Patents
Literature
588 results about "Adder" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An adder is a digital circuit that performs addition of numbers. In many computers and other kinds of processors adders are used in the arithmetic logic units or ALU. They are also used in other parts of the processor, where they are used to calculate addresses, table indices, increment and decrement operators, and similar operations.
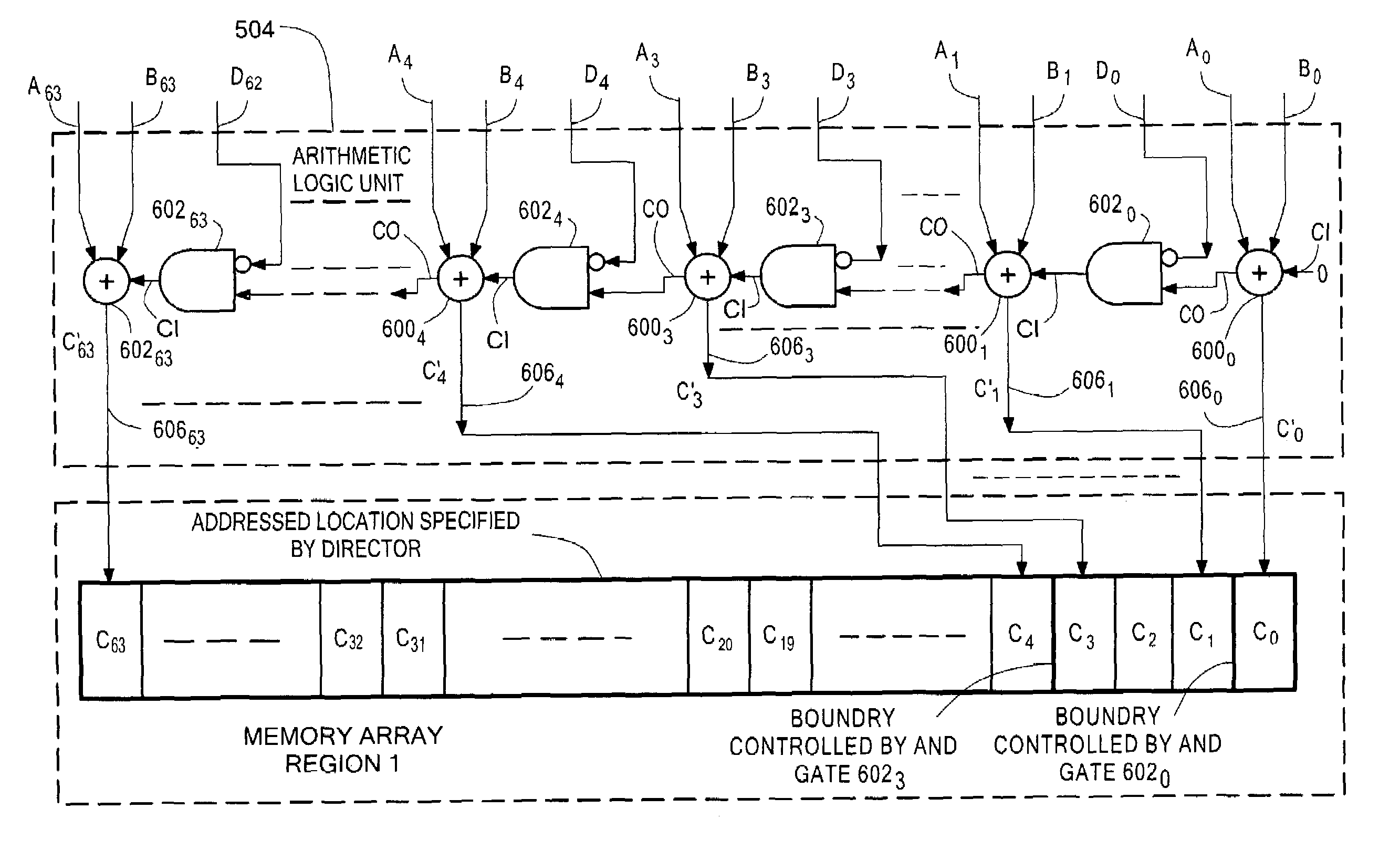
Data storage system having atomic memory operation
ActiveUS6973551B1Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsData storage systemRead-modify-write
A method and system for enabling a director to perform an atomic read-modify-write operation on plural bit read data stored in a selected one of a plurality of memory locations. The method includes providing a plurality of successive full adders, each one of the full adders being associated with a corresponding one of the bits of the plural bit read data. Each one of the full adders has a summation output, a carry bit input and a carry bit output. The method includes adding in each one of the full adders: (a) a corresponding bit of plural bit input data provided by the director; (b) the corresponding one of the bits of the plural bit read data; and, (c) a carry bit fed the carry bit input from a preceding full adder. Each one of the full adders provides: (a) a carry bit on the carry output thereof representative of the most significant bit produced by the full adder; and, (b) a bit on the summation output representative of a least significant bit produced by the full adder. The bit on the summation output is stored in a corresponding bit location in the selected one of a plurality of memory locations. The method selectively couples, or inhibits coupling, the carry bit produced from one of the full adders to the carry bit input of a next successive full adder selectively in accordance with a corresponding bit of a plural bit carry bit mask provided by the director providing a full adder for each one of the bits of the plural bit read stored. The full adder has a carry bit input and a carry bit output. The method includes adding each one of a bits of plural bit input data provided by the director with a corresponding one of the bits of the plural bit read data in the provided full adder together with a carry bit fed the carry bit input of such provided full adder. The full adder provides: a carry output bit; and, a summation of the bits fed to such provided full adder to the corresponding bit location in the selected one of a plurality of memory locations. The method selectively couples, or inhibits coupling, a carry bit produced by one full adder provided for a lower order bit of the plural bit read data to the carry bit input of a second full adder provided by for next, successive higher order bit of the plural bit read data selectively in accordance with one of a plurality of bits of a carry bit mask provided by the director.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
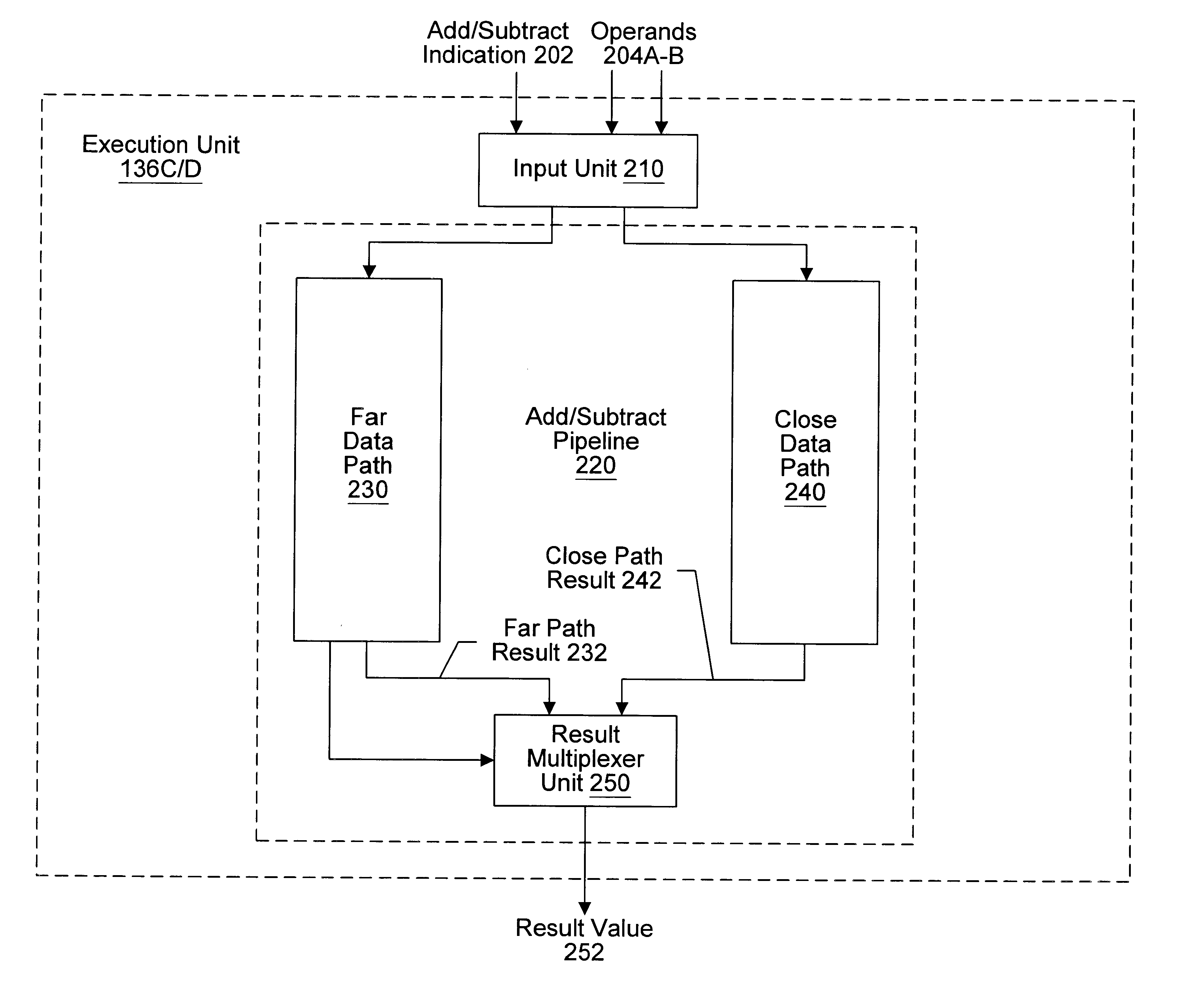
Floating point addition pipeline including extreme value, comparison and accumulate functions
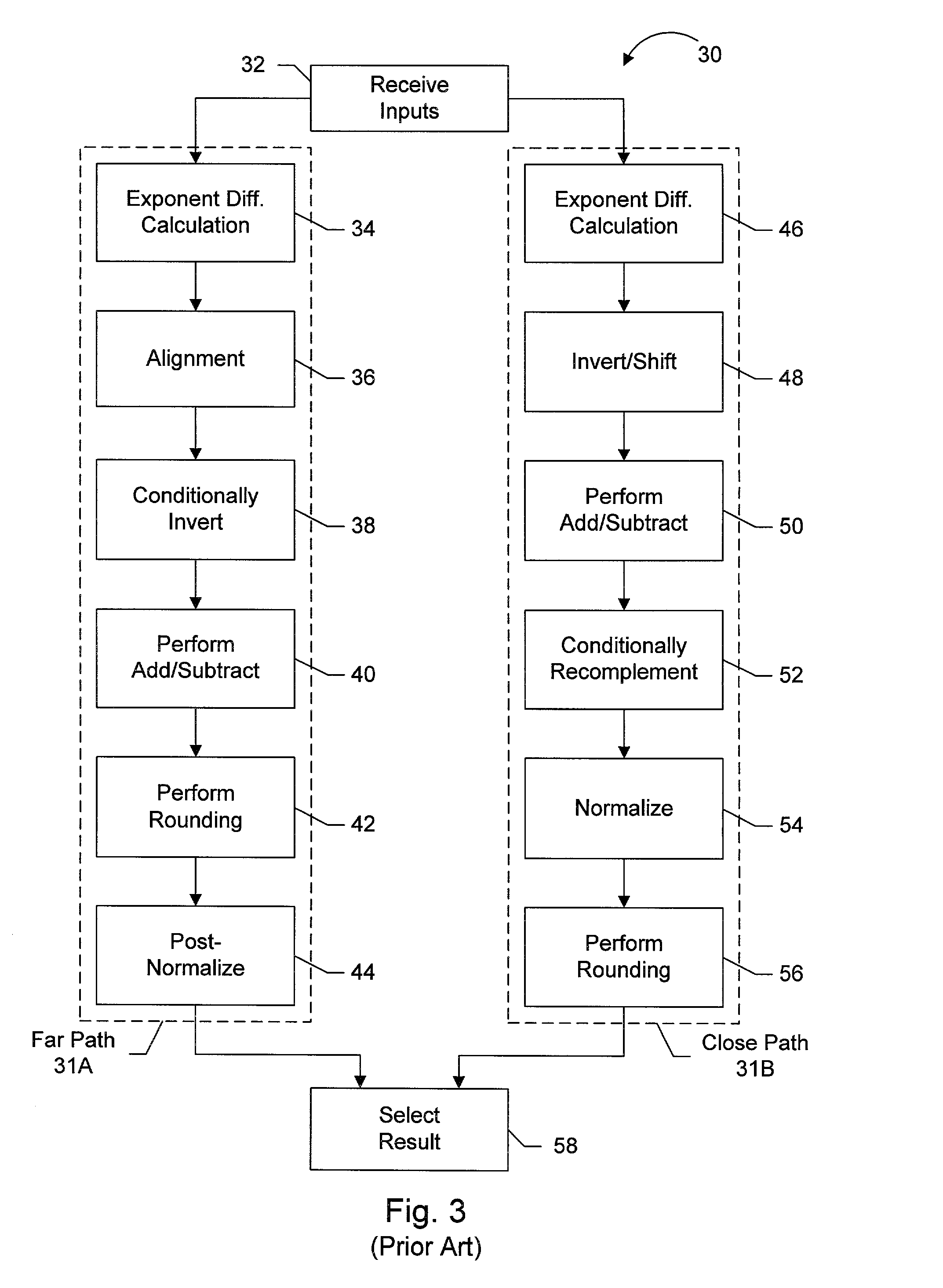
InactiveUS6397239B2Computations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-contact making devicesPathPingExecution unit
A multimedia execution unit configured to perform vectored floating point and integer instructions. The execution unit may include an add / subtract pipeline having far and close data paths. The far path is configured to handle effective addition operations and effective subtraction operations for operands having an absolute exponent difference greater than one. The close path is configured to handle effective subtraction operations for operands having an absolute exponent difference less than or equal to one. The close path is configured to generate two output values, wherein one output value is the first input operand plus an inverted version of the second input operand, while the second output value is equal to the first output value plus one. Selection of the first or second output value in the close path effectuates the round-to-nearest operation for the output of the adder.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
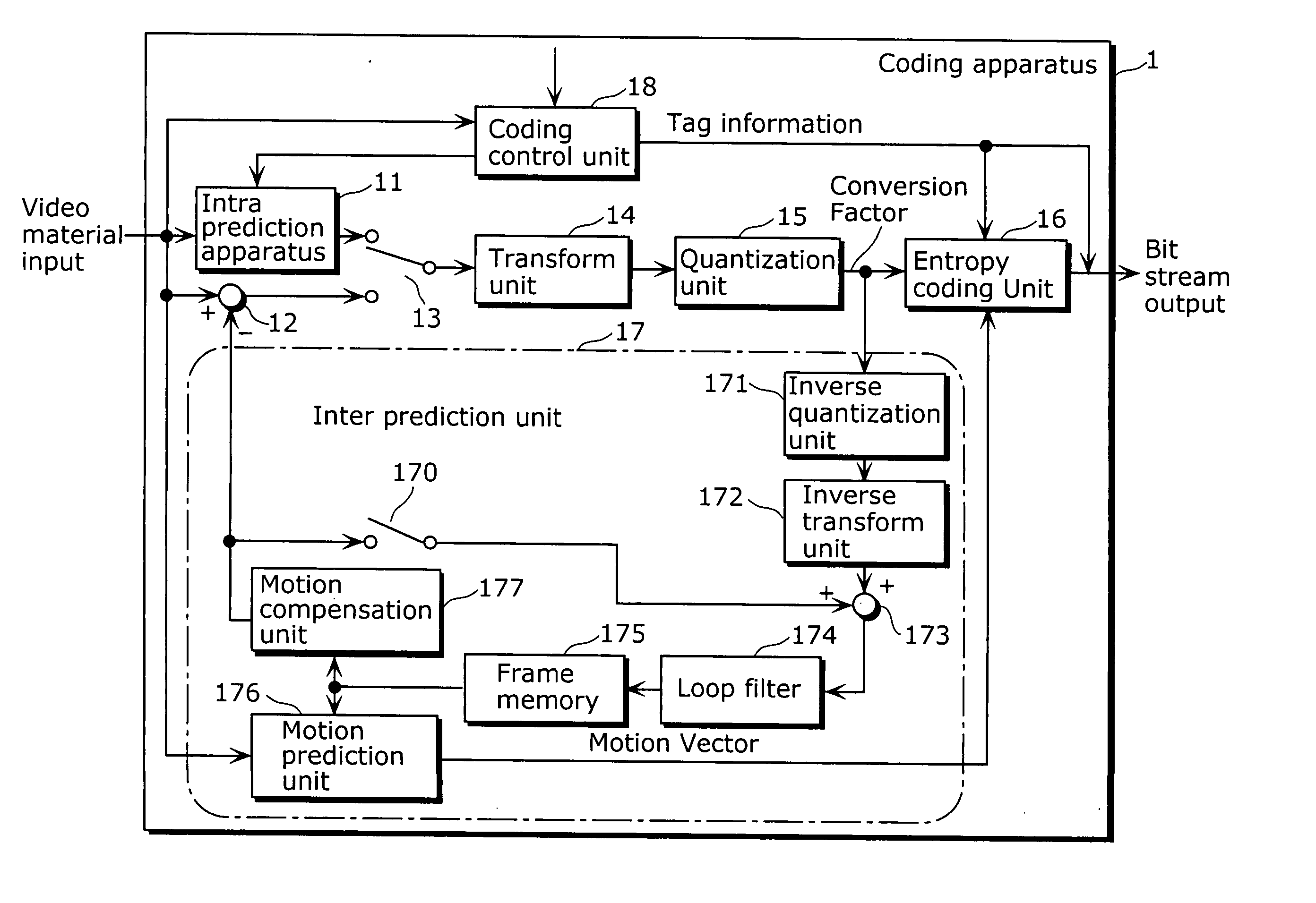
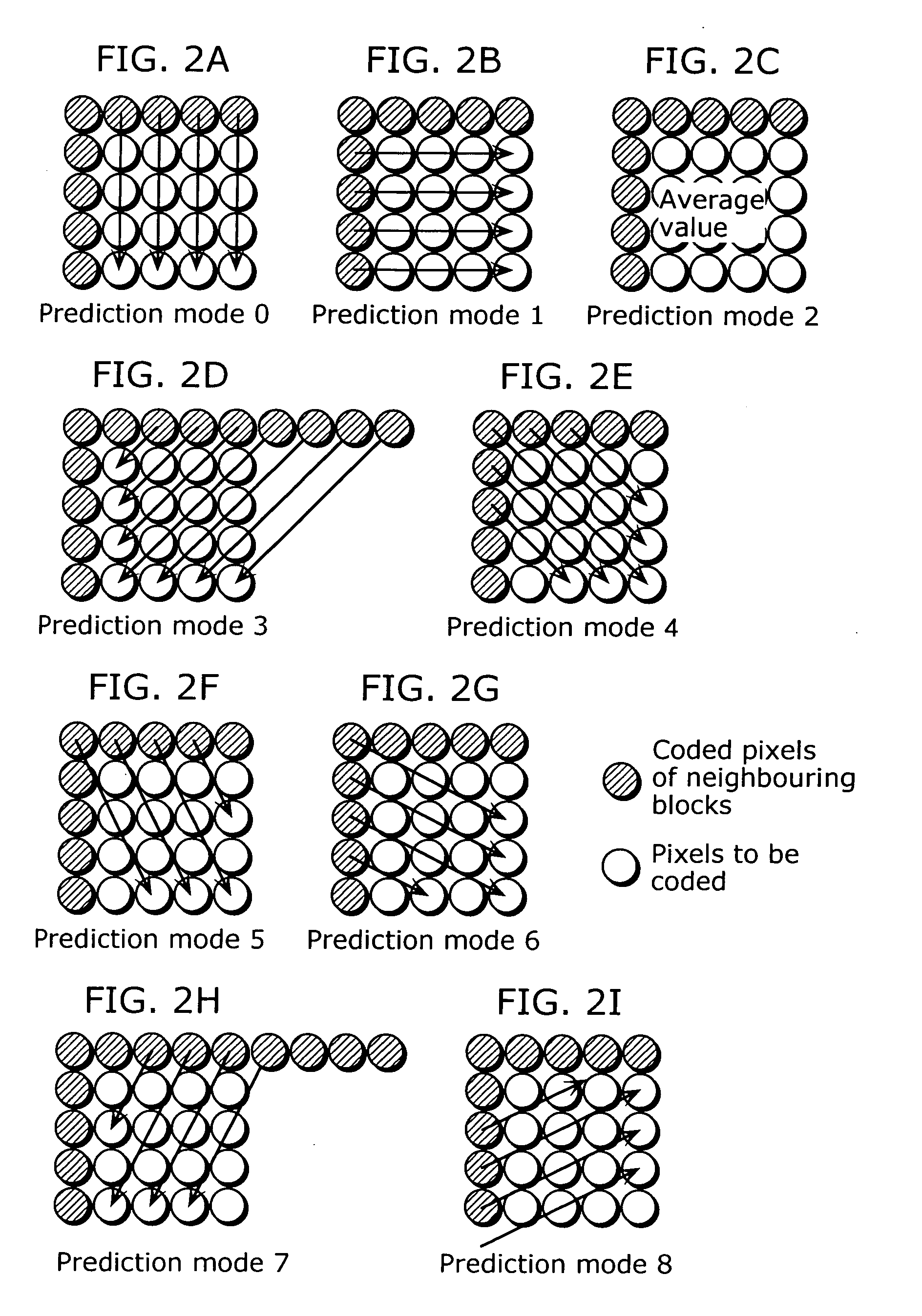
Intra prediction apparatus and intra prediction method
ActiveUS20060126730A1Reduce effectExcellent code efficiencyImage enhancementMultiple-port networksPrediction methodsMacroblock
To provide an intra prediction apparatus which can circumvent a hazard problem and improve the time reduction effect. An intra prediction apparatus 11 performs intra predictions of a picture. The intra predictions include: second intra predictions of respective second blocks (blocks) which are obtained by dividing a first pixel block; and a first intra prediction of the first block (macroblock) which constitutes the picture. The intra prediction apparatus 11 includes: an intra prediction unit (a prediction unit 113, an orthogonal transform and quantization unit 115, an inverse orthogonal transform and inverse quantization unit 116, and an adder 117) which performs the intra predictions; and a control unit 119 which controls the intra prediction unit to perform in parallel the intra prediction of the macroblock and the intra predictions of the respective pixel blocks.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
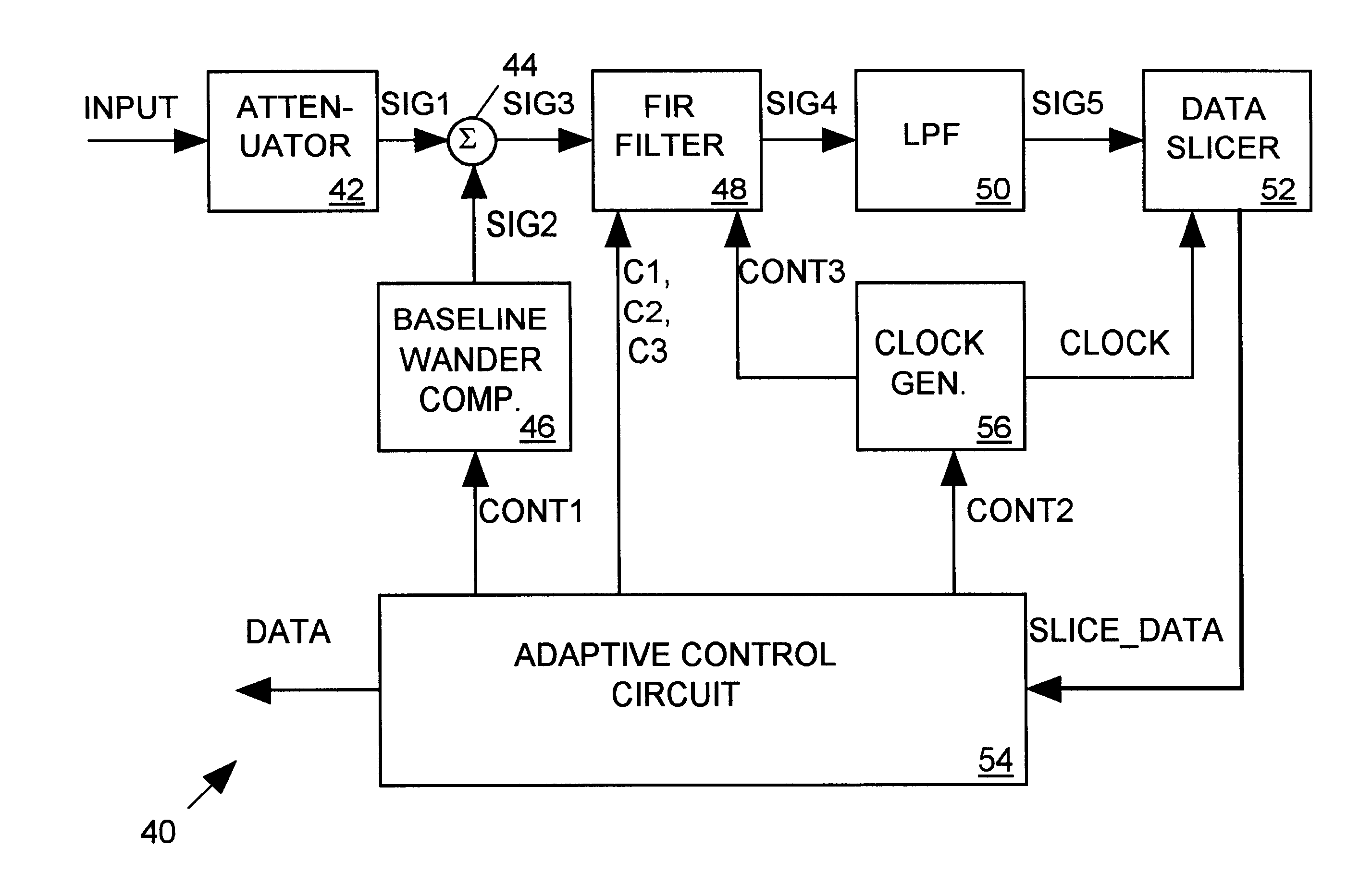
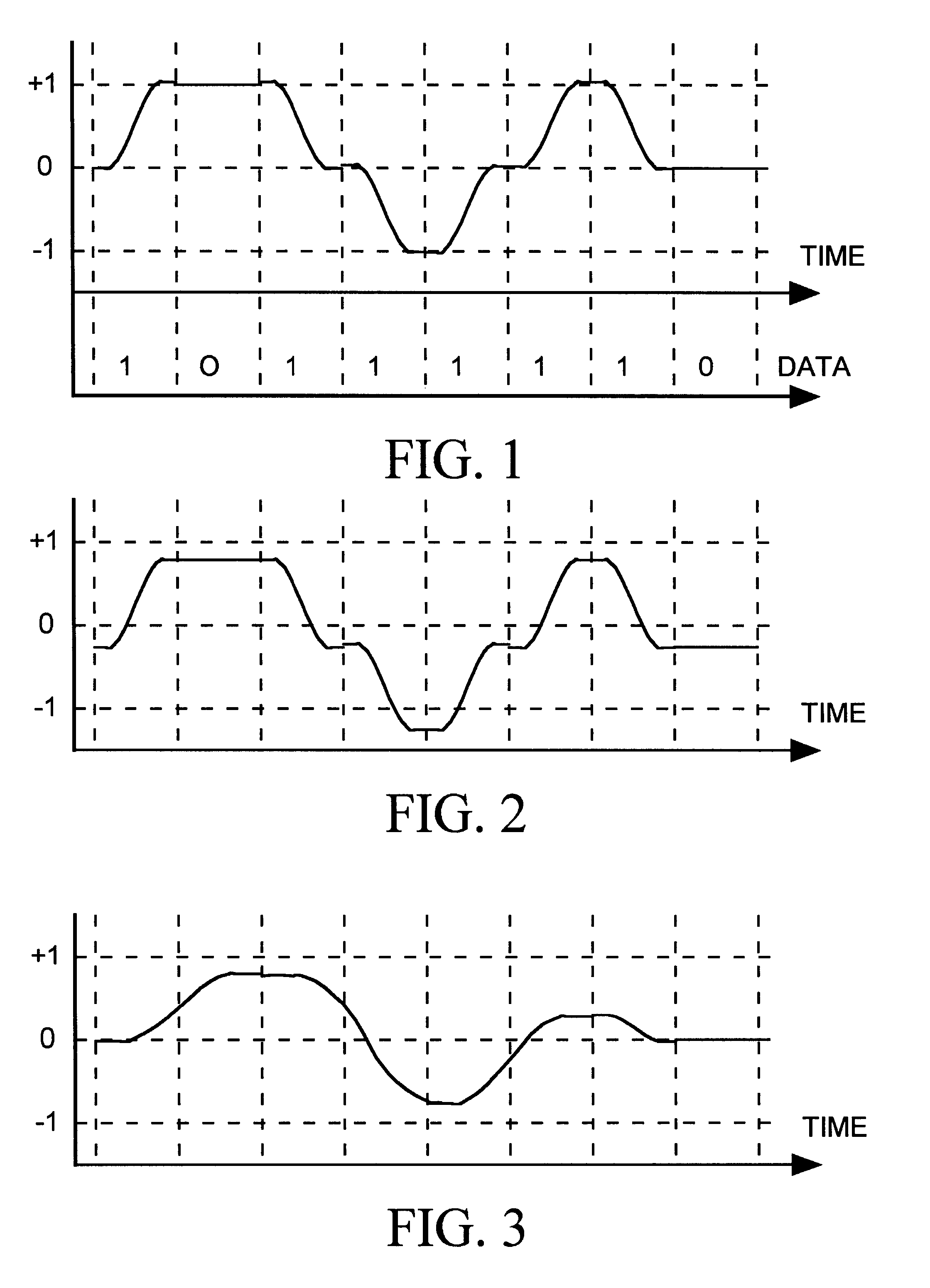
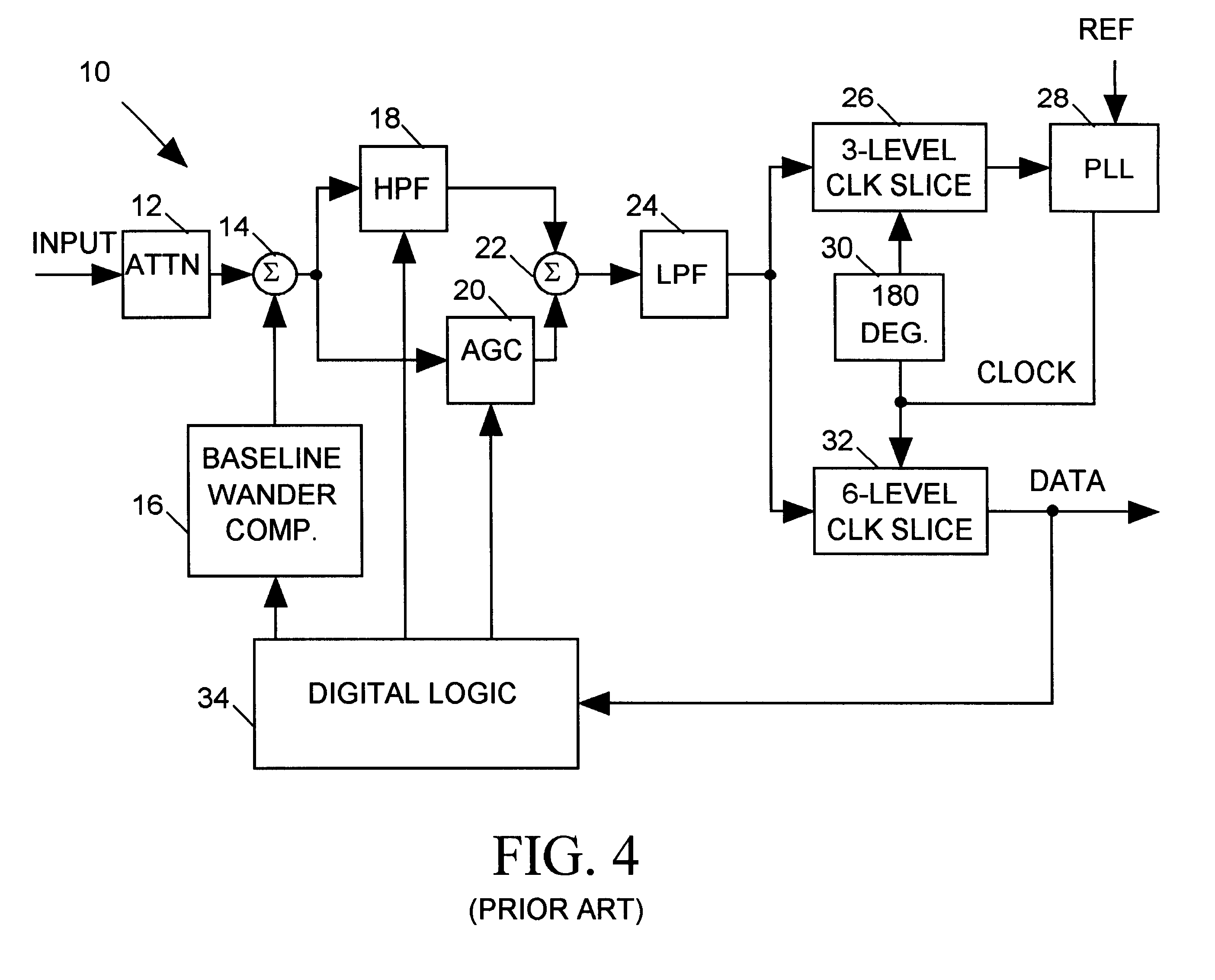
FIR filter architecture for 100Base-TX receiver
A 100Base-TX receiver employs a finite impulse response (FIR) filter to provide both equalization and insertion loss compensation for an MLT-3 input signal. The FIR filter includes three delay stages, each delaying the input signal with an 8 ns delay (the period of one data cycle of the MLT-3 input signal), a set of three amplifiers for amplifying the delay stage outputs with gains C1, C2 and C3, and a summer for summing the outputs of the three amplifiers to produce a compensated, equalized MLT-3 signal. A low-pass filter filters the FIR filter output signal, and a data slicer digitizes the low-pass filter output during each data cycle to produce data representing the incoming MLT-3 as having one of six levels. An adaptive control signal processes the slicer output data to determine how to set the gains C1, C2 and C3 of the three FIR amplifiers to provide the correct amount of equalization and compensation. The adaptive control circuit also processes the slice data to adaptively adjust the phase of a clock signal controlling timing of the data slicer, to adaptively adjust an amount of baseline wander compensation provided to the MLT-3 signal, and to determine the value of data conveyed by the MLT-3 input signal.
Owner:INFINEON TECHNOLOGIES NORTH AMERICA CORPORATION
Dynamically configurable logic gate using a non-linear element
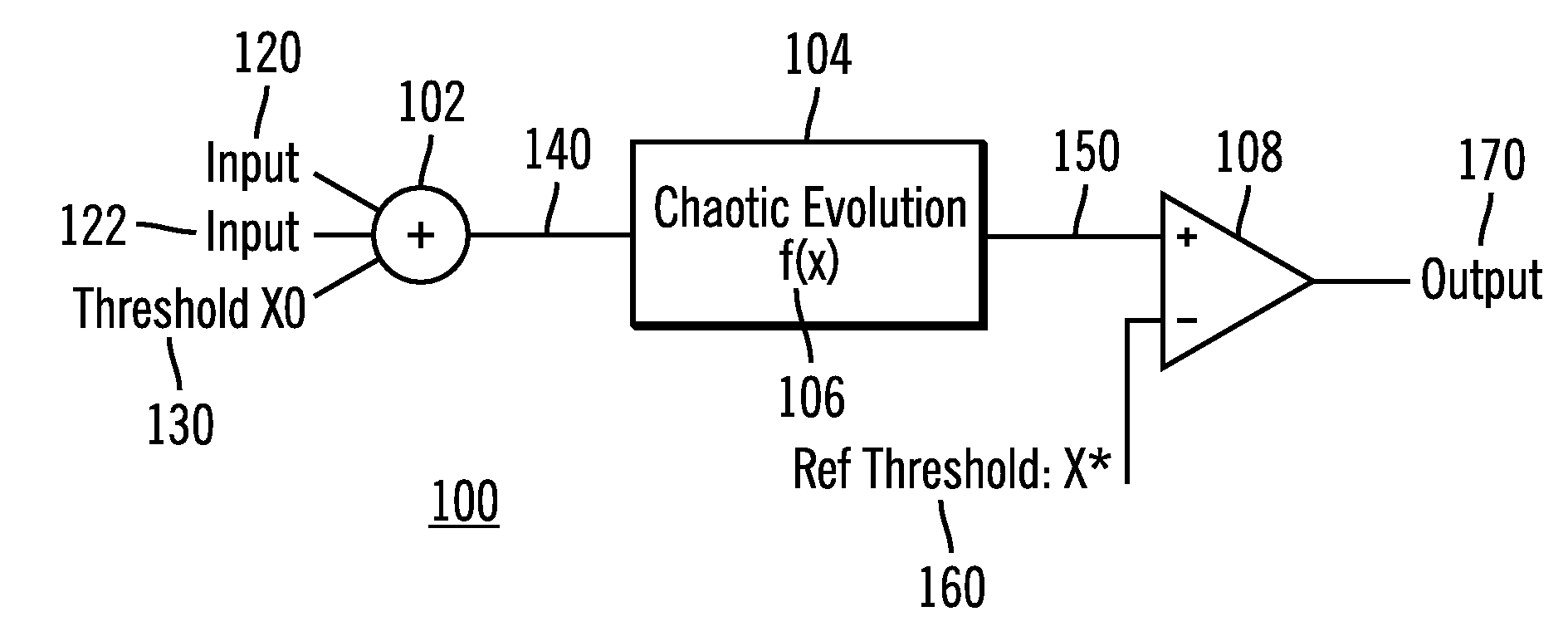
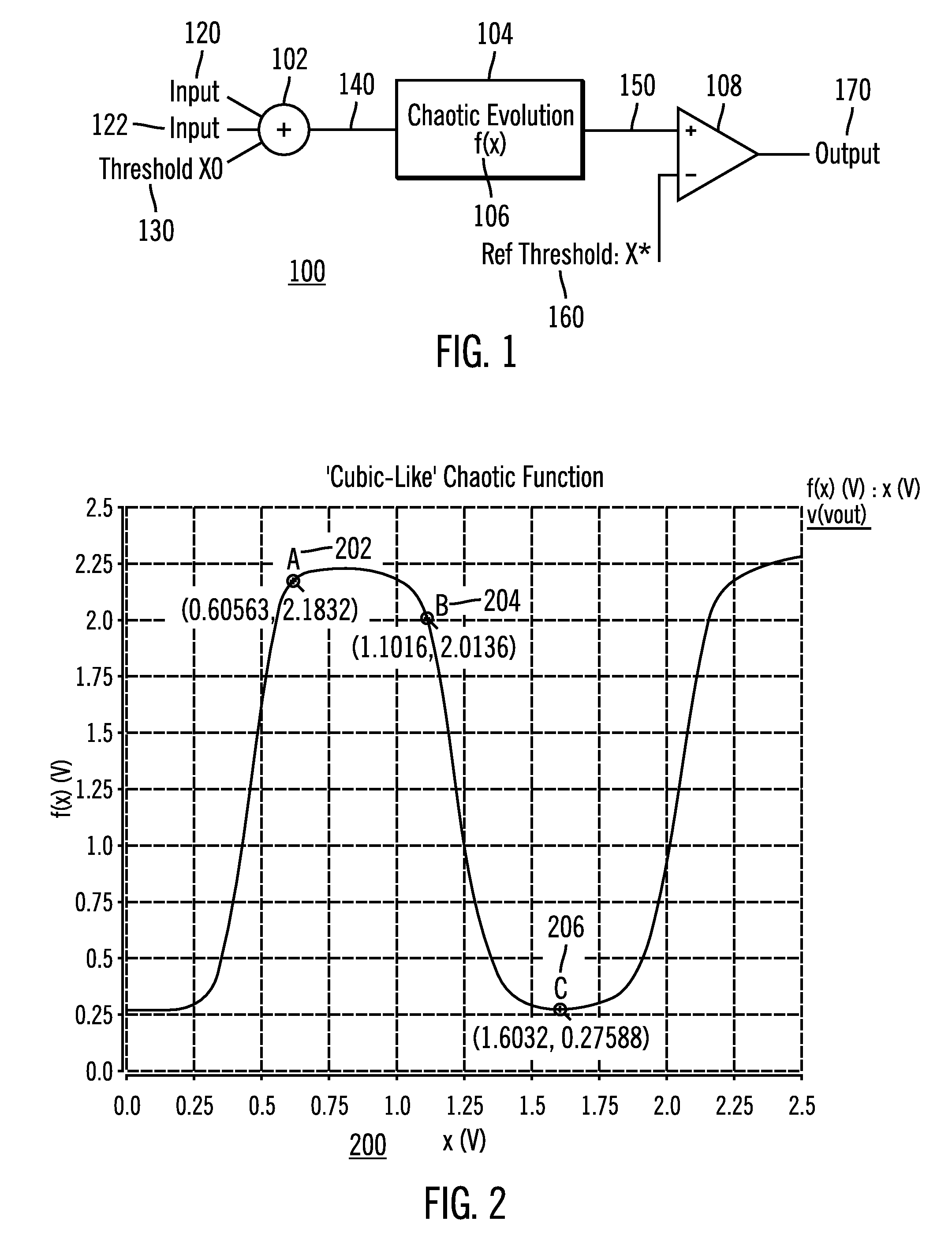
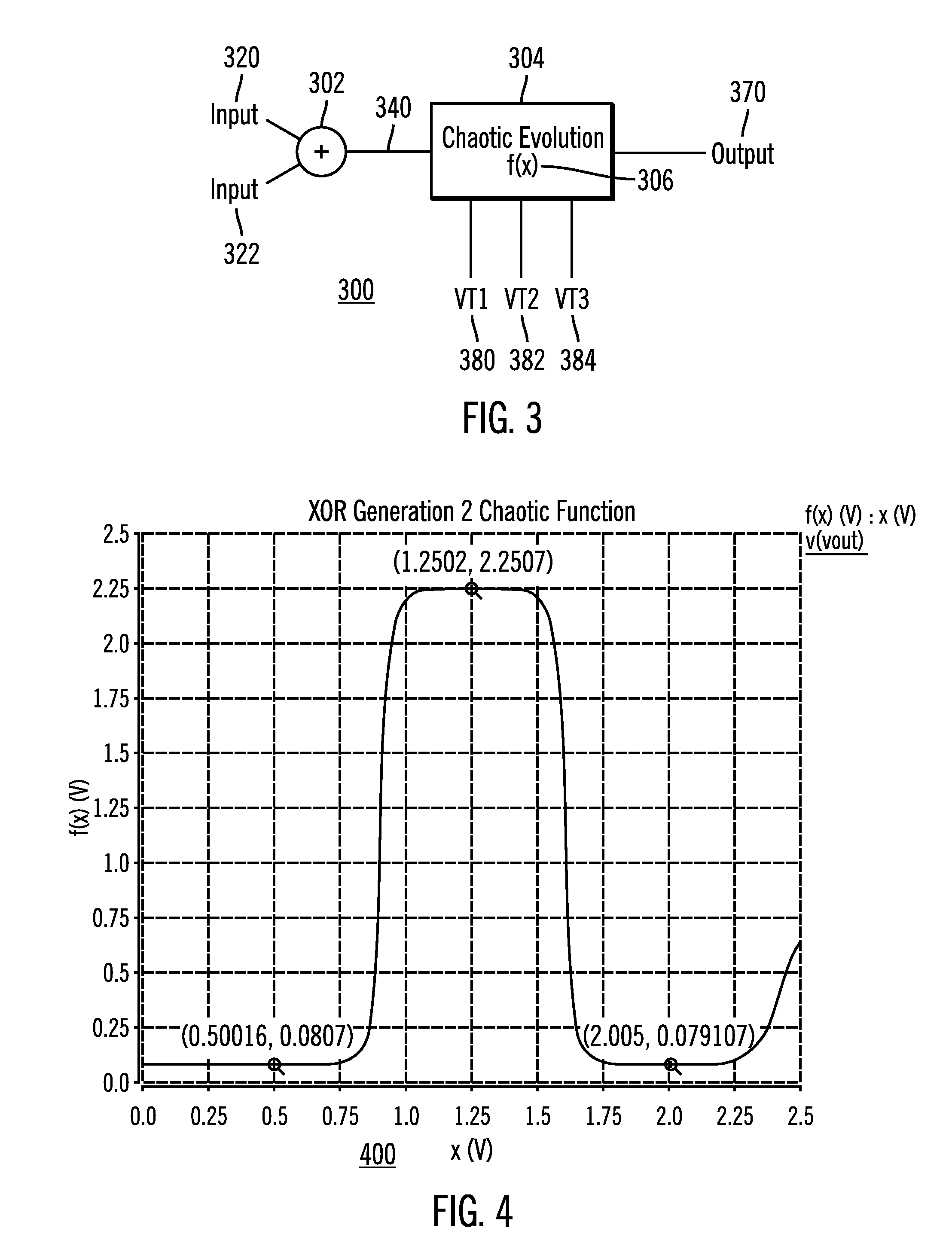
ActiveUS7453285B2Reduce power consumptionLess componentsElectric pulse generatorLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsControl signalLinear element
A dynamically configurable logic gate includes an input summer for receiving a first input signal and a second input signal to generate a summed input signal. Further the dynamically configurable logic gate includes a nonlinear element that applies a nonlinear function to the summed input signal to produce a nonlinear output signal. The dynamically configurable logic gate output signal corresponds to one of a plurality of different logic gates responsive to adjusting the summed input signal and / or the nonlinear function. In another embodiment, the dynamically configurable logic gate includes feedback to one of the inputs. The dynamically configurable logic gate receives the two inputs and operates as one of a plurality of different logic gate types so as to produce an output signal that corresponds to a memory latch according to a selection of the control signal. An array structure of dynamically configurable logic elements is also disclosed.
Owner:CHAOLOGIX INC
Programmable matched filter bank
InactiveUS6842480B1Reduce complexityReduce in quantityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationIntegratorMatched filter bank
A programmable matched filter bank comprises a sliding integrator and compensation calculation circuits. The integrator receives a chip stream of samples derived from a received spread-spectrum signal and integrates a number of the most recent samples, to form a common integration value. Each of the compensation calculation circuits receives the same most recent samples and receives a respective one of the possible reference spreading code sequences. In operation, each compensation calculation circuit derives a compensation value, and an associated circuit modifies the common integration value by the respective compensation value. The result is a value of correlation between the predetermined number of most recent samples, for each respective reference code sequence. The inventive approach reduces the number of bit adders and inverters in the implementation of a matched-filter, a programmable matched filter and a programmable matched filter bank for spread spectrum receivers.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Floating point unit with fused multiply add and method for calculating a result with a floating point unit
InactiveUS20060184601A1Reduce delaysSimplify carry logicComputation using denominational number representationFloating-point unitOperand
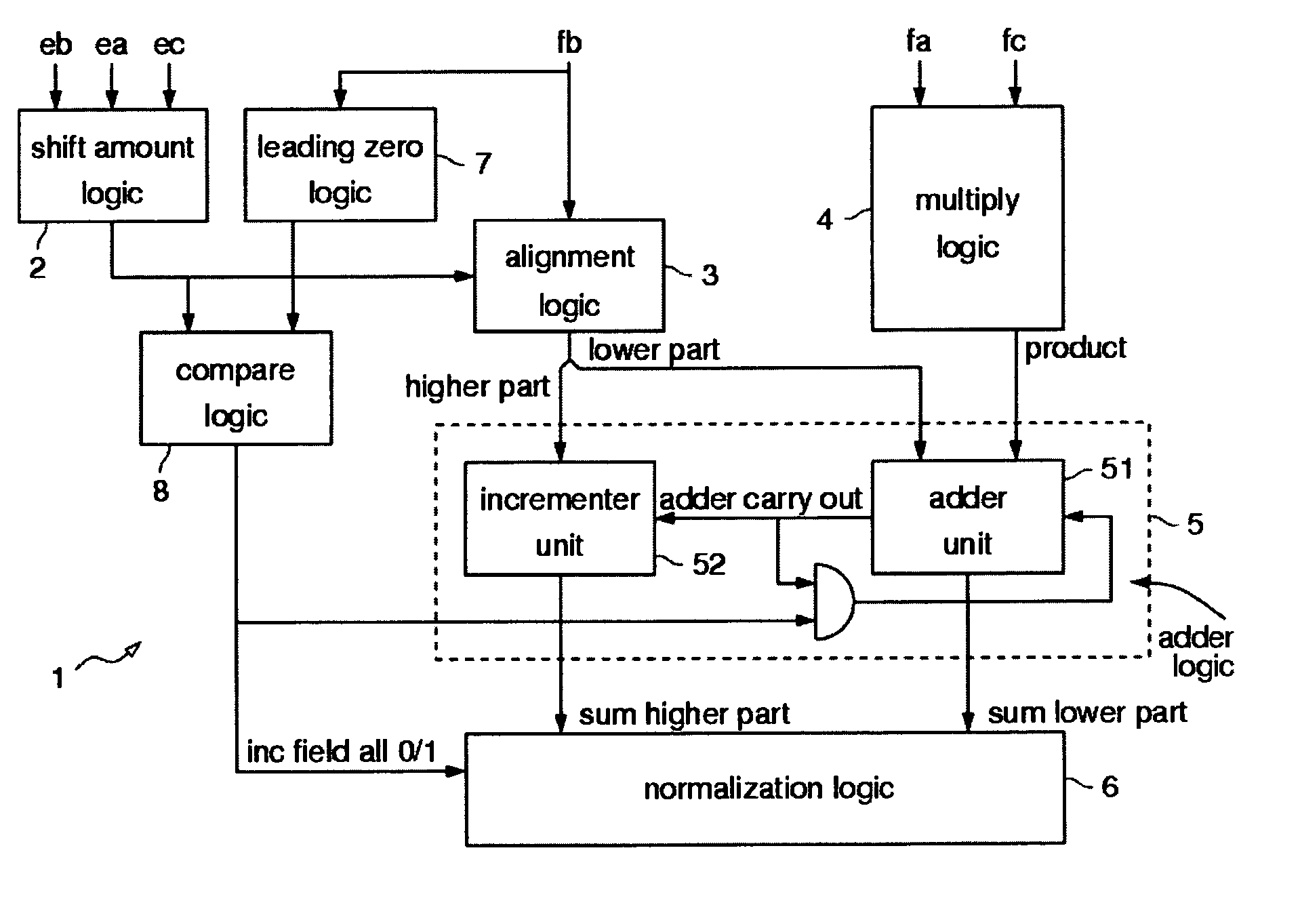
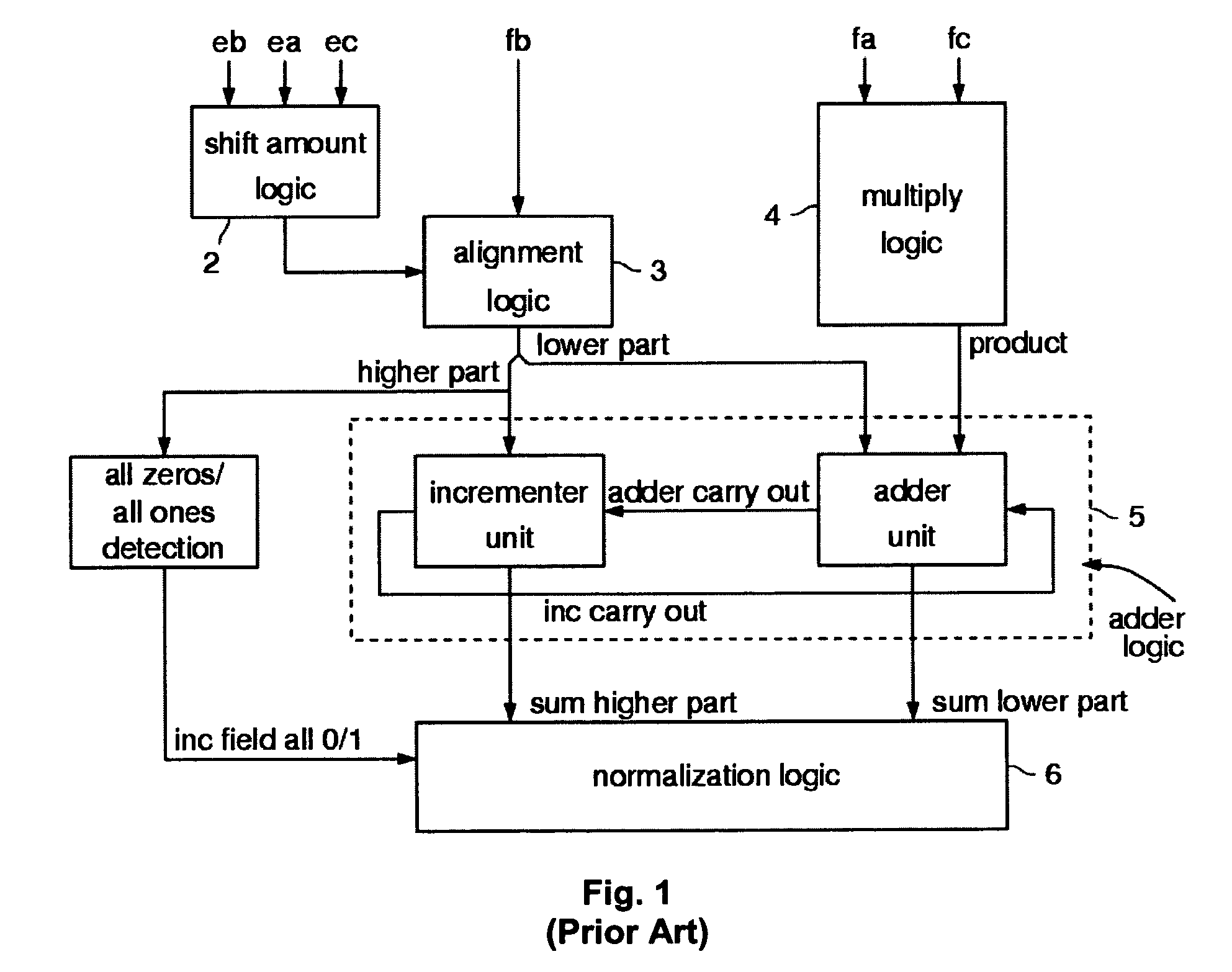
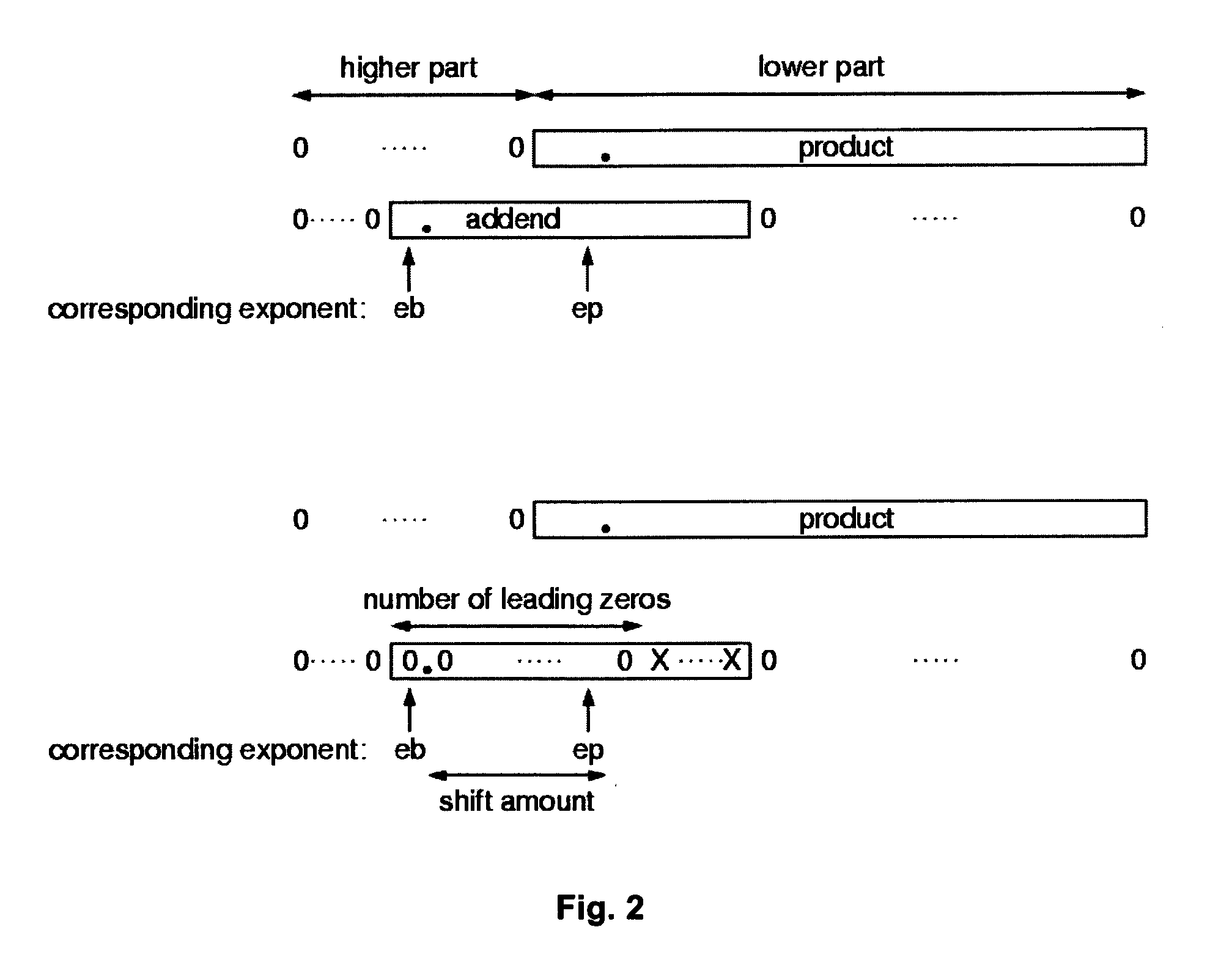
The invention proposes a Floating Point Unit (1) with fused multiply add, with one addend operand (eb, fb) and two multiplicand operands (ea, fa; ec, fc), with a shift amount logic (2) which based on the exponents of the operands (ea, eb and ec) computes an alignment shift amount, with an alignment logic (3) which uses the alignment shift amount to align the fraction (fb) of the addend operand, with a multiply logic (4) which multiplies the fractions of the multiplicand operands (fa, fc), with a adder logic (5) which adds the outputs of the alignment logic (3) and the multiply logic (4), with a normalization logic (6) which normalizes the output of the adder logic (5), which is characterized in that a leading zero logic (7) is provided which computes the number of leading zeros of the fraction of the addend operand (fb), and that a compare logic (8) is provided which based on the number of leading zeros and the alignment shift amount computes select signals that indicate whether the most significant bits of the alignment logic (3) output have all the same value in order to: a) control the carry logic of the adder logic (5) and / or b) control a stage of the normalization logic (6).
Owner:IBM CORP
Time domain self-adaptive equalizer and decision feedback filter included therein
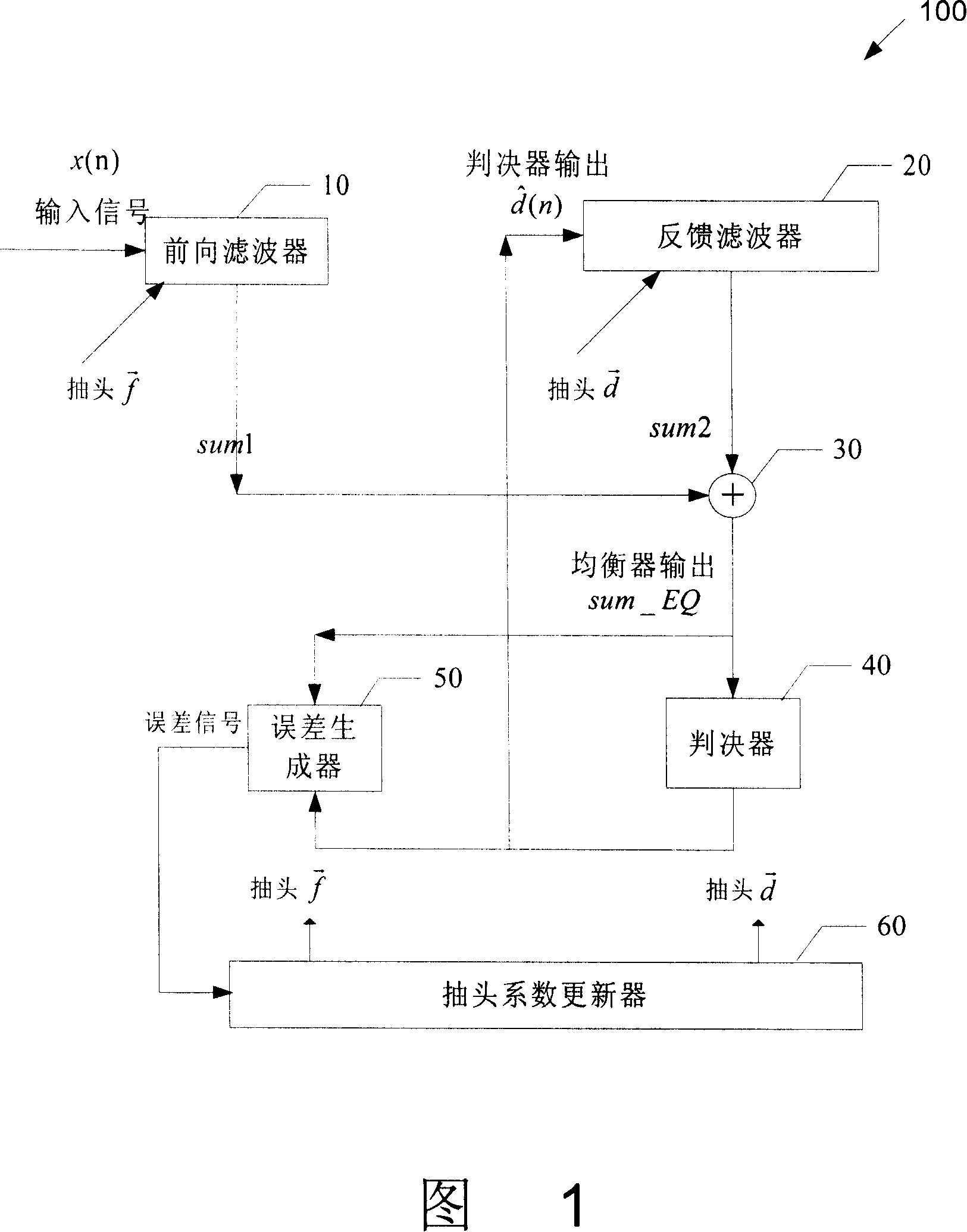
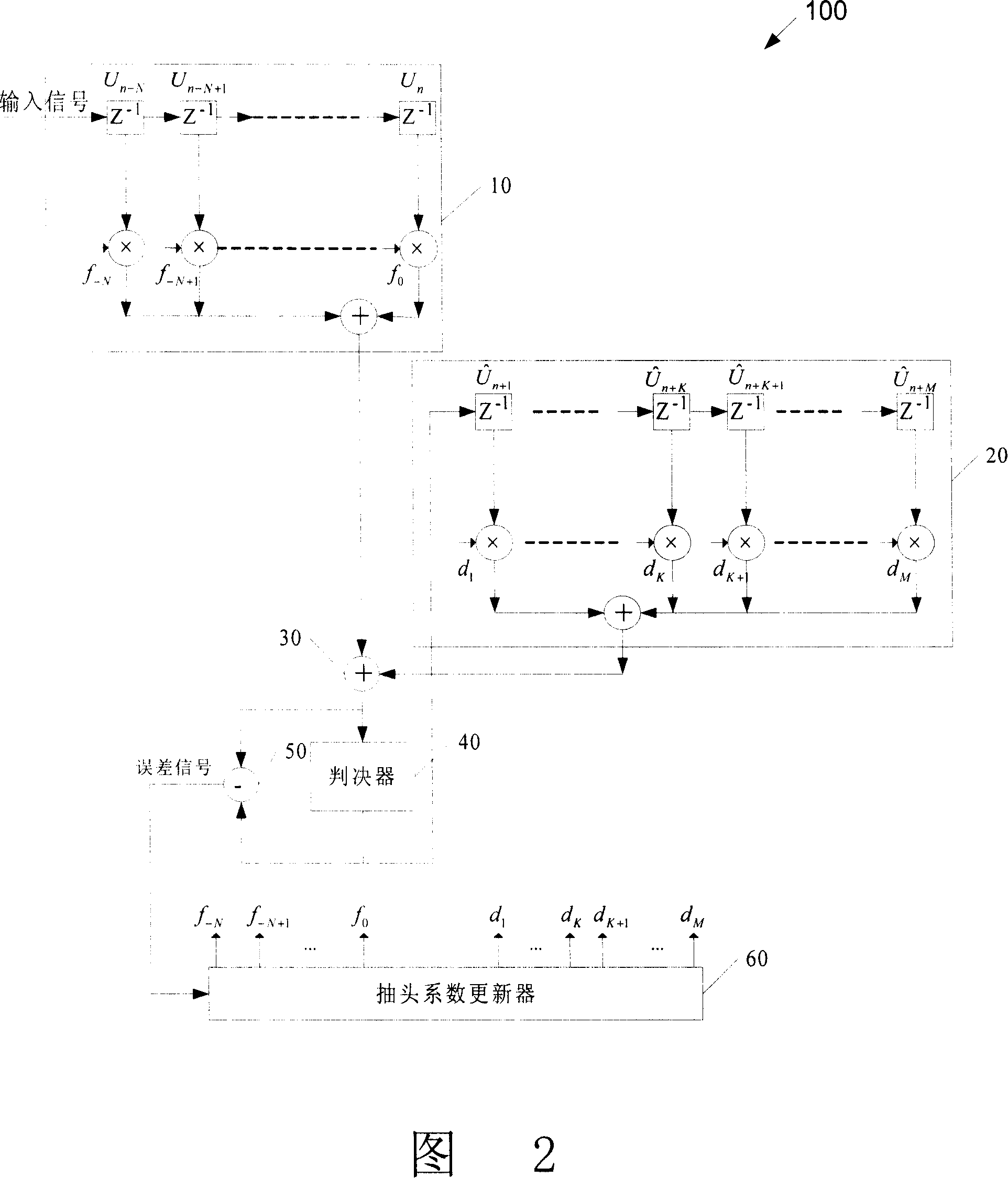
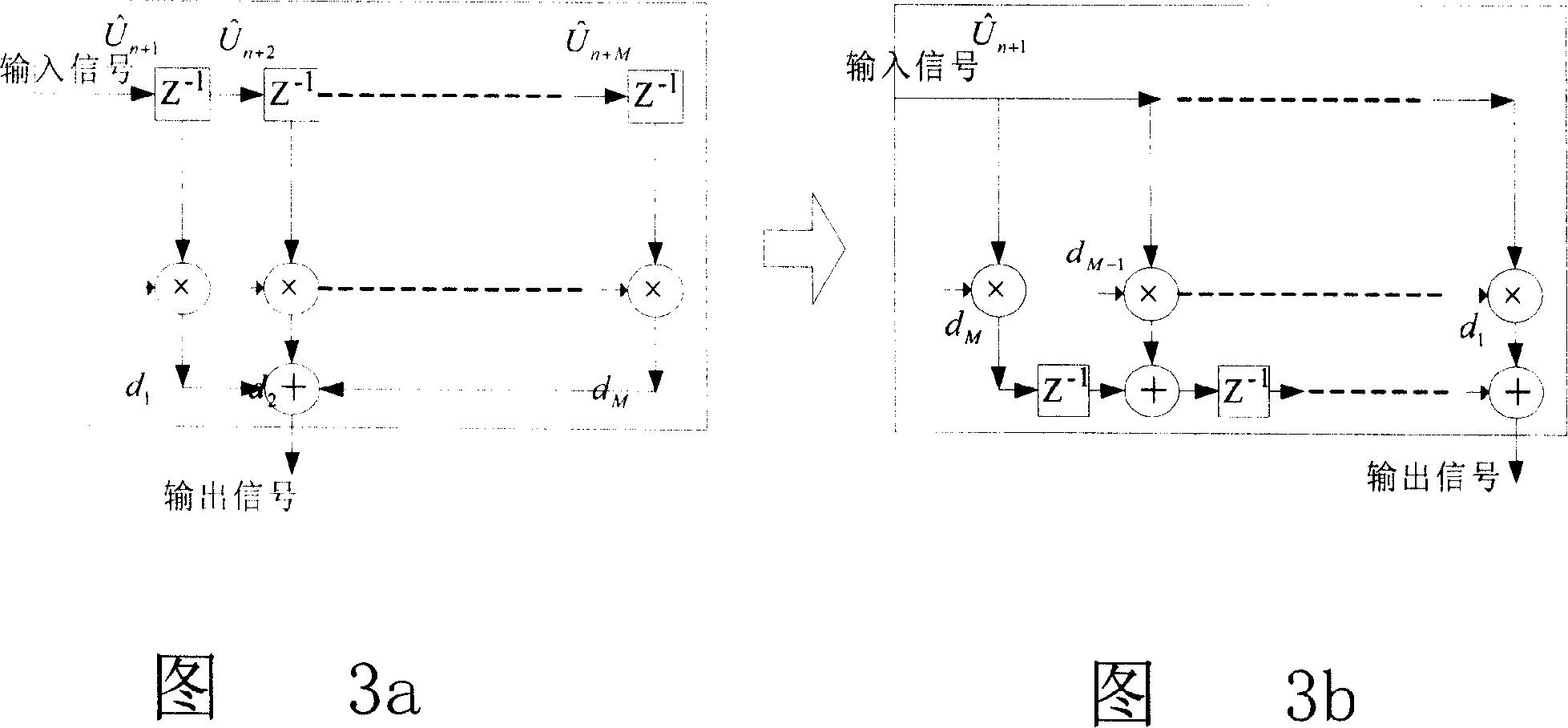
The invention relates to a time domain self-adaptive balancer, wherein input signal flows to a forward filter which output flows into an input of an adder, another two inputs of the adder is the output of a first feedback filter and the output of a second feedback filter, the adder adds the input signals, which output is connected with the input of a judger, an error generator according to the input and output of the judger generates an error signal, a tapping factor refresher according to the error signal generates a tapping factor to refresh the tapping factor of the forward filter and the judgment feedback filter. The first feedback filter uses a rotary structure, and the second feedback filter uses a non-rotary structure, which input has some time delay relative to the input of the first feedback filter. The stage numbers of the rotary structure and non-rotary structure are decided according to the length of last path.
Owner:SHANGHAI HIGH DEFINITION DIGITAL TECH IND
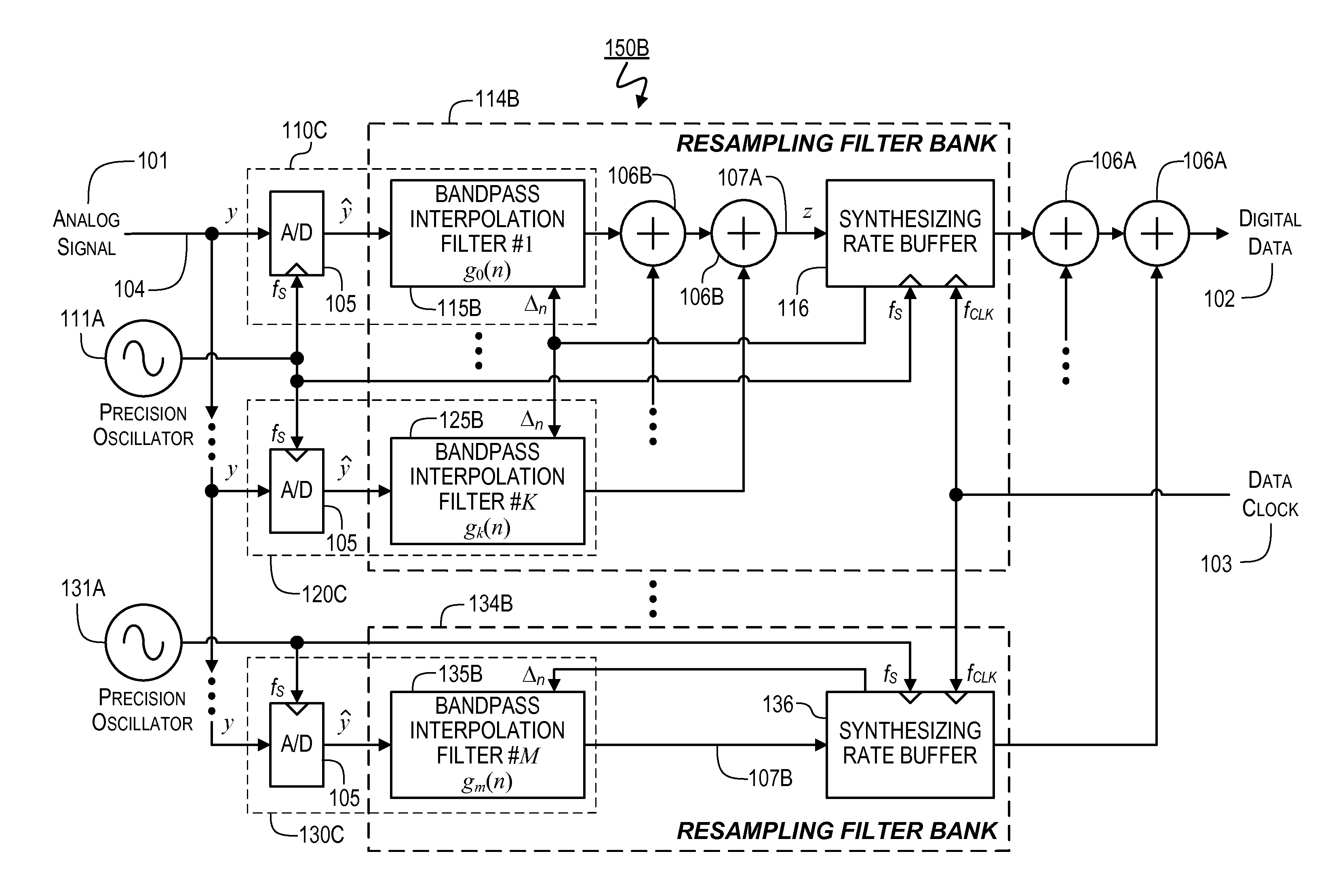
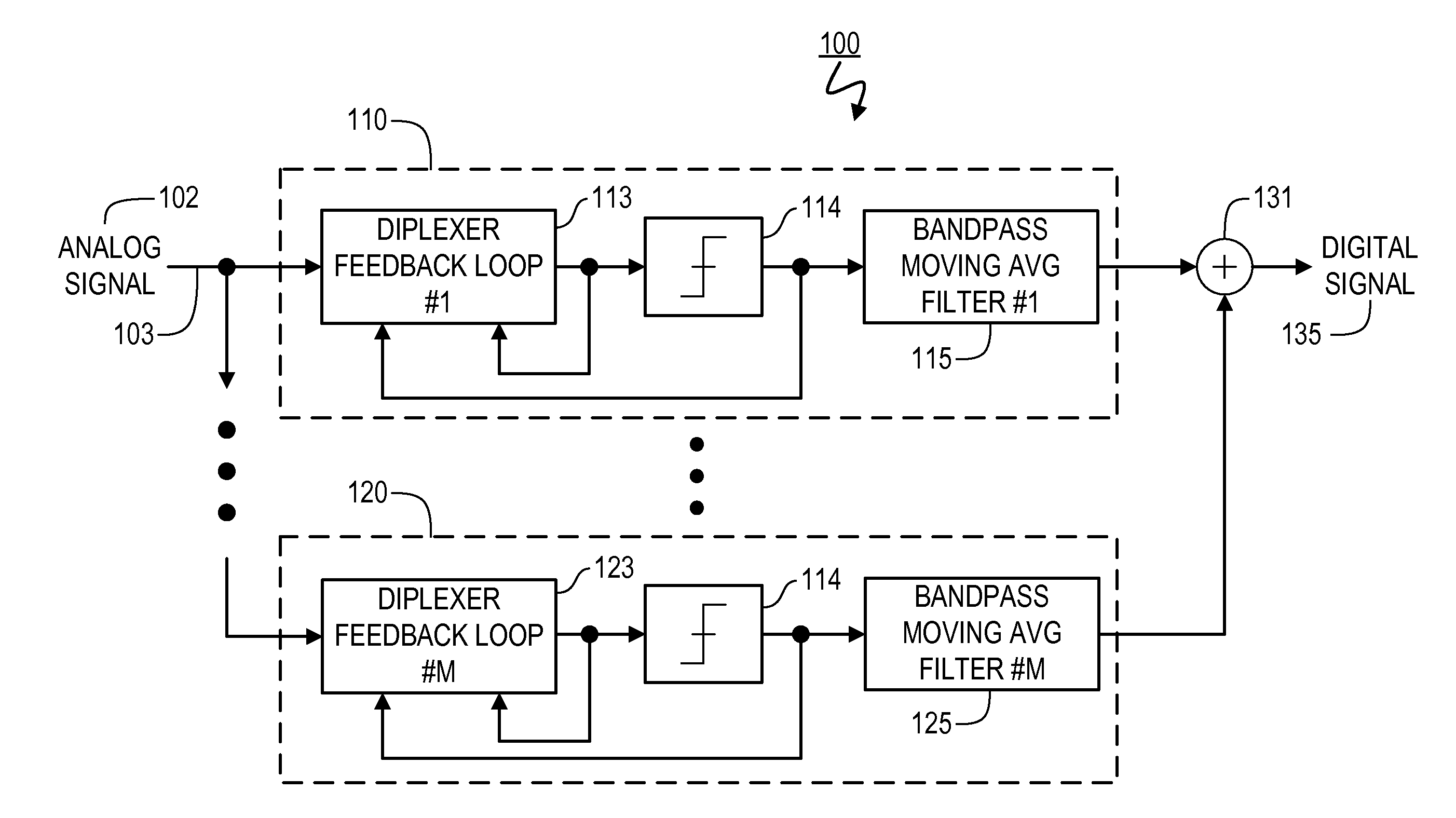
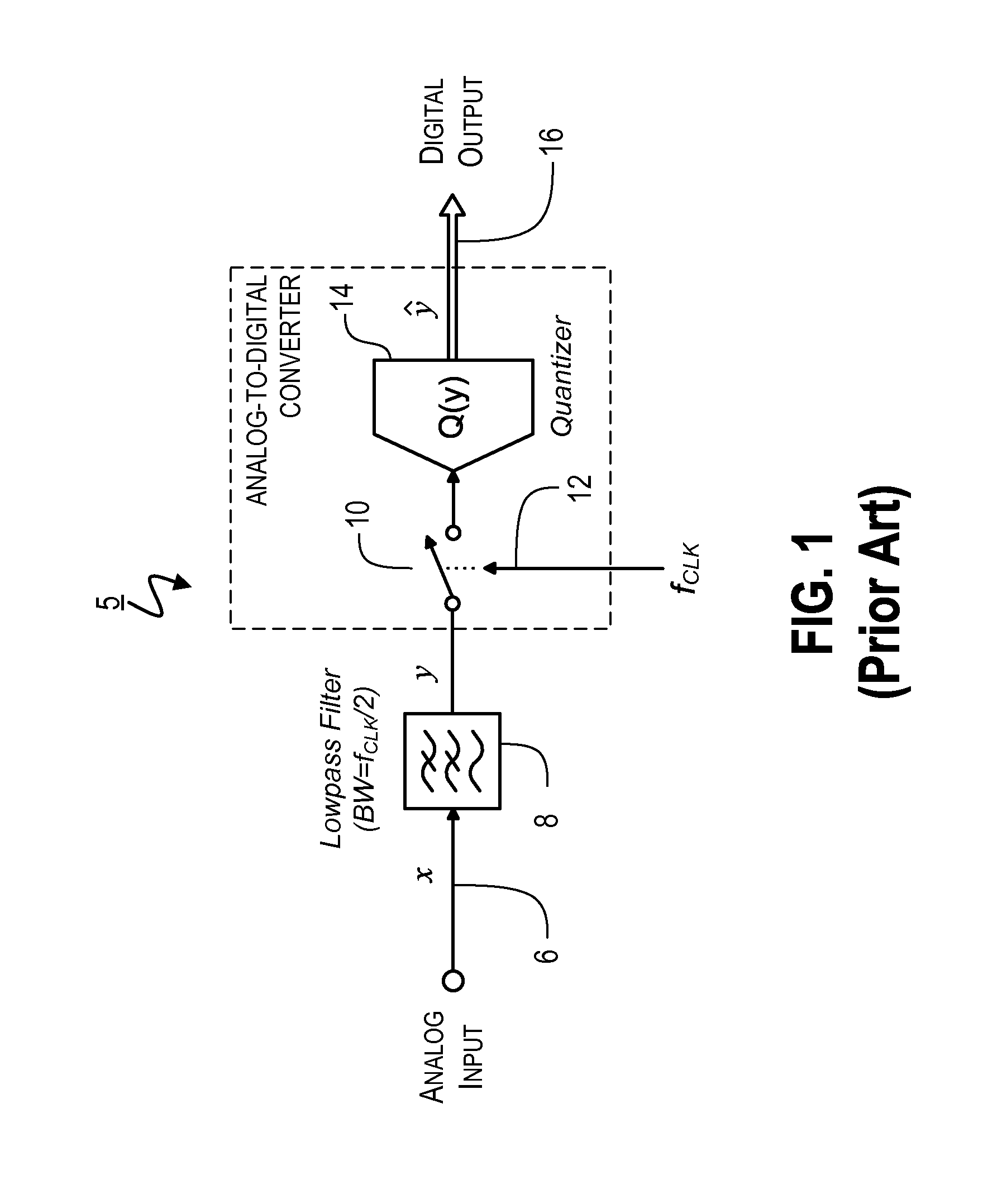
Apparatuses and Methods for Linear to Discrete Quantization Conversion with Reduced Sampling-Variation Errors
ActiveUS20150171890A1Lower Level RequirementsLess sensitiveAnalogue conversionAnalogue-digital convertersLow-pass filterTransverter
Provided is an apparatus for converting a continuous-time, continuously variable signal into a sampled and quantized signal, which includes an input line for accepting an input signal, multiple processing branches coupled to the input line, and an adder coupled to outputs of the plurality of processing branches. Each of the processing branches includes a sampling / quantization circuit and a digital bandpass interpolation filter having an input coupled to an output of the sampling / quantization circuit. The digital bandpass interpolation filters in different ones of the processing branches have frequency responses that are centered at different frequencies. The digital bandpass interpolation filter in at least one of the processing branches includes: (i) a quadrature downconverter, (ii) a first lowpass filter and a second lowpass filter, (iii) a first interpolator and a second interpolator, each having an input for inputting a variable interpolant value, and (iv) a quadrature upconverter.
Owner:PAGNANELLI FAMILY TRUST
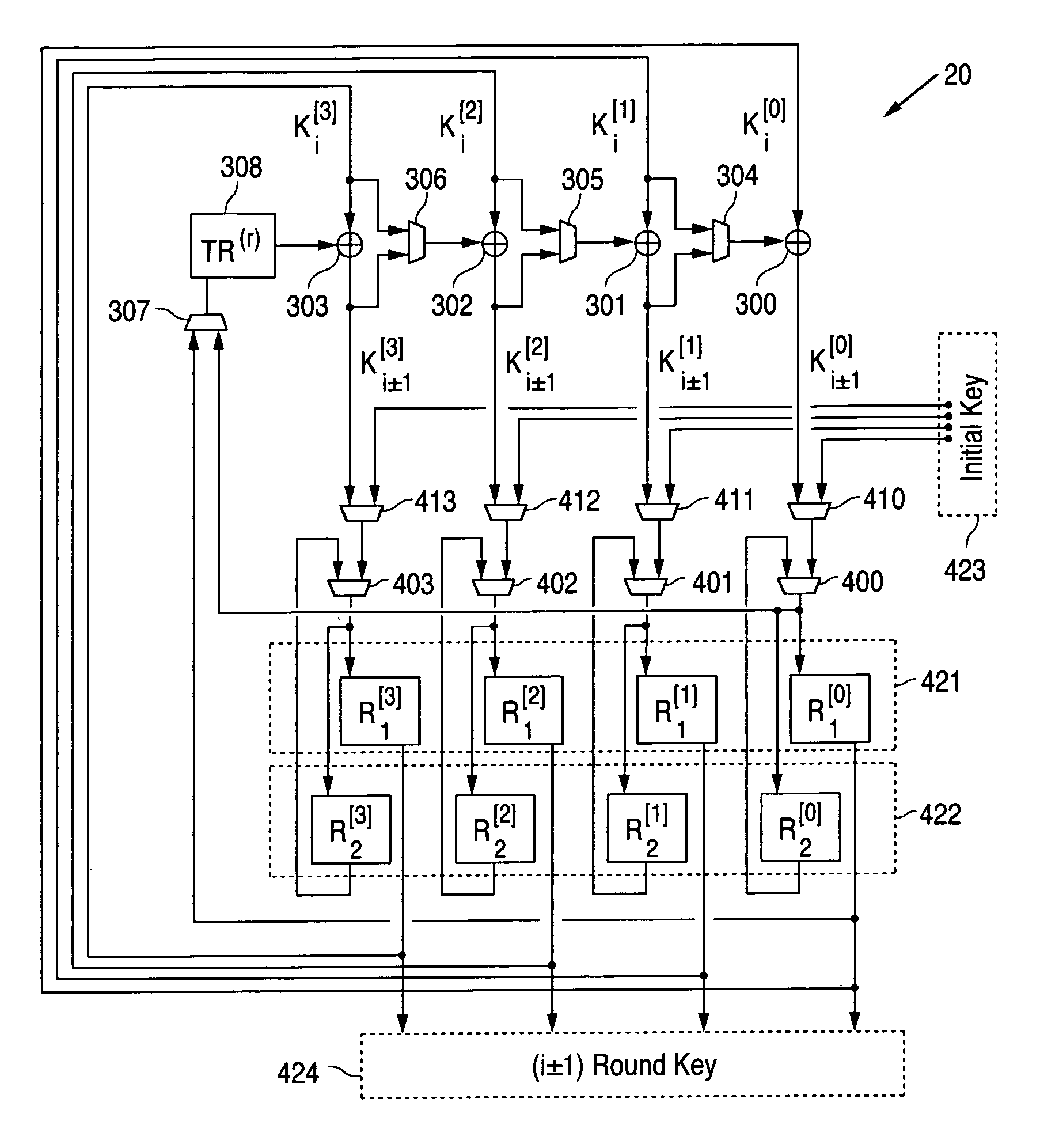
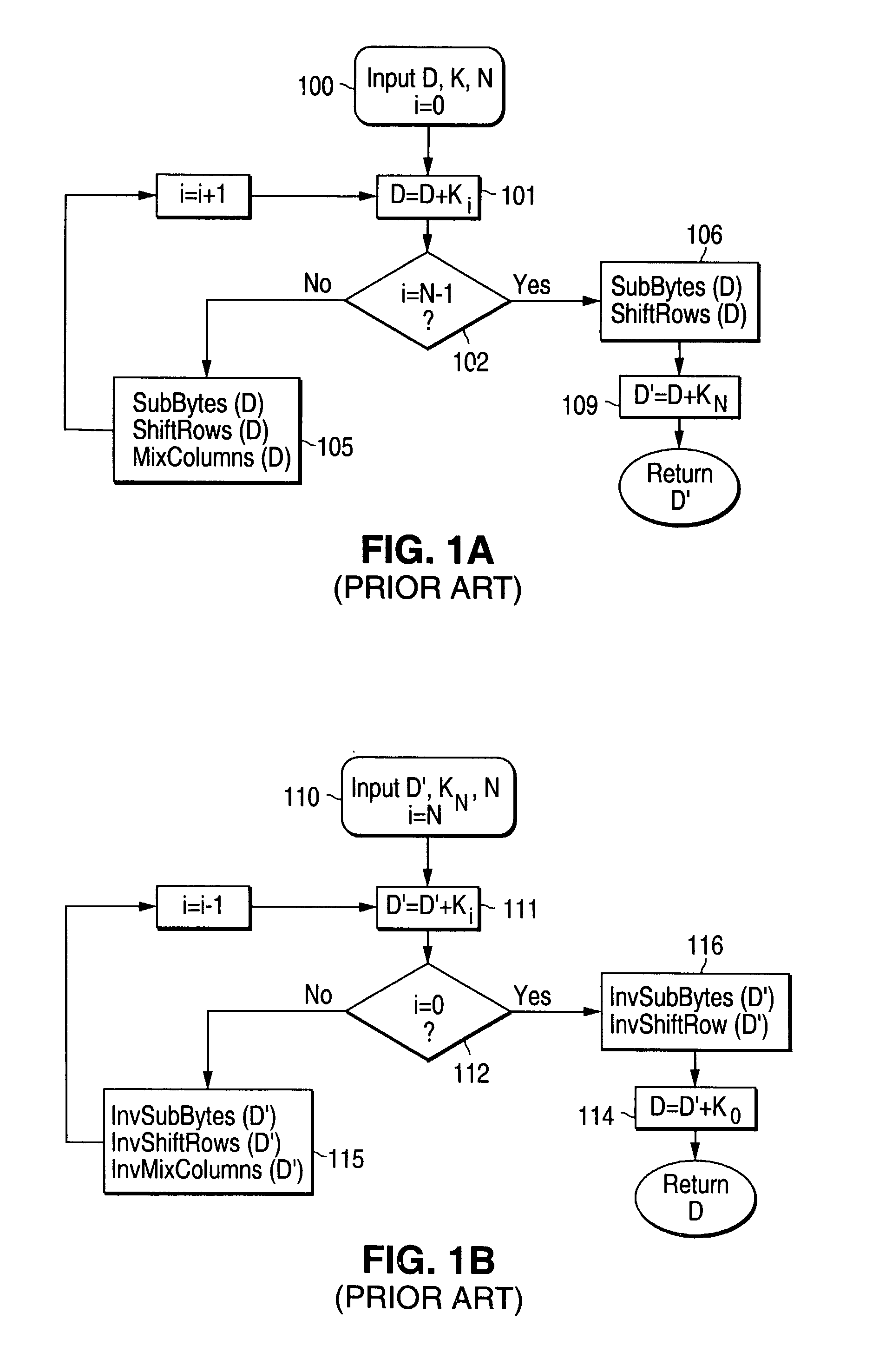
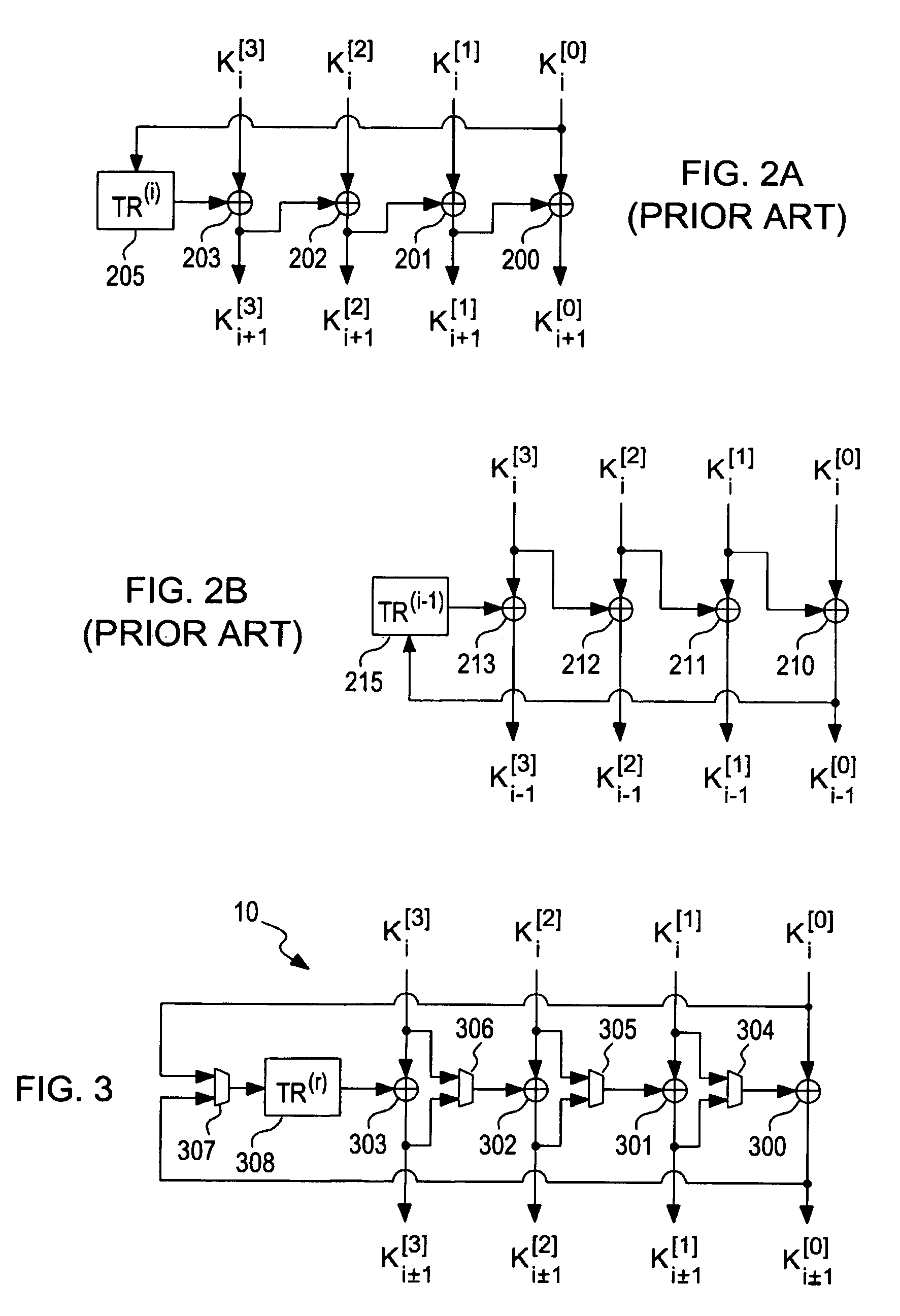
Apparatus and method for key scheduling
A key scheduler for encryption / decryption produces a new ciphering key by a key expansion process or recovers a previous ciphering key by an inverse expansion process. The key scheduler includes a set of adders and transformation circuitry. Each of adders receives a portion of a round key value as its first input. Some of the adders receive either a portion of the round key value or the output of some of the adders, as its second input, be control of arbitration devices. One adder receives as its second input an output from the transformation circuitry, which output is selected by an arbitration device from either a portion of the round key value or an output of an adder. The selection done by the arbitration devices depending on whether the process desired is the key expansion or inverse expansion.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
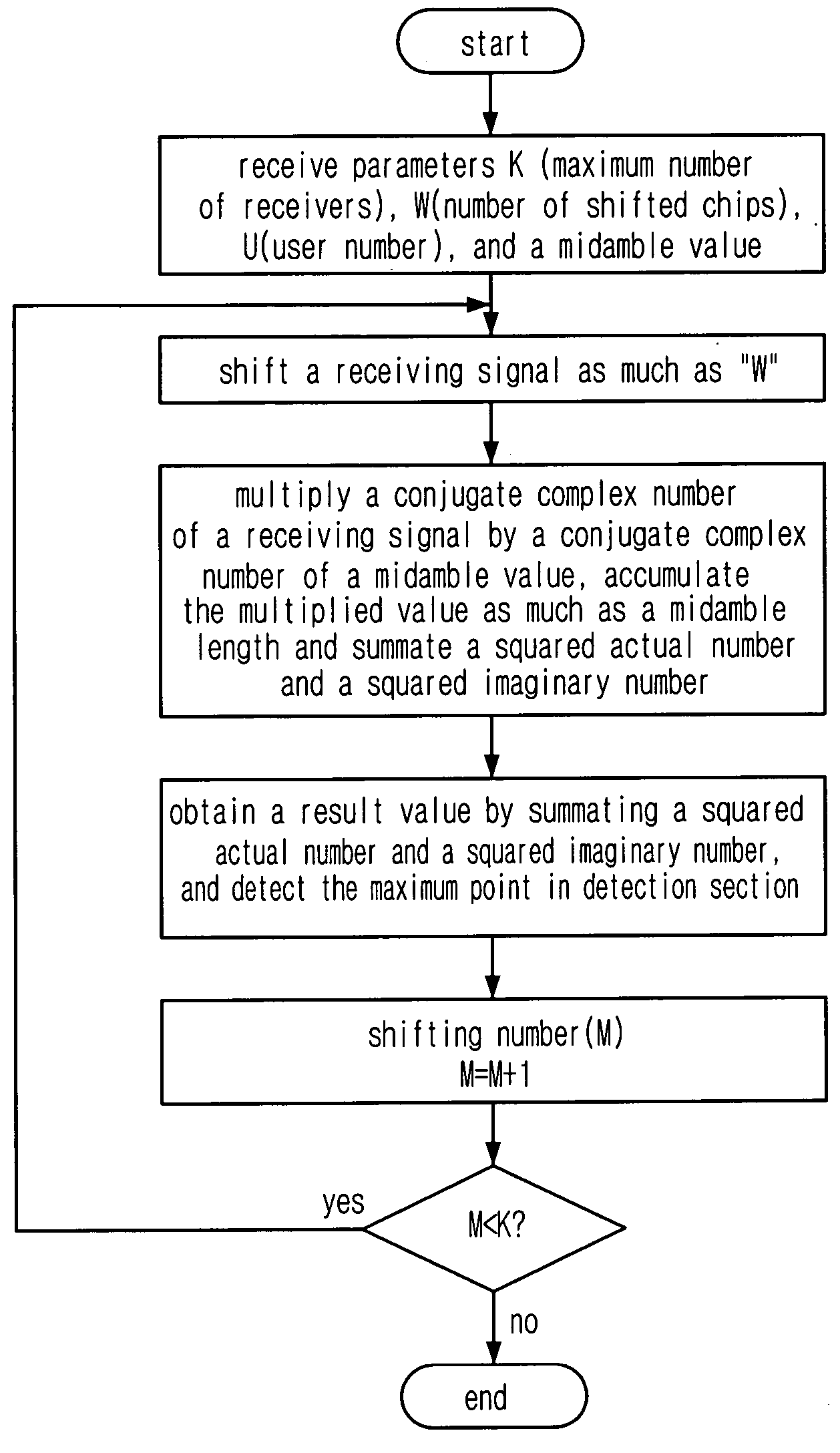
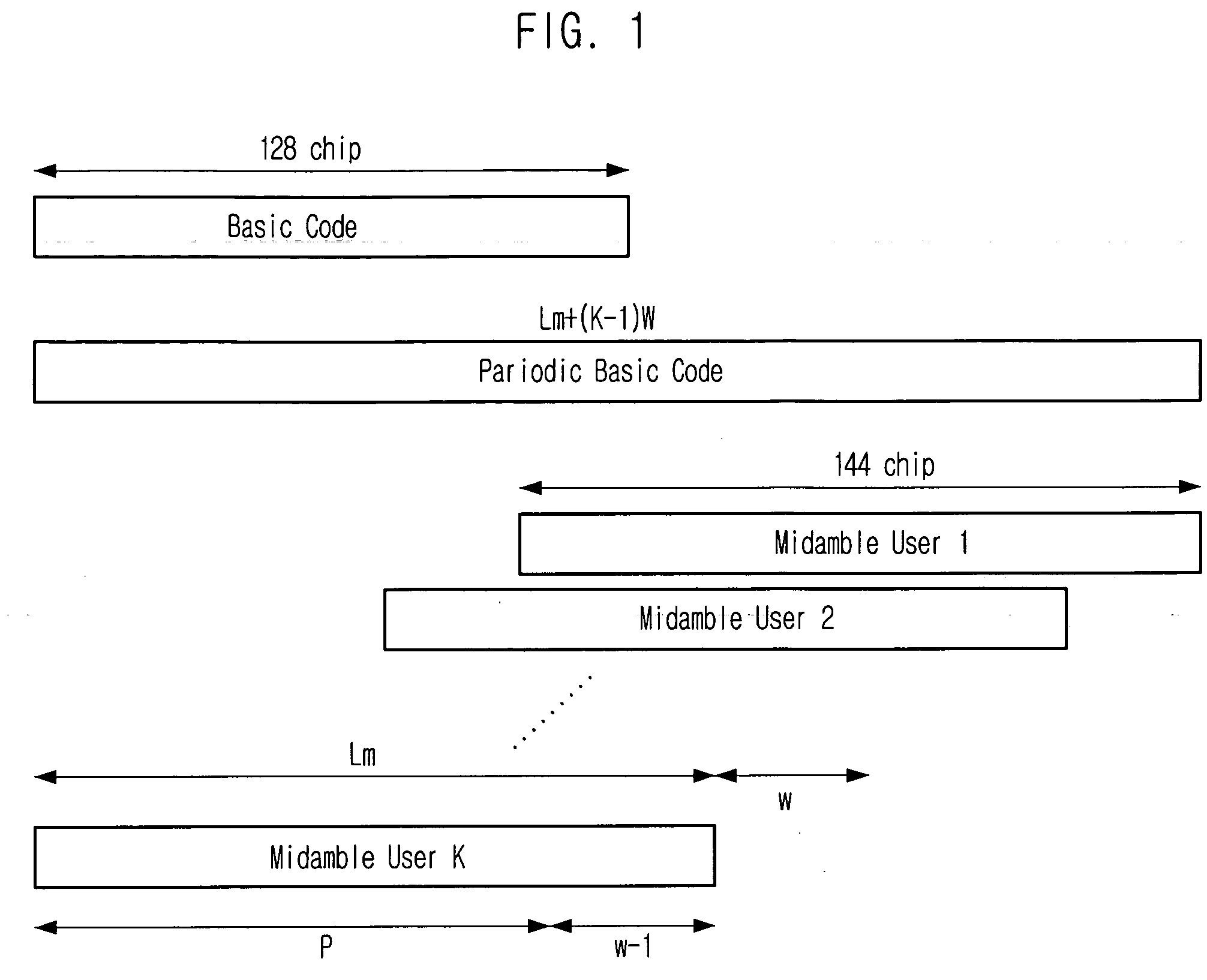
Apparatus and method for detecting timing error based on cyclic correlation
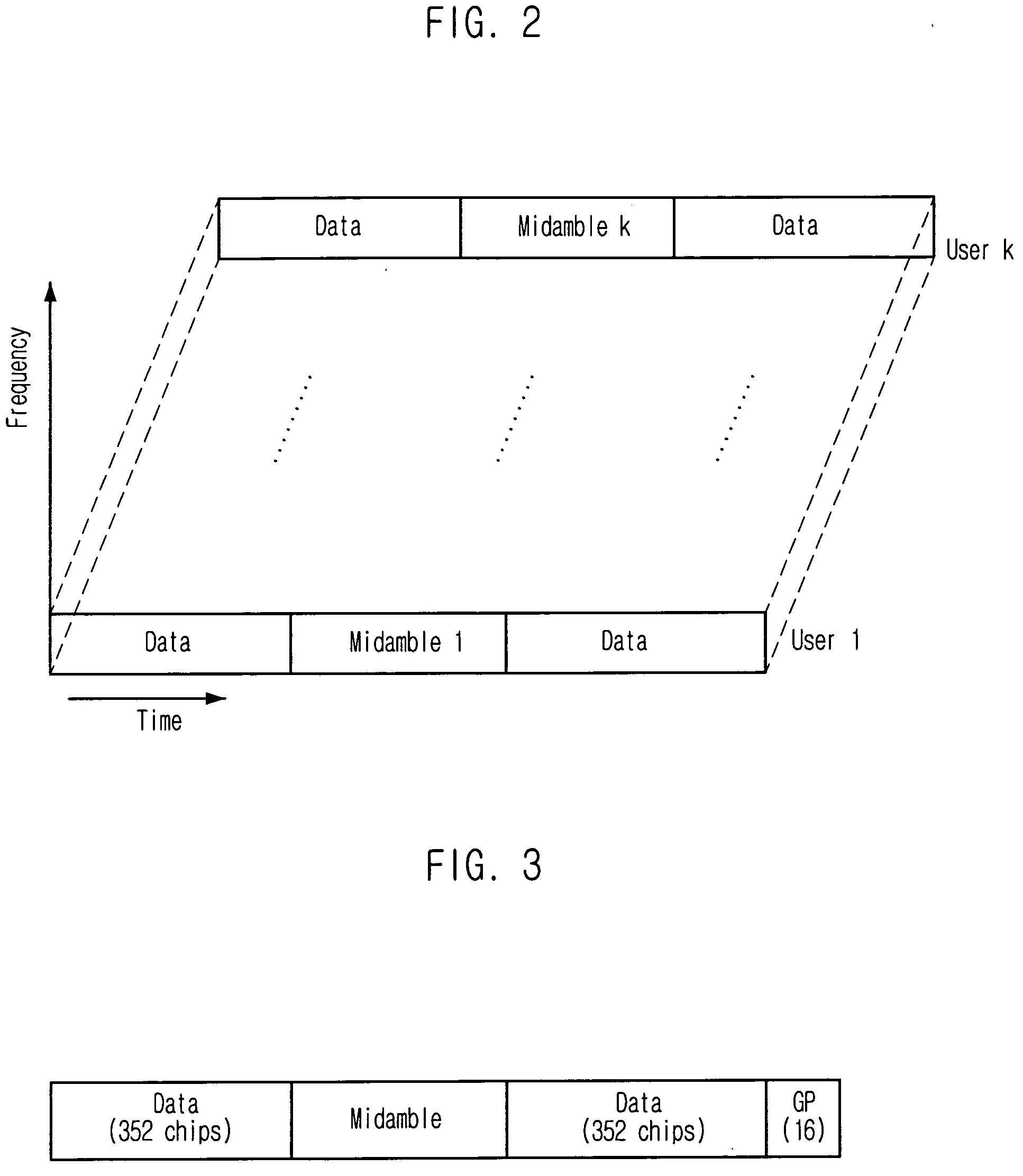
InactiveUS20060126765A1Reduce complexityReduce processing timeTime-division multiplexAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsShift registerTiming error detector
Provided is an apparatus and method for detecting timing errors based on characteristics of cyclic correlation. The apparatus and method can detect the timing errors of many users by using the cyclic characteristics of a midamble code at a time and detects the timing errors based on the characteristics of cyclic correlation to reduce the time required for detecting the users and lower the complexity in terms of Hardware. The apparatus includes a detection section controller, a register, a midamble generator, a midamble shifter, an accumulator, an adder, a shift register and a timing error detector.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
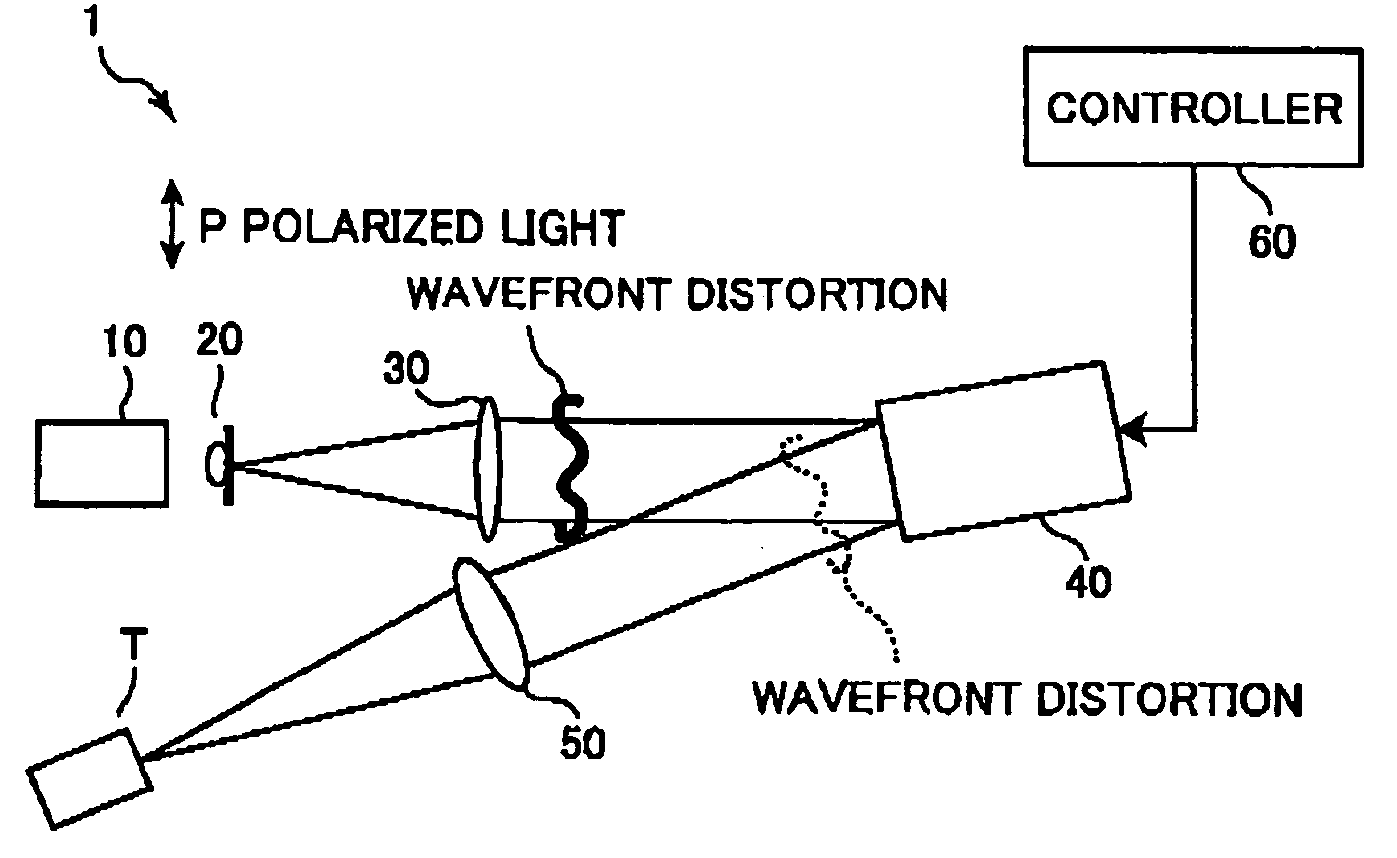
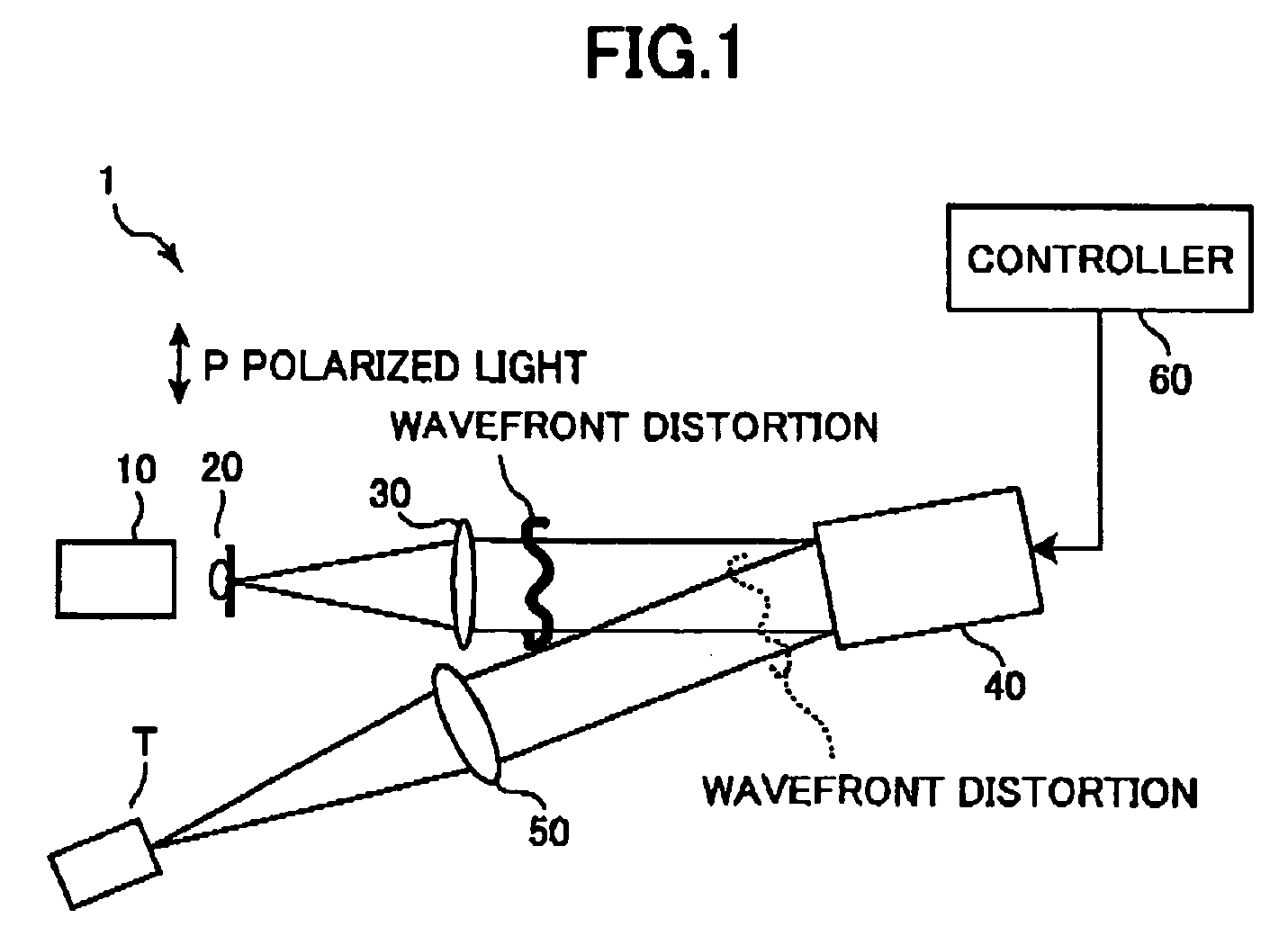
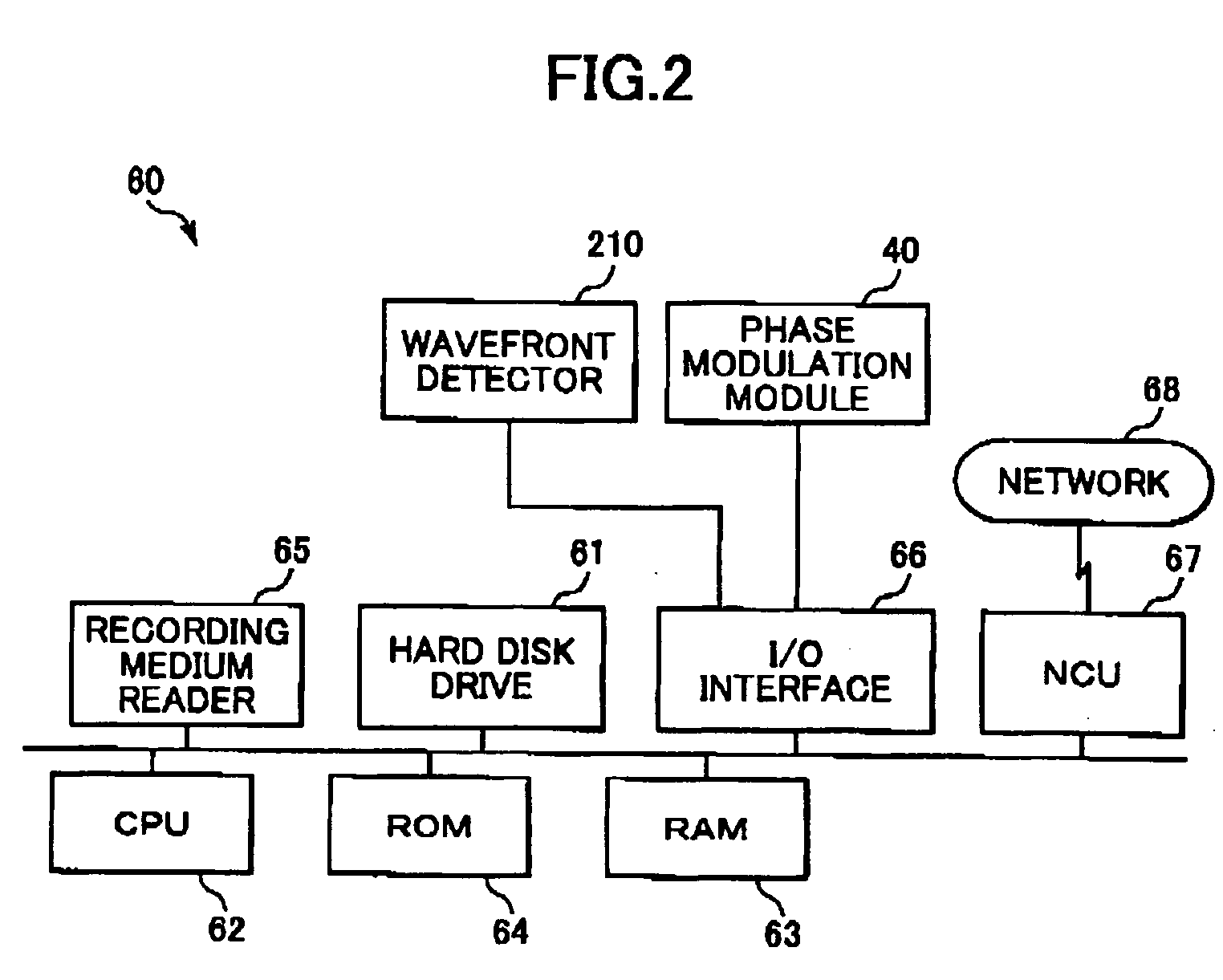
Phase modulation apparatus and phase modulation method
InactiveUS20050063032A1Generate fastFast and accurate generationActive addressable light modulatorHolographic object characteristicsPhysicsDistortion correction
An adder unit (60e) reads a desired CGH pattern from a pattern memory unit (60a) and a phase distortion correction pattern from a distortion-correction pattern memory unit (60d) and adds both patterns together to generate a phase distortion corrected pattern. A control unit (60g) controls a phase modulation module (40) in accordance with the phase distortion corrected pattern. Accordingly, phase-modulated light based on the desired phase pattern can be generated precisely, easily and quickly.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
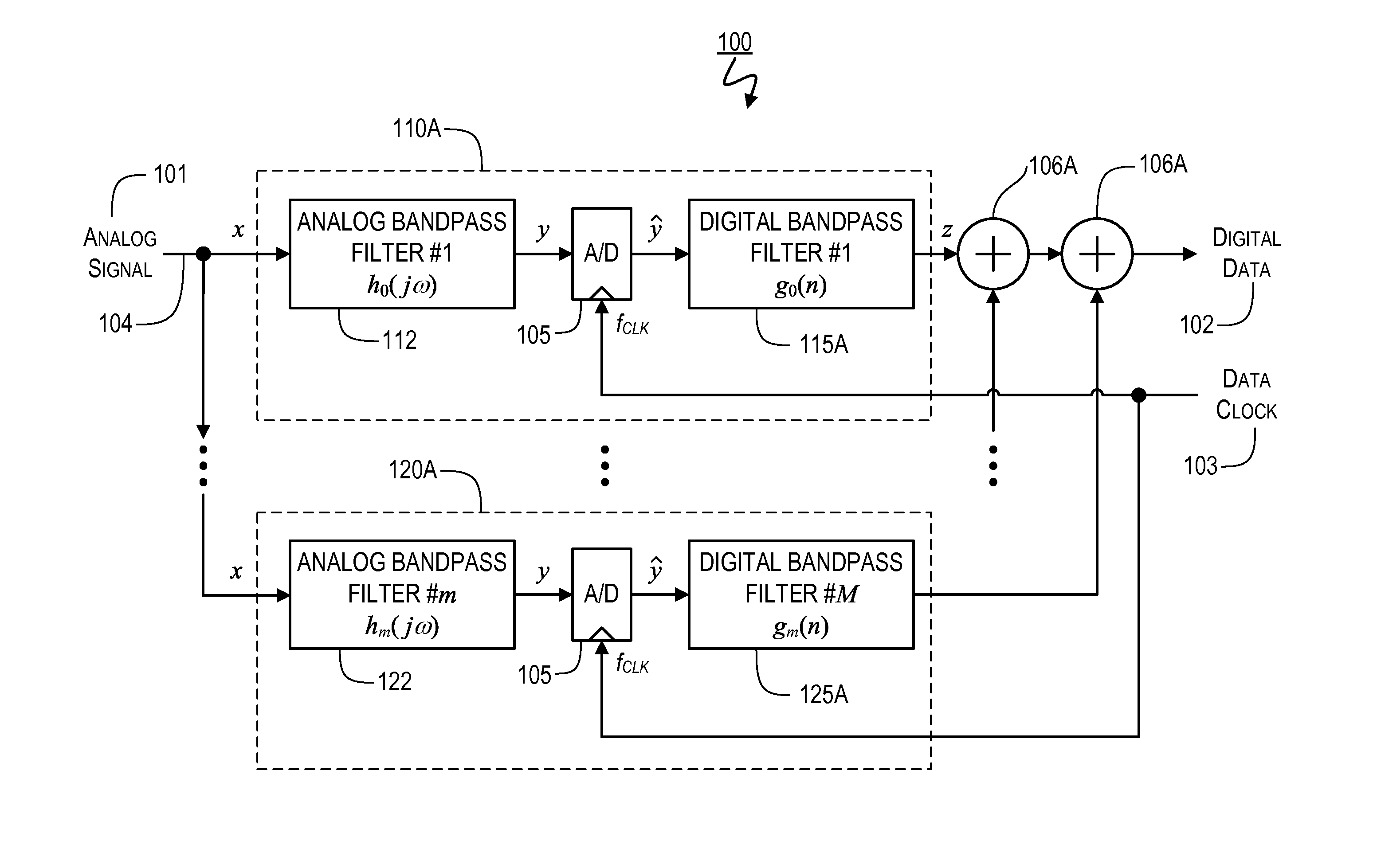
Sampling/Quantization Converters
ActiveUS20110095927A1Improve bindingHigh resolutionElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionNoise shapingMultiple input
Provided are, among other things, systems, methods and techniques for converting a continuous-time, continuously variable signal into a sampled and quantized signal. According to one representative embodiment, an apparatus includes multiple continuous-time quantization-noise-shaping circuits, each in a separate processing branch and having an adder that includes multiple inputs and an output; an input signal is coupled to one of the inputs of the adder; the output of the adder is coupled to one of the inputs of the adder through a first filter; and the output of a sampling / quantization circuit in the same processing branch is coupled to one of the inputs of the adder through a second filter, with the second filter having a different transfer function than the first filter.
Owner:PAGNANELLI FAMILY TRUST
Apparatuses and Methods for Linear to Discrete Quantization Conversion with Reduced Sampling Variation Errors
ActiveUS20140043177A1Lower Level RequirementsLess sensitiveAnalogue/digital conversionAnalogue conversionLow-pass filterTransverter
Provided is an apparatus for converting a continuous-time, continuously variable signal into a sampled and quantized signal, which includes an input line for accepting an input signal, multiple processing branches coupled to the input line, and an adder coupled to outputs of the plurality of processing branches. Each of the processing branches includes a sampling / quantization circuit and a digital bandpass interpolation filter having an input coupled to an output of the sampling / quantization circuit. The digital bandpass interpolation filters in different ones of the processing branches have frequency responses that are centered at different frequencies. The digital bandpass interpolation filter in at least one of the processing branches includes: (i) a quadrature downconverter, (ii) a first lowpass filter and a second lowpass filter, (iii) a first interpolator and a second interpolator, each having an input for inputting a variable interpolant value, and (iv) a quadrature upconverter.
Owner:PAGNANELLI FAMILY TRUST
Floating point addition pipeline including extreme value, comparison and accumulate functions
InactiveUS20010051969A1Computations using contact-making devicesCode conversionPathPingExecution unit
A multimedia execution unit configured to perform vectored floating point and integer instructions. The execution unit may include an add / subtract pipeline having far and close data paths. The far path is configured to handle effective addition operations and effective subtraction operations for operands having an absolute exponent difference greater than one. The close path is configured to handle effective subtraction operations for operands having an absolute exponent difference less than or equal to one. The close path is configured to generate two output values, wherein one output value is the first input operand plus an inverted version of the second input operand, while the second output value is equal to the first output value plus one. Selection of the first or second output value in the close path effectuates the round-to-nearest operation for the output of the adder.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Random number generator bit string filter
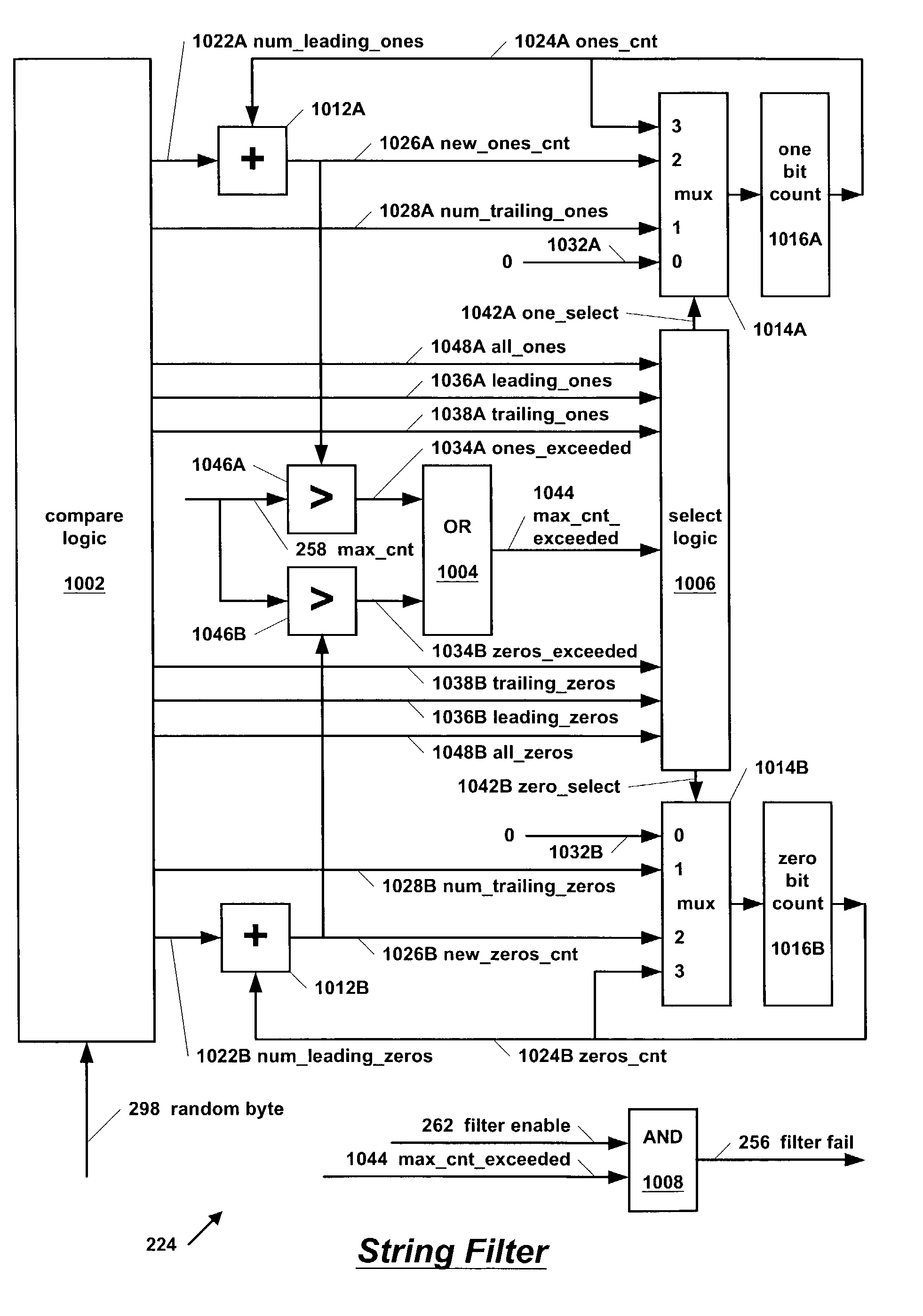
ActiveUS7149764B2Faster rateRandom number generatorsDigital function generatorsLeading zeroNumber generator
A filtering apparatus in a hardware random number generator that prevents the random number generator (RNG) from outputting a contiguous string of zeros or ones longer than a specified length. The maximum length is programmable in the apparatus. The apparatus includes a counter that keeps a current count of contiguous zero bits in a series of bytes generated by the RNG. An adder generates a sum of the current zero bit count and the number of leading zeros in the next byte generated. If the sum exceeds the maximum length, then the filter throws out the byte rather than accumulating it. Otherwise, if the byte contains all zeros, the counter is updated with the sum; or if the byte contains trailing zeros, the counter is updated with the number of trailing zeros; otherwise the counter is cleared. The apparatus does the same for contiguous one bits.
Owner:IP FIRST
Pulse Output Direct Digital Synthesis Circuit
ActiveUS20070276891A1Reduces spurious noiseReduce noiseOscillations generatorsDigital function generatorsInput selectionSignal generator
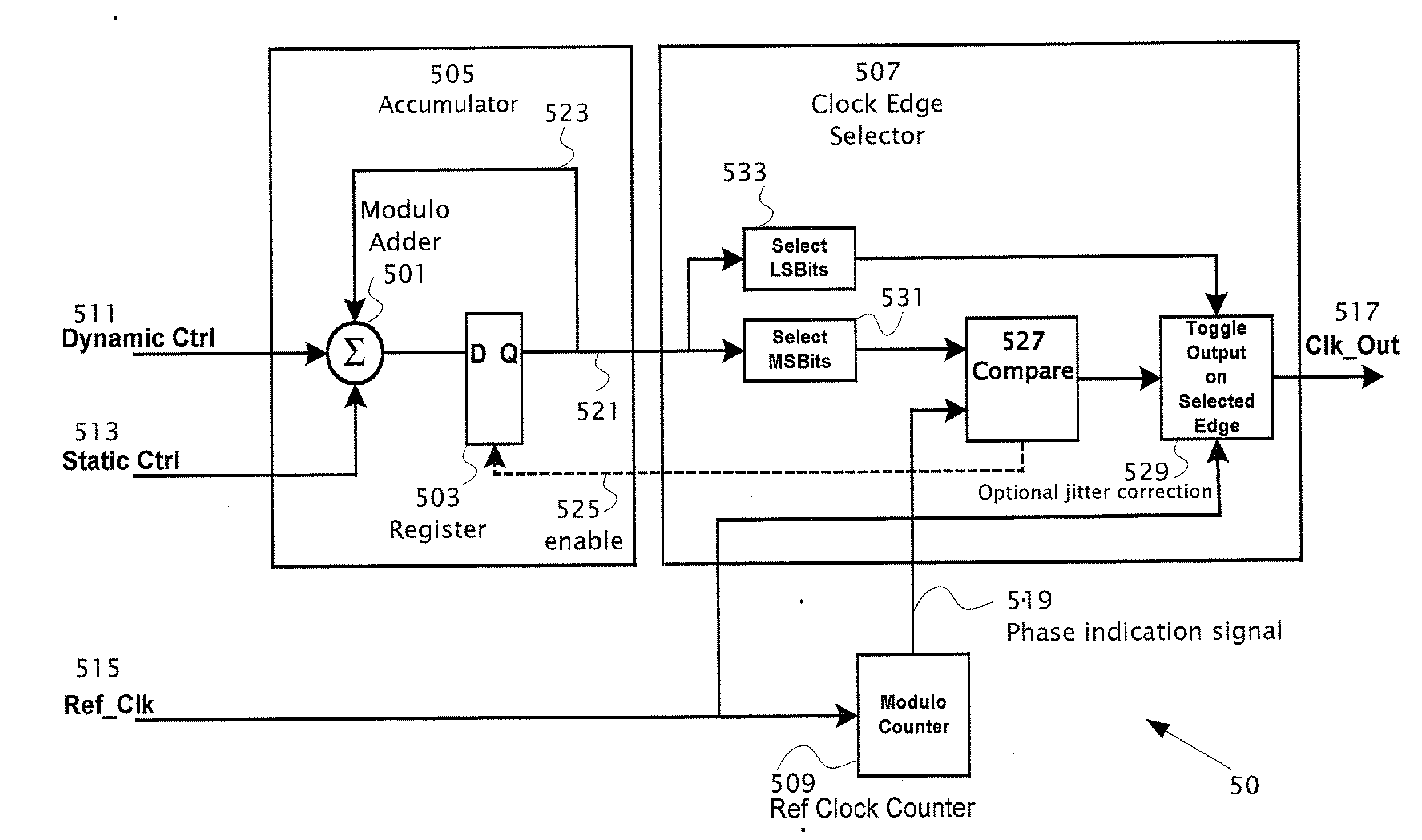
A clock signal generator responsive to a frequency control word and a reference clock signal having a reference clock frequency fref. The clock signal generator generates an output clock signal having a frequency fgen, wherein fgen is less than fref. A modulo-N counter accepts the reference clock signal as input. The modulo-N counter generates a phase-indication signal of the reference clock. The phase indication signal has N clock phases repeating at a frequency of fref / N. An accumulator iteratively accumulates a frequency control word into a modulo-N adder and produces an accumulated value. One or more bits of the accumulated value is fed-back into the modulo-N adder for adding modulo N to the accumulated value in the next iteration. N of the modulo-N adder is the same integer as in the modulo-N counter. A clock edge selector receives as inputs the phase indication signal and one or more bits of the accumulated value and by comparing the inputs selects an edge of the reference clock signal upon which to toggle the state of the output clock signal. The clock edge selector preferably selects the edge from: (i) only rising edges of the reference clock signal, (ii) only falling edges of the reference clock signal or (iii) both rising and falling edges of the reference clock signal. The clock edge selector selects between a rising edge and a falling edge of the reference clock signal preferably based on one or more bits of the accumulated value.
Owner:PMC-SIERRA +1
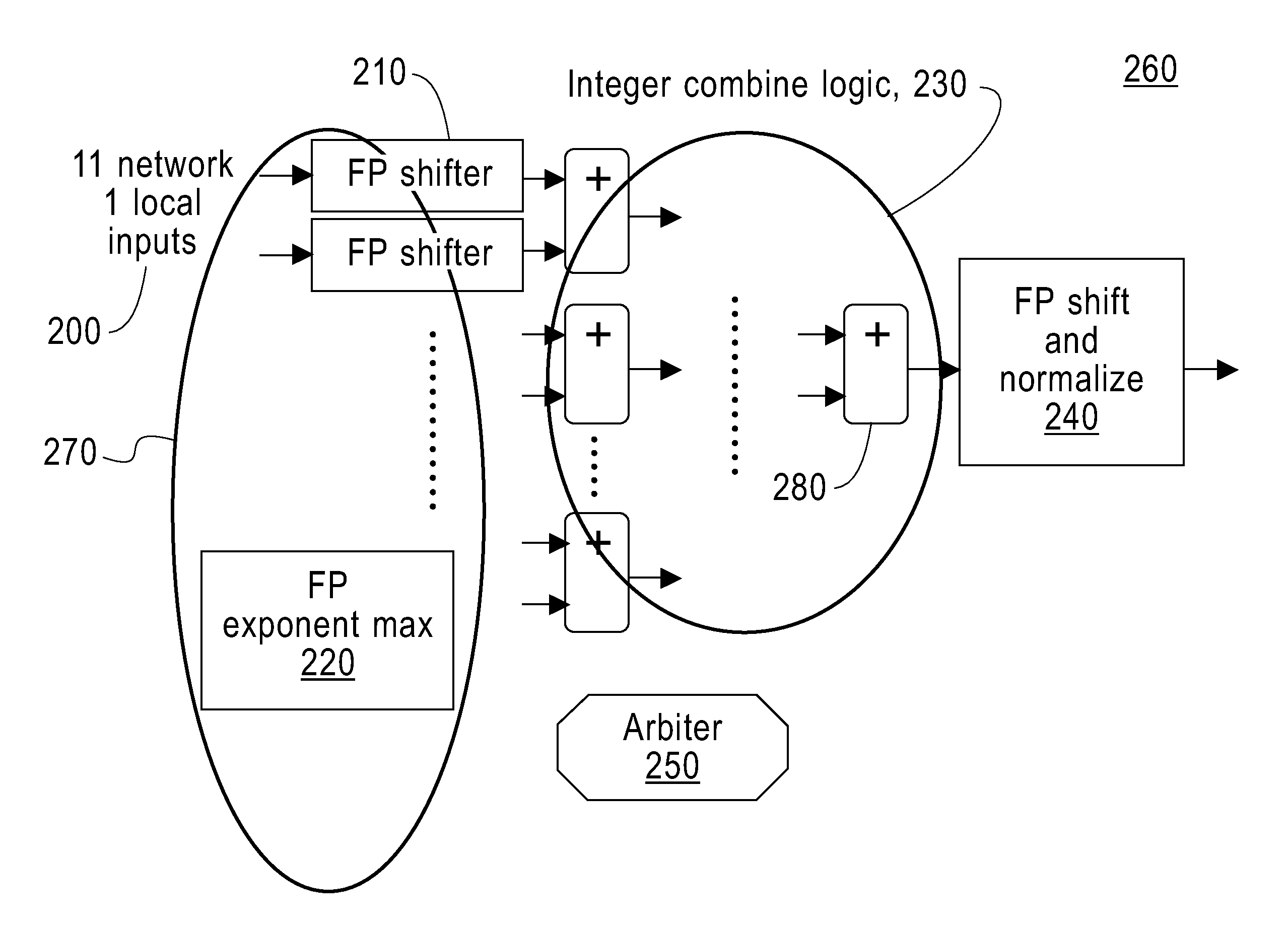
Multi-input and binary reproducible, high bandwidth floating point adder in a collective network
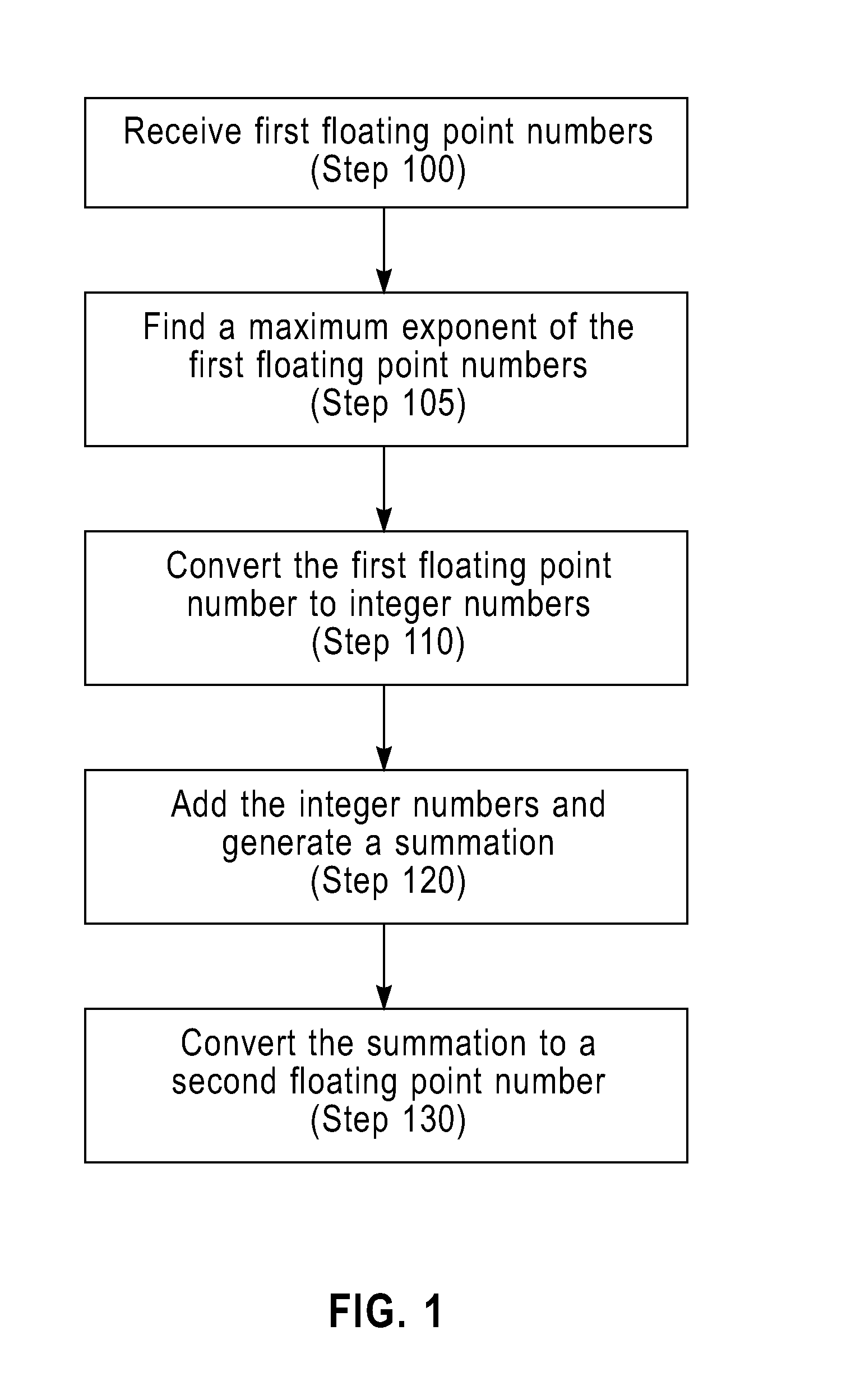
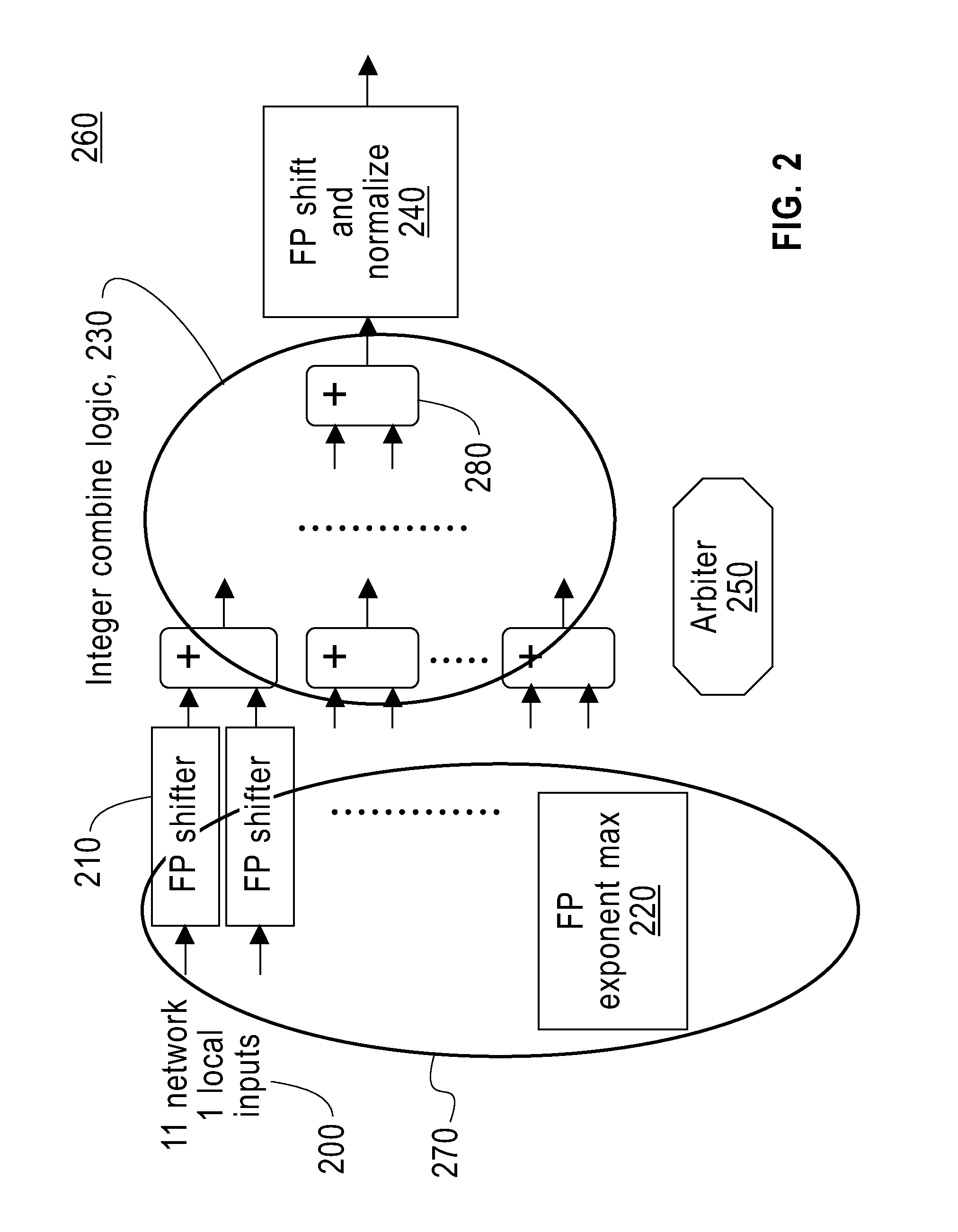
ActiveUS20110173421A1Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsMulti inputConcurrent computation
To add floating point numbers in a parallel computing system, a collective logic device receives the floating point numbers from computing nodes. The collective logic devices converts the floating point numbers to integer numbers. The collective logic device adds the integer numbers and generating a summation of the integer numbers. The collective logic device converts the summation to a floating point number. The collective logic device performs the receiving, the converting the floating point numbers, the adding, the generating and the converting the summation in one pass. One pass indicates that the computing nodes send inputs only once to the collective logic device and receive outputs only once from the collective logic device.
Owner:IBM CORP
Omnibus logic element
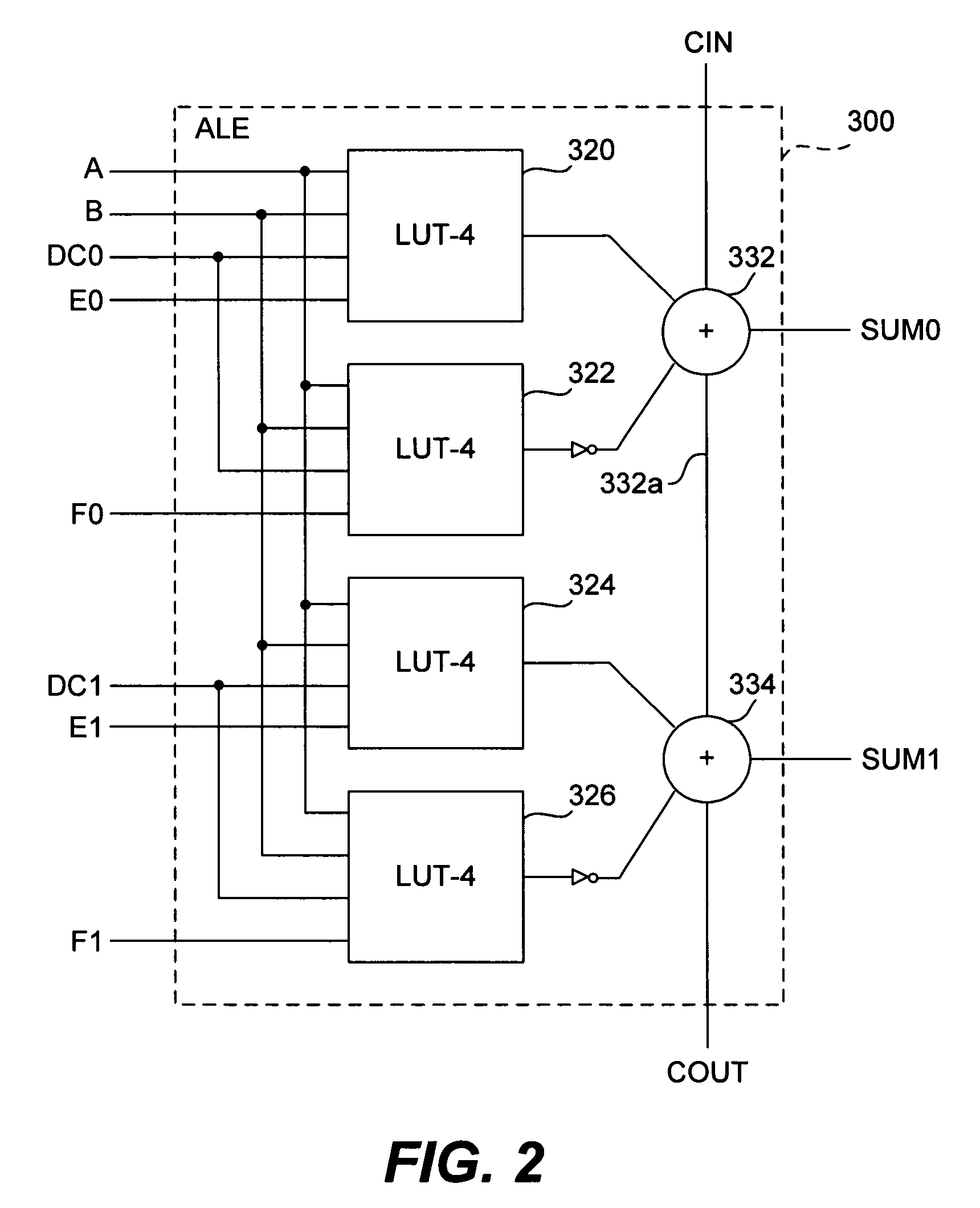
ActiveUS7538579B1Flexible and efficient to useProgrammable logic circuit arrangementsComputation using non-contact making devicesProcessor registerComputer science
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
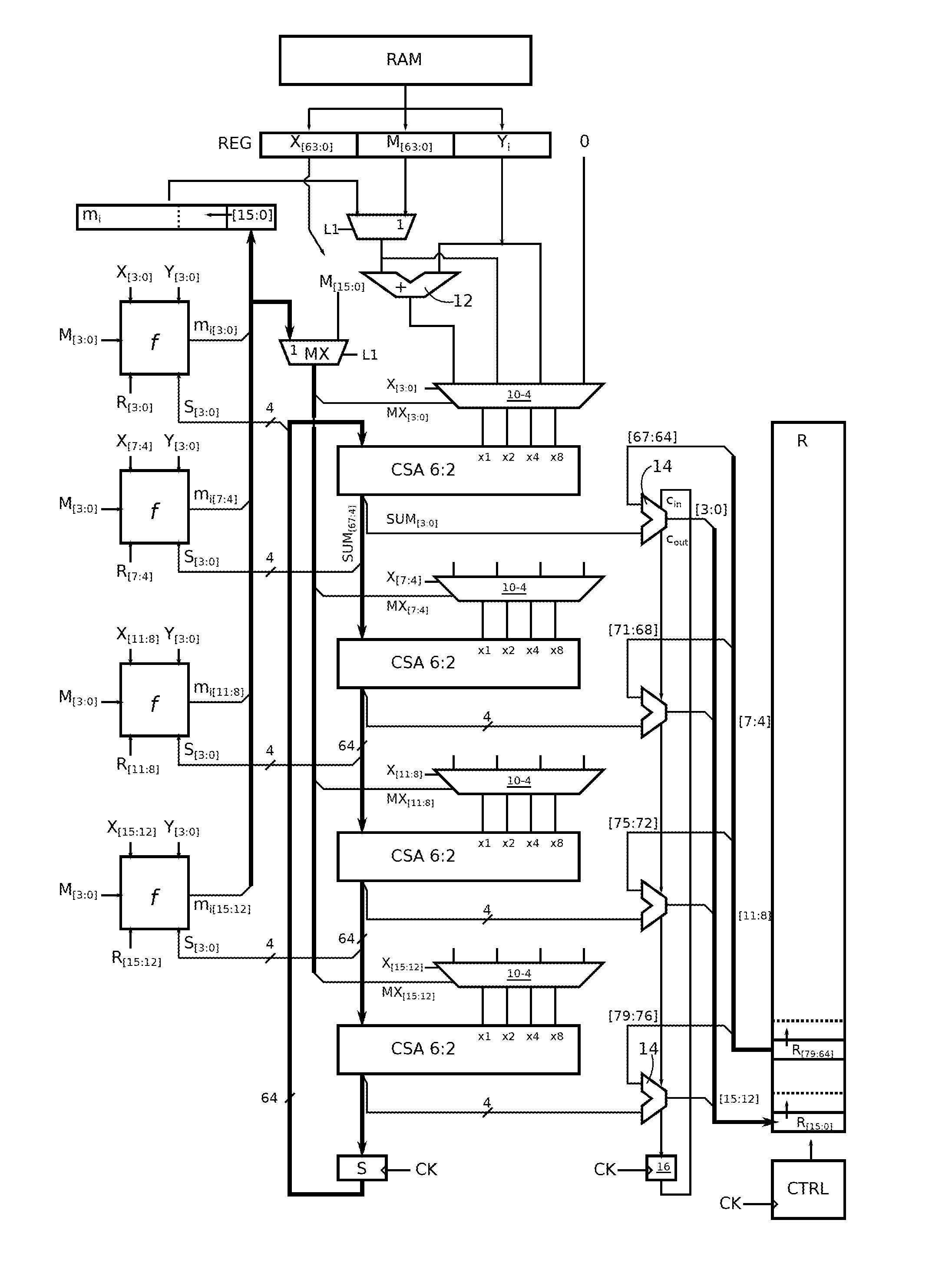
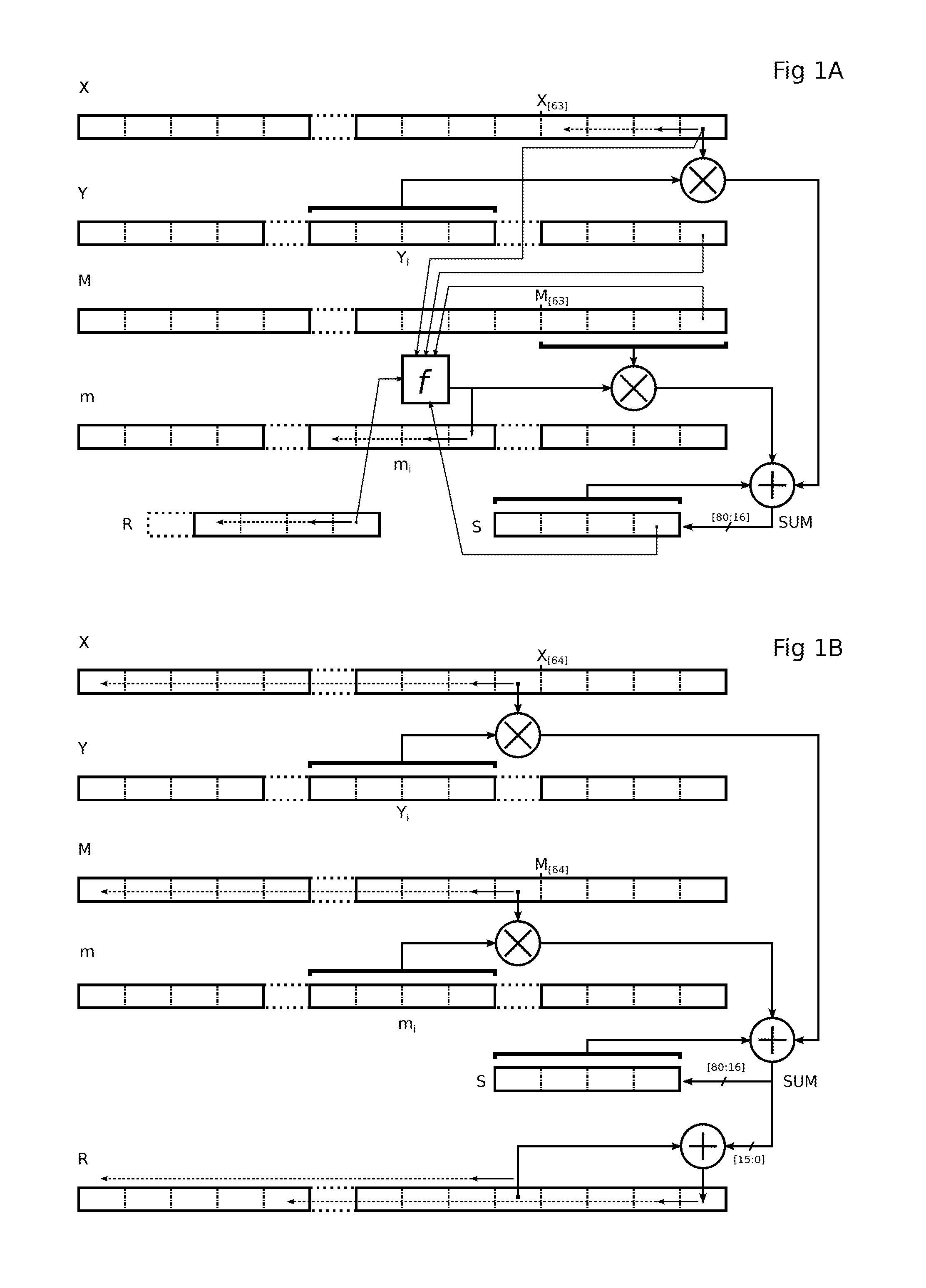
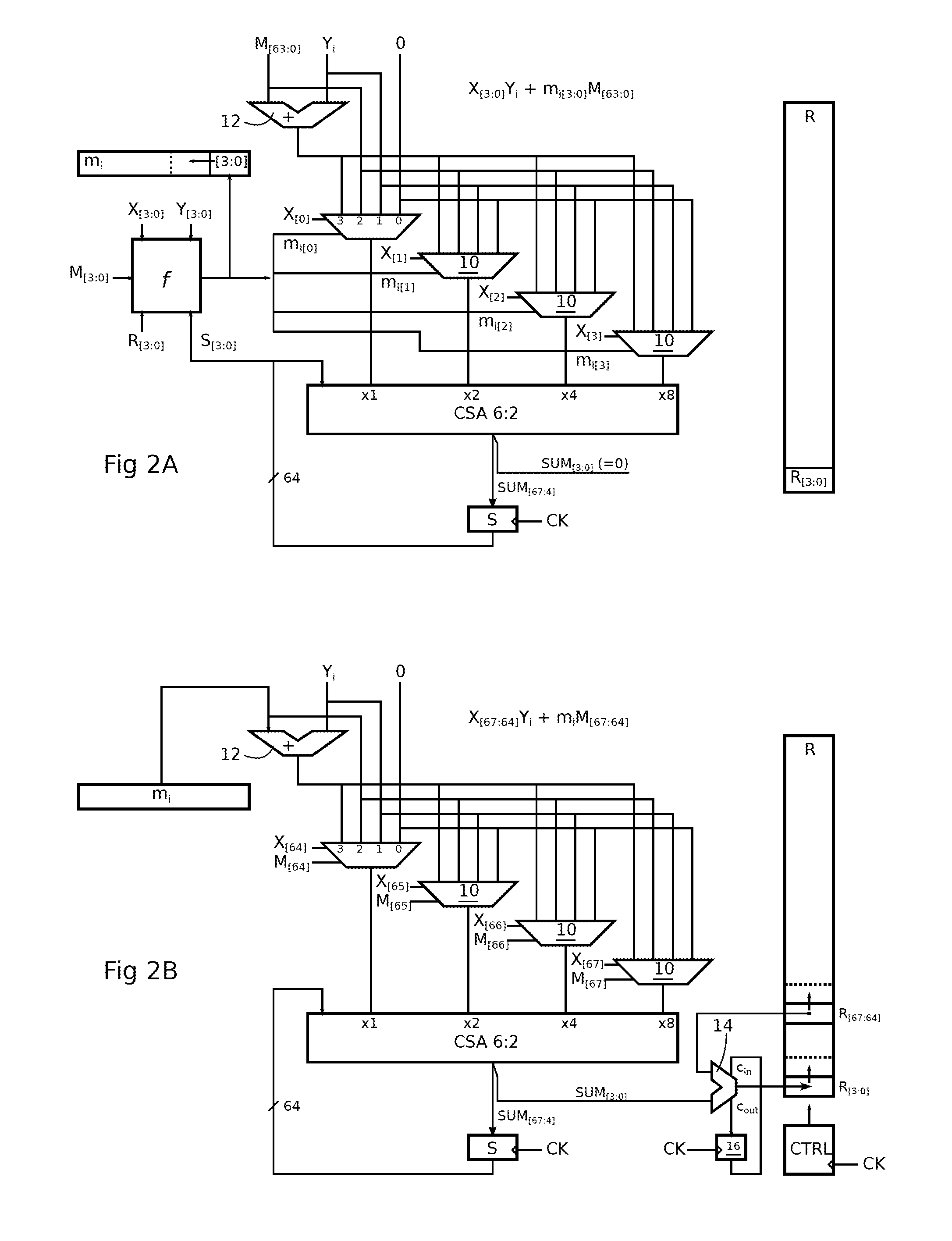
Montgomery multiplication circuit
ActiveUS20120265794A1Computation using non-contact making devicesDigital computer detailsMuxponderMultiplexer
A circuit for calculating a sum of products, each product having a q-bit binary operand and a k-bit binary operand, where k is a multiple of q,includes a q-input carry-save adder (CSA); a multiplexer (10) by input of the adder, having four k-bit channels respectively receiving the value 0, a first (Yi) of the k-bit operands, the second k-bit operand (M[63:0], mi), and the sum of the two k-bit operands, the output of a multiplexer of rank t (where t is between 0 and q−1) being taken into account by the adder with a t-bit left shift; and each multiplexer having first and second path selection inputs, the bits of a first of the q-bit operands being respectively supplied to the first selection inputs, and the bits of the second q-bit operand being respectively supplied to the second selection inputs.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
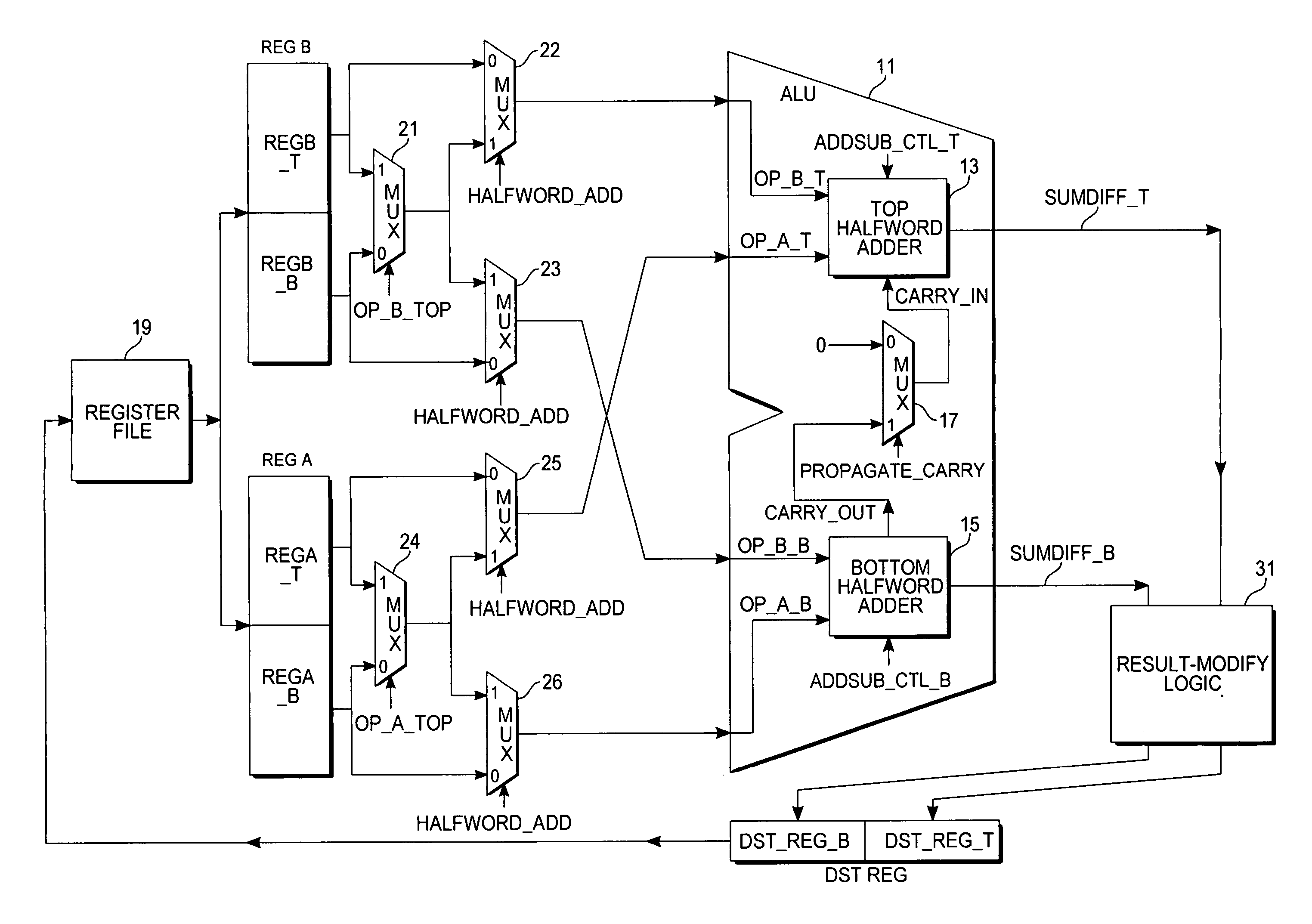
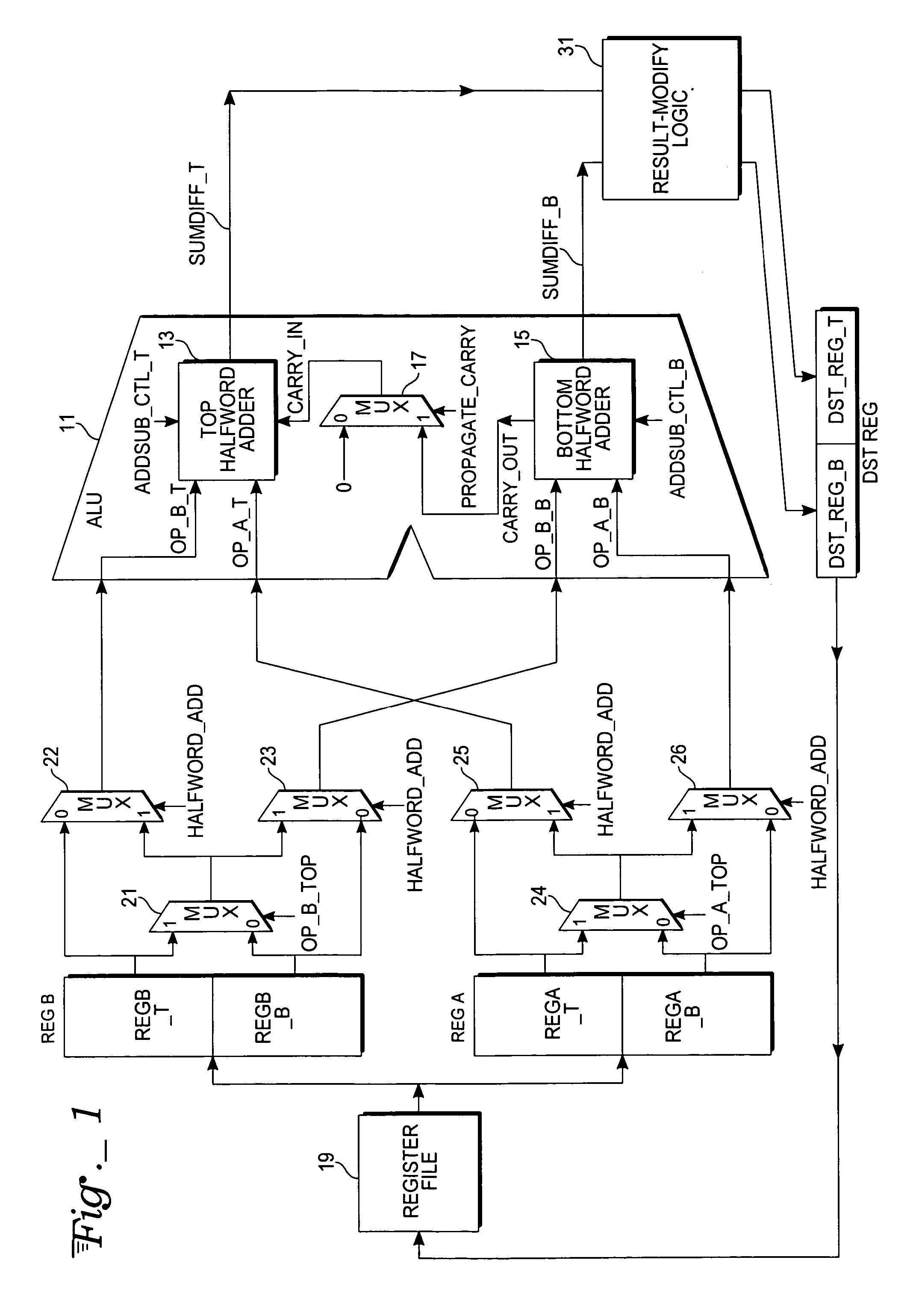
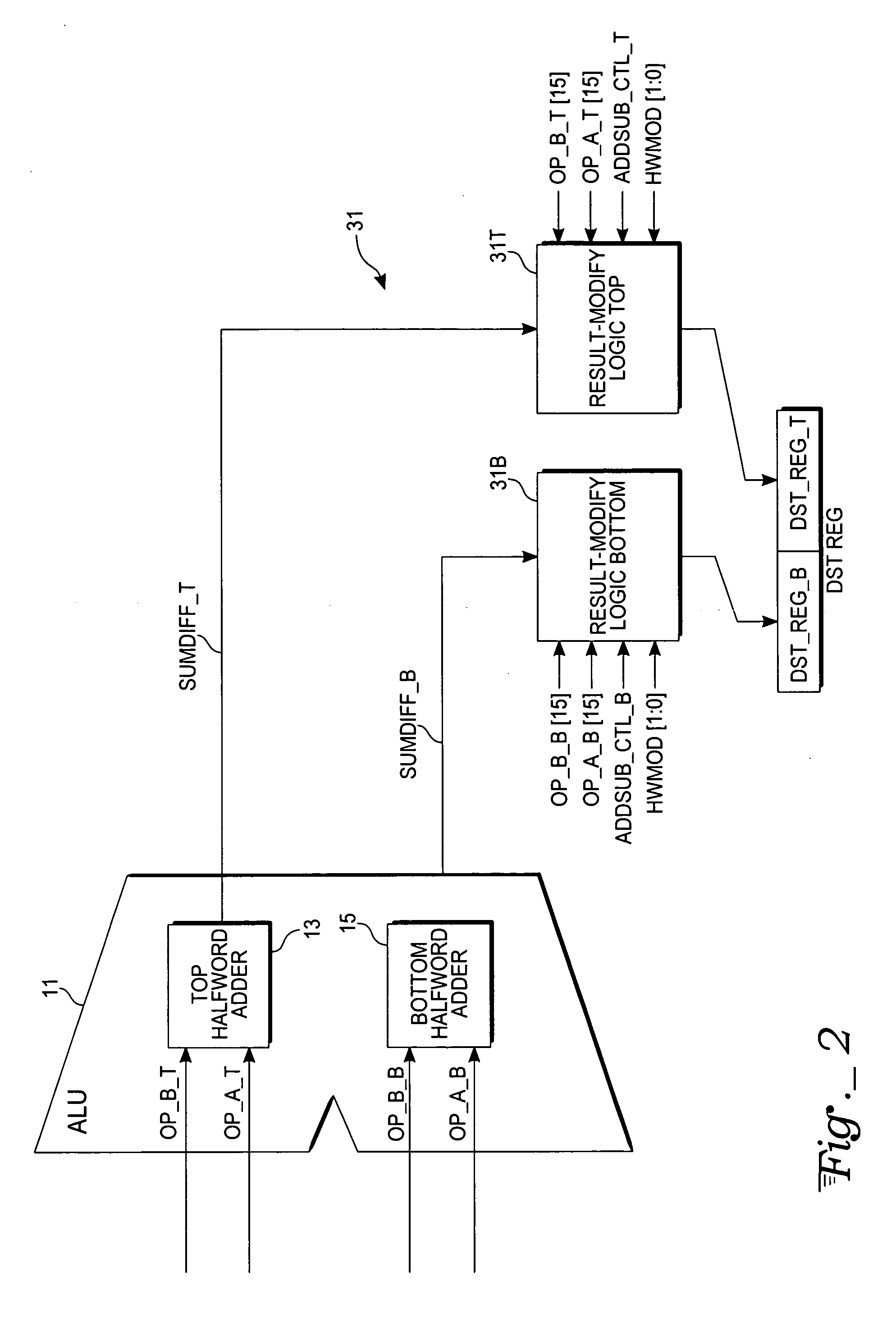
Packed add-subtract operation in a microprocessor
InactiveUS7555514B2Computations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-contact making devicesArithmetic logic unitMultiplexing
A packed half-word addition and subtraction operation is performed by a microprocessor in parallel upon half-word operands obtained from designated top or bottom half-word locations of designated source registers of a register file and the sum and difference results of such operation are packed into respective top and bottom half-word locations of a designated destination register. The microprocessor includes an arithmetic-logic unit (ALU) with adder circuitry that can be selectively split into separate half-word adders that are independently selectable to perform either an addition operation or subtraction operation upon the selected half-word operands. The half-word adders of the ALU access the operands from source registers via a set of multiplexers that select among the top and bottom half-word locations. Operations with halving and saturation modifications to the sum and difference results may also be provided.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
Method and device for tuning and control
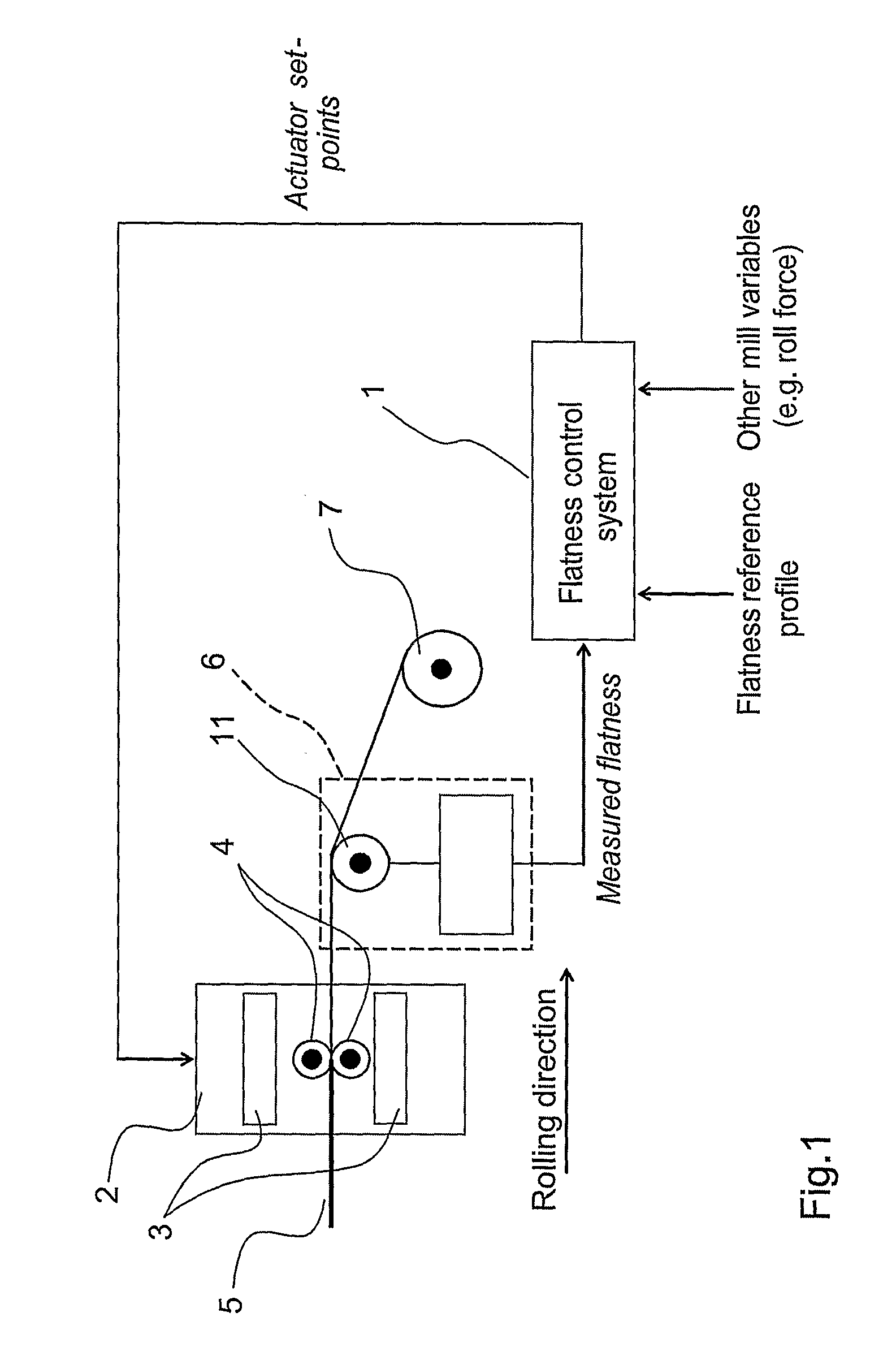
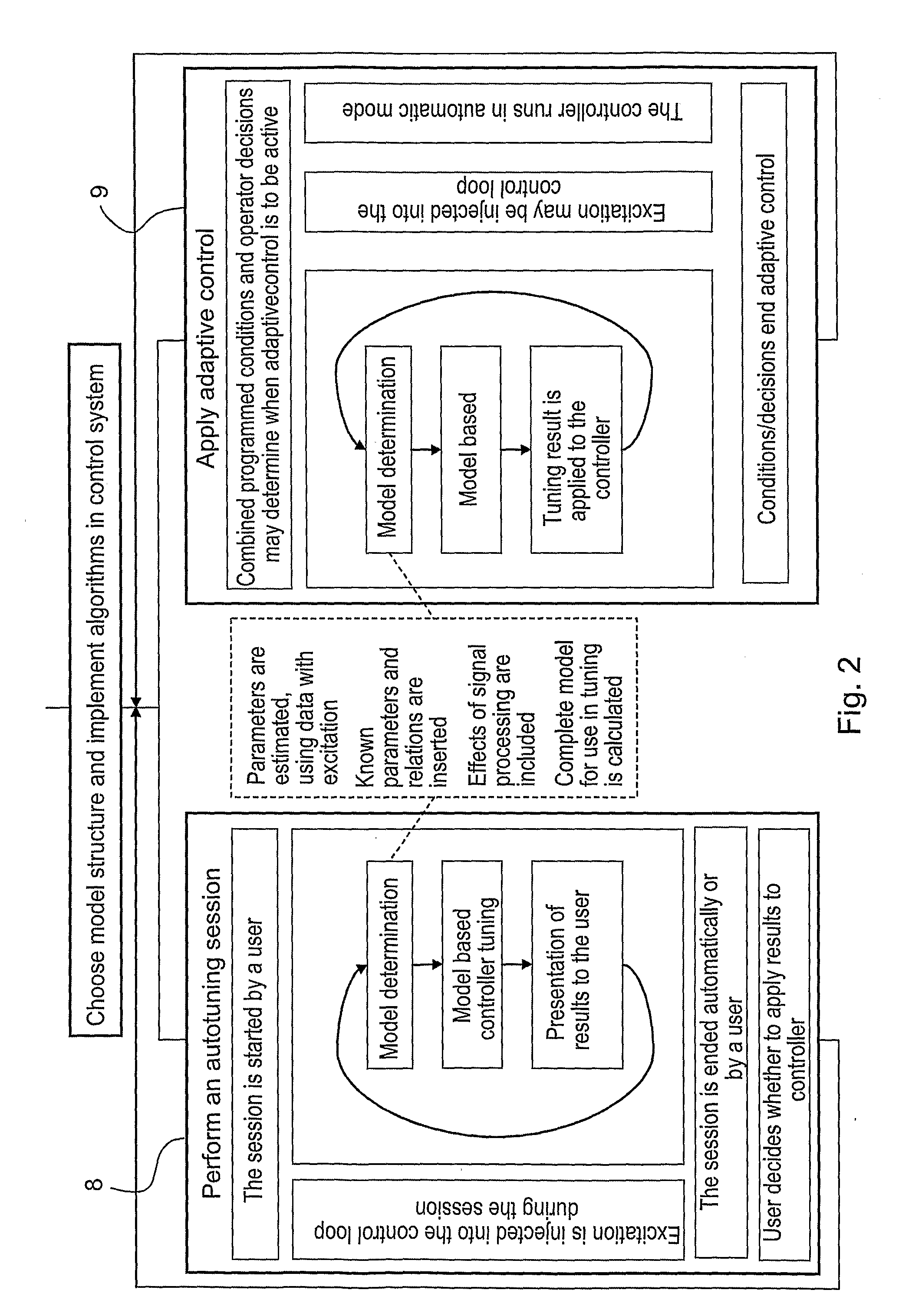
ActiveUS20090138102A1Increase productionLess producedMilling machinesProgram controlModel based controllerEngineering
A method and a device for tuning and control of industrial processes having varying material flow rate. An adder is configured to add excitation signals to the controller output signal. A measurement system is configured to measure a property in response to the excitation signals. A model based tuning unit is adapted to estimate the value of at least one parameter with unknown value of a process model structure describing the effect of varying material flow rate, based on the measurements of the property and the output signal from the controller, and to calculate a model that describes the dynamics from controller output to controller input based on the estimated value of the parameter, and to perform model based tuning of the controller based on the model that describes the dynamics from controller output to controller input.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Triangular wave signal generator
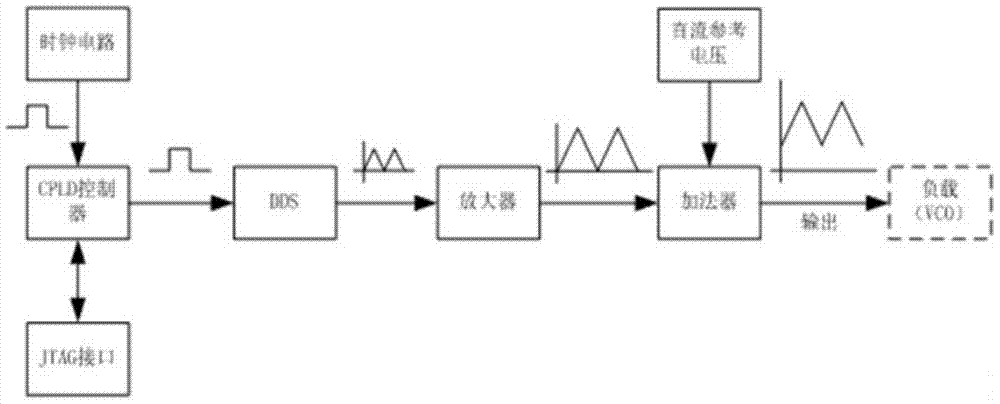
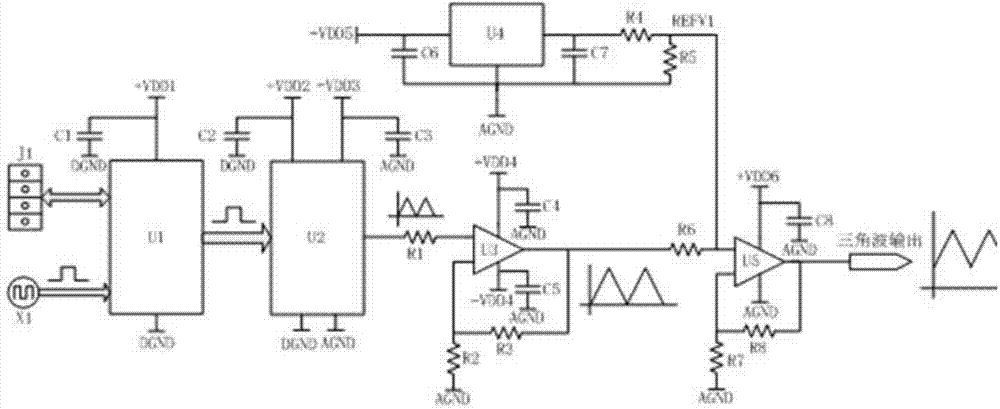
InactiveCN103944540AImprove linearityImprove stabilityPulse generatorDigital signal processingSoftware engineering
The invention discloses a triangular wave signal generator. The triangular wave signal generator comprises a clock circuit unit, a programmable logic controller unit, a DDS unit, an amplifier unit and an adder unit which are connected in sequence, the programmable logic controller unit is further connected with a JTAG interface unit, and the adder unit is further connected with a direct current reference voltage unit. The triangular wave signal generator uses the advanced high-speed digital signal processing technology and direct digital frequency synthesizer technology to overcome the disadvantages of narrow frequency range, complex circuit, various apparatuses, high cost, low independence, and low practicability and so on of an existing triangular wave signal generator.
Owner:成都雷电微力科技股份有限公司
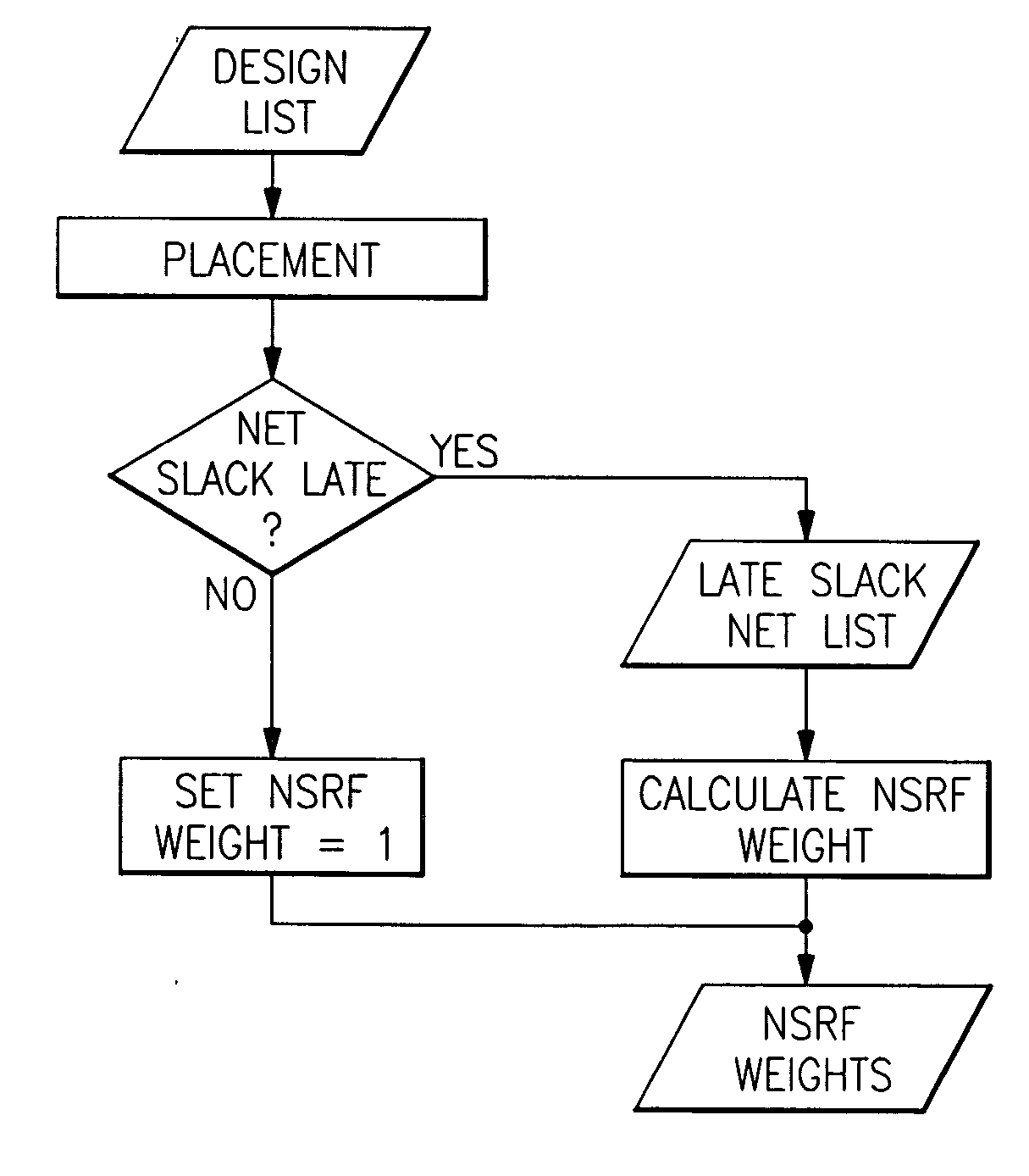
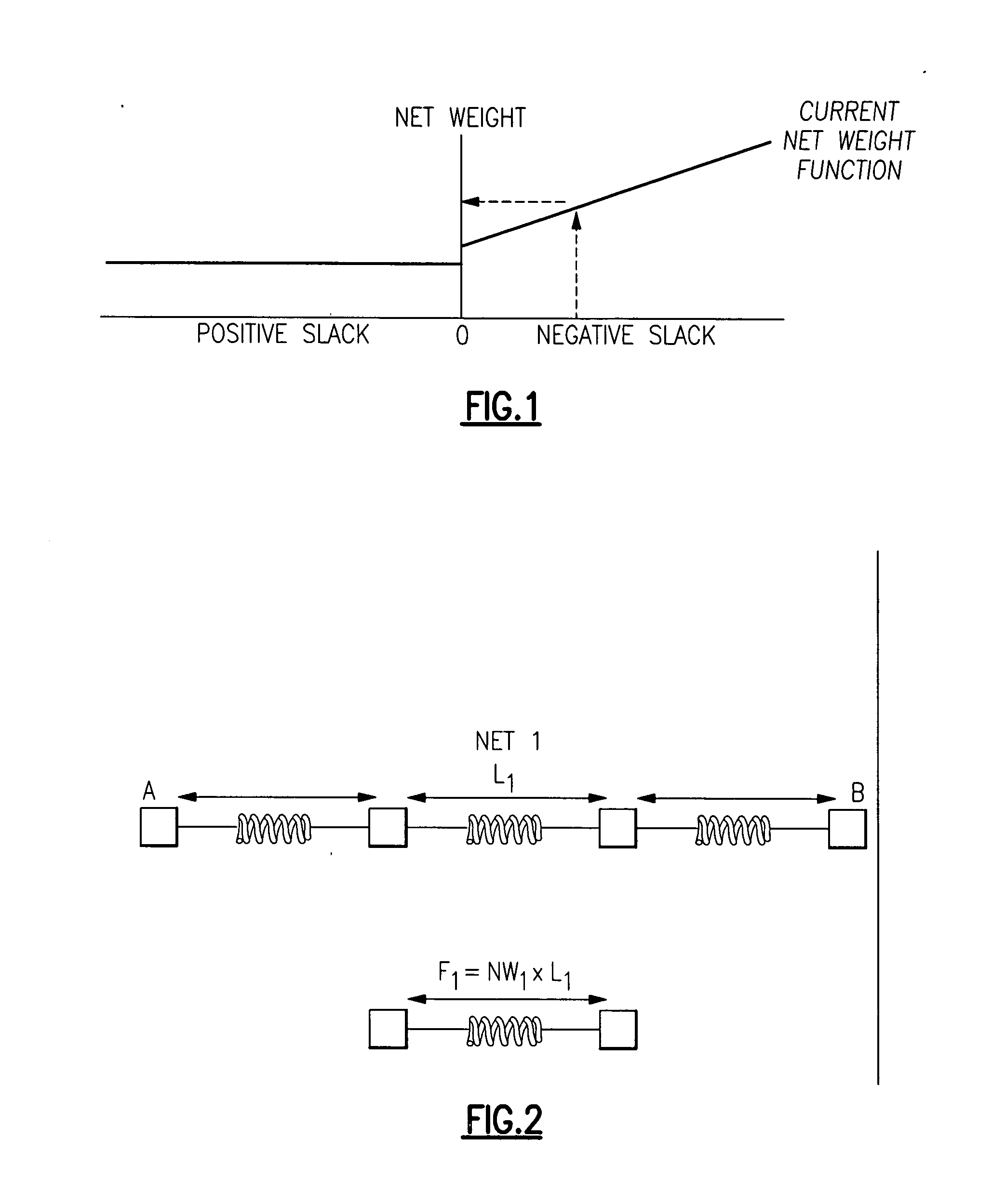
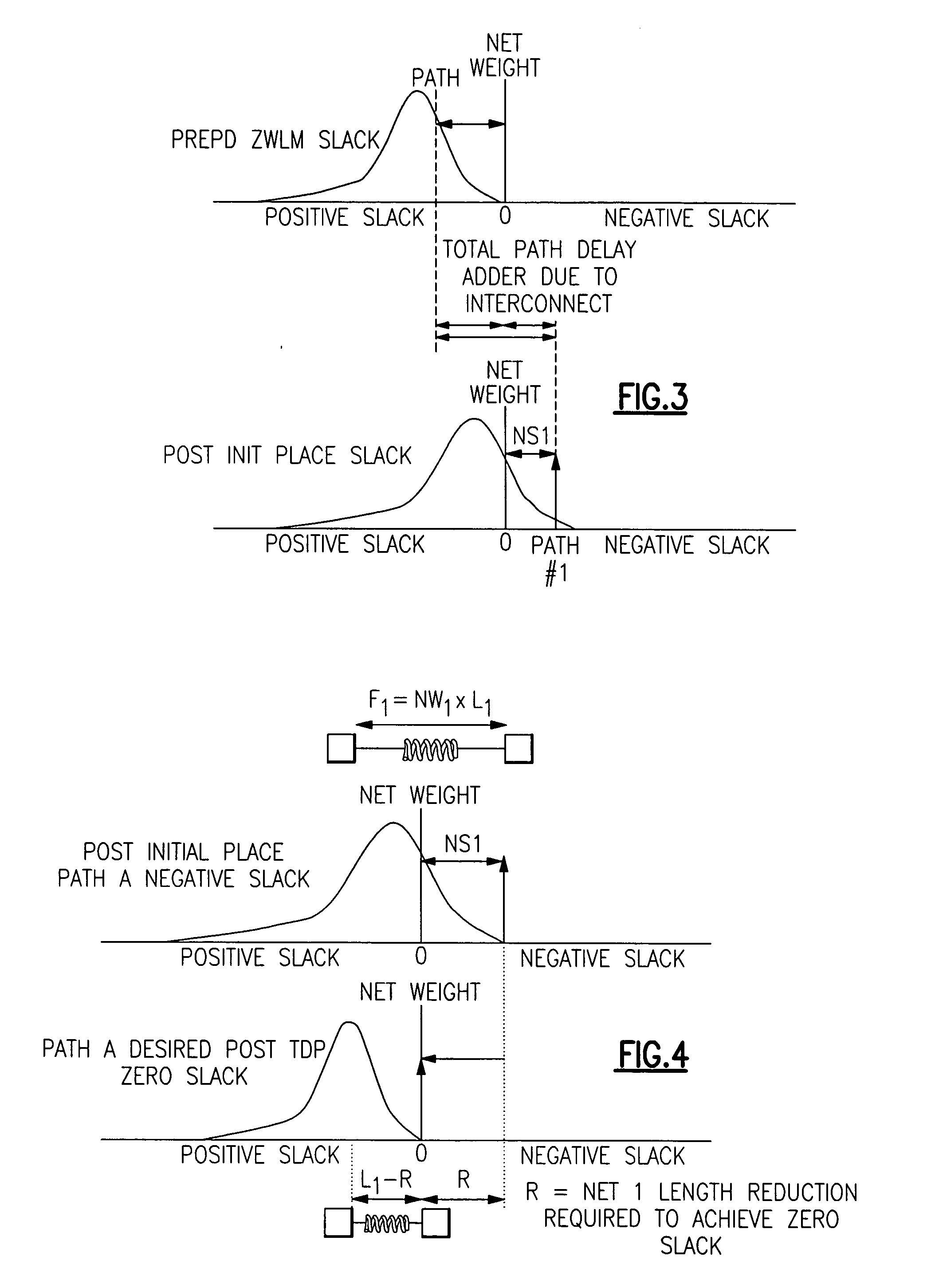
Negative slack recoverability factor - a net weight to enhance timing closure behavior
InactiveUS20060015836A1Enhance timing closure behaviorOvercomes shortcomingComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationLoad modelTiming closure
More “timing closure efficient” Timing Driven Placements by implementing our new net weight for negative slack paths to enhance timing closure behavior is provided by a NSRF (Negative Slack Recover Factor). This new weight would not be based on the absolute amount of negative slack in a path, but rather it would be based on the proportion or percentage of the path's total net delay adder that must be recovered in order to achieve timing closure (zero slack). After an initial or previous placement has been created, then a list of paths with timing violations with a Negative Slack Recover Factor (NSRF) is created for each net in each of the timing paths on the list of paths, and then calculating a NSRF net weight factor for use in subsequent placements and also assigning nets in the list of paths with no timing violations a NSRF default value of one.. The NSRF value is calculated as equaling (ZWLM slack value +negative slack value) / ZWLM slack value=(1+(negative slack value / ZWLM slack value)), where ZWLM is a Zero Wire Load Model (ZWLM) value of timing wherein all wire parasitics are removed from consideration in the timing.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
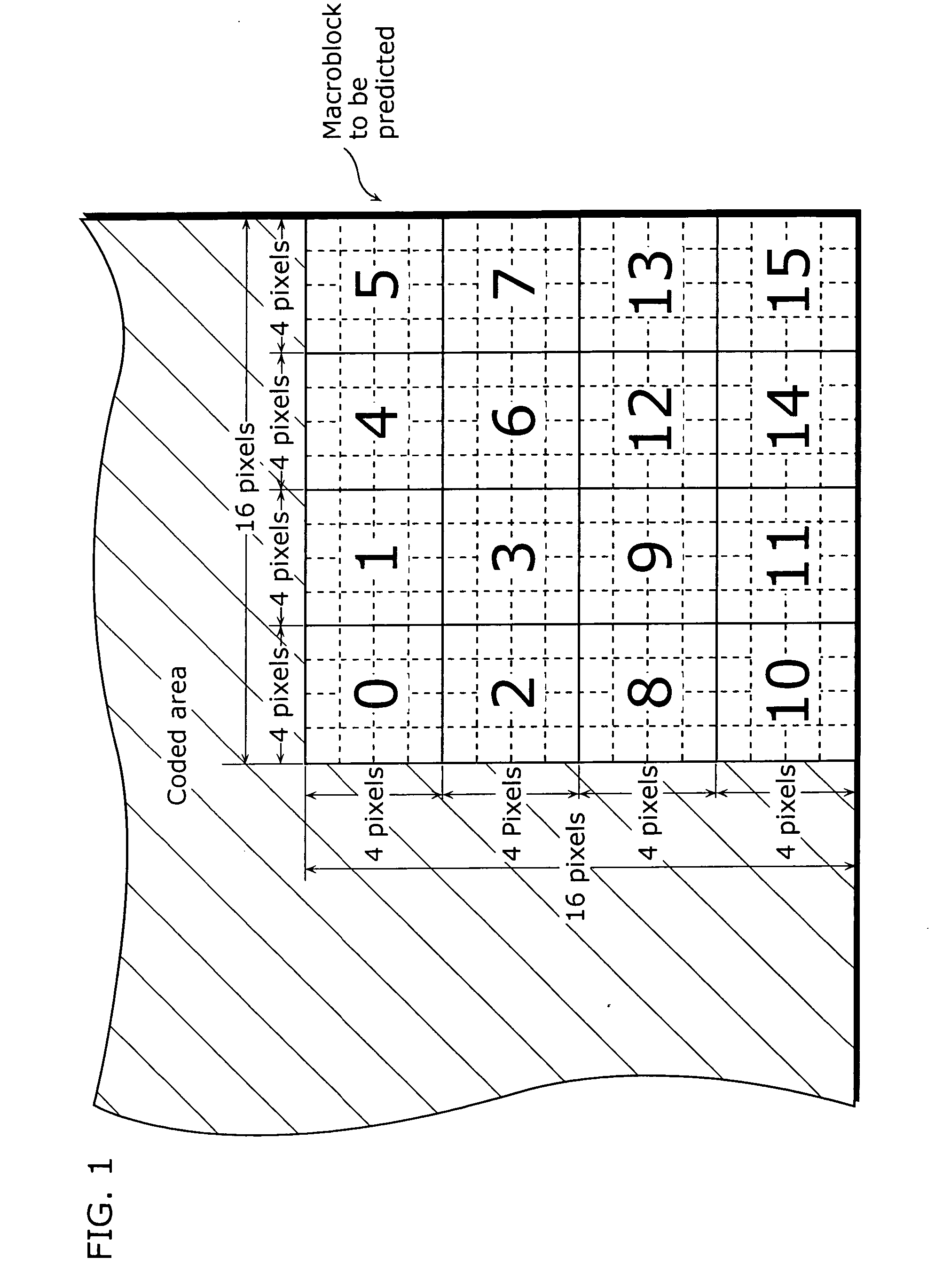
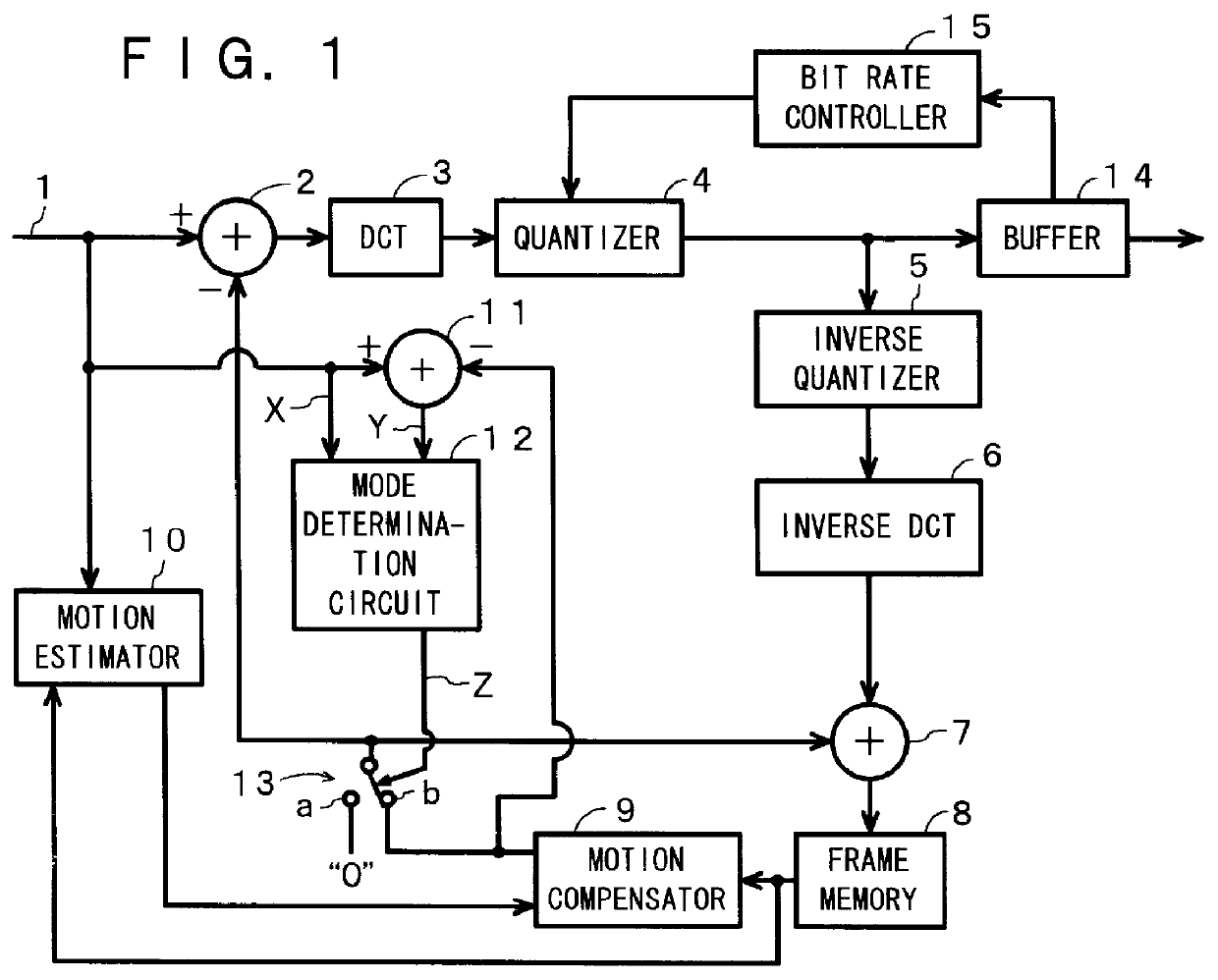
Coding mode determination system
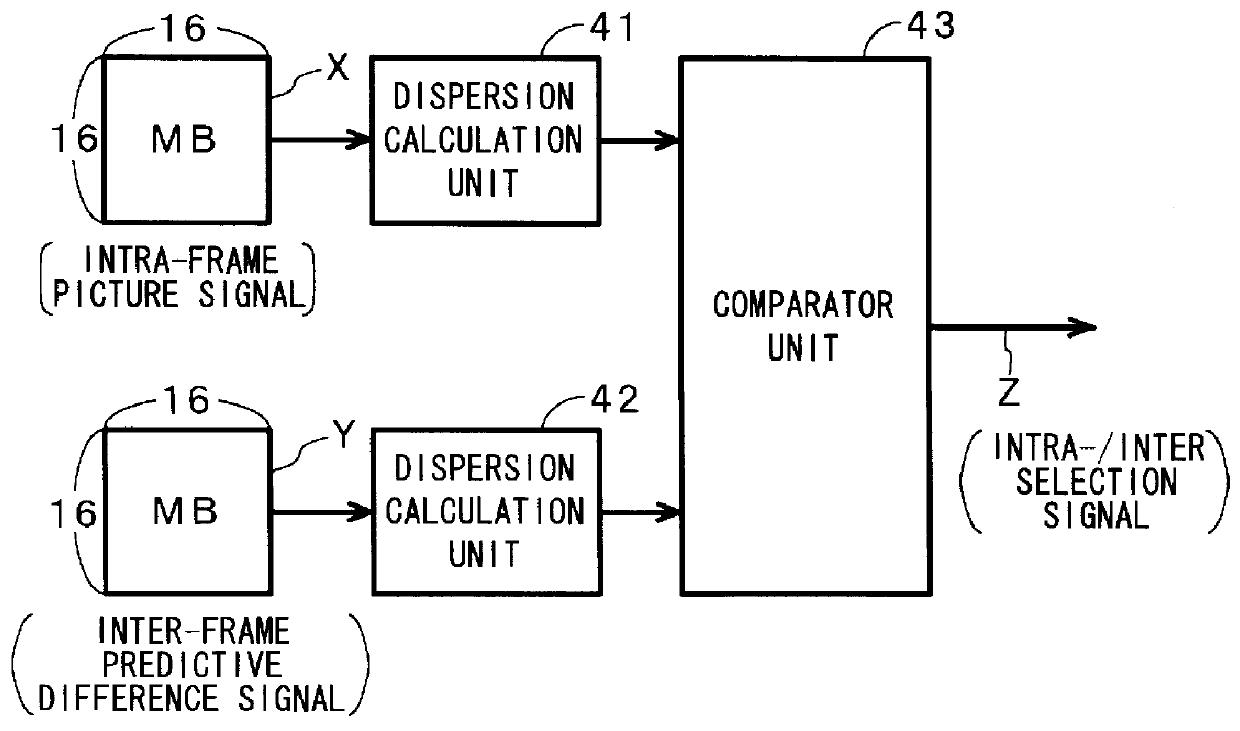
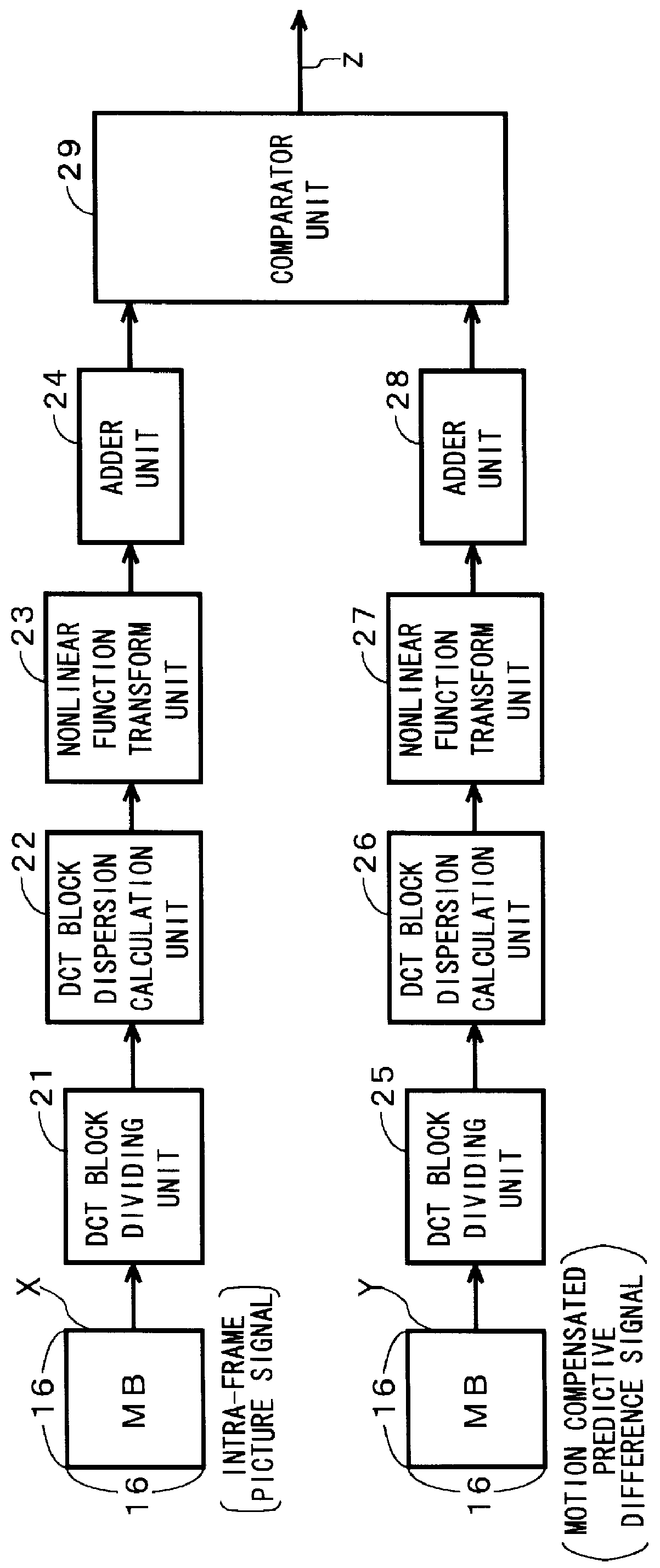
This invention provides a mode determination system for maximizing the coding efficiency by minimizing the amount of generated encoded information. An intra-frame picture signal X of 16 pels 16 lines is divided into four sub-blocks of 8 pelsx8 lines by a DCT block dividing unit. A DCT block dispersion calculation unit calculates the dispersions of the four sub-blocks, and a nonlinear function transform unit transforms the dispersions to values for estimating amounts of generated encoded information. An adder unit adds together the four values for estimating amounts of generated encoded information and outputs the sum. On the other hand, a motion compensated predictive difference Y of 16 pelsx16 lines undergoes a processing similar to said intra-frame picture signal X by a DCT block dividing unit, a DCT block dispersion calculation unit, a nonlinear function transform unit and an adder unit, and a value for estimating an amount of generated encoded information for the motion compensated predictive difference Y is outputted from the adder unit. An comparator unit outputs a signal for selecting a mode according to which of the two values for estimating amounts of generated encoded information is smaller.
Owner:KDDI CORP
Chopper-direct-conversion (CDC) radio architecture
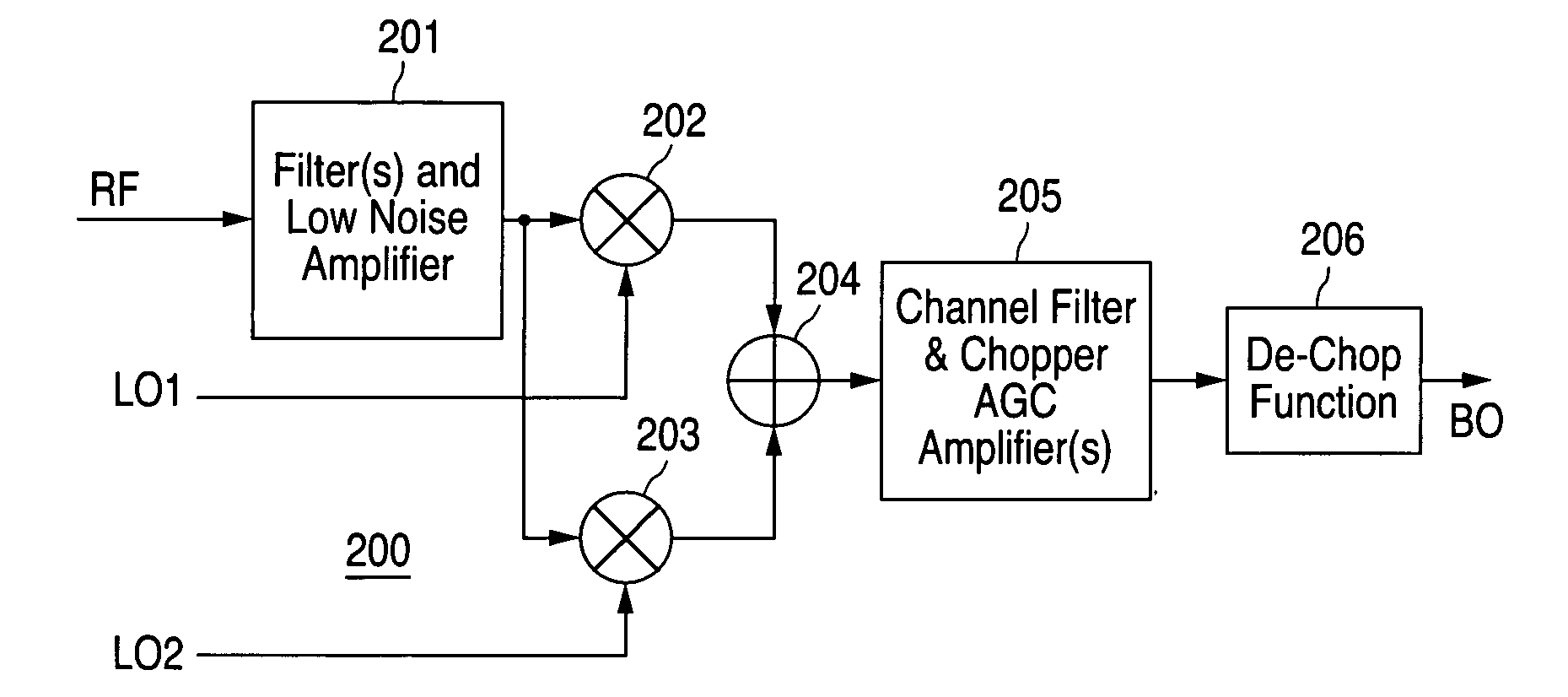
ActiveUS7177609B1Solve the real problemAmplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsModulation with suppressed carrierLocal oscillator signalRadio reception
A chopper-direct-conversion (CDC) radio receiver includes a phase-alternating mixer receiving an antenna input signal and at least one local oscillator signal and generating a double sideband signal in a single mixing step. The phase-alternating mixer may be implemented by two parallel mixers each mixing the input signal with one of two local oscillator signals and an adder receiving and summing outputs from the two parallel mixers, by a track-and-hold circuit sampling the input signal based upon the local oscillator signal, or by a window averaging circuit averaging the input signal across a period of the local oscillator signal. The CDC architecture is suitable for fabrication on a single chip and offers solutions to virtually all problems found in conventional direct-conversion receivers.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Apparatus and method for color dithering
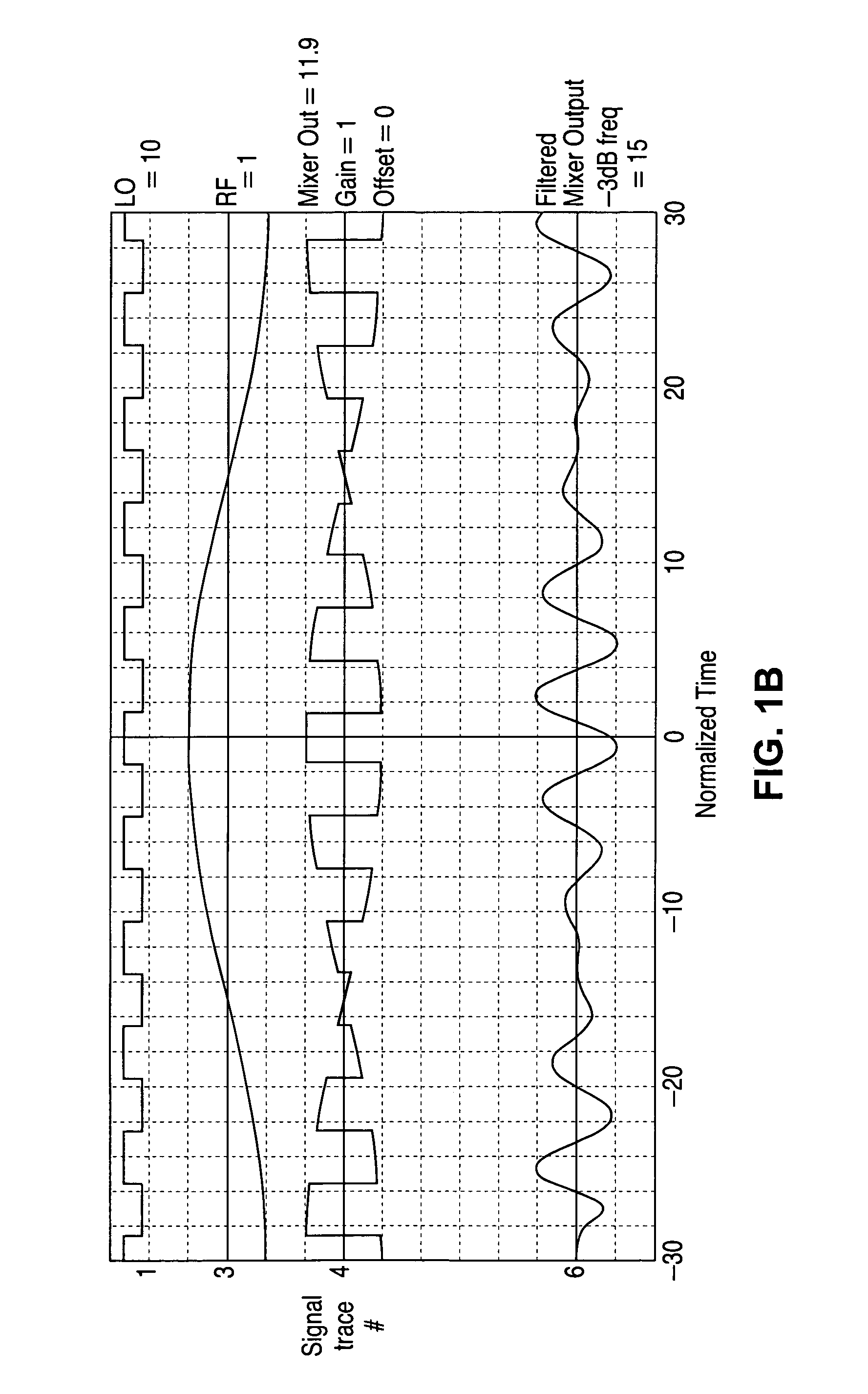
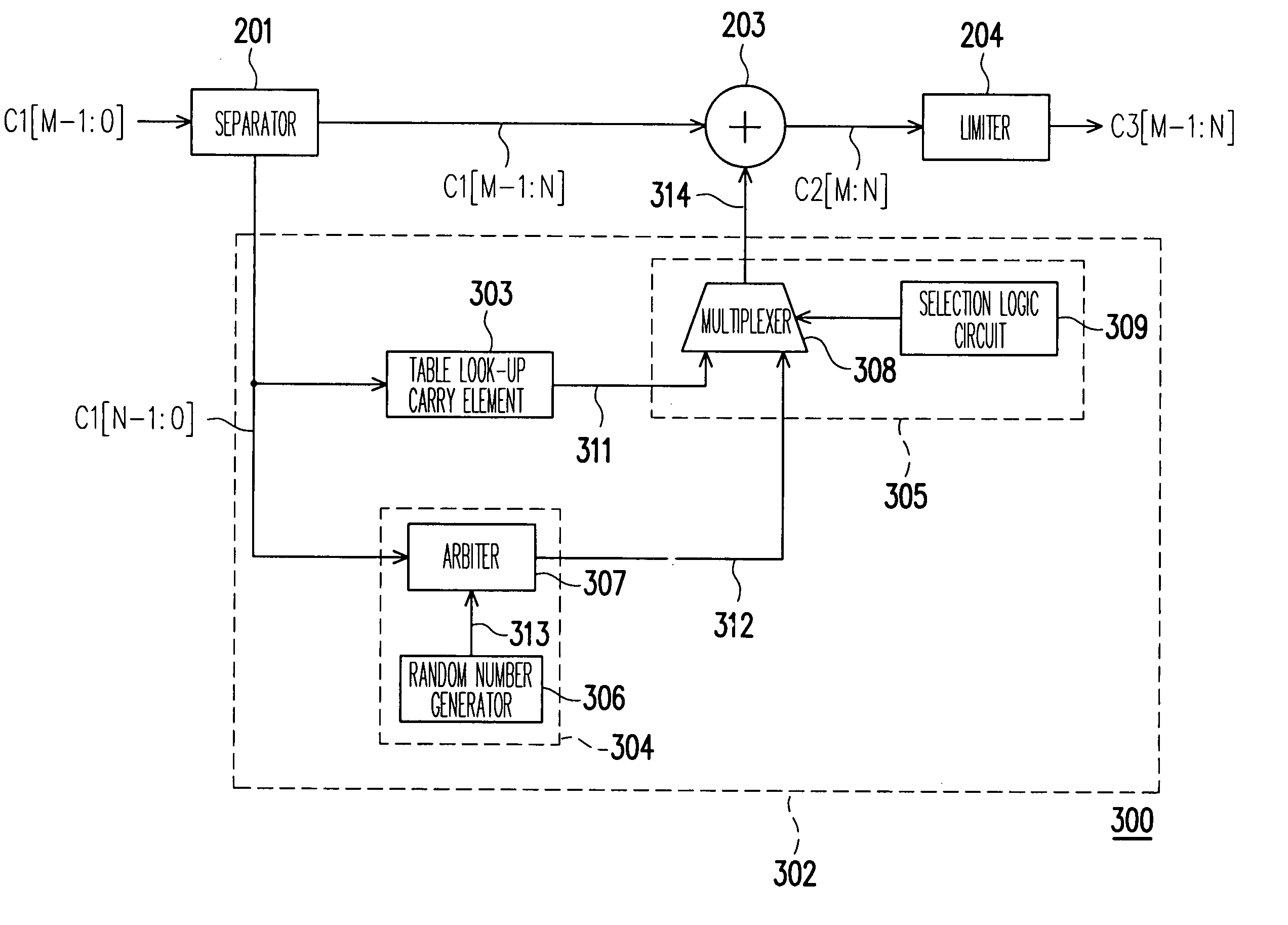
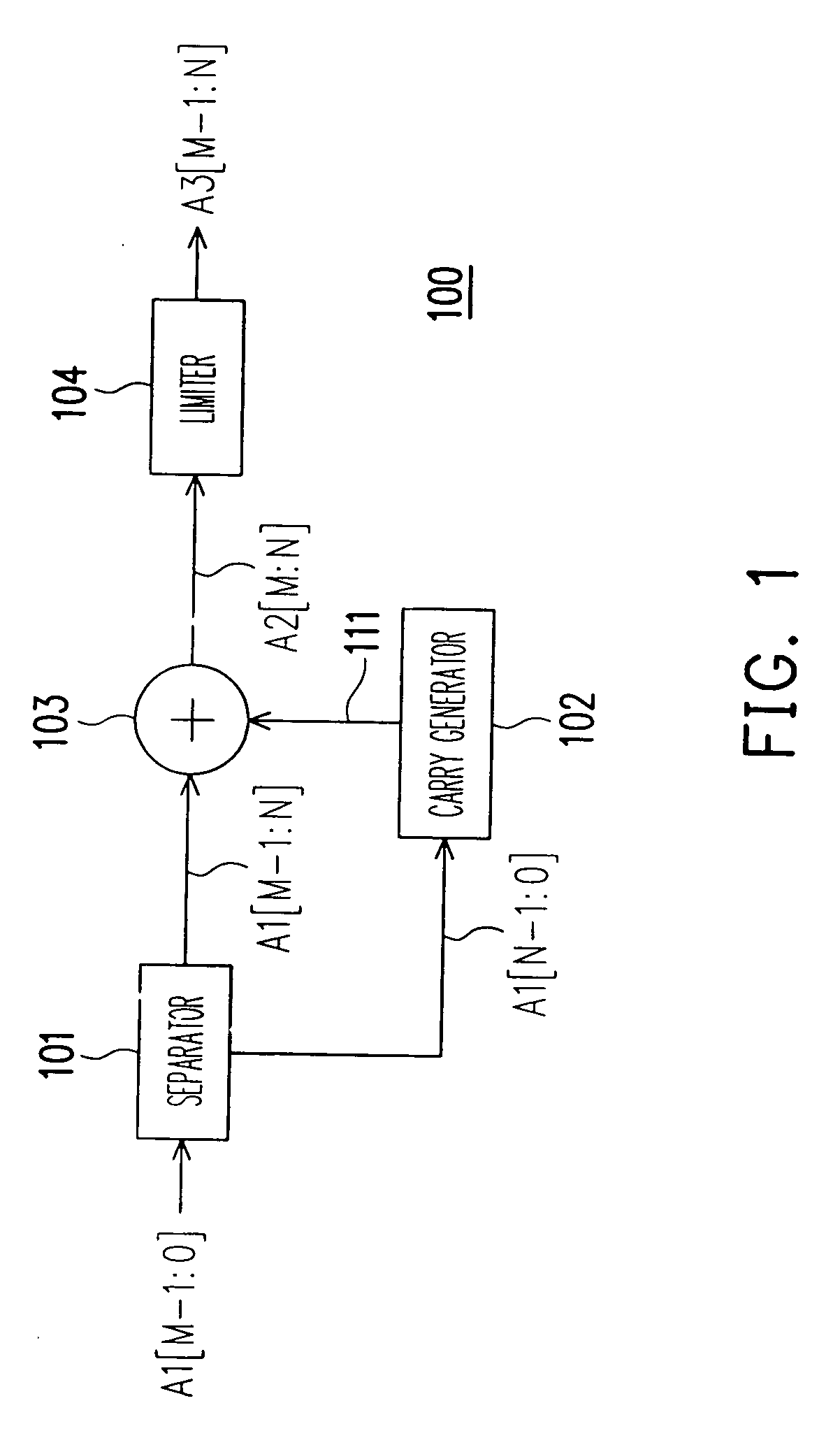
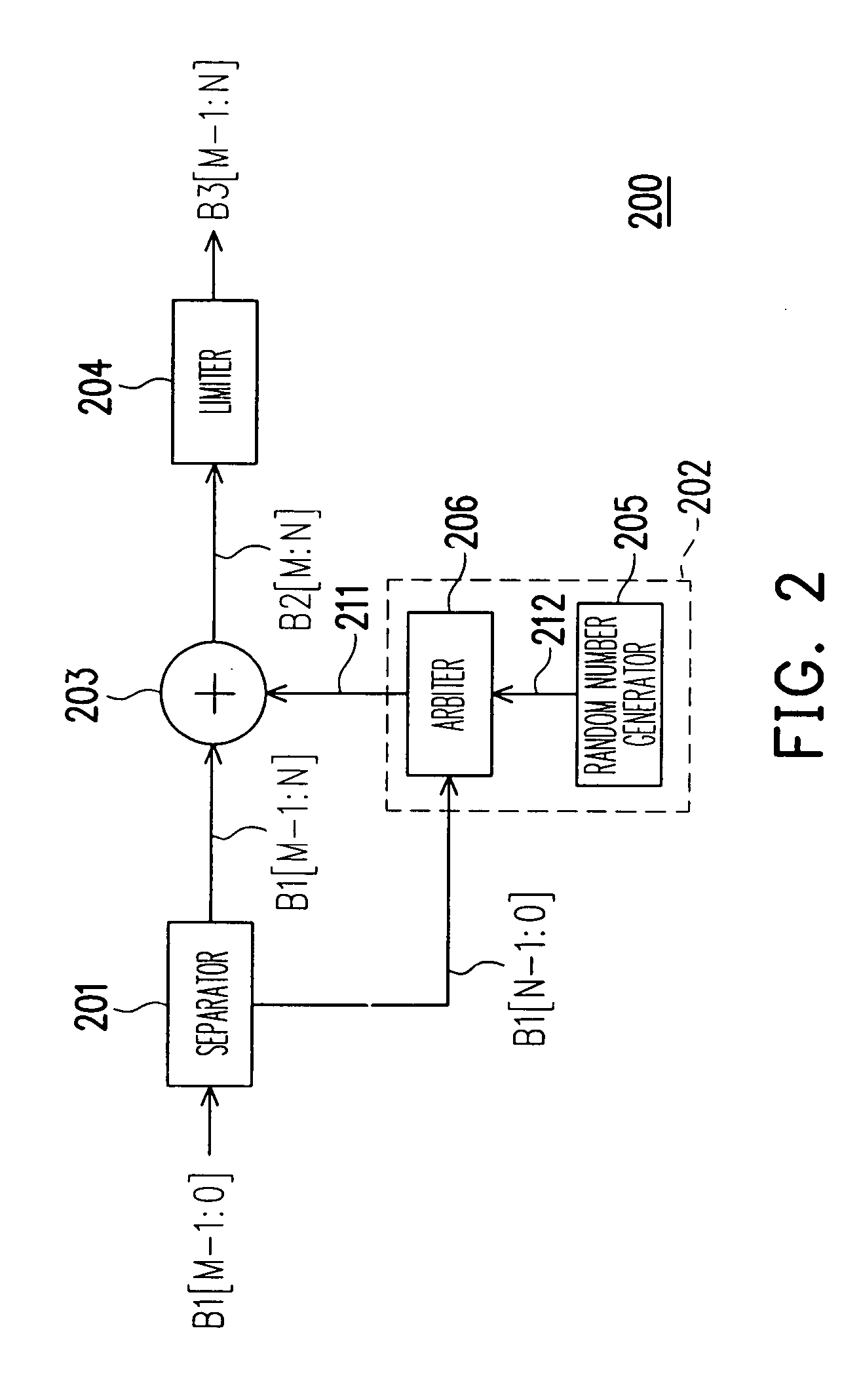
InactiveUS20070024636A1Efficient implementationPreventing perceivable dithering noiseCathode-ray tube indicatorsPattern recognitionNumber generator
An apparatus and the method which implement color dithering having an extended period for preventing perceivable dithering noise caused by the asymmetry and un-ideal characteristics existing in a display system are provided. The apparatus includes a separator, a carry generator, an adder and a limiter. The separator receives a color value and separates the color value into a high-bit color value and a low-bit color value. Then the carry generator provides a carry value to be either one or zero, according to a random number from a random number generator and the low-bit color value. The adder adds the high-bit color value and the carry value, and provides the result as a tentative output value. Finally, the limiter receives the tentative output value and outputs the smaller value of the tentative output value and a pre-set upper limit.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Address automatic distributing method in mobile self organizing network
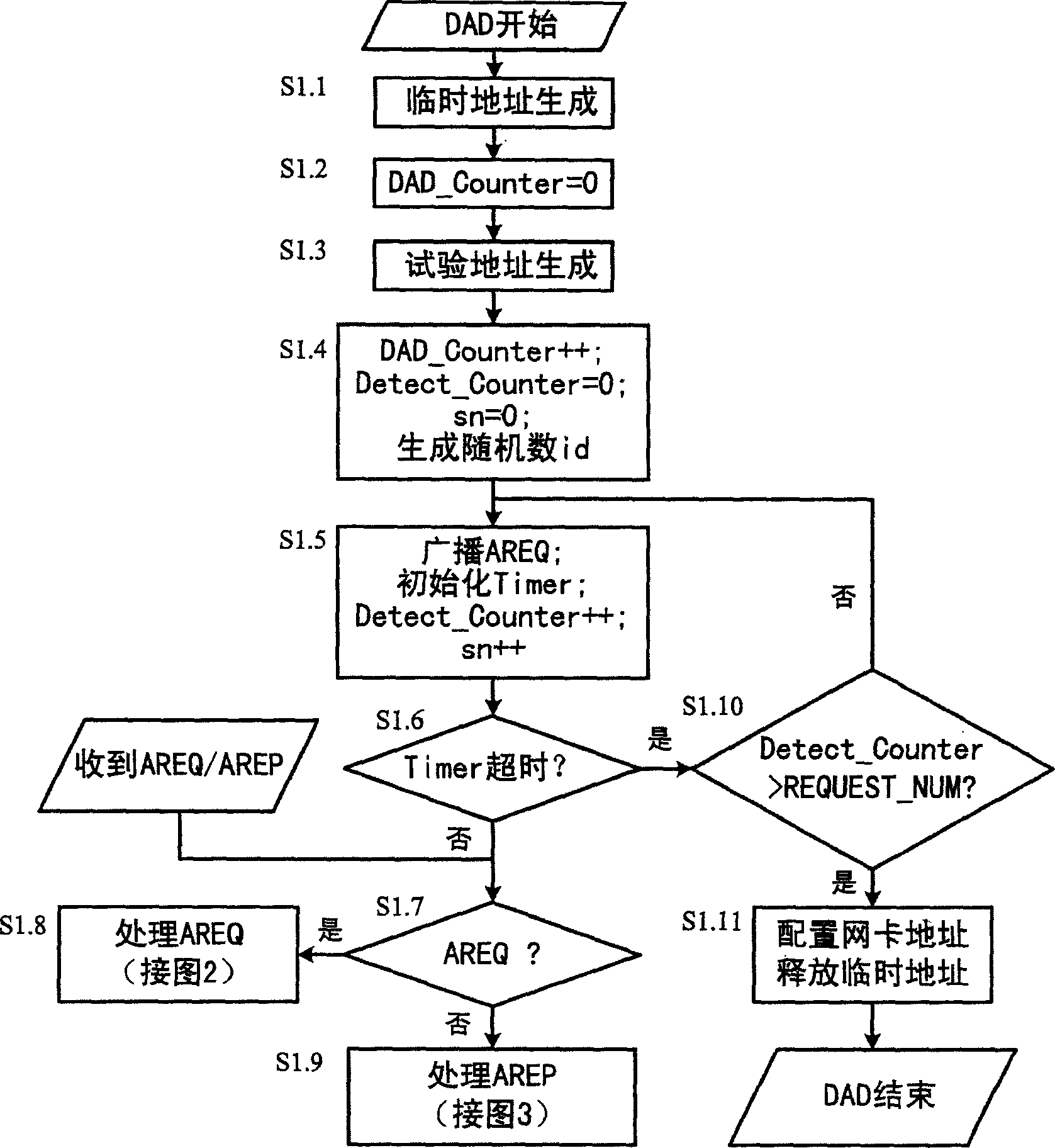
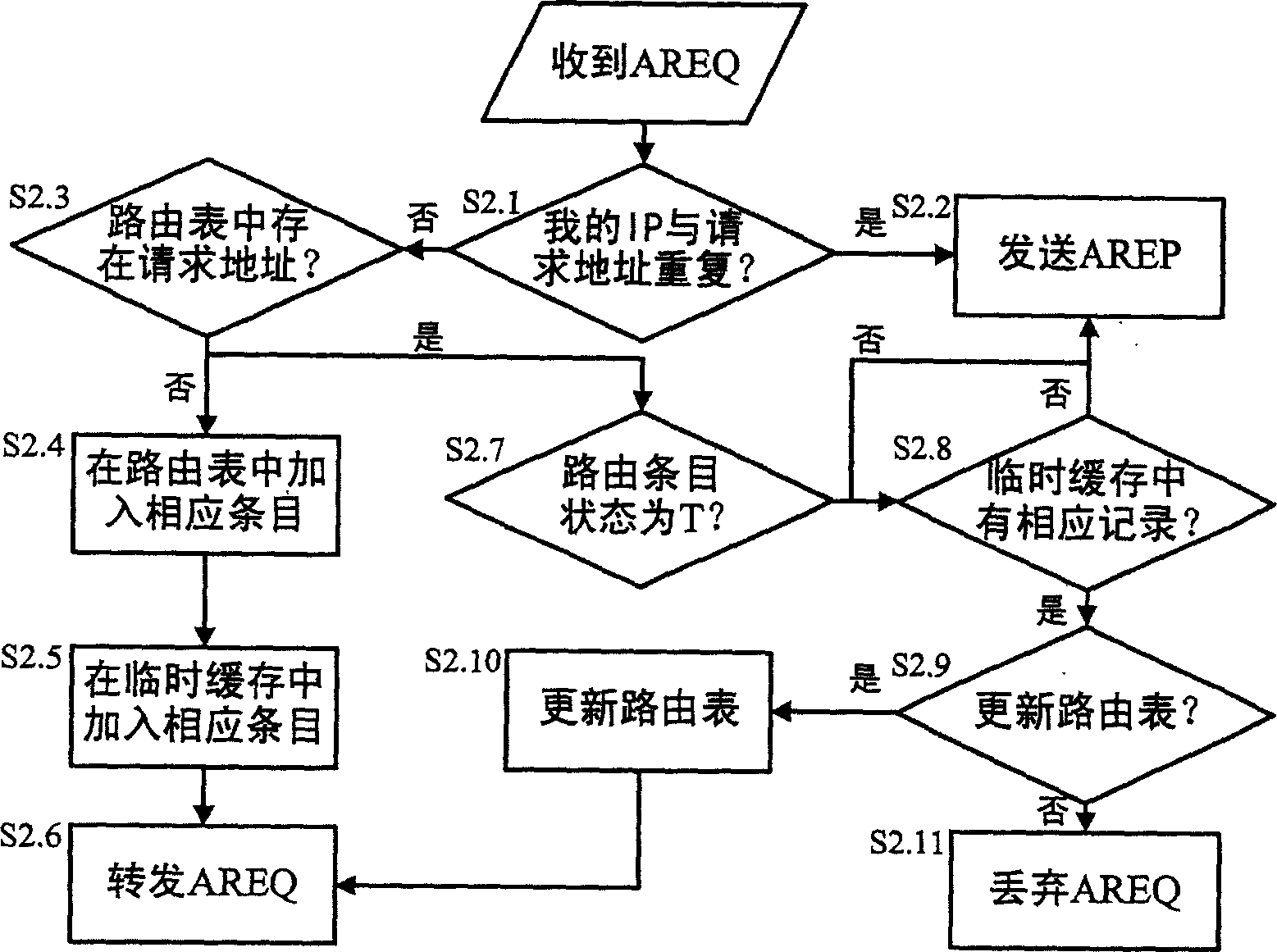
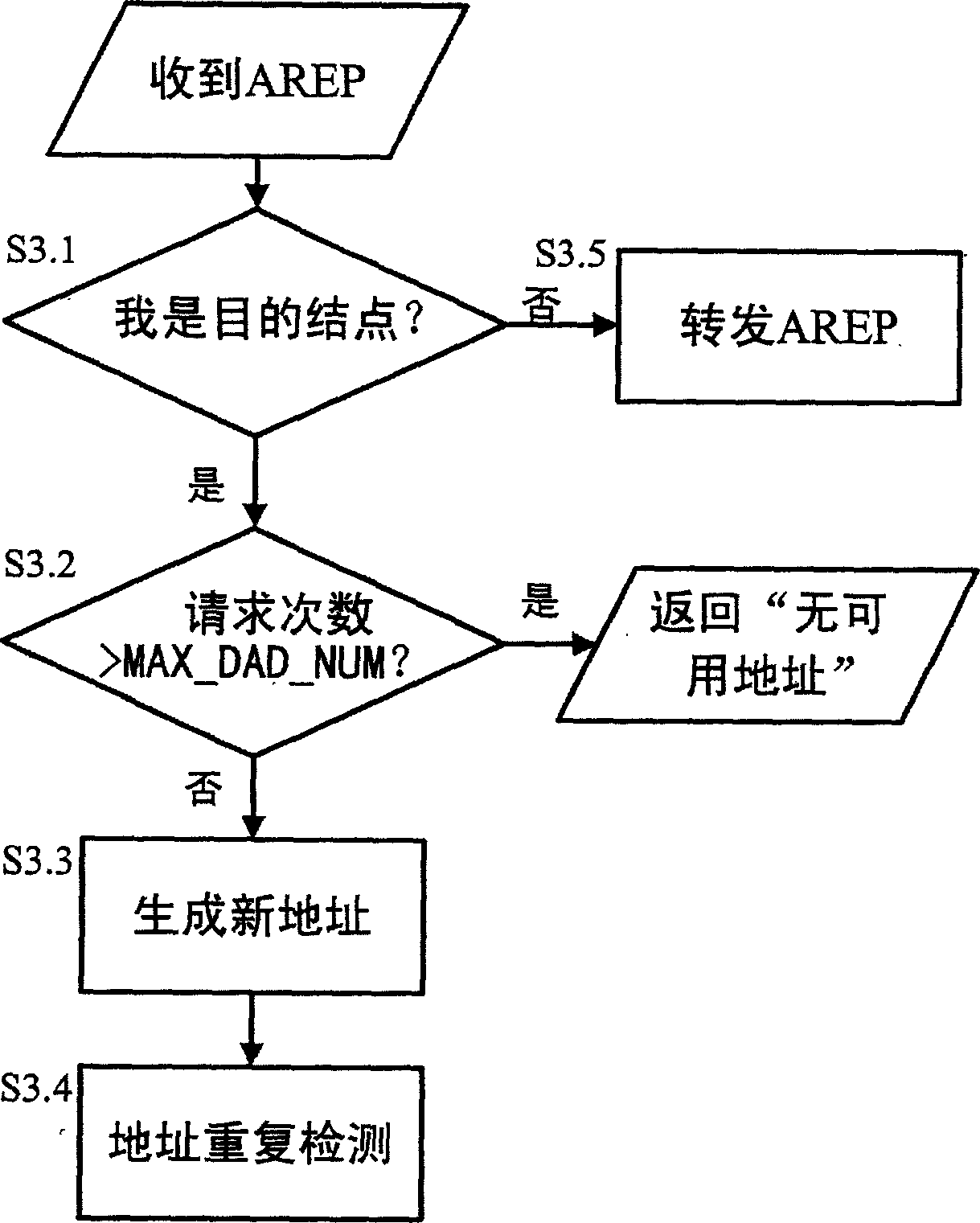
This invention relates to a method for automatically configuring address in MANET which combines itself with AODV route to increase repeated address test efficiency including: first of all, the s, a node of MANET, generates a temporary address for transmitting address configuration information and generates an experiment address then to broadcast AREQ and test the uniqueness of the requested address. The nodes who got the AREQ should refresh the route lists, if MANET node finds its own IP address or that in the route list is the same with the adder, that shows the adder is used. AREP is broadcast to s which generates a new address after receiving AREP and repeats the adder test. If s does not receive AREP, it assigns the adder to netcards.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECHNOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
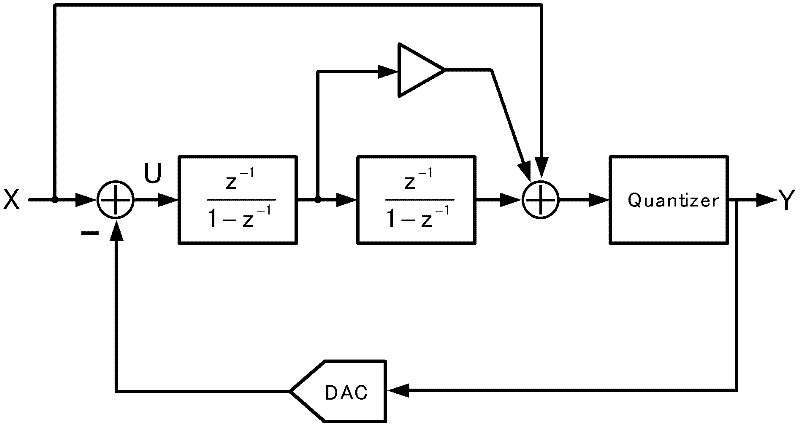
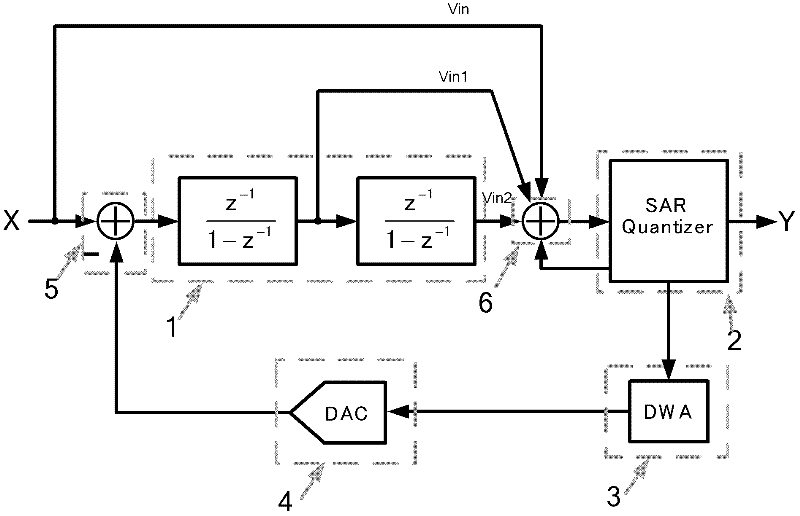
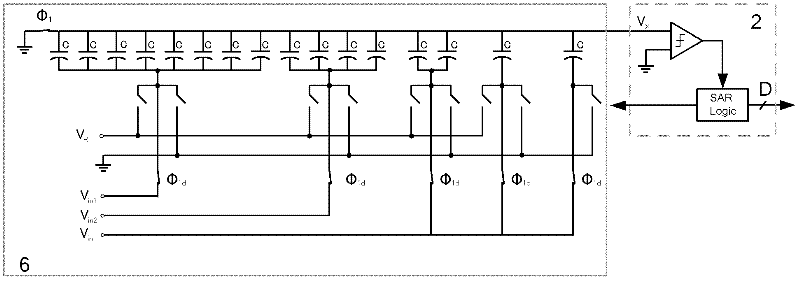
Second-order feedforward Sigma-Delta modulator based on successive comparison quantizer
InactiveCN102545901AReduce power consumptionReduce areaAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsCapacitanceMulti input
The invention discloses a second-order feedforward Sigma-Delta modulator based on a successive comparison quantizer. The Sigma-Delta modulator comprises two integrators (1) based on a switched capacitor structure in the prior art, one multi-bit successive comparison quantizer (2), one digital circuit (3) transforming into a temperature code from a binary code based on the data weighed average algorithm, one feedback digital to analog converter (4) based on a capacitor, a first adder unit (5) for computing difference between an input signal and an output signal of the feedback digital to analog converter, and a second adder unit (6) which is directly formed by a multi-input sampling switched capacitor array of the successive comparator on a feedforward path, wherein the adder unit replaces the existing extra analog adder functional circuit or a digital adder functional circuit. The obtained Sigma-Delta modulator of the invention has the advantages of ultra-low power consumption and high resolution ratio.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
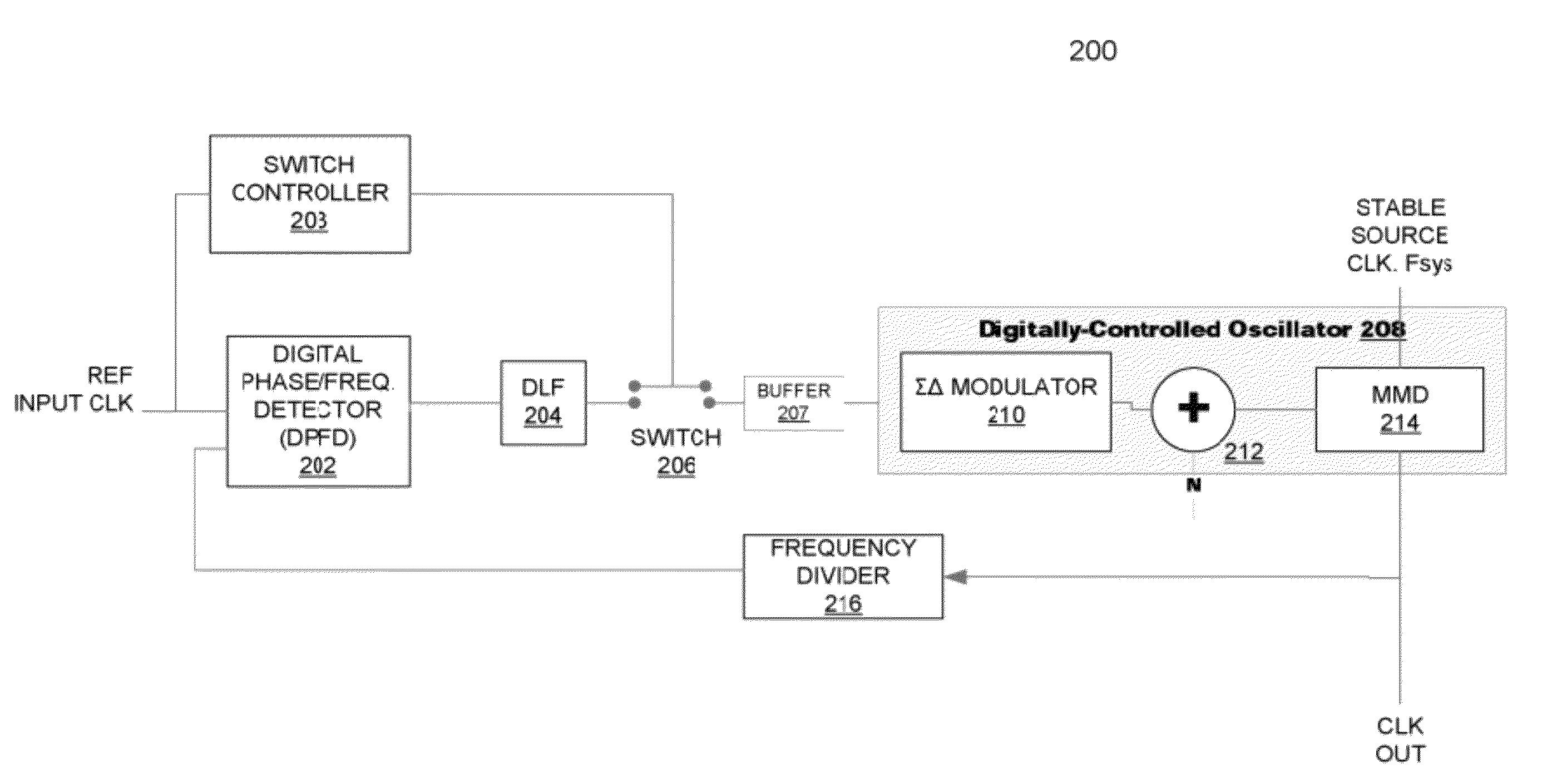
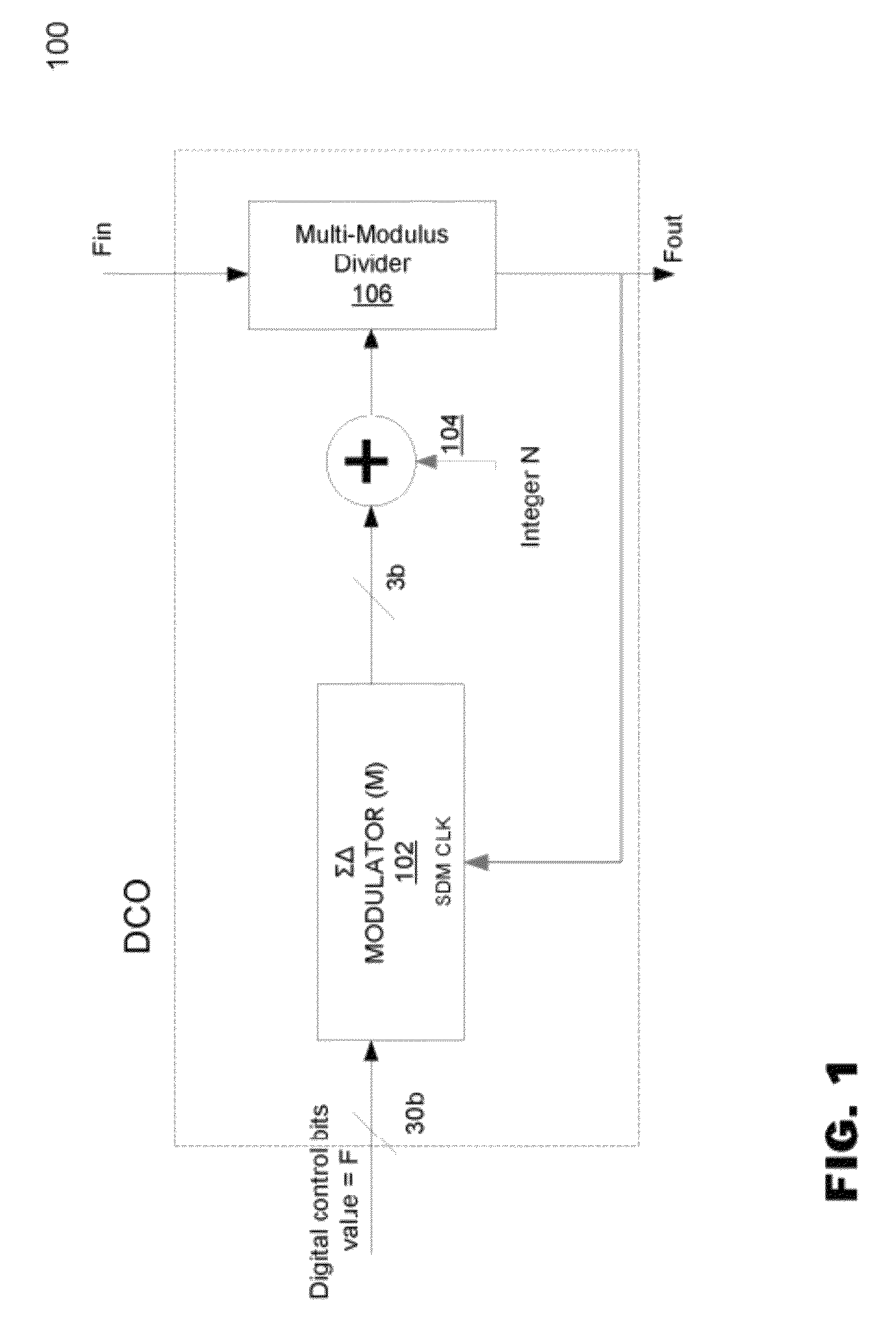
Digital phase-locked loop clock system
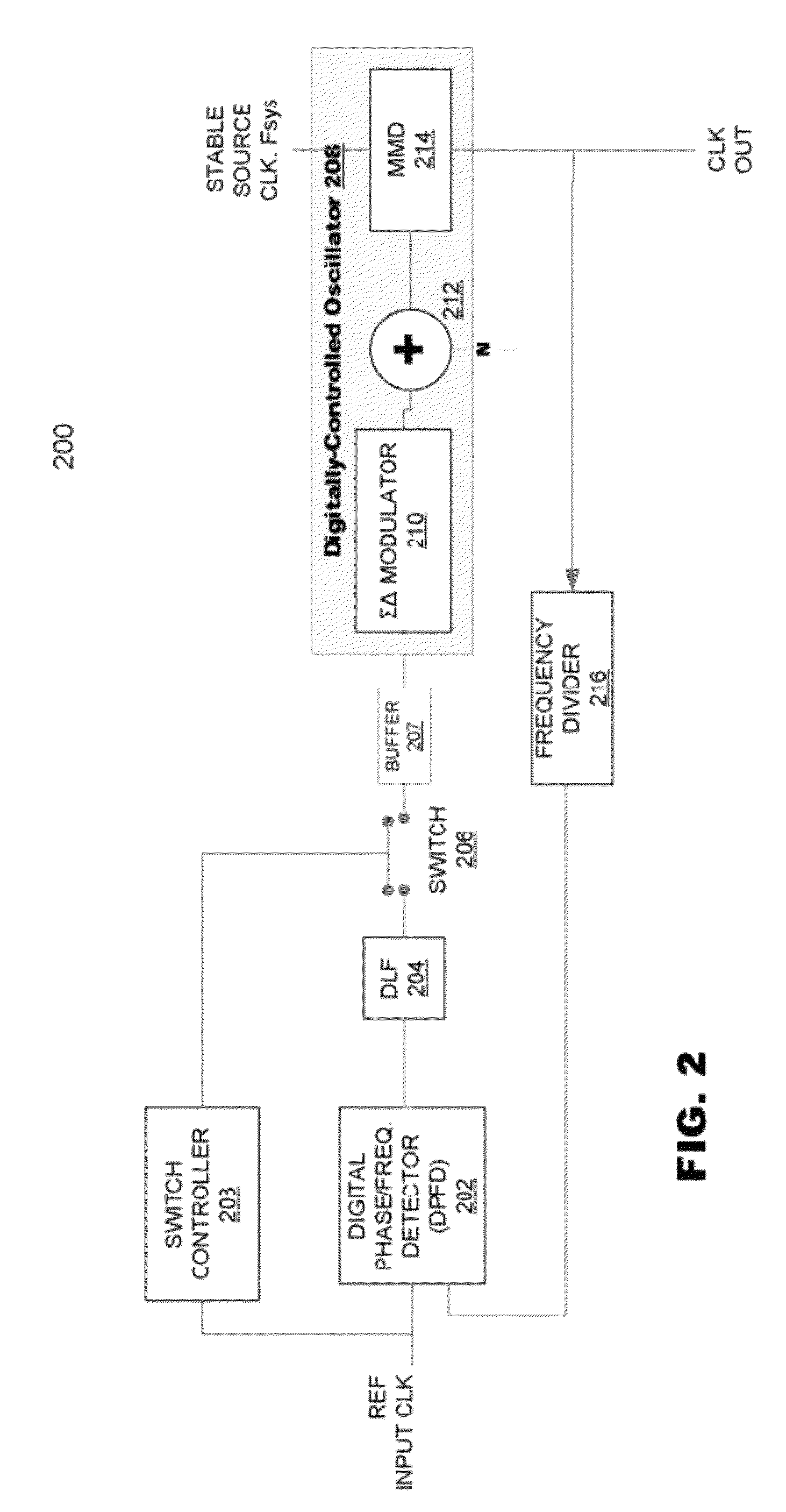
ActiveUS8188796B2Pulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsSoftware engineeringPhase frequency detector
A clock system includes a digital phase / frequency detector (DPFD), a buffer, a digitally-controlled oscillator (DCO) including a sigma-delta modulator (SDM), an adder, a first frequency divider. The DPFD may have a first input for a reference input clock, a second input for a feedback signal, the DPFD generating an output representing a difference between the reference input clock and the feedback signal. The buffer may be coupled to the DPFD for storing the difference signal over time. The SDM may have a control input coupled to the buffer. The adder may have inputs coupled to the SDM and a source of an integer control word. The first frequency divider may have an input for receiving an external clock signal and a control input coupled to the adder, the DCO generating an output clock signal having an average frequency representing a frequency of the external clock signal divided by (N+F / M).
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com