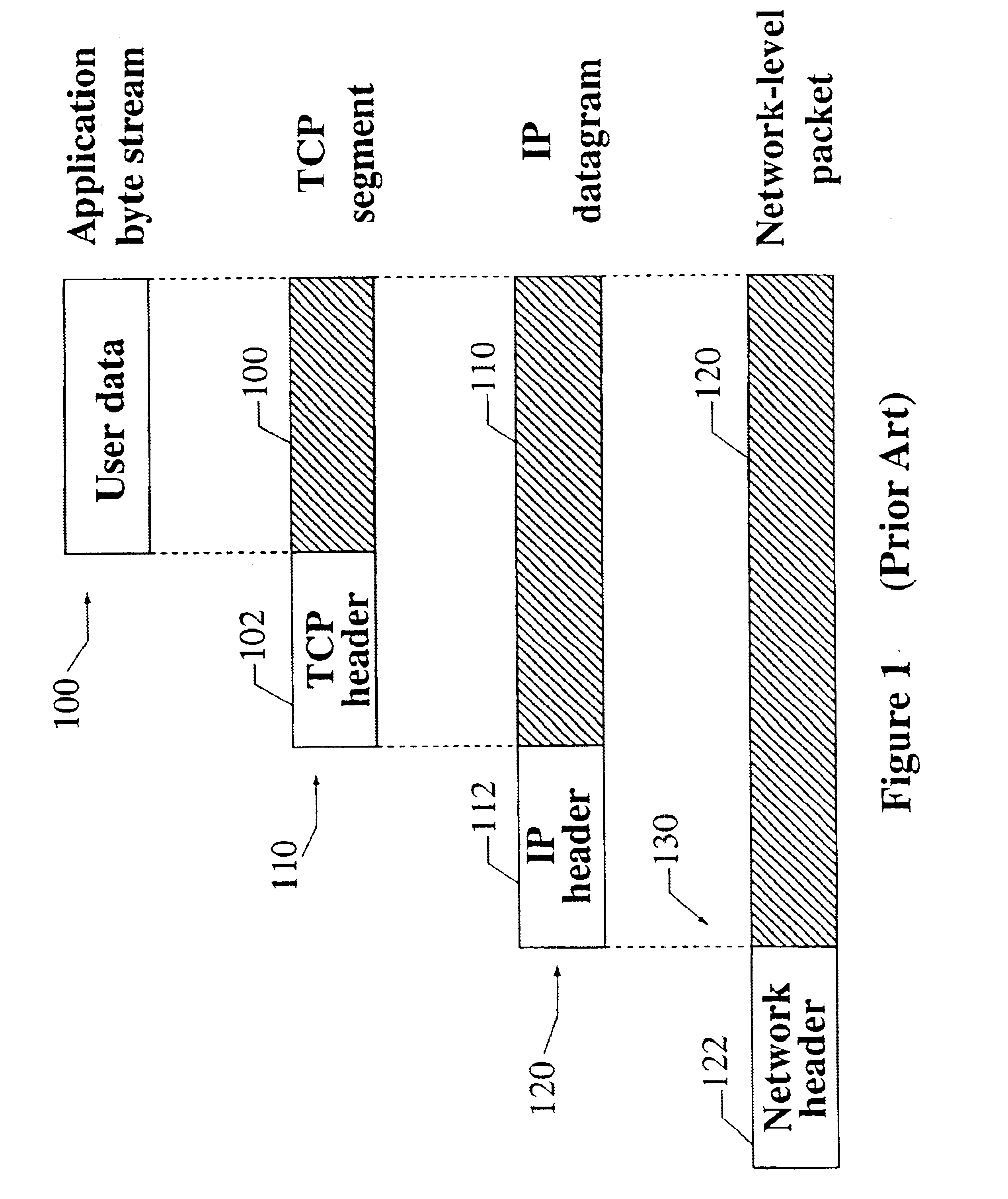
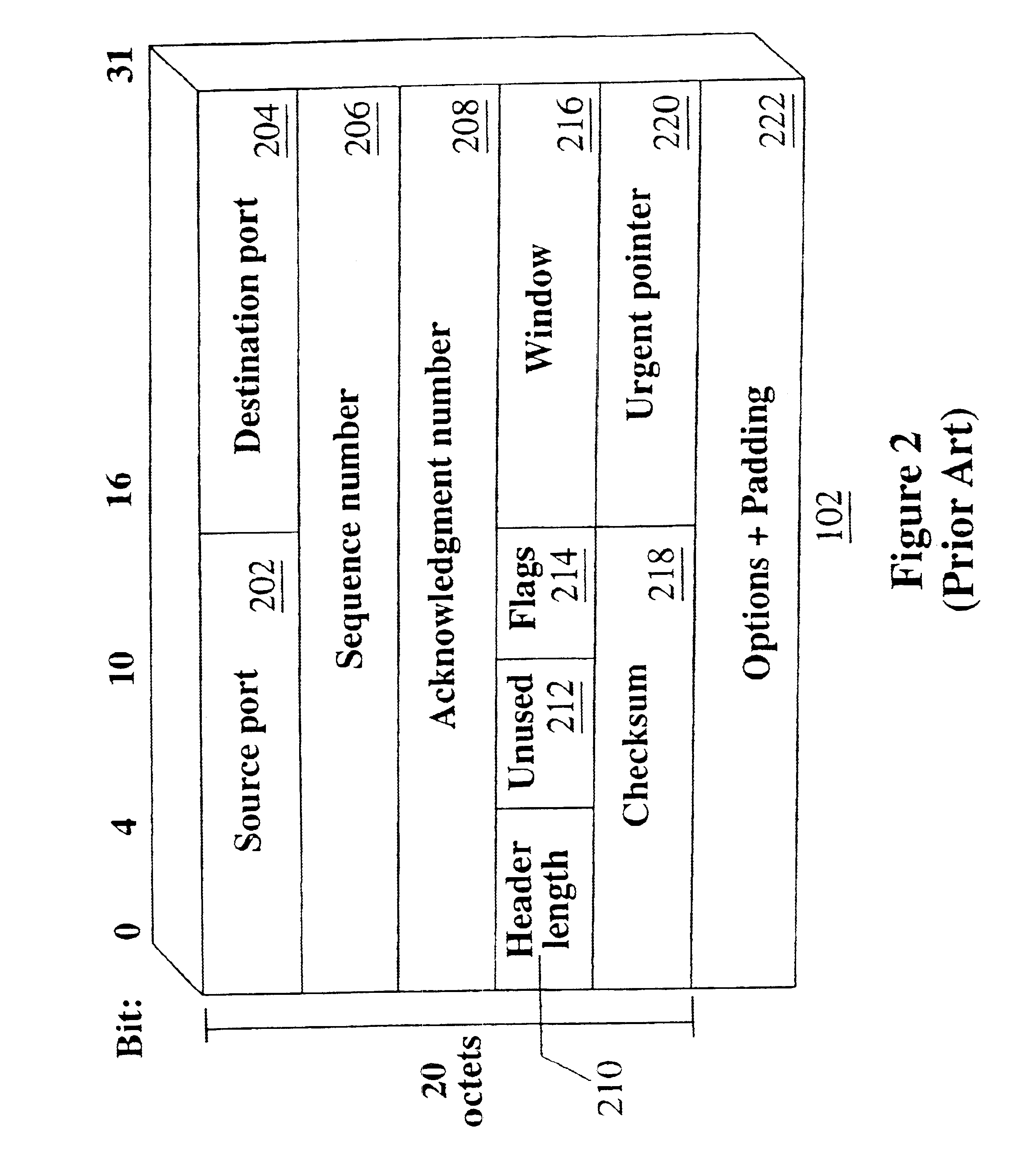
Patents
Literature
264results about How to "To overcome the large delay" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Adaptive jitter buffer for internet telephony
InactiveUS6862298B1Improve audio qualityTo overcome the large delayError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPacket arrivalControl signal
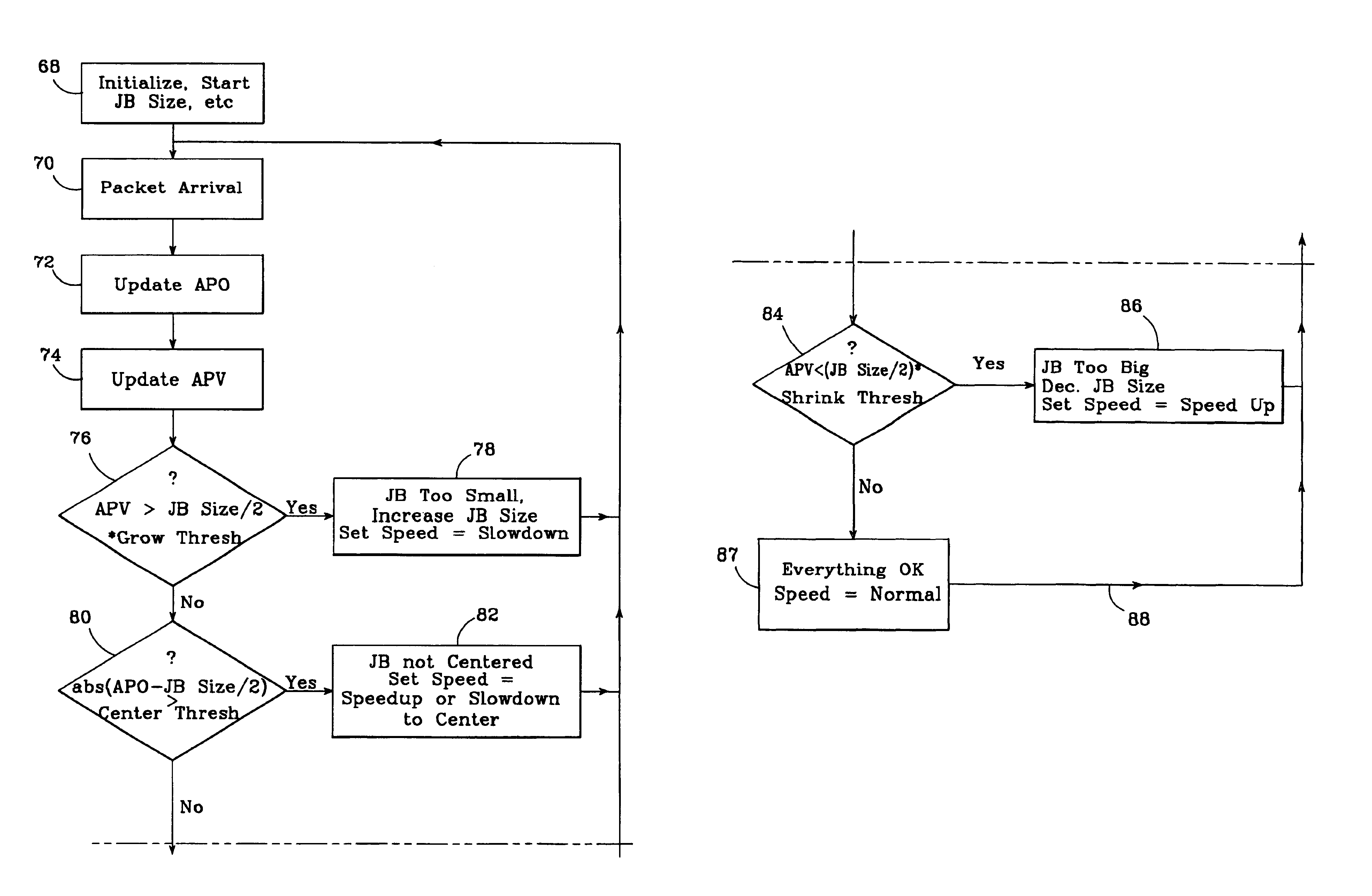
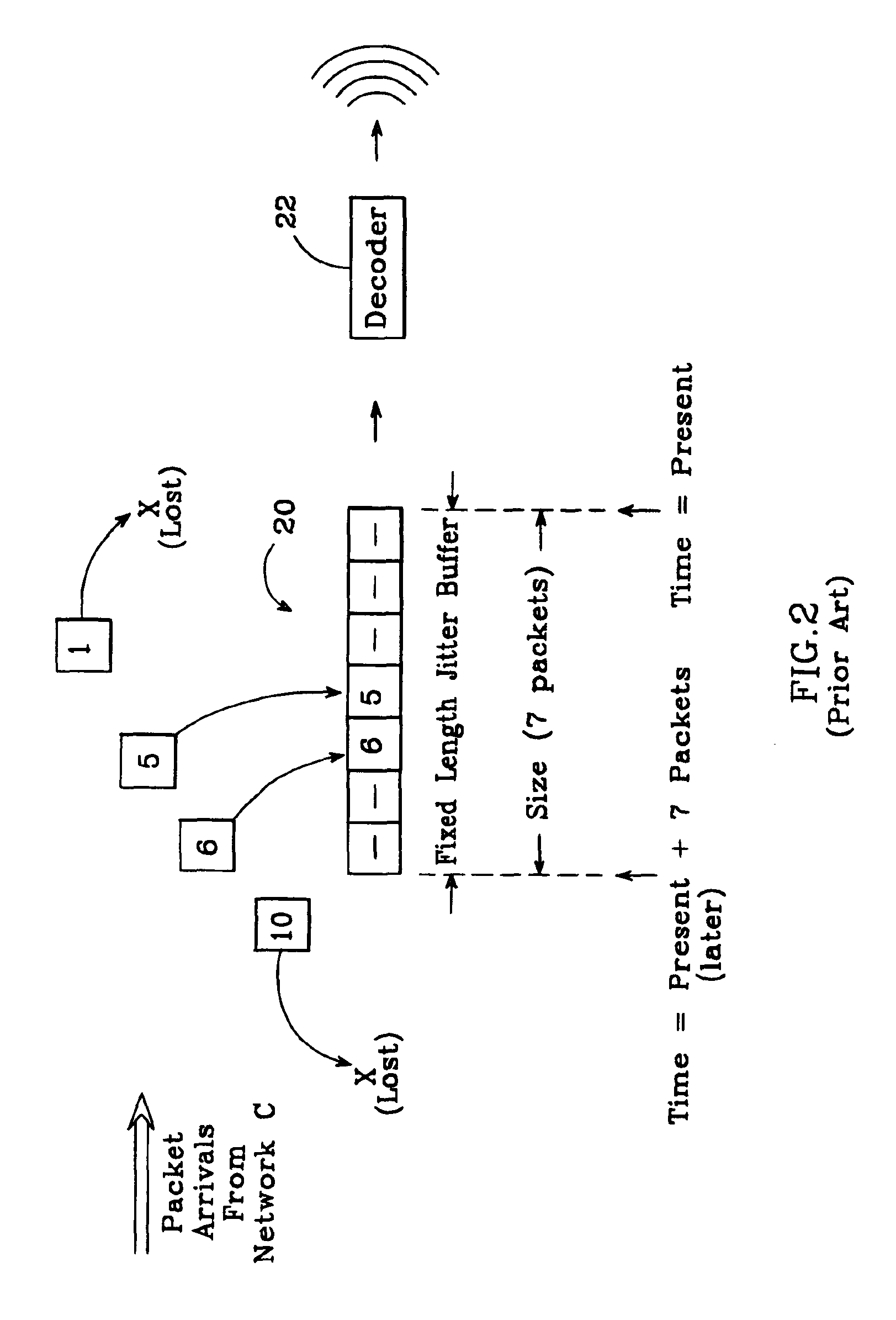
In an improved system for receiving digital voice signals from a data network, a jitter buffer manager monitors packet arrival times, determines a time varying transit delay variation parameter and adaptively controls jitter buffer size in response to the variation parameter. A speed control module responds to a control signal from the jitter buffer manager by modifying the rate of data consumption from the jitter buffer, to compensate for changes in buffer size, preferably in a manner which maintains audio output with acceptable, natural human speech characteristics. Preferably, the manager also calculates average packet delay and controls the speed control module to adaptively align the jitter buffer's center with the average packet delay time.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
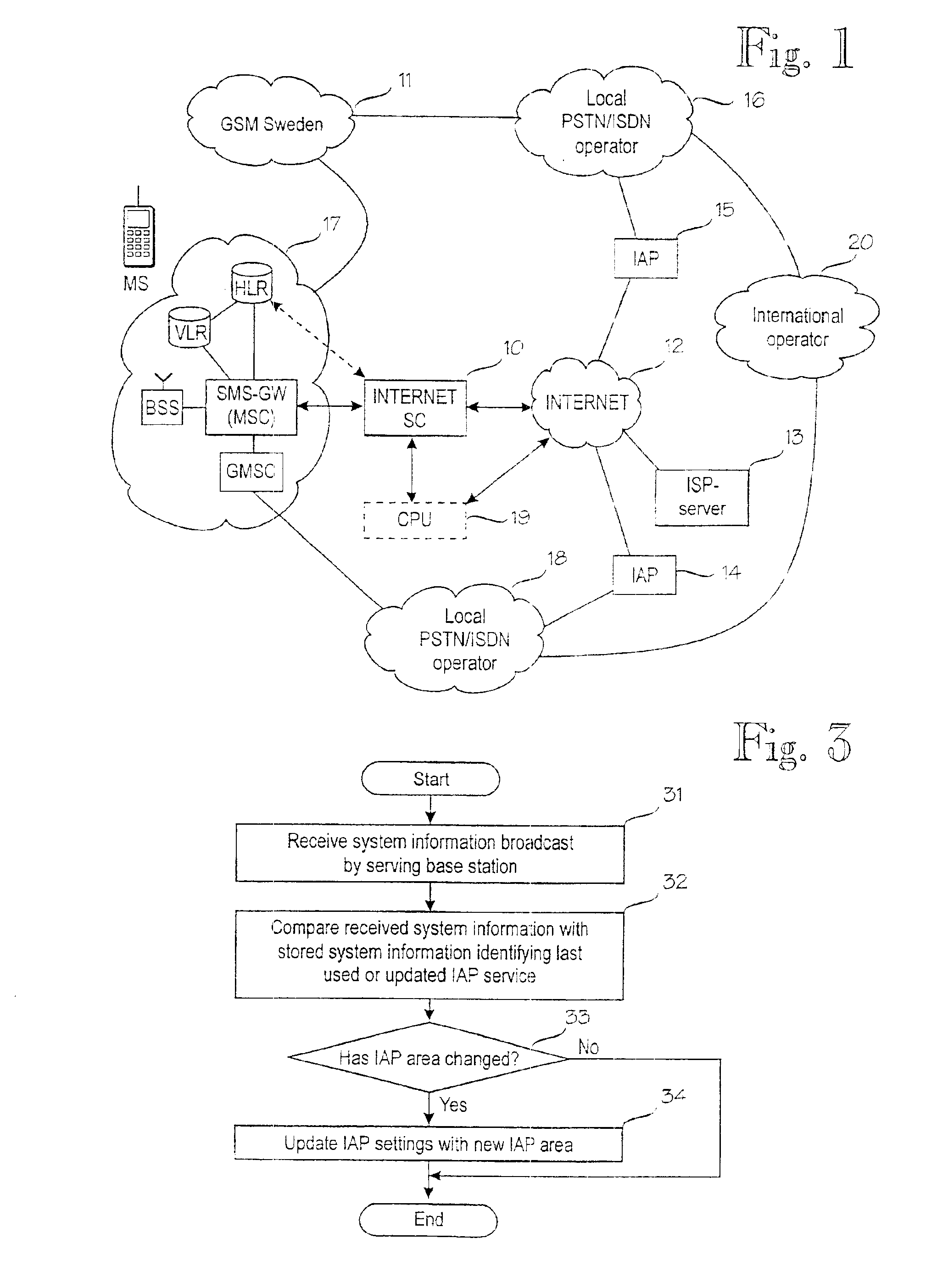
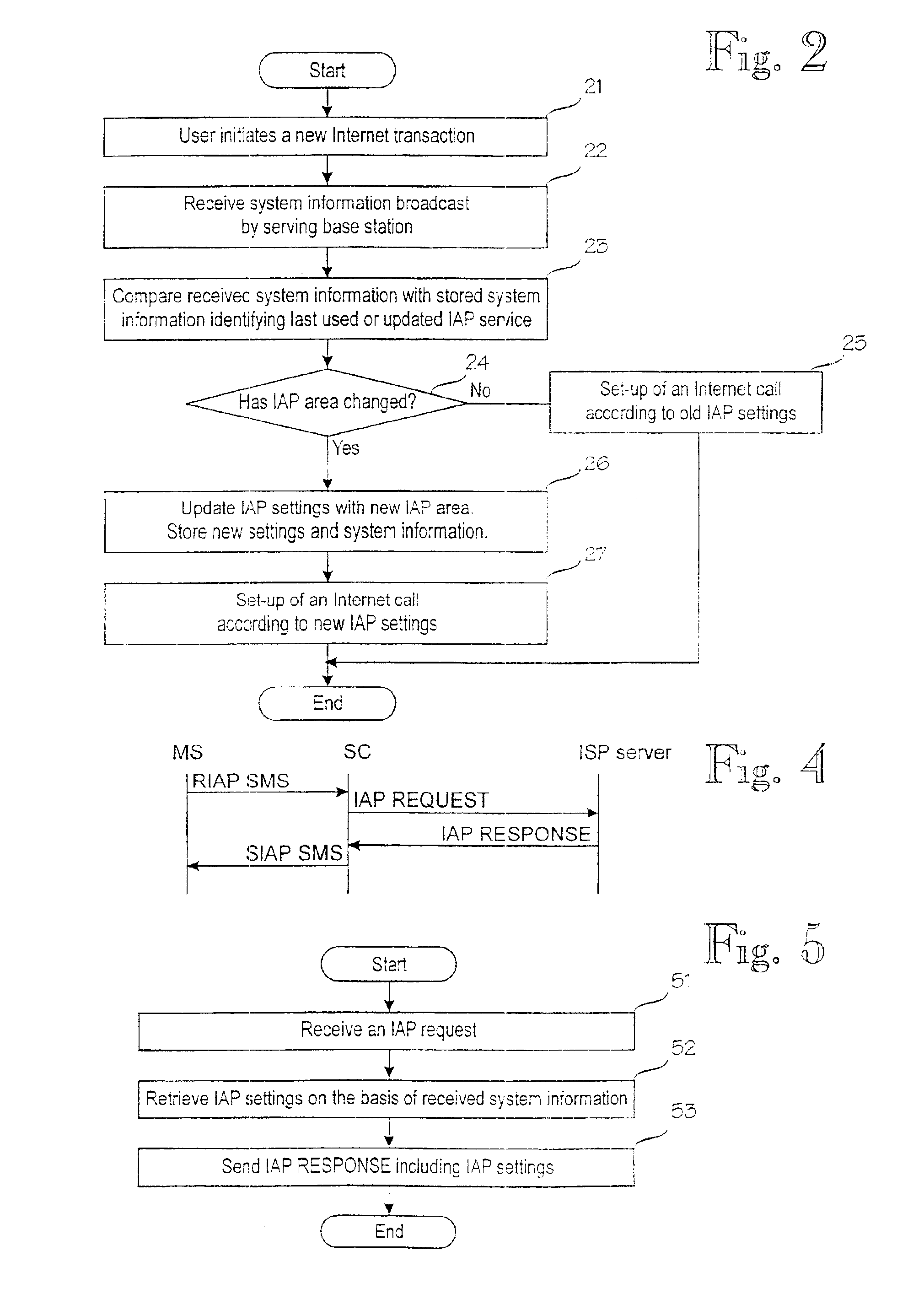
Updating of internet access point settings in a mobile communication system
InactiveUS6904026B1Reduce call costsMinimal amount of workBroadcast service distributionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsClosest pointInternet access
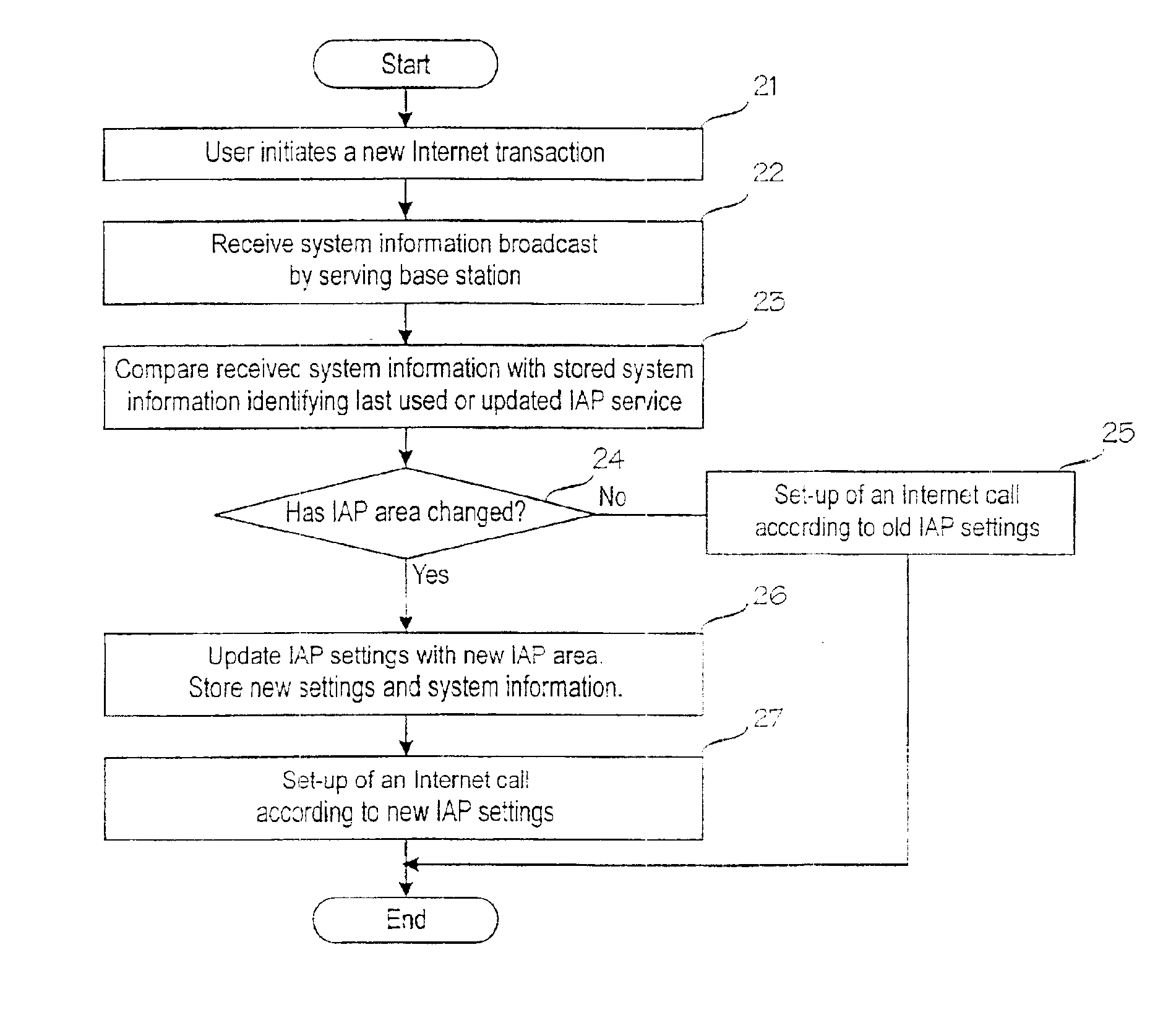
A digital mobile communication system is provided with a facility by means of which it can establish a connection to the Internet network (12) via an Internet access point (14, 15). IAP settings needed for establishing a connection are stored in a mobile station (MS). When a mobile station (MS) roams, the closest point may, however, change, and IAP settings should be updated in the mobile station (MS). The invention comprises dividing the mobile communication system into IAP areas, which are given preferred IAPs. An IAP area may be e.g. a mobile communication network (11, 17). Mobile communication networks broadcast system information on the basis of which a mobile station may detect that the IAP area has changed and start a procedure for updating IAP settings. Updating may comprise retrieval of IAP settings from a special server (13) in the network maintained by an Internet service provider. Retrieval can be done e.g. via a short message service center (10). In one embodiment the mobile communication network broadcasts messages giving recommended IAP settings to mobile stations.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM LLC
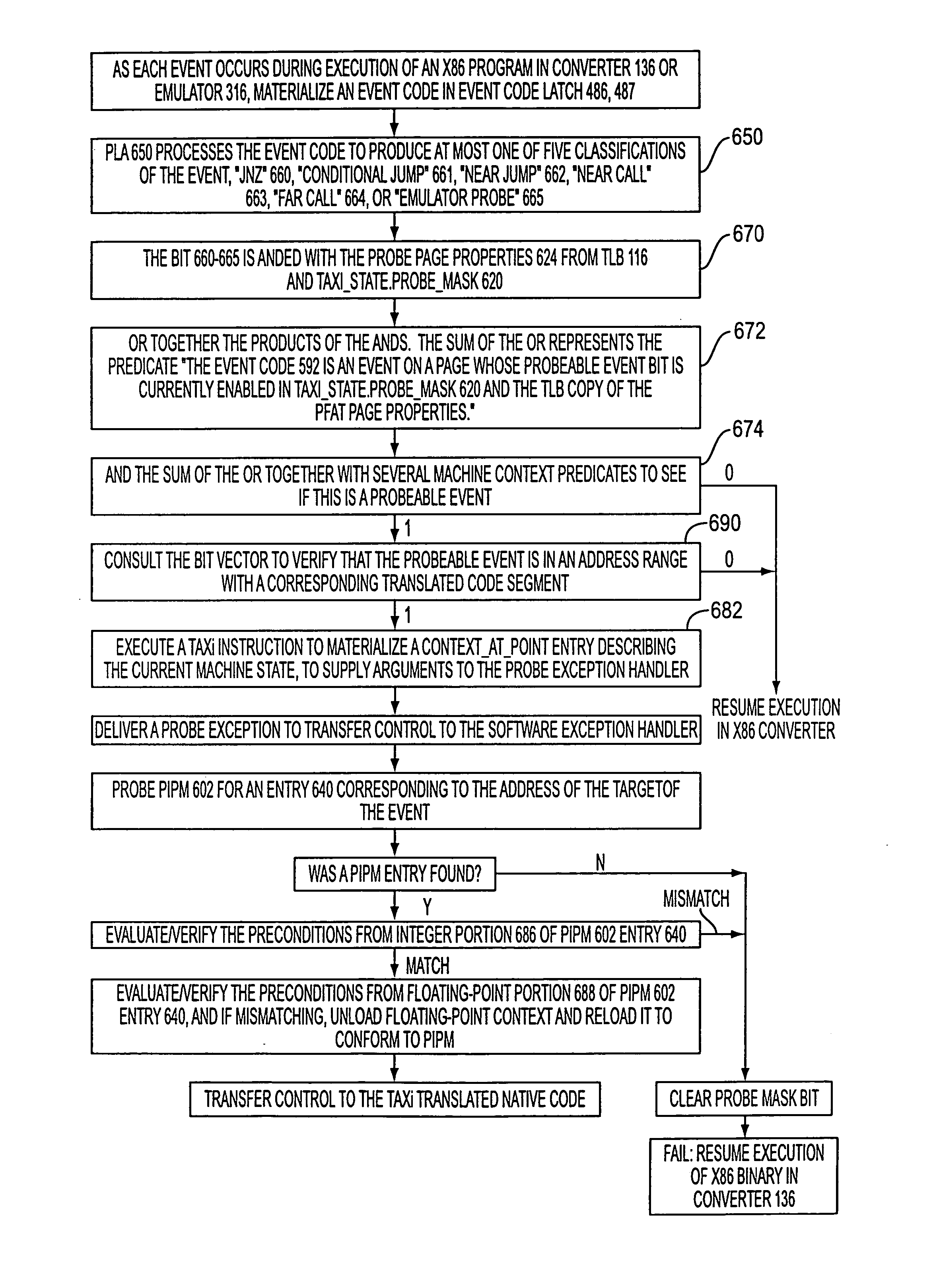
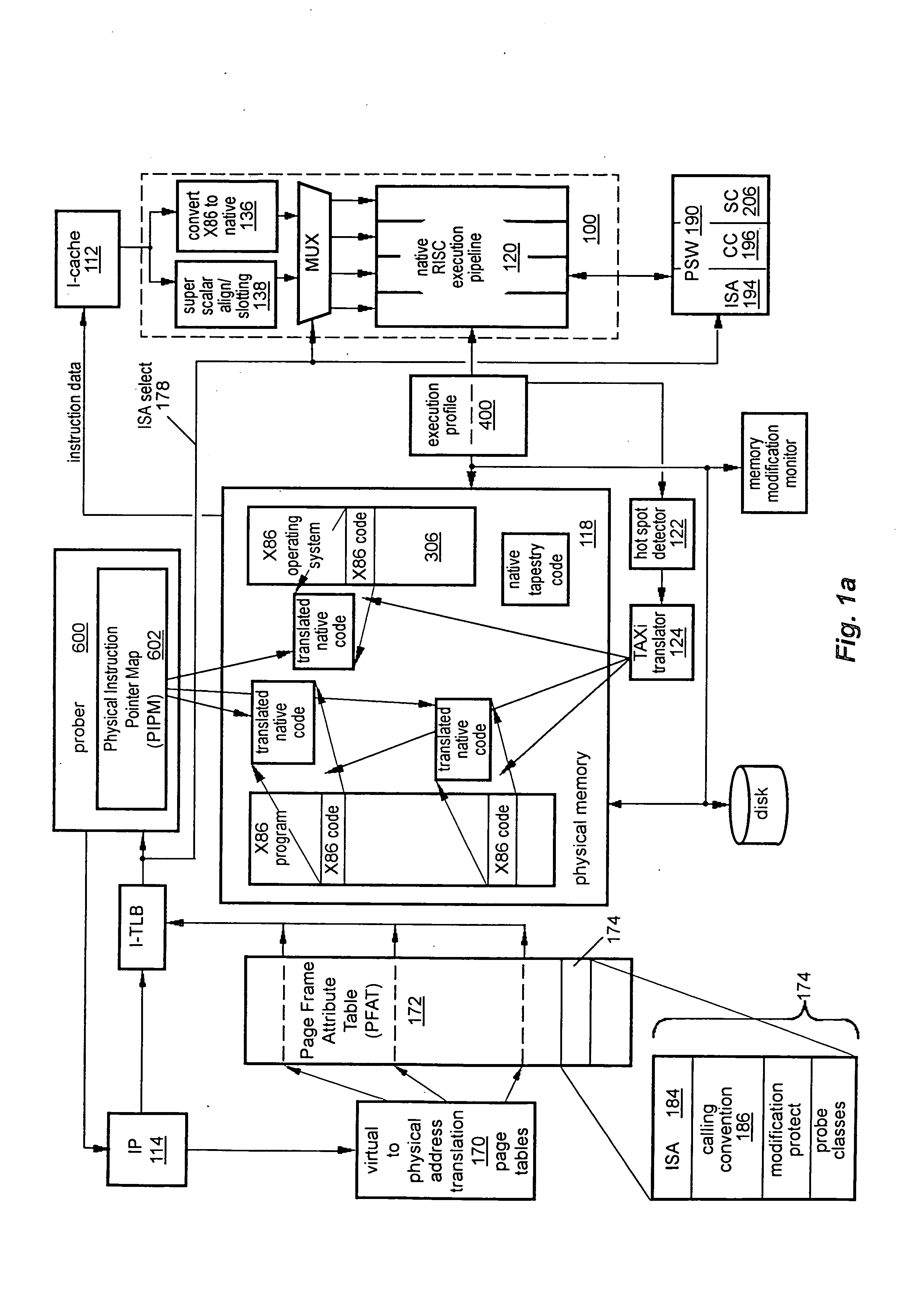
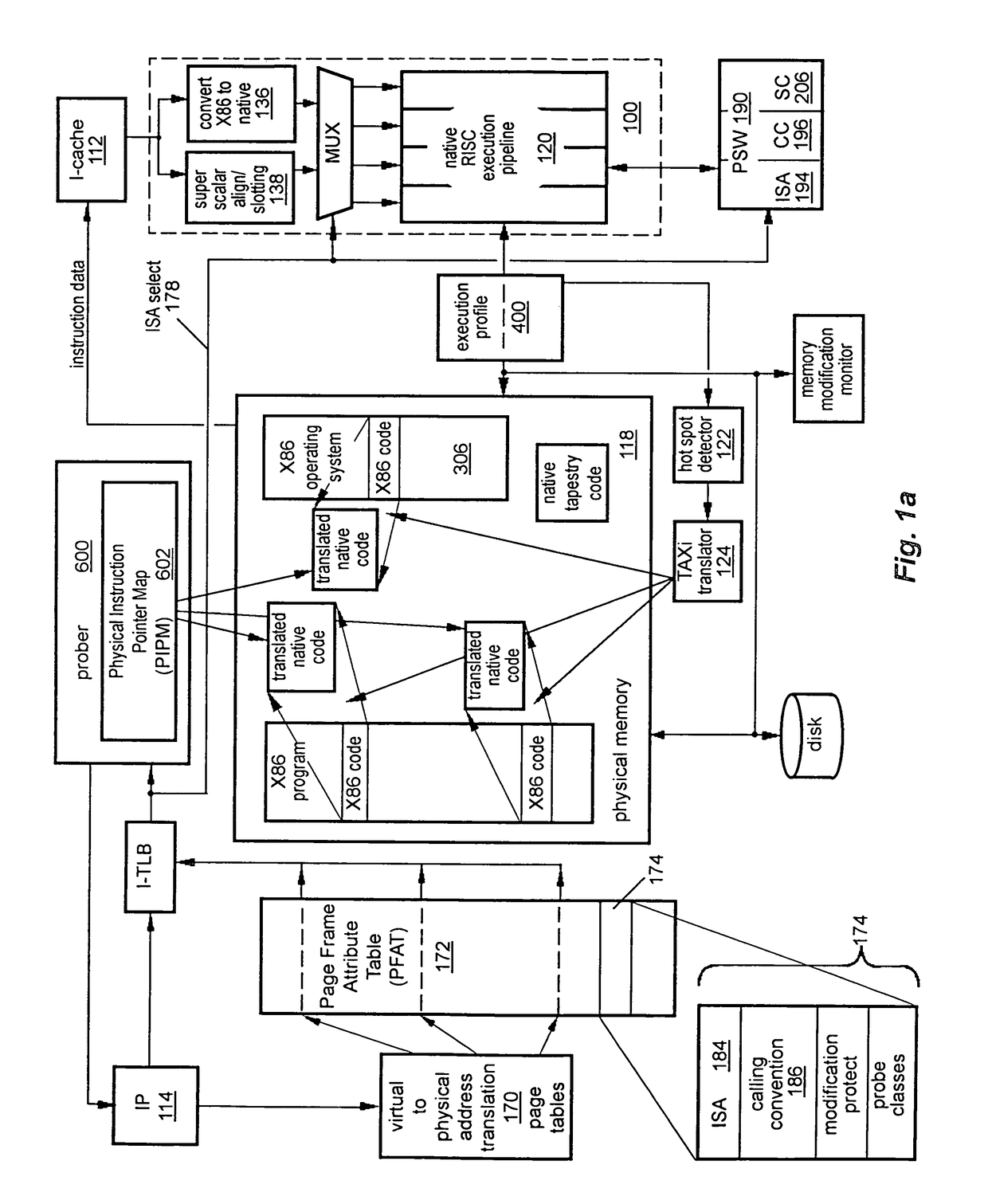
Transferring execution from one instruction stream to another
InactiveUS20050086650A1Improve abilityReduce complexityGeneral purpose stored program computerSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationInstruction setInstruction stream
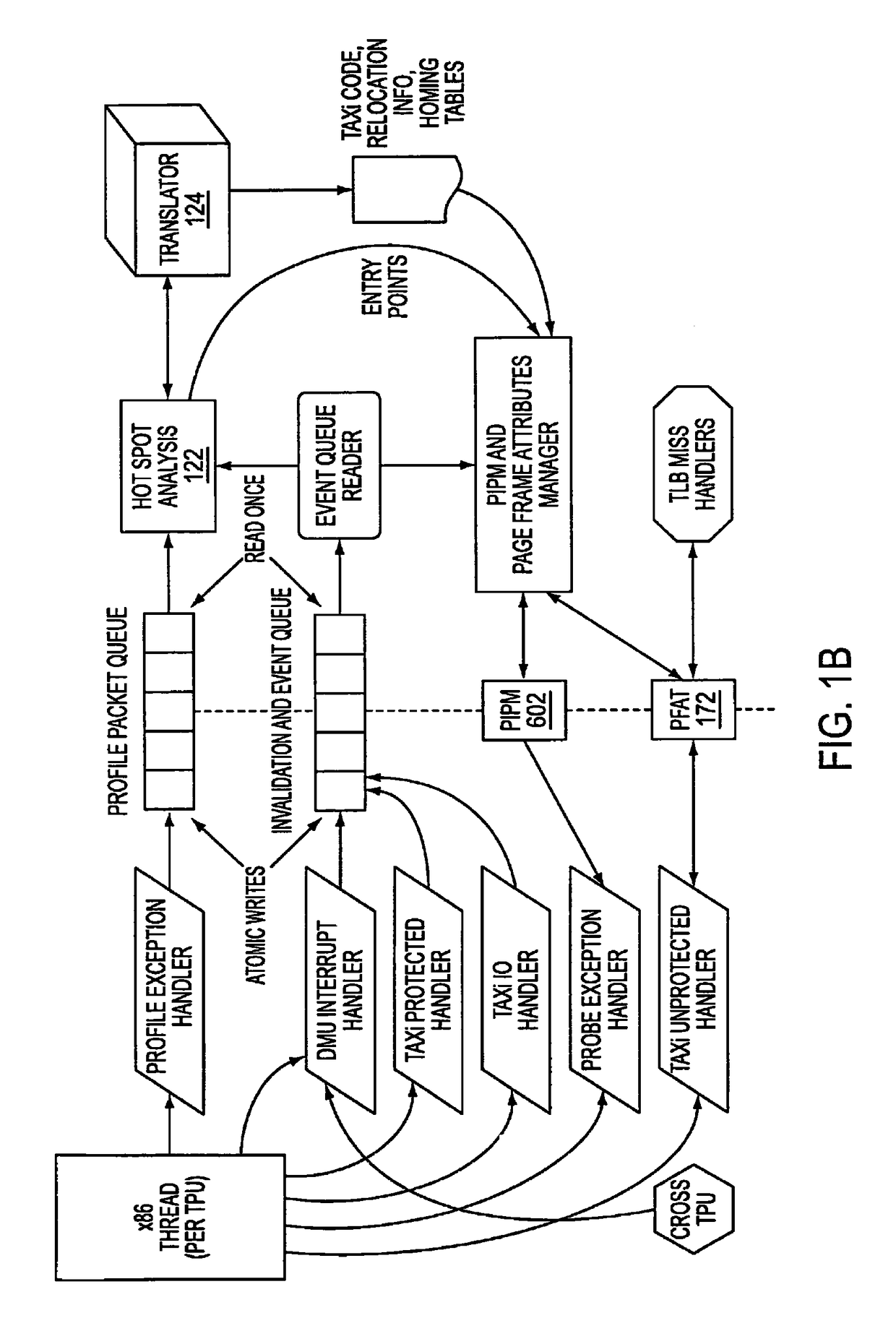
A computer has instruction pipeline circuitry capable of executing two instruction set architectures (ISA's). A binary translator translates at least a selected portion of a computer program from a lower-performance one of the ISA's to a higher-performance one of the ISA's. Hardware initiates a query when about to execute a program region coded in the lower-performance ISA, to determine whether a higher-performance translation exists. If so, the about-to-be-executed instruction is aborted, and control transfers to the higher-performance translation. After execution of the higher-performance translation, execution of the lower-performance region is reestablished at a point downstream from the aborted instruction, in a context logically equivalent to that which would have prevailed had the code of the lower-performance region been allowed to proceed.
Owner:ADVANCED SILICON TECH
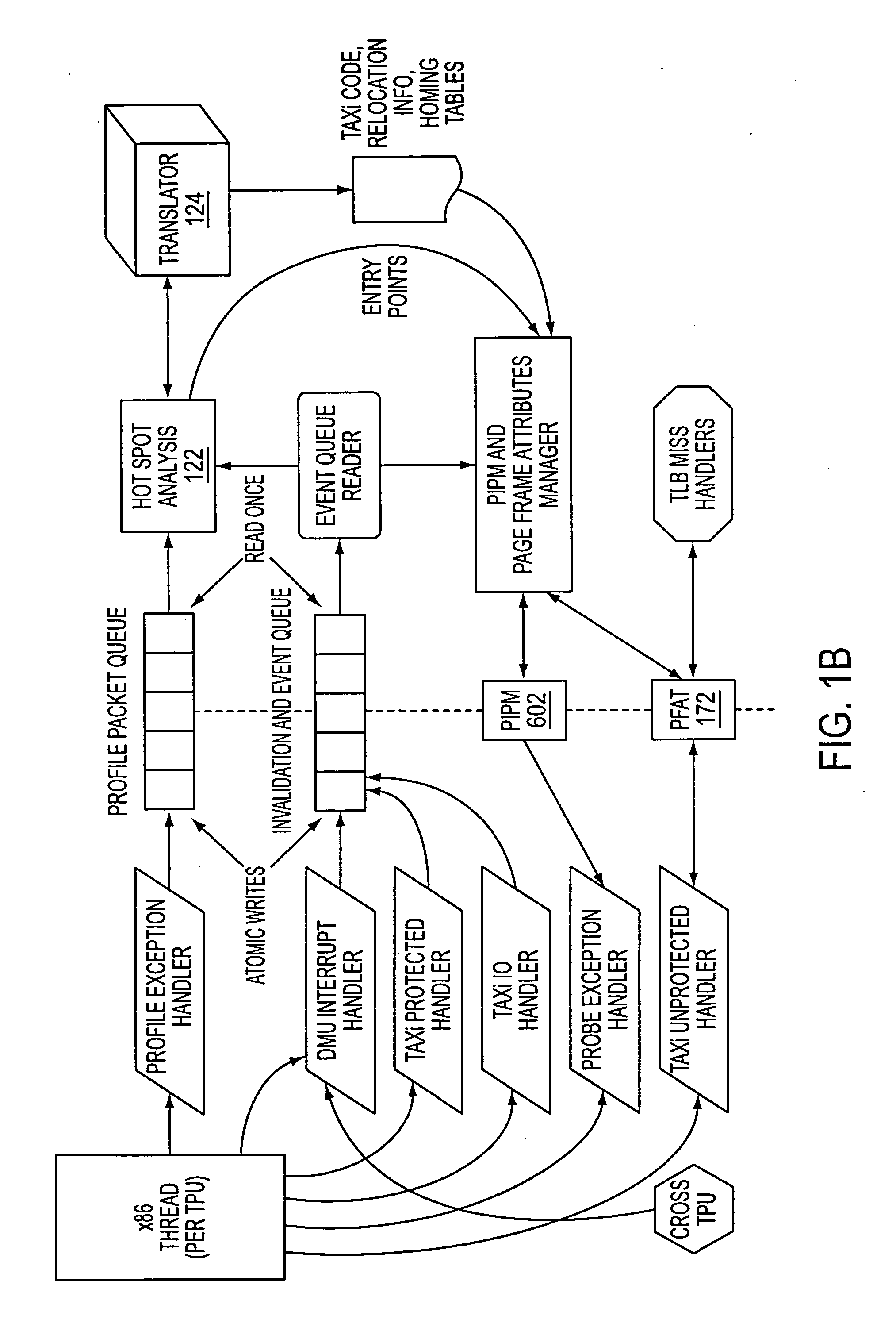
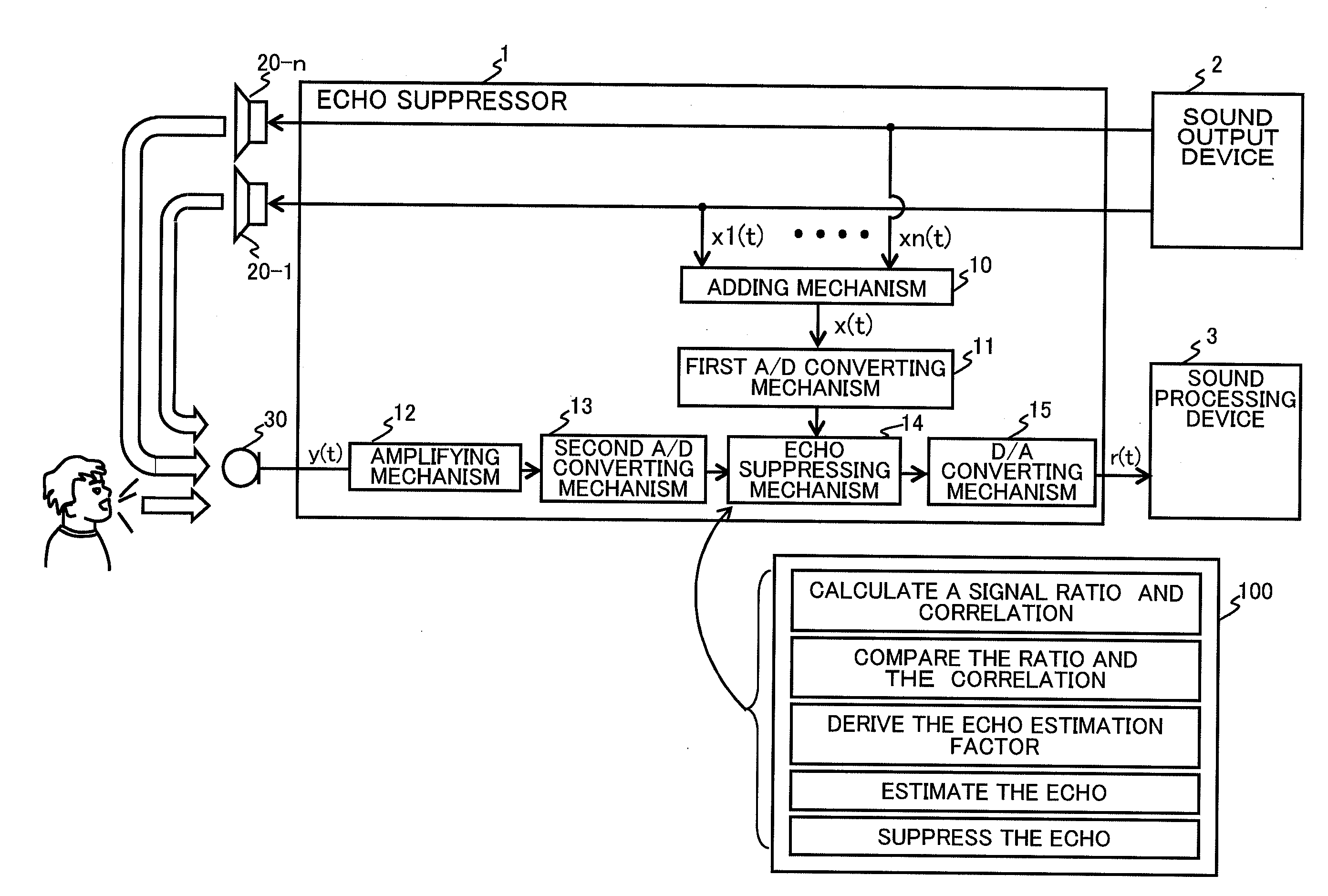
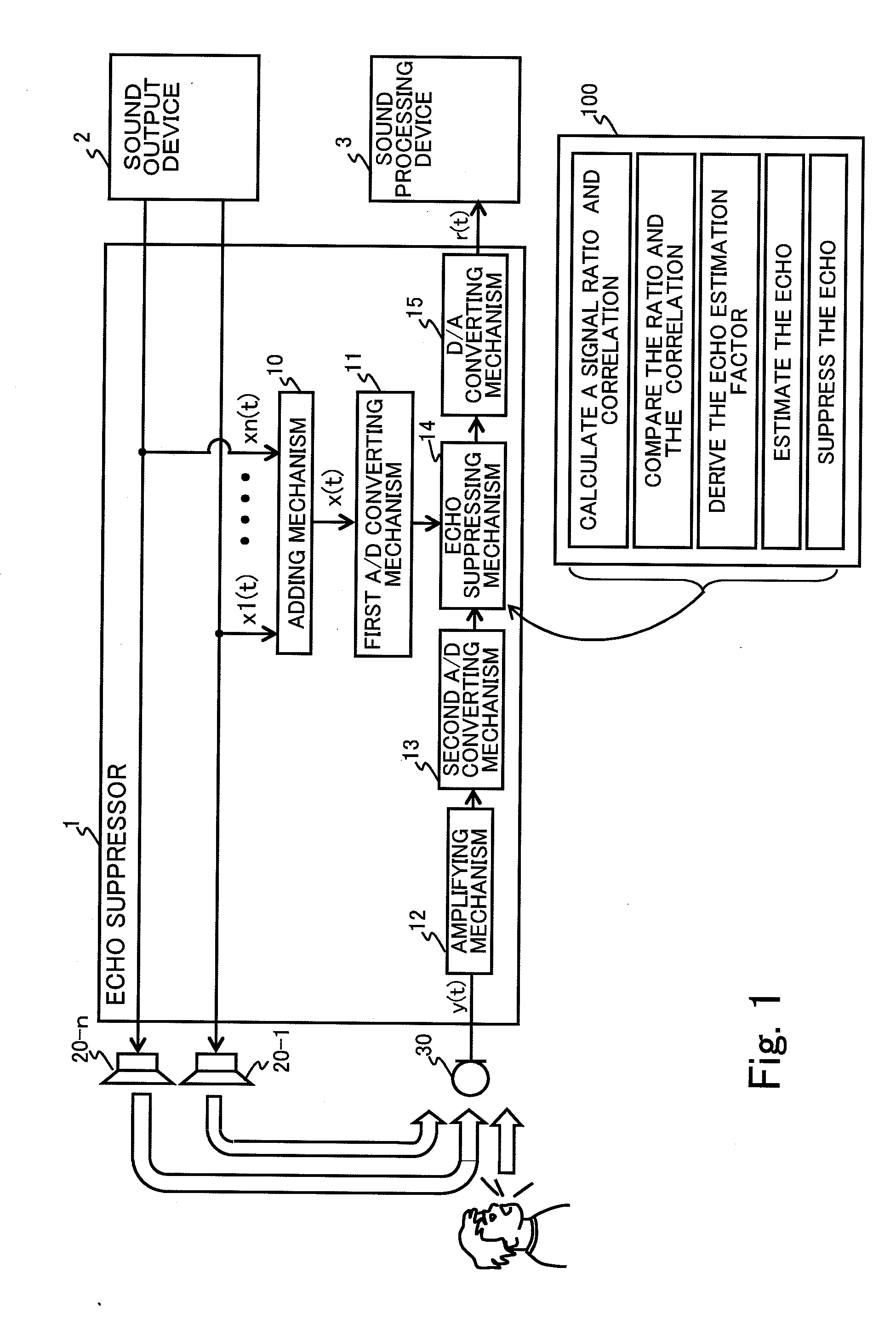
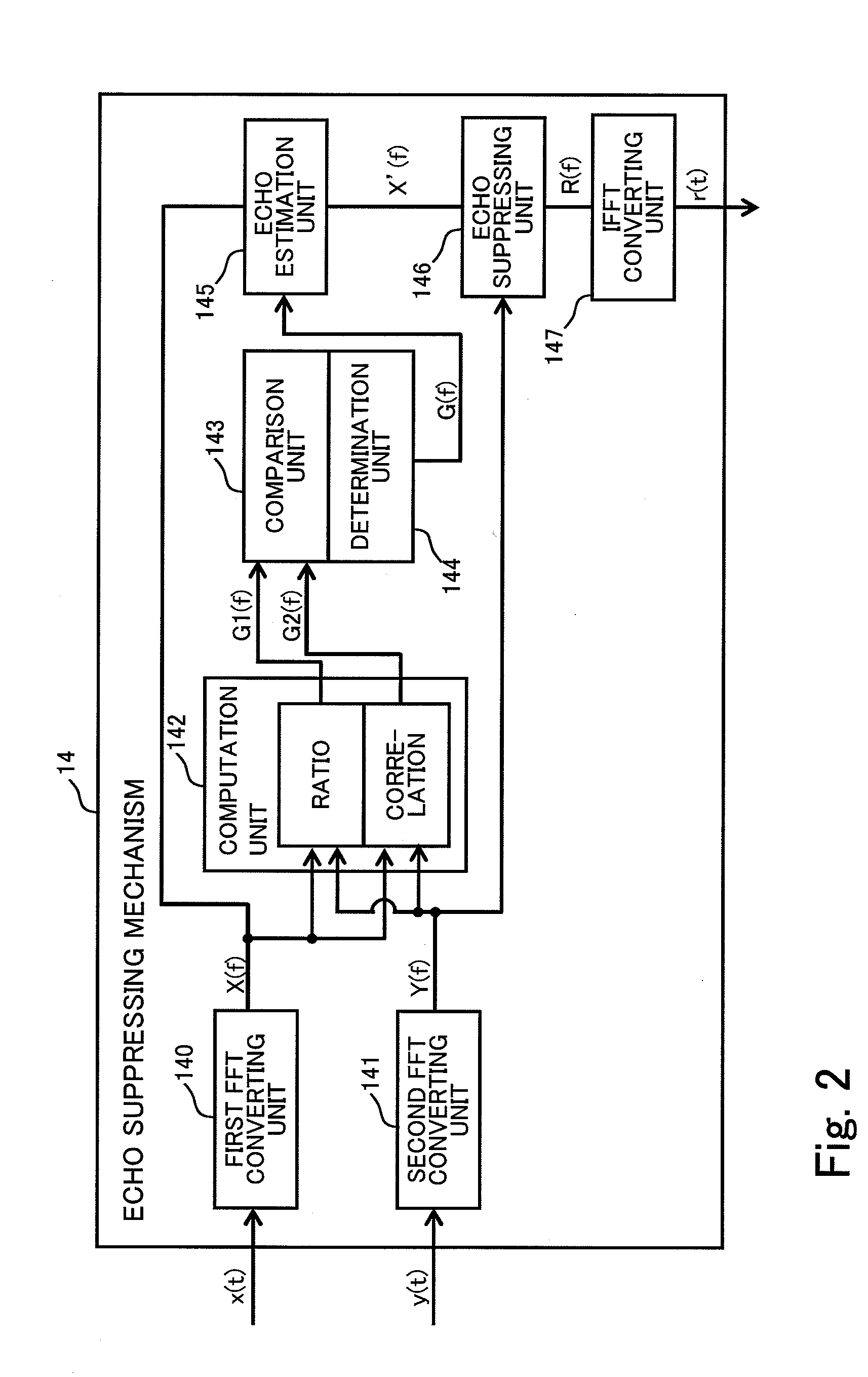
Echo suppressor, echo suppressing method, and computer readable storage medium
ActiveUS20090010445A1Improve detection accuracySuppression of distortionInterconnection arrangementsSpeech analysisTime domainEcho signal
An apparatus is provided for suppressing an echo signal included in a measured signal corresponding to a measured sound. In the apparatus, the measured signal and a reference signal in a time domain are transformed into a frequency domain, and calculated for obtaining each value of a ratio and a correlation between the measured signal and the reference signal in the frequency domain. With executing a comparison of the values of the ratio and the correlation, a coefficient is derived, where a product of the coefficient and the measured sound in the frequency domain gives an estimated value of the echo signal. The echo in the measured signal is suppressed with subtracting the estimation of the echo signal from the measured signal, respectively in the frequency domain.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Delta-sigma A/D converter
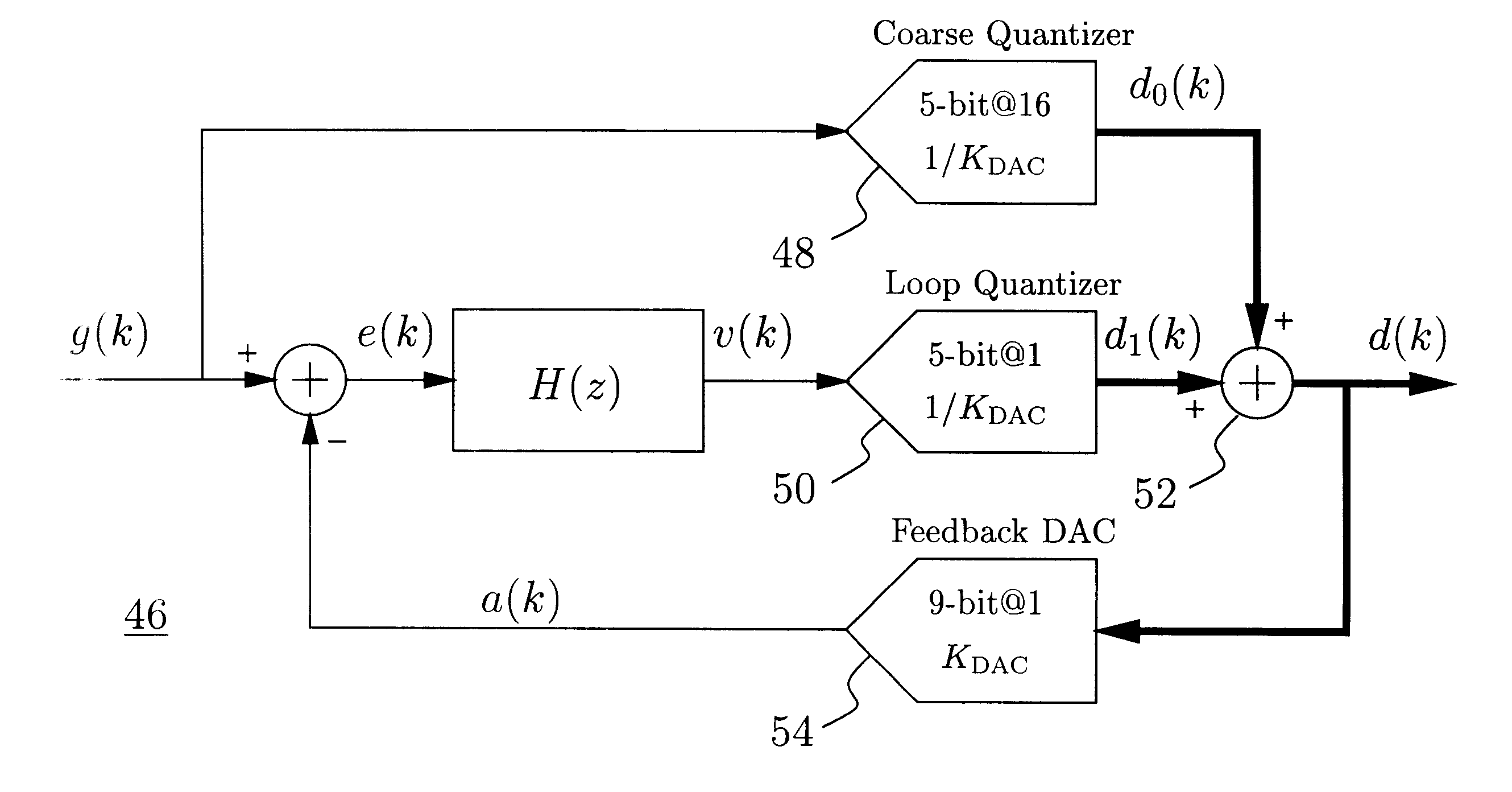
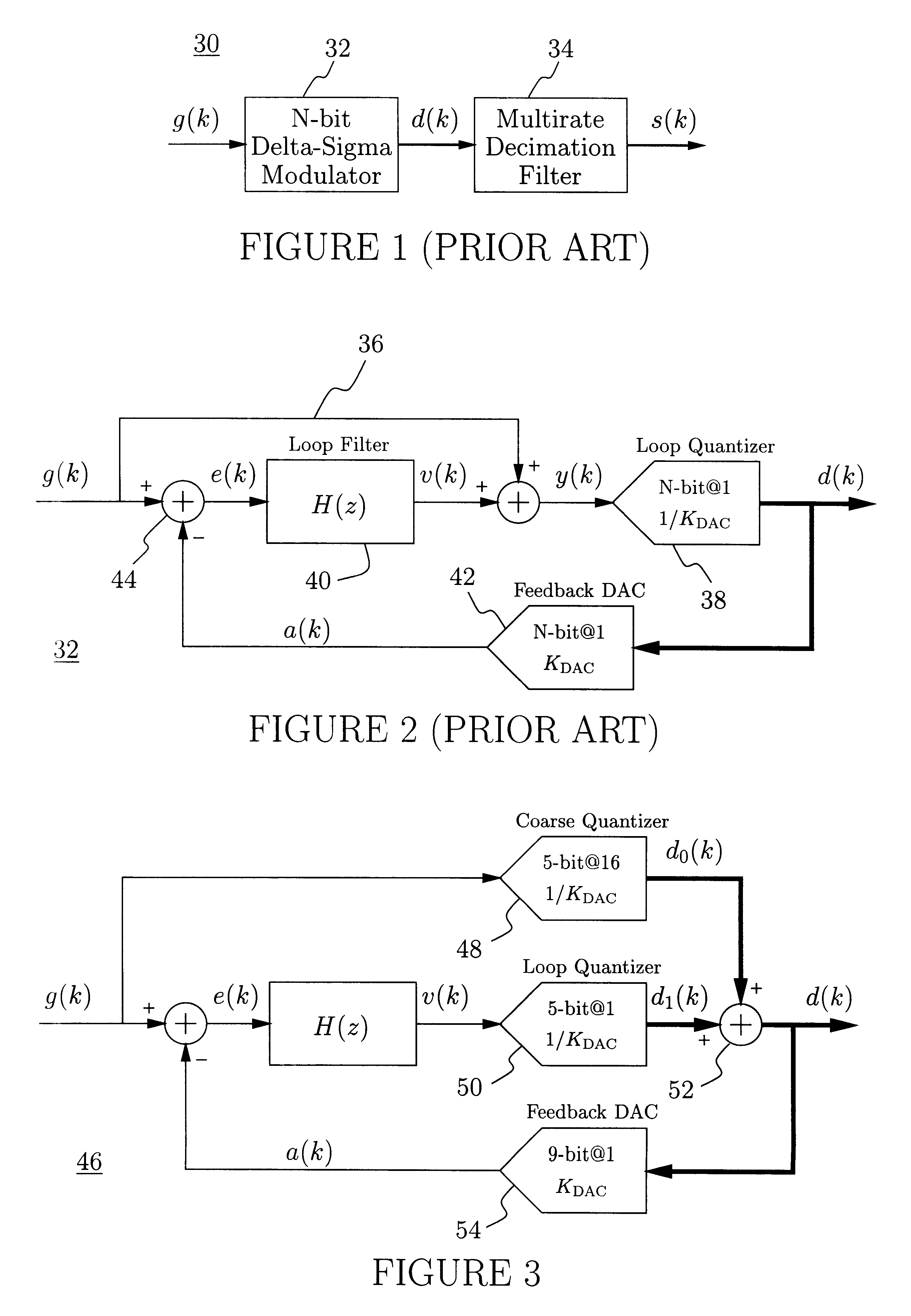
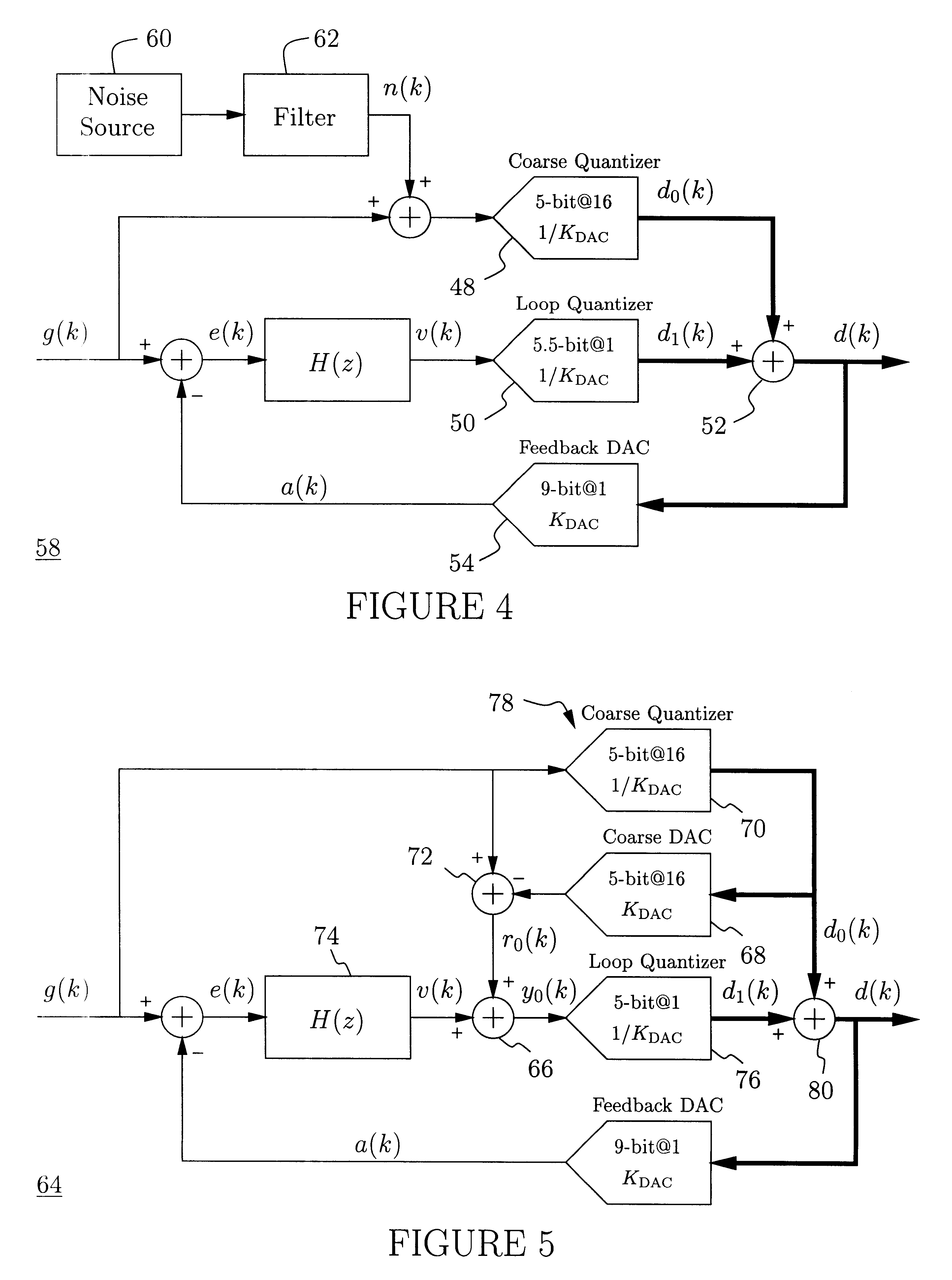
InactiveUS6271782B1Without compromising the modulator's stabilityTo overcome the large delayElectric signal transmission systemsDifferential modulationLoop filterAnalog feedback
A delta-sigma modulator comprising a first quantizer providing a first digital signal d0(k) representing the input signal g(t); a loop filter with input signal paths; a loop quantizer providing a corrective digital signal d1(k) representing the loop filter's output signal y(t); an array of feedback DACs D / A converting the sum d(k)=df(k)=d0(k)+d1(k) of the first and the corrective digital signals and injecting feedback signals into the loop filter.The loop filter's input node is applied the difference of the input signal g(t) and the global analog feedback signal a3(t). The global feedback signal a3(t) is delayed several clock cycles with respect to the digital output signal d(k). The delay is used to carry out mismatch-shaping and deglitching algorithms in the feedback DACs. The feedback DACs' different delays and gain coefficients are designed such that the modulator is stable. The filter's input signal paths and the compensating DAC are designed such that the gain from the input signal g(t) to the loop quantizer is small, ideally zero. Thus, the loop quantizer's resolving range can be a fraction of the first quantizer's resolving range, whereby the output signal's d(k) resolution can be much higher than the individual resolutions of d0(k) and d1(k).The delta-sigma modulator is well suited for the implementation of high-resolution wide-bandwidth A / D converters. Important applications include digital communication systems.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES BV
Methods and apparatus for arbitrating output port contention in a switch having virtual output queuing
InactiveUS6667984B1Implementation reasonableReasonable timeData switching by path configurationTime-division multiplexing selectionComputer networkTelecommunications
A dual round robin arbitration technique for a switch in which input ports include virtual output queues. A first arbitration selects, for each of the input ports, one cell from among head of line cells of the virtual output queues to generate a first arbitration winning cell. Then, for each of the output ports, a second arbitration selects one cell from among the first arbitration winning cells requesting the output port.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INST OF NEW YORK
Method of making resonant tunneling diodes and CMOS backend-process-compatible three dimensional (3-D) integration
InactiveUS7002175B1Improve performanceEase of fabricationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanoinformaticsLow noiseElectrical connection
A double barrier resonant tunneling diode (RTD) is formed and integrated with a level of CMOS / BJT / SiGe devices and circuits through processes such as metal-to-metal thermocompressional bonding, anodic bonding, eutectic bonding, plasma bonding, silicon-to-silicon bonding, silicon dioxide bonding, silicon nitride bonding and polymer bonding or plasma bonding. The electrical connections are made using conducting interconnects aligned during the bonding process. The resulting circuitry has a three-dimensional architecture. The tunneling barrier layers of the RTD are formed of high-K dielectric materials such as SiO2, Si3N4, Al2O3, Y2O3, Ta2O5, TiO2, HfO2, Pr2O3, ZrO2, or their alloys and laminates, having higher band-gaps than the material forming the quantum well, which includes Si, Ge or SiGe. The inherently fast operational speed of the RTD, combined with the 3-D integrated architecture that reduces interconnect delays, will produce ultra-fast circuits with low noise characteristics.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Method and Device for Transmitting Low Rate Signals Over an Optical Transport Network
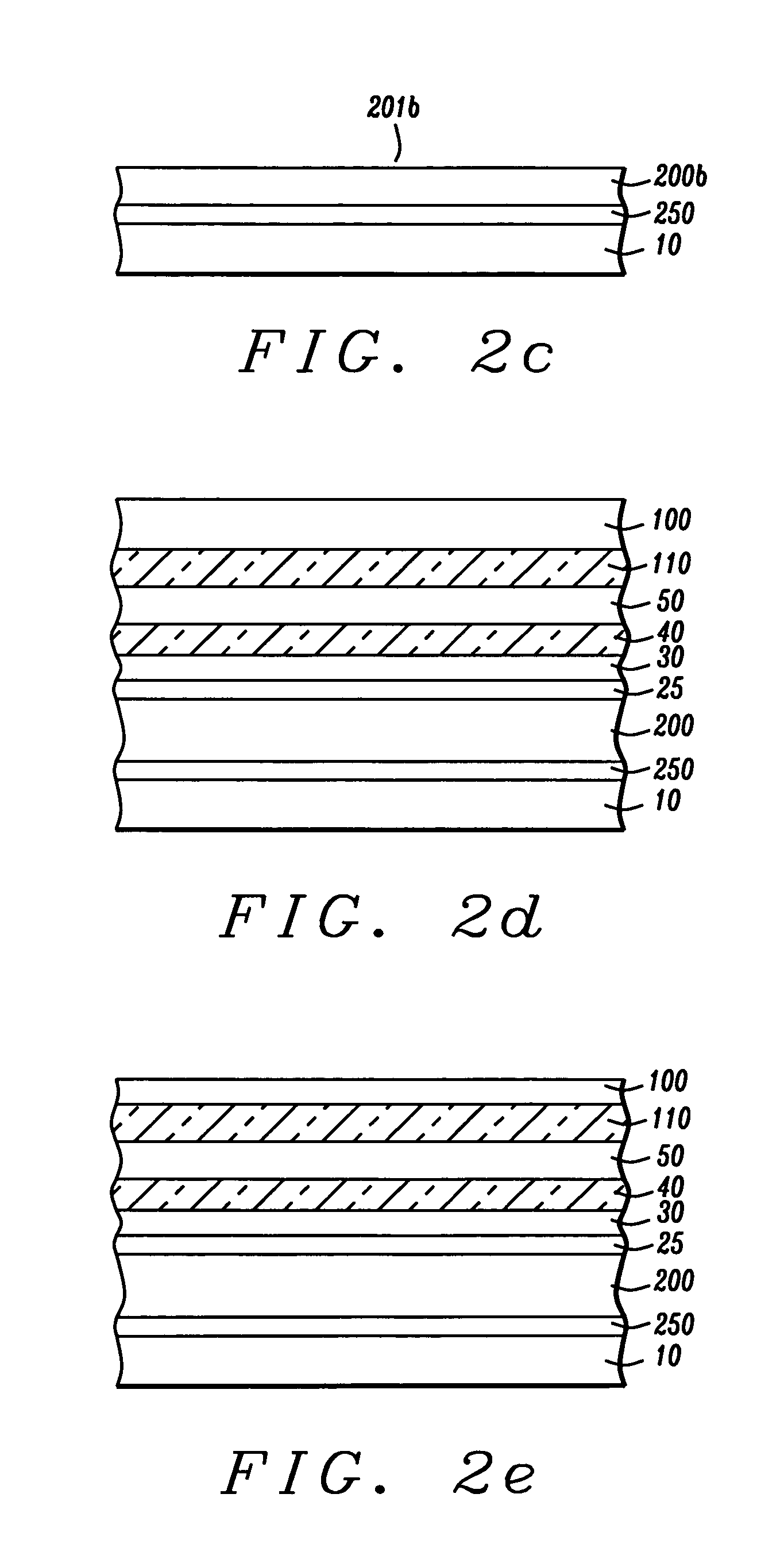
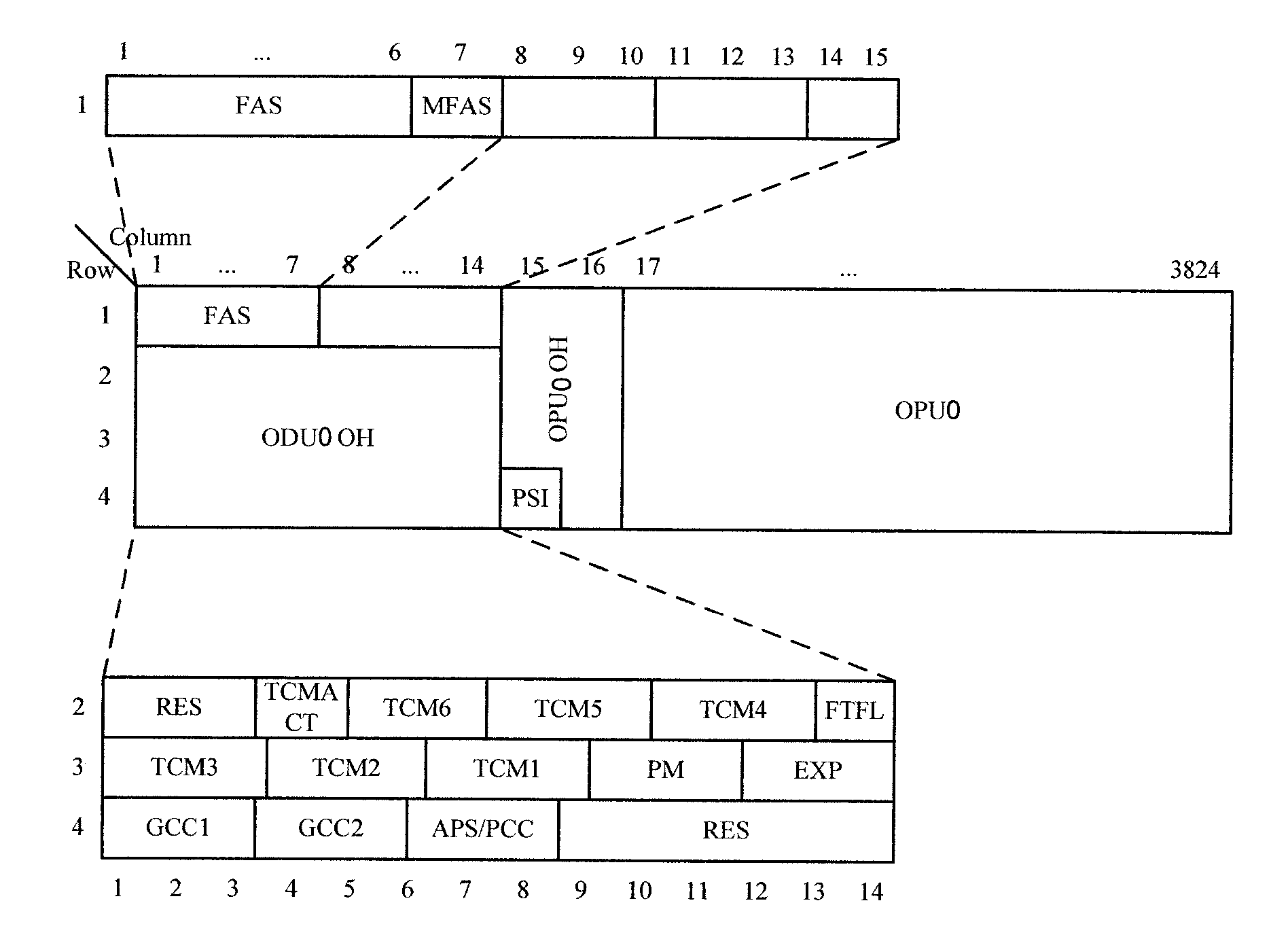
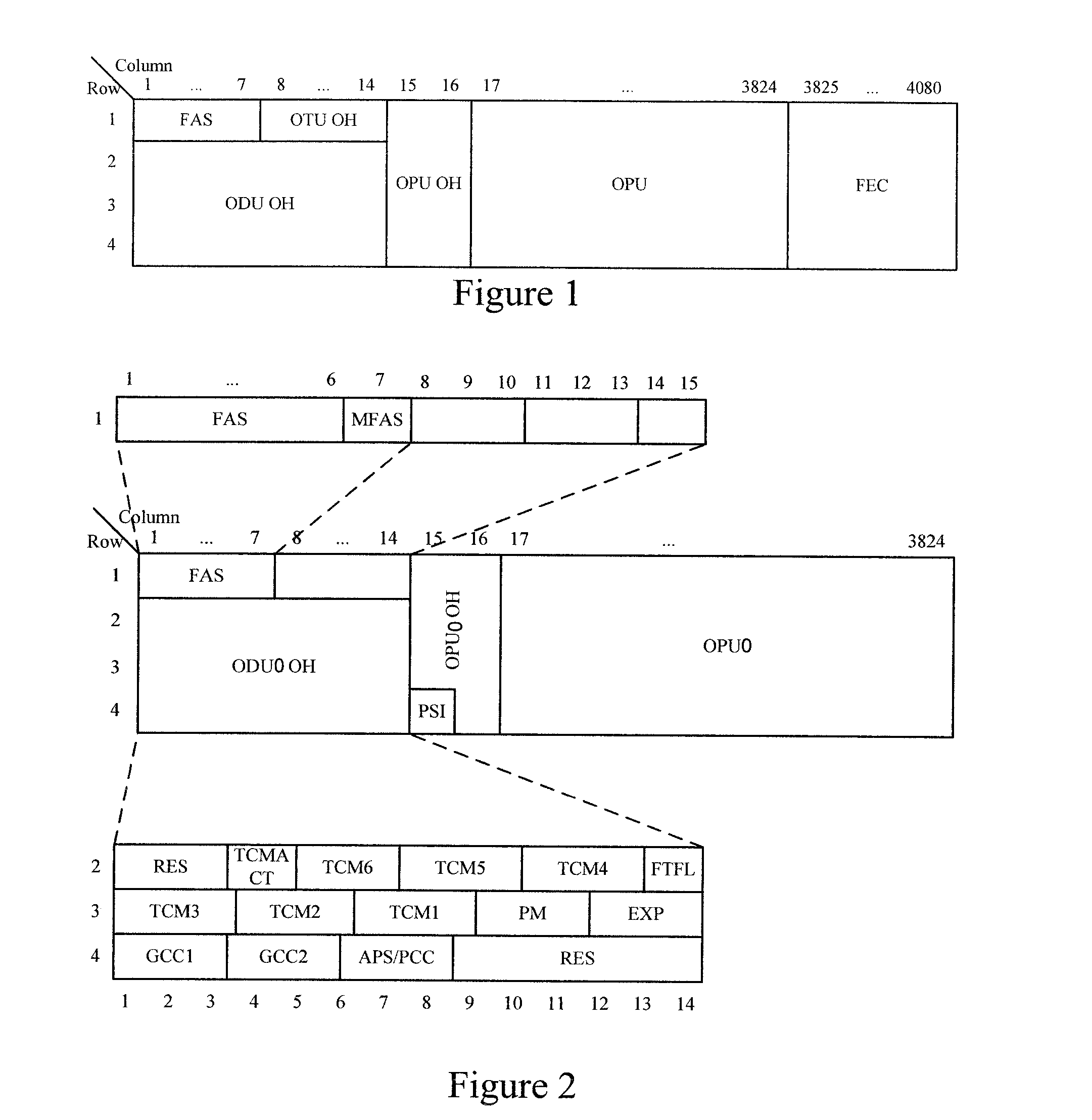
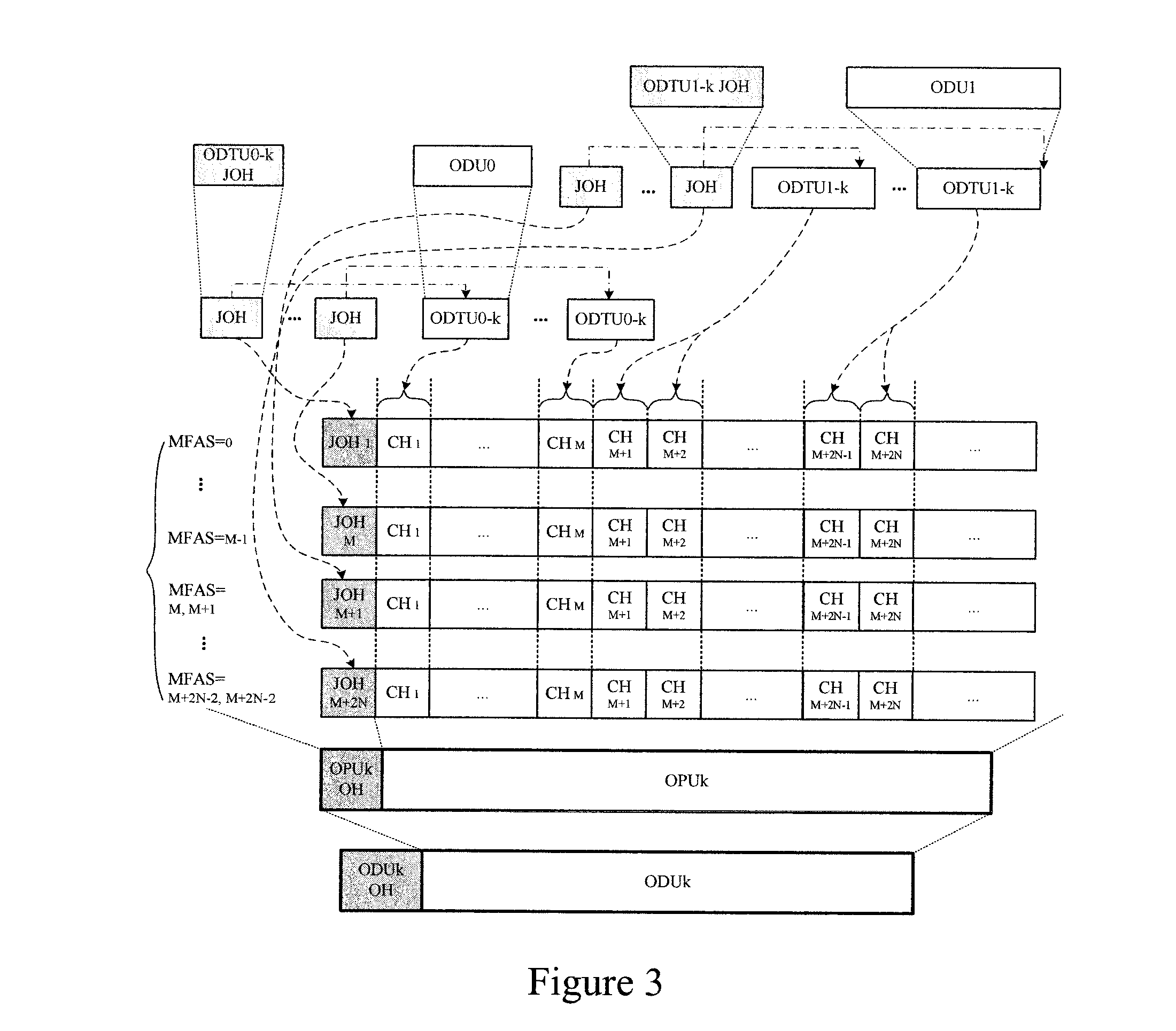
ActiveUS20070248121A1Increase ratingsImprove transmission efficiencyTime-division multiplexOptical multiplexChannel dataMultiplexing
Embodiments of the present invention provide a method for transmitting low rate signals over an optical transport network, including: adapting the low rate signals into low rate optical channel data units of the same rate level with the low rate signals; asynchronously mapping each of the low rate optical channel data units into a low rate optical channel data tributary unit respectively, and generating justification overhead used for rate adaptation for each of the low rate optical channel data units; and forming a higher order optical channel data unit with at least one low rate optical channel data tributary unit and justification overhead corresponding to the low rate optical channel data tributary unit. The present invention enables the optical transport network to support mapping, multiplexing and highly efficient transmission of low rate signals.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Architecture for stack robust fine granularity scalability
InactiveUS20050195896A1Robust error resilience capabilityImprove compression efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionExtensibilityOperating point
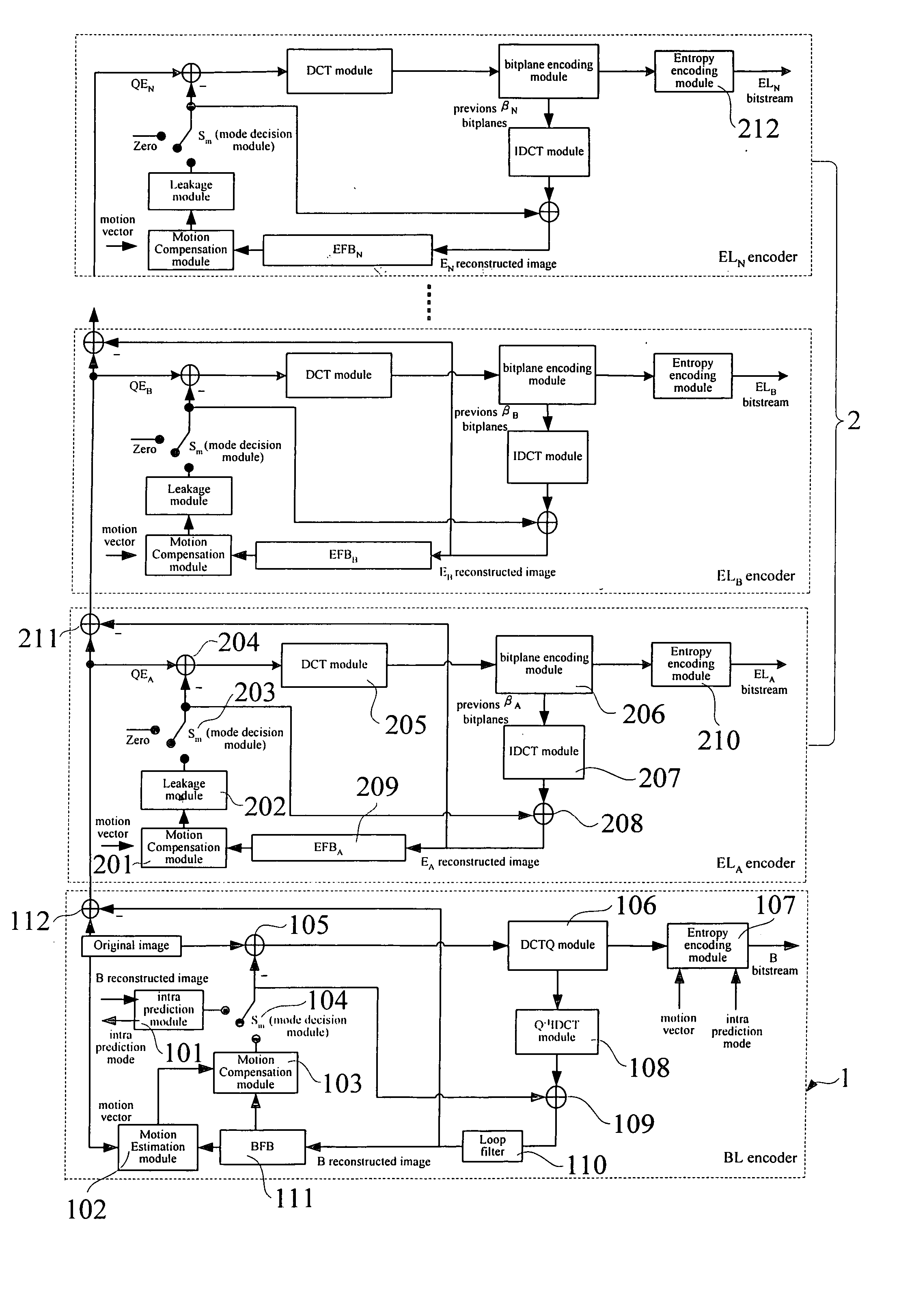
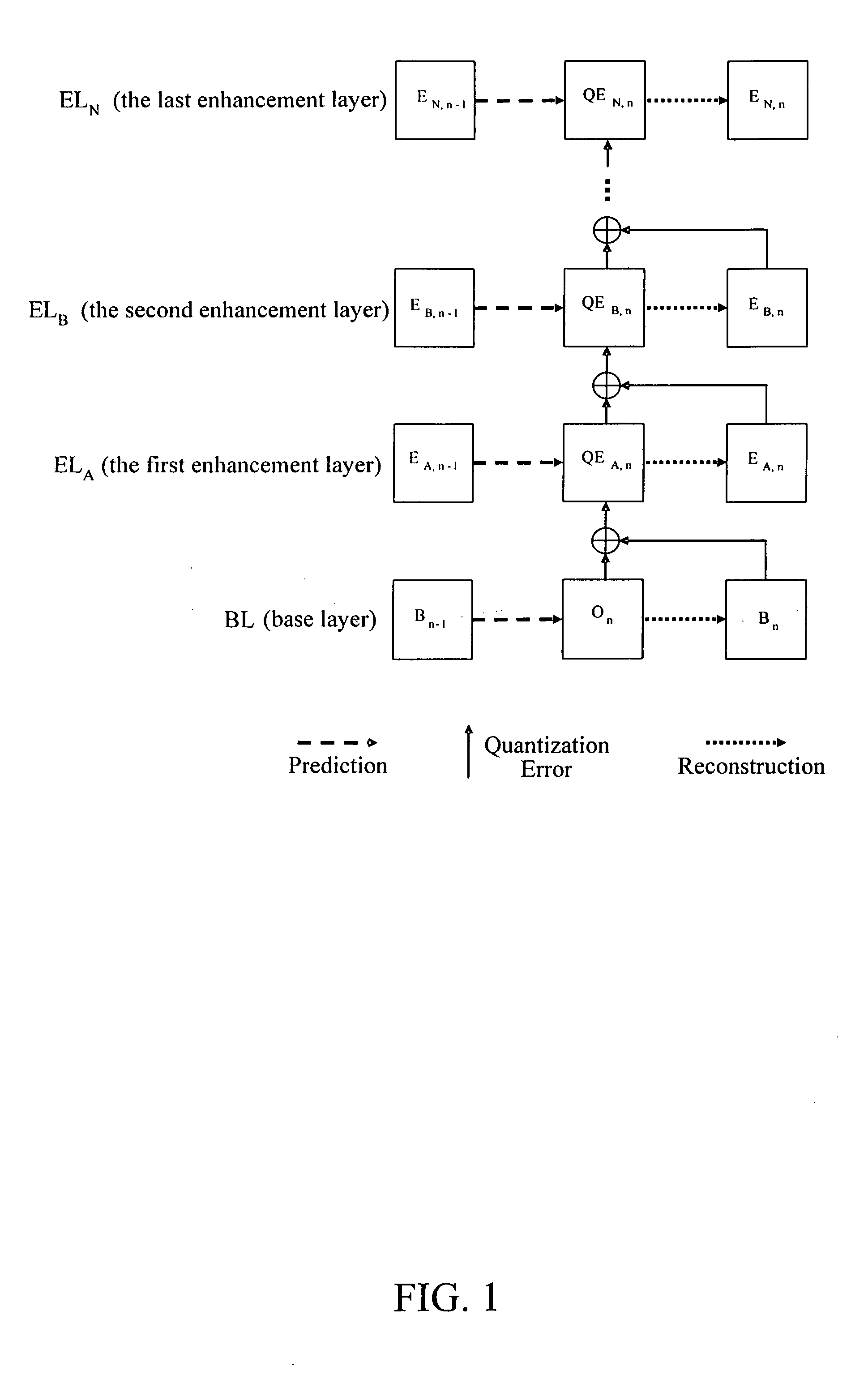
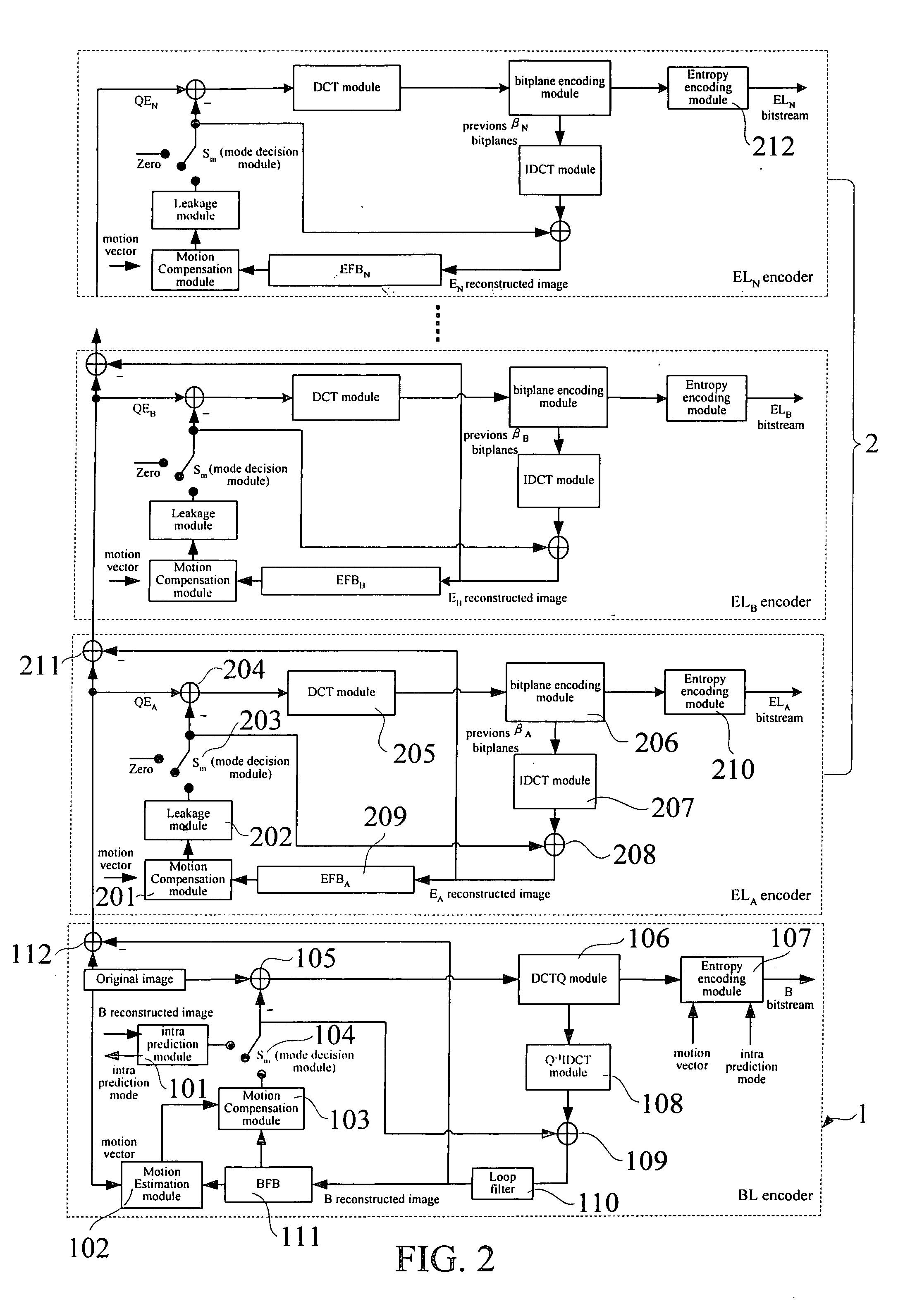
The present invention relates to an architecture for stack robust fine granularity scalability (SRFGS), more particularly, SRFGS providing simultaneously temporal scalability and SNR scalability. SRFGS first simplifies the RFGS temporal prediction architecture and then generalizes the prediction concept as the following: the quantization error of the previous layer can be inter-predicted by the reconstructed image in the previous time instance of the same layer. With this concept, the RFGS architecture can be extended to multiple layers that forming a stack to improve the temporal prediction efficiency. SRFGS can be optimized at several operating points to fit the requirements of various applications while the fine granularity and error robustness of RFGS are still remained. The experiment results show that SRFGS can improve the performance of RFGS by 0.4 to 3.0 dB in PSNR.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Network interface with security association data prefetch for high speed offloaded security processing
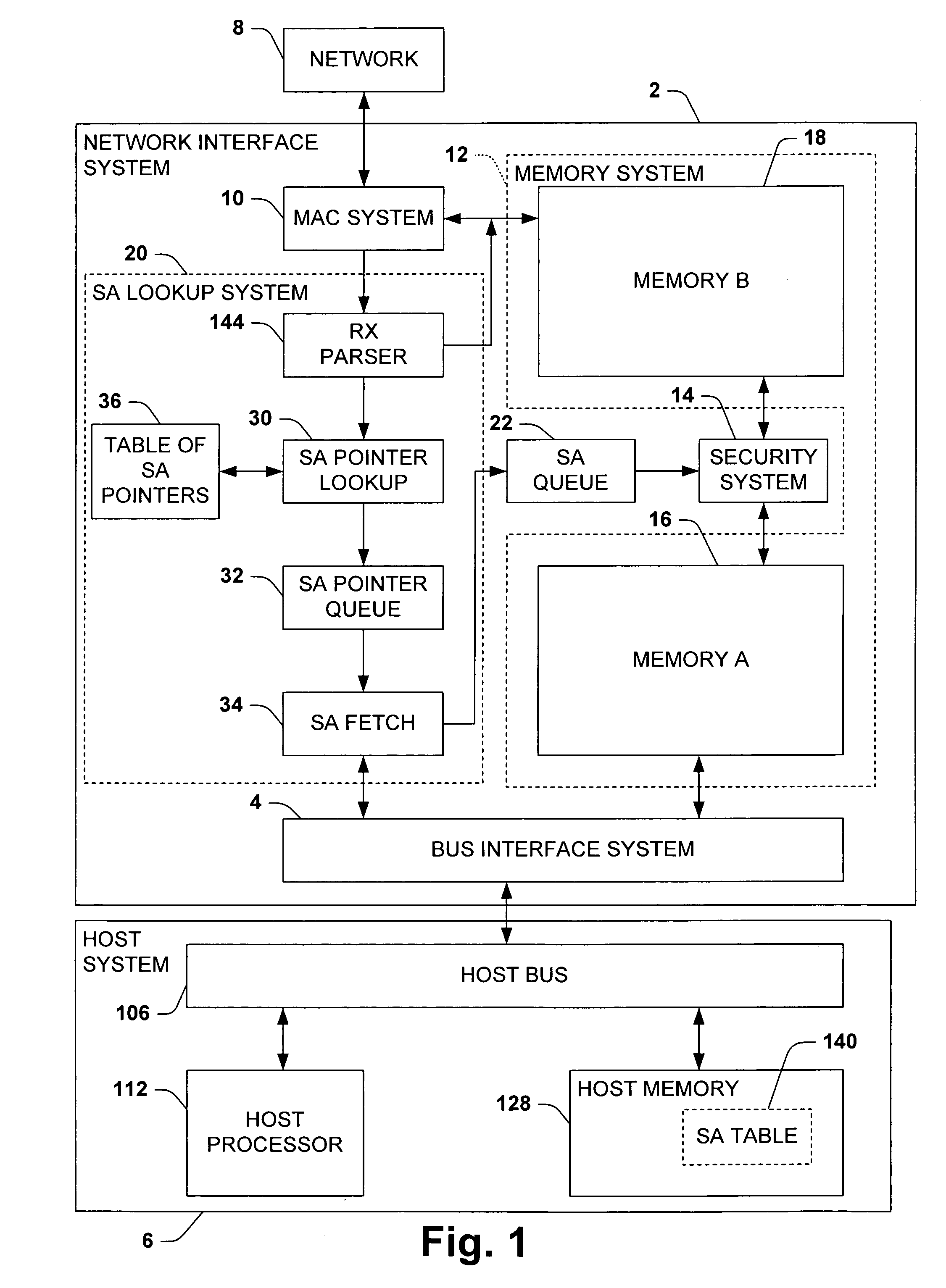
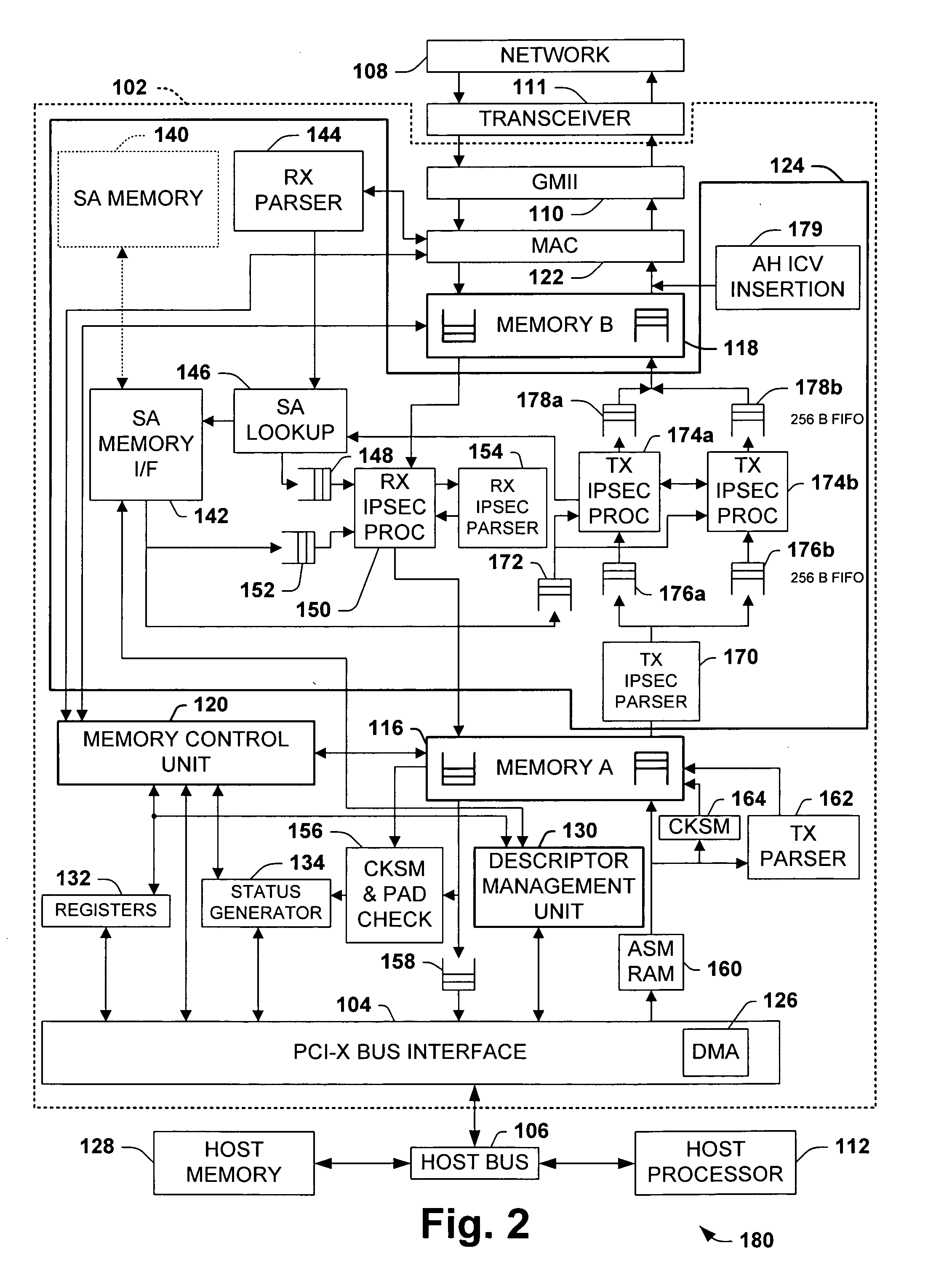
ActiveUS20050256975A1Facilitates high speed security processingTo overcome the large delayMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksExternal storageSecurity association
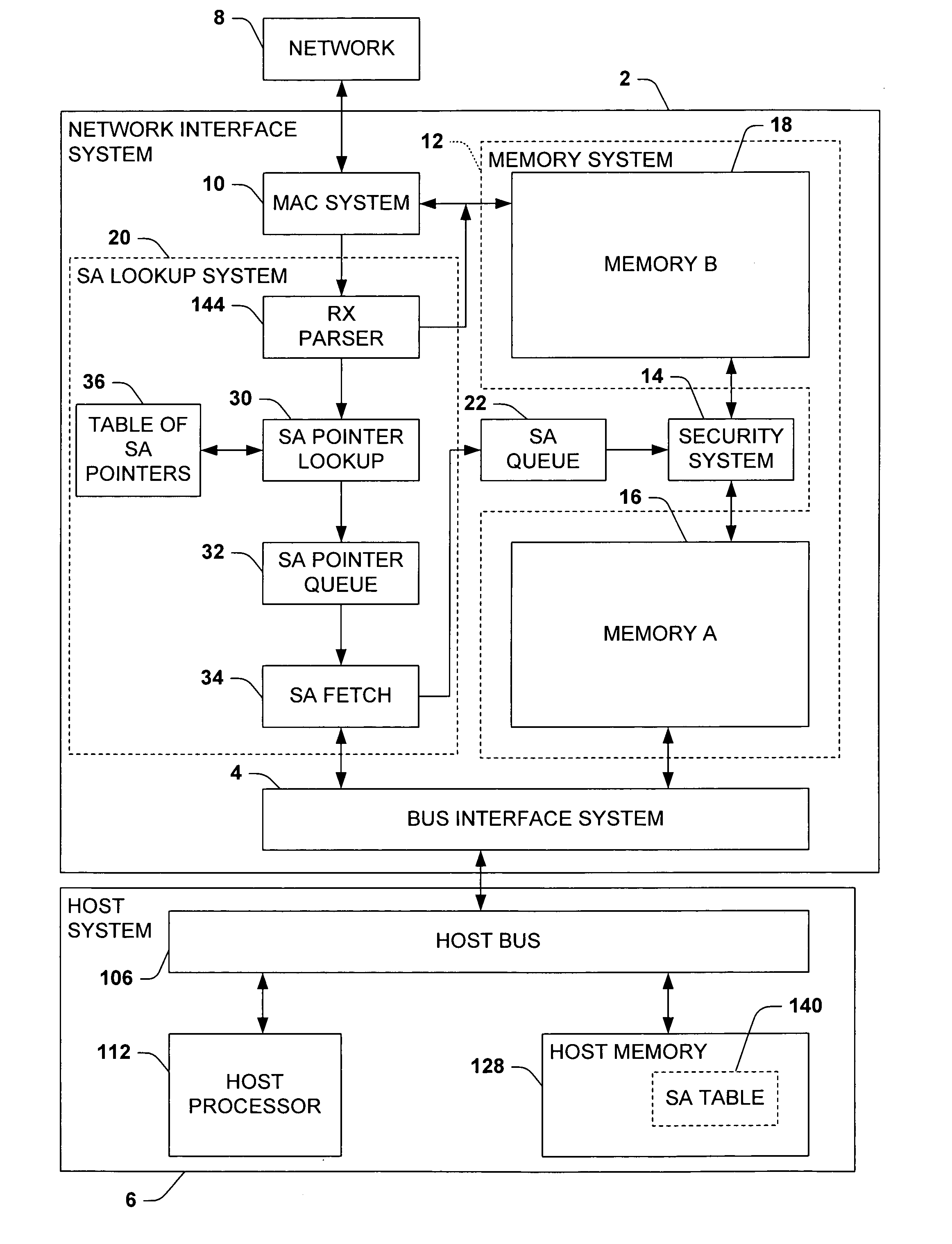
One aspect of the invention relates to a network interface system for interfacing a host system with a network. The network interface system includes a bus interface system, a media access control system, and a security system. The security system selectively perform security processing on data incoming from the network based on security associations stored in a memory external to the network interface system, typically a host system memory. The security association for any given frame, when available, is fetched from the external memory after the frame begins to arrive in the network interface system based in part on information contained in the frame. Preferably, the fetch begins before the frame is fully received and the security association is queued whereby security processing can begin without having to wait for the security association to be fetched.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Robot arm control method and control device
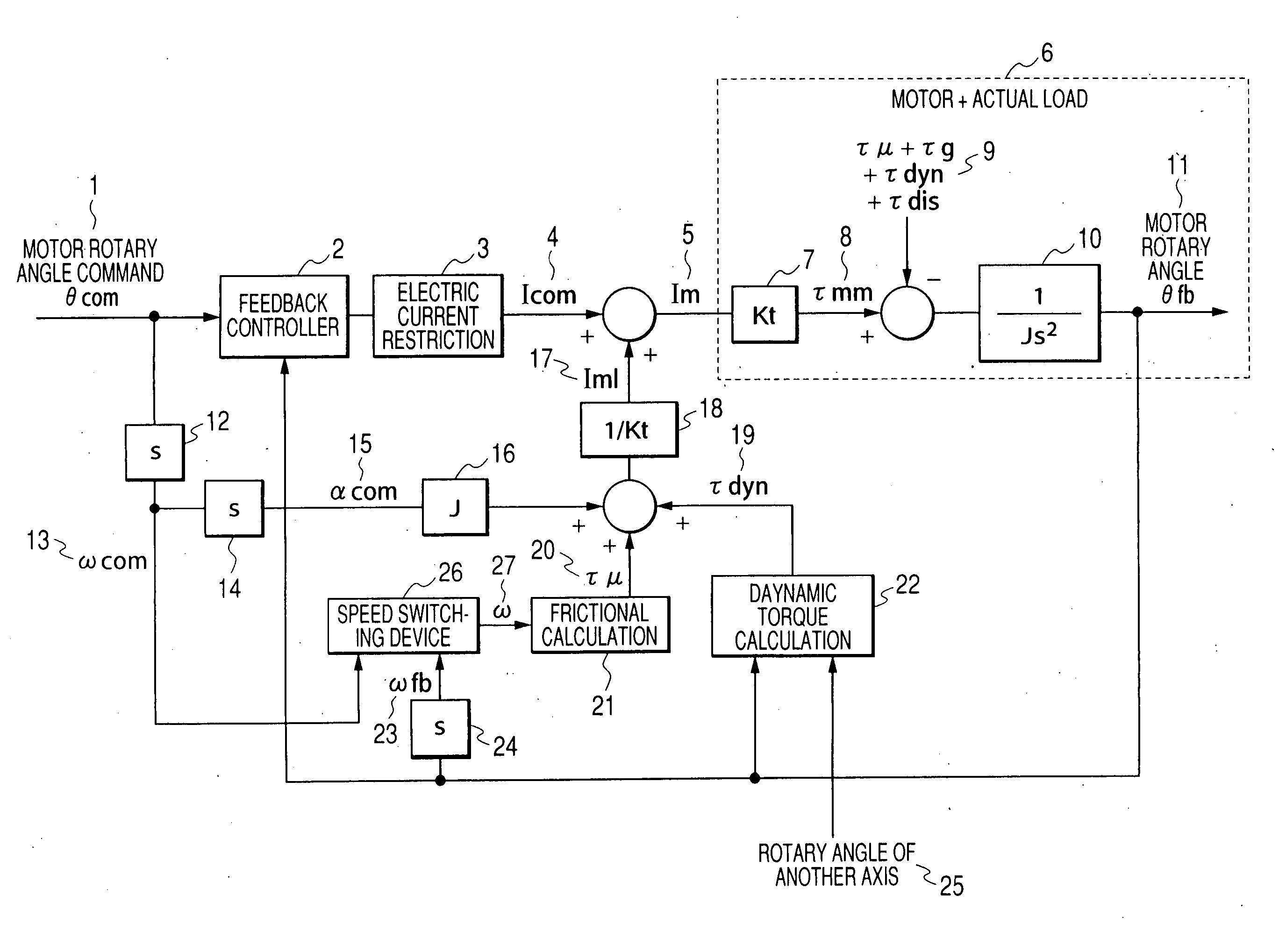
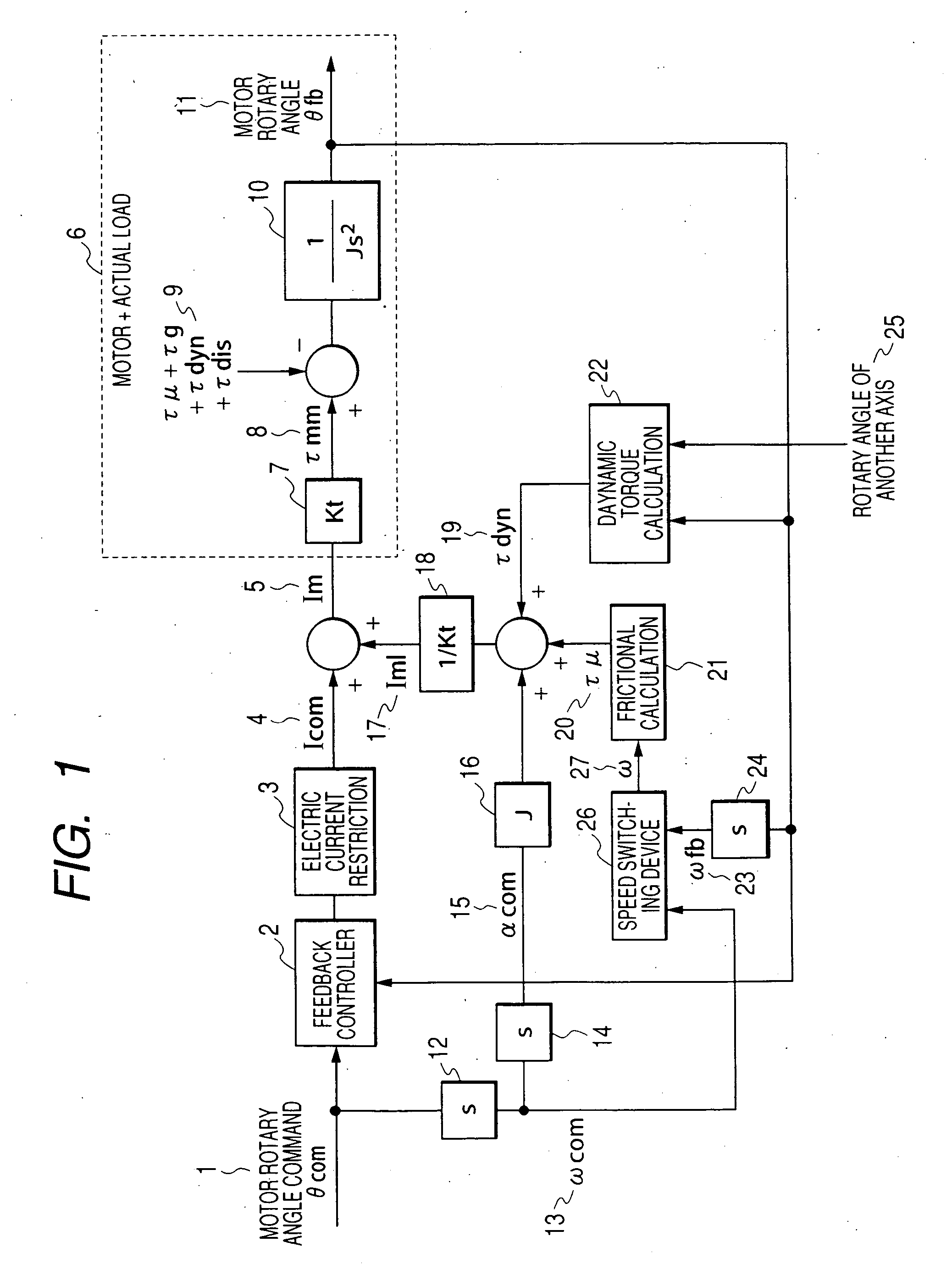
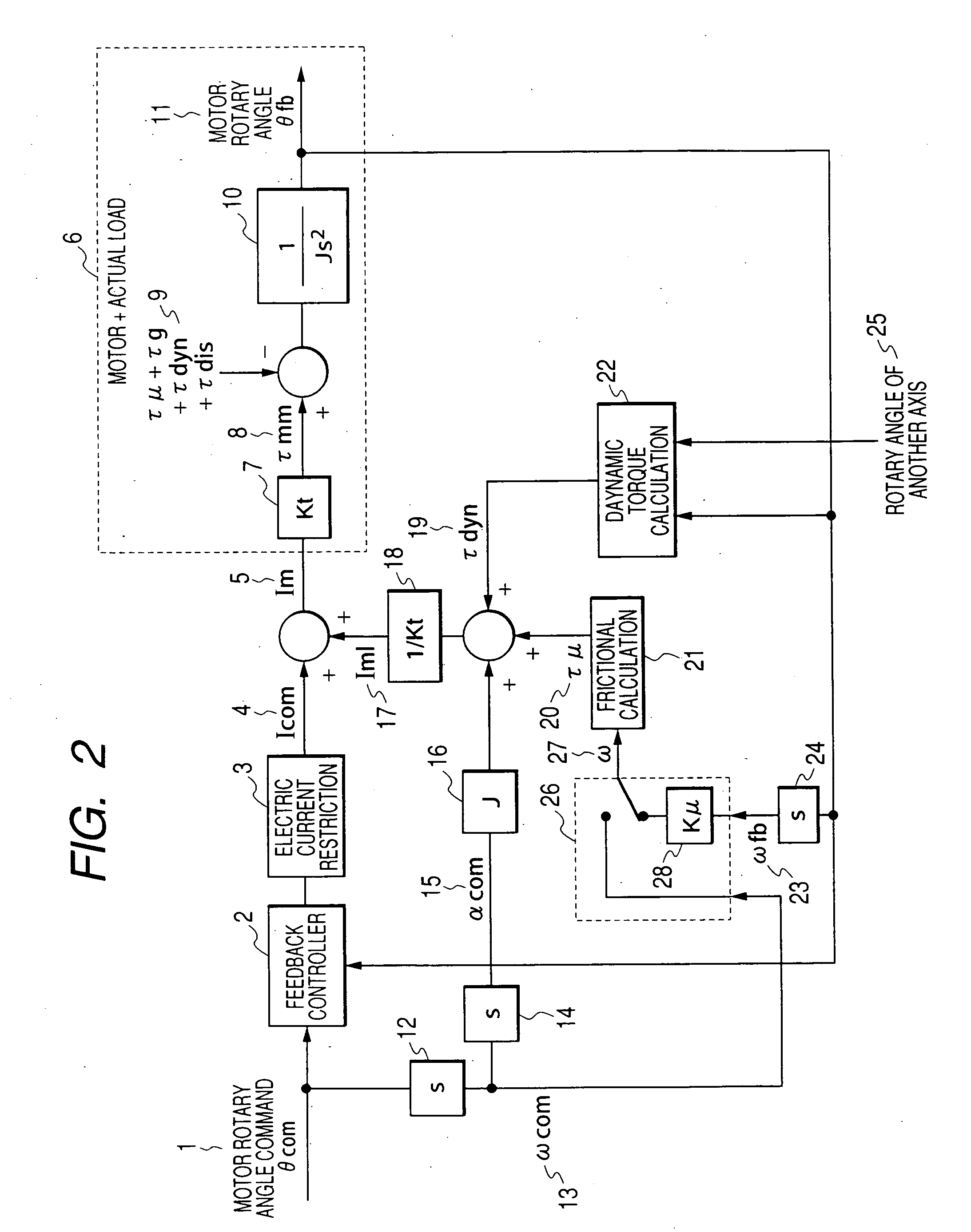
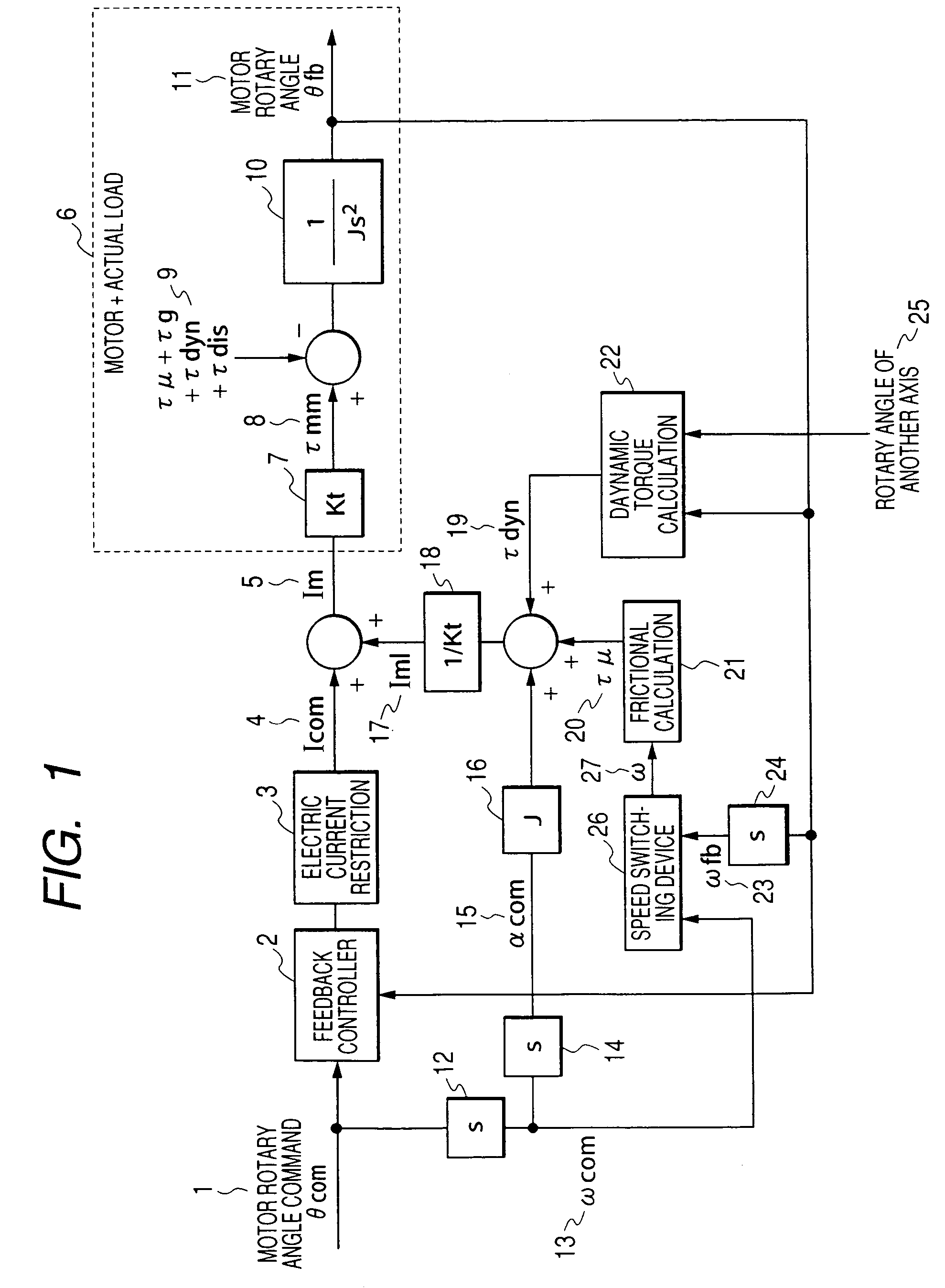
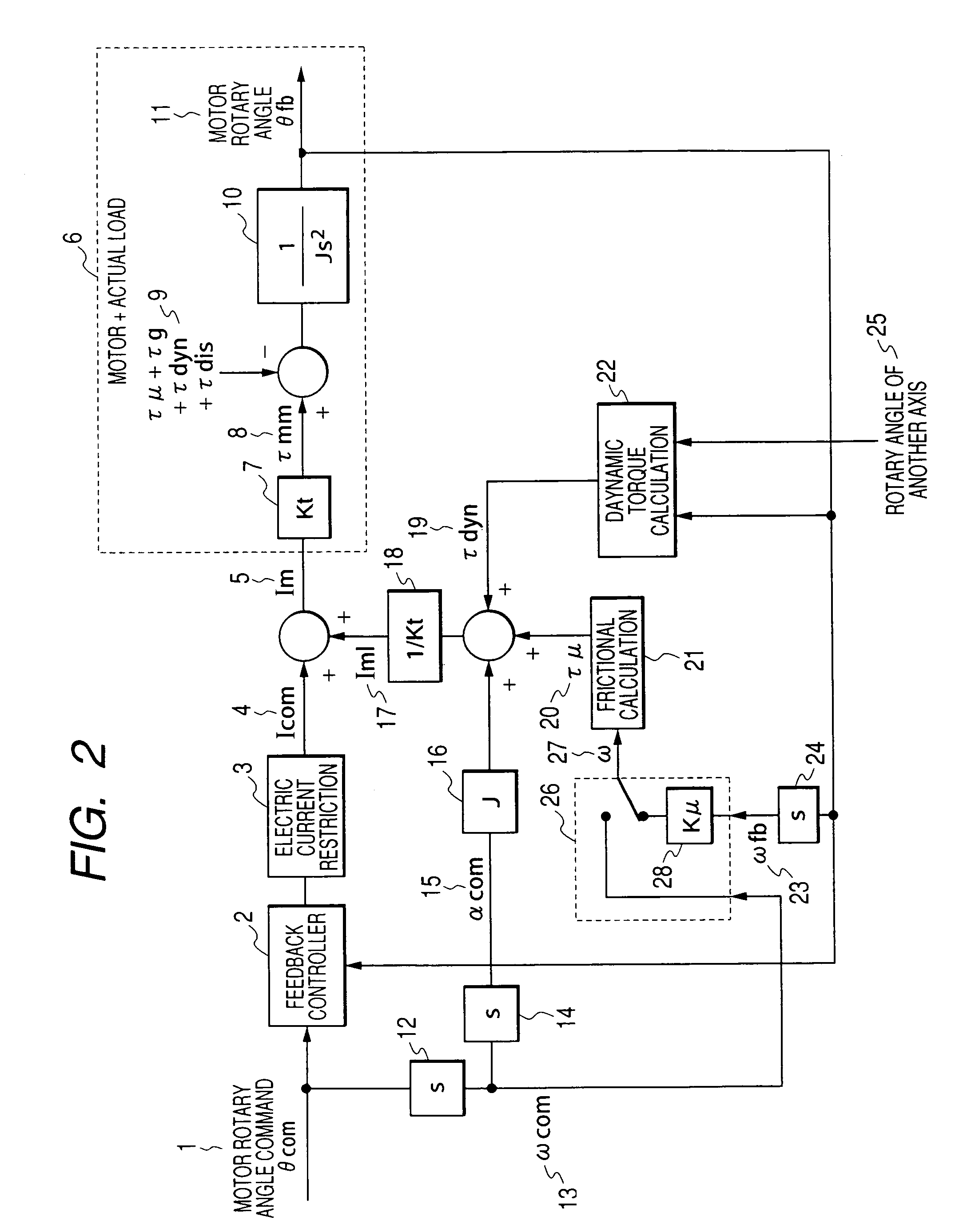
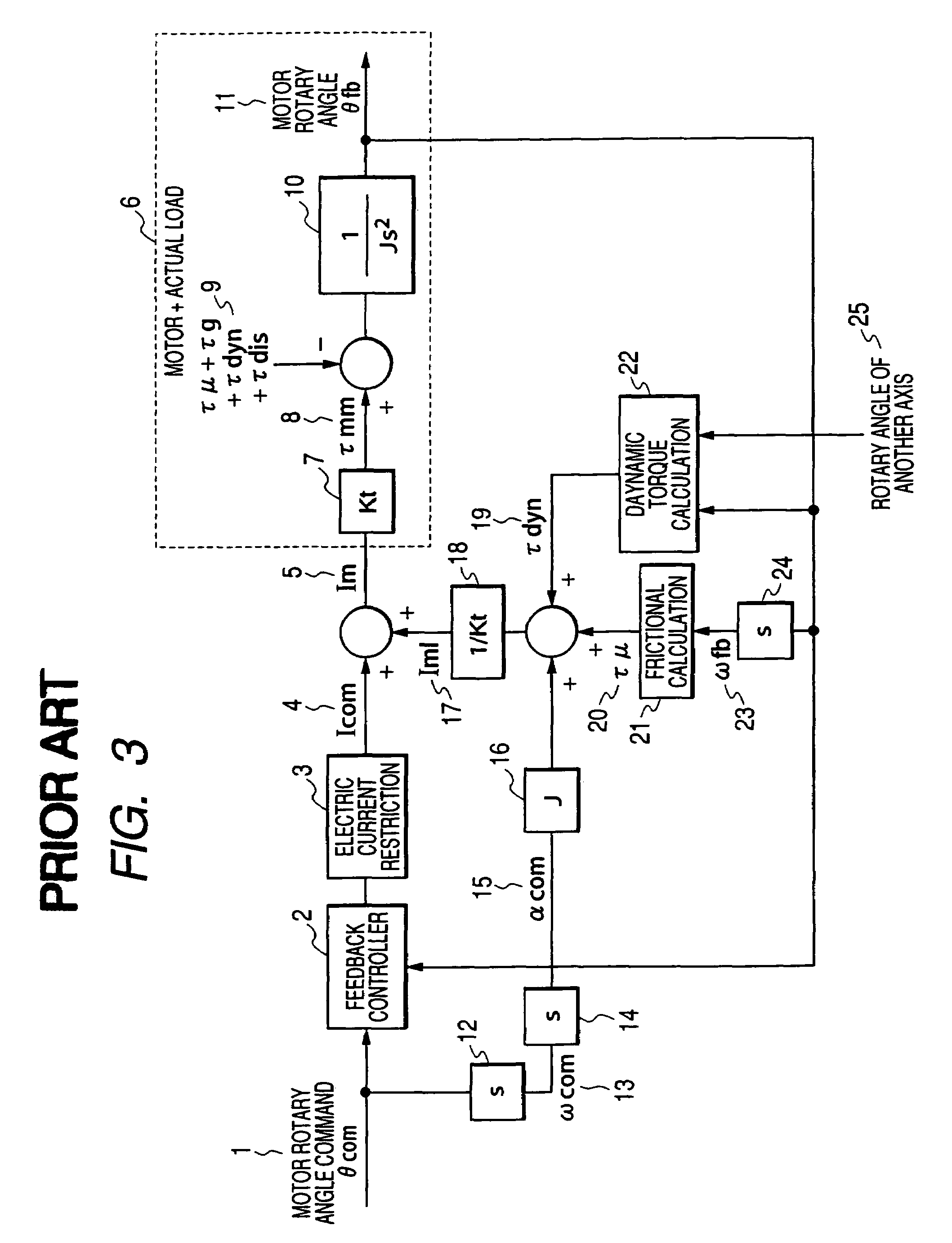
ActiveUS20060071625A1Improve complianceHigh-precision detectionProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorPower flowAngular velocity
When either a command value or an actually measured value is appropriately selected as an angular velocity used for the frictional torque calculation, the frictional compensation can be made valid at all times in both the case in which a robot is actively operated according to an angular velocity command and the case in which the robot is passively operated being pushed by an external force. In the case where a motor rotating direction and a collision direction are reverse to each other after a collision has been detected, the control mode is switched from the positional control to the electric current control and a torque, the direction of which is reverse to the direction of the motor rotation is generated by the motor, so that the motor rotating speed can be reduced and the collision energy can be alleviated. After that, when the motor rotating speed is reduced to a value not more than the setting value, the control mode is switched to the compliance control and the distortion caused in a reduction gear is dissolved. On the other hand, in the case where the motor rotating direction and the collision direction are the same, the control mode is directly switched from the positional control to the compliance control without passing through the electric current control. When the robot is operated whole following a collision force, the collision force can be alleviated.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
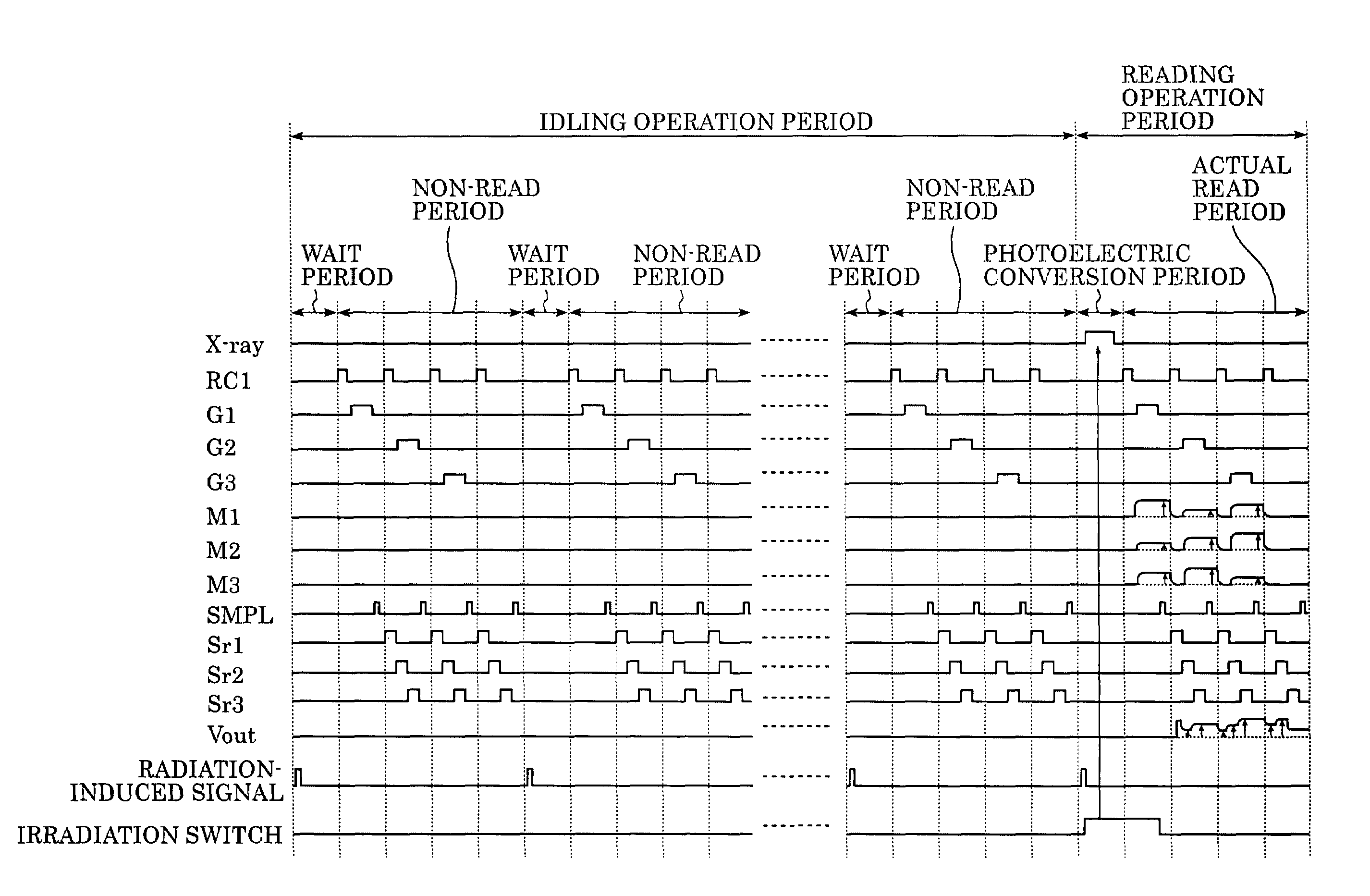
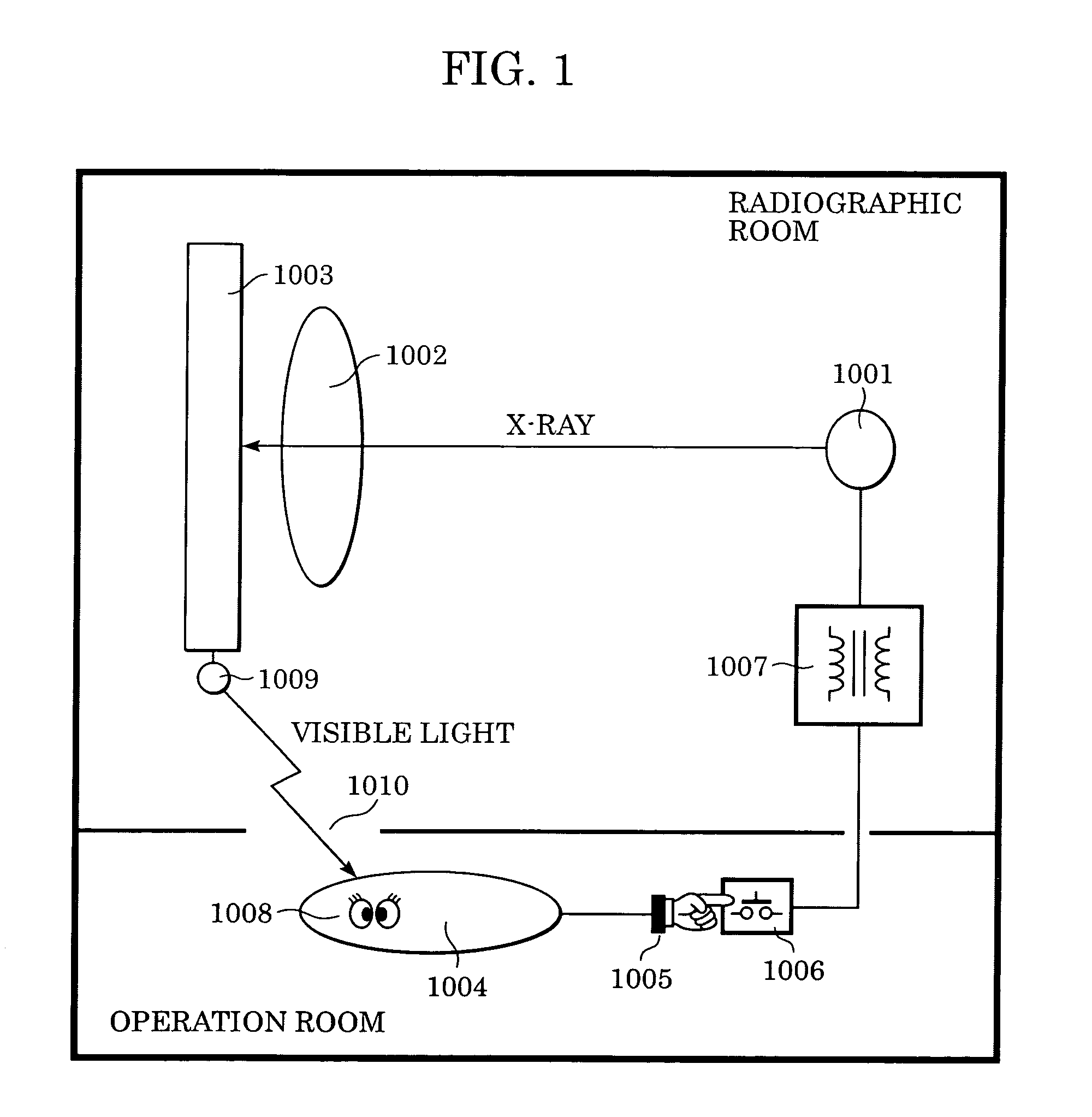
Radiation imaging apparatus and control method therefor
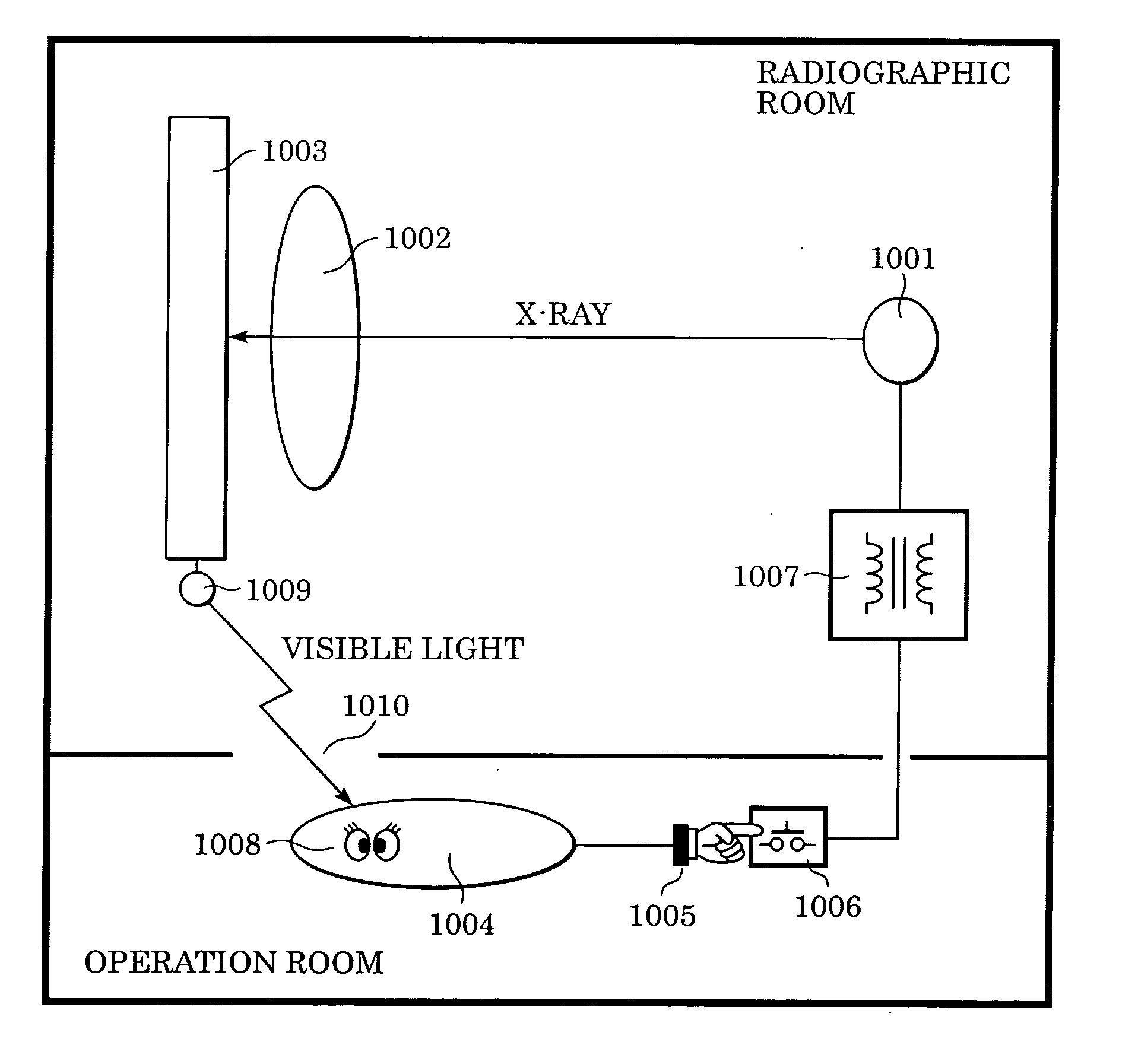
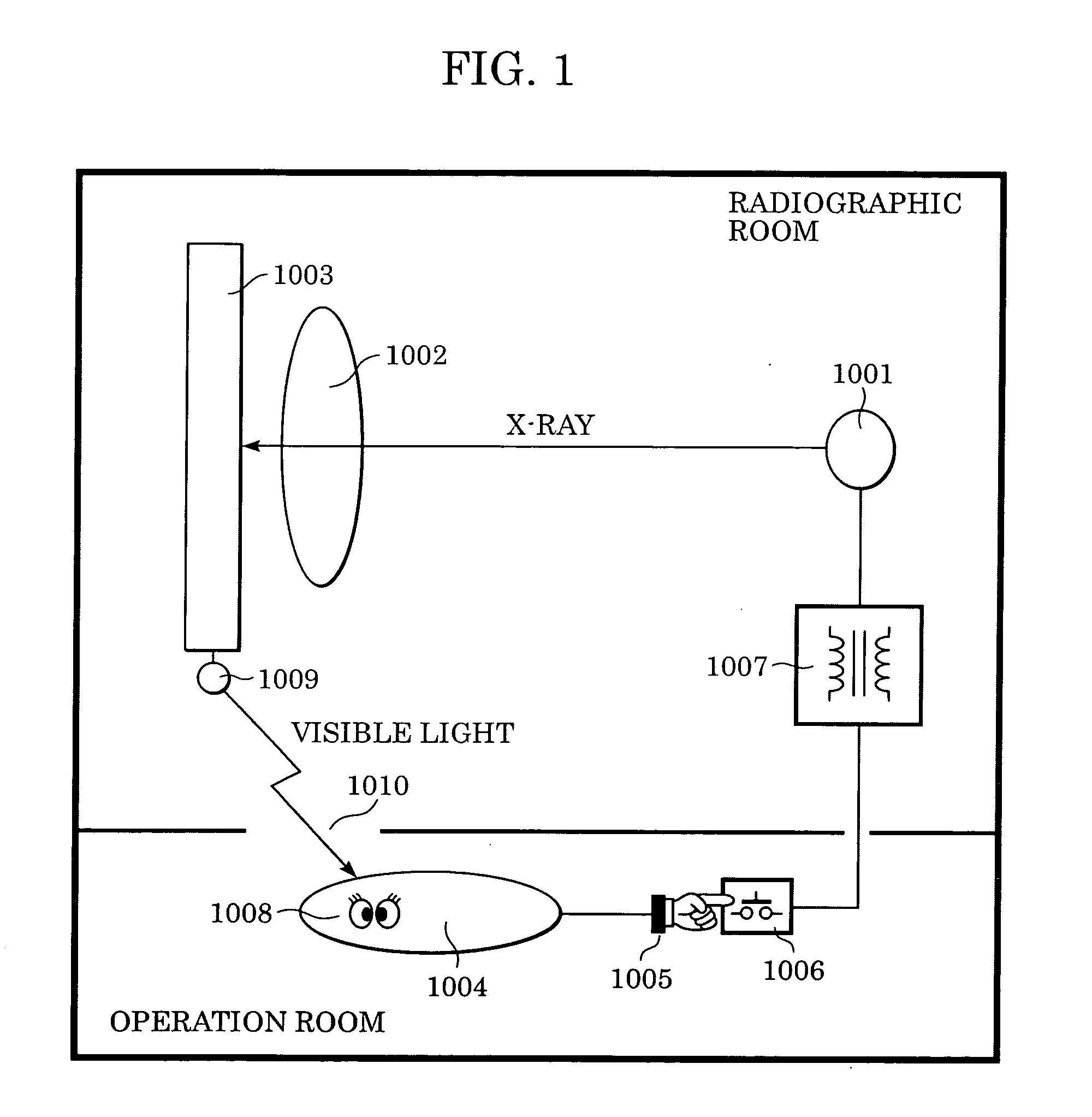
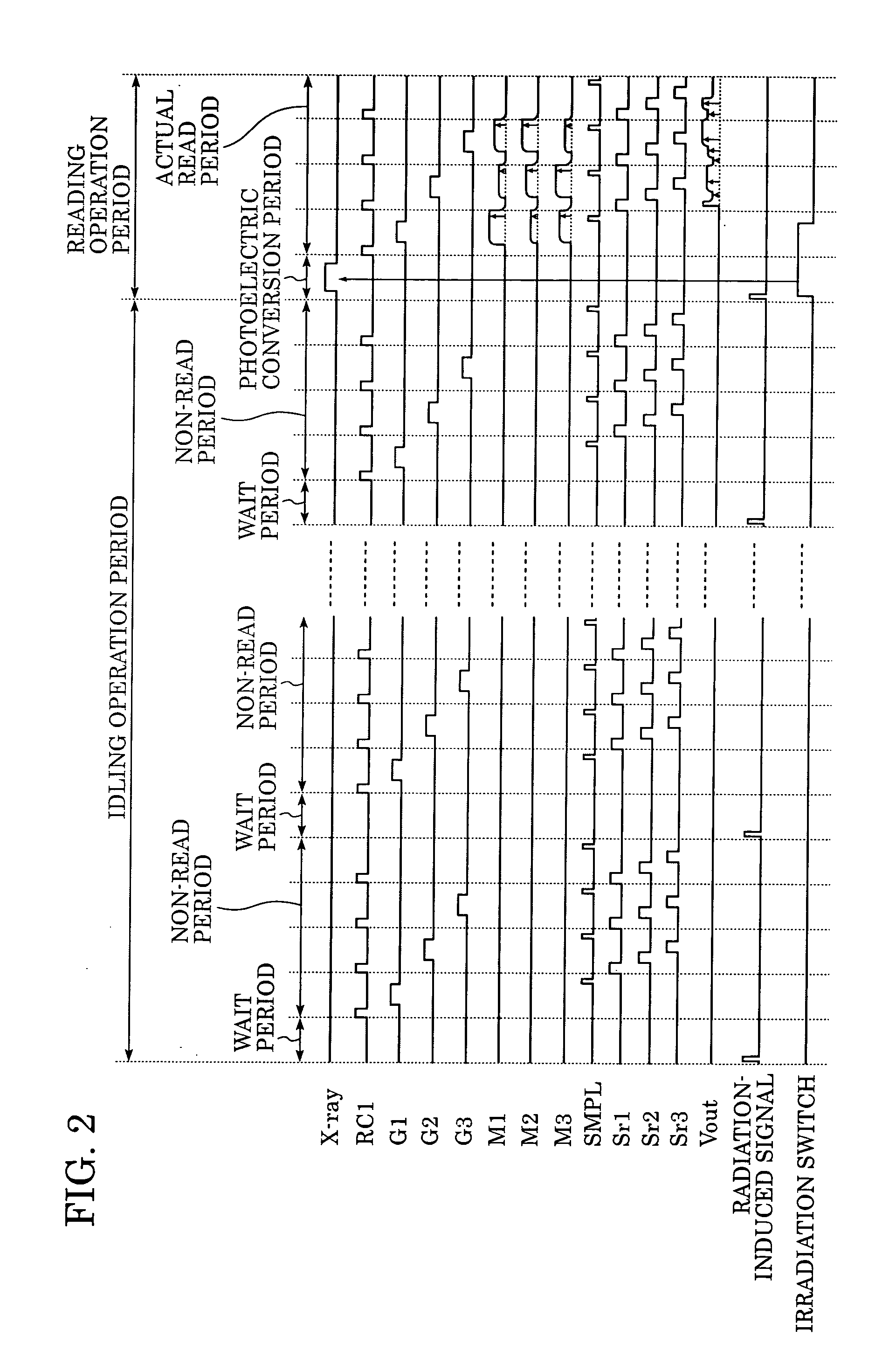
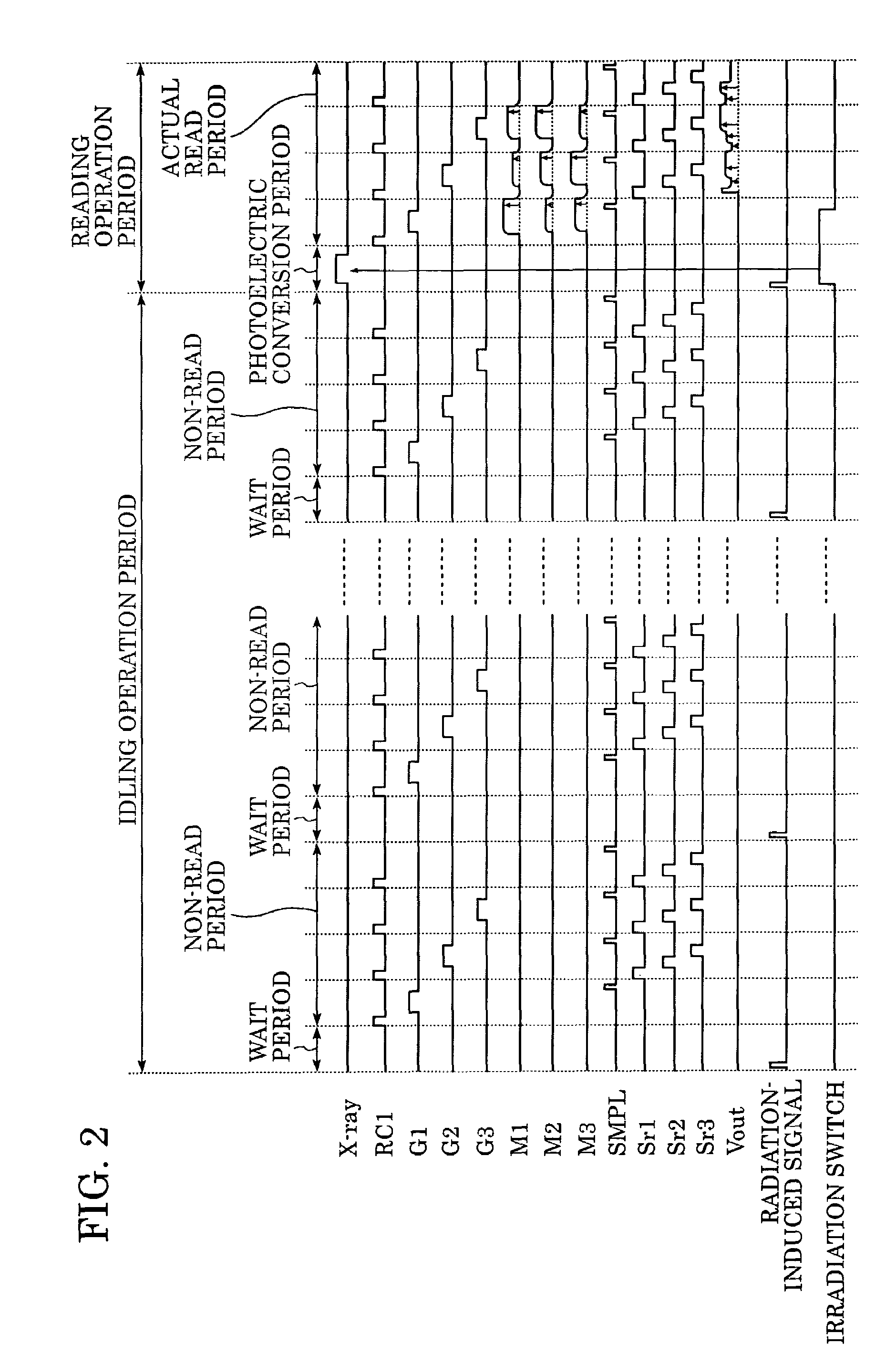
InactiveUS20050220269A1Stably performing radiographyAvoid delayX-ray apparatusRadiation diagnosticsX-rayOpto electronic
A lamp emits pulse-shaped visible light when a wait period begins. If a radiation emission switch is not pressed in the wait period, X-ray radiation is not emitted from an X-ray source, and no charges are accumulated in photoelectric conversion elements of an X-ray imaging apparatus. In a non-read period, although signals are sequentially read from the photoelectric conversion elements, an output signal does not change. When the radiation emission switch is pressed in synchronization with a radiation-induced signal in a certain wait period, the X-ray source emits X-rays. After irradiation of X-rays, a photoelectric conversion period transitions to an actual read period. In the photoelectric conversion period, X-rays are emitted and transmitted X-ray information of a patient are accumulated in the photoelectric conversion elements of the X-ray imaging apparatus. In the actual read period, the accumulated information is read.
Owner:CANON KK
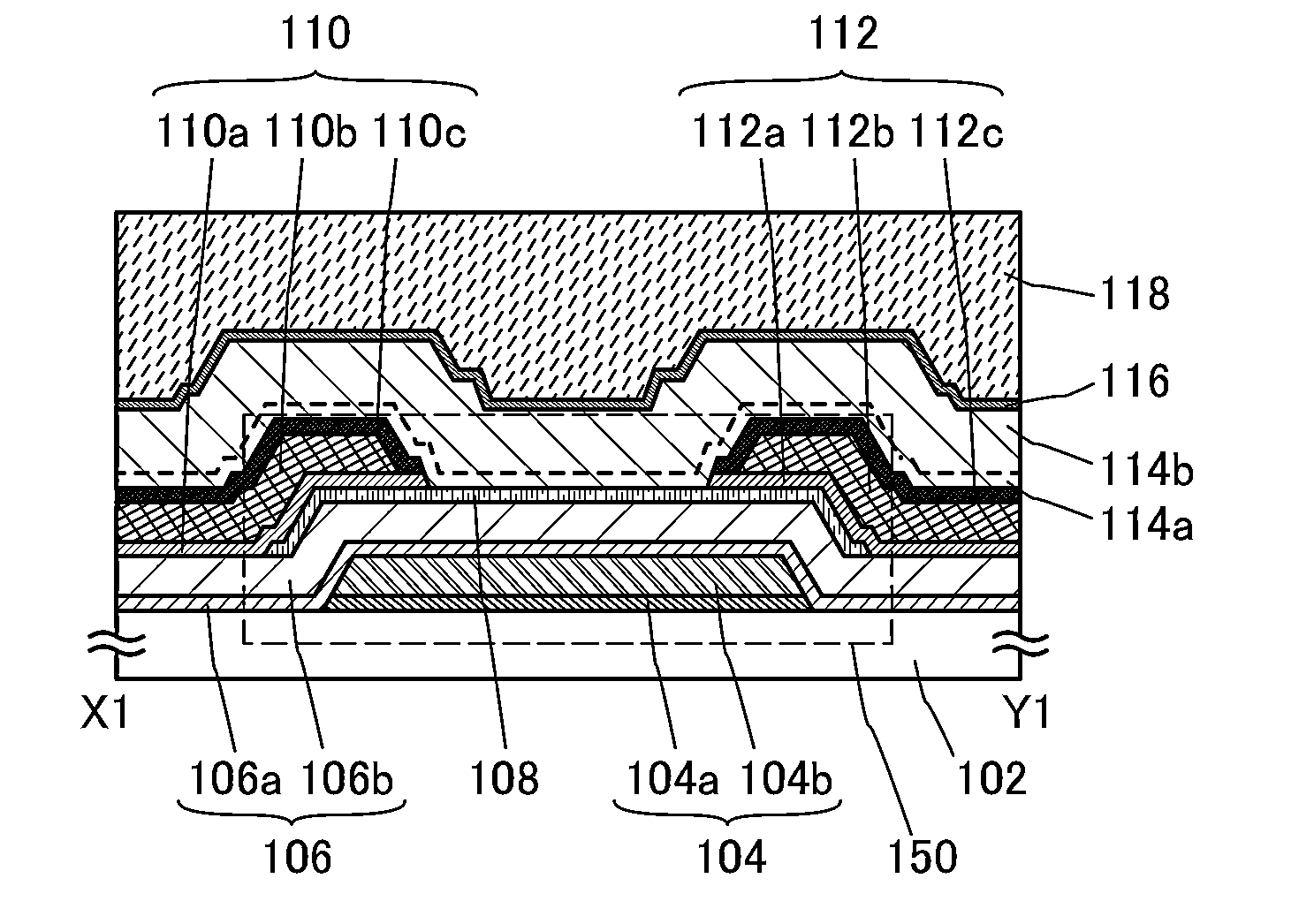
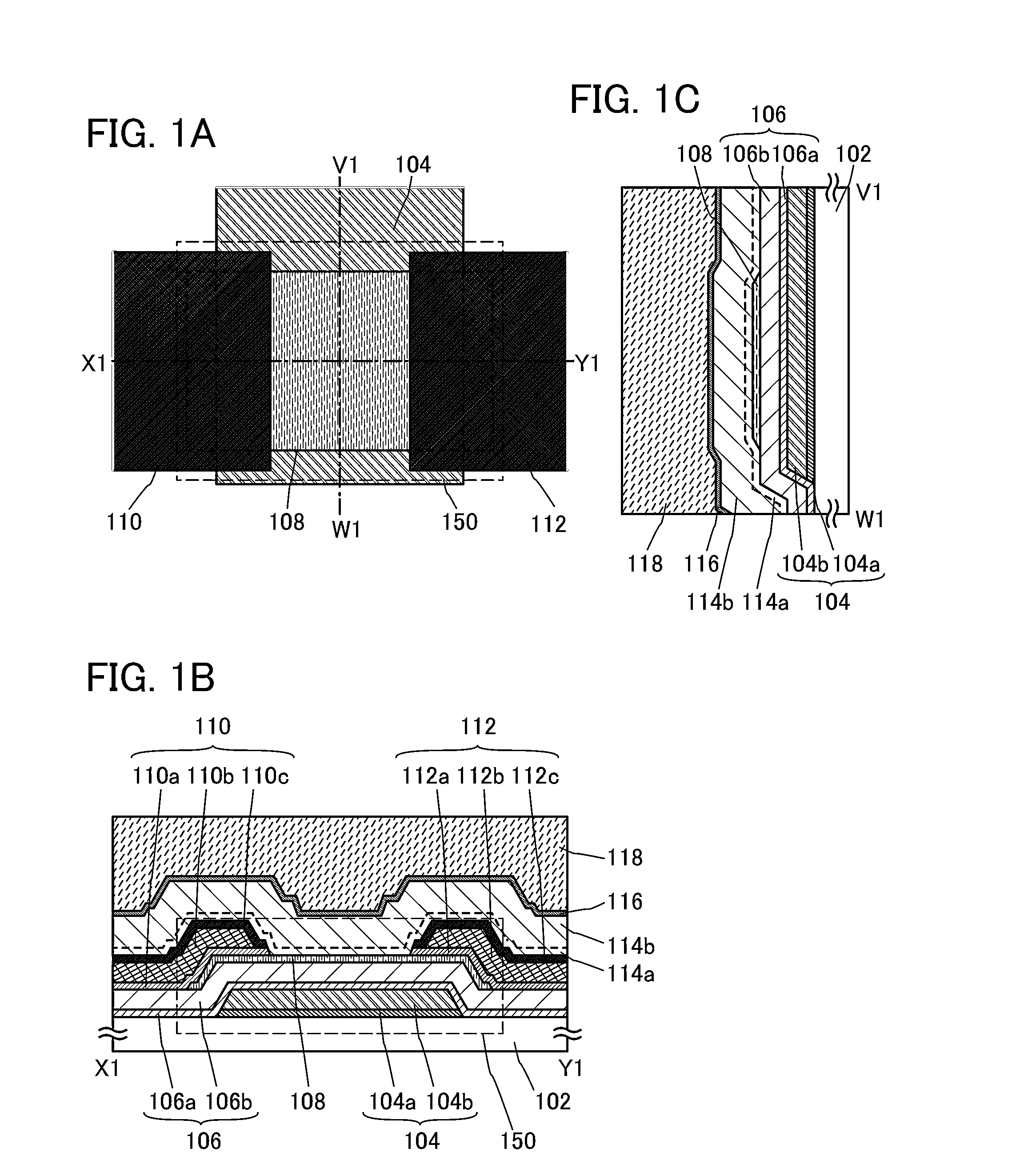
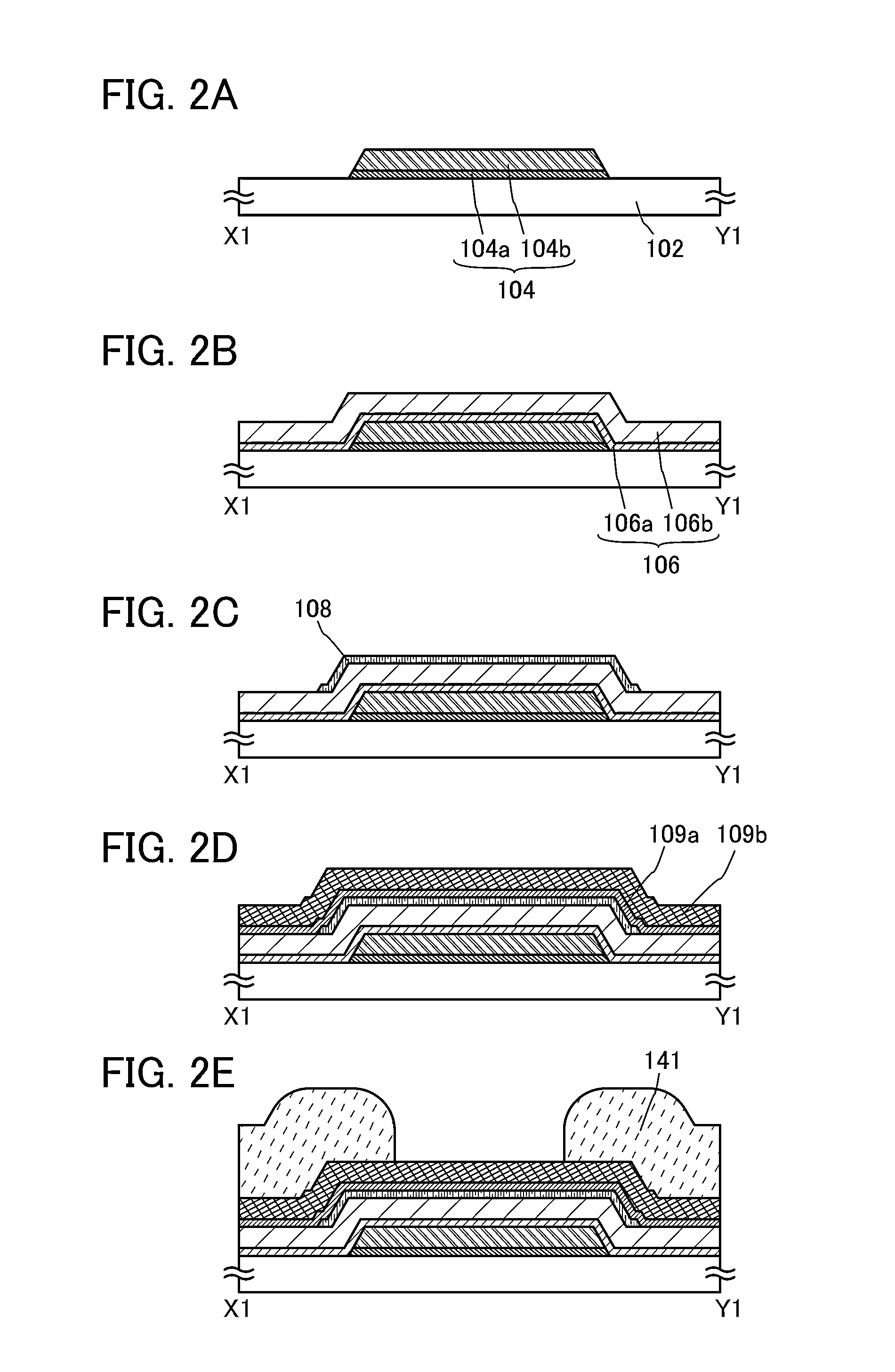
Semiconductor device, display device including semiconductor device, electronic device including semiconductor device, and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20130207111A1Stable electrical characteristicsLittle signal delayTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOxide semiconductorPower semiconductor device
A method for manufacturing a transistor with stable electric characteristics and little signal delay due to wiring resistance, used in a semiconductor device including an oxide semiconductor film. A semiconductor device including the transistor is provided. A high-performance display device including the transistor is provided.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Detecting conditions for transfer of execution from one computer instruction stream to another and executing transfer on satisfaction of the conditions
InactiveUS8121828B2Efficiently tailoredEasy to operateGeneral purpose stored program computerSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationInstruction pipelineInstruction stream
A computer has instruction pipeline circuitry capable of executing two instruction set architectures (ISA's). A binary translator translates at least a selected portion of a computer program from a lower-performance one of the ISA's to a higher-performance one of the ISA's. Hardware initiates a query when about to execute a program region coded in the lower-performance ISA, to determine whether a higher-performance translation exists. If so, the about-to-be-executed instruction is aborted, and control transfers to the higher-performance translation. After execution of the higher-performance translation, execution of the lower-performance region is reestablished at a point downstream from the aborted instruction, in a context logically equivalent to that which would have prevailed had the code of the lower-performance region been allowed to proceed.
Owner:ADVANCED SILICON TECH
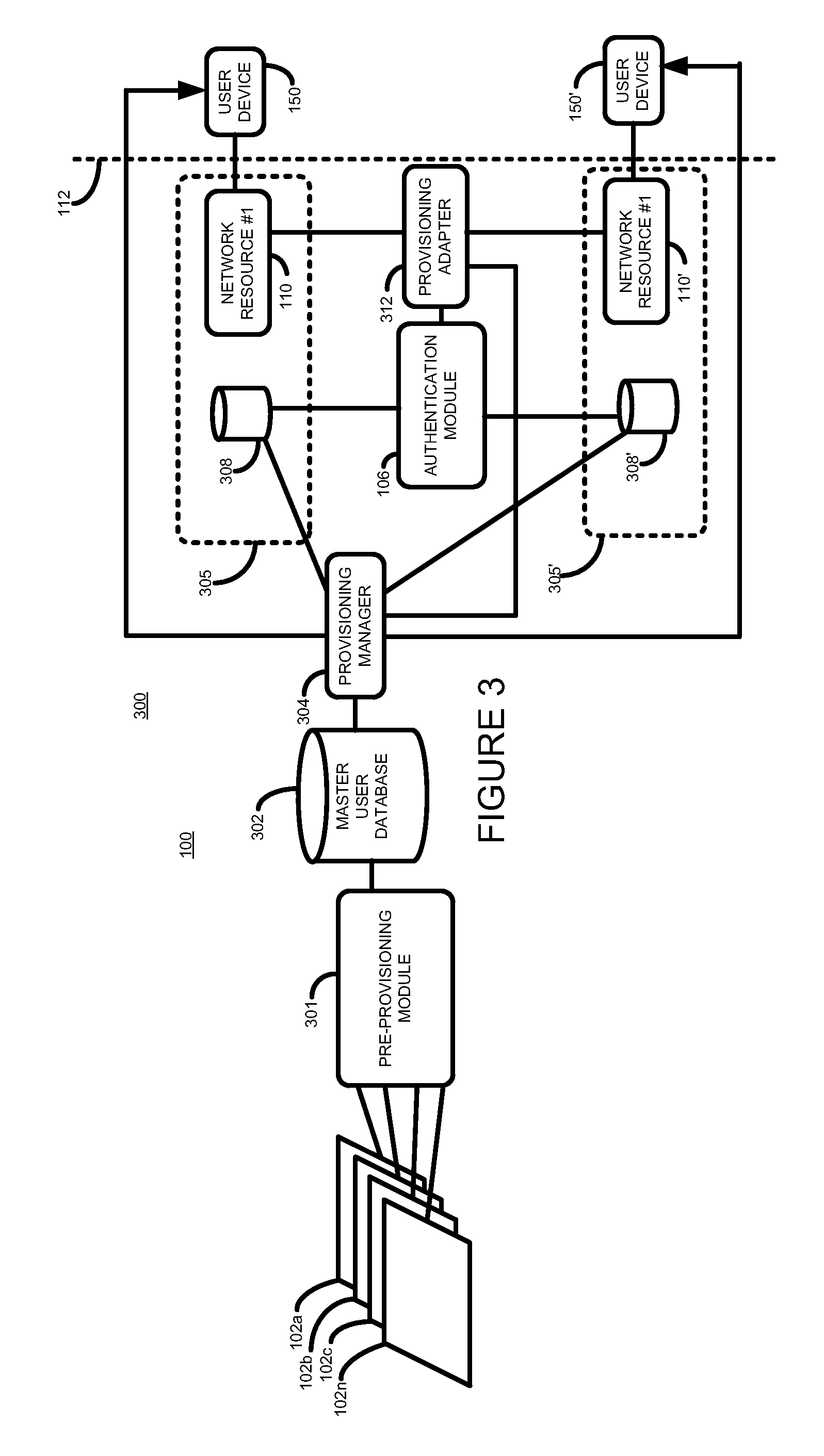
Method and apparatus for controlling access to a network resource
ActiveUS20110185403A1Low costImprove performanceDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationPasswordUser identifier
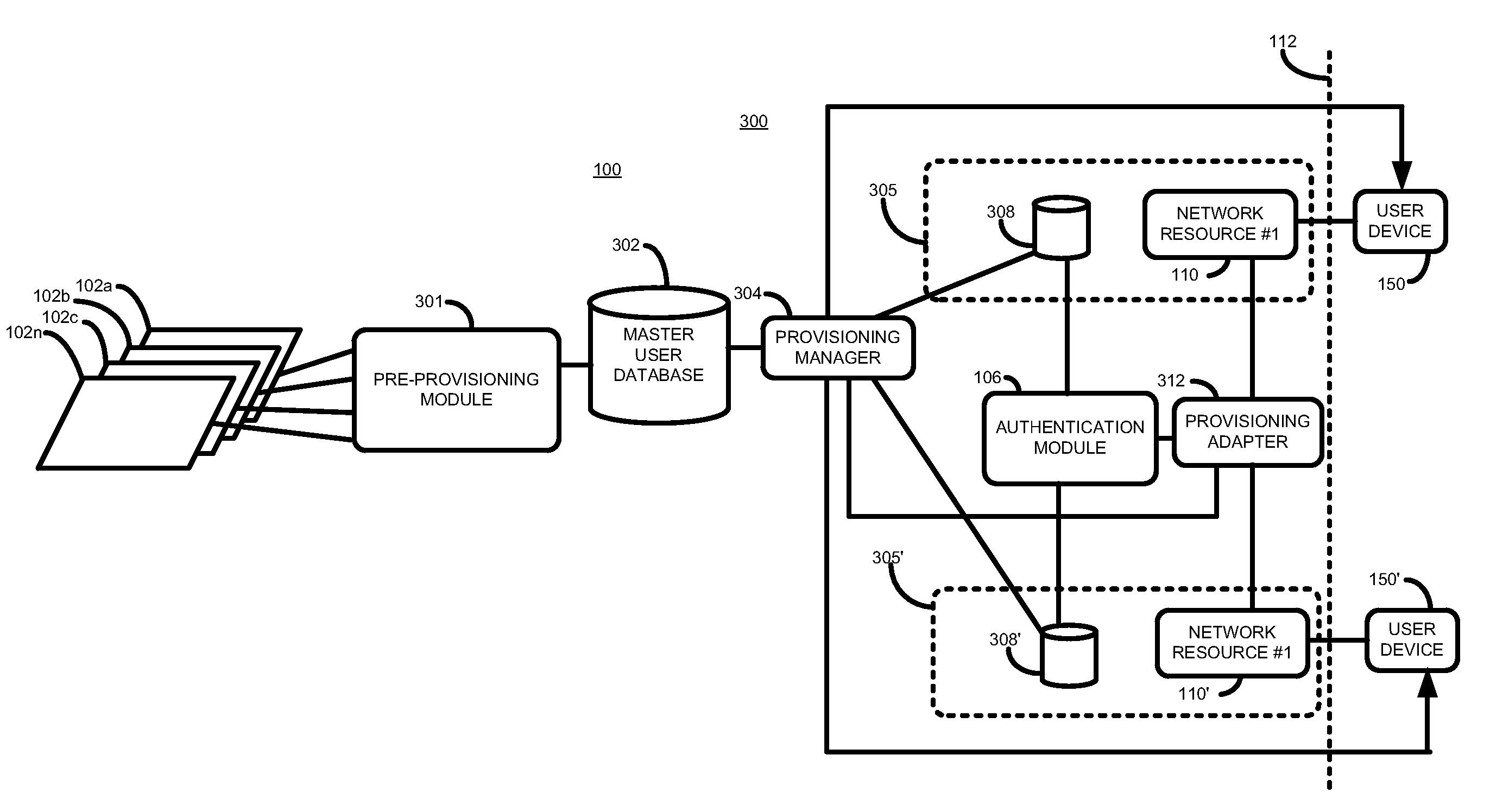
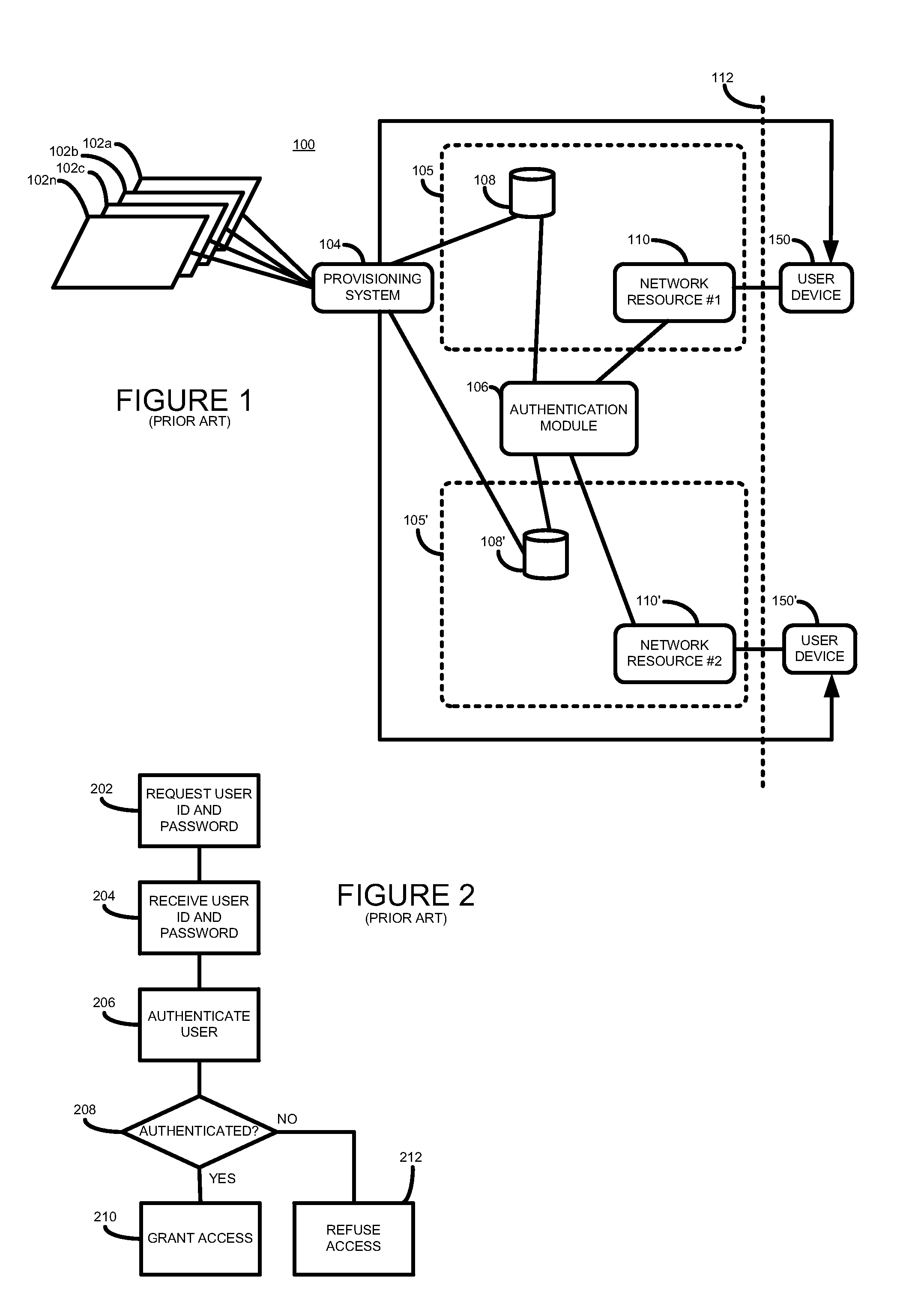
According to one aspect, there is provided a method of controlling access to a network resource. The method comprises receiving a request to grant a user access to the network resource, the request including a user identifier, determining whether the received user identifier is stored in a local user data store associated with the resource, and where it is not so determined determining, from user details stored in a master user data store, whether the user is authorized to access the resource, and where it is so determined obtaining a password, and storing the obtained password and user details in the local data store associated with the network resource.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
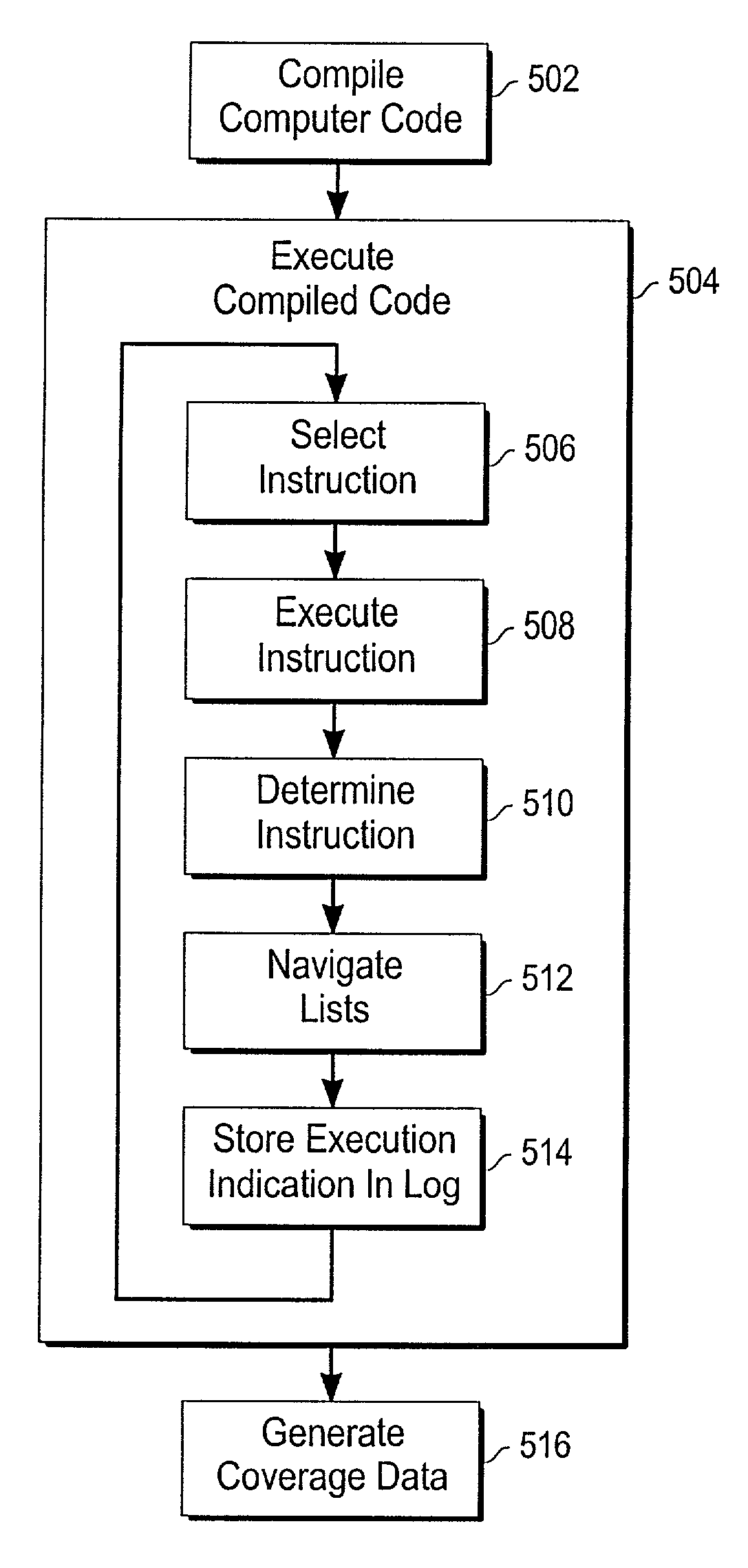
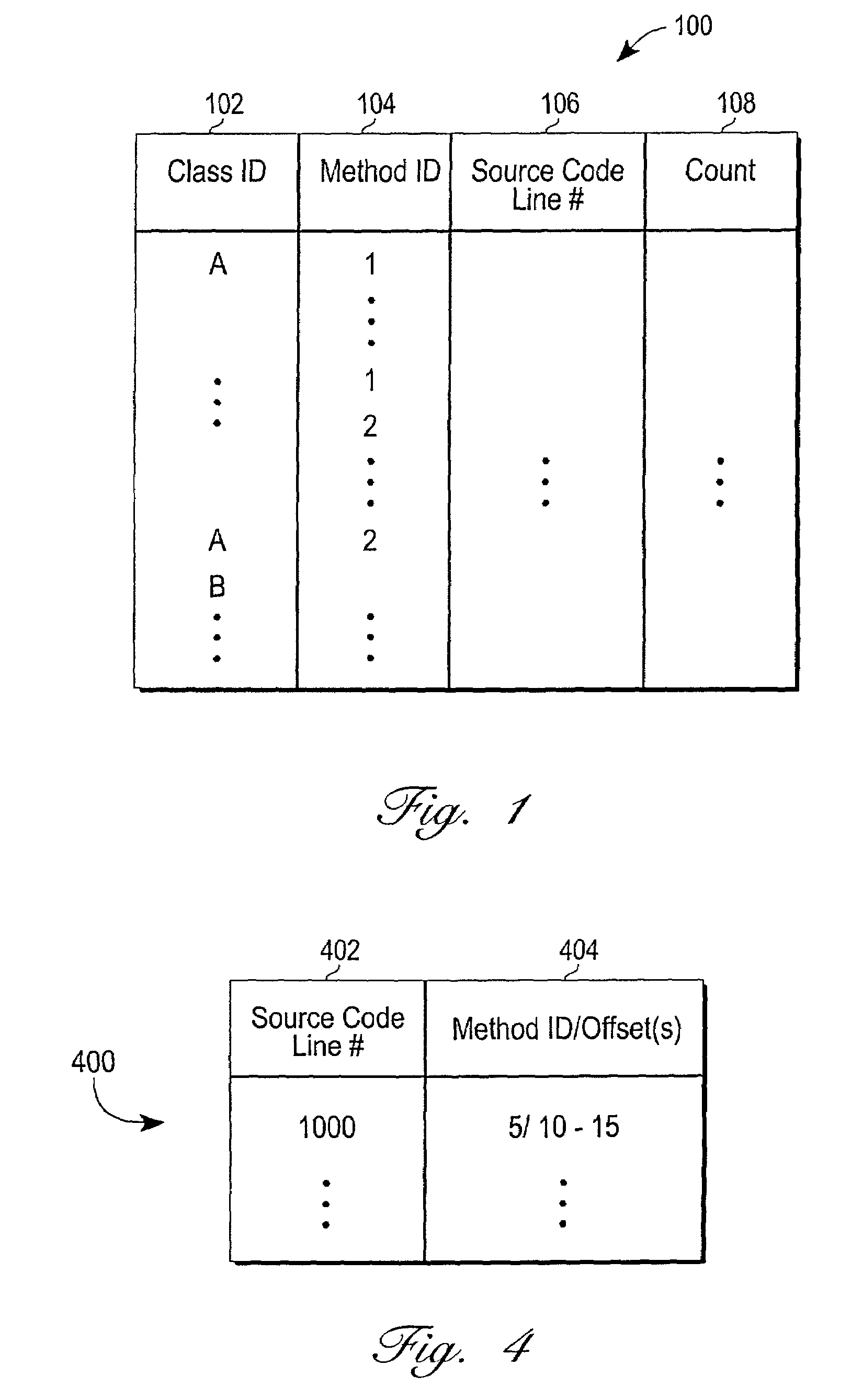
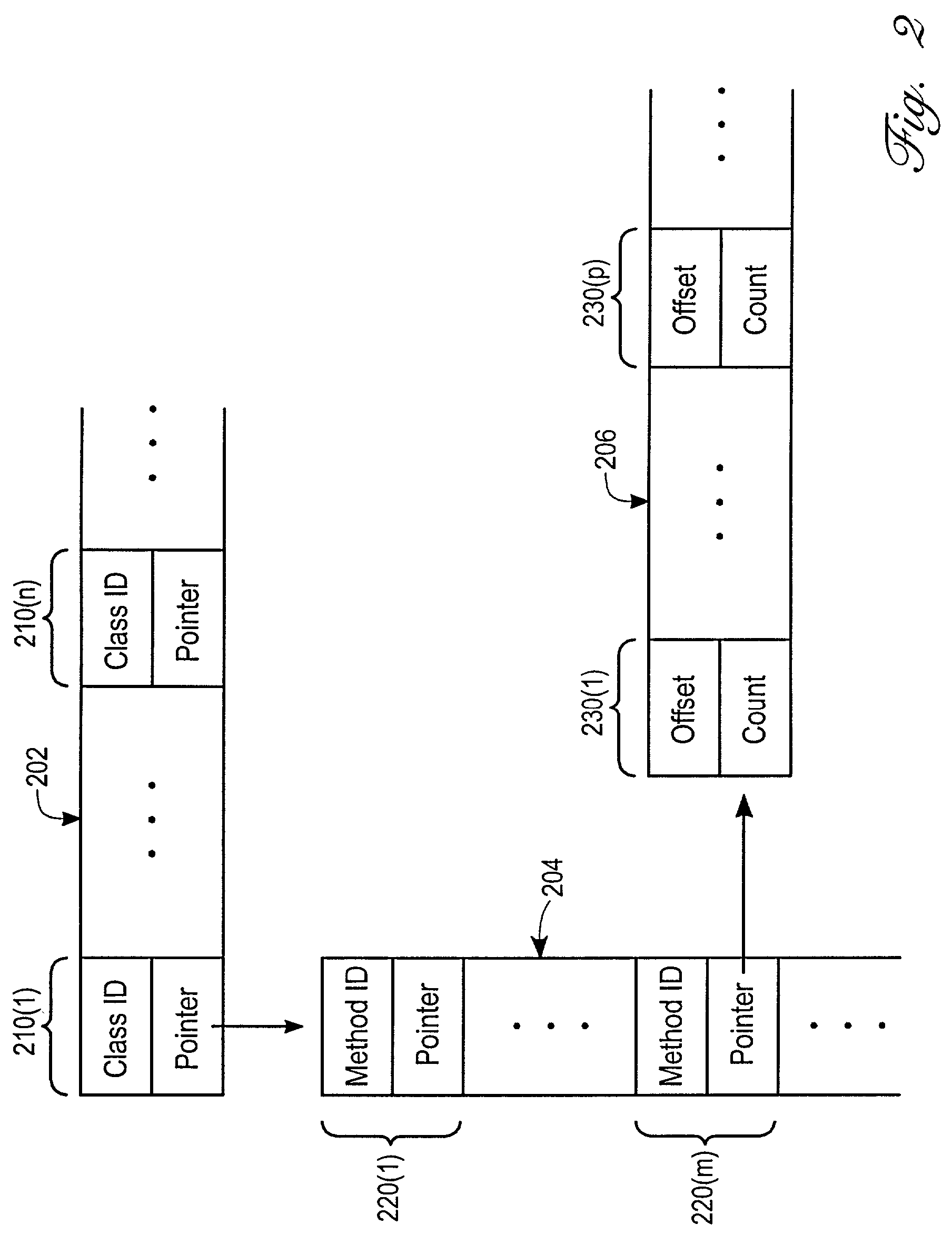
Mechanism for generating an execution log and coverage data for a set of computer code
ActiveUS7080358B2Minimal amount of storageTo overcome the large delaySoftware testing/debuggingSpecific program execution arrangementsParallel computingCoverage data
An improved mechanism is provided for generating an execution log and coverage data for a set of computer code. To minimize the amount of storage required for storing execution log information, the mechanism: (1) stores only information pertaining to instructions that are actually executed during execution; and (2) stores the information in a hierarchically organized set of lists. In addition, to minimize the impact of execution log and coverage data generation on the execution of the computer code, coverage data is generated after execution has completed. By generating the execution log and coverage data in this manner, storage requirements are reduced, and execution performance is improved.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
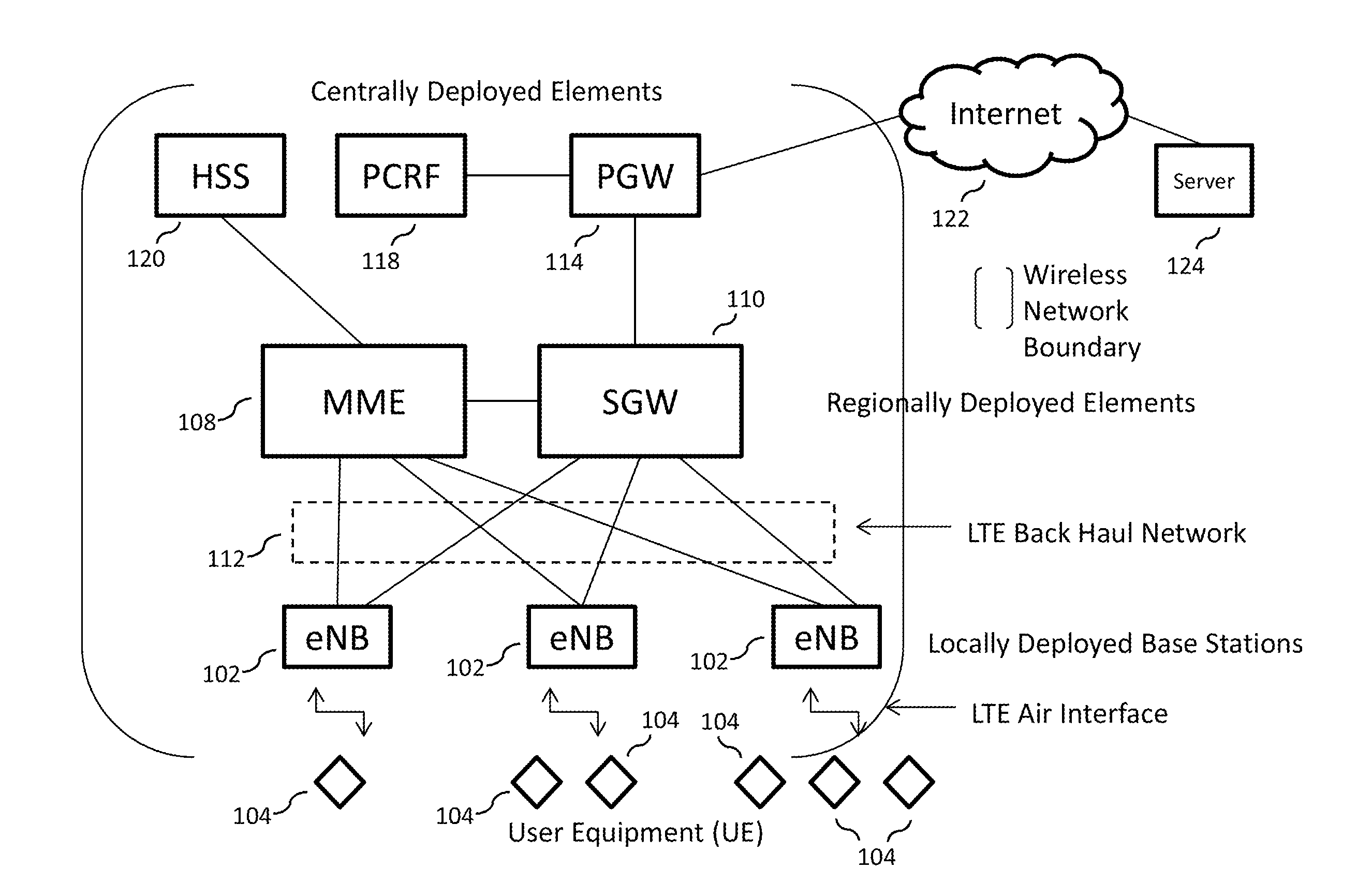
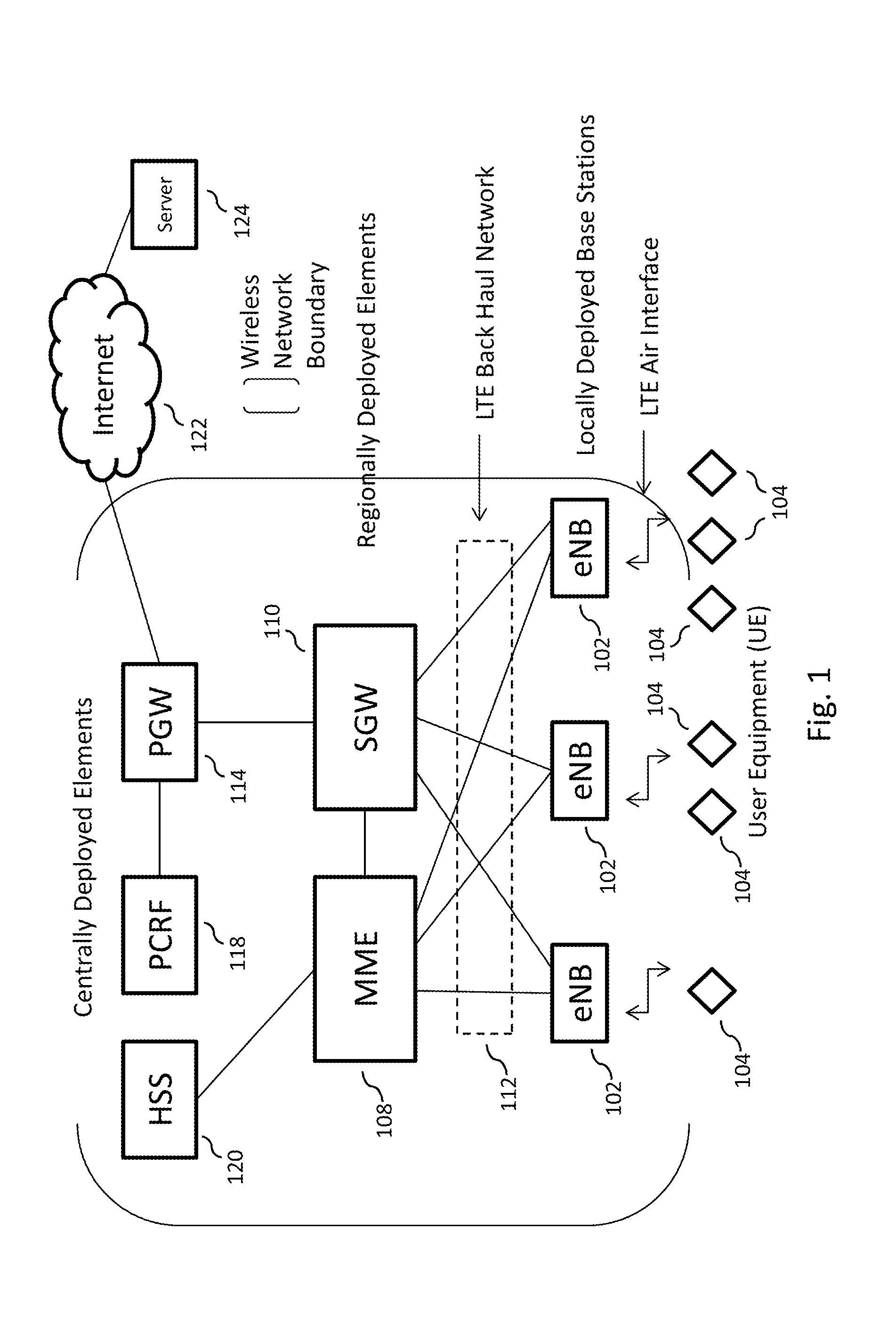
Efficient delivery of real-time asynchronous services over a wireless network
ActiveUS20140153402A1Conserving permanent memory utilizationImprove efficiencyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsStreaming dataData stream
In embodiments of the present disclosure, improved capabilities are described for conserving back haul utilization in a wireless network, where optimization servers utilizing publish-subscribe broker services are provided within the wireless network to provide streaming data services required for applications streaming data to a plurality of mobile cellular devices, where the streaming data is not necessarily delivered to each of the plurality of mobile cellular devices at the same time.
Owner:ALL PURPOSE NETWORKS INC
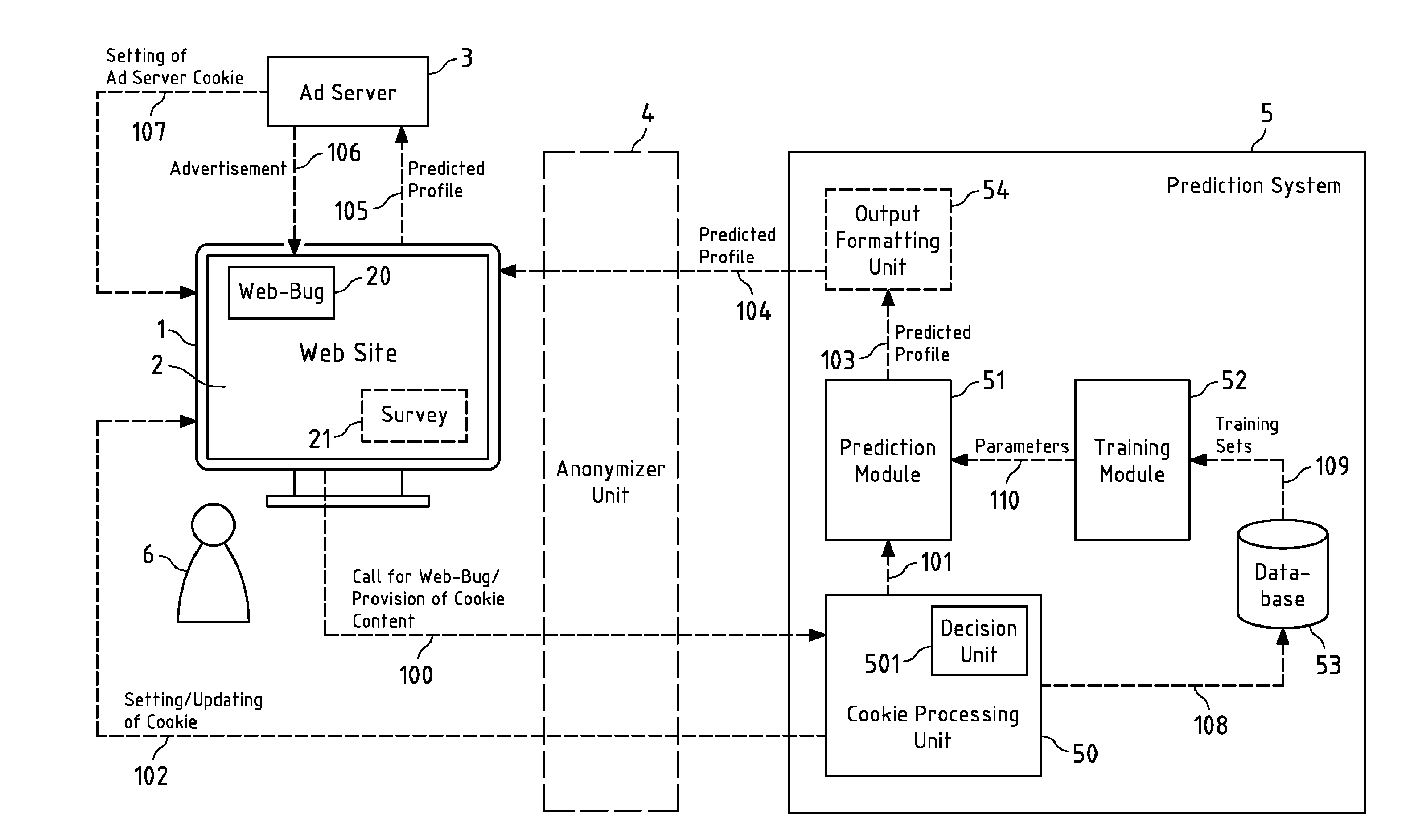
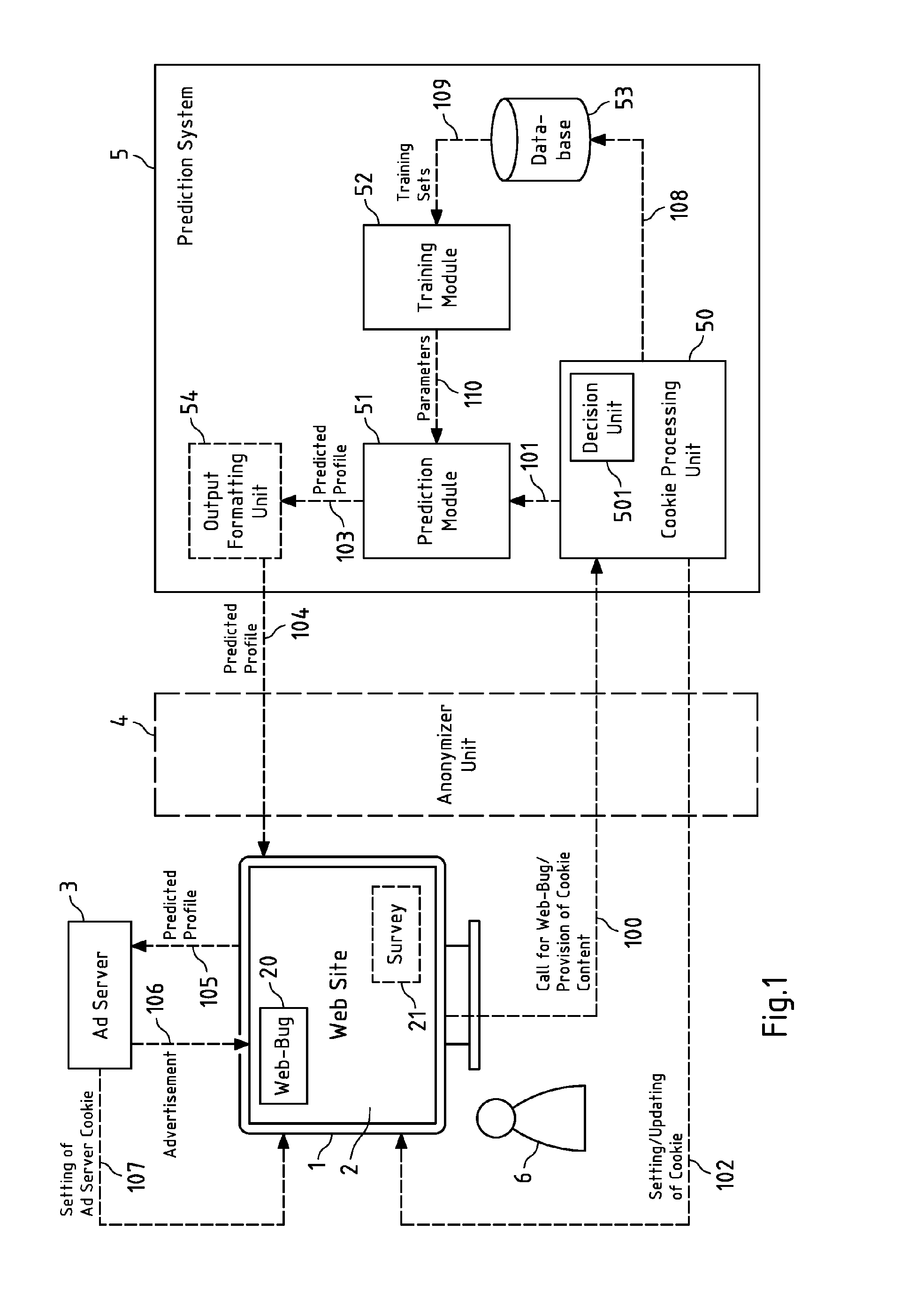
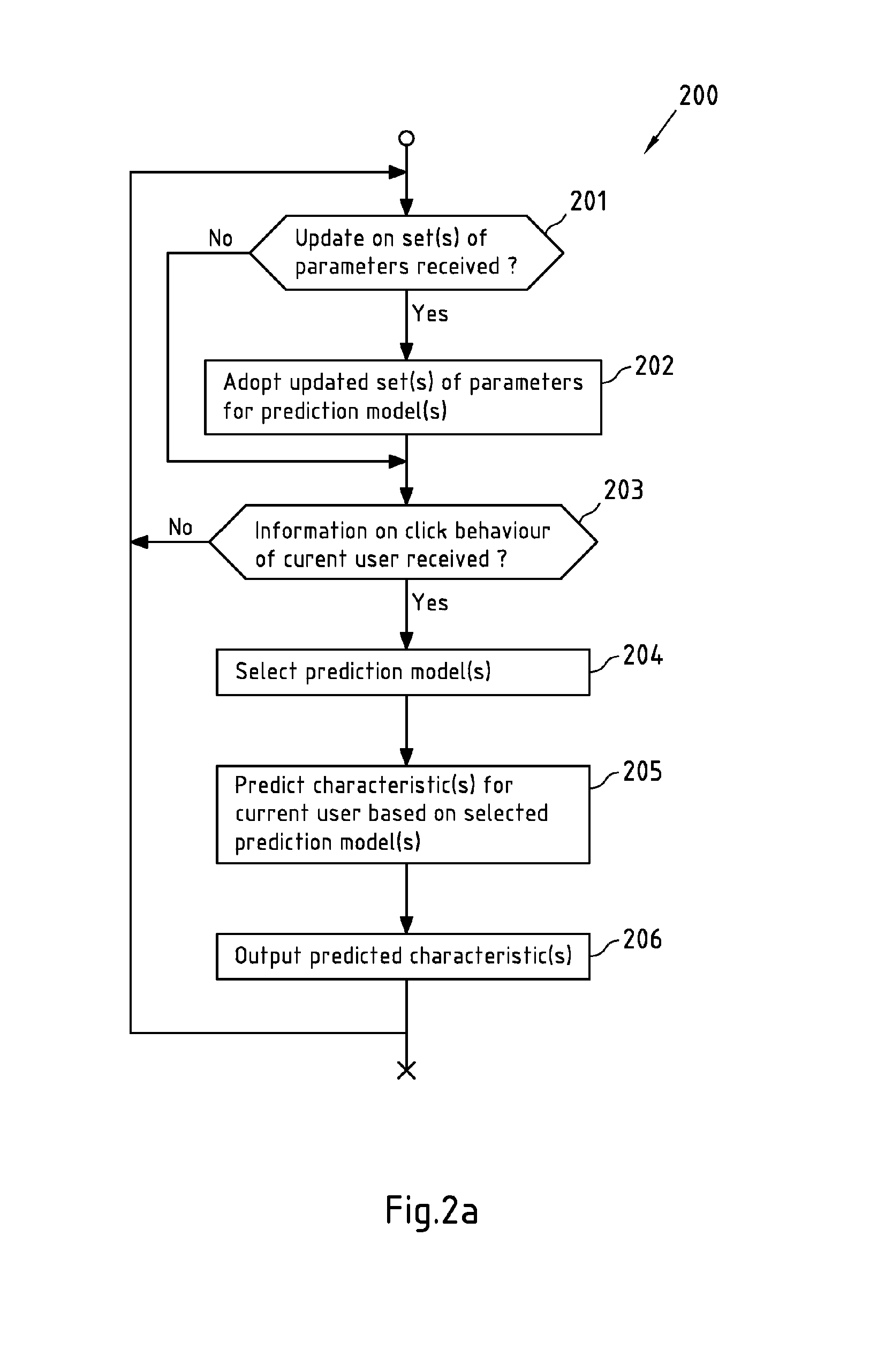
Predictive Behavioural Targeting
InactiveUS20150088662A1Avoid contradictory resultSpeed up the processMachine learningInference methodsData miningData science
It is inter alia disclosed a method, a computer program, an apparatus and a system for predictive behavioural targeting. Information on an access behaviour of a current user accessing content is obtained. At least one characteristic of the current user is predicted by a prediction module of the apparatus in response to the obtaining of the information on the access behaviour of the current user, the prediction at least being based on a model for the characteristic and on the obtained information on the access behaviour of the current user. The model is at least based on a set of parameters determined by a training module at least based on information from a plurality of training sets and provided to the prediction module from time to time for updating purposes.
Owner:NUGG AD
Radiation imaging apparatus and control method therefor
InactiveUS7403594B2Stably performing radiographyAvoid delaySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansSoft x rayX-ray
A lamp emits pulse-shaped visible light when a wait period begins. If a radiation emission switch is not pressed in the wait period, X-ray radiation is not emitted from an X-ray source, and no charges are accumulated in photoelectric conversion elements of an X-ray imaging apparatus. In a non-read period, although signals are sequentially read from the photoelectric conversion elements, an output signal does not change. When the radiation emission switch is pressed in synchronization with a radiation-induced signal in a certain wait period, the X-ray source emits X-rays. After irradiation of X-rays, a photoelectric conversion period transitions to an actual read period. In the photoelectric conversion period, X-rays are emitted and transmitted X-ray information of a patient are accumulated in the photoelectric conversion elements of the X-ray imaging apparatus. In the actual read period, the accumulated information is read.
Owner:CANON KK
Audio signal encoder, audio signal decoder, method for providing an encoded representation of an audio content, method for providing a decoded representation of an audio content and computer program for use in low delay applications
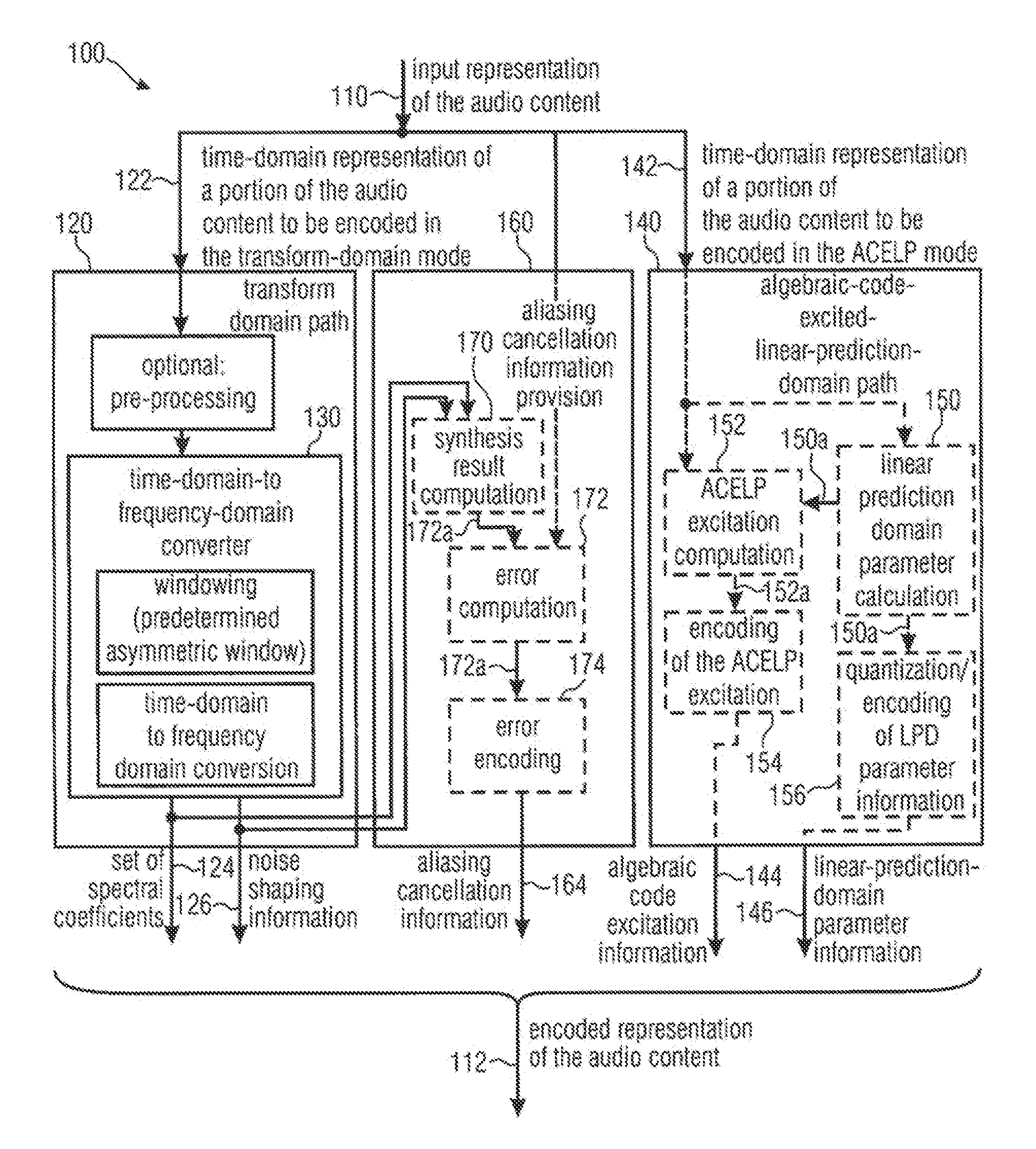
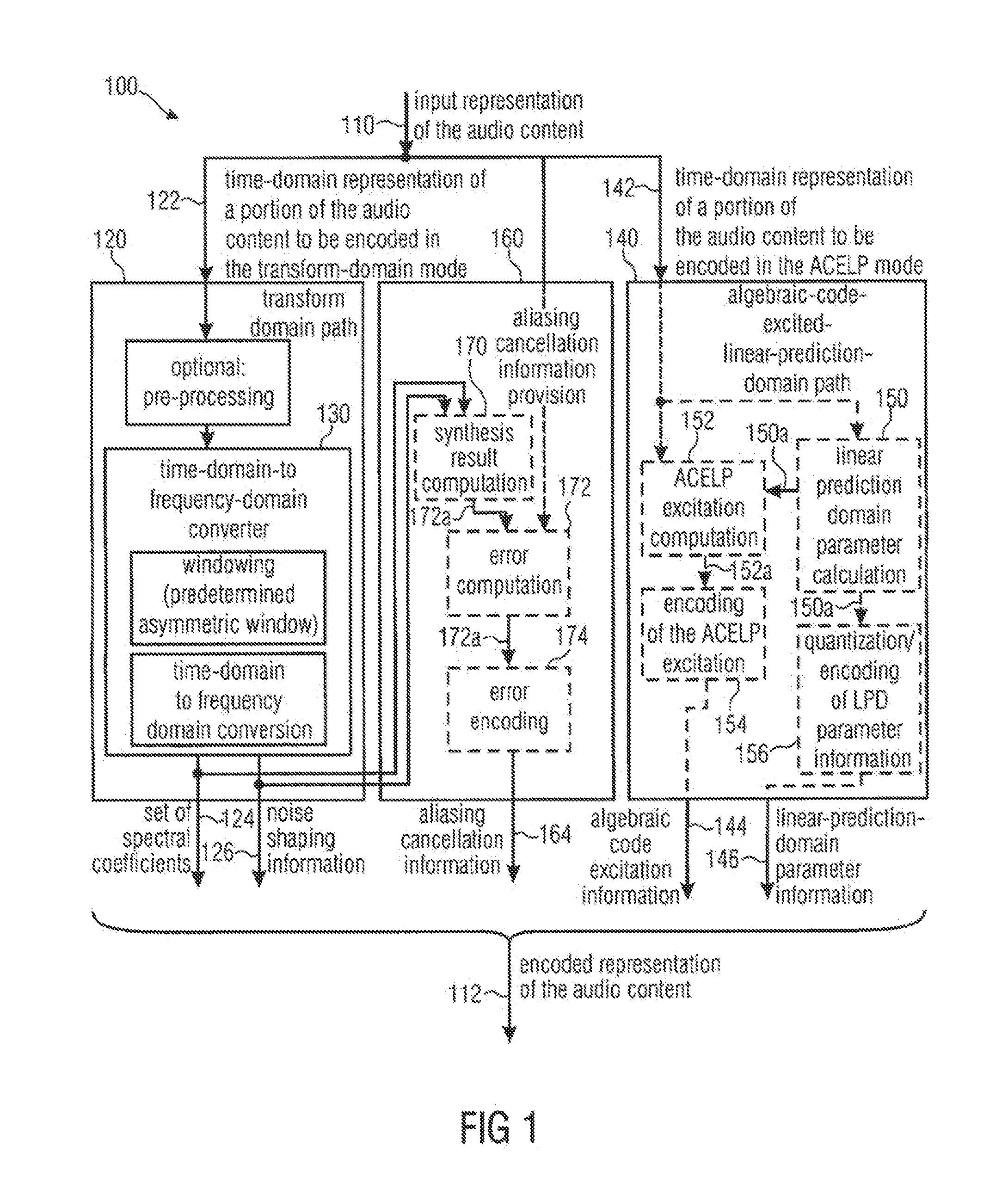
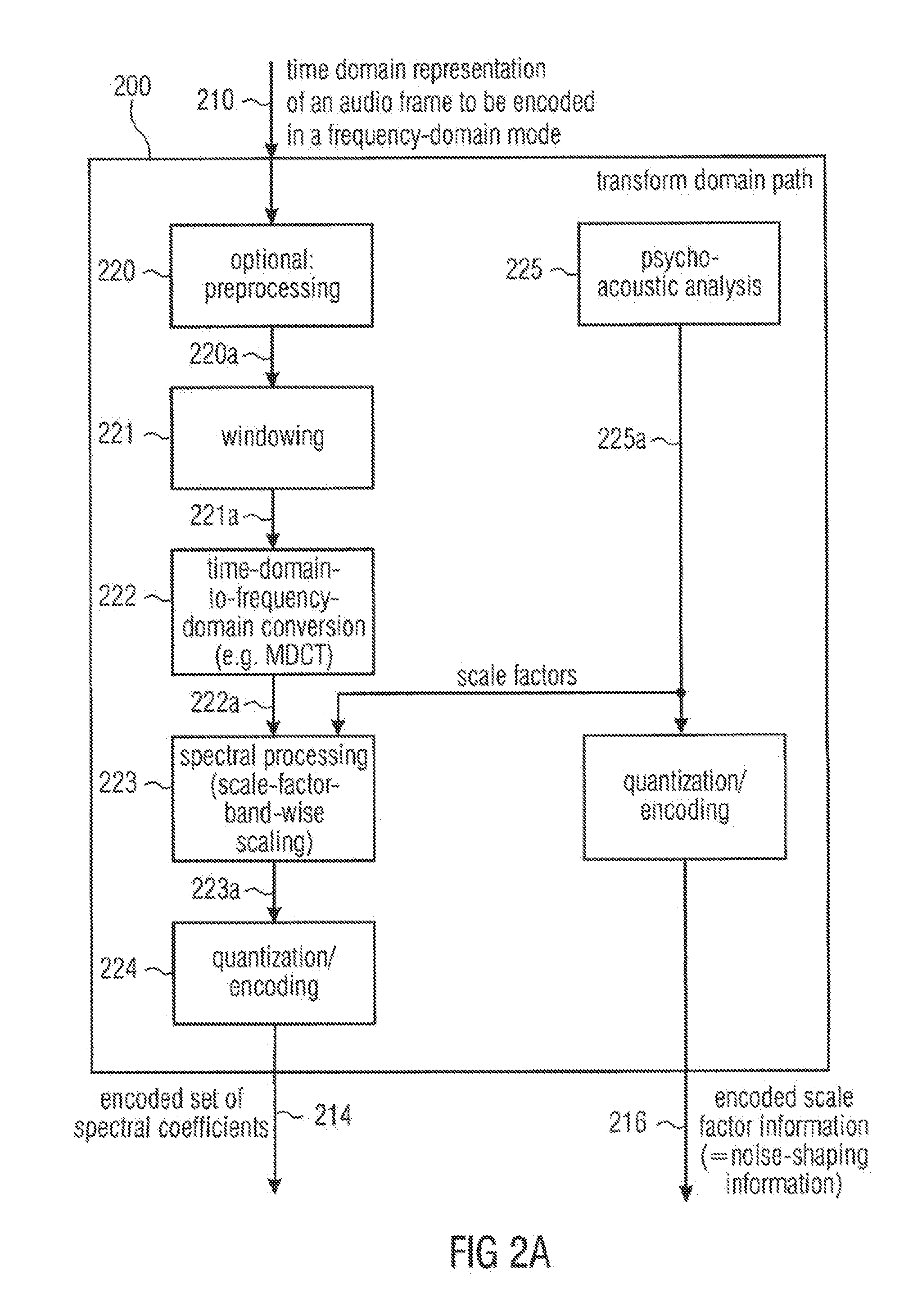
ActiveUS20120265541A1Reduces and cancel aliasing artifactImprove coding efficiencySpeech analysisFrequency spectrumNoise shaping
An audio signal encoder includes a transform-domain path which obtains spectral coefficients and noise-shaping information on the basis of a portion of the audio content, and which windows a time-domain representation of the audio content and applies a time-domain-to-frequency-domain conversion. The audio signal decoder includes a CELP path to obtain a code-excitation information and a LPD parameter information. A converter applies a predetermined asymmetric analysis window in both if a current portion is followed by a subsequent portion to be encoded in the transform-domain mode or in the CELP mode. Aliasing cancellation information is selectively provided in the later case.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Method and system to compensate for the effects of packet delays on speech quality in a Voice-over IP system
ActiveUS7266127B2Increase the lengthDecreased playback speedSpeech analysisTime-division multiplexComputer hardwareNetwork packet
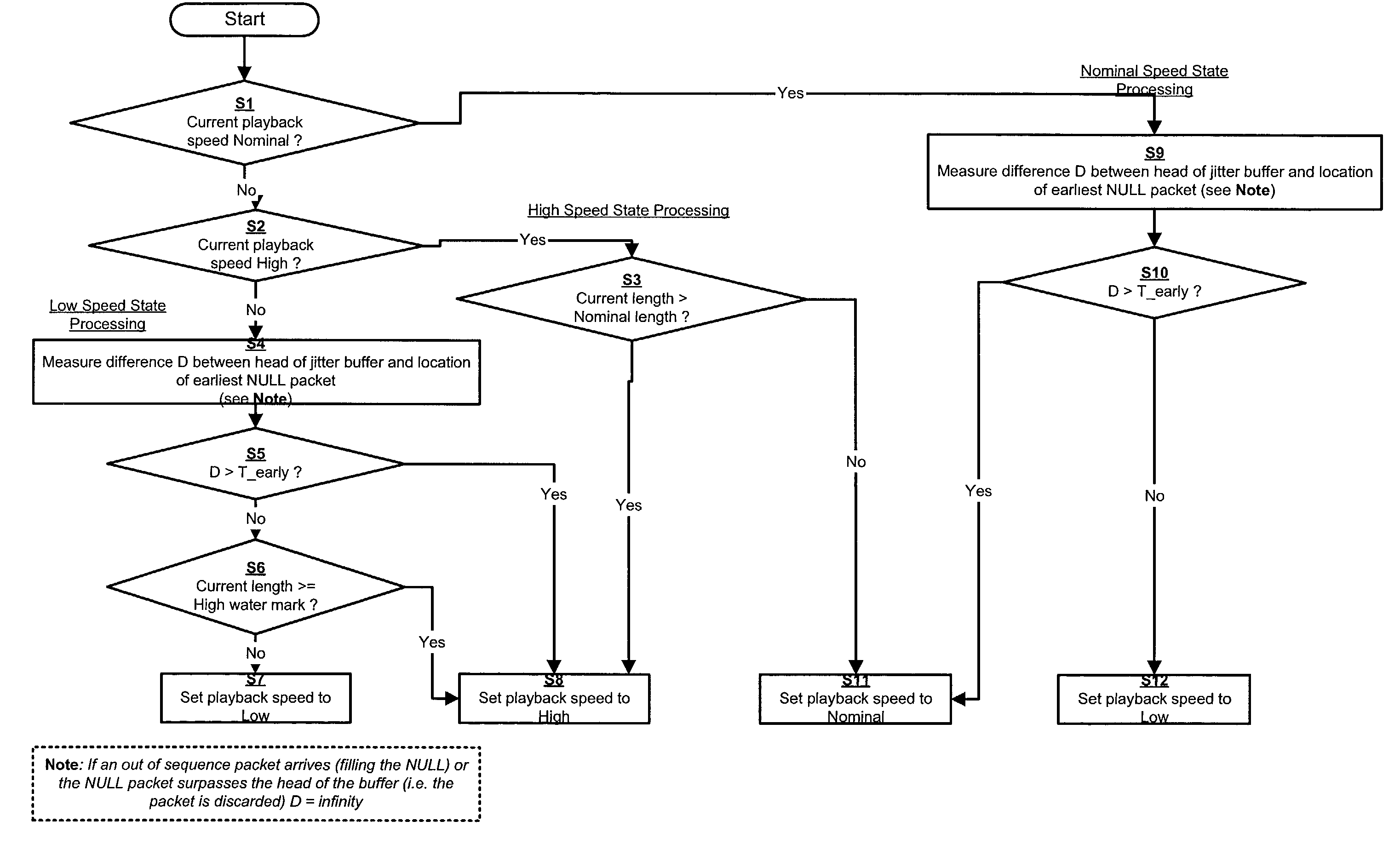
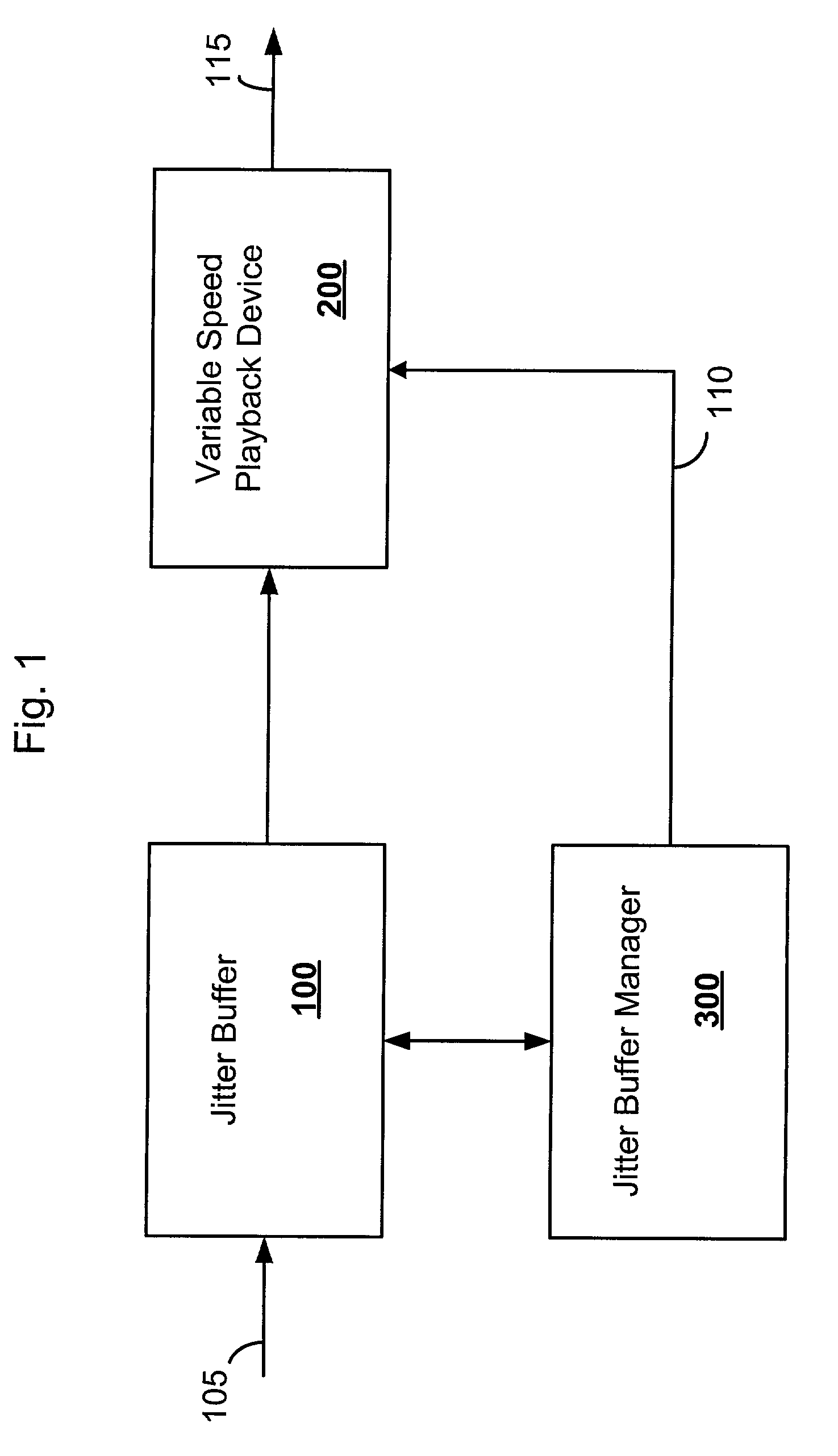
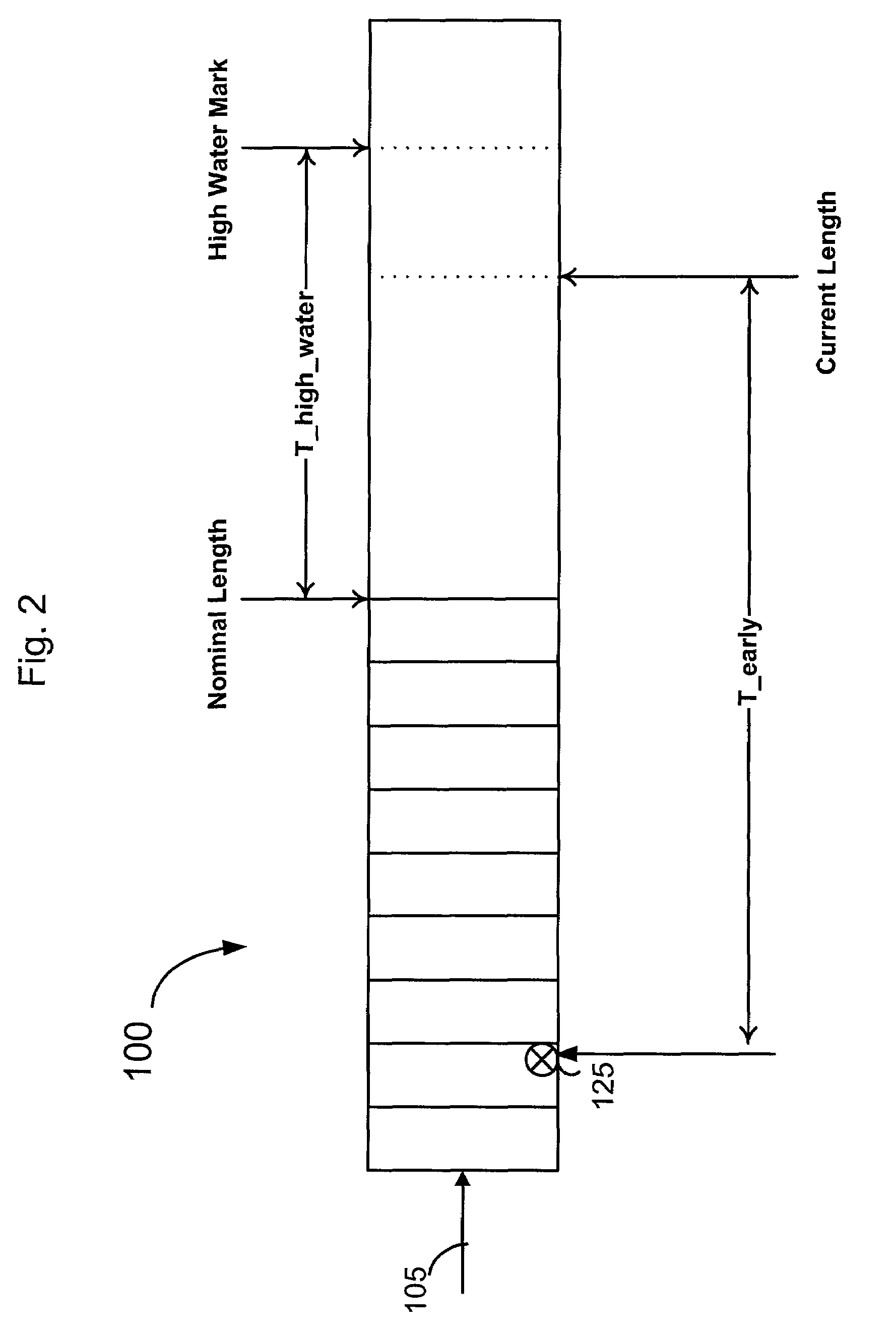
The system includes a jitter buffer for receiving speech packets in a Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) system, a playback device for adjusting the playback speed of the received speed packets, and a jitter buffer manager for detecting out of sequence packets in the jitter buffer and for sending commands to the playback device to adjust playback speed based on the detection. The speech signal is played back at the nominal speed when there are no out of sequence packets. The playback speed is decreased when an out of sequence packet is detected, thereby tending to increase the jitter buffer length. When an out of sequence packet arrives, the playback speed is increased in order to restore jitter buffer length to its nominal length.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
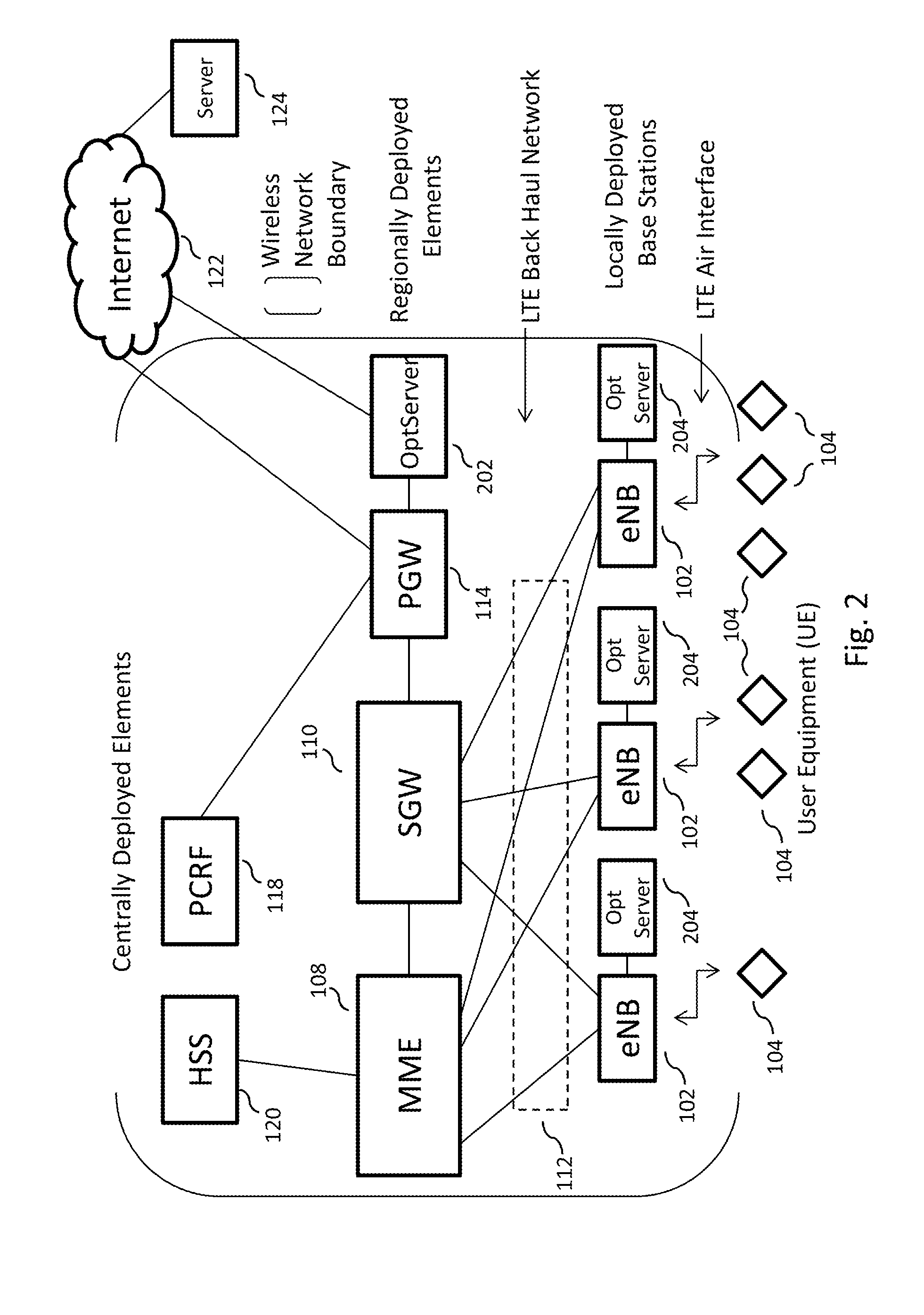
Efficient delivery of real-time asynchronous services over a wireless network
ActiveUS20140334449A1Conserving permanent memory utilizationImprove efficiencySpatial transmit diversityError preventionWireless mesh networkData stream
In embodiments of the present disclosure, improved capabilities are described for conserving back haul utilization in a wireless network, where optimization servers utilizing publish-subscribe broker services are provided within the wireless network to provide streaming data services required for applications streaming data to a plurality of mobile cellular devices, where the streaming data is not necessarily delivered to each of the plurality of mobile cellular devices at the same time.
Owner:ALL PURPOSE NETWORKS INC
Delta caching
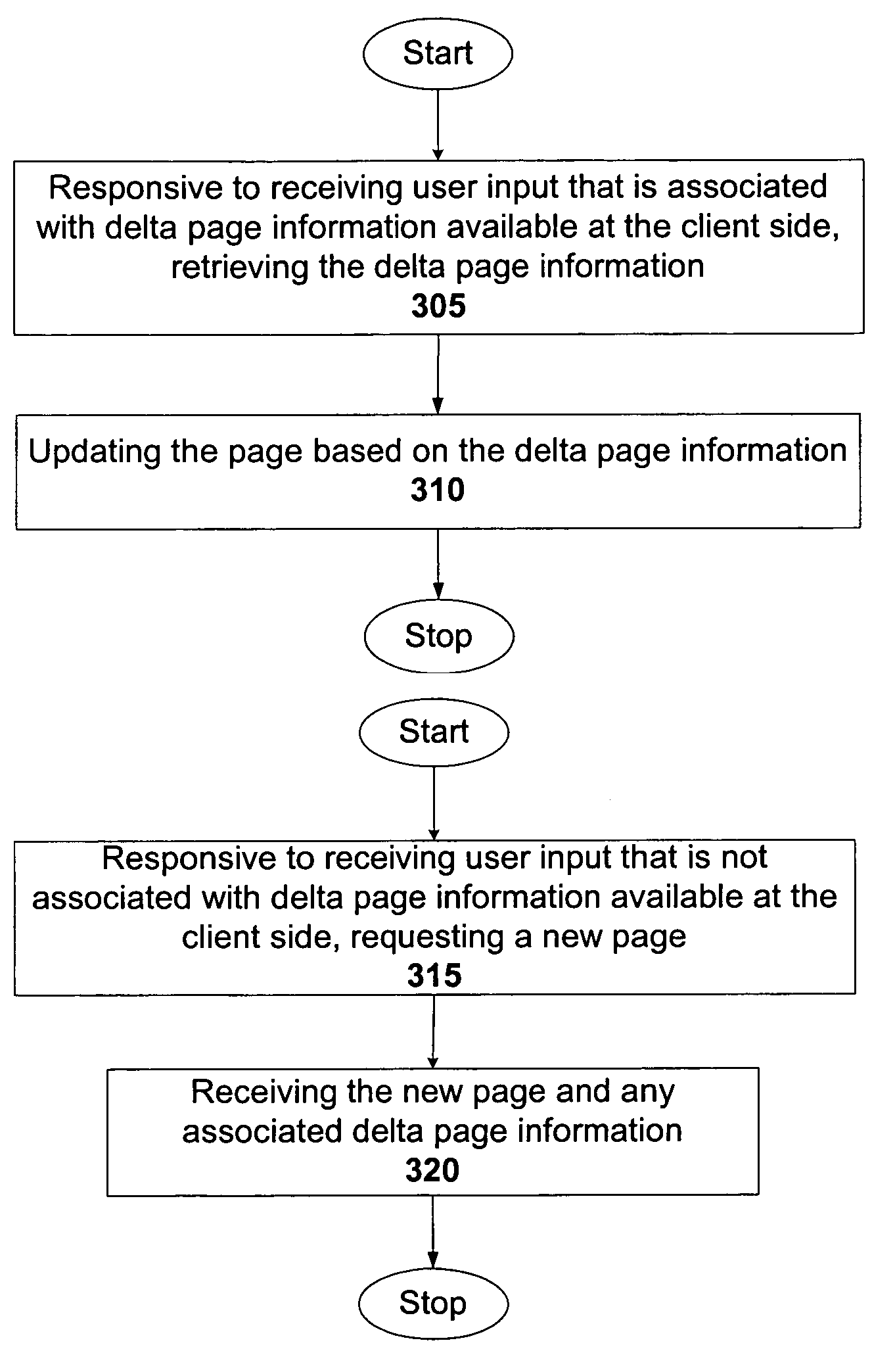
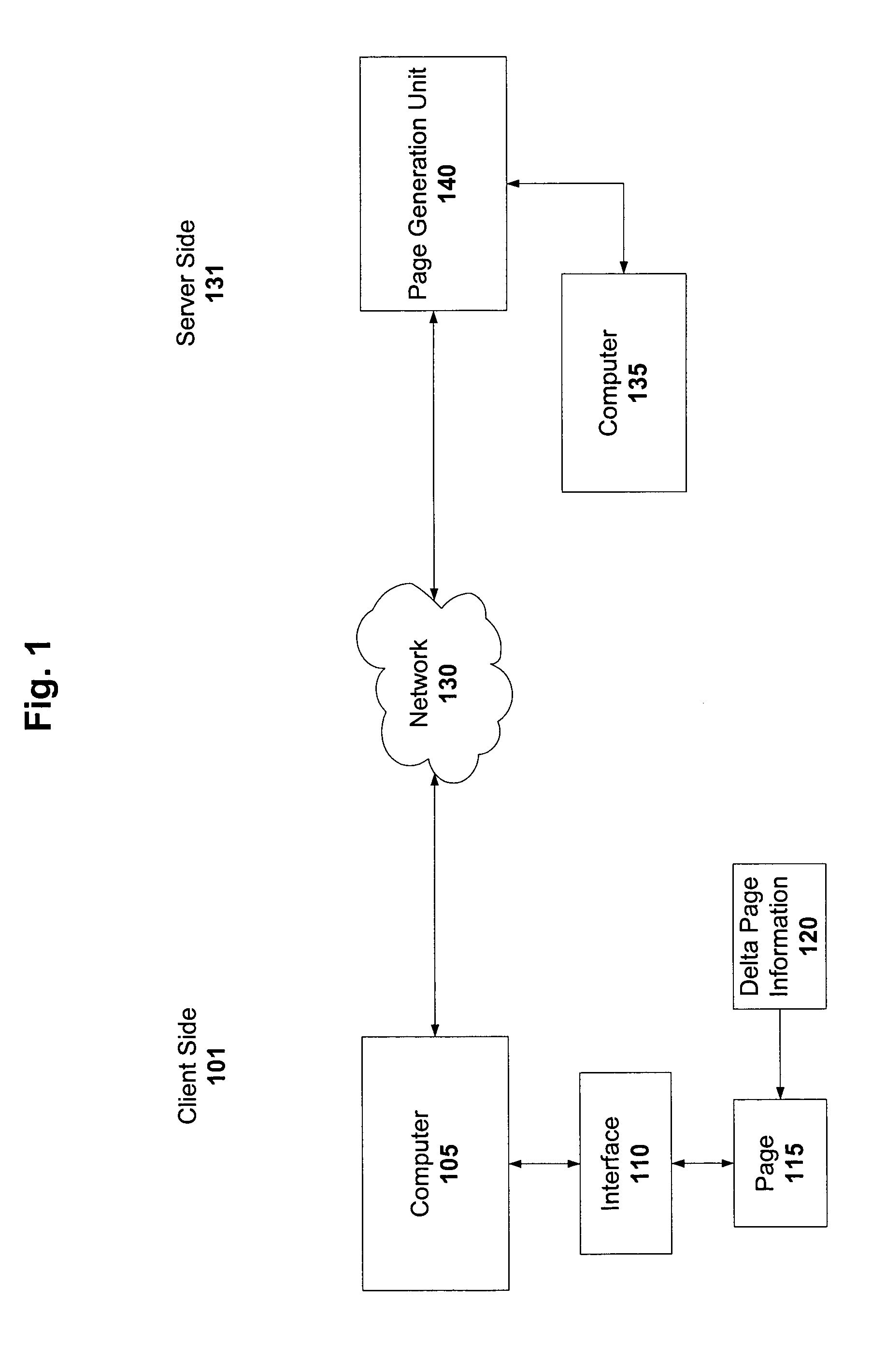
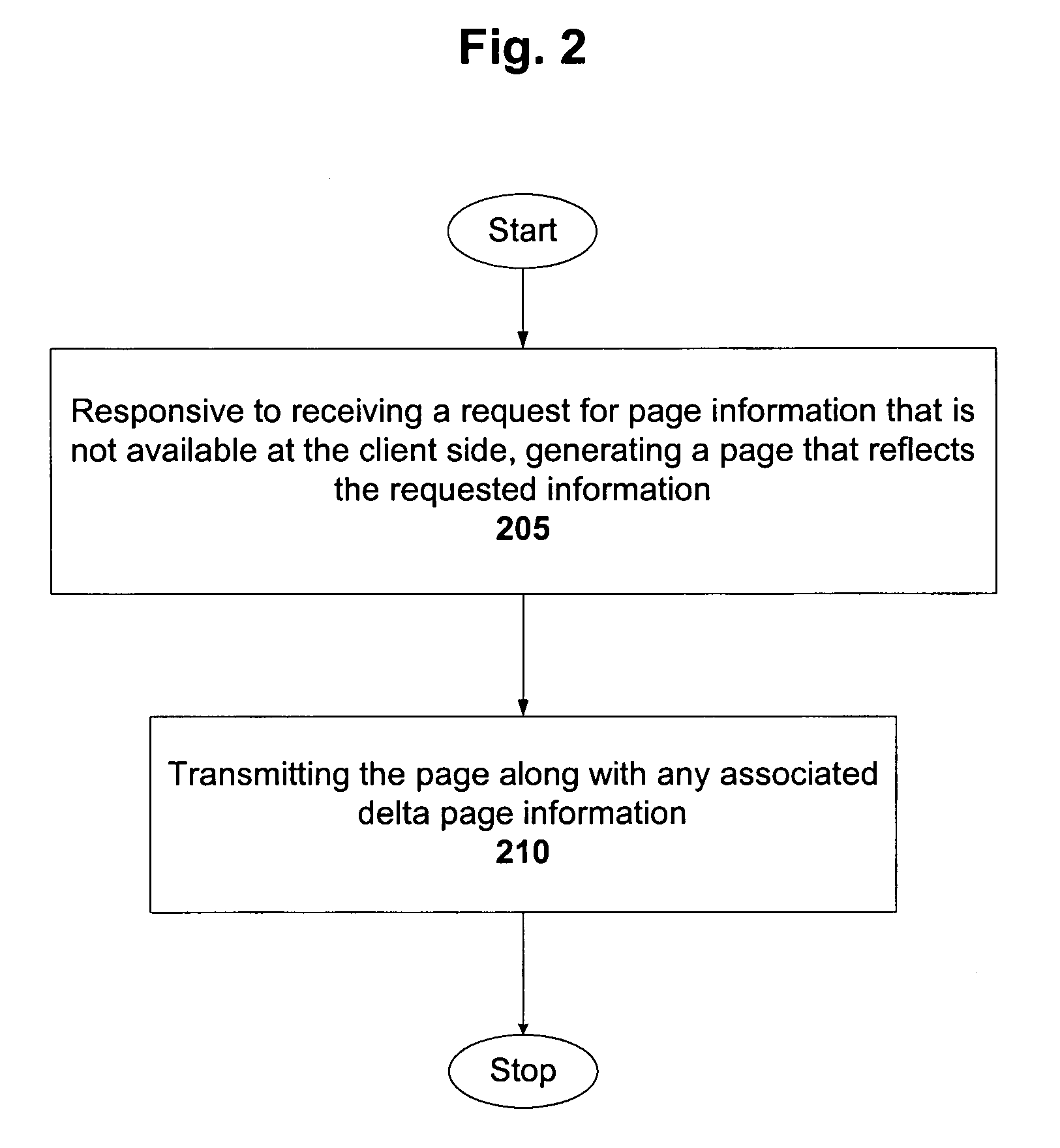
InactiveUS7058700B1Lower latencyReduce latencyDigital data information retrievalDigital computer detailsThe InternetClient-side
A solution to latencies associated with server side processing time, as well as to latency resulting from the transit of information or tools from a server side to a client or user side is provided. The server side and client side can be coupled via a hard link or a network-type connection such as the Internet or a local area network. Select delta page information is stored in a concise manner on client side. As a result, the client does not have to contact the server when a user requests page information that is associated with stored delta page information. The stored delta page information can be accessed and used to update the current page thereby yielding the requested page. Thus, latency from server side processing and network transit time is reduced. An algorithm can be implemented on the client side to identify relevant stored delta page information, and to update the current page with that delta page information.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
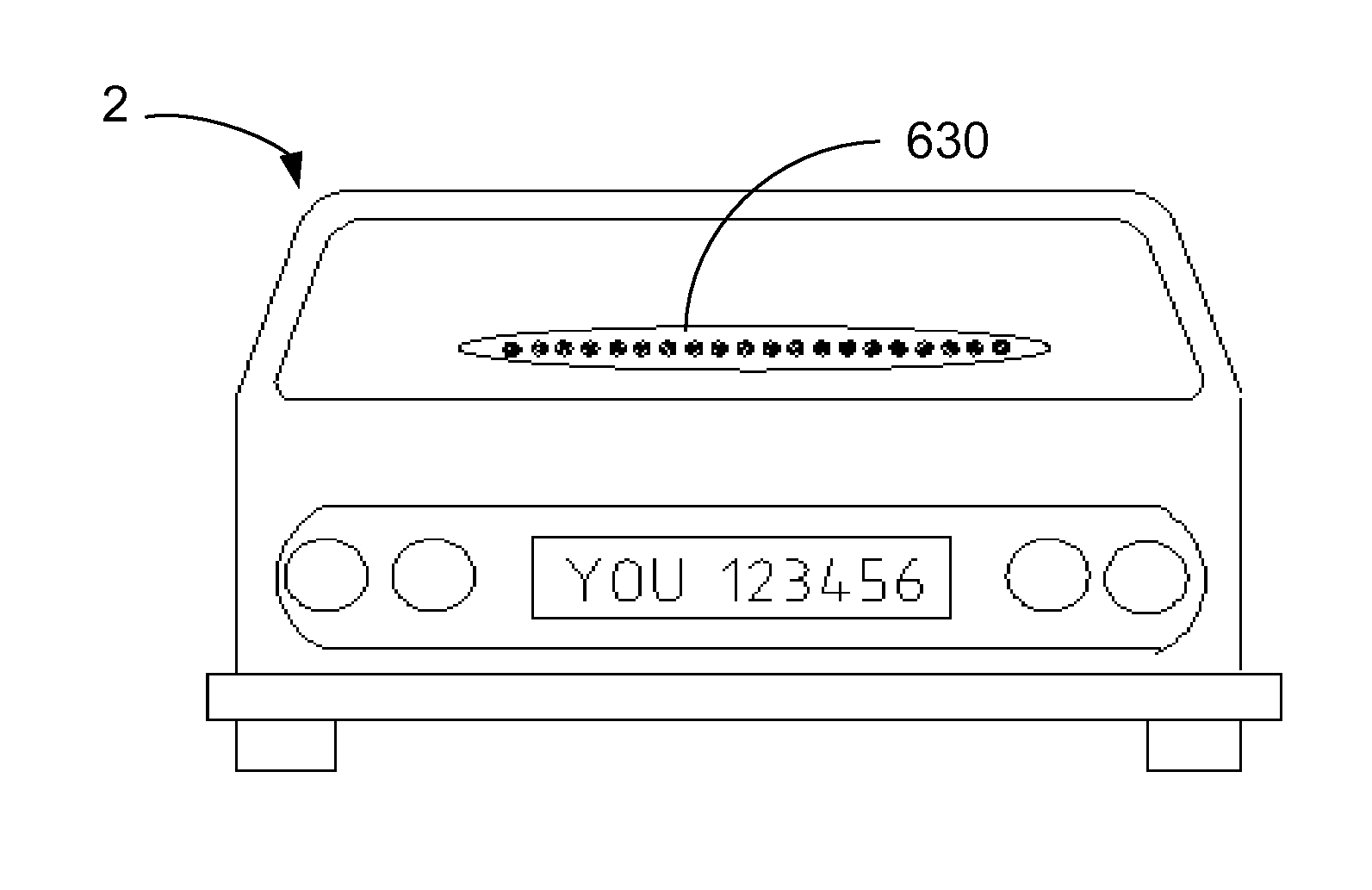
Emergency stop signal device for motor vehicle
An emergency stop signaling device for vehicles is disclosed, including a deceleration sensor which produces deceleration values, an integrated circuit control circuit which receives the deceleration values and produces LED activation control signals. An LED array lights in response to the LED activation control signals from the Integrated Circuit control circuit to produce a light pattern which is distinguishable from an ordinary braking signal. The deceleration sensor is preferably a digital deceleration sensor. The LED array is a flexible LED array, a portable LED array, a linear LED array or a circular LED or a combination of these. The IC control circuit produces signals which activate the LED array to a plurality modes of activity including a tail light mode, a stop light mode, and a panic stop mode.
Owner:QUACH TUAN KIM +2
Distributed Bridging
ActiveUS20090252316A1Efficiently distribute processingLess computationally intensive operationSpecial service for subscribersSubstation equipmentTime domainCommunications system
A communication system that includes multiple conferencing devices connected in a daisy-chain configuration is communicably connected to far-end conference participants. Multiple conferencing devices provide improved sound quality to the far-end participants by reducing aural artifacts resulting from reverberation and echo. The daisy-chain communication system also reduces the processing and transmission time of the near-end audio signal by processing and transmitting the audio signal in frequency domain. Each conferencing device in the daisy chain performs signal conditioning on its audio signal before transmitting it in the frequency domain to a mixer. The output signal of the mixer is converted back to the time domain before being transmitted to the far-end. The daisy-chain configuration also provides a distributed bridge to external communication devices that can be connected to each conferencing device.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Compact ATE with time stamp system
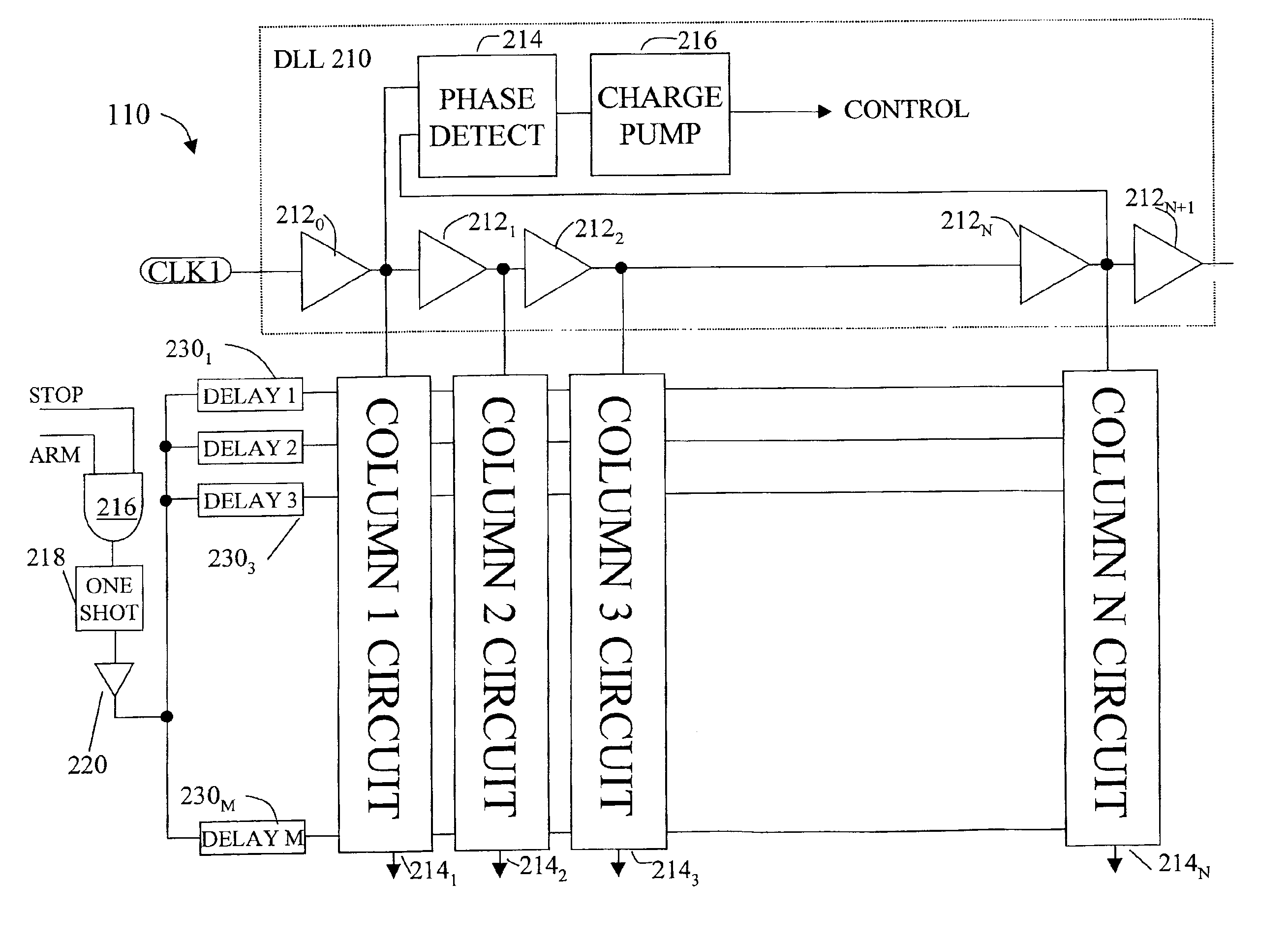
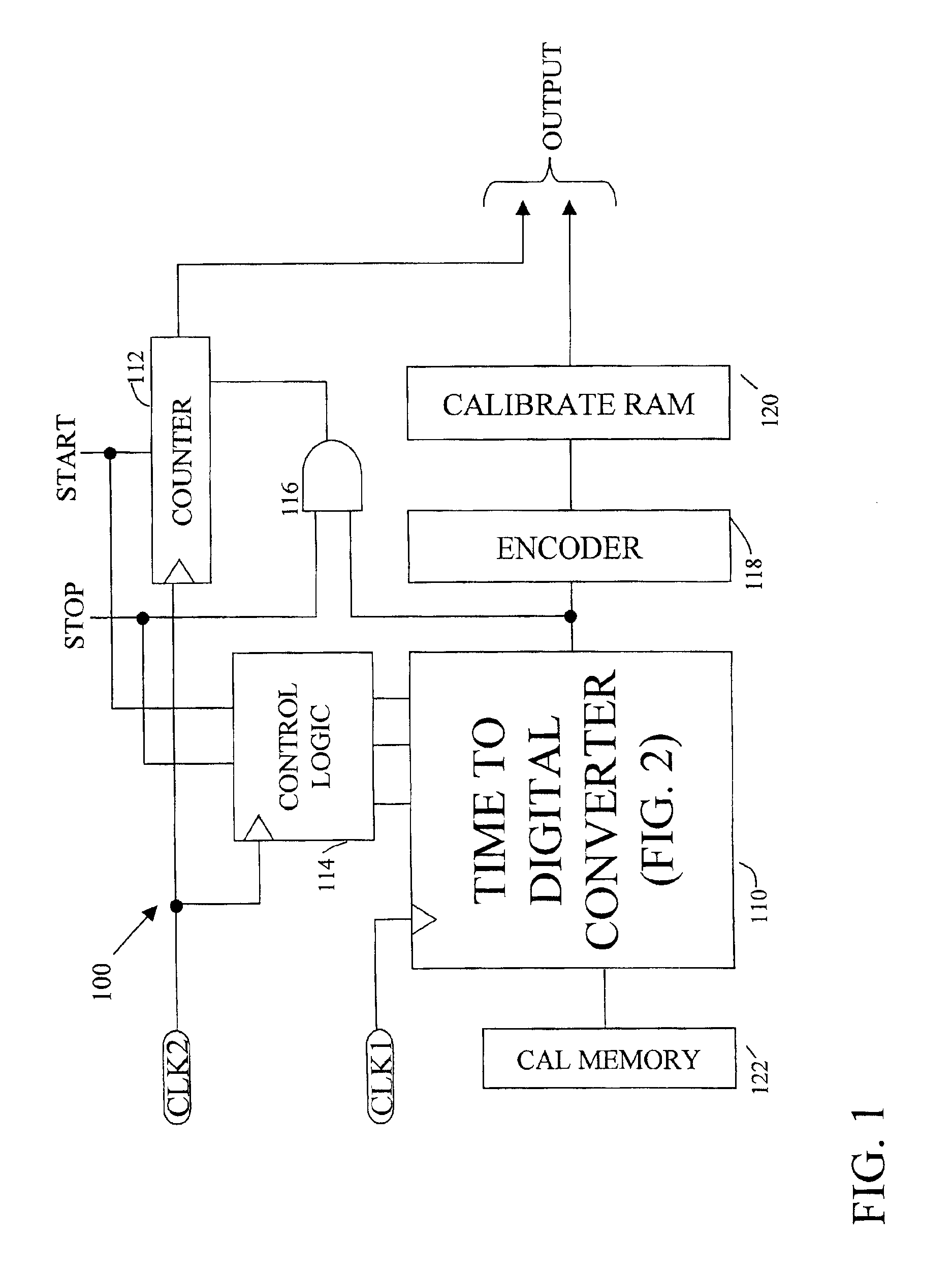
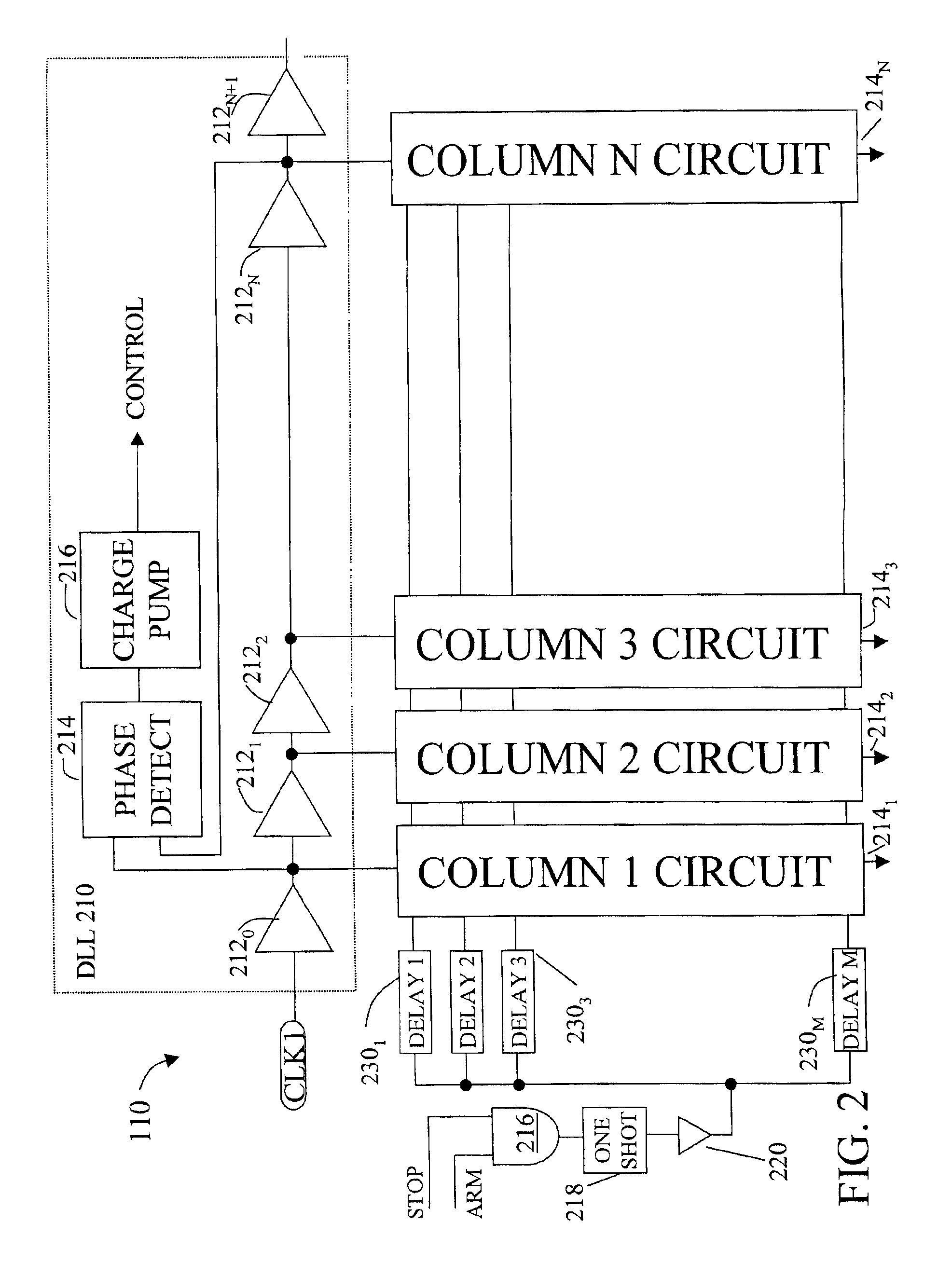
InactiveUS6868047B2Low costIntegrated reductionElectronic circuit testingElectromechanical unknown time interval measurementAutomatic test equipmentDelay-locked loop
A accurate time measurement circuit. The design is amenable to implementation as a CMOS integrated circuits, making the circuit suitable for a highly integrated system, such as automatic test equipment where multiple time measurement circuits are required. The circuit uses a delay locked loop to generate a plurality of signals that are delayed in time by an interval D. The signal to be measured is fed to a bank of delay elements, each with a slightly different delay with the difference in delay between the first and the last being more than D. An accurate time measurement is achieved by finding coincidence between one of the TAP signals and one of the delay signals. The circuit has much greater accuracy than a traditional delay line based time measurement circuit with the same number of taps. It therefore provides both accuracy and fast re-fire time and is less susceptible to noise.
Owner:TERADYNE
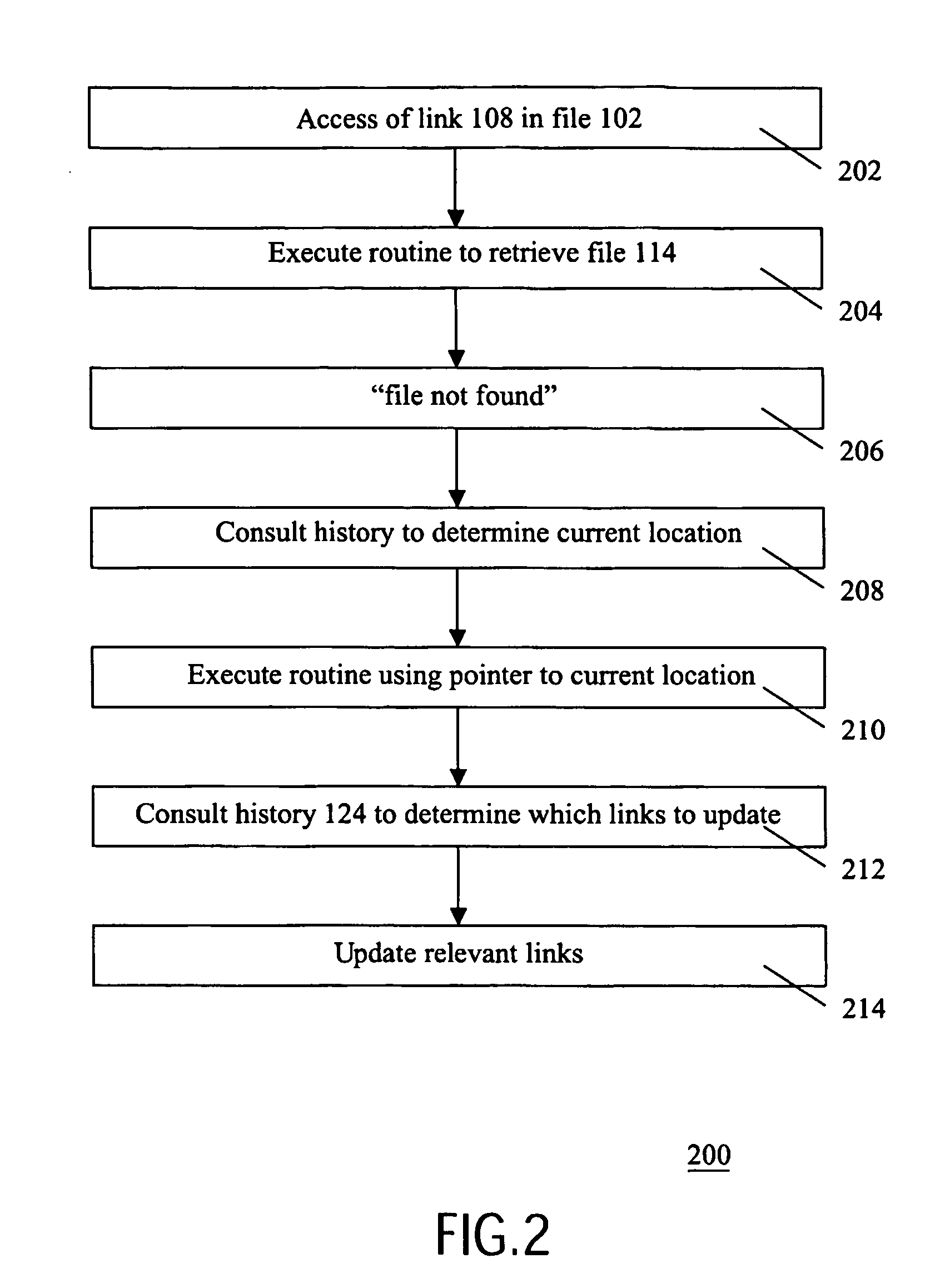
File migration history controls updating or pointers
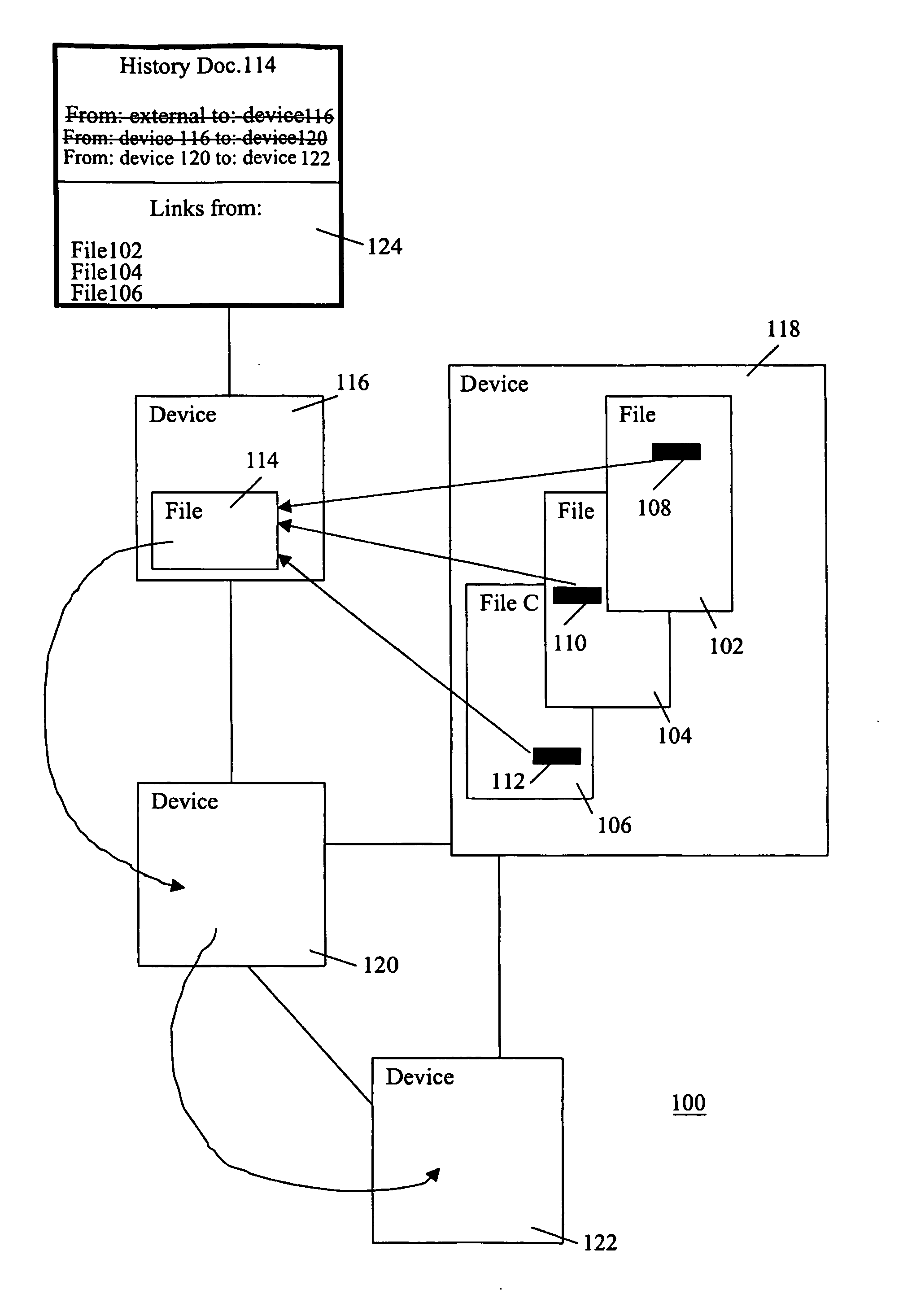
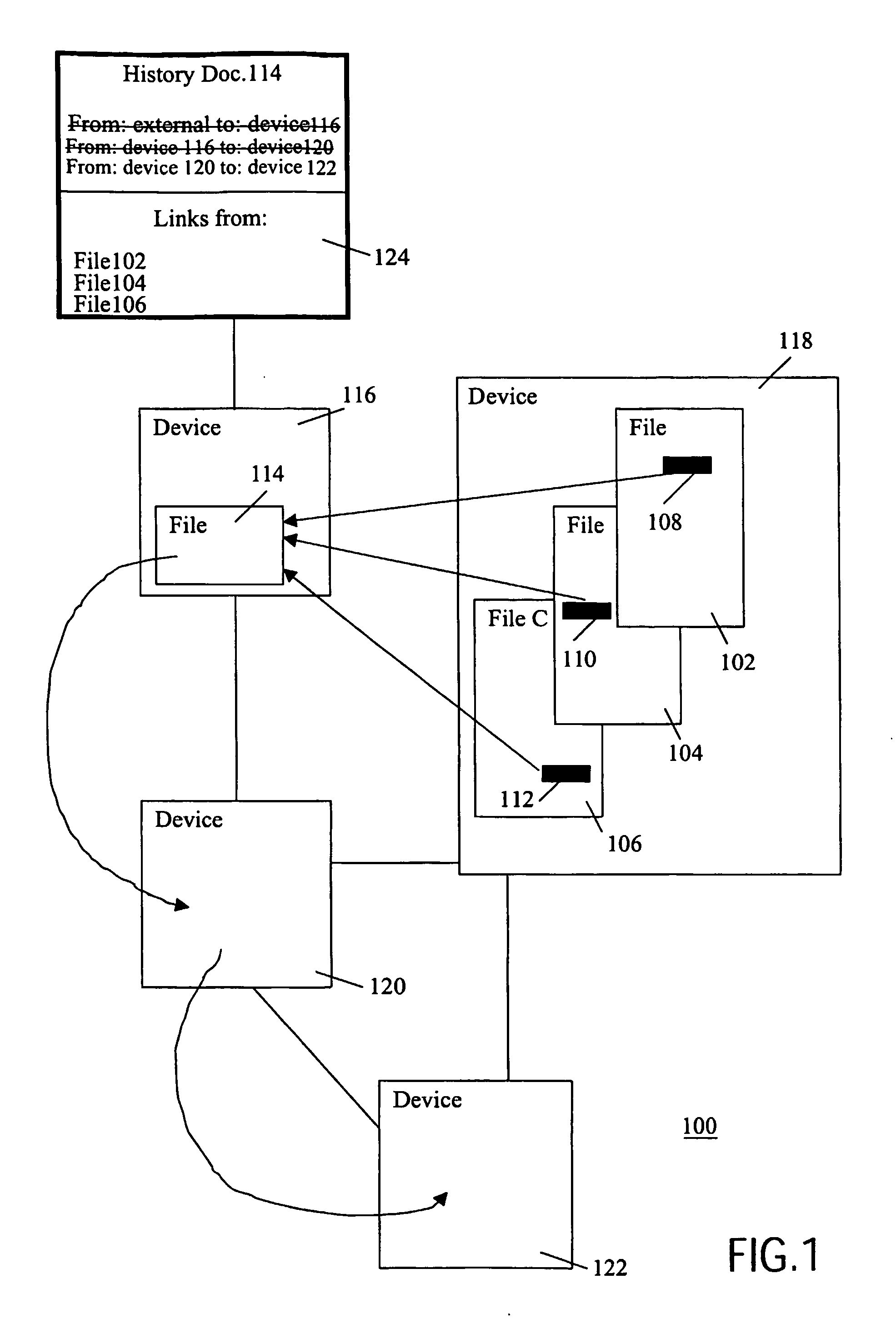
InactiveUS20060294039A1To overcome the large delayEasy to implementDigital computer detailsFile metadata searchingData processing systemData treatment
On a distributed data processing system, a history of file migration is maintained. When access to a file is requested and the file is not found, the migration history is consulted to determine the current location of the file, and to update links contained in other files that point to the request file.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
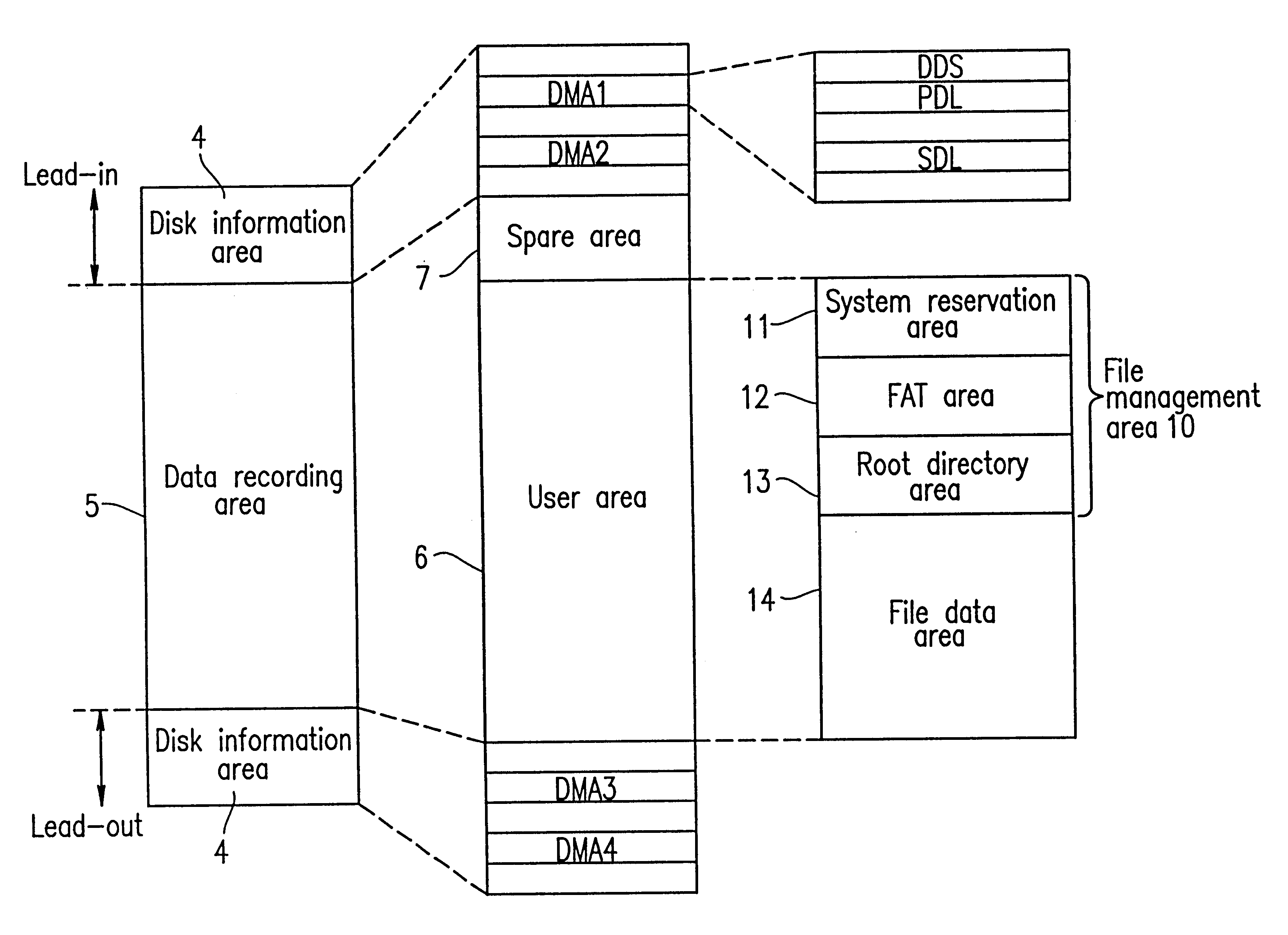
Information recording medium, and method and apparatus for managing defect thereof
InactiveUS6742147B1To overcome the large delayDisc-shaped record carriersRecord information storageComputer hardwareRecording media
An information recording medium includes a disk information area; a user area including a plurality of sectors; and a spare area including at least one sector which, when at least one of the plurality of sectors included in the user area is a defective sector, is usable instead of the at least one defective sector. The spare area is located radially inward from the user area. A physical sector number of a sector to which a logical sector number "0" is assigned, among the plurality of sectors included in the user area and the at least one sector included in the spare area, is recorded in the disk information area.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Robot arm control method and control device
ActiveUS7102315B2High-precision detectionTo overcome the large delayProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorGear wheelAngular velocity
When either a command value or an actually measured value is appropriately selected as an angular velocity used for the frictional torque calculation, the frictional compensation can be made valid at all times in both the case in which a robot is actively operated according to an angular velocity command and the case in which the robot is passively operated being pushed by an external force. In the case where a motor rotating direction and a collision direction are reverse to each other after a collision has been detected, the control mode is switched from the positional control to the electric current control and a torque, the direction of which is reverse to the direction of the motor rotation is generated by the motor, so that the motor rotating speed can be reduced and the collision energy can be alleviated. After that, when the motor rotating speed is reduced to a value not more than the setting value, the control mode is switched to the compliance control and the distortion caused in a reduction gear is dissolved. On the other hand, in the case where the motor rotating direction and the collision direction are the same, the control mode is directly switched from the positional control to the compliance control without passing through the electric current control. When the robot is operated whole following a collision force, the collision force can be alleviated.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Packet switching system, packet switching network and packet switching method
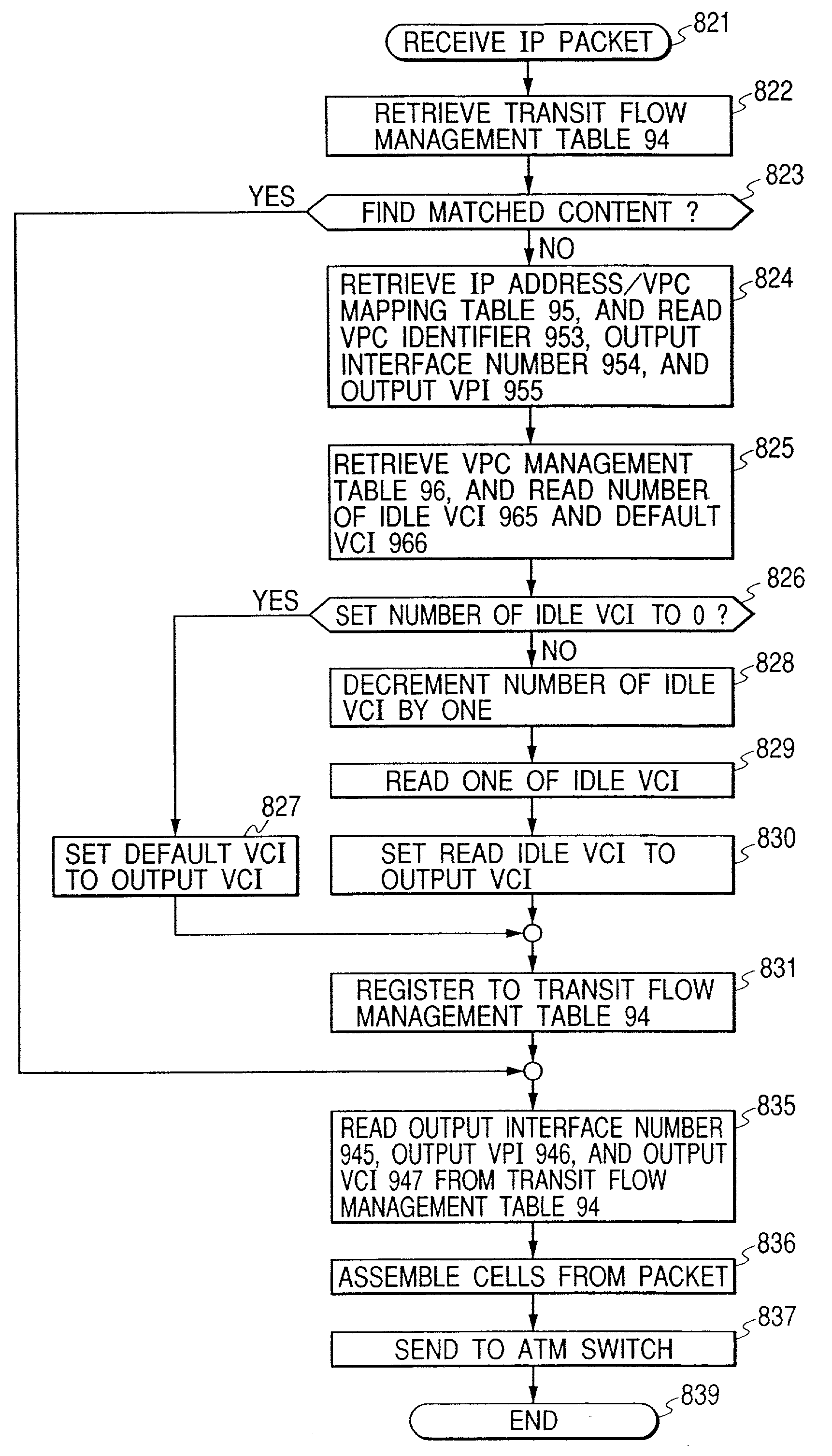
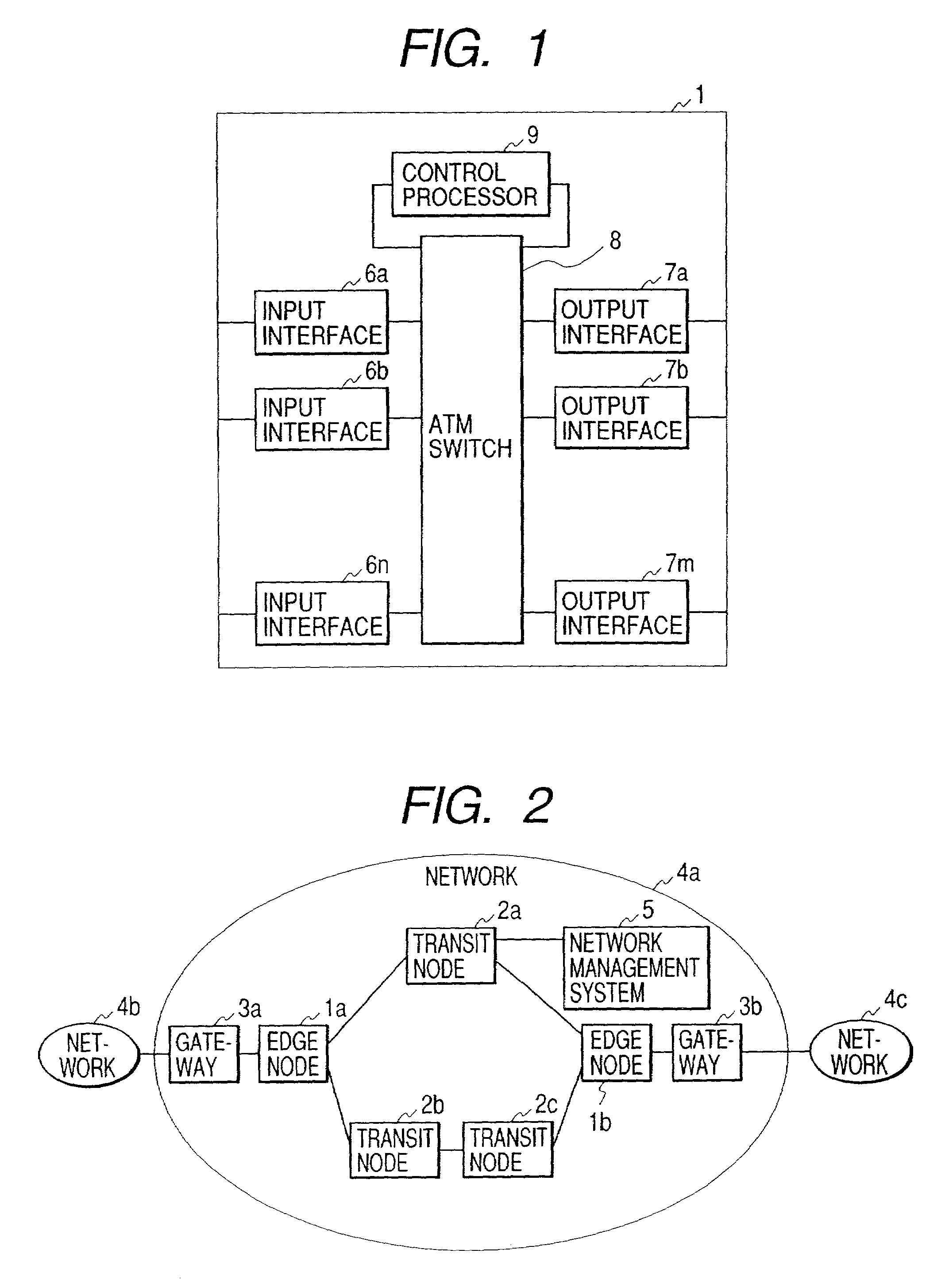
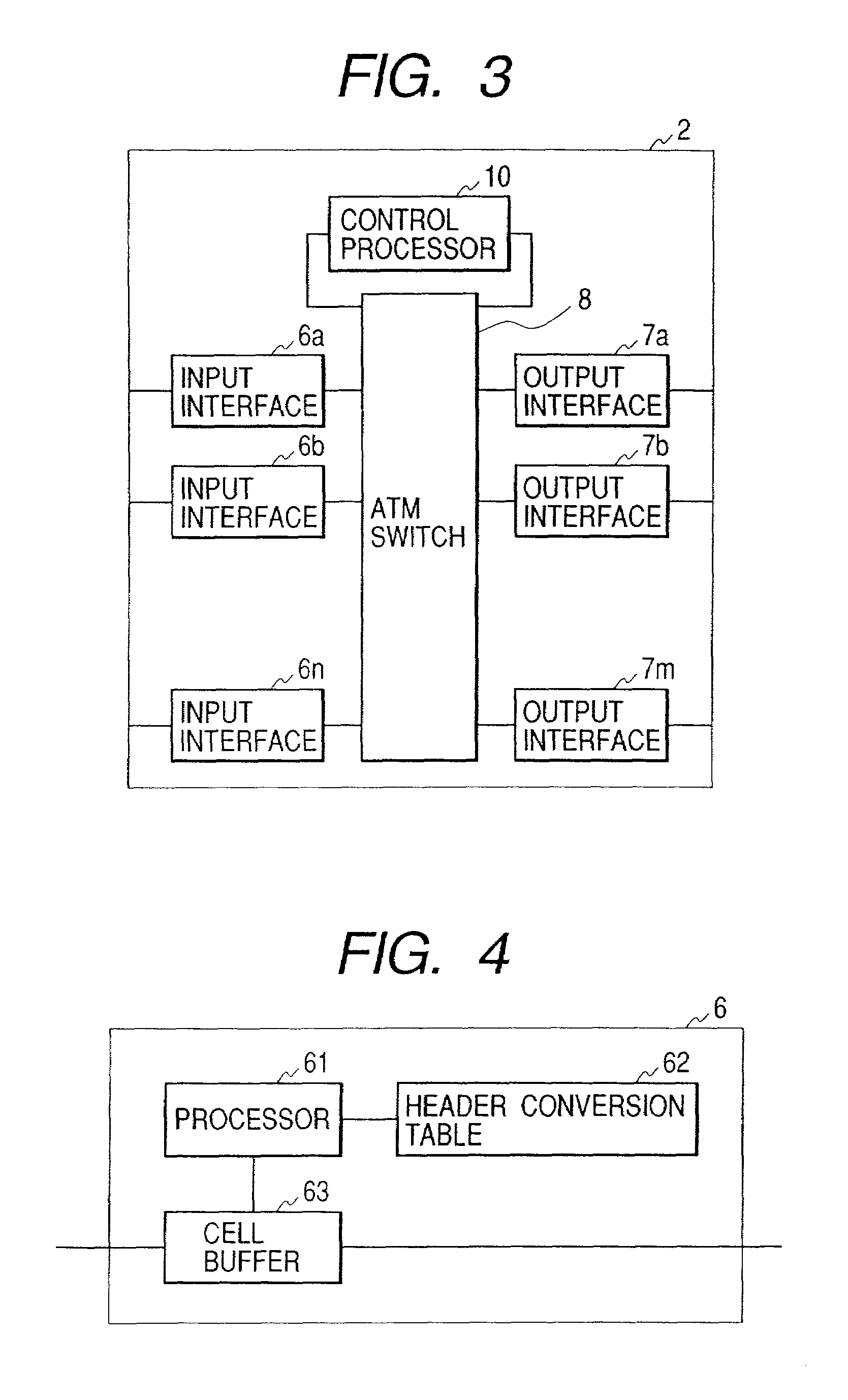
InactiveUS7463633B2To overcome the large delayConstraint is somewhat limitingData switching by path configurationTime-division multiplexing selectionIp addressEdge node
Upon initialization, a VPC is set up between edge nodes. A control processor of each node creates an IP address / VPC mapping table using IP routing information and an address mapping table mapping correspondence between IP addresses and ATM addresses and supplied by a network management system. A gateway assigns a VCC to each packet input to the network. A sending-side edge node inputs the packet to the VPC corresponding to its destination by referring to the IP address / VPC mapping table. A transit node performs packet switching over VP. A receiving-side edge node transfers each packet to the gateway corresponding to its destination. If a series of packets meet a predetermined condition in a given edge node, its control processor sends VCC information to input interfaces of the edge node so that the packets are switched by an ATM switch in the edge node without intervention of the control processor.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com