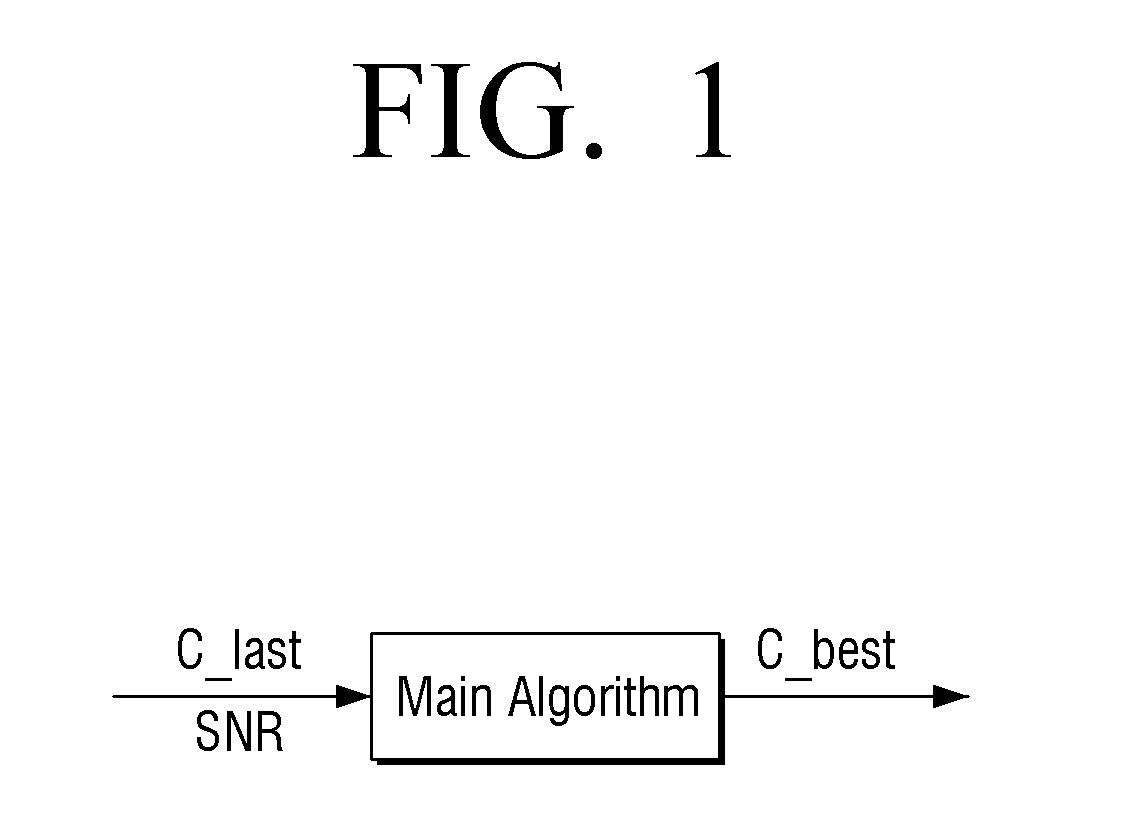
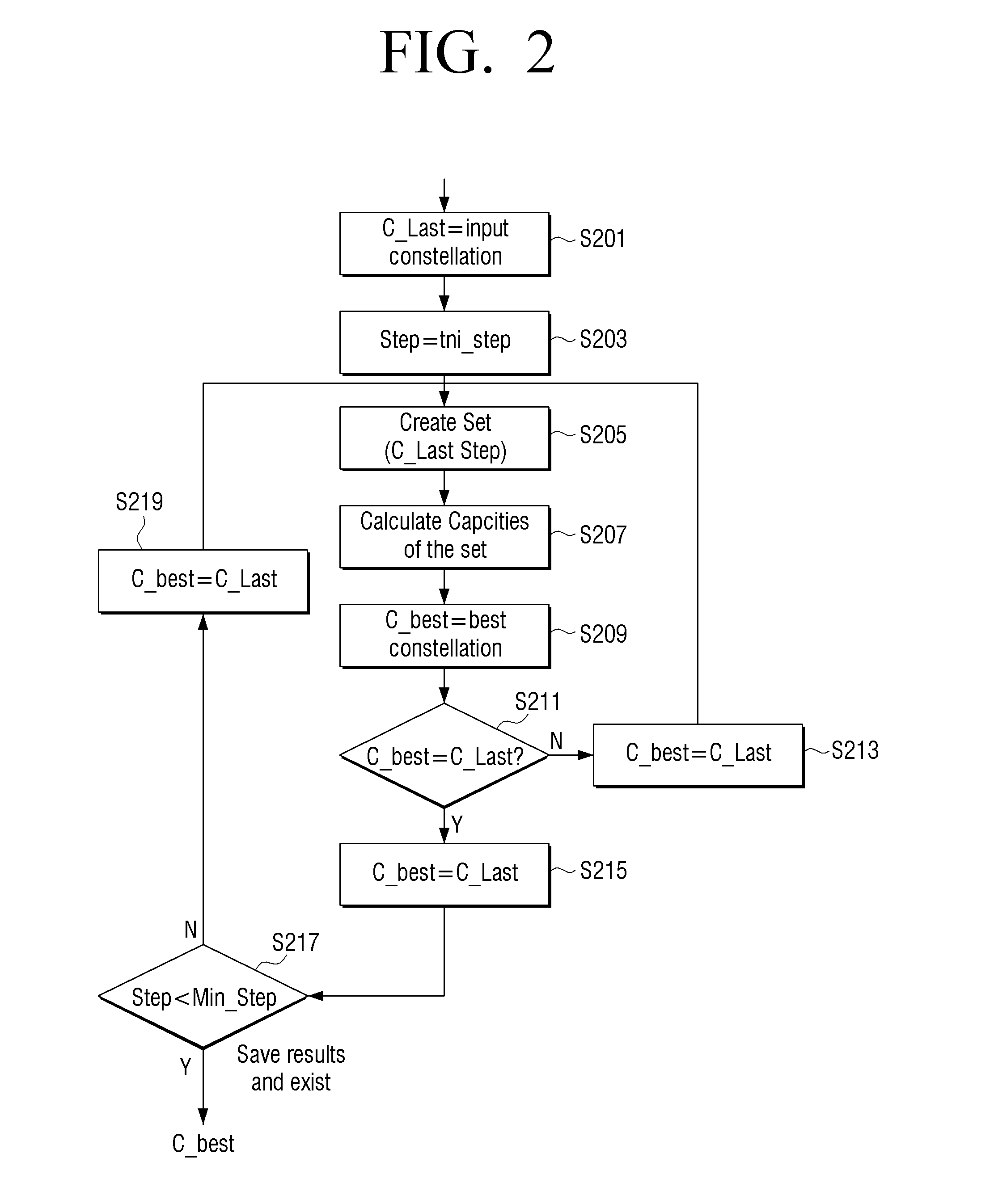
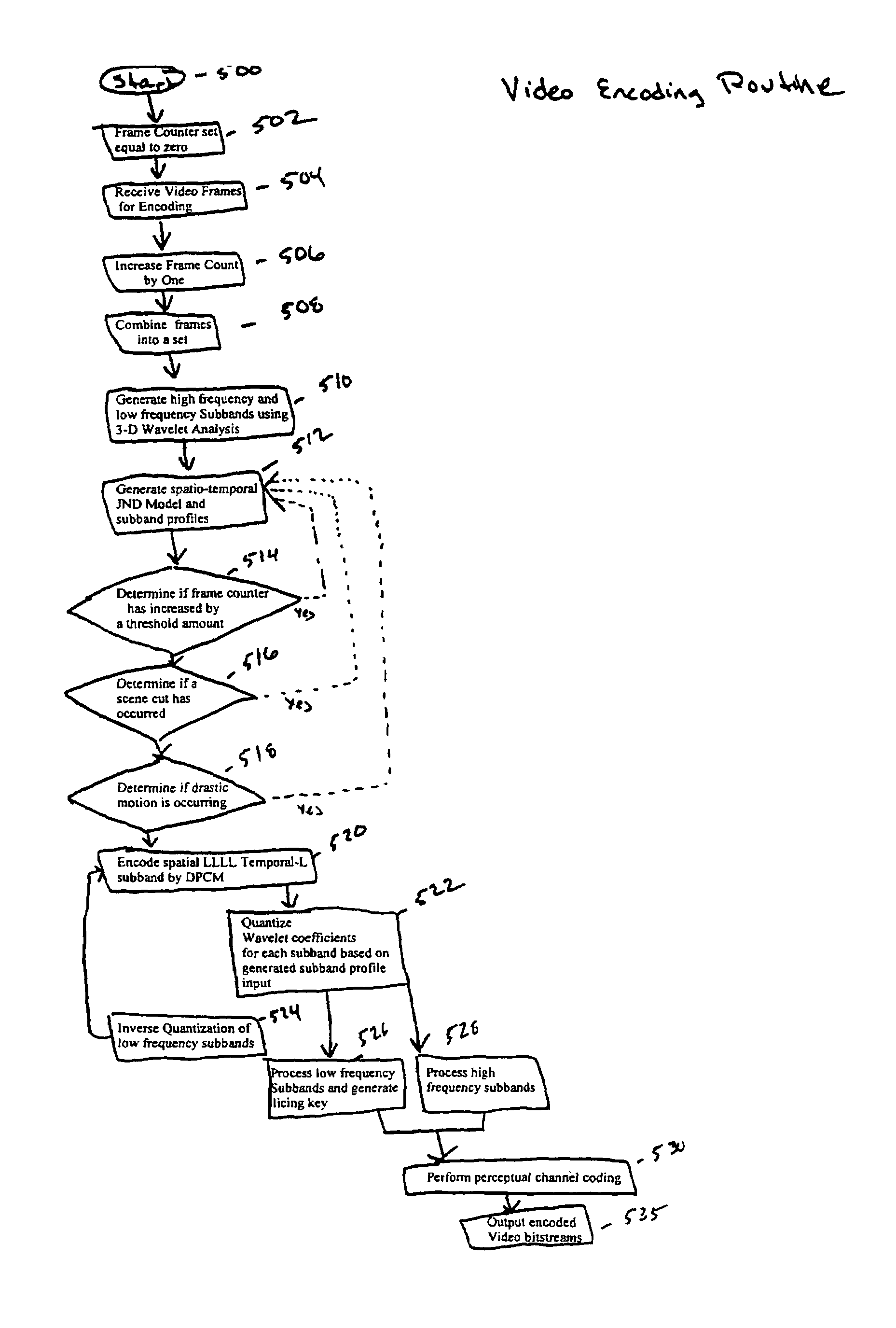
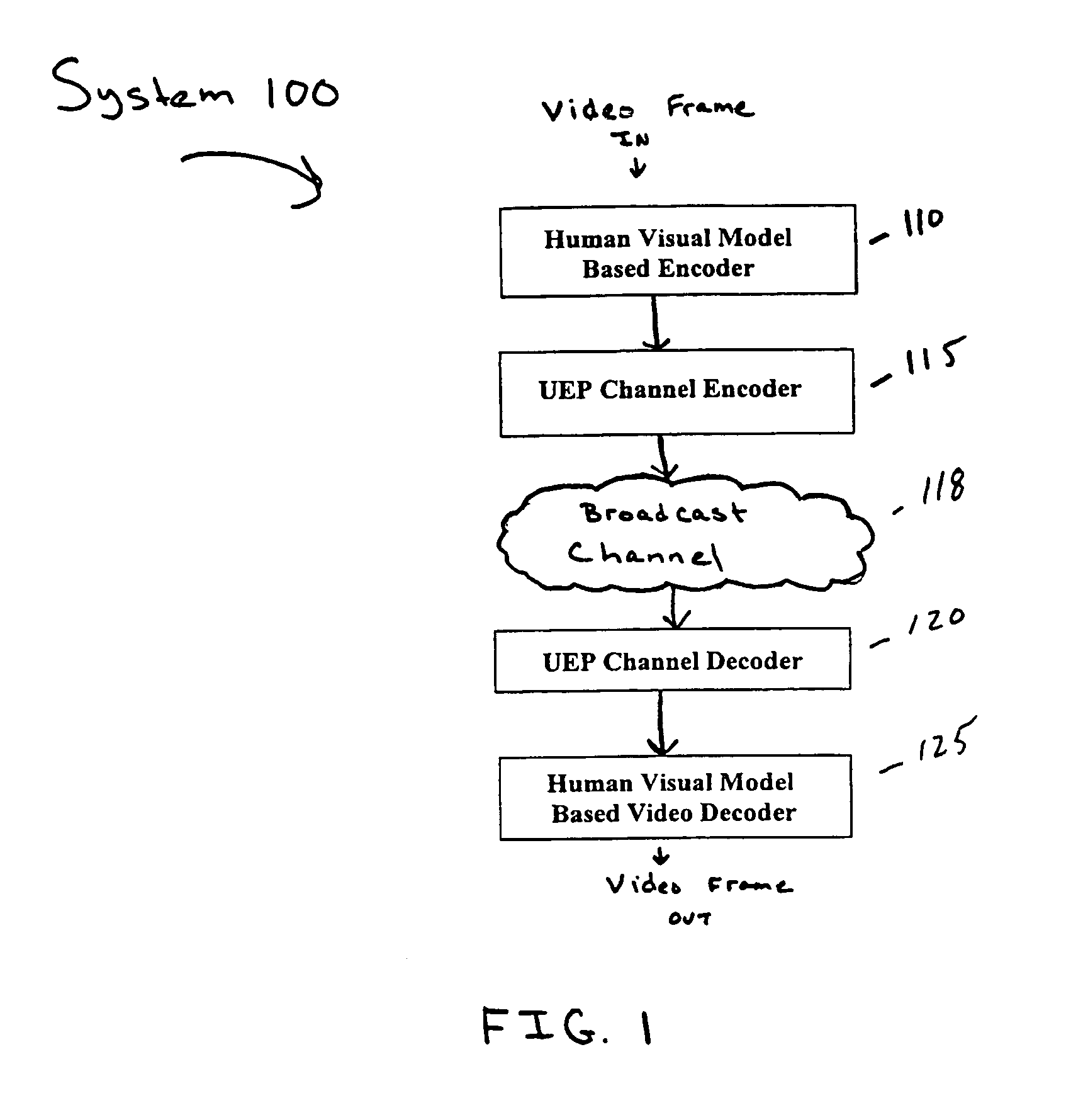
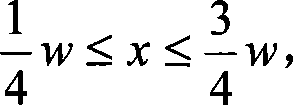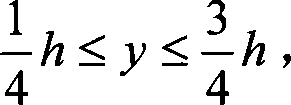Patents
Literature
1699 results about "Channel encoding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In telecommunication: Channel encoding As described in Source encoding, one purpose of the source encoder is to eliminate redundant binary digits from the digitized signal. The strategy of the channel encoder, on the other hand, is to add redundancy to the transmitted signal—in this case so that….
Multicarrier sub-layer for direct sequence channel and multiple-access coding
InactiveUS7430257B1Low costPolarisation/directional diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsUltra-widebandTransmission protocol
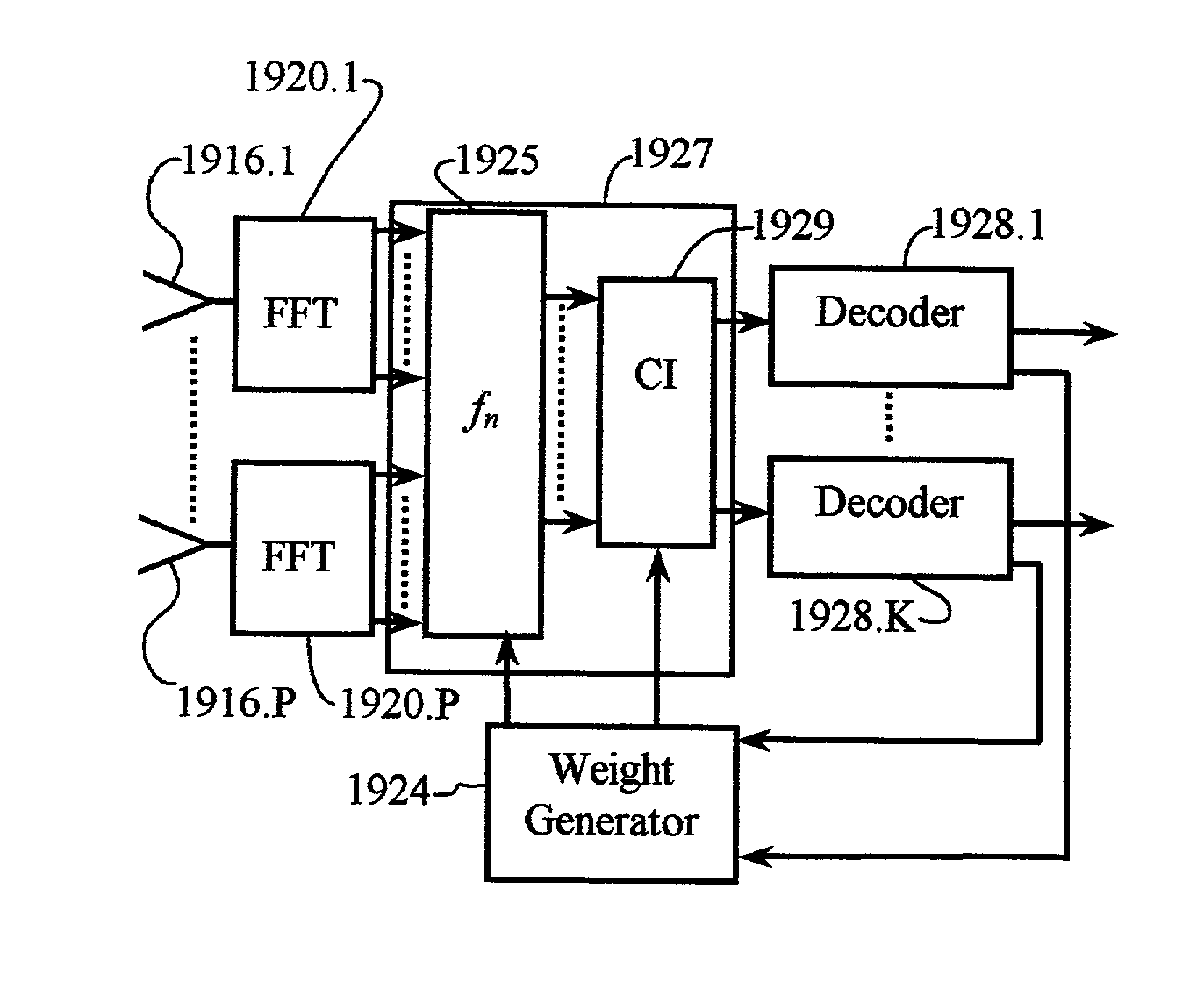
Carrier Interferometry (CI) provides wideband transmission protocols with frequency-band selectivity to improve interference rejection, reduce multipath fading, and enable operation across non-continuous frequency bands. Direct-sequence protocols, such as DS-CDMA, are provided with CI to greatly improve performance and reduce transceiver complexity. CI introduces families of orthogonal polyphase codes that can be used for channel coding, spreading, and / or multiple access. Unlike conventional DS-CDMA, CI coding is not necessary for energy spreading because a set of CI carriers has an inherently wide aggregate bandwidth. Instead, CI codes are used for channelization, energy smoothing in the frequency domain, and interference suppression. CI-based ultra-wideband protocols are implemented via frequency-domain processing to reduce synchronization problems, transceiver complexity, and poor multipath performance of conventional ultra-wideband systems. CI allows wideband protocols to be implemented with space-frequency processing and other array-processing techniques to provide either or both diversity combining and sub-space processing. CI also enables spatial processing without antenna arrays. Even the bandwidth efficiency of multicarrier protocols is greatly enhanced with CI. CI-based wavelets avoid time and frequency resolution trade-offs associated with conventional wavelet processing. CI-based Fourier transforms eliminate all multiplications, which greatly simplifies multi-frequency processing. The quantum-wave principles of CI improve all types of baseband and radio processing.
Owner:GENGHISCOMM HLDG
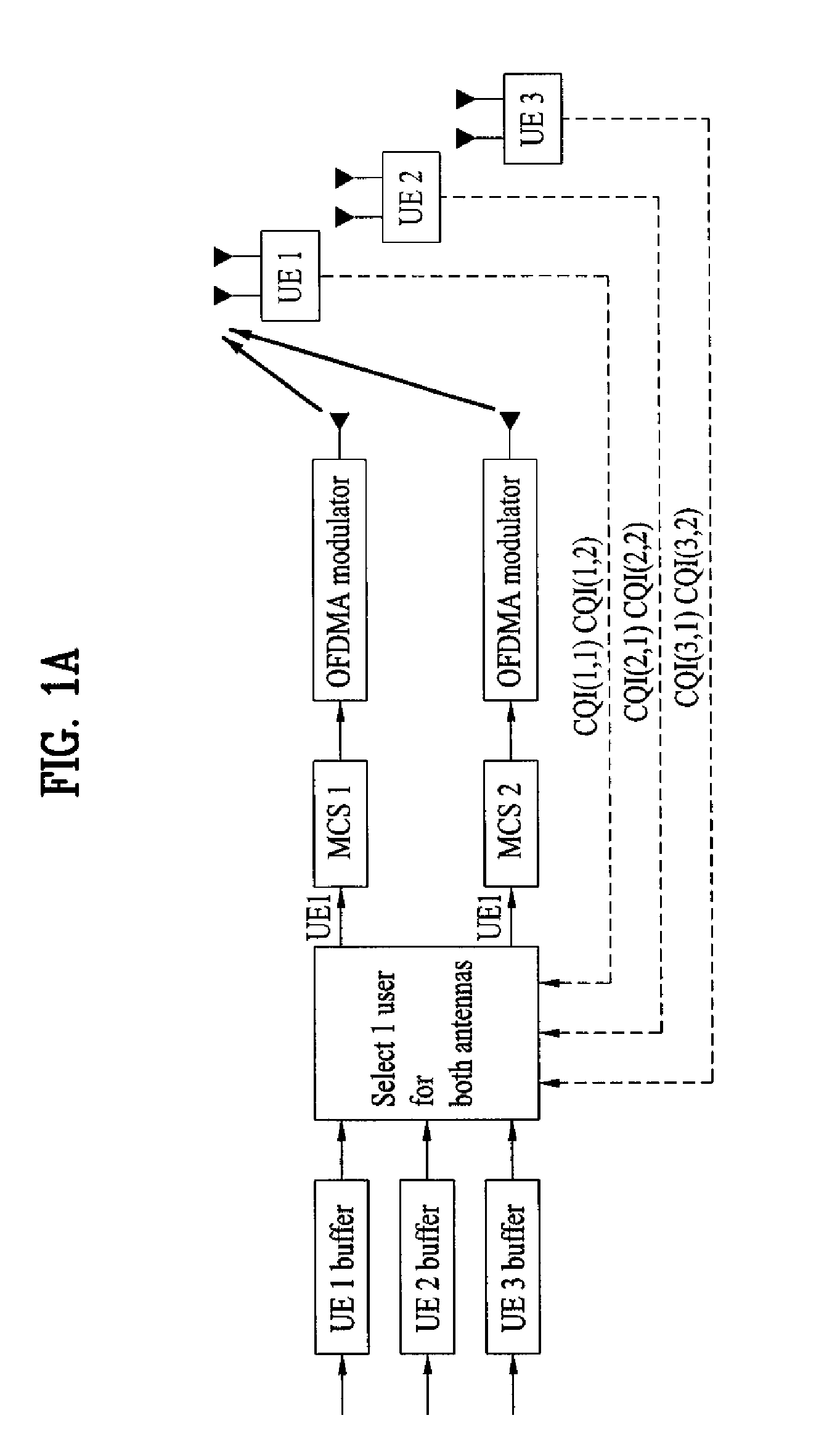
Apparatus for OFDMA transmission and reception for coherent detection in uplink of wireless communication system and method thereof
InactiveUS20050135324A1Improve channel estimation performanceFrequency-division multiplexSecret communicationCommunications systemResource block
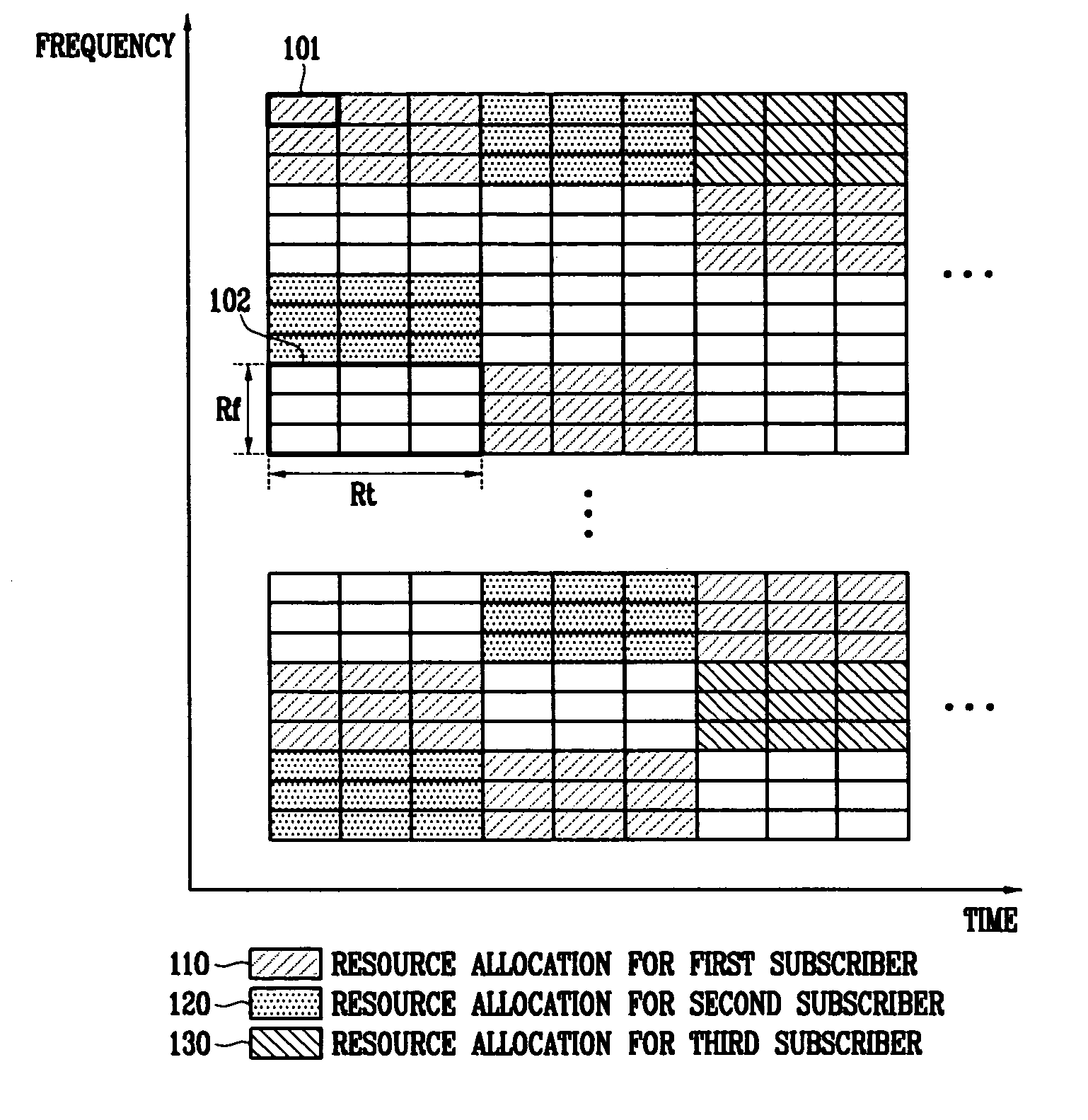
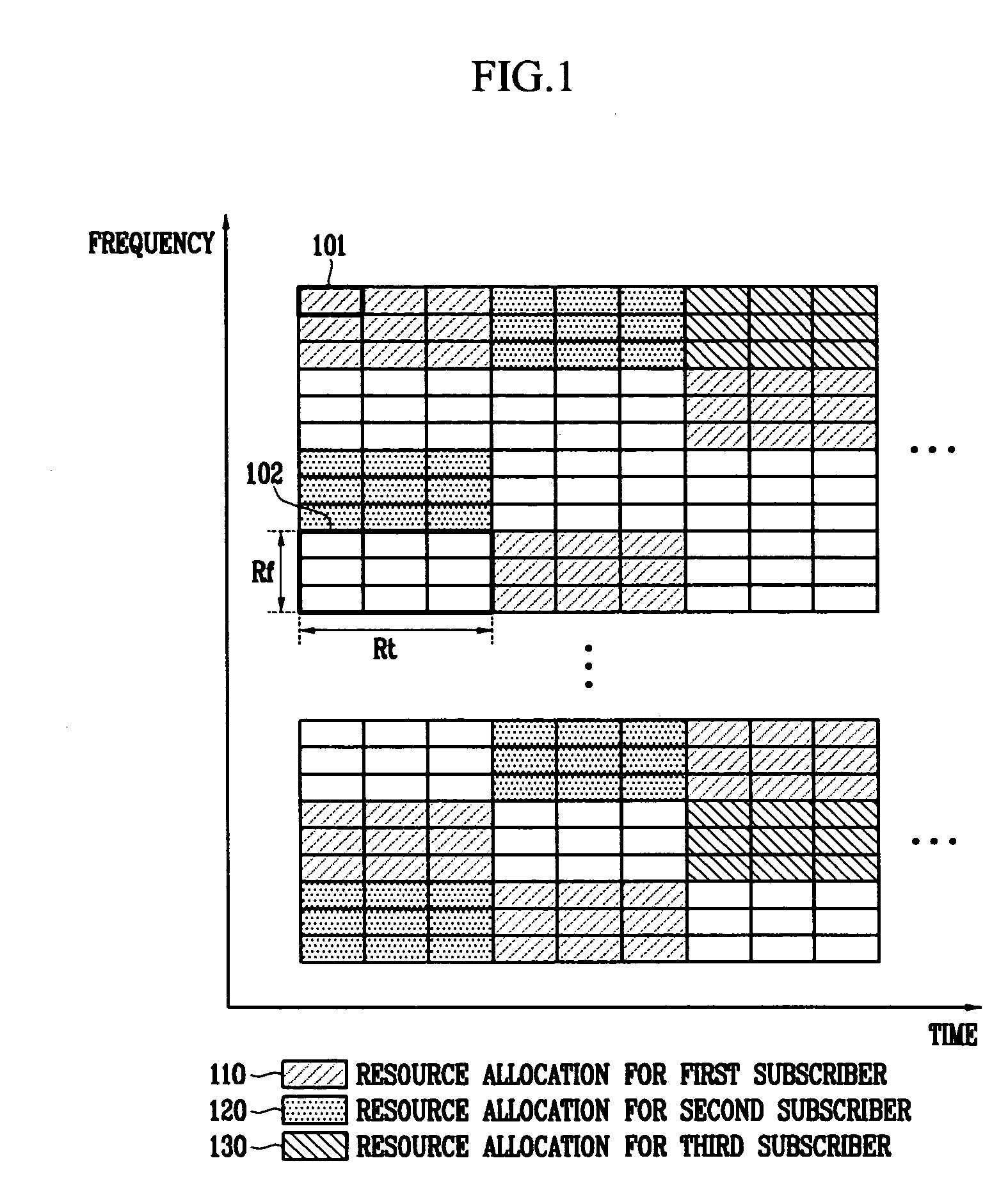
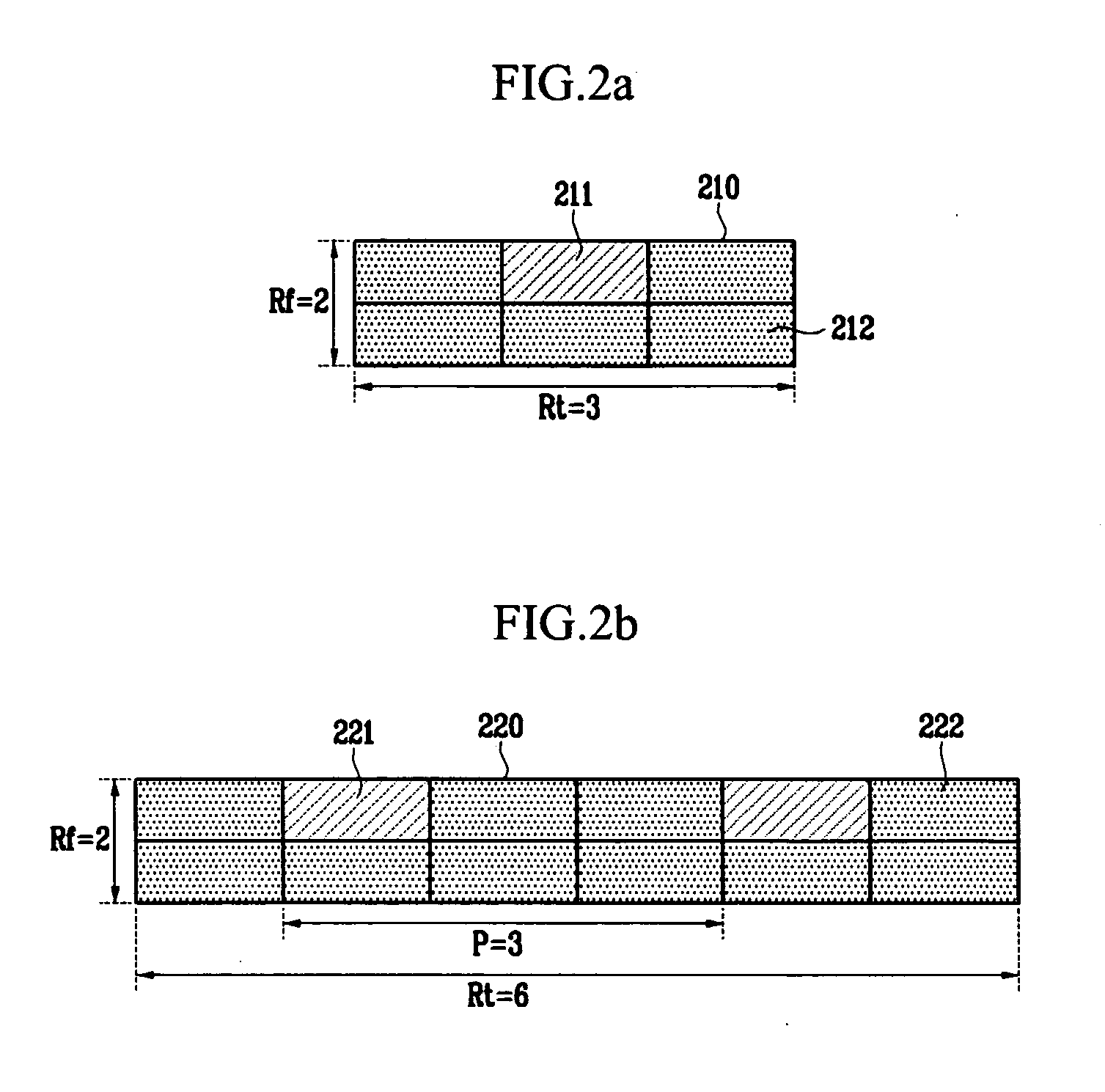
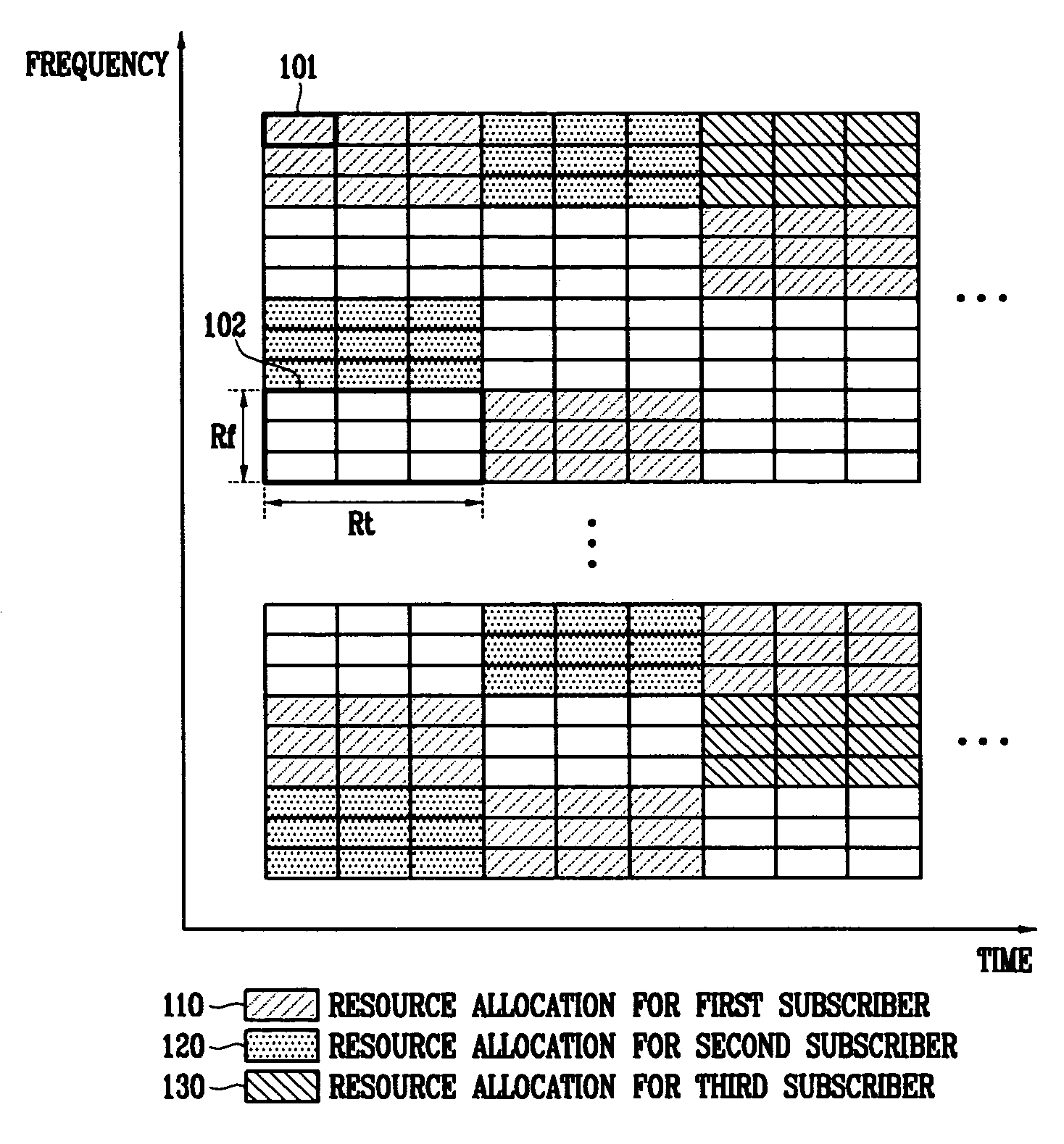
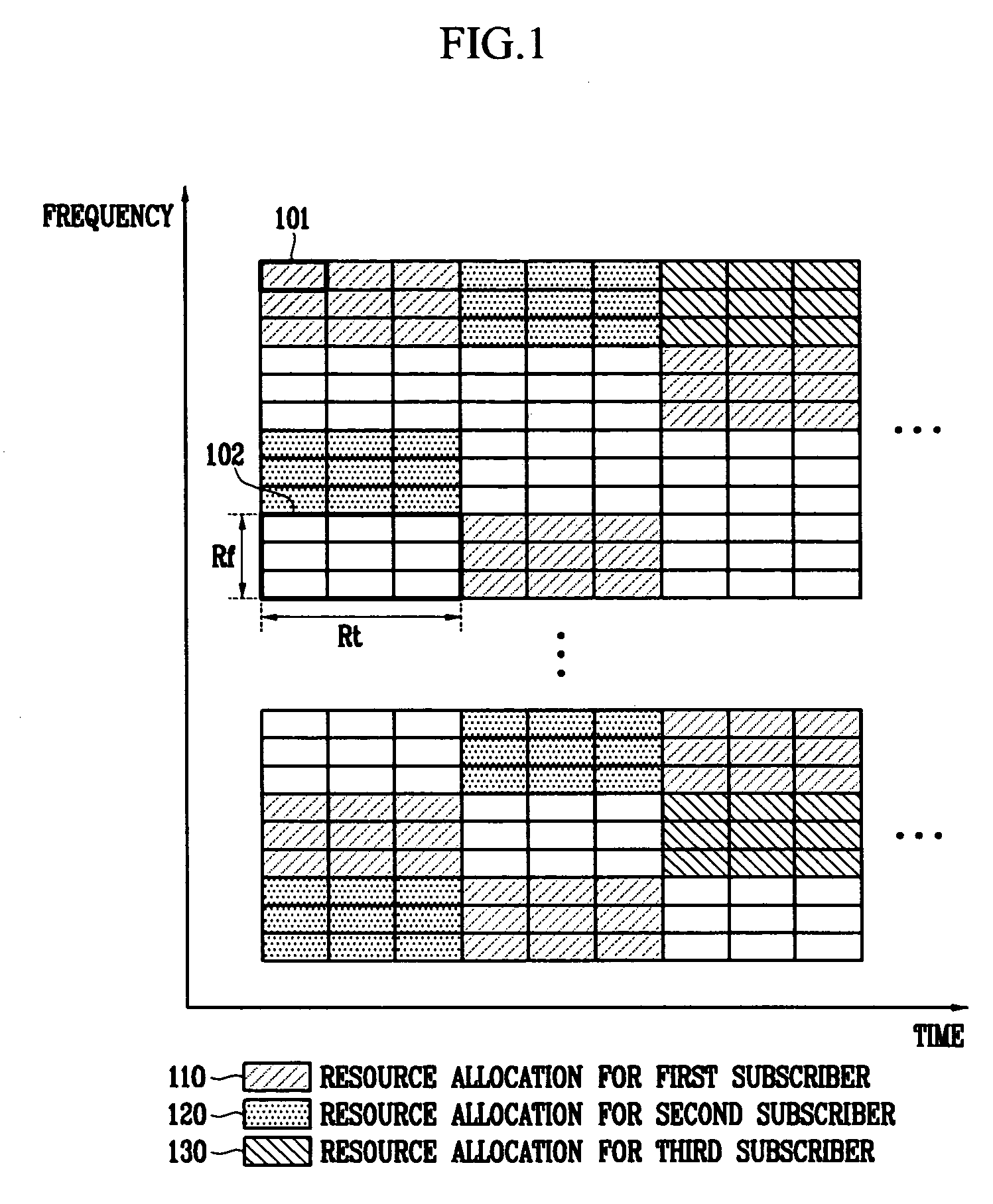
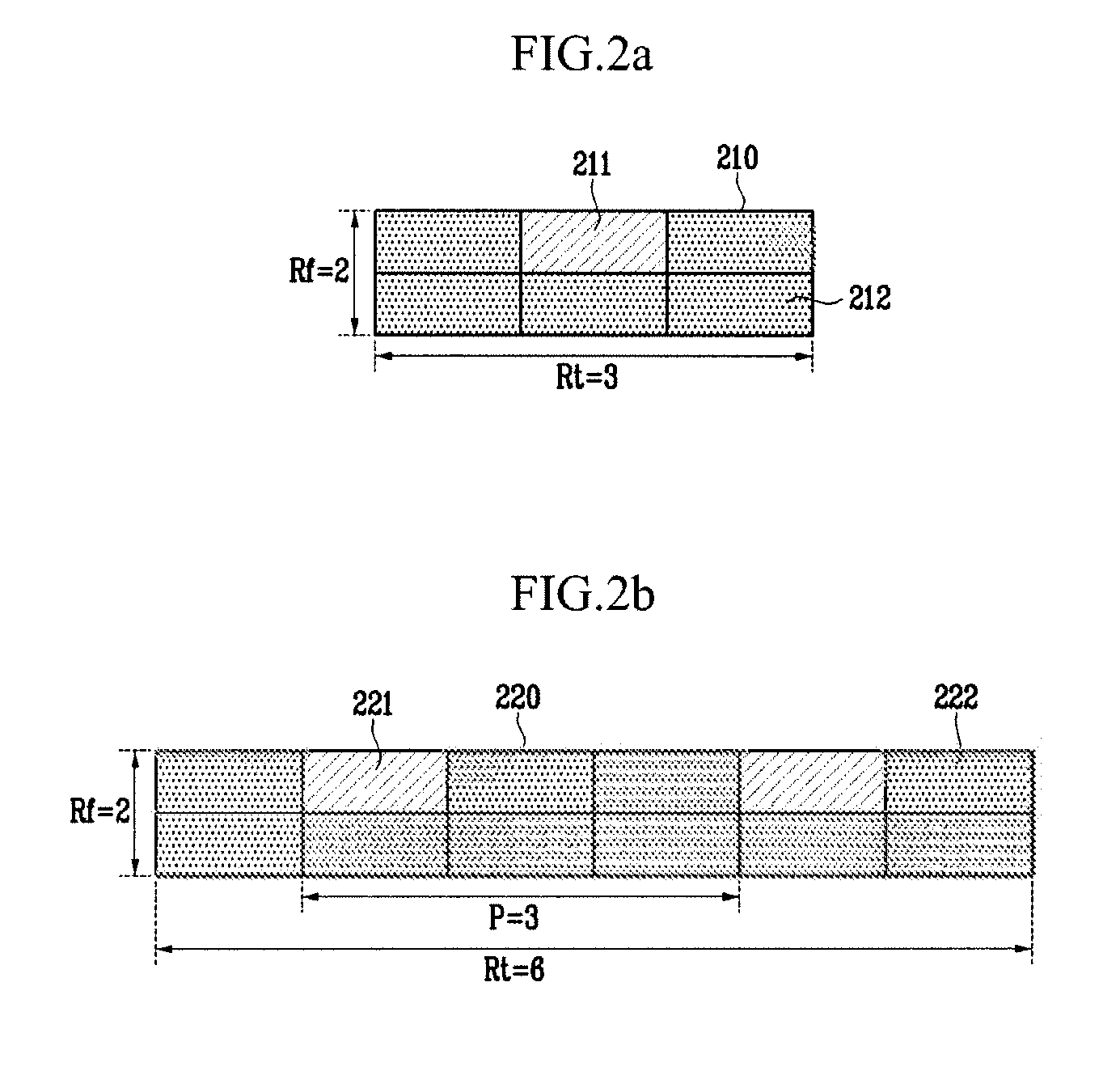
In the resource mapping method for data transmission, a time-frequency resource of a slot interval including OFDM symbols is divided into traffic channels and shared among the subscribers, the traffic channel including resource blocks uniformly distributed in the whole transmit frequency band, the resource block including consecutive subcarriers of consecutive received symbols having at least one inserted pilot symbol. The pilot symbols and the channel-encoded and modulated data symbols are processed by time-frequency mapping according to the resource-block-based mapping method to generate received symbols. The receiver separates the received symbols by subscribers according to the resource-block-based mapping method in a frequency domain, and performs iterative channel estimation, demodulation, and decoding by using the pilot and a data reference value after decoding for each traffic channel.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Data and real-time media communication over a lossy network
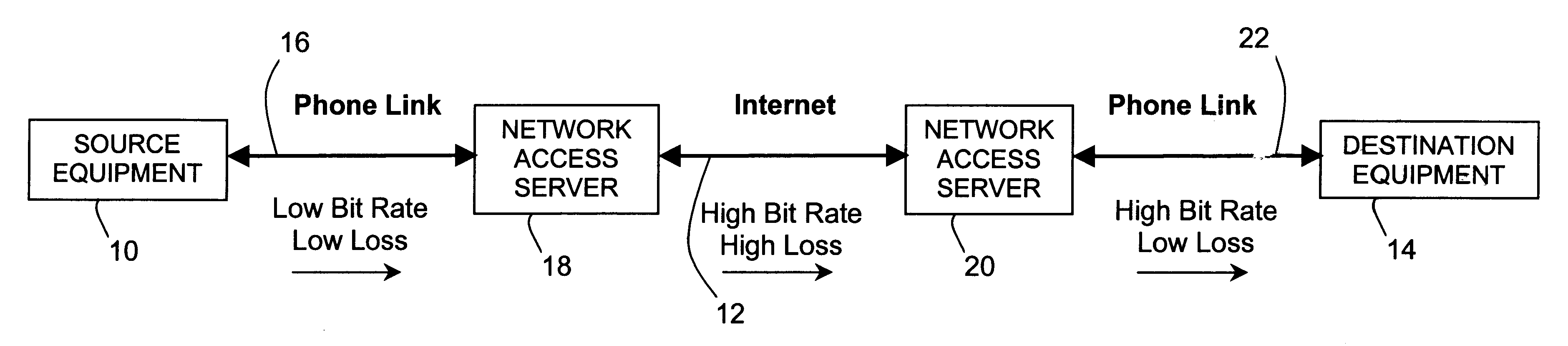
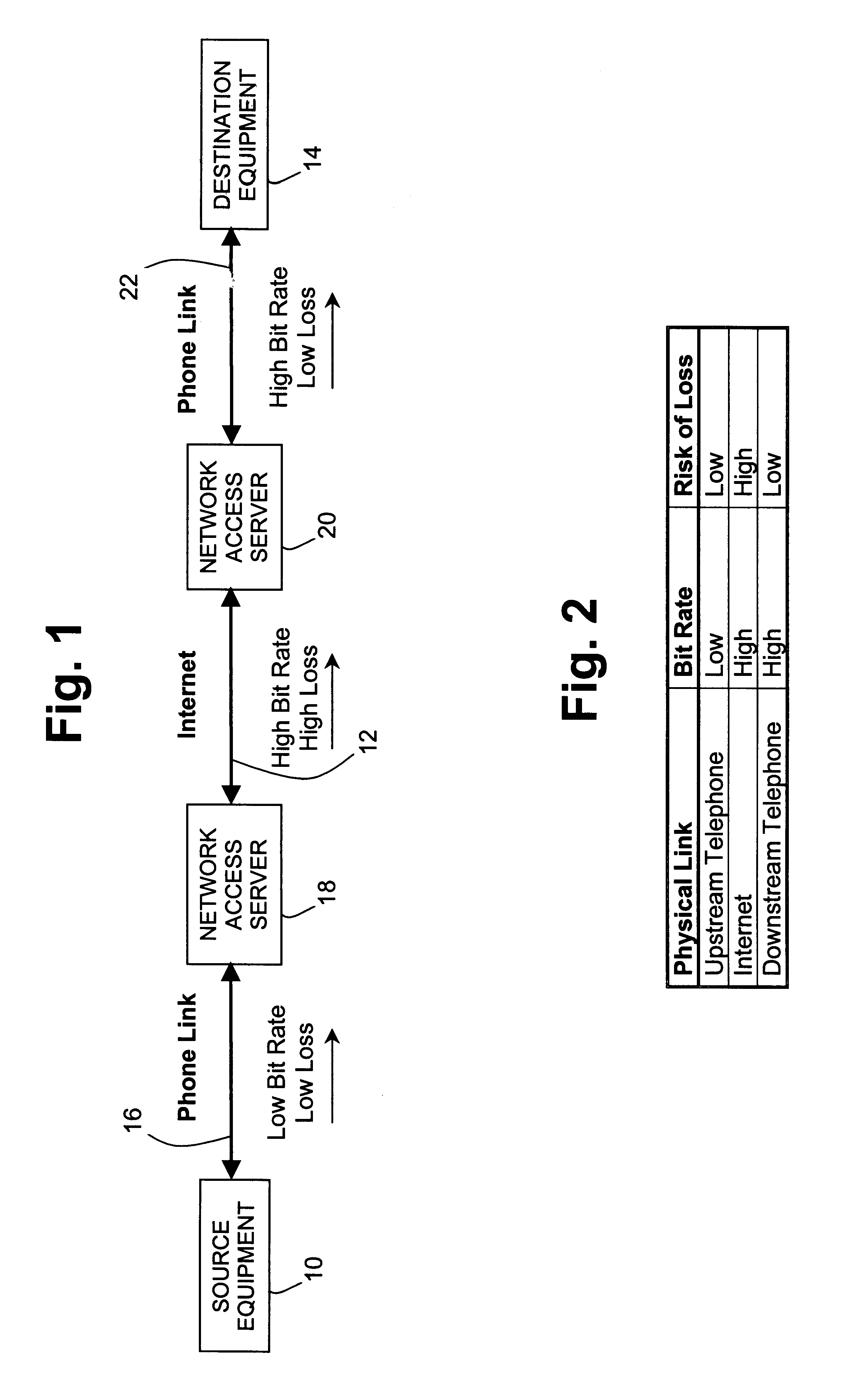
A method and apparatus for improving the speed and quality of end-to-end data or real-time media transmissions over an internet is disclosed. A media stream being transmitted to the internet is channel coded at the edge of the internet in order to free upstream bit rate for use in source coding the media. The channel coded media stream may then be decoded at a remote edge of the internet to recover lost packets.
Owner:UTSTARCOM INC
Segmented CRC assisted polar code encoding and decoding method
ActiveCN105227189ASave storage spaceFacilitate real-time communicationError preventionError detection onlyComputer architectureProcessor register
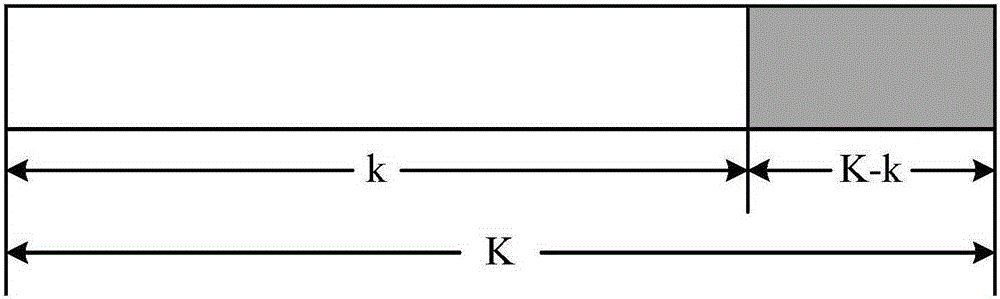
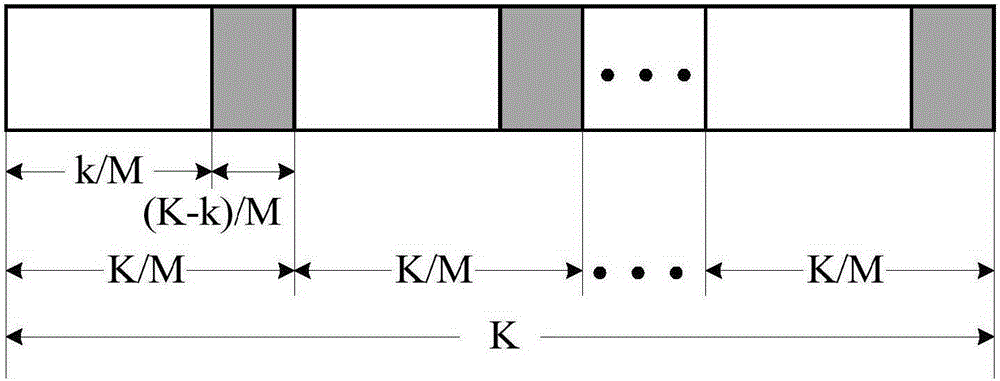
The invention belongs to the field of channel encoding, and particularly relates to a polar code coding and decoding method with segmented cyclic redundancy check (Cyclic Redundancy Check, CRC) auxiliary check. According to the polar code coding and decoding method provided by the invention, certain information bits are sacrificed to check polar codes to improve the decoding performance, and assuming that the length of used CRC is K-k bits, the information is averagely divided into M segments by segmented CRC check, k / M bits of information and (K-k) / M bits of CRC check information constitute an information structure of each segment, as shown in Fig.2. The information bits are encoded and transmitted by a channel, finally, SCL decoding and check are carried out on the information received by a receiving end, and L maximum storage paths are available. The polar code coding and decoding method provided by the invention can be used for shortening the time delay, bringing great convenience for real-time communication, saving the memory space of a register and providing great convenience for hardware realization.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Apparatus for OFDMA transmission and reception for coherent detection in uplink of wireless communication system and method thereof
InactiveUS7639660B2Improve channel estimation performanceFrequency-division multiplexSecret communicationCommunications systemResource block
In the resource mapping method for data transmission, a time-frequency resource of a slot interval including OFDM symbols is divided into traffic channels and shared among the subscribers, the traffic channel including resource blocks uniformly distributed in the whole transmit frequency band, the resource block including consecutive subcarriers of consecutive received symbols having at least one inserted pilot symbol. The pilot symbols and the channel-encoded and modulated data symbols are processed by time-frequency mapping according to the resource-block-based mapping method to generate received symbols. The receiver separates the received symbols by subscribers according to the resource-block-based mapping method in a frequency domain, and performs iterative channel estimation, demodulation, and decoding by using the pilot and a data reference value after decoding for each traffic channel.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
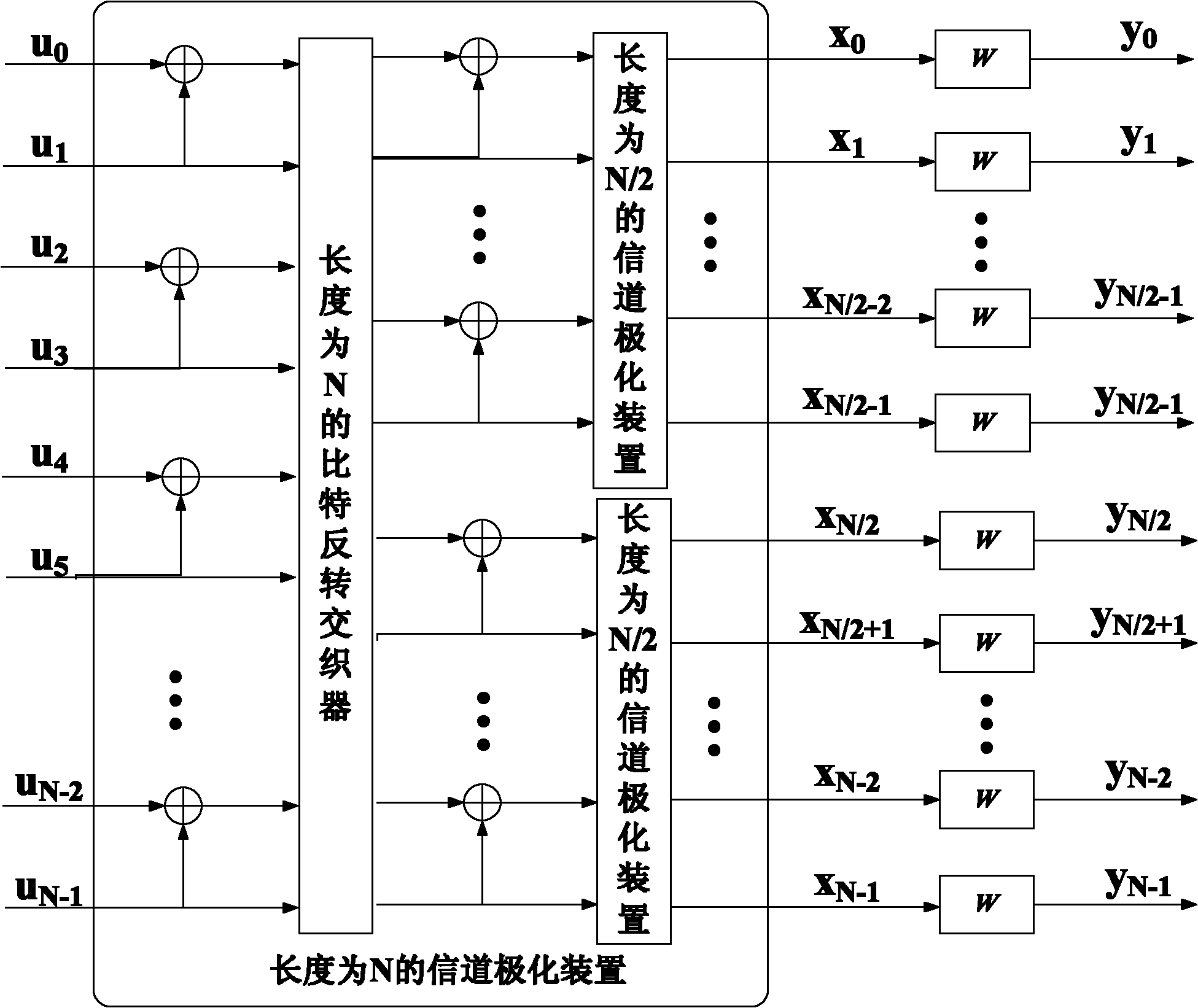
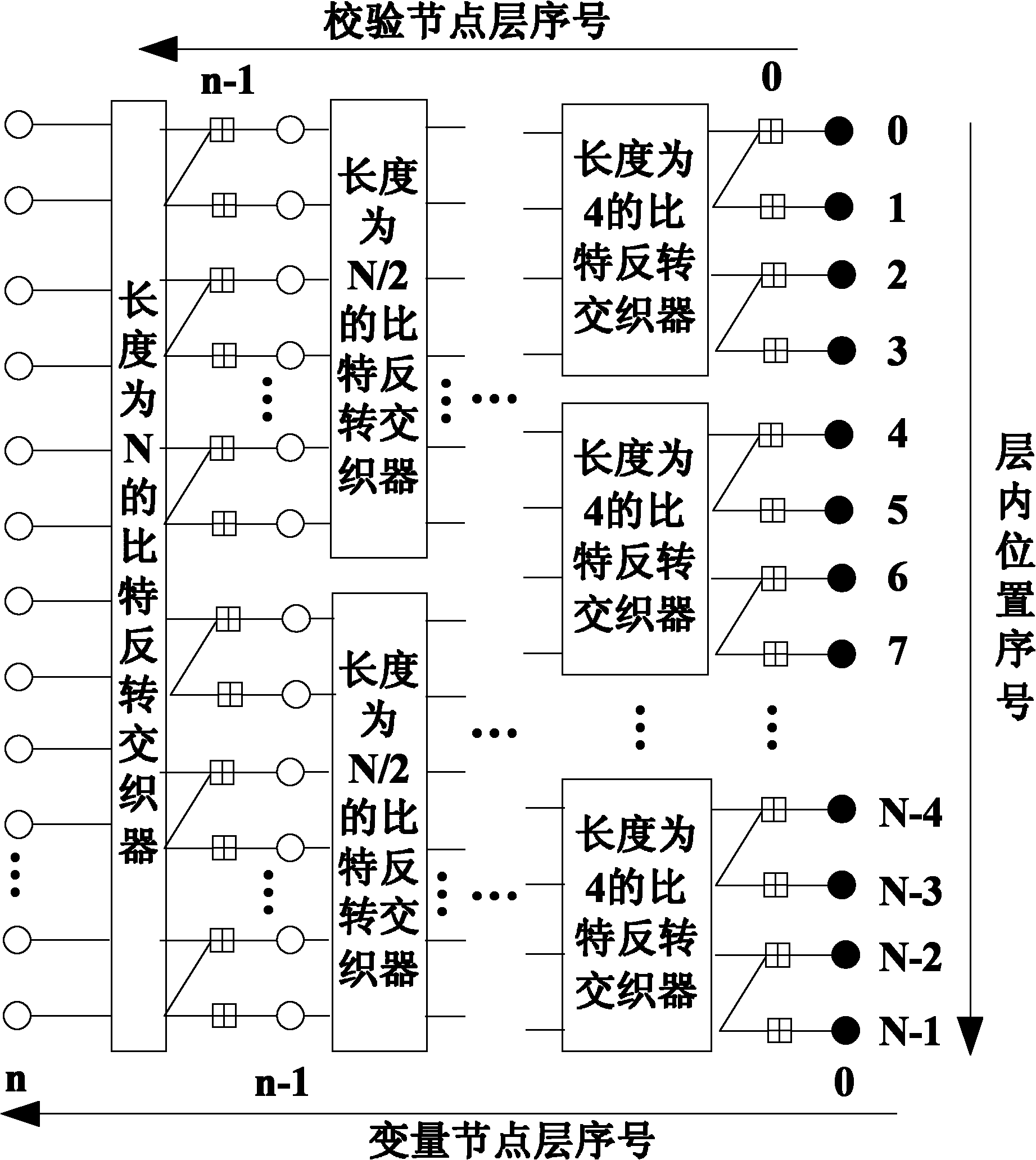
Coder based on repeated coding and channel polarization and coding/decoding method thereof
InactiveCN102164025AStrong error correction abilityNo added decoding complexityError preventionError correction/detection using linear codesCode moduleChannel polarization
The invention discloses a coder based on repeated coding and channel polarization and a coding / decoding method thereof. The coder comprises two coding modules with the same structure; each coding module is provided with a repeated coder group, a bit position mapper with the length of N and a channel polarization device with the length of N, wherein the repeated coder group has m*L output ports and is composed of L sequentially-arranged repeated coders with the repeating times of m; and the two coding modules are connected together through a coding mode selector between the repeated coder and the bit position mapper. The invention provides a concrete method of embedding repeated codes in the channel polarization process to perform channel coding and decoding based on the coder; and compared with the polarization code of the limited length in the prior art, the coding / decoding method disclosed by the invention has stronger error correction capability and obviously improves the transmission performance on the premise of rarely increasing the decoding complexity, is particularly suitable for the practical engineering systems of mobile communication, satellite communication, underwatercommunication and the like, and has good popularization and application prospects.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method of transmitting using phase shift-based precoding and apparatus for implementing the same in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20080205533A1Eliminate the problemEnergy efficient ICTSpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemPhase shifted
A method of transmitting data using a plurality of subcarriers in a multi-antenna wireless communication system is disclosed. More specifically, the method includes receiving feedback information from a mobile station (MS), performing channel encoding and modulation independently on user data to be transmitted by each antenna using the received feedback information, determining a phase shift-based precoding matrix for increasing a phase angle of the user data by a fixed amount, and performing precoding using the determined phase shift-based precoding matrix on the user data.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Radio base station device, communication terminal device, and control information transmission method
ActiveUS20050238053A1Curb consumptionFully extractedPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementMultiplexingInformation transmission
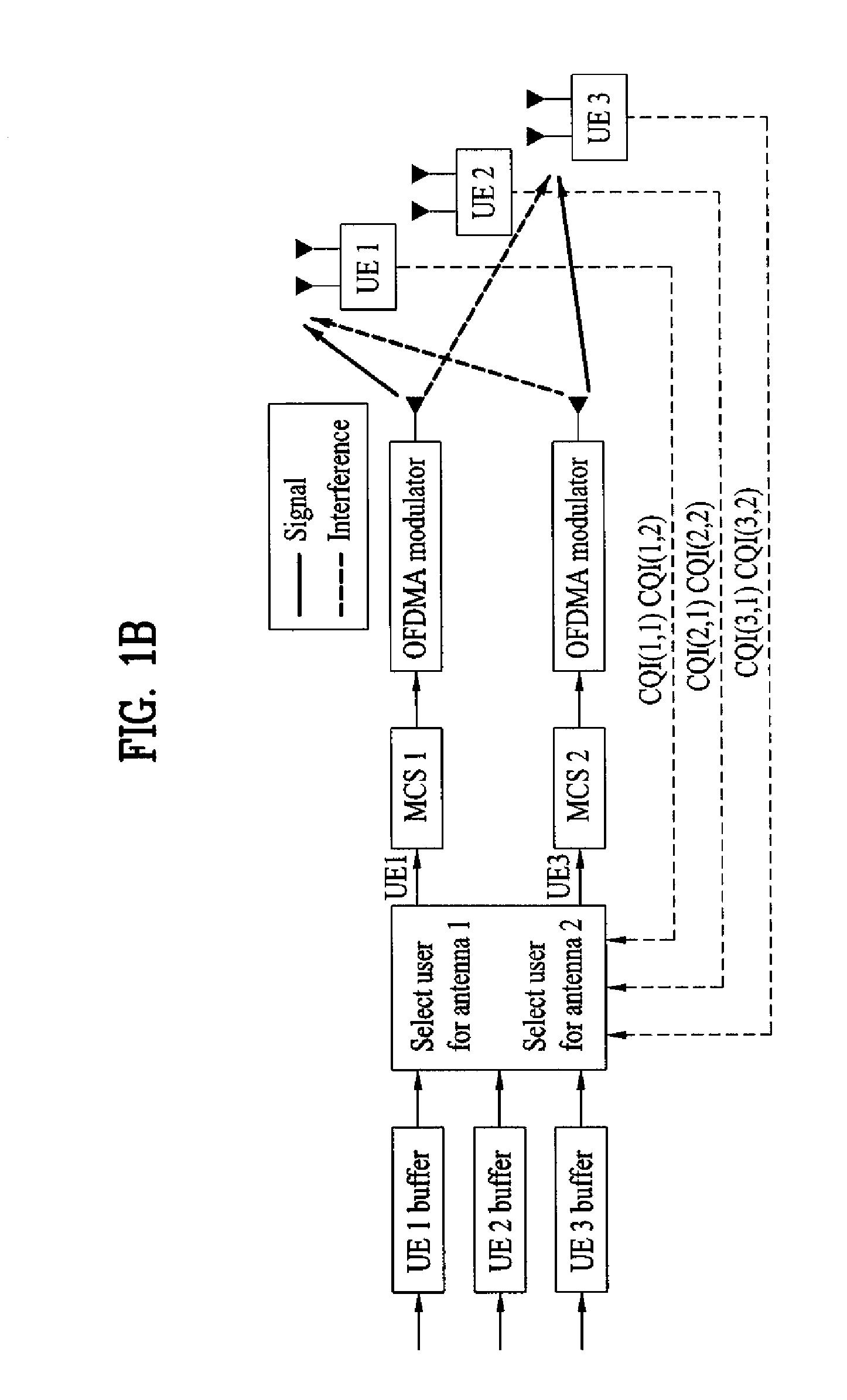
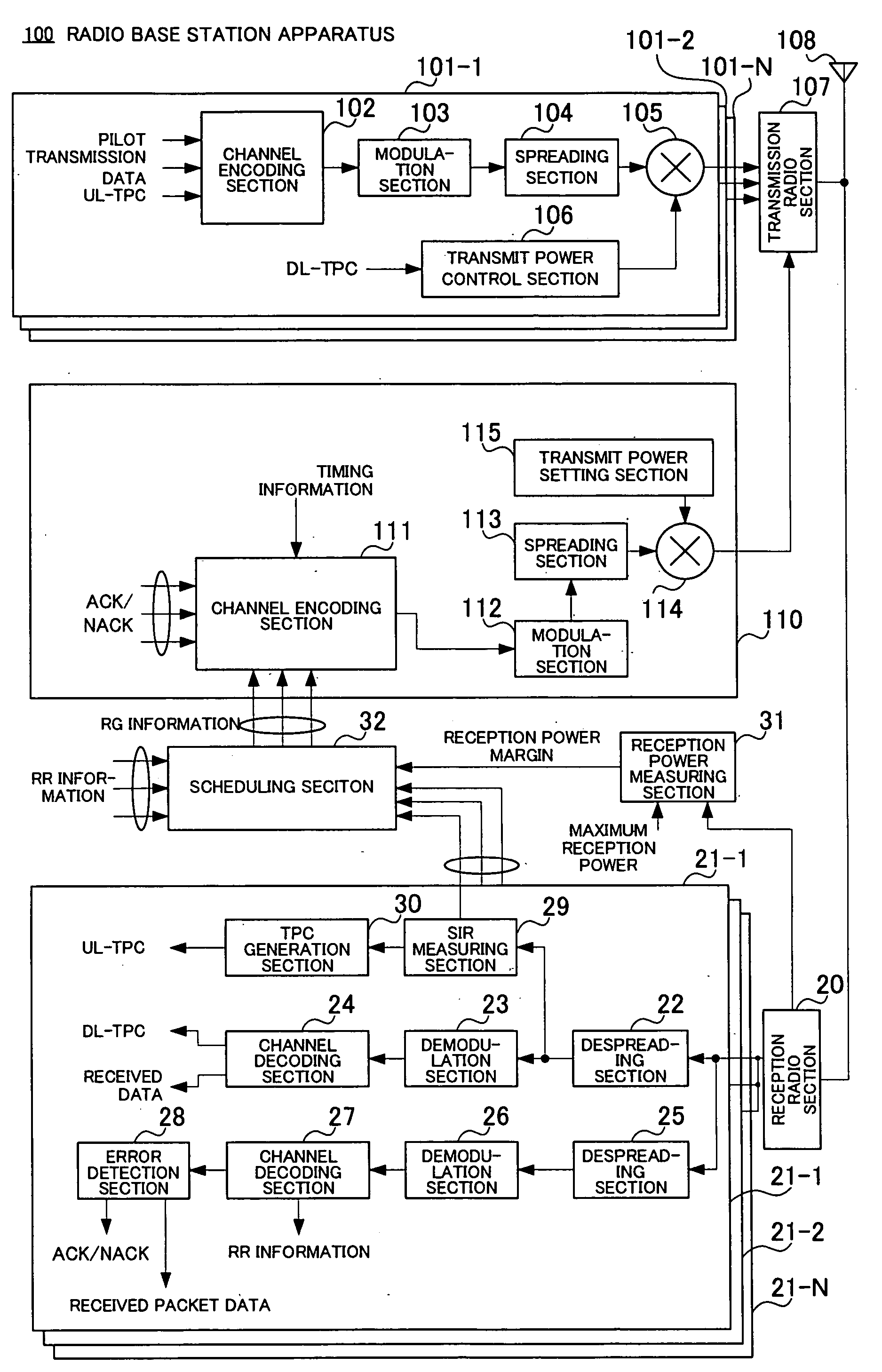
In addition to dedicated channel signal formation units 101-1 to 101-N, control information channel signal formation unit 110 is provided and this control information channel signal formation unit 110 forms control information for carrying out uplink packet transmission. The control information channel signal formation unit 110 multiplexes control information (RG information, ACK / NACK, etc.) directed to a plurality of communication terminals through a channel encoding section 111 according to a multiplexing rule preset between the base station apparatus and each communication terminal and spreads the control information using a spreading code common to the communication terminals through a spreading section 113 and thereby forms a control information channel signal for uplink packet transmission.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
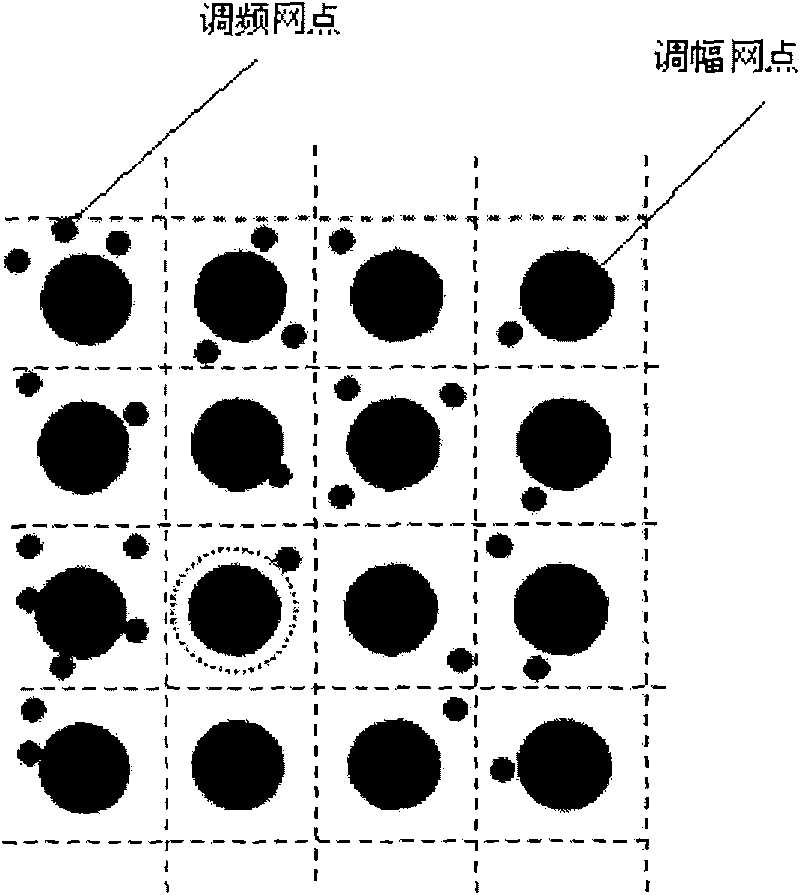
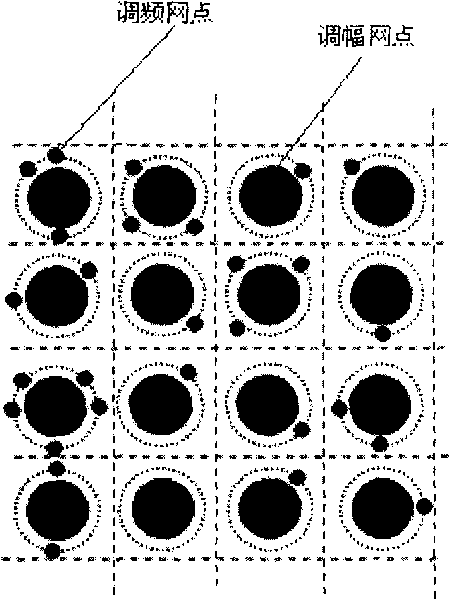
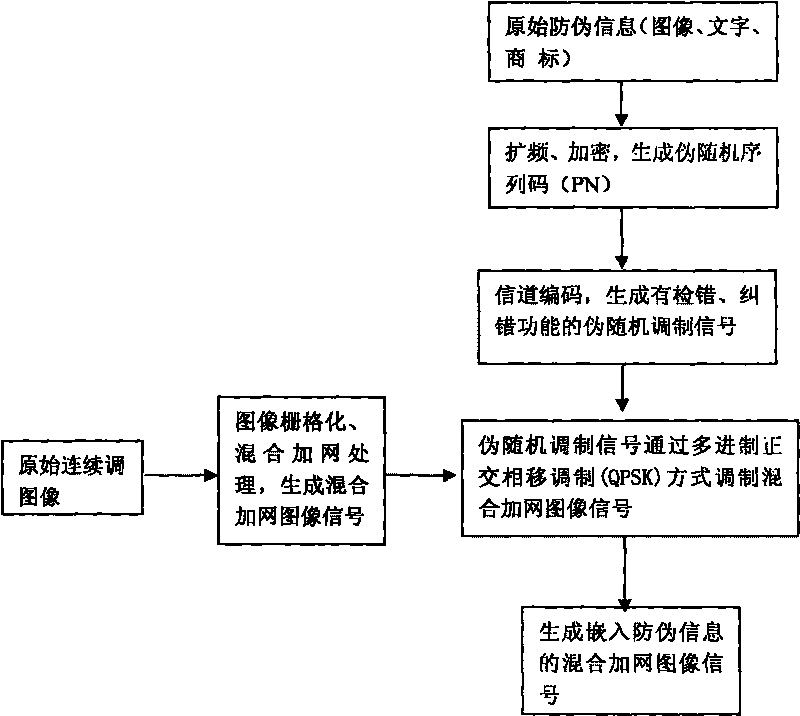
Encryption counterfeit printing technology of frequency modulated halftone dot space position for pseudo random signal modulation printed matter
InactiveCN101699845ACombating Illegal CopyingStrong anti-counterfeiting abilityPictoral communicationElectronic documentDocumentation
The invention discloses an encryption counterfeit printing technology based on the frequency modulated halftone dot space position in a pseudo random signal modulation hybrid screening. The counterfeit printing technology can change the counterfeit information into the pseudo random modulation signal through spread spectrum, encryption and channel coding to generate, embed the counterfeit information in the entire page though the quadrature phase shift keying (QPSK), and identify the counterfeit information in any fragment when identifying the printing matter so that the technology of the invention has strong shatter resistant, can more effectively counter the illegal copying behavior based on cameras, scanners, electronic documents and the like, and can be widely applied in the counterfeit field of the printing matter.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF GRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
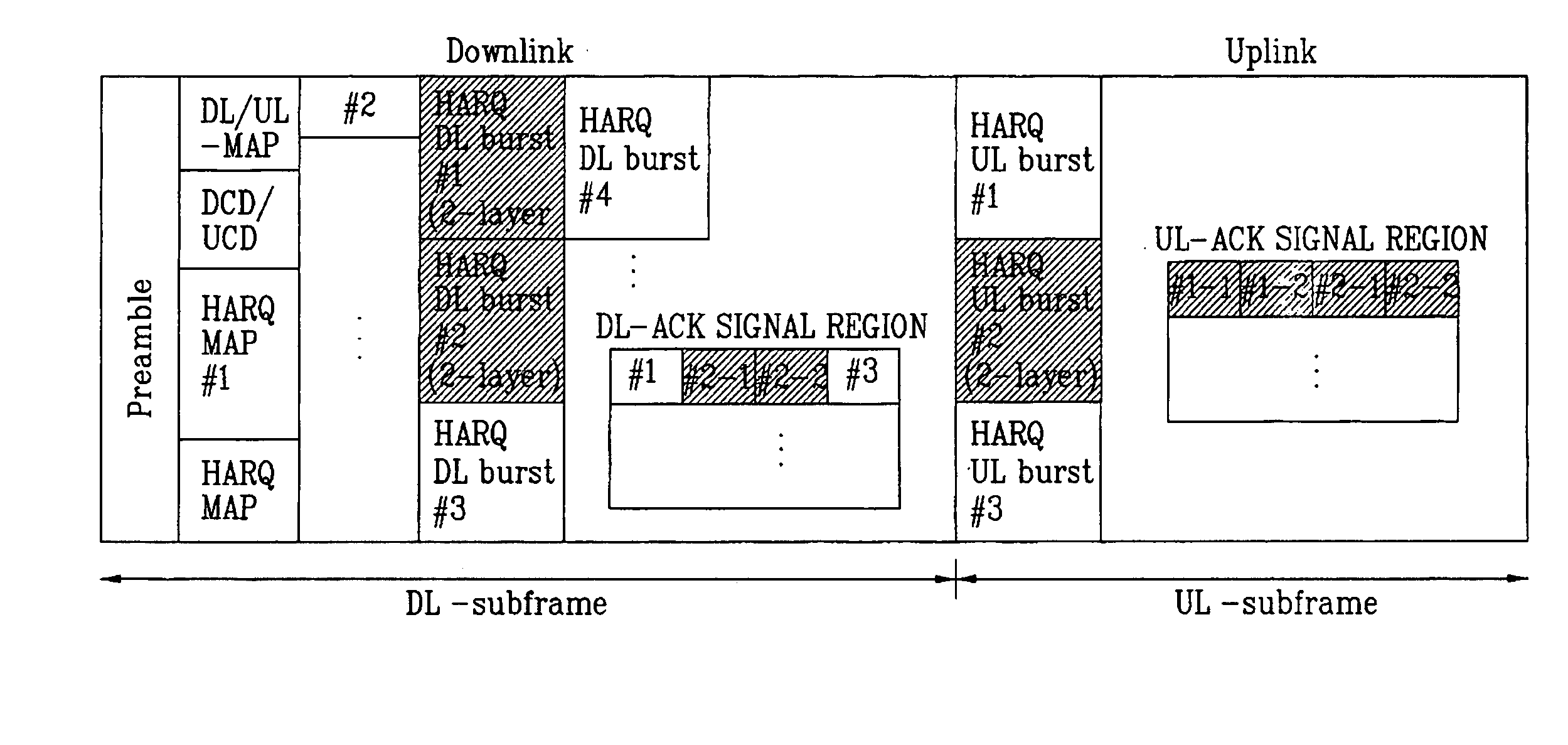
Supporting hybrid automatic retransmission request in orthogonal frequency division multiplexing access radio access system
InactiveUS20060195767A1Error preventionCode conversionSpace time transmit diversityTelecommunications
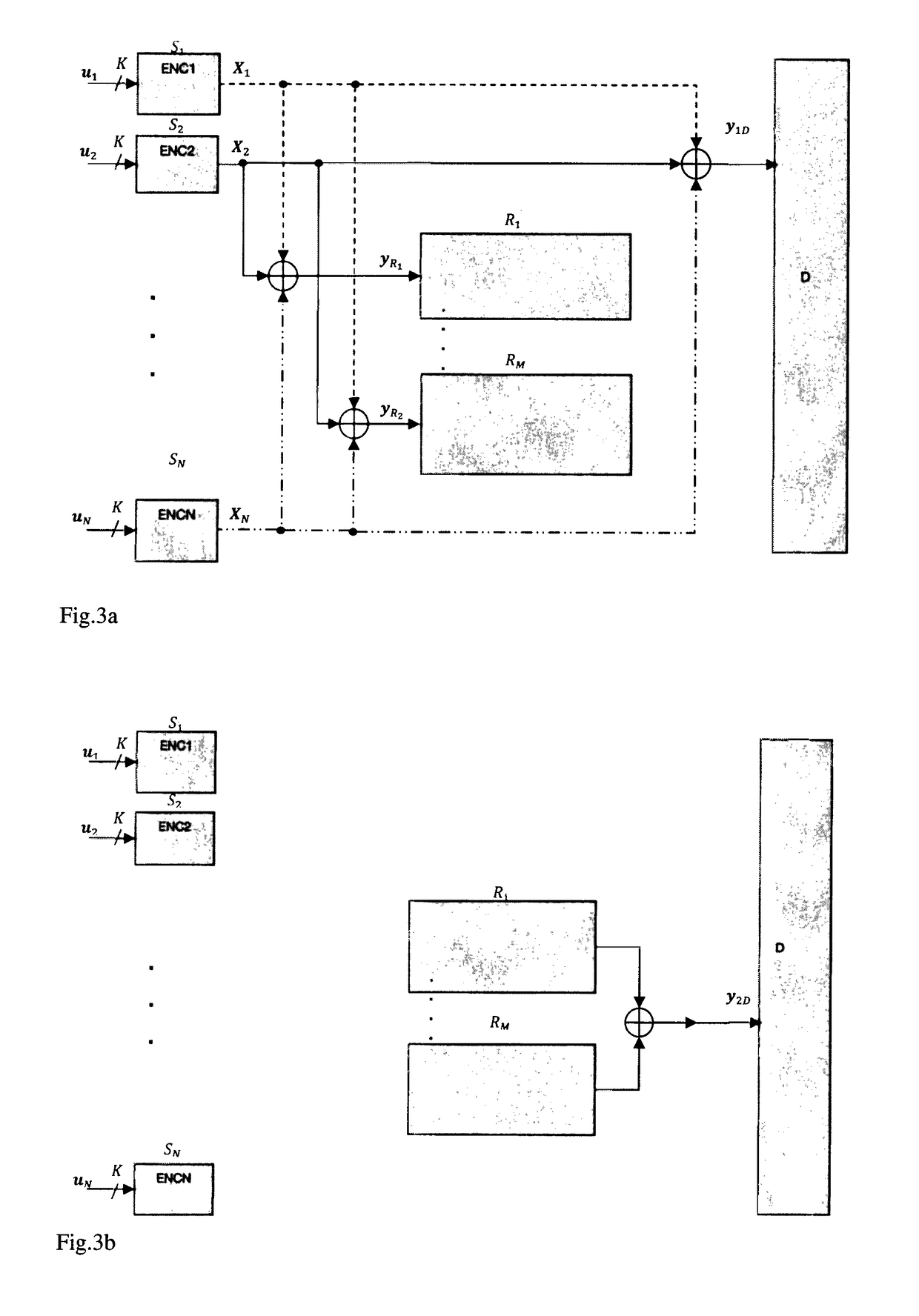
A method of supporting a hybrid automatic retransmission request (HARQ) in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing access (OFDMA) radio access system is disclosed. Preferably, the method comprises receiving a downlink data frame comprising a data map information element and a data burst comprising a plurality of layers, wherein each layer is encoded with a corresponding channel encoder, and wherein the data map information element is configured to support multiple antennas to achieve space time transmit diversity by providing control information associated with each one of the plurality of layers, wherein the control information comprises allocation of acknowledgement status channels corresponding to the plurality of layers, and transmitting in an uplink data frame a plurality of acknowledgement status, each acknowledgement status being associated with whether a corresponding layer of the plurality of layers is properly decoded.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Data transmission using arithmetic coding based continuous error detection
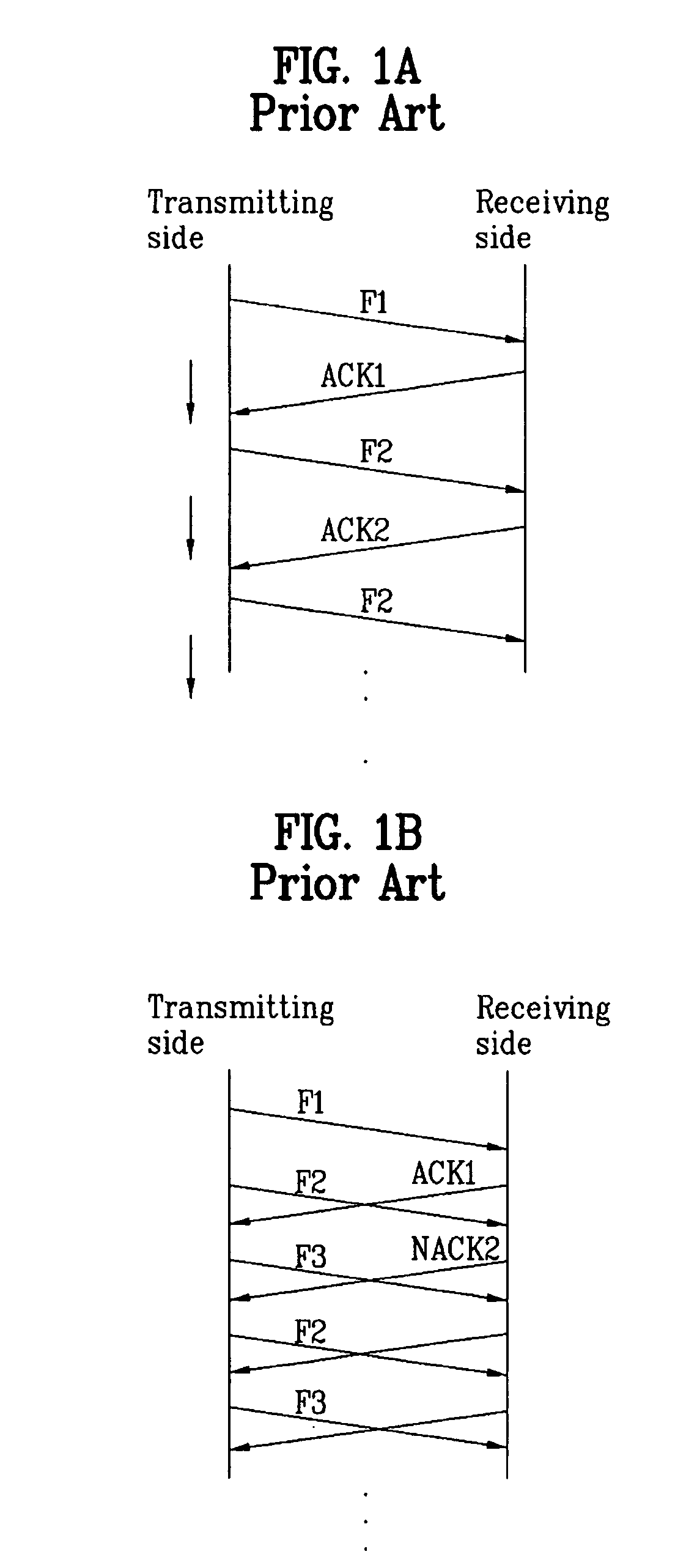
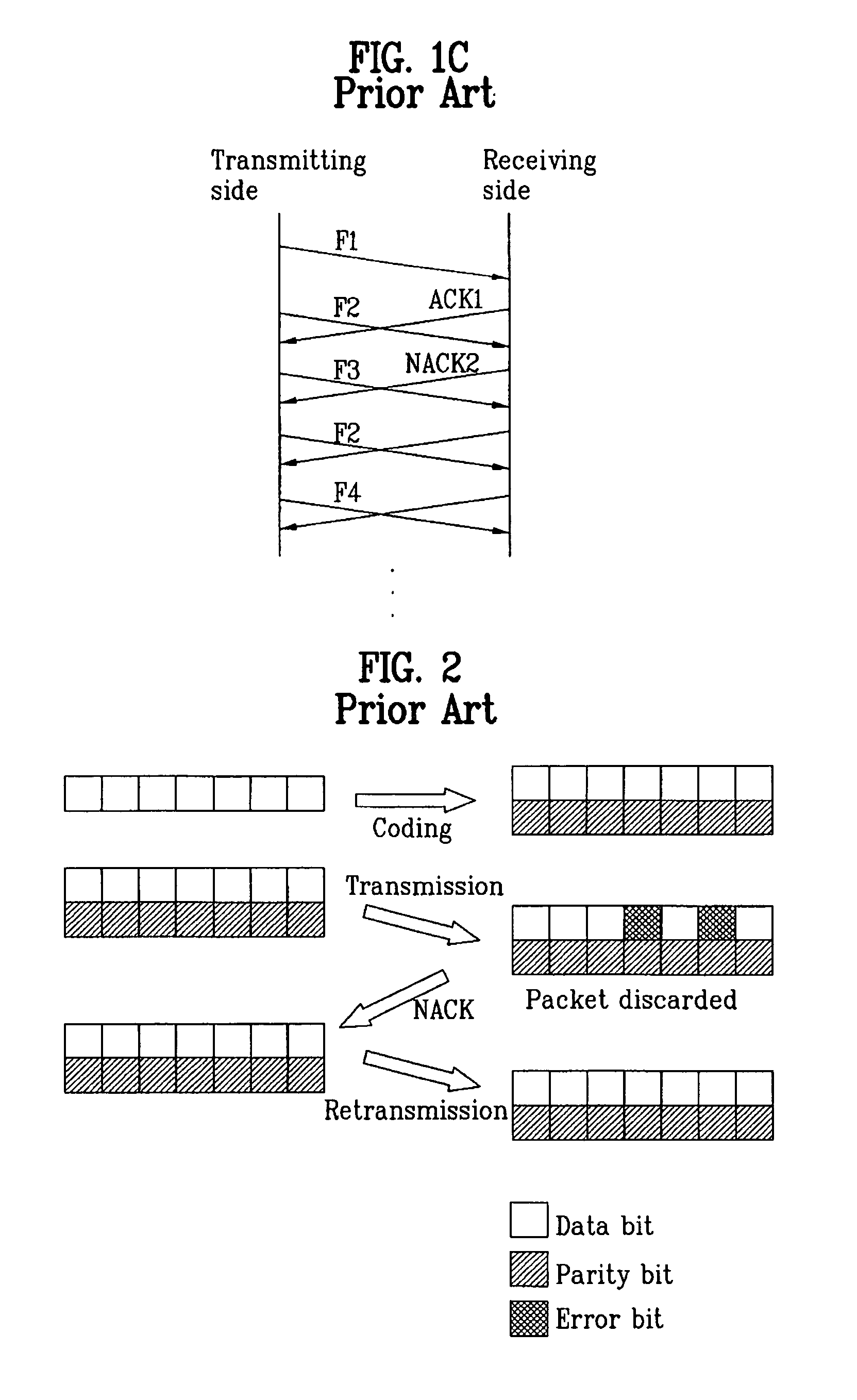
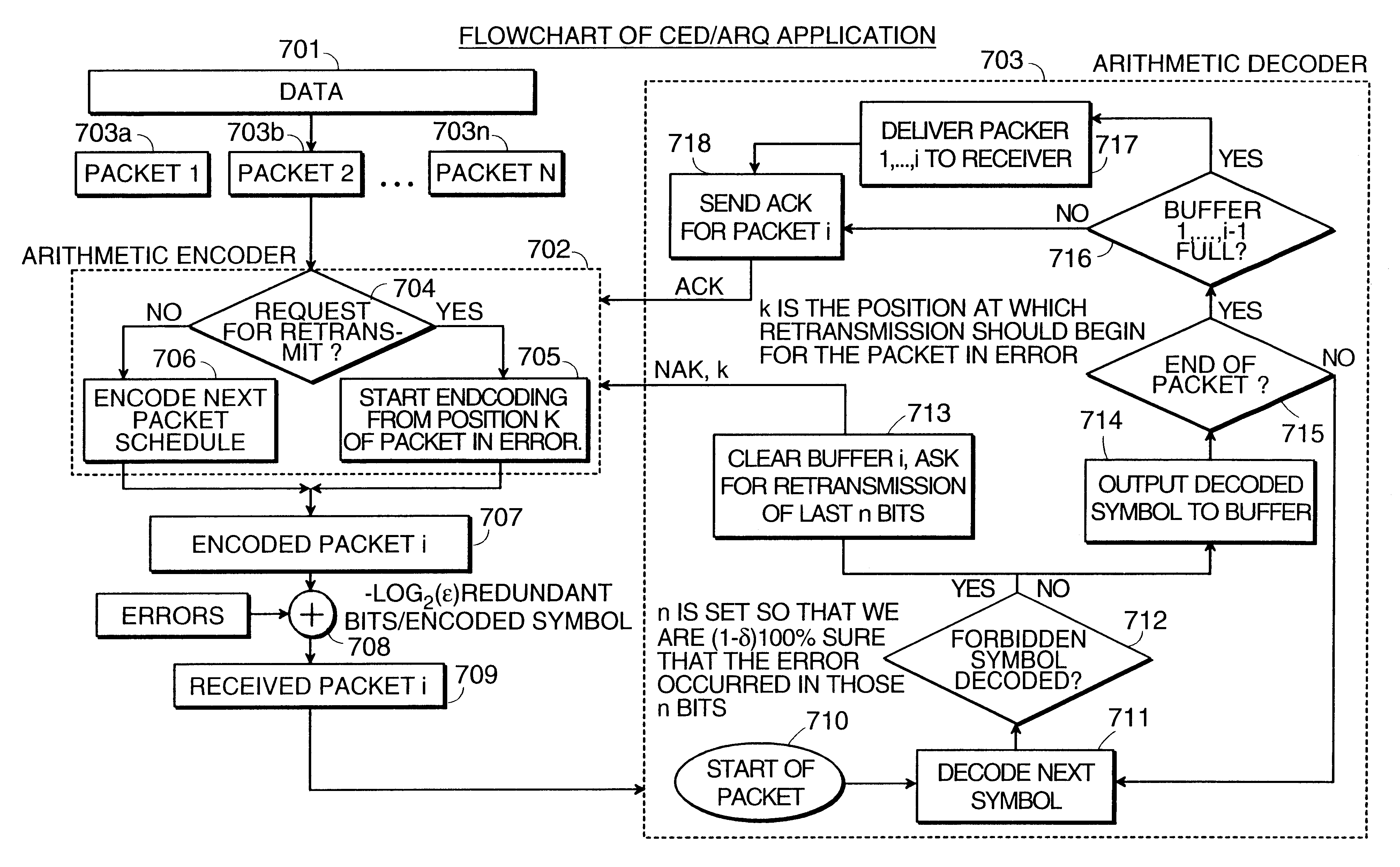
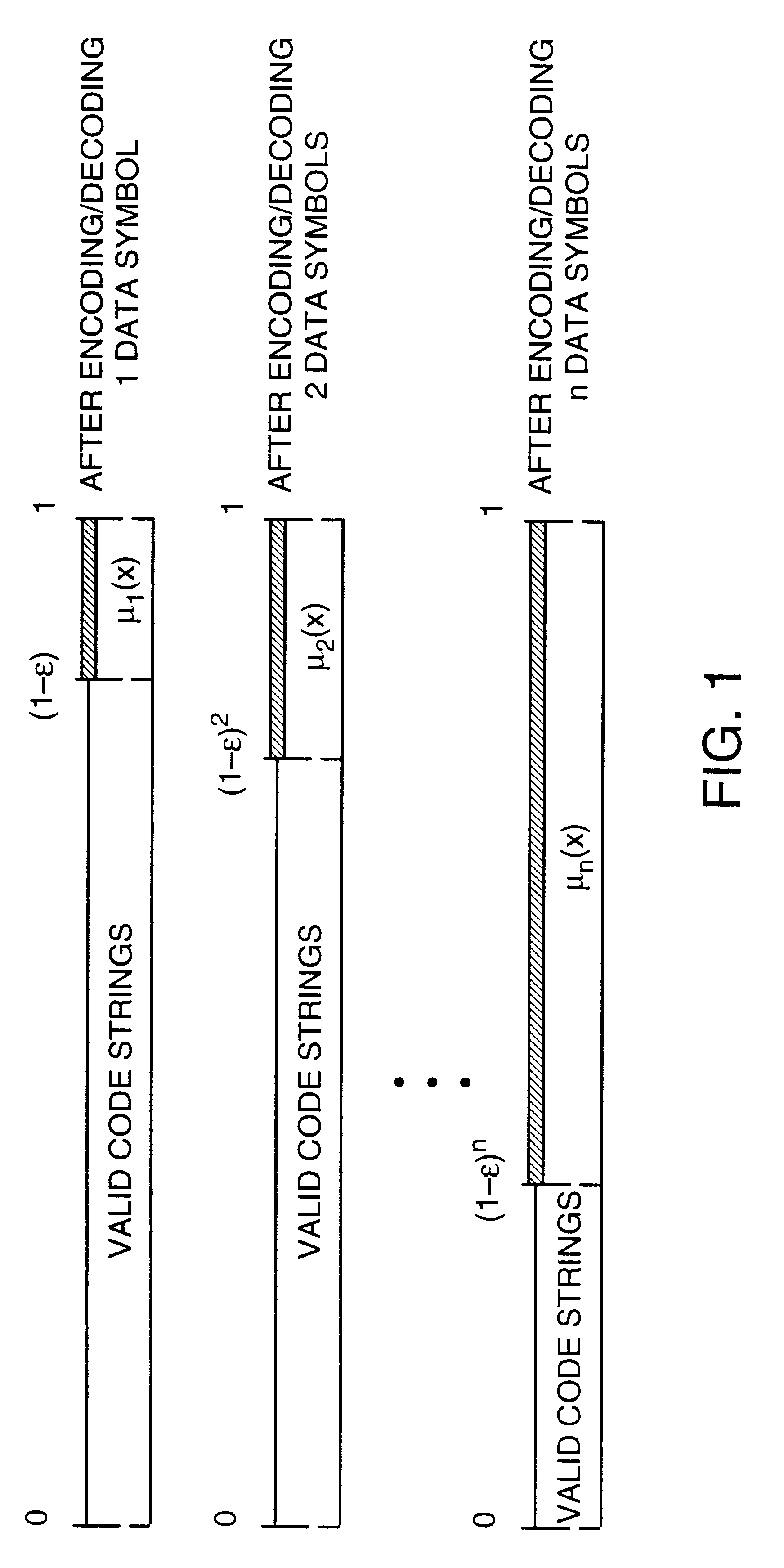
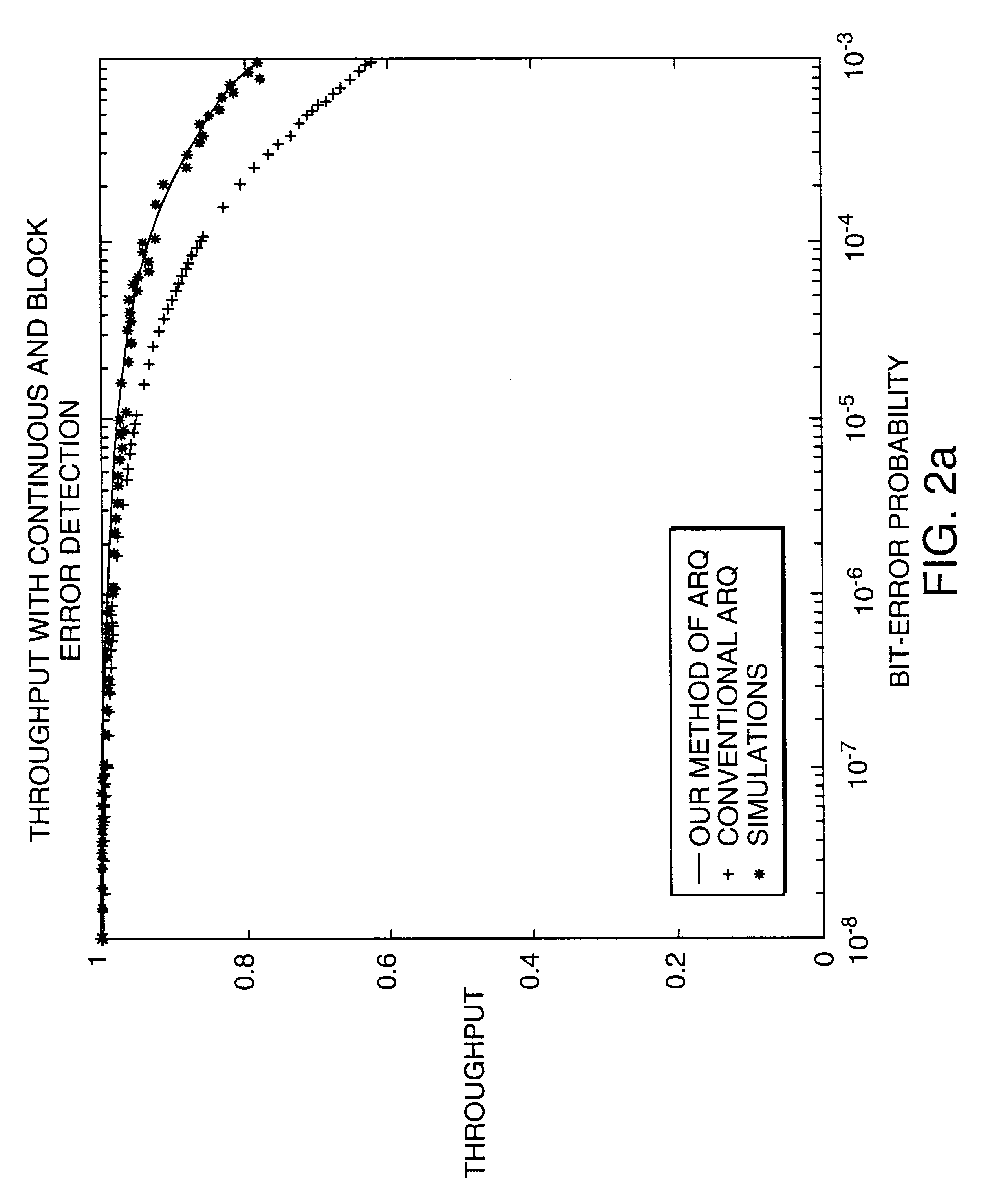
InactiveUS6418549B1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsAutomatic repeat requestTrade offs
Method and apparatus for image transmission using arithmetic coding, based on continuous error detection uses a controlled amount of added redundancy. A continuous error detection scheme is provided, wherein there is a trade-off between the amount of added redundancy and the time needed to detect an error once it occurs. Herein, there is no need for the cyclic redundancy check (CRC) to wait until an entire block of data has been received and processed before an error can be detected. The invention can be used to great advantage both in the automatic repeat request (ARQ) and other concatenated coding schemes. Errors in the received bit stream are detected by introducing added redundancy, e.g., a forbidden symbol, in the arithmetic coding operation. The forbidden symbol is never intended to be encoded. The redundancy error causes loss of synchronization, which is used to detect errors. If a forbidden symbol gets decoded, it means that an error has occurred. In this invention, there is direct control over the amount of redundancy added vs. the amount of time it takes to detect an error. For image compression systems, by using the invention and ARQ, only one device would suffice both for source compression and channel coding.
Owner:MERU NETWORKS
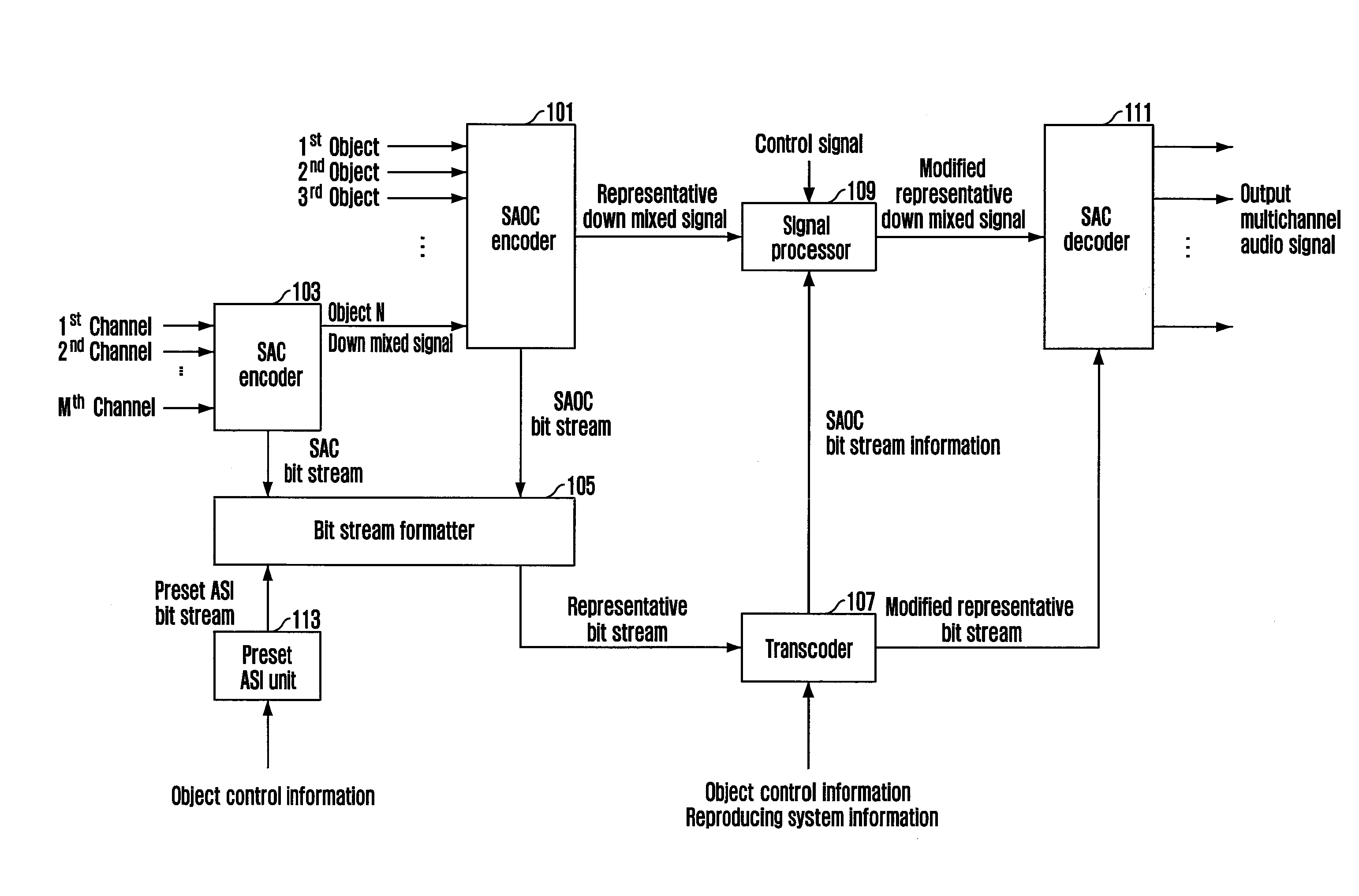
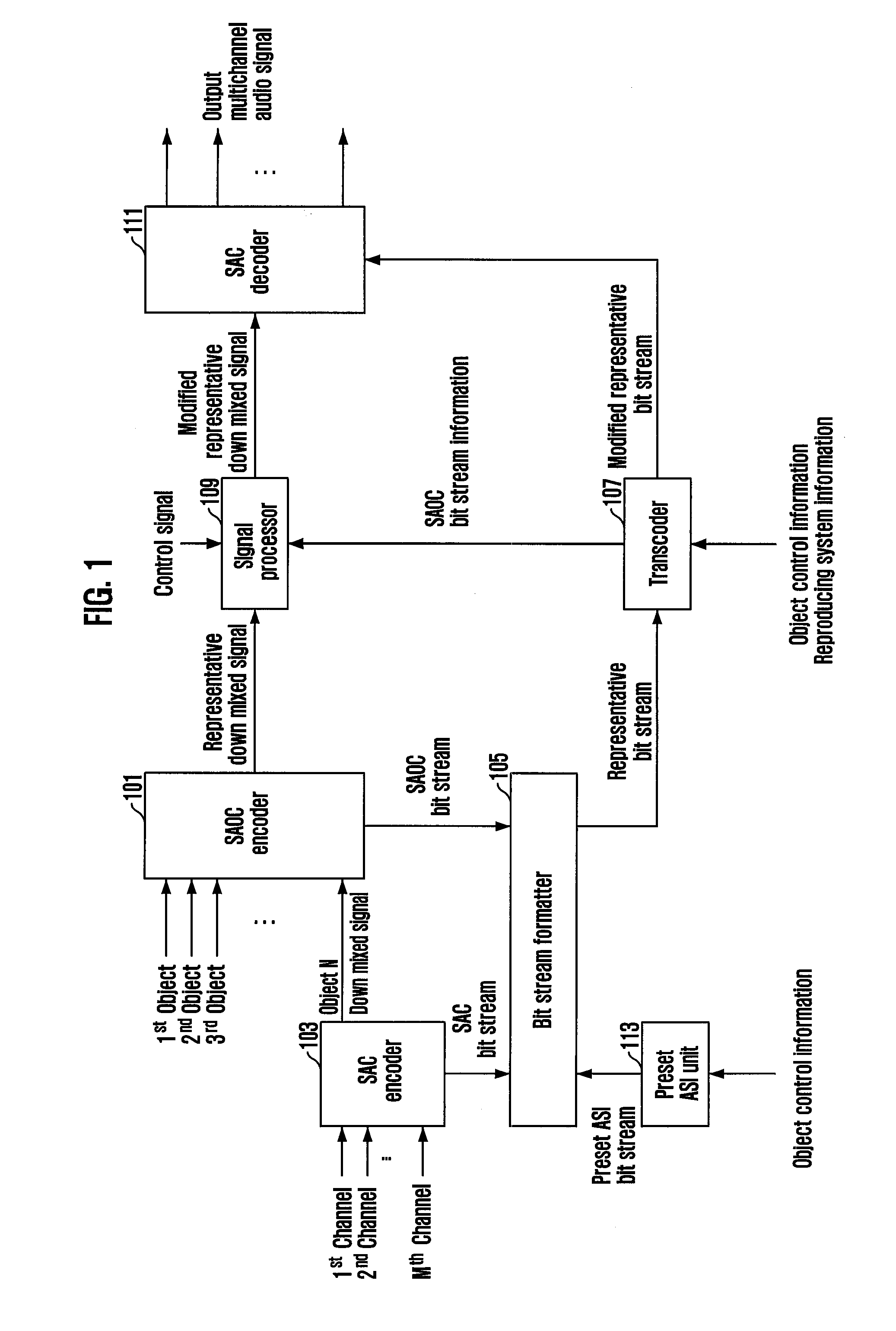
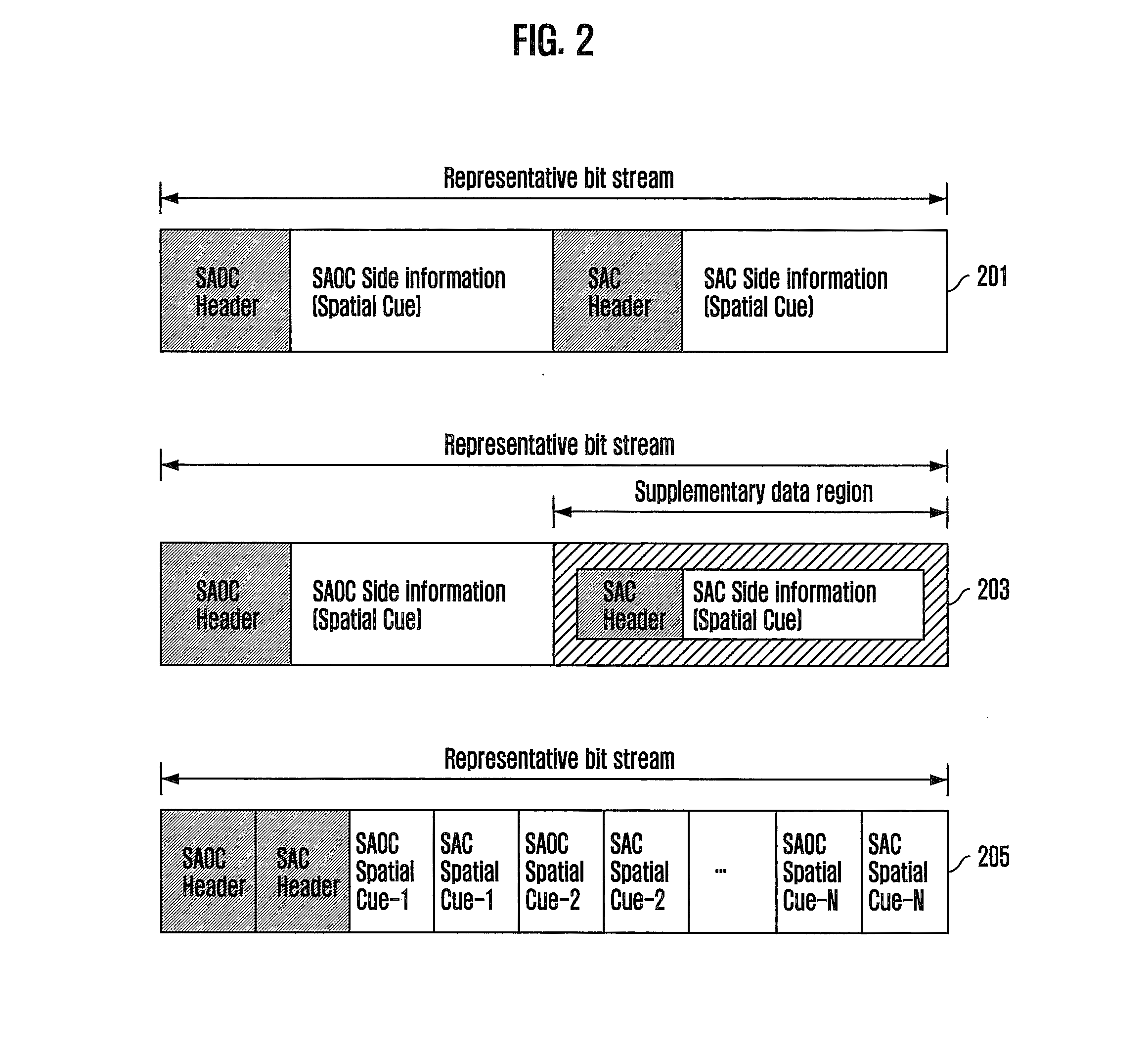
Apparatus and method for coding and decoding multi object audio signal with multi channel
Provided are an apparatus and method for coding and decoding a multi object audio signal with multi channel. The apparatus includes: a multi channel encoding means for down-mixing an audio signal including a plurality of channels, generating a spatial cue for the audio signal including the plurality of channels, and generating first rendering information including the generated spatial cue; and a multi object encoding unit for down-mixing an audio signal including a plurality of objects, which includes the down-mixed signal from the multi channel encoding unit, generating a spatial cue for the audio signal including the plurality of objects, and generating second rendering information including the generated spatial cue, wherein the multichannel encoding unit generates a spatial cue for the audio signal including the plurality of objects regardless of a Coder-DECoder (CODEC) scheme the limits the multi channel encoding unit.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
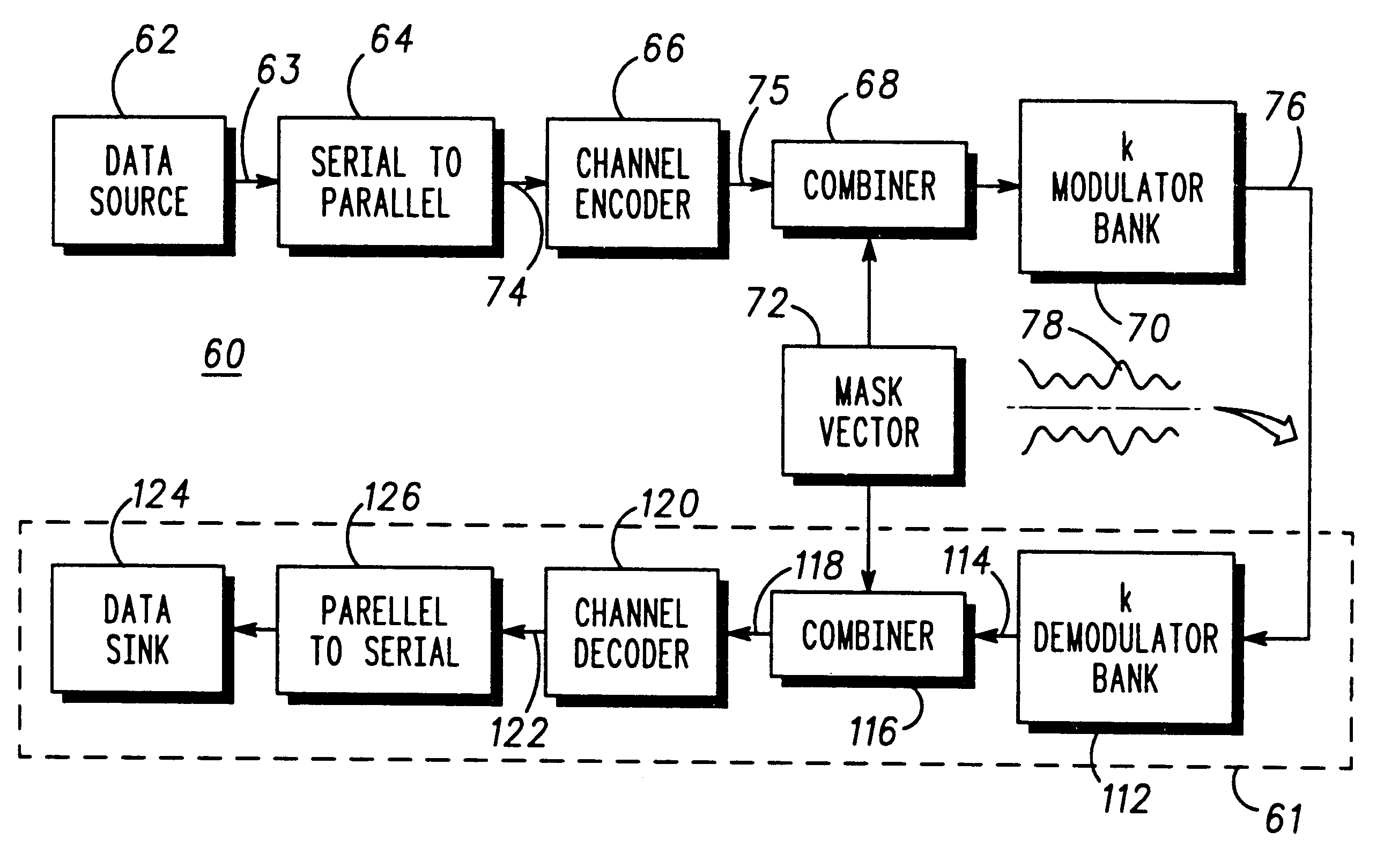
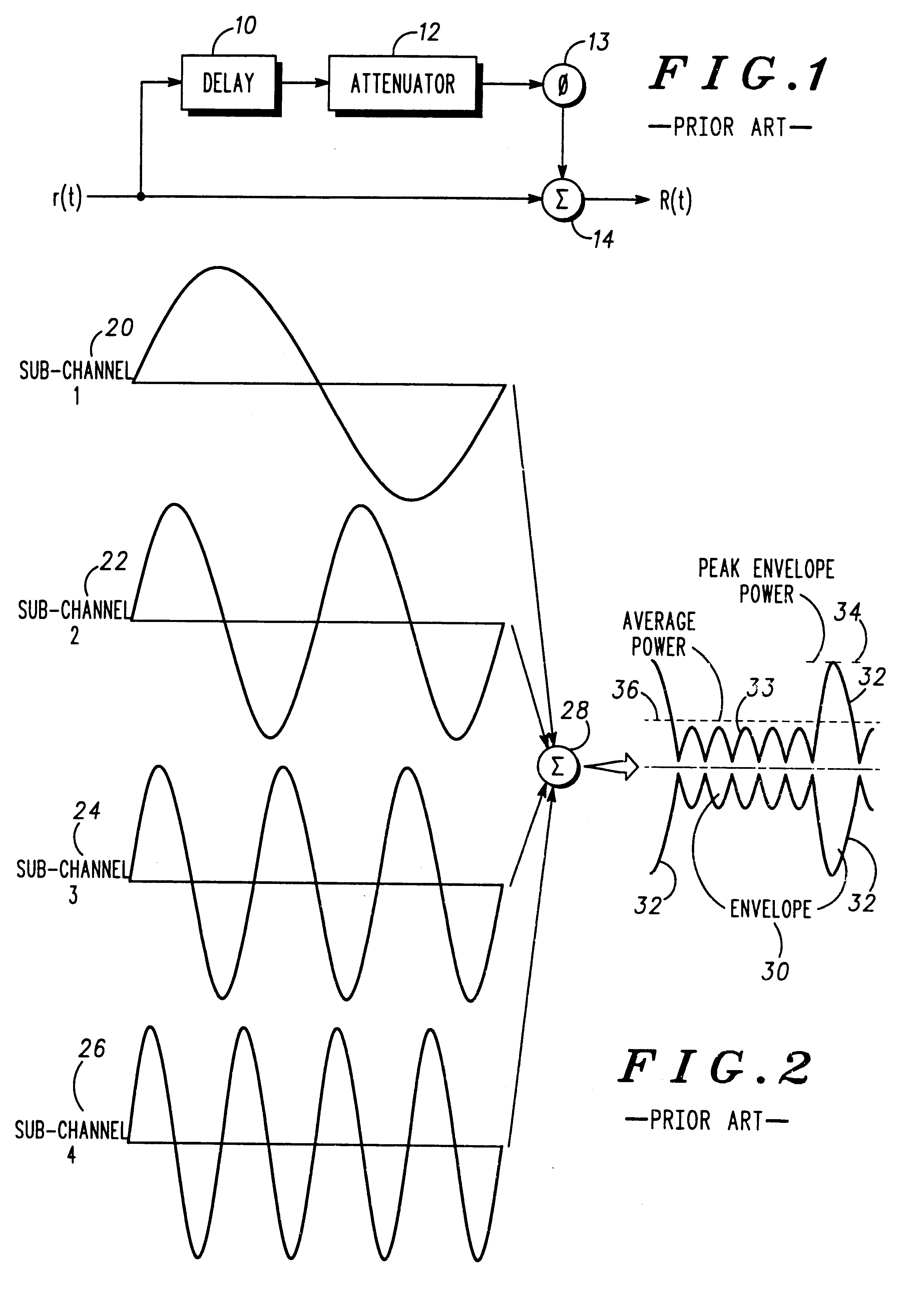
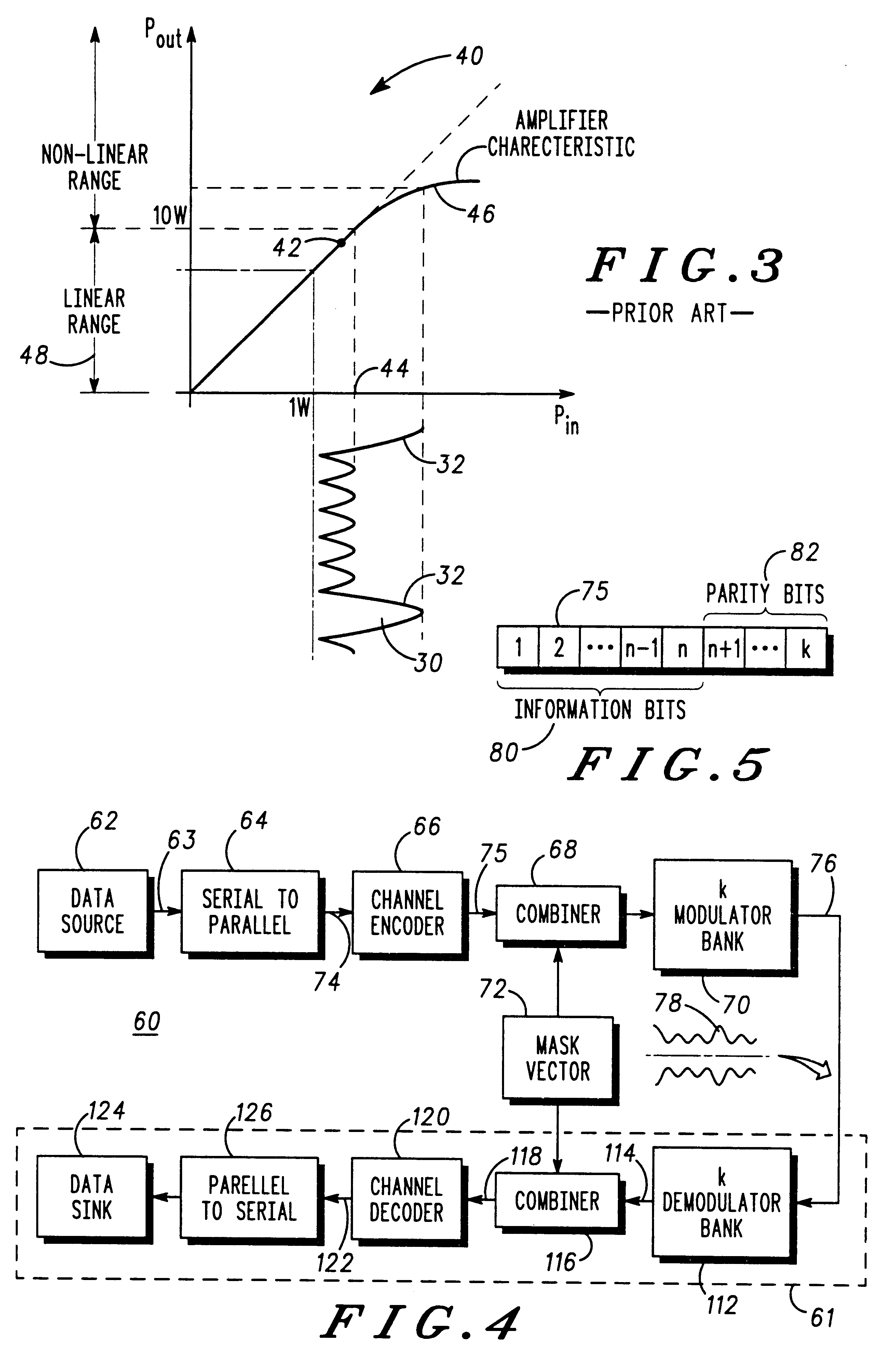
Multicarrier communication system and method for peak power control
InactiveUS6307892B1Remove distortion effectsImprovement in PMEPRSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsCommunications systemPeak value
A communication device for simultaneously transmitting information on multiple sub-channels encodes information for each of the multiple sub-channels with a coding scheme to produce channel encoded information. A mask vector derived from a redundancy in the coding scheme, encodes the channel encoded information to transform the channel encoded information into codewords having pairwise Euclidean distance properties identical to those of the channel encoded information, Modulation of the sub-channels in accordance with the codewords in a modulator then produces a composite signal envelope having a peak-to-mean error power ratio (PMEPR) reduced relative to a PMEPR for correspondingly modulated channel encoded information.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
Adaptive Joint Source and Channel Coding Scheme for H.264 Video Multicasting Over Wireless Networks
InactiveUS20100226262A1Improve system performanceImprove performancePulse modulation television signal transmissionError preventionTopology informationJoint source and channel coding
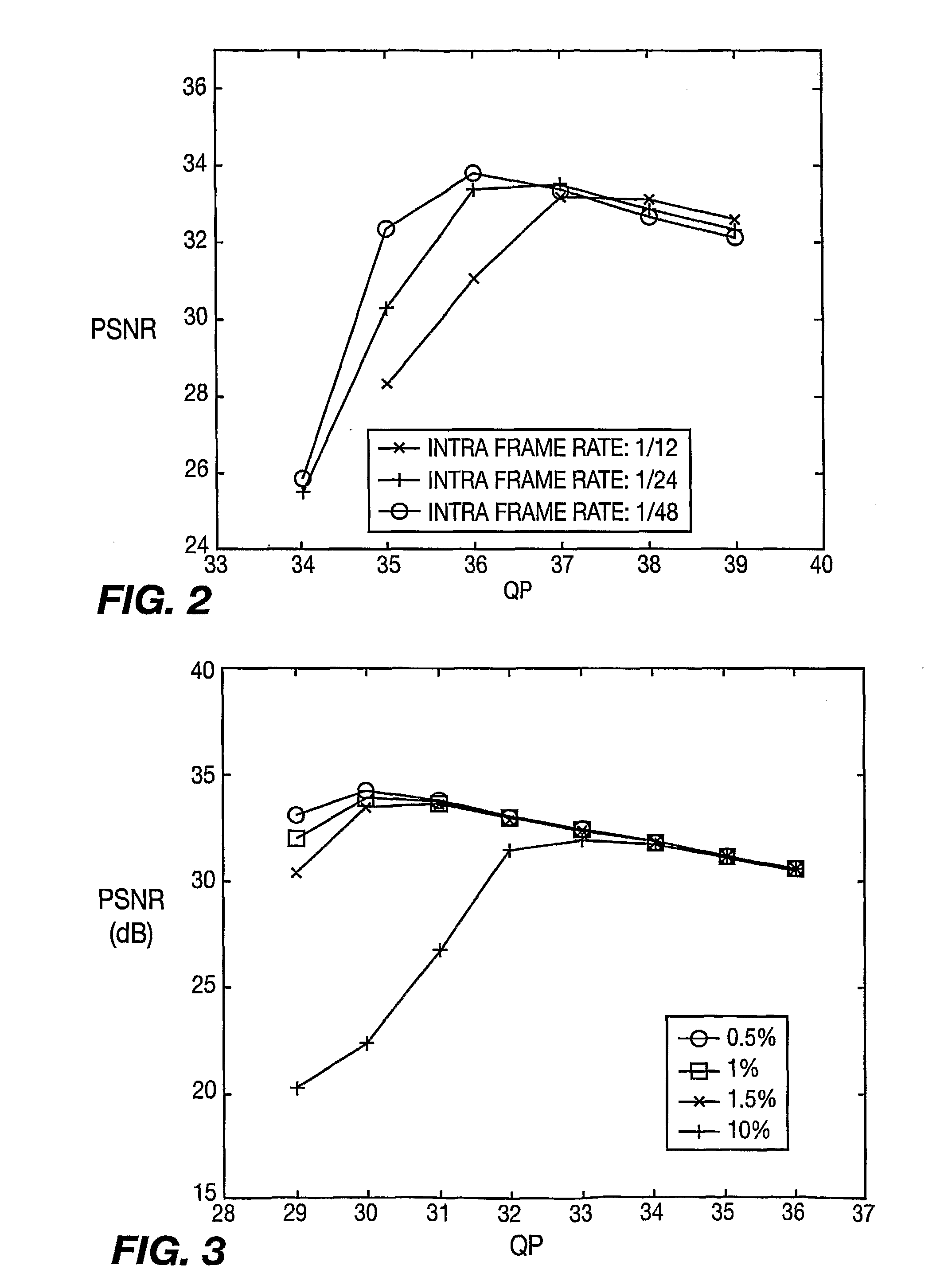
A method and apparatus for estimating packet loss rate are described including calculating a real packet loss rate in a time slot at the end of the time slot, estimating average packet loss rate for a subsequent time slot, estimating variance of packet loss rate for the subsequent time slot and estimating the packet loss rate for the subsequent time slot. A method and apparatus and also described for dynamically allocating available bandwidth for video multicast including selecting an intra-frame rate, determining a packet loss rate threshold, receiving user topology information, receiving channel conditions for each user, determining an optimal operation point for encoding and transmitting video frames in a subsequent time slot, adapting dynamically quantization parameters and a forward error correction code rate, encoding the video frames using the quantization parameters and applying forward error correction code with the forward error correction code rate to data packets of the video frames to generate forward error correction packets.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Method of transmitting a digital signal for a semi-orthogonal MS-marc system, and a corresponding program product and relay device
ActiveUS9634797B2Improve reliabilitySimple to ensureData representation error detection/correctionError detection/correctionComputer hardwareFrequency spectrum
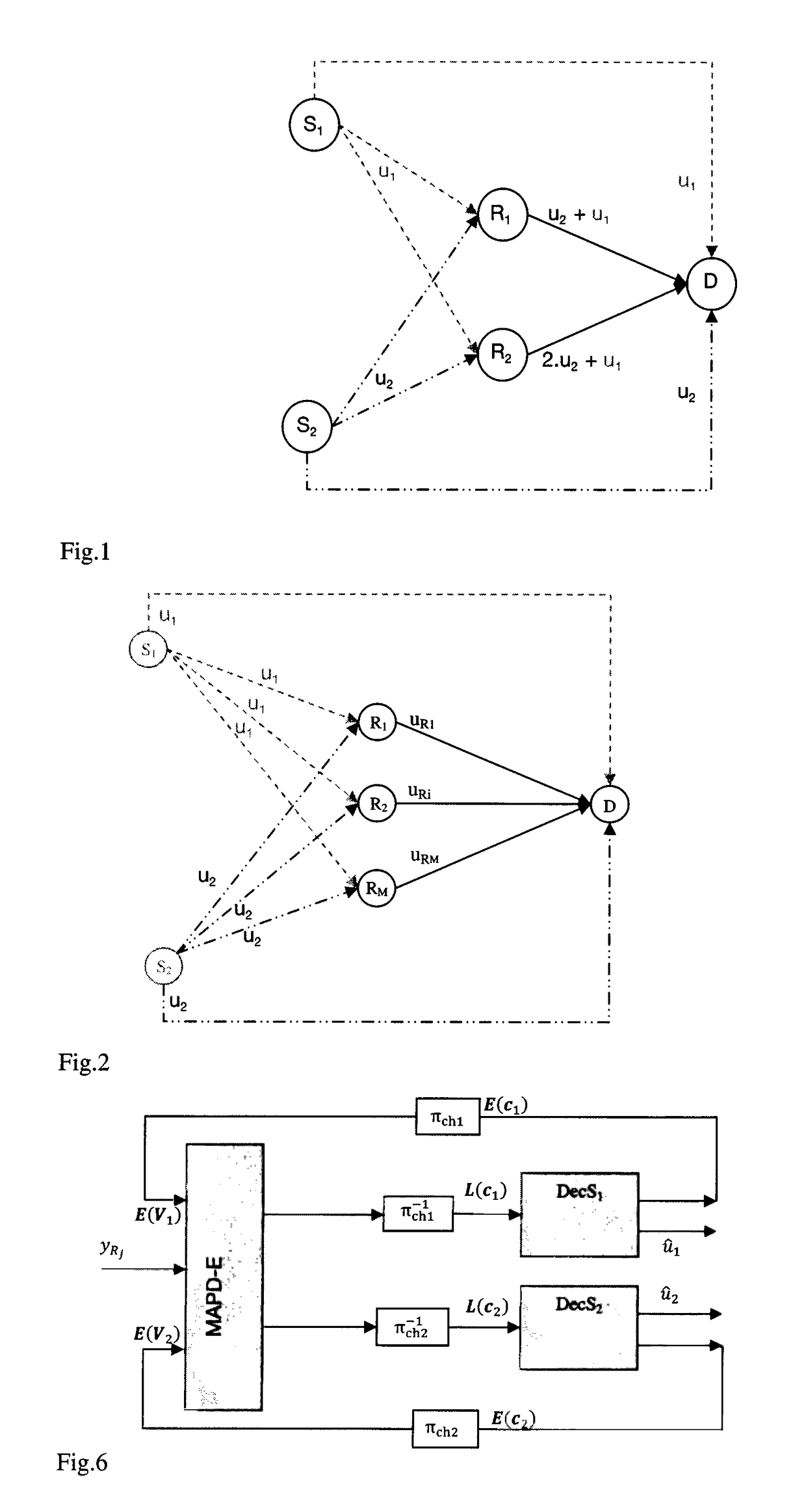
A method for semi-orthogonal transmission of a signal intended for a system with N sources, M relays and a single receiver whereby the simultaneous transmission on a same spectral resource by the relays is successive and not simultaneous to a simultaneous transmission on a same spectral resource by the sources. The includes, by relay: joint iterative detection / decoding of messages transmitted respectively by the sources to obtain decoded messages, detecting errors on the decoded messages, interleaving the detected messages without errors followed by algebraic network coding consisting of a linear combination in a finite group of an order strictly higher than two of the interleaved messages to obtain a coded message, the linear combinations being independent, two by two, between the relays of the system, and formatting including channel coding to generate a signal representative of the network coded message.
Owner:ORANGE SA (FR)
Method and device for allocating radio resources in wireless portable network system
ActiveUS20070010268A1Reduce power consumptionGood curative effectTransmission path divisionSignal allocationTelecommunicationsResource block
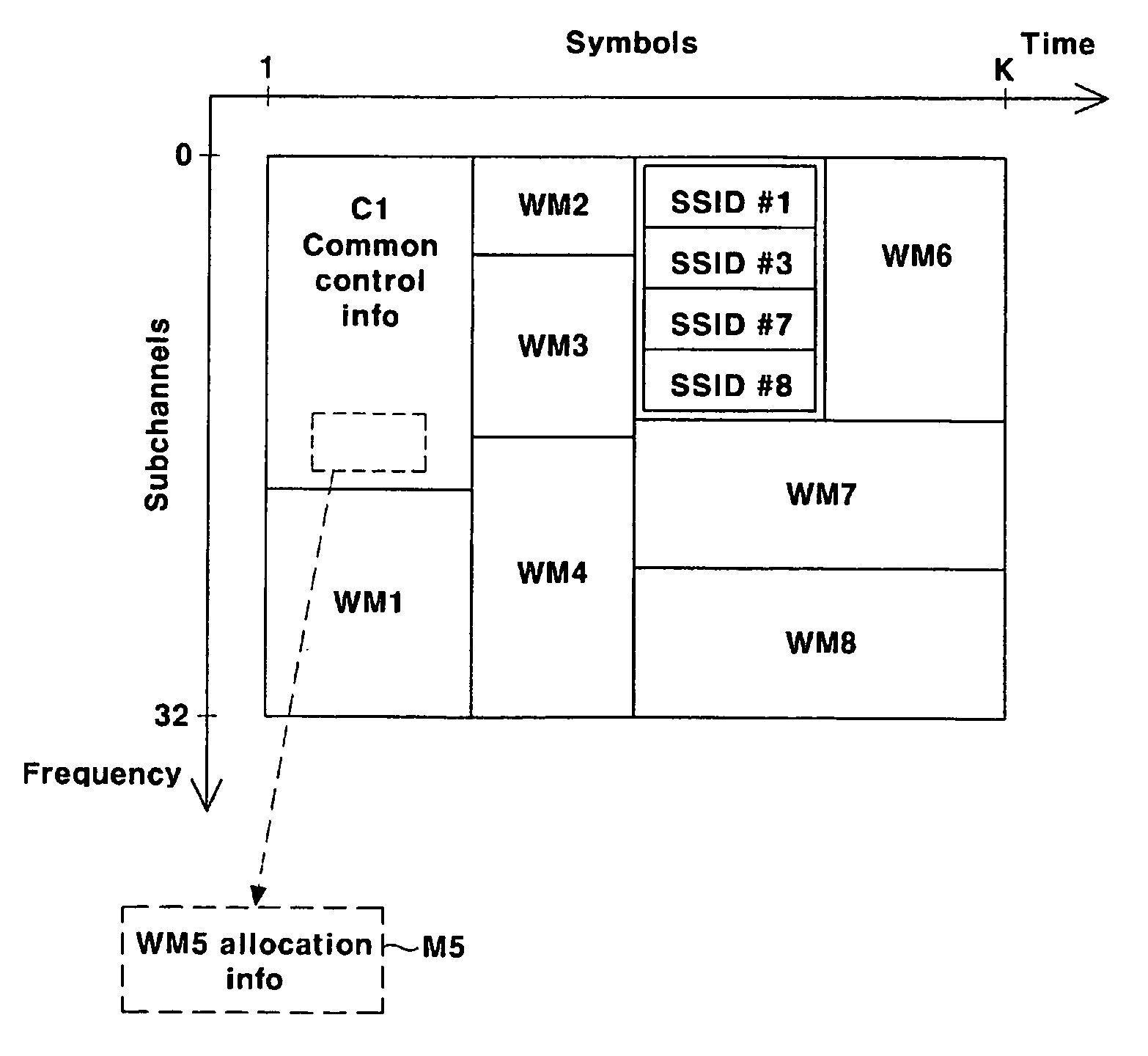
Information for different subscribers of a service with the same modulation and channel encoding method is transmitted by allocating radio resources in a wireless portable Internet system. Also, identifier information on the subscriber of a concurrently allocated radio resource is transmitted through common control information. Therefore, information for a plurality of subscribers coexists in a single radio resource block, and it can be easily transmitted. Since a subscriber station which has received downlink information can know to which radio resource block the information for the corresponding station is allocated through the subscriber identifier information transmitted as common control information, the subscriber station can access desired information by accessing a specific radio resource block to which information for the subscriber is allocated in the received frame.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +4
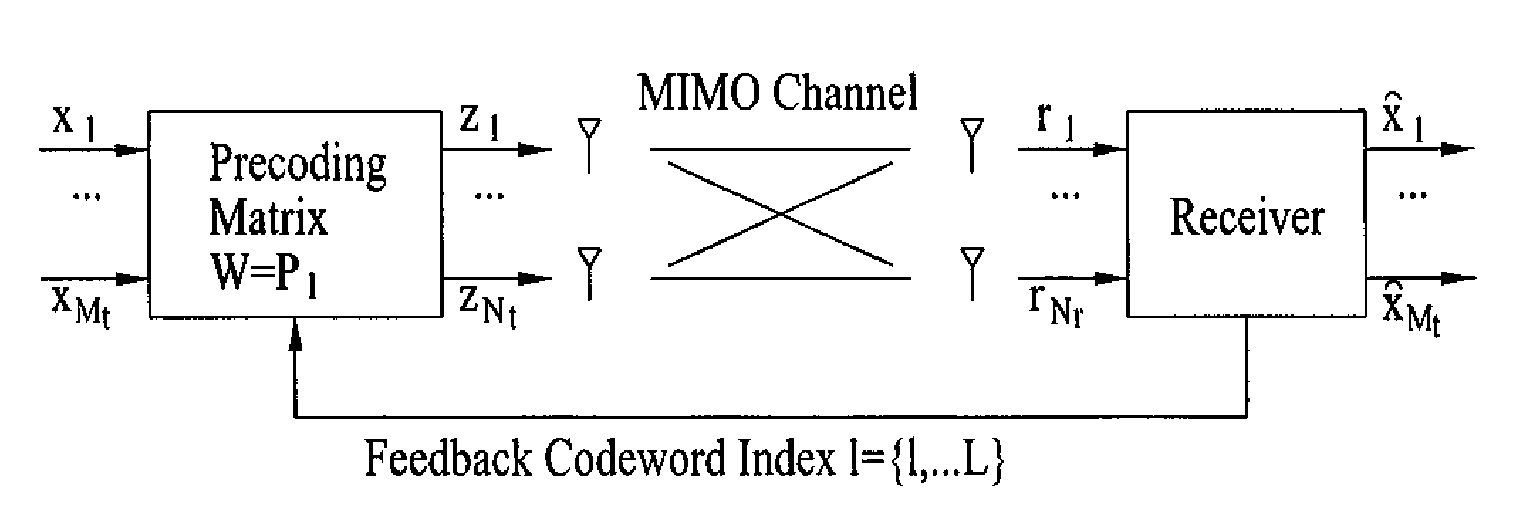
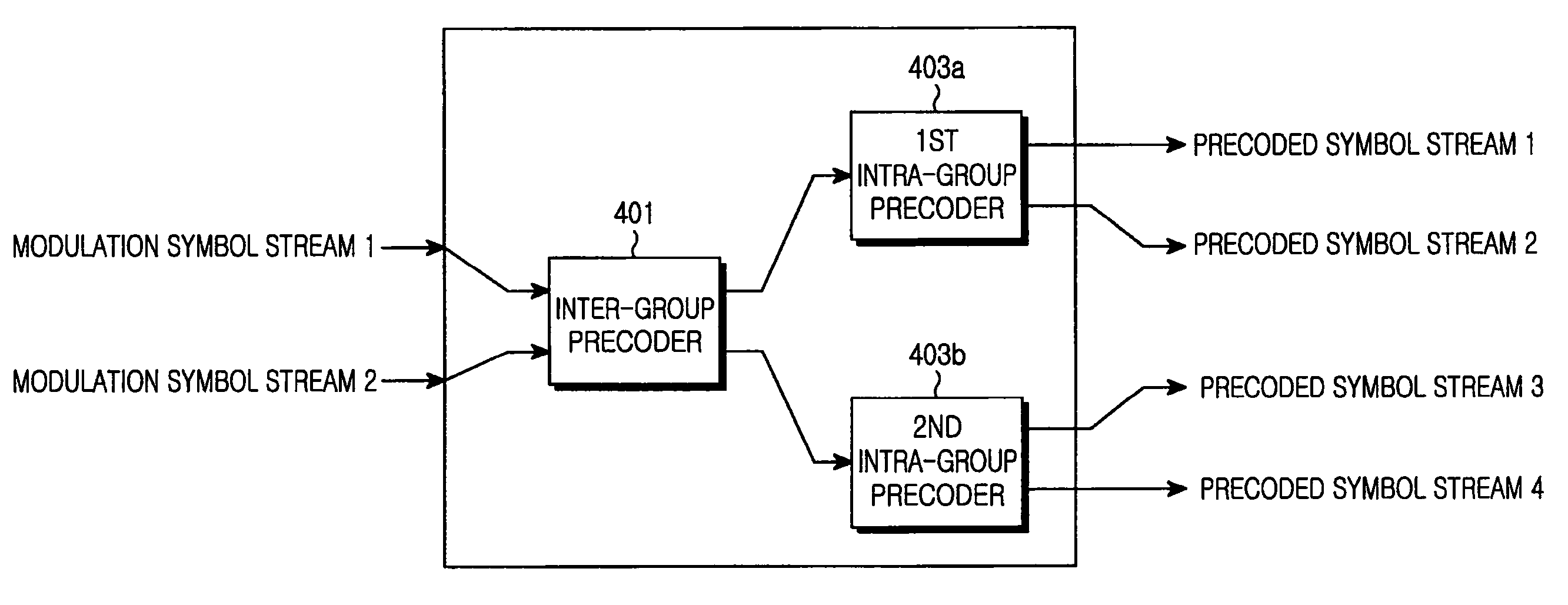
Precoding apparatus and method in a wireless communication system using multiple input multiple output
ActiveUS20080240274A1Improve transmission efficiencySpatial transmit diversitySecret communicationPrecodingCommunications system
A transmission apparatus in a Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO)-based wireless communication system. The transmission apparatus includes at least two antenna groups each having at least two antennas, wherein the antenna groups are spaced apart by a first distance and transmit antennas in each antenna group are spaced apart by a second distance which is shorter than the first distance. A channel coding and modulation unit channel-codes and modulates a desired transmission data stream. A precoding unit precodes the channel-coded and modulated signal separately for each antenna group and each antenna in the same antenna group. Thereafter, a transmission processing unit transmission-processes the output signal from the precoding unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
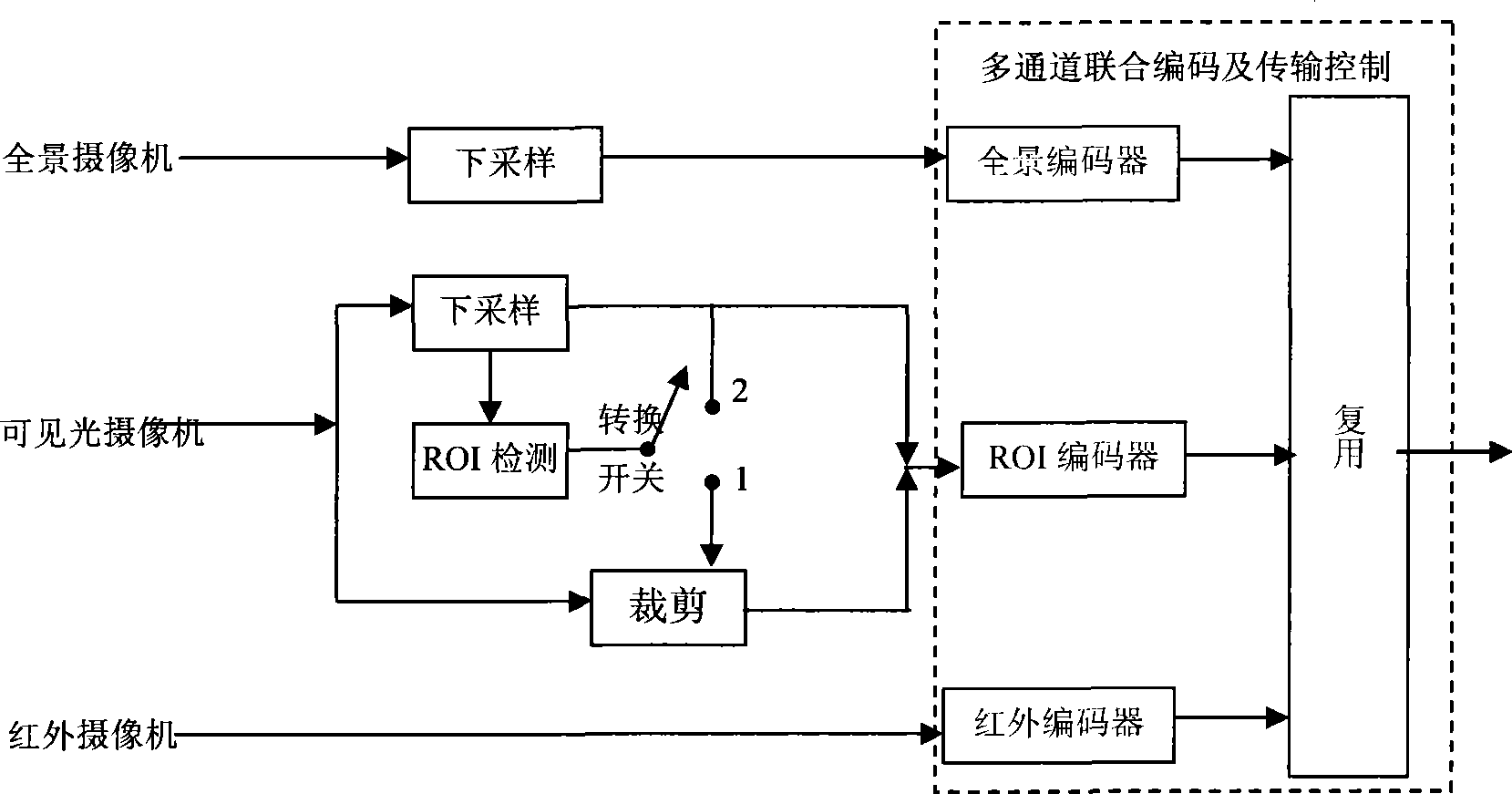
Method for implementing multichannel combined interested area video coding and transmission
ActiveCN101252687AAccurate detectionReal-time trackingTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationImage resolutionVideo encoding
The invention relates to a region-of-interest video encoding and transmitting method which realize multi-channel combination, and belongs to the technical field of the video encoding and transmission. The method adopts the following steps: step one, space down sampling is performed to the panoramic video with high resolution collected by a panoramic camera, and then encoding is performed after video with low resolution is obtained; step two, region-of-interest detection is performed to video with high definition collected by a visible-light camera, and self-adaptive switching is performed to the two channels of video, namely, downsized video and down-sampled video, according to the area and the position of the region-of-interest detection; step three, an an infrared thermal imager is used for performing detection and tracking to interest targets, encoding infrared region-of-interest video with primary low resolution, and adjusting quantization parameter to realize code rate control; step four, the priority of the three channels of video is set, protecting channel encoding for non-uniform channel is performed according to the priority, and the code is multiplexed into one channel of code stream to be sent to the channel for transmission, and code rate distribution of the channel bandwidth is performed according to the priority. The method guarantees precise detection and high quality encoding to the region of interest when ensuring global detection on the complete scene.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT OF DIGITAL TELEVISION
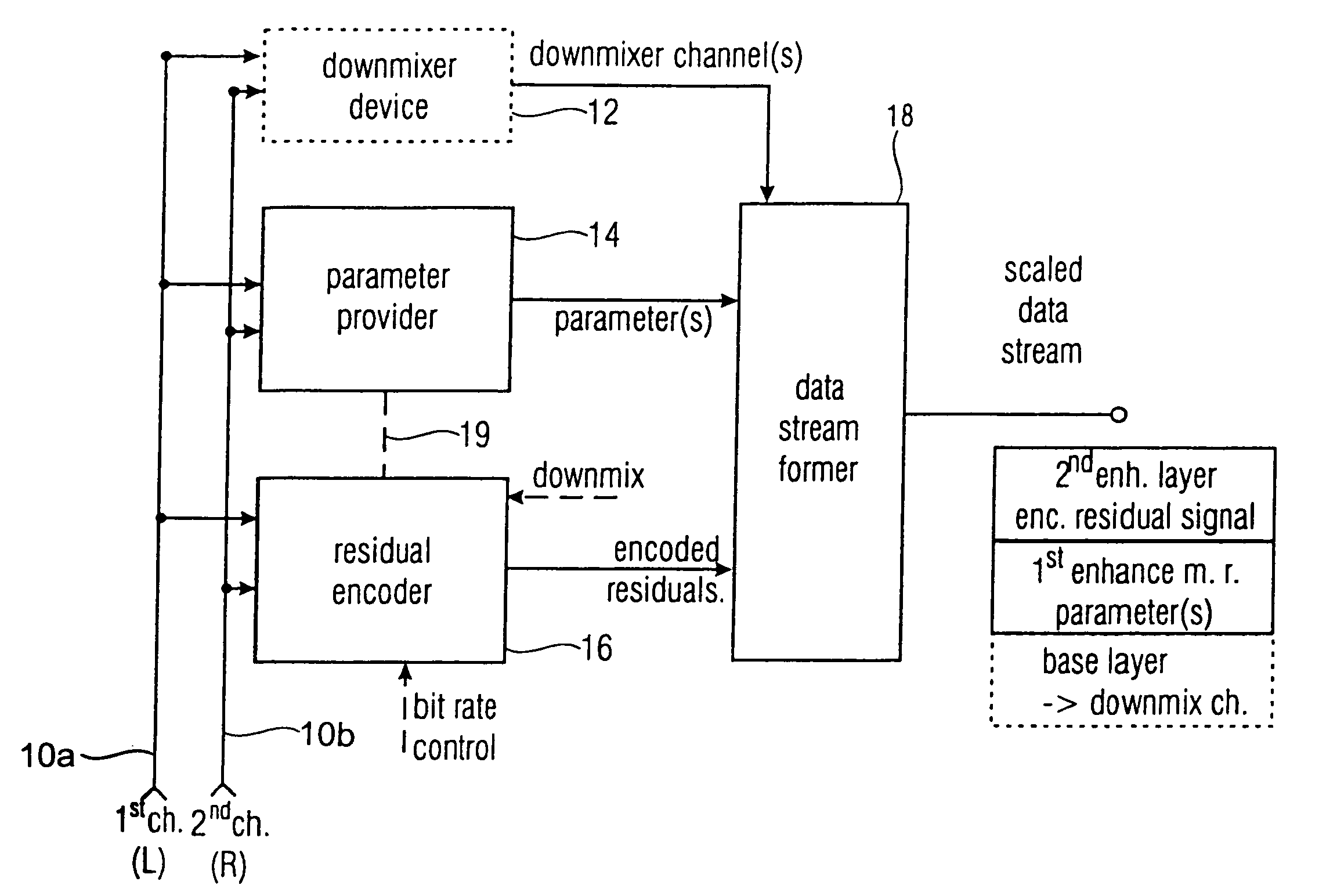
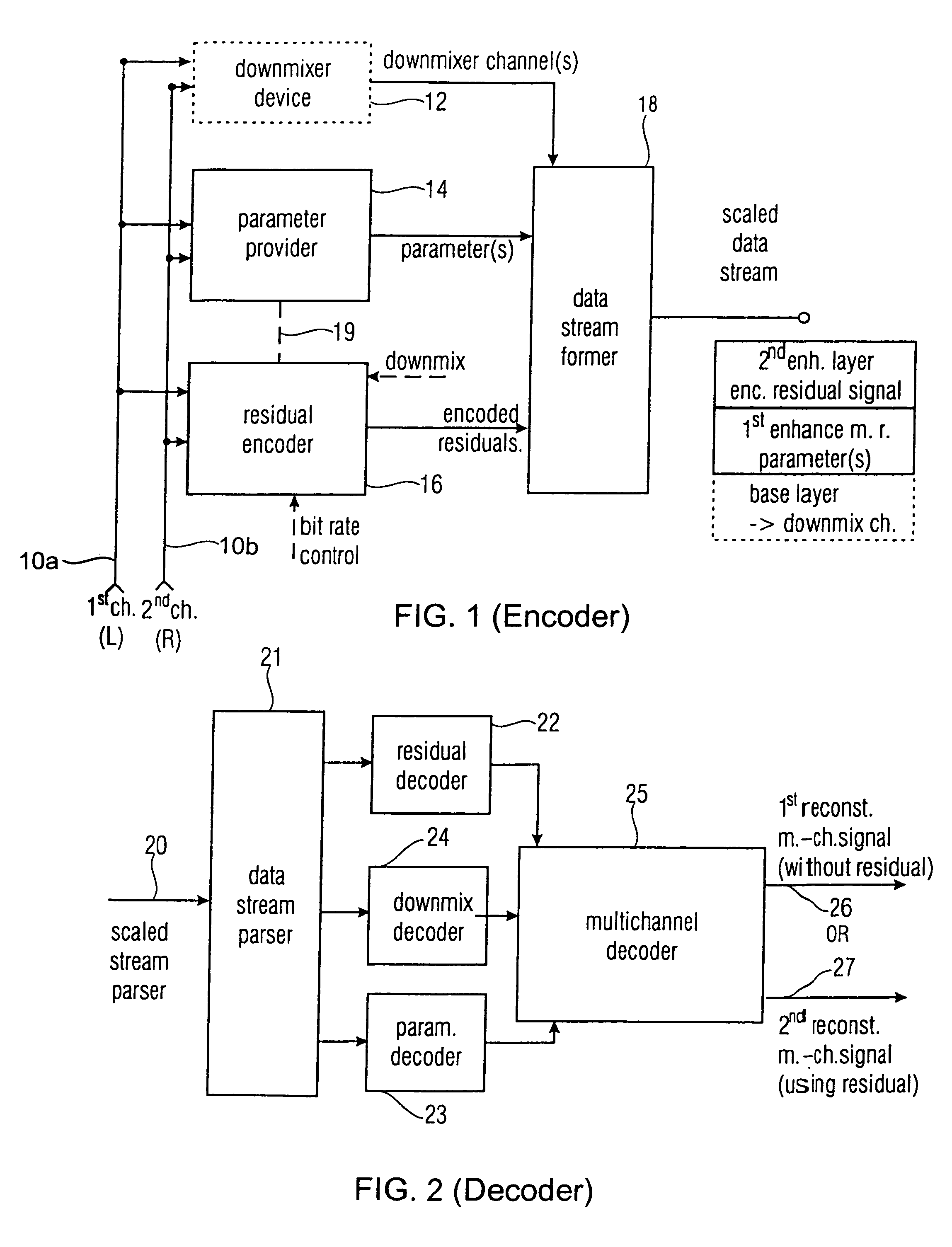
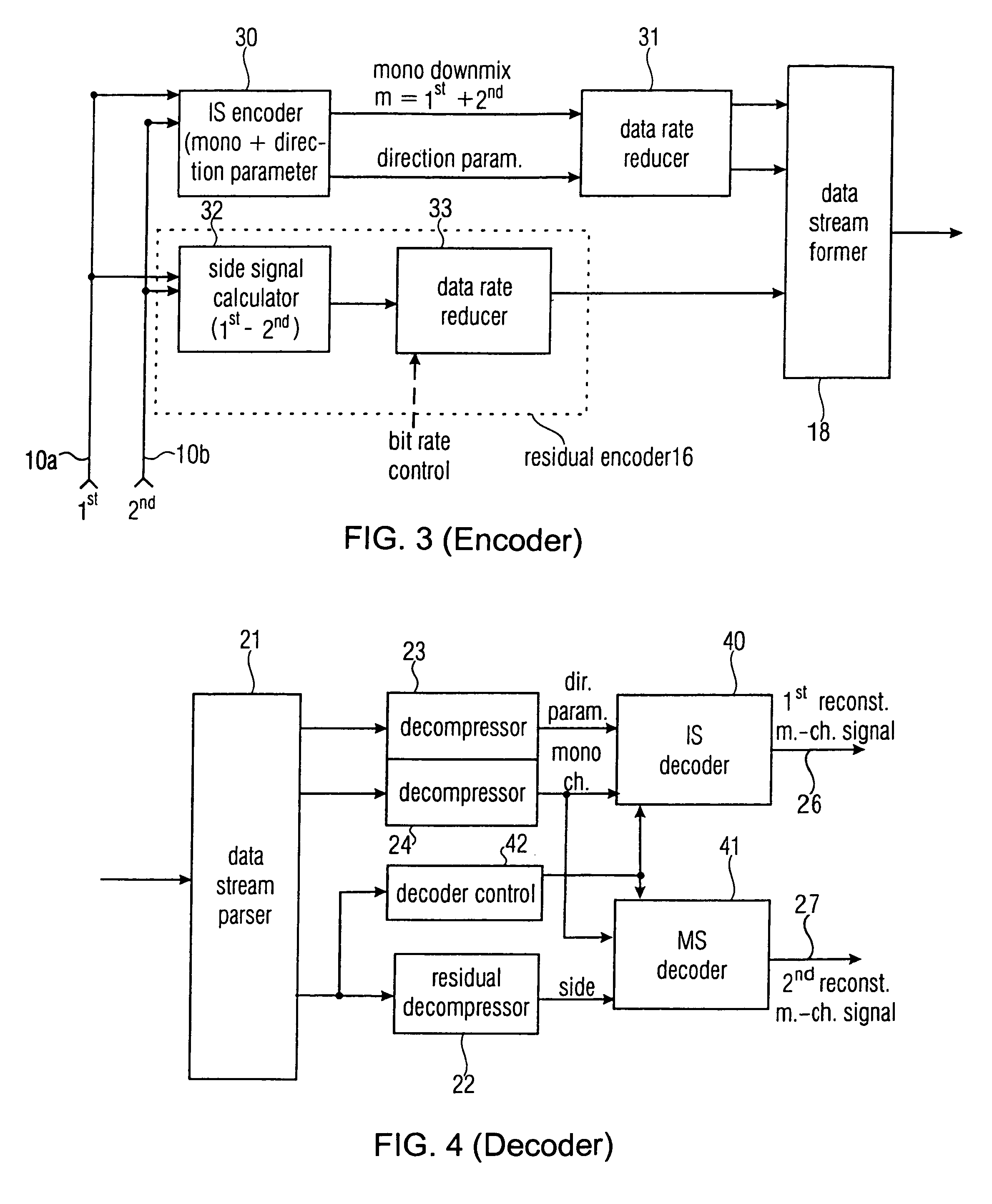
Near-transparent or transparent multi-channel encoder/decoder scheme
ActiveUS7573912B2Quality improvementReduce bitrateError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsWave shapeComputer science
A multi-channel encoder / decoder scheme additionally preferably generates a waveform-type residual signal. This residual signal is transmitted together with one or more multi-channel parameters to a decoder. In contrast to a purely parametric multi-channel decoder, the enhanced decoder generates a multi-channel output signal having an improved output quality because of the additional residual signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
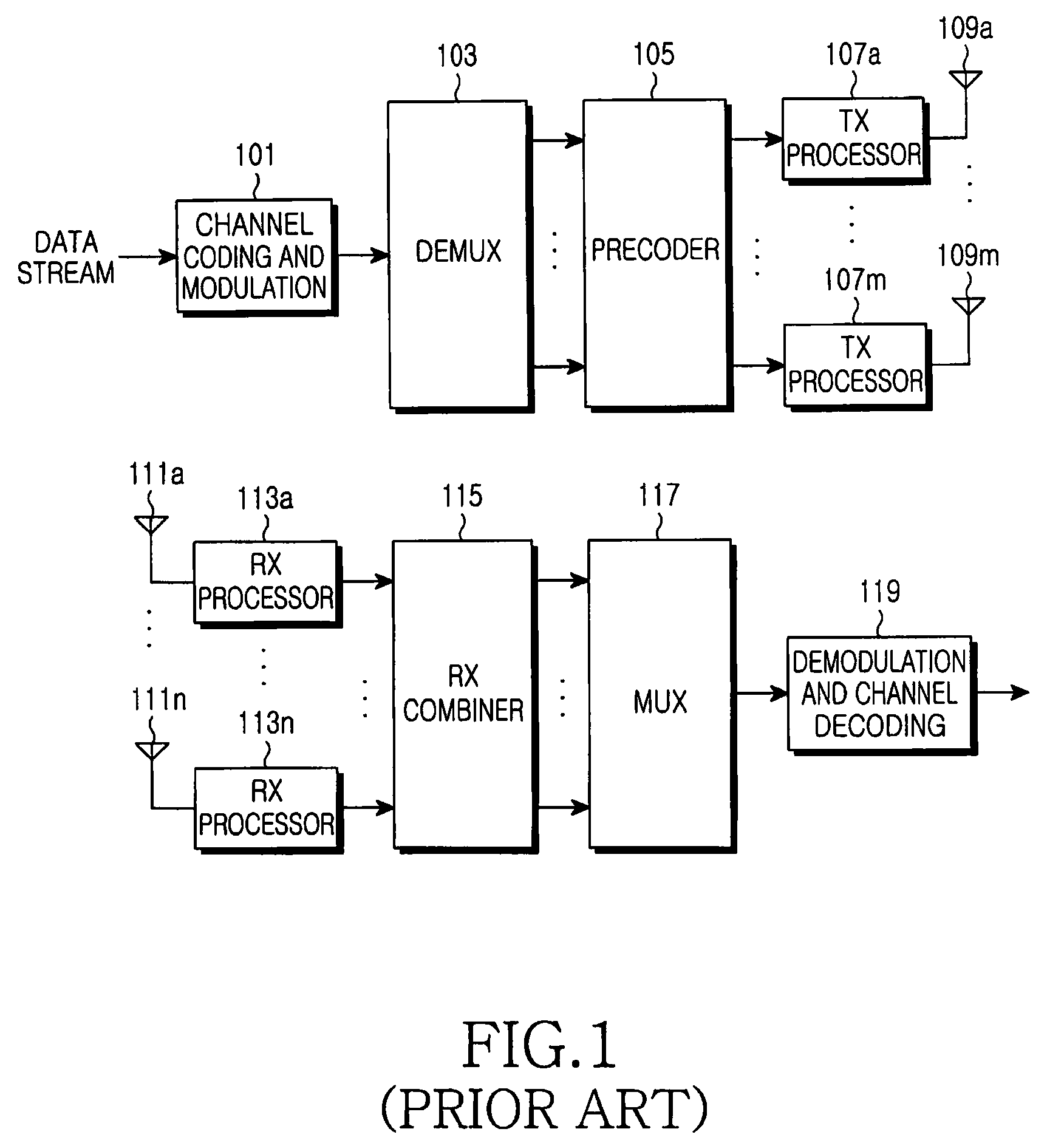
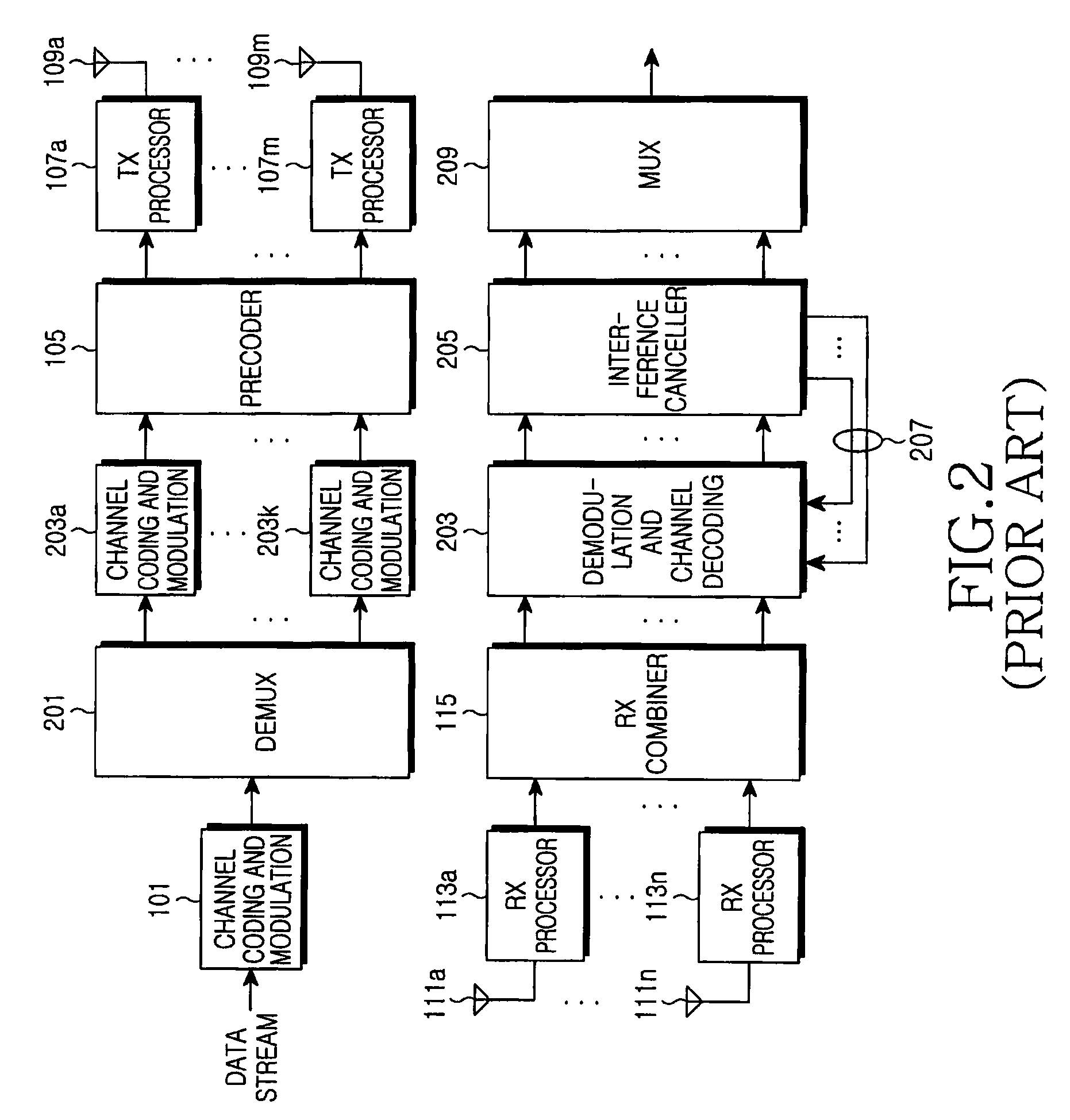
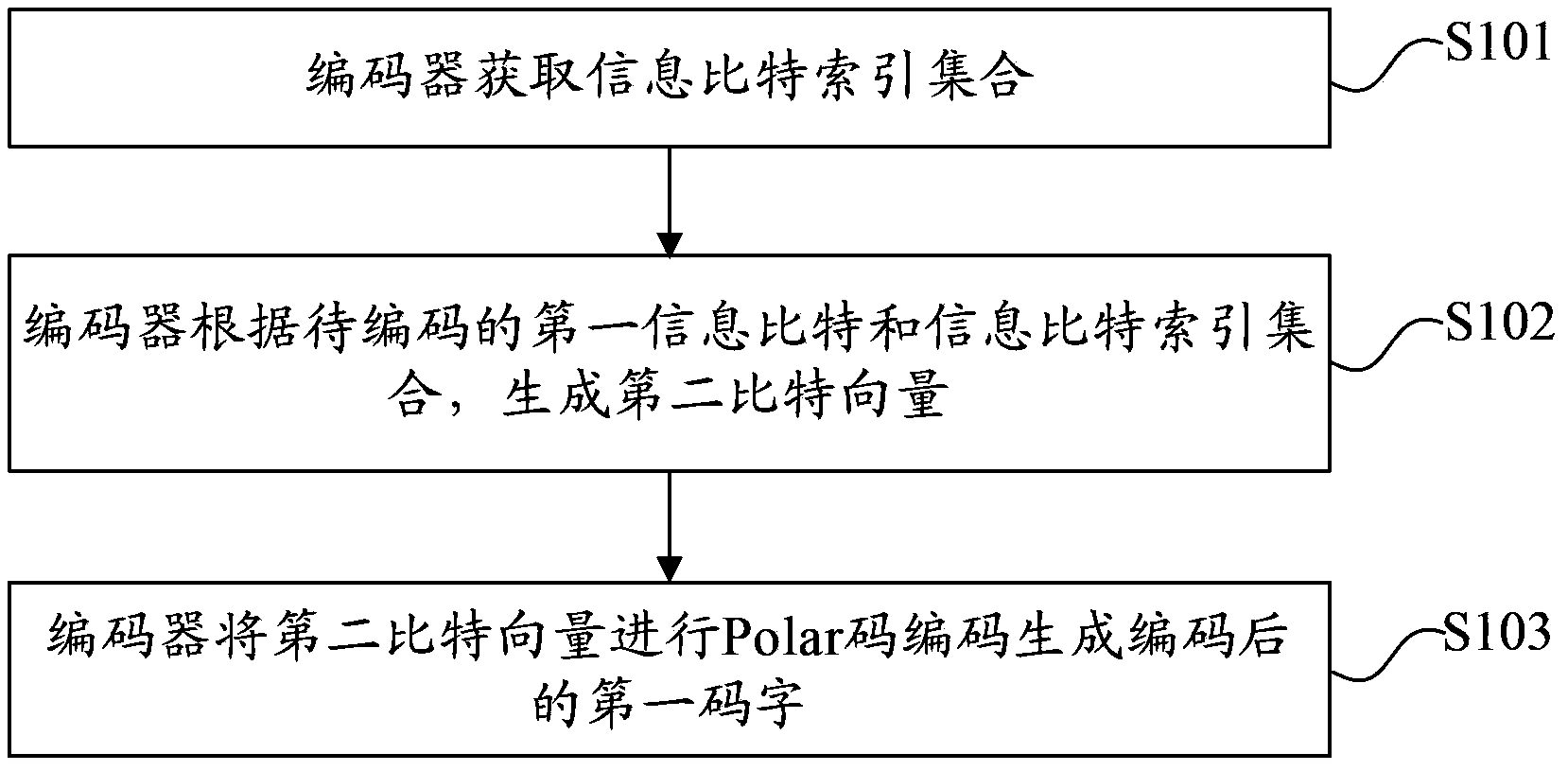
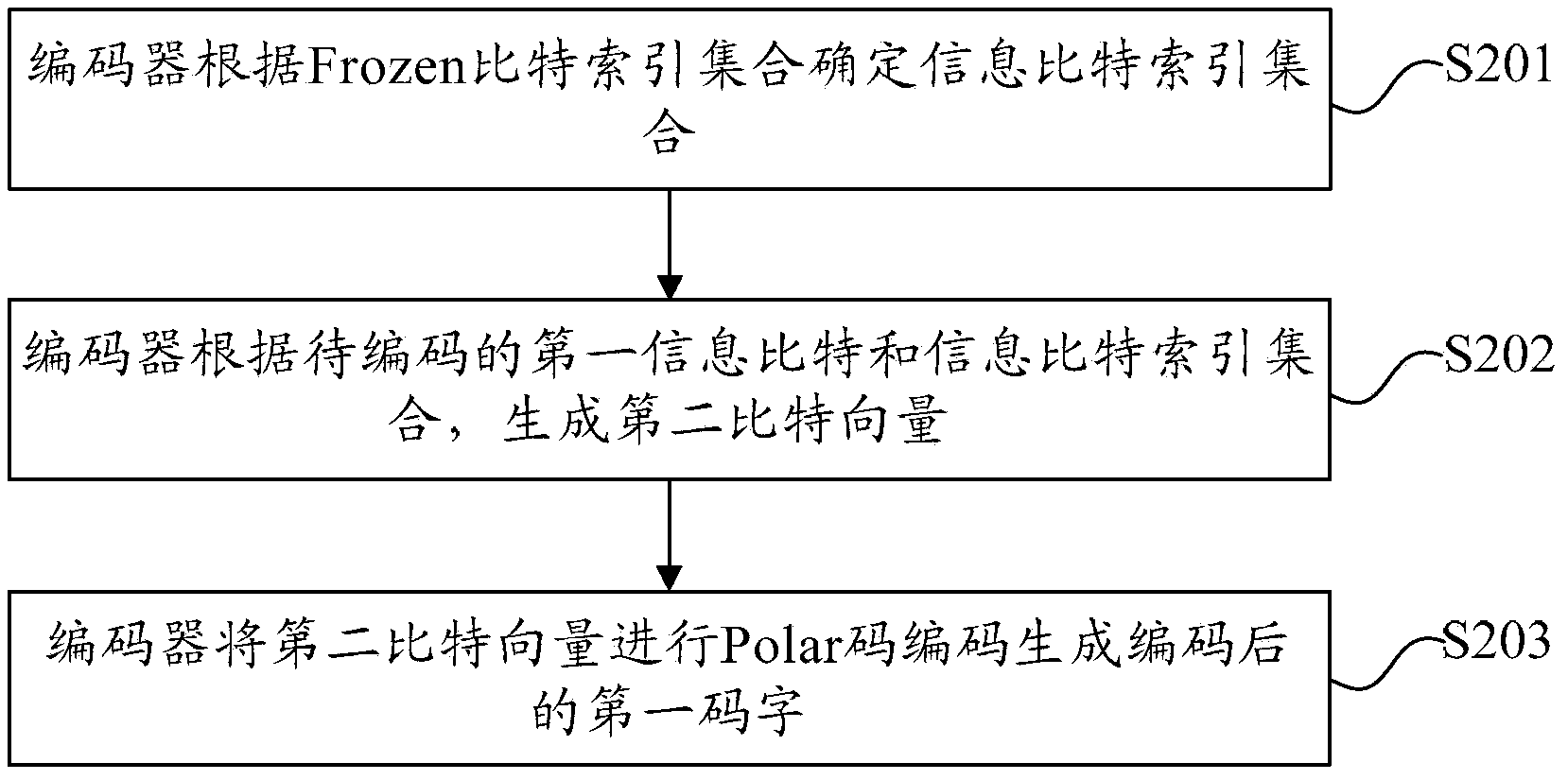
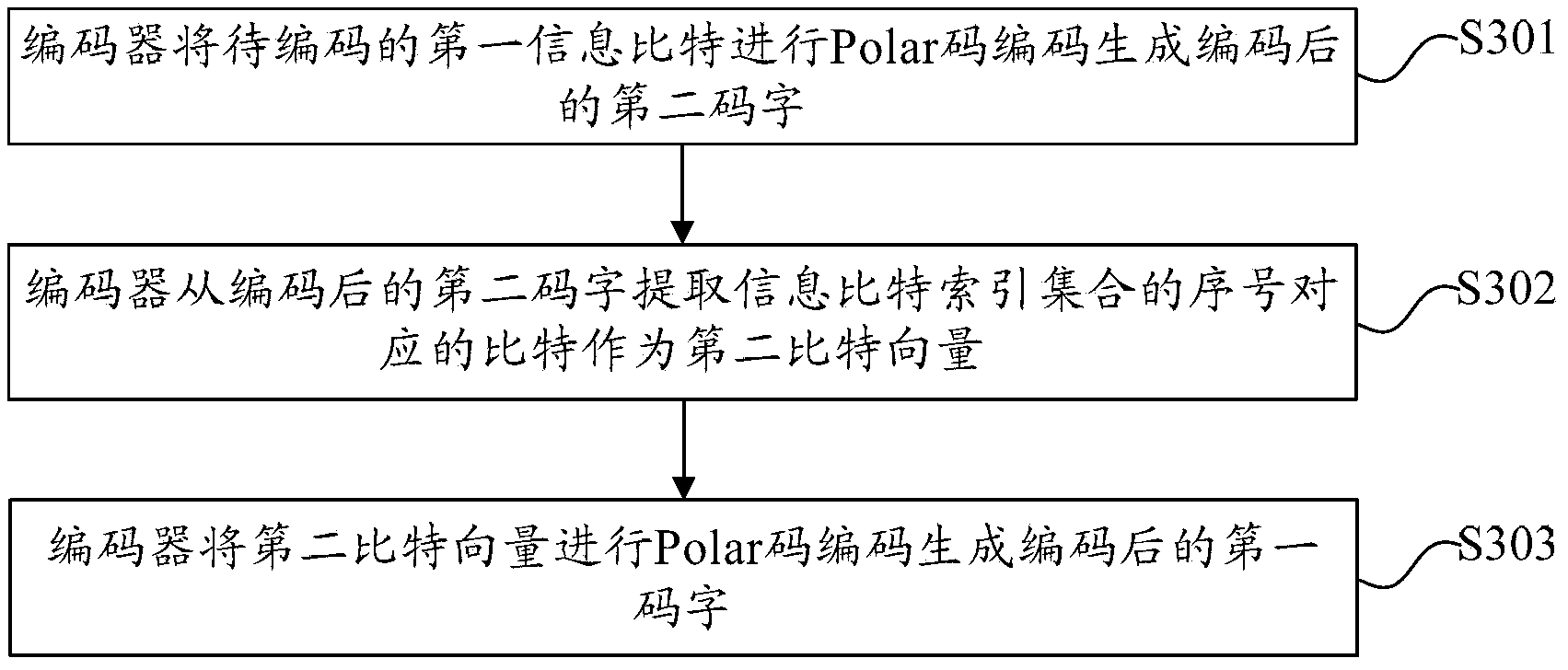
Channel coding and decoding method and device
ActiveCN104079370AReduce complexityImprove bit error rate performanceError preventionError correction/detection using linear codesChannel encodingBit rate
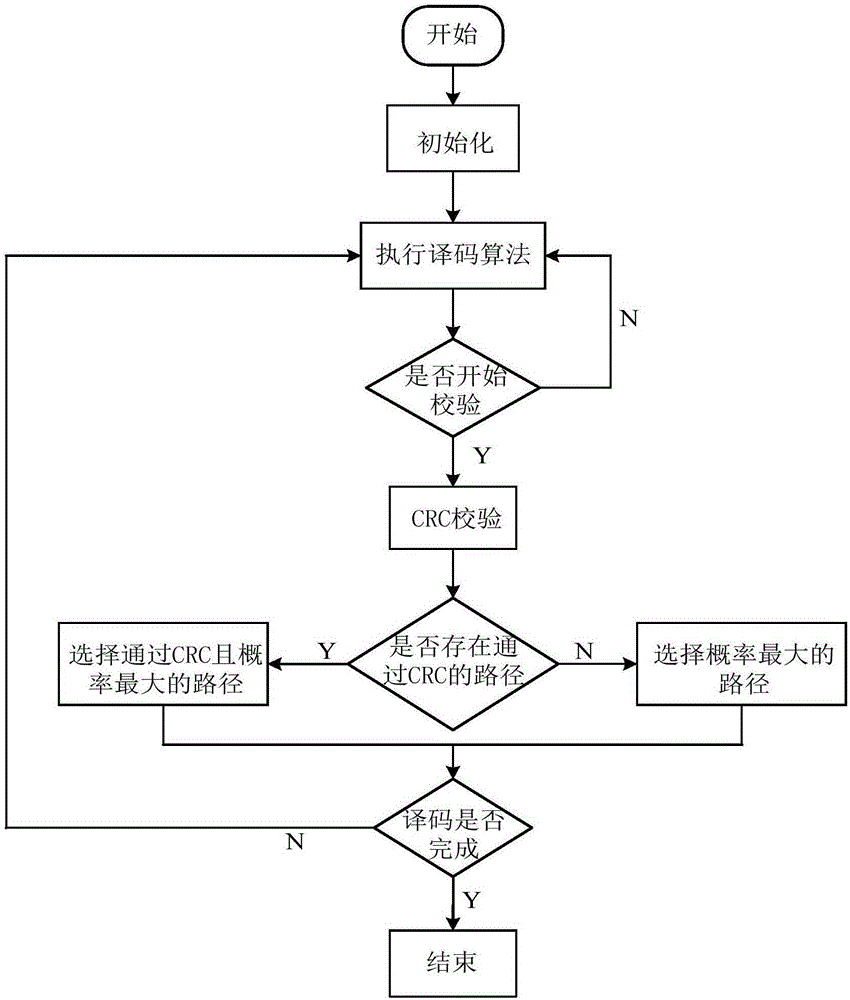
The embodiment of the invention provides a channel coding and decoding method and device, wherein the channel coding method comprises the steps that: a coder obtains an information bit index set; the coder generates a second bit vector according to a to-be-coded first information bit and the information bit index set; and the coder performs Polar code coding on the second bit vector to generate a coded first codeword. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, the coder firstly obtains the information bit index set, generates the second bit vector according to the to-be-coded first information bit and the information bit index set, and performs Polar code coding on the second bit vector to generate the coded first codeword, thus the channel coding method can realize that a Polar code is converted into a system code at a lower level of complexity, and can reduce the bit error rate so as to improve the performance of the Polar code.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for sending physics uplink control signal in TDD system
ActiveCN101227233ASolve highFulfil requirementsError preventionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTime domainSignal on
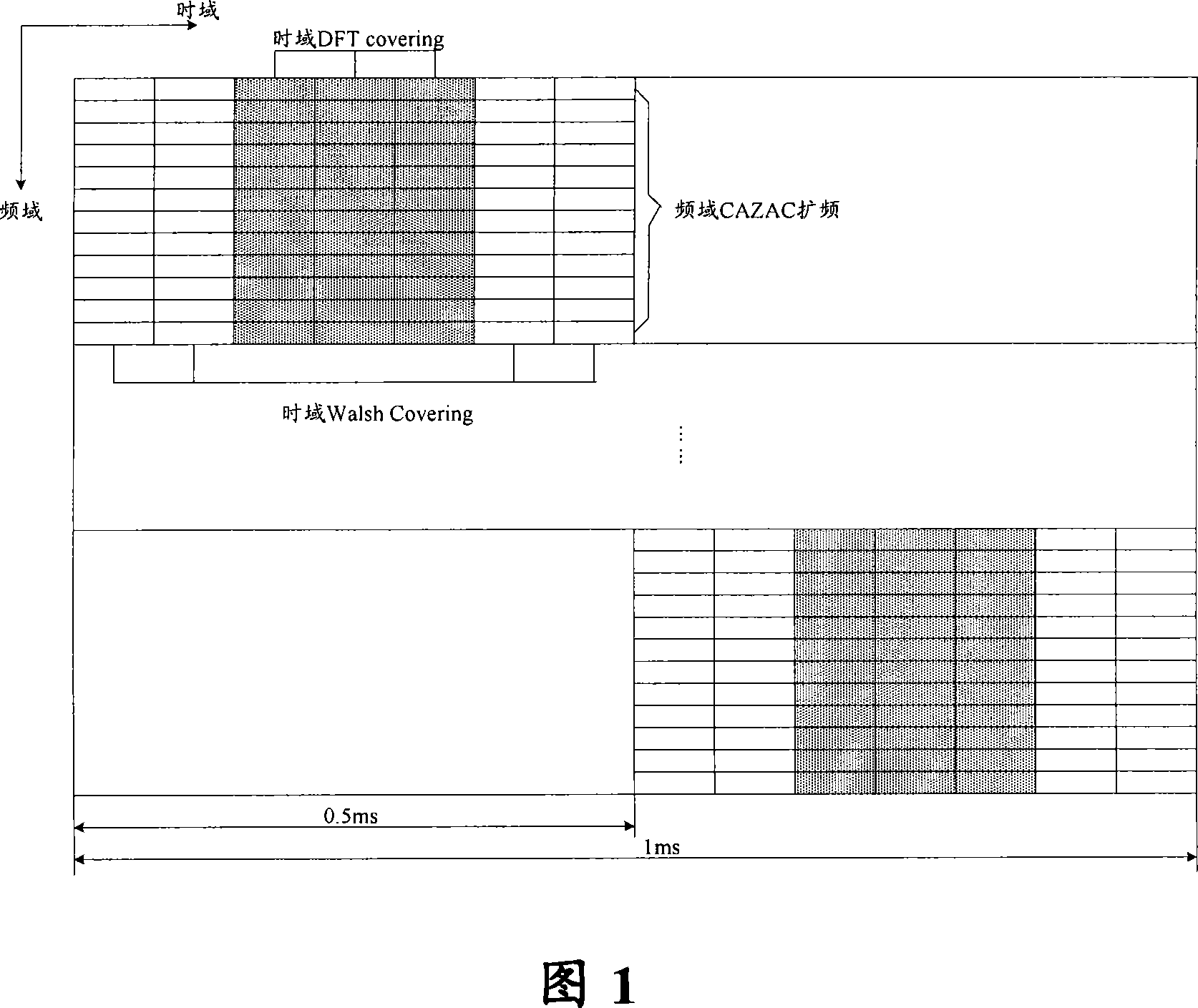
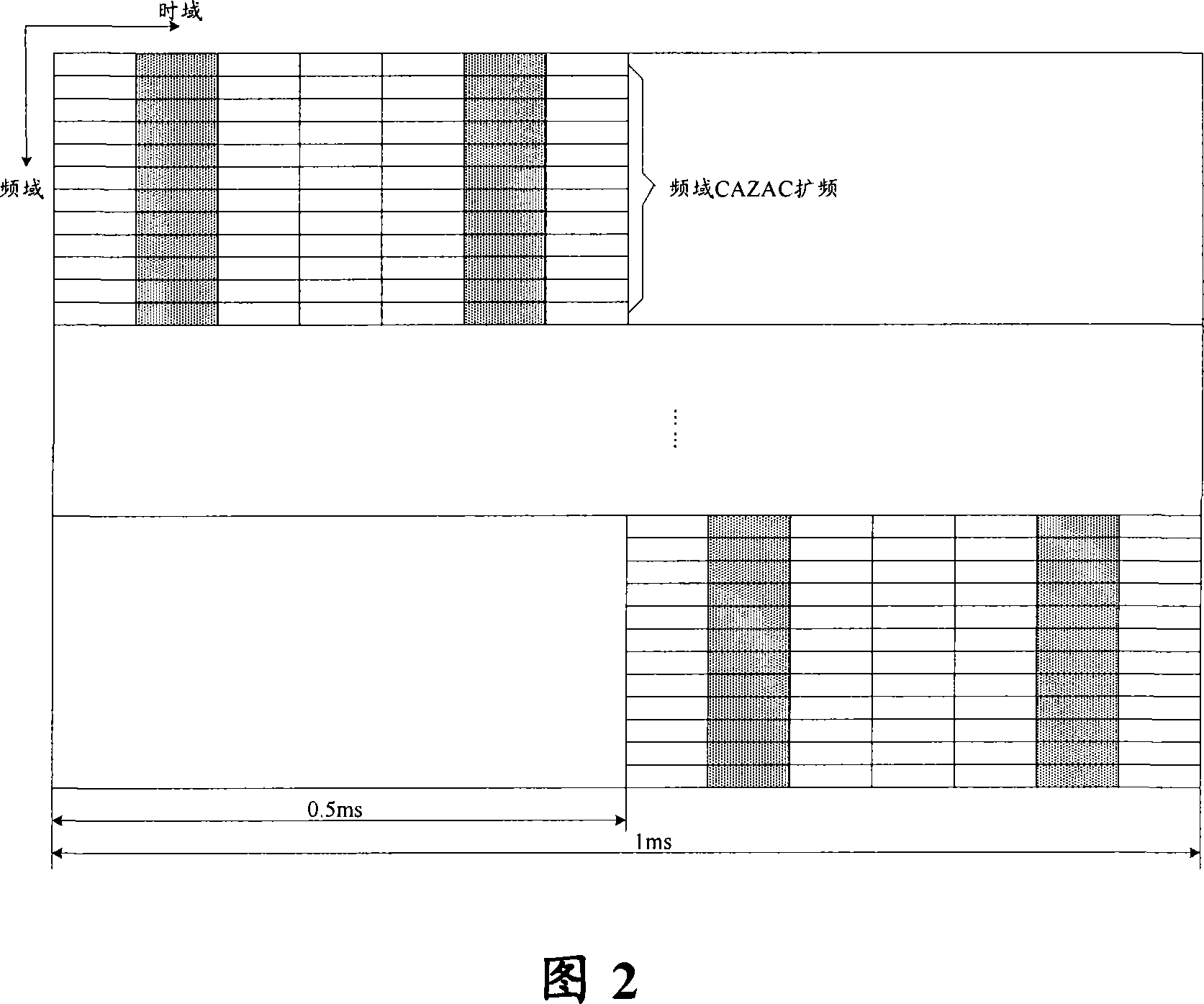
The invention provides a method and a device for sending physical uplink control signals in a time-division duplex system, the method comprises following steps: encoding the uplink control signals with a communication channel to obtain coded bits, modulating the coded bits with QPSK to obtain modulation symbols, transforming the modulation symbols with DFT to obtain symbols on a frequency domain,expanding the symbols on the frequency domain with time-domain through adopting a CAZAC root sequence to respectively obtain a first signal and a second signal which are sent on two time slots, mapping the first signal and the second signal on an information symbol which is corresponded with a PUCCH reference signal structure 2, and combining the information symbol and the reference signal into asignal which will be sent by a sub-frame. The invention can well satisfy the performance requirement and the covering requirement that a plurality of ACK / NACK can be sent on an uplink sub frame.
Owner:ZTE CORP
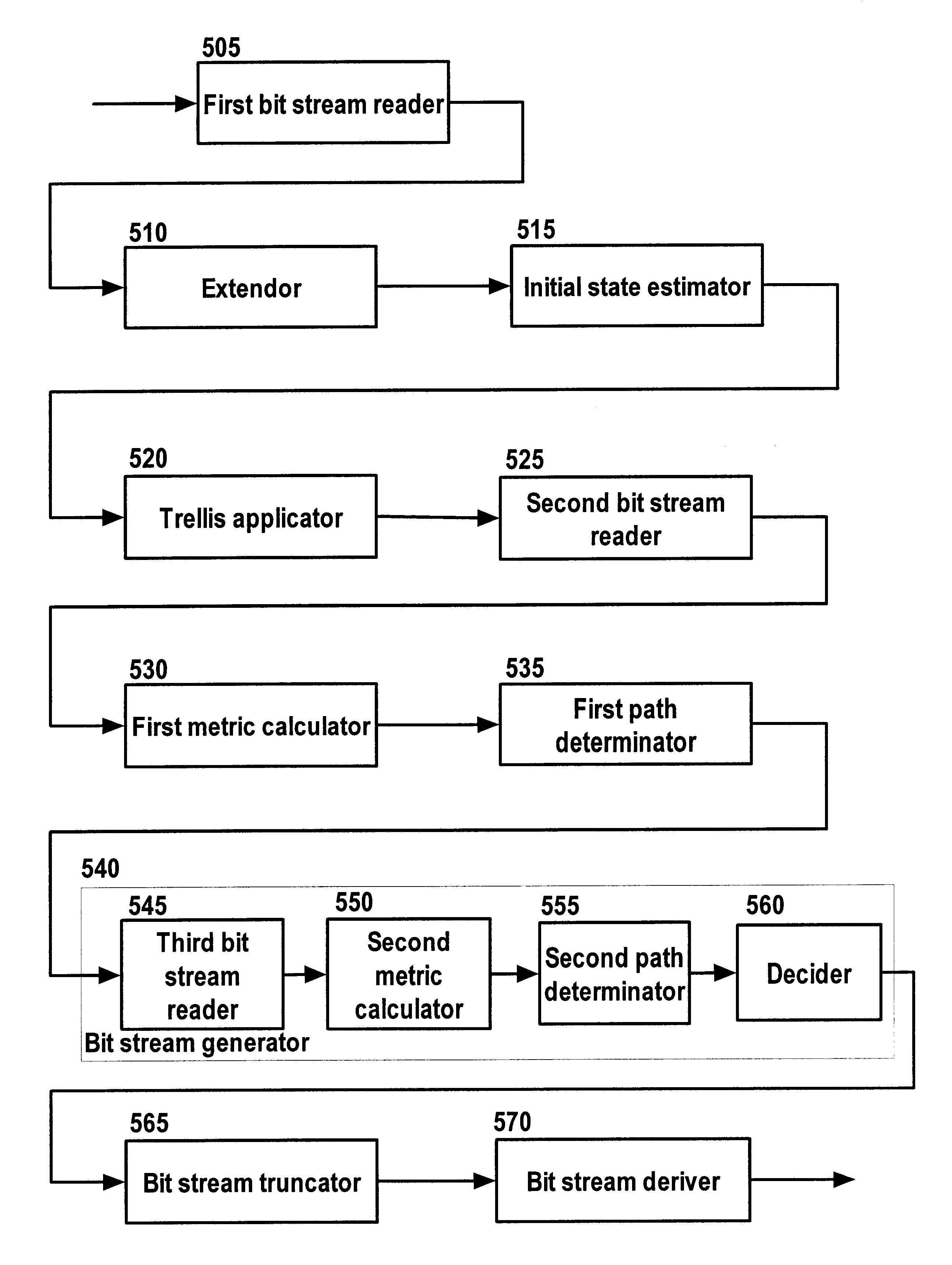
Method and apparatus for channel decoding of tail-biting convolutional codes
InactiveUS6877132B1Error correction/detection using convolutional codesOther decoding techniquesMajority logic decodingMajority logic
A method for hard-decision channel decoding of tail-biting convolutional codes includes the step of receiving from a channel an input bit stream encoded by a tail-biting convolutional channel encoder. The encoder includes a number of memory elements and a rate. The input bit stream includes a series of symbols; each symbol includes a number of bits; the number of bits is related to the rate of the encoder. The method further includes the step of assuming a probability for each possible initial state of the encoder. The method further includes the step of decoding each symbol of the input bit stream using majority logic, with reference to a trellis structure corresponding to the encoder. The trellis structure represents: a number of states related to the number of memory elements of the encoder; a plurality of transitional branches; and a number of stages related to the number of symbols in the input bit stream.
Owner:APPLE INC
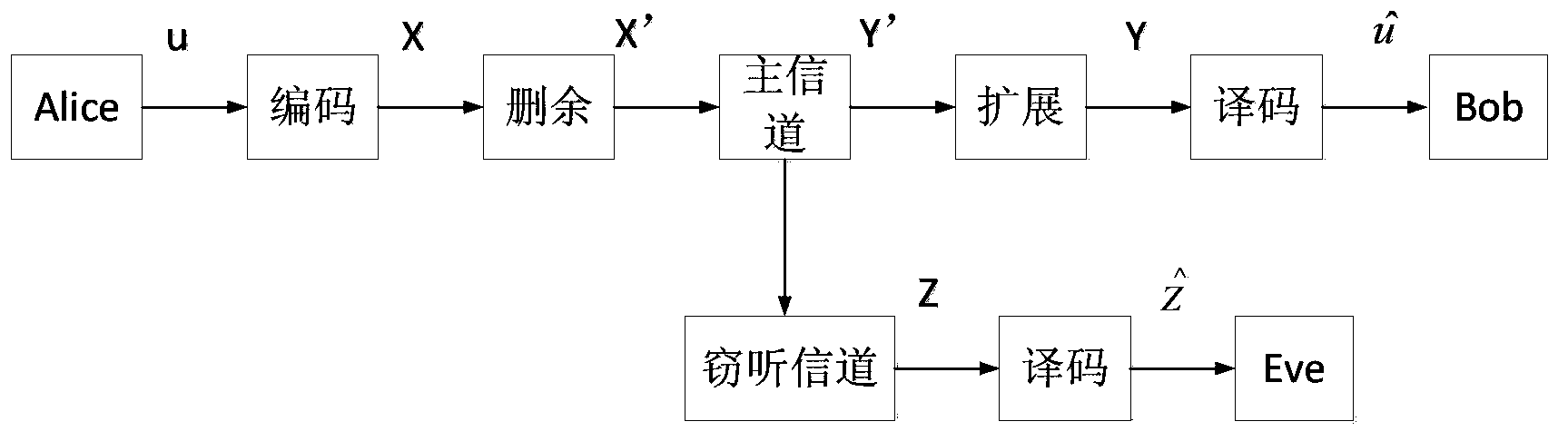
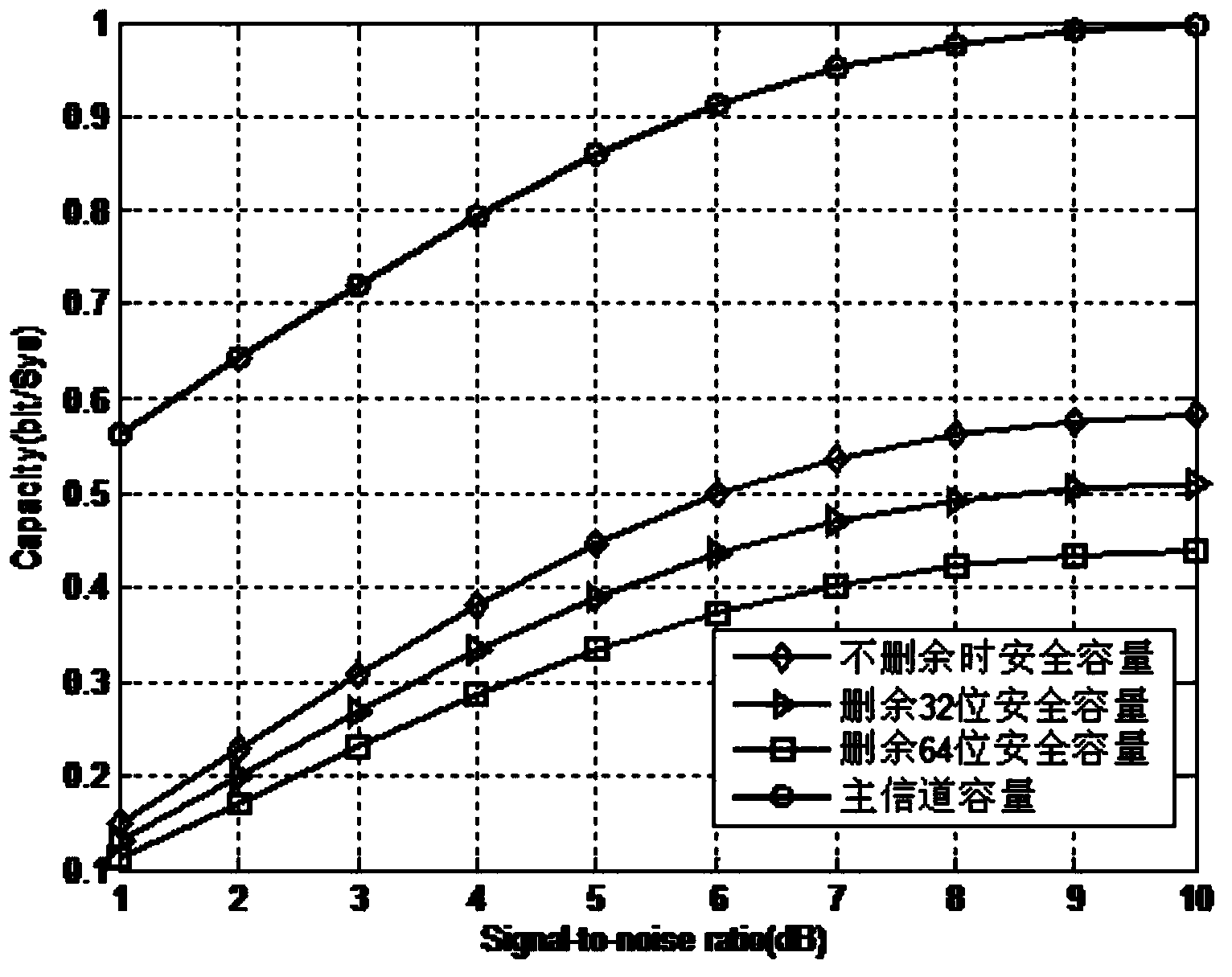
Degraded eavesdropping channel rate compatible method based on Polar code
InactiveCN103414540AIncrease safety capacityEnsure safetyError preventionEavesdroppingComputer science
The invention discloses a degraded eavesdropping channel rate compatible method based on a punctured Polar code. According to the method, the punctured Polar code is combined with a degraded eavesdropping channel model; according to construction features of the Polar code, a safe bit-channel used for transmitting information is given; according to channel rate requirements of a degraded eavesdropping channel, a proper puncturing matrix is built, and the degraded eavesdropping channel rate compatible method based on the Polar code is achieved; because eavesdroppers do not know the puncturing matrix, the coded code word length is reduced through puncturing operation, information is hidden through the puncturing operation, the complexity that the eavesdroppers recover original information through code words received through wiretapping is increased, and system safety is guaranteed; furthermore, the puncturing method ensures that all codes in the same group of rate-compatible codes can be achieved through the same group of encoders, and therefore the complexity of emitters and receivers is greatly reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
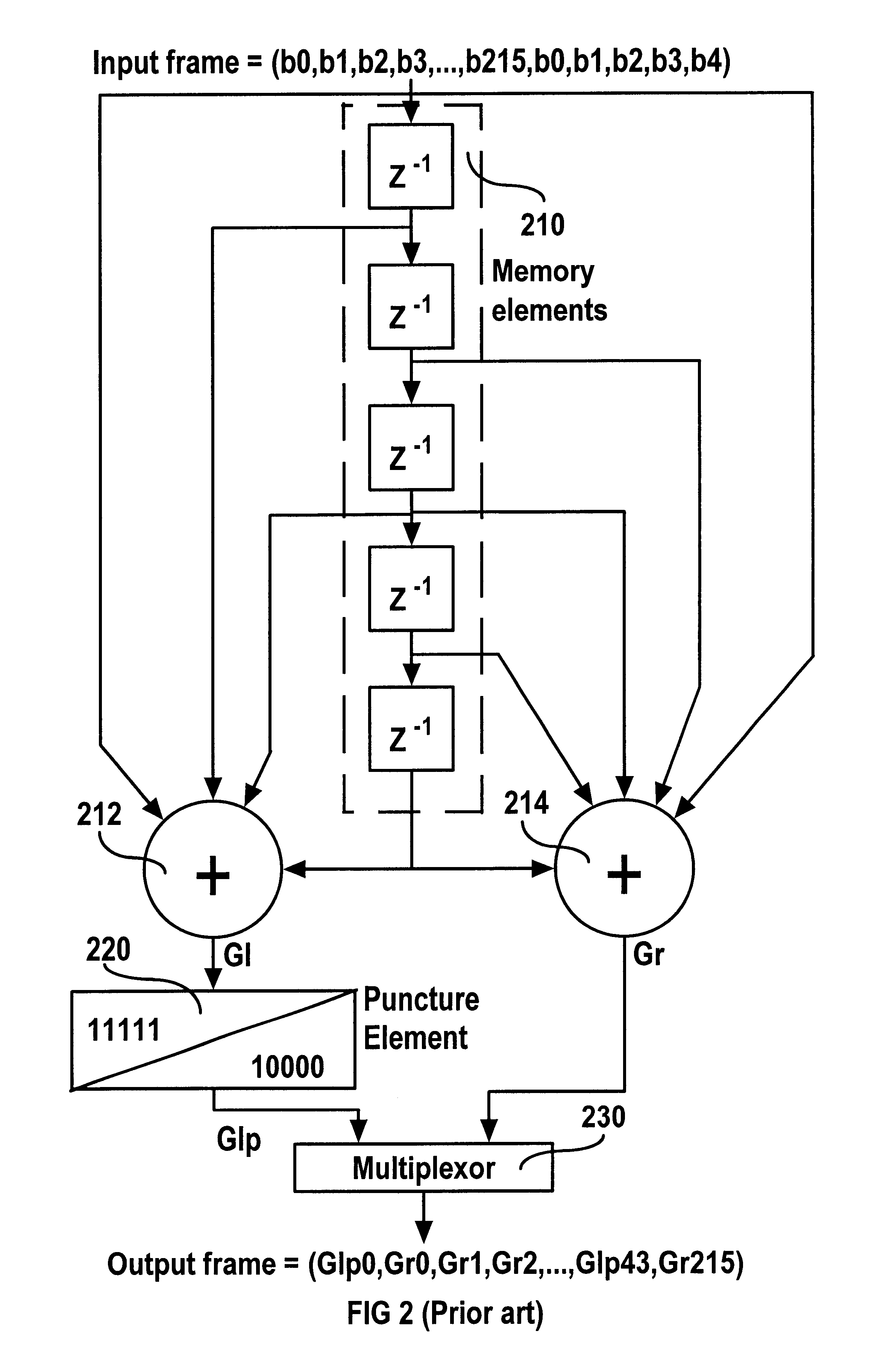
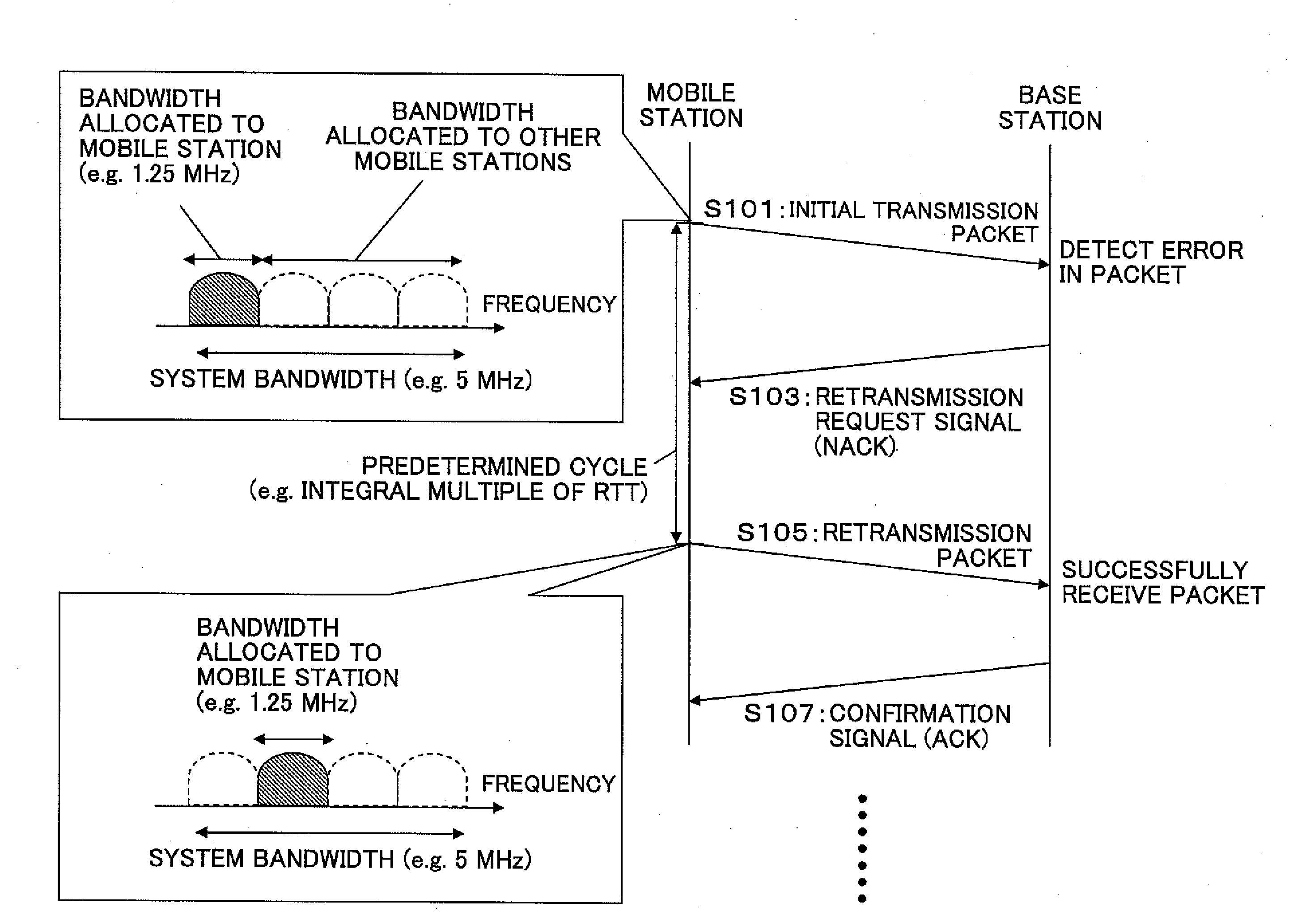
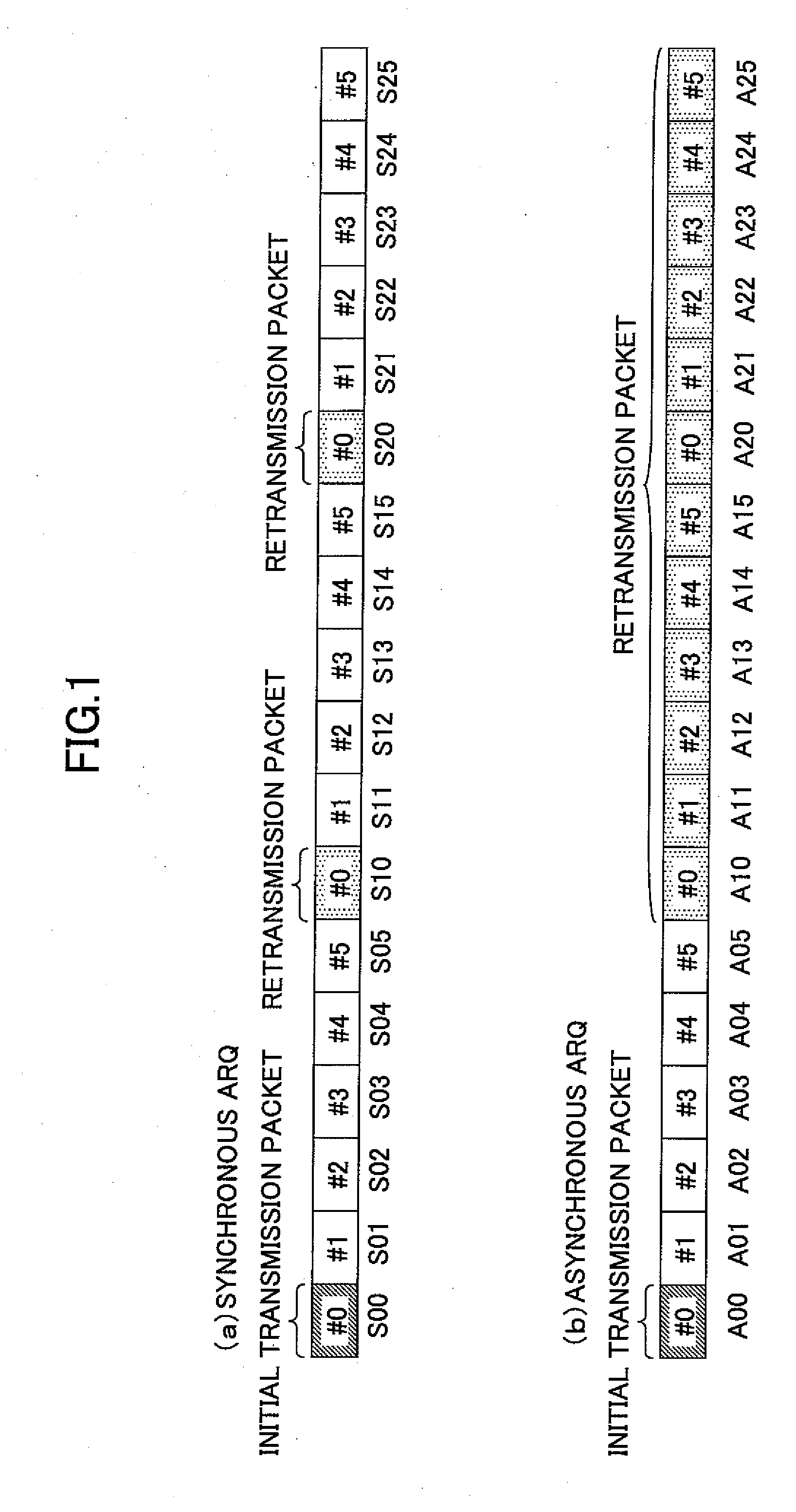
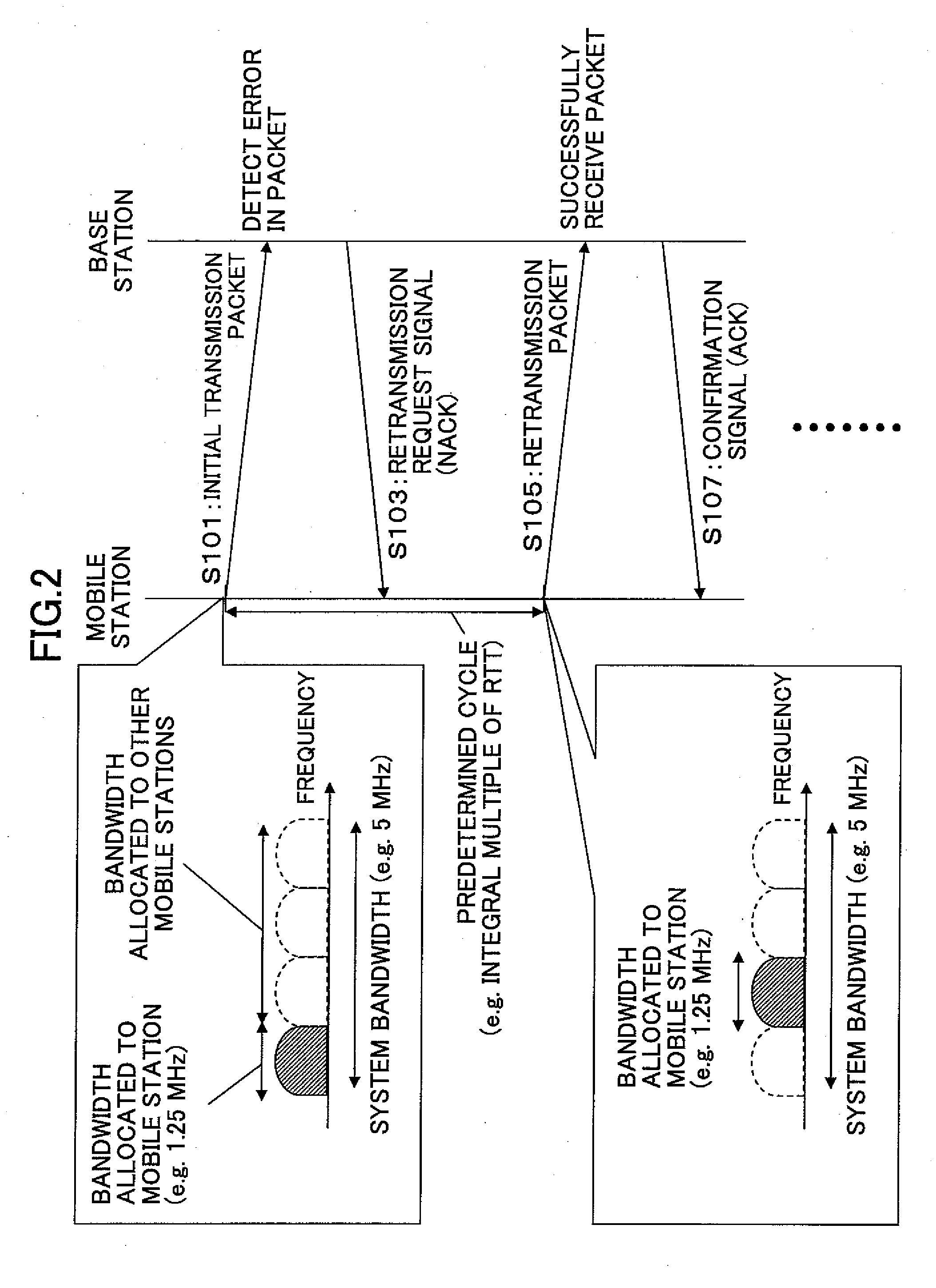
Mobile station and a base station
ActiveUS20090175369A1Improve reception qualityError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission path divisionControl signalMobile station
A mobile station includes a control unit configured to change at least one parameter for a retransmission packet from that of a transmission packet, where the at least one parameter is selected from a data modulation scheme; a channel coding rate; a puncturing pattern; a spreading factor; a frequency bandwidth; a frequency allocation position; and transmission power. A base station includes a retransmission format determining unit configured to determine a pattern used for changing at least one parameter for a retransmission packet from that of a transmission packet to determine a format for the retransmission packet, where the at least one parameter is selected from a data modulation scheme; a channel coding rate; a puncturing pattern; a spreading factor; a frequency bandwidth; a frequency allocation position; and transmission power; and a control signal generating unit configured to generate a control signal based on the format for the retransmission packet determined by the retransmission format determining unit.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
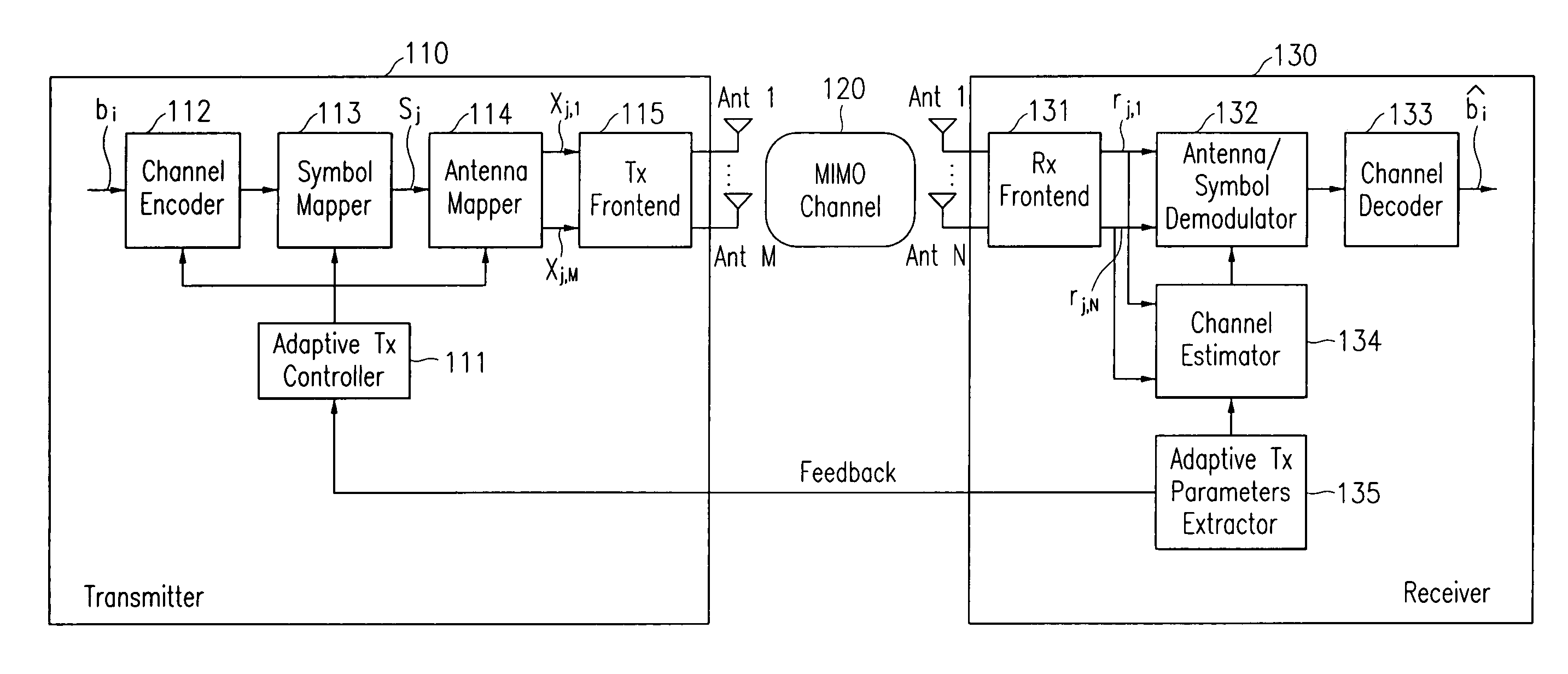
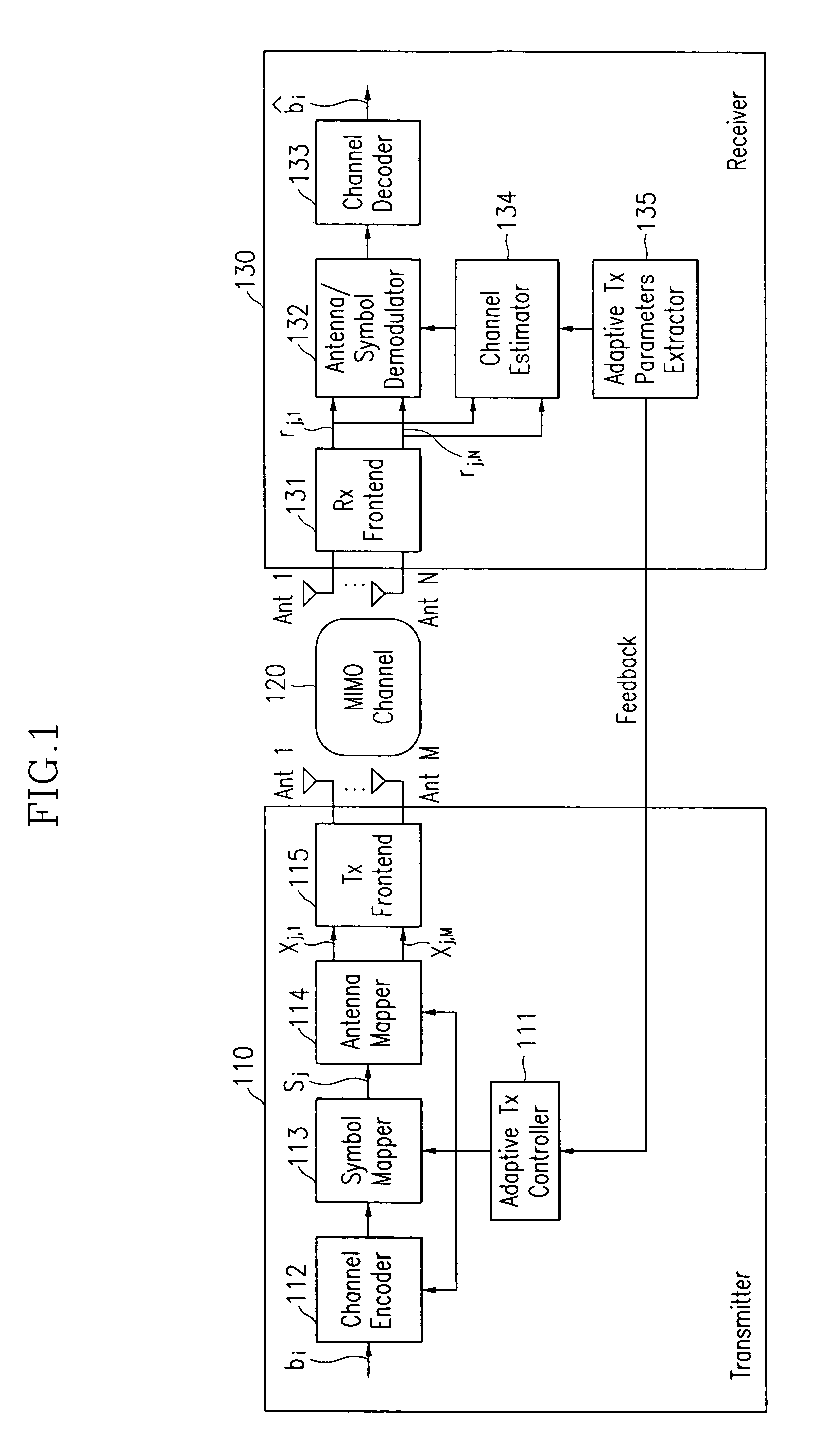
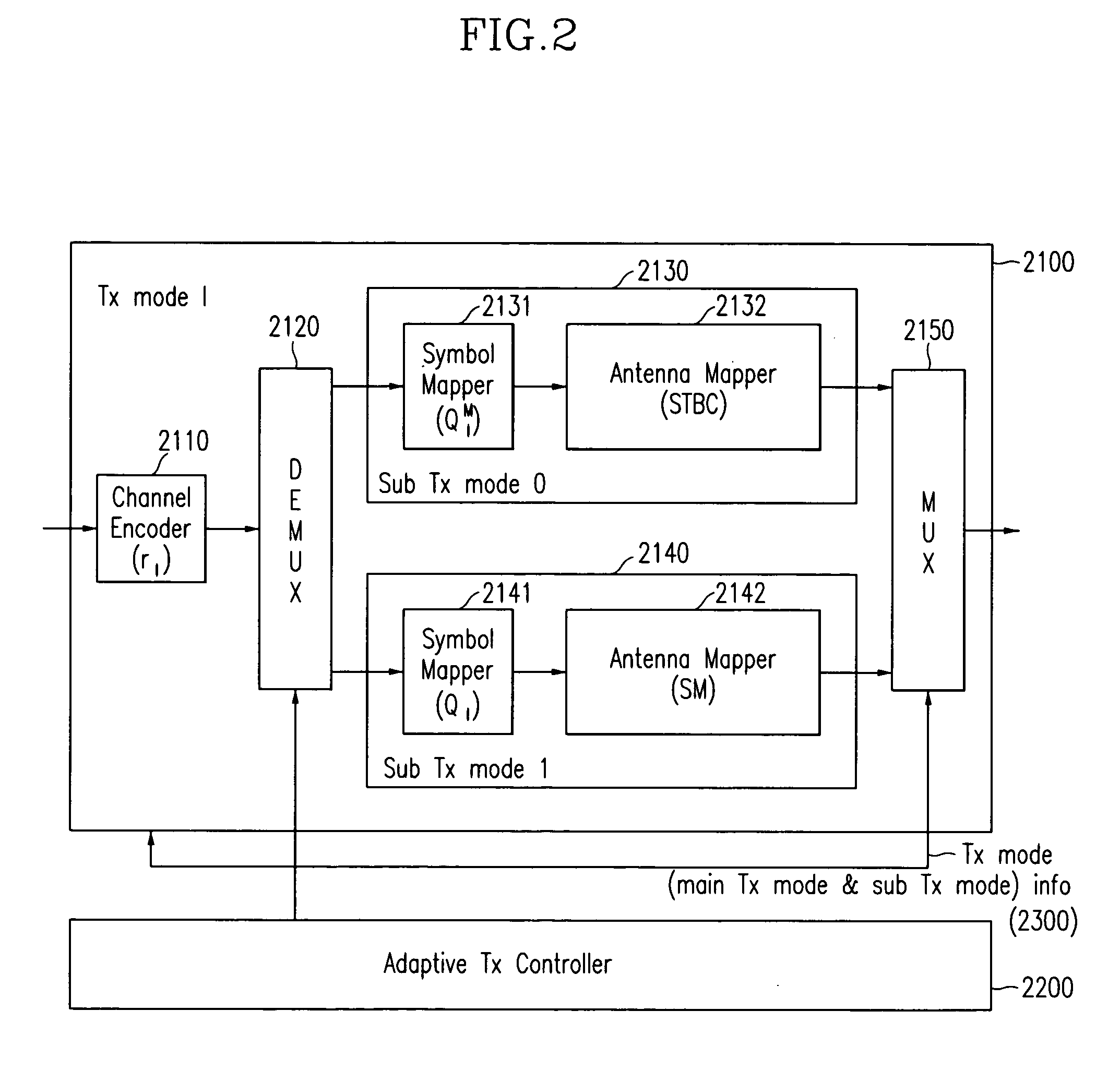
Adaptive transmission and receiving method and device in wireless communication system with multiple antennas
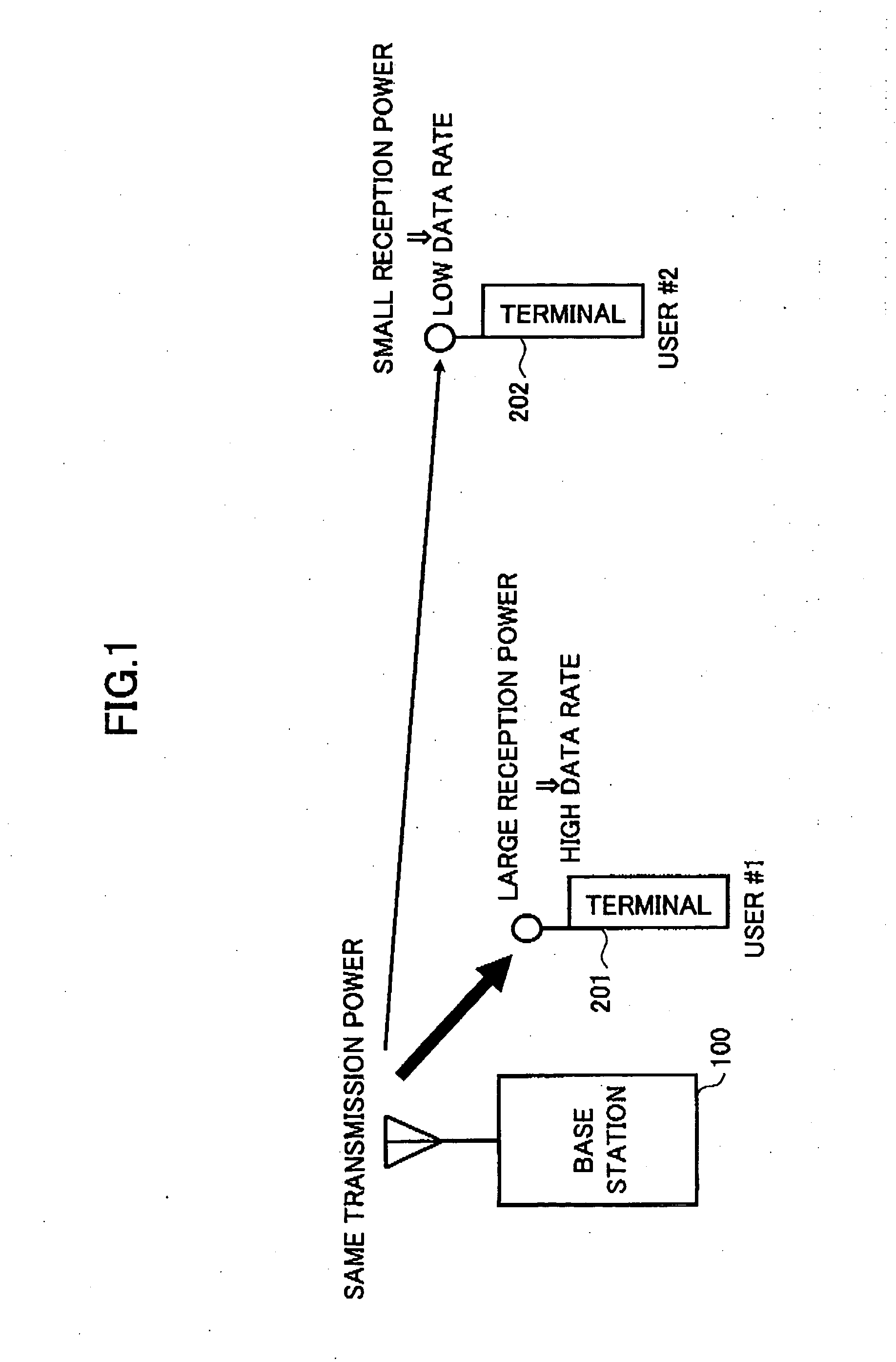
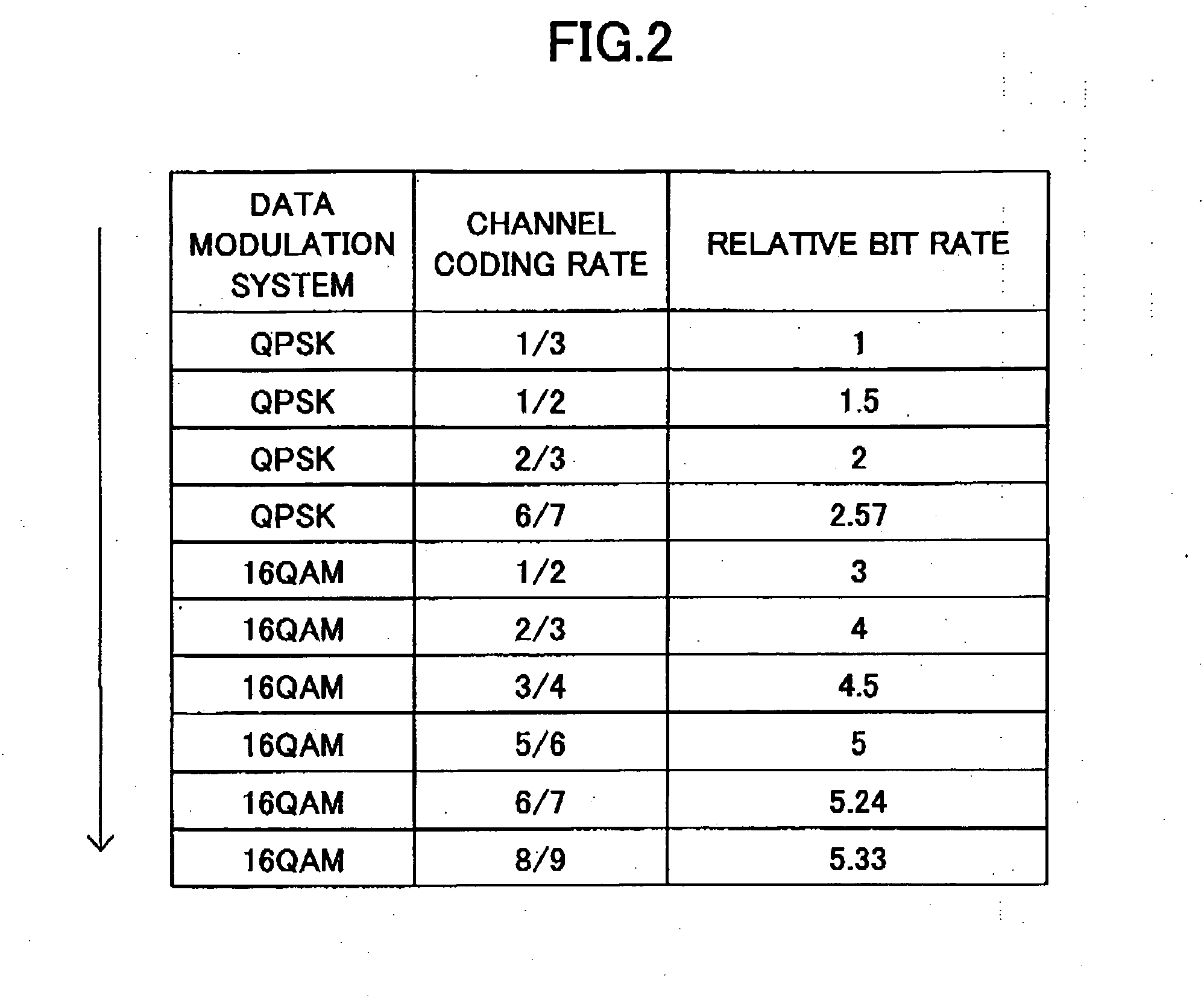
ActiveUS7123887B2Different data rateReduce transmit powerEnergy efficient ICTSpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemData rate
Disclosed is an adaptive transmit and receive method and device in a multiple-antenna wireless communication system. A transmit mode comprises different main transmit modes each of which includes one or both of a sub-transmit mode based on STBC and a sub-transmit mode based on SM. A receiver calculates an STBC performance parameter and a SM performance parameter, and a transmitter uses the parameters to determine a main transmit mode with maximum data rates and select a sub-transmit mode for minimizing power consumption. The transmitter channel-encodes, modulates and antenna-maps input data according to the selected transmit mode, and outputs results to the receiver. The receiver antenna / symbol-demodulates and channel-decodes the received data.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
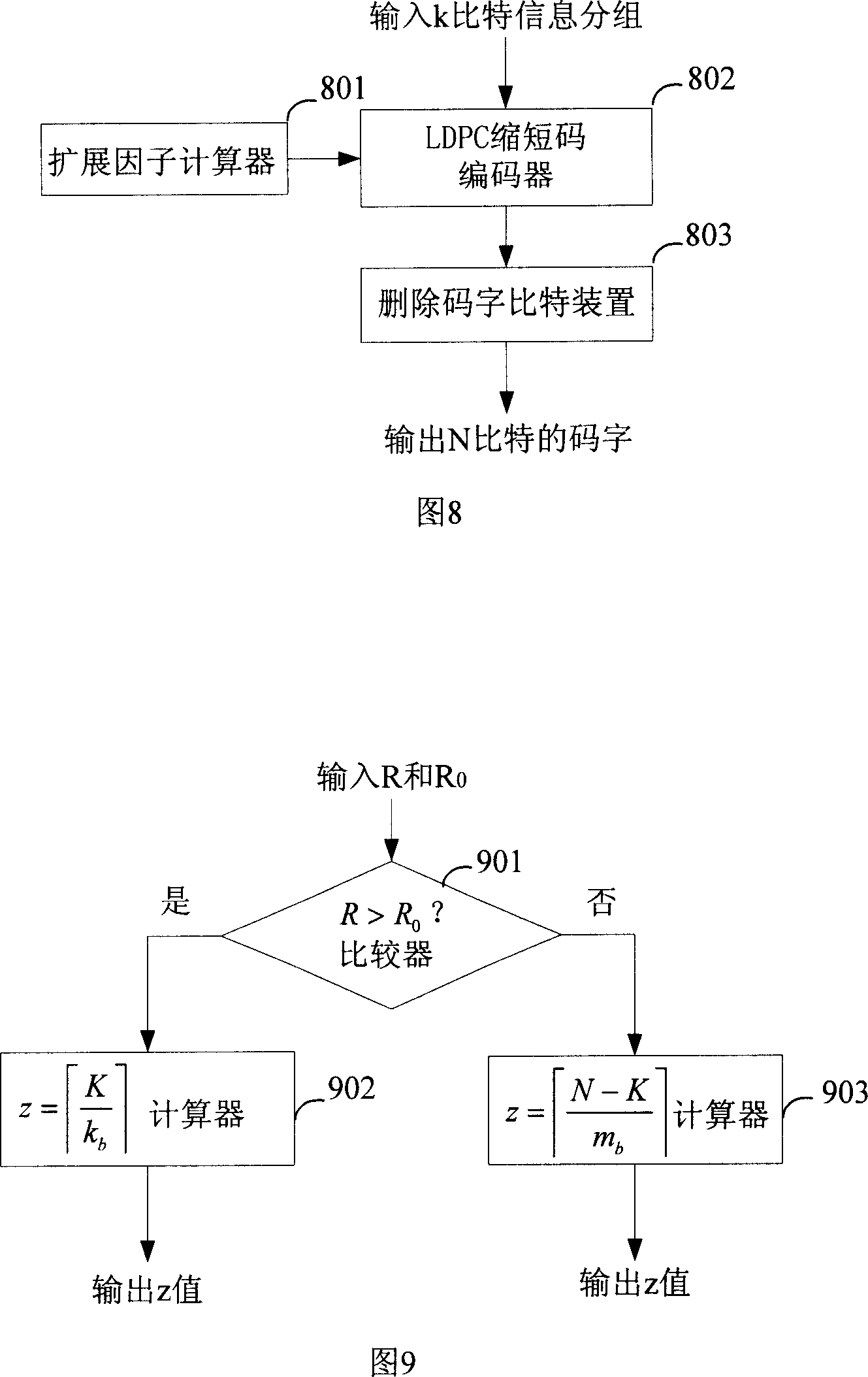
A coding device and method for low density parity check code of supporting any code rate/code length
ActiveCN1953335AIncrease flexibilityLow costError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionComputer hardwareLow-density parity-check code
The invention relates to a low-density parity check code method which supports any code rate / length, and a relative device. Wherein, said device comprises an expand factor z calculator, to calculate out expand factor and output z value to shorten coder; a shorten coder for obtaining the shortened data and outputting it to delete code bit device; a delete code bit device for inputting shorten code, selecting and deleting the bit at certain position with confirmed property of delete code, and outputting the code after deletion. The invention can produce a coder with different code ratios and different code lengths of LDPC code, while they have unique base matrix. The invention can save hardware cost, improve code flexibility and improve its application.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Transmitting apparatus of OFDM system and method thereof
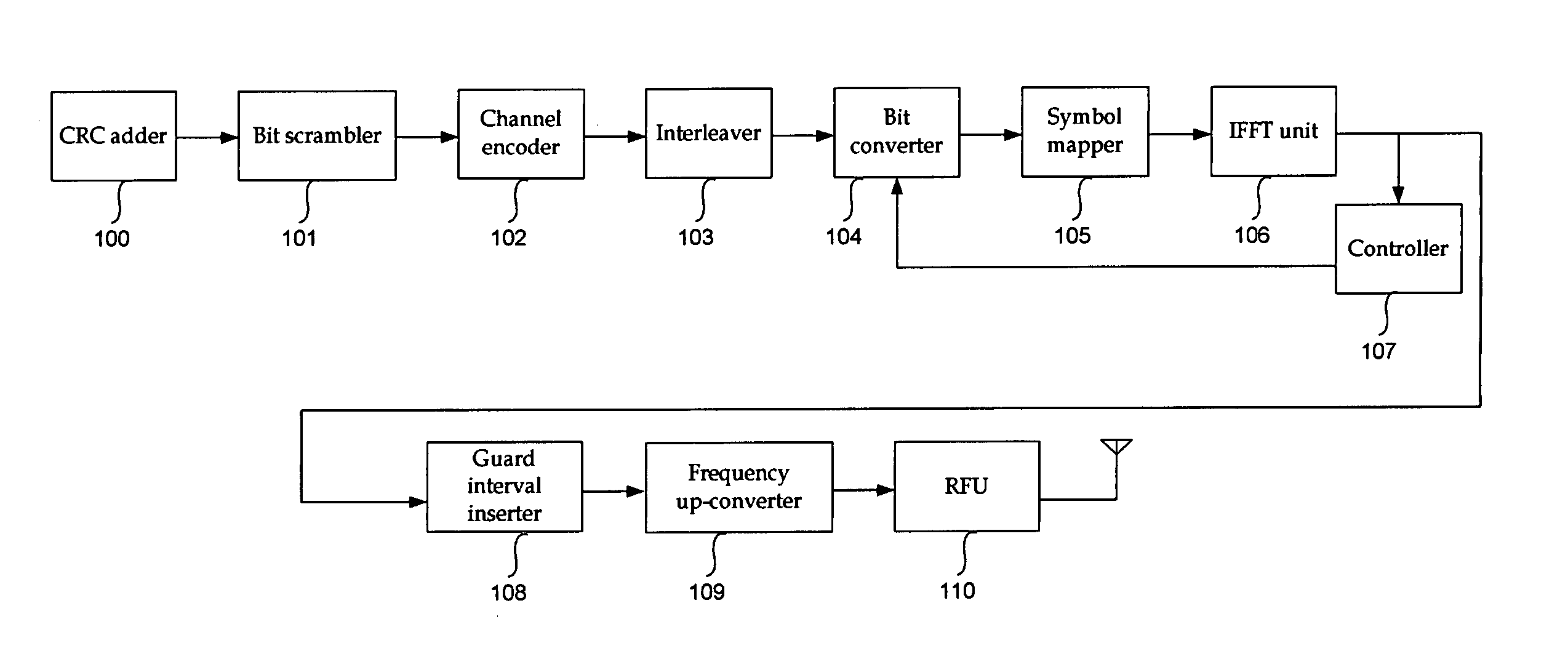
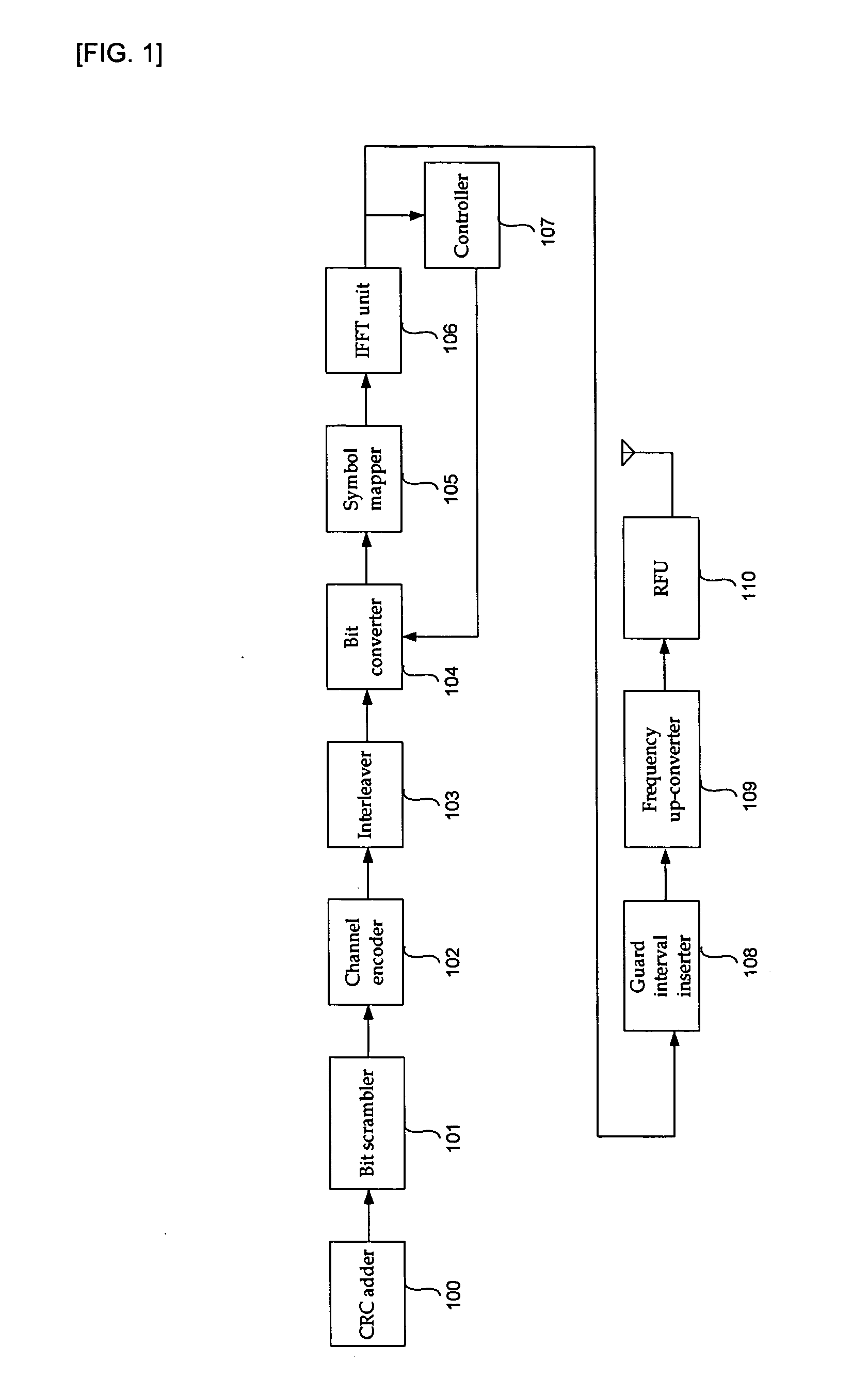
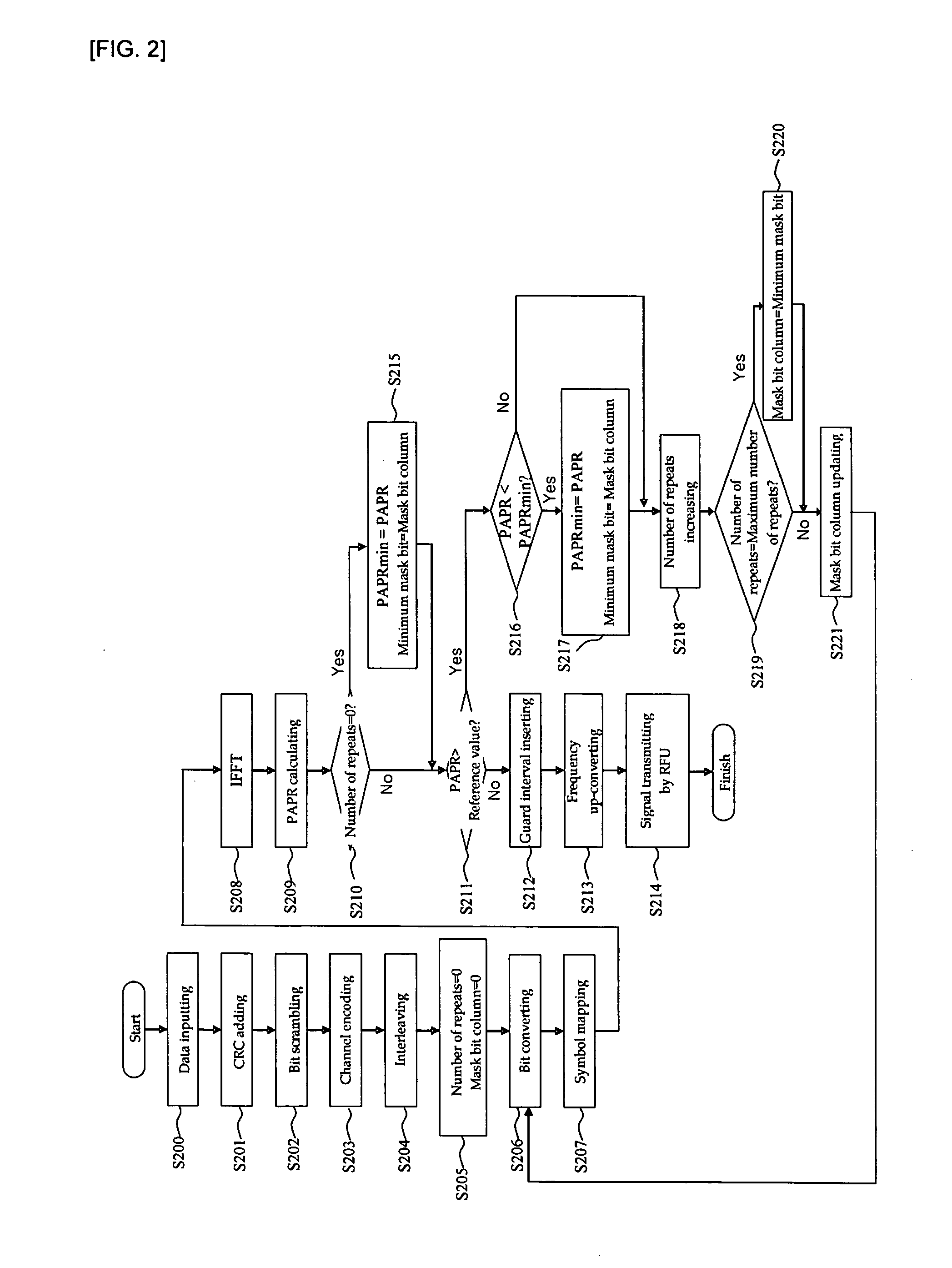
InactiveUS20060120269A1Reduce ratio of average powerQuality improvementSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsRadio channelData transmission
The present invention relates to a transmitter in an OFDM system for improving the PAPR, and a method thereof. According to the exemplary embodiment of the present invention, channel encoding is performed in order to correct a data transmission error of a radio channel, a predetermined bit of the channel encoded data is bit-inverted by using a mask bit or a mask bit sequence, and a PAPR of the signal is reduced. Accordingly, reduction of transmission efficiency which has been generated in block coding and DSI methods is not generated when the signal is transmitted because an additional bit is not required.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Transmitting apparatus and modulation method thereof
ActiveUS20150222471A1Reduce gapImprove performanceSecret communicationError correction/detection using interleaving techniquesComputer scienceChannel encoding
A transmitting apparatus is disclosed. The transmitting apparatus includes an encoder to perform channel encoding with respect to bits and generate a codeword, an interleaver to interleave the codeword, and a modulator to map the interleaved codeword onto a non-uniform constellation according to a modulation scheme, and the constellation may include constellation points defined based on various tables according to the modulation scheme.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
3D wavelet based video codec with human perceptual model
InactiveUS7006568B1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionData compressionSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
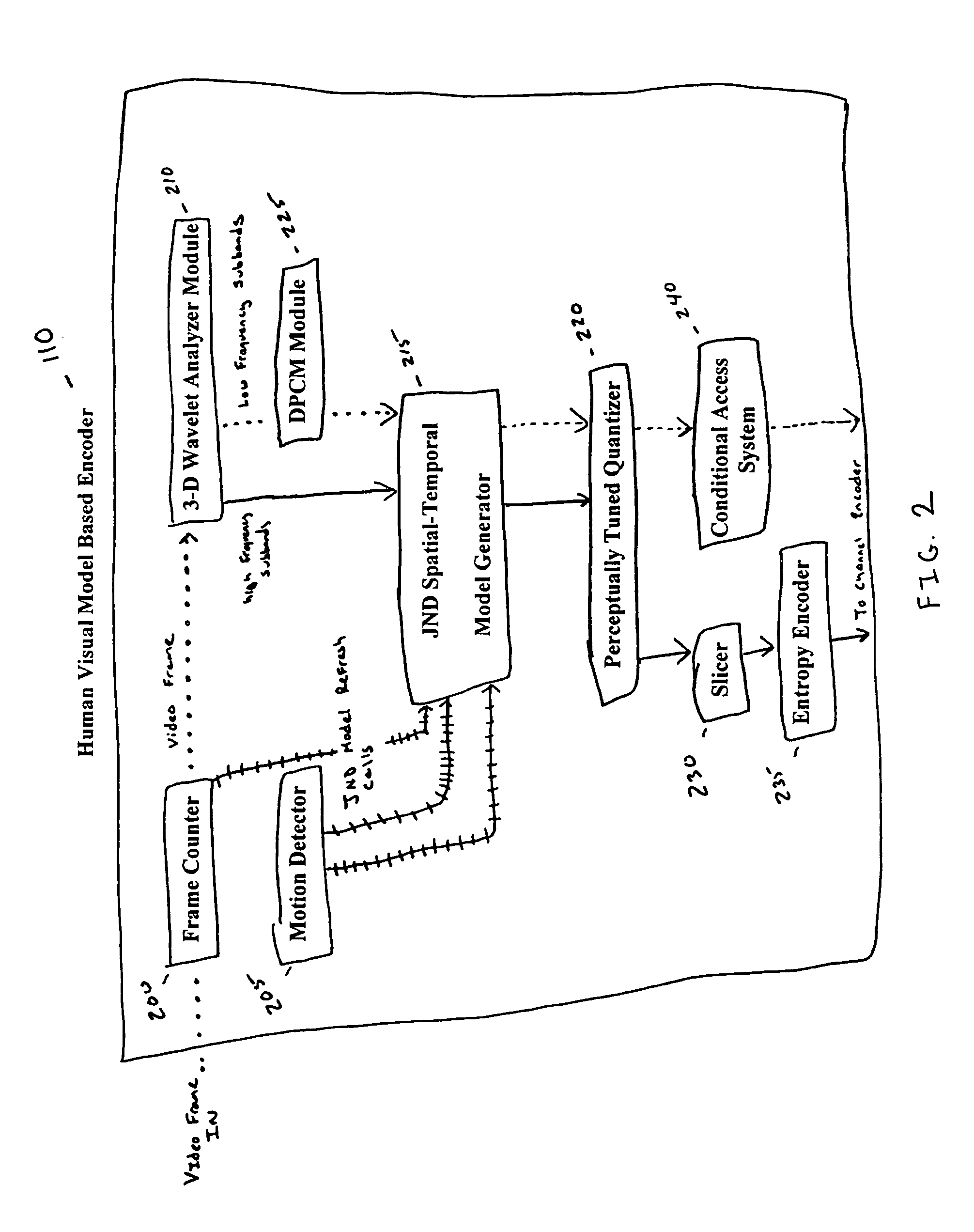
A video encoding / decoding system based on 3D wavelet decomposition and the human perceptual model is implemented. JND is applied in quantizer design to improve the subjective quality of compressed video. The 3D wavelet decomposition helps to remove spatial and temporal redundancy and provides scalability of video quality. In order to conceal the errors that may, occur under bad wireless channel conditions, a slicing method and a joint source channel coding scenario, that combines RCPC with CRC and utilizes the distortion information to allocate convolutional coding rates are proposed. A new subjective quality index based on JND is presented and used to evaluate the overall system performance at different signal to noise rations (SNR) and at different compression ratios. Due to the wide use of arithmetic coding (AC) in data compression, it is considered as a readily available unit in the video codec system for broadcasting. A new scheme for conditional access (CA) sub-system is designed based on the compression graphic property of arithmetic coding. Its performance is analyzed along with its application in a multi-resolution video compression system. This scheme simplifies the conditional access sub-system and provides satisfactory system reliability.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF THE COLLEGE PARK
MIMO multiple transmission device and method
InactiveUS20060209813A1Little dataLittle workMultiplex system selection arrangementsModulated-carrier systemsData streamComputer science
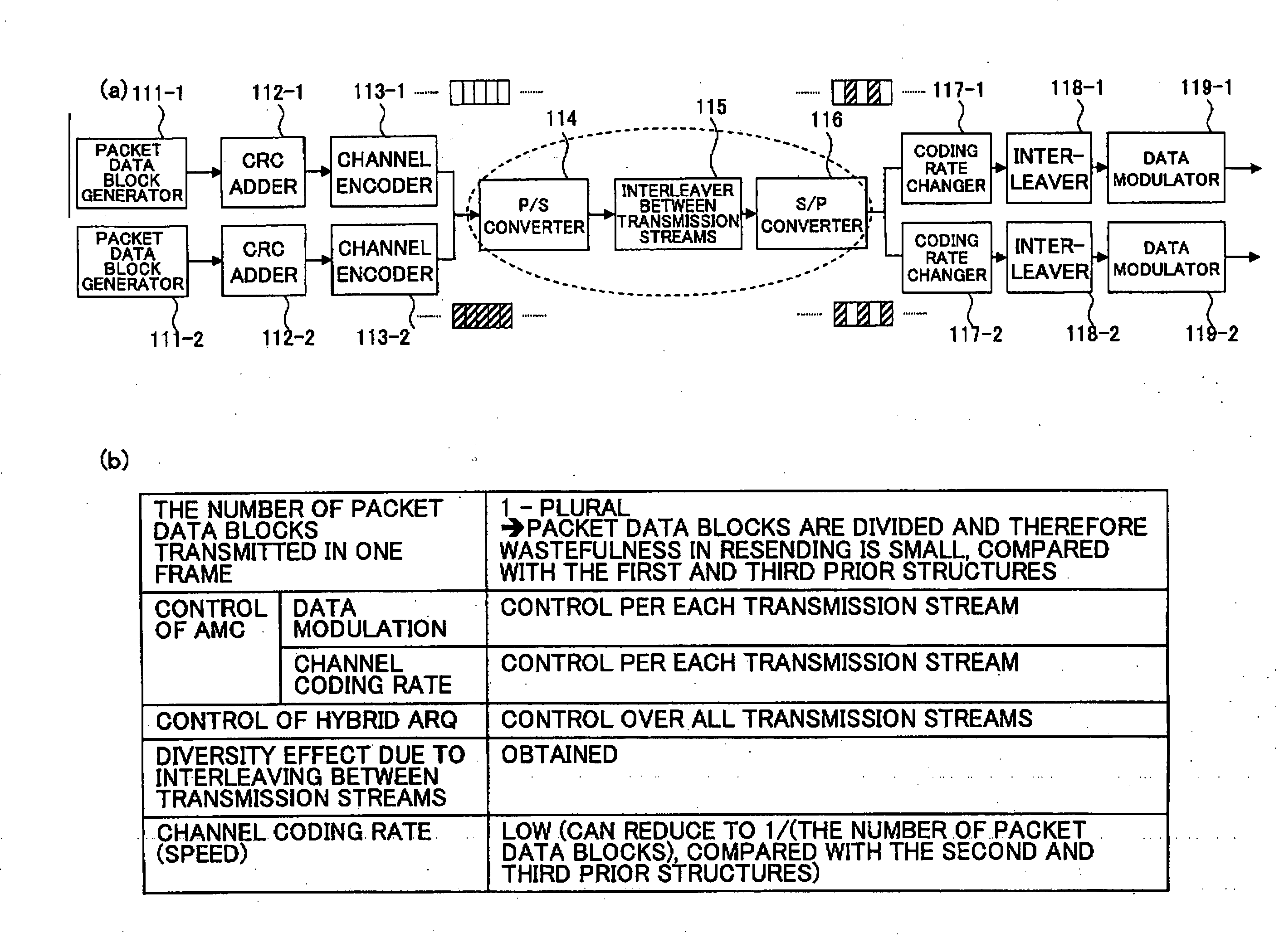
A MIMO multiple transmission device, comprising a packet data block generator (111) for generating a packet data block as a resent unit for hybrid ARQ; a CRC adder (112) for adding an error detection code; a channel encoder (113) for performing channel encoding, the packet data block generator, the CRC adder and the channel encoder being coupled in series in one or more data streams; a parallel-to-serial converter (114) for converting output of the channel encoder to serial form; an interleaver between transmission streams (115) for performing interleaving between transmission streams on outputs from the parallel-to-serial converter; a serial-to-parallel converter (116) for converting outputs from the interleaver between transmission streams to parallel form; a coding rate changer (117) for changing a coding rate; and a data modulator (119) for modulating data, the coding rate changer and the data modulator being connected in series in plural data streams divided by the serial-to-parallel converter.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com