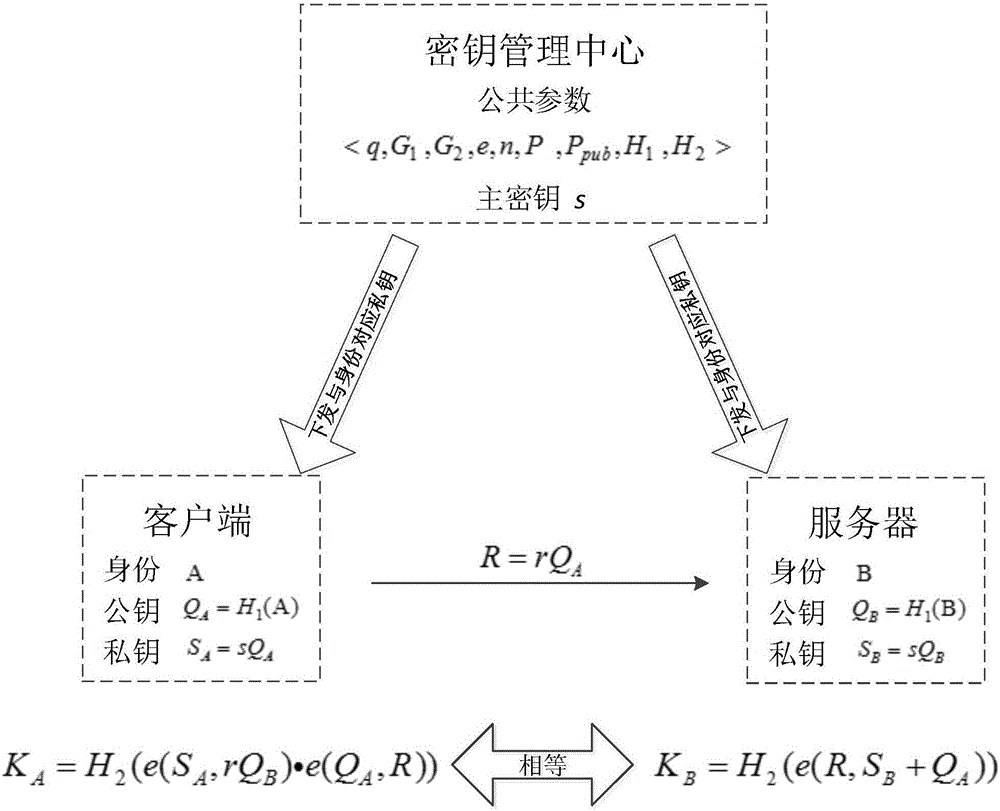
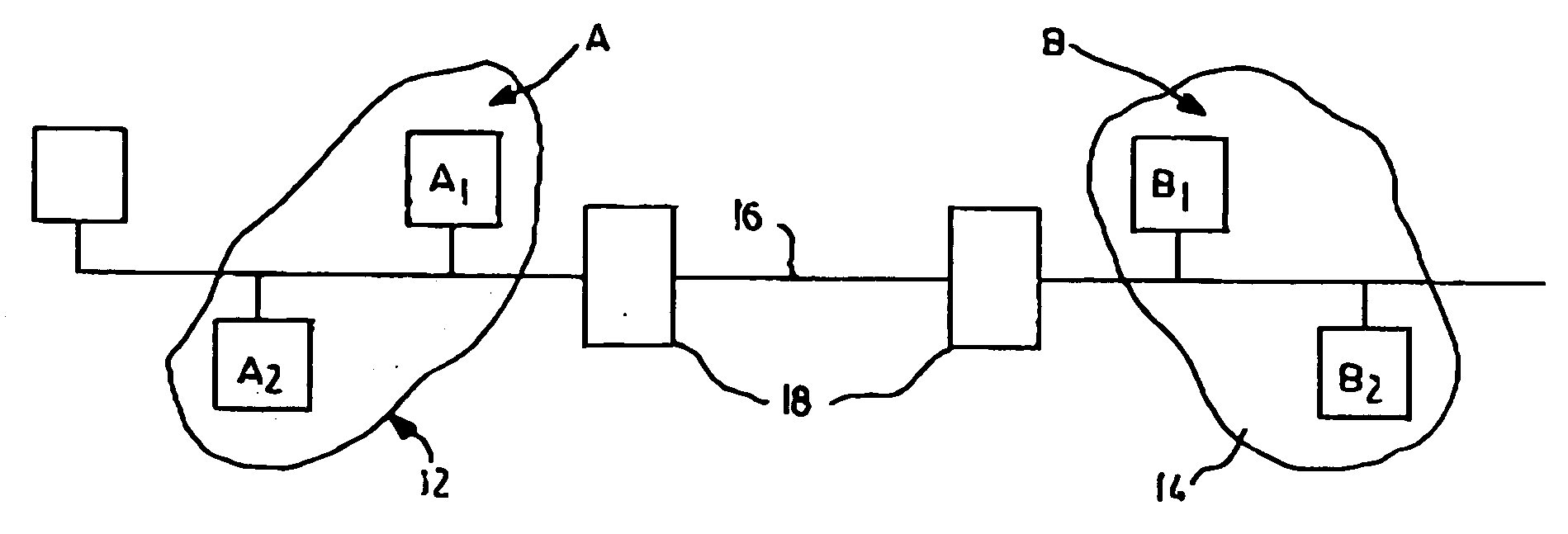
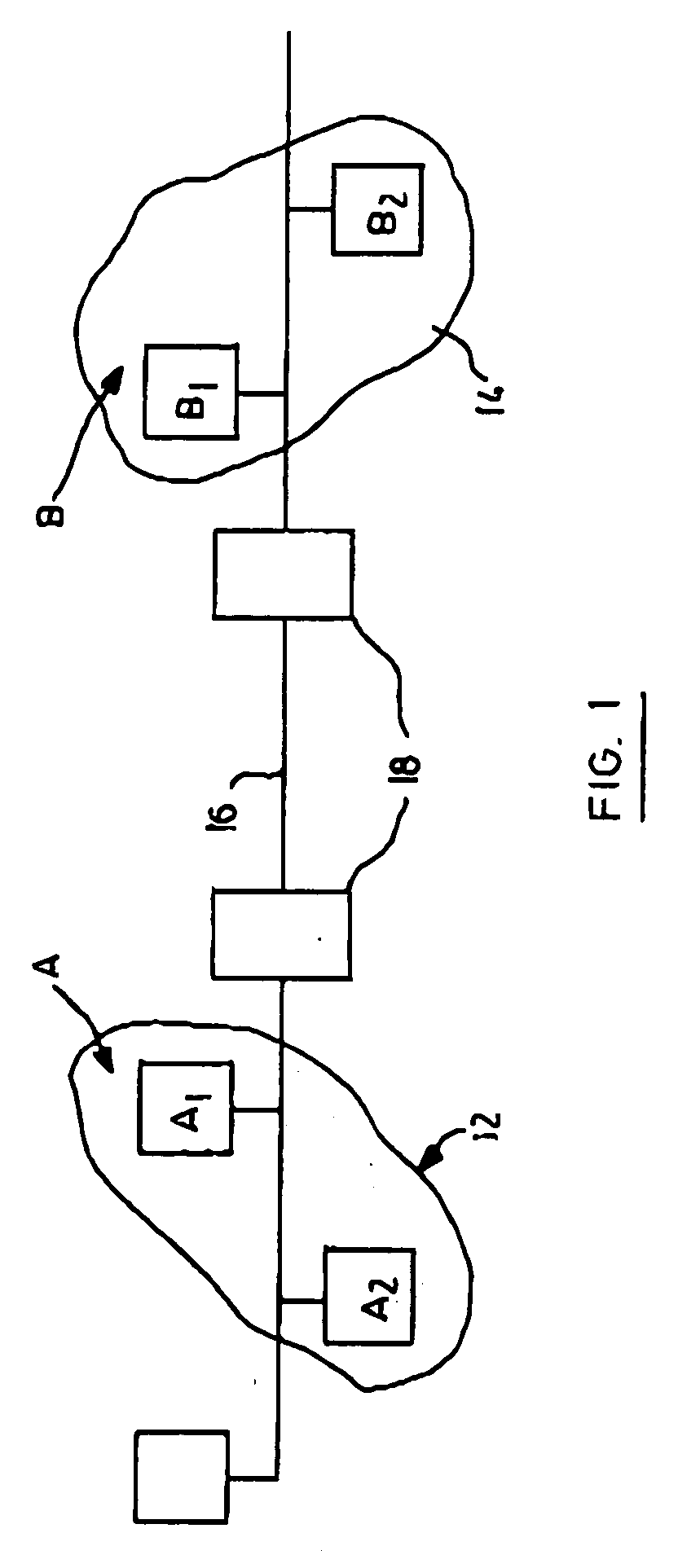
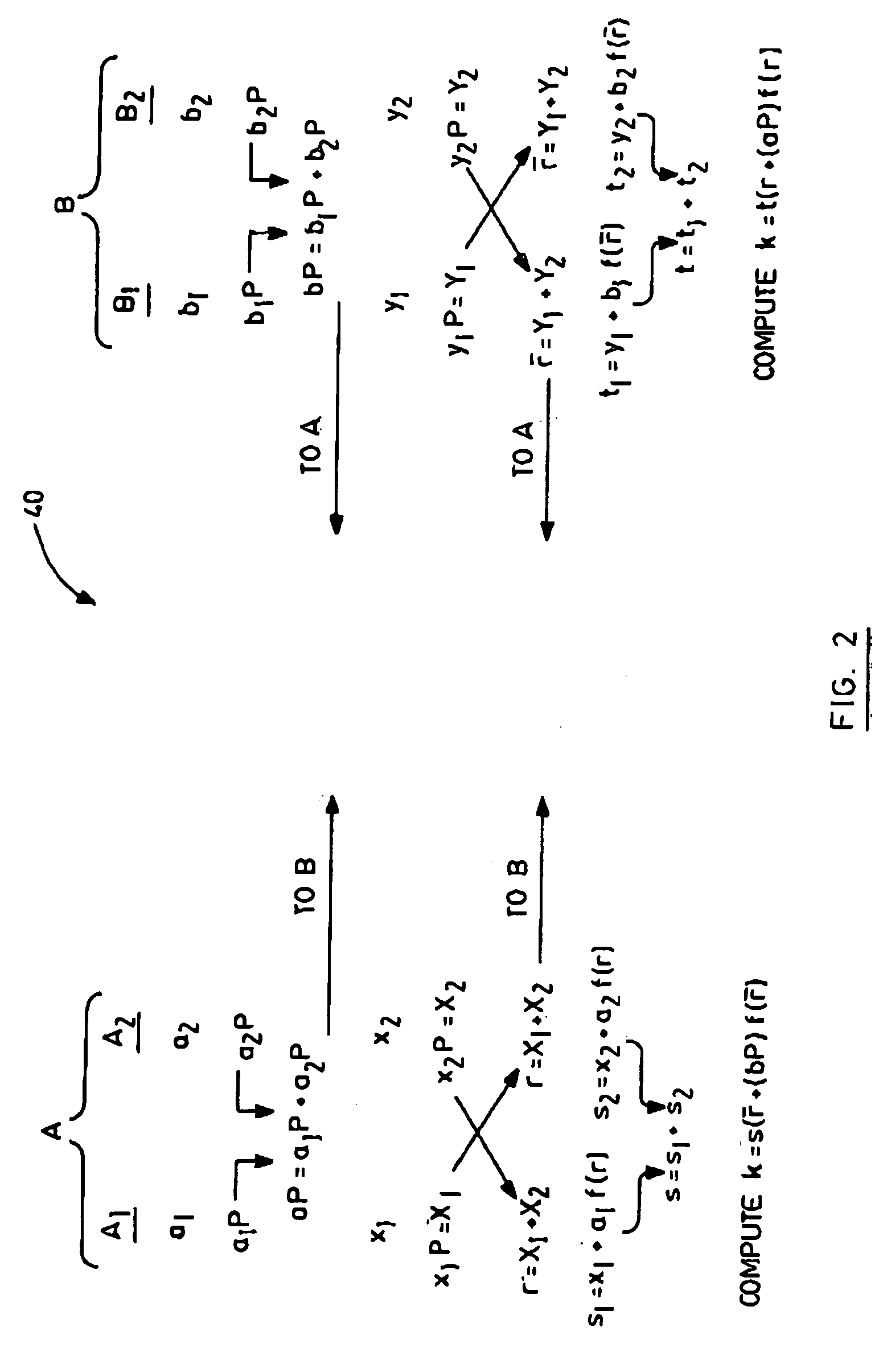
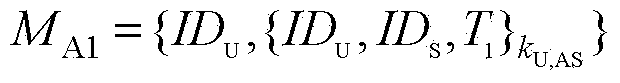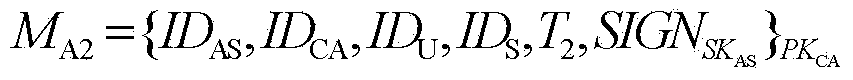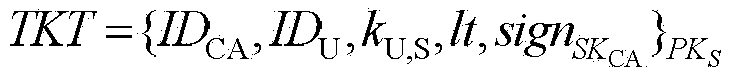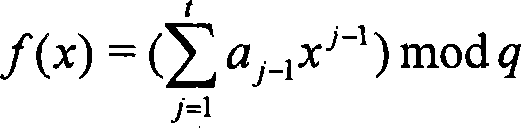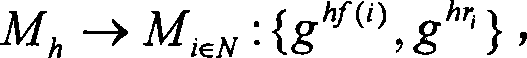Patents
Literature
121 results about "Key-agreement protocol" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In cryptography, a key-agreement protocol is a protocol whereby two or more parties can agree on a key in such a way that both influence the outcome. If properly done, this precludes undesired third parties from forcing a key choice on the agreeing parties. Protocols that are useful in practice also do not reveal to any eavesdropping party what key has been agreed upon.
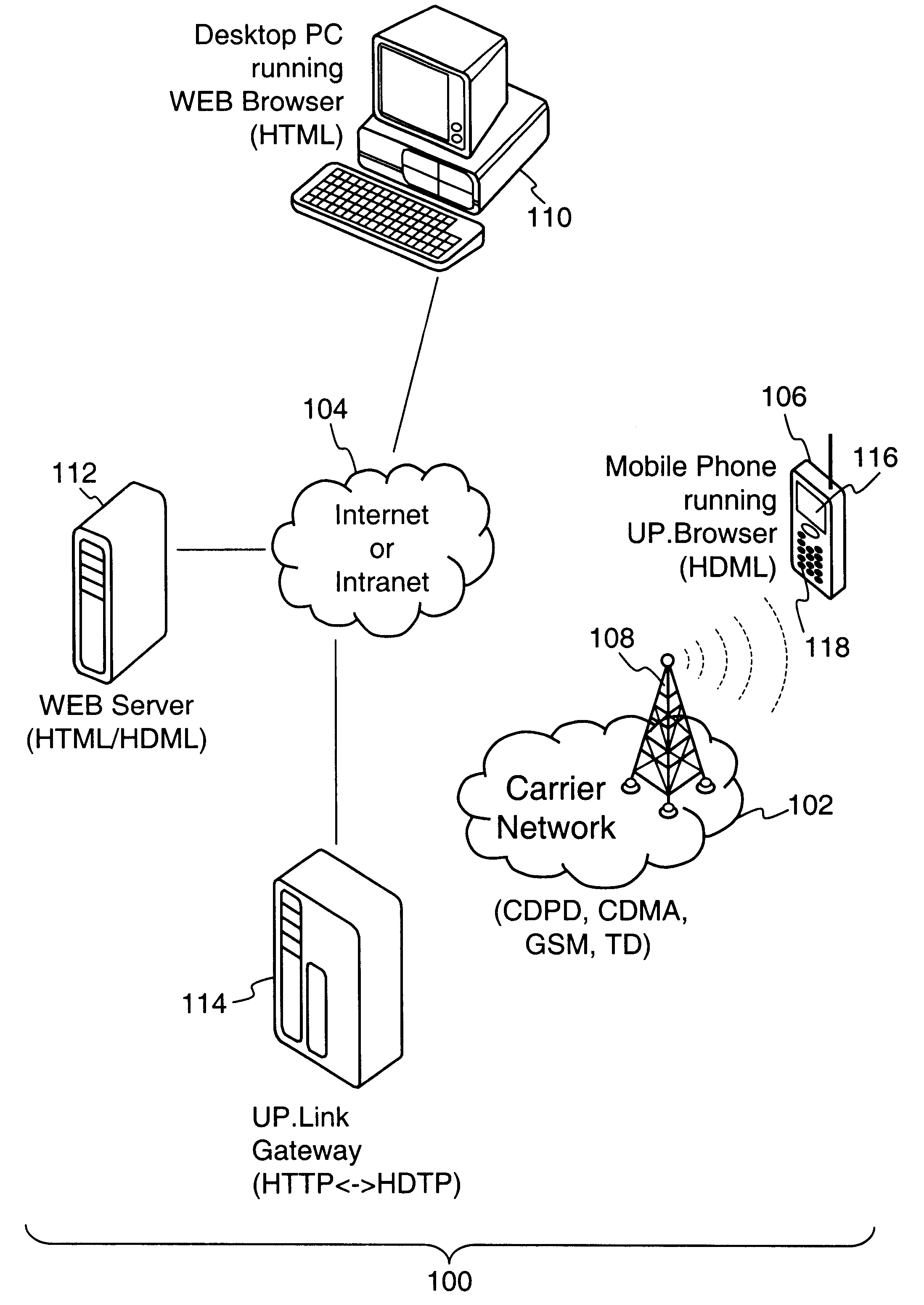
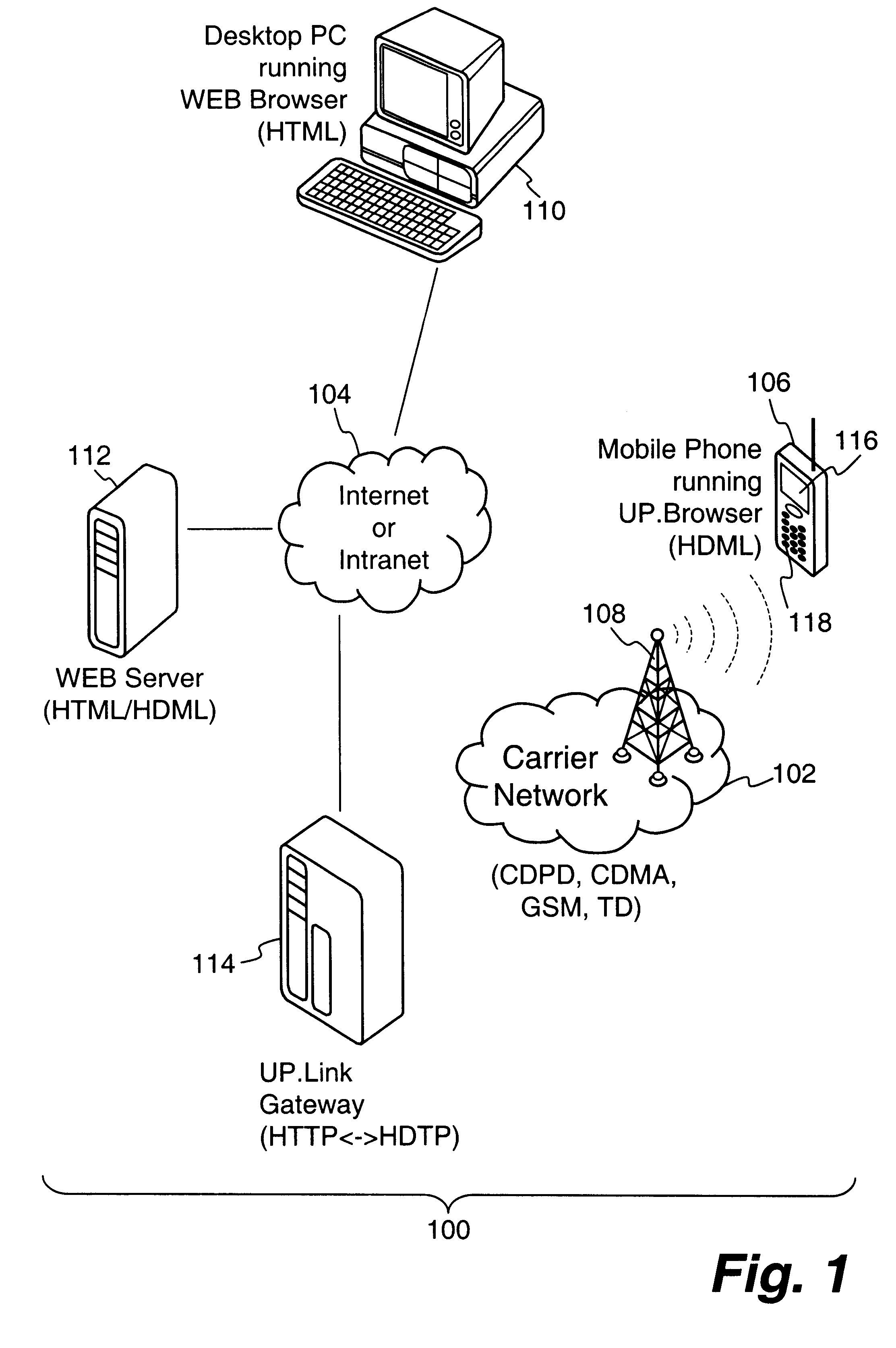
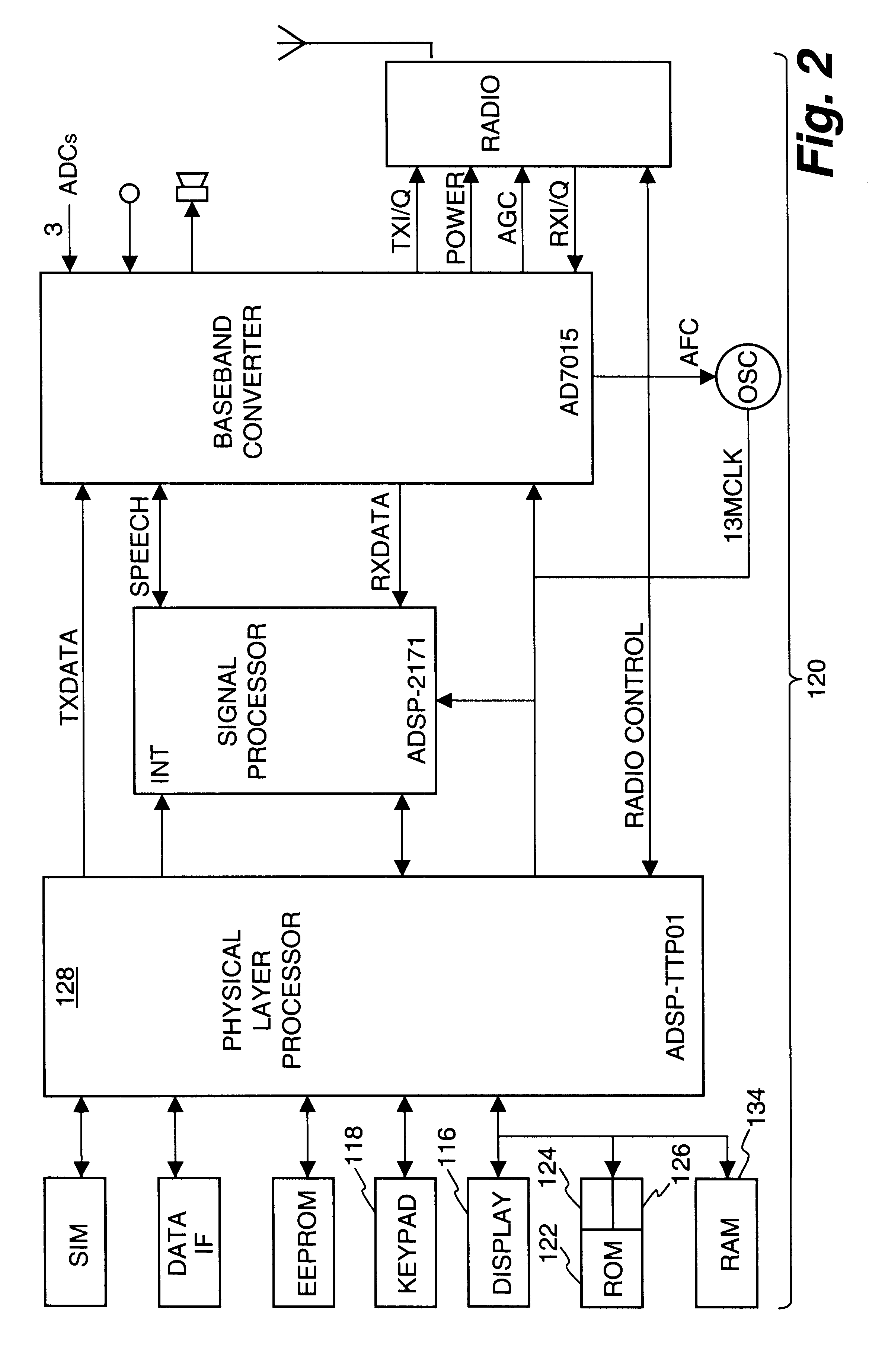
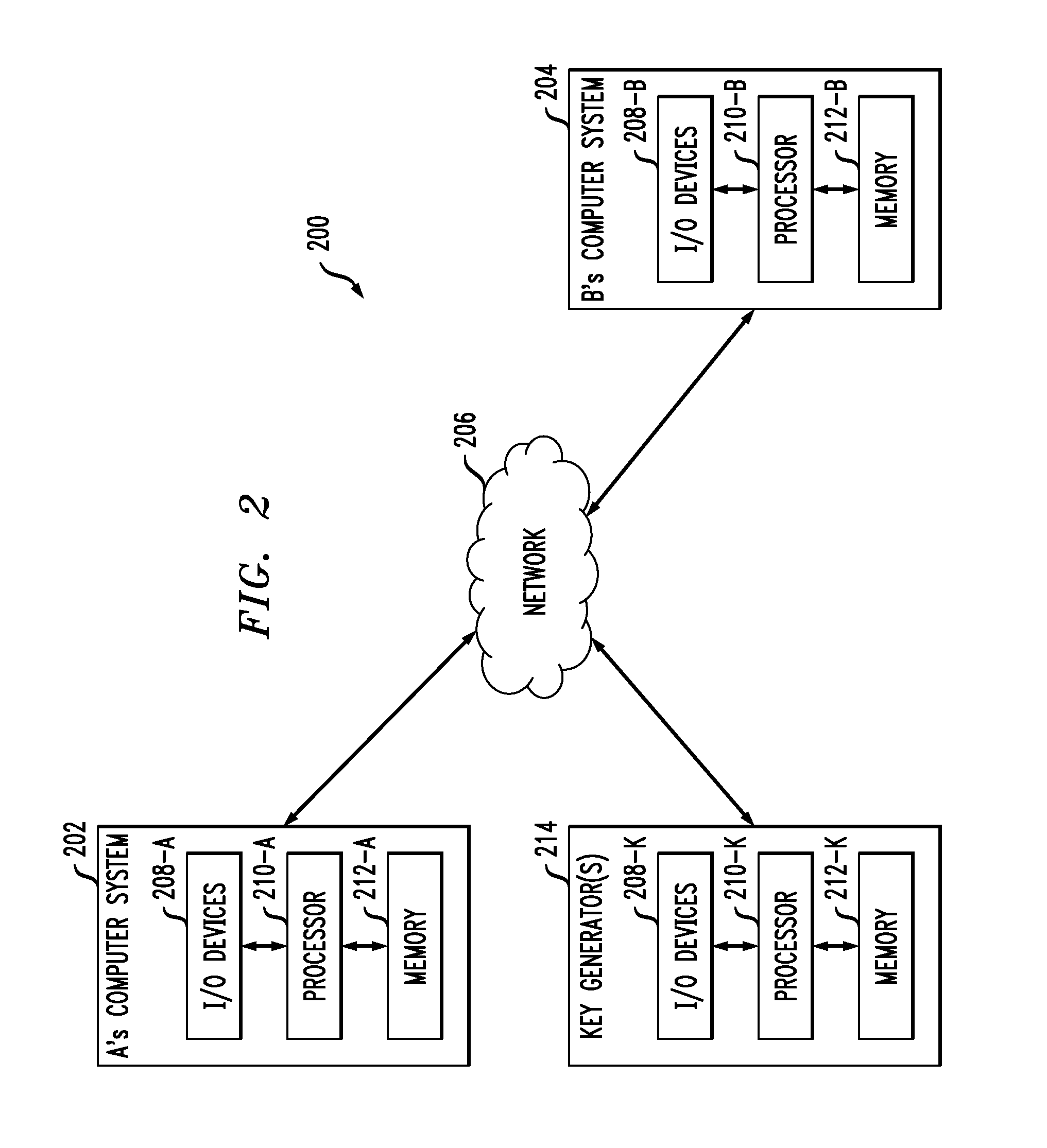
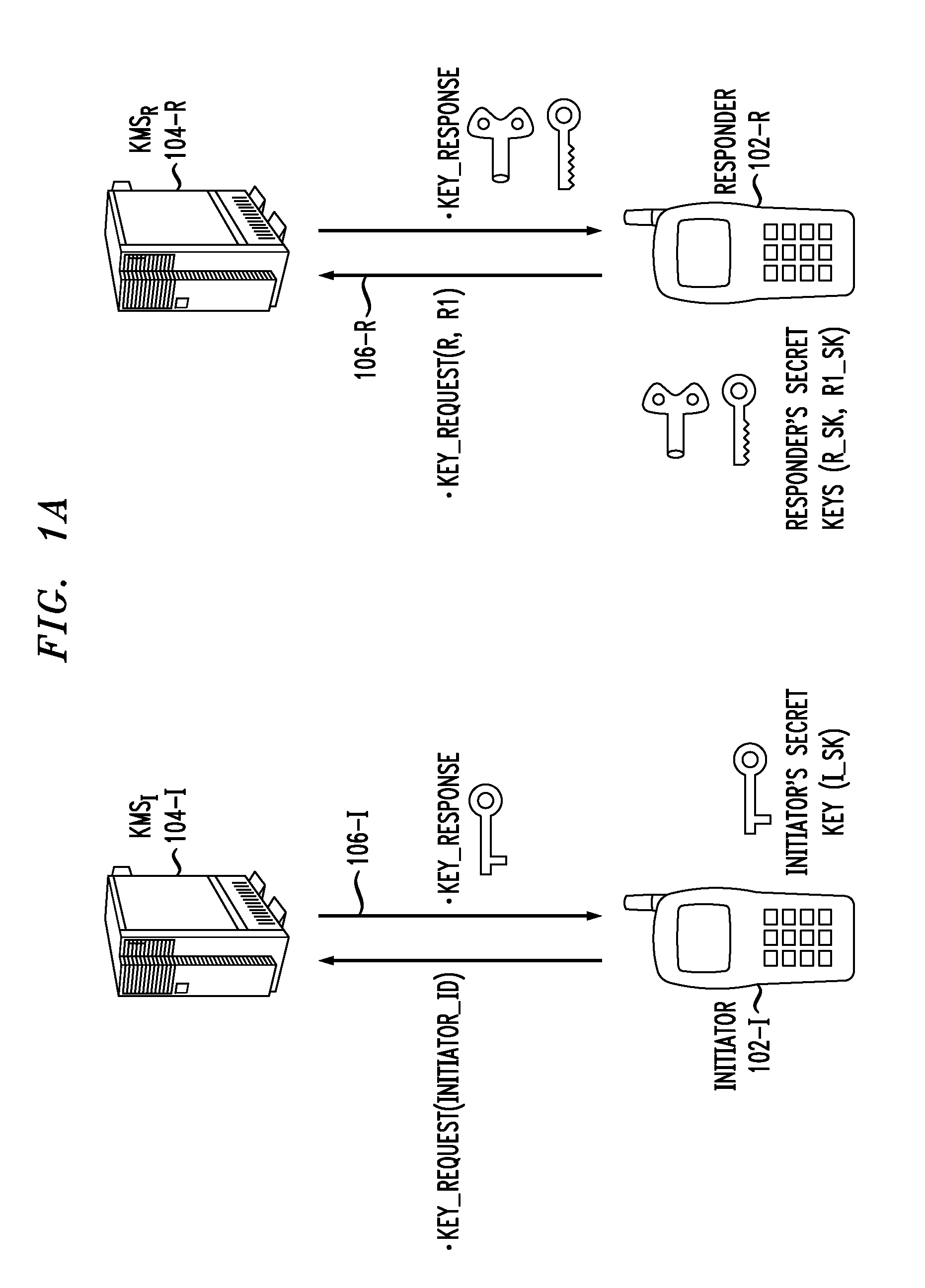
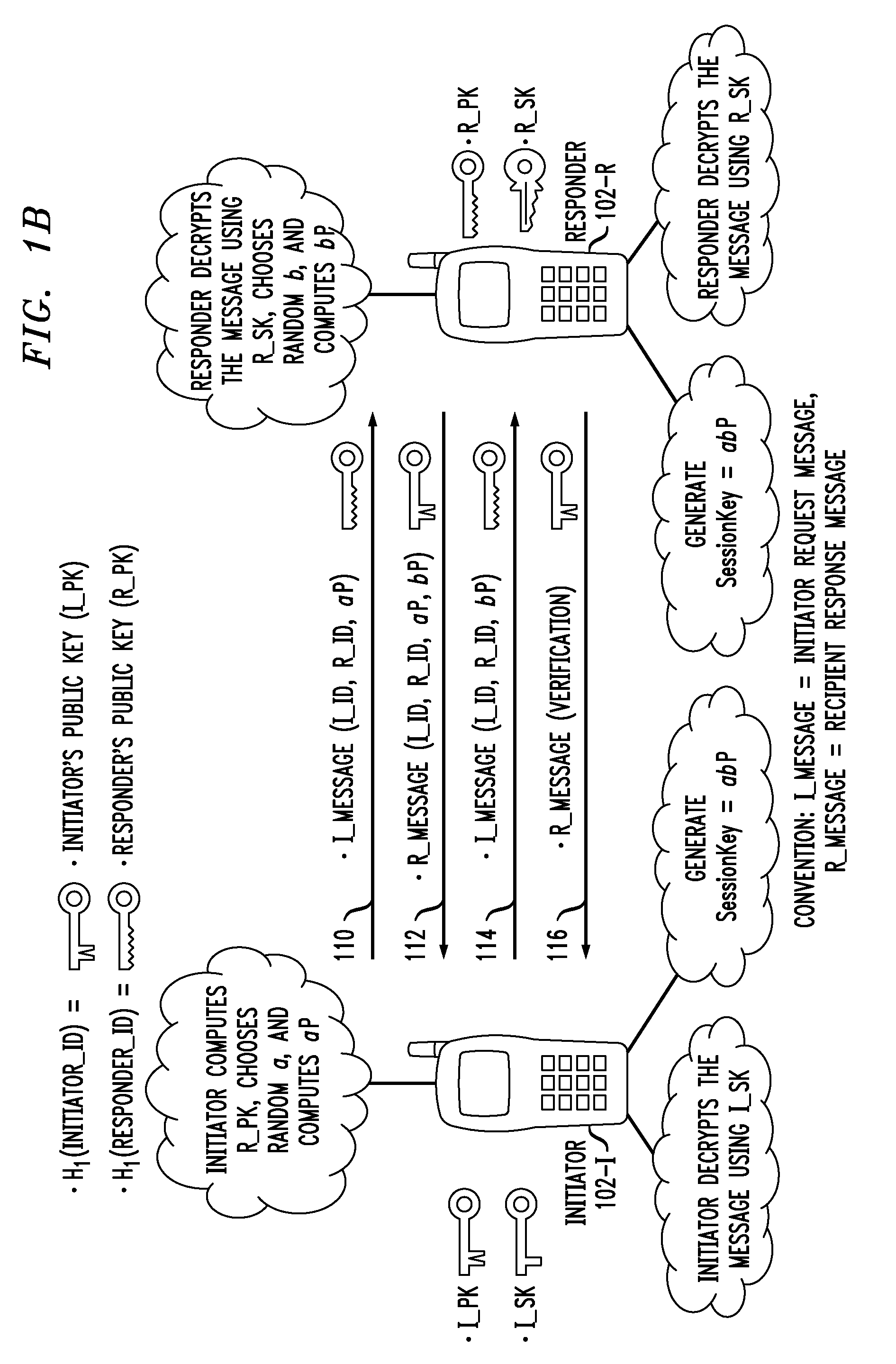
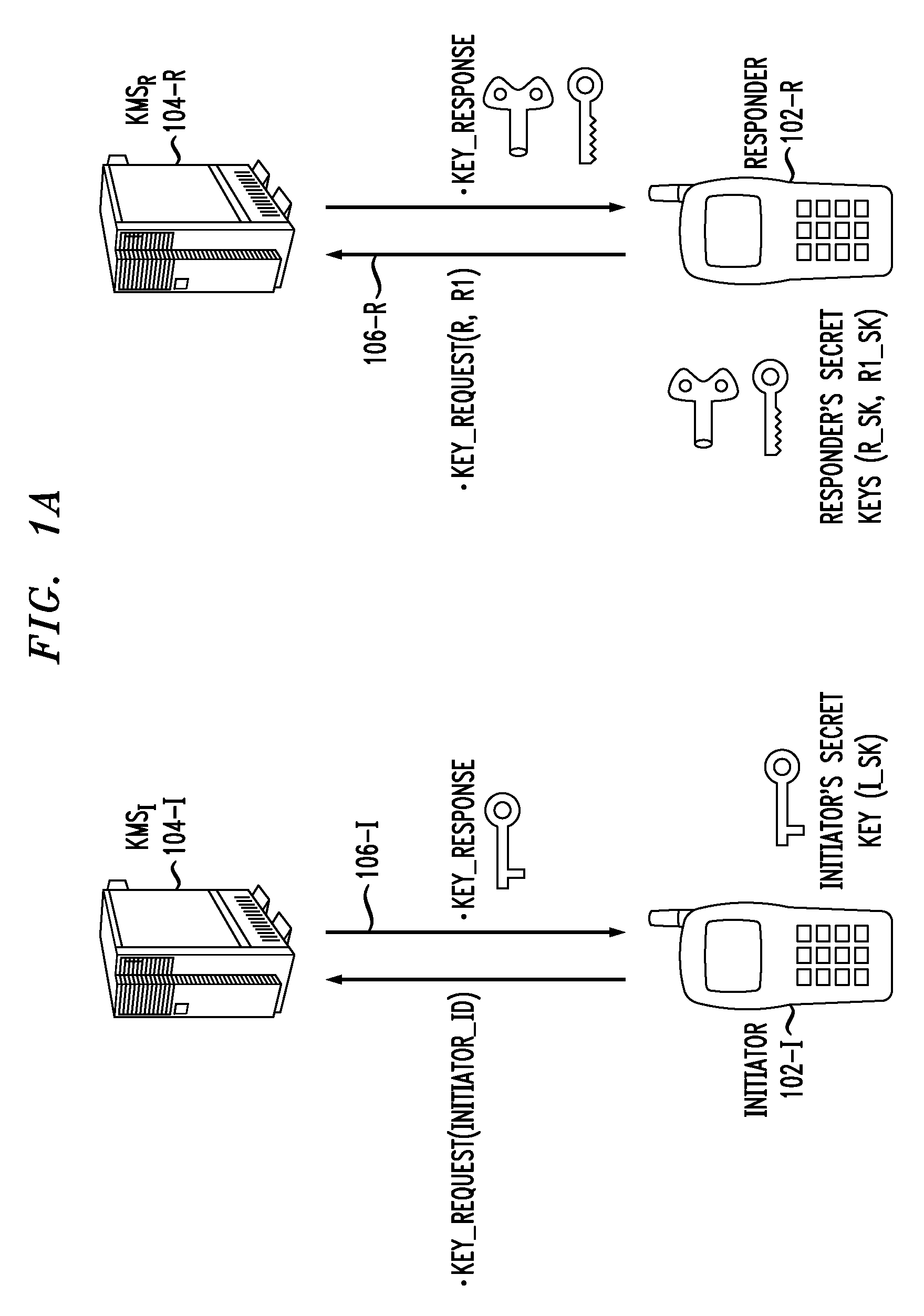
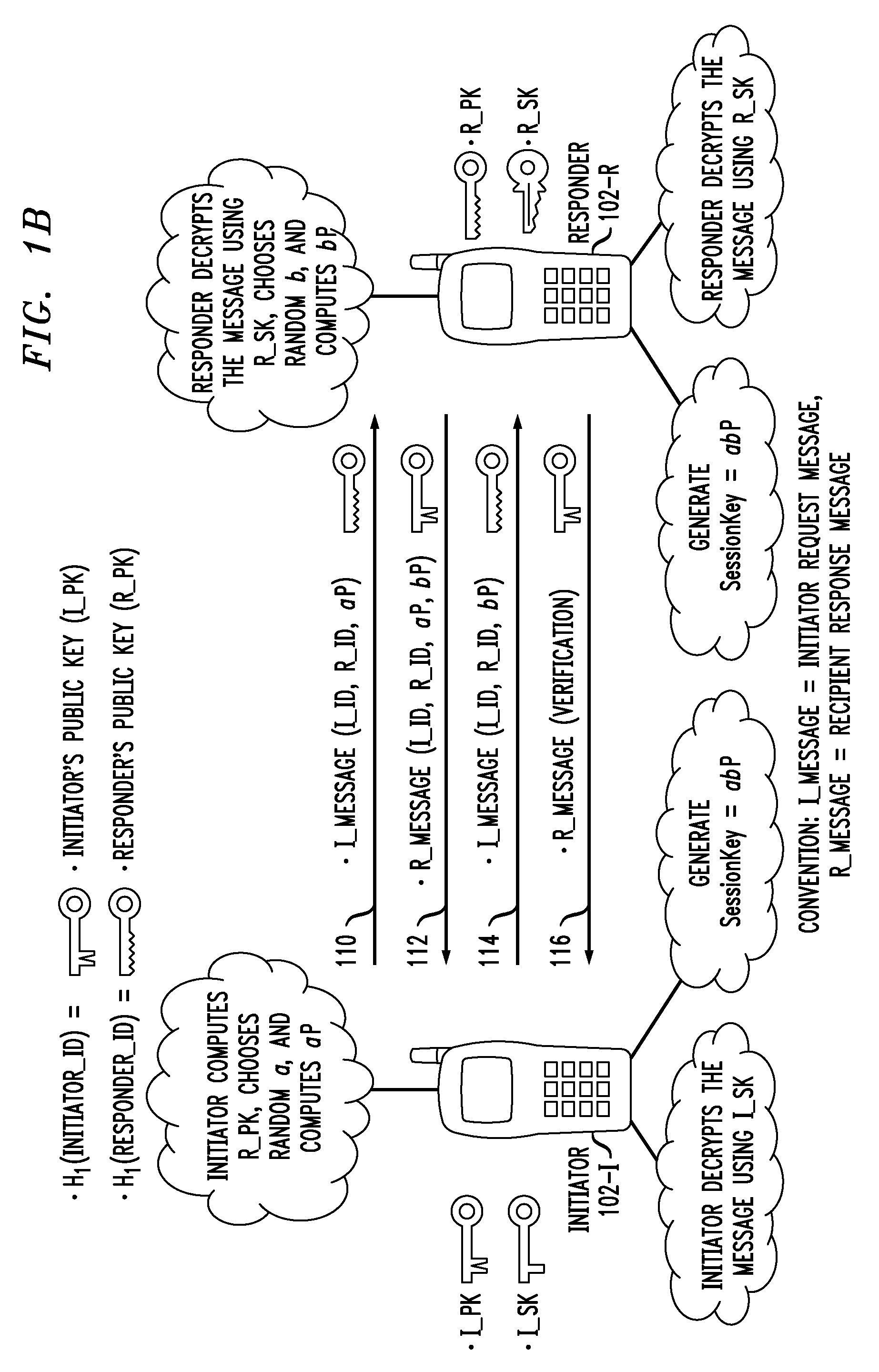
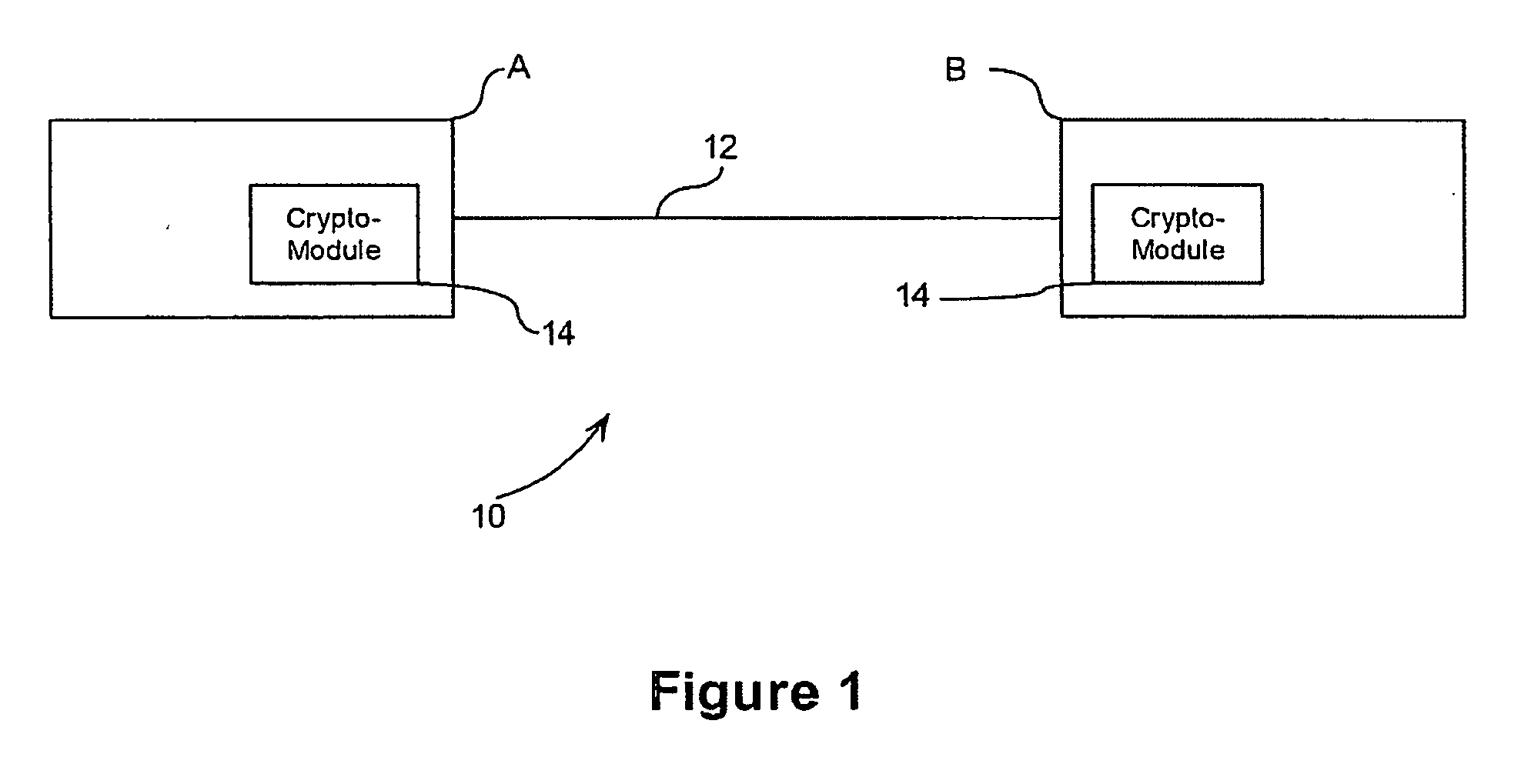
Method and apparatus for conducting crypto-ignition processes between thin client devices and server devices over data networks
InactiveUS6263437B1Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageTraffic capacityKey-agreement protocol
A crypto-ignition process is needed to establish an encrypted communication protocol between two devices connected by an insecure communication link. The present invention introduces a method of creating an identical secret key to two communicating parties is conducted between a thin device and a server computer over an insecure data network. The thin device generally has limited computing power and working memory and the server computer may communicate with a plurality of such thin devices. To ensure the security of the secret key on both sides and reduce traffic in the network, only a pair of public values is exchanged between the thin device and the server computer over the data network. Each side generates its own secret key from a self-generated private value along with the received counterpart's public value according to a commonly used key agreement protocol, such as the Diffie-Hellman key agreement protocol. To ensure that the generated secret keys are identical on both sides, a verification process is followed by exchanging a message encrypted by one of two generated secret keys. The secret keys are proved to be identical and secret when the encrypted message is successfully decrypted by the other secret key. To reduce network traffic, the verification process is piggybacked with a session request from the thin device to establish a secure and authentic communication session with the server computer. The present invention enables the automatic delivery of the secret keys, without requiring significant computing power and working memory, between each of the thin clients respectively with the server computer.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
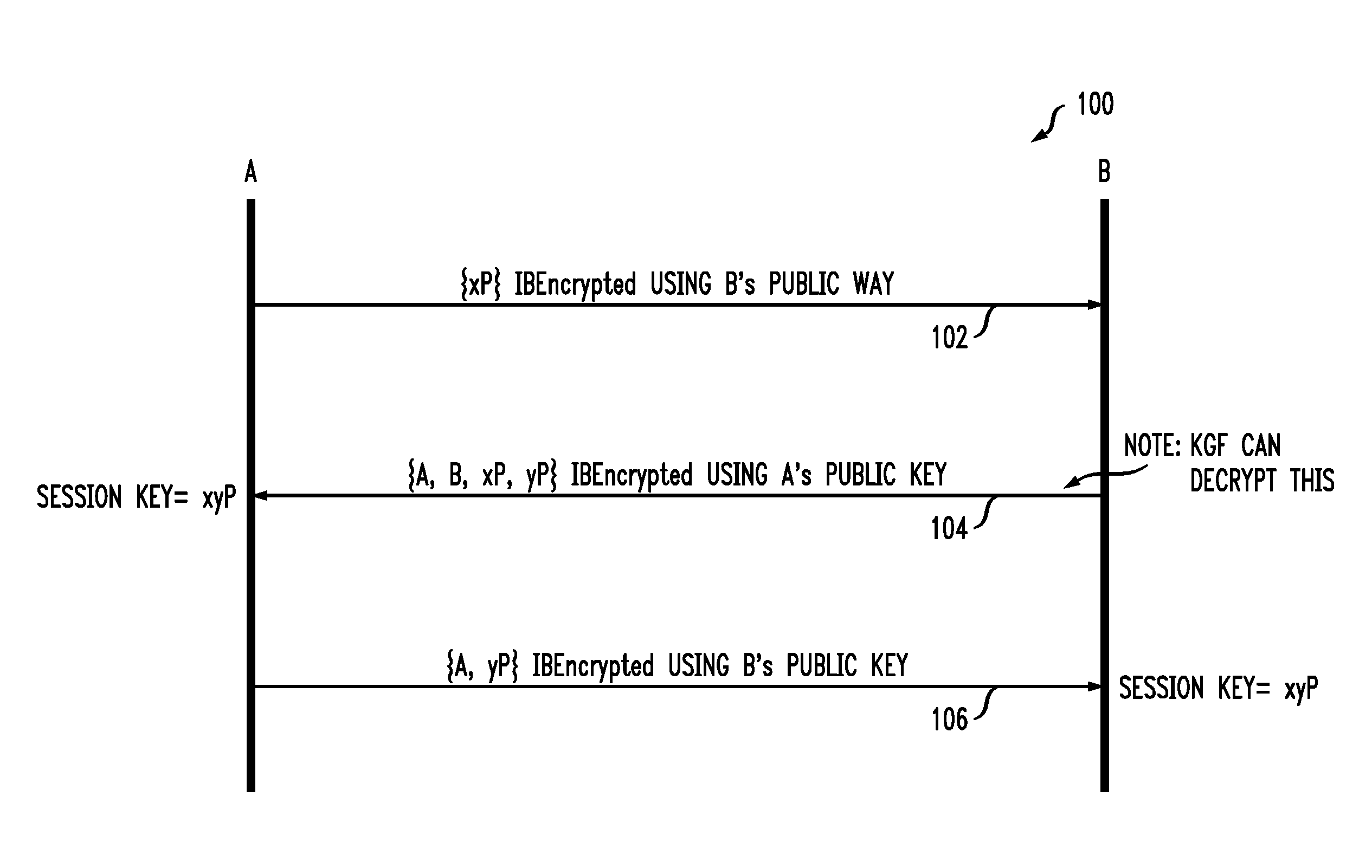
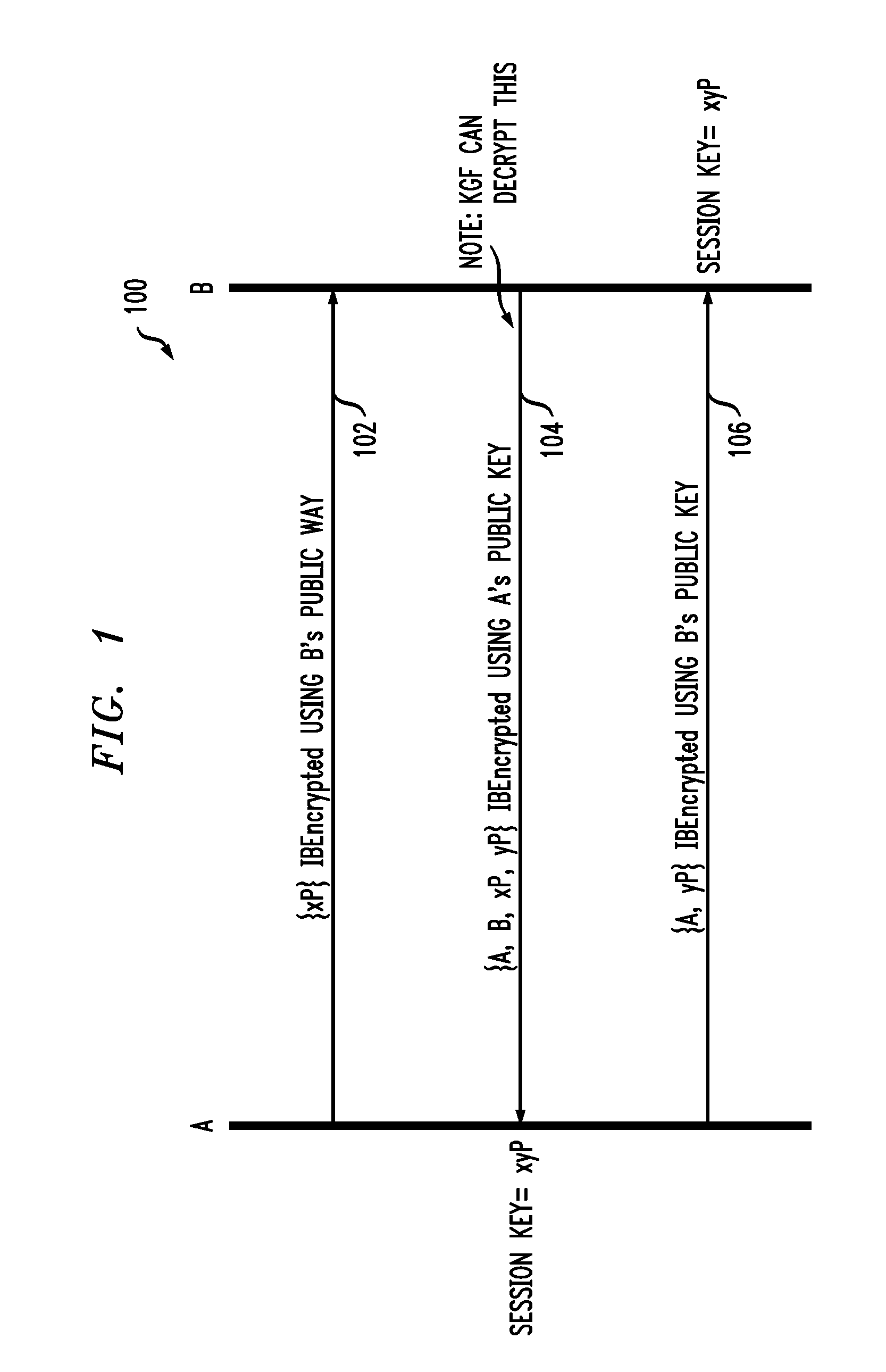
Identity Based Authenticated Key Agreement Protocol
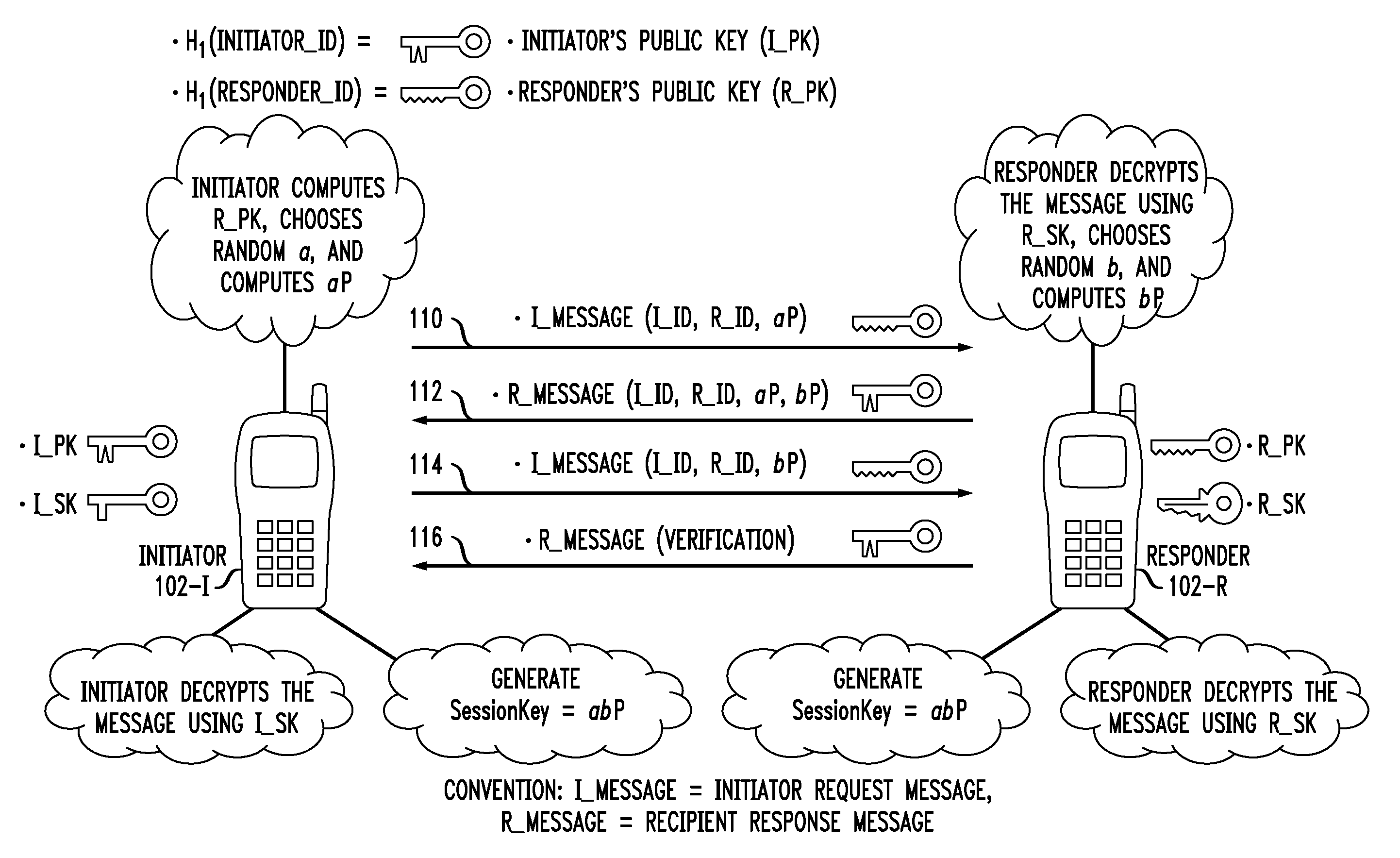
ActiveUS20100211779A1Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageAuthenticated key agreement protocolKey-agreement protocol
A key agreement protocol between a first party and a second party comprises the following steps from the first party perspective. An encrypted first random key component is sent to the second party, the first random key component being encrypted using a public key of the second party in accordance with an identity based encryption operation. An encrypted random key component pair is received from the second party, the random key component pair being formed from the first random key component and a second random key component computed at the second party, and encrypted at the second party using a public key of the first party in accordance with the identity based encryption operation. The second random key component, in encrypted form, is sent to the second party, the second random key component being encrypted using the public key of the second party. A key for use in subsequent communications between the first party and the second party is computable at the first party based on the second random key component. The key may be computed at the second party based on the first random key component.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
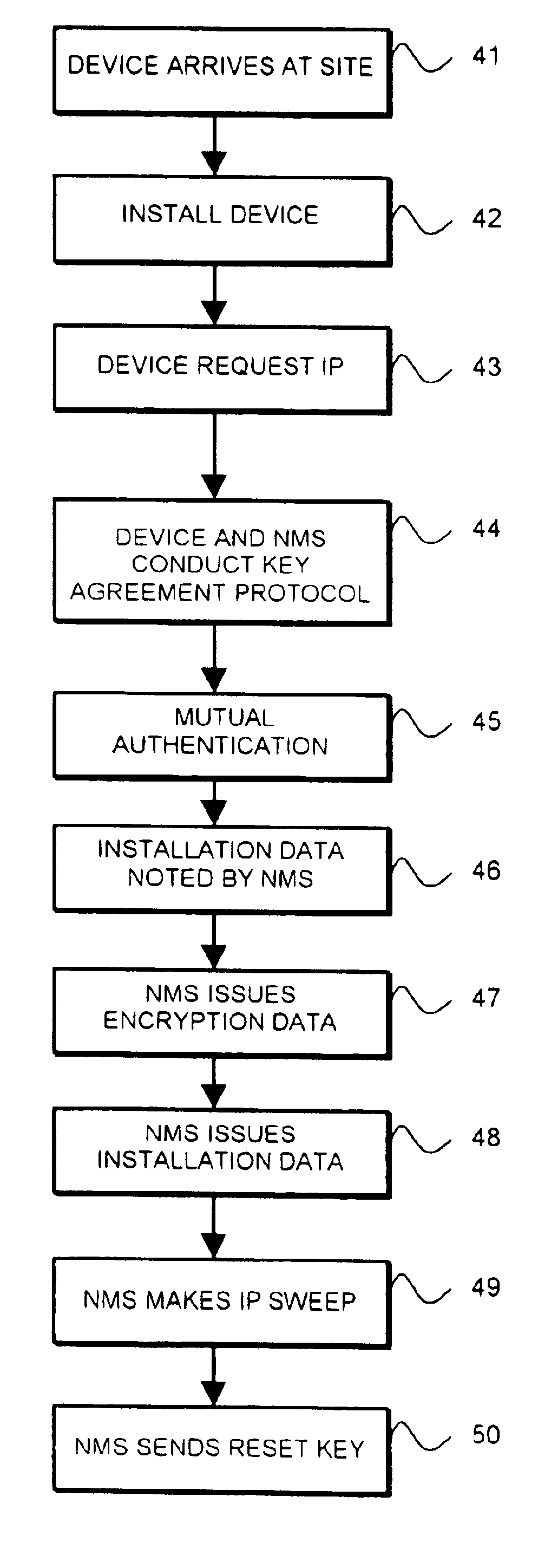
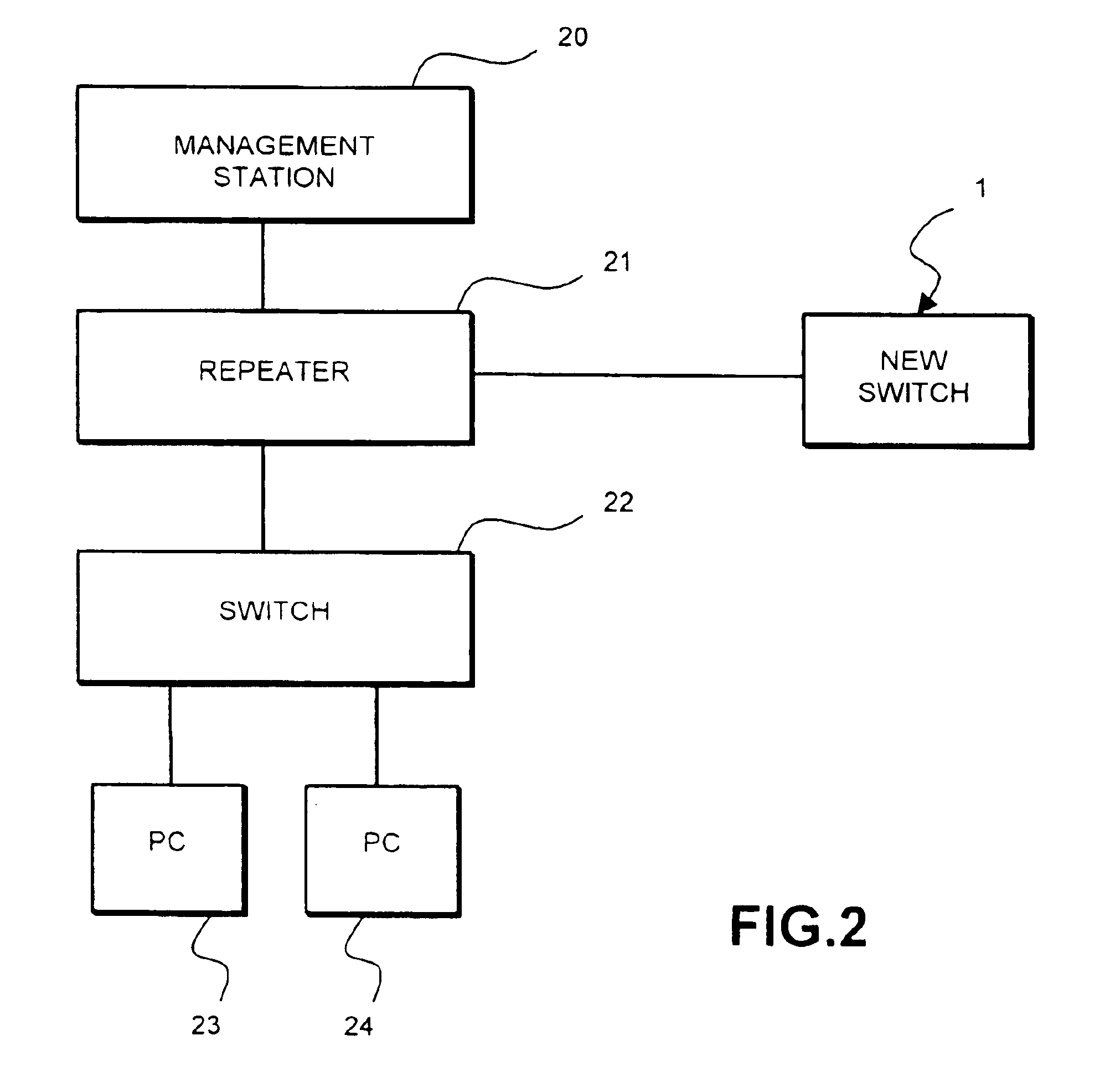
Method for secure installation of device in packet based communication network
InactiveUS6865673B1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationKey-agreement protocolComputer science
A method of installing a network device in a packet-based data communication network and checking the authenticity of the installation includes: (a) communicating identification information of the device to a management system; (b) installing the device; (c) obtaining from a protocol address administrator a protocol address for the device; (d) sending a communication from the device to the management system; (e) conducting a key agreement protocol exchange between the device and the management system to establish a set of encryption keys; (f) using the set of encryption keys to provide mutual authentication by the device and the management system; (g) associating, within the management system, the time of the communication in step (d) with the identification information and the protocol address of the device; and (h) communicating from the management system to the administrator a message including the identification information, the protocol address and the time.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
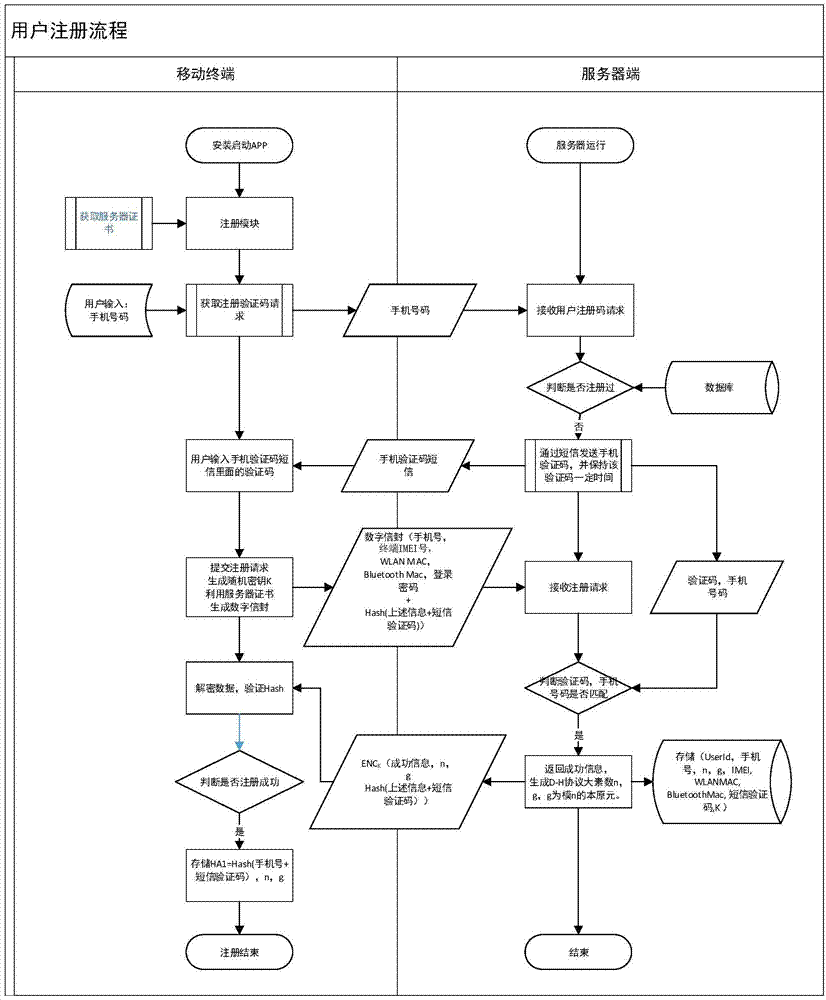
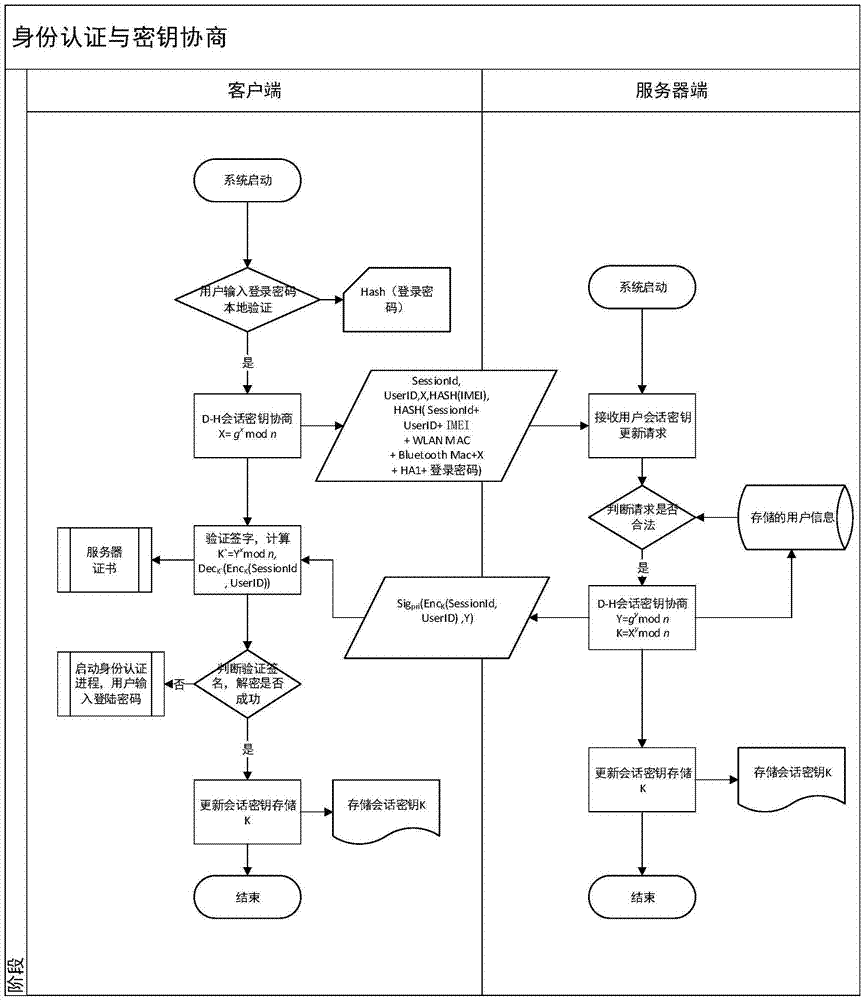
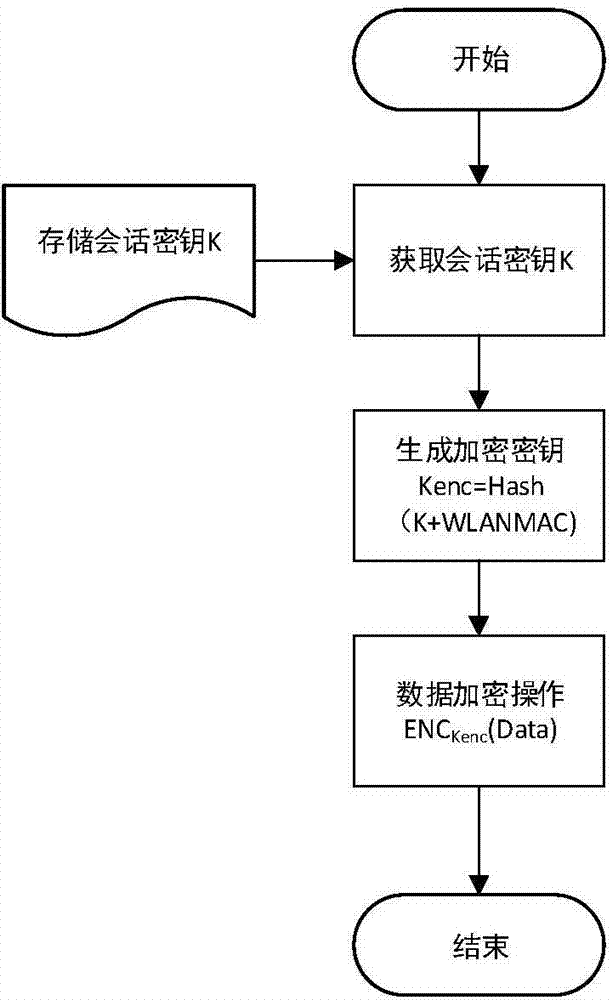
Safety communication secret key negotiation interaction scheme
ActiveCN104506534AGuarantee authenticityEnsure communication securityKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationThe InternetNetwork service
The invention provides a method for safety communication between an application on a mobile terminal and a network server. Shared secrets of a user and a server are overlapped and bound with an identification code of mobile intelligent terminal equipment and a mobile phone number of the user by utilizing a cryptology; then the obtained product is applied to an identity authentication system to implement authentication on a client side; a digital certificate and a digital signature mechanism are utilized to implement authentication on the server; a session key is established with a network server by utilizing a Differ-Hellman secret key negotiation protocol so as to carry out safety data communication. The method is characterized in that the shared secrets are overlapped and bound with identification code of the machine and the mobile phone number of the user and the shared secrets are updated regularly; even though information is stolen by an attacker, a system still cannot be influenced. The user not only needs to provide a login password, but also needs to use the system on designated equipment. The method can ensure that the user carries out safety communication with the server on internet by the mobile equipment.
Owner:QINGDAO WEIZHIHUI INFORMATION
Method and apparatus for providing bootstrapping procedures in a communication network
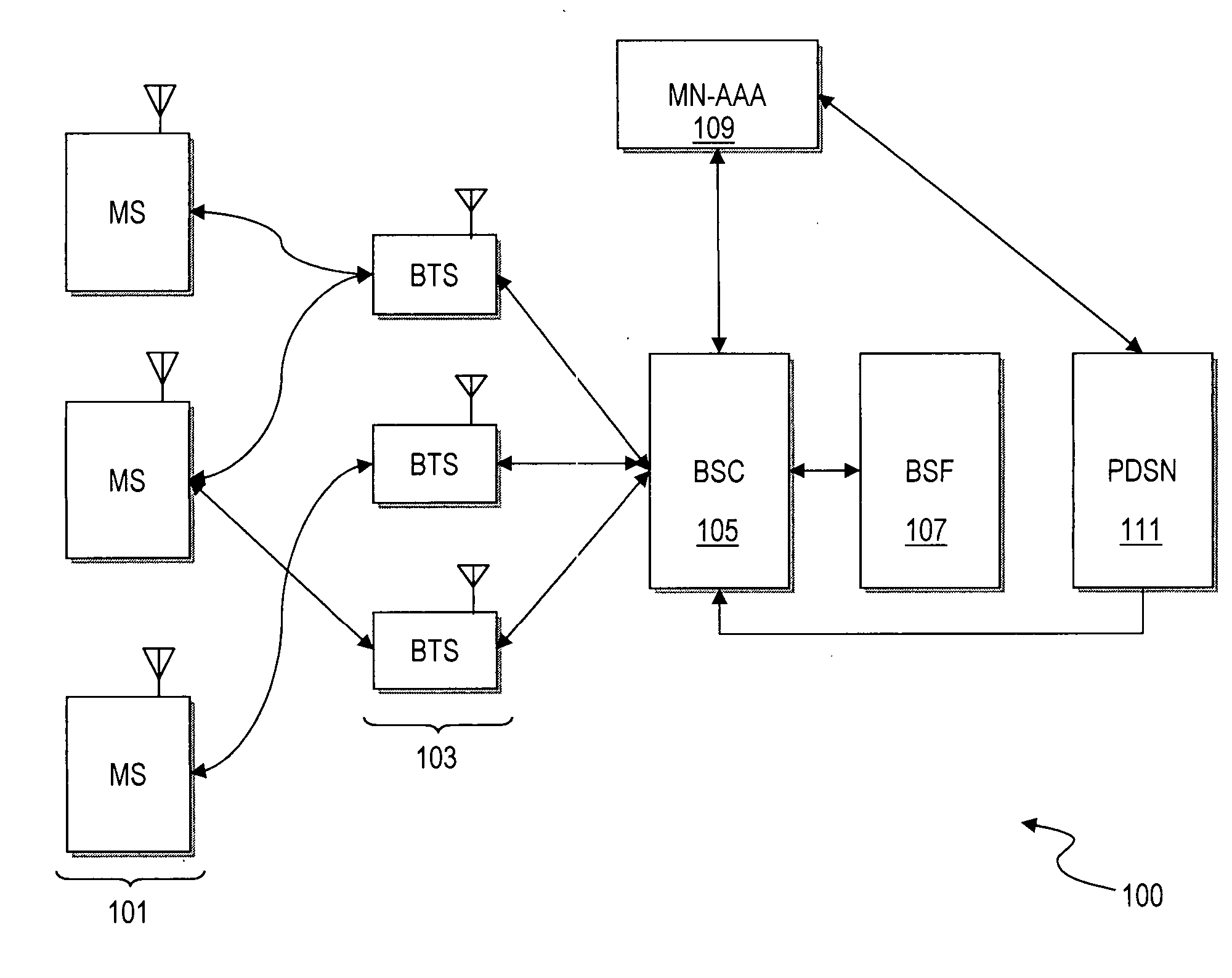
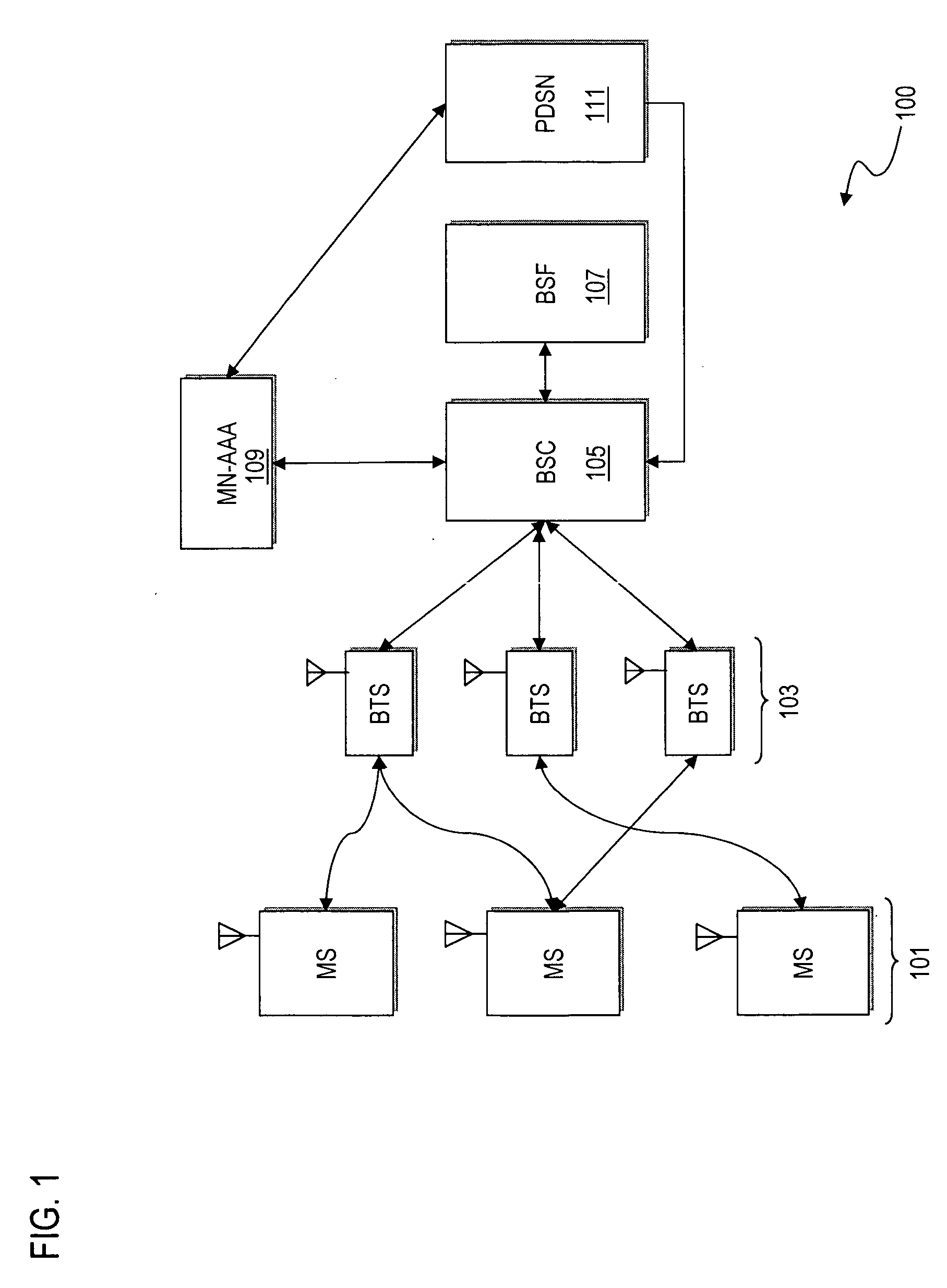
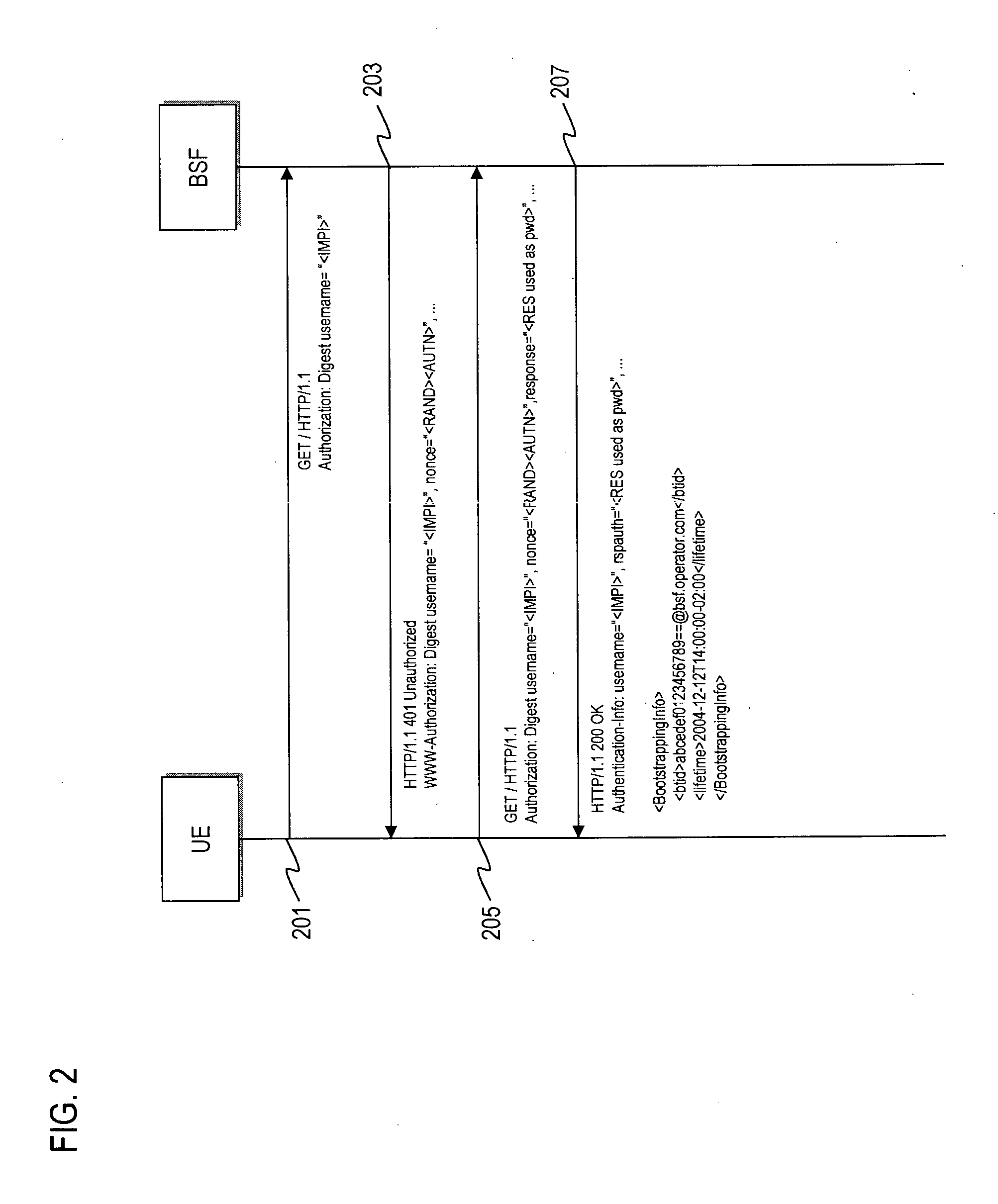
ActiveUS20060182280A1Efficient executionSecret communicationProgram controlComputer hardwareKey exchange
An approach is provided for performing authentication in a communication system. In one embodiment, a key is established with a terminal in a communication network according to a key agreement protocol. The agreed key is tied to an authentication procedure to provide a security association that supports reuse of the key. A master key is generated based on the agreed key. In another embodiment, digest authentication is combined with key exchange parameters (e.g., Diffie-Hellman parameters) in the payload of the digest message, in which a key (e.g., SMEKEY or MN-AAA) is utilized as a password. In yet another embodiment, an authentication algorithm (e.g., Cellular Authentication and Voice Encryption (CAVE)) is employed with a key agreement protocol with conversion functions to support bootstrapping.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
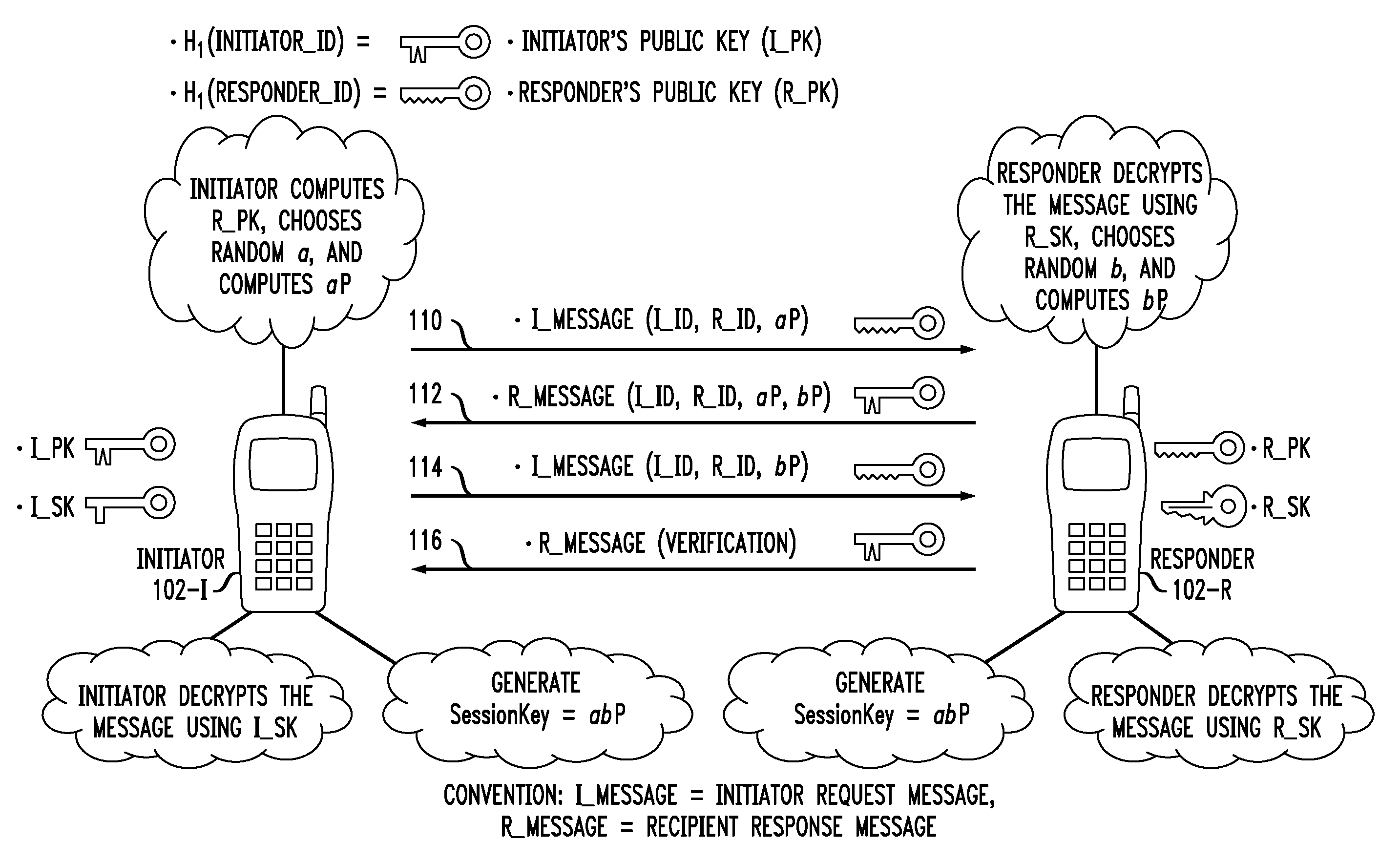
Secure Key Management in Multimedia Communication System
ActiveUS20110055567A1Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageID-based encryptionCommunications system
Principles of the invention provide one or more secure key management protocols for use in communication environments such as a media plane of a multimedia communication system. For example, a method for performing an authenticated key agreement protocol, in accordance with a multimedia communication system, between a first party and a second party comprises, at the first party, the following steps. Note that encryption / decryption is performed in accordance with an identity based encryption operation. At least one private key for the first party is obtained from a key service. A first message comprising an encrypted first random key component is sent from the first party to the second party, the first random key component having been computed at the first party, and the first message having been encrypted using a public key of the second party. A second message comprising an encrypted random key component pair is received at the first party from the second party, the random key component pair having been formed from the first random key component and a second random key component computed at the second party, and the second message having been encrypted at the second party using a public key of the first party. The second message is decrypted by the first party using the private key obtained by the first party from the key service to obtain the second random key component. A third message comprising the second random key component is sent from the first party to the second party, the third message having been encrypted using the public key of the second party. The first party computes a secure key based on the second random key component, the secure key being used for conducting at least one call session with the second party via a media plane of the multimedia communication system.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
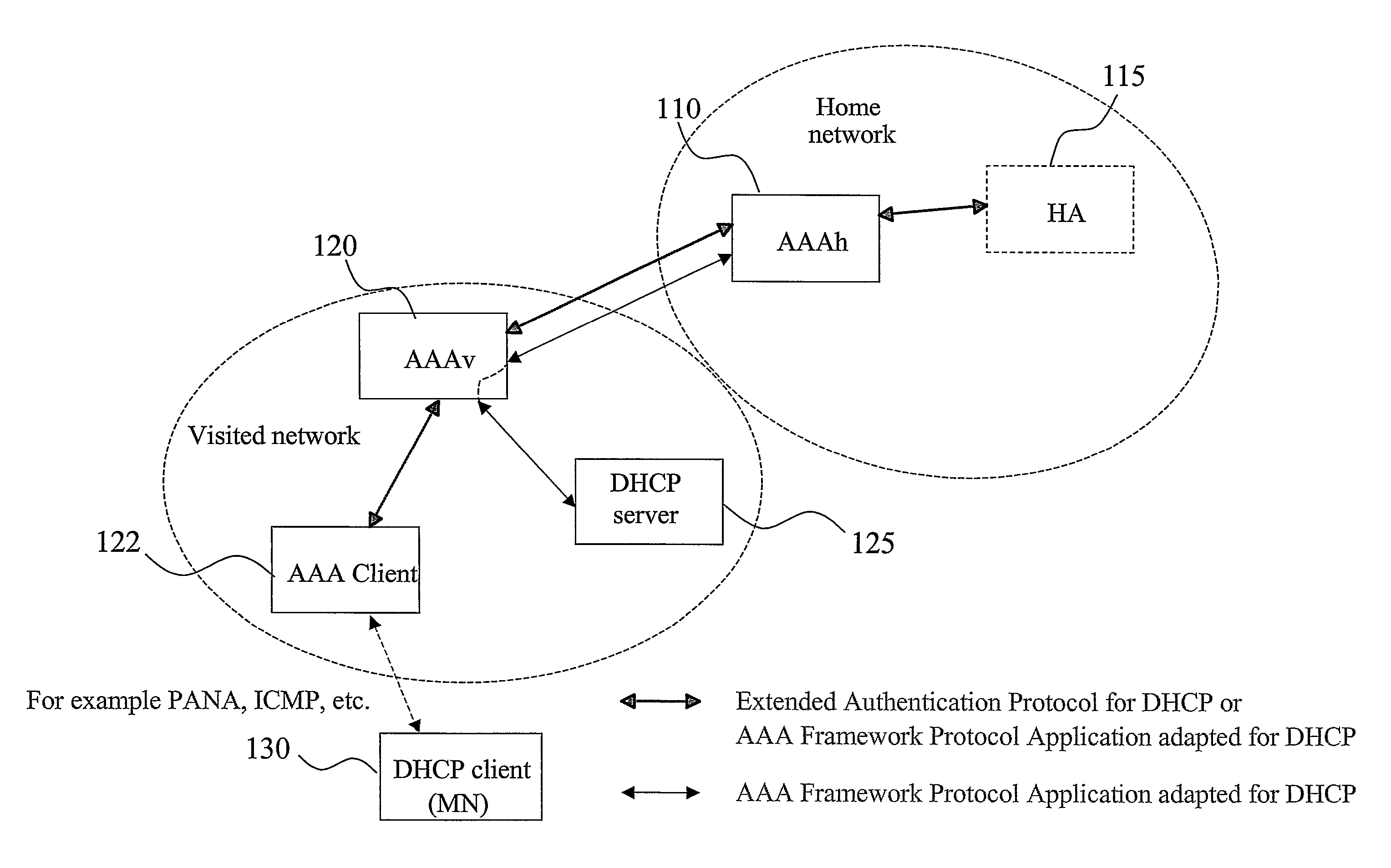
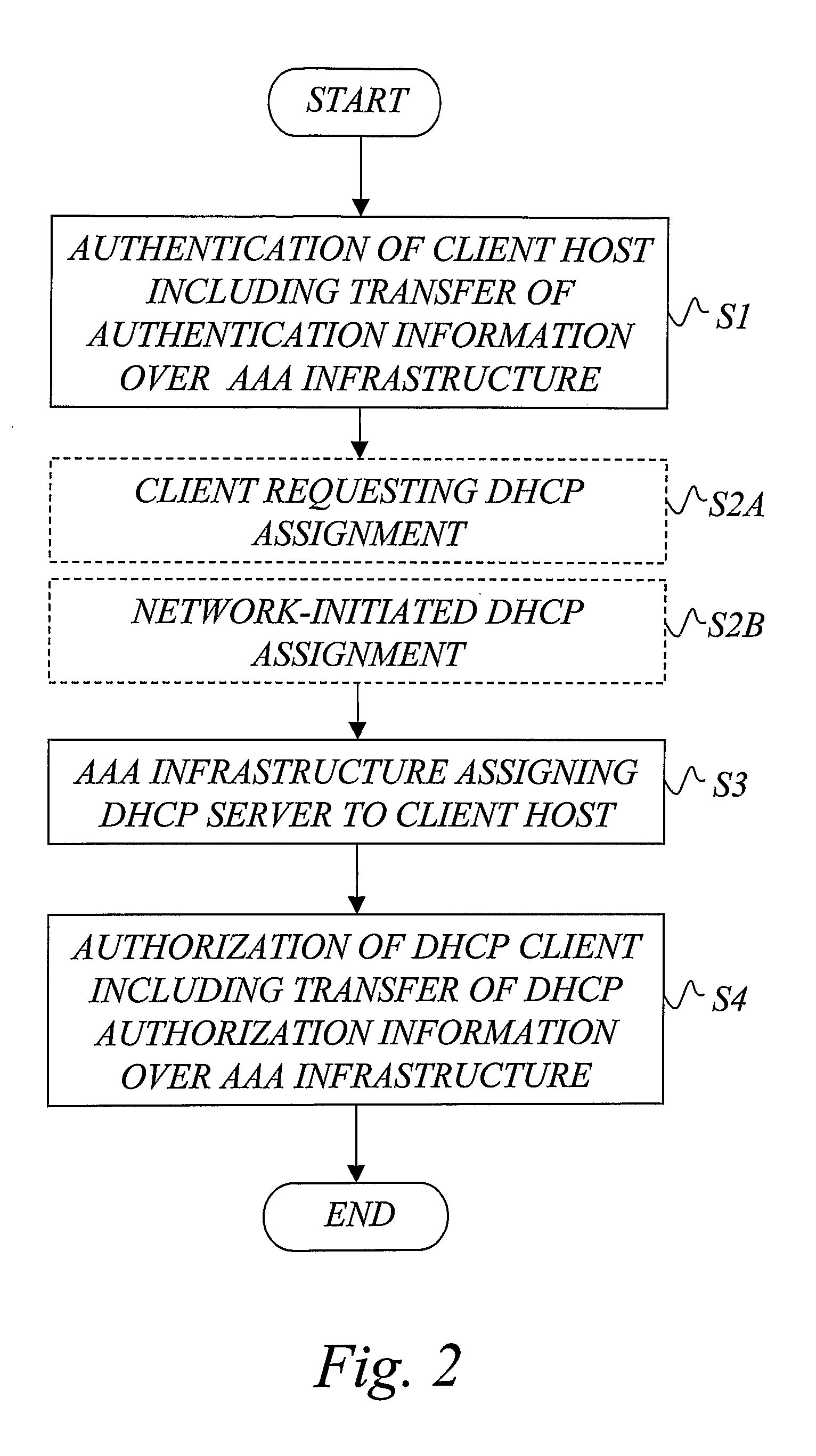
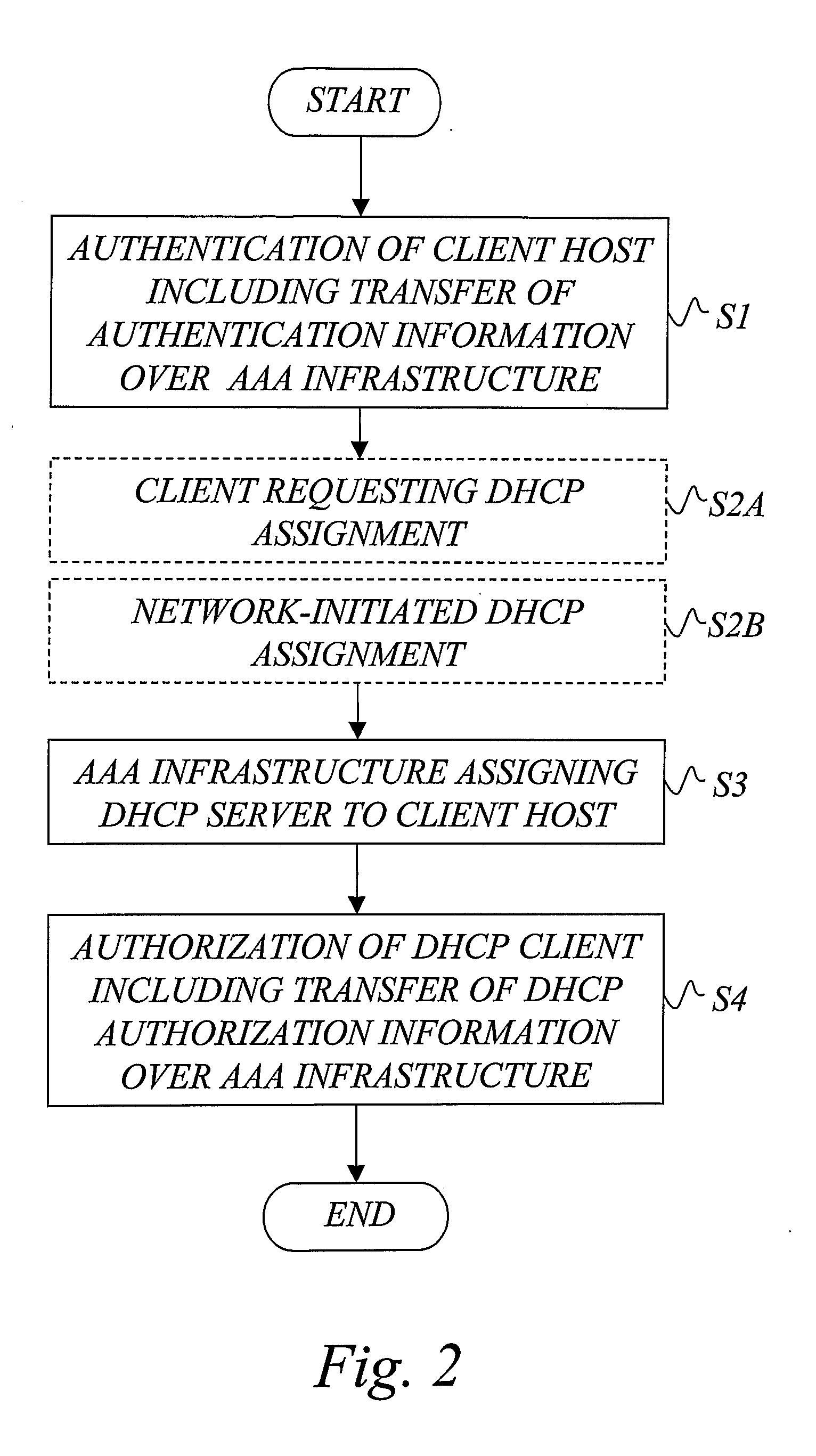
AAA support for DHCP
InactiveUS7983418B2Add supportEasy transferDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsKey-agreement protocolClient-side
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Bidirectional authentication method
InactiveCN101431415AImprove encryption efficiencyShort ciphertext lengthKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationPlaintextCiphertext
The present invention discloses a method of mutual authentication which is suitable for digital right management domain of interactive network TV. The invention comprises the following procedures: registering in an authentication server by a user terminal; executing key agreement between user terminal and authentication server; executing mutual authentication between user terminal and authentication server; obtaining license certificate for content broadcasting by user terminal. Mutual authentication is established between server of IPTVDRM and client taking advantage of high encryption efficiency of ECC and short length of cipher text by adopting the technical scheme described in the invention; obtaining session key from key protocol agreement before mutual authentication, authenticating ID of mutual parties through certificate mutually, and preventing certificate from tampering attack in transmitting process; making authentication valid and encryption and decryption efficiency higher than RSA mutual authentication by adopting mutual authentication of the certificate, and obtaining information of counterpart in plaintext by both parties for mutual confirmation without leaking plaintext simultaneously.
Owner:天柏宽带网络技术(北京)有限公司
Method for cross-isomerism domain identity authentication and session key negotiation based on access authorization ticket
ActiveCN103780618AHigh security requirementsStrong computing powerUser identity/authority verificationPublic key authenticationKey-agreement protocol
The invention provides a method for cross-isomerism domain identity authentication and session key negotiation based on an access authorization ticket. The method mainly comprises the steps that firstly, a first-level trust relationship is established between a CA of a PKI domain and an AS of a Kerberos domain through a distributed trust model based on a public key authentication mechanism; on the basis, the authorization ticket allowing an outer-domain user to have access to resources of the domain is generated and distributed by the CA or the AS united with a TGS, and through design of a two-way cross-domain authentication and key negotiation protocol based on a symmetric key cryptosystem, a second-level trust relationship allowing the outer-domain user to have access to the resources of the domain is established. On the premise that the requirements for safety of the levels are satisfied, the calculated amount and the communication traffic of a terminal are effectively reduced, public key encryption and decryption operations of a Kerberos domain terminal can be completely avoided, and the implementation is good in the cross-isomerism domain identity authentication process of a dynamic distributed type system, session key negotiation is completed when identity authentication is conducted, and the protocol efficiency is high.
Owner:四川华创智能科技有限公司
Robust authentication and key agreement protocol for next-generation wireless networks
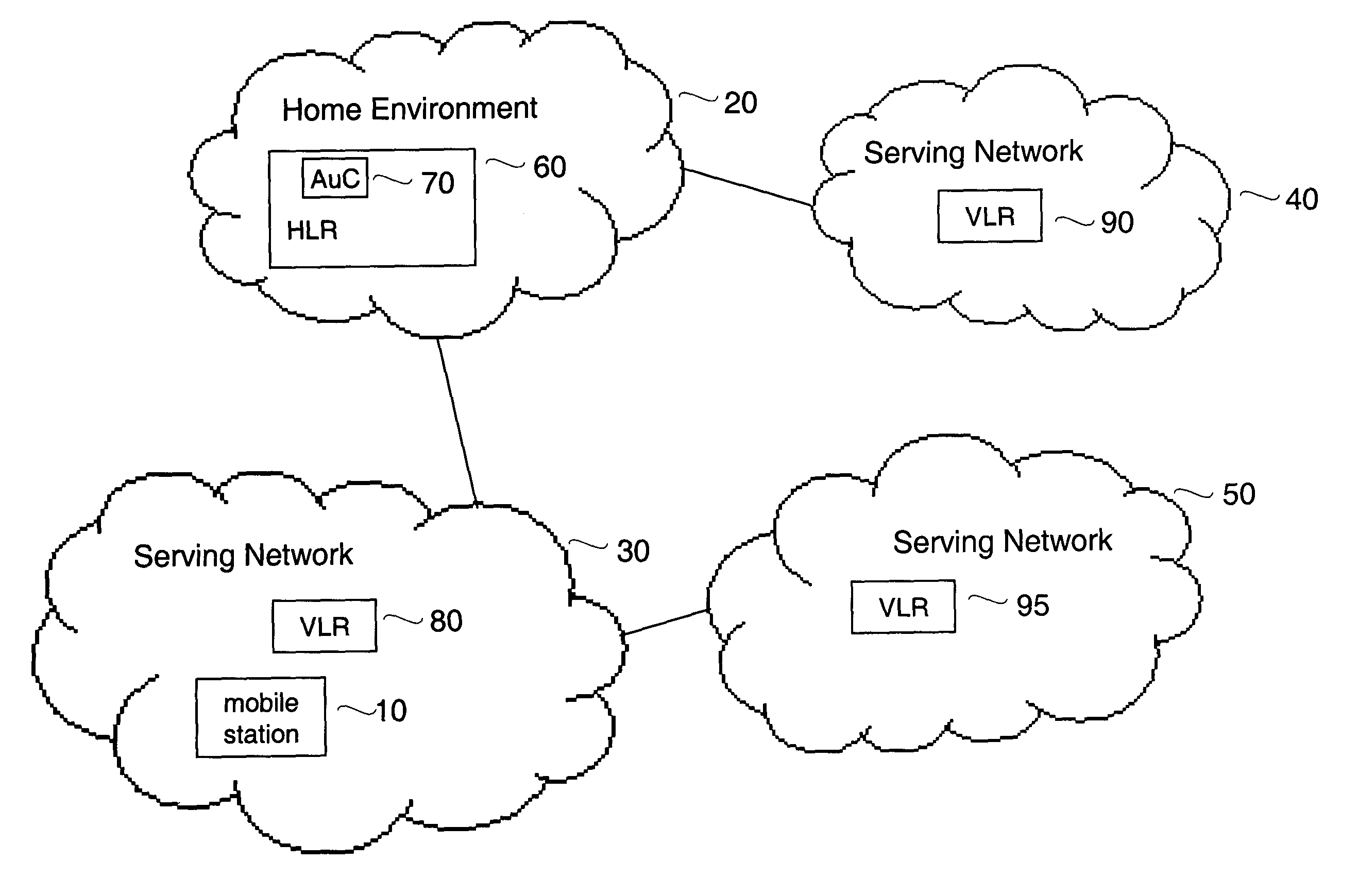
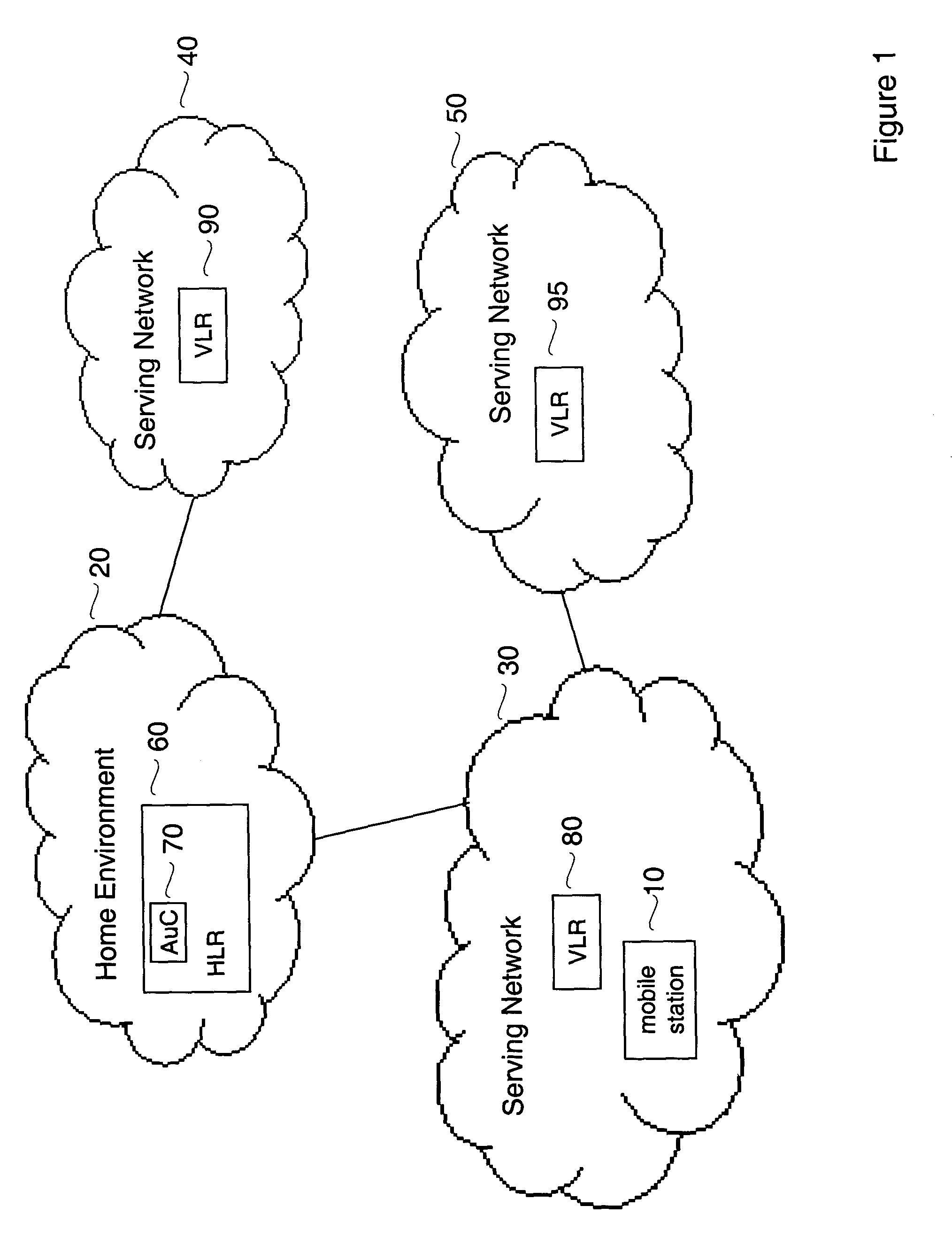
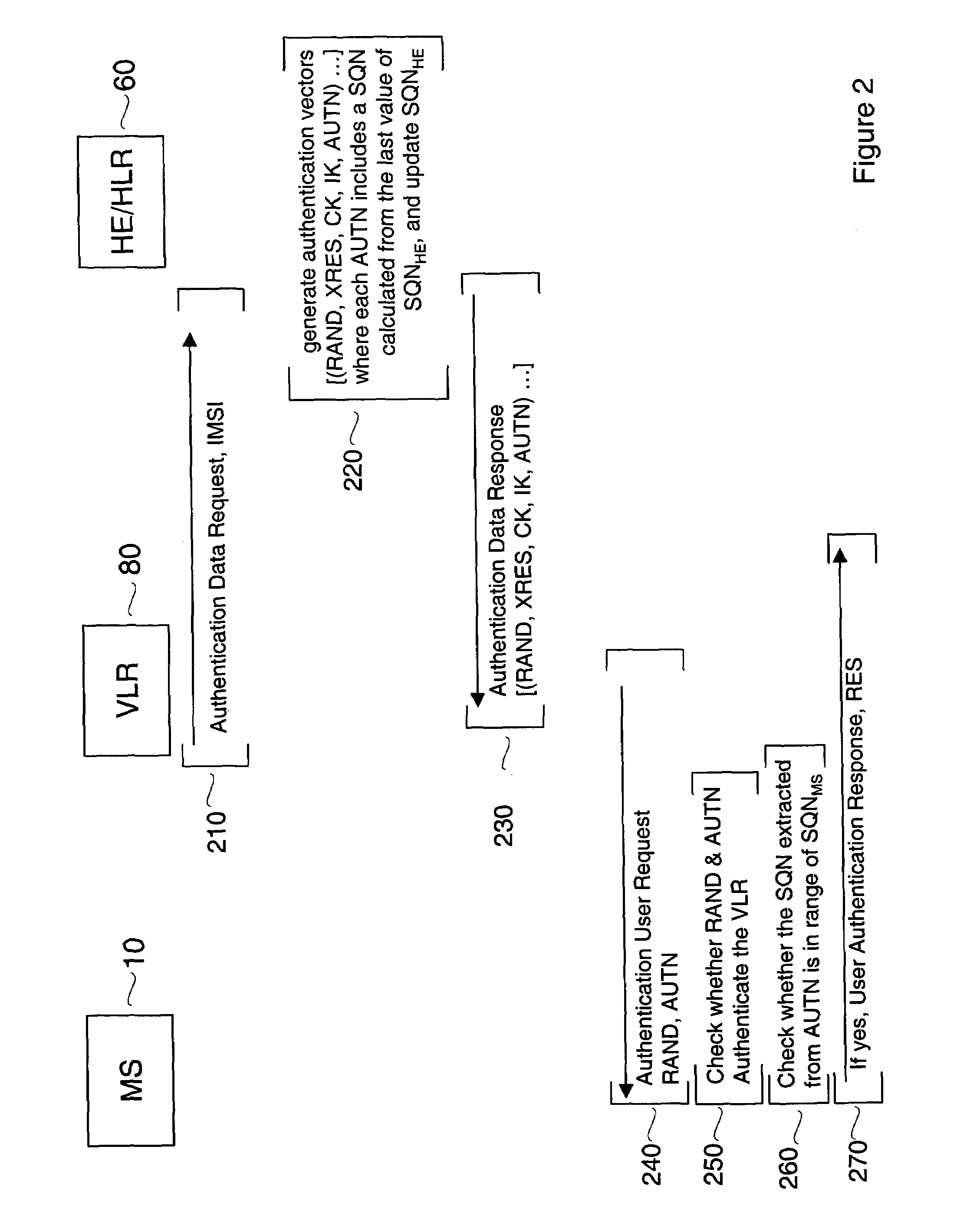
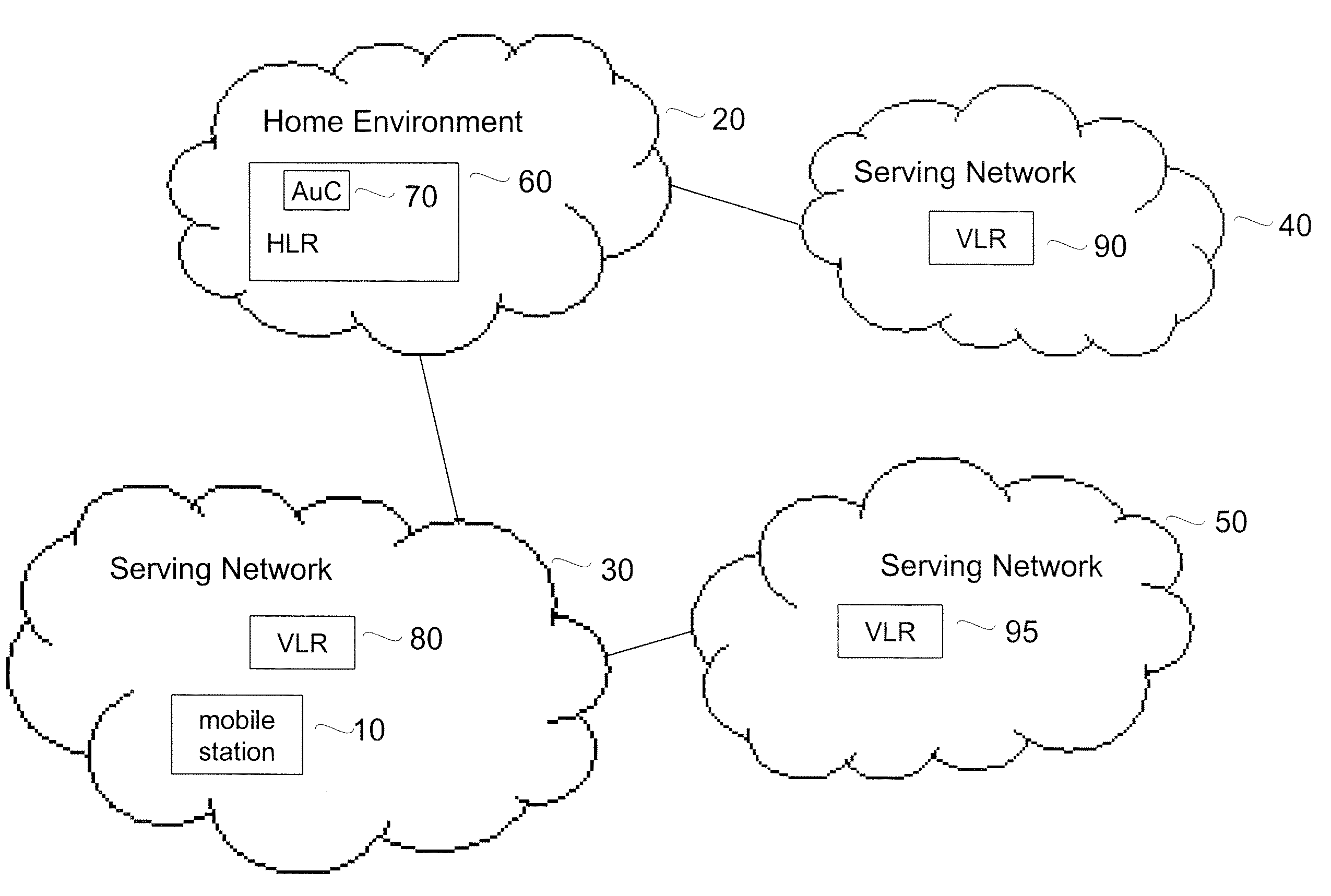
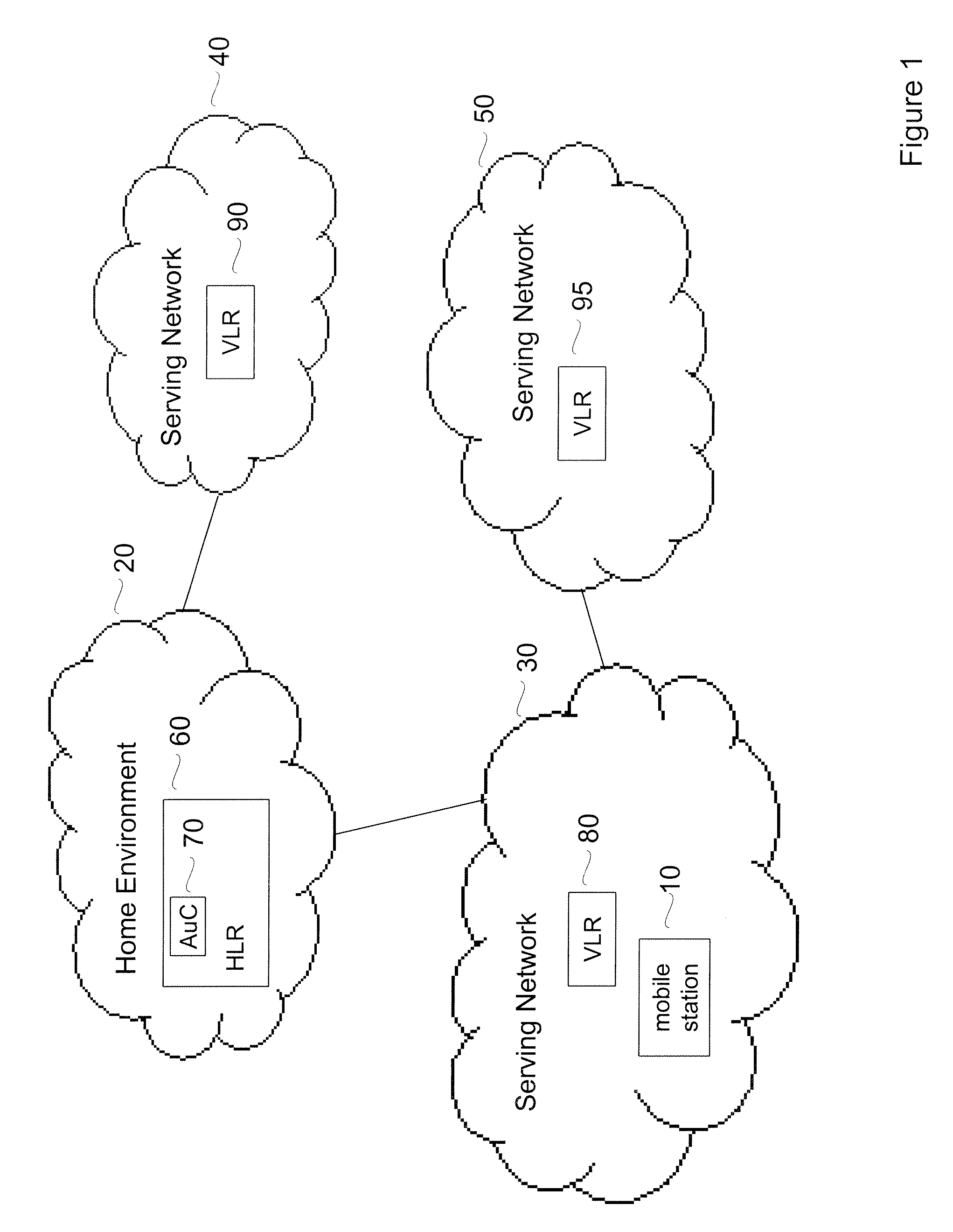
ActiveUS7574599B1Reduce probabilityImprove interoperabilityUser identity/authority verificationNetwork topologiesKey-agreement protocolHome environment
Embodiments of the invention may be used to provide an authentication and key agreement protocol that is more robust against base station, replay and other attacks compared to previously known systems. The nonce-based authentication and key agreement protocol provides security against such attacks while avoiding the problems that arise in systems that use sequence number counters on the home environment and mobile station-sides. In an embodiment, a nonce that is transmitted from the user to the home environment through the serving network, as well as subsequent values for the nonce that are derived from the initial nonce, are used as indices for authentication vectors.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Aaa Support for Dhcp
InactiveUS20080282325A1Minimum of backward compatibility problemFlexible useDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationKey-agreement protocolClient-side
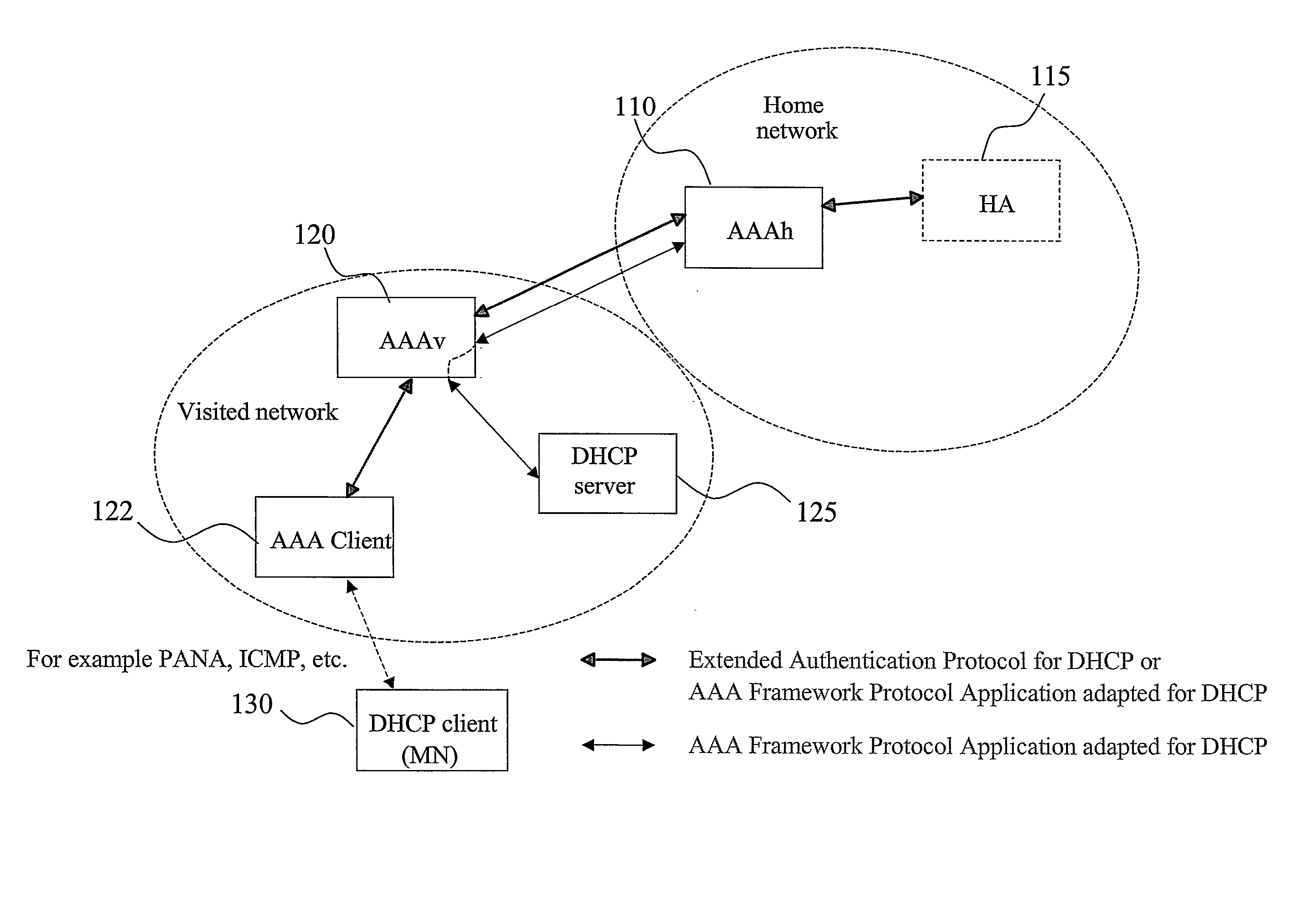
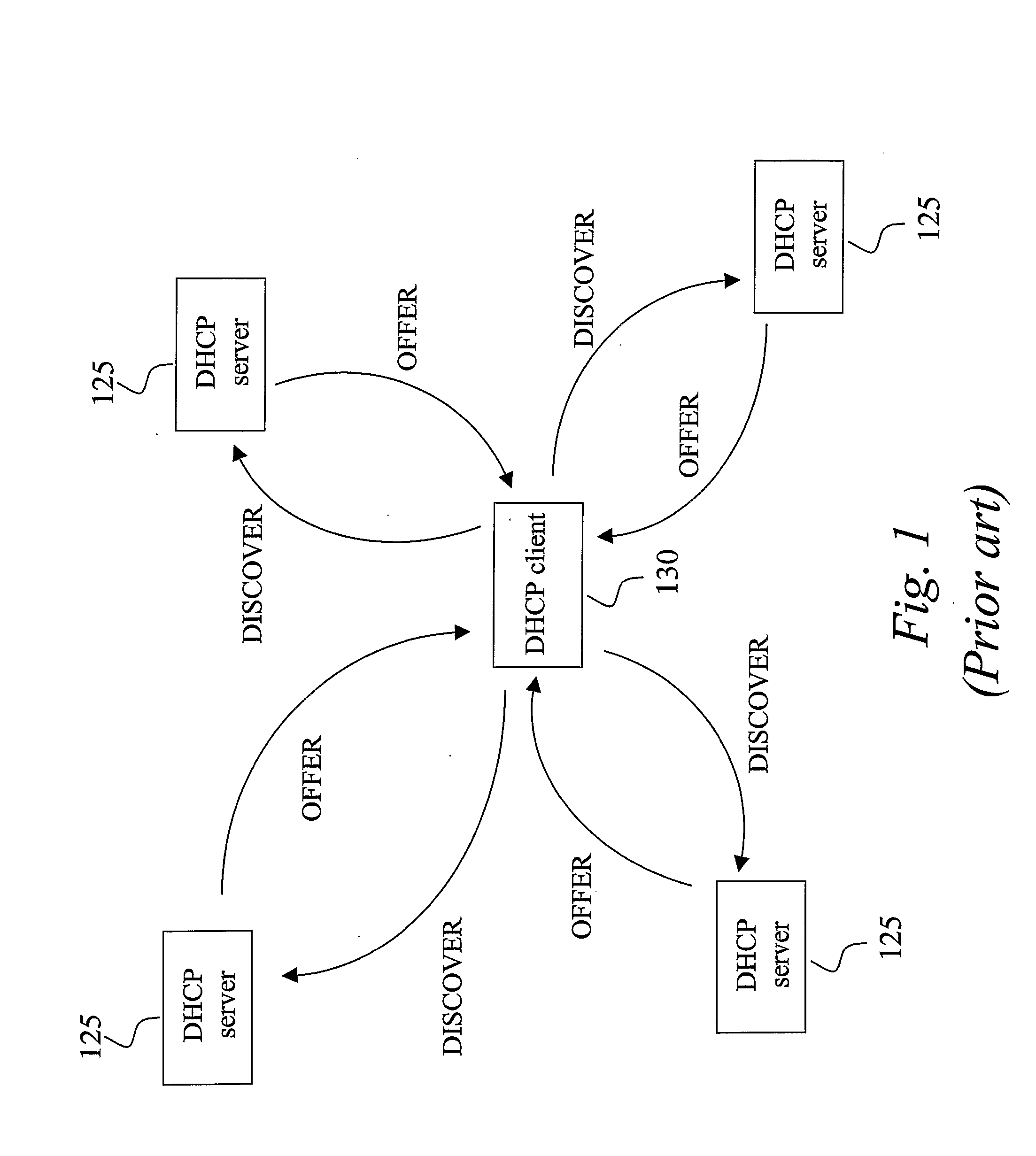
A basic idea is to use the AAA infrastructure to assign (S3) an appropriate DHCP server to DHCP client for the DHCP service, and transferring DHCP-related information over the AAA infrastructure for authenticating (S1) and authorizing (S4) the DHCP client for DHCP service with the assigned DHCP server. Instead of the more complex DHCP server discovery process known from the prior art, the AAA infrastructure, and more particularly a suitable AAA server or equivalent AAA component, is used for assigning an appropriate DHCP server to the DHCP client. Consequently, there is no longer any mandatory dependency on the DHCP discovery-related messages. The invention preferably provides AAA protocol support for facilitating assignment of appropriate DHCP servers and providing an out-of-band key agreement protocol for DHCP clients and servers by carrying DHCP related information facilitating the bootstrapping of DHCP authentication extension (RFC3118).
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
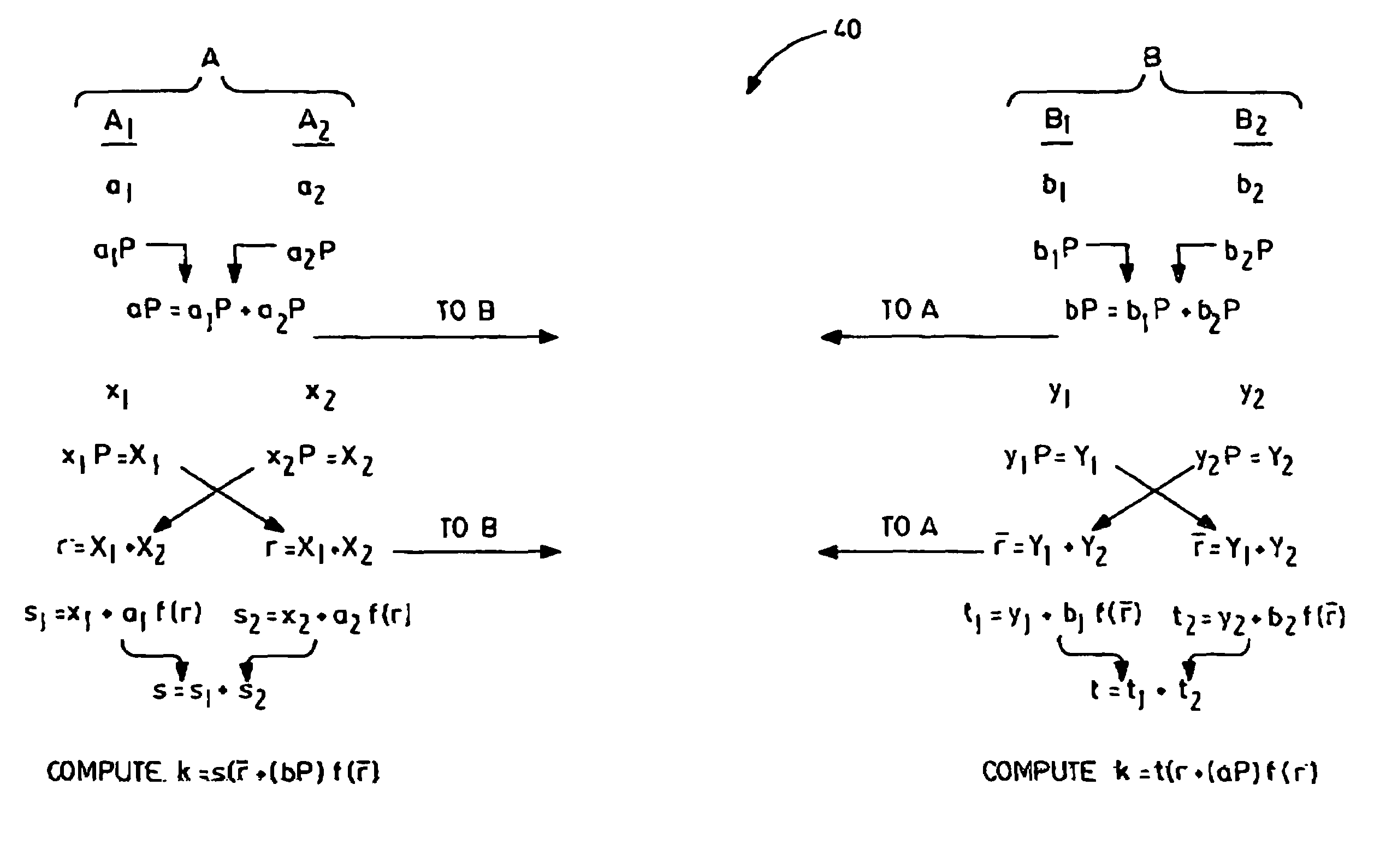
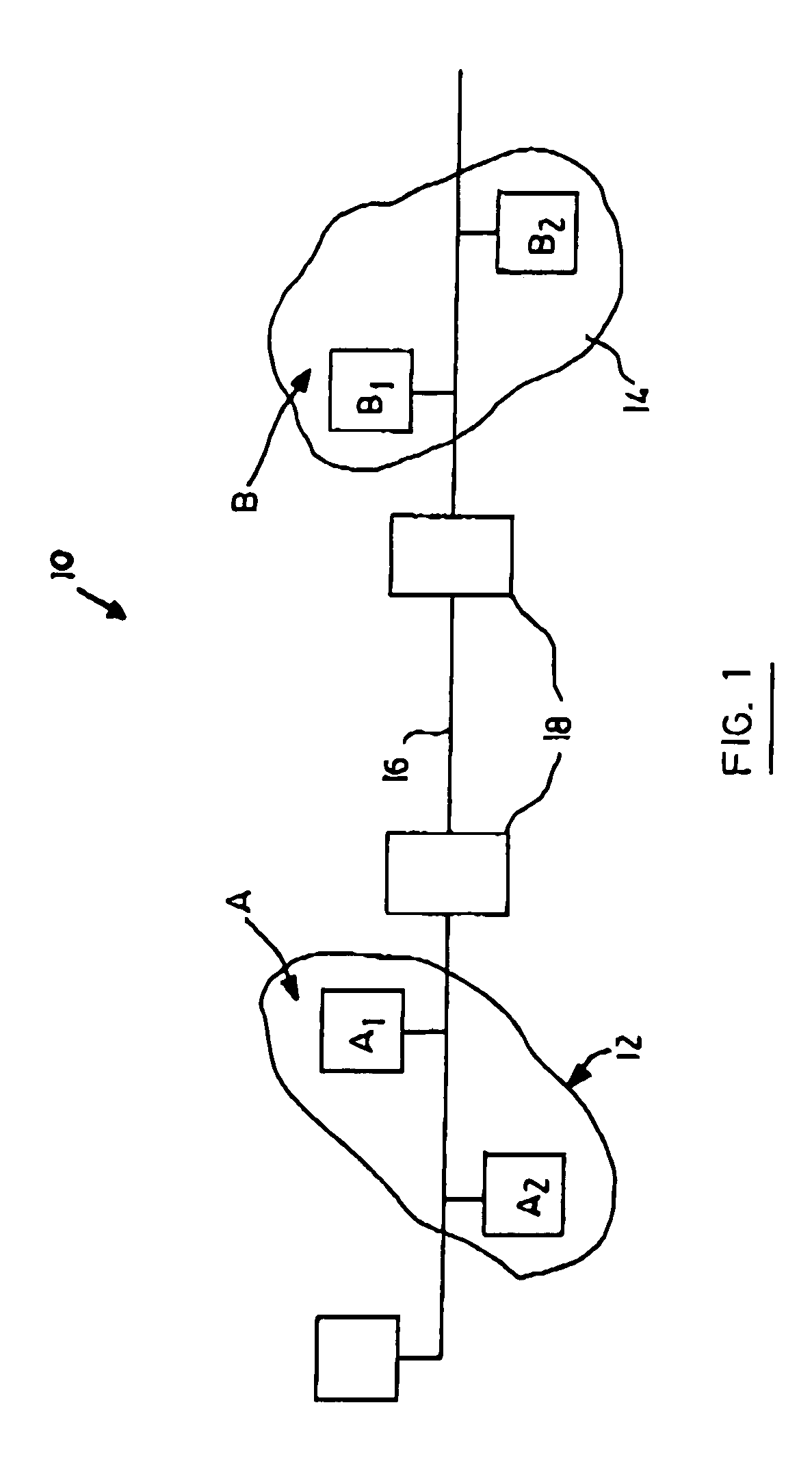
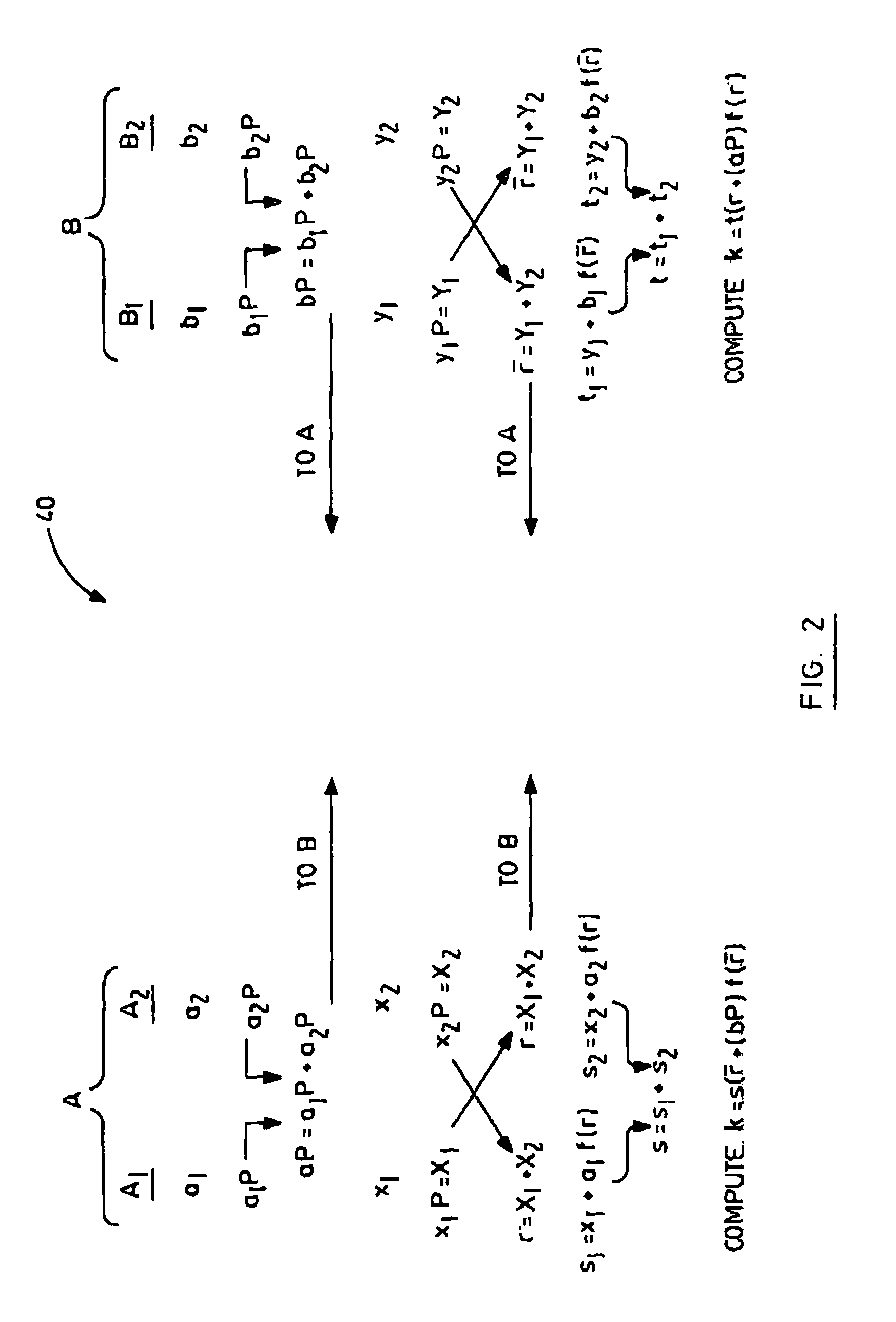
Split-key key-agreement protocol
InactiveUS6934392B1Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationCommunications systemKey-agreement protocol
This invention relates to a method for generating a shared secret value between entities in a data communication system, one or more of the entities having a plurality of members for participation in the communication system, each member having a long term private key and a corresponding long term public key. The method comprises the steps of generating a short term private and a corresponding short term public key for each of the members; exchanging short term public keys of the members within an entity. For each member then computing an intra-entity shared key by mathematically combining the short term public keys of each the members computing an intra-entity public key by mathematically combining its short-term private key, the long term private key and the intra-entity shared key. Next, each entity combines intra-entity public keys to derive a group short-term Si public key; each entity transmitting its intra-entity shared key and its group short term public key to the other entities; and each entity computing a common shared key K by combining its group short term public key (Si), with the intra-entity shared key ({overscore (X)}i), and a group short term public ({overscore (S)}i) key received from the other entities.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Pseudonym-based anonymous authentication and key negotiation optimization method and optimized authentication analysis method for Internet of Things
ActiveCN106657124AAchieve non-traceabilityAvoid attackTransmissionKey-agreement protocolThe Internet
The invention provides a pseudonym-based anonymous authentication and key negotiation optimization method and optimized authentication analysis method for the Internet of Things. The method comprises the following steps: S1, a user and a sensor node separately register a gateway node, and for the difference of the user and the sensor node, a user registration protocol and a sensor node registration protocol different from each other are adopted; and S2, after the registration, the user logs in the system through a user login protocol and an authentication and key negotiation protocol, and under the assistance of the gateway node, the sensor node requiring access realizes mutual authentication and a negotiation shared session key. By adoption of the method provided by the invention, better anonymity, non-traceability and security are realized.
Owner:YICHUN UNIVERSITY
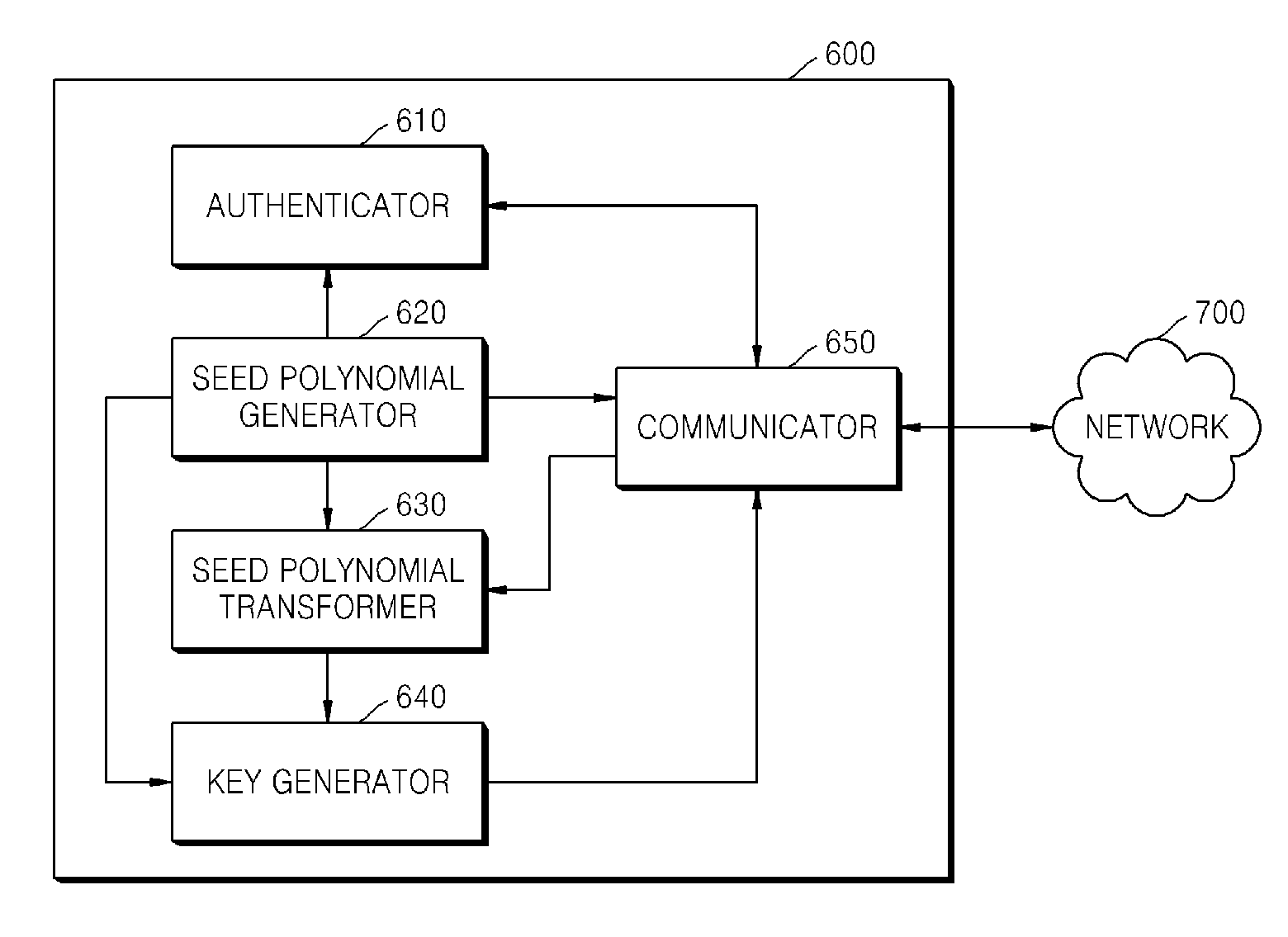
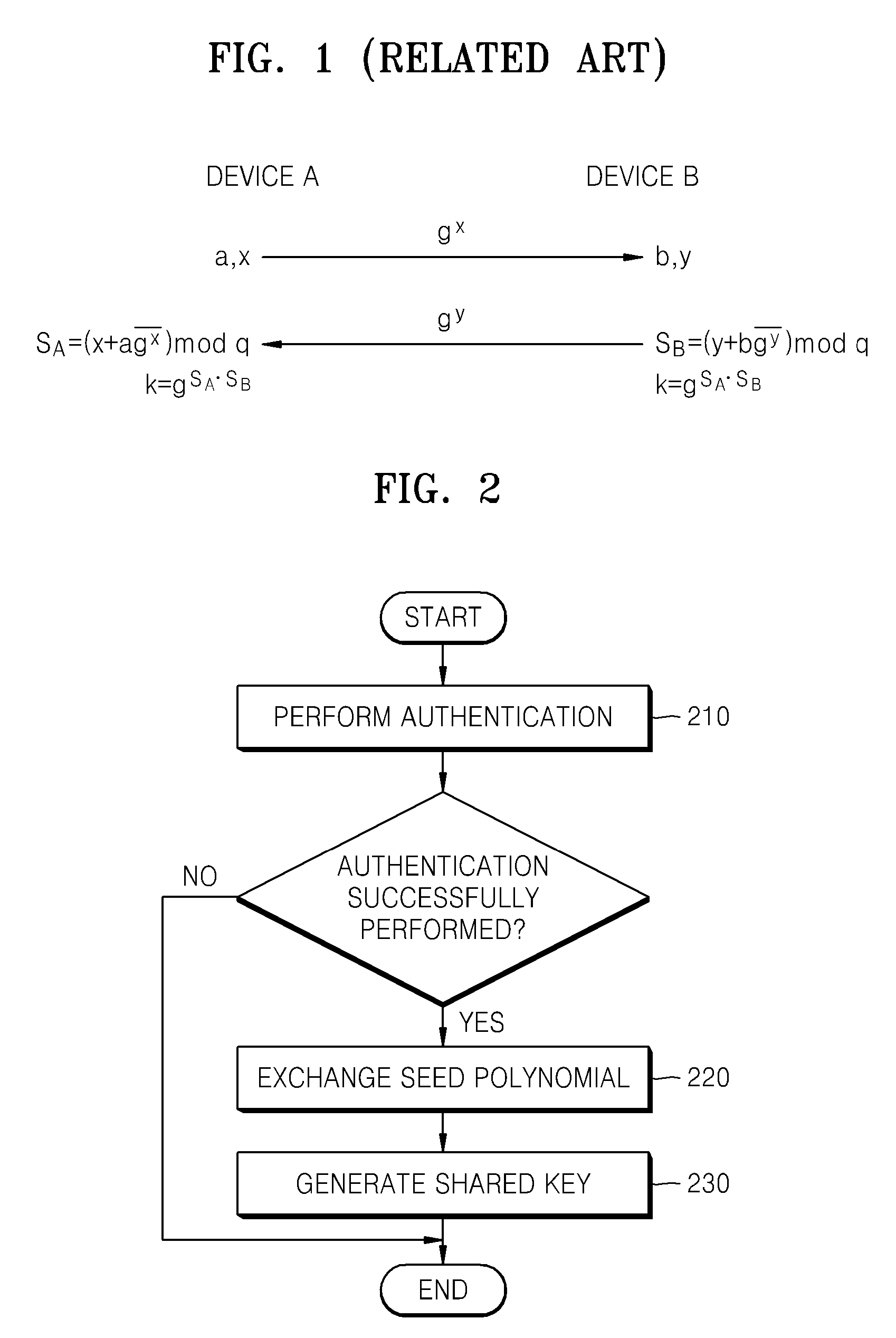
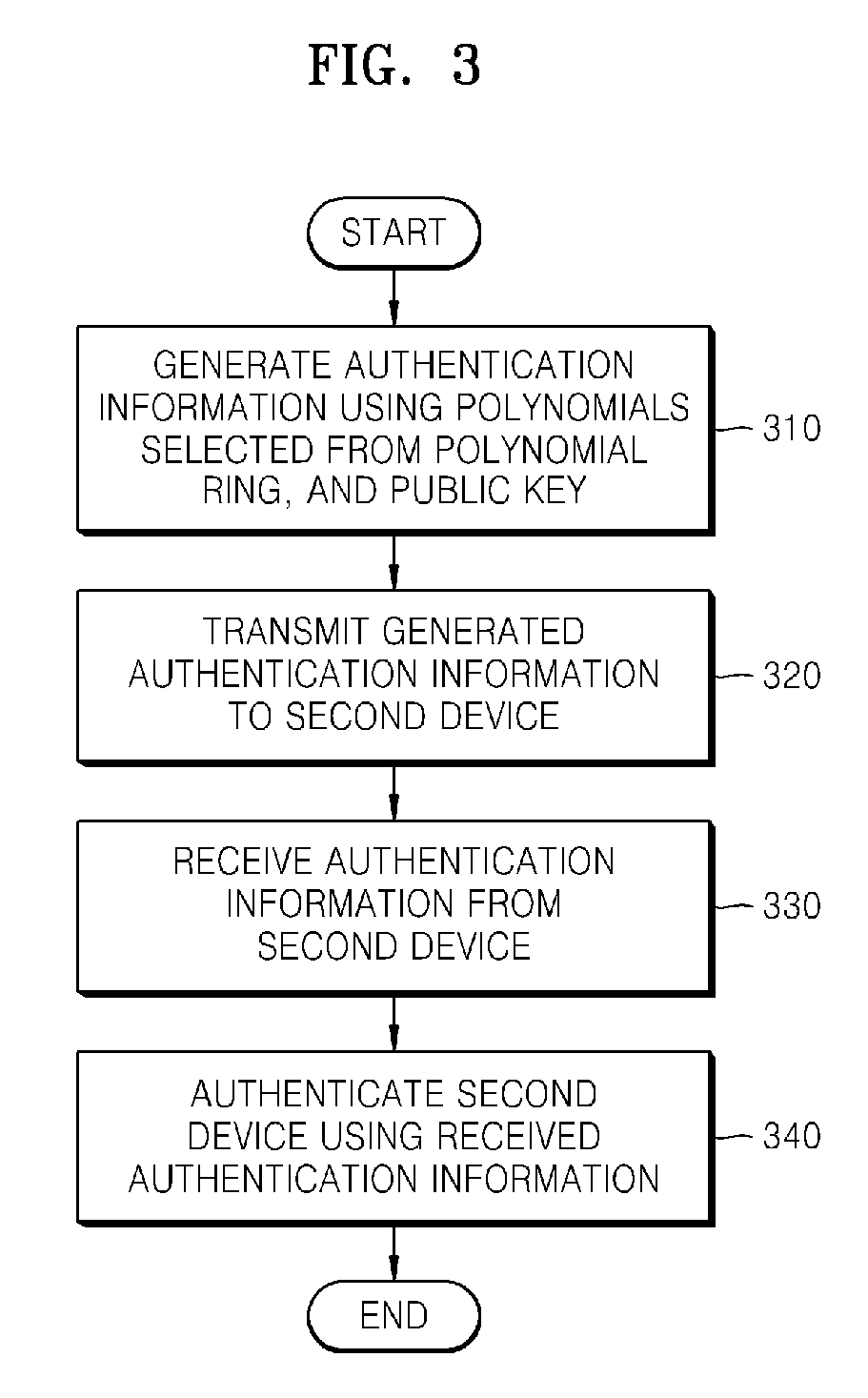
Method and apparatus for key agreement between devices using polynomial ring
InactiveUS20080069344A1Improve securitySynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesPublic key for secure communicationAuthenticated key agreement protocolKey-agreement protocol
Provided is a method of key agreement between devices. Using the method, two devices on a network can exchange information using polynomials of a polynomial ring, authenticate each other using the exchanged information, and generate a shared key. Accordingly, an authenticated key agreement protocol, which has better security and a faster processing speed than a conventional encoding system, can be realized.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for managing network key and updating session key
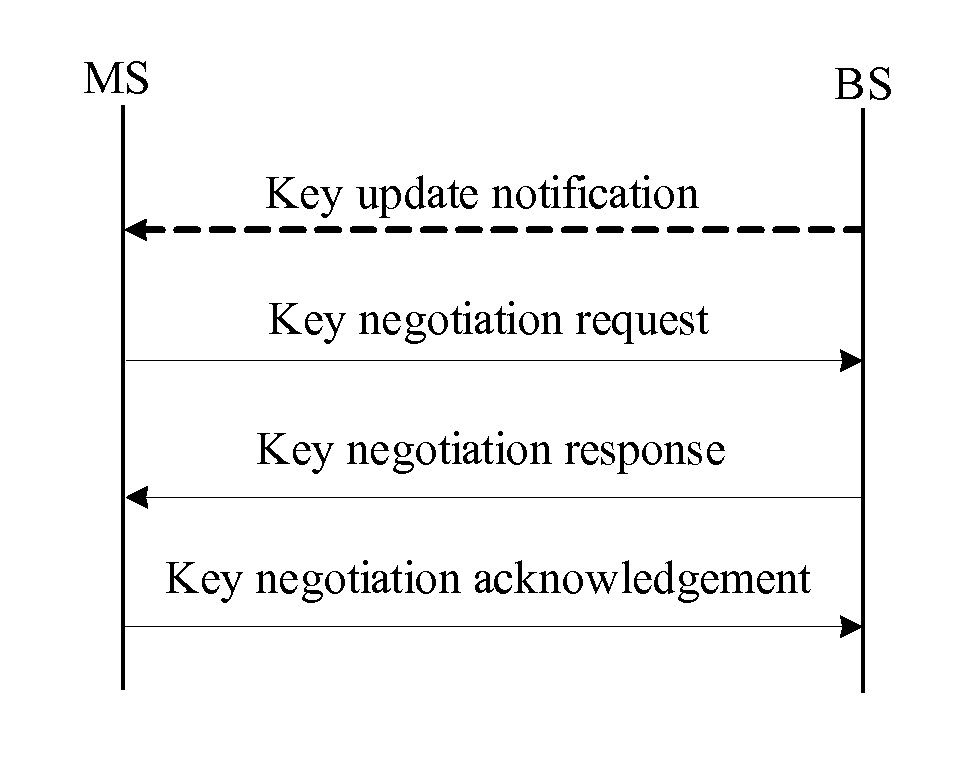
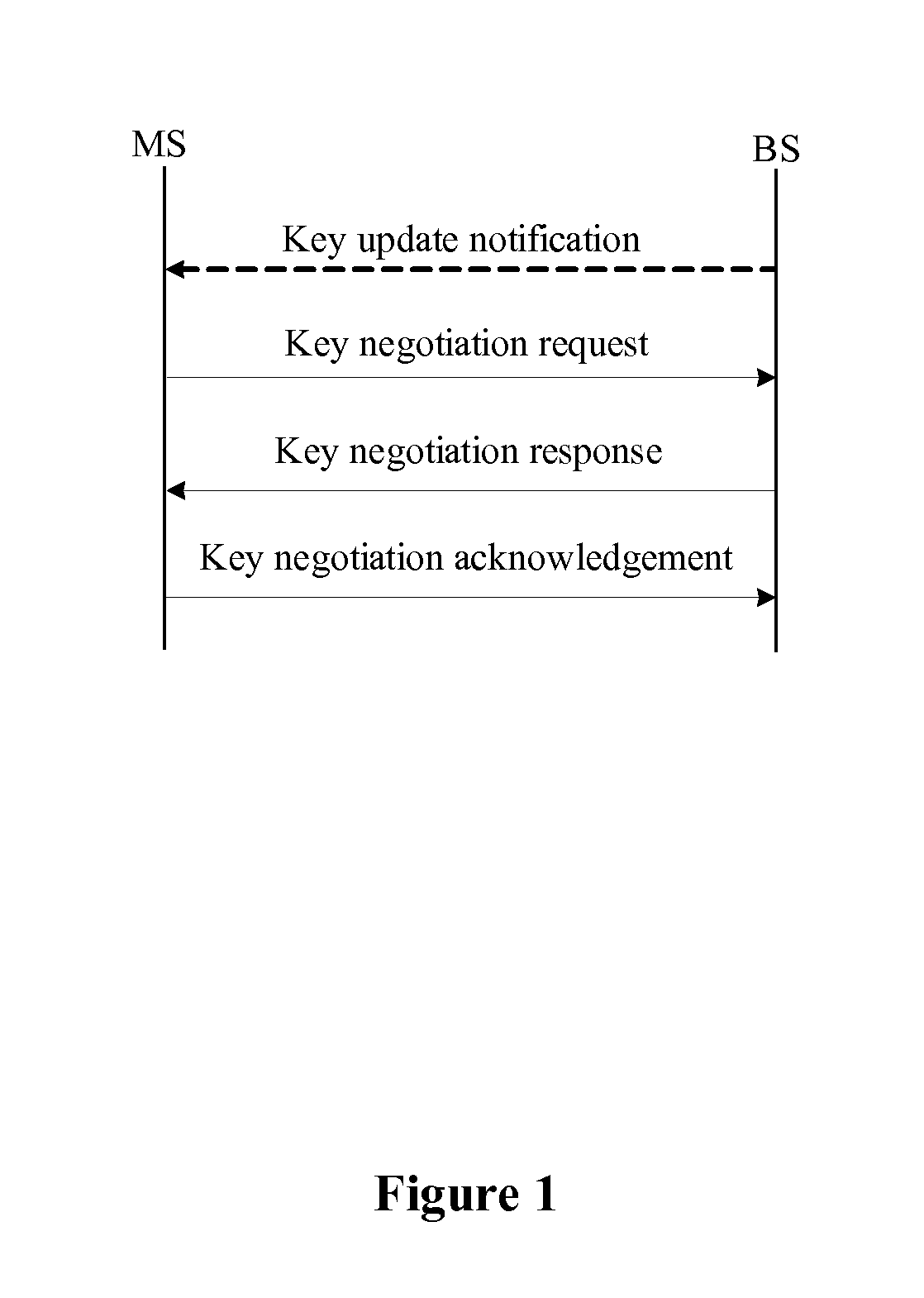
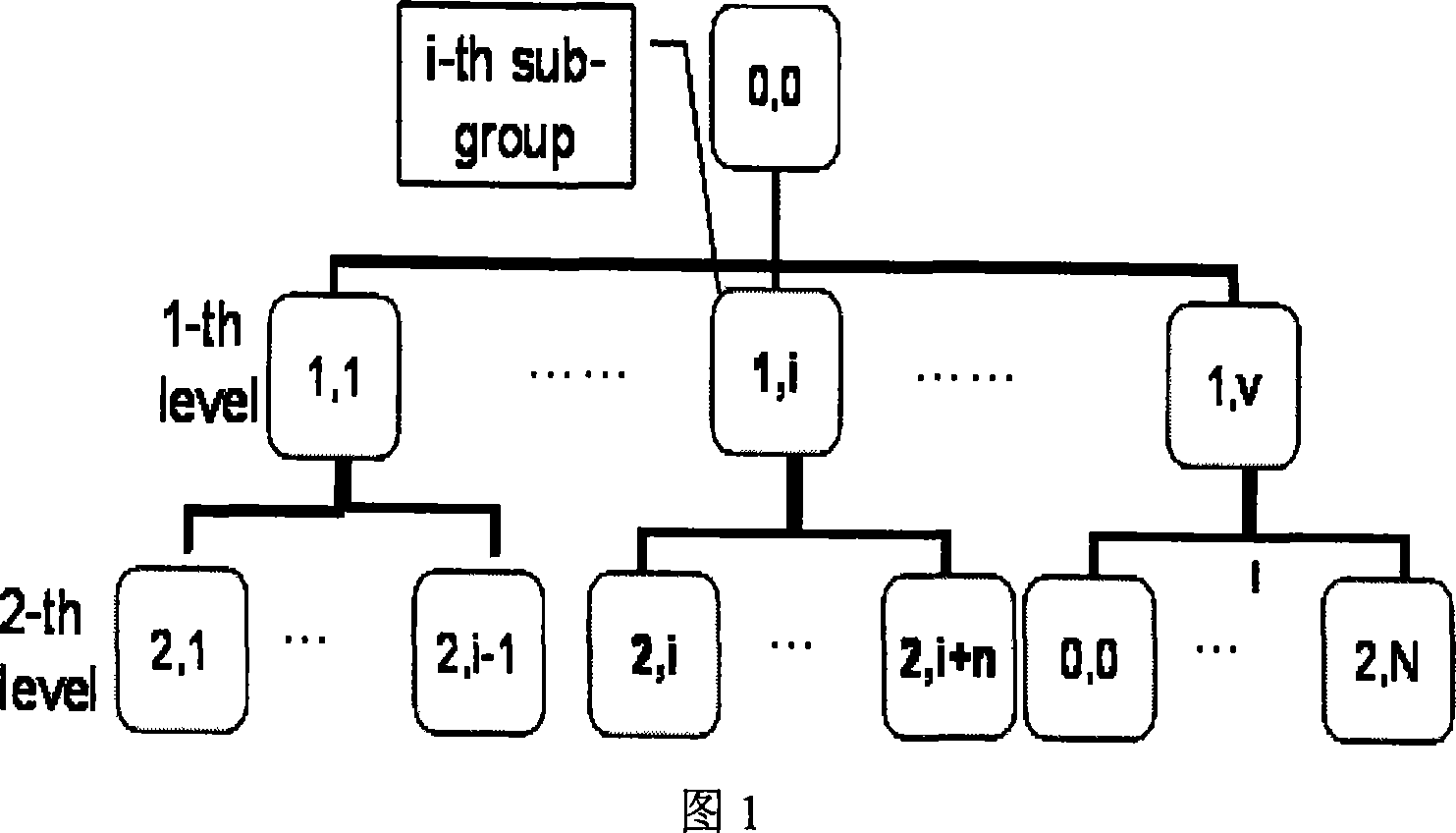
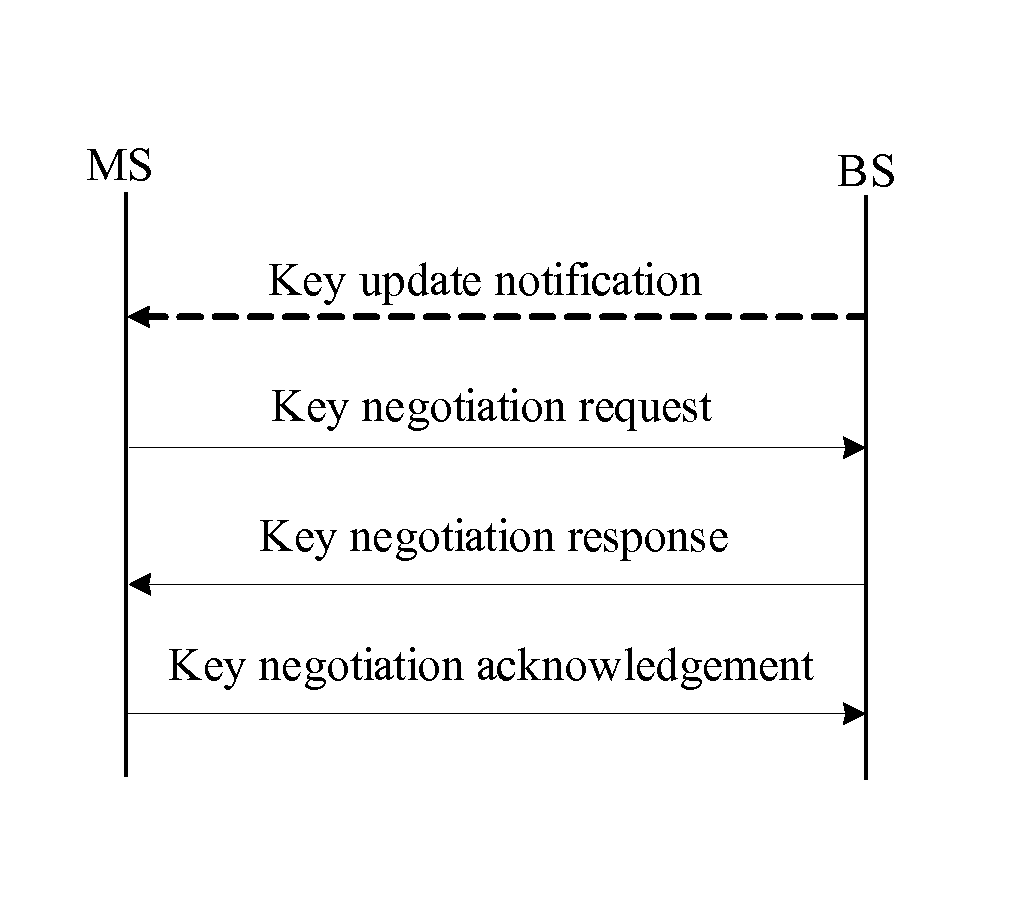
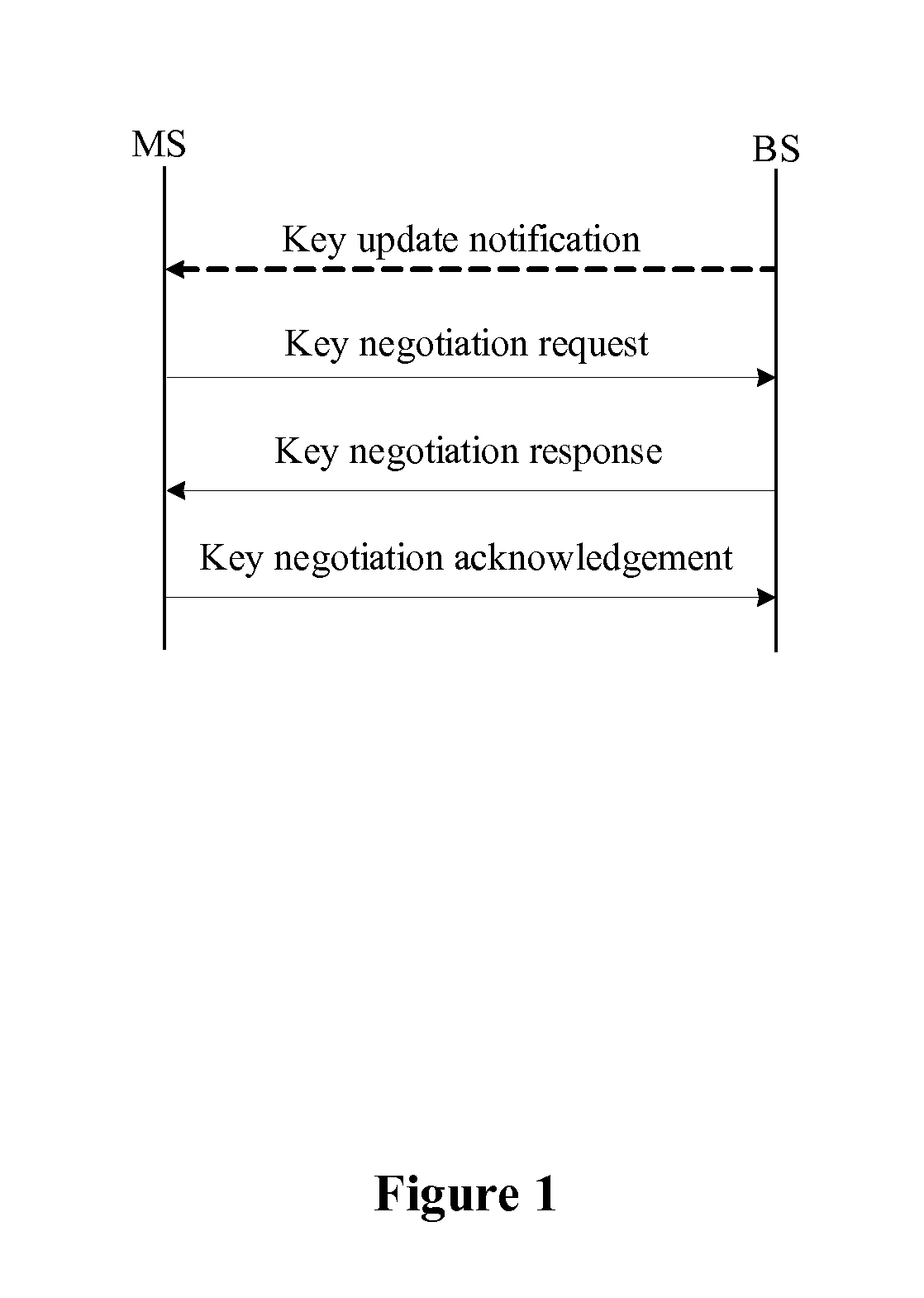
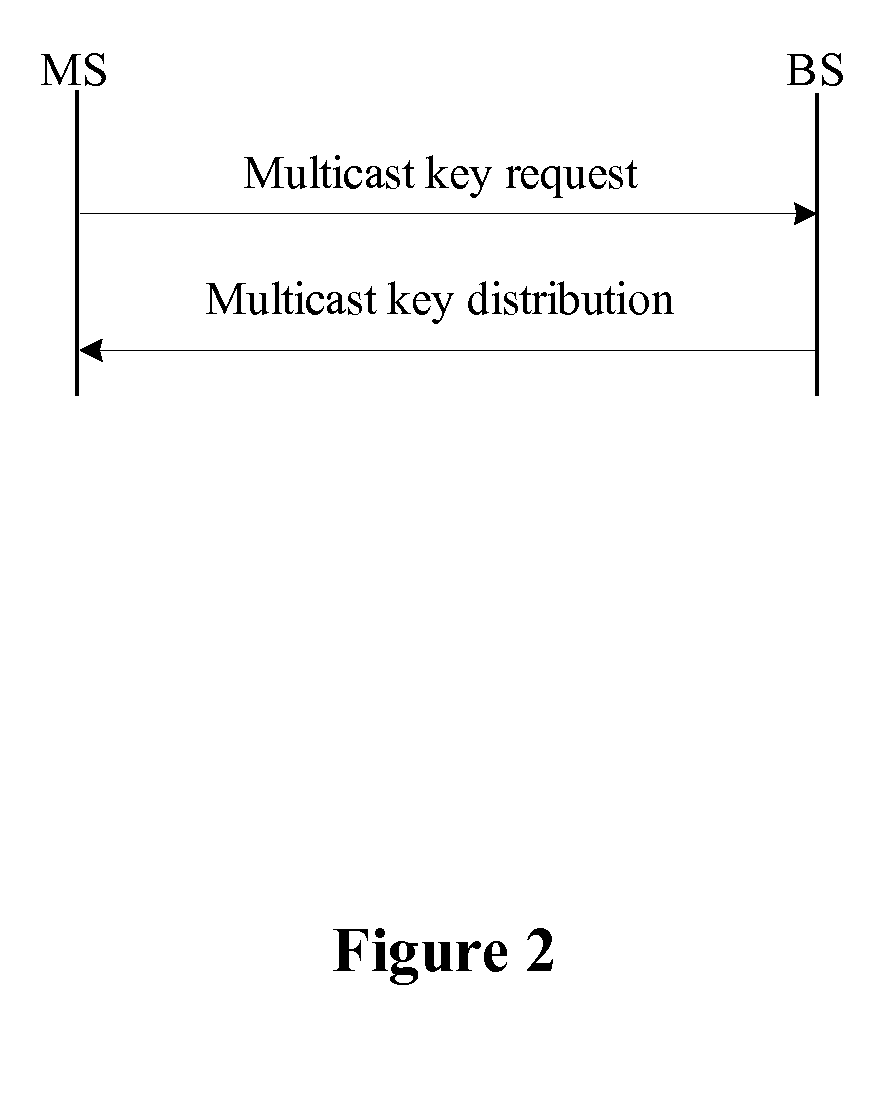
ActiveUS20090300358A1Improve performanceSimplifies state managementKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesKey-agreement protocolNetwork key
A method for managing network key and updating session key is provided. The step of the key management includes: constructing key request group, constructing key negotiation response group, and constructing key negotiation acknowledgement group. The step of multicasting key management method includes multicasting main key negotiation protocol and multicasting session key distribution protocol. The multicasting main key negotiation protocol comprises key updating informs group, constructing encryption key negotiation request group, constructing key negotiation response group and constructing key negotiation acknowledgement group. The multicasting session key distribution protocol comprises multicasting session key request and multicasting session key distribution.
Owner:CHINA IWNCOMM
Secure key management in multimedia communication system
ActiveUS8850203B2Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageCommunications systemAuthenticated key agreement protocol
Principles of the invention provide one or more secure key management protocols for use in communication environments such as a media plane of a multimedia communication system. For example, a method for performing an authenticated key agreement protocol, in accordance with a multimedia communication system, between a first party and a second party comprises, at the first party, the following steps. Note that encryption / decryption is performed in accordance with an identity based encryption operation. At least one private key for the first party is obtained from a key service. A first message comprising an encrypted first random key component is sent from the first party to the second party, the first random key component having been computed at the first party, and the first message having been encrypted using a public key of the second party. A second message comprising an encrypted random key component pair is received at the first party from the second party, the random key component pair having been formed from the first random key component and a second random key component computed at the second party, and the second message having been encrypted at the second party using a public key of the first party. The second message is decrypted by the first party using the private key obtained by the first party from the key service to obtain the second random key component. A third message comprising the second random key component is sent from the first party to the second party, the third message having been encrypted using the public key of the second party. The first party computes a secure key based on the second random key component, the secure key being used for conducting at least one call session with the second party via a media plane of the multimedia communication system.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Single interaction authenticated key agreement protocol of identity-based cryptosystem
ActiveCN106209369AReduce usageResist attackKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationCryptosystemMaster key
The invention discloses a single interaction authenticated key agreement protocol of an identity-based cryptosystem, and relates to the field of cryptography. The key agreement efficiency can be effectively enhanced and the interaction frequency can be reduced. The solving technical scheme is that a random number is self-selected through combination of an opposite side public key and an own side private key, and a session key of both communication sides is constructed through bilinear operation and Hash operation. The single interaction authenticated key agreement protocol of the identity-based cryptosystem comprises the following steps that 1) a PKG generates system parameters and generates and distributes corresponding private keys to all the hosts in a local domain; and 2) a client side initiates a key agreement request to a server side and transmits key information, and generates the session key according to the algorithm and stores the session key. Natural binding of the identity and the public key is completed based on the identity-based cryptographic technology so that use of a certificate can be avoided; a master key and a temporary key are combined so as to meet the known session key security, partial forward security, partial key resistant disguise leaking, unknown key resistant sharing, message independence and known session temporary secret information security and resist the man-in-the-middle attack; and operation is easy and convenient and the computational complexity is low.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Split-key key-agreement protocol
InactiveUS20060123235A1Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationCommunications systemKey-agreement protocol
This invention relates to a method for generating a shared secret value between entities in a data communication system, one or more of the entities having a plurality of members for participation in the communication system, each member having a long term private key and a corresponding long term public key. The method comprises the steps of generating a short term private and a corresponding short term public key for each of the members; exchanging short term public keys of the members within an entity. For each member then computing an intra-entity shared key by mathematically combining the short term public keys of each the members computing an intra-entity public key by mathematically combining its short-term private key, the long term private key and the intra-entity shared key. Next, each entity combines intra-entity public keys to derive a group short-term Si public key; each entity transmitting its intra-entity shared key and its group short term public key to the other entities; and each entity computing a common shared key K by combining its group short term public key (Si), with the intra-entity shared key ({overscore (X)}i), and a group short term public ({overscore (S)}i) key received from the other entities.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Robust Authentication and Key Agreement Protocol for Net-Generation Wireless networks
ActiveUS20090267730A1Reduce probabilityImprove interoperabilityProgramme controlElectric signal transmission systemsKey-agreement protocolHome environment
Embodiments of the invention may be used to provide an authentication and key agreement protocol that is more robust against base station, replay and other attacks compared to previously known systems. The nonce-based authentication and key agreement protocol provides security against such attacks while avoiding the problems that arise in systems that use sequence number counters on the home environment and mobile station-sides. In an embodiment, a nonce that is transmitted from the user to the home environment through the serving network, as well as subsequent values for the nonce that are derived from the initial nonce, are used as indices for authentication vectors.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
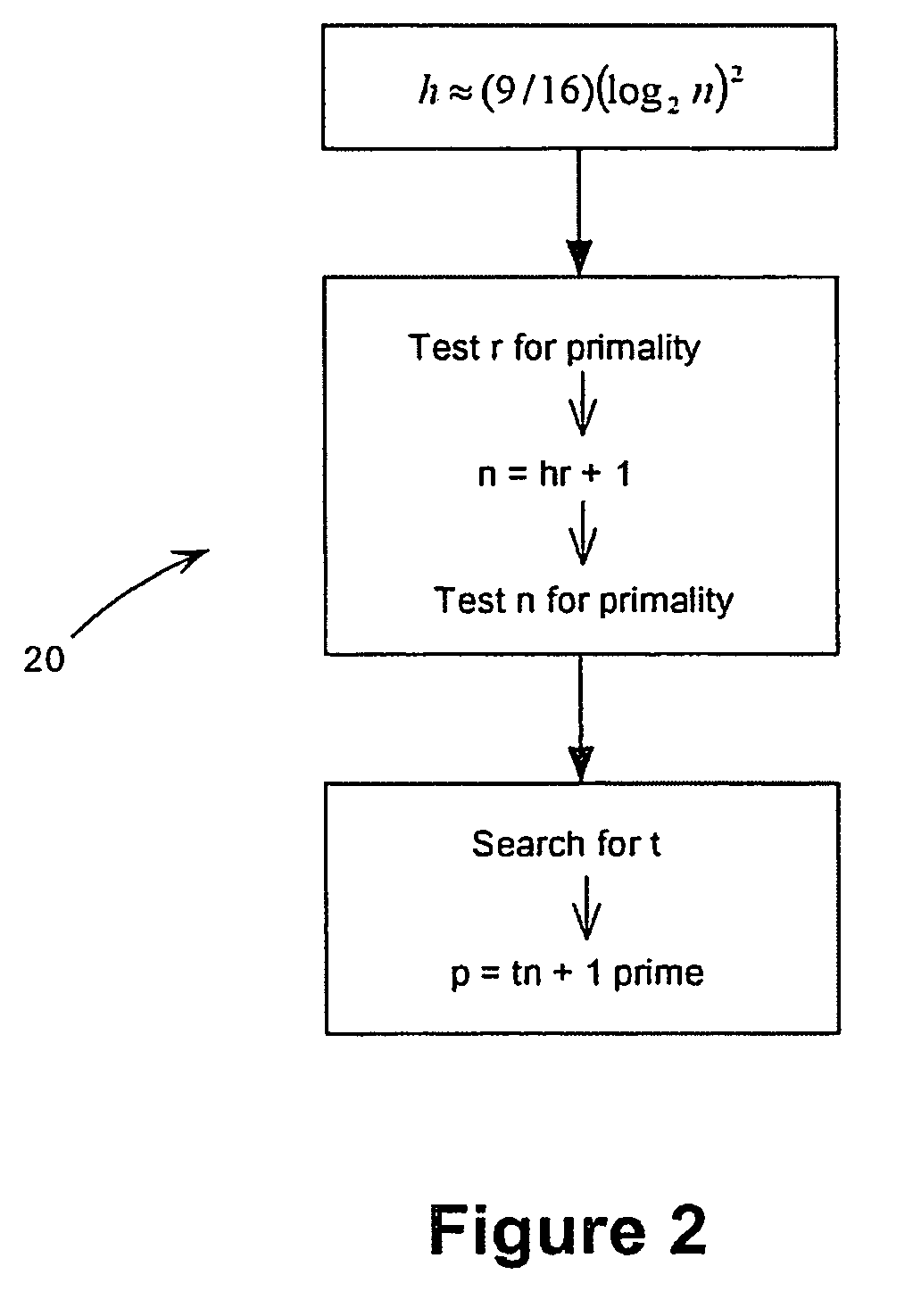
Custom static Diffie-Hellman groups
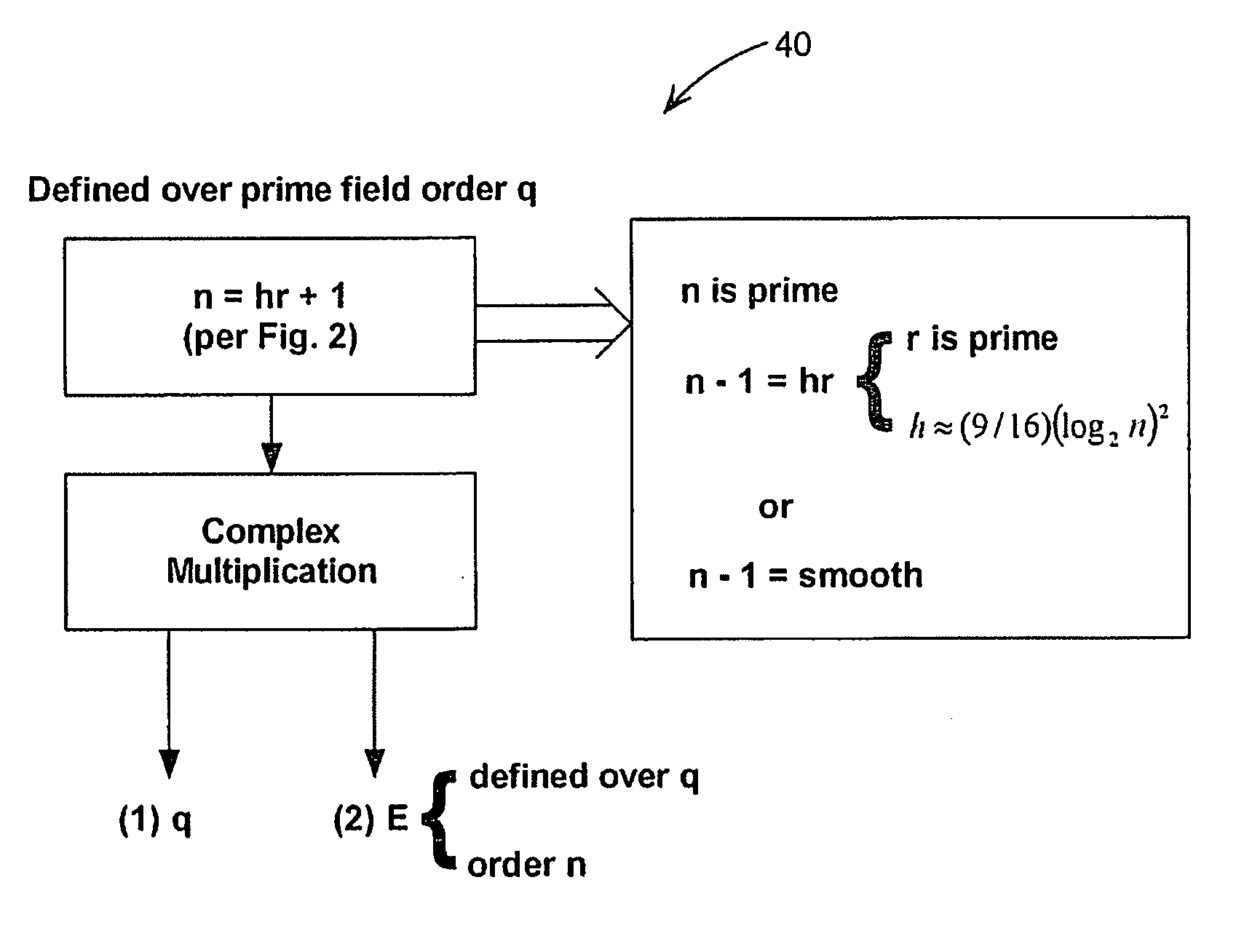
ActiveUS20070071237A1Inhibit active attackAvoid attackPublic key for secure communicationSecret communicationKey-agreement protocolComputer science
Methods for choosing groups for a static Diffie-Hellman key agreement protocol to inhibit active attacks by an adversary are provided. In mod p groups, an even h is chosen of value approximately (9 / 16)(log2n)2, values r and n are determined using sieving and primality testing on r and n, and a value t is found to compute p=tn+1 wherein p is prime. In elliptic curve groups defined over a binary filed, a random curve is chosen, the number of points on the curve is counted and this number is checked for value of 2n wherein n is prime and n−1 meets preferred criteria. In elliptic curve groups defined over a prime field of order q, a value n=hr+1 is computed, wherein n is prime and n−1 meets preferred criteria, and a complex multiplication method is applied on n to produce a value q and an elliptic curve E defined over q and having an order n.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
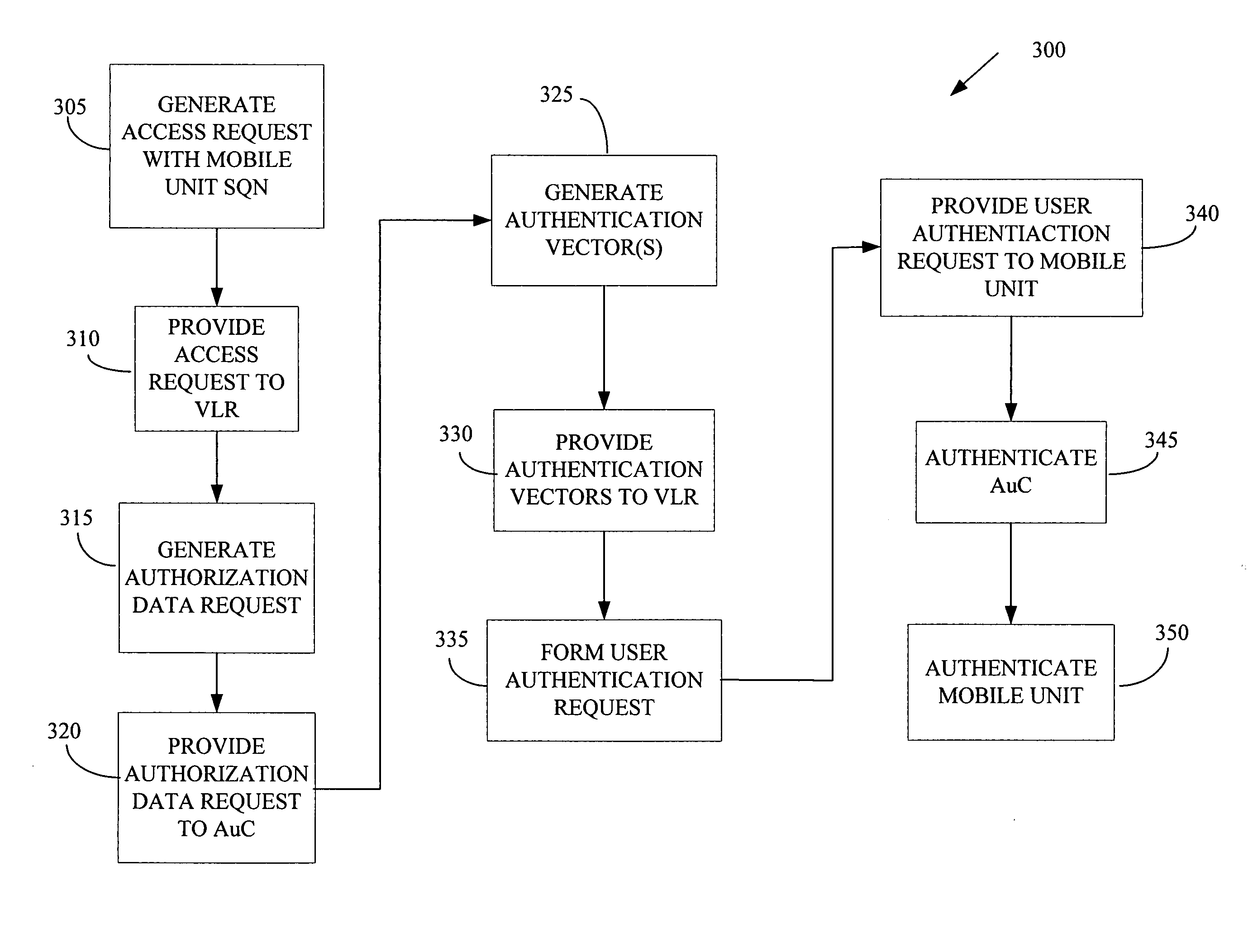
Self-synchronizing authentication and key agreement protocol
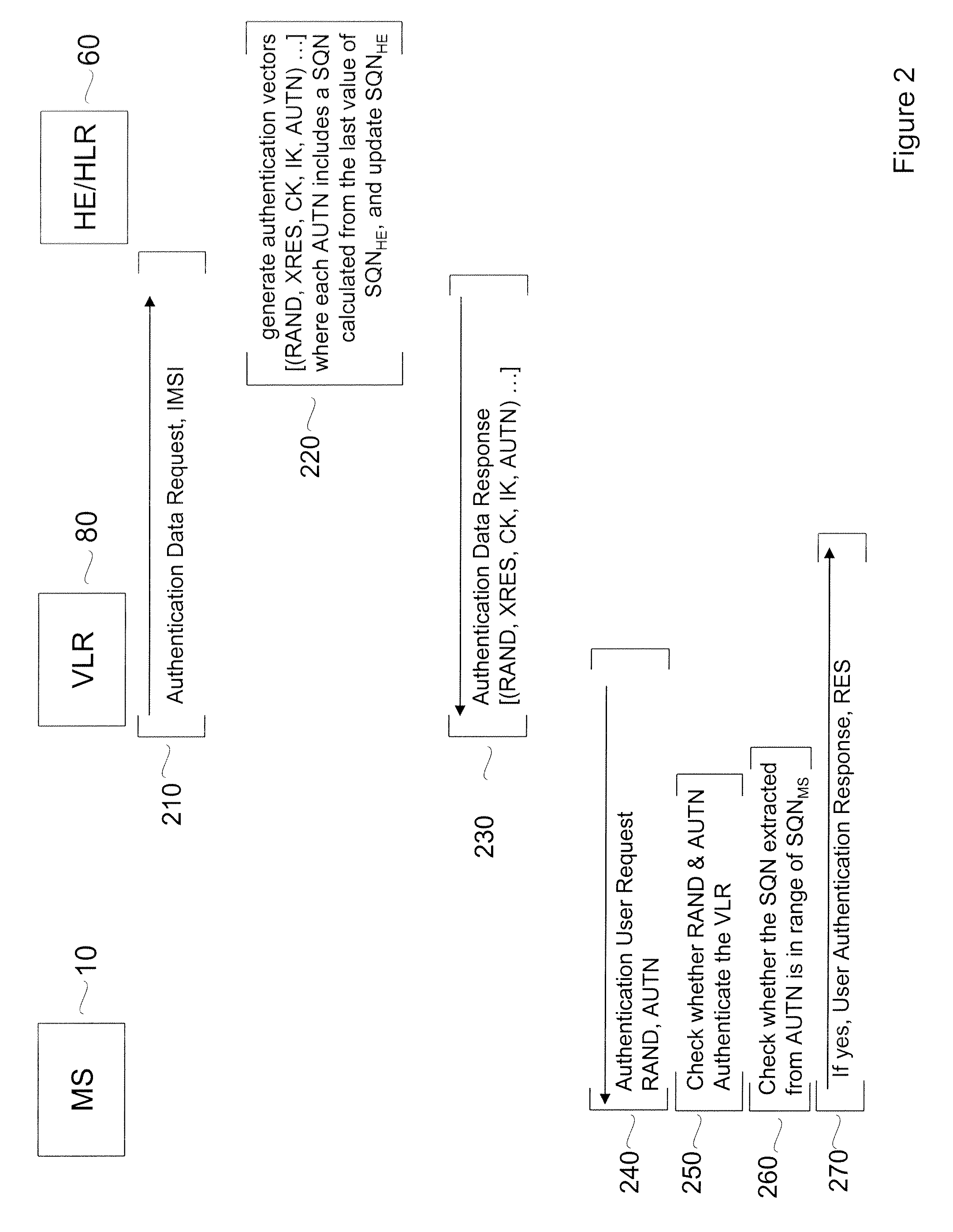
ActiveUS20050272406A1Key distribution for secure communicationUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionAKAKey-agreement protocol
The present invention provides a method of wireless communication with at least one mobile unit and at least one authentication center in a wireless telecommunications network. The method includes generating at least one access request based upon at least one first sequence number associated with the mobile unit and receiving at least one message formed based upon the access request, the message including at least one second sequence number associated with the authentication center, the second sequence number selected to be acceptable to the mobile unit.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Lightweight authentication and key agreement protocol applicable to electric information acquisition
InactiveCN102882688AReduce the number of interactionsResistance to asynchronous attacksUser identity/authority verificationAttackKey-agreement protocol
The invention relates to a lightweight authentication and key agreement protocol applicable to electric information acquisition. An identify authentication stage is completed on the basis of communication of a digital certificate of an authentication center of a state grid cooperation of China and a shared key. In a key agreement stage, new and old parameter protection keys which are updated dynamically are utilized, and lightweight operators are utilized for computation, and the key agreement is completed by communication circulations only. In a key updating stage, a session key group and the new and old parameter protection keys are synchronized. During key agreement, parameters are protected alternatively by the new and old parameter protection keys so that nonsynchronous attack can be resisted effectively. The protocol can be analyzed by combination of BAN logic formal analysis and informal analysis methods, can be approved to have safety attributes such as two-way entity authentication, perfect forward security and the like when reaching first-level faith and second-level faith, resists to various attacks, and can complete identify authentication and key agreement in real time effectively on the premises of security guarantee and meet requirements of an electric information acquisition system to key application.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Cross-cloud security certification system and method based on identifier
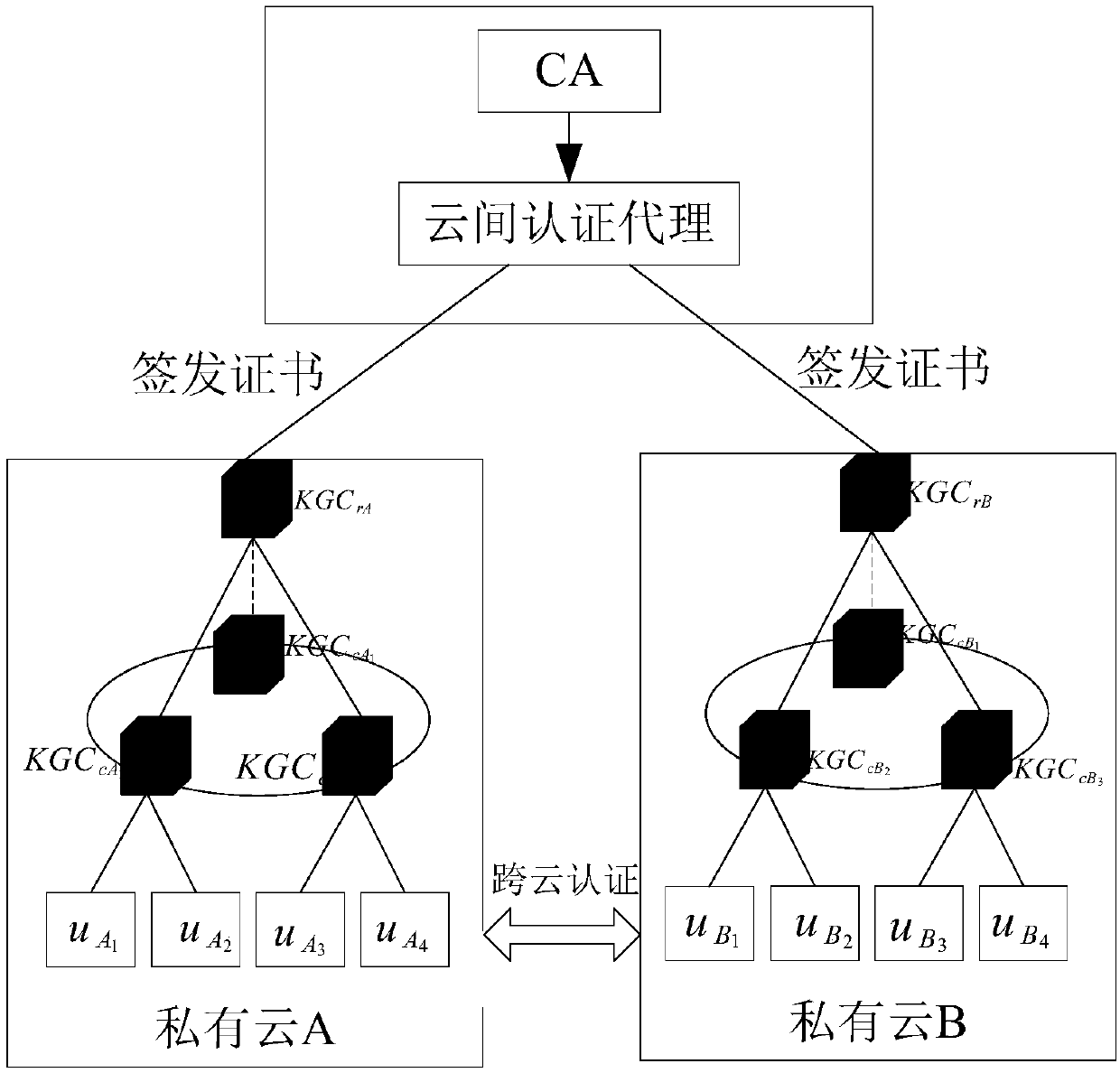
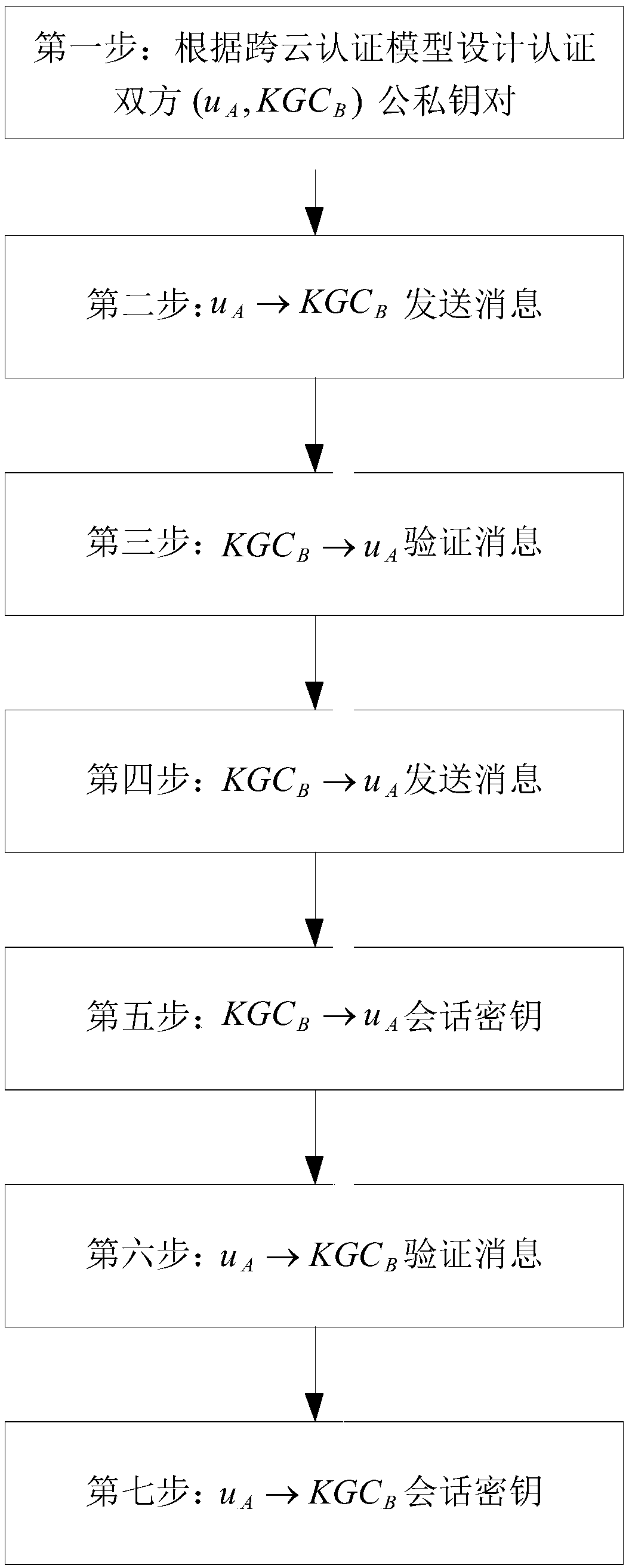
ActiveCN108667616ANot easy to attackAvoid safety hazardsKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationRound complexityComputation complexity
The invention discloses a cross-cloud security certification system and a cross-cloud security certification method based on an identifier, in order to mainly solve the problem that cloud service providers within cloud domains securely manage privacy data of users. The cross-cloud security certification system introduces a layered identifier model and adopts a shared key ring structure, so that identity identifier of the user is unique; the user can get rid of a series of complicated certificate operations, thereby expanding a large-scale cloud network environment. The cross-cloud security certification method comprises the steps of: designing public and private key pairs for the users and the cloud service providers respectively by using the cross-cloud security certification system; sending and verifying messages; and performing key agreement to achieve identifier certification of both certification sides. The cross-cloud security certification system and the cross-cloud security certification method of the invention have the beneficial effects that: a cross-cloud certification model is built and a certificateless key agreement protocol is adopted, each link has safety protection, thus security and reliability of the whole system can be ensured; in addition, a computation complexity is low, thus certification and secure access requirements on the condition that the users in acloud environment respectively belong to different cloud domains can be met, and a practical application requirement that only one-time certification is needed for different cloud domains also can bemet.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
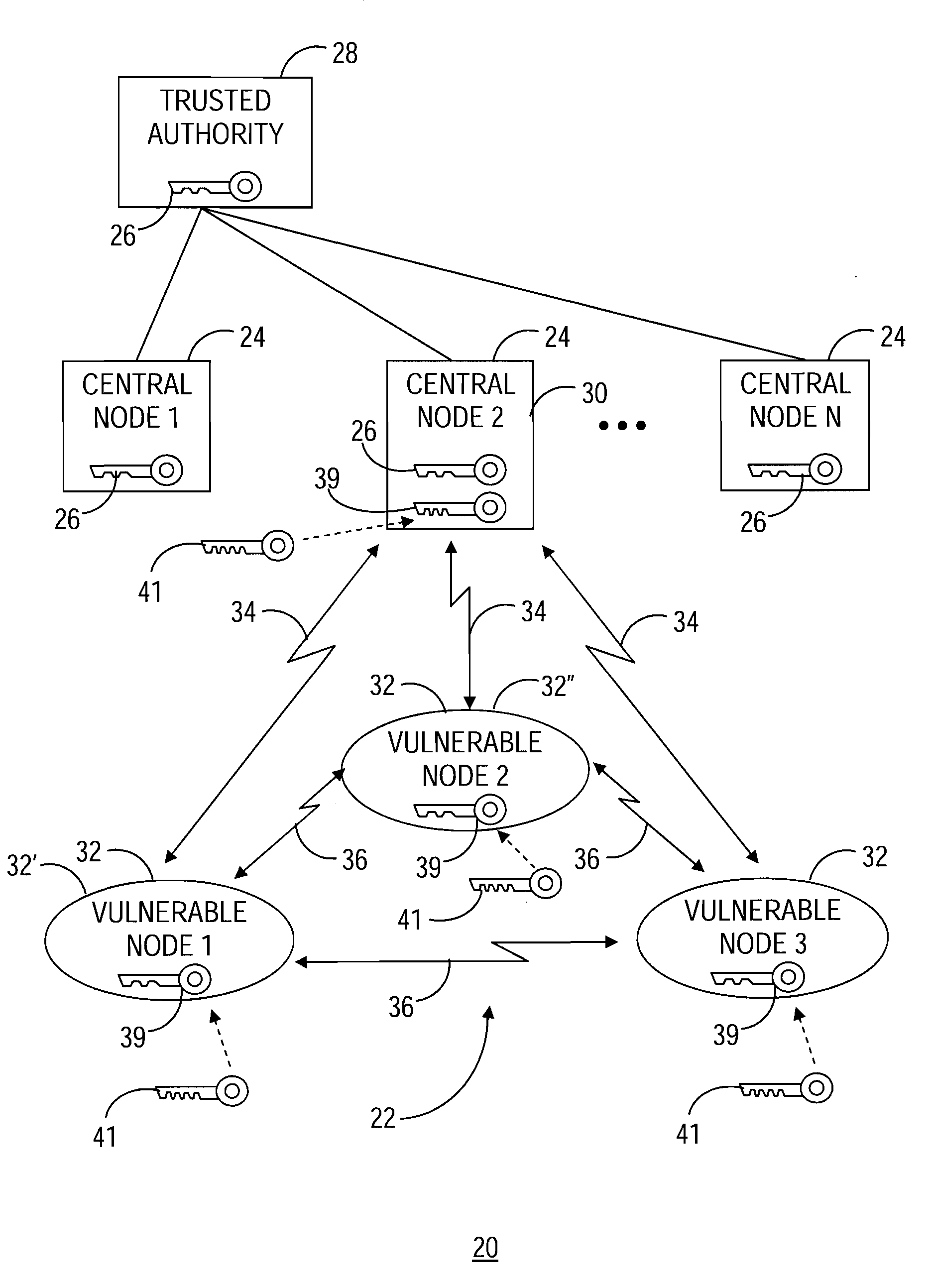
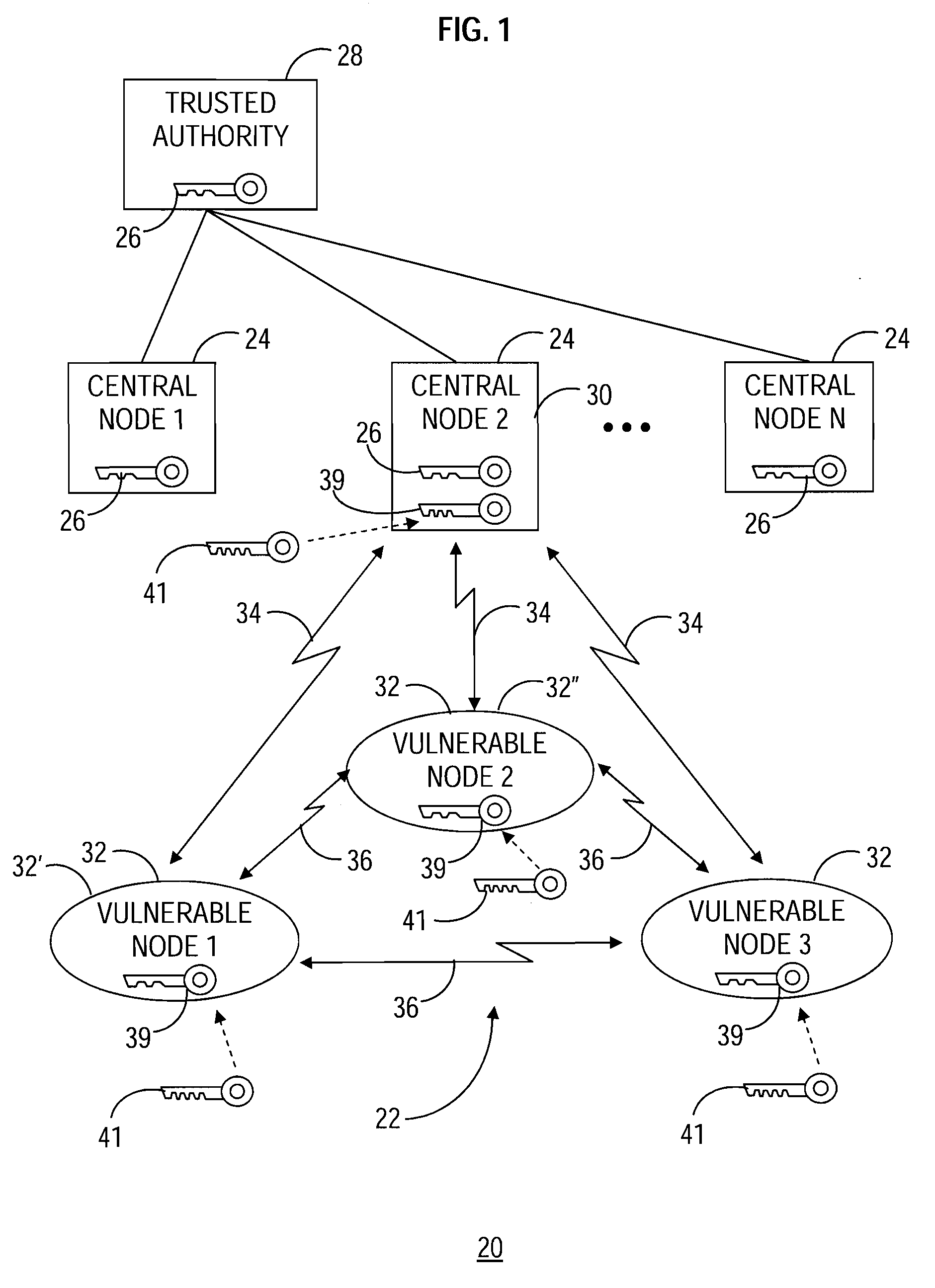
Cryptographic key management in a communication network
InactiveUS20080085004A1Communication securityPromote recoveryKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationSecure communicationKey-agreement protocol
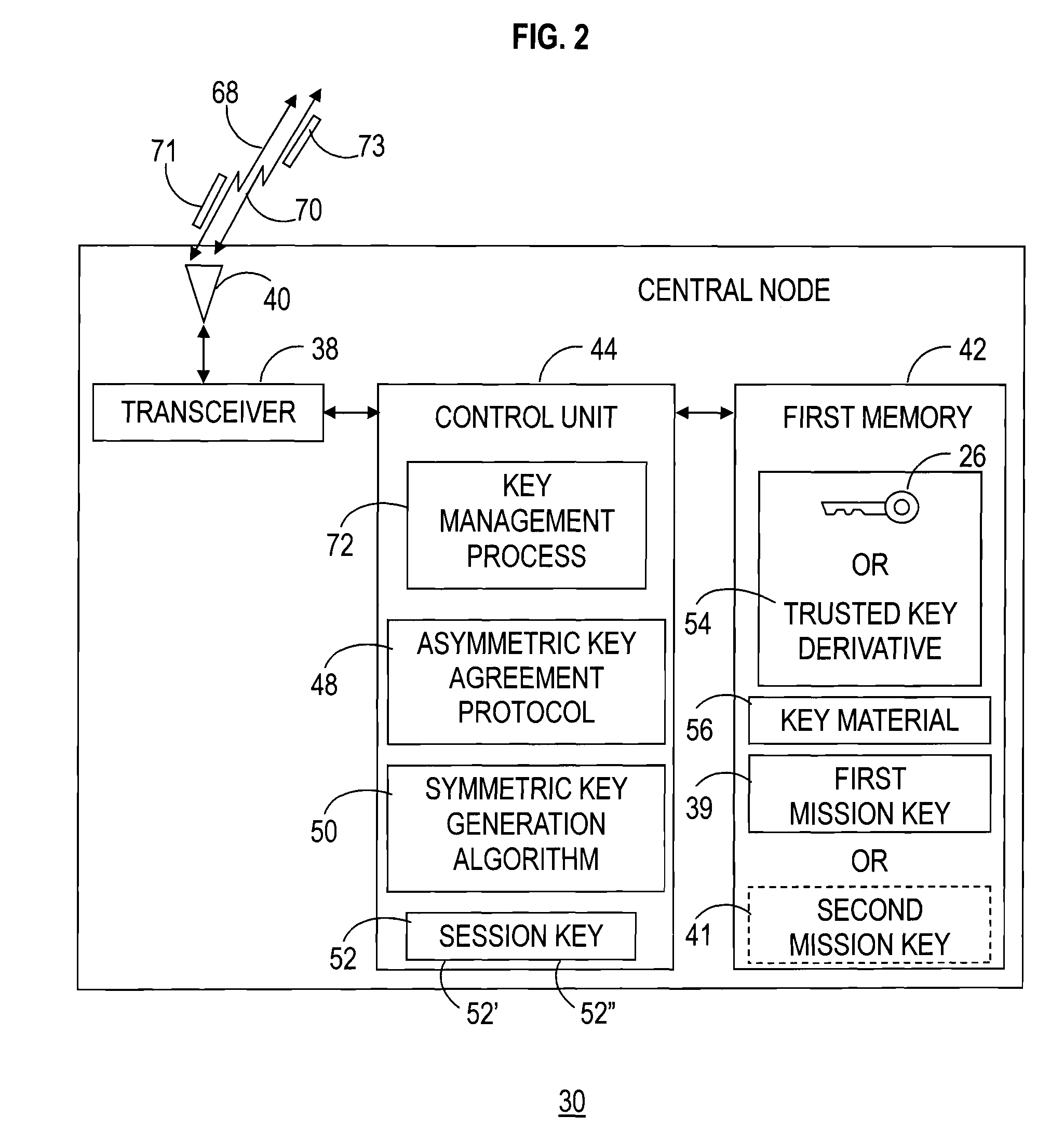
A communication network (22) includes a central node (30) loaded with a trusted key (26) and key material (56) corresponding to an asymmetric key agreement protocol (48). The network (22) further includes vulnerable nodes (32) loaded with key material (69) corresponding to the protocol (48). Successive secure connections (68, 70) are established between the central node (30) and the vulnerable nodes (32) using the key material (56, 69) to generate a distinct session key (52) for each of the secure connections (68, 70). The trusted key (26) and one of the session keys (52) are utilized to produce a mission key (39). The mission key (39) is transferred from the central node (30) to each of the vulnerable nodes (32) via each of the secure connections (68, 70) using the corresponding current session key (52). The mission key (39) functions for secure communication within the communication network (22).
Owner:GENERAL DYNAMICS MISSION SYST INC
Three-factor identity authentication and key negotiation method in multi-server environment
ActiveCN108965338AAchieve securityImprove confidentialityKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationConfidentialityKey-agreement protocol
The invention discloses a three-factor identity authentication and key negotiation method in a multi-server environment. The method comprises the following phases: a registration center initializationphase, a server registration phase, a client registration phase and an authentication and key negotiation phase, and a functional portion of client password replacement. By adoption of the three-factor identity authentication and key negotiation method disclosed by the invention, the participation of a trusted third party registration / authentication center is not required in the authentication phase, thus reducing the communication steps and costs, improving the protocol operation efficiency and ensuring the security of the protocol at the same time. The mutual authentication of the two parties is realized by a static DH value shared by the client and the server uniquely, and the confidentiality of a session key is realized by a dynamic DH value shared by both parties uniquely and used for calculating the session key so as to ensure the security of an established channel. The three-factor identity authentication and key negotiation method disclosed by the invention has authenticationproperty and confidentiality, is secure and provides an efficient multi-server three-factor identity authentication and key negotiation protocol on the communication.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method and apparatus for establishing a key agreement protocol
ActiveUS20060280308A1Organic active ingredientsKey distribution for secure communicationSecure communicationMethod selection
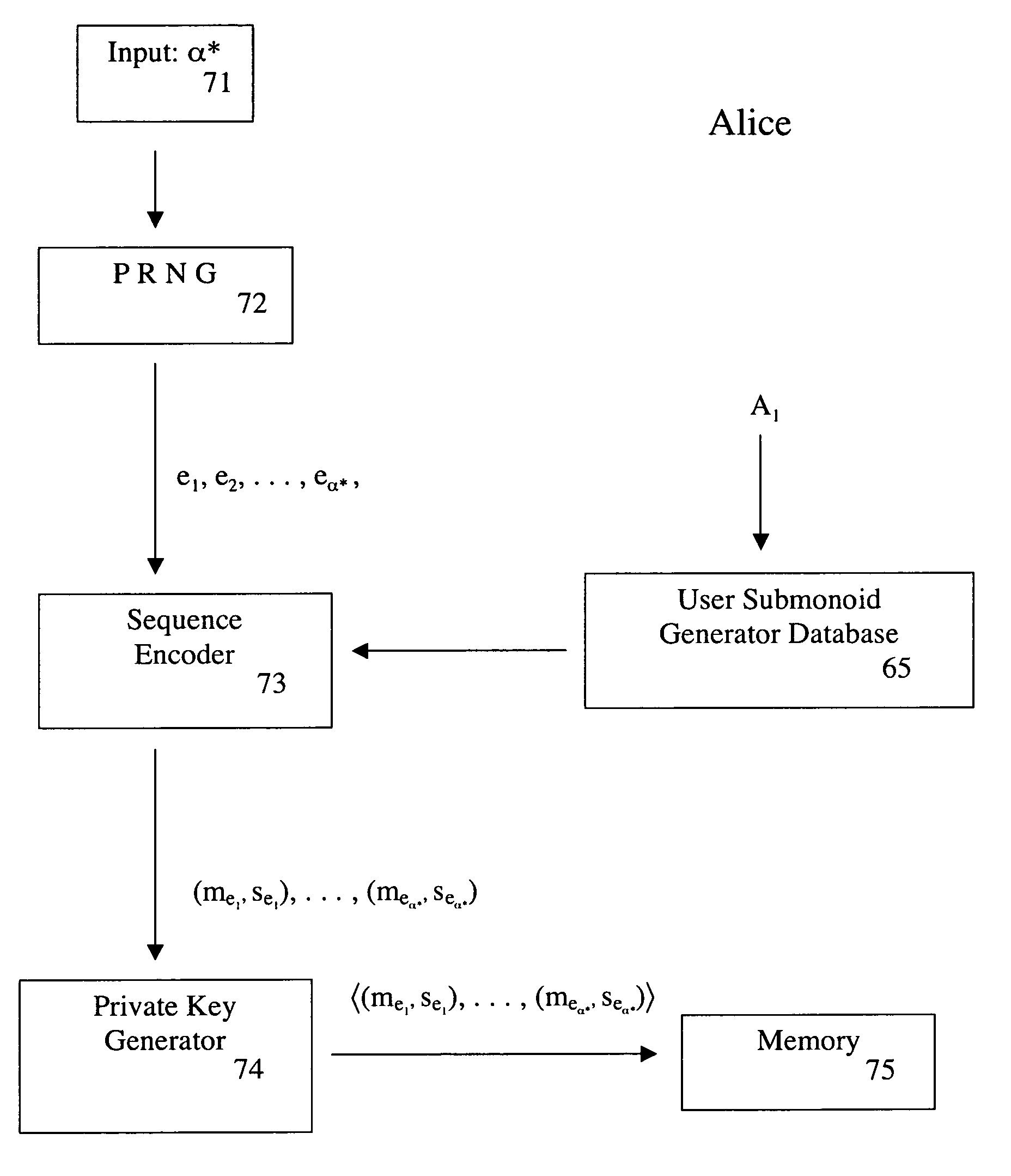
A system and method for generating a secret key to facilitate secure communications between users. A first and second and a function between the two monoids are selected, the function being a monoid homomorphism. A group and a group action of the group on the first monoid is selected. Each user is assigned a submonoid of the first monoid so that these submonoids satisfy a special symmetry property determined by the function, a structure of the first and second monoids, and the action of the group. A multiplication of an element in the second monoid and an element in the first monoid is obtained by combining the group action and the monoid homomorphism. First and second users choose private keys which are sequences of elements in their respective submonoids. A first result is obtained by multiplying an identity element by the first element of the sequence in a respective submonoid. Starting with the first result, each element of the user's private key may be iteratively multiplied by the previous result to produce a public key. Public keys are exchanged between first and second users. Each user's private key may be iteratively multiplied by the other user's public key to produce a secret key. Secure communication may then occur between the first and second user using the secret key.
Owner:SECURERF CORP
Mutual anonymous authentication and key agreement protocol in mobile network
InactiveCN107360571AImprove protectionPrevent theftSecurity arrangementInformation transmissionKey-agreement protocol
The invention discloses a mutual anonymous authentication and key agreement protocol in a mobile network. The protocol is implemented as follows: step A, at a registration stage, a legal mobile device user initiates a request to register own information to a server; step B, the operation is carried out at an authentication and key agreement stage. Therefore, a server in a mobile network carries out authentication of an anonymous mobile device and session key sharing is established, so that privacy information of the two communication sides is protected from leakage; and security of the information transmission between the mobile devices is guaranteed. The protocol has high security and efficiency in the same kinds of protocols.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Authenticating Ad Hoc group cipher key negotiation protocol
InactiveCN101119364AKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationKey-agreement protocolCryptographic protocol
The present invention relates to an Ad Hoc group cipher key negotiation which is capable of being authenticated, and drafting the cryptographic key protocol through the method which is based on a code tree. The present invention adopts a threshold cryptographic key and a Contributory type cryptographic key negotiation; and adopts the tree-shaped method when transmitting, not only increasing the flexibility and the efficiency, but the invention is more suitable for the situations whose communication environment is execrable; and the invention adopts authenticates the whole negotiation process through utilizing the Schonorr signature method, increasing the safety performance of the system. The result produced by the present invention is simple and safe, and the invention has a function of error resistance.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method for managing network key and updating session key
ActiveUS8306229B2Low efficiencyImprove performanceKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationKey-agreement protocolNetwork key
A method for managing network key and updating session key is provided. The step of the key management includes: constructing key request group, constructing key negotiation response group, and constructing key negotiation acknowledgement group. The step of multicasting key management method includes multicasting main key negotiation protocol and multicasting session key distribution protocol. The multicasting main key negotiation protocol comprises key updating informs group, constructing encryption key negotiation request group, constructing key negotiation response group and constructing key negotiation acknowledgement group. The multicasting session key distribution protocol comprises multicasting session key request and multicasting session key distribution.
Owner:CHINA IWNCOMM
Two-factor authentication key agreement protocol suitable for multi-gateway wireless sensor network
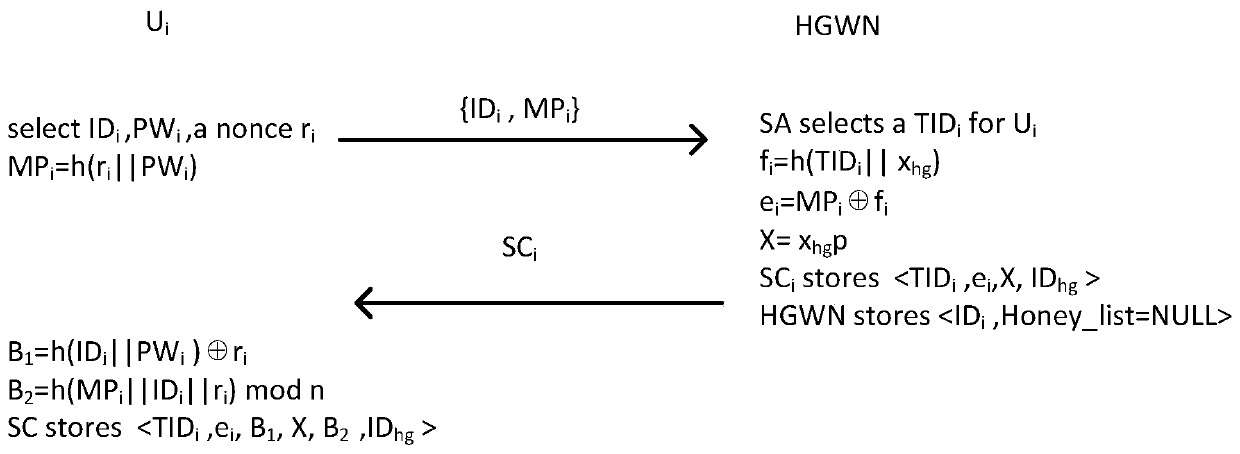
ActiveCN110234111AResistance to replay attacksResistance to insider attacksSecurity arrangementKey-agreement protocolPassword
The invention provides a double-factor authentication key agreement protocol suitable for a multi-gateway wireless sensor network. The protocol is divided into five stages: an initialization stage, aregistration stage, a login stage, an authentication stage and a key change stage. Fuzzy verification and honeywords methods are adopted in the user authentication part, so that the united password identity guessing attack based on the stolen intelligent card is effectively resisted. In the scheme, key negotiation is based on discrete elliptic curve encryption and can resist sensor capture attacks, so that the forward security of the protocol is ensured.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com