Patents
Literature
570 results about "Noise shaping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
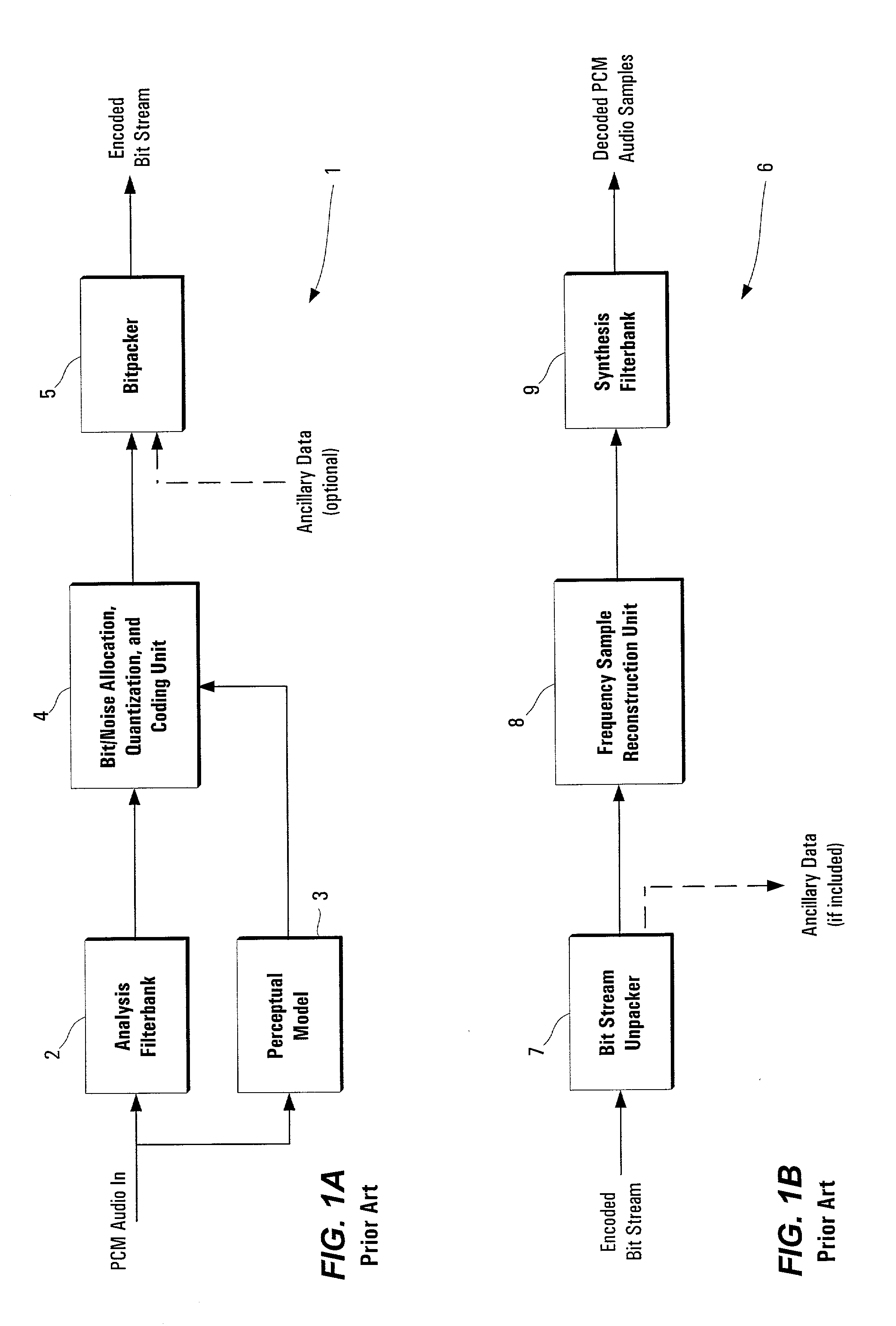
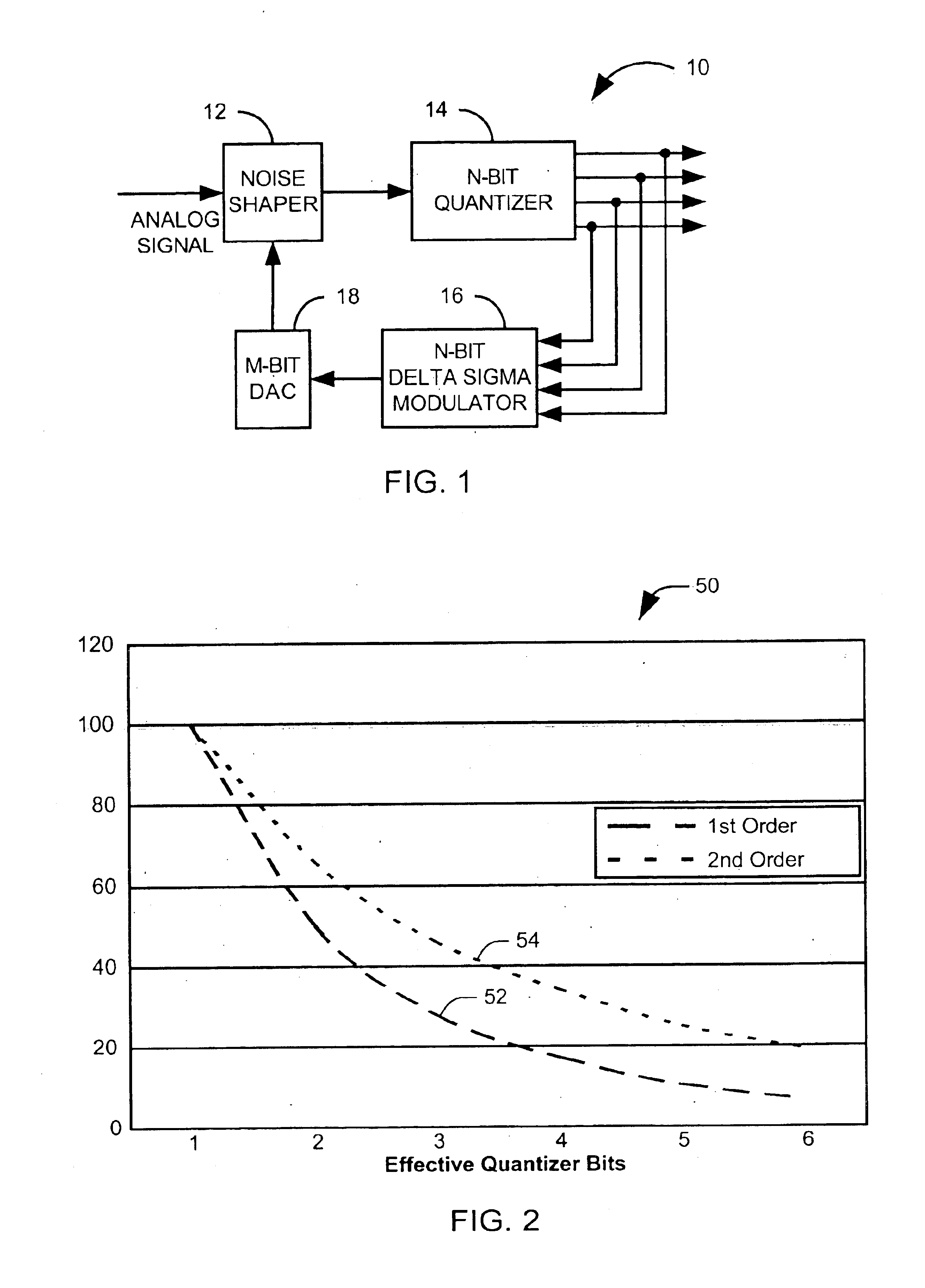
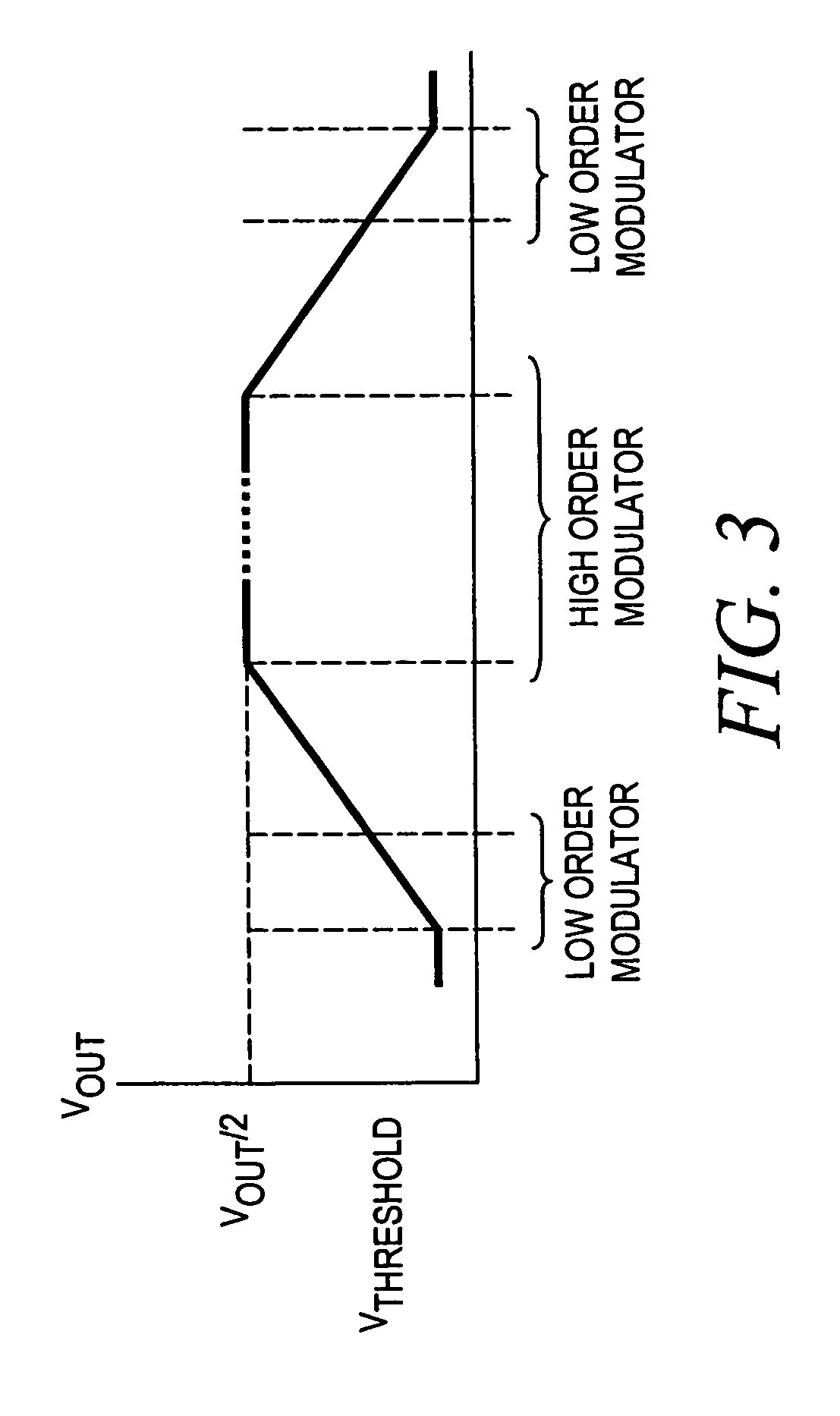
Noise shaping is a technique typically used in digital audio, image, and video processing, usually in combination with dithering, as part of the process of quantization or bit-depth reduction of a digital signal. Its purpose is to increase the apparent signal-to-noise ratio of the resultant signal. It does this by altering the spectral shape of the error that is introduced by dithering and quantization; such that the noise power is at a lower level in frequency bands at which noise is considered to be less desirable and at a correspondingly higher level in bands where it is considered to be more desirable. A popular noise shaping algorithm used in image processing is known as ‘Floyd Steinberg dithering’; and many noise shaping algorithms used in audio processing are based on an ‘Absolute threshold of hearing’ model.
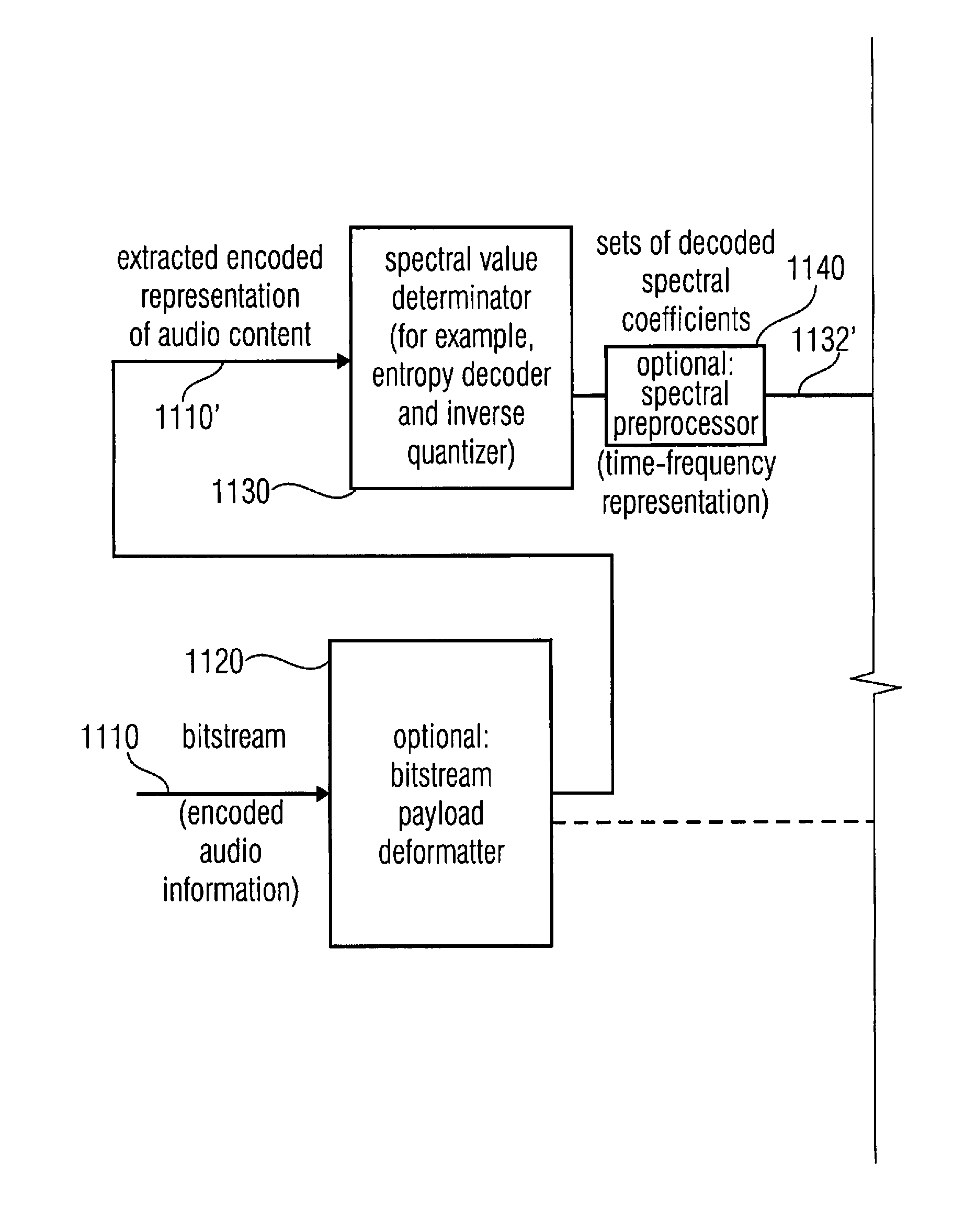
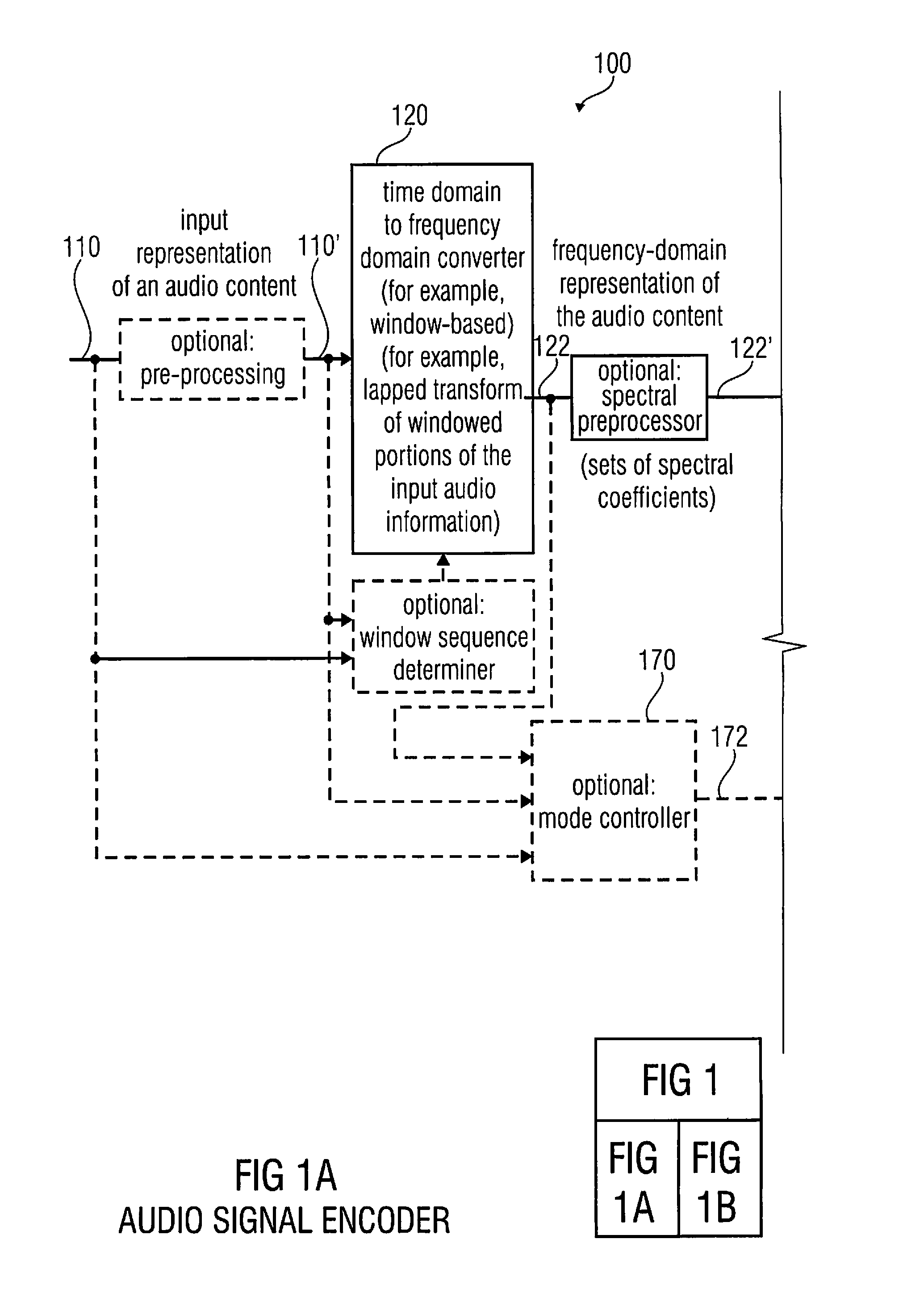
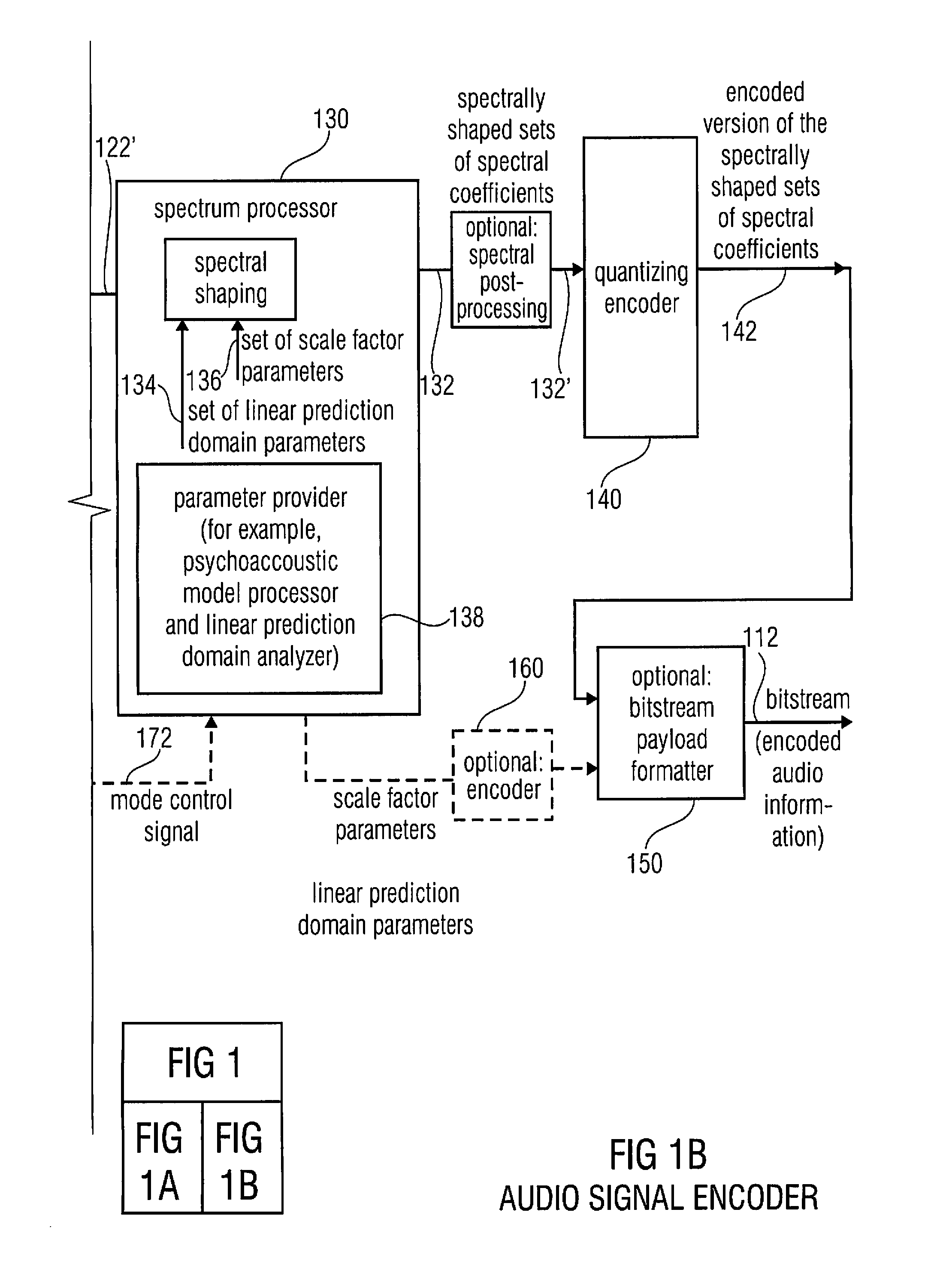
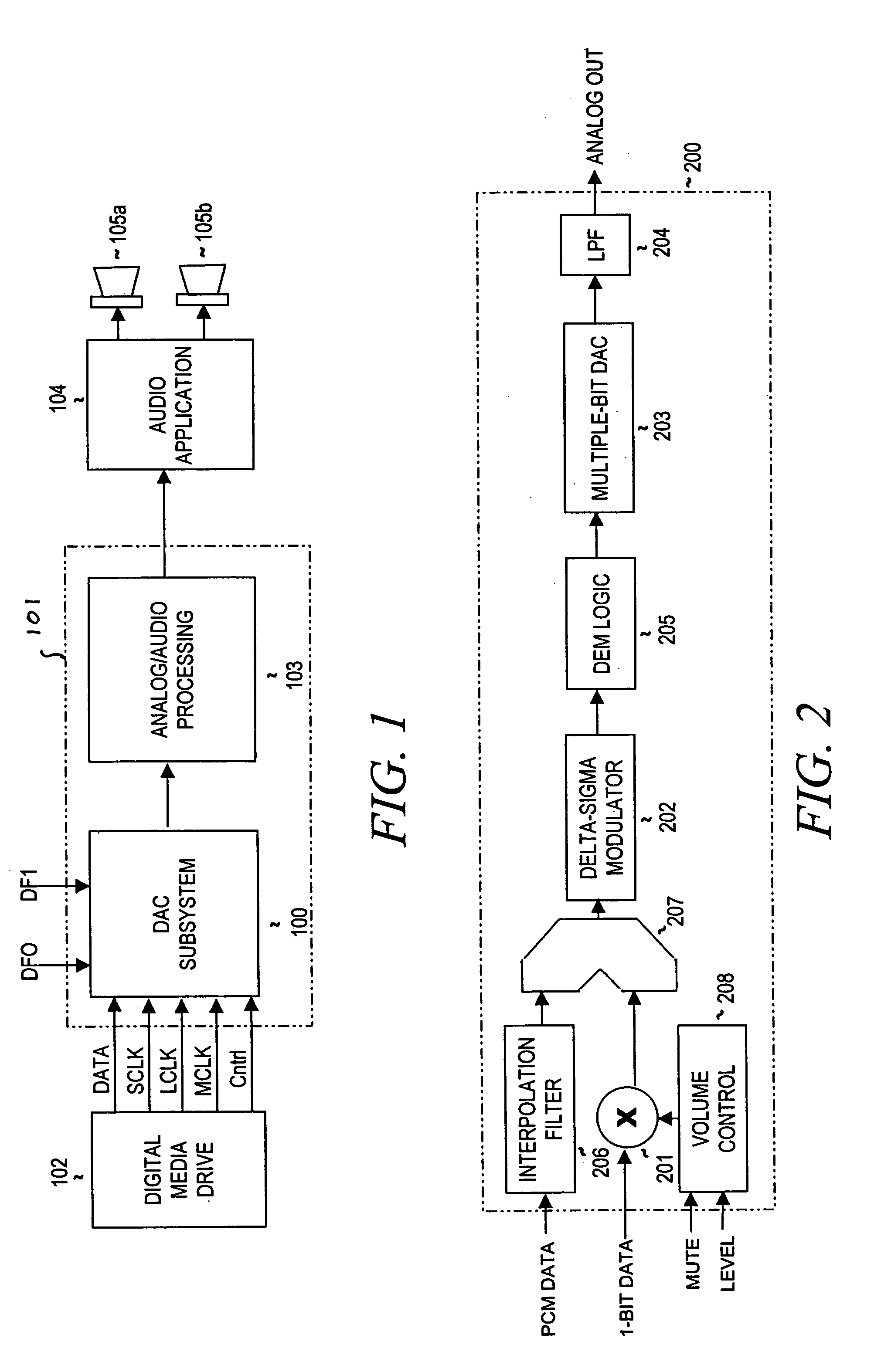
Multi-mode audio signal decoder, multi-mode audio signal encoder, methods and computer program using a linear-prediction-coding based noise shaping
ActiveUS20120245947A1Without inacceptable artifactEasy transitionSpeech analysisLinear prediction codingFrequency spectrum
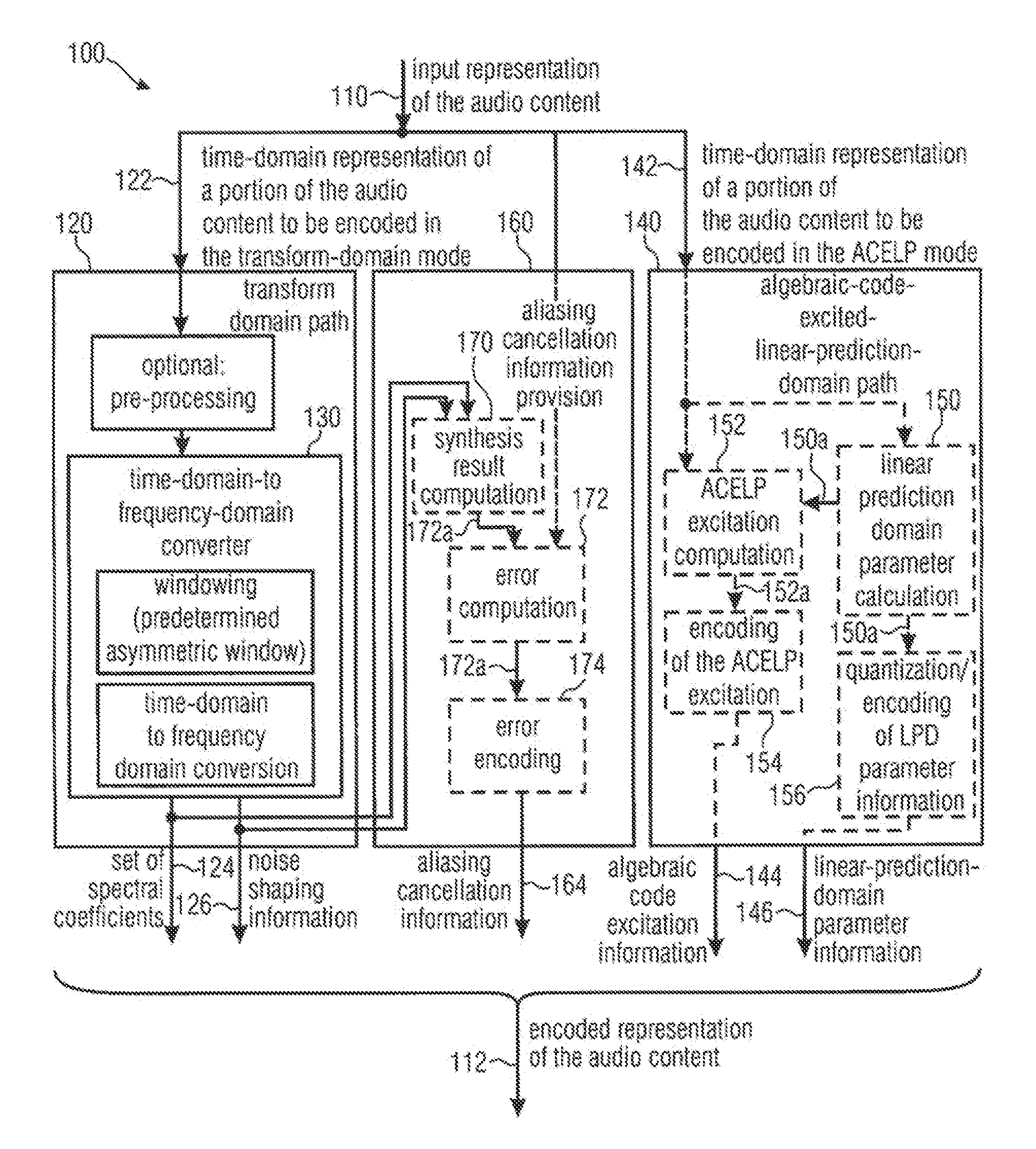
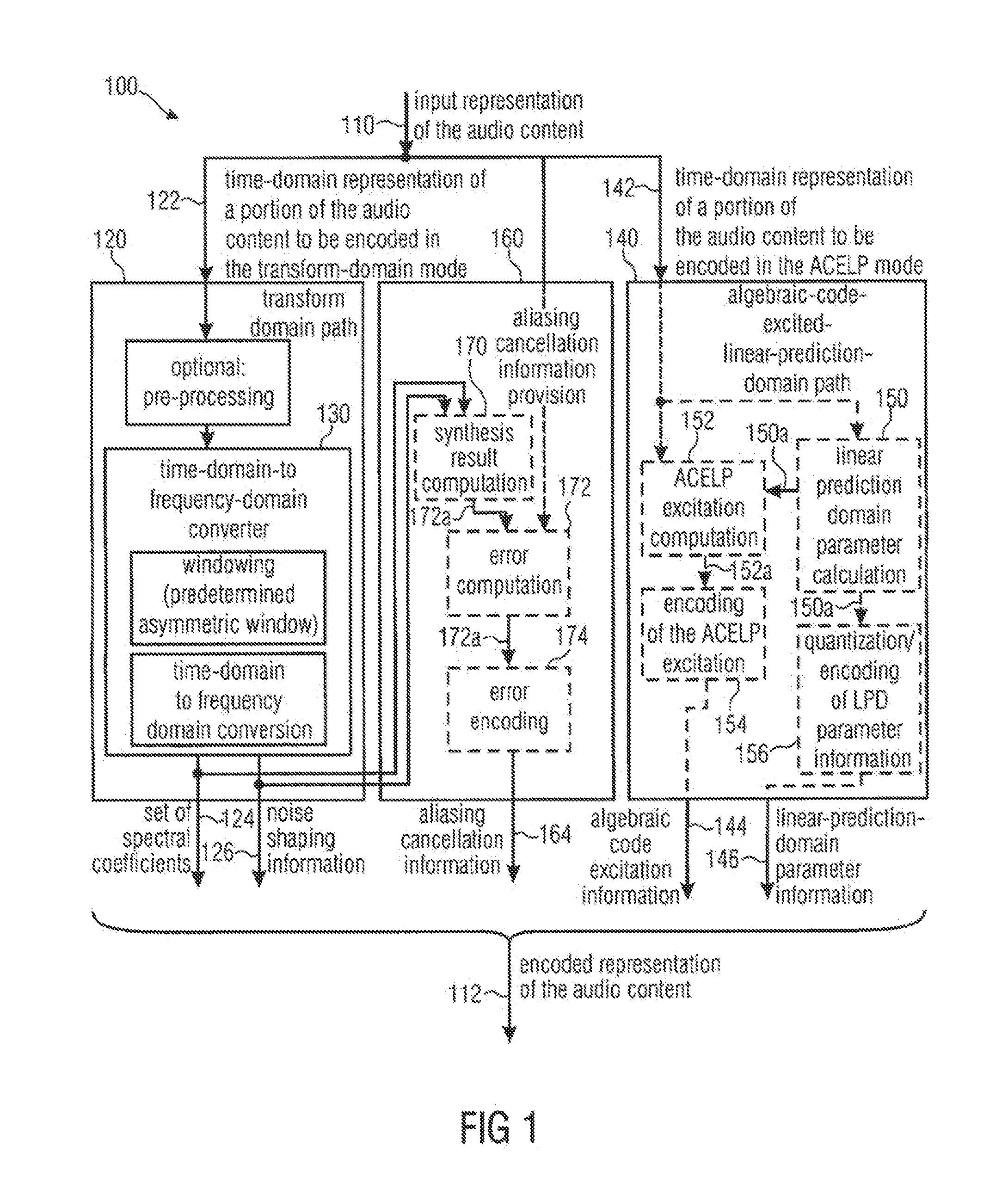
A multi-mode audio signal decoder has a spectral value determinator to obtain sets of decoded spectral coefficients for a plurality of portions of an audio content and a spectrum processor configured to apply a spectral shaping to a set of spectral coefficients in dependence on a set of linear-prediction-domain parameters for a portion of the audio content encoded in a linear-prediction mode, and in dependence on a set of scale factor parameters for a portion of the audio content encoded in a frequency-domain mode. The audio signal decoder has a frequency-domain-to-time-domain converter configured to obtain a time-domain audio representation on the basis of a spectrally-shaped set of decoded spectral coefficients for a portion of the audio content encoded in the linear-prediction mode and for a portion of the audio content encoded in the frequency domain mode. An audio signal encoder is also described.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
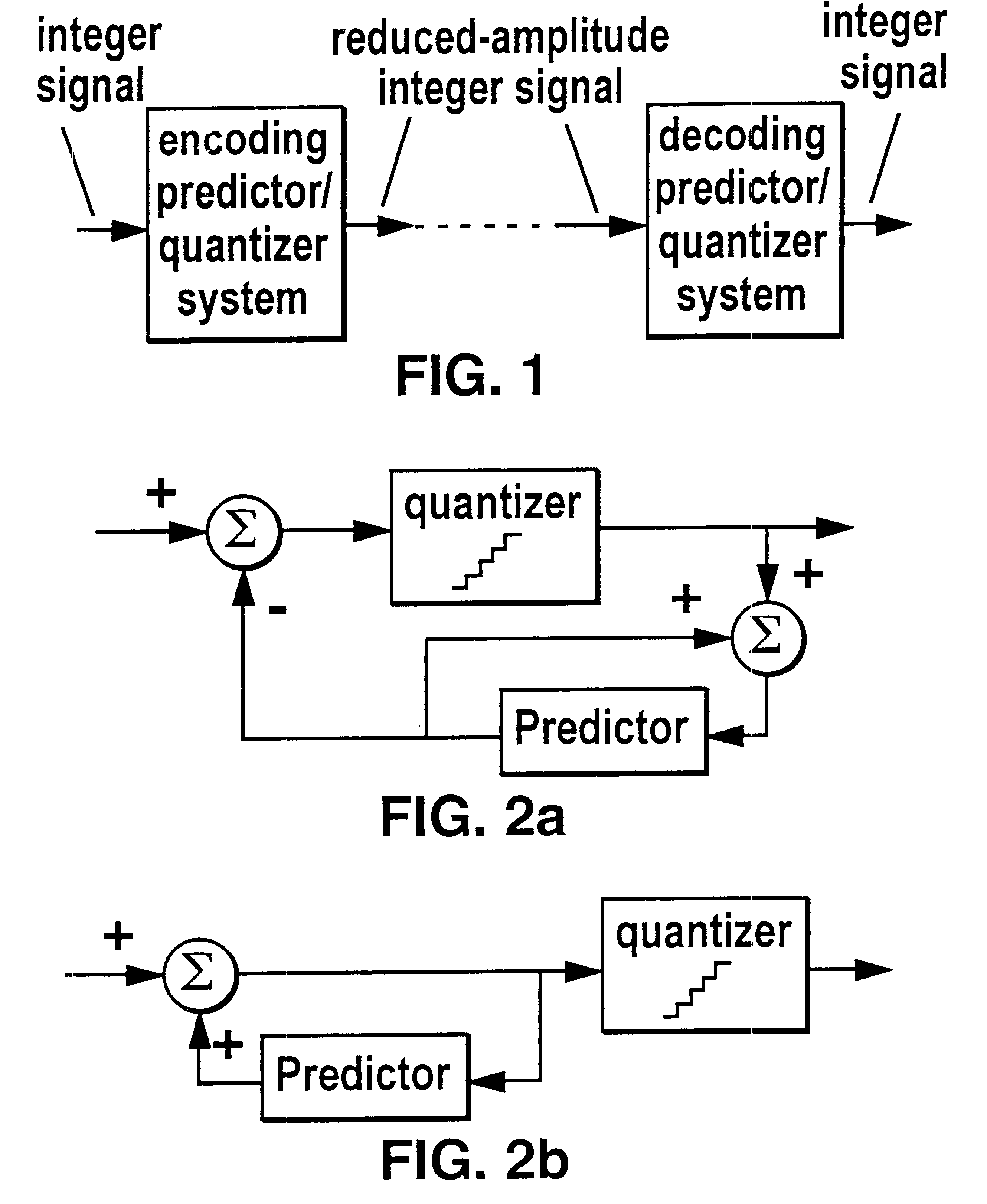
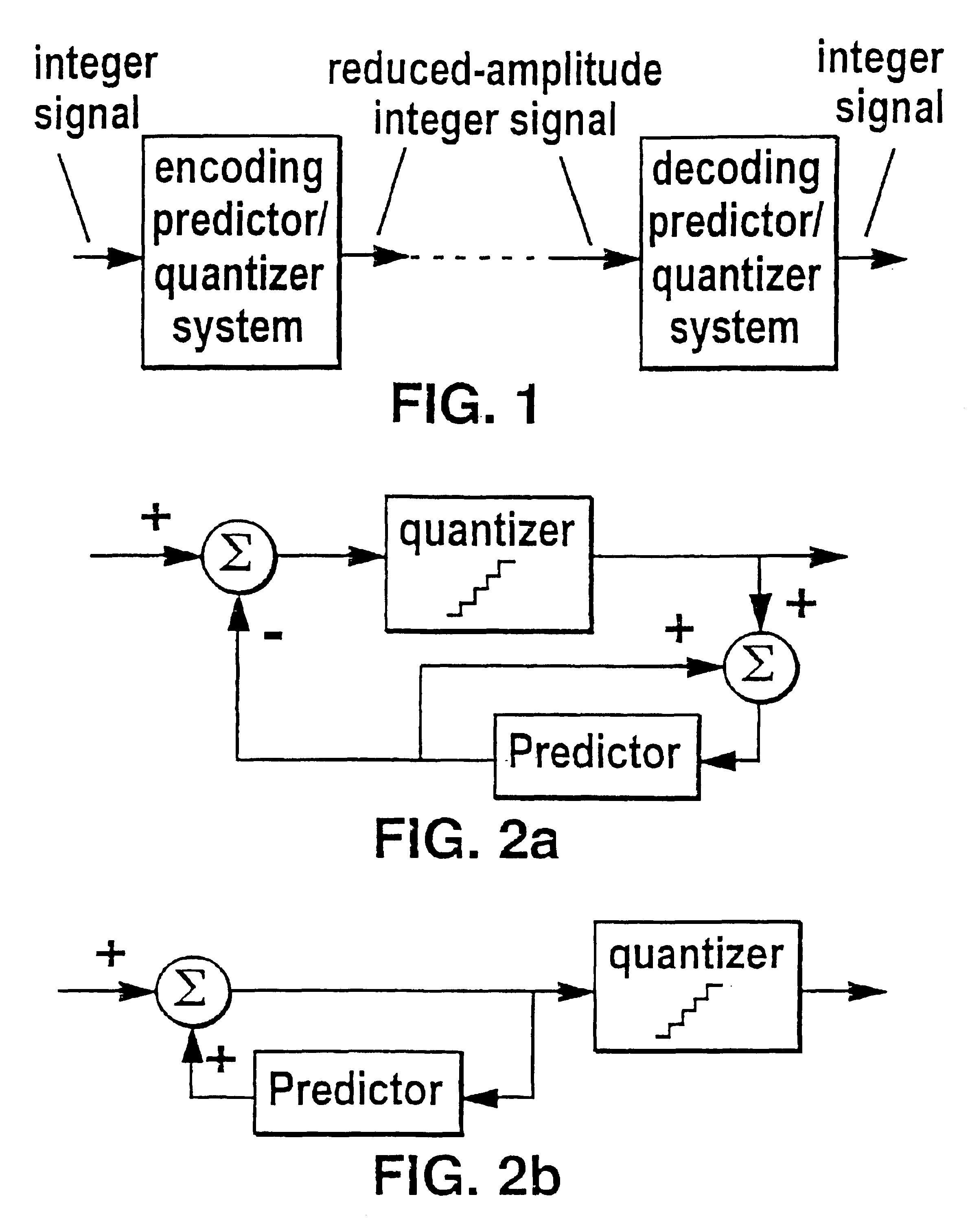
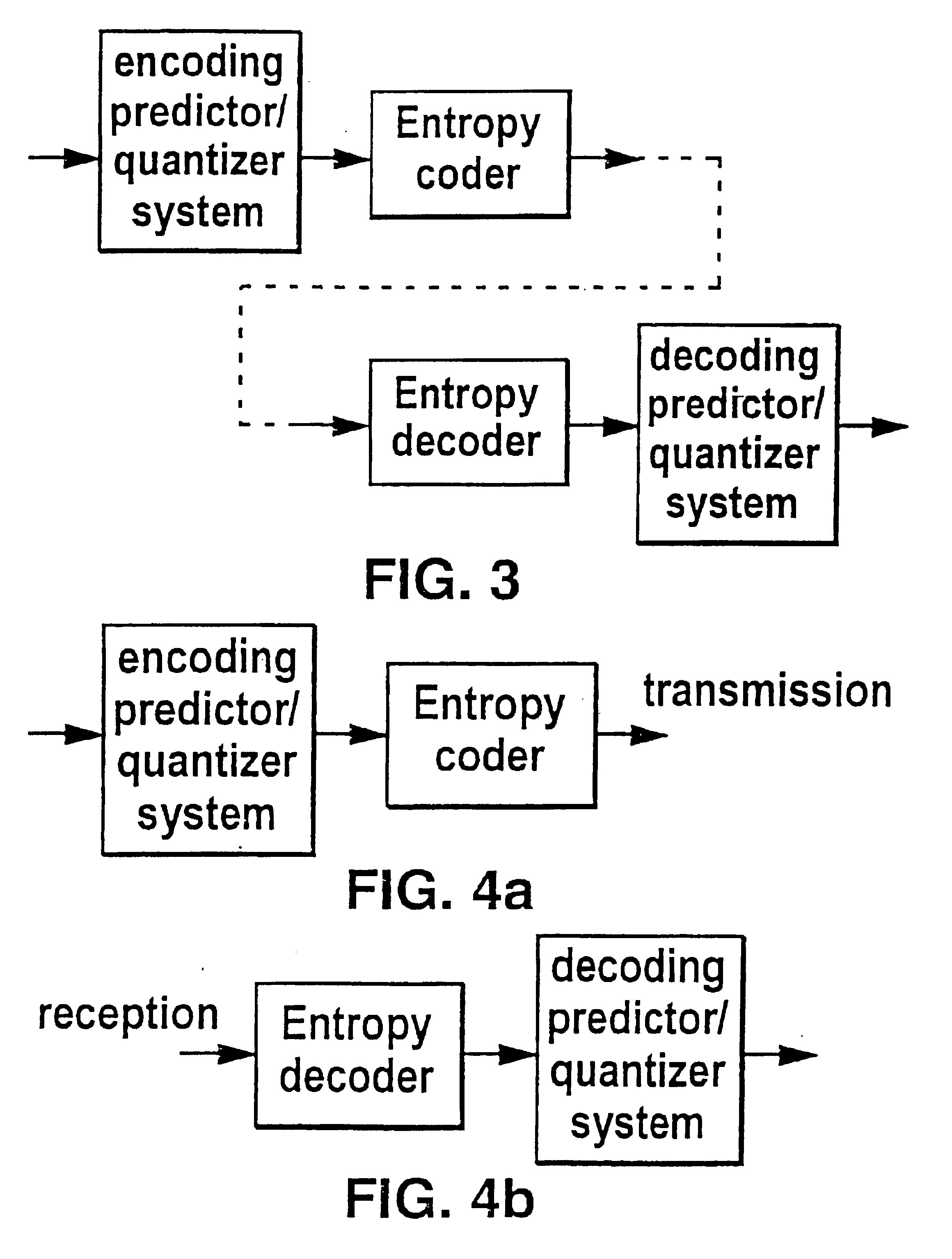
Lossless coding method for waveform data
InactiveUS6664913B1Preserve integrityAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsLossless codingSampling instant
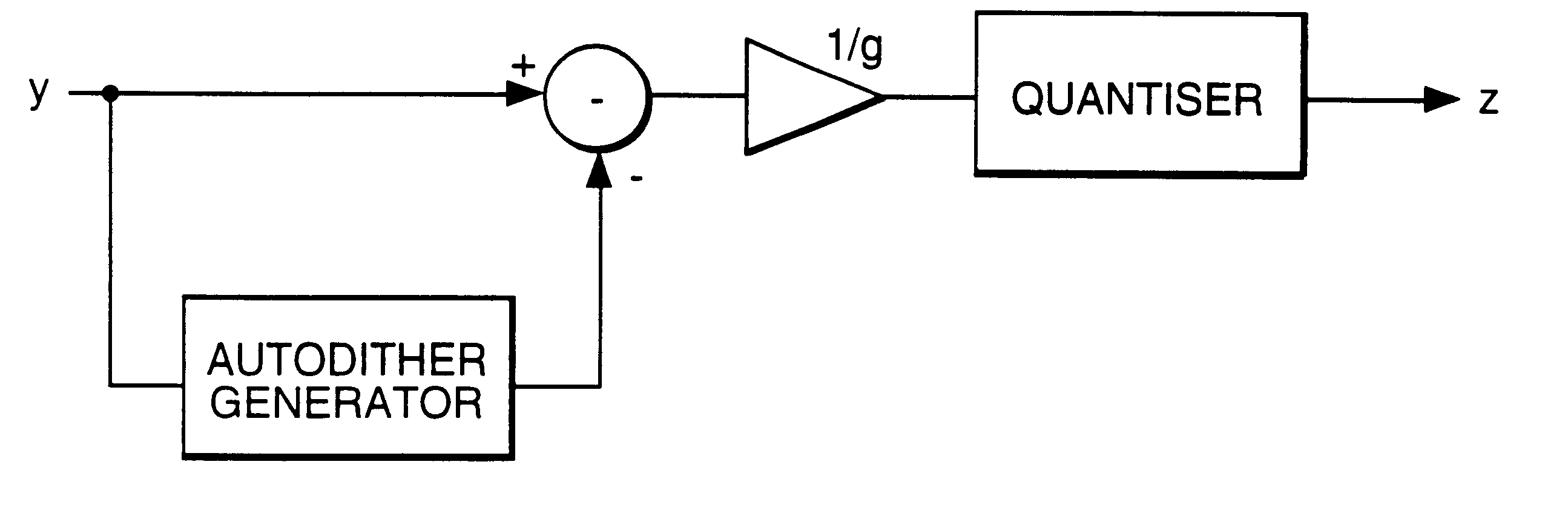
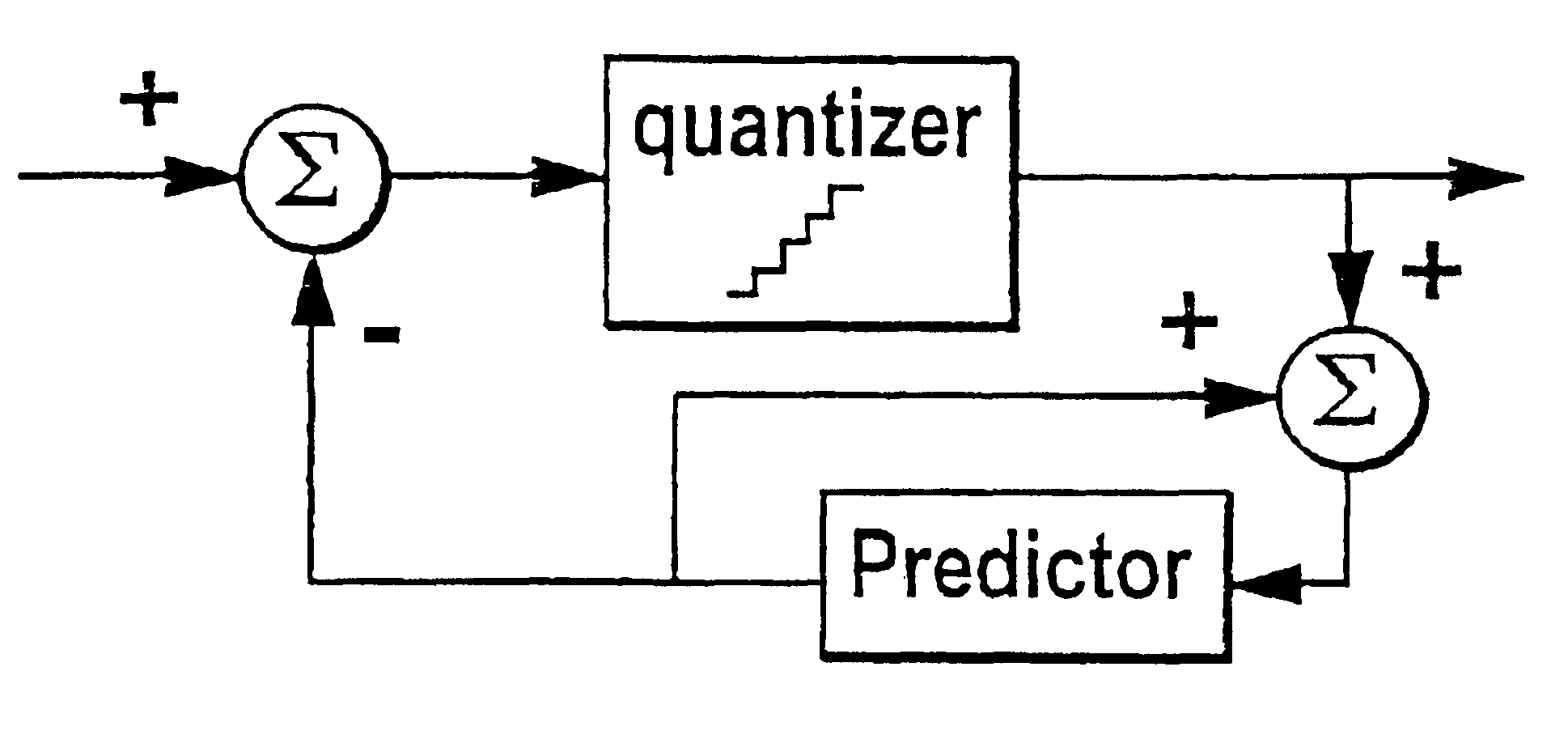
In a method of lossless processing of an integer value signal in a prediction filter which includes a quantiser, a numerator of the prediction filter is implemented prior to the quantiser and a denominator of the prediction filter is implemented recursively around the quantiser to reduce the peak data rate of an output signal. In the lossless processor, at each sample instant, an input to the quantiser is jointly responsive to a first sample value of a signal input to the prediction filter, a second sample value of a signal input to the prediction filter at a previous sample instant, and an output value of the quantiser at a previous sample incident. In a preferred embodiment, the prediction filter includes noise shaping for affecting the output of the quantiser.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
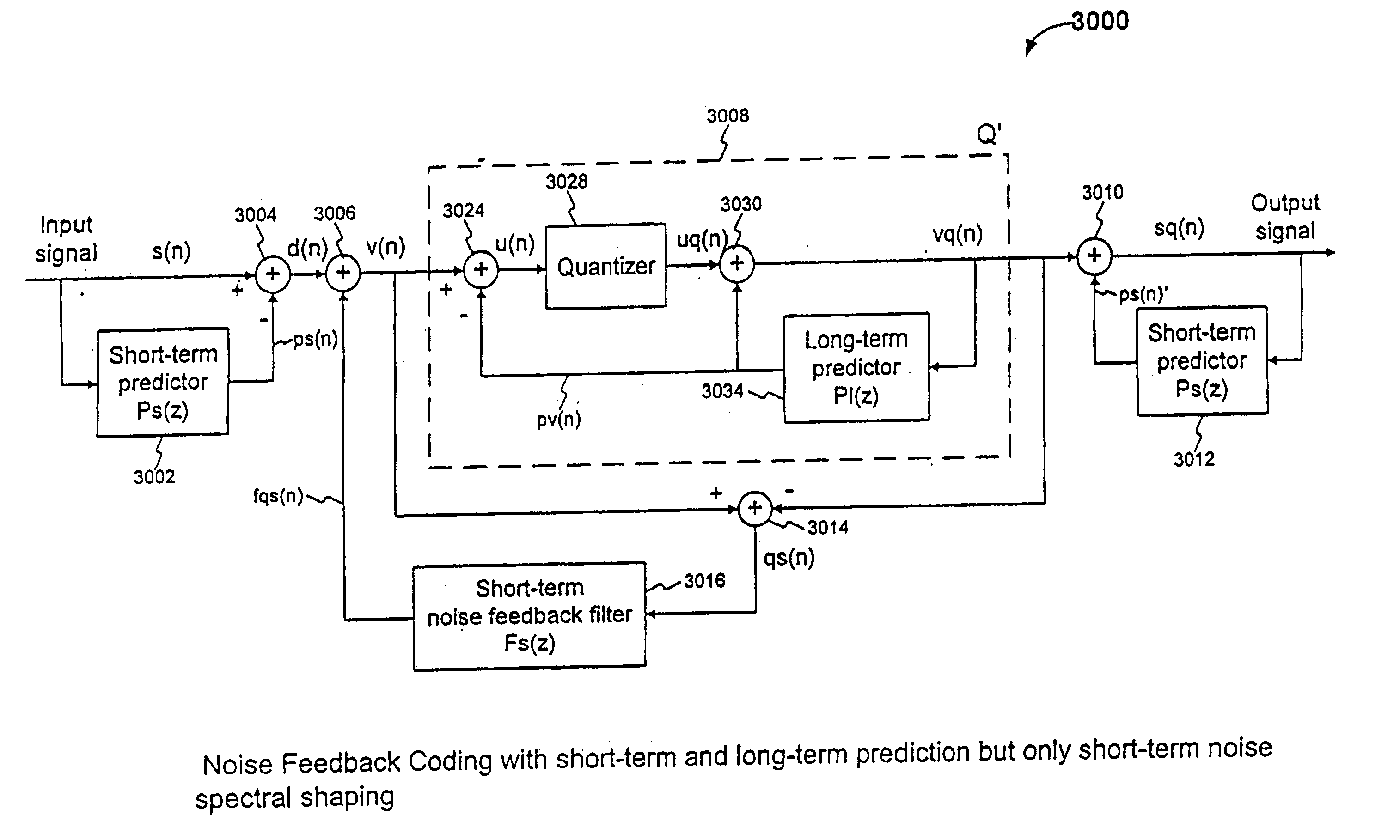
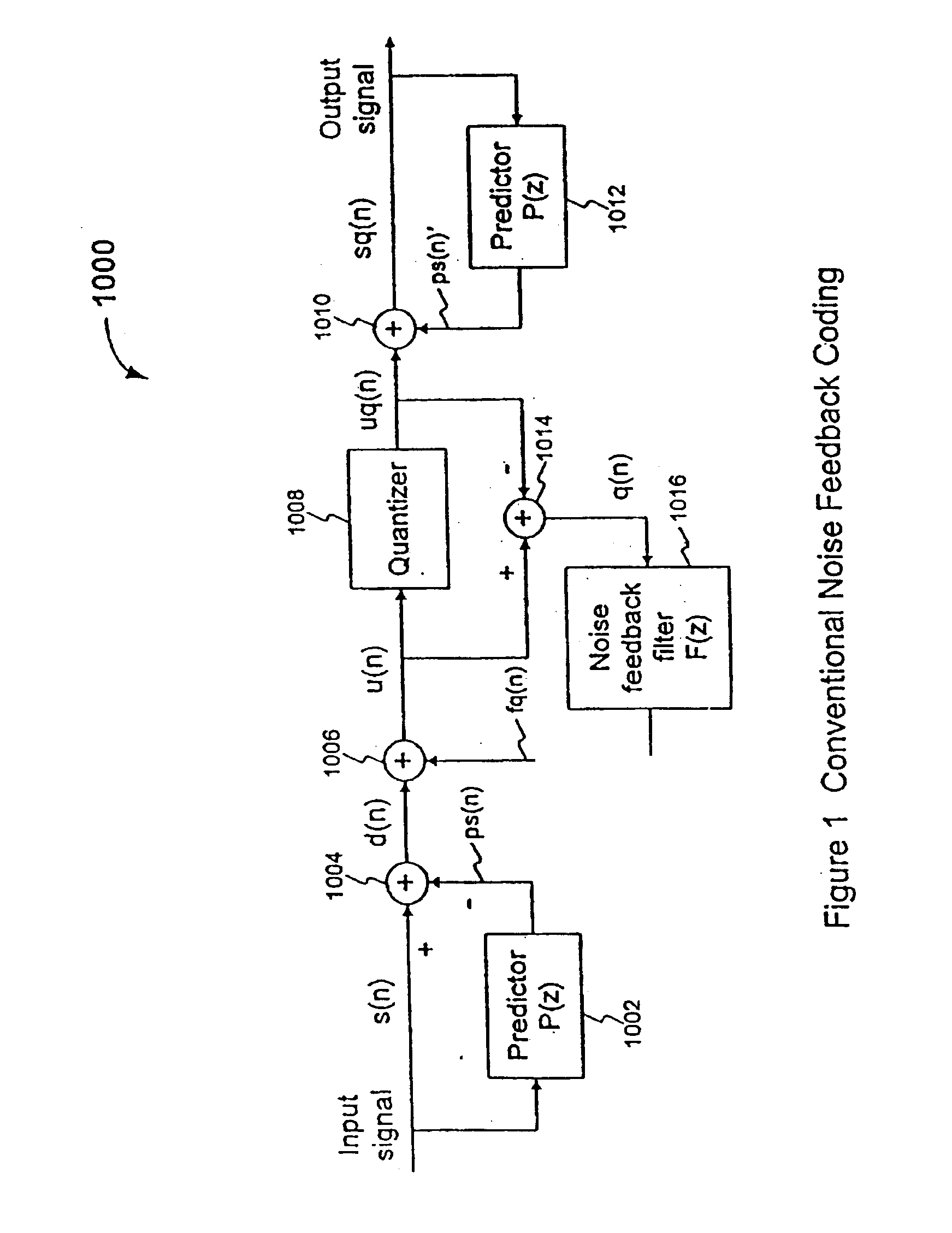
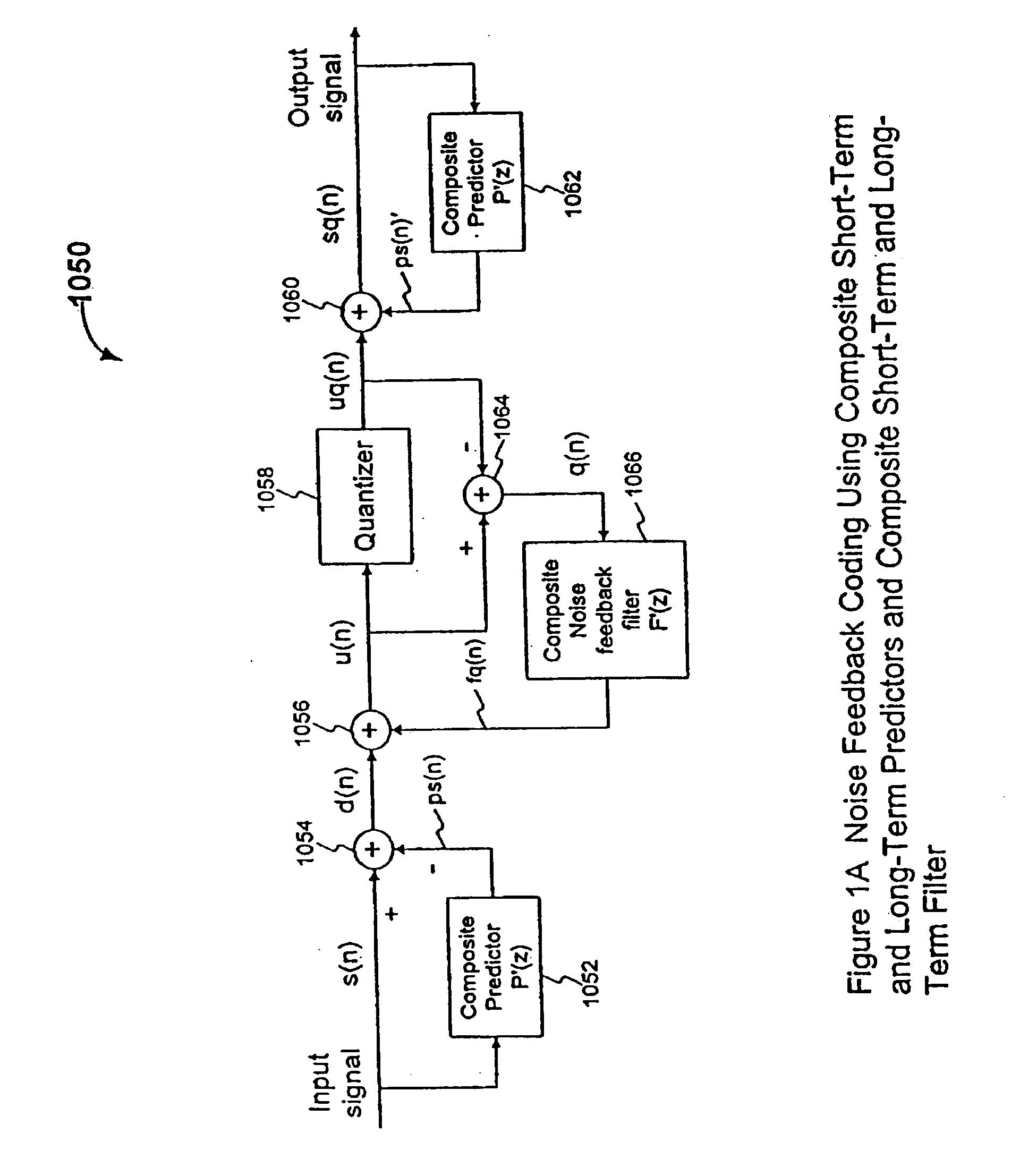
Efficient excitation quantization in noise feedback coding with general noise shaping
InactiveUS6751587B2Speech analysisVacuum gauge using compression chambersNoise shapingComputer science
In a Noise Feedback Coding (NFC) system having a corresponding ZERO-STATE filter structure, the first ZERO-STATE filter structure including multiple filters, a method of producing a ZERO-STATE response error vector. The method includes: (a) transforming the first ZERO-STATE filter structure to a second ZERO-STATE filter structure including only an all-zero filter, the all-zero filter having a filter response substantially equivalent to a filter response of the ZERO-STATE filter structure including multiple filters; and (b) filtering a VQ codevector with the all-zero filter to produce the ZERO-STATE response error vector corresponding to the VQ codevector.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
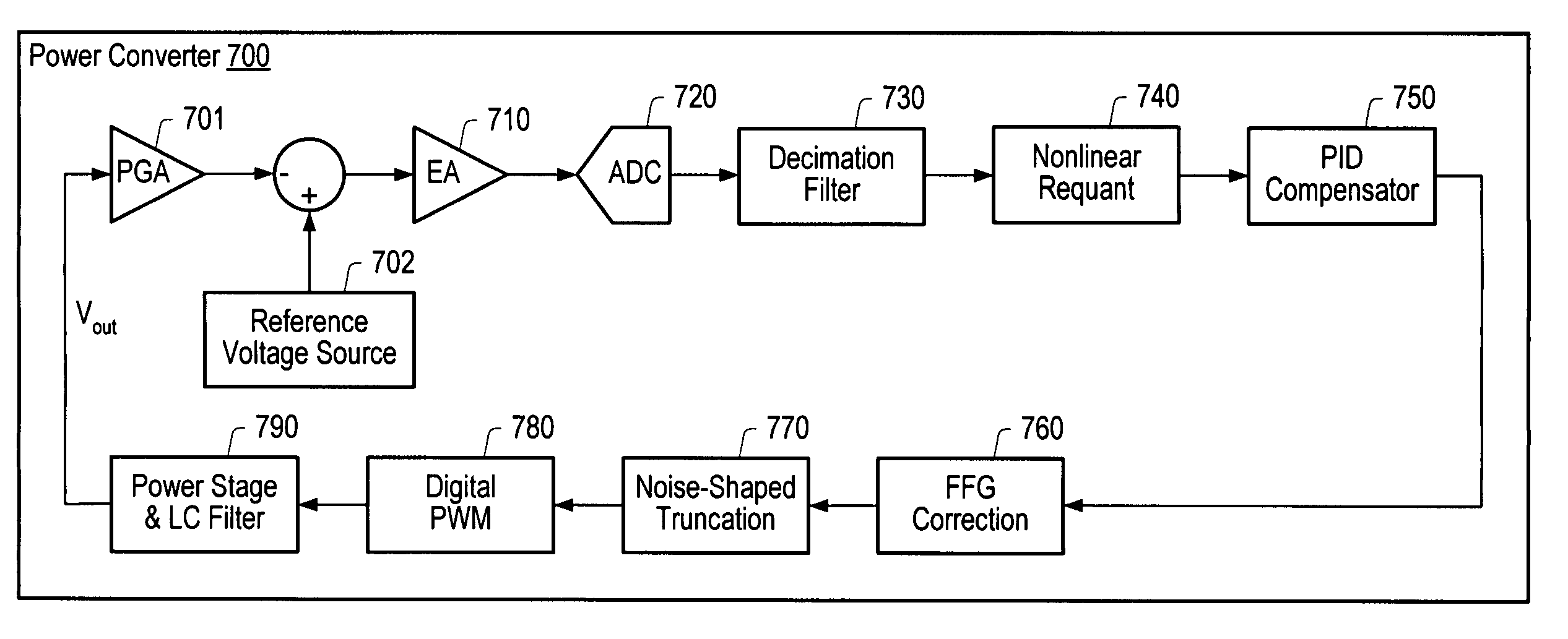
Hardware efficient digital control loop architecture for a power converter
ActiveUS7239257B1Reduce in quantityElectric signal transmission systemsConversion with intermediate conversion to dcImage resolutionNoise shaping
A power converter including a hardware efficient control loop architecture. Error detection circuitry may generate an error signal based on the difference between a power converter output voltage and a reference voltage. An oversampling ADC may digitize the error signal. The transfer function associated with the ADC may include quantization levels spaced at non-uniform intervals away from a center code. A digital filter may calculate the average of the digitized error signal. A nonlinear requantizer may reduce the number of codes corresponding to the output of the digital filter. A proportional integral derivative (PID) unit may multiply the output of the nonlinear requantizer by PID coefficients to generate a PID duty cycle command, and a gain compensation unit may dynamically adjust the PID coefficients to maintain a constant control loop gain. A noise-shaped truncation unit including a multi-level error-feedback delta sigma modulator may reduce the resolution of the PID duty cycle command.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Method for reducing DAC resolution in multi-bit sigma delta analog-to digital converter (ADC)
A method for reducing the resolution of a digital-to-analog converter in a multi-bit sigma-delta ADC is described. With the addition of digital sigma-delta modulators in the feedback path of a sigma-delta ADC, the truncation errors between the digital word output of the multi-bit sigma-delta ADC to the DAC input can be shaped to higher order than that of the quantization error. Thus, the DAC resolution can be reduced and the implementation of DEM for multi-bit DAC can be avoided. A preferred embodiment comprises selecting an outermost feedback loop in a sigma-delta ADC that has not been replaced and replacing it with a circuit with an equivalent transfer function. The circuit can be further enhanced with an additional term if the order of the noise shaping of the circuit is less than the order of the noise shaping of the sigma-delta ADC.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Jointly nonlinear delta sigma modulators
A signal processing system includes a jointly non-linear delta sigma modulator. In one embodiment, the jointly non-linear delta sigma modulator includes a non-linear quantization transfer function, and the output of the delta sigma modulator is defined, at least in part, by a non-linear interrelationship of multiple noise-shaping filter state variables. A look-ahead delta-sigma modulator can be implemented as a noise shaping filter and a function generator. State variables of the noise shaping filter provide the input data from which the function generator determines a quantizer output signal. Latter state variables are more dominant in determining the quantizer output signal. Accordingly, earlier state variables can be approximated to a greater degree than latter state variables without significant compromise in quantization accuracy.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
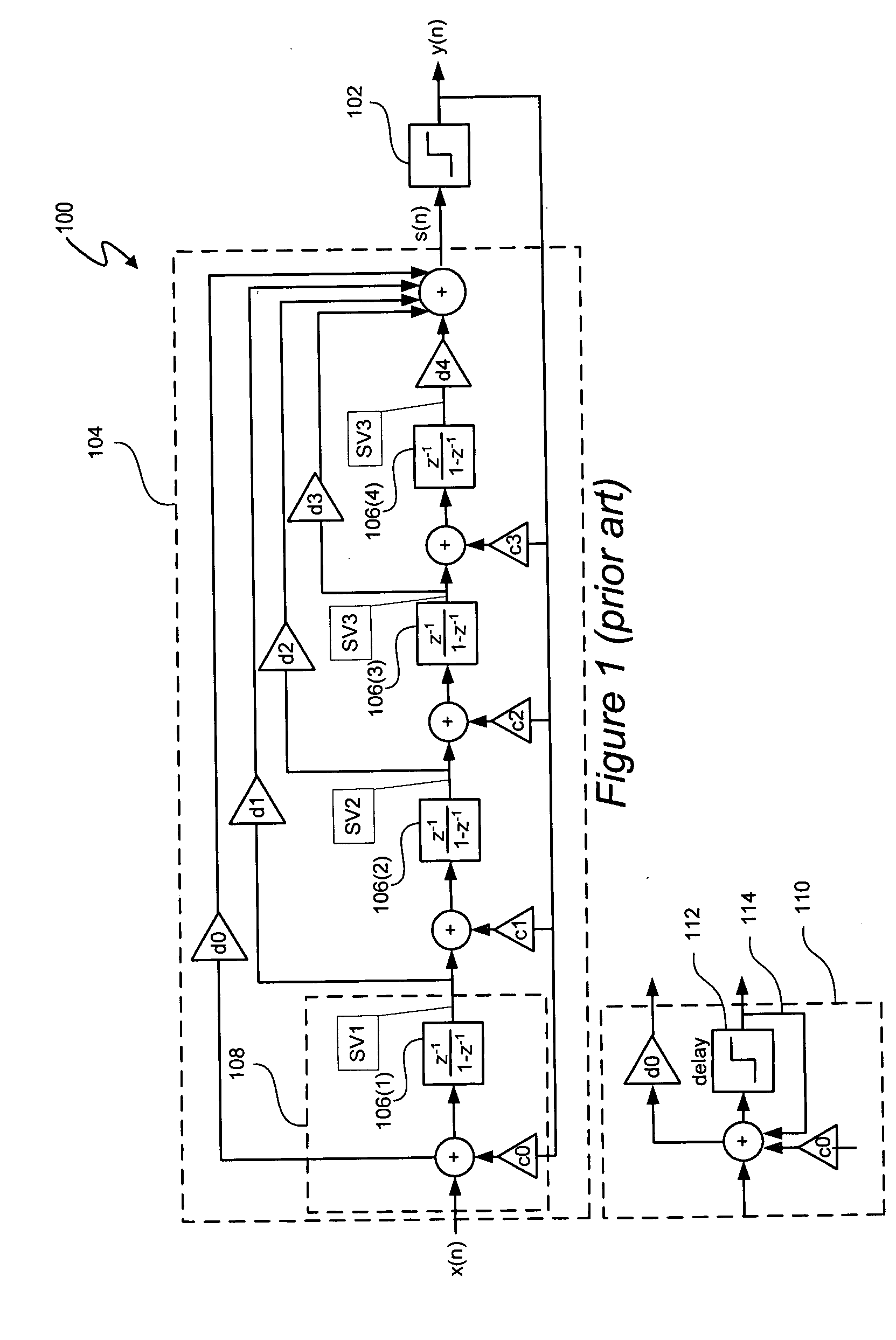
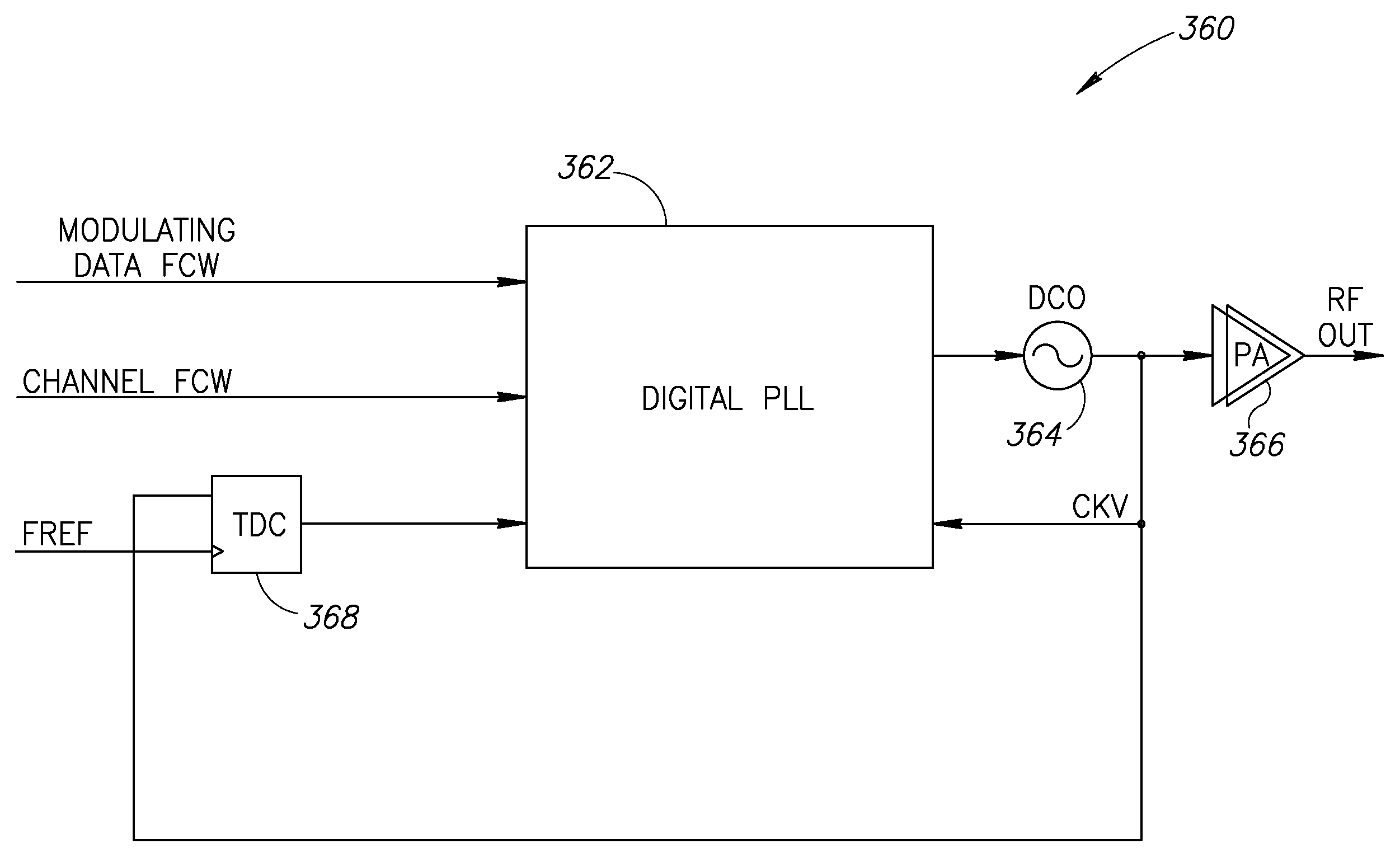
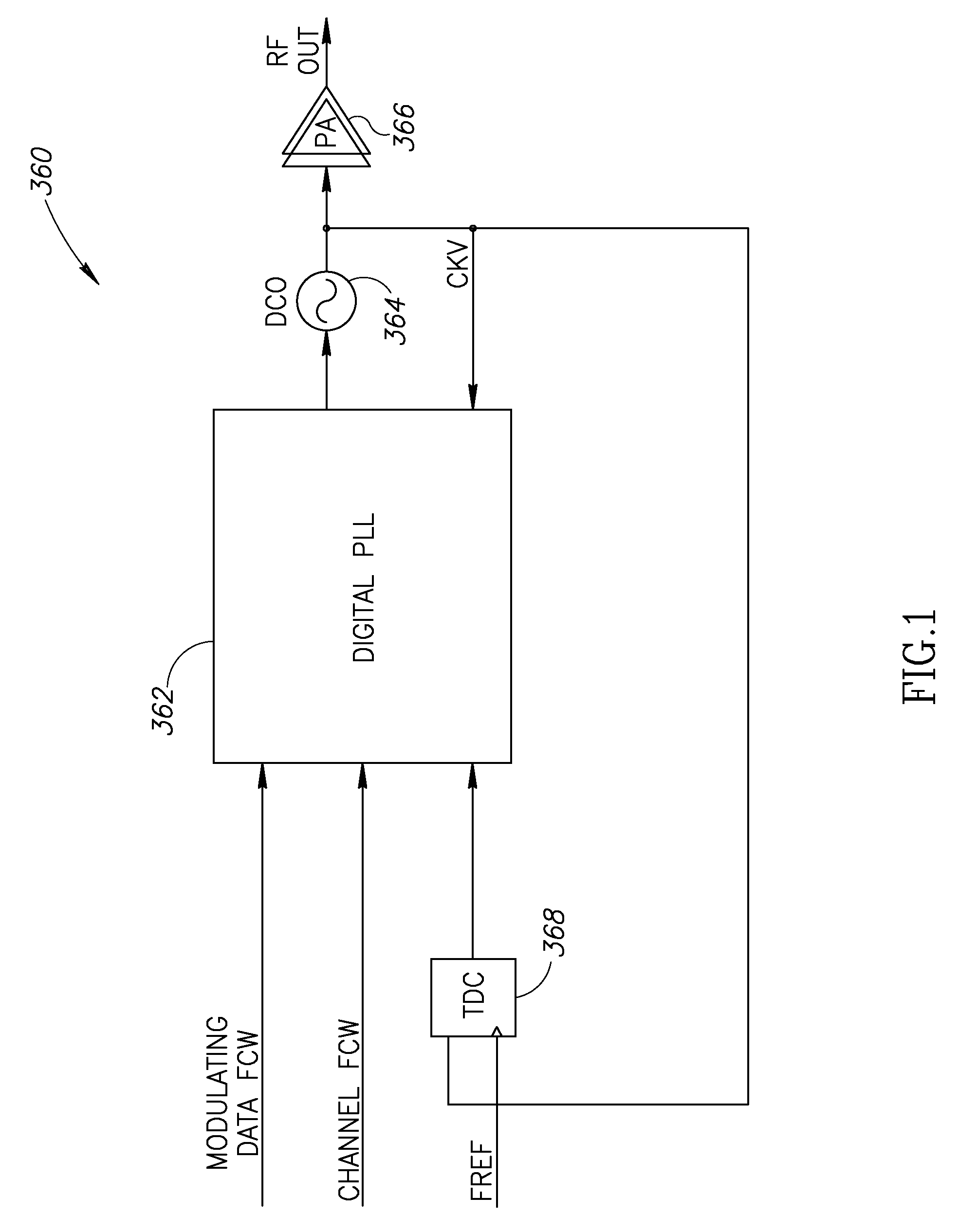
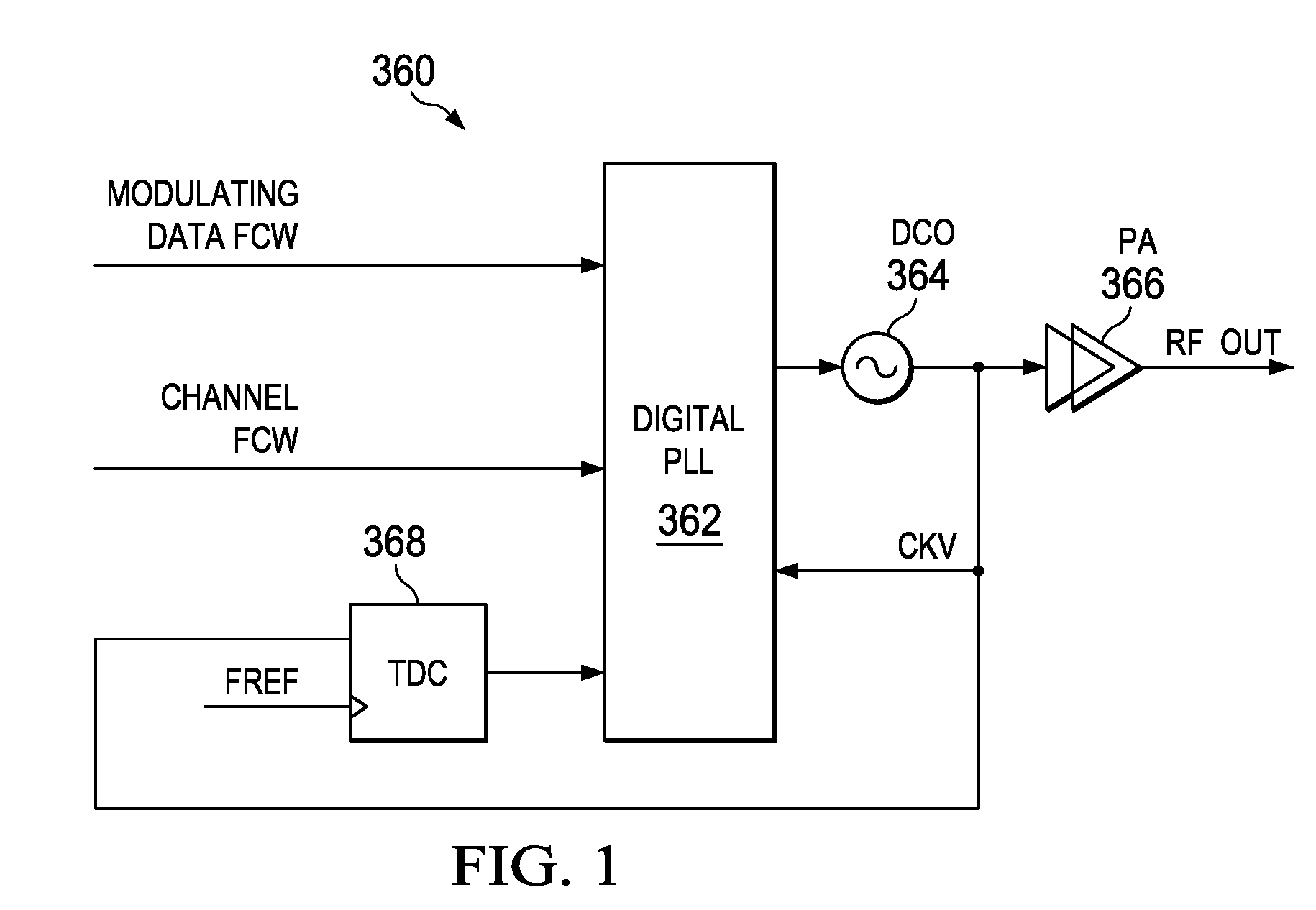
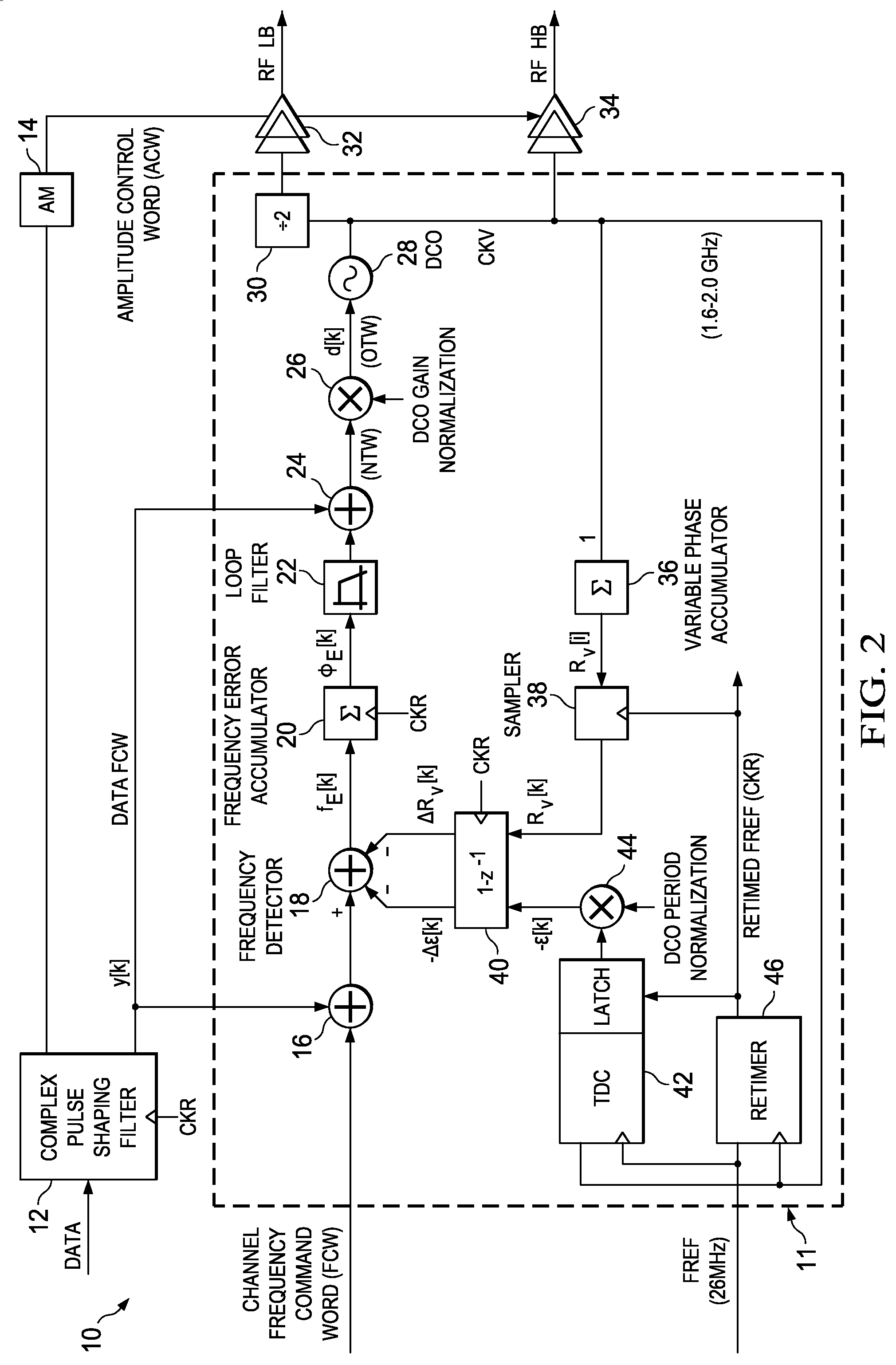
Adaptive spectral noise shaping to improve time to digital converter quantization resolution using dithering
ActiveUS20080068236A1High resolutionHigh frequency noiseElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionFrequency spectrumNoise shaping
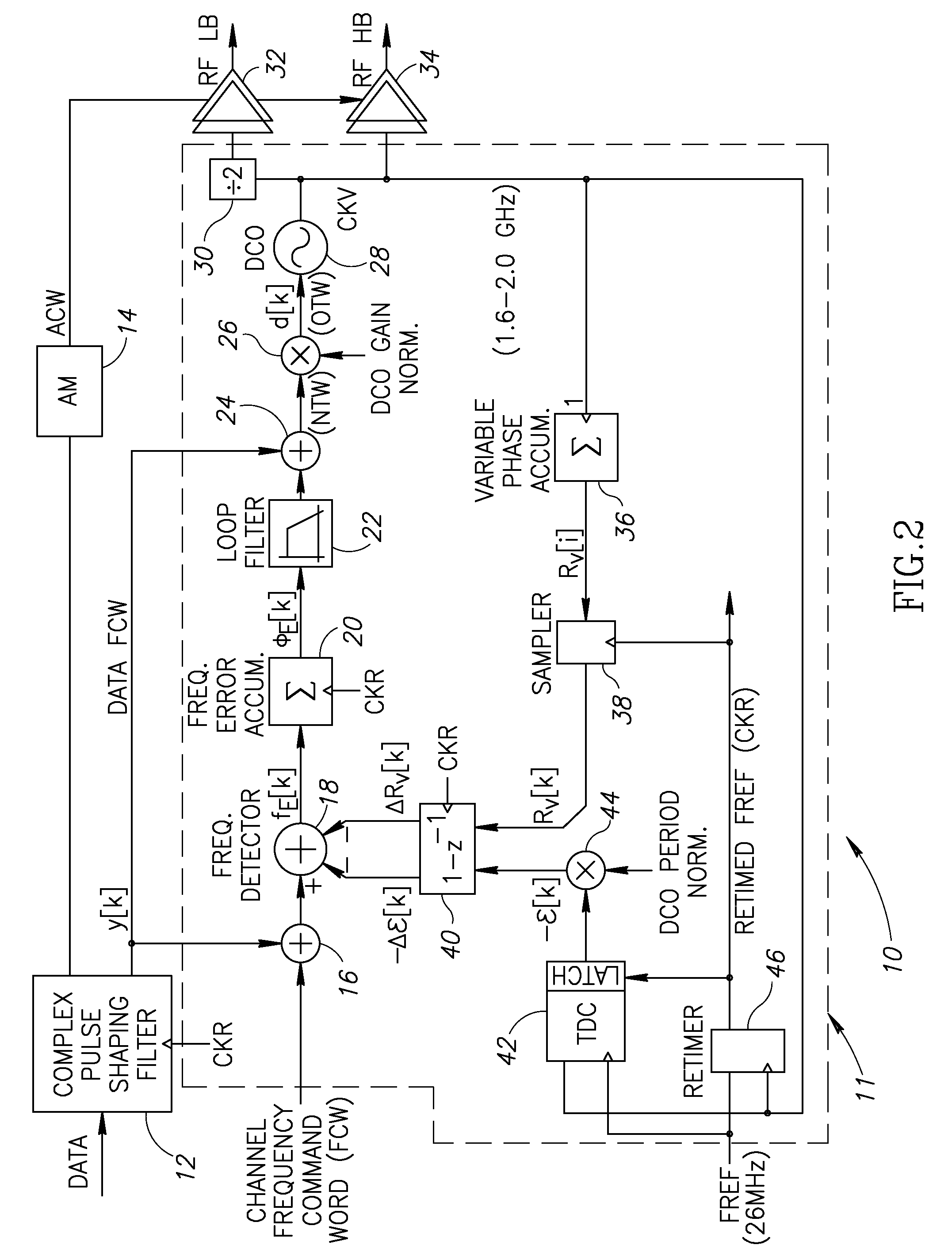
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of improving the quantization resolution of a time to digital converter in a digital PLL using noise shaping. The TDC quantization noise shaping scheme is effective to reduce the TDC quantization noise to acceptable levels especially in the case of integer-N channel operation. The mechanism monitors the output of the TDC circuit and adaptively generates a dither (i.e. delay) sequence based on the output. The dither sequence is applied to the frequency reference clock used in the TDC which adjusts the timing alignment between the edges of the frequency reference clock and the RF oscillator clock. The dynamic alignment changes effectively shape the quantization noise of the TDC. By shaping the quantization noise, a much finer in-band TDC resolution is achieved resulting in the quantization noise being pushed out to high frequencies where the PLL low pass characteristic effectively filters it out.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
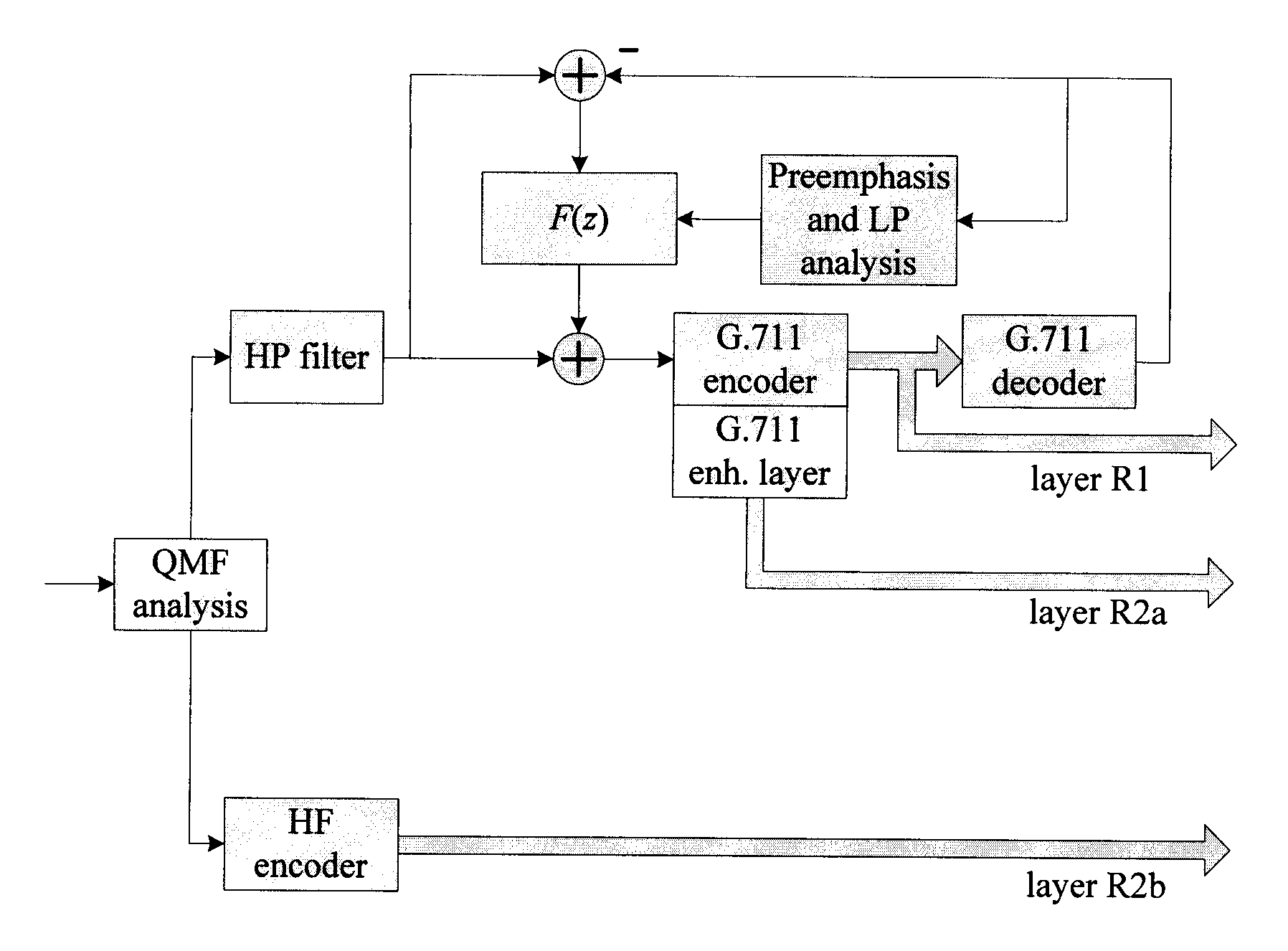
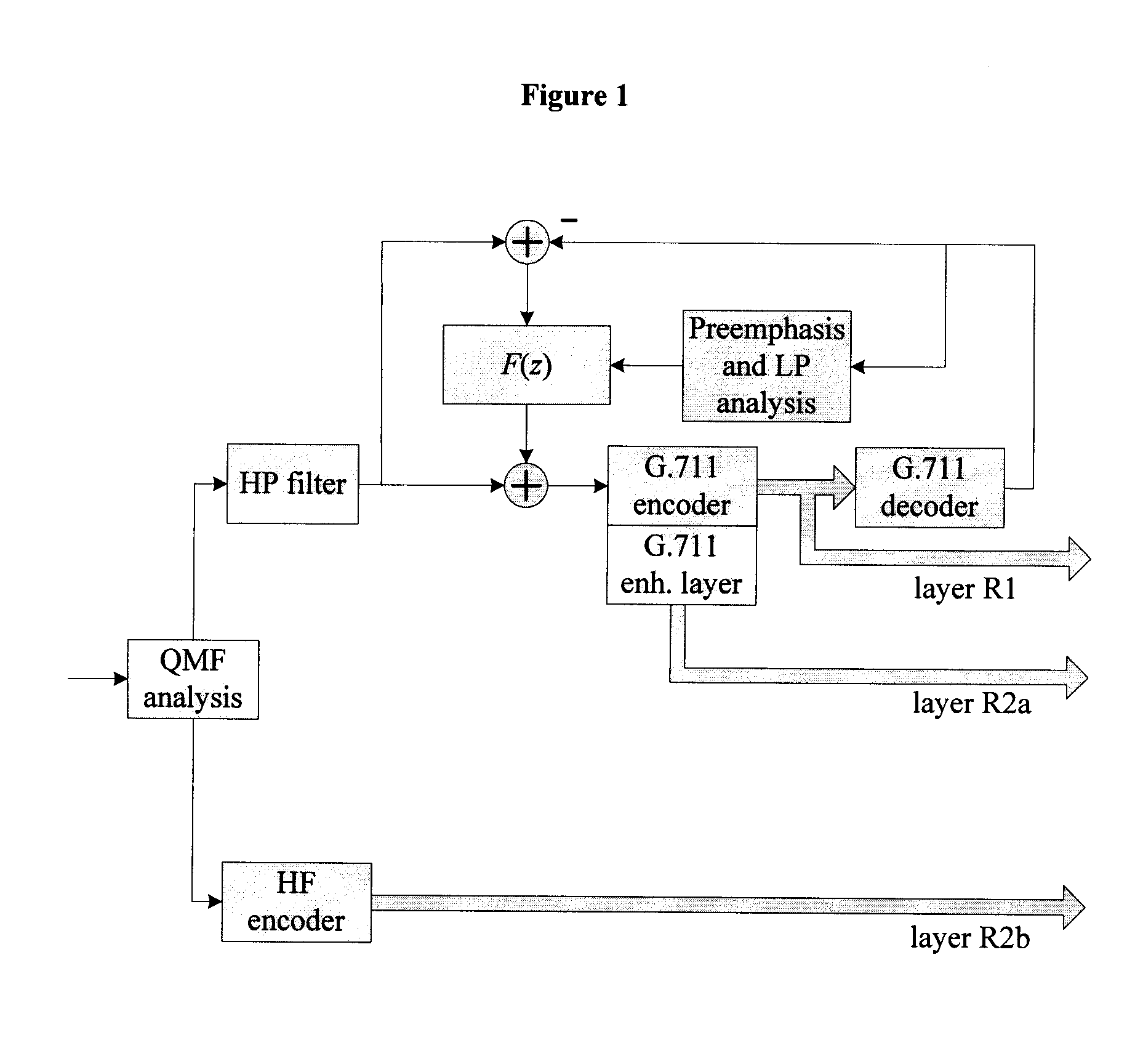
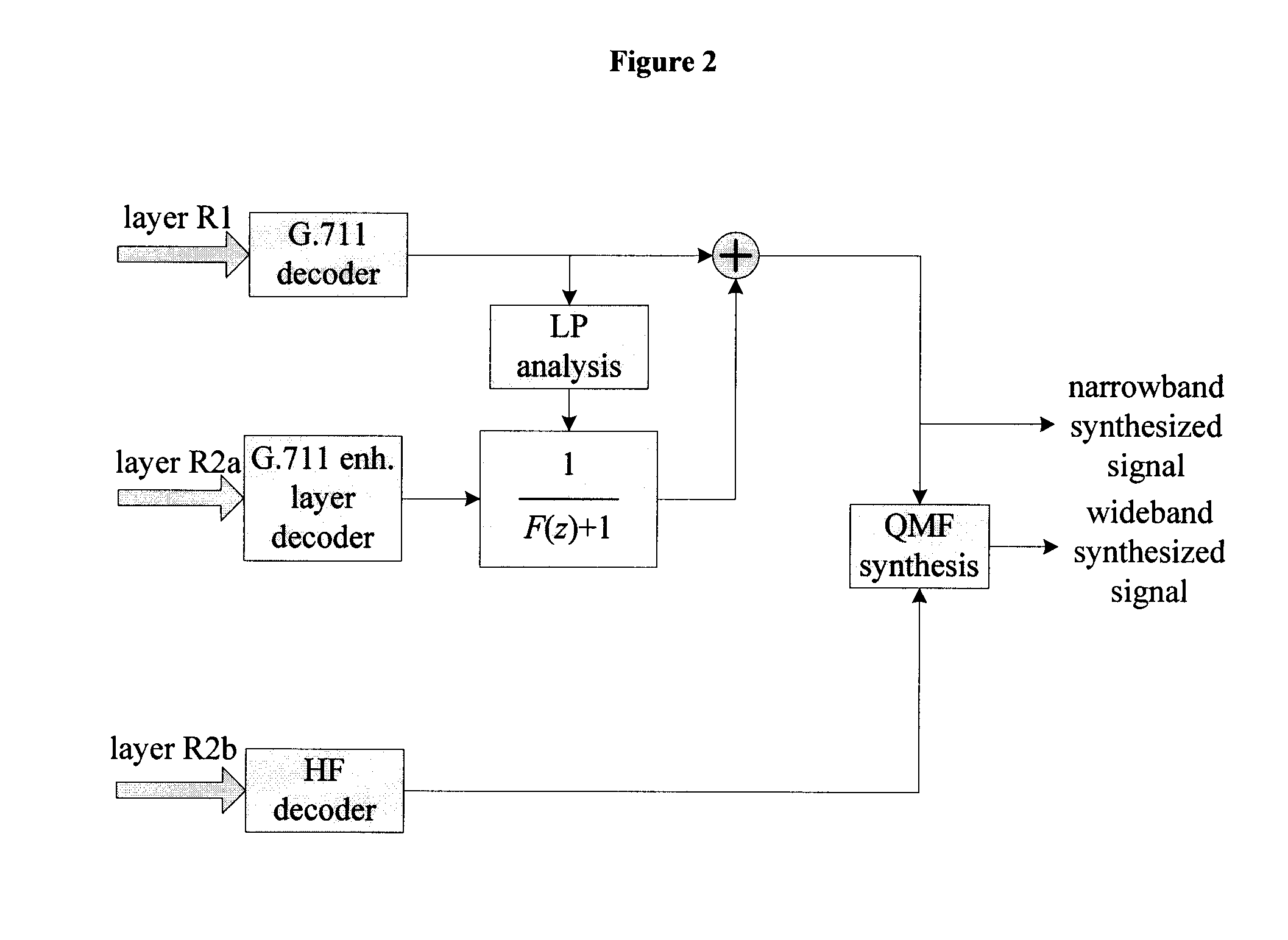
Device and Method for Noise Shaping in a Multilayer Embedded Codec Interoperable with the ITU-T G.711 Standard
A device and method for shaping noise during encoding of an input sound signal comprise pre-emphasizing the input signal or a decoded signal from a given sound signal codec to produce a pre-emphasized signal, computing a filter transfer function based on the pre-emphasized signal, and shaping the noise by filtering the noise through the transfer function to produce a shaped noise signal, wherein the noise shaping comprises producing a noise feedback. A device and method for noise shaping in a multilayer codec, including at least Layer 1 and 2, comprise: at an encoder, producing an encoded sound signal in Layer 1 including Layer 1 noise shaping, and producing a Layer 2 enhancement signal; at a decoder, decoding the Layer 1 encoded sound signal to produce a synthesis signal, decoding the enhancement signal, computing a filter transfer function based on the synthesis signal, filtering the enhancement signal through the transfer function to produce a Layer 2 filtered enhancement signal, and adding the filtered enhancement signal to the synthesis signal to produce an output signal including contributions from Layer 1 and 2.
Owner:VOICEAGE CORP
Sigma Delta Over-Sampling Charge Pump Analog-To-Digital Converter
ActiveUS20140085985A1Eliminate low frequency noiseRead-only memoriesApparatus without intermediate ac conversionImage resolutionNoise shaping
Techniques are presented for determining current levels based on the behavior of a charge pump system while driving a load under regulation. While driving the load under regulation, the number of pump clocks during a set interval is counted. This can be compared to a reference that can be obtained, for example, from the numbers of cycles needed to drive a known load current over an interval of the duration. By comparing the counts, the amount of current being drawn by the load can be determined. This technique can be applied to determining leakage from circuit elements, such as word lines in a non-volatile memory. The accuracy and level of resolution can be further increased through use of sigma delta noise shaping.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
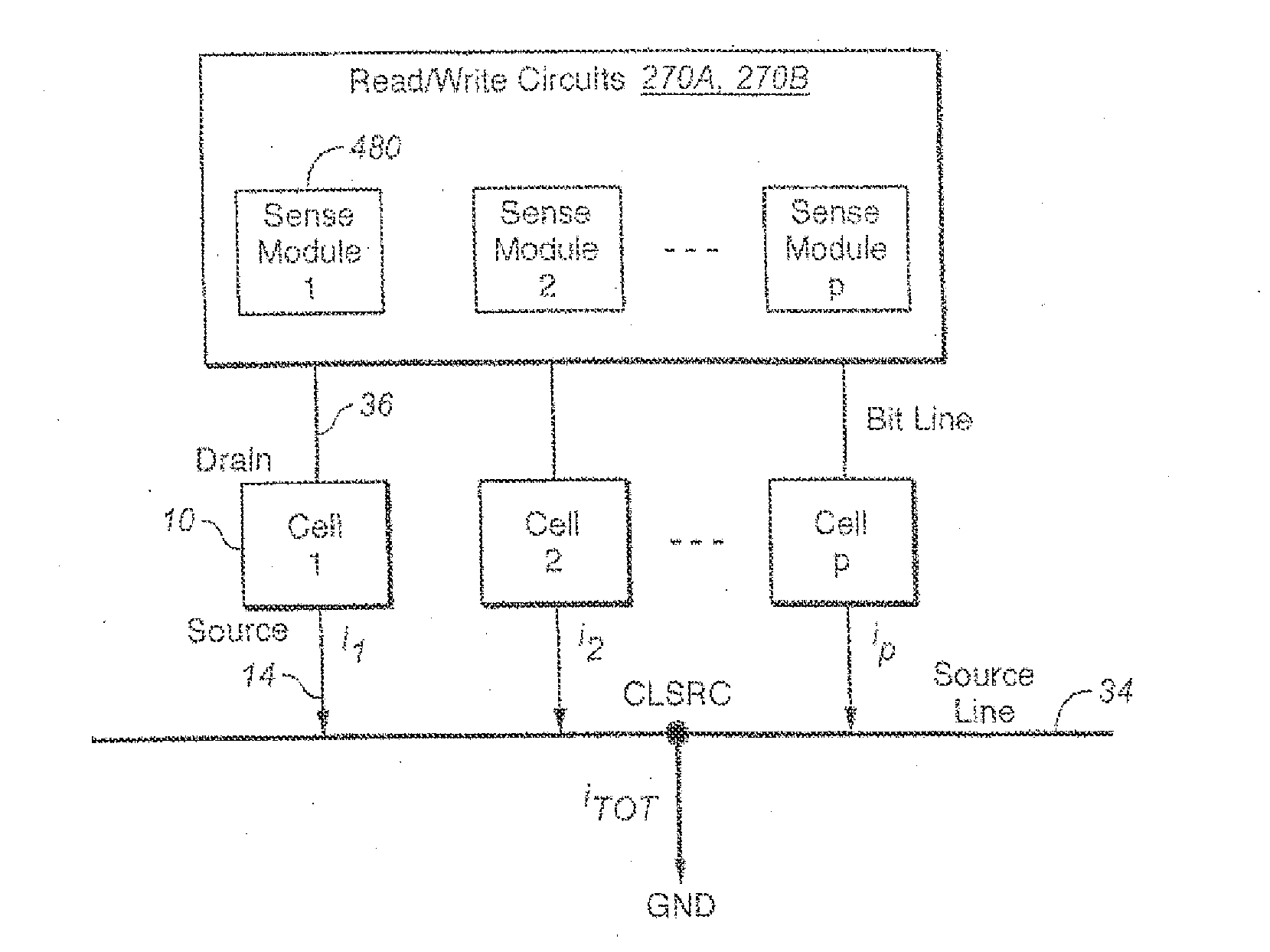
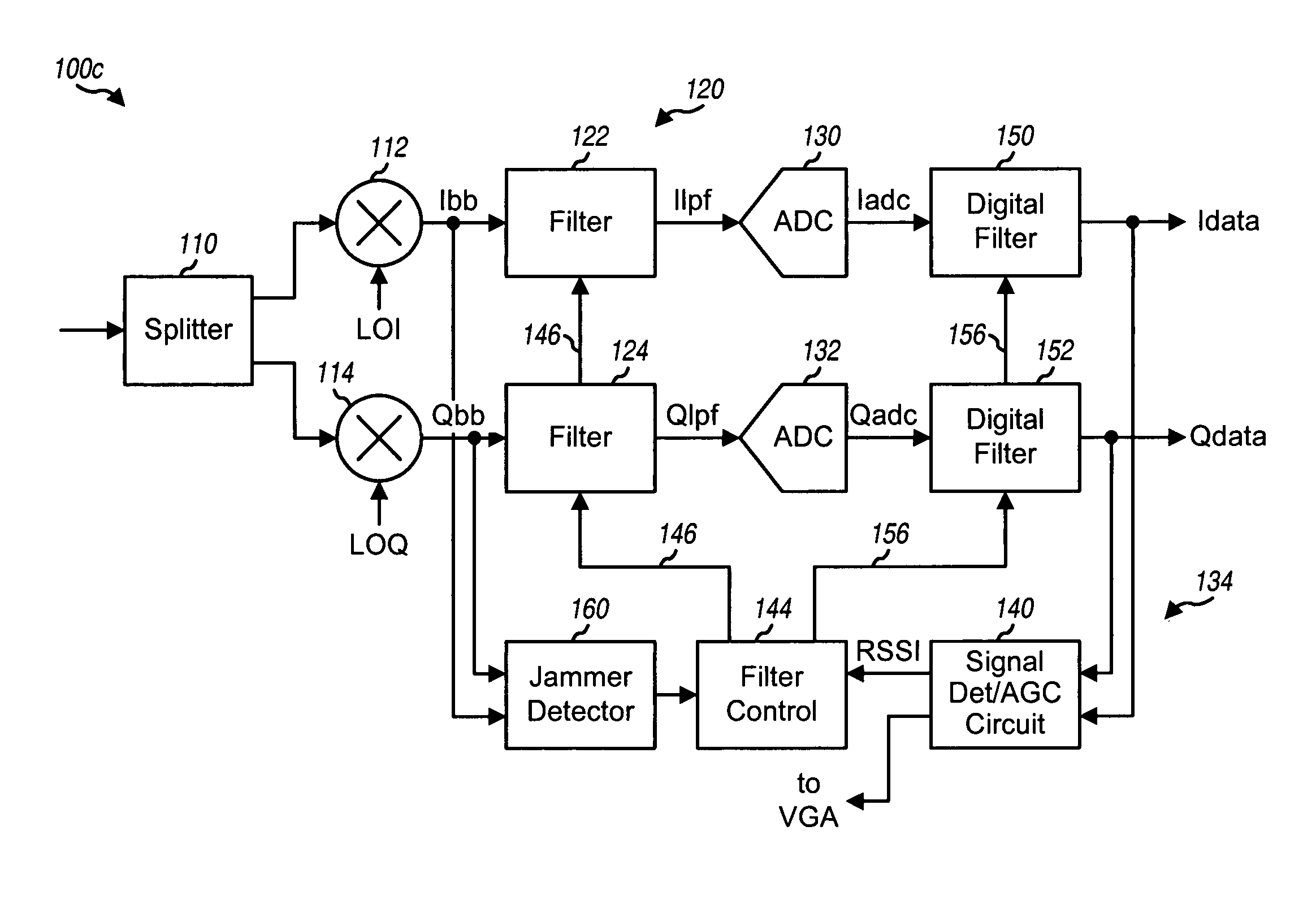
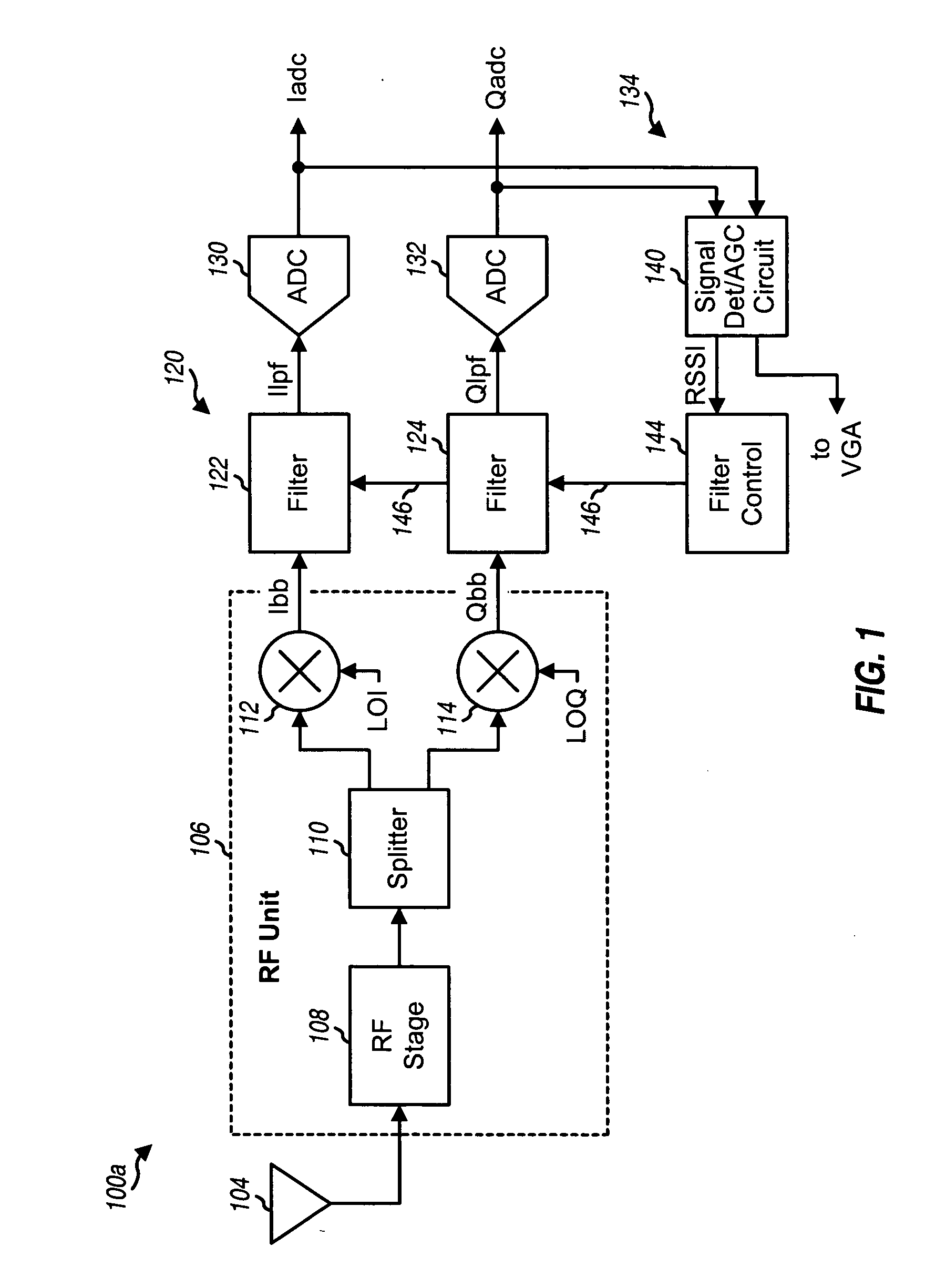
Noise reduction filtering in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20060109939A1Avoid performanceLower performance requirementsError preventionDigital technique networkControl signalNoise shaping
A technique for noise reduction in a wireless communication system uses controllable bandwidth filters (120) to filter a received signal. In a typical implementation, the filters (120) are used at baseband frequencies. A measurement (RSSI) is indicative of the strength of the received signal. A control circuit (144) generates a control signal (146) to control the bandwidth of the filters (120). If the received signal strength is above a first threshold, a wider bandwidth may be used for the filters (120). If the received signal is below a second threshold, the control circuit (144) generates the control signal (146) to set the filters (120) to a more narrow bandwidth. The system (100) may also be used with digital filters (150, 152) following digitization by analog to digital converters (ADCs) (130, 132). The system (100) is particularly well-suited for operation with noise-shaped ADCs (130, 132), such as Delta-Sigma converters.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
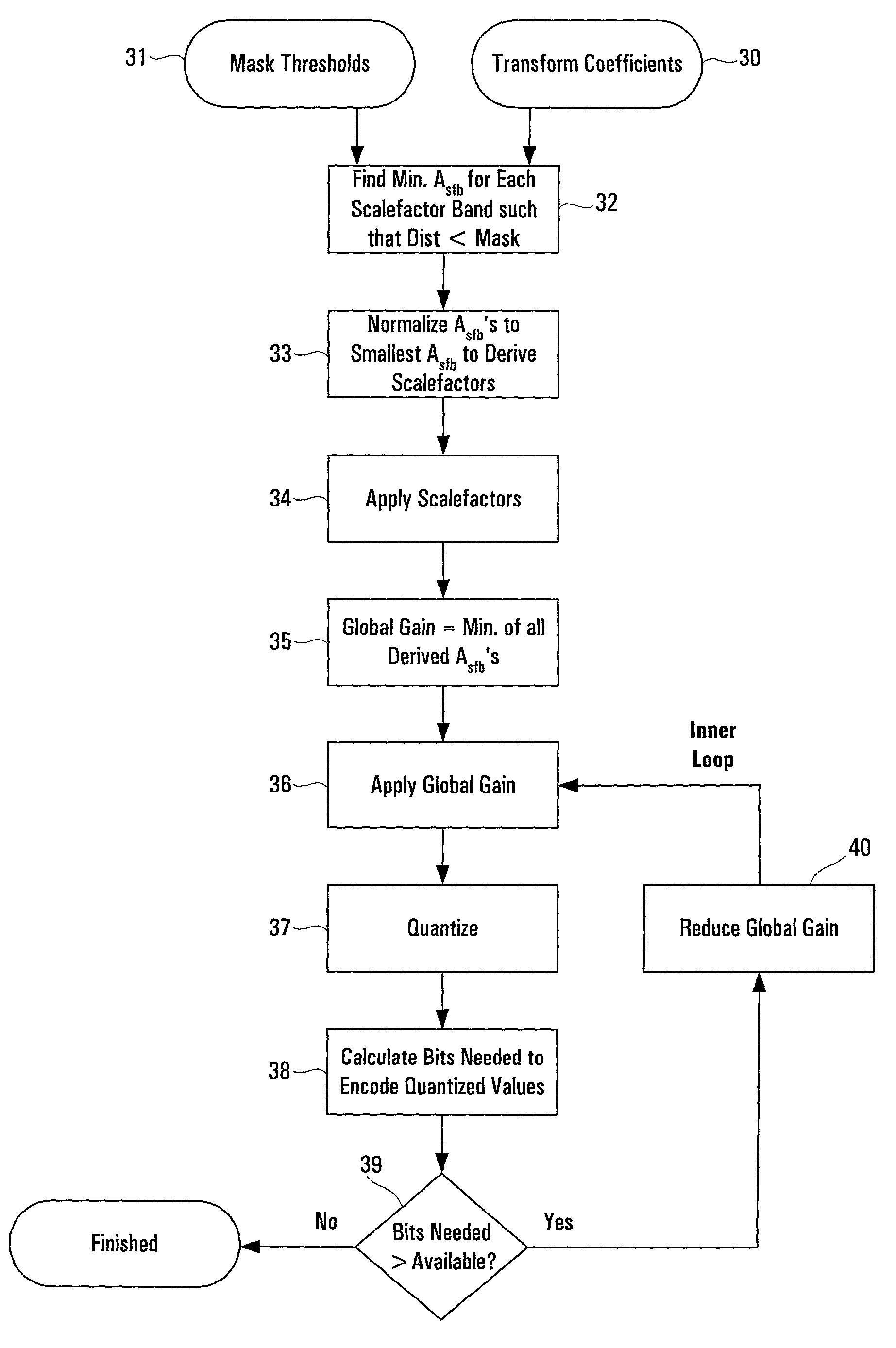
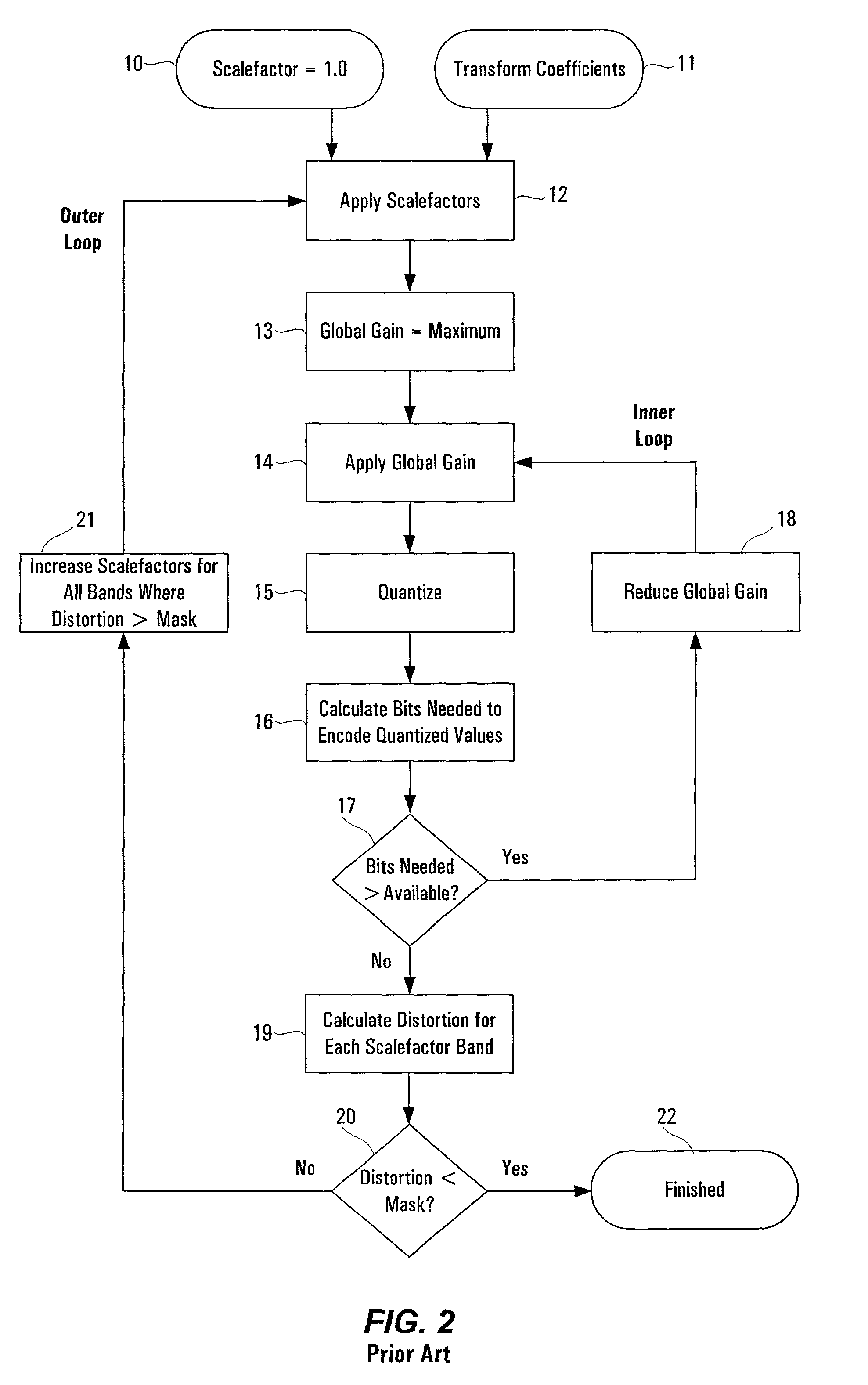
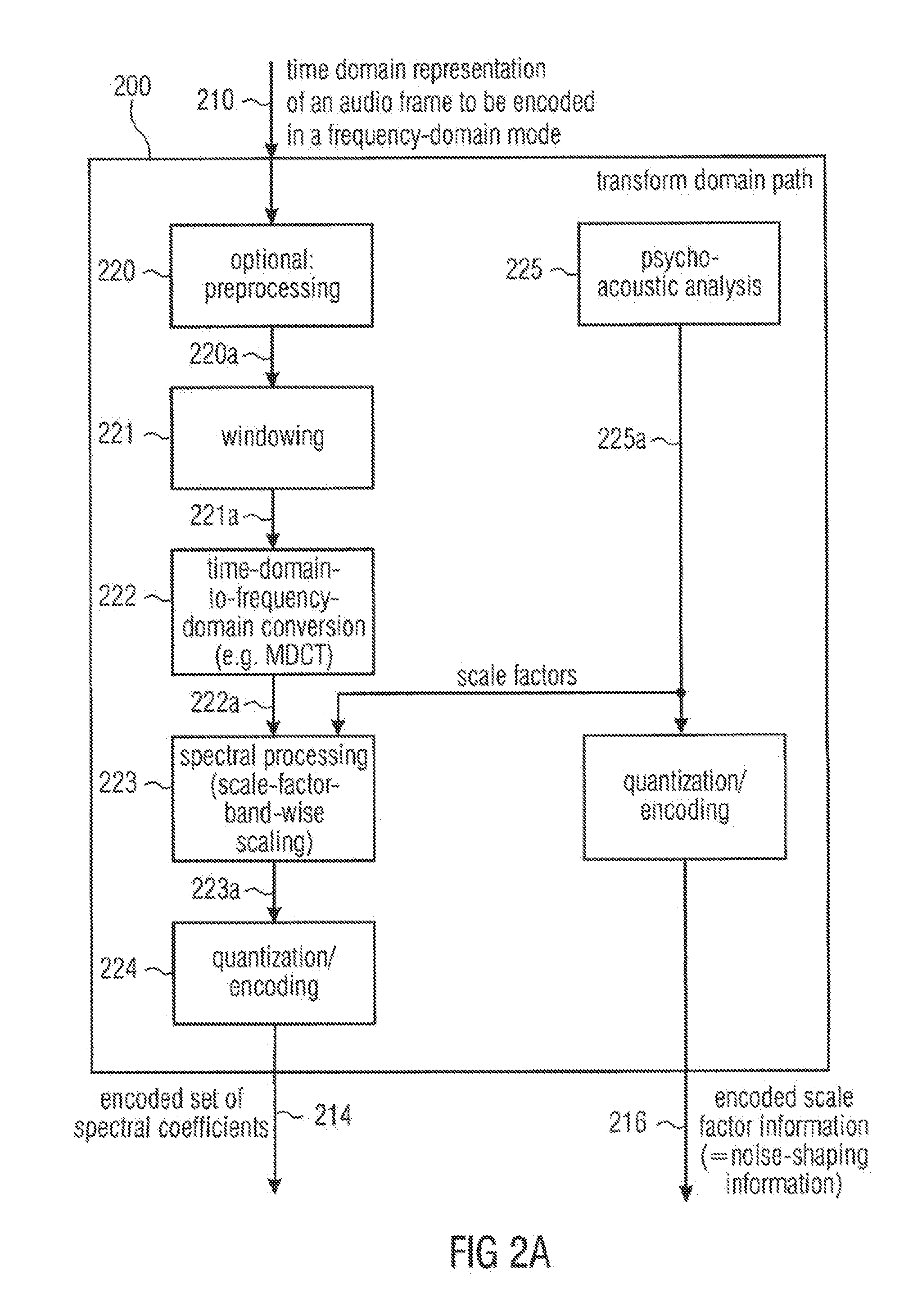
Feedforward prediction of scalefactors based on allowable distortion for noise shaping in psychoacoustic-based compression
A method of encoding a digital signal, particularly an audio signal, which predicts favorable scalefactors for different frequency subbands of the signal. Distortion thresholds which are associated with each of the frequency subbands of the signal are used, along with transform coefficients, to calculate total scaling values, one for each of the frequency subbands, such that the product of a transform coefficient for a given subband with its respective total scaling value is less than a corresponding one of the distortion thresholds. In an audio encoding application, the distortion thresholds are based on psychoacoustic masking. The invention may use a novel approximation for calculating the total scaling values, which obtains a first term based on a corresponding distortion threshold, and obtains a second term based on a sum of the transform coefficients. Both of these terms may be obtained using lookup tables. The total scaling values can be normalized to yield scalefactors by identifying one of the total scaling values as a minimum nonzero value, and using that minimum nonzero value to carry out normalization. Encoding of the signal further includes the steps of setting a global gain factor to this minimum nonzero value, and quantizing the transform coefficients using the global gain factor and the scalefactors.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
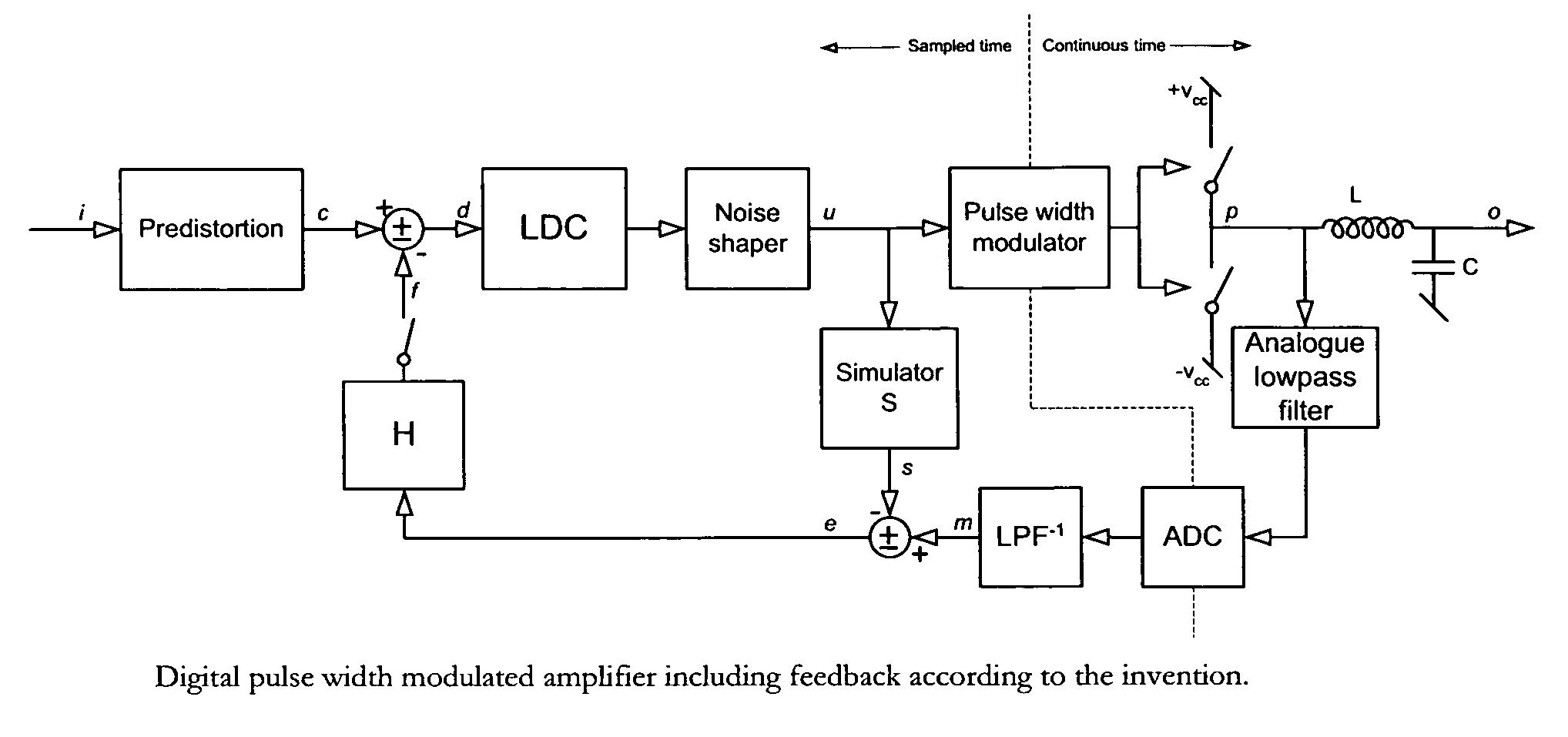
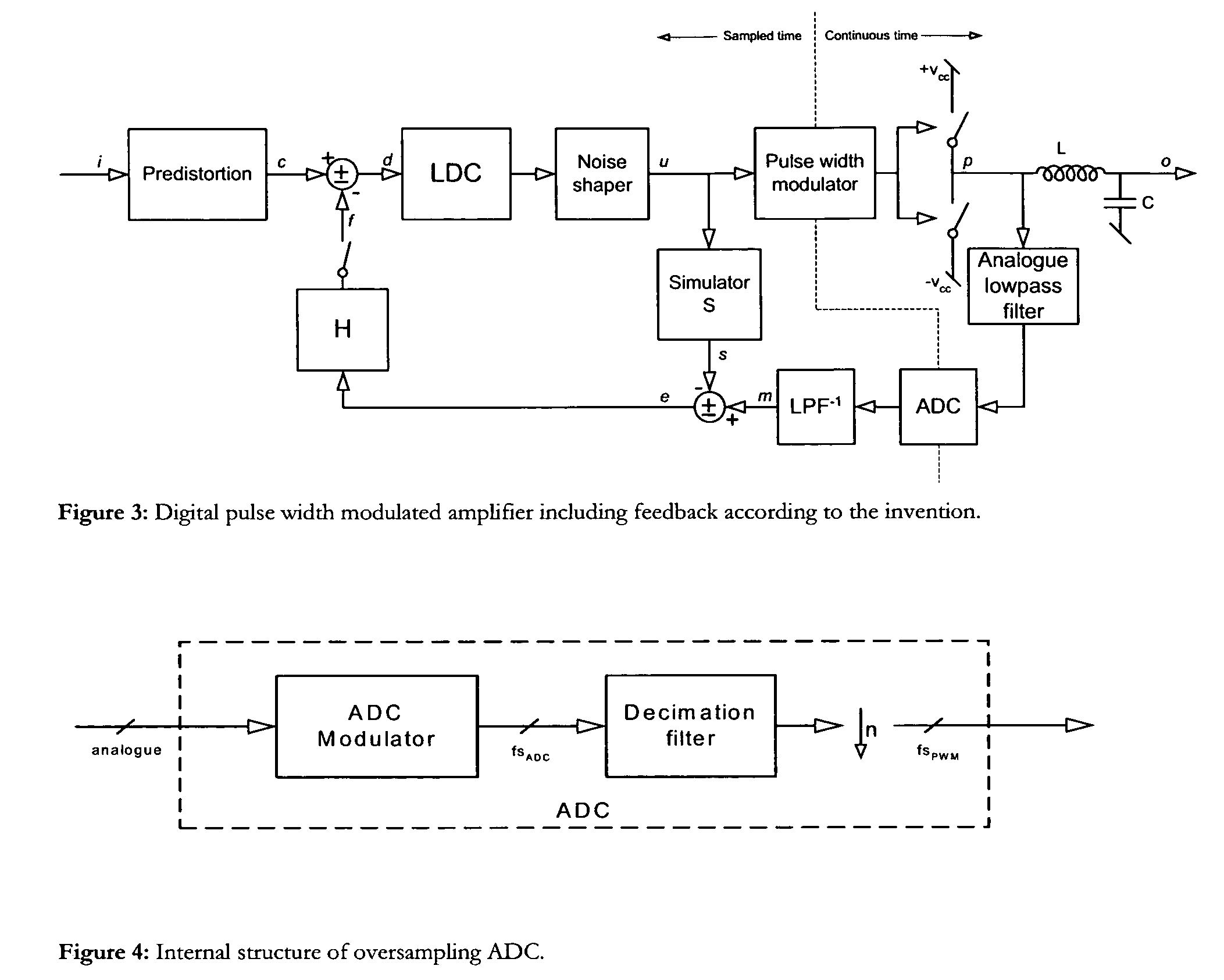
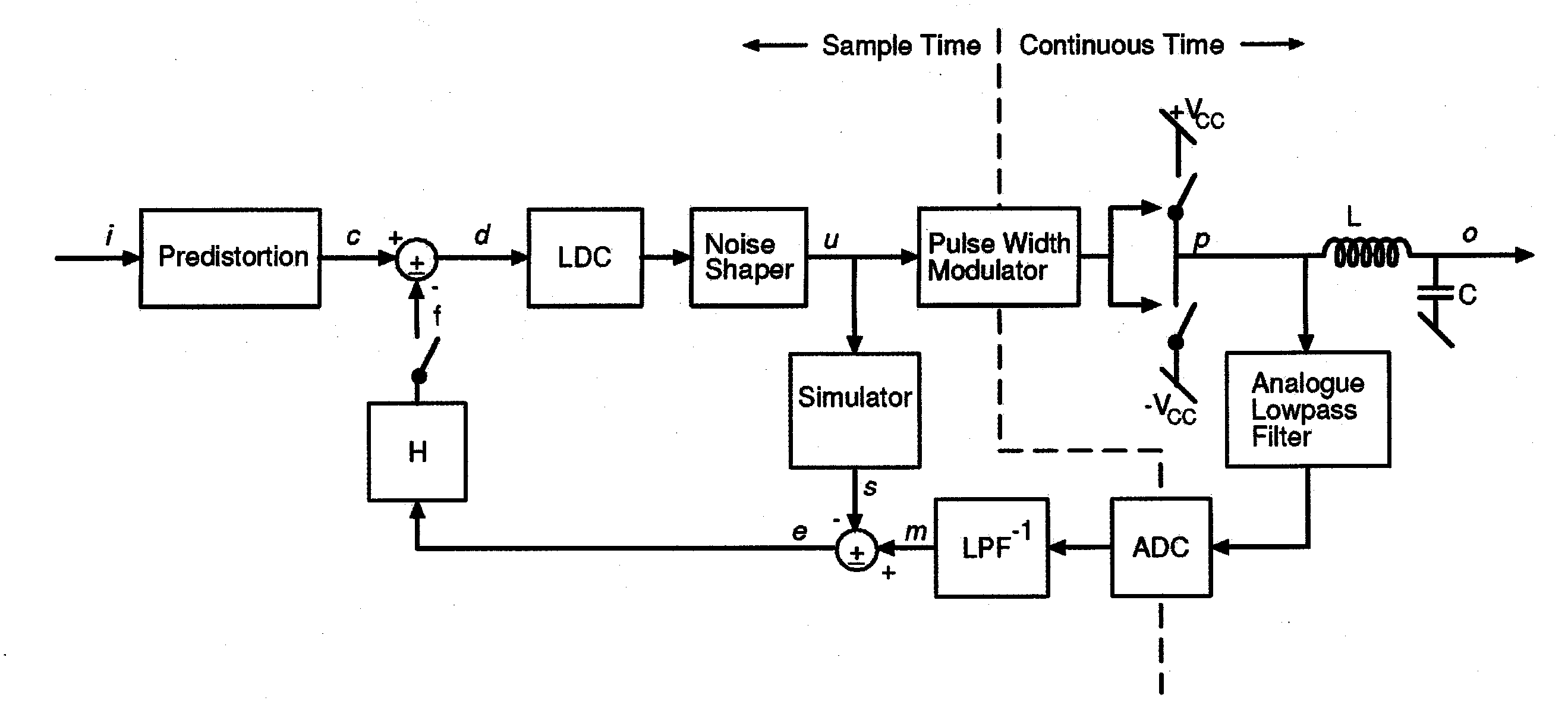
Digital PWM amplifier with simulation-based feedback
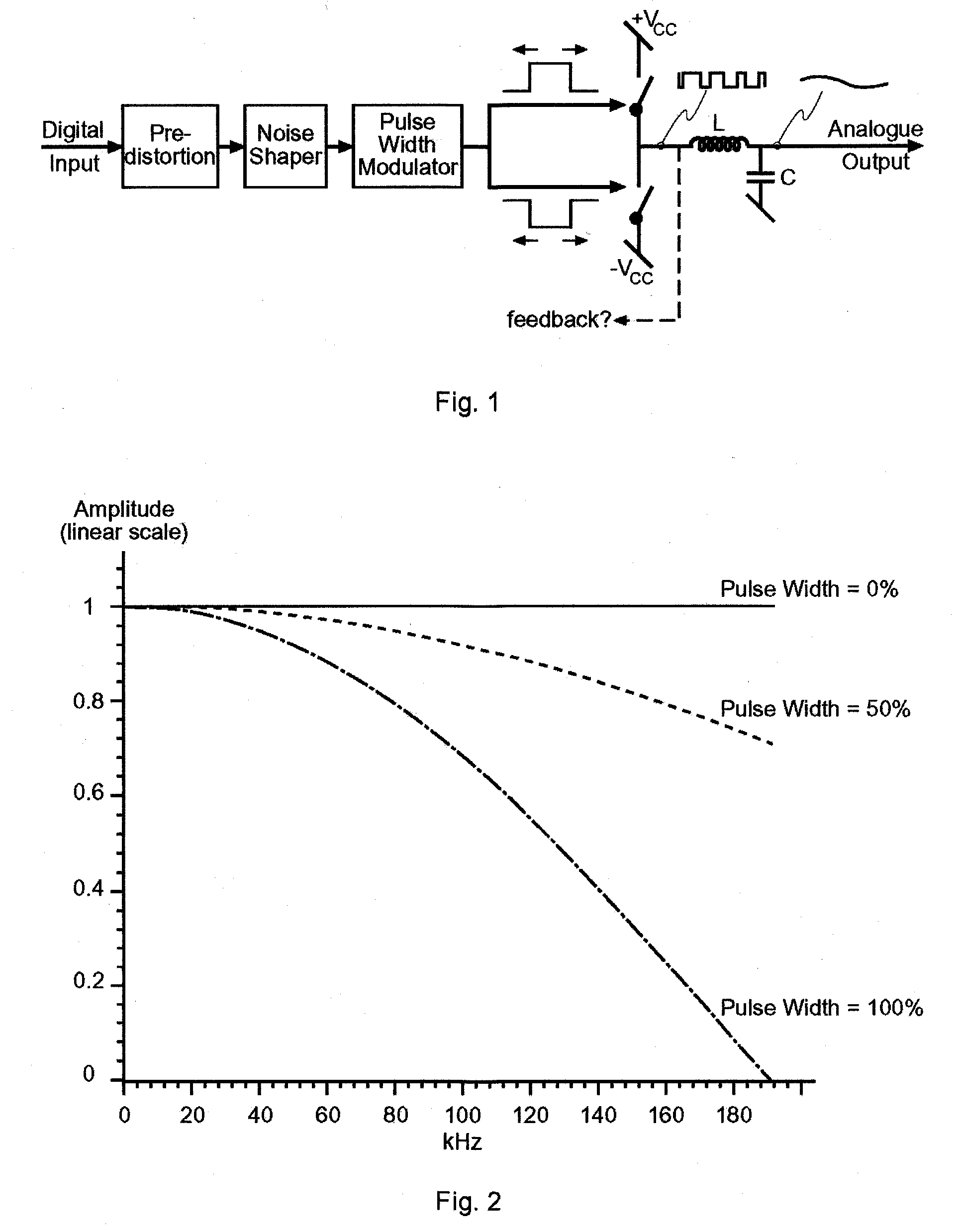
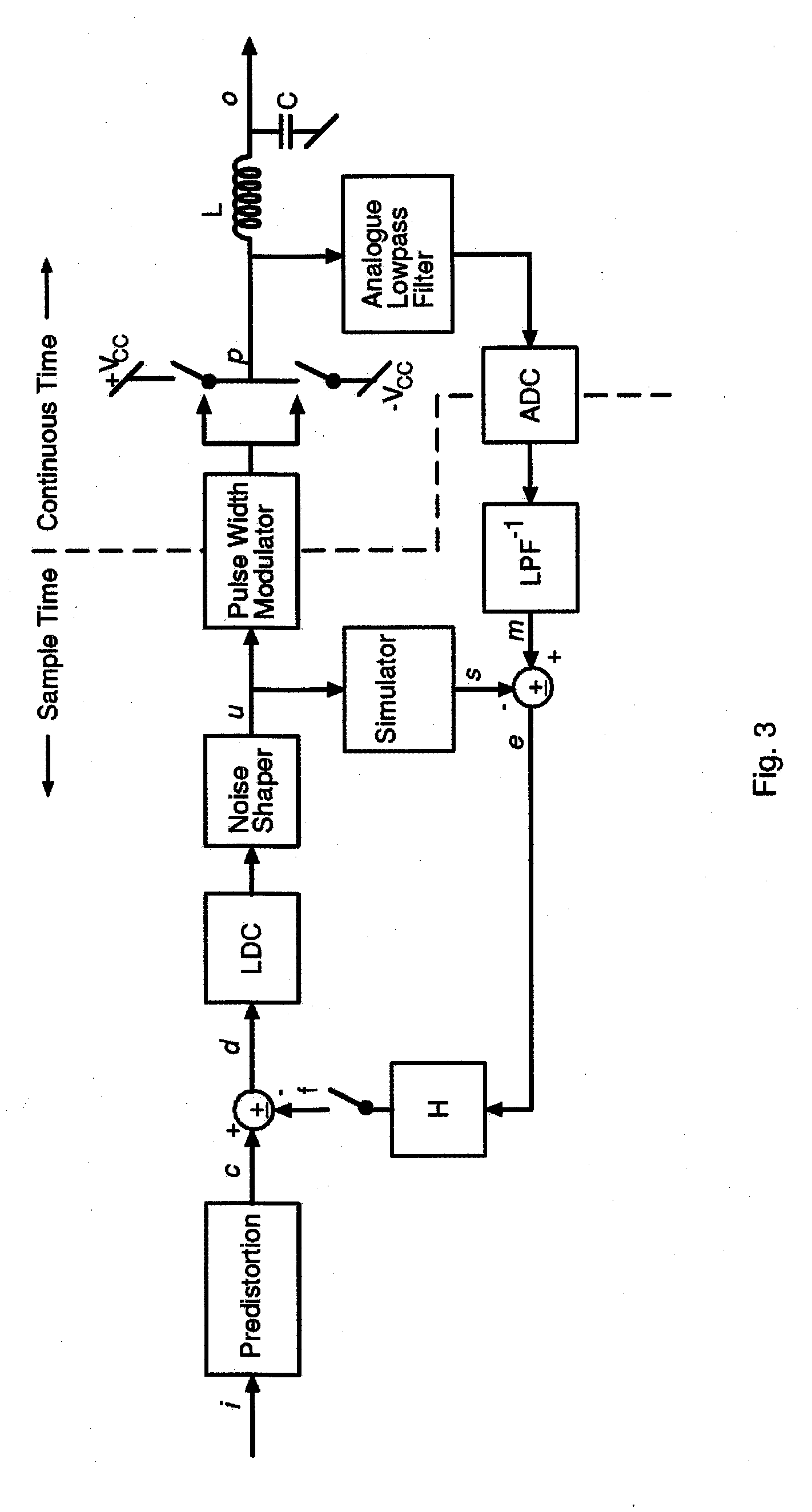
InactiveUS7286009B2Compensation delayAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAudio power amplifierNoise shaping
Systems and methods for performance improvements in digital switching amplifiers using simulation-based feedback. In one embodiment, a digital pulse width modulation (PWM) amplifier includes a signal processing plant configured to receive and process an input audio signal. The amplifier also includes a simulator configured to model processing of audio signals by the plant. The outputs of the plant and the simulator are provided to a subtractor, the output of which is then added to the input audio signal as feedback. The plant may consist of a modulator and power switch, a noise shaper, or any other type of plant. An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) may be provided to convert the output audio signal to a digital signal for input to the subtractor. Filtering may be implemented before or after the ADC, and a decimator may be placed after the ADC if it is an oversampling ADC.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
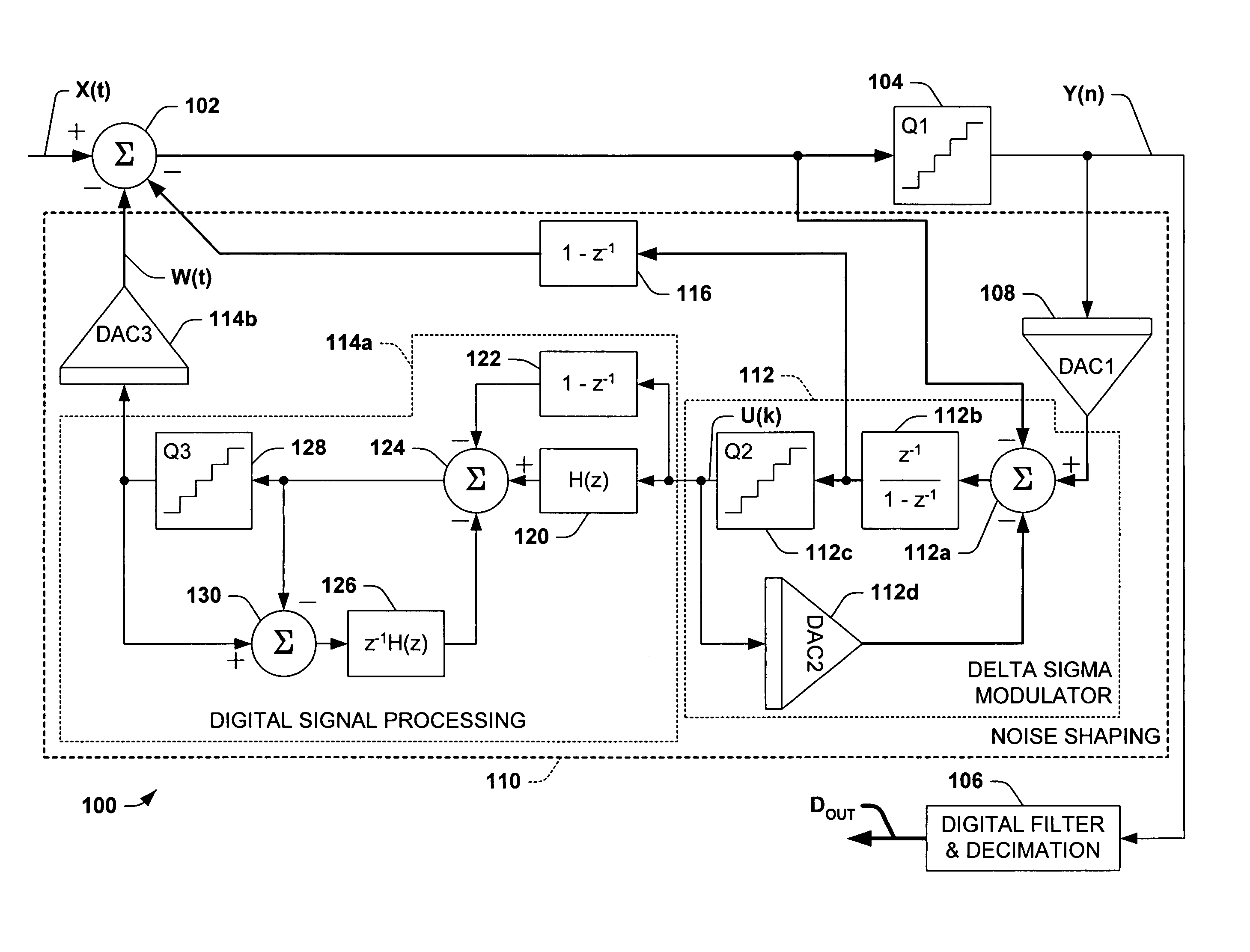
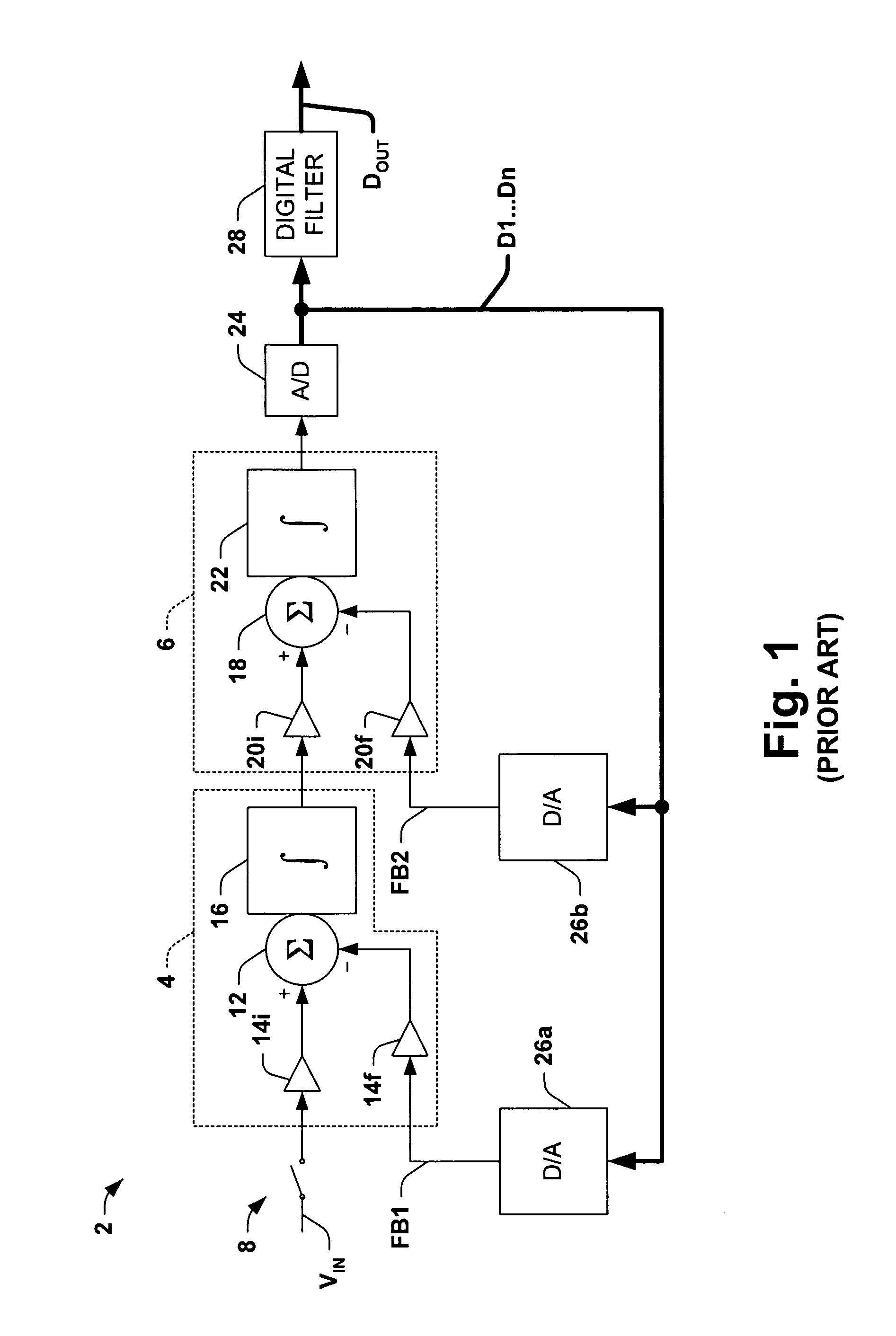
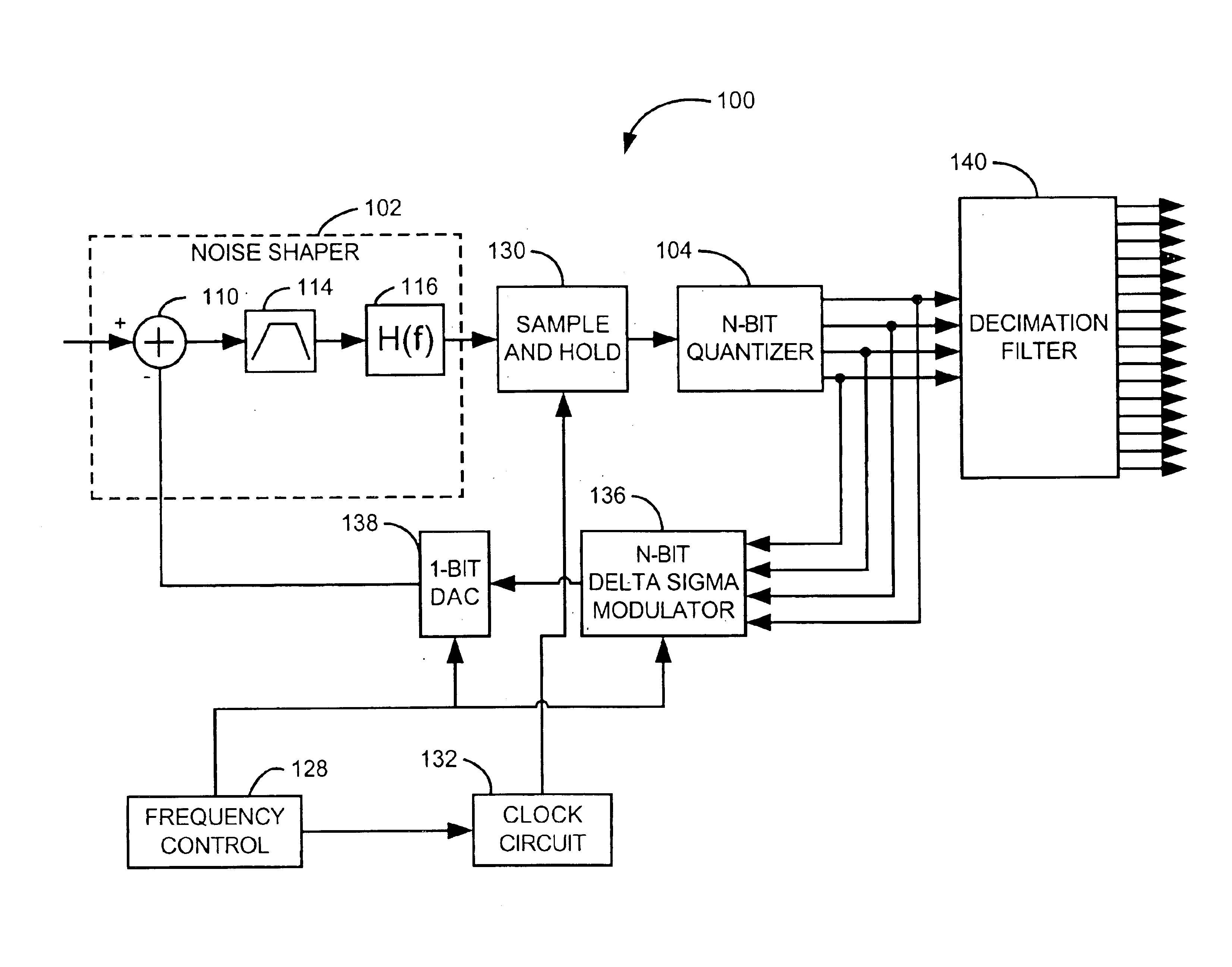
Analog-to-digital conversion system with second order noise shaping and a single amplifier
ActiveUS20050093726A1Well formedElectric signal transmission systemsDifferential modulationDigital signal processingIntegrator
A analog-to-digital converters and second order noise shaping systems are presented for providing a noise shaped analog feedback signal to a A / D converter in an analog-to-digital conversion system. The noise shaping system comprises a first order integrator having a single amplifier, and a digital error feedback system comprising a digital signal processing system, in which the digital error feedback system provides an analog feedback signal to the A / D converter with second order noise shaping with respect to a quantization error associated with the A / D converter.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Adaptive spectral noise shaping to improve time to digital converter quantization resolution using dithering
ActiveUS7570182B2Quantization noise resolutionReduce noiseElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionFrequency spectrumNoise shaping
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
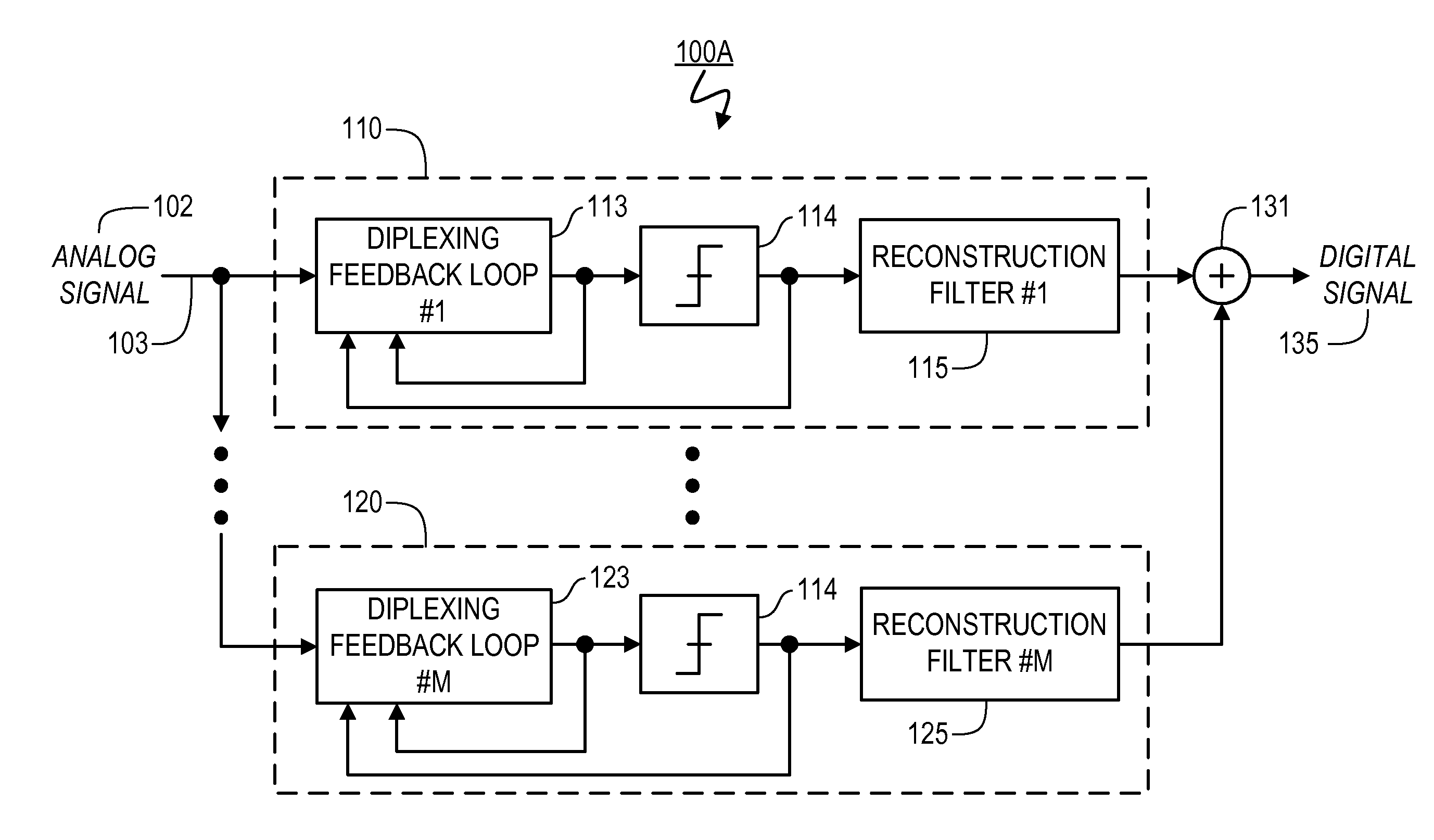
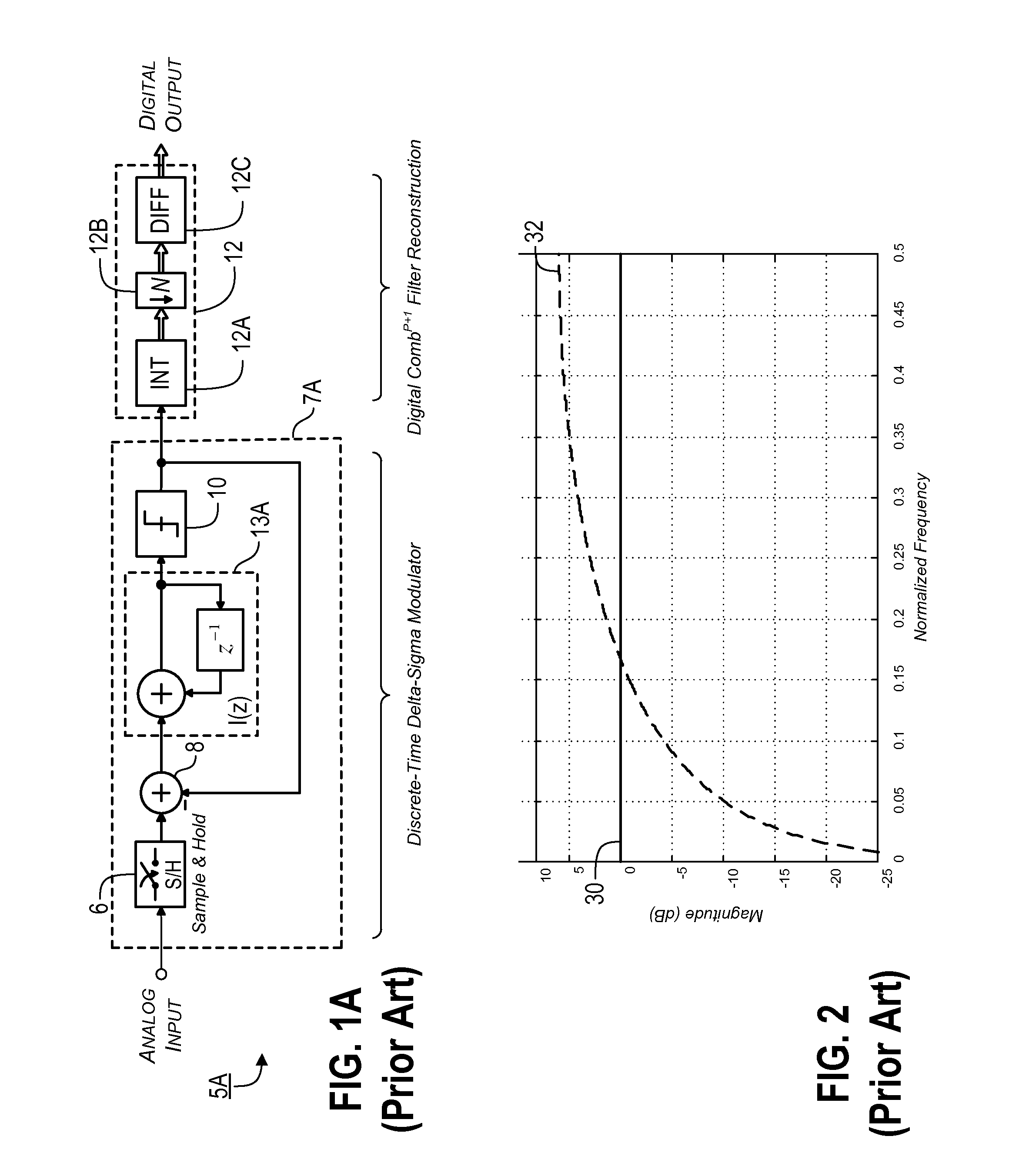
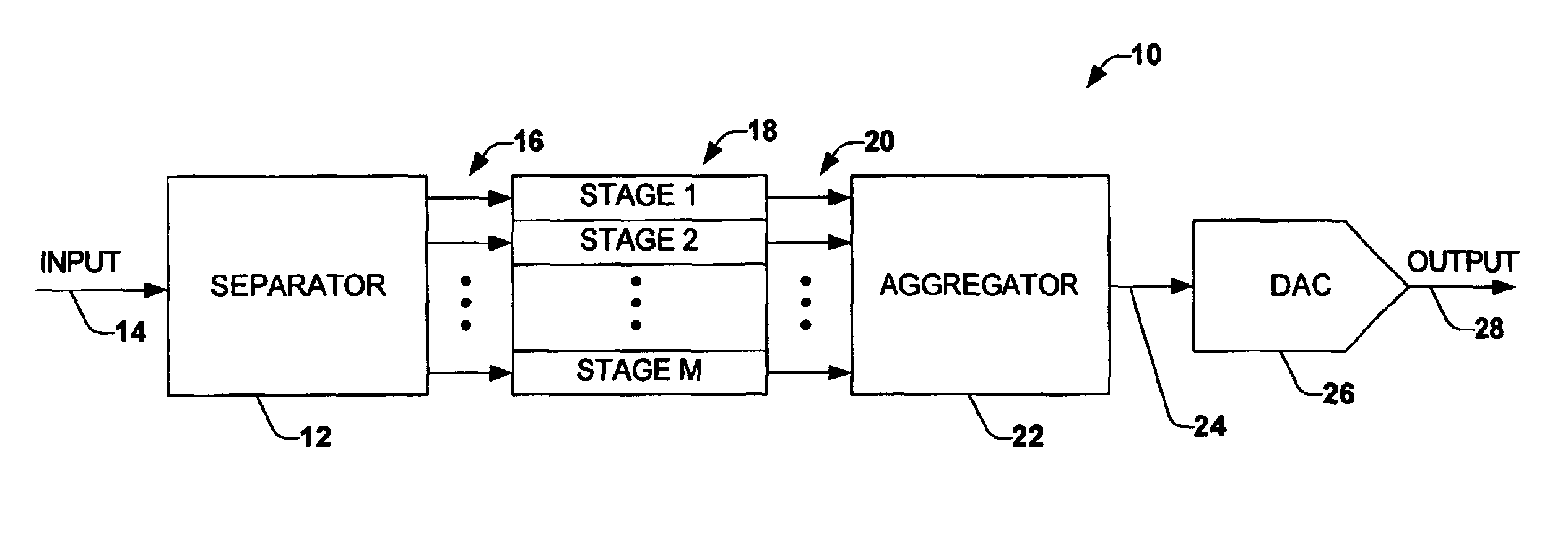
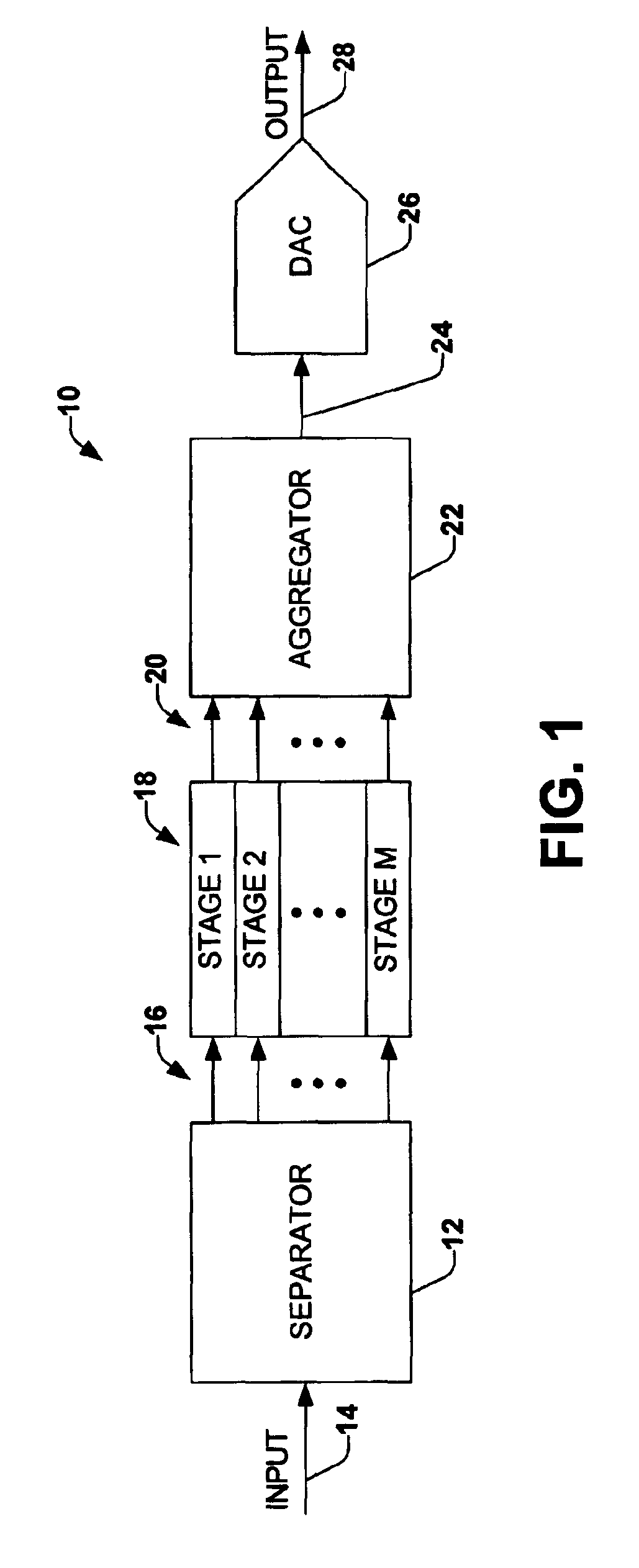
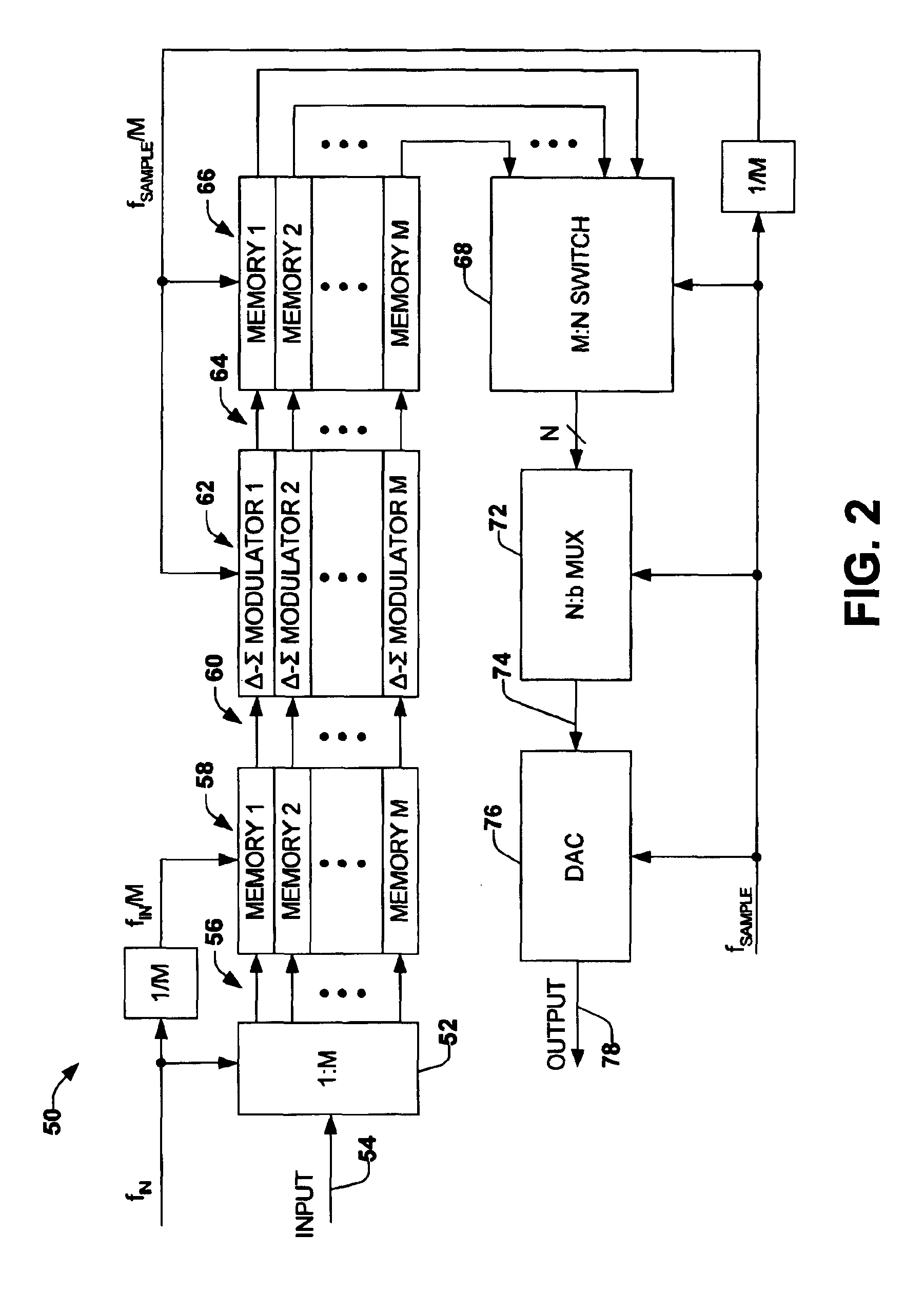
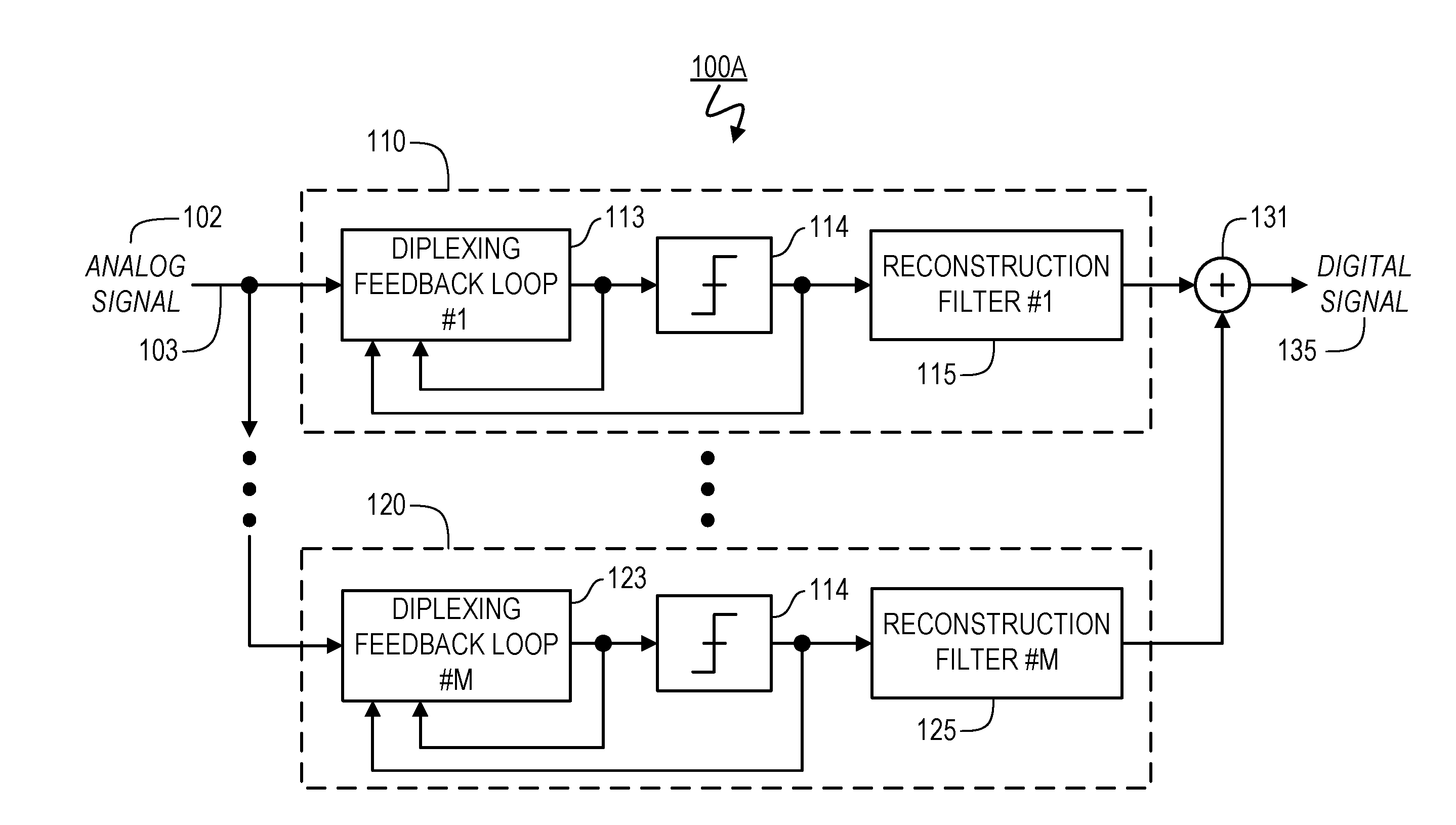
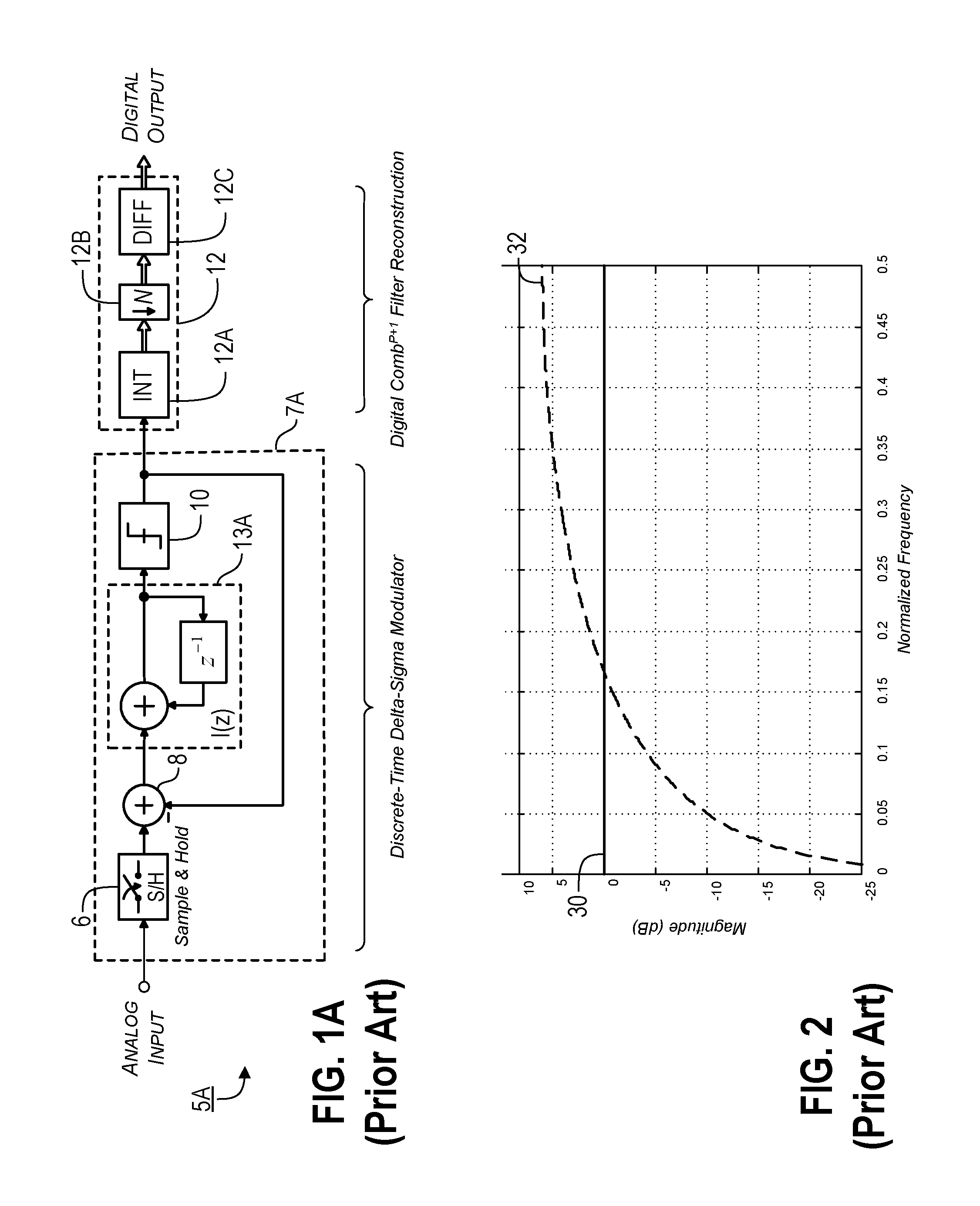
Sampling/Quantization Converters
Owner:PAGNANELLI FAMILY TRUST
Double-closed-loop control circuit of micromechanical gyroscope
ActiveCN102620726AEasy to controlHigh precisionPulse automatic controlTurn-sensitive devicesGyroscopeSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses a double-closed-loop control circuit of a micromechanical gyroscope and belongs to the field of guide or control devices based on a Coriolis effect. The circuit is used for closed-loop control of driving and detection modes of the micromechanical gyroscope. A simplified self-oscillation closed-loop control circuit based on automatic gain control (AGC) is employed for the driving mode of the circuit, and the frequency stability and amplitude stability of the micromechanical gyroscope in the driving mode can be effectively improved; and a six-order continuous band-pass Sigma Delta M closed-loop control circuit for the detection mode has six-order noise reshaping capacity, and the signal to noise ratio (SNR), linearity and zero-bias stability of a system detection signal can be improved. The double-closed-loop control circuit of the micromechanical gyroscope is easy to control and simple, the accuracy of a system is improved, the SNR of the system is high, and the system is self-adaptively adjusted and high in stability.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Conversion employing delta-sigma modulation
InactiveUS6873280B2Efficient implementationImprove performanceElectric signal transmission systemsDelta modulationNoise shapingData rate
Signal conversion of an input signal can be achieved by processing portions of the signal through plural parallel paths, which collectively approximate a desired infinite impulse response (IIR) filter, either alone or implemented with other signal processing functions. In one aspect, each of the paths can perform filtering, noise-shaping and / or quantization on a respective portion of the input signal to provide a corresponding representation of the respective portion of the input signal, for example, a coarser representation at a higher data rate. The corresponding representations from the parallel paths can be aggregated and further processed in a desired manner, such as conversion to an analog signal.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Lossless coding method for waveform data
In a method of lossless processing of an integer value signal in a prediction filter which includes a quantiser, a numerator of the prediction filter is implemented prior to the quantiser and a denominator of the prediction filter is implemented recursively around the quantiser to reduce the peak data rate of an output signal. In the lossless processor, at each sample instant, an input to the quantiser is jointly responsive to a first sample value of a signal input to the prediction filter, a second sample value of a signal input to the prediction filter at a previous sample instant, and an output value of the quantiser at a previous sample incident. In a preferred embodiment, the prediction filter includes noise shaping for affecting the output of the quantiser.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Analog-to-digital conversion system with second order noise shaping and a single amplifier
InactiveUS6940436B2Electric signal transmission systemsDifferential modulationDigital signal processingAudio power amplifier
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Audio signal encoder, audio signal decoder, method for providing an encoded representation of an audio content, method for providing a decoded representation of an audio content and computer program for use in low delay applications
ActiveUS20120265541A1Reduces and cancel aliasing artifactImprove coding efficiencySpeech analysisFrequency spectrumNoise shaping
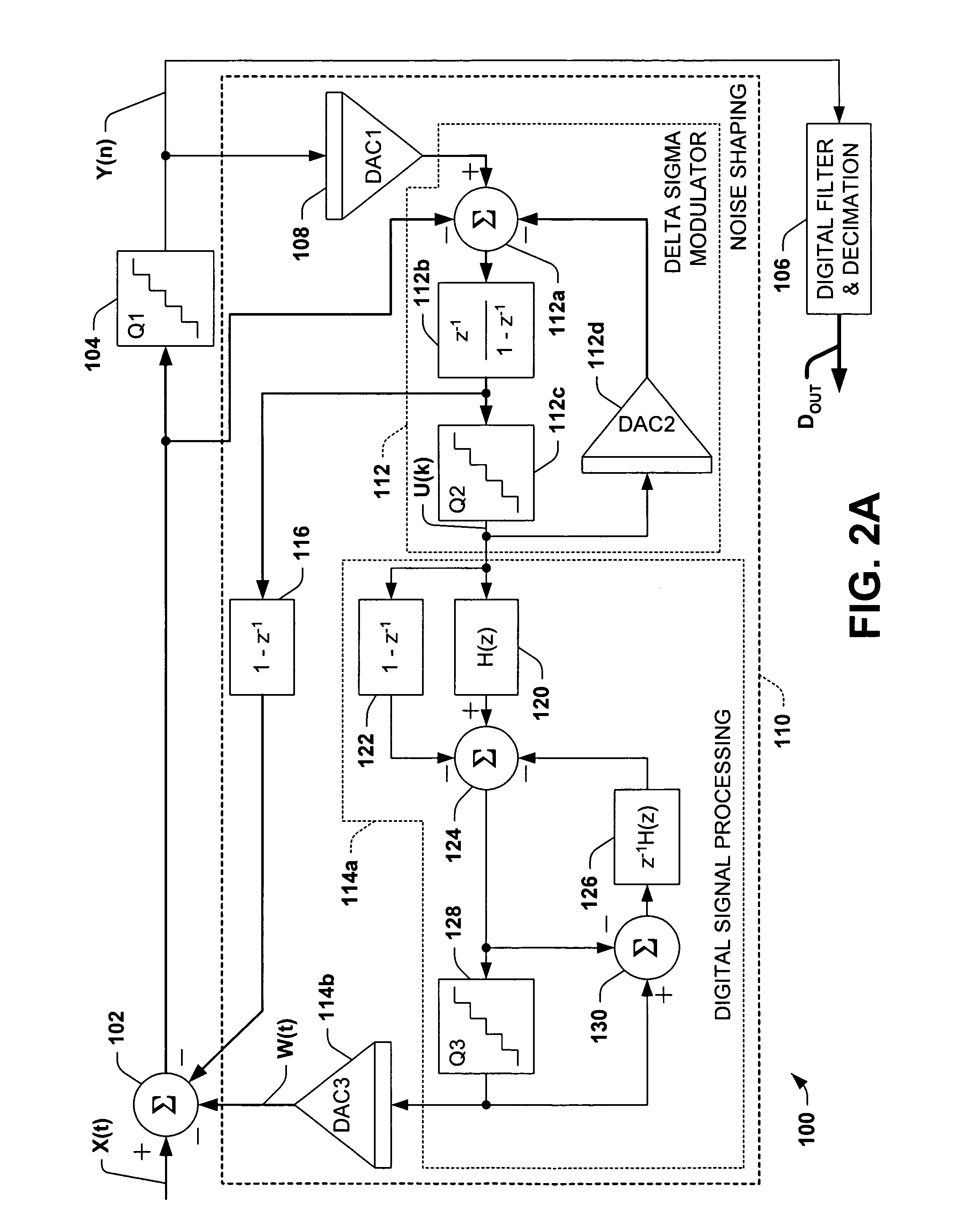
An audio signal encoder includes a transform-domain path which obtains spectral coefficients and noise-shaping information on the basis of a portion of the audio content, and which windows a time-domain representation of the audio content and applies a time-domain-to-frequency-domain conversion. The audio signal decoder includes a CELP path to obtain a code-excitation information and a LPD parameter information. A converter applies a predetermined asymmetric analysis window in both if a current portion is followed by a subsequent portion to be encoded in the transform-domain mode or in the CELP mode. Aliasing cancellation information is selectively provided in the later case.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Programmable bandpass analog to digital converter based on error feedback architecture
ActiveUS6864818B1Improve programmabilityReduce circuit sizeDifferential modulationNoise shapingEngineering
A delta sigma modulator based analog to digital converter is presented, having a first quantizer and a digital error feedback system comprising a second quantizer and a digital bandpass noise shaping system. The second quantizer provides a second quantized output to the noise shaping system according to the first quantized output, the system analog input, and the noise shaped feedback signal. The digital noise shaping system provides a feedback signal to the first quantizer according to the second quantized output, where the feedback signal is bandpass noise shaped with respect to a quantization error of the first quantizer.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
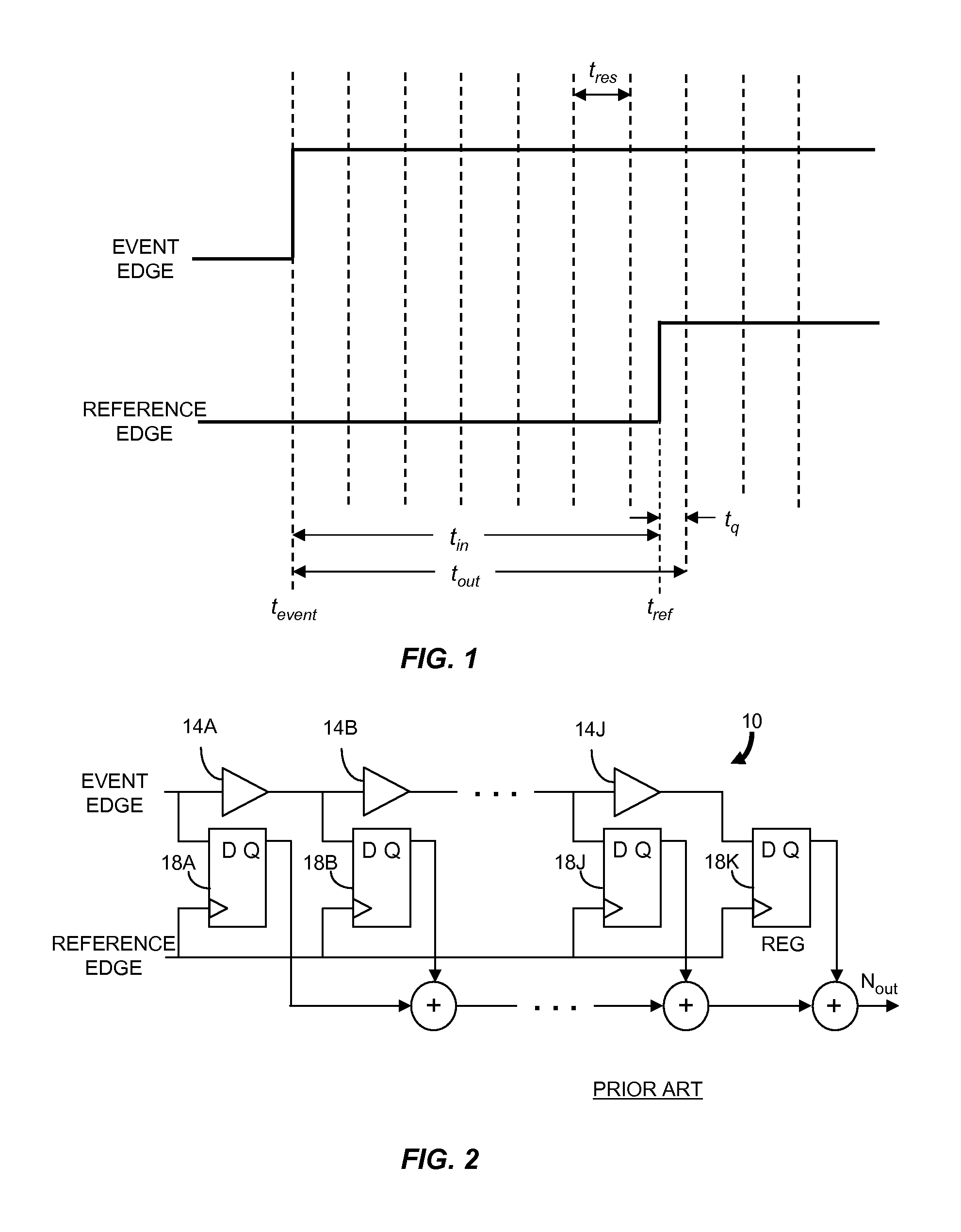
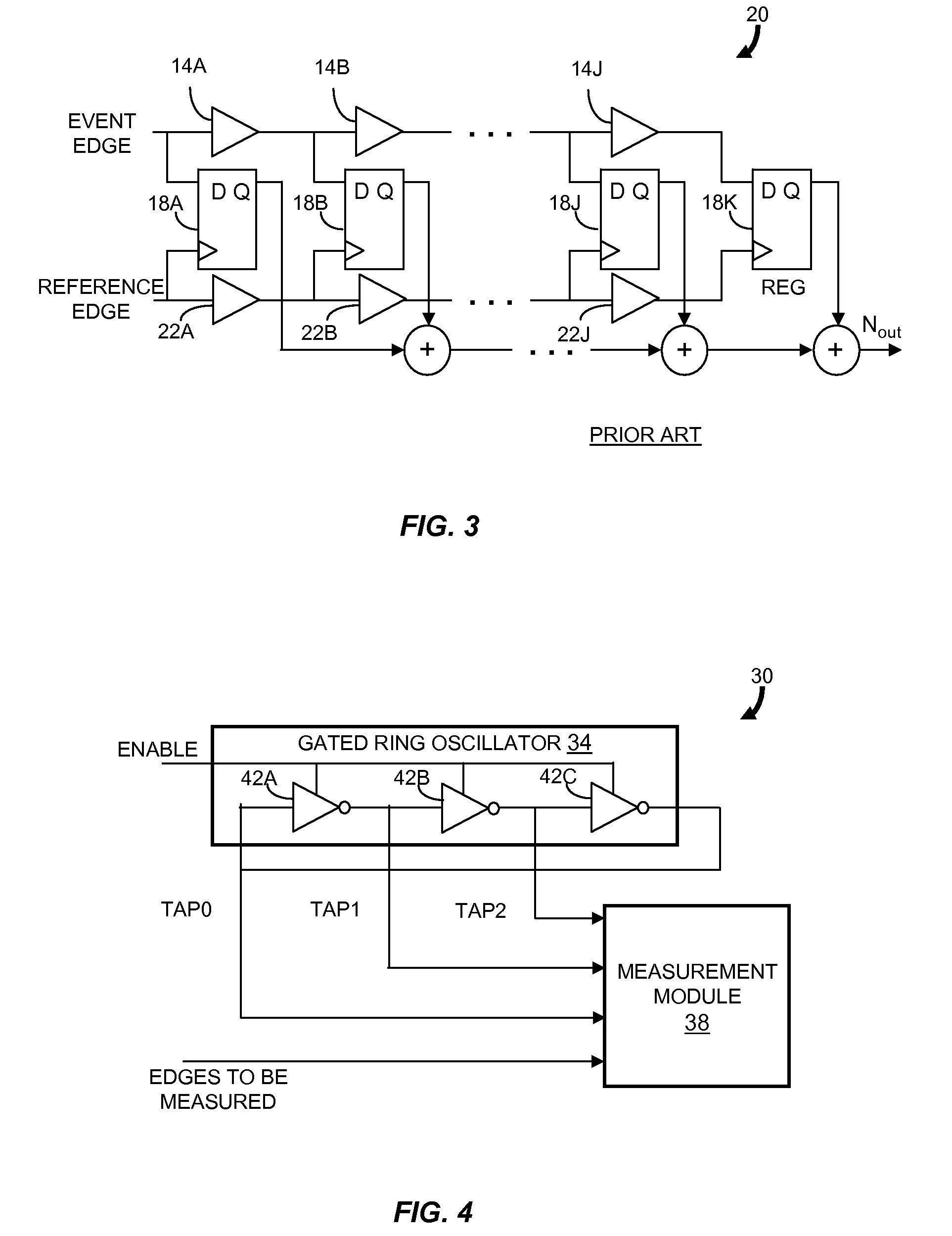
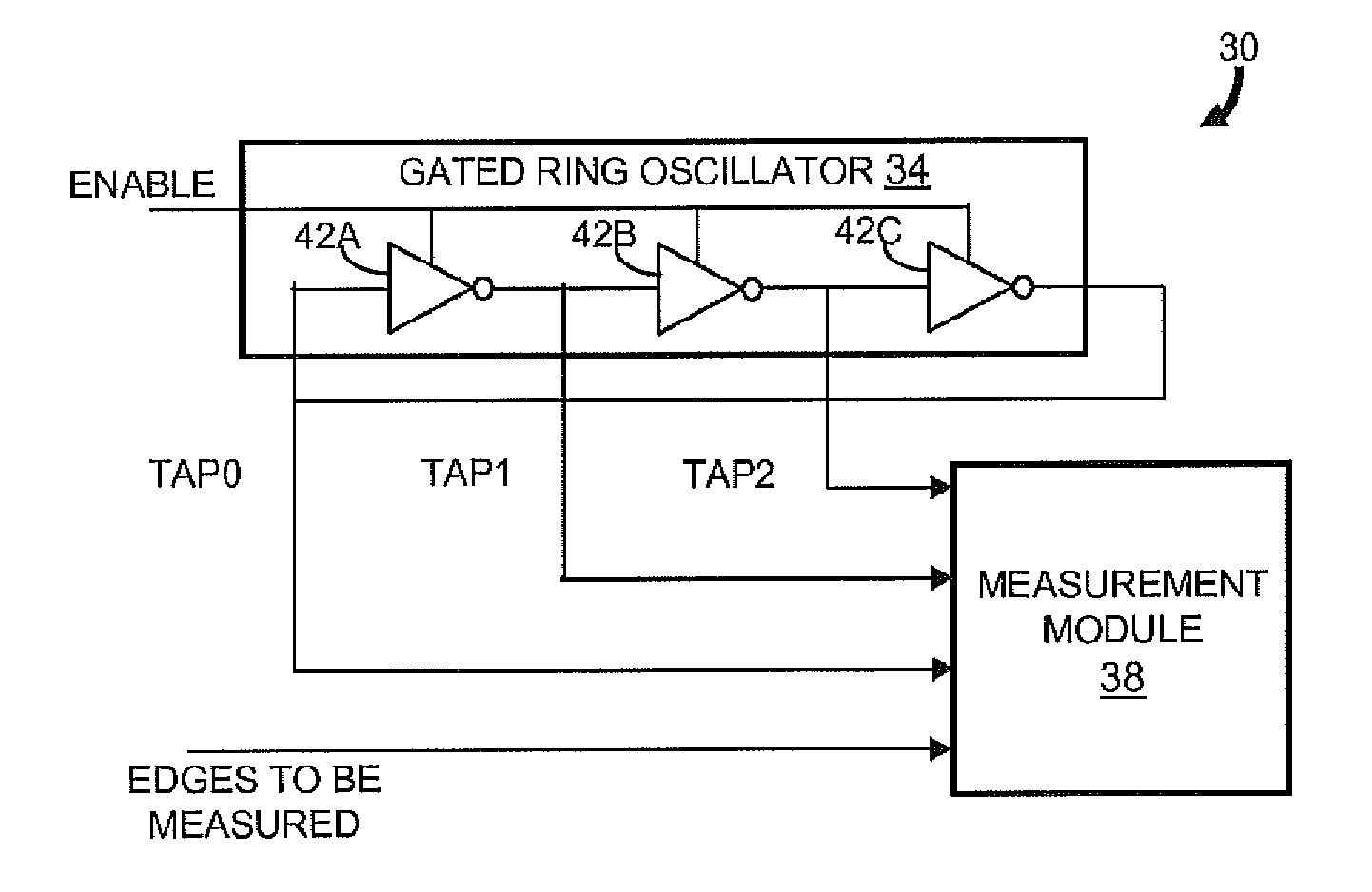
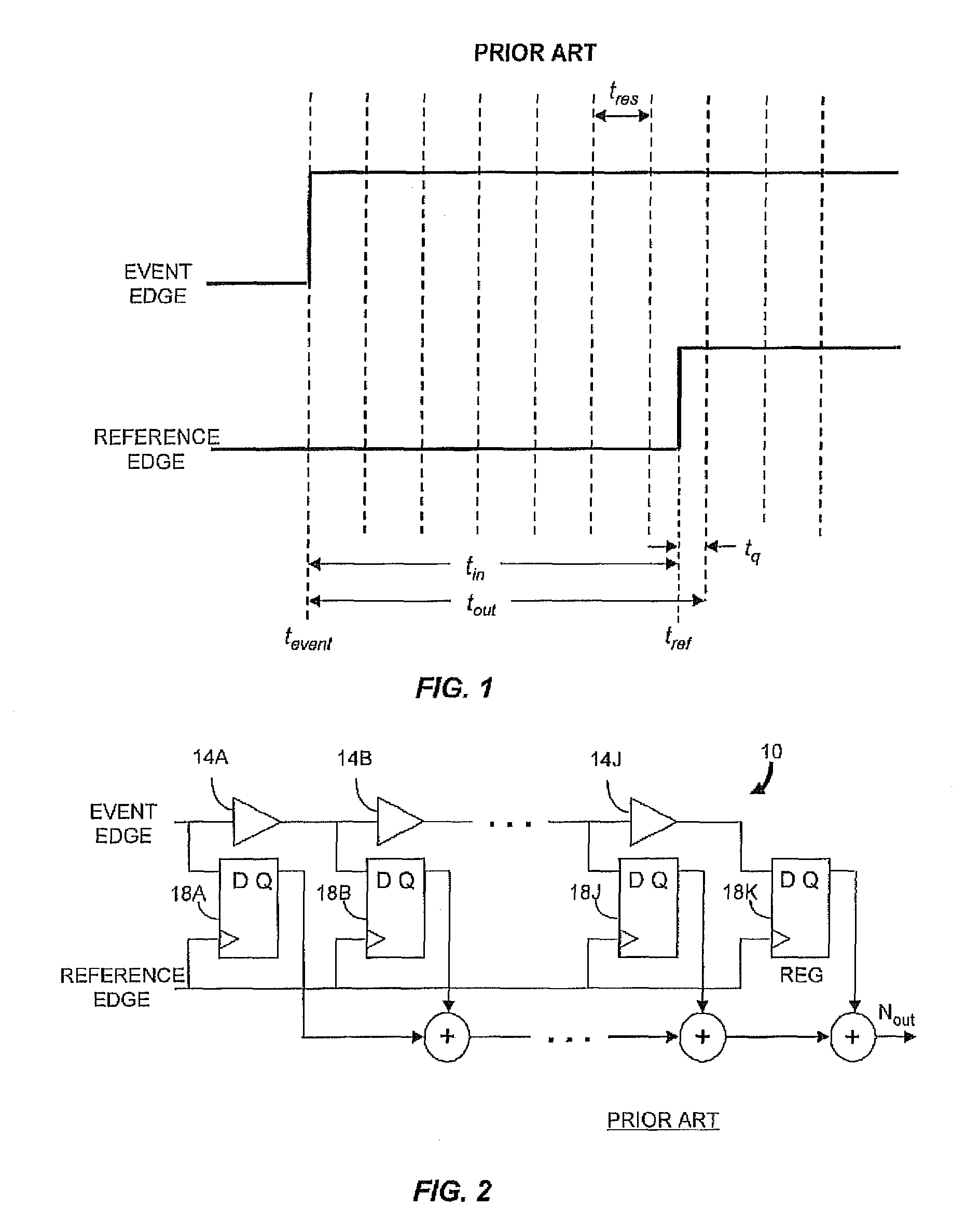
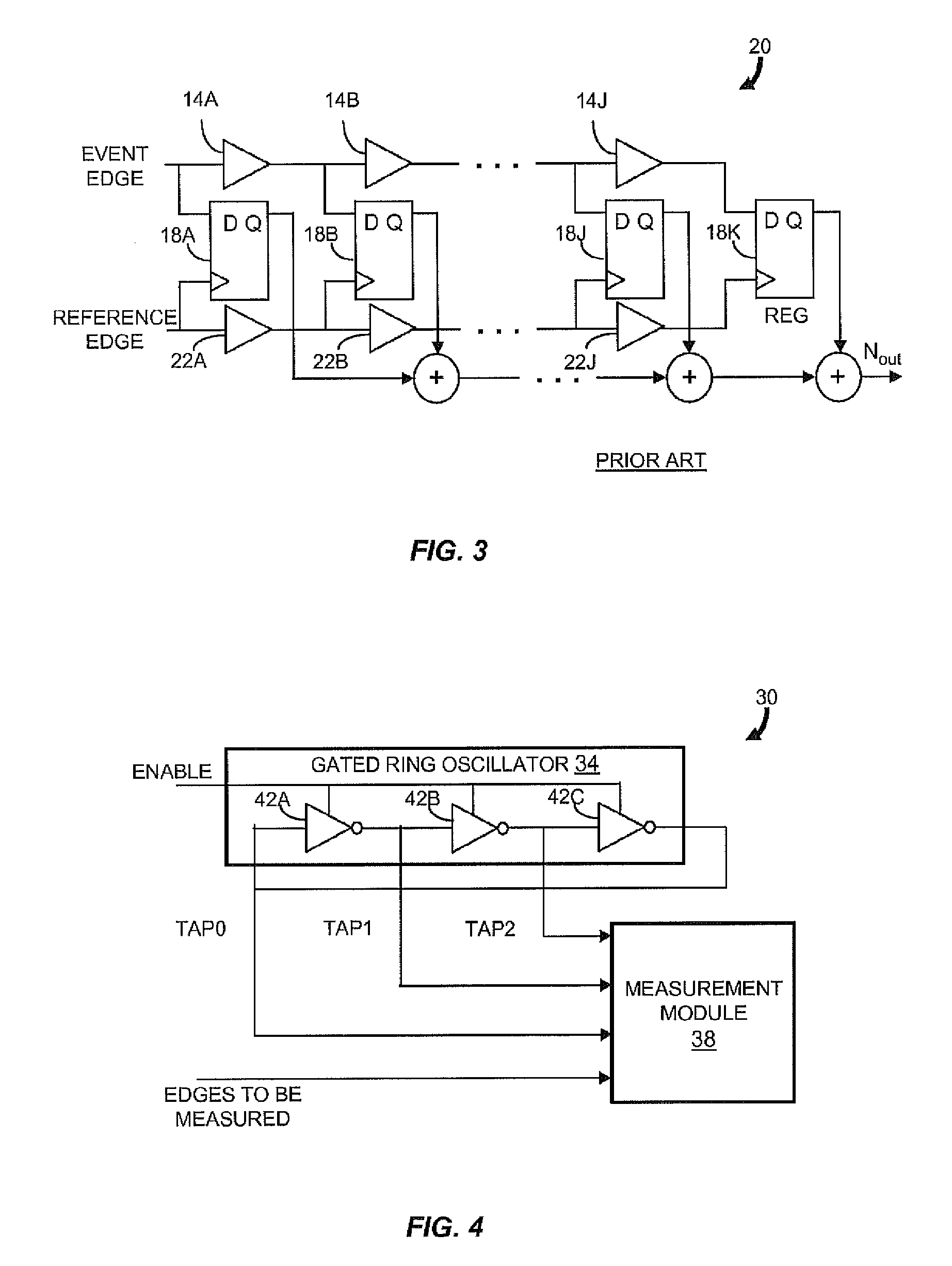
Gated ring oscillator for a time-to-digital converter with shaped quantization noise
ActiveUS20080069292A1Resolution timeContinuously circulated pulse countersCounting chain synchronous pulse countersImage resolutionNoise shaping
Described is a compact, lower power gated ring oscillator time-to-digital converter that achieves first order noise shaping of quantization noise using a digital implementation. The gated ring oscillator time-to-digital converter includes a plurality of delay stages configured to enable propagation of a transitioning signal through the delay stages during an enabled state and configured to inhibit propagation of the transitioning signal through the delay stages during a disabled state. Delay stages are interconnected to allow sustained transitions to propagate through the delay stages during the enabled state and to preserve a state of the gated ring oscillator time-to-digital converter during the disabled state. The state represents a time resolution that is finer than the delay of at least one of the delay stages. A measurement module determines the number of transitions of the delay stages.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Delta-sigma analog-to-digital converter
ActiveUS6842129B1Electric signal transmission systemsDifferential modulationDigital analog converterDigital down converter
Systems and methods are provided for providing feedback to a delta-sigma analog-to-digital converter assembly. A noise shaper preprocesses an analog input signal according to an analog feedback signal and an associated transfer function. A quantizer converts the preprocessed analog input signal into a digital output signal. A delta-sigma modulator shapes noise within a sample of the digital output signal. A digital-to-analog converter converts the shaped digital signal into an analog signal to provide the analog feedback signal.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Tri-level dynamic element matcher allowing reduced reference loading and dac element reduction
ActiveUS20100245142A1Reduce power consumptionTotal current dropElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionCircuit complexityNoise shaping
Systems and methods using the same to achieve a tri-level multi-bit delta-sigma DAC having reduced power consumption and voltage droop have been achieved. A new rotation-based first order noise-shaping Dynamic Element Matcher (DEM) technique for use with 3-level unit elements have been disclosed. Reduced reference loading has been achieved when the tri-level DEM scheme is applied to switched capacitor implementations in particular. Furthermore a differential switched-capacitor DAC implementation, which enables use of the DEM technique is disclosed. The invention allows reduced circuit complexity required to implement a N-bit DAC when constructed using 3-level unit elements.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
Sampling/Quantization Converters
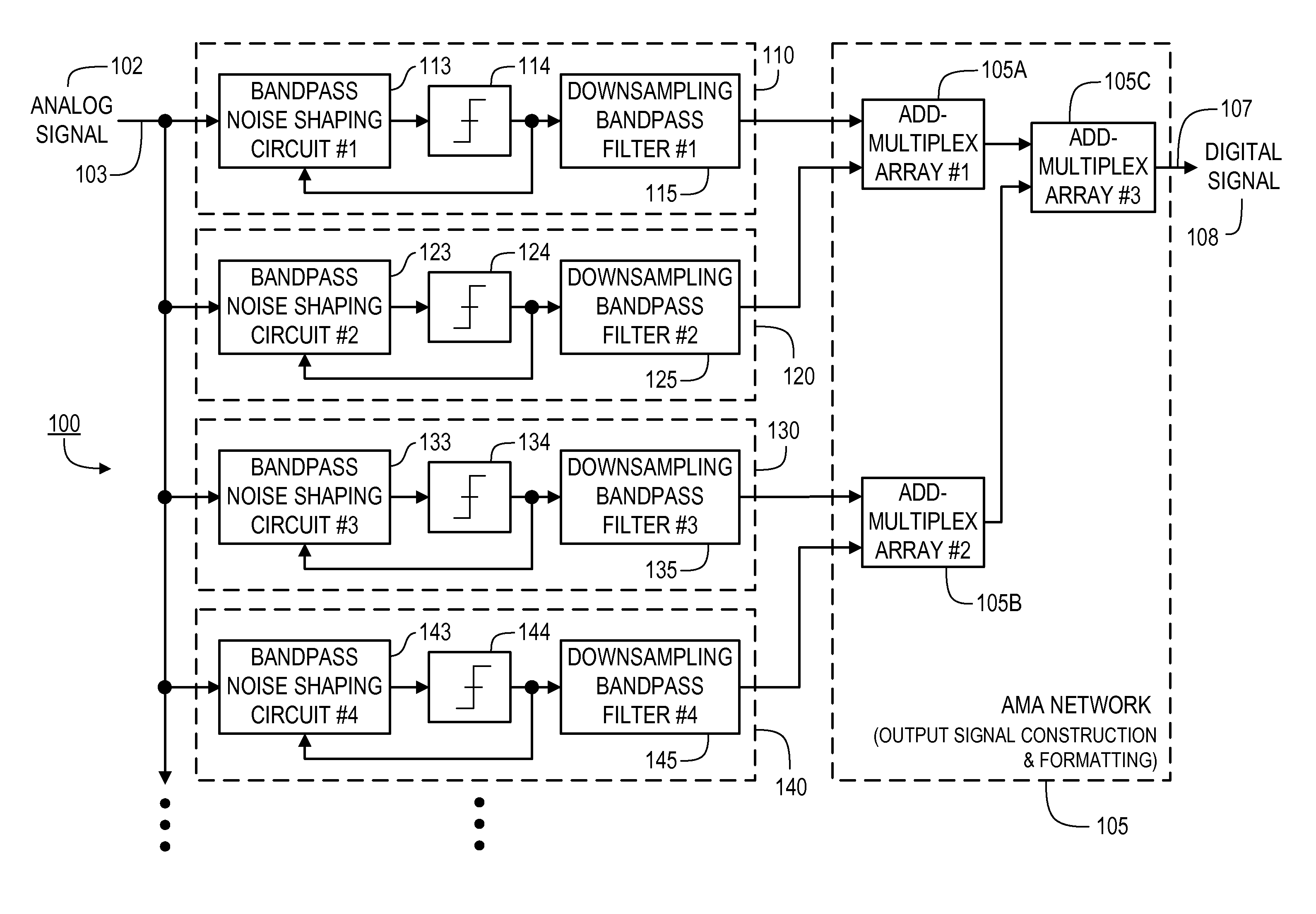
ActiveUS20160373125A1Minimizes level detector outputImprove bindingElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionBandpass filteringNoise shaping
Provided are, among other things, systems, apparatuses, methods and techniques for converting a continuous-time, continuously variable signal into a sampled and quantized signal. One such apparatus includes an input line for accepting an input signal that is continuous in time and continuously variable, multiple processing branches coupled to the input line, and an adder coupled to outputs of the processing branches, with each of the processing branches including a bandpass noise-shaping circuit, a sampling / quantization circuit coupled to an output of the bandpass noise-shaping circuit, a digital bandpass filter coupled to an output of the sampling / quantization circuit, and a line coupling an output of the sampling / quantization converter circuit back into the bandpass noise-shaping circuit. A center frequency of the digital bandpass filter in each processing branch corresponds to a stopband region in a quantization noise transfer function for the bandpass noise-shaping circuit in the same processing branch.
Owner:PAGNANELLI FAMILY TRUST
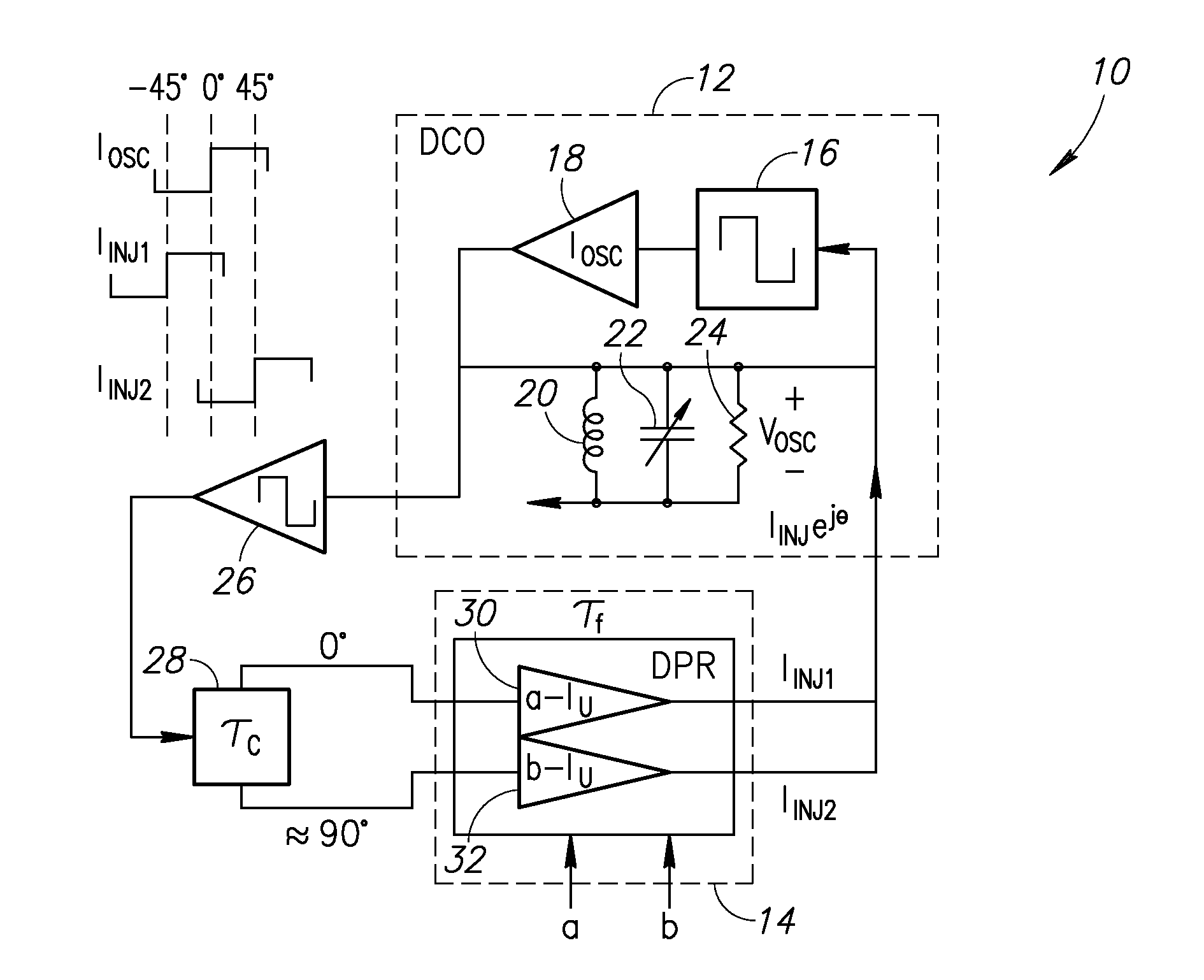
Wideband Digitally Controlled Injection-Locked Oscillator
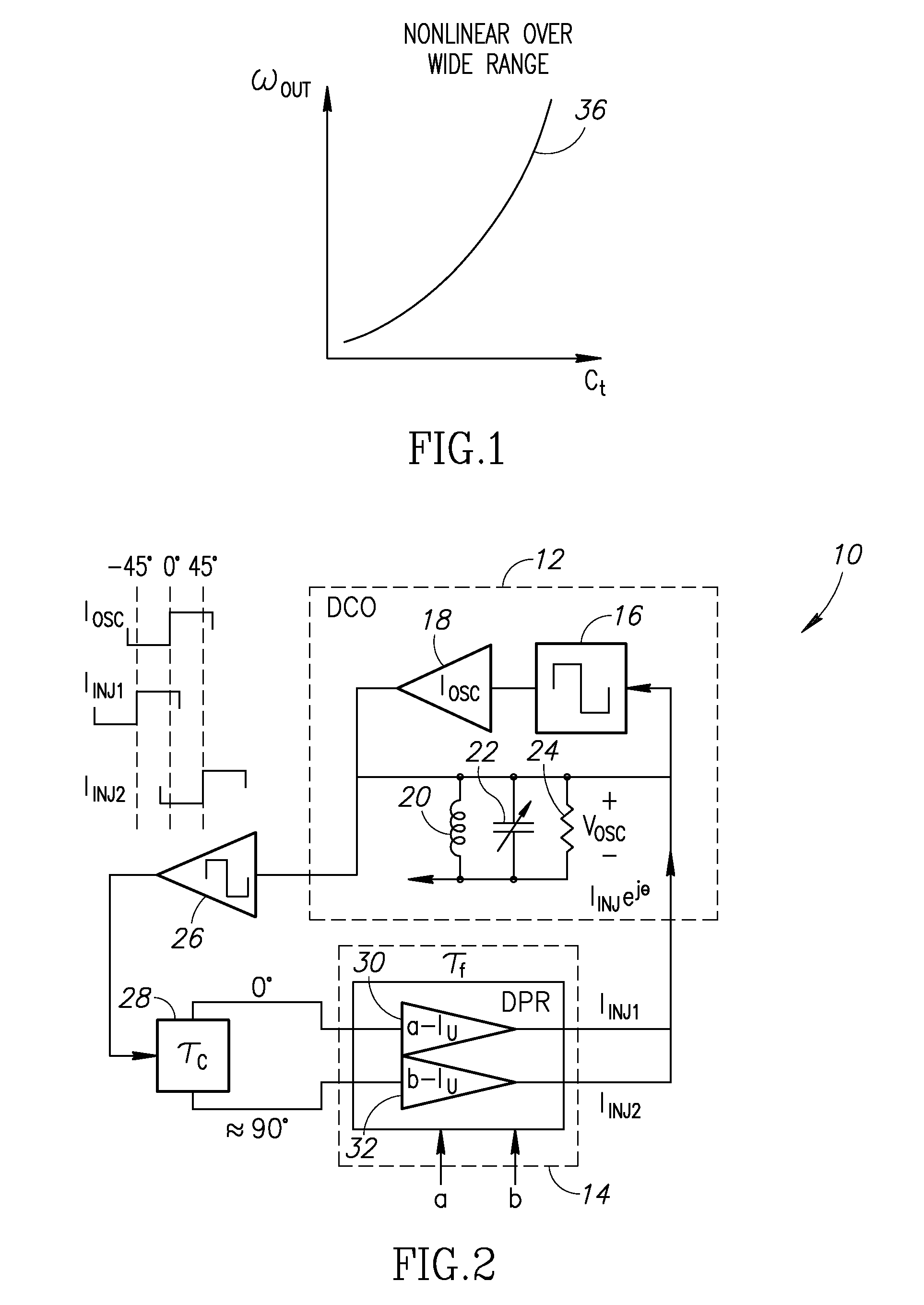
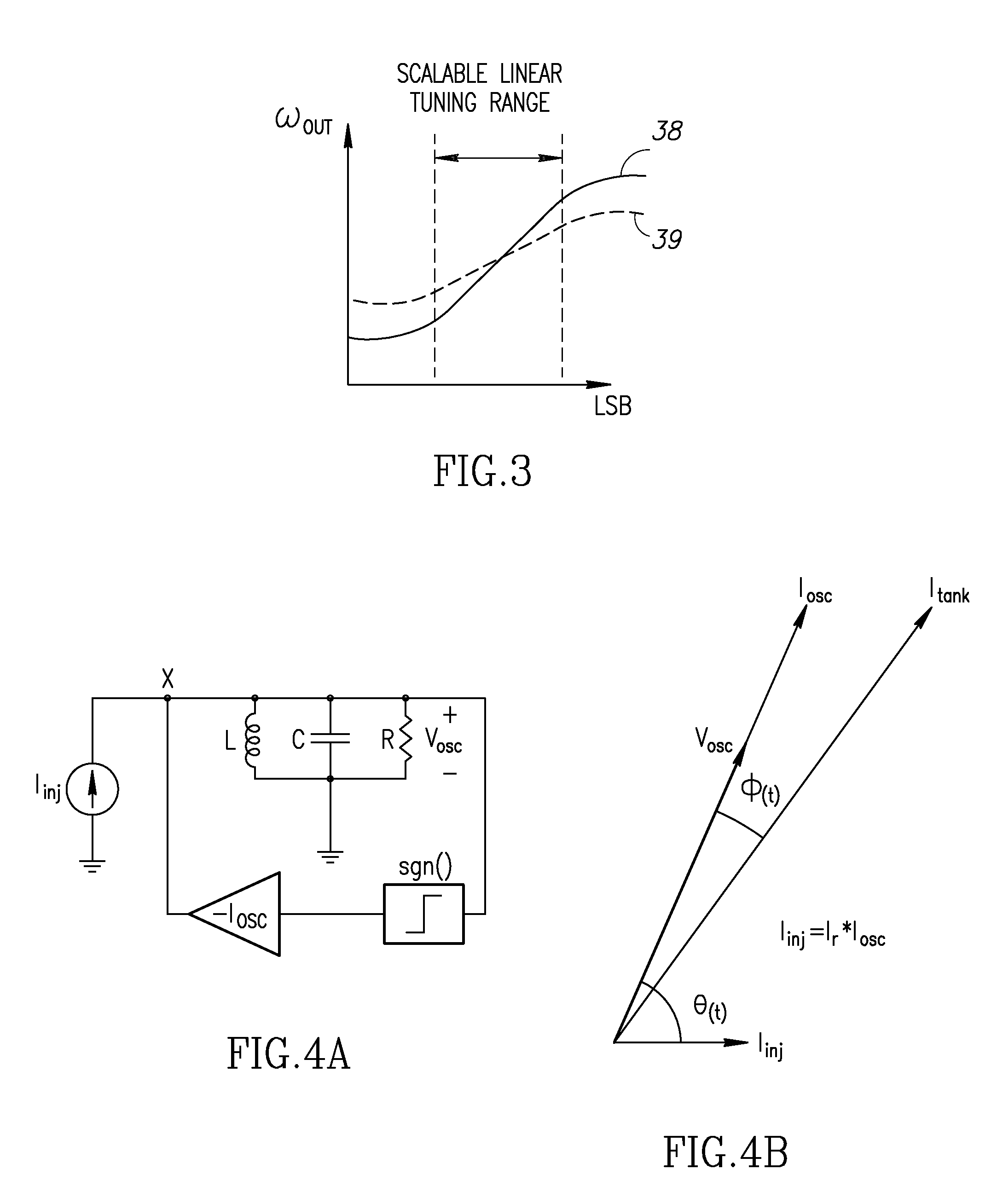
A novel and useful digitally controlled injection-locked RF oscillator with an auxiliary loop. The oscillator is injection locked to a time delayed version of its own resonating voltage (or its second harmonic) and its frequency is modulated by manipulating the phase and amplitude of injected current. The oscillator achieves a narrow modulation tuning range and fine step size of an LC tank based digitally controlled oscillator (DCO). The DCO first gets tuned to its center frequency by means of a conventional switched capacitor array. Frequency modulation is then achieved via a novel method of digitally controlling the phase and amplitude of injected current into the LC tank generated from its own resonating voltage. A very linear deviation from the center frequency is achieved with a much lower gain resulting in a very fine resolution DCO step size and high linearity without needing to resort to oversampled noise shaped dithering.
Owner:SHORT CIRCUIT TECH LLC
Gated ring oscillator for a time-to-digital converter with shaped quantization noise
ActiveUS8138843B2Continuously circulated pulse countersCounting chain synchronous pulse countersDigital down converterImage resolution
Described is a compact, lower power gated ring oscillator time-to-digital converter that achieves first order noise shaping of quantization noise using a digital implementation. The gated ring oscillator time-to-digital converter includes a plurality of delay stages configured to enable propagation of a transitioning signal through the delay stages during an enabled state and configured to inhibit propagation of the transitioning signal through the delay stages during a disabled state. Delay stages are interconnected to allow sustained transitions to propagate through the delay stages during the enabled state and to preserve a state of the gated ring oscillator time-to-digital converter during the disabled state. The state represents a time resolution that is finer than the delay of at least one of the delay stages. A measurement module determines the number of transitions of the delay stages.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
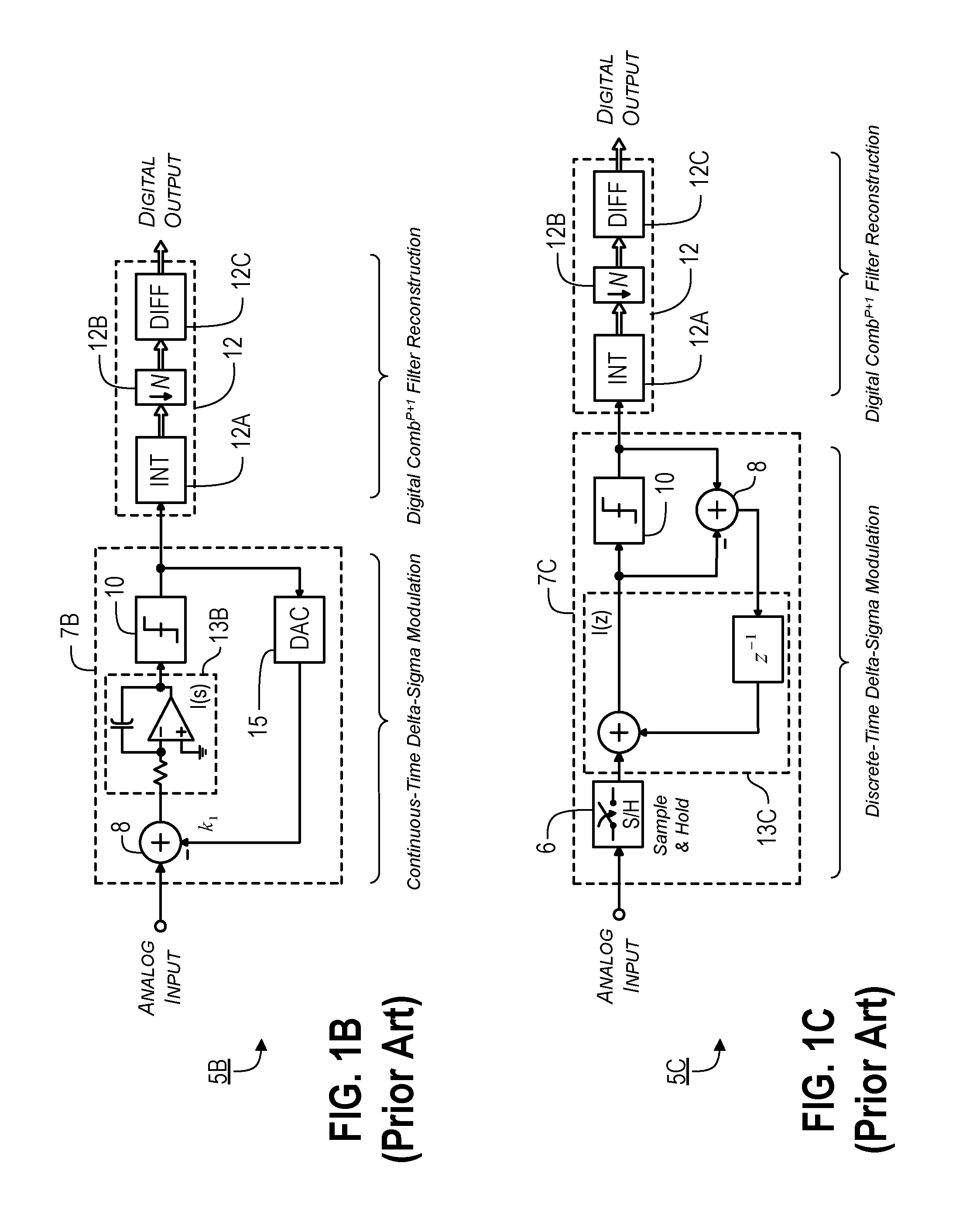
Multimode Sampling/Quantization Converters
ActiveUS20110163900A1High resolutionGood combination of high resolutionElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionBandpass filteringNoise shaping
Provided are, among other things, systems, methods and techniques for converting a continuous-time, continuously variable signal into a sampled and quantized signal. According to one implementation, an apparatus includes multiple processing branches, each including: a continuous-time quantization-noise-shaping circuit, a sampling / quantization circuit, and a digital bandpass filter. A combining circuit then combines signals at the processing branch outputs into a final output signal. The continuous-time quantization-noise-shaping circuits include adjustable circuit components for changing their quantization-noise frequency-response minimum, and the digital bandpass filters include adjustable parameters for changing their frequency passbands.
Owner:PAGNANELLI FAMILY TRUST
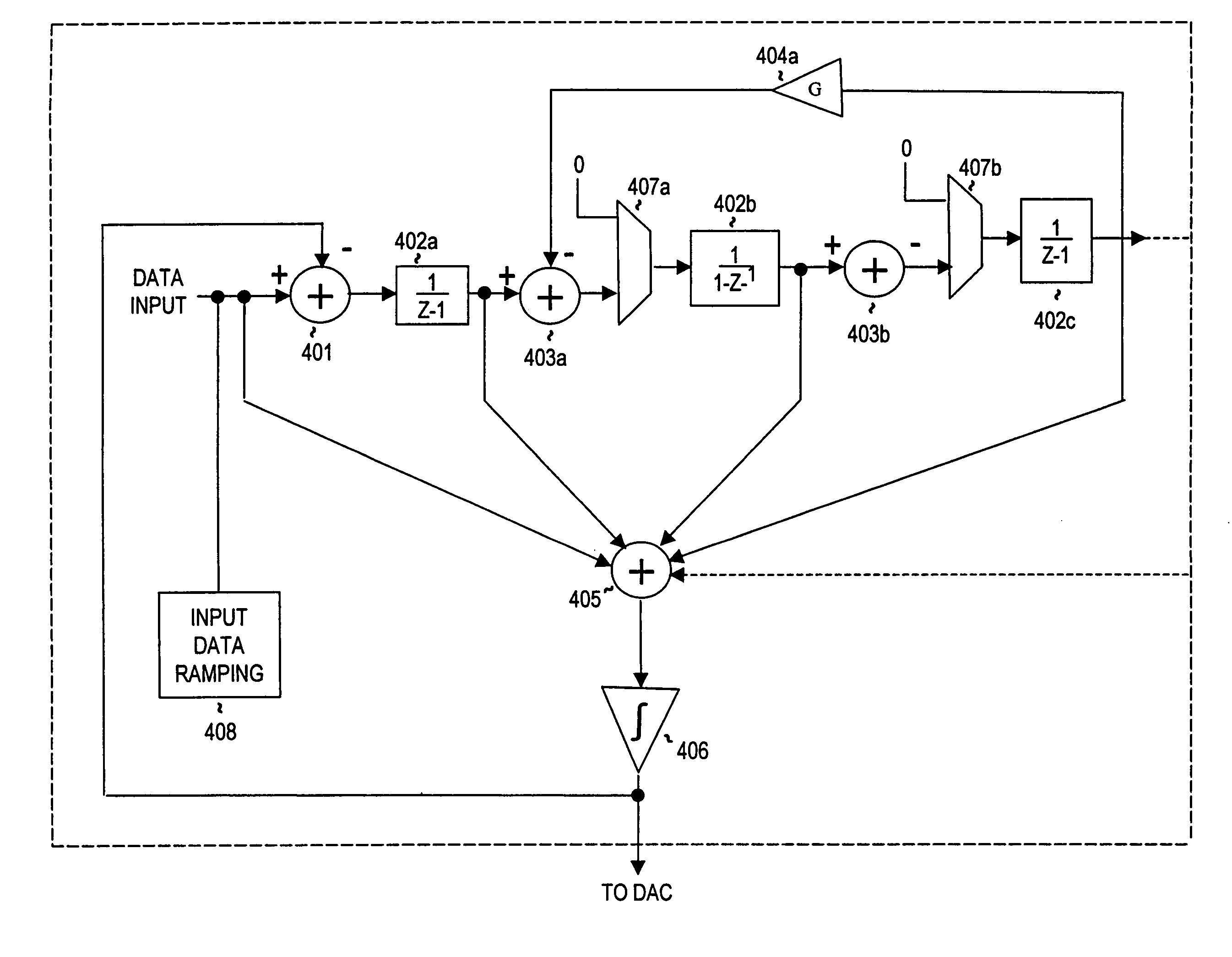
Feedback steering delta-sigma modulators and systems using the same
InactiveUS6933871B2Reduce and eliminate outputDigital variable displayElectric signal transmission systemsNoise shapingDigital-to-analog converter
A digital to analog converter including an input for receiving an input signal, a ramp generator, and a delta-sigma modulator responsive to the input signal and an output of the ramp generator. An order of a noise shaping transfer function of the delta-sigma modulator is response to a level of the output of the ramp generator.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Low-Noise, Low-Distortion Digital PWM Amplifier
InactiveUS20090027117A1Compensation delayAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceGain controlLow noiseLow distortion
Systems and methods for performance improvements in digital switching amplifiers using low-pass filtering to reduce noise and distortion. In one embodiment, a digital pulse width modulation (PWM) amplifier includes a signal processing plant configured to receive and process an input audio signal. The amplifier also includes a low-pass filter configured to filter audio signals output by the plant. The filtered output of the plant is added to the input audio signal as feedback. The plant may consist of a modulator and power switch, a noise shaper, or any other type of plant. An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) may be provided to convert the output audio signal to a digital signal. Filtering may be implemented before or after the ADC, and a decimator may be placed after the ADC if it is an oversampling ADC.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com