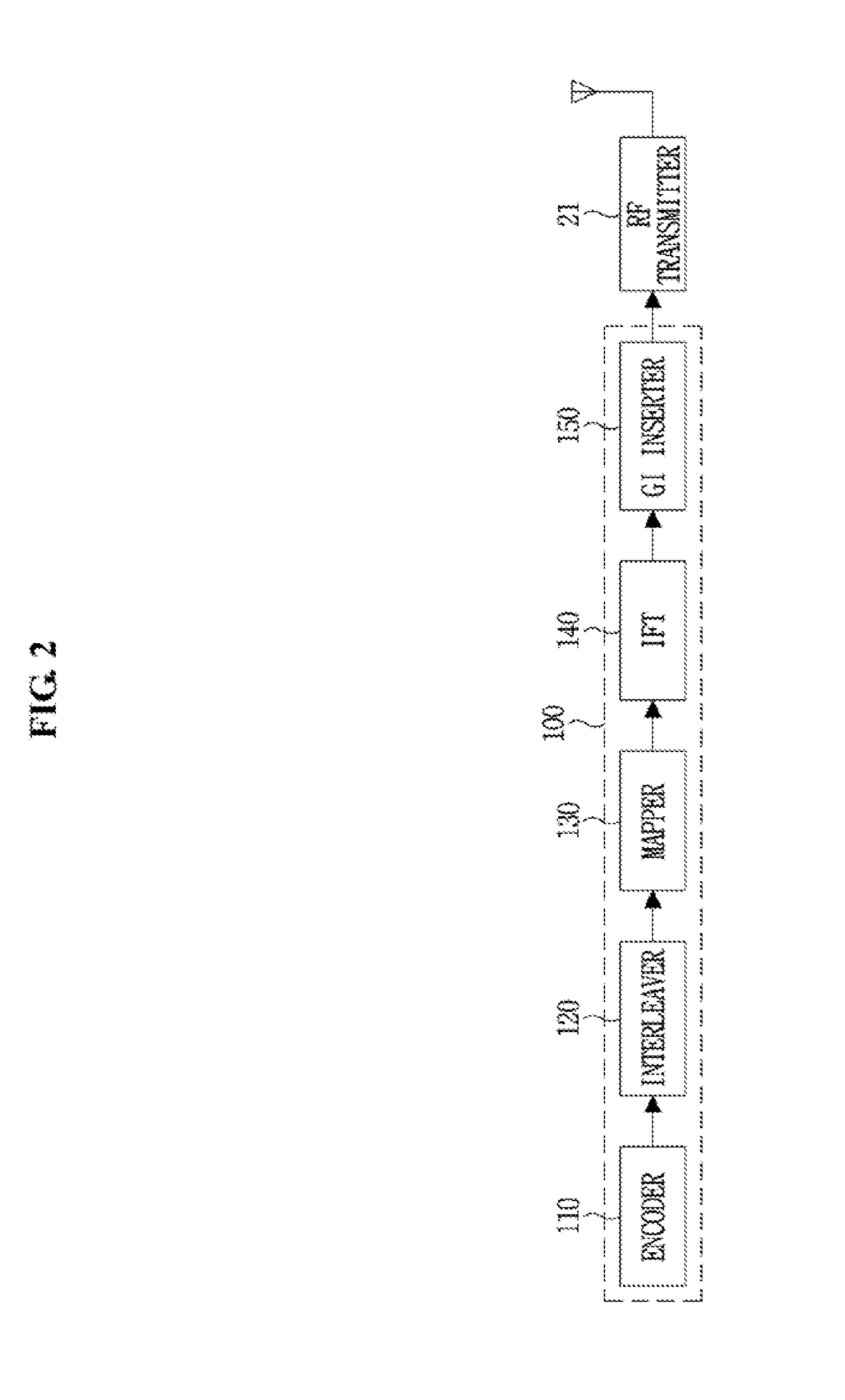
Patents
Literature
1452 results about "Basic service" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
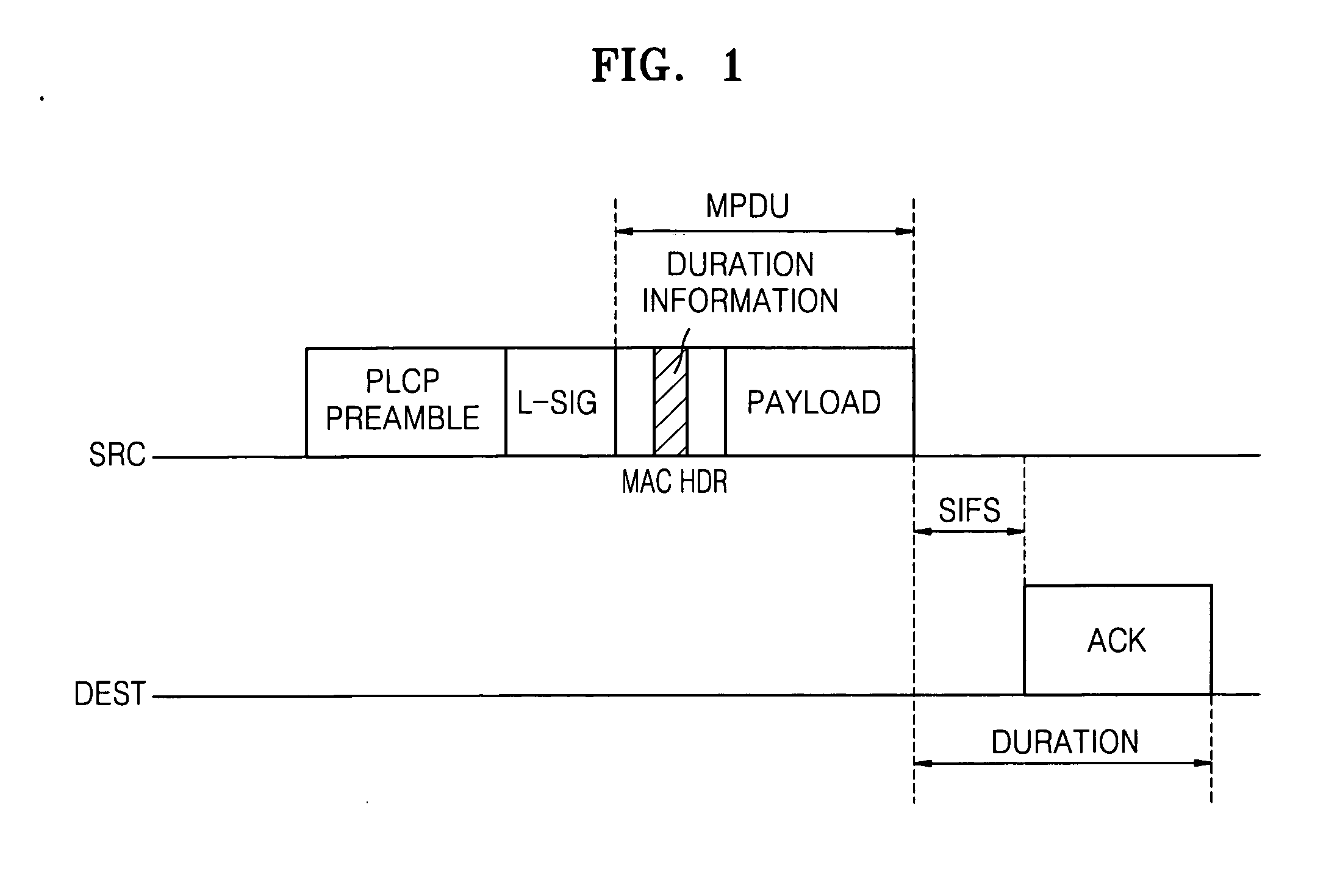
In telecommunications, basic service is: 1. A pure transmission capability over a communication path that is virtually transparent in terms of its interaction with customer-supplied information. 2. The offering of transmission capacity between two or more points suitable for a user's transmission needs and subject only to the technical parameters of fidelity and distortion criteria, or other conditioning.
System for transactionally deploying content across multiple machines
InactiveUS20050080801A1Easy to deployDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram planningBasic service
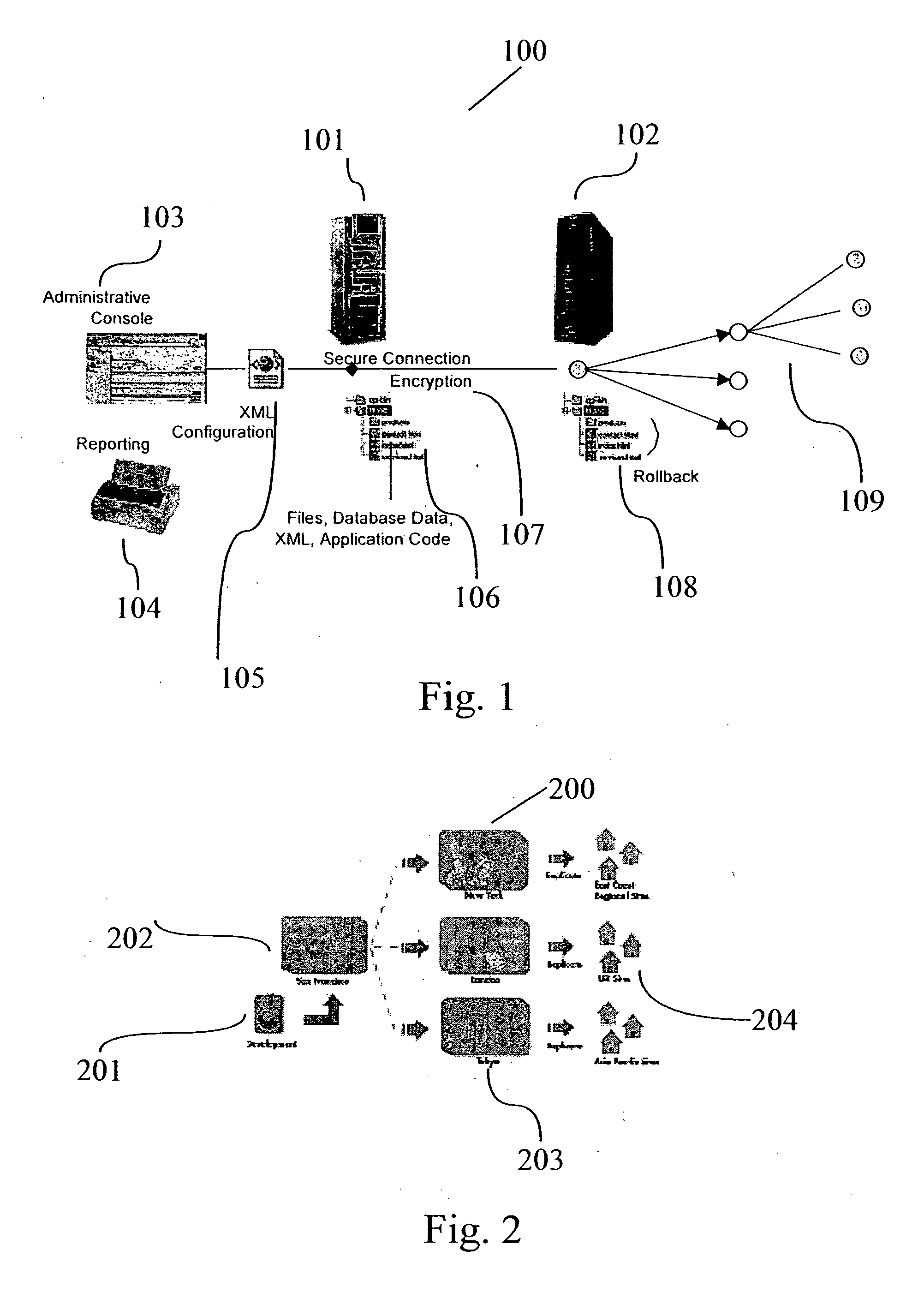
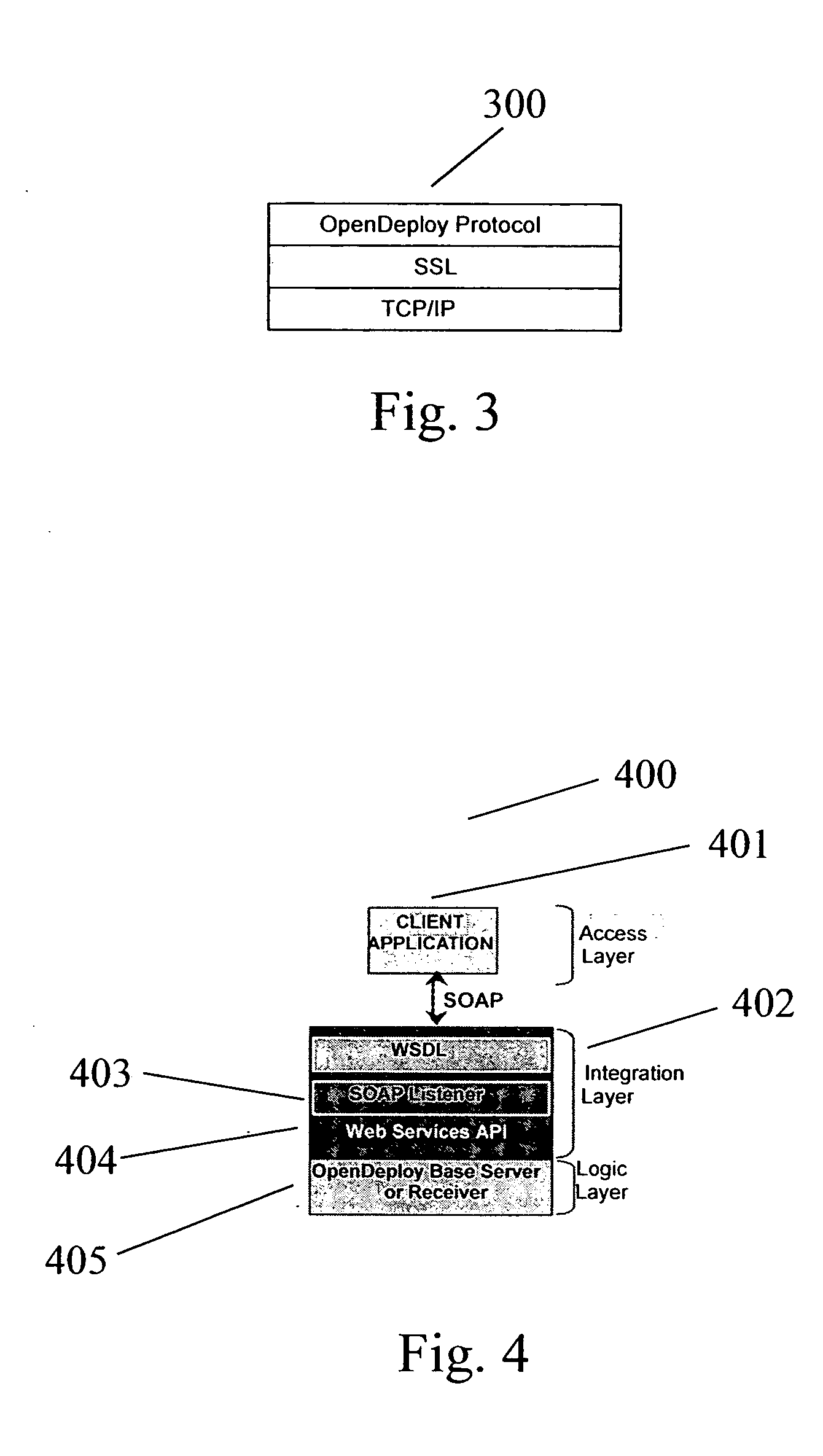
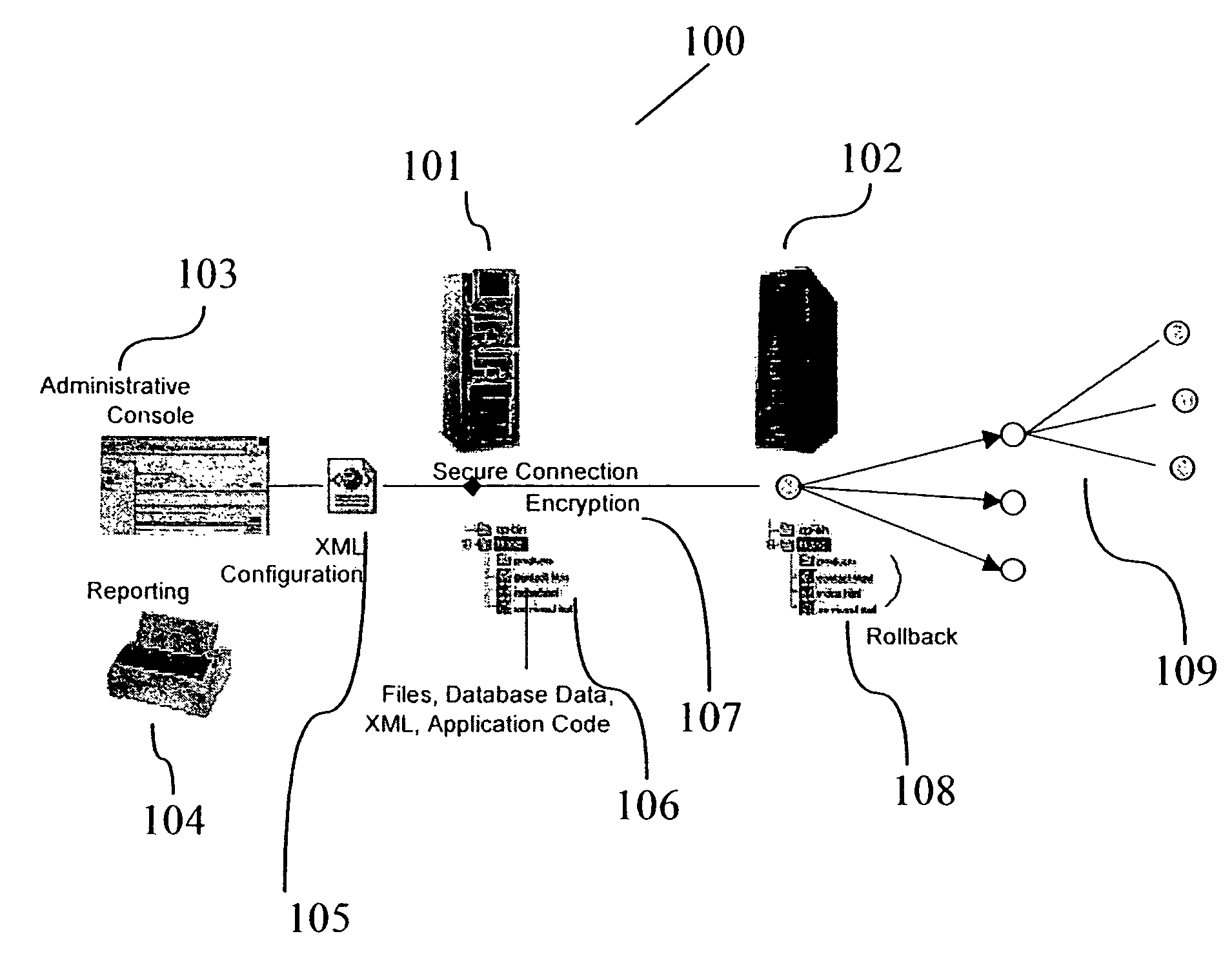
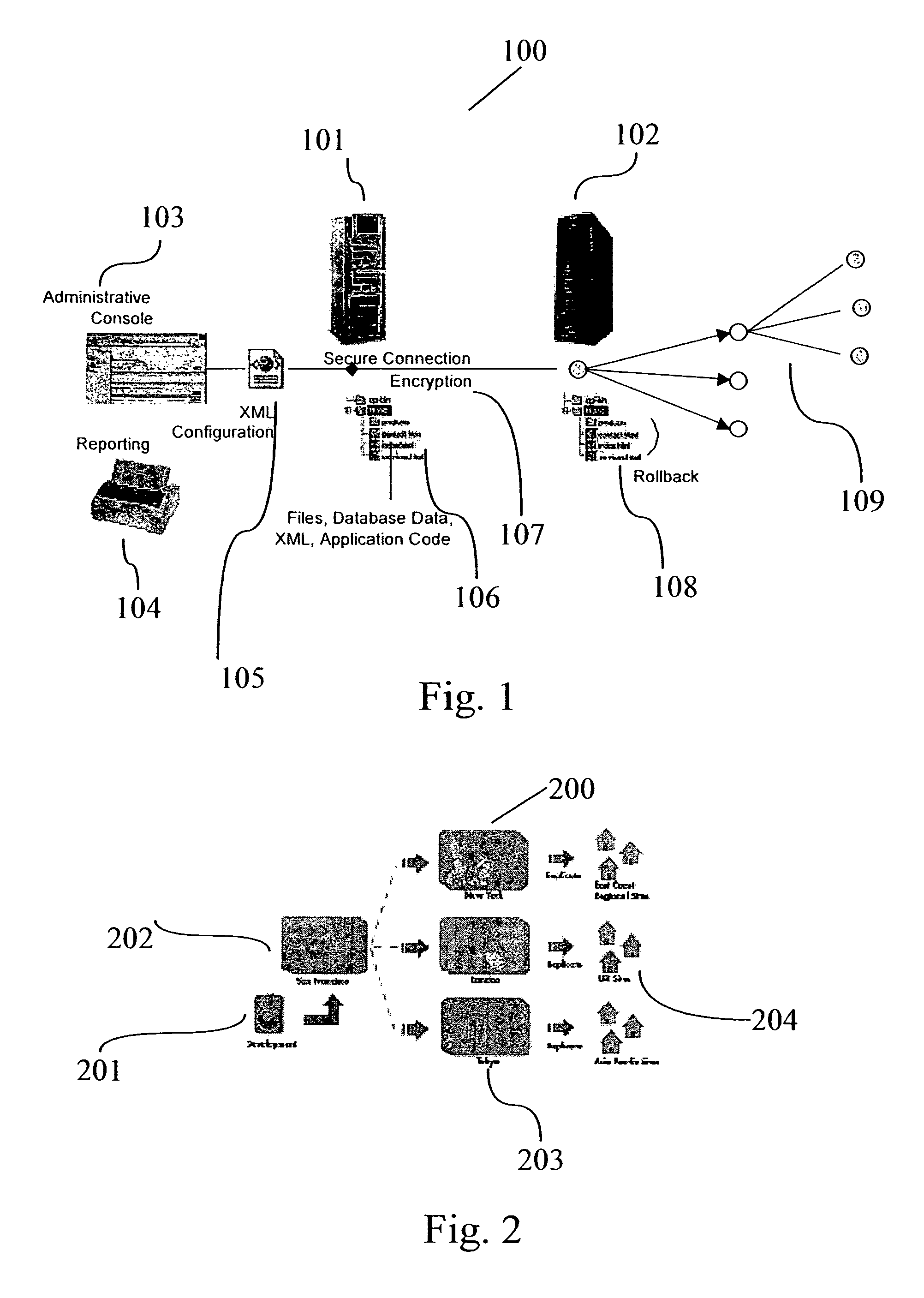
A system for transactionally deploying content across multiple machines in a network environment automates and synchronizes secure and reliable distribution of digital assets to multiple network locations, allowing controlled provisioning and synchronization of code and content updates to live applications. A distributed architecture includes at least one receiver—a secure listener configured to process incoming distribution jobs—and at least one base server—a sender that may also act as a receiver. An administration interface allows administrative and reporting services and deployment management. Using the administrative interface, users are enabled to launch, simulate, schedule and monitor activities for any network location at any time. The system provides fan-out and multi-tiered deployment topologies expandable to hundreds of servers. Each deployment is fully transactional, permitting rollback of the system to it “last known good” state in the case of failure.
Owner:OPEN TEXT CORPORATION
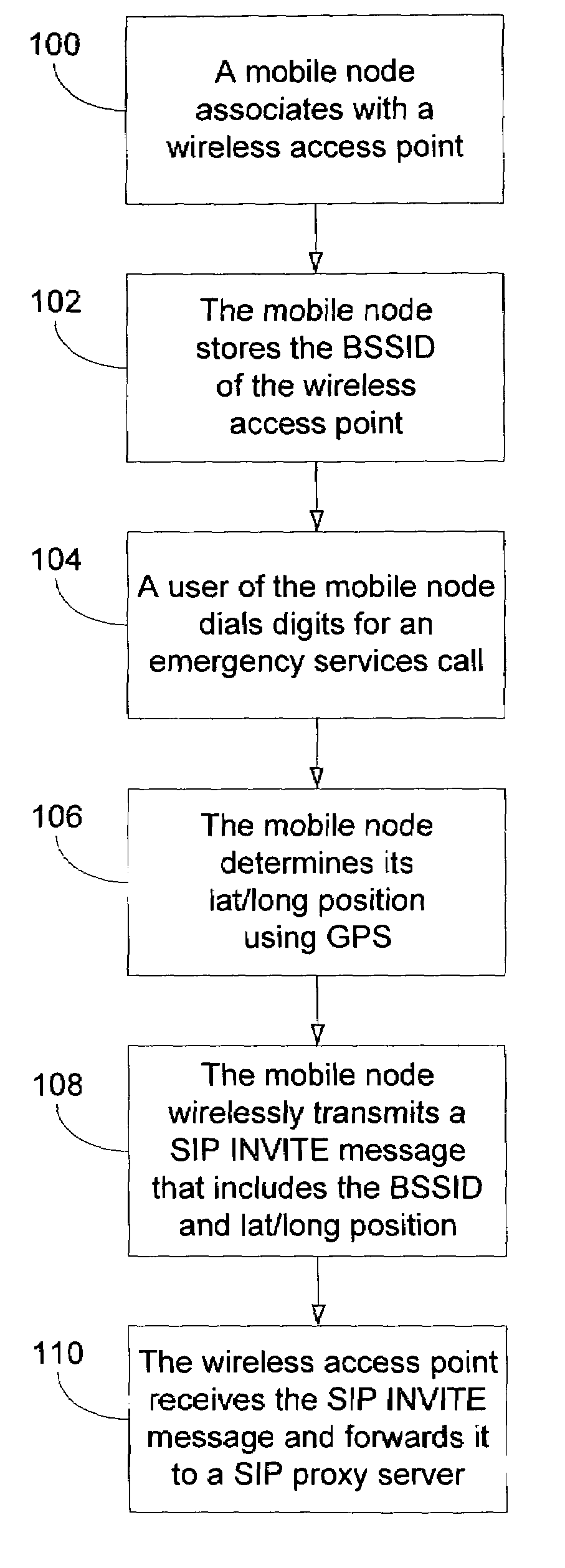
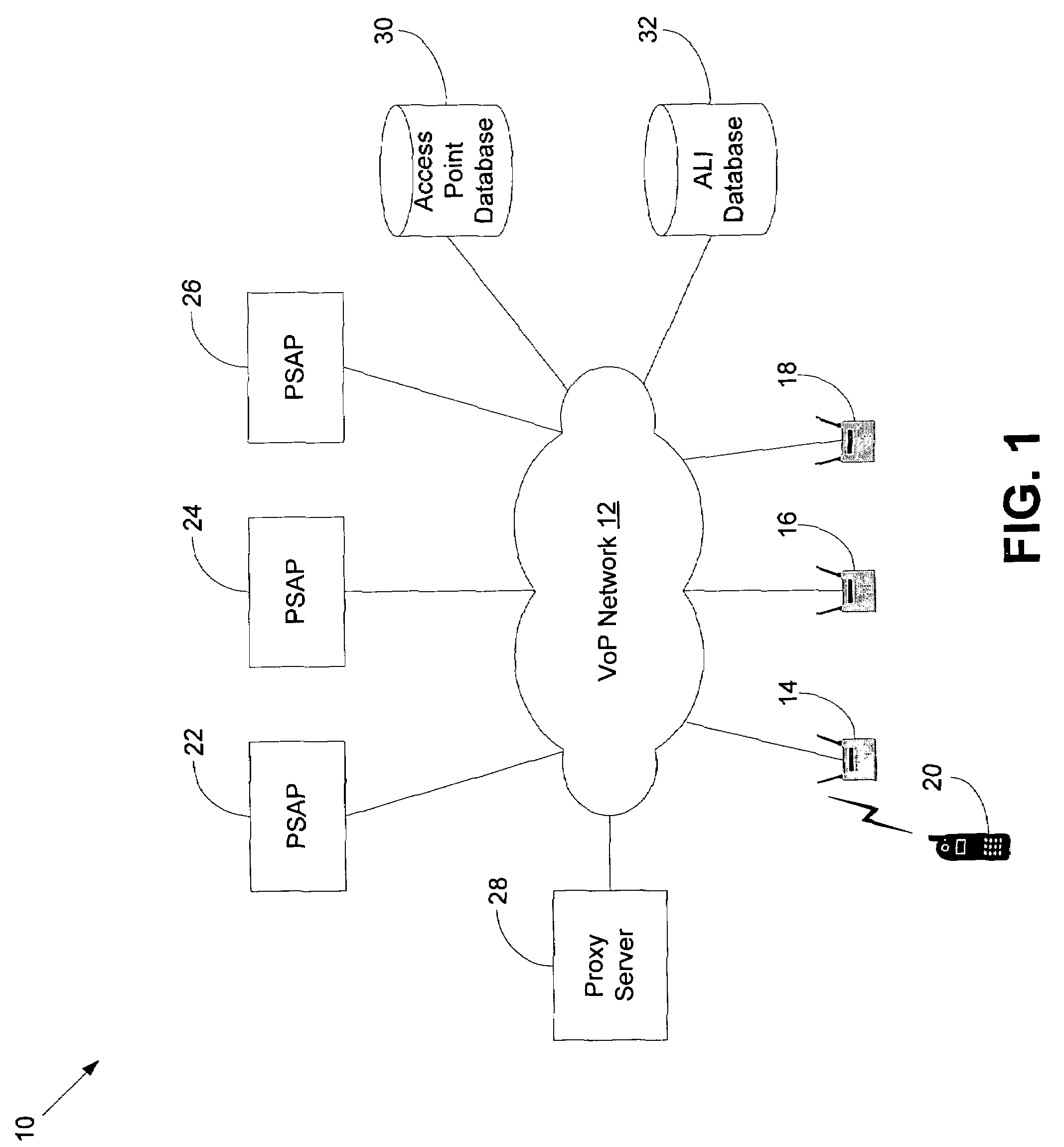
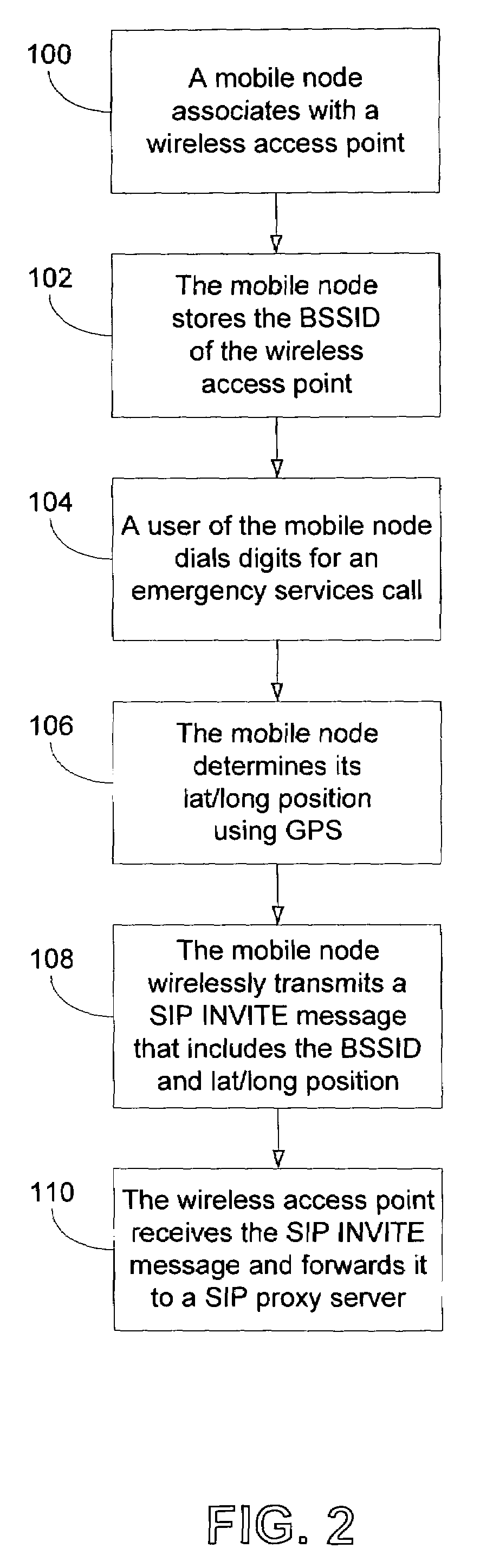
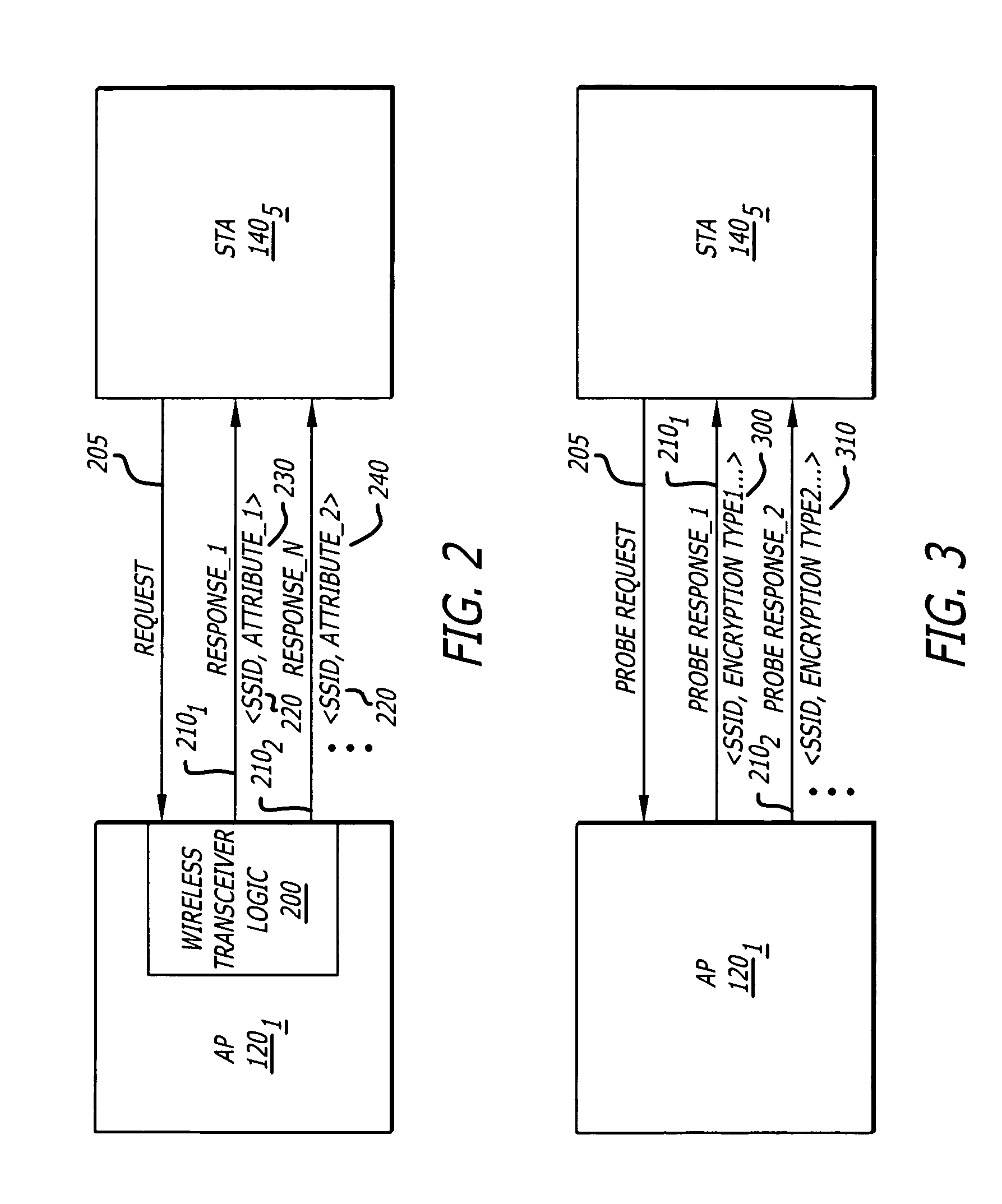
Method and system for using basic service set identifiers (BSSIDs) for emergency services routing
A plurality of public safety answering points (PSAPs) are accessible via a voice-over-packet (VoP) network. Each wireless access point of the VoP network is identified by a basic service set identifier (BSSID). A mobile node associates with a wireless access point and stores the wireless access point's BSSID as an indicator of the mobile node's location. A user of the mobile node dials digits for an emergency services call. In response, the mobile node transmits a SIP INVITE message that includes the BSSID and an additional indicator of the mobile node's location, e.g., determined using GPS or tower triangulation. A SIP proxy server receives the SIP INVITE message and attempts to determine the appropriate PSAP to answer the call based on the BSSID. If the attempt is unsuccessful, the SIP proxy server determines the appropriate PSAP based on the additional indicator.
Owner:SPRINT SPECTRUM LLC
System and method for advertising the same service set identifier for different basic service sets
According to one embodiment of the invention, a method comprises advertising services by a first wireless device. The services are provided by different basic service sets, each basic service set having the same service set identifier (SSID). Thereafter, one of the basic service sets is selected.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
System and method for building wireless applications with intelligent mapping between user interface and data components
ActiveUS20050057560A1Reduce complexitySimplify development workDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsData domainBasic service
A system and method is described for effective management of a User Interface (UI) of a wireless device by implementing direct mapping between the application data domain and UI screens and controls. The device has an intelligent wireless device runtime environment (Device Runtime) that provides a set of basic services to manage the wireless application, including a series of linked screen and data component definitions, and their interactions can simplify the development effort and reduce resource allocation. The data domain for this category of applications is defined using the atomic data component definitions. The communication between a device user interface and data components is defined using atomic screen component definitions. Both screen and data component definitions are described in metadata using a structured definition language such as XML. The relationships between the screen and data component definitions are embedded in the XML definitions in the form of screen / data mappings. Typically, rendered screens for display are derived from some underlying data component and screens controls affected by user events impact the current state (or data representation) of the application Changes to the application domain data are automatically synchronized with the user interface, and user-entered data is automatically reflected in the application domain data. The primary mechanism behind this synchronization is the mapping of screens and data. This mechanism enables creation of dynamic and interactive screens. All changes to the data component can be immediately reflected on the screen and vice versa. This model allows building effective wireless applications based on server-to-device notifications. The data updates asynchronously pushed from the server are instantaneously reflected at the UI screen.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
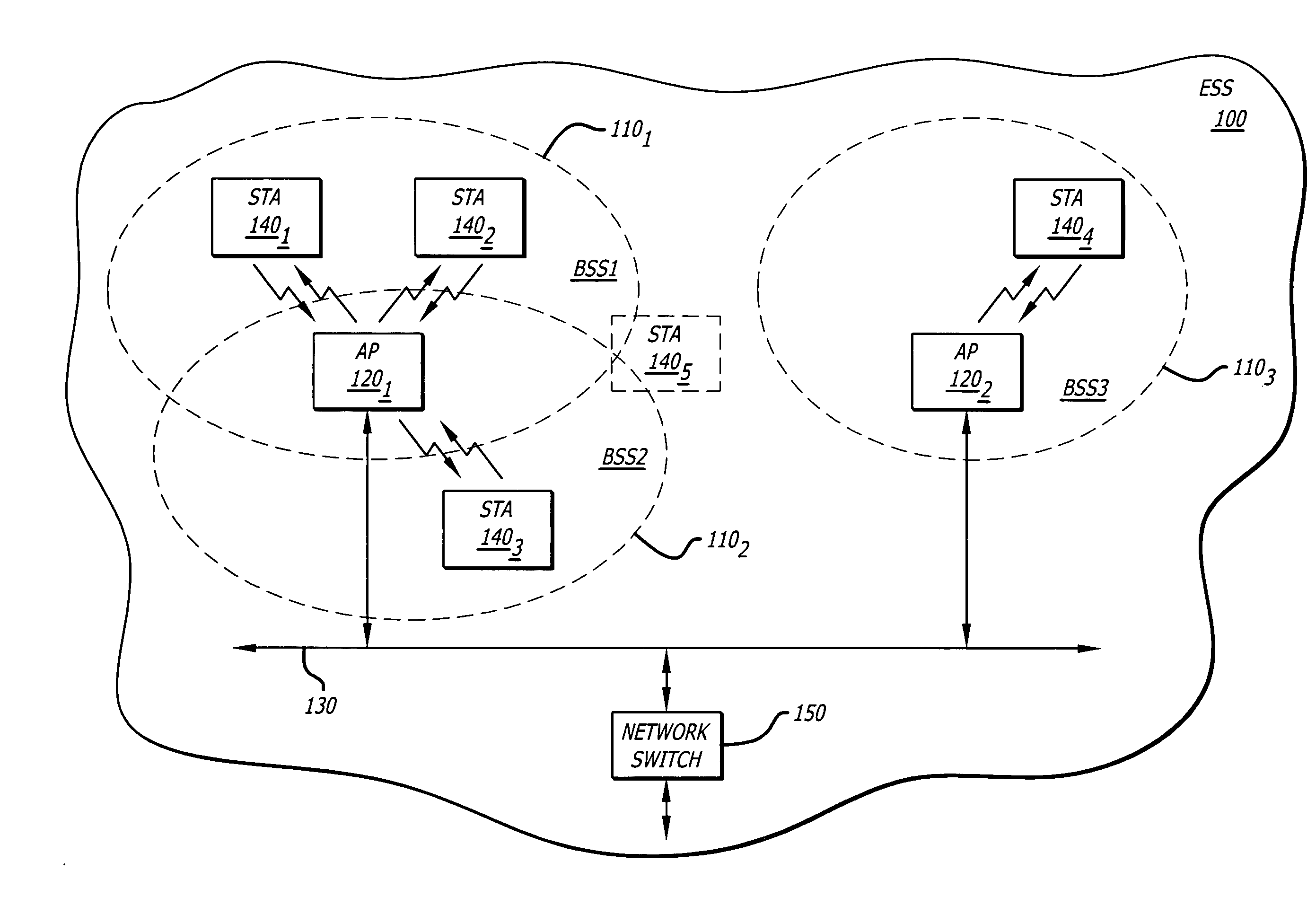
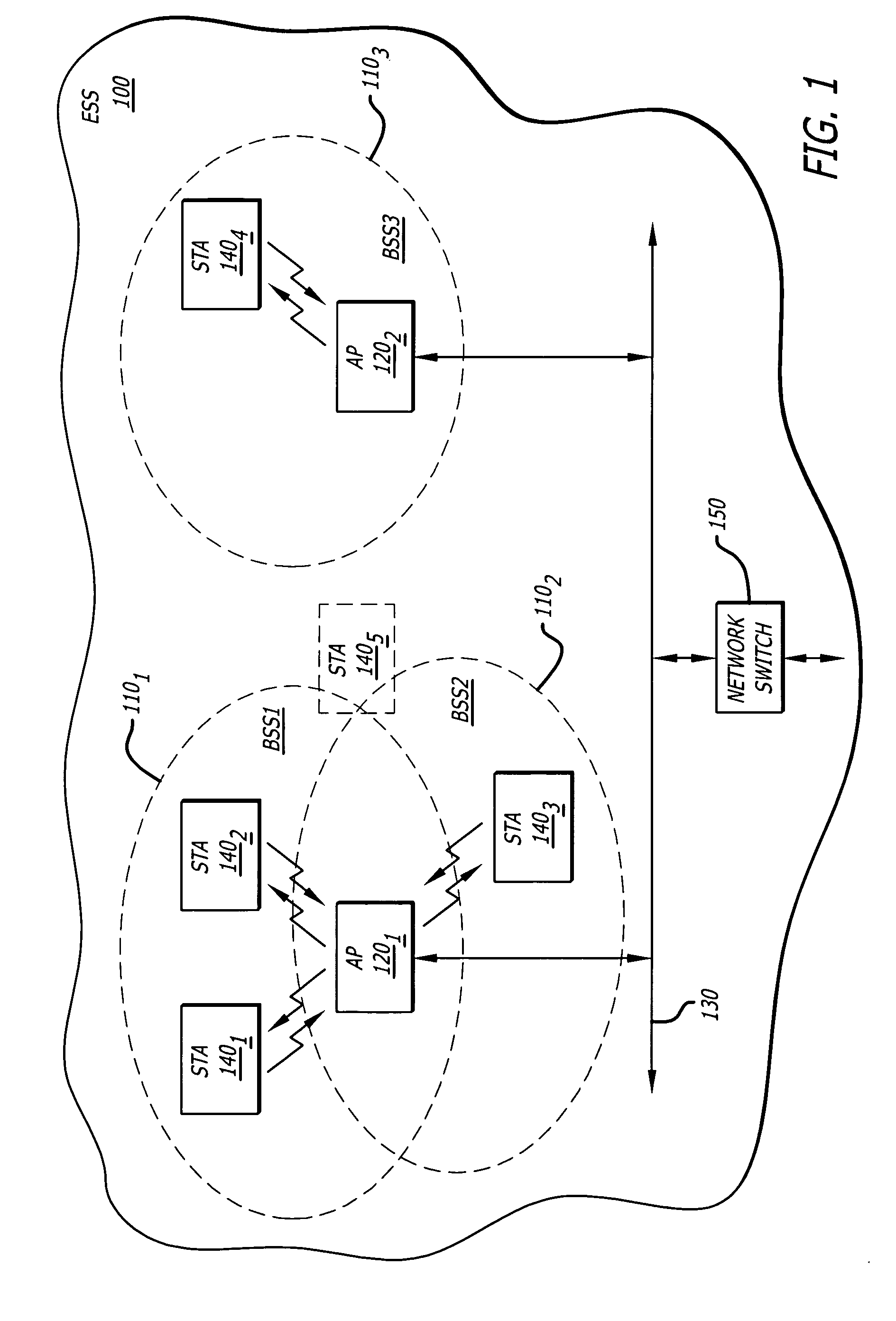
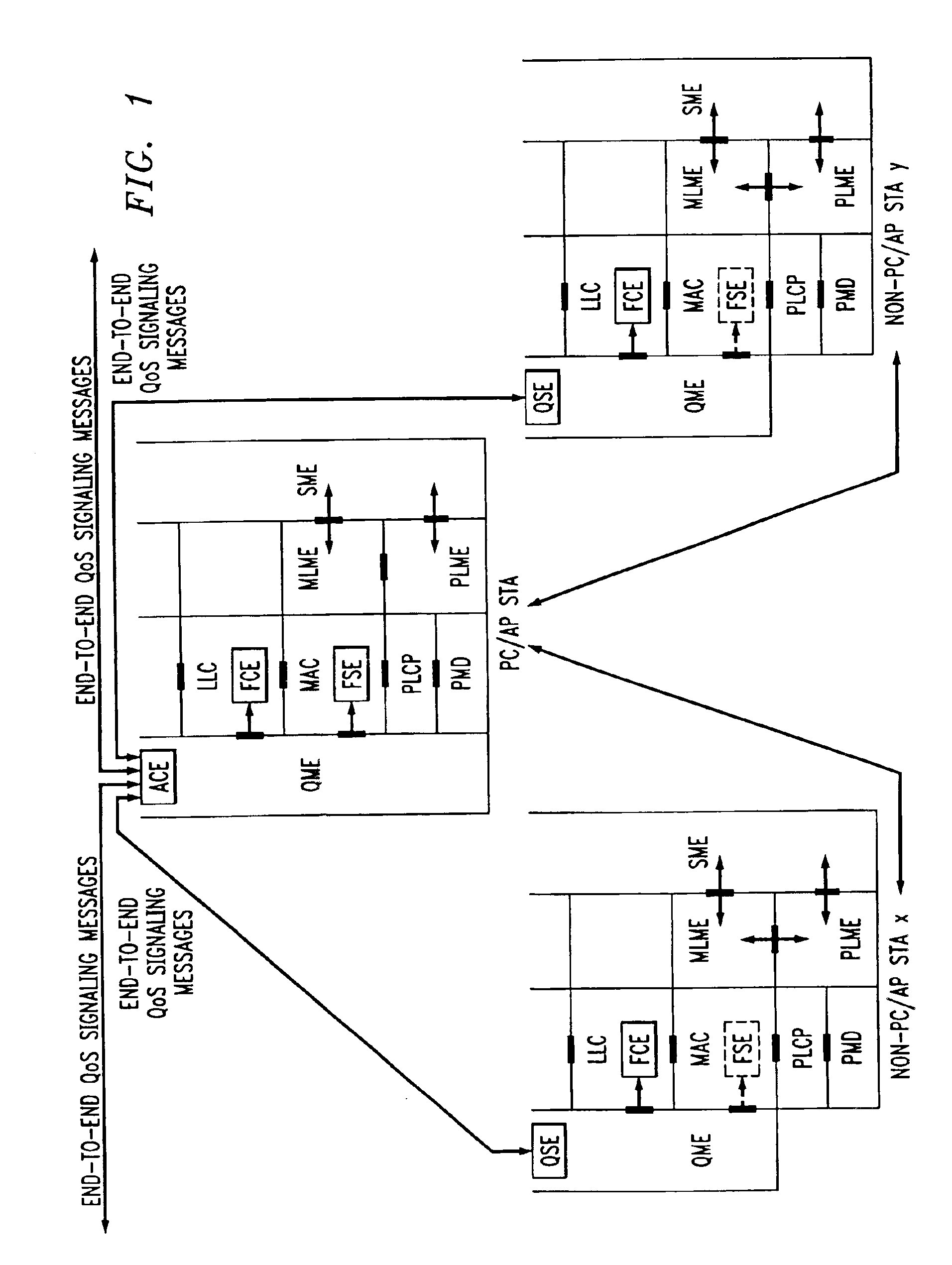
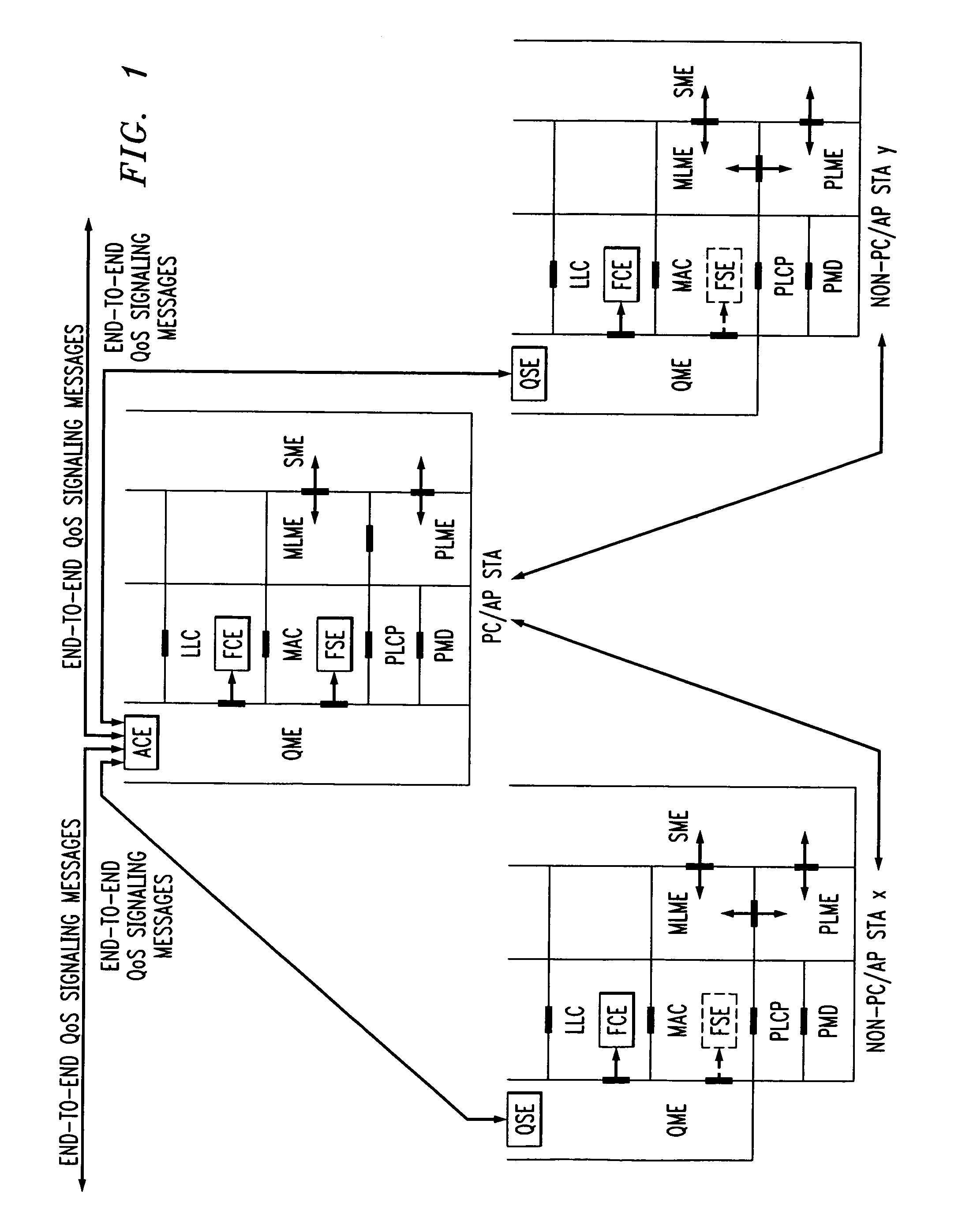
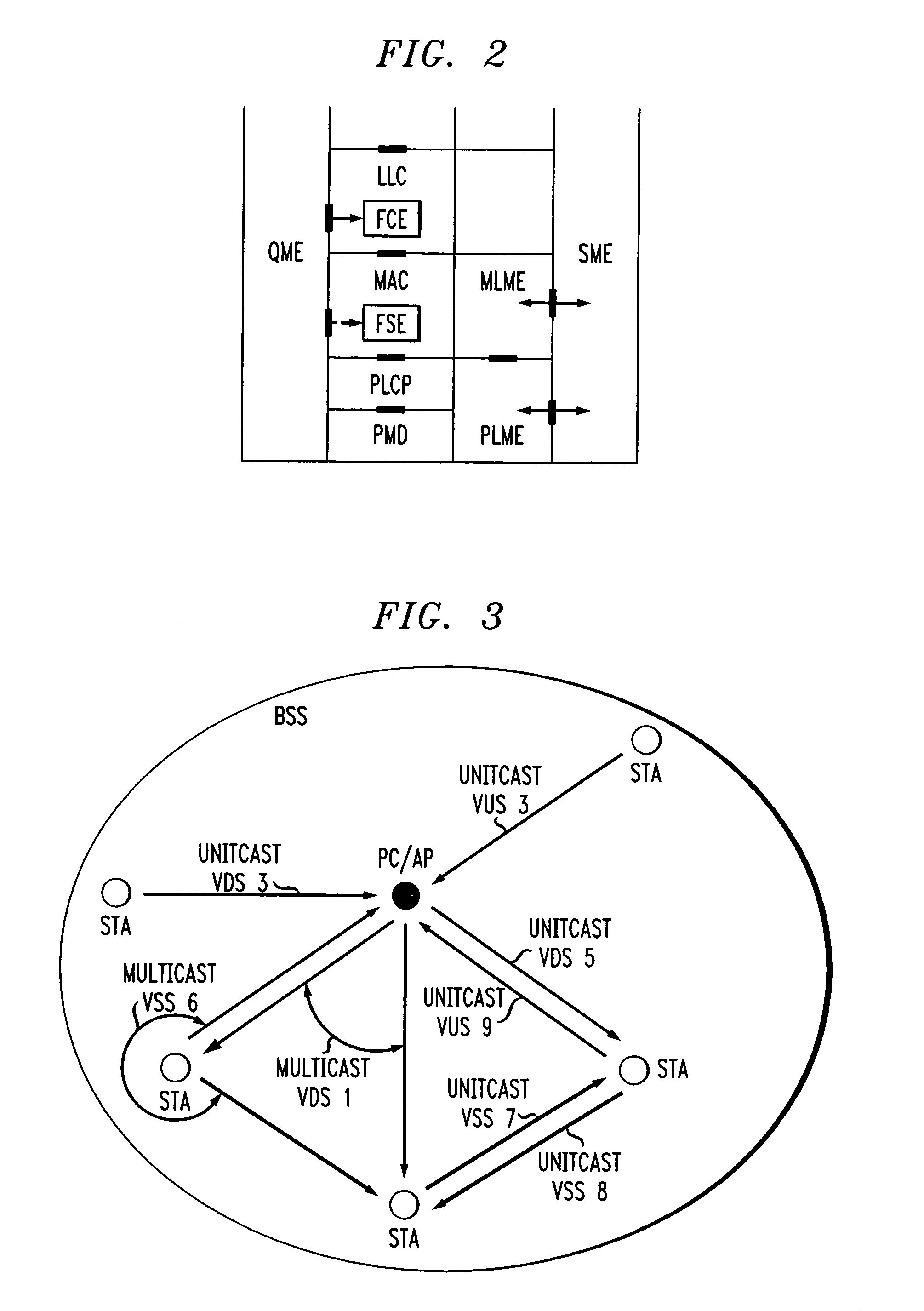
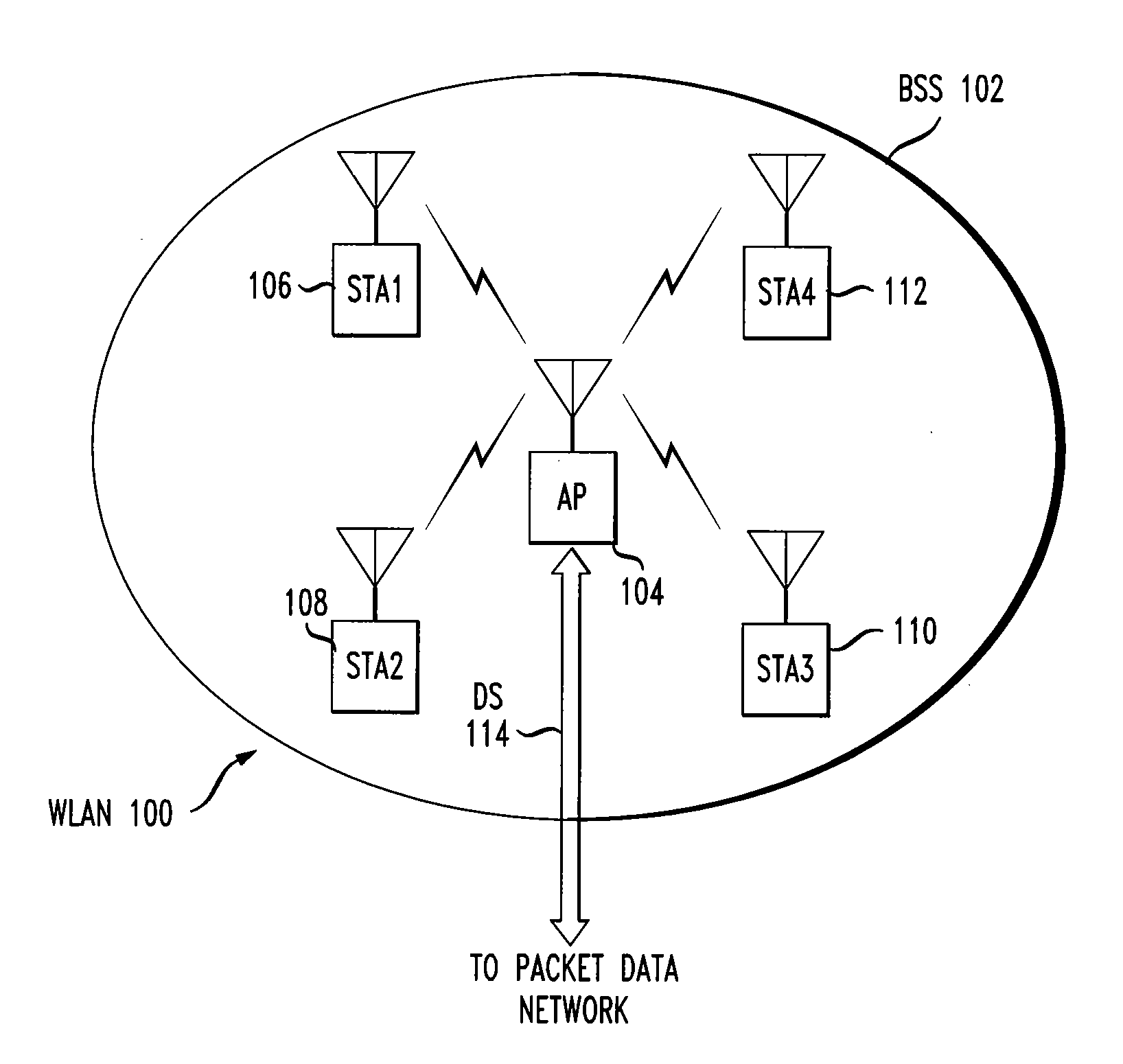
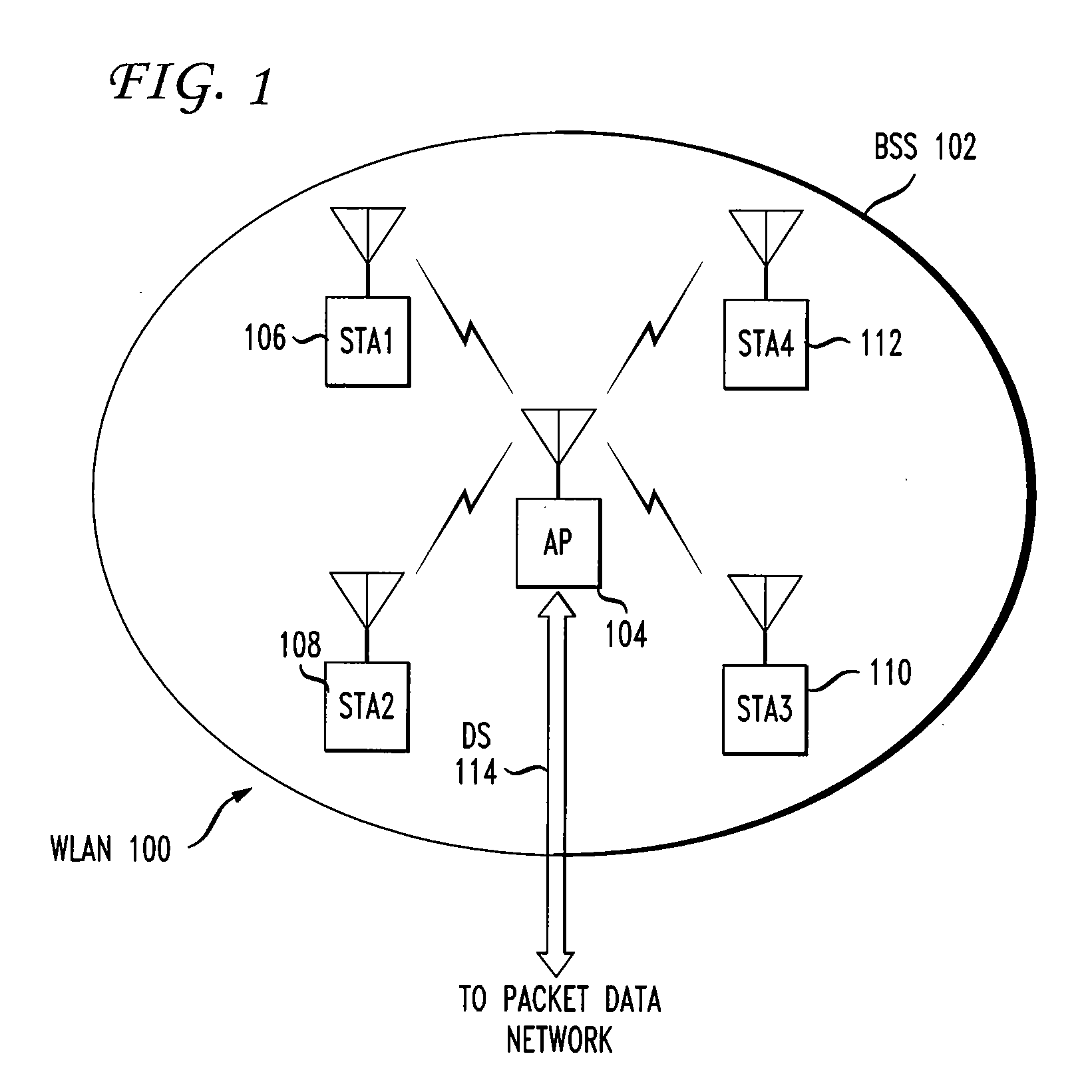
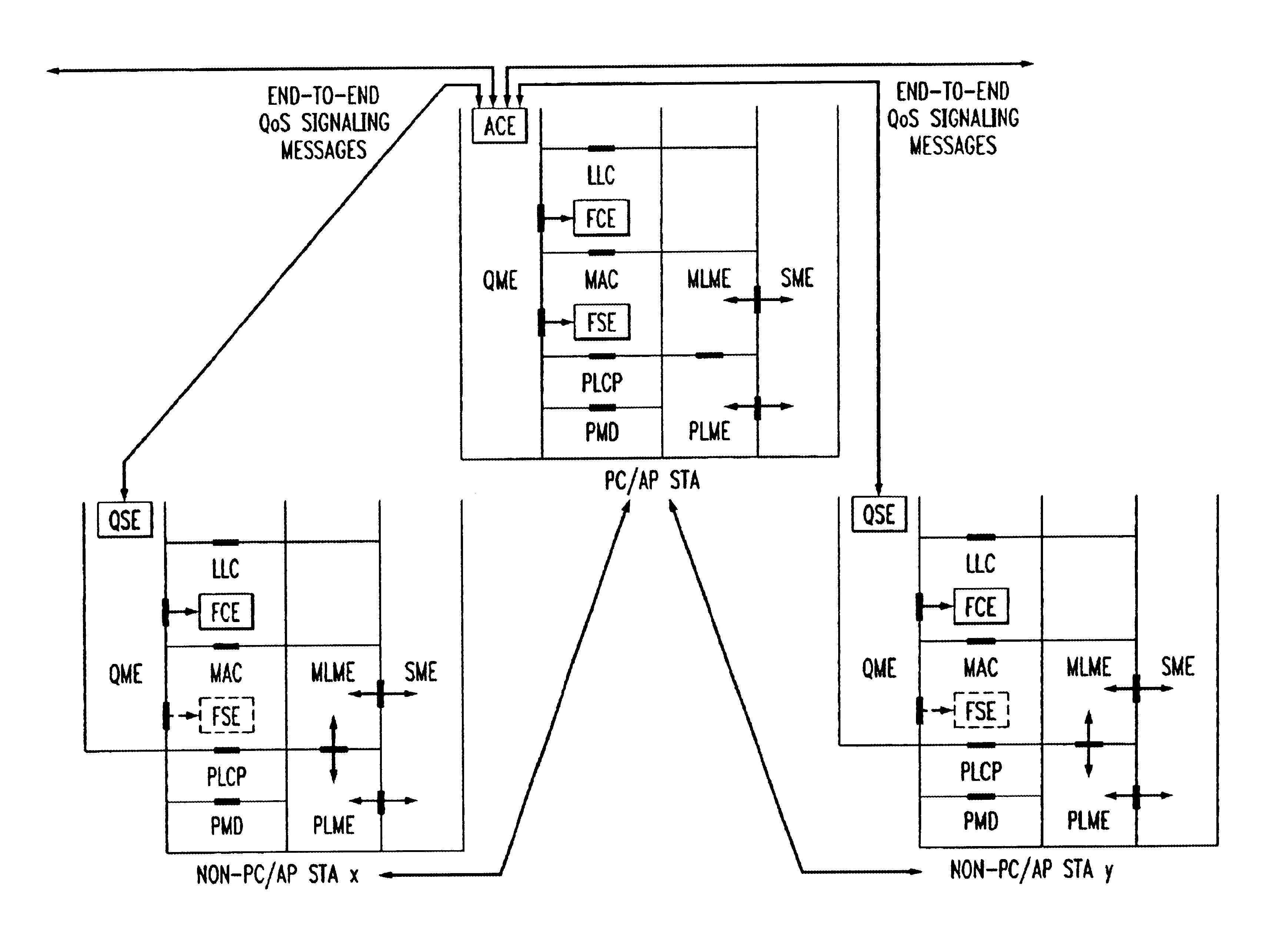
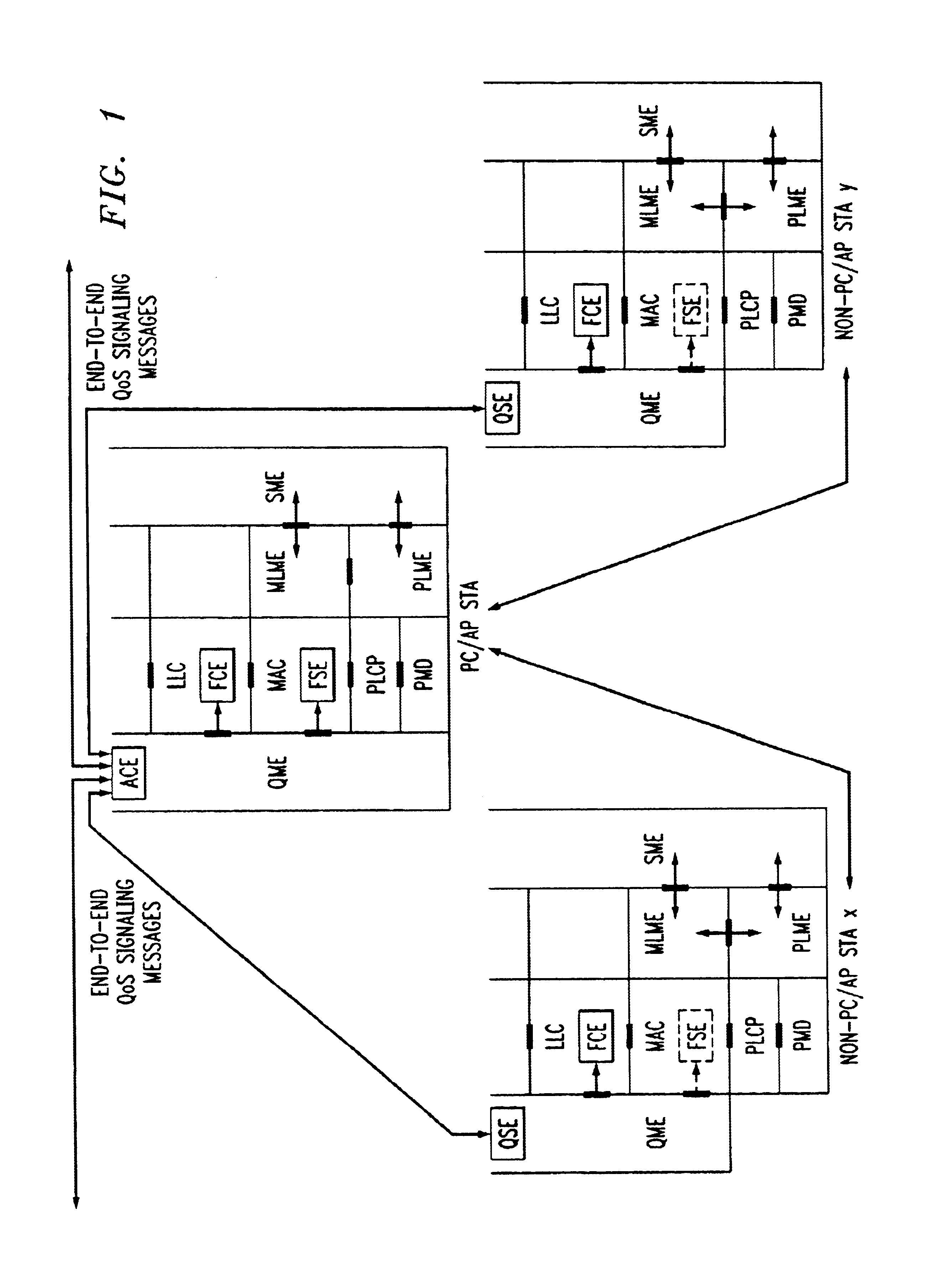
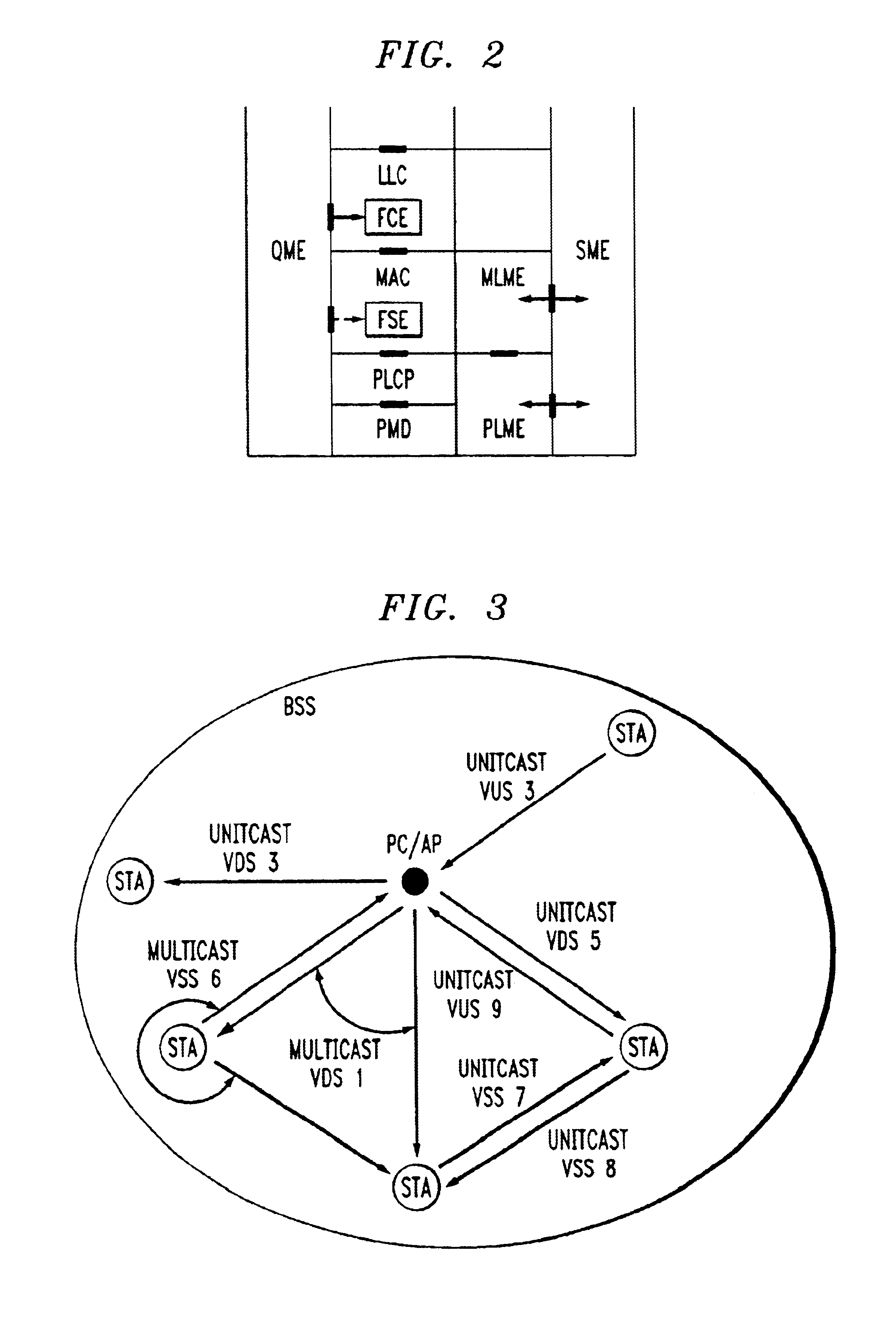
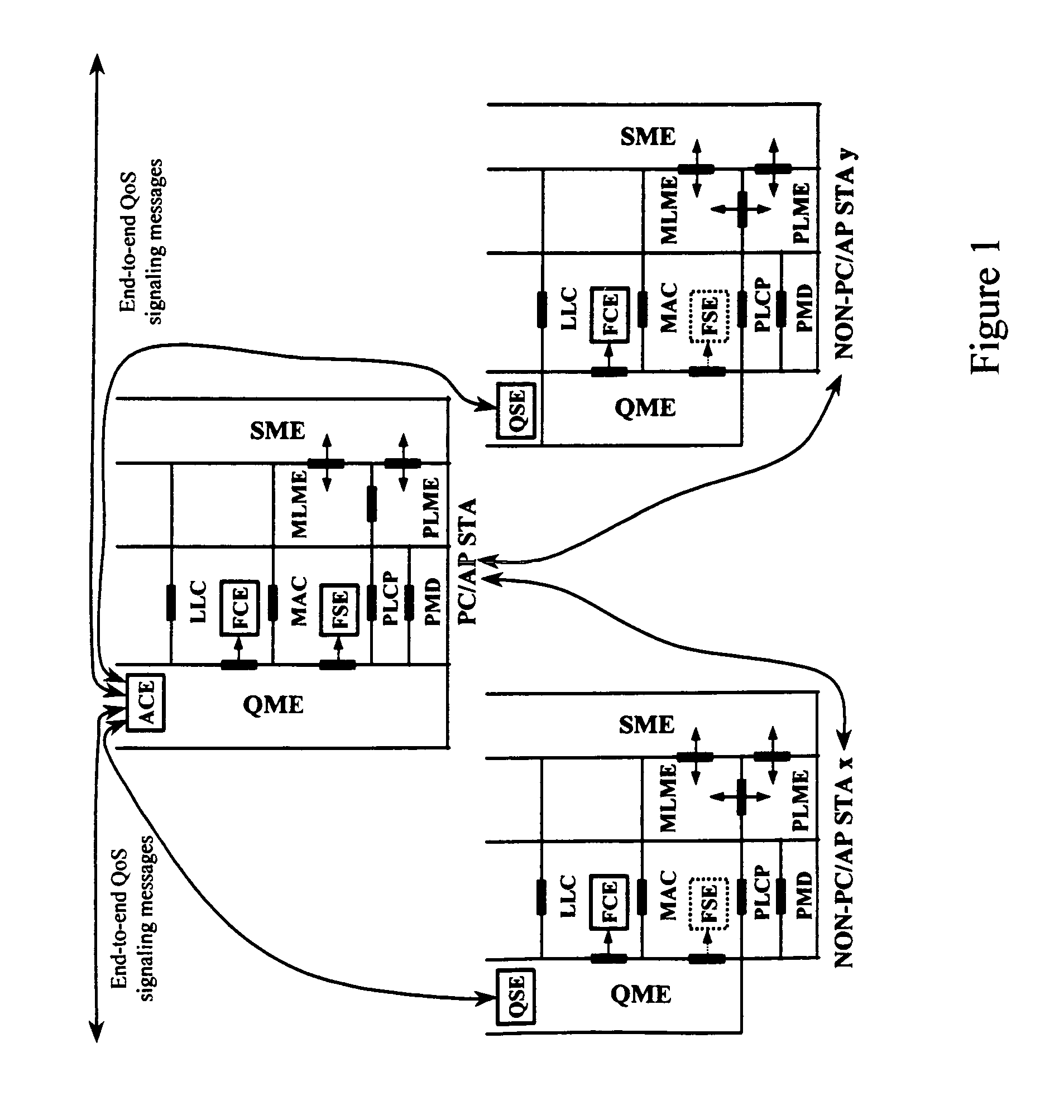
Architectural reference model for QoS-driven wireless LANs
InactiveUS6862270B1Enhanced channel accessImprove bandwidth utilizationNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesOpen Systems InterconnectionEnd to end qos
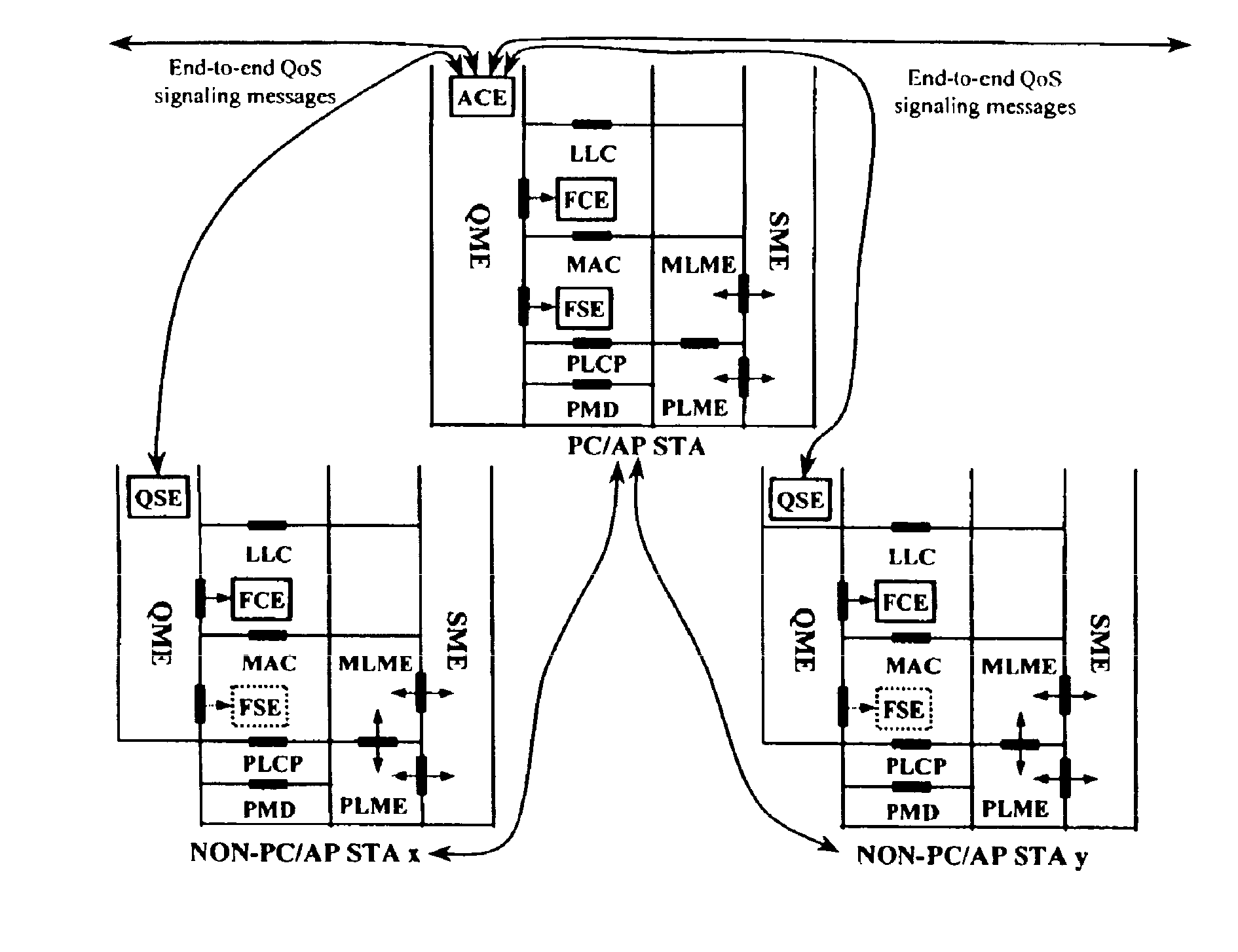
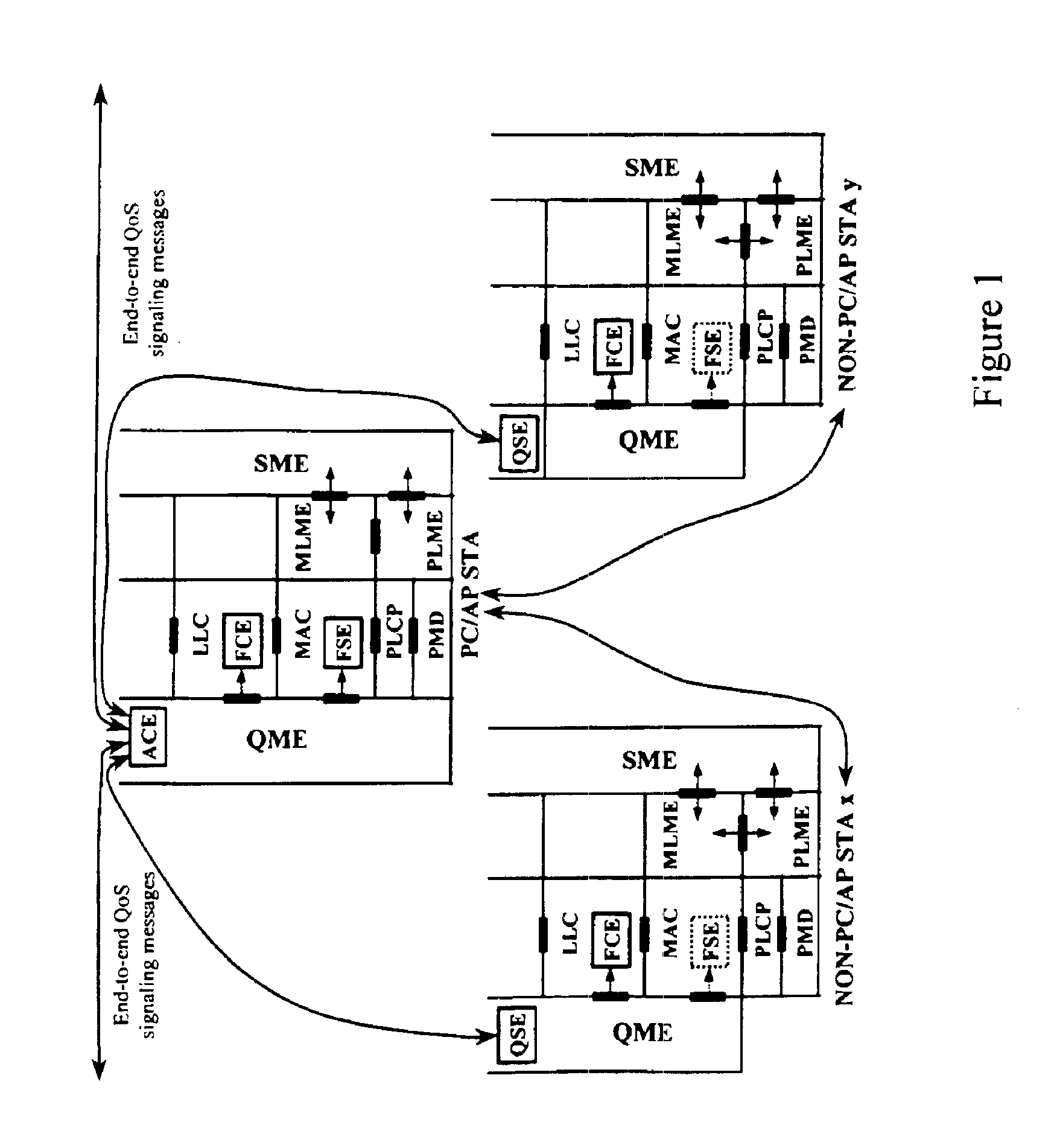
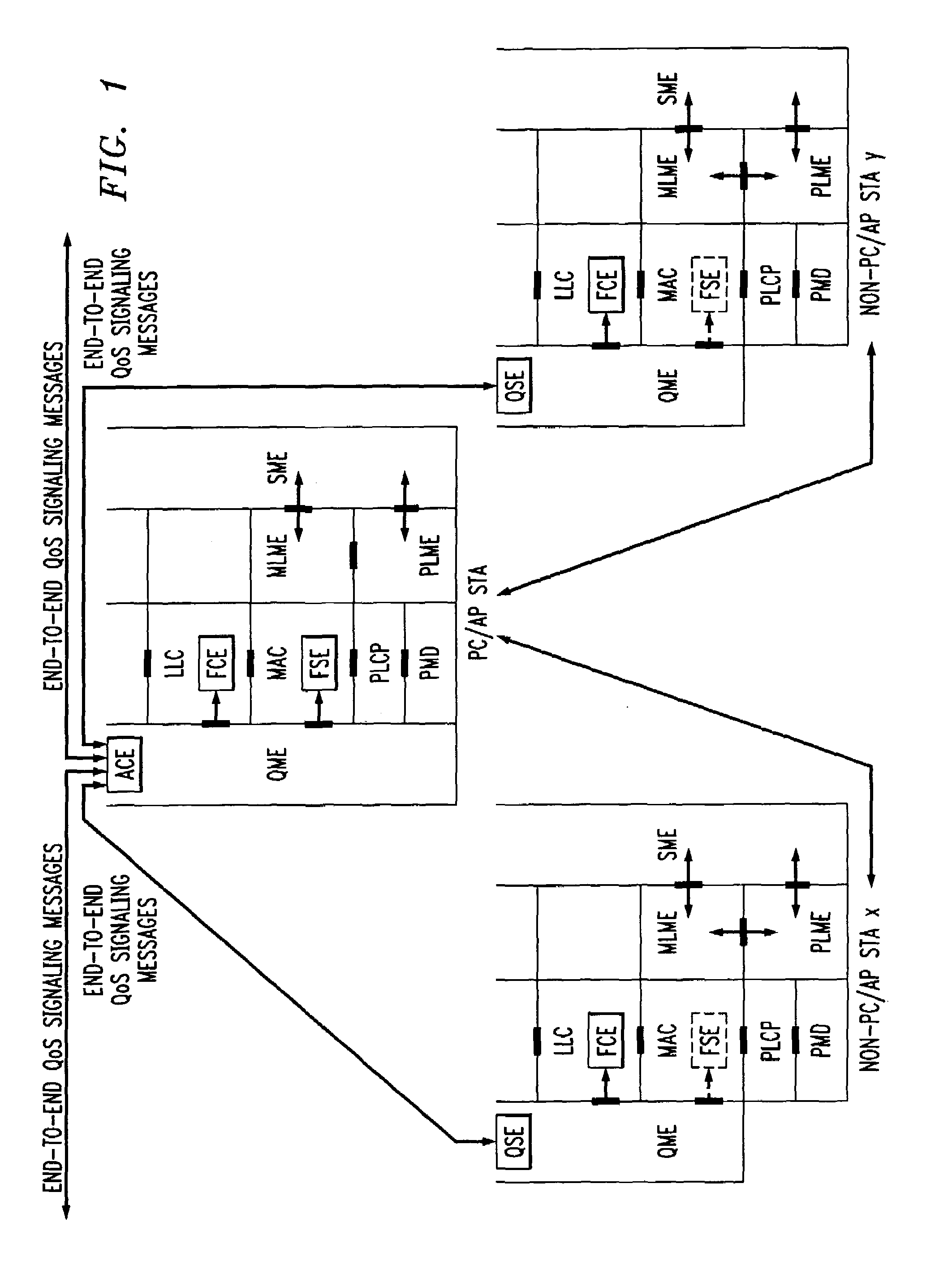
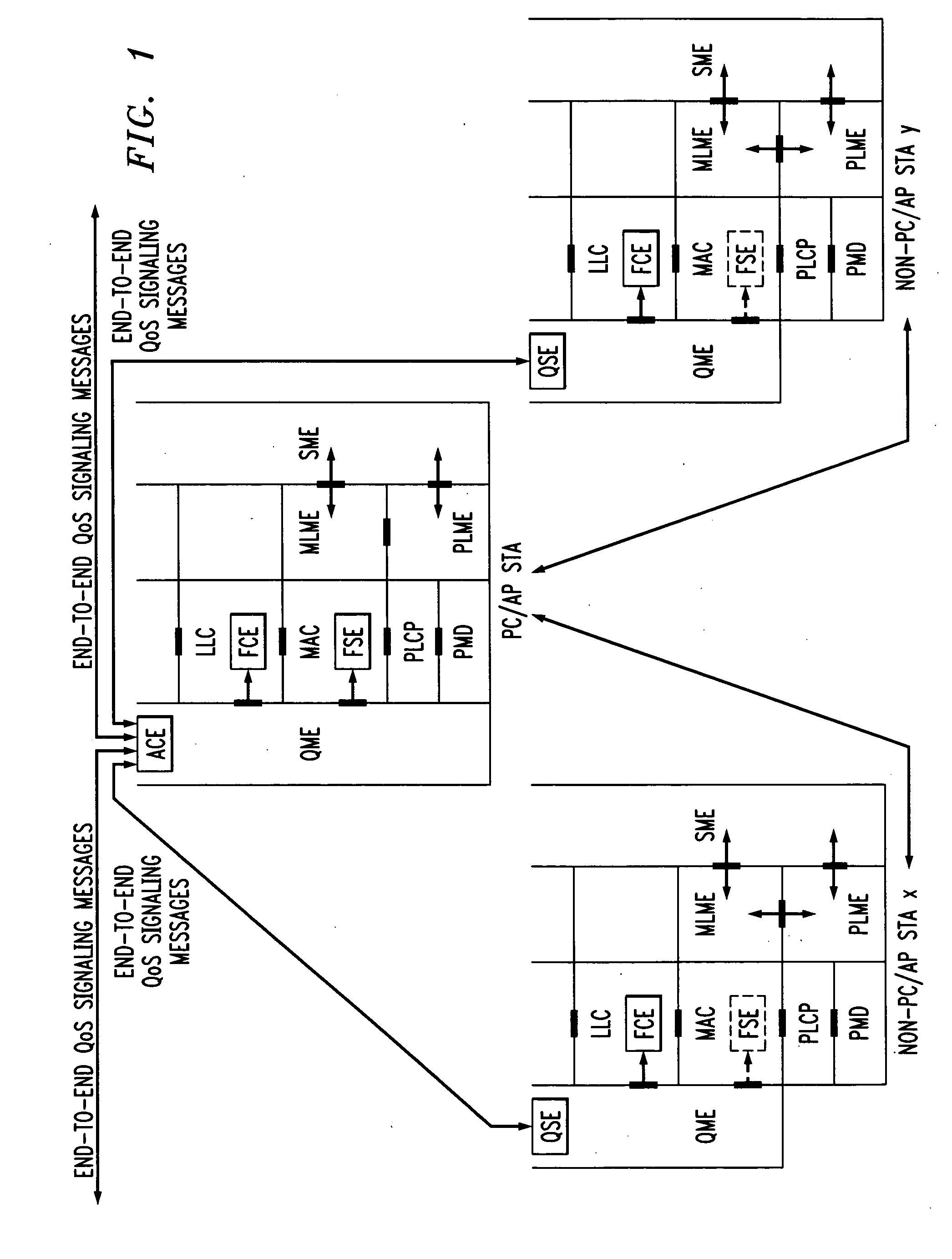
A quality of service (QoS) station is disclosed containing a point coordinator (PC) for a basic service set (BSS) in a wireless LAN. The PC station includes a QoS management entity (QME) and an admission control entity (ACE). The QME receives at least one end-to-end QoS message that characterizes a user application, such as a voice call, a video call, a data call and a multimedia call. The at least one end-to-end QoS message includes at least one QoS parameter set that is expressed at layer 3 and higher of an ISO / IEC basic reference model of Open Systems interconnection (OSI) (ISO / IEC 7498-1) and is to be passed down to layer 2 of the PC-station for enabling QoS traffic transport of the application. The ACE performs an admission control decision relating to the application based on the at least one end-to-end QoS message characterizing the application. The ACE reserves a resource based on a QoS parameter set contained in the end-to-end QoS message. The ACE can be part of the QME and can include a resource control module that performs at least one admission control decision based on resource permission, and a policy control module that performs at least one admission control decision based on policy permission.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Wireless access point simultaneously supporting basic service sets on multiple channels
InactiveUS20050124294A1Create efficientlyImprove economyData switching by path configurationRadio transmissionTime segmentBasic service
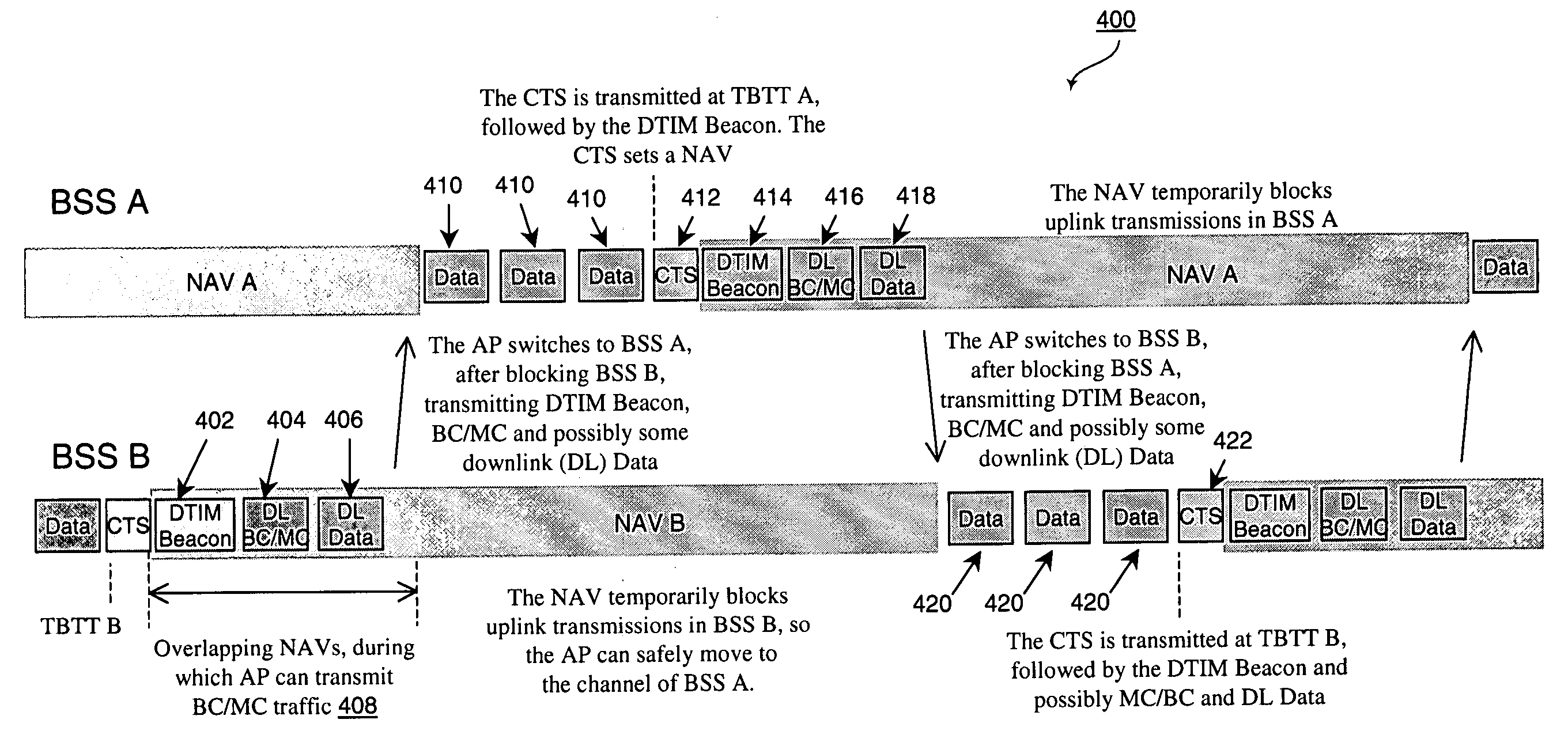
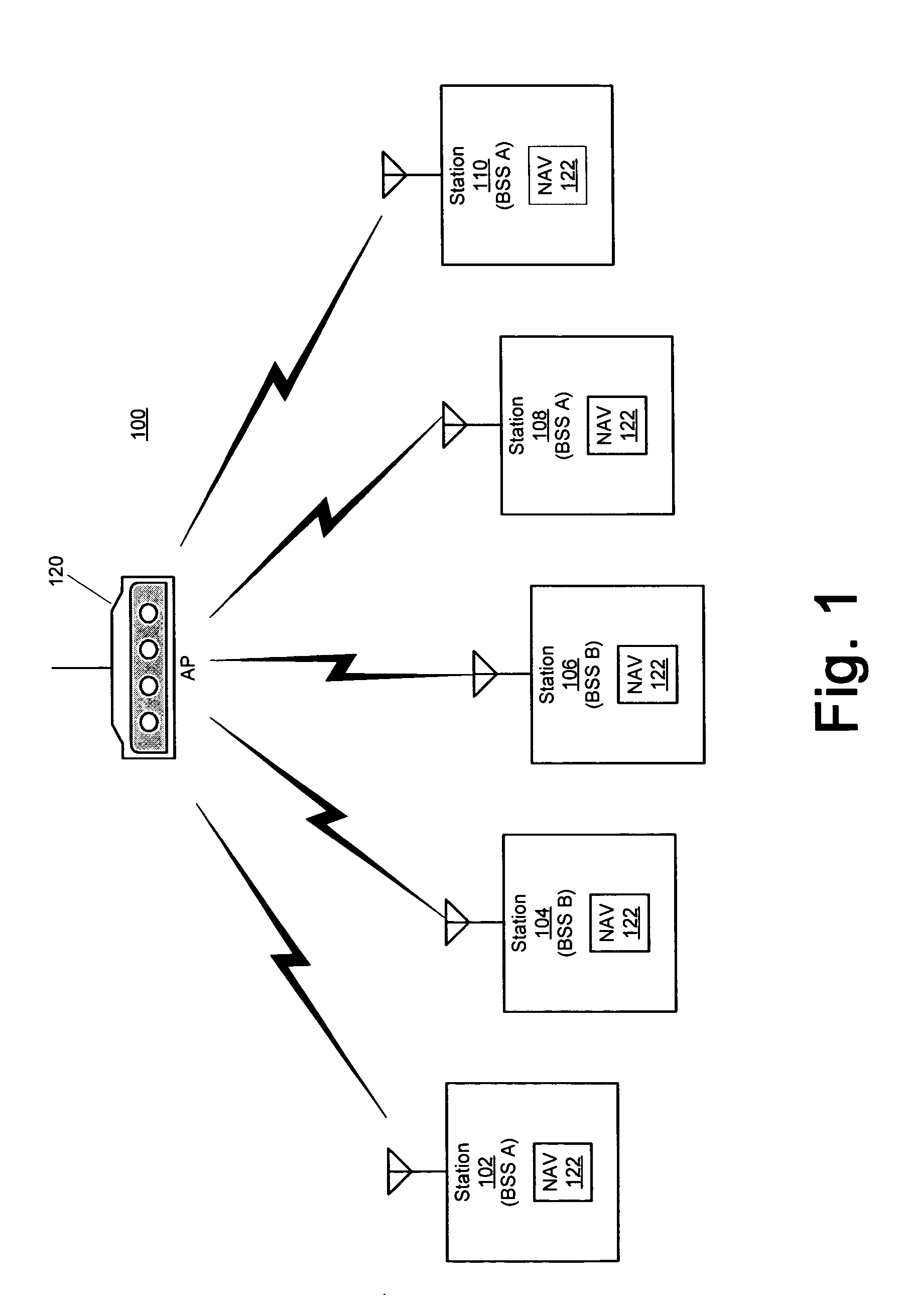
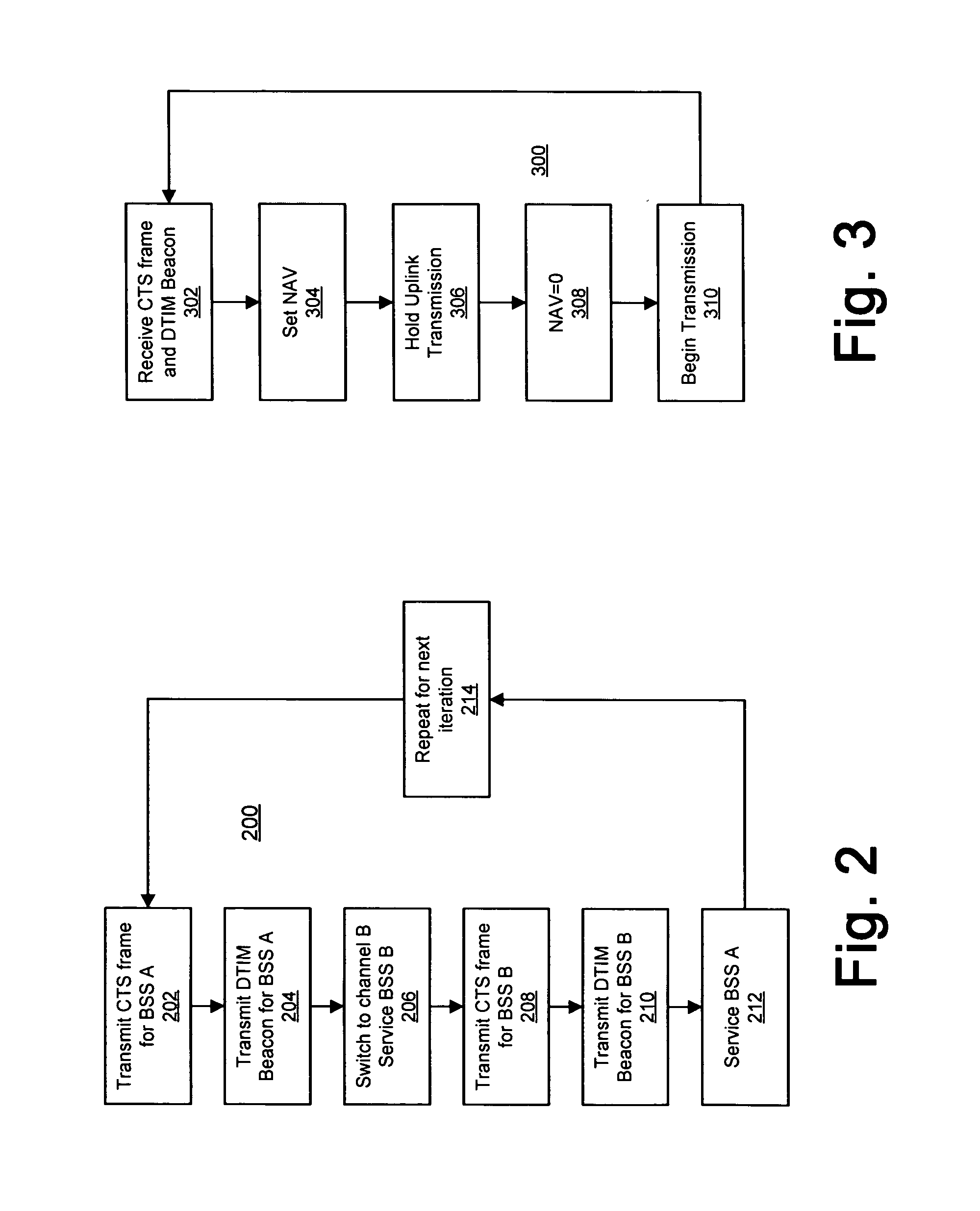
The present invention provides a technique for an access point (AP) to maintain a basic service set (BSS) on two or more channels simultaneously by temporarily blocking one BSS and servicing the other BSS while the other BSS is blocked, thereby providing an efficient way to create a dual cell AP with only a single radio. In an embodiment of the invention, a method for servicing a first set of wireless stations operating on a first channel of an access point and a second set of wireless stations operating on a second channel of the access point comprises transmitting, at a first time, a first frame from the access point to the first set of wireless stations via the first channel, the first frame having duration data directing the first set of wireless stations to cease transmitting until a second time represented by the duration data and servicing the second set of wireless stations via the second channel of the access point for at least a part of a time period between the first time and the second time. The method further comprises transmitting, at the second time, a second frame from the access point to the second set of wireless stations via the second channel, the second frame having duration data directing the second set of wireless stations to cease transmitting until a third time represented by the duration data of the second frame and servicing the first set of wireless stations via the first channel of the access point for at least a part of a time period between the second time and the third time. The method also may comprise transmitting a Delivery Transmission Indication Map (DTIM) frame prior to transmitting each of the first and second frames. The transmission of the DTIM frame preferably occurs substantially simultaneously with a Target Beacon Transmission Time (TBTT) of the access point.
Owner:GLOBESPANVIRATA
Modular outlet
ActiveUS20050010954A1Easy and simple upgradingSubstations coupling interface circuitsImproving S/N for transmission/receivingExpansion cardModularity
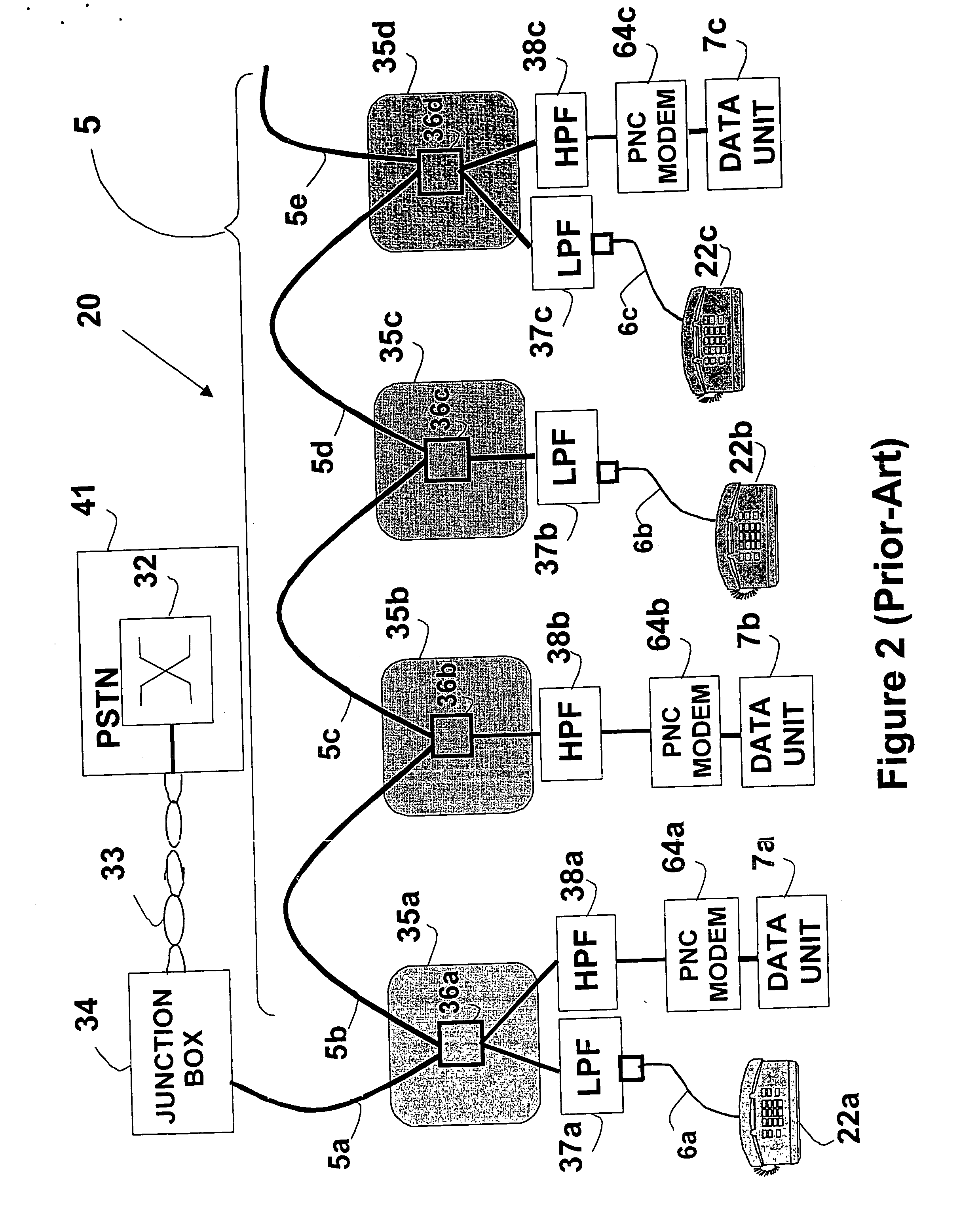
In conjunction with a wiring in a house carrying data network signal, a modular outlet comprising of a base module and interface module. The base module connects to the wiring and attached to a wall. The interface module provides a data unit connection. The interface module is mechanically attached to the base module and electrically connected thereto. The wiring may also carry basic service signal such as telephone, electrical power and cable television (CATV). In such a case, the outlet will provide the relevant connectivity either as part of the base module or as part of the interface module. Both proprietary and industry standard interfaces can be used to interconnect the module. Furthermore, a standard computer expansion card (such as PCI, PCMCIA and alike) may be used as interface module.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC +1
Method and apparatus of multiple entity wireless communication adapter
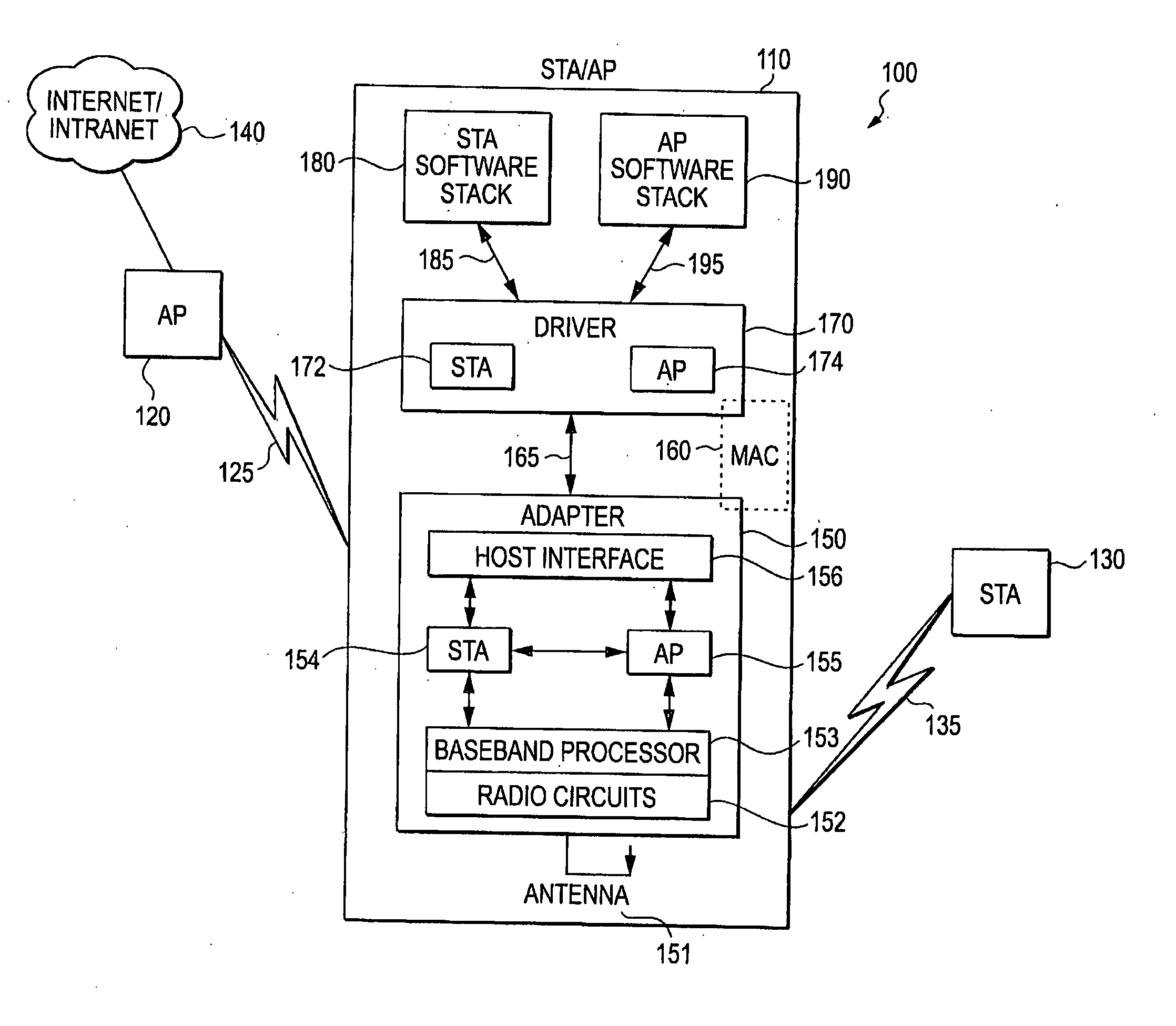
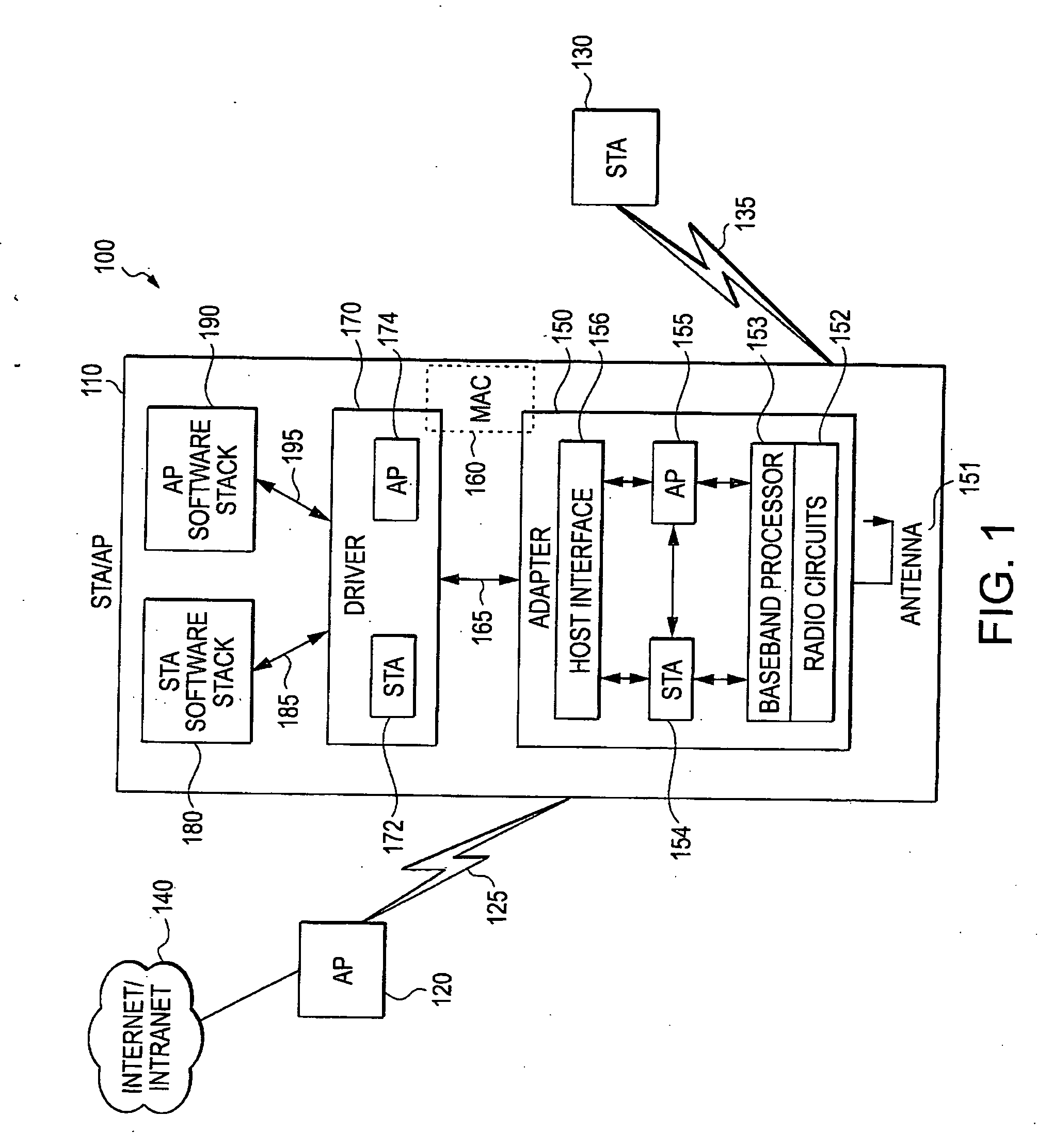
Embodiments of the present invention provide a method and apparatus for a multiple-entity wireless communication adapter, including at least a first connection module to communicate first signal traffic corresponding to a basic service set station entity, a second connection module to communicate second signal traffic corresponding to an entity that is not a basic service set station, and a shared physical layer able to process both the first and the second signal traffic. Additional features are described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
System for transactionally deploying content across multiple machines
InactiveUS7657887B2Easy to deployDigital data processing detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsProgram planningBasic service
A system for transactionally deploying content across multiple machines in a network environment automates and synchronizes secure and reliable distribution of digital assets to multiple network locations, allowing controlled provisioning and synchronization of code and content updates to live applications. A distributed architecture includes at least one receiver—a secure listener configured to process incoming distribution jobs—and at least one base server—a sender that may also act as a receiver. An administration interface allows administrative and reporting services and deployment management. Using the administrative interface, users are enabled to launch, simulate, schedule and monitor activities for any network location at any time. The system provides fan-out and multi-tiered deployment topologies expandable to hundreds of servers. Each deployment is fully transactional, permitting rollback of the system to it “last known good” state in the case of failure.
Owner:OPEN TEXT CORPORATION
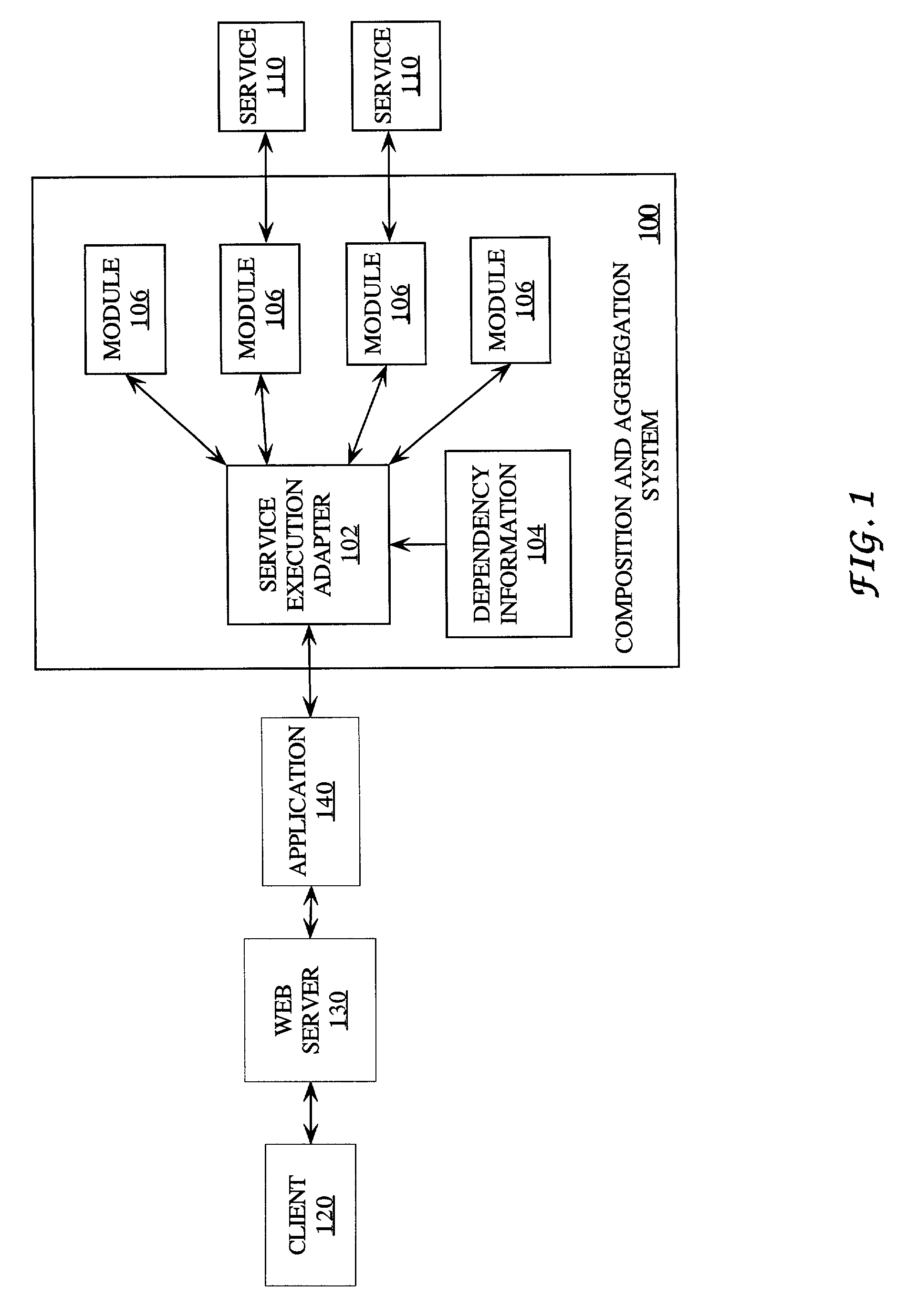
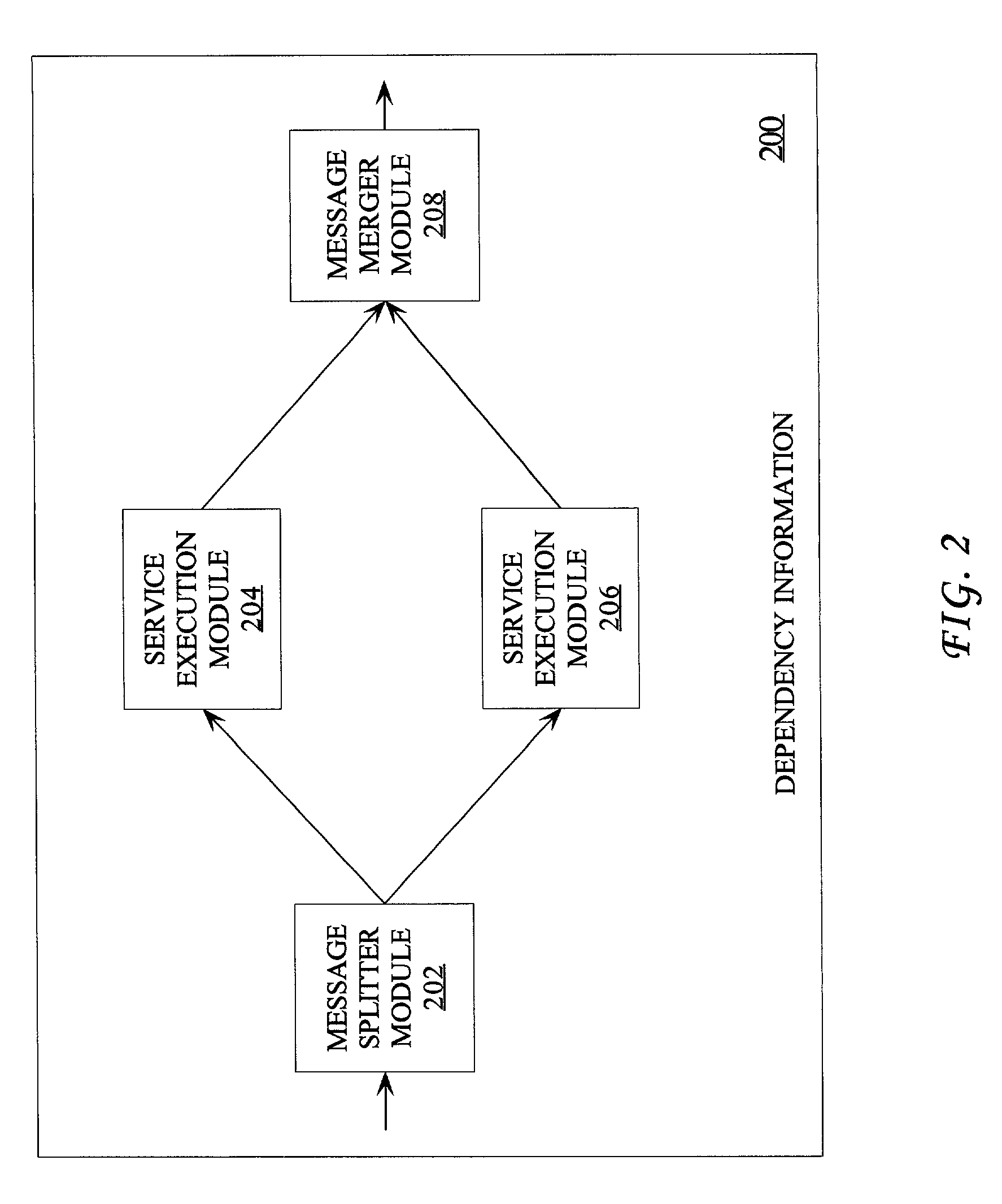
Distributed service aggregation and composition
ActiveUS7185342B1Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsBasic serviceDistributed services
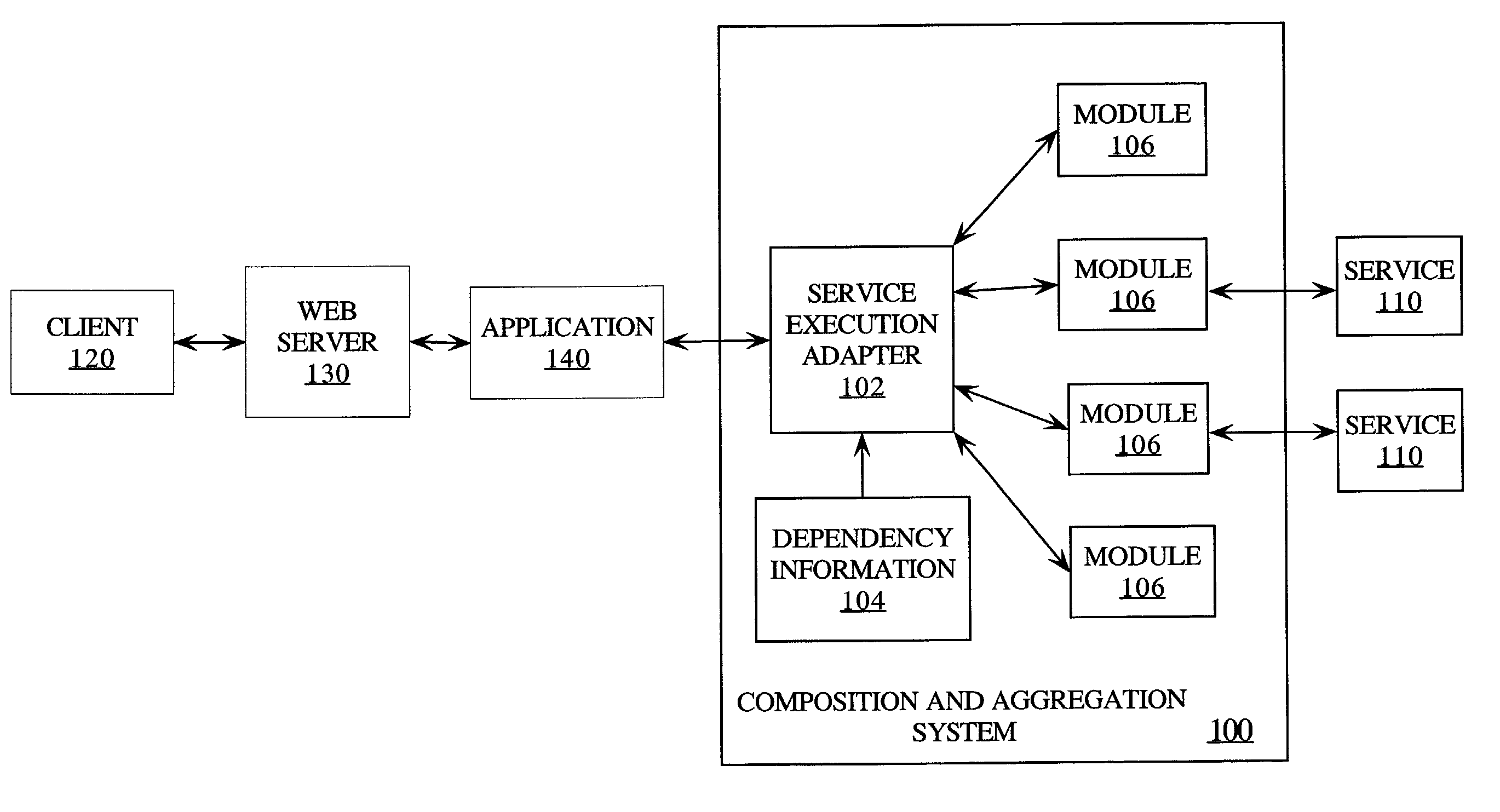
Techniques are provided for defining and coordinating execution of a compound service, which uses results from a plurality of base services, over a network. A sequence in which a plurality of modules must be executed to perform the compound service is specified in dependency information, and the modules in the sequence are executed according to the dependency information and under the management of a service execution adapter. Each module operates upon messages according to module properties, and is able to communicate using event messages.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
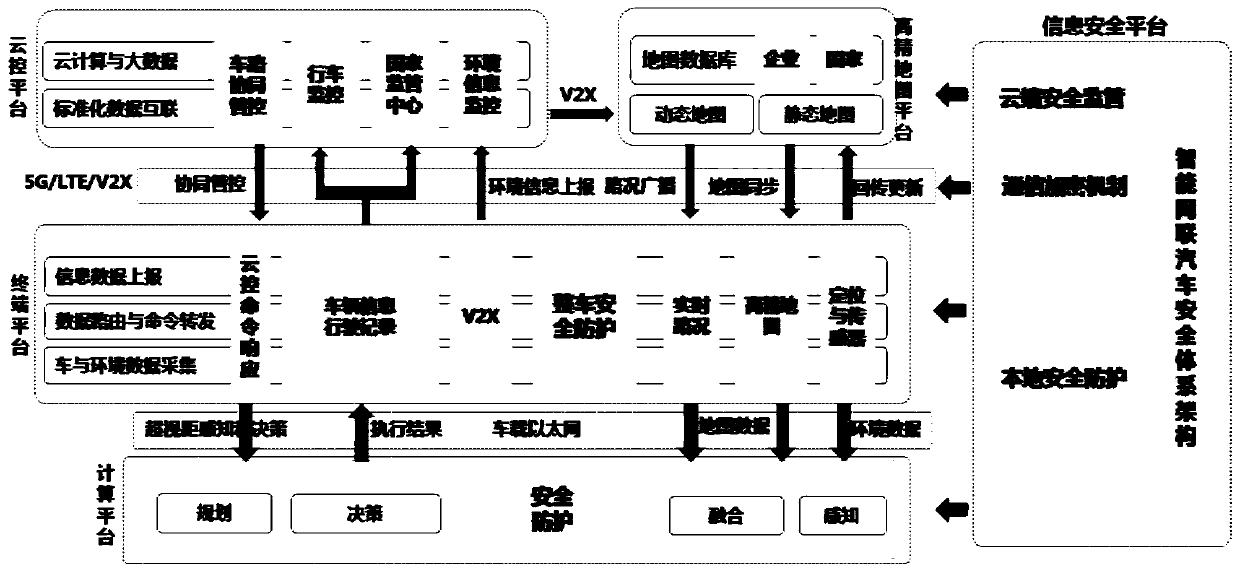
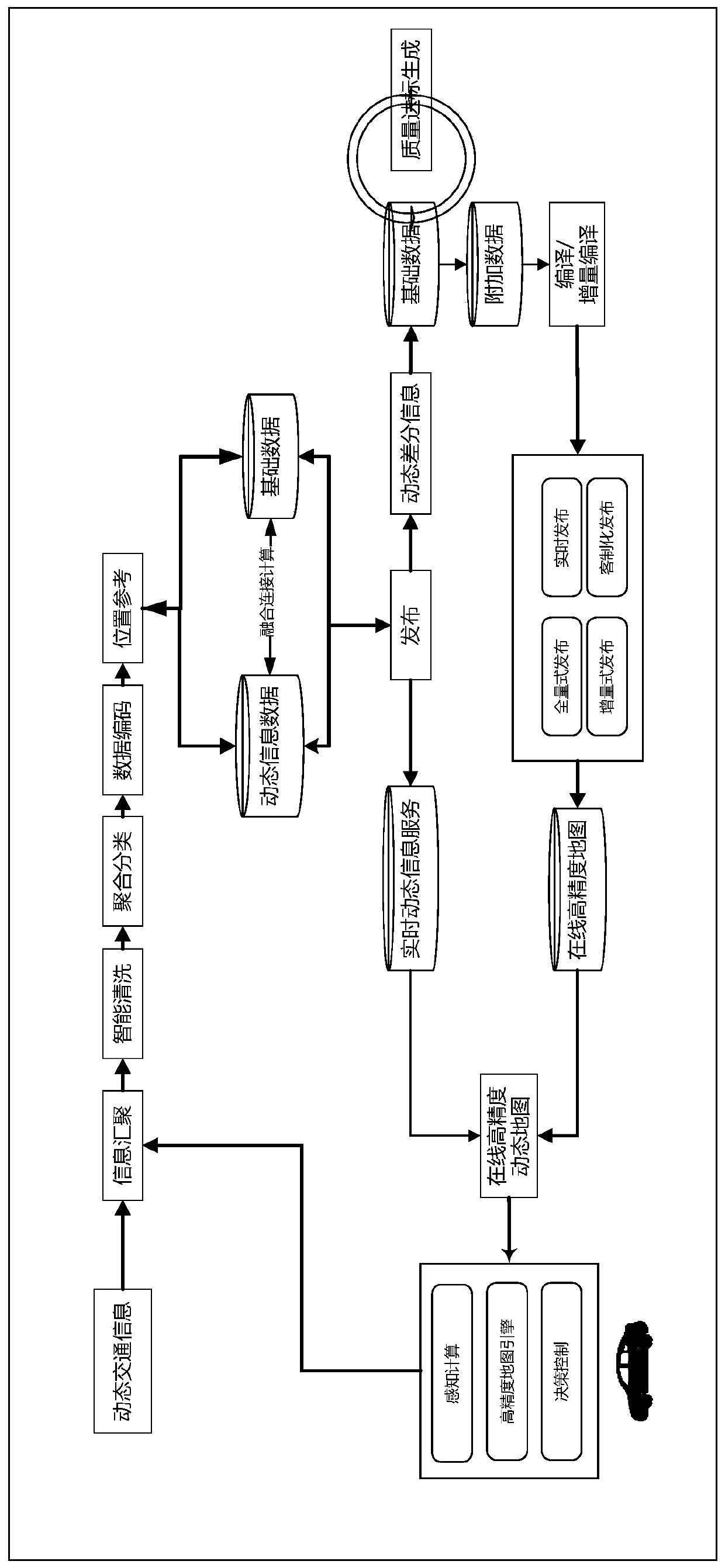
An intelligent network-connected automobile operation system based on vehicle-road collaboration
ActiveCN109714421ARealize data standardization and interconnectionMeet different applicationsParticular environment based servicesDetection of traffic movementHorizonVehicle driving
The invention discloses an intelligent network-connected automobile operation system based on vehicle-road collaboration. The intelligent networked automobile operation system comprises a high-precision map platform, a cloud control platform, a vehicle-mounted terminal platform, a vehicle-mounted computing platform and an information security platform. The high-precision map platform provides a real-time dynamic high-precision map; the cloud control platform and the vehicle-mounted terminal platform are subjected to cooperative management and control through a communication network; the cloudcontrol platform executes data storage, cloud computing and standardized data interconnection; the vehicle-mounted terminal platform executes information reporting; wherein the vehicle-mounted computing platform is connected with the vehicle-mounted terminal platform through the vehicle-mounted Ethernet, over-the-horizon perception data, map data, environment data and the like are obtained, a vehicle driving scheme is formulated through fusion calculation, and the cloud control platform, the vehicle-mounted terminal platform, the vehicle-mounted computing platform and the map platform are allprovided with safety monitors. Common basic services are provided for operation of the intelligent network connection automobile, and national and industrial development requirements are met.
Owner:CHINA INTELLIGENT & CONNECTED VEHICLES (BEIJING) RES INST CO LTD +1
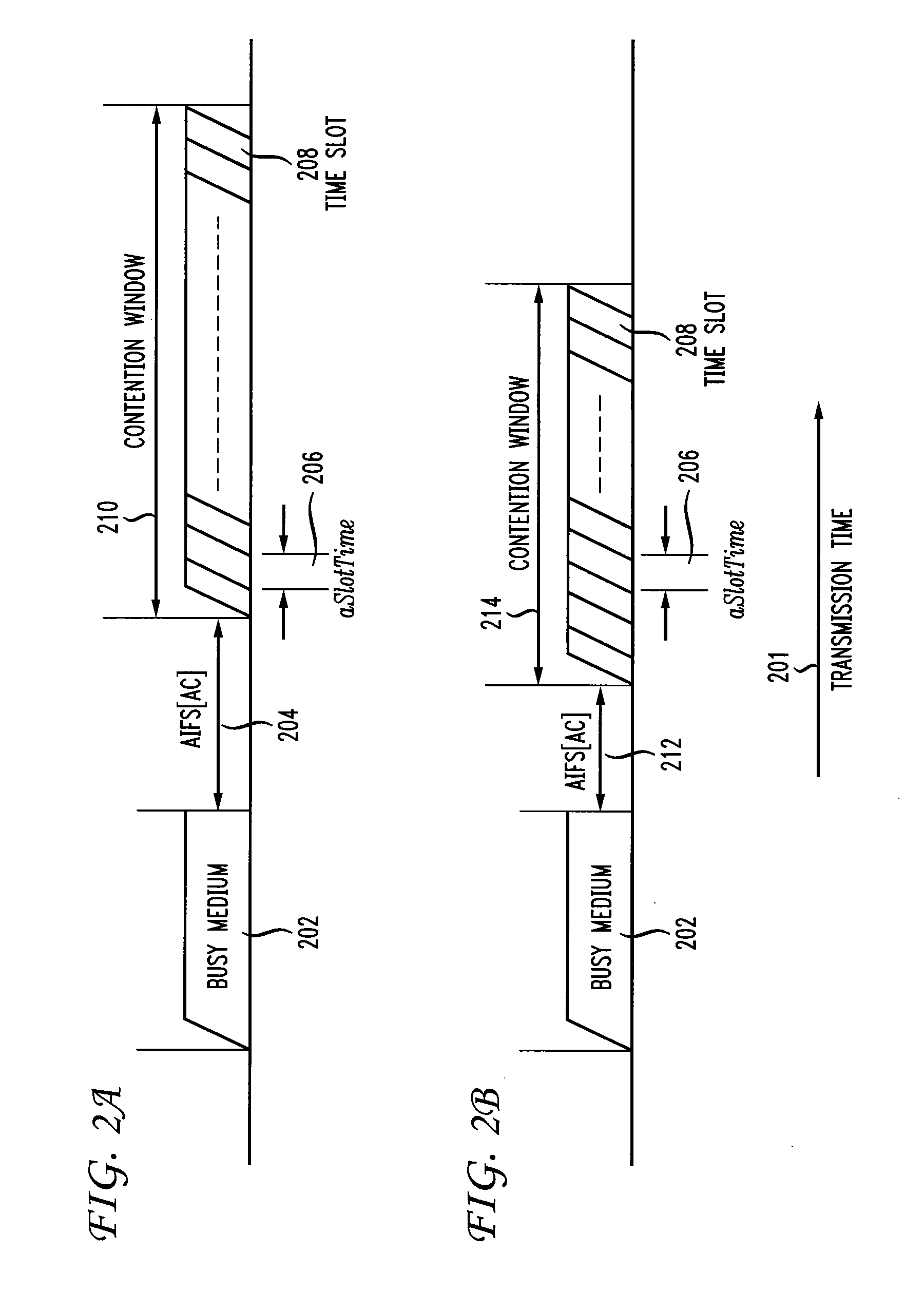
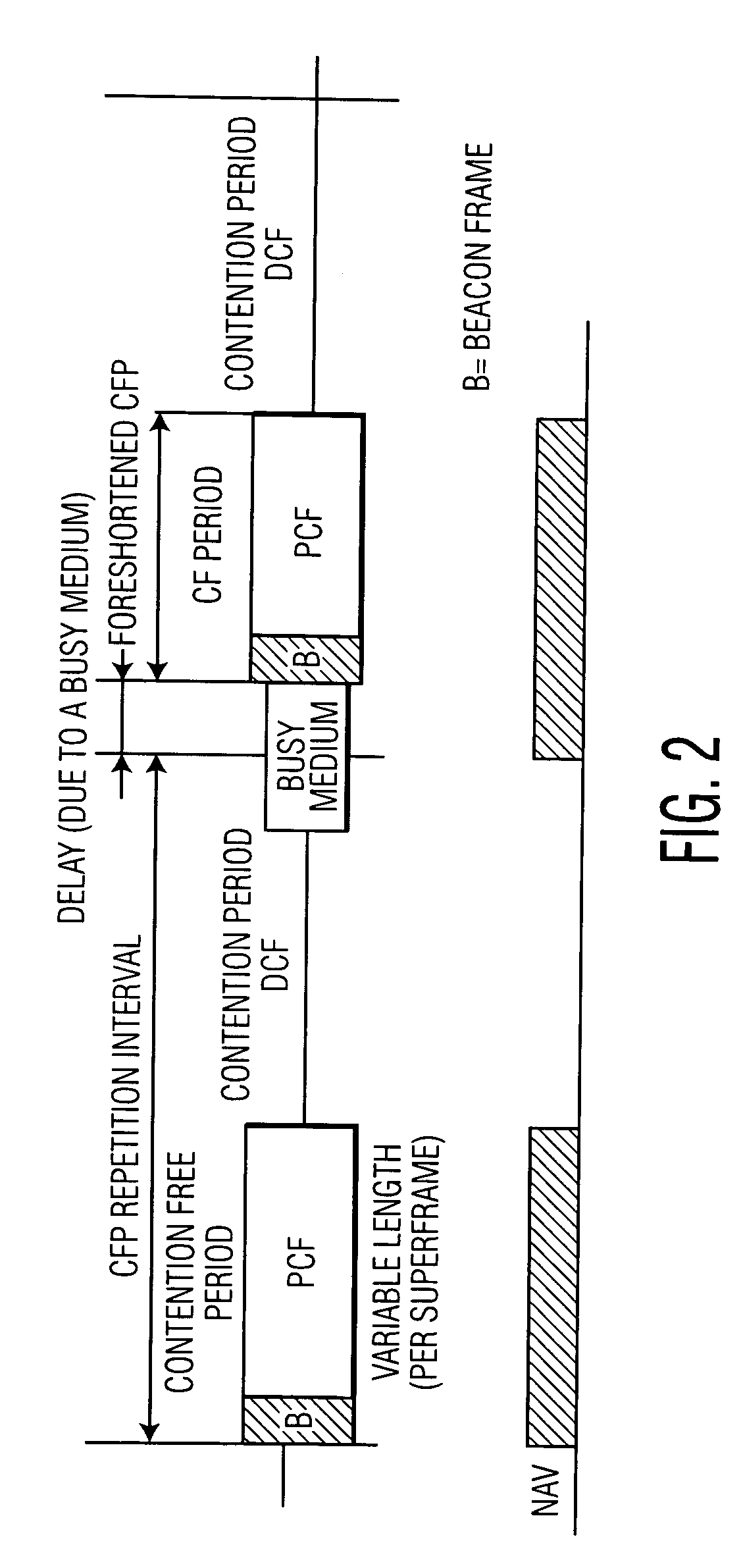
Centralized contention and reservation request for QoS-driven wireless LANs
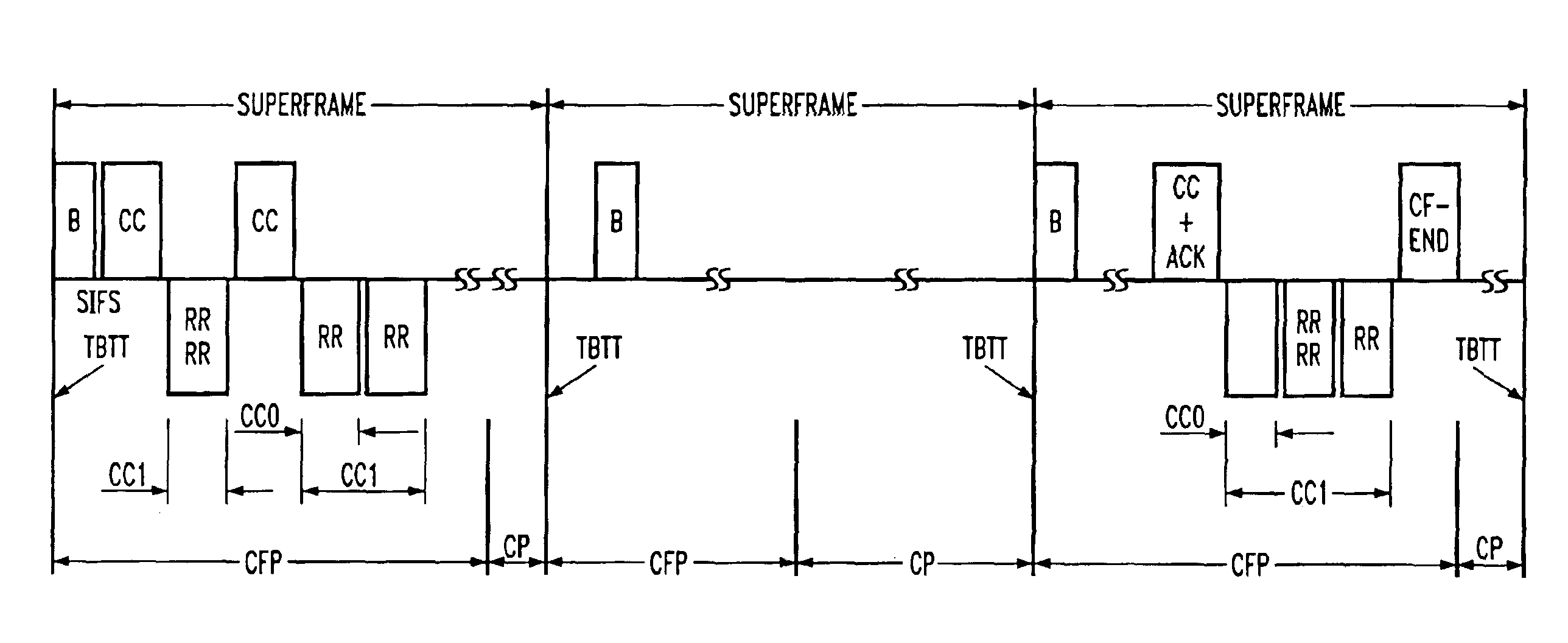
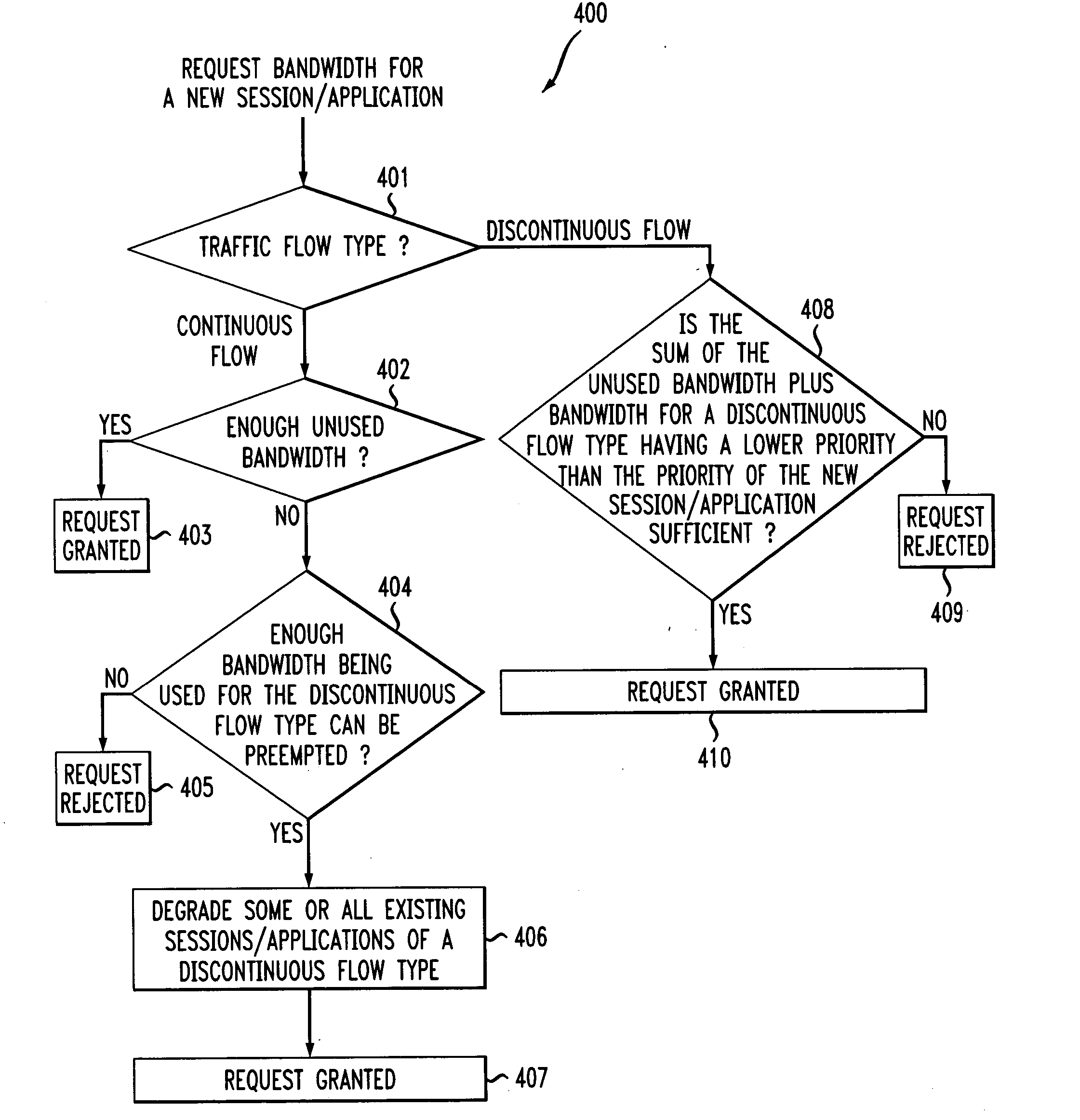
InactiveUS7031287B1Maximizes channel throughputNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesQuality of serviceBasic service
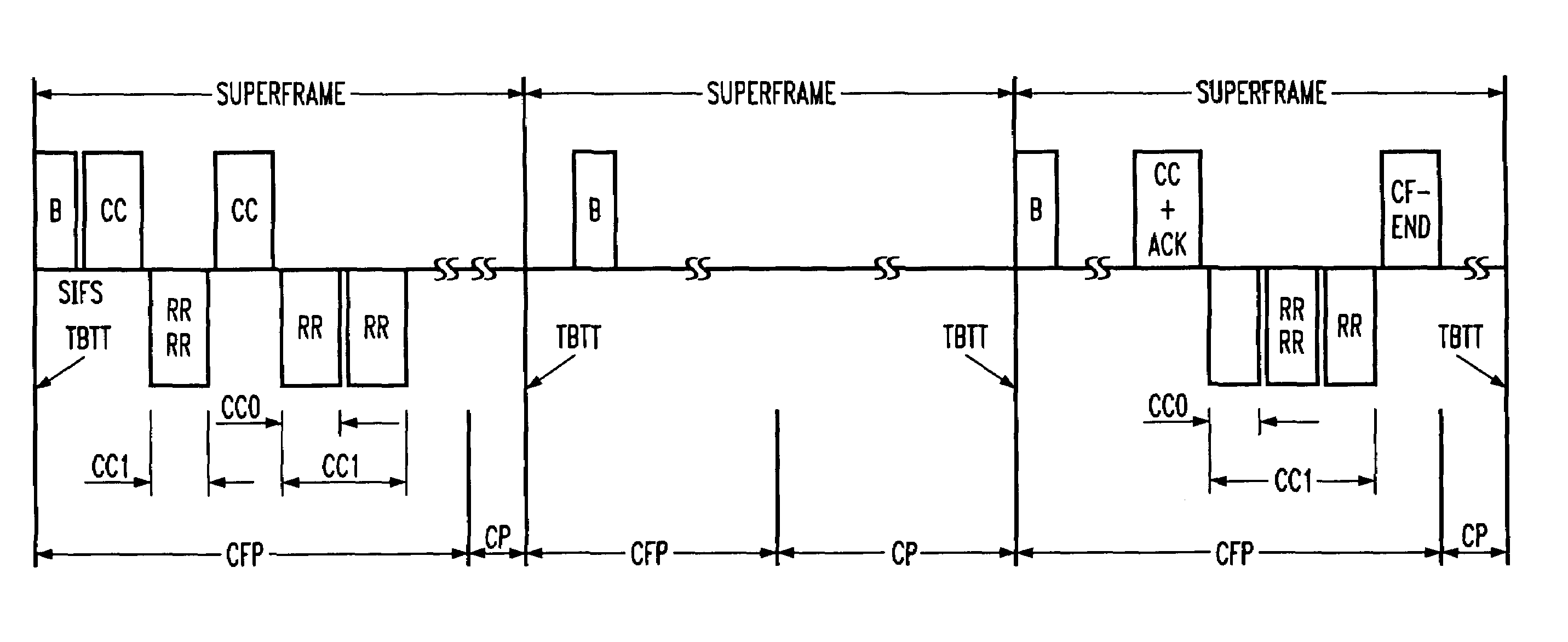
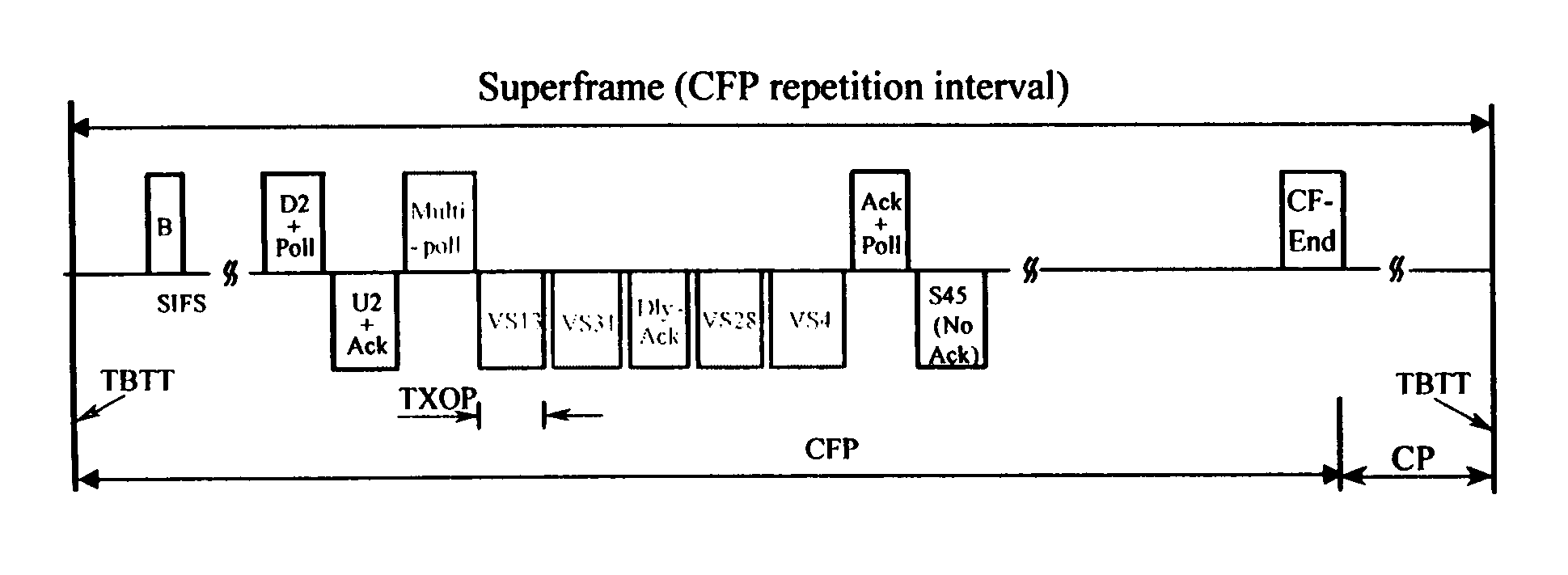
A method and a system is disclosed for providing quality of service (QoS)-driven channel access within a basic service set (BSS) in a wireless local area network (WLAN). A contention control (CC) frame is sent from a point coordinator (PC) of the BSS during a contention-free period (CFP) of a superframe that includes the contention-free period (CFP) and a contention period (CP). The CC frame contains information relating to at least one of a priority limit for a next centralized contention interval (CCI), a length of the next CCI, a permission probability associated with the next CCI and information relating to a reservation request (RR) frame successfully received by the PC in a previous CCI. A non-colliding RR frame is then received at the PC in the CCI following the CC frame. The received RR frame is sent from a non-PC station in the BSS when at least one centralized contention opportunity (CCO) is available during the CCI after the CC frame. The RR frame indicates that the non-PC station sending the RR frame has at least one buffered data frame for transmission.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
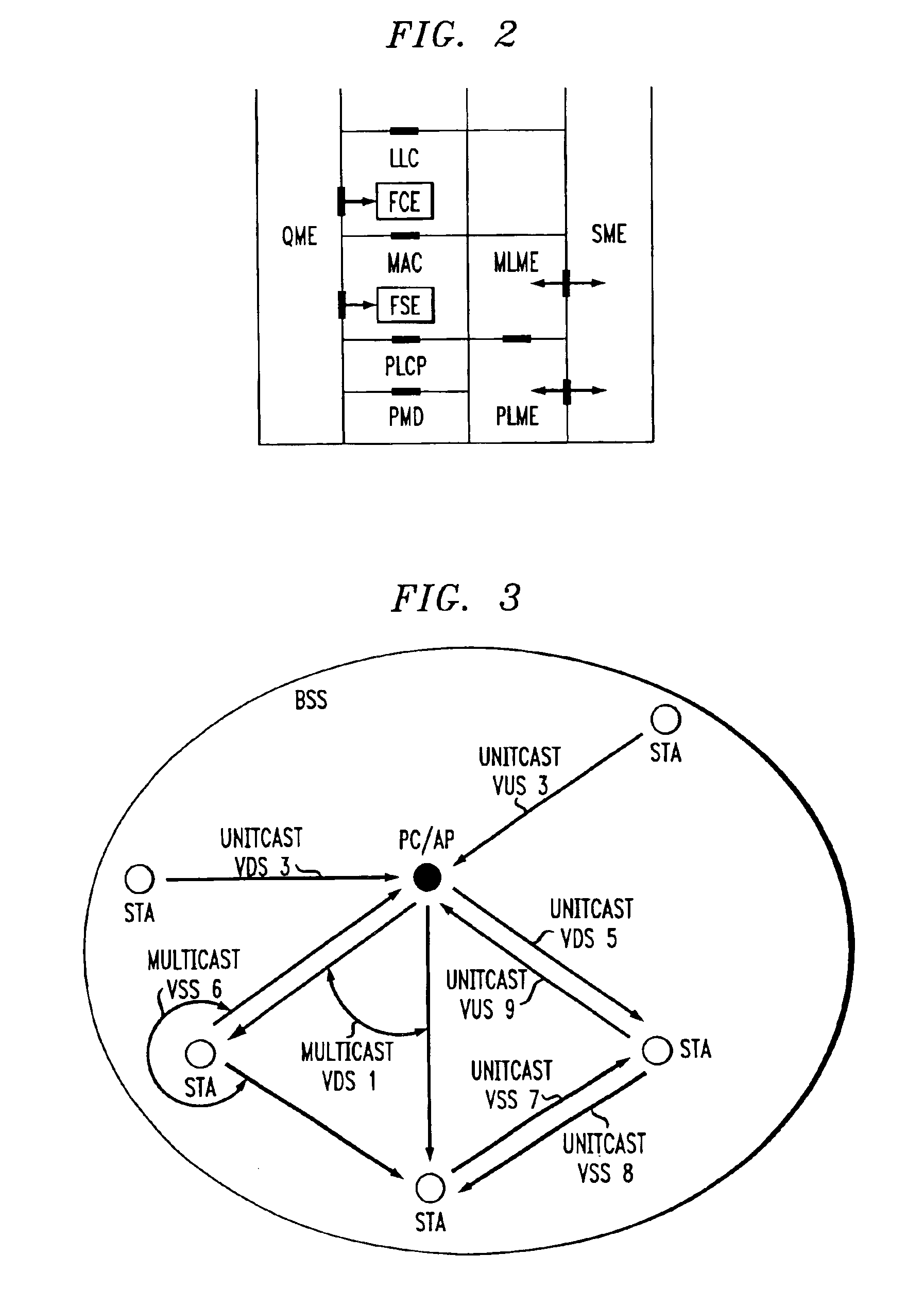
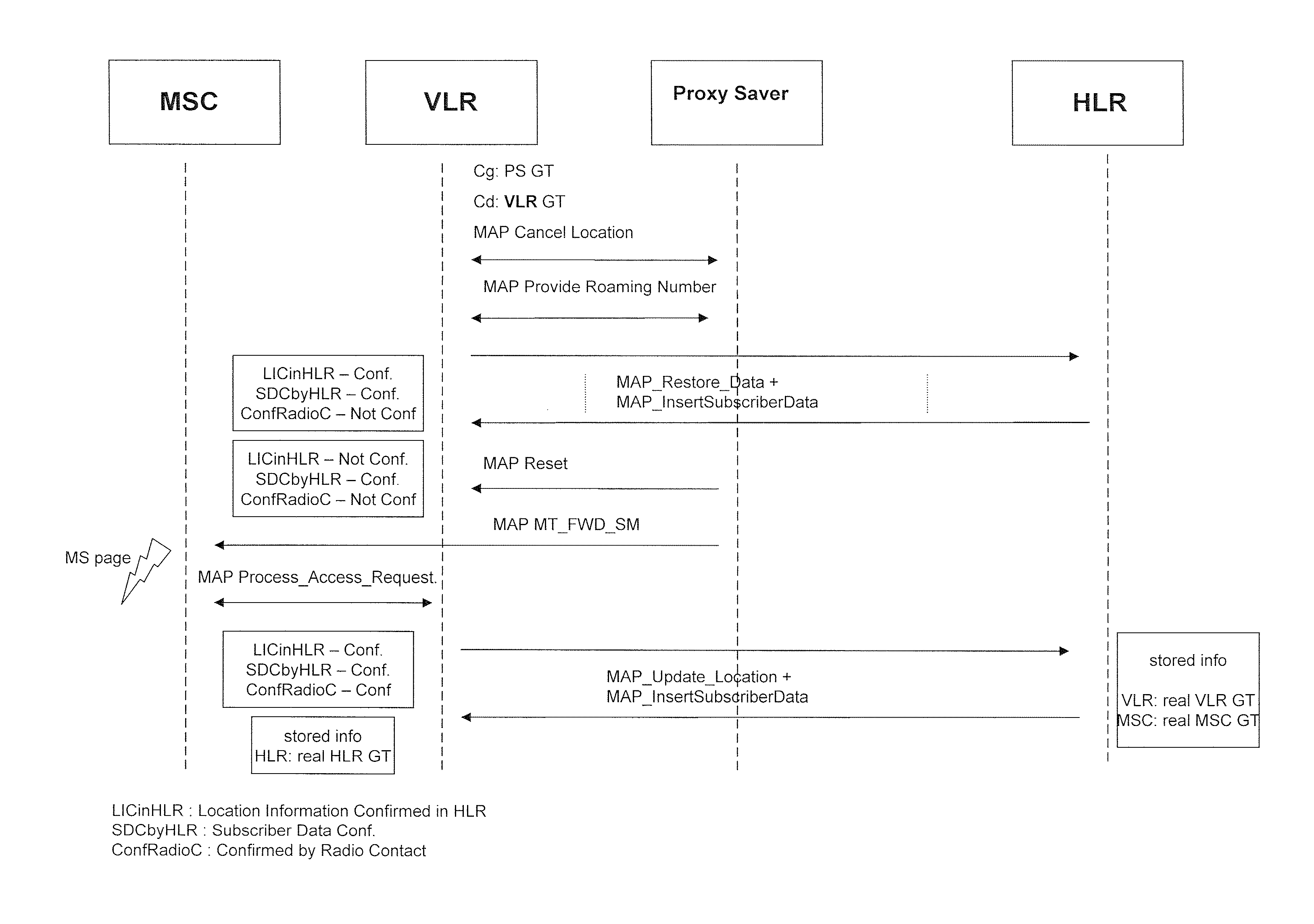
Virtual streams for QoS-driven wireless LANs
InactiveUS7151762B1Network traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesQuality of serviceBasic service
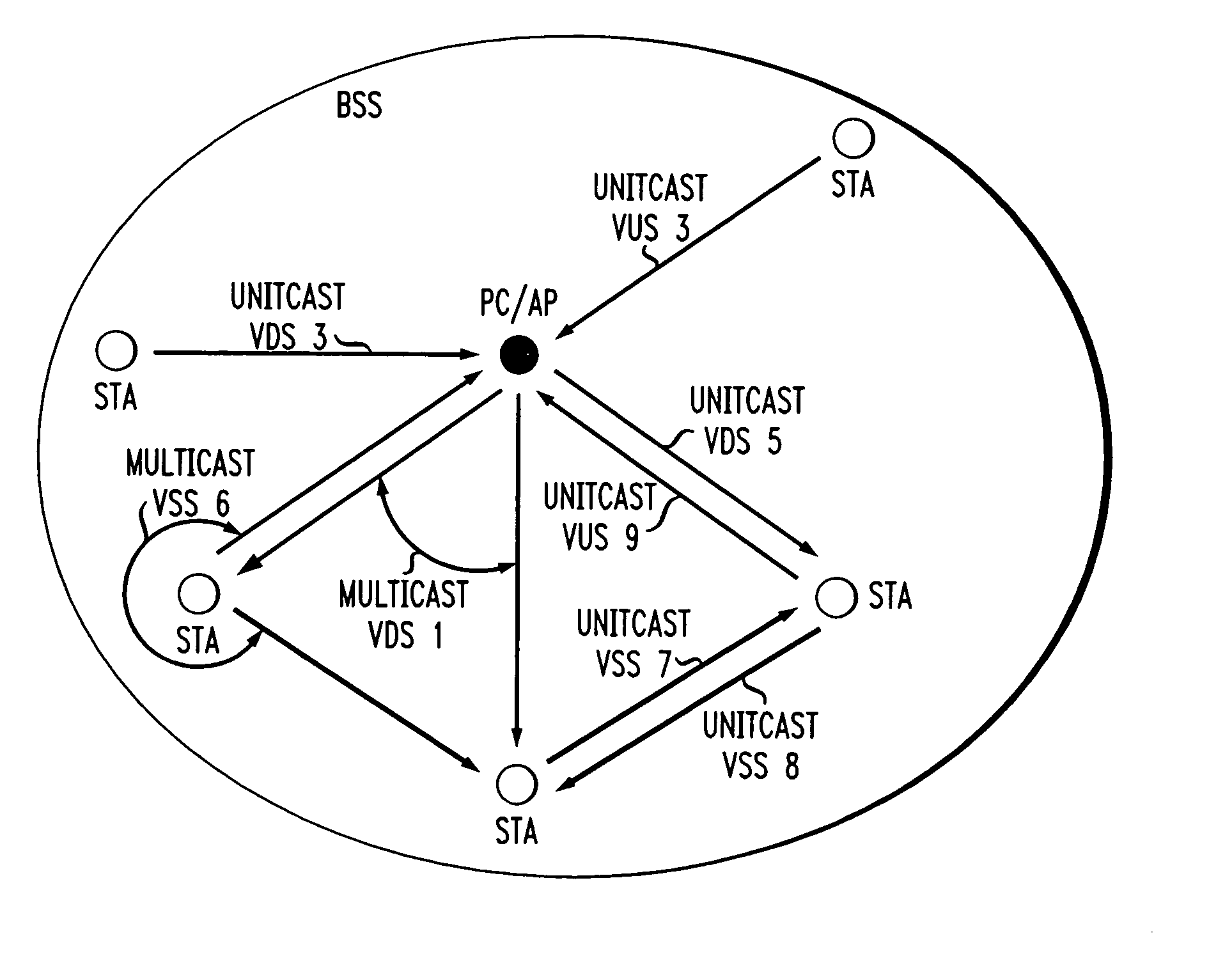
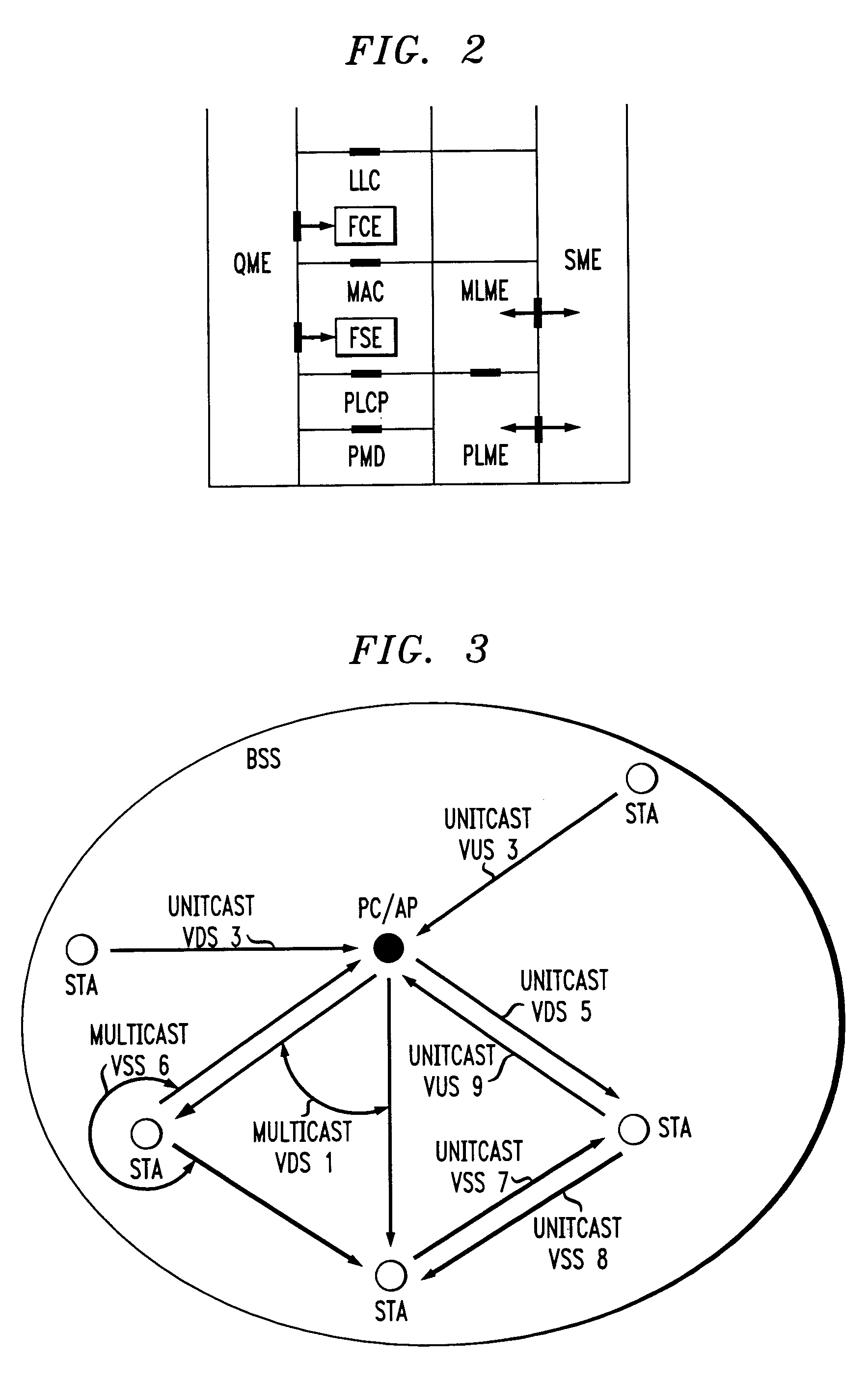
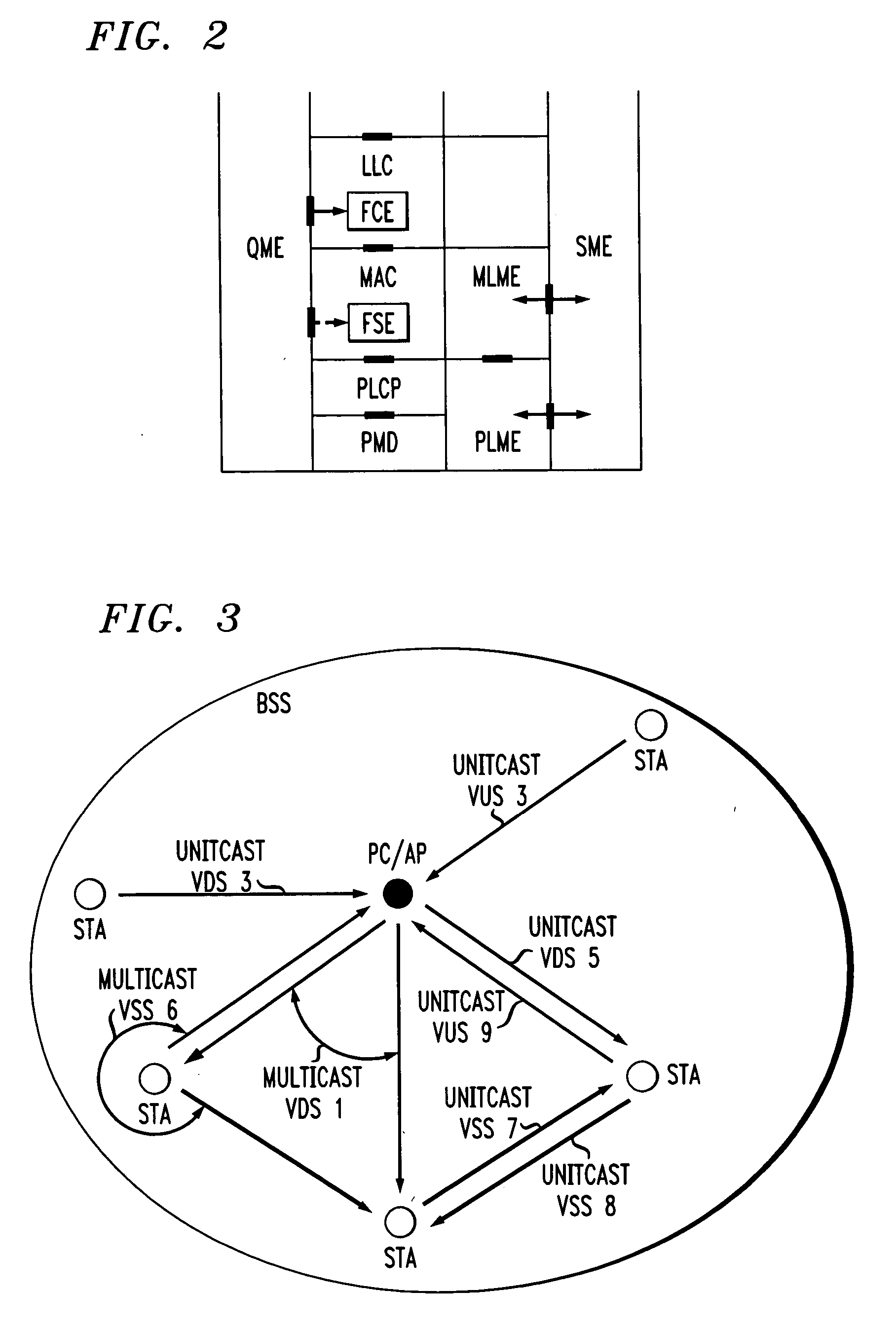
A virtual stream (VS) in a basic service set (BSS) in a wireless local area network (WLAN) that exists solely within the medium access control (MAC) sublayer of the WLAN. The VS includes a unidirectional path in the wireless network between a station sourcing a quality of service (QoS) session and at least one station receiving the QoS session in the same BSS. The VS is defined by a VS identifier (VSID) that is unique within and local to the BSS, an address of the sourcing station, and an address of the at least one receiving station. The VS can be a virtual down-stream (VDS), a virtual up-stream (VUS) or a virtual side-stream (VSS). The VS can be a unitcast or a multicast VS.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
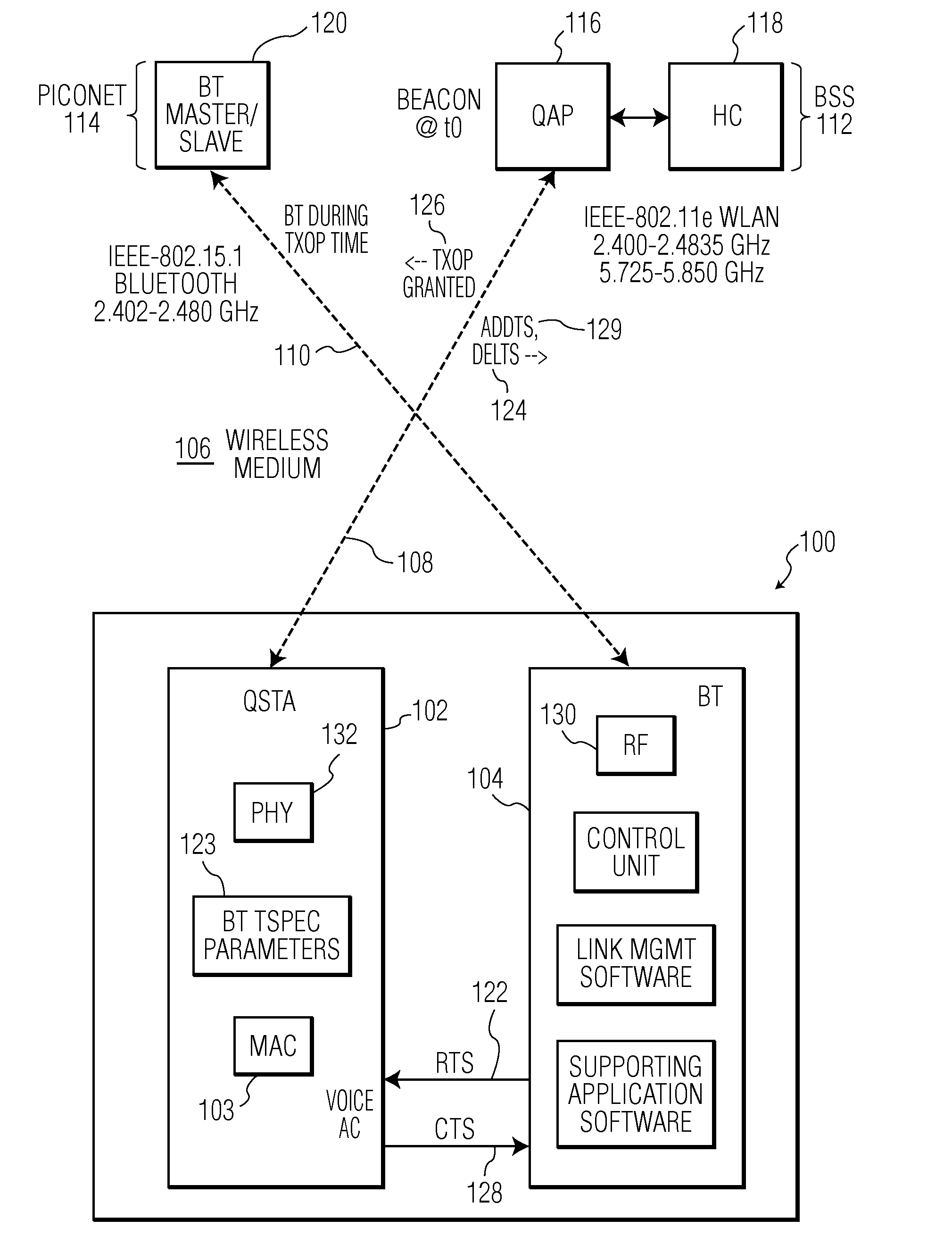
Quality of service for WLAN and bluetooth combinations
ActiveUS20100284380A1Easy to useNetwork topologiesMultiple digital computer combinationsQuality of serviceBluetooth piconets
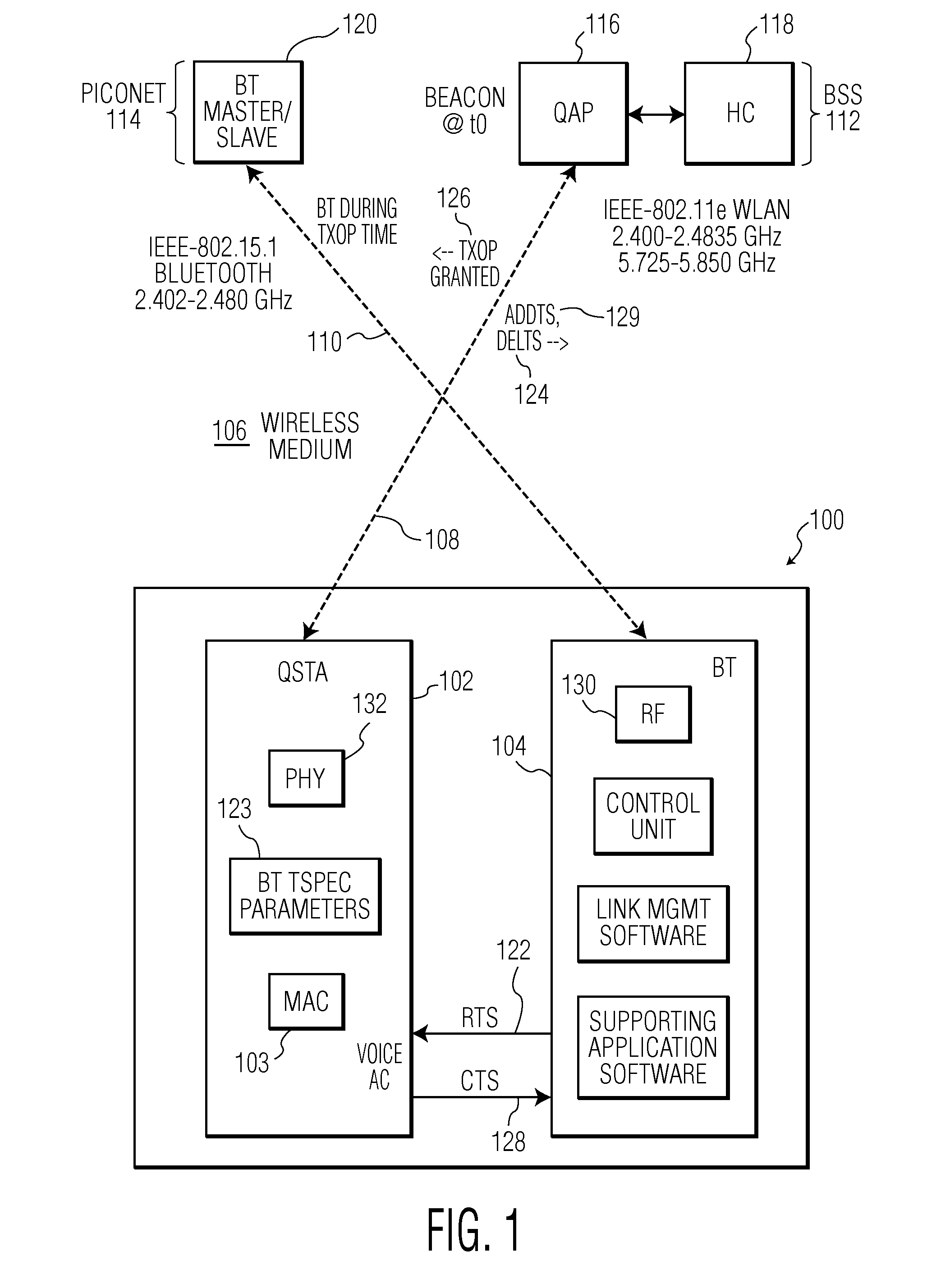
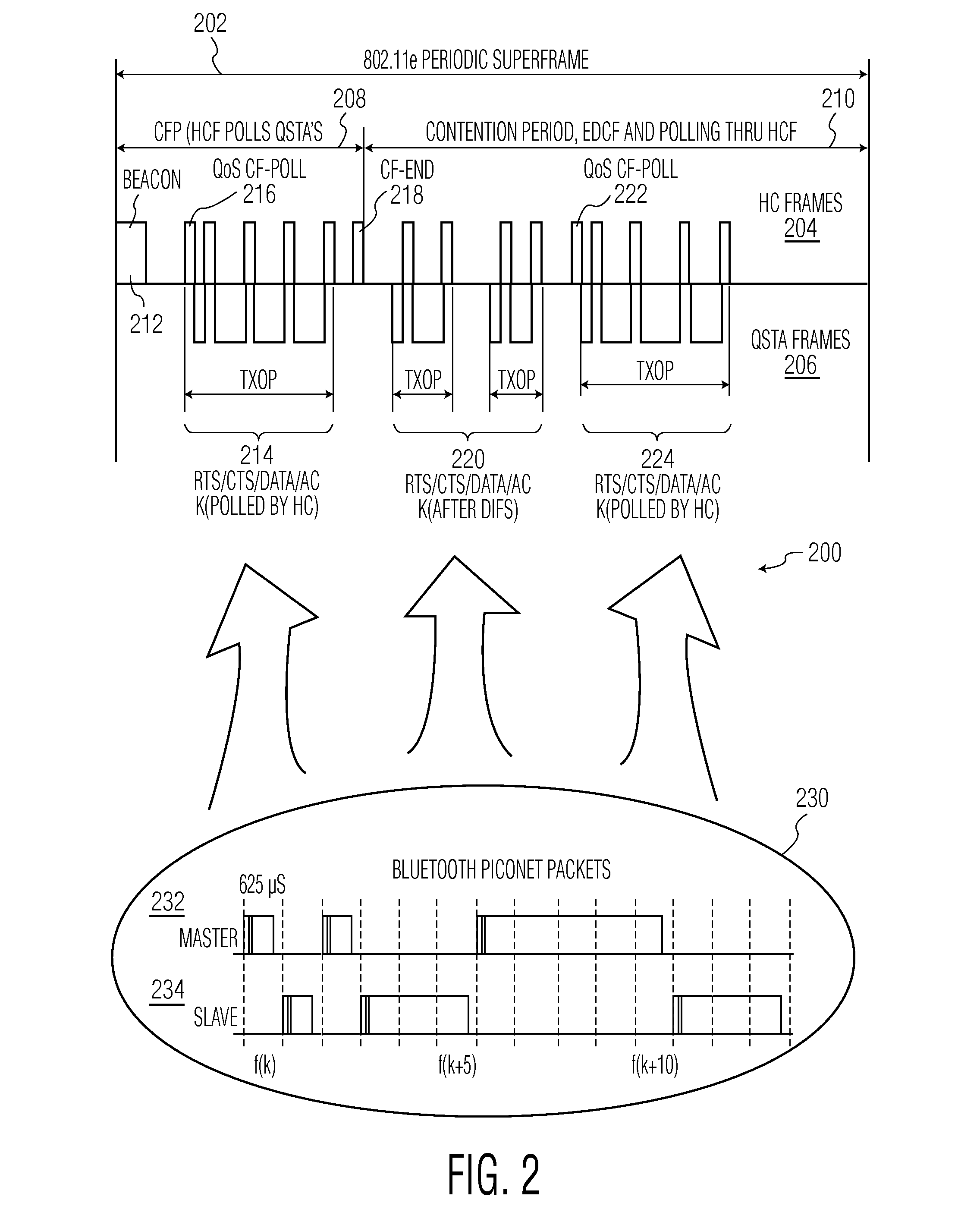
A hybrid device (100) includes both a IEEE-802.11e type WLAN client station (QAP) (102) and a BLUETOOTH piconet unit (104) interconnected such that the BLUETOOTH transmissions are scheduled to occur according to a transmission opportunity (TXOP) (126) that was granted by a quality of service (QoS) access point (QAP) (116) in a basic service set (BSS) (112). Requests for BLUETOOTH traffic are handled by the associated QSTA (102) which generates an add traffic service (ADDTS) (124) to the QAP.
Owner:NXP BV
Internet of things intelligent home system and method
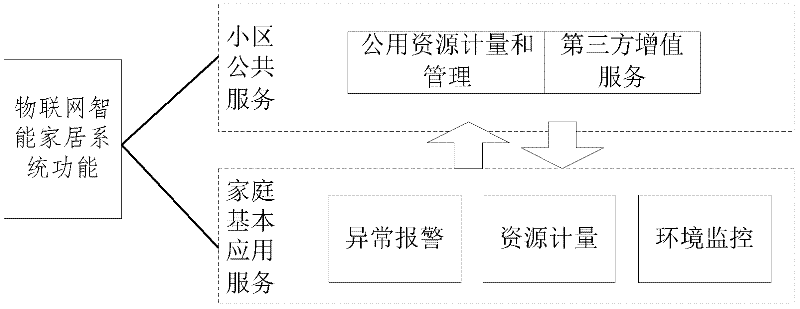
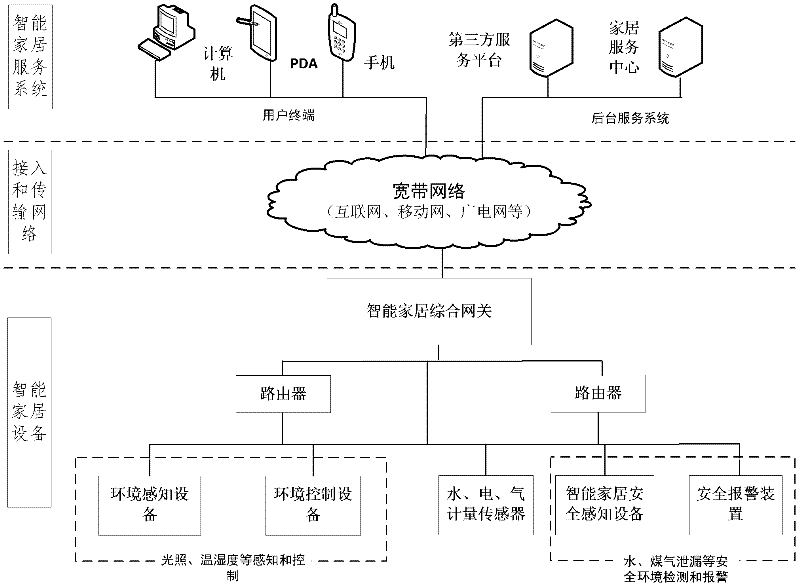
The invention discloses an Internet of things intelligent home system and a method. The system comprises intelligent home equipment, an access and transmission network and an intelligent home service system, wherein the intelligent home equipment comprises sensing equipment, control equipment, an alarm device, a router and an intelligent home comprehensive gateway; the access and transmission network is a remote transmission broadband network for finishing interaction between the intelligent home service system and a background service system; and the intelligent home service system comprises a user terminal and the background service system. According to the method, the Internet of things intelligent home system is divided into an intelligent home basic service and a cell public service; the intelligent home basic service comprises abnormal situation alarming, environment monitoring and home energy metering; and the cell public service comprises public resource metering, comprehensive data acquisition and analysis, management and optimization and other services supplied by a third party. The Internet of things intelligent home system can alarm abnormal situations, monitor environments, meter home energy and comprehensively manage and control home information, so that the security of the system is guaranteed.
Owner:感知企银科技(无锡)有限责任公司
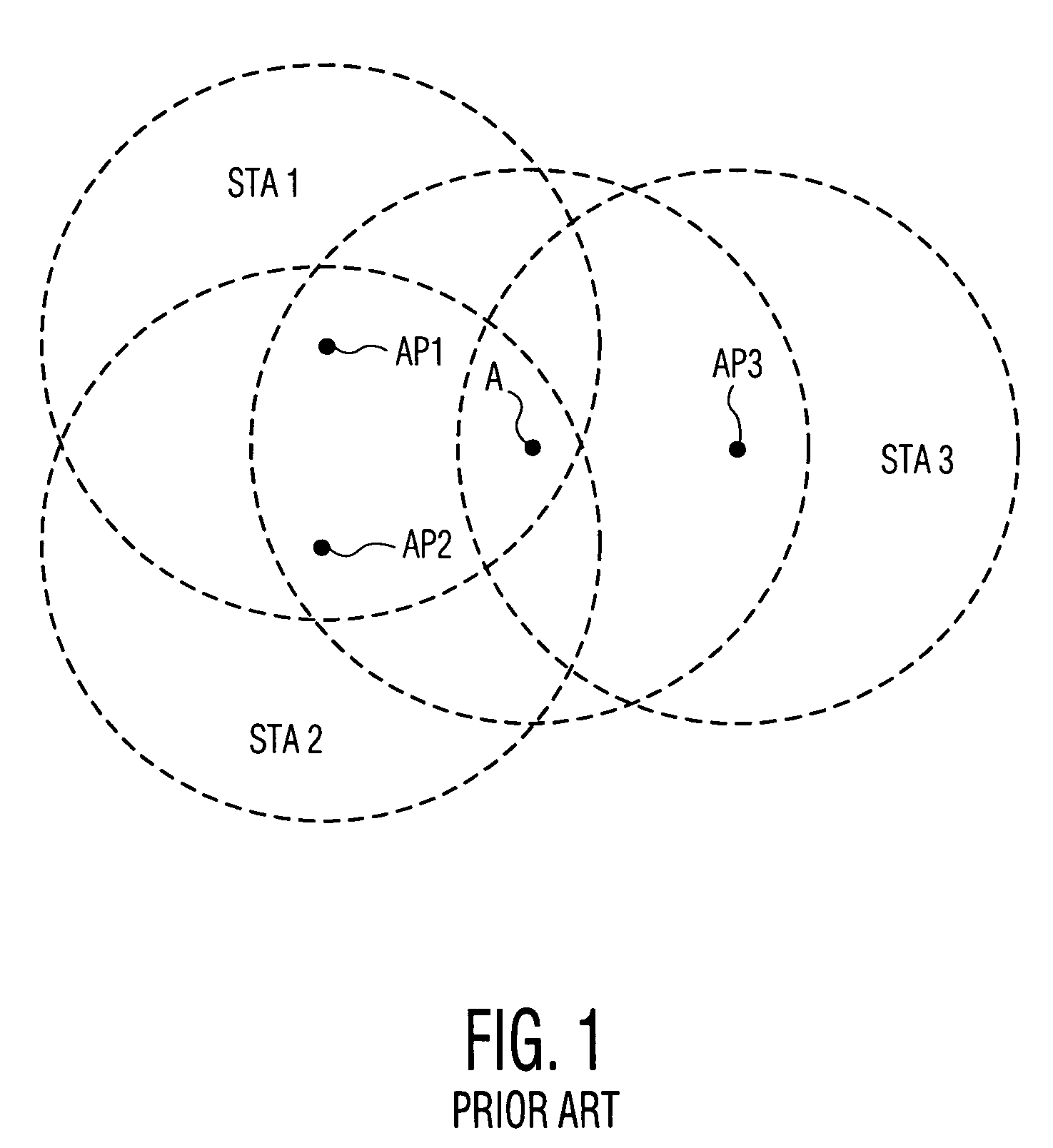
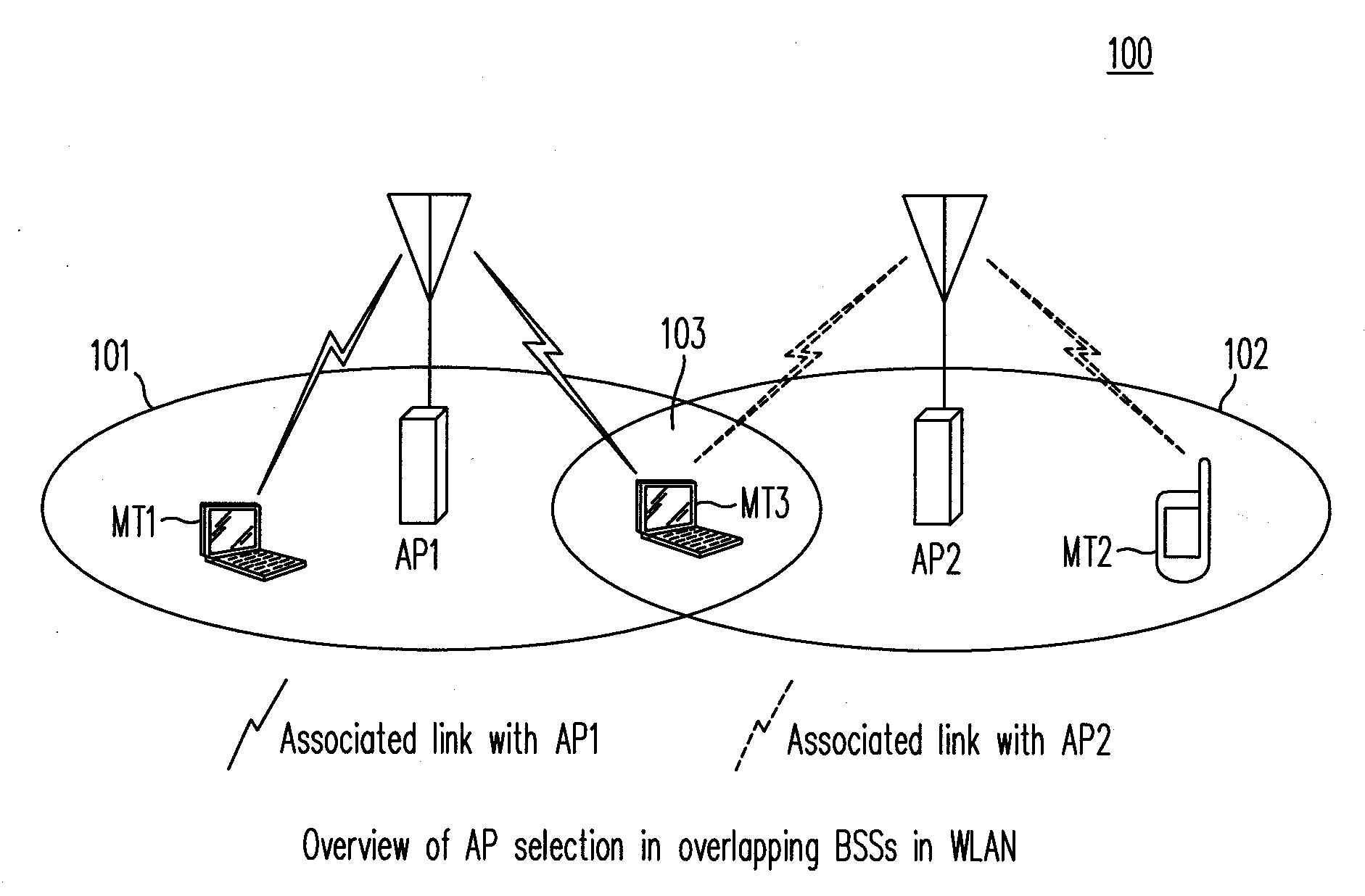
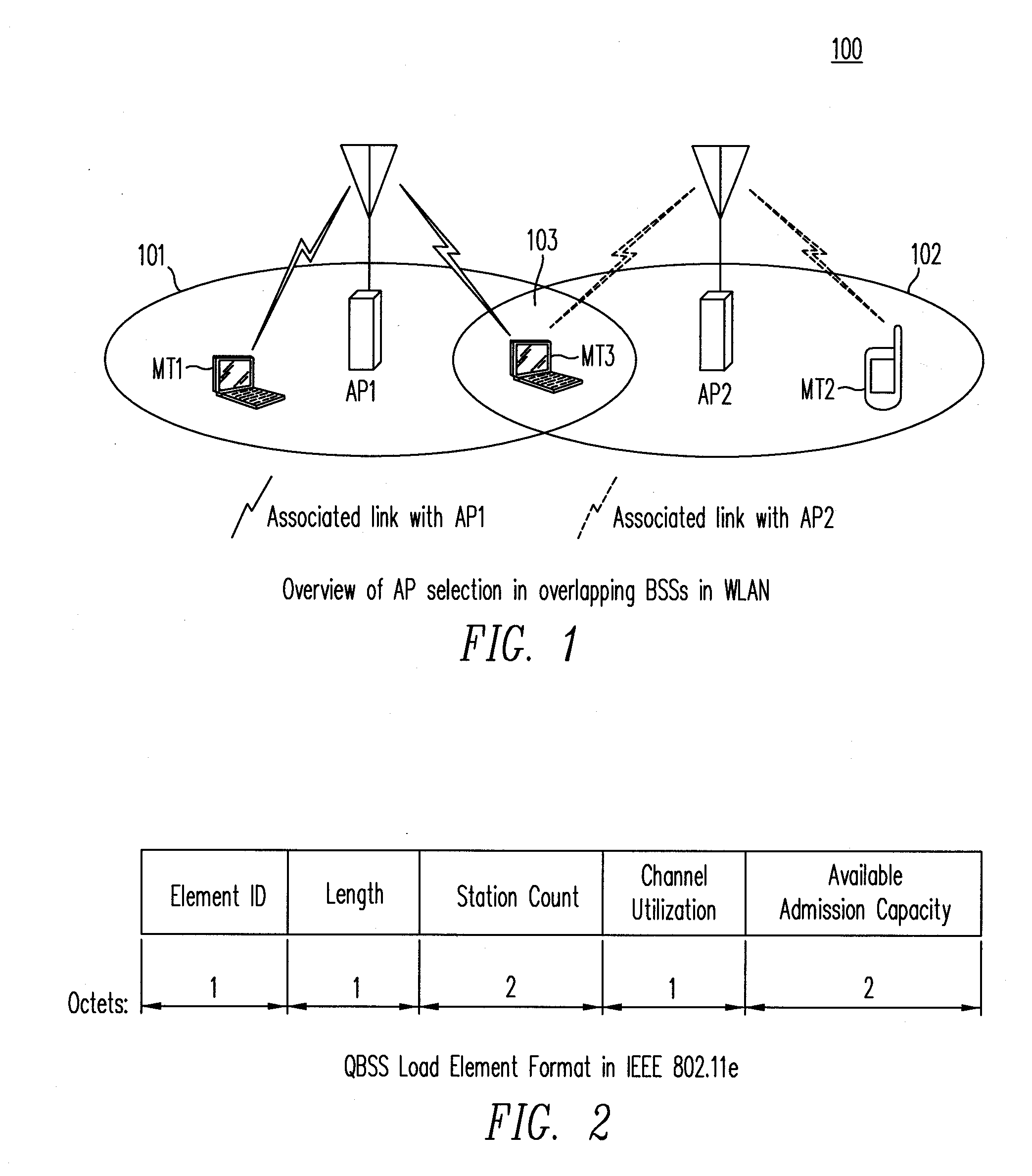
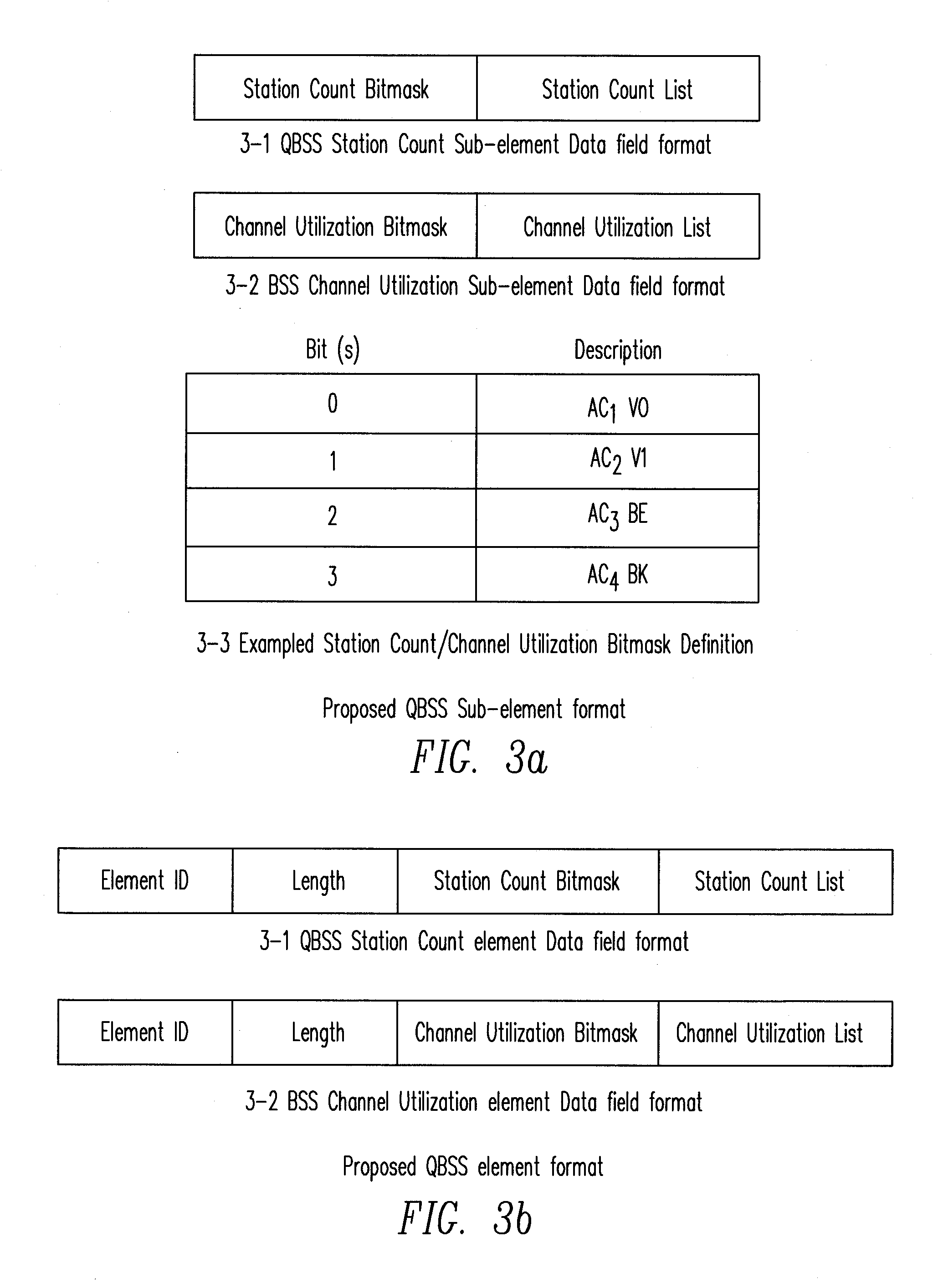
Control of Quality of Service in Overlapping Basic Service Sets in Wireless Local Area Networks
Access priority for wireless devices located in an area in which radiofrequency (RF) coverage areas of a first wireless access point and a second wireless access point overlap is controlled by coordinating operation of the first wireless access point and the second wireless access point. The wireless devices access a common RF channel via a collision sense multiple access / collision avoidance mechanism. The probability of accessing the RF channel may be varied by adjusting the length of interframe spacings and the length of contention windows. The length of the interframe spacings and the length of the contention windows associated with the first access point and associated with the second access point are configured such that the probability of wireless devices associated with the first wireless access point accessing the RF channel is greater than the probability of wireless devices associated with the second wireless access point accessing the RF channel.
Owner:LYFT INC
Enhanced channel access mechanisms for QoS-driven wireless lans
InactiveUS7068633B1Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionQuality of serviceWireless lan
A method and a system is disclosed for providing quality of service (QoS)-driven channel access within a basic service set (BSS) in a wireless network. A contention control (CC) frame is sent from a point coordinator (PC) station of the BSS. The CC frame contains information relating to a number of available centralized contention opportunities (CCOs) for receiving a reservation request (RR) in a centralized contention interval (CCI) following the CC frame. The CC frame also contains information relating to the identification of stations from which an RR was successfully received by the PC station in a preceding CCI. The CC frame is sent by the PC station during a contention-free period (CFP) of a superframe. The superframe includes a contention-free period (CFP) and a contention period (CP). The CC frame is received at a non-PC station in the BSS. An RR is then sent in a selected one of the available CCOs in the CCI in response to the received CC frame. The RR is sent from the non-PC station when the non-PC station has a burst of data frames to send, and the RR indicating an amount of bandwidth requested by the non-PC station sending the RR for transmitting the burst. The RR frame is received at the PC-station in one of the CCOs of the CCI. A multipoll frame is then sent from the PC station containing information relating to at least two transmission opportunities (TOs) assigned to at least one non-PC station in the BSS for data transmission. The information contained in the multipoll frame can include information relating to a length of each TO.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
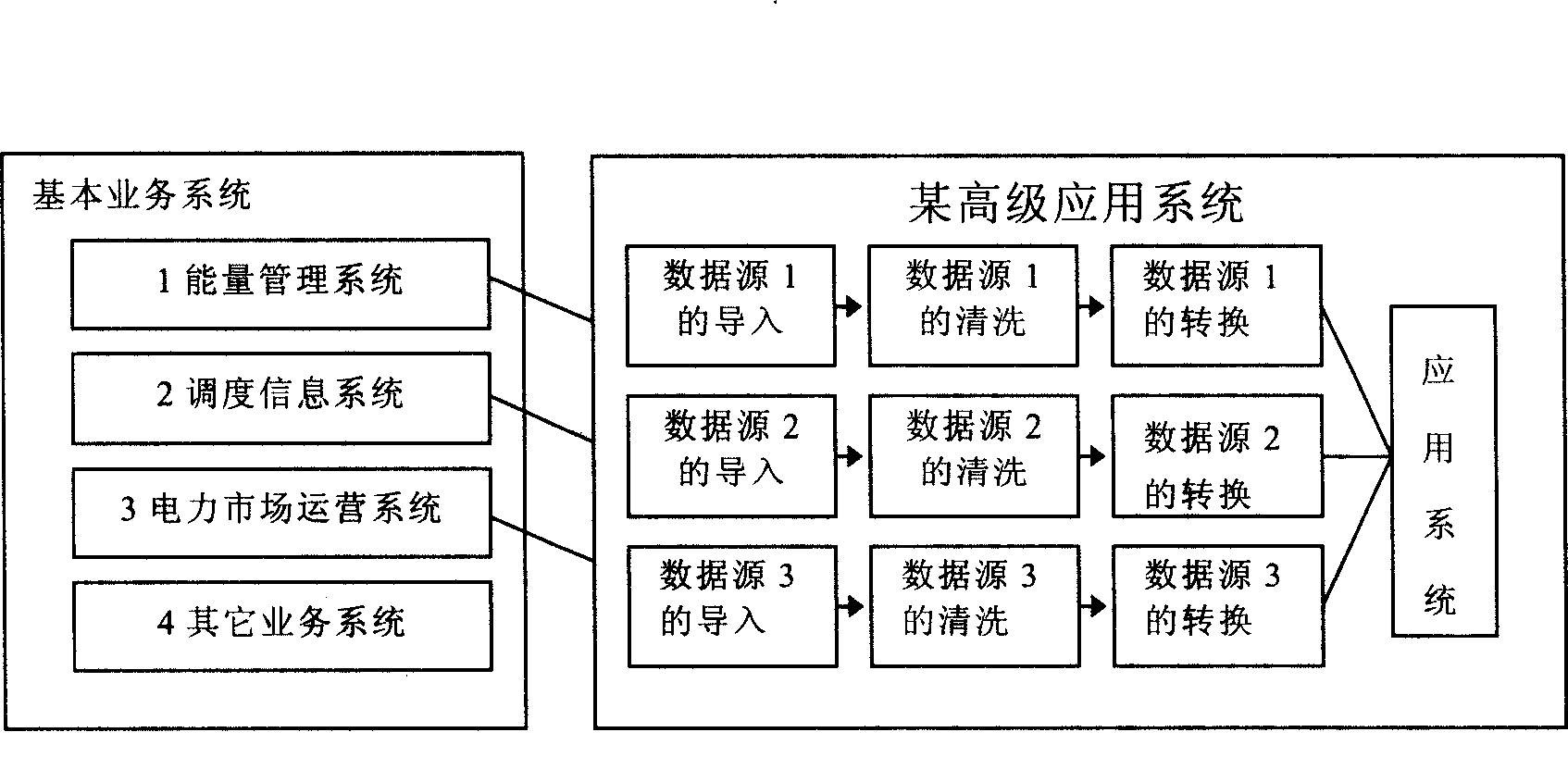
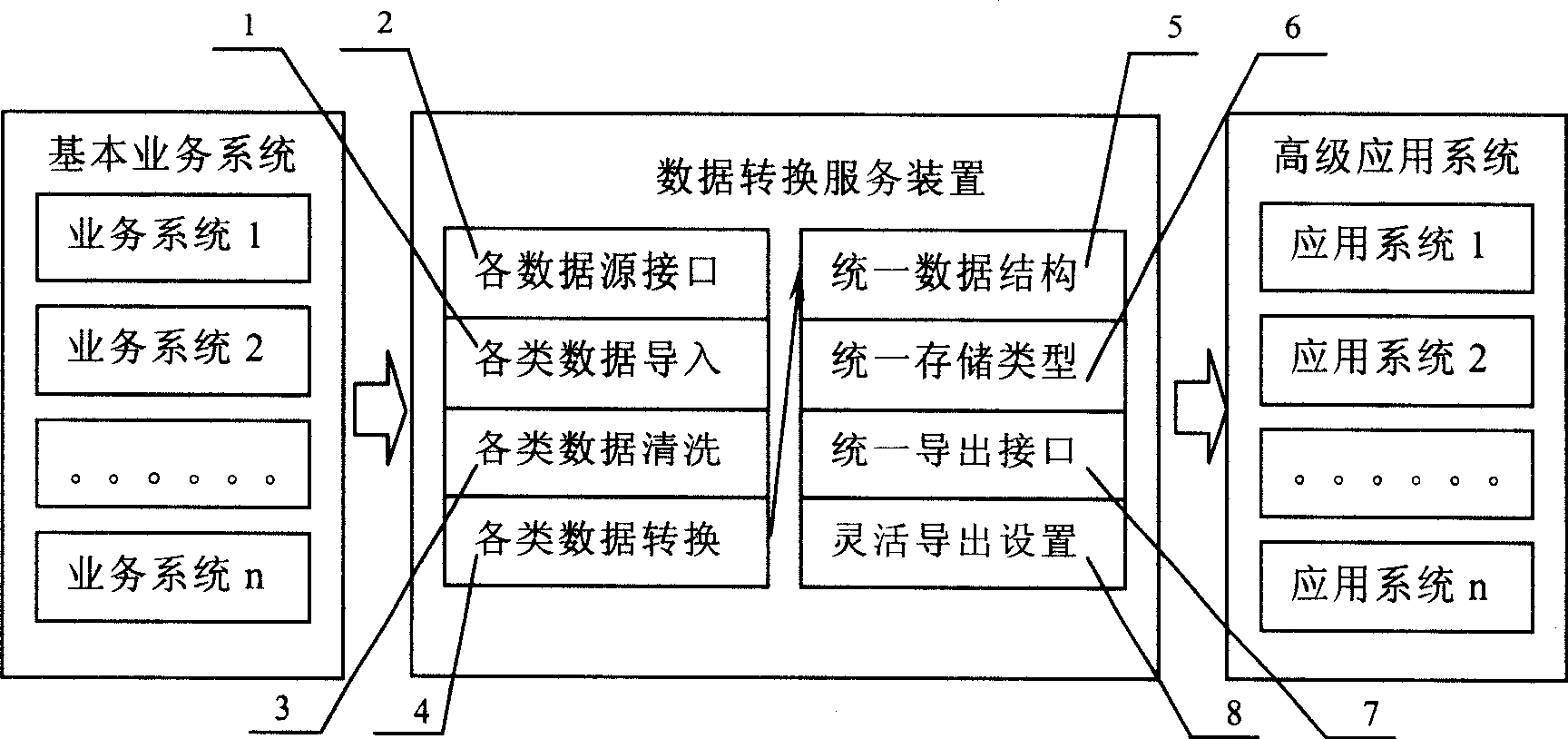
Multiple source data conversion service method and apparatus thereof
InactiveCN101452450AGuaranteed correctnessImprove data conversion efficiencyData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsData sourceBasic service
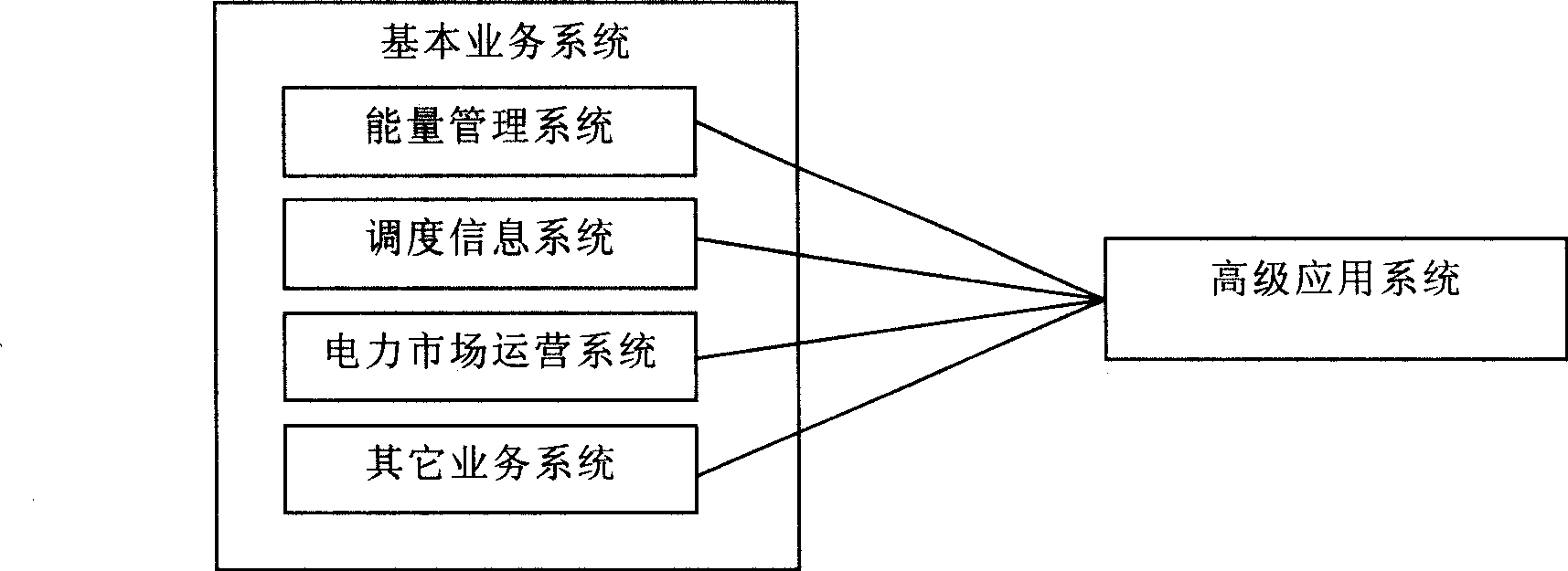
The invention relates to a service method and a service device for converting multi-source data. The device comprises a data source interface module, a data importing module, a data cleaning module, a data converting module, a consolidated data structure module, a consolidated storage type module, a consolidated exporting interface module and a flexible export setting module. The service method and the service device for converting the multi-source data have the following advantages: 1) an independent device is specially responsible for operations, such as data exchange of various advanced application systems and various basic service systems in a power dispatching center, thereby improving efficiency of data conversion, and ensuring correctness and timeliness of the data conversion; 2) each advanced application system only needs to acquire data from a data conversion service device, thereby saving complicated workload of data conversion, and saving development cost and maintenance cost; and 3) the advanced application system is separated from data conversion, thereby saving hardware resource, and improving operating efficiency and operating stability of the application system.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
System and method of frame scheduling for QoS-driven wireless local area network (WLAN)
InactiveUS6850981B1Network traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesLogical link controlBasic service
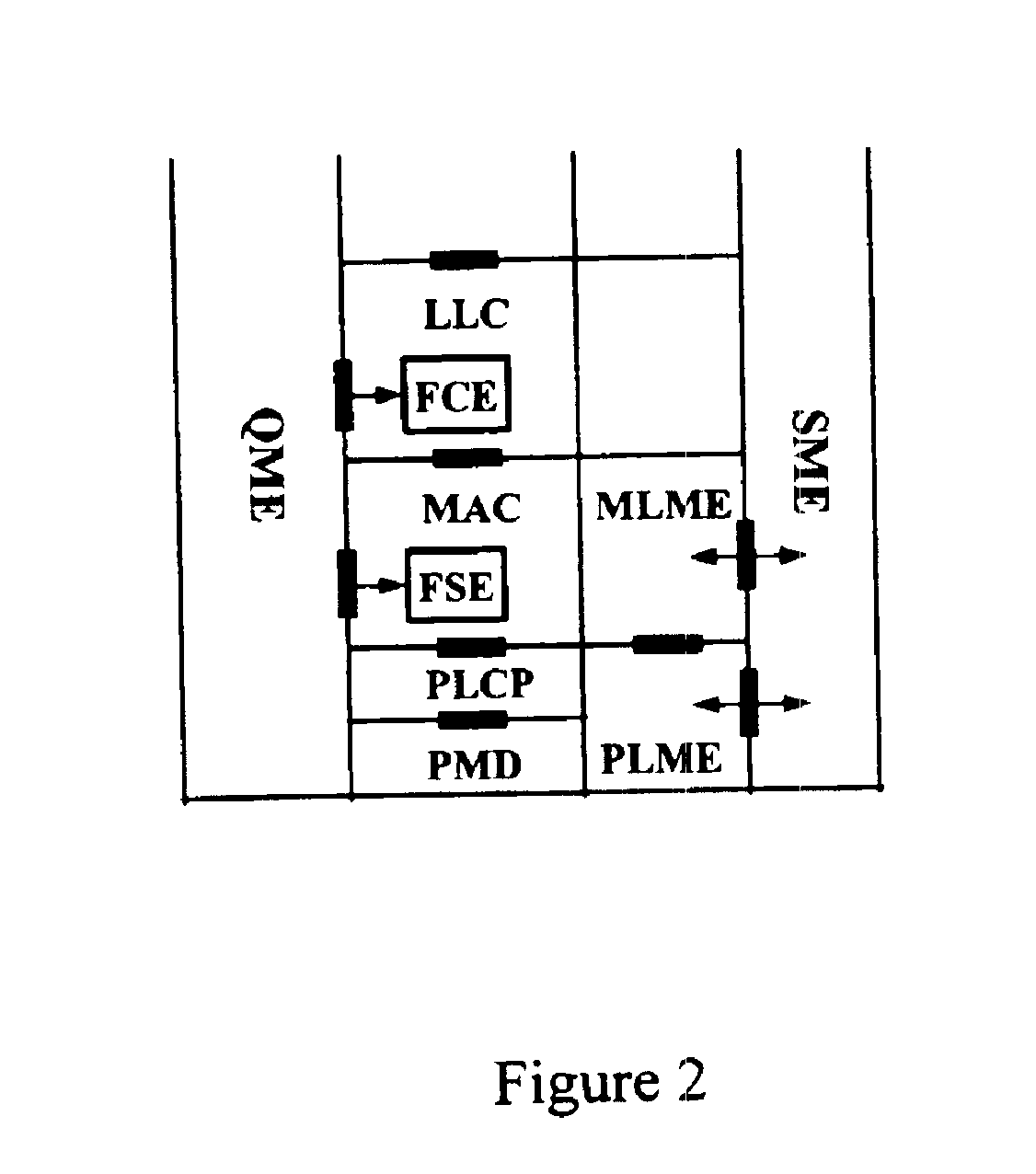
A frame scheduling entity (FSE) for a station having a point coordinator (PC) in a basic service set (BSS) in a wireless local area network (WLAN) is disclosed. The FSE is located at a medium access control (MAC) sublayer of the station, and includes a scheduling table and a scheduling element. The scheduling table is logically located at a medium access control (MAC) sublayer of the station, and contains at least one entry corresponding to a session admitted to transmit traffic over the wireless network. The entry contains a virtual stream (VS) identifier (VSID), a QoS parameter set, and a data size that are each associated with the session. The scheduling table also includes a permanent entry containing a null QoS parameter set and corresponding to best-effort (asynchronous) traffic from the PC to a non-PC station associated with the PC. The scheduling element schedules transmission of a data frame for a session between peer logical link control (LLC) sublayer entities of the BSS based on the information contained in the entry for the session. The data frame scheduled by the scheduling element is labeled by the VSID contained in the entry.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
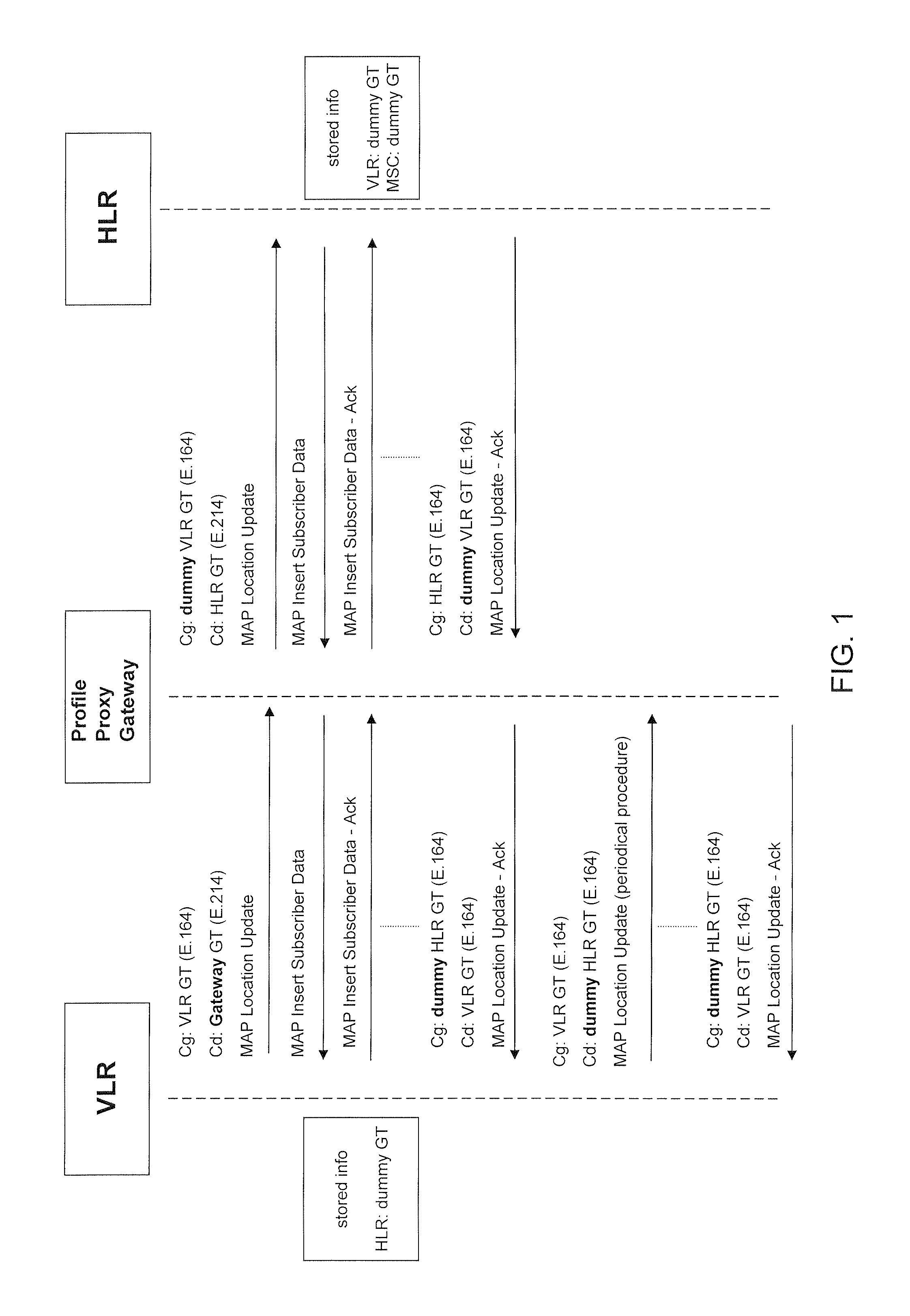
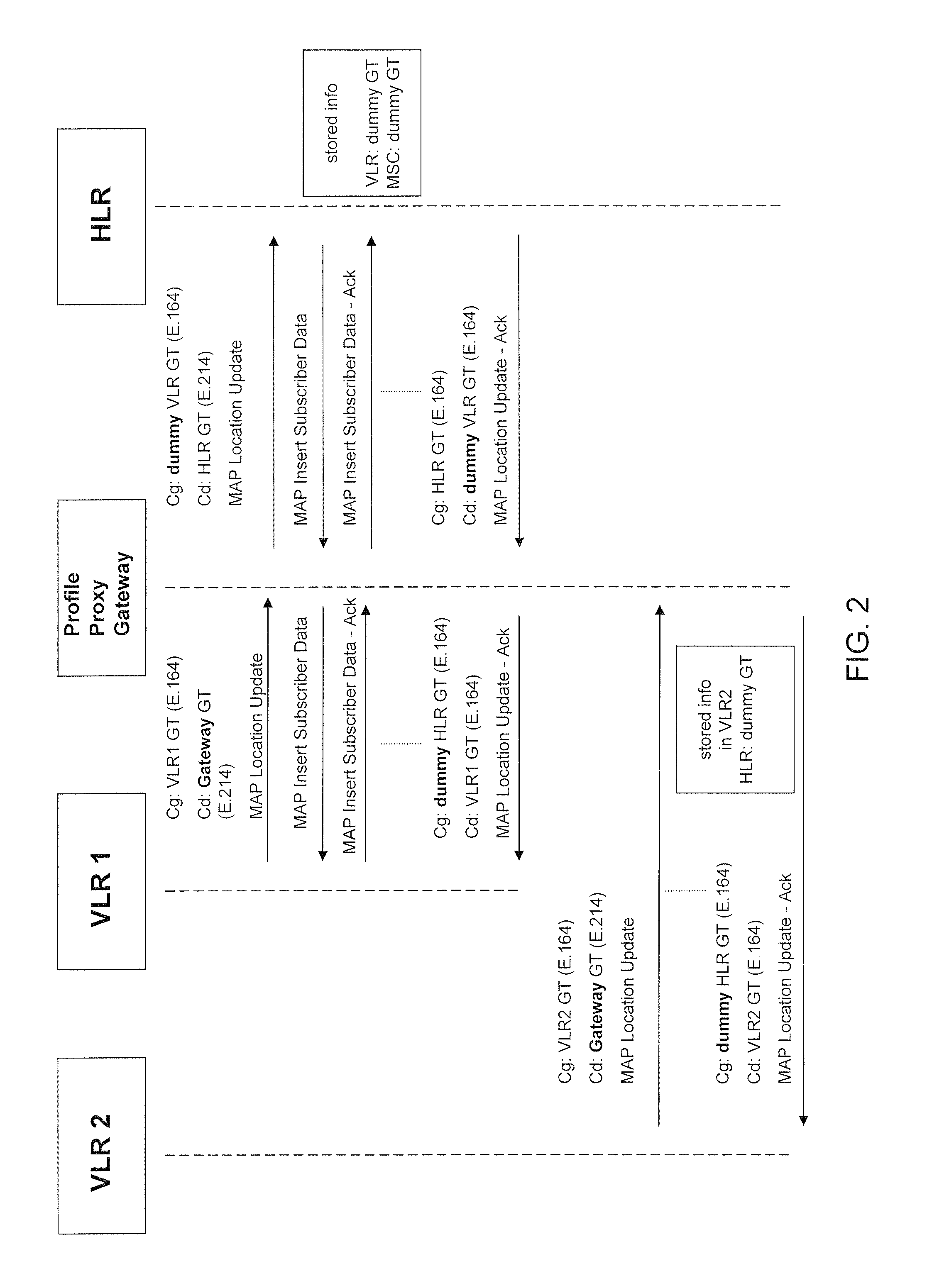
Method and system for ensuring service continuity in case of a proxy profile gateway failure or interruption
Aspects of the present invention relate to methods, systems and computer products that guarantee the availability of basic services to subscribers during the failure of a Proxy-Profile Gateway. An independent module equipped with monitoring probes for tracking the actual location of the end-customer, an interface for controlling the Gateway availability, and an active SS7 signaling interface are also provided, in order to initiate the recovery procedures, along with a database for storing the relevant information necessary to apply the restoration procedures.
Owner:MOBILEUM INC
System of wireless local area network based on transmit power control and method for controlling transmit power
InactiveUS20050250528A1Power managementTransmission control/equalisingTelecommunicationsTransmitted power
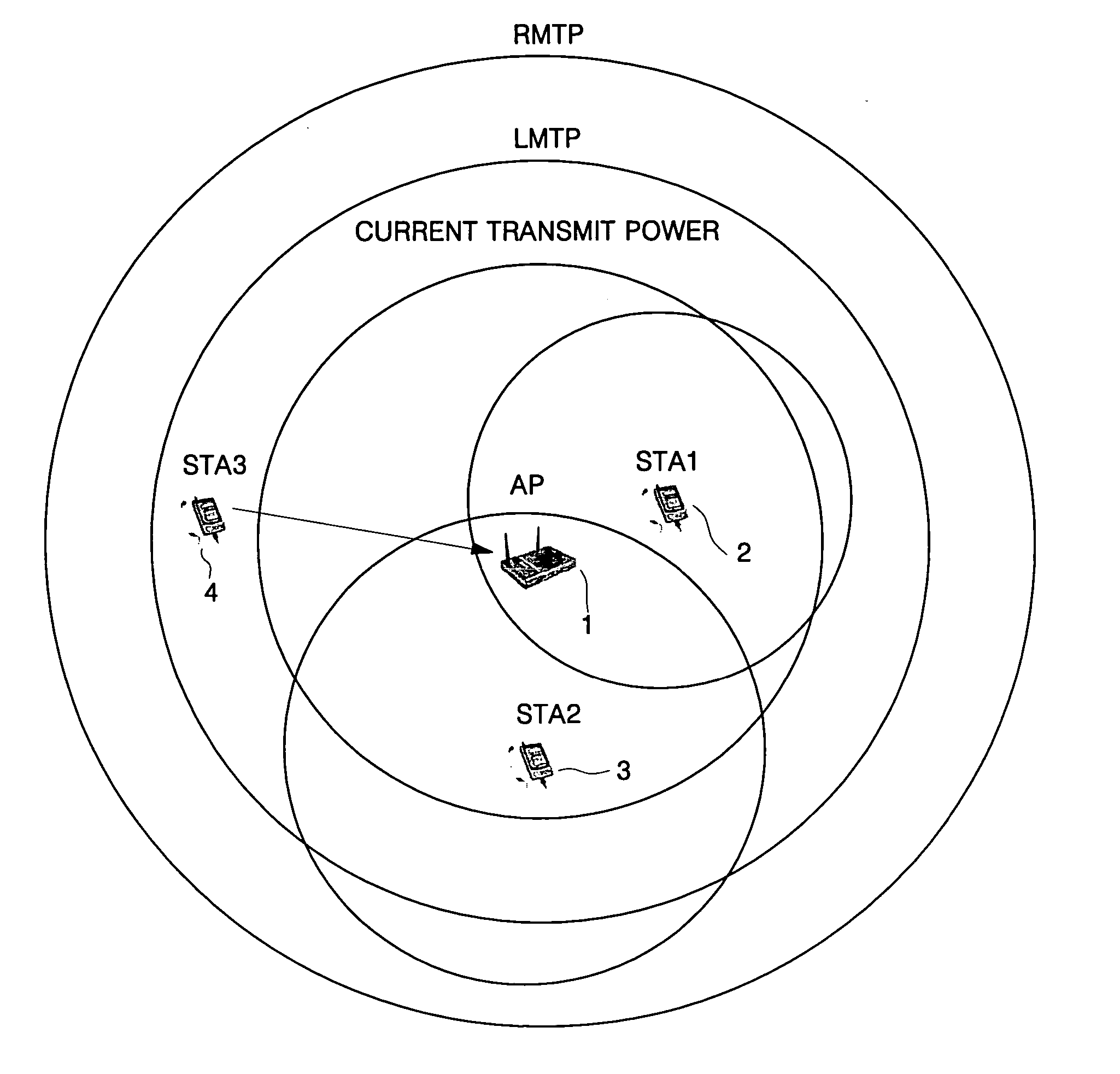
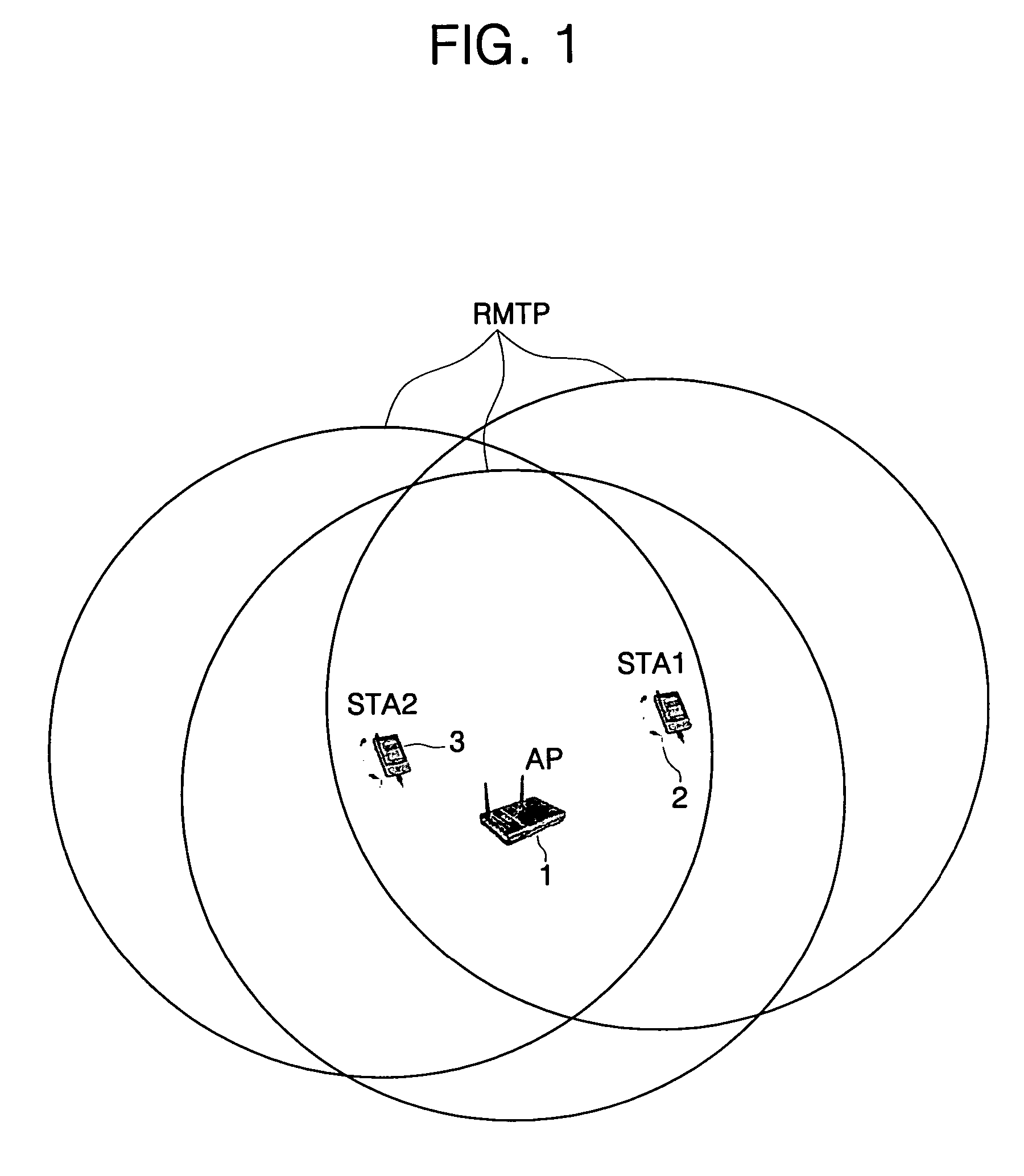
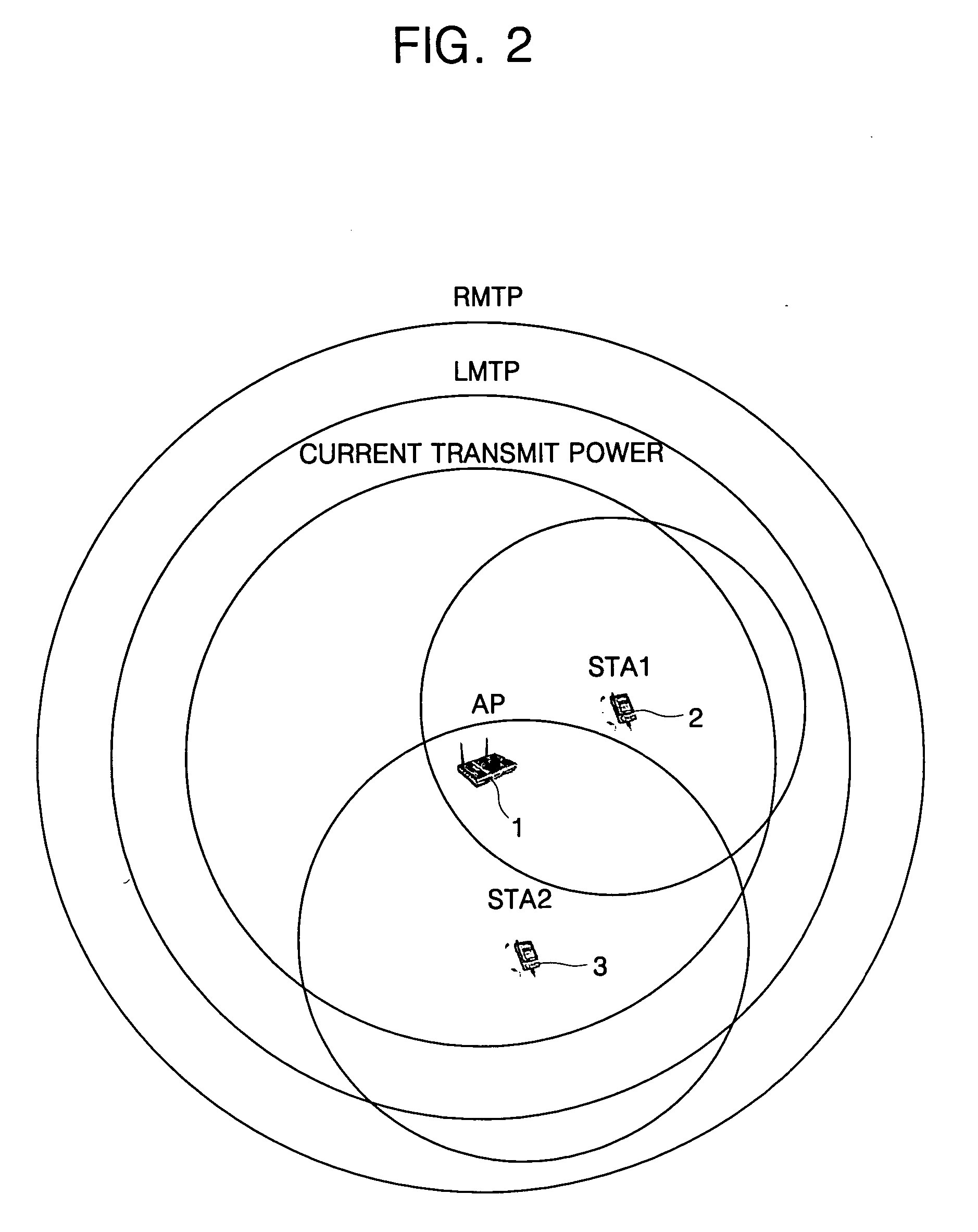
A system of a wireless local area network (LAN) based on transmit power control comprises: an access point (AP) for broadcasting a beacon frame to an area that is outside a service coverage of a first transmit power by using a second transmit power higher than the first transmit power already set when it reaches a set period, and for increasing the first transmit power if there is a request for increase of the first transmit power based on the beacon frame broadcast by the second transmit power; and a station which requests an increase in the first transmit power on the basis of the received beacon frame so as to enable the station to have an association with the AP. The increase is requested when the station receives the beacon frame broadcast from the AP with the second transmit power when the station is outside the service coverage of the first transmit power. The AP periodically transmits a strong beacon frame having local maximum transmit power (LMTP), and then provides a station existing outside the transmit power coverage of a current AP with basic service set (BSS) information. In this way, a newly approaching station can be provided with a basis for associating and communicating with the BSS with ease.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
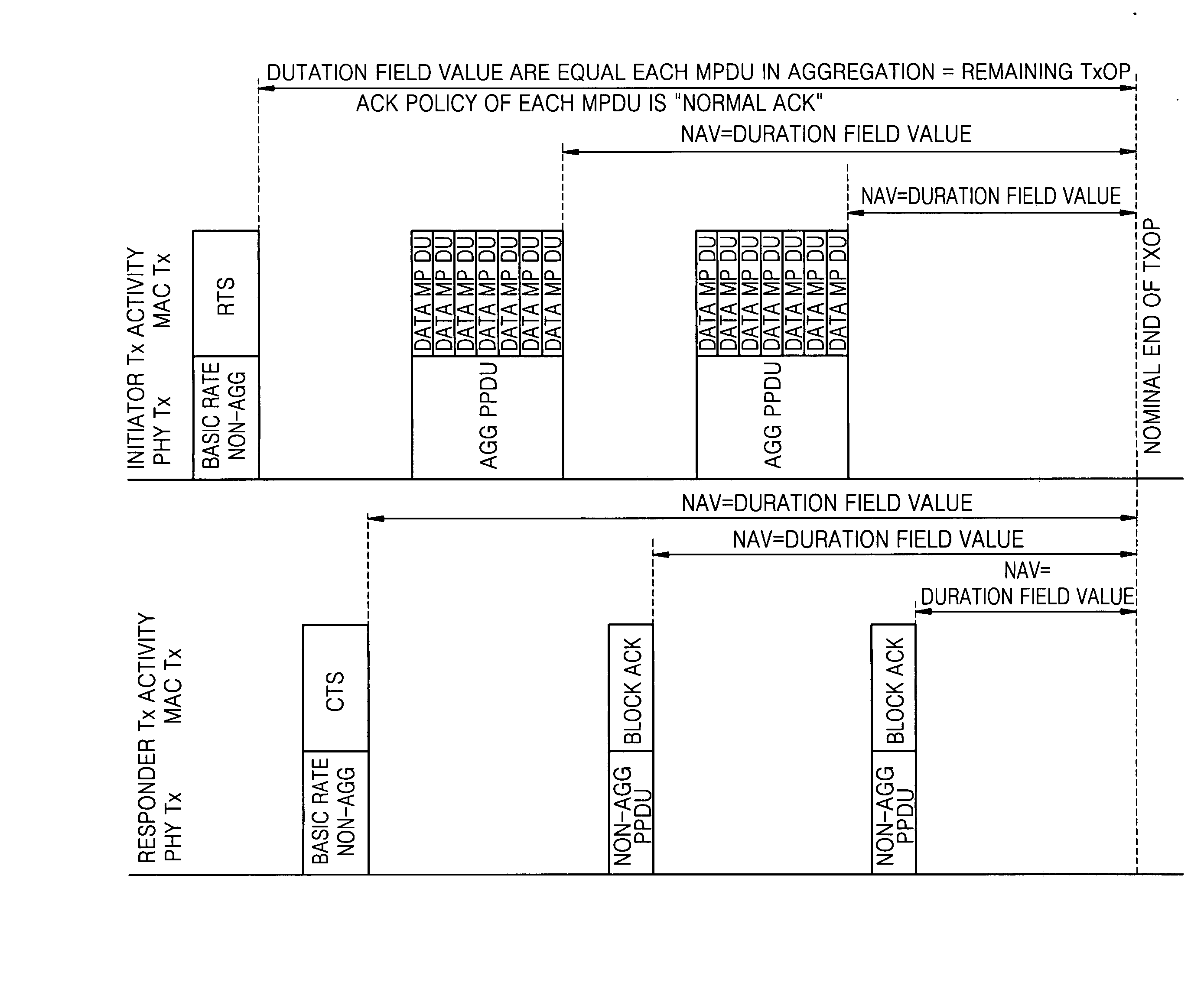
Collision avoidance in IEEE 802.11 contention free period (CFP) with overlapping basic service sets (BSSs)
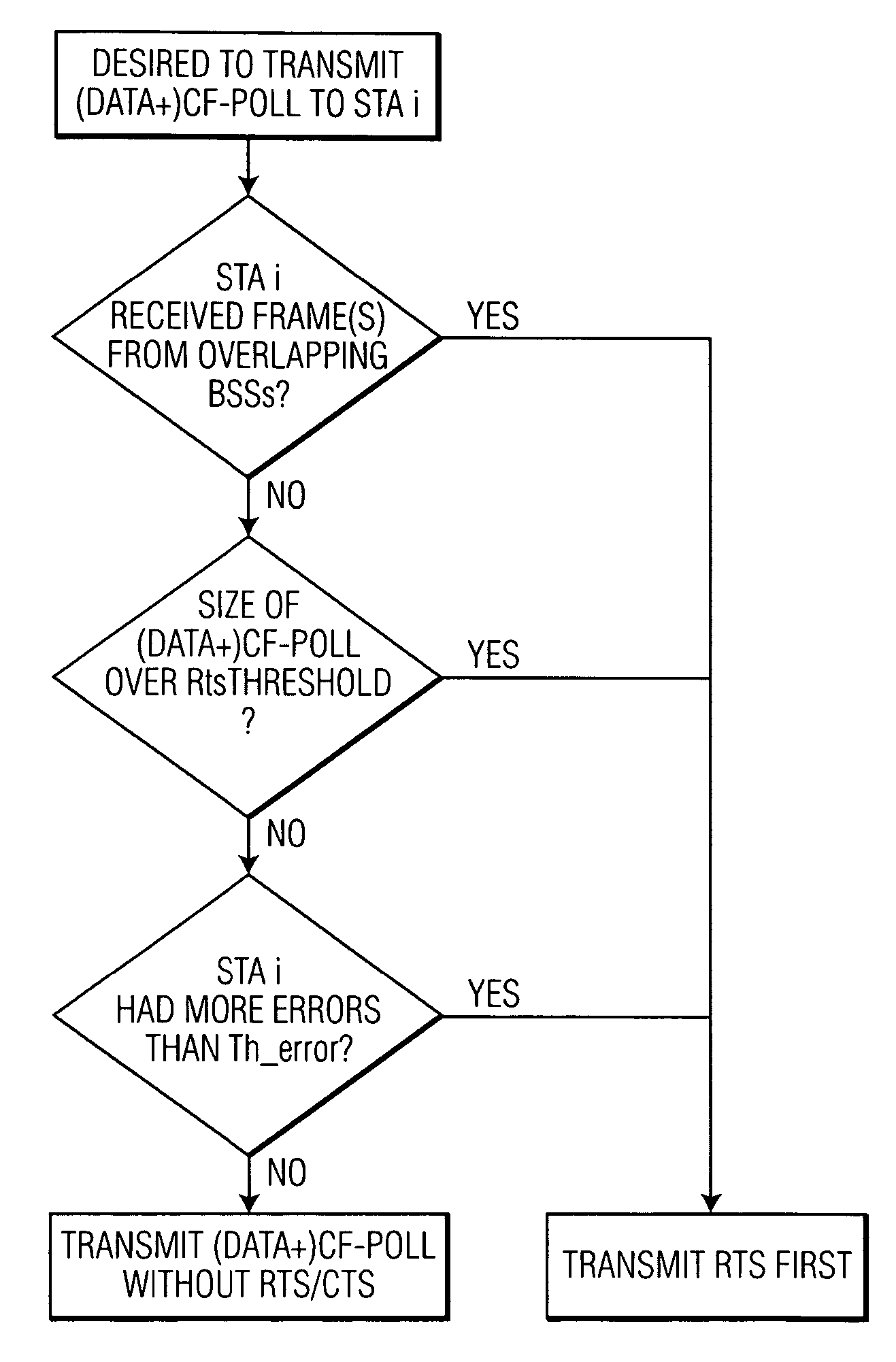
InactiveUS20060029073A1Improve efficiencyAvoid contentionNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationClear to sendBasic service
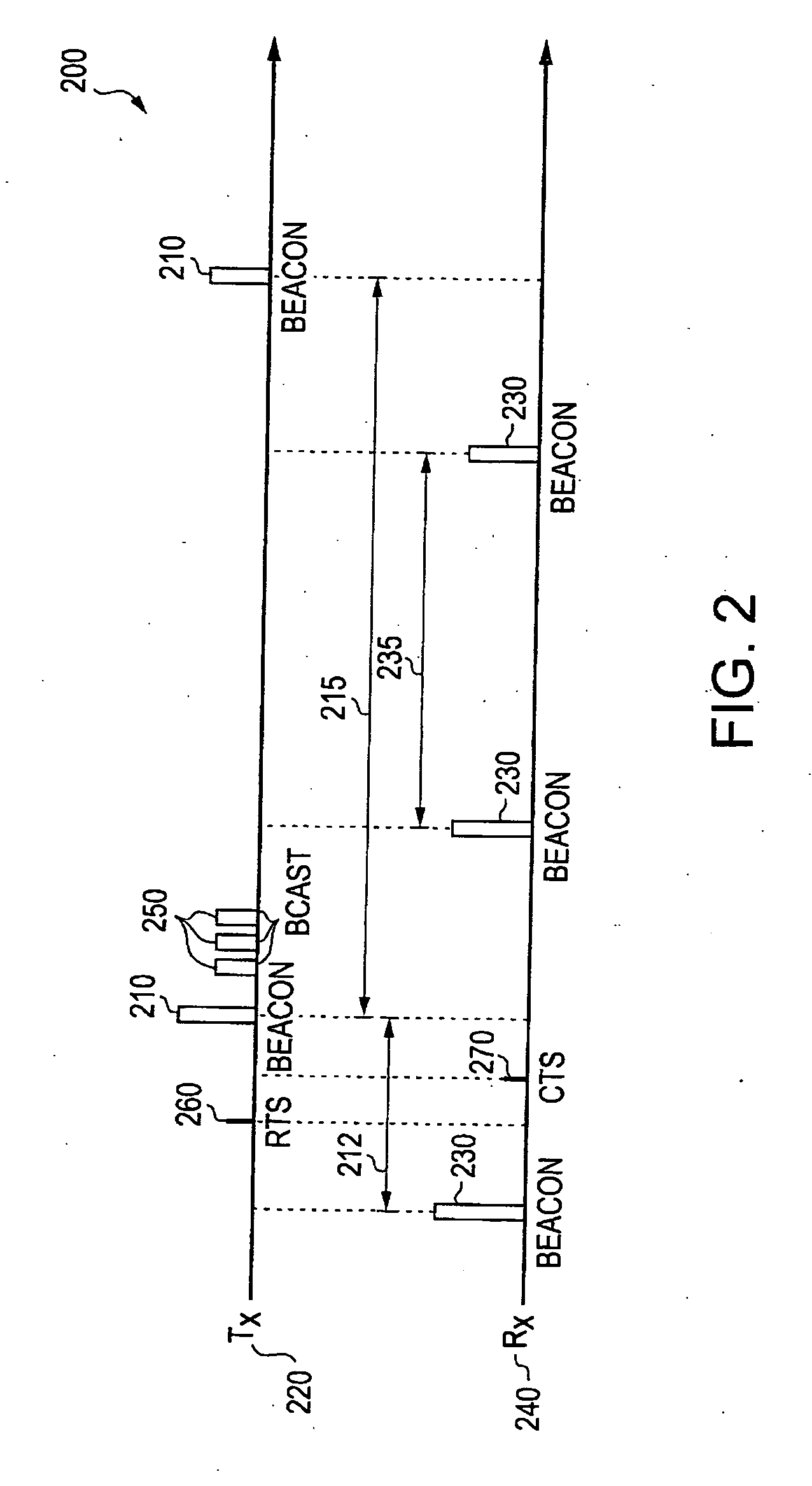
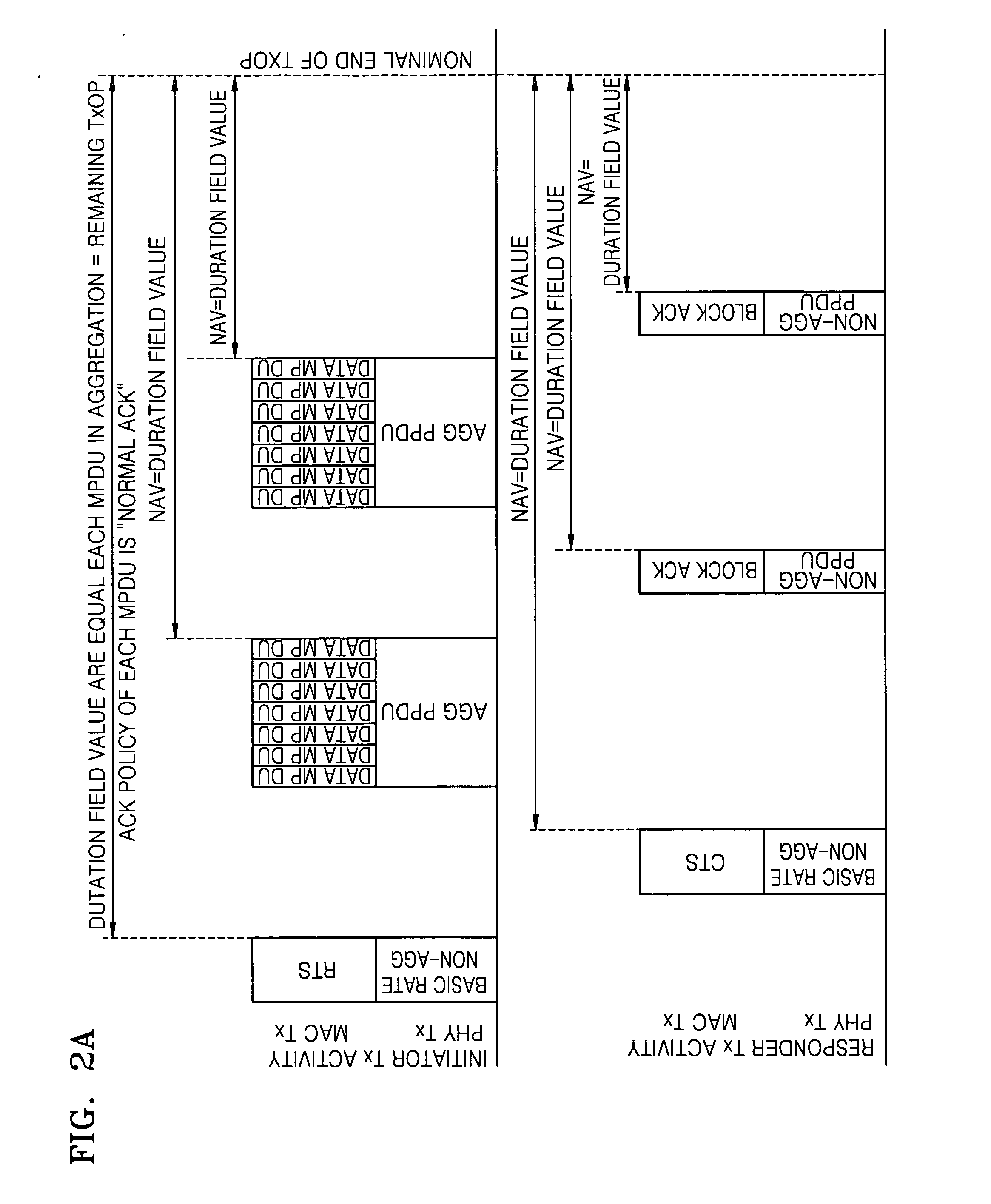
A medium access control (MAC) protocol is provided for avoiding collisions from stations (STAs) comprising two or more IEEE 802.11 basic service sets (BSSs) collocated and operating in the same channel during contention free periods (CFPs). The MAC protocol includes hardware / software for utilizing ready-to-send (RTS) / clear-to-send(CTS) exchange during CFPs to avoid potential collision from STAs in overlapping BSSs and hardware / software for providing overlapping network allocation vectors (ONAV) in addition to a network allocation vector (NAV), the ONAV included to facilitate the effectiveness of the RTS / CTS during CFPs.
Owner:CERVELLO GERARD +1
Method and apparatus for processing ppdu based on bss identification information in a high efficiency wireless LAN
Methods and apparatus for processing Physical layer Protocol Data Unit (PPDU) based on Basic Service Set (BSS) identification information in a High Efficiency WLAN (HEW) are described. An embodiment is a method for processing a PPDU by a station (STA) in a wireless local area network. The method may include determining whether the PPDU is transmitted from a different Basic Service Set (BSS) from a BSS to which the STA belongs or a same BSS as the BSS to which the STA belongs; and processing the PPDU using a first type of Clear Channel Assessment (CCA) threshold when the PPDU is determined to be transmitted from the different BSS, wherein the first type of CCA threshold is greater than a second type of CCA threshold which is used when the PPDU is determined to be transmitted from the same BSS.
Owner:ATLAS GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and Apparatus for Access Point Selection in Wireless LAN
ActiveUS20080102852A1Improve performanceSensitive to delay characteristicError preventionTransmission systemsTransmission throughputQos quality of service
A method and an apparatus select an access point (AP) in a wireless LAN to associate or reassociate, based on considerations that take into account the quality-of-service (QoS) status of the stations (STAs) and the potential hidden terminal effect. The method utilizes advertised or requested information obtained from an AP which includes the QoS status in each basic service set (BSS) and estimates the potential hidden terminal (HT) effect based on local channel sensing by the STA. The method selects the AP in a manner that reduces the possibility of collision from equal and higher priority HTs, thus providing greater transmission throughput and improving performance.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
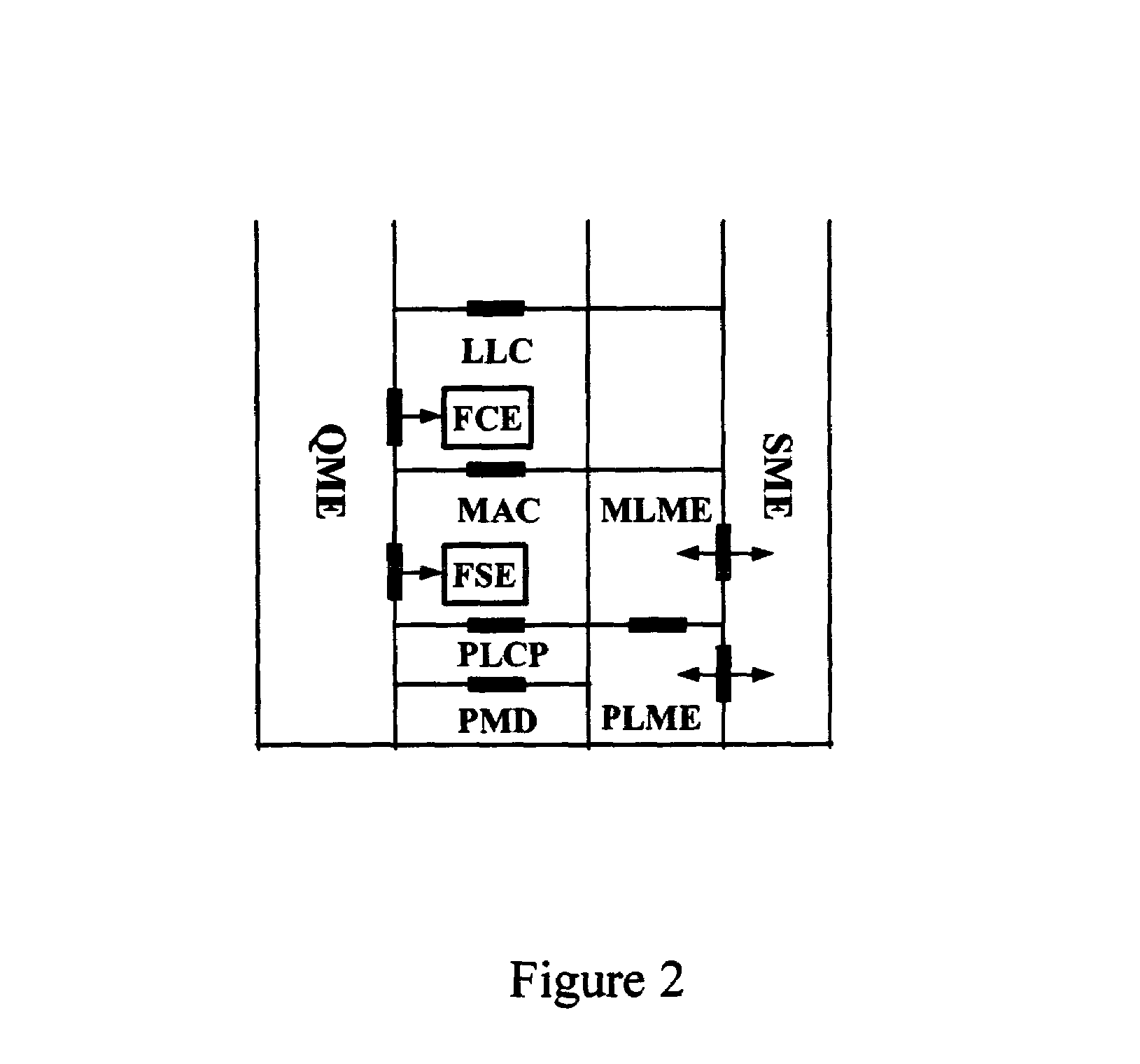
In-band QoS signaling refernce model for QoS-driven wireless lans
InactiveUS20050041670A1Function increaseError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsQuality of serviceFrame based
A station, such as a point coordinator (PC) or a non-PC station, in a basic service set (BSS) in a wireless local area network (WLAN) is disclosed. The station includes a frame classification entity (FCE), a frame scheduling entity (FSE) and a QoS management entity (QME). The FCE is logically located in a logical link control (LLC) layer of the station and has a classification table containing at least one classifier entry. Each classifier entry contains a virtual stream identifier (VSID) and a frame classifier associated with a user session. The FCE receives a data frame associated with the user session, which can be one of a voice session, a video session, a data session and a multimedia session. The data frame contains in-band quality of service (QoS) signaling information for the user session. The FCE classifies the received data frame to a selected VSID contained in a classifier entry in the classification table based on a match between an in-band frame classification information contained in the received frame and the frame classifier contained in the classifier entry. The FSE is logically located in a medium access control (MAC) sublayer of the station and has a frame scheduling table containing at least one entry. Each entry in the frame scheduling table contains a VSID and a QoS parameter set associated with a user session identified by the VSID. The FSE is responsive to the classified data frame by scheduling a transmission opportunity (TO) for the classified data frame based on the at least one QoS parameter value associated with the VSID and characterizing the user session. The QME interfaces with the FCE and The FSE.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Multipoll for QoS-Driven wireless LANs
InactiveUS7039032B1Enhanced channel accessNetwork traffic/resource managementElectric testing/monitoringQuality of serviceWireless lan
A method and a system are disclosed for providing quality of service (QoS)-driven channel access within a basic service set (BSS) in a wireless network. A point coordinator (PC) station determines whether at least one of upstream traffic and side-stream traffic is scheduled to be transmitted from at least one non-PC station At least one available TO is allocated to each selected non-PC having at least one traffic to transmit. A multipoll frame containing information relating to at least two allocated TOs is then sent from the PC station containing information relating to each allocated TO.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Wireless LAN handover method, wireless terminal, program product for use in the wireless terminal, and wireless communications system
InactiveUS20060079232A1Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityEnergy efficient ICTPower managementCommunications systemBasic service
A wireless terminal is associated with a Basic Service Set (BSS) or an Independent Basic Service Set (IBSS). The wireless terminal notifies the currently associated target of transition into power saving mode, before migrating from the currently associated BSS or IBSS to another BSS or IBSS. Subsequently, the wireless LAN terminal starts searching for another BSS or IBSS which is the next candidate target to be associated with.
Owner:NEC CORP
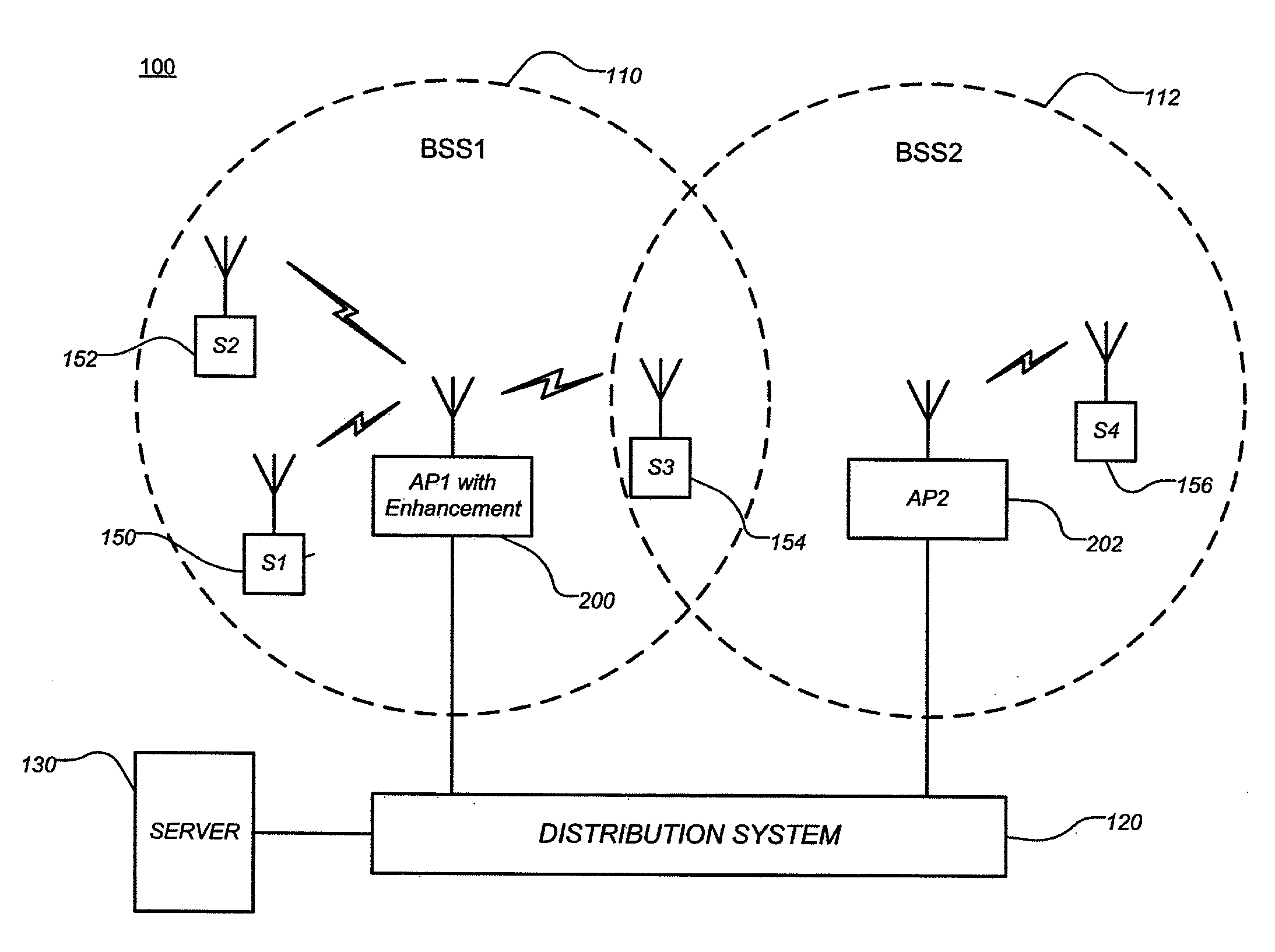
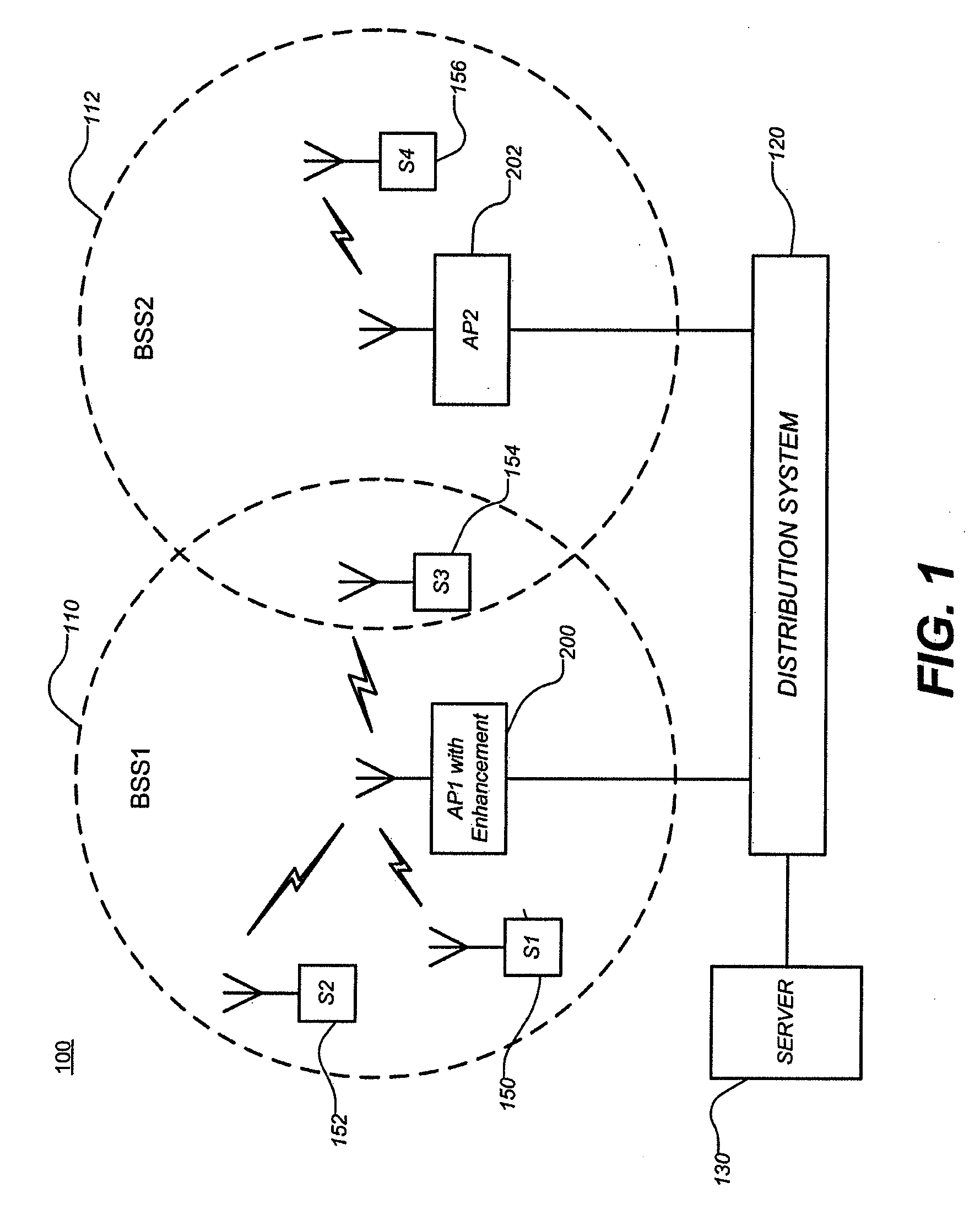
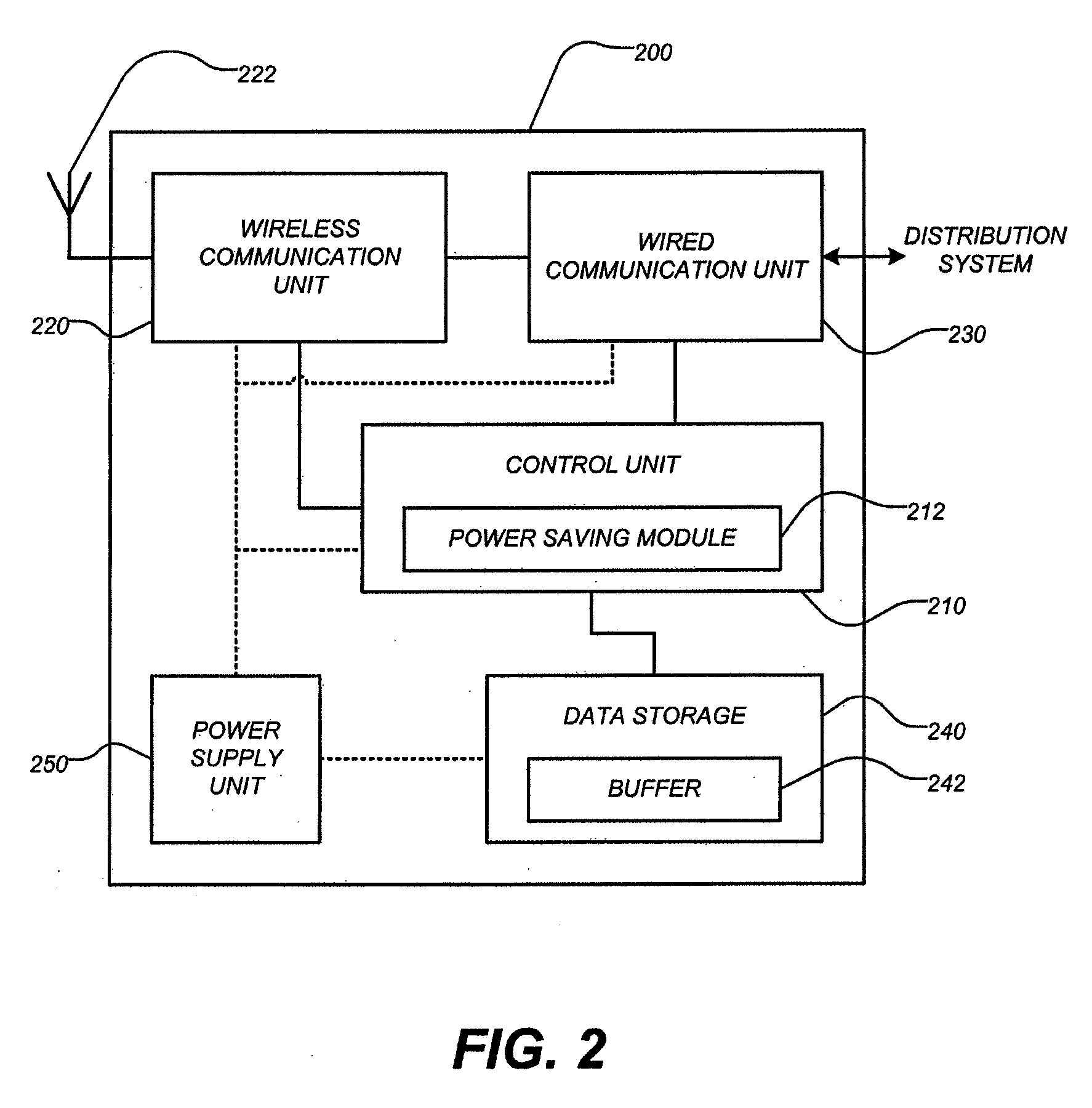
Portable ap enhancements
An access point configured to connect a station to a wireless network includes a wireless communication unit configured to send data to the station, and a control unit configured to adjust one or more operational parameters of the access point based on indicative parameters of a basic service set (BSS), which includes the access point and the station.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Access point for providing WLAN virtualization, WLAN virtualization system and method of providing access to wireless communication network
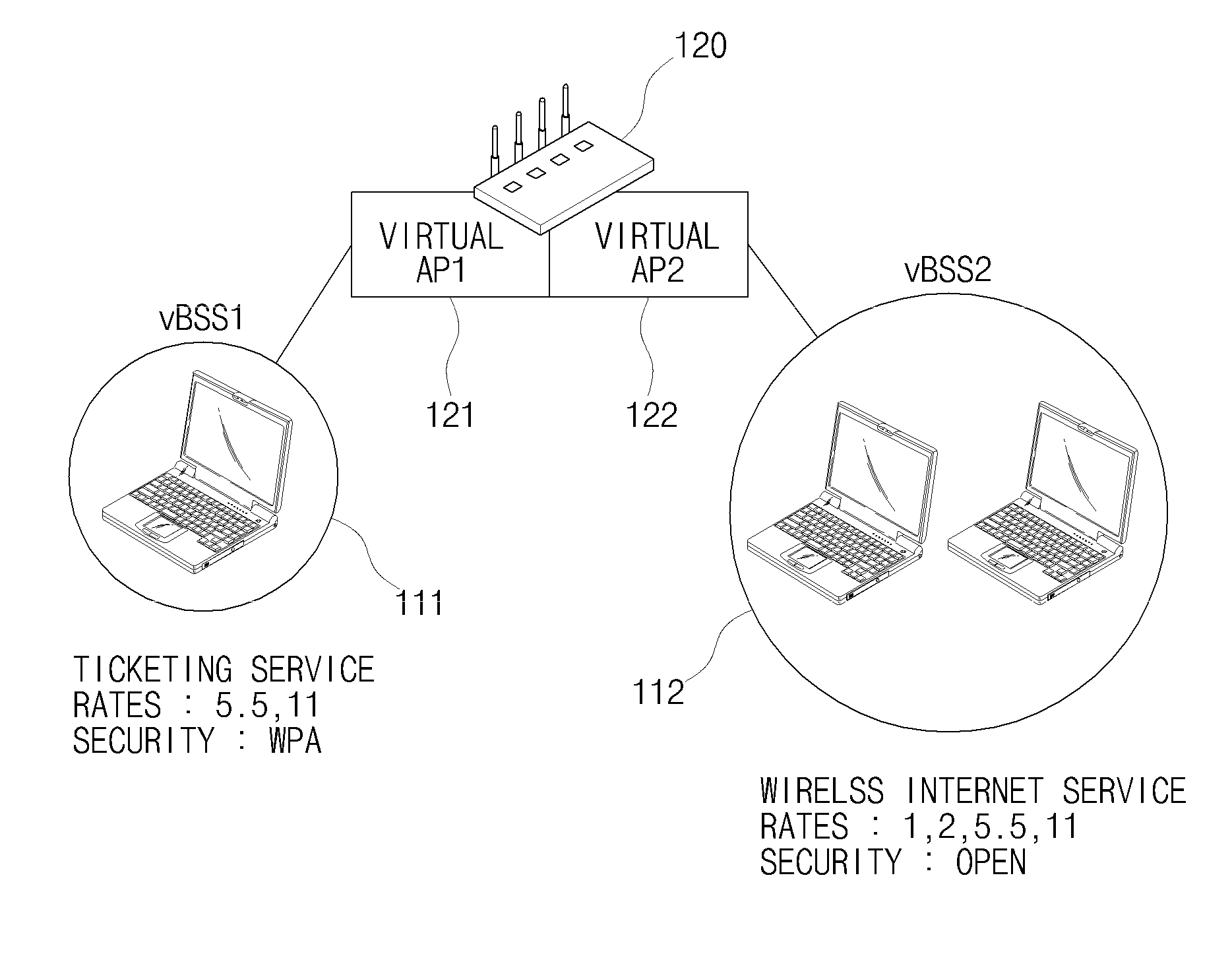
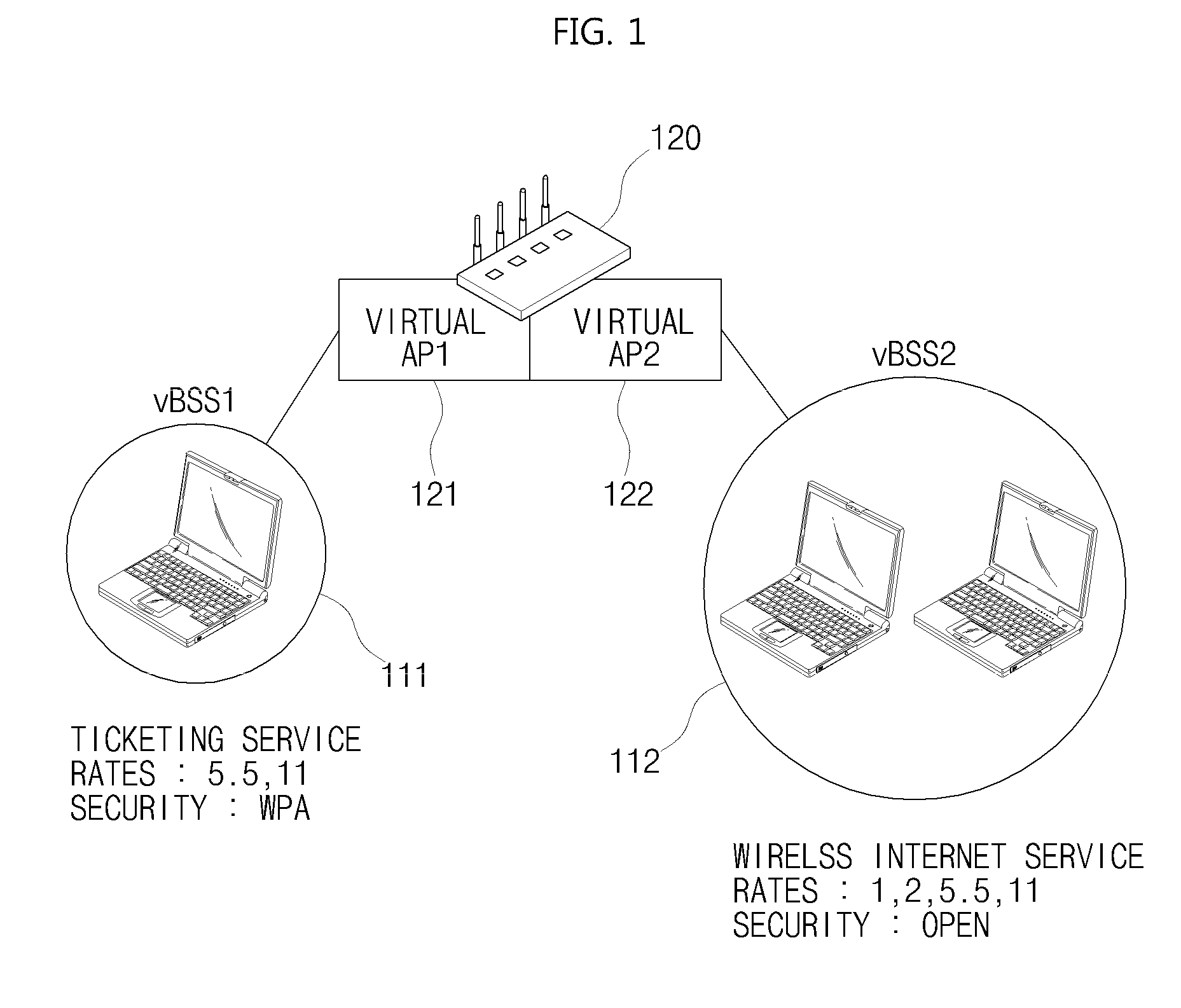
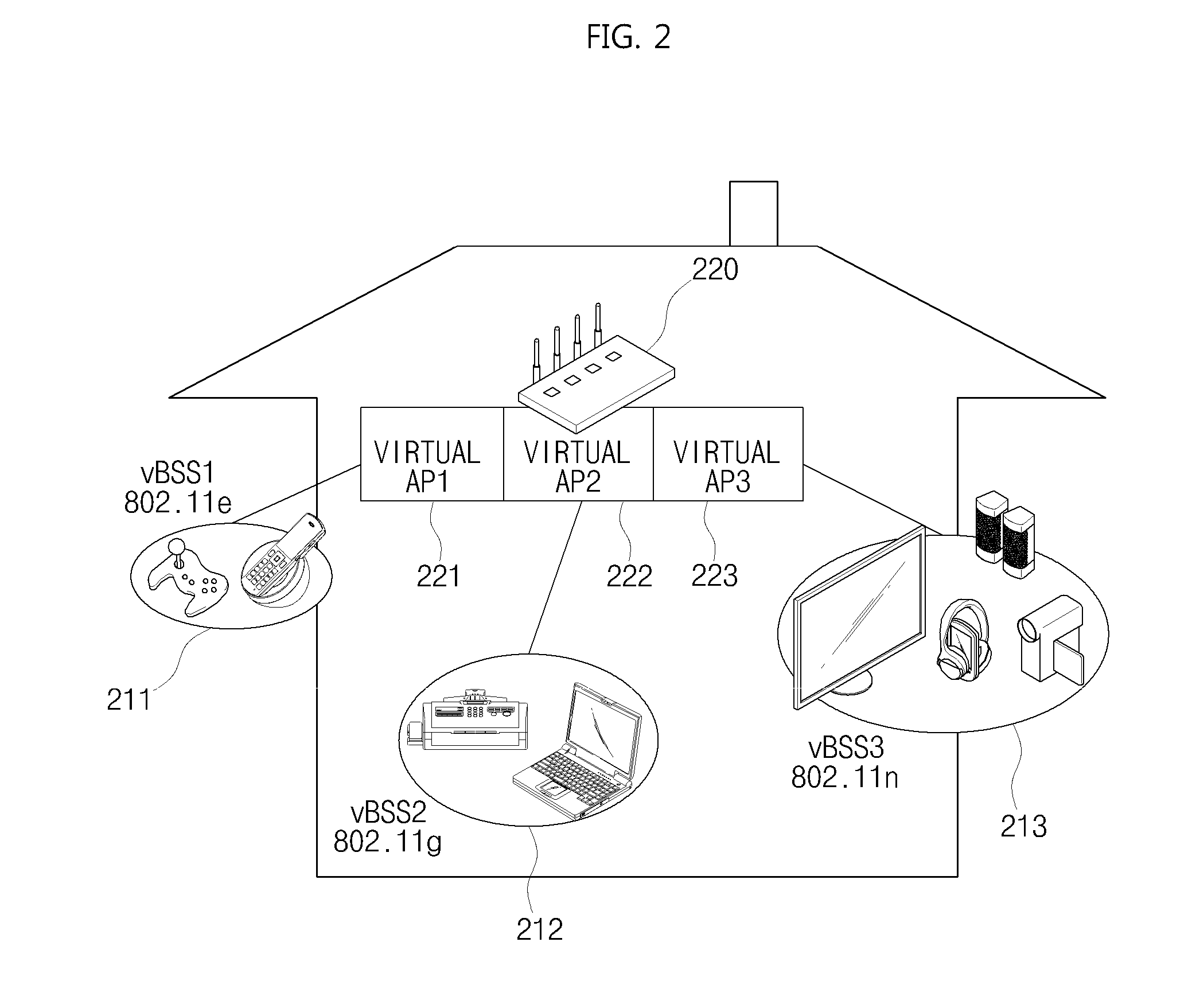
ActiveUS20110013608A1Guaranteed independenceImprove throughputNetwork topologiesLoop networksVirtualizationService provision
The present invention relates to a WLAN virtualization system which is capable of efficiently separating a Basic Service Set (BSS) into a plurality of virtual BSSs in a Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) manner. The WLAN virtualization system includes an Access Point (AP) for providing a plurality of vBSSs, and a plurality of stations corresponding to the vBSSs provided by the AP. Each of the vBSSs is operated on a superframe basis, the superframe being scheduled by a beacon frame transmitted from the AP. The superframe includes the beacon frame, one contention-free period, and one contention period. The CPs of the vBSSs include intervals which do not overlap each other. The vBSSs can be classified into any groups designated by a service provider based on certain criteria such as physical layer, QoS, security level, or network access authority, and times can be allocated to superframes at different rates or frequencies.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Method and apparatus for transmitting control frame to hidden node in wireless LAN
ActiveUS20070217352A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork traffic/resource managementTime informationTelecommunications
A method and apparatus informs nodes included in a wireless local area network (LAN) of how to avoid access collision in a wireless LAN. A wireless LAN access point or an independent basic service set (IBSS) control station receives a Contention-Free-End (CF-End) frame, compares a basic service set ID (BSSID) of the received CF-End frame of the access point or the IBSS, and rebroadcasts the received CF-End frame if the comparison result indicates that the two BSSIDs coincide with each other. Thus, all stations included in one BSS can receive the same time information for controlling medium access.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com