Patents
Literature
554 results about "Security association" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
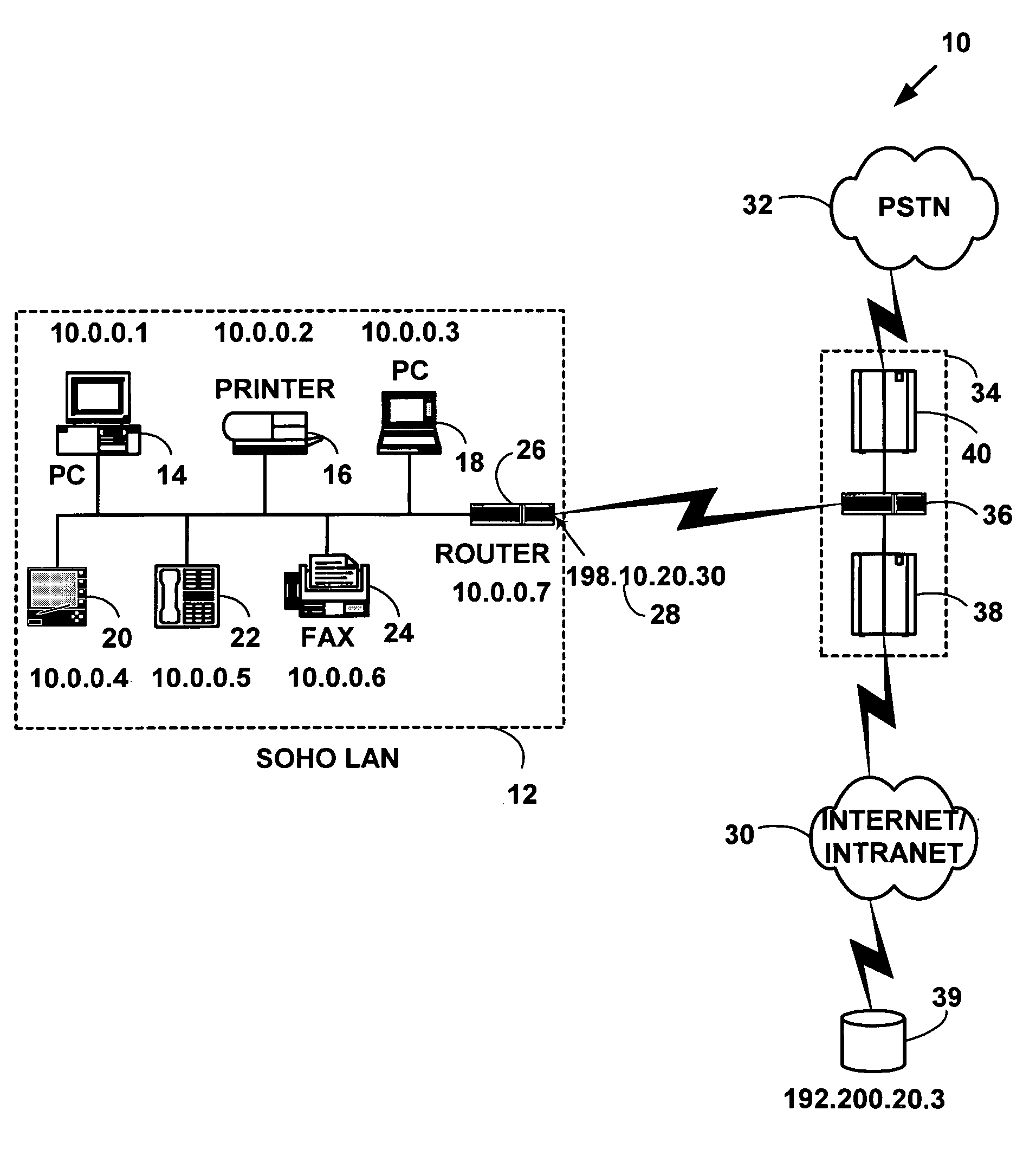
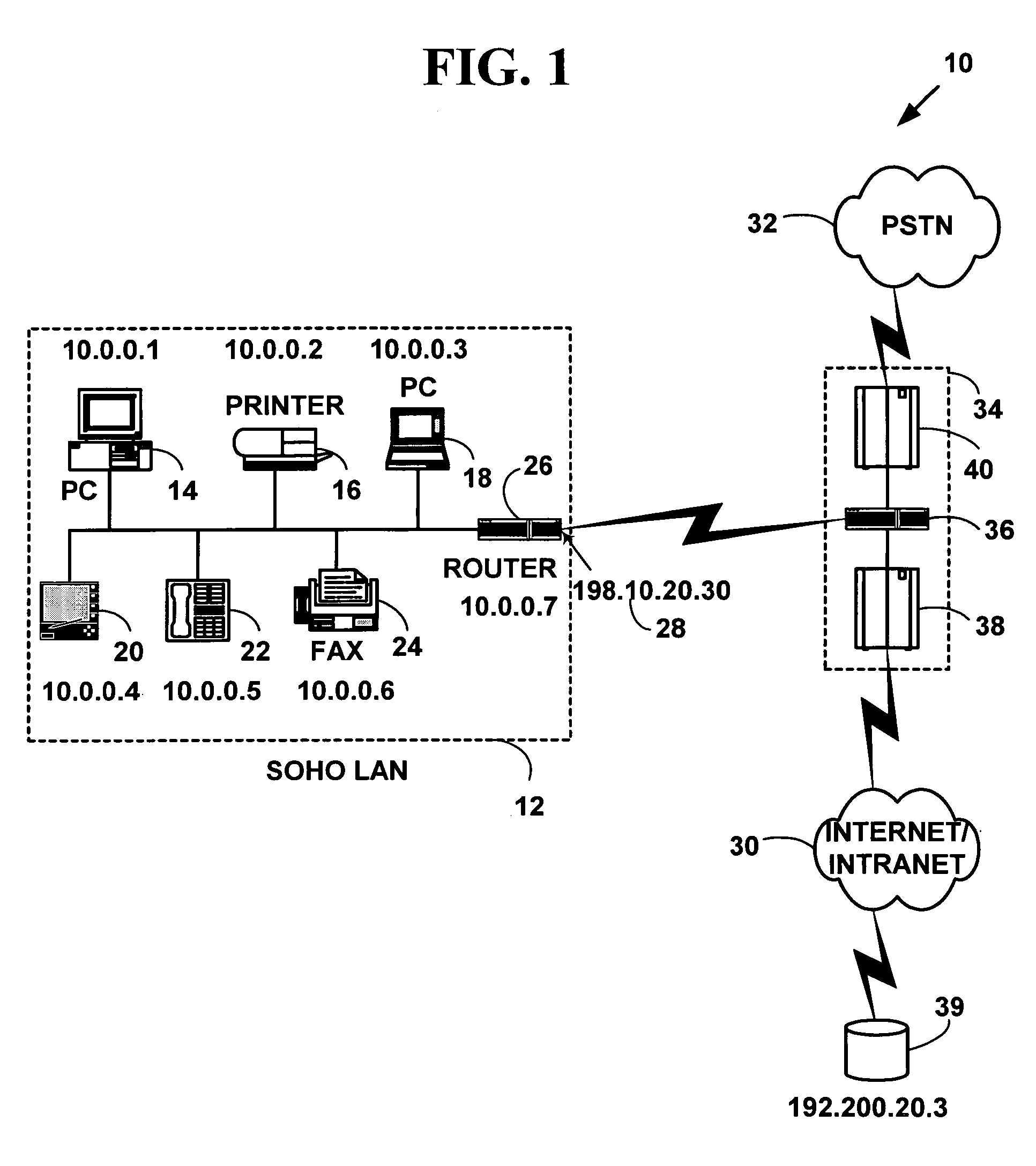
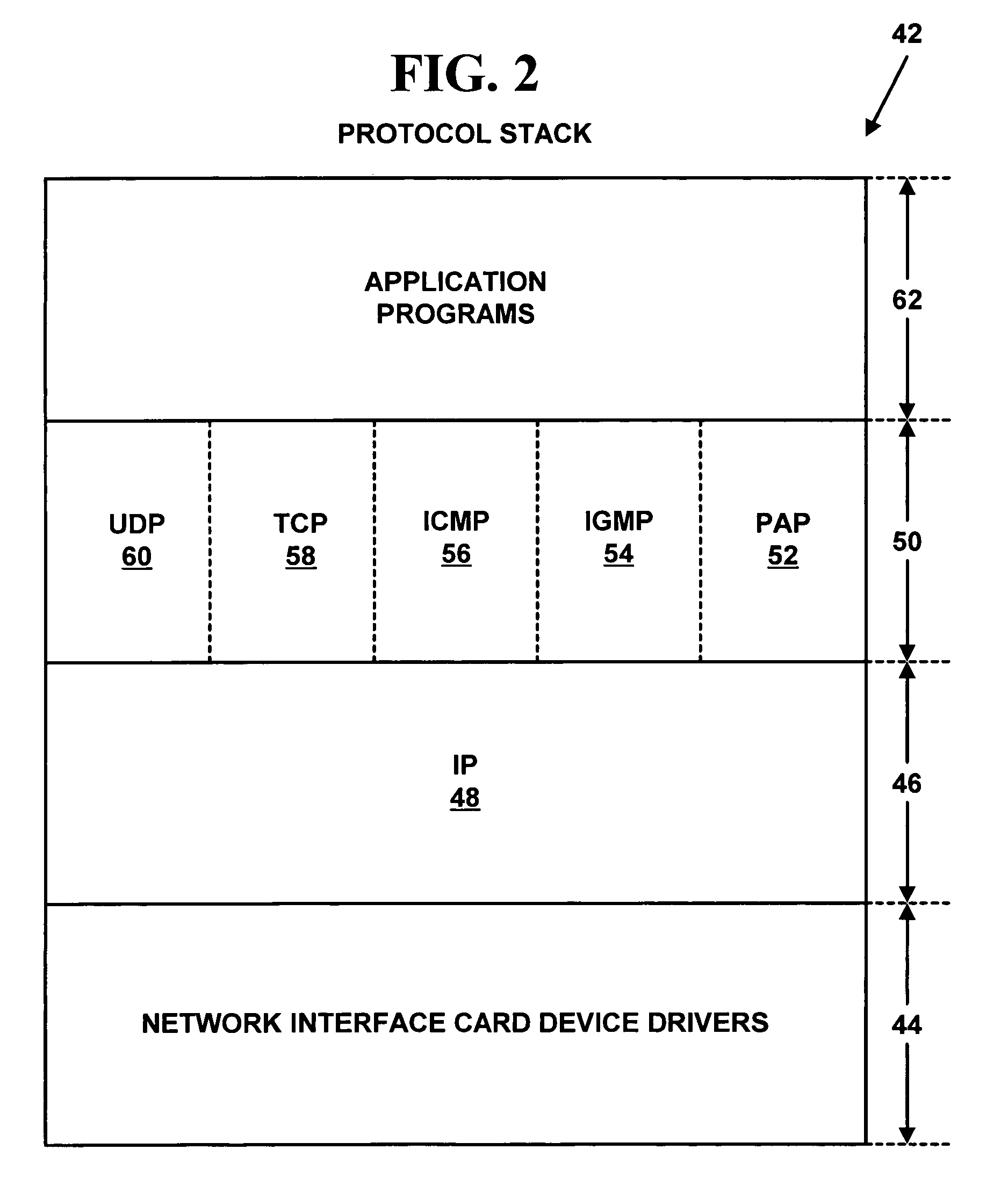
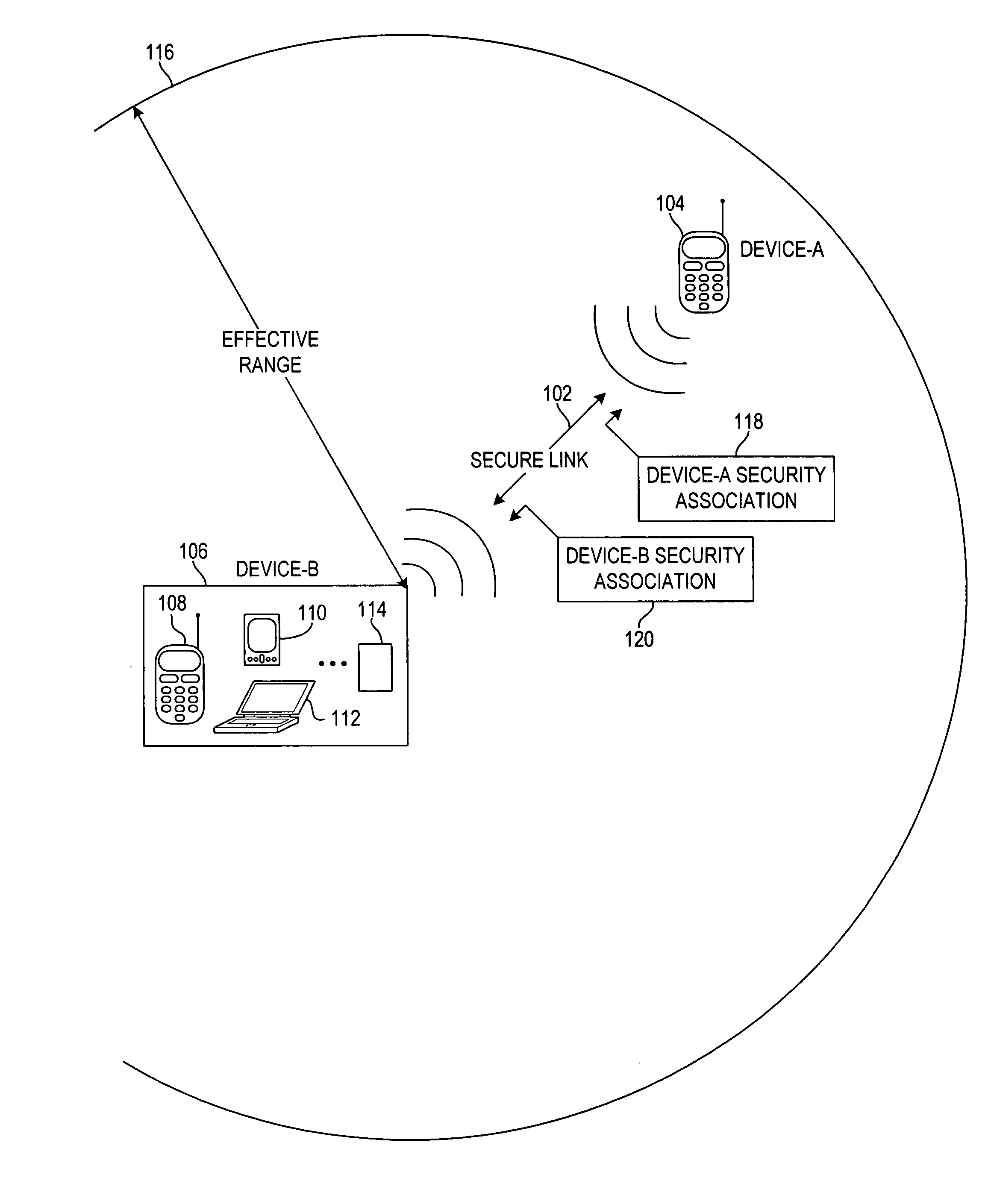
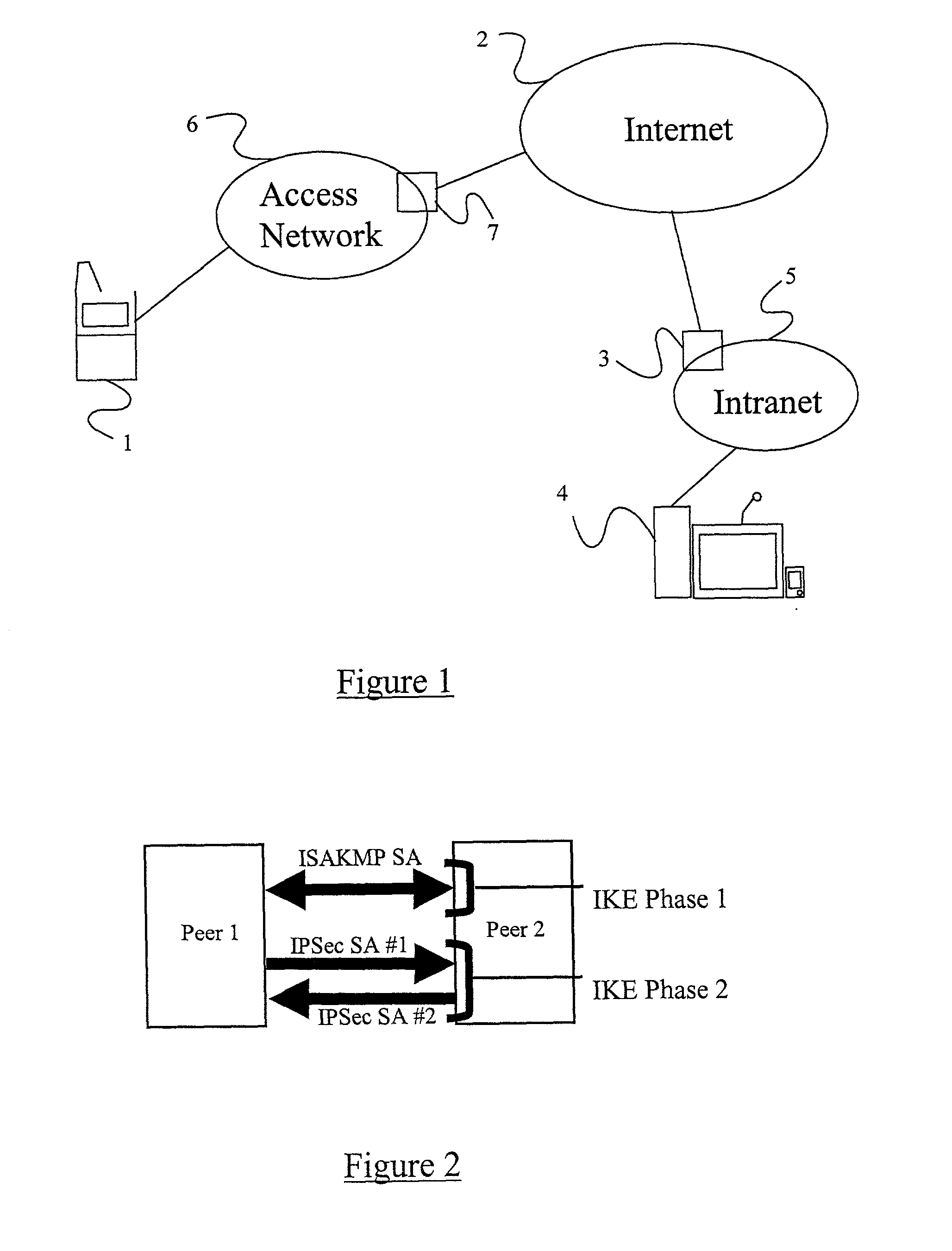
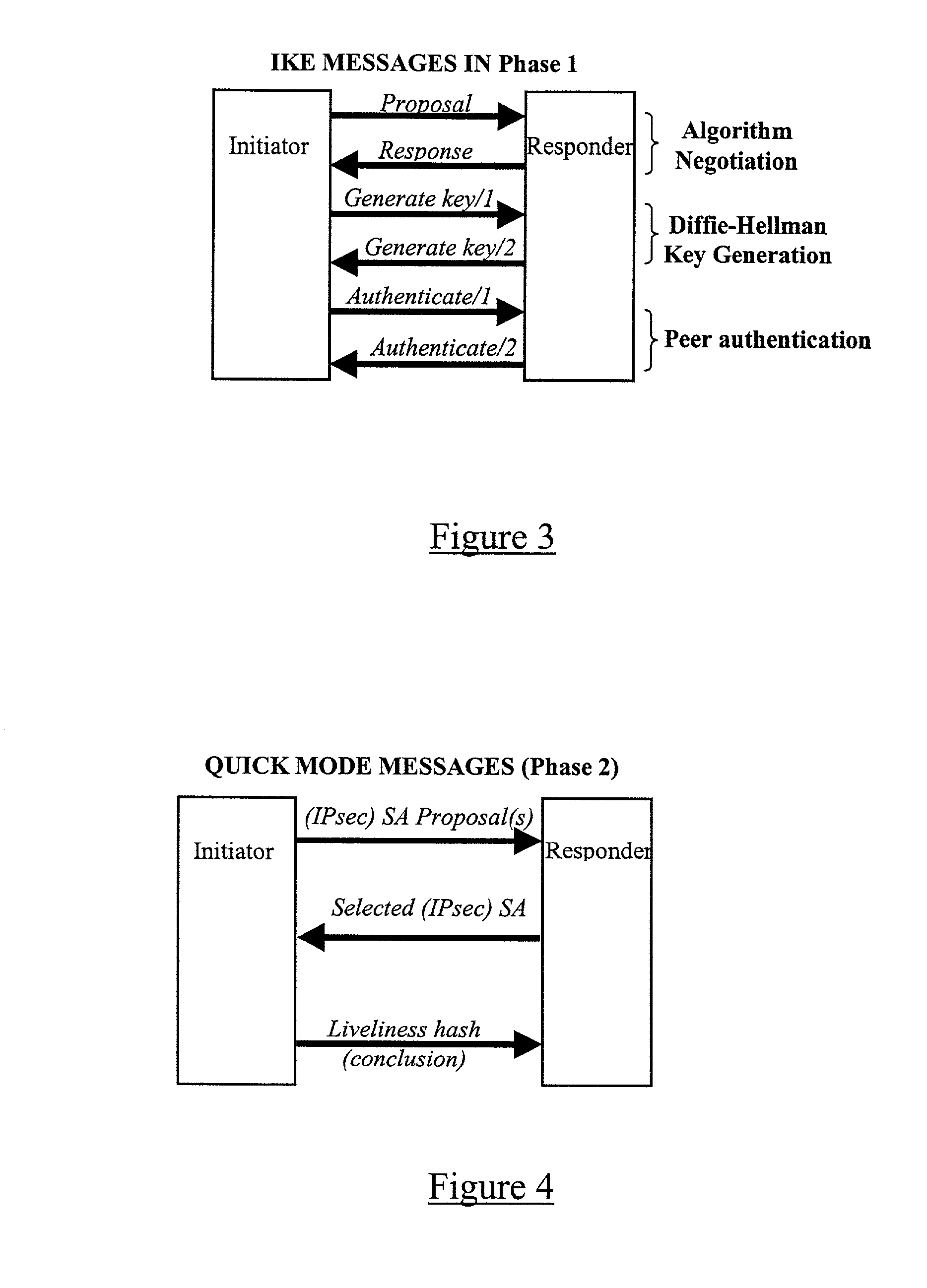
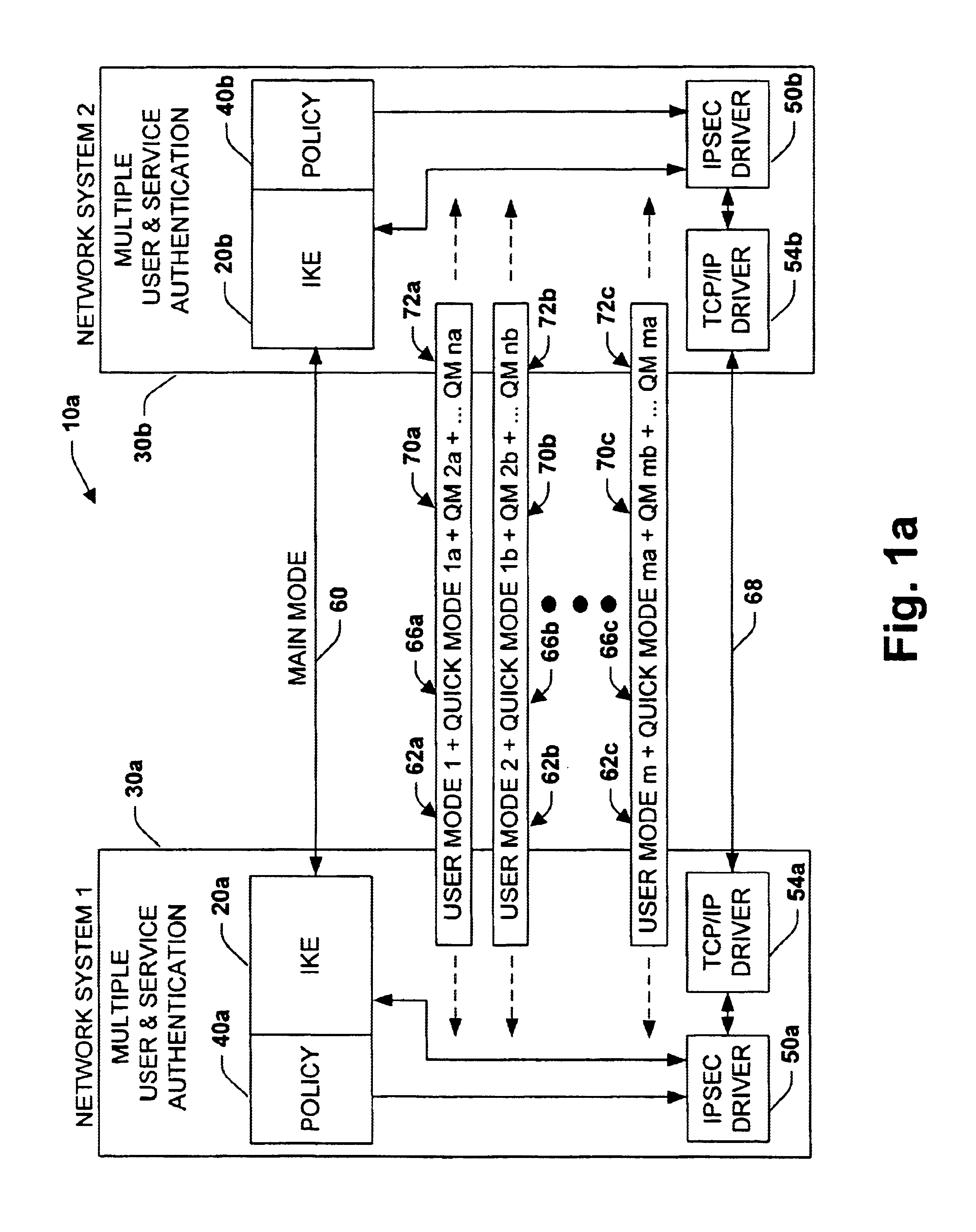
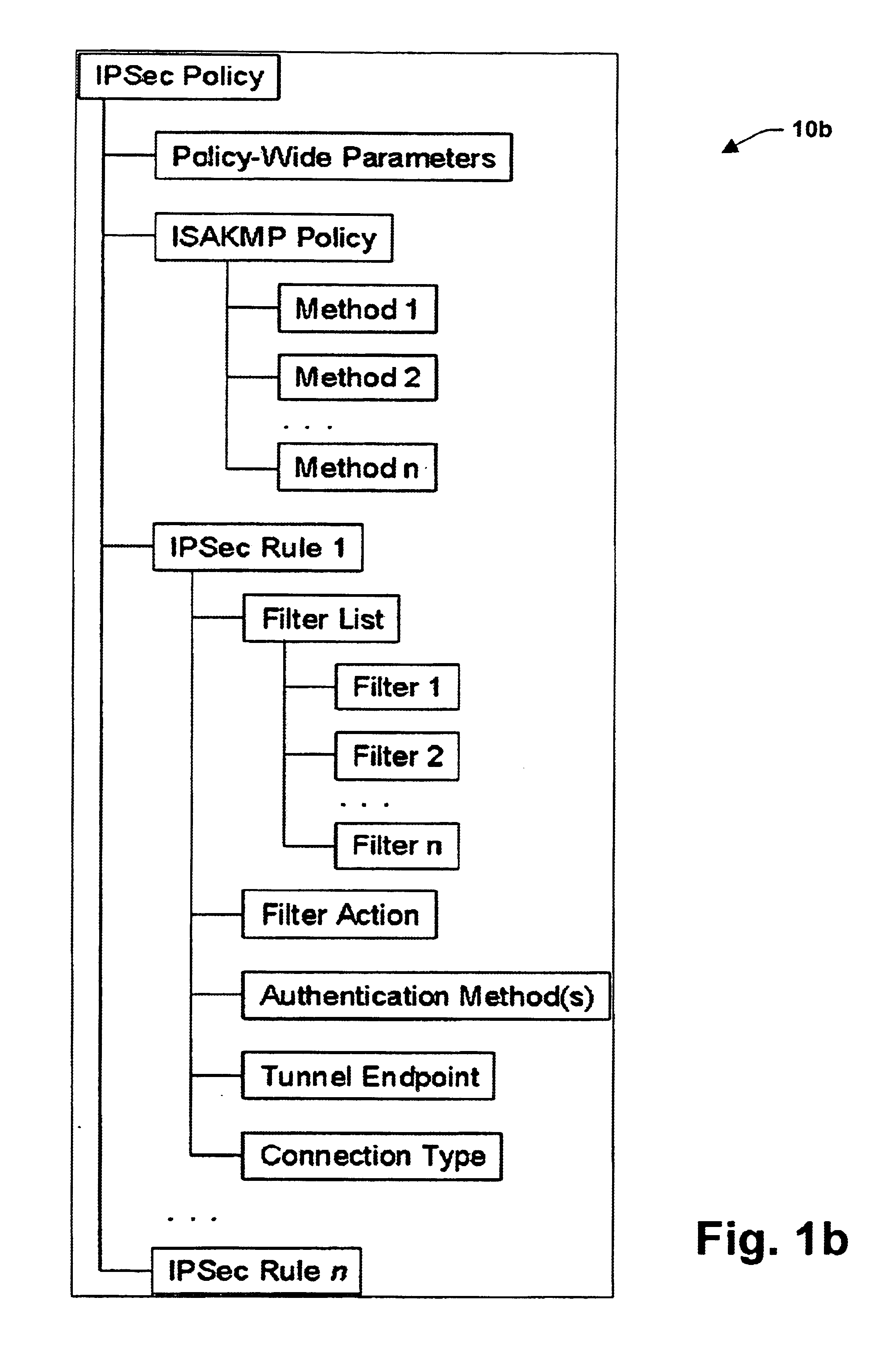
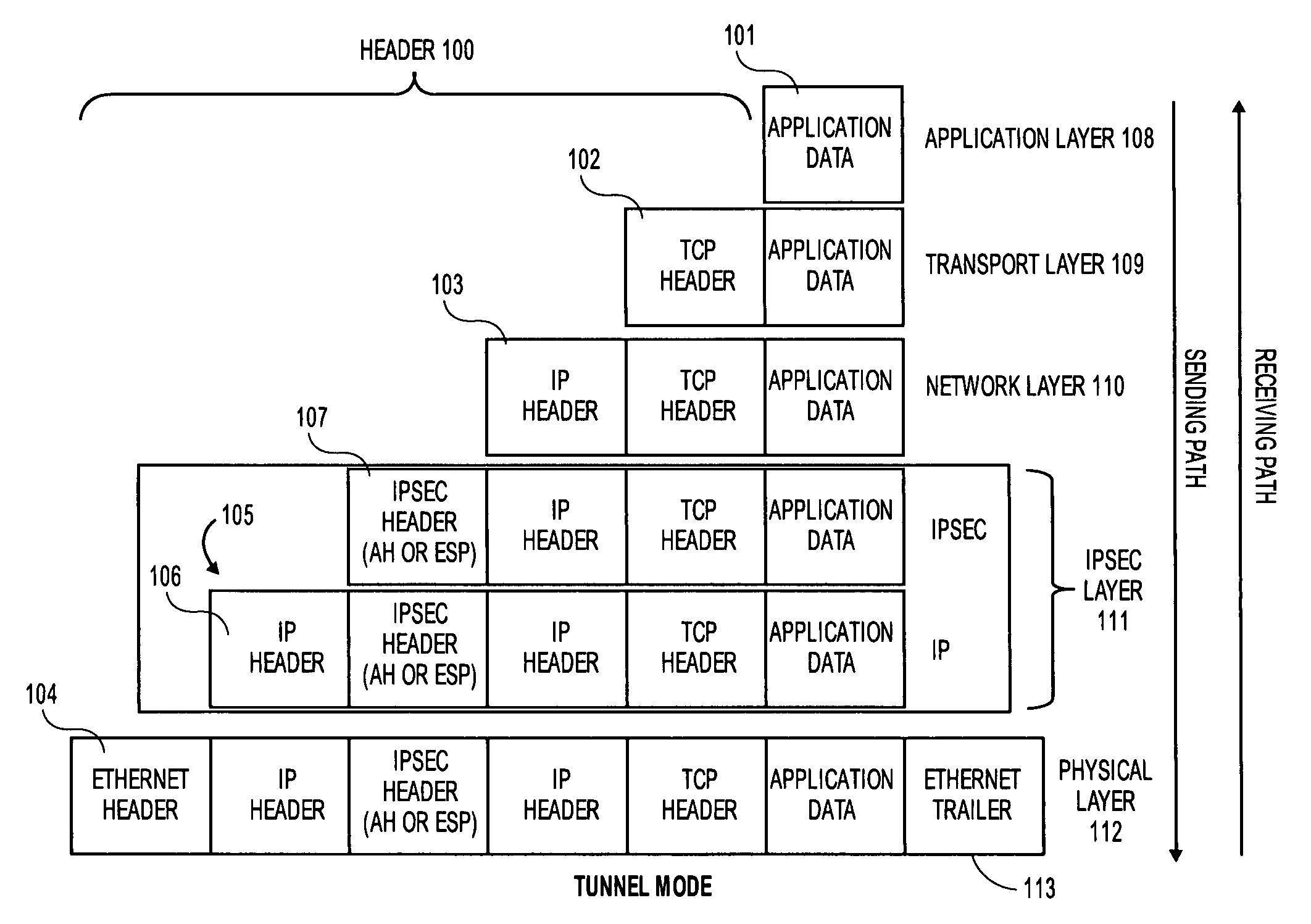
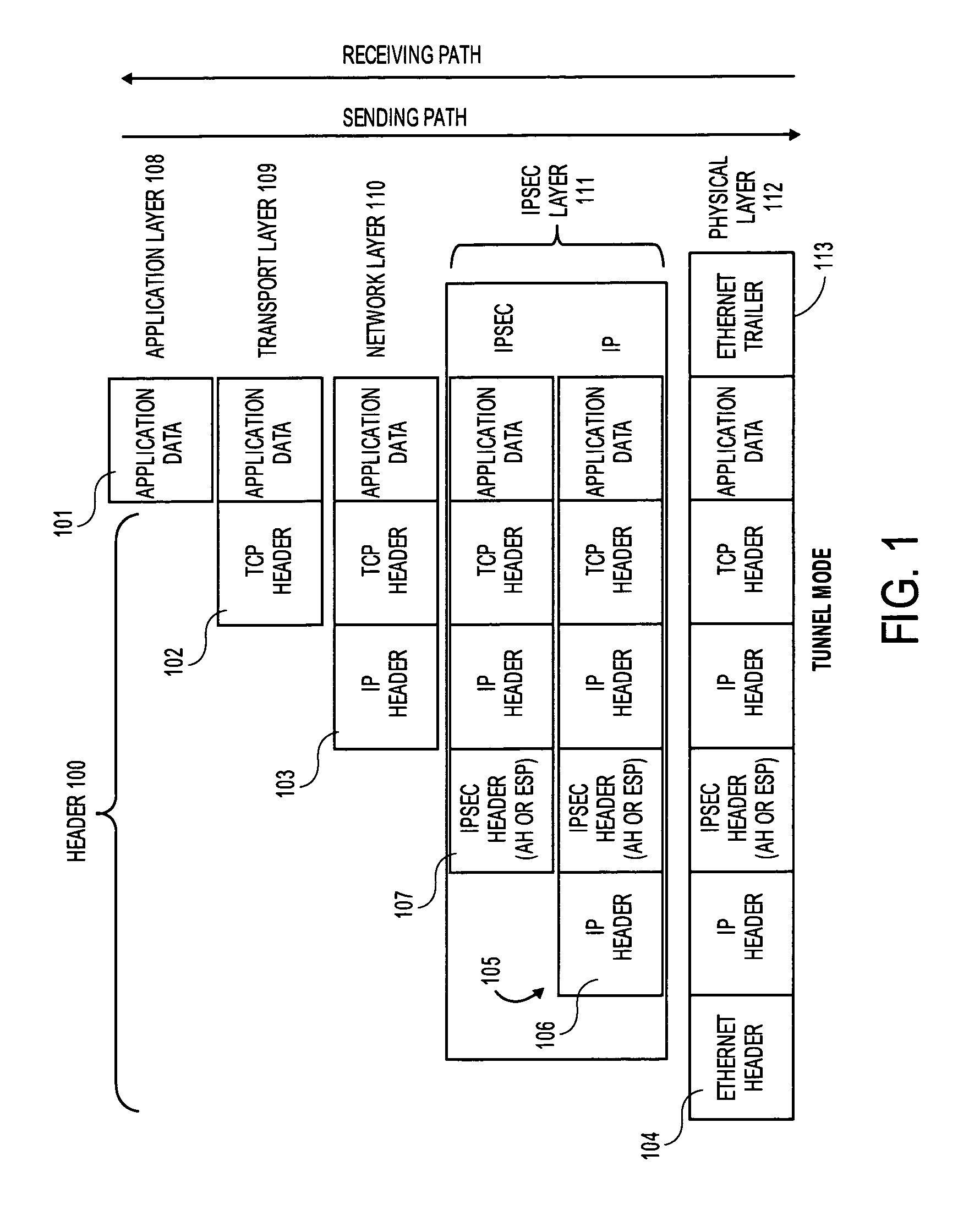
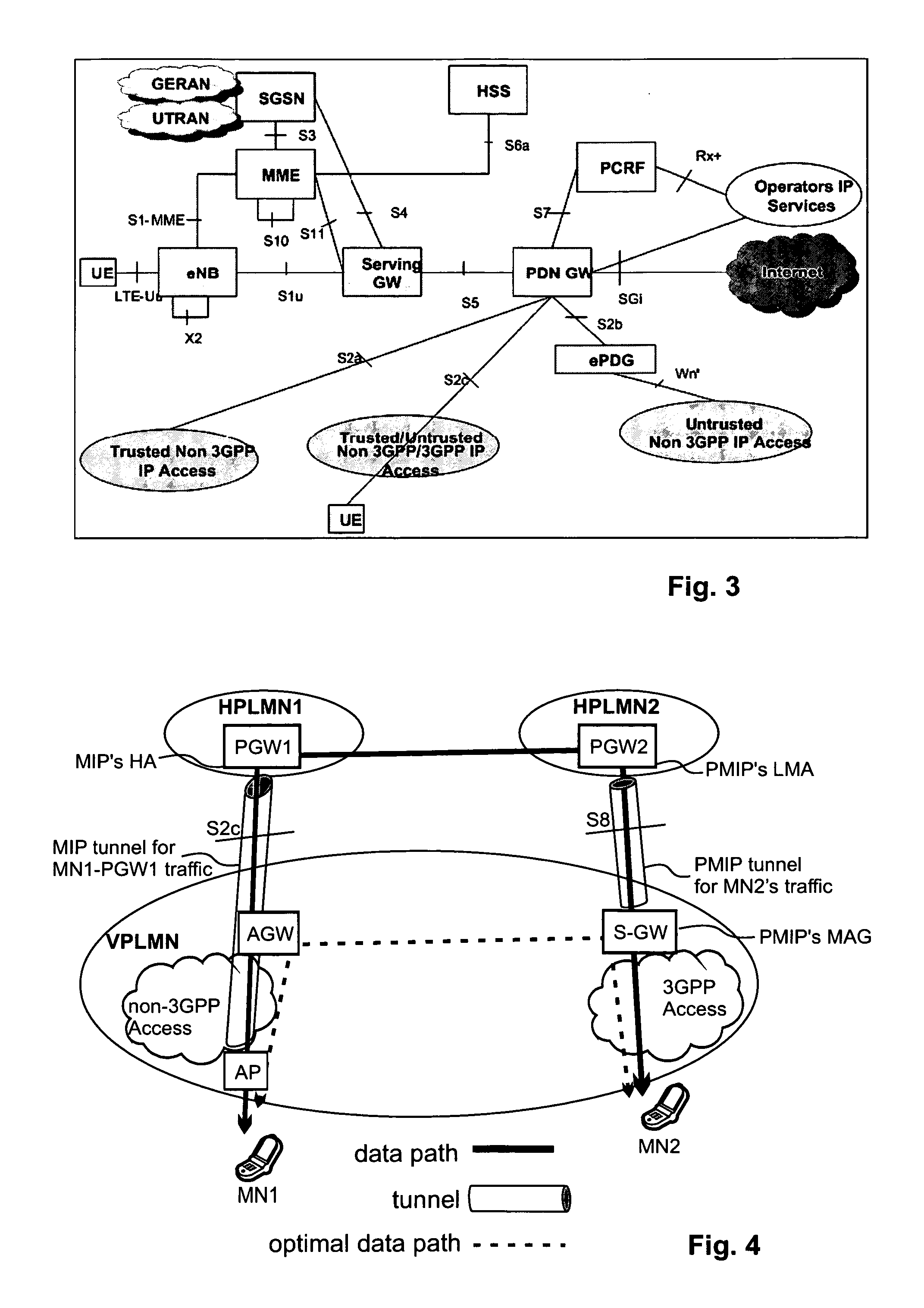
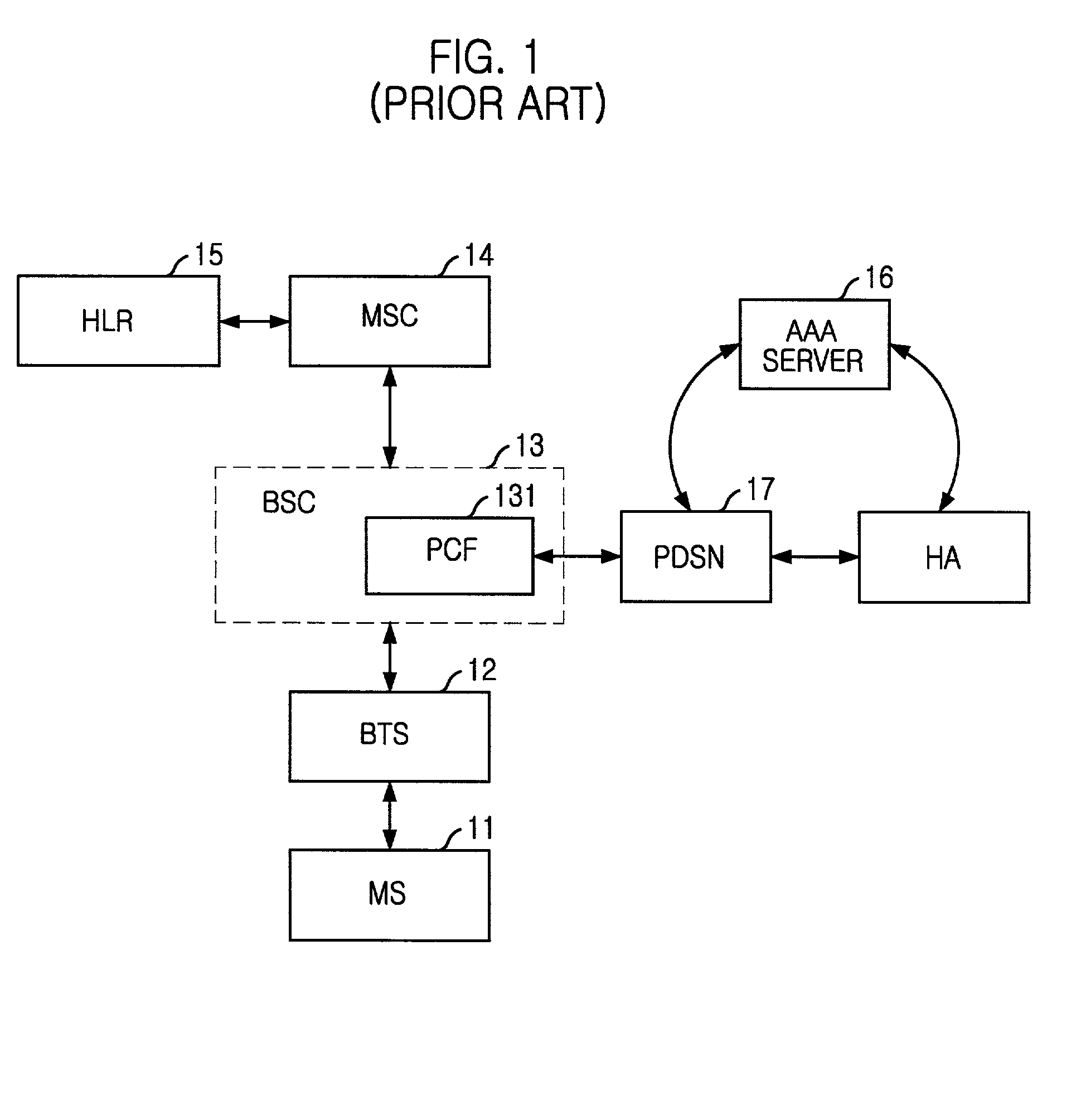
A security association (SA) is the establishment of shared security attributes between two network entities to support secure communication. An SA may include attributes such as: cryptographic algorithm and mode; traffic encryption key; and parameters for the network data to be passed over the connection. The framework for establishing security associations is provided by the Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP). Protocols such as Internet Key Exchange (IKE) and Kerberized Internet Negotiation of Keys (KINK) provide authenticated keying material.
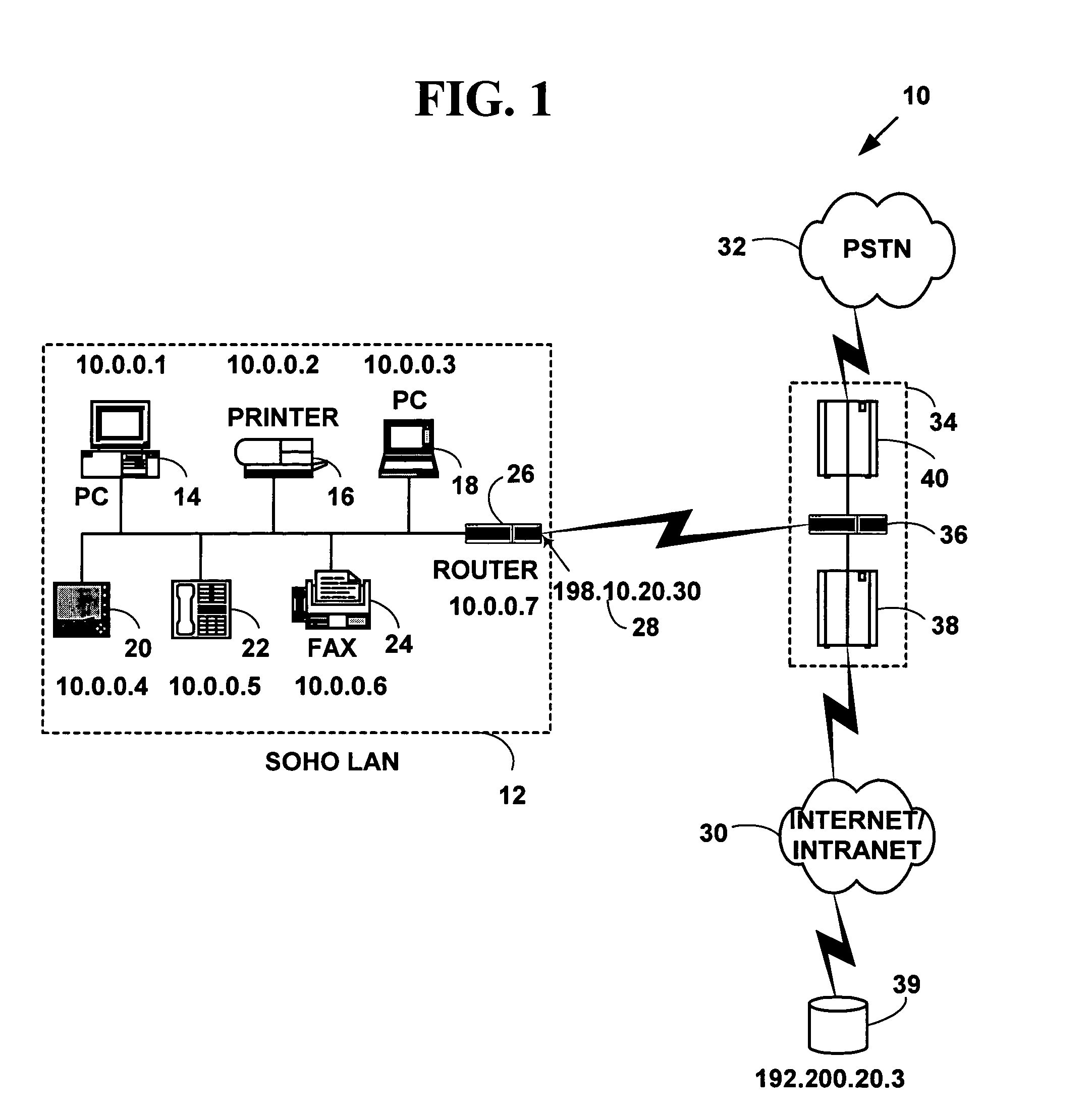
Method and system for distributed network address translation with network security features
InactiveUS7032242B1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationSecurity associationIp address
A method and system for distributed network address translation with security features. The method and system allow Internet Protocol security protocol (“IPsec”) to be used with distributed network address translation. The distributed network address translation is accomplished with IPsec by mapping a local Internet Protocol (“IP”) address of a given local network device and a IPsec Security Parameter Index (“SPI”) associated with an inbound IPsec Security Association (“SA”) that terminates at the local network device. A router allocates locally unique security values that are used as the IPsec SPIs. A router used for distributed network address translation is used as a local certificate authority that may vouch for identities of local network devices, allowing local network devices to bind a public key to a security name space that combines a global IP address for the router with a set of locally unique port numbers used for distributed network address translation. The router issues security certificates and may itself be authenticated by a higher certificate authority. Using a security certificate, a local network device may initiate and be a termination point of an IPsec security association to virtually any other network device on an IP network like the Internet or an intranet. The method and system may also allow distributed network address translation with security features to be used with Mobile IP or other protocols in the Internet Protocol suite.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
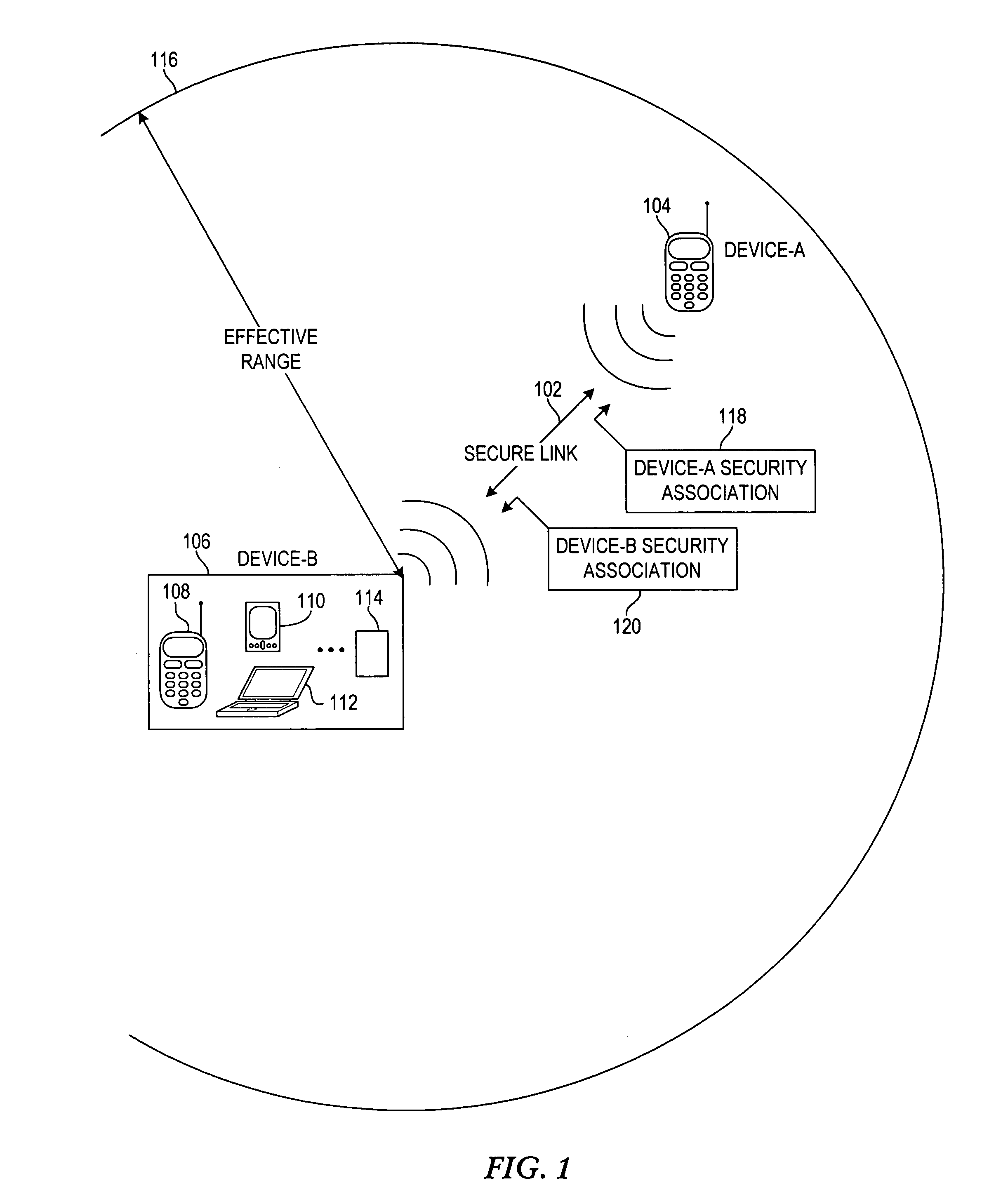
Linking security association to entries in a contact directory of a wireless device
InactiveUS20050266798A1Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsSecurity associationBluetooth
A system, apparatus and method for relating a security association to a contact in a namespace familiar to the user, and using this association to make access control decisions. An identifier of a first device is received at a second device. Using the identifier, the second device locates a contact entry corresponding to the identifier in a contact directory. A contact name associated with the identified contact entry is presented to the user of the second device to facilitate user authorization of the wireless proximity connection. An authorization identifier, e.g., a Bluetooth link key, is associated with the contact entry if authorized by the user of the second device. A wireless proximity connection, e.g., a Bluetooth connection, is established between the first and second devices in response to associating the authorization identifier with the entry. When subsequent wireless proximity connection are attempted between the first and second devices, the connection may be automatically established.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
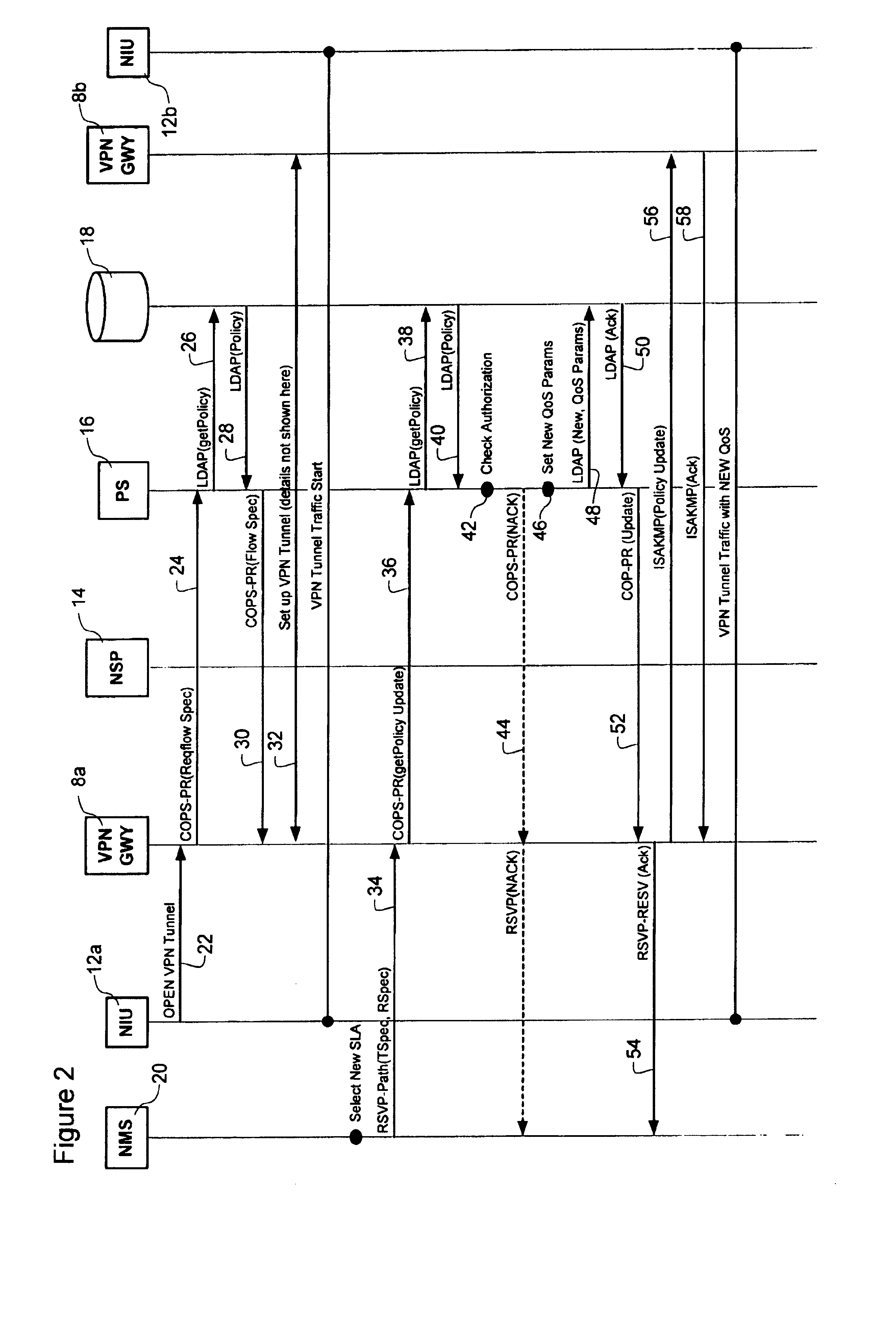
Dynamic virtual private network (VPN) tunnel quality of service (QoS) treatment
InactiveUS20050088977A1Sufficient available bandwidthNetworks interconnectionTraffic capacityQuality of service
Dynamic Quality of Service (QoS) treatment of traffic within a secure Virtual Private Network (VPN) tunnel is provided by attaching a QoS marker to data traffic at an ingress end of the VPN tunnel. The QoS marker is obtained by querying a policy database. The policy database returns QoS information, from which the QoS marker is derived. The policy data base can be queried by a VPN Gateway at an ingress end of the tunnel during tunnel setup, and / or at any time following tunnel setup to obtain updated QoS information. This updated QoS information is then propagated through the VPN tunnel to a VPN gateway at the opposite end of the VPN Tunnel, so that it can be used for egress processing of the tunnel. traffic without renegotiating the Security Association. Consequently, re-establishment of the tunnel is not required in order to change the QoS treatment of tunnel traffic.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
Method for establishing a security association between a wireless access point and a wireless node in a UPnP environment
InactiveUS20050266826A1Network traffic/resource managementUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionUser deviceSecurity association
A system and method provide for the intuitive establishment of a security association between devices. To join a network of devices, a user device sends user parameters for the user device to an administrator device using an out-of-band communication protocol. The administrator device sends the user parameters to an access point device using a Universal Plug and Play Simple Object Access Protocol (UPnP SOAP) Set action. The access point device saves the user parameters in a local database. The administrator device retrieves access point parameters from the access point device using the UPnP SOAP Get action. The administrator device sends the access point parameters to the user device using the out-of-band communication protocol. The user device connects to the access point device using the access point parameters to configure a secure connection. Preferably, a location limited channel is used by the user device to communicate with the administrator device.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
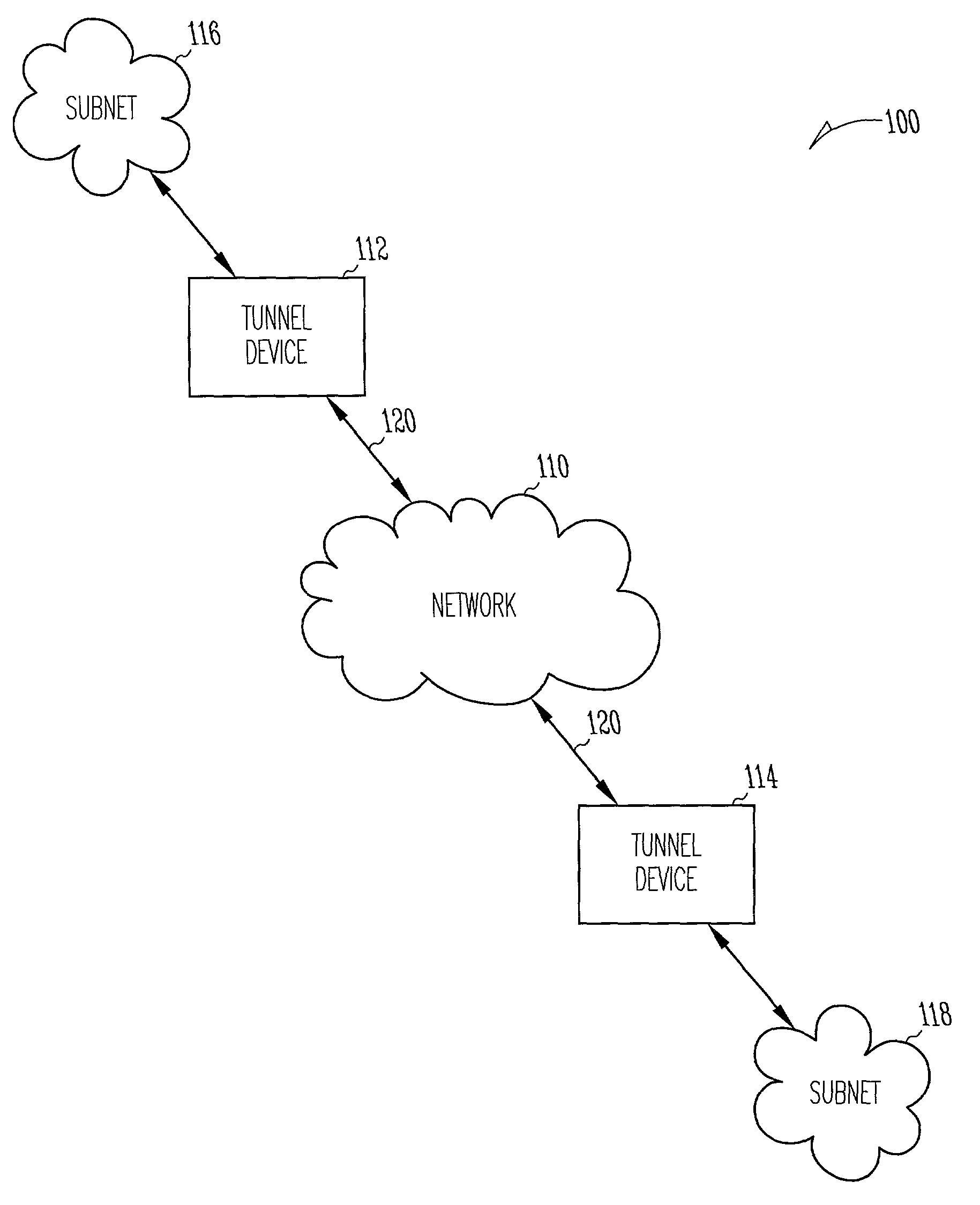
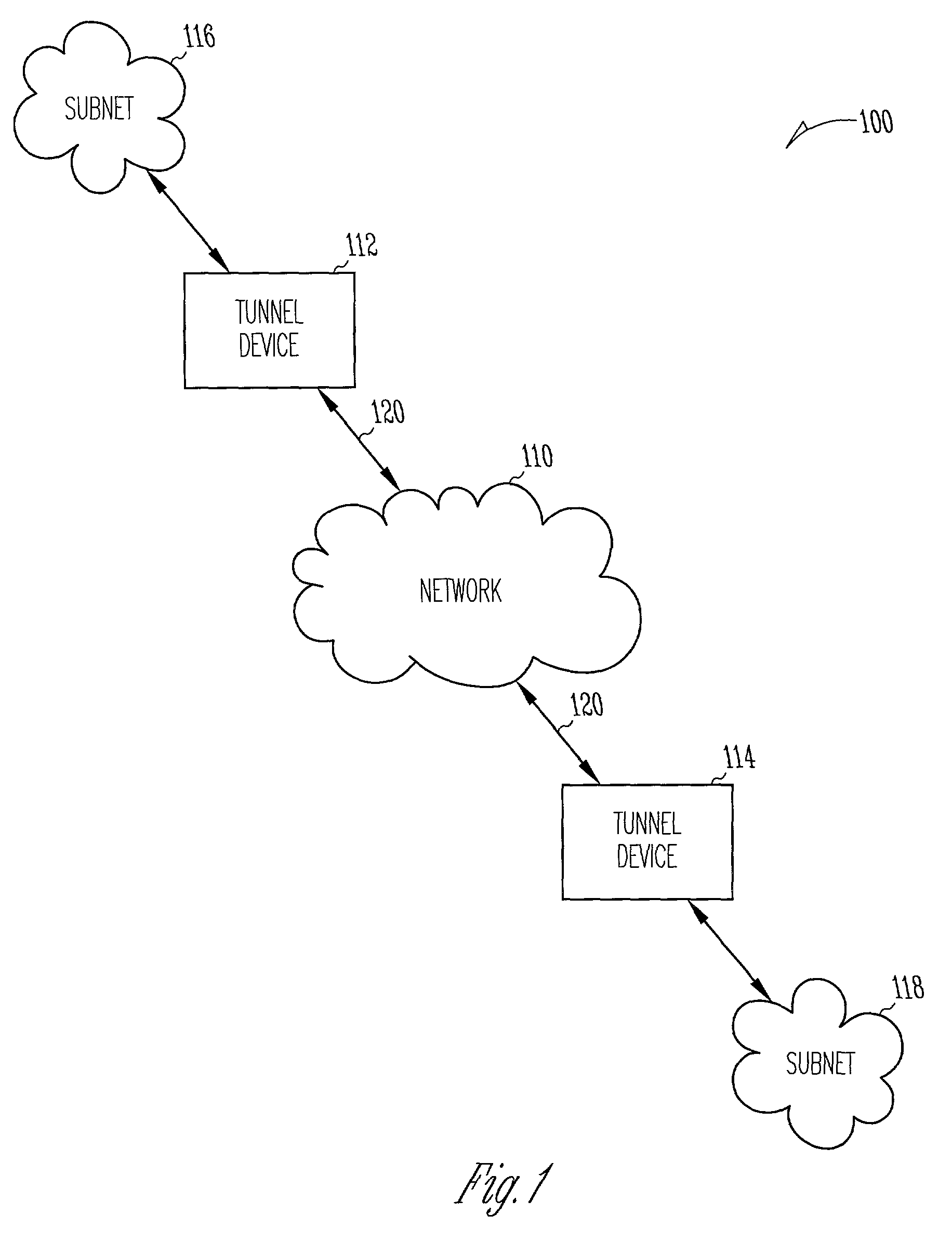
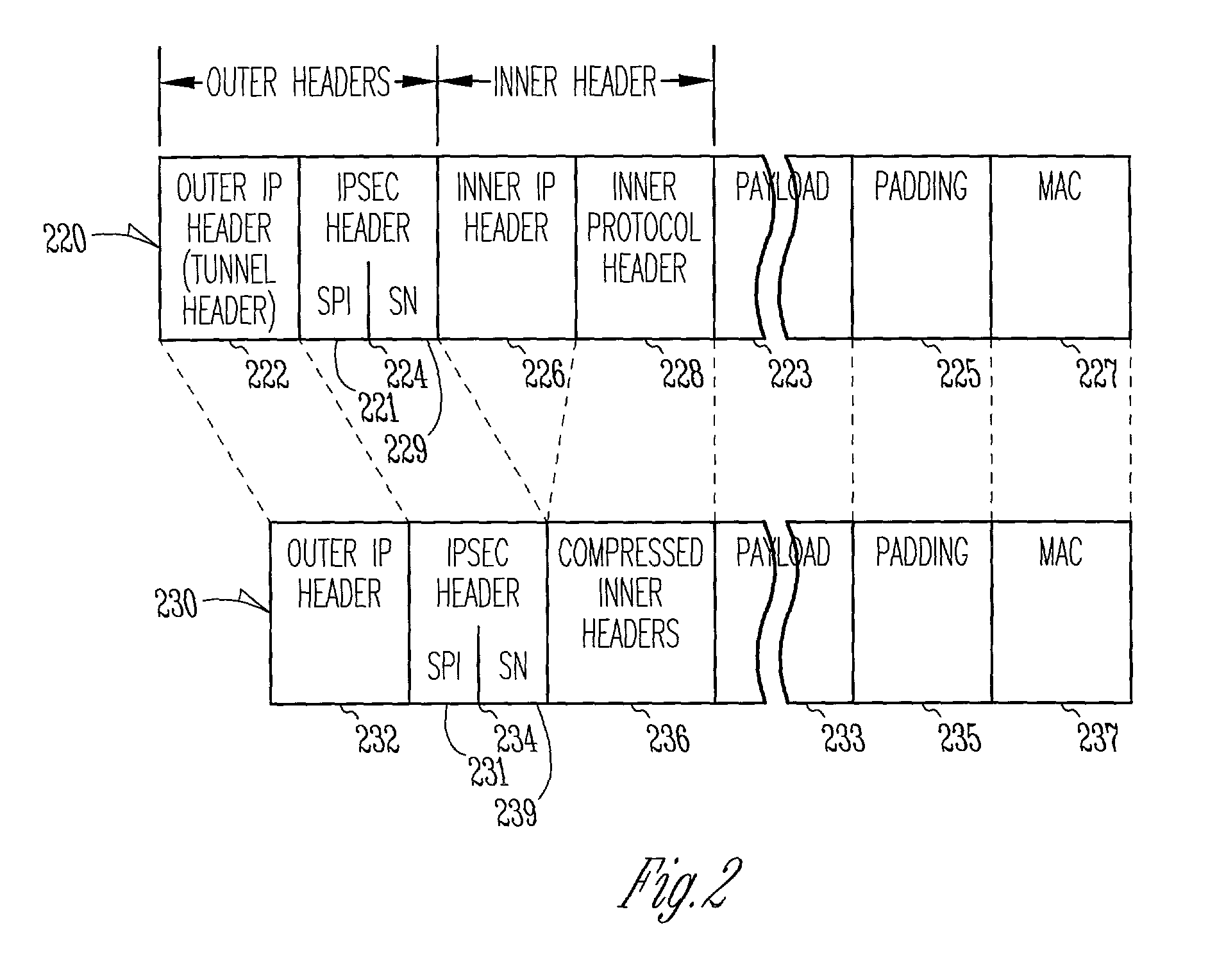
System and method for communicating IPSec tunnel packets with compressed inner headers
Compression of inner headers of IPSec tunnel packets is achieved by storing an inner IP header and an inner protocol header in a context sub-table associated with the security association database entry at a destination tunnel device. IPSec tunnel packets having compressed inner headers may be identified by the LSBs of the SPI number in the IPSec header. The SPI number may also identify whether the IPSec tunnel packet is a TCP packet. A portion of padding in the encapsulated portion may identify a particular context sub-table used for decompressing the inner headers. The context sub-table may be updated as portions of the inner headers change.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
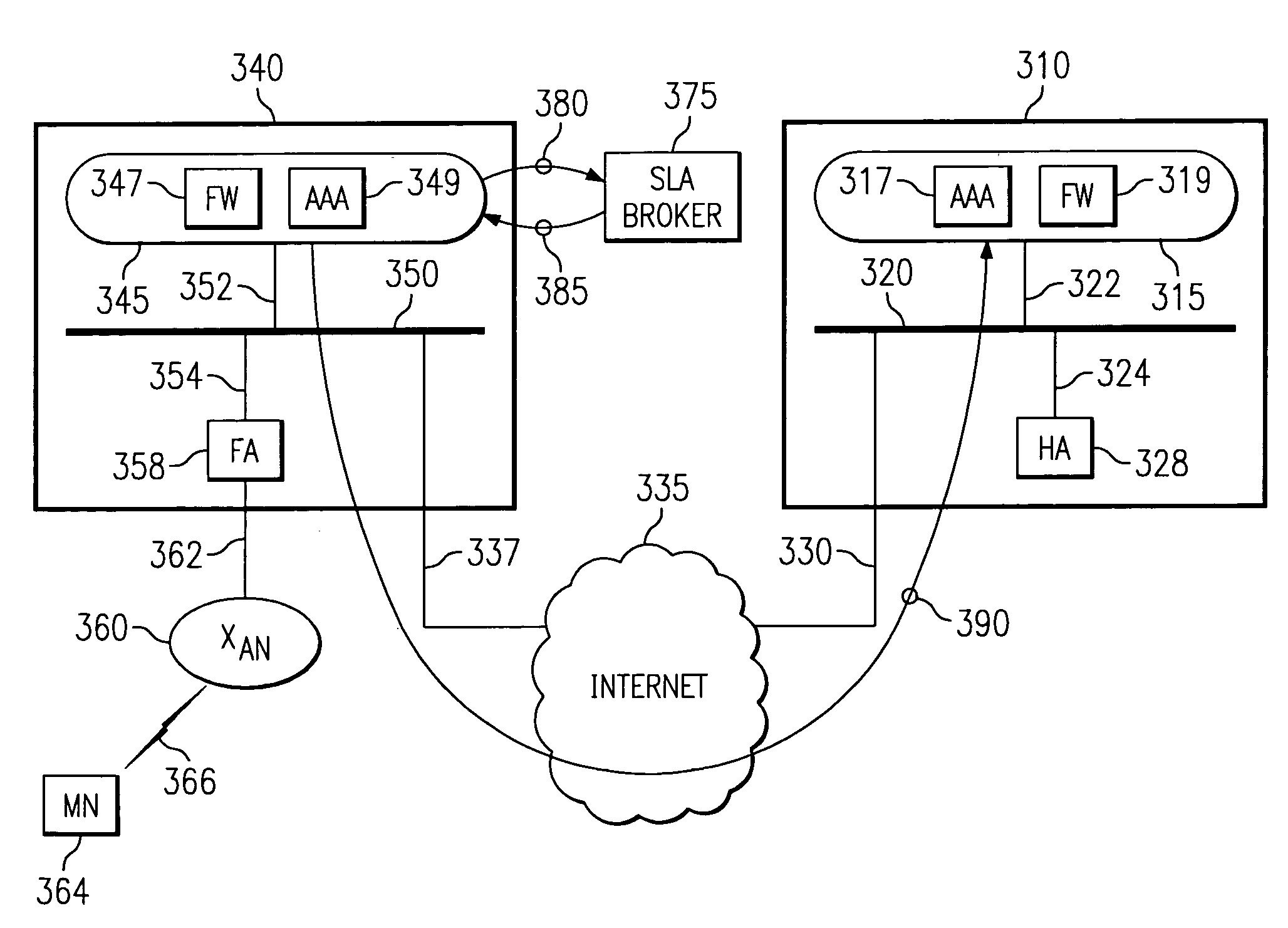
Security framework for an IP mobility system using variable-based security associations and broker redirection
InactiveUS7174018B1Improve securityPromote large-scale roamingWireless network protocolsSecret communicationService-level agreementSecurity association
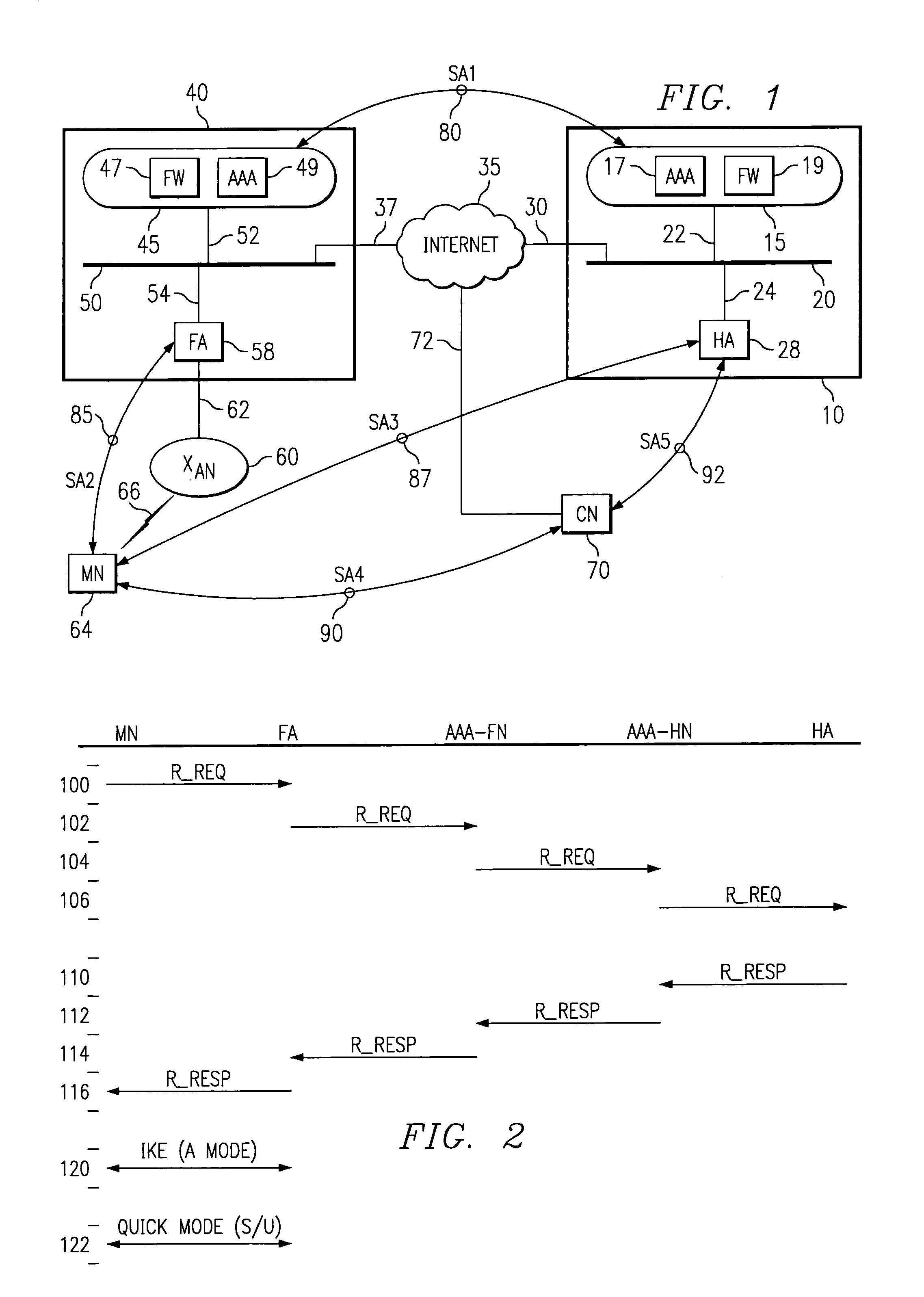
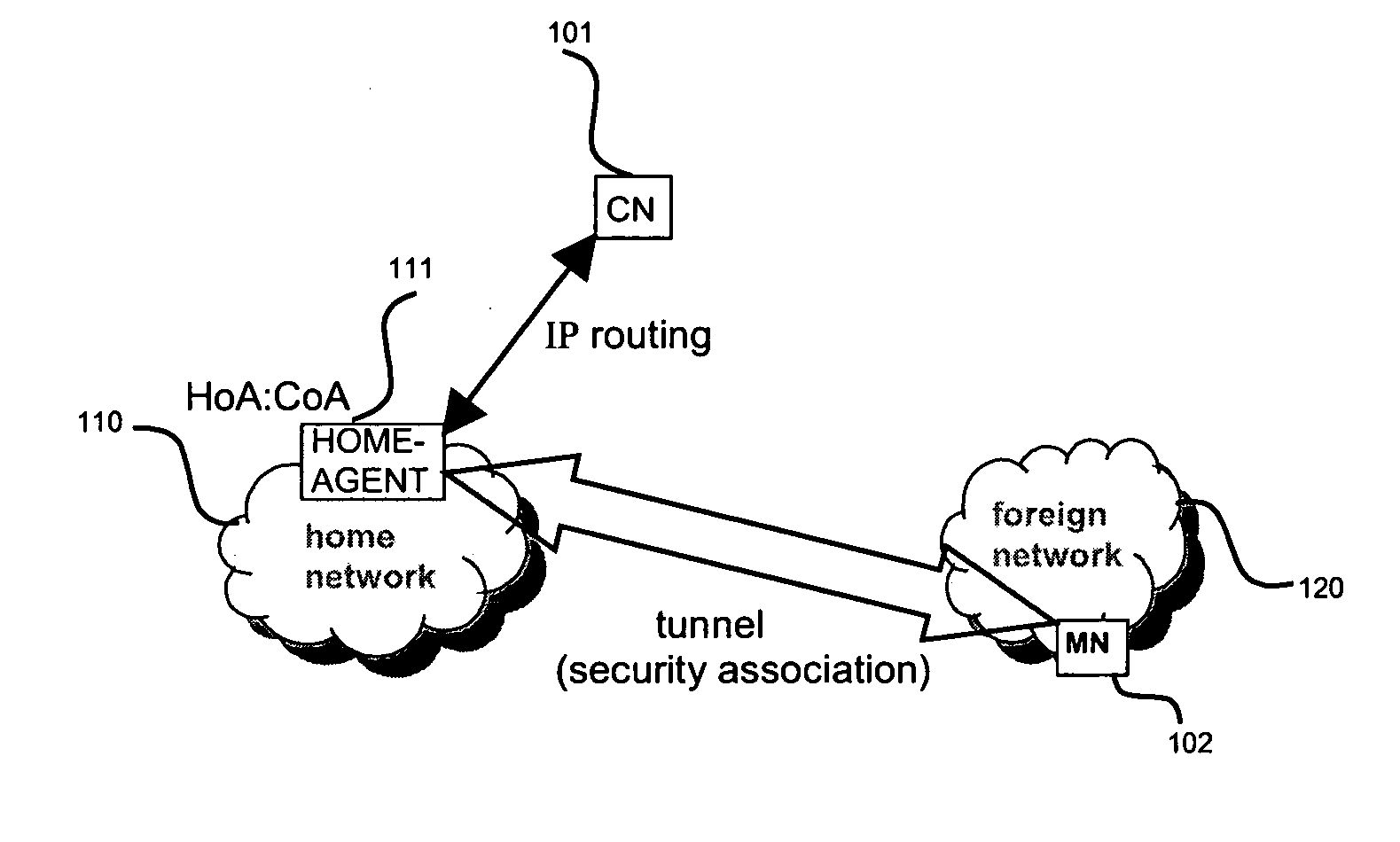
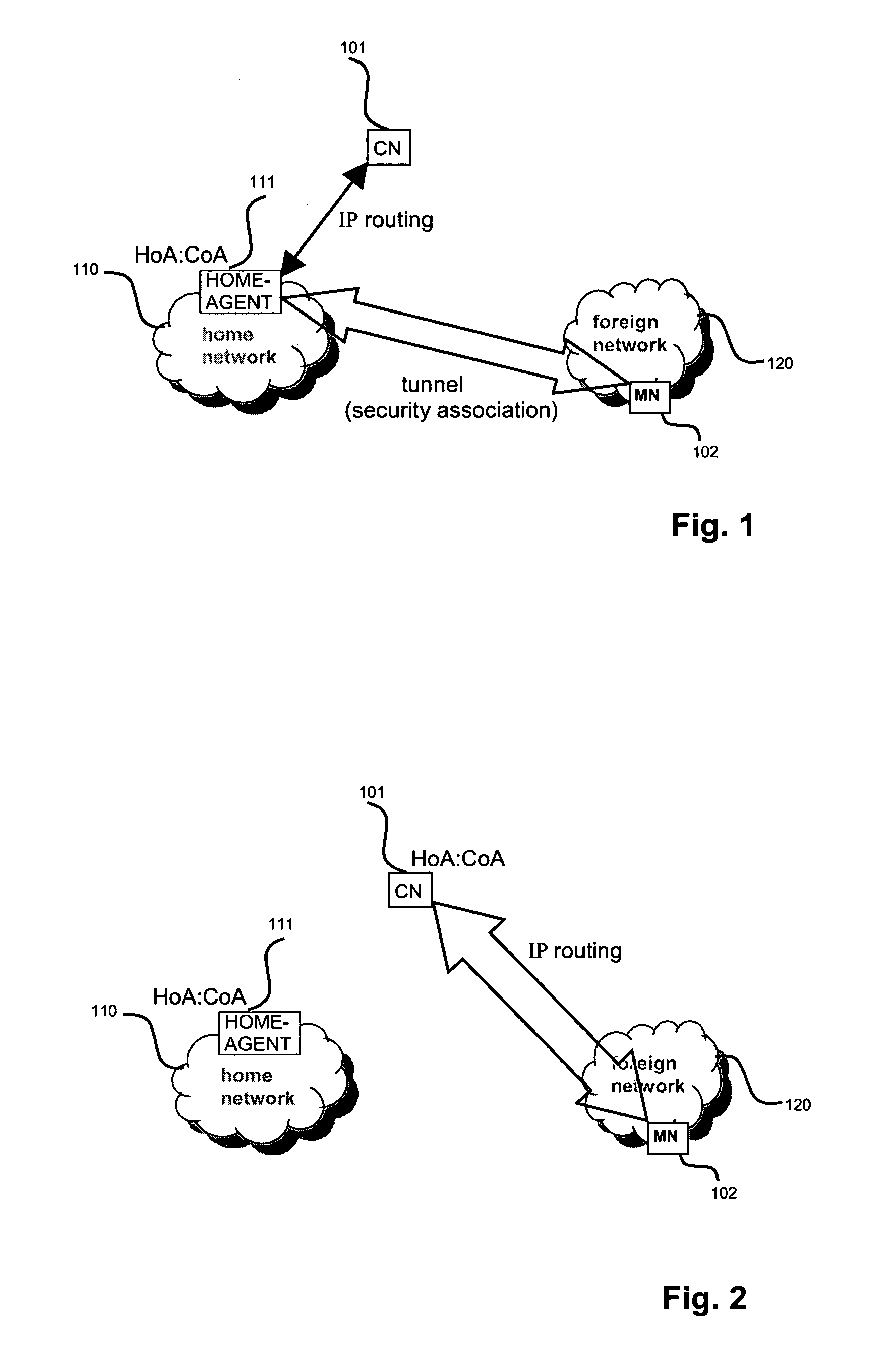
In an IP-based mobile communications system, the Mobile Node changes its point of attachment to the network while maintaining network connectivity. Security concerns arise in the mobile system because authorized users are subject to the following forms of attack: (1) session stealing where a hostile node hijacks session from mobile node by redirecting packets, (2) spoofing where the identity of an authorized user is utilized in an unauthorized manner to obtain access to the network, and (3) eavesdropping and stealing of data during session with authorized user. No separate secure network exists in the IP-based mobility communications system, and therefore, it is necessary to protect information transmitted in the mobile system from the above-identified security attacks.The present invention improves the security of communications in a IP mobile communications system by creating variable-based Security Associations between various nodes on the system, a Virtual Private Network supported by an Service Level Agreement between various foreign networks and a home network, and an SLA Broker to promote large-scale roaming among different SLAs supported by the SLA Broker or agreements with other SLA Brokers.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
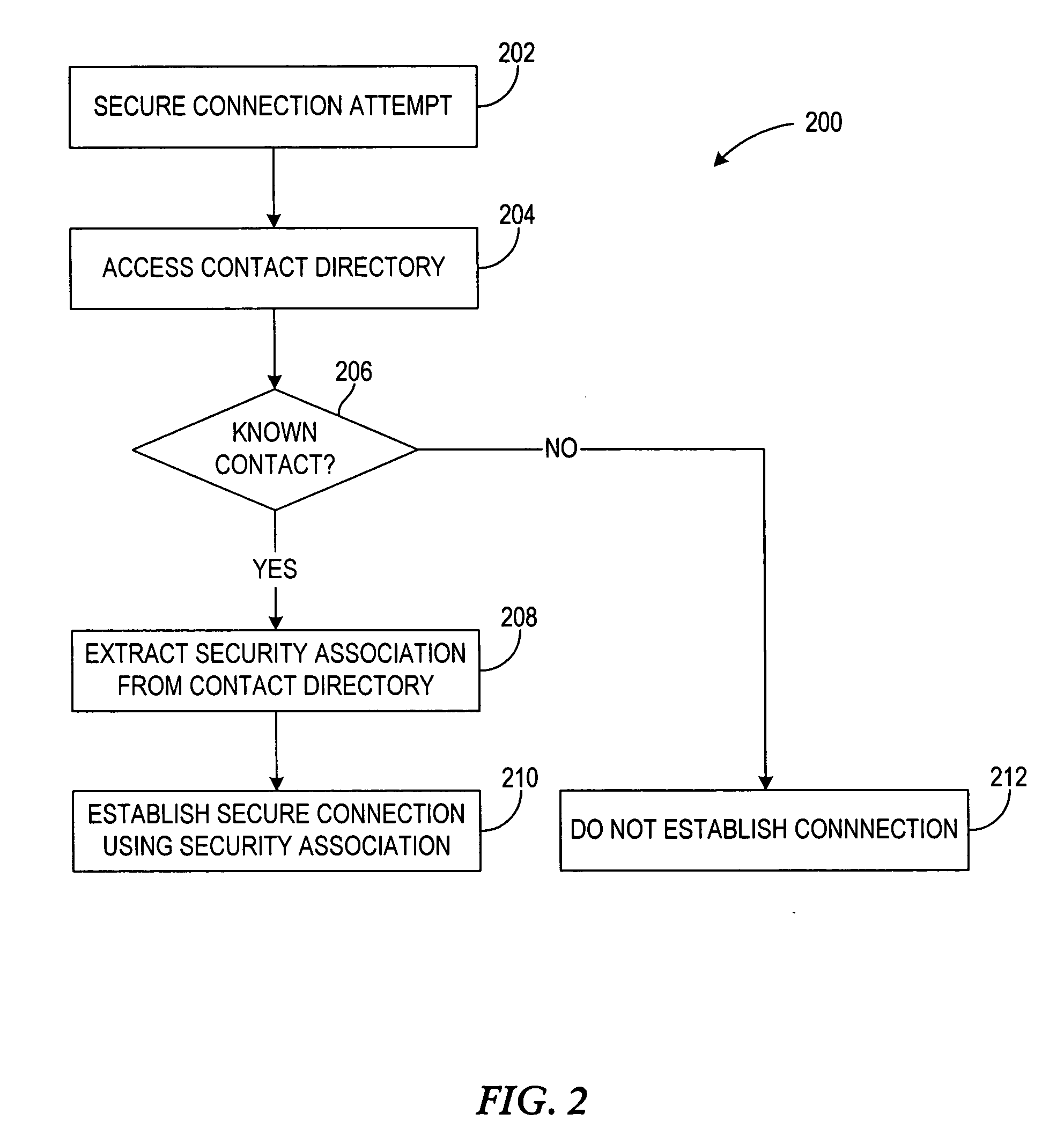
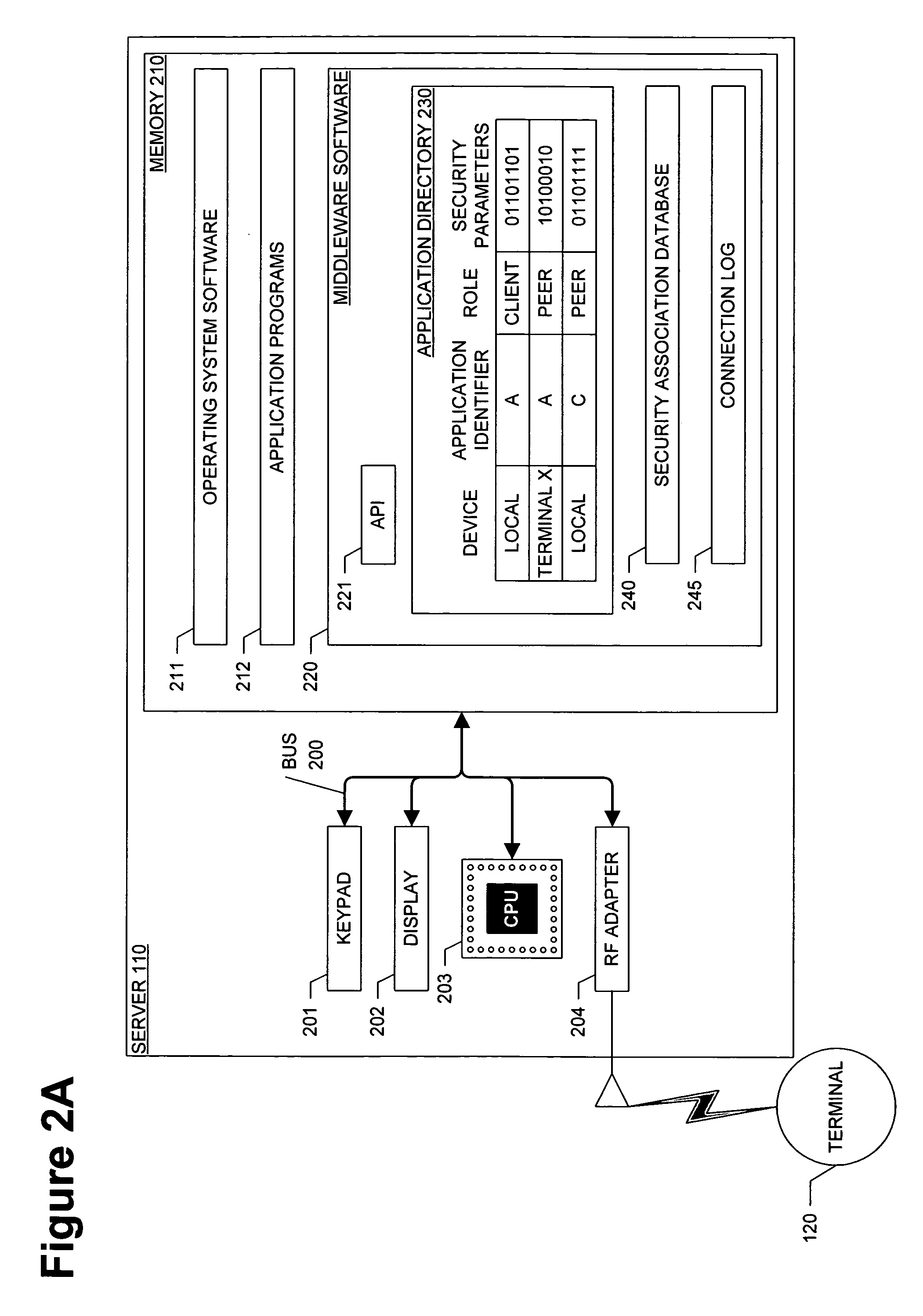
Method of initializing and using a security association for middleware based on physical proximity
InactiveUS20050059379A1Maintain confidentialityEnsure integrityUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionDigital data processing detailsComputer networkSecurity association
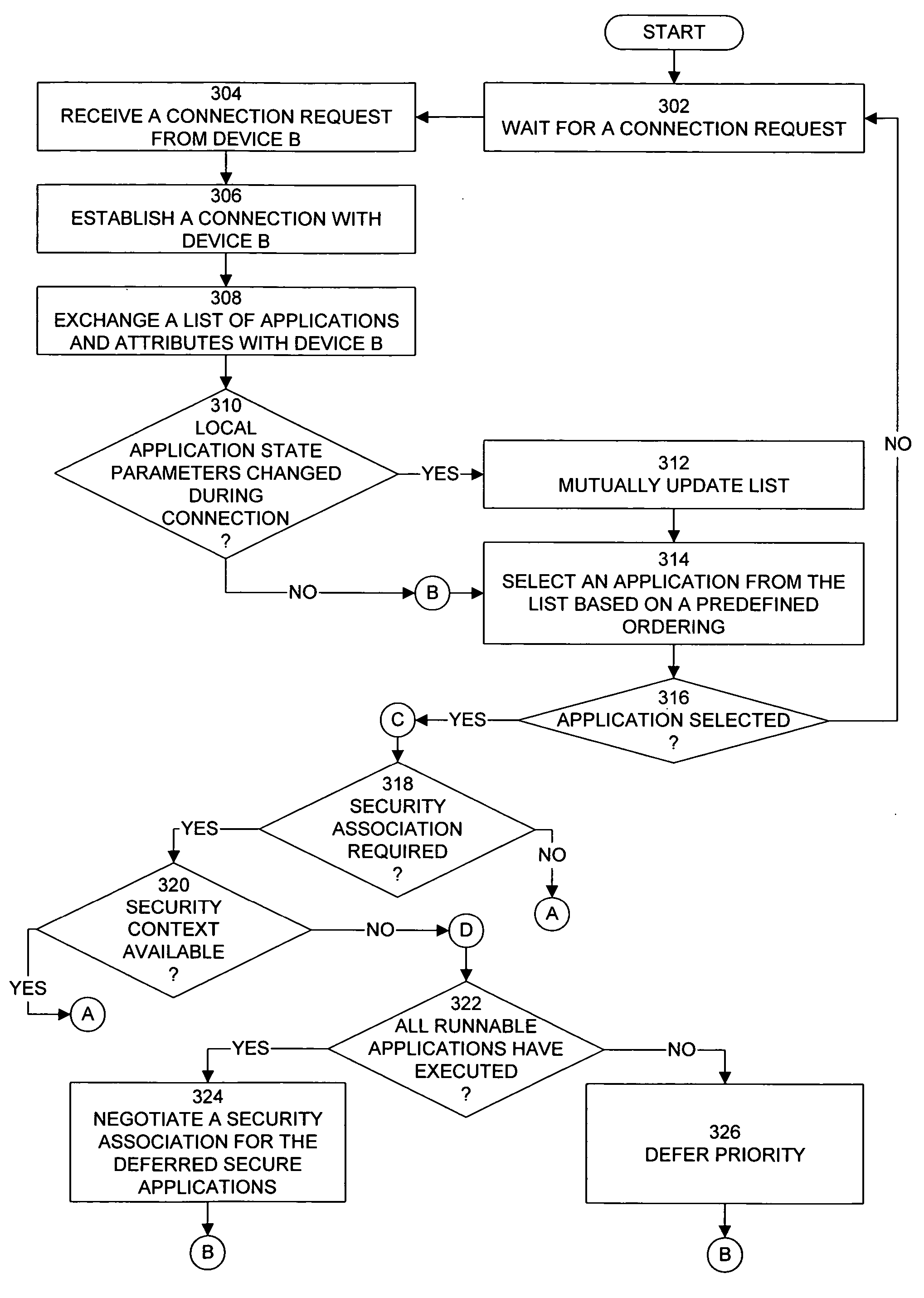
A computer system, method, and computer program product for controlling data communication in an ad-hoc network that connects a wireless device and a nearby wireless device. The method stores an application directory, determines a priority for each entry in the application directory, identifies a selected entry based on the priority, and examines the attributes and security parameters associated with the selected entry. When the security parameters indicate to use a secure connection, the method establishes a security association to support the data communication by querying a database for an existing security association that will satisfy the security parameters. When the query is successful, the method reuses the existing security association. When the query is unsuccessful, the method creates a new security association by establishing a privileged side channel to the nearby wireless device, negotiating the new security association over the privileged side channel, and storing the new security association.
Owner:NORDIC INTERACTIVE TECH LLC
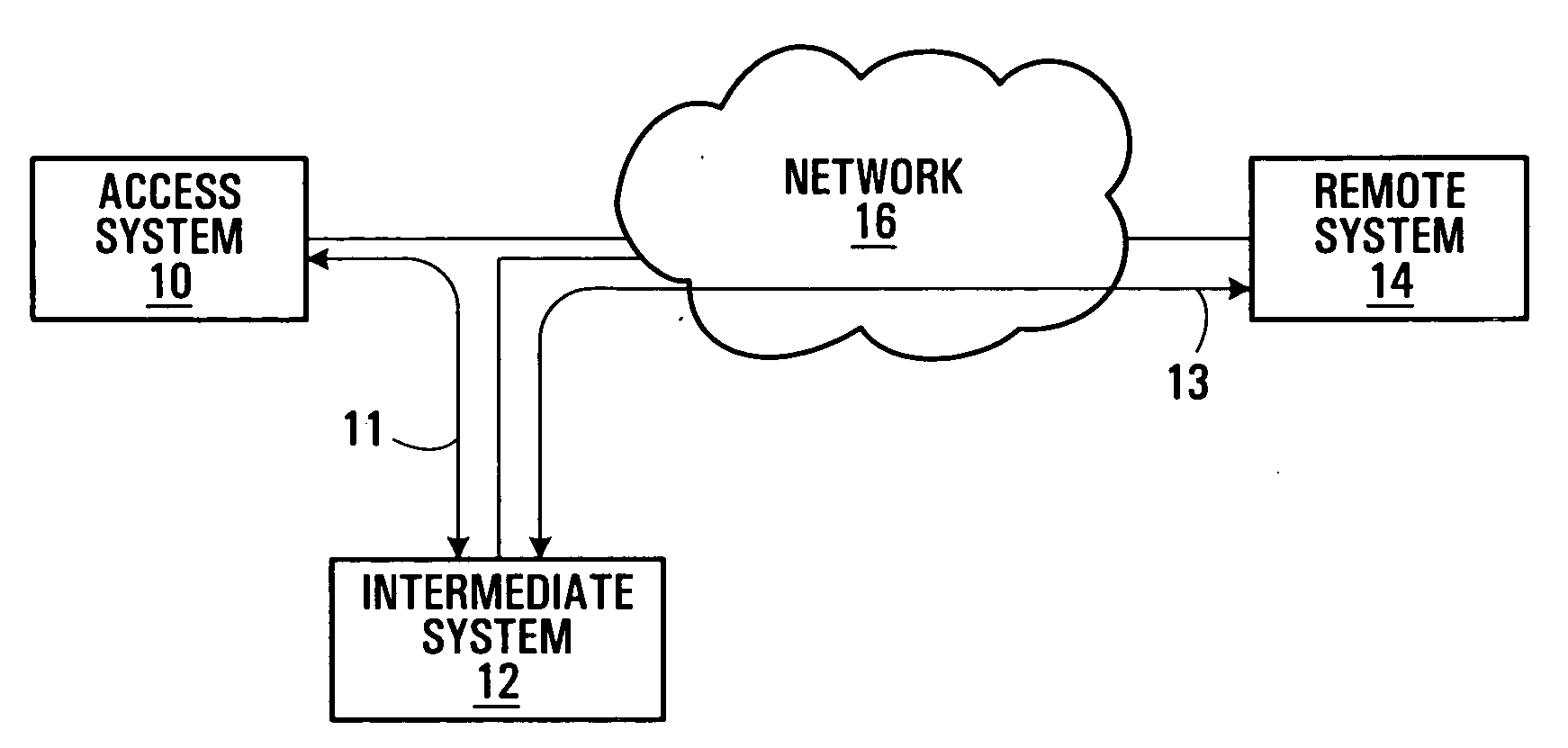
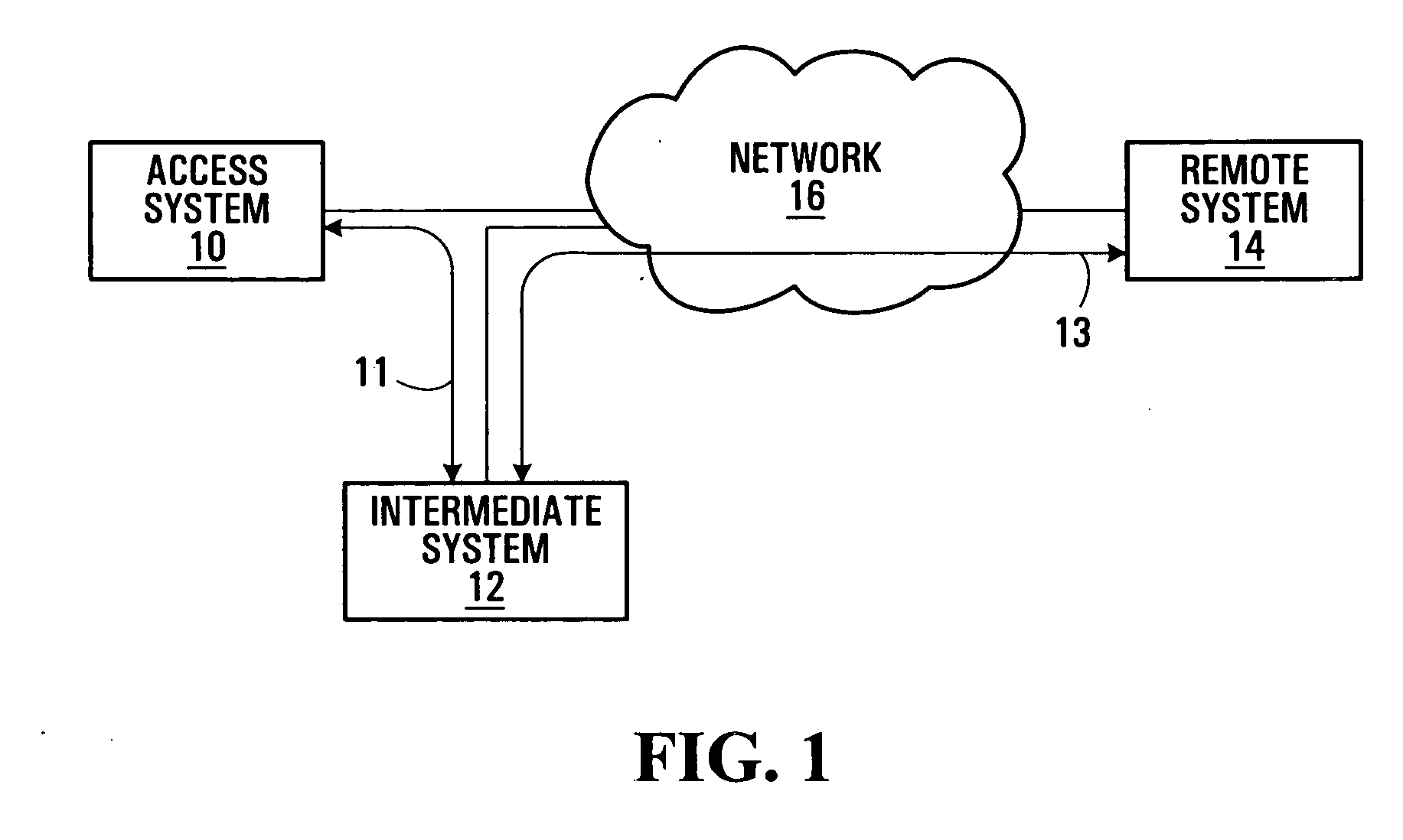
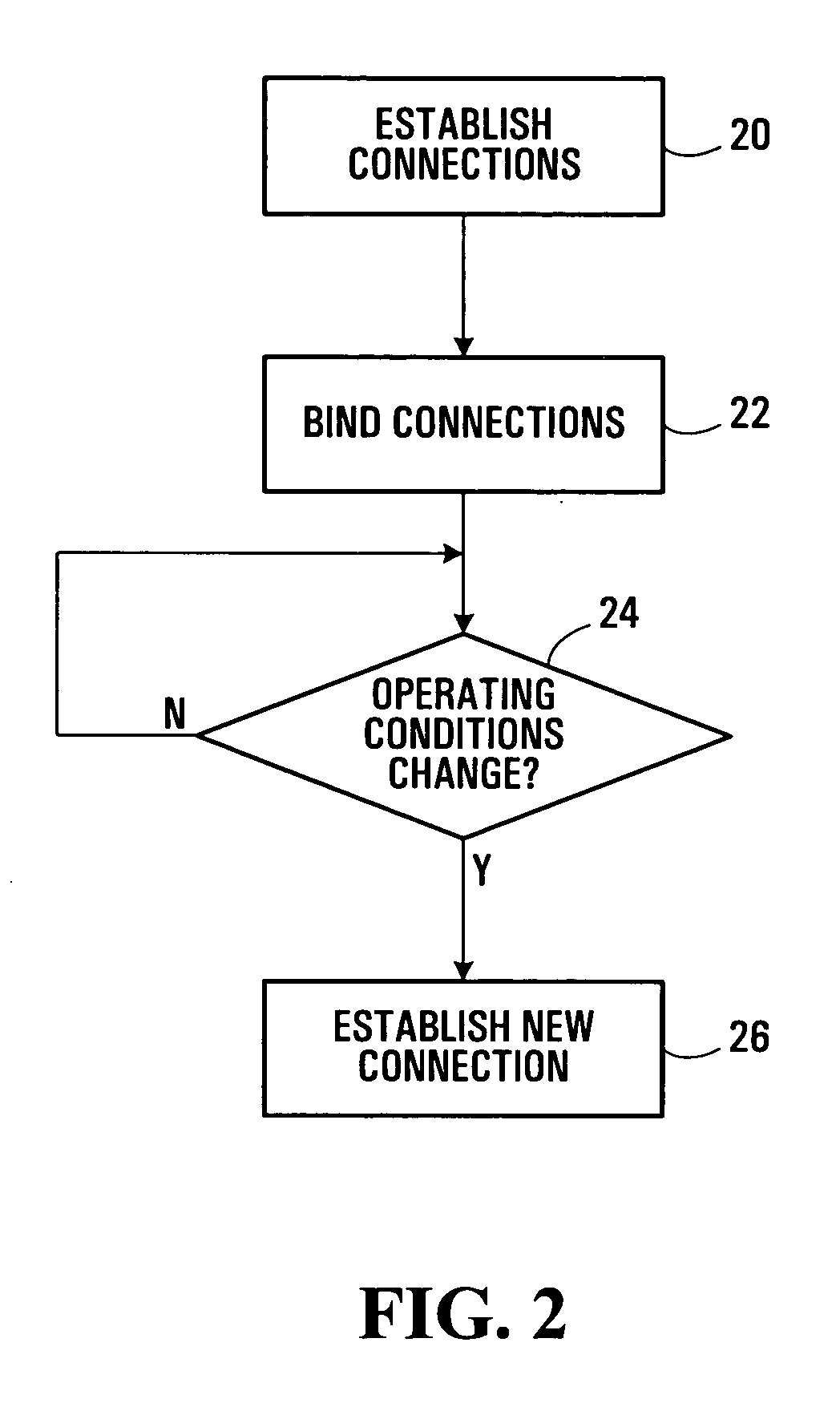
Secure communication methods and systems
InactiveUS20060020787A1Reduce signal delayMultiple digital computer combinationsWireless network protocolsSecure communicationSecurity association
Methods and systems for secure communications are provided. Secure end-to-end connections are established as separate multiple secure connections, illustratively between a first system and an intermediate system and between a second system and an intermediate system. The multiple secure connections may be bound, by binding Internet Protocol Security Protocol (IPSec) Security Associations (SAs) for the multiple connections, for example, to establish the end-to-end connection. In the event of a change in operating conditions which would normally require the entire secure connection to be re-established, only one of the multiple secure connections which form the end-to-end connection is re-established. Separation of end-to-end connections in this manner may reduce processing resource requirements and latency normally associated with re-establishing secure connections.
Owner:RPX CORP
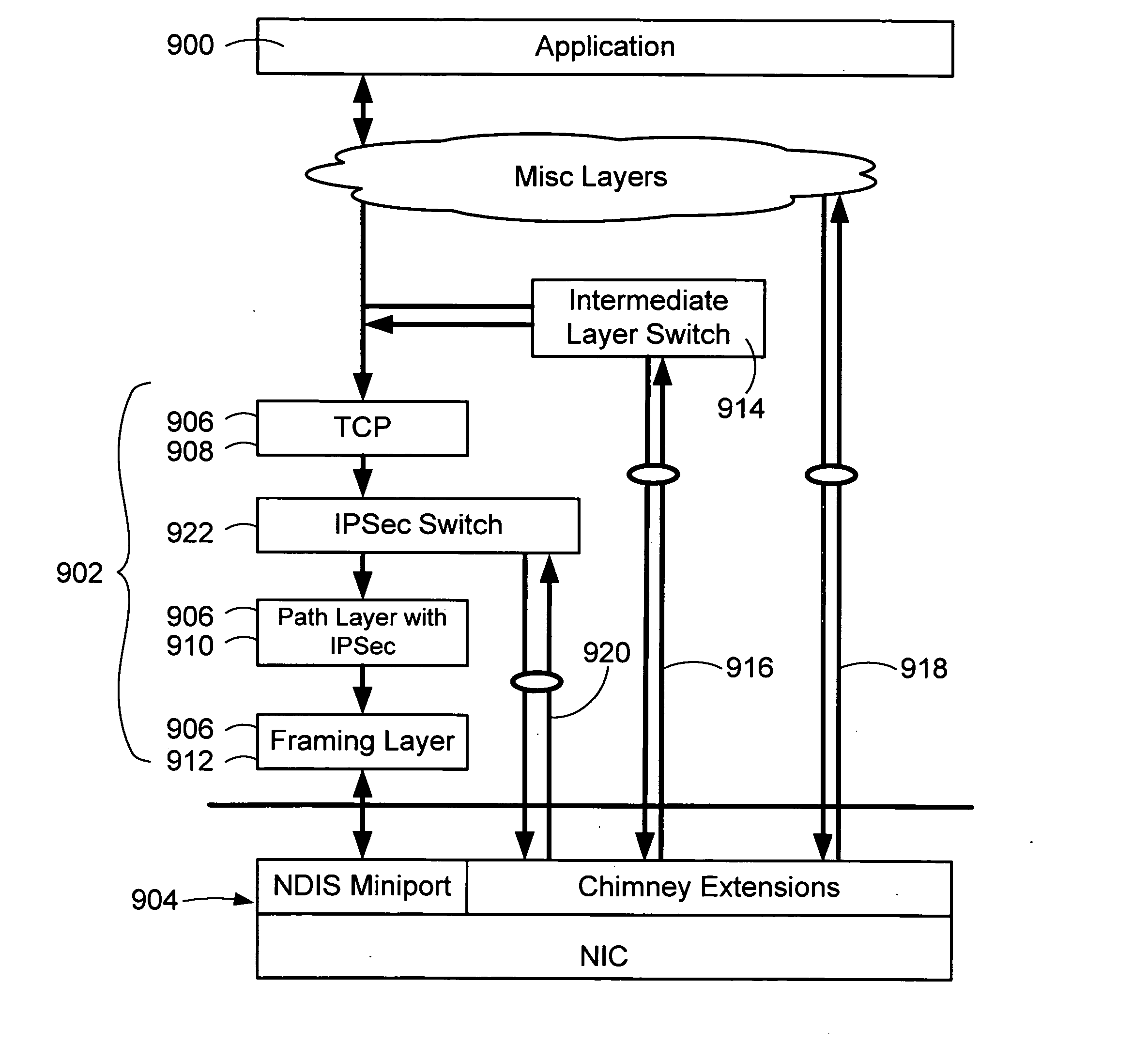
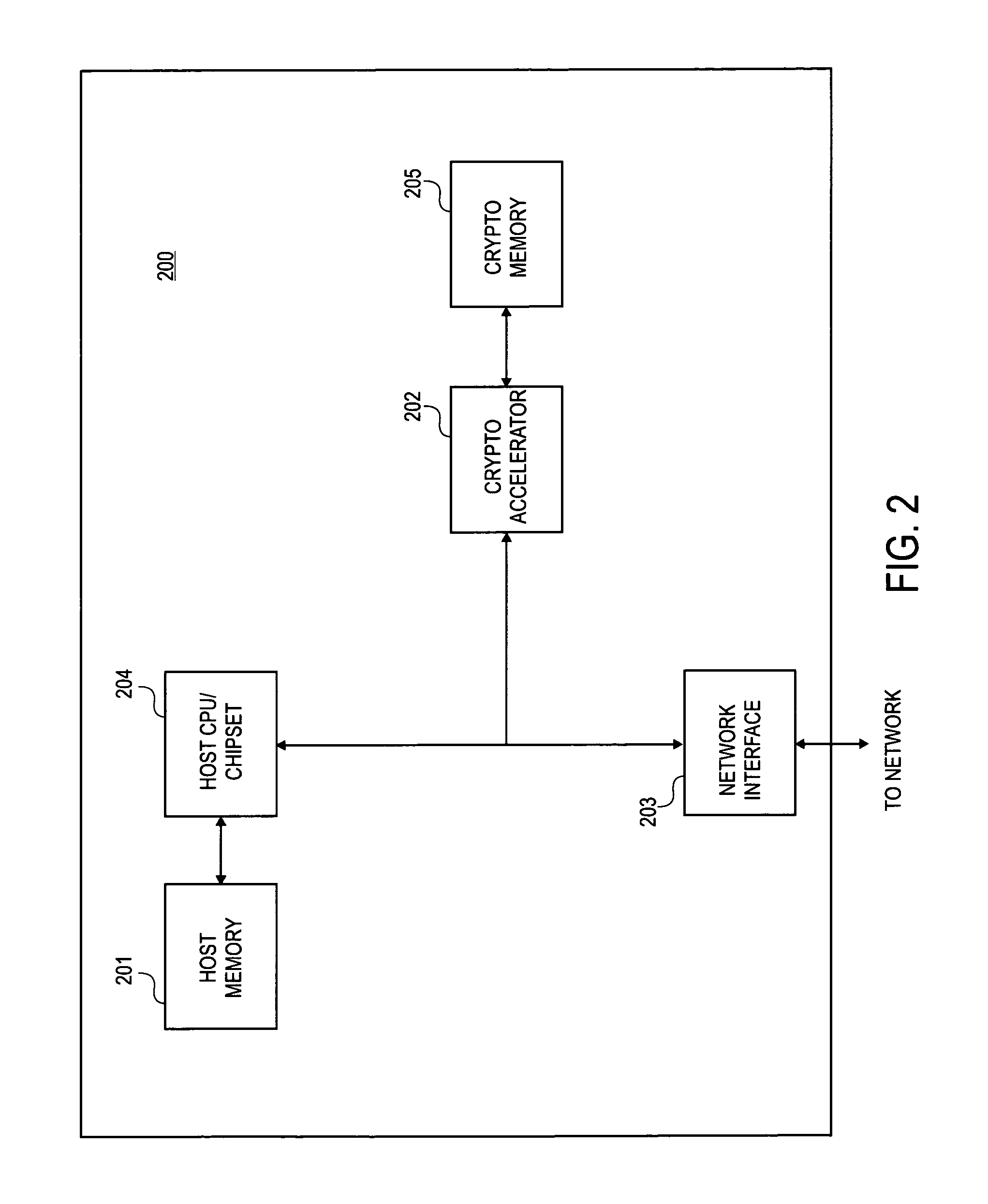
Method and apparatus for secure internet protocol (IPSEC) offloading with integrated host protocol stack management
ActiveUS20060104308A1Requires minimizationDigital data processing detailsTime-division multiplexComputer hardwareSecurity association
The invention provides mechanisms for transferring processor control of secure Internet Protocol (IPSec) security association (SA) functions between a host and a target processing devices of a computerized system, such as processors in a host CPU and a NIC. In one aspect of the invention, the computation associated with authentication and / or encryption is offloaded while the host maintains control of when SA functions are offloaded, uploaded, invalidated, and re-keyed. The devices coordinate to maintain metrics for the SA, including support for both soft and hard limits on SA expiration. Timer requirements are minimized for the target. The offloaded SA function may be embedded in other offloaded state objects of intermediate software layers of a network stack.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and system for controlling attacks on distributed network address translation enabled networks
InactiveUS7028335B1Readily apparentDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationSecurity associationNetwork address translation
A method and system for distributed network address translation with security for controlling and limiting the disruption caused by denial of service attacks. The method and system have a first network device and a second network device on a first network, and a third network device on a second network external to the first network, with an established security association between the first network device and the third network device. The first network device specifies an external address of the third network device for the security association to the second network device, which stores the external address in a table. The second network device then maps at least one of an internal address and a security value to the external address in the table. Any packets sent from the third network device to the first network device are intercepted by the second network device, which determines the external address and security value of the packet. If the security value of the packet has been allocated to the first network device, and the external address of the packet has been specified by the first network device as being valid, the packet is sent from the second network device to the first network device using distributed network address translation with security. Otherwise, the packet is discarded by the second network device.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
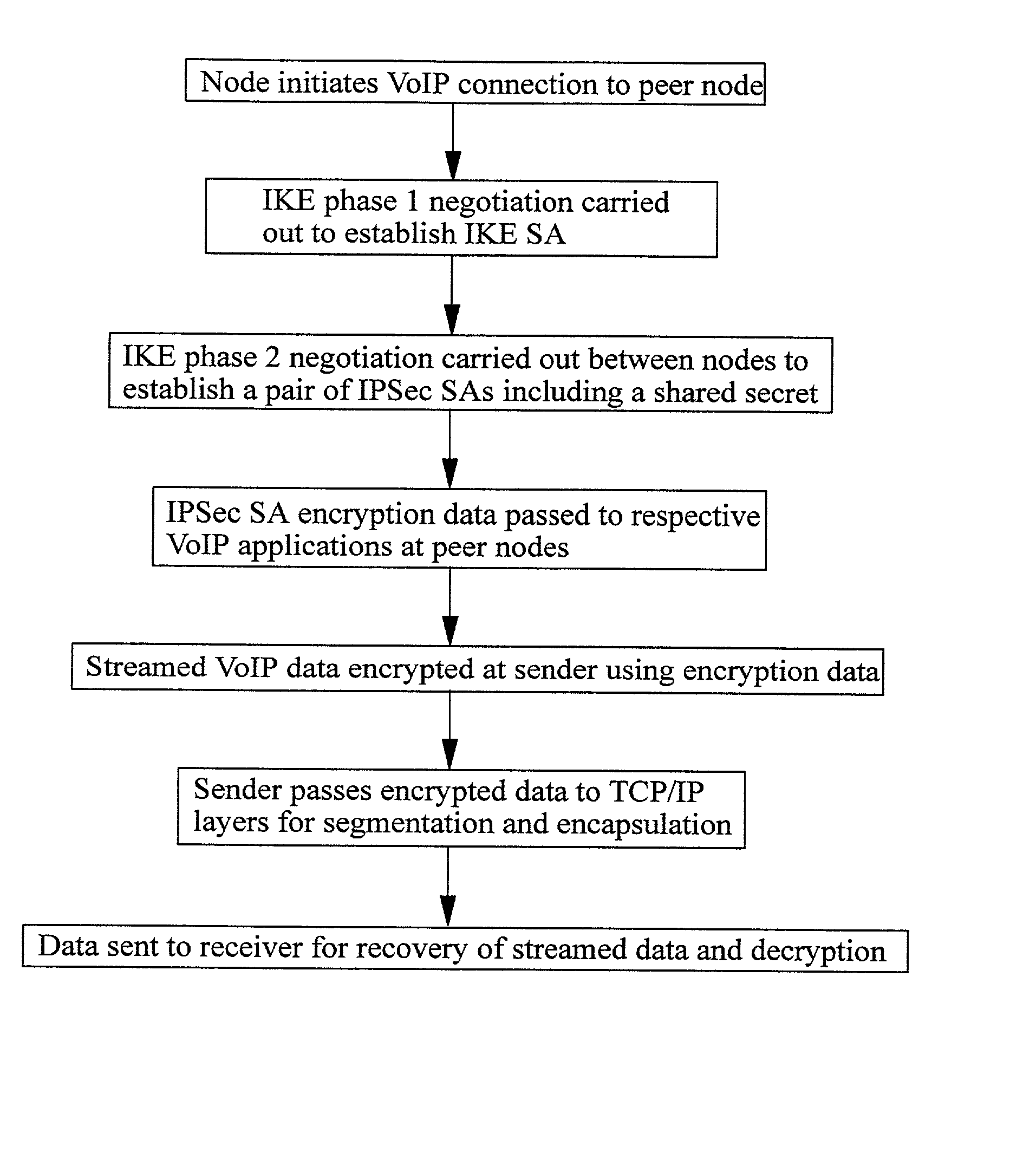
Securing Voice over IP traffic
A method of sending streamed data over an IP network from a first node 1 to a second node 4, the method comprising using Internet Key Exchange (IKE) to establish an IKE security association (SA) between the first and second nodes 1,4. A shared secret is established between the first and second nodes using the IKE SA, and the streamed data encrypted at the first node 1 with a cipher using the shared secret or a key derived using the shared secret. IP datagrams are constructed containing in their payload, segments of the encrypted streamed data, the datagrams not including an IPSec header or headers. The IP datagrams are then sent from the first node 1 to the second node 4.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
System and method for security association between communication devices within a wireless personal and local area network
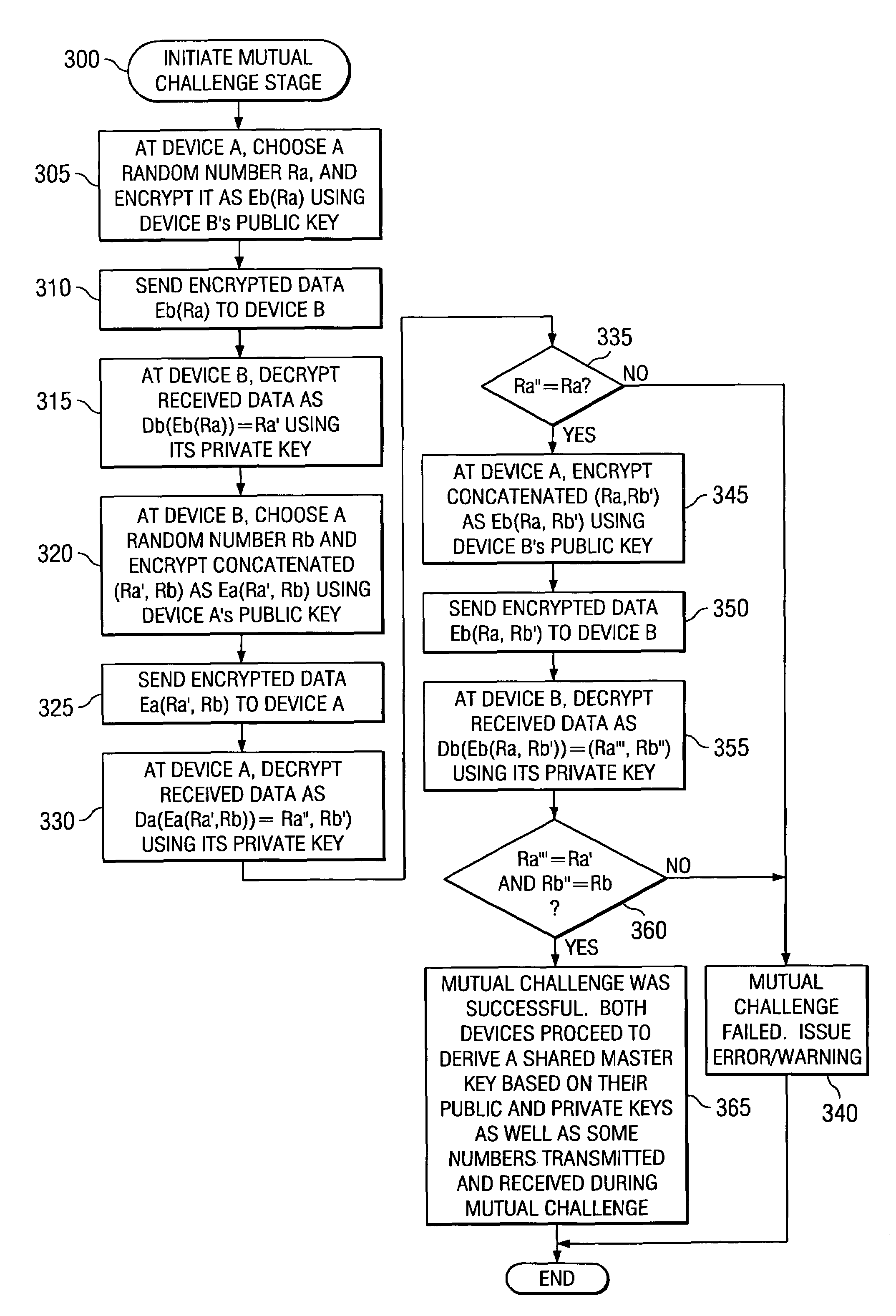
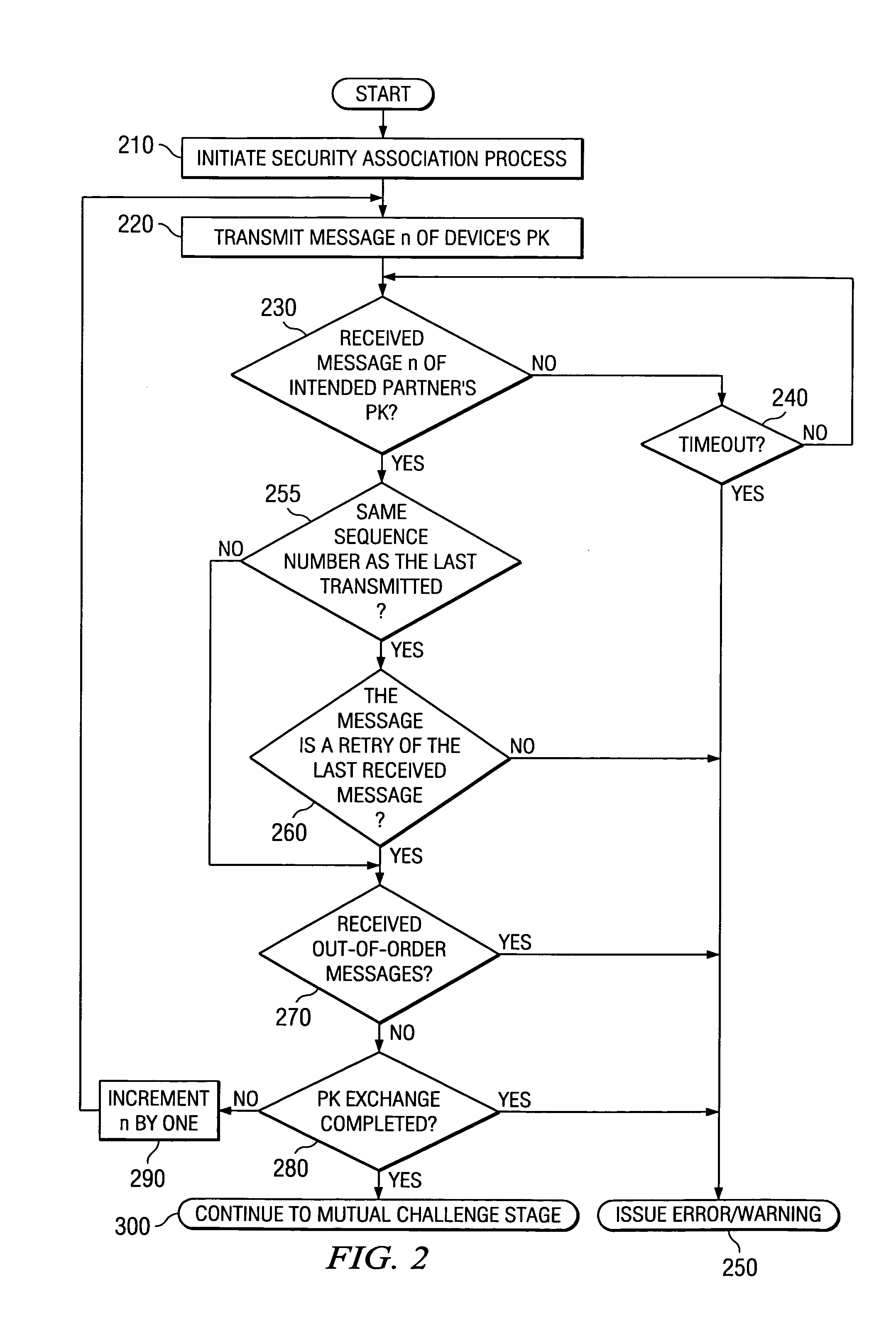
ActiveUS7660419B1Improve securityImprove integrityUser identity/authority verificationSecret communicationSecurity associationMaster key
The present application describes a method and system for discovering and authenticating communication devices within a wireless network. According to an embodiment, communication devices exchange public keys using multiple messages each including at least a portion of the public key of the sending device. The devices authenticate the receipt of the public key and establish a shared master key. The shared master key is used to further derive a session key for securing the application data between the communicating devices for a current session.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
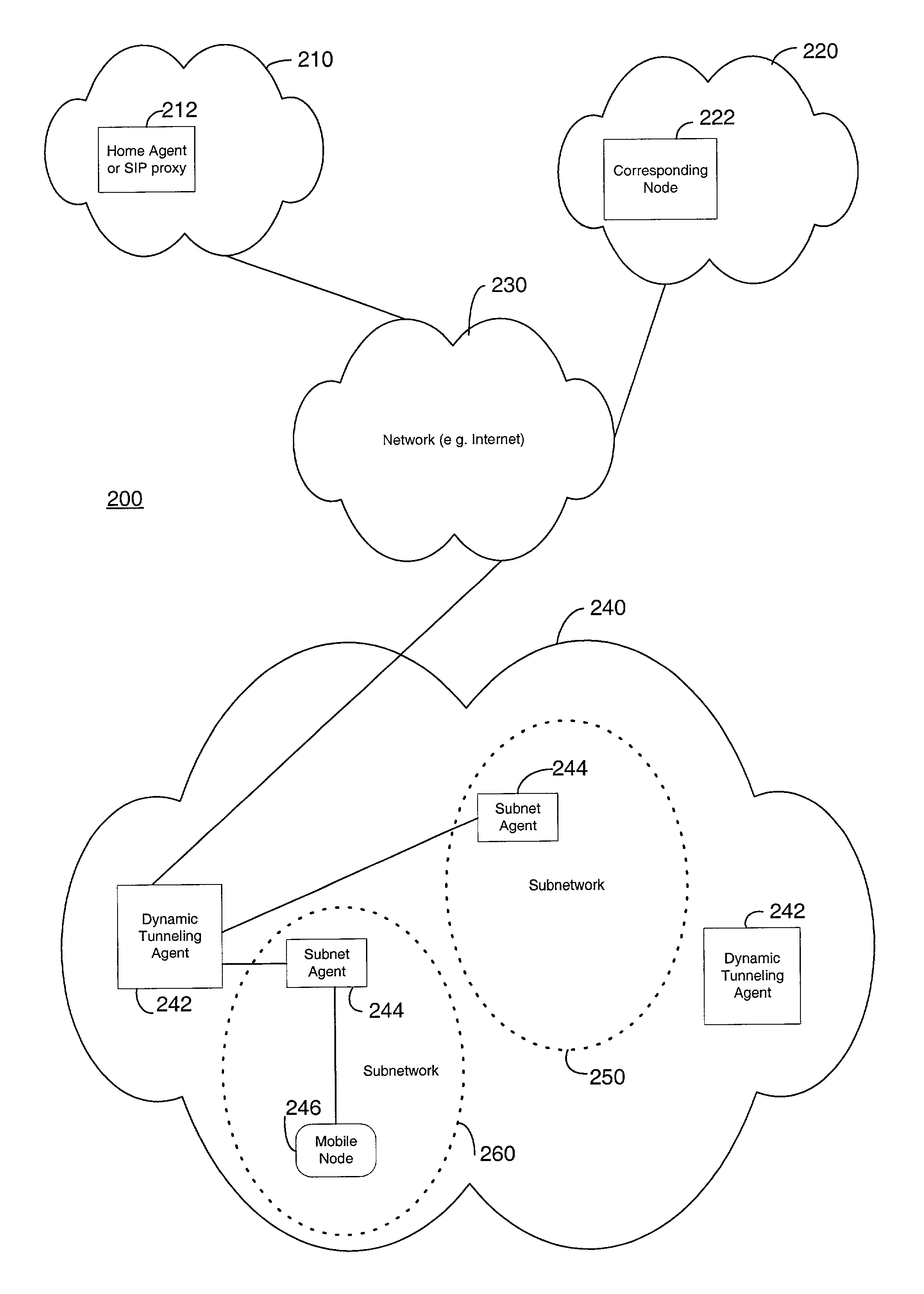
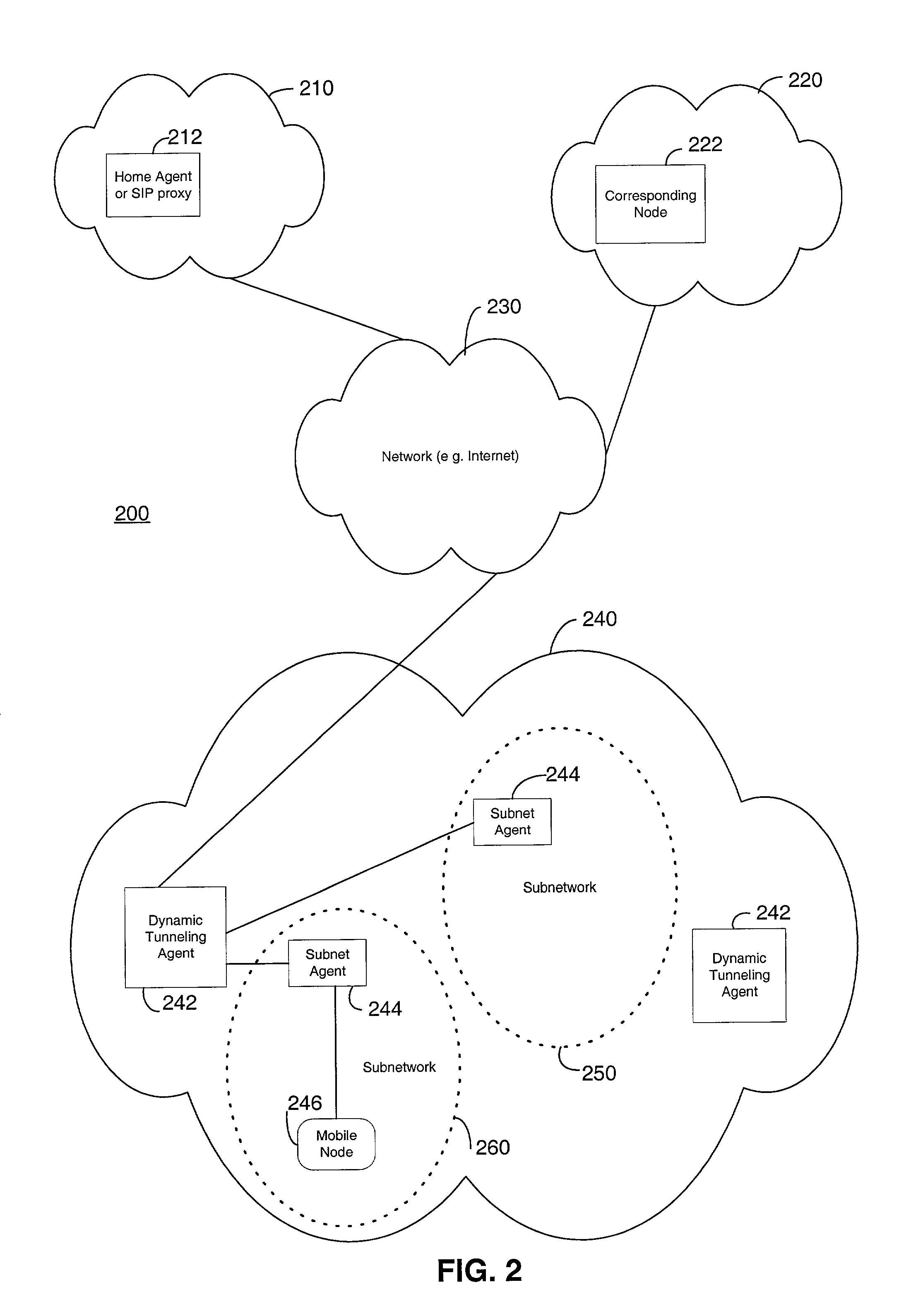
Methods and systems for a generalized mobility solution using a dynamic tunneling agent
ActiveUS6992994B2Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsSecurity associationComputer science
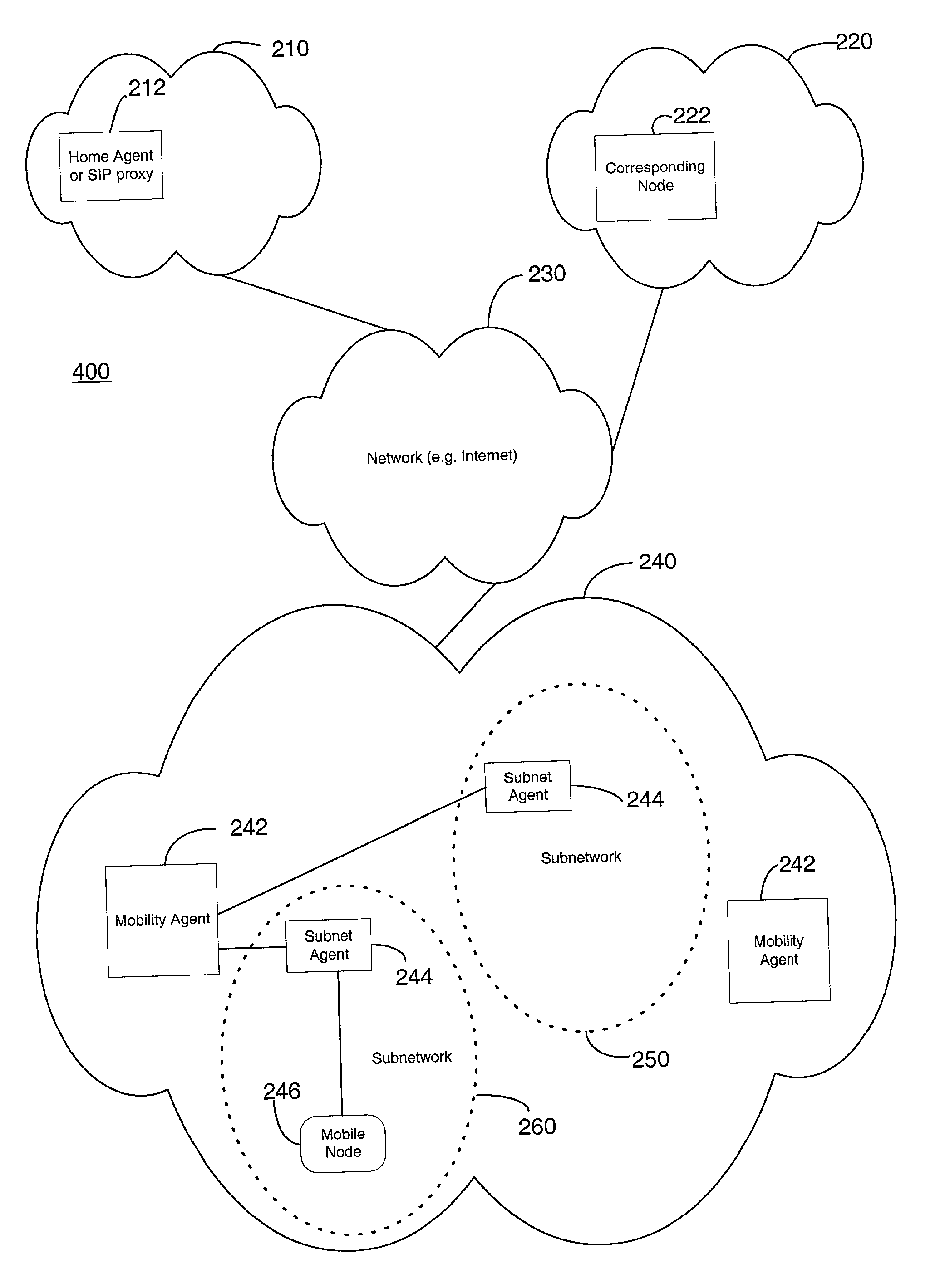
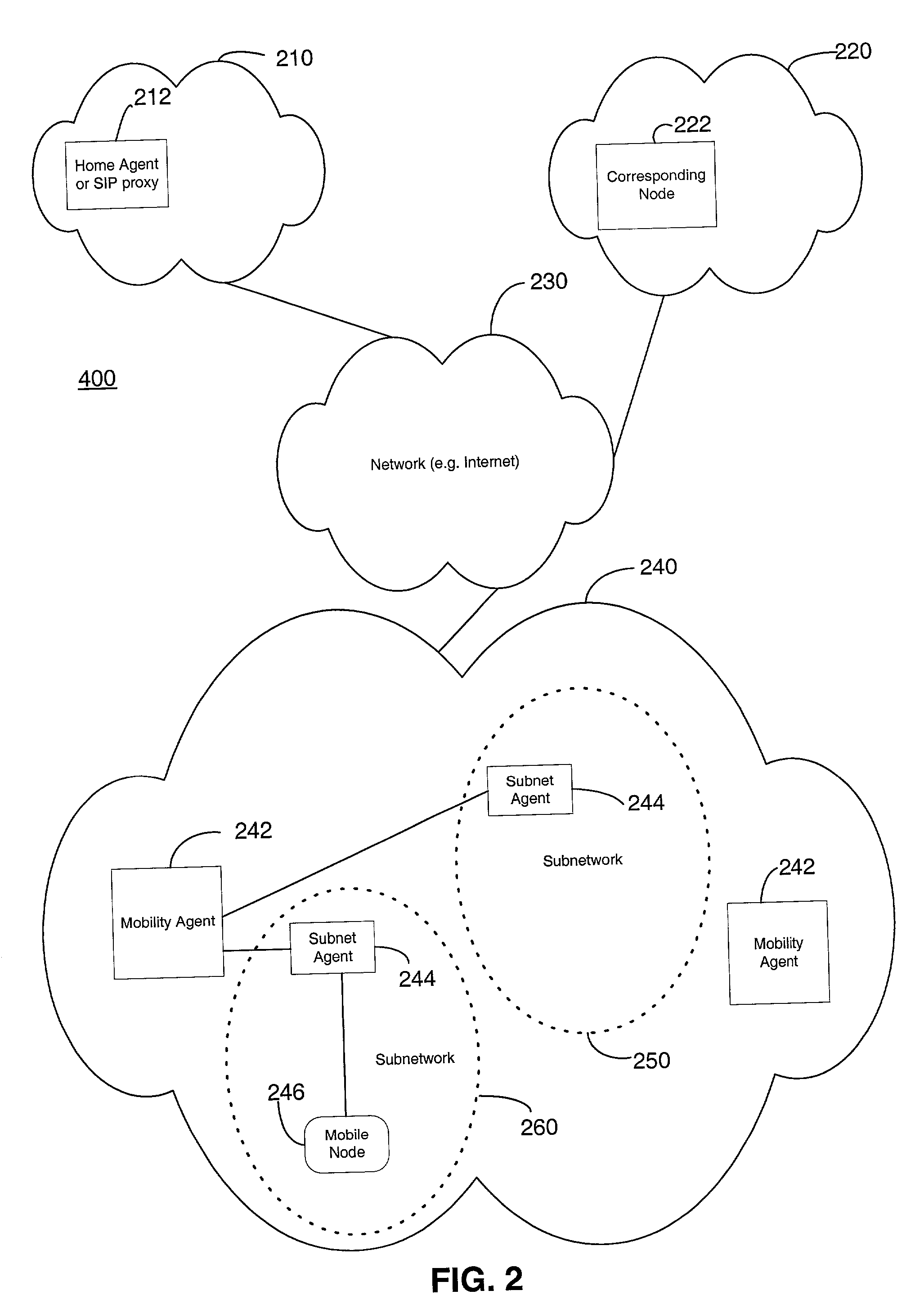
Methods and systems are provided for facilitating intra-domain mobility. A first network or domain includes a home agent or SIP proxy of a mobile node. A second network includes two or more subnetworks and at least one dynamic tunneling agent (DTA). Each subnetwork includes an associated subnet agent. To communicate, the mobile node first registers with a subnet agent, receives a local care-of-address and a global care-of-address, and then registers with a DTA. The local care-of-address received from the subnet agent may enable communication with the mobile node without determining a specific route to the mobile node. The global care-of-address received from the subnet agent may include the address of the DTA with which to register. On registering with the DTA, the DTA may provide the mobile node with a unique, globally reachable global care-of-address, which the mobile node may then forward to a home agent, SIP proxy, or a correspondent node. Accordingly, the mobile node may transition from any of the subnetworks to another subnetwork without communicating to the home agent information about the transition and without communicating to the DTA information about a security association between the mobile node and the home agent.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
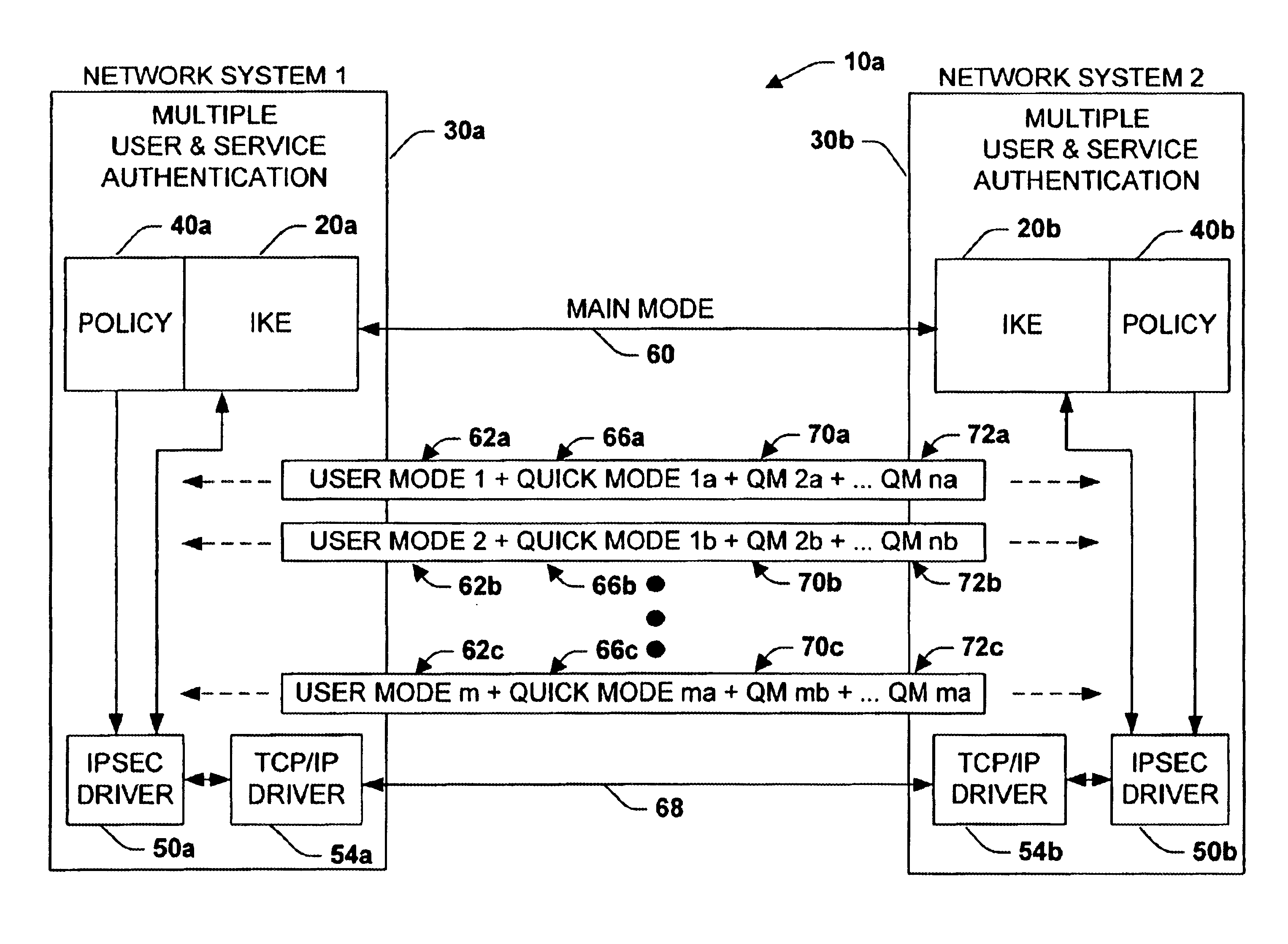
System and method for improved network security
InactiveUS6915437B2Improve performanceImprove securityDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationTraffic capacityInternet Key Exchange
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
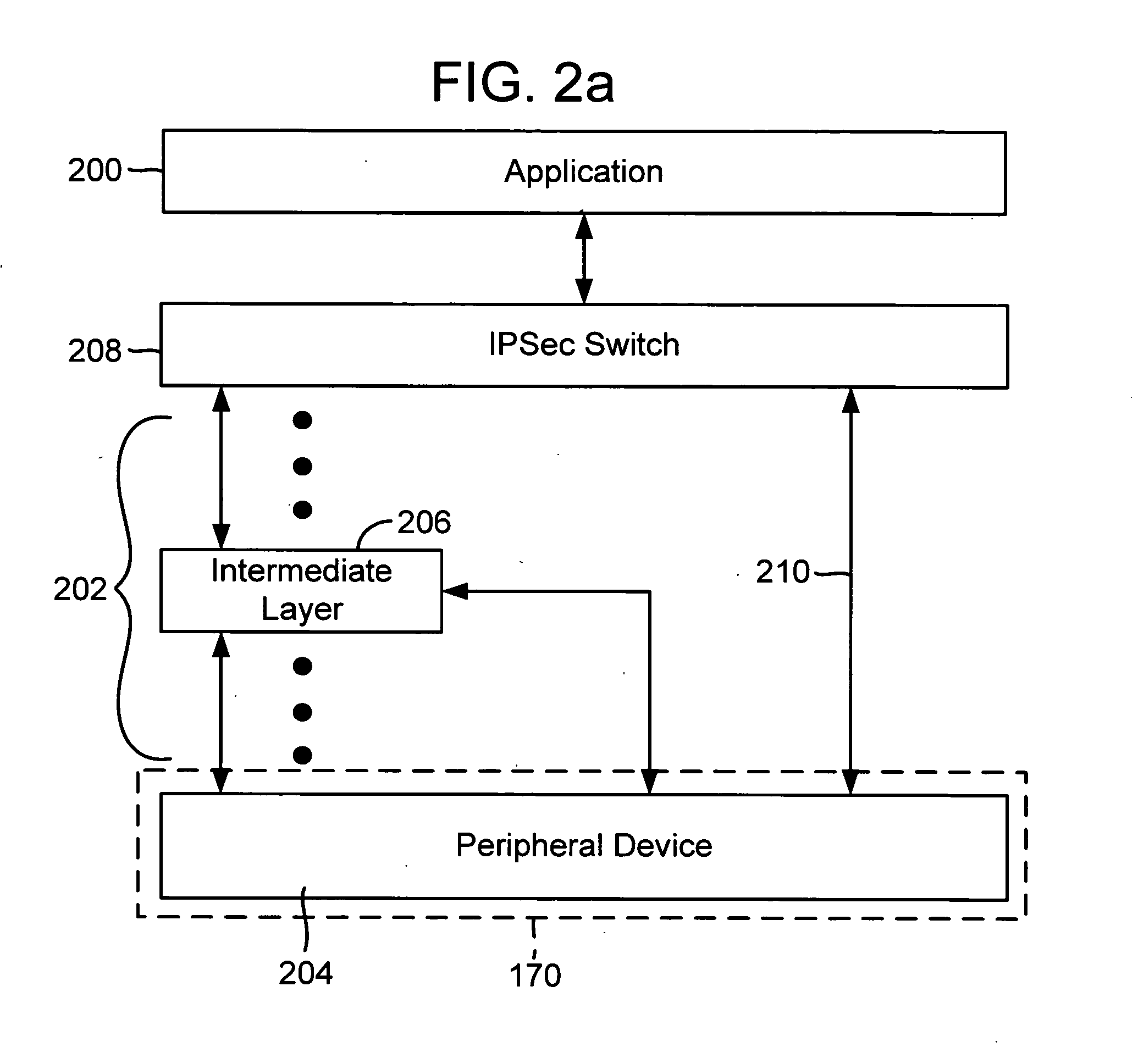
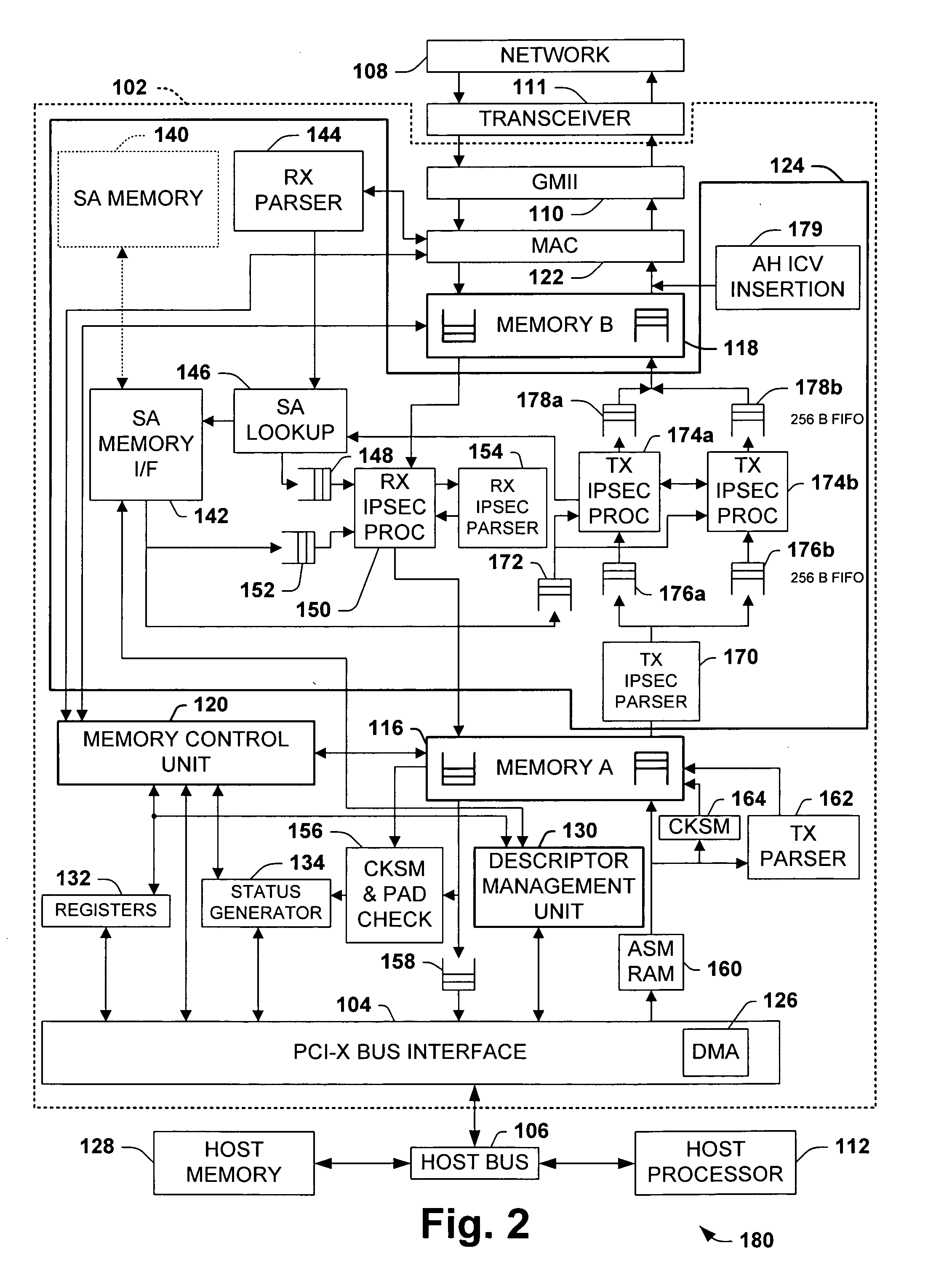
Method and circuit to accelerate IPSec processing
ActiveUS7017042B1Unauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringNetwork packetSecurity association
Methods and apparatus' for performing IPSec processing on an IP packet being transmitted onto a network and being received from a network are described. The methods and apparatus' further described perform IPSec processing inline which results in a reduced number of transfers over the system bus, reduced utilization of system memory, and a reduced utilization of the system CPU. An IP packet which requires IPSec processing enters an acceleration device. In one embodiment, the acceleration device is coupled to a security policy database (SPD) and security association database (SAD). IPSec processing is performed at the acceleration device without sending the IP Packet to system memory for processing.
Owner:DIGITAL ARCHWAY +1
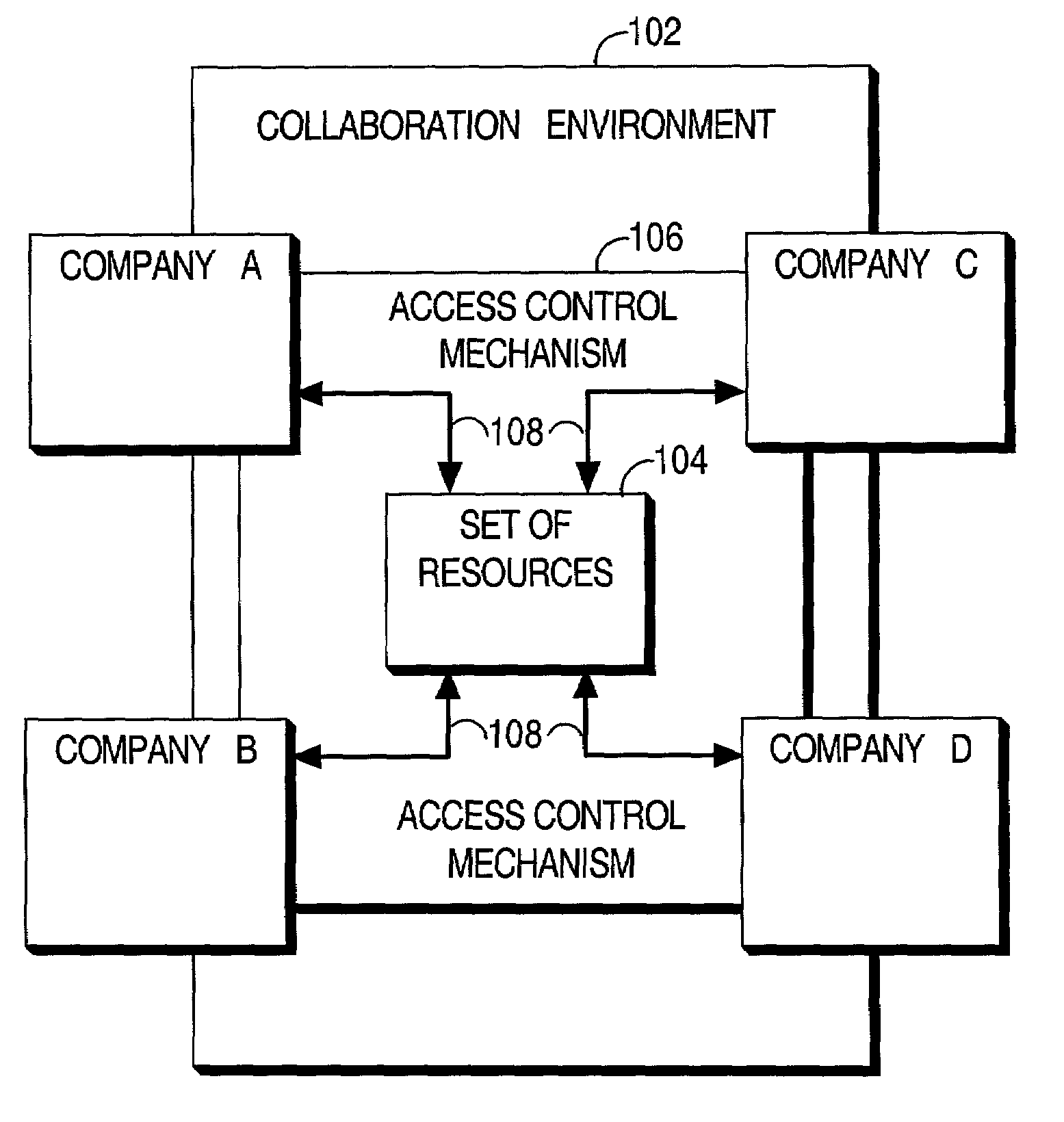
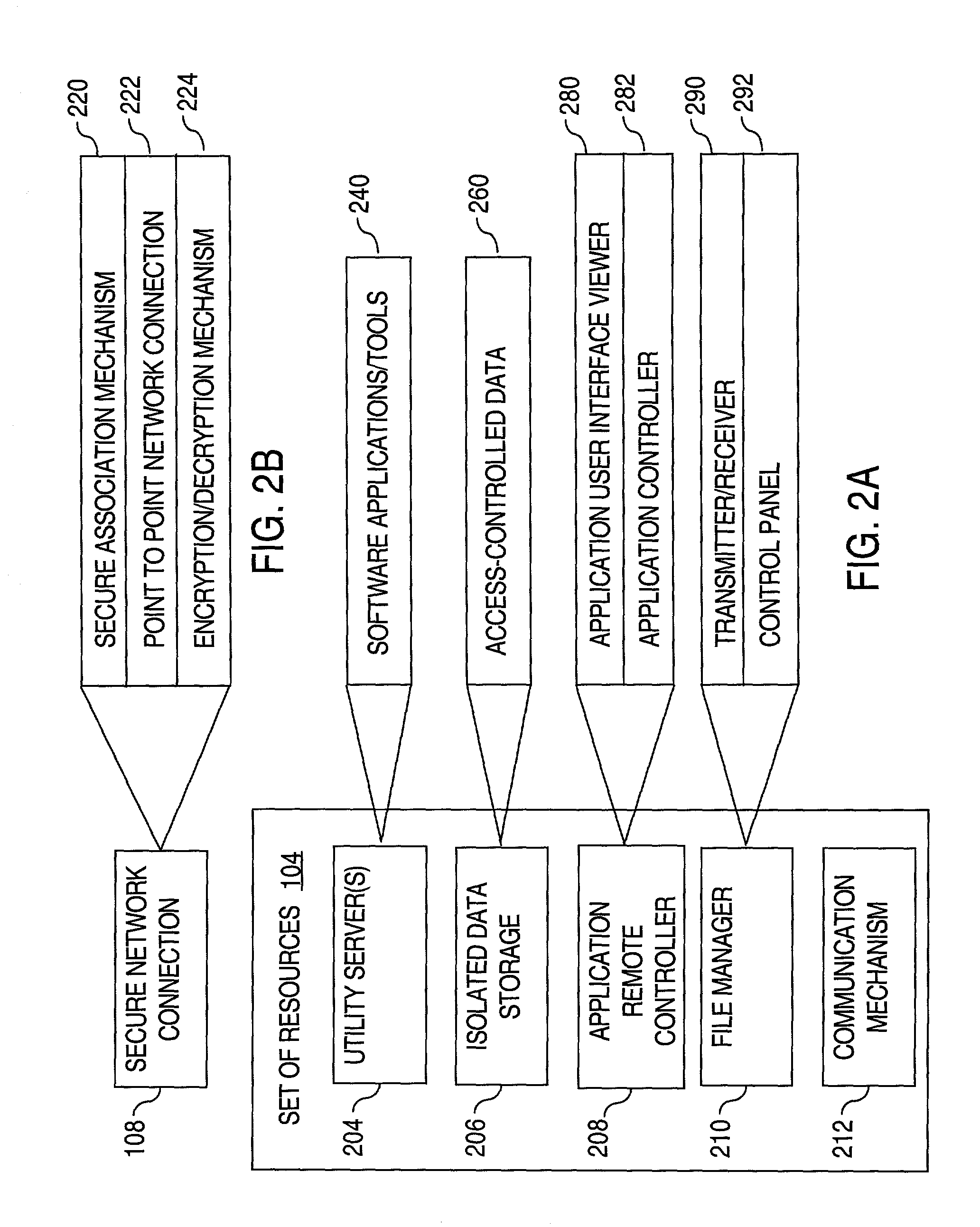
Secure inter-company collaboration environment
InactiveUS7143136B1Multiple digital computer combinationsOffice automationSecurity associationEngineering
An environment is described in which multiple companies can securely collaborate on a design or other project. The environment includes a set of resources residing on a set of one or more utility servers maintained by a first company, an access control mechanism for controlling access to the set of resources, a secure network connection between the set of utility servers and a second company, and a remote controller for remotely viewing, by an authorized individual from the second company, a user interface of an application while an authorized individual from the first company is executing the application on the set of utility servers. The secure network connection includes a secure association mechanism for establishing a secure association between participating parties, a virtual point-to-point network connection for transmitting data between associated parties, and an encryption / decryption mechanism.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
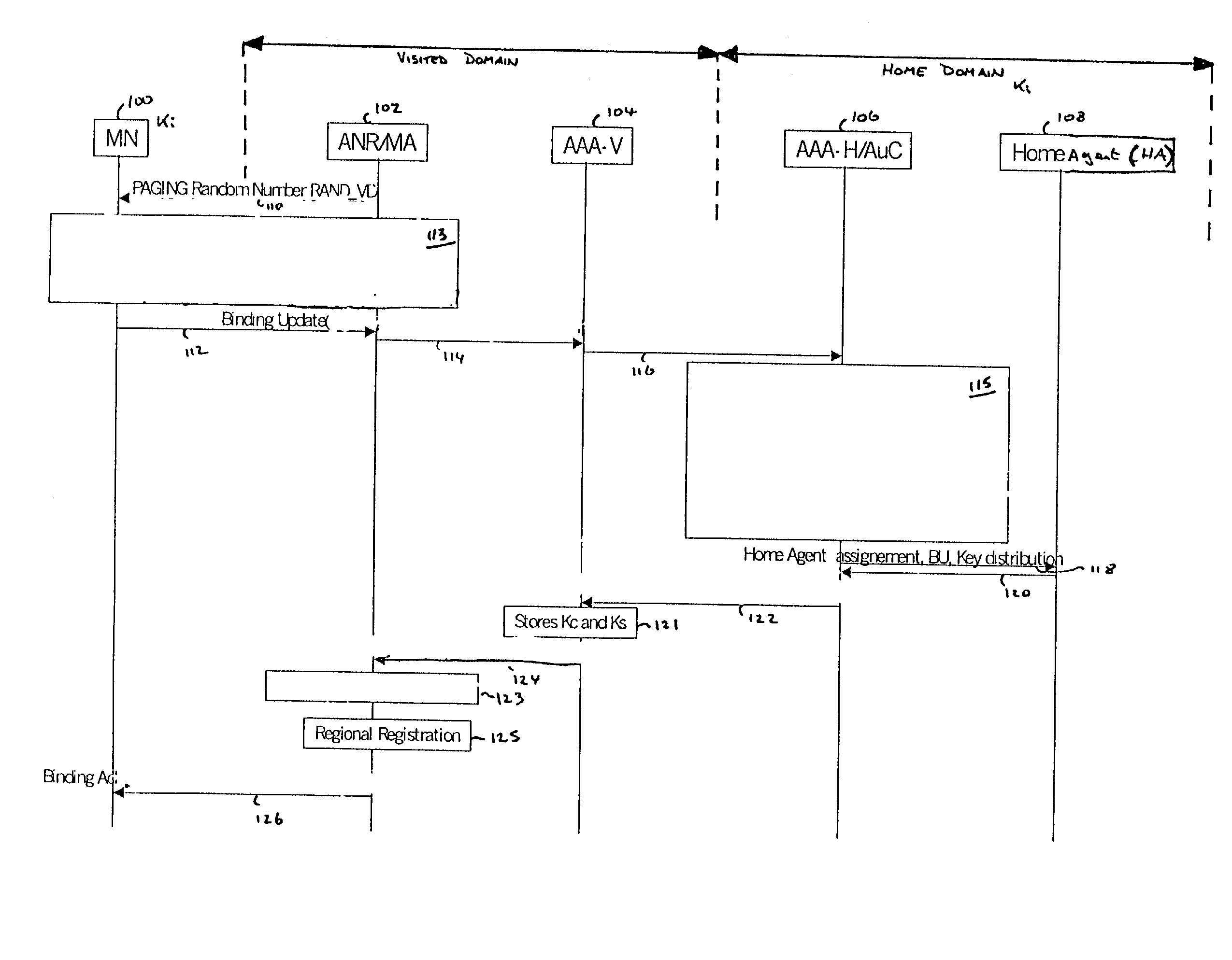
Authentication and distribution of keys in mobile IP network
InactiveUS20020120844A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationTelecommunicationsSecurity association
There is disclosed a method of establishing a connection between a mobile station and a serving domain, in which a first security association exists between the mobile node and an associated home domain, and a second security association exists between the serving domain and the home domain, the method comprising: transmitting a first message from the mobile node to the serving domain, the first message being encrypted in accordance with the first security association; transmitting the first message from the serving domain to the home domain; decrypting the first message in the home domain in accordance with the first security association; transmitting a second message from the home domain to the serving domain, the second message being encrypted according to the first security association; transmitting the second message from the serving domain to the mobile node; decrypting the second message in the mobile node in accordance with the first security association.
Owner:NOKIA NETWORKS OY
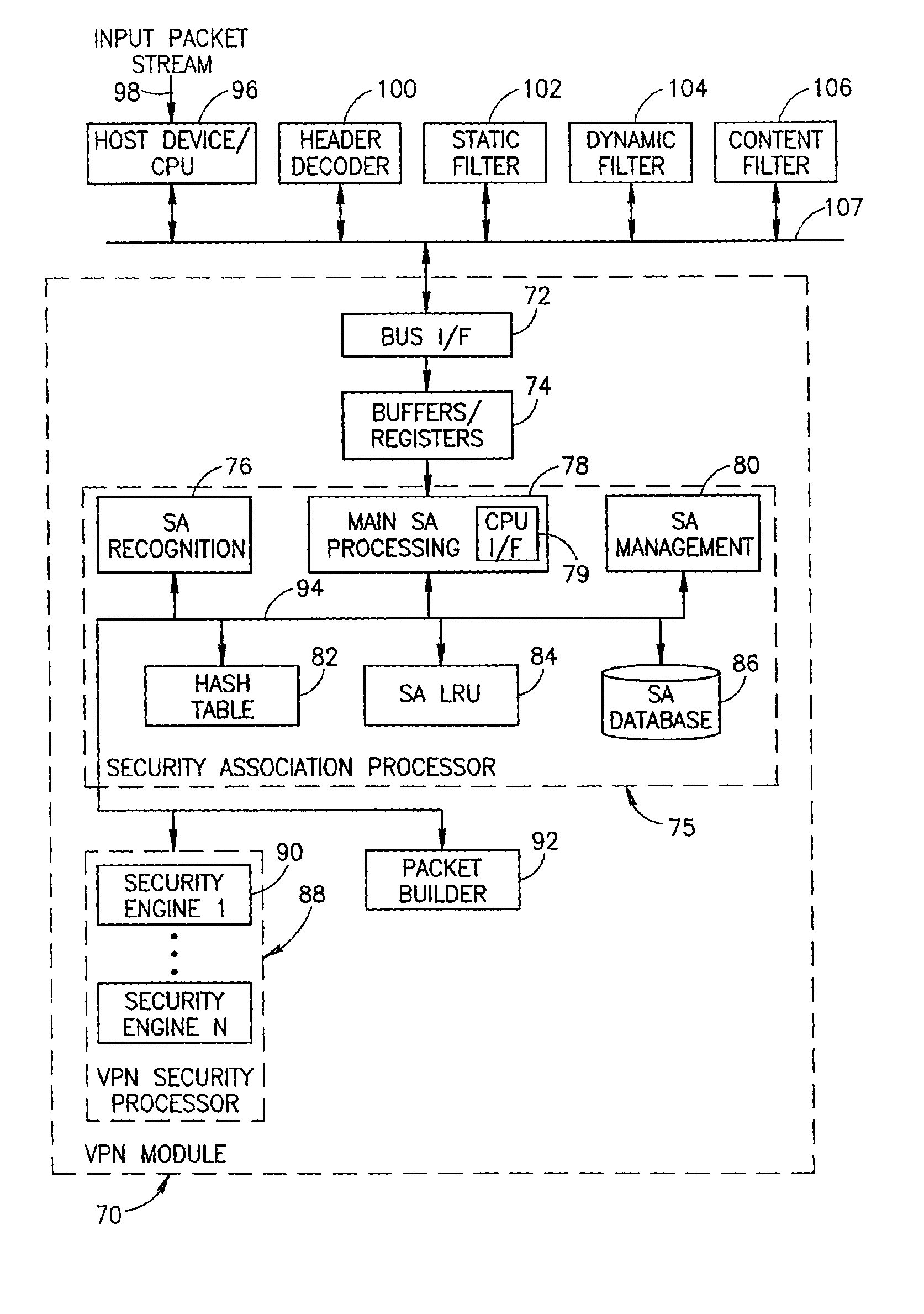
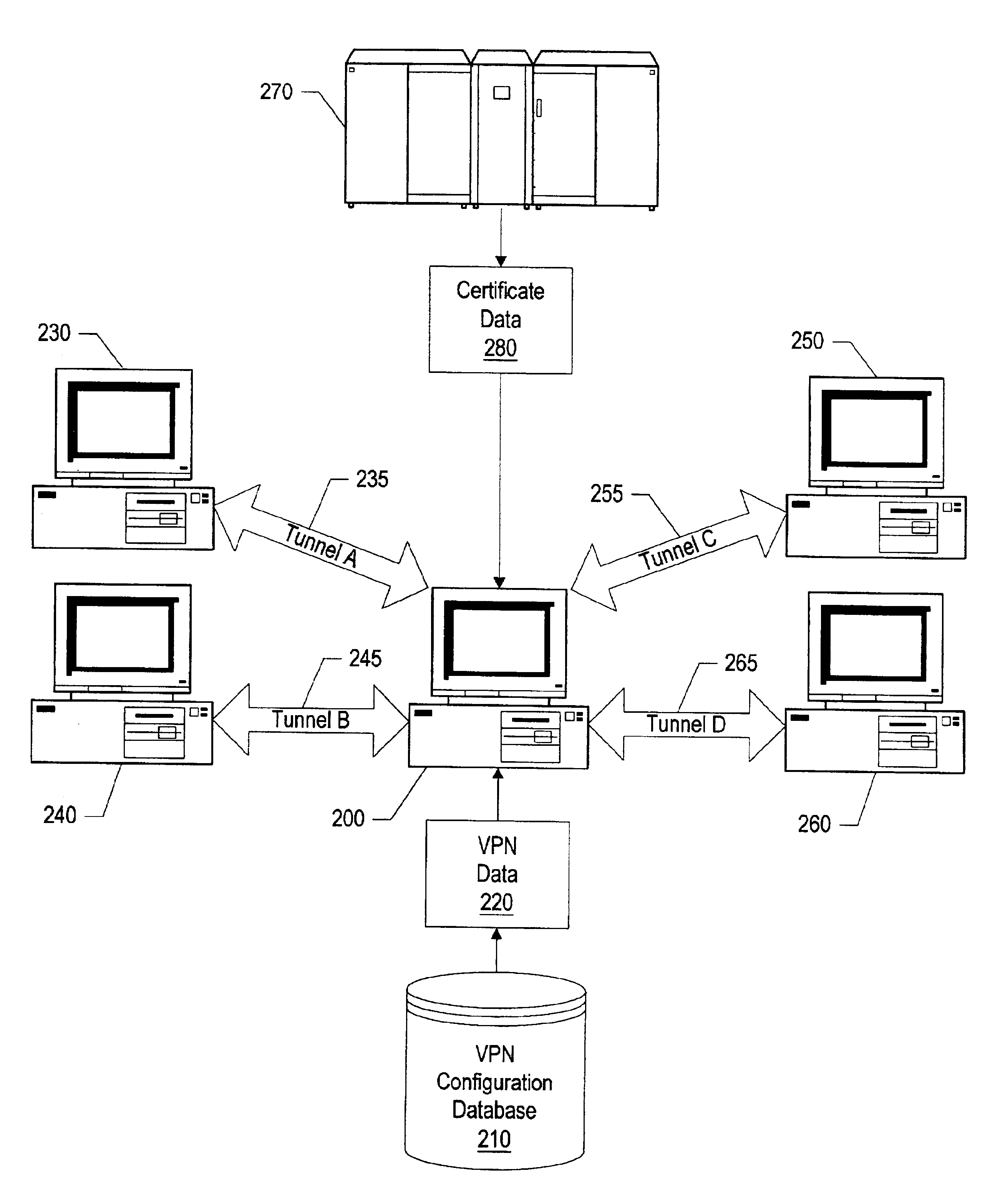
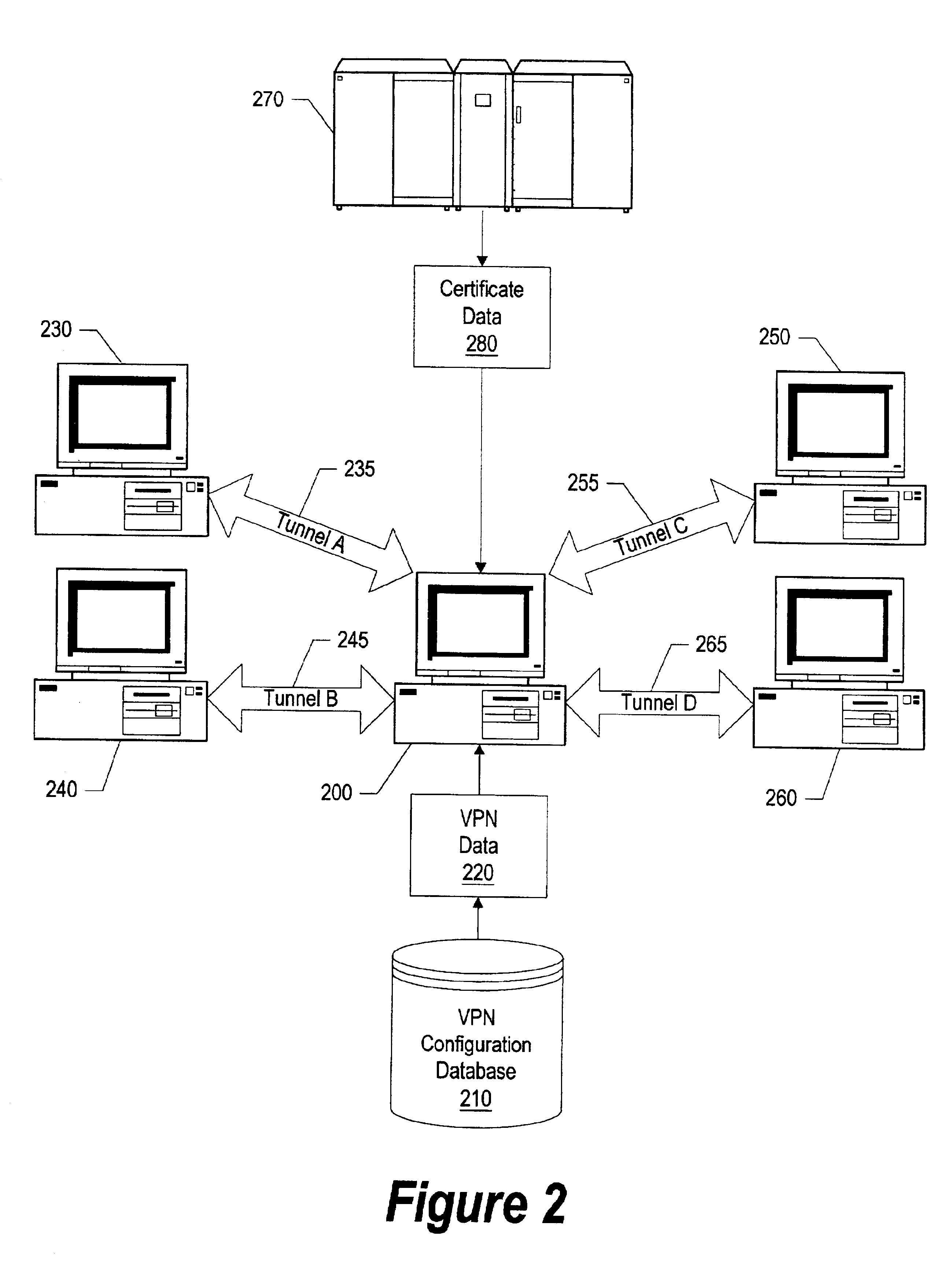
Virtual private network mechanism incorporating security association processor
ActiveUS7107464B2Low costLow-cost implementationMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlSecurity associationPrivate network
A novel and useful virtual private network (VPN) mechanism and related security association processor for maintaining the necessary security related parameters to perform security functions such as encryption, decryption and authentication. A security association database (SAD) and related circuitry is adapted to provide the necessary parameters to implement the IPSec group of security specifications for encryption / decryption and authentication. Each security association (SA) entry in the database comprises all the parameters that are necessary to receive and transmit VPN packets according to the IPSec specification.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
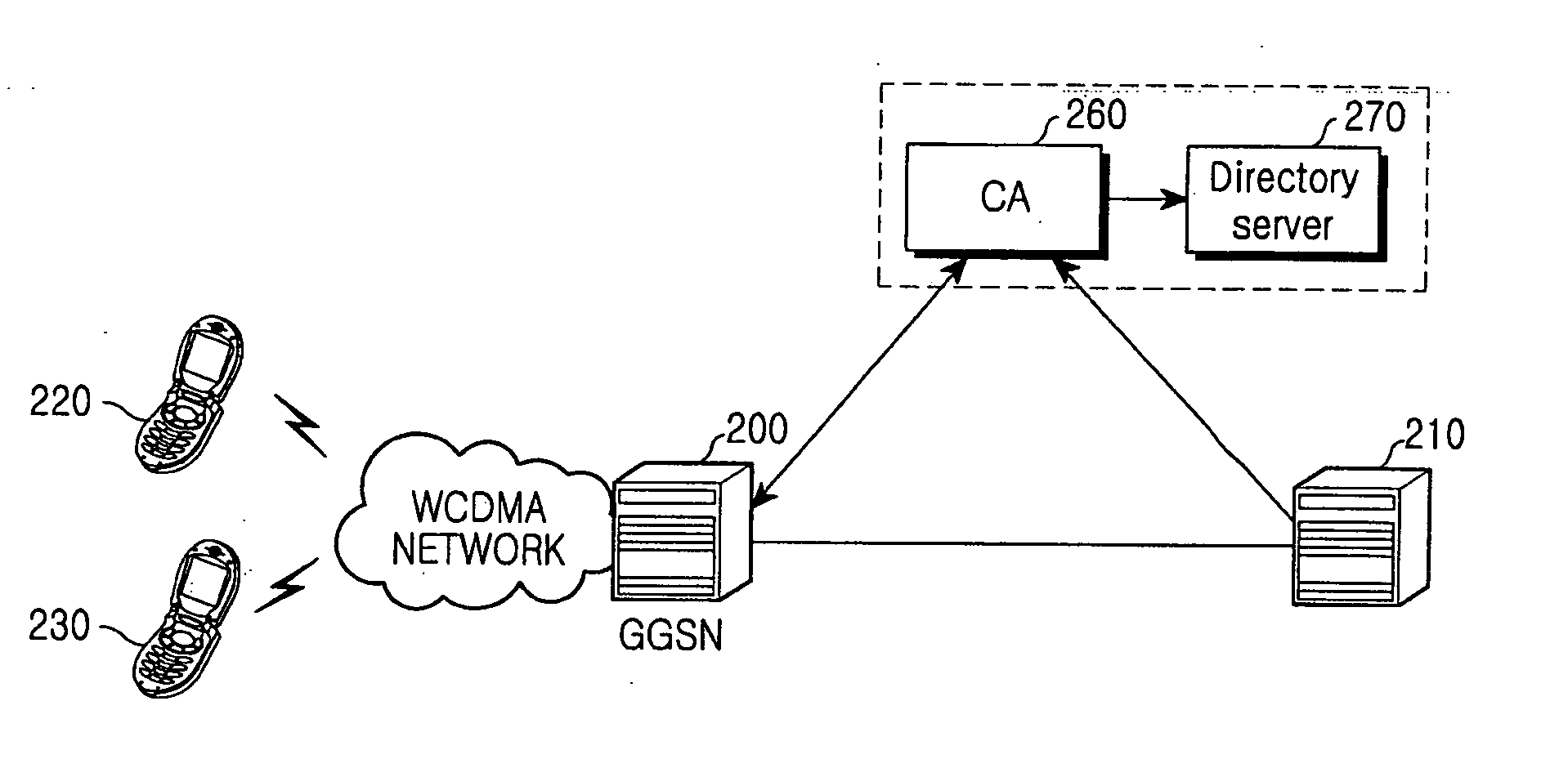
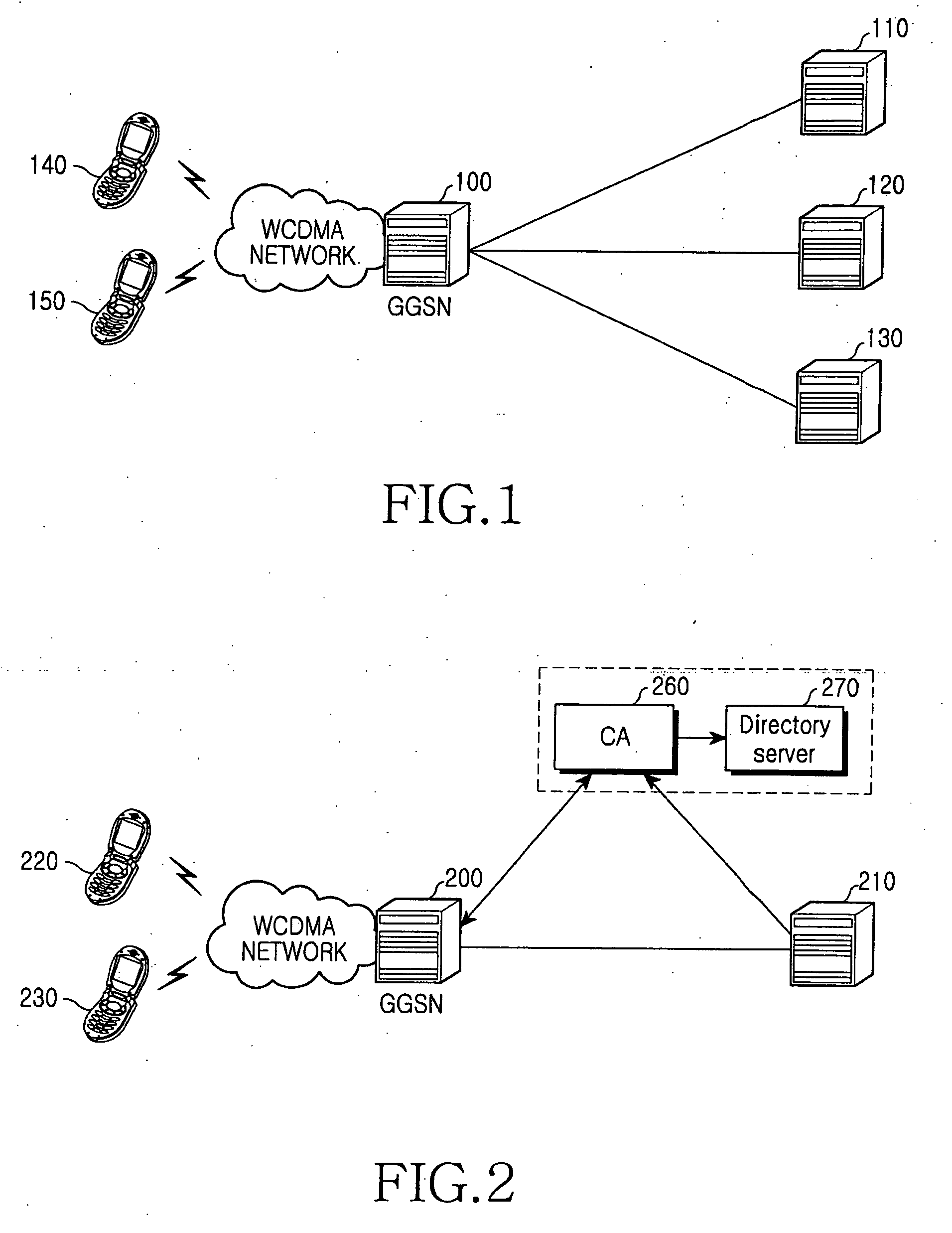
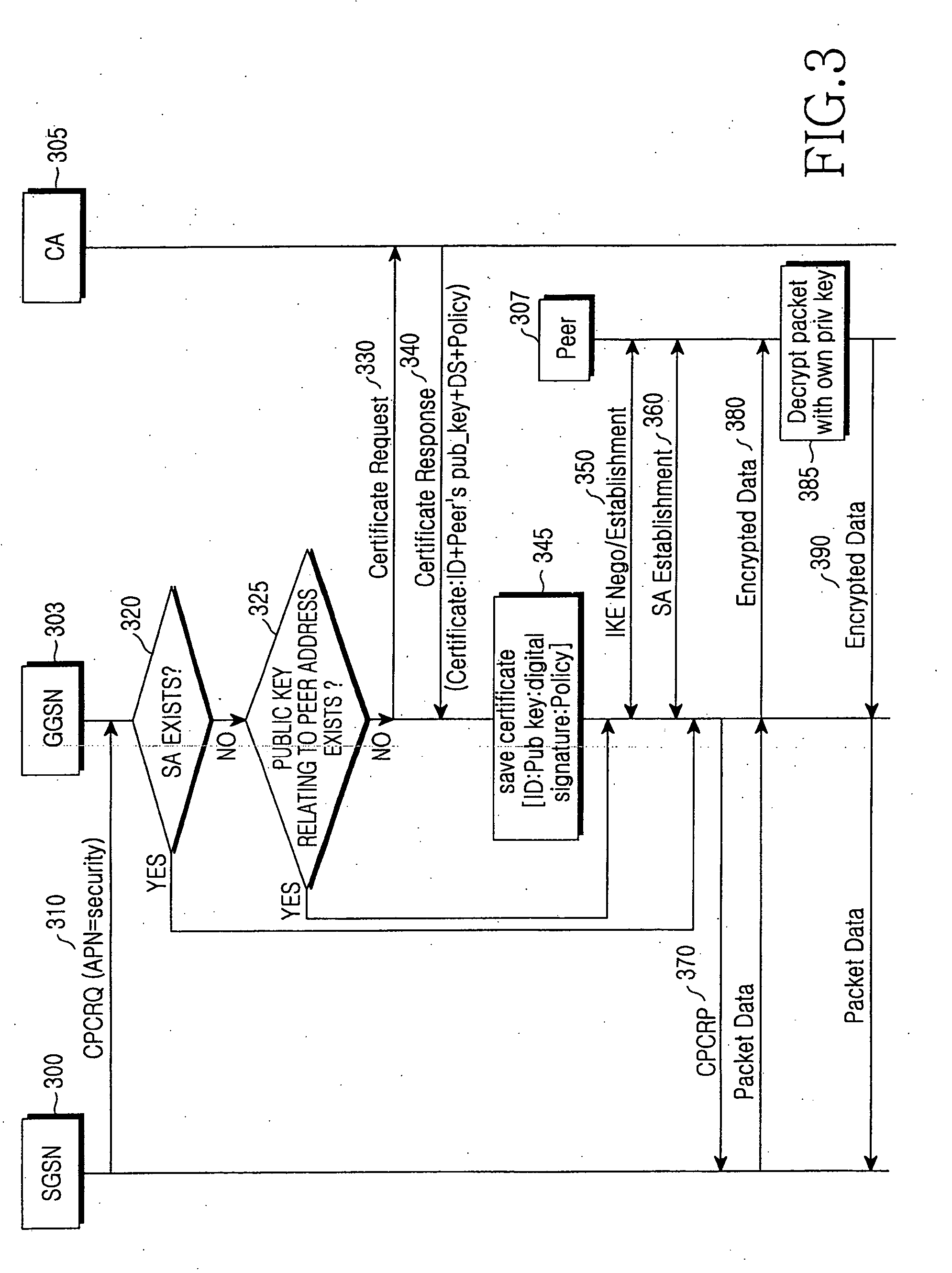
Method and apparatus for security of IP security tunnel using public key infrastructure in mobile communication network
InactiveUS20060105741A1Applied load reductionUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsKey exchangeInternet Key Exchange
A method and apparatus is provided for security of an IP security tunnel using public key infrastructure, including the steps of receiving a request message which relates to a security service requested by a mobile node, determining if there is security association (SA) for the security service and determining if there is a public key related to a peer address when the SA does not exist, sending a certificate request message to a certificate authority (CA) when the public key does not exist and receiving a certificate response message which has a certificate that includes a public key. The method further includes the steps of performing an internet key exchange and SA establishment procedure with a peer corresponding to the peer address by using the certificate, completing the internet key exchange and the SA establishment, and encrypting a packet received from the mobile node, transmitting the encrypted packet to the peer, decrypting a packet received from the peer, and transmitting the decrypted packet to the mobile node.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
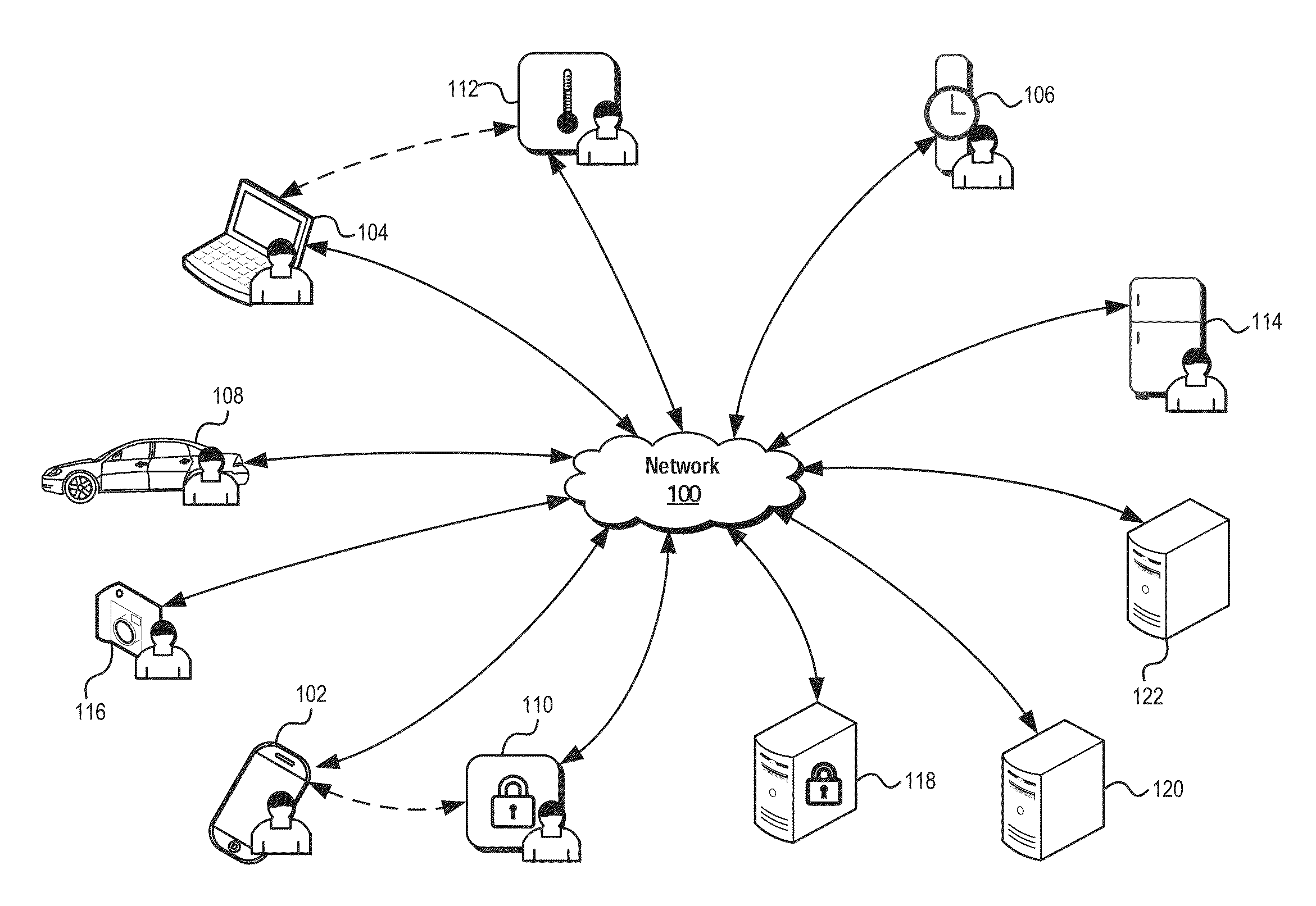
Network security systems and methods
ActiveUS20150237071A1Easy for users to understandEnhanced interactionComputer security arrangementsSecurity arrangementSecurity associationPrivate network
This disclosure relates to systems and methods for managing connected devices and associated network connections. In certain embodiments, trust, privacy, safety, and / or security of information communicated between connected devices may be established in part through use of security associations and / or shared group tokens. In some embodiments, these security associations may be used to form an explicit private network associated with the user. A user may add and / or manage devices included in the explicit private network through management of various security associations associated with the network's constituent devices.
Owner:INTERTRUST TECH CORP
Method for reconfiguring security mechanism of a wireless network and the mobile node and network node thereof
InactiveUS20090119760A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationSecurity associationWireless network
A method for reconfiguring the security mechanism of a wireless network system includes steps of: sending a packet from a network node to a mobile node; sending a negotiation packet from the mobile node to the network node according to a selected authentication protocol; the mobile node and the network node proceeding the authentication process if the received negotiation packet is valid; the mobile node and the network node generating a security association after the authentication process is completed.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
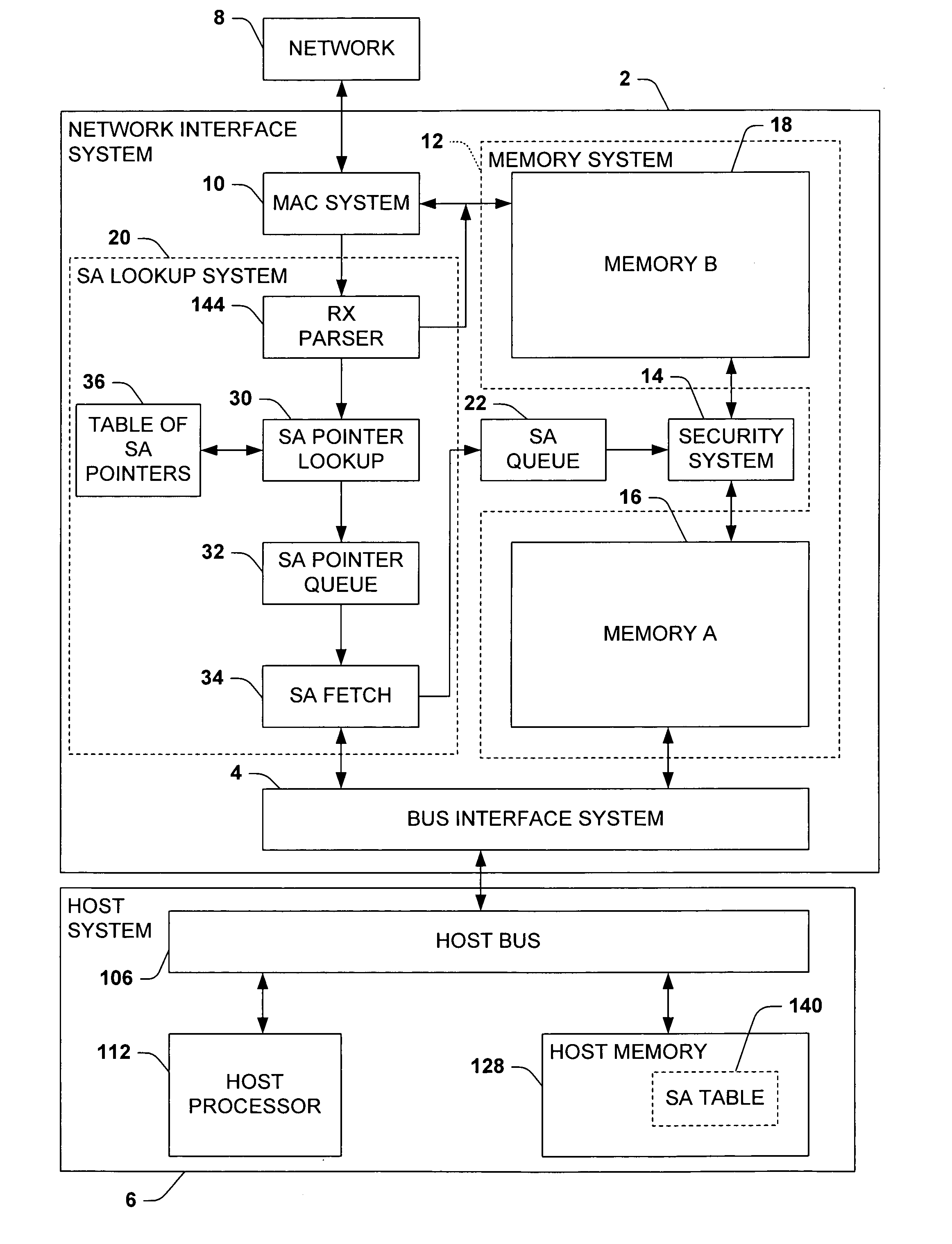
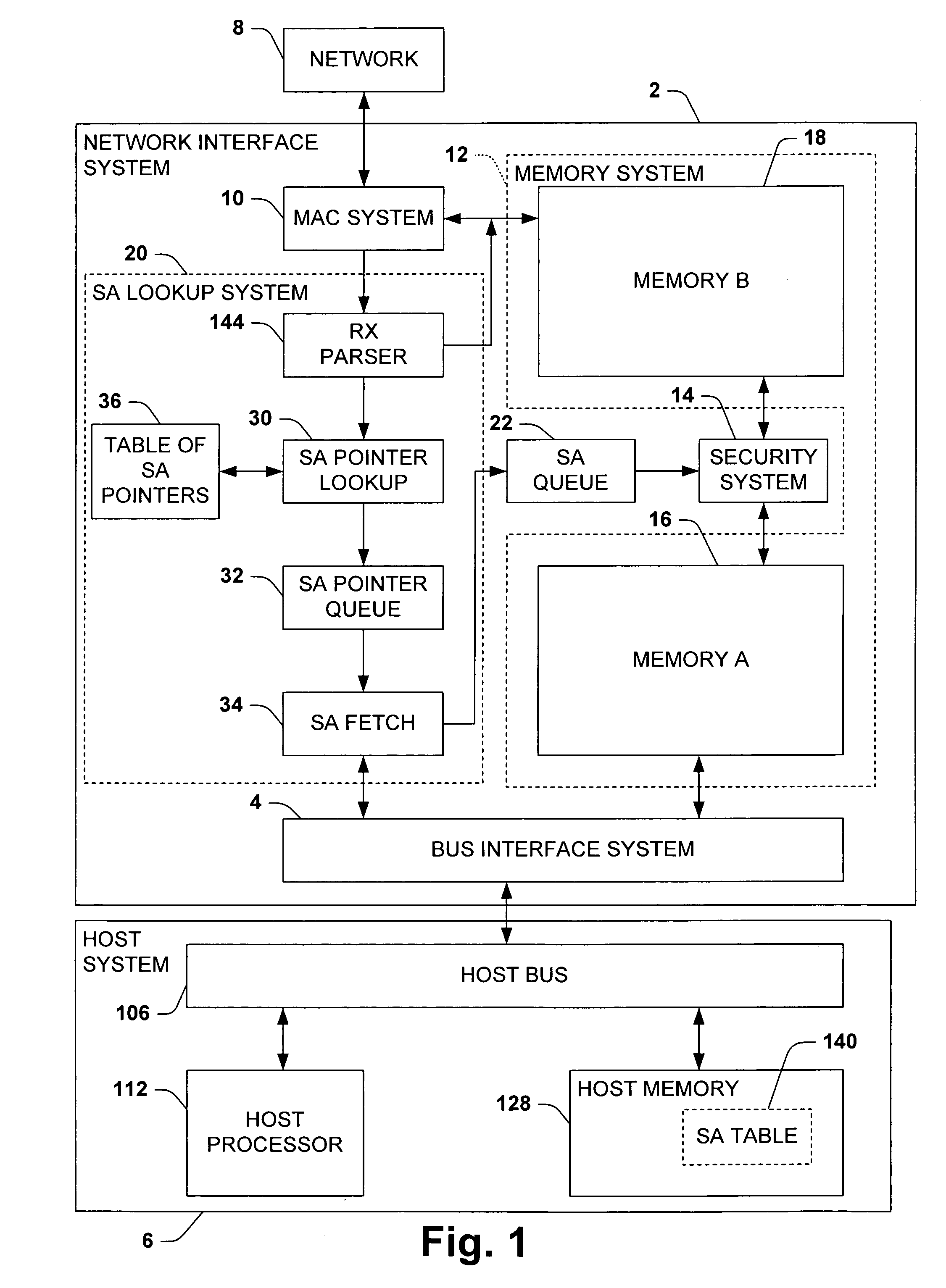
Network interface with security association data prefetch for high speed offloaded security processing
ActiveUS20050256975A1Facilitates high speed security processingTo overcome the large delayMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksExternal storageSecurity association
One aspect of the invention relates to a network interface system for interfacing a host system with a network. The network interface system includes a bus interface system, a media access control system, and a security system. The security system selectively perform security processing on data incoming from the network based on security associations stored in a memory external to the network interface system, typically a host system memory. The security association for any given frame, when available, is fetched from the external memory after the frame begins to arrive in the network interface system based in part on information contained in the frame. Preferably, the fetch begins before the frame is fully received and the security association is queued whereby security processing can begin without having to wait for the security association to be fetched.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
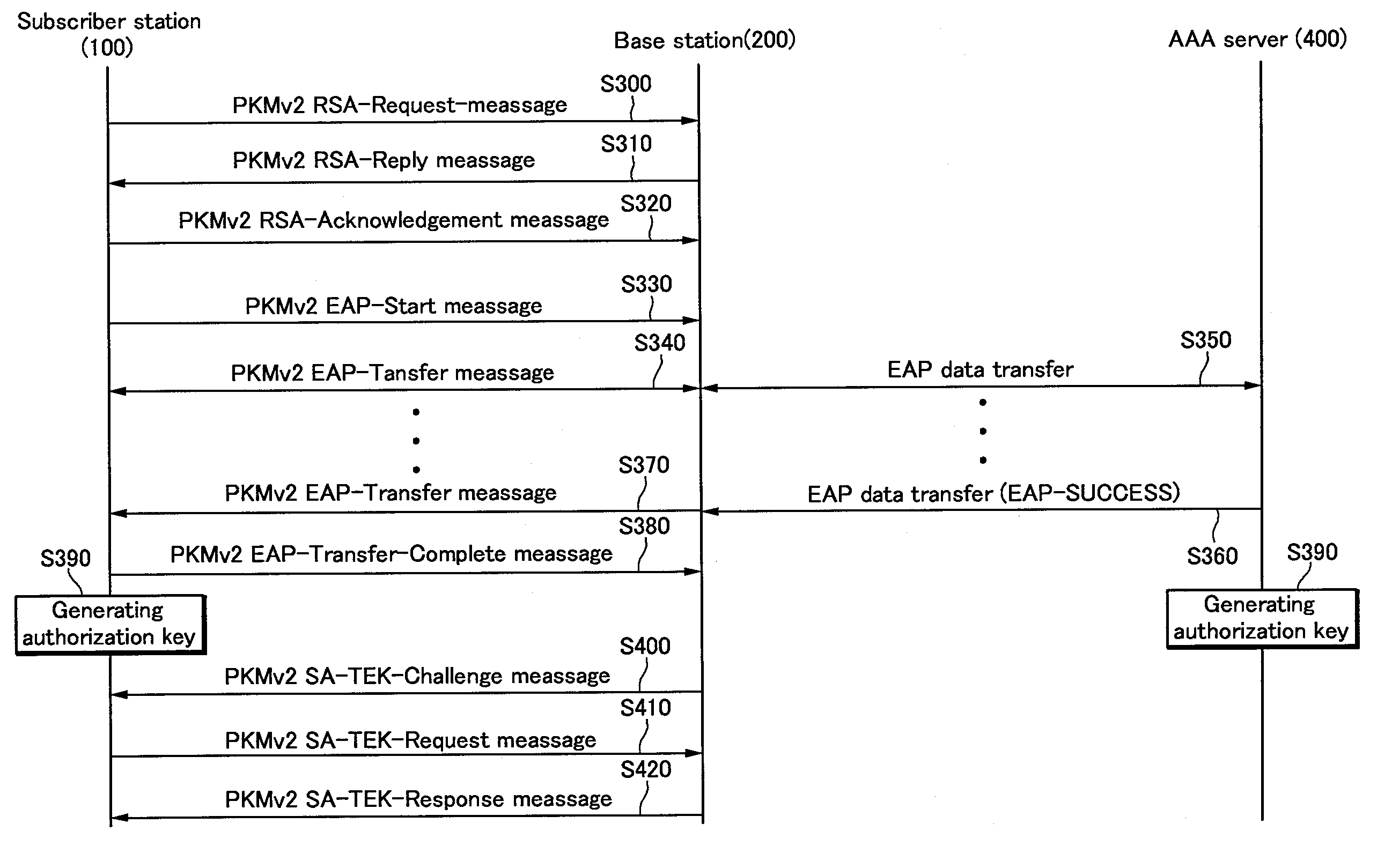
Authentication method and key generating method in wireless portable internet system
InactiveUS20090019284A1User identity/authority verificationSecurity arrangementSecurity associationThe Internet
An authentication method and authorization key generation method in a wireless portable Internet system is provided. In a wireless portable Internet system, the base station and the subscriber station share an authorization key when an authentication process is performed according to a predetermined authentication method negotiated therebetween. Particularly, the subscriber station and the base station perform an additional authentication process including an authorization key-related parameter and a security-related parameter and exchanges a security algorithm and SA (Security Association) information. In addition, an authorization key is derived from one or more basic key obtained through various authentication processes as an input key of an authorization key generation algorithm. Therefore, reliability of a security related parameter received from the receiving node can be enhanced and an authorization key having a hierarchical and secure structure can be provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +4
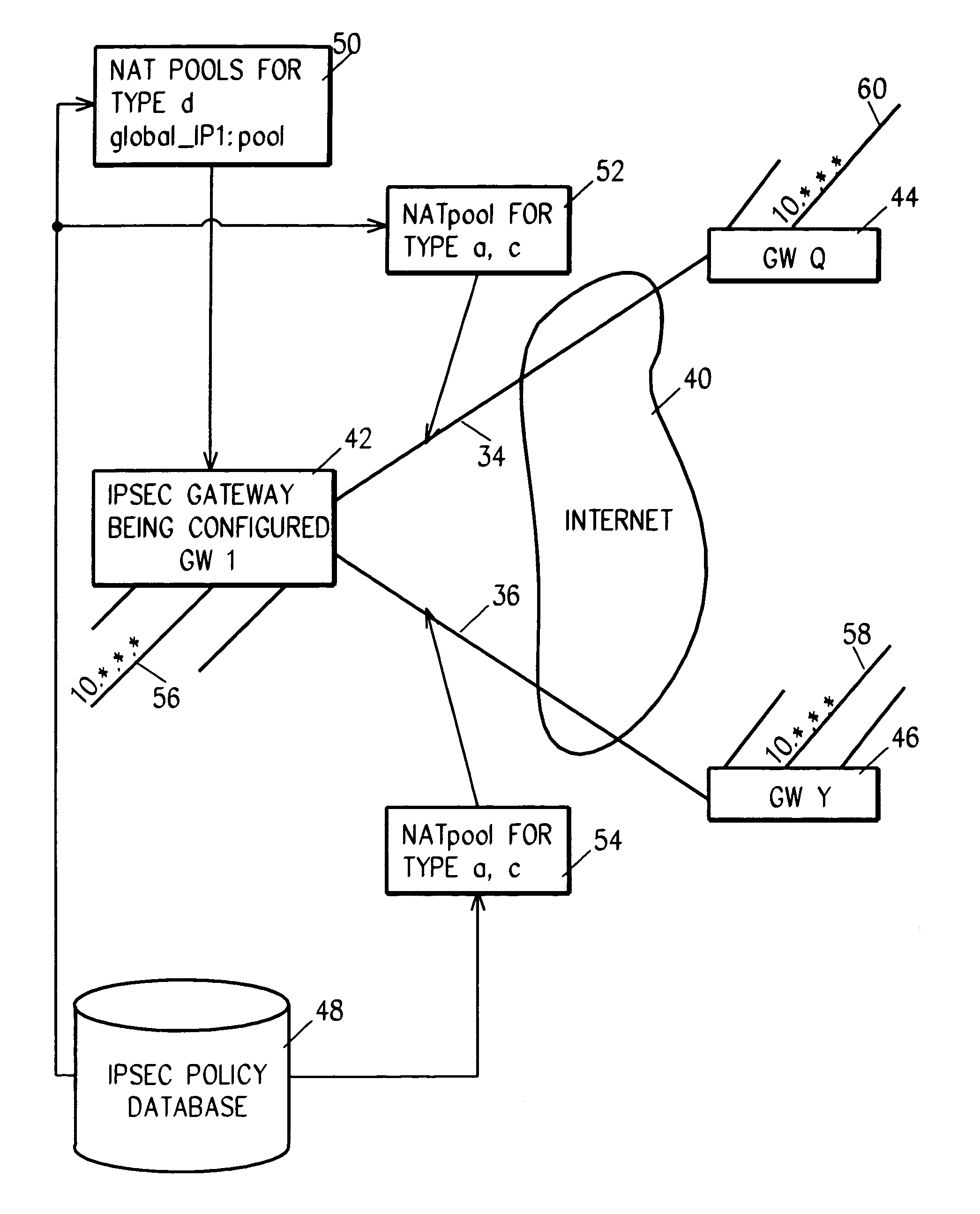
System and method for network address translation integration with IP security
InactiveUS7107614B1Increase likelihoodMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlSecurity associationPrivate network
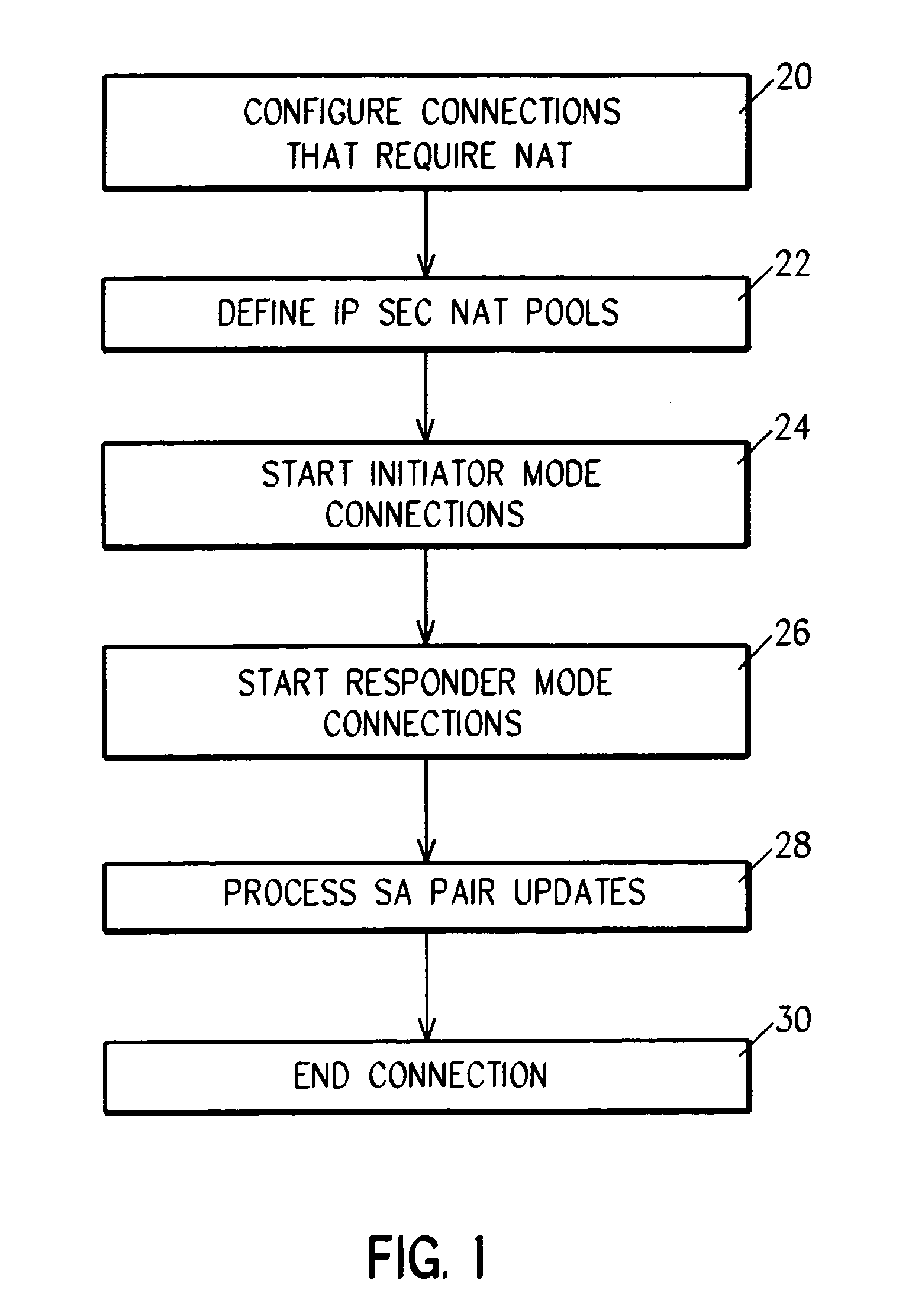
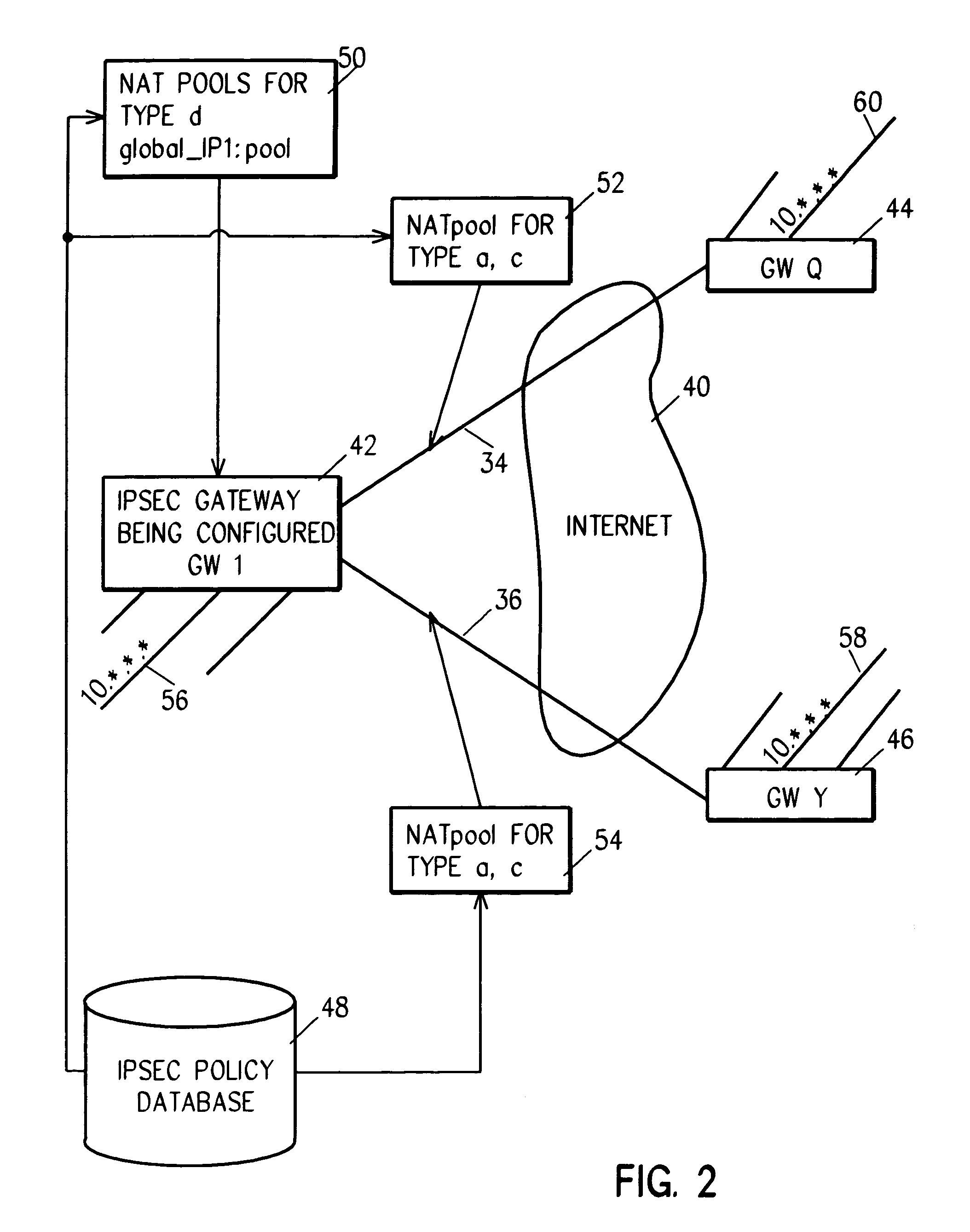
IP security is provided in a virtual private network using network address translation (NAT) by performing one or a combination of the four types of VPN NAT, including VPN NAT type ‘a source-outbound’ IP NAT, VPN NAT type ‘b destination-outbound, VPN NAT type ‘c inbound-source’ IP NAT, and VPN NAT type ‘d inbound-destination’ IP NAT. This involves dynamically generating NAT rules and associating them with the manual or dynamically generated (IKE) Security Associations, before beginning IP security that uses the Security Associations. Then, as IP Sec is performed on outbound and inbound datagrams, the NAT function is also performed.
Owner:TREND MICRO INC
Route optimization of a data path between communicating nodes using a route optimization agent
InactiveUS20120044949A1Easy to optimizeImprove directionAssess restrictionData switching by path configurationSecurity associationDatapath
The invention relates to optimizing a data path between two communication nodes. A route optimization agent (ROA) is determined in the current network of the second communication node, preferably on the data path between the two communication nodes. Then, an IP tunnel is established between the first communication node and the ROA, the IP tunnel and the corresponding security association of said IP tunnel being based on the home address of the first communication node in its home network. The first communication node may have two IP tunnels based on the same home address, one to its home agent and one to the ROA. Corresponding routing entries and binding cache entries need to be established in the ROA and the first communication node so that all data packets between the two communication nodes are exchanged via the established IP tunnel over the ROA.
Owner:OPTIS WIRELESS TECH LLC
System and method for multiple virtual private network authentication schemes
InactiveUS6938155B2Multiple digital computer combinationsElectric digital data processingPrivate networkRemote system
A system and method for providing multiple virtual private networks from a computer system. The computer system communicates with a remote computer system in order to allow encrypted data traffic to flow between the respective systems. Two phases are used to authenticate the computer systems to one another. During the first phase, digital certificates or pre-shared keys are used to authenticate the computer systems. A phase 1 ID rules list contains authentication rules for local-remote computer pairs. During the second phase, a hash value is used to authenticate the computer systems and a security association payload is created. The remote system's IP address is used for connecting. The phase 1 ID rules list corresponds to one or more phase 2 ID rules lists. If the remote ID is not found in the phase 2 ID rules list, a default rule is used based upon the phase 1 ID rules list.
Owner:TREND MICRO INC
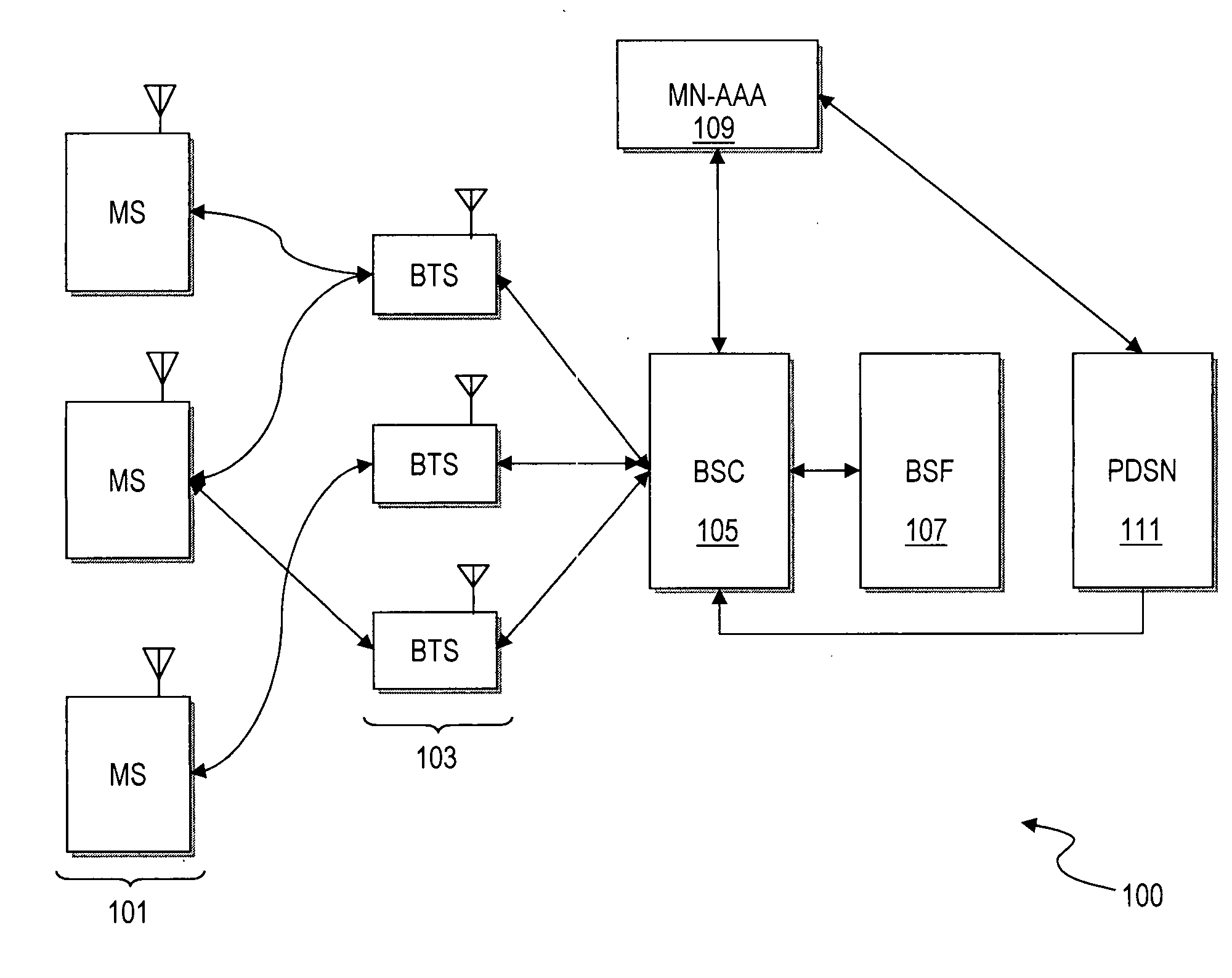
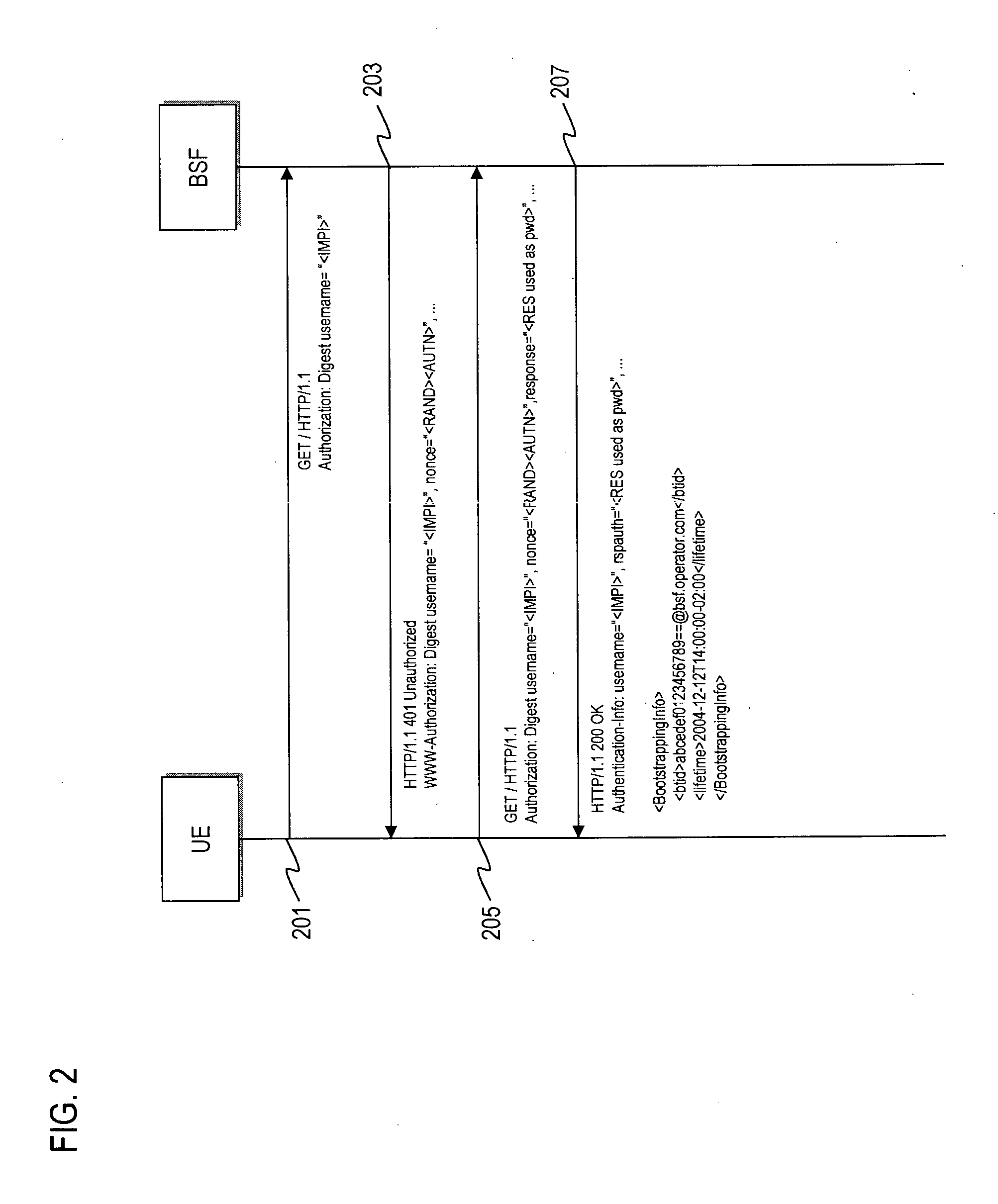
Method and apparatus for providing bootstrapping procedures in a communication network
ActiveUS20060182280A1Efficient executionSecret communicationProgram controlComputer hardwareKey exchange
An approach is provided for performing authentication in a communication system. In one embodiment, a key is established with a terminal in a communication network according to a key agreement protocol. The agreed key is tied to an authentication procedure to provide a security association that supports reuse of the key. A master key is generated based on the agreed key. In another embodiment, digest authentication is combined with key exchange parameters (e.g., Diffie-Hellman parameters) in the payload of the digest message, in which a key (e.g., SMEKEY or MN-AAA) is utilized as a password. In yet another embodiment, an authentication algorithm (e.g., Cellular Authentication and Voice Encryption (CAVE)) is employed with a key agreement protocol with conversion functions to support bootstrapping.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
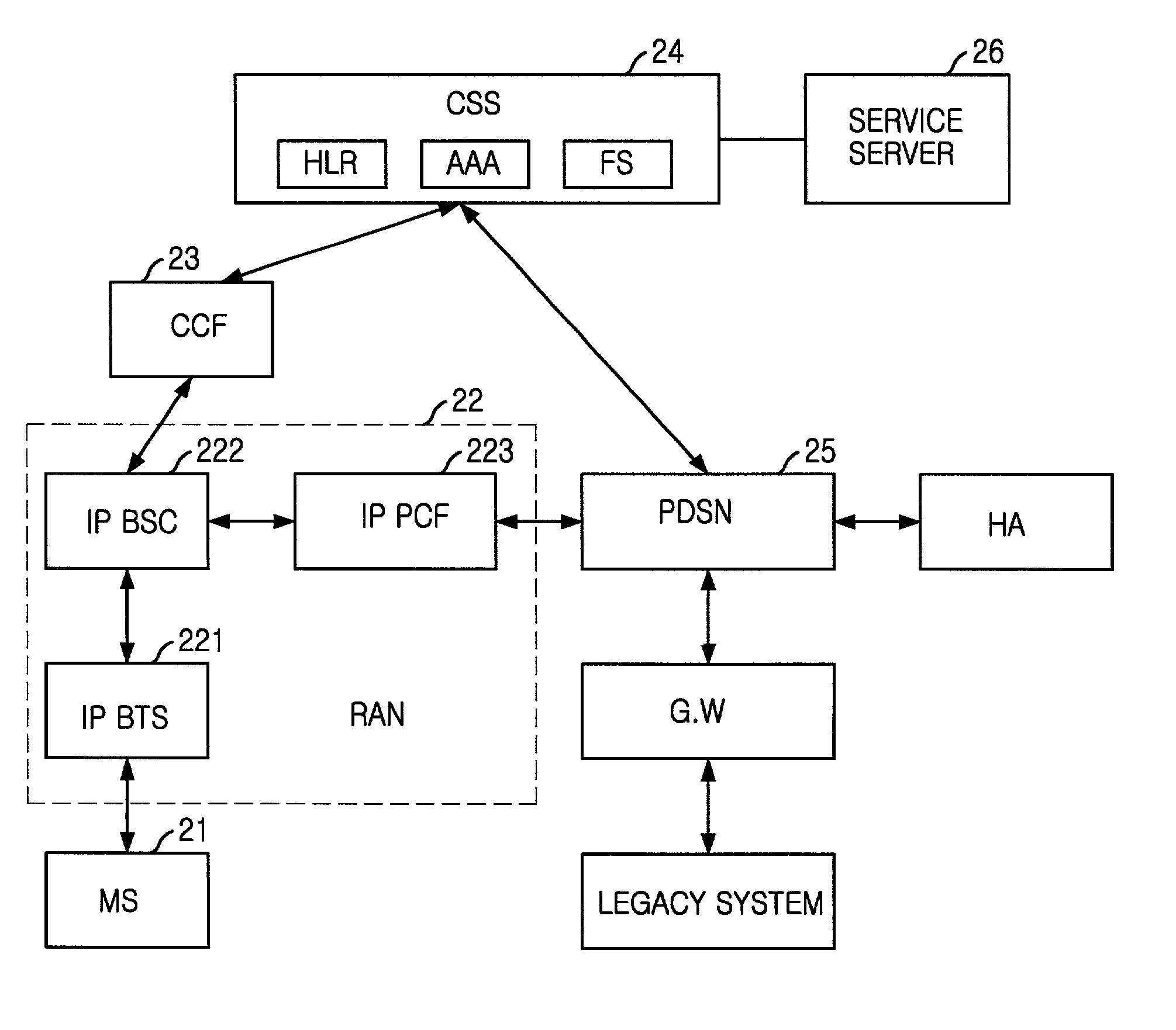
Common subscriber managing apparatus and method based on fuctional modeling of a common subscriber server for use in an ALL-IP network
InactiveUS20020003789A1Hybrid switching systemsCommmunication supplementary servicesQuality of serviceSecurity association
A common subscriber managing apparatus and method for use in an all Internet Protocol network integrating a circuit network for voice and a packet network for data. The apparatus comprises a portable user terminating unit satisfying media standards supported in the network, a wireless interfacing unit controlling wireless resources of the user terminating unit and wireless traffic, controlling handoff, realigning data from and to the packet network upon interface request of the user terminating unit, providing realigned data to the user terminating unit and transferring media to another user terminating unit, a call controlling unit controlling a call between the wireless interfacing unit and common subscriber managing unit, and common subscriber managing unit for providing Security Association setup function for voice processing and commonly managing mobility management, Quality of Service, authentication and authorization management, accounting management and service management functions for the user terminating unit through a common subscriber database.
Owner:PANTECH CORP
Telecommunication enhanced mobile IP architecture for intra-domain mobility
ActiveUS6992995B2Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsSecurity associationCare-of address
Methods and systems are provided for facilitating intra-domain mobility. A first network or domain includes a home agent or SIP proxy of a mobile node. A second network includes two or more subnetworks and at least one mobility agent (MA). Each subnetwork includes an associated subnet agent. To communicate, the mobile node first registers with a subnet agent, receives a local care-of-address and a global care-of-address, and then registers with an MA. The mobile node may then provide the global care-of-address to the home agent. The local care-of-address may enable communication with the mobile node without determining a specific route to the mobile node. The global care-of-address received from the subnet agent may include the address of the MA. Accordingly, the mobile node may transition from any of the subnetworks to another subnetwork without communicating to the home agent information about the transition and without communicating to the MA information about a security association between the mobile node and the home agent.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
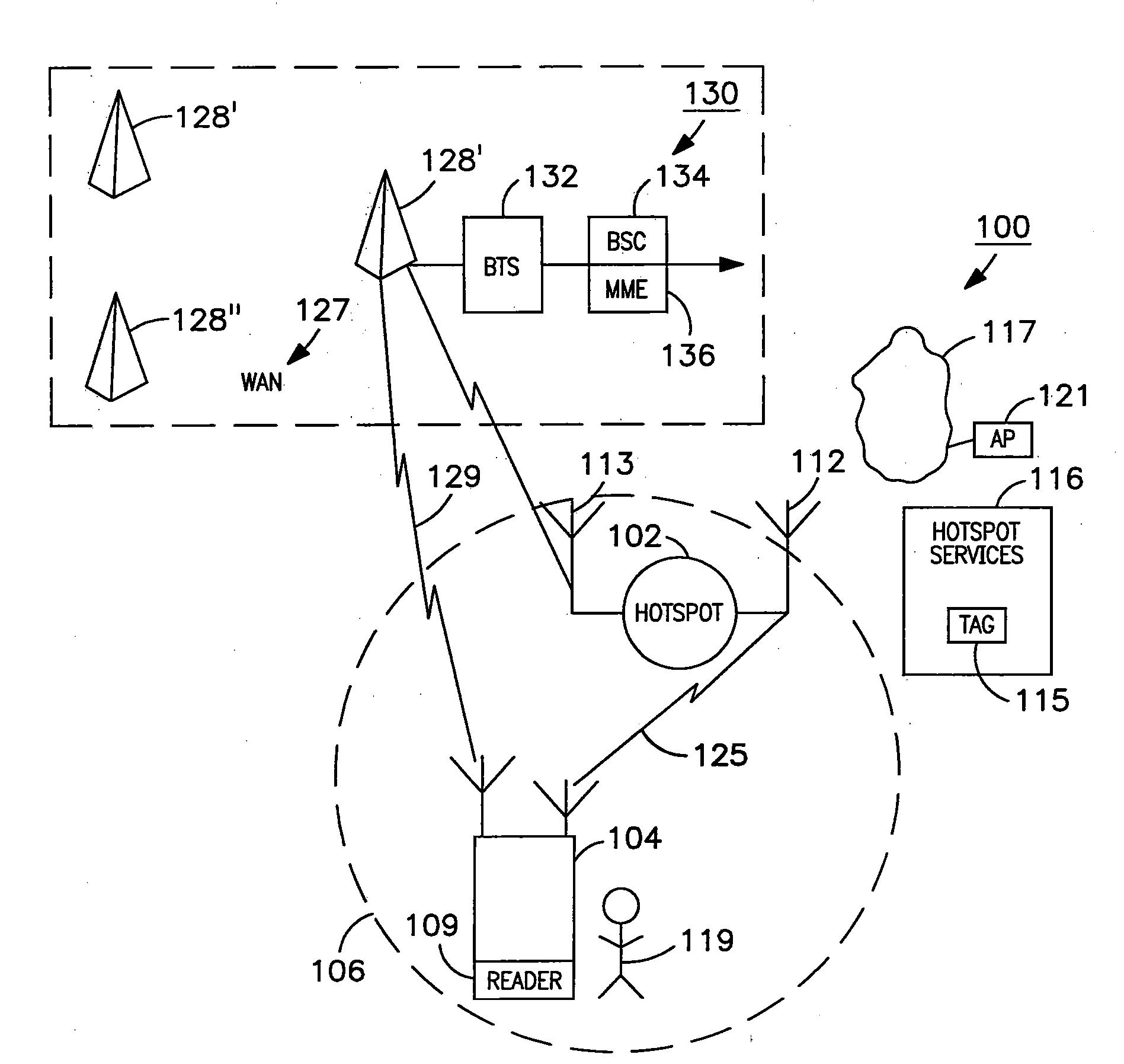
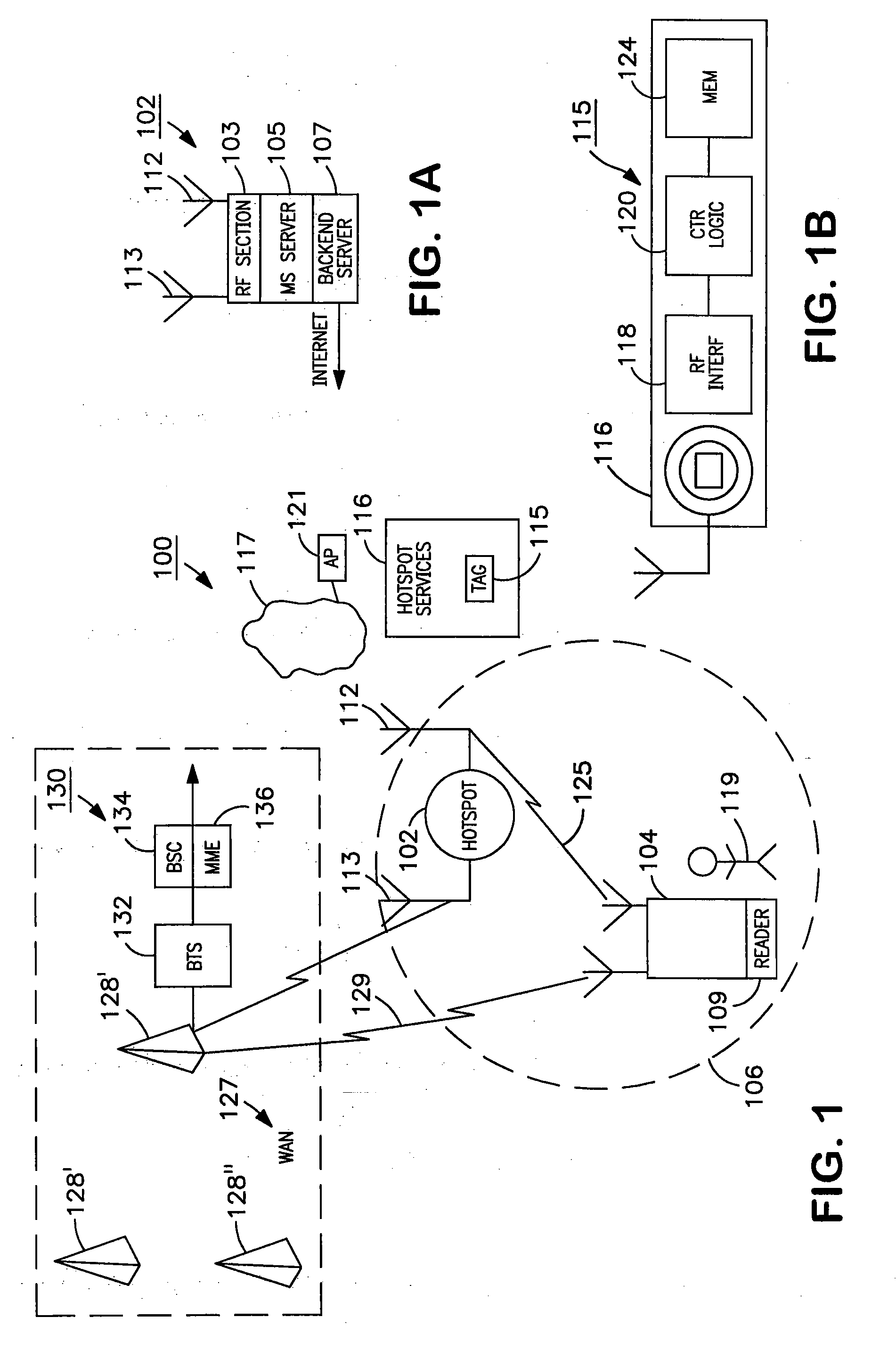
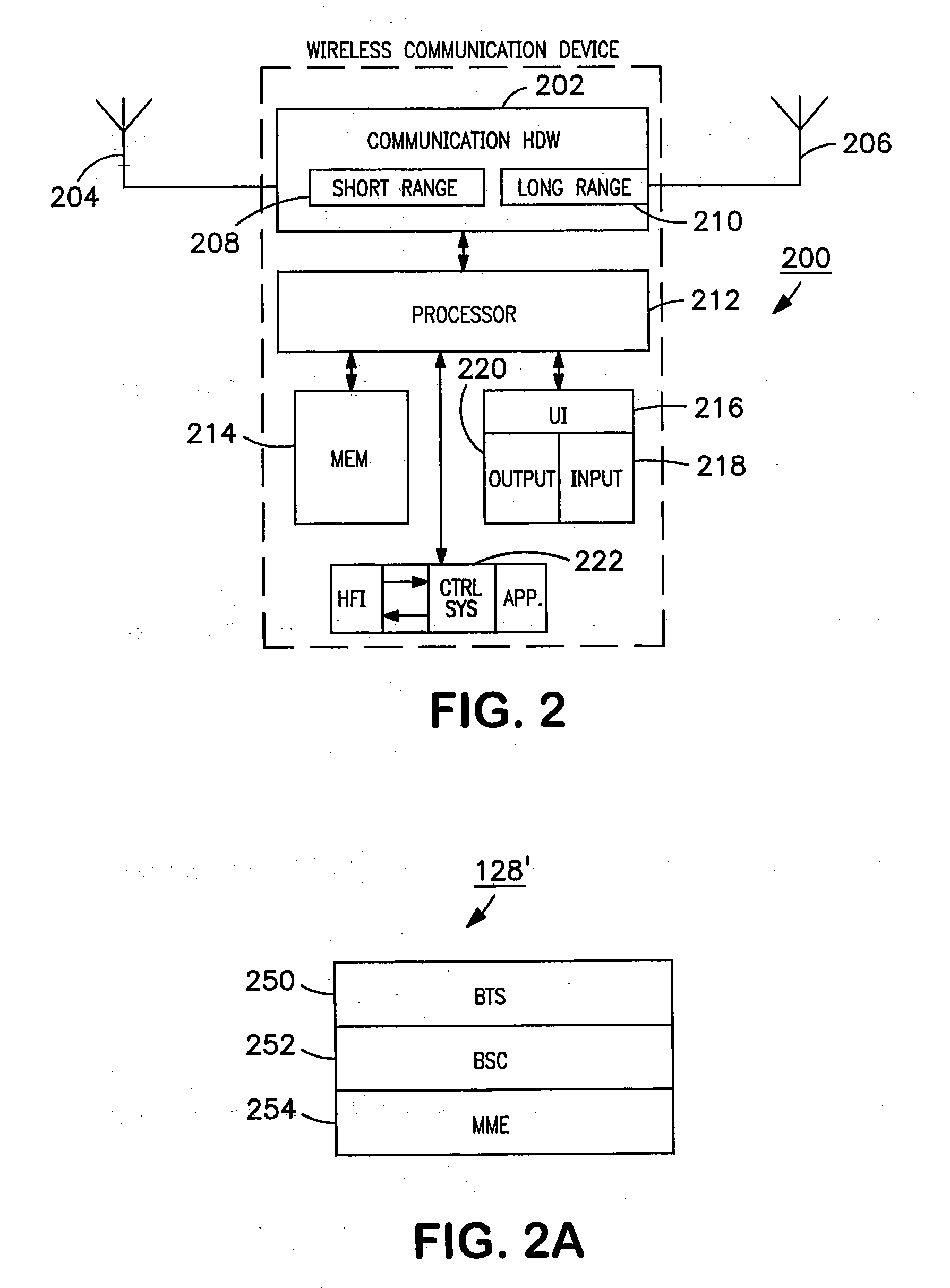
Managing attachment of a wireless terminal to local area networks
The invention relates to managing and controlling access by a user wireless device (MD) to a wireless local area network (WLAN) at an access point or “hotspot”, while protecting the security of the WLAN. The hotspot and associated advertisement describe an available communication service at the hotspot. A RFID device is embedded in the advertisement providing instructions for attachment of the user's mobile device (MD) to the communication service, e.g. a WLAN. After evaluation of the instructions and establishing a security relation between the MD and a mobile management entity (MME) included in a wide area network (WAN), the MME provides attachment information for the MD to the WLAN. The attachment is completed after verification by the WLAN of the MME approval of the MD attachment, and establishing a session key for messages between the MD and the WLAN.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com