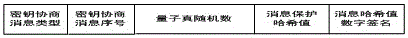Patents
Literature
841 results about "Eavesdropping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
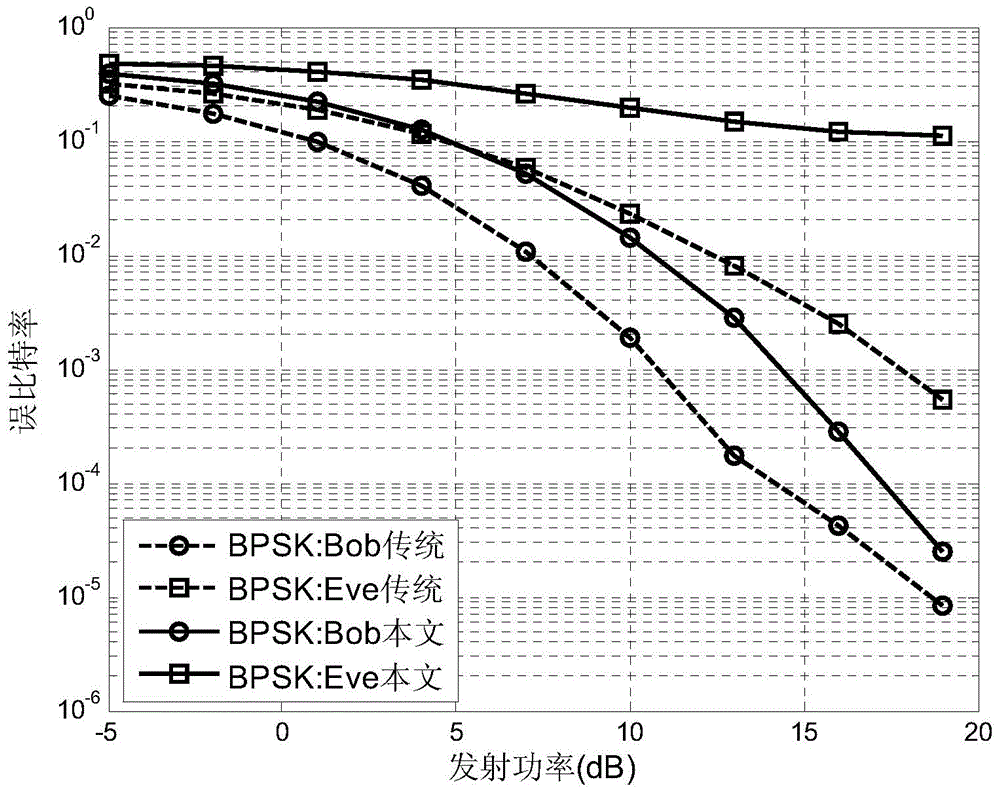
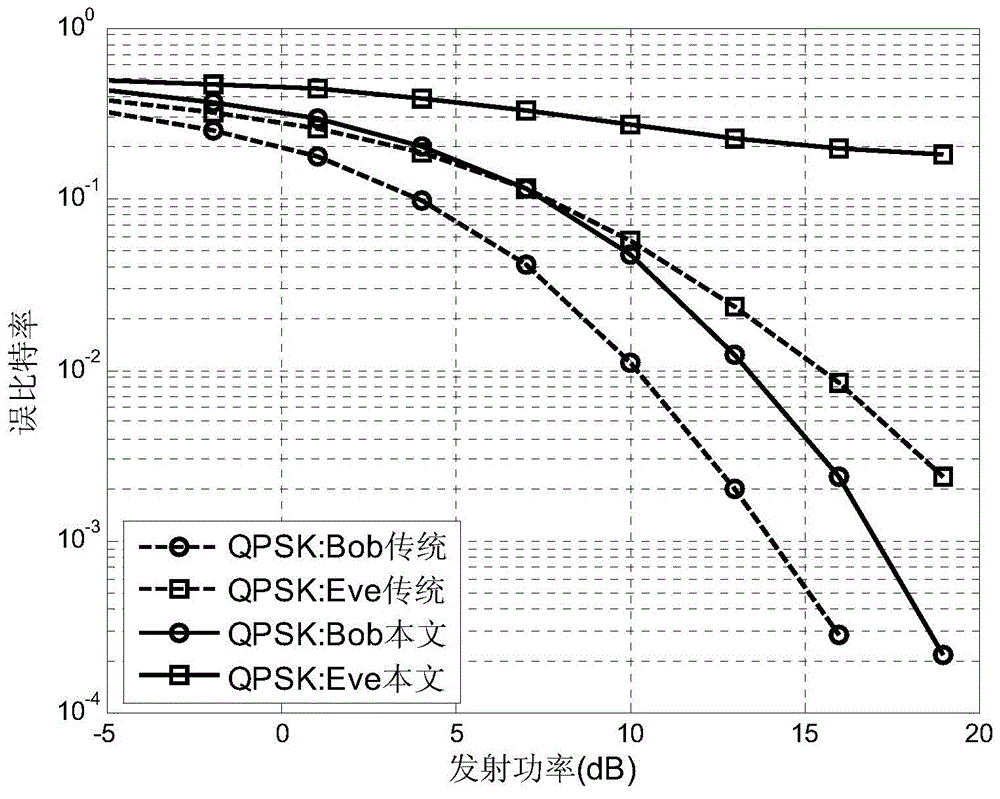
Eavesdropping is the act of secretly or stealthily listening to the private conversation or communications of others without their consent. The practice is widely regarded as unethical, and in many jurisdictions is illegal.
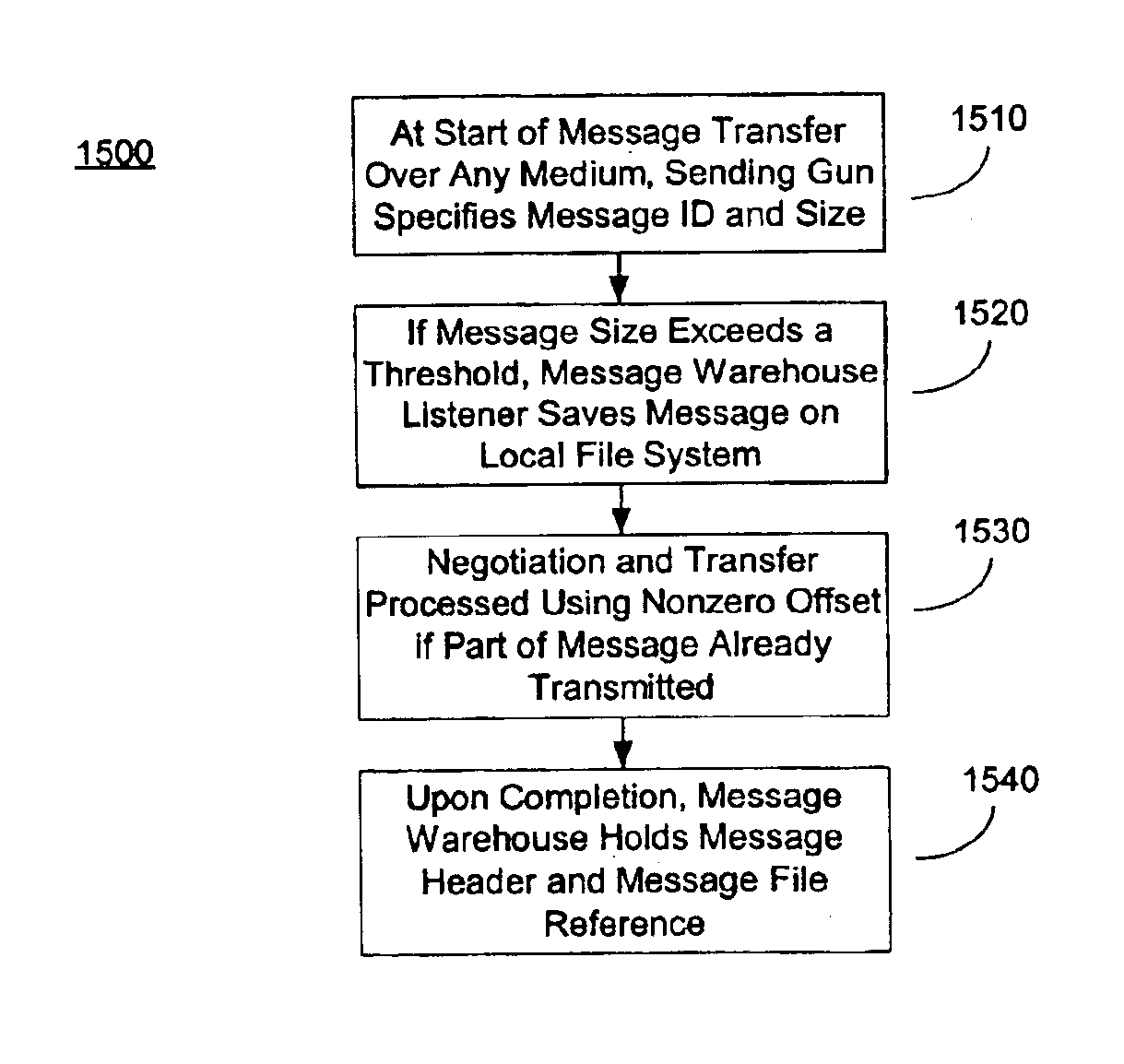
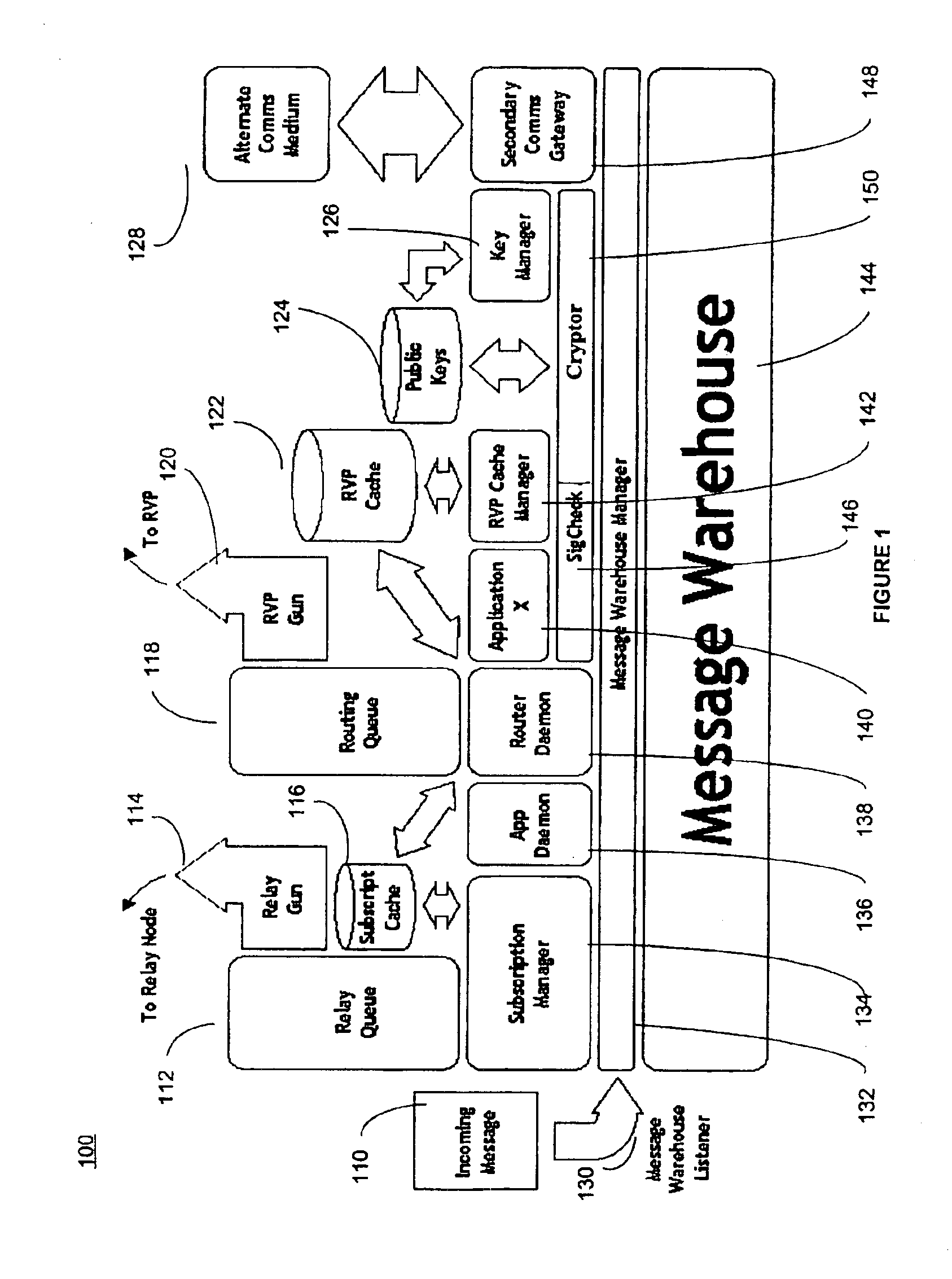
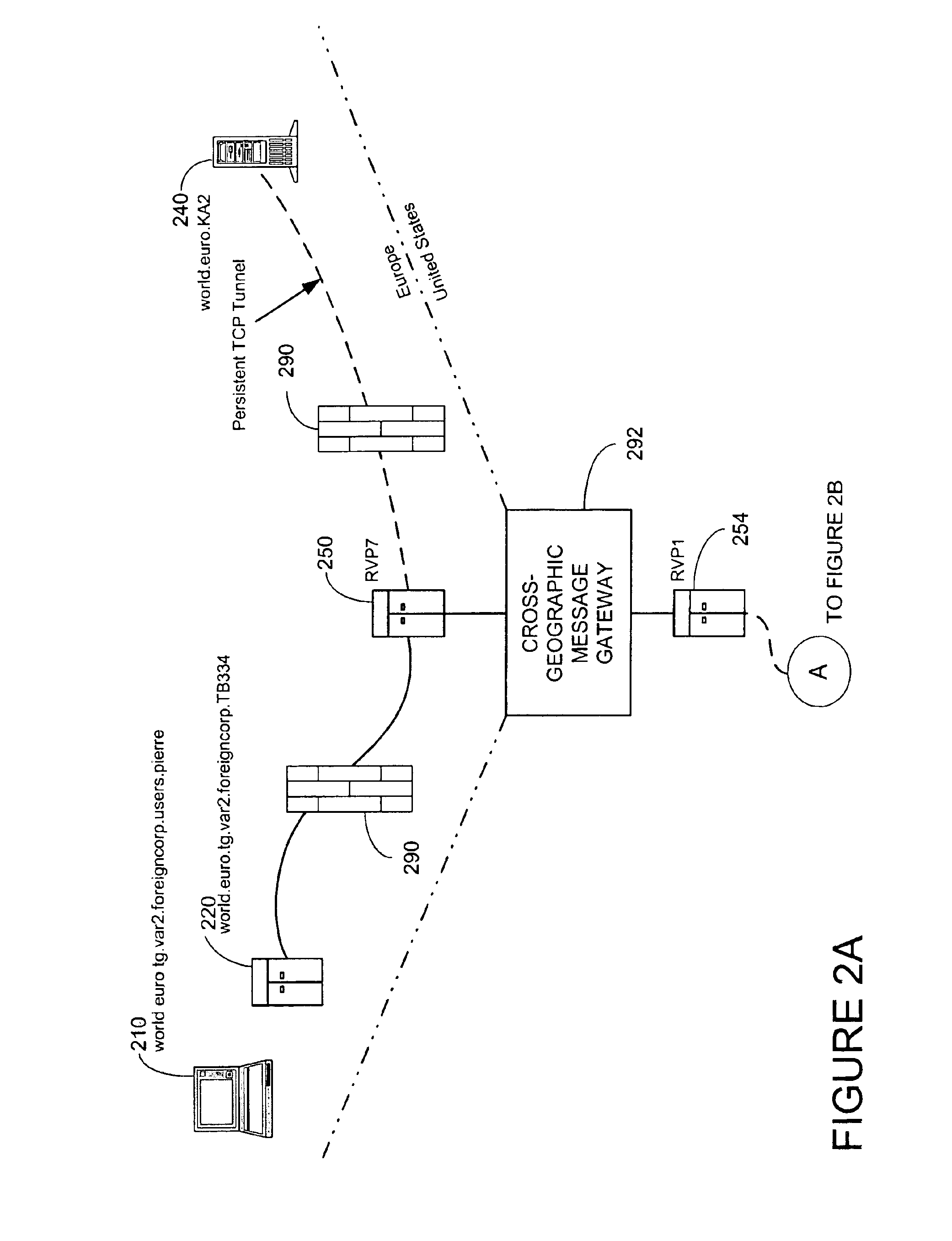
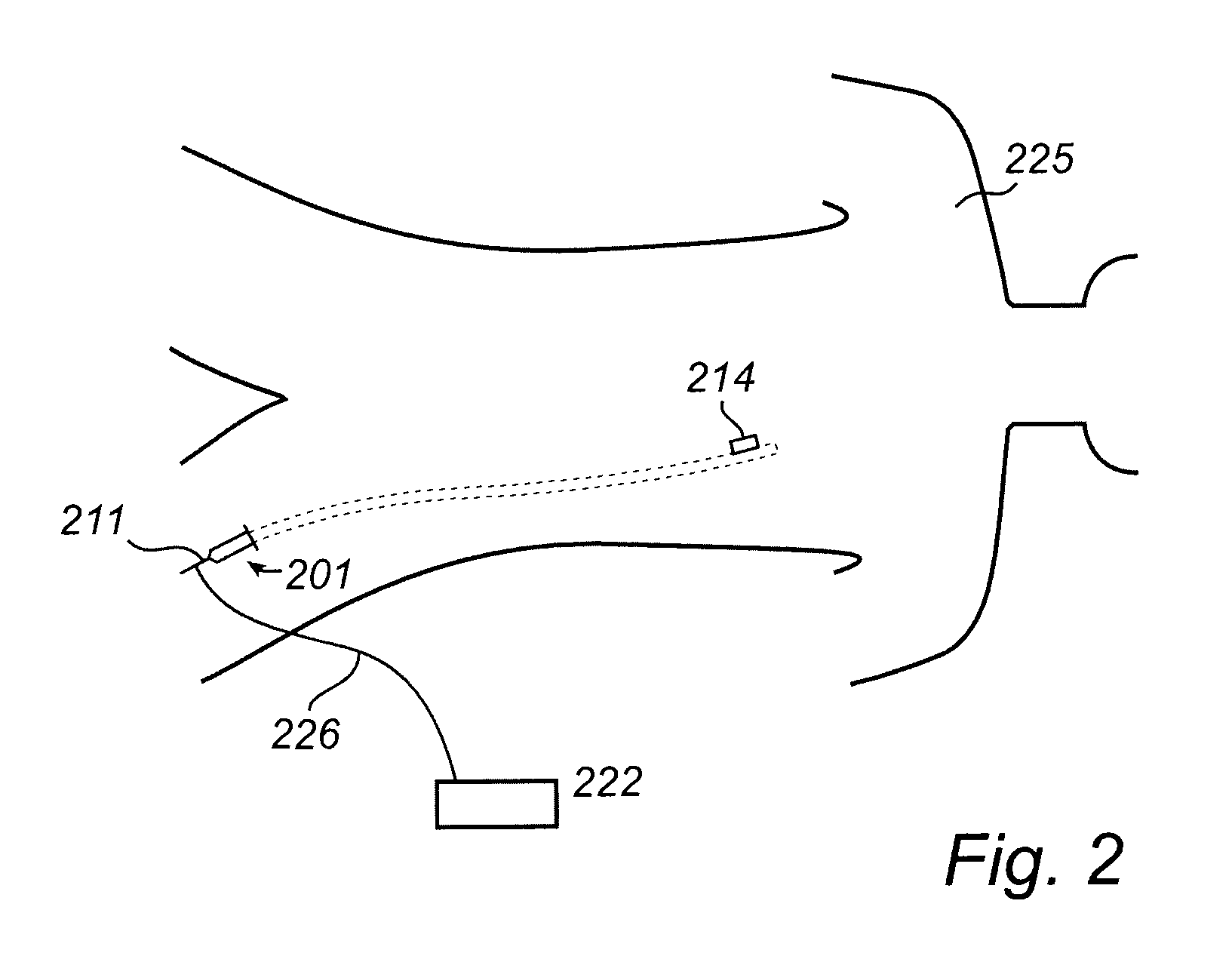
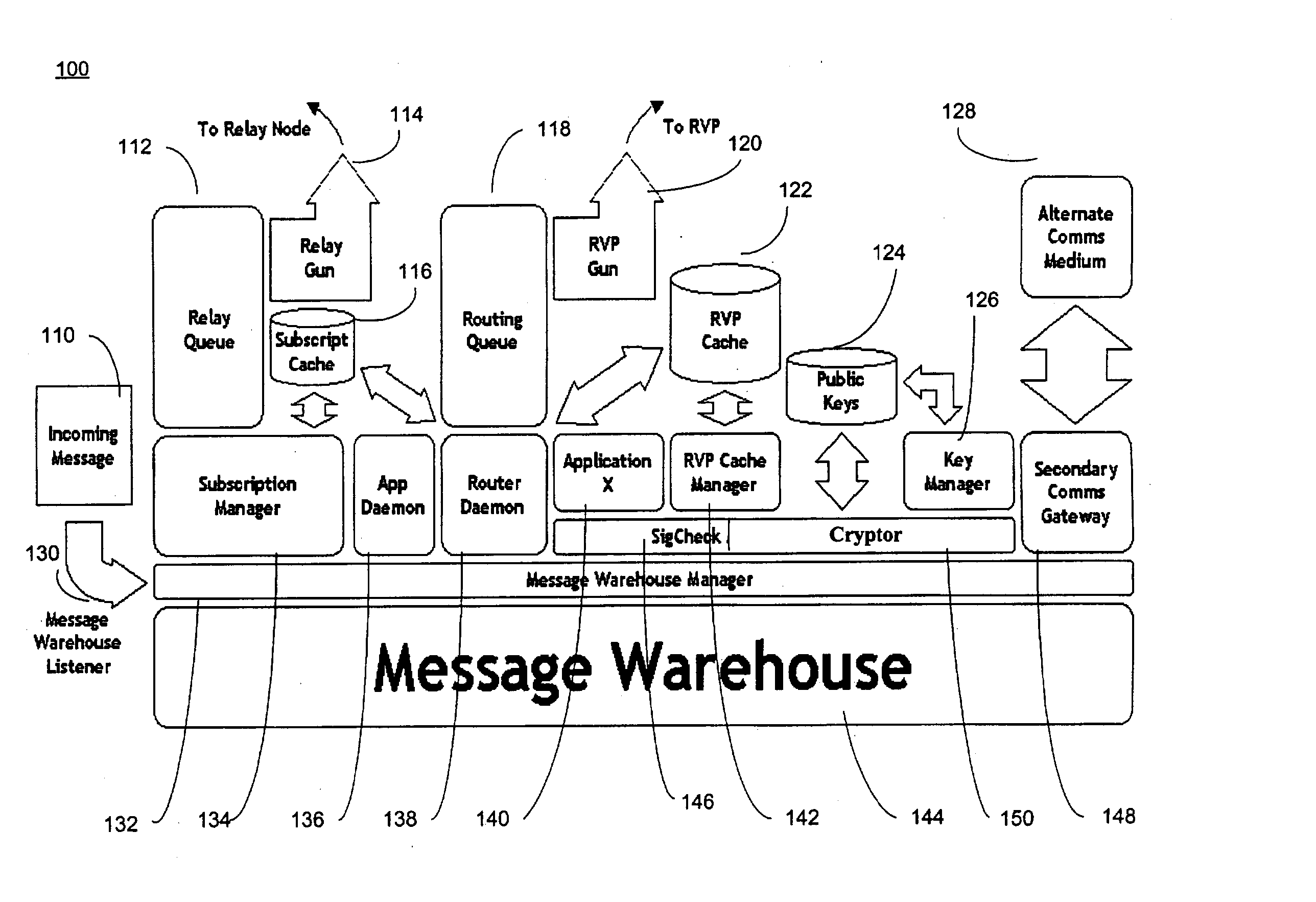
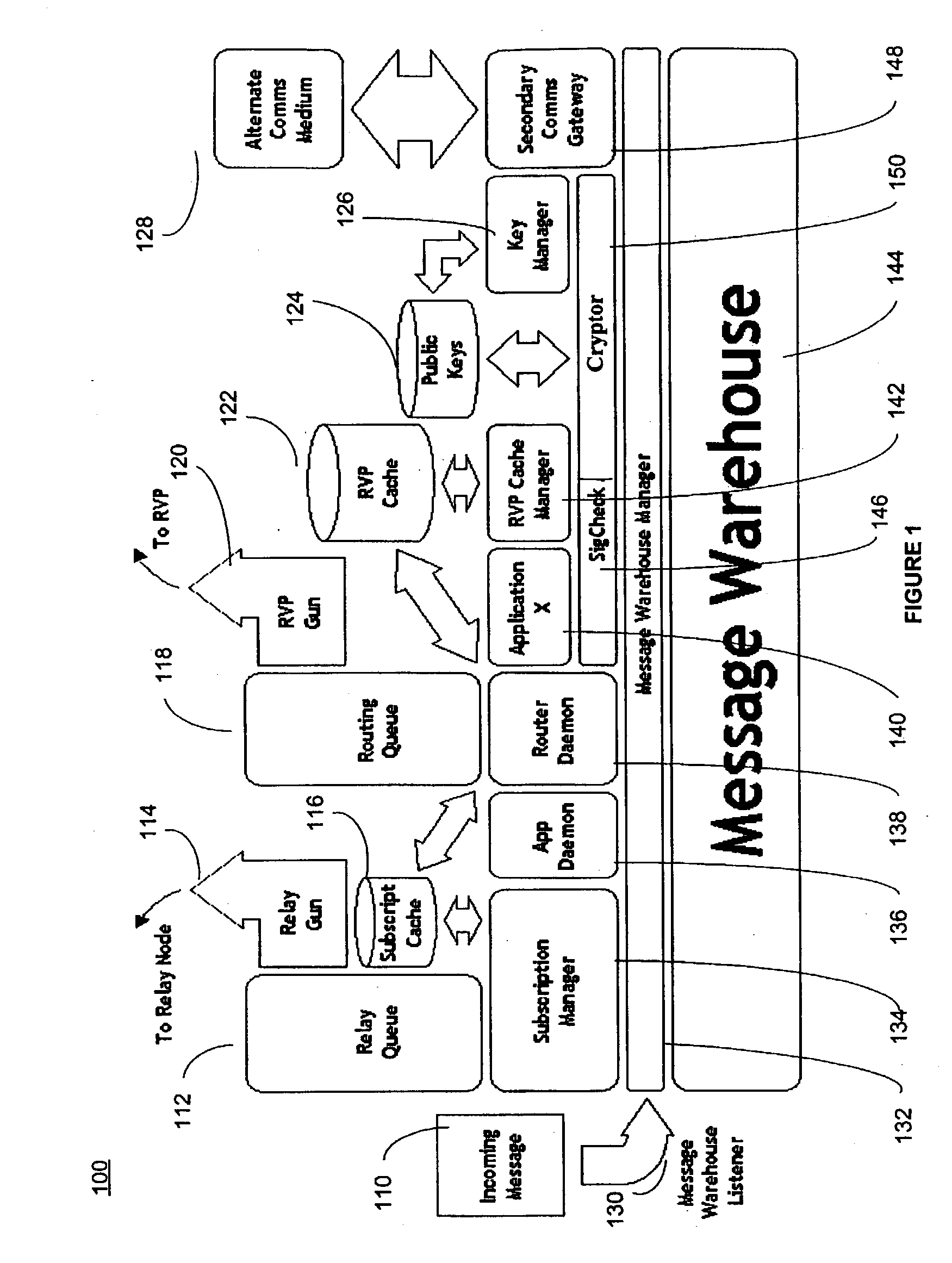
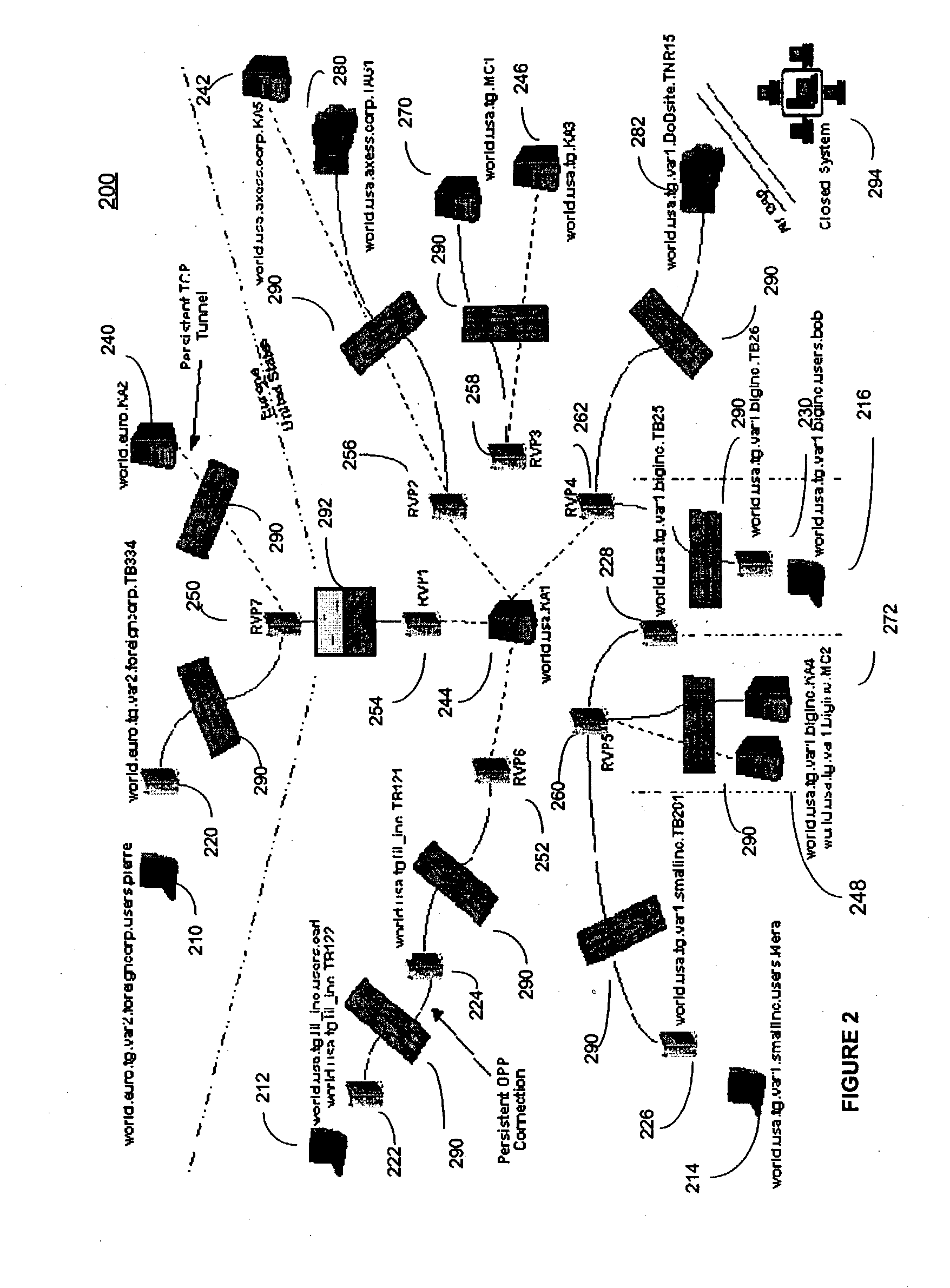
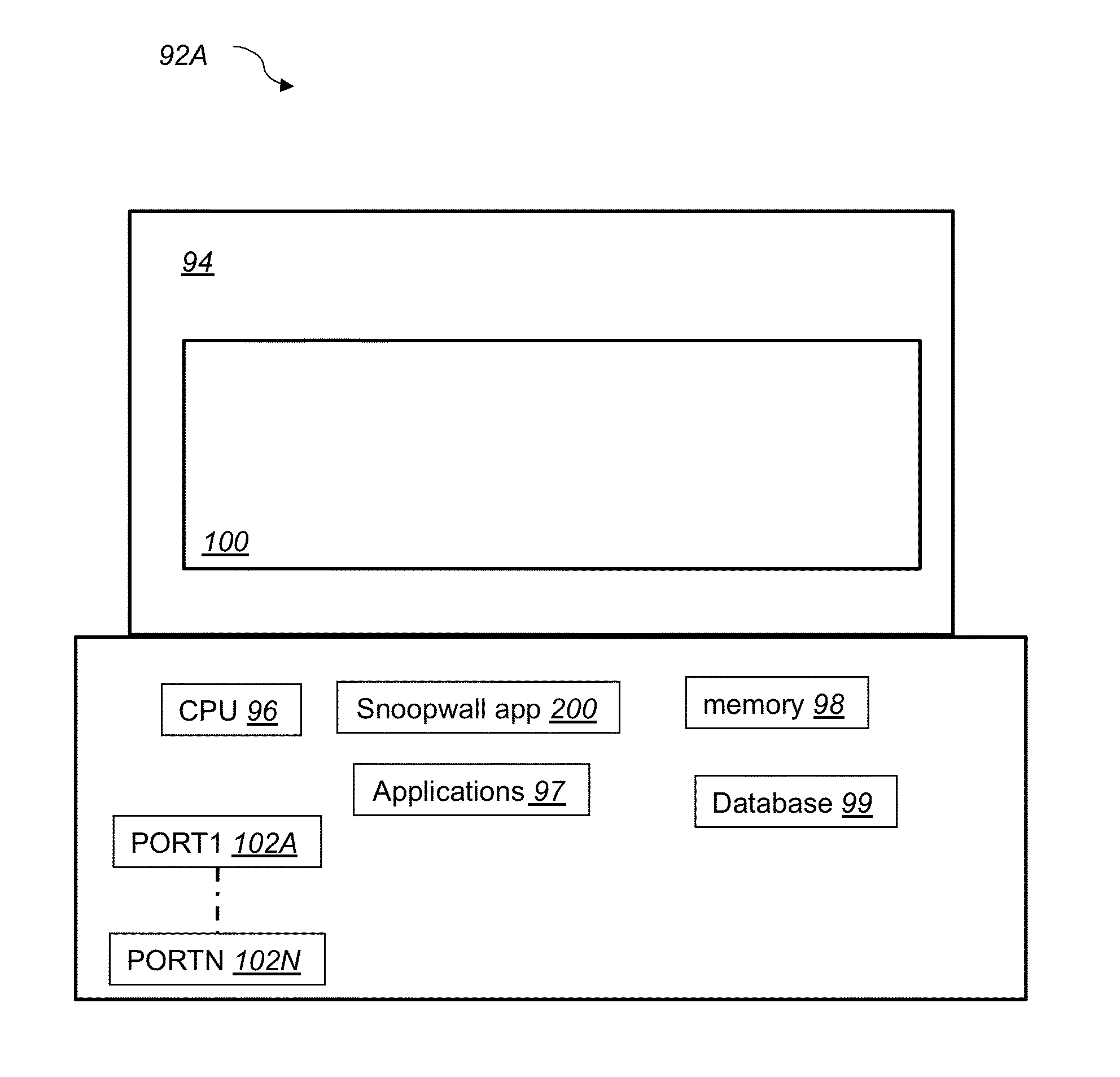
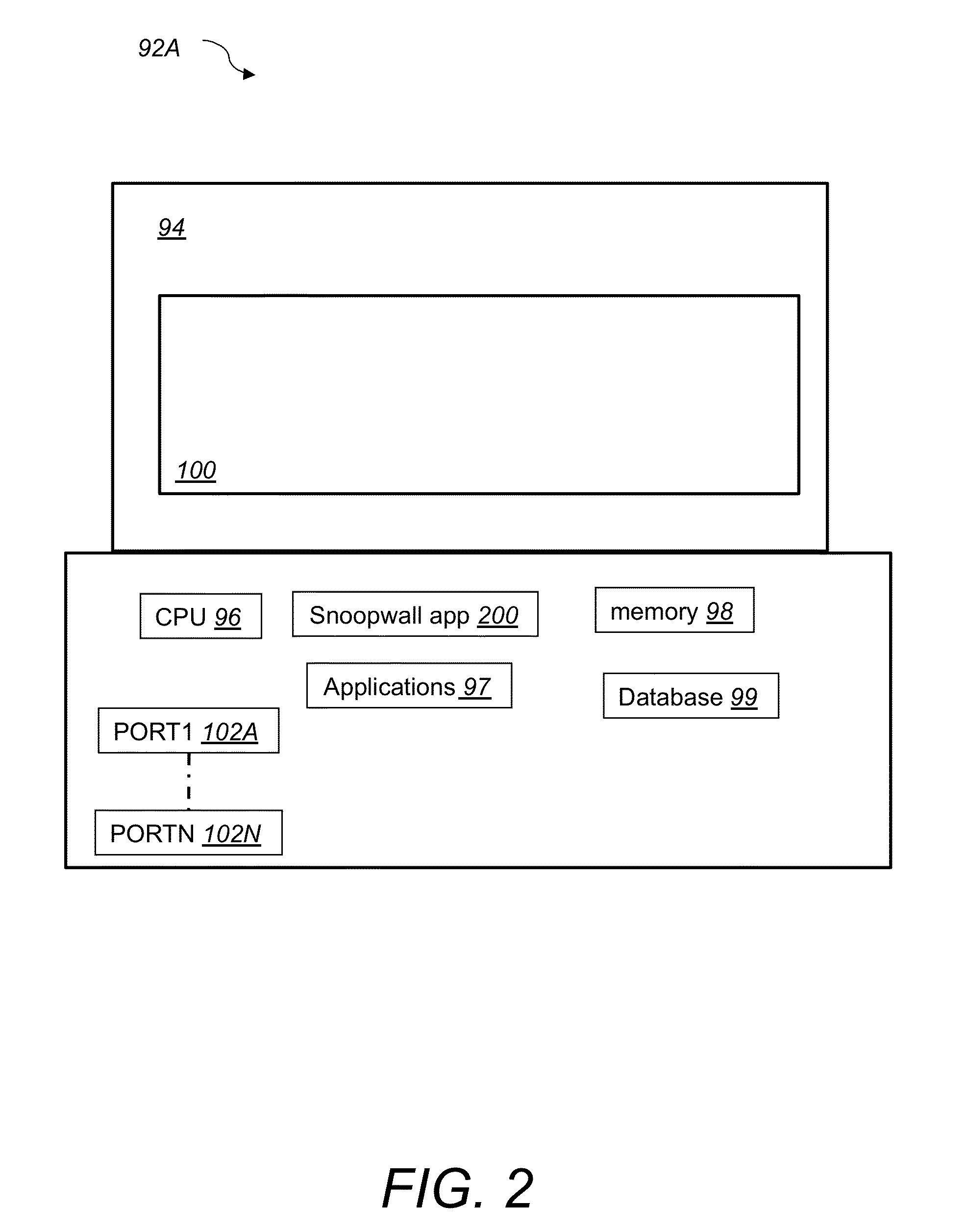
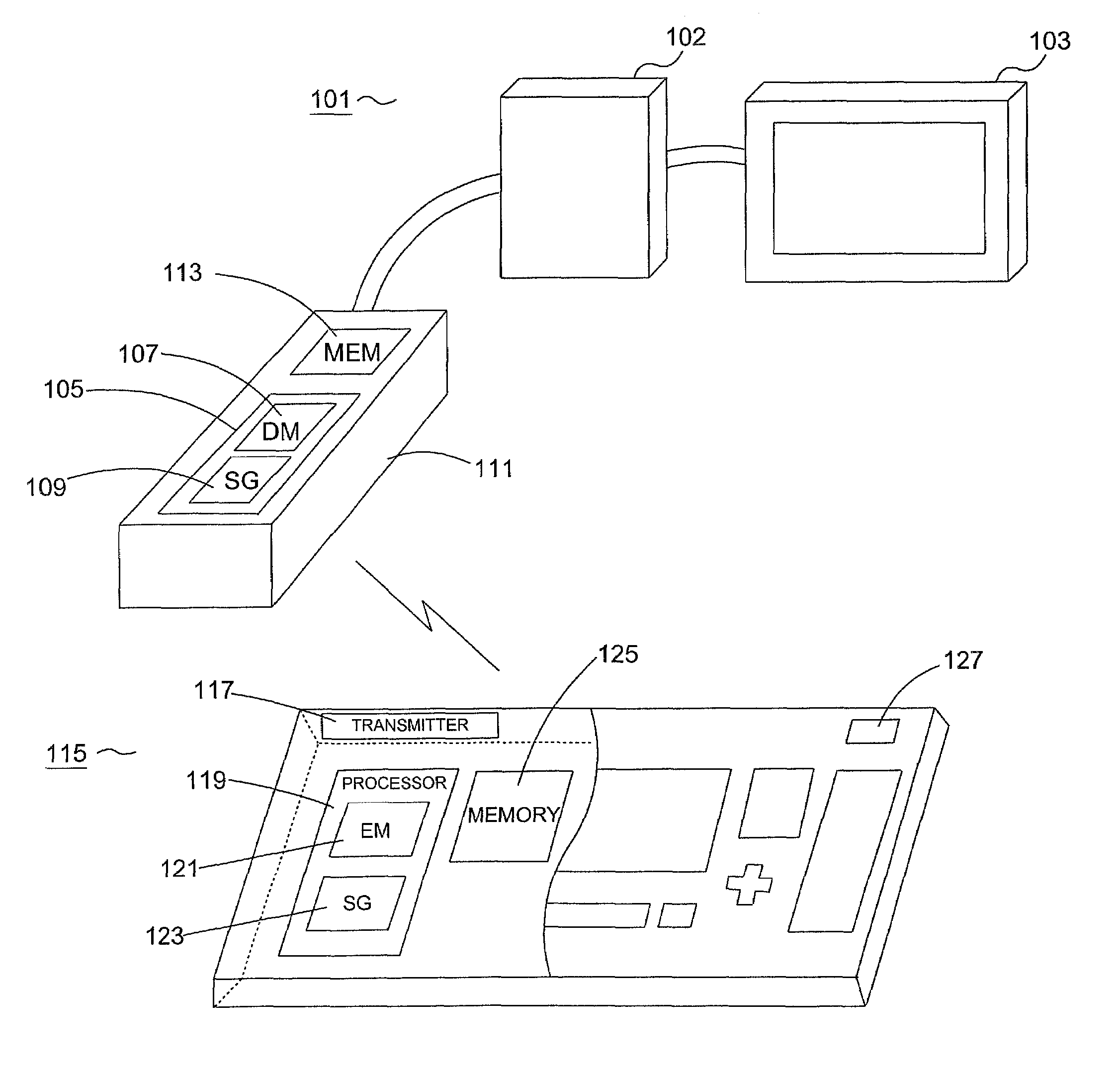
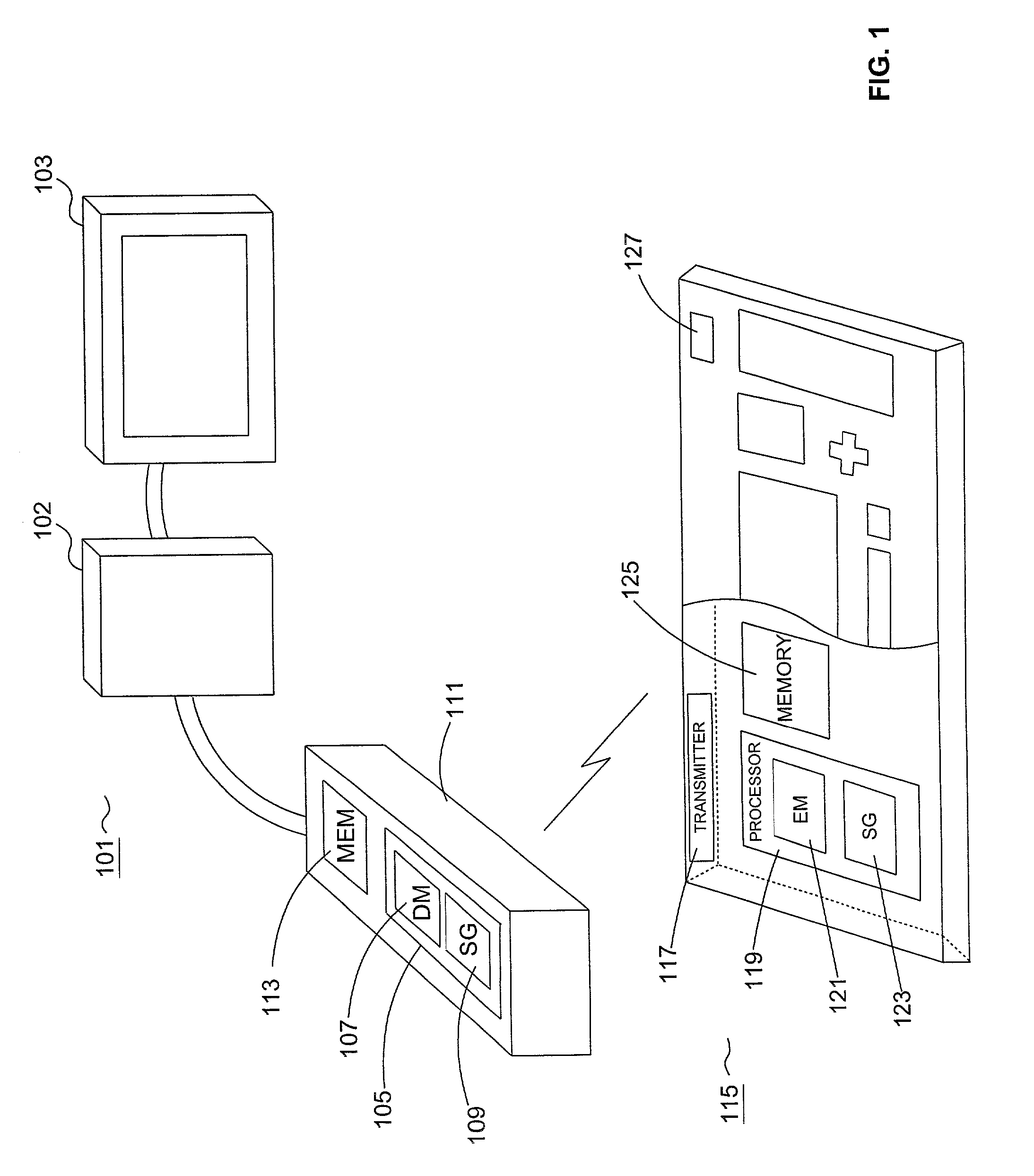
System and method for secure message-oriented network communications
InactiveUS6959393B2Minimize threatFacilitate and control accessKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsSecurity MeasureNetwork communication
The present invention provides a message-oriented middleware solution for securely transmitting messages and files across public networks unencumbered by intervening network barriers implemented as security measures. It also provides a dynamic, dedicated, application level VPN solution that is facilitated by the message-oriented middleware. Standard encryption algorithms are used to minimize the threat of eavesdropping and an Open-Pull Protocol (OPP) that allows target nodes to pull and verify the credentials of requestors prior to the passing of any data. Messaging can be segregated into multiple and distinct missions that all share the same nodes. The security network's architecture is built to resist and automatically recover from poor, slow, and degrading communications channels. Peers are identifiable by hardware appliance, software agent, and personally identifiable sessions. The security network provides a dynamic, private transport for sensitive data over existing non-secure networks without the overhead and limited security associated with traditional VPN solutions.
Owner:THREATGUARD
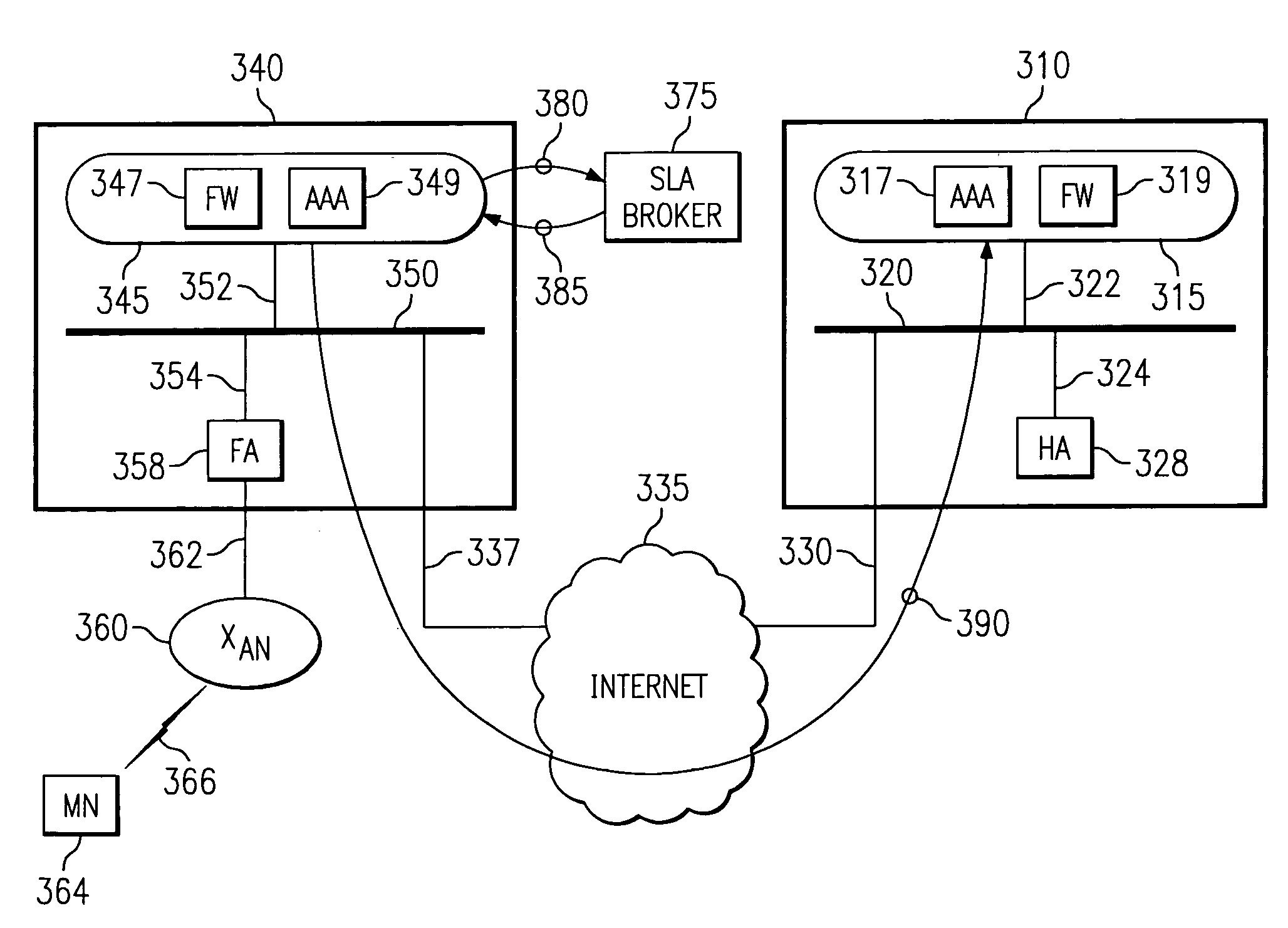
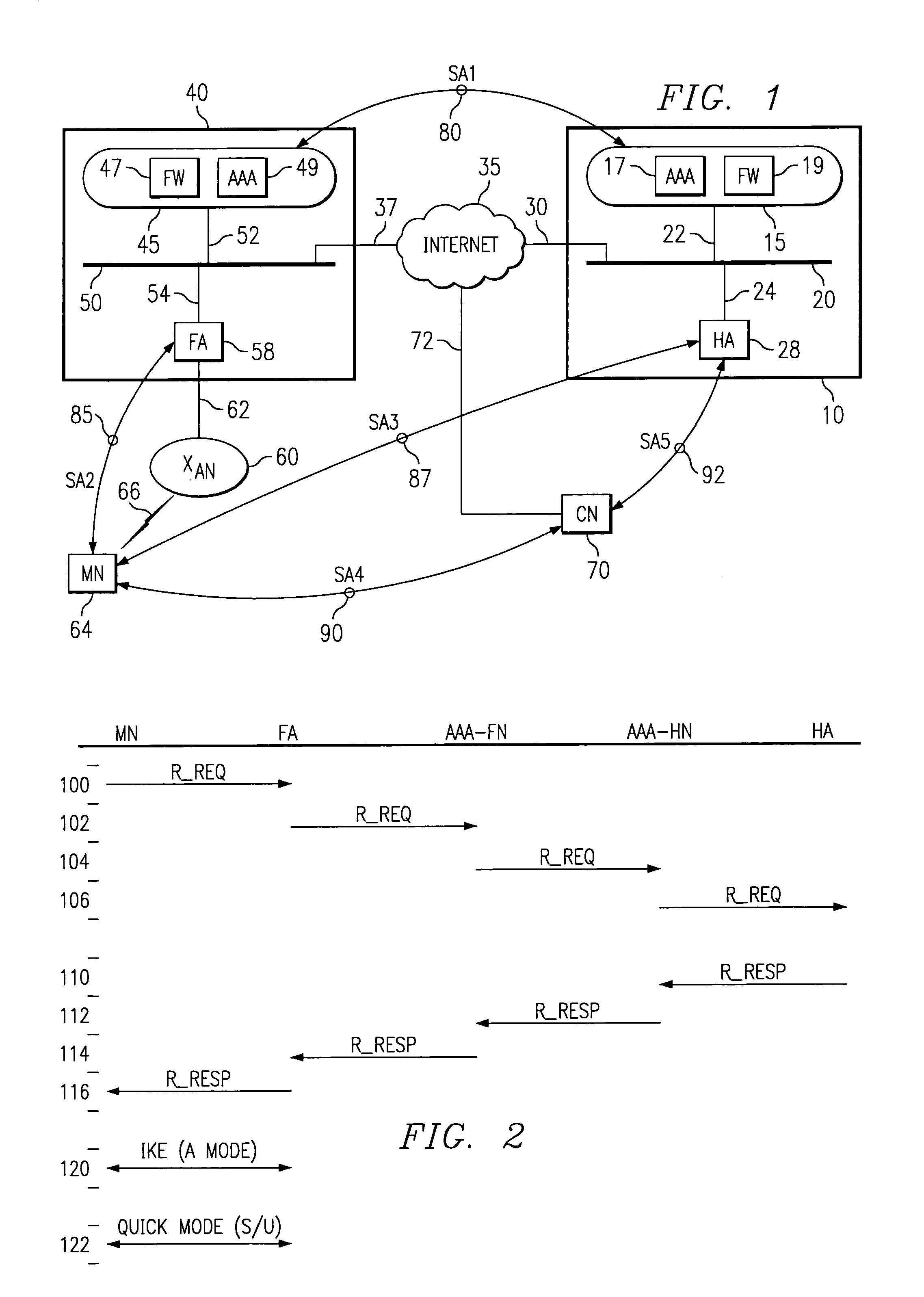
Security framework for an IP mobility system using variable-based security associations and broker redirection
InactiveUS7174018B1Improve securityPromote large-scale roamingWireless network protocolsSecret communicationService-level agreementSecurity association
In an IP-based mobile communications system, the Mobile Node changes its point of attachment to the network while maintaining network connectivity. Security concerns arise in the mobile system because authorized users are subject to the following forms of attack: (1) session stealing where a hostile node hijacks session from mobile node by redirecting packets, (2) spoofing where the identity of an authorized user is utilized in an unauthorized manner to obtain access to the network, and (3) eavesdropping and stealing of data during session with authorized user. No separate secure network exists in the IP-based mobility communications system, and therefore, it is necessary to protect information transmitted in the mobile system from the above-identified security attacks.The present invention improves the security of communications in a IP mobile communications system by creating variable-based Security Associations between various nodes on the system, a Virtual Private Network supported by an Service Level Agreement between various foreign networks and a home network, and an SLA Broker to promote large-scale roaming among different SLAs supported by the SLA Broker or agreements with other SLA Brokers.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
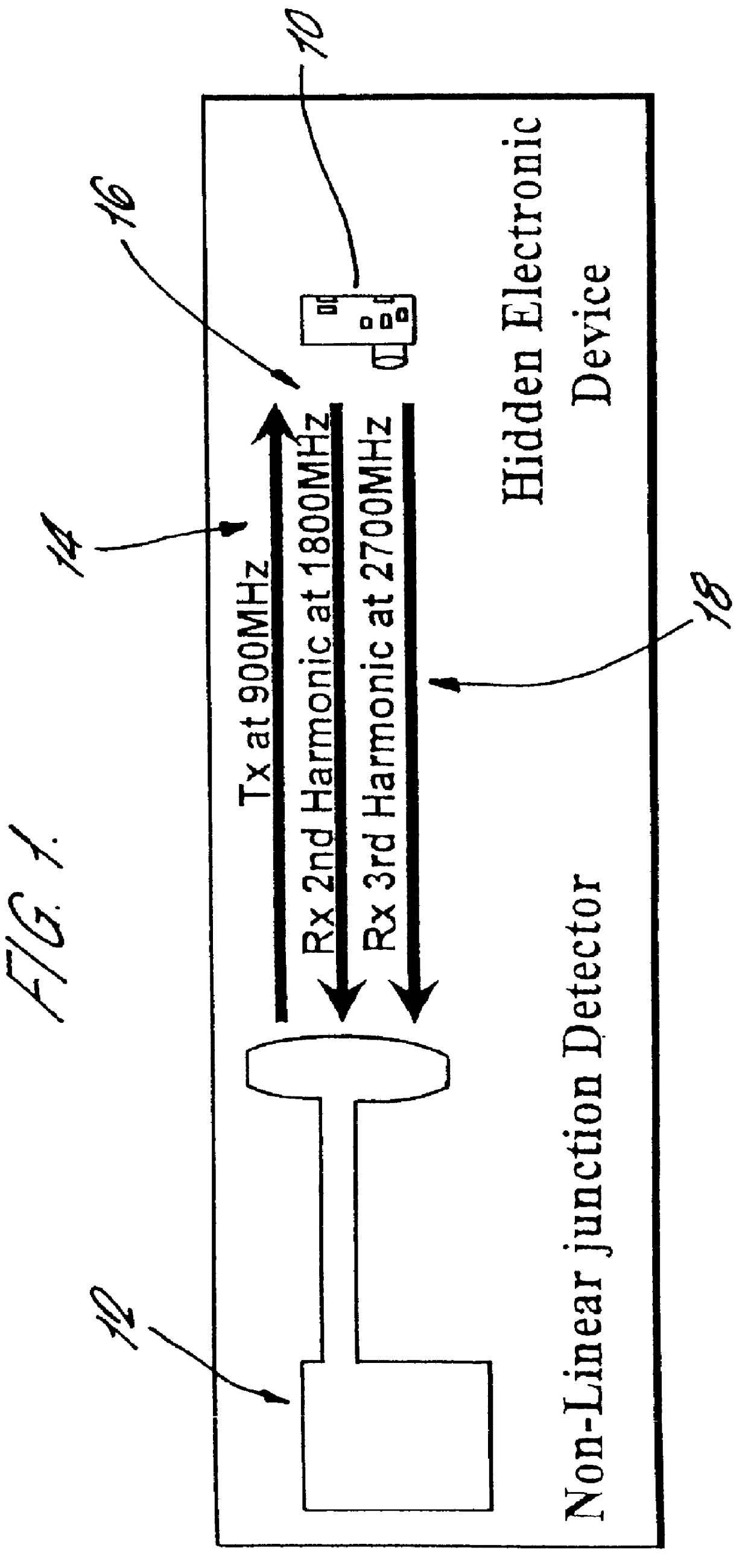
Pulse transmitting non-linear junction detector
InactiveUS6163259AHigh and effective peak power levelCost-effective and convenient to useBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalDetection using electromagnetic wavesData displayTransmitted power
A non-linear junction detector designed for counter surveillance measures achieves superior performance by transmitting a series of pulses and receiving harmonics of the transmitted pulse signals that are re-radiated by a non-linear junction such as would be found in an eavesdropping device containing a semiconductor. The transmit power of the series of pulses is varied and the amplitudes of the harmonics received at the different power levels are compared to determine the type of non-linear junction detected. The received harmonic signals are demodulated to create signals having a frequency in the audible range of human ears. The demodulated signals are broadcast so that an operator of the non-linear junction detector can audibly distinguish between the noise responses produced by the different types of non-linear junctions. The harmonic signals are analyzed to determine if the harmonic, signals correspond to signals produced by a known type of non-linear junction device such as a video camera or tape recorder. Data generated by the non-linear junction detector is displayed to an operator of the detector and may be stored for later analysis.
Owner:RES ELECTRONICS INT
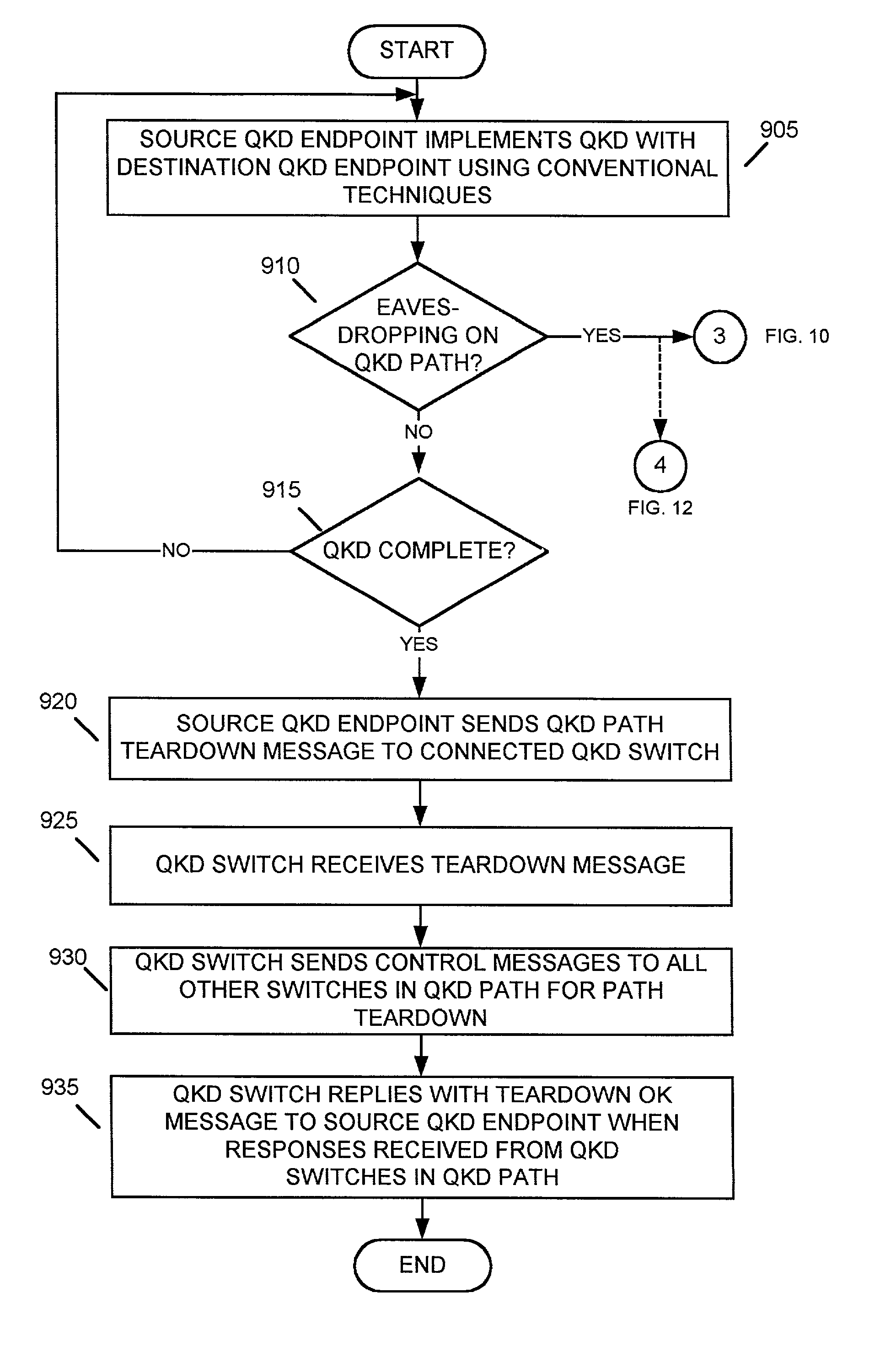
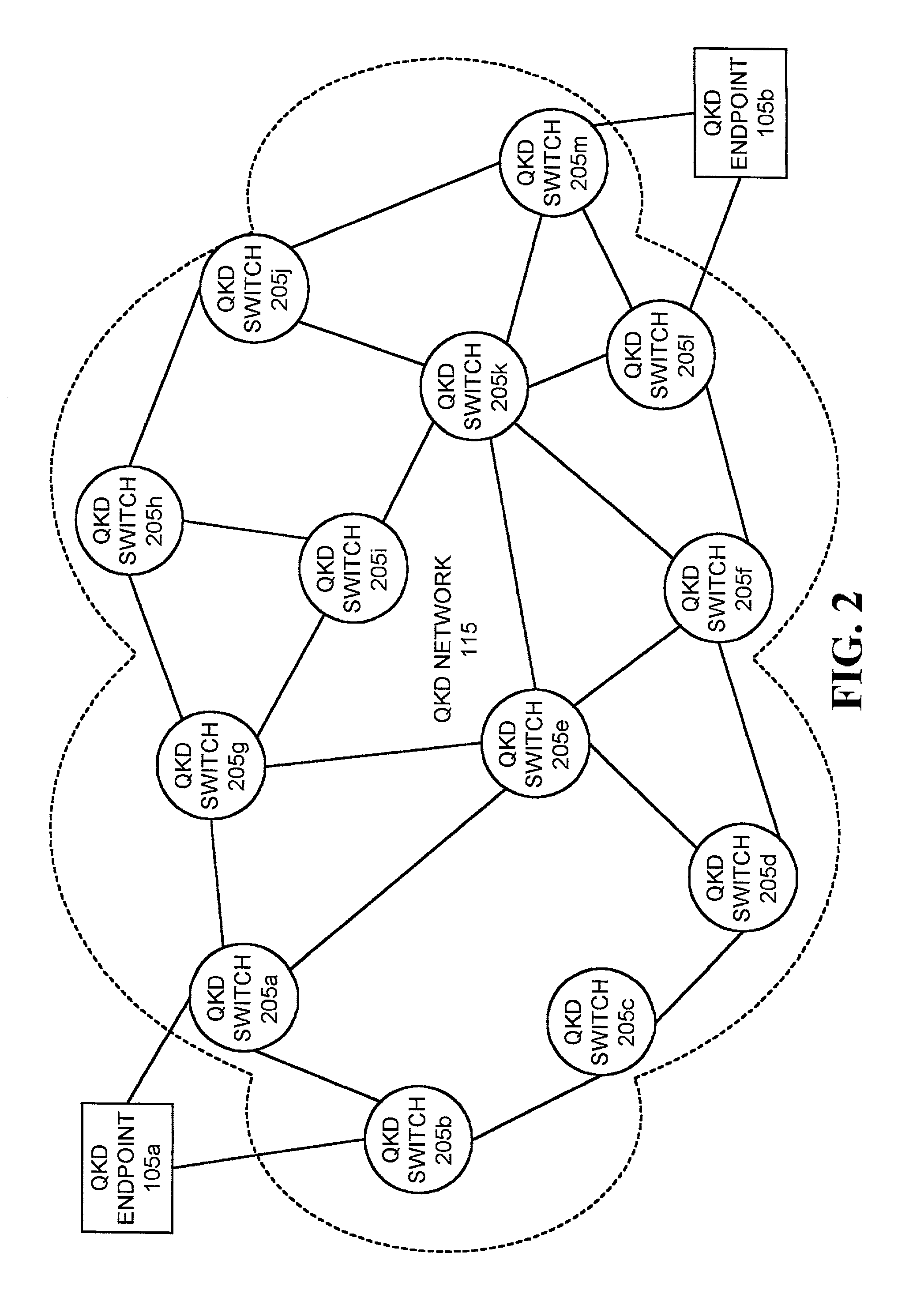
Systems and methods for path set-up in a quantum key distribution network
InactiveUS7068790B1Low costReduce complexityKey distribution for secure communicationWavelength-division multiplex systemsKey distributionEavesdropping
A system establishes a path for distributing data through an optical network (115). The system includes an optical switch (205a) and a data distribution endpoint (105a). The optical switch (205a) establishes a first encryption key distribution path through the optical network (115), the first encryption key distribution path including multiple optical switches and optical links. The data distribution endpoint (105a) determines whether eavesdropping has occurred on the first encryption key distribution path using quantum cryptography. The optical switch (205a) further establishes a second data distribution path through the optical network (115) responsive to the eavesdropping determination. The second encryption key distribution path includes multiple optical switches and optical links.
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP
Secure remote access to voice mail
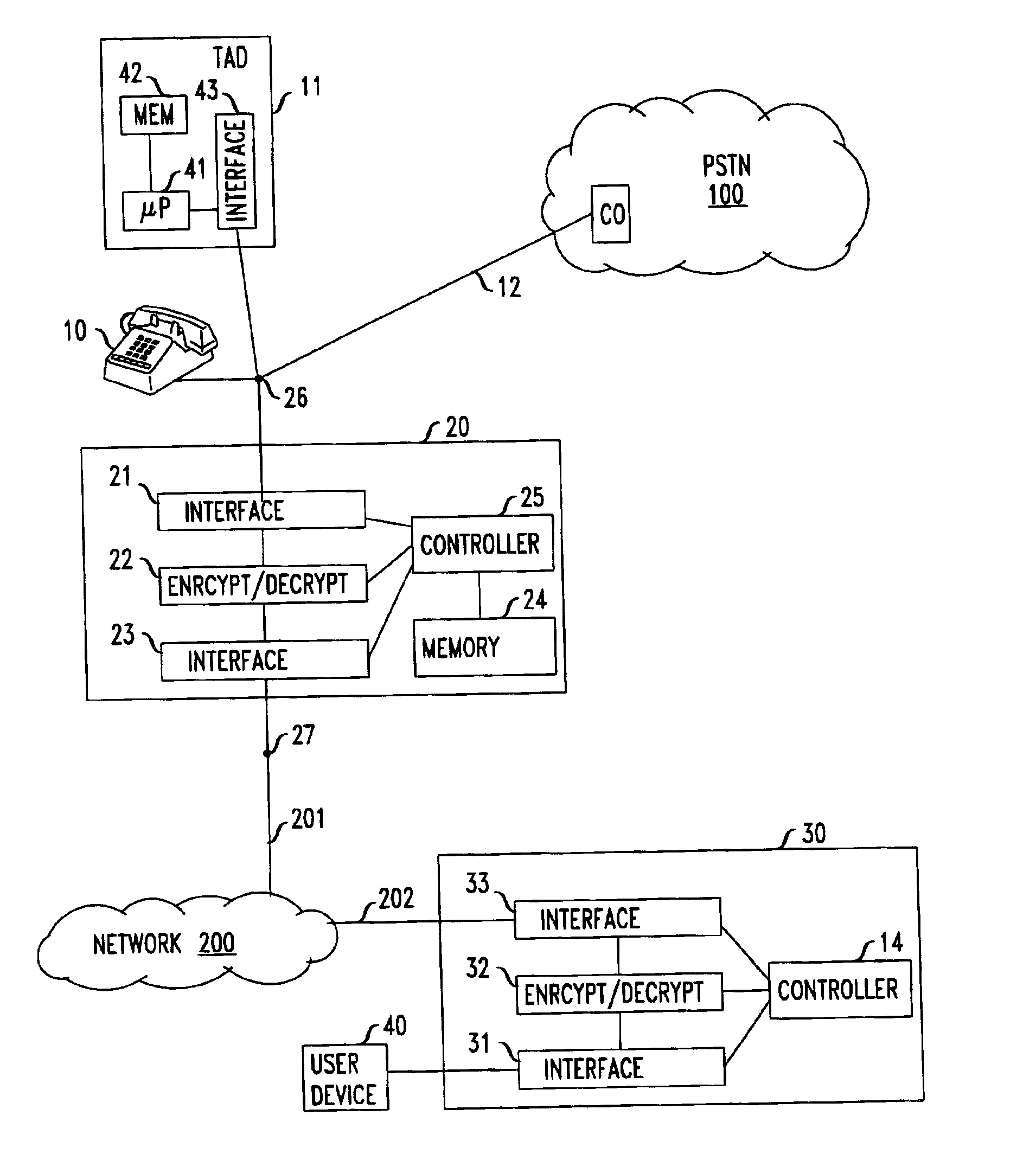
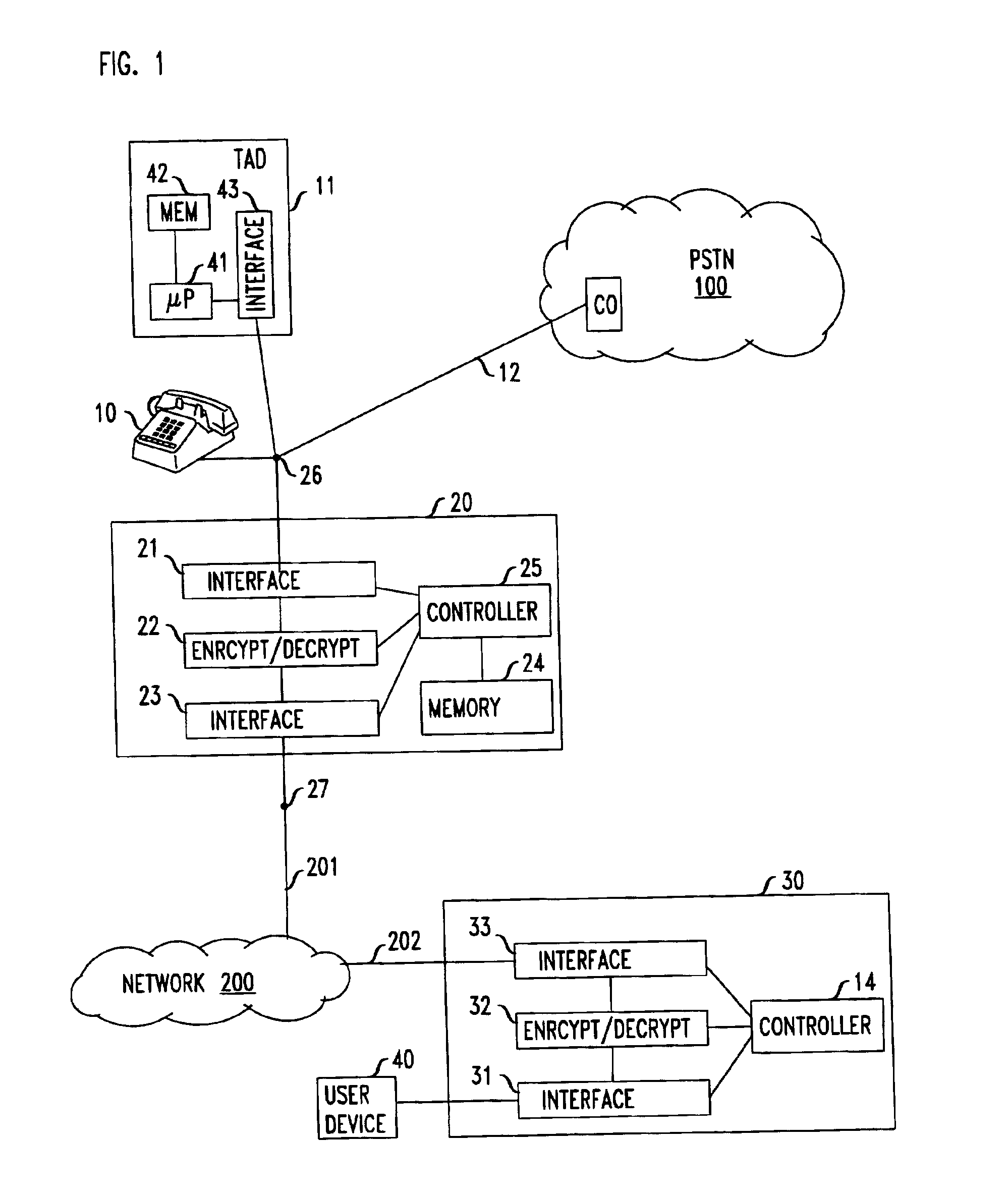
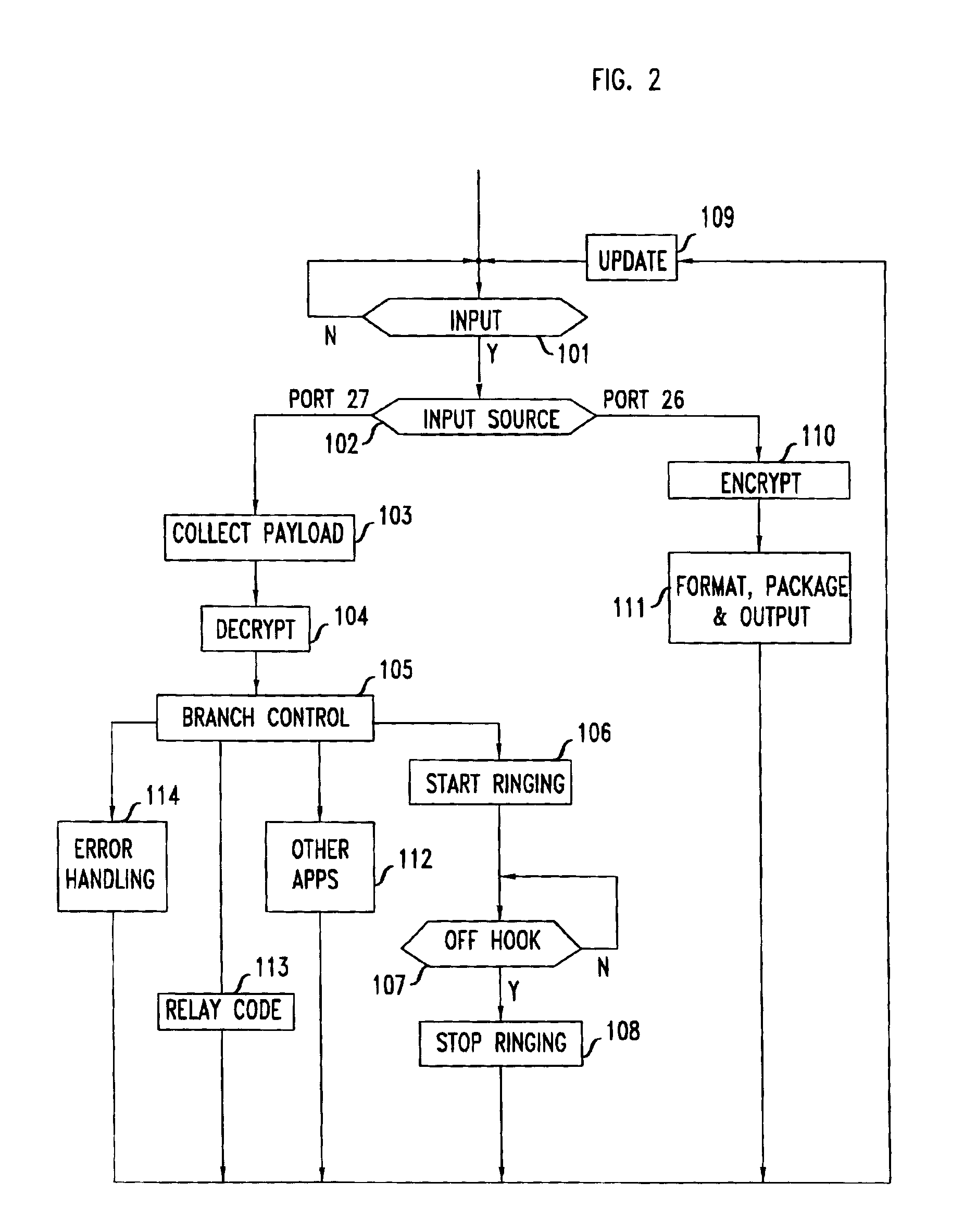
InactiveUS6912275B1Overcome problemsEavesdropping prevention circuitsAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingTelephone networkEavesdropping
A coupler includes an analog port for interfacing with a telephone answering system a network port that is adapted for connection to an insecure network. The security problem associated with eavesdropping over insecure network is overcome by encrypting the messages that exit through the coupler's network port. In one embodiment, the coupler and the telephone answering system are distinct hardware elements and the coupler is connected to the TAD. In another embodiment, a single processor and associated memory perform the functions of the coupler's controller and of the telephone answering system, thus forming a single device that has an analog port for connecting to the public switched telephone network, as well as a port for connection to the insecure network. In yet another embodiment, the coupler / TAD combination includes a control port to allow connection to the control port of an ISDN telephone.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Detecting and diagnosing performance problems in a wireless network through neighbor collaboration
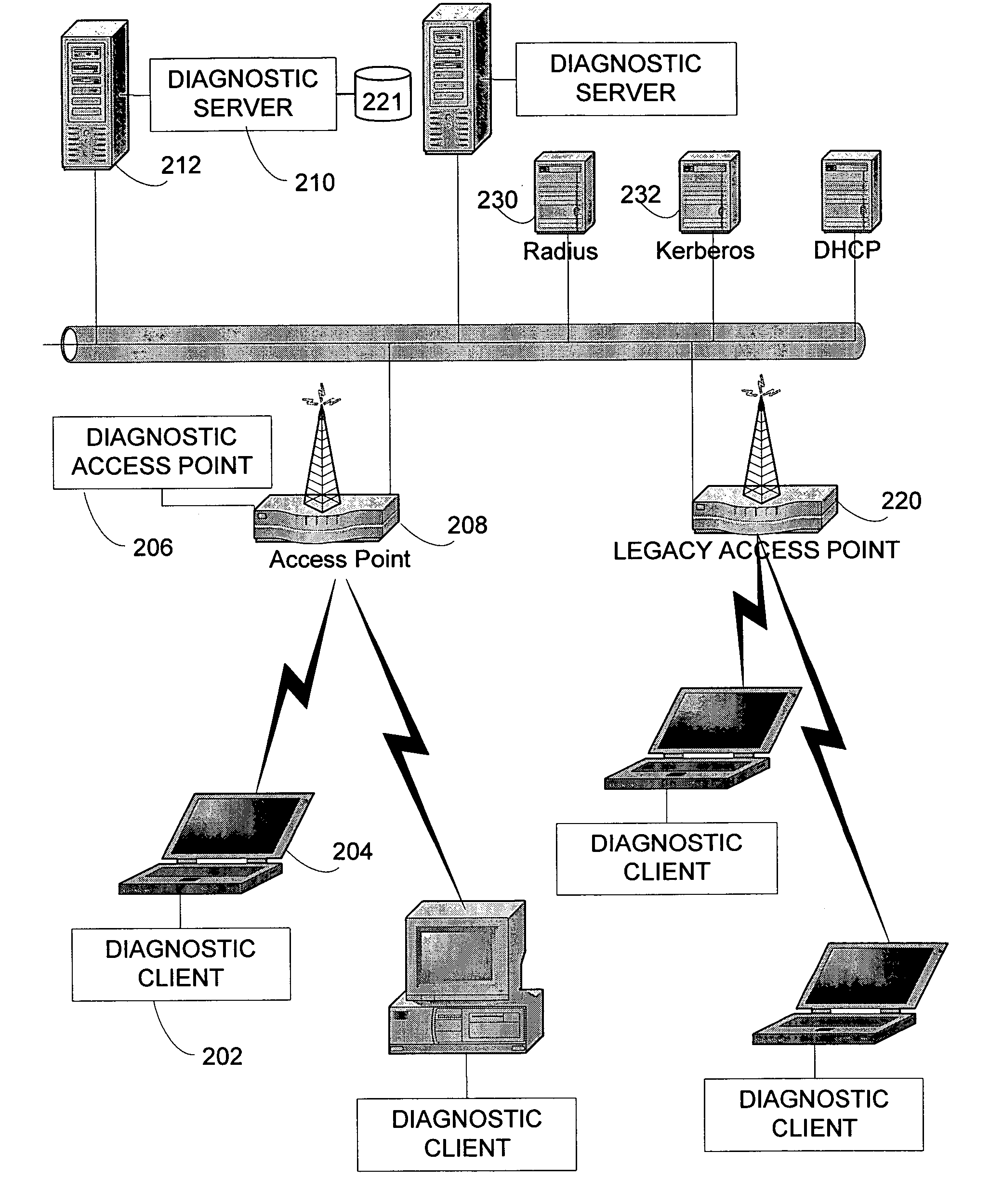
InactiveUS20060068769A1Easy diagnosisDiagnosing communicationNetwork traffic/resource managementDigital computer detailsDiagnostic programWireless mesh network
Systems and methods are described for detecting and diagnosing performance problems in wireless communications networks. Diagnostic programs execute on a wireless device, neighboring devices, and a wireless access point to collaborate in diagnosing network problems. The neighboring devices eavesdrop on a diagnostic session between the device and the access point to determine problems at the device, the access point, and in the wireless medium. Data from the eavesdropping devices can be summarized and sent to a network administrator for further action. The diagnostic programs are described to contain a passive component for detecting problems, and an active component for running the diagnostic techniques.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
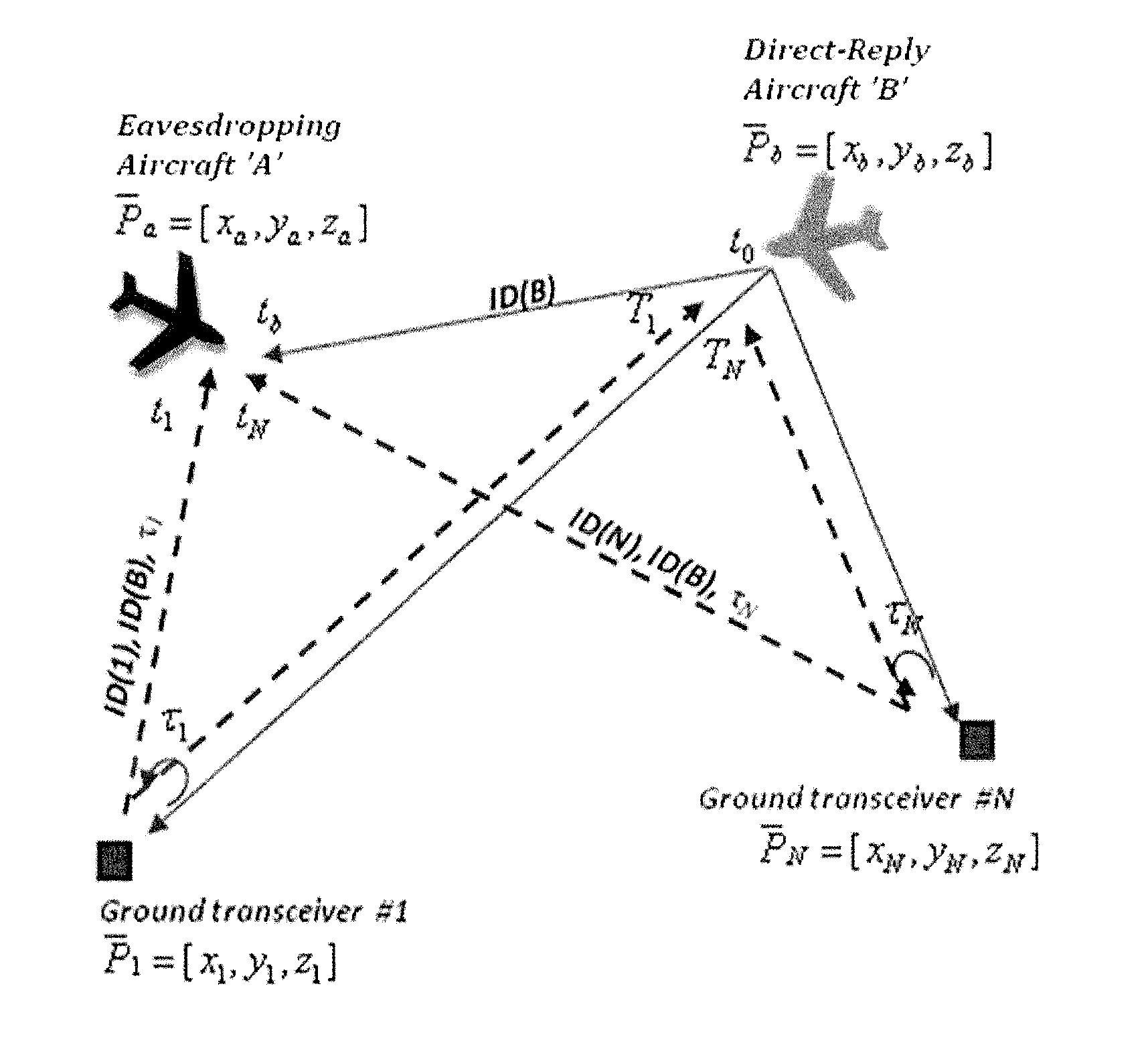
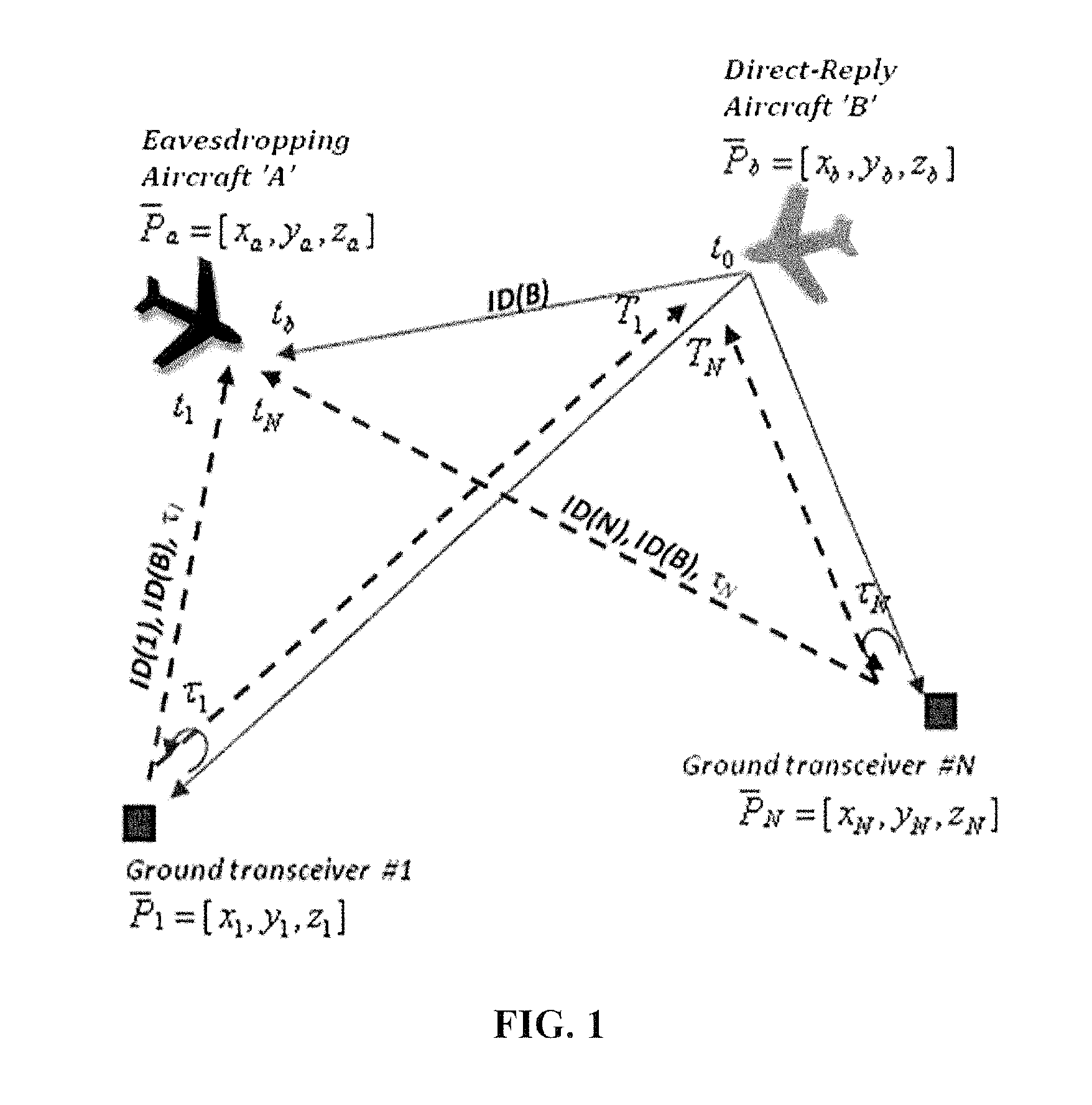
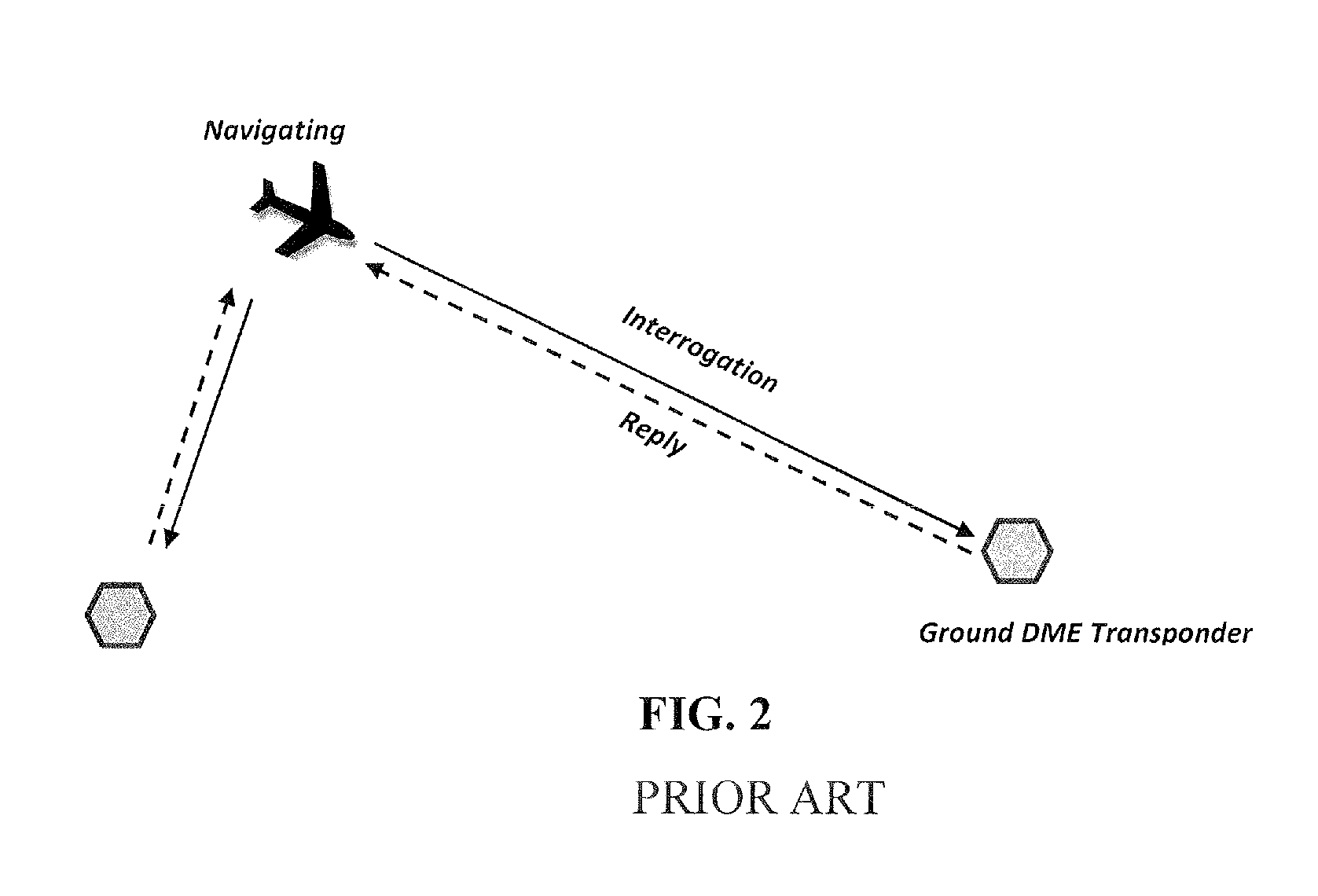
System and method for aircraft navigation based on diverse ranging algorithm using ads-b messages and ground transceiver responses
A method of aircraft navigation via receiving signals emitted by other aircraft and corresponding reply message transmitted by ground transceivers and the using a new diverse-ranging algorithm that solves for the positions of a eavesdropping aircraft and the positions of direct-reply aircraft emitting the signals received by the eavesdropping aircraft.
Owner:SAAB INC
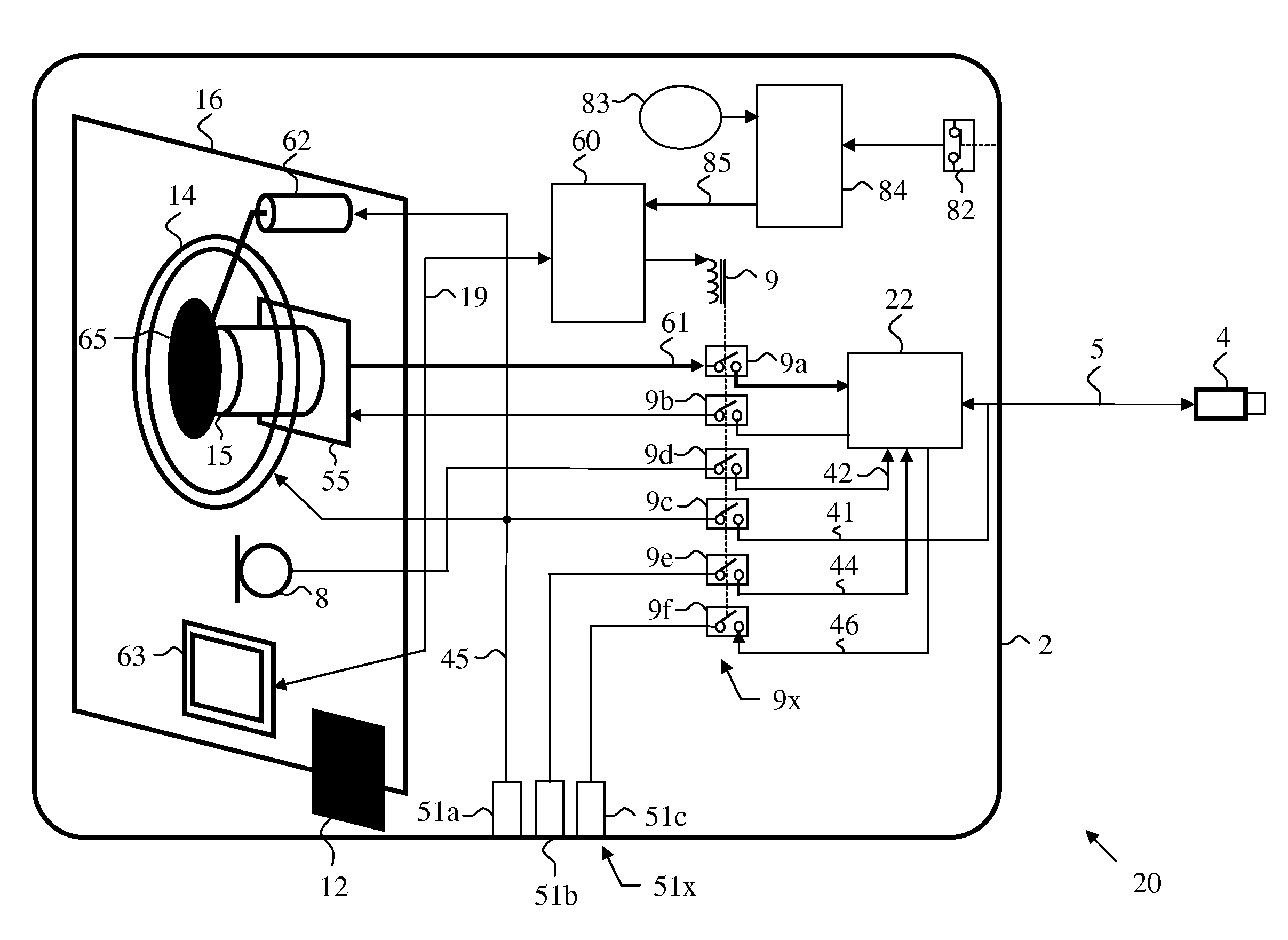
Secure video camera device
ActiveUS20130222609A1Efficient and secure switchingExtend activation timeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensComputer hardware
A secure video camera device for reducing the risk of visual and audio eavesdropping has a video camera and an electromechanical shutter behind a transparent cover in a secured enclosure. The shutter optically obscures the camera lens when the device is in secure state. A visual indicator indicates when the device is in operational state. A switch controllable by the user, select the state of the device by concurrently disabling the camera turning off the visual indicator in a secure state; and setting said device in an operational state by concurrently enabling the camera and turning on said lighted indicator. The device has a built in, or auxiliary microphone, and audio outputs which are disabled in secure state of the device. The device is tempered proof by an anti-tempering circuitry.
Owner:HIGH SEC LABS LTD
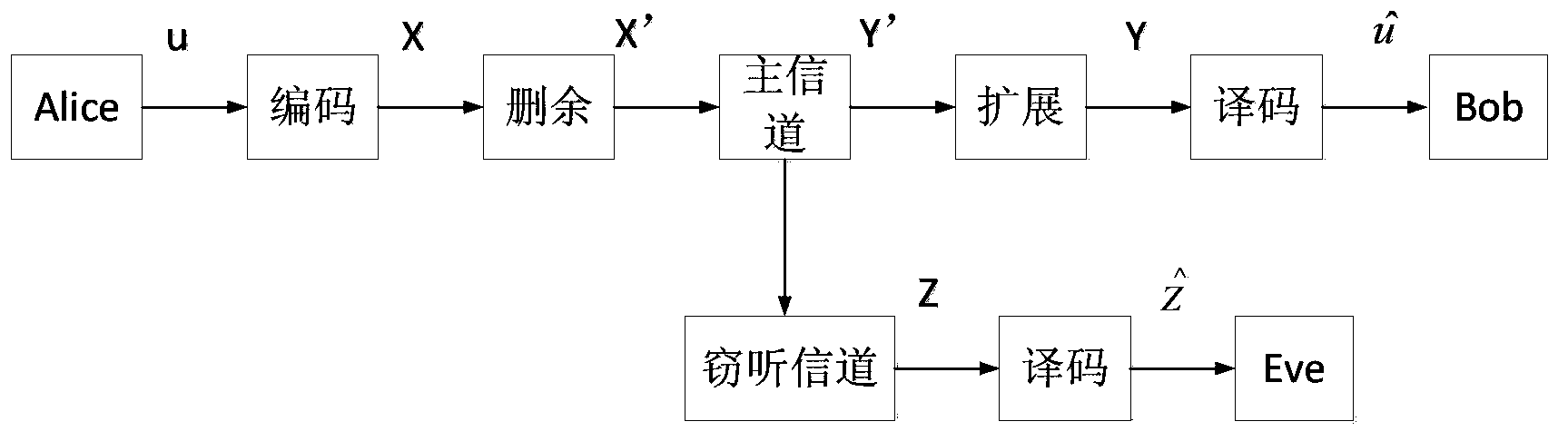
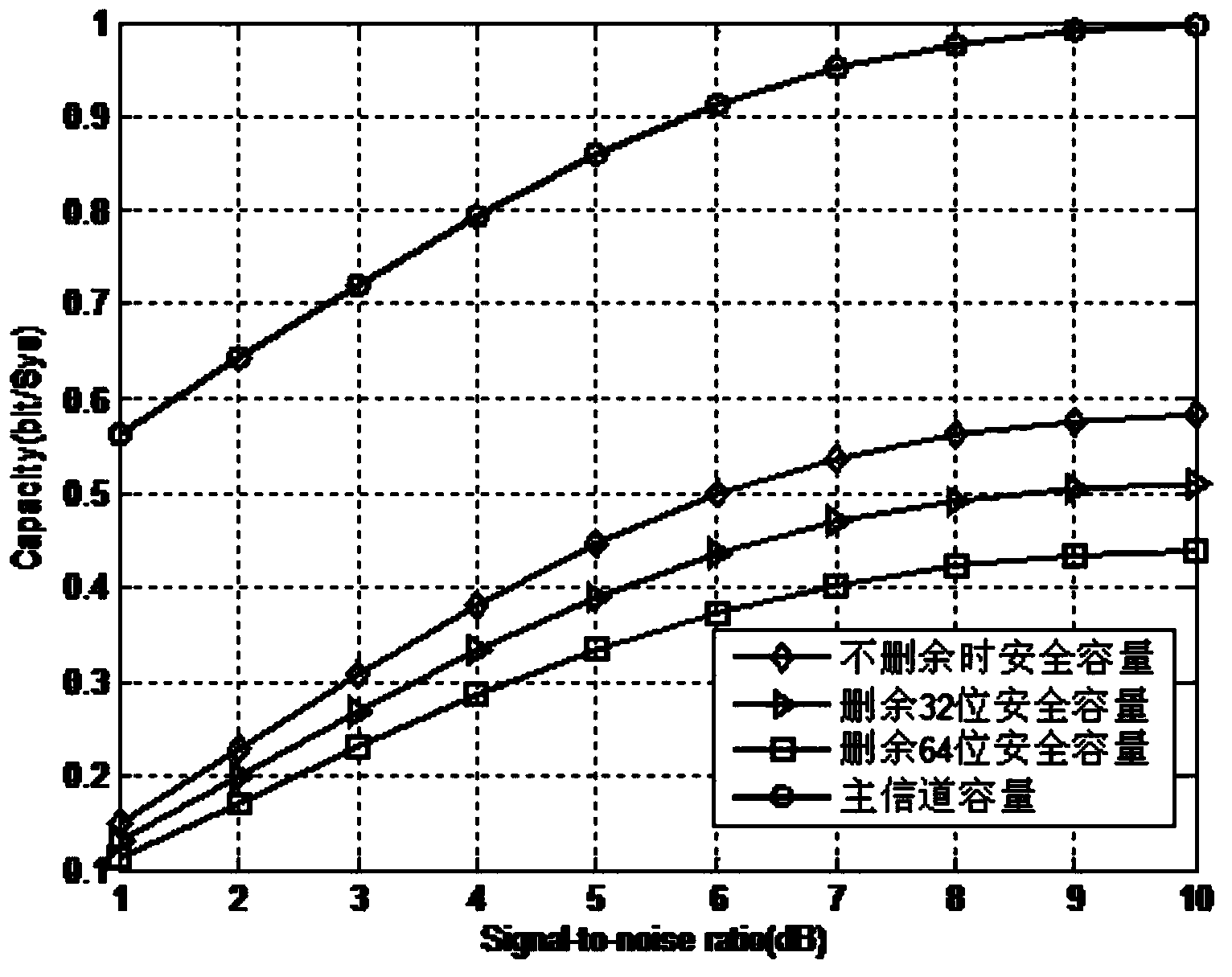
Degraded eavesdropping channel rate compatible method based on Polar code
InactiveCN103414540AIncrease safety capacityEnsure safetyError preventionEavesdroppingComputer science
The invention discloses a degraded eavesdropping channel rate compatible method based on a punctured Polar code. According to the method, the punctured Polar code is combined with a degraded eavesdropping channel model; according to construction features of the Polar code, a safe bit-channel used for transmitting information is given; according to channel rate requirements of a degraded eavesdropping channel, a proper puncturing matrix is built, and the degraded eavesdropping channel rate compatible method based on the Polar code is achieved; because eavesdroppers do not know the puncturing matrix, the coded code word length is reduced through puncturing operation, information is hidden through the puncturing operation, the complexity that the eavesdroppers recover original information through code words received through wiretapping is increased, and system safety is guaranteed; furthermore, the puncturing method ensures that all codes in the same group of rate-compatible codes can be achieved through the same group of encoders, and therefore the complexity of emitters and receivers is greatly reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
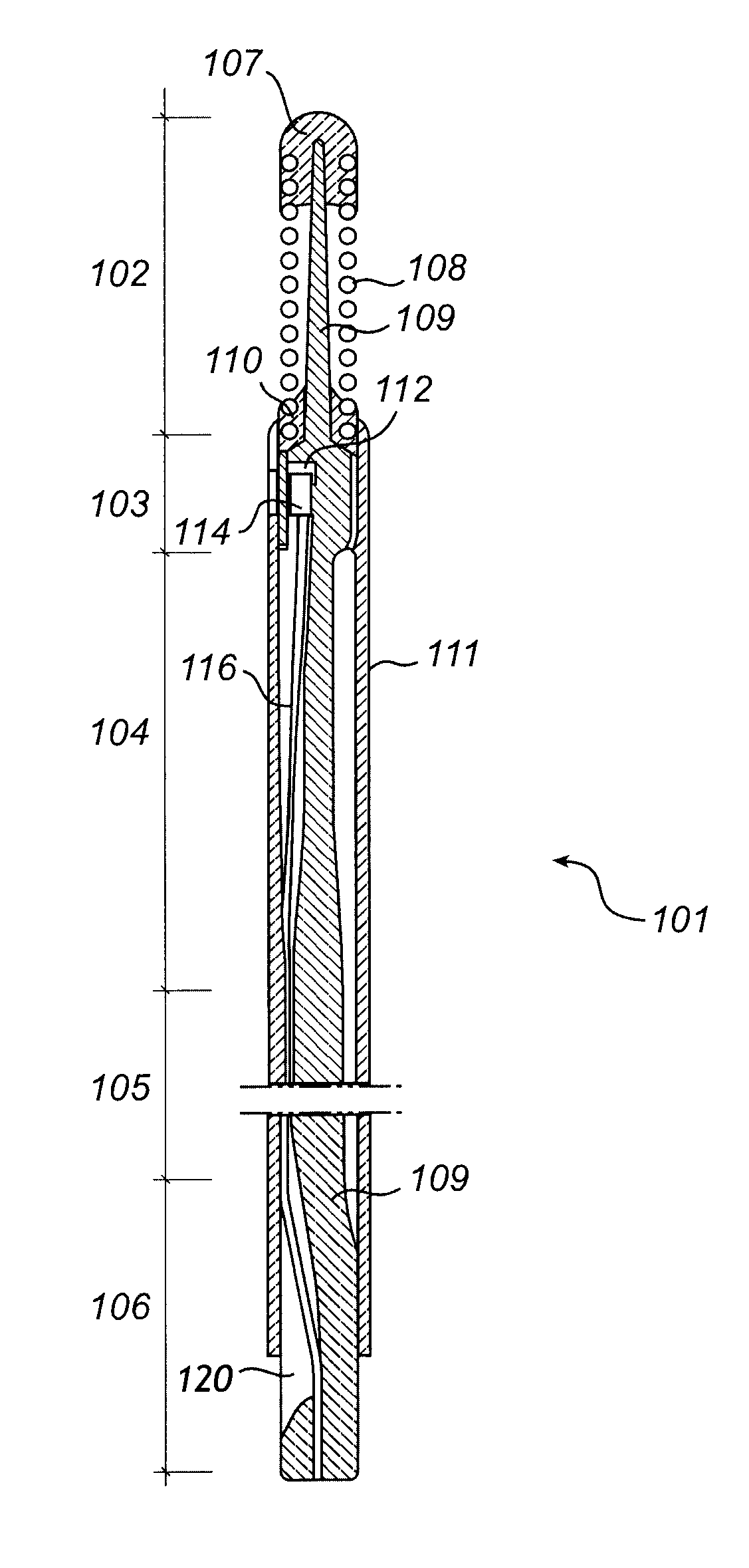
Device for acquiring physiological variables measured in a body
ActiveUS20110071407A1Firmly connectedReduce in quantityEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterCommunication interfaceTelecommunications link
The present invention relates to an eavesdropping device for monitoring measured physiological variables of an individual, which eavesdropping device comprises a receiver and a communication interface. The eavesdropping device of the present invention is typically applied in a system comprising a first sensor arranged to be disposed in or outside the body of the individual for measuring aortic blood pressure Pa, and a second sensor arranged for measuring distal blood pressure Pd. Further, the system comprises a central monitoring device for monitoring the measured physiological variables and a communication link between the sensors and the central monitoring device for communicating signals representing the measured physiological variables from the sensors to the central monitoring device. The eavesdropping device is configured such that the communication interface is arranged at the communication link to communicate at least the signal representing the aortic blood pressure to a monitor of the eavesdropping device. Moreover, the receiver of the eavesdropping device is connected to the communication link, in parallel with the central monitoring device. The signal representing the aortic blood pressure Pa is communicated to the receiver via a high-impedance connection at the communication interface, and the receiver of the eavesdropping device is further arranged to receive the signal representing the measured distal blood pressure Pd from the communication link. By means of the blood pressure signals of the respective sensor, FFR can be calculated.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL COORDINATION CENT
System and Method for Secure Message-Oriented Network Communications
InactiveUS20030202663A1Minimize threatFacilitate and control accessKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsCommunications systemSecurity Measure
The present invention provides a message-oriented middleware solution for securely transmitting messages and files across public networks unencumbered by intervening network barriers implemented as security measures. It also provides a dynamic, dedicated, application level VPN solution that is facilitated by the message-oriented middleware. Standard encryption algorithms are used to minimize the threat of eavesdropping and an Open-Pull Protocol (OPP) that allows target nodes to pull and verify the credentials of requestors prior to the passing of any data. Messaging can be segregated into multiple and distinct missions that all share the same nodes. The security network's architecture is built to resist and automatically recover from poor, slow, and degrading communications channels. Peers are identifiable by hardware appliance, software agent, and personally identifiable sessions. The security network provides a dynamic, private transport for sensitive data over existing non-secure networks without the overhead and limited security associated with traditional VPN solutions.
Owner:THREATGUARD
Methods and systems for generating encryption keys using random bit generators
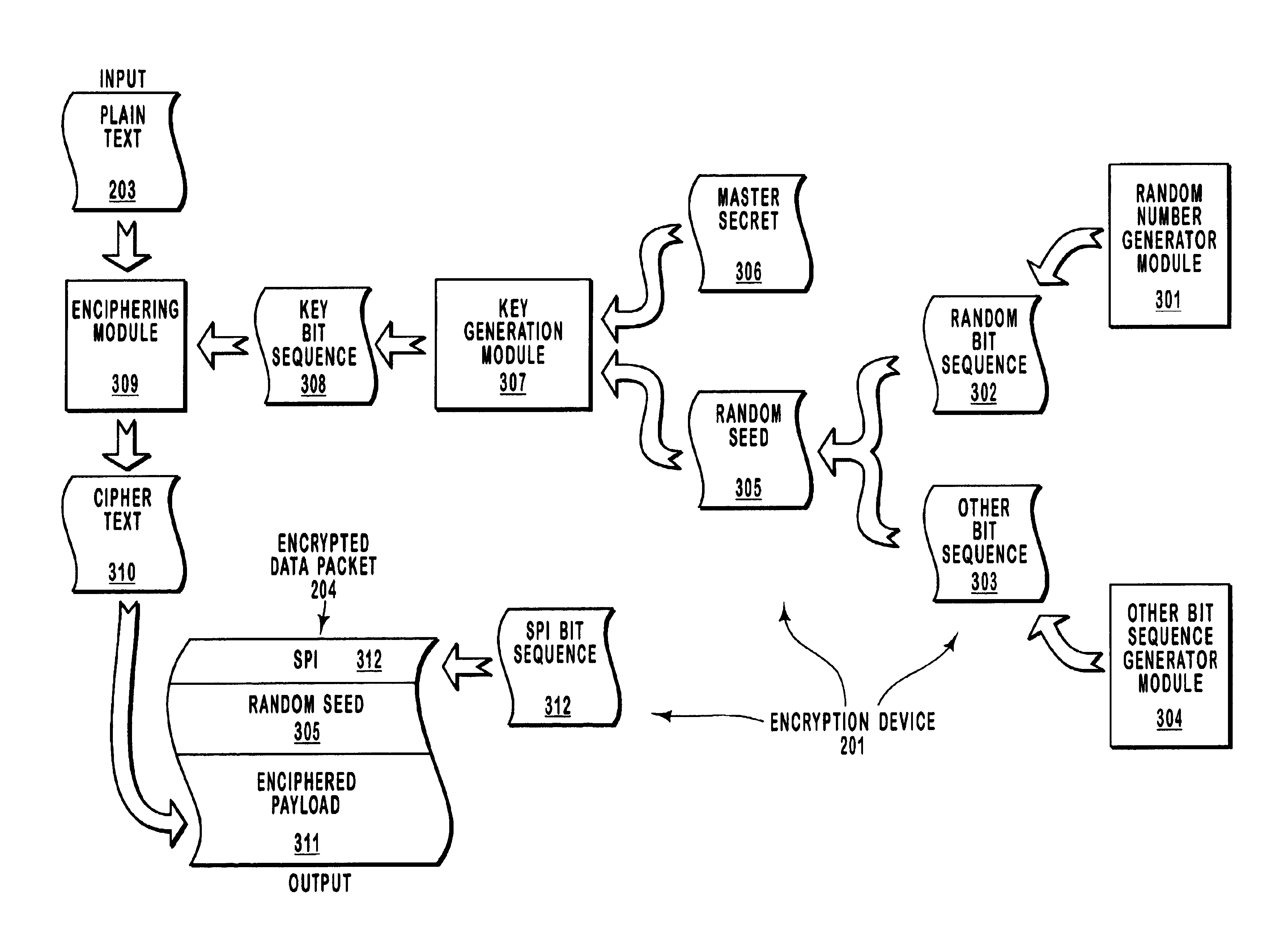
InactiveUS6931128B2Reduce rewardAvoid breakingKey distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationNetwork packetRandom seed
A security key, such as an encryption key, is generated so as to make it more difficult for eavesdroppers to identify the key. Specifically, a cryptographically secure random number generator generates a random bit sequence that is included in a seed. This random seed is provided along with a negotiated master secret to a key generation module. The key generation module may implement a pseudo random function that is in accordance with the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol or the Wireless Transport Layer Security (WTLS) protocol. This key may then be used to encrypt a plain text message to form an encrypted data packet. The encrypted data packet also includes the random seed in unencrypted form. The encrypted data packet may be transmitted over a public network to a recipient with reduced risk of eavesdropping.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Quantum Cryptographic Communication Method
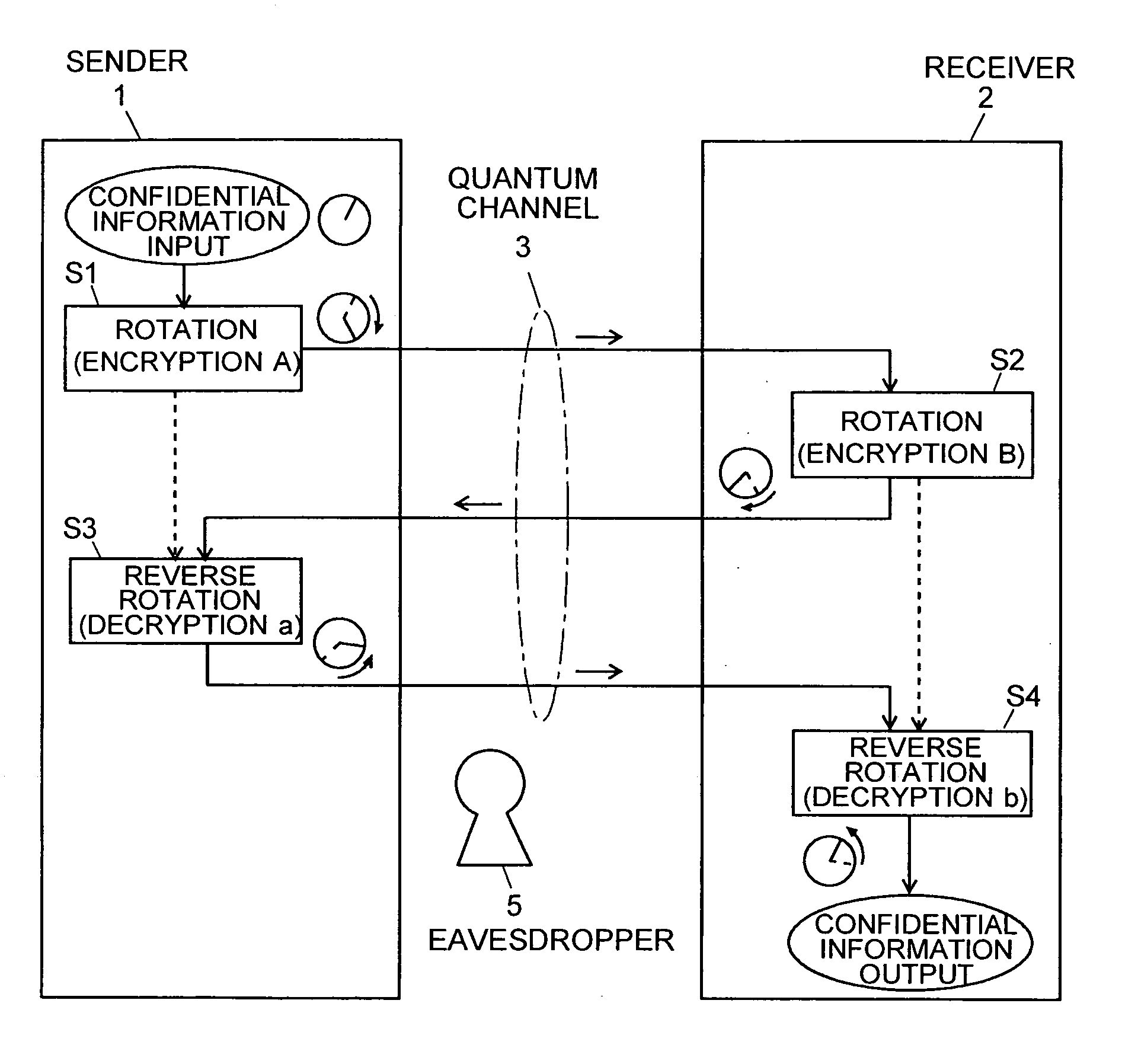
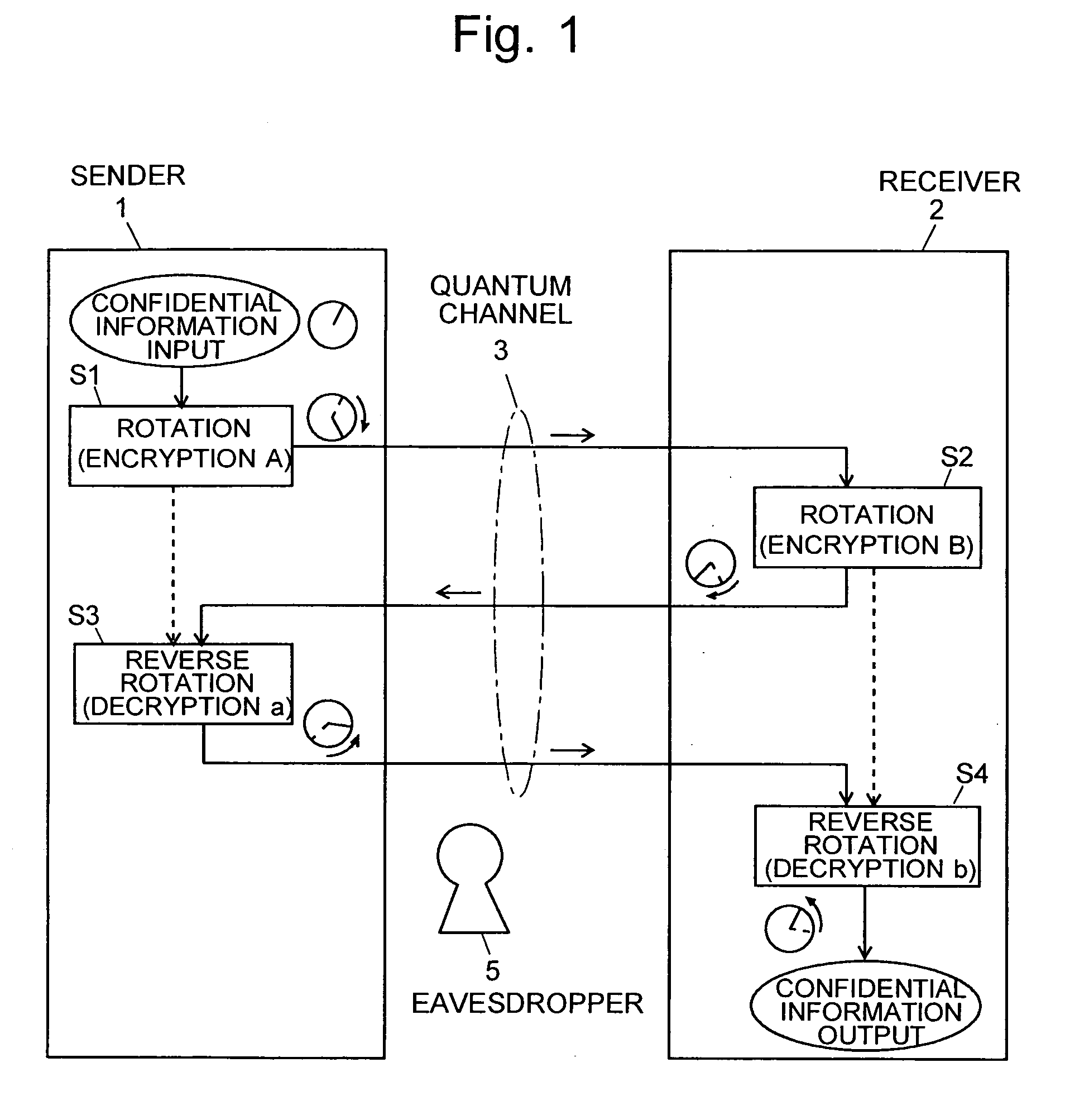
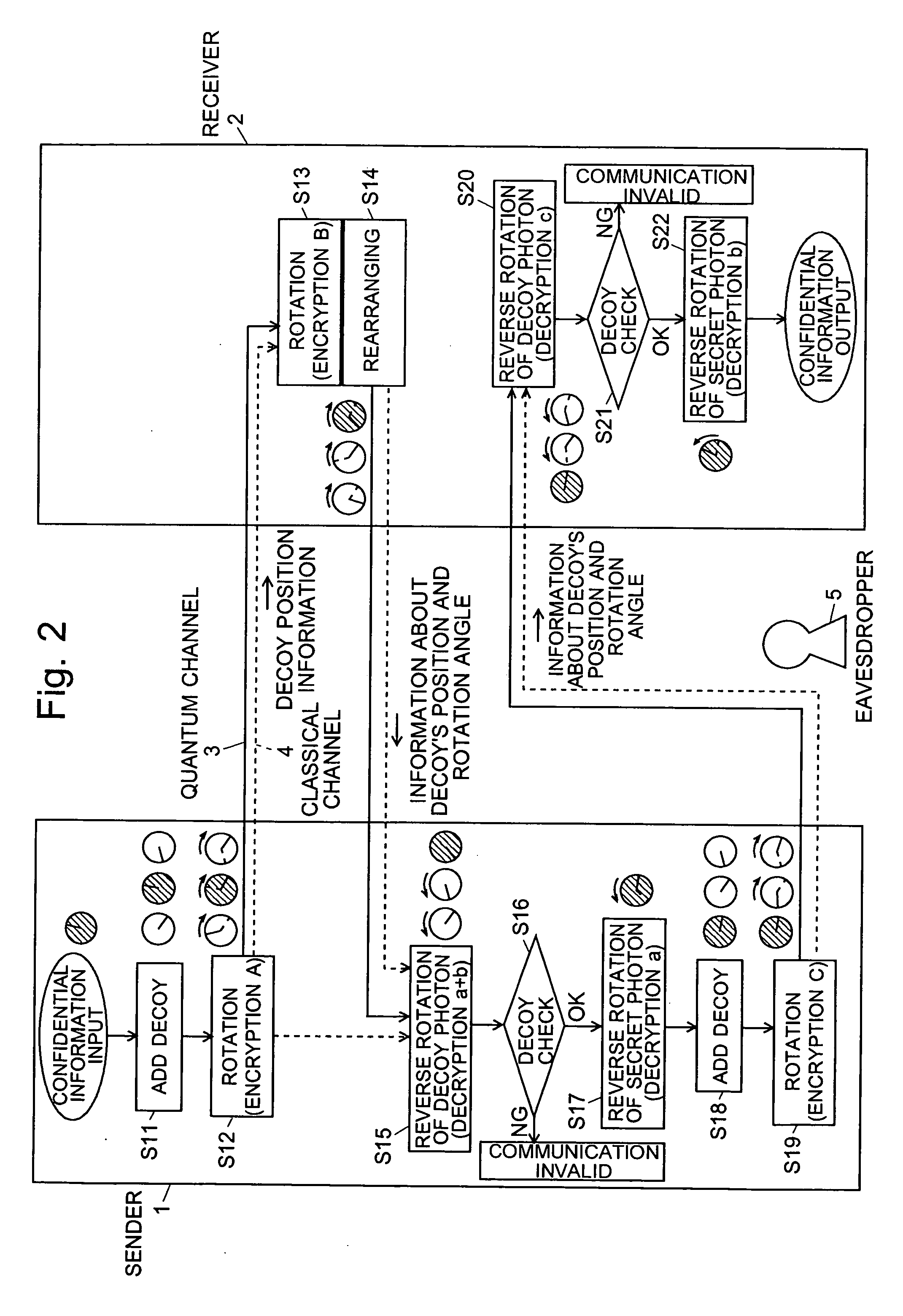
A sender (1) adds decoy photons to a secret photon having confidential information, then, subjects each photon to a different rotational manipulation, and passes the photons along a quantum channel (3) (S11 and S12). A receiver (2) receives those photons and then obtains information about the position of the decoy photons from the sender (1) through a classical channel (4). Using the information, the receiver (2) subjects each of the decoy and secret photons to a different rotational manipulation and transmits the photons in a rearranged order (S13 and S14). The receiver (1) obtains information about the position and manipulation quantities of the decoy photons from the receiver (2) and decodes the decoy photons. If the quantum state of the decoys is identical to their initial quantum state, the sender (1) determines that no eavesdropper (5) should be present (S15 and S16), cancels only the encryption of the secret photon performed by himself or herself in S12, and transmits the secret photon (S17). The receiver (2) cancels the encryption of the secret photon performed by himself or herself in S13 and thereby obtains the confidential information (S18). The present method can securely send quantum information as well as classical information such as key information, and also effectively detect eavesdropping.
Owner:NARA INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
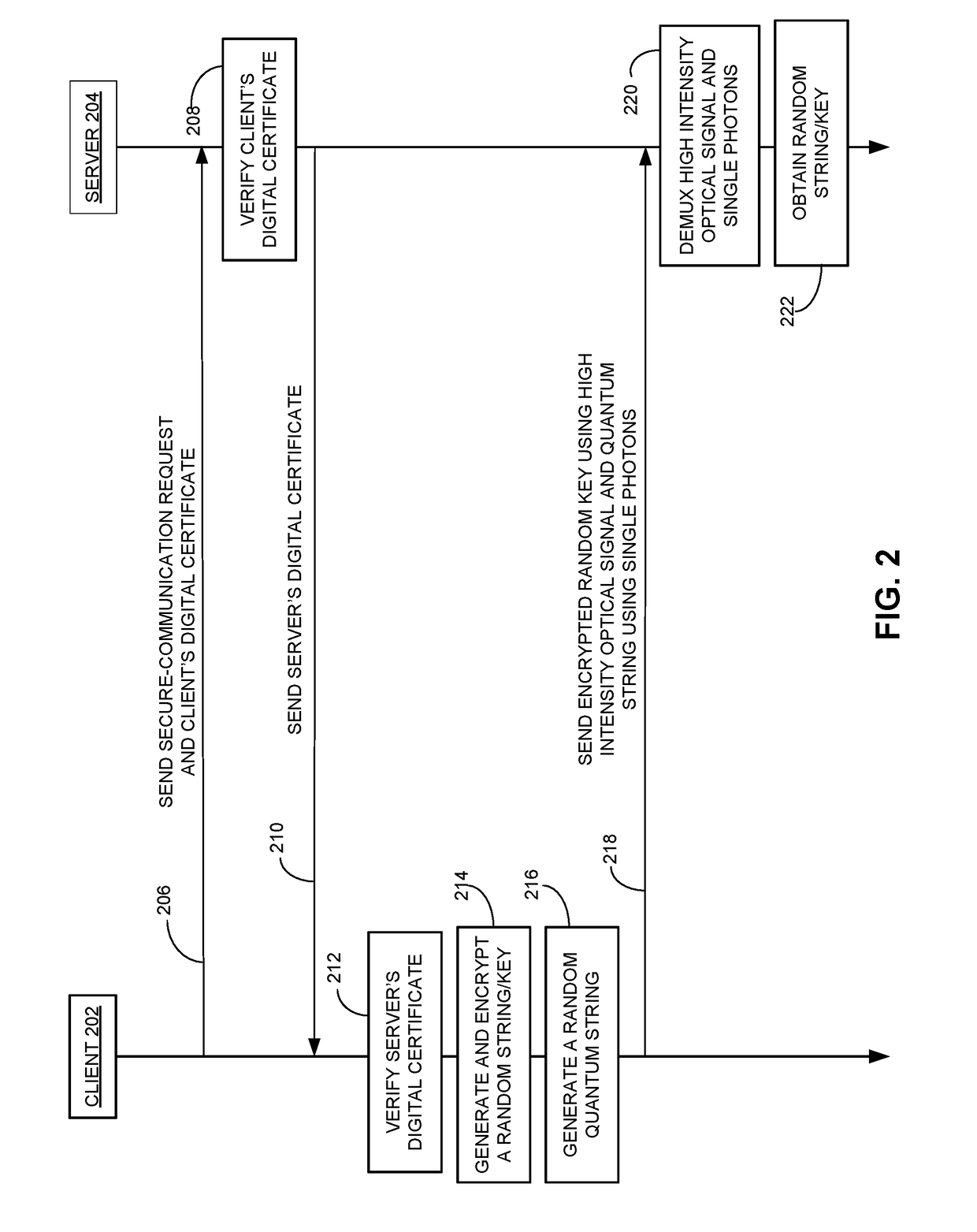
Method and system for detecting eavesdropping during data transmission
ActiveUS20170331623A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsKey distribution for secure communicationSecure communicationEavesdropping
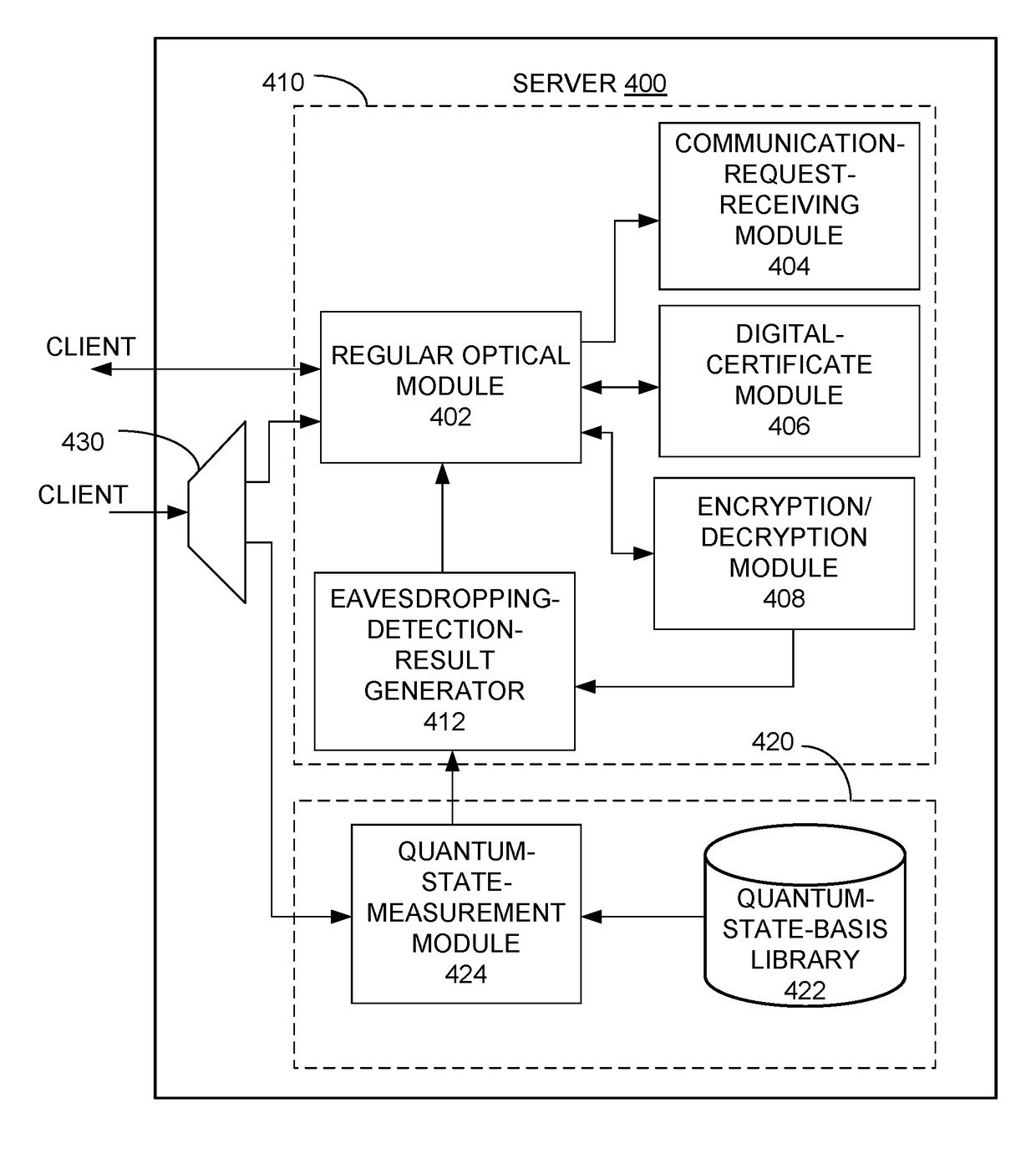
One embodiment provide a system and method for detecting eavesdropping while establishing secure communication between a local node and a remote node. During operation, the local node generates a random key and a regular optical signal based on the random key. The local node also generates a quantum optical signal based on a control sequence and a set of quantum state bases, and multiplexes the regular optical signal and the quantum optical signal to produce a hybrid optical signal. The local node transmits the hybrid optical signal to the remote node, sends information associated with the control sequence and information associated with the set of quantum state bases to the remote node, and receives an eavesdropping-detection result from the remote node based on measurement of the quantum optical signal, the information associated with the control sequence, and the information associated with the set of quantum state bases.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
Secure Data Management Device and Method
InactiveUS20070278285A1Coin-freed apparatus detailsUser identity/authority verificationLogistics managementConfidentiality
The invention concerns a secure data management device and a method for providing communication between a remote device in a chain of logistics and a host computer via a data network which ensures the identity, authenticity, integrity and confidentiality of collected information. This is provided by an item which is attached to a product subjected to a chain of logistics. The item can collect information about the product or use of the product and communicates such information to a host computer via a data network in a secure manner, which will assure the recipient of the information that the communication is made with the correct item and that the information communicated has not been manipulated and the transmission is protected from eavesdropping. The information collected by the item can be generated by sensors integrated or attached to the product.
Owner:CYPAK
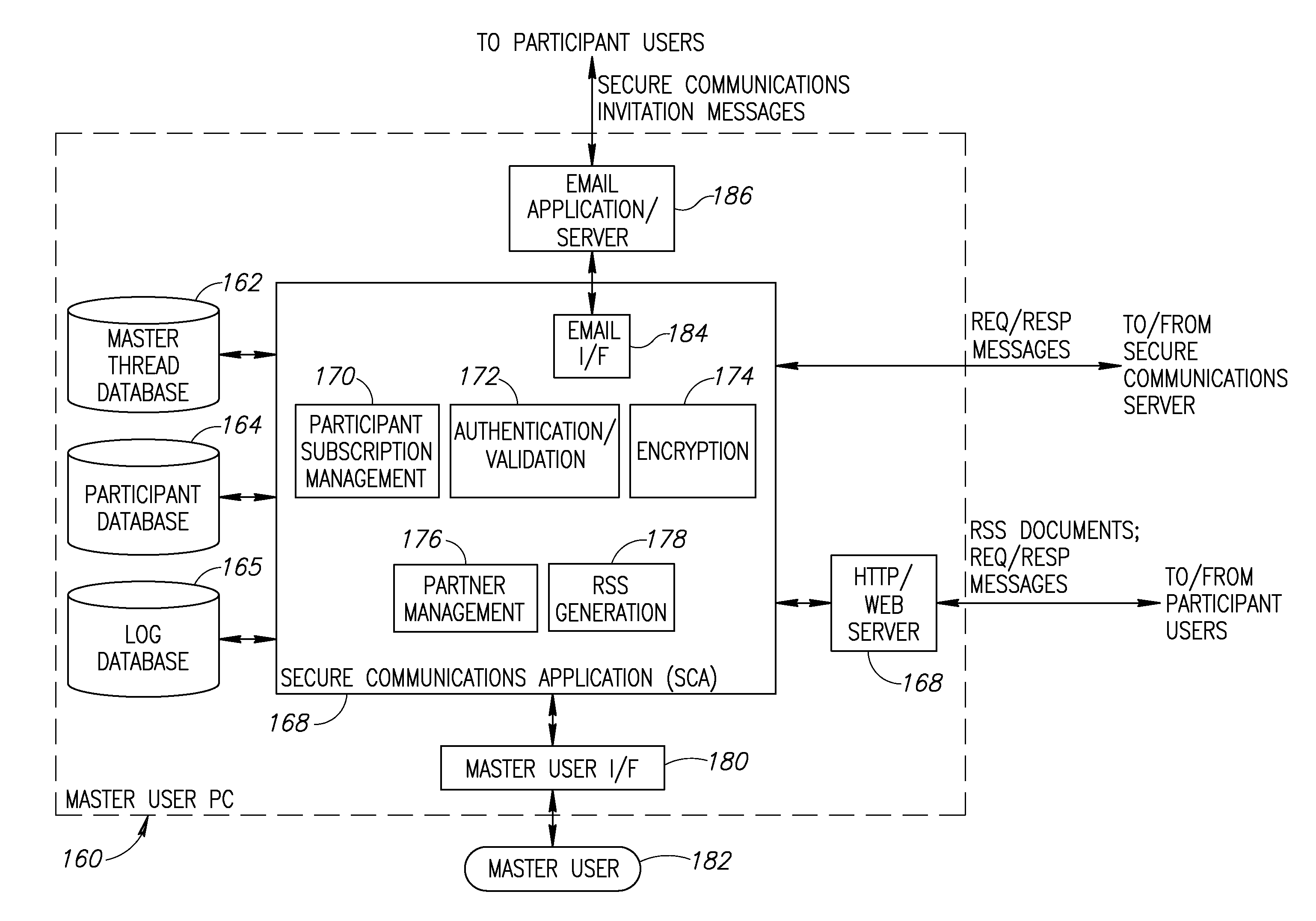
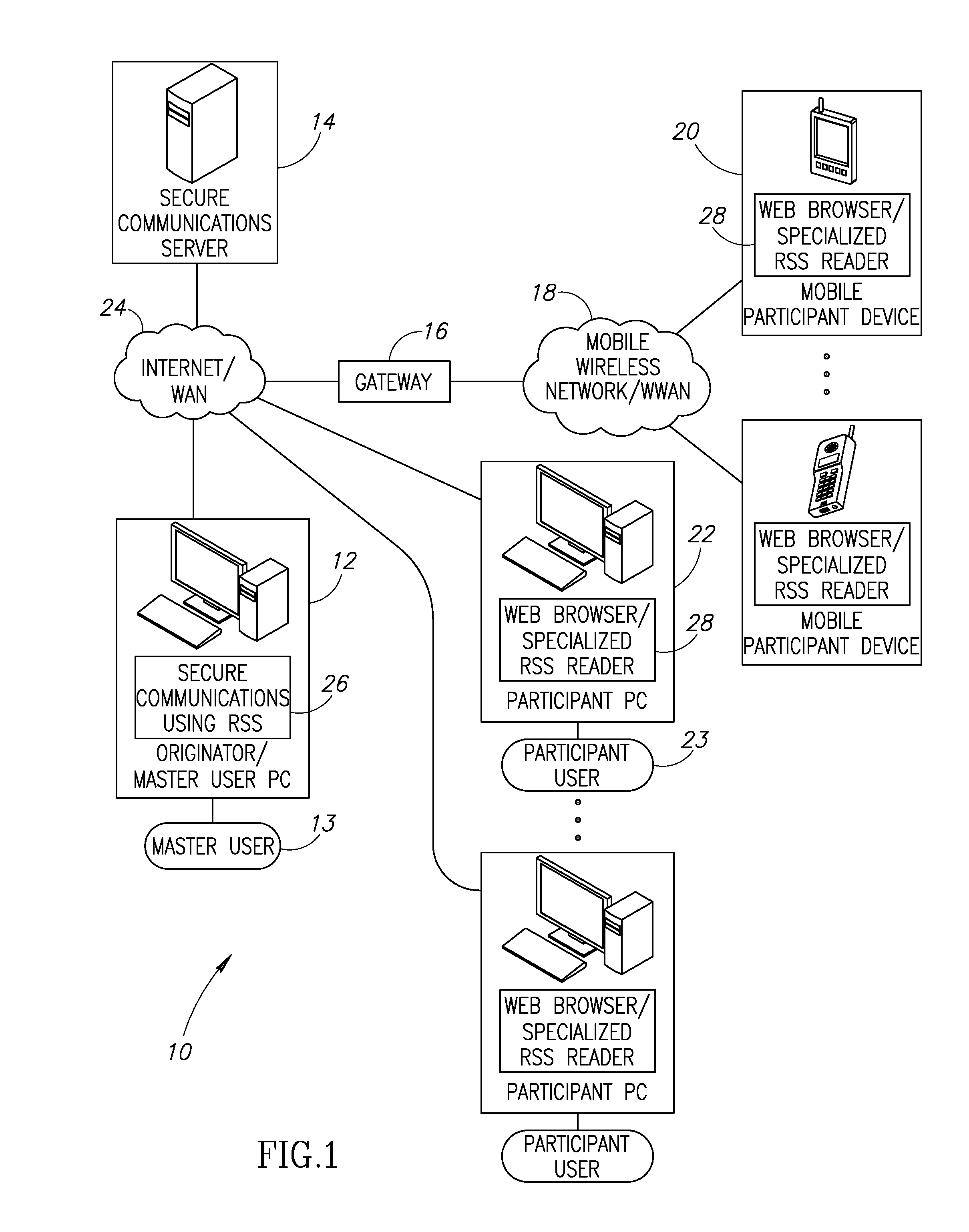
System and method for secure communications utilizing really simple syndication protocol
InactiveUS20070055731A1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksSecure communicationWeb browser
A novel system and method for providing secure communication between two or more users via a really simply syndication (RSS) document feed through a conventional email client. Users exchange messages via RSS documents in lieu of sending email messages using conventional email applications with the problem of spam, security and network bandwidth that typically plague conventional email systems. A unique RSS document feed exchange is established using conventional email. Once established, however, all messages in the communications session are transmitted between users using RSS documents. Users can create, edit and delete message threads on their standard web browsers or use a specialized RSS reader. The communication event messages may also be encrypted using any suitable well known encryption technique to foil malicious interception and eavesdropping.
Owner:THIBEAULT JASON
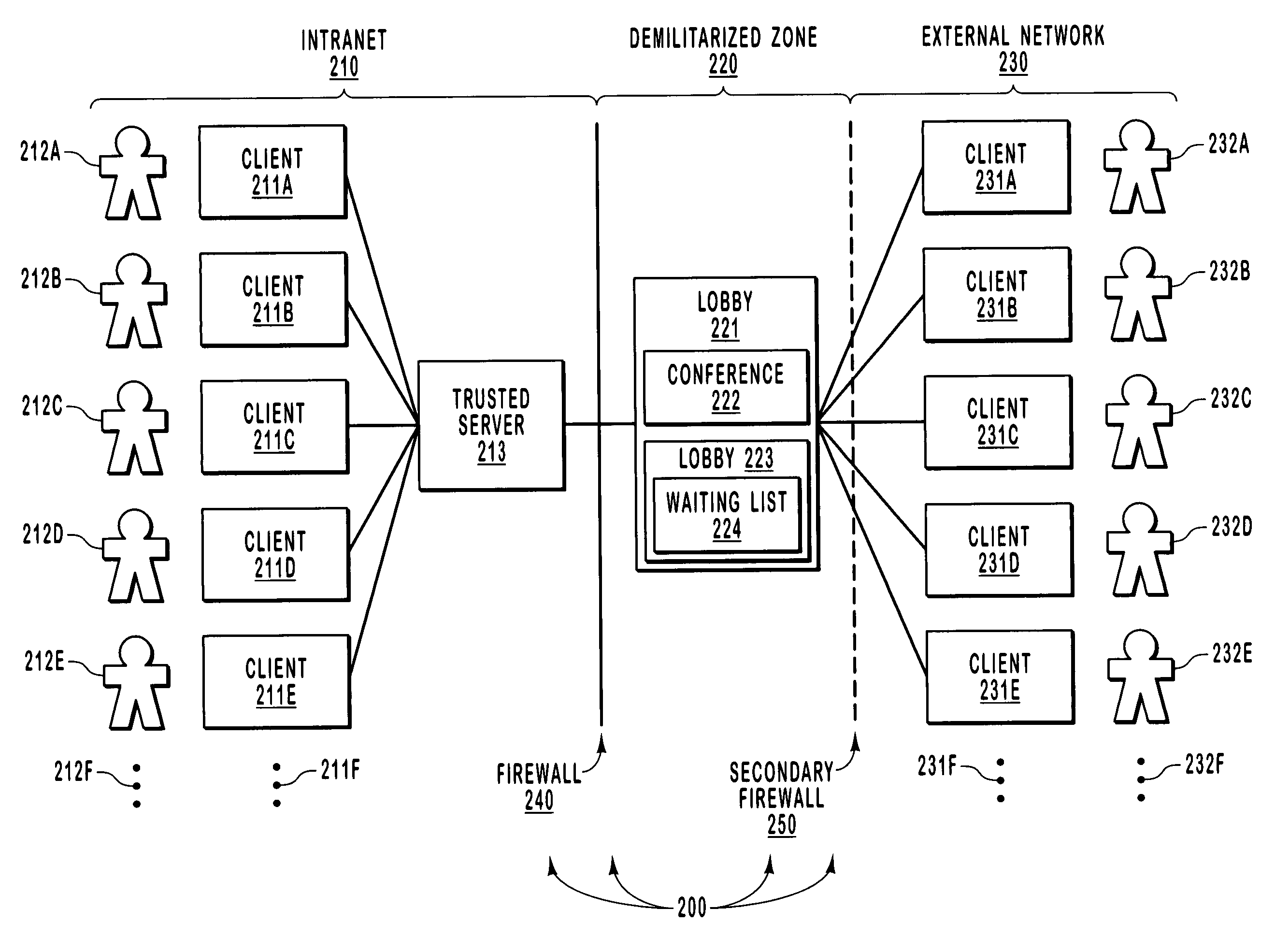
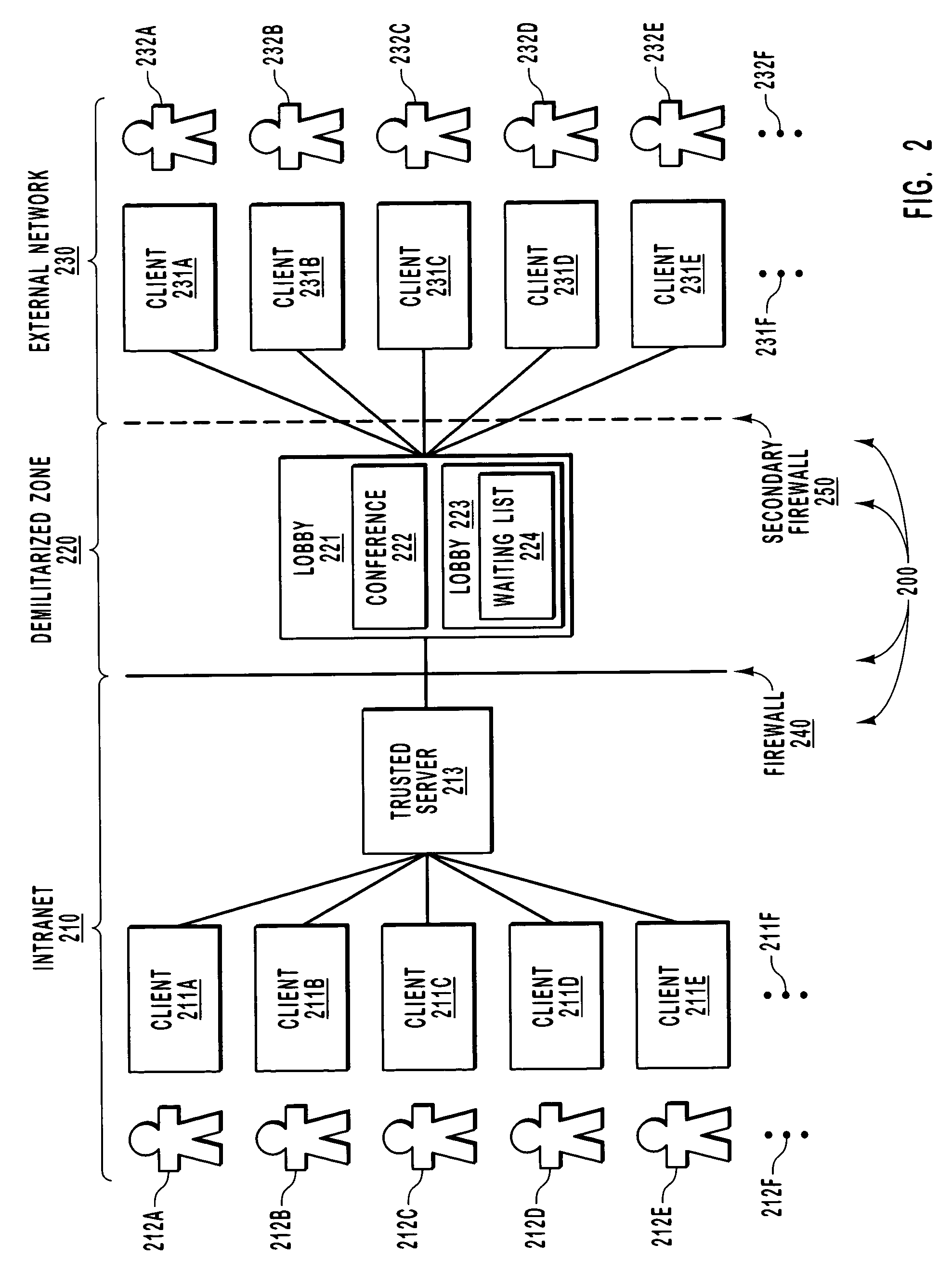
Virtual lobby for data conferencing
ActiveUS7398295B2Great and flexible level of securityReduce riskSpecial service provision for substationMultiple digital computer combinationsReal-time dataData exchange
Allowing external computing systems to access a data conference with low risk of eavesdropping. An external computing system accesses a virtual lobby before joining the data conference. The virtual lobby is an object that may include a list of computing systems admitted to the lobby. An external computing system joins the lobby when it is included in a waiting list associated with the lobby. Being joined to the lobby does not allow full access to the live data exchanges in the data conference, but does facilitate functions that are less sensitive such as notifying a conference organizer that the joined party in the lobby would like to join the data conference. Upon receiving notice that an external computing system has joined the lobby, the conference organizer then provides further authorization for the external computing system to enter the data conference using any number of in-band or out-of-band mechanisms.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
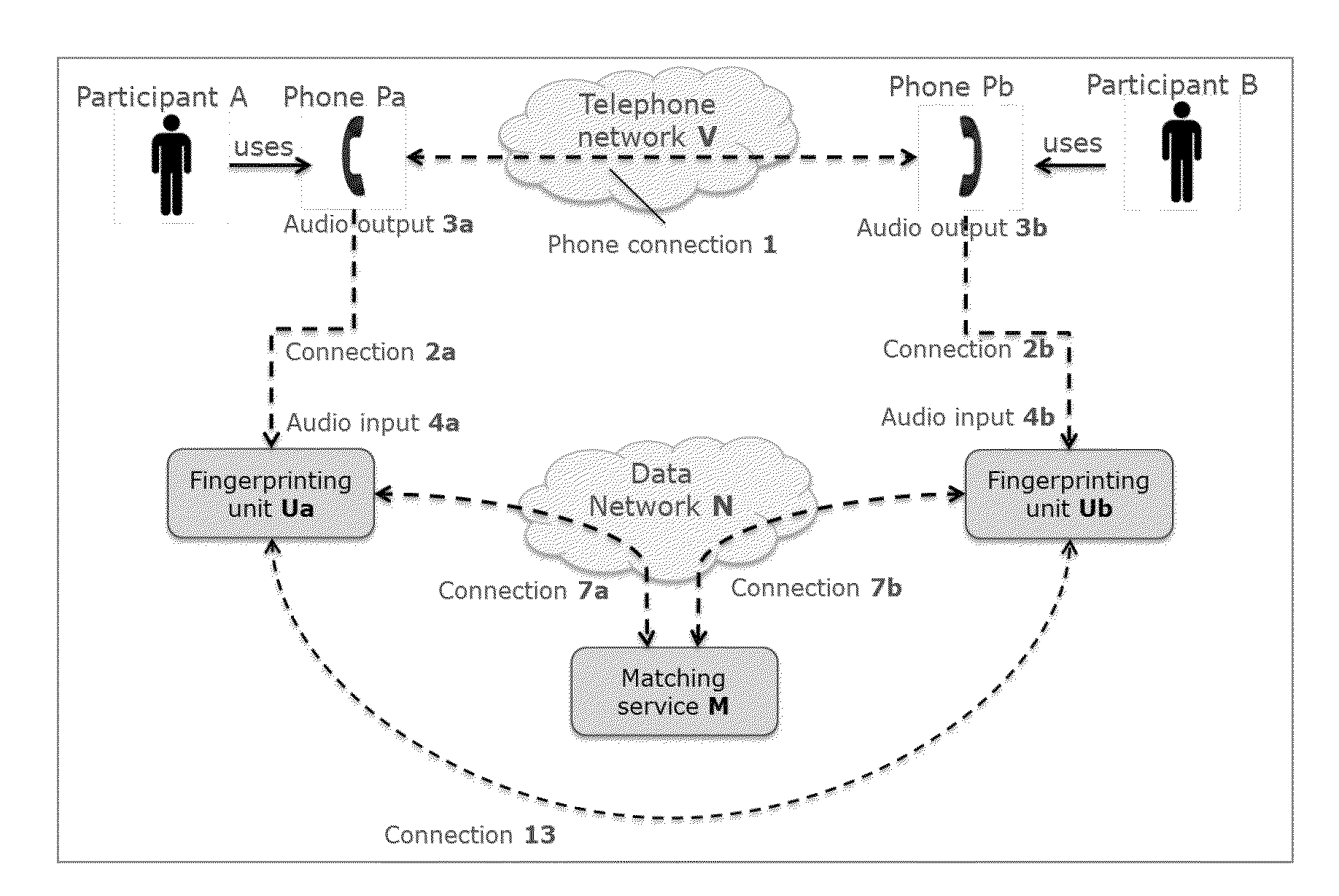
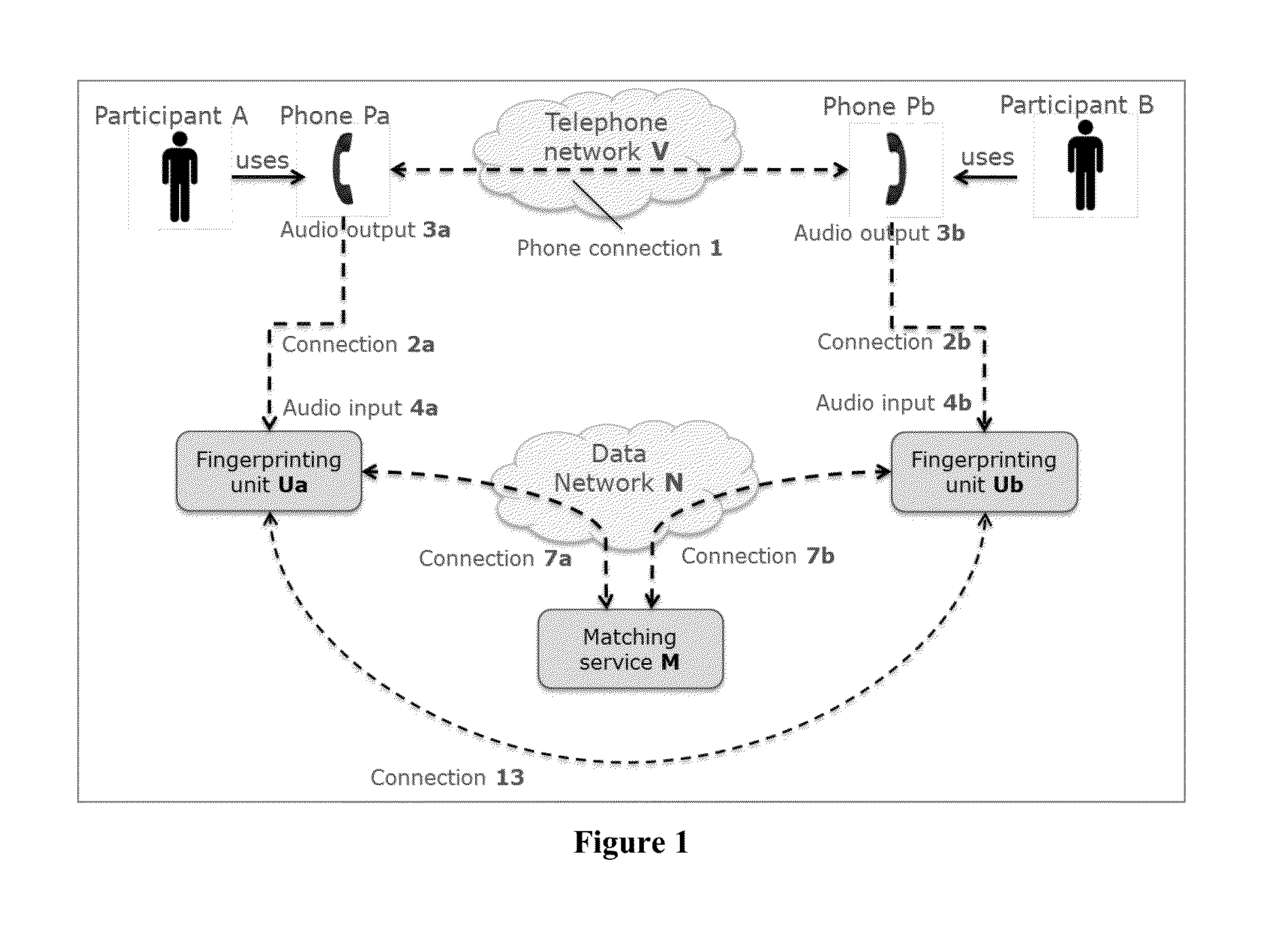
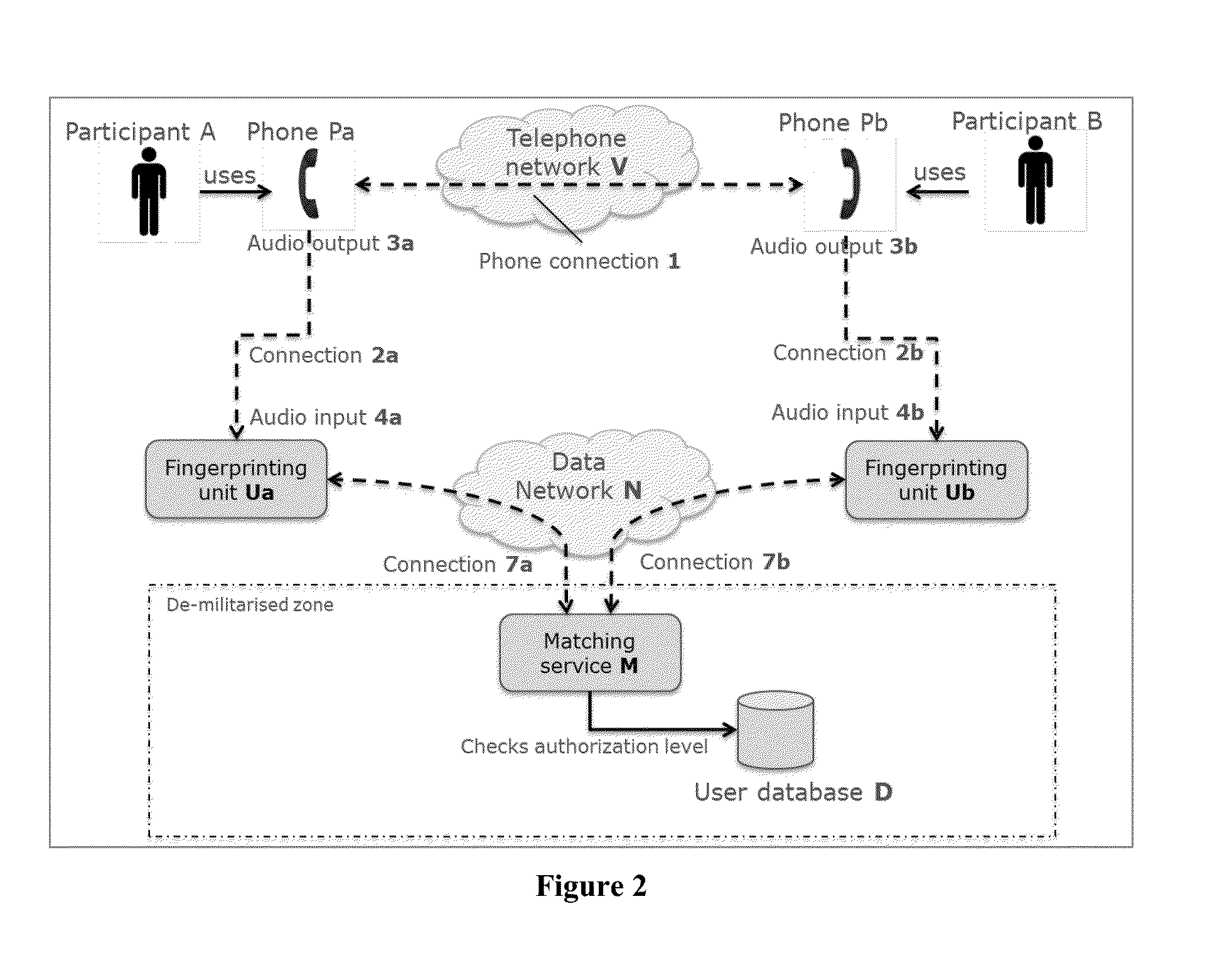
Ad hoc one-time pairing of remote devices using online audio fingerprinting
ActiveUS20150287416A1Improve protectionEasy to useSpecial service for subscribersSpeech analysisData connectionPassword
Participants of a phone conference can share electronic data without a need to exchange passwords to link two devices nor to login to access data. The invention is resistant to eavesdropping, and provides methods, devices and systems to easily and automatically find, identify and authenticate participants on a computer network for electronic data exchange. Samples of the audio are used to create a stream of audio fingerprints which are sent to a matching service. This matching service finds the fingerprints that correspond to the same conversation, and exchanges identifiers. When instructed by the user, the device can setup a secure data connection.
Owner:BARCO NV
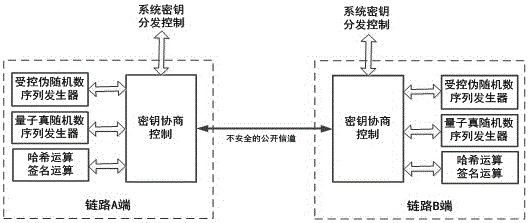
Negotiation system and negotiation method based on quantum truly random number negotiation secret key
ActiveCN106612176AEliminate channel eavesdropping attack vectorsKey distribution for secure communicationEavesdroppingComputer science
The invention provides a negotiation system and a negotiation method based on a quantum truly random number negotiation secret key. Based on a controlled pseudo random number sequence generator and a quantum truly random number sequence generator at both ends of a link, two groups of quantum truly random number sequences are exchanged mutually by a negotiation protocol; after carrying out hash value operation, each end of the link compares the quantum truly random number sequence exchanged from the opposite end with the group of quantum truly random number sequence of the local end, which is used for exchange, to acquire position marking information with the same bit value; and one group of pseudo random number sequence is read, according to the position marking information, taking out bit values of corresponding positions one by one to form an original material bit string of the secret key, and by hash operation, a shared secret key is obtained. Compared with the prior art, a channel-eavesdropping attack channel of an opponent can be completely eliminated, and in the secret key negotiating process, any information related to the original material of the secret key is not transferred, so that the opponent cannot acquire any information related to the generated shared secret key on the basis of a channel eavesdropping or decoding means.
Owner:NO 30 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP
System and method for detecting, alerting and blocking data leakage, eavesdropping and spyware
InactiveUS20140143864A1Efficient methodMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionMonitoring statusGraphics
A computer implemented method for detecting, alerting and blocking data leakage, eavesdropping and spyware in one or more networked computing devices includes providing a graphical user interface (GUI) and displaying all available hardware device interfaces in each networked computing device. Next, providing a turn-on switch and a turn-off switch for each displayed hardware device interface in each networked computing device. Next, providing a turn-all-on switch and a turn-all-off switch for all displayed hardware device interfaces in each networked computing device. Next, monitoring status of each available hardware device interface and data traffic across each available hardware device interface. Upon detecting an unauthorized change of status of a specific hardware device interface or unauthorized data traffic across a specific hardware device interface providing a warning signal, turning off the specific hardware device interface by activating the turn-off switch for the specific hardware device interface or the turn-all-off switch.
Owner:NETSHIELD CORP
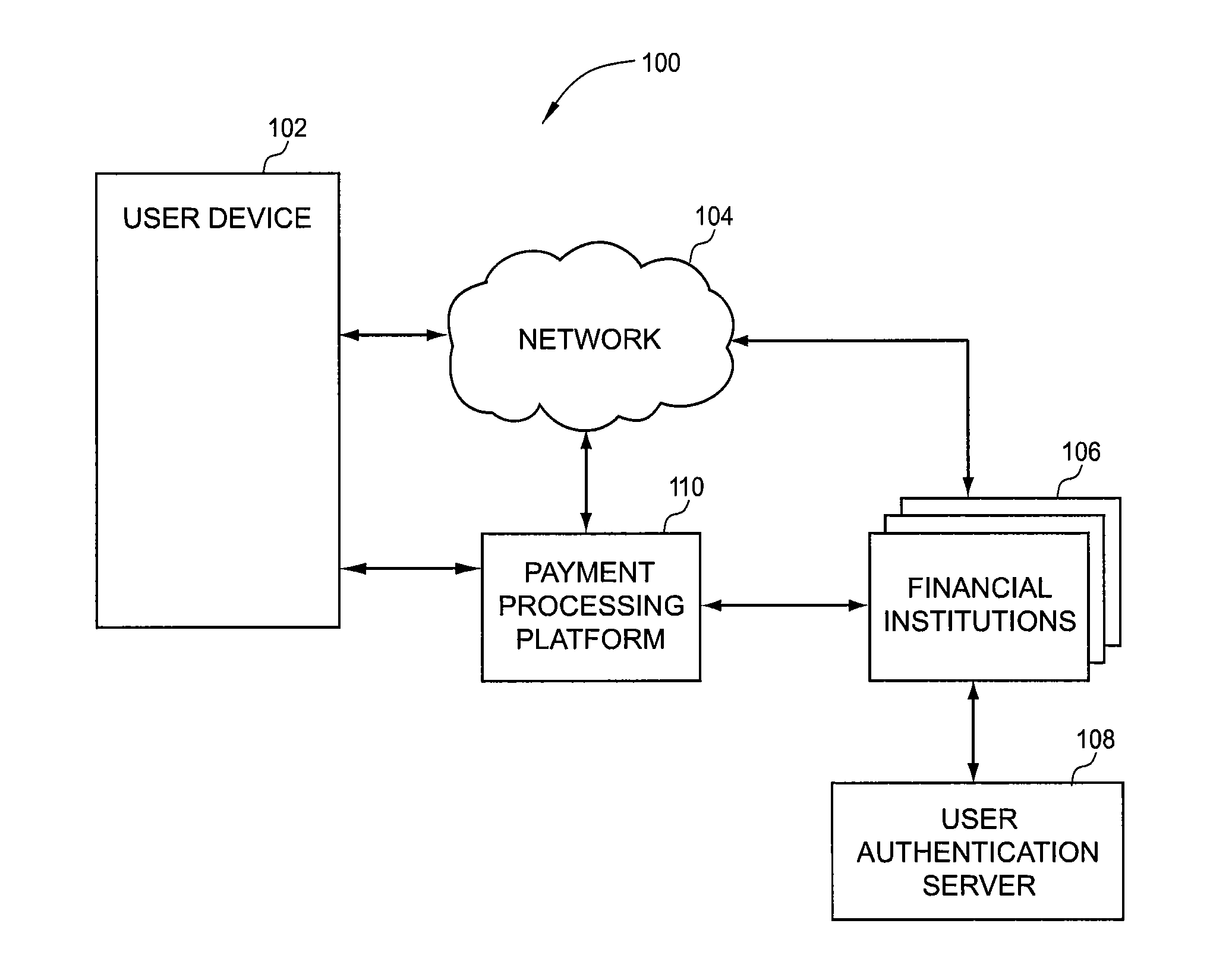
Apparatus and methods for payment transactions using near field communication
In one embodiment, the mobile device includes an NFC tag for near field communication. The NFC tag may include a first storage device and a second storage device. Personal data is stored on the first storage device, which is not accessible by a NFC reader device. Prior to a transaction, the personal data is transmitted from the first storage device to the second storage device, where the data is readable or accessible by the reader device. After transmission of the data to the reader device, the data on the second storage is erased. In this respect, the data is not available for eavesdropping by an unauthorized reader device. In one embodiment, the data remains stored in the first storage device and available for future use. In another embodiment, the data comprises financial product data.
Owner:VERIENT
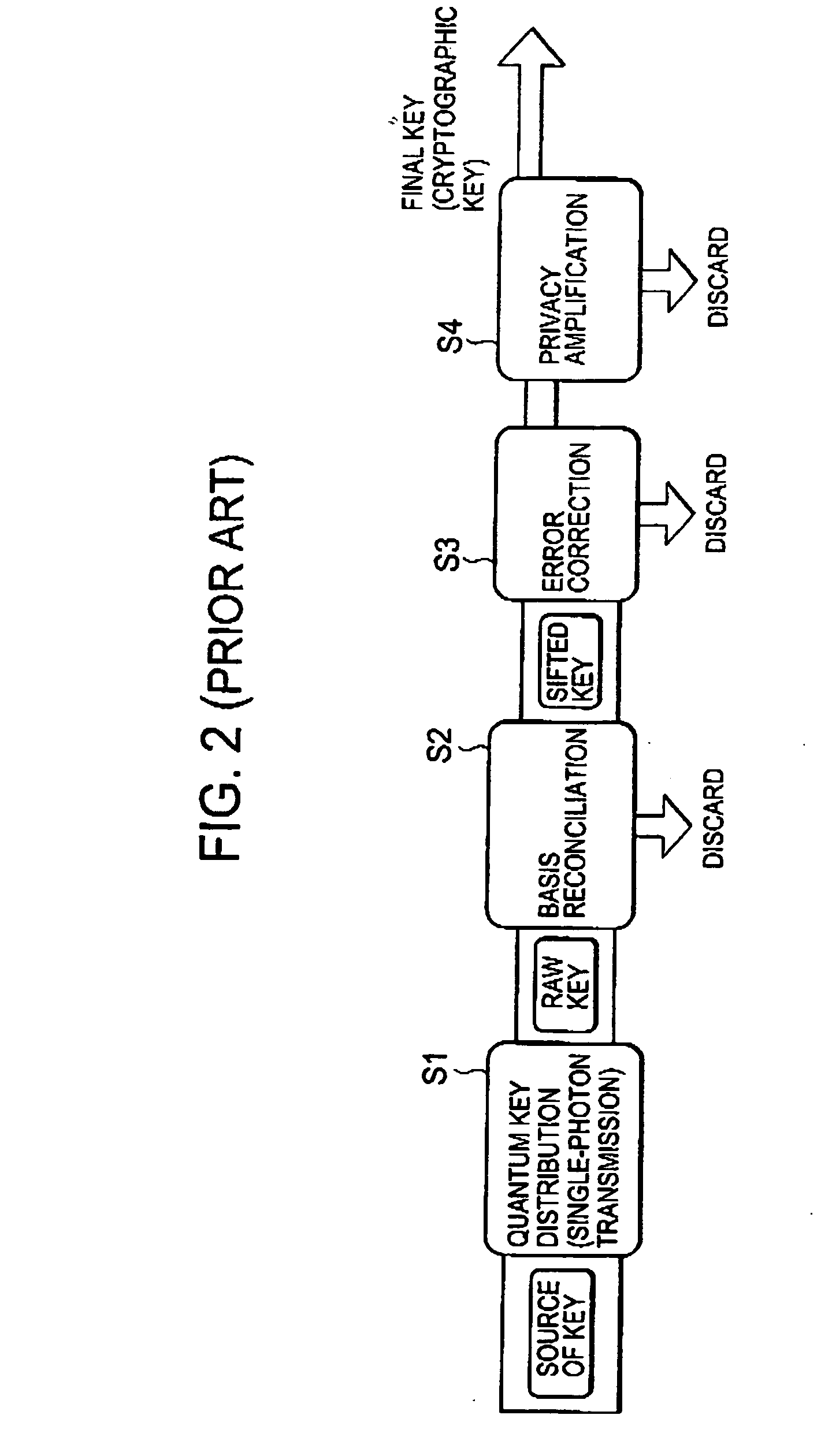
Communication system and method for controlling the same
InactiveUS20070009098A1Minimize error rateEfficient processingSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesError preventionPhase correctionCommunications system
For an error rate QBER, threshold values are preset, including a threshold value Qbit for frame synchronization processing, a threshold value Qphase for phase correction processing, and a threshold value QEve for eavesdropping detection. Upon the distribution of a quantum key from a sender to a receiver, when the measurement value of QBER is deteriorated more than Qbit, frame synchronization processing is performed. When the measurement value of QBER is deteriorated more than Qphase, phase correction processing and frame synchronization processing are performed. When QBER does not become better than QEve even after these recovery-processing steps are repeated N times, it is determined that there is a possibility of eavesdropping, and the processing is stopped.
Owner:NEC CORP
Wireless secure device
InactiveUS7224801B2Internal/peripheral component protectionSecret communicationComputer hardwareJoystick
A method and apparatus for securely connecting one or more wireless peripheral devices such as keyboards, mice, gamepads, remote controllers, joysticks and one or more host systems such as personal computers or workstations, the secure connection reducing the vulnerability of wireless communications between a wireless peripheral device and a host system to accidental or malicious interference or eavesdropping.
Owner:LOGITECH EURO SA
Business process for improving electronic mail
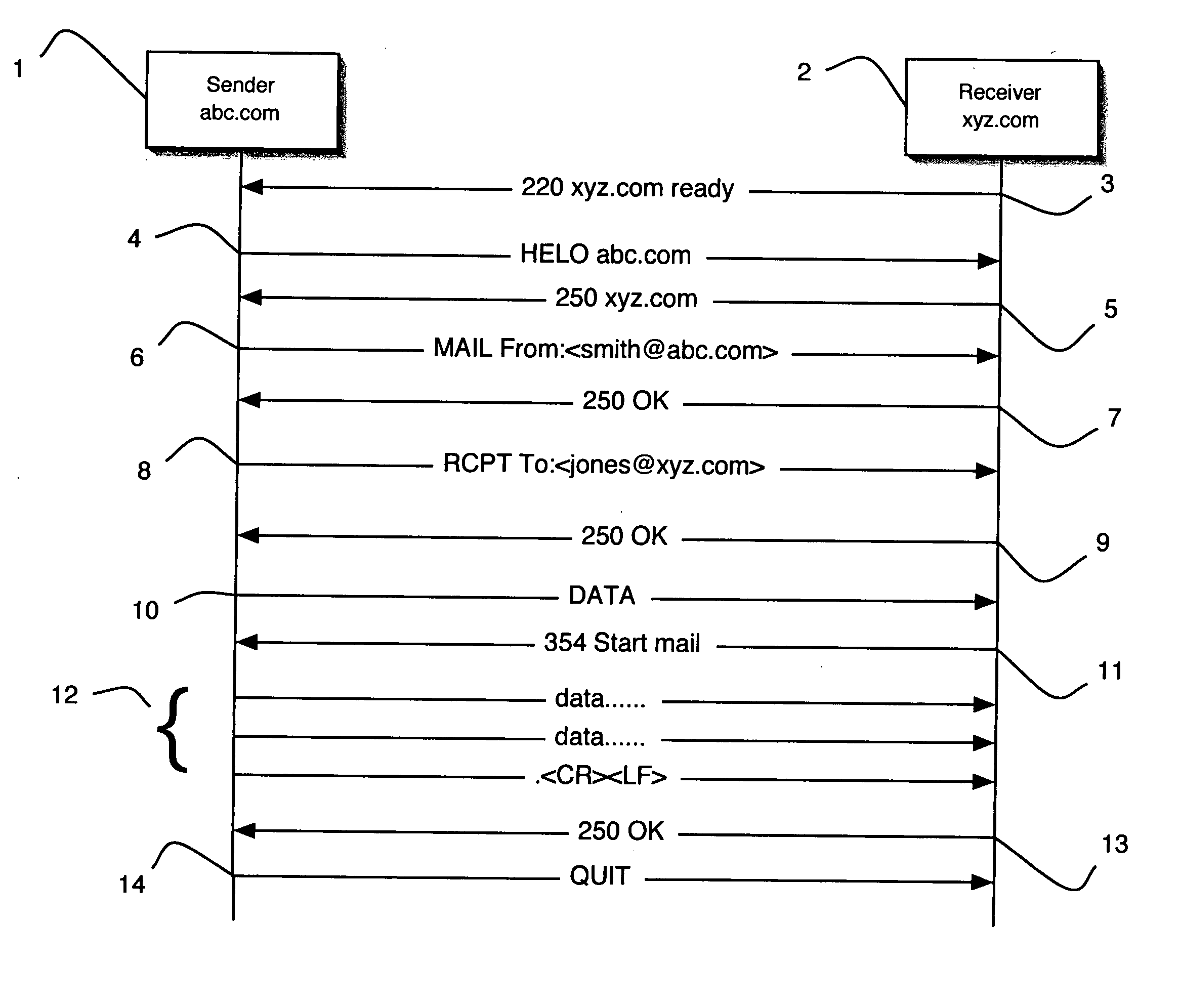
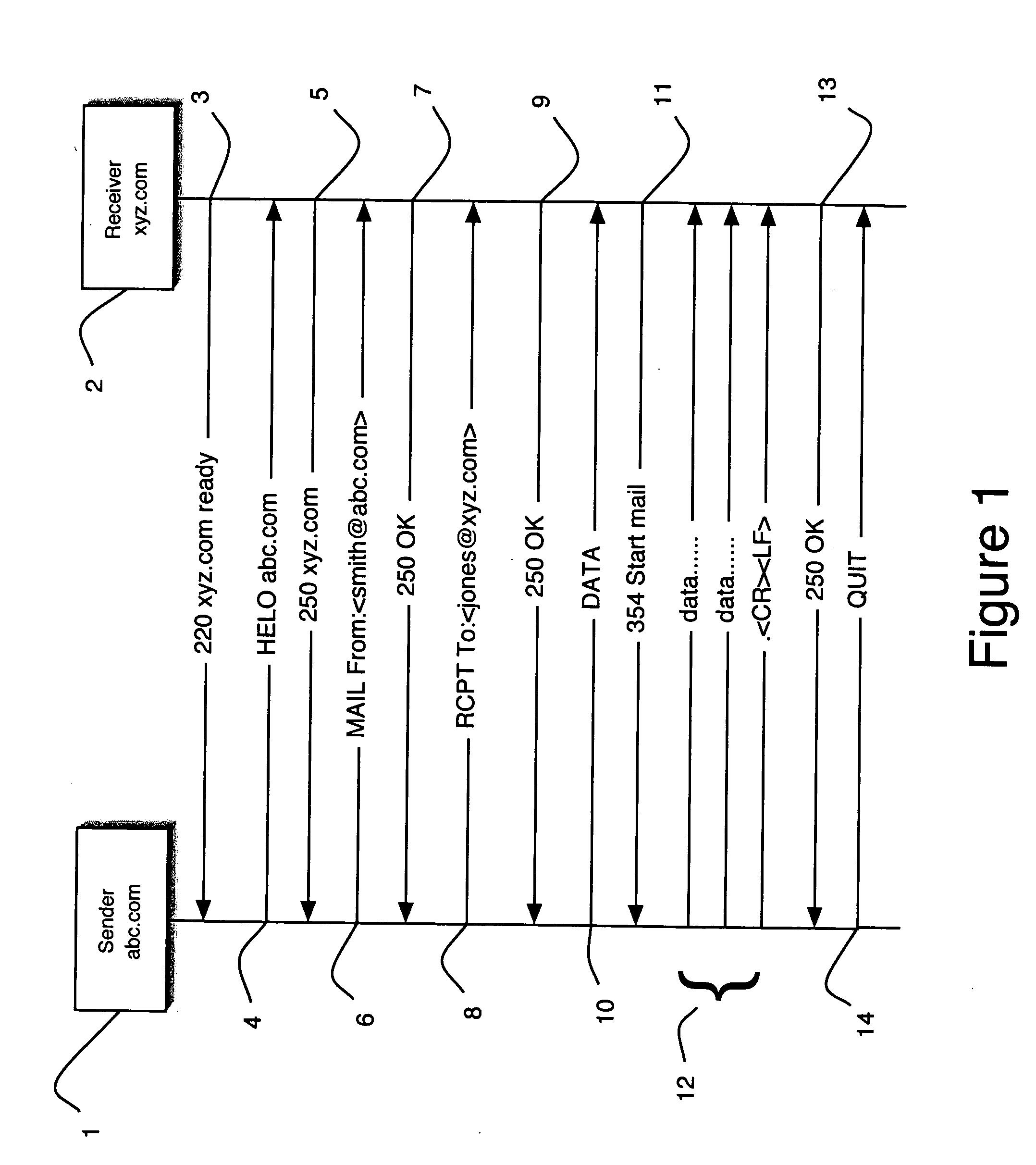
InactiveUS20050097177A1ConfidenceAdditional exchangeMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksThird partyEavesdropping
A business process for effectively sending, receiving, and managing electronic mail over computer networks is provided. Problems of unsolicited, fraudulent, and malicious email are solved by the new process by providing the following capabilities which are absent in current electronic mail exchanges: Definitive identification of the sender, definitive identification of the receiver, precise recording of all email exchanges, preventing third party eavesdropping on email, and ensuring that senders conform to a set of rules disallowing unsolicited, fraudulent, and malicious email. The new process is easily integrated into existing processes, and does not preclude email communication with others who do not employ the new process.
Owner:MCUMBER WILLIAM E +1
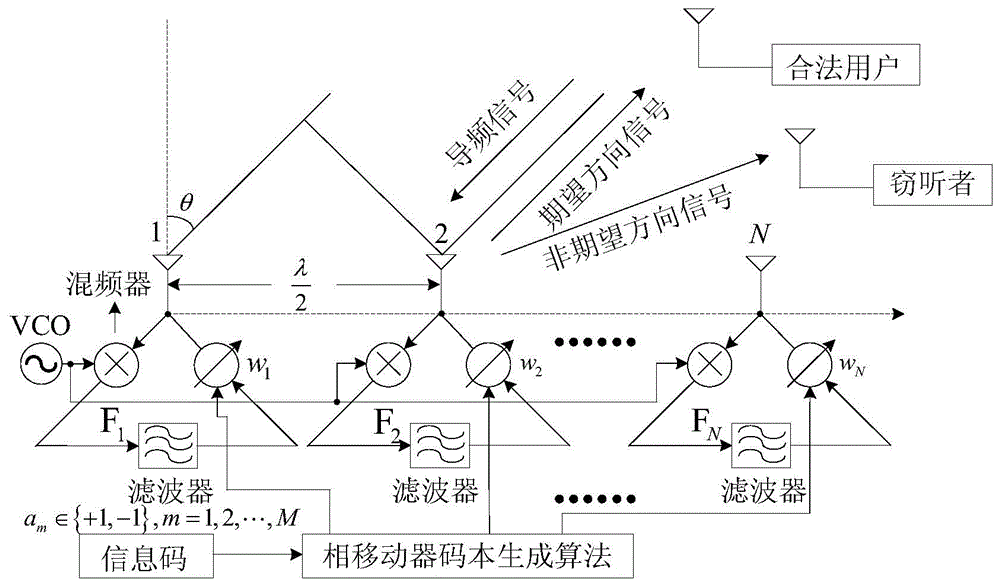
Directional modulation signal design method based on reverse antenna array.
ActiveCN104579440AReduce the difficulty of implementationSpatial transmit diversityPhase-modulated carrier systemsEavesdroppingSpatial direction
The invention discloses a directional modulation signal design method based on a reverse antenna array. According to the method, the reverse antenna array is adopted to enable an incident wave phase position to conjugate and enable a digital phase shifter to construct a directional modulation signal planisphere codebook, and an expected directional modulation signal is synthesized in any spatial direction; according to the invention, a directional modulation signal transmitter and two common digital signal receivers in different spatial directions are included; the spatial direction where the legal user receiver is positioned is the expected direction, and the spatial direction where the eavesdropping receiver is positioned is the unexpected direction. A legal user can normally demodulate a received signal by utilizing the directional modulation signal transmitted through the method; however, the eavesdropping receiver cannot demodulate useful communication information even if receives signal energy similar to that of the legal user due to the dynamic distortion of a received signal planisphere. Therefore, the transmitted directional modulation signal provides a secure transmission method for wireless transmission of communication information.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Anti-eavesdrop optimal secure transmission method based on collaboration interference
InactiveCN108712228AImprove securityMaximize confidentiality capacitySecret communicationCommunication jammingSecure transmissionConfidentiality
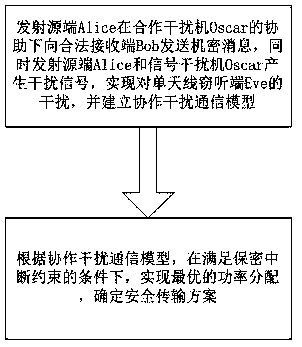
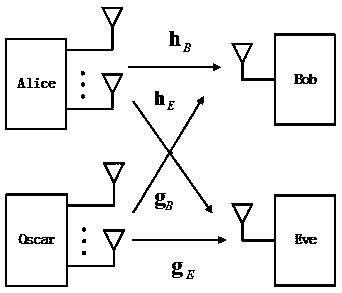
The invention discloses an anti-eavesdrop optimal secure transmission method based on collaboration interference, and the method comprises the following steps: S1, a transmitting source end Alice transmits a confidential message to a legal receiving end Bob with the help of a collaboration jammer Oscar, meanwhile, the transmitting source end Alice and a signal jammer Oscar generate interference signals, thus, interference on a single-antenna eavesdropping end Eve is realized, and a collaboration interference communication model is established; S2, according to the collaboration interference communication model, under a condition of satisfying confidentiality interruption constraint, optimal power distribution is realized, and a secure transmission scheme is determined. The invention provides the anti-eavesdrop optimal secure transmission method based on collaboration interference, in a collaboration interference communication process where channel estimation error exists, confidentiality capacity is maximized based on confidentiality interruption probability constraint, and optimization of secure transmission performance is realized.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Multi-relay physical layer safety method based on known eavesdropping end channel information
InactiveCN104540124AIncrease freedomMaximize safe capacitySecurity arrangementHigh level techniquesInformation transmissionPhysical layer
The invention discloses a multi-relay physical layer safety method based on known eavesdropping end channel information to achieve safety communication of a physical layer. Based on known eavesdropping end channel information, a relay group is divided into a relay forwarding group part and a relay interference group part, effectiveness and safe transmission of information are guaranteed for a first information transmission time slot by means of the beam forming technology and the artificial interference technology, and information is effectively prevented from being received by an eavesdropping end in a second time slot by means of the known eavesdropping end channel information and the beam forming technology. On the premise that relay power distribution is considered, the beam forming vector of the relay forwarding group part and the beam forming vector of the relay interference group part are optimized, and the maximum safe capacity of a system is obtained finally.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification Device) mutual authentication method based on secret key and cache mechanism
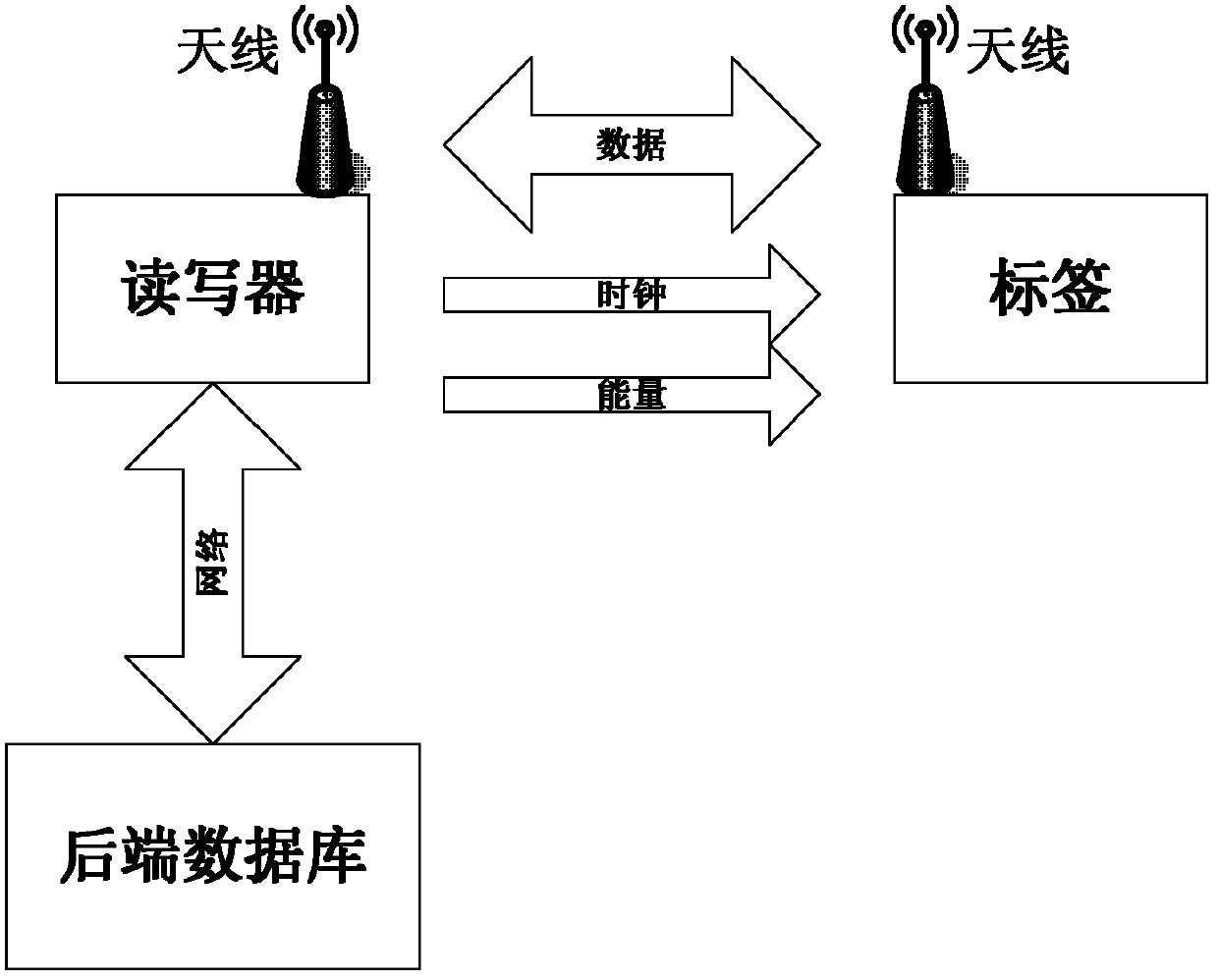
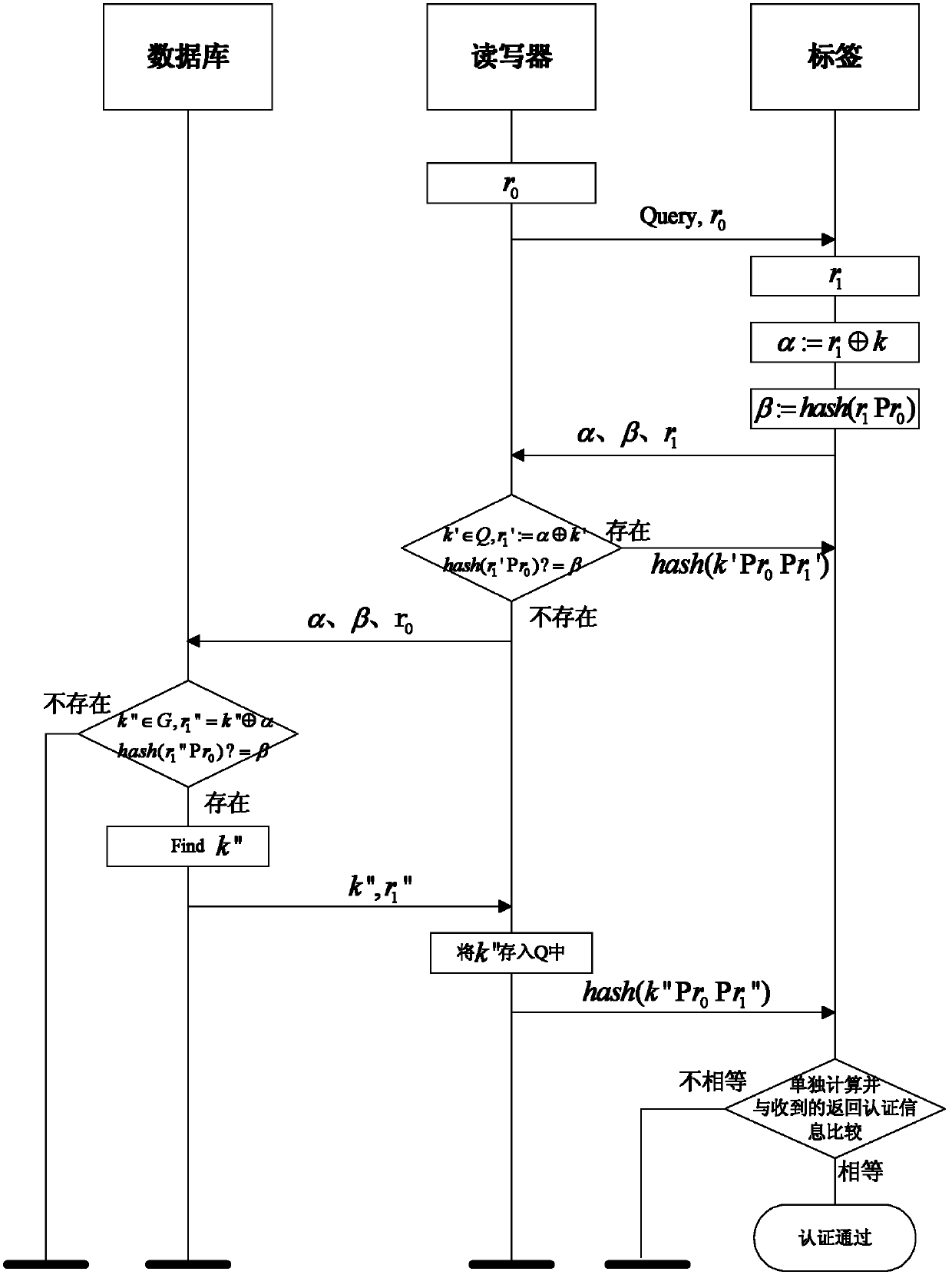
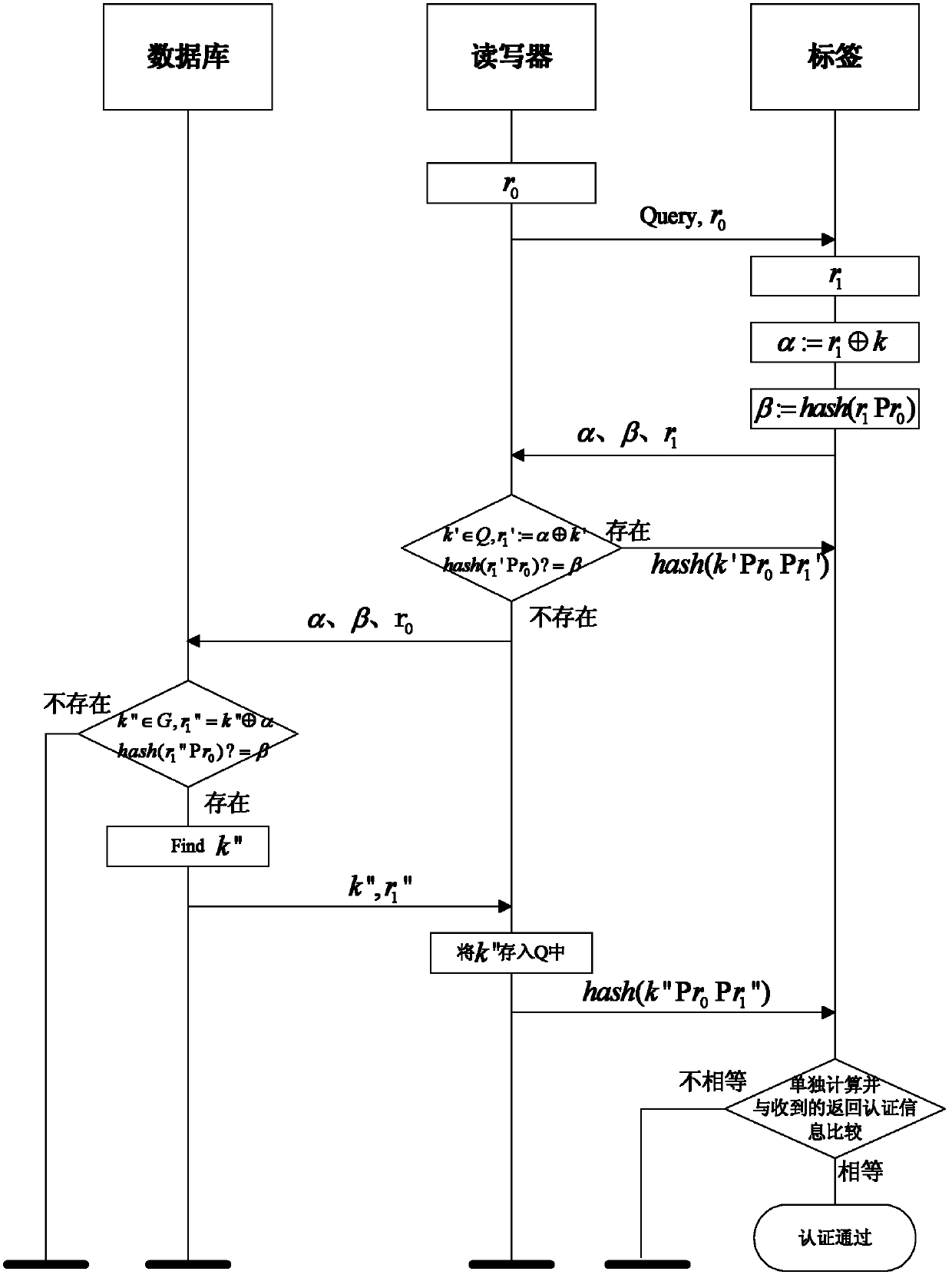
ActiveCN102394753AWith anti-eavesdropping performancePrevent location tracking issuesUser identity/authority verificationCo-operative working arrangementsComputer hardwareLimited resources
The invention provides an RFID (Radio Frequency Identification Device) mutual authentication method based on a secret key and a cache mechanism, which mainly solves the problems in the prior art that illegal reading, position tracking, eavesdropping, camouflage cajoling and unsafe resetting can not be resisted simultaneously. The achieving steps are as follows: a reader-writer and a tag adopt typical inquire response mechanism, the tag generates two authentication information values, namely beta is equal to hash (rl and Pr0), and sends the authentication information values to the reader-writer, the reader-writer compares received information value with self-computed information value, if the comparison results are same, returning authentication information hash (k' Pr0 and Prl') is sent to the tag through authentication. If the comparison results are different, the information is sent to back-end data base, authentication judgment is conducted by the back-end data base, the returning authentication information hash (k'' Pr0 and Prl'') is sent to the tag, after the tag receives the returning authentication information, authentication is carried out on the reader-writer by comparing the tag with self-computed value hash (k Pr0 and Prl), if the tag and the self-computed value hash (k Pr0 Prl) are same, the authentication is passed. The RFID (Radio Frequency Identification Device) mutual authentication method has the advantages of high safety performance and high execution efficiency, and can be applied to the RFID application context with limited resources and high safety requirements.
Owner:北京中科蓝信科技有限公司
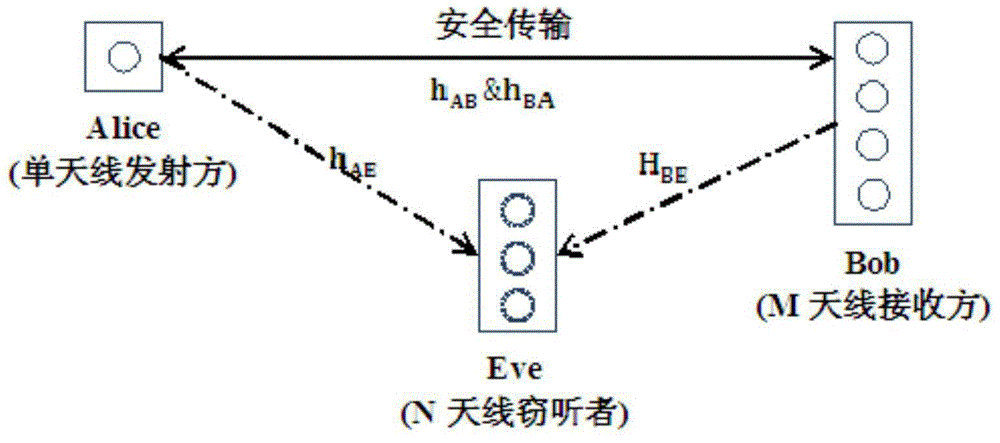
Physical layer safety transmission method used for SIMO wireless communication system
ActiveCN103986545AImprove physical layer security performanceImprove security and confidentialitySpatial transmit diversitySecret communicationCommunications systemSecure transmission
The invention discloses a physical layer safety transmission method used for an SIMO wireless communication system. Firstly, a receiving expecting party emits a random reference signal reversely, an emitting party scrambles and transmits symbols to be transmitted through the received reference signal, and finally the receiving expecting party demodulates the received signal through the known reference signal to obtain information transmitted by the emitting party. In the first step, the multi-antenna receiving party sends not only the reference signal, but also an artificial noise signal, the space where the artificial noise signal is located is in quadrature with a main channel vector, so that the artificial noise has no influence on receiving the reference signal of the emitting expecting party. For an eavesdropper, due to different channels, eavesdropping is interfered with by artificial noise signals, the random reference signal is difficult to evaluate accurately, the probability of successfully eavesdropping encrypted signals is greatly reduced, and safety transmission of the SIMO wireless communication system is guaranteed finally.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
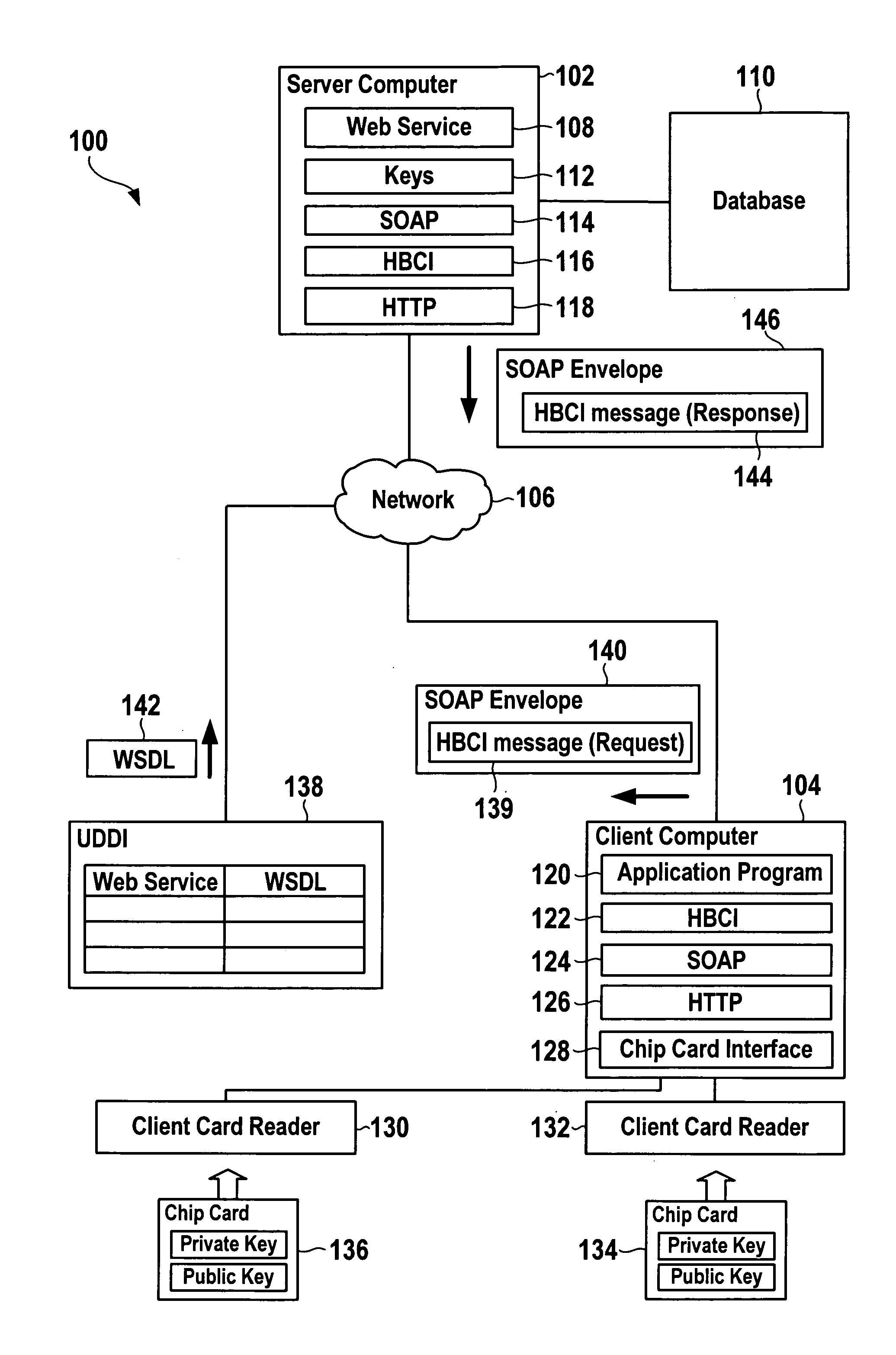
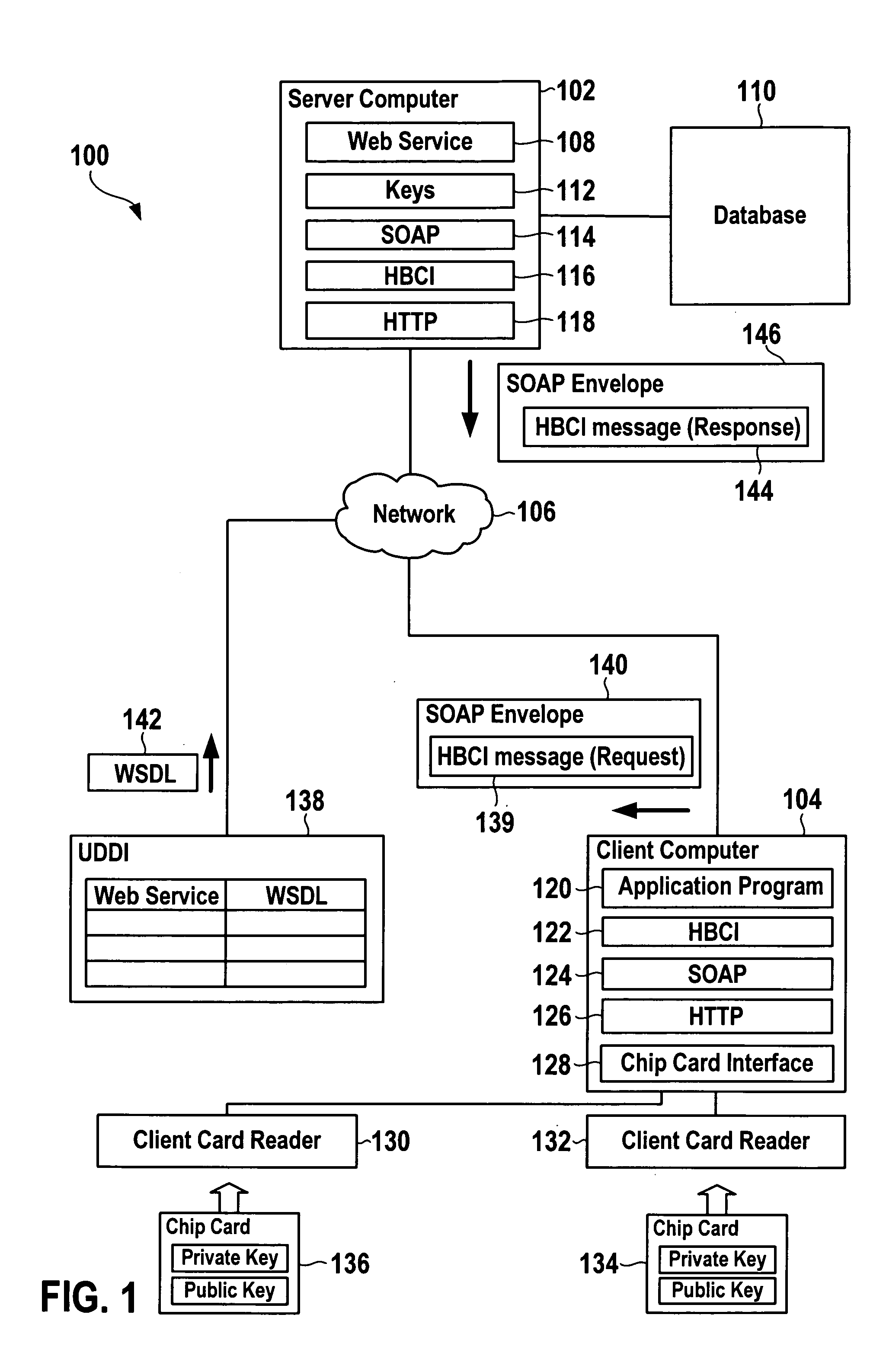
Computer systems and data processing methods for using a web service
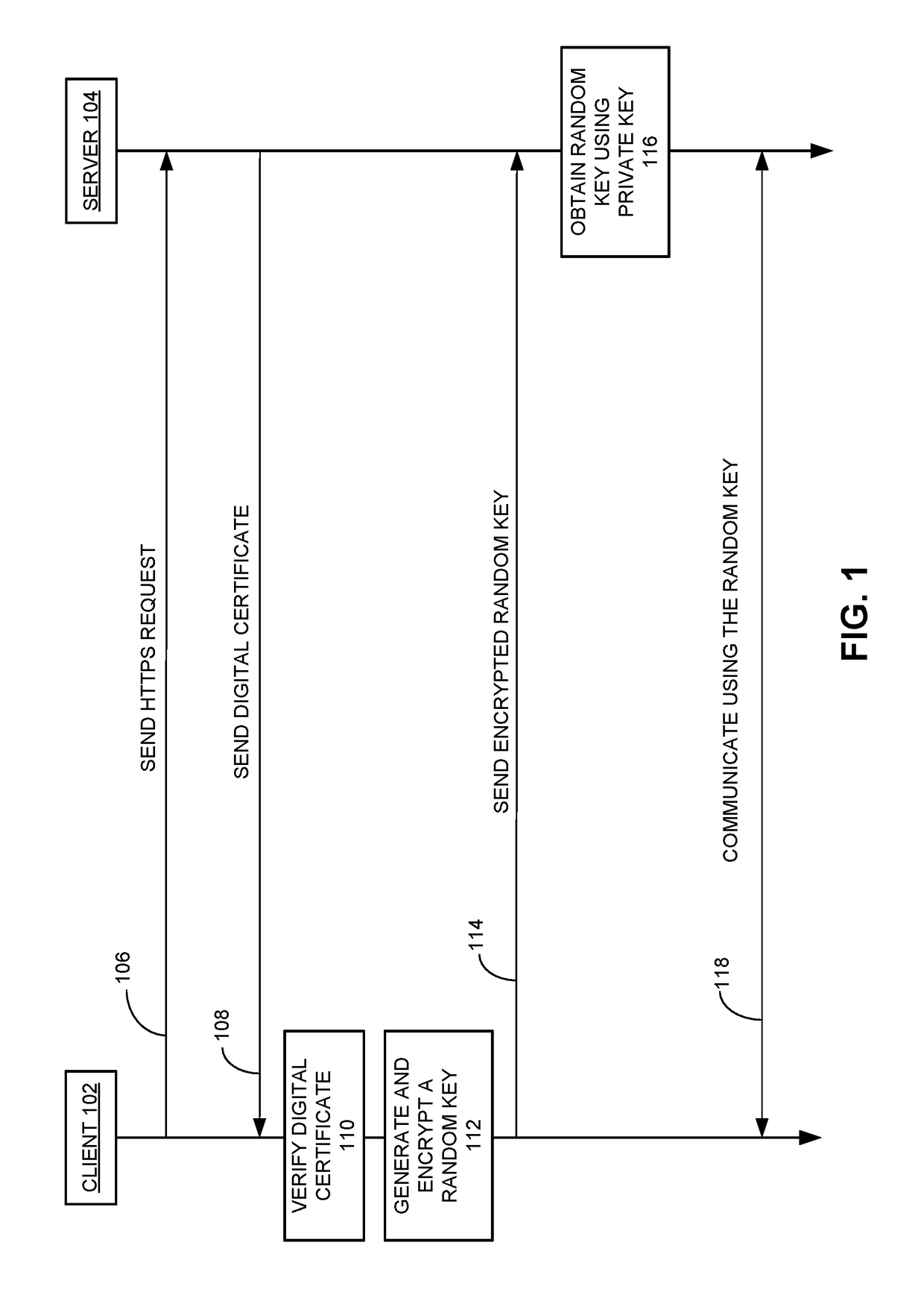
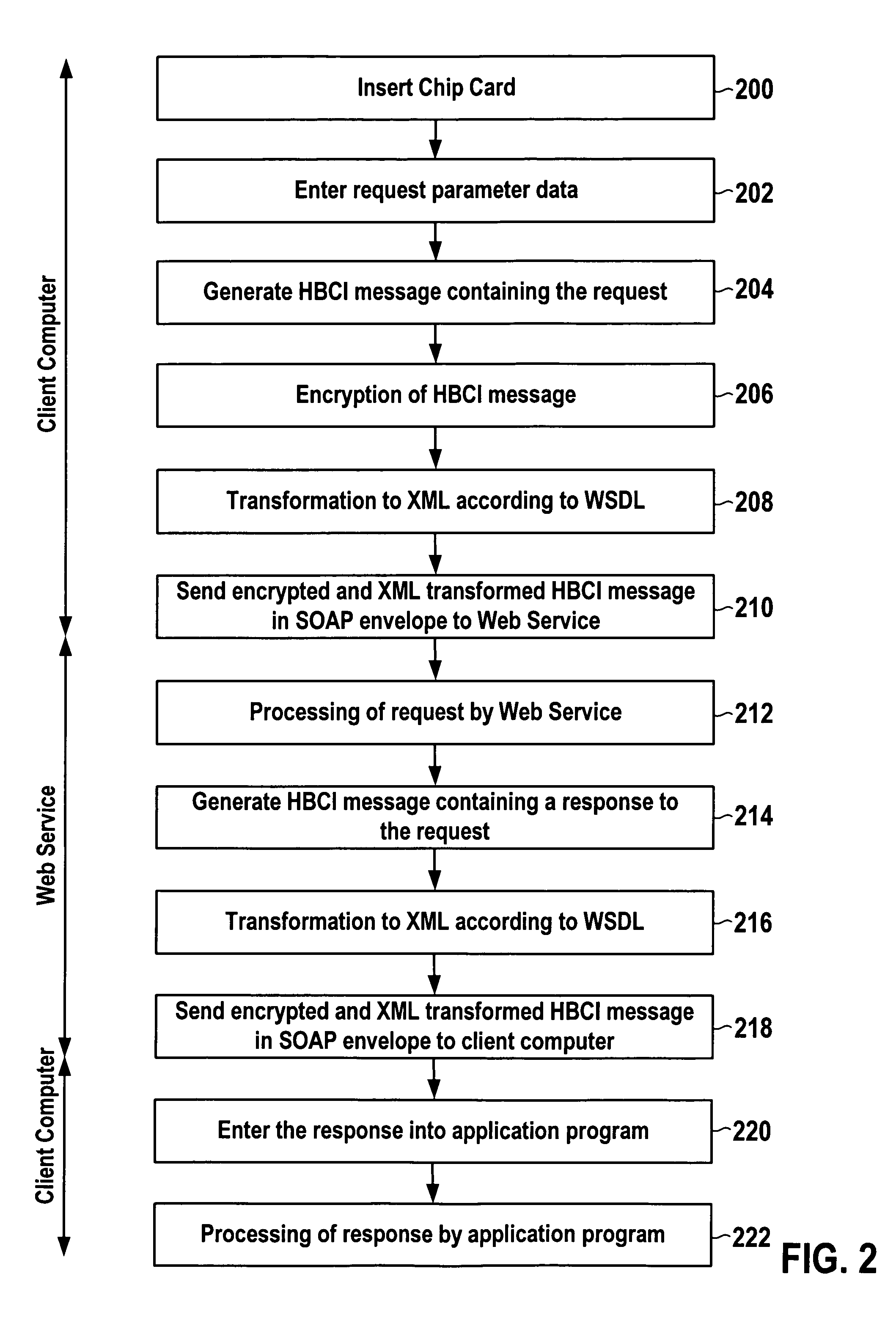
ActiveUS20060004771A1Improve the level ofImprove confidentialityDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsSecure communicationData processing system
Data processing systems and methods are disclosed that utilize the Home Banking Computer Interface (HBCI) protocol for secure communication with a web service. Usage of the HBCI protocol protects the communication of a requester with the web service against eavesdropping and tampering. Further, implementation of a dual control business procedure is facilitated.
Owner:SAP AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com