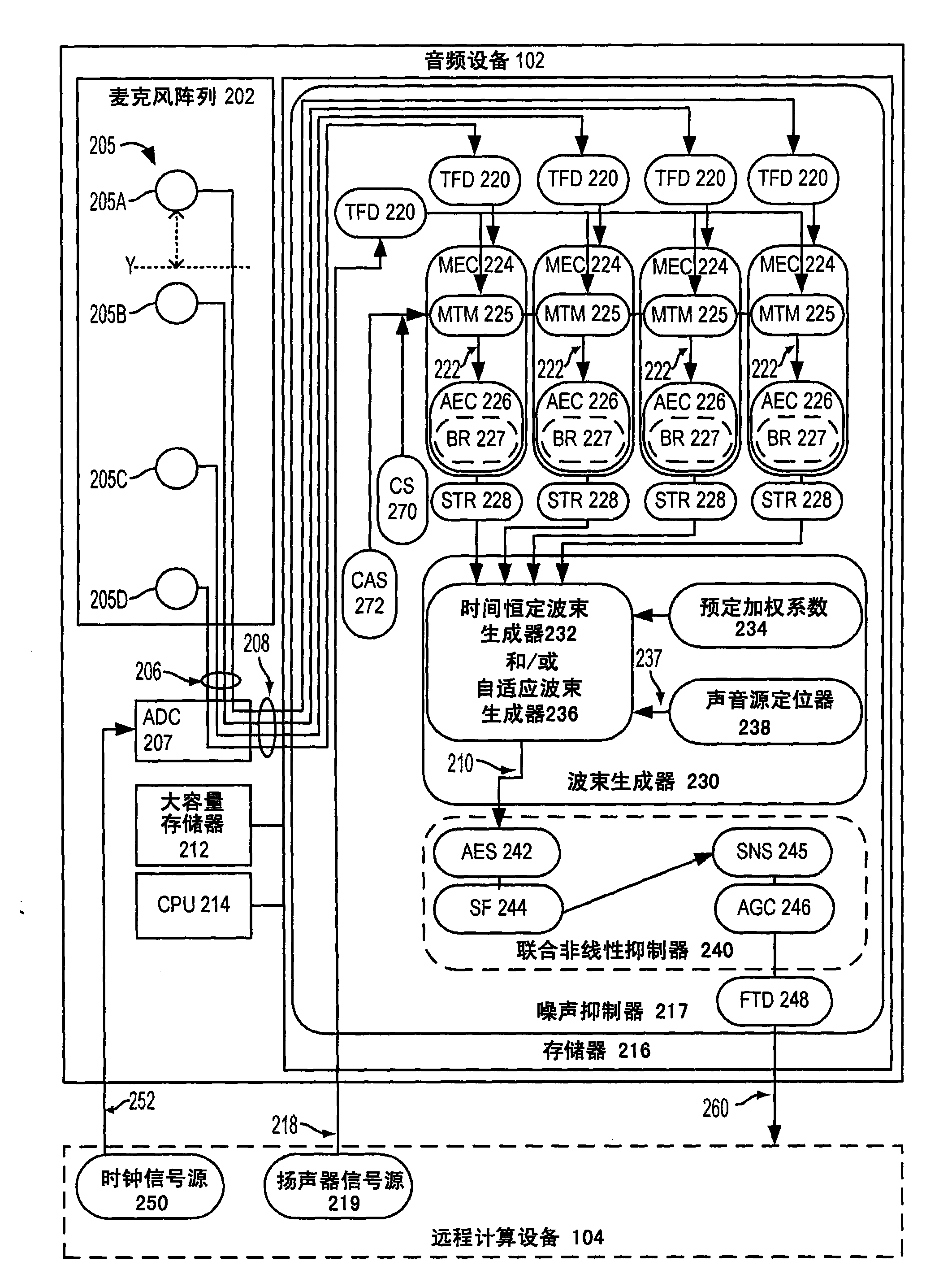
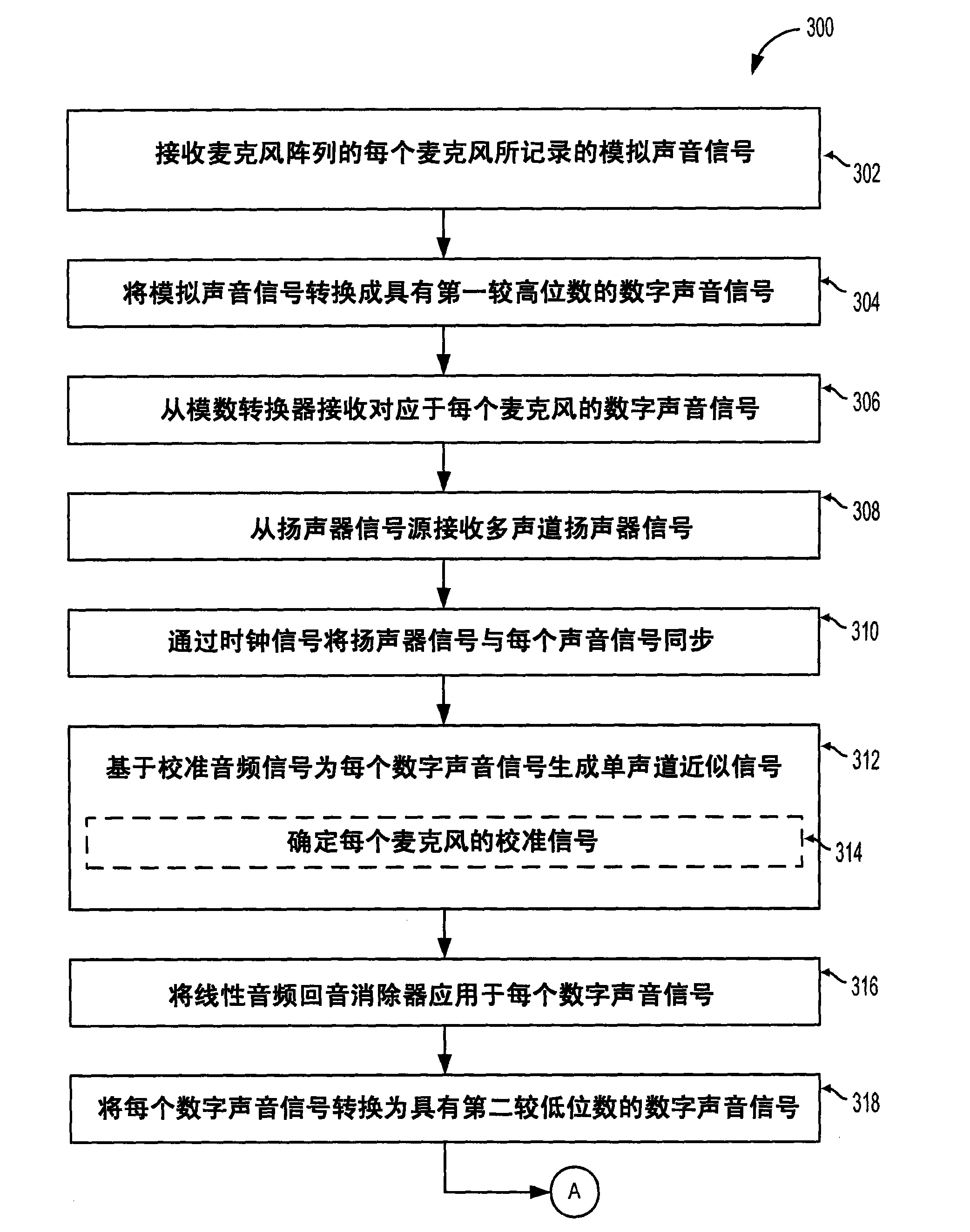
Adaptive ambient sound suppression and speech tracking
A device for suppressing ambient sounds from speech received by a microphone array is provided. One embodiment of the device comprises a microphone array, a processor, an analog-to-digital converter, and memory comprising instructions stored therein that are executable by the processor. The instructions stored in the memory are configured to receive a plurality of digital sound signals, each digital sound signal based on an analog sound signal originating at the microphone array, receive a multi-channel speaker signal, generate a monophonic approximation signal of the multi-channel speaker signal, apply a linear acoustic echo canceller to suppress a first ambient sound portion of each digital sound signal, generate a combined directionally-adaptive sound signal from a combination of each digital sound signal by a combination of time-invariant and adaptive beamforming techniques, and apply one or more nonlinear noise suppression techniques to suppress a second ambient sound portion of the combined directionally-adaptive sound signal.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
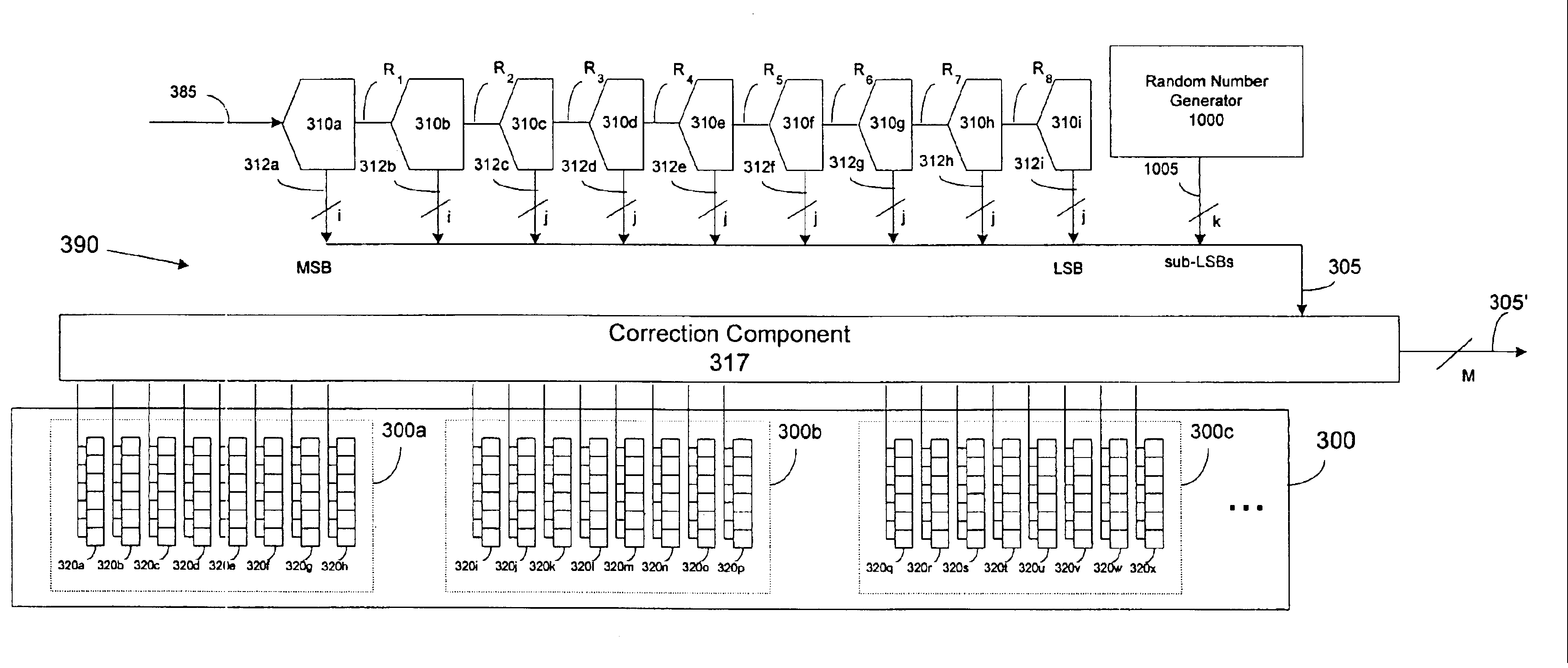
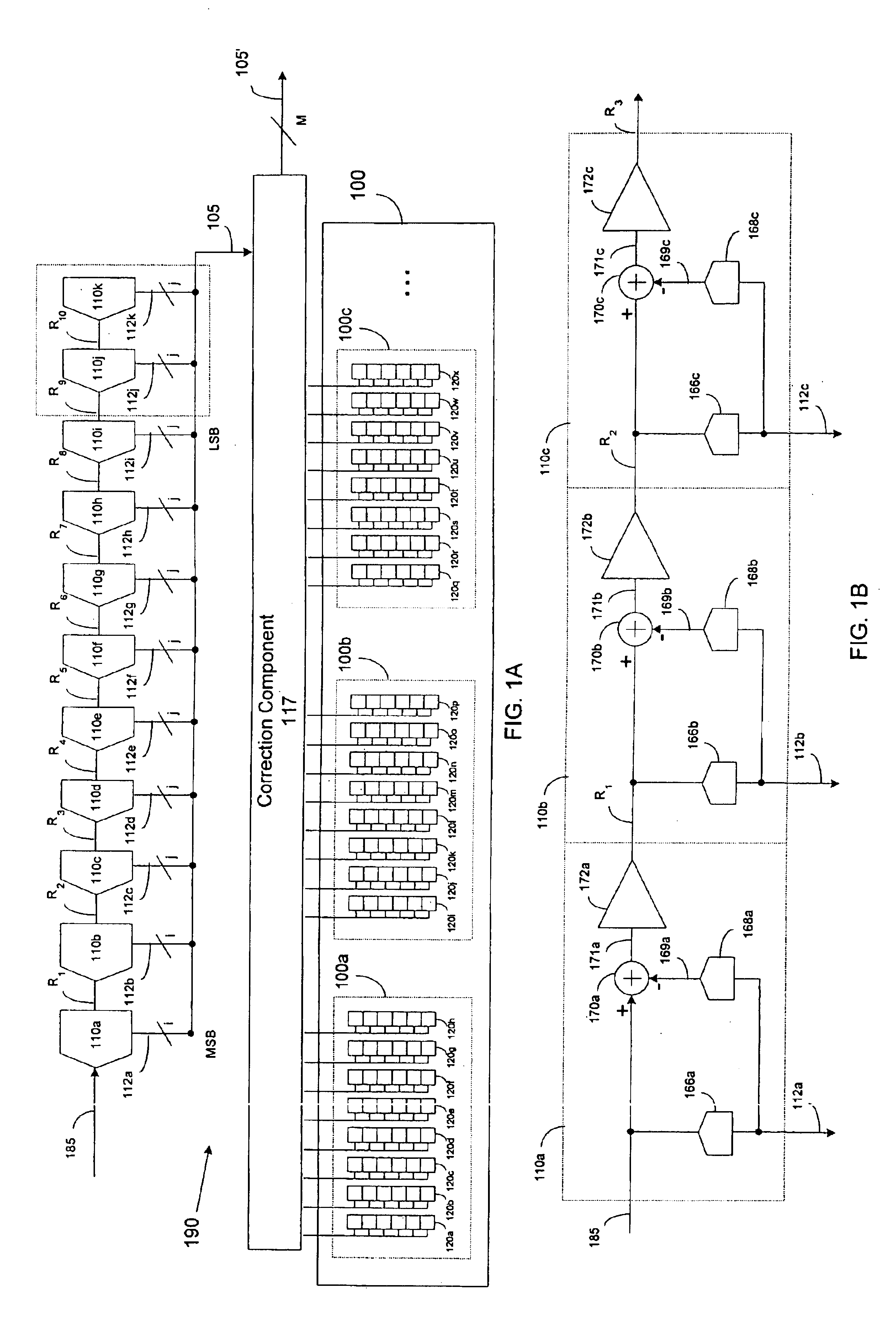
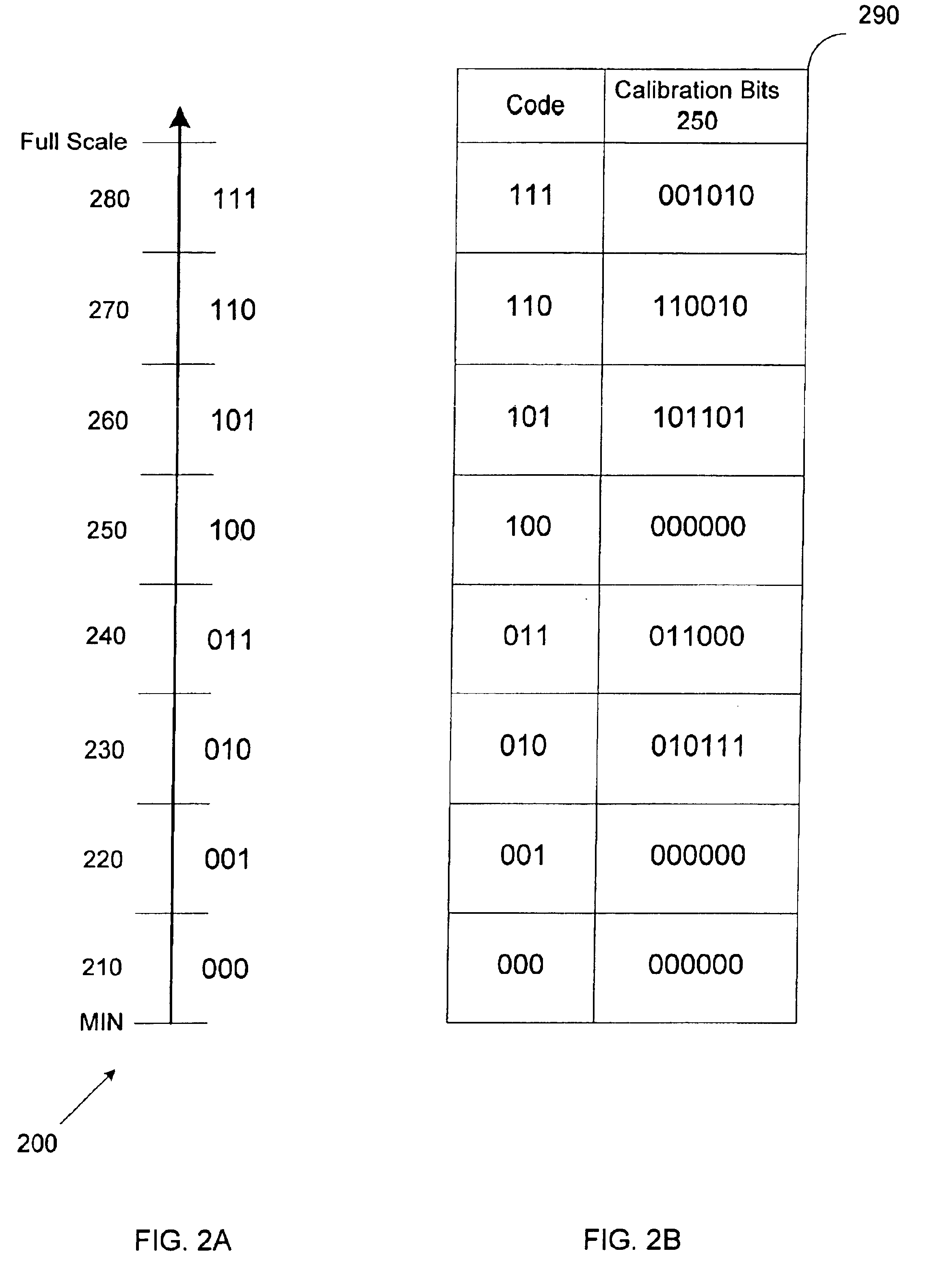
Pipeline ADC digital dithering for increased digital calibration resolution
ActiveUS6894631B1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersDigital down converterImage resolution
An pipeline analog-to-digital converter (ADC) is provided that is capable of applying calibration at a resolution greater than the resolution of a digital output signal provided by the ADC. The ADC includes a calibration component adapted to apply calibration bits to digital output bits generated by stages of the pipeline and corresponding to samples of an analog input signal. The ADC also includes a random number generator that provides at least one random bit having a sub-LSB bit weight. The calibration bits and the at least one random bit are applied as a dither to the digital output bits such that, on average, the digital output signal provided by the ADC is calibrated at a sub-LSB resolution.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
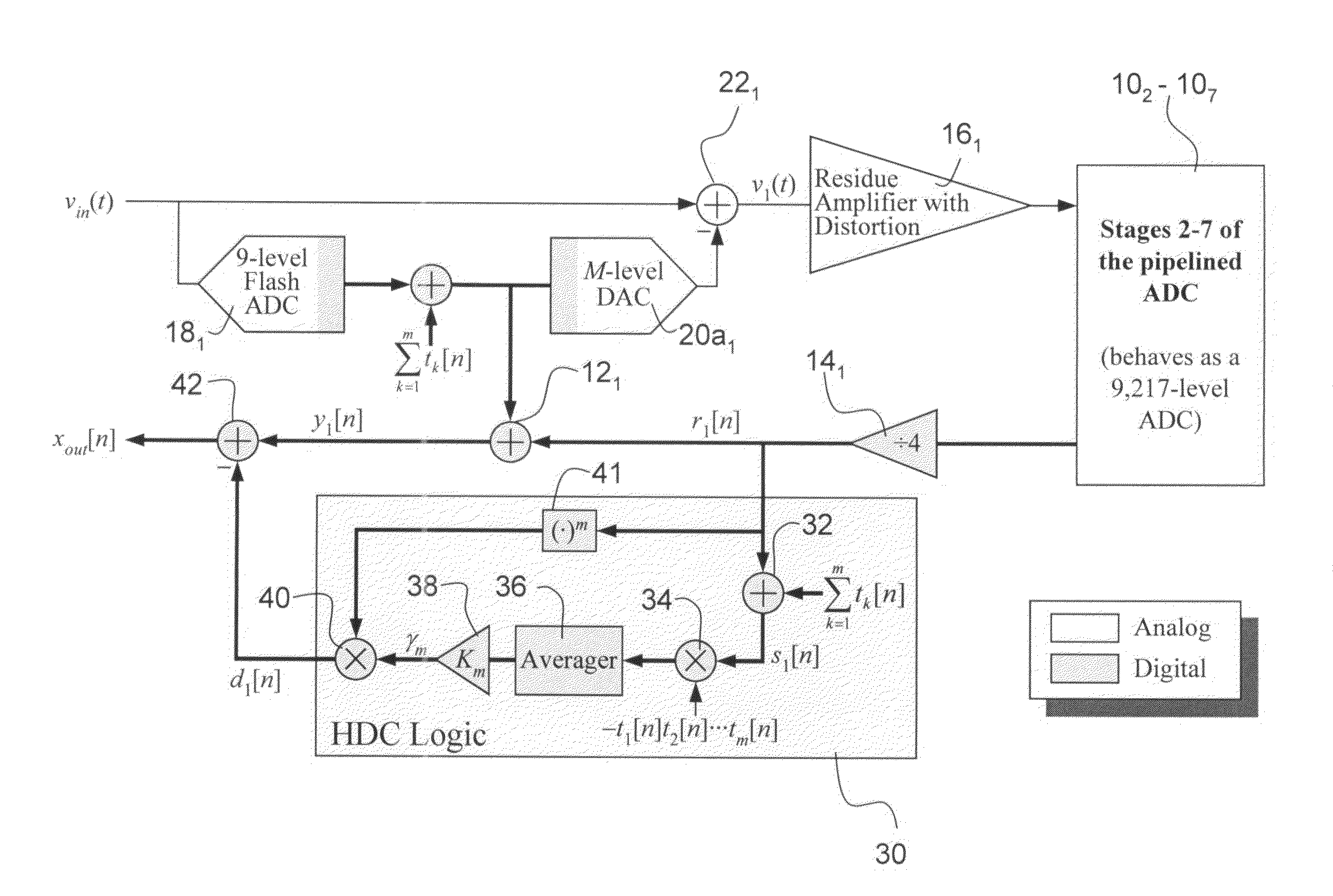
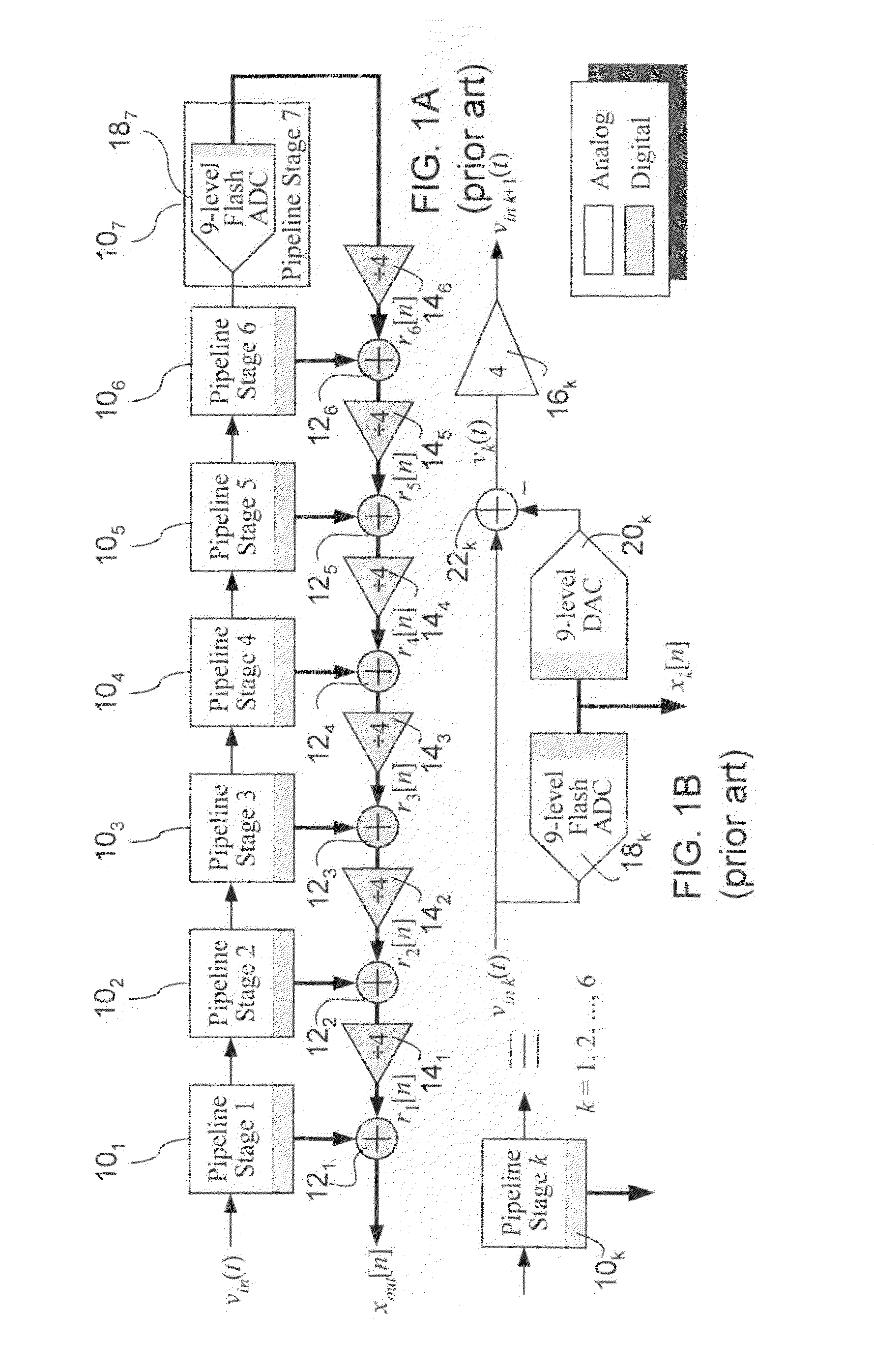
Digital background correction of nonlinear error ADC's
ActiveUS7602323B2Electric signal transmission systemsPhysical parameters compensation/preventionNonlinear circuit elementsDigital down converter
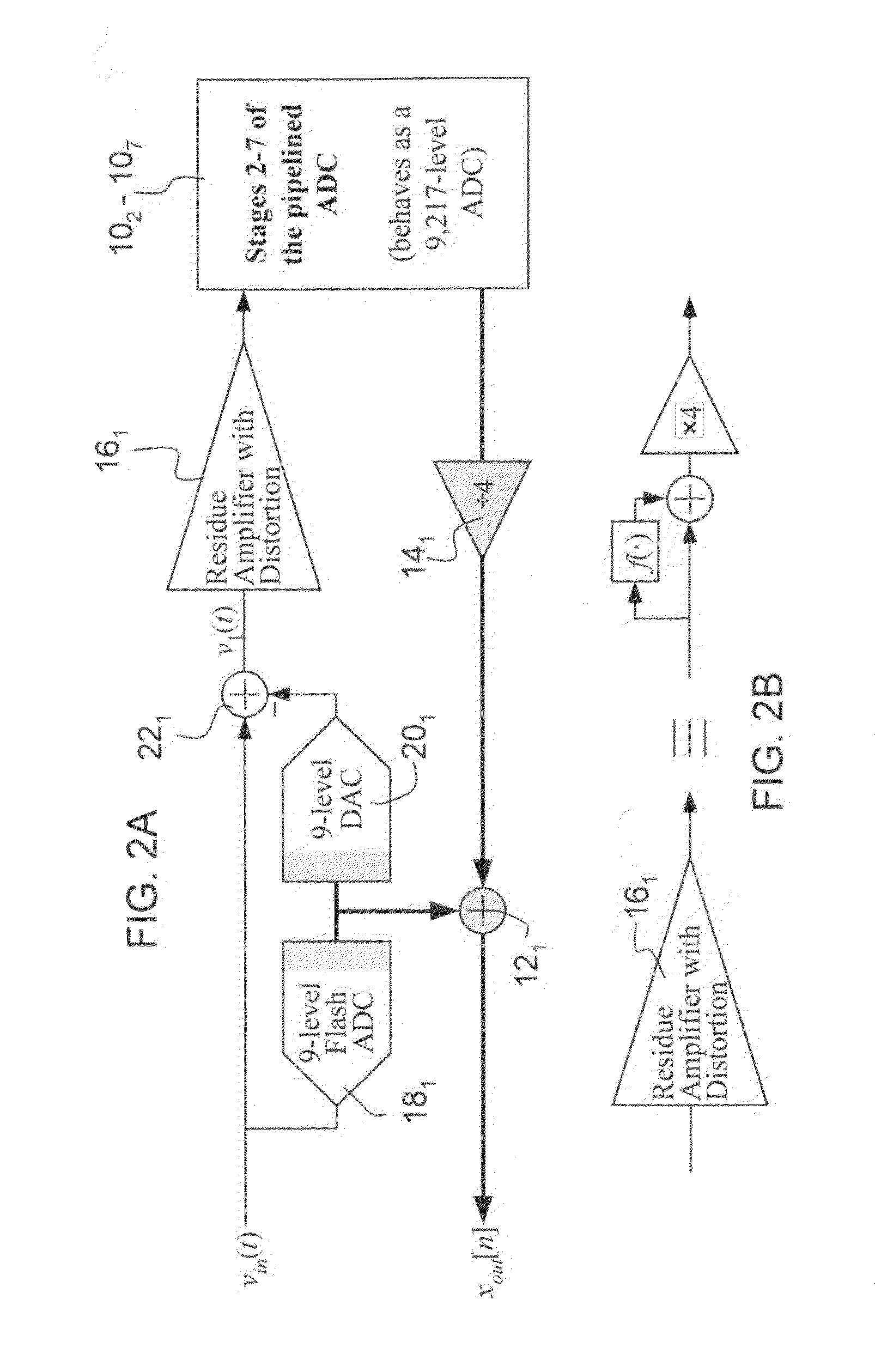
The invention provides circuits and methods for estimating and correcting nonlinear error in analog to digital converters that is introduced by nonlinear circuit elements, for example one or more residue amplifiers in a pipelined analog to digital converter integrated circuit. In a preferred method of the invention, pseudo random calibration sequences are introduced into the digital signal to be converted by a flash digital to analog converter in one or more initial stages of the pipelined analog to digital converter circuit. A digital residue signal of the output of the one or more initial pipelined analog to digital converter stages is sampled. Intermodulation products of the pseudo random calibration sequences that are present in the digital residue signal are determined to estimate nonlinear error introduced by the residue amplifier in the one or more stages. A digital correction signal is provided to the output of the one or more stages to cancel estimated nonlinear error.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Transducer array imaging system
ActiveUS8079263B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSensor arrayDigital data
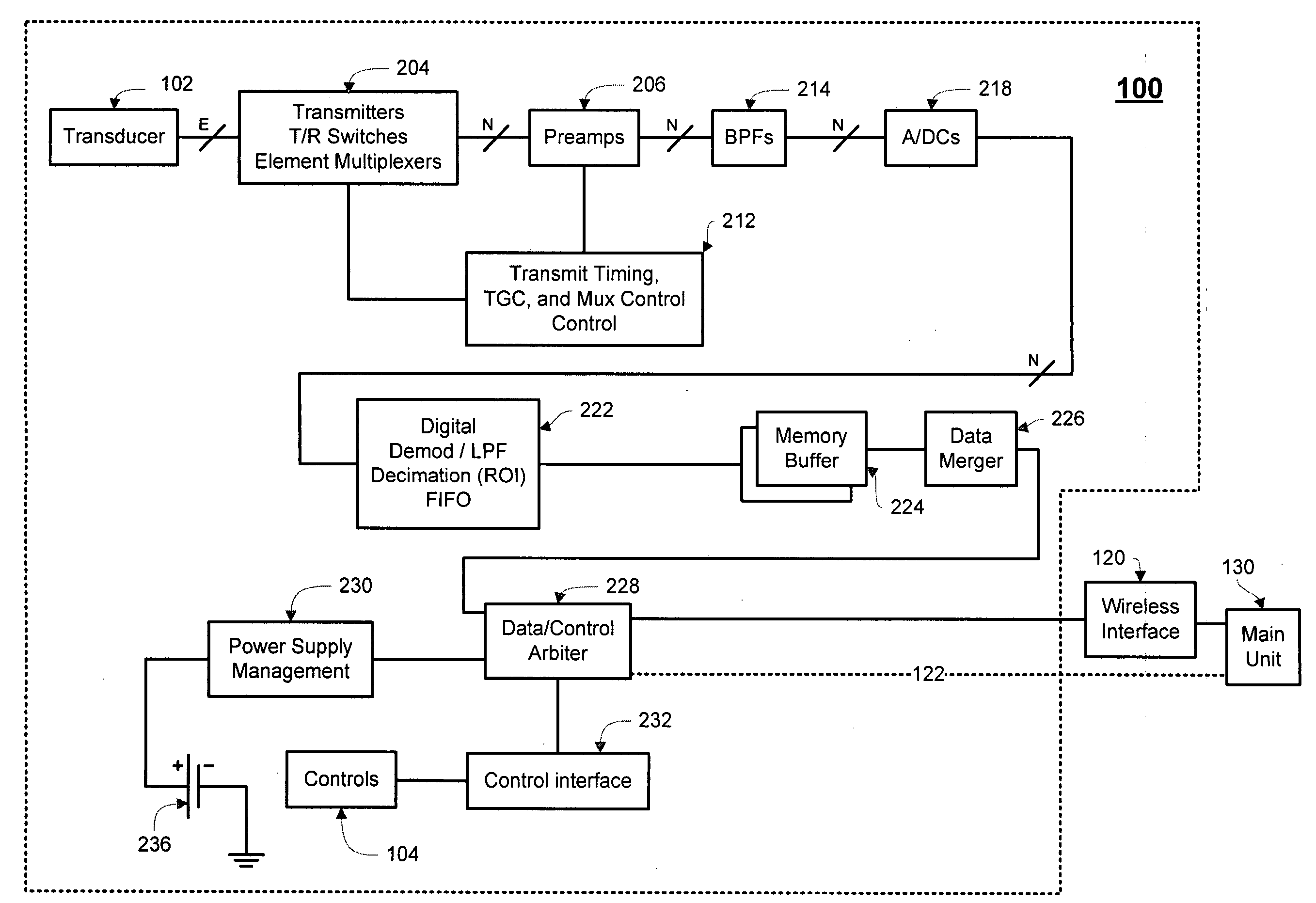
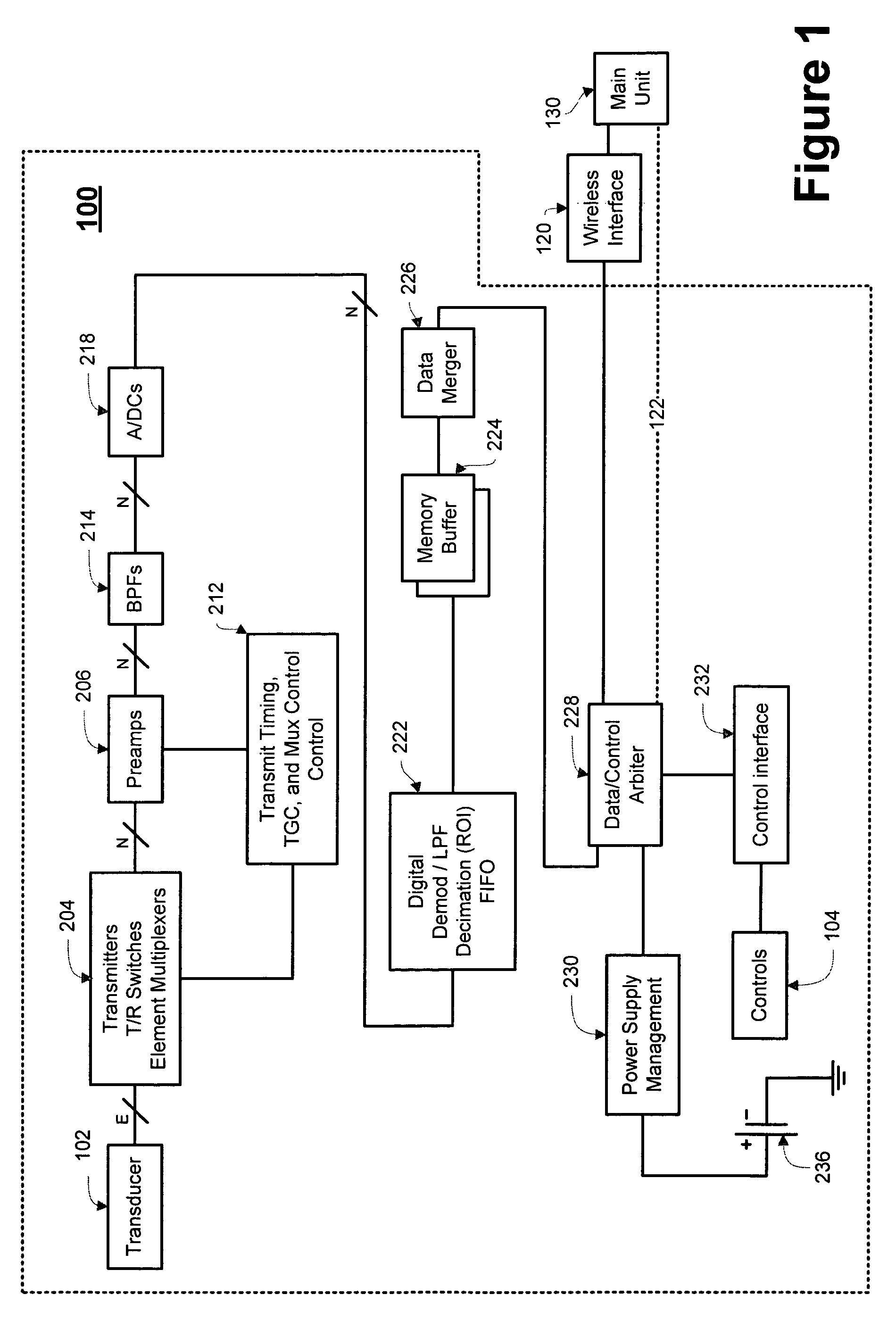
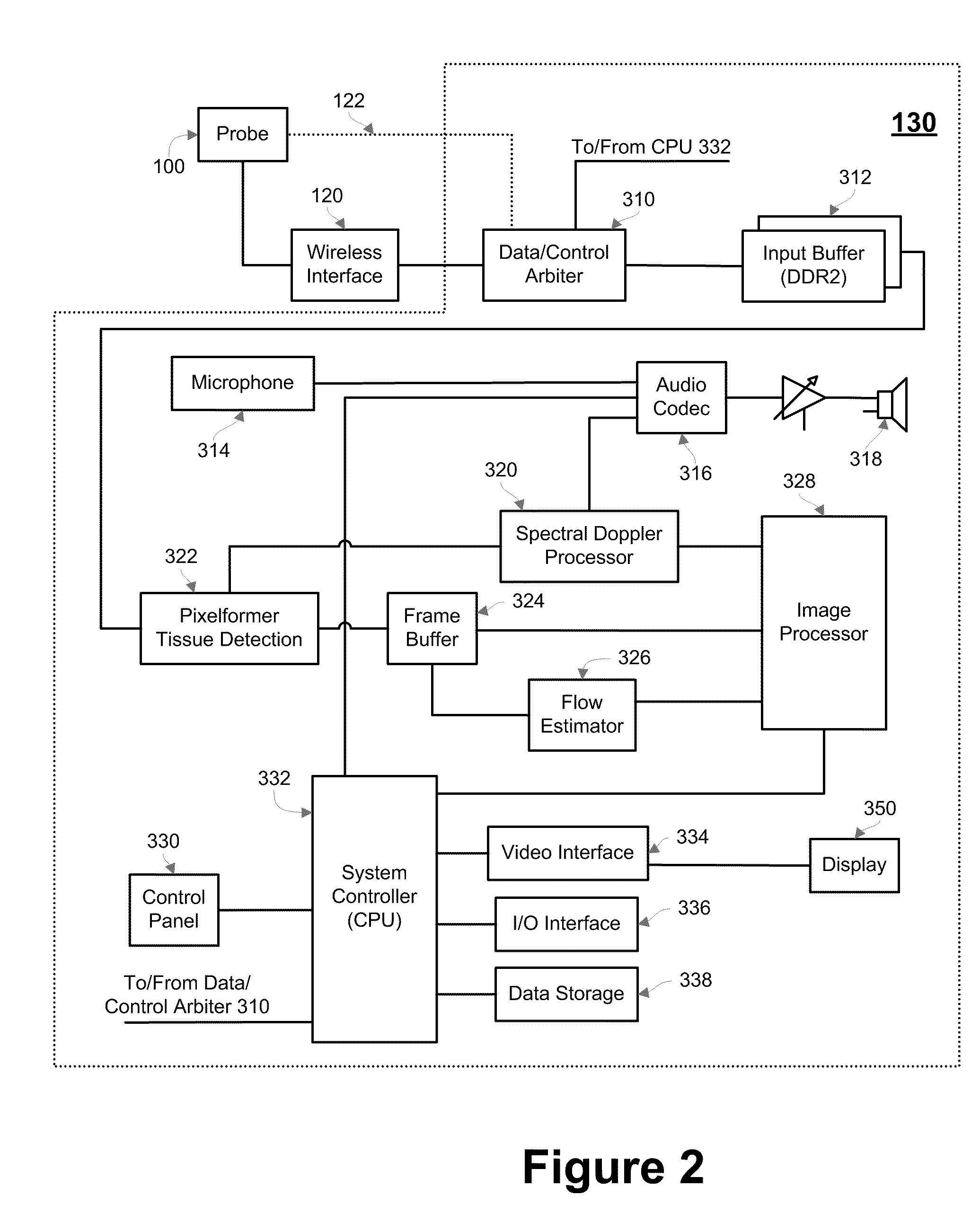
The disclosed embodiments include a method, system, and device for conducting ultrasound interrogation of a medium. The novel method includes transmitting a non-beamformed or beamformed ultrasound wave into the medium, receiving more than one echoed ultrasound wave from the medium, and converting the received echoed ultrasound wave into digital data. The novel method may further transmit the digital data. In some embodiments, the transmitting may be wireless. The novel device may include transducer elements, an analog-to-digital converter in communication with the transducer elements, and a transmitter in communication with the analog-to-digital converter. The transducers may operate to convert a first electrical energy into an ultrasound wave. The first electrical energy may or may not be beamformed. The transducers also may convert an echoed ultrasound wave into a second electrical energy. The analog-to-digital converter may convert the electrical energy into digital data, and the transmitter may transmit the digital data.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
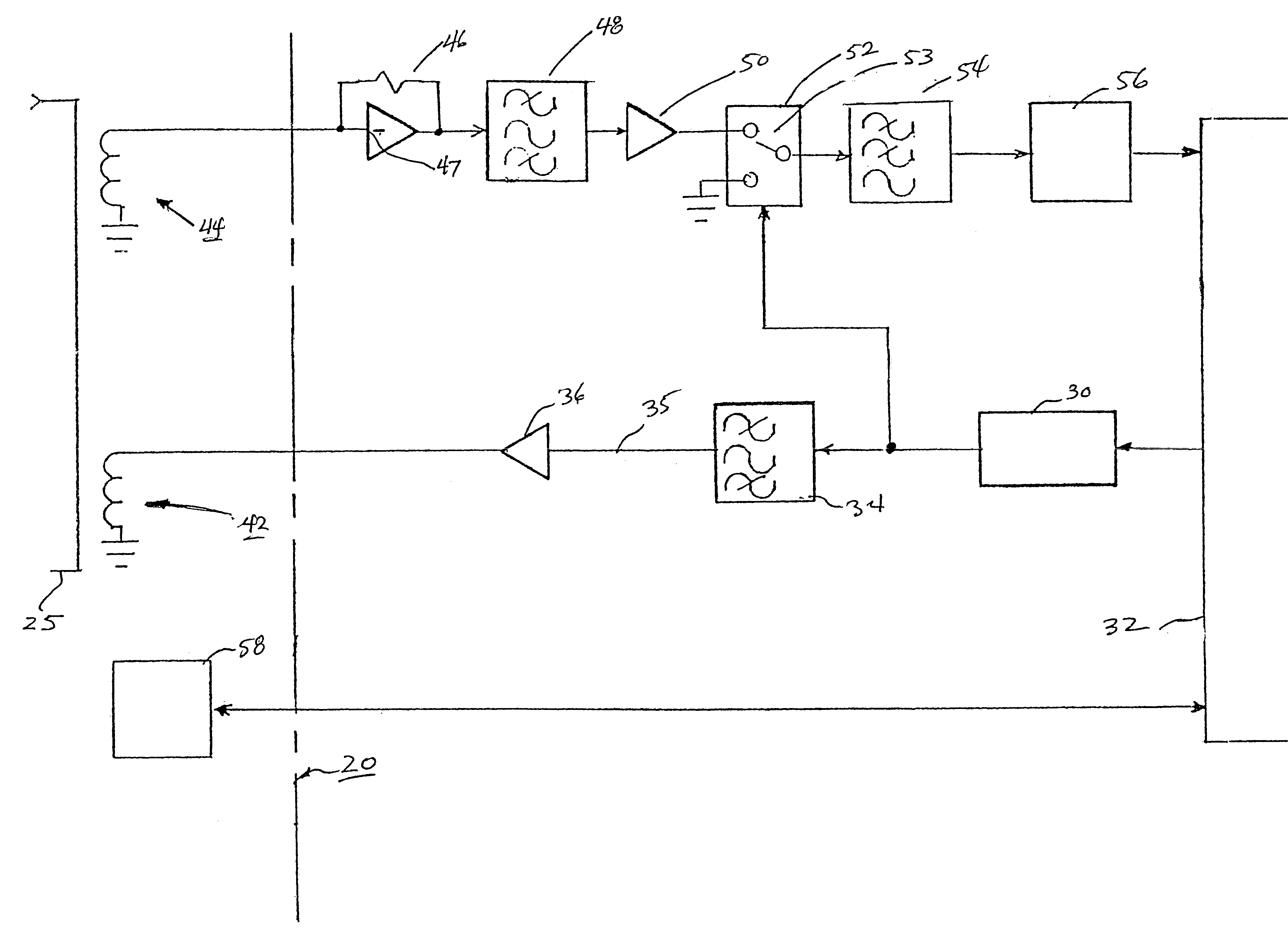
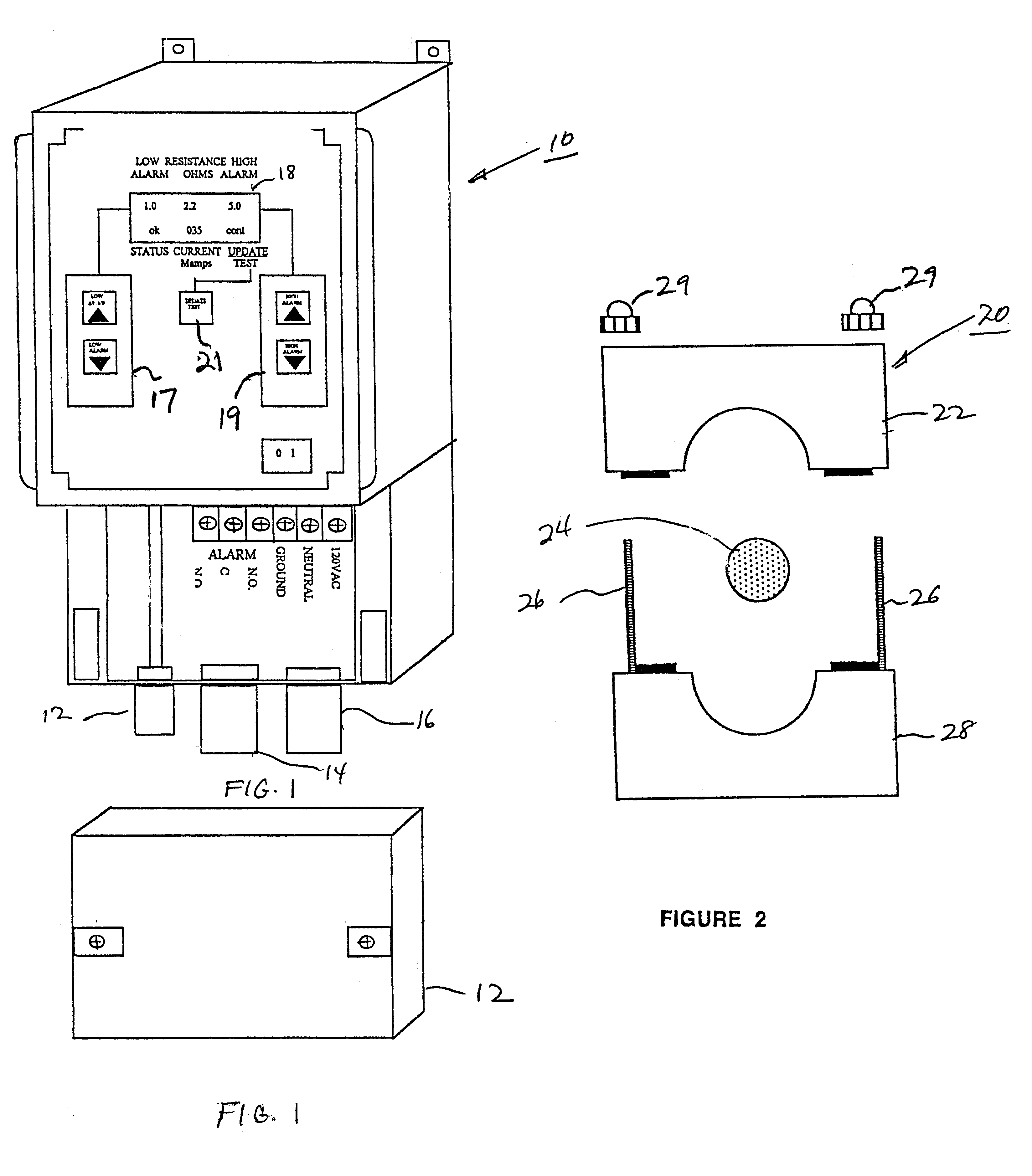
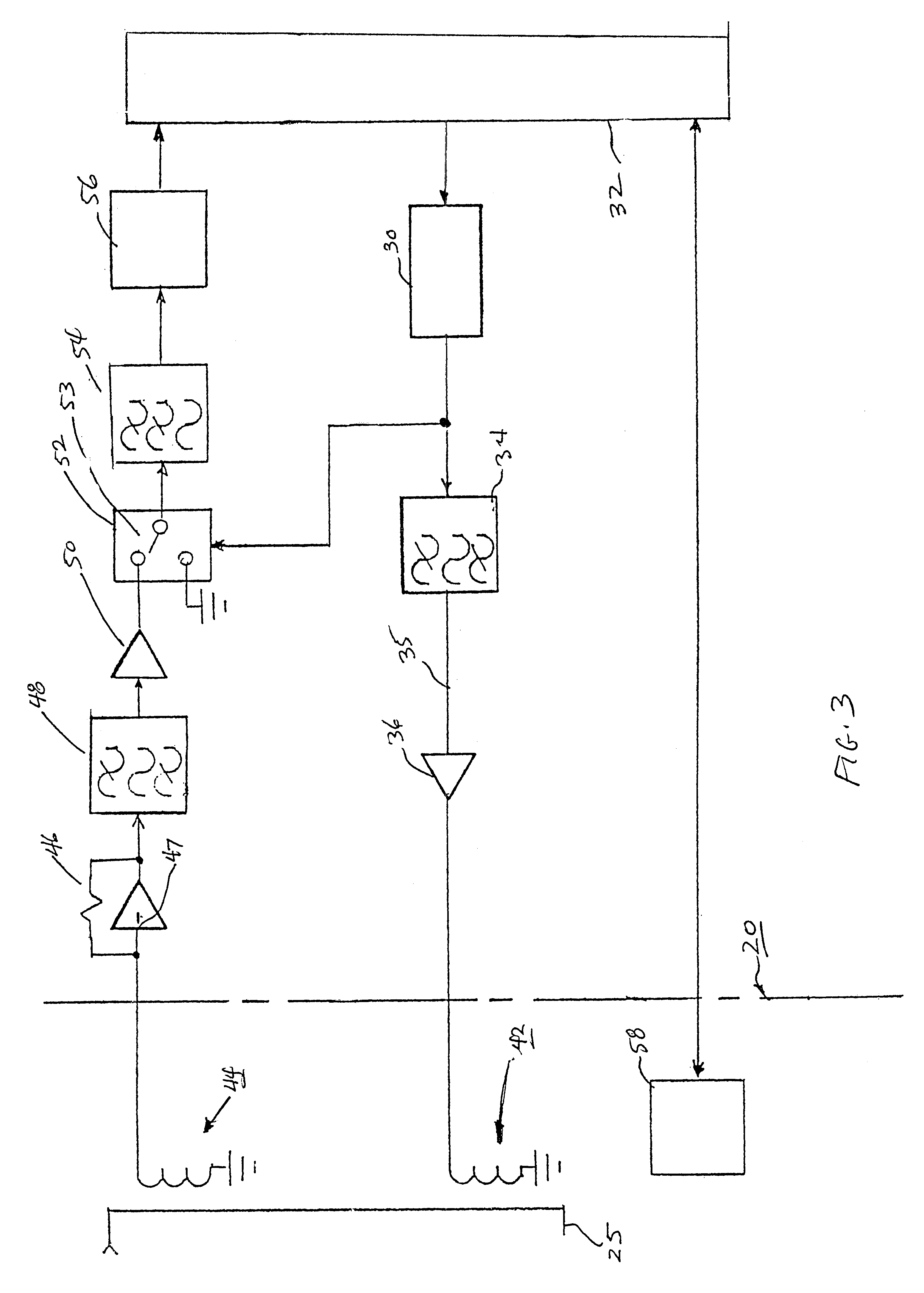
Ground resistance monitor
InactiveUS6396284B1Reduce complexityLow costElectronic circuit testingEarth resistance measurementsDigital down converterDisplay device
A permanently mounted AC powered control / display unit and a remote sensor for use in measuring ground resistance. The sensor is permanently mounted around the earth grounding cable. The control display unit generates a 1953 Hz, 5 Vac sine wave which is sent via a cable to a 100:1 ratio drive transformer in the remote sensor. The transformer induces a 0.05 Vac sine wave in the ground cable. The resulting current is detected by a 100:1 turns ratio sense transformer. The current is returned via the cable to the control display unit and converted to a voltage, filtered, amplified and rectified by a synchronous rectifier. The rectified voltage is again filtered and presented to an analog to digital converter. A microprocessor reads the output of the analog to digital converter and the ground resistance is computed by using Ohm's Law (R=E / I), the result being shown on a display.
Owner:RANCOM SYSTNS
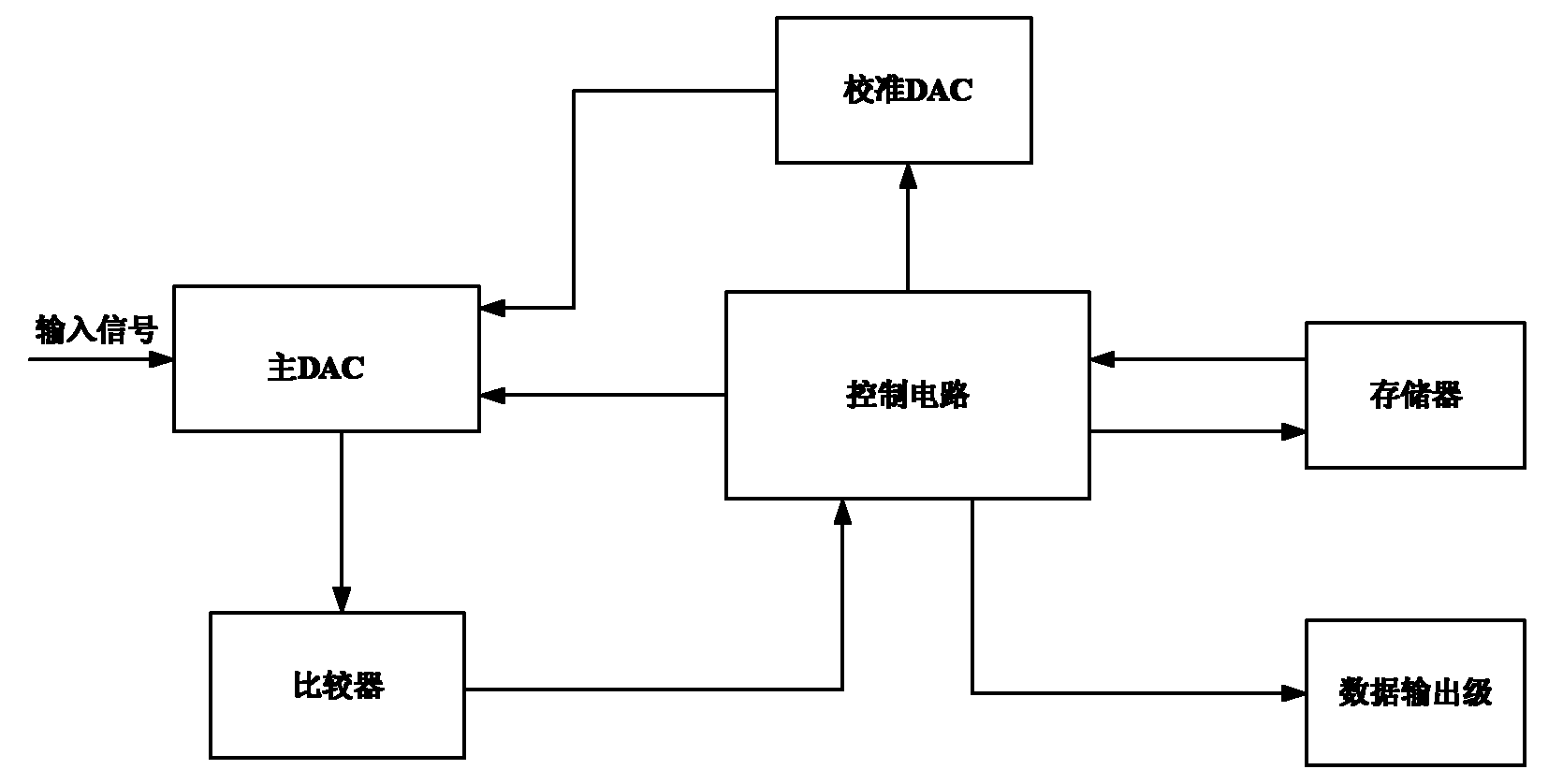
Sequential approximation analog to digital converter with digital correction and processing method thereof
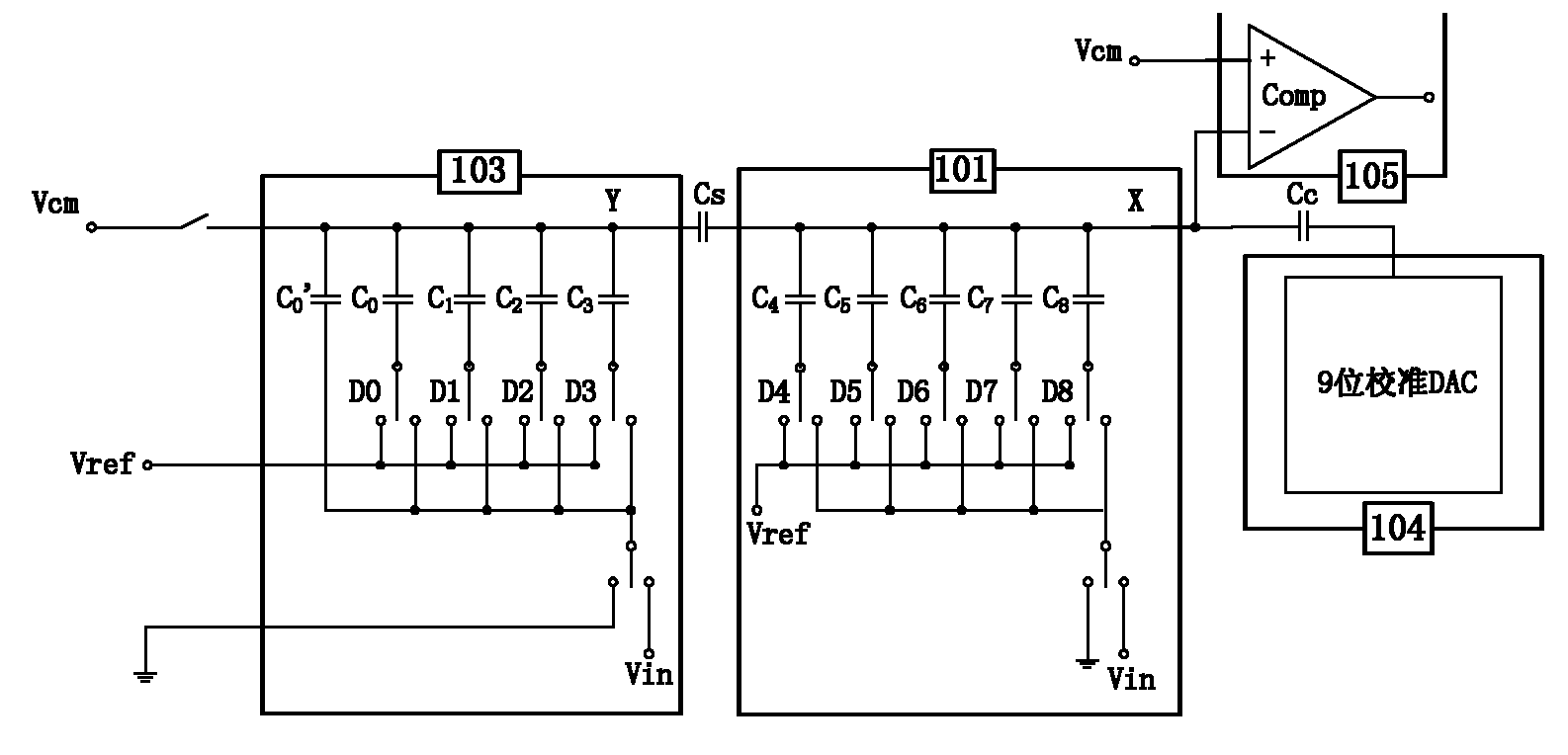
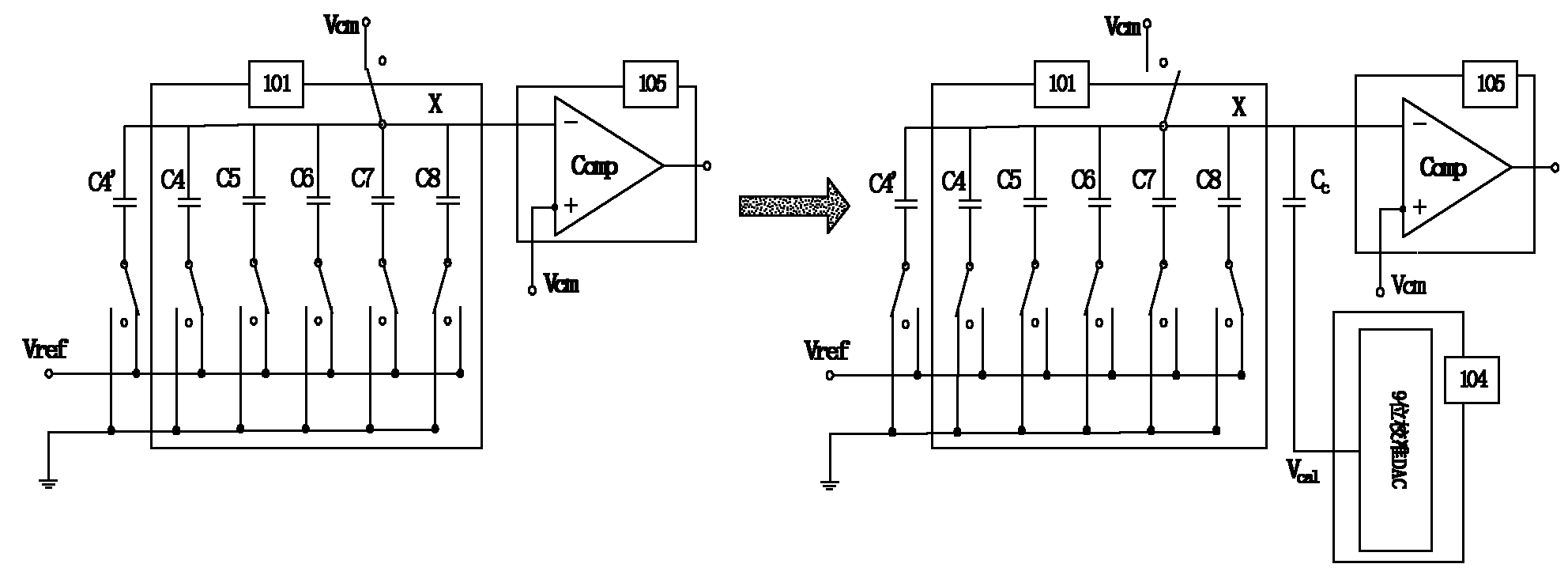
InactiveCN101977058AAvoid makingImprove matchElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue/digital conversion calibration/testingCapacitanceDigital down converter
The invention discloses a sequential approximation analog to digital converter with digital correction and a processing method thereof aiming at the defect of difficult composition manufacture of a coupling capacitor in the traditional sequential approximation analog to digital converter. The sequential approximation analog to digital converter comprises a main DAC (Digital Analogue Converter), acalibration DAC, a comparer, a control circuit and a storage. The sequential approximation analog to digital converter is characterized in that the main DAC comprises a high-K-bit CDAC (Capacitance Digital Analogue Converter) and a low-N-bit CDAC. Introduced system errors and capacitance matching errors are digitally corrected and eliminated, error voltages corresponding to capacitors in the high-K-bit CDAC are quantized and stored in the storage, and two-digit 0 are added behind the tail of the quantized residual error voltage digital code and participate in the calculation of the error voltages. When normal conversion is carried out, the error voltage digital codes are accumulated and then last two digits are discarded, the remain digital codes are used as the input of the calibration DAC, thus the accuracy of the analog to digital converter is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
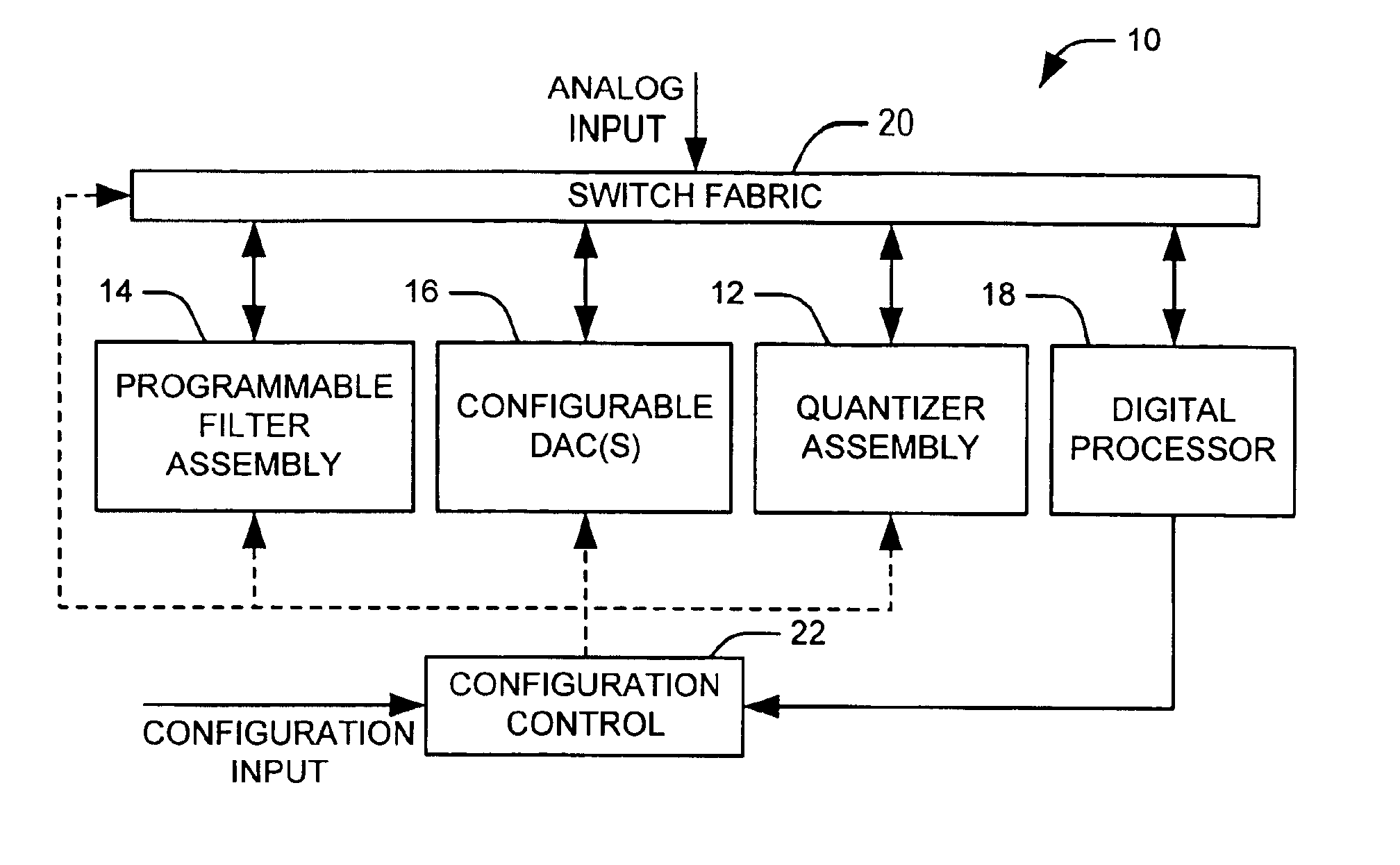
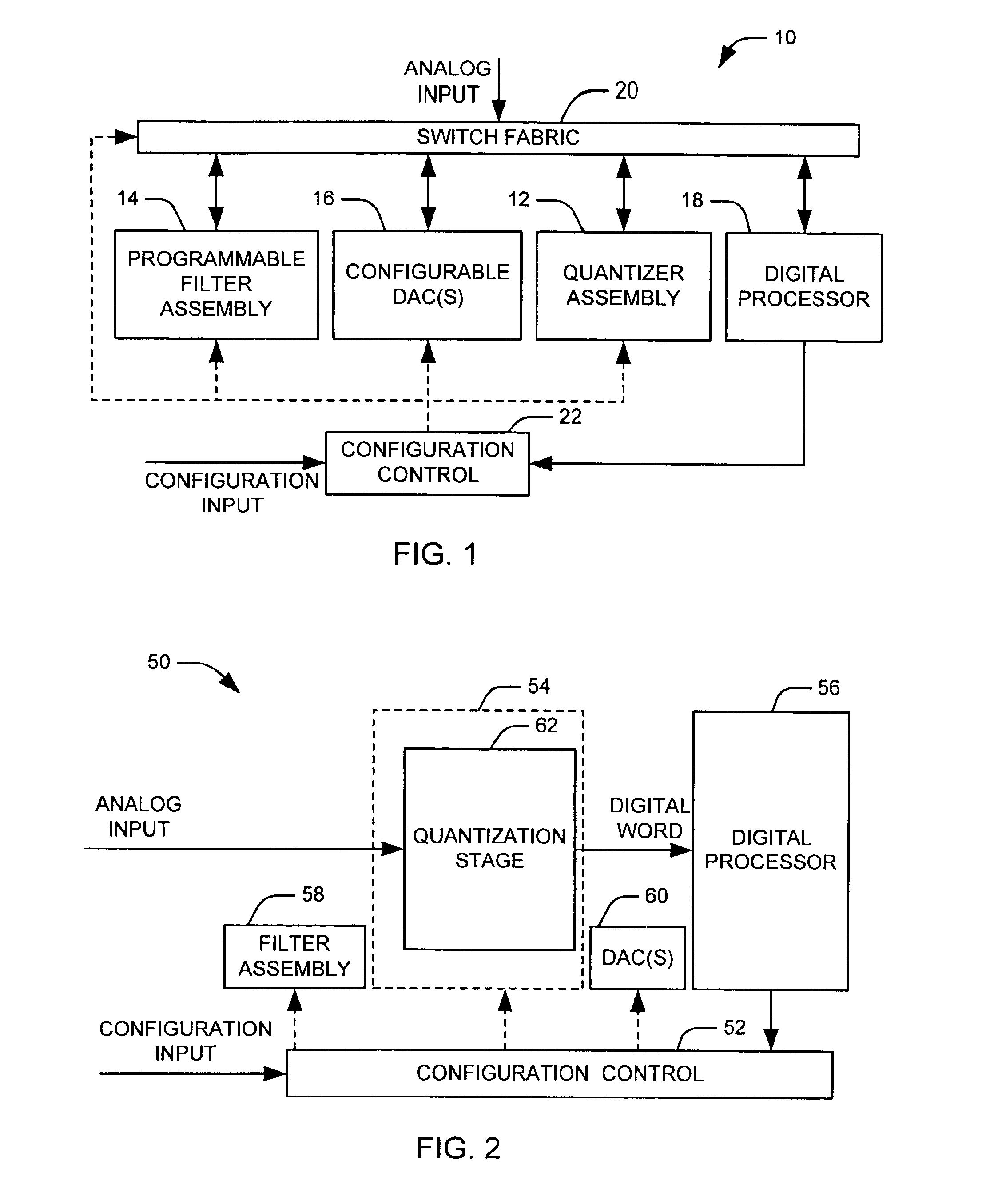
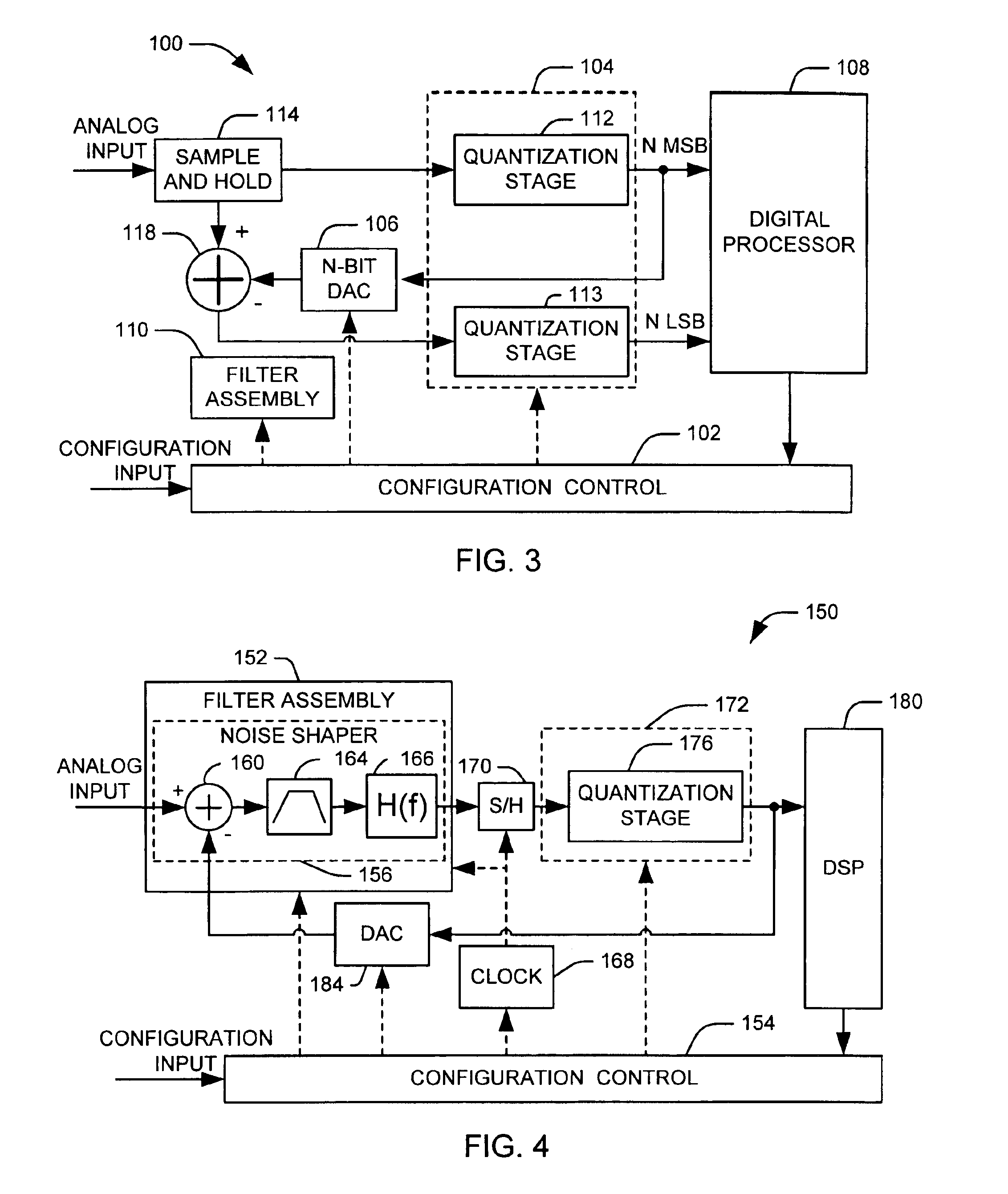
Programmable analog-to-digital converter
ActiveUS6894632B1Electric signal transmission systemsReconfigurable analogue/digital convertersDigital down converterEngineering
Systems and methods are disclosed that employ a programmable analog-to-programmable digital converted system. A programmable analog-to-digital converter system comprises a quantizer assembly and configuration control. The quantizer assembly is configurable to provide at least one quantization stage. A given quantization stage converts an associated analog signal into an associated digital output signal. The configuration control selects among a plurality of configurations and configures the analog-to-digital converter system according to the selected configuration. The quantizer assembly is configurable to provide a plurality of quantization stages arranged in series in a first configuration, or to provide a single quantization stage in a second configuration.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com