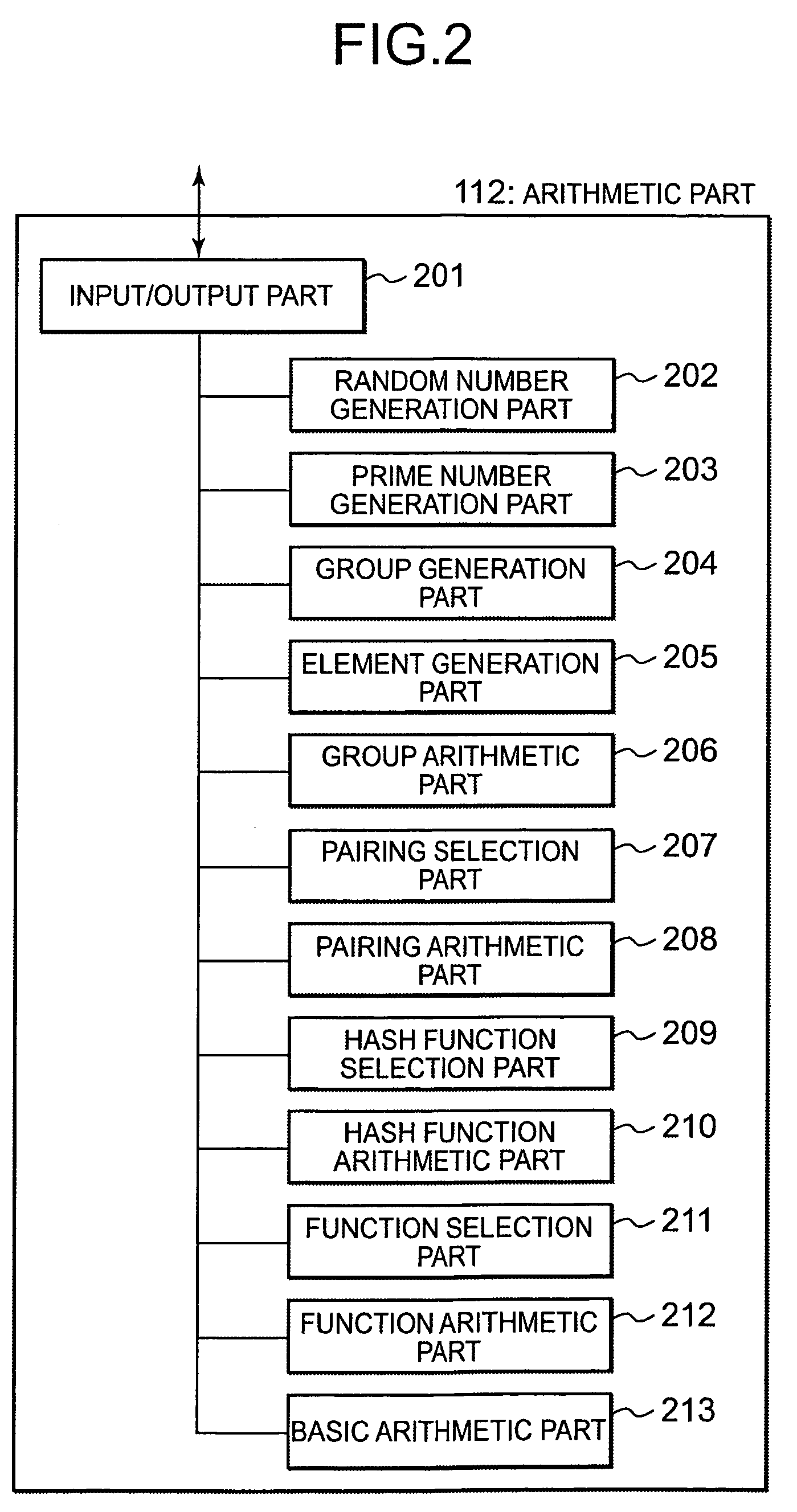
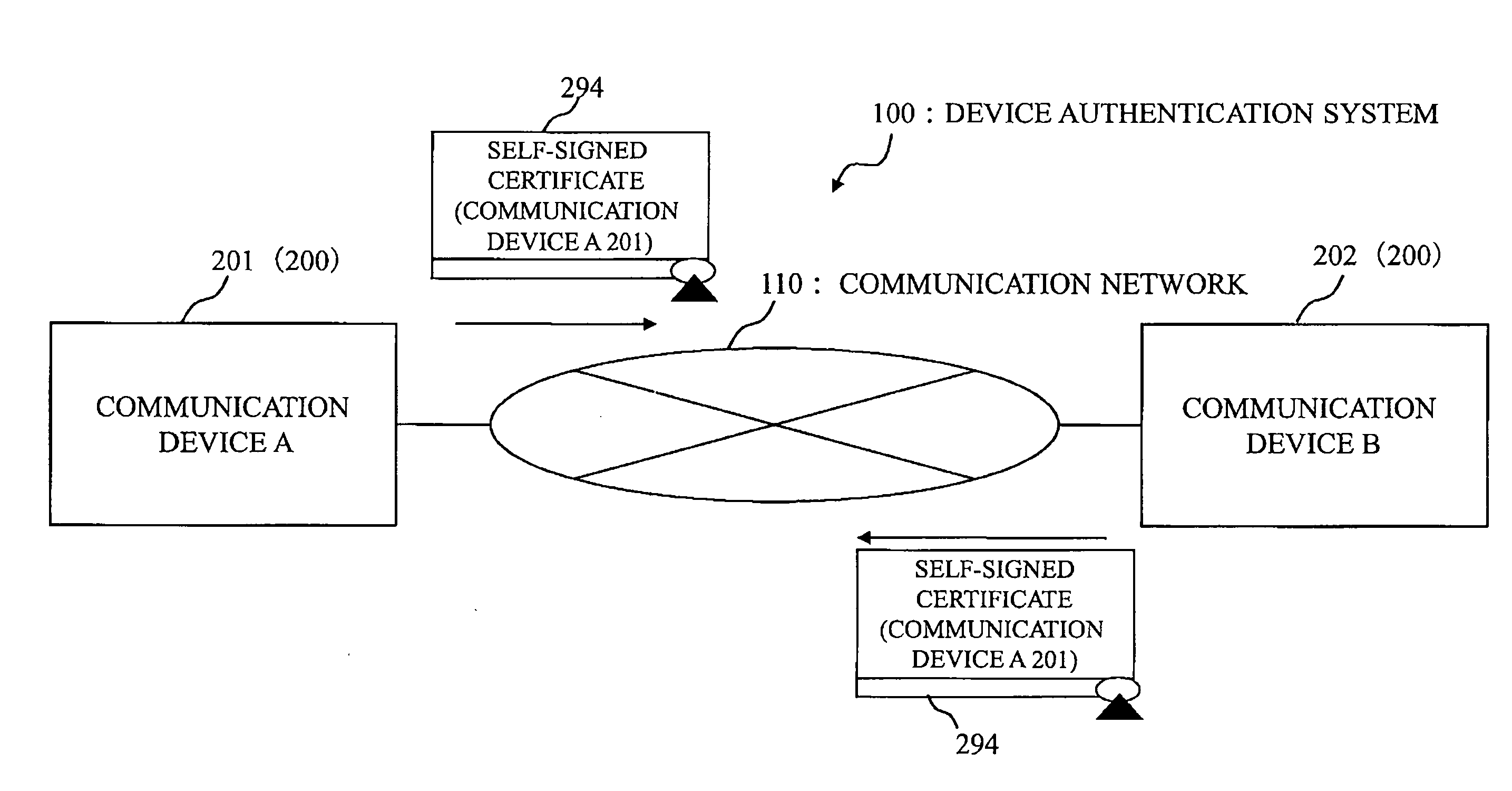
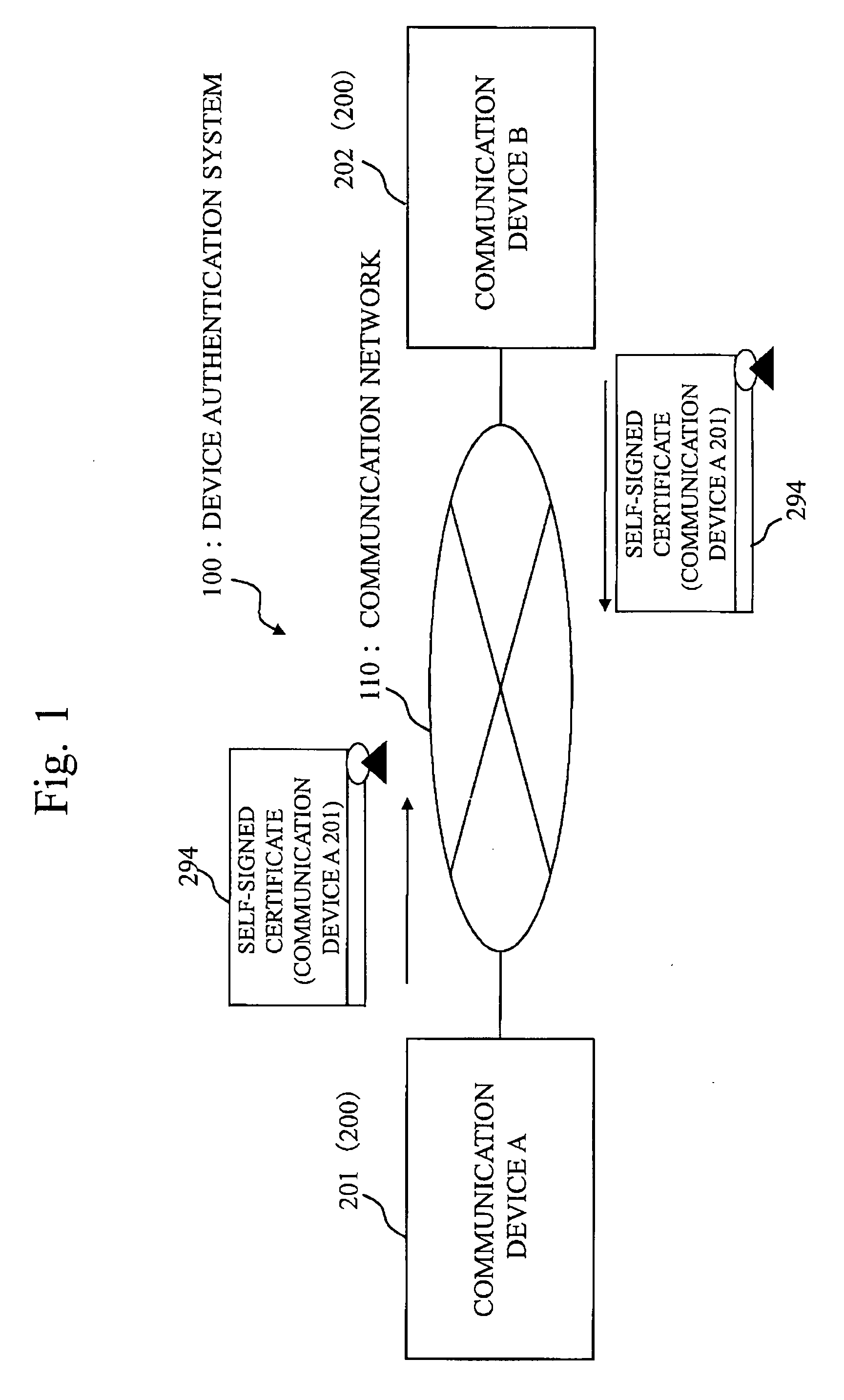
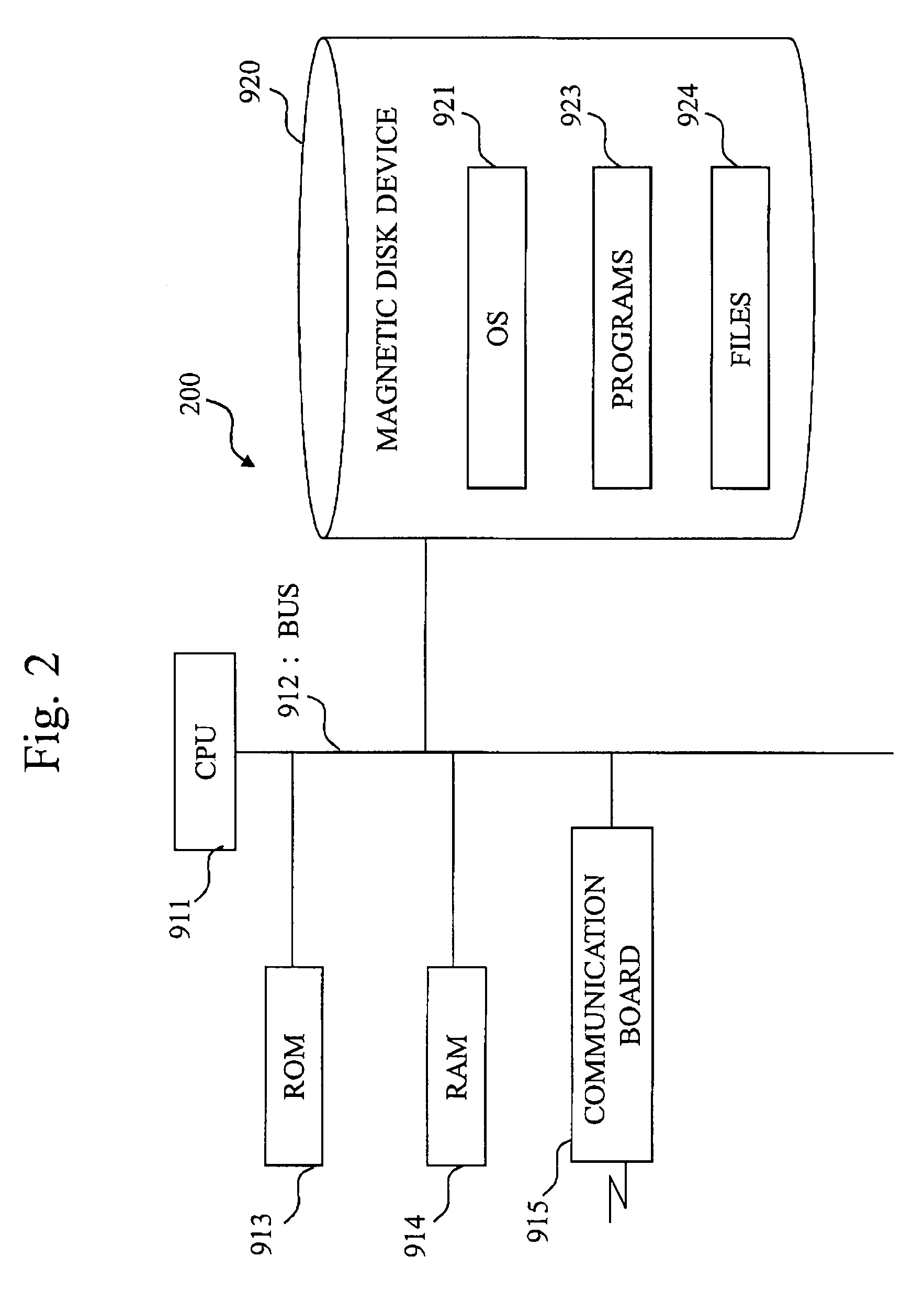
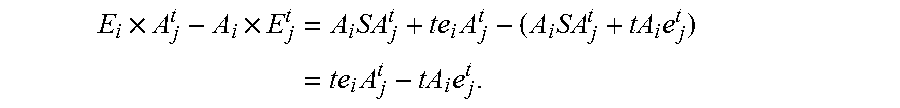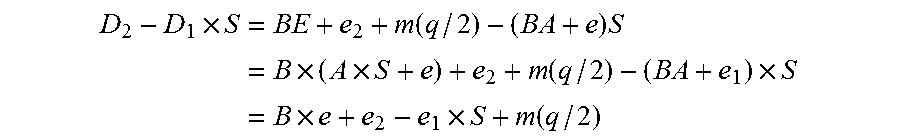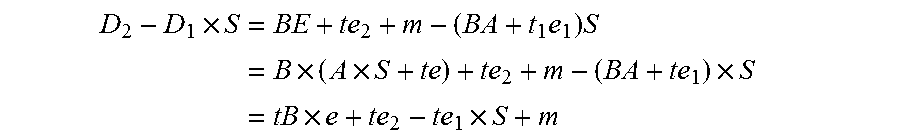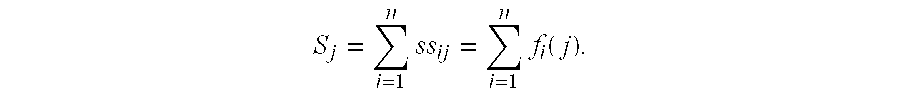Patents
Literature
50 results about "ID-based encryption" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
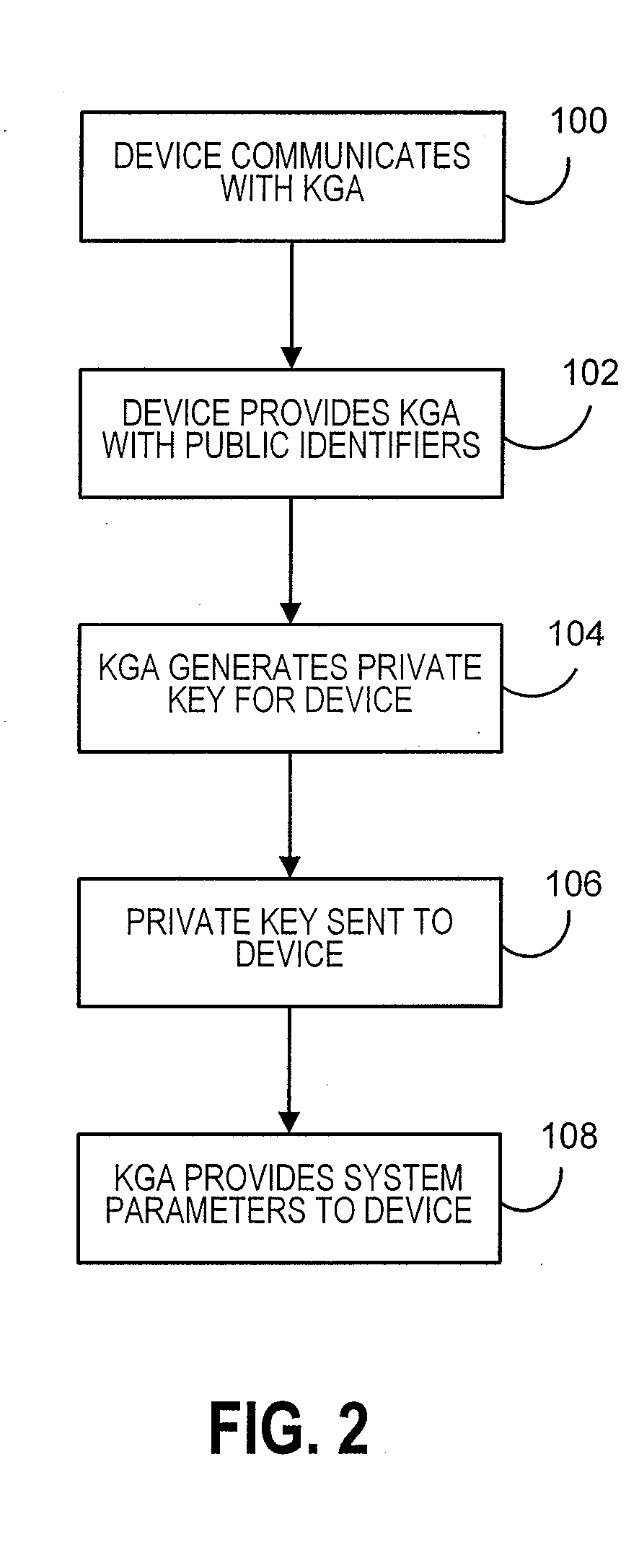
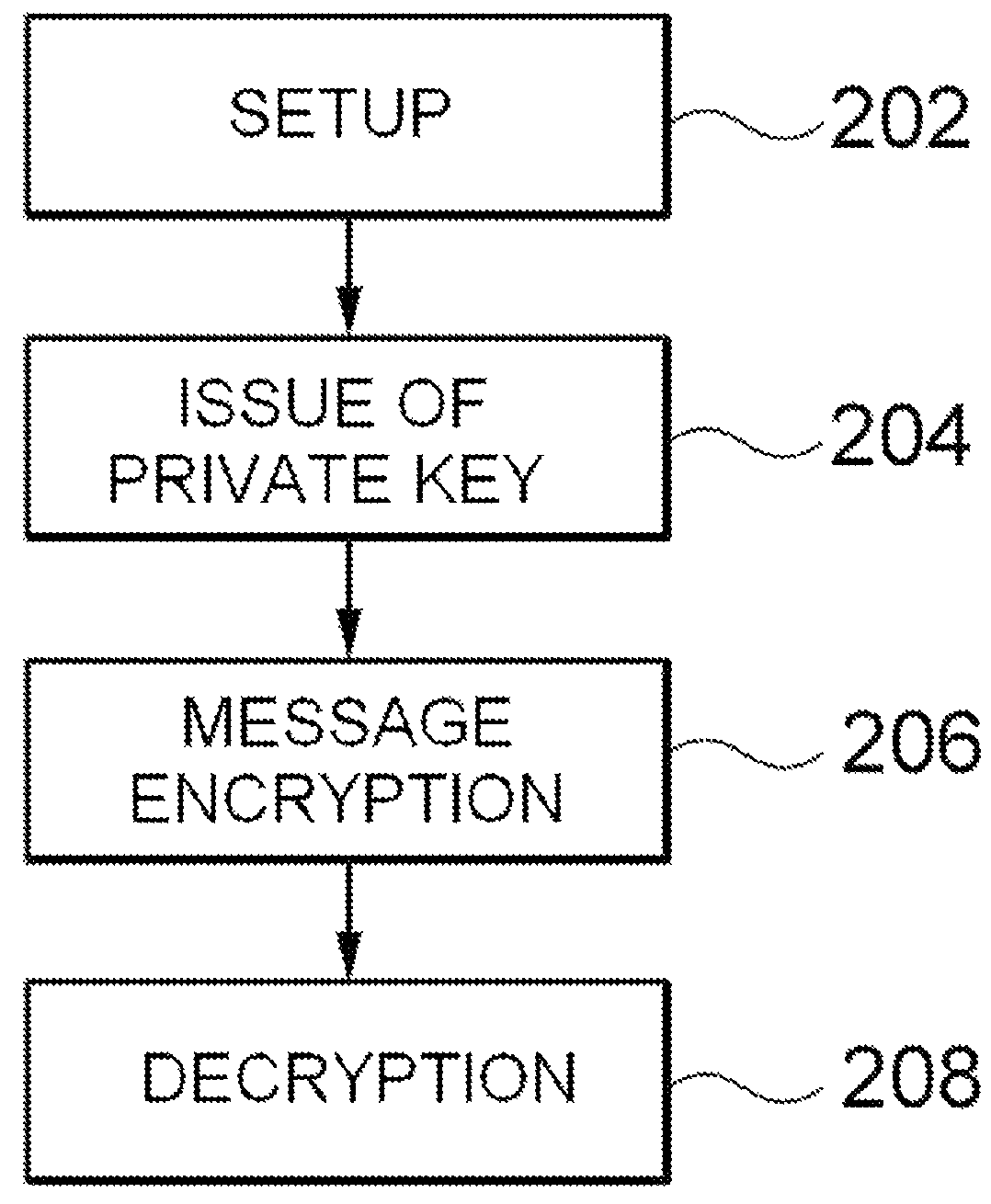
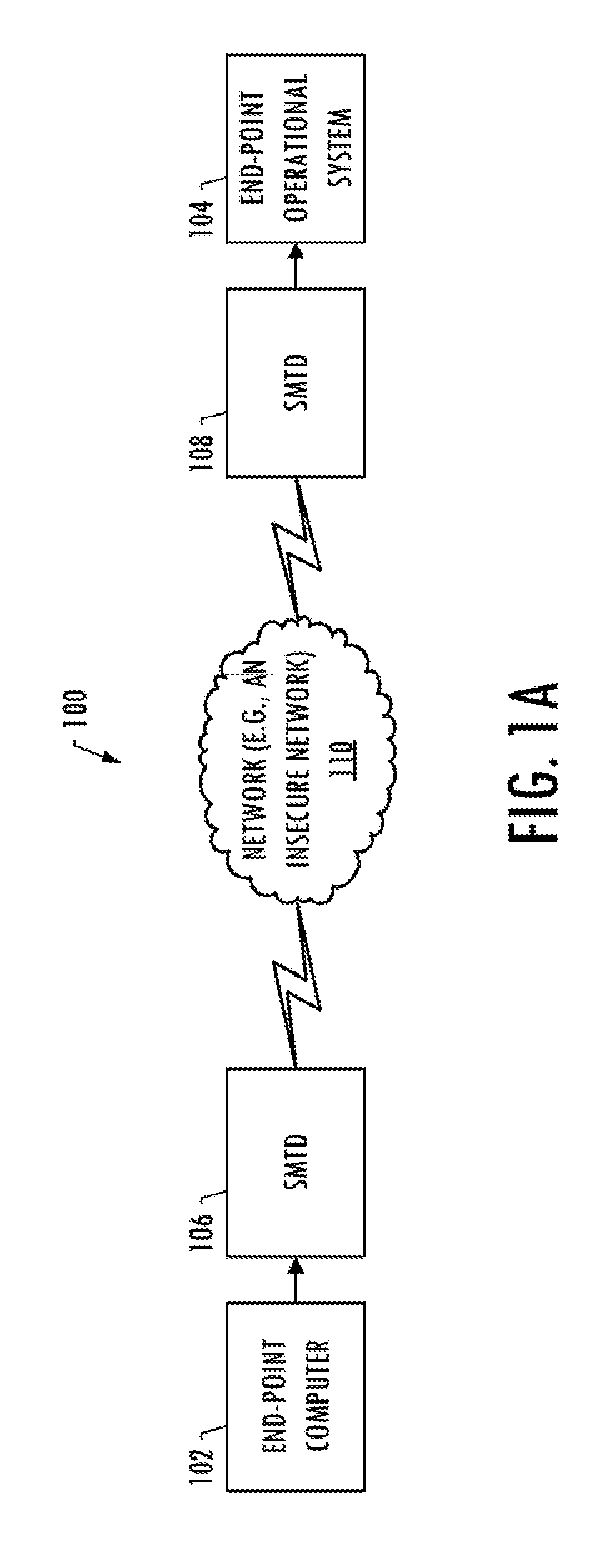
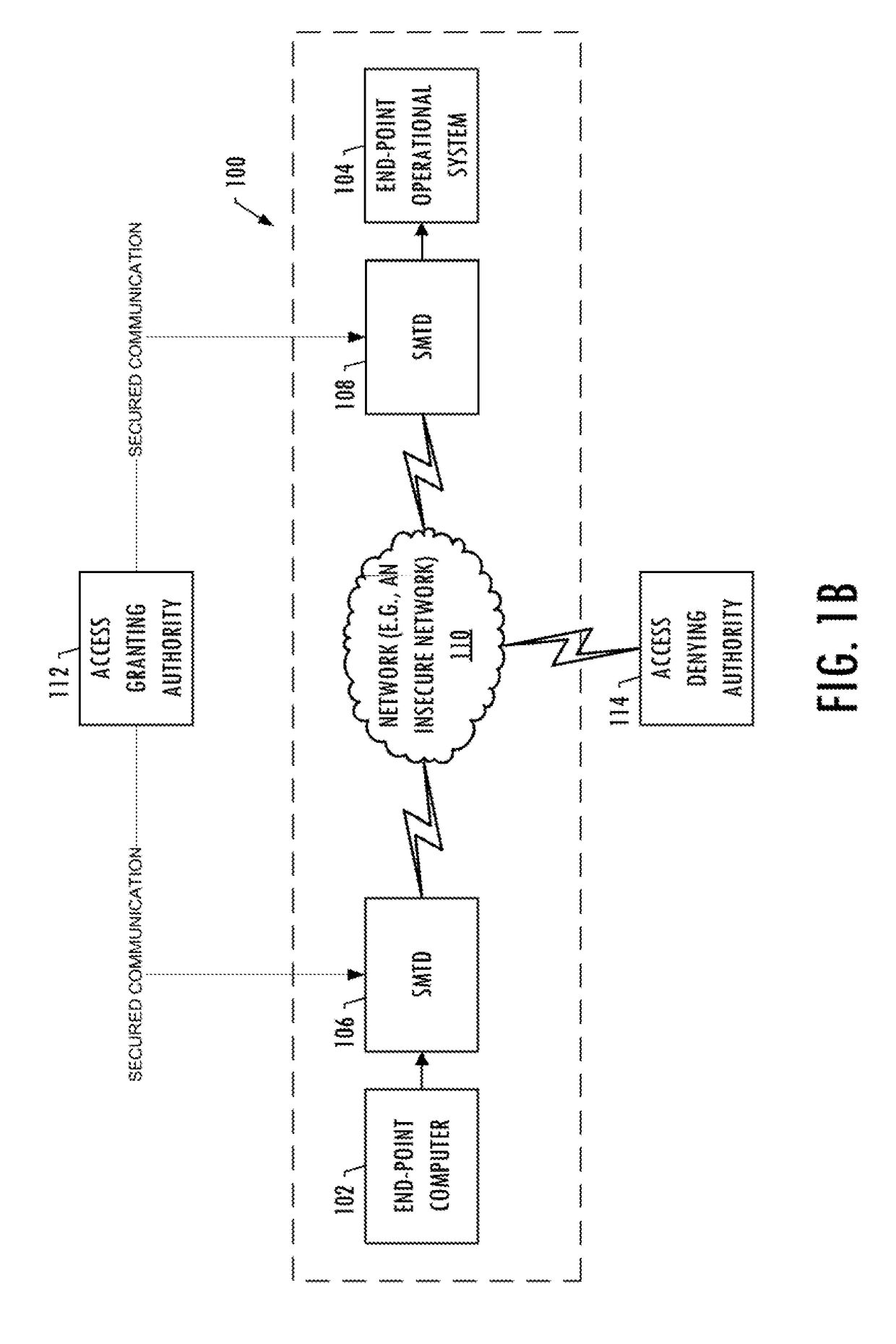
ID-based encryption, or identity-based encryption (IBE), is an important primitive of ID-based cryptography. As such it is a type of public-key encryption in which the public key of a user is some unique information about the identity of the user (e.g. a user's email address). This means that a sender who has access to the public parameters of the system can encrypt a message using e.g. the text-value of the receiver's name or email address as a key. The receiver obtains its decryption key from a central authority, which needs to be trusted as it generates secret keys for every user.
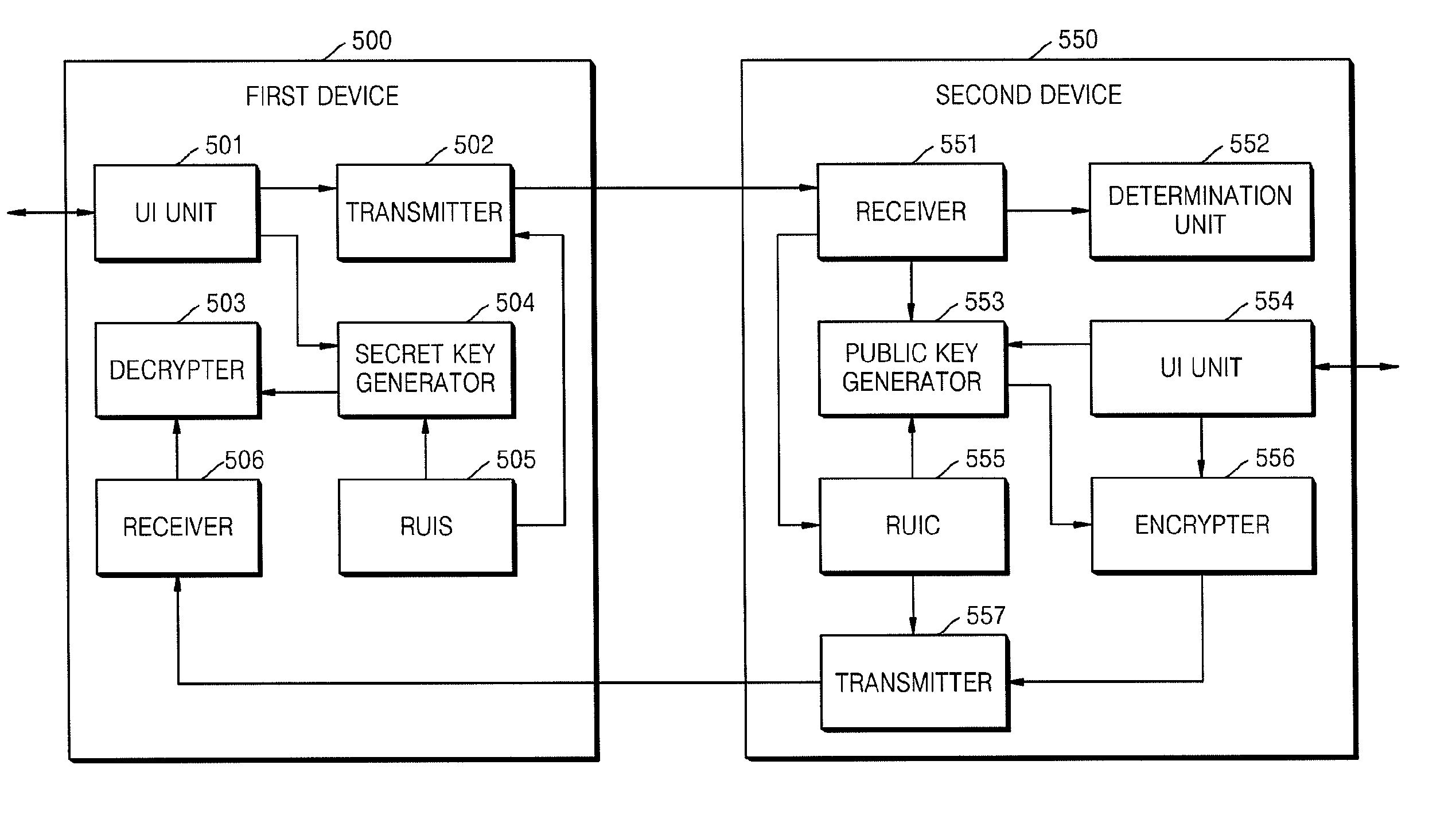
Method of and apparatus for sharing secret information between device in home network
InactiveUS20090055648A1Reduce traffic problemsAvoid complex calculationsKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationID-based encryptionPassword
A method and apparatus for sharing secret information between devices in a home network are provided. In the method and apparatus, home network devices receive a password (credential) input by a user and encrypt secret information based on the credential by using keys generated according to a predetermined identity-based encryption (IBE) scheme. Accordingly, it is possible to securely share the secret information between home network devices without any certificate authority or certificate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
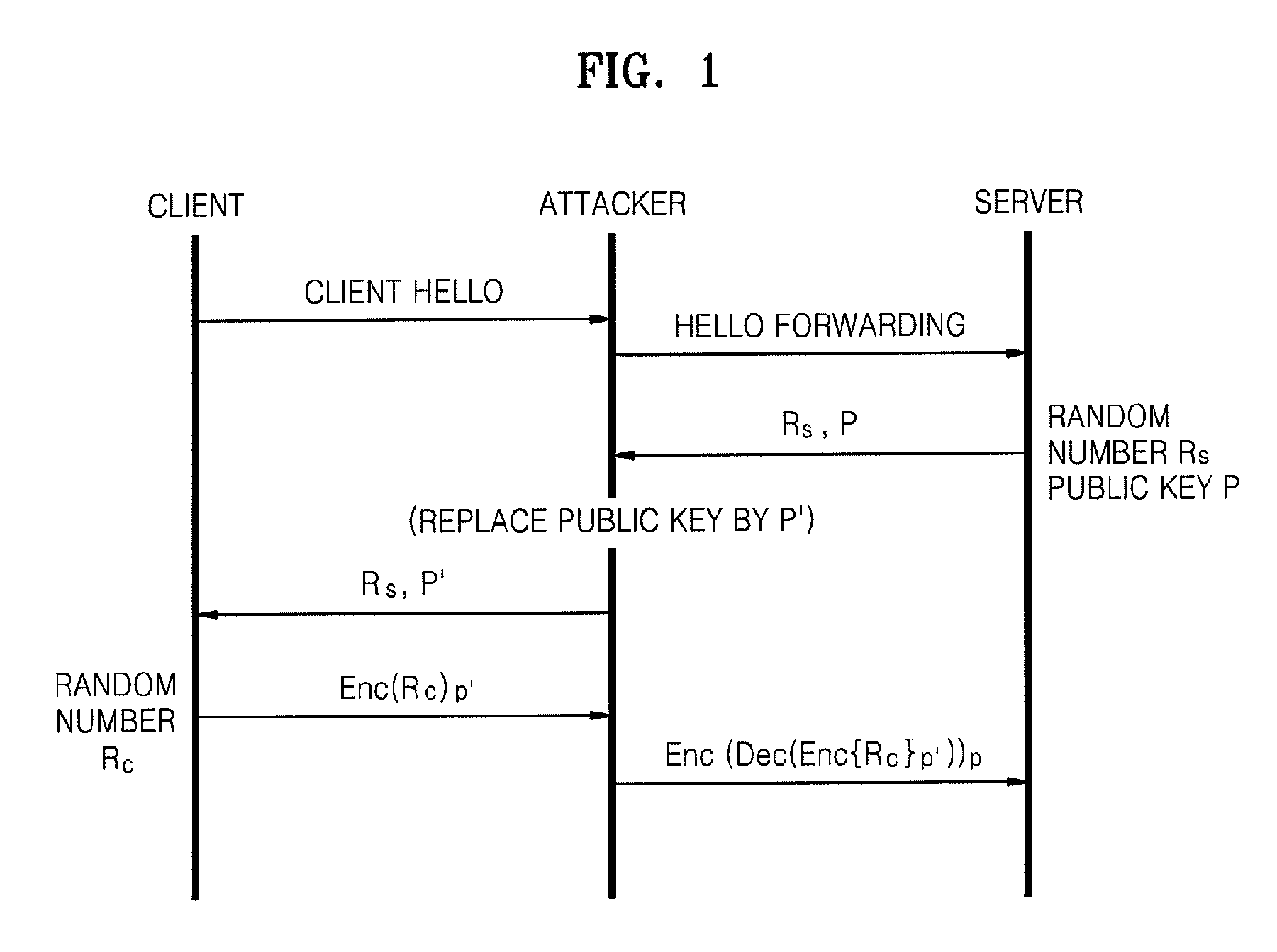
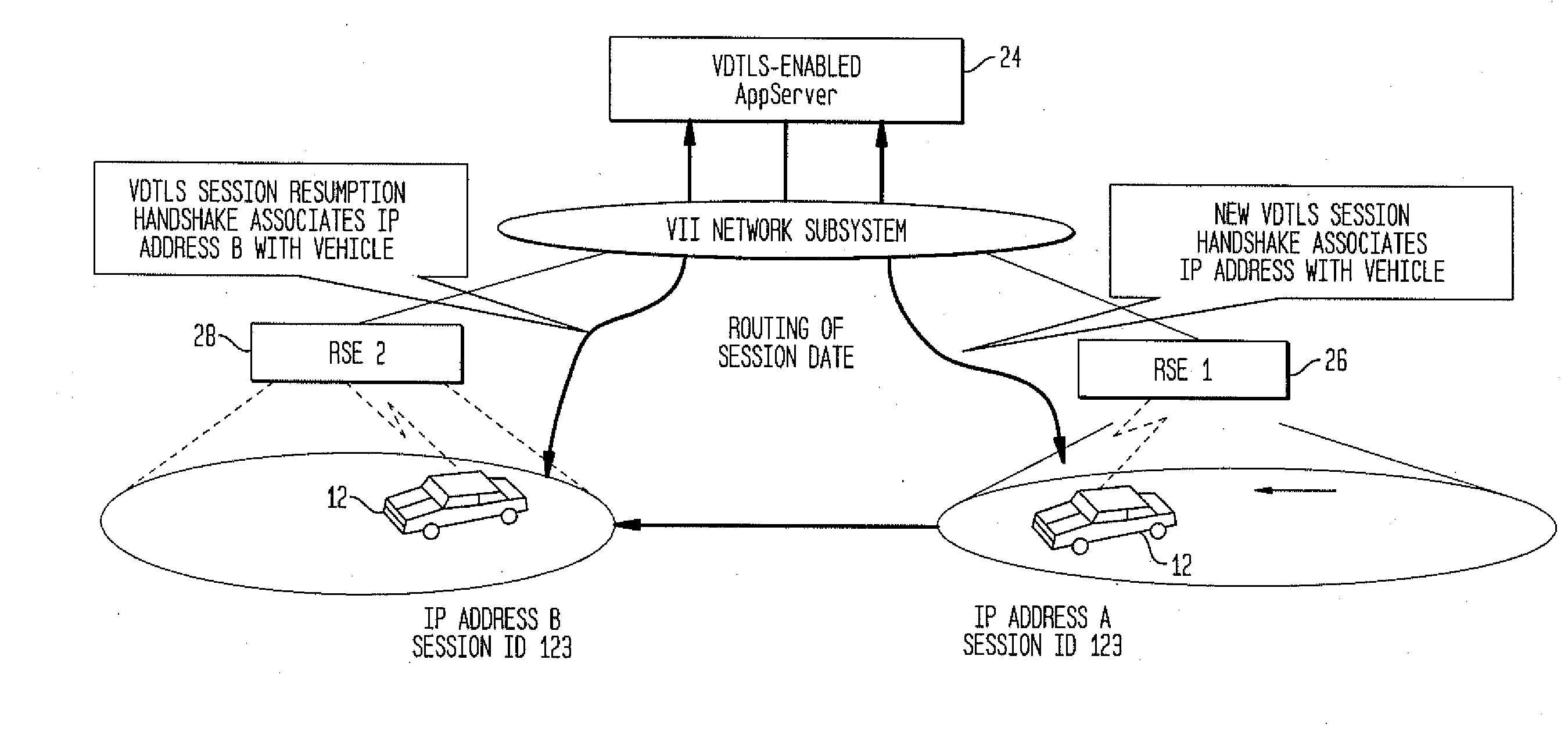
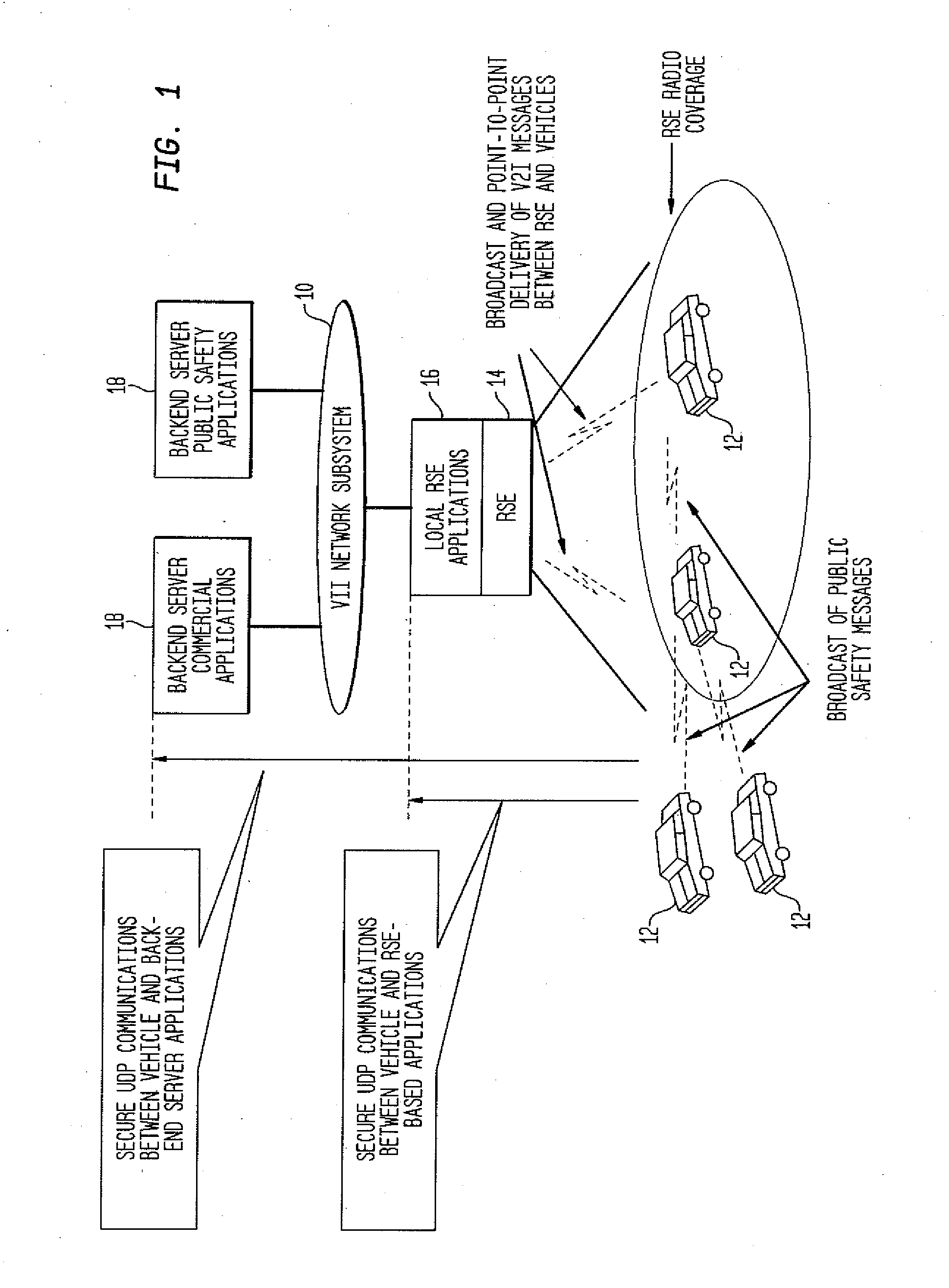
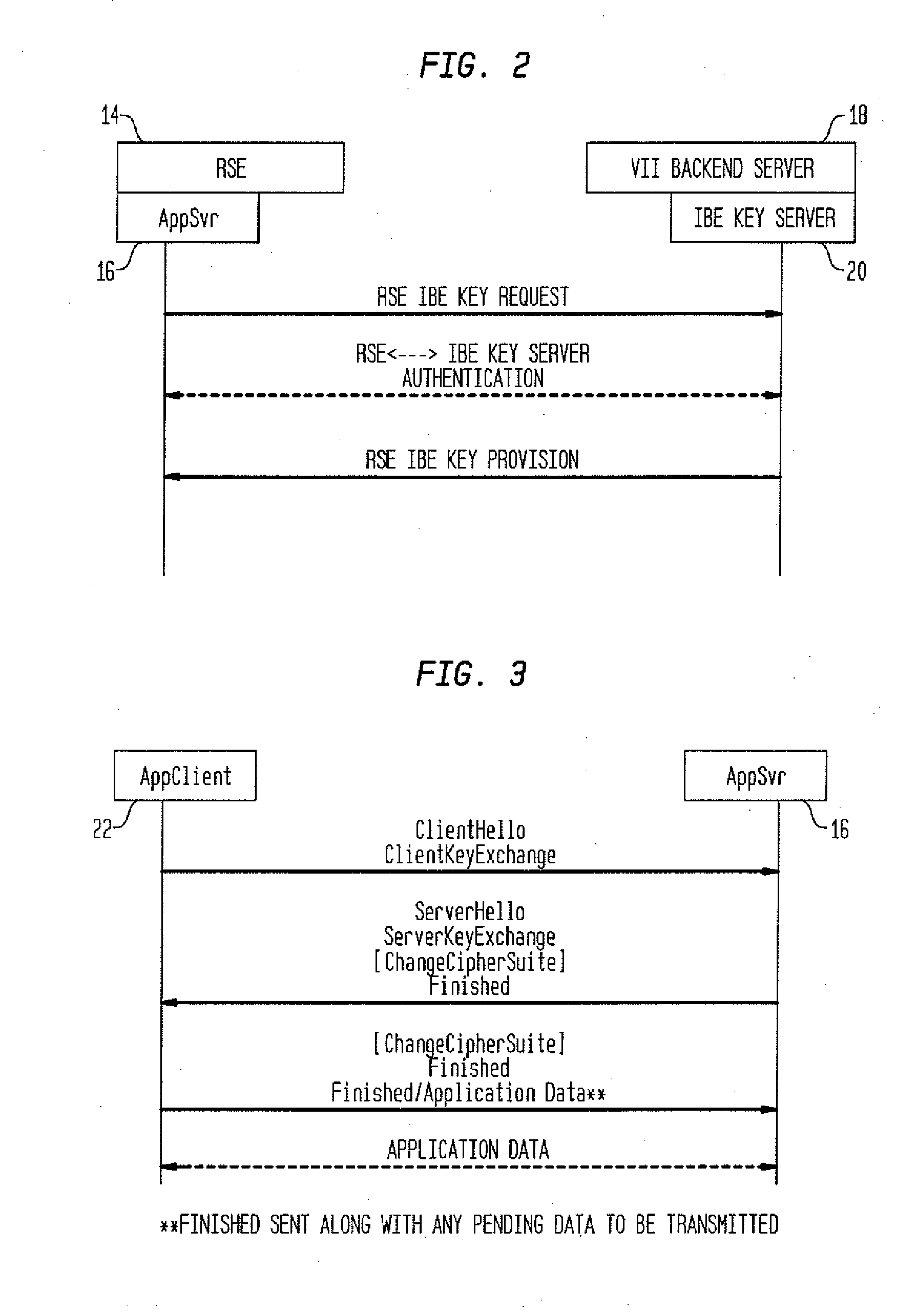
Method and System for Secure Session Establishment Using Identity-Based Encryption (VDTLS)
ActiveUS20100031042A1Communication securityPrivacy protectionUser identity/authority verificationSecurity arrangementID-based encryptionSecure communication
The inventive system for providing strong security for UDP communications in networks comprises a server, a client, and a secure communication protocol wherein authentication of client and server, either unilaterally or mutually, is performed using identity based encryption, the secure communication protocol preserves privacy of the client, achieves significant bandwidth savings, and eliminates overheads associated with certificate management. VDTLS also enables session mobility across multiple IP domains through its session resumption capability.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
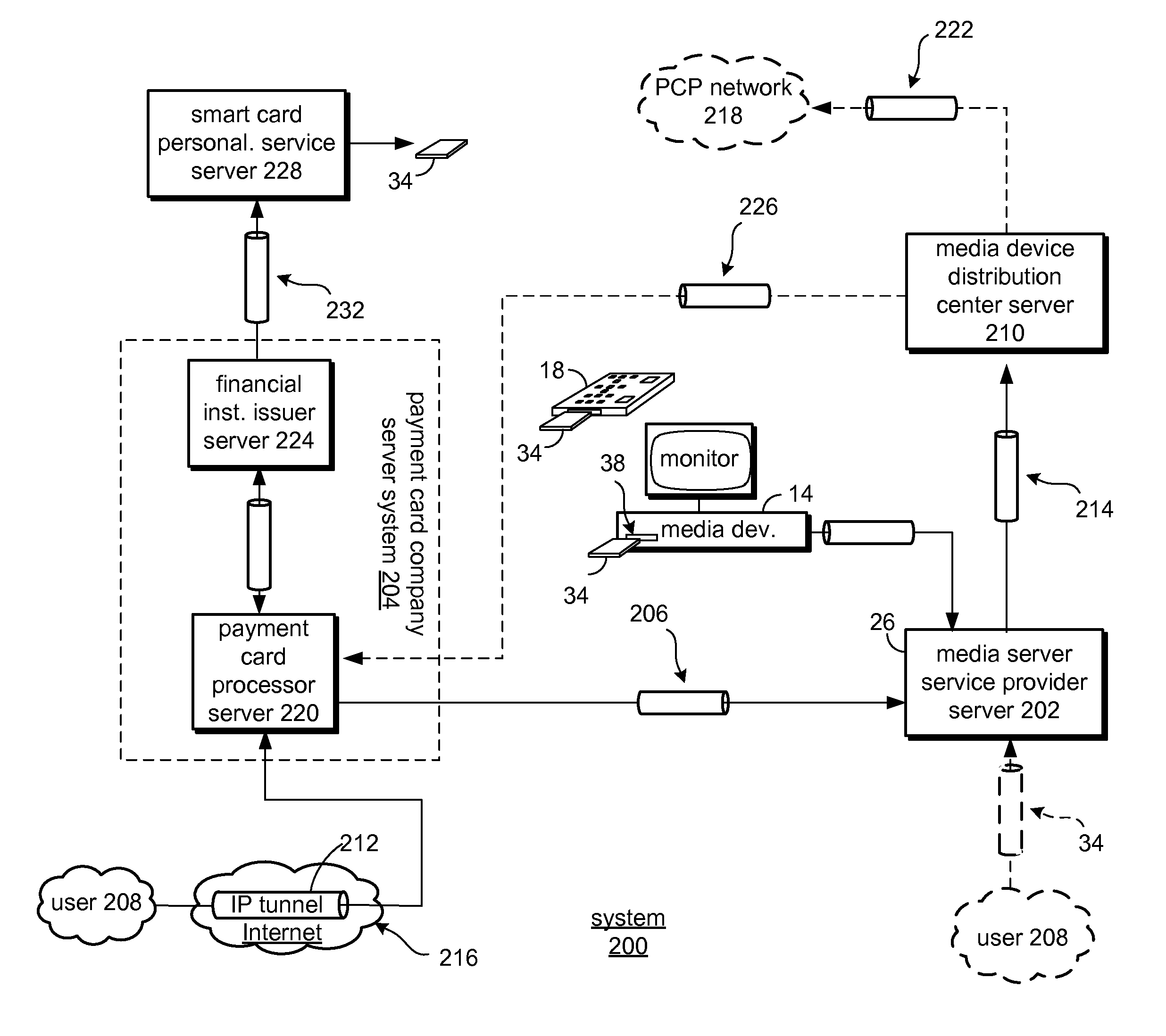
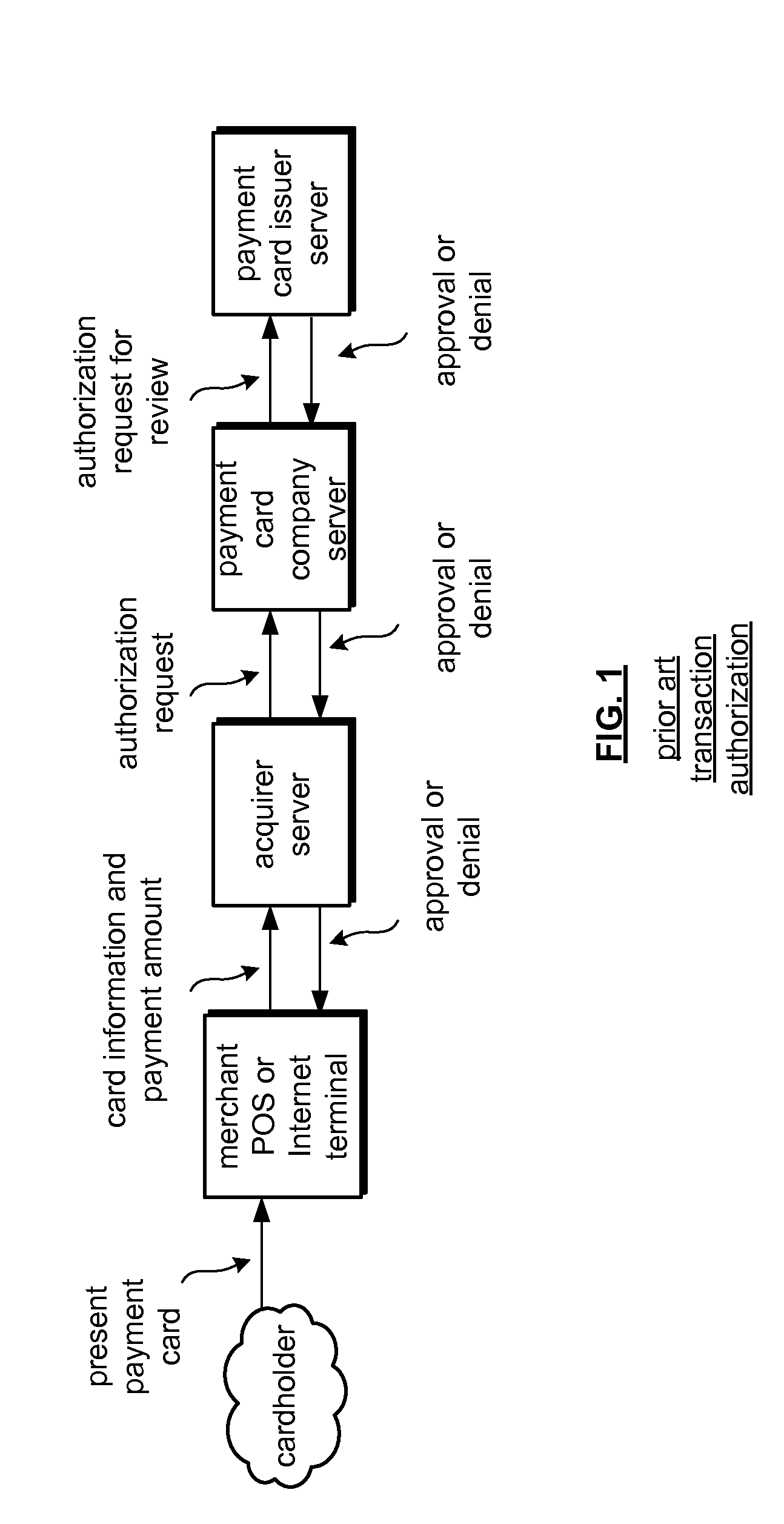
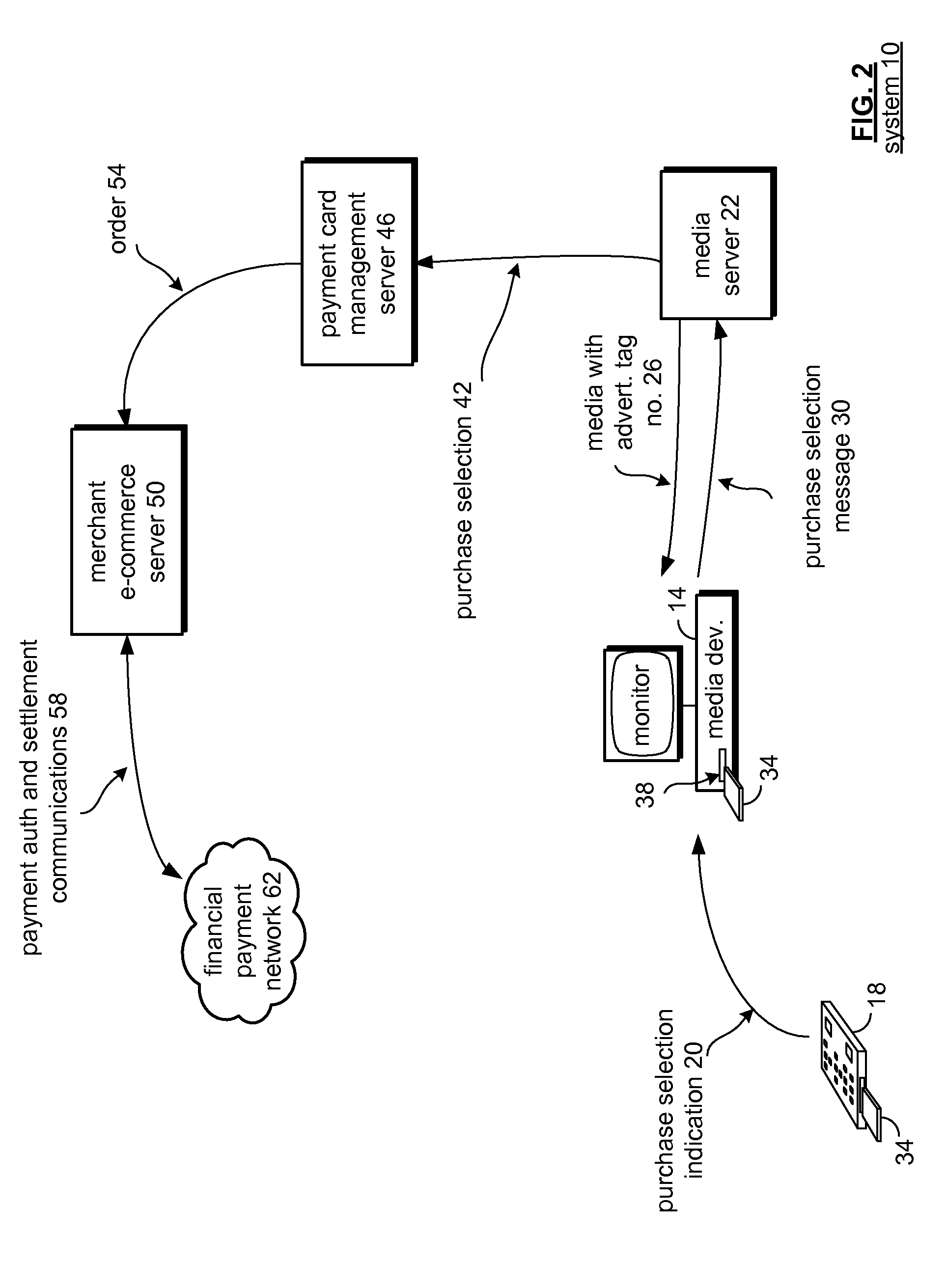
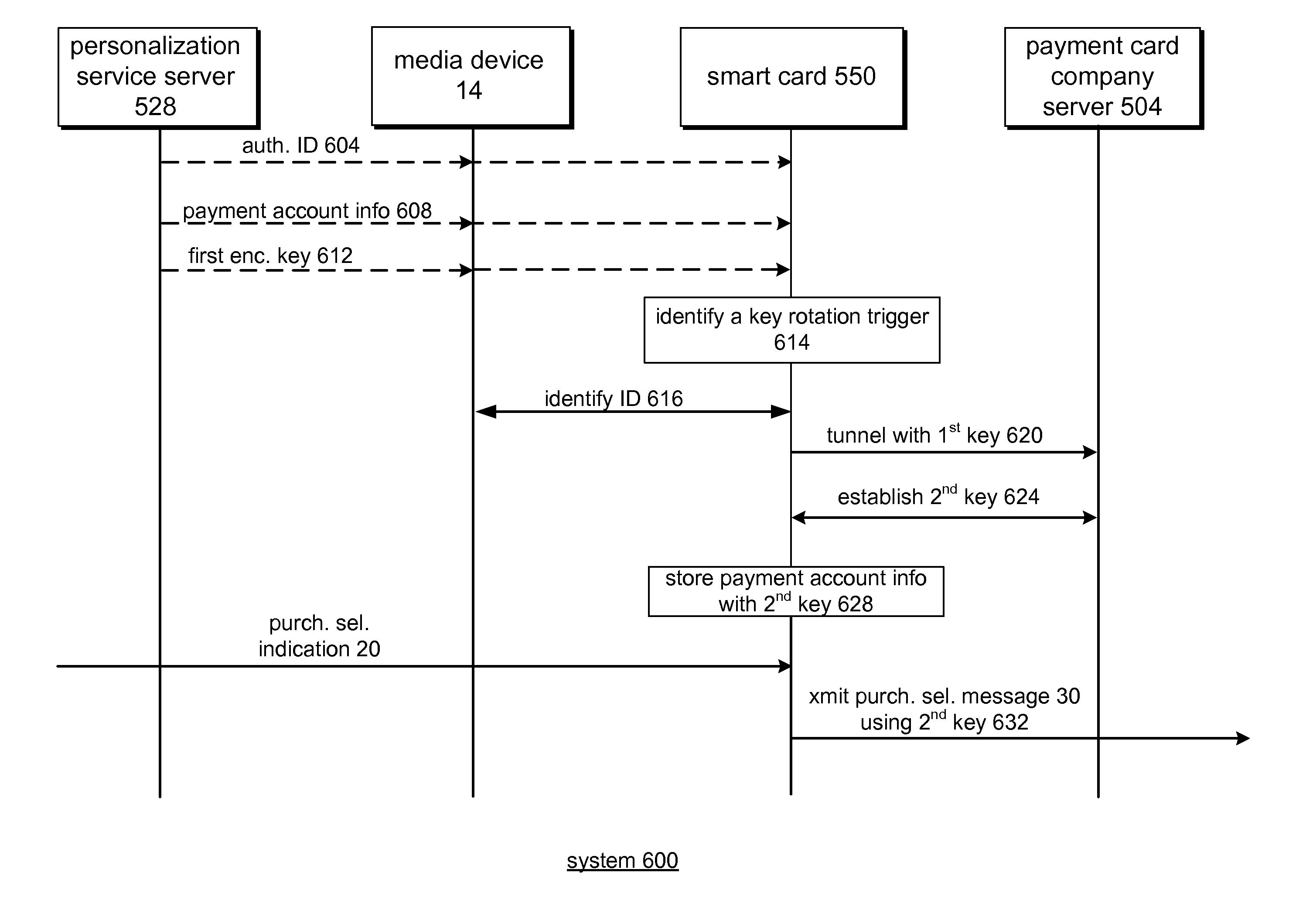
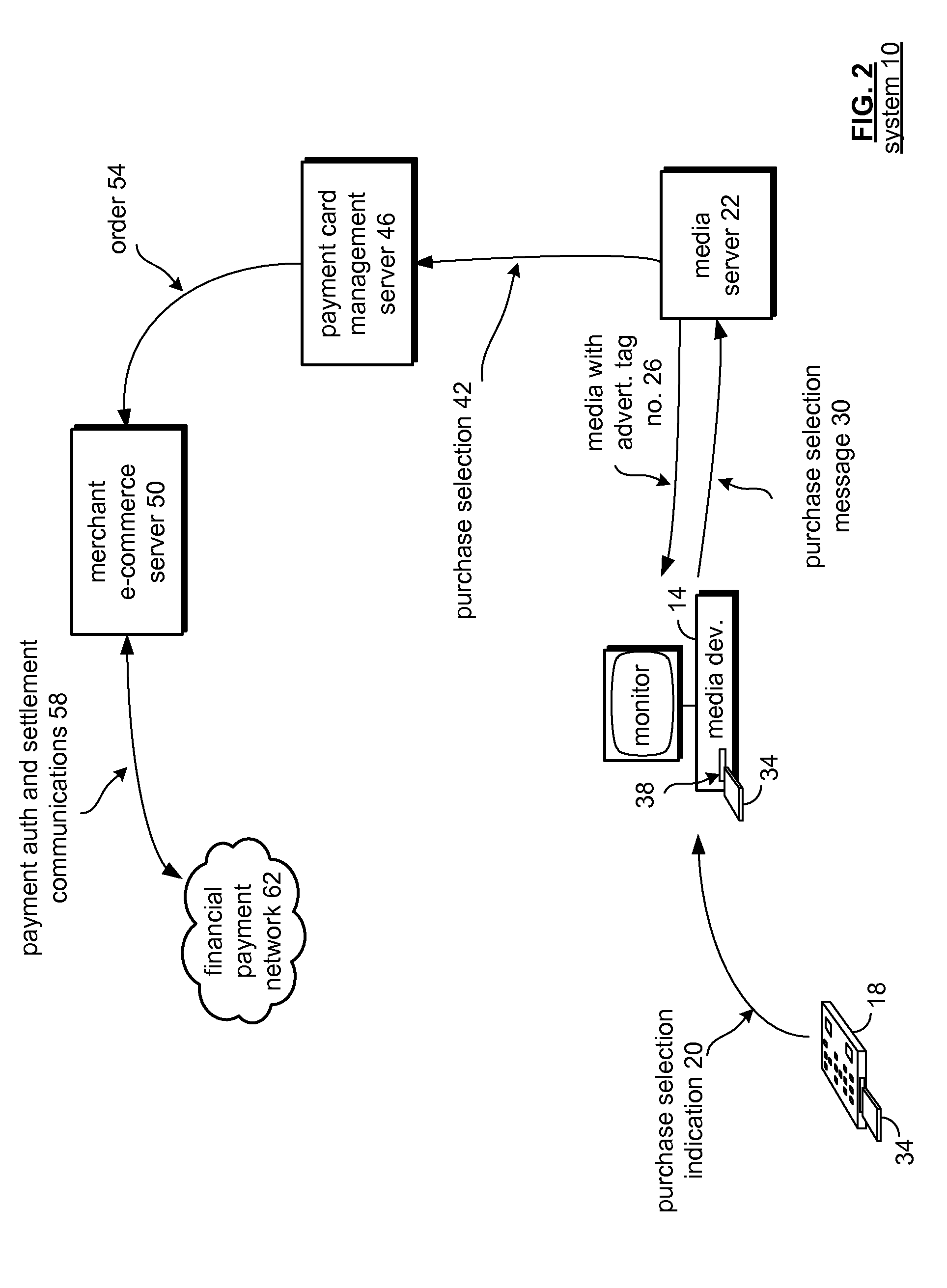
Module id based encryption for financial transactions
A server is operable to receive a media device identifying number (ID) and establish an association between a media device and a payment account and, in one embodiment, supports at least one of payment authorization and payment clearing based at least in part on the media device ID and the payment account. A network and system includes a payment card processor server that is operable to receive a payment authorization request and to determine if an authorized media device generated a purchase selection message and to determine to approve a received payment authorization request based, in part, if the media device was authorized for the purchase selection based upon a received media device ID. The system is further operable to perform a key rotation to protect payment account information.
Owner:VISA USA INC (US)
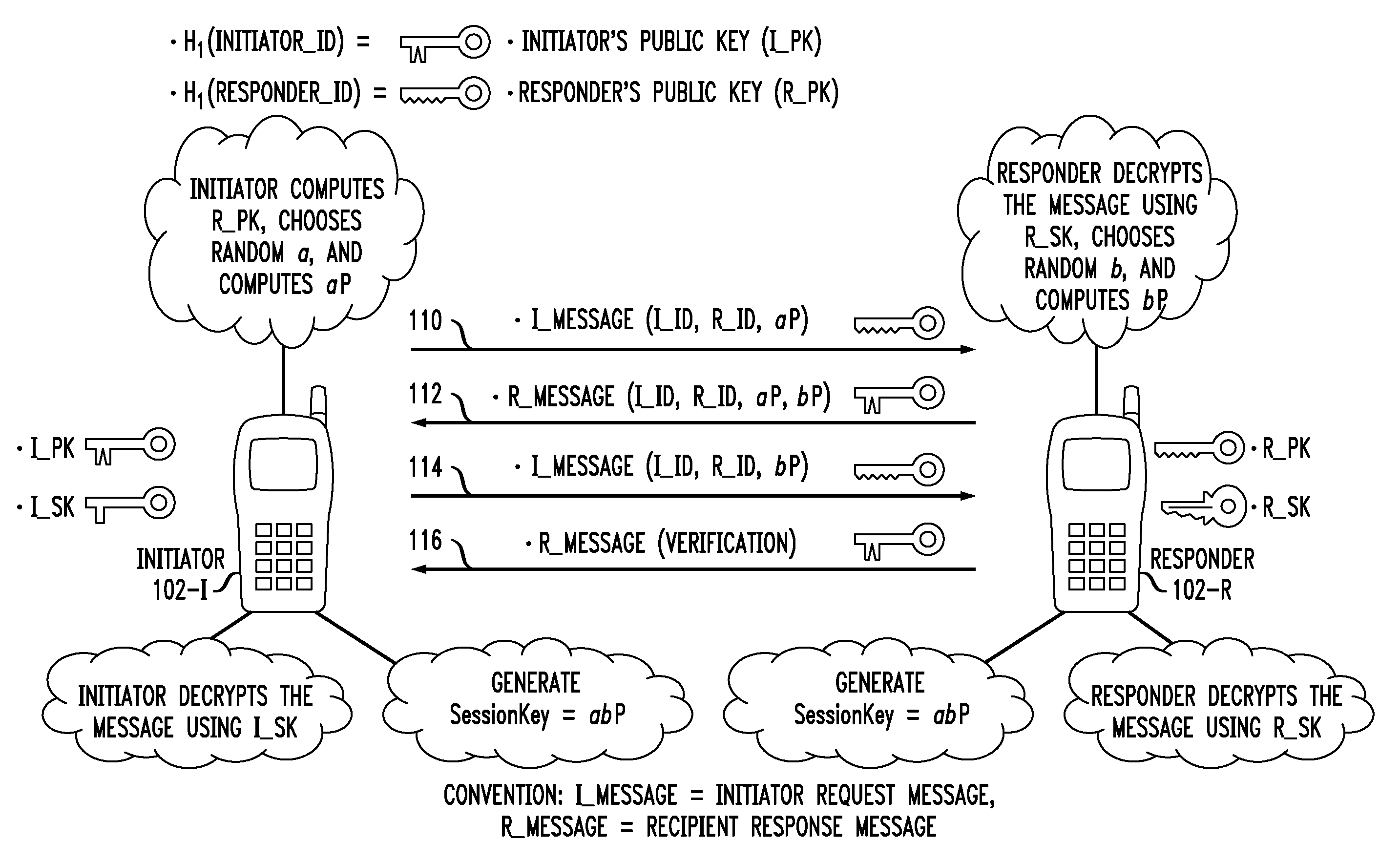
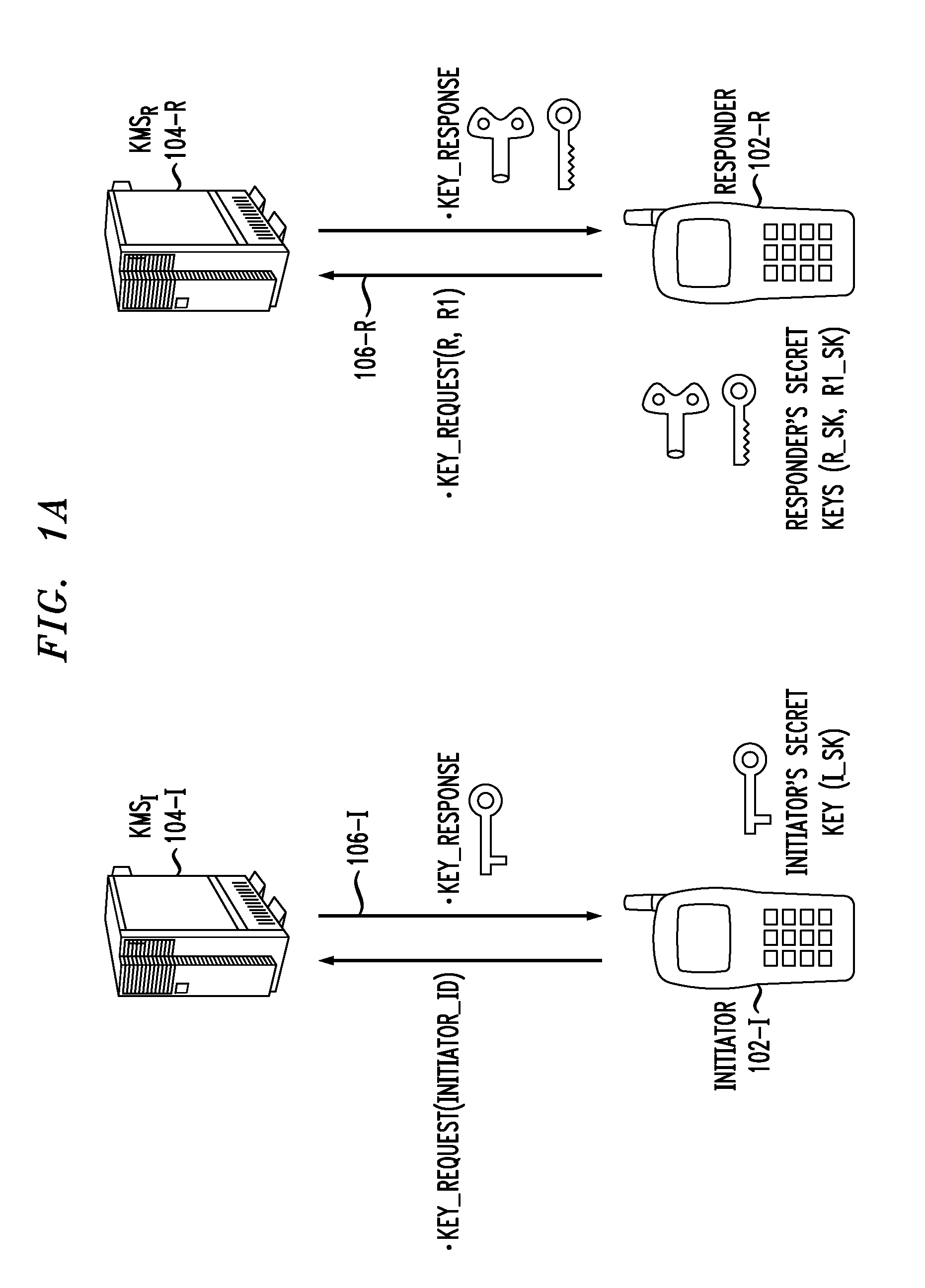
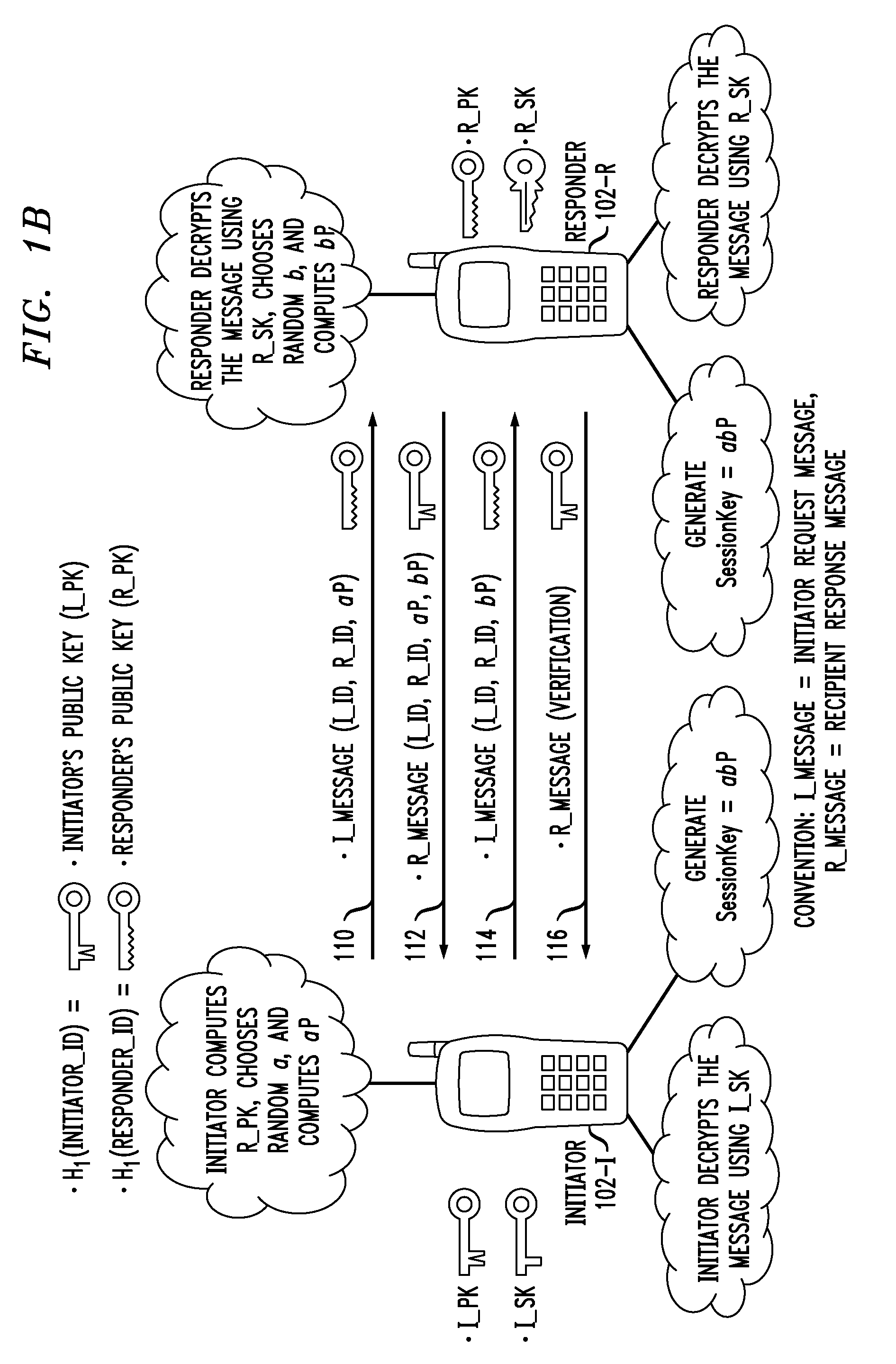
Secure Key Management in Multimedia Communication System
ActiveUS20110055567A1Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageID-based encryptionCommunications system
Principles of the invention provide one or more secure key management protocols for use in communication environments such as a media plane of a multimedia communication system. For example, a method for performing an authenticated key agreement protocol, in accordance with a multimedia communication system, between a first party and a second party comprises, at the first party, the following steps. Note that encryption / decryption is performed in accordance with an identity based encryption operation. At least one private key for the first party is obtained from a key service. A first message comprising an encrypted first random key component is sent from the first party to the second party, the first random key component having been computed at the first party, and the first message having been encrypted using a public key of the second party. A second message comprising an encrypted random key component pair is received at the first party from the second party, the random key component pair having been formed from the first random key component and a second random key component computed at the second party, and the second message having been encrypted at the second party using a public key of the first party. The second message is decrypted by the first party using the private key obtained by the first party from the key service to obtain the second random key component. A third message comprising the second random key component is sent from the first party to the second party, the third message having been encrypted using the public key of the second party. The first party computes a secure key based on the second random key component, the secure key being used for conducting at least one call session with the second party via a media plane of the multimedia communication system.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
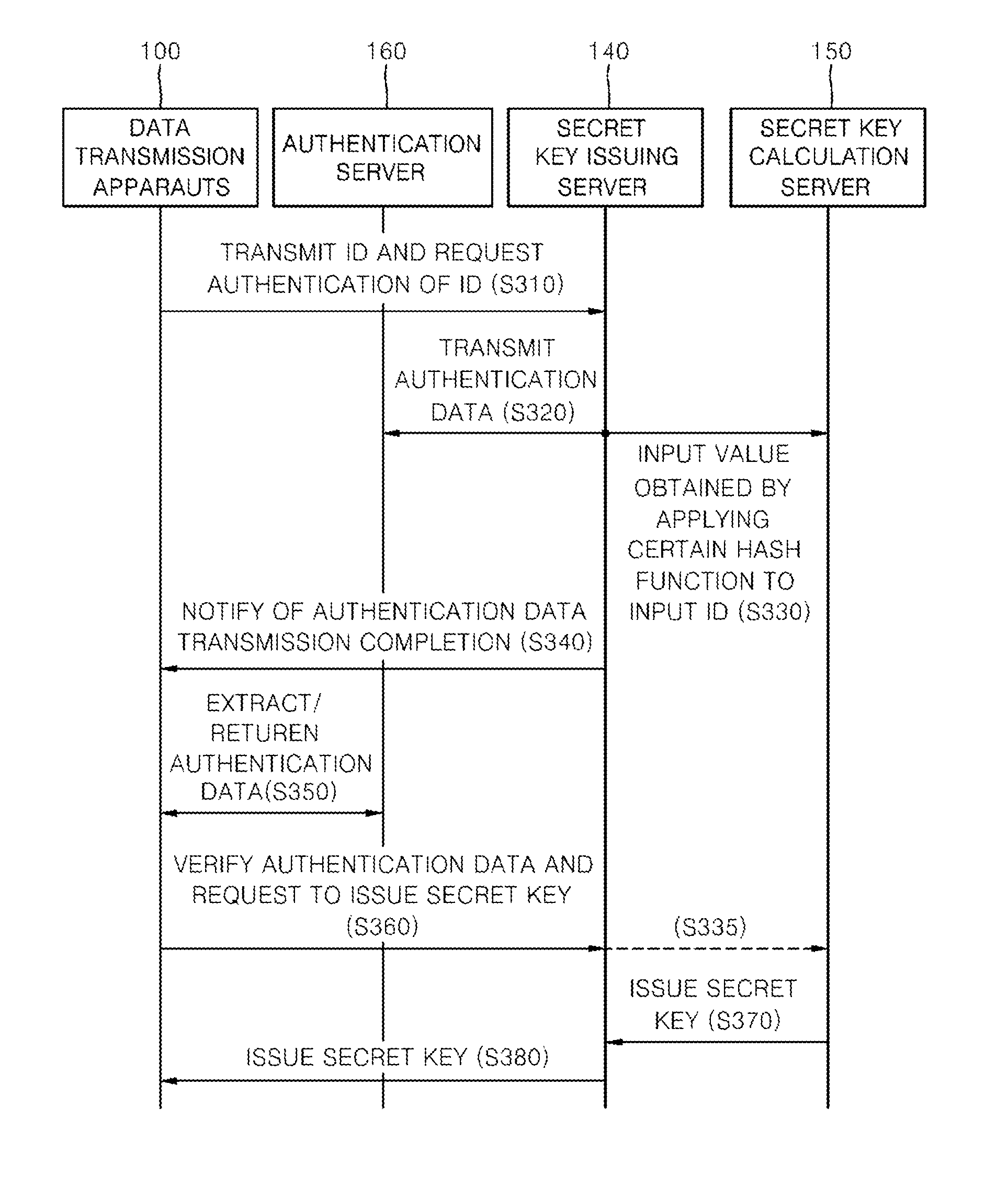
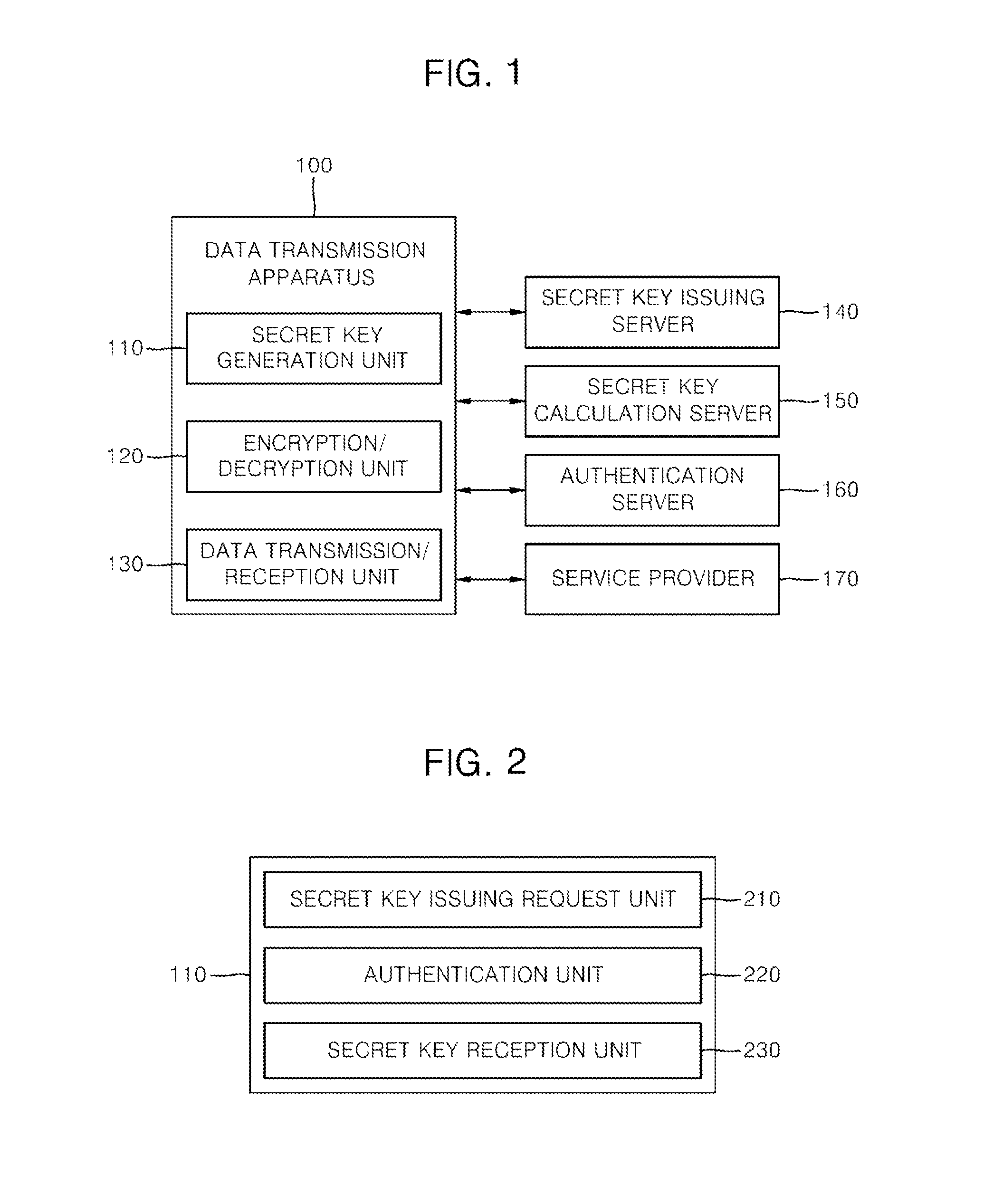
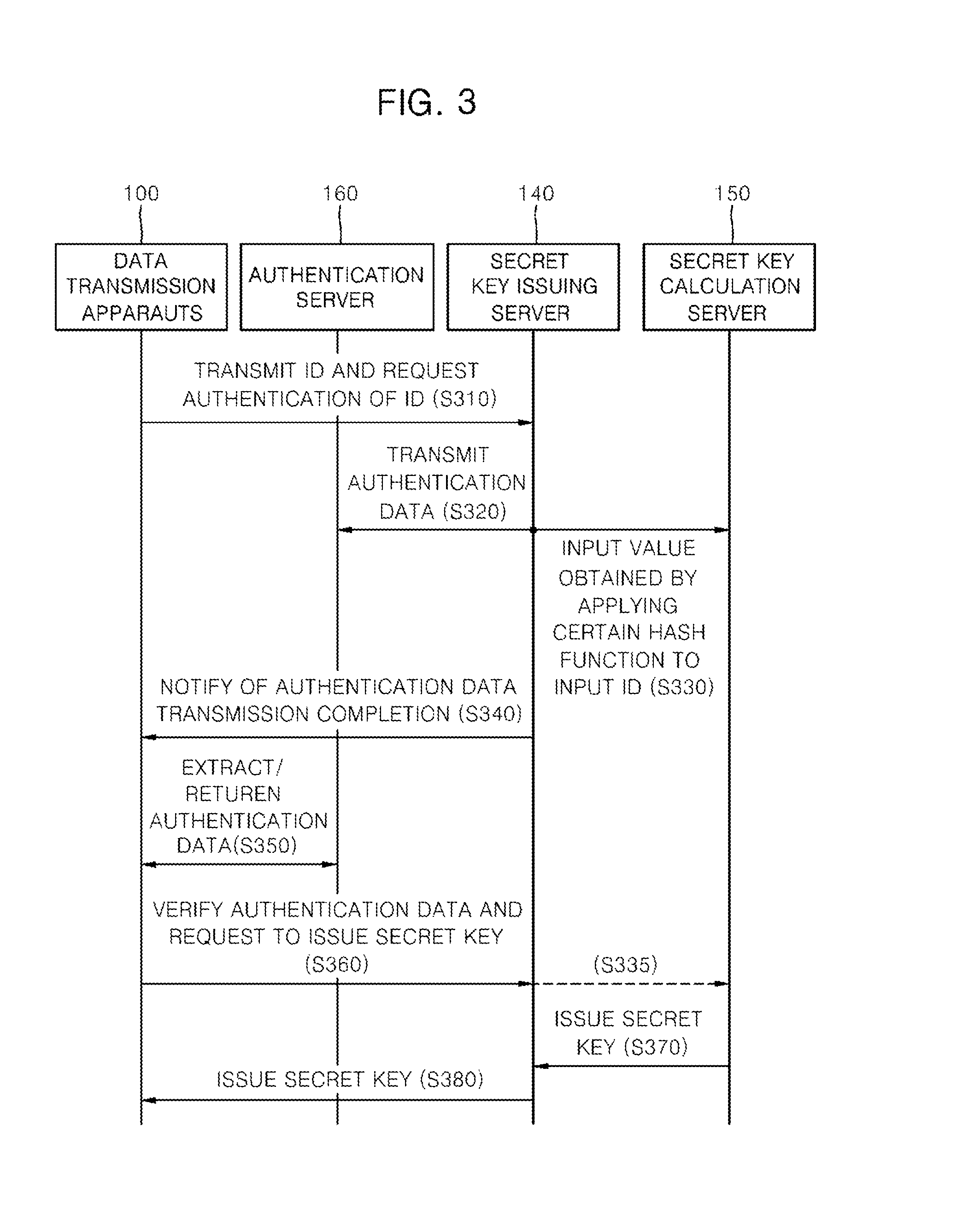
Apparatus and method for transmitting data, and recording medium storing program for executing method of the same in computer
ActiveUS20140101444A1Communication securitySafely encryptedKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationSecure communicationID-based encryption
Disclosed are a data transmission / reception apparatus and method. A secret key generation unit uses a user ID as a public key to generate a secret key corresponding to the user ID. An encryption / decryption unit sets a user ID intended to receive data as an input value to encrypt the data using a certain method and decrypt the encrypted data using a certain method on the basis of a secret key corresponding to a user ID of a receiver generated by the secret key generation unit. The transmission apparatus and method according to the present invention allow for secure communication between terminals without server intervention by encrypting data using an ID-based encryption technique for safe data communication and then communicating the encrypted data.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDS CO LTD
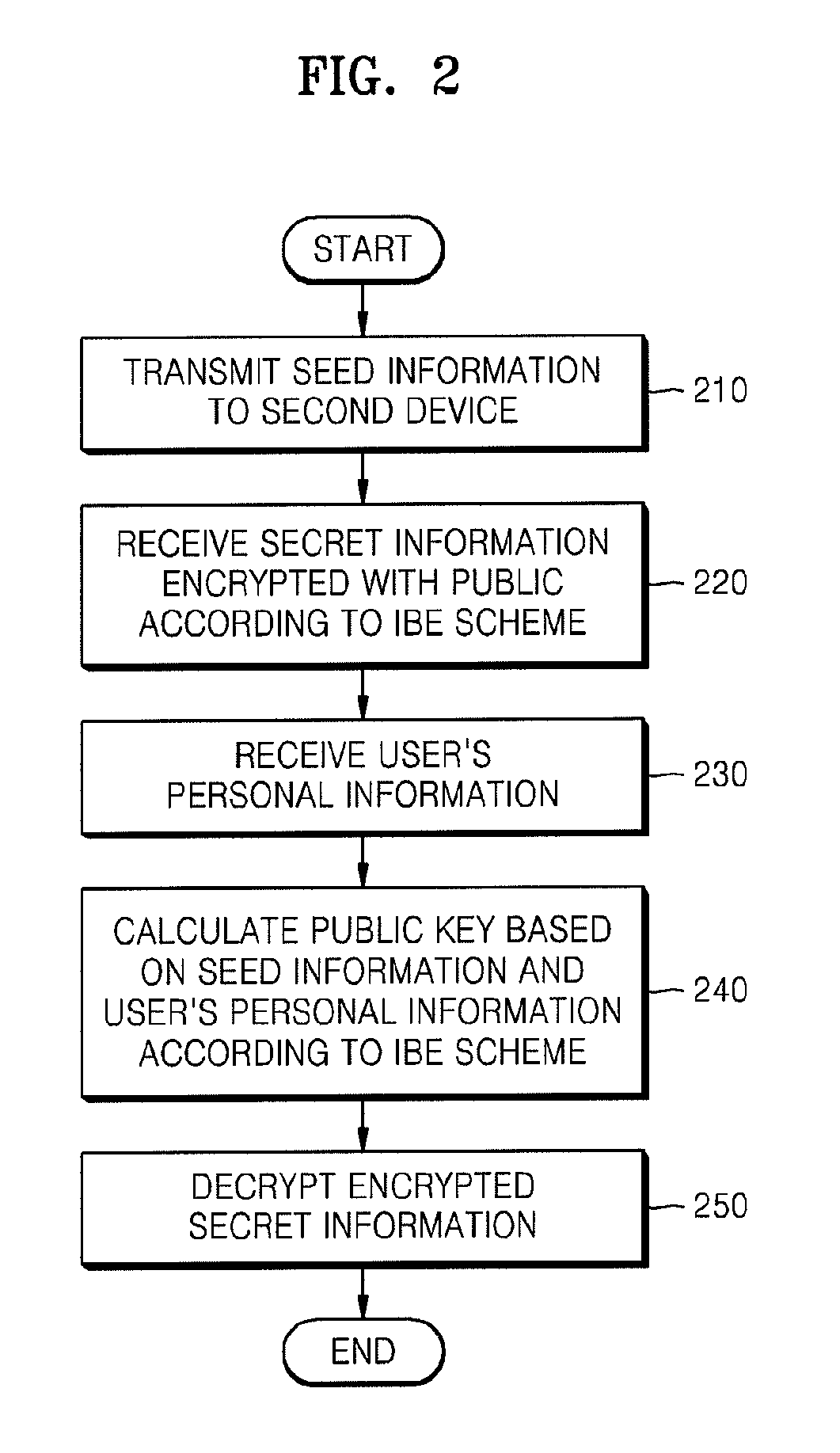
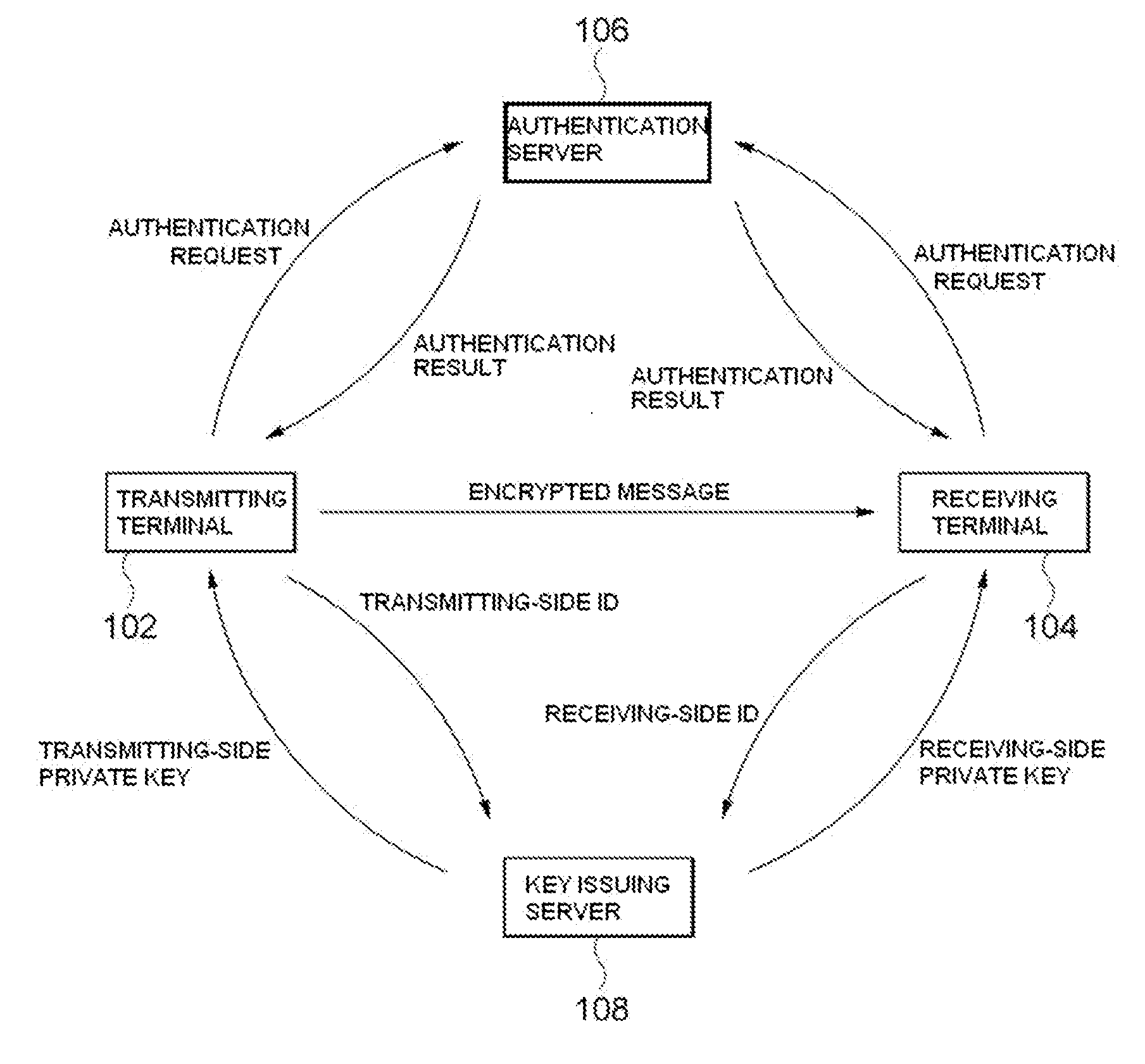
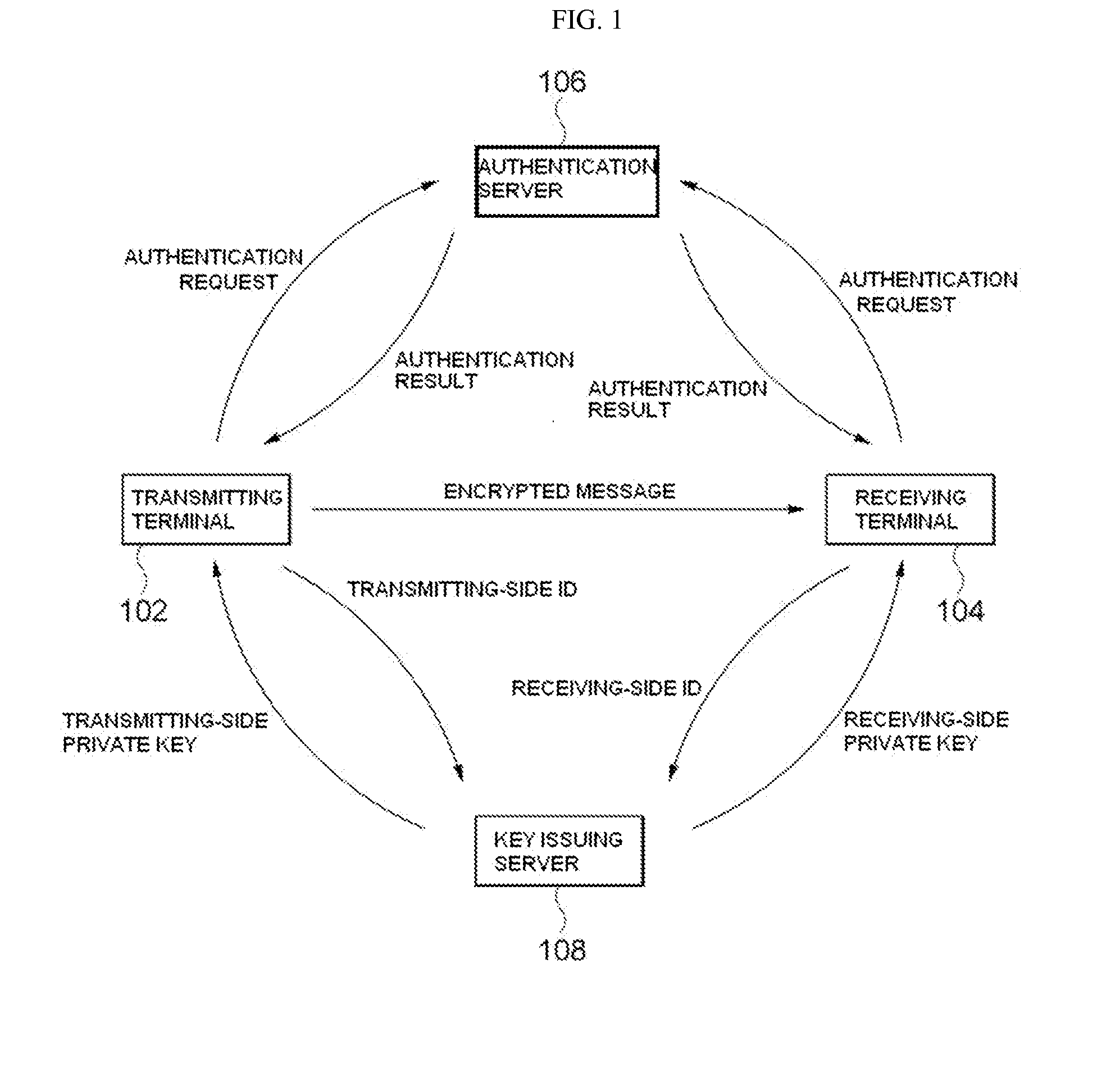
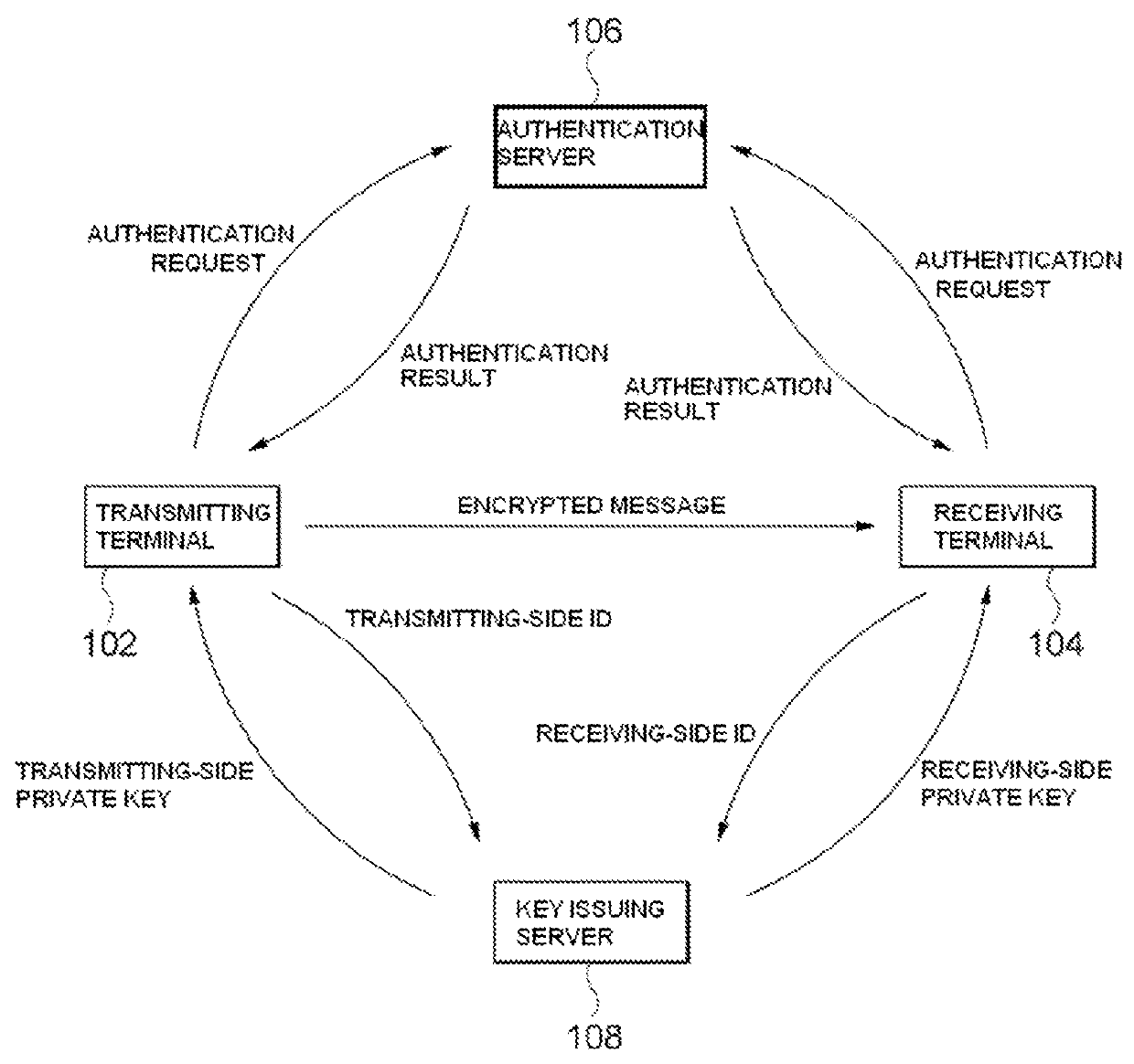
Method and system for id-based encryption and decryption
ActiveUS20140192976A1Improve stabilityKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageID-based encryptionSession key
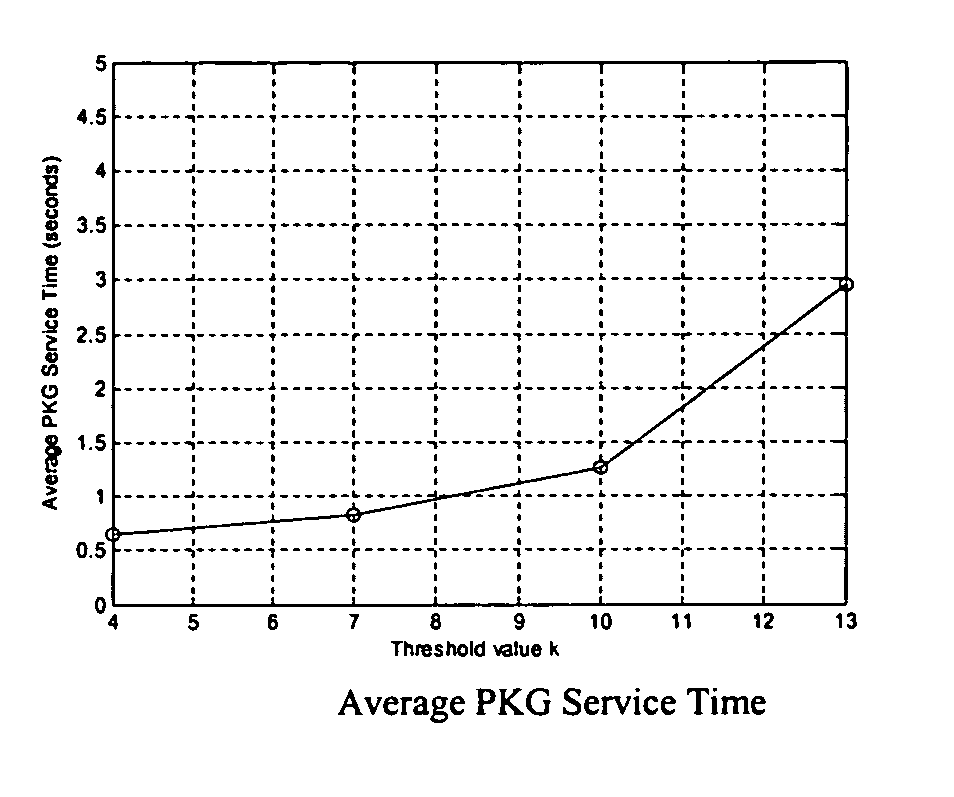
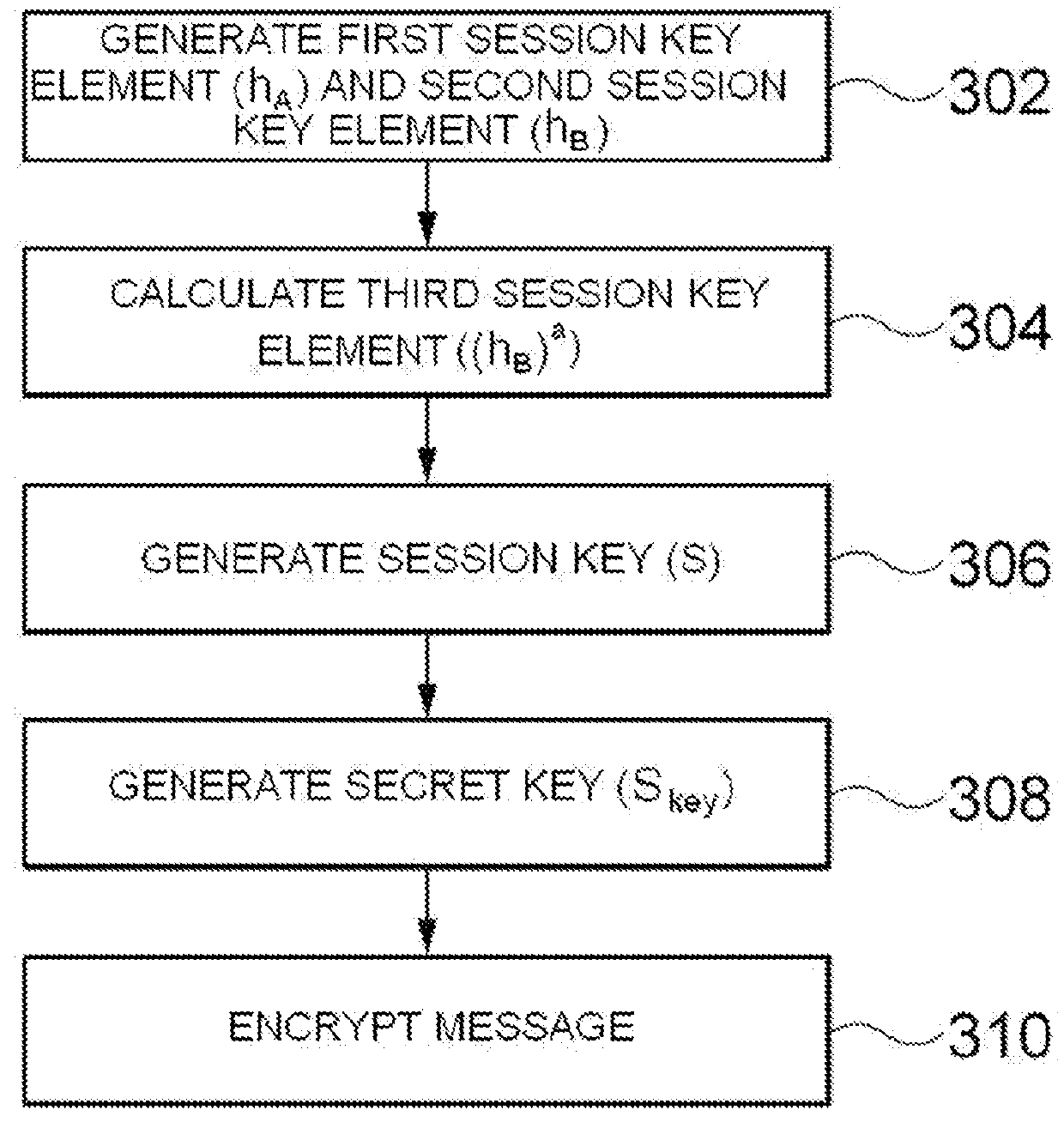
Provided are identifier (ID)-based encryption and decryption methods and apparatuses for the methods. The ID-based encryption method includes having, at a transmitting terminal, a transmitting-side private key corresponding to a transmitting-side ID issued by a key issuing server, generating, at the transmitting terminal, a session key using the transmitting-side ID, a receiving-side ID, and the transmitting-side private key, extracting, at the transmitting terminal, a secret key from at least a part of the session key, and encrypting, at the transmitting terminal, a message using a previously set encryption algorithm and the secret key.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDS CO LTD +1
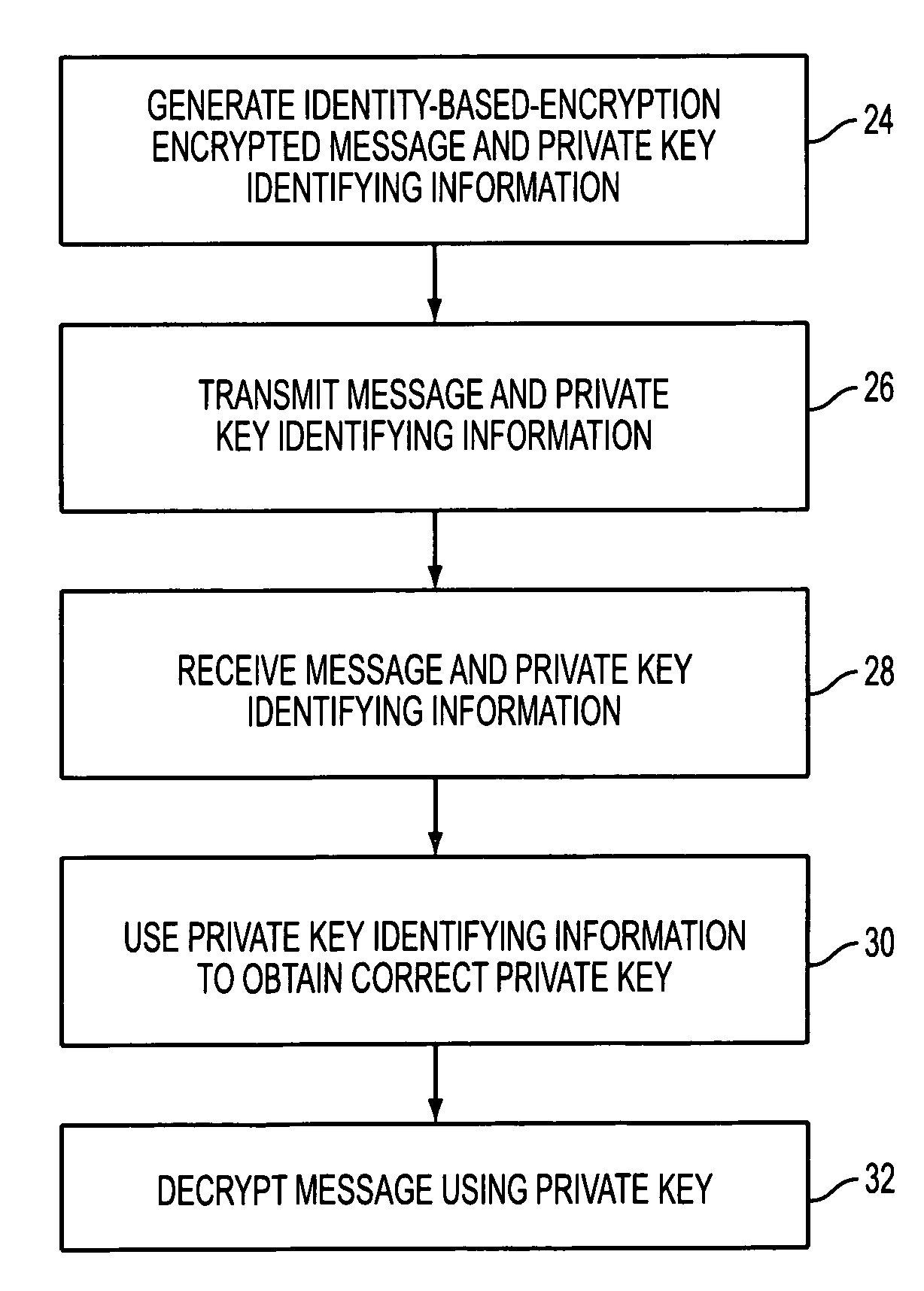
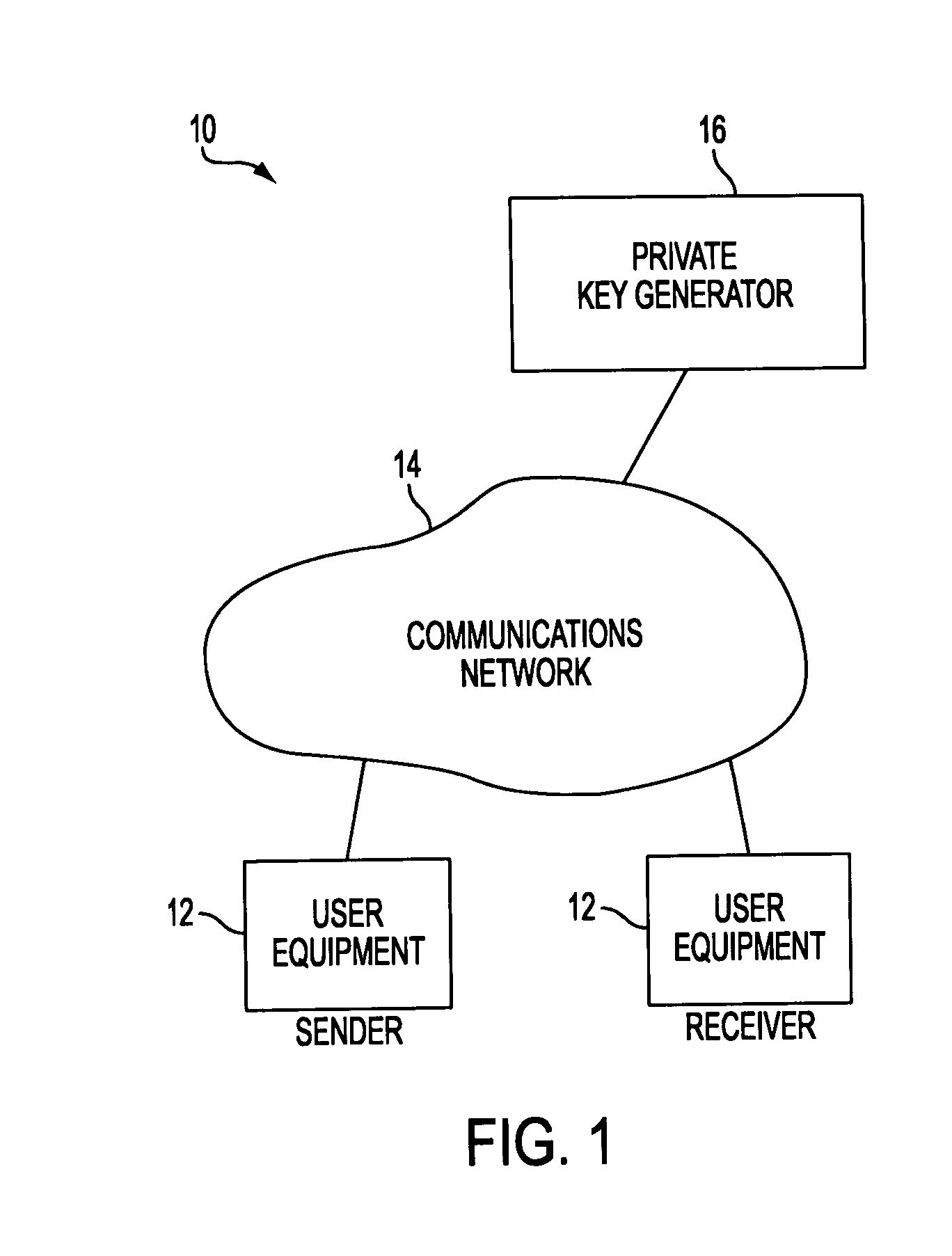
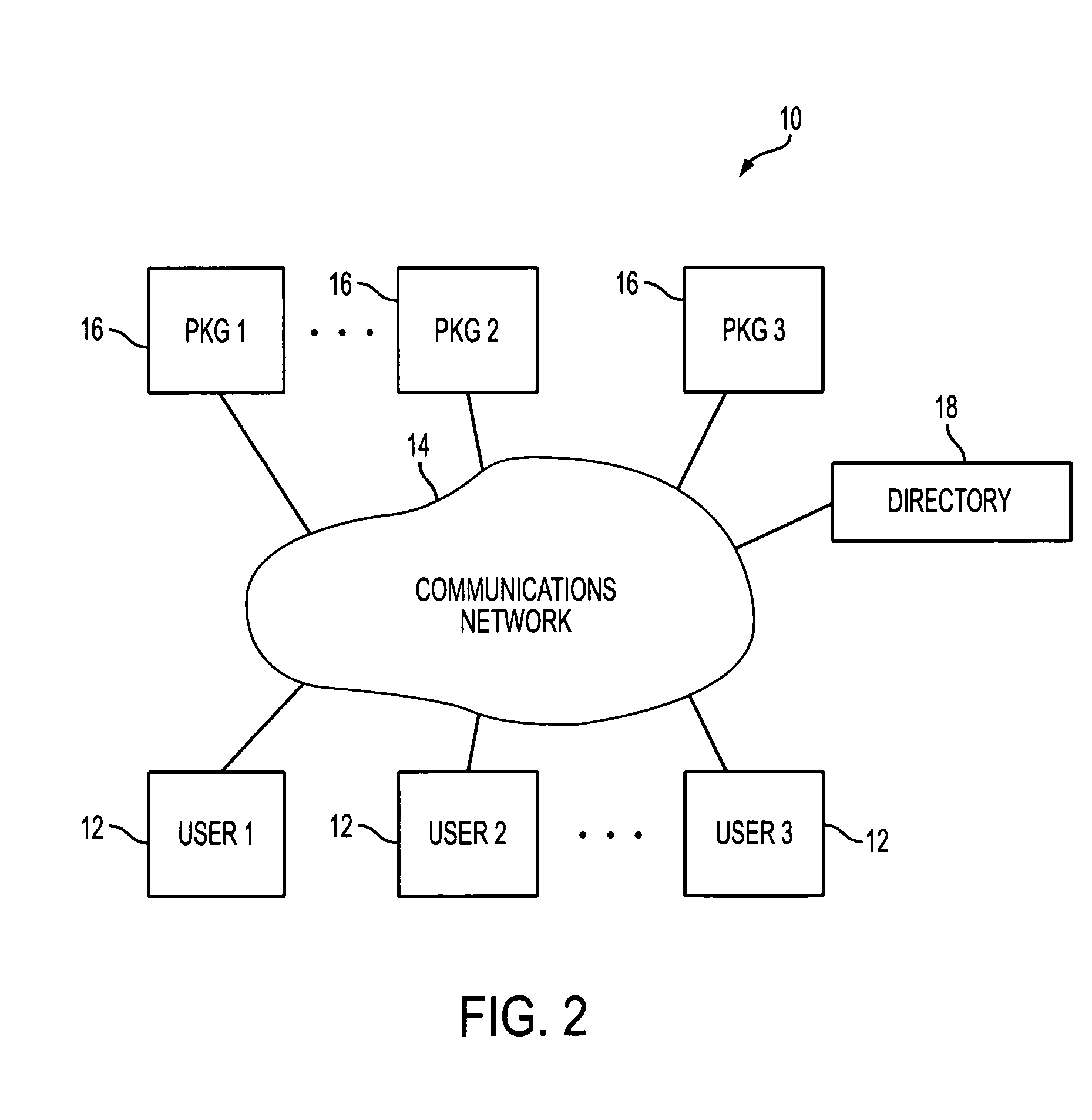
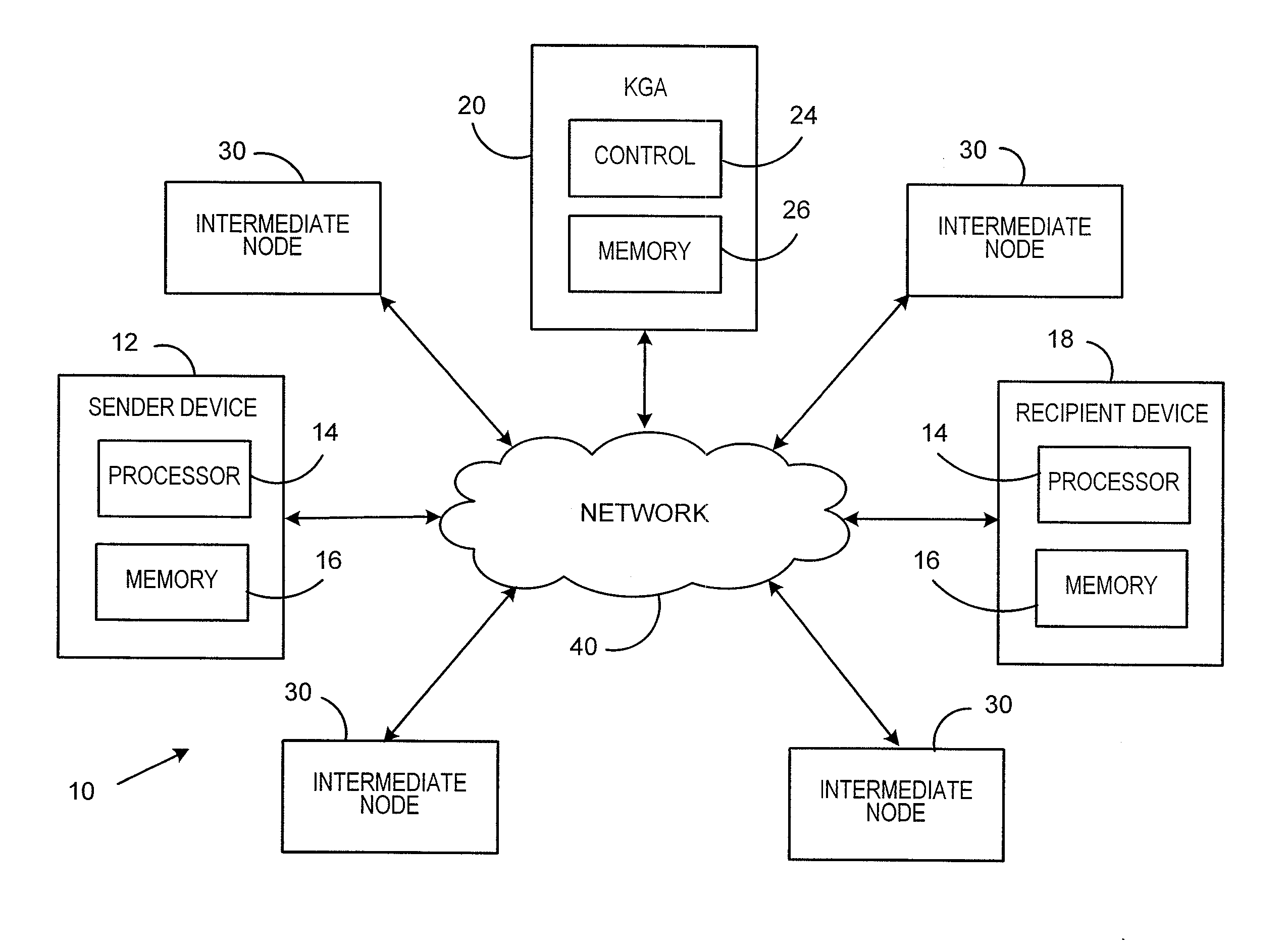
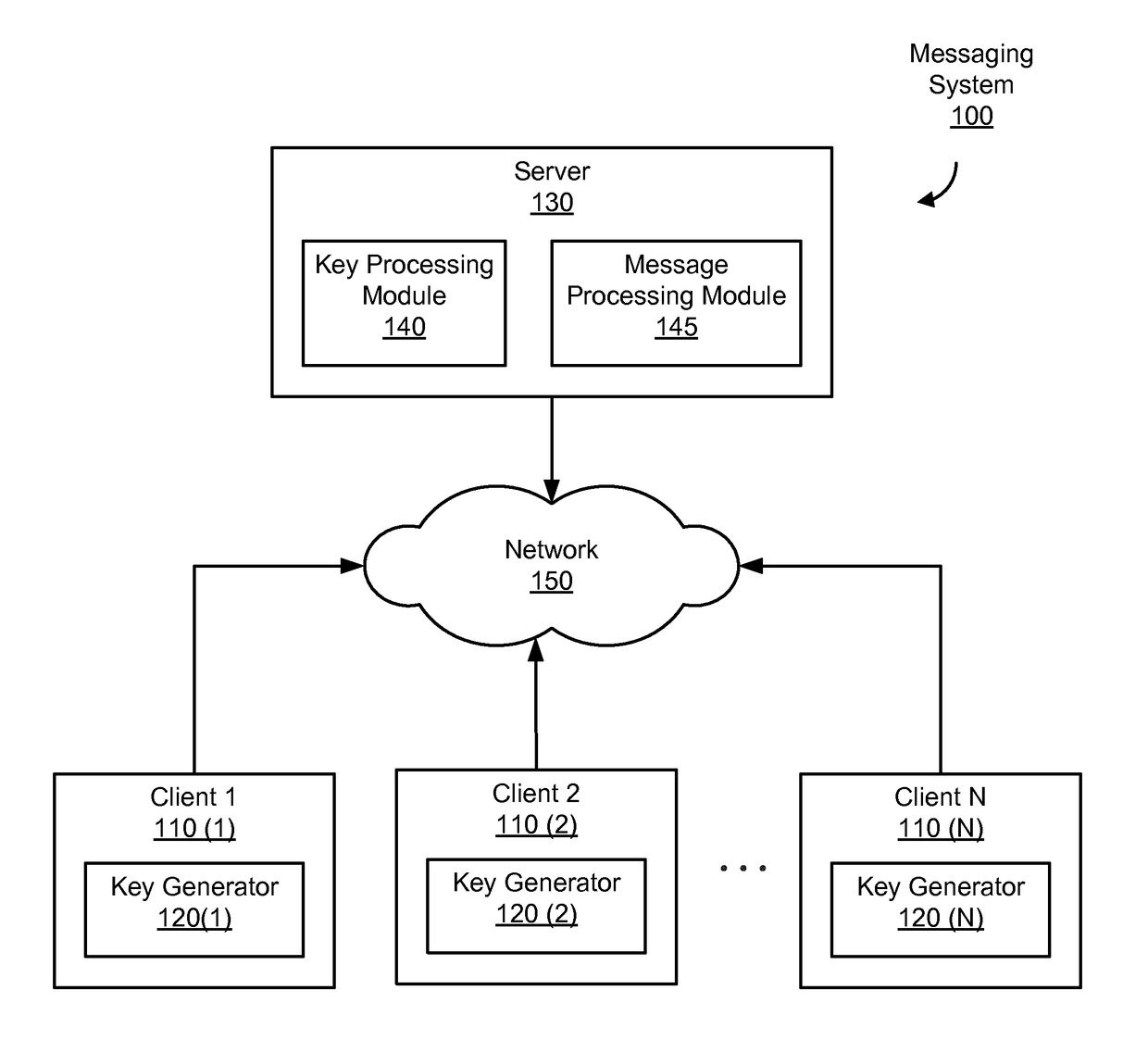
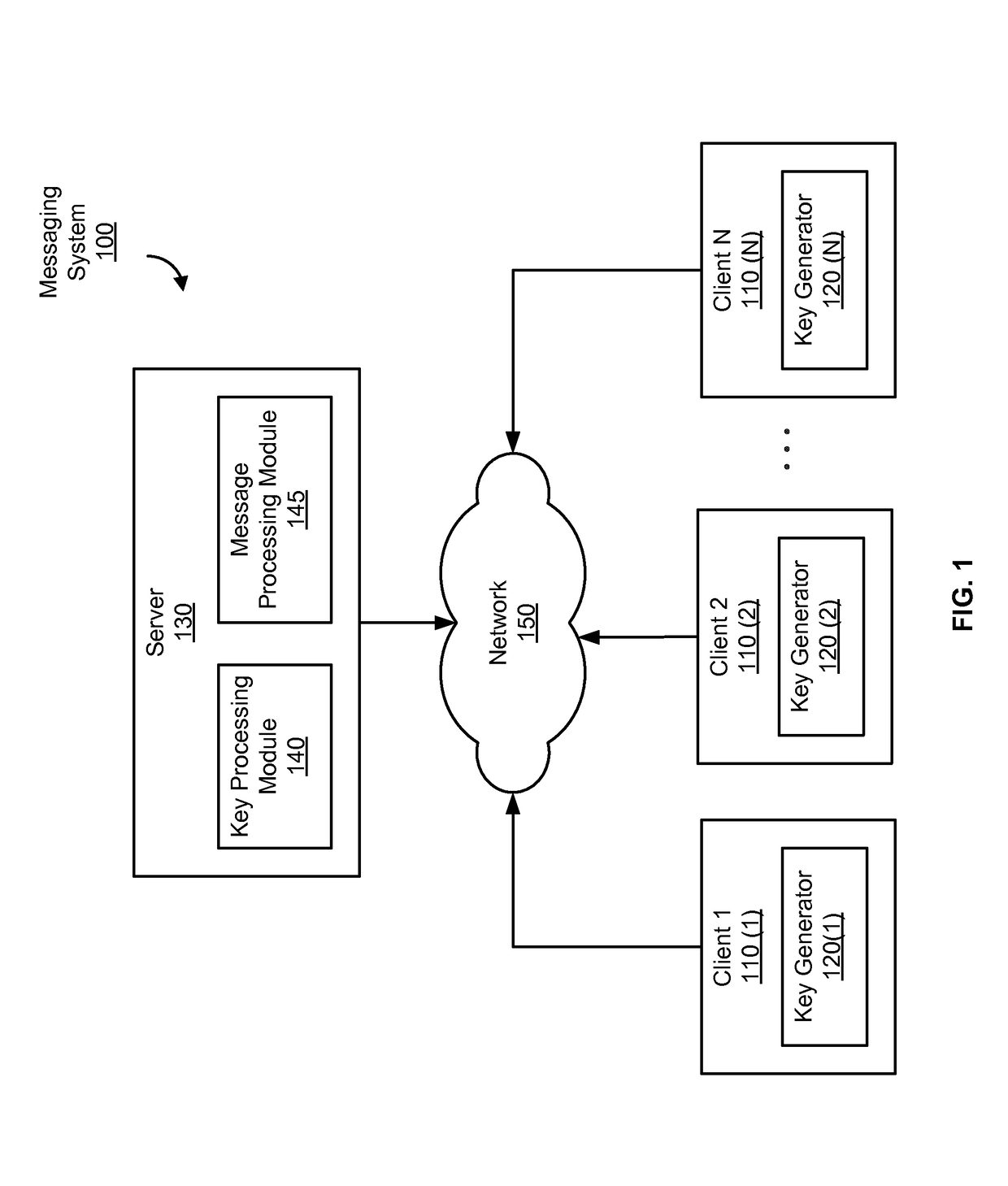
Identity-based-encryption messaging system
InactiveUS7571321B2Reduce decreaseKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsSecure communicationKey generator
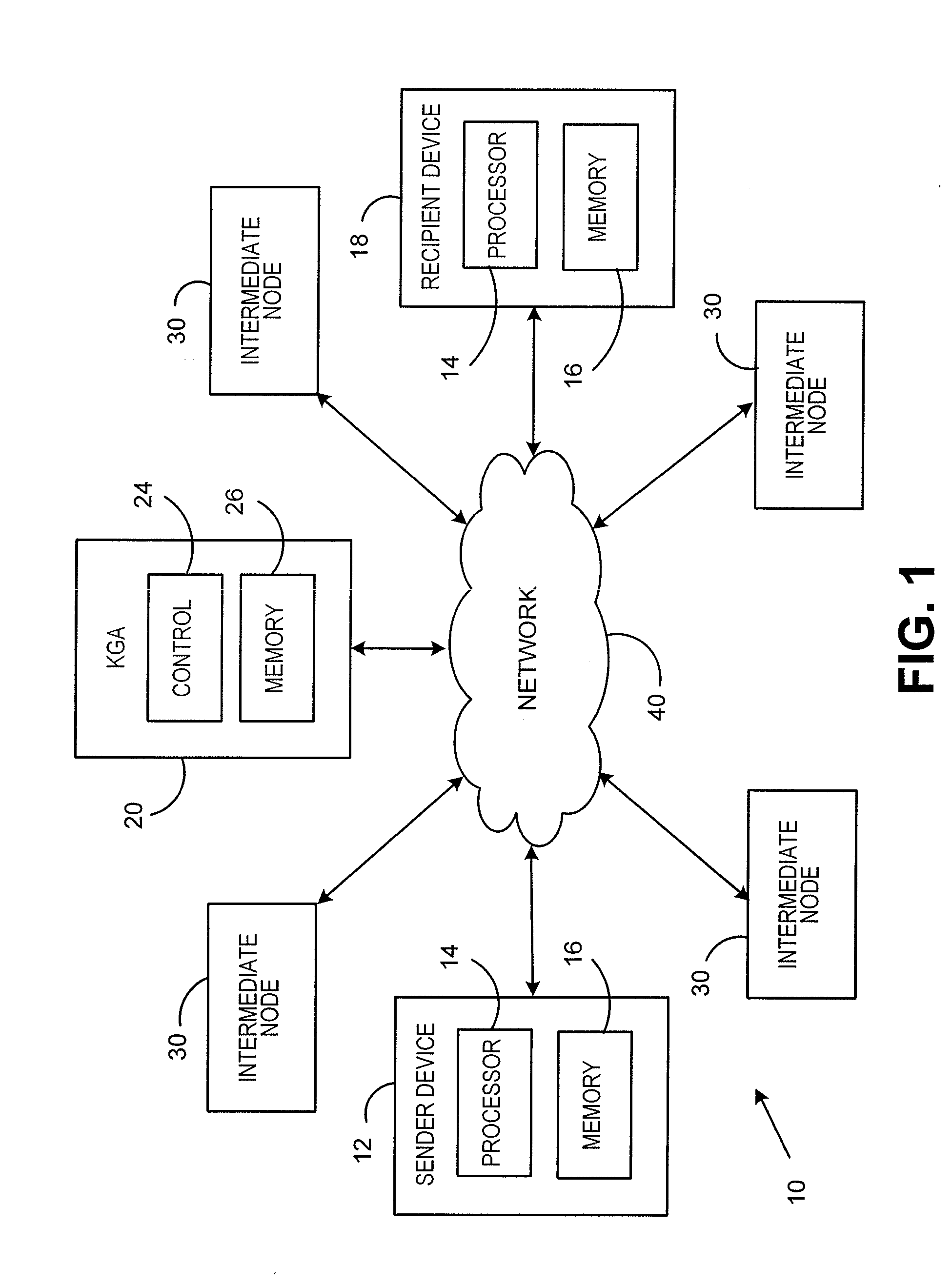
A system is provided that uses identity-based encryption to support secure communications between senders and recipients over a communications network. Private key generators are used to provide public parameter information. Senders encrypt messages for recipients using public keys based on recipient identities and using the public parameter information as inputs to an identity-based encryption algorithm. Recipients use private keys to decrypt the messages. There may be multiple private key generators in the system and a given recipient may have multiple private keys. Senders can include private key identifying information in the messages they send to recipients. The private key identifying information may be used by the recipients to determine which of their private keys to use in decrypting a message. Recipients may obtain the correct private key to use to decrypt a message from a local database of private keys or from an appropriate private key server.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS LLC
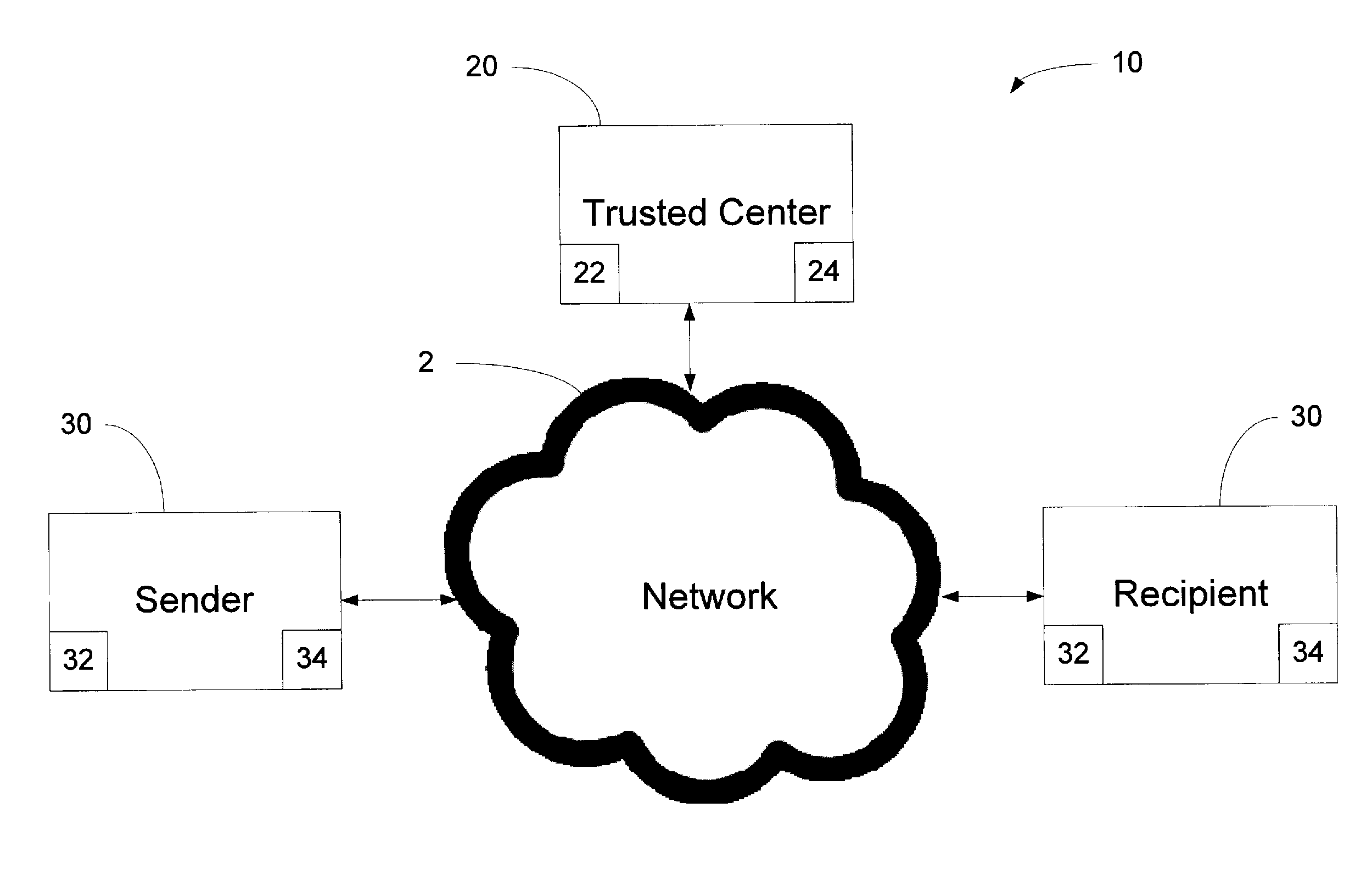
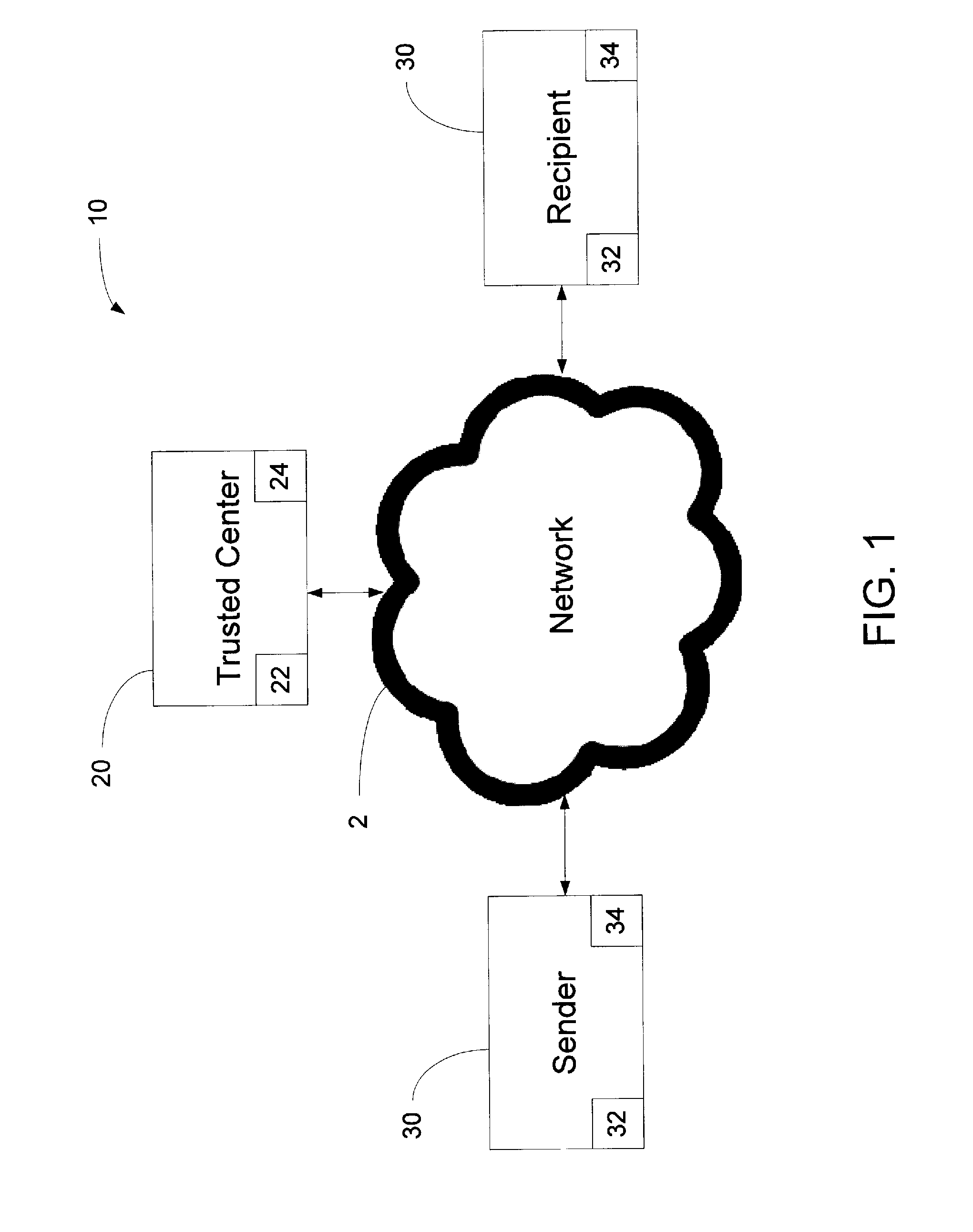
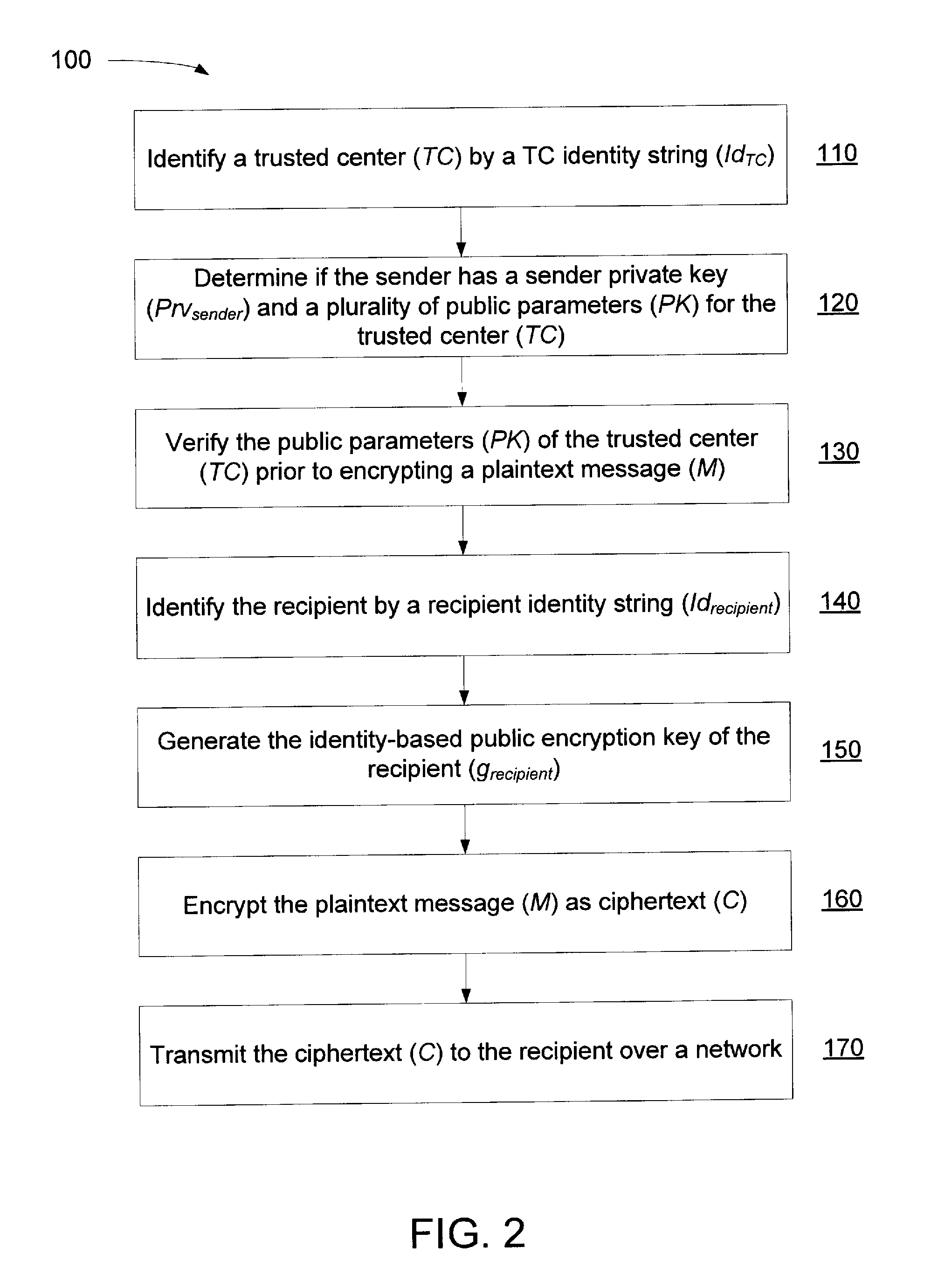
Method and System for a Certificate-less Authenticated Encryption Scheme Using Identity-based Encryption
ActiveUS20130212377A1Good flexibilityEliminate needPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationPlaintextID-based encryption
A method of verifying public parameters from a trusted center in an identity-based encryption system prior to encrypting a plaintext message by a sender having a sender identity string may include: identifying the trusted center by a TC identity string, the trusted center having an identity-based public encryption key of the trusted center based on the TC identity string; determining if the sender has a sender private key and the public parameters for the trusted center including the public encryption key of the trusted center and a bilinear map; and verifying the public parameters using the TC identity string prior to encrypting the plaintext message into a ciphertext by comparing values of the bilinear map calculated with variables from the trusted center. The ciphertext may include a component to authenticate the sender once the ciphertext is received and decrypted by the recipient using the private key of the recipient.
Owner:VIBE CYBERSECURITY IP LLC
Systems and methods for identity-based encryption and related cryptographic techniques
InactiveUS20070041583A1Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationID-based encryptionEmail address
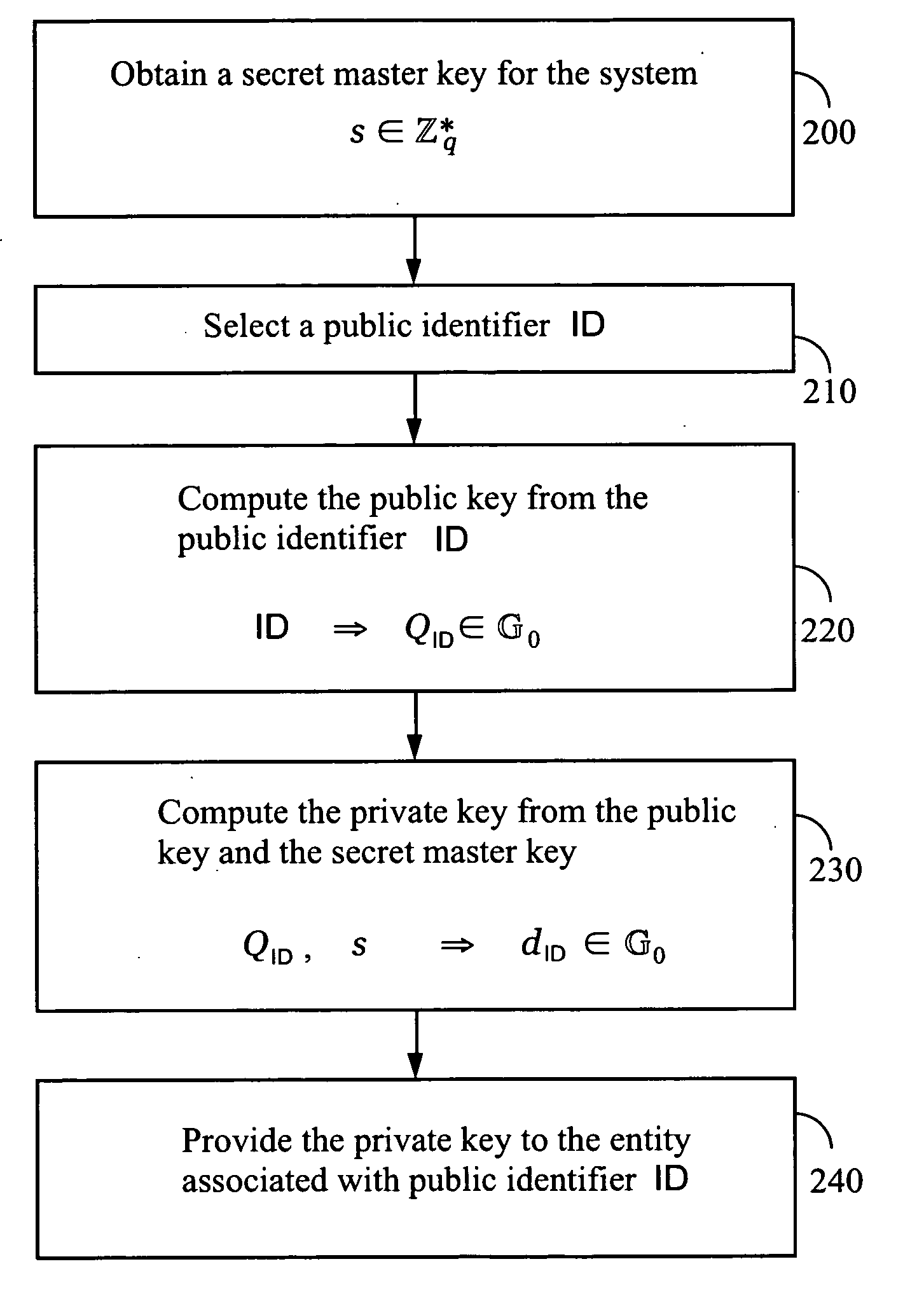
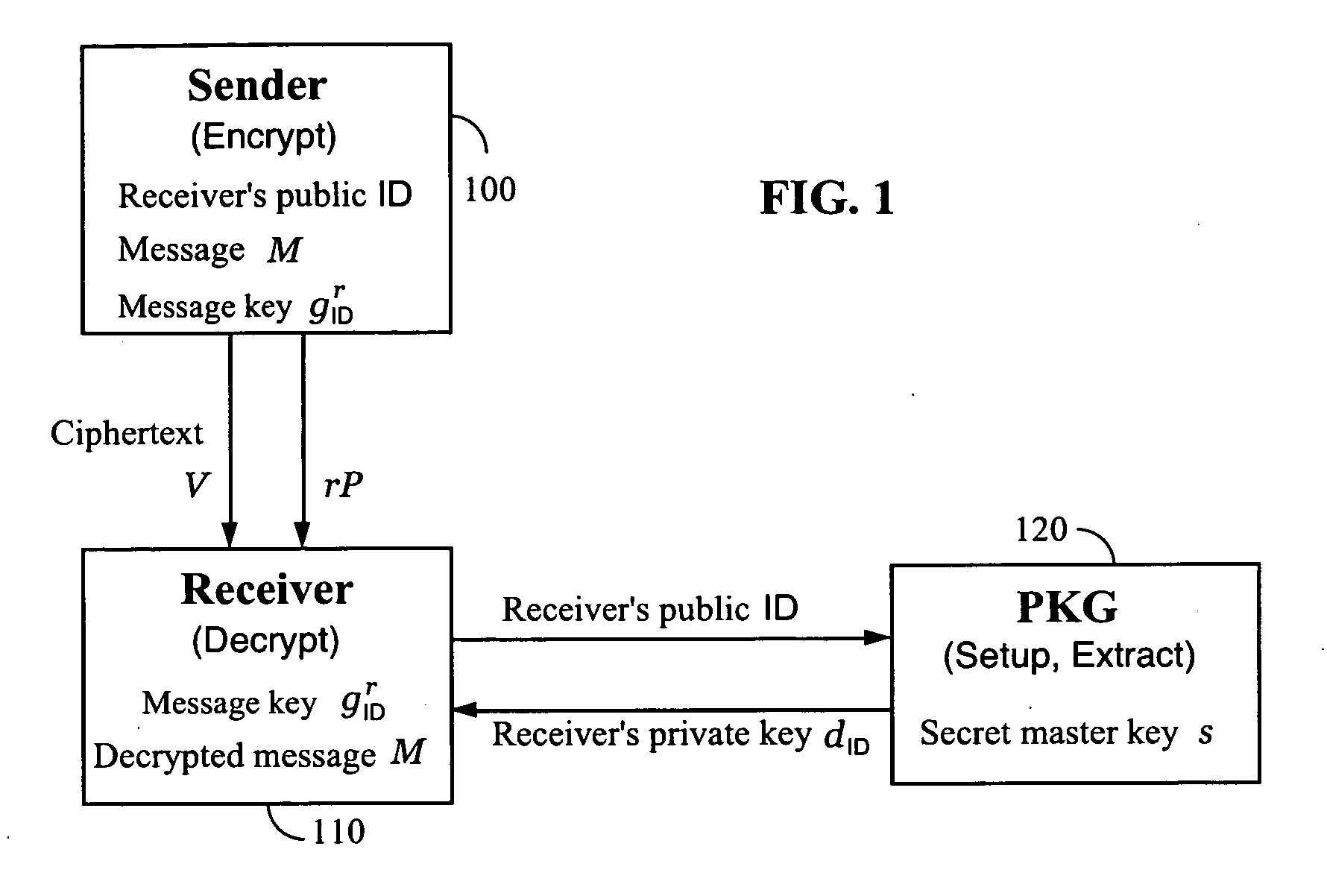
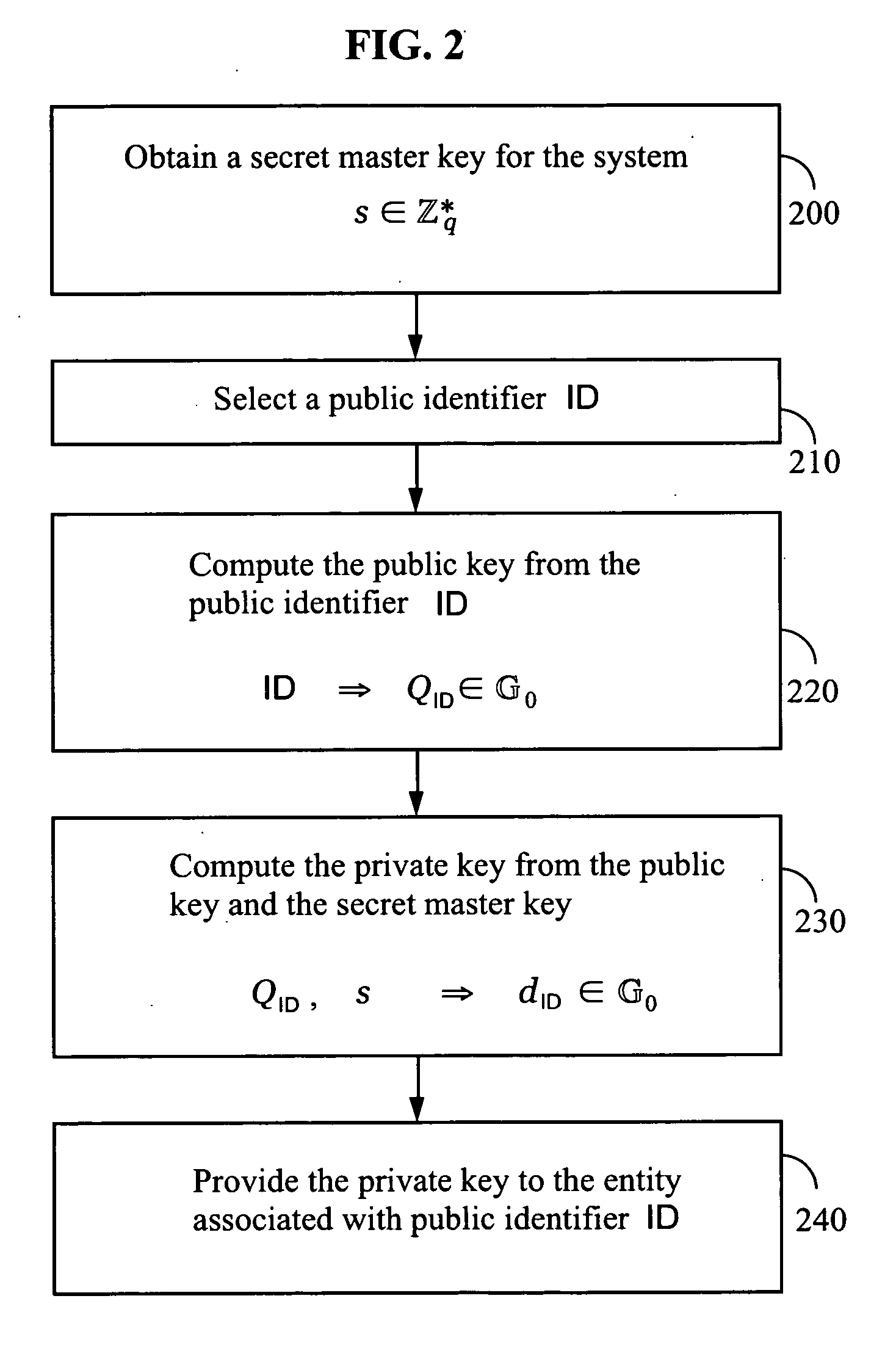
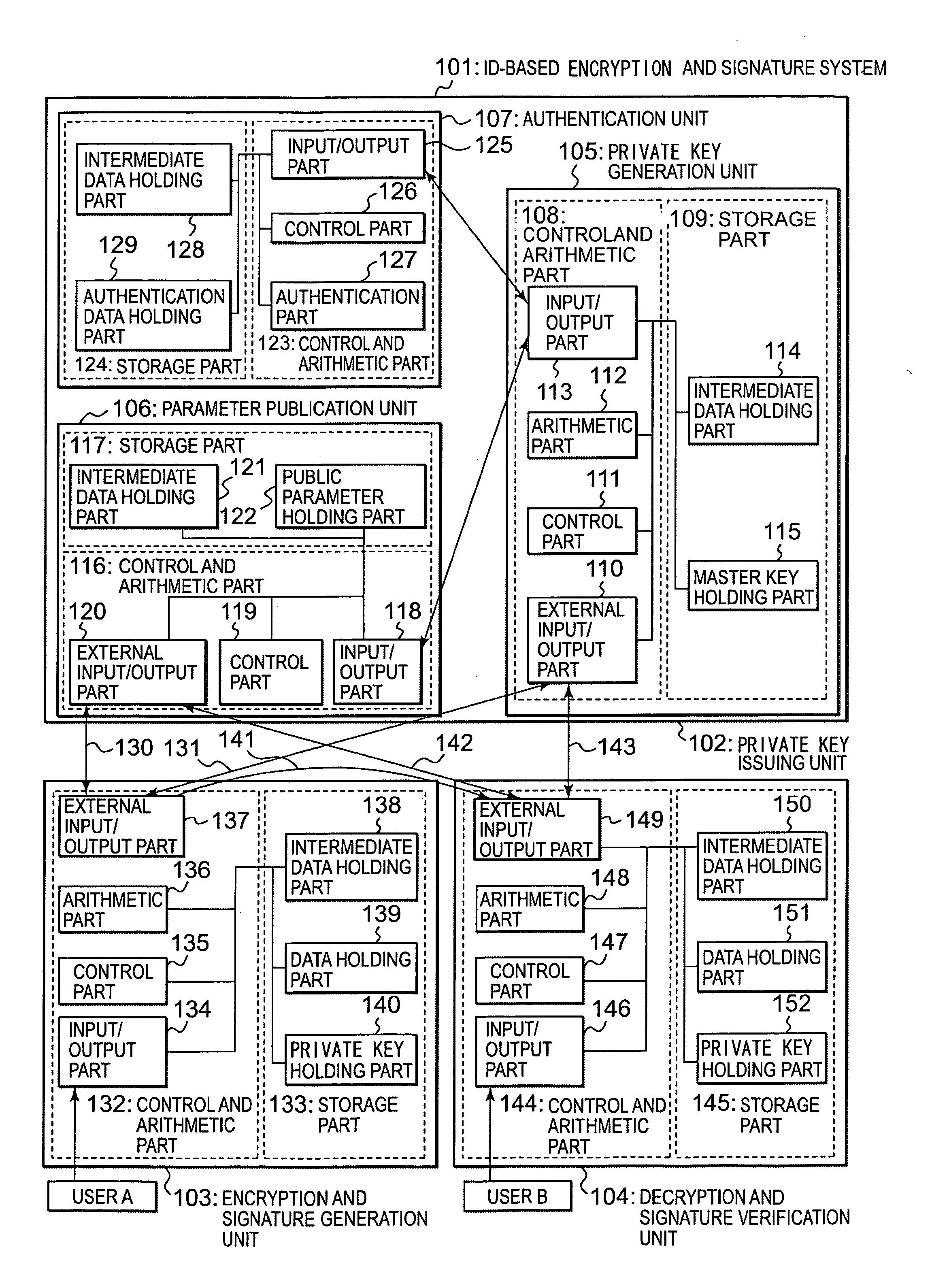
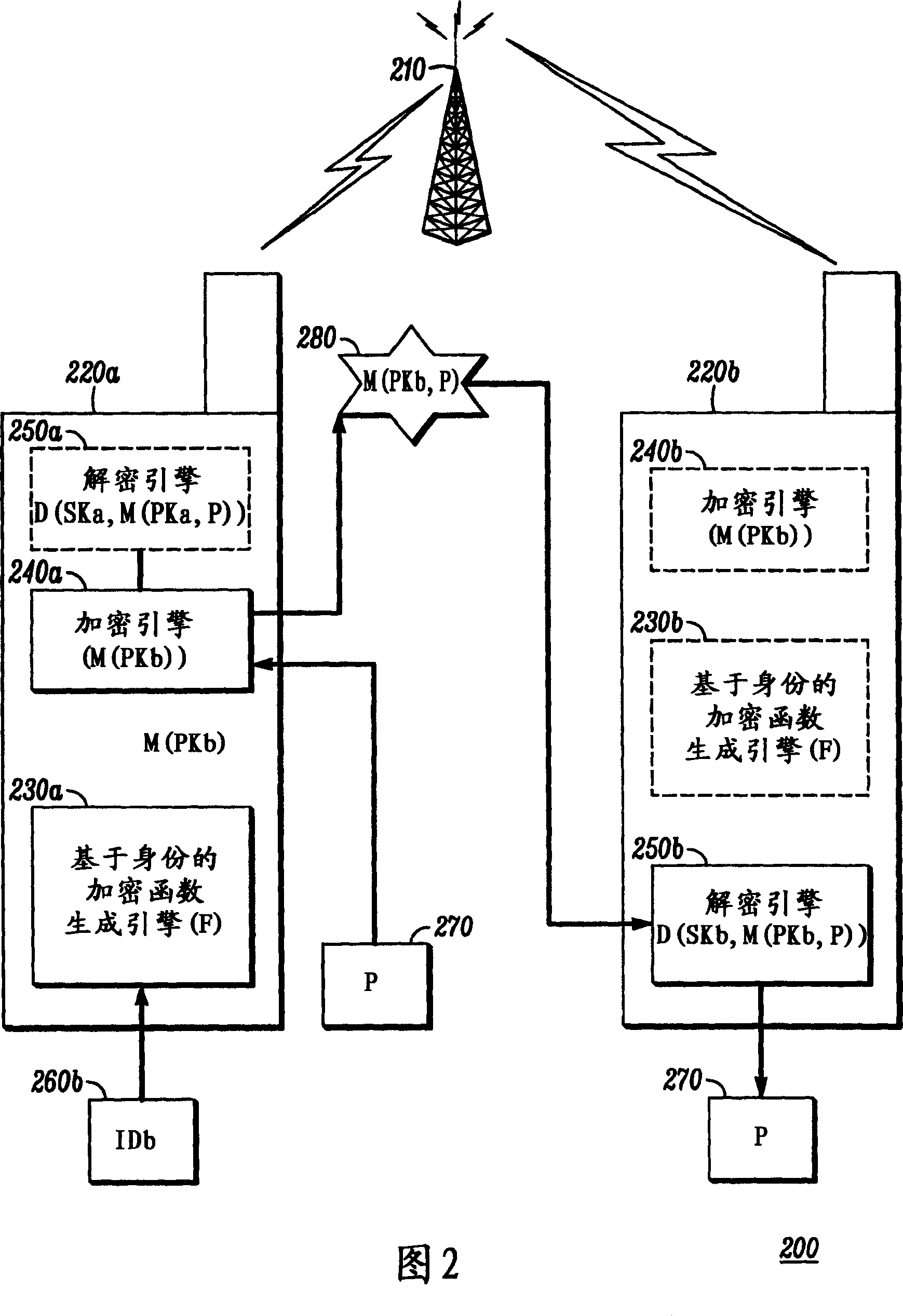
A method and system for encrypting a first piece of information M to be sent by a sender [100] to a receiver [110] allows both sender and receiver to compute a secret message key using identity-based information and a bilinear map. In a one embodiment, the sender [100] computes an identity-based encryption key from an identifier ID associated with the receiver [110]. The identifier ID may include various types of information such as the receiver's e-mail address, a receiver credential, a message identifier, or a date. The sender uses a bilinear map and the encryption key to compute a secret message key gIDr, which is then used to encrypt a message M, producing ciphertext V to be sent from the sender [100] to the receiver [110] together with an element rP. An identity-based decryption key dID is computed by a private key generator [120] based on the ID associated with the receiver and a secret master key s. After obtaining the private decryption key from the key generator [120], the receiver [110] uses it together with the element rP and the bilinear map to compute the secret message key gIDr, which is then used to decrypt V and recover the original message M. According to one embodiment, the bilinear map is based on a Weil pairing or a Tate pairing defined on a subgroup of an elliptic curve. Also described are several applications of the techniques, including key revocation, credential management, and return receipt notification.
Owner:UNIV OF CALIFORNIA DAVIS +1
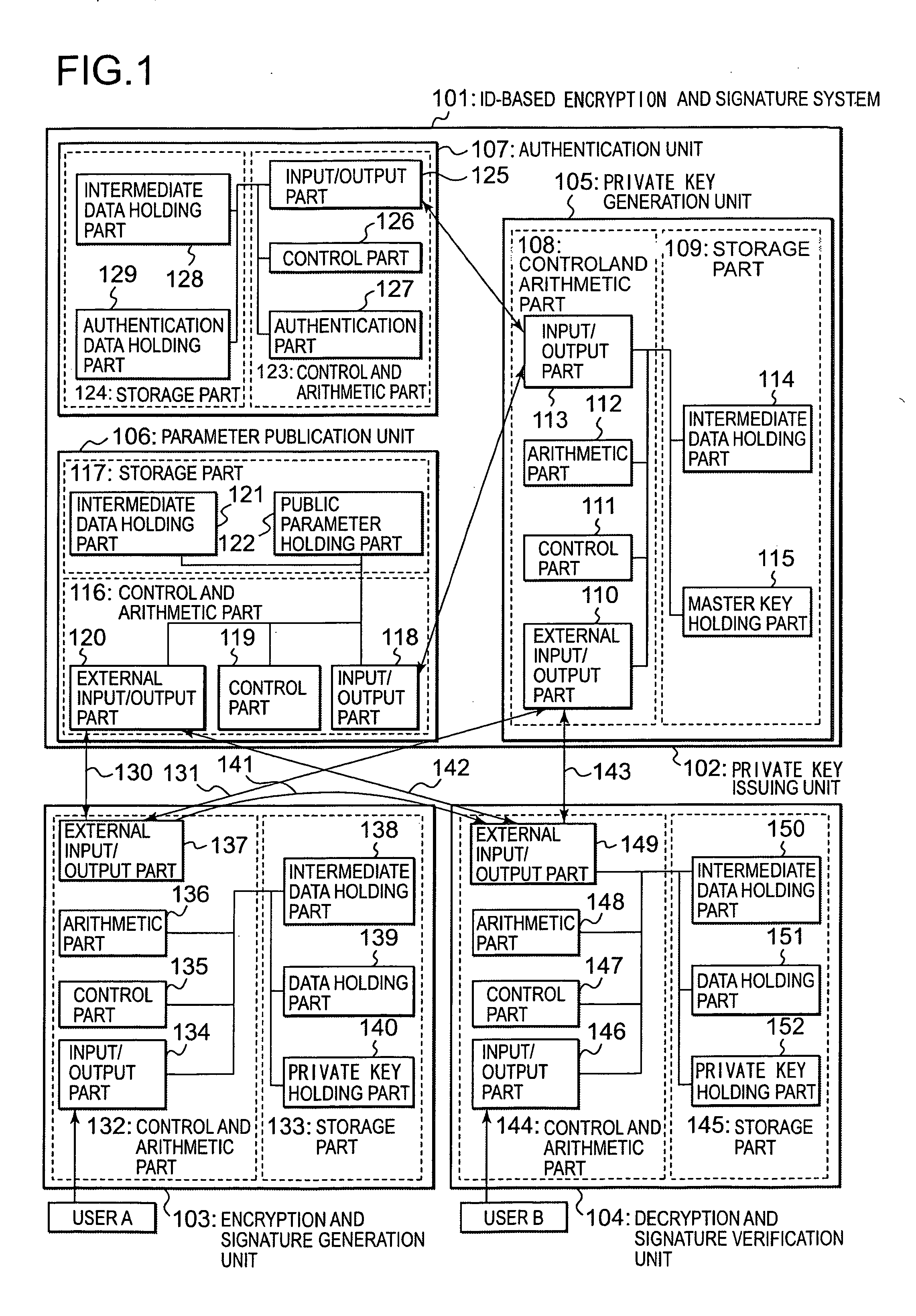
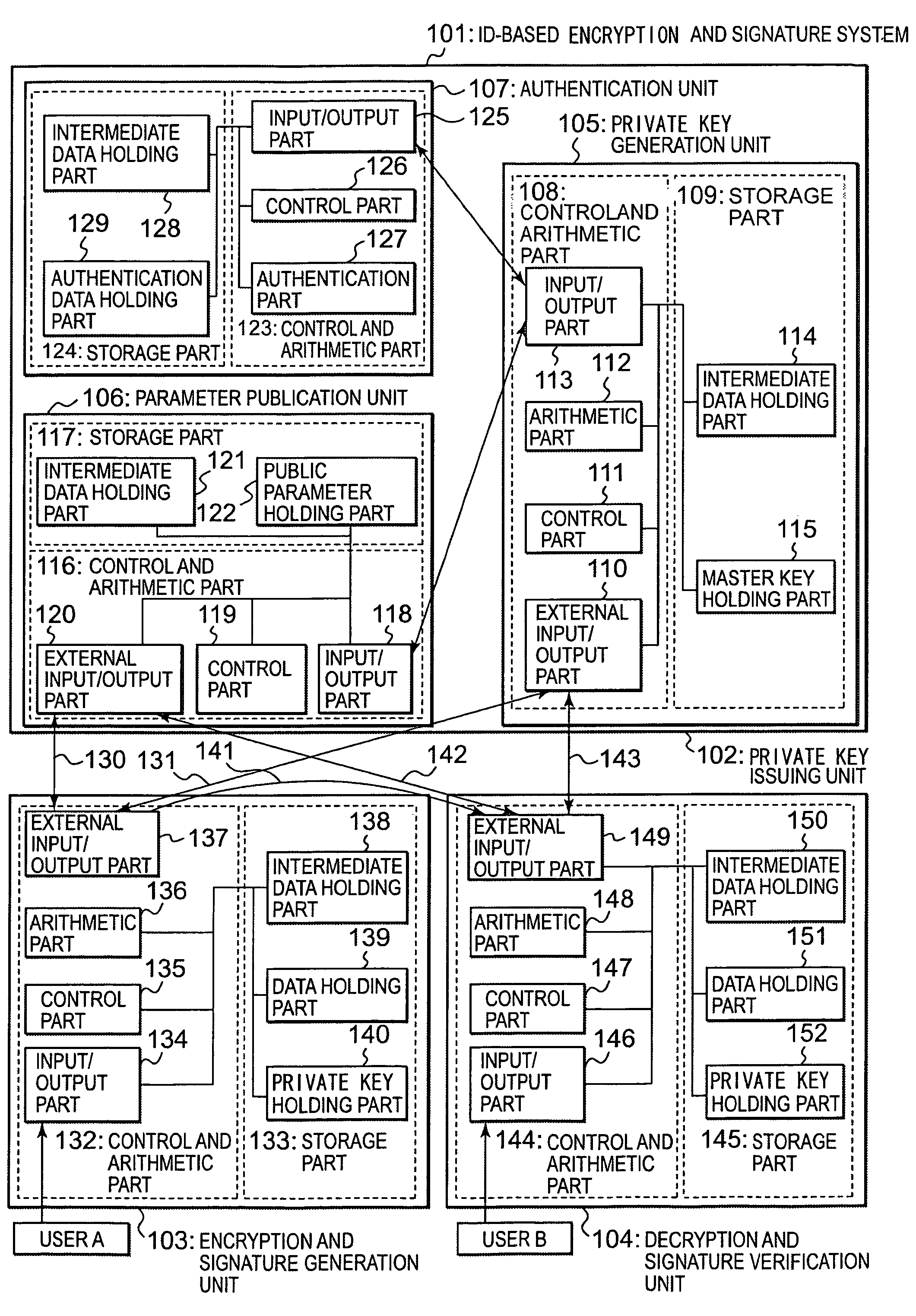
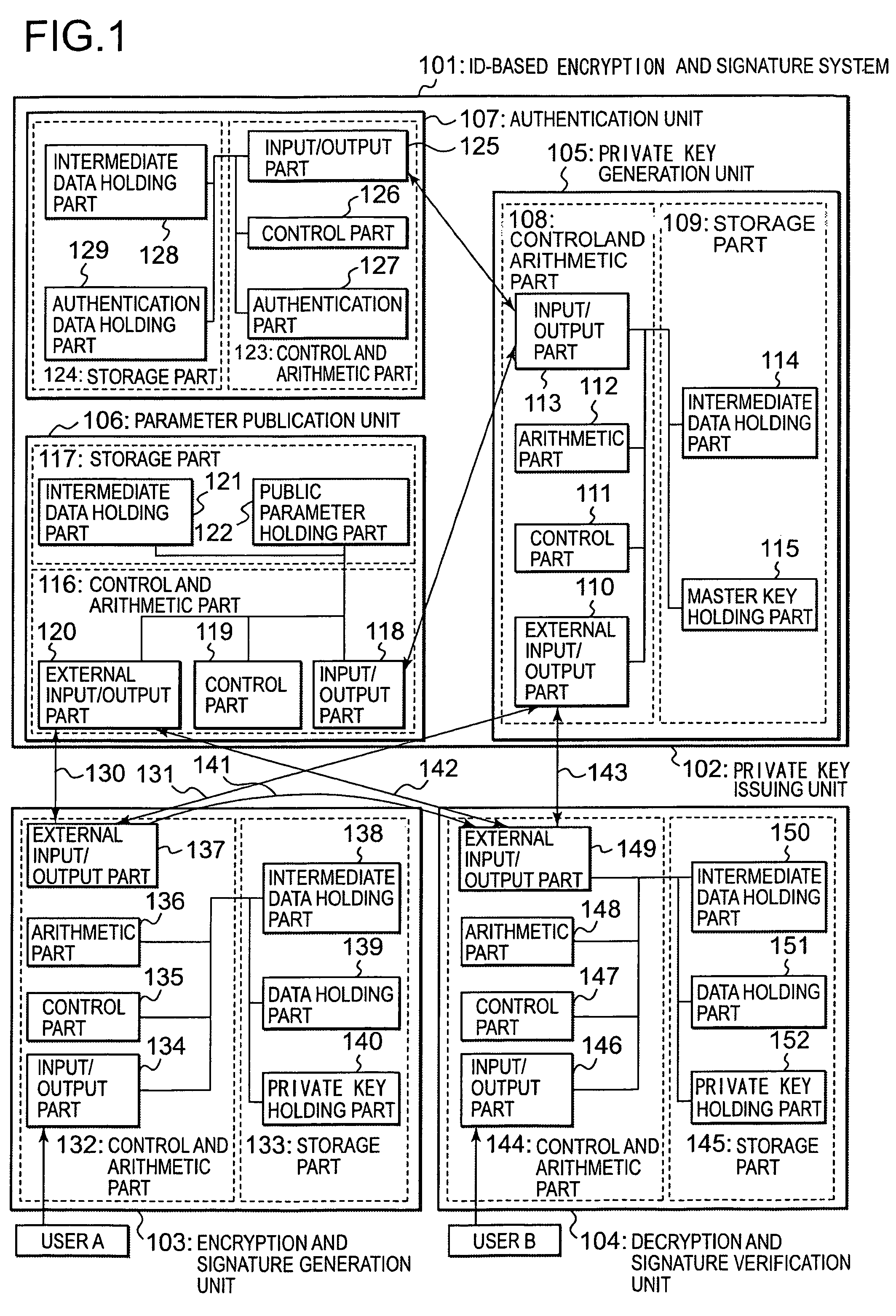
ID-based signature, encryption system and encryption method
InactiveUS20060126832A1Degree of improvementIncrease speedPublic key for secure communicationSecret communicationID-based encryptionMaster key
An ID-based encryption and signature technique, according to which more efficient and higher speed processing is possible. In generation of public parameters, an element P of a group G1 of order q is selected, and then, g=e(P, P) calculated in advance is added to the public parameters. At the time of encryption and verification, a public key ID is associated with an element PID of the group G1, using u∈Zq* and two elements P1 and P2 (included in the public parameters) of G1 and calculating PID=P1+uP2. The above-mentioned elements P1 and P2 are determined by P1=s1P and P2=s2P using random numbers s1, s2∈Zq* as a part of a master key, and a private key of a user is determined by dID=(s1+us2)−1P.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Module ID based encryption for financial transactions
A server is operable to receive a media device identifying number (ID) and establish an association between a media device and a payment account and, in one embodiment, supports at least one of payment authorization and payment clearing based at least in part on the media device ID and the payment account. A network and system includes a payment card processor server that is operable to receive a payment authorization request and to determine if an authorized media device generated a purchase selection message and to determine to approve a received payment authorization request based, in part, if the media device was authorized for the purchase selection based upon a received media device ID. The system is further operable to perform a key rotation to protect payment account information.
Owner:VISA USA INC (US)
Cryptographic systems using pairing with errors
ActiveUS9246675B2Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageKey exchangeID-based encryption
Using the same mathematical principle of paring with errors, which can be viewed as an extension of the idea of the LWE problem, this invention gives constructions of a new key exchanges system, a new key distribution system and a new identity-based encryption system. These new systems are efficient and have very strong security property including provable security and resistance to quantum computer attacks.
Owner:ALGO CONSULTING INC
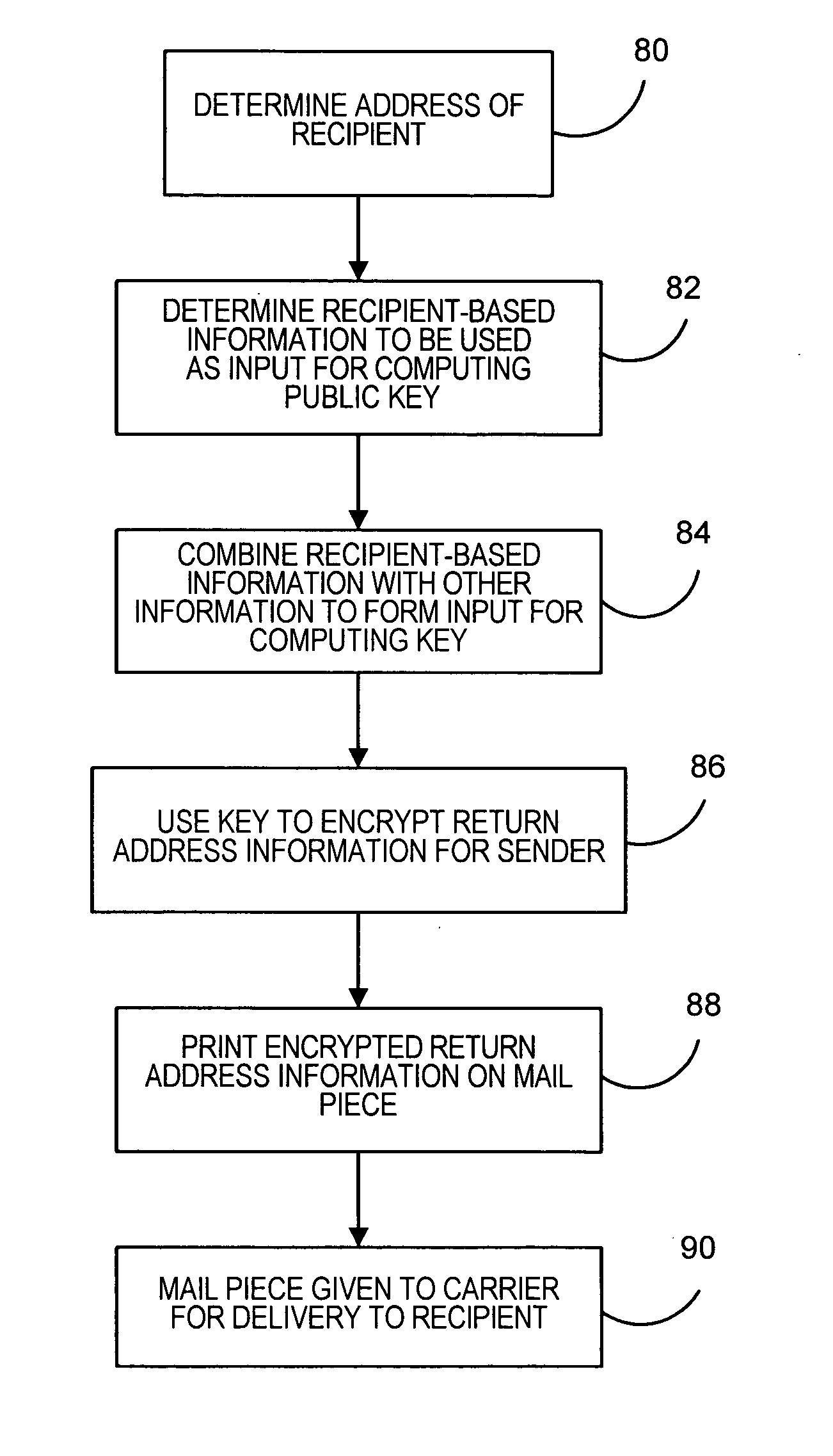
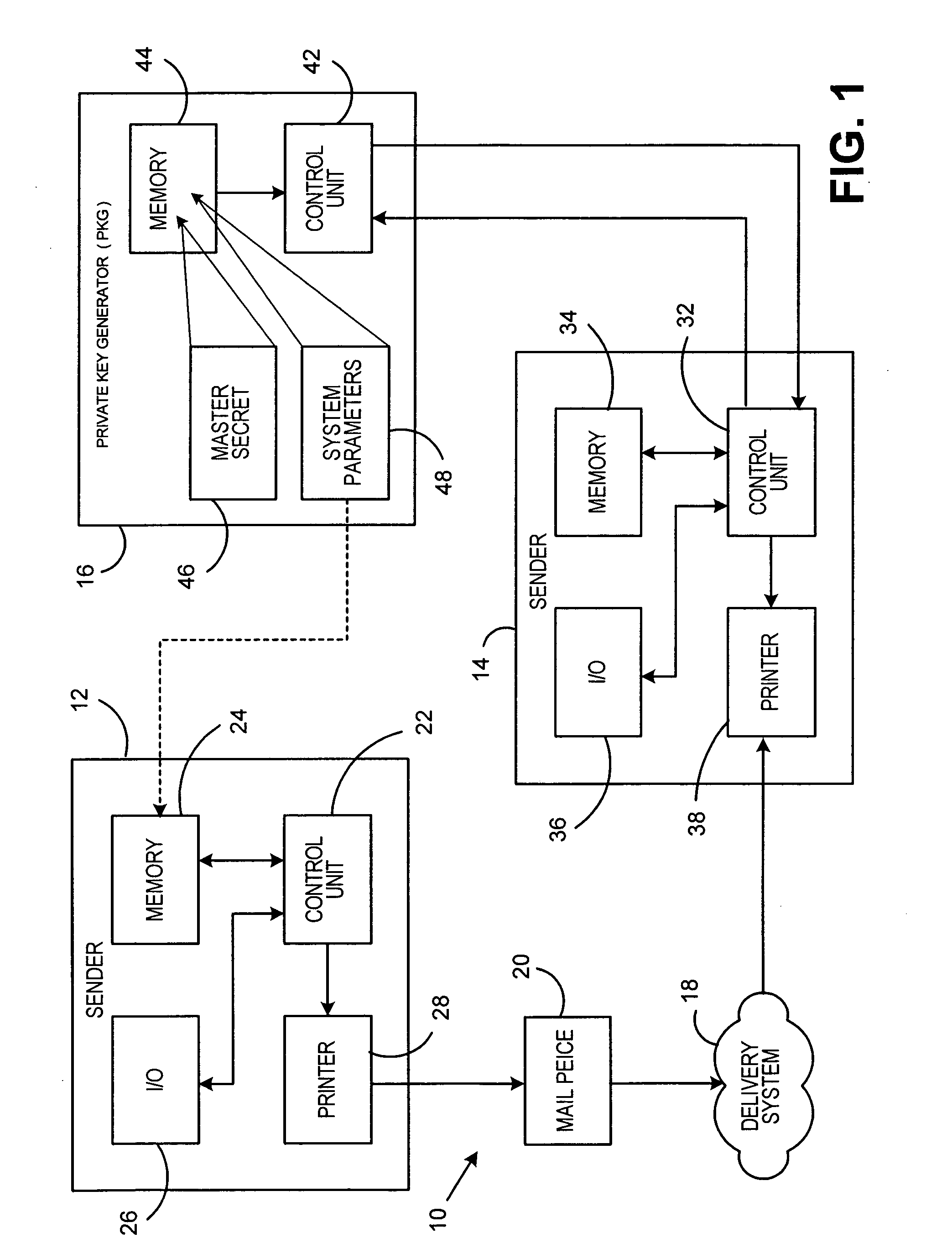
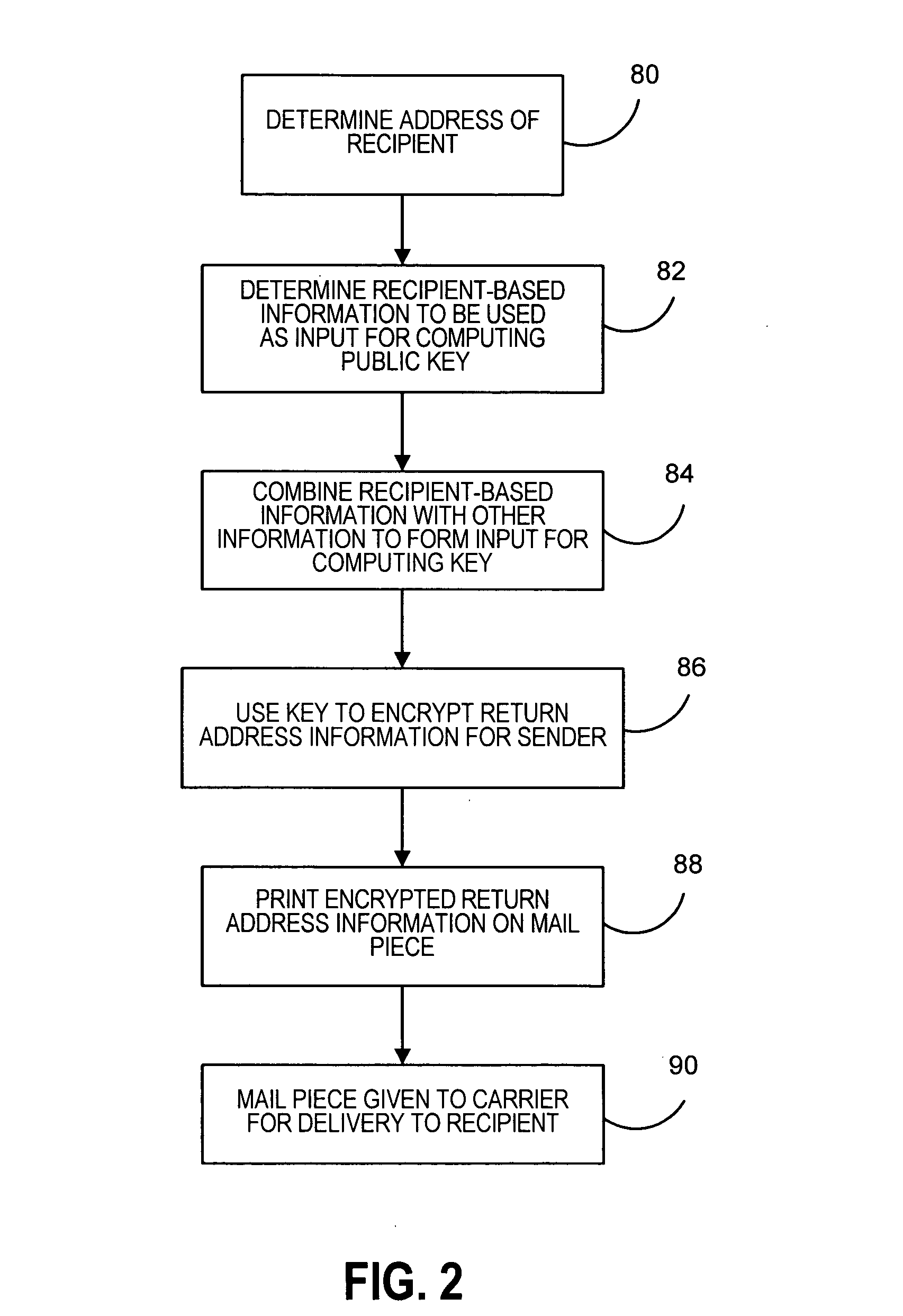
Method and system for providing privacy to sender of a mail piece
InactiveUS20070104323A1Easy to getReduce decreasePublic key for secure communicationSecret communicationID-based encryptionTrusted third party
Methods and systems for keeping information related to the sender of a mail piece private, while still allowing authorized parties to easily obtain the sender information if desired, is provided. Sender information for a mail piece is encrypted utilizing an identity-based encryption (IBE) scheme. The encryption key used to encrypt the sender information can be computed using recipient information. The corresponding decryption key can only be obtained from a trusted third party acting as a Private Key Generator (PKG). Only those parties authorized to have access to the sender information will be provided with the corresponding decryption key. The corresponding decryption key can then be used to decrypt the sender information into human readable form.
Owner:PITNEY BOWES INC
Method and system for securing routing information of a communication using identity-based encryption scheme
ActiveUS20090103734A1Easy to implementReduce decreaseKey distribution for secure communicationID-based encryptionConfidentiality
Methods and systems for providing confidentiality of communications sent via a network that is efficient, easy to implement, and does not require significant key management. The identity of each node of the routing path of a communication is encrypted utilizing an identity-based encryption scheme. This allows each node of the routing path to decrypt only those portions of the routing path necessary to send the communication to the next node. Thus, each node will only know the immediate previous node from which the communication came, and the next node to which the communication is to be sent. The remainder of the routing path of the communication, along with the original sender and intended recipient, remain confidential from any intermediate nodes in the routing path. Use of the identity-based encryption scheme removes the need for significant key management to maintain the encryption / decryption keys.
Owner:PITNEY BOWES INC
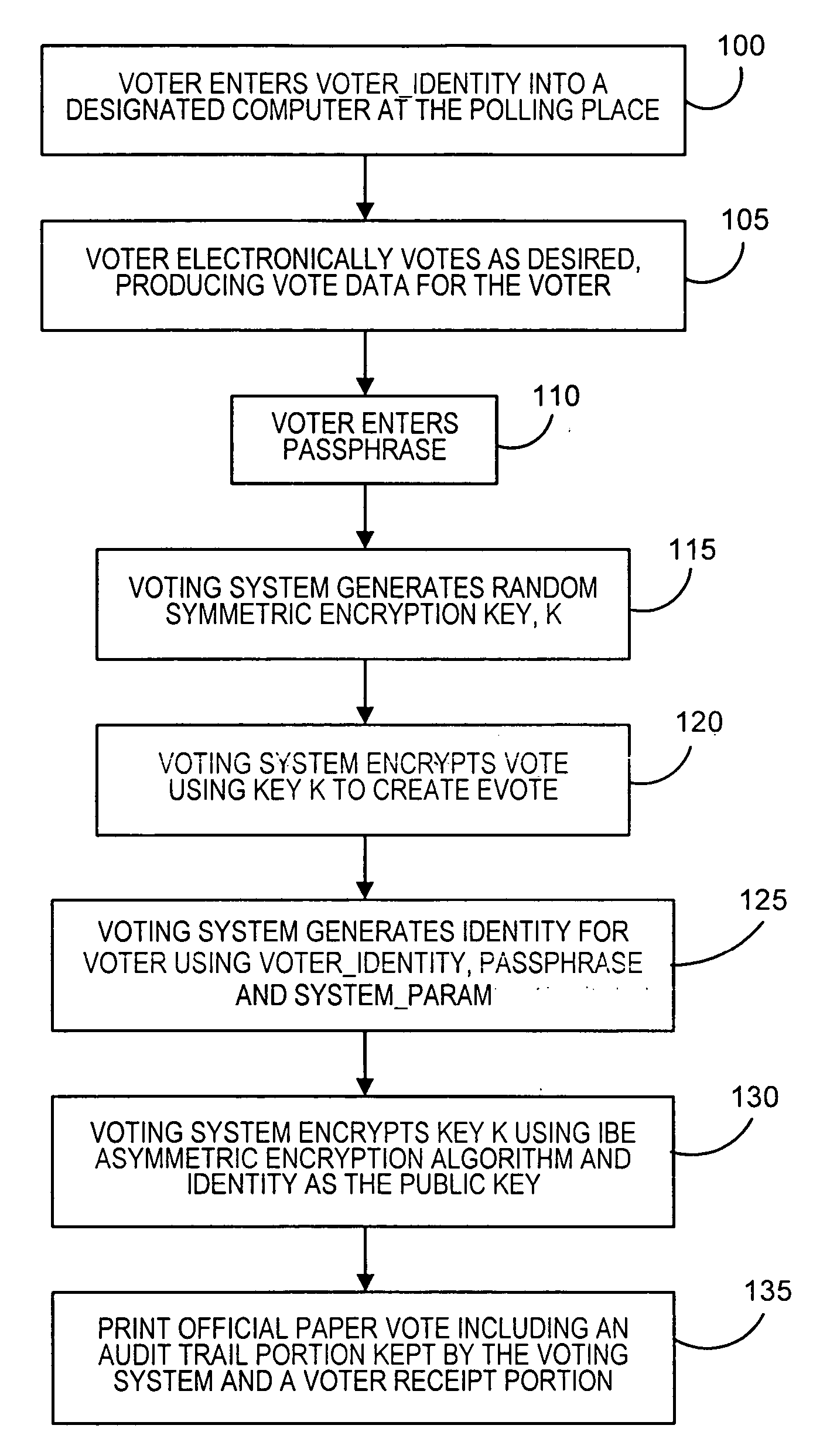
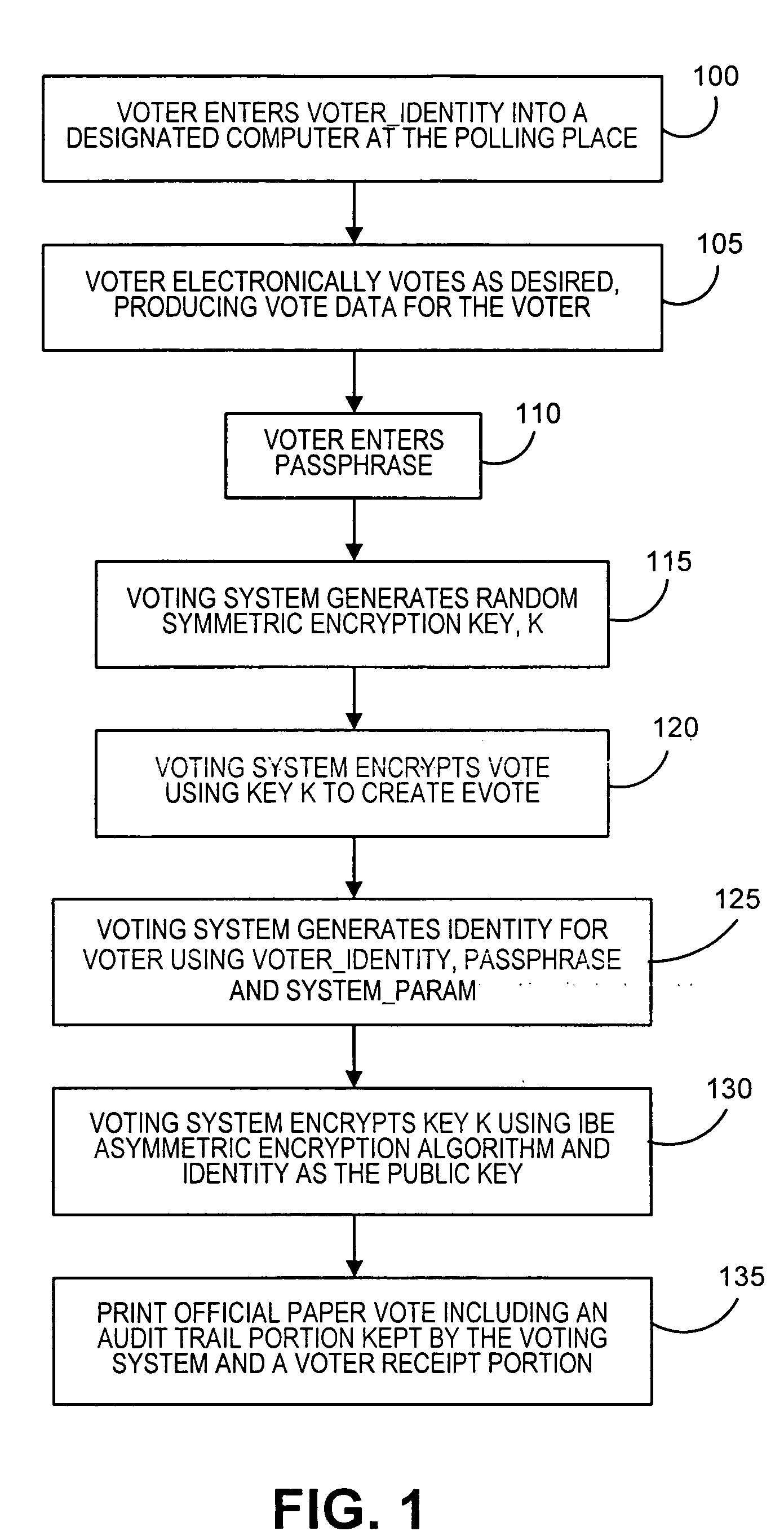
Method and system for electronic voting using identity based encryption
A voting method includes receiving identity-based information, vote data and a passphrase for a voter, encrypting the vote data using a symmetric key, generating second identity-based information for the voter, and generating an identity-based public key using at least the second identity-based information and a voting system parameter. The symmetric key is encrypted using the identity-based public key and an identity-based asymmetric encryption algorithm. The encrypted symmetric key may be decrypted using a private key corresponding to the identity-based public key and an identity-based asymmetric decryption algorithm, wherein the private key is generated from at least the identity-based public key and a secret master key. The voter is provided with information that includes at least the encrypted vote data and the encrypted symmetric key, and the system retains anonymous identity information, encrypted vote data and the encrypted symmetric key as a paper audit trail.
Owner:PITNEY BOWES INC
New Cryptographic Systems Using Pairing with Errors
ActiveUS20150067336A1Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageKey exchangeID-based encryption
Using the same mathematical principle of paring with errors, which can be viewed as an extension of the idea of the LWE problem, this invention gives constructions of a new key exchanges system, a new key distribution system and a new identity-based encryption system. These new systems are efficient and have very strong security property including provable security and resistance to quantum computer attacks.
Owner:ALGO CONSULTING INC
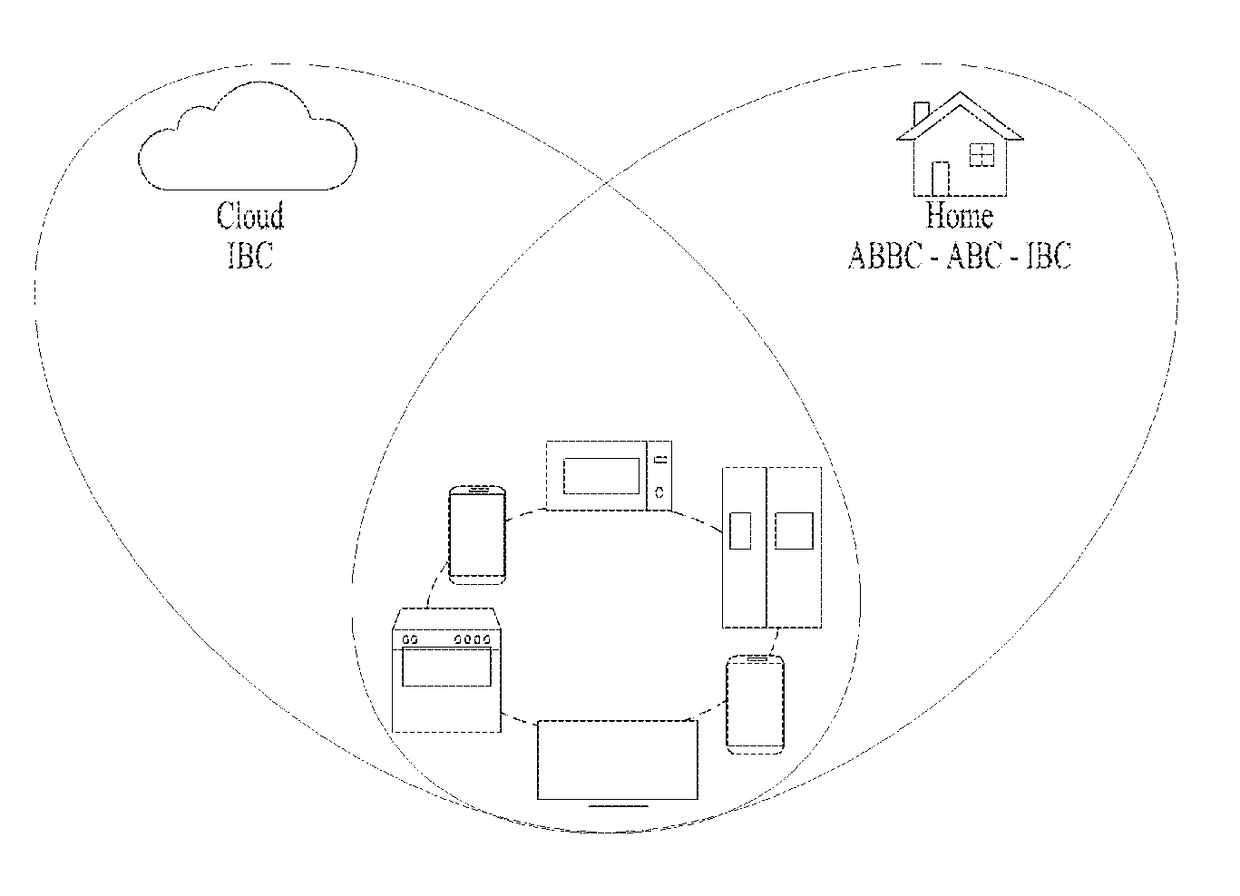
System and method for authentication of things
ActiveUS20170214529A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationID-based encryptionPairwise key
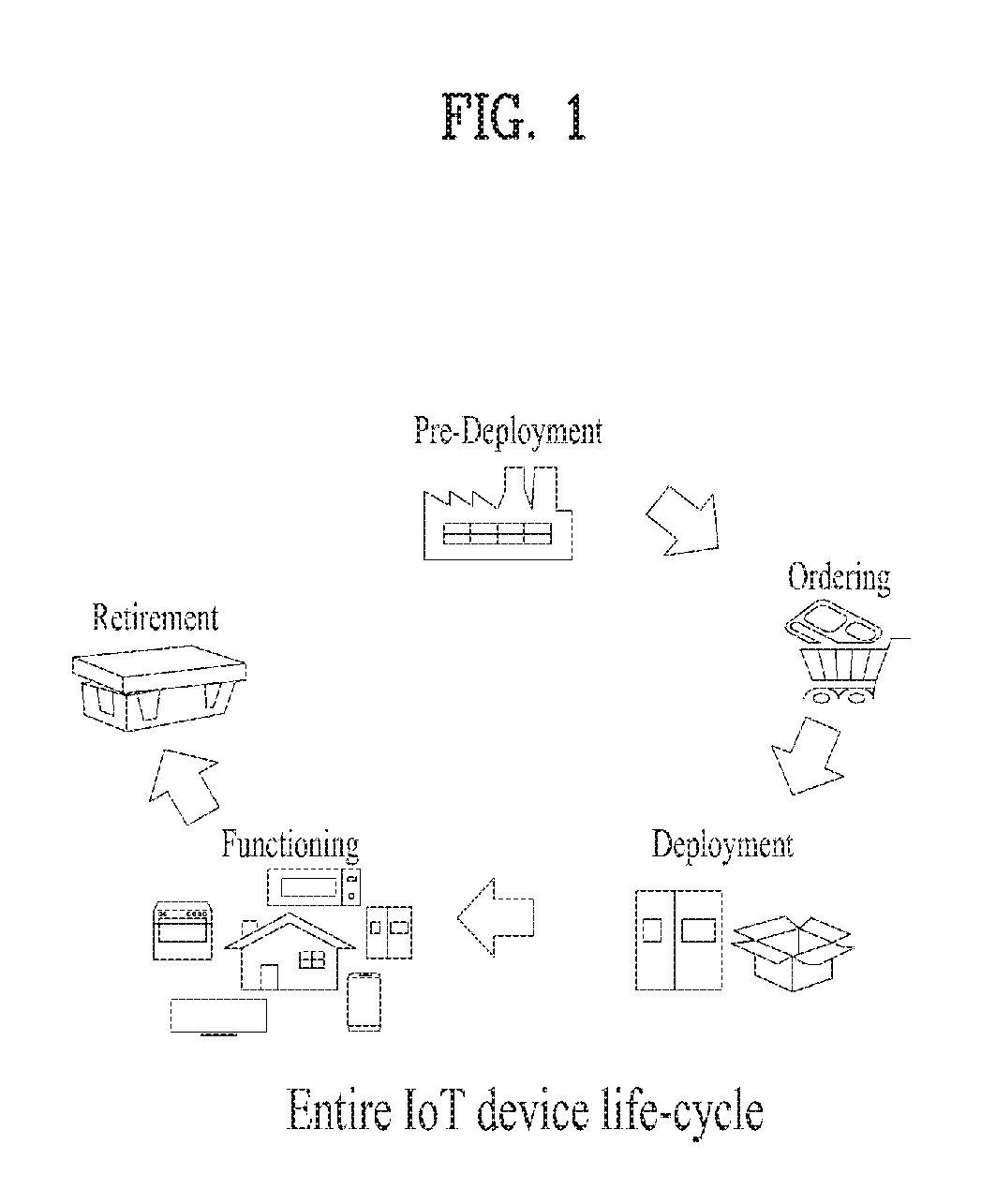
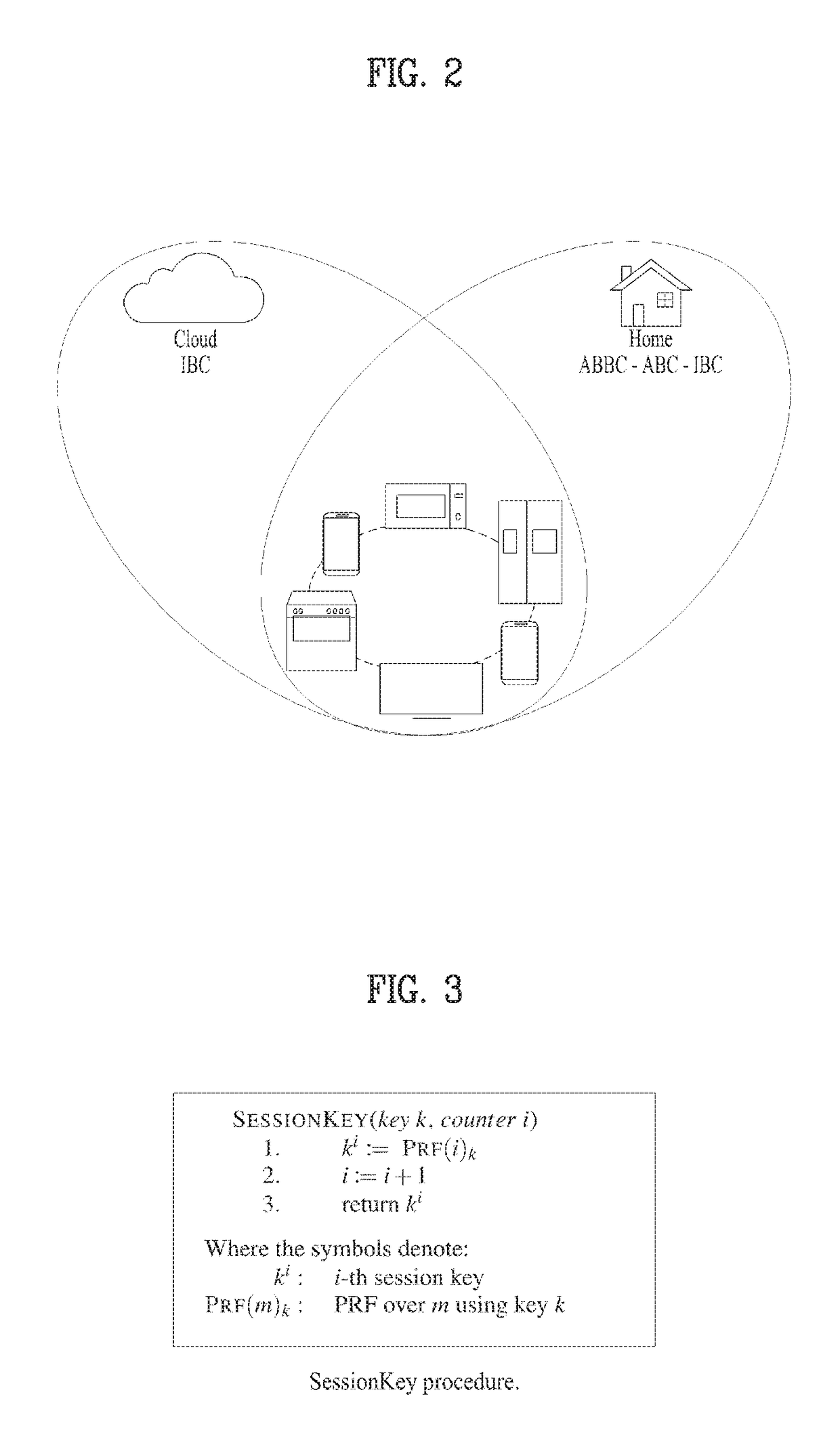
An Authentication Of Things (AOT) system includes a cloud server configured to control a cloud domain connected with a plurality of devices, a home server configured to control a home server connected with a plurality of devices, a first device corresponding to a new device, and a second device of a root user connected with the home domain while authentication is completed in the home server. In this case, the first device loads cryptographic material of the cloud server from the cloud server in a pre-deployment stage, the cryptographic material includes at least one selected from the group consisting of an identifier of the first device in the cloud server, a first private key of an ID-based cryptography system of the first device in the cloud server, a first pairwise key of the first device in the cloud server, and a counter of the first device, and if the first device is shipped to a trader, the cloud server deletes the first private key from the cloud server.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC +1
Threshold and identity-based key management and authentication for wireless ad hoc networks
InactiveUS8050409B2Reduce usageReduce resource requirementsKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationID-based encryptionConfidentiality
As various applications of wireless ad hoc network have been proposed, security has become one of the big research challenges and is receiving increasing attention. The present invention provides for a distributed key management and authentication approach by deploying the recently developed concepts of identity-based cryptography and threshold secret sharing. Without any assumption of pre-fixed trust relationship between nodes, the ad hoc network works in a self-organizing way to provide the key generation and key management service, which effectively solves the problem of single point of failure in the traditional public key infrastructure (PKI)-supported system. The identity-based cryptography mechanism provided not only to provide end-to-end authenticity and confidentiality, but also saves network bandwidth and computational power of wireless nodes.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
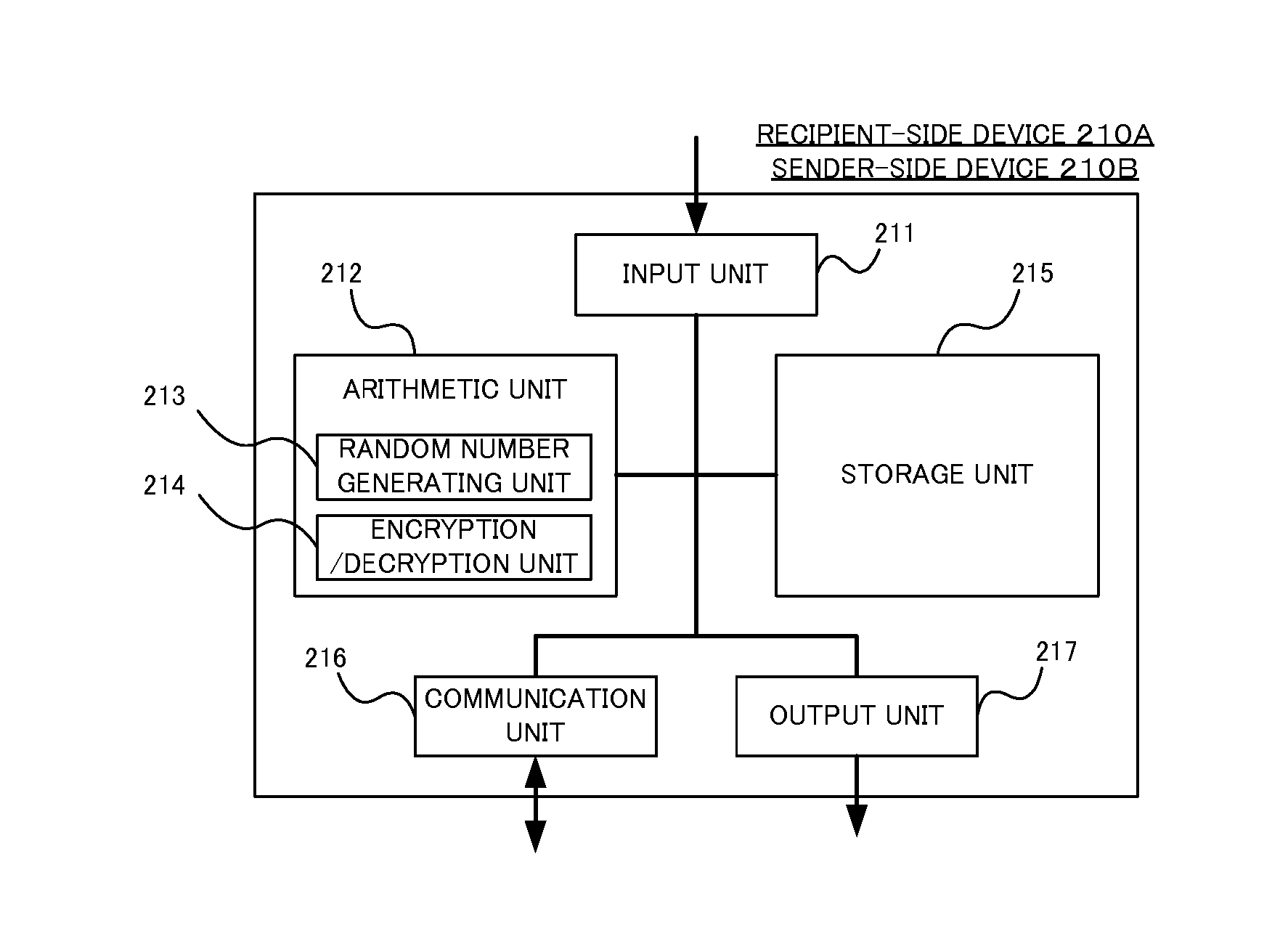
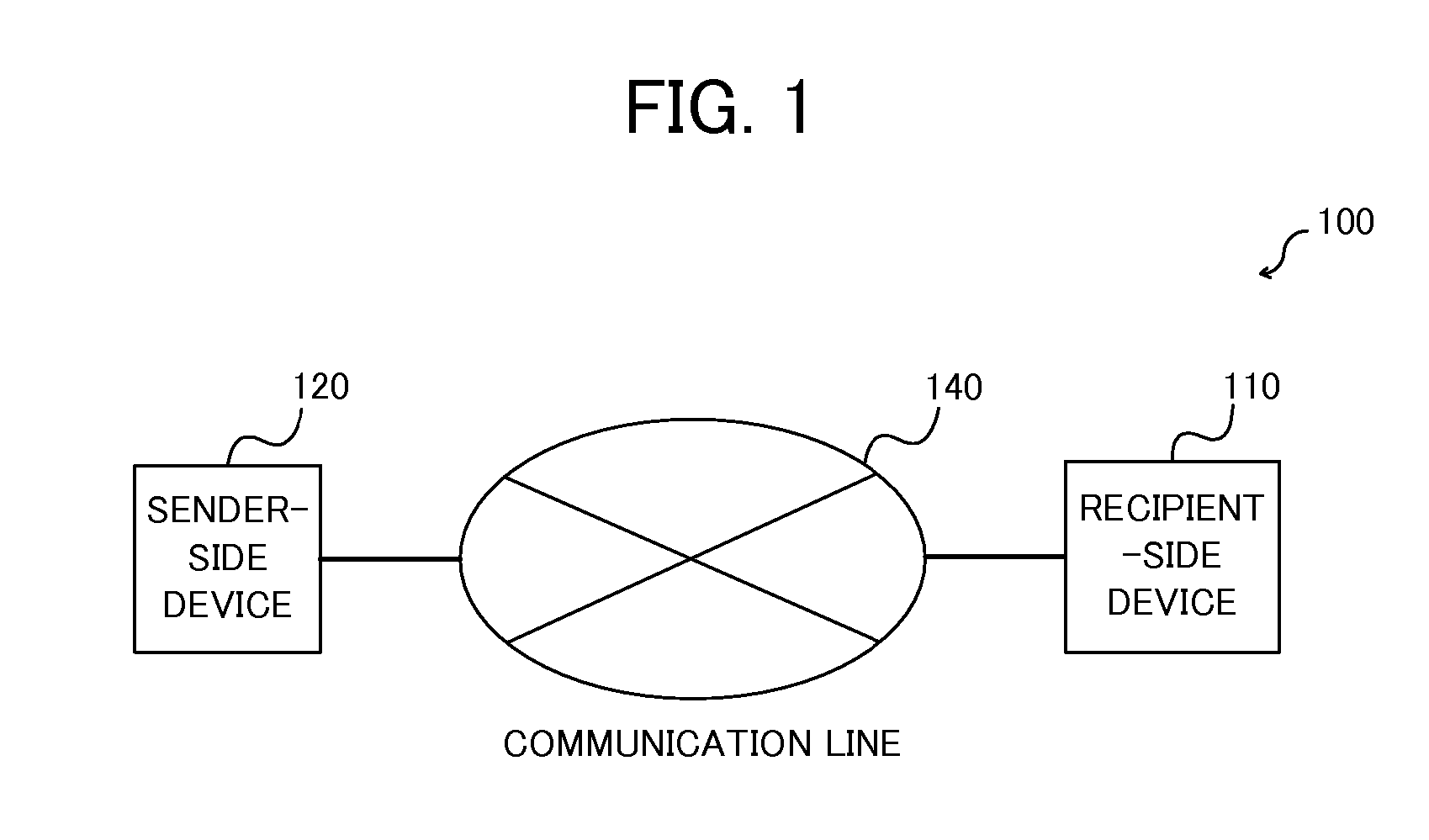
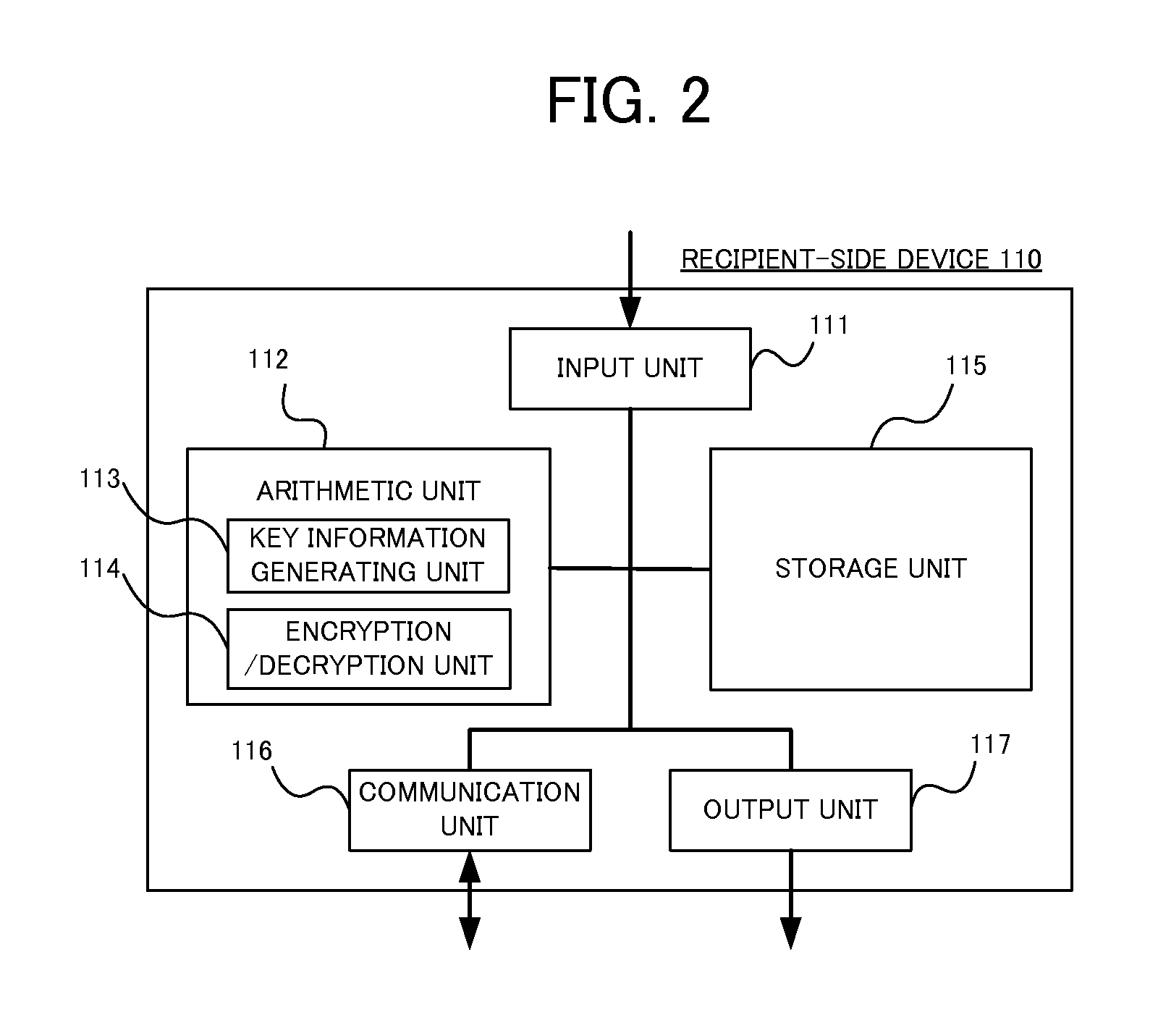
Crypto-communication method, recipient-side device, key management center-side device and program
InactiveUS20080063193A1Improve securityTight security reductionRandom number generatorsPublic key for secure communicationID-based encryptionCryptogram
A public key encryption system and an ID-based encryption system are provided, each exhibiting high security and having a tight security reduction, in which a BDH problem is a cryptographic assumption. A recipient-side device (110) serving as a recipient of a cryptogram selects random numbers s1 and s2, generates P, QεG1 and a bilinear mapping e: G1×G1→G2 as part of public key information, and further generates P1=s1P and P2=s2P as part of the public key information. A sender-side device (120) serving as a sender of the cryptogram calculates e(Q, P1) and e(Q, P2) by use of the public key information Q of the recipient-side device (110) and the bilinear mapping e, and further generates a cryptogram to be transmitted to the recipient-side device (110) by use of those pieces of information e(Q, P1) and e(Q, P2).
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Virtual power plant security scheduling and trading method based on dual blockchain technology
PendingCN112434343ASafe storageEnsure normal communicationFinanceDigital data protectionID-based encryptionCurrent electric
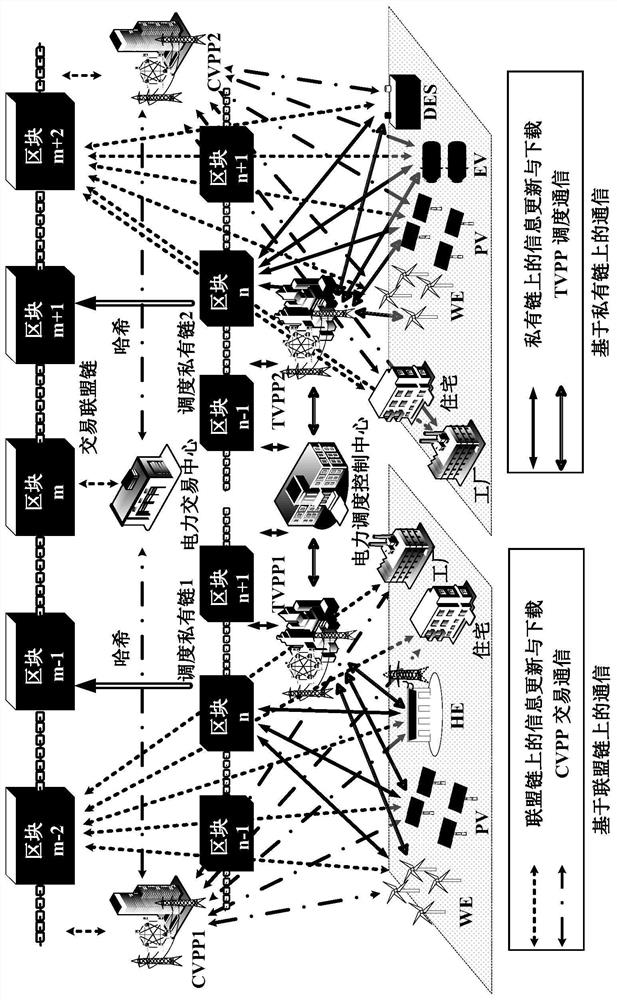
A virtual power plant security scheduling and transaction method based on a dual blockchain technology comprises a scheduling private chain for scheduling and a transaction alliance chain for transaction, adopts a hybrid proxy re-encryption algorithm based on a ciphertext strategy, and is formed by combining an identity-based encryption algorithm and an attribute proxy re-encryption algorithm based on the ciphertext strategy. The agent converts the ciphertext based on attribute encryption into the ciphertext based on identity encryption, so that the decryption cost of the data accessor is reduced, and the non-repudiation and reliability of production information are ensured. In the transaction process, a continuous bilateral auction mechanism based on reputation is adopted, participants can continuously adjust their own quotation according to the current electric quantity transaction price, benefit maximization is achieved, transaction information and a reputation value are recorded inan alliance chain, and tamper resistance and transparency of the information are guaranteed. A low-cost, open and transparent information and transaction platform is provided for a virtual power plant, and the safety, tamper resistance, non-repudiation, integrity and the like of data are guaranteed.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and system for ID-based encryption and decryption
ActiveUS9379891B2Improve stabilityKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageID-based encryptionComputer terminal
Provided are identifier (ID)-based encryption and decryption methods and apparatuses for the methods. The ID-based encryption method includes having, at a transmitting terminal, a transmitting-side private key corresponding to a transmitting-side ID issued by a key issuing server, generating, at the transmitting terminal, a session key using the transmitting-side ID, a receiving-side ID, and the transmitting-side private key, extracting, at the transmitting terminal, a secret key from at least a part of the session key, and encrypting, at the transmitting terminal, a message using a previously set encryption algorithm and the secret key.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDS CO LTD +1
ID-based signature, encryption system and encryption method
InactiveUS7711113B2Degree of improvementIncrease speedPublic key for secure communicationSecret communicationID-based encryptionMaster key
An ID-based encryption and signature technique, according to which more efficient and higher speed processing is possible. In generation of public parameters, an element P of a group G1 of order q is selected, and then, g=e(P, P) calculated in advance is added to the public parameters. At the time of encryption and verification, a public key ID is associated with an element PID of the group G1, using uεZq* and two elements P1 and P2 (included in the public parameters) of G1 and calculating PID=P1+uP2. The above-mentioned elements P1 and P2 are determined by P1=s1P and P2=s2P using random numbers s1, s2εZq* as a part of a master key, and a private key of a user is determined by dID=(s1+us2)−1P.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Self-authentication communication device and device authentication system
InactiveUS8479001B2Public key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationID-based encryptionSecure communication
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Identity-based encryption method allowing revocation at lattice
ActiveCN105024821AImplement identity managementImprove computing efficiencyKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationIdentity managementKey generation
The invention discloses an identity-based encryption method allowing revocation at the lattice, and specifically includes the steps of: 1. establishing an algorithm; 2. establishing a private key generation algorithm; 3. updating a secret key generation algorithm; 4. decrypting the secret key generation algorithm; 5. encrypting an algorithm; 6. decrypting the algorithm; and 7. revoking the algorithm. The identity-based encryption method allowing revocation at the lattice adds a user identity revocation mechanism, and thus identity management of user can be effectively realized; and the method is based on the problem of LWE difficulty at the lattice, can resist quantum attack, has relatively high computational efficiency, proves that the scheme is adaptively safe, security of the scheme is stipulated to the problem of LWE difficulty, and the problem existing in the prior art that an encryption method causes disclosure of a user private key and difficulty in resisting quantum attack.
Owner:广东恒睿科技有限公司
Secured data transmission using identity-based cryptography
ActiveUS20170366520A1Secure transmissionKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key infrastructure trust modelsID-based encryptionData file
A system is provided for secure data transmission. The system stores a public master key, private decryption key and secure messaging module for securely transmitting and receiving a digital model data file for transmission via a work order message. For transmitting and receiving the work order message, the system generate public encryption keys using a key generation algorithm in which each of the public encryption keys are unique to a designated message recipient and generated using an input including the public master key, a validity period, and an identifier of the designated message recipient. The system may also store a revocation list that includes identifiers of message recipients that have revoked access to the public master key or private decryption key, and based thereon determine whether or not to encrypt and transmit the work order message, or receive and decrypt the work order message.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
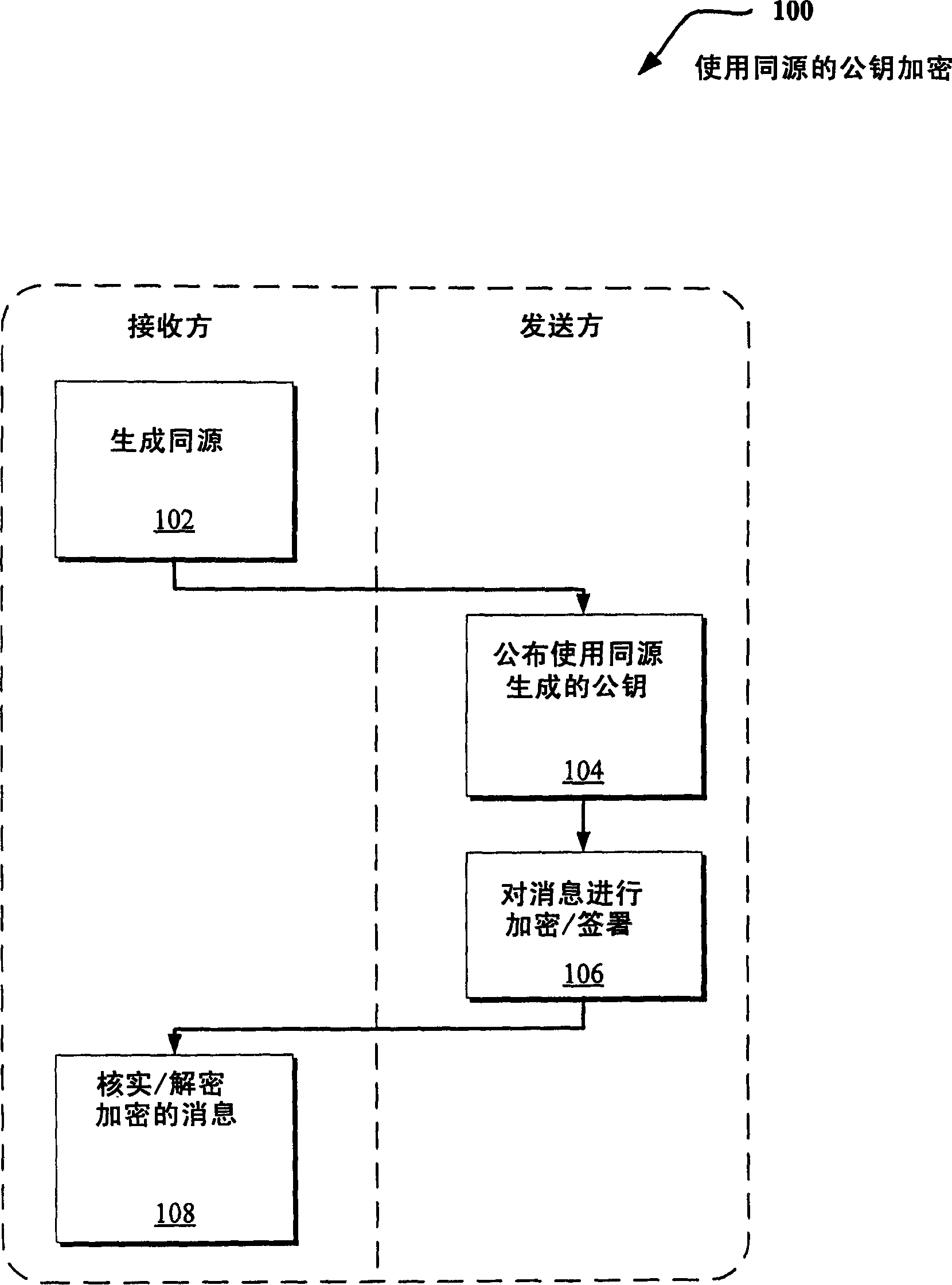
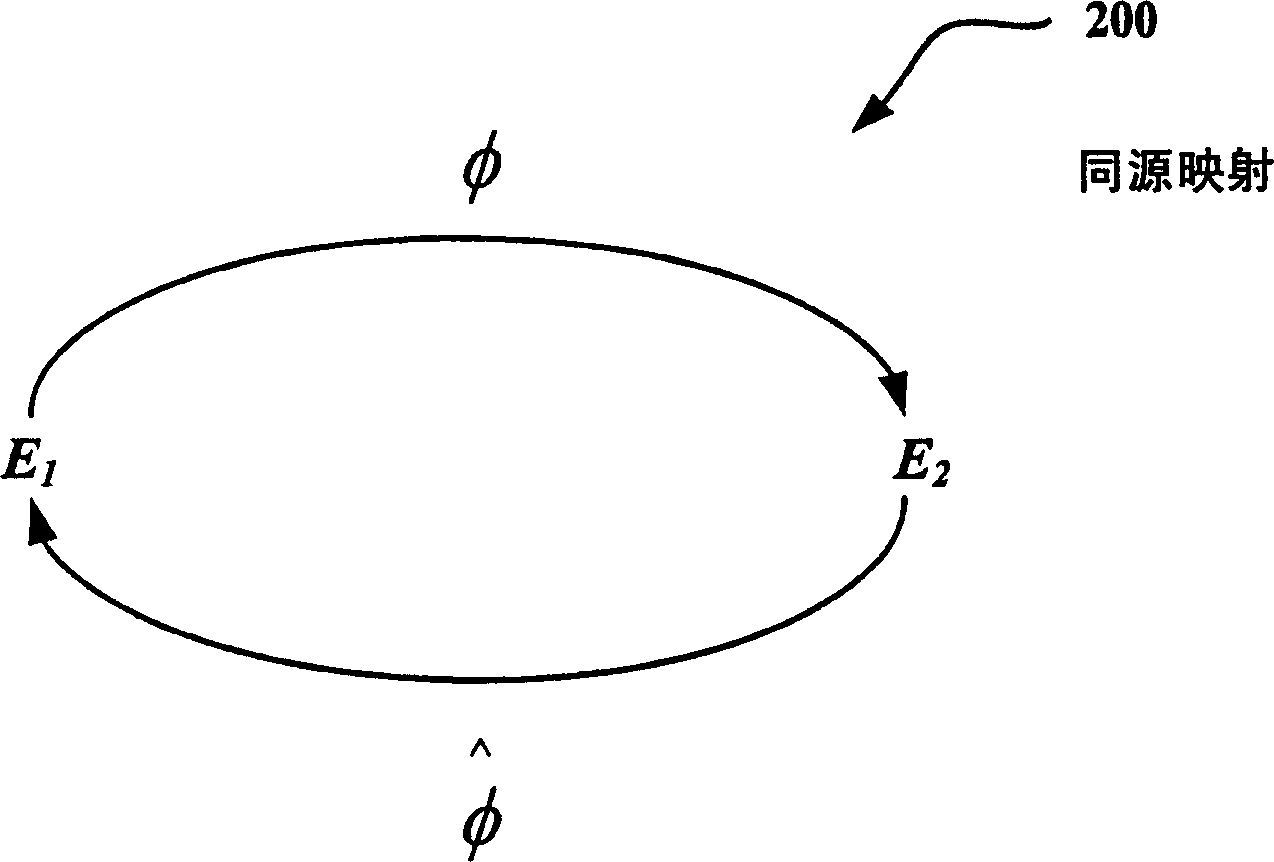
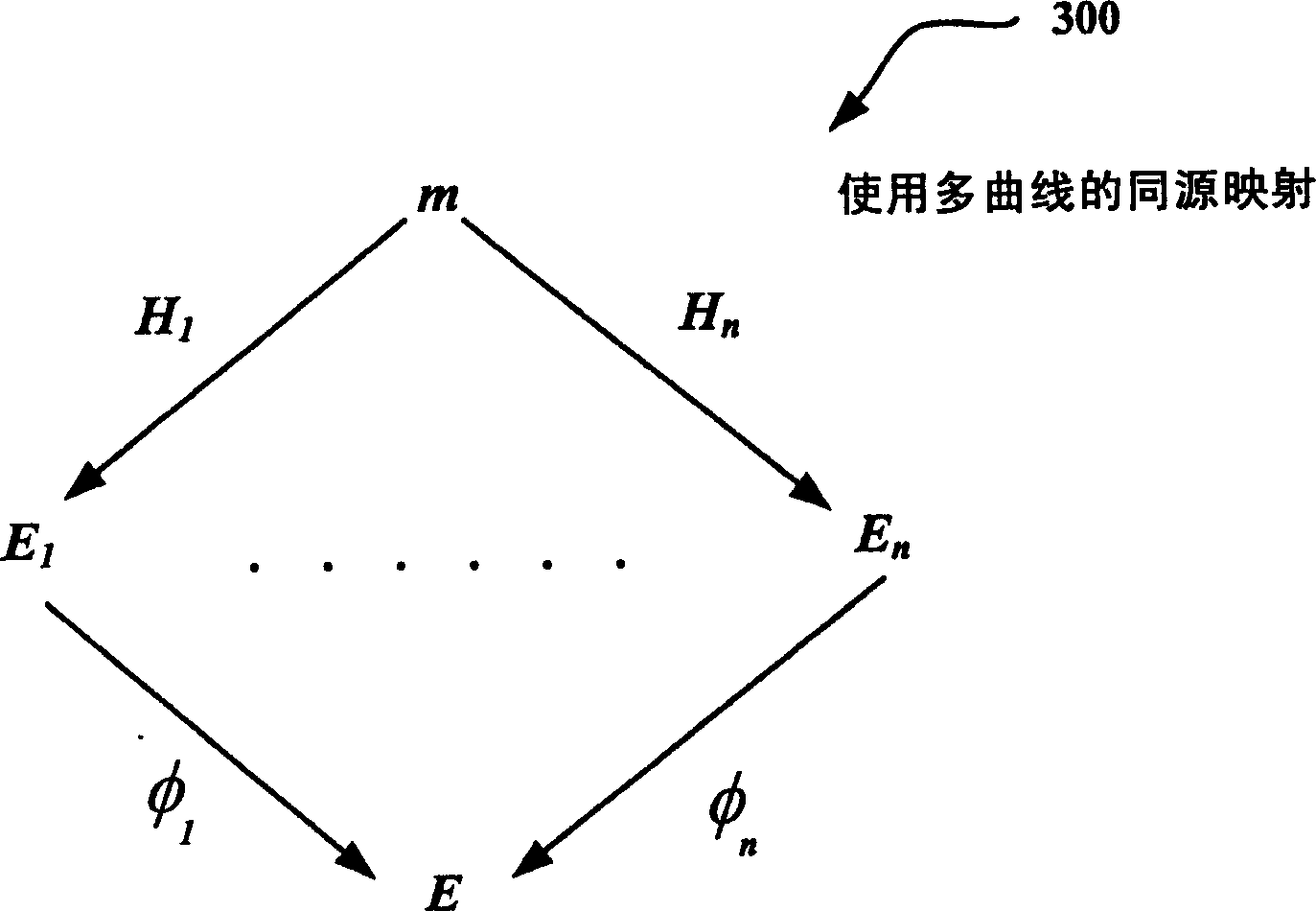
Use of isogenies for design of cryptosystems
ActiveCN1614922AKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationID-based encryptionSAFER
Techniques for providing public key cryptography systems are revealed. More specifically, public key cryptography systems are provided using homologs of Abelian varieties (eg, elliptic curves in the one-dimensional case). For example, homology allows the use of multiple curves instead of a single curve to provide more secure encryption. The technology can be applied to digital signing and / or identity-based encryption (IBE) solutions. Additionally, same origins can be used in other applications such as blind signing, rating systems, etc. In addition, the solution for generating homology is revealed.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Identification-based encryption system
InactiveCN1992587AMultiple keys/algorithms usagePublic key for secure communicationID-based encryptionGeneration process
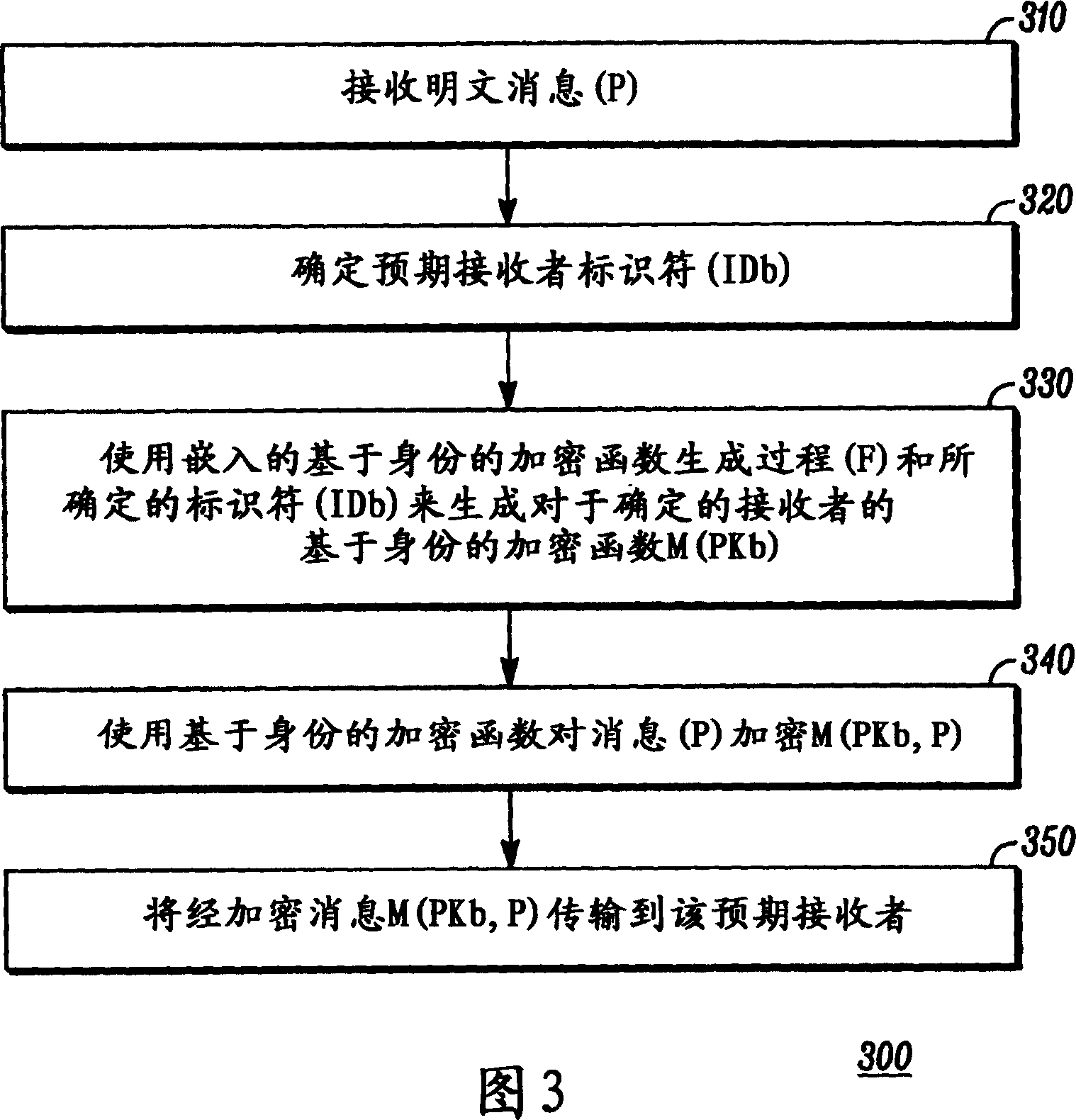
This invention relates to an identity-based encryption system. The invention provides the method (300) to exchange information safely by unsafe communication system, and which provides the electronic equipment (100) for implementing the method (300).This method makes sure (320) the identifier associated to the expected recipient of user's information, and then which uses a generation process of identity-based encryption function and identified identifier to generate (330) an encryption function related to the expected recipient based on identity. Next, the method decrypts (340) the user's information by using identity-based encryption function, and then which transports messaging (350) to the expected recipients by the decrypted user.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
Methods and Systems For Blockchain-Implemented Event-Lock Encryption
PendingCN110999204APrevent malicious activityKey share protectionKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationID-based encryptionDigital signature
There may be provided a computer-implemented method. It may be implemented at least in part using a blockchain network such as, for example, the Bitcoin network. The computer-implemented method includes: i) encrypting a plaintext message to a cryptographic public key in accordance with an identity-based encryption scheme using at least a congress public key to generate an encrypted message, wherein the congress public key is associated with members of a congress, respective members of the congress having access to private key shares usable in a threshold decryption scheme in which at least a threshold of private key shares are sufficient to derive a decryption key through the combination of partial contributions to the decryption key on behalf of the congress; ii) generating, using at least a cryptographic private key corresponding to the cryptographic public key, a digital signature over a first set of instructions to perform cryptographic operations upon an occurrence of an event; and iii) broadcasting one or more transactions to a proof-of-work blockchain network, the one or more transactions comprising the encrypted message, the cryptographic public key, at least the first setof instructions, and a second set of instructions to the members of the congress to cooperate to: in response to reaching a consensus on the event occurring and contingent upon the digital signature being authentic, deploy a ghost chain to perform the first set of instructions, wherein performing the first set of instructions includes at least deriving the decryption key from the cryptographic keyand a plurality of private key shares that satisfies the threshold, the decryption key being sufficient cryptographic material to obtain the plaintext message from the encrypted message.
Owner:NCHAIN HLDG LTD
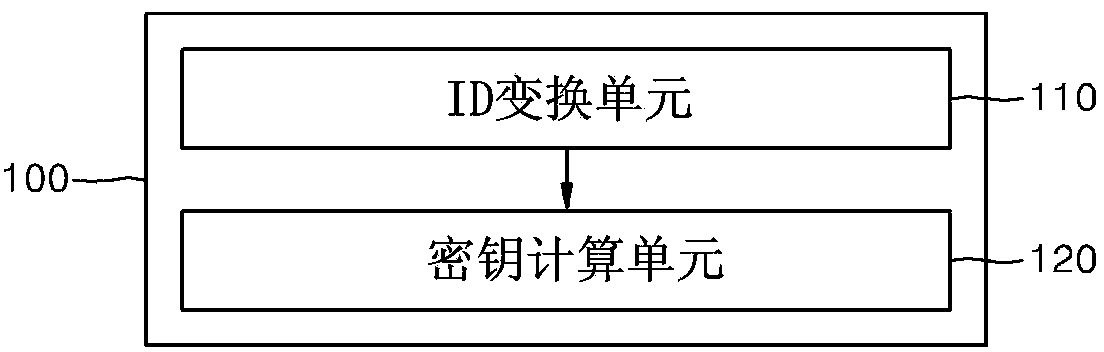
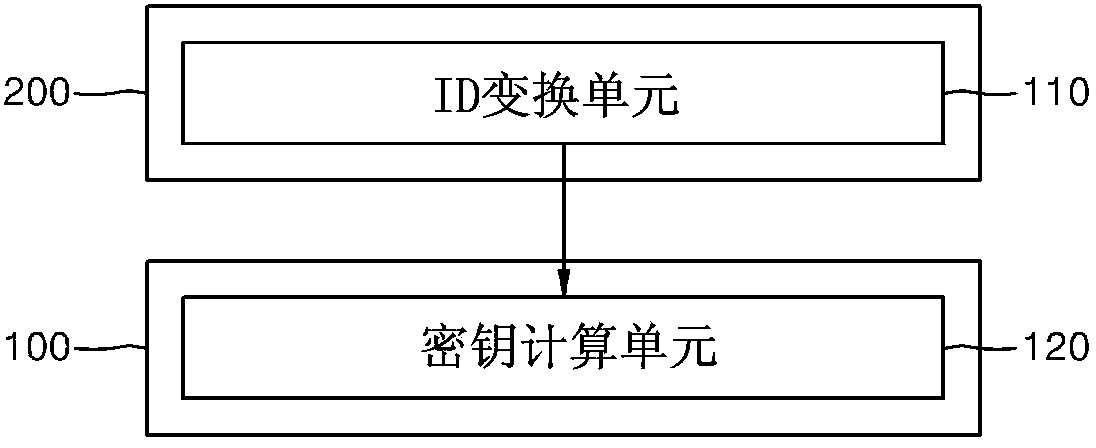
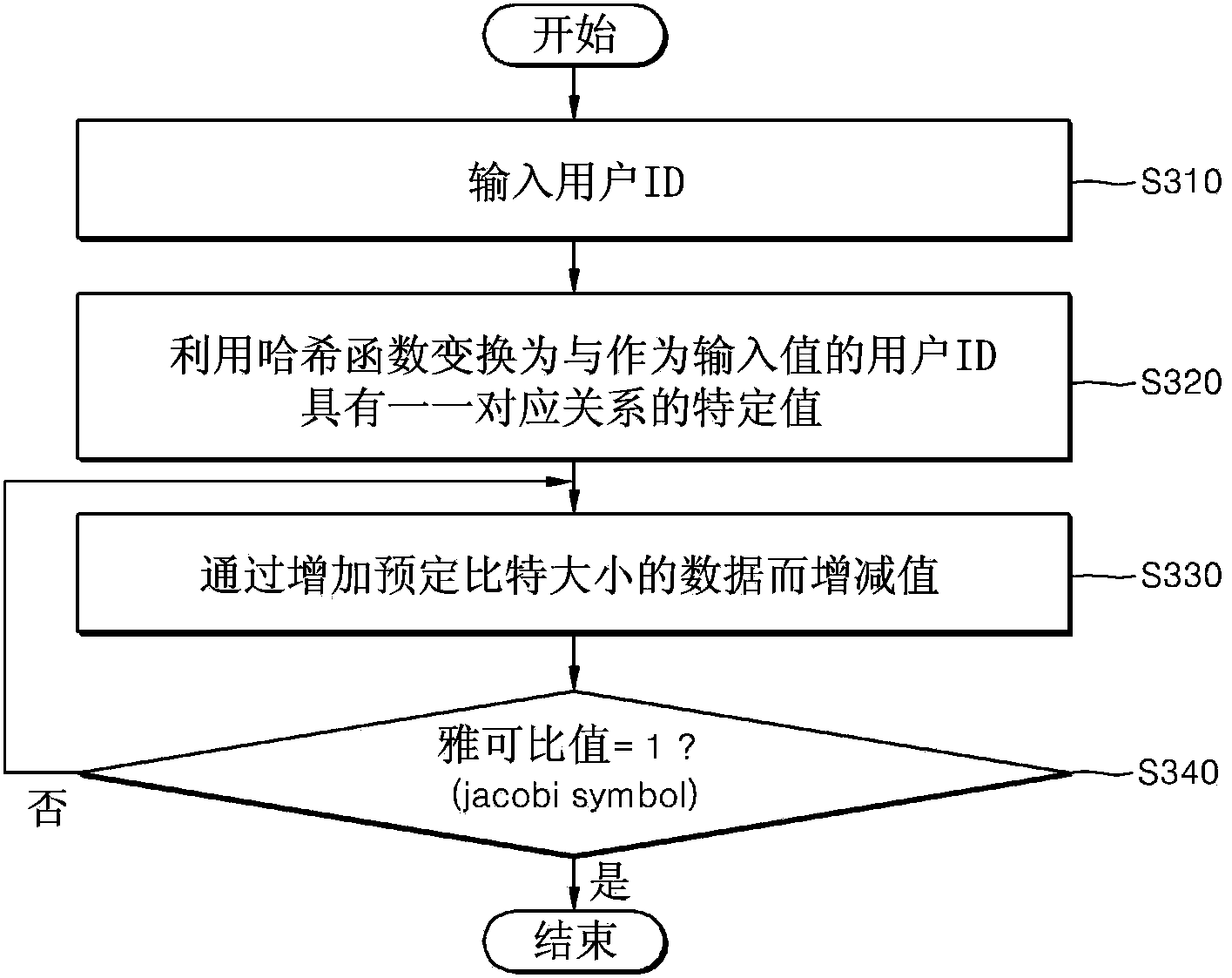
Apparatus and method for generating secret key for id-based encryption system and recording medium having program recorded thereon for causing computer to execute the method
ActiveCN103457720AKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageID-based encryptionComputer hardware
A private key generation apparatus for generating a private key corresponding to a user ID using the user ID as a public key is disclosed. When a user ID is input, an ID conversion unit outputs a specific element value of a discrete logarithm cyclic group having a one-to-one correspondence relationship with an input user ID. A private key calculation unit calculates a discrete logarithm result value based on the output specific element value of the discrete logarithm cyclic group and calculates a private key having a one-to-one correspondence relationship with the user ID. According to the present invention, it is possible to concretely propose a method of calculating a secret key, capable of guaranteeing a one-to-one correspondence relationship between the ID and the private key by applying a method of calculating a discrete logarithm using the pre-computation table in an ID-based encryption system.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com