Patents
Literature
981 results about "Media access" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
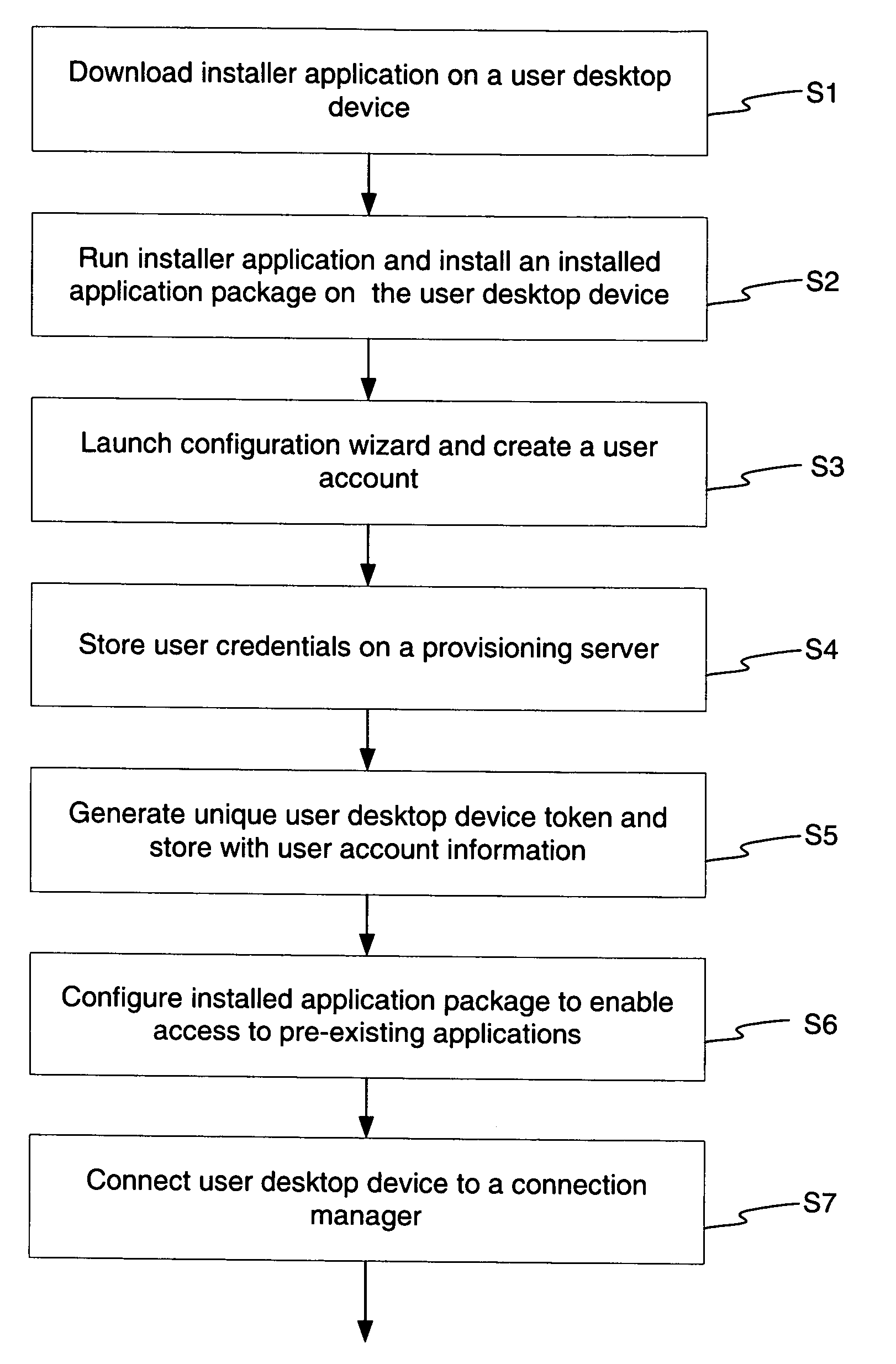
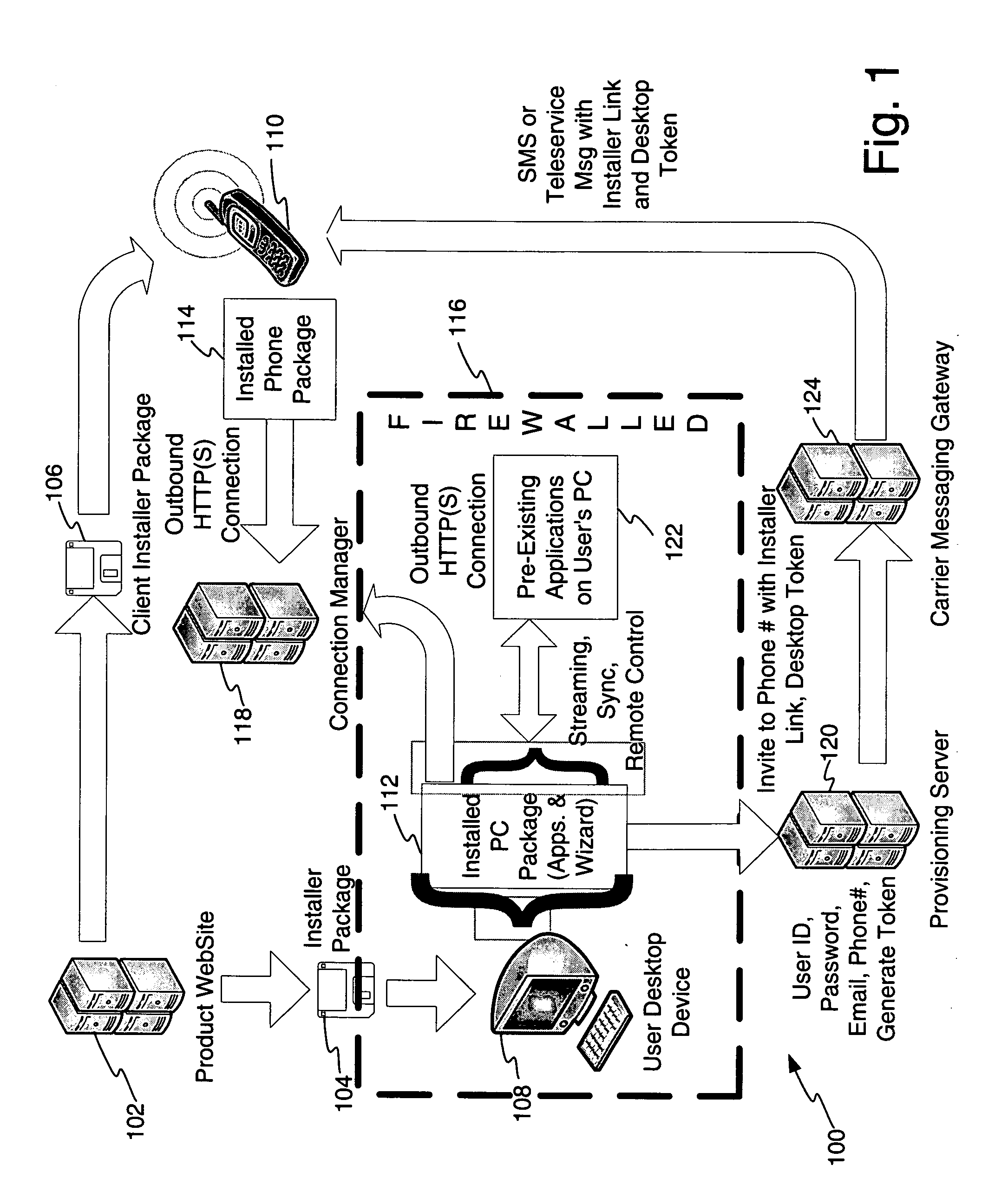
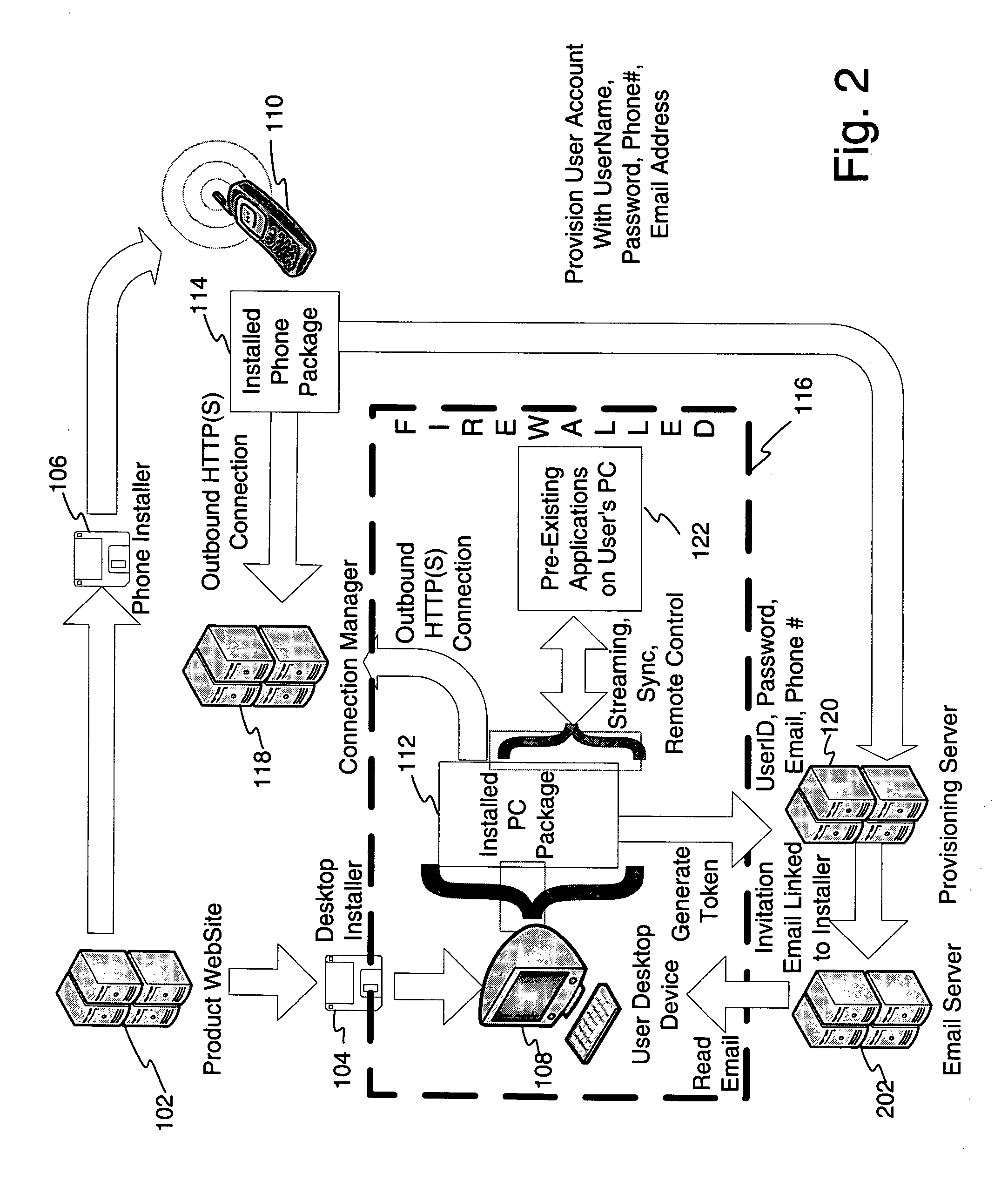
System and method for providing mobile access to personal media
InactiveUS20060173974A1Facilitates authorized accessEasy accessMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionPersonalizationClient-side
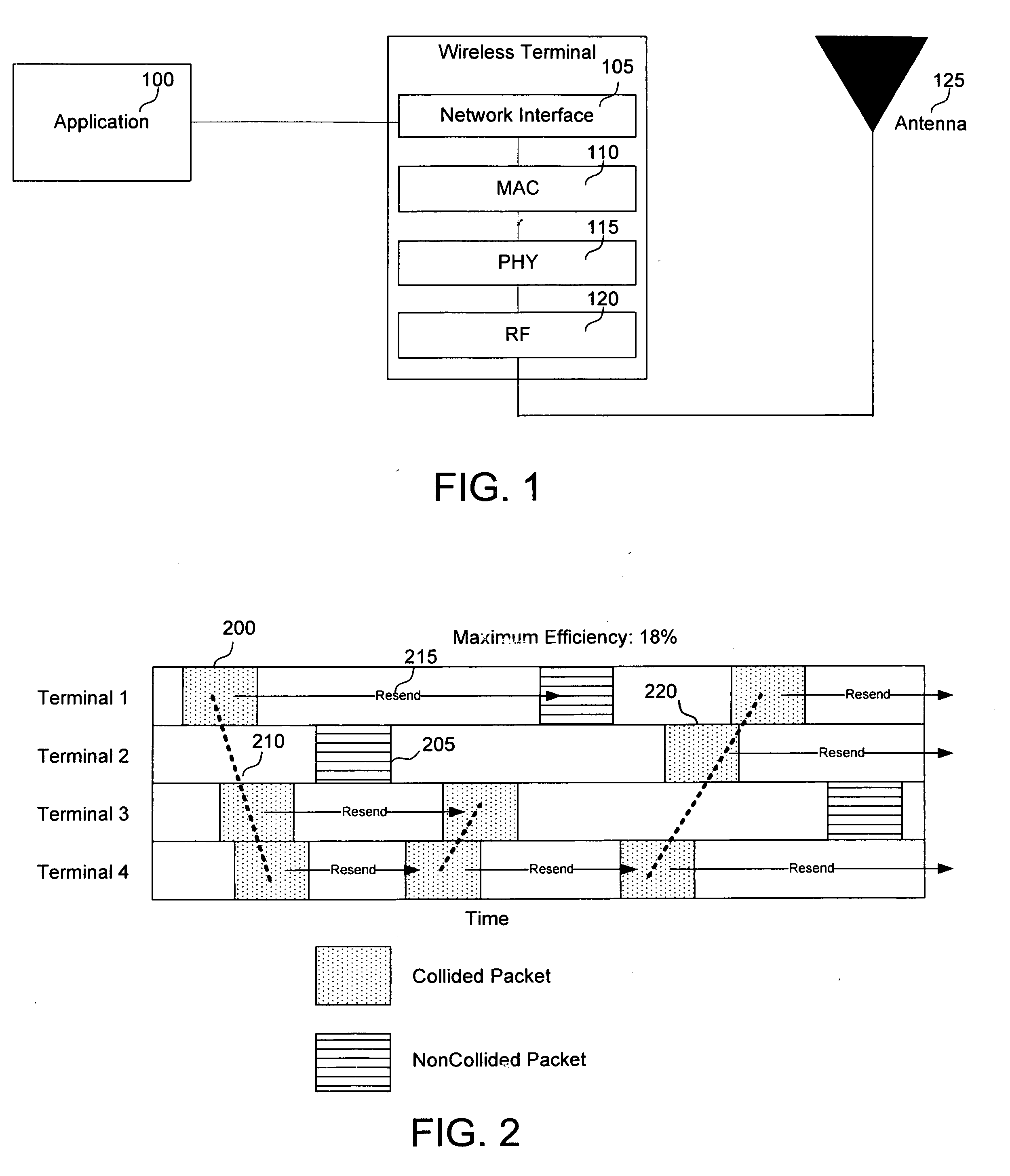
The invention is a media access system. A multipoint installation may create a connection system which permits client devices, such as wireless media playback devices, to connect to host devices in a partnered relationship which permits authorized access to selected media located on the host device, without a need to physically synchronize the partnered client devices. Playback of media content may be configured on a variety of devices where new media content may be offered for purchase. Furthermore, the system permits authorized storage of additional selected media on the host devices. A personalized music radio for receiving personalized music services is also described. Media accessed may be tracked and stored along with user preferences in a personalization engine.
Owner:TANG VICTOR
Wireless Media Transmission Systems and Methods
InactiveUS20080201751A1Remove temporal redundancyFacilitate transmissionTwo-way working systemsTransmissionTransceiverNetwork connection
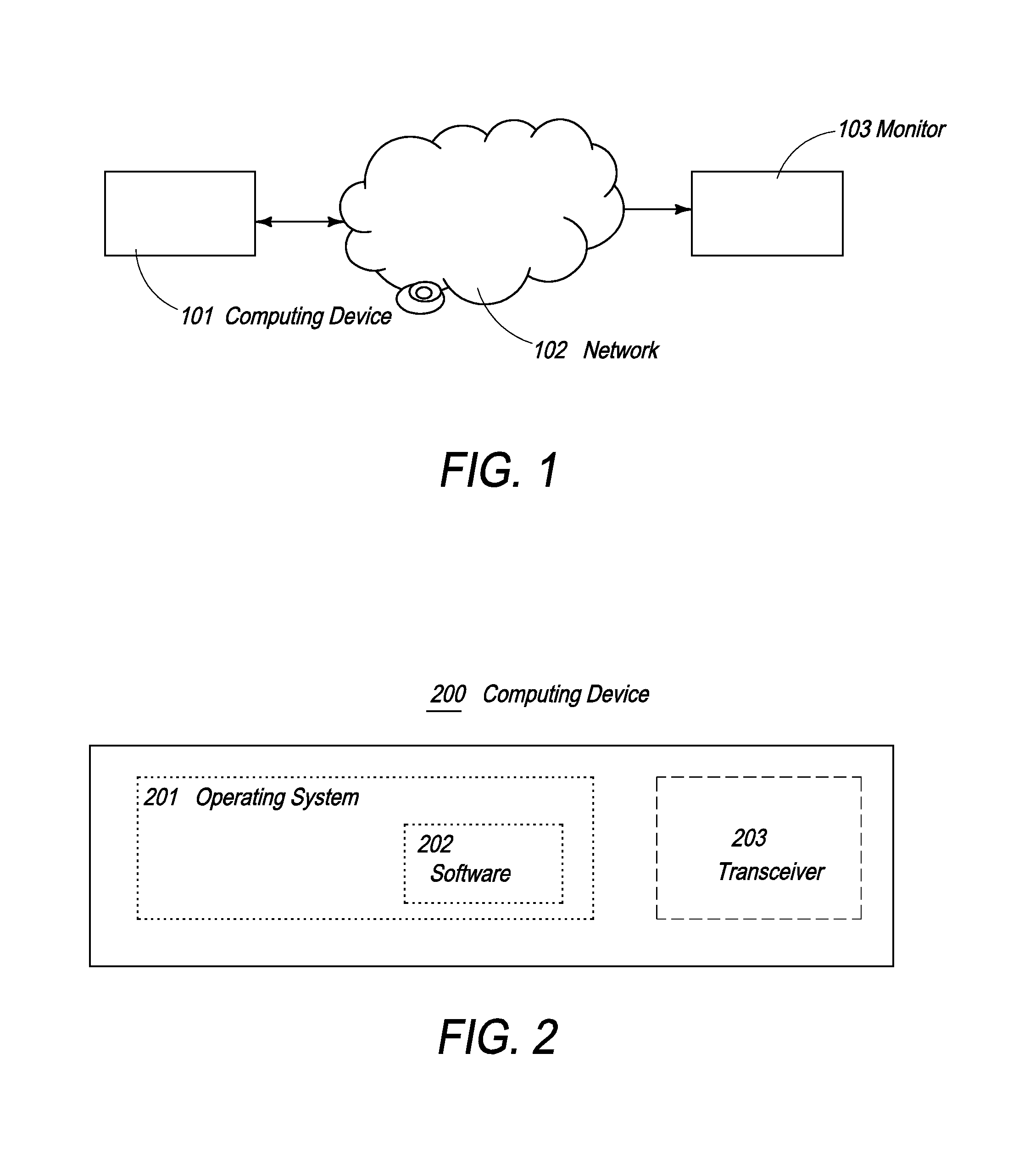
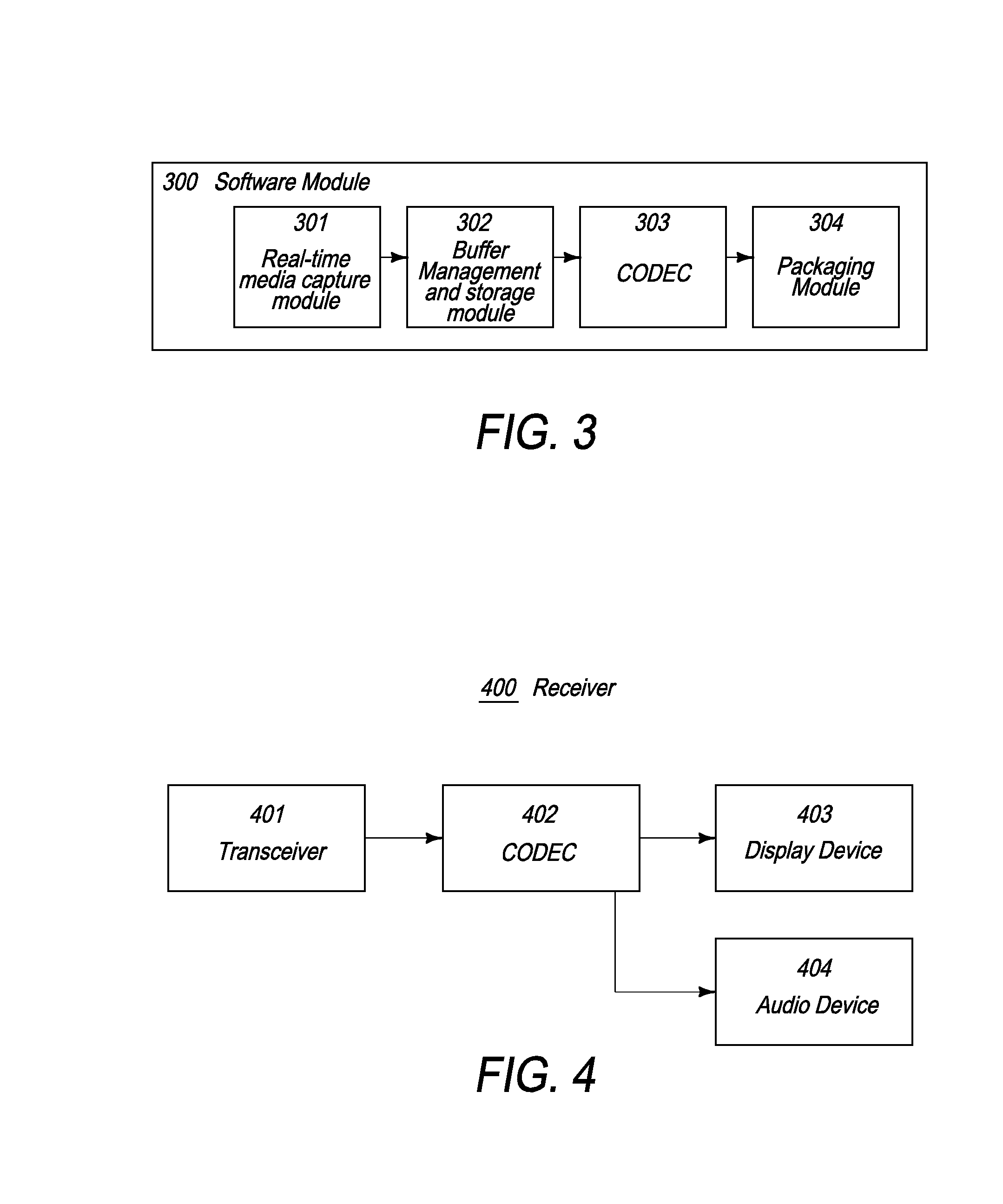
The present invention relates to a media transmission and reception system that is implemented, in the form of programs stored in a satellite device having a memory, an input mechanism for receiving commands from a user, and a transceiver capable of wirelessly accessing a network, and in a computing device having a memory and a transceiver capable of accessing a network. The program stored in the memory of the satellite device causes user commands to be processed, causes the satellite device to connect to the computing device through the network, and causes the satellite device to transmit command instructions, derived from the commands, to the computing device through the network. The program stored in the memory of the computing device causes the computing device to access media stored in a memory, causes the computing device to process the media, captures the processed media, compresses the media, and causes the computing device to transmit the compressed media to the satellite device. The media access, media processing, media compression, and media transmission occurs in real-time and in response to the command instructions.
Owner:QUARTICS
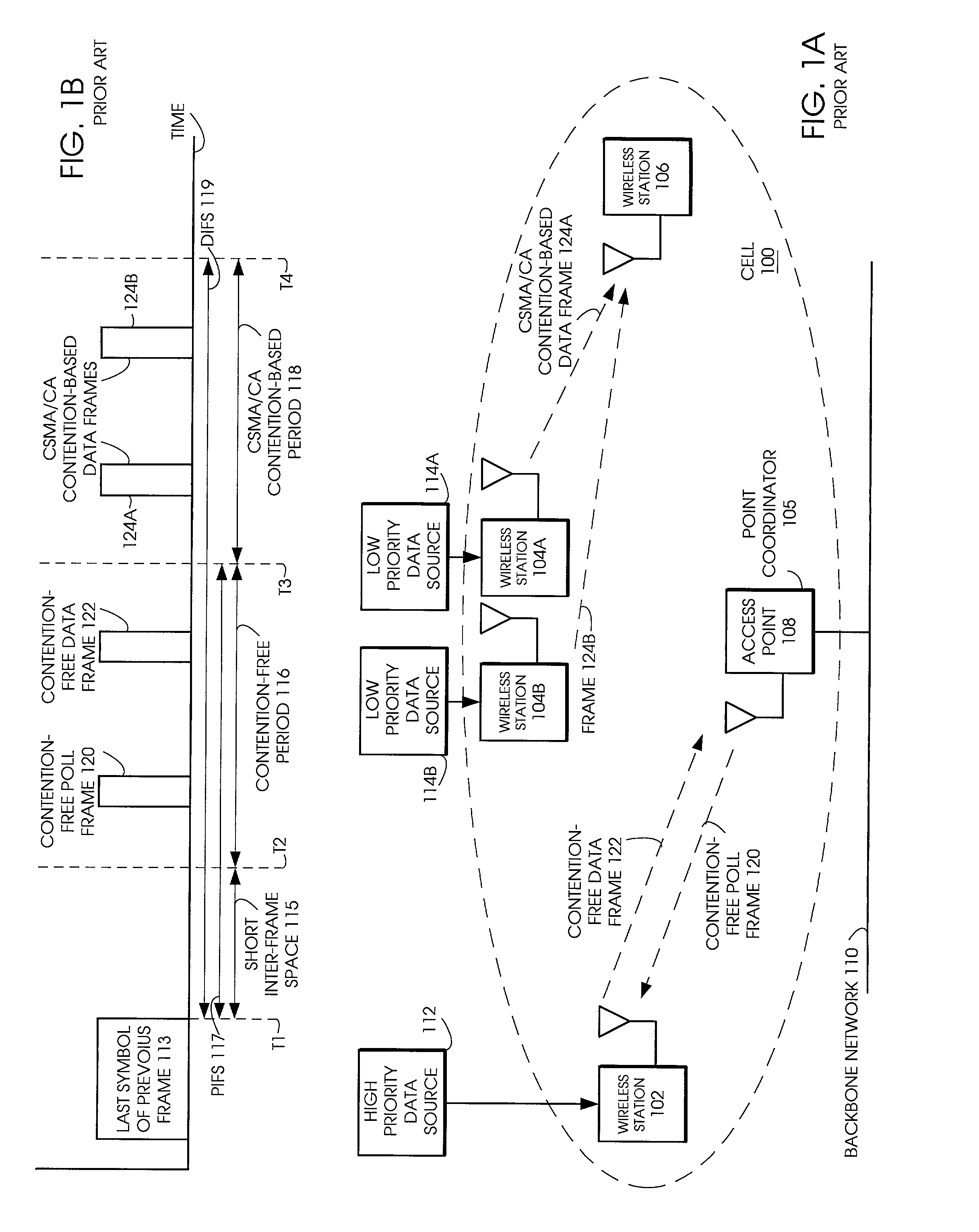
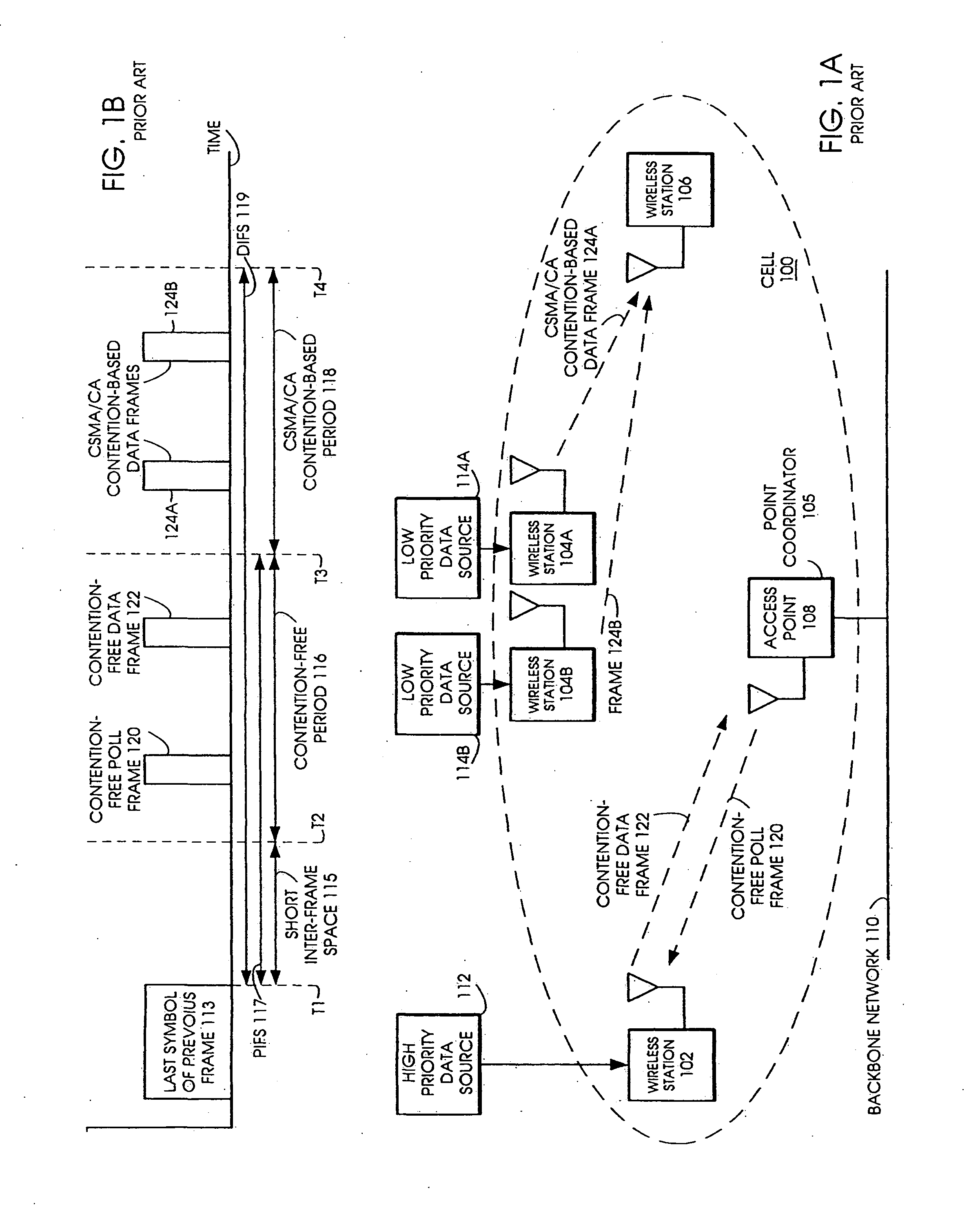
Tiered contention multiple access (TCMA): a method for priority-based shared channel access
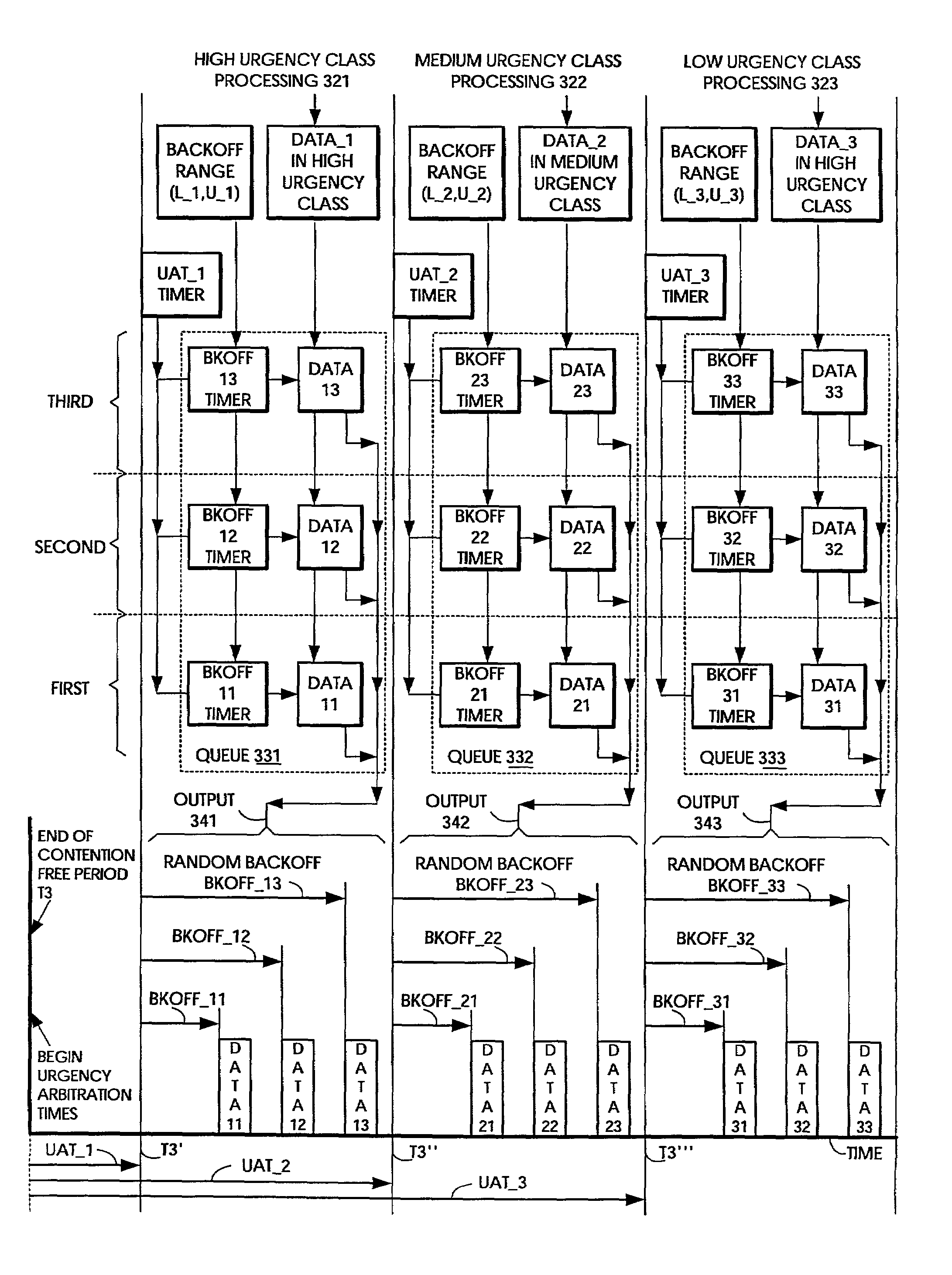
ActiveUS7095754B2Minimizing chanceLower latencySynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementService-level agreementIdle time
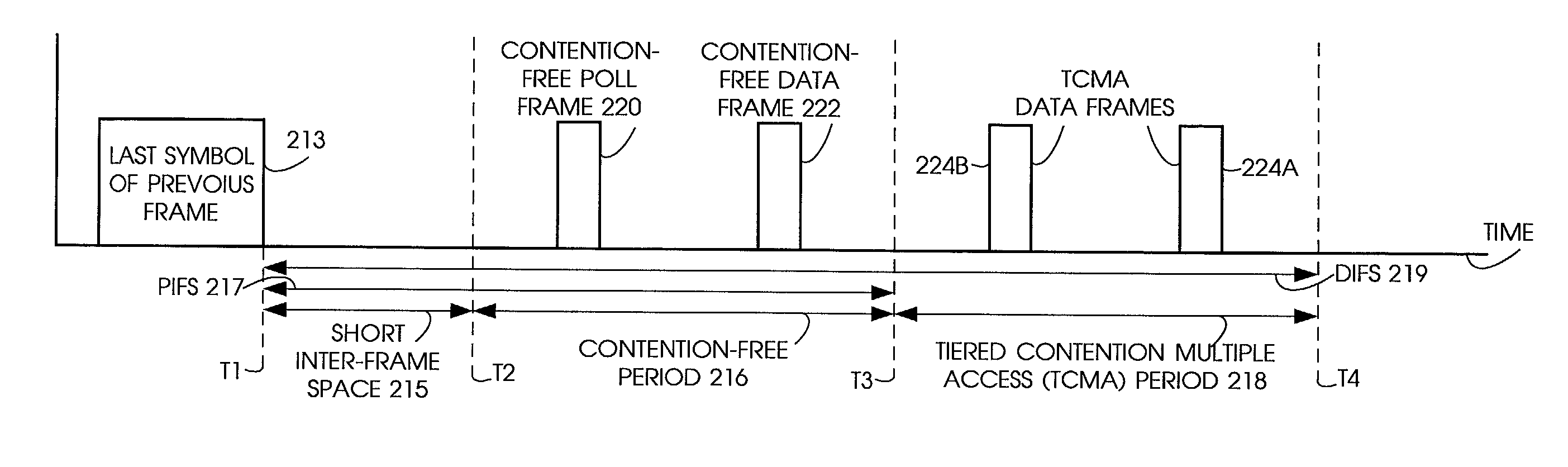
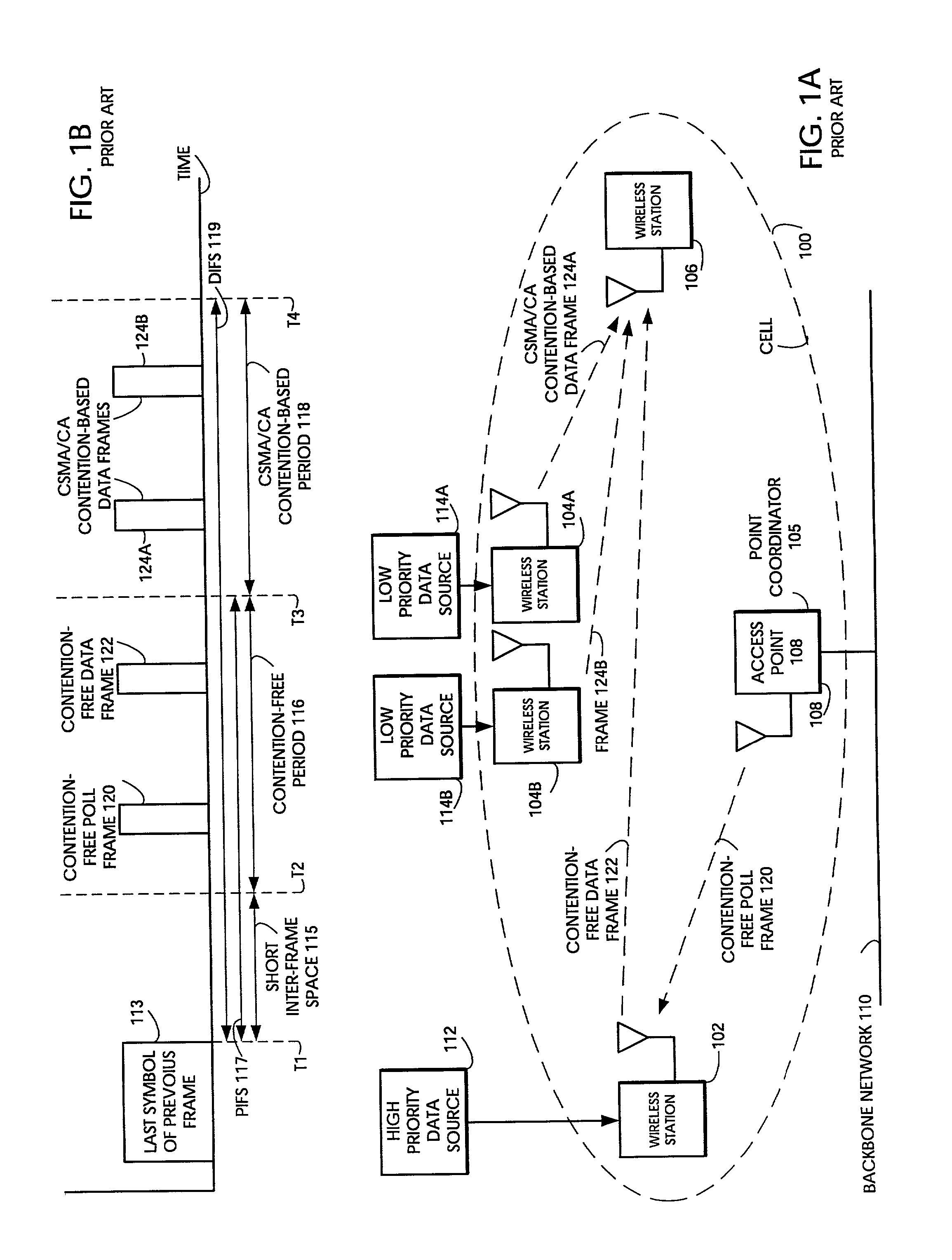
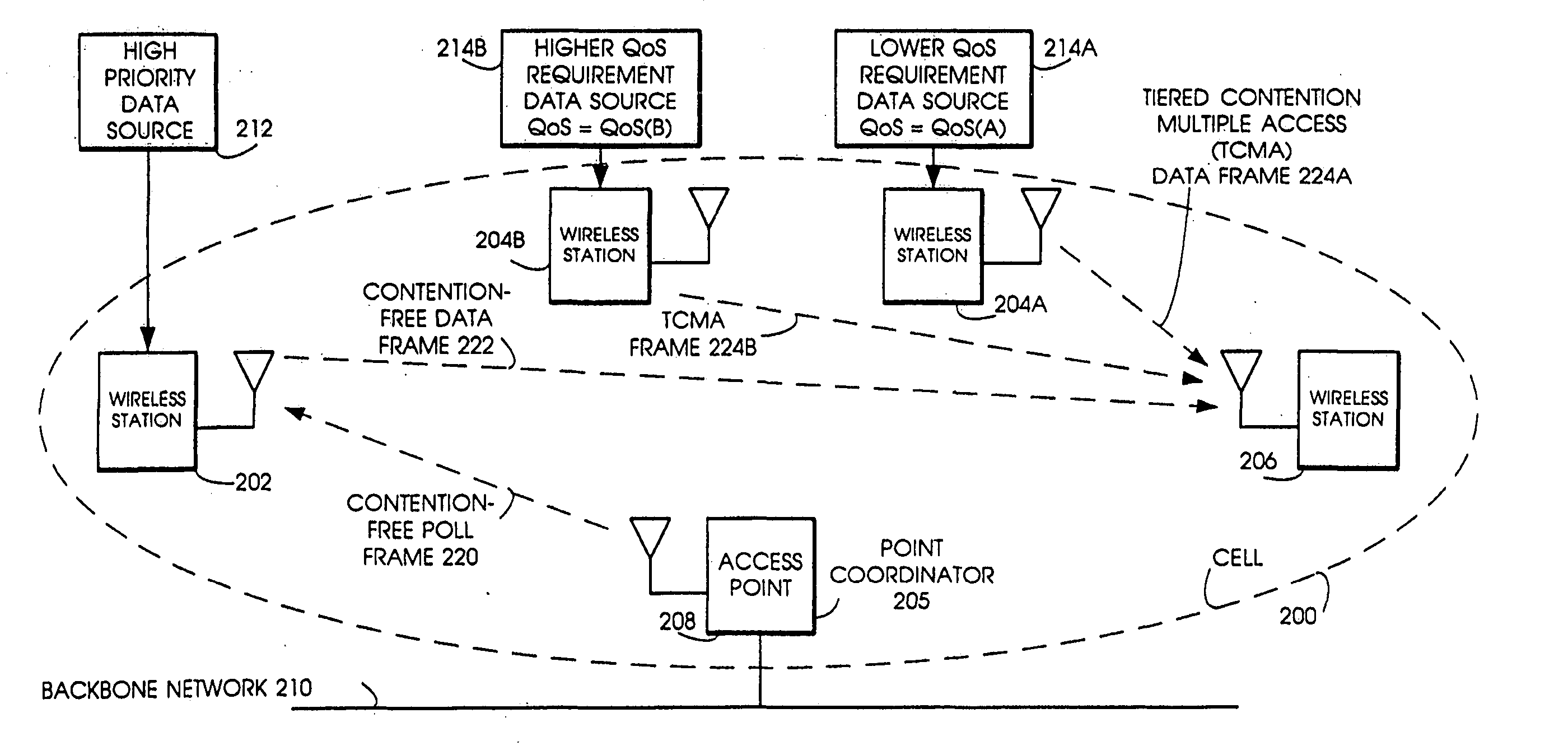
Quality of Service (QoS) support is provided by means of a Tiered Contention Multiple Access (TCMA) distributed medium access protocol that schedules transmission of different types of traffic based on their service quality specifications. In one embodiment, a wireless station is supplied with data from a source having a lower QoS priority QoS(A), such as file transfer data. Another wireless station is supplied with data from a source having a higher QoS priority QoS(B), such as voice and video data. Each wireless station can determine the urgency class of its pending packets according to a scheduling algorithm. For example file transfer data is assigned lower urgency class and voice and video data is assigned higher urgency class. There are several urgency classes which indicate the desired ordering. Pending packets in a given urgency class are transmitted before transmitting packets of a lower urgency class by relying on class-differentiated urgency arbitration times (UATs), which are the idle time intervals required before the random backoff counter is decreased. In another embodiment packets are reclassified in real time with a scheduling algorithm that adjusts the class assigned to packets based on observed performance parameters and according to negotiated QoS-based requirements. Further, for packets assigned the same arbitration time, additional differentiation into more urgency classes is achieved in terms of the contention resolution mechanism employed, thus yielding hybrid packet prioritization methods. An Enhanced DCF Parameter Set is contained in a control packet sent by the AP to the associated stations, which contains class differentiated parameter values necessary to support the TCMA. These parameters can be changed based on different algorithms to support call admission and flow control functions and to meet the requirements of service level agreements.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
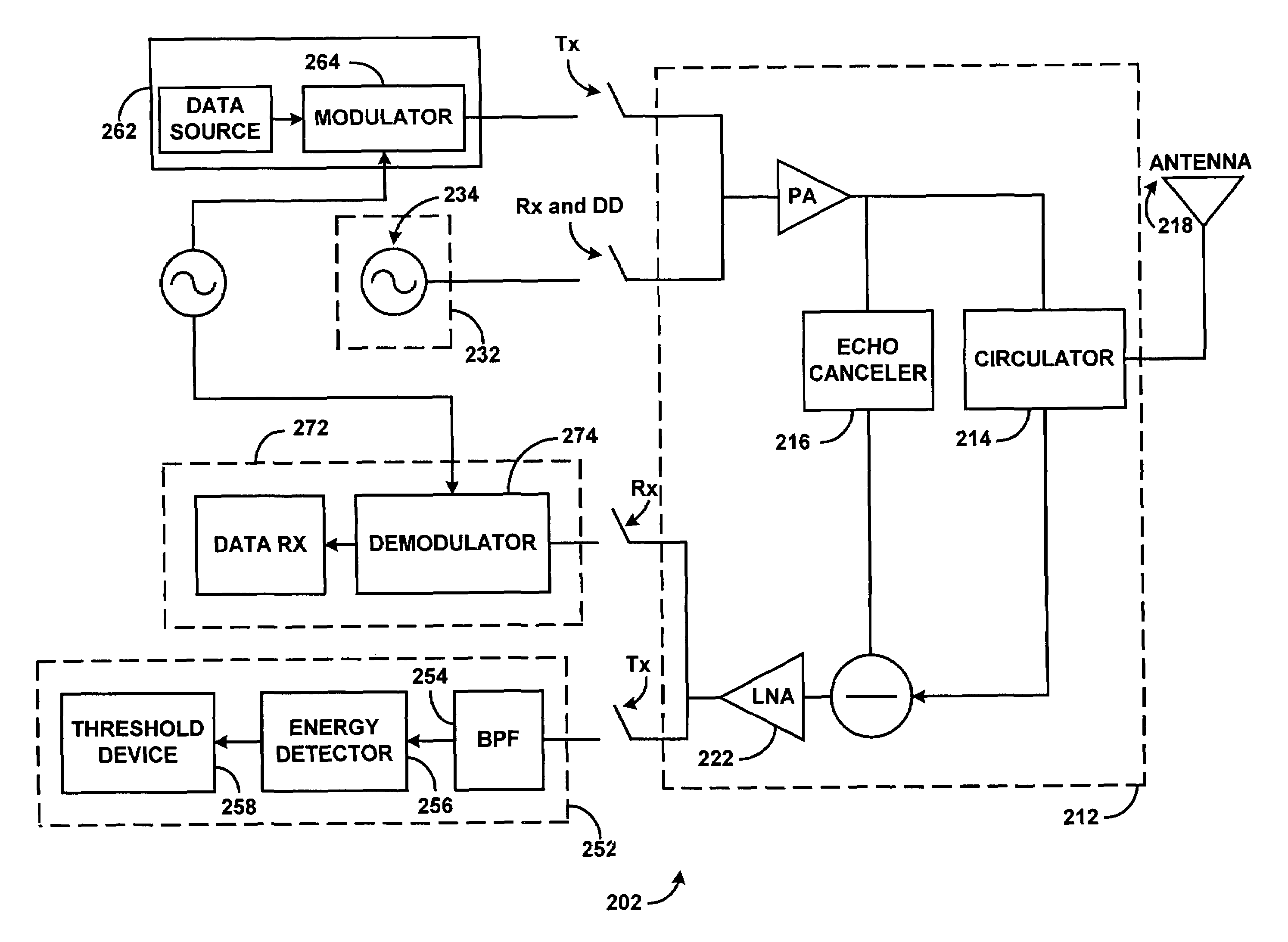
System and method for providing high speed wireless media access
InactiveUS7061877B1Improve efficiencyIncrease data rateNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmission control/equalisingWireless transceiverTransceiver
A system and method for providing high speed wireless media access is disclosed. A local transceiver is provided, which is capable of transmitting data via a transmit path while receiving a feedback signal via a receive path. The local transmitter is connected to a feedback generator for generating and transmitting a feedback signal in response to receiving data from a wireless transceiver. A feedback detector is also connected to the local transceiver for detecting feedback signals received from other wireless transceivers. When a feedback signal is detected, data associated with the signal is decoded. The wireless transceivers then transmit a feedback signal within the series of wireless transceivers in order to stop the transmission of data until a destination of the data is determined. A destination address associated with a destination wireless transceiver is then identified and the transmission of feedback signals by all wireless transceivers within the system then ceases, except from the identified destination wireless transceiver.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Fiber to the home (FTTH) multimedia access system with reflection PON
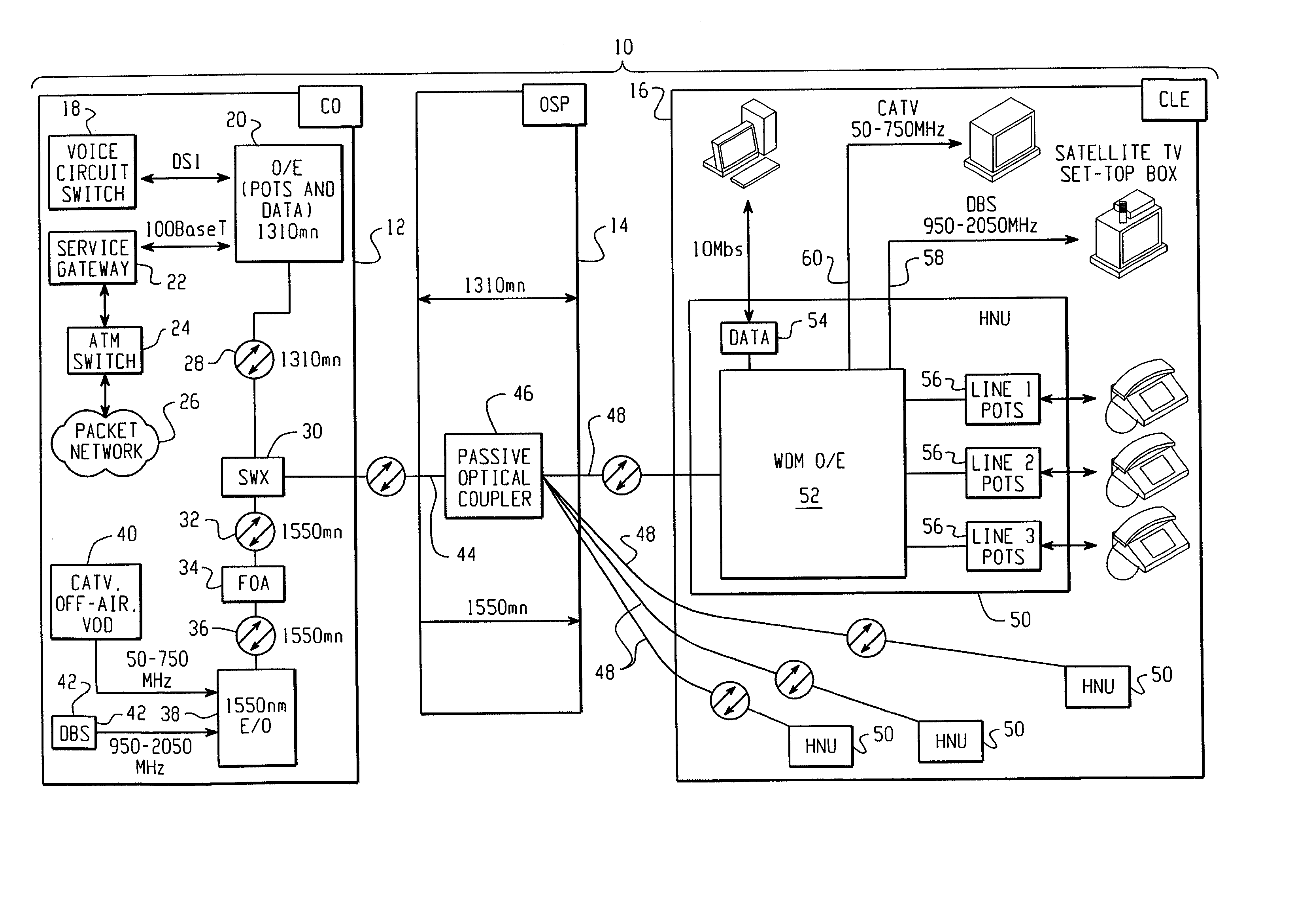
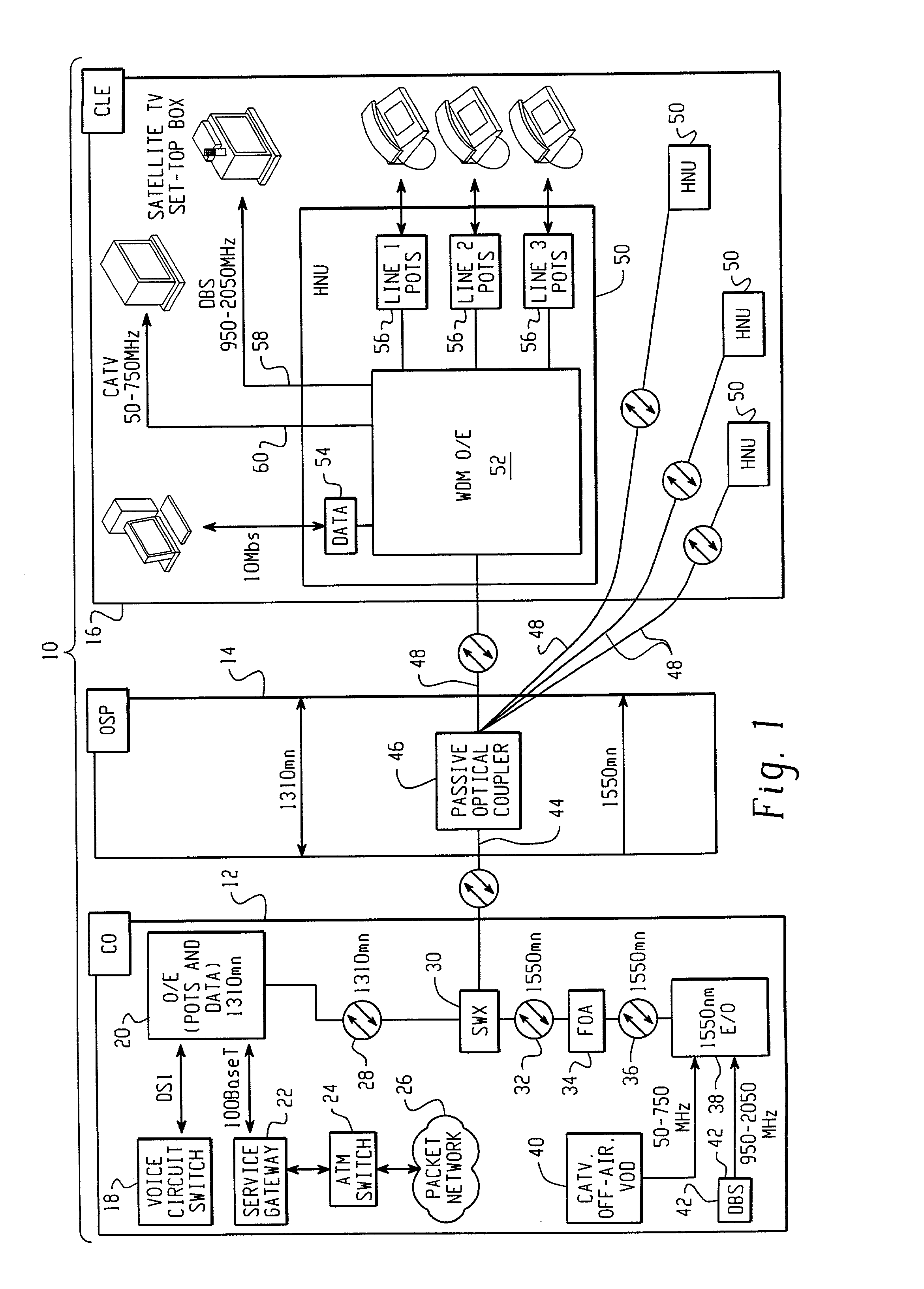
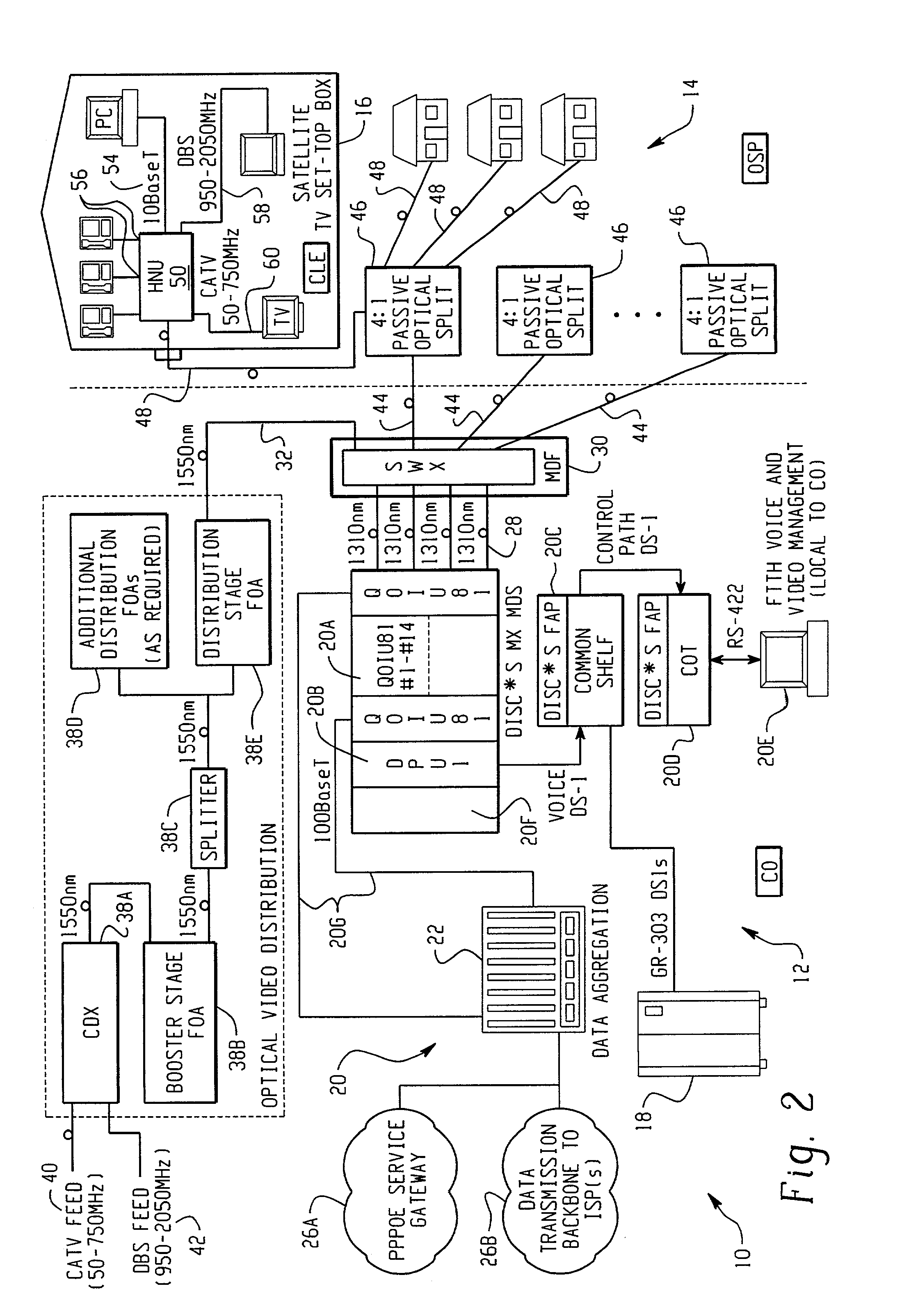
InactiveUS20020063924A1Inexpensive, easy-to-serviceEasy to scaleBroadband local area networksWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexingData signal
A Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) multi-media access system and method are provided in which voice, video and data signals are transported over a passive optical network (PON) between a central office location and a plurality of subscriber home network units (HNUs). Optical video distribution circuitry and telephony / data distribution circuitry at the central office location are included in the system and operate to send and receive CATV video, PBS video television, telephony and Packet data signals to and from the HNUs via the PON. Optical multiplexing / demultiplexing circuitry operating at the central office combines the video signals, which are operating at one optical wavelength, with the telephony / data signals, which are operating at a second, distinct optical wavelength. These combined optical signals are then transported over the PON to the HNUs. The PON includes a plurality of distribution fibers coupled to a plurality of passive optical splitters, which are each coupled to a plurality of drop fibers that connect to the HNUs. The HNUs receive the combined optical signals, demultiplex and convert the optical signals into corresponding electrical signals, which are in turn coupled through the HNU to the video, data and telephony networks within the home. The HNUs also receive upstream electrical signals from devices within the home, multiplex and convert these electrical signals into upstream optical signals, and transmit these upstream optical signals to the central office.
Owner:ADVANCED FIBER ACCESS CORP
Method and system for controlling medium access in a wireless network
InactiveUS20060164969A1Simple designEasy to manufactureEnergy efficient ICTSpatial transmit diversityFrequency spectrumSpectral efficiency
A method and system are disclosed that can be applied to achieve high-throughput in a WLAN. Central to the present invention is the use of an SDMA compatible multi-beam antenna system by a WLAN access point. A system based on two types of antennas-dynamic beam forming and fixed beam antennas—is described. A mechanism and protocol are described that implement simultaneous transmissions with respect to an SDMA compatible access point and thereby improve spectral efficiency, and by extension achieve higher throughput. Based on the recognition that current WLAN MAC has major limitations in throughput, certain MAC extensions (that can be applied independently of SDMA) are described. Also disclosed are power-saving and power control techniques that improve battery performance and contribute to a reduction in station size, and a means of reducing channel interference. The present invention also deals with the problem of backward compatibility with conventional devices that implement the protocol that is a subset covered by the present invention.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
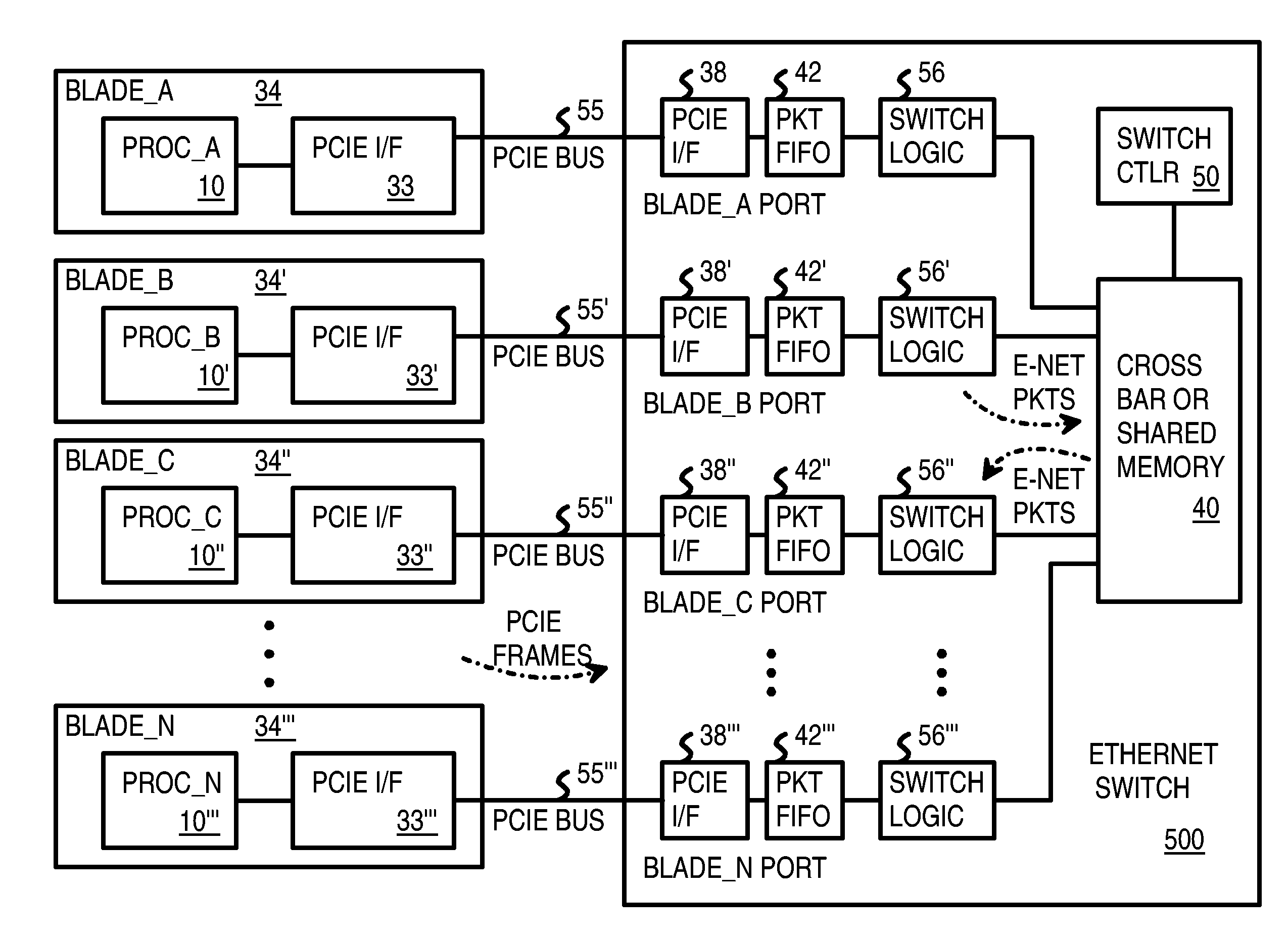
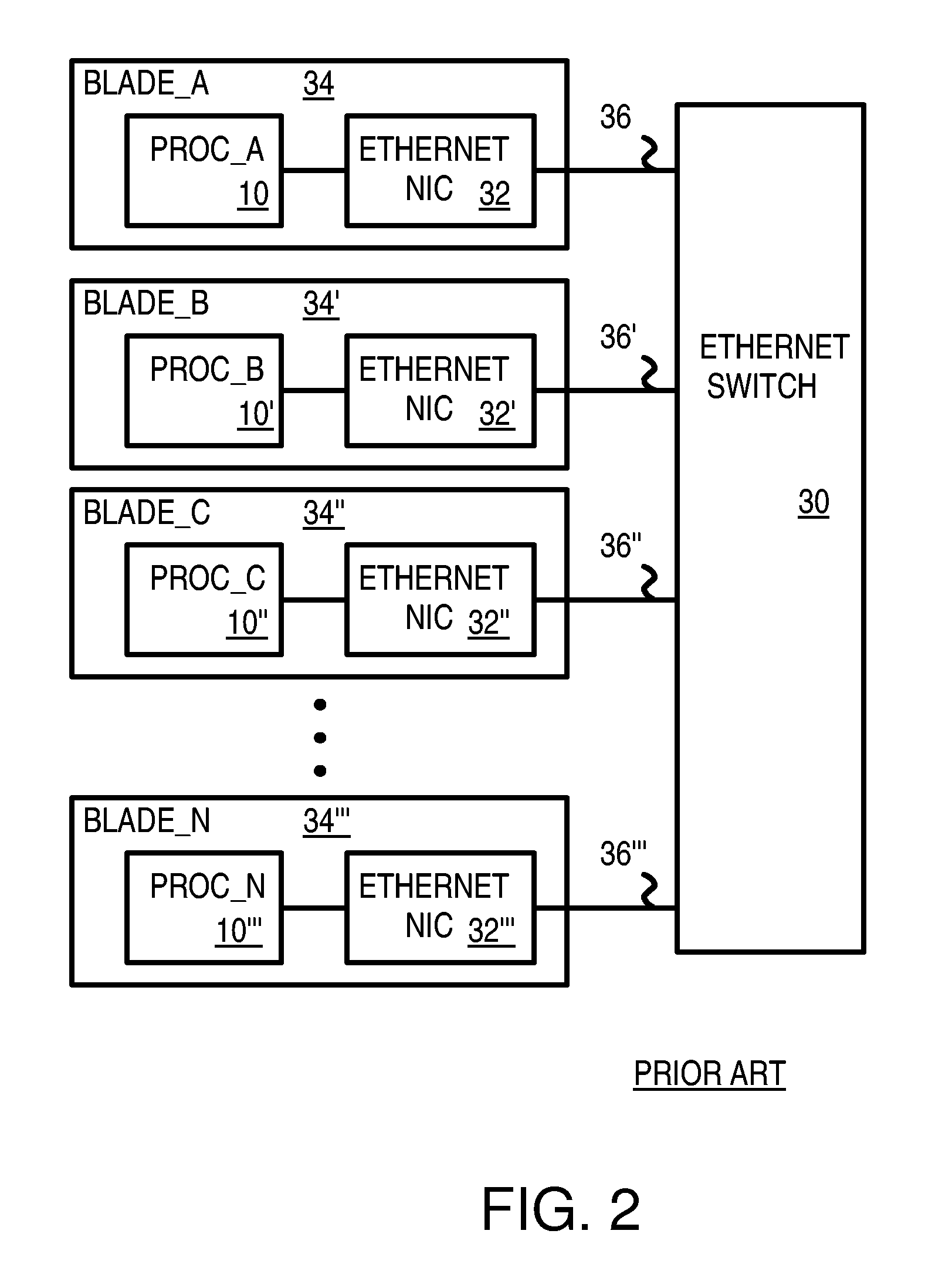
Pseudo-ethernet switch without ethernet media-access-controllers (MAC's) that copies ethernet context registers between PCI-express ports
A Pseudo-Ethernet switch has a routing table that uses Ethernet media-access controller (MAC) addresses to route Ethernet packets through a switch fabric between an input port and an output port. However, the input port and output port have Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIE) interfaces that read and write PCI-Express packets to and from host-processor memories. When used in a blade system, host processor boards have PCIE physical links that connect to the PCIE ports on the Pseudo-Ethernet switch. The Pseudo-Ethernet switch does not have Ethernet MAC and Ethernet physical layers, saving considerable hardware. The switch fabric can be a cross-bar switch or can be a shared memory that stores Ethernet packet data embedded in the PCIE packets. Write and read pointers for a buffer storing an Ethernet packet in the shared memory can be passed from input to output port to perform packet switching.
Owner:DIODES INC
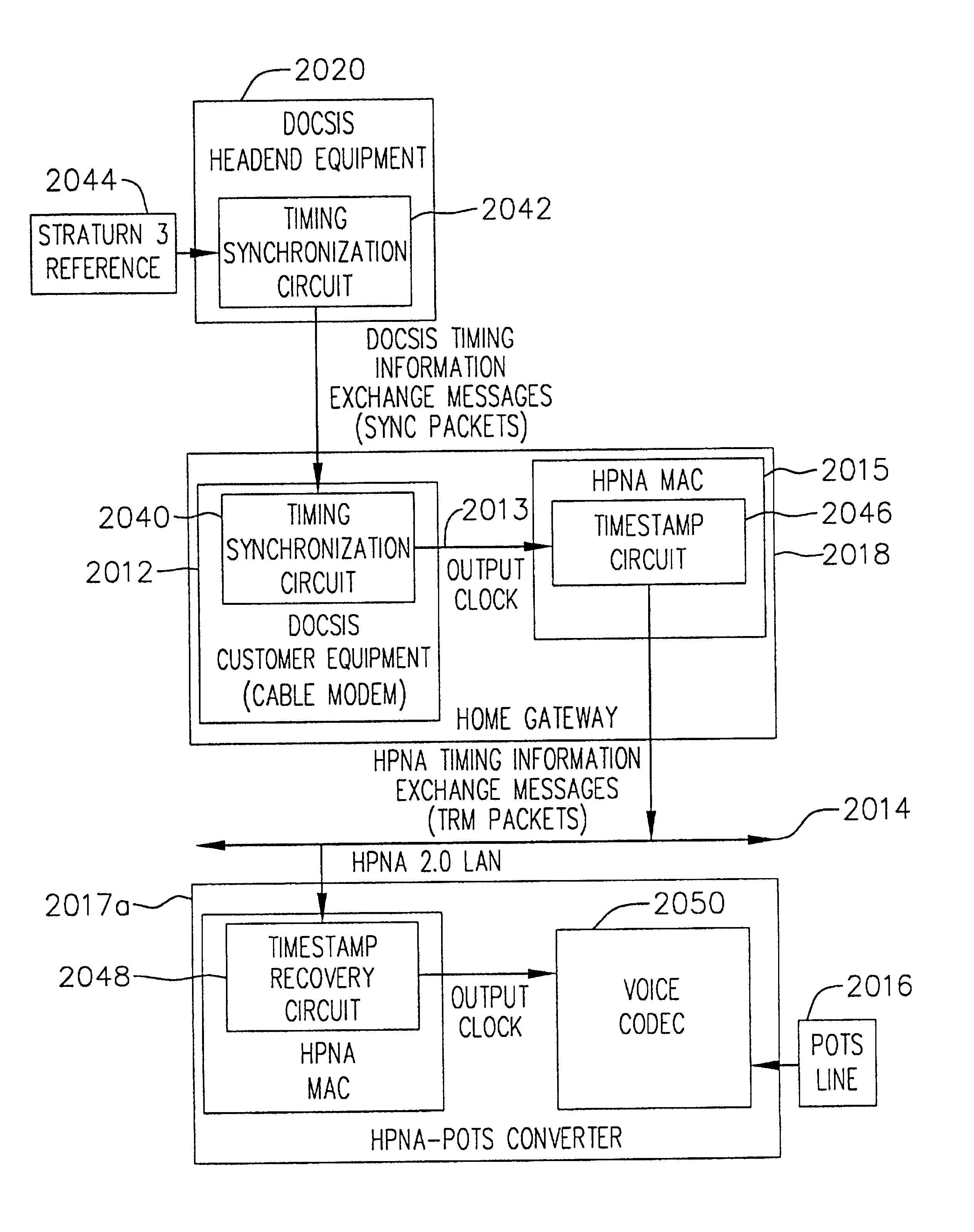
Method of controlling data sampling clocking of asynchronous network nodes in a frame-based communications network
InactiveUS6975655B2Energy efficient ICTError prevention/detection by using return channelTimestampFrame based
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Radio communication system using point-to-point and point-to-multipoint user information communications
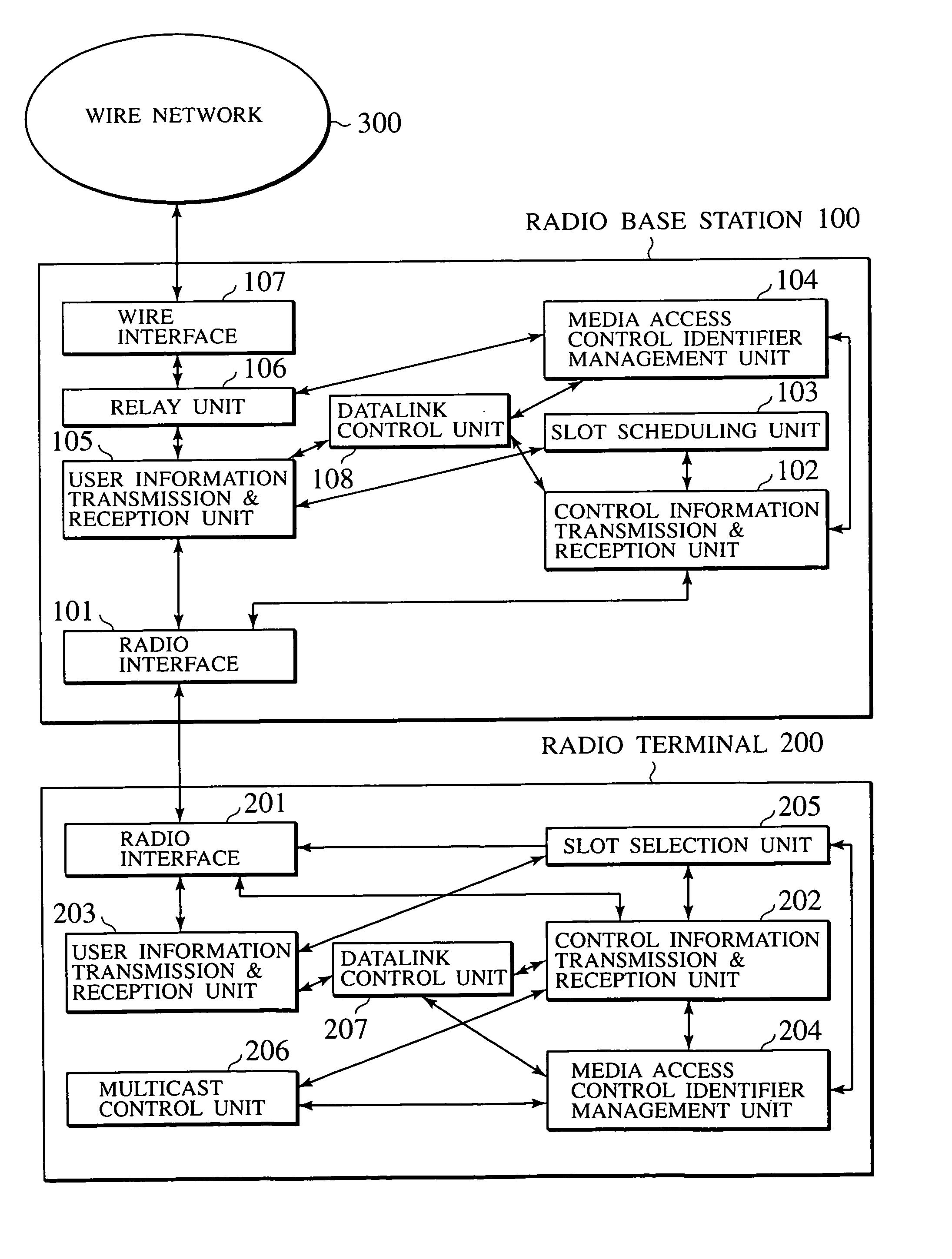
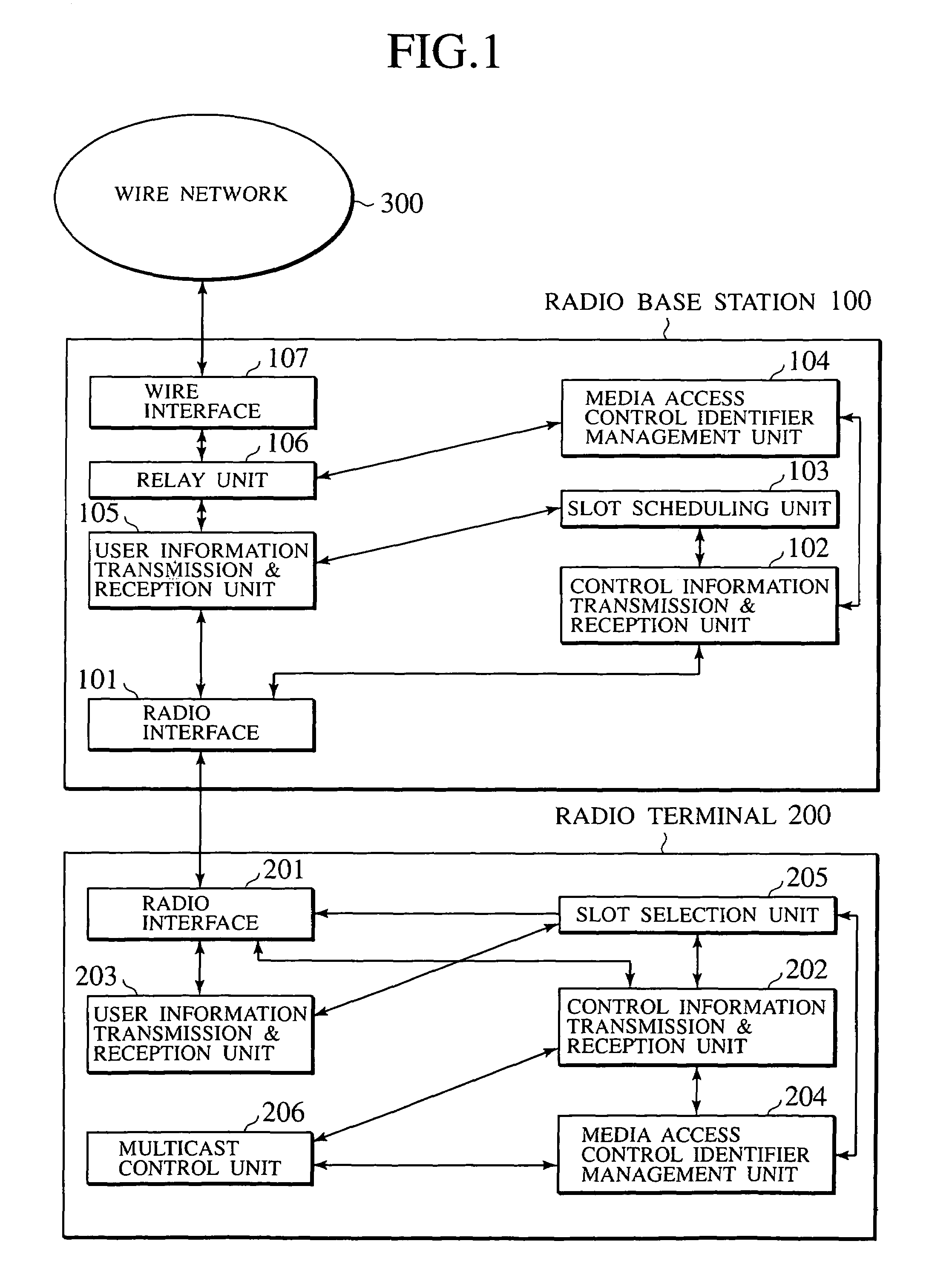
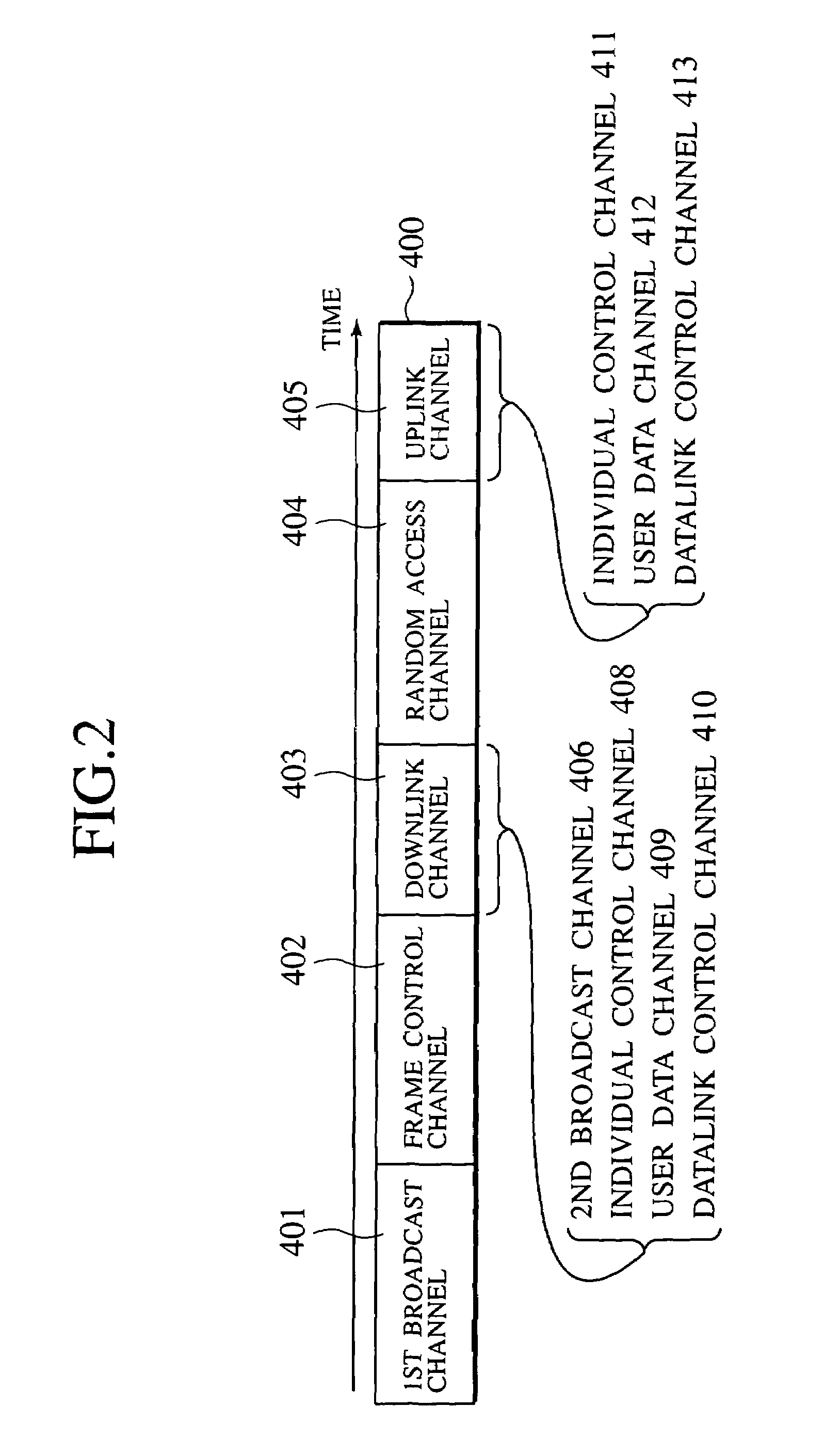
InactiveUS6965580B1Broadcast transmission systemsTime-division multiplexCommunications systemMedia access control
An information communication scheme for enabling the radio base station to carry out both point-to-point user information communications and point-to-multipoint user information communications with respect to radio terminals is disclosed. A first media access control identifier is allocated to a radio terminal which made a connection request, a correspondence between the first media access identifier and the radio terminal is broadcast, and a user information destined to the radio terminal is transmitted using a time-slot corresponding to the first media access control identifier. On the other hand, a second media access control identifier is allocated to a multicast information identifier, a correspondence between the second media access control identifier and the multicast information identifier is transmitted, and the multicast information is transmitted using a time-slot corresonding to the second media access control identifier.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
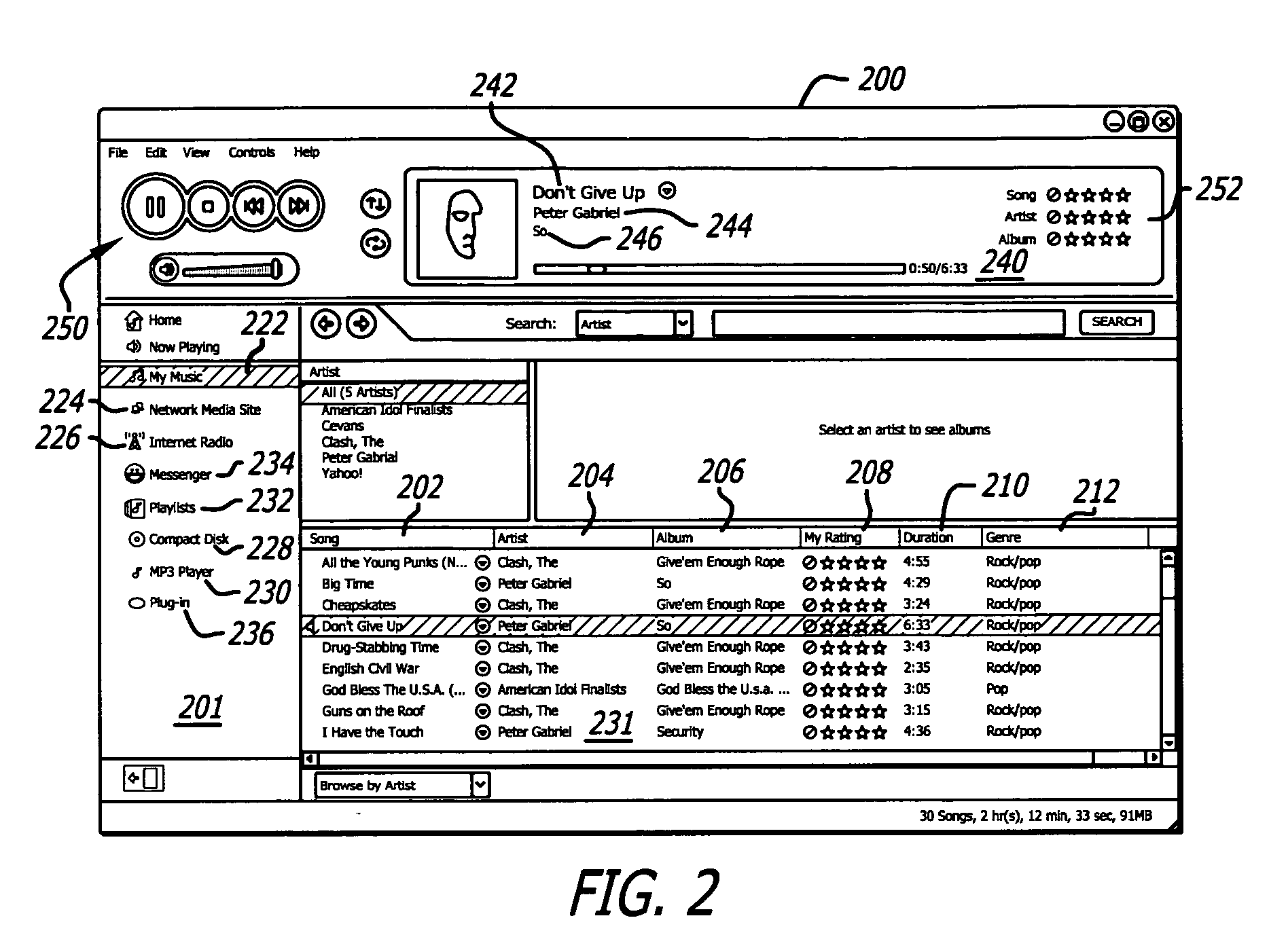
Methods, computer readable mediums and systems for requesting, retrieving and delivering metadata pages
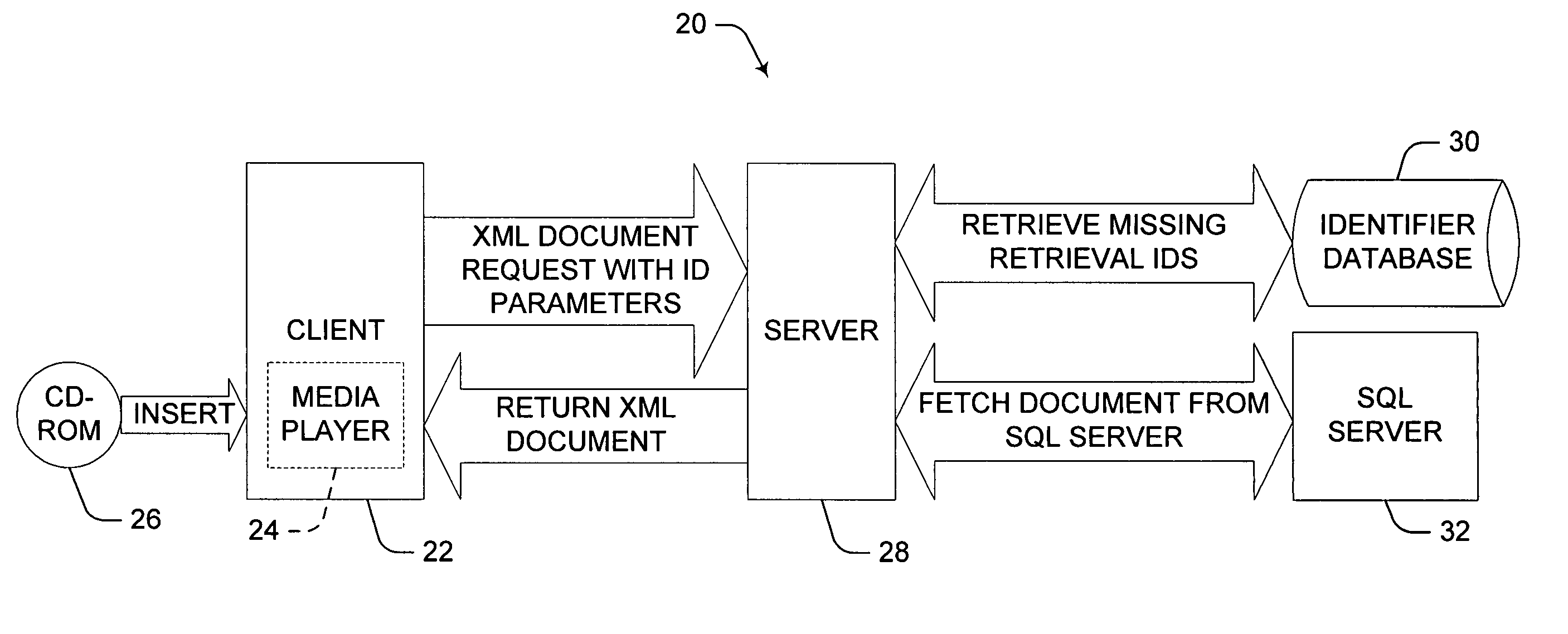
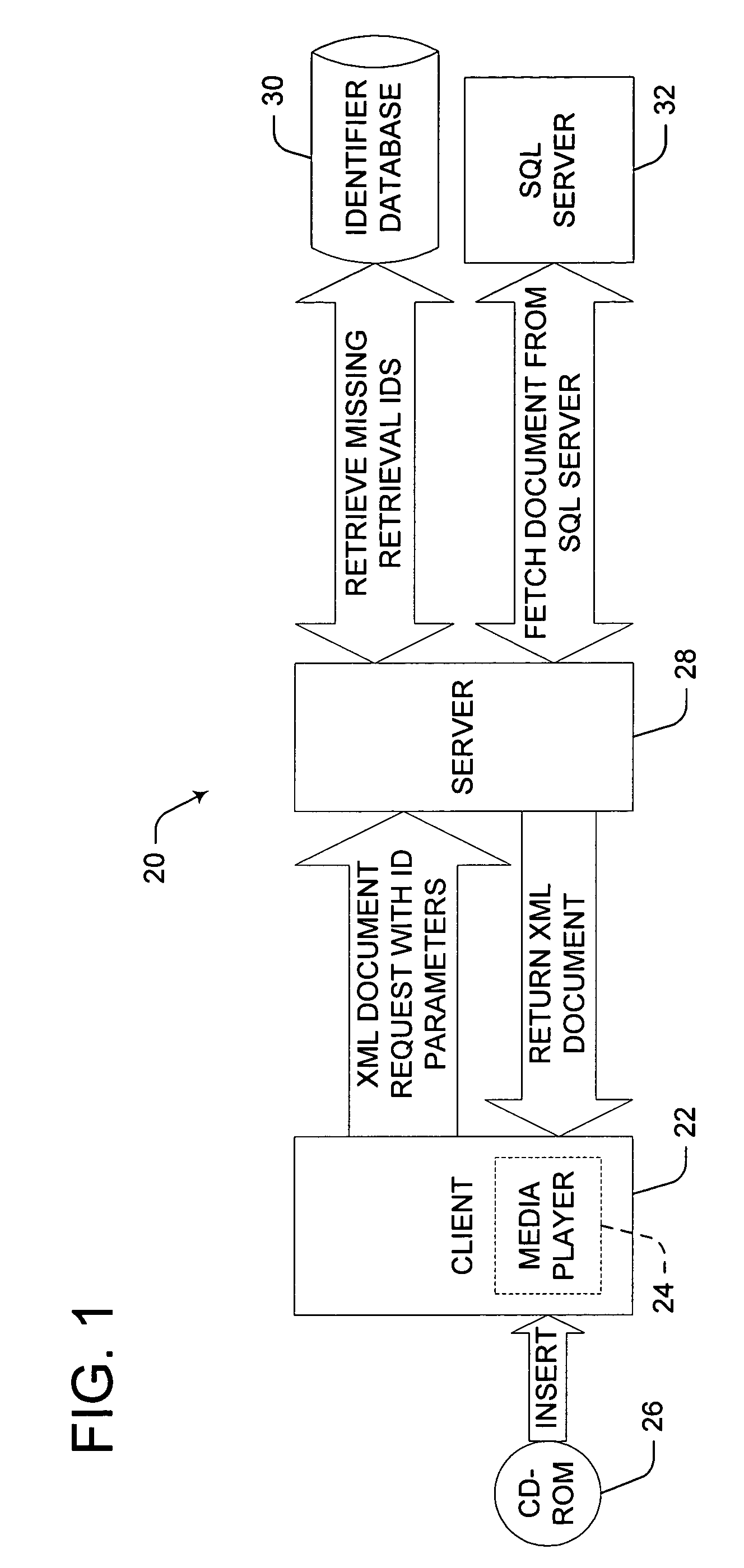
ActiveUS20050015551A1Improve experienceEnhances overall contextual metadata experienceMetadata audio data retrievalData processing applicationsMultiple formsCD-ROM
Methods, computer readable mediums and systems provide media player users with a full contextual metadata experience. Metadata include multiple forms of property data, or information, relating to media accessed by a media player, such as a CD in a CD-ROM drive of a computer. Metadata is transferred from a server to a client. Identification parameters associated with the accessed media file are submitted by the client to a server, and property data is retrieved and forwarded to the client. The metadata provides the user with integrated, contemporaneous property data directly related to the media file being played, providing automatic, integrated access to data from multiple databases, simply by accessing a related media file through a media player, without further direction from the user.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
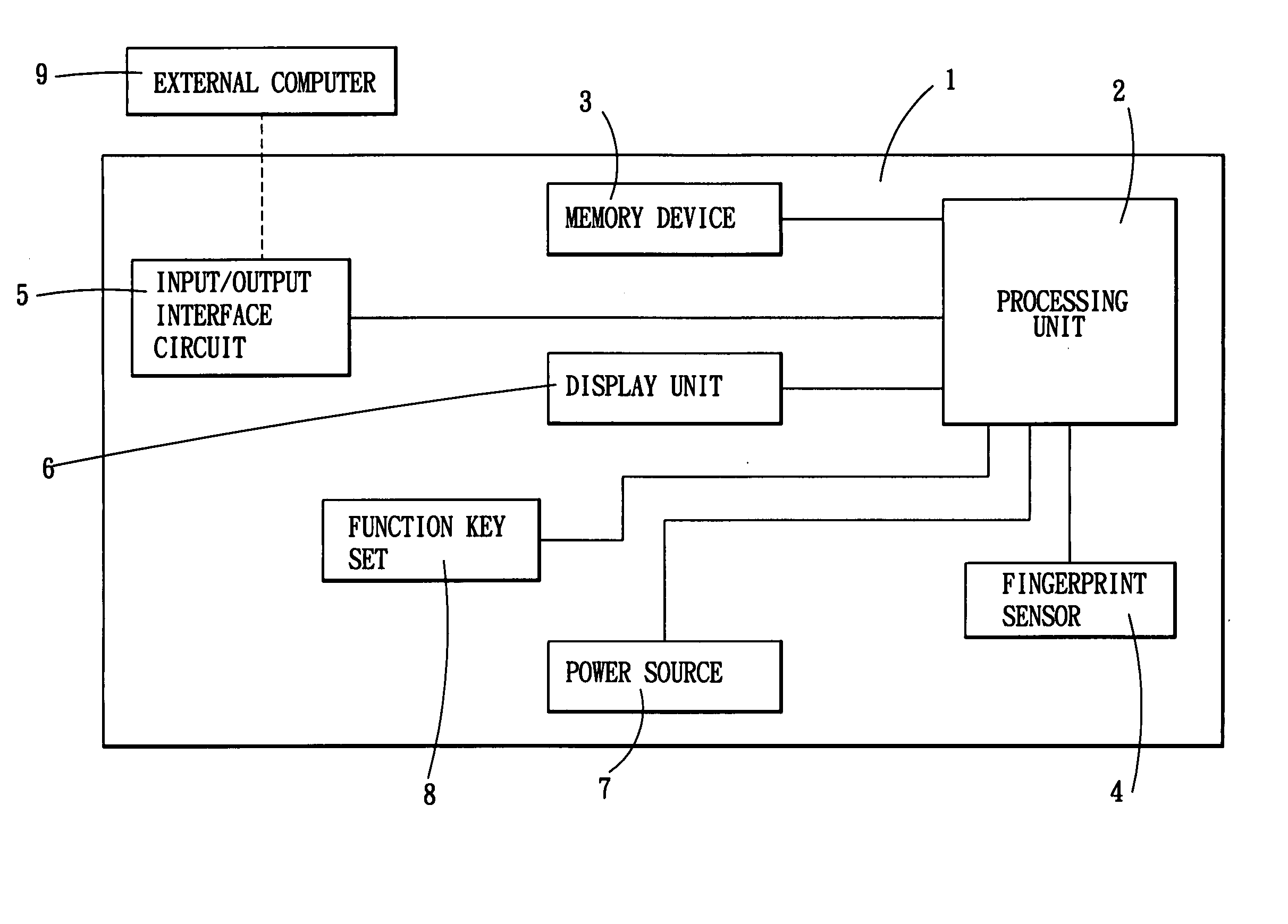
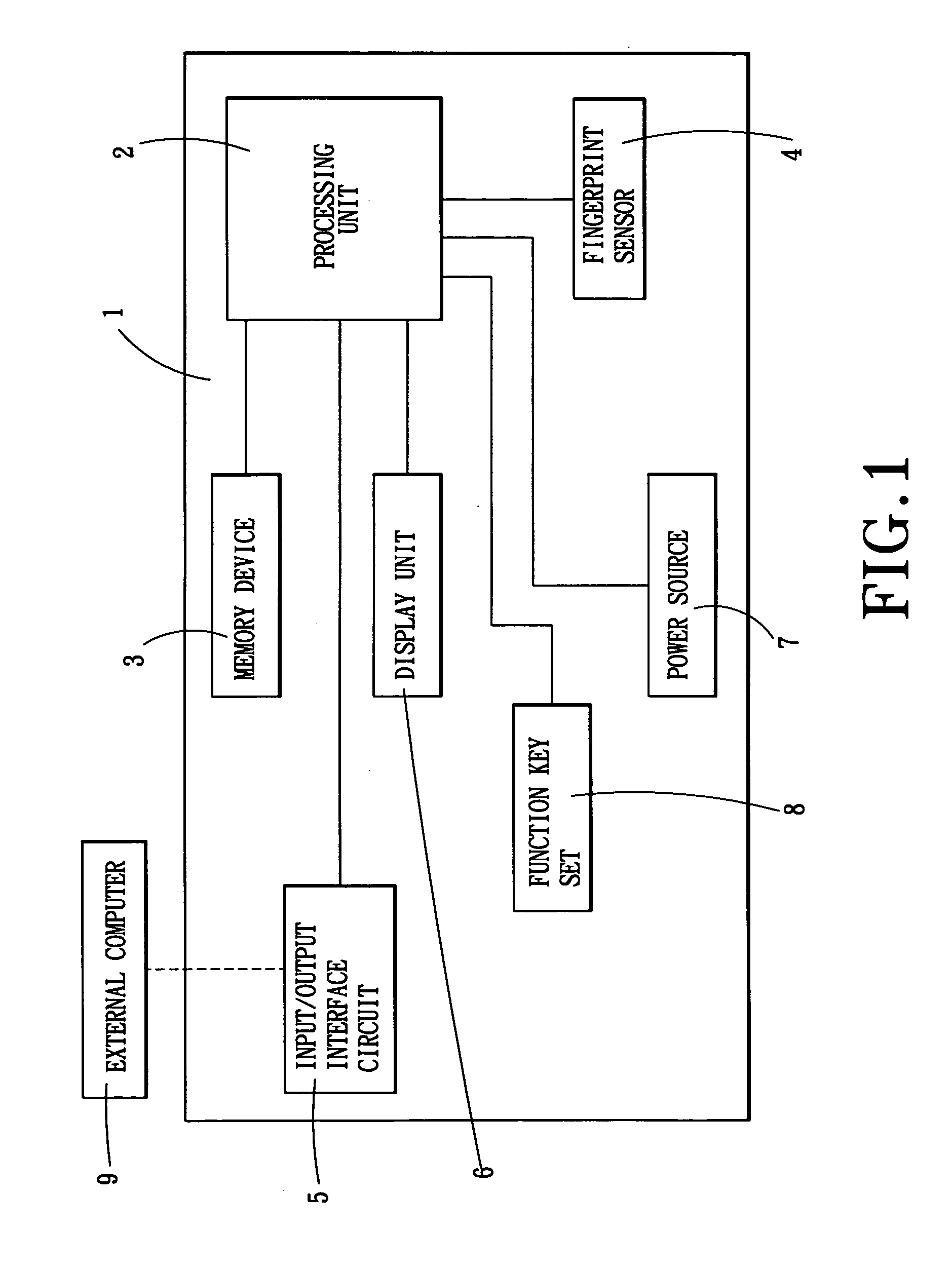
Electronic data storage medium with fingerprint verification capability
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
Synchronized plural channels for time division duplexing
InactiveUS7068639B1Efficient use ofEasy to useTime-division multiplexRadio transmissionTime-division multiplexingMedia access
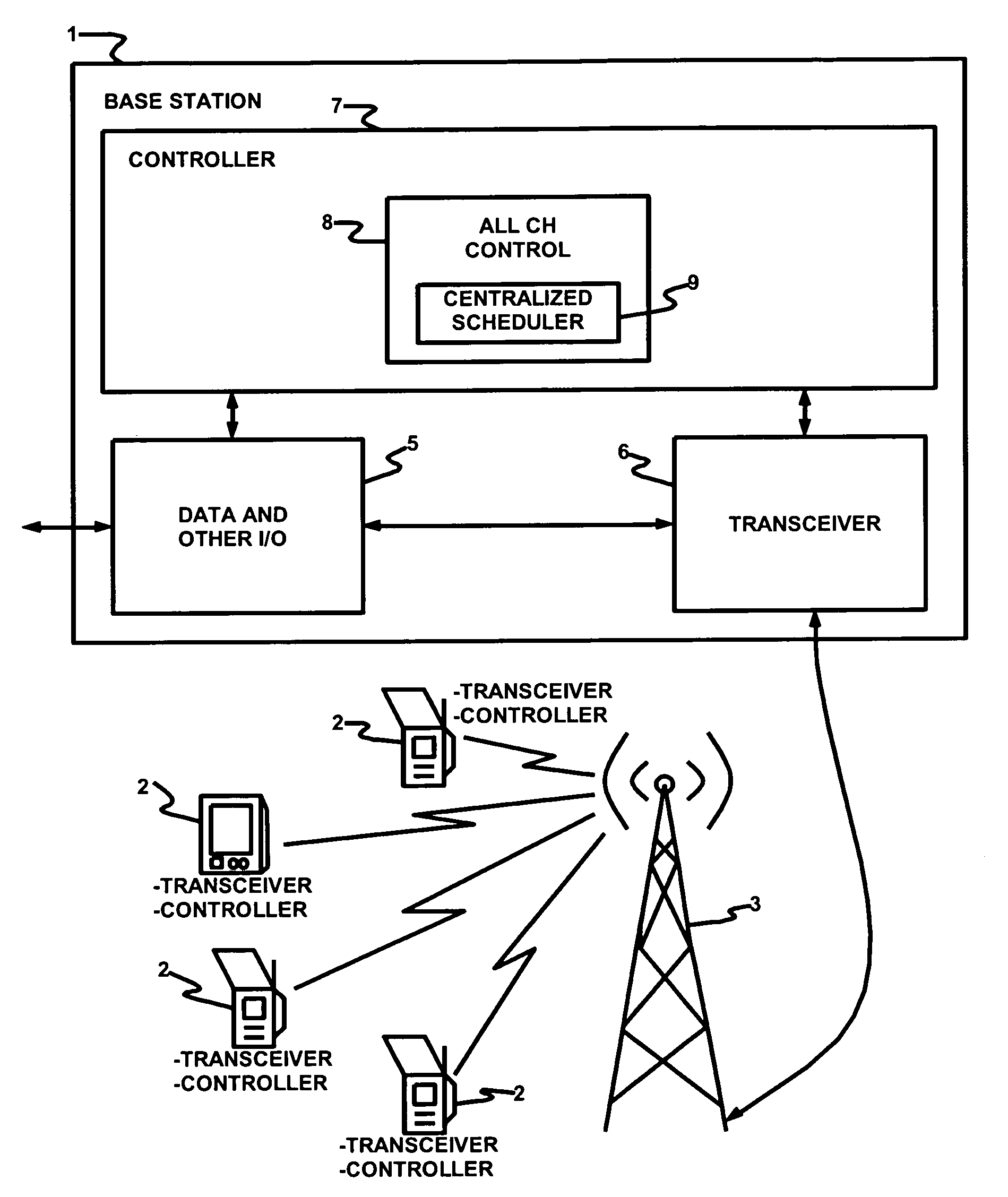
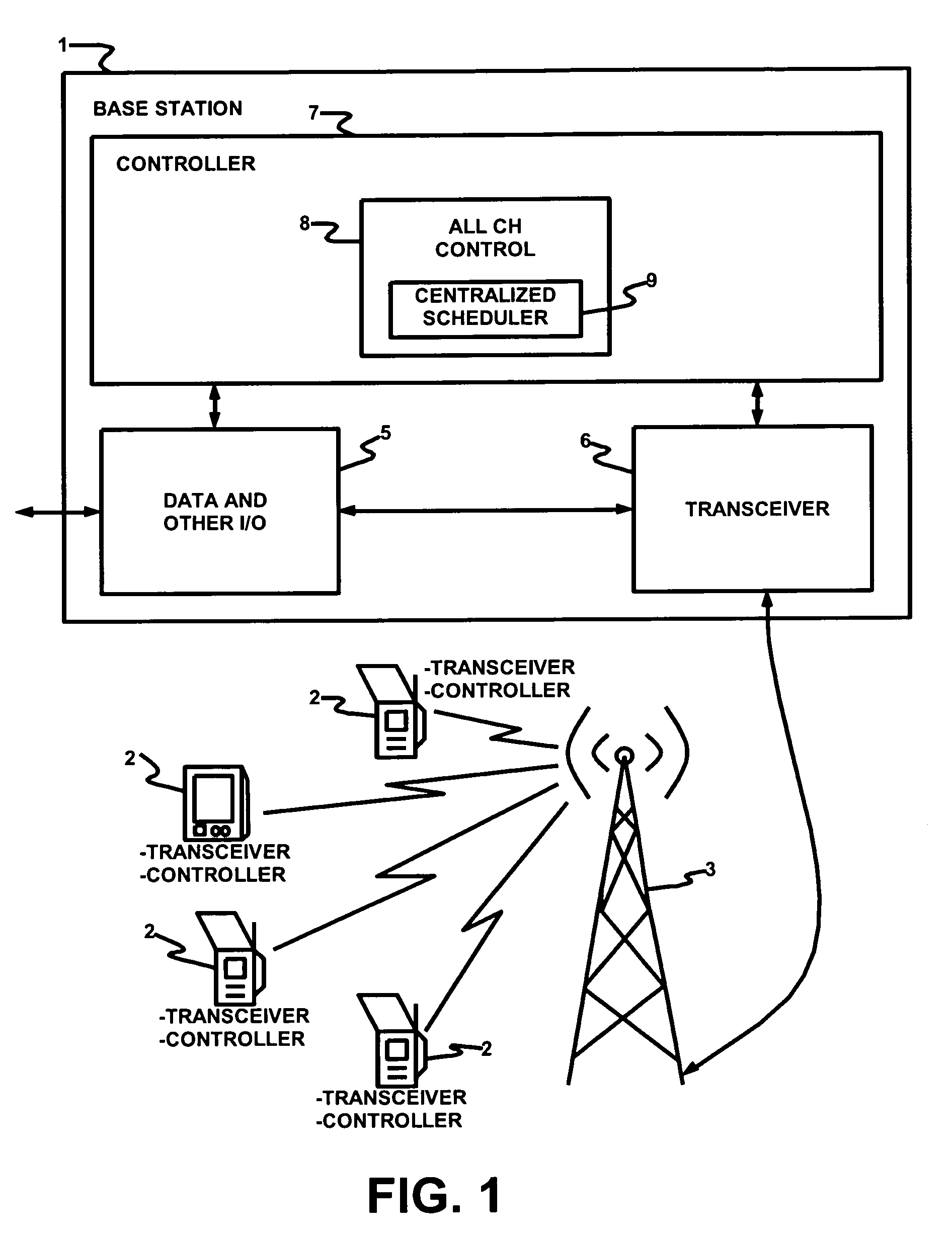
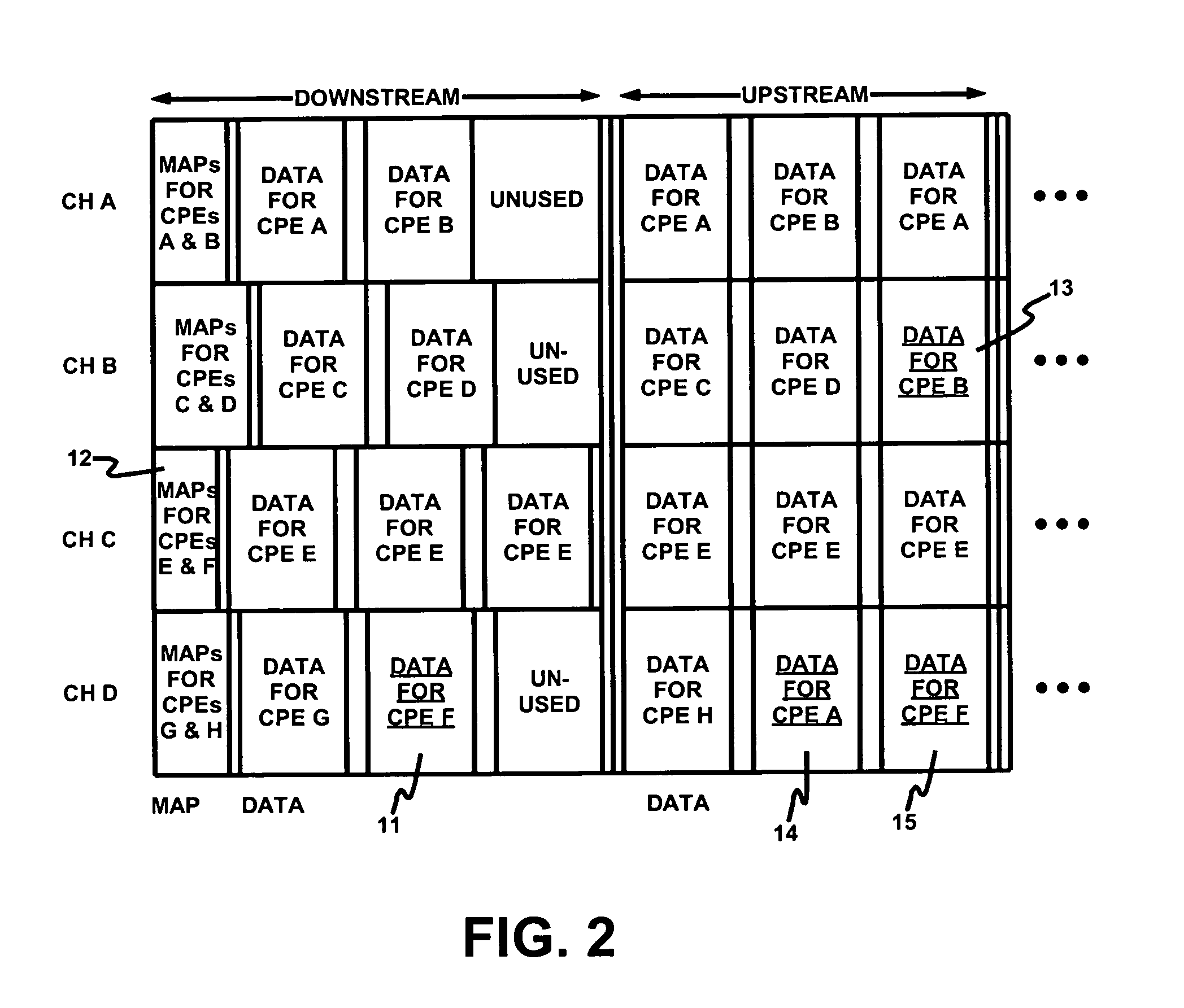
A method of managing TDD across plural channels. In the method, frames are synchronized across the plural channels so that upstream frames and downstream frames coincide across the plural channels. Preferable, one channel is assigned to each of plural CPEs. Each CPE receives MAP messages on its assigned channel. A base station controller preferably generates the MAP messages. The MAP messages instruct the CPEs to switch channels so as to receive data bursts. The base station controller preferably includes a centralized scheduler that allocates channels and slots in those channels to the CPEs for receipt of the data bursts. Also, a method of receiving TDD messages. According to the method, CPEs switch channels based on received media access protocol messages so as to receive data bursts on plural channels. The channel to which a CPE switches need not be the same channel as the one on which the CPE receives its MAP messages. Additionally, systems, base stations, CPEs, and / or software that utilizes and / or implements these methods.
Owner:MONUMENT BANK OF INTPROP LLC
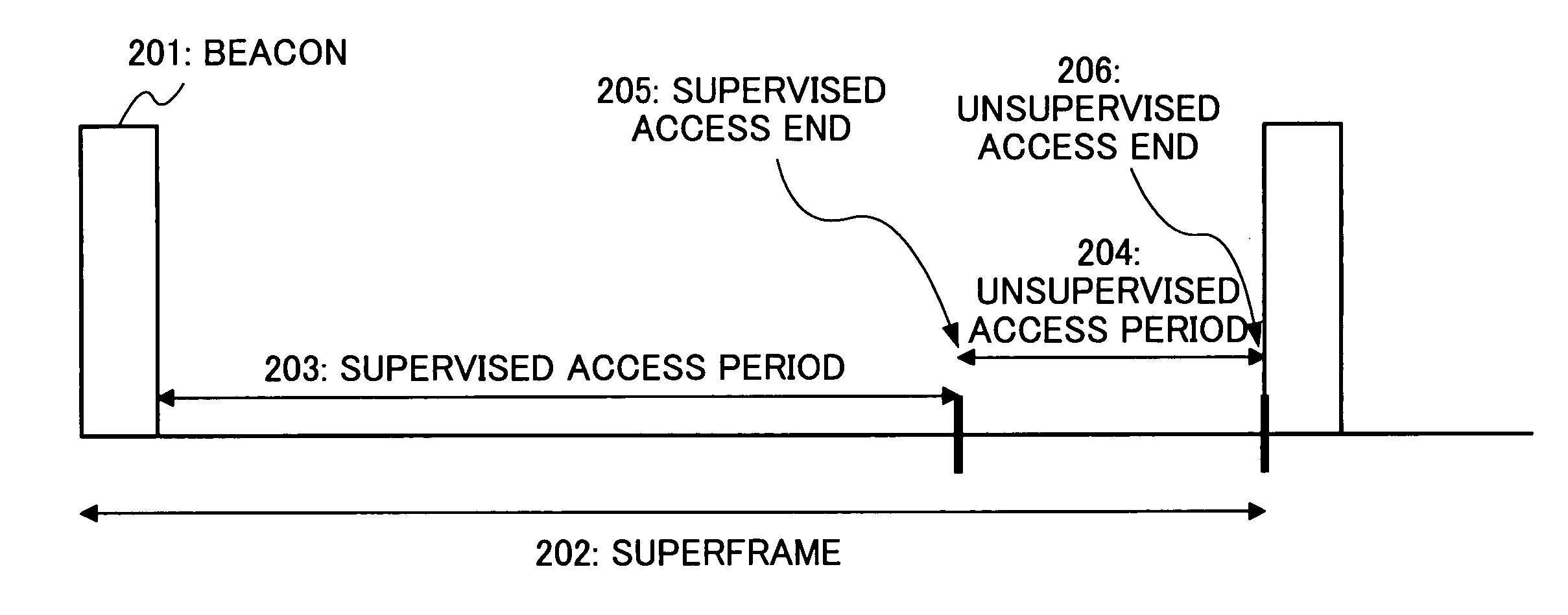
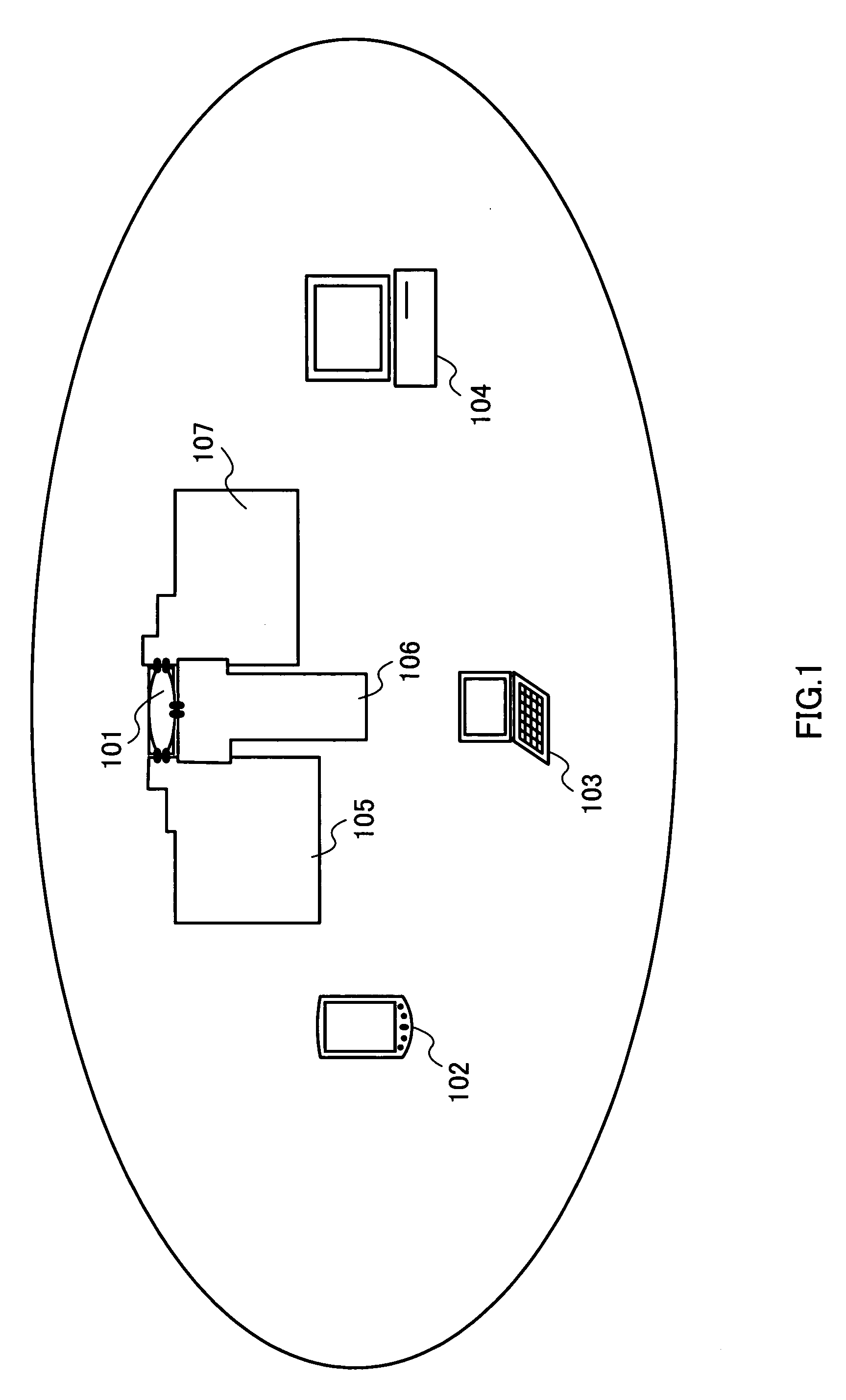
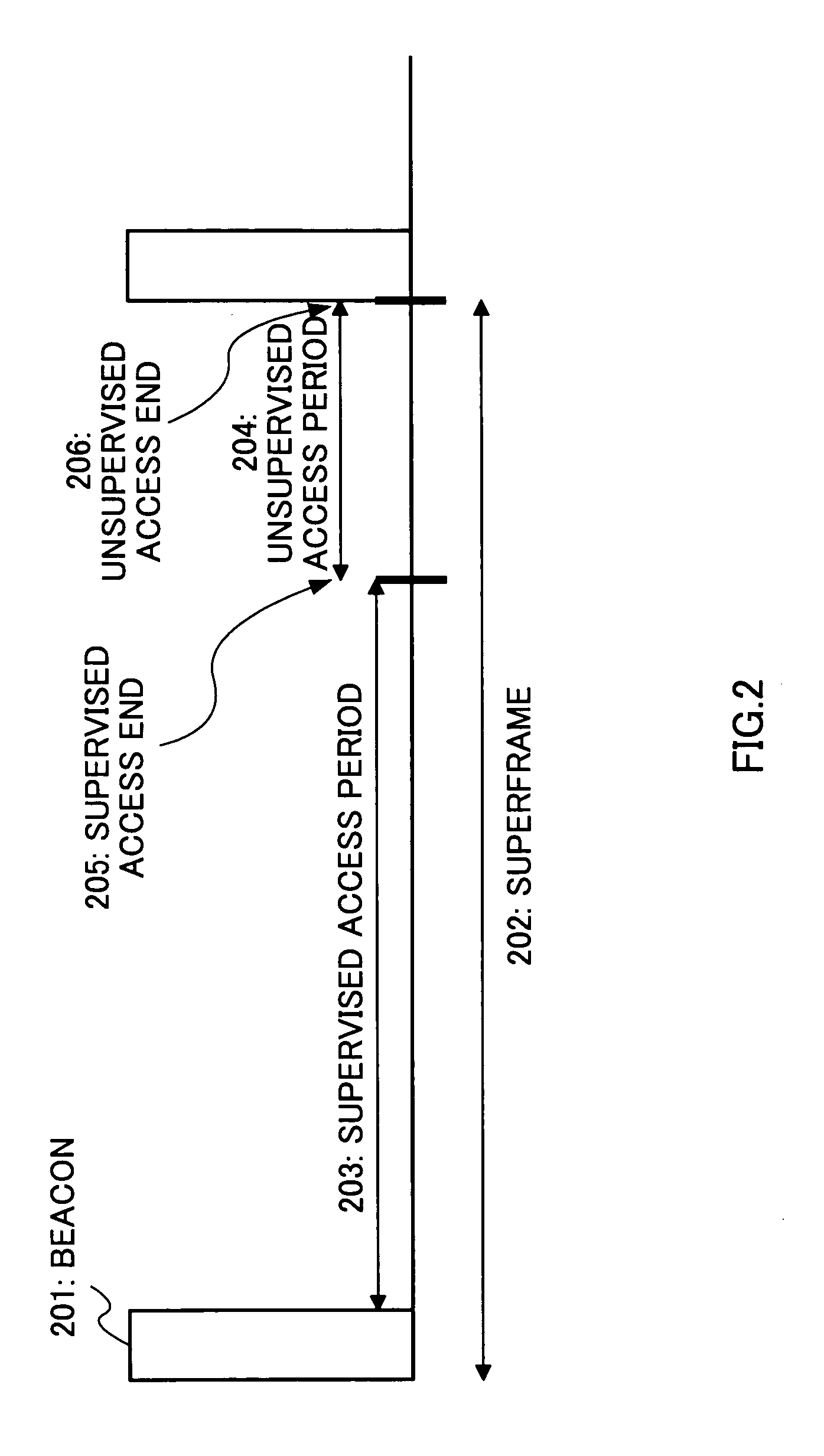
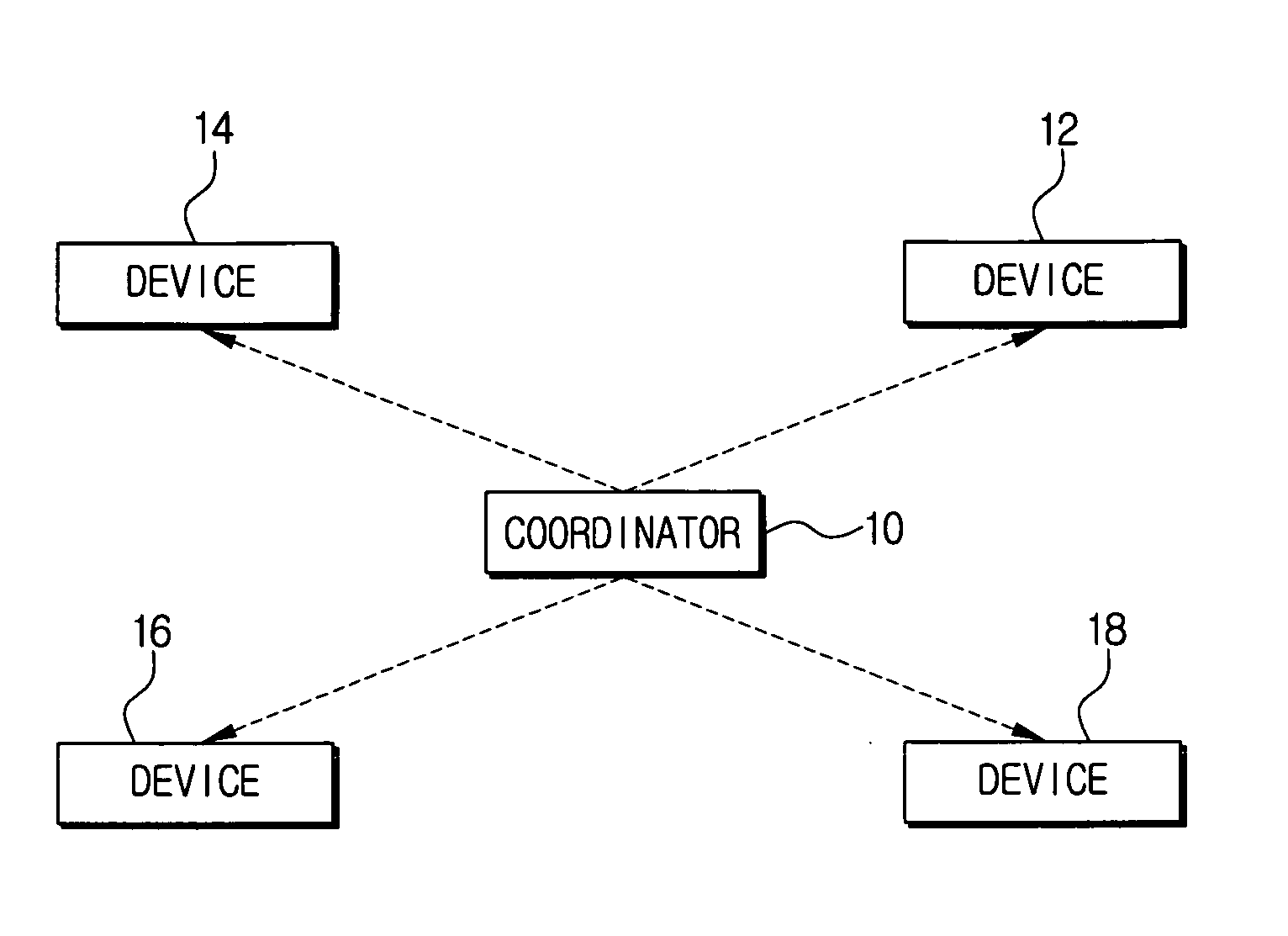
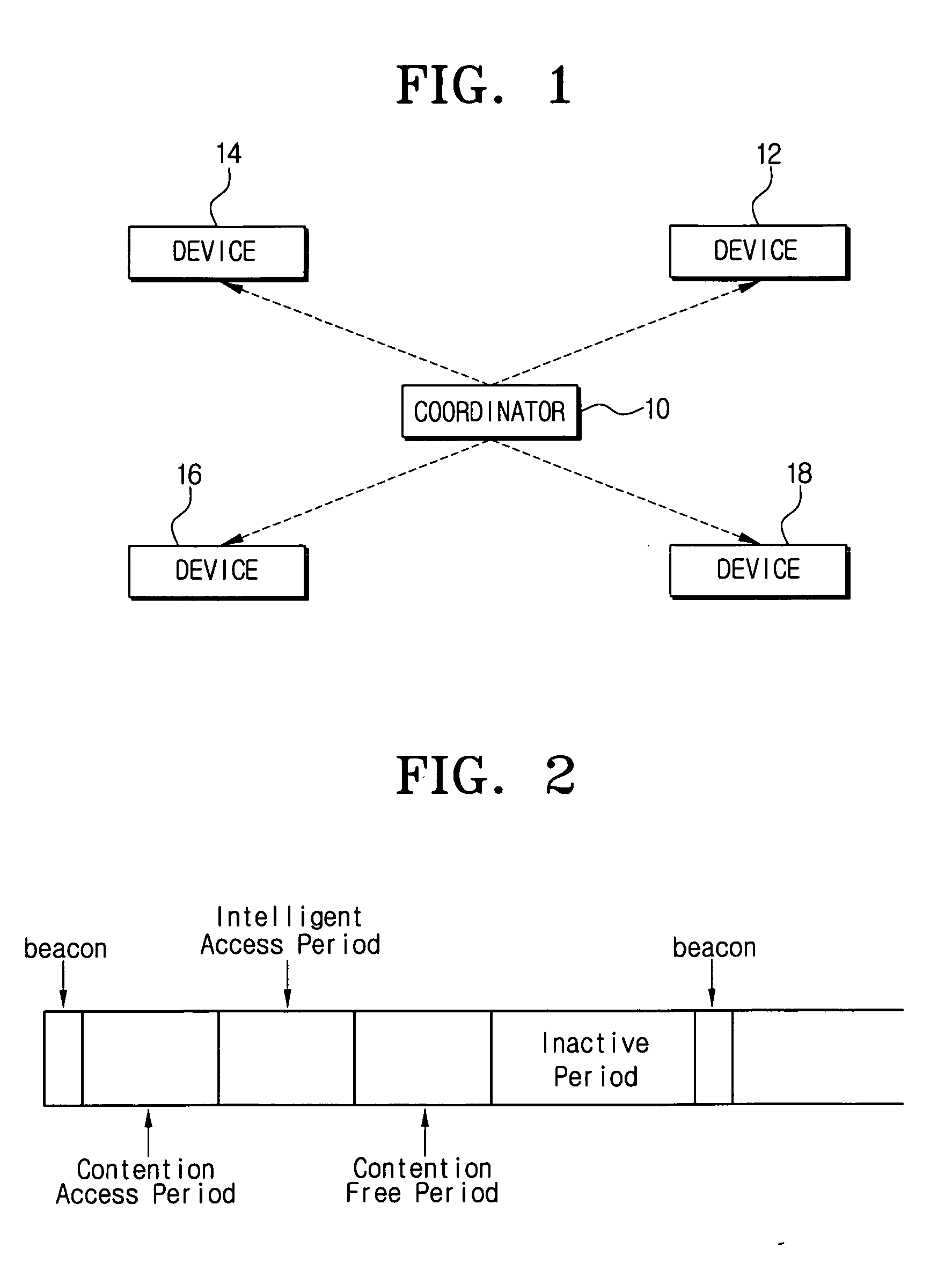
Wireless media access method
The present invention is a wireless media access method on a wireless network synchronized by a synchronizing signal broadcasted from a coordinator. In the method, priority is assigned to a plurality of devices interconnected over the wireless network for securing wireless resources in accordance with application characteristics of a packet to be transmitted, and if the devices request communication, dividing at least one slot within a superframe into a plurality of minislots. Minislots are then allocated to the devices, respectively, according to the priority, and information about the allocated minislots is inserted into the synchronizing signal. The information is then broadcast, thereby allowing each of the devices with the allocated minislots to exclusively use the allocated minislot for data communication.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Systems and methods for visible light communication
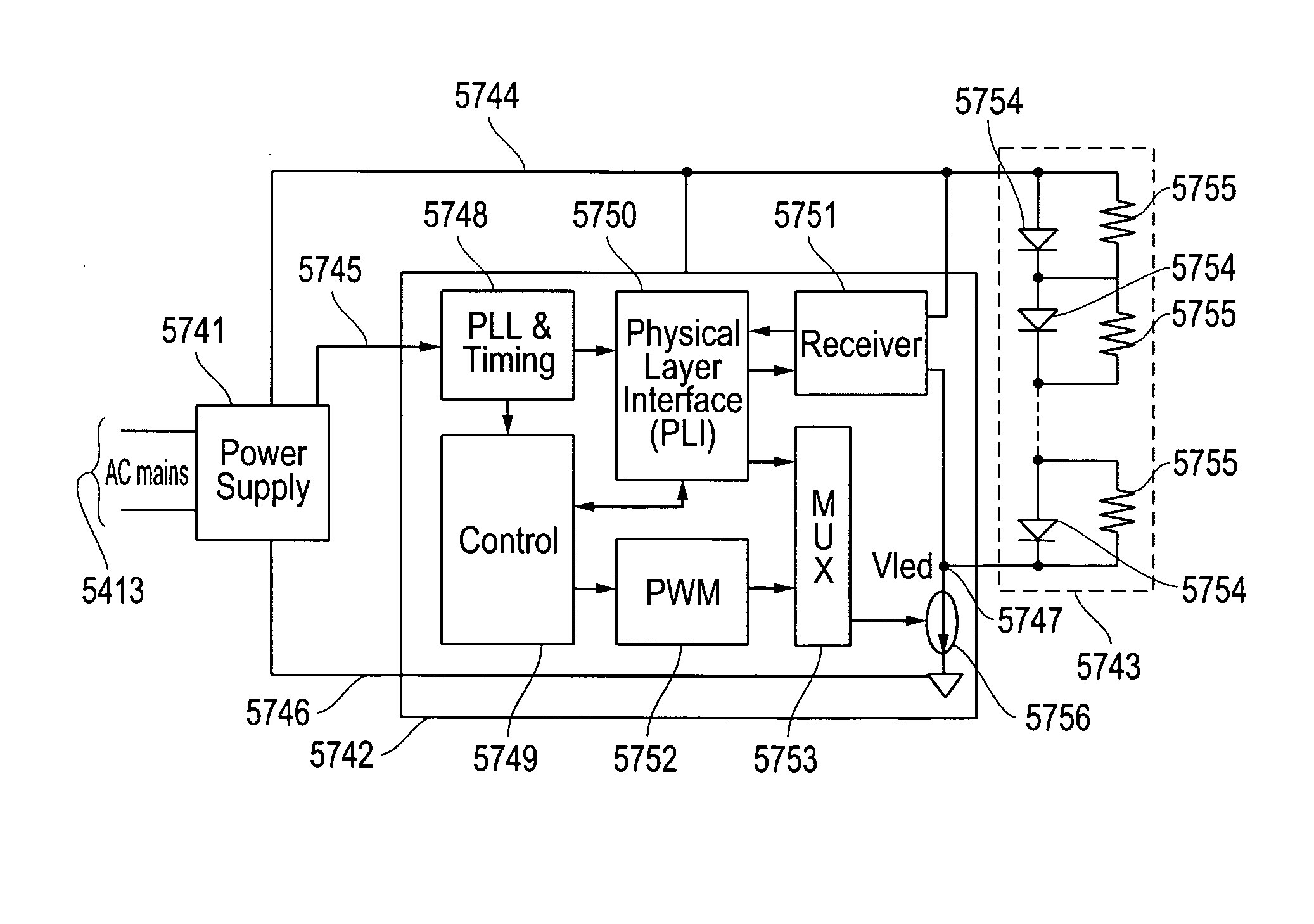
ActiveUS20110069960A1Low additional costIncreased complexityVehicle testingInstruments for road network navigationLight equipmentPhysical layer
Systems and methods for visible light communication are disclosed. In part, illumination devices and related systems and methods are disclosed that can be used for general illumination, lighting control systems, or other applications. The illumination devices synchronize preferentially to the AC mains to produce time division multiplexed channels in which control information can be communicated optically by the same light source that is producing illumination. Such illumination devices preferentially comprise LEDs for producing illumination, transmitting data, detecting ambient light, and receiving data, however, other light sources and detectors can be used. The physical layer can be used with a variety of protocols, such as ZigBee, from the Media ACcess (MAC) layer and higher.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
Frame Structure for Medium Access in Body Area Networks (BAN)
ActiveUS20100202354A1Optimize amountOptimize of hibernation timeResourcesWireless commuication servicesBody area networkBody area
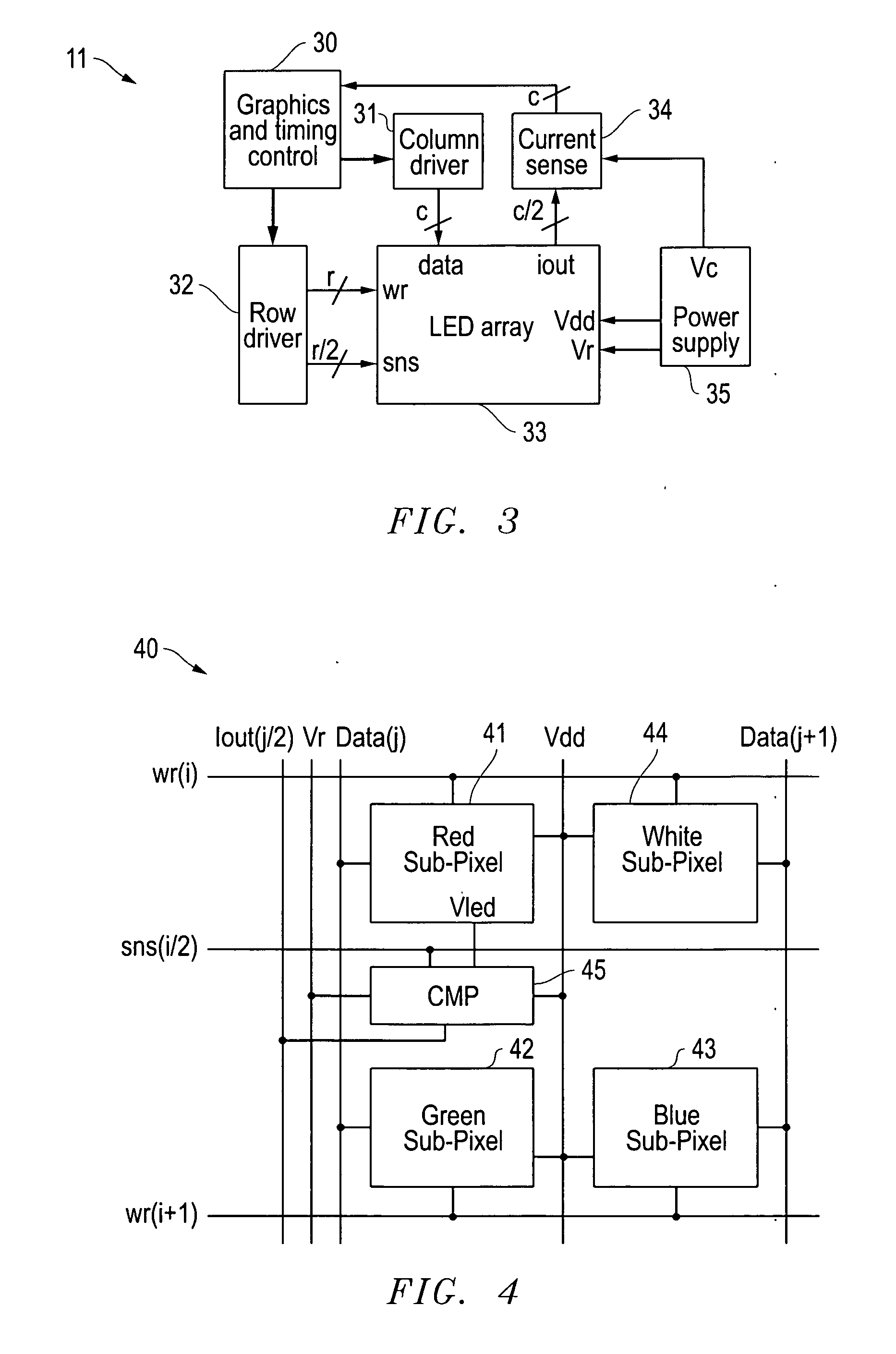
A system and method for providing a variety of medium access and power management methods are disclosed. A defined frame structure allows a hub and a node to use said methods for secured or unsecured communications with each other. Contended access is available during a random access phase. The node uses an alternate doubling of a backoff counter to reduce interference and resolve collisions with other nodes attempting to communicate with the hub in the random access phase. Non-contended access is also available, and the hub may schedule reoccurring or one-time allocation intervals for the node. The hub and the node may also establish polled and posted allocation intervals on an as needed basis. The node manages power usage by being at active mode at times during the beacon period when the node is expected to transmit or receive frames.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
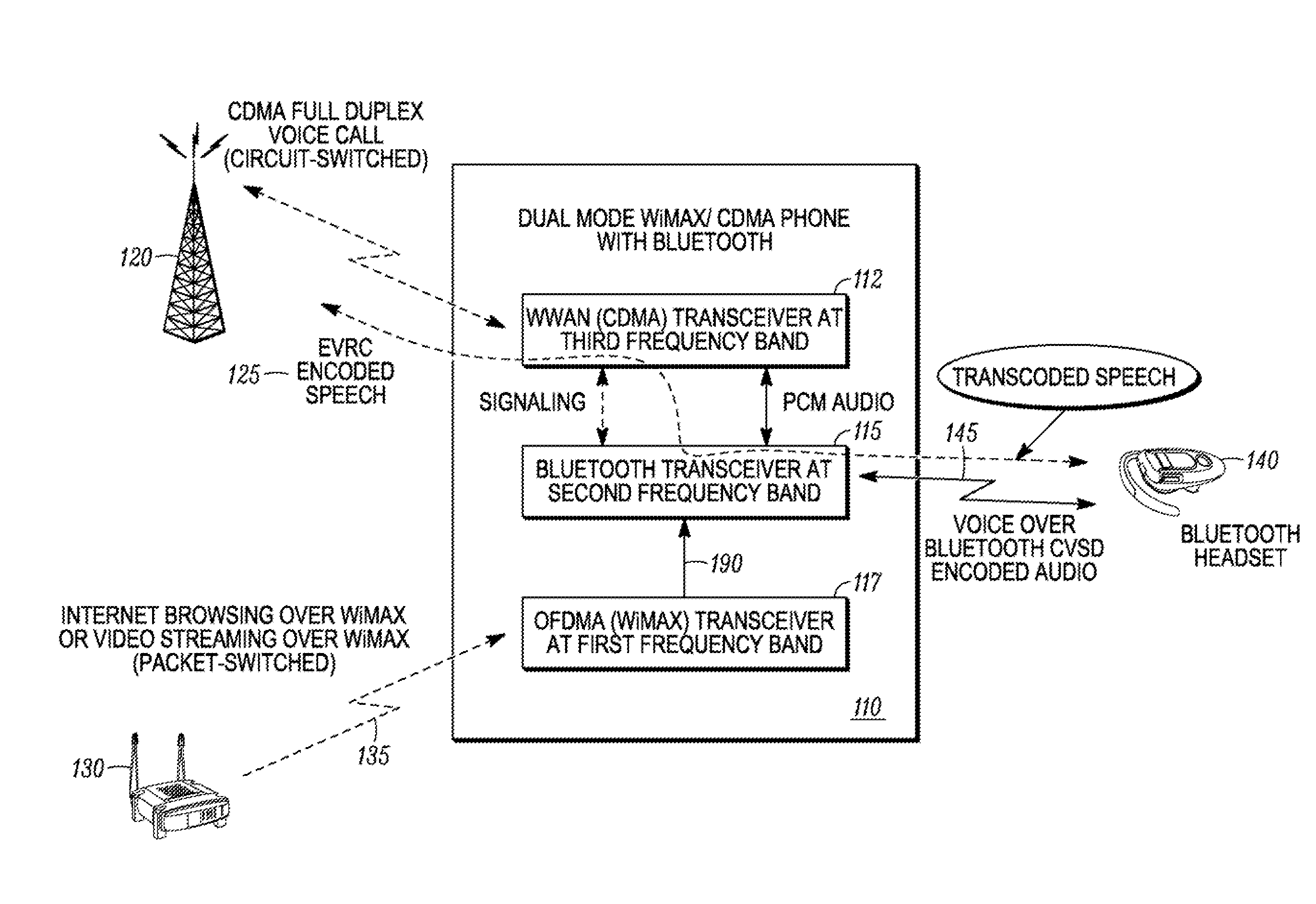
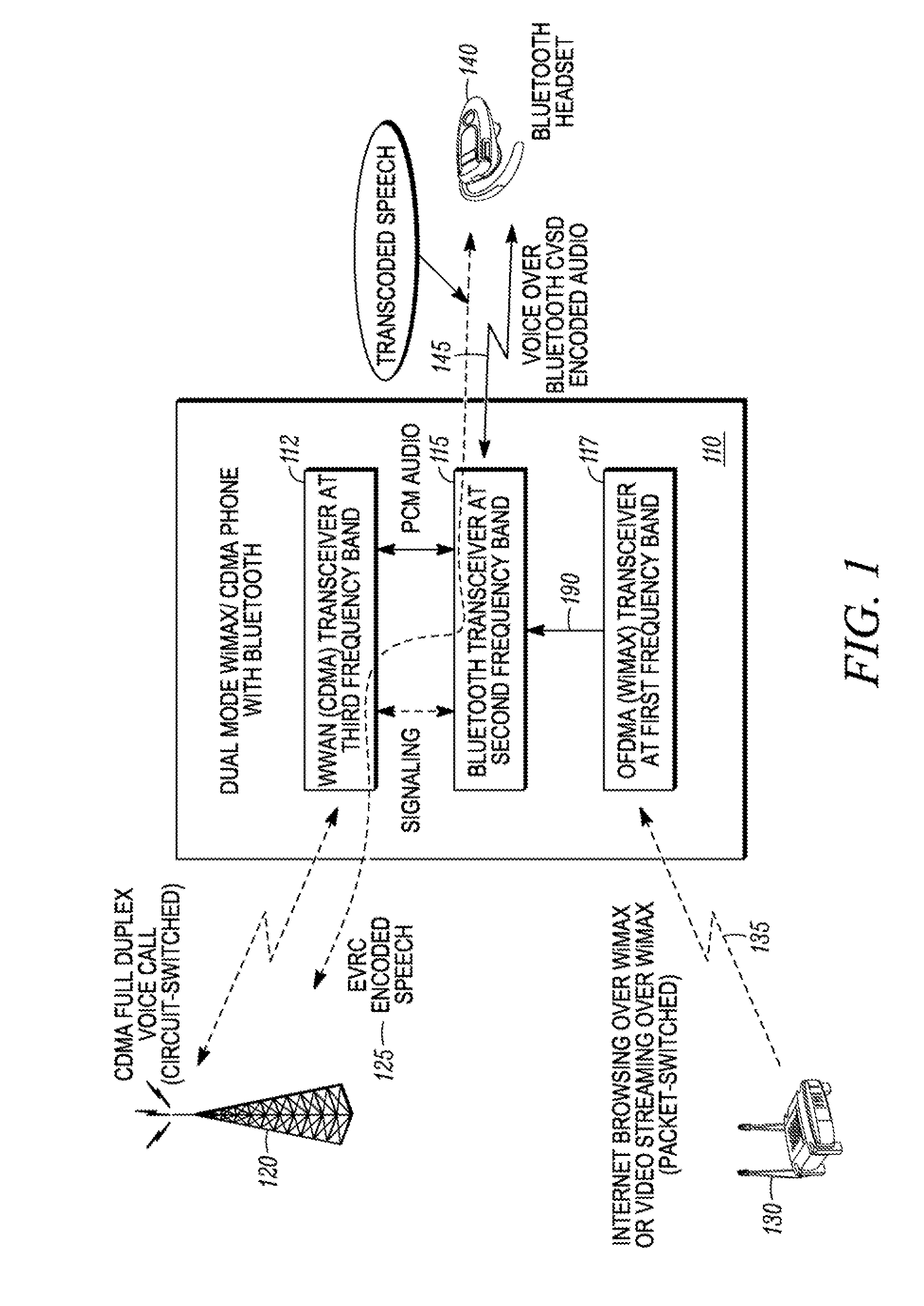
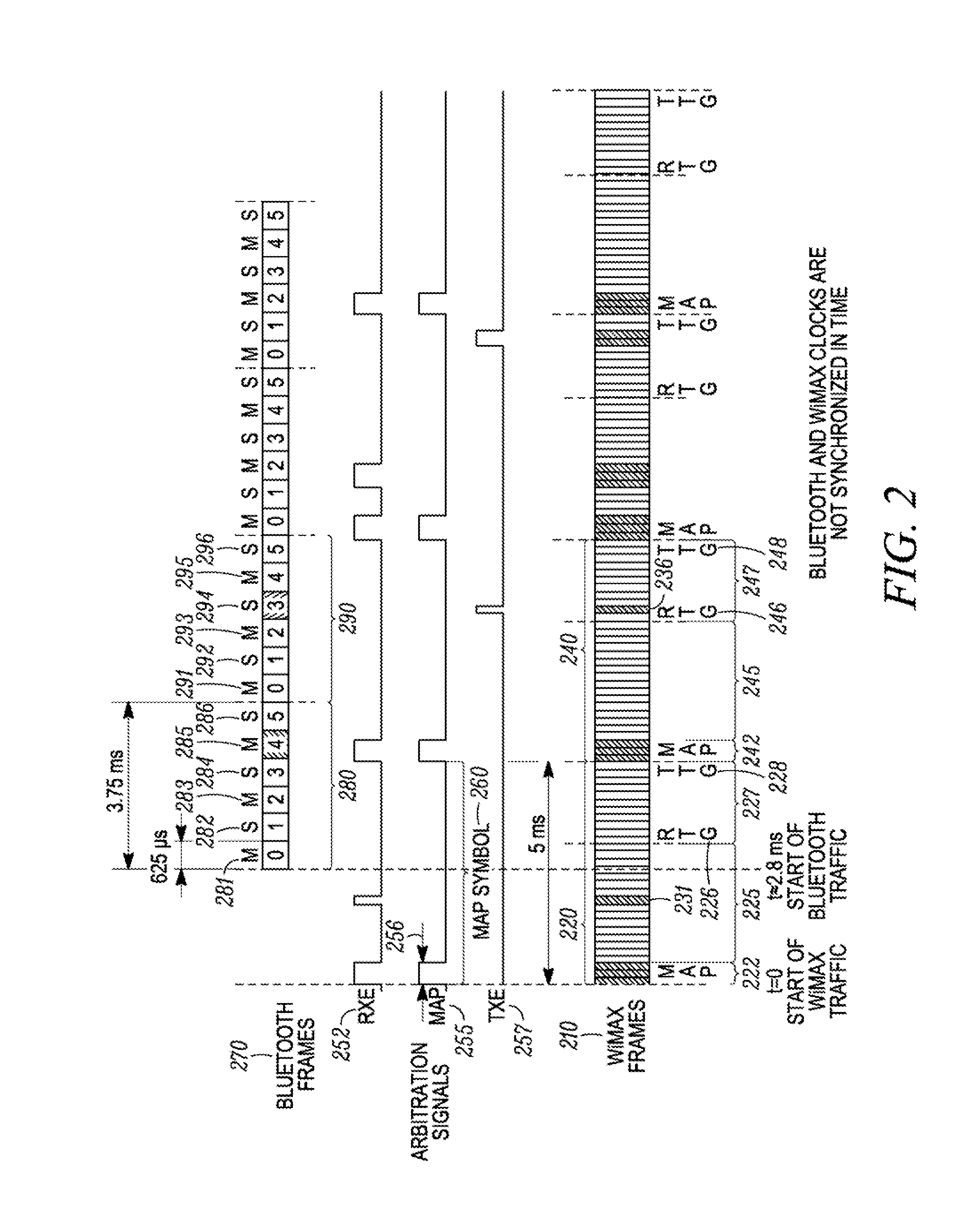
Method and apparatus for coexistence
A method for coexistence of an orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) receiver (117) such as a WiMAX receiver with a synchronous frame-based transmitter (115) such as a Bluetooth transmitter within a mobile station (110) receives an estimated media access protocol (MAP′) signal indicating when a MAP message is expected to be received by the OFDMA receiver (117) and uses it at a Bluetooth shutdown signal (190) at least when a MAP message is expected to be received. The MAP′ signal can be taken directly from the ODFMA transceiver (117) or it may be produced through analysis of a receiver-enable (RXE) signal that includes not only MAP symbols but also downlink data symbols. The RXE signal can be analyzed using interrupt-and-timer, Fast Fourier Transform, covariance, and / or delay-locked loop techniques to extract historical MAP symbol information and generate expected MAP symbol information. Shutting down a Bluetooth transmitter during expected MAP message receipt permits the OFDMA receiver to maintain synchronicity with an access point while not requiring the Bluetooth transmitter to shut down every time the OFDMA receiver expects to receive an OFDMA symbol.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
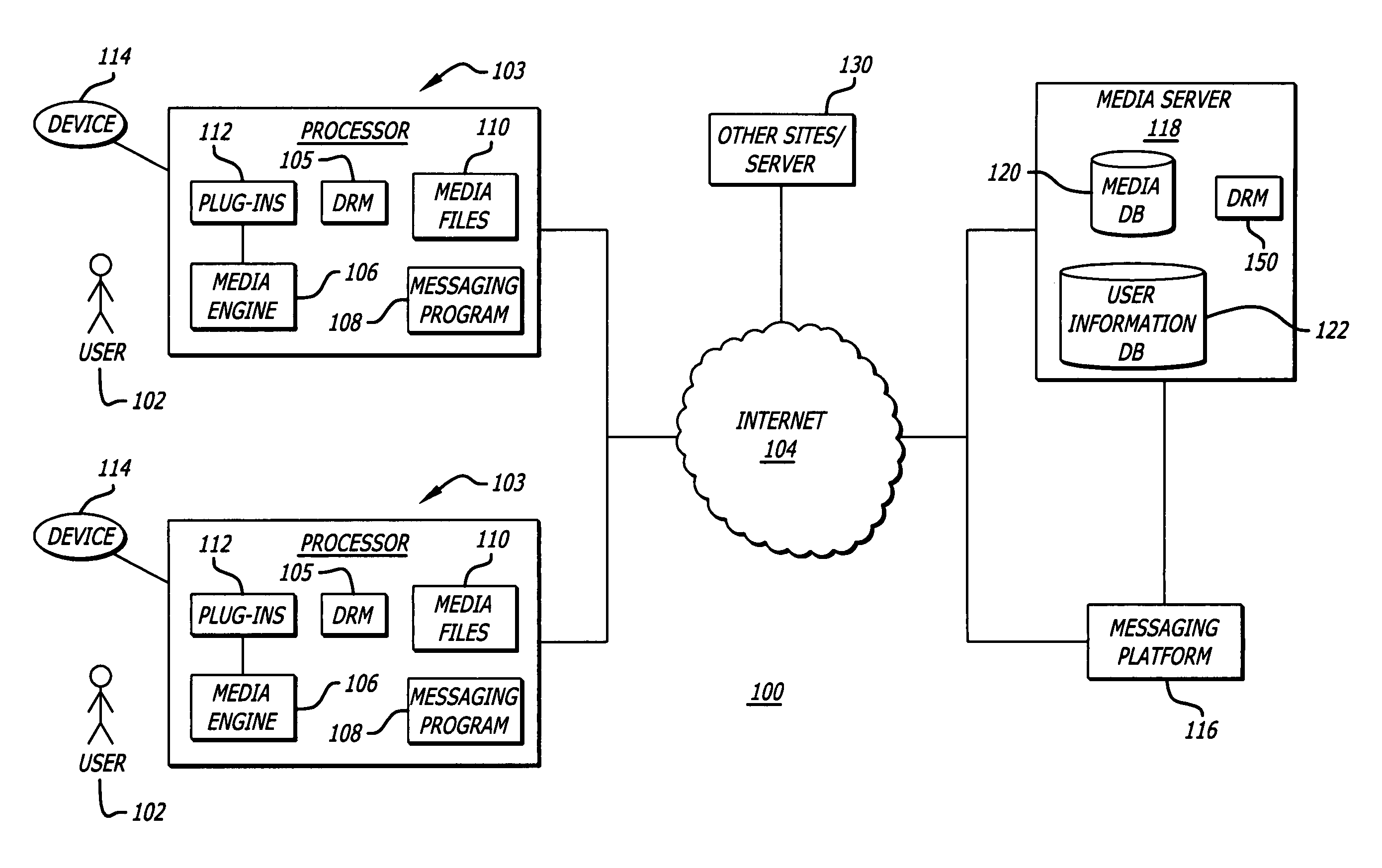
System and method for networked media access
ActiveUS20060195513A1Record information storageMultiple digital computer combinationsMedia accessMultimedia
A method, system, and media management application for providing a user access to a media file from multiple locations on a network. In one aspect, a user communicates a desire to access a media file at a future time and is able to access the bookmarked media file from various locations on a network at any future time. In one aspect, the media file is available from multiple locations on the network and in different media formats.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
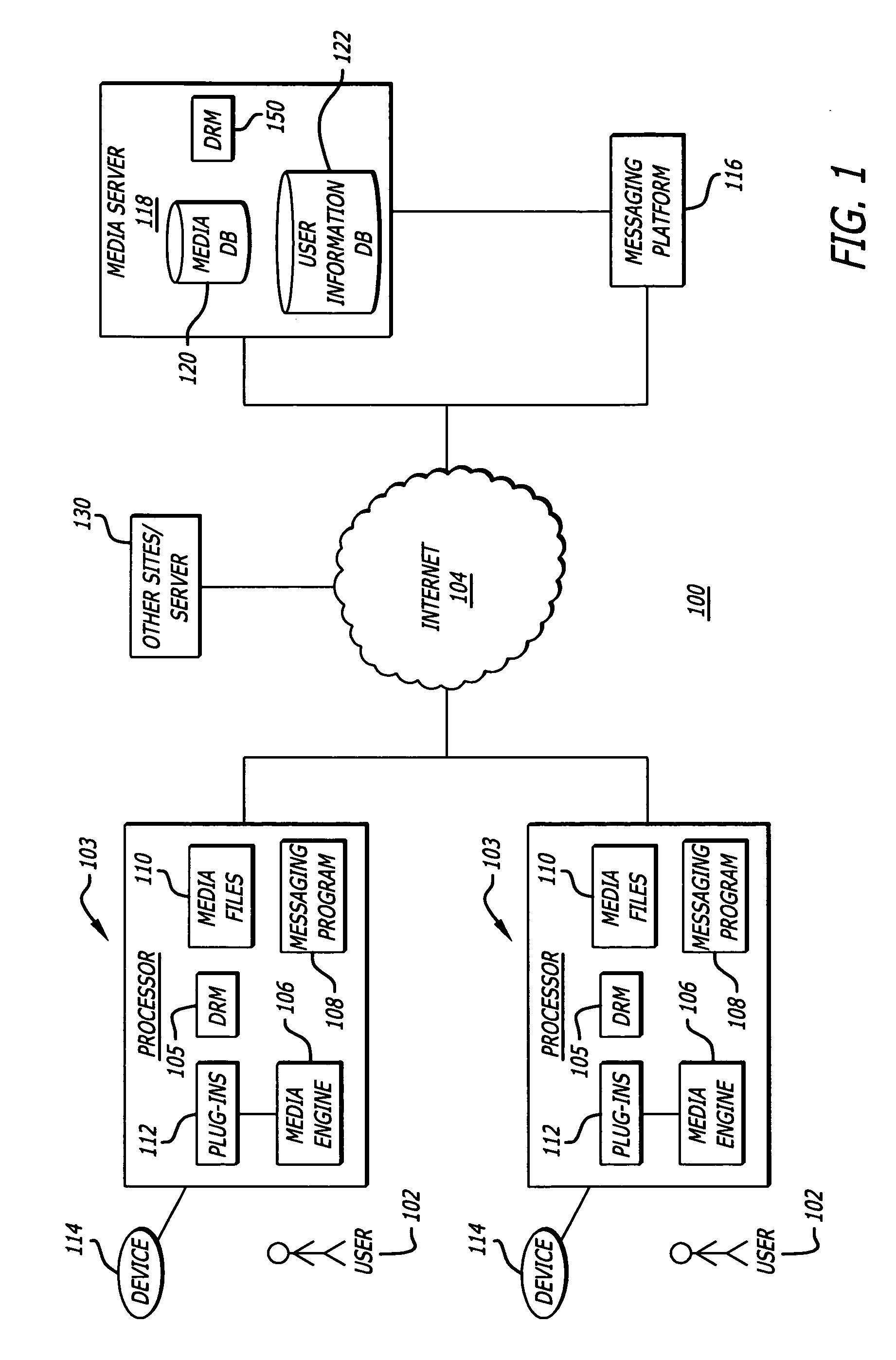
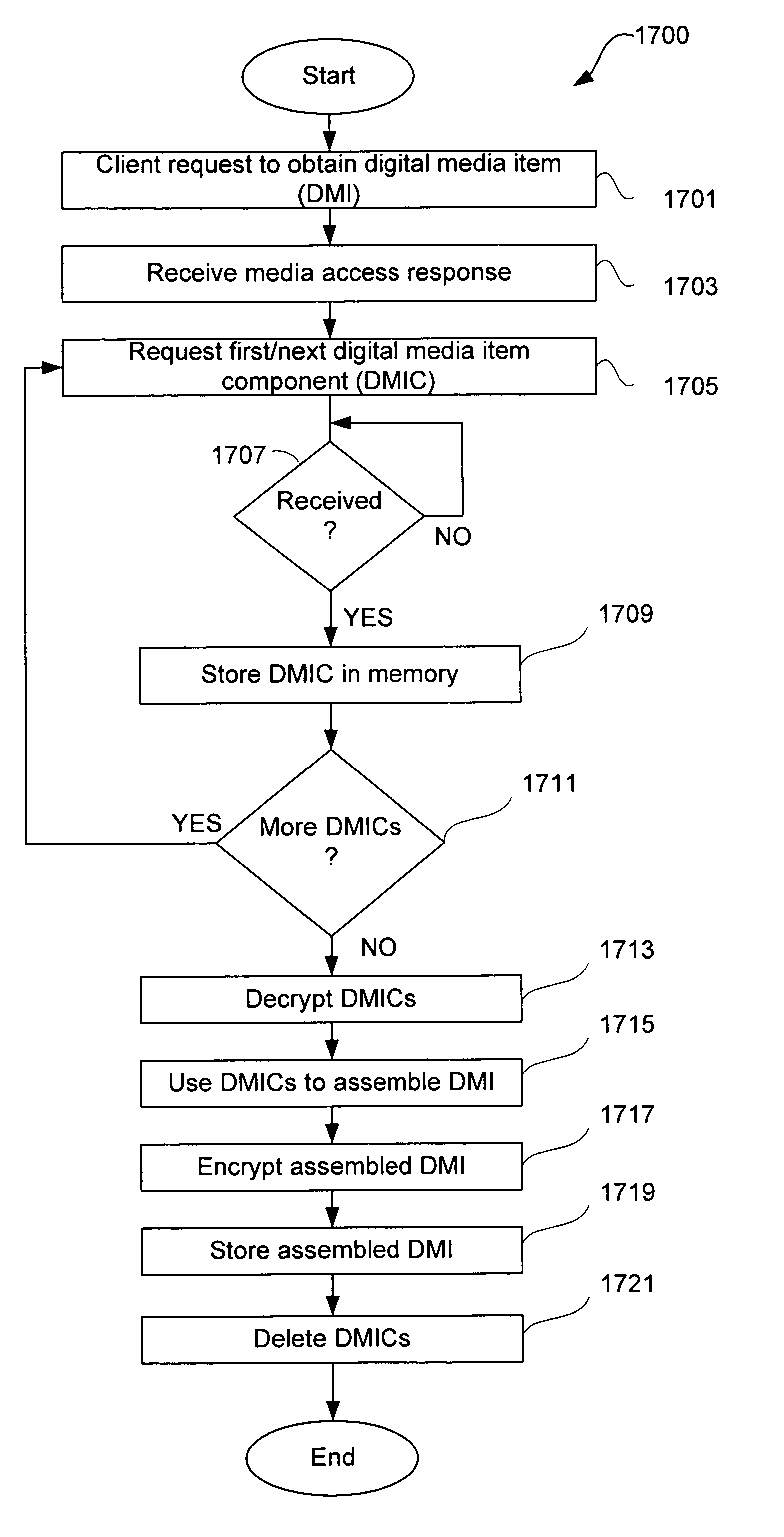
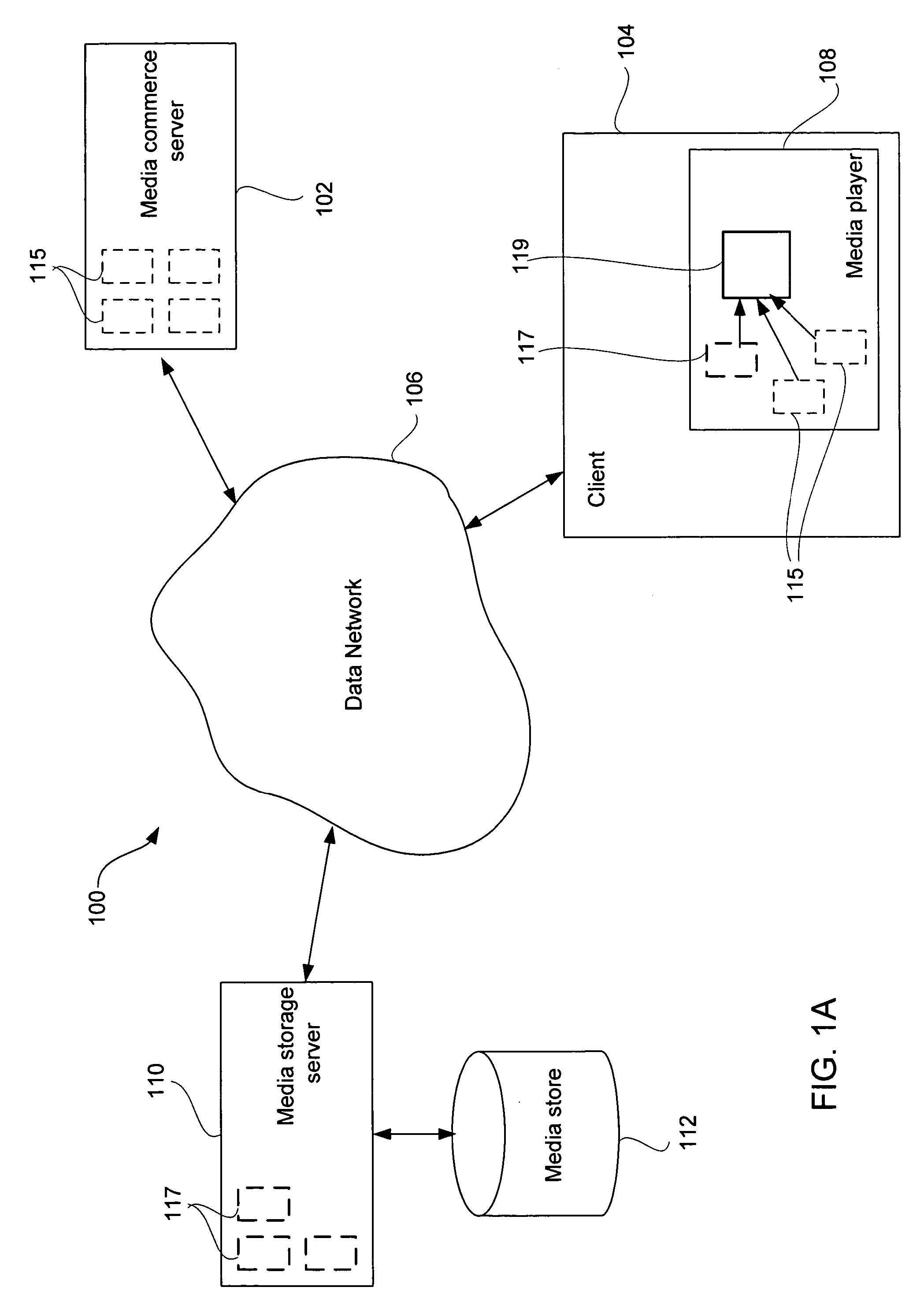
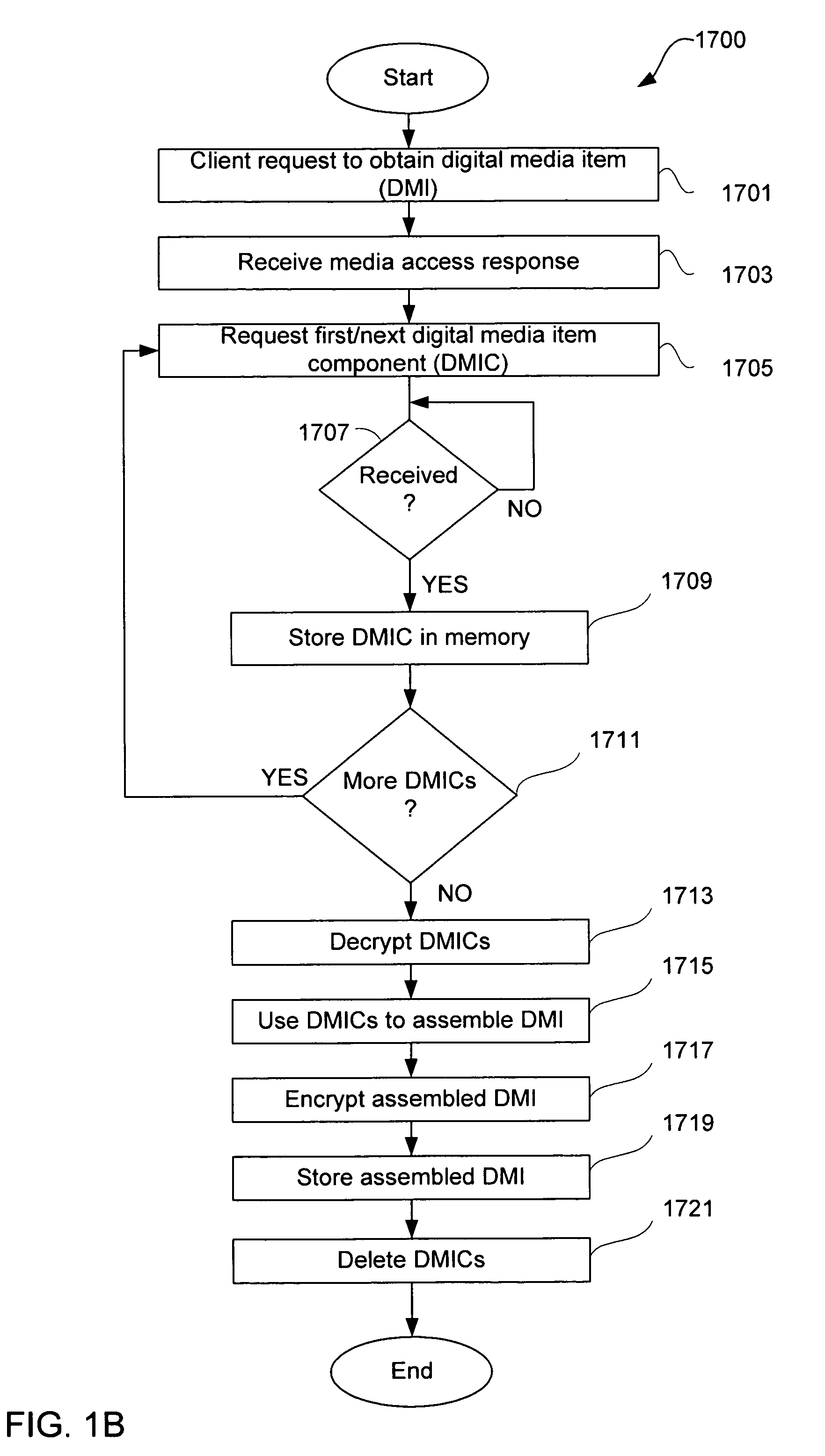
Network-based purchase and distribution of digital media items
Methods and systems for network-based purchase and distribution of media are disclosed. The purchase and distribution of media by these methods and systems are not only secure but also controlled. The media takes the form of a digital media item, which is assembled by a client application from one or more digital media item components, including at least one digital graphic associated with the media content contained in the digital media item. The digital media item components are stored on one or more server computers and are obtained by the client application, which requests, from a server computer, a media access response containing one or more pointers to digital media item components on one or more server computers. The assembled digital media item can then be encrypted for the purchaser's use and stored on the purchaser's machine. Thereafter, the purchaser can make use of the digital media item (e.g., play the digital media item).
Owner:APPLE INC
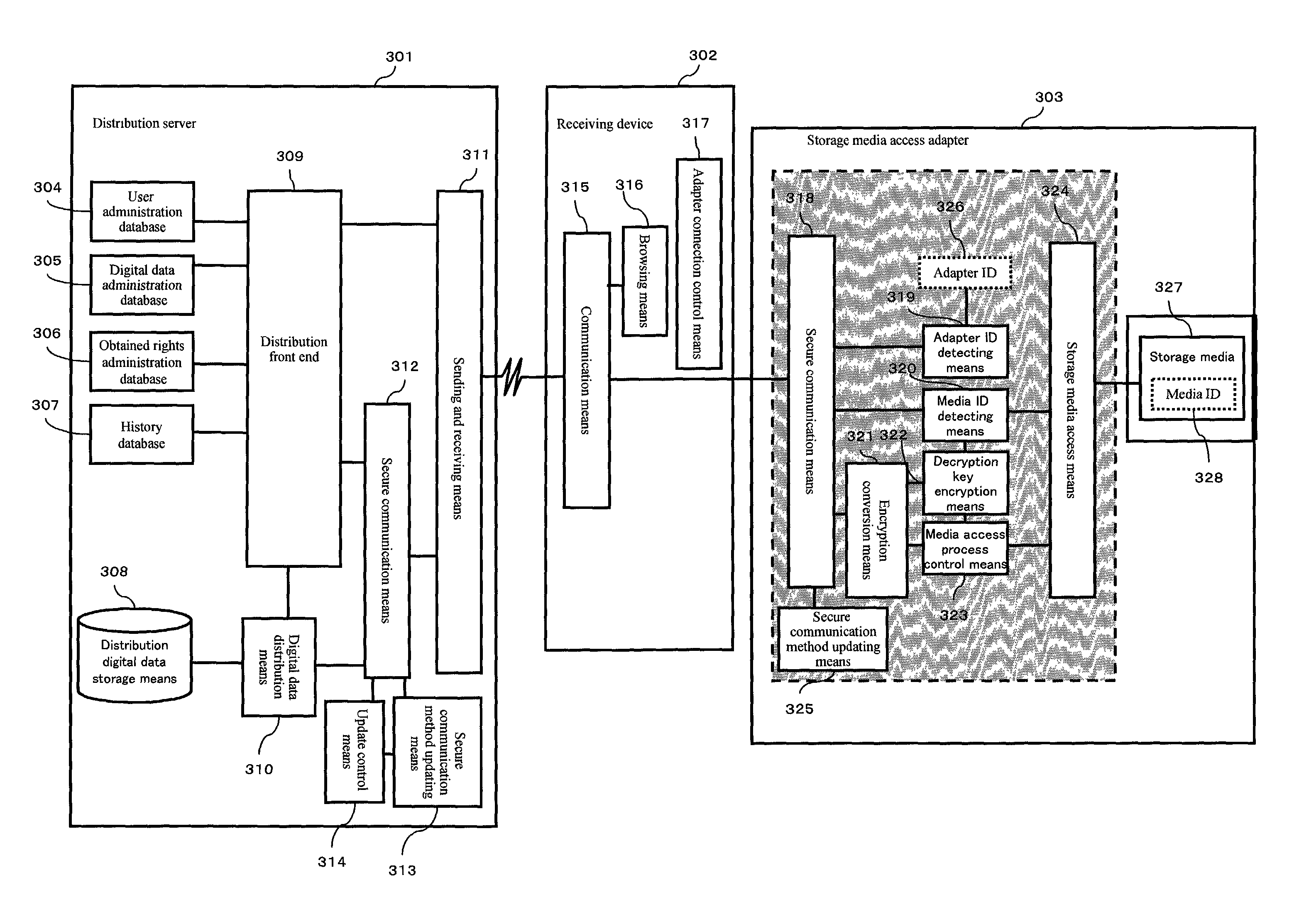
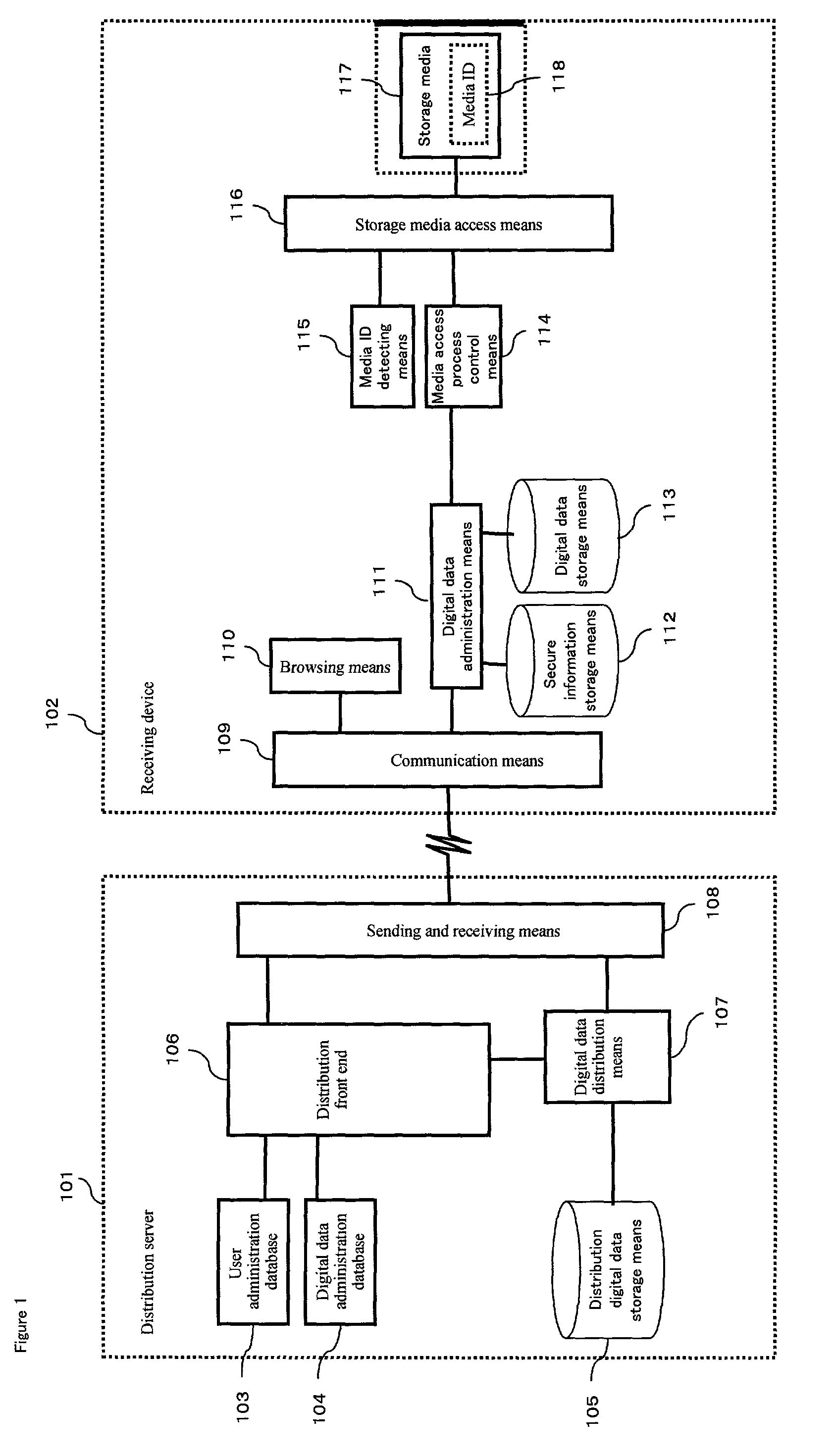
Digital data distributing system
An object of the invention is to provide a system in which various services can be received by a plurality of receiving devices having different structures, without having to take into consideration the difference in the structures, by connecting an adapter that corresponds to the service the user wishes to receive. The distribution server 301 communicates with the storage media access adapter 303 via the receiving device 302, and thereby controls distribution of digital data.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
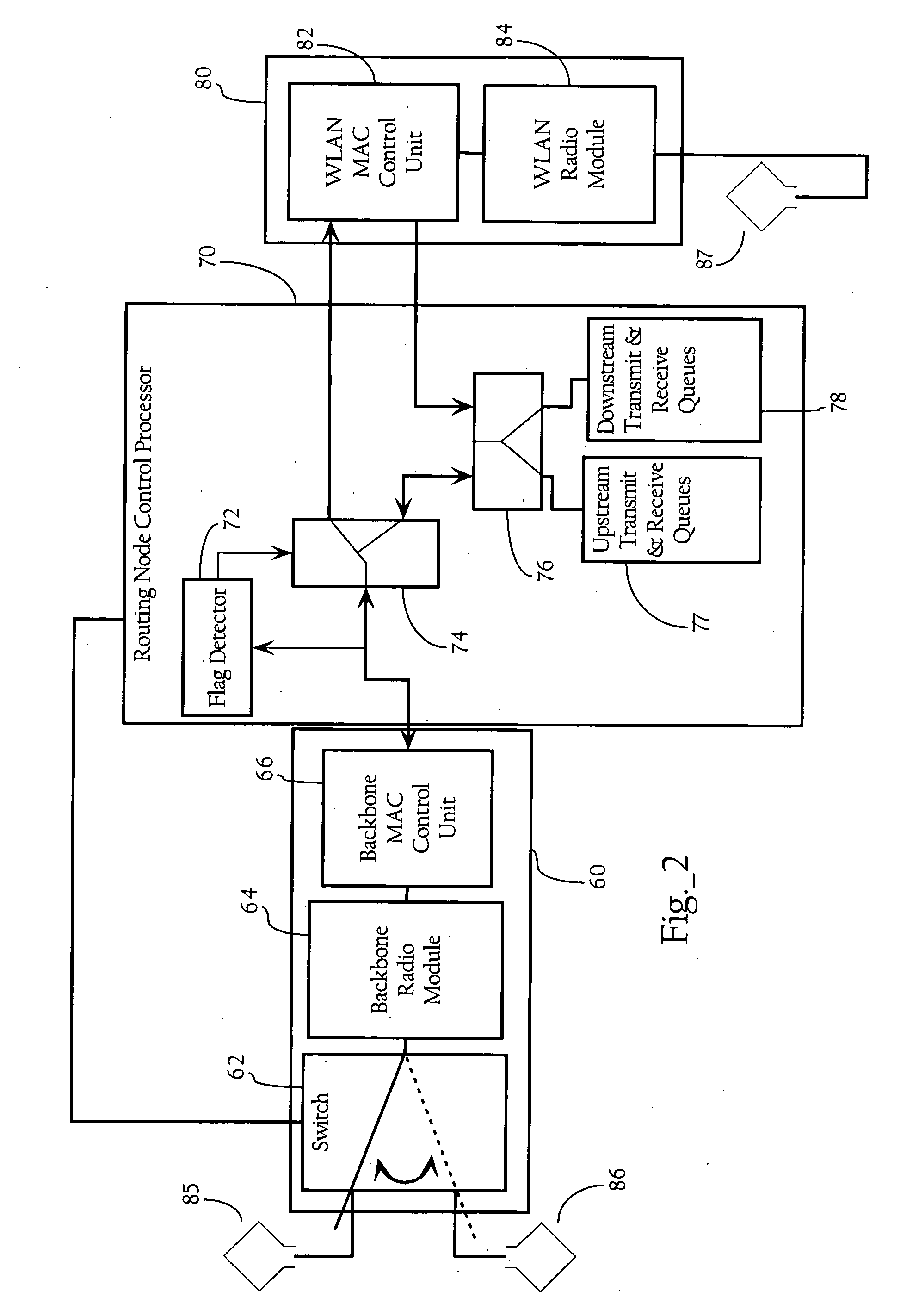
Media access control architecture
InactiveUS20070058661A1Data switching by path configurationWireless commuication servicesTraffic flow managementStation
Owner:OPTIMAL INNOVATIONS INC
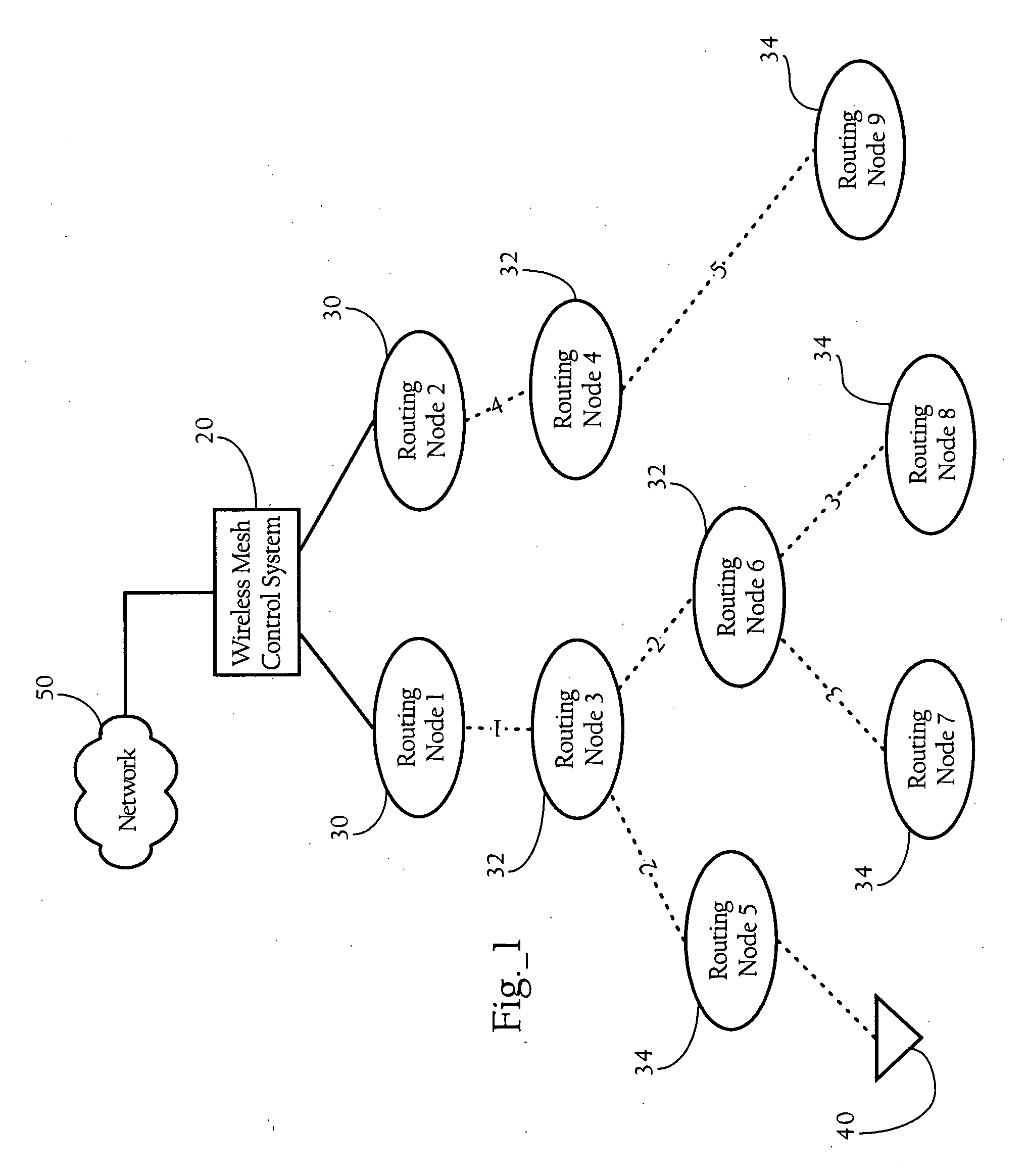
Dynamic modification of contention-based transmission control parameters achieving load balancing scheme in wireless mesh networks
ActiveUS20070206547A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsWireless mesh networkMedia access
Methods, apparatuses and systems directed to facilitating load balancing and bandwidth allocation in wireless mesh networks. Generally, according to one implementation of the present invention, routing nodes implement a contention-based media access mechanism and self-allocate bandwidth within a wireless mesh network by dynamically modifying one or more contention-based transmission control parameters. The routing nodes determine a hop count and adjust one or more contention parameters based at least in part on the hop count.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Medium access for shared or unlicensed spectrum
ActiveUS20160212625A1Wireless commuication servicesNetwork planningFrequency spectrumTelecommunications
Methods, systems, and devices are described for wireless communication at a UE. A wireless devices may use a shared or unlicensed spectrum configuration based on a prioritization scheme for the shared frequency resources. The prioritization scheme may assign a priority to different operators and may enable devices associated with a prioritized operator to access the shared band over non-prioritized devices. For example, a non-prioritized device may win the channel and begin communicating over the shared or unlicensed spectrum. The non-prioritized device may then periodically cease transmission for a set interval (i.e., a preemption opportunity) and listen for an indication that a prioritized device wishes to use the channel. If a prioritized device begins transmitting (or, in some cases, if the prioritized device transmits a medium preemption indication) the non-prioritized device may relinquish control of the channel.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Advanced multi-network client device for wideband multimedia access to private and public wireless networks
InactiveUS7437158B2Agile and robustSupports accessAssess restrictionPosition fixationCDMA2000Broadband
Owner:INCNETWORKS
Systems and methods for visible light communication
ActiveUS8521035B2Low additional costIncreased complexityVehicle testingInstruments for road network navigationLight equipmentPhysical layer
Systems and methods for visible light communication are disclosed. In part, illumination devices and related systems and methods are disclosed that can be used for general illumination, lighting control systems, or other applications. The illumination devices synchronize preferentially to the AC mains to produce time division multiplexed channels in which control information can be communicated optically by the same light source that is producing illumination. Such illumination devices preferentially comprise LEDs for producing illumination, transmitting data, detecting ambient light, and receiving data, however, other light sources and detectors can be used. The physical layer can be used with a variety of protocols, such as ZigBee, from the Media ACcess (MAC) layer and higher.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
Random medium access methods with backoff adaptation to traffic
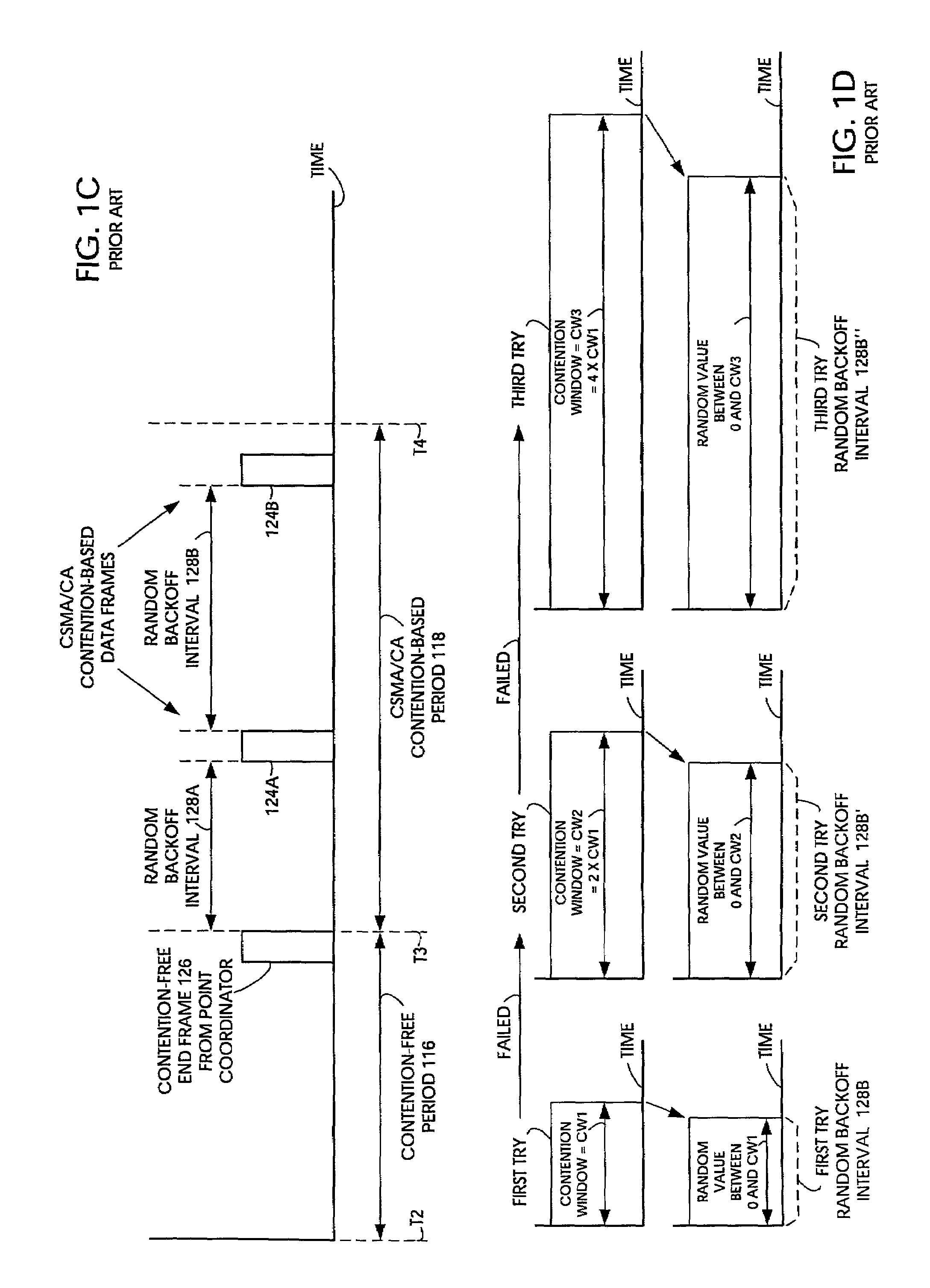
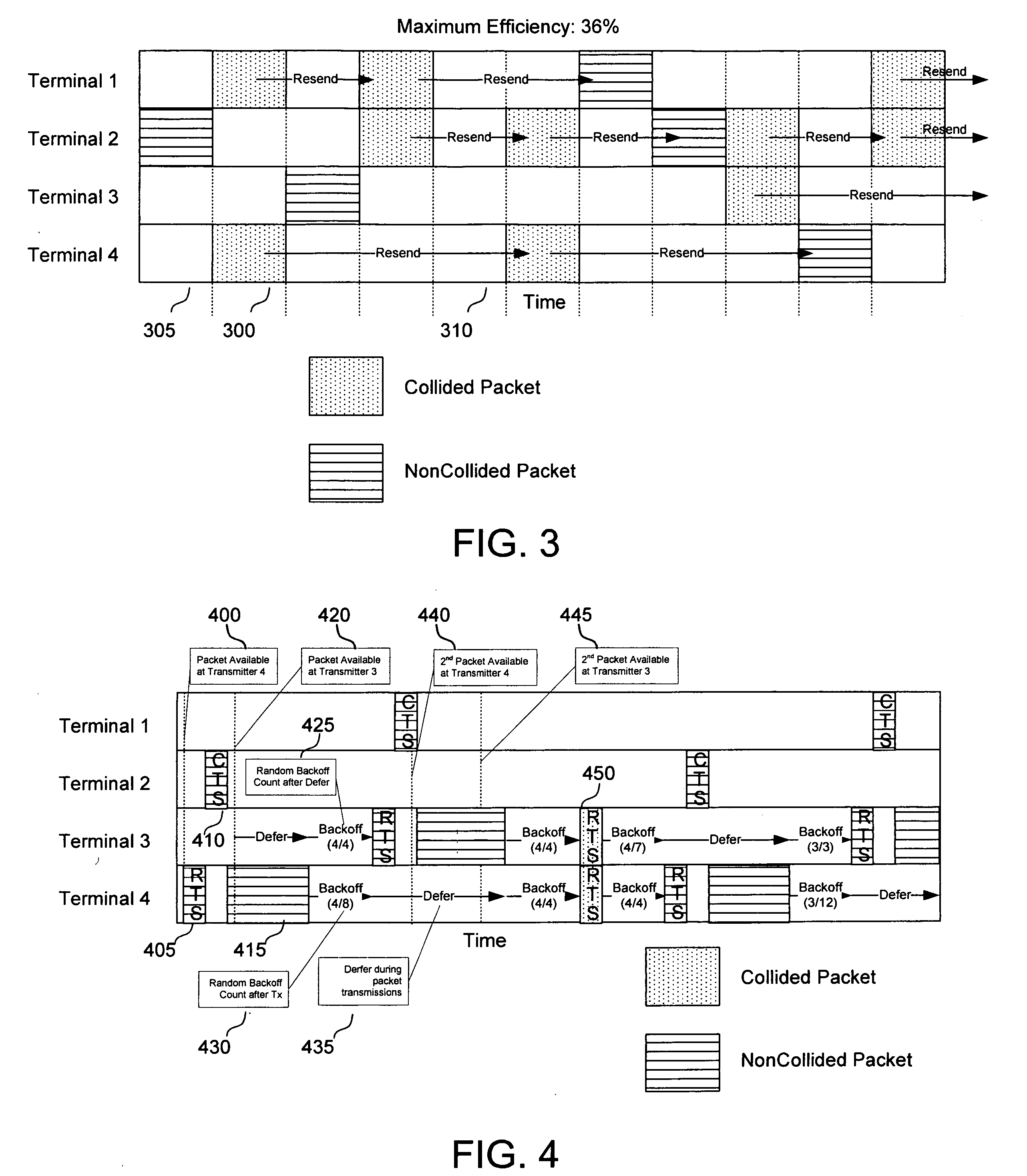
InactiveUS7027462B2Synchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementComputer scienceMedia access
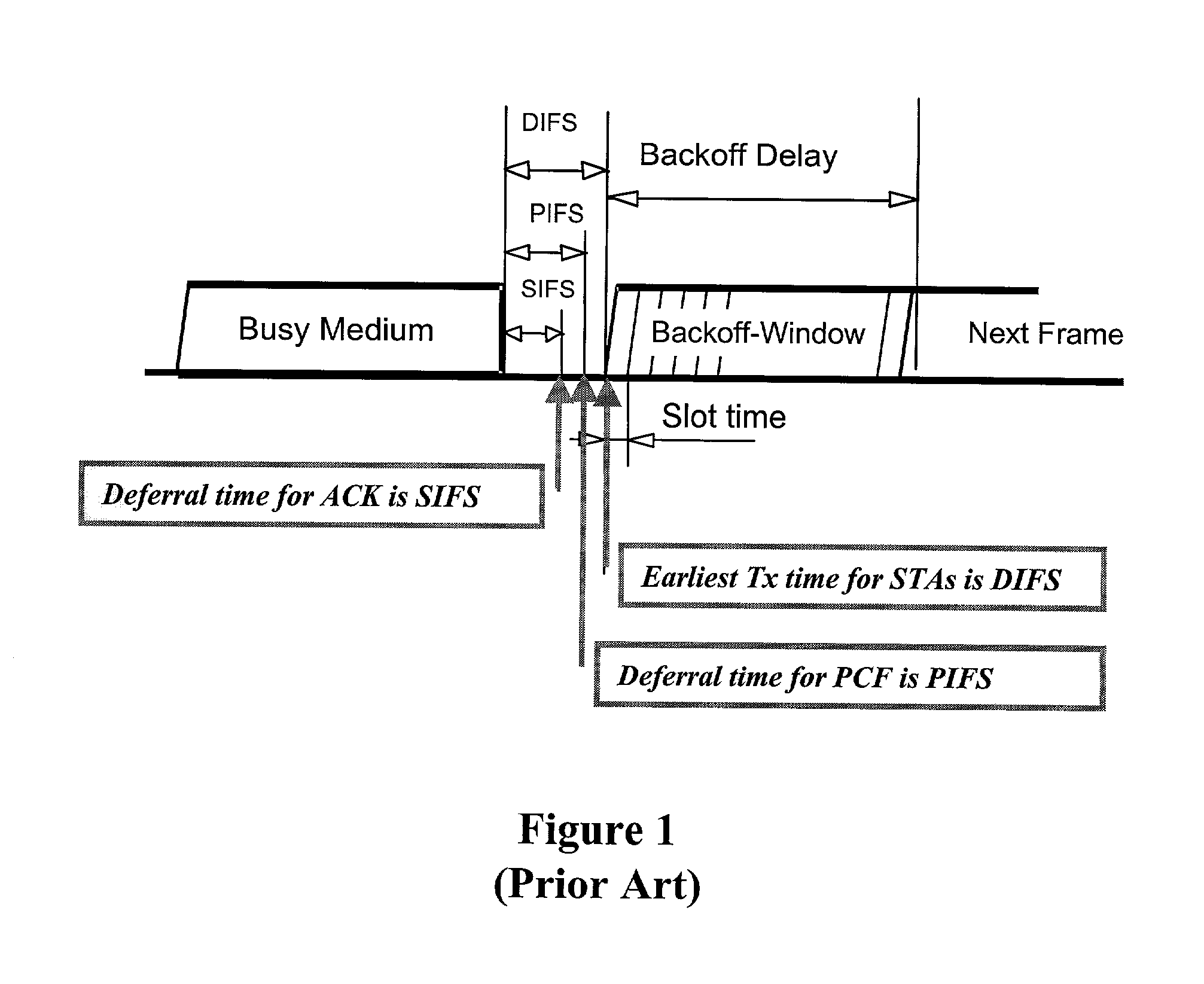
Using low PF values in conjunction with traffic-adapted contention windows leads to substantial decreases in delay and jitter. In general, adaptation to traffic reduces contention or delay: opening up the contention window in congestion and closing it on relief. Residual backoff adaptation provides for the reduction of the already decremented backoff values of stations that interrupted the backoff countdown process due to a transmission. It is good to adapt both the contention window and the residual backoff in order to avoid jitter. Otherwise, if the contention window is reduced but residual backoffs stay unchanged, new arrivals will enjoy shorter backoff delays than older ones, resulting in greater jitter. Adjusting both preserves the relative ordering of backoff counter values, which implies also some form of age ordering. Different adjustments can be applied to different priority traffic.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
Tiered contention multiple access (TCMA): a method for priority-based shared channel access
InactiveUS20070019664A1Minimizing chanceLower latencySynchronisation arrangementError preventionService-level agreementClass of service
Quality of Service (QoS) support is provided by means of a Tiered Contention Multiple Access (TCMA) distributed medium access protocol that schedules transmission of different types of traffic based on their service quality specifications. In one embodiment, a wireless station is supplied with data from a source having a lower QoS priority QoS(A), such as file transfer data. Another wireless station is supplied with data from a source having a higher QoS priority QoS(B), such as voice and video data. Each wireless station can determine the urgency class of its pending packets according to a scheduling algorithm. For example file transfer data is assigned lower urgency class and voice and video data is assigned higher urgency class. There are several urgency classes which indicate the desired ordering. Pending packets in a given urgency class are transmitted before transmitting packets of a lower urgency class by relying on class-differentiated urgency arbitration times (UATs), which are the idle time intervals required before the random backoff counter is decreased. In another embodiment packets are reclassified in real time with a scheduling algorithm that adjusts the class assigned to packets based on observed performance parameters and according to negotiated QoS-based requirements. Further, for packets assigned the same arbitration time, additional differentiation into more urgency classes is achieved in terms of the contention resolution mechanism employed, thus yielding hybrid packet prioritization methods. An Enhanced DCF Parameter Set is contained in a control packet sent by the AP to the associated stations, which contains class differentiated parameter values necessary to support the TCMA. These parameters can be changed based on different algorithms to support call admission and flow control functions and to meet the requirements of service level agreements.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
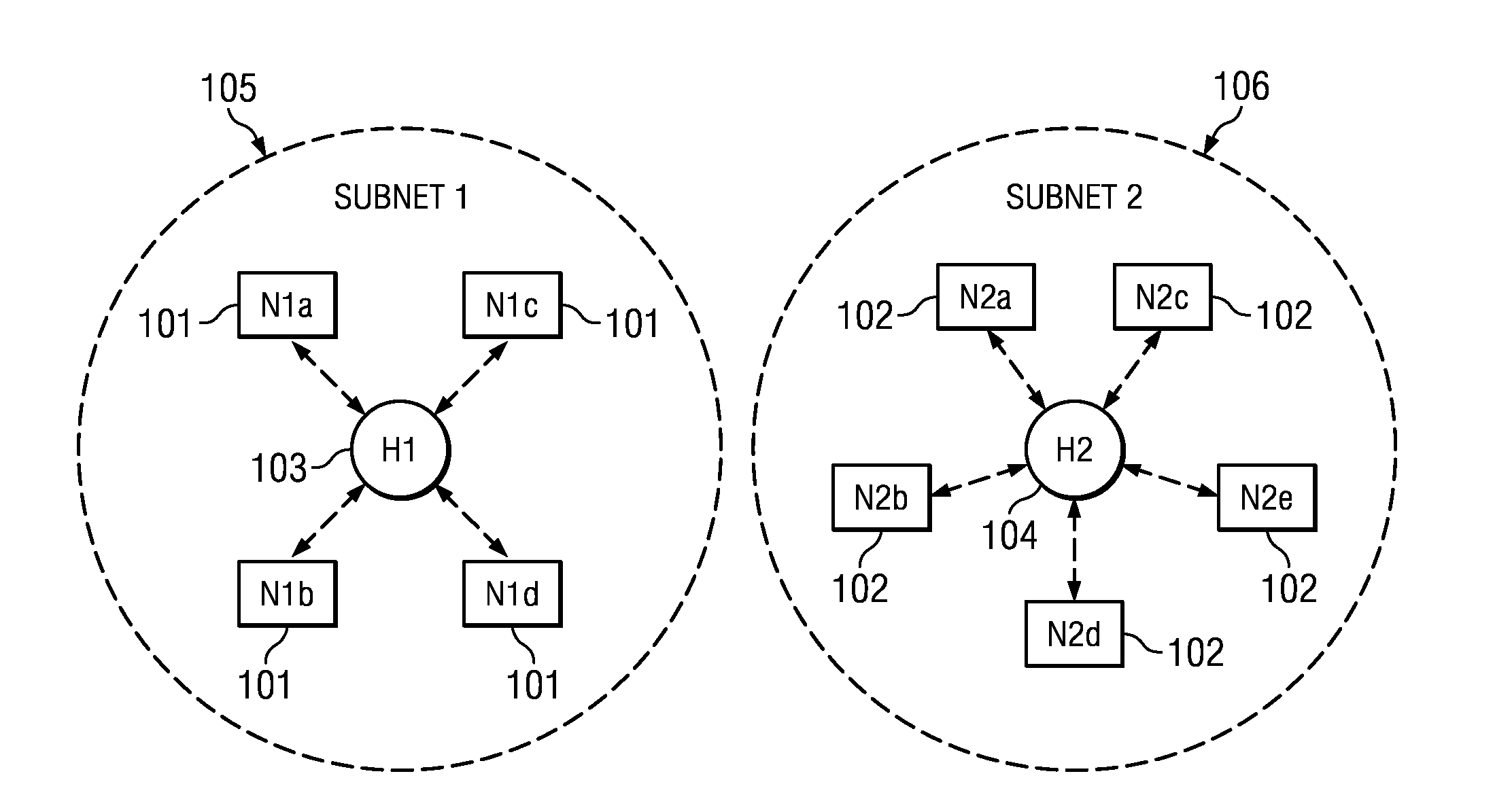
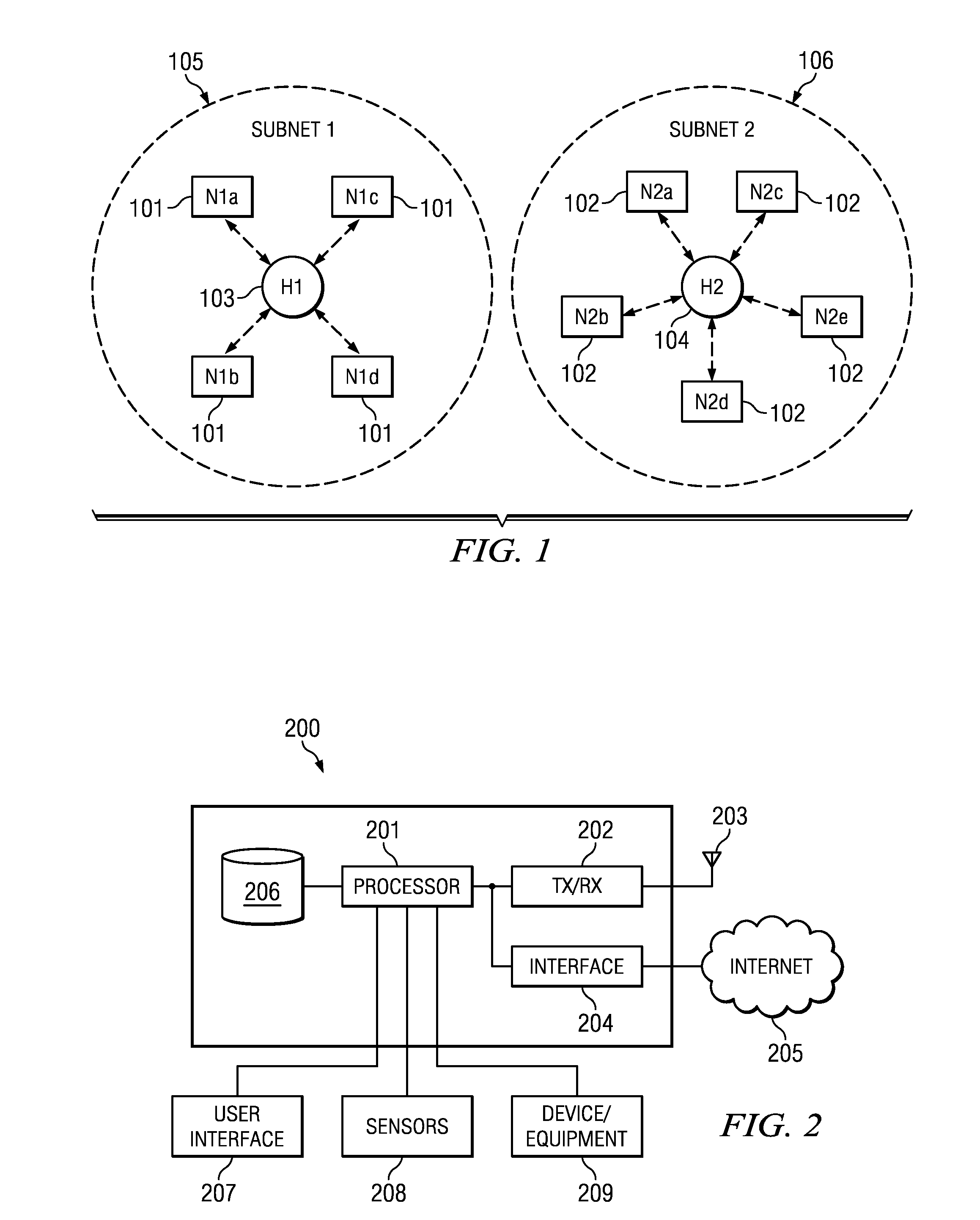
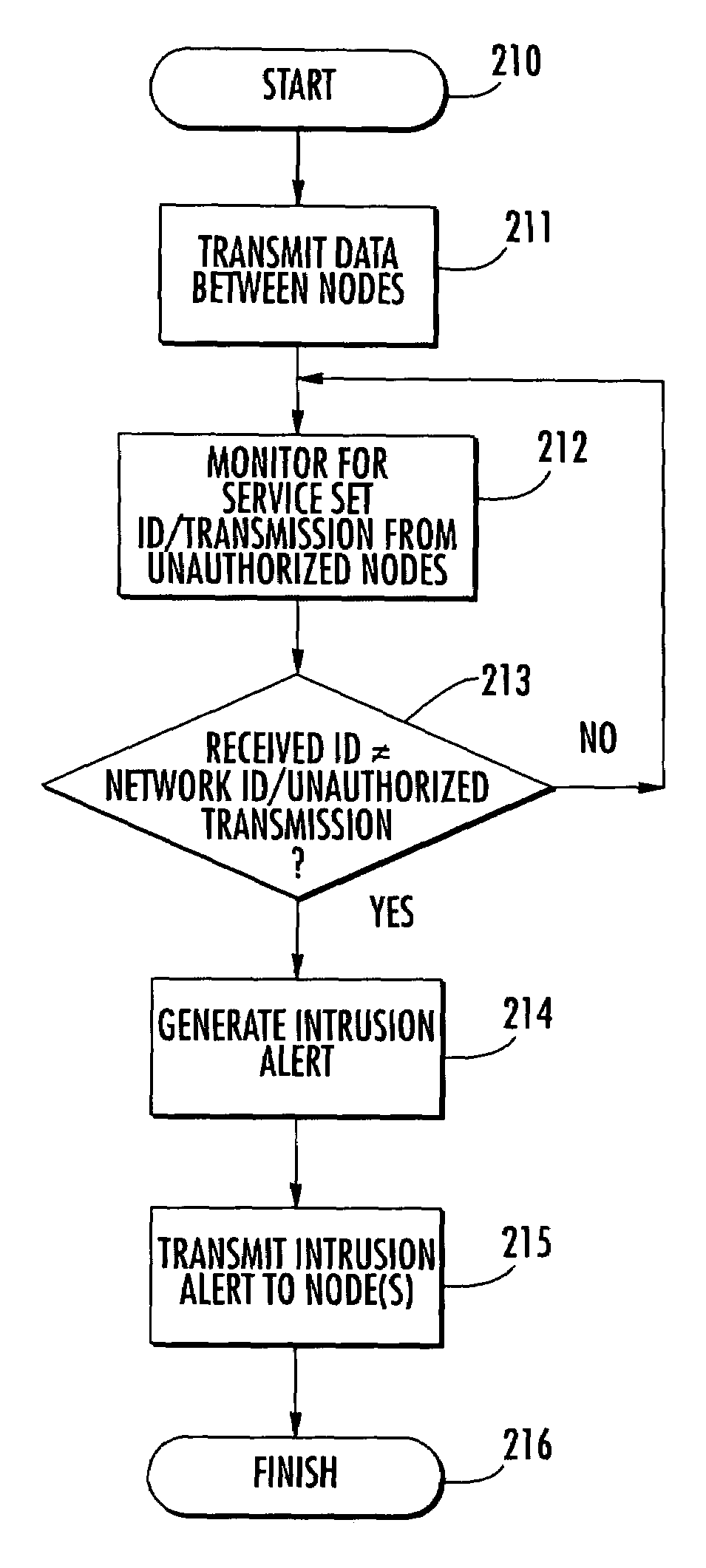
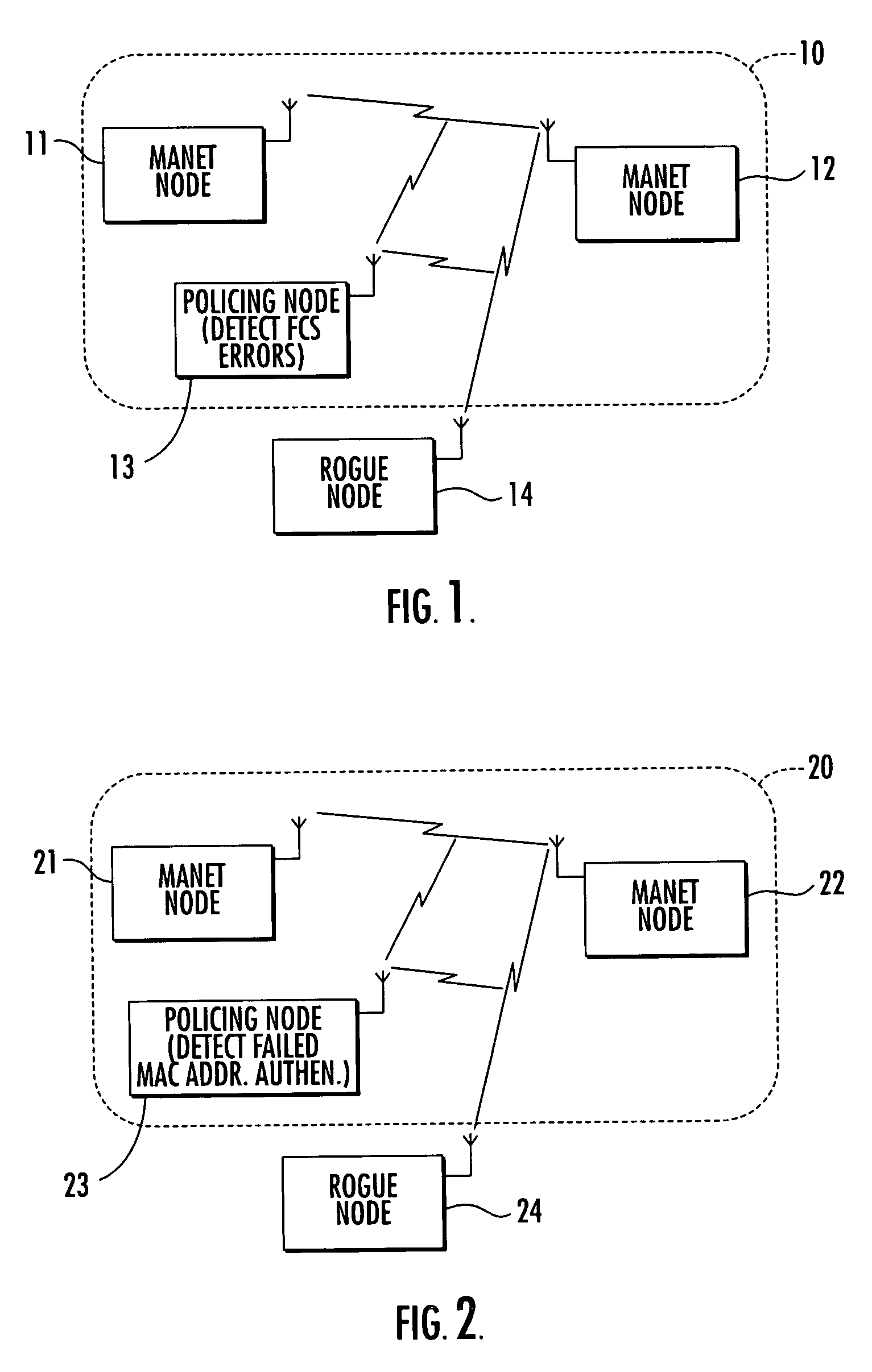
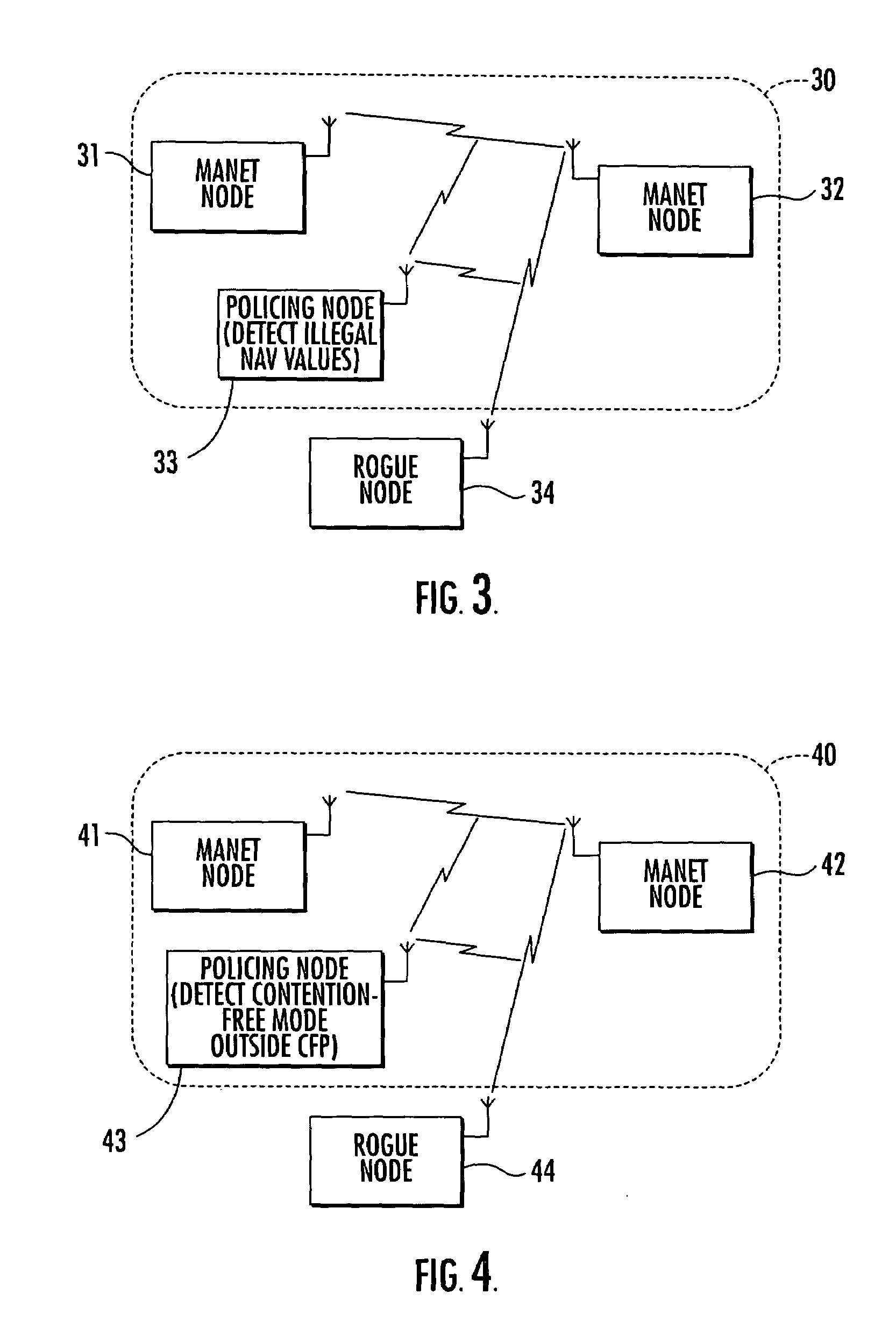
Mobile ad-hoc network with intrusion detection features and related methods
InactiveUS7082117B2Error preventionBroadcast transmission systemsNetwork allocation vectorMedia access
A mobile ad-hoc network (MANET) may include a plurality of nodes for transmitting data therebetween using a media access layer (MAC), where each of the nodes has a respective MAC address associated therewith. The MANET may also include a policing node for detecting intrusions into the MANET by monitoring transmissions among the plurality of nodes to detect frame check sequence (FCS) errors from a MAC address, and generating an intrusion alert based upon detecting a number of FCS errors for the MAC address exceeding a threshold. The policing node may also detect intrusions based upon one or more of failed MAC address authentications, illegal network allocation vector (NAV) values, and unexpected contention or contention-free operation.
Owner:STINGRAY IP SOLUTIONS LLC
Programmable output interface for lower level open system interconnection architecture
InactiveUS6049837ABroadband local area networksMultiple digital computer combinationsControl signalData rate
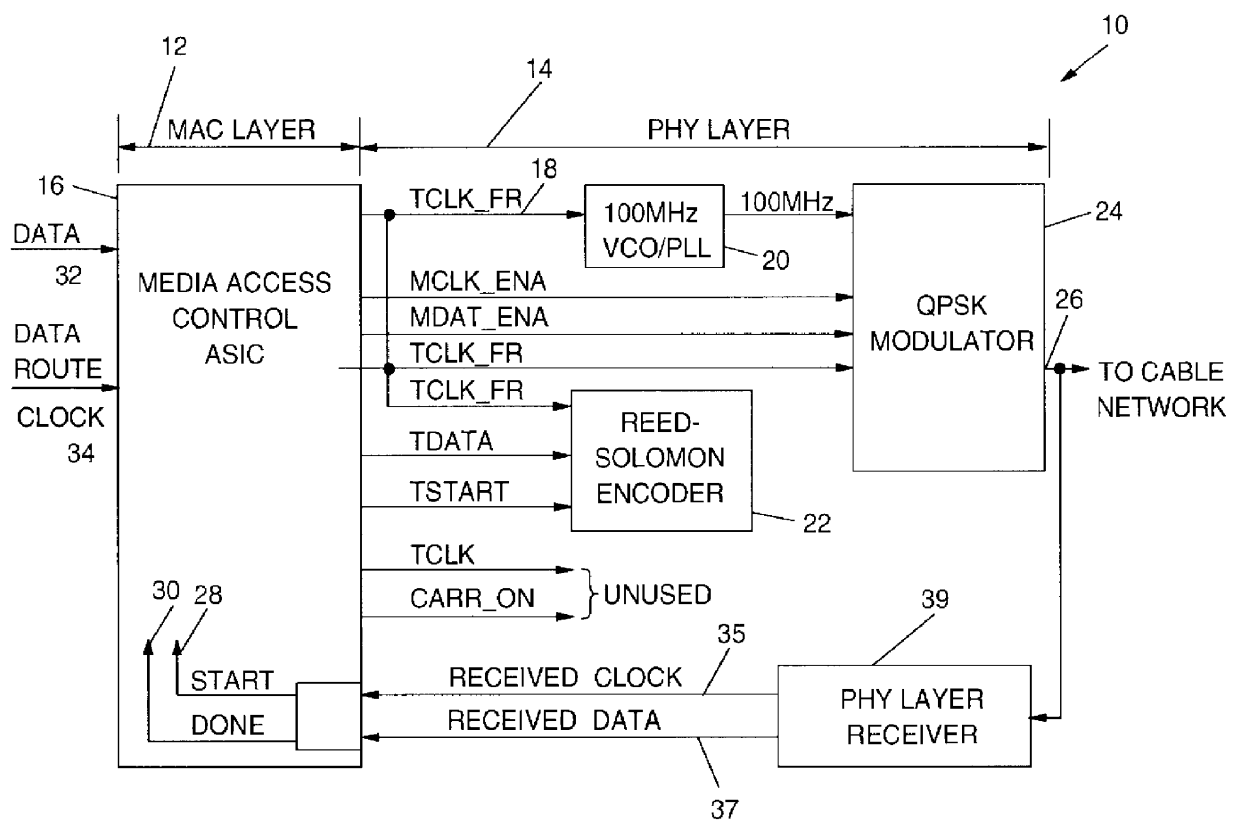
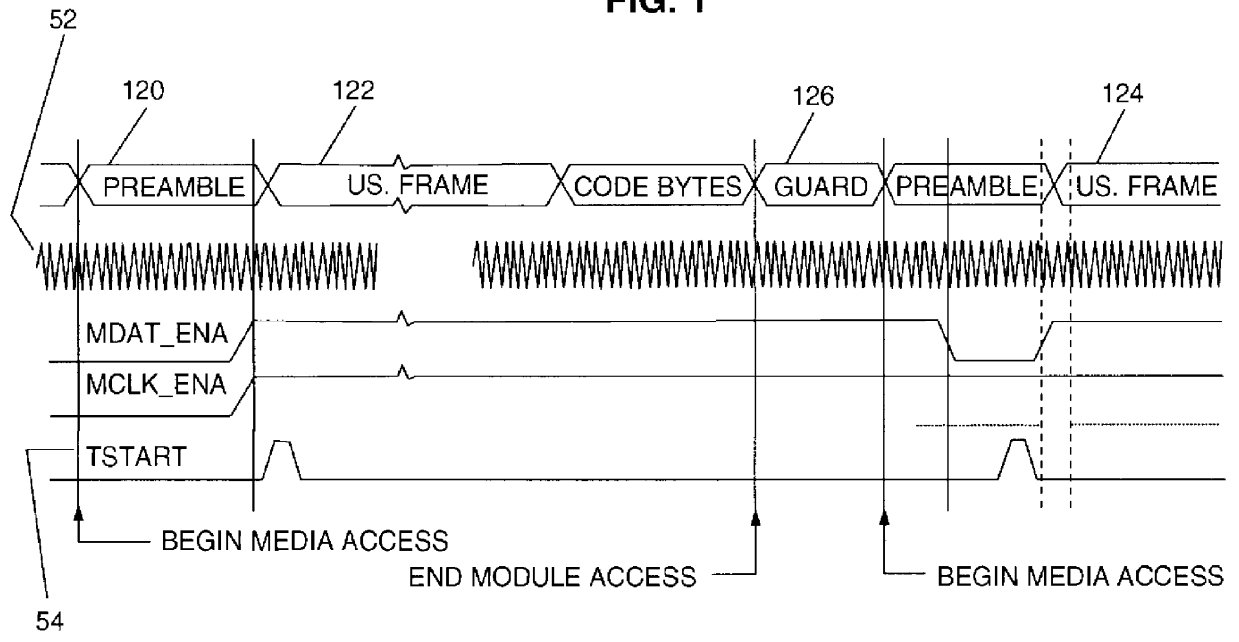
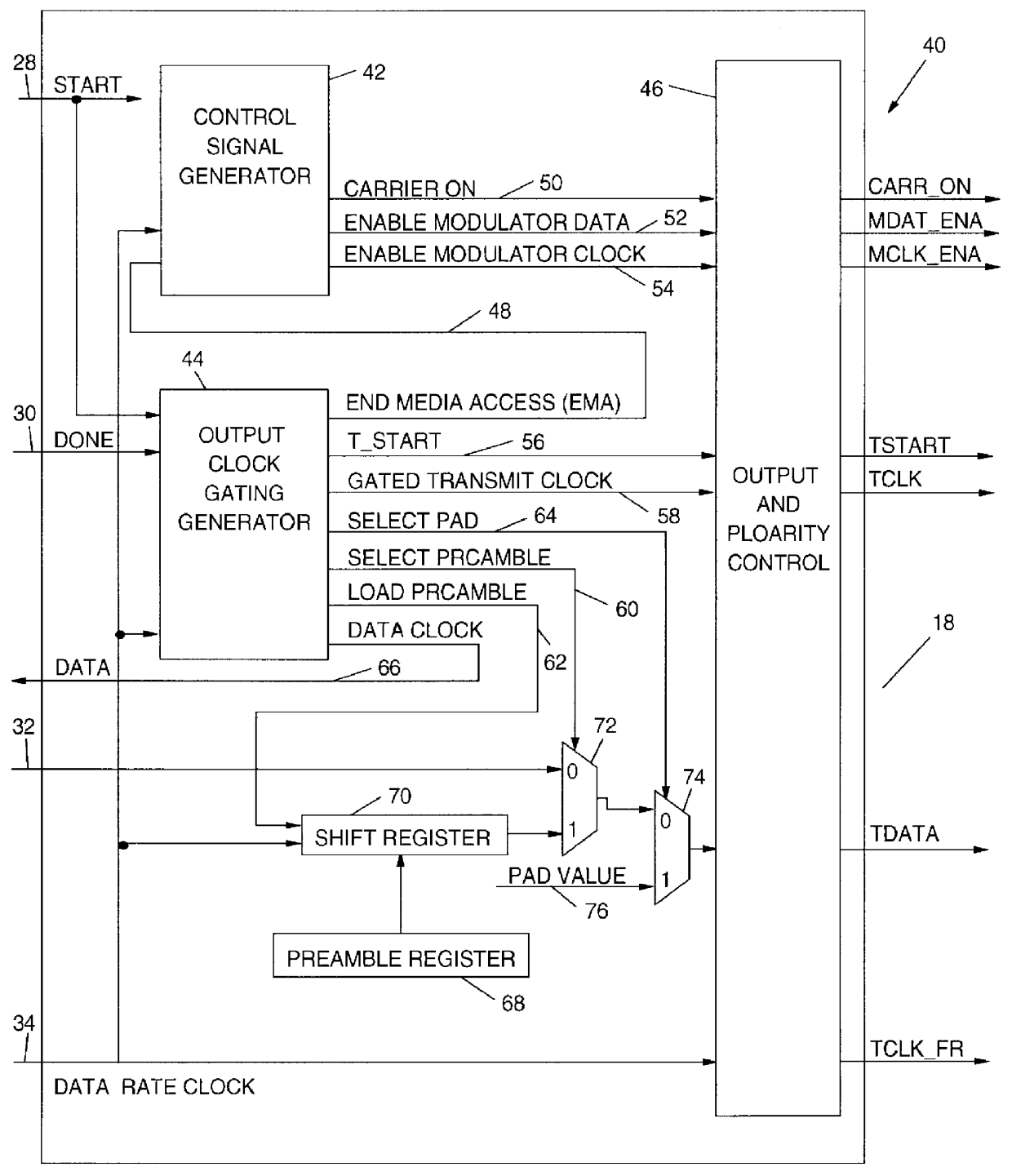
A programmable output interface in an Open System Interconnection (OSI) enables a Media Access (MAC) Layer to access a variety of Physical (PHY) Layer implementations without redesign of the interface. The programmable interface includes a control signal generator; an output clock gating generator, and an output polarity control device coupled to the PHY layer. The interface receives media access Start; media access Done signals; a Data Rate clock signal and a data signal. The control signal generator provides control signals for the physical layer components via the polarity control device. The active signal polarity and the relative timing of the control signals are controlled by programmable registers. The output clock gating generator provides clock signals to the physical layer components via the polarity control in response to the Start; Done and Data Rate signals. The output generator clock includes programmable interval registers for the various frame intervals including a User Pause Interval (UPI); Preamble Interval (PI); User Send Interval (USI), etc. The polarity control provides the correct signal polarity for each control, clock, and data signal.
Owner:IBM CORP
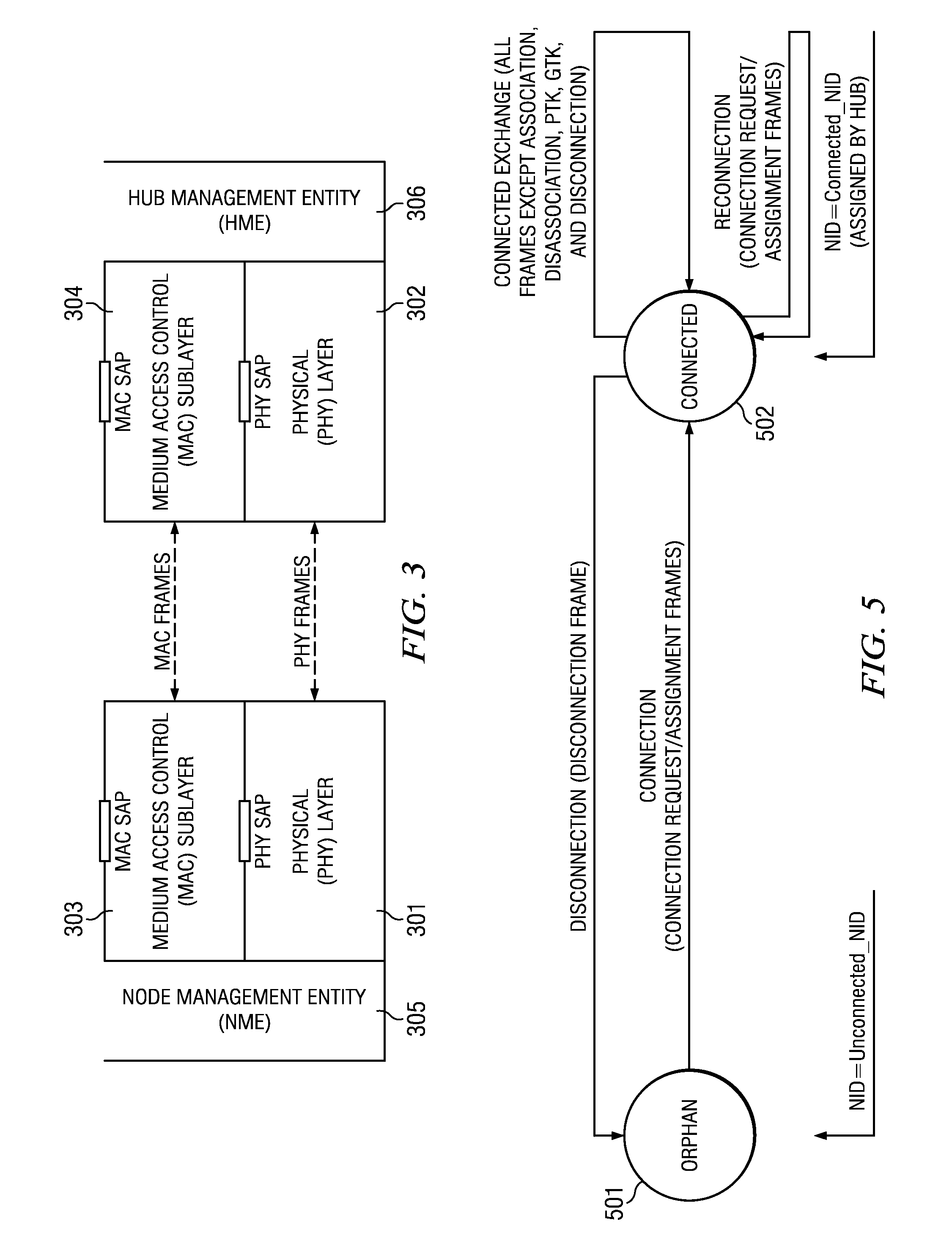
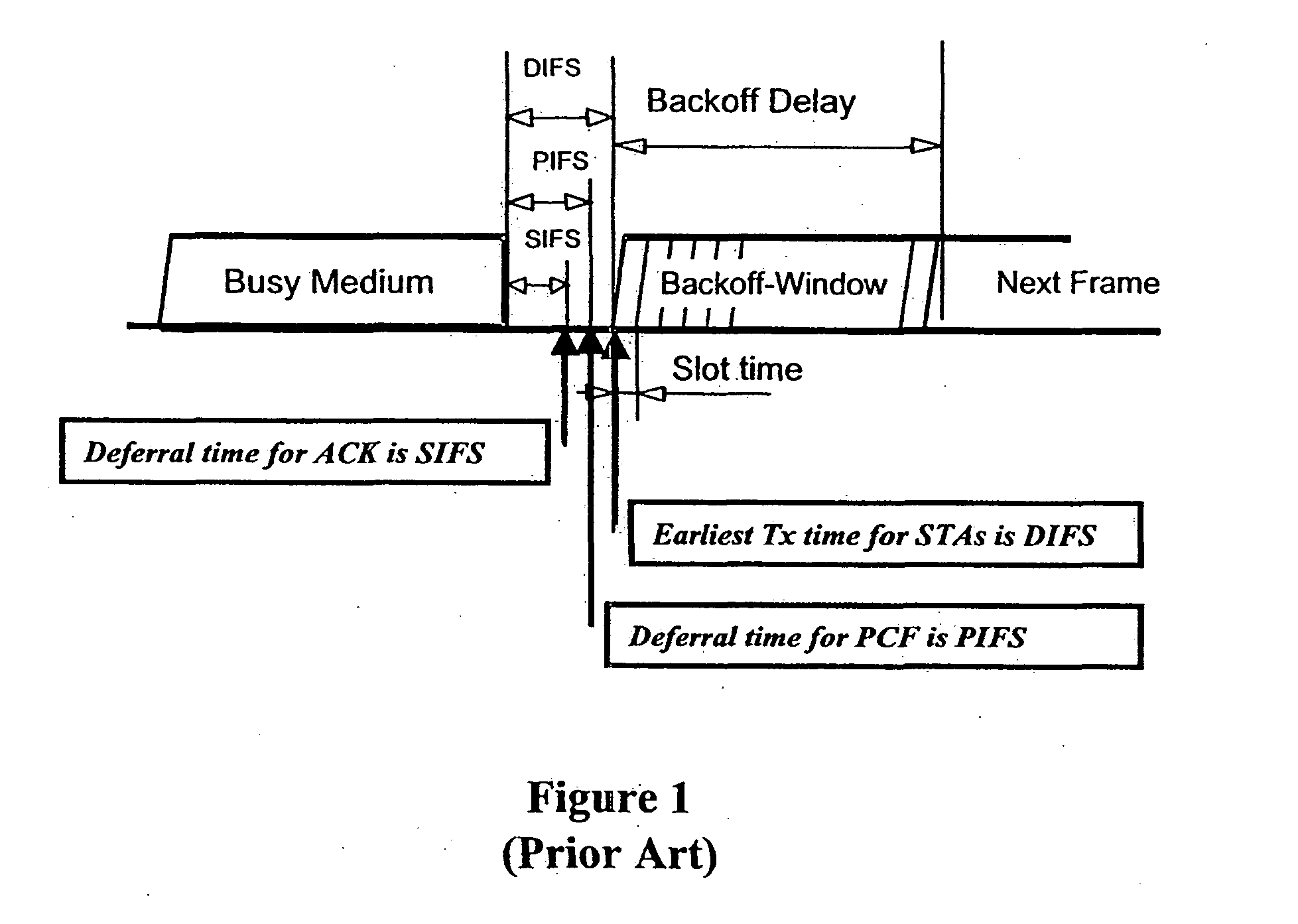
Contention protocols for wireless medium access in communication networks
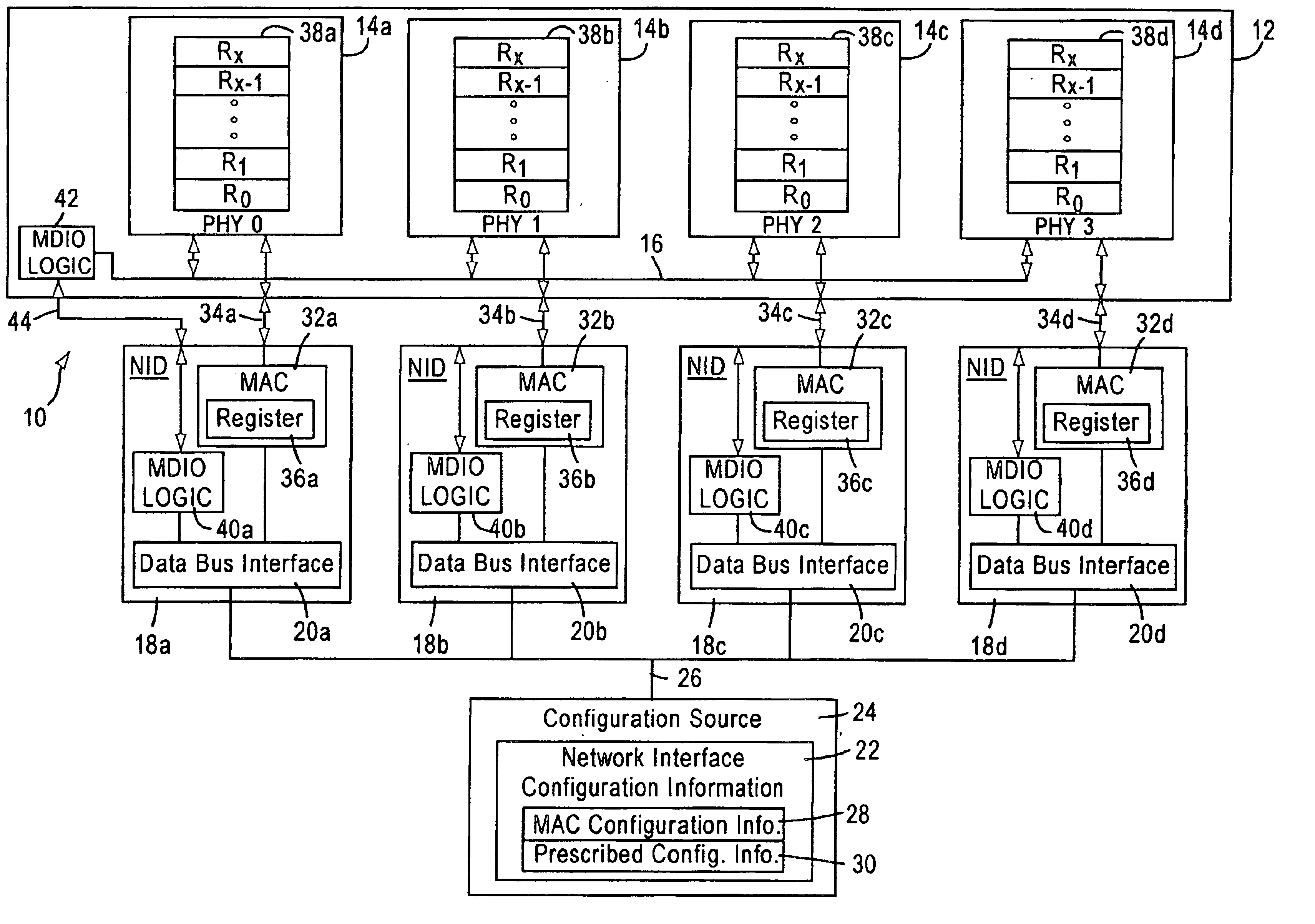
ActiveUS20090213815A1Minimizing number of timeMinimize the numberTime-division multiplexData switching networksComputer scienceMedia access
Wireless medium access in a communication network having a number of terminals is controlled by defining protocol message units for transmission by a given terminal which units correspond to operational states of at least one of the terminal and the medium. A number of time slots are allocated for transmission of packets from each terminal, and a number of contention opportunities are defined at the beginning of each time slot. Priority and backoff mechanisms are defined and applied at each terminal during the contention opportunities in the slots. Packets are then transmitted by the terminal within the slots while (1) minimizing the occurrence of empty slots at times when packets are available for transmission, and (2) minimizing the number of slots during which two or more packets are detected on the medium simultaneously at the terminal.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
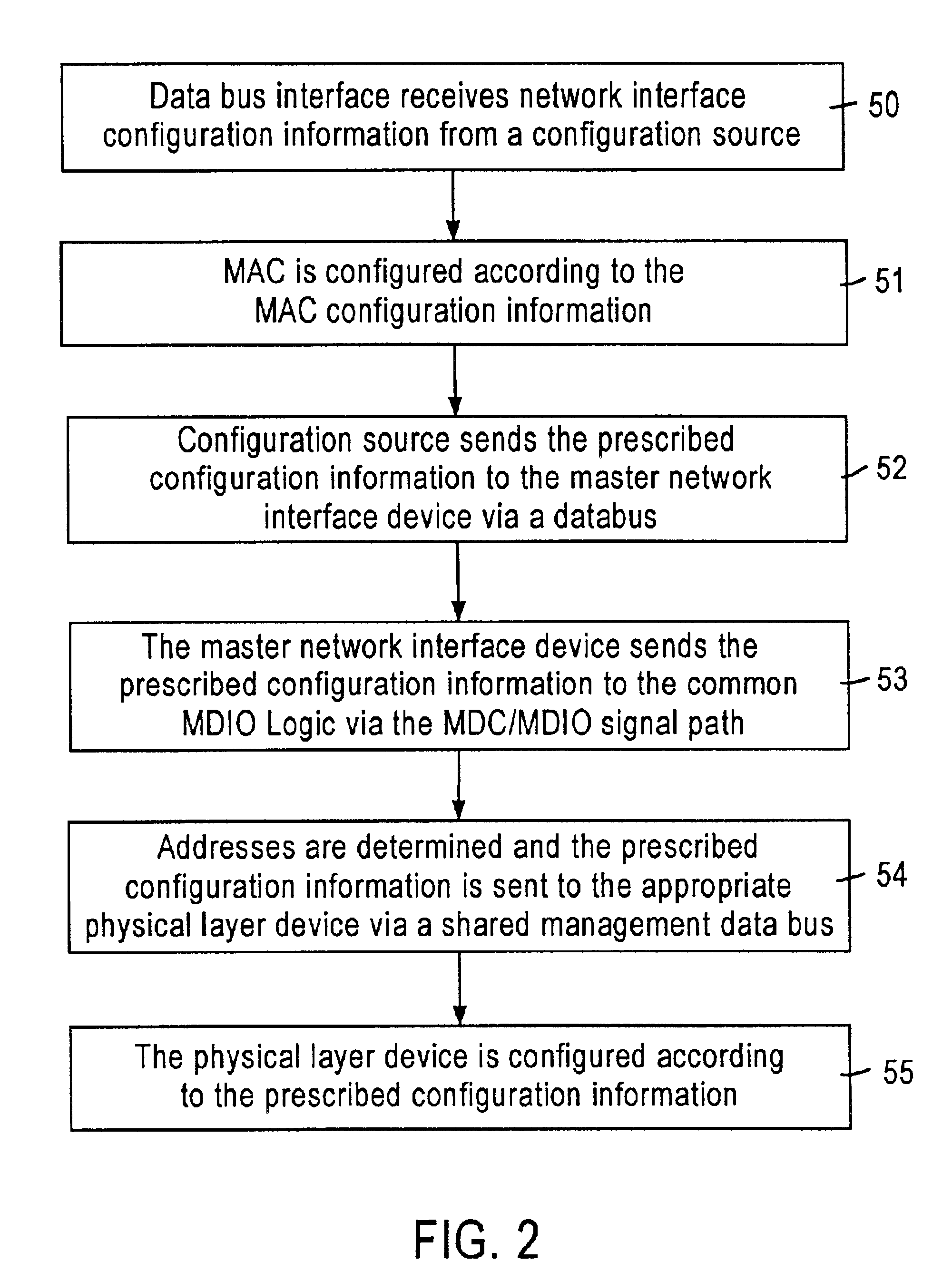
System and method enabling configuration of physical layer devices and corresponding link partners for communicating network data via a configuration source or auto-negotiation
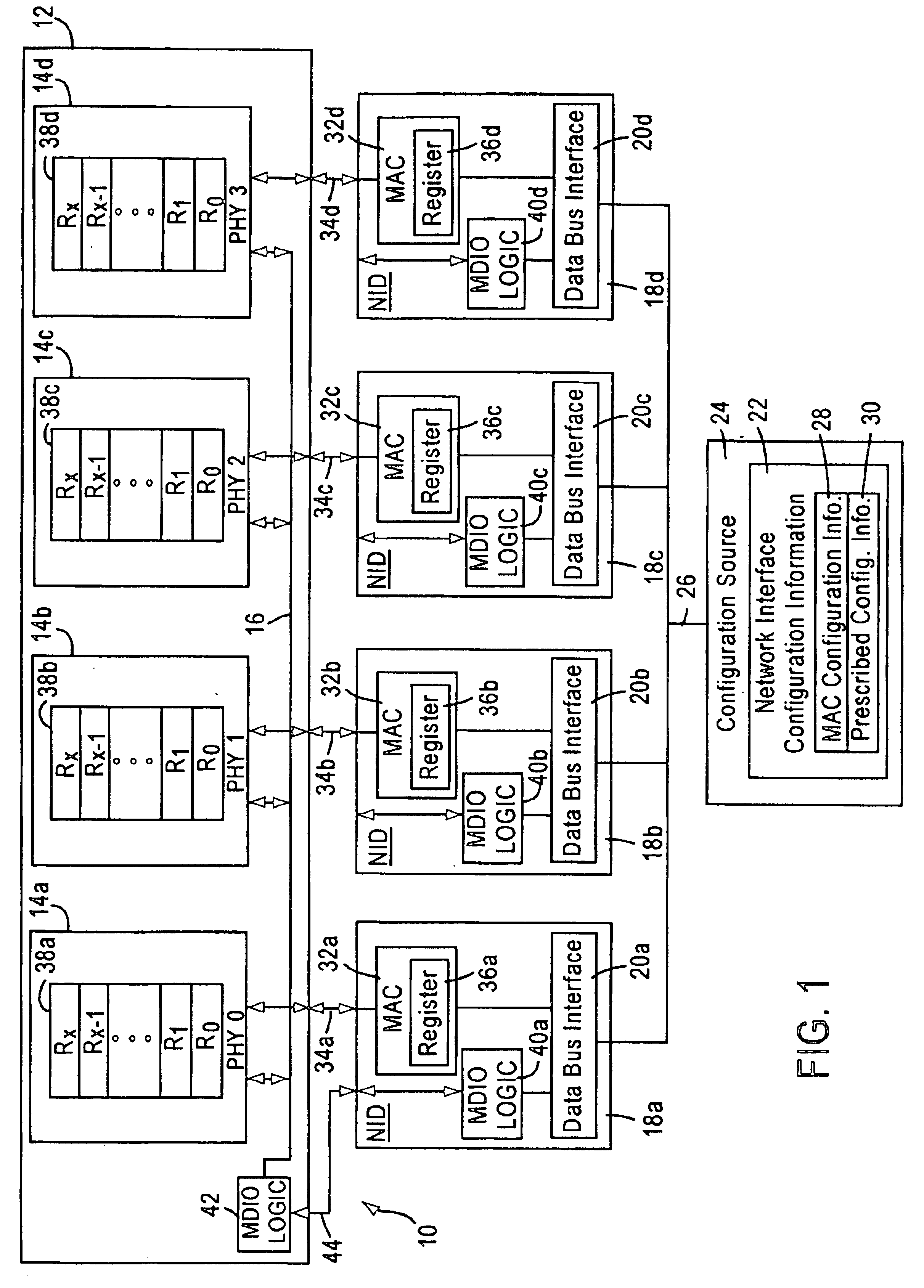
InactiveUS6859825B1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksProgrammable read-only memoryNetwork interface device
A network interface configures a plurality of physical layer devices and a corresponding plurality of network interface devices to allow for the communication of network data between the physical layer devices and corresponding link partners. At least one of the network interface devices is configured as a master device that communicates management information and autonegotiation results with the physical layer devices, while the other network interface devices do not. A configuration source, such as a central processing unit (CPU) or electronic erasable programmable read only memory (EEPROM), receives the autonegotiation results from the physical layer devices, through the master device, and configures the media access controllers (MACs) of each of the network interface devices in accordance with the autonegotiation results. This forces the MACs into their respective proper configurations even though the network interface devices that are not master devices do not receive the autonegotiation results directly from their corresponding physical layer devices.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com