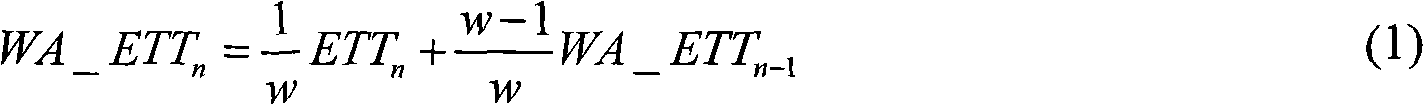Patents
Literature
152 results about "Network allocation vector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
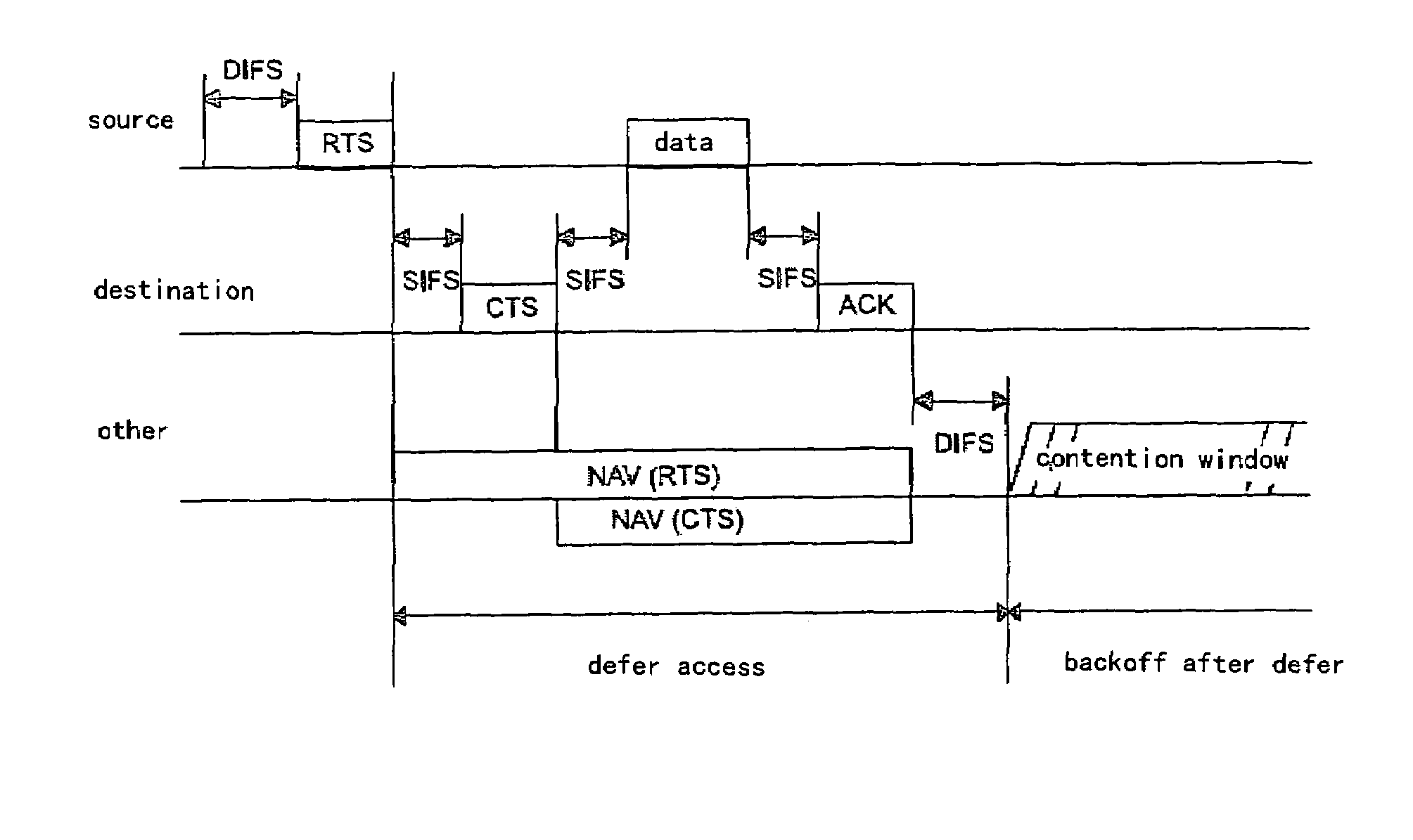
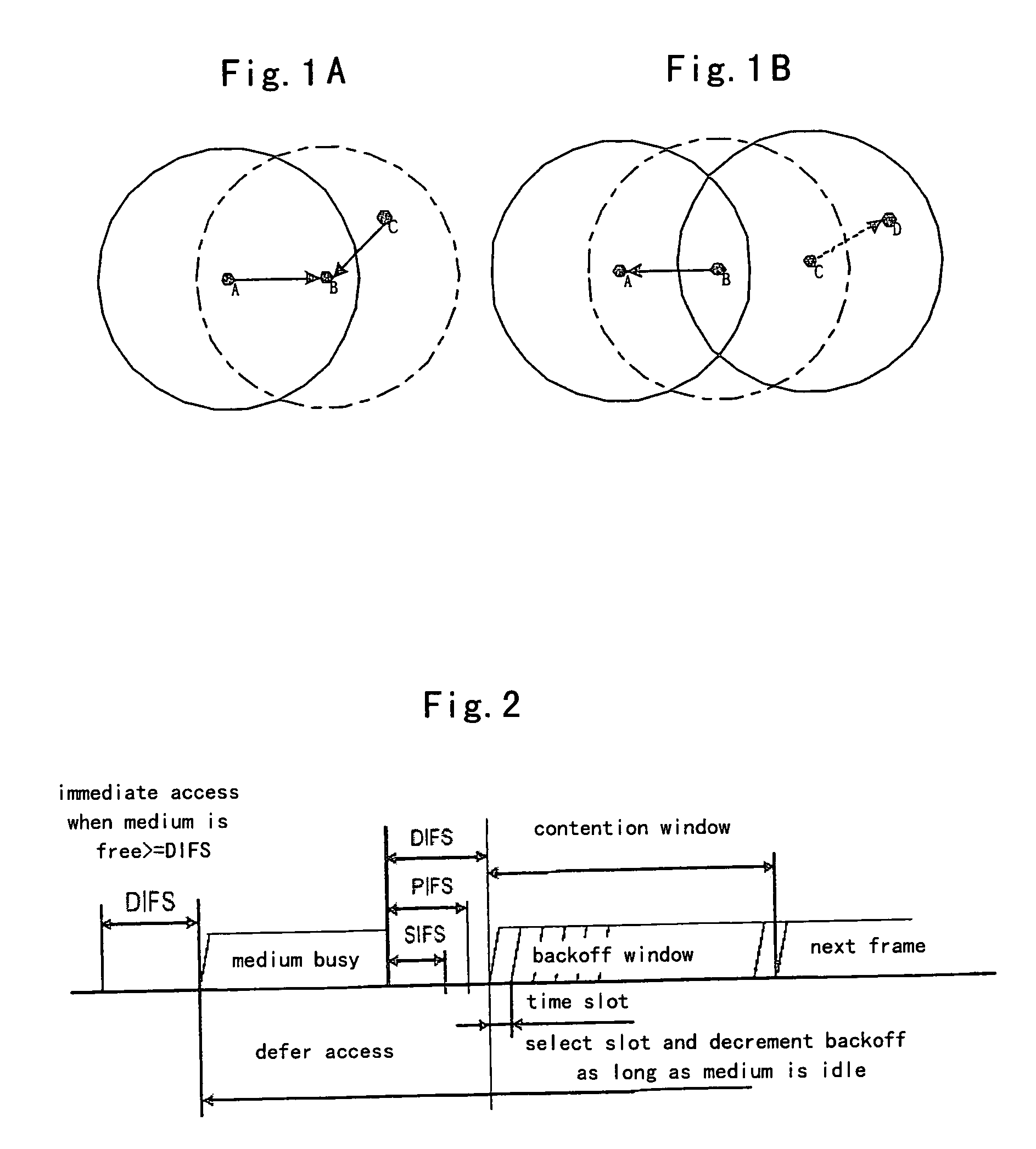
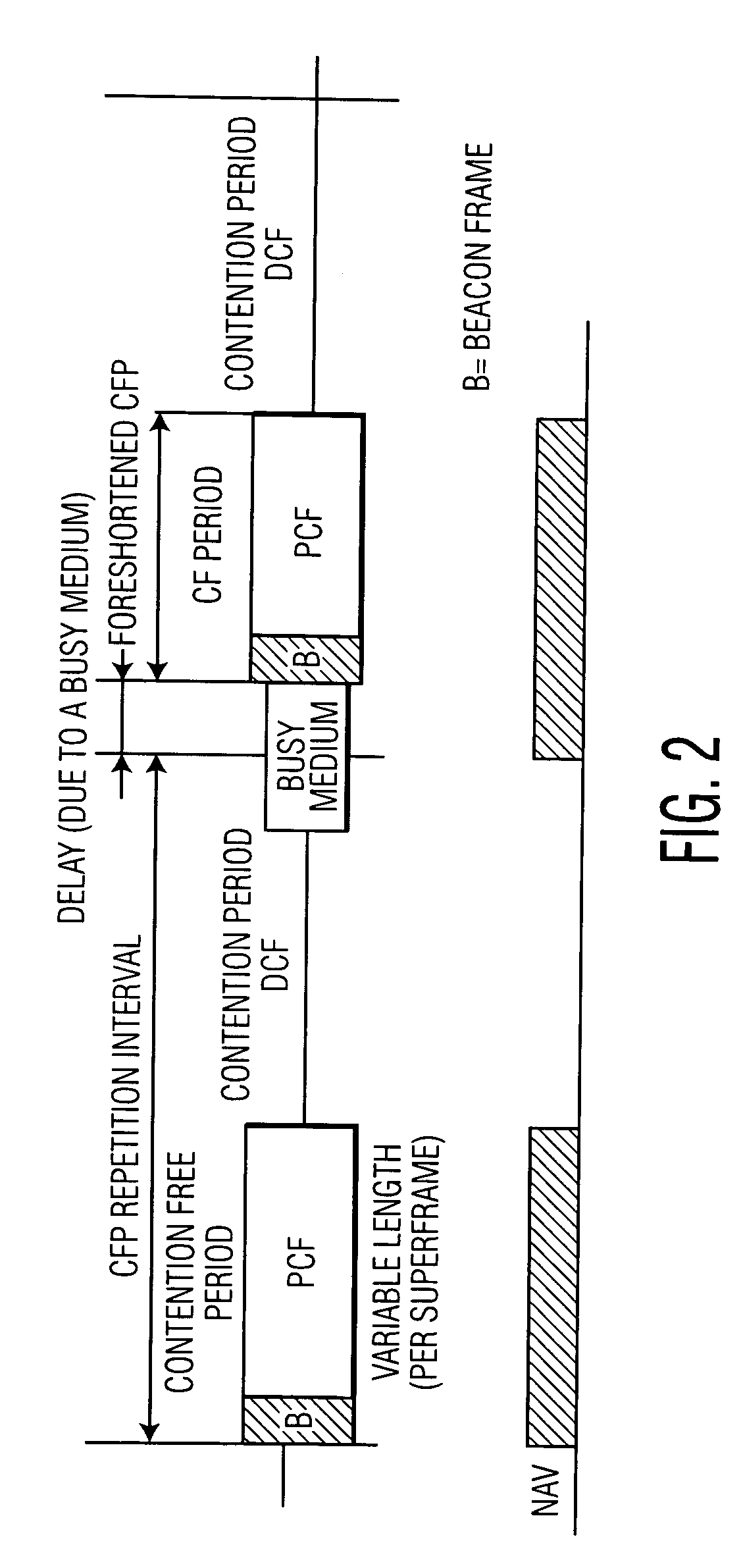
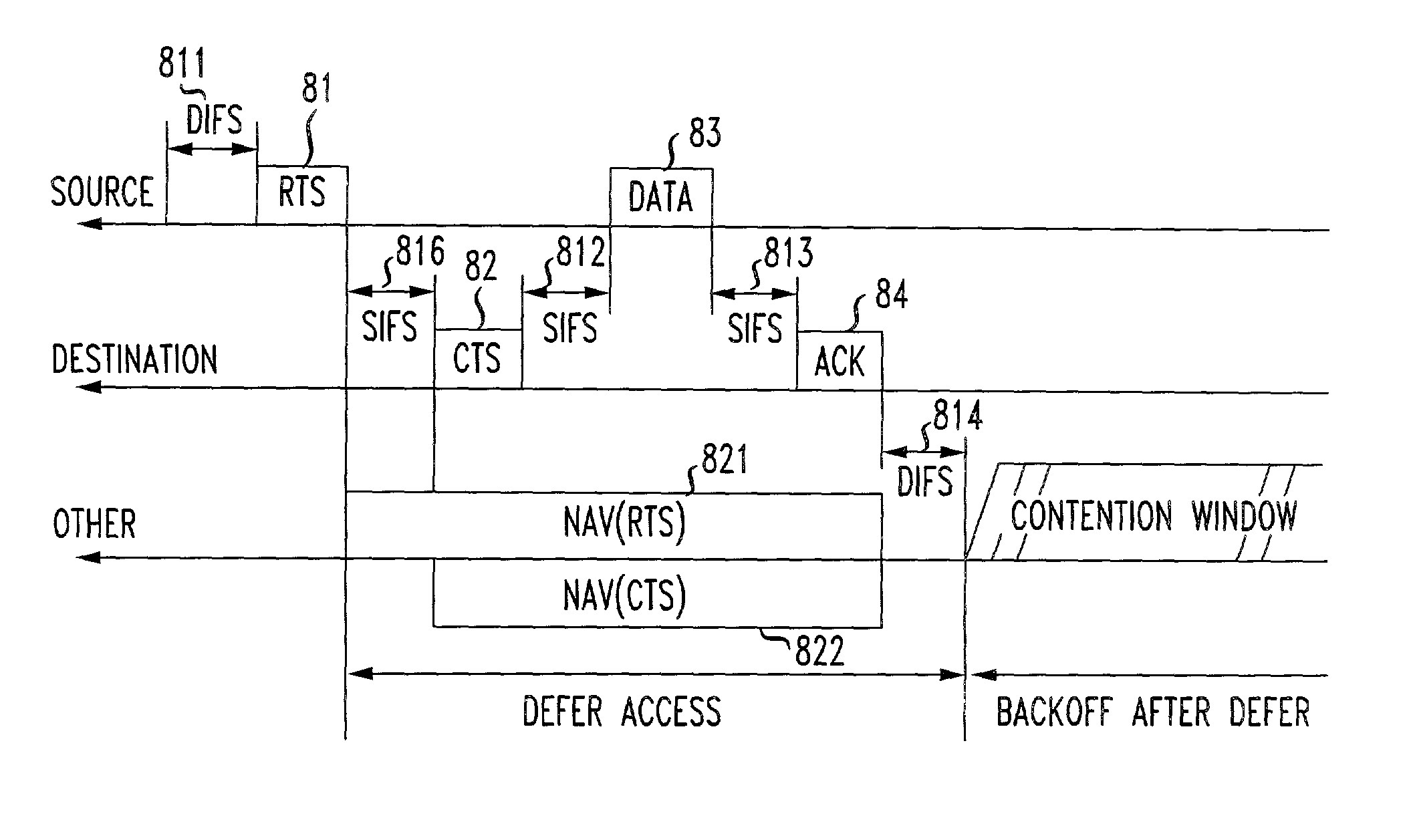
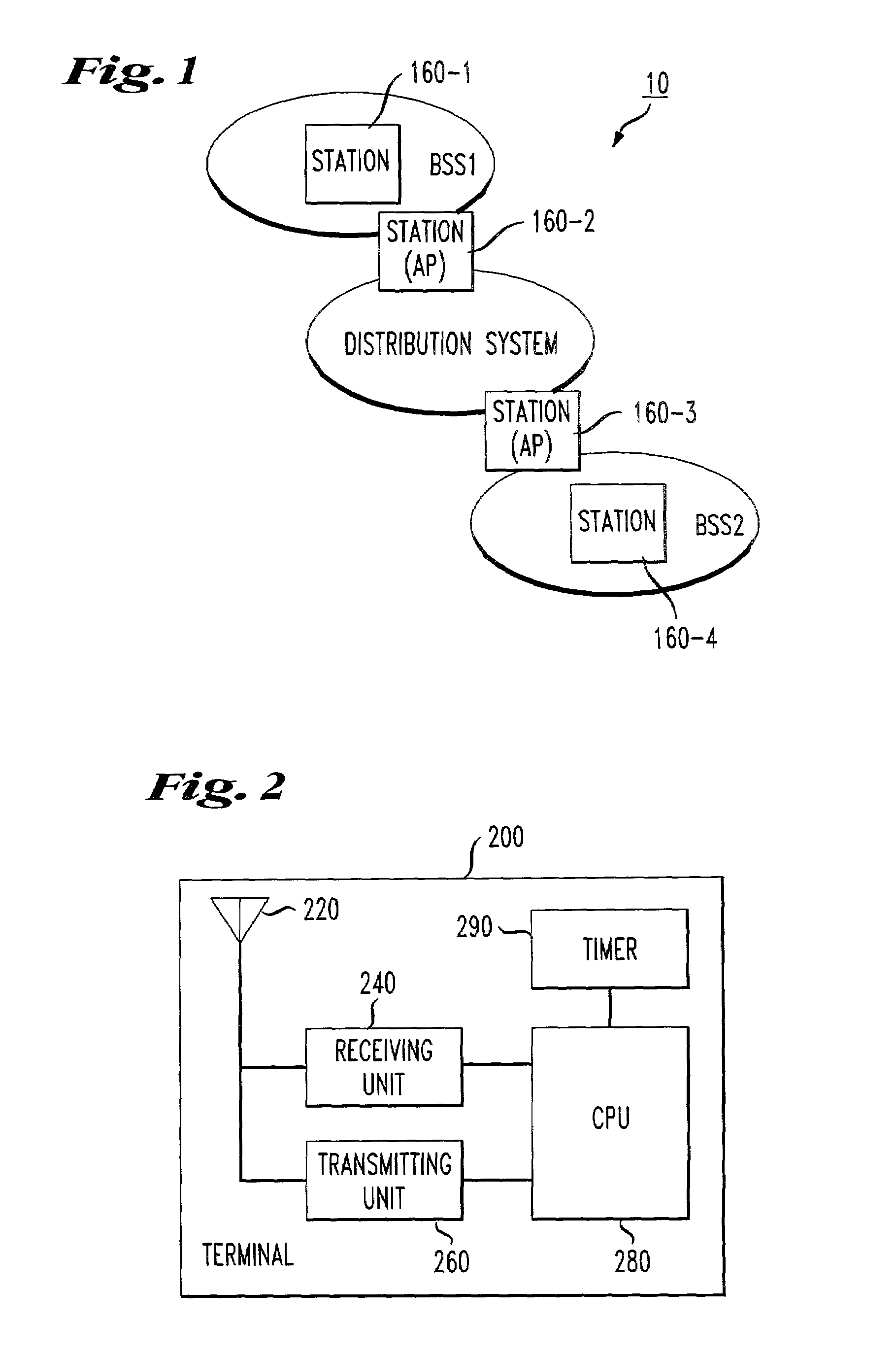
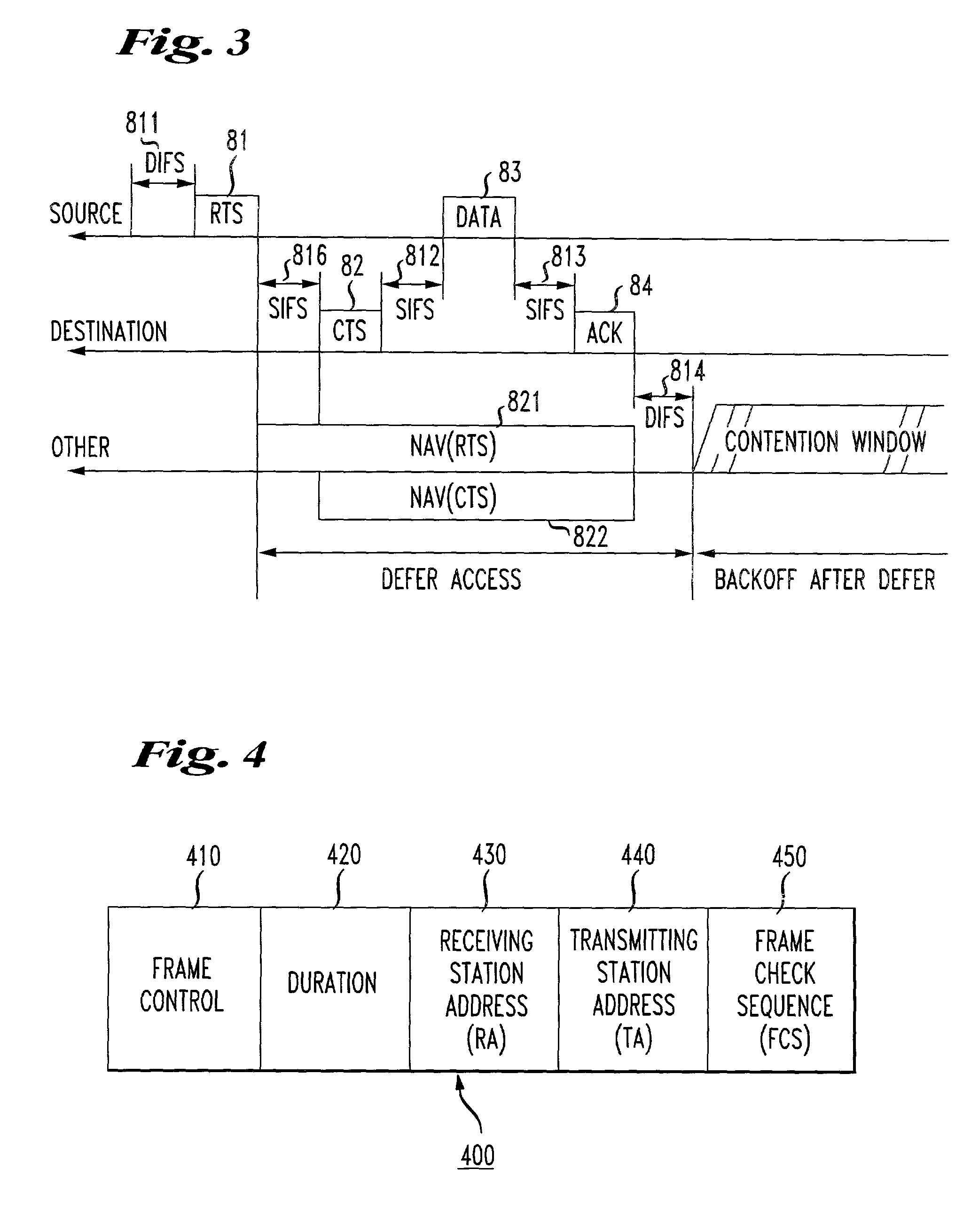
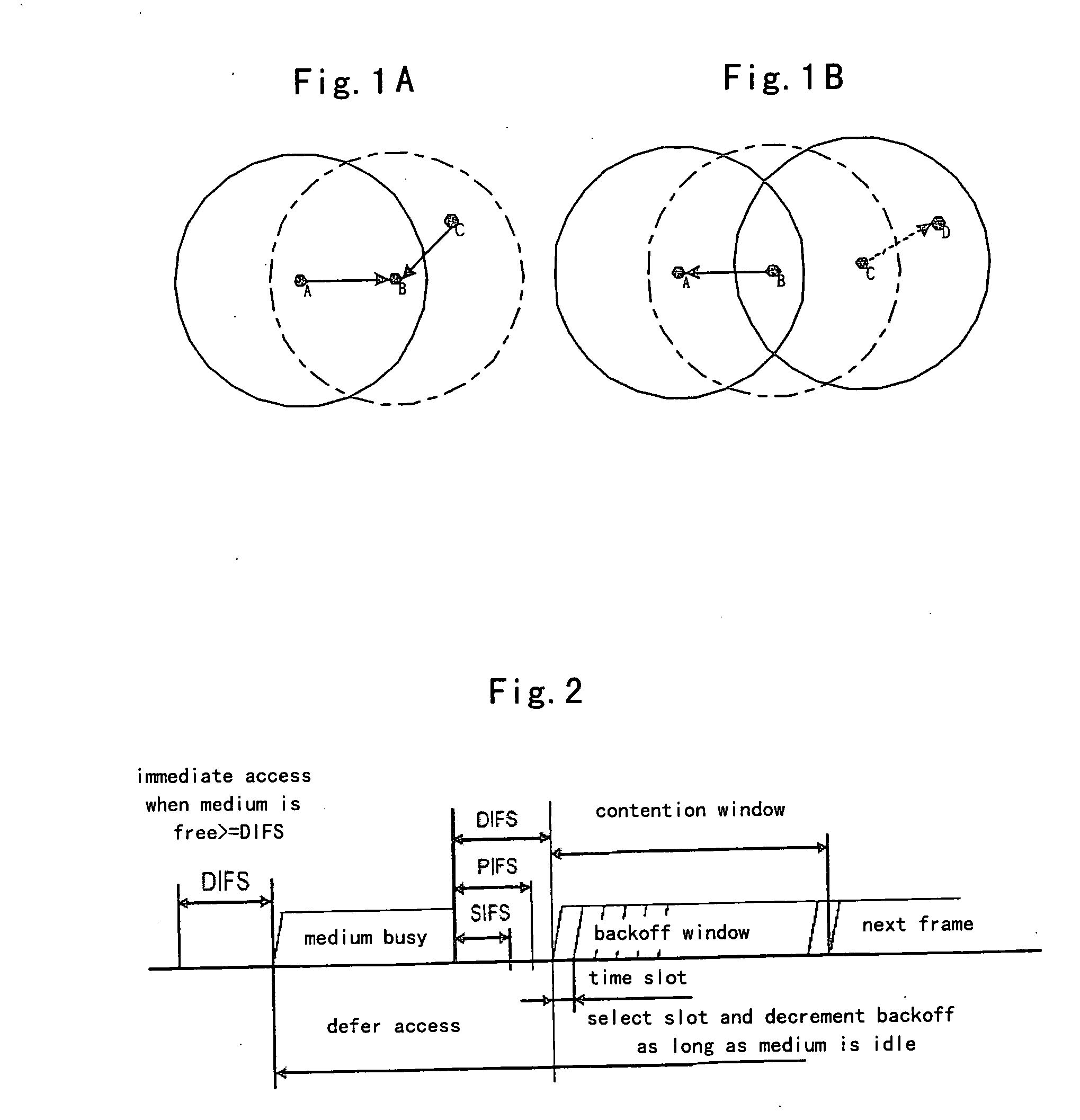
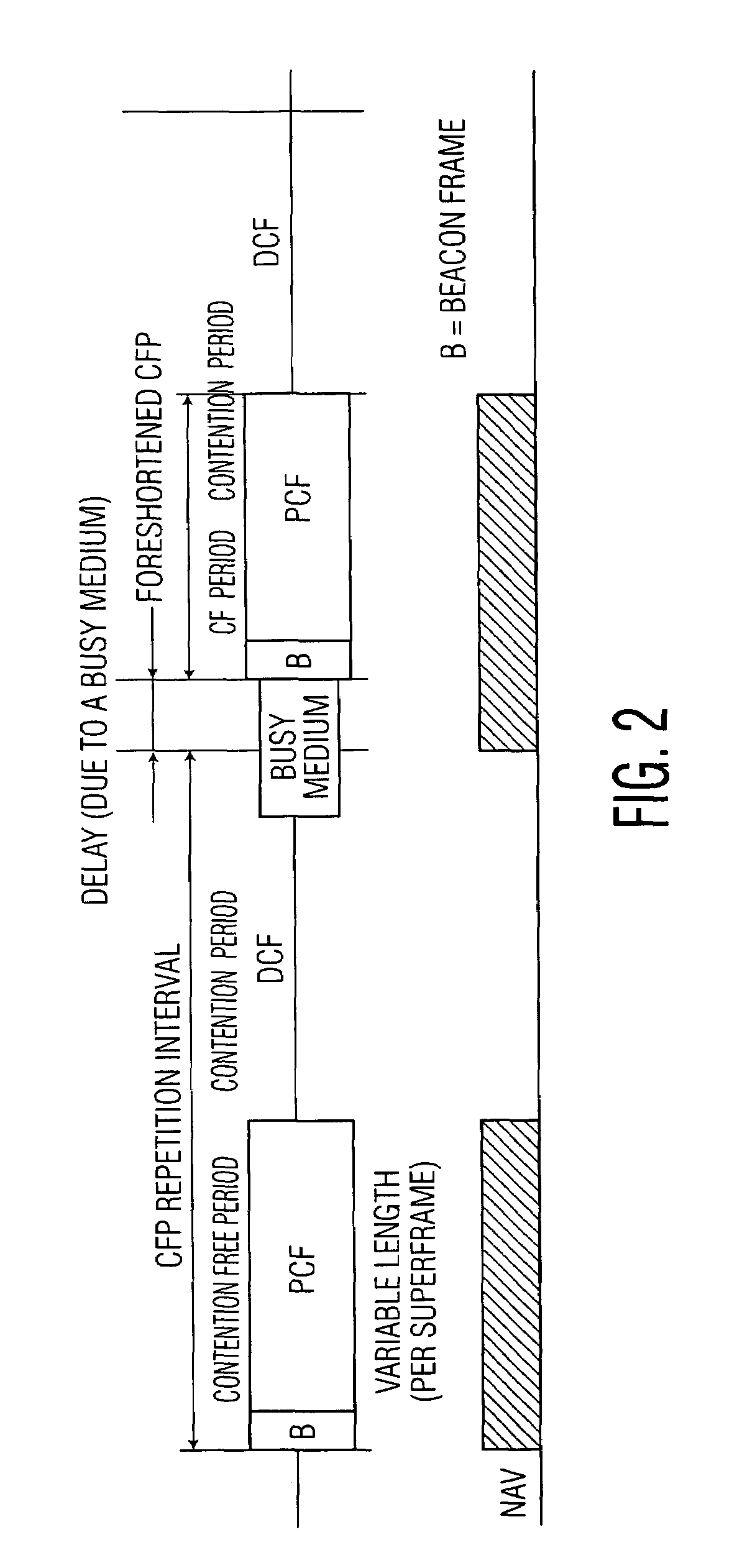
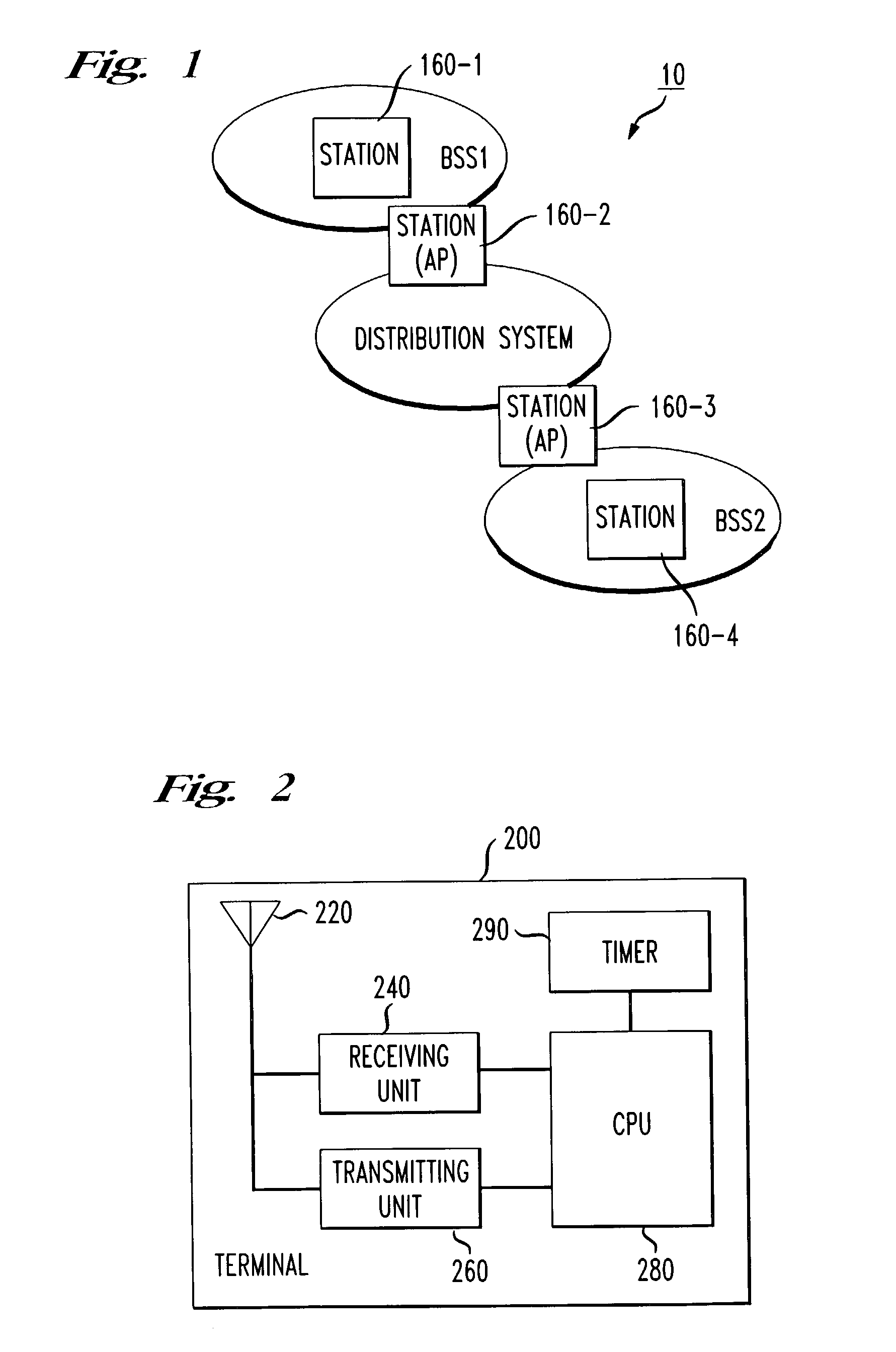
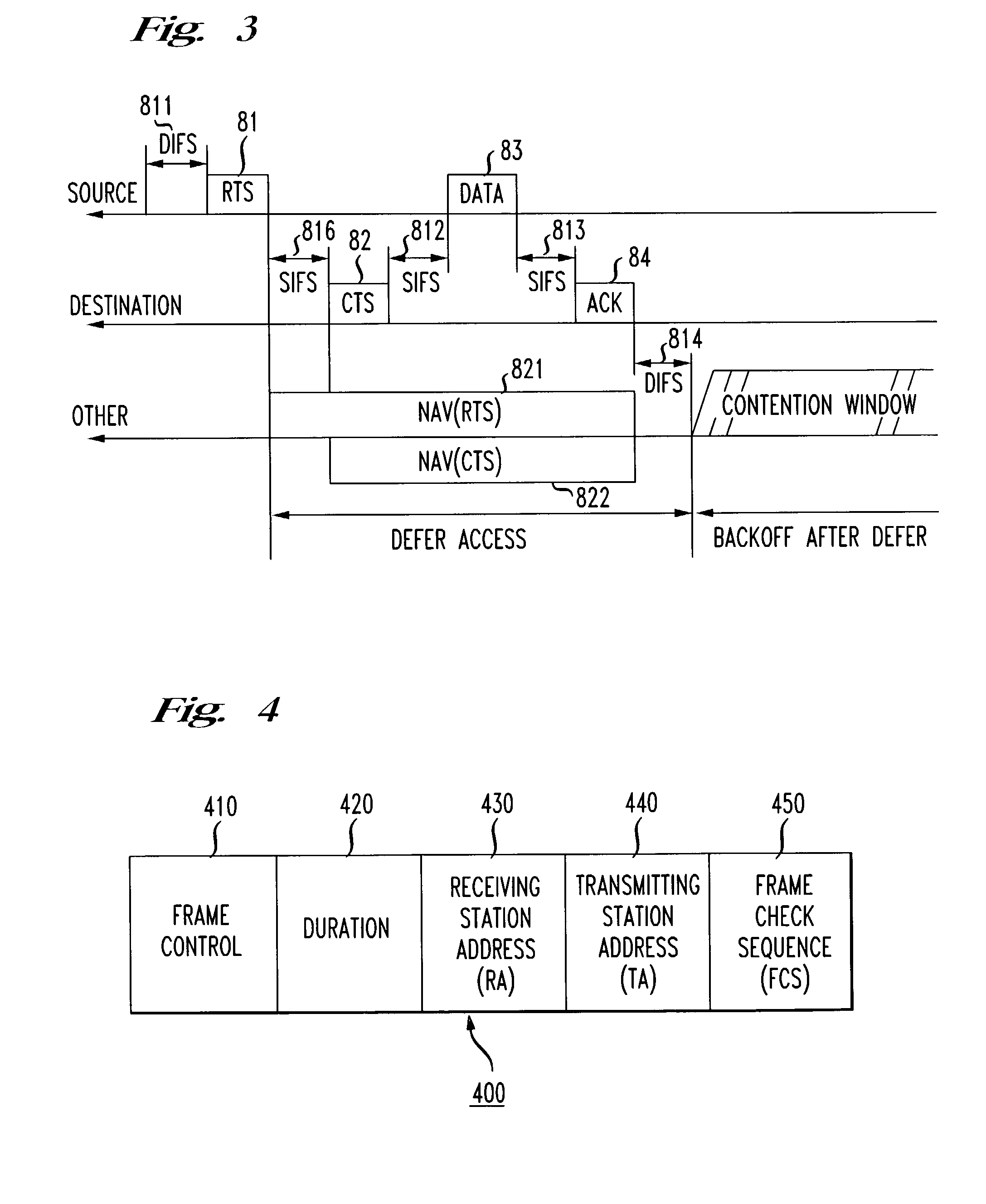
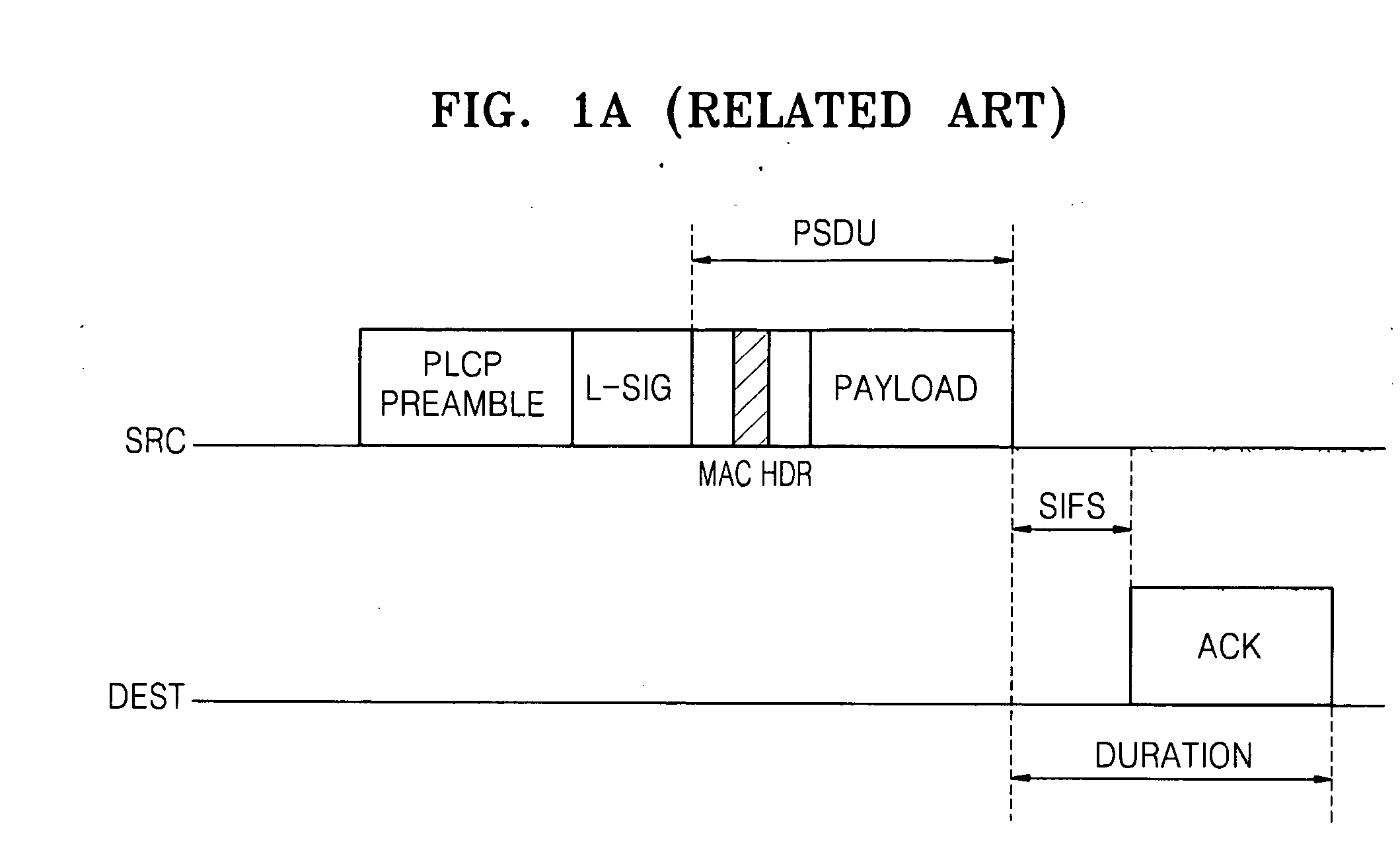
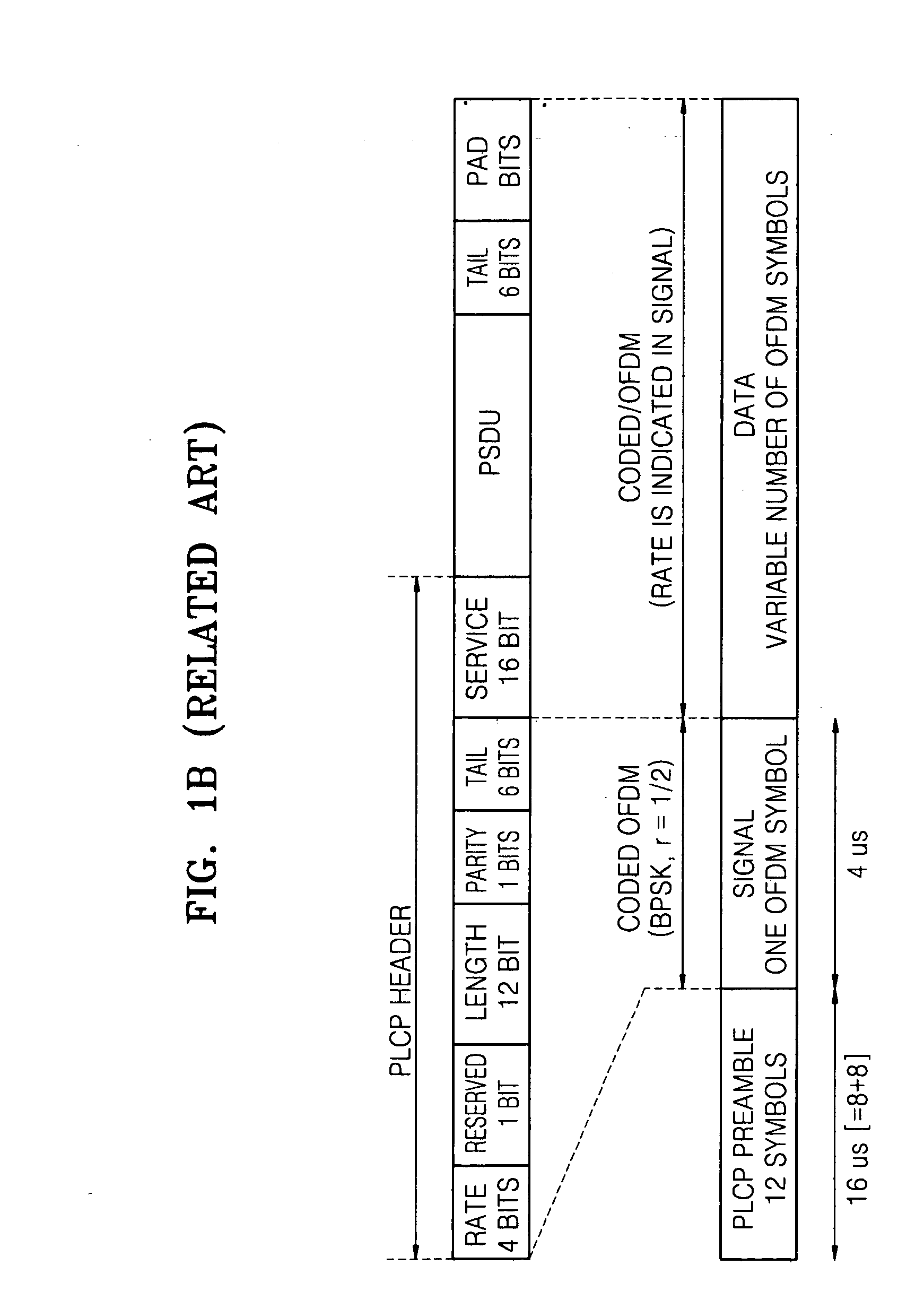
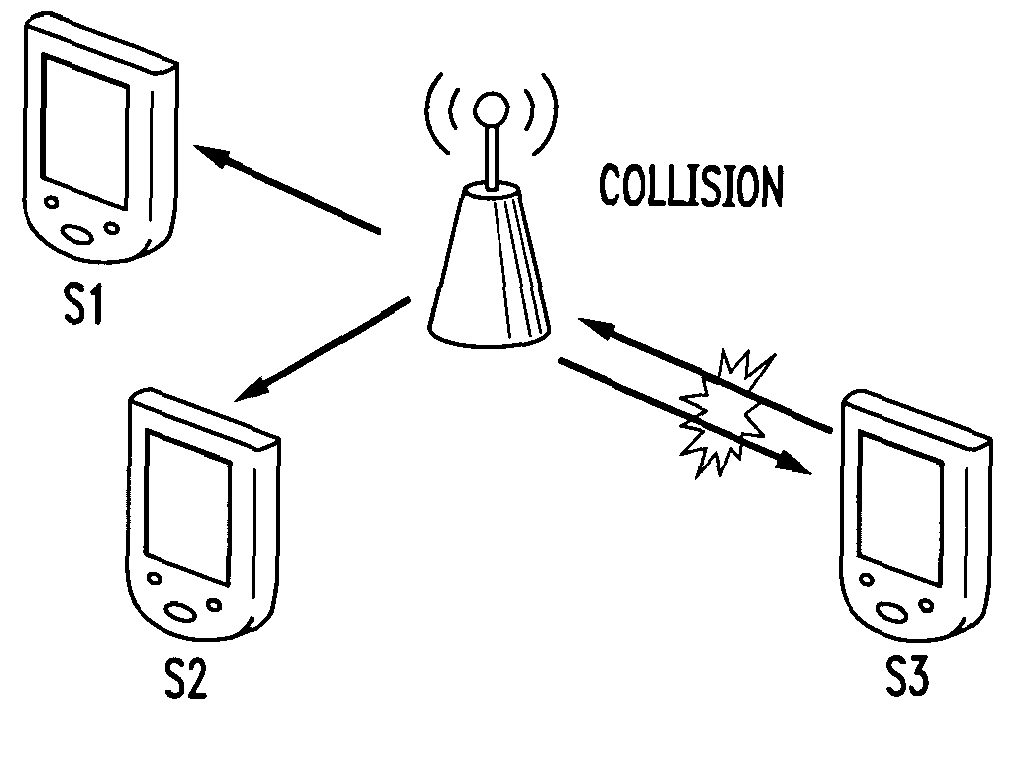
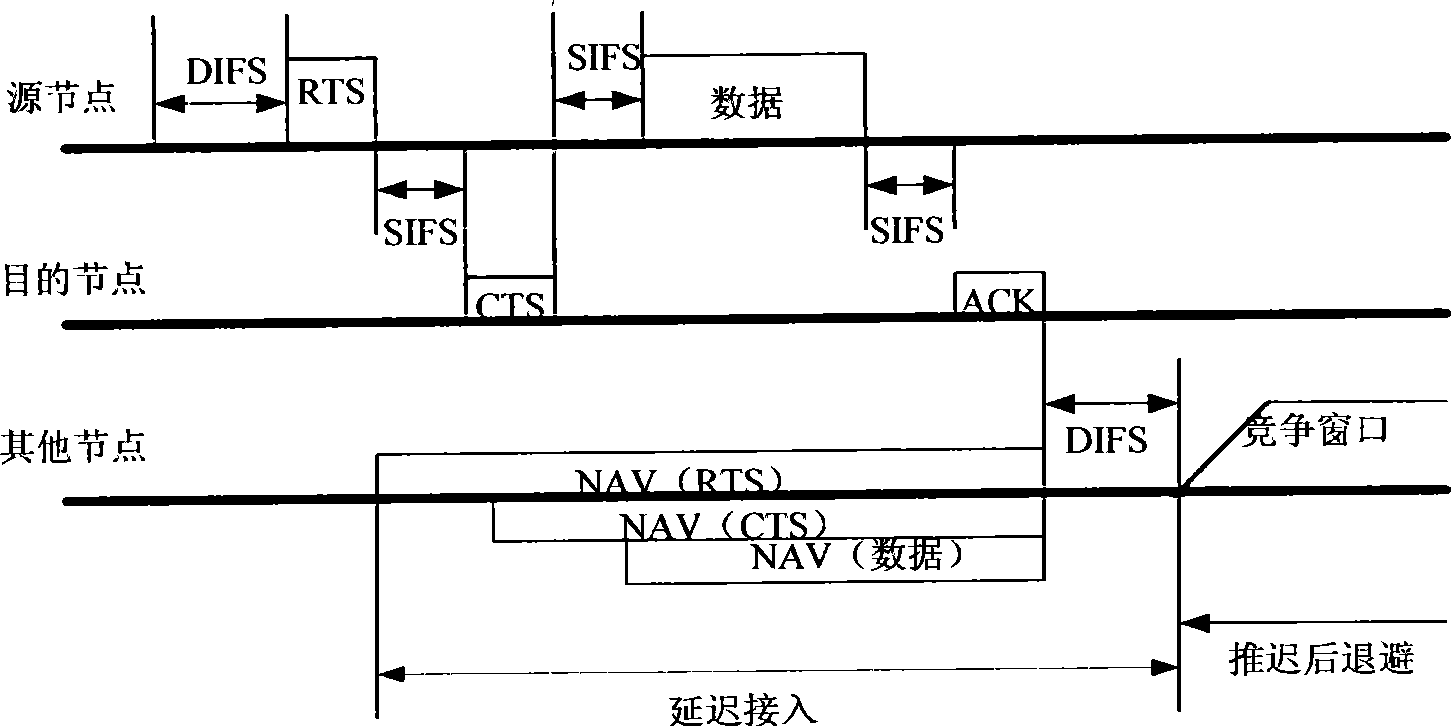
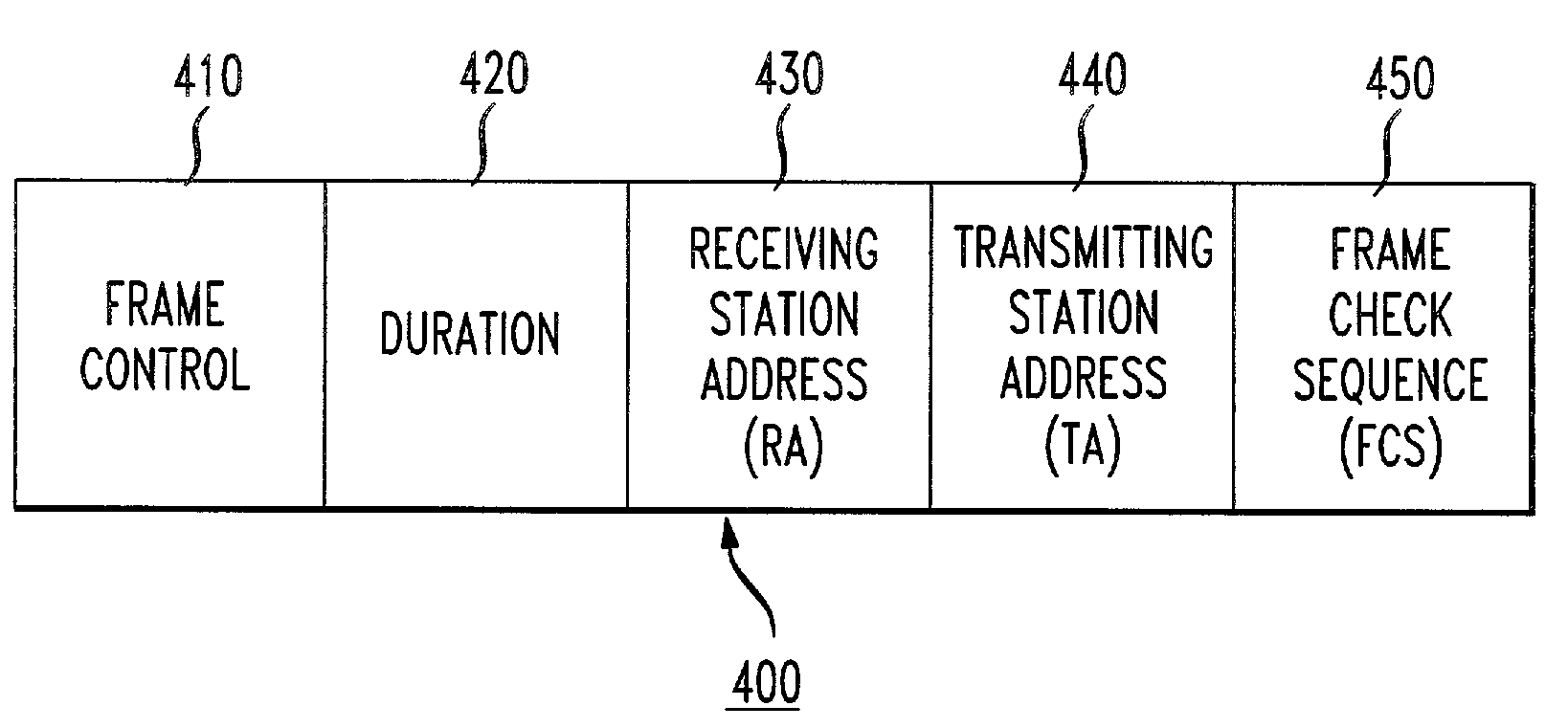
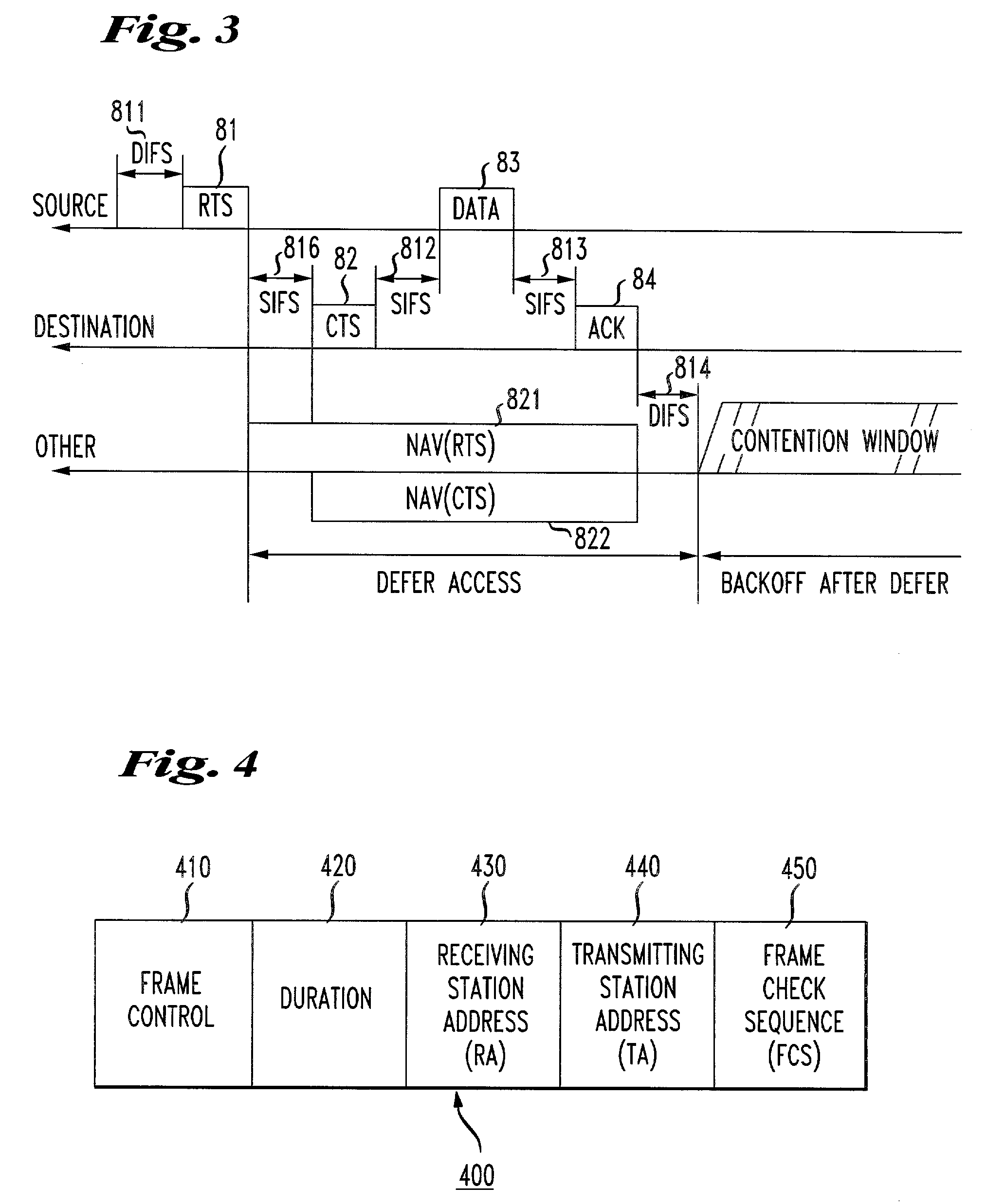
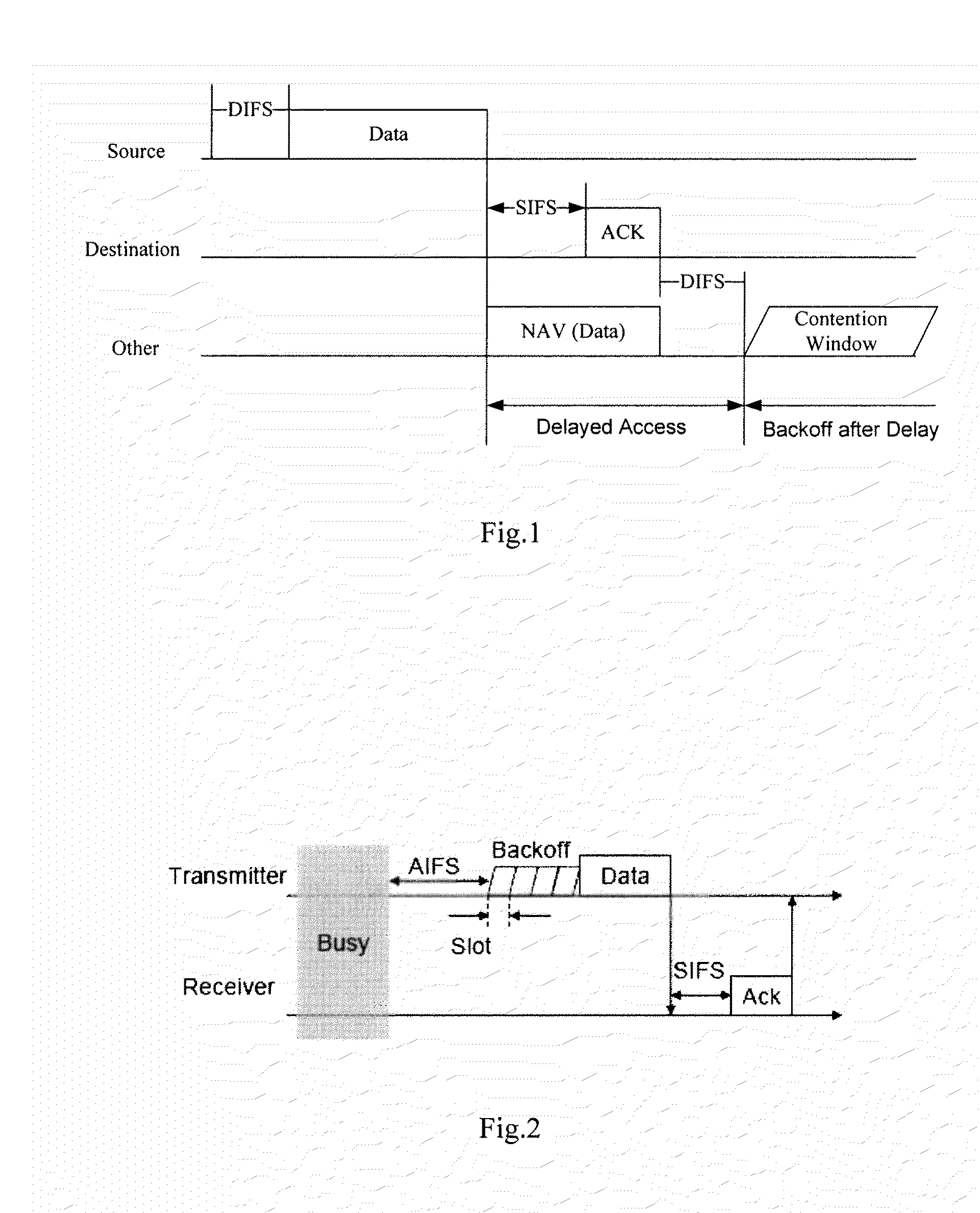
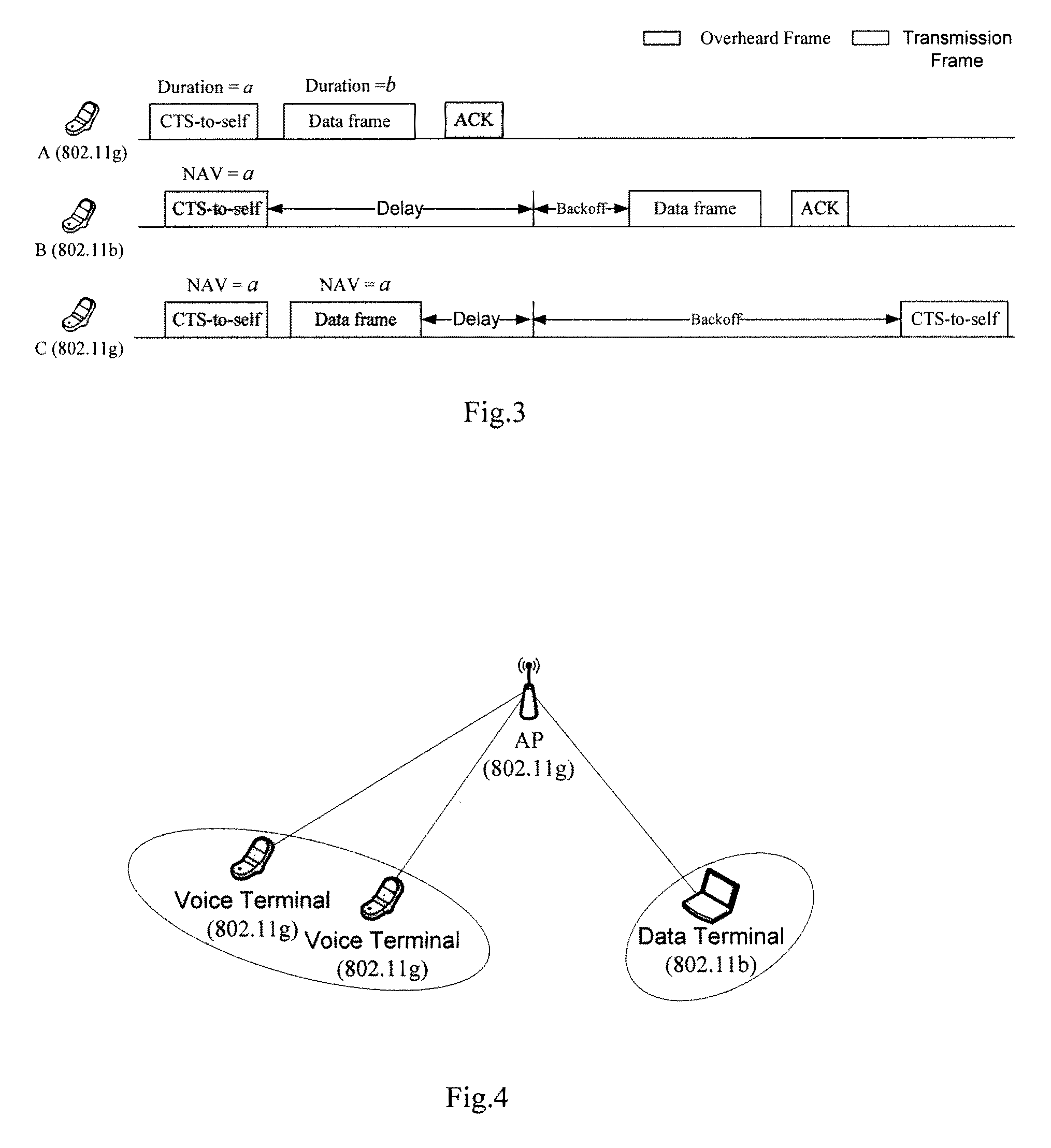
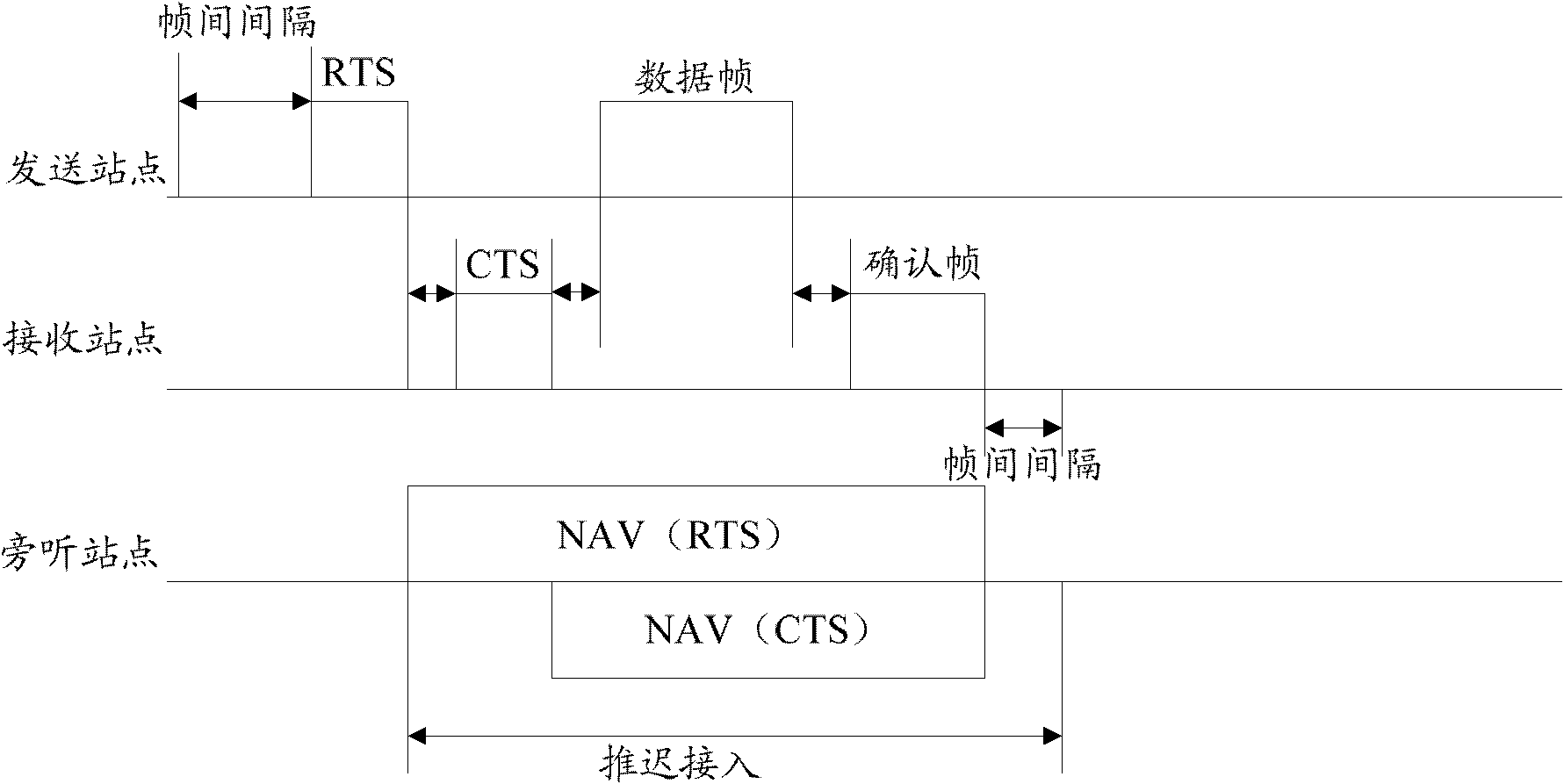
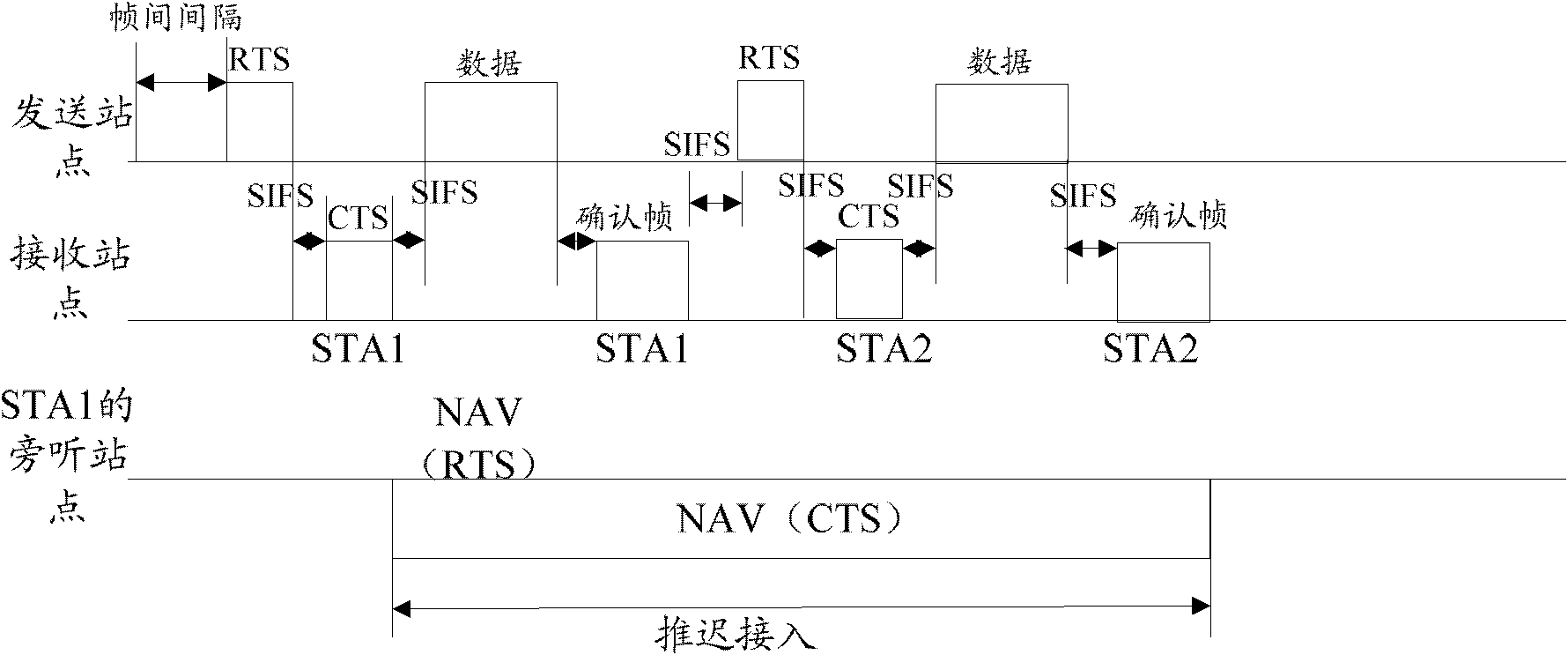
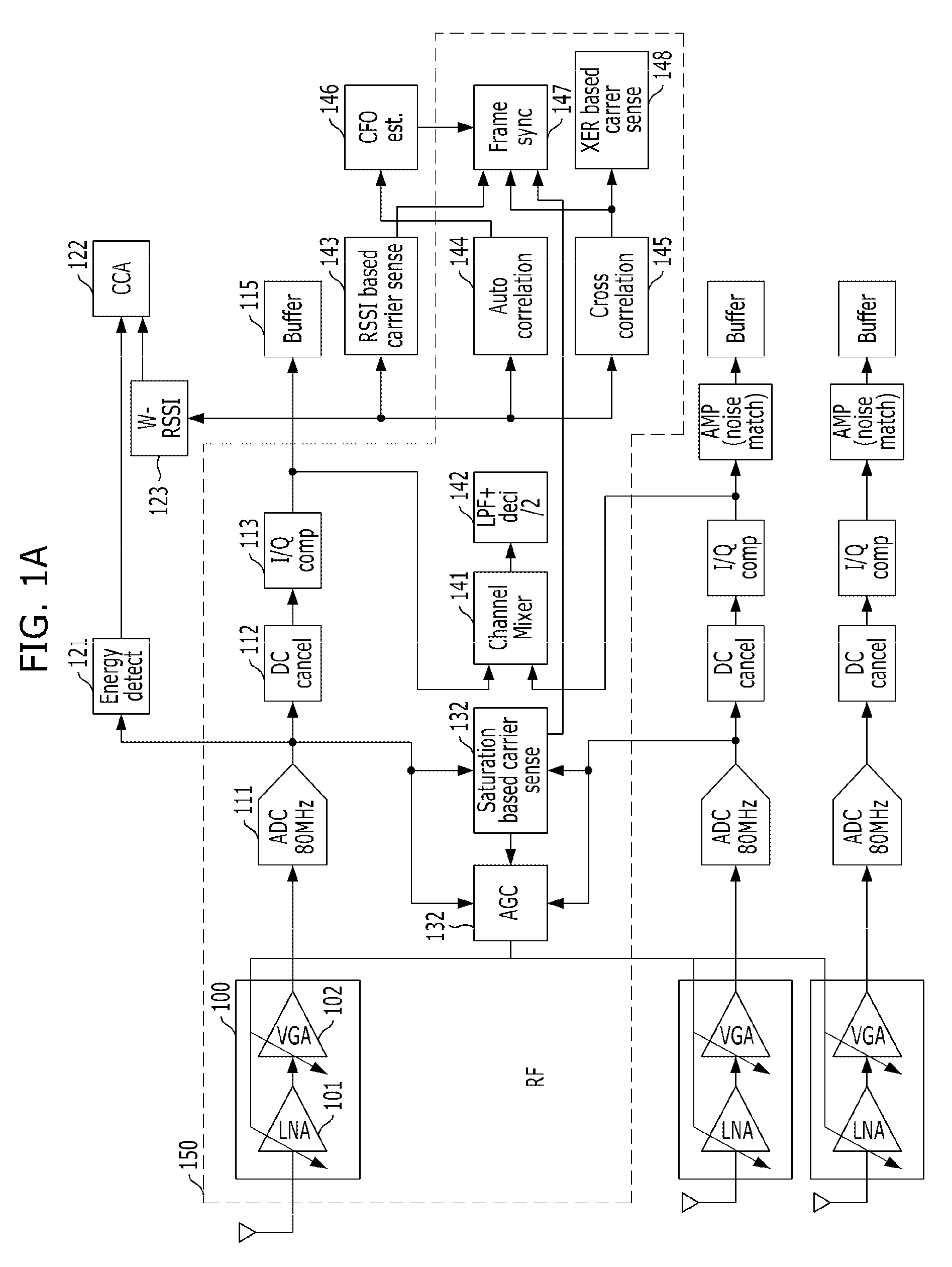
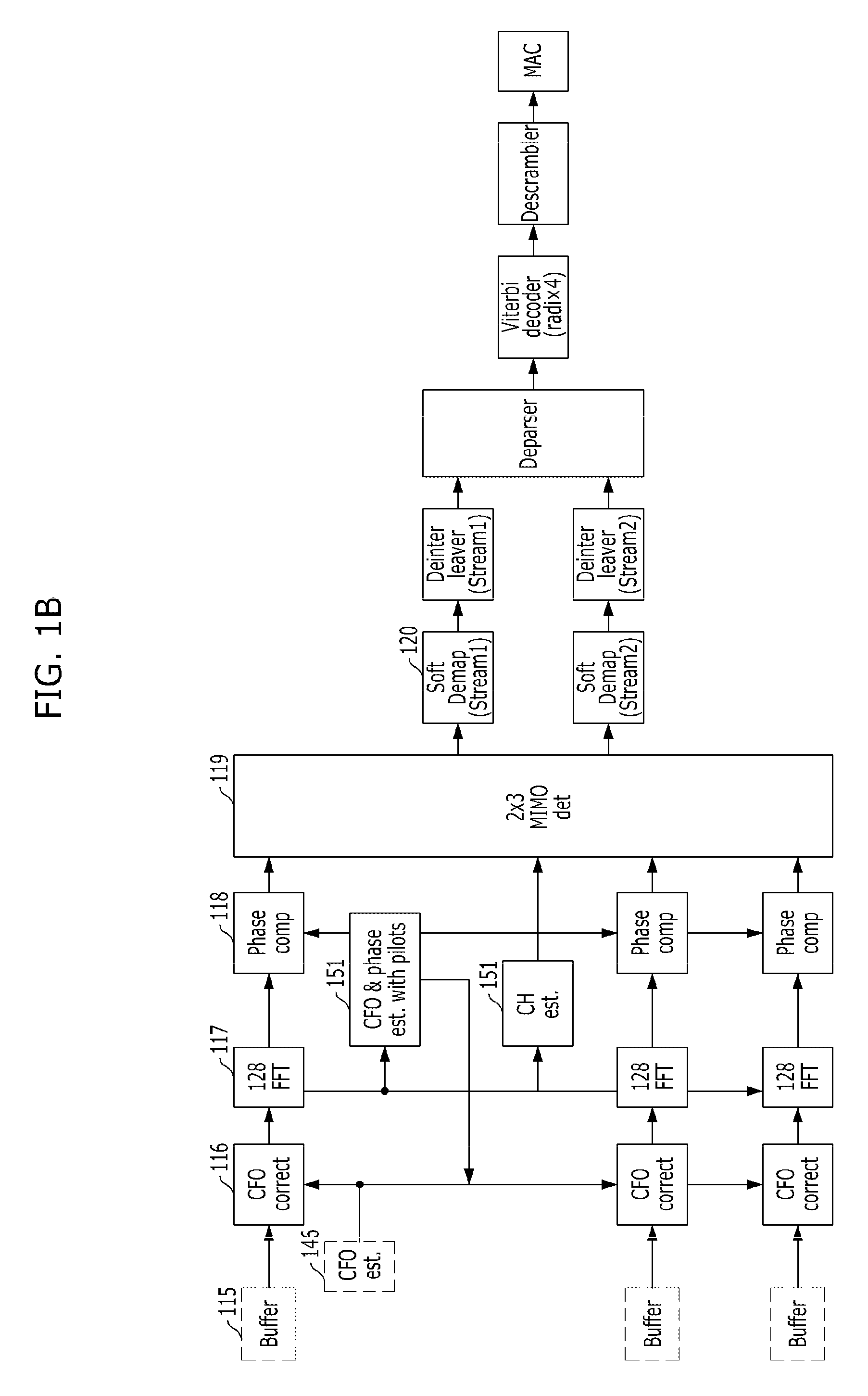
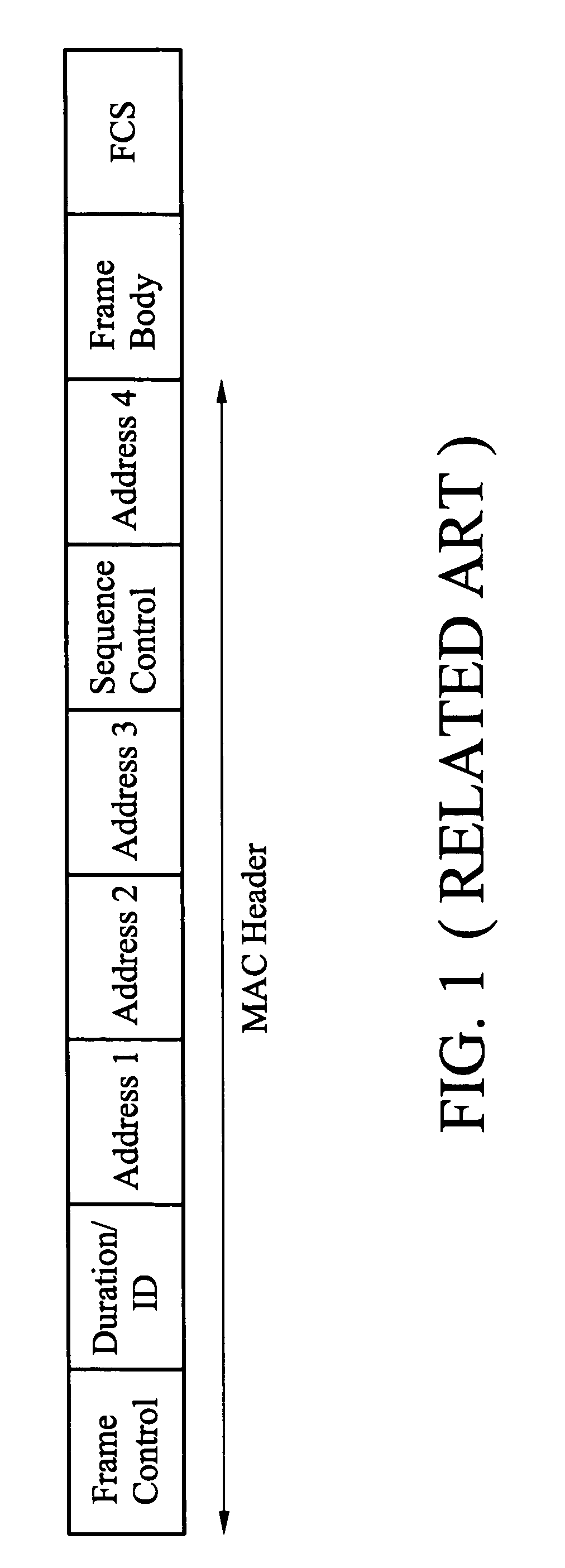
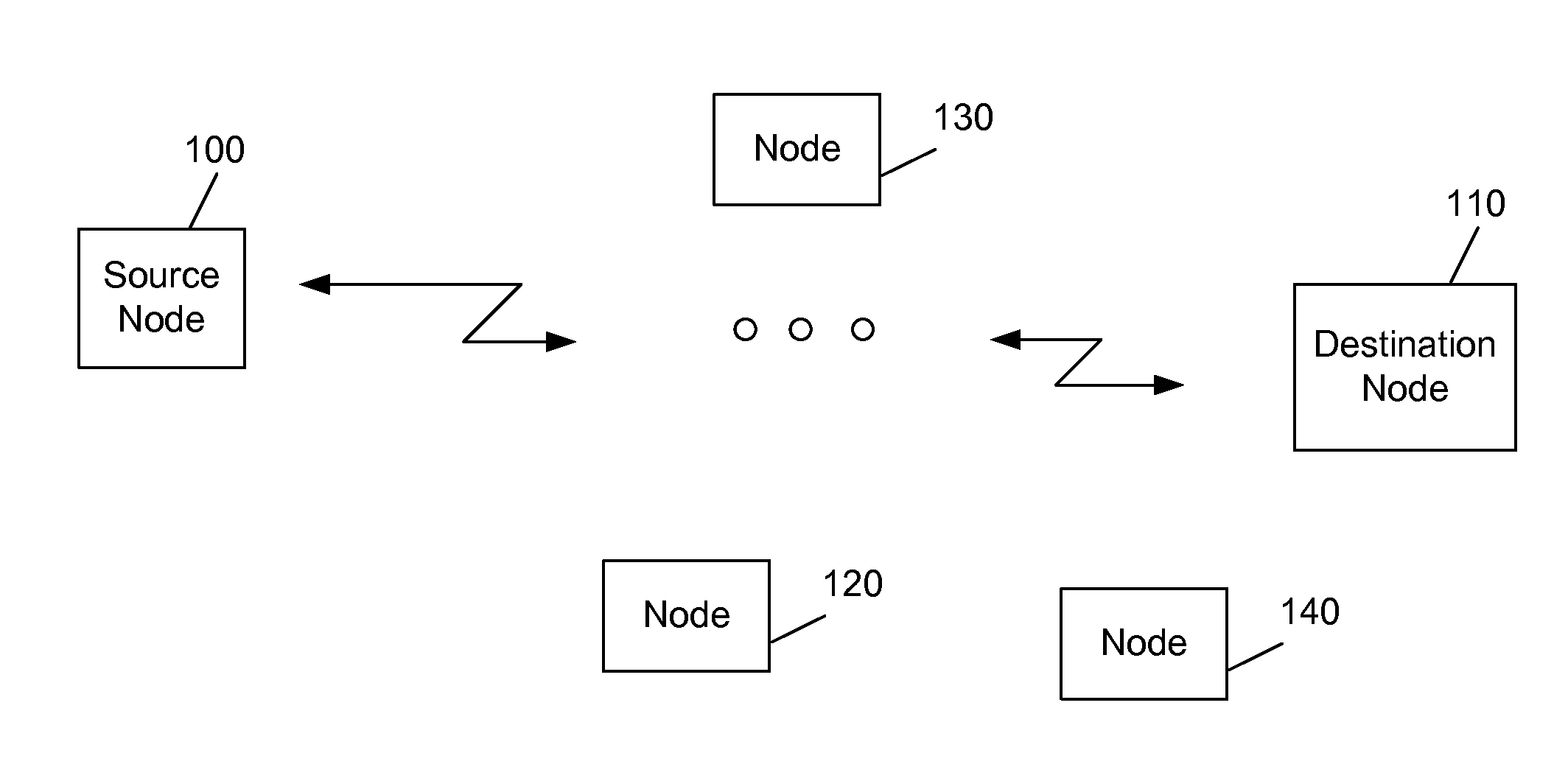
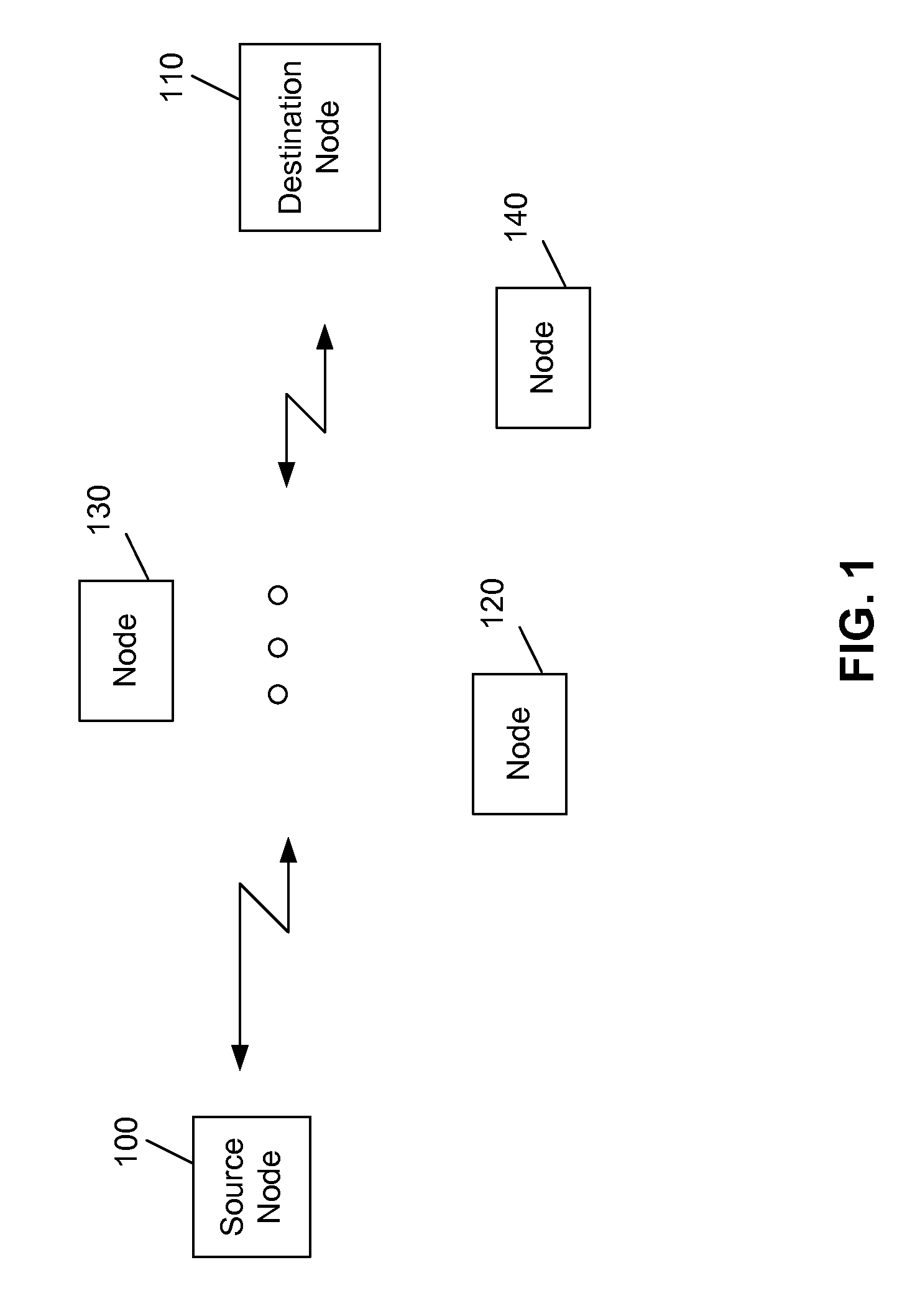
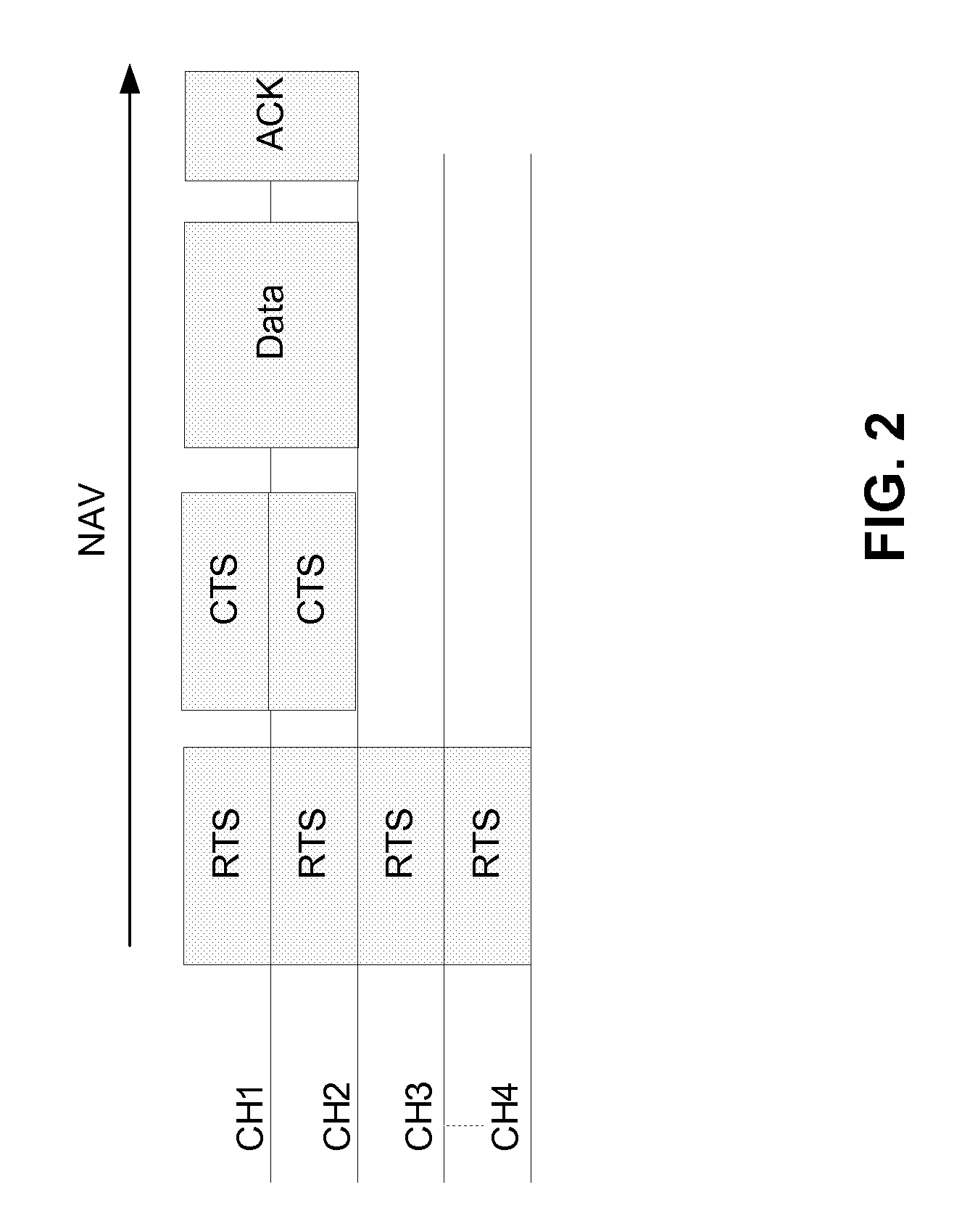
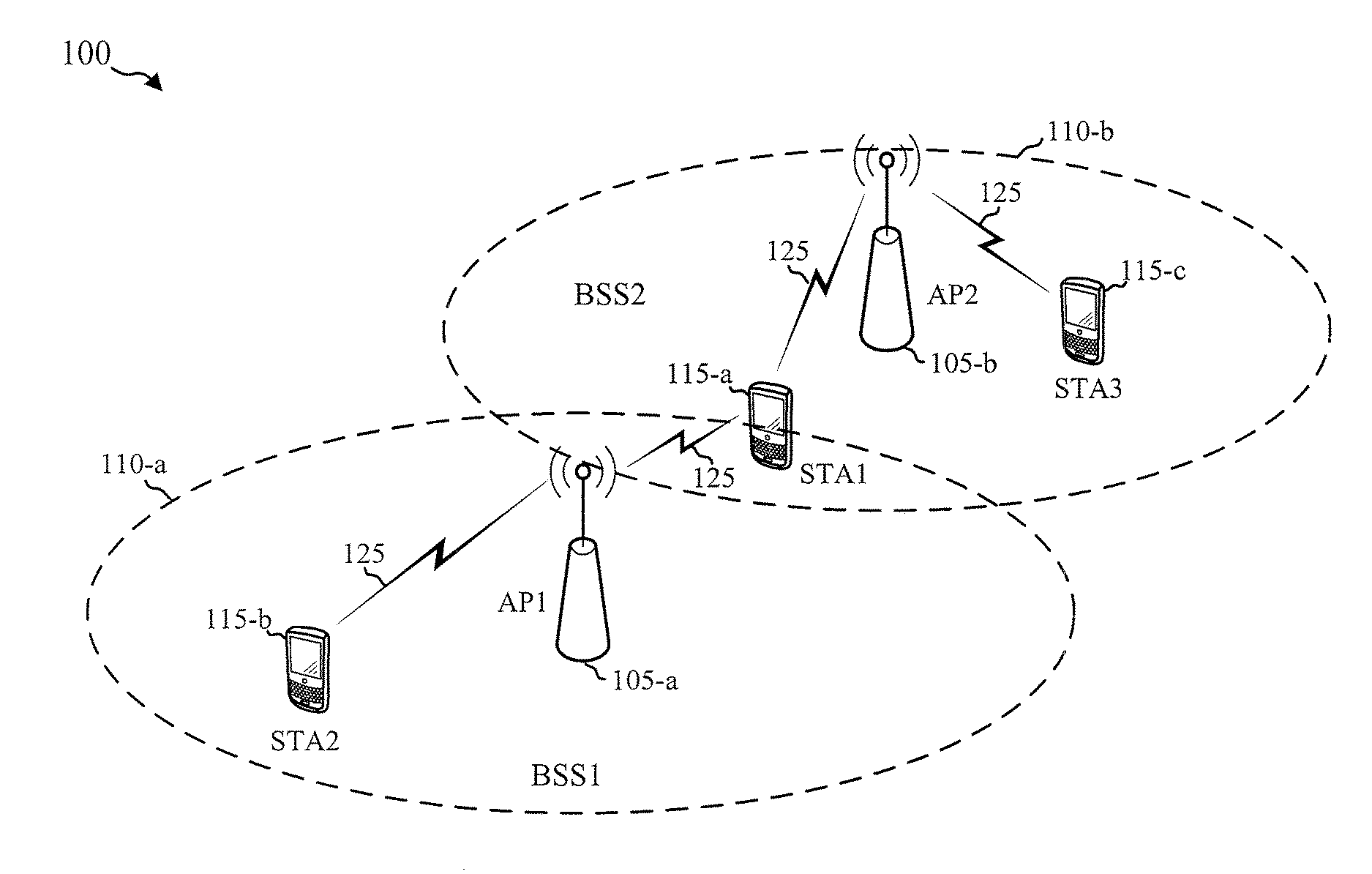
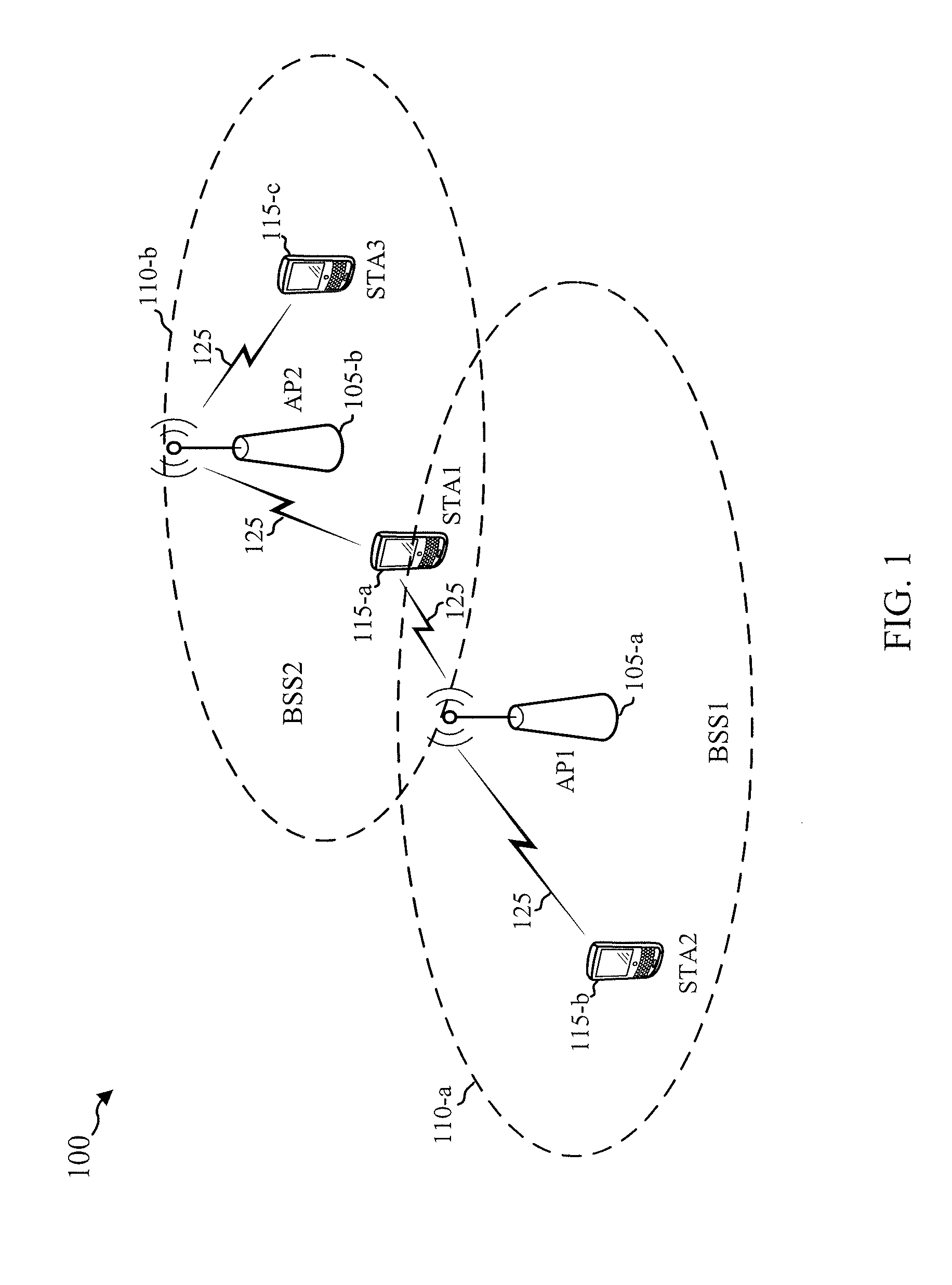
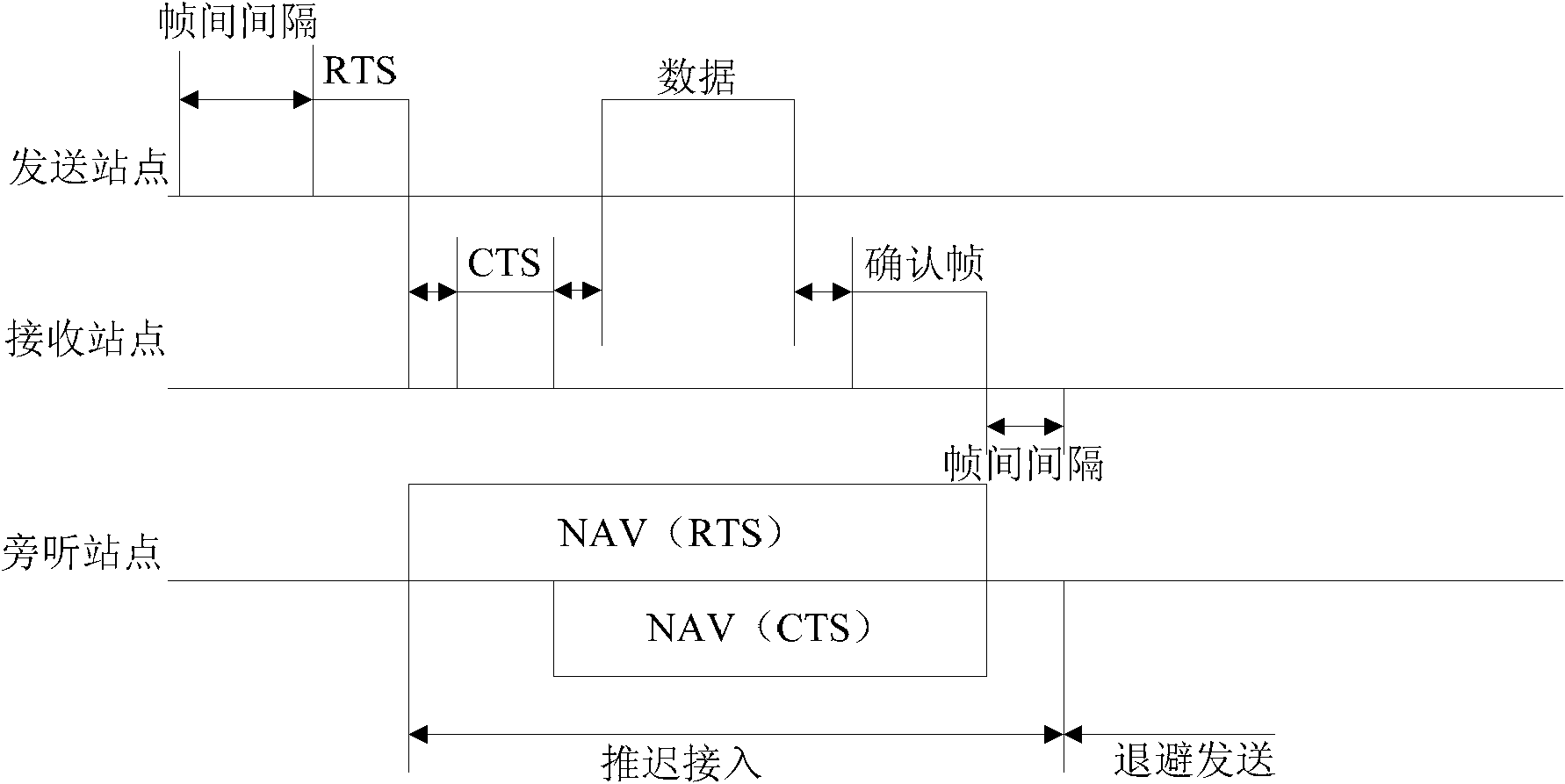
The network allocation vector (NAV) is a virtual carrier-sensing mechanism used with wireless network protocols such as IEEE 802.11 (Wi-Fi) and IEEE 802.16 (WiMax). The virtual carrier-sensing is a logical abstraction which limits the need for physical carrier-sensing at the air interface in order to save power. The MAC layer frame headers contain a duration field that specifies the transmission time required for the frame, in which time the medium will be busy. The stations listening on the wireless medium read the Duration field and set their NAV, which is an indicator for a station on how long it must defer from accessing the medium.
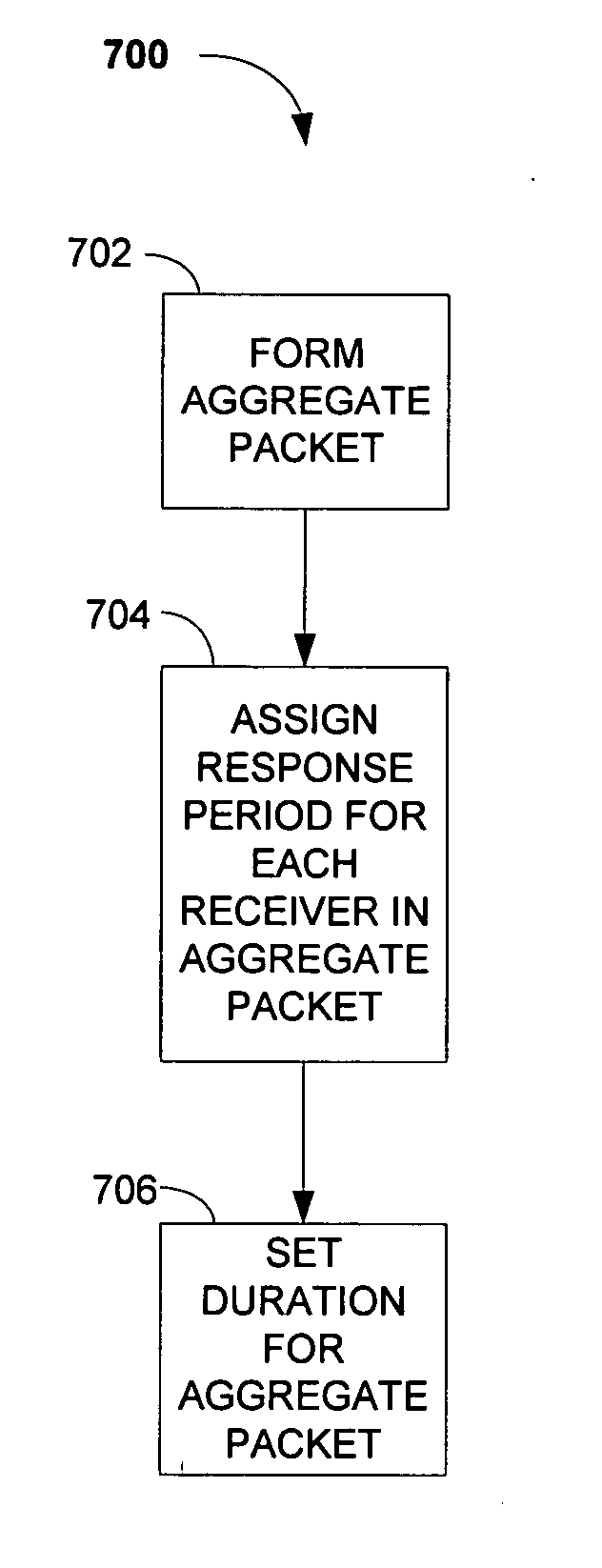
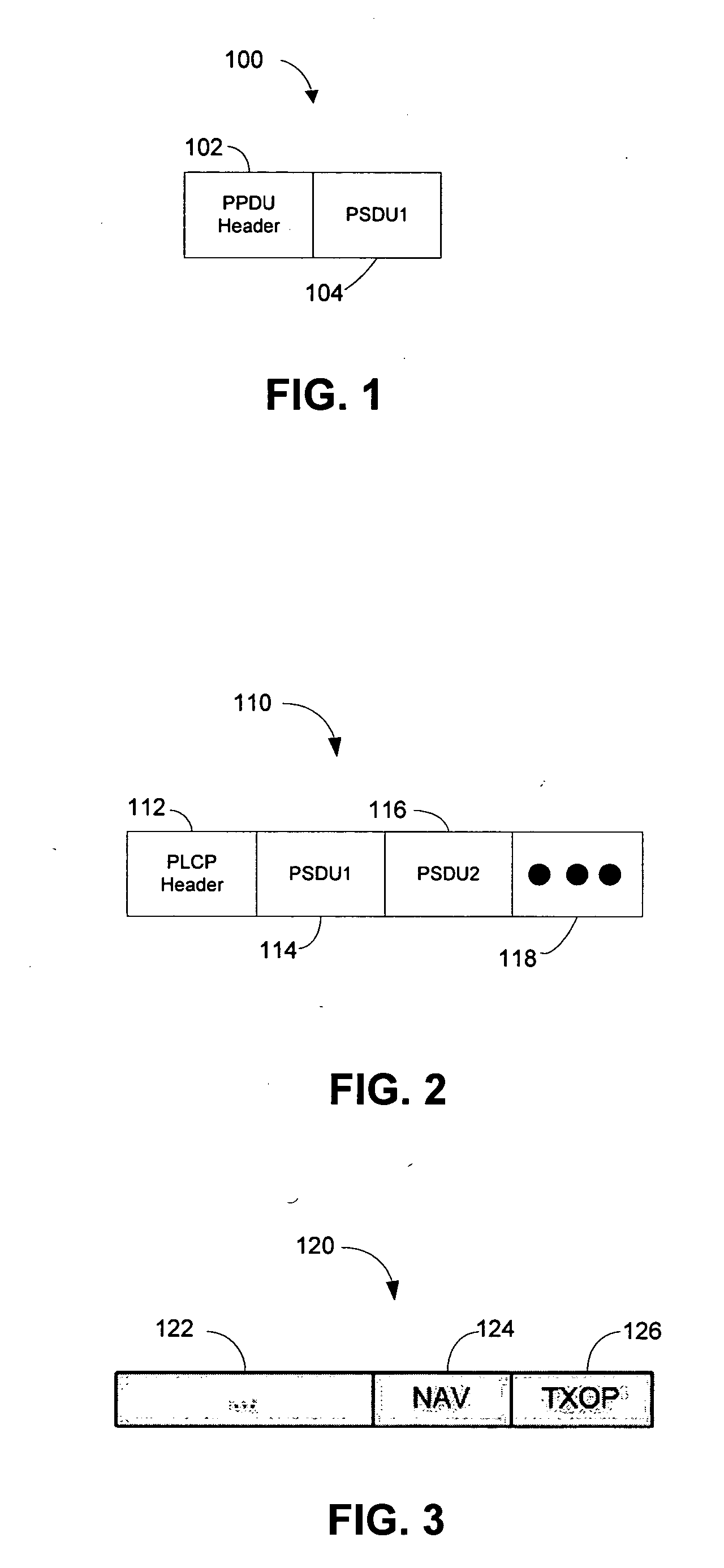
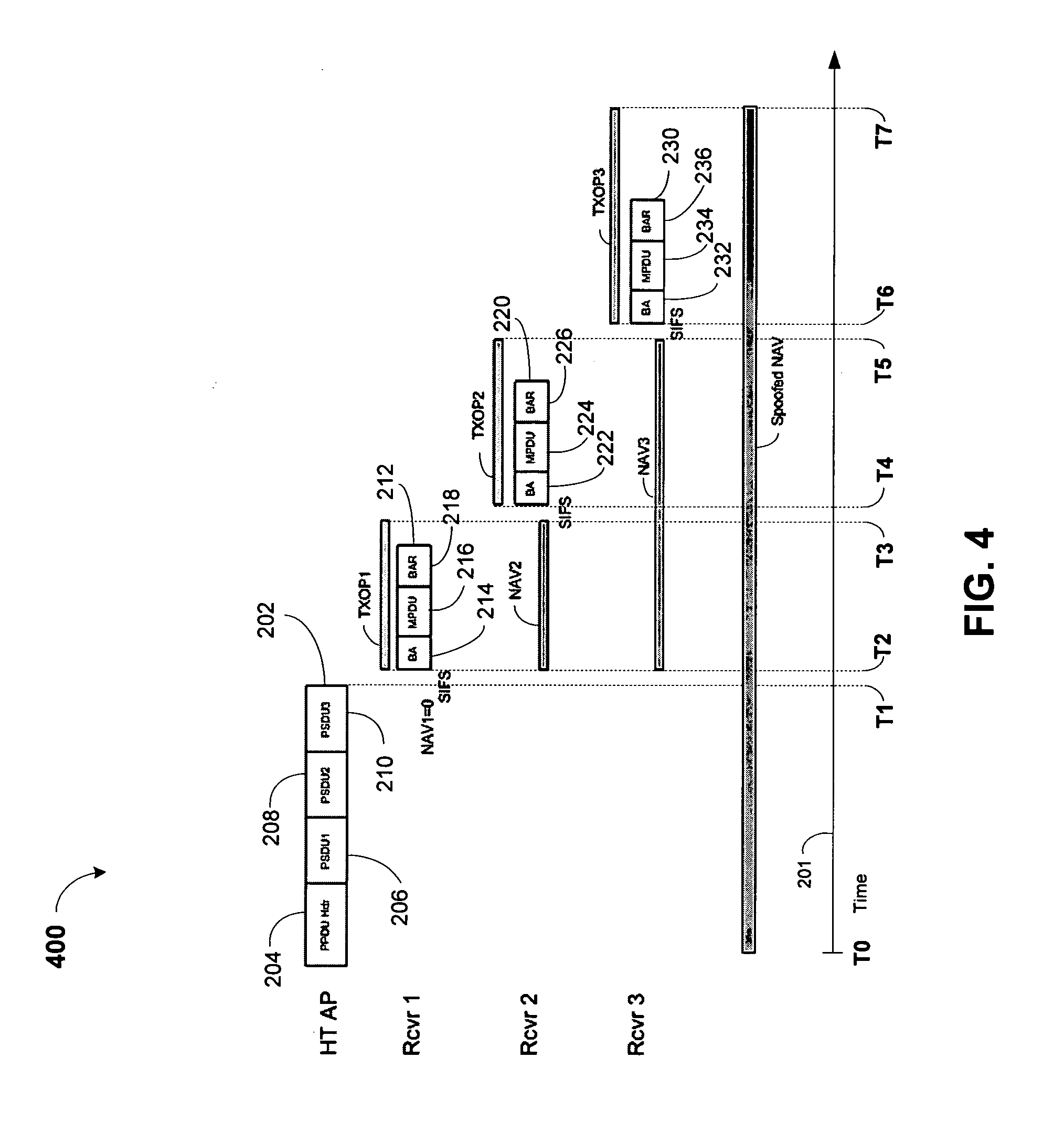
Multiple receiver aggregation
ActiveUS20050226273A1Error preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork allocation vectorReal-time computing
A technique for multiple receiver aggregation that allows for multiple immediate responses of acknowledgements or block acknowledgements. The technique uses a spoofed network allocation vector (NAV) implemented within an aggregate's PLCP header to protect the aggregate and all of the immediate responses from multiple receivers. The immediate responses are scheduled, the information indicating the scheduled offset time and granted transmission duration for response of each receiver being included in the physical sublayer data unit (PSDU) headers within the aggregate.
Owner:CISCO SYSTEMS INC
Distributed wireless access method based on network allocation vector table and apparatus of the same
ActiveUS7522576B2Reducing packet collision and waste of resourceImprove system throughput and utilization rateNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesClear to sendAccess method
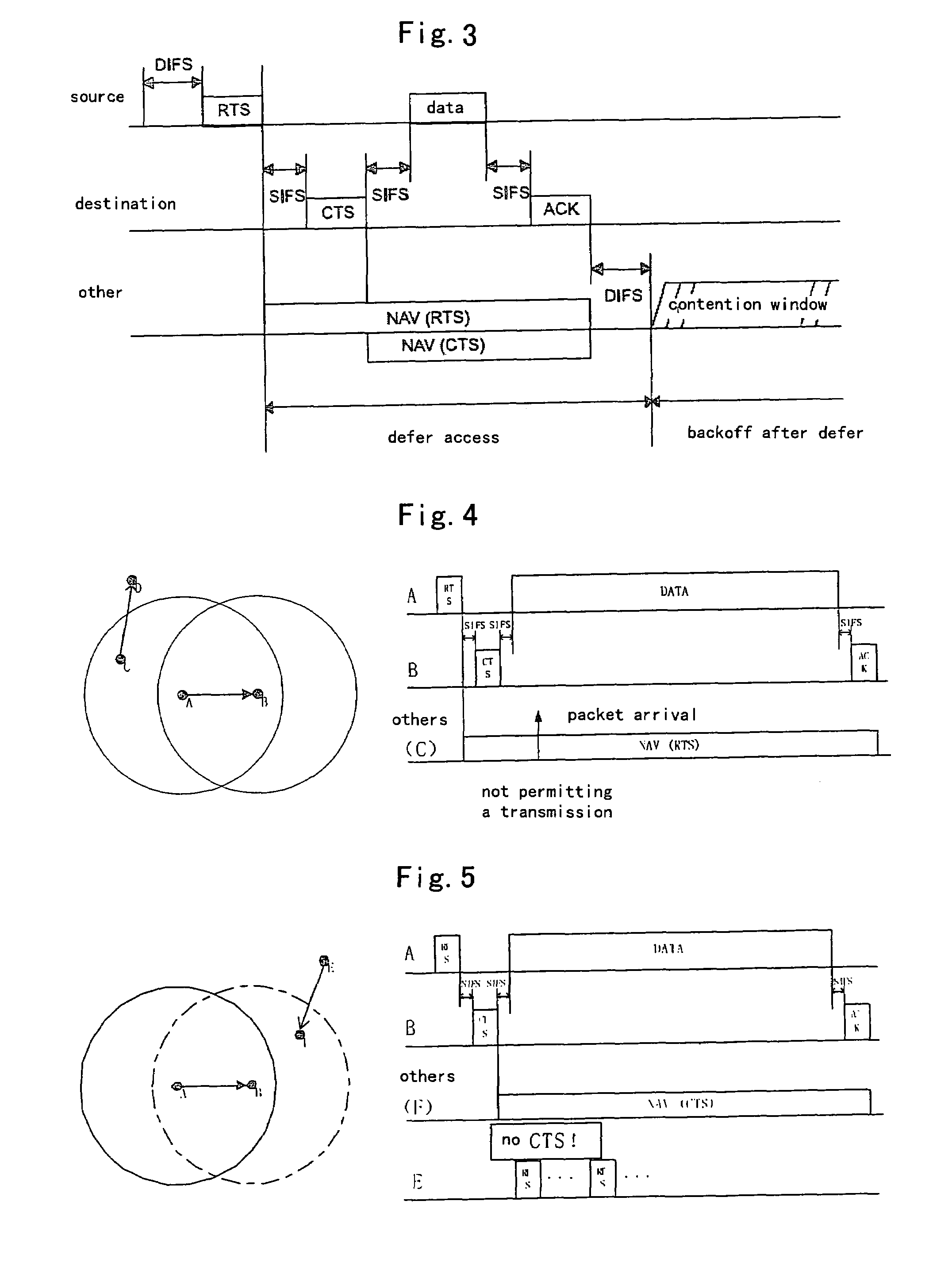
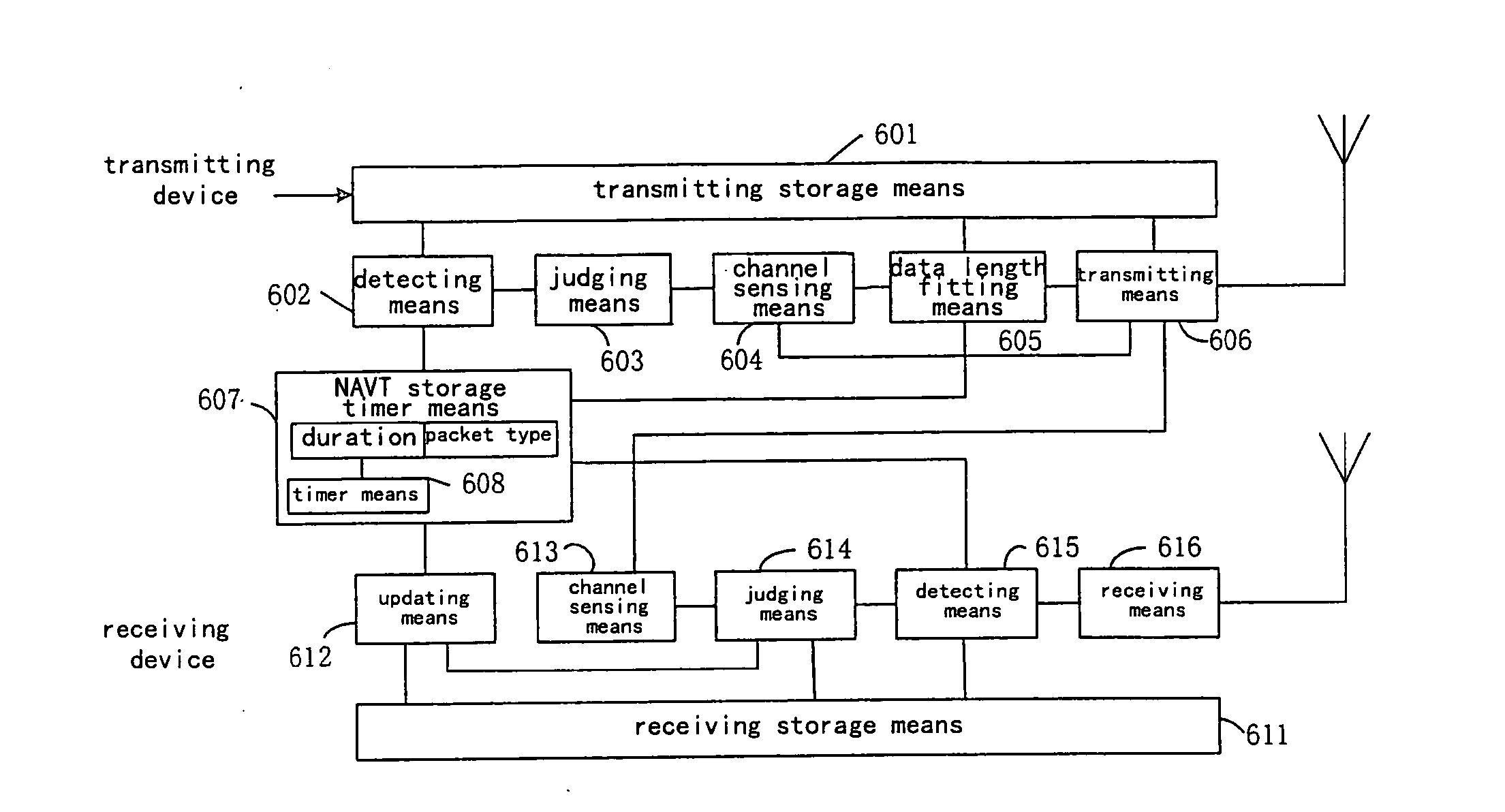
Embodiments of the present invention include a wireless access method based on a NAVT (Network allocation vector table), which is applied to a distributed wireless mobile communication system comprising a plurality of nodes, the NAVT comprises a packet type field and a duration field and is stored in the respective nodes of the communication system, comprising: on a transmitting side, determining whether only a RTS (request to send) item is contained in the NAVT when a packet arrives; sensing channel to judge whether the channel is busy after determining that only the RTS item is contained in the NAVT; sending a RTS packet based on the RTS item to the receiving side after determining that the channel is busy; and on a receiving side, determining whether the NAVT is empty or not when the RTS packet is received; sending a CTS (clear to send) packet back to the transmitting side after determining that the NAVT is empty.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
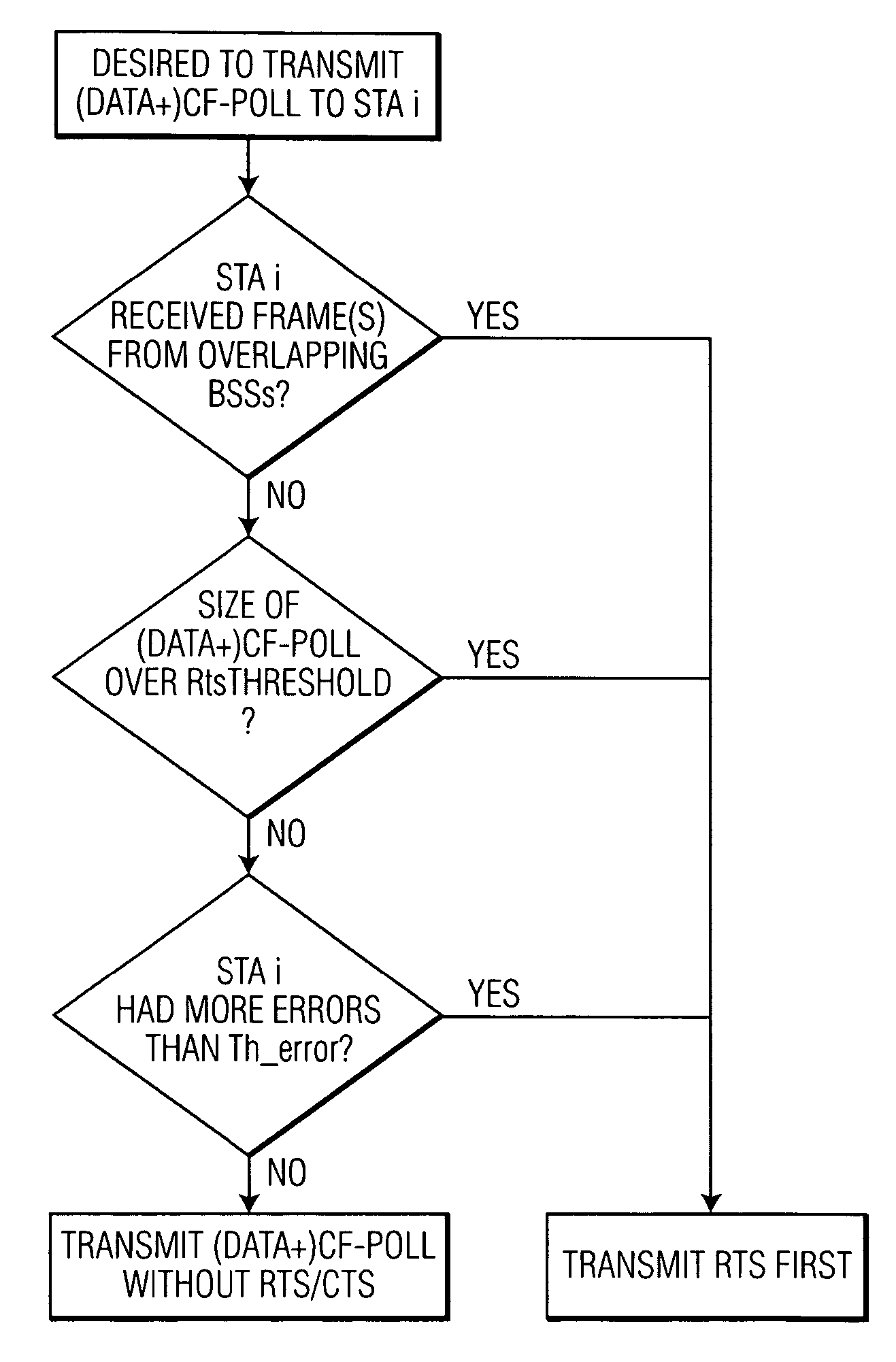
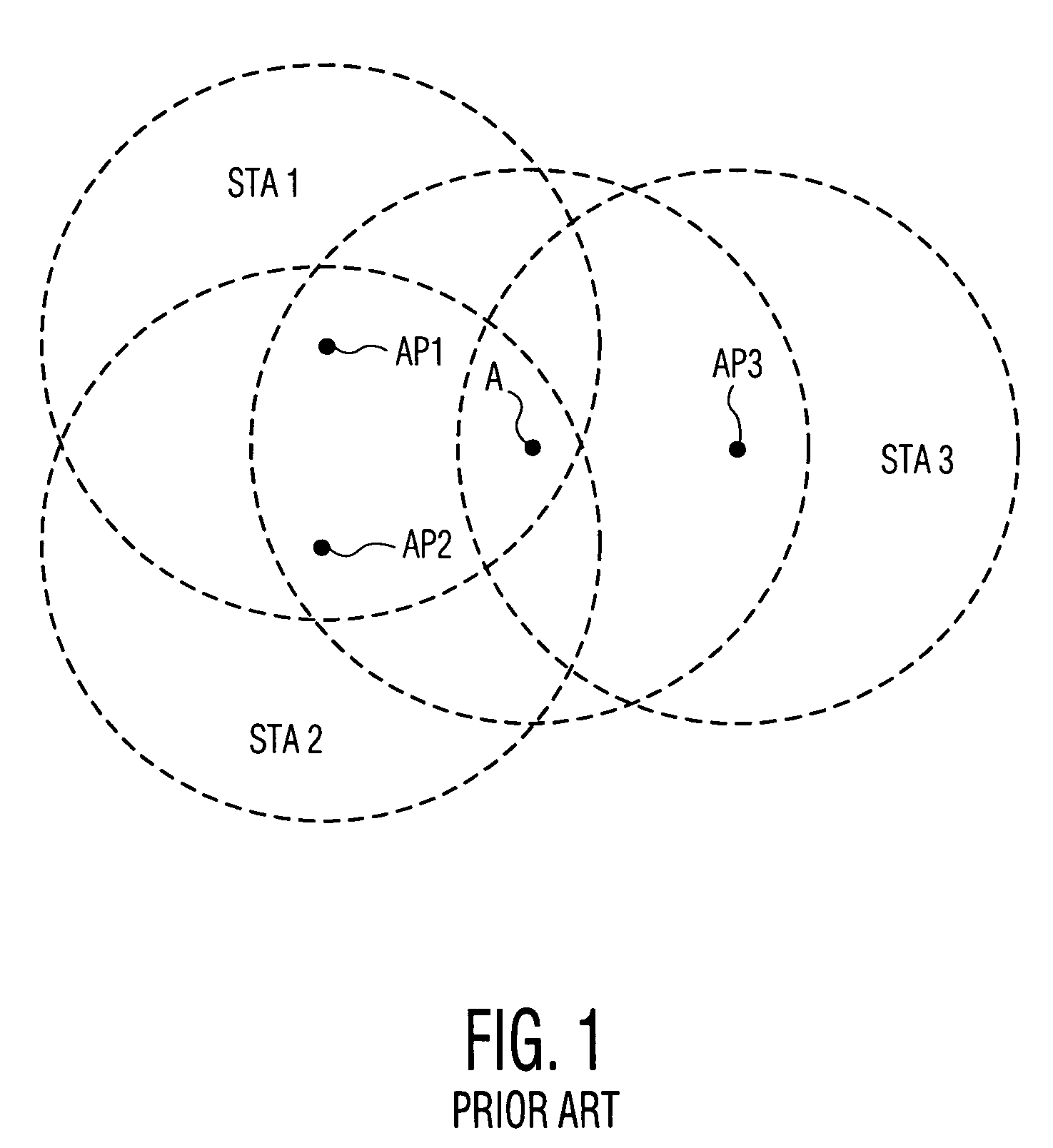
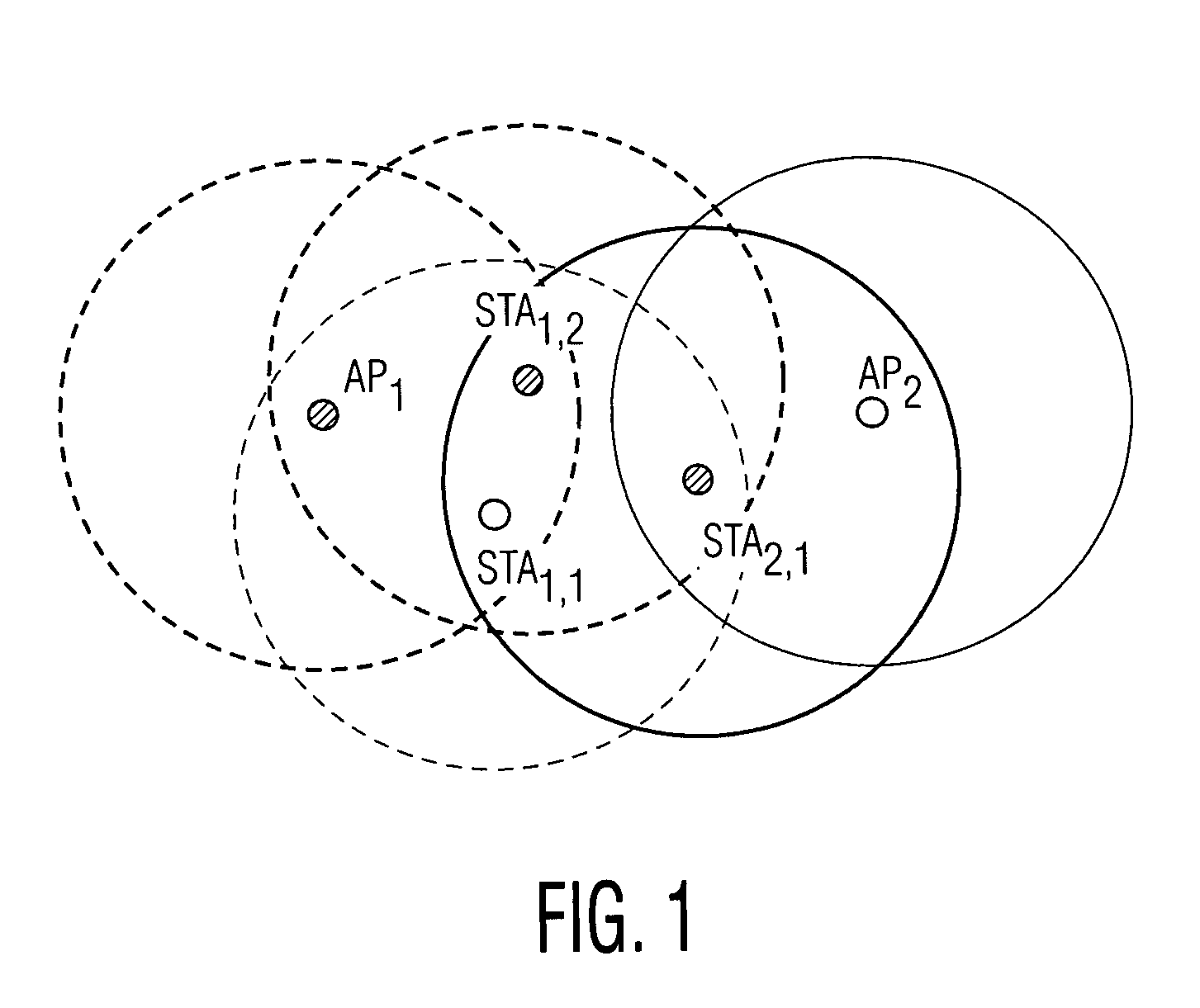
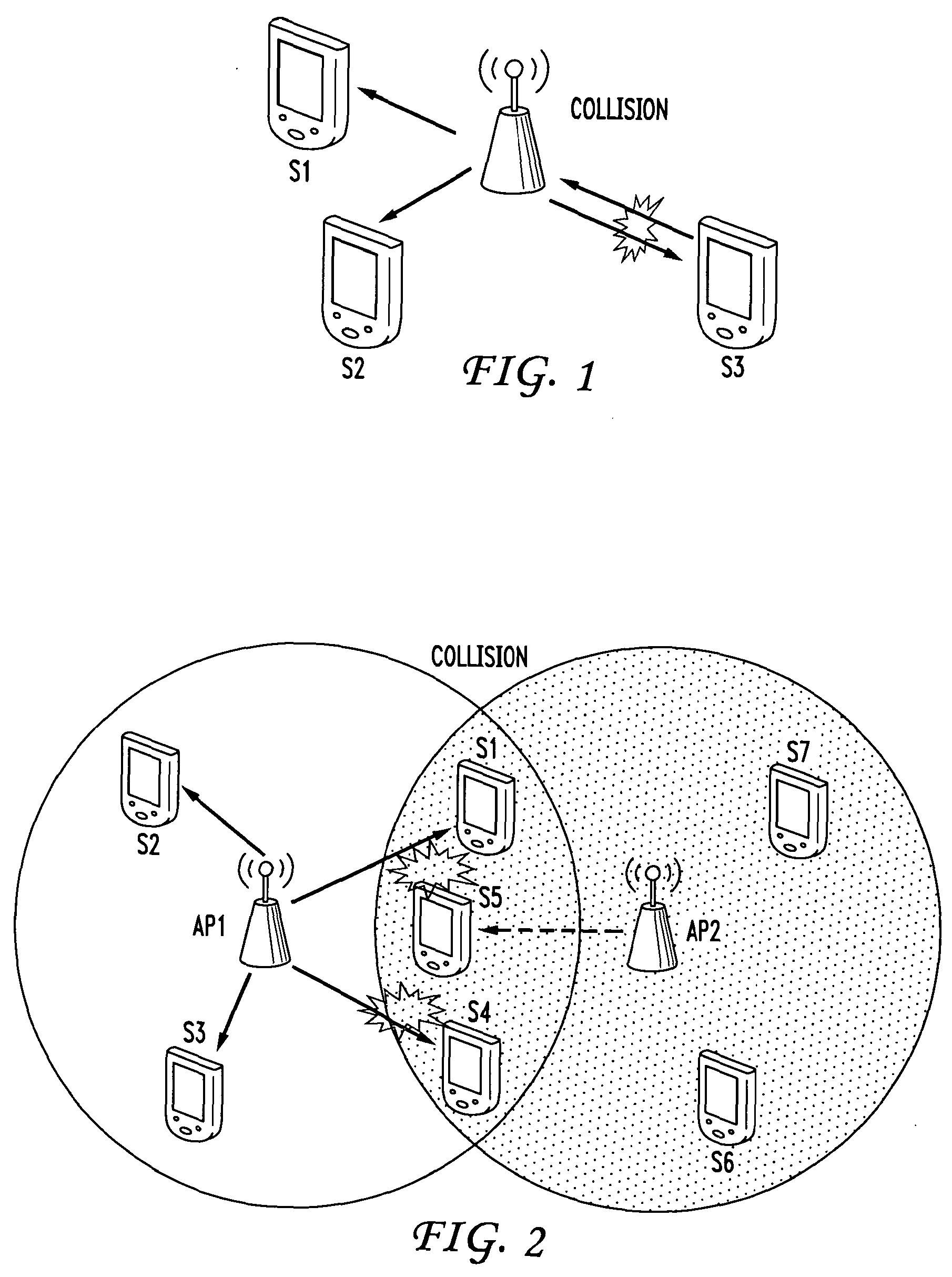
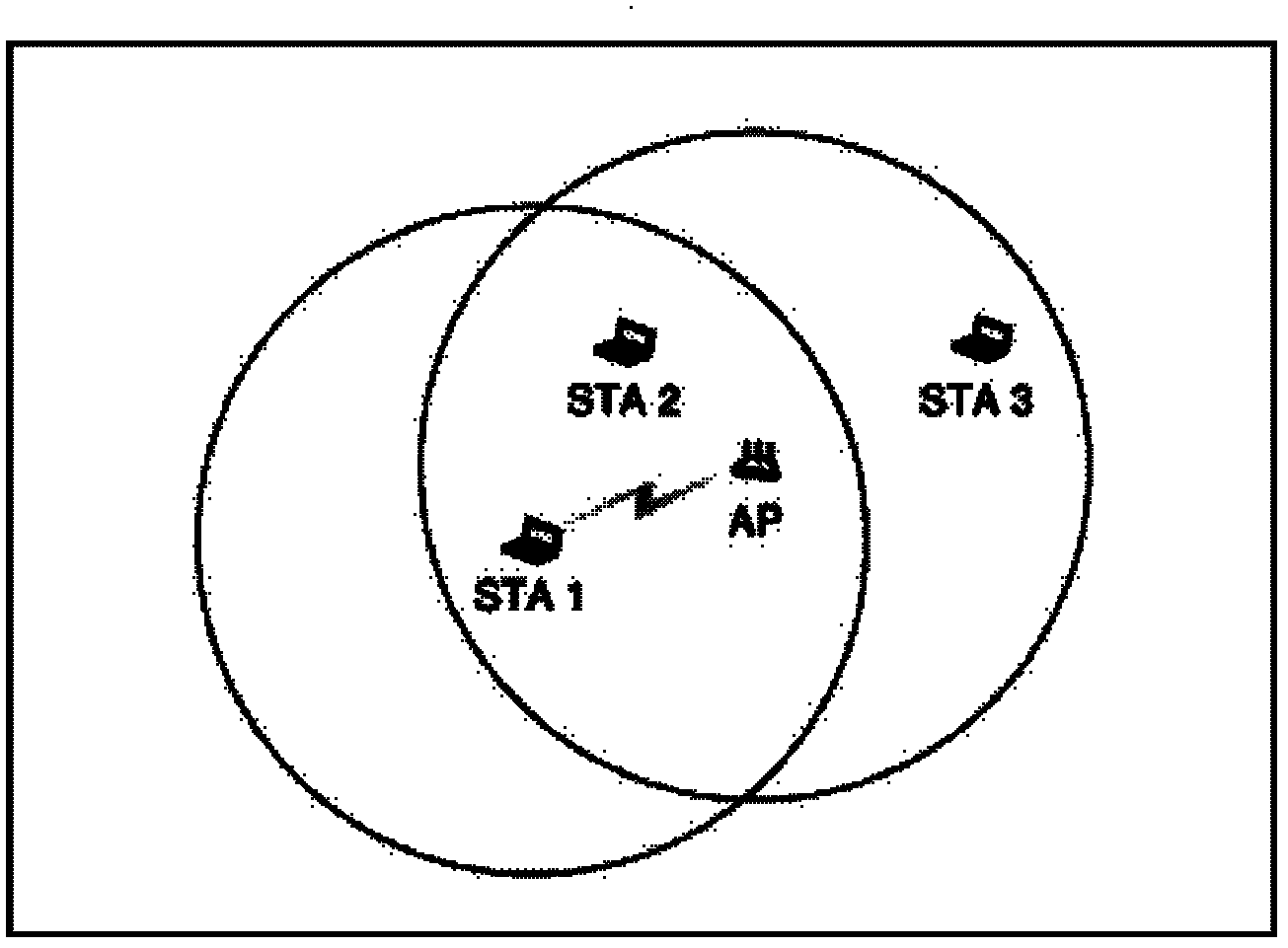
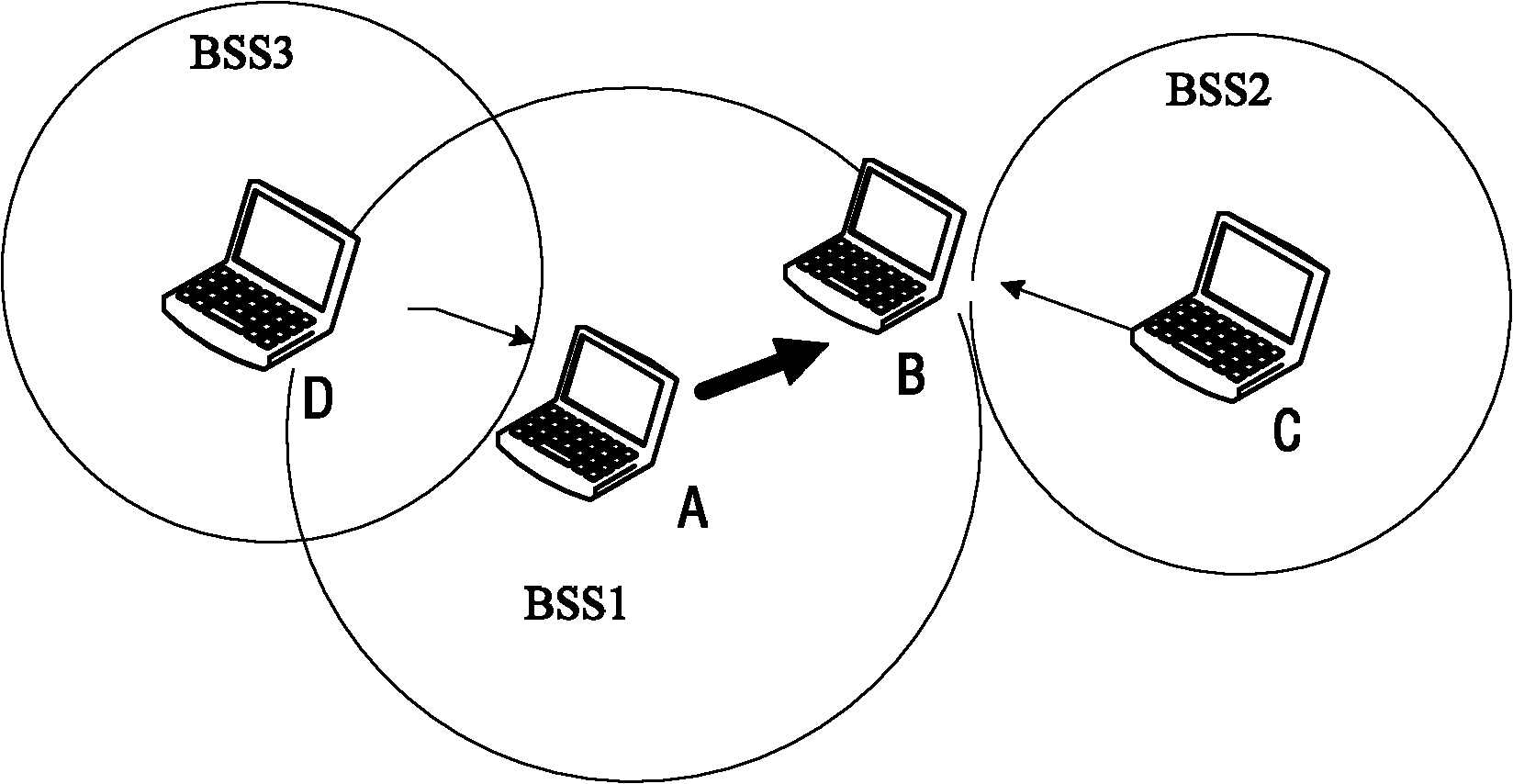
Collision avoidance in IEEE 802.11 contention free period (CFP) with overlapping basic service sets (BSSs)
InactiveUS20060029073A1Improve efficiencyAvoid contentionNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationClear to sendBasic service
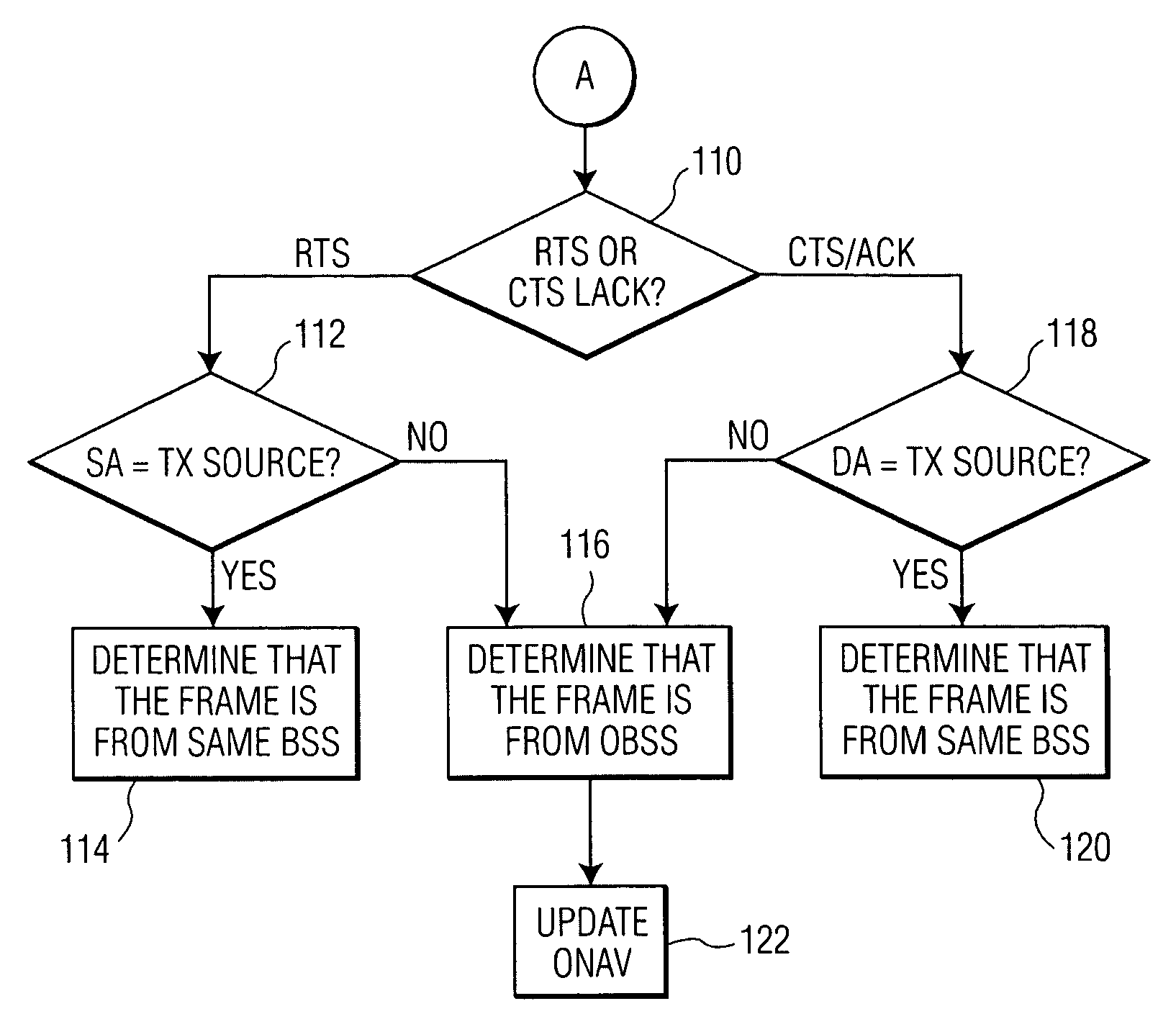
A medium access control (MAC) protocol is provided for avoiding collisions from stations (STAs) comprising two or more IEEE 802.11 basic service sets (BSSs) collocated and operating in the same channel during contention free periods (CFPs). The MAC protocol includes hardware / software for utilizing ready-to-send (RTS) / clear-to-send(CTS) exchange during CFPs to avoid potential collision from STAs in overlapping BSSs and hardware / software for providing overlapping network allocation vectors (ONAV) in addition to a network allocation vector (NAV), the ONAV included to facilitate the effectiveness of the RTS / CTS during CFPs.
Owner:CERVELLO GERARD +1
Mobile ad-hoc network with intrusion detection features and related methods
InactiveUS7082117B2Error preventionBroadcast transmission systemsNetwork allocation vectorMedia access
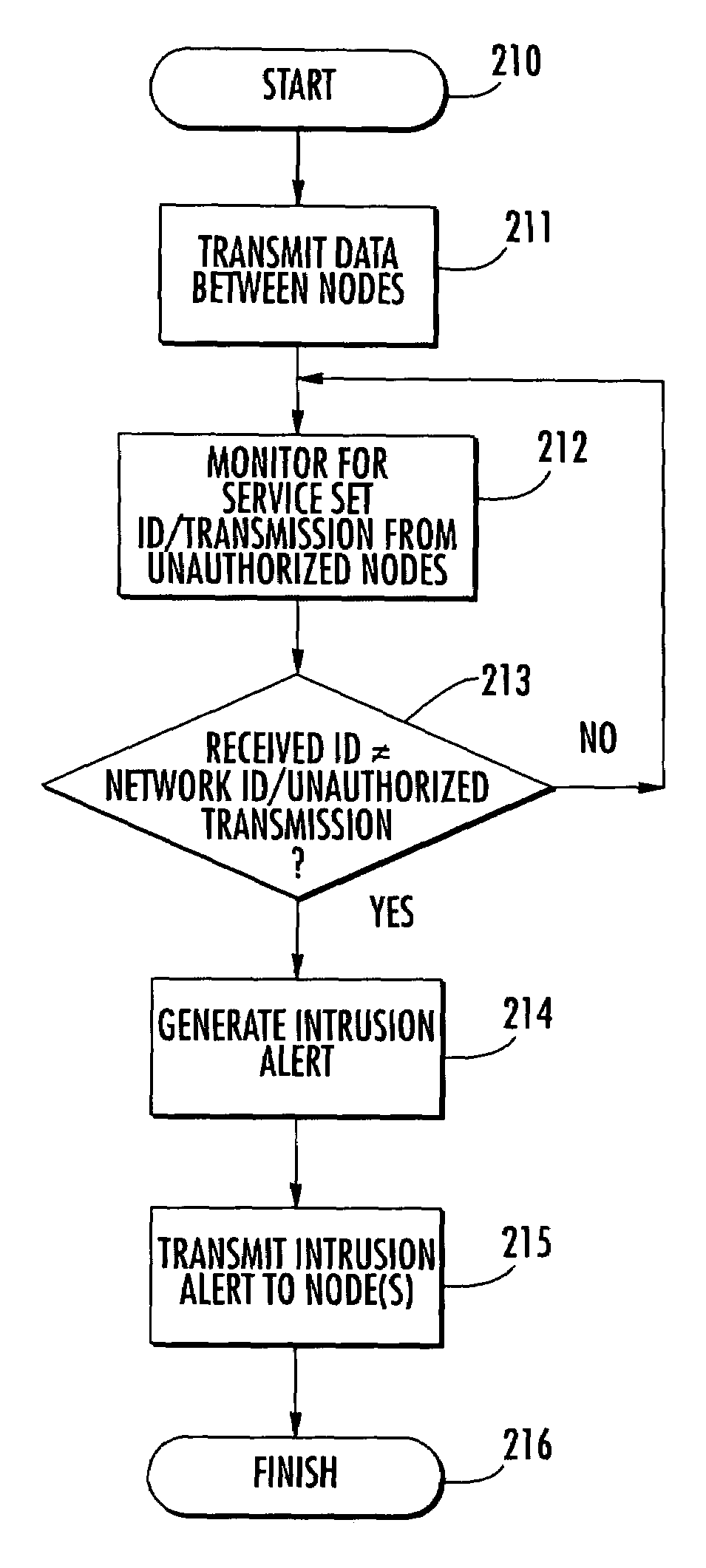
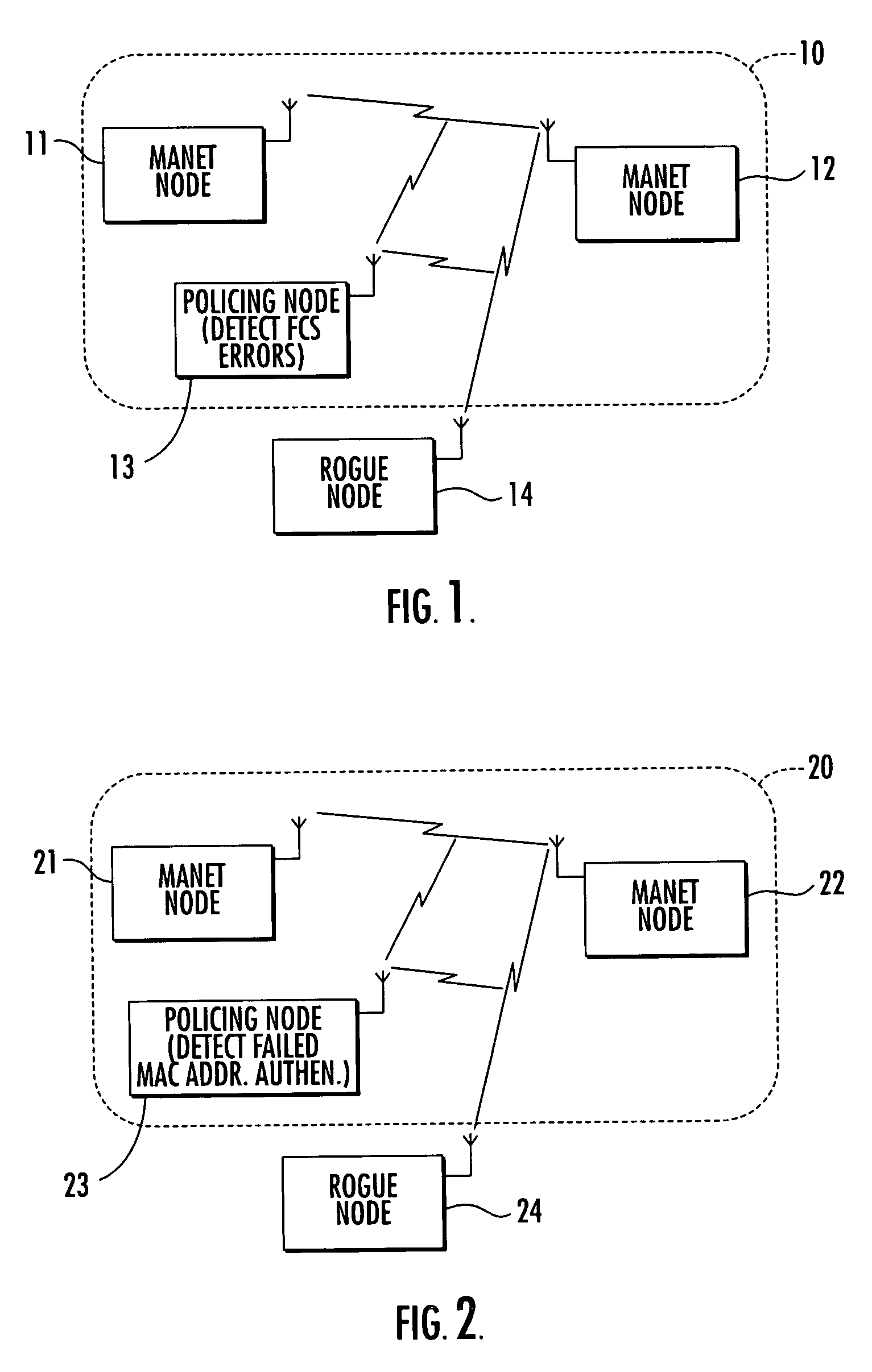
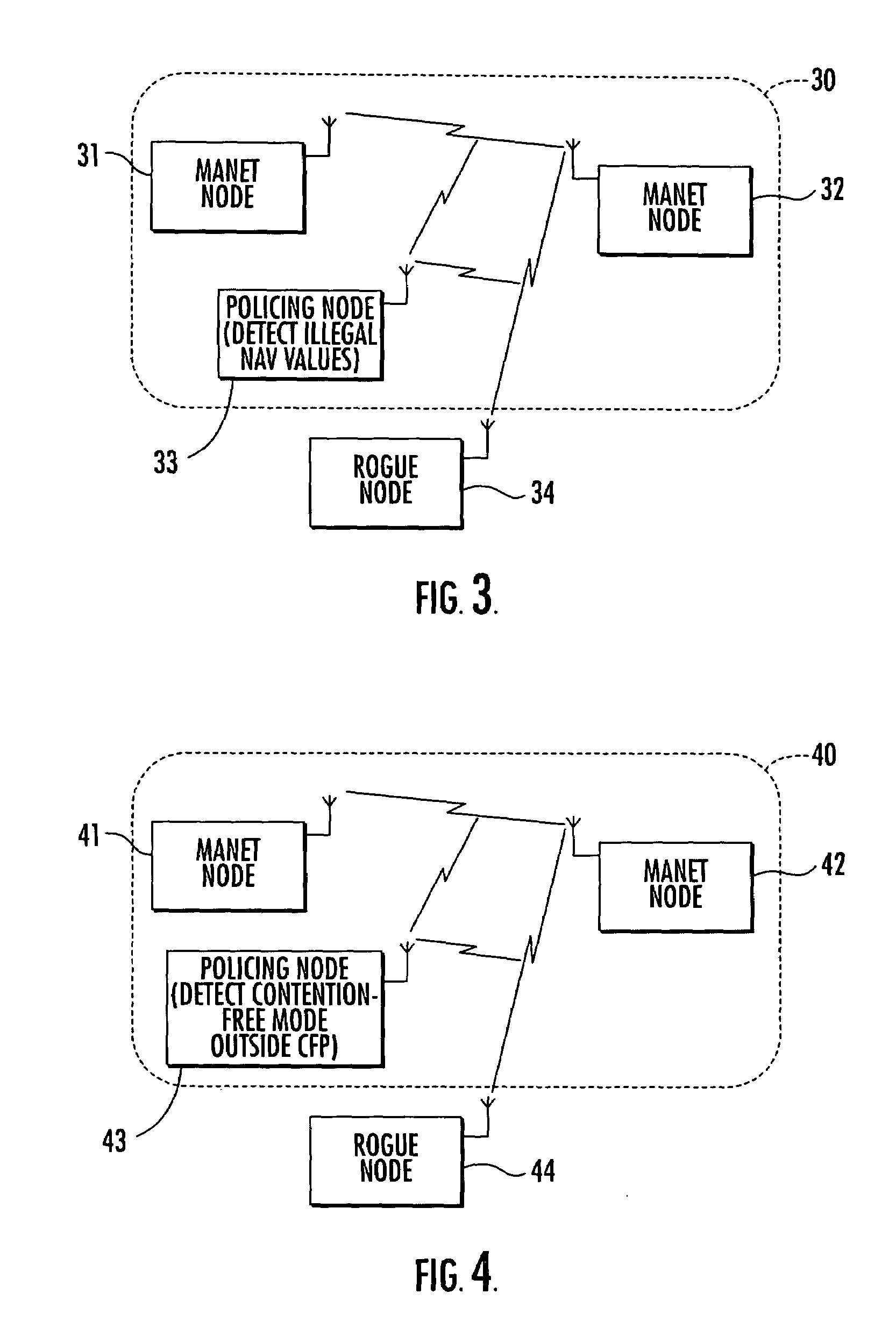
A mobile ad-hoc network (MANET) may include a plurality of nodes for transmitting data therebetween using a media access layer (MAC), where each of the nodes has a respective MAC address associated therewith. The MANET may also include a policing node for detecting intrusions into the MANET by monitoring transmissions among the plurality of nodes to detect frame check sequence (FCS) errors from a MAC address, and generating an intrusion alert based upon detecting a number of FCS errors for the MAC address exceeding a threshold. The policing node may also detect intrusions based upon one or more of failed MAC address authentications, illegal network allocation vector (NAV) values, and unexpected contention or contention-free operation.
Owner:STINGRAY IP SOLUTIONS LLC
Setting of network allocation vectors in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20100074198A1Maintain communication qualityMultiplex communicationNetwork topologiesCompletion timeCommunications system
Owner:SONY CORP
Interference suppression methods for 802.11
ActiveUS7046690B2Avoid lostAvoid interferenceError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementGeneral purposeTelecommunications
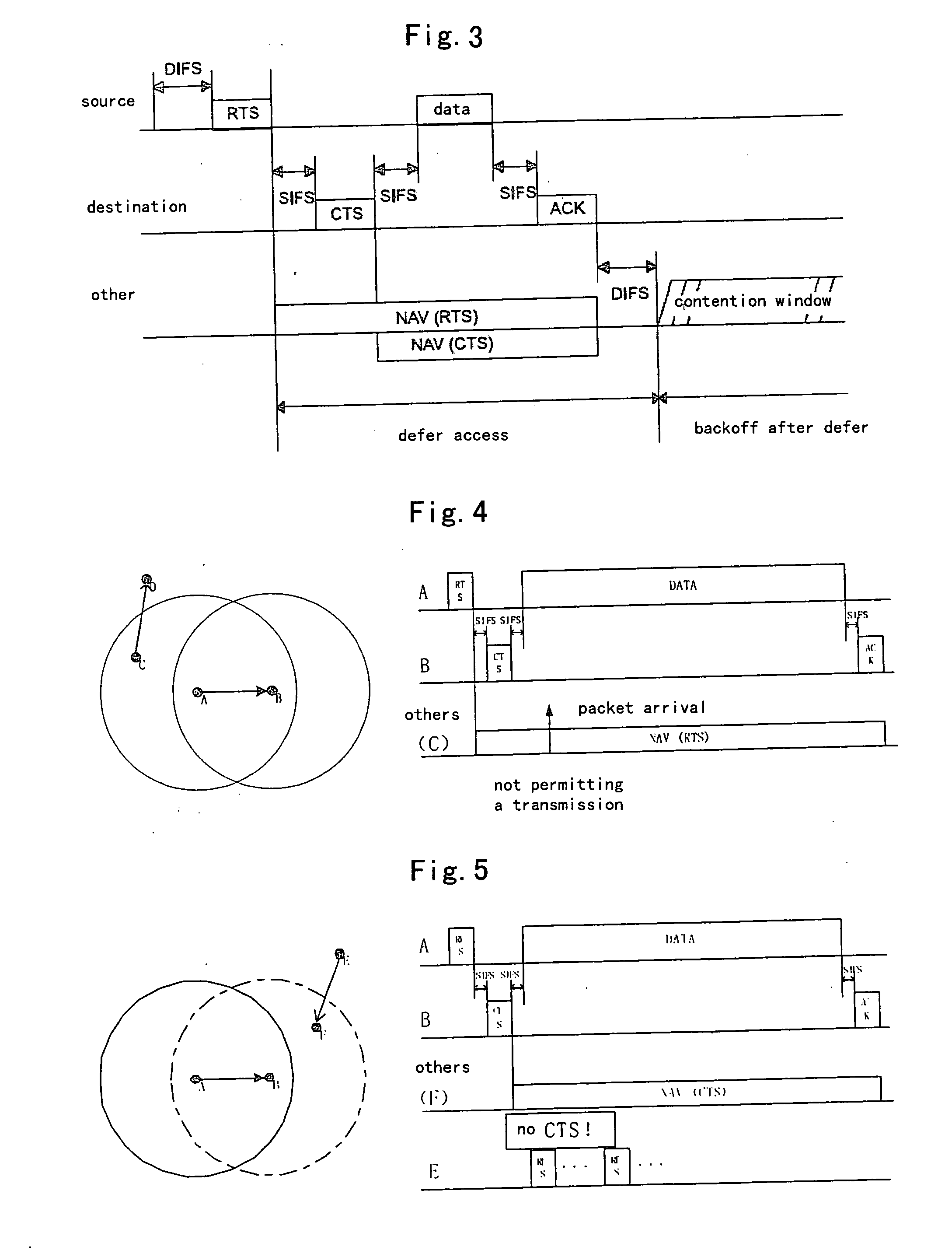
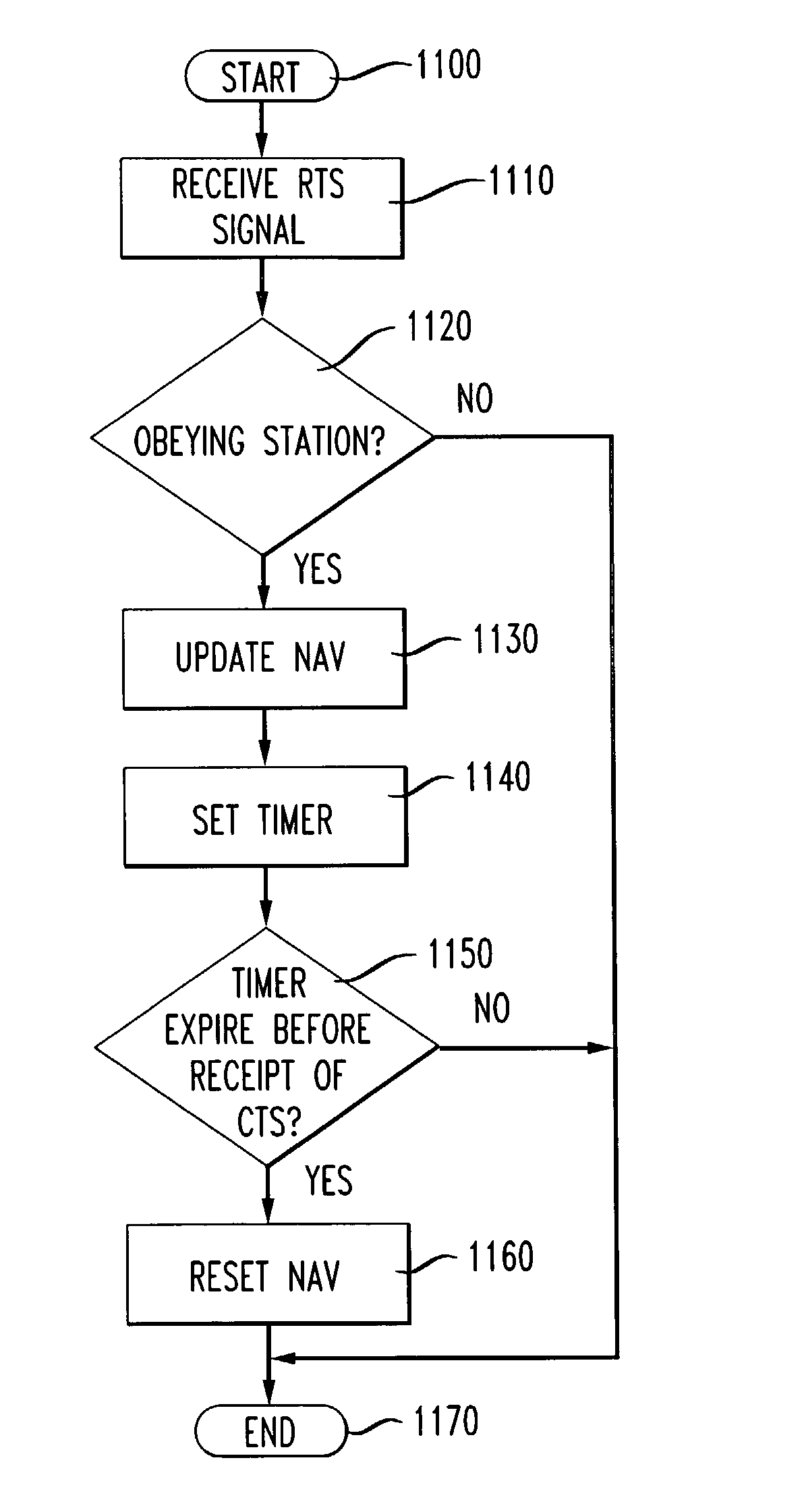
An 802.11 source station transmits a message, such as a CF-End message, to reset a network allocation vector at a time other than that required for indicating the end of the contention free period. That is, the source station uses the CF-End message to spoof stations within range of the message into resetting the stations' network allocation vectors as if the contention free period were active. Thus, the spoofing source station is allowed to release the medium for general use after the medium has been reserved for a specific use, for a greater time than necessary. Accordingly, spoofed stations may, for example, 1) delay transmission until a more critical transmission has completed, 2) allow unknown or foreign protocol to have preferential use of the medium, 3) prevent interference from hidden stations, and 4) allow sharing of the medium by overlapping basic service sets. After the specific use, if the medium is still reserved, the medium may be released for general use.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Access method for periodic contention-free sessions
ActiveUS7180905B2Reduce distractionsReduce conflictSynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementQuality of serviceAccess method
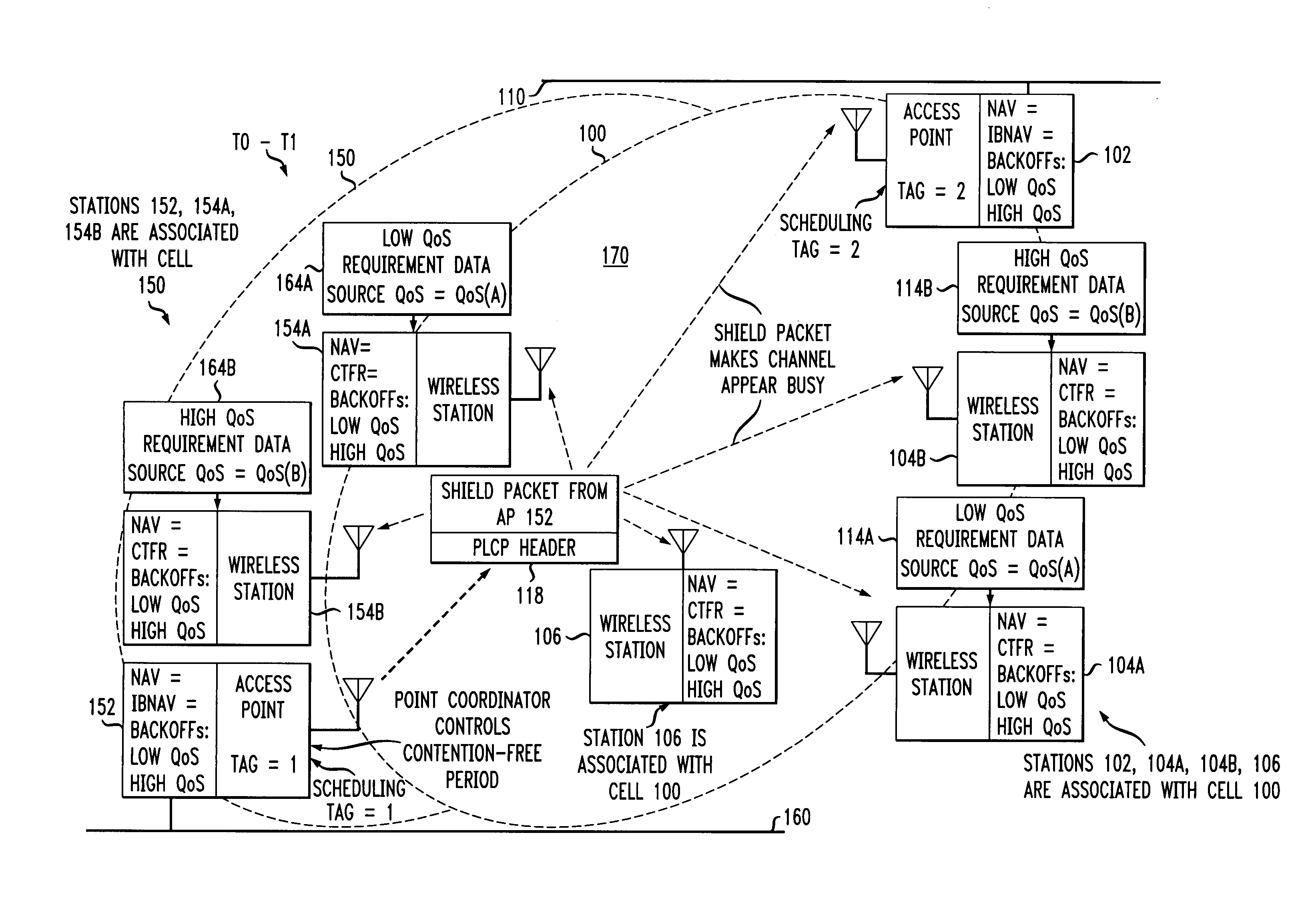
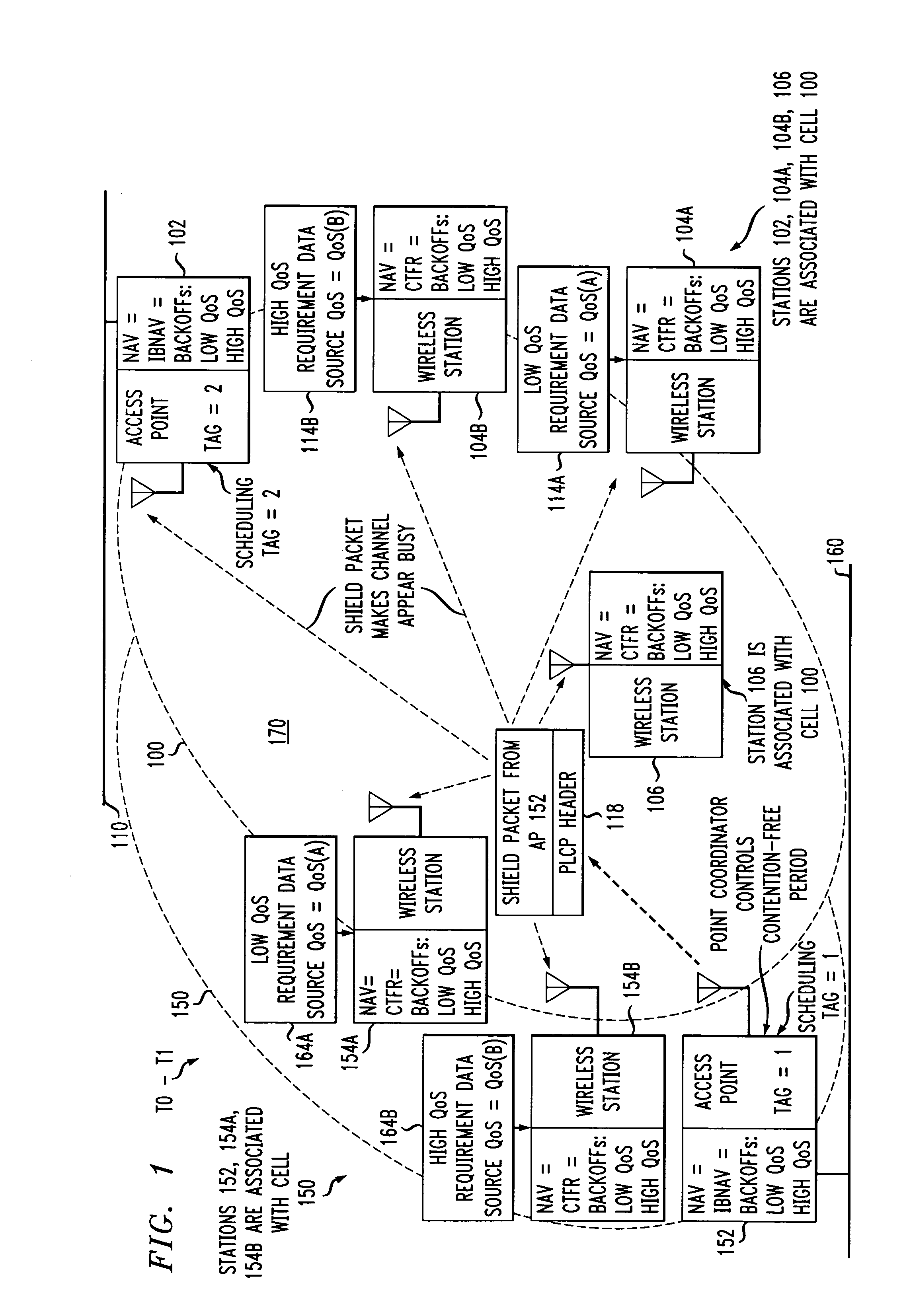
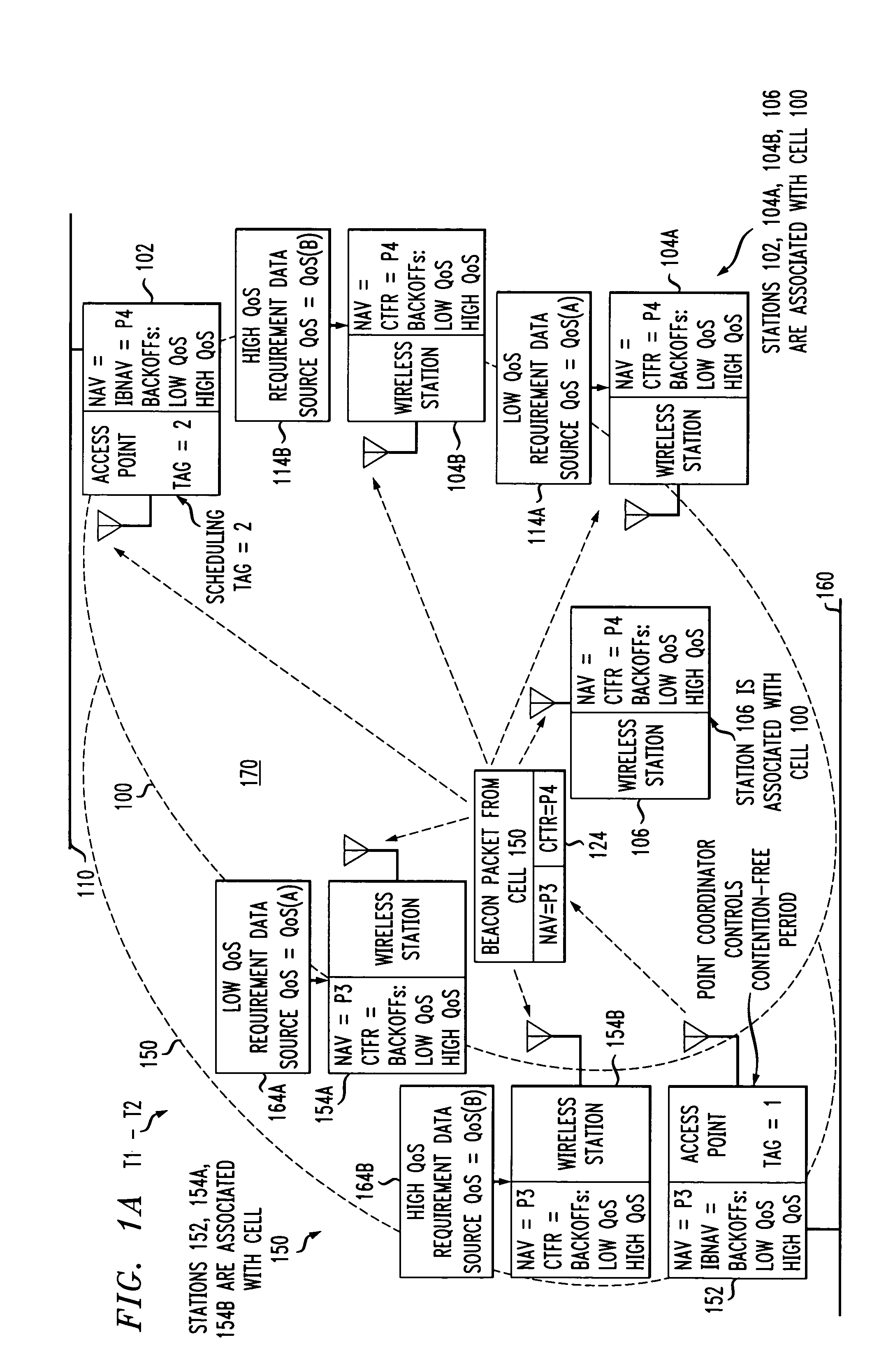
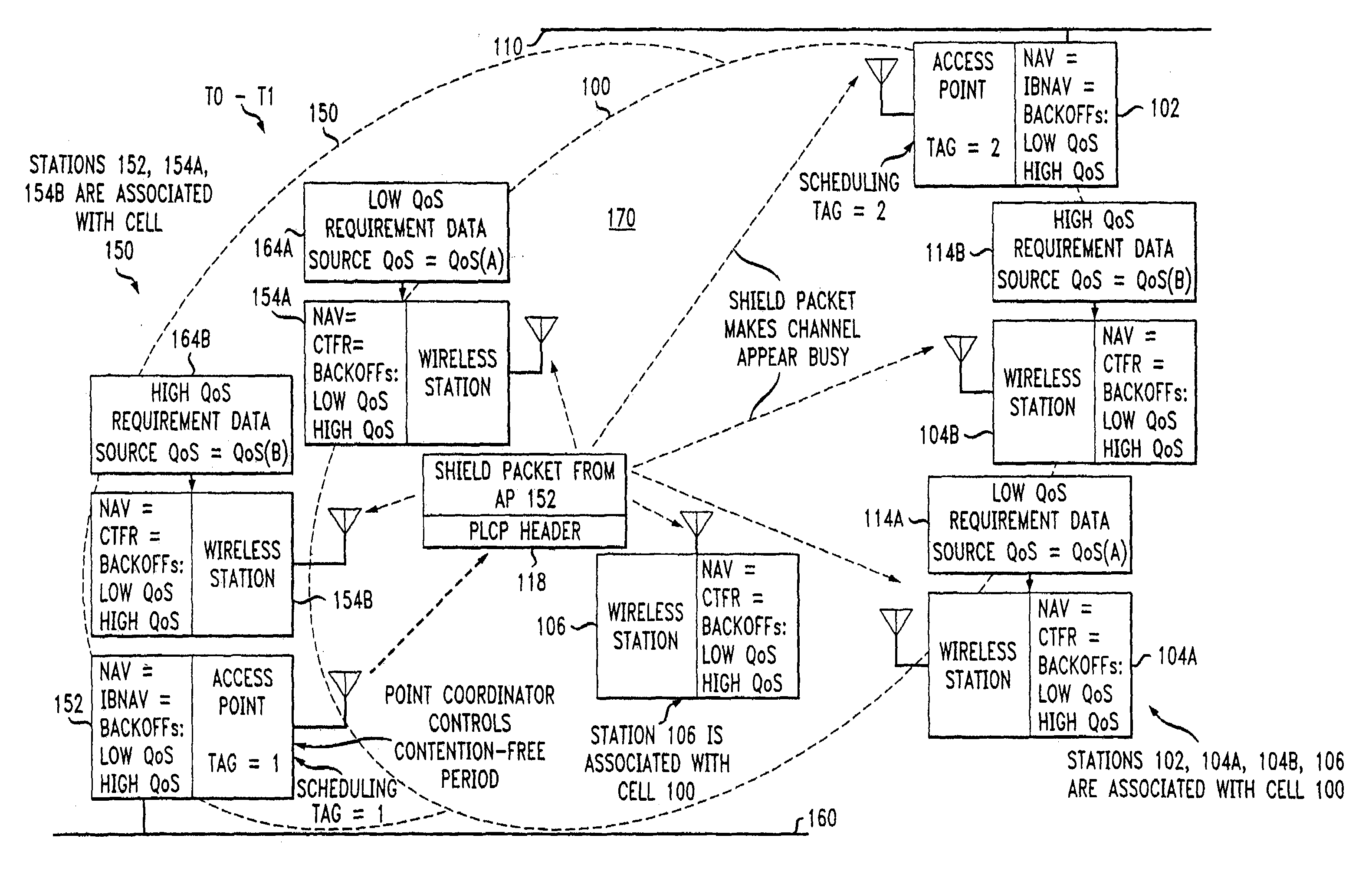
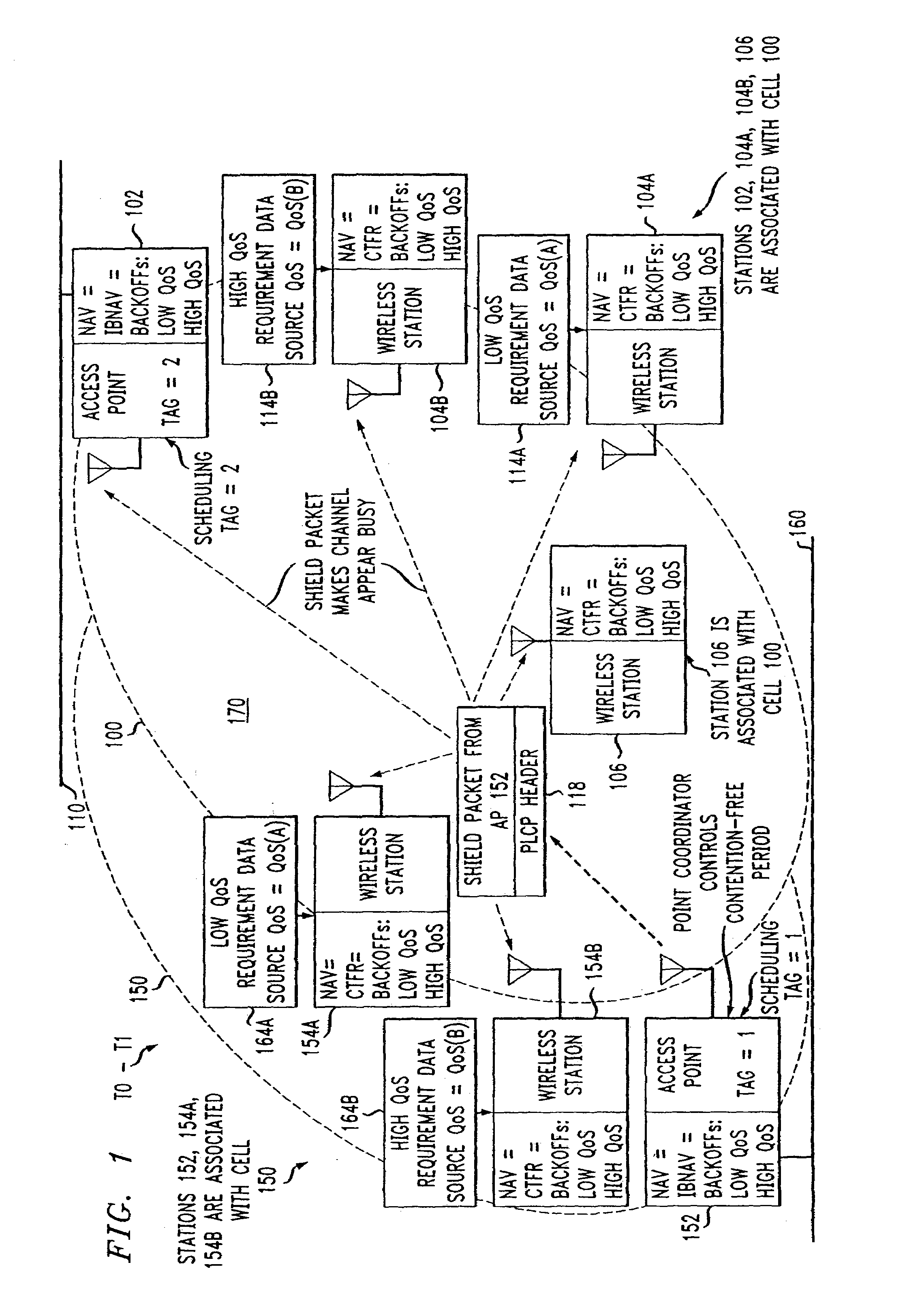
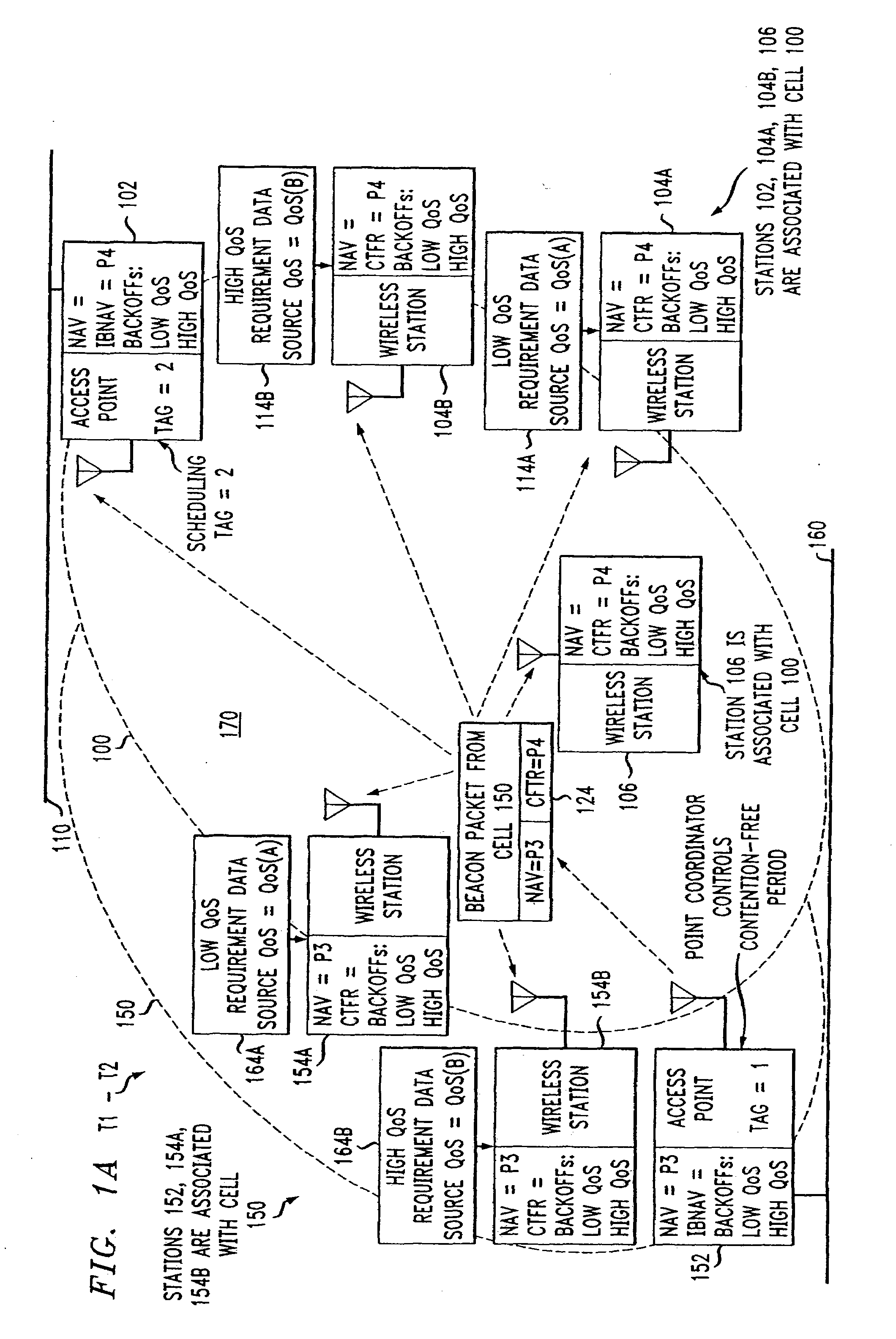
An access method for periodic contention-free sessions (PCFS) reduces interference between overlapping first and second wireless LAN cells contending for the same medium. Each cell includes a respective plurality of member stations and an access point (AP) station. The access method for periodic contention-free sessions (PCFS) includes a fixed cycle time that reduces conflicts with PCFS from other cells. The PCFS from several cells are repeated in cycles of cycle period (CP), which is the contention-free period (CFP) of an access point times a factor that is a function of the number of overlapping cells. Periodic contention-free sessions (PCFSs) are generated, one from each overlapping cell. PCFS transmission attempts occur at the fixed specified time spacing following the start of the previous cycle. Each active AP sets a timer at CP and a PCFS is initiated when the timer expires. The timer is then reset to CP and this starts a new cycle. Contention transmissions are attempted by stations based on their assigned priority. If a channel is busy at the designated start time for transmitting a PCFS, the PCFS is shortened by the time lost. Interleaving PCFSs and CFSs reduces conflicts with CFSs from other cells. To lessen the contention between APs of different cells, each station's Network Allocation Vector (NAV) and Inter-BSS Network Allocation Vector (IBNAV) is updated by an increased value of the next CFS length, the increment being the inter-BSS contention period (IBCP). APs will attempt to access the channel during the IBCP only for transmitting a PCFS, while they will wait for the NAV and IBNAV expirations before attempting to transmit a CFS. Interleaving PCFSs and CFSs also enables maintaining quality of service (QoS).
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
Distributed wireless access method based on network allocation vector table and apparatus of the same
ActiveUS20060114867A1Reducing packet collisionReduce wasteNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesClear to sendCommunications system
Embodiments of the present invention include a wireless access method based on a NAVT (Network allocation vector table), which is applied to a distributed wireless mobile communication system comprising a plurality of nodes, the NAVT comprises a packet type field and a duration field and is stored in the respective nodes of the communication system, comprising: on a transmitting side, determining whether only a RTS (request to send) item is contained in the NAVT when a packet arrives; sensing channel to judge whether the channel is busy after determining that only the RTS item is contained in the NAVT; sending a RTS packet based on the RTS item to the receiving side after determining that the channel is busy; and on a receiving side, determining whether the NAVT is empty or not when the RTS packet is received; sending a CTS (clear to send) packet back to the transmitting side after determining that the NAVT is empty.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Overlapping network allocation vector (ONAV) for avoiding collision in the IEEE 802.11 WLAN operating under HCF
ActiveUS7164671B2Efficient use ofAvoid collisionError preventionTransmission systemsTelecommunicationsBasic service
The present invention is related to a medium access control (MAC) protocol for avoiding collisions among ESTAs when two or more overlapping basic service sets (OBSSs) co-exist and operate in the same channel. To achieve this, each mobile station operating under HCF maintains a first counter known as Network Allocation Vector (NAV) and a second counter known as Overlapping Network Allocation Vector (ONAV), which is updated within a mobile station by frames coming from OBSSs, during the Contention Free Period (CFP) or during a Contention Free Burst (CFB) granted by a polling frame. The mobile station uses the NAV to update only to the medium occupancy in its own BSS to ensure that the mobile station will not interfere with the transmissions in its own QBSS, while the ONAV is used to avoid collisions with the mobile stations from the OBSS.
Owner:UNILOC 2017 LLC
Interference suppression methods for 802.11
ActiveUS7046650B2Avoid interferenceAvoid lostError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementCarrier signalNetwork allocation vector
An 802.11 source station transmits a signal with the duration field other than that required for the transmission to prevent transmission by other stations during known sequences. Thus, the source station uses the duration field to spoof the actual time the medium will be occupied, to stations within range of the signal. A station within range of the transmitted signal will check the duration field of the transmitted signal, and update the station's network allocation vector. Thus, the station will not transmit because the station's network allocation vector indicates that the medium is in use, even though the station maybe unable to hear the carrier. Accordingly, spoofed stations may, for example, 1) delay transmission until a more critical transmission has completed, 2) allow unknown or foreign protocol to have preferential use of the medium, 3) prevent interference from hidden stations, and 4) allow sharing of the medium by overlapping basic service sets.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Medium access apparatus and method for preventing a plurality of stations in a wireless local area network from colliding with one another
ActiveUS20070110091A1Ensure fairnessModulated-carrier systemsAssess restrictionTelecommunicationsPhysical layer
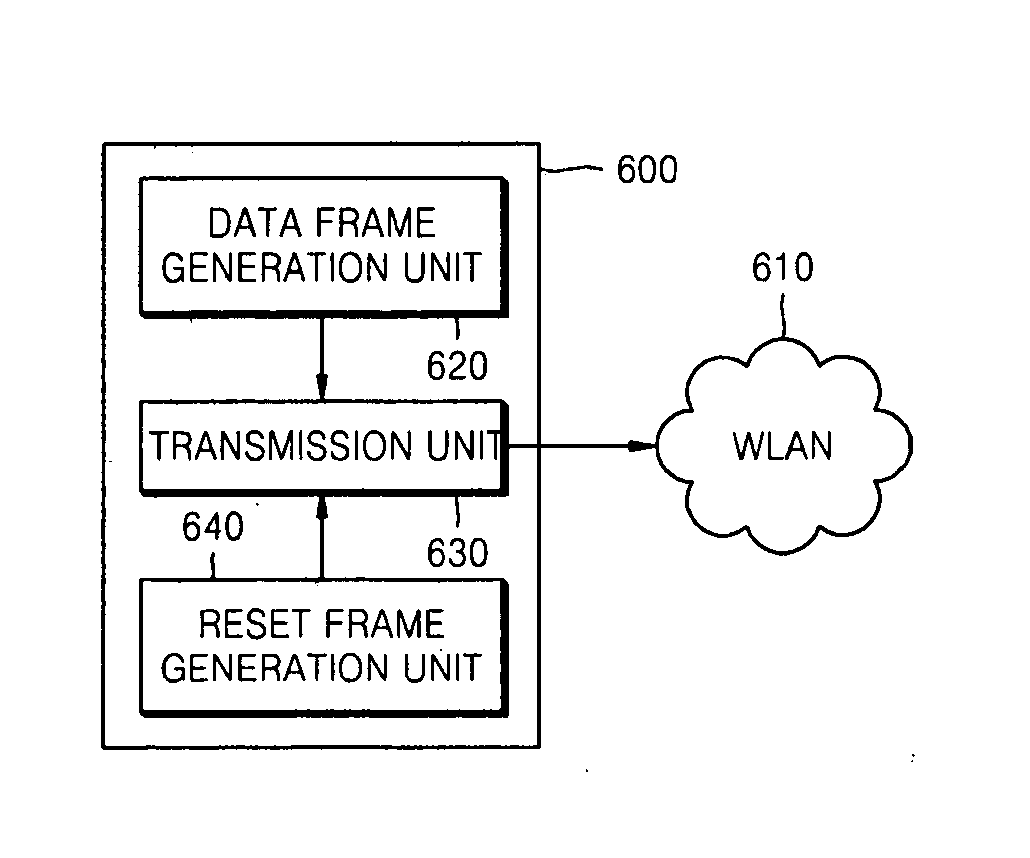
A method and apparatus for preventing a plurality of stations in a wireless local area network (WLAN) where a plurality of high throughput (HT) stations and a plurality of 802.11 legacy stations coexist from colliding are provided. The method includes generating a data frame having an HT format by inserting information indicating that a medium will be unavailable until the reception of an acknowledgement (ACK) frame is concluded into a physical layer (PHY) header having a format that can be interpreted by both the HT stations and the legacy stations; transmitting the data frame; and transmitting a reset frame which resets network allocation vectors (NAVs) of a plurality of stations which have heard the data frame, and has a format that can be interpreted by both the HT stations and the legacy stations. The apparatus includes a data frame generation unit; a reset frame generation unit; and a transmission unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Scheme for operating a wireless station having directional antennas
InactiveUS20060240780A1Enhancing 802.11 Wireless NetworksEasy to produceNetwork topologiesSubstation equipmentDirectional antennaAntenna correlation
Disclosed is a wireless station having a receiver and a network allocation vector associated with each of a plurality of directional antennas. The receivers concurrently listen for frames from remote stations. When any receiver detects a frame from a remote station, the receiver activates its associated NAV. The station has one or more transmitters that can transmit using the antennas. While transmitting a signal using an antenna, the receivers associated with any non-transmitting antennas continue to listen for signals from remote stations. The station cancels any signals from the transmitting antenna received by the non-transmitting antennas. To perform the cancellation, the station performs a self-calibration procedure. The station can self-calibrate by either silencing neighboring stations or by inserting null tones into a transmitted calibration signal.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Contention based medium reservation for multicast transmission in wireless local area networks
ActiveUS20110069628A1Reduce the probability of collisionProtect normal transmissionNetwork traffic/resource managementFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork allocation vectorMulticast transmission
A method and apparatus are described including multicasting a medium reservation message and receiving a response to the medium reservation message. Also described are a method and apparatus including receiving a medium reservation message, determining if a medium is idle and transmitting a response to the medium reservation message responsive to the determination. Further described are a method and apparatus including receiving a medium reservation message, determining if a received network allocation vector in the medium reservation message has a value greater than a current network allocation vector, determining if transmission over a medium during a time interval is detected and resetting the current network allocation vector responsive to the determination of transmission. Yet further described are a method and apparatus including receiving a response to a medium reservation message, determining if a network allocation vector in the response is greater than a current network allocation vector and updating the current network allocation vector responsive to the determination.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
Method for establishing layer-striding dynamic source route protocol based on load balance
InactiveCN101415248AReduce the scope of query floodingReduce the number of discoveriesNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesIdle timeNetwork allocation vector
The invention relates to the technical field of wireless communication and discloses a building method for a layer-spanning dynamic source routing protocol based on load balance. With a single-path routing mode adopted and based on the dynamic source routing protocol, the method comprises the following steps: based on IEEE802.11 MAC layer technology, a cycle T is determined, network distribution vectors in a request frame and an allowing frame sent by a neighbor node S are intercepted within the cycle T, and the idle time of the node is calculated to obtain the residual available bandwidth of the node; the residual available bandwidth, the load, the hop count and the data quantity in a buffer queue of the node S are transferred to the network layer to form routing metrics, and a path parameter with the biggest metric is selected; a plurality of gateways used for shifting flows are built for shunting the flows to separate gateway. The building method for the layer-spanning dynamic source routing protocol based on the load balance can maintain the load balance of the whole network, reduce the routing query flooding range, reduce the times of routing discovery and improve the throughput of WMN.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Interference suppression methods for 802.11
InactiveUS7305004B2Avoid interferenceAvoid lostNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesTelecommunicationsCarrier signal
An 802.11 source station transmits a signal with the duration field other than that required for the transmission to prevent transmission by other stations during known sequences. Thus, the source station uses the duration field to spoof the actual time the medium will be occupied, to stations within range of the signal. A station within range of the transmitted signal will check the duration field of the transmitted signal, and update the station's network allocation vector. Thus, the station will not transmit because the station's network allocation vector indicates that the medium is in use, even though the station maybe unable to hear the carrier. Accordingly, spoofed stations may, for example, 1) delay transmission until a more critical transmission has completed, 2) allow unknown or foreign protocol to have preferential use of the medium, 3) prevent interference from hidden stations, and 4) allow sharing of the medium by overlapping basic service sets.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
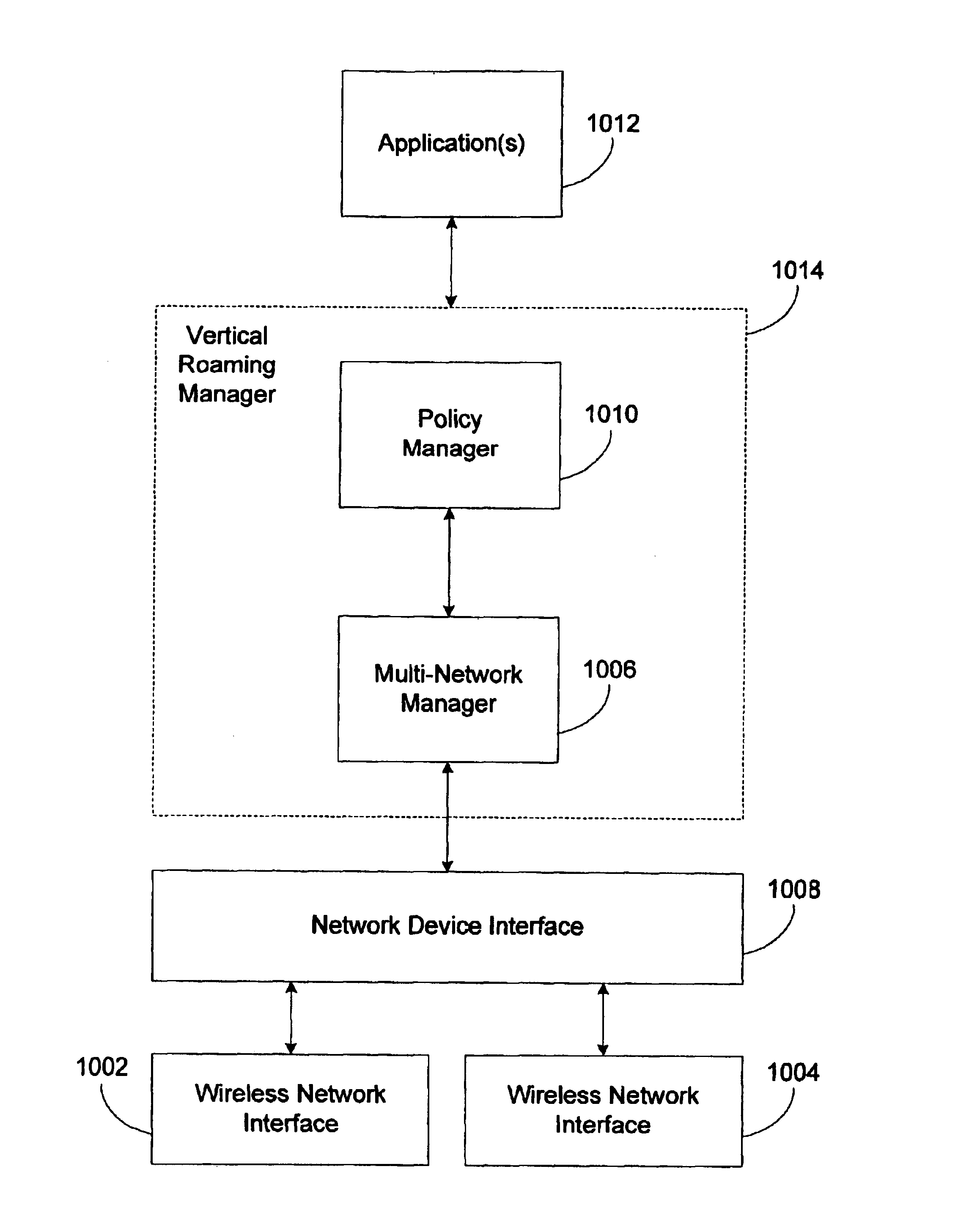
Vertical roaming in wireless networks through improved wireless network cell boundary detection
InactiveUS6982949B2Improved vertical handoffReliable detectionTime-division multiplexRadio transmission for post communicationQuality of servicePacket collision
A system and method for improved vertical handoff between different types of wireless network. Network allocation vector occupation and packet collision probability are used as quality of service measures, enabling vertical handoffs to be delayed until actually beneficial to quality of service. Improved wireless network cell boundary detection in vertical handoff scenarios is achieved with a Fourier-based technique in conjunction with an adaptively determined minimum operating signal strength threshold. Improved wireless network cell boundary detection enables vertical handoffs from high quality of service networks to be delayed as long as possible. Together, practical wireless network quality of service measures and improved detection of wireless network cell boundaries in vertical handoff scenarios reduce the rate of unnecessary vertical handoff resulting in higher overall quality of service experienced by a mobile computing device roaming between wireless network types.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Relay apparatus, communication terminal, communication system, and semiconductor integrated circuit
InactiveUS20070206628A1Improve reliabilityAvoid Signal ConflictsEnergy efficient ICTPower managementWireless transmissionCommunications system
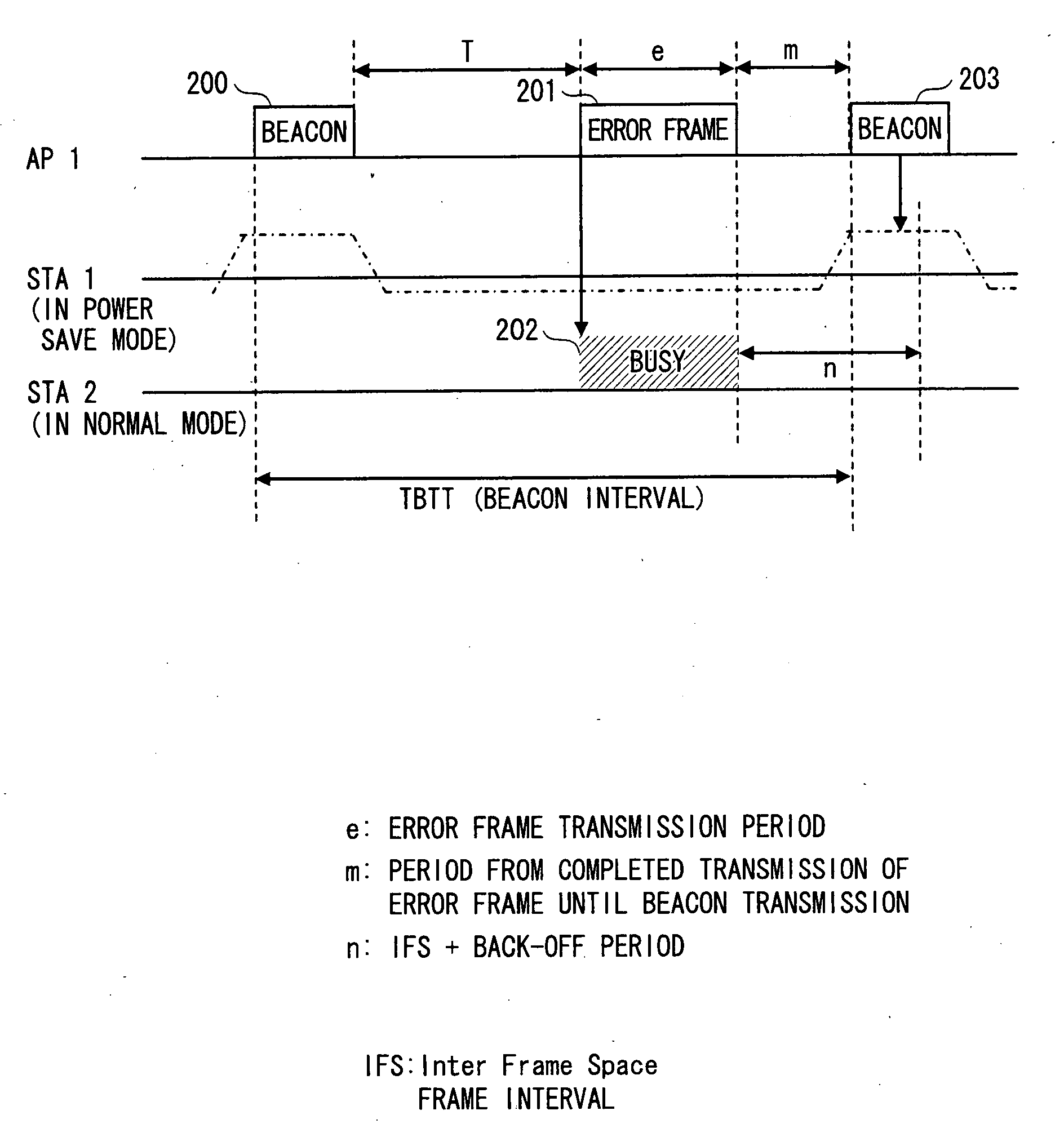
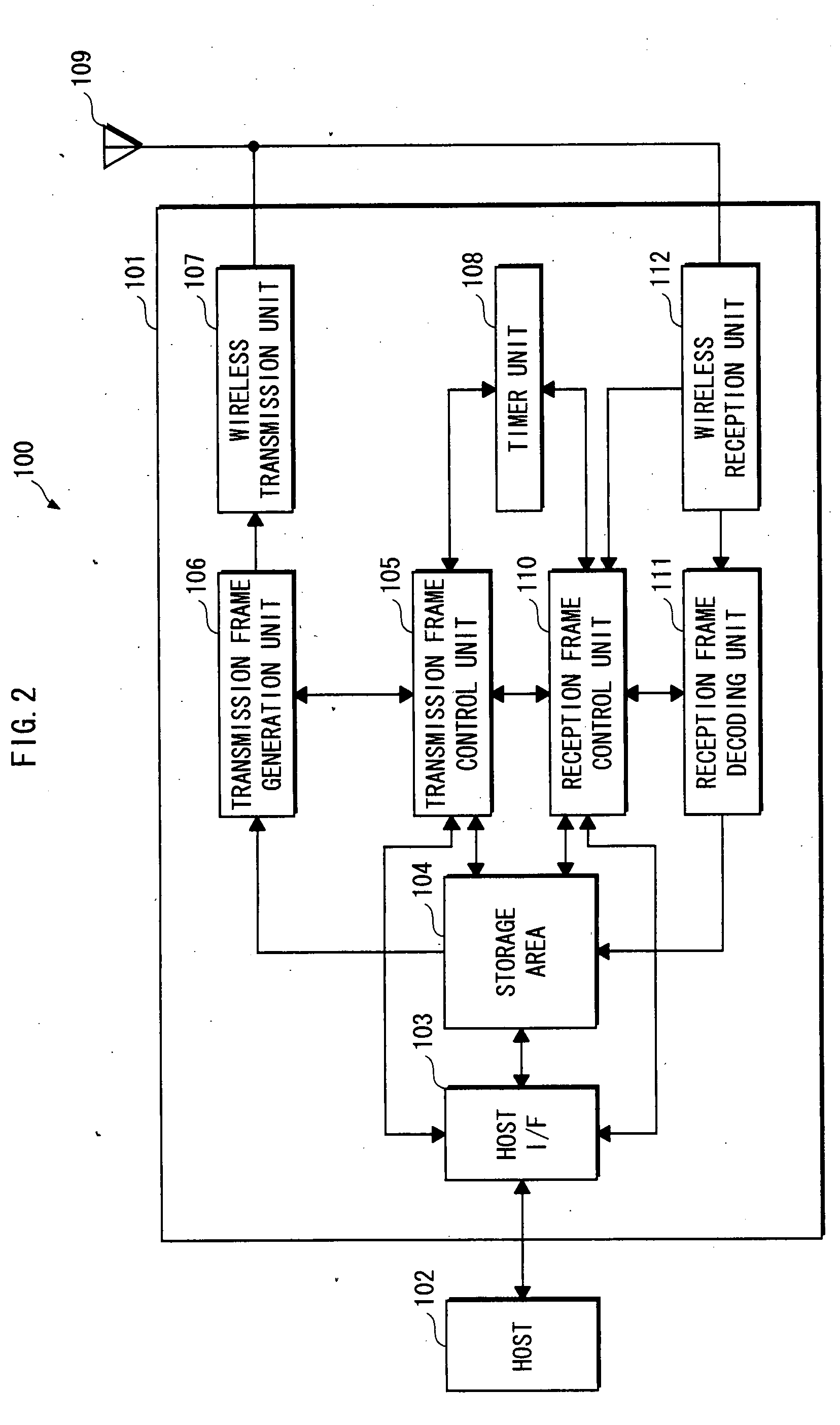
The present invention relates to a wireless LAN (Local Area Network) communication system. Upon a timer unit 108 clocking a predetermined time T after an access point 100 has transmitted a beacon signal 200, a transmission frame control unit 105 generates a CTS frame 301, and transmits an error frame 401 via a transmission frame generation unit 106, a wireless transmission unit 107 and an antenna 109. Accordingly, upon receiving the CTS frame 301, a communication terminal 20 ceases transmitting data for a NAV (Network Allocation Vector, transmission prohibition interval) period in accordance with IEEE 802.11 standard.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
Request to send (RTS) and clear to send (CTS) for multichannel operations
Certain aspects of the present disclosure provide techniques and apparatus for signaling the bandwidth to be used for wireless communications using an RTS / CTS (Request to Send / Clear to Send) frame exchange, providing for bandwidths of at least 20 MHz, 40 MHz, 80 MHz, 160 MHz, or higher. This exchange of bandwidth information may be performed implicitly-by determining the channels in which the RTS / CTS frames are actually sent-or explicitly. In addition to this bandwidth information exchange, aspects of the present disclosure may also allow for Network Allocation Vector (NAV) protection in multiple channels. In this manner, the wireless medium may be reserved, and the transmission may be protected from hidden nodes.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and apparatus for reducing control signaling overhead in hybrid wireless network
InactiveUS20090279524A1Reduce control signaling overheadIncrease capacityNetwork topologiesWireless commuication servicesTelecommunicationsControl signal
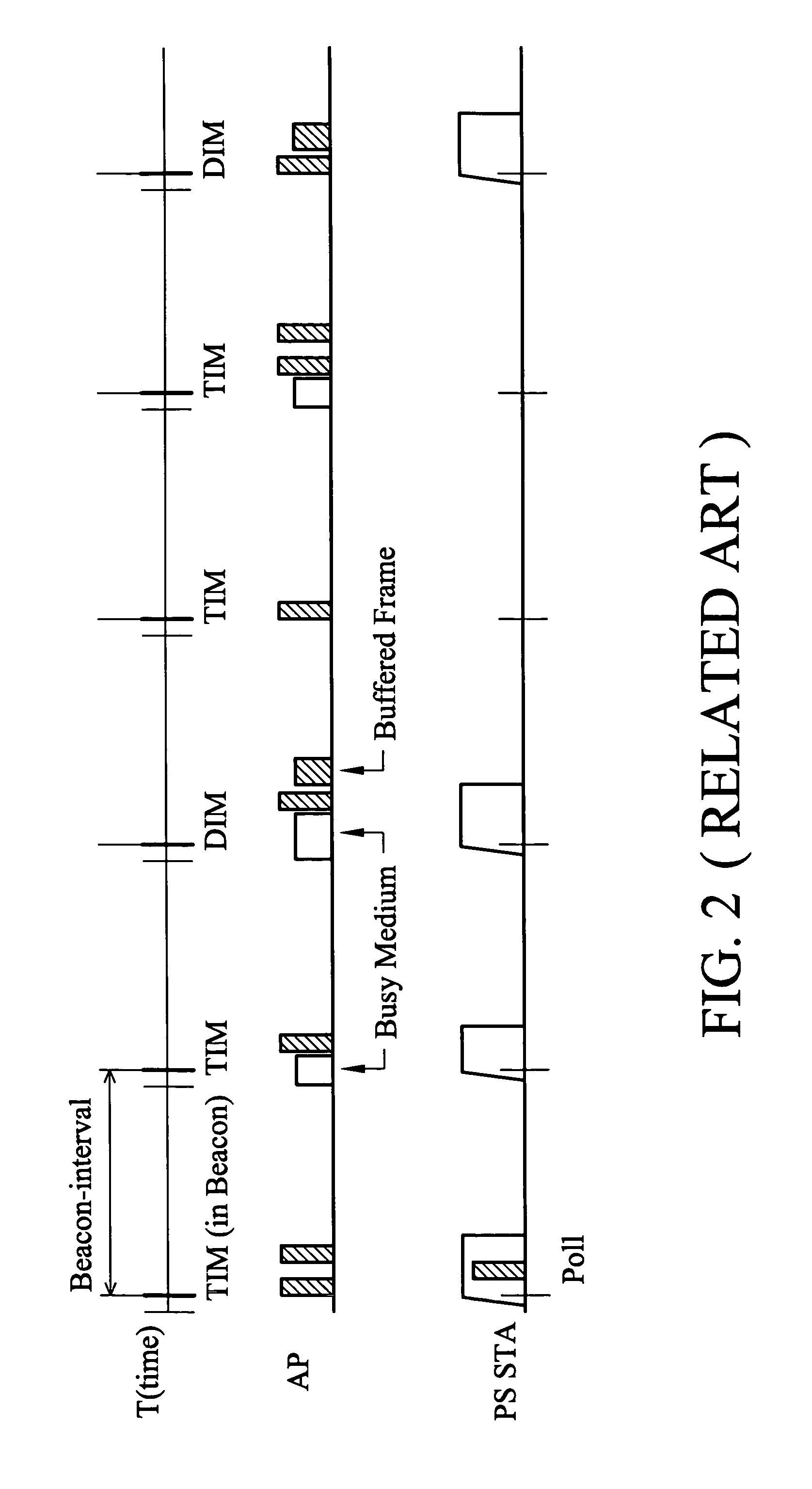
Embodiments of the present invention include a method and apparatus for reducing control signaling overhead in a hybrid wireless network. The method comprises receiving a wireless frame in the hybrid wireless network at a first terminal, and determining whether the received wireless frame is a control frame for a wireless channel reservation; if the received wireless frame is a control frame for the wireless channel reservation, reading by the first terminal a value of Duration field in control frame, and updating a timer for a channel reservation period in the first terminal with the value of Duration field, instead of updating network allocation vector of the first terminal; determining whether the remaining time of the timer for the channel reservation period is longer than the time required for transmitting the data frame or not before transmitting a data frame by the first terminal; and transmitting the data frame directly by the first terminal without transmission of a control frame for the wireless channel reservation if the remaining time is longer than the time required for transmitting the data frame.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC +1
Multi-frame transmission method and multi-frame transmission system
ActiveCN102595623AImprove efficiencyImprove throughputWireless communicationTime informationObject based
The invention discloses a multi-frame transmission method. The method comprises the following steps that: based on amount and / or length of data to be sent to the current receiving station in the current access queue, a sending station determines the time for occupying a channel to perform frame exchange with the current receiving station; the sending station generates channel reservation time information according to the determined time for occupying the channel to perform frame exchange with the current receiving station; and the sending base station performs frame exchange with the current receiving station according to the generated channel reservation time information. The invention further discloses a multi-frame transmission system. With the method and the system, the channel reservation time of the stations in an OBSS (Object Based Storage System) is reduced, thus, an auditing station can set shorter NAV (Network Allocation Vector) settings, the system throughput of the OBSS is improved, and the high efficiency of each station in the OBSS under the condition of large-bandwidth is ensured.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Access method for periodic contention-free sessions
InactiveUS20070211749A1Reduce conflictReduce distractionsSynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementQuality of serviceAccess method
An access method for periodic contention-free sessions (PCFS) reduces interference between overlapping first and second wireless LAN cells contending for the same medium. Each cell includes a respective plurality of member stations and an access point (AP) station. The access method for periodic contention-free sessions (PCFS) includes a fixed cycle time that reduces conflicts with PCFS from other cells. The PCFS from several cells are repeated in cycles of cycle period (CP), which is the contention-free period (CFP) of an access point times a factor that is a function of the number of overlapping cells. Periodic contention-free sessions (PCFSs) are generated, one from each overlapping cell. PCFS transmission attempts occur at the fixed specified time spacing following the start of the previous cycle. Each active AP sets a timer at CP and a PCFS is initiated when the timer expires. The timer is then reset to CP and this starts a new cycle. Contention transmissions are attempted by stations based on their assigned priority. If a channel is busy at the designated start time for transmitting a PCFS, the PCFS is shortened by the time lost. Interleaving PCFSs and CFSs reduces conflicts with CFSs from other cells. To lessen the contention between APs of different cells, each station's Network Allocation Vector (NAV) and Inter-BSS Network Allocation Vector (IBNAV) is updated by an increased value of the next CFS length, the increment being the inter-BSS contention period (IBCP). APs will attempt to access the channel during the IBCP only for transmitting a PCFS, while they will wait for the NAV and IBNAV expirations before attempting to transmit a CFS. Interleaving PCFSs and CFSs also enables maintaining quality of service (QoS).
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
Power saving method in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20120213177A1Wide bandwidthImprove consumption efficiencyEnergy efficient ICTPower managementClear to sendCommunications system
A method and apparatus of accessing a channel in a wireless local area network is provided. A destination station receives a request to send (RTS) frame to allocate a network allocation vector from a source station over a first bandwidth and transmits a clear to send (CTS) frame over a second bandwidth to the source station in response to the RTS frame. The second bandwidth is dynamically determined when a first parameter has a predetermined value.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
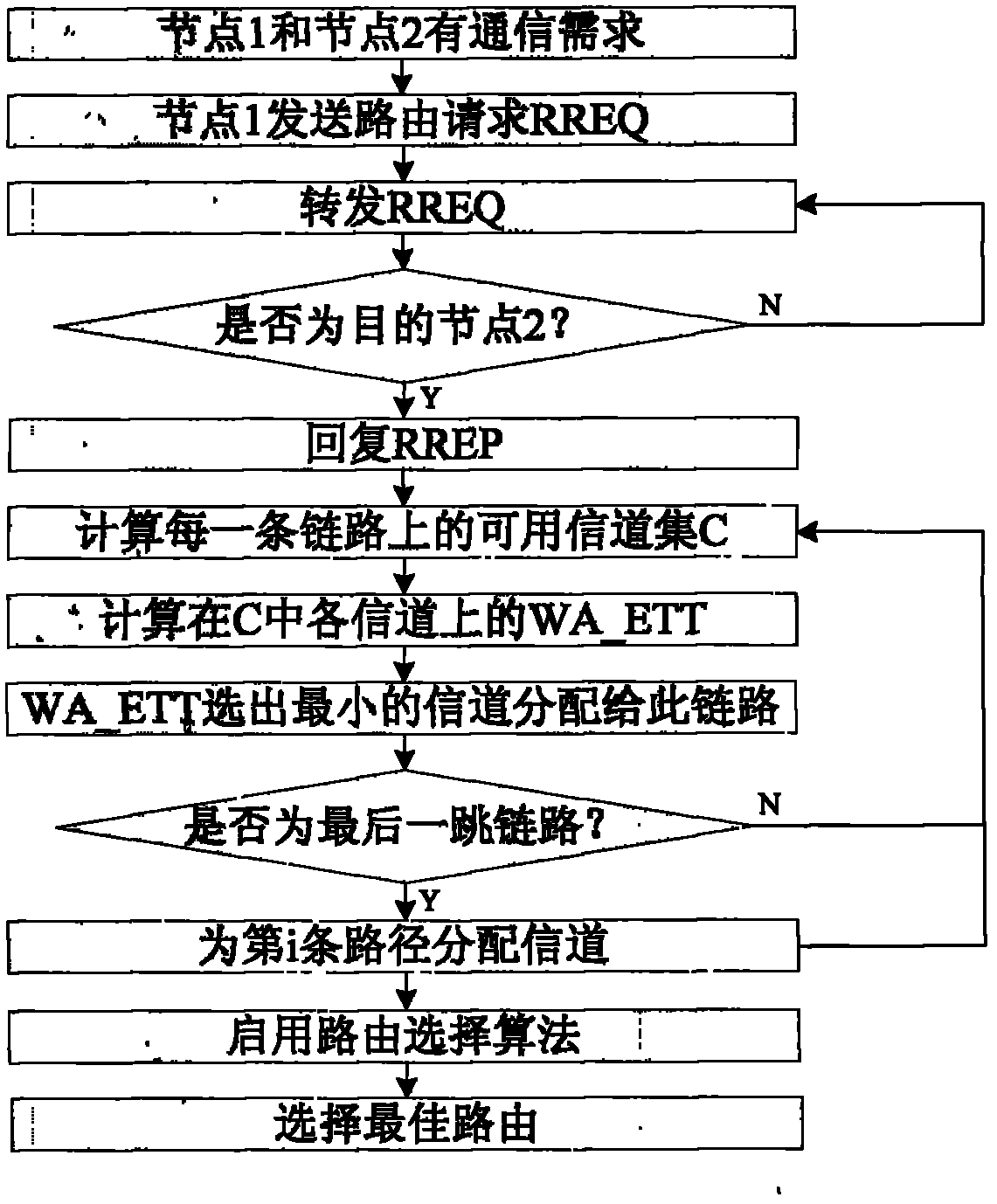
Distributed channel allocating method in multi-channel multi-radio wireless Mesh network
The invention relates to a distributed channel allocating method in a multi-channel multi-radio wireless Mesh network, which comprises the steps of: initiating a route request by a node needing route discovery, after a target node receives a request message, figuring out a channel free degree and a surplus available bandwidth through a network allocation vector (for short NAV) when replying along a reverse route, solving weighted average expected transmission time (WA ETT), selecting a channel with the minimum WA ETT as a channel for allocating to a link, after allocating the channel for each jump in each path, respectively figuring out a value of a route metric EWCETT (Evoluted Weighted Accumulation Expected Transmission Time) of each path, and selecting the path with the minimum EWCETT value as an optimal route for transmitting and maintaining. According to the invention, channel allocation and route selection are fused together, the time of channel allocation and route selection is effectively reduced, and network throughput, end-to-end time delay and network overhead of the multi-channel multi-radio wireless Mesh network can be effectively improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Space division interference avoiding method for wireless local area network OBSS (object-based storage system) site
InactiveCN103052077ASolve the problem of quality of service requirementsImprove throughputNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesMulti inputQuality of service
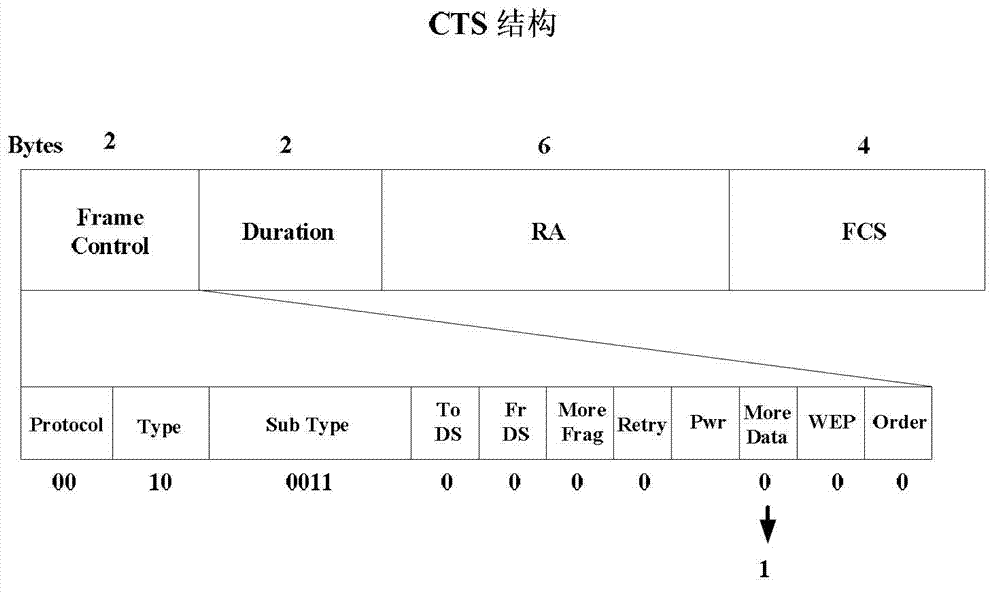
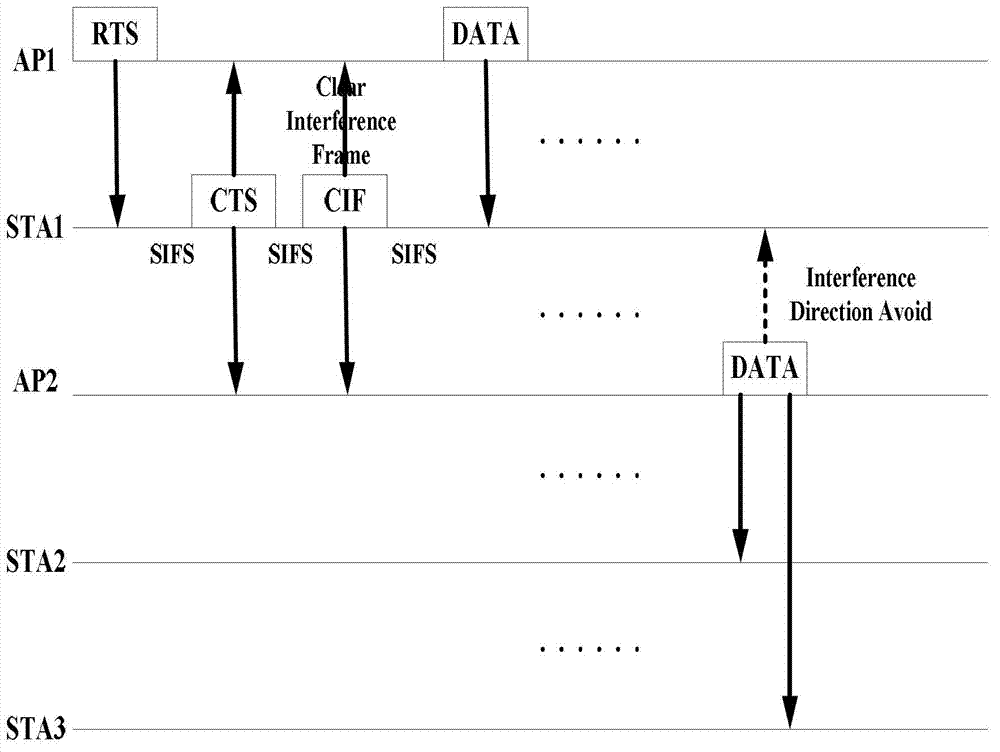
The invention discloses a space division interference avoiding method for a wireless local area network OBSS (object-based storage system) site. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, a site at the OBSS is enabled to carry beam vector information used by the site through modifying the structure of an RTS (ready to send) frame and a CTS (clear to send) frame, and an MU-MIMO (multi-user multi-input multi-output) sending mode is realized; and step 2, interference AP (access point) in the MU-MIMO sending mode considers the zero-forcing beam direction as an extra constraint condition in the protection time interval of network allocation vector. The space division interference avoiding method for the wireless local area network OBSS site can effectively satisfy the service quality requirement of the site at the OBSS under scarce spectrum resource.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Methods and devices for sending and receiving data, and network system
InactiveCN102547917ATimely replyEffective protection mechanismAssess restrictionConnection managementClear to sendProtection mechanism
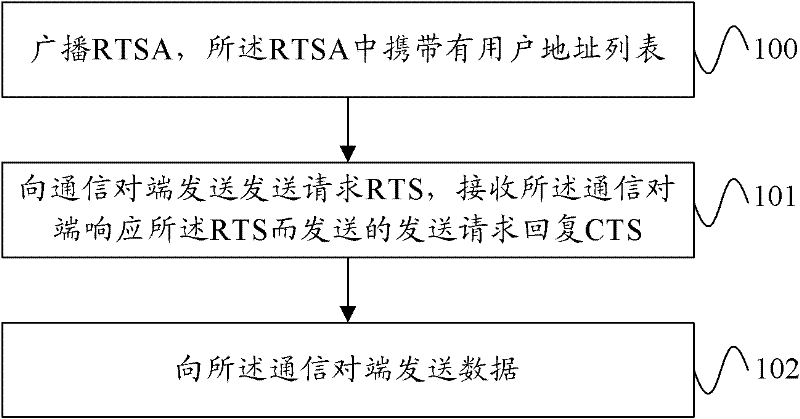
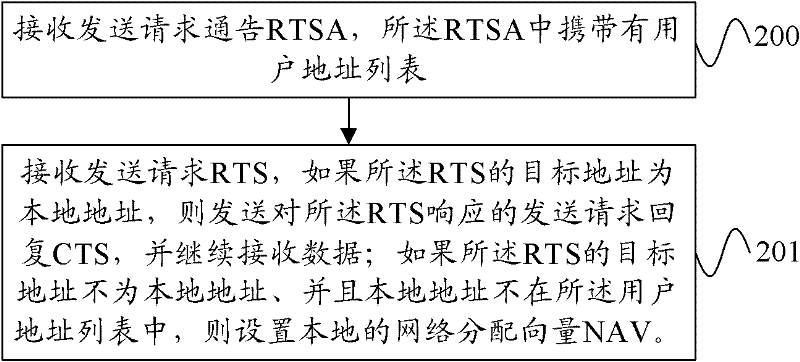
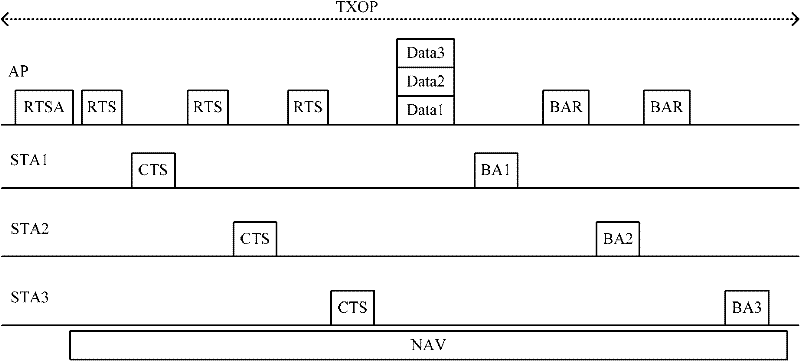
The embodiment of the invention provides methods and devices for sending and receiving data, and a network system. The method for sending the data comprises the following steps of: broadcasting a request to send announcement (RTSA) which carries a user address list; sending a request to send (RTS), and receiving a clear to send (CTS) returned by an opposite end in response to the RTS; and sending data to the opposite end, wherein the user address list is used for indicating whether a user receiving the RTSA is provided with a network allocation vector (NAV) after receiving the RTS or the CTS. According to the embodiments of the invention, the RTSA is added so as to be used as supplementation and expansion of an RTS / CTS mechanism; an STA user receiving the RTSA selects whether to be provided with the NAV according to the indication of the user address list in the RTSA after receiving the RTS / CTS, and can timely reply the data sent by a data sending end; and therefore, the problems of mutual confliction, difficult realization and the like in the prior art are solved, and an effective protection mechanism is supplied to data transmission.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
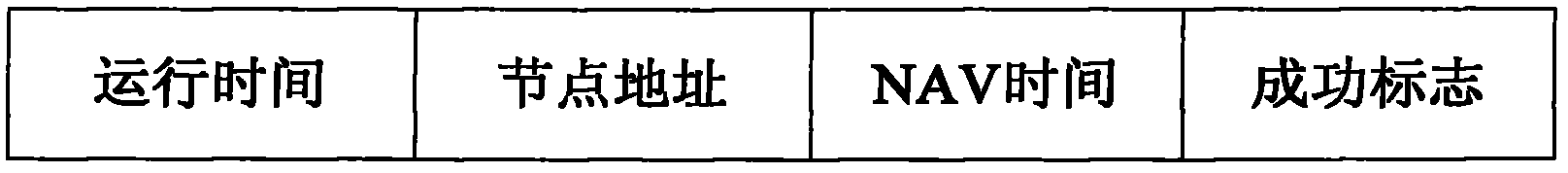
Nodes and NAV (network allocation vector) control method, device and system therefor
ActiveCN103002591ASolve the problem of geographical discriminationCriteria allocationNetwork topologiesNetwork allocation vectorMedia access control
The invention discloses nodes and NAV (network allocation vector) control method, device and system therefor. The method includes: judging that a preset first field of a monitored MAC (media access control) frame carries a first identifier, upgrading a local NAV value into a preset first value smaller than the local current NAV value; and after a TXOP (transmit opportunity) responder receives a last MAC frame transmitted by a TXOP holder, transmitting the MAC frame with the preset first field carrying the first identifier. The method, device, system and nodes allow hidden sites to timely compete for channel access, so that the problem of regional discrimination is solved for the sites.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
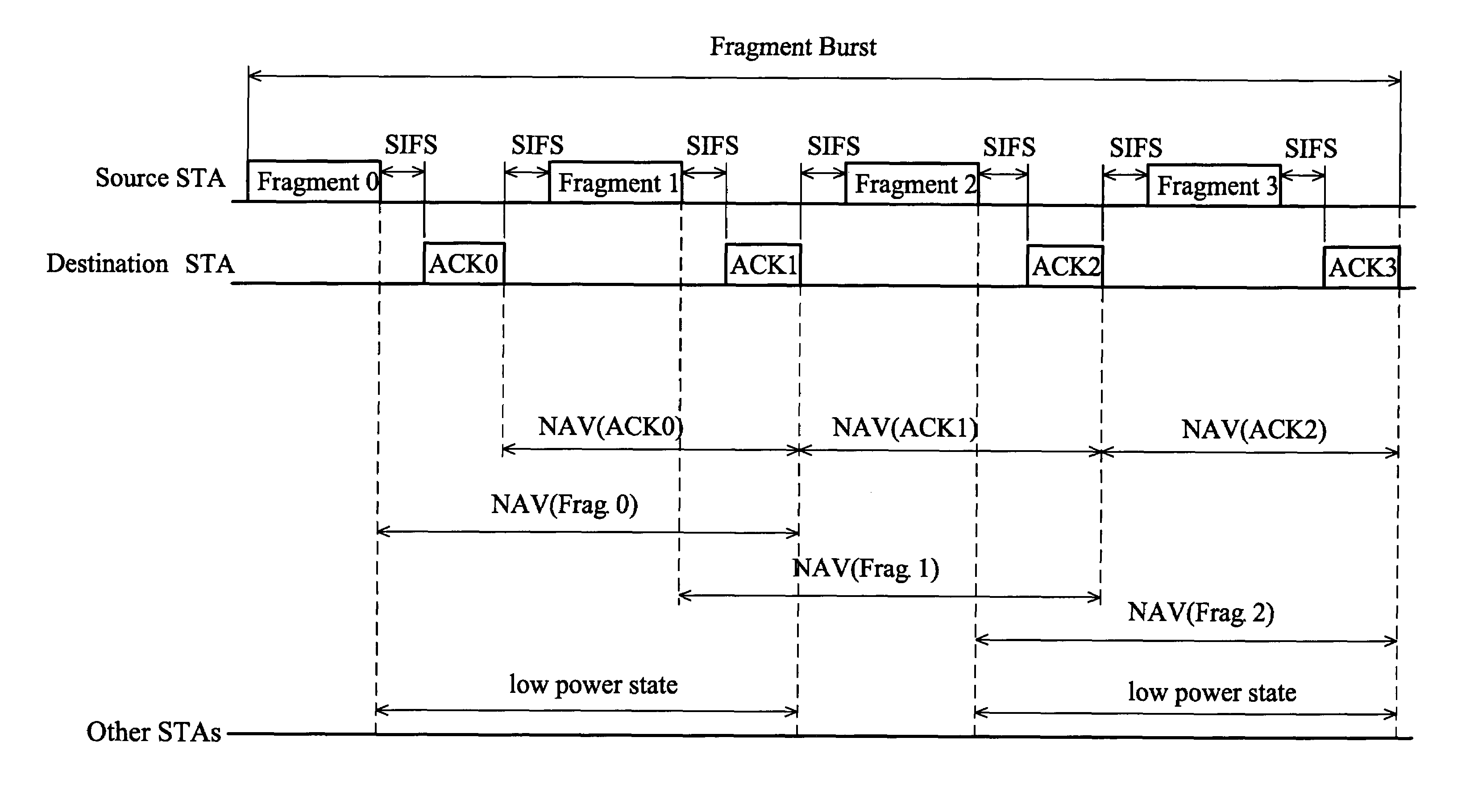
Power management method
A power management method. The power management method for a wireless network having a plurality of stations (STAs) comprises receiving a data frame, detecting a destination STA in accordance with the data frame, and entering a low power state if not the destination STA for a first power-save (PS) duration determined according to a network allocation vector (NAV) of each STA not the destination STA, updated with a duration information of the received data frame duration determined according to a network allocation vector (NAV) of the data frame.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Apparatus and method for transmission and recovery modes for an rts/cts system that utilizes multichannels
ActiveUS20130070668A1Network topologiesWireless commuication servicesData transmissionNetwork allocation vector
A method, apparatus and computer readable medium for an RTS / CTS system that utilizes a plurality of channels for data transfer, includes sending, by a first device, an RTS frame over the plurality of channels; receiving, by a second device, the RTS frame and outputting a CTS frame to the first device based on receipt of the RTS frame, the CTS frame being output over at least one of the plurality of channels; setting, by each device within a network that receives the RTS frame, a network allocation vector (NAV) to a time duration that is based in part on information included in the RTS frame; and transmitting, by the first device, data to the second device within the time duration set by the NAV using the at least one of the plurality of channels.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Backoff mechanism techniques for spatial reuse
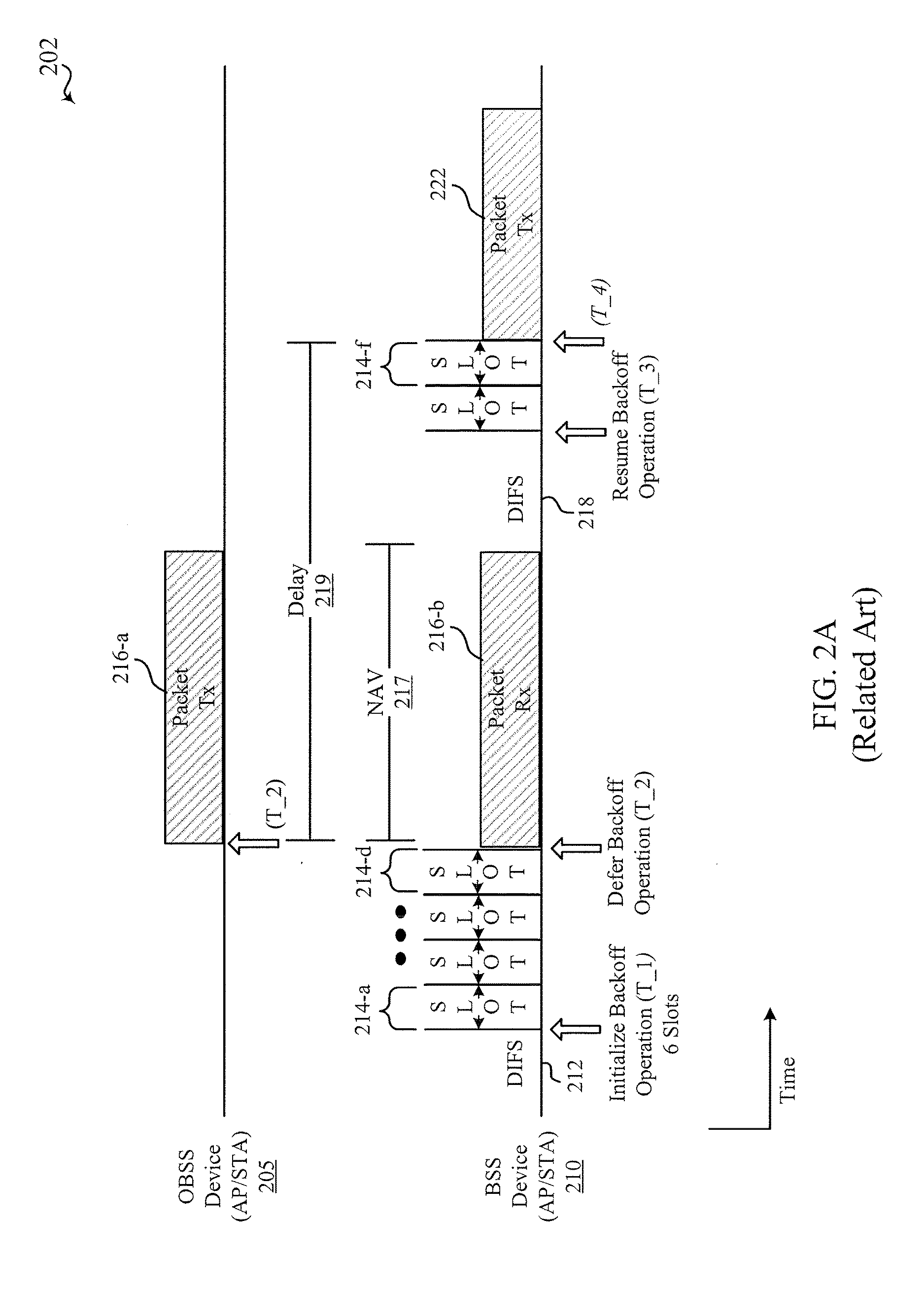
Techniques for reducing delay in scheduling traffic transmission in an overlapping basic service set (OBSS) environment by modifying backoff mechanisms are disclosed. In some examples, a device (e.g., station (STA) or access point (AP)) may decode at least a portion of a preamble of a received packet to determine whether the packet is sent by a member of an OBSS (e.g., STA or AP from a different BSS). Backoff operations are typically deferred as a result of the decoding. Aspects of the present disclosure provide a method, apparatus, and system to reduce delay in scheduling traffic transmissions by resuming the backoff operations prior to expiration of the period reserved for an OBSS packet by the network allocation vector (NAV). In other words, the device may not honor the NAV of the OBSS packet, and instead perform spatial reuse by transmitting another packet (or signal) on the same frequency channel during the NAV of the OBSS packet.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and apparatus for network allocation vector resetting
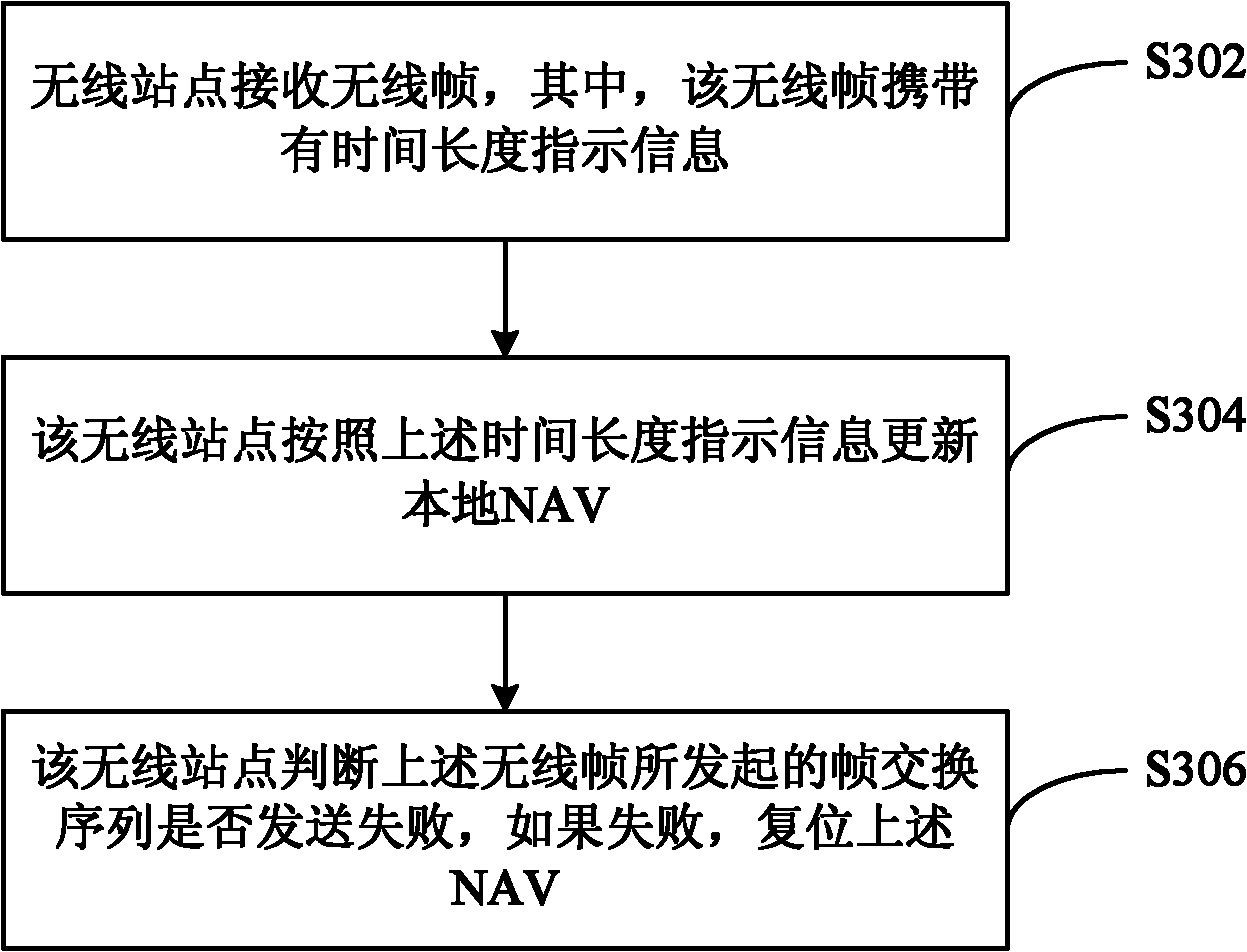
InactiveCN102695286ASolve the problem of not being able to compete fairly for channelsIncrease profitWireless communicationTelecommunicationsNetwork allocation vector
The invention provides a method and apparatus for network allocation vector (NAV) resetting. The method comprises the following steps that: a radio station receives a radio frame carrying time length indication information; the radio station updates a local NAV according to the time length indication information; and the radio station determines whether a frame switch sequence initiated by the radio frame is failed to be sent; if so, the NAV is reset. According to the invention, a problem that all stations can not compete for channels fairly when a frame switch sequence is failed can be solved, thereby enabling all the radio stations to compete for channels quickly and further improving a channel utilization rate.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com