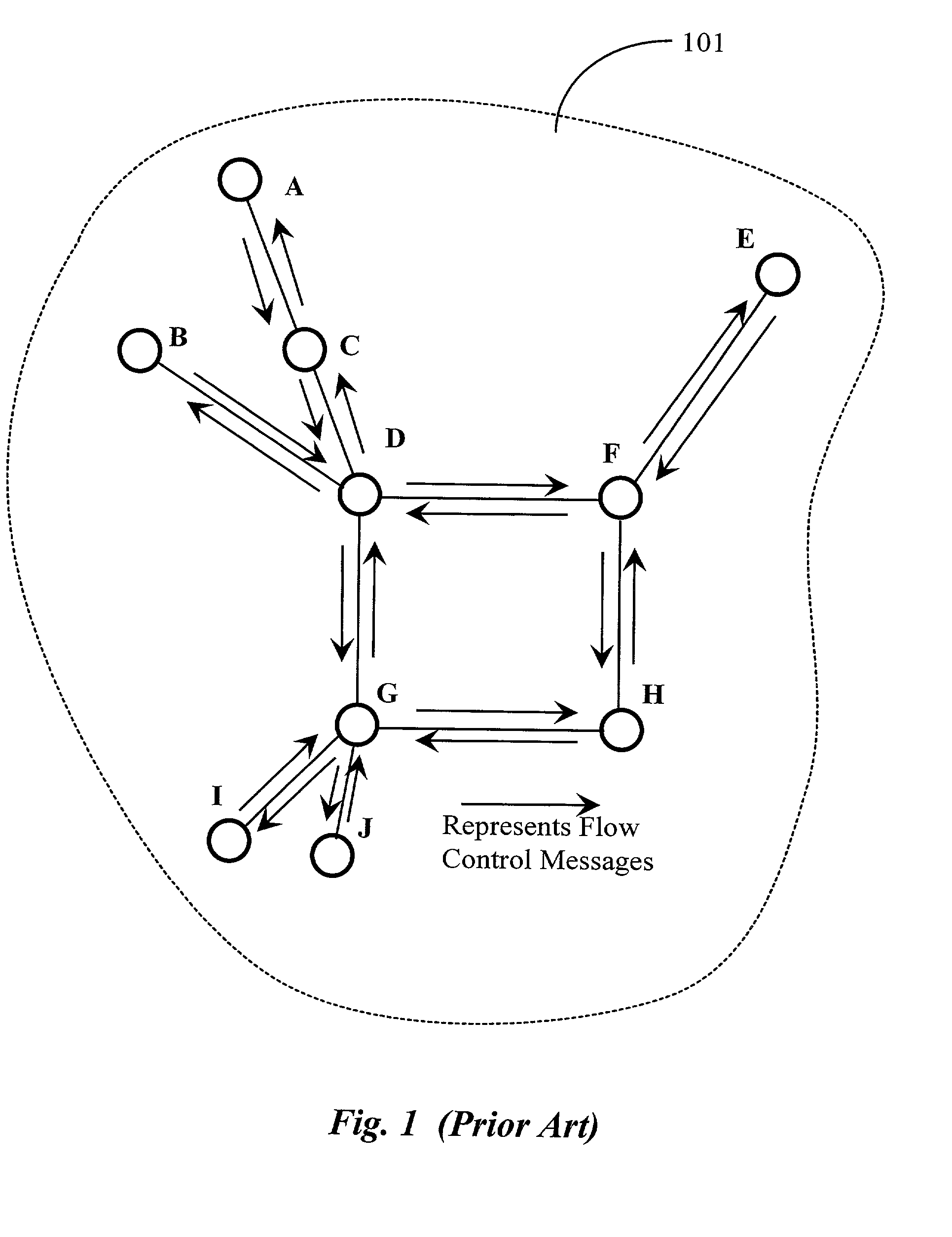
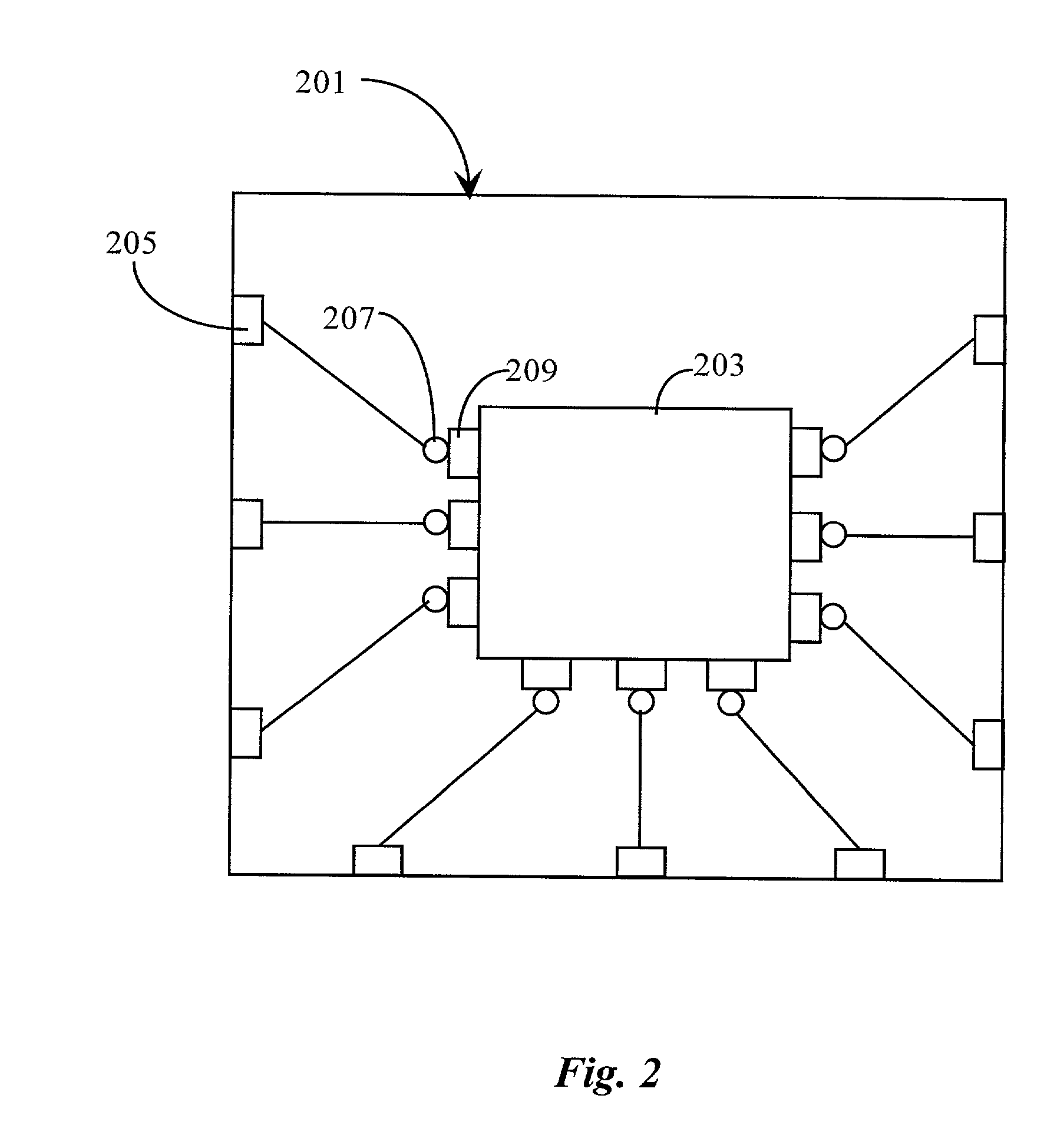
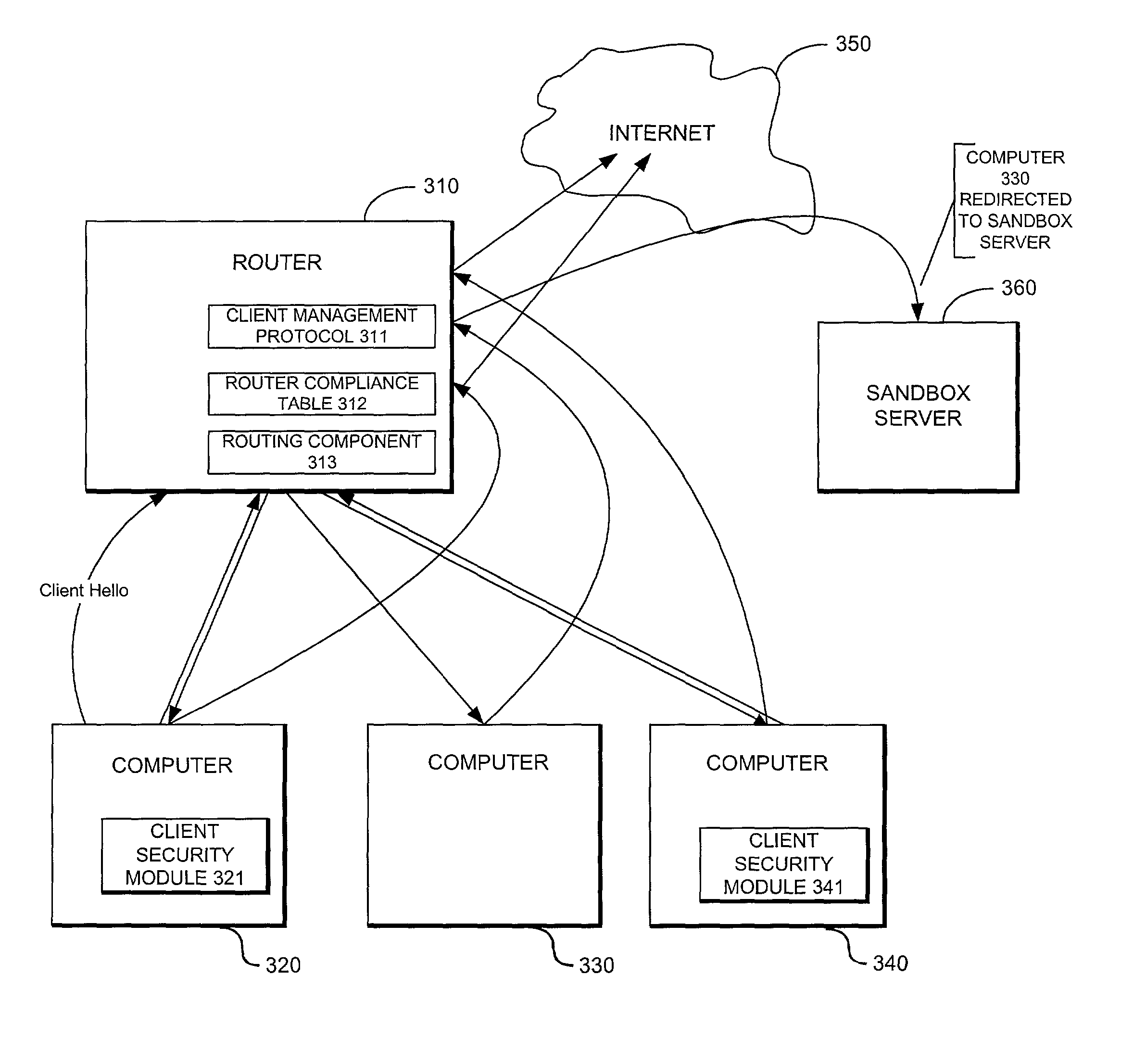
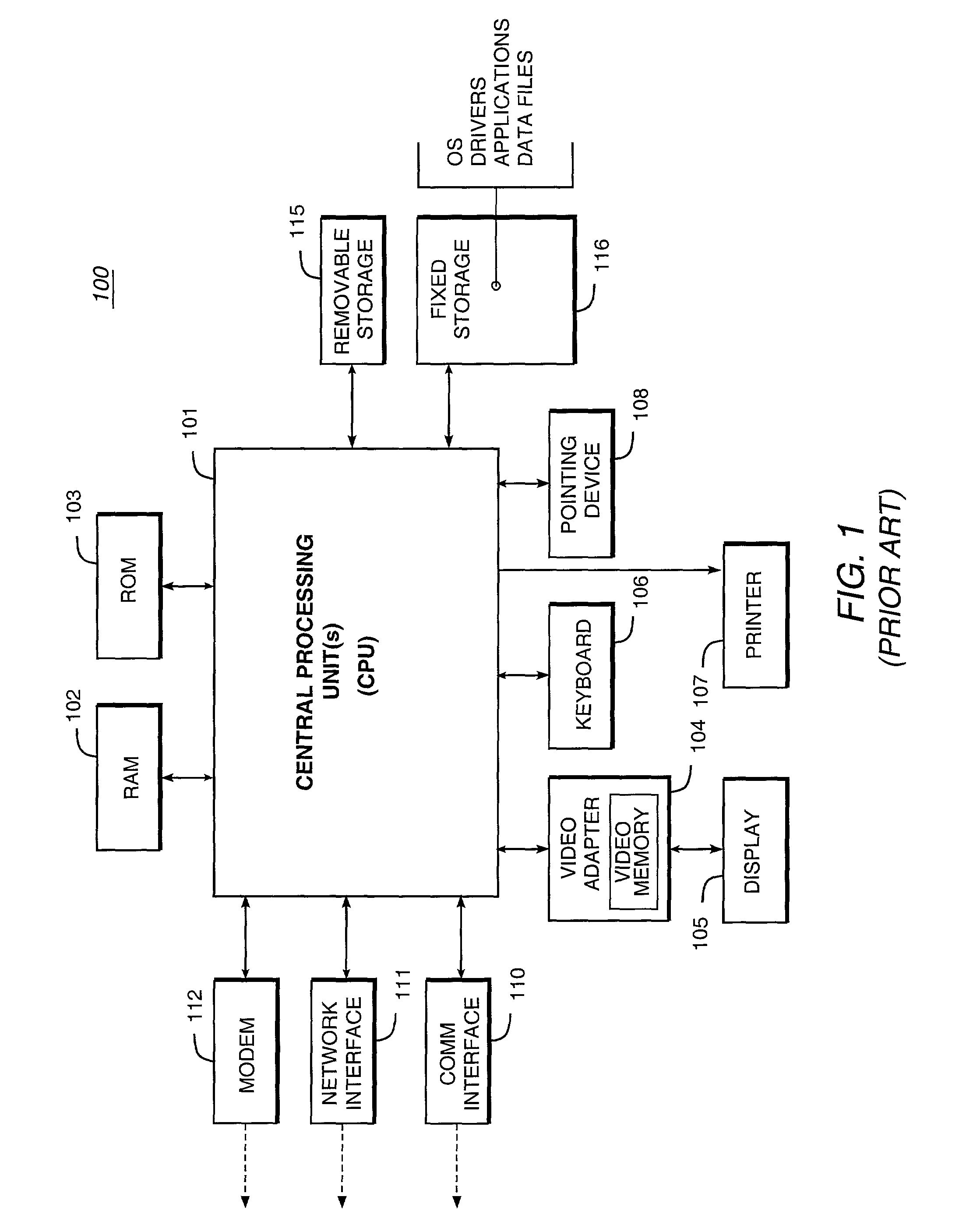
Patents
Literature
4816 results about "Router" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
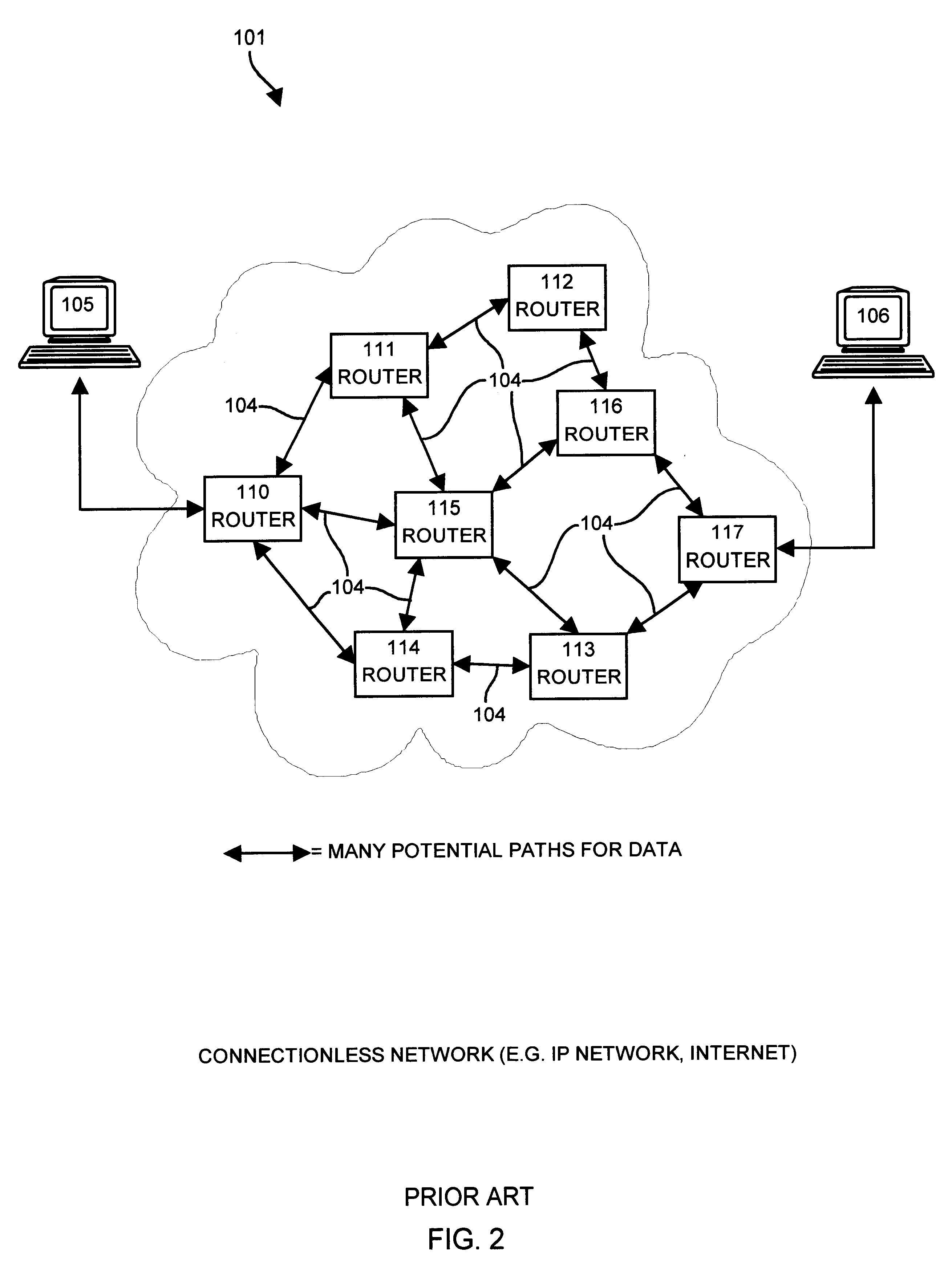
A router is a hand tool or power tool that a worker uses to rout (hollow out) an area in relatively hard material like wood or plastic. Routers are mainly used in woodworking, especially cabinetry. Routers are typically handheld or fastened cutting end-up in a router table.
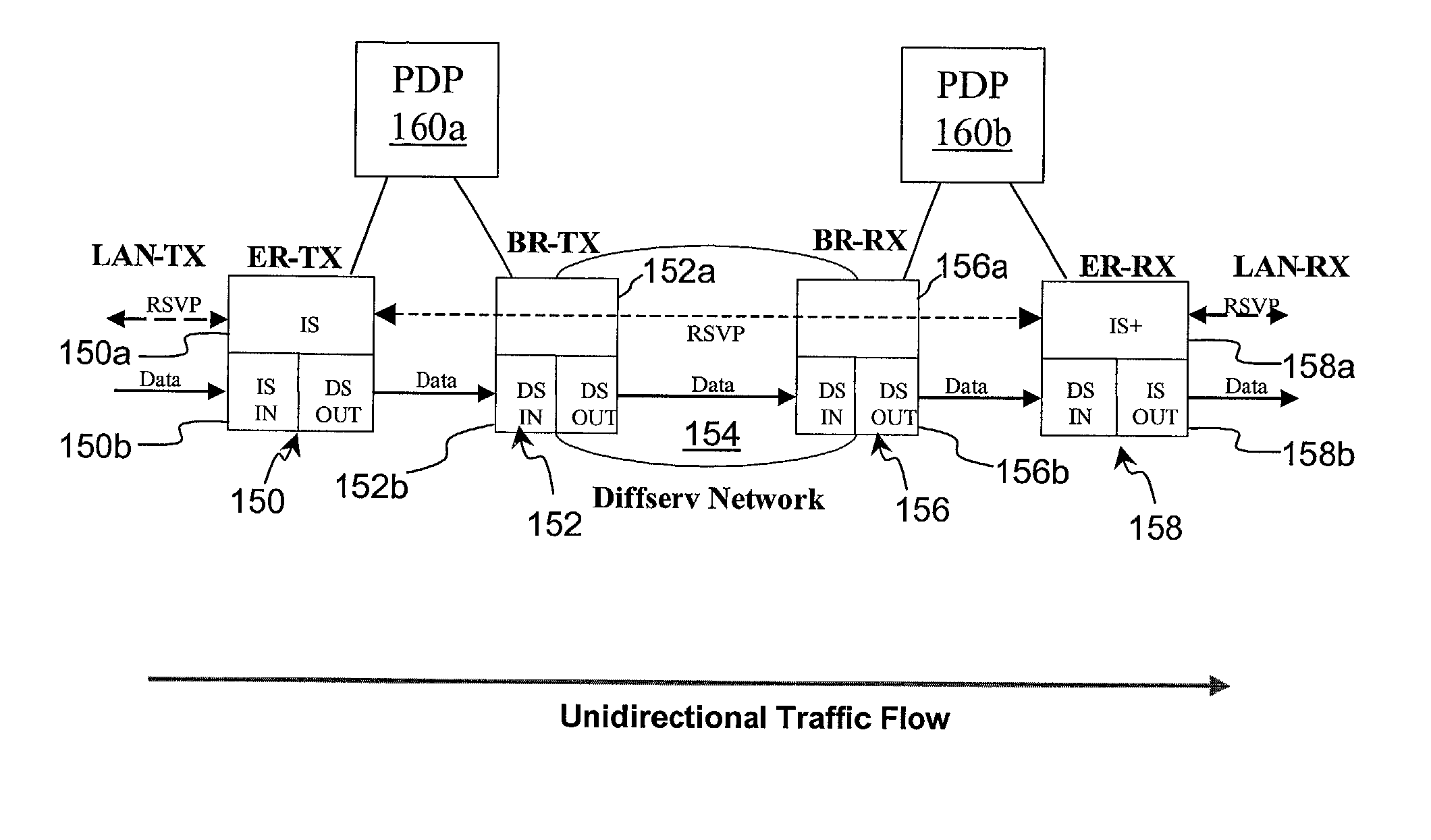
Policy-based synchronization of per-class resources between routers in a data network
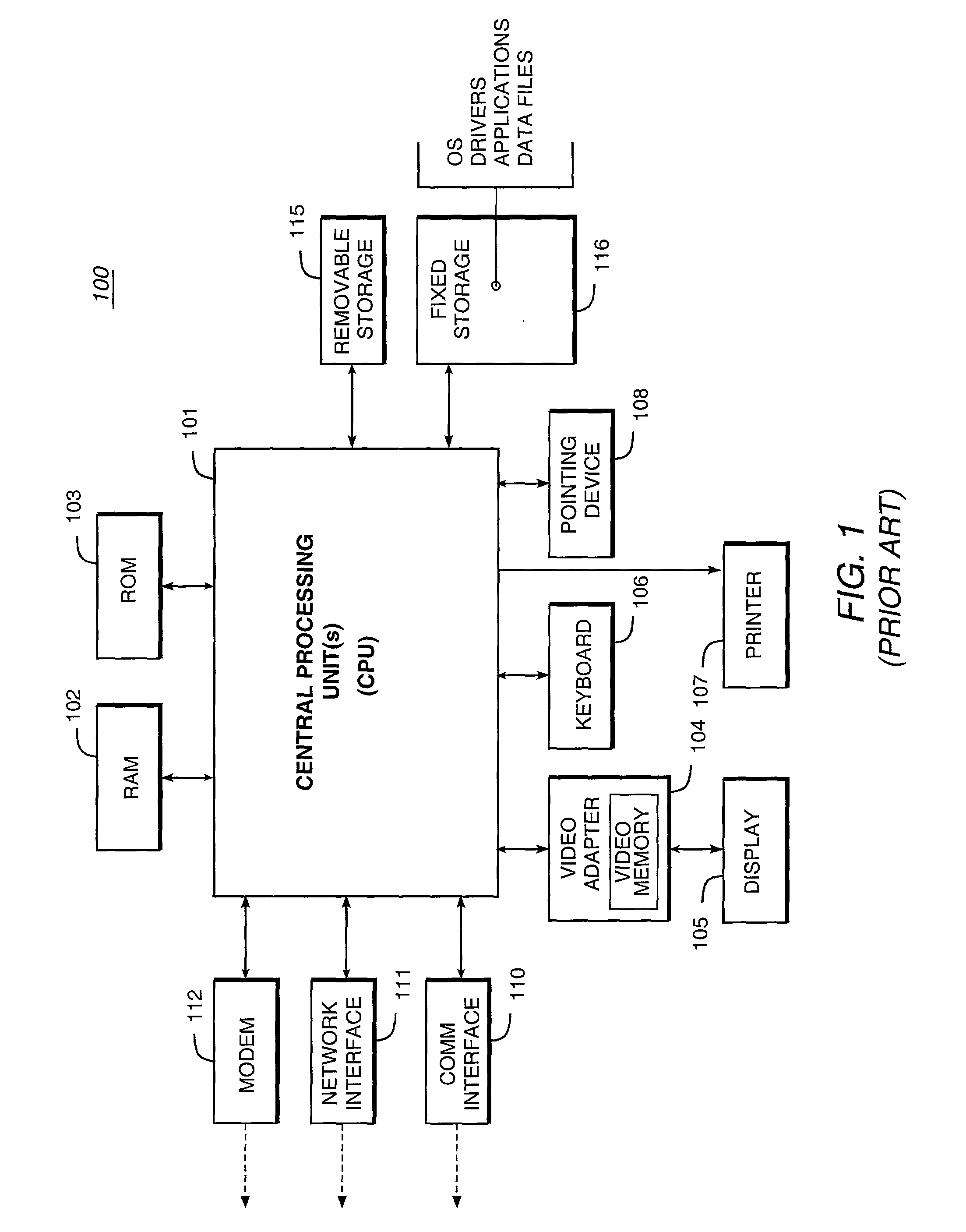
ActiveUS20020194369A1Multiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlCommunication interfaceData stream
A data network may include an upstream router having one or more data handling queues, a downstream router, and a policy server. In one embodiment, the policy server includes processing resources, a communication interface in communication with the processing resources, and data storage that stores a configuration manager executable by the processing resources. The configuration manager configures data handling queues of the upstream router to provide a selected bandwidth to one or more of a plurality of service classes of data flows. In addition, the configuration manager transmits to the downstream router one or more virtual pool capacities, each corresponding to a bandwidth at the upstream router for one or more associated service classes among the plurality of service classes. In one embodiment, the configuration manager configures the data handling queues on the upstream router only in response to acknowledgment that one or more virtual pool capacities transmitted to the downstream router were successfully installed.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
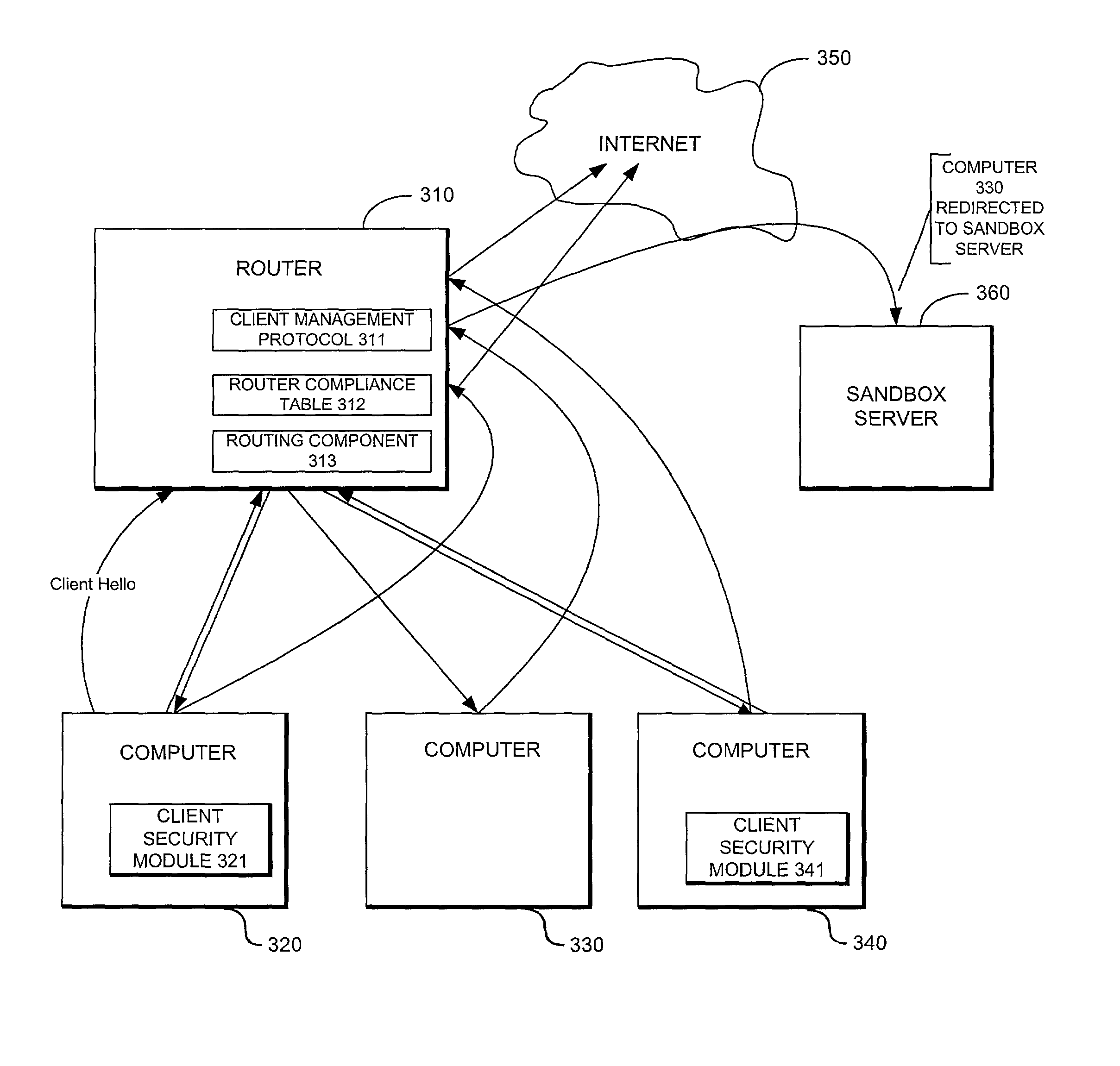
System providing internet access management with router-based policy enforcement
ActiveUS20030055962A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionInternet accessApplication software
A computing environment with methods for monitoring access to an open network such as the Internet, is described. The system includes one or more client computers, each operating applications (e.g., Netscape Navigator or Microsoft Internet Explorer) requiring access to an open network, such as a WAN or the Internet, and a router or other equipment that serves a routing function (e.g., a cable modem) for the client computers. A centralized security enforcement module on the router maintains access rules for the client computers and verifies the existence and proper operation of a client-based security module on each client computer. The router-side security module periodically sends out a router challenge via Internet broadcast to the local computers on the network. If the client-side security module is installed and properly operating, the client-side security module responds to the router challenge. The responses received by the router-side security module are maintained in a table. Each time the router receives a request from a client computer to connect to the Internet, the router-side security module reviews the table and analyzes whether or not the computer requesting a connection to the Internet properly responded to the most recent router challenge. If it determines that the computer has properly responded to the router challenge, then it permits the computer to connect to the Internet. If a computer has not properly responded or if a computer has not answered the router challenge, then the computer is not allowed to connect to the Internet as requested.
Owner:CHECK POINT SOFTWARE TECH INC
Applying blocking measures progressively to malicious network traffic
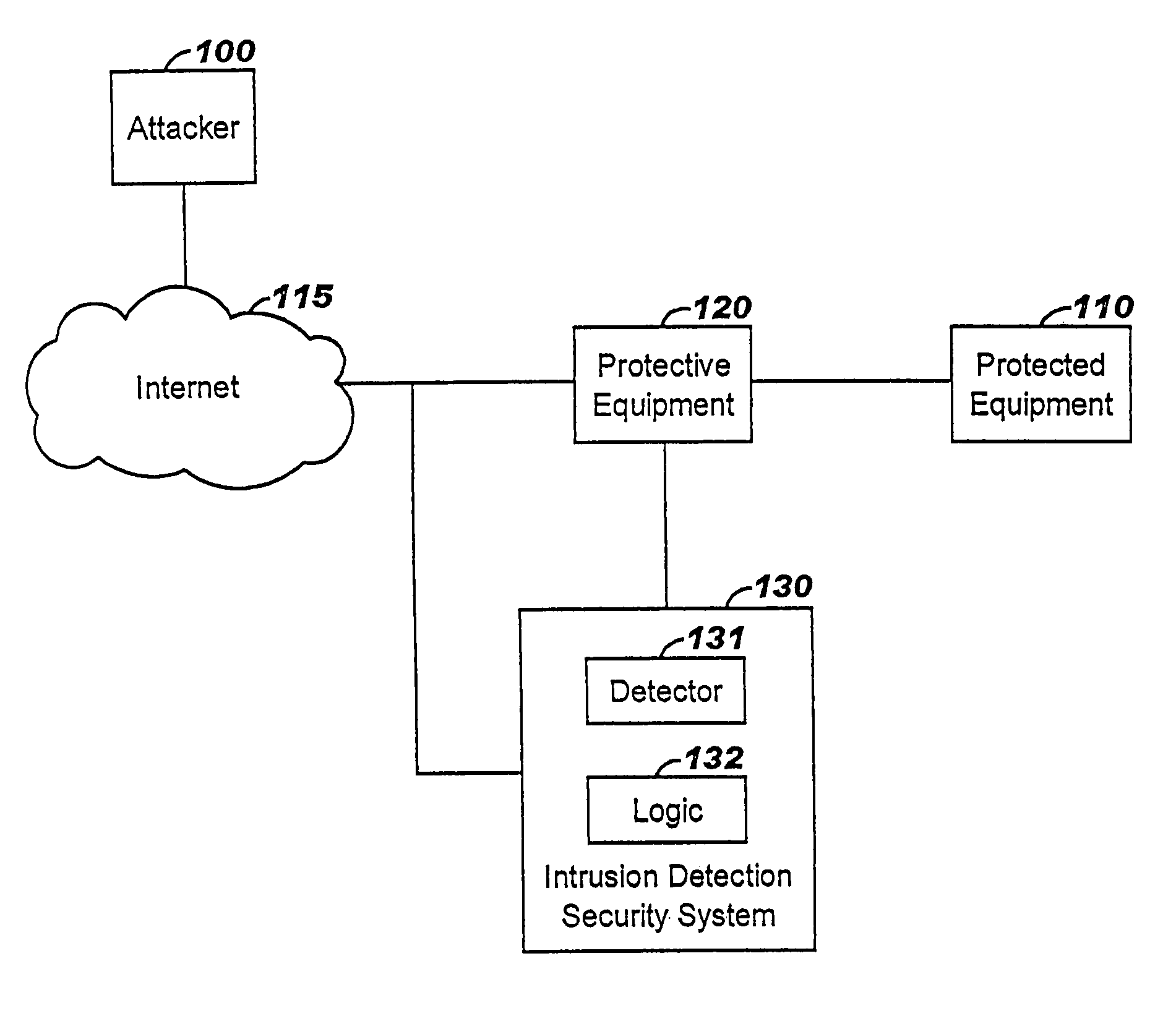
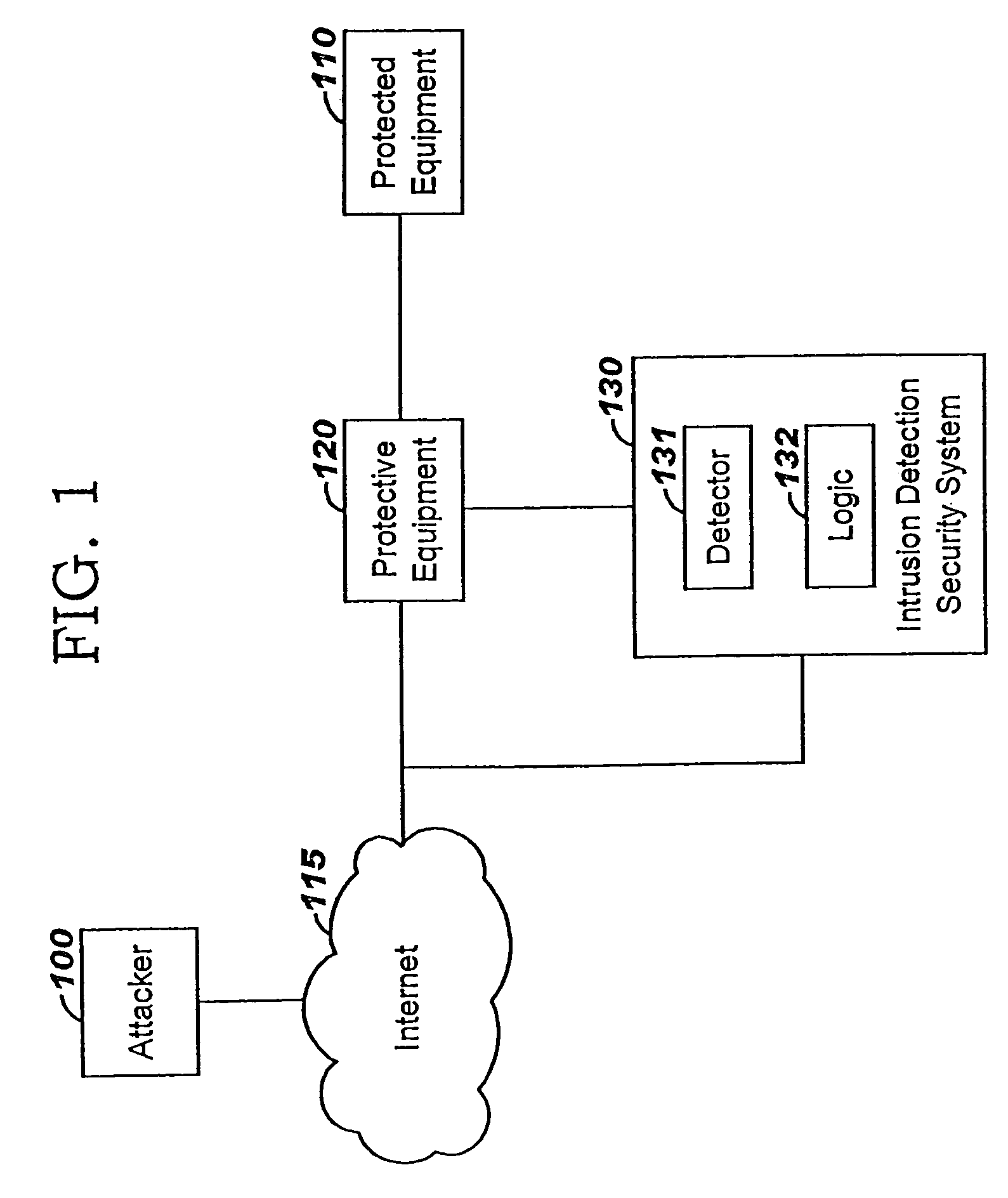
InactiveUS20060075496A1Minimizing adverse consequenceMinimize consequencesMemory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionResponse methodFalse positives and false negatives
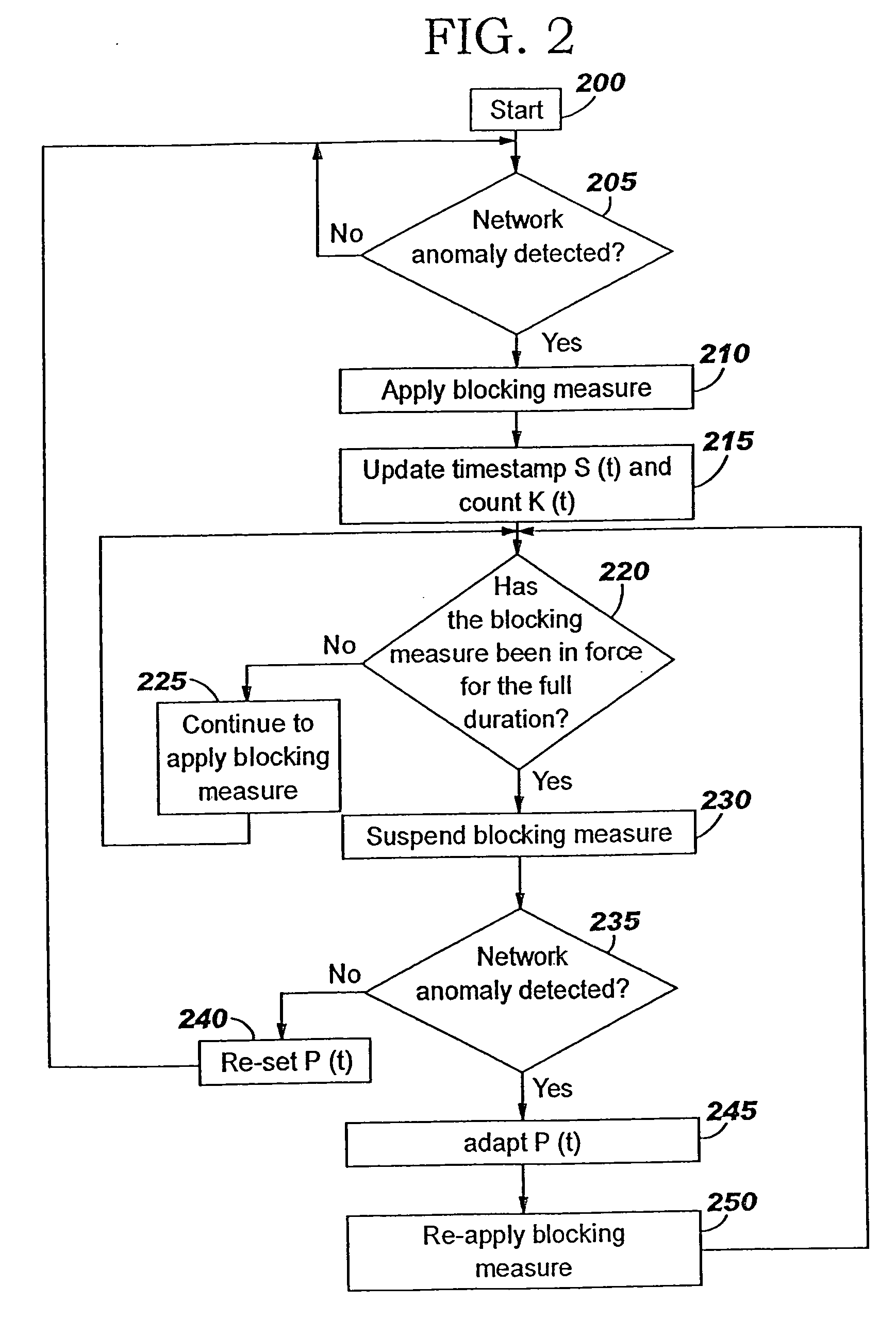
A method of progressive response for invoking and suspending blocking measures that defend against network anomalies such as malicious network traffic so that false positives and false negatives are minimized. When a truncated secure session attack is detected, the detector notifies protective equipment such as a firewall or a router to invoke a blocking measure. The blocking measure is maintained for an initial duration, after which it is suspended while another test for the anomaly is made. If the attack is no longer evident, the method returns to the state of readiness. Otherwise, a loop is executed to re-applying the blocking measure for a specified duration, then suspend the blocking measure and test again for the attack. If the attack is detected, the blocking measure is re-applied, and its duration is adapted. If the attack is no longer detected, the method returns to the state of readiness.
Owner:TREND MICRO INC
Methods and apparatus and data structures for providing access to an edge router of a network
Aggregating physical connections from customers for presentation to an access router and de-aggregating traffic from a shared link(s) from the access router. Ports of an aggregation unit may be configured such that each has a unique identifier in the place of information (e.g., the layer 2 address) originally in the layer 2 header. The layer 2 (e.g., MAC) address of the customer device connected with the port can be associated with, and therefore determined from, the IP address of the attached device. When a packet is received from a customer, information in the layer 2 header is changed to a unique identifier assigned to a logical port or interface associated with the physical port. When a packet is received from the access router, it is placed on the port assigned to the logical port associated with the destination layer 2 address (or associated with other bits of the unique bit string and at least some of those bits are replaced with the destination layer 2 address of the device associated with the port.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Negotiated routing in telephony systems
InactiveUS7231032B2Solve problemsInterconnection arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersService controlDistribution system
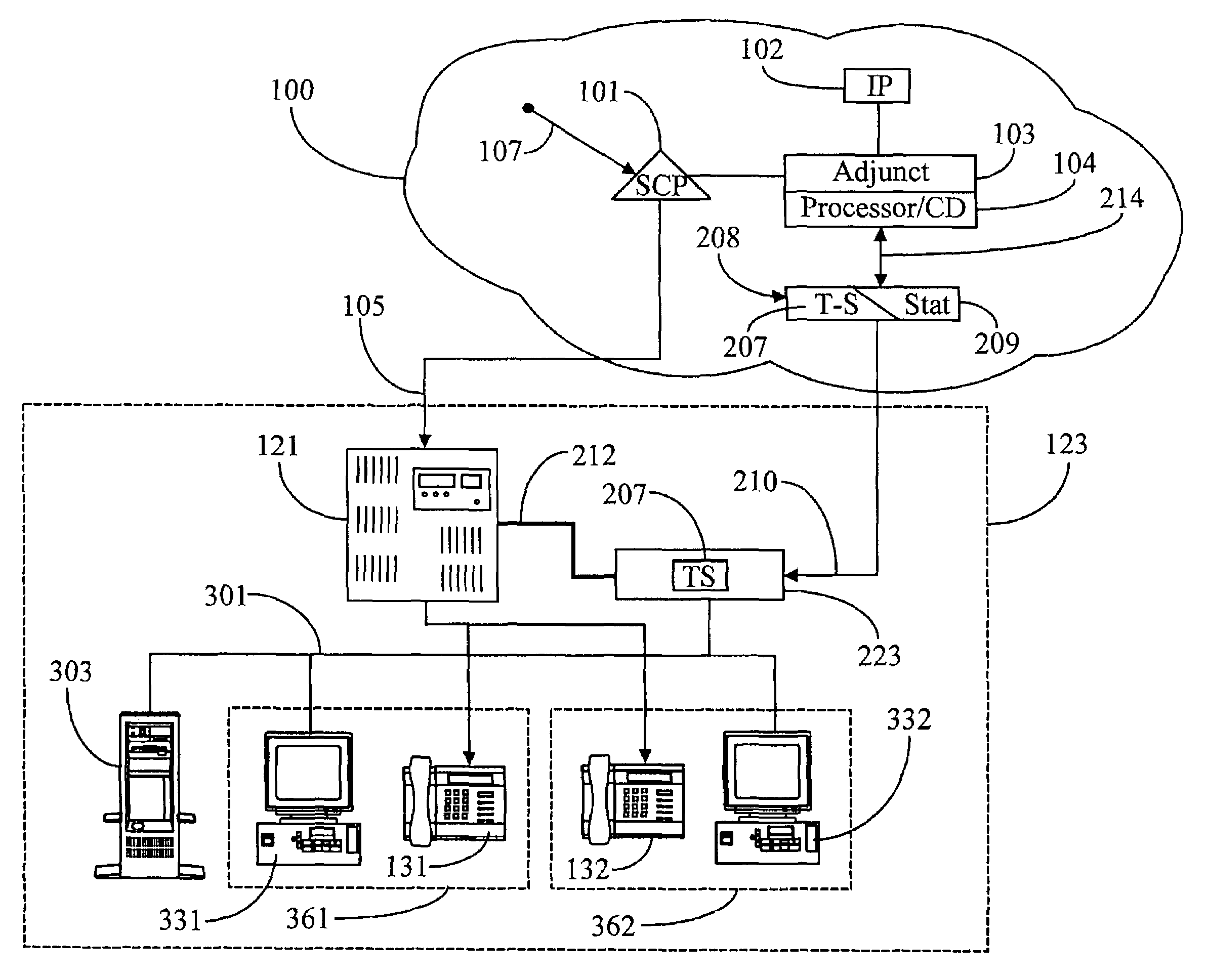
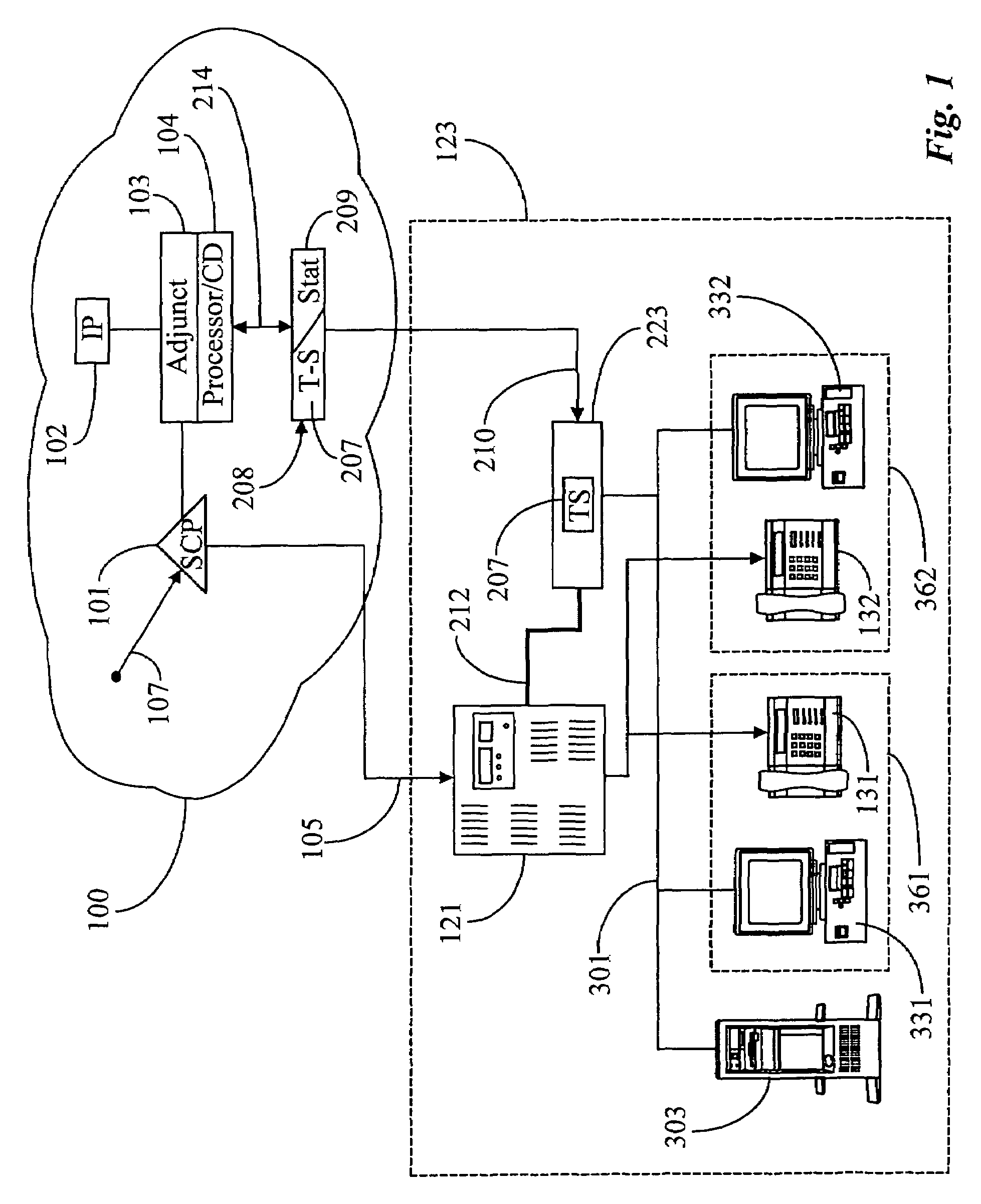
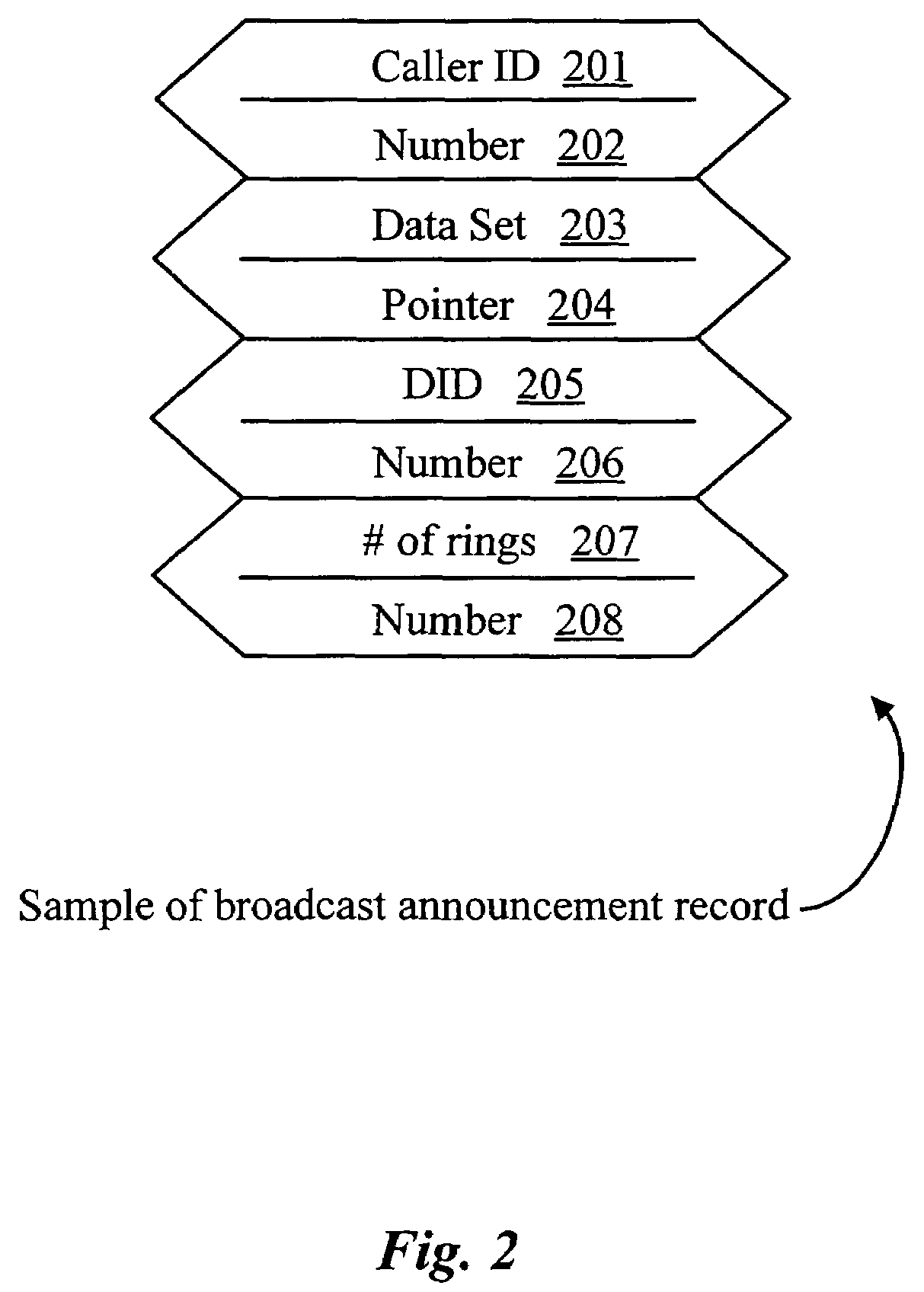
A telephone call distribution system for determining destination for an incoming telephone call in a telephony network including a service control point (SCP) operates with a plurality of workstations each comprising a telephone coupled to the telephony network and a proximate computer station having a video display unit (PC / VDU), the PC / VDO connected to the SCP via a wide area network (WAN), and a personal router associated with each PC / VDU. The SCP broadcasts data pertaining to the incoming telephone call and a request for a destination to individual ones of the PC / VDUs via the WAN, and the personal routers negotiate a destination based on individual routing rules and the data pertaining to the call. At least one of the individual routers responds to the SCP with a destination for the call. In some instances the workstations are associated with a call center, and the call center may be CTI-enhanced. Individual routers in this instance may be executed on a server on a local area network connecting workstations at the call center, the server providing individual routers to workstations in a client-server relationship.
Owner:GENESYS TELECOMM LAB INC AS GRANTOR +3
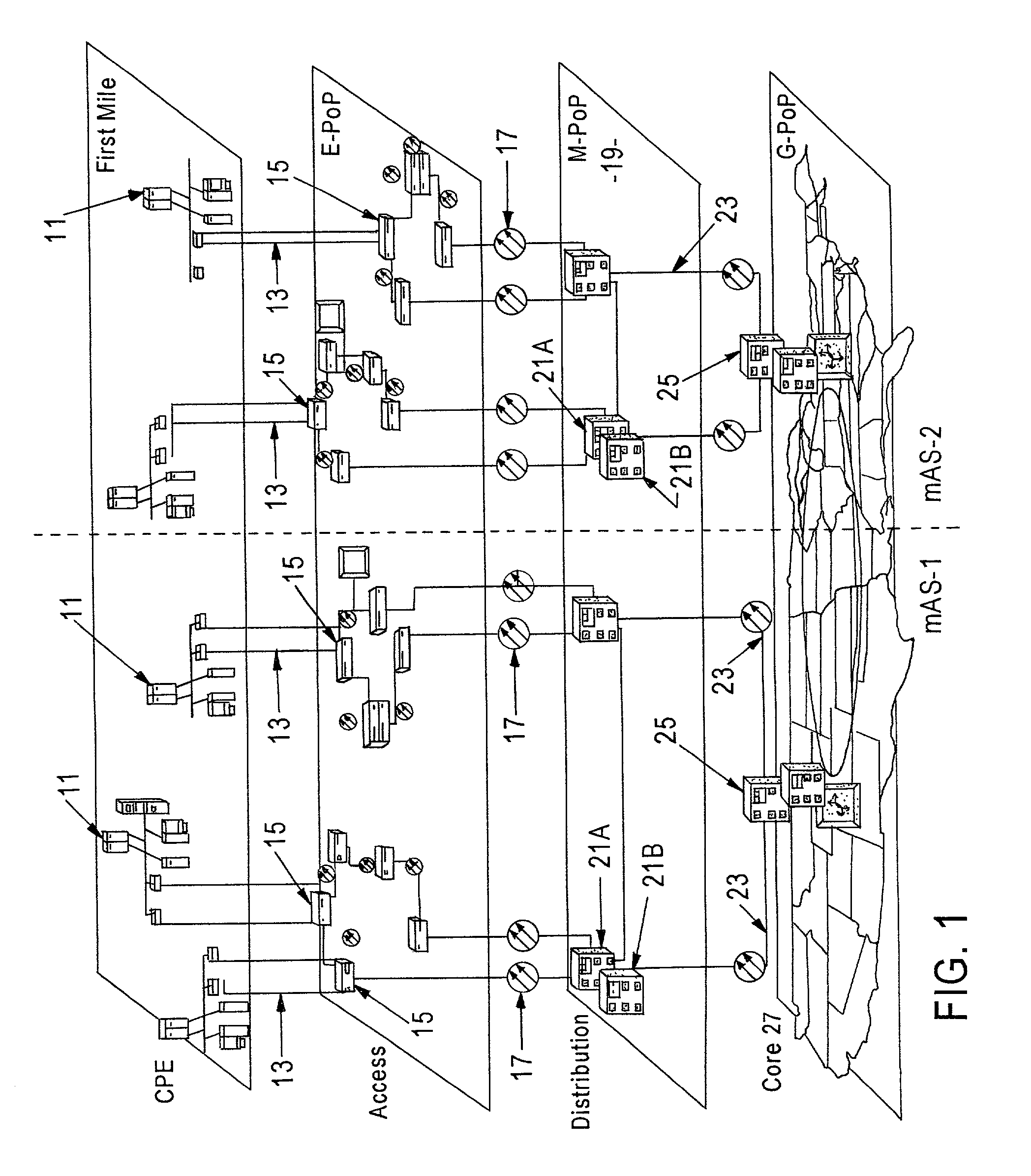
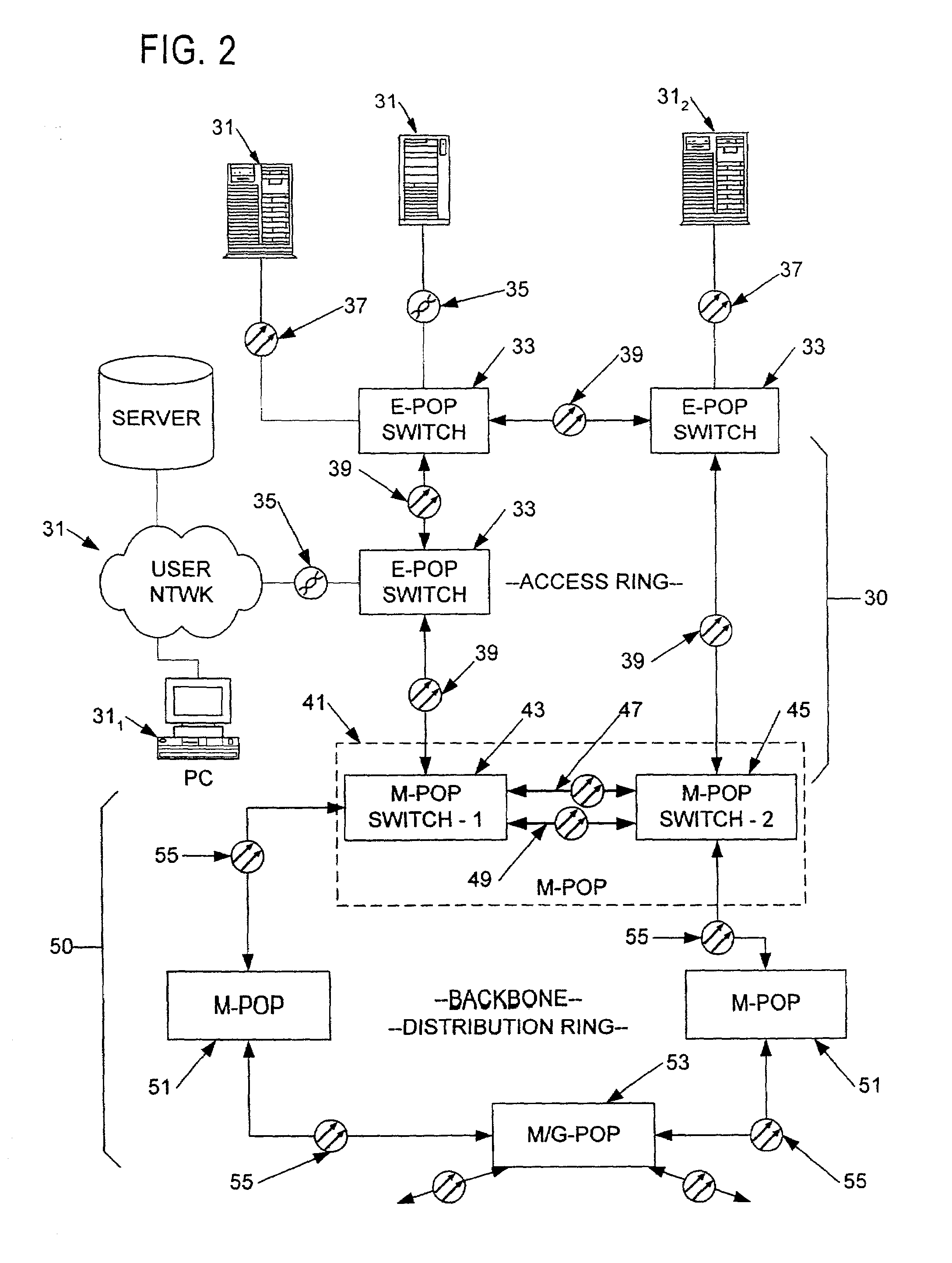
Enhanced data switching/routing for multi-regional IP over fiber network
InactiveUS6963575B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsNetworks interconnectionWide areaBorder Gateway Protocol
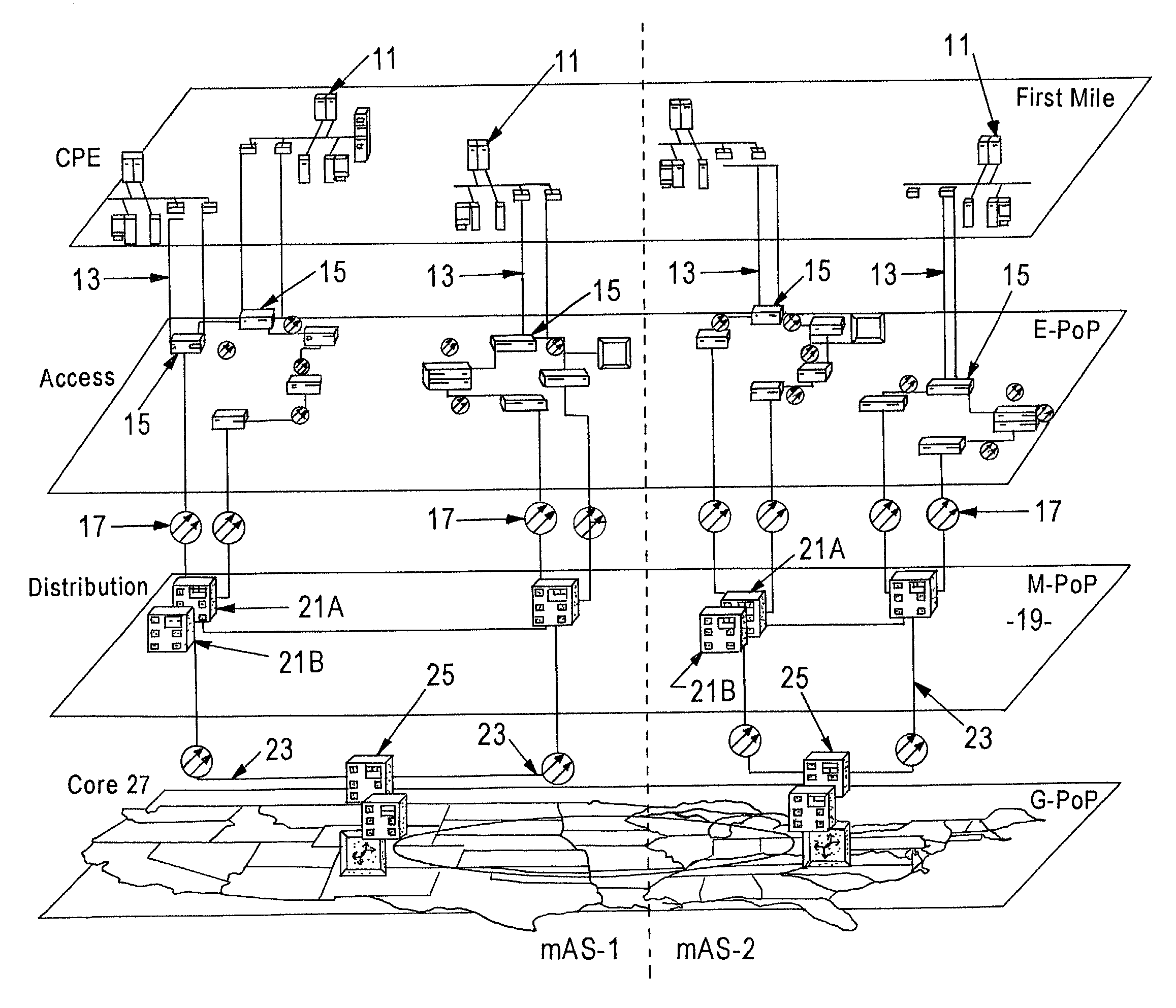
Wide-area data communications utilize regional networks transporting IP-over-Ethernet on fiber. For certain Layer 2 services, a regional implementation of the network makes limited use of spanning tree protocol on a backbone ring. Learning bridge operations in switches on associated access rings involve a short default for an aging timer. For use of Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), the connection of each access ring to the backbone ring uses a pair of routers with dual links therebetween. One of these links is bonded to the backbone (OSPF Area 0), whereas the other link is bonded to the Area of the respective access ring. Also, certain routers within each regional network form a mini-autonomous system, for boundary gateway protocol (BGP). The mini-autonomous systems of the regional networks form a confederation. The network utilizes route reflectors in the mini-autonomous systems. The Internet carries confederation commands to and from a designated hub.
Owner:YIPES ENTERPRISE SERVICES
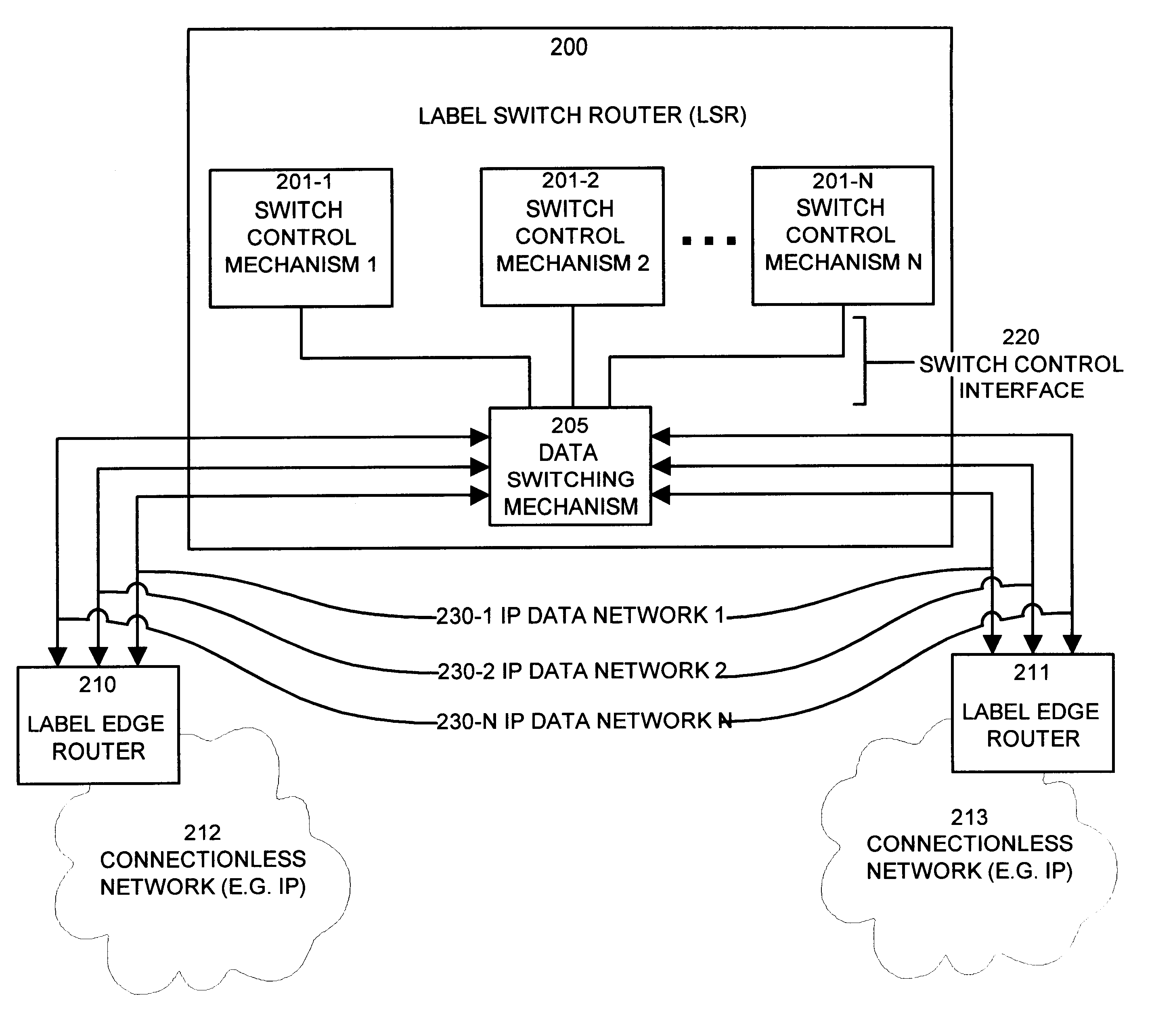
Apparatus and methods providing redundant routing in a switched network device
InactiveUS6628649B1Improve fault toleranceHigh degreeMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationData transmissionData loss
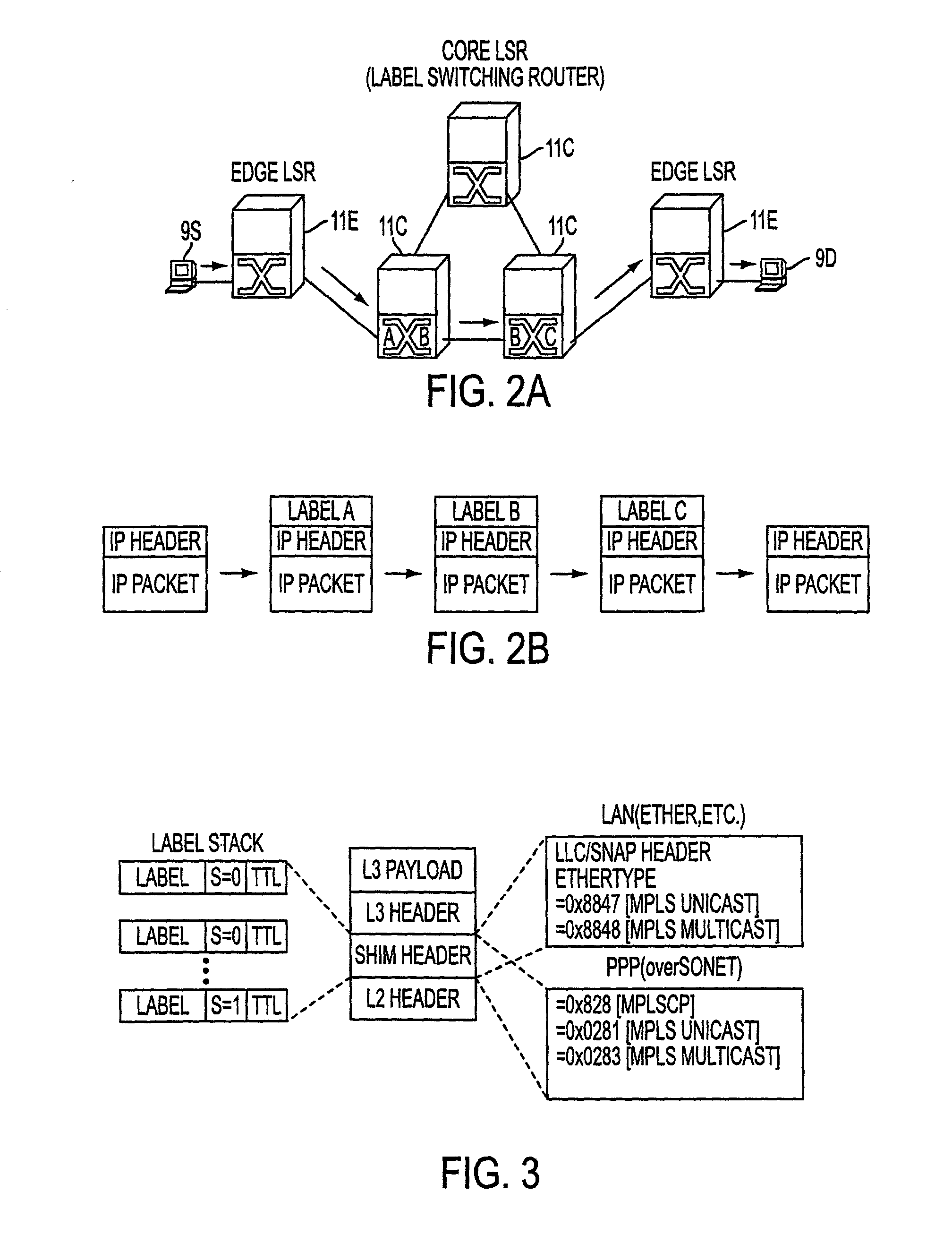
The invention provides unique architectures and techniques for routing redundancy in a data switch configured to use label switching. Multiple label switch controllers (LSCs) each operate concurrently but independently of each other to provide routes through a data switching mechanism. Preferred embodiments provide a plurality of LSCs offering MPLS capabilities coupled to a single switch, such as an ATM switch. The similarly configured LSCs each can concurrently support a route for data (e.g., labeled ATM cells) within the data switching mechanism in parallel, thereby providing the ability to support redundant and multiple parallel data networks. The configuration is called a label switch router (LSR). A fully-meshed embodiment allows selected routes to share bandwidth on ports, while a fully parallel embodiment provides separate ports for selected routes. Since each LSC provides parallel routes with the other LSCs in an LSR, a communications between an LSR and a label edge router (LER) can use multipath routing to concurrently distribute data equally across the parallel routes for each destination. Alternatively, unipath routing techniques can select one route for use for each destination from the available routes concurrently offered by each LSC. In the event of a failure of one of the LSCs, multipath routing implementations can exclude transmission of data onto the failed network, while continuing to use the other parallel networks supported by non-failed LSCs in a concurrent manner. Alternatively, if a failure occurs with unipath routing, a new route offered by another LSC can be selected for data transfers. In either case, the LSC that fails does not need to provide state or connection information to the LSCs that operate subsequently to the failure, since they are already configured in parallel to support the same route. Upon an LSC failure, switch resources such as bandwidth that were used by the failed LSC are made available to the remaining non-failed LSCs. The design allows failures are handled gracefully without diminished network capacity or data loss resulting in a highly reliable routing capability provided within connection-based or circuit-switched networks.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
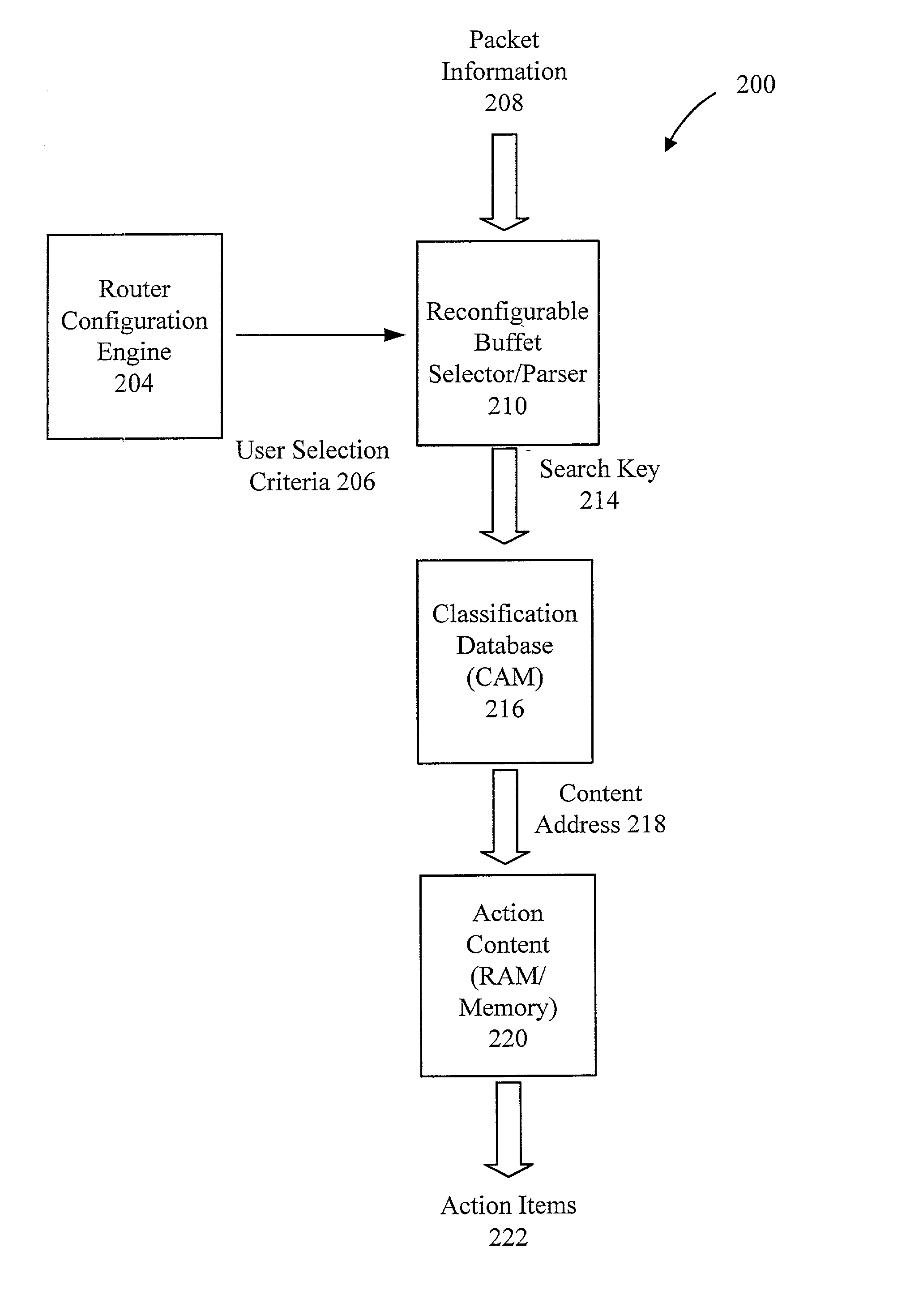
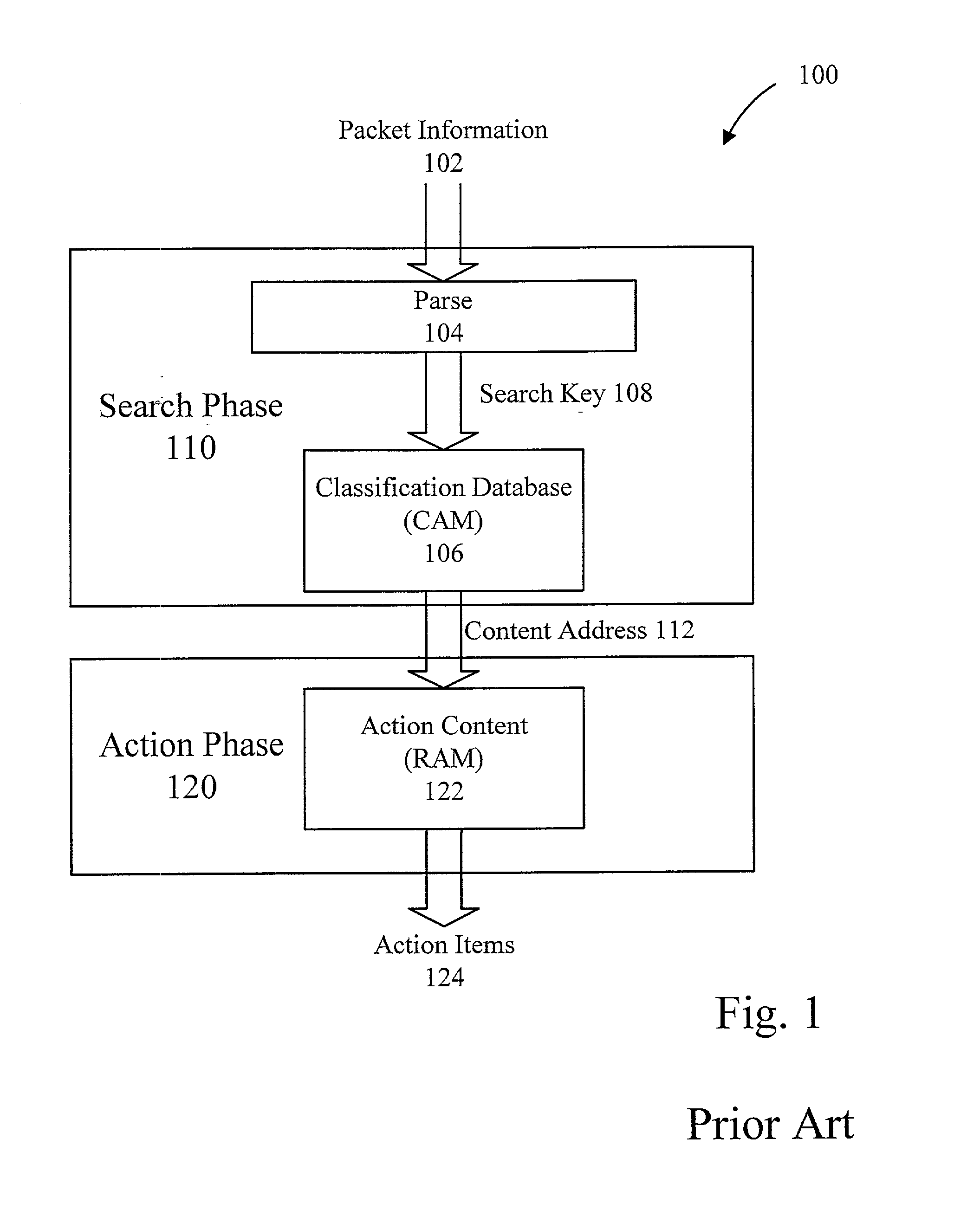
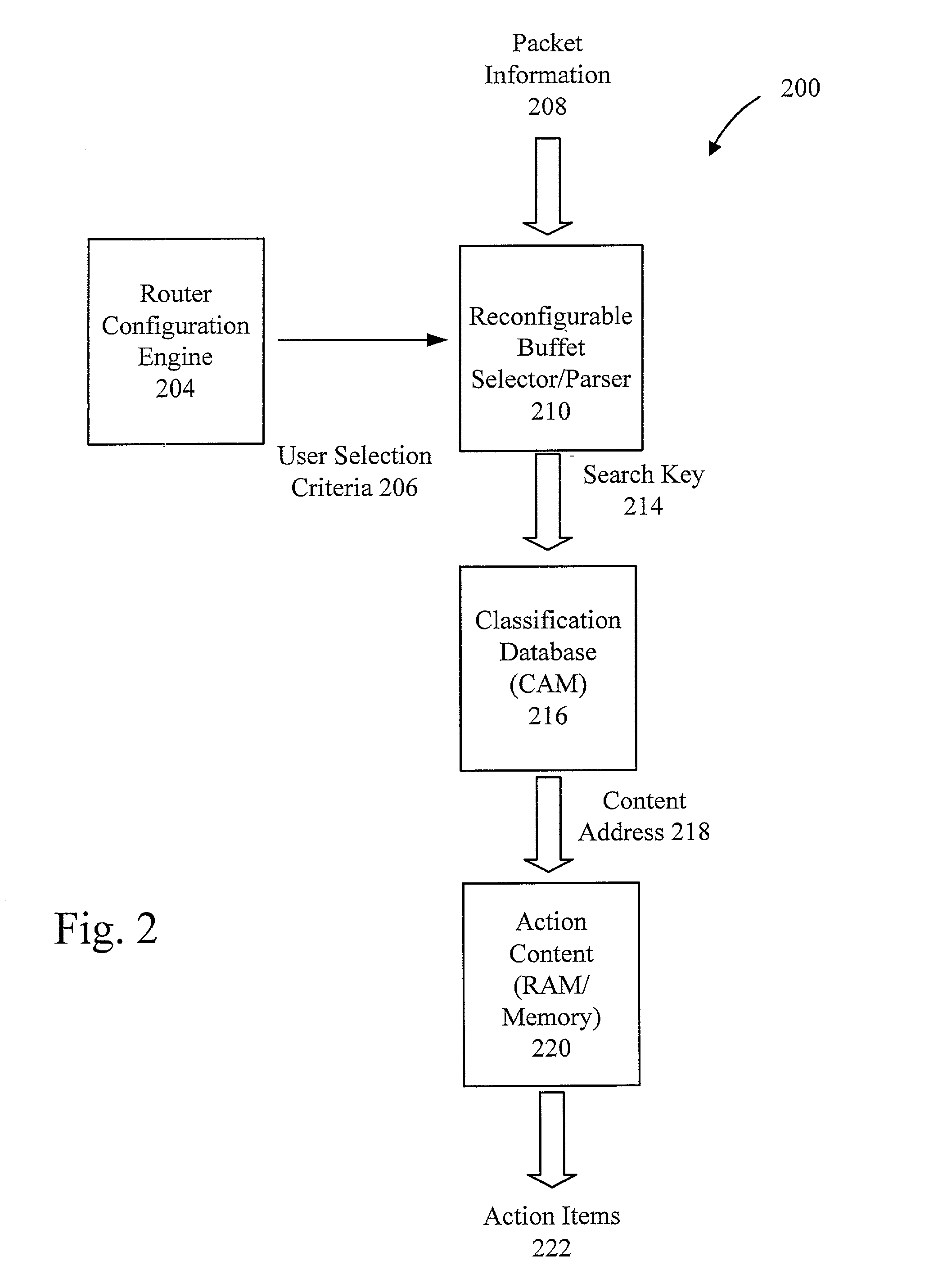
Method and apparatus for a flexible and reconfigurable packet classifier using content addressable memory
InactiveUS20020126672A1Low costFlexibility of deploymentData switching by path configurationSecuring communicationCustomer requirementsTernary content addressable memory
The present invention provides for a reconfigurable packet classifier using CAM. The invention is directed to packet classification for switching / routing systems where the router's system resources are limited and the customer requirements from the router are variable. The invention addresses the CAM constraint (e.g. search key width) problems of CAM-based classification systems, by allowing a reconfigurable selection of packet fields and / or payload bits to be used in the definition of the search key. For any given incoming packet, a subset of that incoming packet may be statically chosen to fit that particular CAM architecture and to create a particular CAM search key. This provides router deployment flexibility within networks and, thus, cuts costs.
Owner:ACUTE COMM CORP
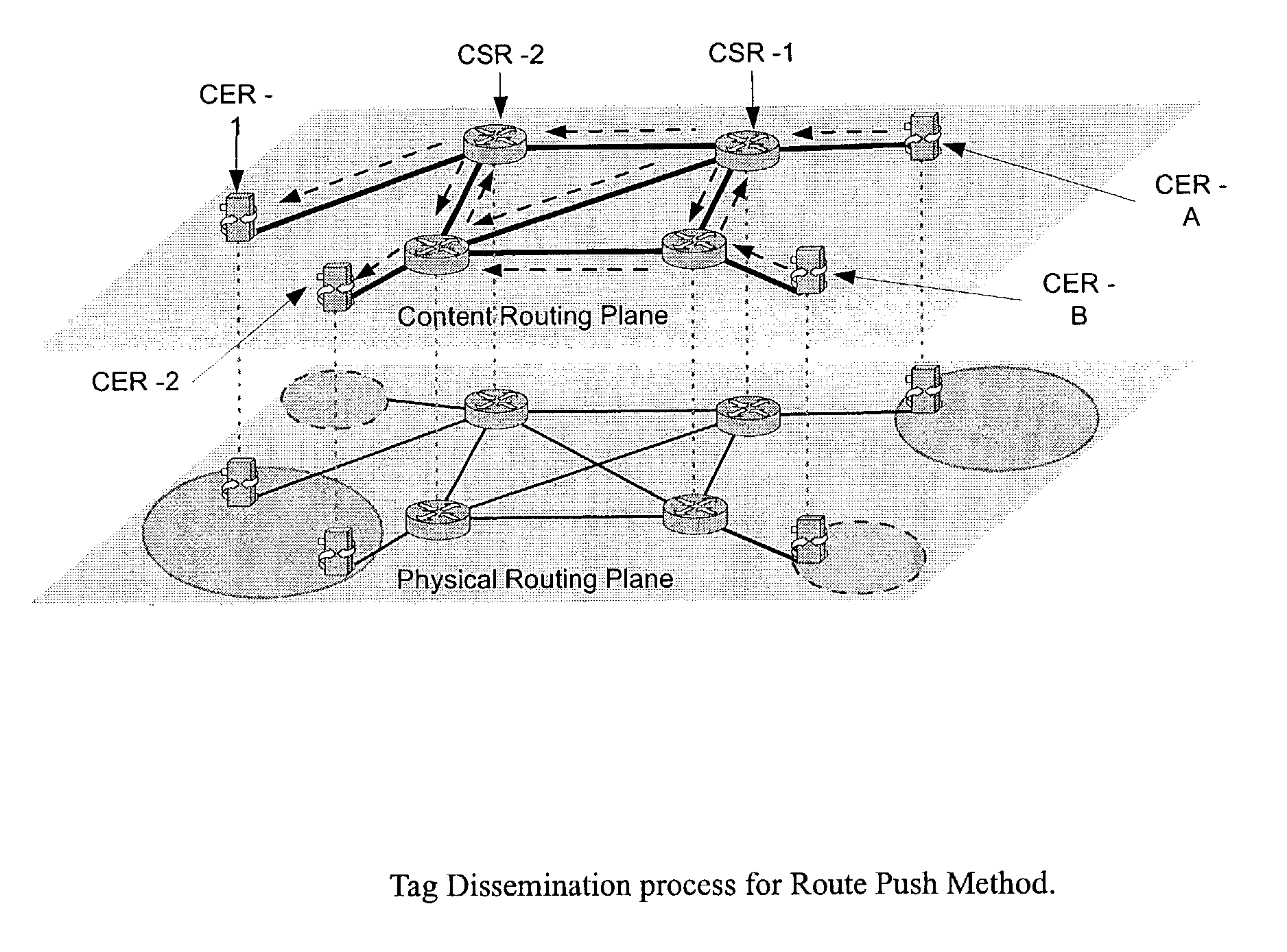
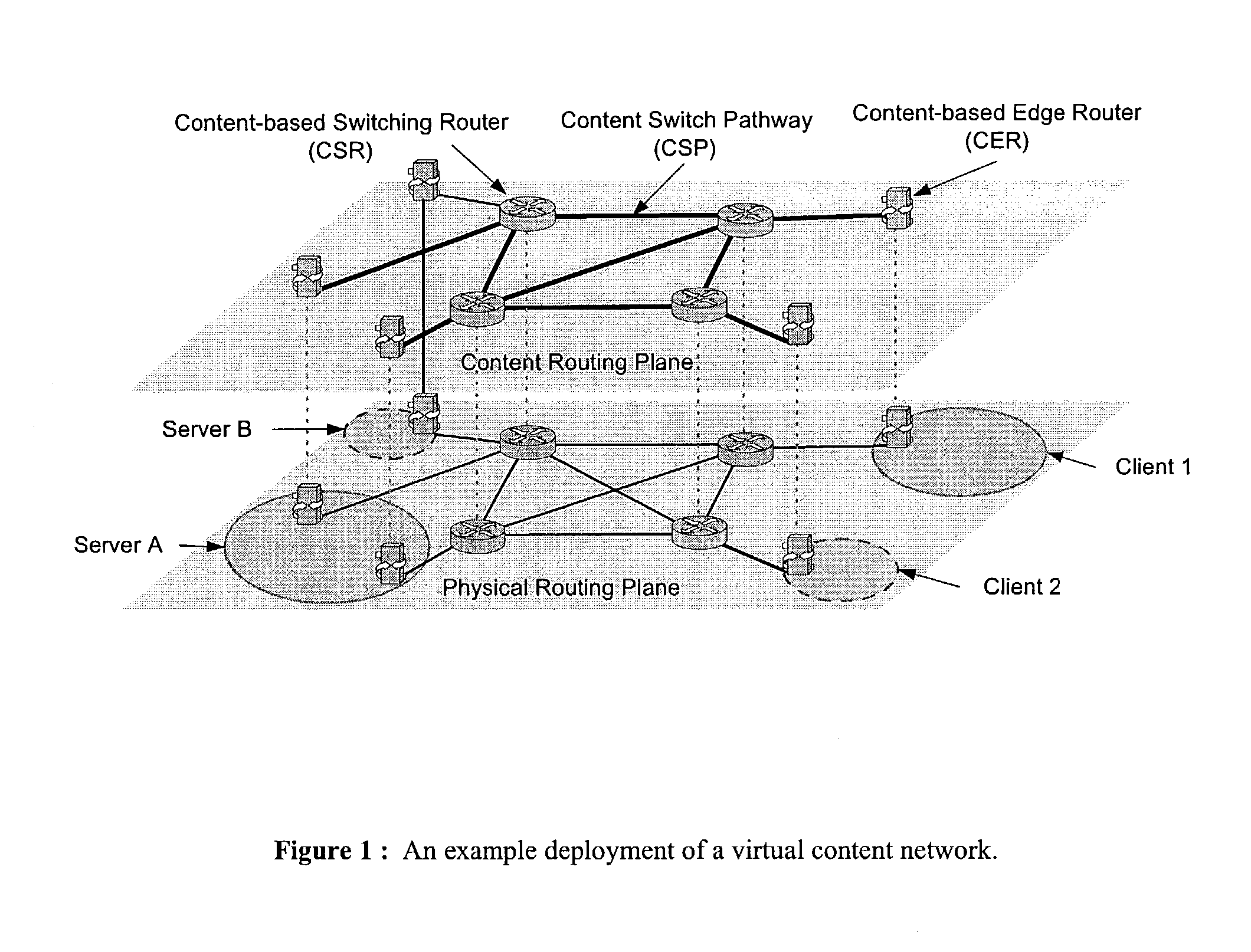
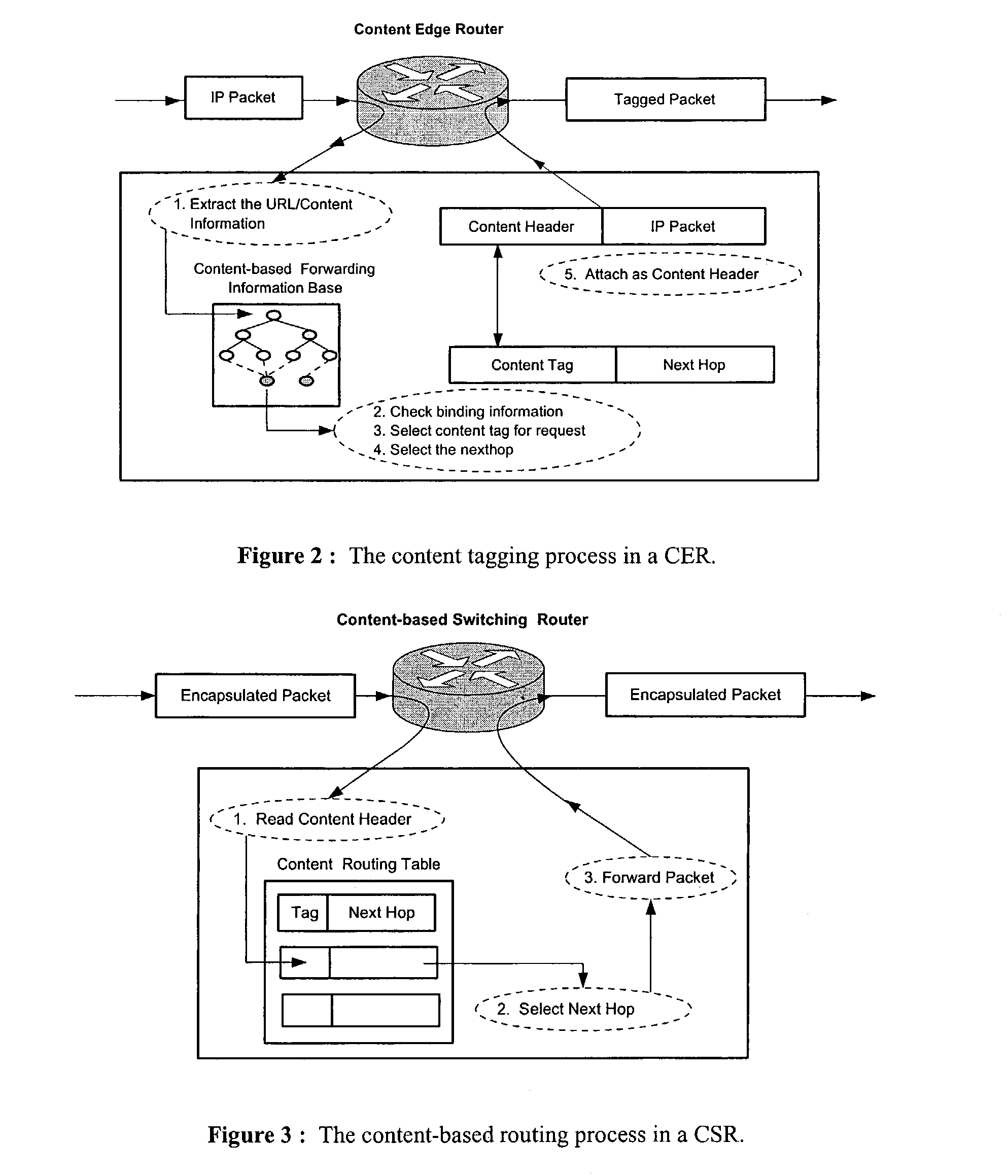
Wide-area content-based routing architecture
Owner:TELECOMM RES LAB
Method and apparatus for distributing routing instructions over multiple interfaces of a data router
InactiveUS20020126671A1Special service provision for substationError preventionCommunication interfaceInformation repository
A software application in a multi-processor data router in which a forwarding information base for the router is maintained is provided with a server module and one or more client modules, each client module associated with one or more communication interfaces of the data router. The application is characterized in that the server module sends to each client module only that portion of the forwarding information base specific to the communication interfaces associated with the client module.
Owner:PLURIS
System providing internet access management with router-based policy enforcement
ActiveUS8200818B2Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionInternet accessApplication software
A computing environment with methods for monitoring access to an open network such as the Internet, is described. The system includes one or more client computers, each operating applications (e.g., Netscape Navigator or Microsoft Internet Explorer) requiring access to an open network, such as a WAN or the Internet, and a router or other equipment that serves a routing function (e.g., a cable modem) for the client computers. A centralized security enforcement module on the router maintains access rules for the client computers and verifies the existence and proper operation of a client-based security module on each client computer. The router-side security module periodically sends out a router challenge via Internet broadcast to the local computers on the network. If the client-side security module is installed and properly operating, the client-side security module responds to the router challenge. The responses received by the router-side security module are maintained in a table. Each time the router receives a request from a client computer to connect to the Internet, the router-side security module reviews the table and analyzes whether or not the computer requesting a connection to the Internet properly responded to the most recent router challenge. If it determines that the computer has properly responded to the router challenge, then it permits the computer to connect to the Internet. If a computer has not properly responded or if a computer has not answered the router challenge, then the computer is not allowed to connect to the Internet as requested.
Owner:CHECK POINT SOFTWARE TECH INC
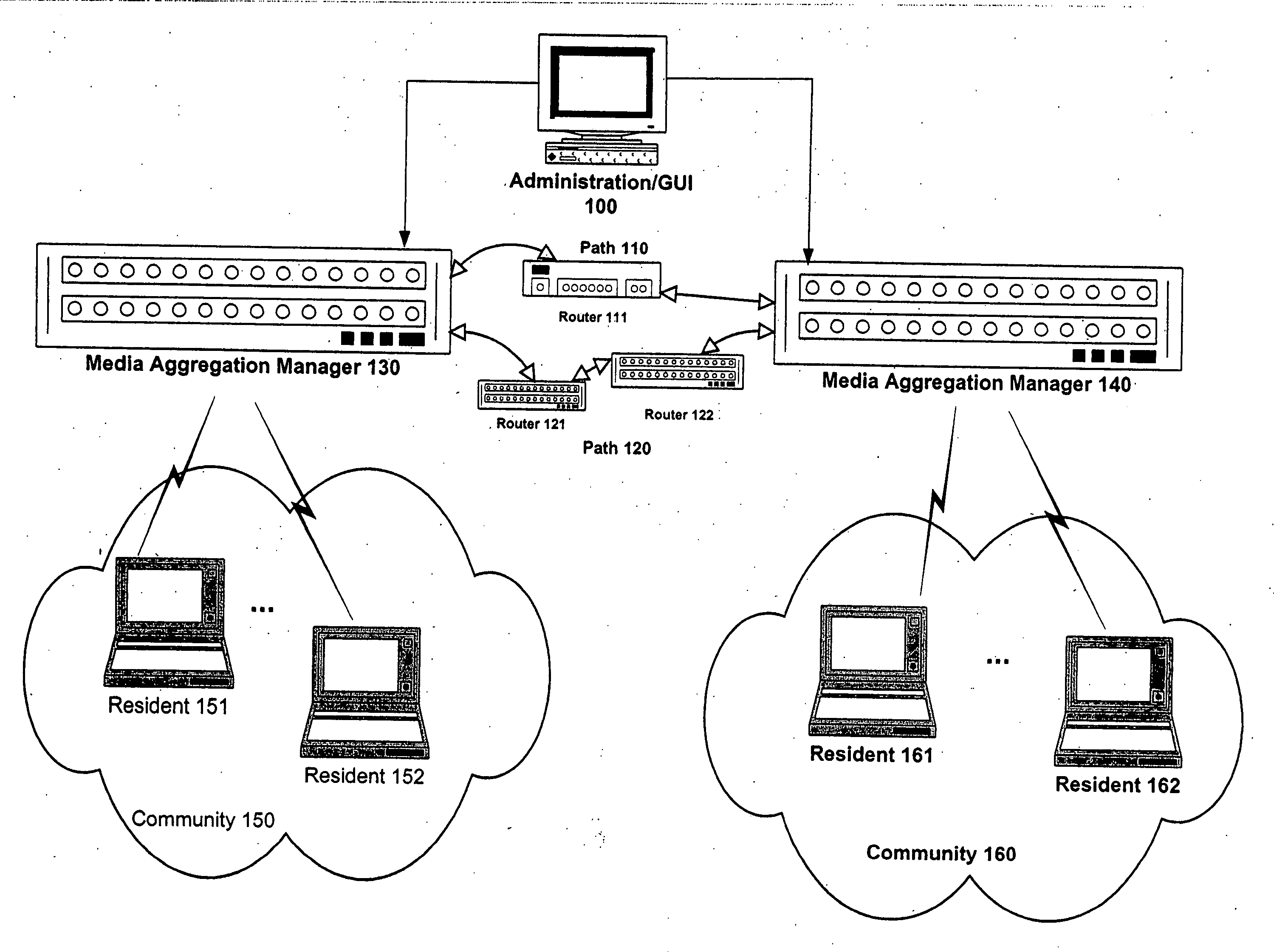
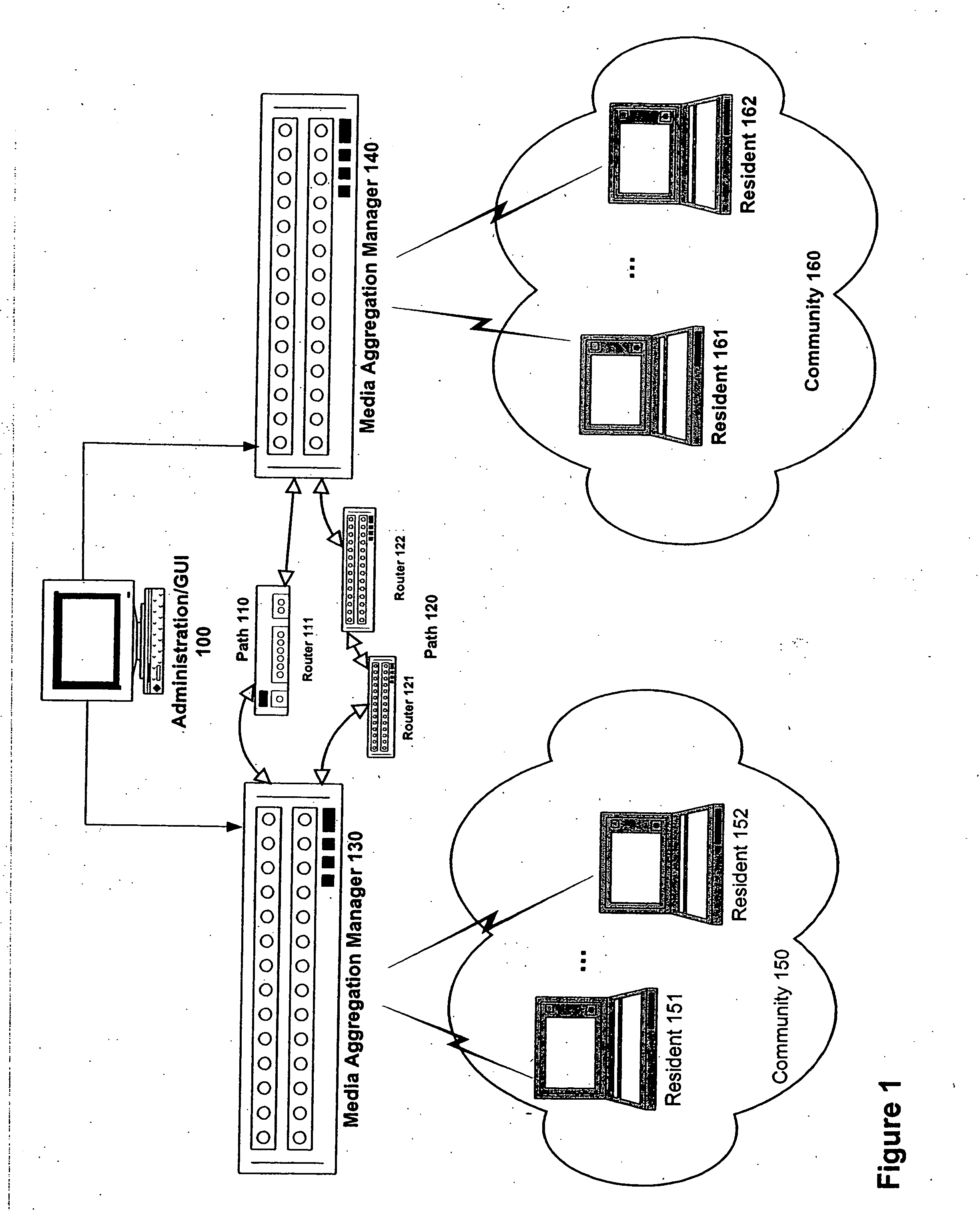
Administering a communication network
ActiveUS20060020694A1Interconnection arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork methodTraffic volume
Methods and apparatus are provided for administering a communication network. In one embodiment, a first interface screen depicts nodes within a network. The nodes include a pair of media aggregation managers providing multiplexing / demultiplexing of media traffic associated with multiple application sessions between a pair of communities onto a preallocated reservation protocol session between the media aggregation managers. The media aggregation managers are visually distinguishable from other nodes. A second interface screen depicts potential paths through the network. Each potential path is capable of transferring media packets between the media aggregation managers. Via the second user interface screen, a network administrator is capable of initiating (1) path-level configuration of routers that are part of a selected potential path to cause the routers to route media packets exchanged between the pair of communities over the selected path, and (2) establishment of the preallocated reservation protocol session between the media aggregation managers.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES ASSETS 169 LLC
Method and apparatus for simple IP-layer bandwidth allocation using ingress control of egress bandwidth
InactiveUS6628609B2Reduce the possibilityMinimum bandwidthError preventionTransmission systemsDynamic bandwidth allocationData transmission
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
Transmission path controlling apparatus and transmission path controlling method as well as medium having transmission path controlling program recorded thereon
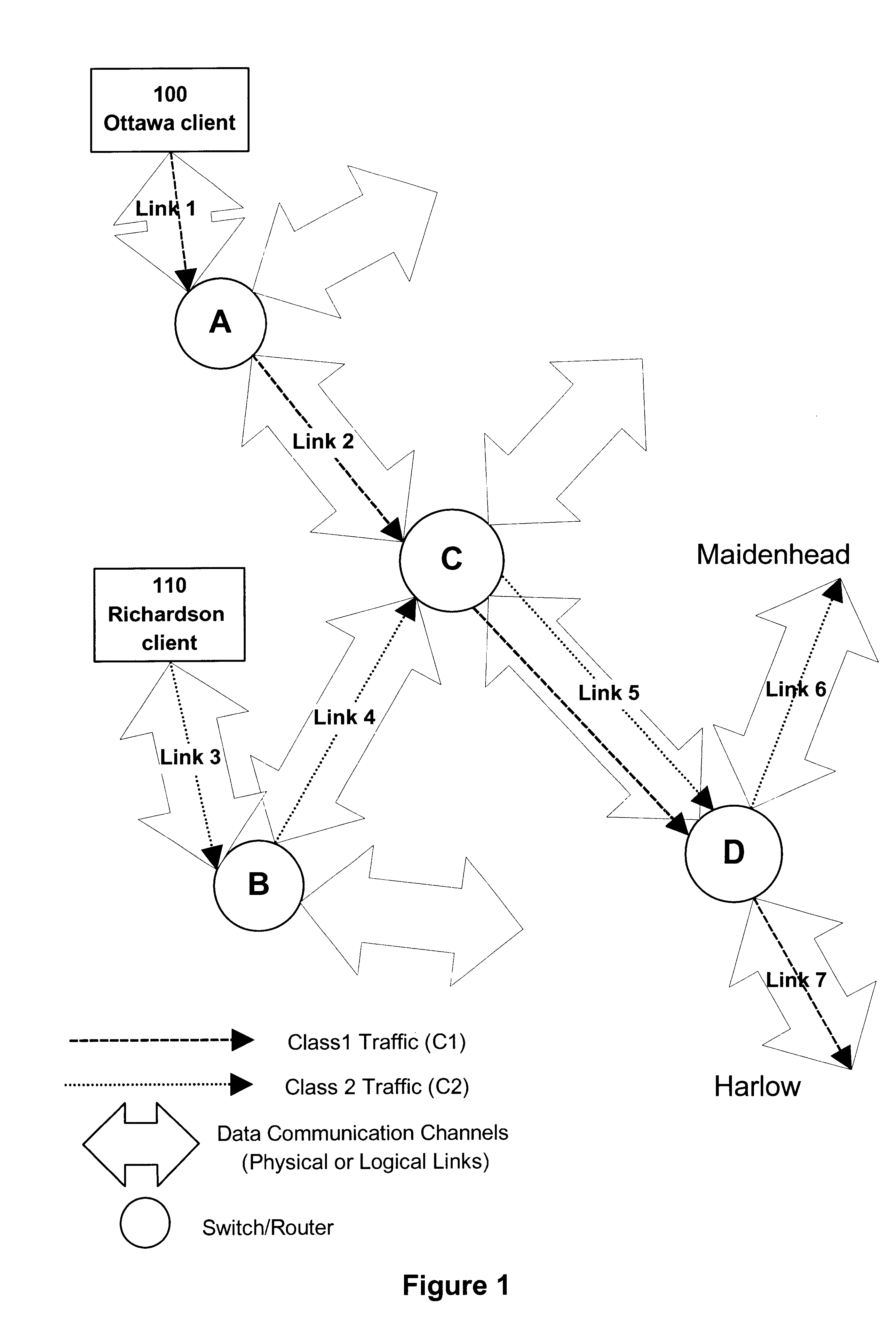
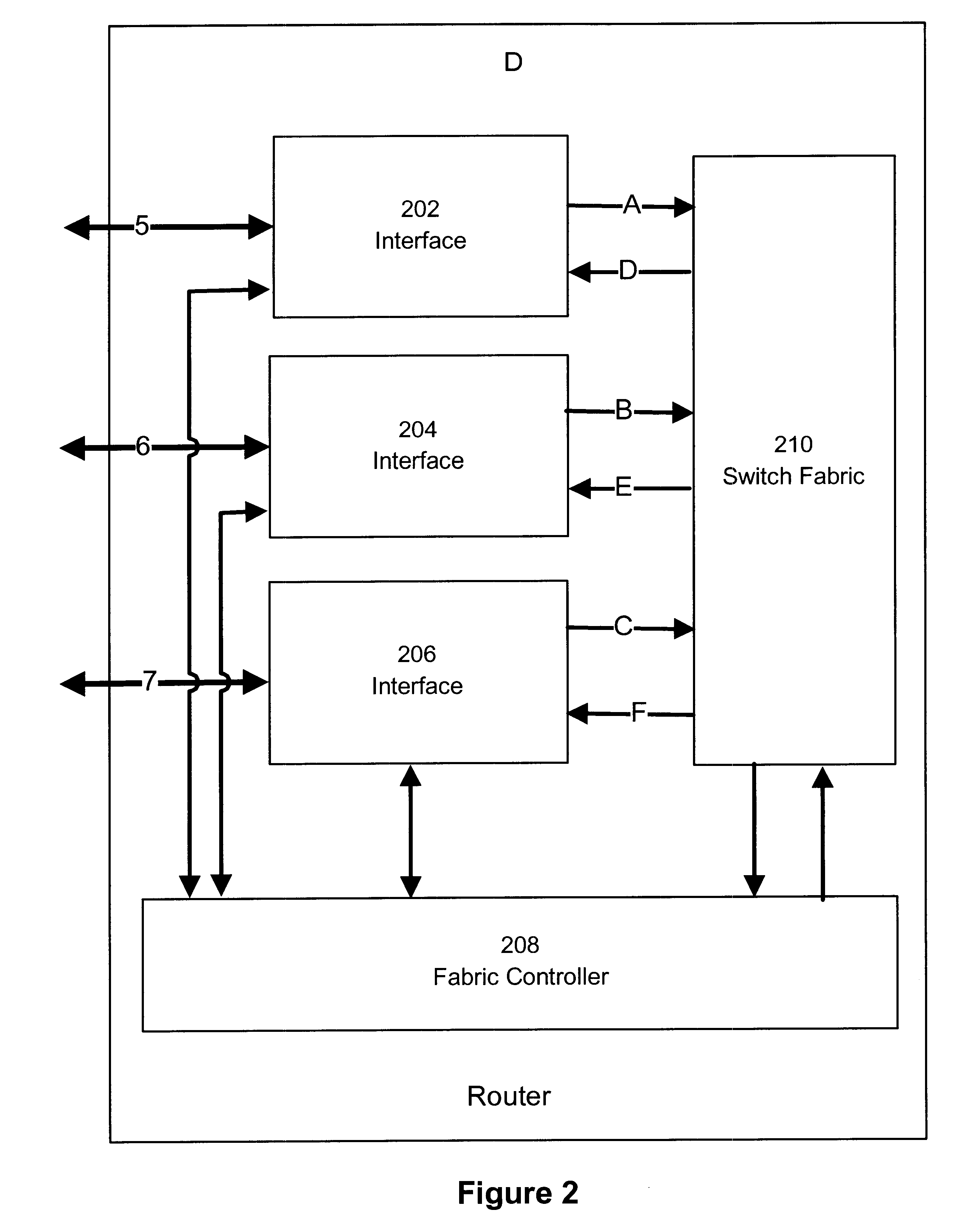
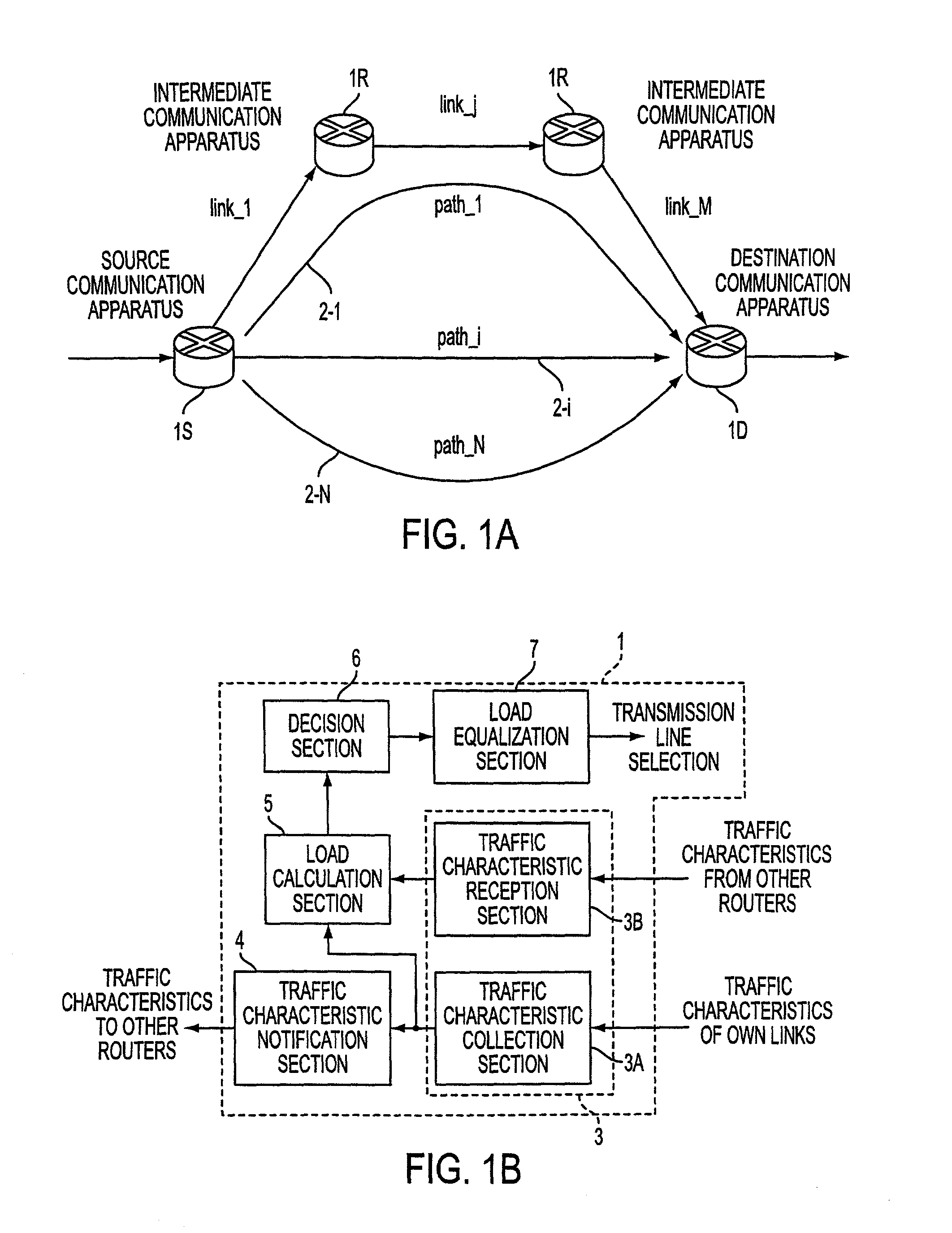
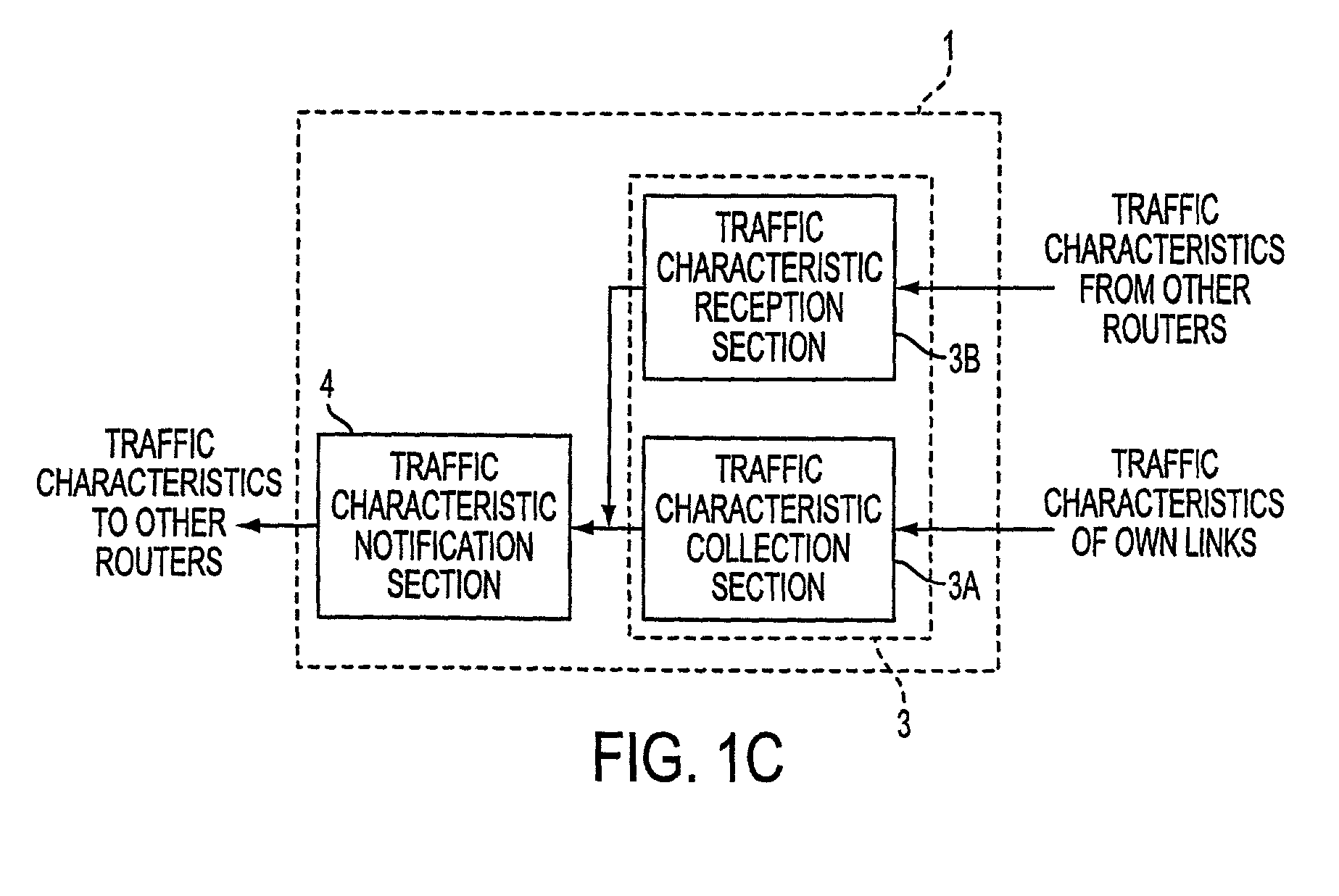
InactiveUS20010037401A1Efficient loadingLoad estimation can be avoidedError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic characteristicPathPing
The present invention relates to distributing the load between the set routes among a plurality of routes between a communication apparatus which serves as a start point to another communication apparatus which serves as an end point. An apparatus provided in a router in a network collects traffic characteristics of transmission paths connected to the router, notifies other routers of the collected traffic characteristics, calculates load based on the collected traffic characteristics, decides based on the calculated load information whether or not a transmission path should be added or deleted, and equalizes the load among the plurality of transmission paths.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Layer 3 switching logic architecture in an integrated network switch
InactiveUS7079537B1Improve performanceTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationNetwork switchEthernet
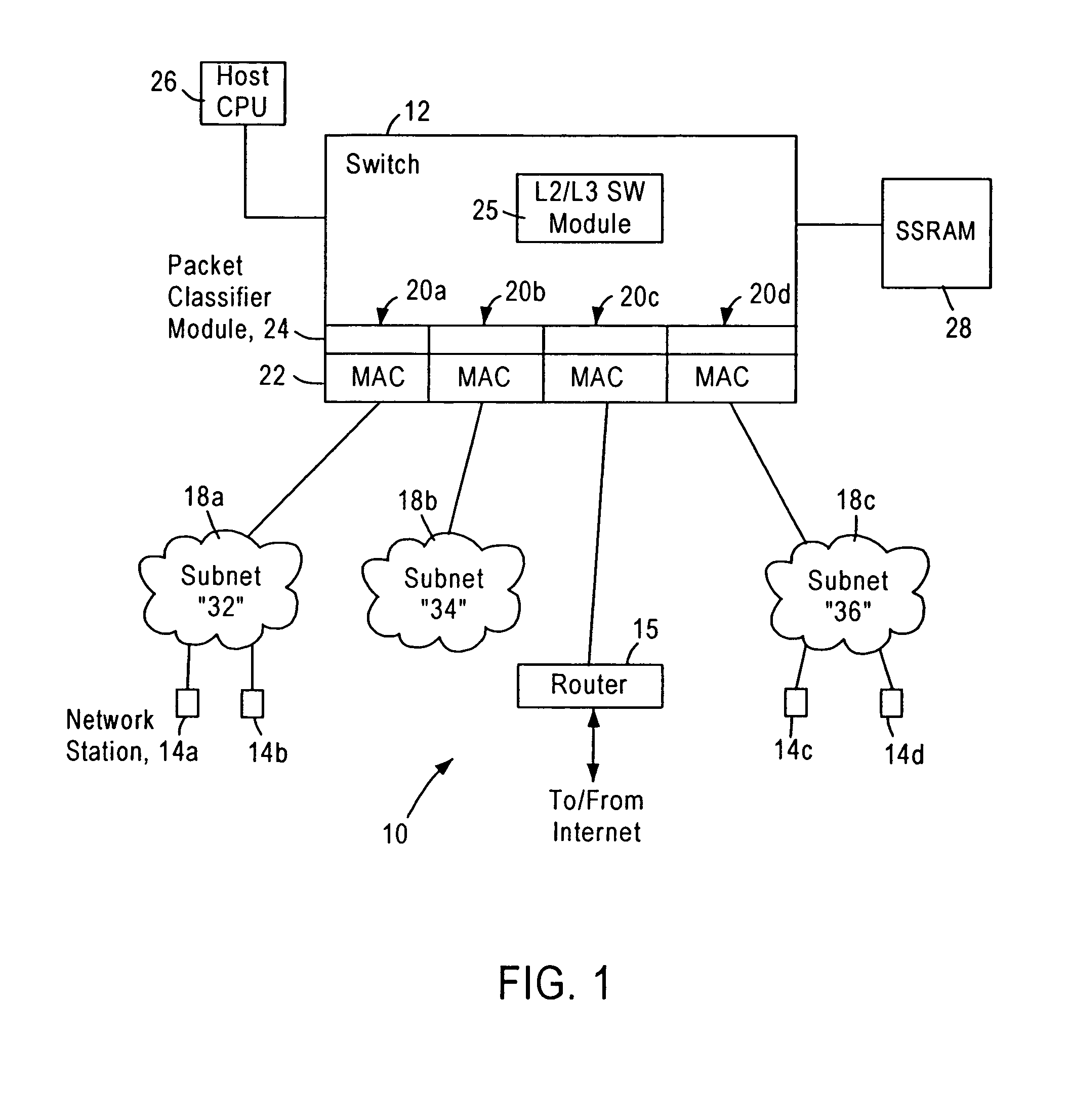
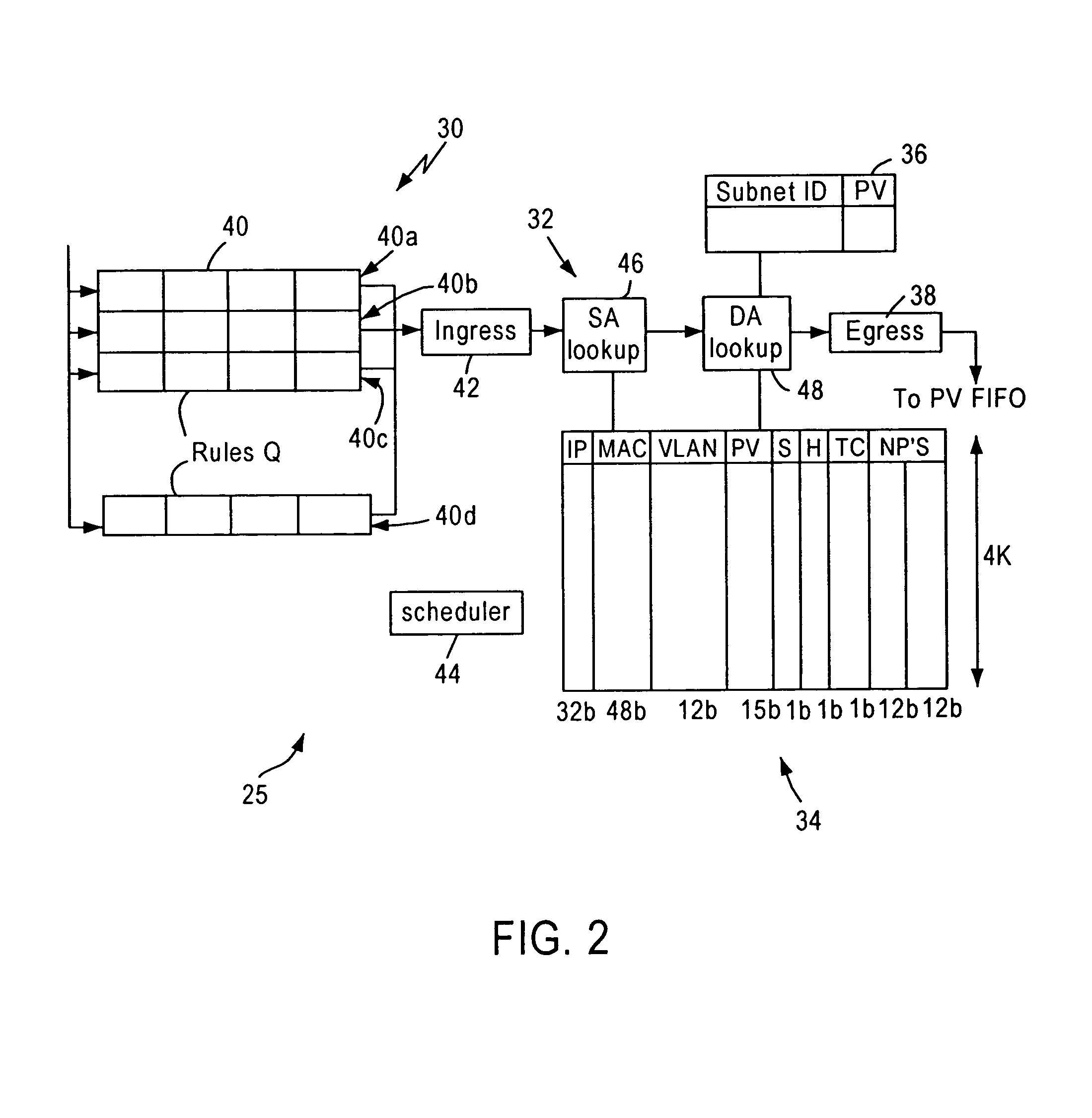
A network switch, configured for performing layer 2 and layer 3 switching in an Ethernet (IEEE 802.3) network without blocking of incoming data packets, includes a switching module for performing layer 2 and layer 3 (specifically Internet Protocol) switching operations, and a plurality of network switch ports, each configured for connecting the network switch to a corresponding subnetwork. The switching module includes address tables for storing address information (e.g., layer 2 and layer 3 address and switching information). The network switching module is configured for performing prescribed layer 3 switching that enables transfer of data packets between subnetworks, bypassing a router that normally would need to manage Internet protocol switching between subnetworks of the network. Hence, the network switch performs Internet Protocol switching for intranetwork (i.e., inter-subnetwork) traffic, improving efficiency of the router by enabling the router resources to support more subnetworks.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Mobile robotic router with web server and digital radio links
InactiveUS7096090B1Increases scope and flexibilityCostAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficRobot controlWeb server
The invention is a computerized mobile robotic router with an onboard internet web server, and a capability of establishing a first connection to a remote web browser on the internet for robotic control purposes, and a capability of establishing a second short range bi-directional digital radio connection to one or more nearby computerized digital radio equipped computers or devices external to the robot. The short-range bi-directional digital radio connection will typically have a maximum range of about 300 feet. In a preferred embodiment, this short-range wireless digital connection will use the 2.4 gHz band and digital protocols following the IEEE 802.11, 802.15, or other digital communications protocol. By employing the proper set of external short-range digital radio devices capable of interfacing with the robot (such as sensors, mechanical actuators, appliances, and the like), a remote user on the internet may direct the robot to move within range of the external devices or computers, and connect these devices or computers to the internet.
Owner:ZWEIG STEPHEN ELIOT
Method and system for transparent in-line protection of an electronic communications network
InactiveUS20060190997A1Improve performanceDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationComputing systemsAggregate data
The invention provides a method and system for enabling in-line communications channels between a plurality of computational systems and a switch, and / or a plurality of switches and a router. In a first version of the invention an in-line system receives uplinks of aggregated data from a plurality of switches and applies policies to the each aggregated data stream prior to transmission of the aggregated data streams from the in-line system to the router. At least one computational system provides a user identification associated with a user profile to the in-line system. The user profile informs indicates to the in-line system of the constraints imposed upon and activities permitted to the computational system originating the user identification. The constraints may include (a) one or more customized policies, (b) policies applicable to a group associated with the user identification, (c) virus / worm detection & protection, (d) a firewall, (e) virtual private network rules, and / or (f) encryption / decryption. In a second version the in-line system is configured to communicate directly with one or more computational systems as well as one or more switches.
Owner:NEVIS NETWORKS INC
Routing data packets in a compressed-header domain
InactiveUS20060075134A1Reduce loadReduce processing loadDigital computer detailsData switching networksData packReal-time computing
The invention concerns routing of data packets in a header-compressed domain. According to the method described, routing a data packet with a compressed header section and an uncompressed payload section comprises steps of receiving the data packet at an ingress interface, routing the data packet to an egress interface, and forwarding the data packet to the egress interface. According to this method, the compressed header section remains unchanged between the ingress interface and the egress interface. Various implementations of this method are described, including the use of the header compression context identifier (HCCID) by for routing the packets to the correct egress interface. Accordingly, a decompressor and a router are also disclosed.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
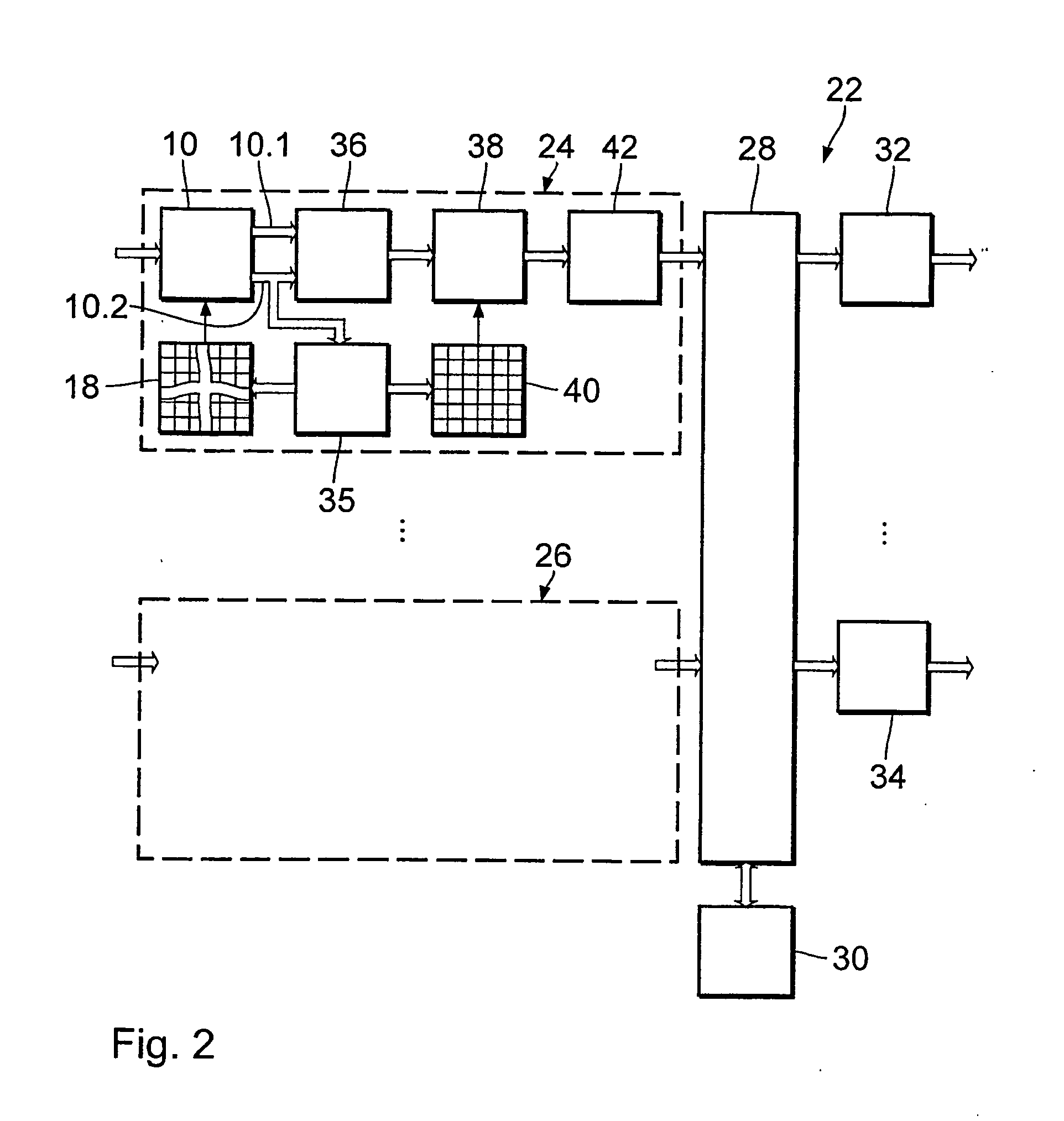
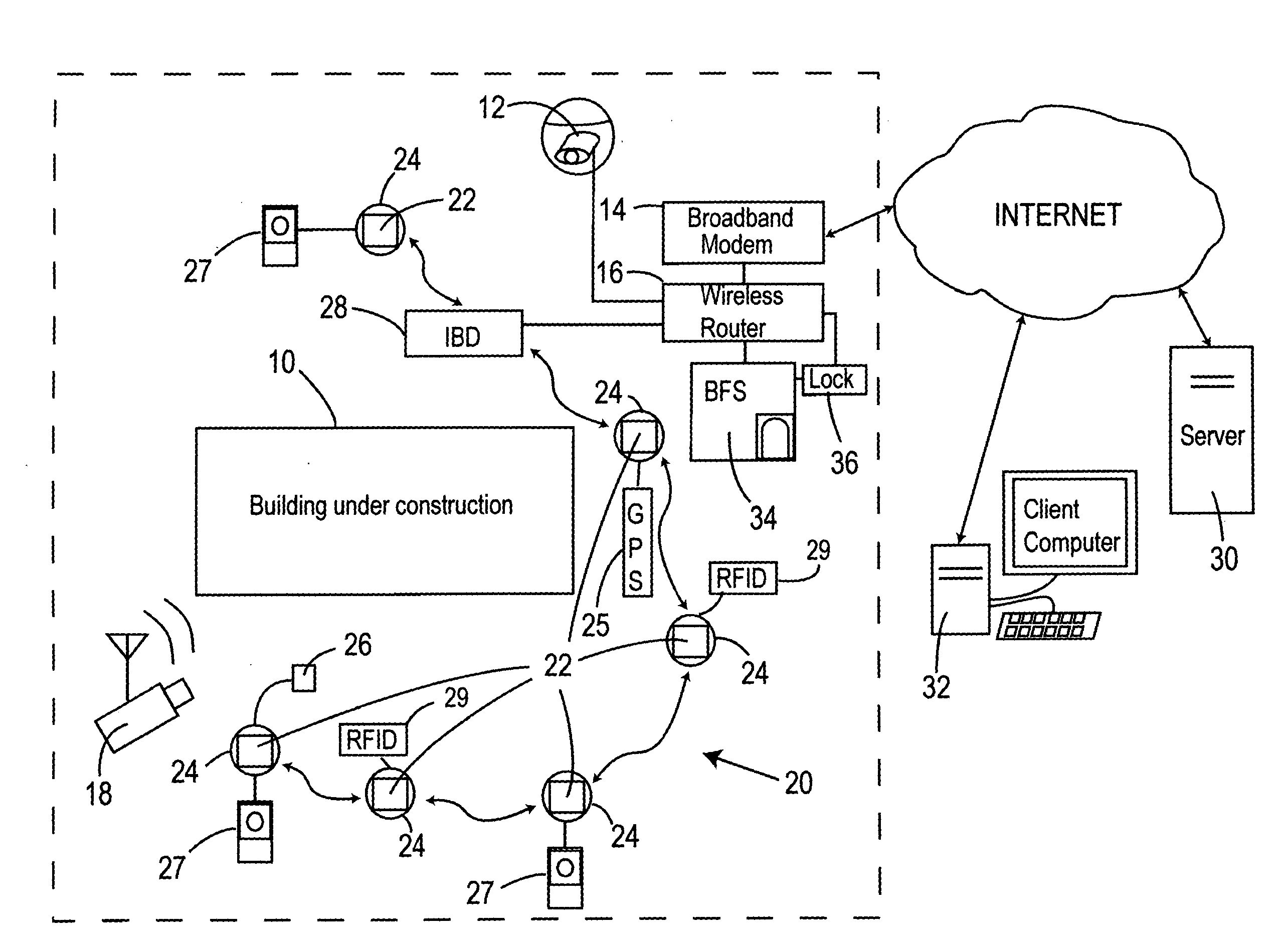
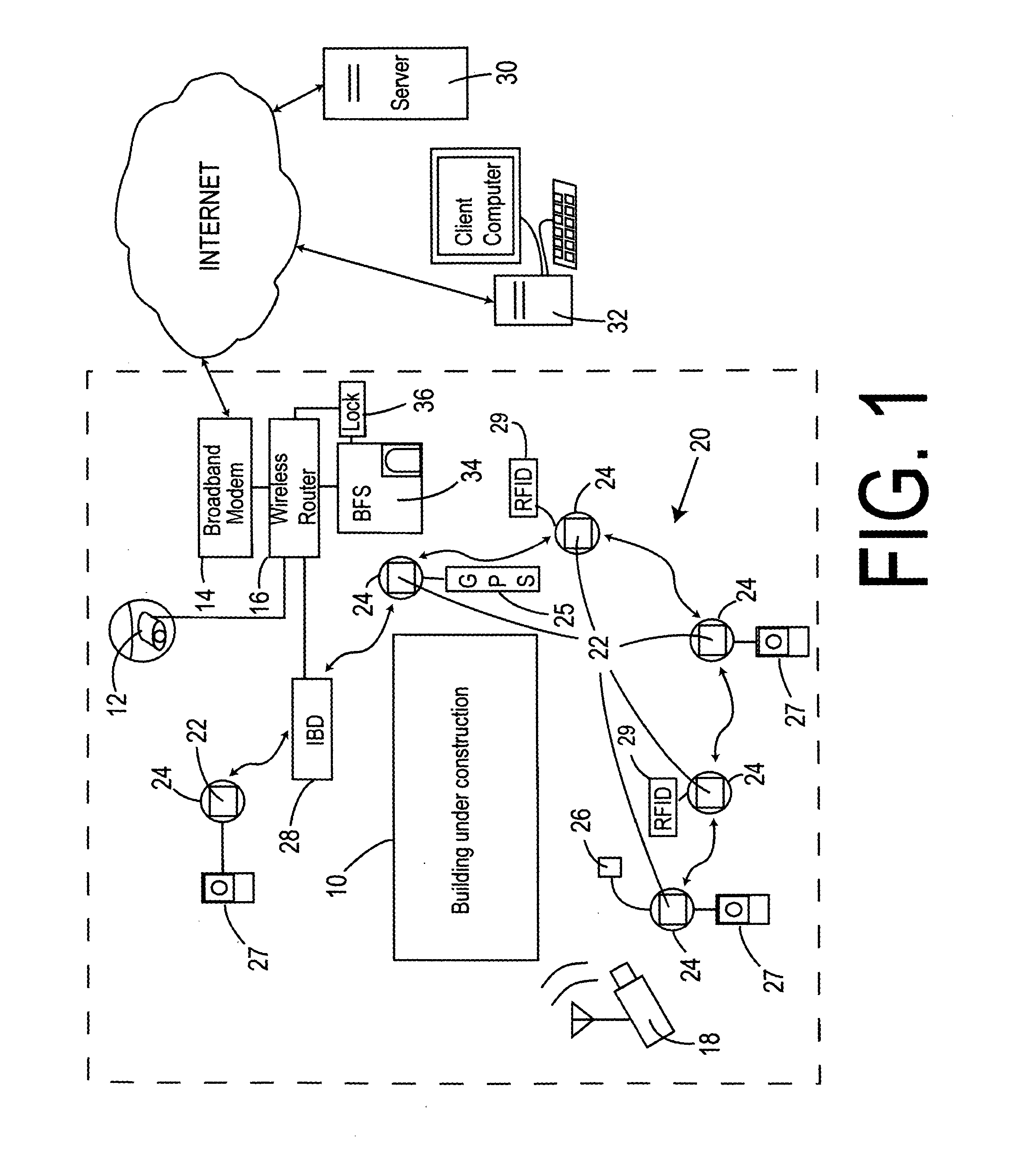
Work site remote monitoring and employee time tracking system and method
InactiveUS20080177646A1Security monitoring be enhanceReduce bandwidth requirementsElectric signal transmission systemsImage analysisBroadbandFingerprint
A work site monitoring and employee time tracking system that includes a work site Internet connection having a broadband modem in communication with a router for transporting data to and from the work site and a work site IP camera in communication with the router for transporting images from the work site to client computers in communication with the Internet. A biometric fingerprint scanner for identifying and clocking-in and clocking-out work site workers is also included. The biometric scanner is in communication with the router for transmitting identification, clock-in and clock-out data to a server computer in communication with the Internet.
Owner:PROPERTY MONITORS
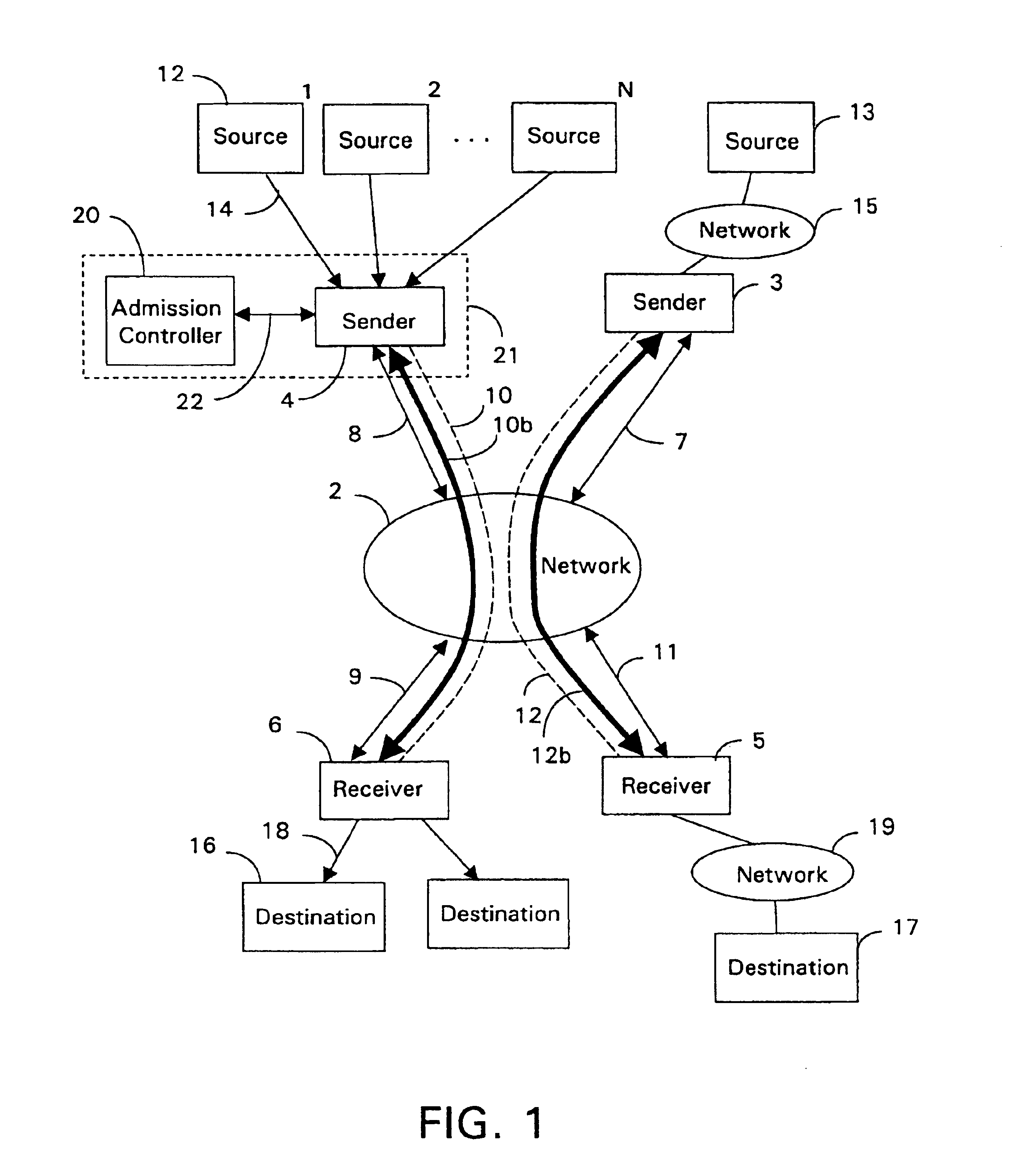
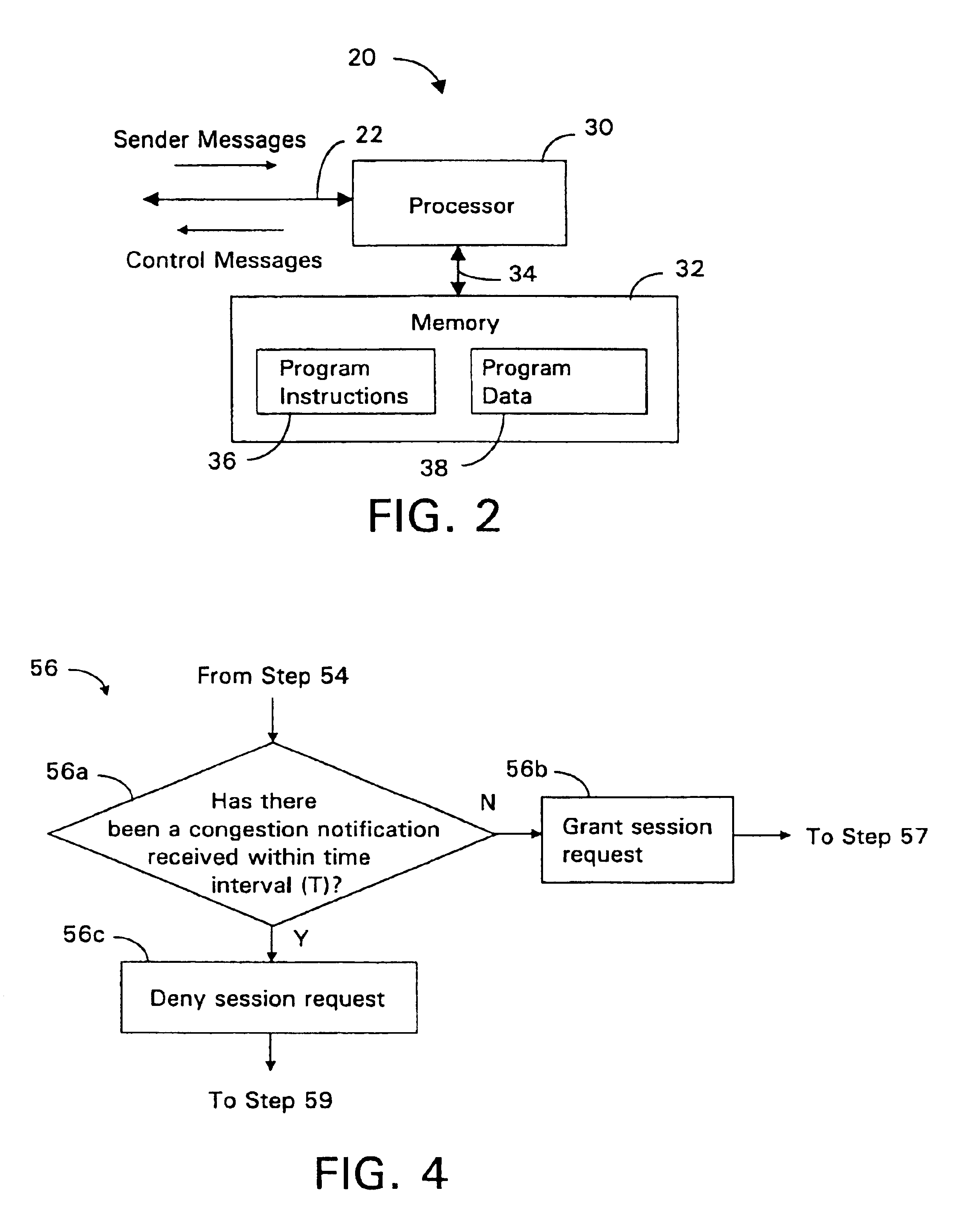
Admission control for aggregate data flows based on a threshold adjusted according to the frequency of traffic congestion notification
InactiveUS6839767B1Guaranteed bandwidthExacerbating congestion condition is avoidedError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityData stream
An admission controller and its method of operation for controlling admission of data flows into an aggregate data flow are described. Admitted data flows are aggregated into an aggregate data flow for transmission by a router, for example, over a data network. The aggregate data flow typically follows a pre-established path through the network; for example a multi-protocol label switched (MPLS) path. The path has minimum and maximum bandwidth limits assigned to it. The admission controller controls admission of new data flows into the aggregate data flow by granting or denying new session requests for the new data flows. Congestion notifications received from the network and bandwidth limits of the path are considered in determining whether to grant or deny a new session request. In this way, the admission controller provides elastic sharing of network bandwidth among data flows without exacerbating network congestion and while remaining within the path's bandwidth limits. The data flows may include transaction oriented traffic.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Method and apparatus for establishing and sharing a virtual change notification list among a plurality of peer nodes
InactiveUS6938095B2Special service provision for substationDigital computer detailsEvent objectDistributed computing
A data structure has a list of event objects, one or more producers creating the event objects for the list, and a finite set of consumers accessing the object list. The structure is characterized in that the event objects are each associated with a first reference number indicating the number of consumers currently accessing the event object, and in that, as each consumer completes access the reference number is decremented, and when the reference number for an event object is zero, and the event object is at the head of the list, indicating that all consumers have accessed the object, that event object is removed from the list. A use of the structure for propagating route changes to nodes in a multiple-processor router, and to peer routers in a network is also taught.
Owner:PLURIS
Method and system for authorizing a commercial transaction
InactiveUS6934849B2HandlingEasy to handleInterconnection arrangementsFinanceAuthorizationAuthentication
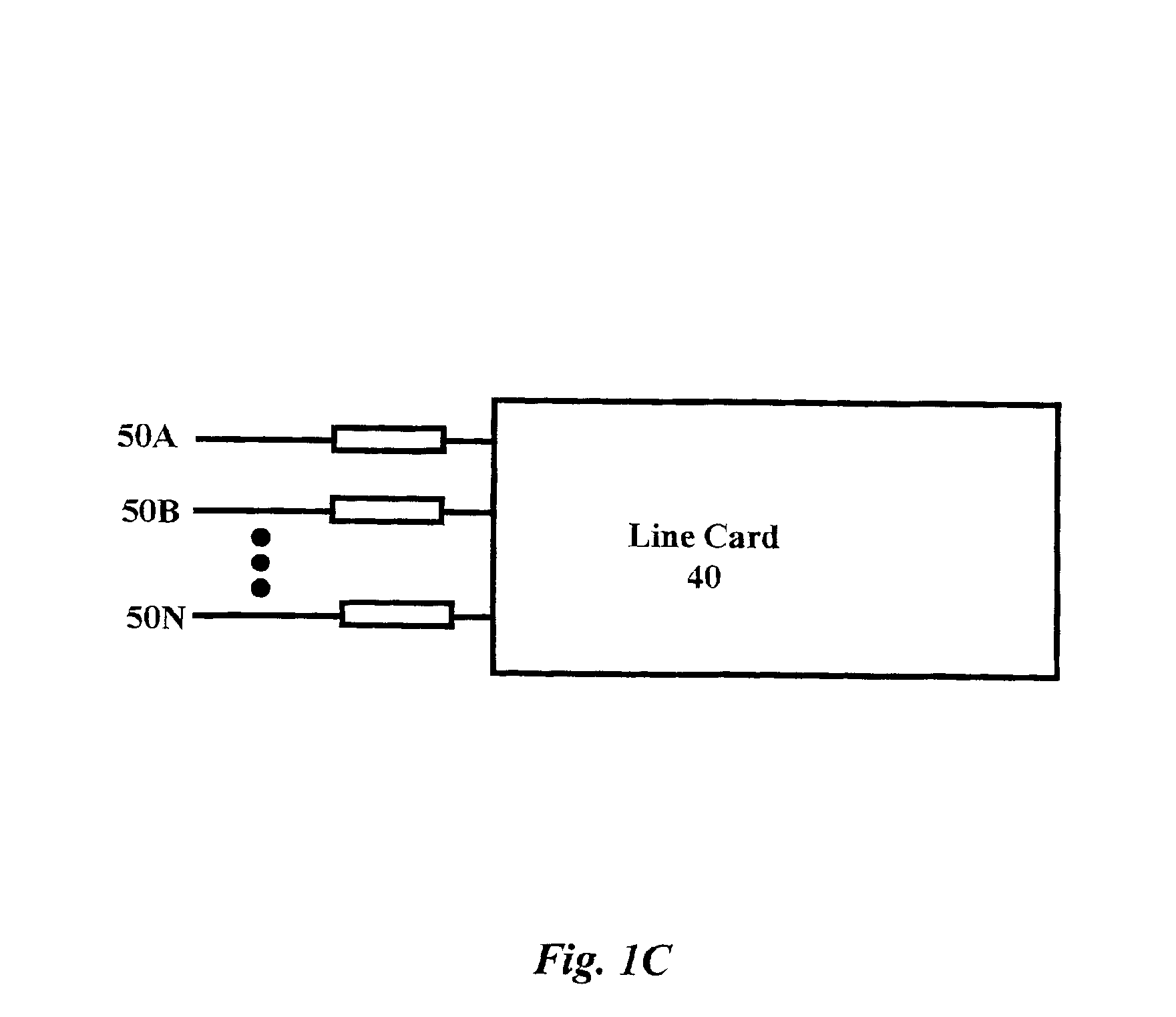
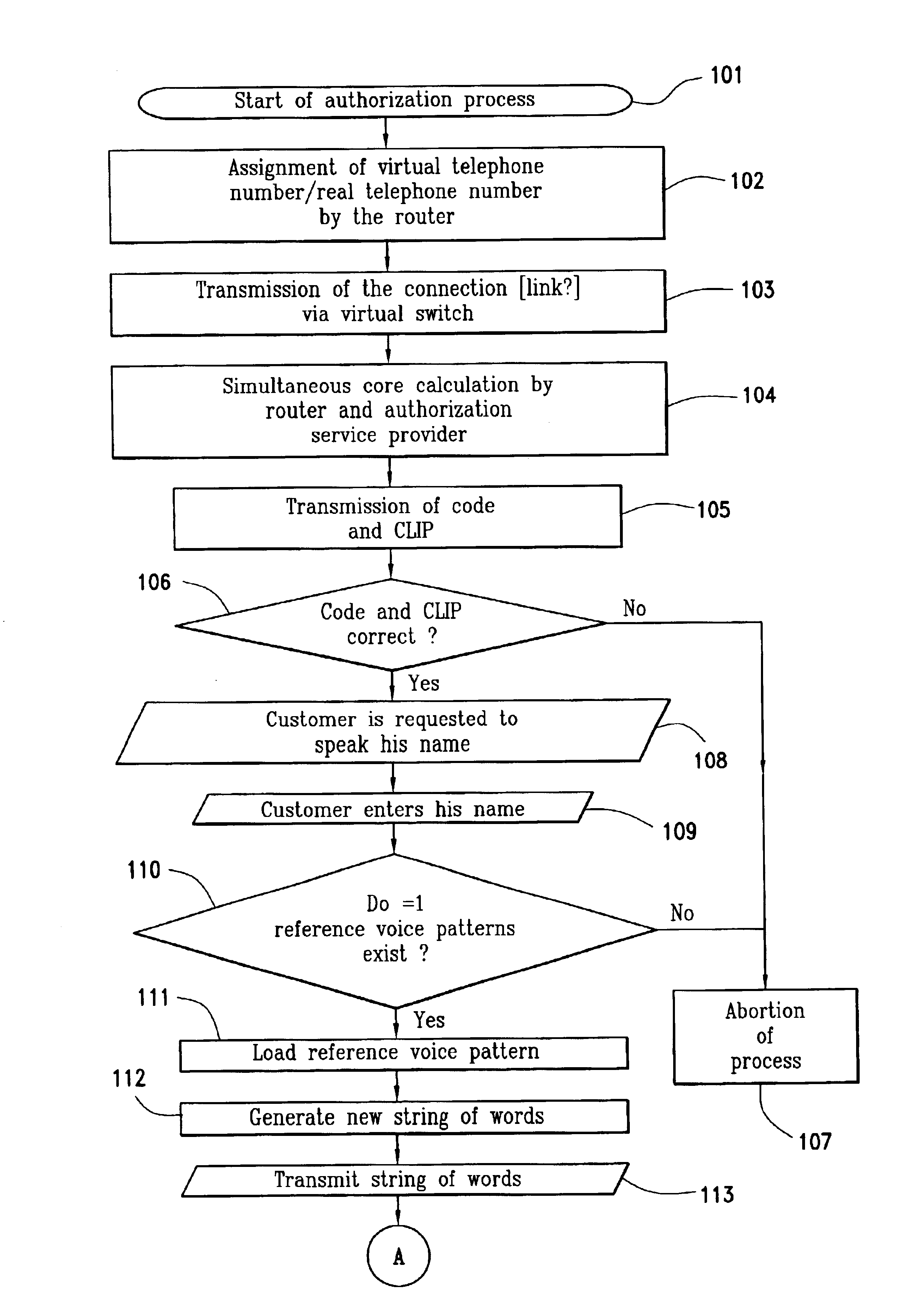
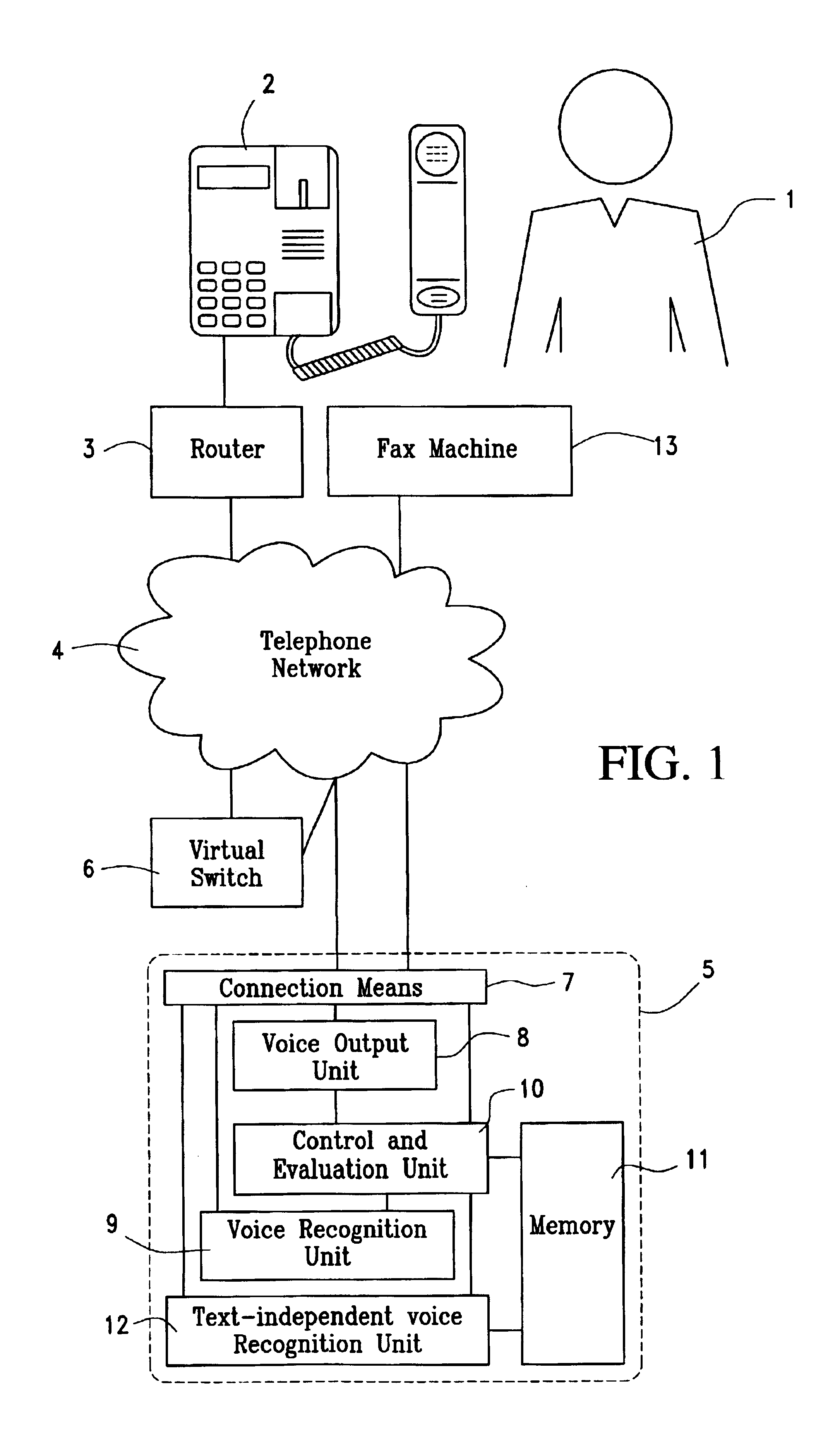
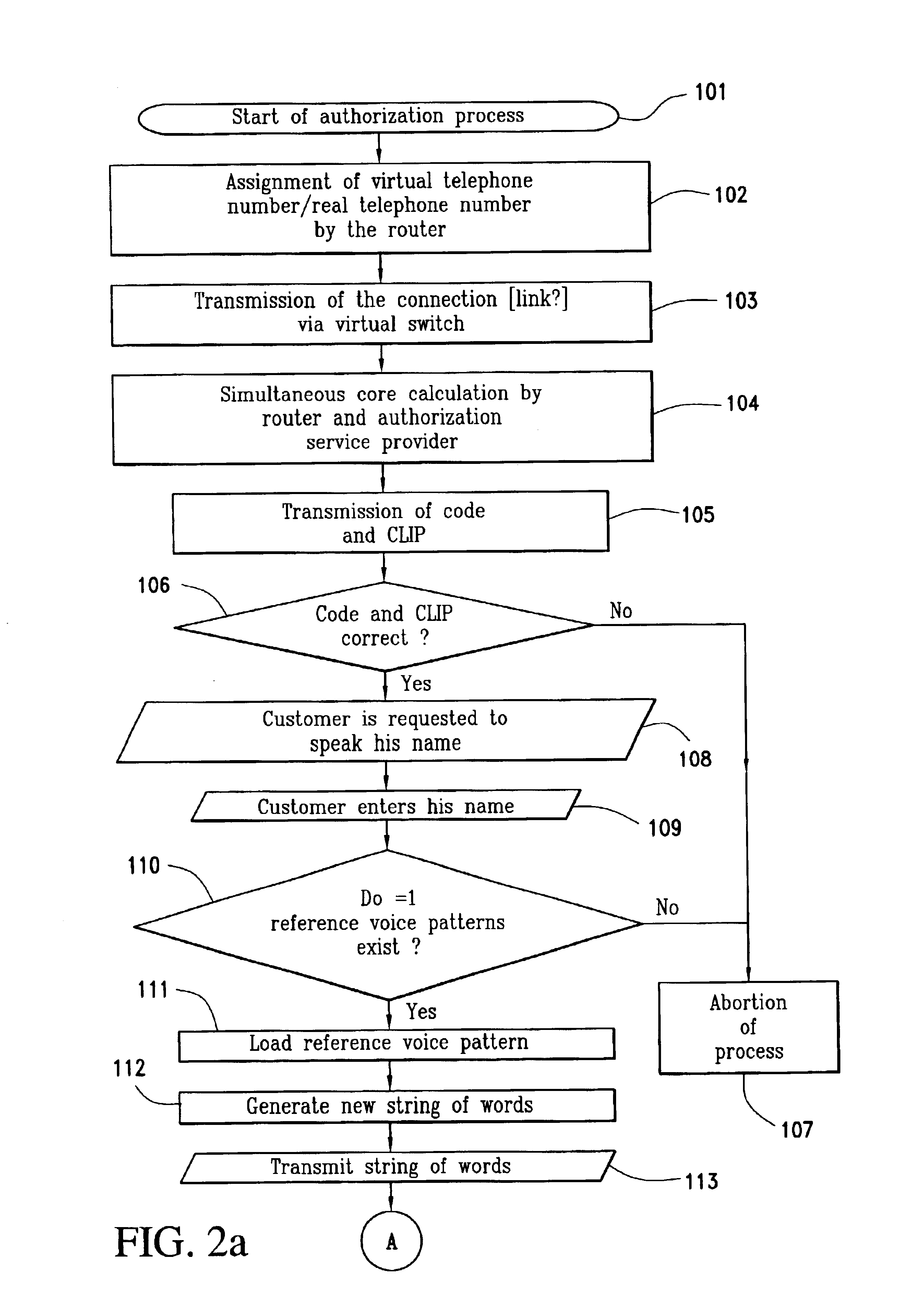
The invention relates to a method and system for authorizing a commercial transaction between a customer and a goods or service provider via an authorization service provider with authentication of the customer by comparing a biometric sample of the customer with a biometric model of the customer stored with the authorization service provider. The telephone link between the supplier and the authorization service provider is set up via a router which associates the real telephone number of the authorization service provider and the telephone number of the supplier with a virtual telephone number and transmits a code which is isochronously calculated by the router and the authorization provider with the aid of the same algorithm. The telephone link is accepted by the authorization service provider if the supplier is registered with the authorization service provider if the supplier is registered with authorization service provider under the transmitted number and if the transmitted code corresponds to the calculated code contained by said authorization service provider. An identifier and biometric code of the customer are transmitted to the authorization service provider in addition to the amount which is to be transferred. The transaction is initiated by the authorization provider if the correspondence between the biometric sample and the stored biometric model exceeds a predetermined thresh old value.
Owner:LUMENVOX CORP
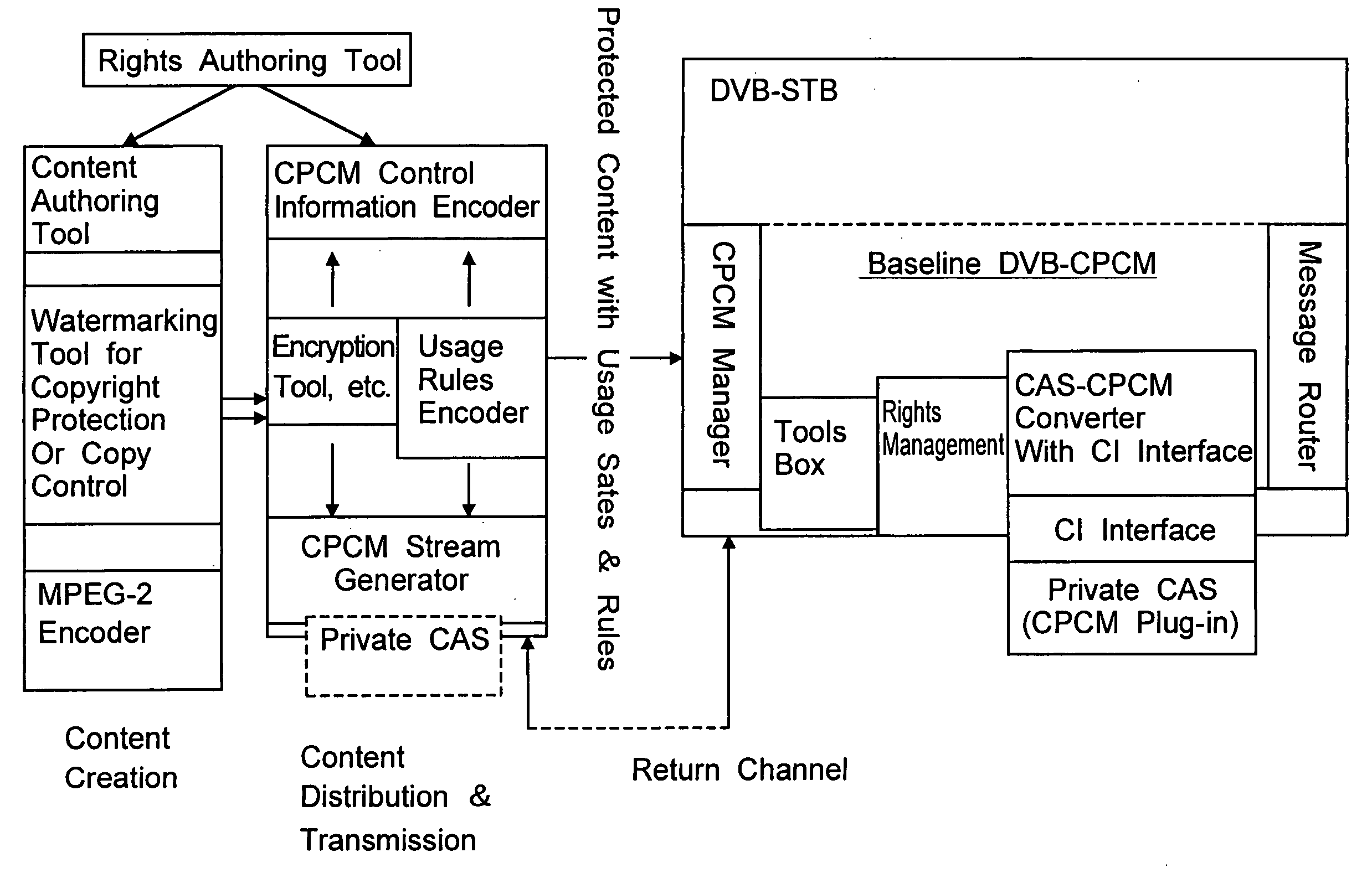
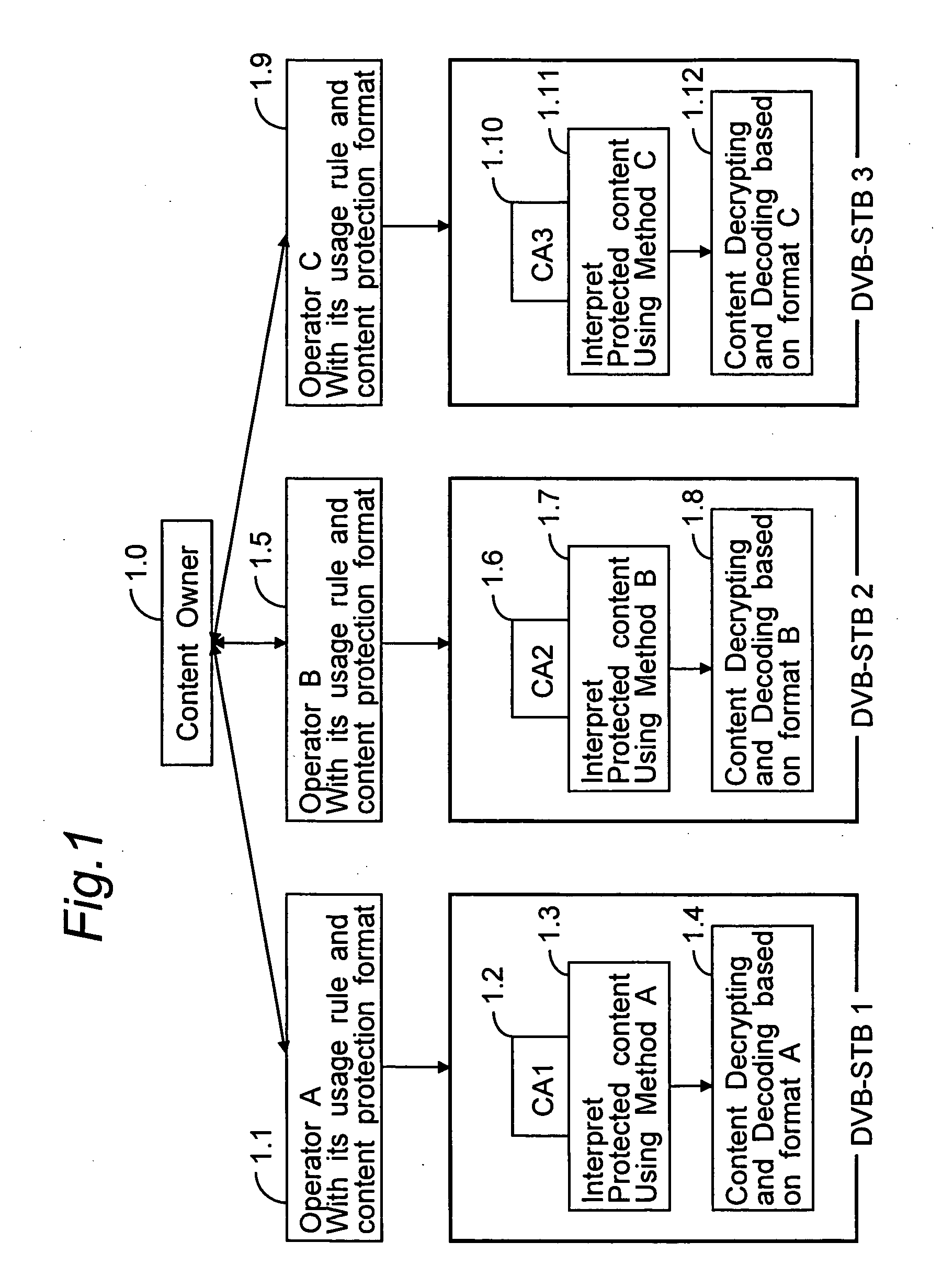
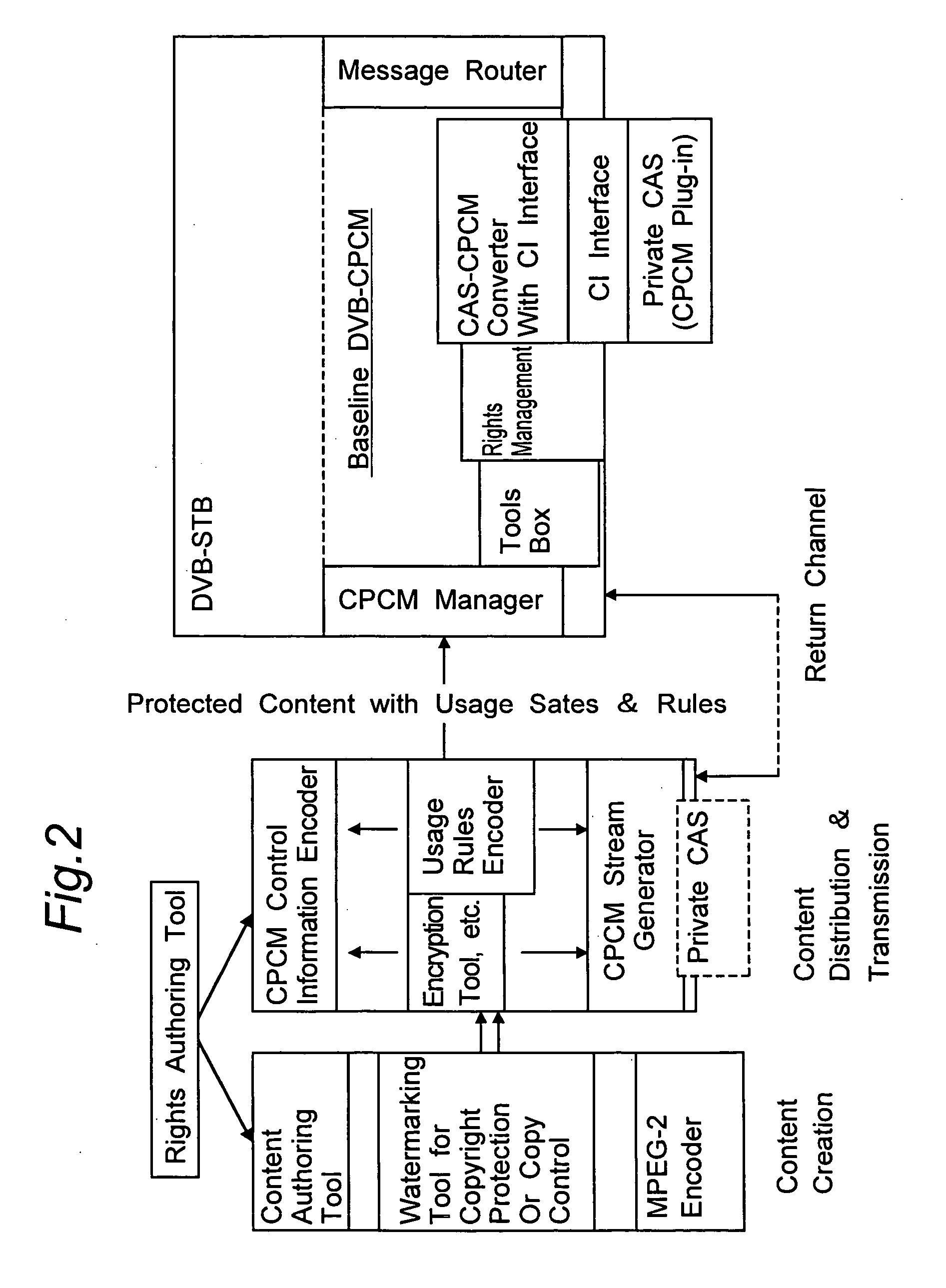
Apparatus of a baseline dvb-cpcm
ActiveUS20050022227A1Improve interoperabilityTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionRights managementContent delivery
A Baseline DVB-CPCM is presented in this proposal to provide a secure and interoperable content delivery and transferring apparatus. The proposed Baseline DVB-CPCM is a unit to be implemented in a compliant CPCM device, and it consists of five major modules to be used for end-to end solution and content transferring between devices. These modules are CPCM Manager, Tools Box, Rights Management Module, Message Router, and CAS-CPCM Converter.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
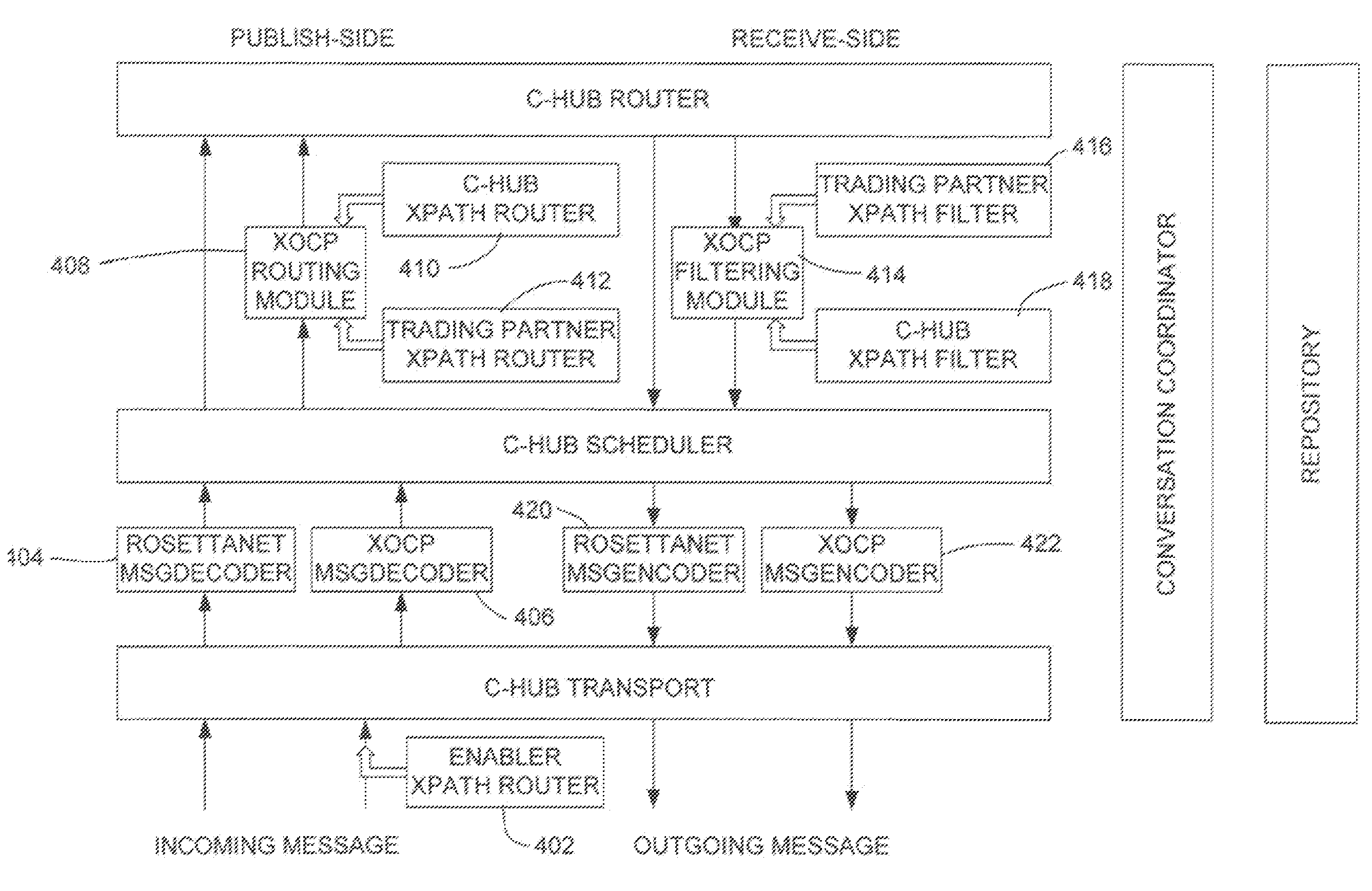
Pluggable hub system for enterprise wide electronic collaboration
InactiveUS7143186B2Increase speedEnsure qualityFinanceMultiple digital computer combinationsSession managementMessage flow
An enterprise wide electronic commerce system allows trading partners to act as participants in a complex trading process. Participants communicate with one another by joining conversations that are hosted in a collaboration space and managed by a collaboration hub. In this manner, the enterprise workflow may have an effect on, or be affected by, local workflows. The invention provides a pluggable hub system for enterprise wide electronic collaboration. An embodiment of the invention includes a collaboration hub for use with a collaboration system, comprising a hub transport for receiving messages from participants and sending messages to participants, a hub router for routing messages from a first participant to a second participant, a hub scheduler for scheduling the flow of messages between the hub router and the hub transport, a conversation manager for managing the flow of messages between participants, and a repository for storing conversation management data.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
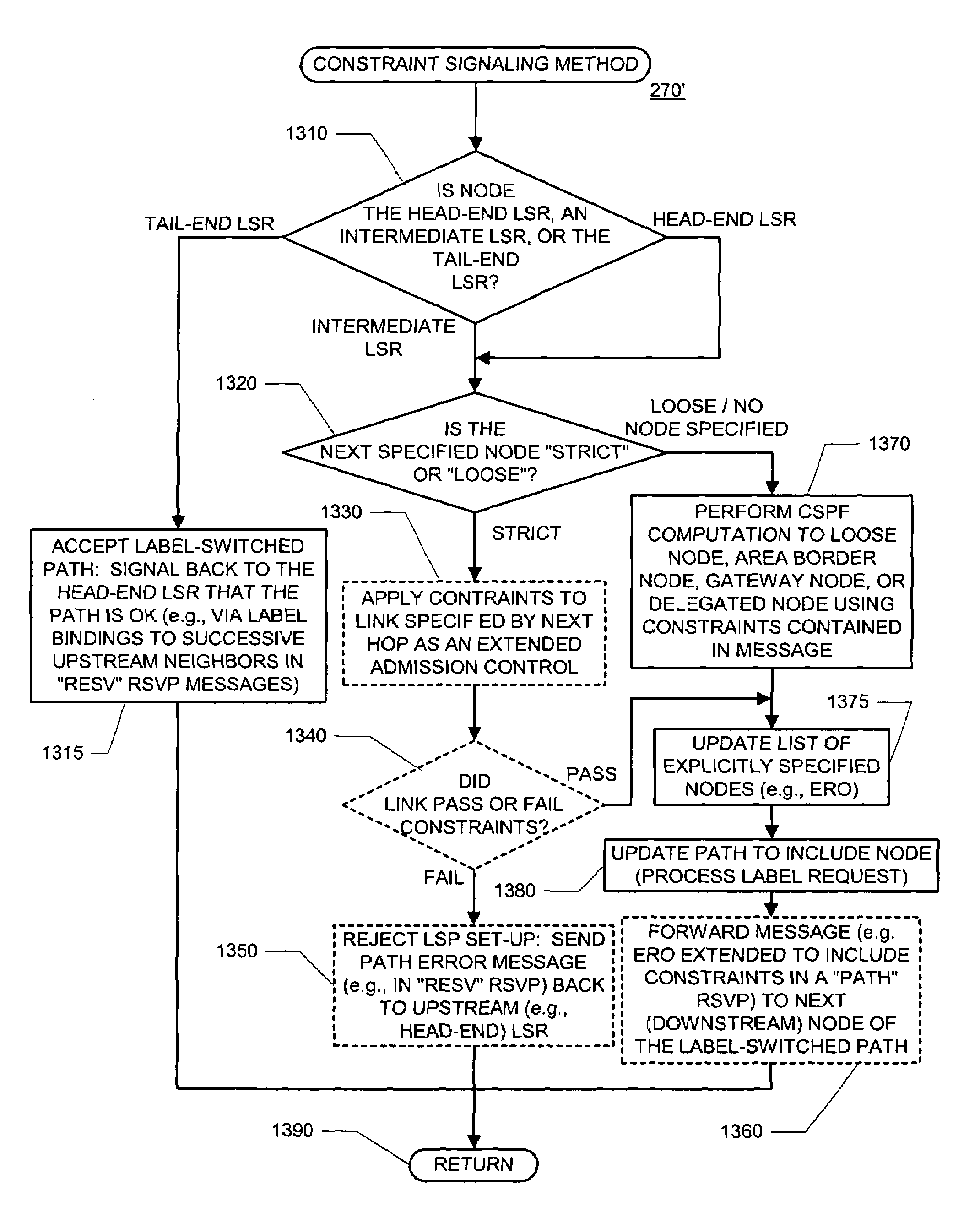
Communicating constraint information for determining a path subject to such constraints
InactiveUS7319700B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPathPingDistributed computing
Path determination constraints may be encoded in the form of a program having one or more instructions. Each of instructions may include an operation code, and operands (or pointers to locations where operands are stored). In this way, an extensible, interoperable way for a nodes (e.g., label-switching routers) to communicate constraints within a network is provided. Such constraints may be inserted (e.g., as one or more CONSTRAINT objects) into signaling messages (e.g., a PATH RSVP message). By enabling the signaling of constraints, the determination of constraint-based (label-switched) paths can be distributed among a number of (label-switching) routers or other nodes. Upon receiving a message with constraints (e.g., a CONSTRAINT object(s)), a node may (i) ignore the constraints if the node is a tail-end node (label-switching router), (ii) apply the constraints to a link if the next hop in the (label-switched) path is strict, and / or (iii) perform a constraint-based path determination to a next hop if the next hop is loose.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Performing multicast communication in computer networks by using overlay routing
InactiveUS7080157B2Efficient managementSpecial service provision for substationData switching by path configurationNetwork managementService provision
An overlay protocol and system for allowing multicast routing in the Internet to be performed at the application level. The overlay protocol uses “native” Internet multicast and multicast routing protocols to route information, according to overlay routing tables. Overlay groups are mapped to native multicast groups to exploit native multicasting in regional or local forwarding domains. Use of the overlay protocol allows overlay distribution to be handled in a more intelligent and bandwidth-managed fashion. Overlay routers are placed at each of several local area networks, Internet service provider's point of presence, enterprise, or other cohesively-managed locations. The overlay computers are configured according to bandwidth and security policies, and perform application-level multicast distribution across the otherwise disjoint multicast networks by using the overlay routing. The result is an overlay multicast network that is effectively managed according to local network management policies. Application-level control can be applied to the transferred data at the overlay routers.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
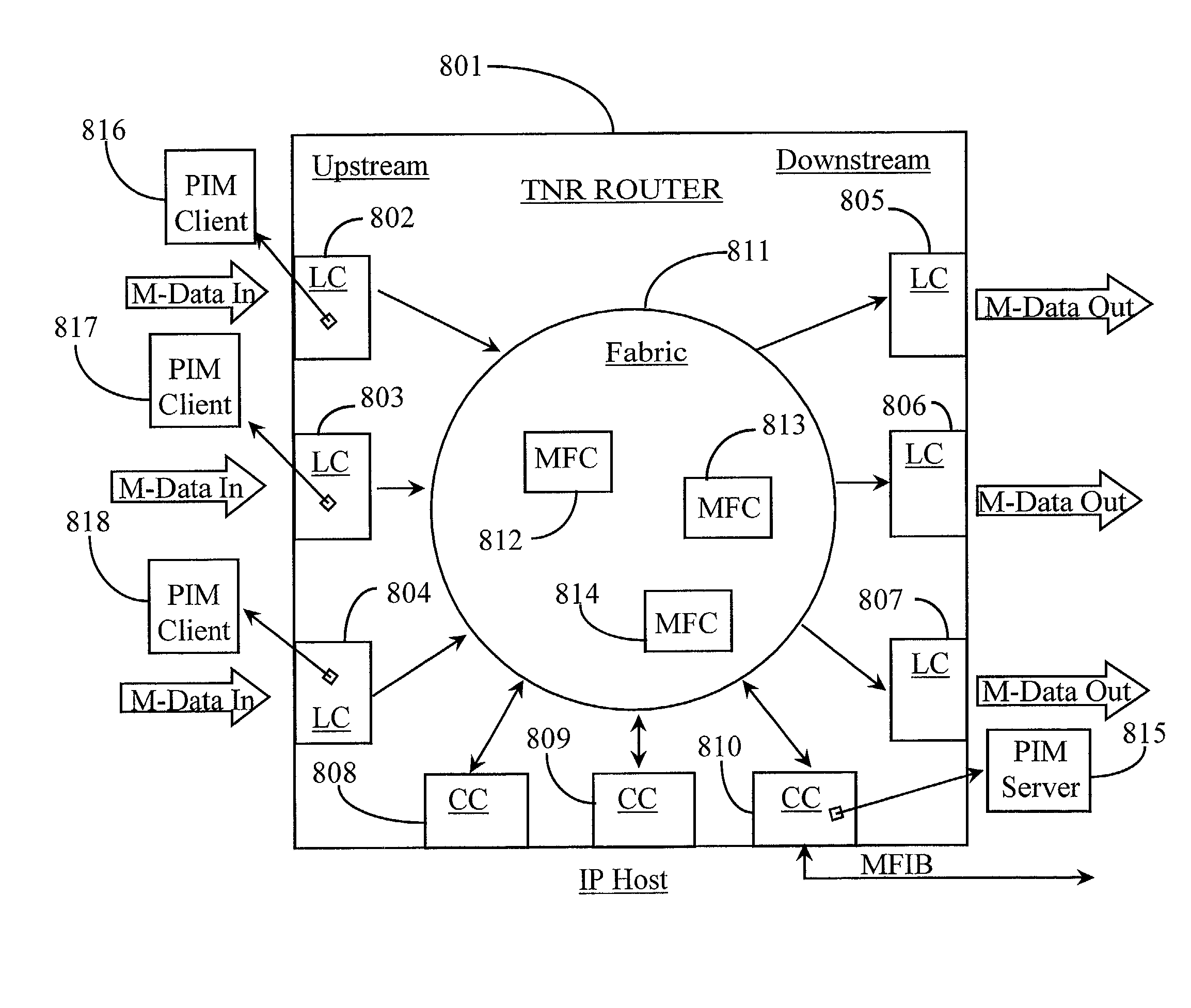
Method and apparatus for providing multi-cast transmissions using a distributed router
InactiveUS6914907B1Special service provision for substationTime-division multiplexTraffic volumeTraffic capacity
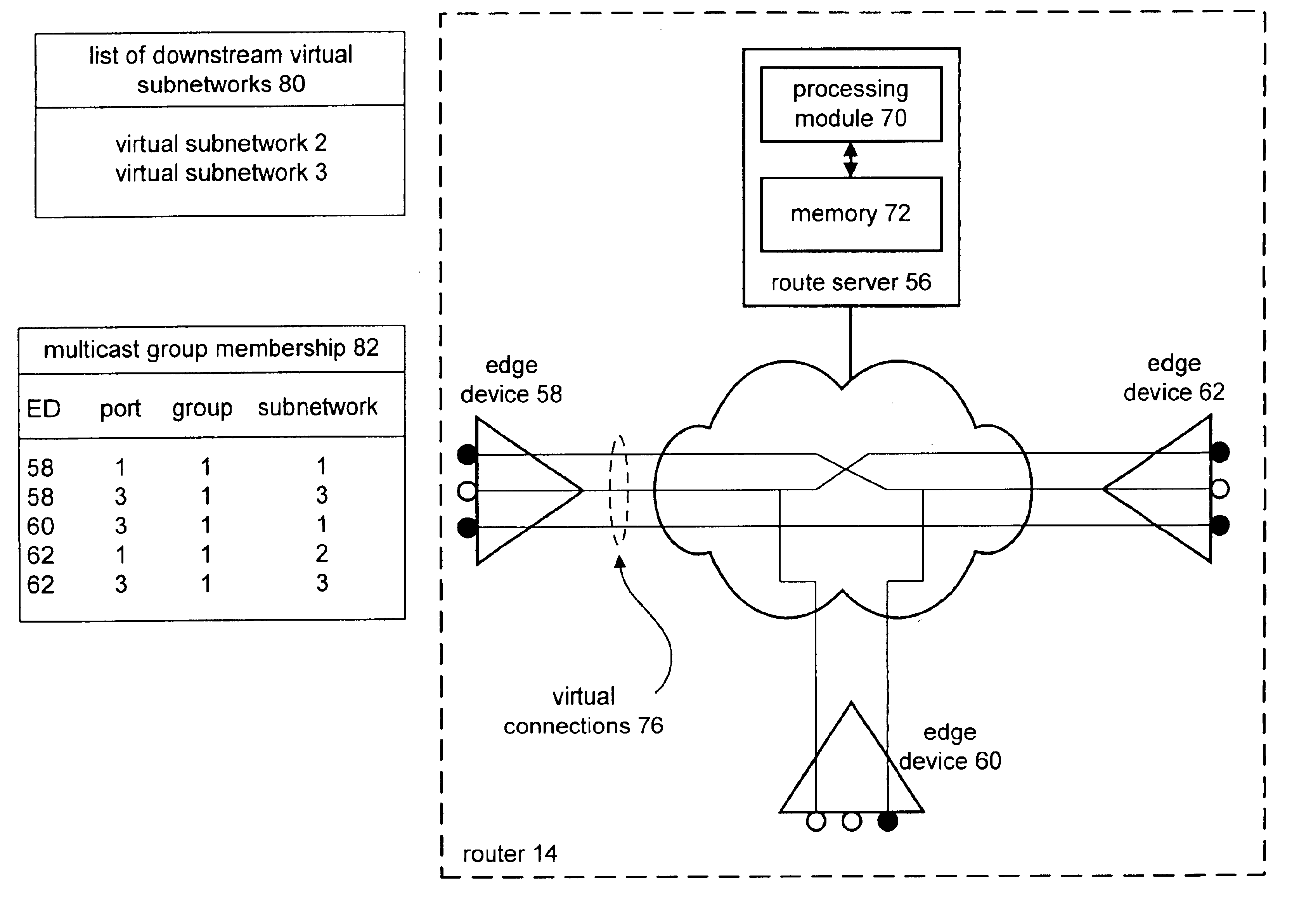
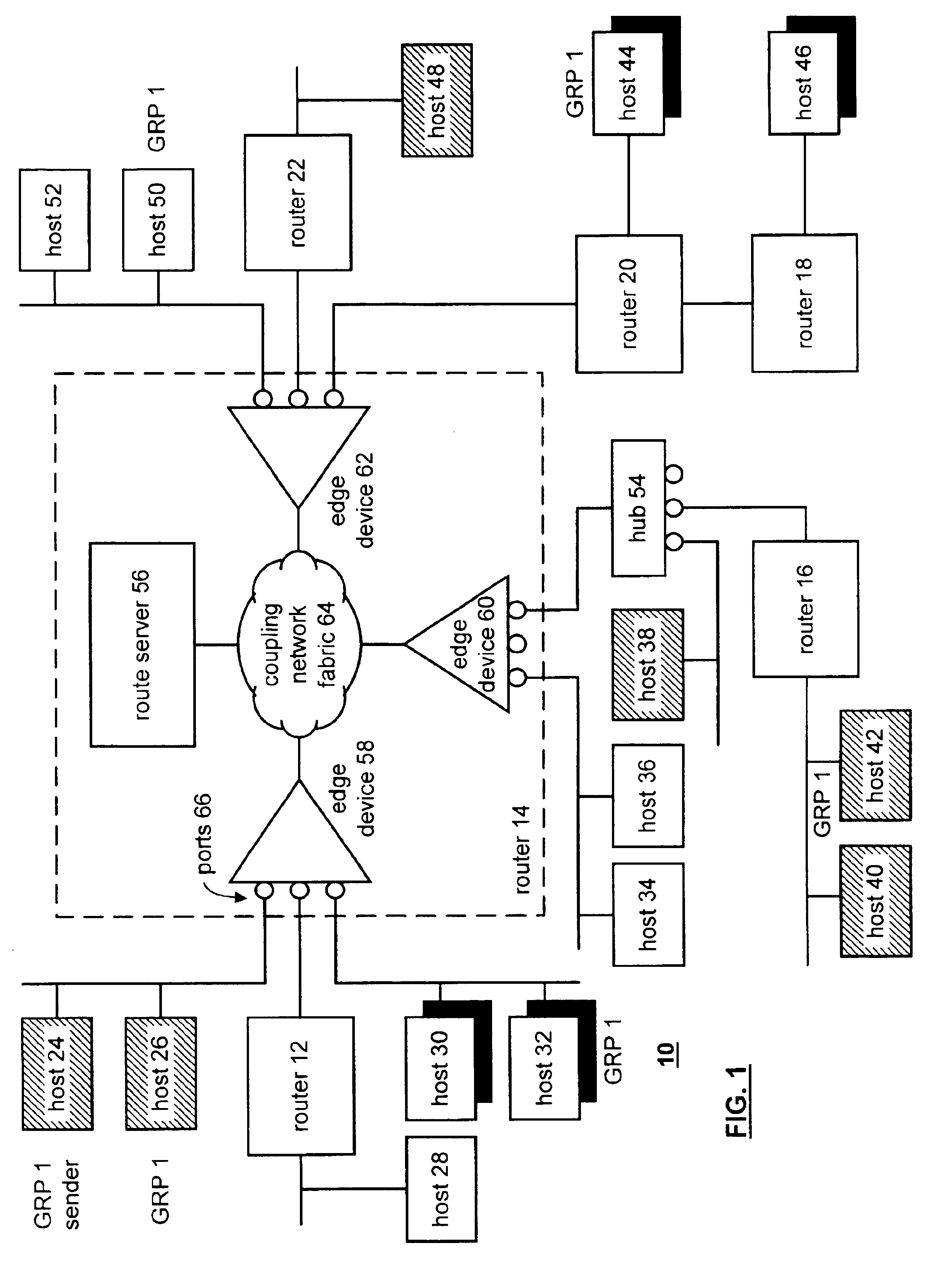
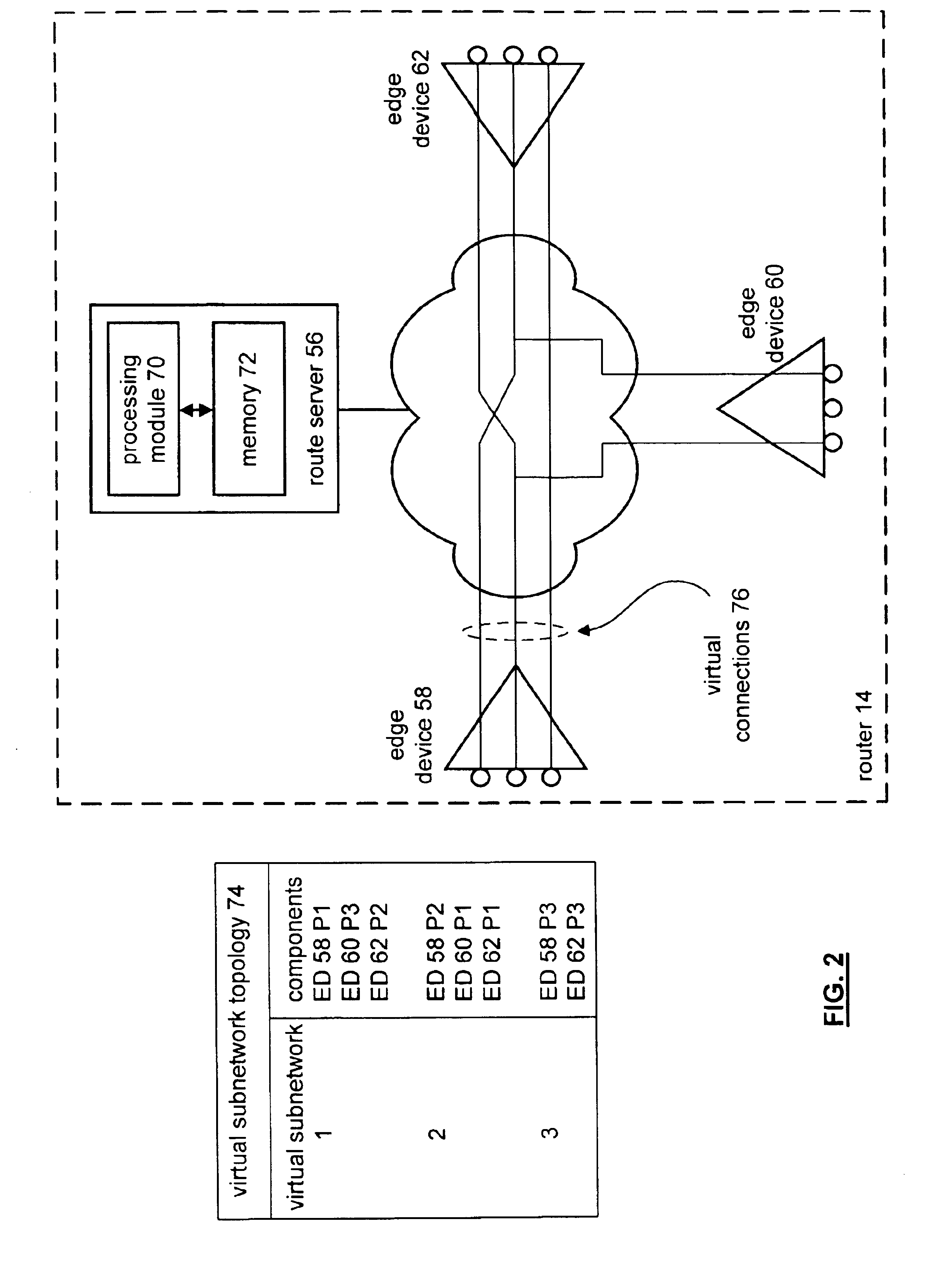
A method and apparatus that includes processing for providing multi-cast transmissions within a data network begins by determining, for a source virtual network, a list of downstream virtual sub-networks for multi-cast traffic based on a multi-cast routing protocol. The processing then continues by determining multi-cast group membership on as per downstream virtual sub-network, edge device, and port basis. The process continues when a data packet is received via the source virtual network. The processing then continues by generating a multi-cast session table entry based on the list of downstream virtual sub-networks and the multi-cast group membership. The process continues by establishing virtual connections between the source virtual network and edge devices coupled to virtual sub-networks identified in the list of downstream virtual sub-networks. Having generated the virtual connections, the processing continues by downloading the multi-cast session table to the edge devices. The edge devices utilize the multi-cast session table entry to determine where the received data packets are to be forwarded.
Owner:NEWBRIDGE NETWORKS
Managing L3 VPN virtual routing tables
InactiveUS20050188106A1Efficiently setupEffective maintenanceDigital computer detailsNetworks interconnectionRouting tablePrivate network
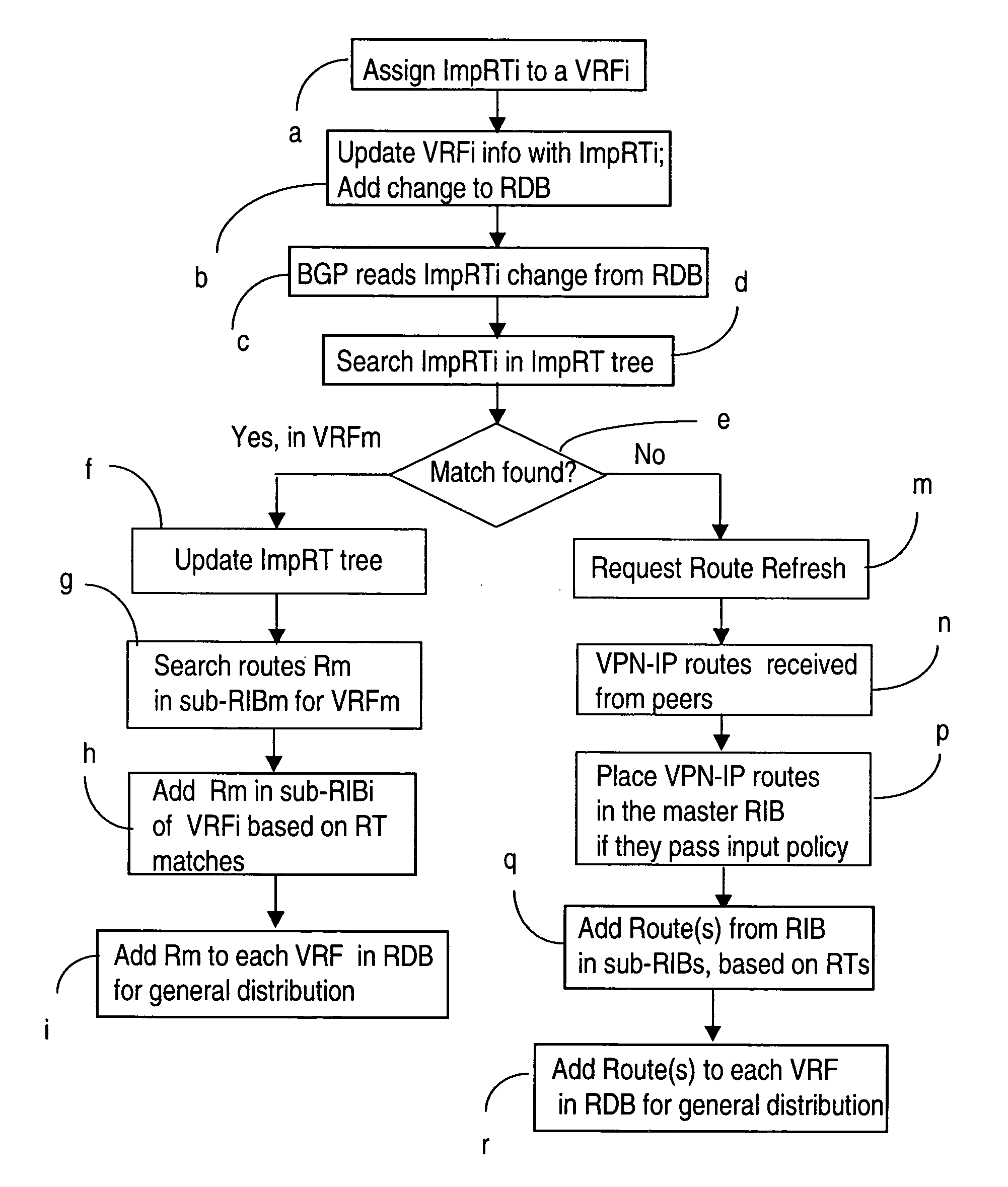
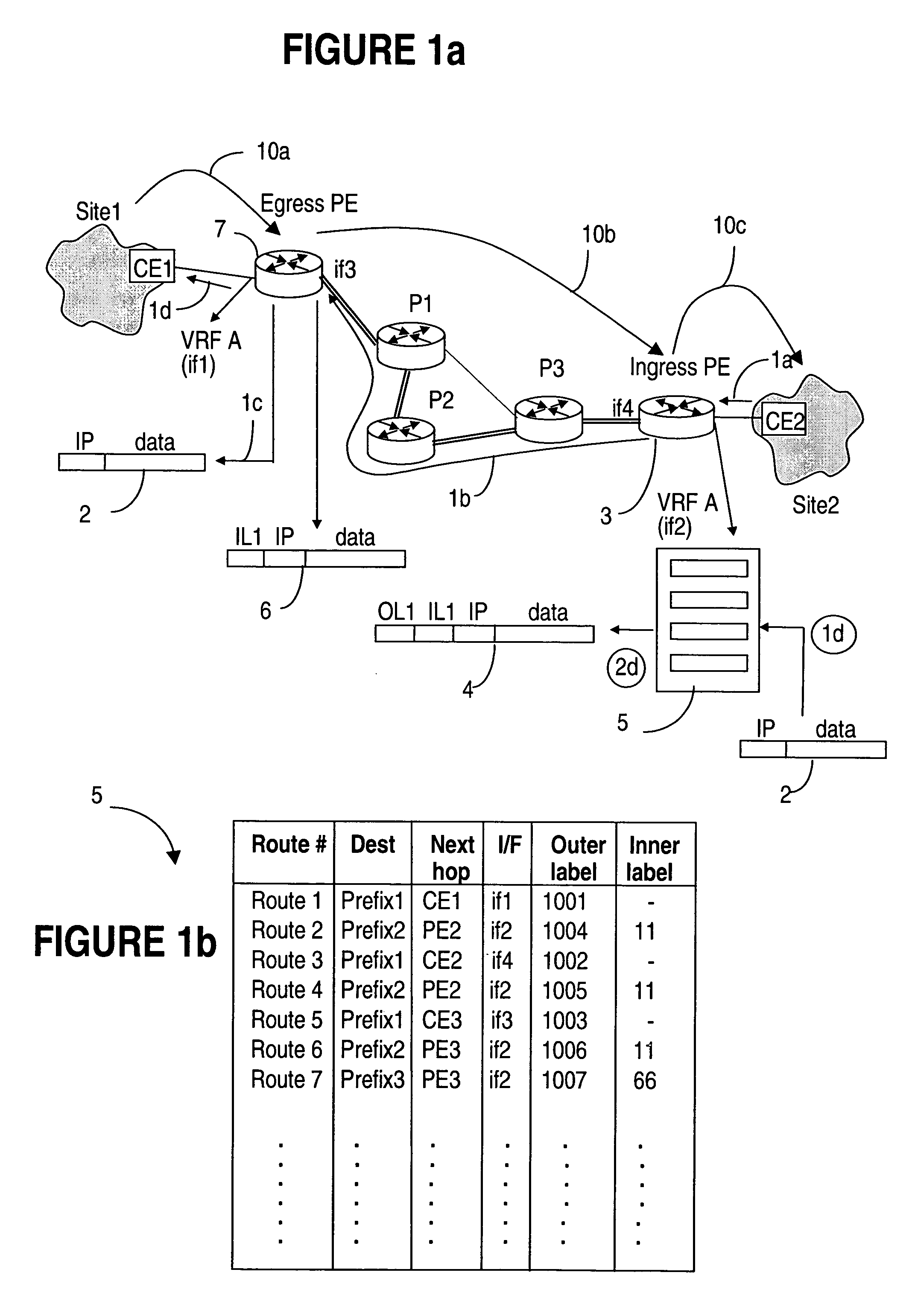
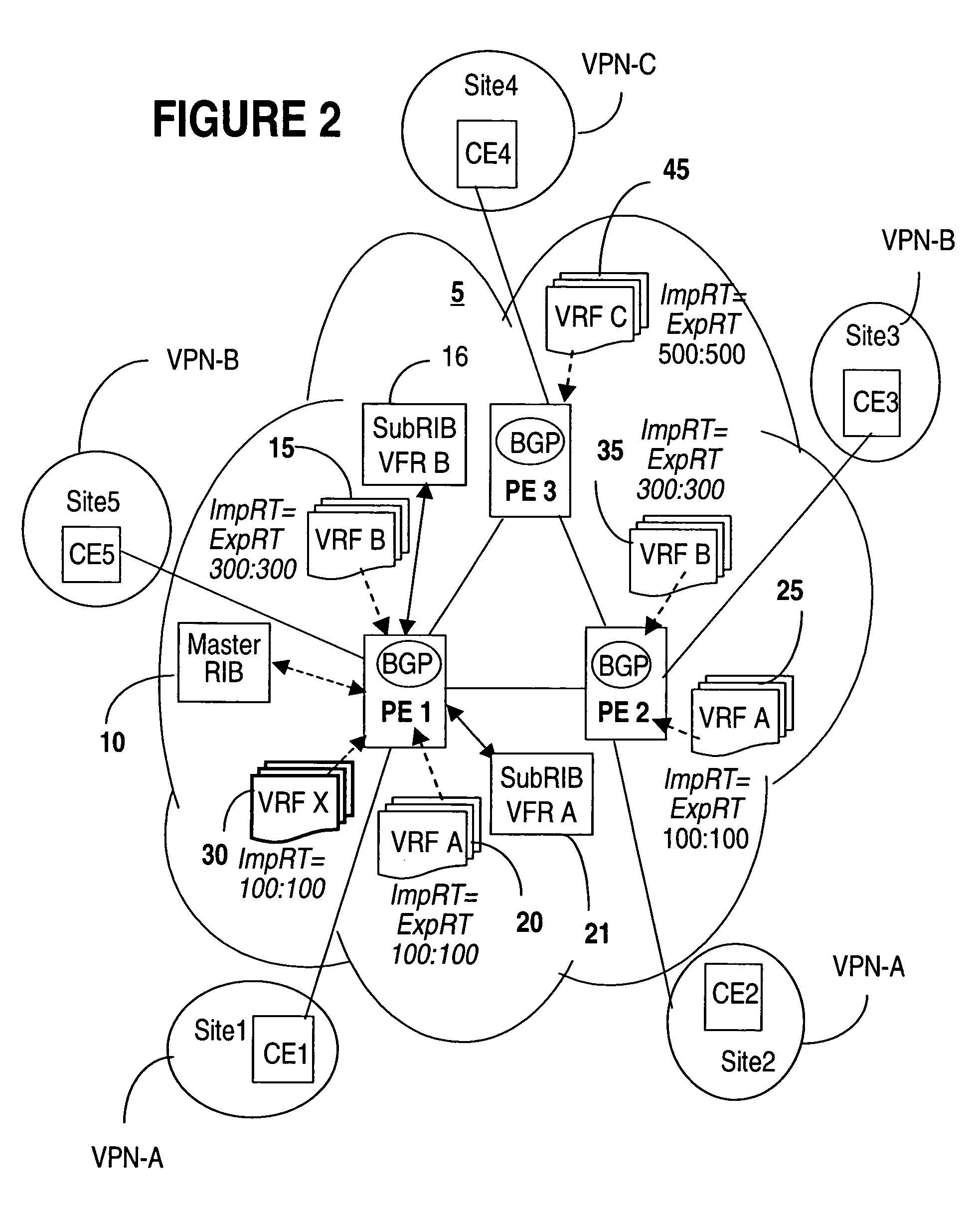
A method of managing virtual routing forwarding (VRF) tables at a provider edge PE router of a L3 virtual private network (VPN) is provided. An import route target (ImpRT) tree is maintained at the PE router, which keeps the association between all ImpRT attributes currently configured on said PE router and the virtual routing table VRF at that router. When an ImpRT attribute is configured on a VRF table, the PE router first searches the tree to identify a local VRF table that contains a route(s) with that ImpRT attribute. If this information is available locally, the VRF is updated by copying the route information, and there is no need to do a route refresh. When an ImpRT is deleted from a VRF, a route refresh is avoided by parsing all the routes in the VRF and removing the routes that no longer have a matching route target. In an alternative implementation, the local source is the master RIB (routing information base) which includes all routes in all VRFs at the router, and optionally even rejected routes that were filtered out using ImpRTs. In this variant, even routes associated with ImpRTs that are new to the router would be available to update the VRF without requiring a route refresh.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
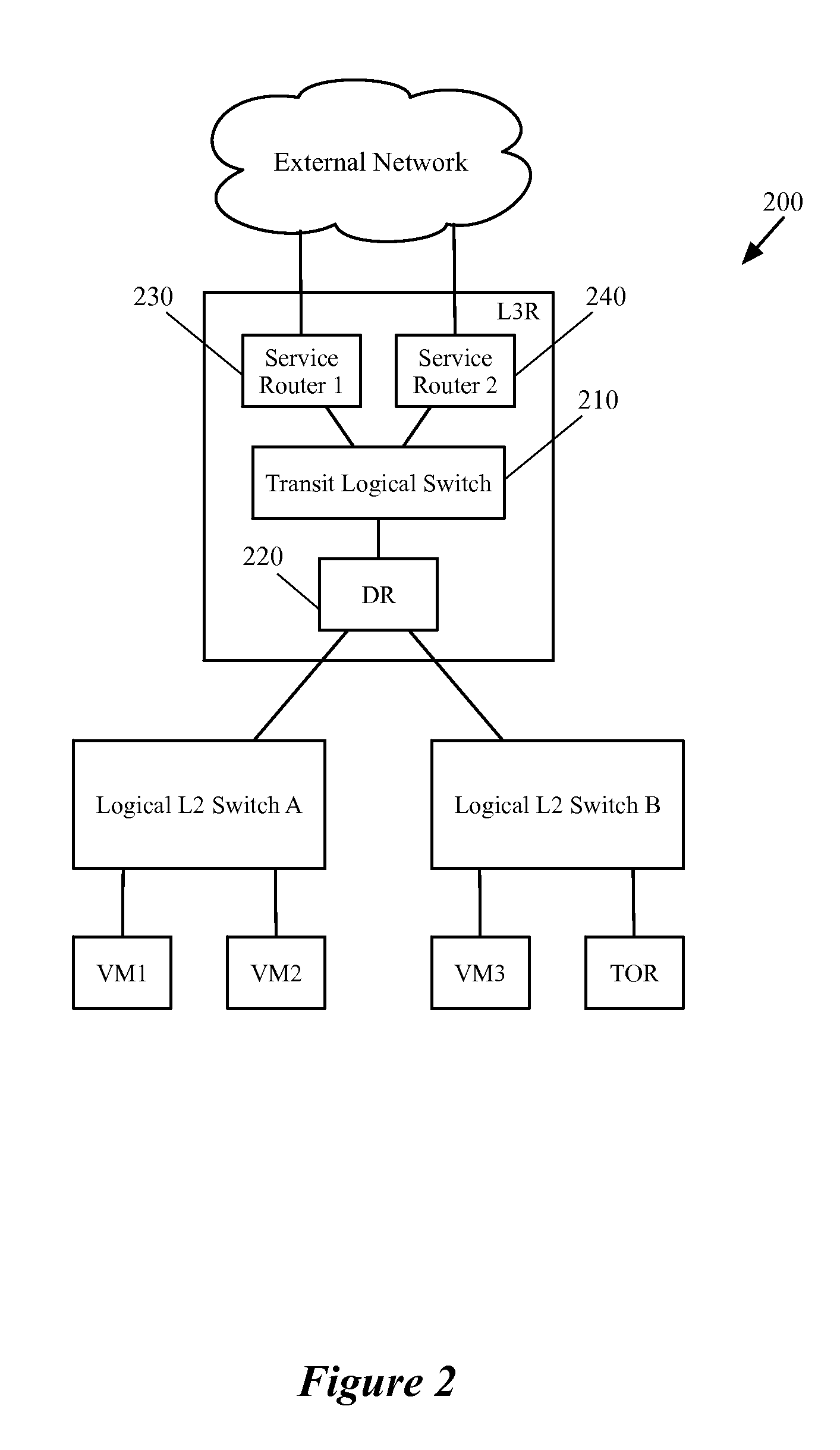
Configuring a Hardware Switch as an Edge Node for a Logical Router
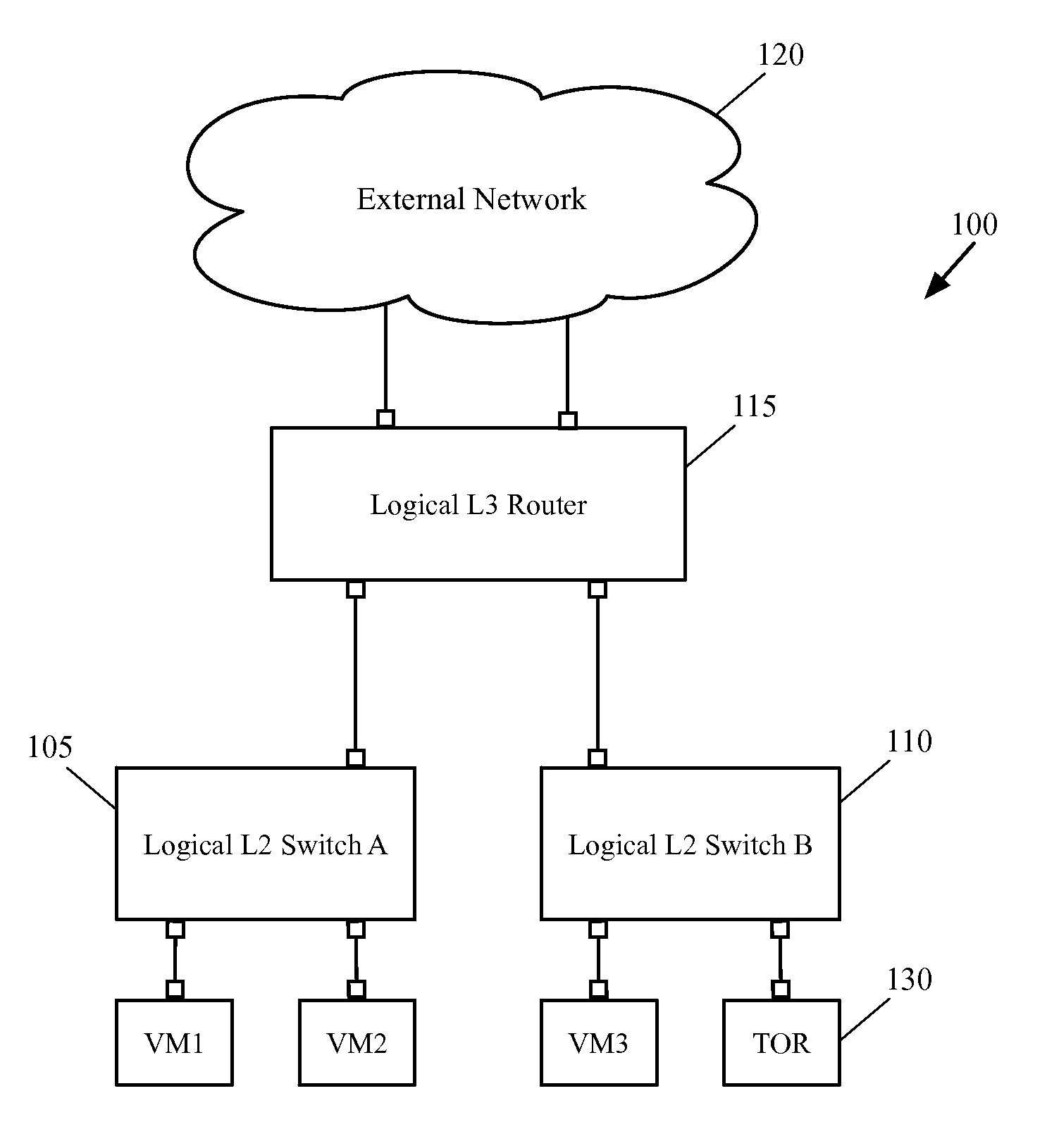
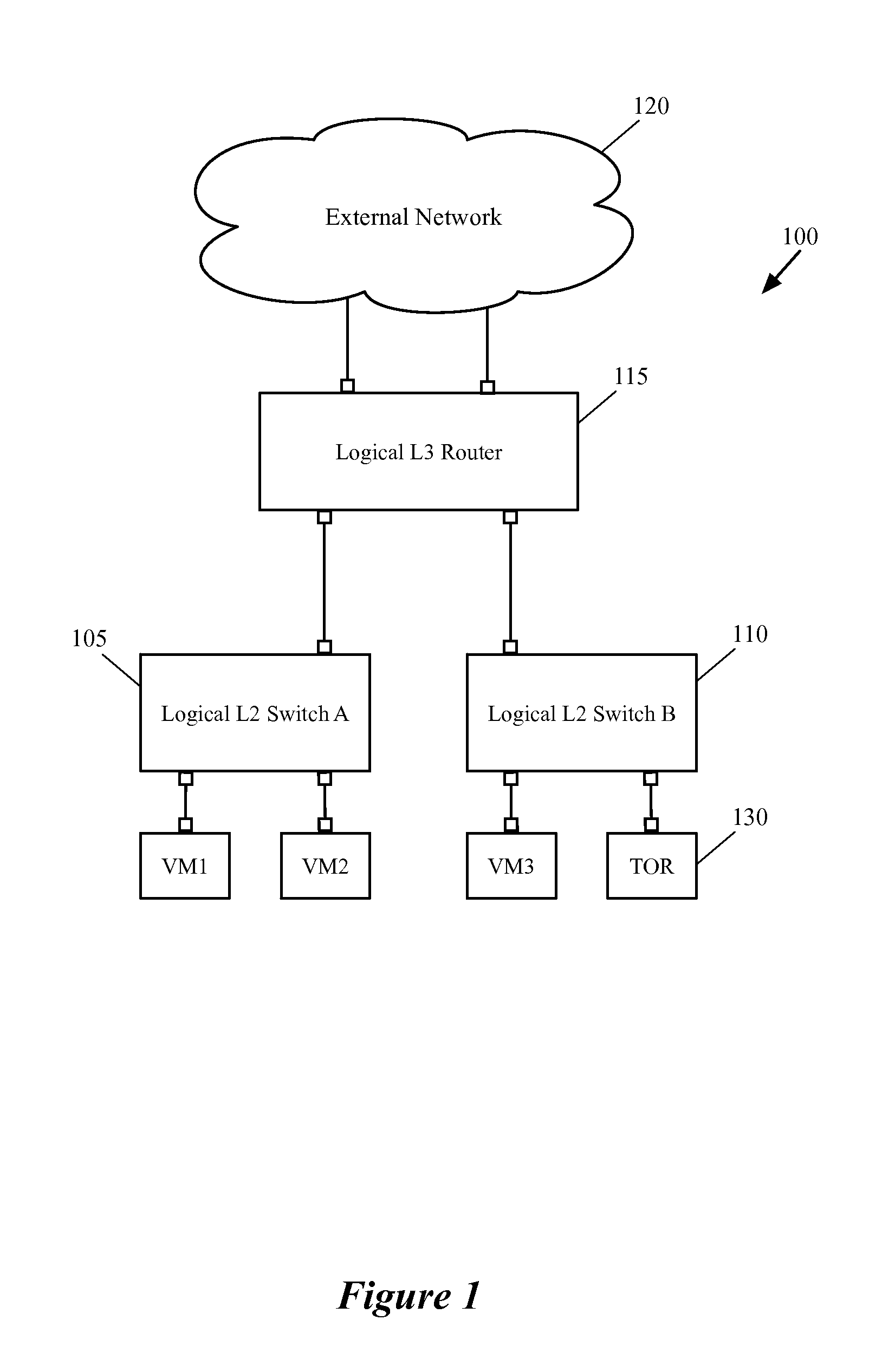
A method for configuring an edge MHFE for a logical network to communicate with other networks is described. The method receives data for the logical network that defines a logical router and a set of logical switches for logically connecting several end machines that operate on different host machines. The method, based on the received logical network data, identifies a physical port of the MHFE to bind a logical uplink port of the logical router to the identified physical port. The uplink port is for connecting the logical router to the external network. The method then binds the logical uplink port to the identified physical port by defining an uplink logical switch with a logical port that is associated with the identified physical port and assigning network and data link addresses of the logical uplink port to the logical port of the uplink logical switch.
Owner:NICIRA
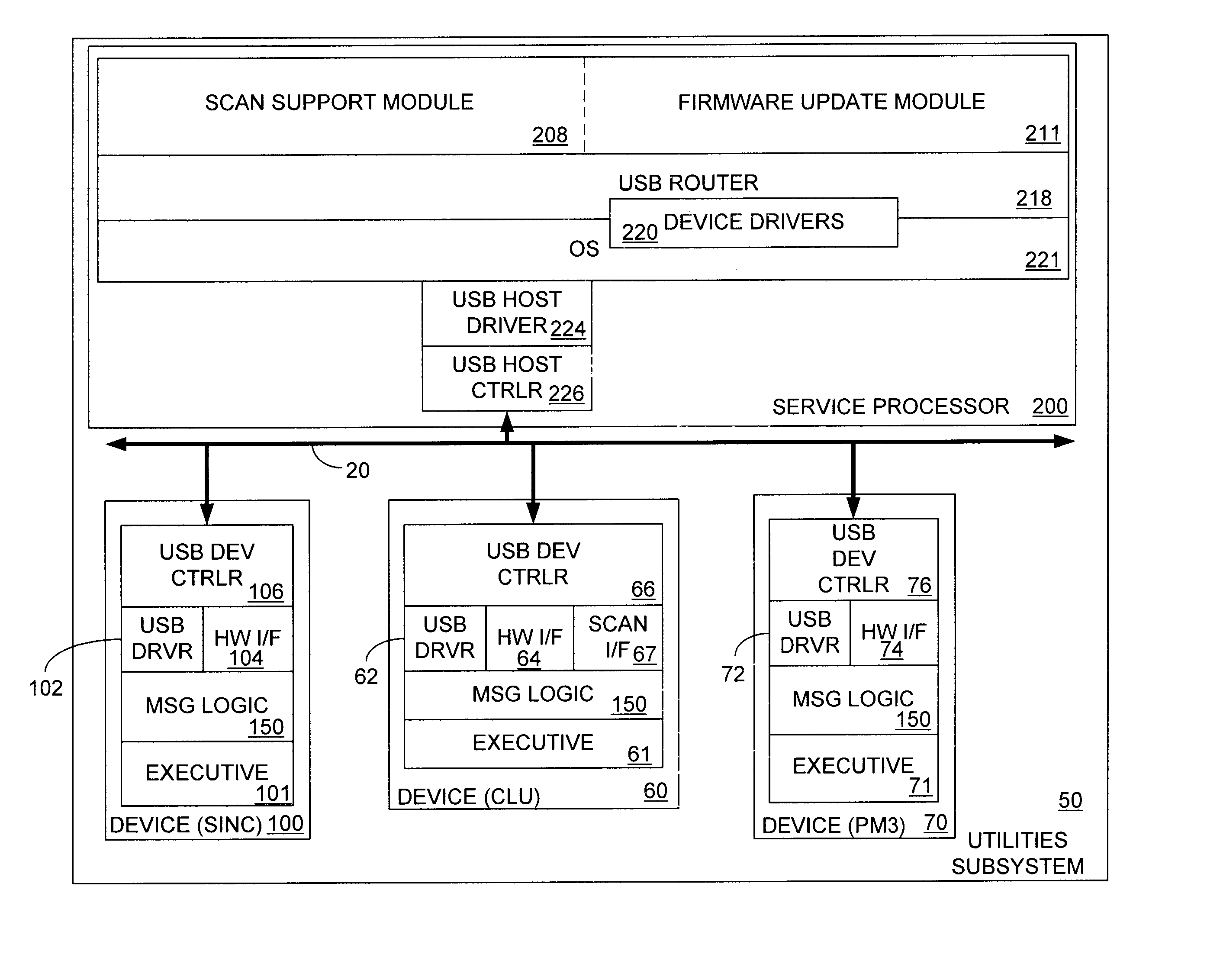
Method and system for using a universal serial bus (USB) as a peer-to-peer network
InactiveUS6839771B1Multiple digital computer combinationsElectric digital data processingMessage handlingNetwork Communication Protocols
In one embodiment, the system includes a host processor and a plurality of devices connected to the host processor via a USB interface. Each of the devices includes at least a processor and USB controller hardware. The host processor includes message handling logic and each of the devices also include message handling logic that is configured to cooperate with the device to prepend a communication protocol header to a message that one of the devices desires to send to the host or to another of the devices. The host processor and each of the devices are peers with respect to each other. A router located in the host processor analyzes the communication protocol header to determine whether the message is destined for the host processor or for one of the other devices.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com