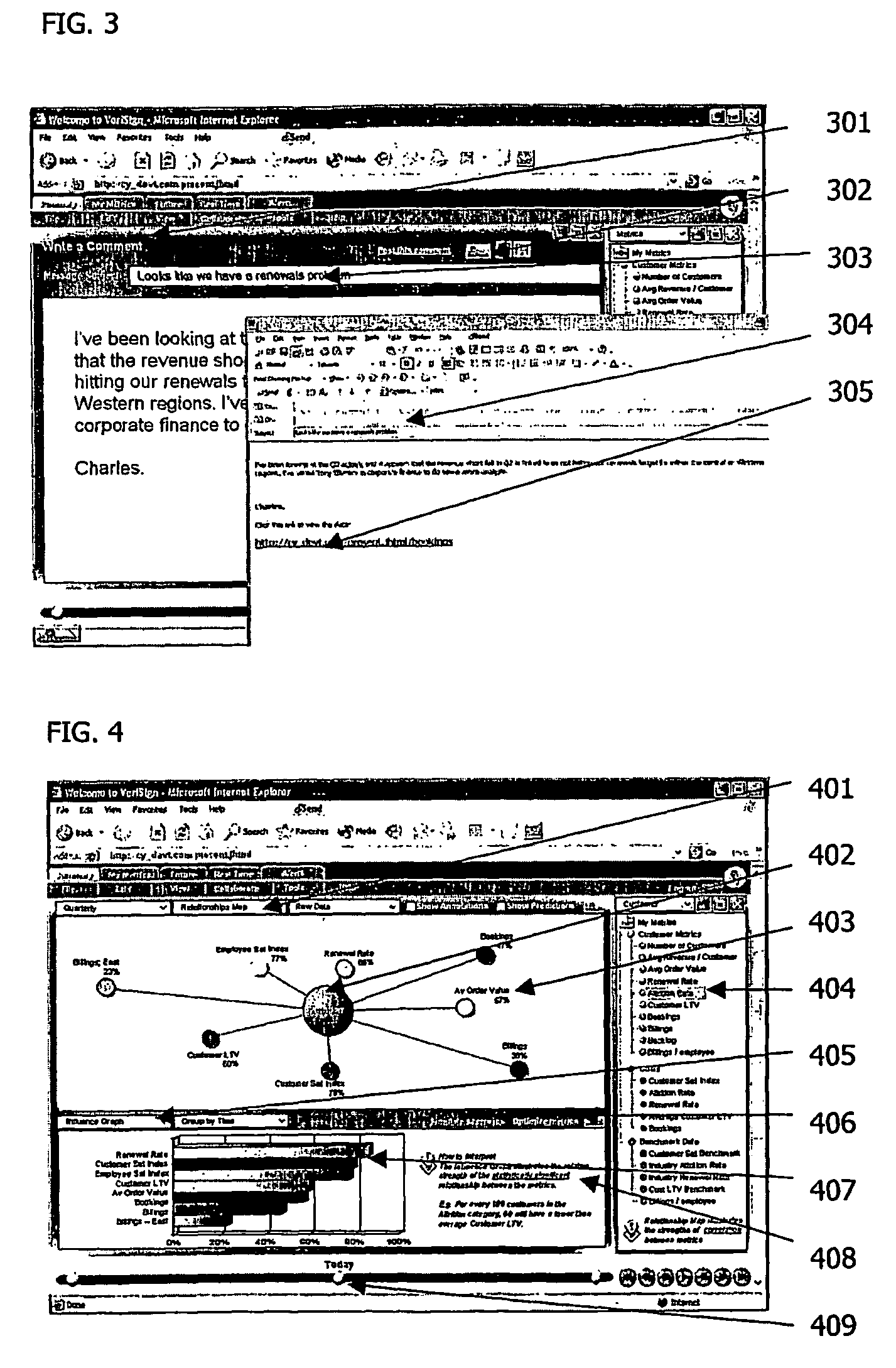
Patents
Literature
6078 results about "Time delayed" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Time delay in British. (taɪm dɪˈleɪ) noun. 1. a delay that separates the occurrence of two events. Soviet scientists believed the bacteria survive in a quiescent form, but this would imply a shorter time delay between population peaks and outbreaks.
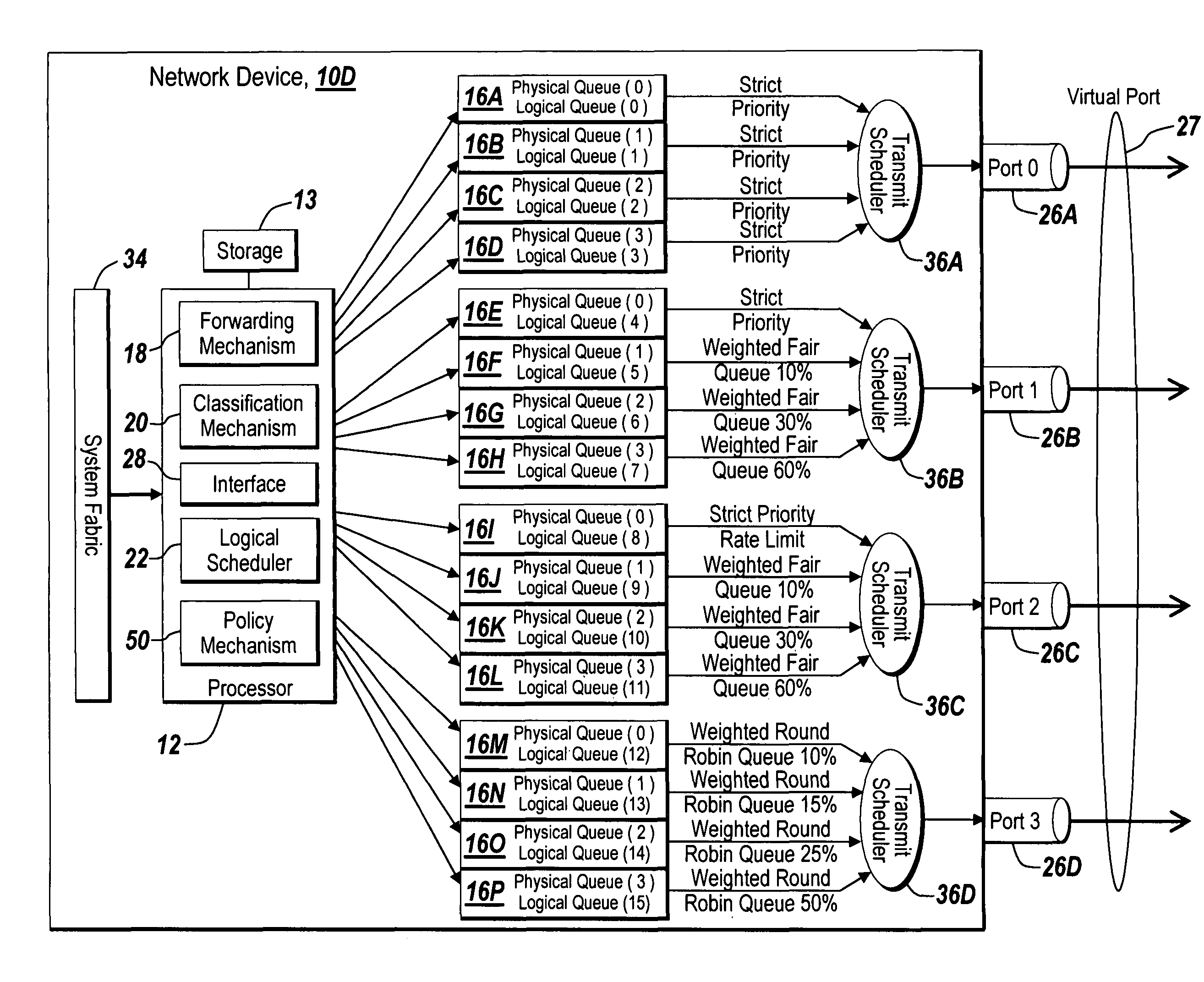
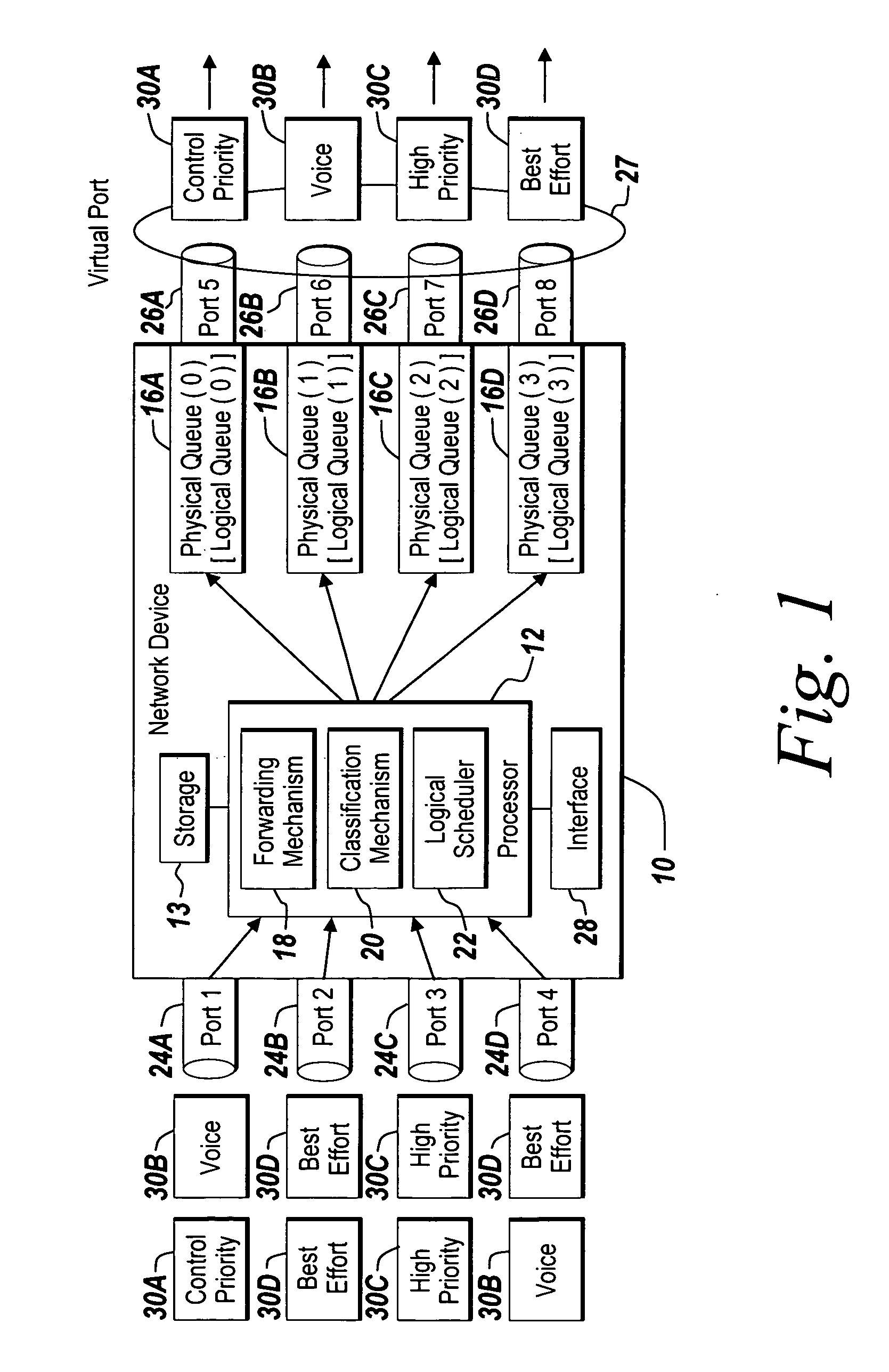
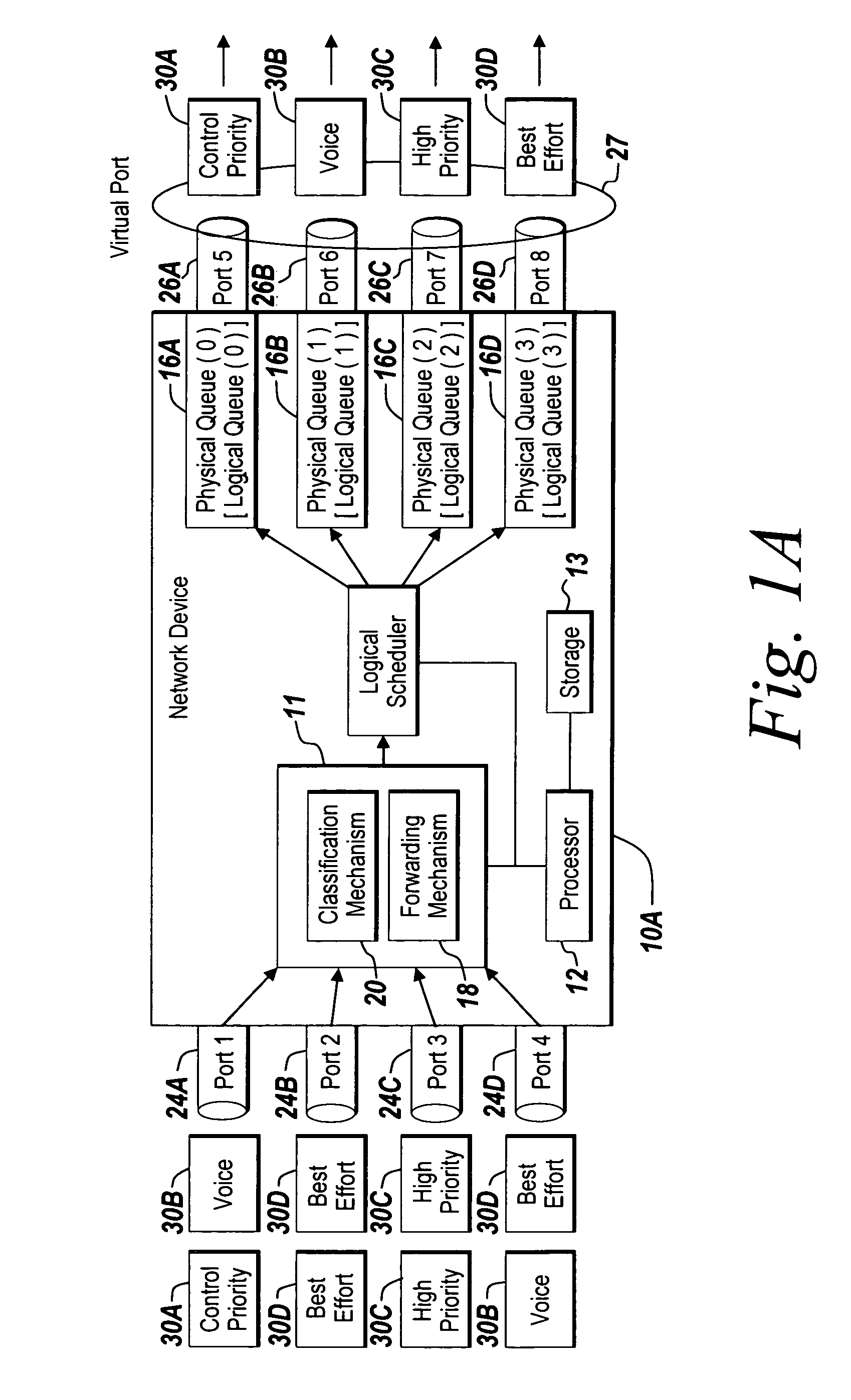
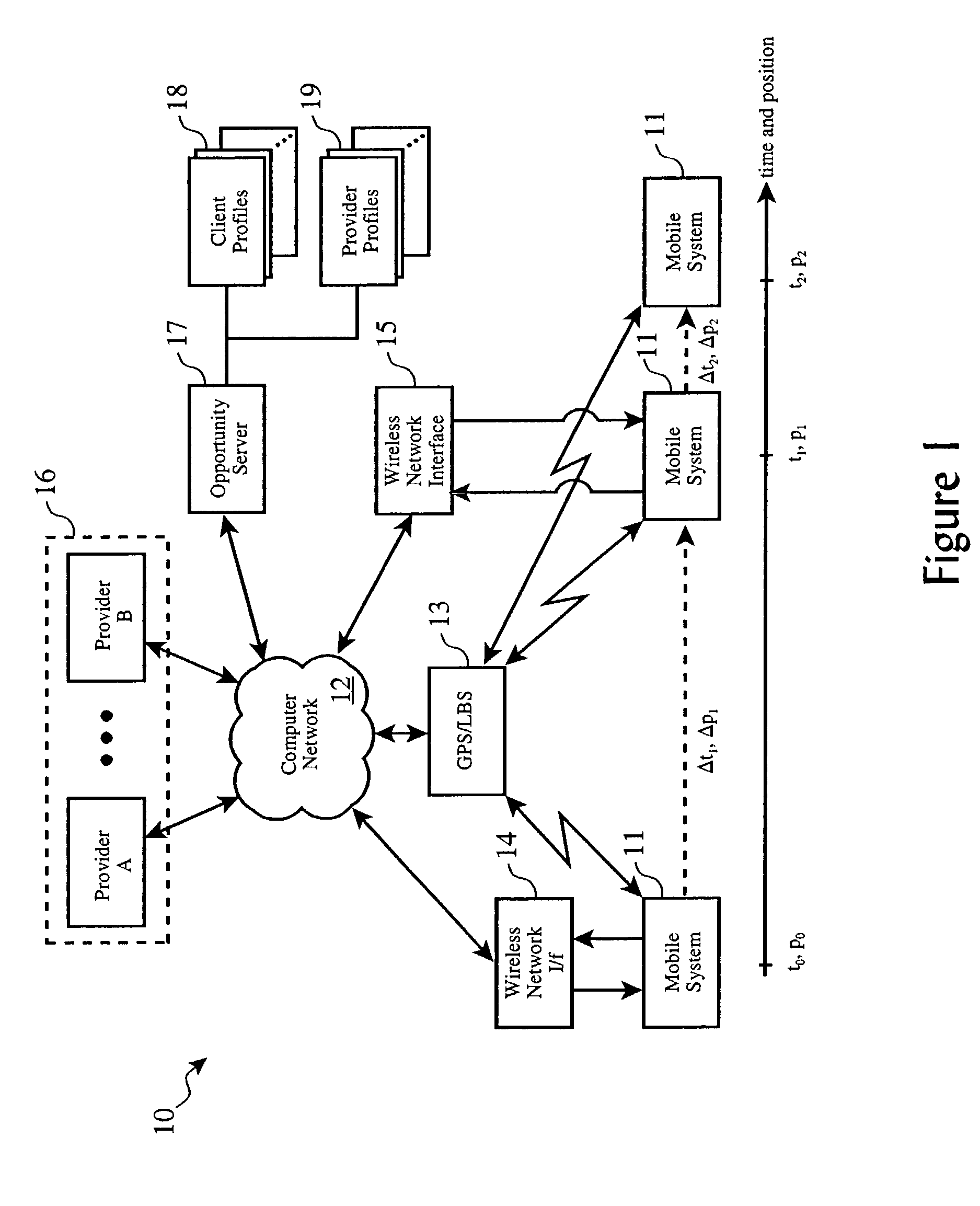
Method and apparatus of virtual class of service and logical queue representation through network traffic distribution over multiple port interfaces
ActiveUS7936770B1Improve abilitiesIncrease volumeMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityVirtual class
A method and apparatus are provided that allows for the representation of a larger number of classes of network traffic and logical queues than is physically available on a per port basis within a network device. A number of logical queues, whose number can match the number of classes of network traffic a network device handles, may be supported across an aggregated set of ports even though the network device has fewer physical queues per port than there are classes of network traffic. The method and apparatus improve the management of network traffic sensitive to time delay and jitter, and further facilitates the operation of these applications in a simultaneous or near simultaneous manner.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
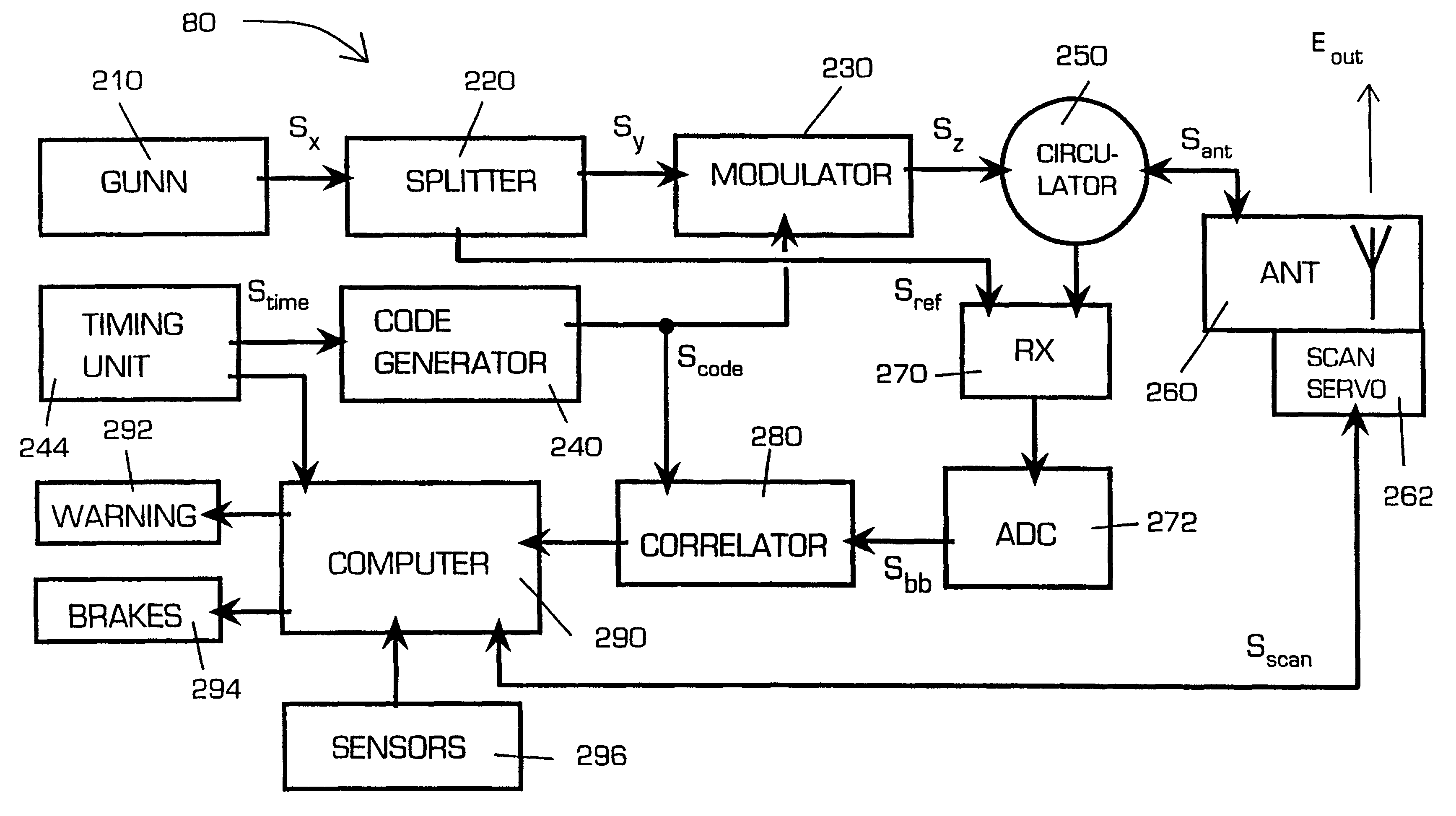
Proximity measuring apparatus
InactiveUS6614387B1Reduced risk of collisionAnti-collision systemsCode division multiplexMeasurement deviceSignature Code
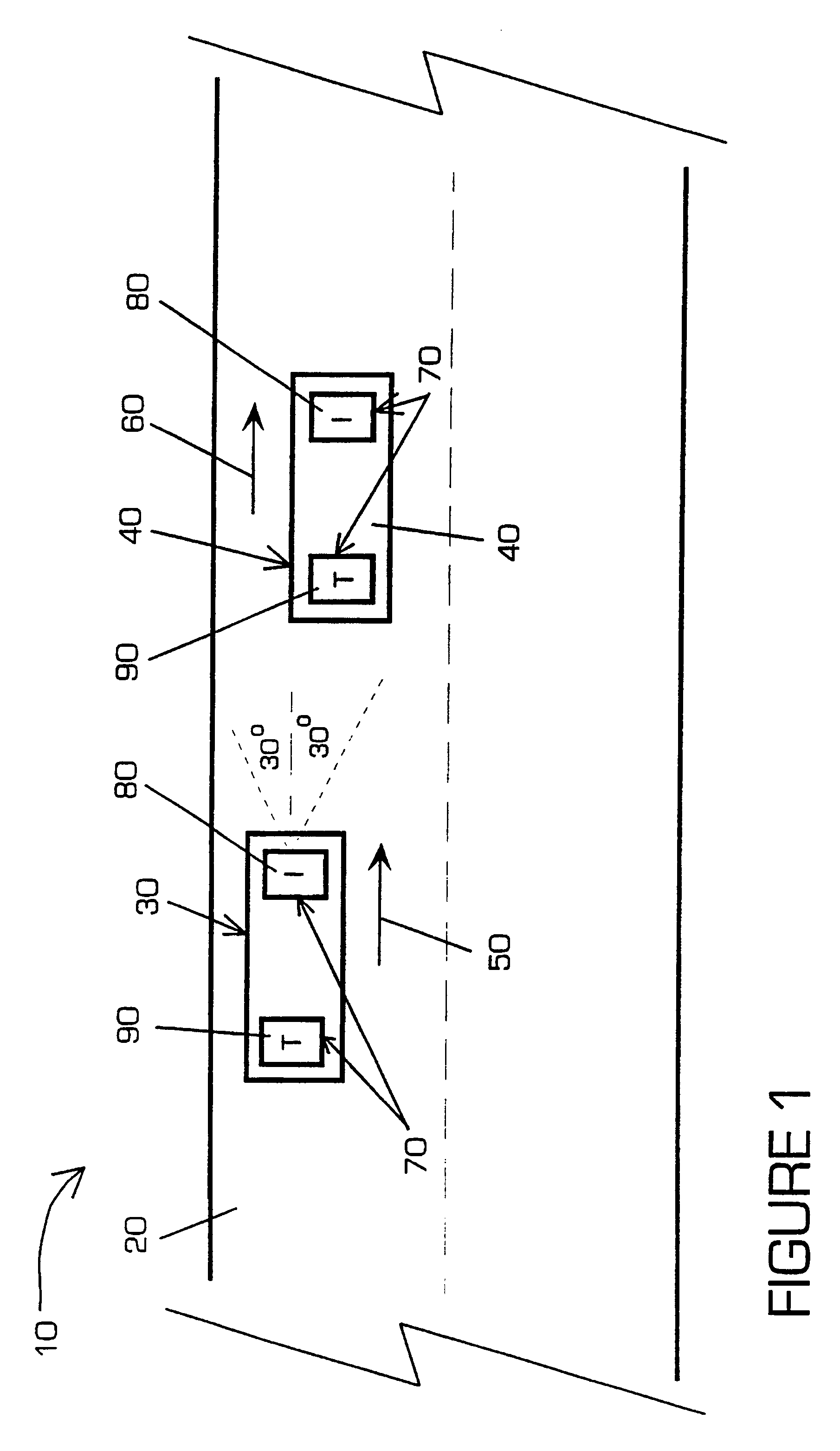
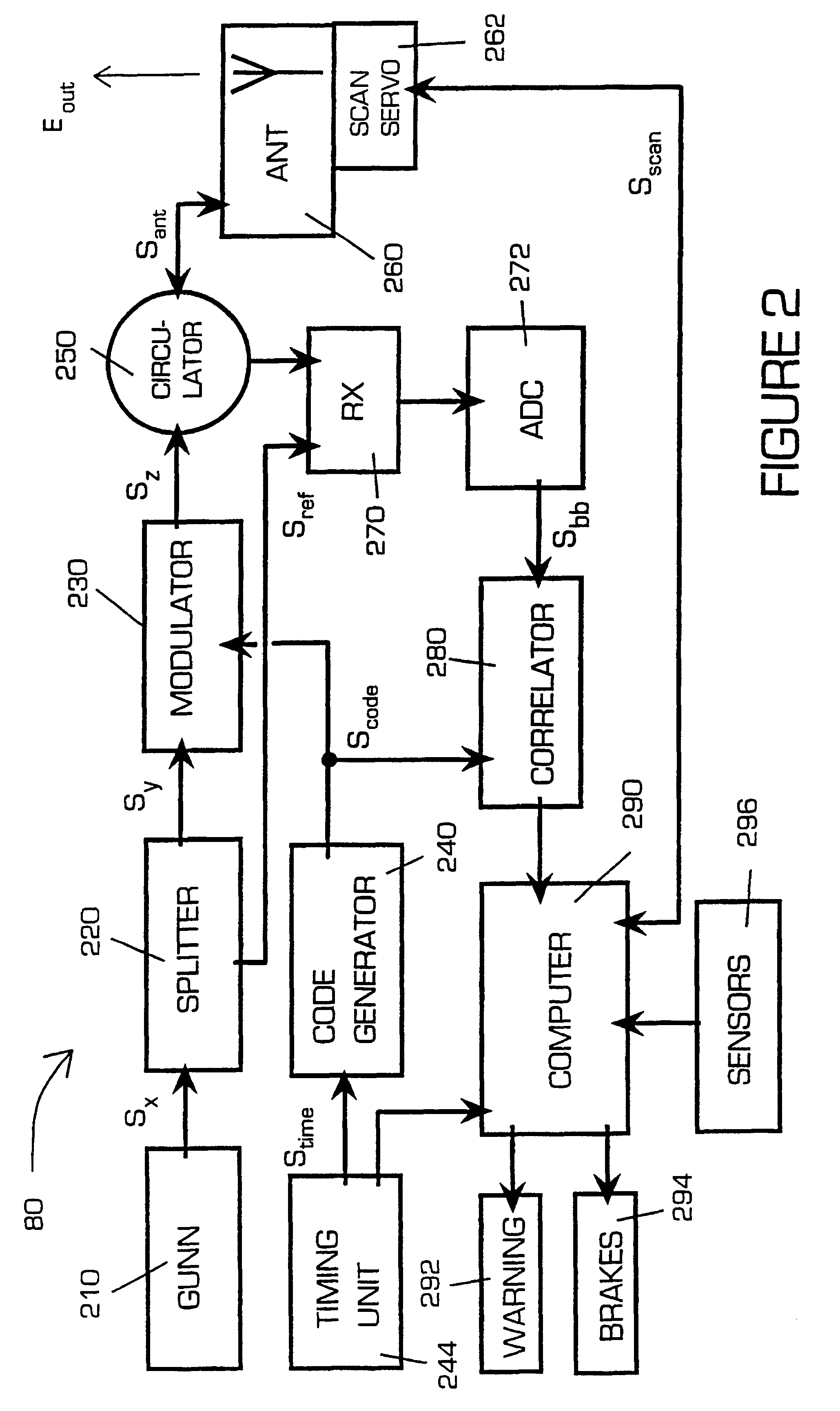
A proximity measuring apparatus (70) comprises an interrogator (80) for generating an interrogation signal encoded with a reference signature code comprising concatenated codes and emitting it as interrogating radiation. It also incorporates a transponder (90) for receiving the interrogating radiation, demodulating it to extract its signature code and then remodulating it after a delay period to provide a signal for reemission as return radiation therefrom. The interrogator (80) receives return radiation at its antenna (260) and demodulates it to extract its signature code and then correlates the code with the reference code to determine mutual correlation thereof. The interrogator (80) incorporates a computer (290) for controlling a scan direction of the antenna (260) and for measuring time delay between emission of the interrogating radiation therefrom and receipt of corresponding return radiation. The computer (290) computes distance and relative bearing of a transponder (90) providing the return radiation from the scan direction and the time delay. The apparatus (70) may be used for improving road vehicle safety.
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
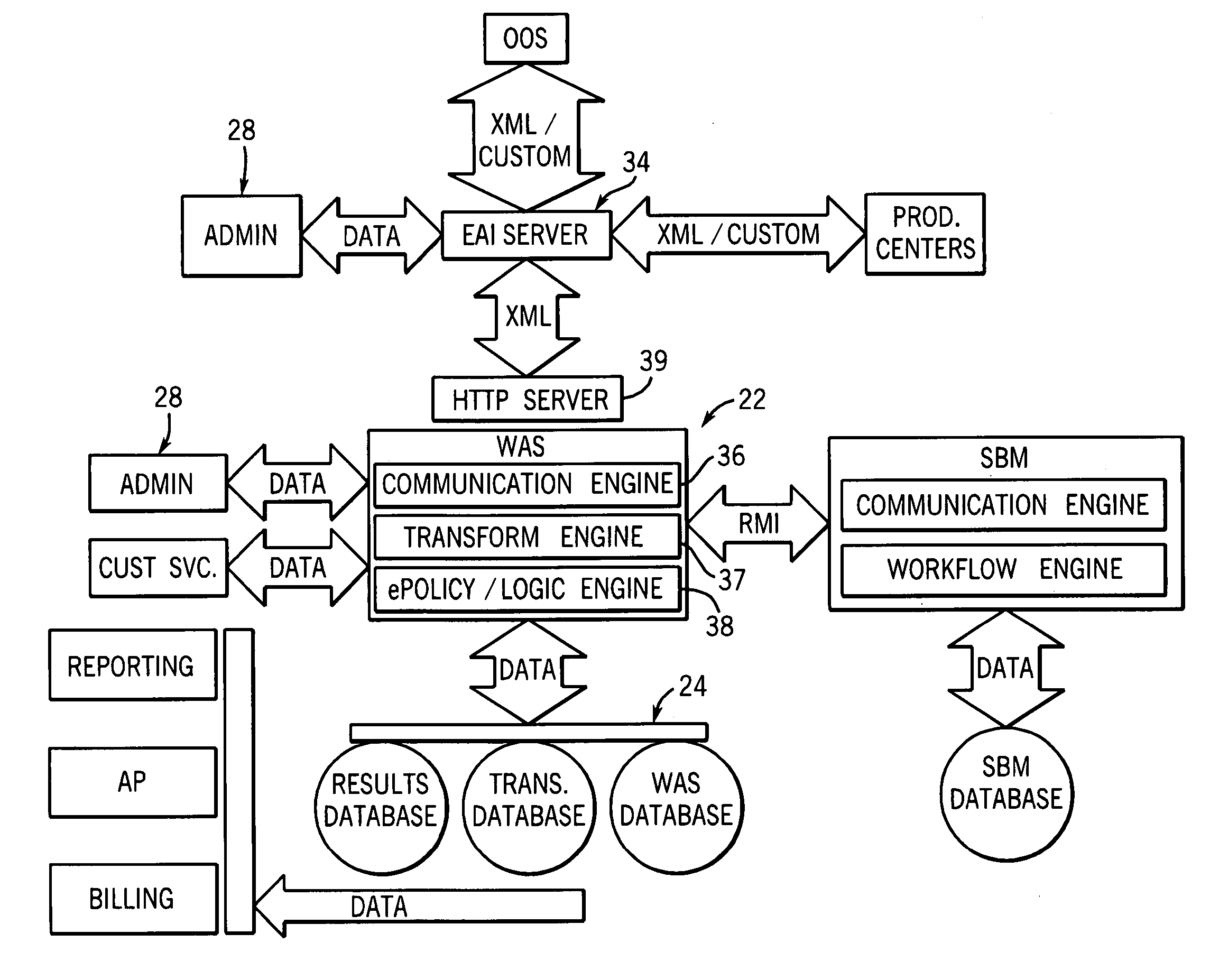
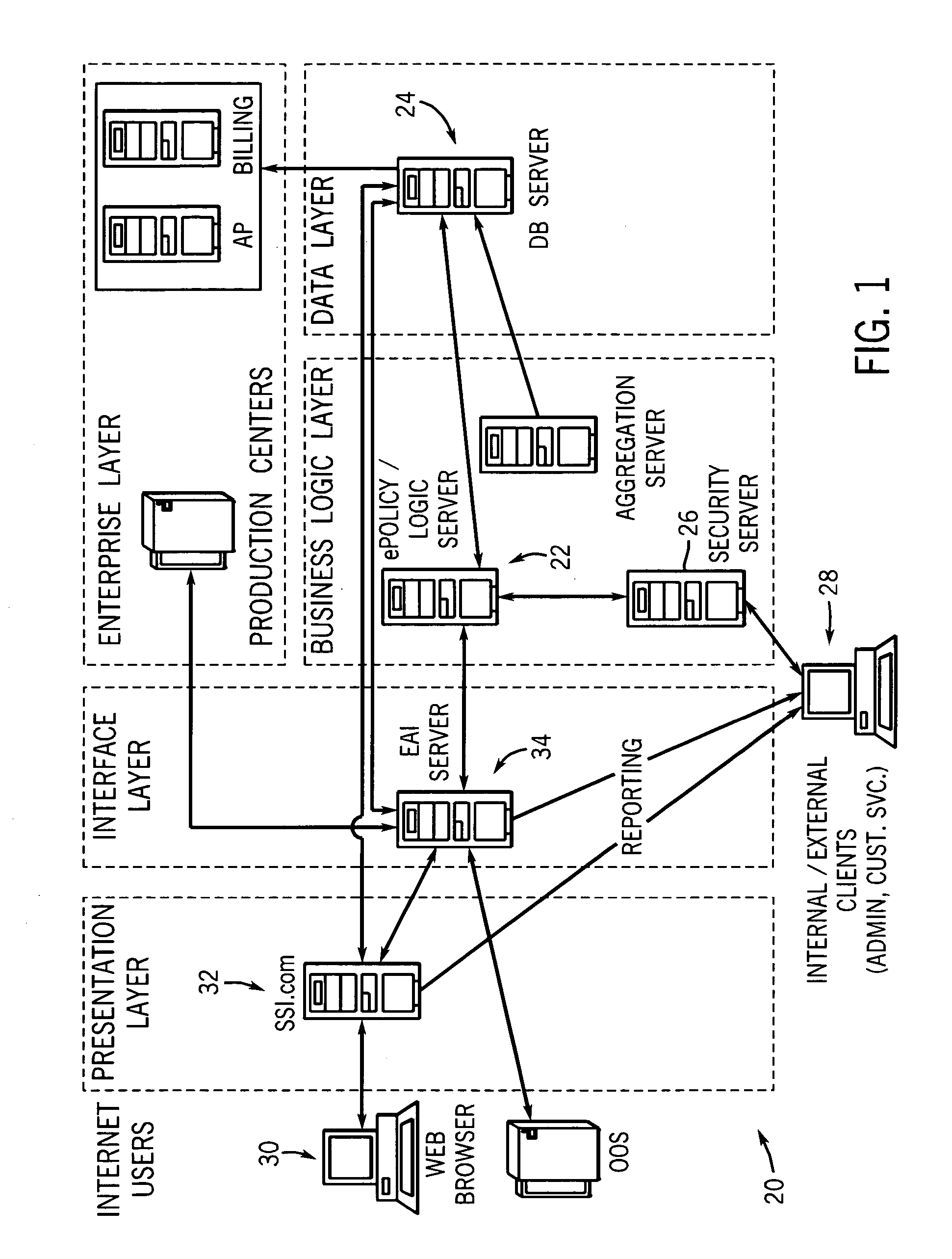
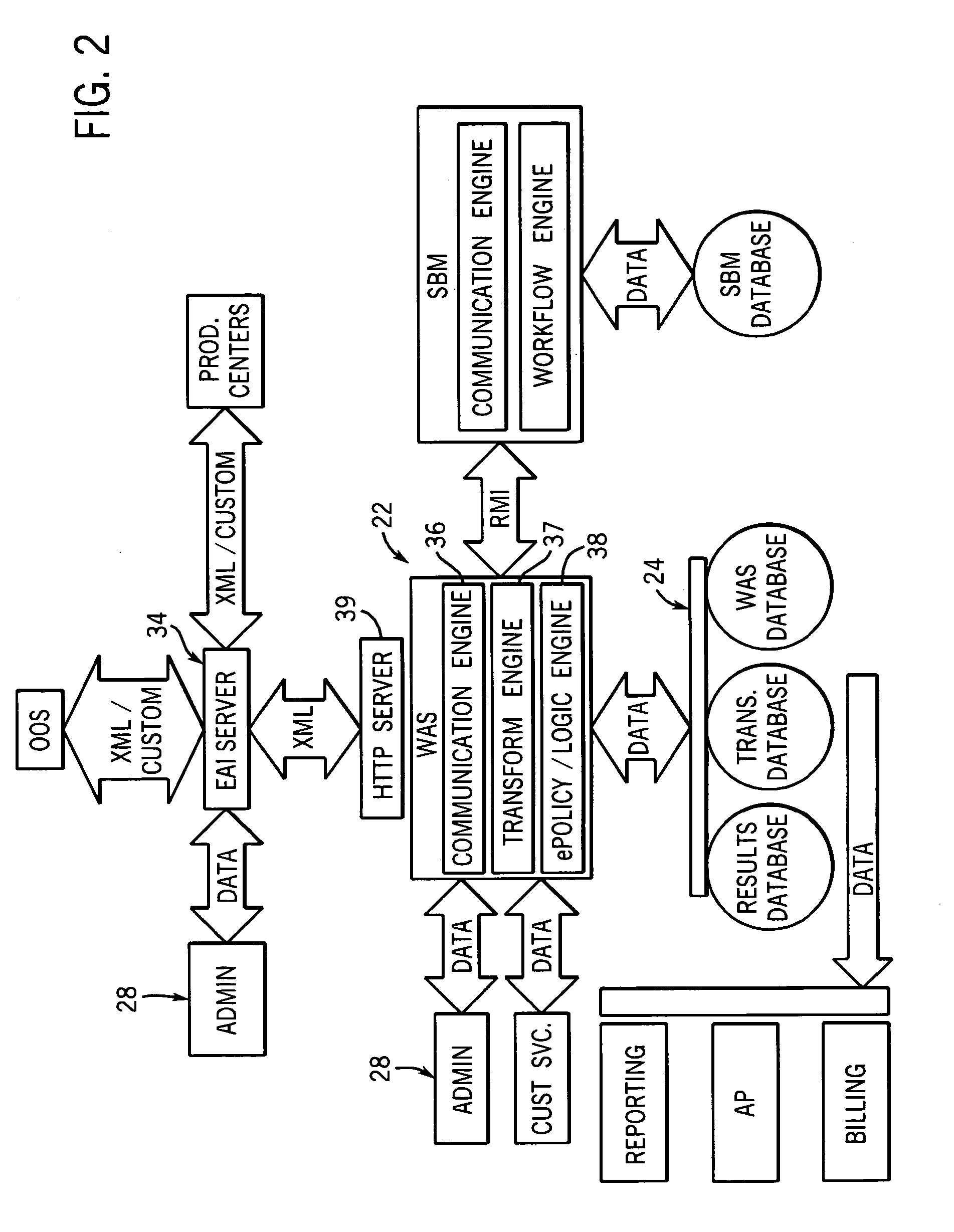
Computer system and method for business data processing
ActiveUS20060167704A1Improve predictabilityImprove performanceOffice automationCommerceTime informationBusiness Personnel
The system enables business people to understand the impact of business transactions, changes and events in real-time using advanced rules and analytics to filter, categorize and interpret the significance of streams of real-time information. Most business performance analysis today is done manually and this process is a time consuming and skilled task leading to a time delay in producing the analysis. This time lag between the transaction or event happening and being able to take action on the analysis is measured in weeks or months at many companies. By blending real-time information with historical data and performance goals, this system enables business users to assess business events and collaborate within teams to drive optimal business performance. Using forecasting techniques enables business managers to predict the likelihood of achieving a particular goal without relying on manual analysis by a skilled analyst. The system automatically updates the forecast based on real-time changing data, enabling the business manager to have an up to the minute and statistically valid projection of future business performance.
Owner:SEEWHY ACQUISITION CORP +1
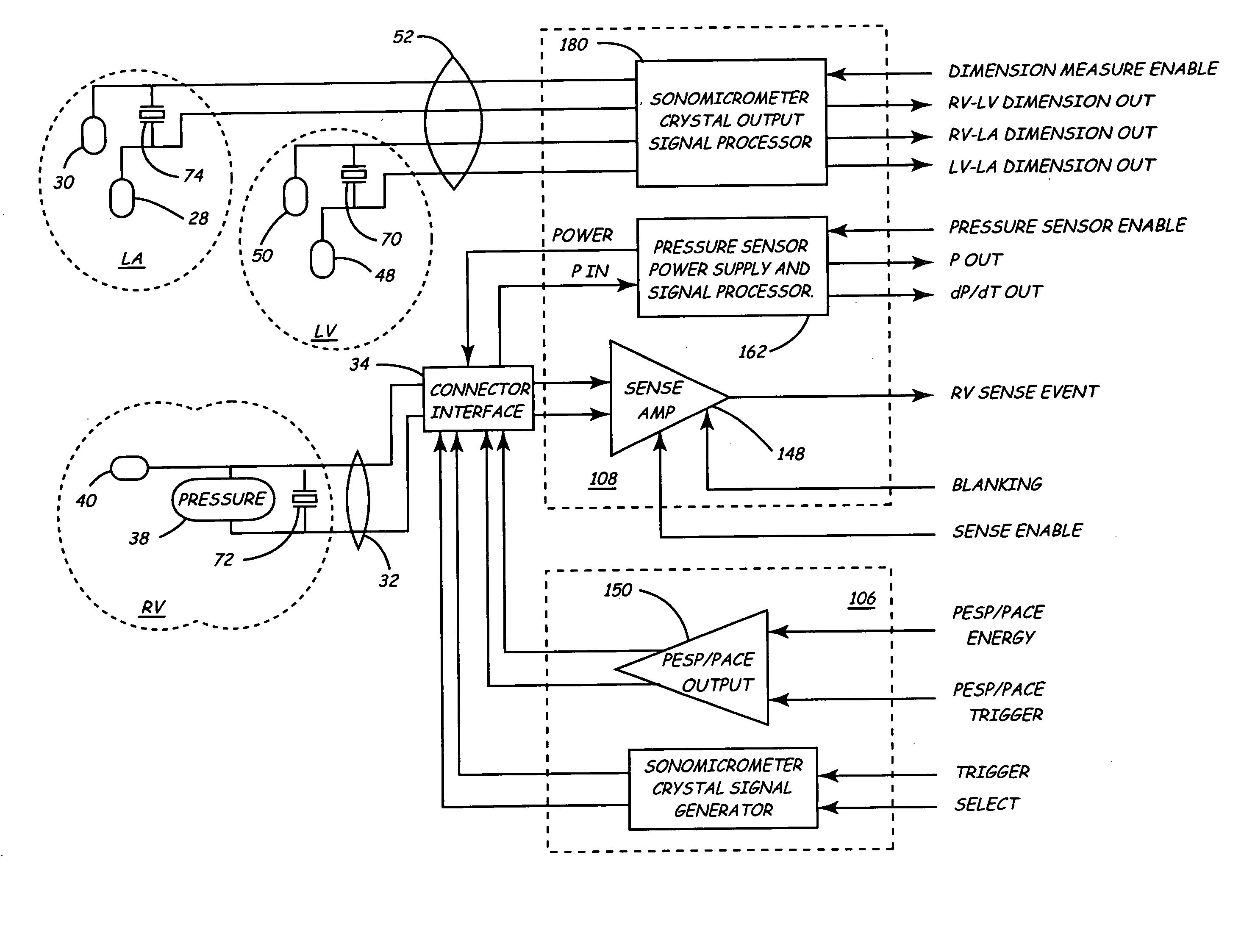
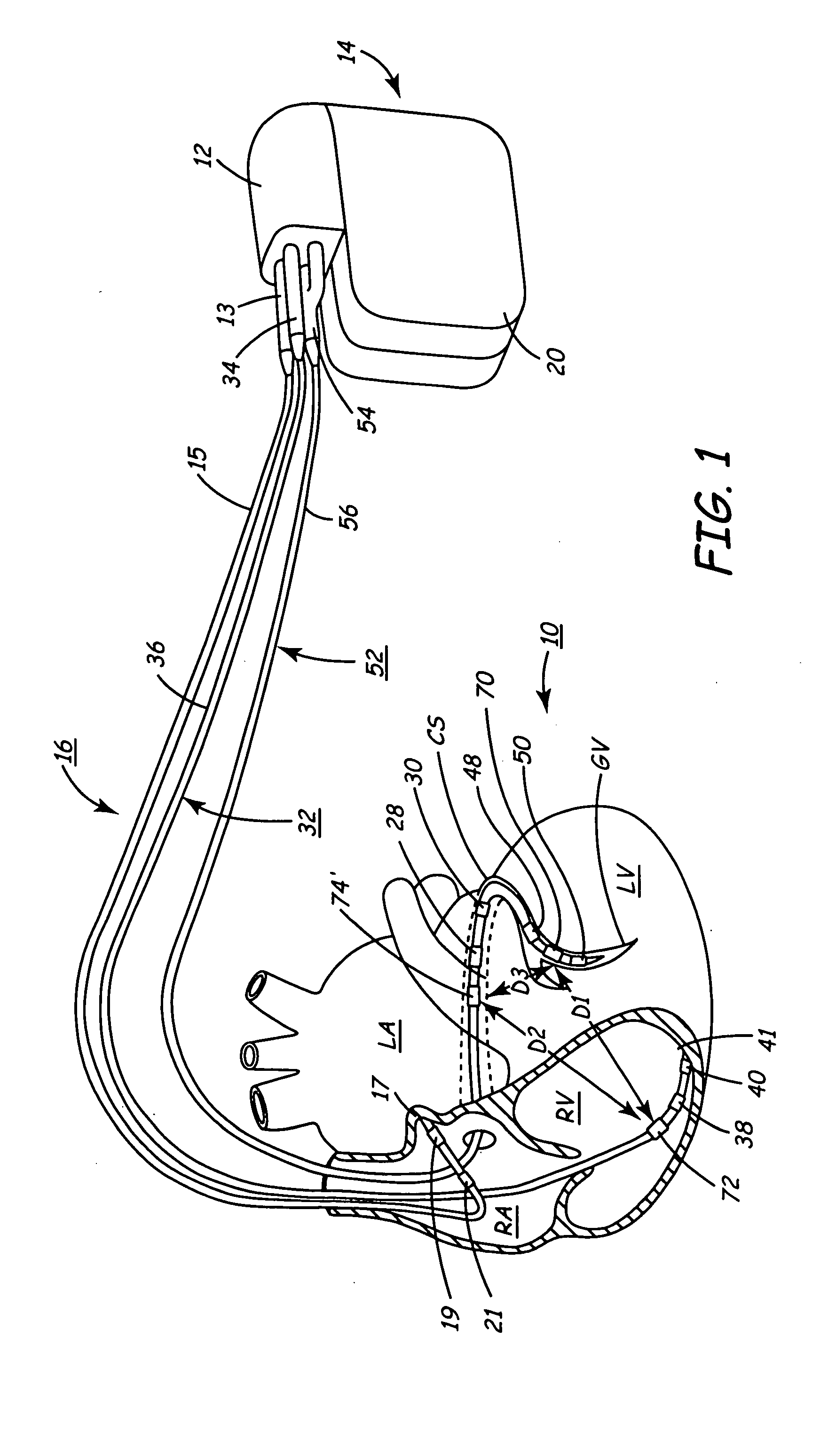
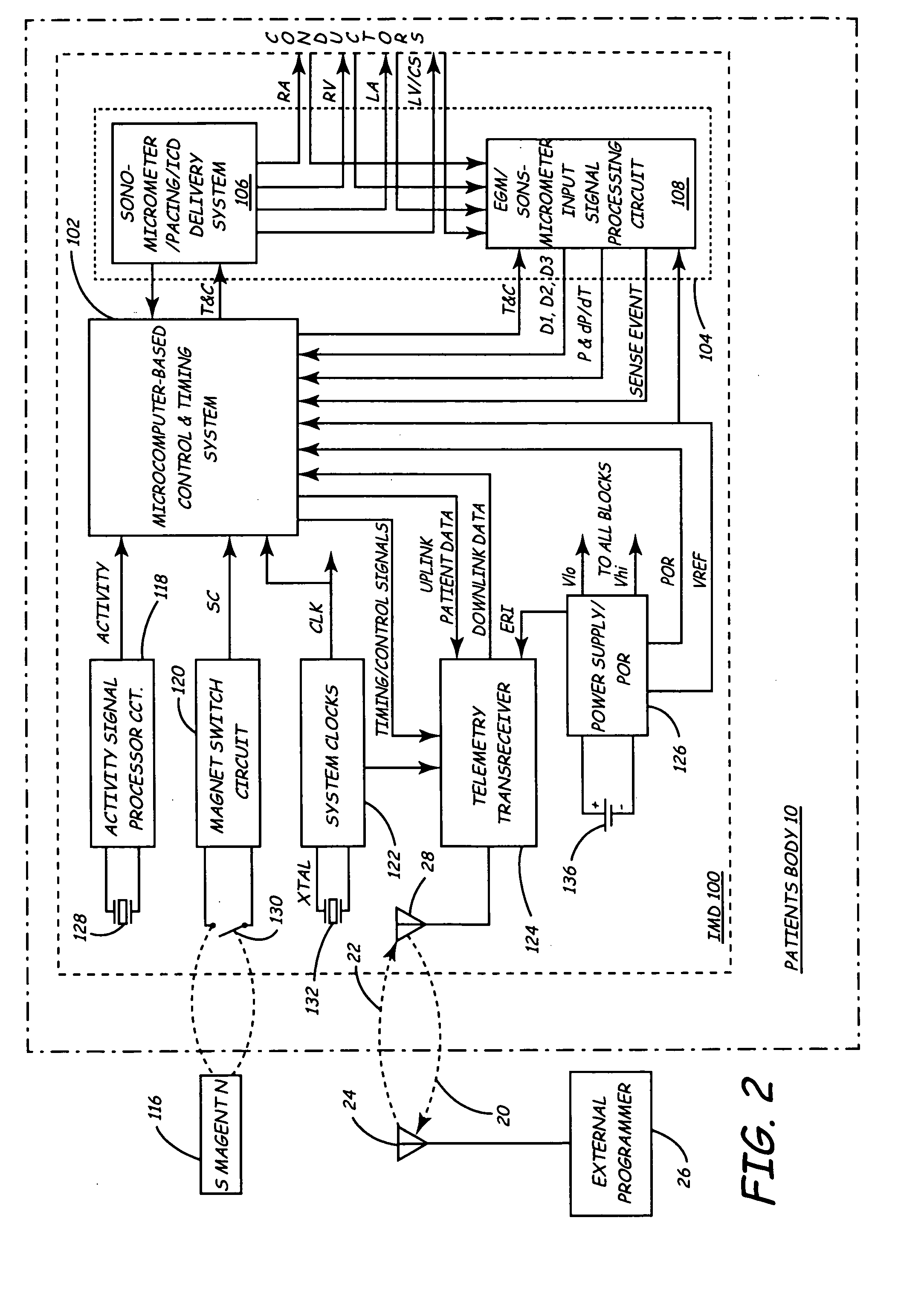
Implantable medical device for monitoring cardiac blood pressure and chamber dimension
InactiveUS20050027323A1Maximize cardiac outputConvenient timeCatheterHeart stimulatorsSonificationHeart chamber
Implantable medical devices (IMDs) for monitoring signs of acute or chronic cardiac heart failure by measuring cardiac blood pressure and mechanical dimensions of the heart and providing multi-chamber pacing optimized as a function of measured blood pressure and dimensions are disclosed. The dimension sensor or sensors comprise at least a first sonomicrometer piezoelectric crystal mounted to a first lead body implanted into or in relation to one heart chamber that operates as an ultrasound transmitter when a drive signal is applied to it and at least one second sonomicrometer crystal mounted to a second lead body implanted into or in relation to a second heart chamber that operates as an ultrasound receiver. The ultrasound receiver converts impinging ultrasound energy transmitted from the ultrasound transmitter through blood and heart tissue into an electrical signal. The time delay between the generation of the transmitted ultrasound signal and the reception of the ultrasound wave varies as a function of distance between the ultrasound transmitter and receiver which in turn varies with contraction and expansion of a heart chamber between the first and second sonomicrometer crystals. One or more additional sonomicrometer piezoelectric crystal can be mounted to additional lead bodies such that the distances between the three or more sonomicrometer crystals can be determined. In each case, the sonomicrometer crystals are distributed about a heart chamber such that the distance between the separated ultrasound transmitter and receiver crystal pairs changes with contraction and relaxation of the heart chamber walls.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
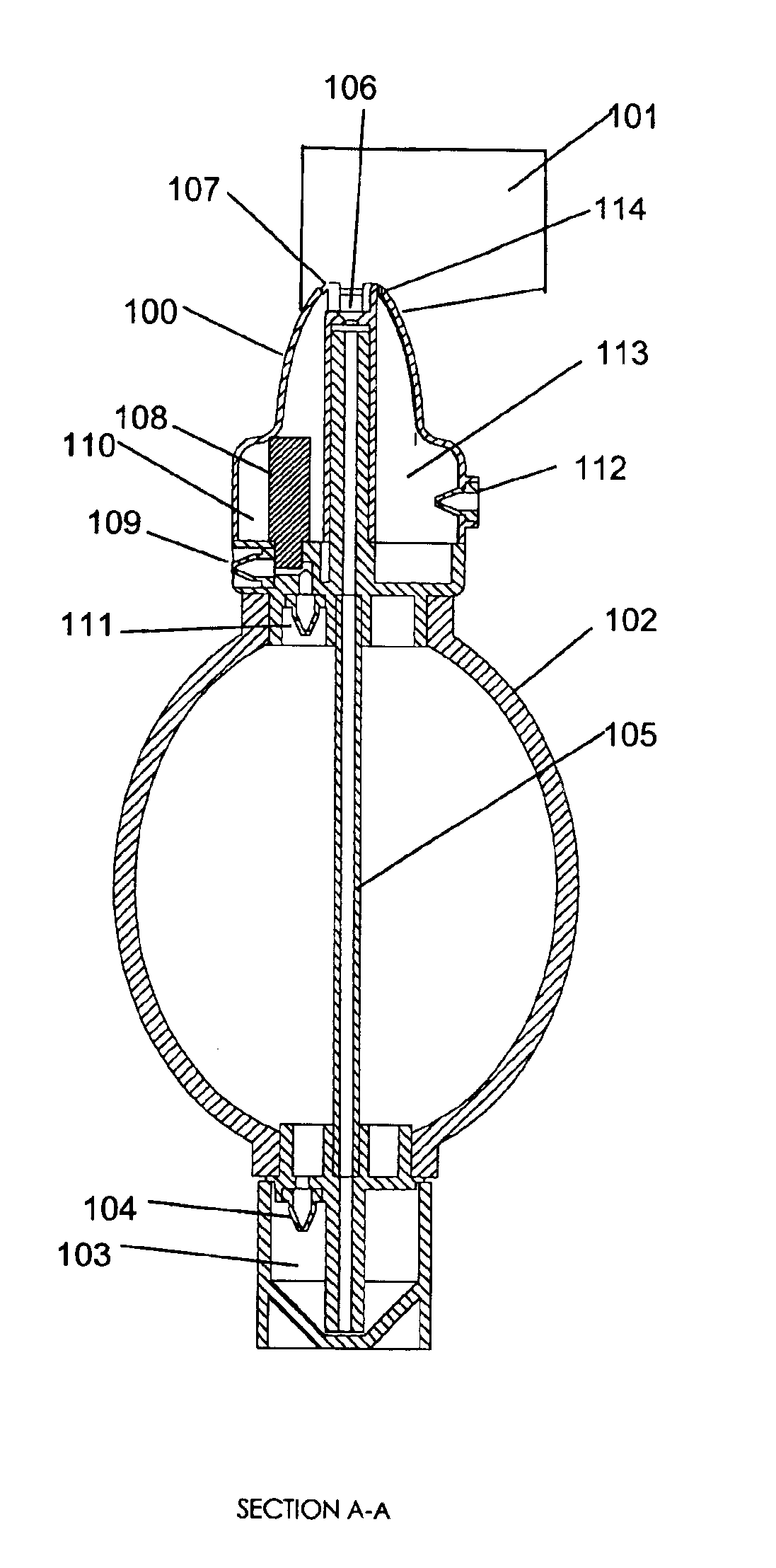
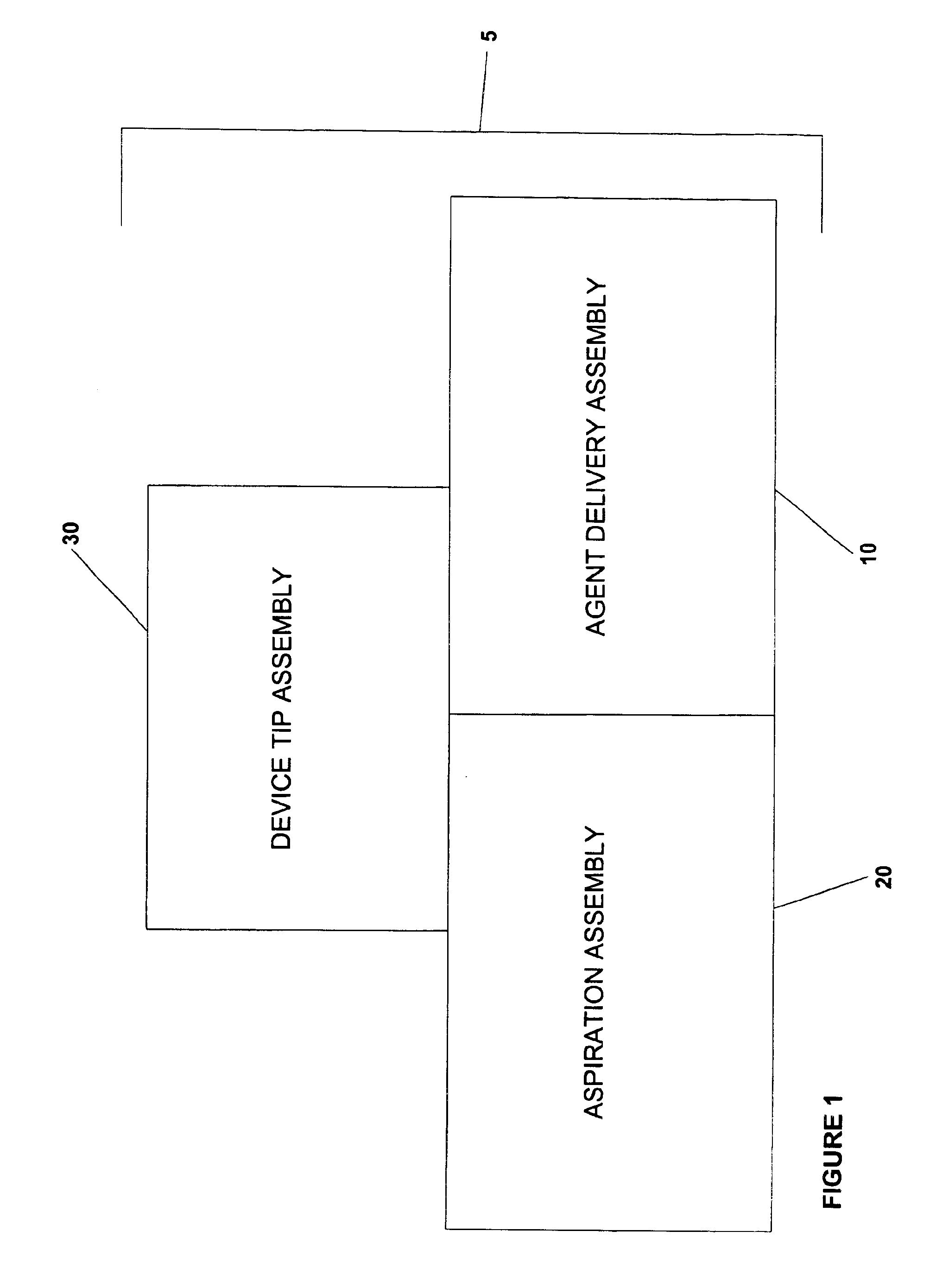
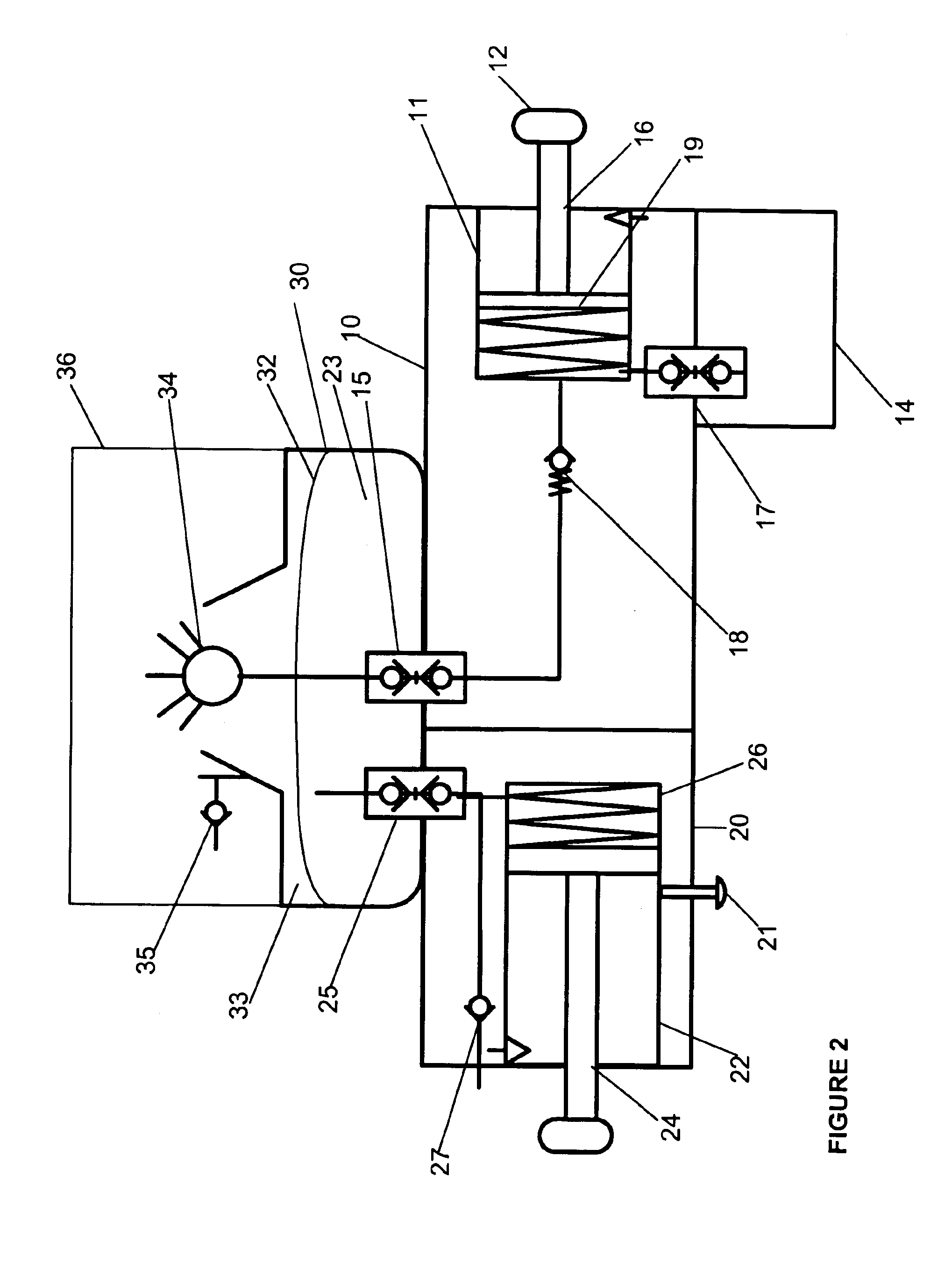
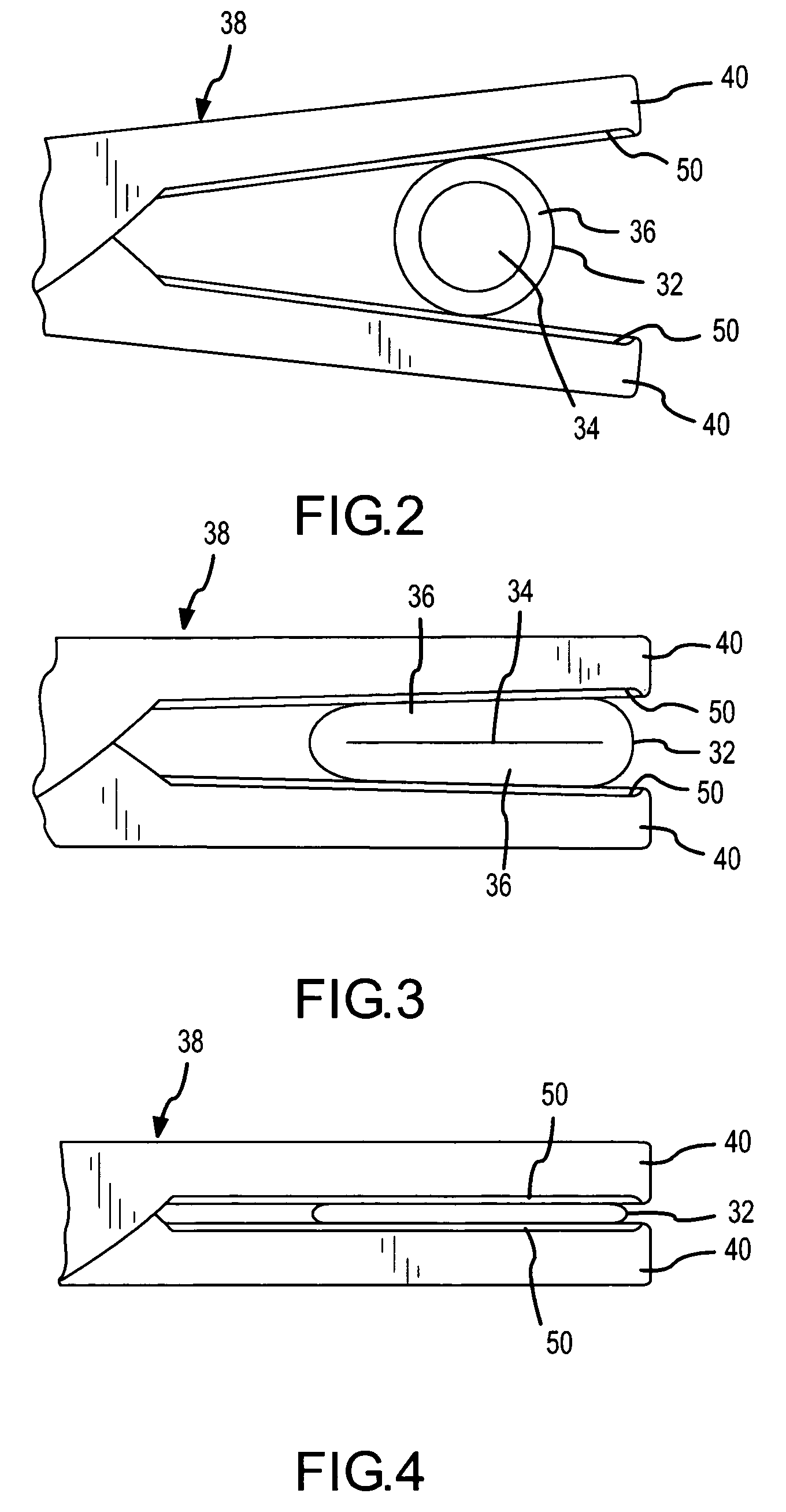
Agent delivery and aspiration device
The methods and devices disclosed provides for the delivery of agents to an orifice cavity and subsequent aspiration of the agent and orifice contents from the orifice cavity and related areas. In one form, the delivery and aspiration system comprises an agent delivery sub-assembly, an aspiration sub-assembly and a device tip sub-assembly. The subassemblies operate to first deliver an agent contained within the device to an orifice cavity and after an optional time delay, subsequently aspirate the delivered agent and orifice contents from the orifice cavity and related areas. In another form, a removable reservoir is provided whereby the aspirated agent and orifice contents from the orifice are assayed either independent of or within the device itself.
Owner:NDT
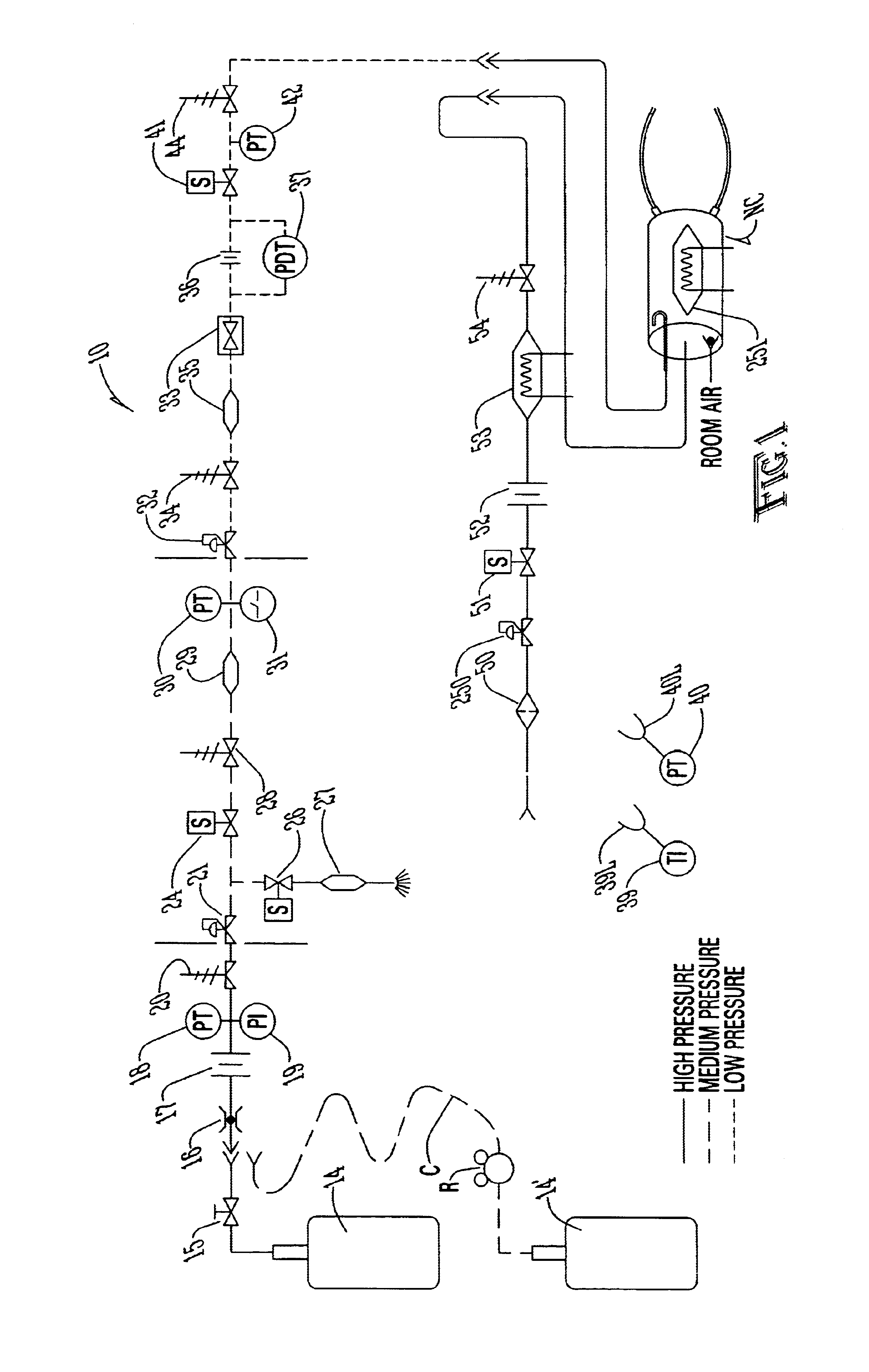
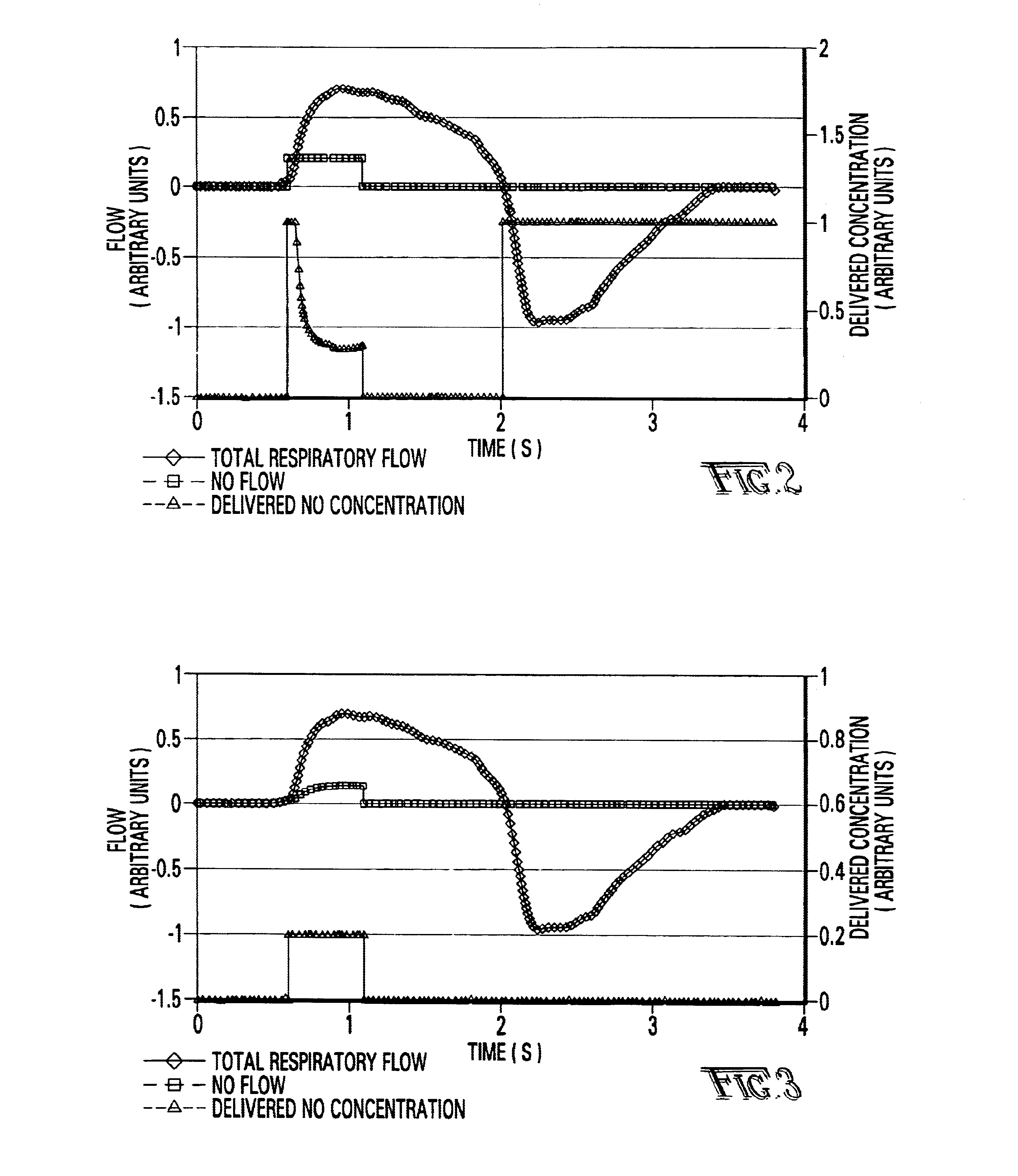
System and elements for managing therapeutic gas administration to a spontaneously breathing non-ventilated patient
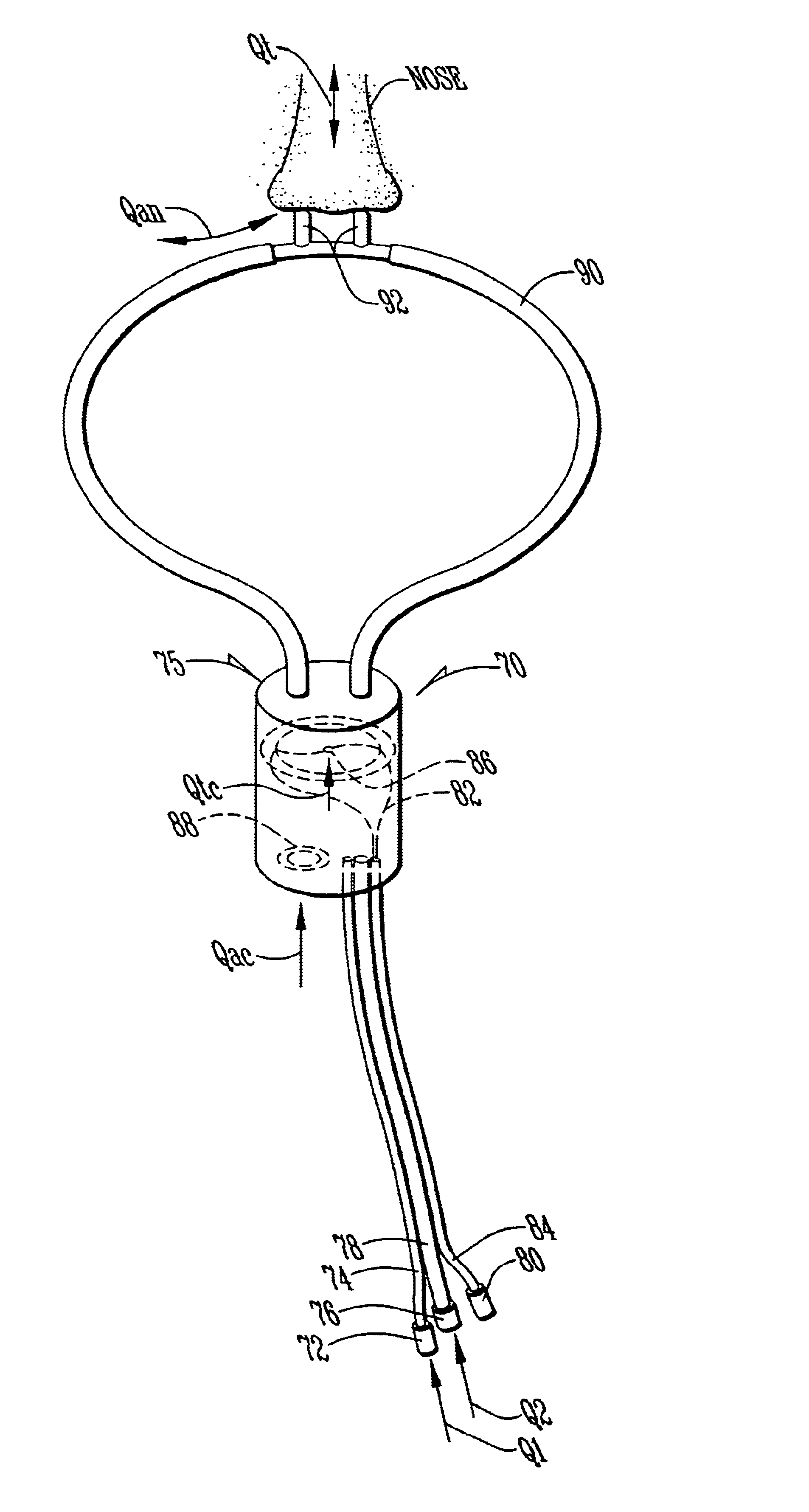
InactiveUS6668828B1Reduce in quantityLower the volumeOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksDistal portionNose
A system controls and manages administration of a therapeutic gas, such as NO, O2, or the like, to a spontaneously breathing, non-ventilated patient such that concentrated NO is as low as reasonably possible while delivering the desired amount of NO to the distal portions of the lungs. The system includes an entrainment cell that provides remote, turbulent mixing with low temporal latency and can be used with a nasal cannula or a mask. The entrainment cell uses room air to dilute the therapeutic gas; however, supplementary gases can also be used. A baffle can be included to promote mixing and a flow sensor can also be used if desired. Multiple ports can be included in the entrainment cell. An equalizing valve is also disclosed.
Owner:ADVANCED INHILATION THERAPIES AIT LTD
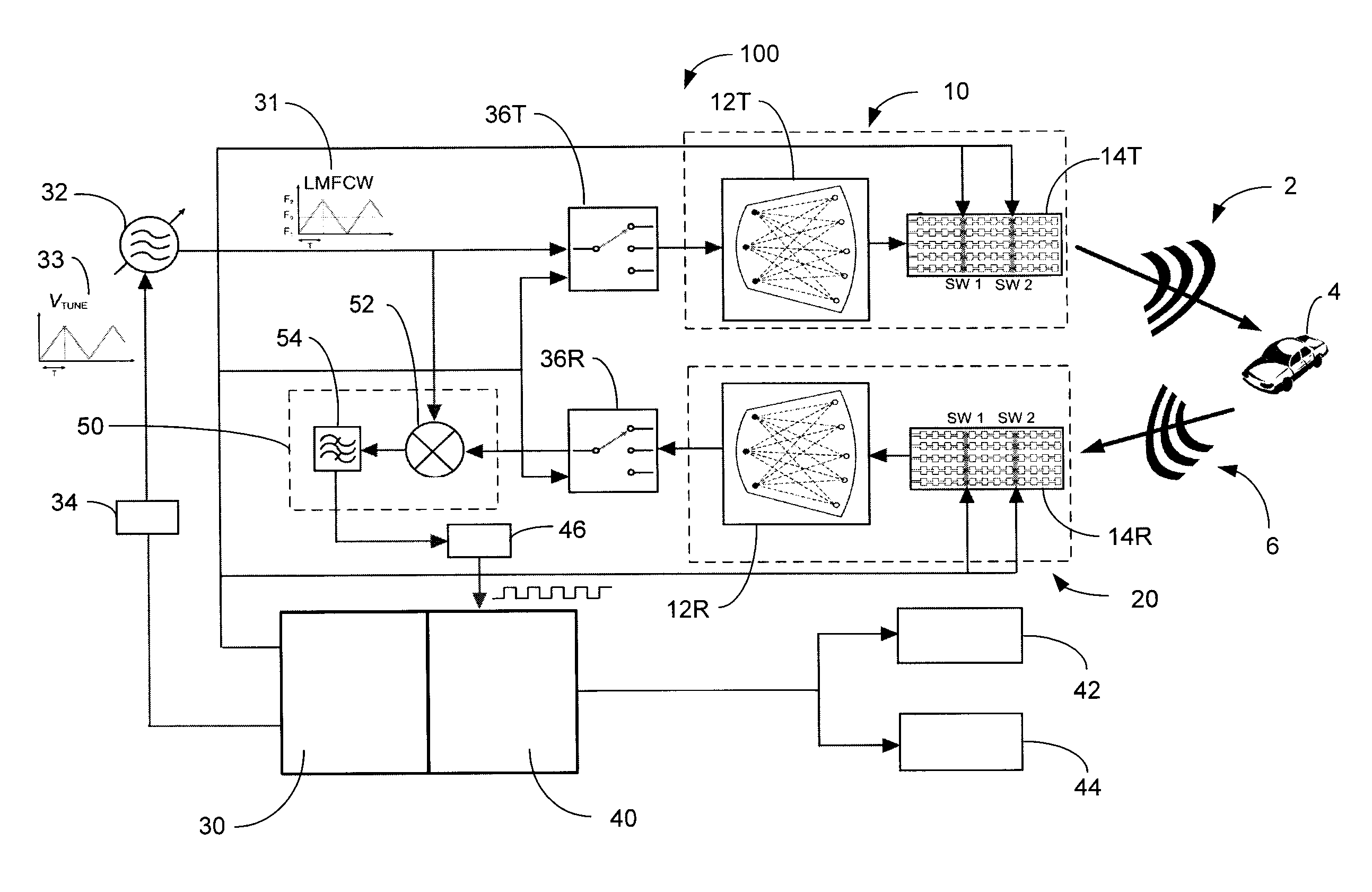
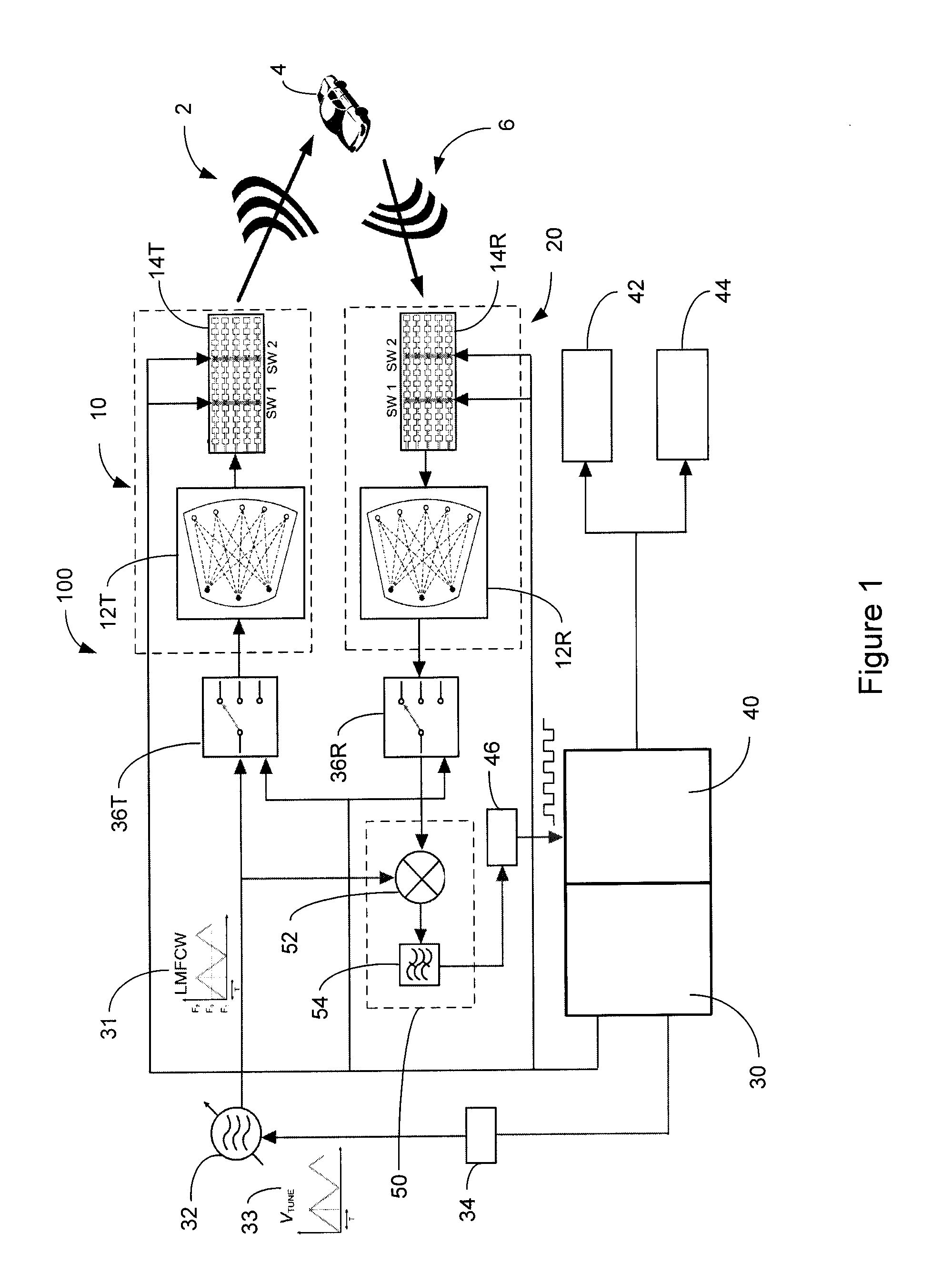
Radar system and method of manufacturing same
ActiveUS20130027240A1Increase speedThe signal is accurate and reliableAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesParallel-plate/lens fed arraysRadar systemsEngineering
A radar system (100) is described including a transmitting assembly (10), a receiving assembly (20), a control unit (30) and a signal processing unit (40). The transmitting assembly (10) receives an input signal (31) and transmits an incident radar signal (2). The transmitting assembly (10) includes a Rotman lens (12) having a lens cavity (74), a plurality of beam ports (60), a plurality of array ports (62) and a patch antenna assembly (14). The lens cavity (74) has a lens gap (h) between 10 microns to 120 microns, and preferably 40 microns to 60 microns. The patch antenna assembly (14) includes a plurality of antenna arrays (130) operable to receive a plurality of time-delayed, in-phase signals from the Rotman lens (12) and to transmit the incident radar signal (2) towards a target (4). The receiving assembly (20) receives a reflected radar signal (6) and produces an output signal. The signal processing unit (40) compares the input signal (31) to the output signal and implements an algorithm determining the range, velocity and position of the target (4).
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WINDSOR
Flow cytometry apparatus and method
InactiveUS6256096B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce contributionParticle size analysisIndividual particle analysisBiological cellStatistical analysis
A flow cytometer for detecting target particles such as microorganisms including biological cells and viruses as well as molecular species. The flow cytometer includes a detection system involving a CCD having a time delay integration capability to thereby increase the signal from the target particle and decrease the noise detected by the CCD. Calibration particles can be included in the sample stream of the flow cytometer for coordinating the readout of the CCD with the rate of flow of the sample stream to improve the detection capability of the CCD. Statistical analysis techniques can also be used to determine the rate of flow of target particles in the sample stream to thereby coordinate the readout rate of the CCD with the rate of flow of the target particles.
Owner:SOFTRAY
Segmented CRC assisted polar code encoding and decoding method
ActiveCN105227189ASave storage spaceFacilitate real-time communicationError preventionError detection onlyComputer architectureProcessor register
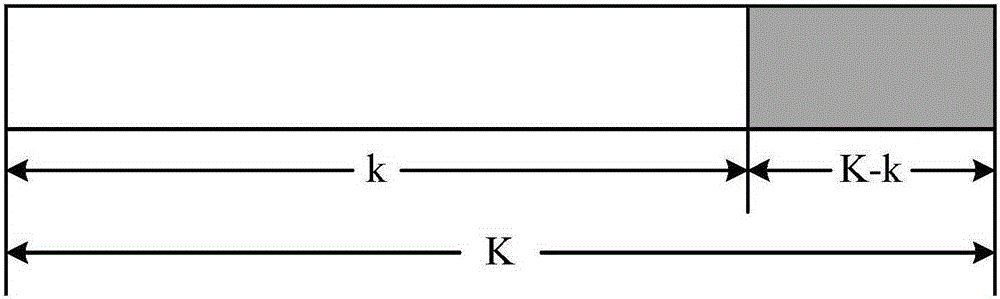
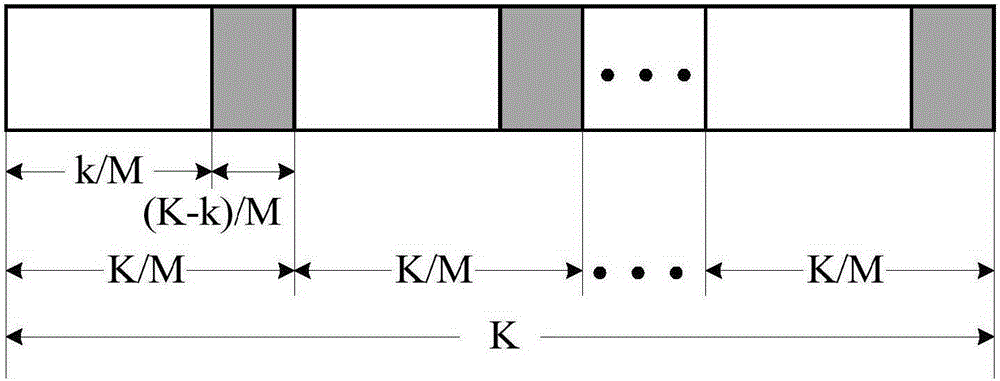
The invention belongs to the field of channel encoding, and particularly relates to a polar code coding and decoding method with segmented cyclic redundancy check (Cyclic Redundancy Check, CRC) auxiliary check. According to the polar code coding and decoding method provided by the invention, certain information bits are sacrificed to check polar codes to improve the decoding performance, and assuming that the length of used CRC is K-k bits, the information is averagely divided into M segments by segmented CRC check, k / M bits of information and (K-k) / M bits of CRC check information constitute an information structure of each segment, as shown in Fig.2. The information bits are encoded and transmitted by a channel, finally, SCL decoding and check are carried out on the information received by a receiving end, and L maximum storage paths are available. The polar code coding and decoding method provided by the invention can be used for shortening the time delay, bringing great convenience for real-time communication, saving the memory space of a register and providing great convenience for hardware realization.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
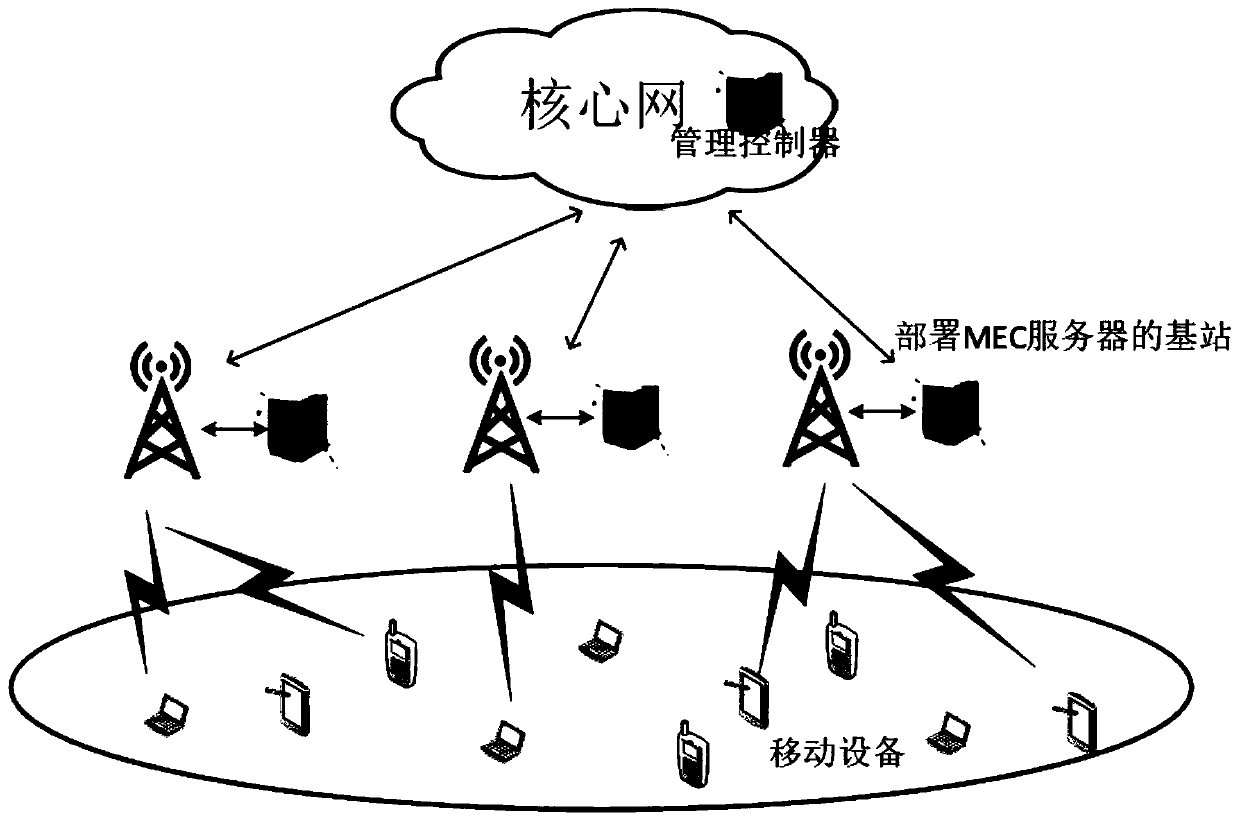
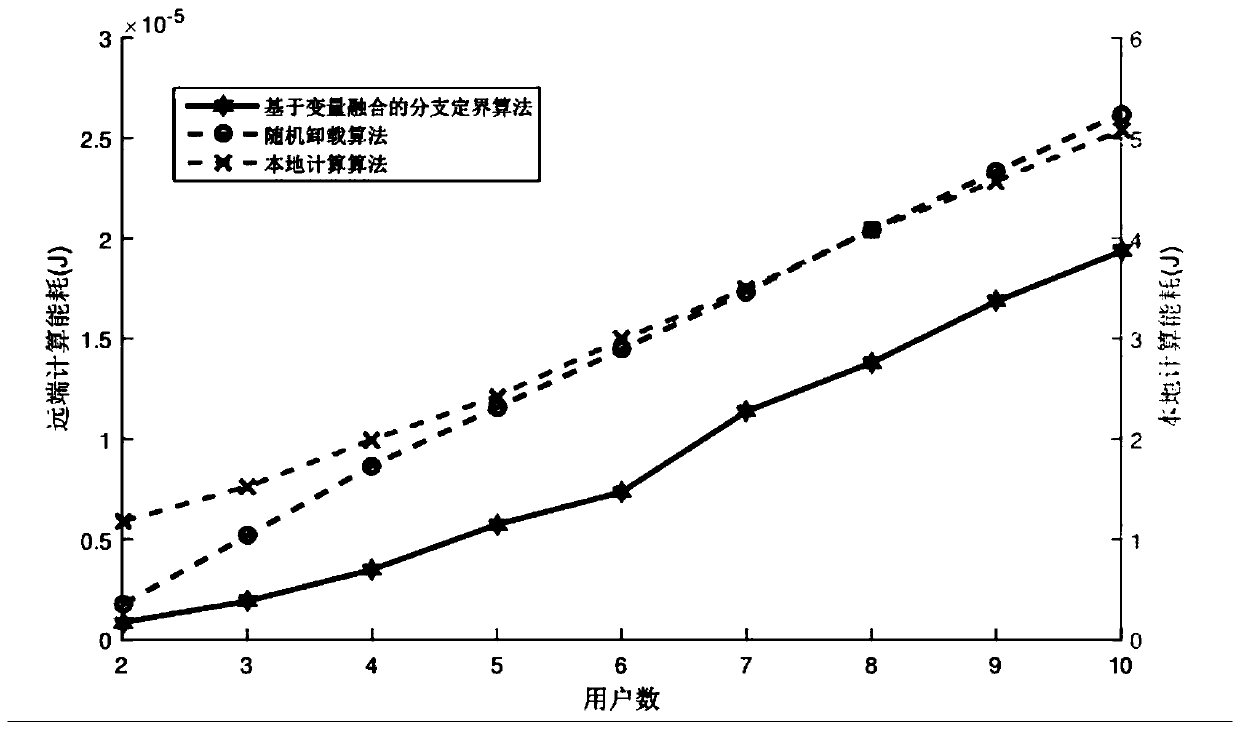
A joint optimization method for task unloading and resource allocation in a mobile edge computing network
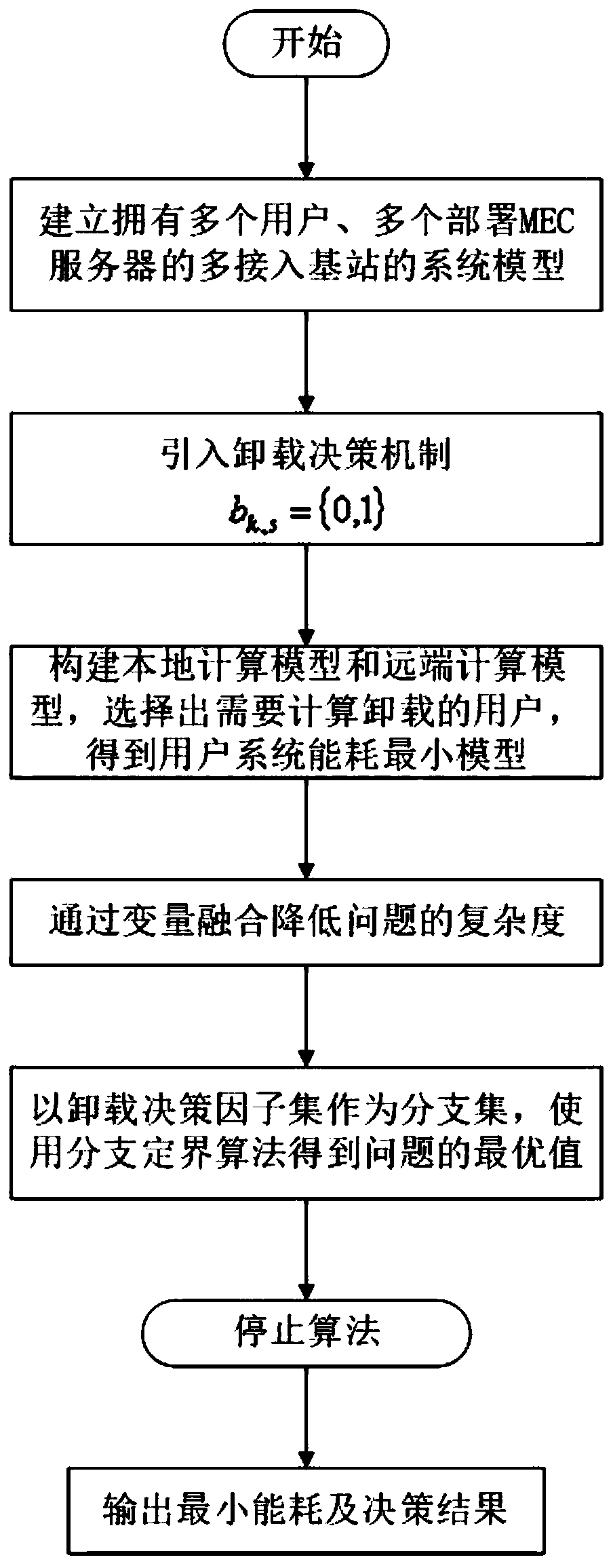
ActiveCN109814951AFull restorationUniversalService provisioningProgram loading/initiatingDecision takingWireless resource allocation
The invention discloses a joint optimization method for task unloading and resource allocation in a mobile edge computing network, which comprises the following steps of 1, establishing an OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access)-based multi-MEC (Mobile Edge Computing) base station and a multi-user scene model, wherein the MEC base station supports the multi-user access; 2, introducing an unloading decision mechanism; Meanwhile, constructing a local calculation model and a remote calculation model, selecting a user needing to perform calculation unloading, and establishing a calculation task unloading and resource allocation scheme based on minimum energy consumption under the condition of meeting the time delay constraint according to the conditions; 3, carrying out variablefusion on three mutually constrained optimization variables, namely an unloading decision variable, a wireless resource distribution variable and a computing resource distribution variable, so as to simplify the problem; and 4, obtaining an unloading decision and a resource allocation result which enable the total energy consumption of the user in the MEC system to be minimum through a branch andbound algorithm. The method has the advantage that the energy consumption of the system can be effectively reduced on the premise that strict time delay limitation is guaranteed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
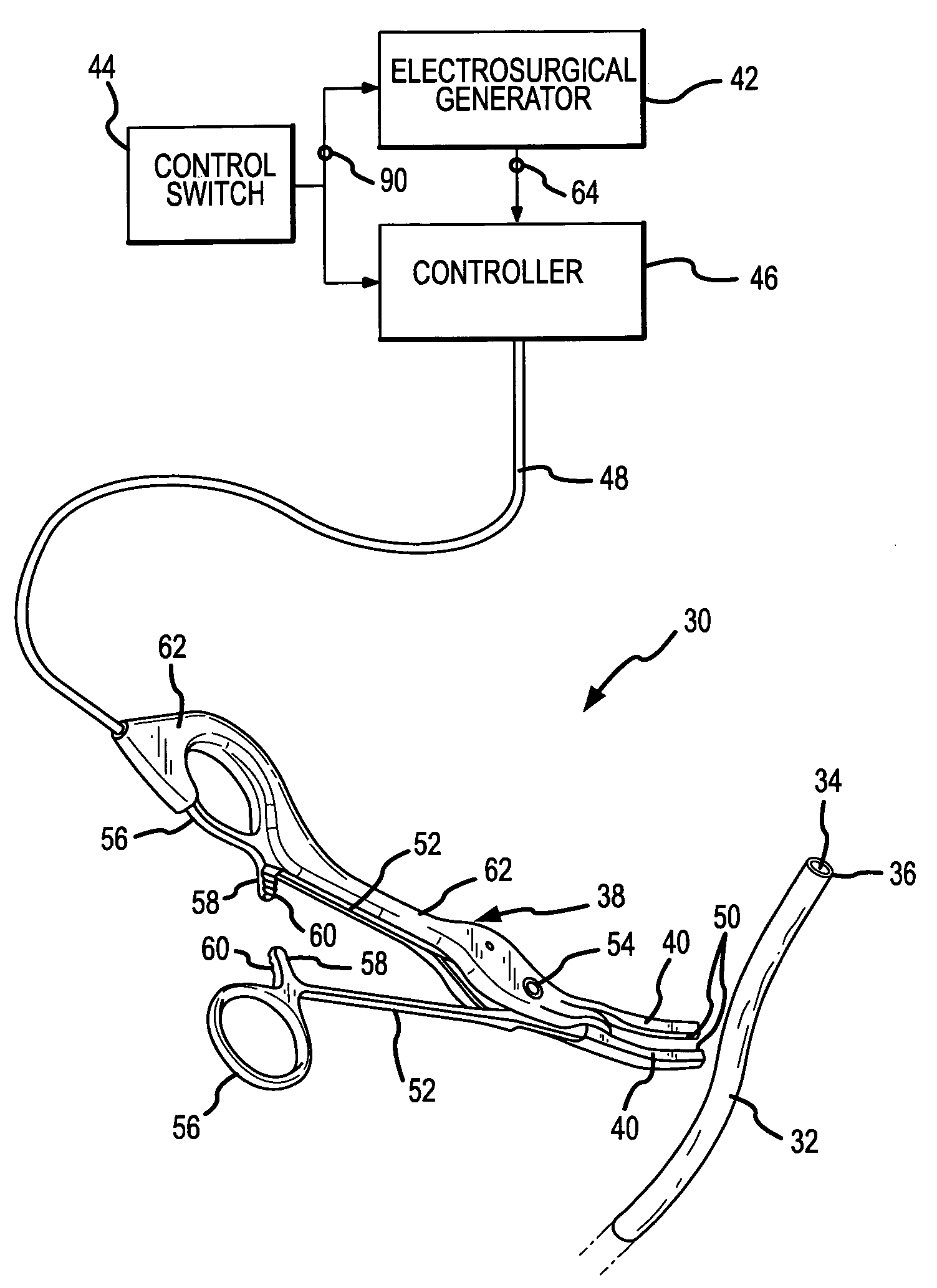
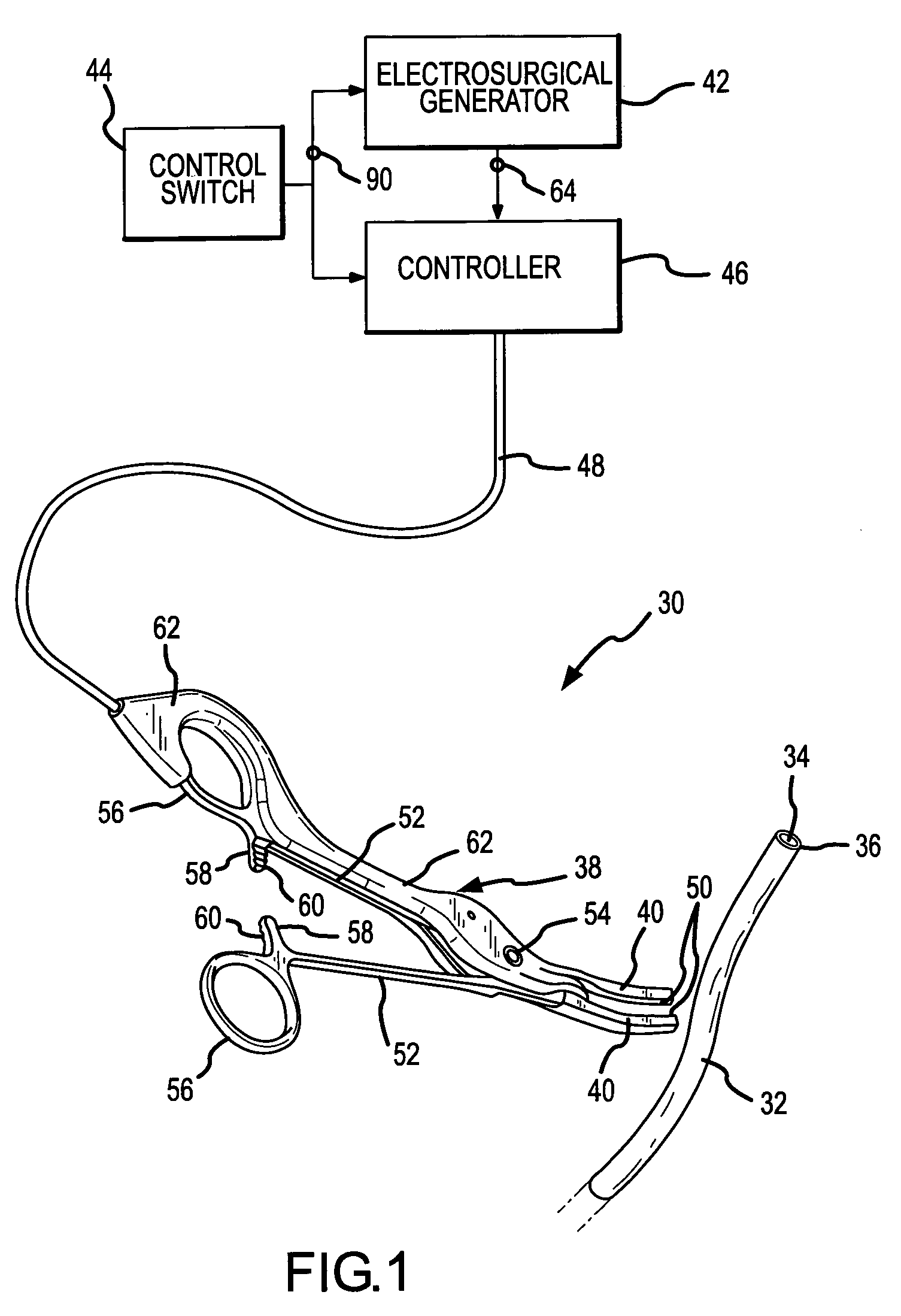
Method and apparatus for precursively controlling energy during coaptive tissue fusion
ActiveUS7678105B2Easily sensed and determinedEqually or more effectiveSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsFiberPeak value
A sidewall of biological tissue which surrounds and defines an opening in the tissue is sealed or fused to occlude the opening by compressing apposite sidewall portions and applying sufficient energy to cause the fibers of the compressed apposed sidewall portions to intertwine and fuse with one another to form a permanent seal. The energy application is controlled by detecting a precursor fusion condition while applying the energy and before sufficient energy has been applied to achieve an adequate seal. The application of energy is terminated in a time-delayed relationship to the detection of the precursor fusion condition such that sufficient energy has been applied to achieve an effective seal. The precursor fusion condition is detected upon the peak RF current delivered to the tissue remaining below a threshold value for a threshold time.
Owner:CONMED CORP
Loan underwriting system and method
An automated loan underwriting system and method automates the logic implemented by a loan underwriter, saving the loan originator time and money. Each lending institution can set up its own decisioning criteria, enabling customers to customize the process in which a proper evaluation, owners and encumbrance report, or title product is selected for a loan application within a given set of characteristics. The system and method allow for the automatic upgrading to another product without involvement of the loan processor, helping to reduce time delays in the loan origination process. The speed and automation allow for more underwriting checks to be applied against each loan.
Owner:DATAQUICK LENDING SOLUTIONS +1
System for identifying patient response to anesthesia infusion
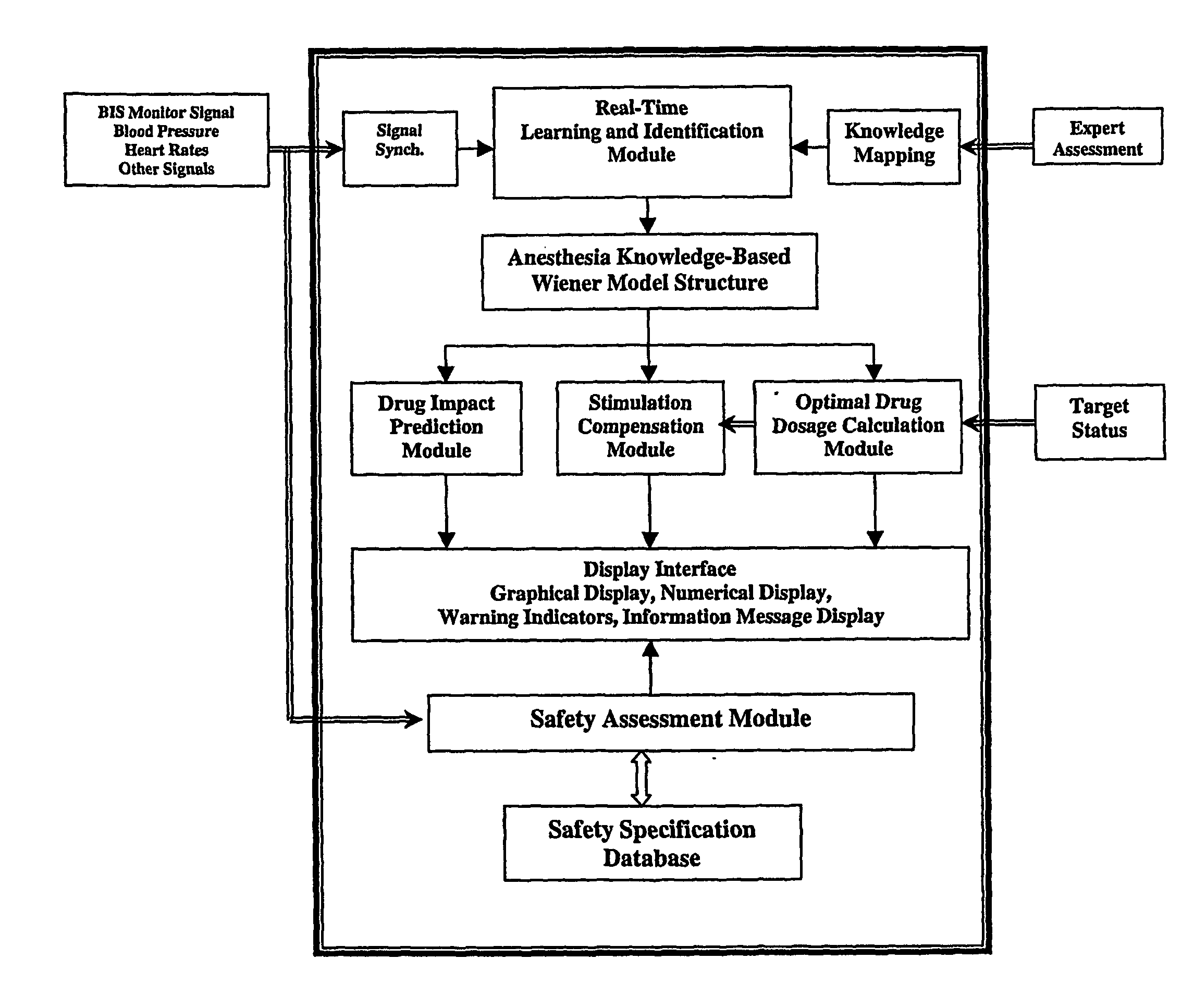
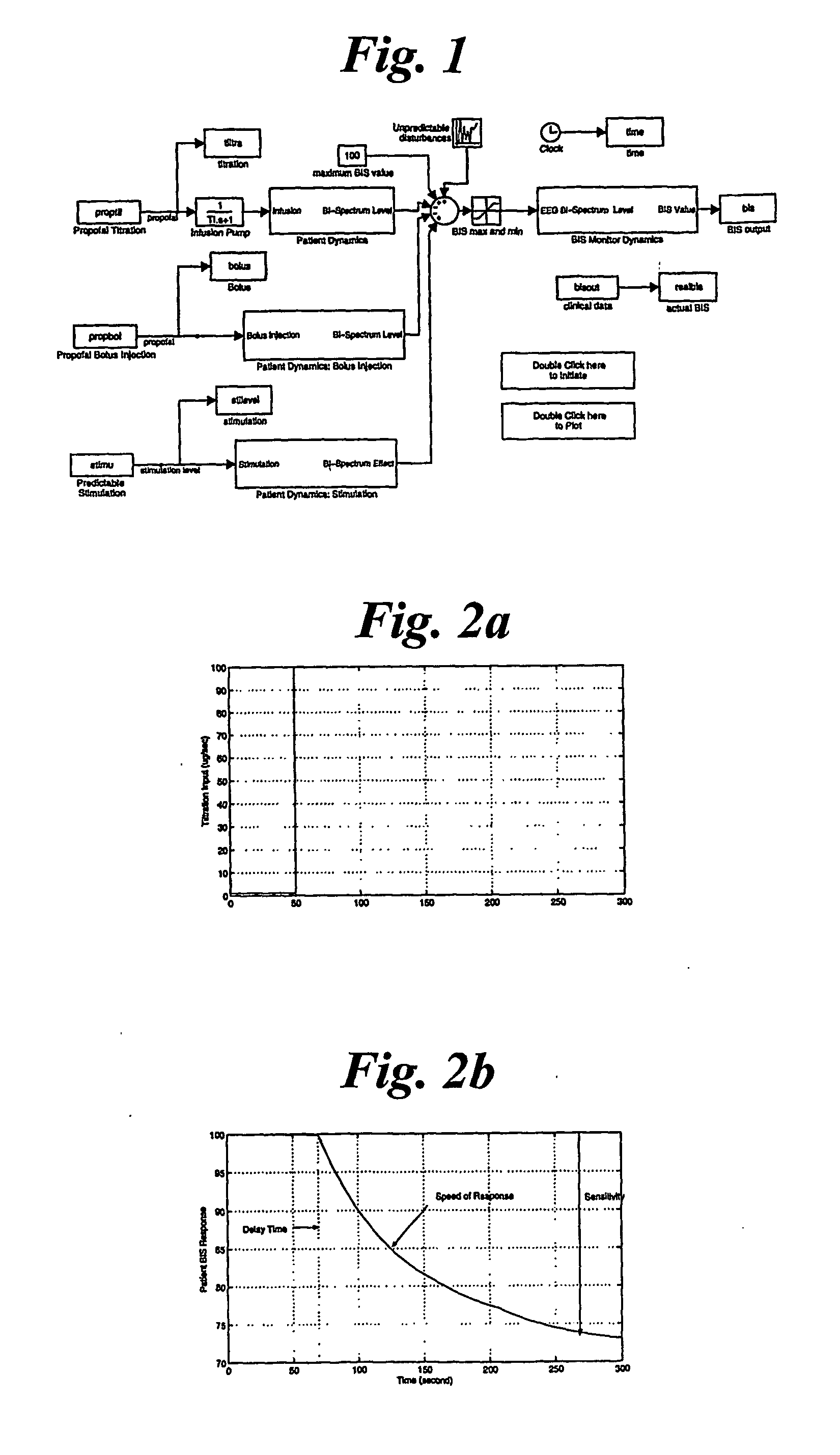
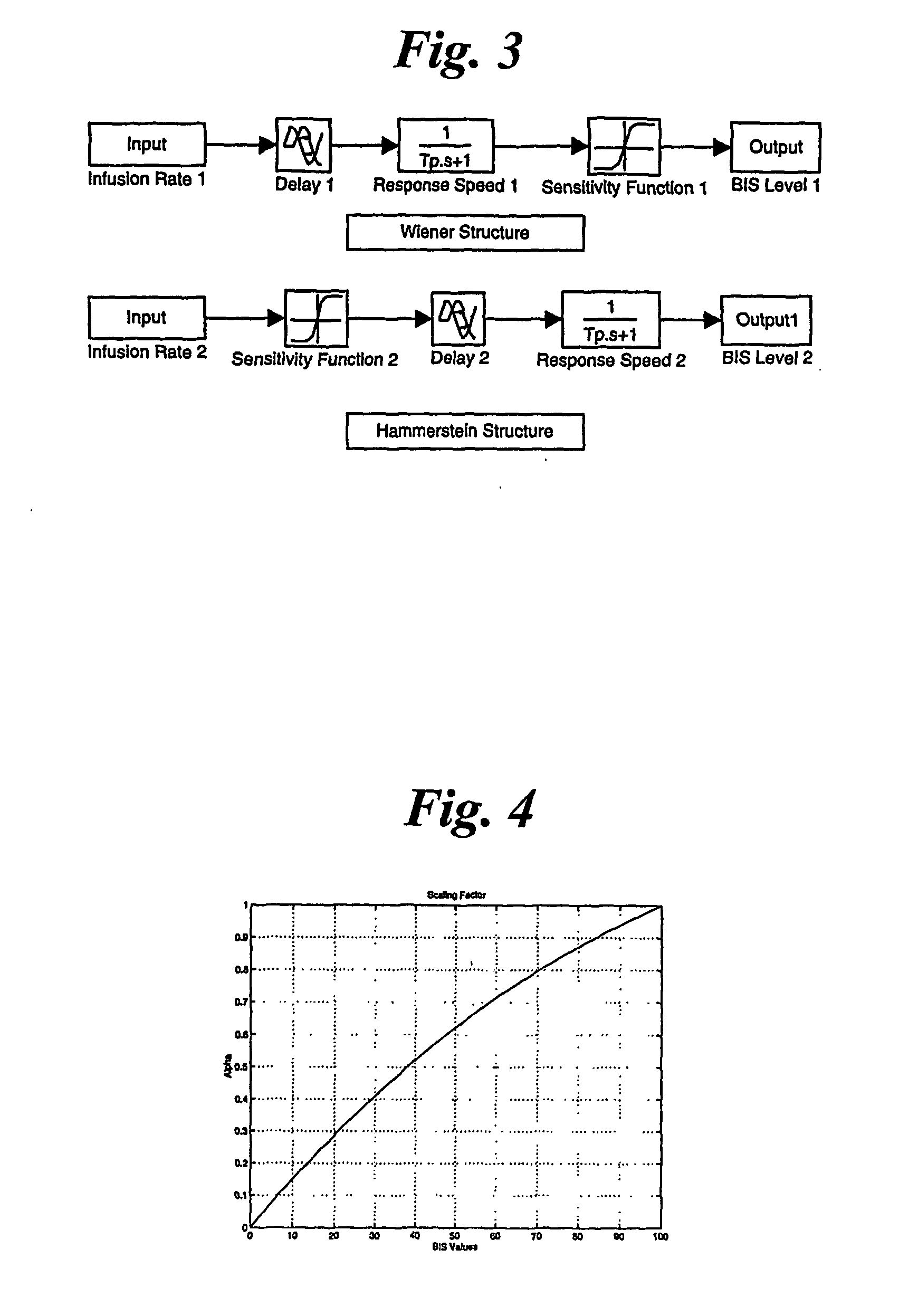
InactiveUS20070015972A1Avoid large fluctuations in BIS valuesReduce the valueElectroencephalographyMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesPatient modelDrugs sensitivity
A generic model structure captures basic characteristics in BIS-based patients' responses to anesthesia and surgical stimulation, the model being used in combination with the insight of an anesthesiologist. The model structure represents the patient response with a time delay, a time constant for response speed, and a nonlinear function for drug sensitivity. Clinical data confirms the model structure and is used to establish parameters and function forms for individual patients. A feedback and predictive control strategy for anesthesia drug infusion is then introduced on the basis of the patient model. Feedback control alone cannot avoid large fluctuations in BIS values when significant surgical stimulation is imposed, as a result of time delays in a patient's response to drug infusion. Predictive control attenuates fluctuations of BIS levels from surgical stimulation.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
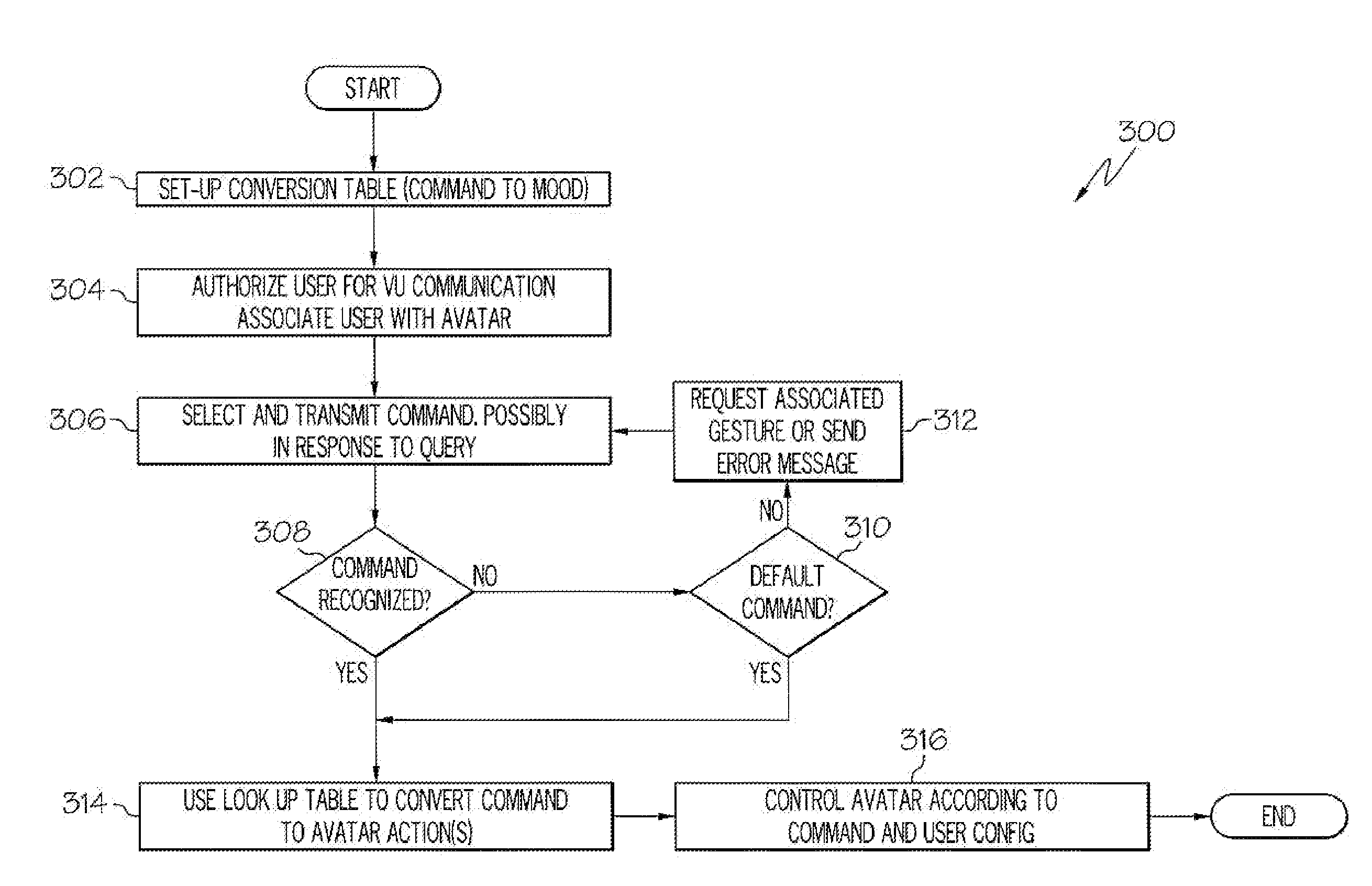
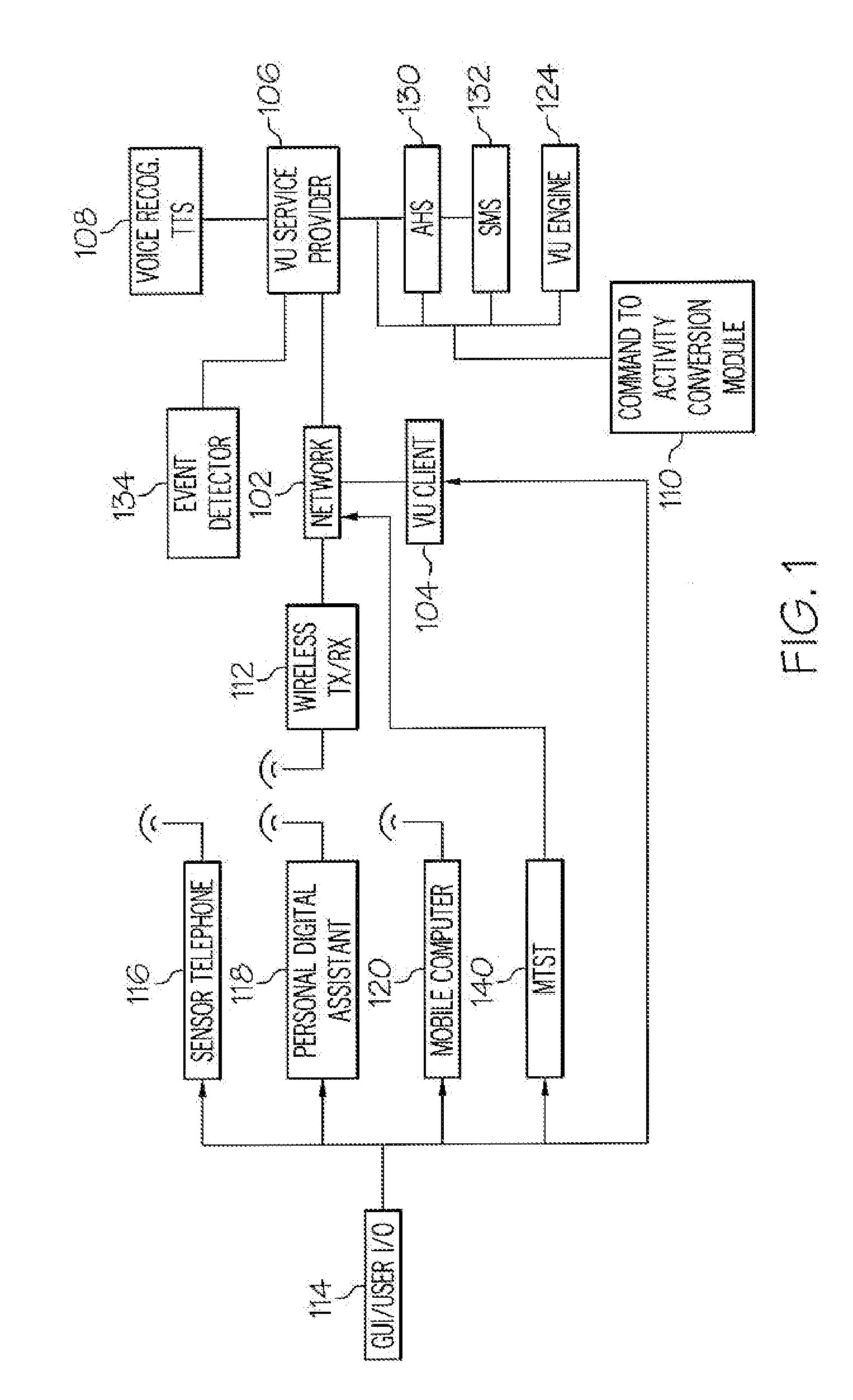
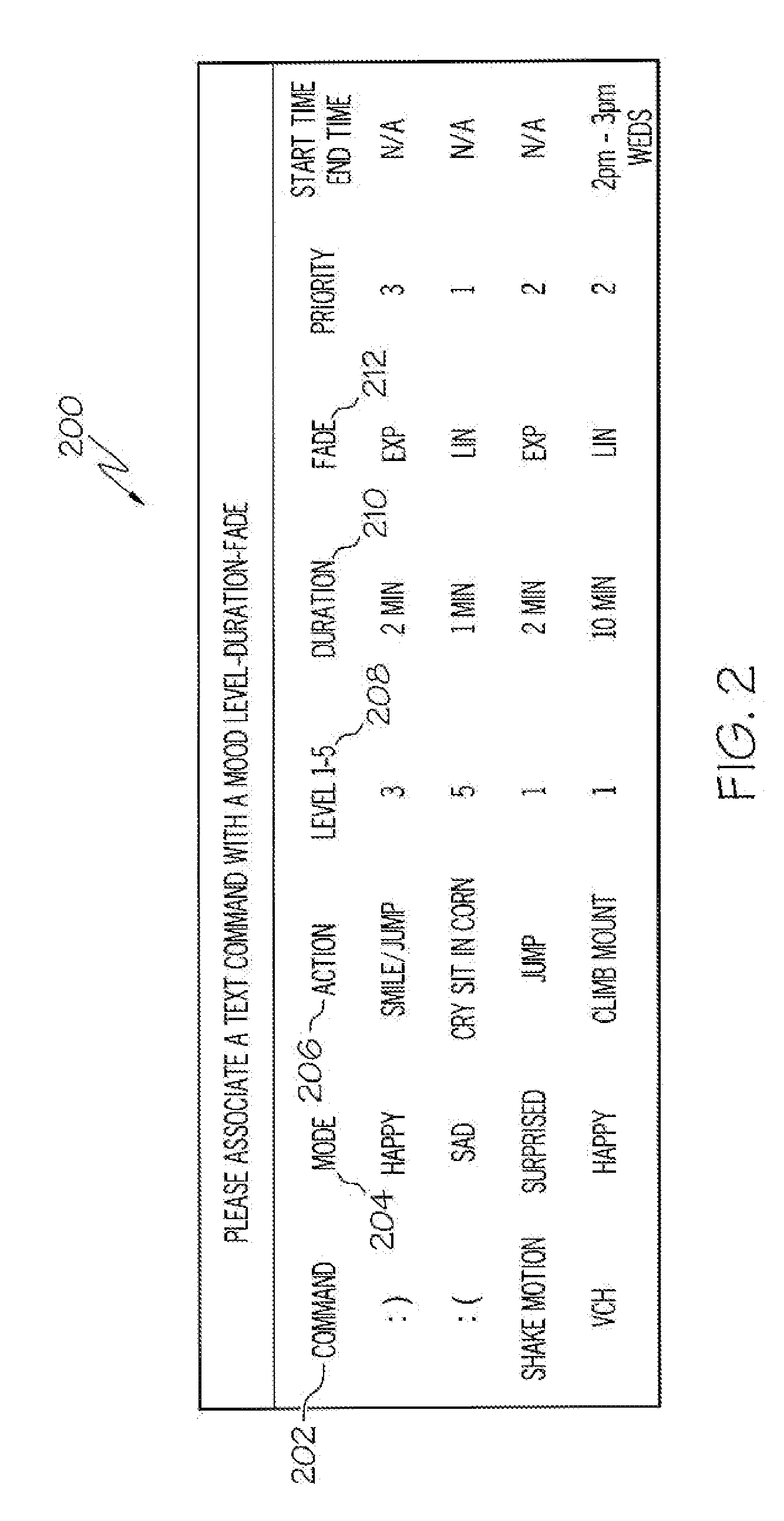
Arrangements for controlling activites of an avatar
Systems are disclosed herein that allow a participant to be associated with an avatar and receive a transmission from the participant in response to a participant activated transmission. The transmission can include a participant selectable and time delayed mood and / or activity command which can be associated with a user configurable command to avatar activity conversion table. The associated avatar activity table can provide control signal to the VU system controlling the participant's avatar for extended time periods, where the activity commands allow the avatar to exhibit a mood and to conduct an activity. The preconfigured time controlled activity commands allow the user to control their avatar without being actively engaged in a session with a virtual universe client or logged on and the control configuration can be set up such that a single mood / activity control signal can initiate moods and activities that occur over an extended period of time.
Owner:ACTIVISION PUBLISHING
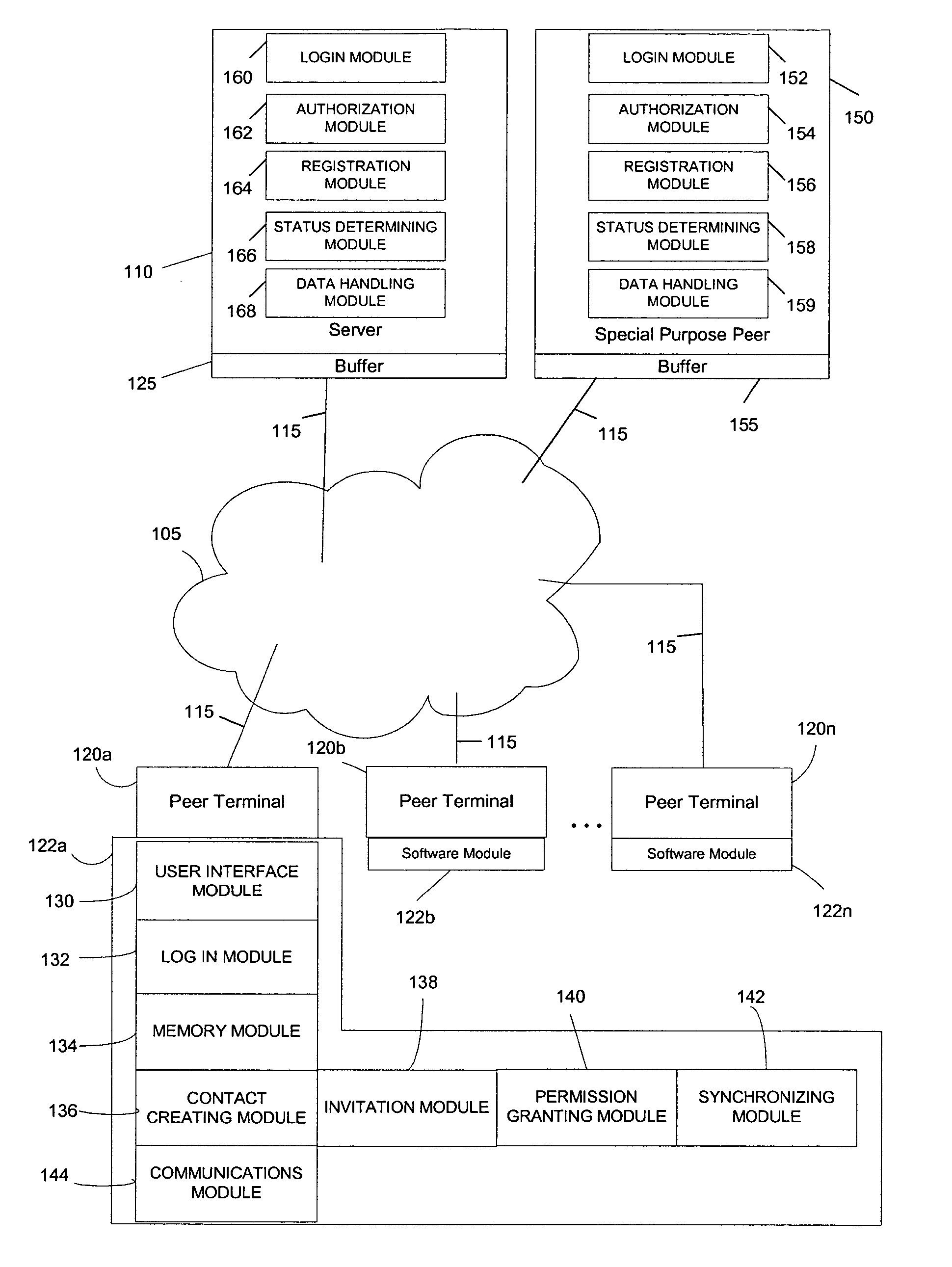
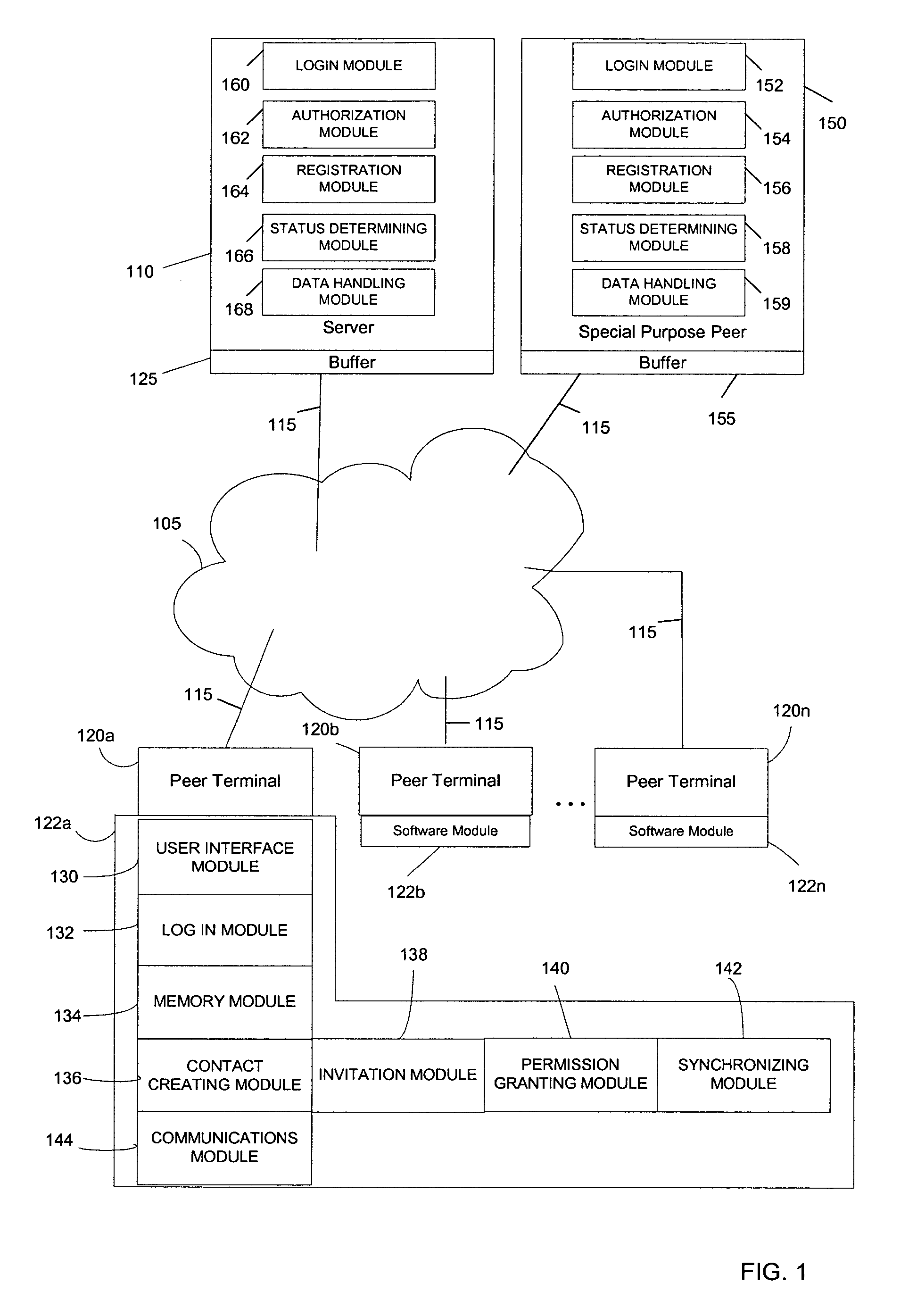
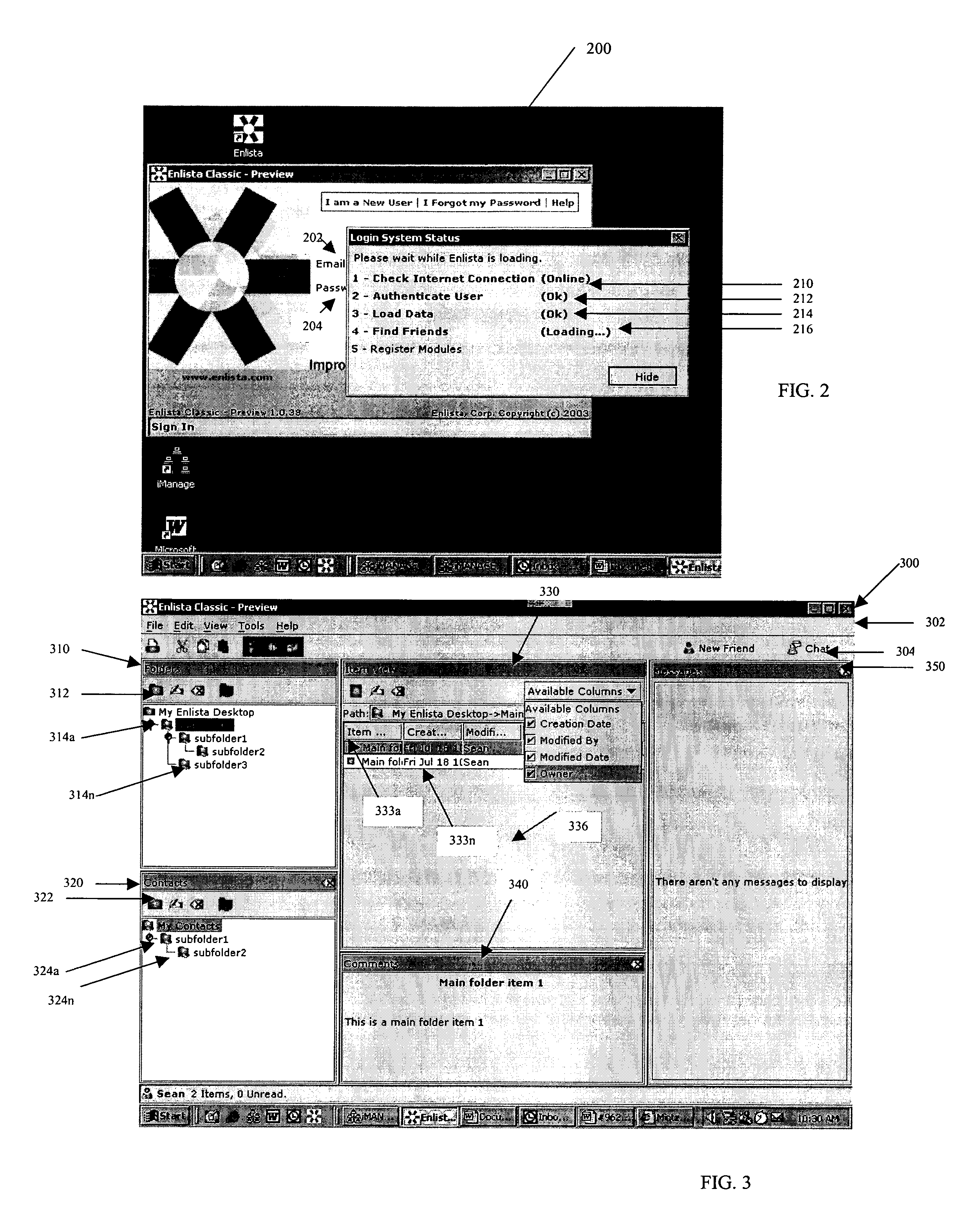
System and method for creating and selectively sharing data elements in a peer-to-peer network
InactiveUS20050091316A1Facilitate communicationFacilitate automatic synchronizationMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionInformation sharingData element
A system and method are provided for sharing information in a distributed peer-to-peer network wherein an information owner invites one or more trusted users to participate in information sharing and wherein the information owner designates permission levels for each of one or more trusted users. Upon accepting the invitation, the one or more trusted users may be granted with complete access, read only access, or blocked access to the shared information. The one or more trusted users may selectively decide to accept or decline to share information on a folder-to-folder basis. Any modifications made to the shared information may be disseminated to all the trusted users in real-time, upon log-in to a central server, or after a predetermined time delay.
Owner:ENLISTA
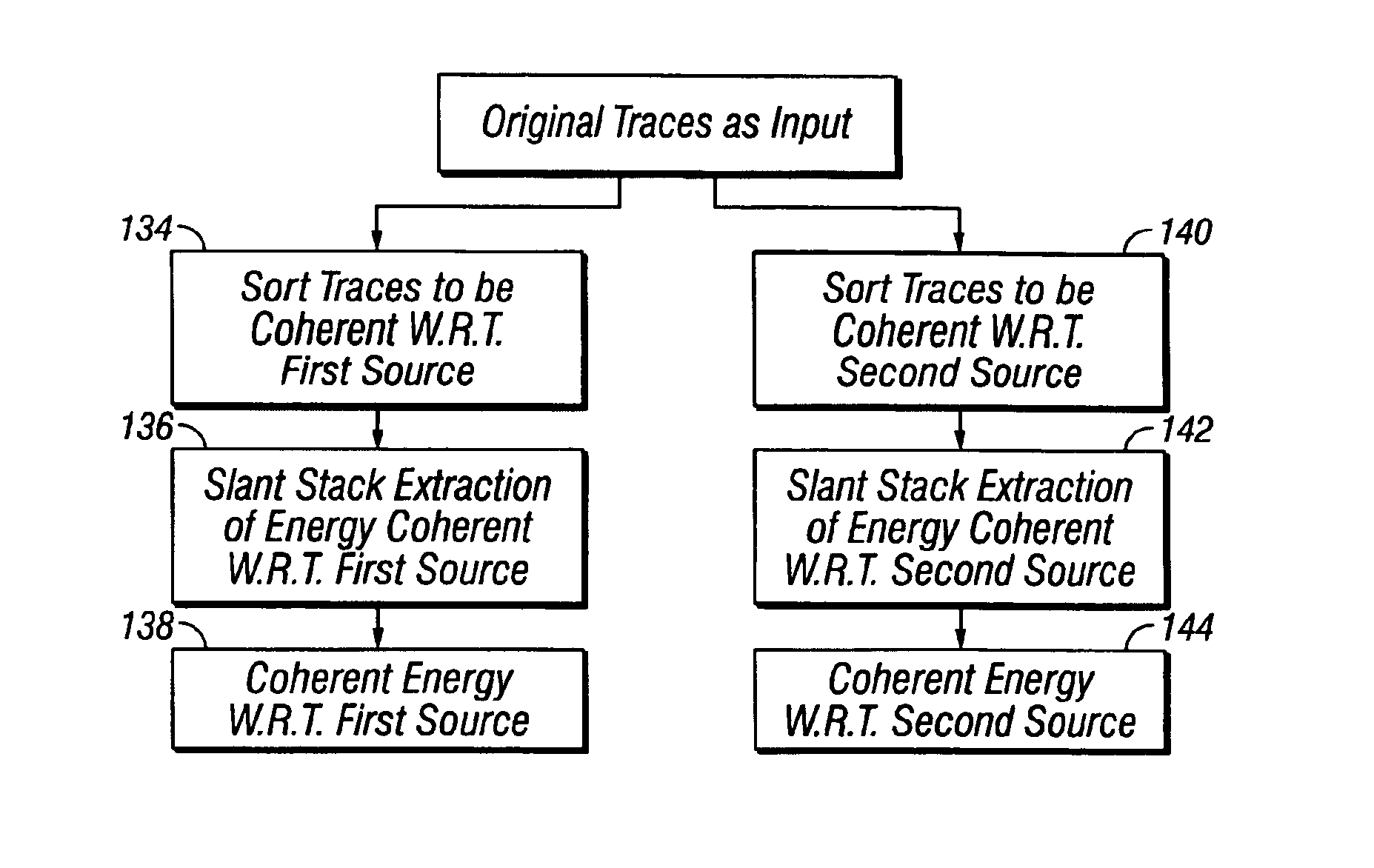
Method for separating seismic signals from two or more distinct sources
InactiveUS6882938B2Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsSpatial directionSeismic energy
A method is disclosed for separating energy resulting from actuating at least two different seismic energy sources from seismic signals. The sources are actuated to provide a variable time delay between successive actuations of a first one and a second one of the sources. The method includes sorting the seismic signals such that events therein resulting from actuations of the first source are substantially coherent in all spatial directions, coherency filtering the first source coherency sorted signals, sorting the seismic signals such that events therein resulting from actuations of the second source are substantially coherent in all spatial directions, and coherency filtering the second source coherency sorted signals.
Owner:PGS AMERICA INC
Transaction verification processing method, apparatus and node device
ActiveCN107077674ASimplify the verification processThe verification process is fast and efficientEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesProtocol authorisationPaymentFinancial transaction
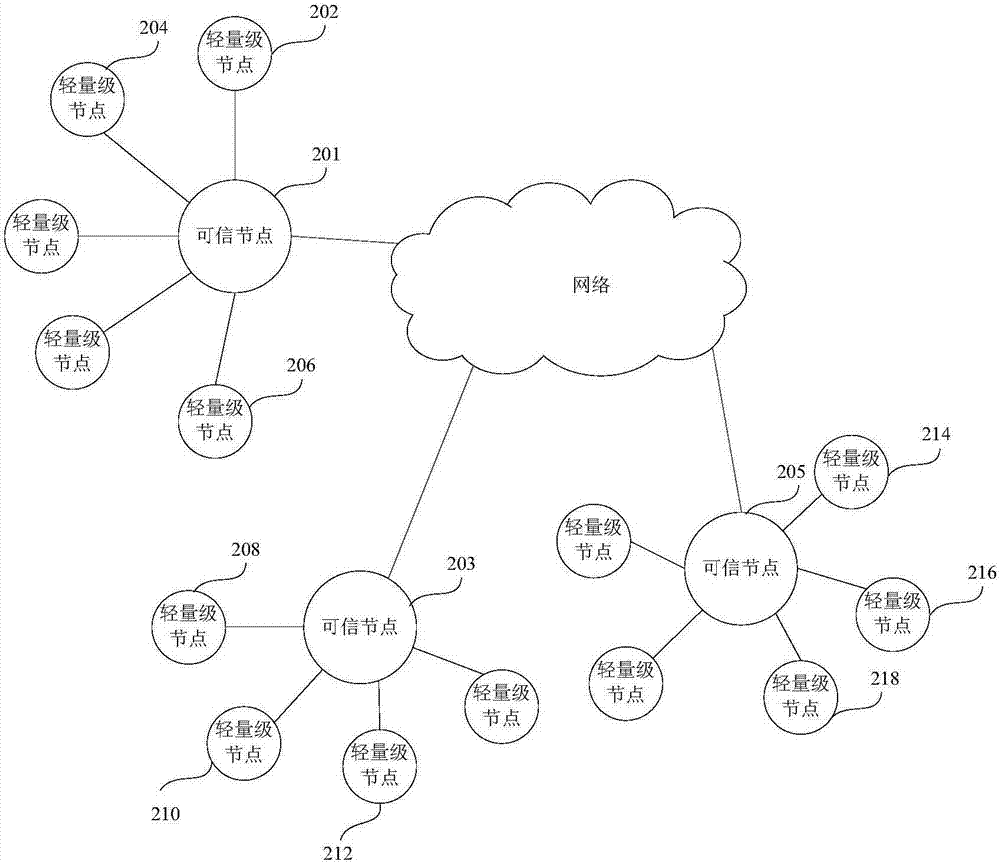
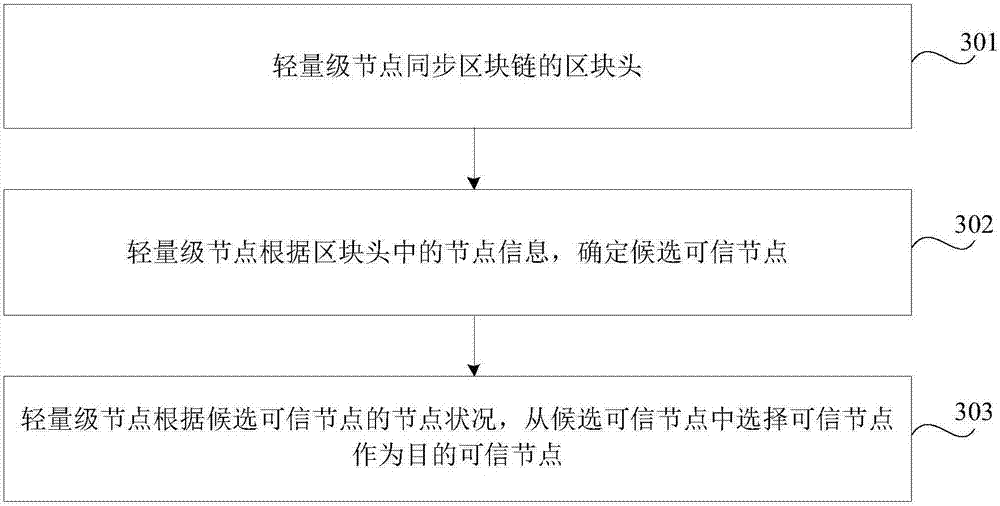
The invention relates to a transaction verification processing method, apparatus and node device. The transaction verification processing method includes the following steps: transmitting a transaction hash of a to-be-verified transaction to a destination credible node which can establish new block and save a complete block chain; and receiving a verification result which is returned by the destination credible node which conducts payment verification and transaction verification on the to-be-verified transaction based on the transaction hash. According to the invention, the credible node verifies the to-be-verified transaction of lightweight nodes, simplifies the verification process of lightweight nodes, can at the same time conducts transaction verification and payment verification; since the lightweight nodes can determine credible nodes based on the node condition of the credible nodes, can effectively ensure safety of the verification process, ensures information synchronization, reduces verification time delay and increases verification efficiency.
Owner:CLOUDMINDS SHANGHAI ROBOTICS CO LTD
Ultra small microphone array
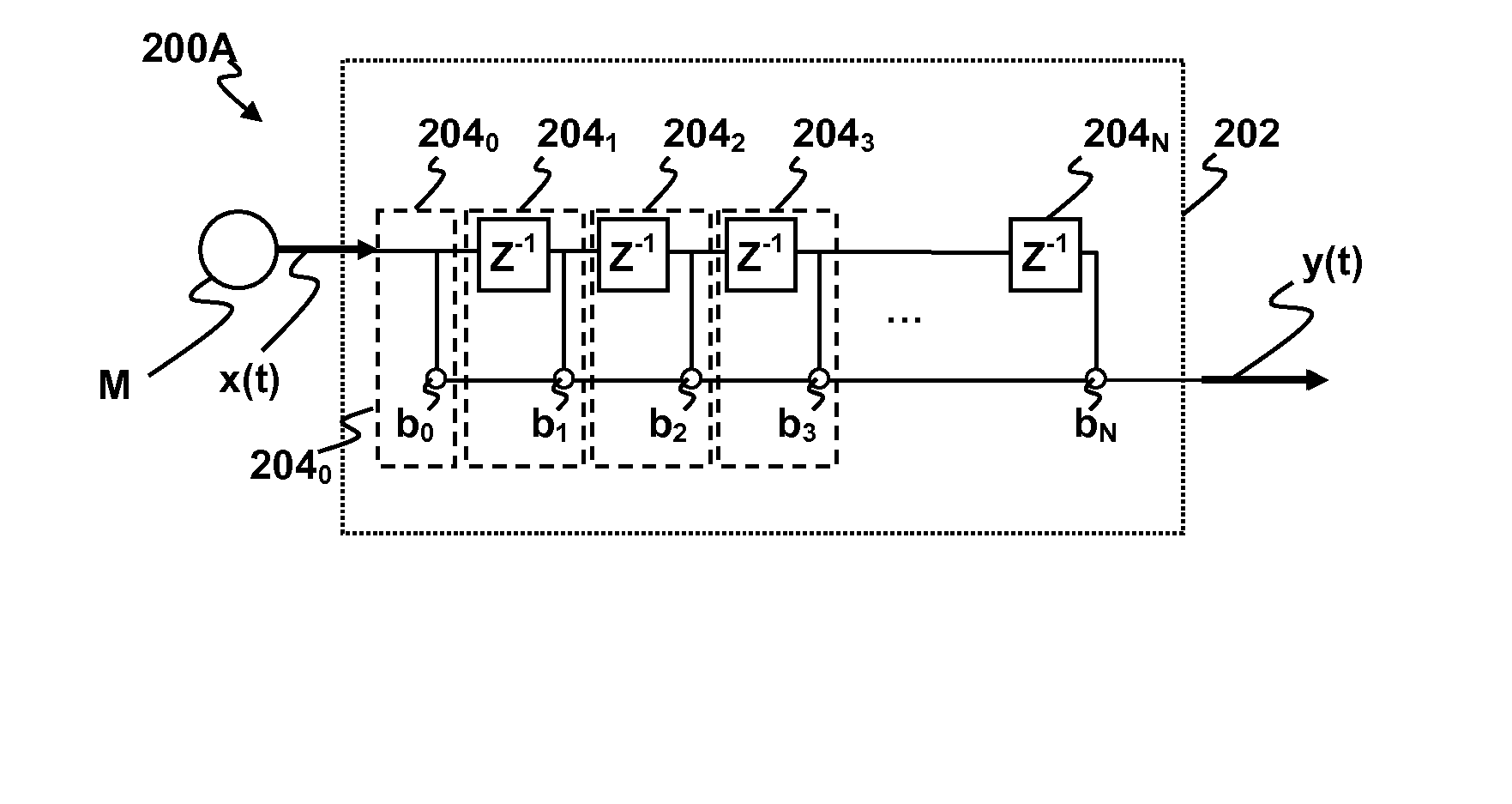
ActiveUS20070260340A1MicrophonesAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceFinite impulse responseTime domain
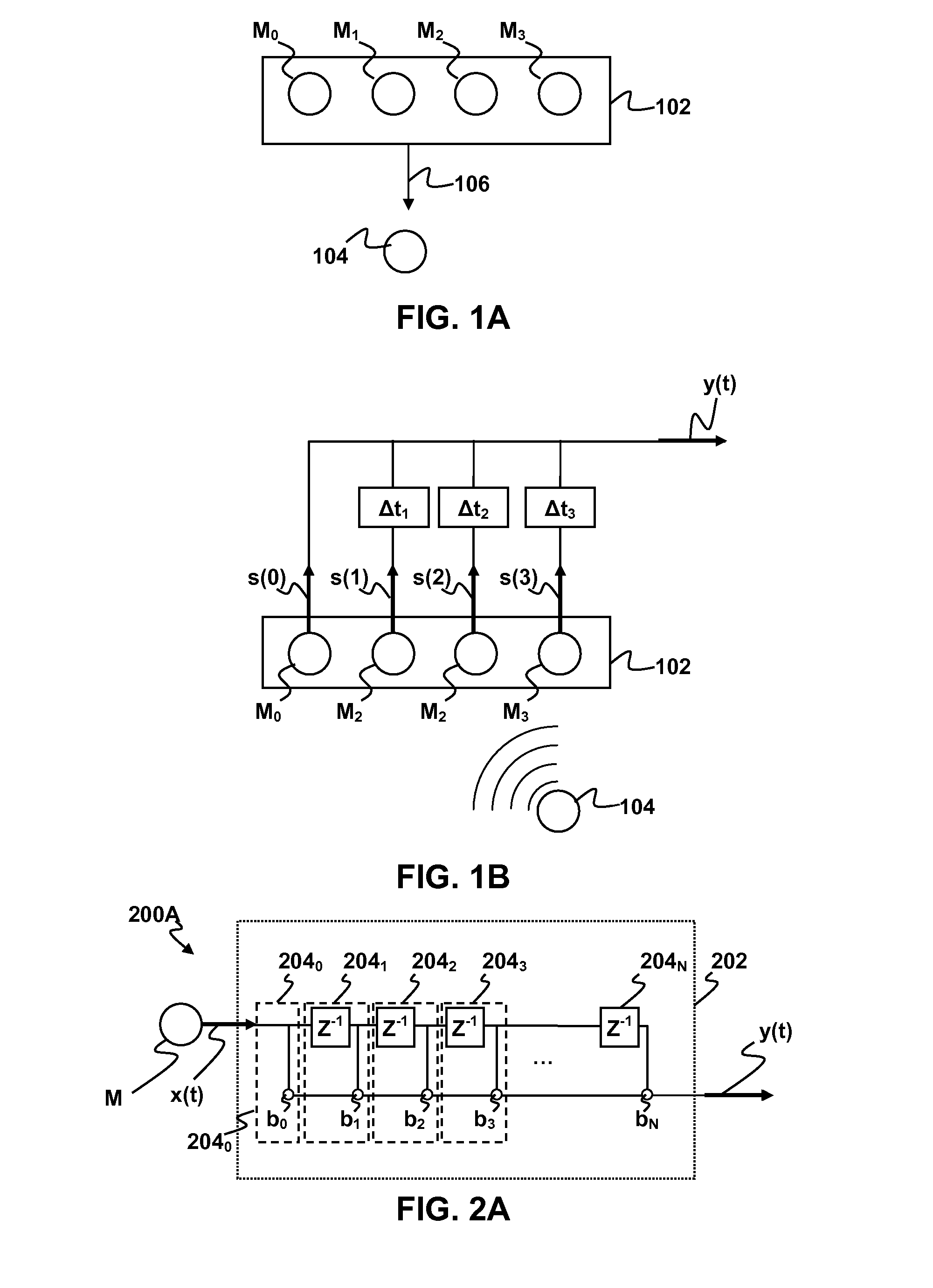
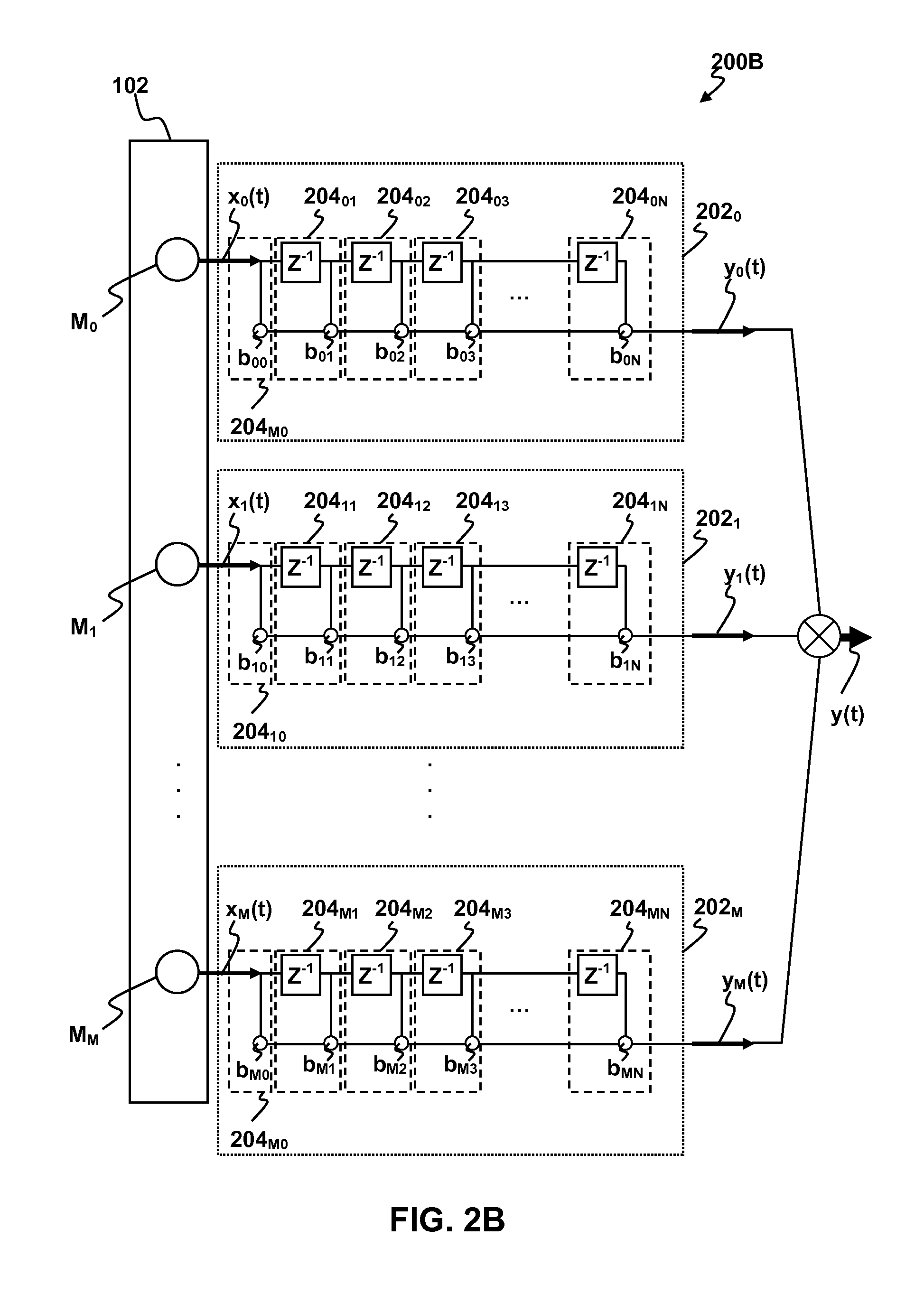
Methods and apparatus for signal processing are disclosed. A discrete time domain input signal xm(t) may be produced from an array of microphones M0 . . . MM. A listening direction may be determined for the microphone array. The listening direction is used in a semi-blind source separation to select the finite impulse response filter coefficients b0, b1 . . . , bN to separate out different sound sources from input signal xm(t). One or more fractional delays may optionally be applied to selected input signals xm(t) other than an input signal x0(t) from a reference microphone M0. Each fractional delay may be selected to optimize a signal to noise ratio of a discrete time domain output signal y(t) from the microphone array. The fractional delays may be selected to such that a signal from the reference microphone M0 is first in time relative to signals from the other microphone(s) of the array. A fractional time delay Δ may optionally be introduced into an output signal y(t) so that: y(t+Δ)=x(t+Δ)*b0+x(t−1+Δ)*b1+x(t−2+Δ)*b2+ . . . +x(t−N+Δ)bN, where Δ is between zero and ±1.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC +1
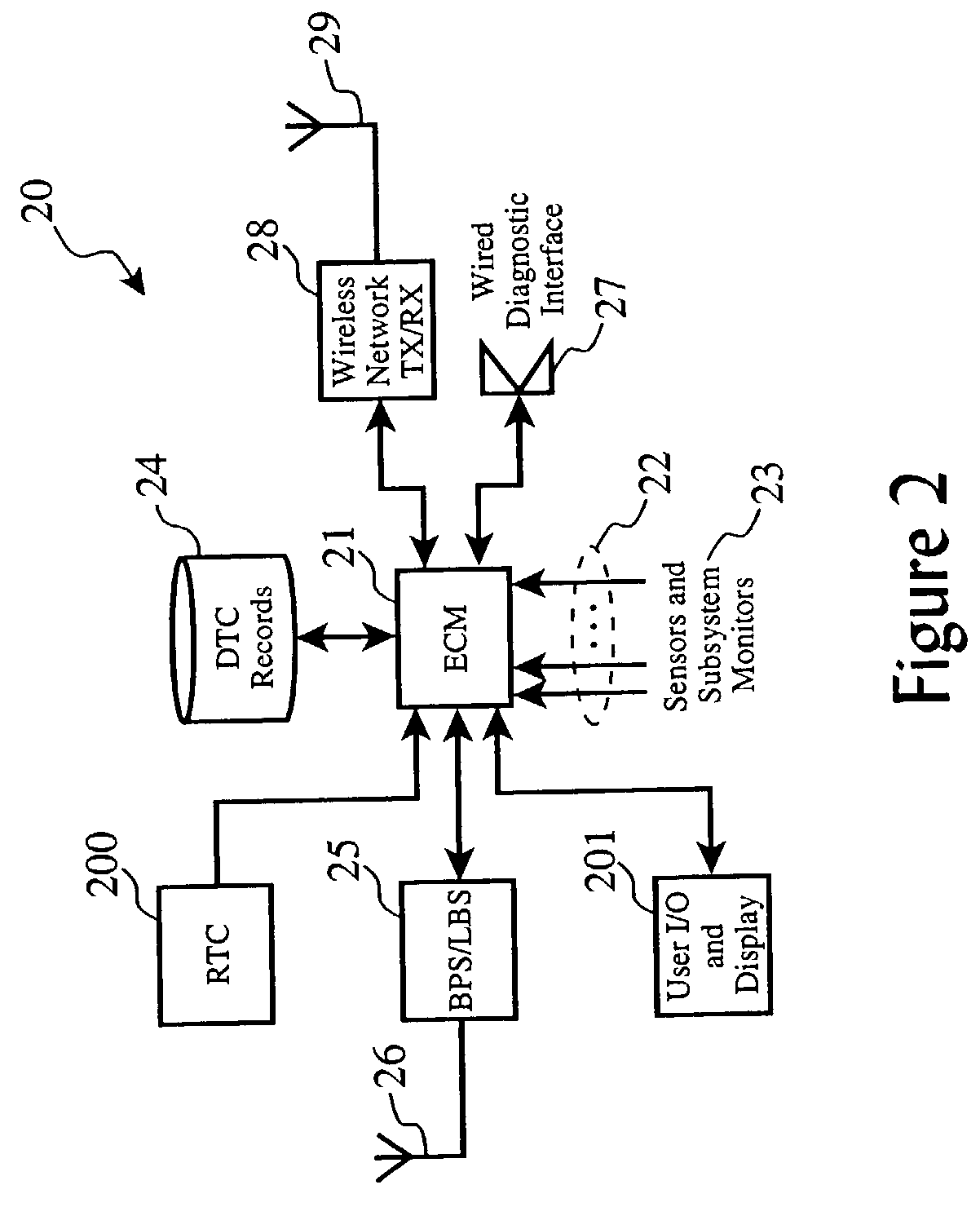
Timed delay for redelivery of treatment therapy for a medical device system
Apparatus and method support a repetitive administration of a therapeutic treatment through a delivery unit during a neurological event, such as a seizure, of a nervous system disorder. The medical device system monitors signal data from a sensor and through an amplifier. A neurological event is detected by a medical device system using a detection algorithm. Consequently, a electrical stimulation pulse is applied to an electrode. During the delivery of the electrical stimulation pulse, the medical device system blanks signal data that is associated with the electrode. Subsequently, additional blanking is providing during a time interval in which signal artifacts may occur and the amplifier is stabilizing. The medical device system then collects signal data for the detection algorithm to stabilize. Subsequently, the medical device system collects additional signal data in order to obtain statistically meaningful data. If the medical device system detects a continuation of the seizure, therapeutic treatment continues.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Airborne inventory and inspection system and apparatus
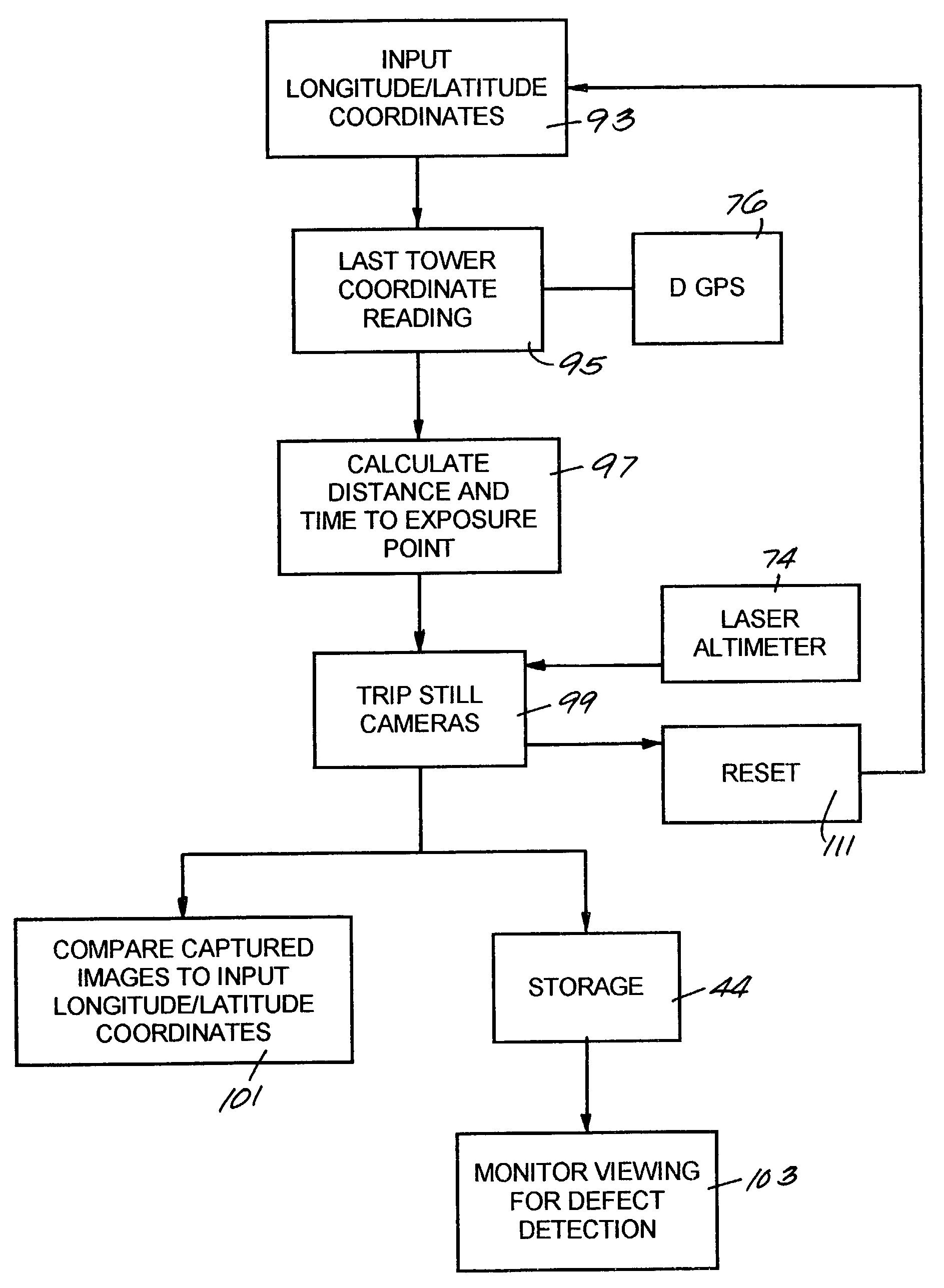
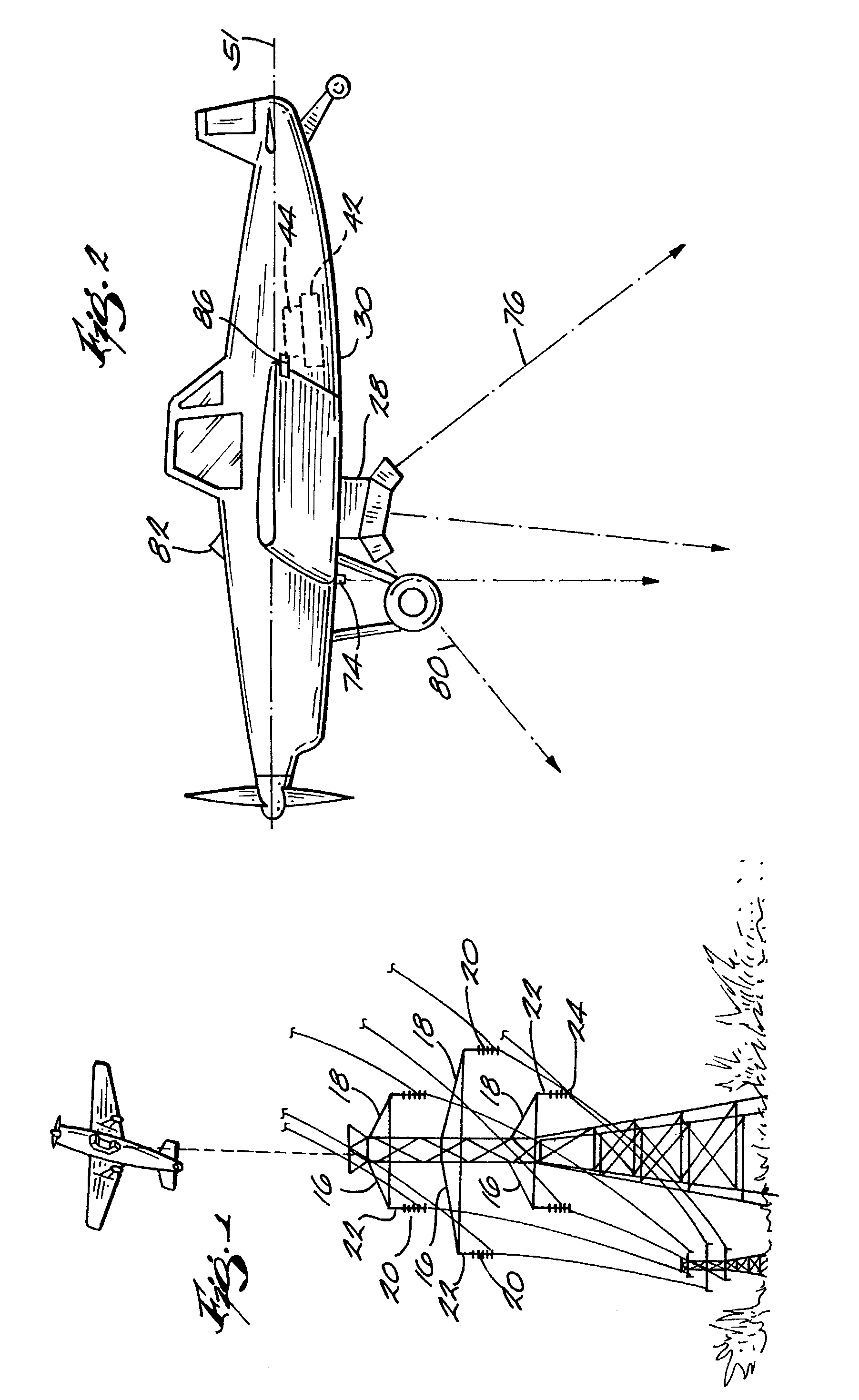
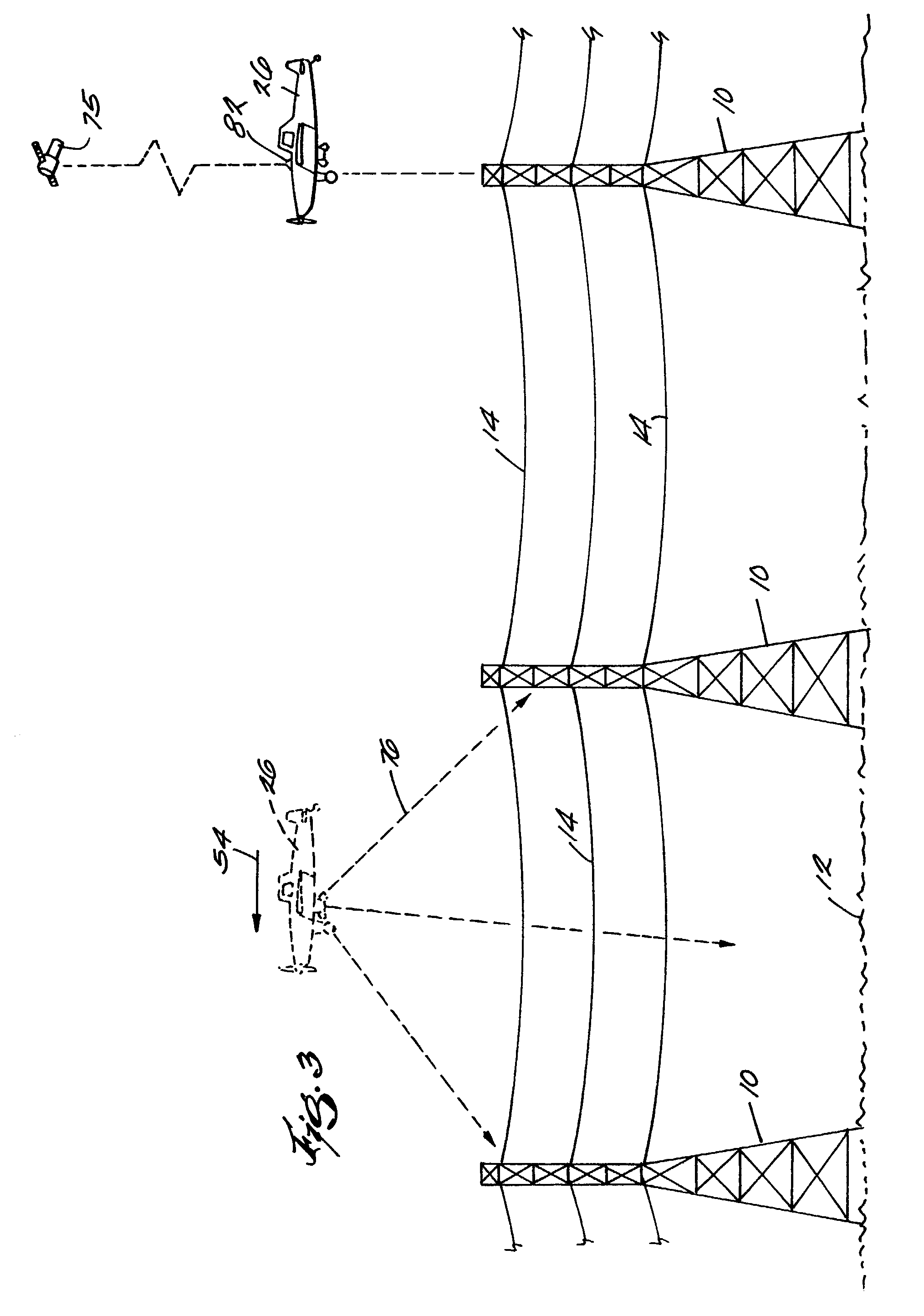
InactiveUS7184072B1Enhance the photos being takenDigital data processing detailsPicture taking arrangementsElectric power transmissionLongitude
A system and apparatus for acquiring images of electric transmission line tower structures, equipment attached to said tower structures, and transmission lines suspended from said towers. The system uses a fixed wing aircraft and an arrangement of at least one still camera, means for detecting a tower structure, a data storage unit, and a central processing unit containing operational software. The central processing unit is connected to the camera, the means for detecting a tower structure, and the storage unit. The detection means is a laser altimeter or a combination of preset longitude / latitude coordinates for tower locations and a GPS unit which supplies continuous longitude / latitude coordinates for the aircraft location for comparison to those preset coordinates. The aircraft is flown along the transmission line at a predetermined altitude above the tops of said towers (60–100 feet). The still camera points rearwardly relative to the line of flight of the aircraft and take a picture from between two adjacent towers and along an exposure line directed downwardly at an angle to the line of flight, 30–60 degrees and preferably 45 degrees. The detecting means transmits a signal to the central processing indicative of the presence of a tower to be photographed. The central processing unit calculates the time delay necessary for said aircraft to fly past the tower to a predetermined exposure point located between the tower to be photographed and the next tower in said transmission line after the tower to be photographed. The still camera is activated at the exposure point to acquire an image of the tower structure. The data corresponding to the acquired image is transmitted to a data storage unit for later retrieval and examination to identify defects in the tower or the equipment or transmission lines suspended form the tower. The system is reset to continue acquiring images along the transmission lines. The system is also provided with a video capability to film the towers and transmission lines and the line right-of-way.
Owner:POWER VIEW COMPANY L L C
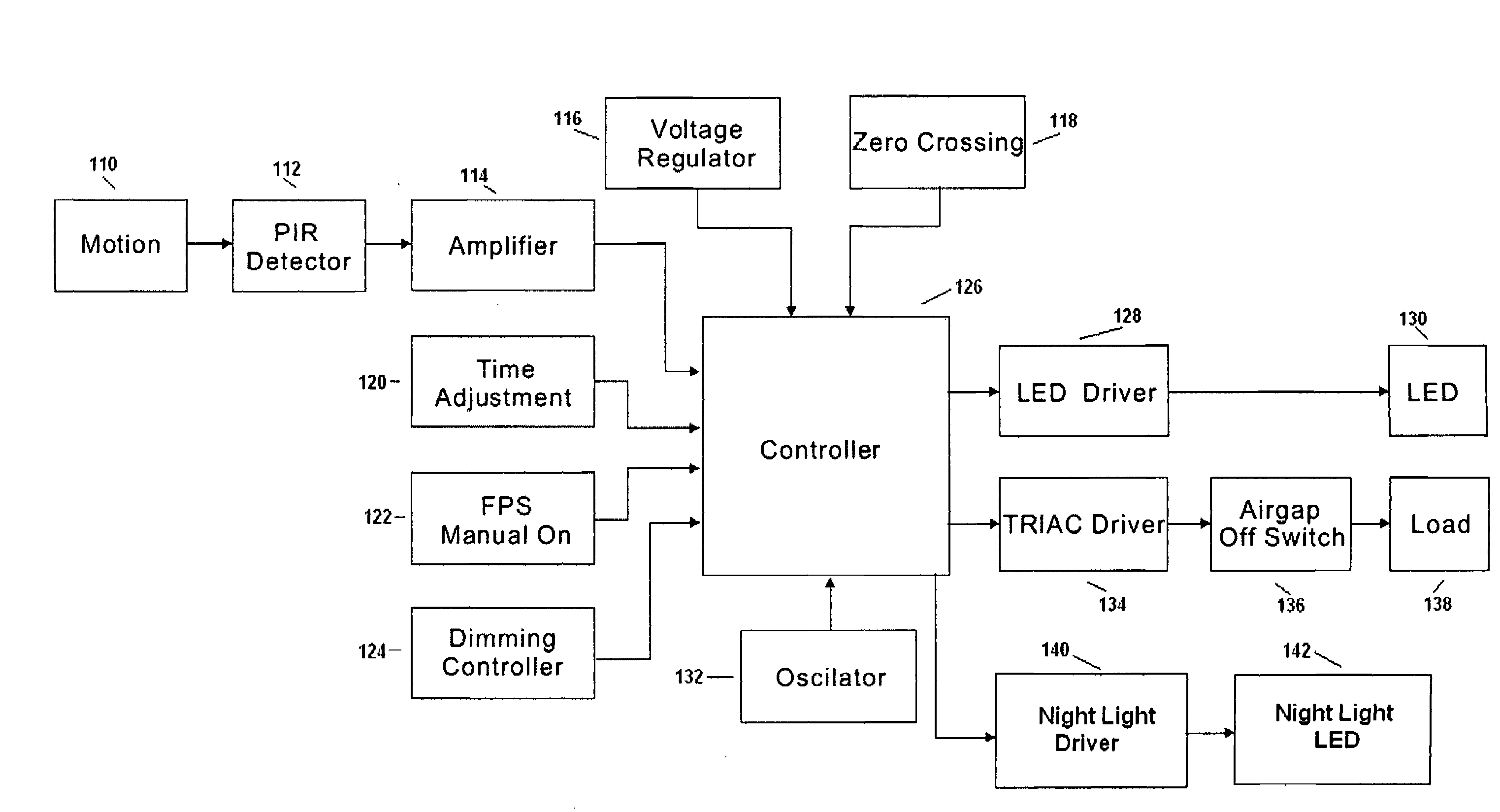
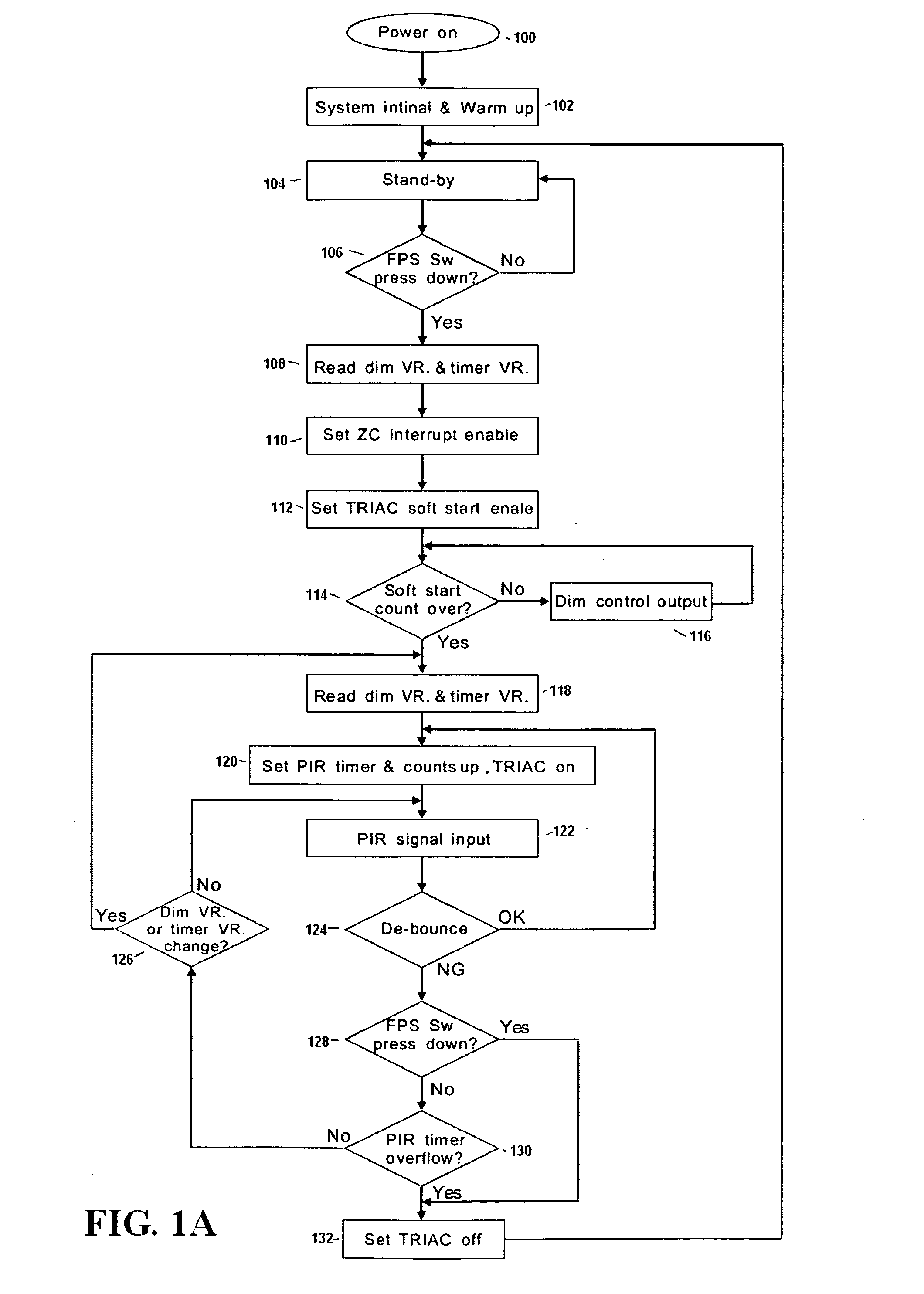
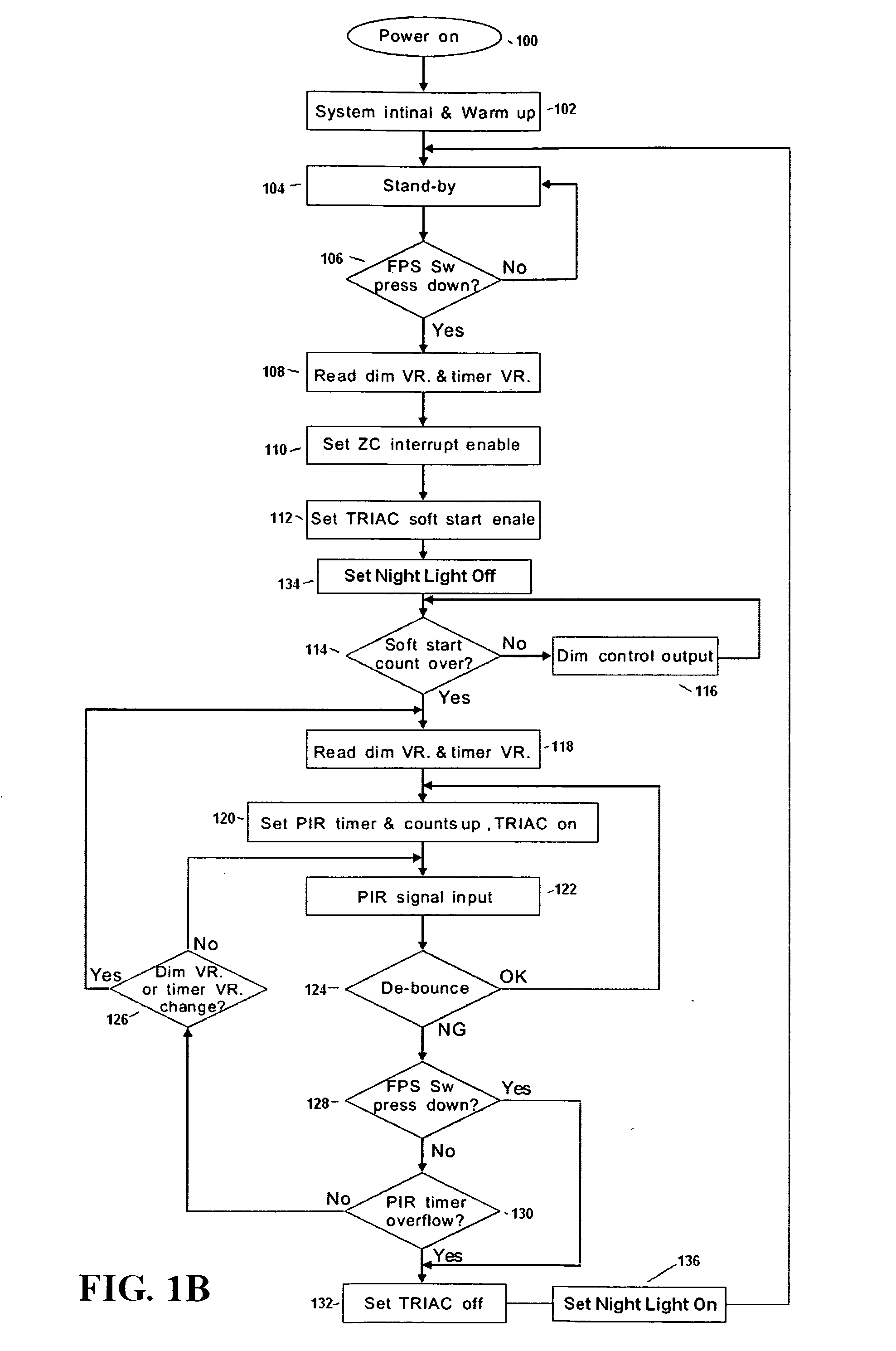
Occupancy sensor with dimmer feature and night light and method of lighting control using the same
ActiveUS20080079568A1Light would become directionalElectrical apparatusElectric circuit arrangementsDimmerEngineering
System and method are provided where an occupancy sensor with a time delay function designed to dim the lights, for example as a warning, after a first period of time has expired without detecting room occupancy. The lights remain dimmed for a second period of time, and then are turned off after a third period of time has expired without detecting room occupancy. If occupancy is detected during the first period of time, the lights will remain on. If occupancy is detected during the second or third period of time, the lights will be turned on to, for example, previous brightness. A night light can be added to, and / or incorporated in, an occupancy sensor which includes the dimmer feature.
Owner:HUBBELL INC
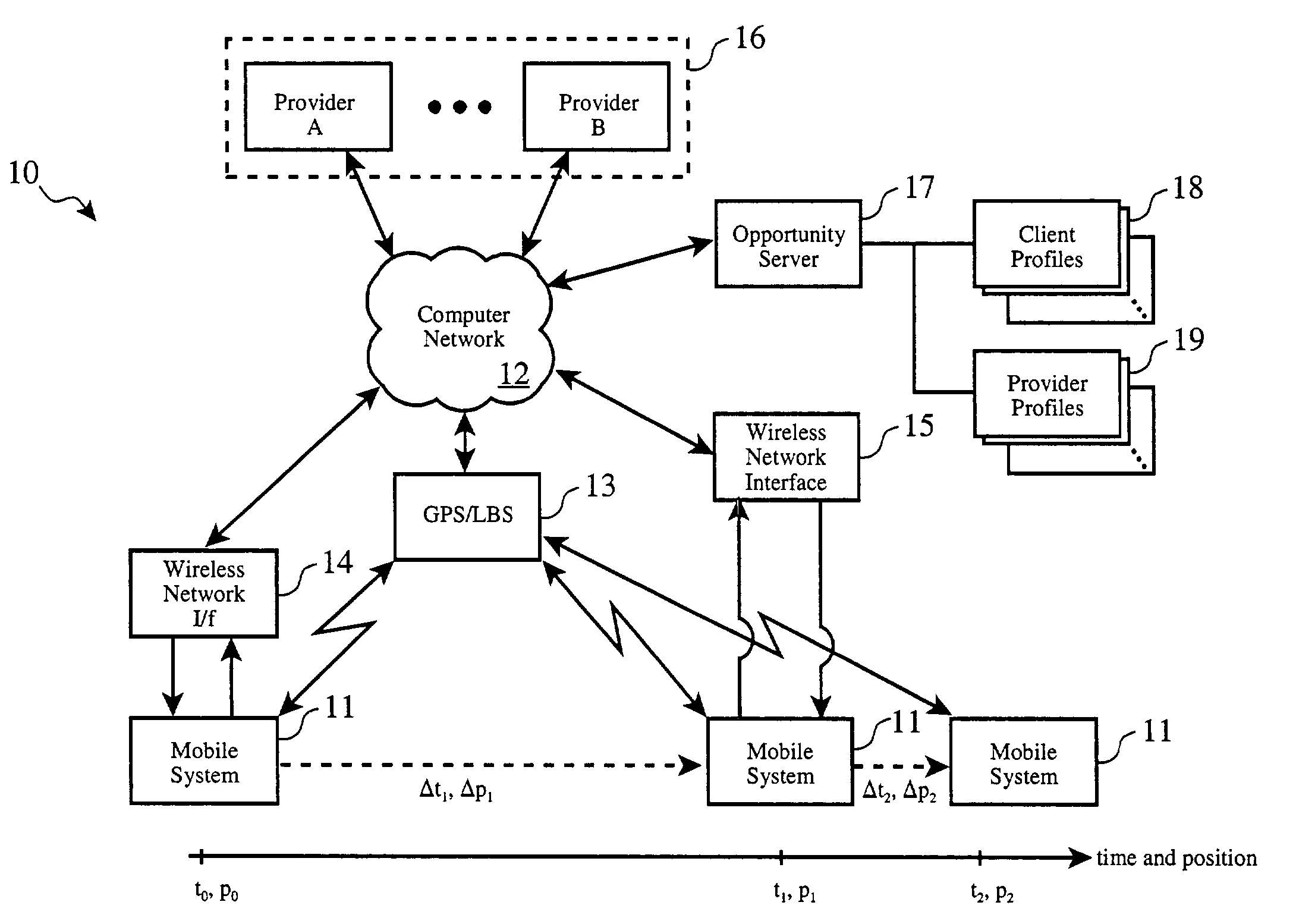
Location-based intelligent remote vehicle function control
ActiveUS7346439B2Increase costWide deploymentDigital data processing detailsRoad vehicles traffic controlTime segmentIn vehicle
An in-vehicle monitor detects the occurrence of a meta-event related to the operation of a vehicle, such as the vehicle's operation over a maximum allowable speed, operation in a prohibited geographic area, operation during a specific time frame, or combinations thereof. The monitor signals a server via a wireless data link, and the server determines an appropriate deferred action to be taken by an in-vehicle controller, such as disabling the engine, limiting vehicle speed, and locking vehicle doors, upon occurrence of a second meta-event including conditions such as time delays, vehicle speed and direction, and vehicle location. The system can thereby allow orderly and safe control of vehicle functions for purposes such as terminating a pursuit, enforcing legal sentences and operator restrictions, and controlling fleet vehicle operations.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
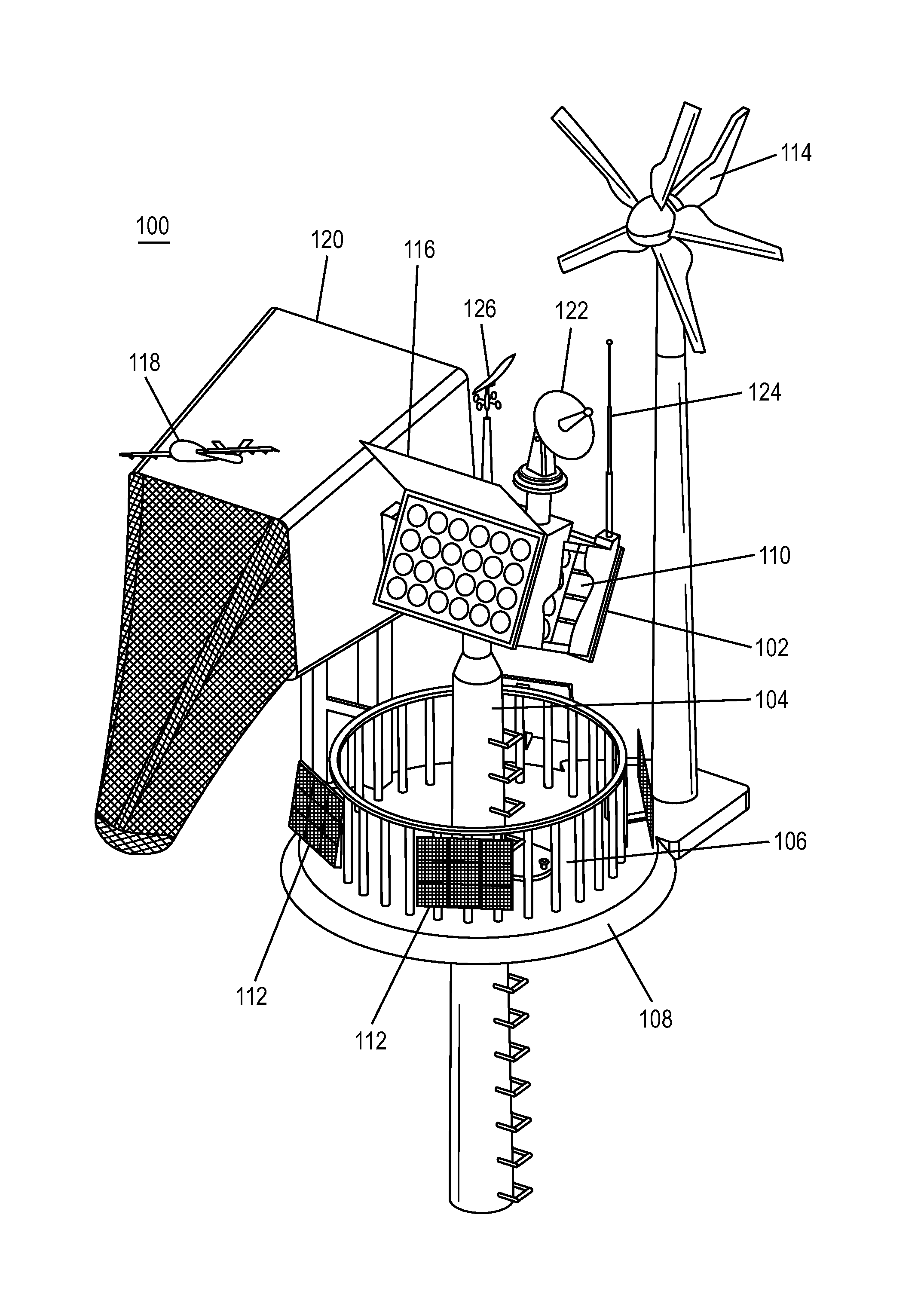
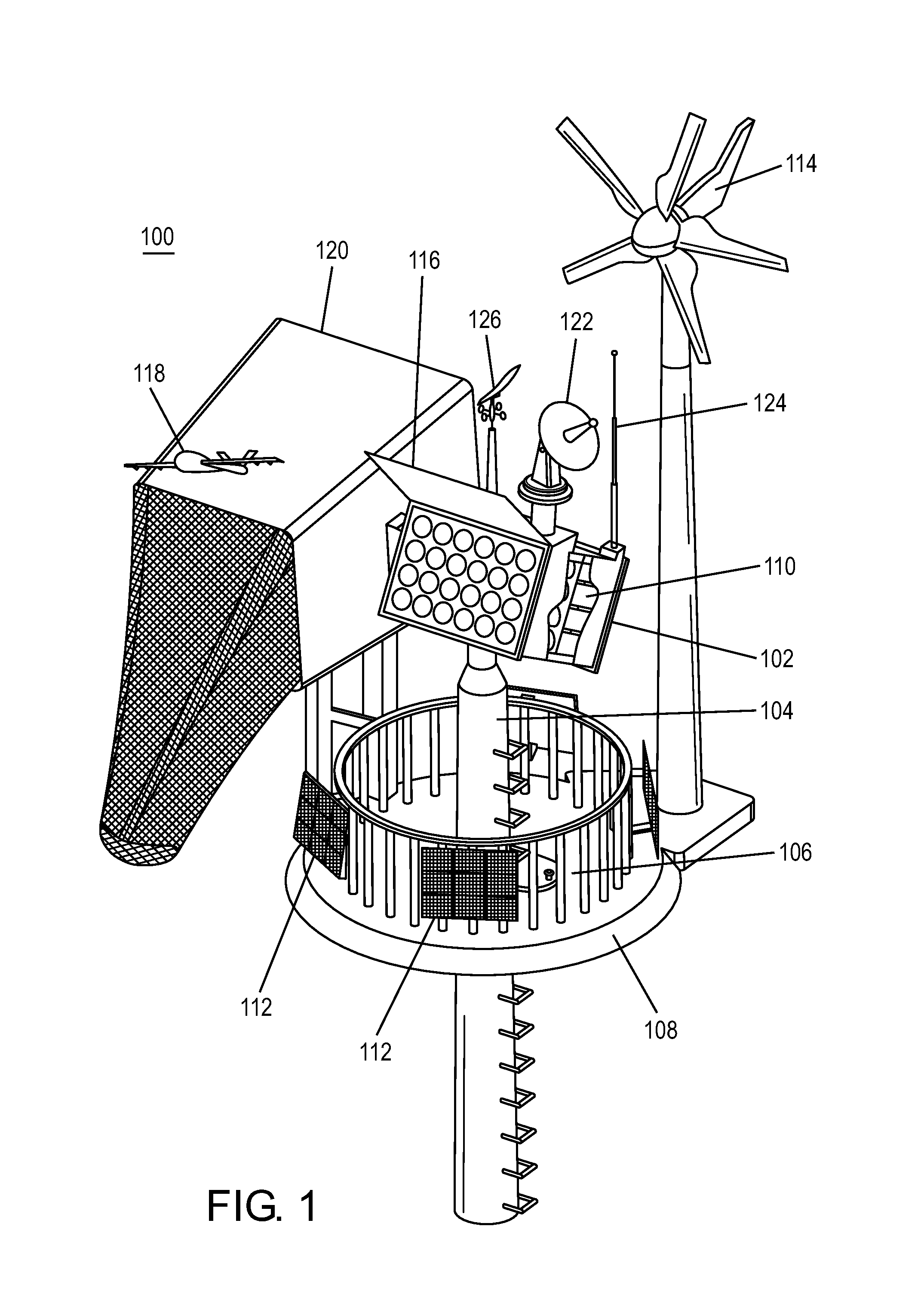
Systems and methods for deployment and operation of unmanned aerial vehicles
InactiveUS8439301B1Extended shelf lifeImprove launch reliabilityRocket launchersArresting gearLogistics managementCommand and control
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) system provides for UAV deployment and remote, unattended operation with reduced logistics requirements. The system includes a launcher that can include one or more launch tubes, each launch tube configured to house a UAV in a canister and one or more gas generators operatively connected to each canister and configured to push the UAV out of the launch tube by releasing gas into the canister. A controller for activating the gas generators can sequentially, and with a predetermined time delay, expel the UAV with a desired velocity and acceleration. The system further includes a UAV recovery device, a power supply, a security subsystem, a command and control subsystem and a communications subsystem. Command, control and communications can be provided between a remote station and the UAV.
Owner:SEACORP LLC
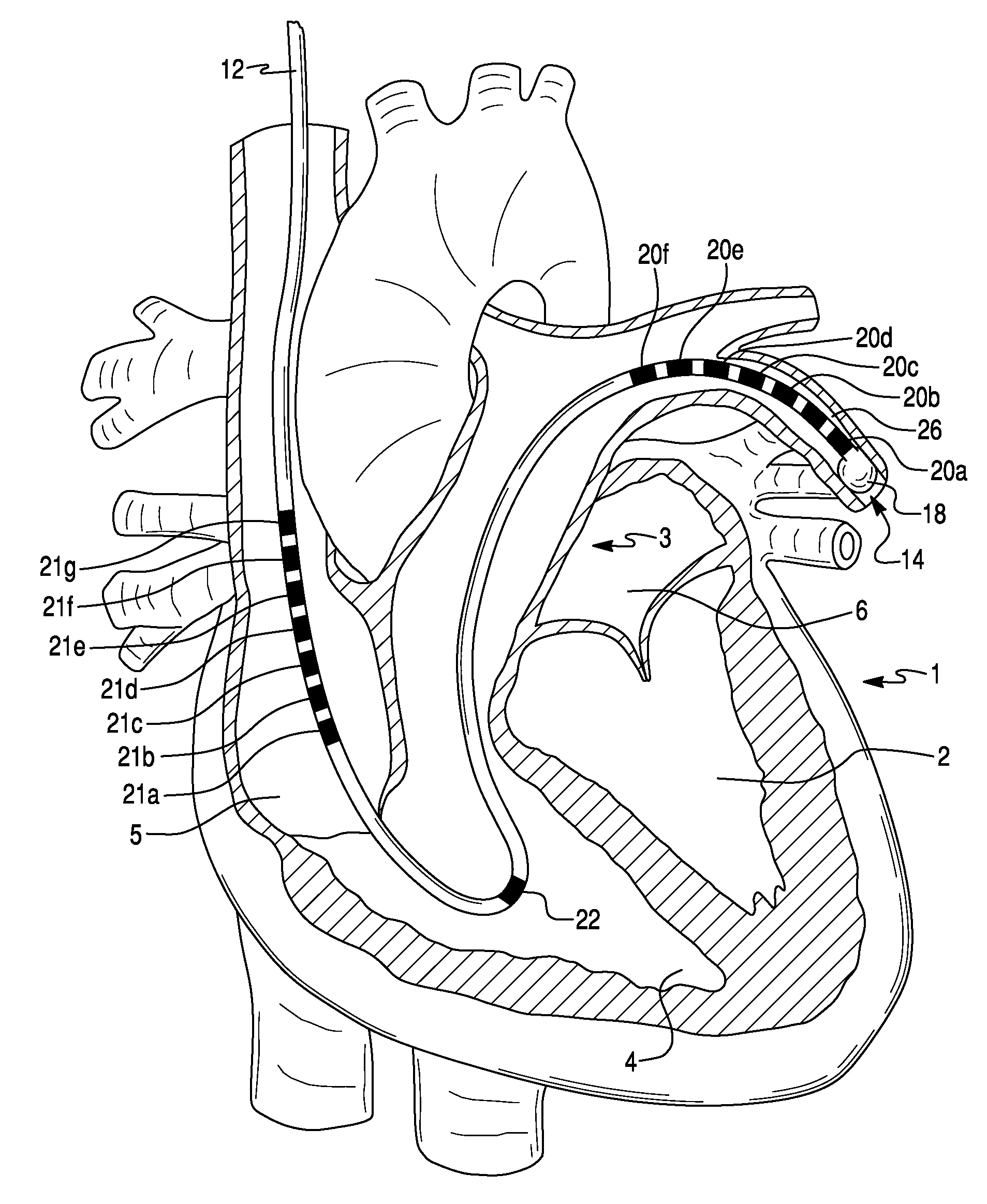
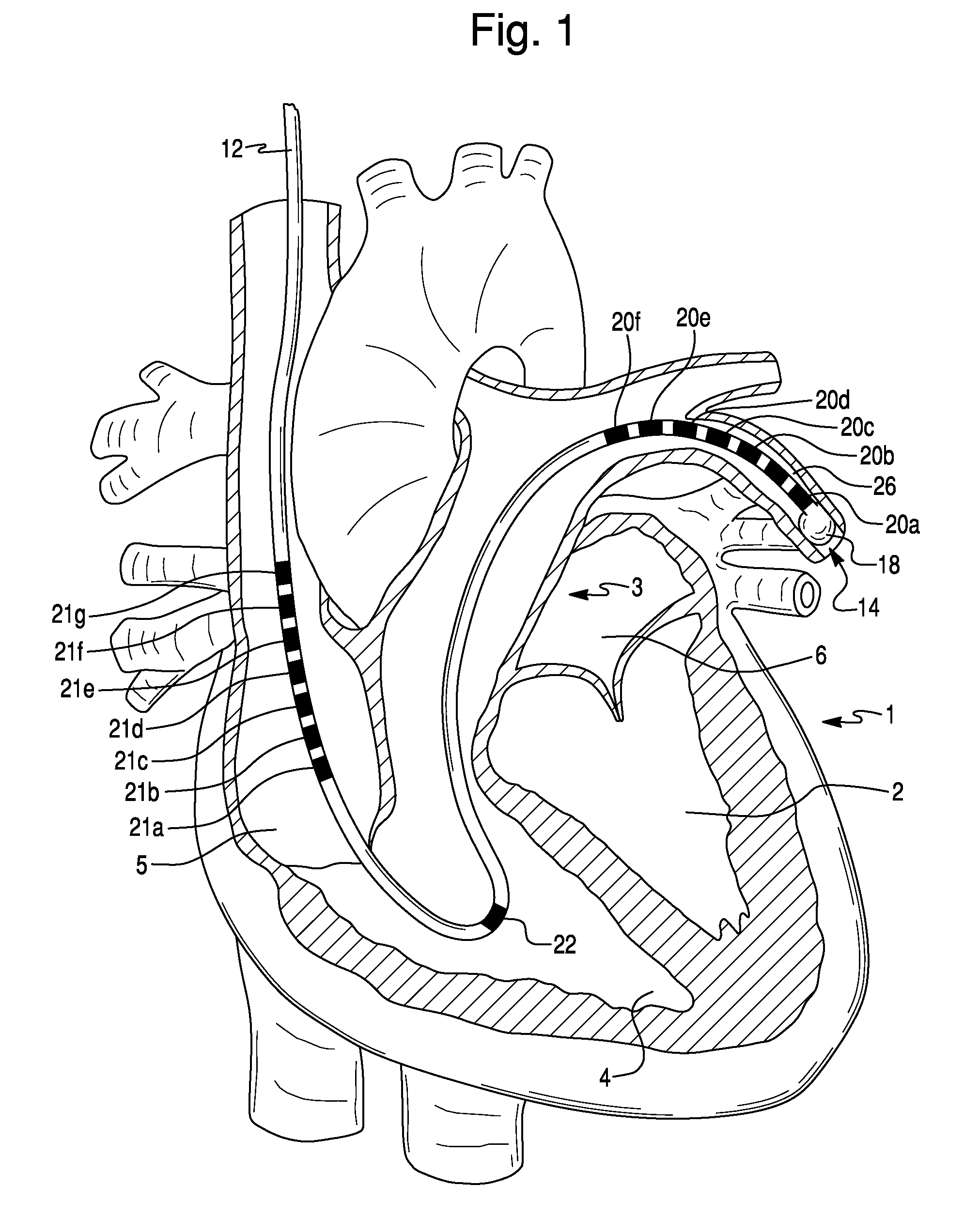
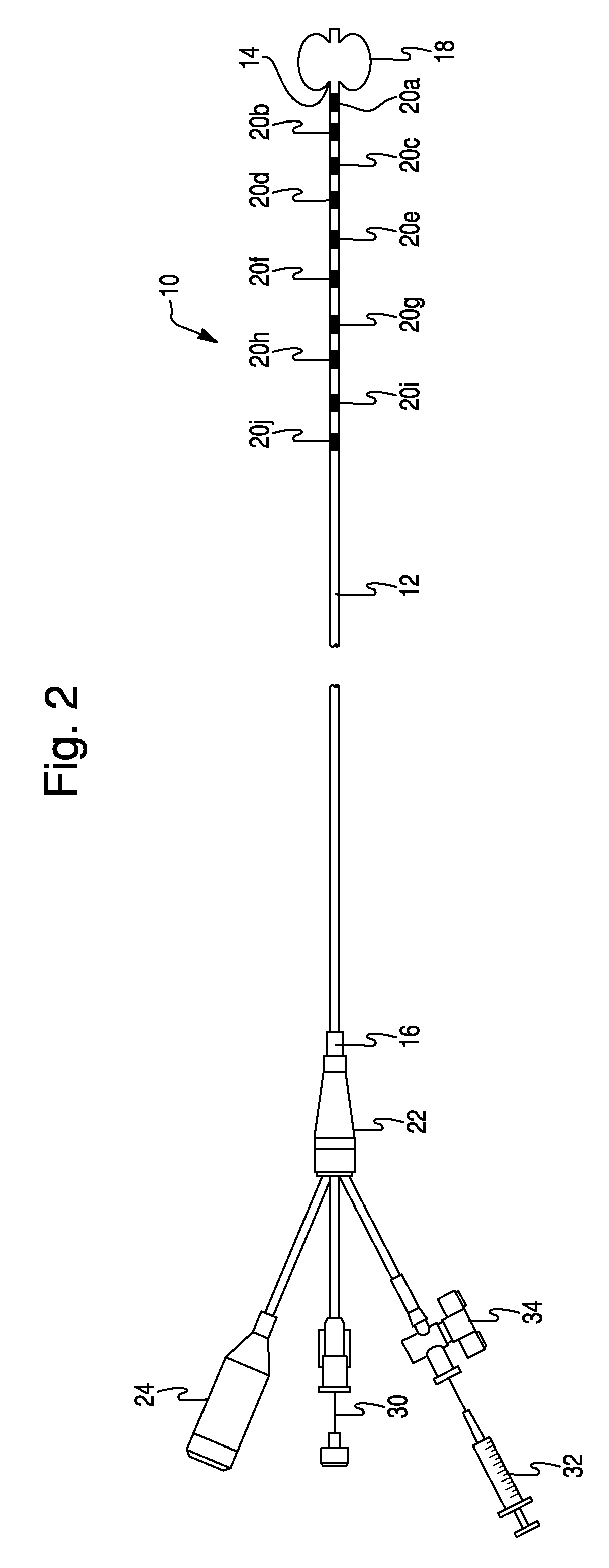
Method For Simultaneous Bi-Atrial Mapping Of Atrial Fibrillation
InactiveUS20070232949A1High resolutionFast informationElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyCardiac pacemaker electrodeDisplay device
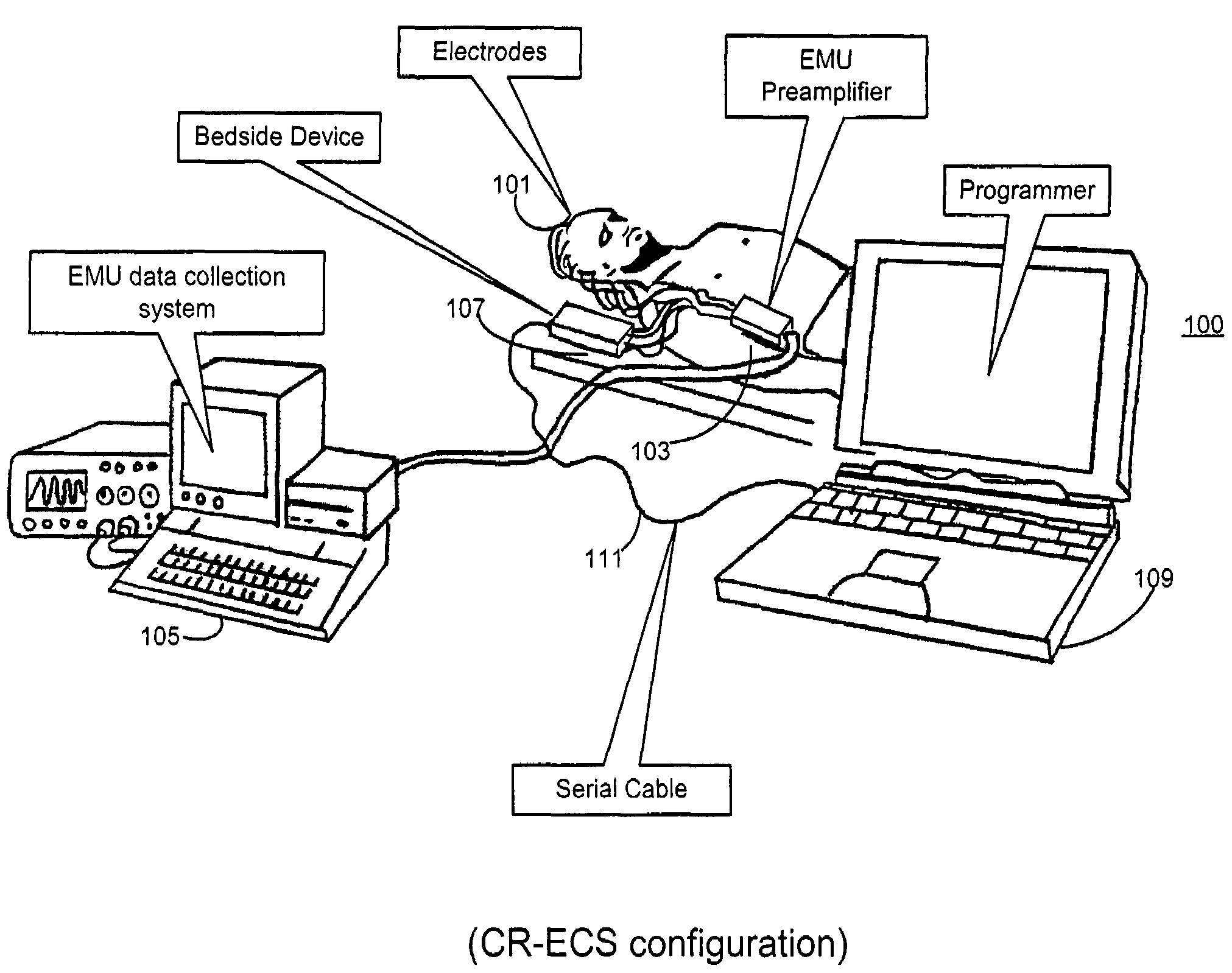
A method for diagnosing and mapping atrial fibrillation correlates recordings of electrical activity from intracardiac multielectrode catheters with the locations of electrodes within the heart to obtain a global mapping of cardiac electrical activity. Time delay and / or amplitude information in the recorded electrical activities is fused with electrode location information to generate a display on a 3-D anatomical template of the heart. Time delay and / or amplitude information is displayed using color code and / or lines of equal value, to aid diagnosis and localization of electrical activity irregularities. Mapping of atrial fibrillation enables physicians to treat arrhythmia by ablation, pacing, shock therapy and / or drugs at initiation or during an episode based on therapy delivery at critical mapped locations for arrhythmia onset or maintenance. Locations for placement of pacing leads and pacemaker timing parameters may also be obtained from the display.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
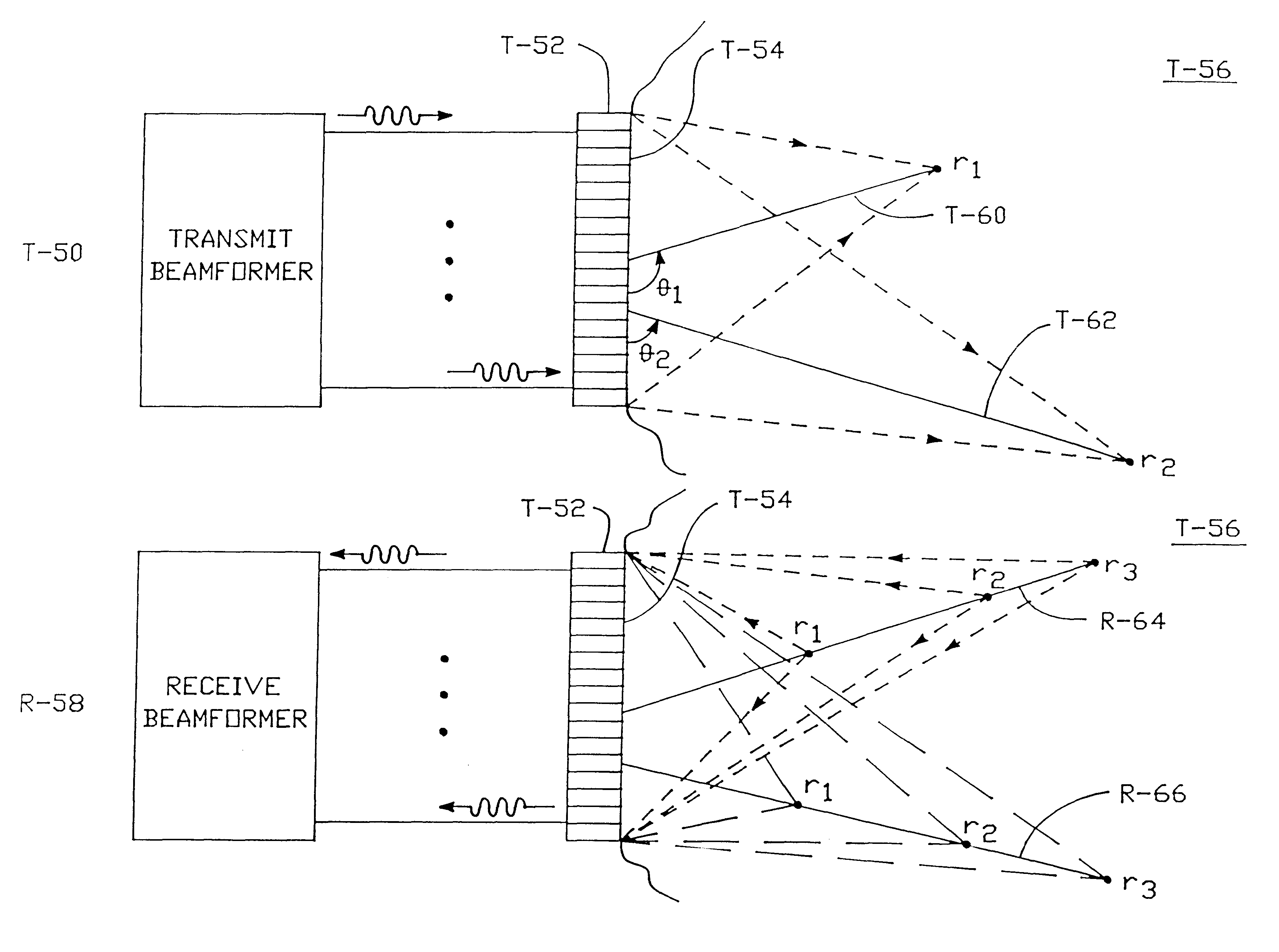
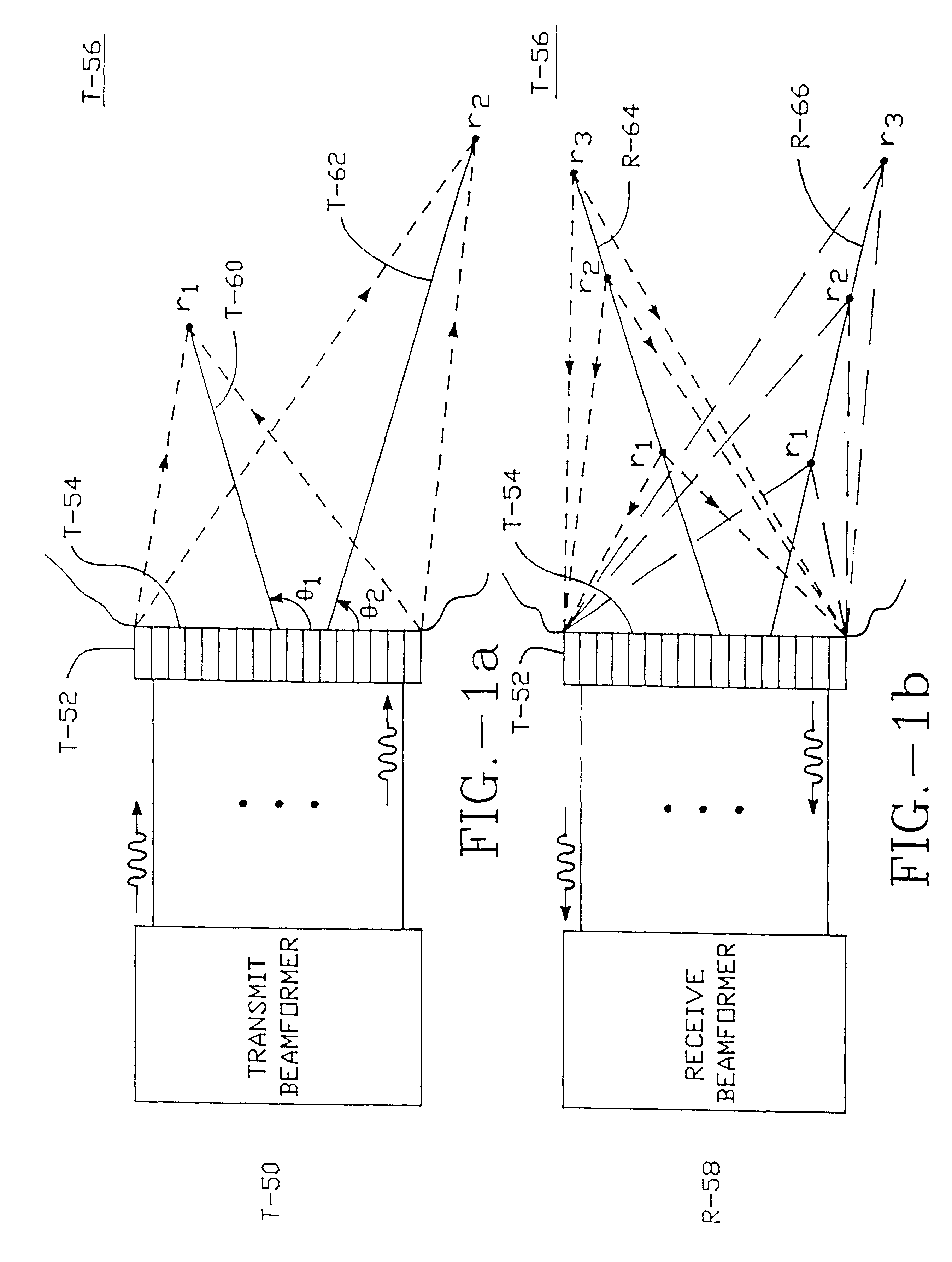
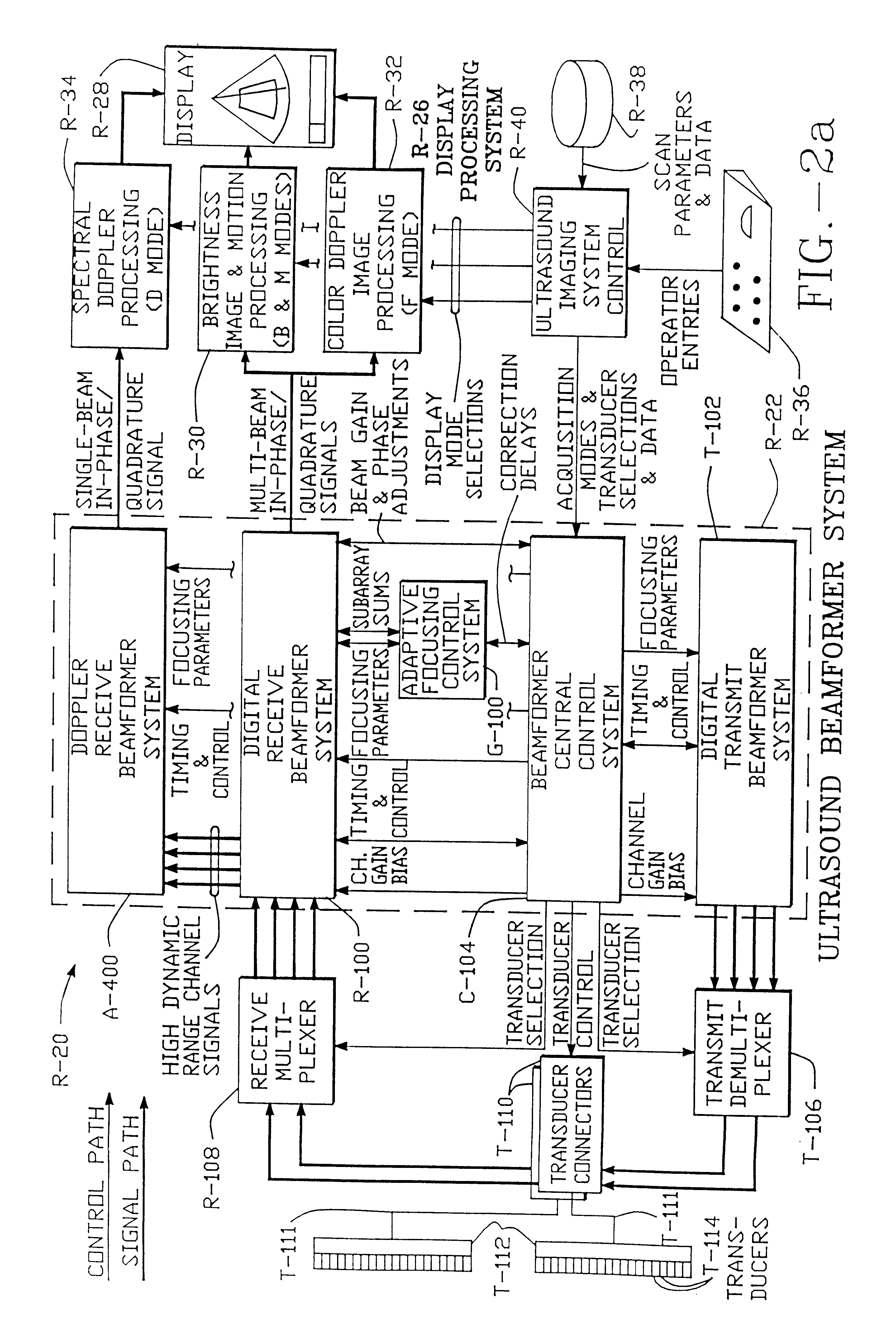
Method and apparatus for transmit beamformer system
InactiveUS6363033B1Improve programmabilityMaximum flexibilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsProcessing detected response signalTrade offsApodization
A digital transmit beamformer system with multiple beam transmit capability has a plurality of multi-channel transmitters, each channel with a source of sampled, complex-valued initial waveform information representative of the ultimate desired waveform to be applied to one or more corresponding transducer elements for each beam. Each multi-channel transmitter applies beamformation delays and apodization to each channel's respective initial waveform information digitally, digitally modulates the information by a carrier frequency, and interpolates the information to the DAC sample rate for conversion to an analog signal and application to the associated transducer element(s). The beamformer transmitters can be programmed per channel and per beam with carrier frequency, delay, apodization and calibration values, For pulsed wave operation, pulse waveform parameters can be specified to the beamformer transmitters on a per firing basis, without degrading the scan frame rate to non-useful diagnostic levels. Waveform parameters can be specified to the transmitters by an external central control system which is responsible for higher level flexibility, such as scan formats, focusing depths and fields of view. The transmit pulse delay specified per-channel to each transmitter is applied in at least two components: a focusing time delay component and a focusing phase component. The carrier frequency can be specified for each transmit beam, to any desired frequency within a substantially continuous predefined range of frequencies, and a beam-interleaved signal processing path permits operation in any of several predefined processing modes, which define different parameter sets in a trade-off among (1) the number of beams produced; (2) per-beam initial waveform sample interval; and (3) transmit frequency.
Owner:ACUSON
Automatic target box in methods and systems for editing content-rich layouts in media-based projects
ActiveUS20160139761A1Raise countNatural language data processingPictoral communicationDrag and dropAnimation
Methods and systems for editing media rich photo projects are disclosed. In one embodiment, the present invention uses drag and drop features to add a photo to a spread, to remove a photo from the spread, and / or to create a new spread. In another embodiment, drop areas are utilized to facilitate addition and removal of photos at an editor. In another embodiment, drop targets are determined by an animated highlight of a drop target, a time delay allowing a user to wait until a drop target is auto-selected by the pre-set rules of the editor, and pre-set rules of a drop target as determined by the location of a drop. Furthermore, drop targets are determined by location coordinates of a photo over the spread before being dropped, proximity of a dragged photo with a photo slot, or a pre-calculated photo slot based on pre-set rules.
Owner:INTERACTIVE MEMORIES
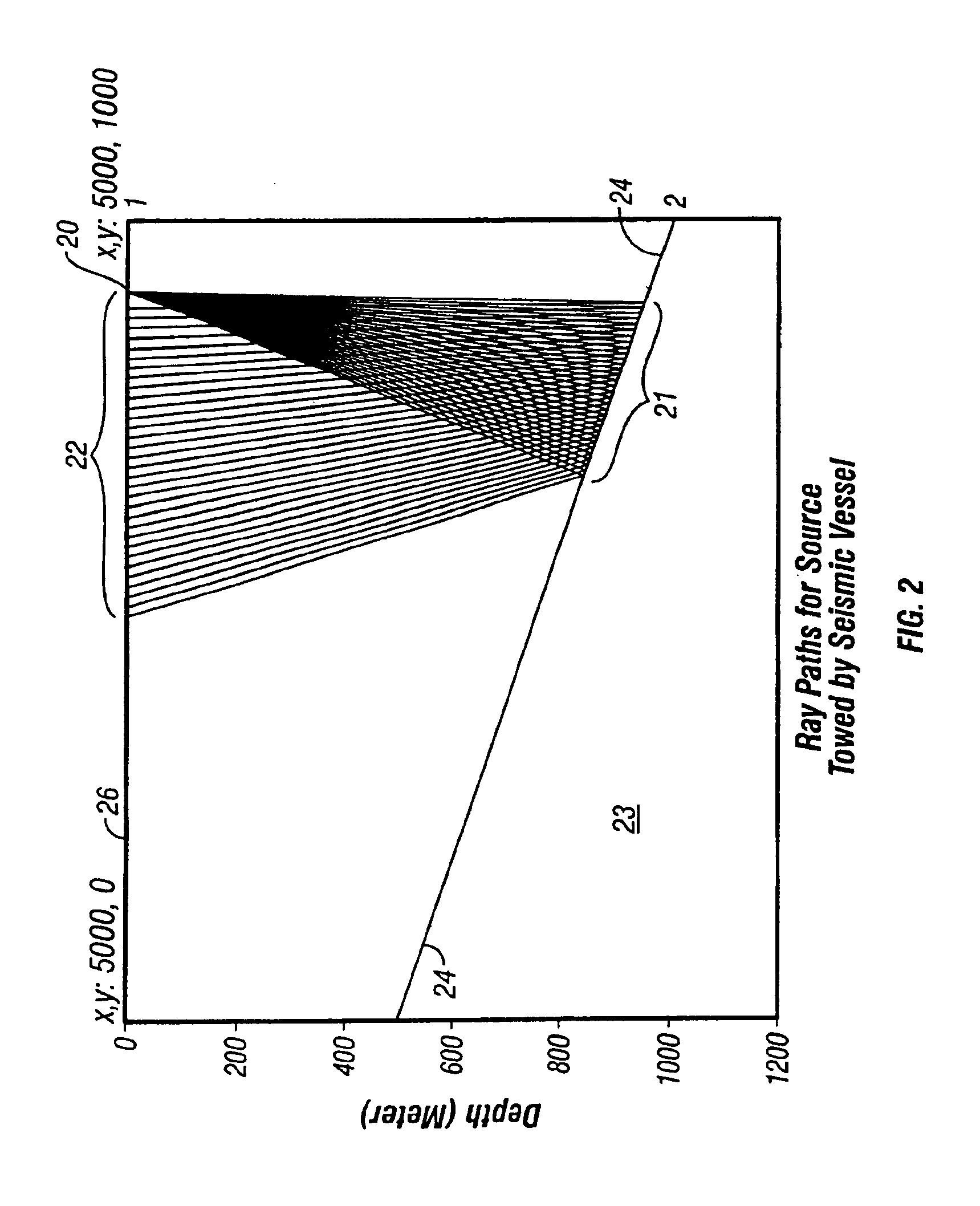
Method of seismic surveying
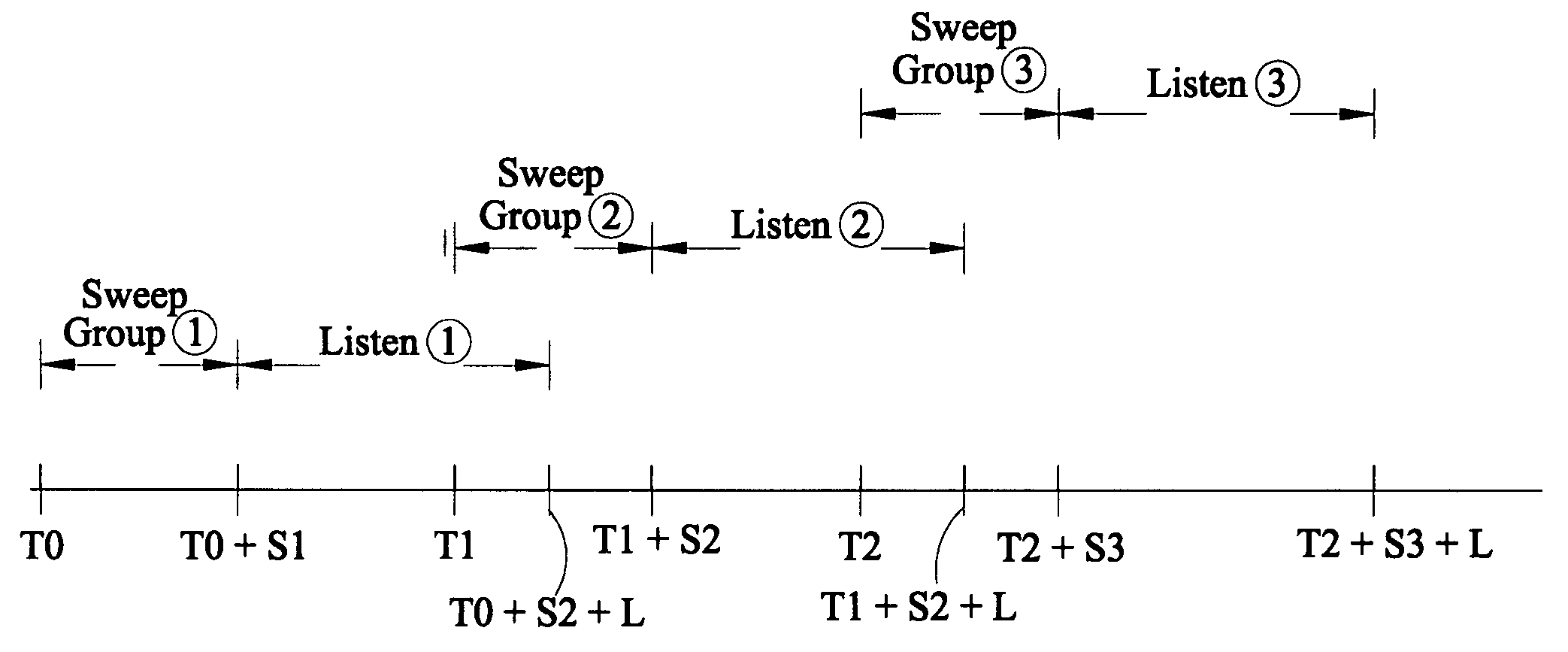
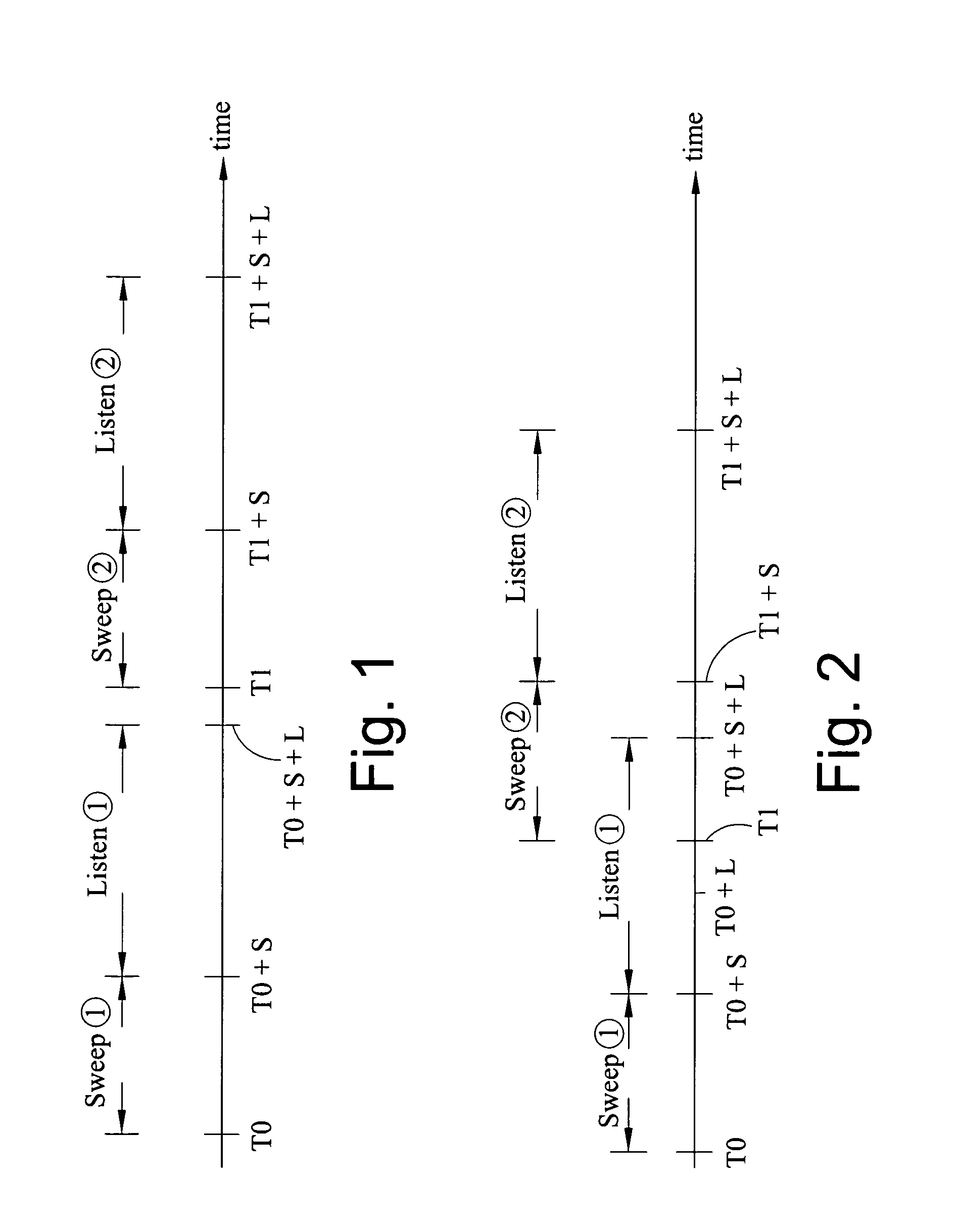
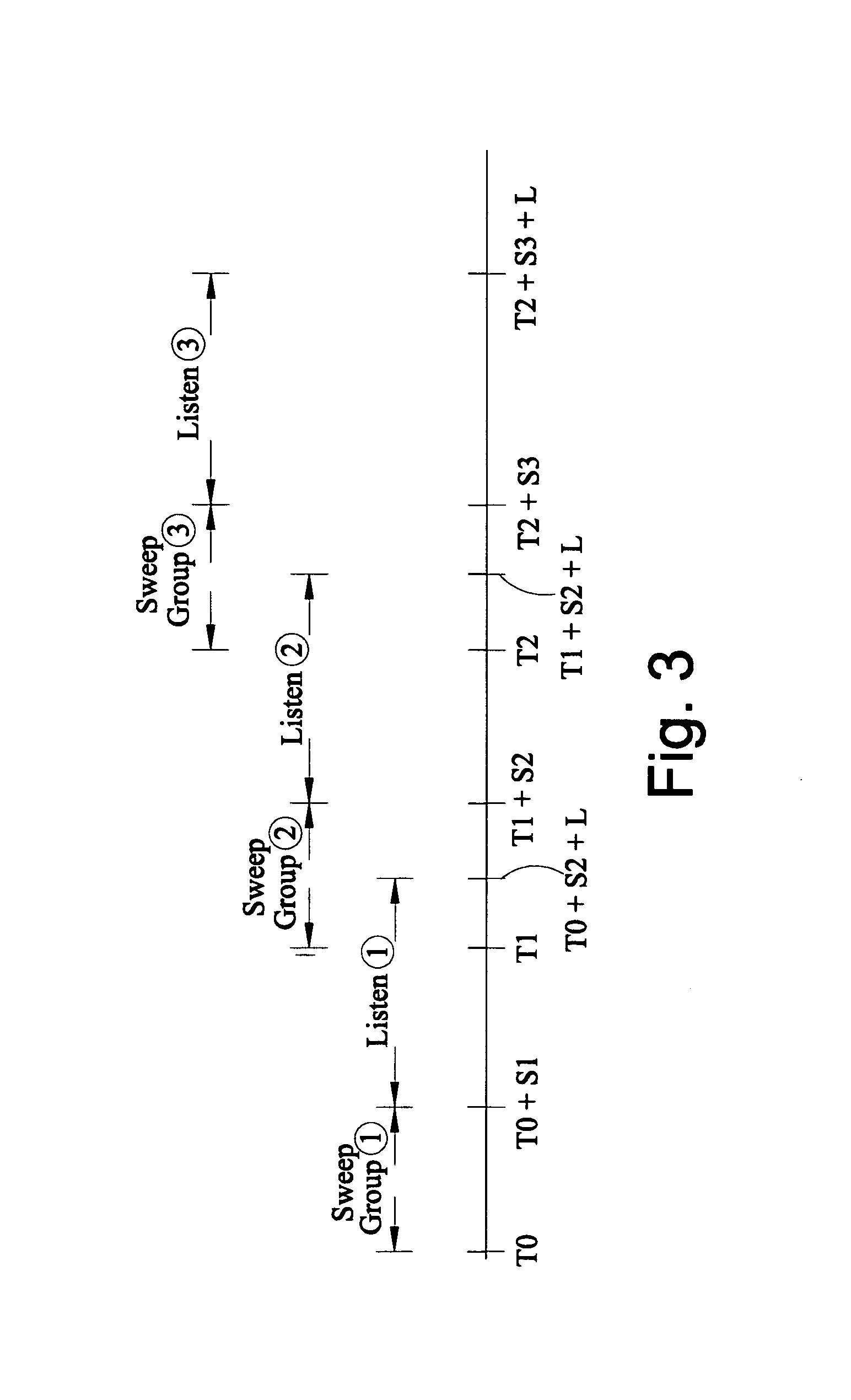
A method of seismic surveying comprising the steps of actuating the or each vibrator in a first vibrator group at time T0, and subsequently actuating the or each vibrator in a second vibrator group at time T1 that satisfies T0<T1<T0+S1+L where S1 is the sweep time of the first vibrator group and L is the listening time. At least one of the first vibrator group and the second vibrator group comprises at least two vibrators. The first group and the second group of vibrators may be the same group, or they may be different groups. This method enables the time required to complete a seismic survey to be reduced compared to the prior art “simultaneous shooting” and “slip-sweep shooting” techniques.In a case where the first group and the second group of vibrators are different, the method may further comprise actuating the or each vibrator in the first vibrator group at time T2, where T1<T2<T1+S2+L and S2 is the sweep time of the first vibrator group, and then actuating the or each vibrator in the second vibrator group at time T3 where T2<T3<T2+S1+L and where T3−T2≠T1−T0. The varying time delay between a shot of the first vibrator group and the corresponding shot of the second vibrator group means that harmonic noise will occur at different times in the shot records so that the noise may be eliminated by appropriately combining the shot records.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Method and apparatus for preparing signals to be compared to establish predistortion at the input of an amplifier
InactiveUS20030156658A1Improve electricity efficiencyImprove performance efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionElectric signal transmission systemsAudio power amplifierUnit of time
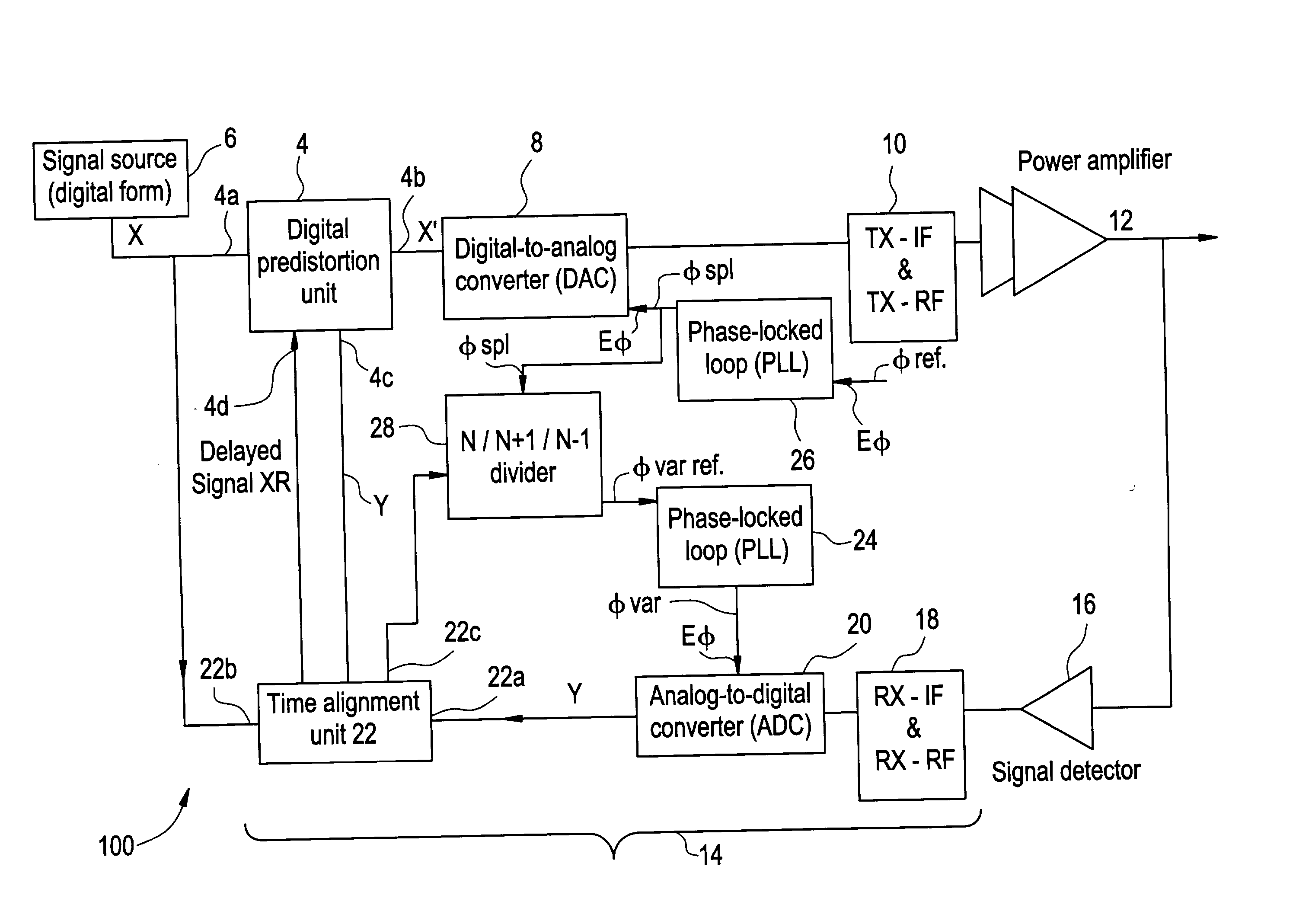
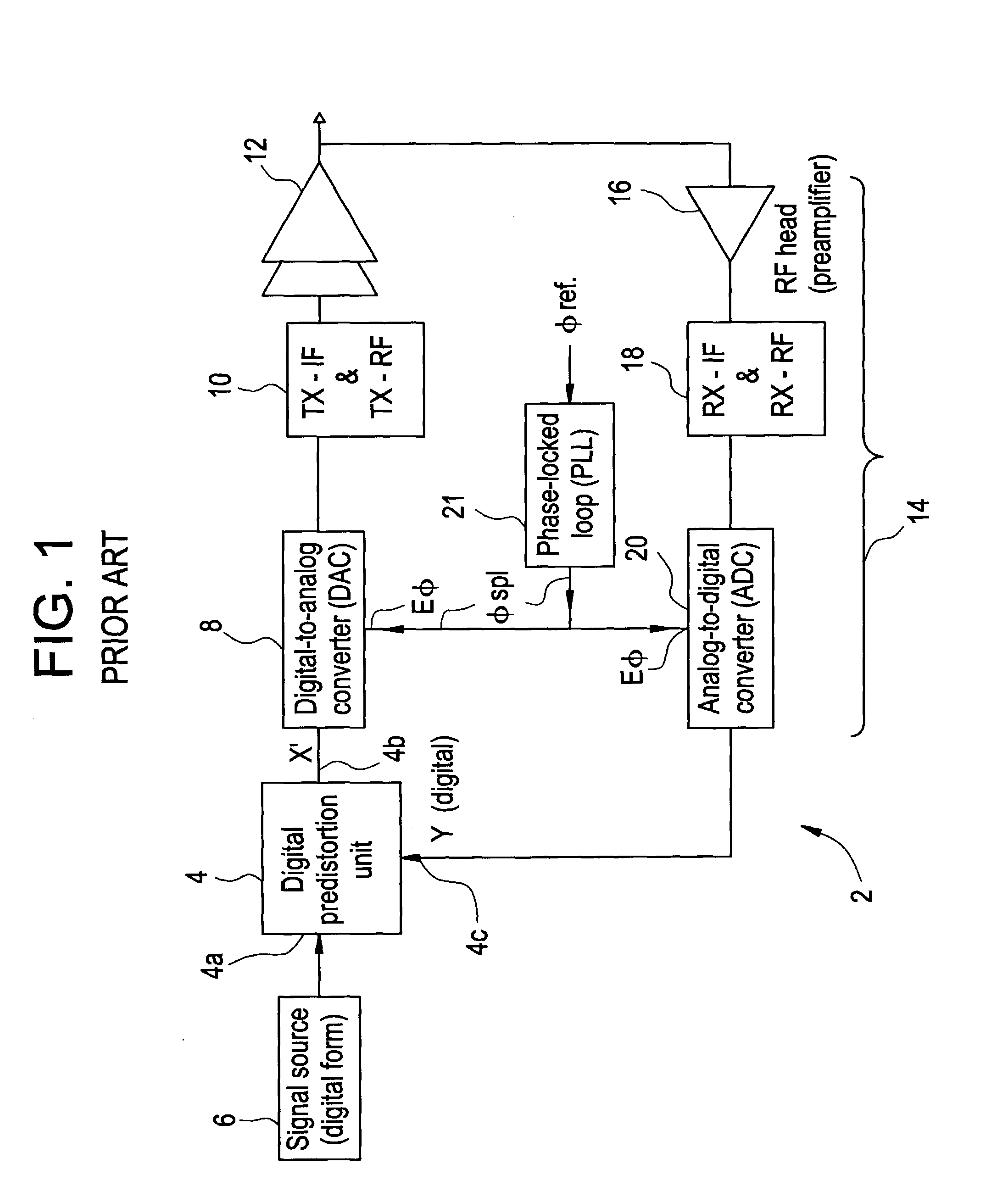
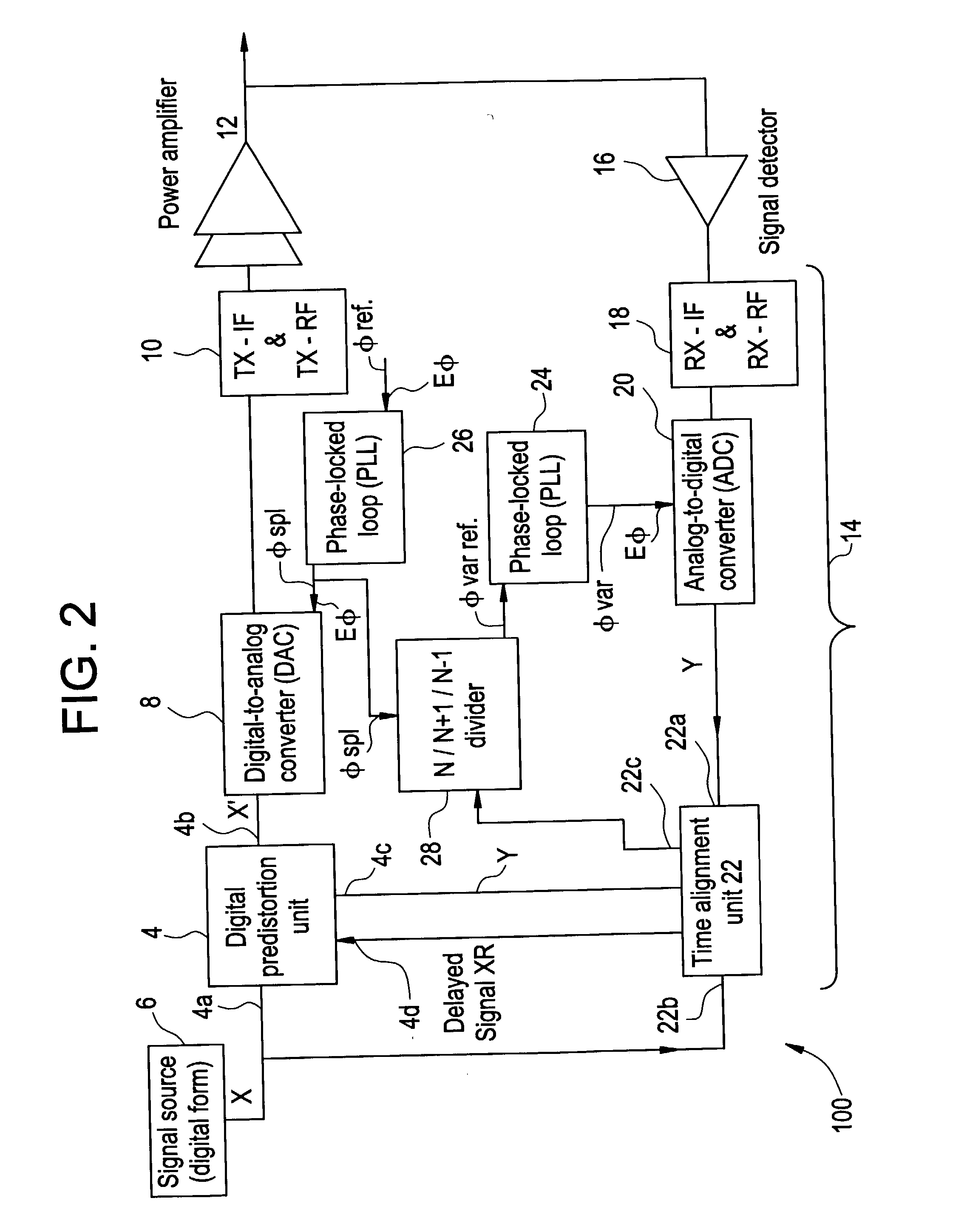
The invention relates to a method of preparing signals (X and Y) to be compared to establish predistortion at the input of an amplifier (12), the signals comprising a signal (X) before amplification and a signal (Y) after amplification by said amplifier. Preparation includes time aligning (22) the signal before amplification (X) with the signal after amplification (Y) before using them to establish said predistortion. The invention preferably operates in two stages, namely a stage of coarse time alignment, in which the signal before amplification (X) is subjected to a time delay comprising an integer number of first time units, and a stage of fine time alignment, in which a delay or advance value of a fraction of the first time unit is determined.
Owner:EVOLIUM
Multispectral or hyperspectral imaging system and method for tactical reconnaissance
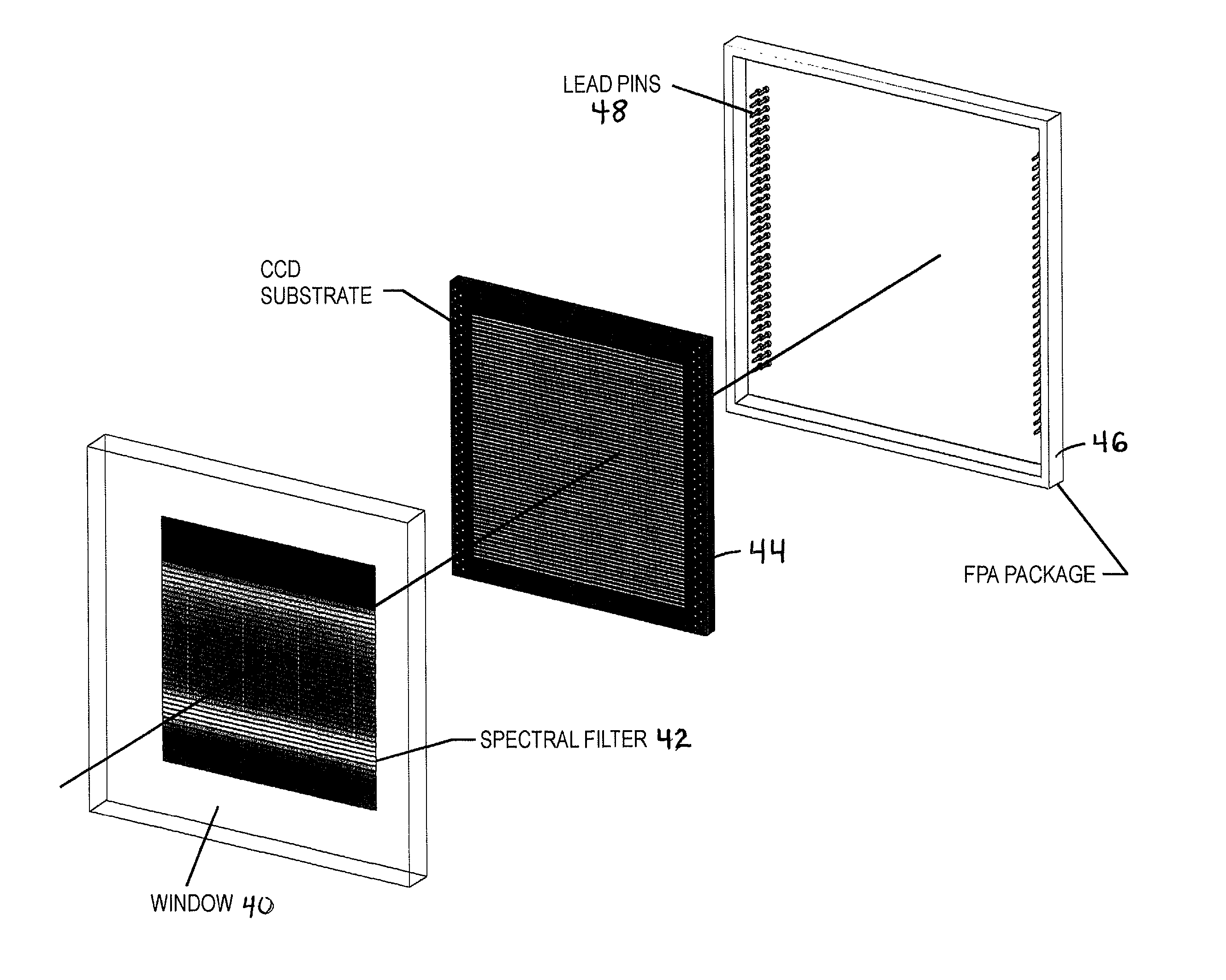
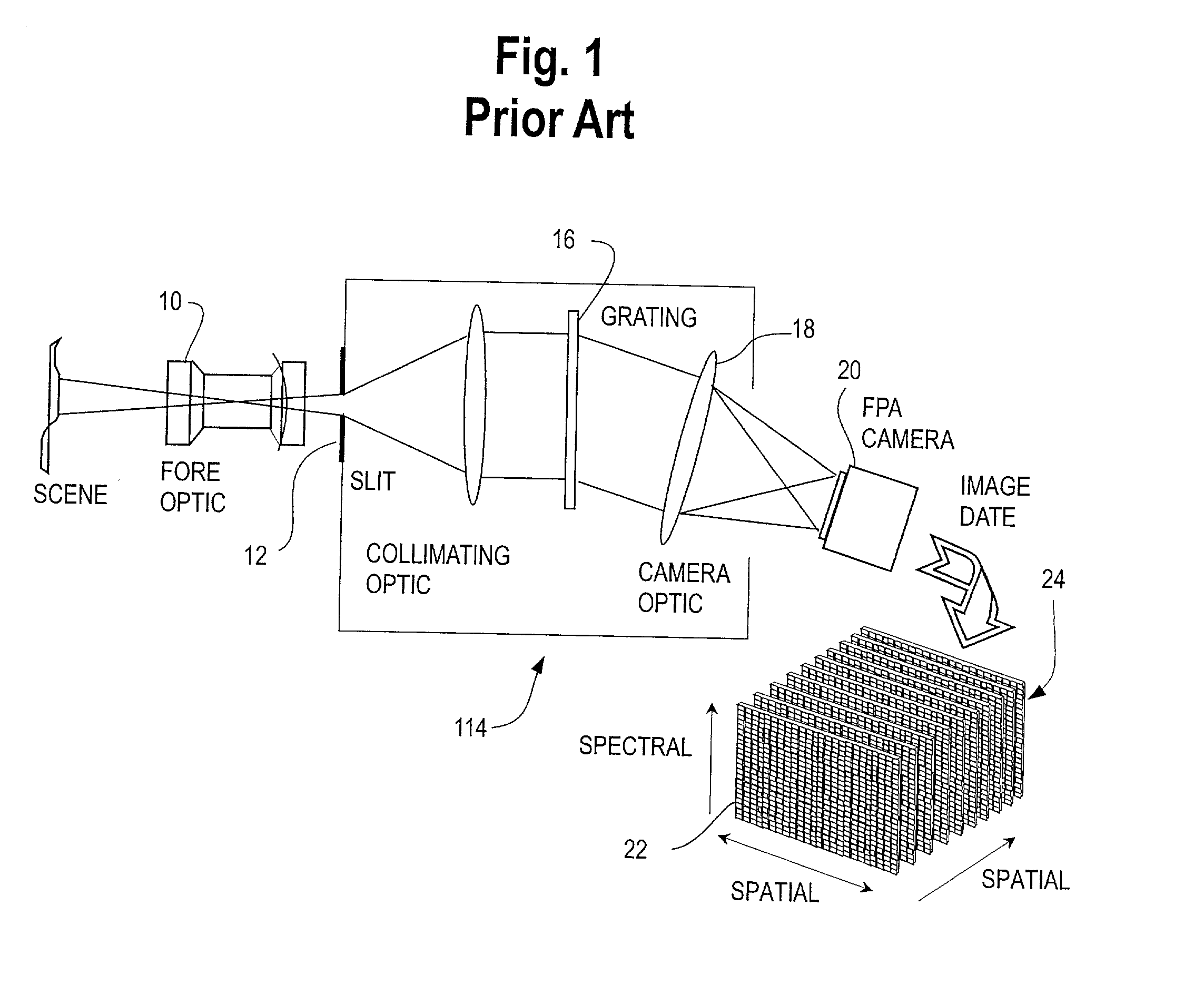
A two-dimensional focal plane array (FPA) is divided into sub-arrays of rows and columns of pixels, each sub-array being responsive to light energy from a target object which has been separated by a spectral filter or other spectrum dividing element into a predetermined number of spectral bands. There is preferably one sub-array on the FPA for each predetermined spectral band. Each sub-array has its own read out channel to allow parallel and simultaneous readout of all sub-arrays of the array. The scene is scanned onto the array for simultaneous imaging of the terrain in many spectral bands. Time Delay and Integrate (TDI) techniques are used as a clocking mechanism within the sub-arrays to increase the signal to noise ratio (SNR) of the detected image. Additionally, the TDI length (i.e., number of rows of integration during the exposure) within each sub-array is adjustable to optimize and normalize the response of the photosensitive substrate to each spectral band. The array provides for parallel and simultaneous readout of each sub-array to increase the collection rate of the spectral imagery. All of these features serve to provide a substantial improvement in the area coverage of a hyperspectral imaging system while at the same time increasing the SNR of the detected spectral image.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Comparing audio using characterizations based on auditory events
InactiveUS7283954B2Simple and computationally efficientReduce and eliminate effectTelevision system detailsSpeech analysisTime shiftingA domain
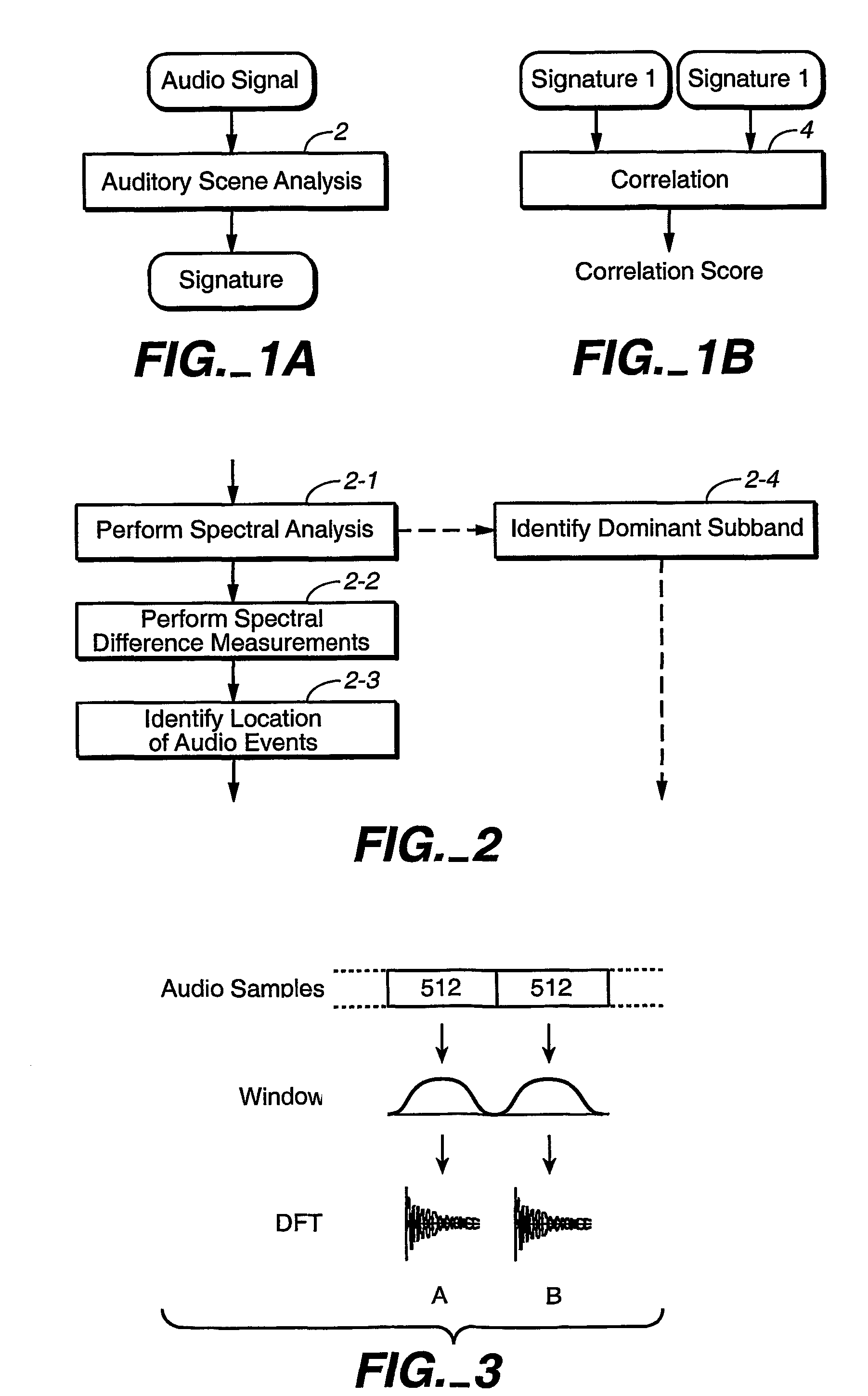
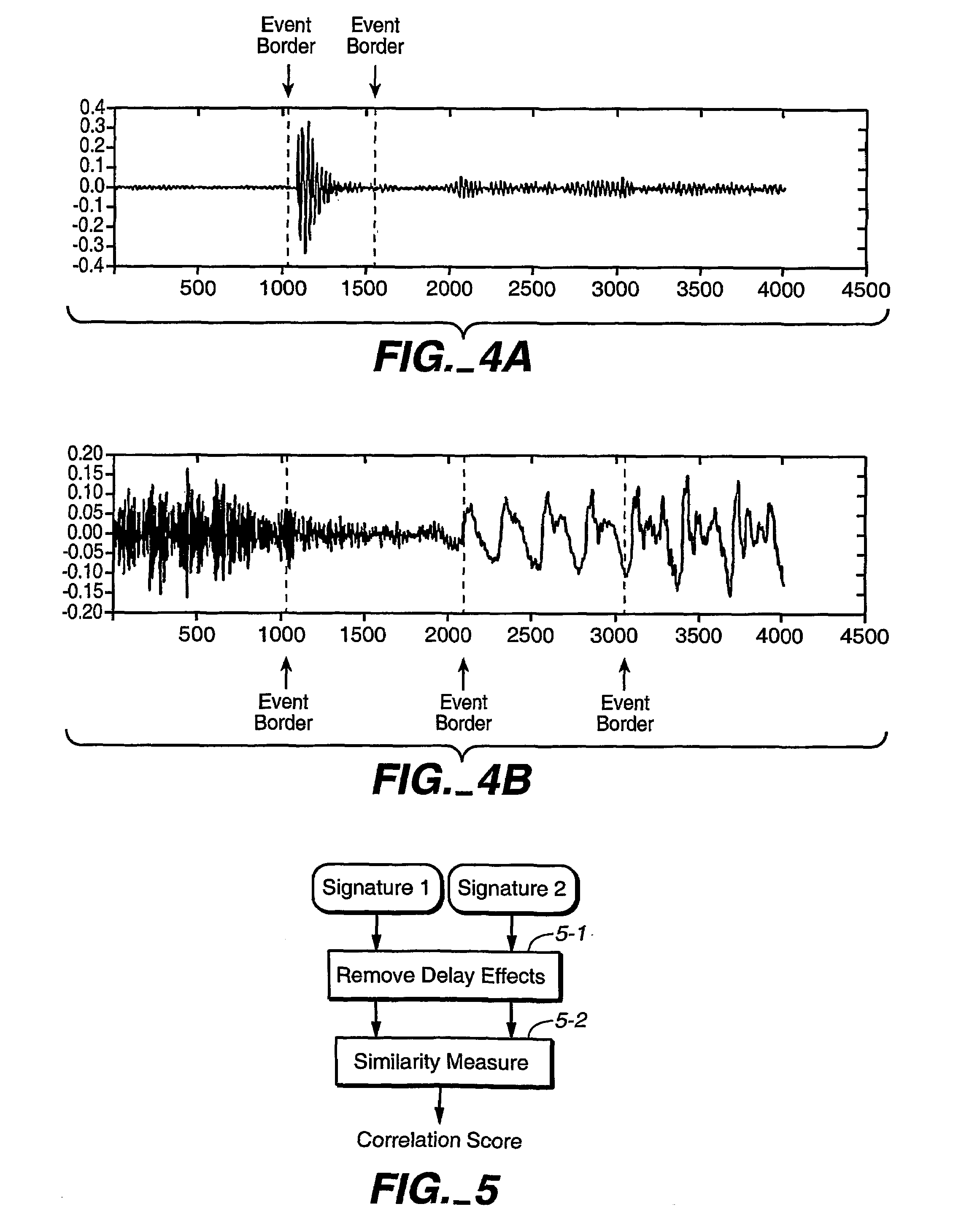
A method for determining if one audio signal is derived from another audio signal or if two audio signals are derived from the same audio signal compares reduced-information characterizations of said audio signals, wherein said characterizations are based on auditory scene analysis. The comparison removes from the characterisations or minimizes in the characterisations the effect of temporal shift or delay on the audio signals (5-1), calculates a measure of similarity (5-2), and compares the measure of similarity against a threshold. In one alternative, the effect of temporal shift or delay is removed or minimized by cross-correlating the two characterizations. In another alternative, the effect of temporal shift or delay is removed or minimized by transforming the characterizations into a domain that is independent of temporal delay effects, such as the frequency domain. In both cases, a measure of similarity is calculated by calculating a coefficient of correlation.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com