Patents
Literature
478 results about "Ternary content addressable memory" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
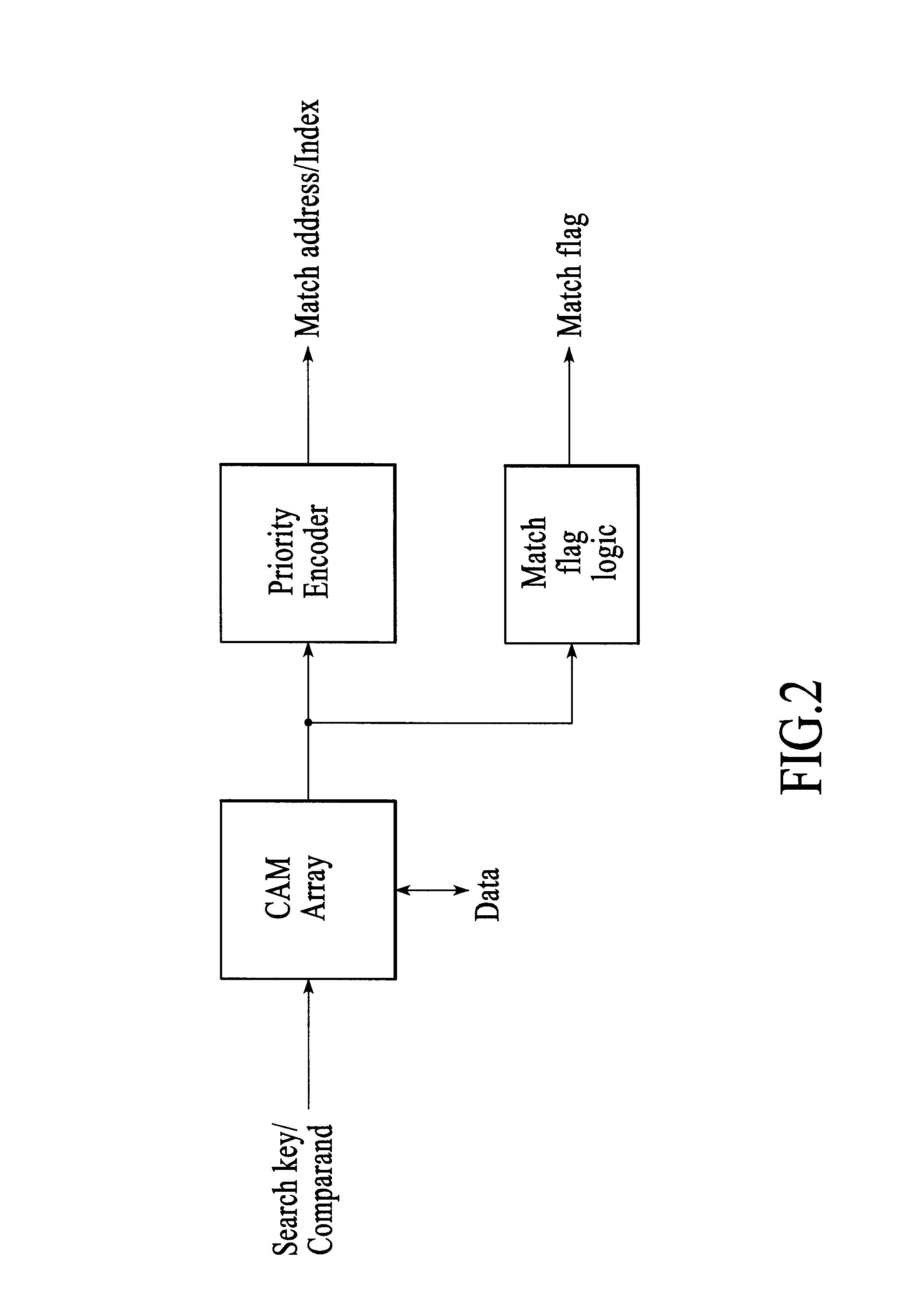
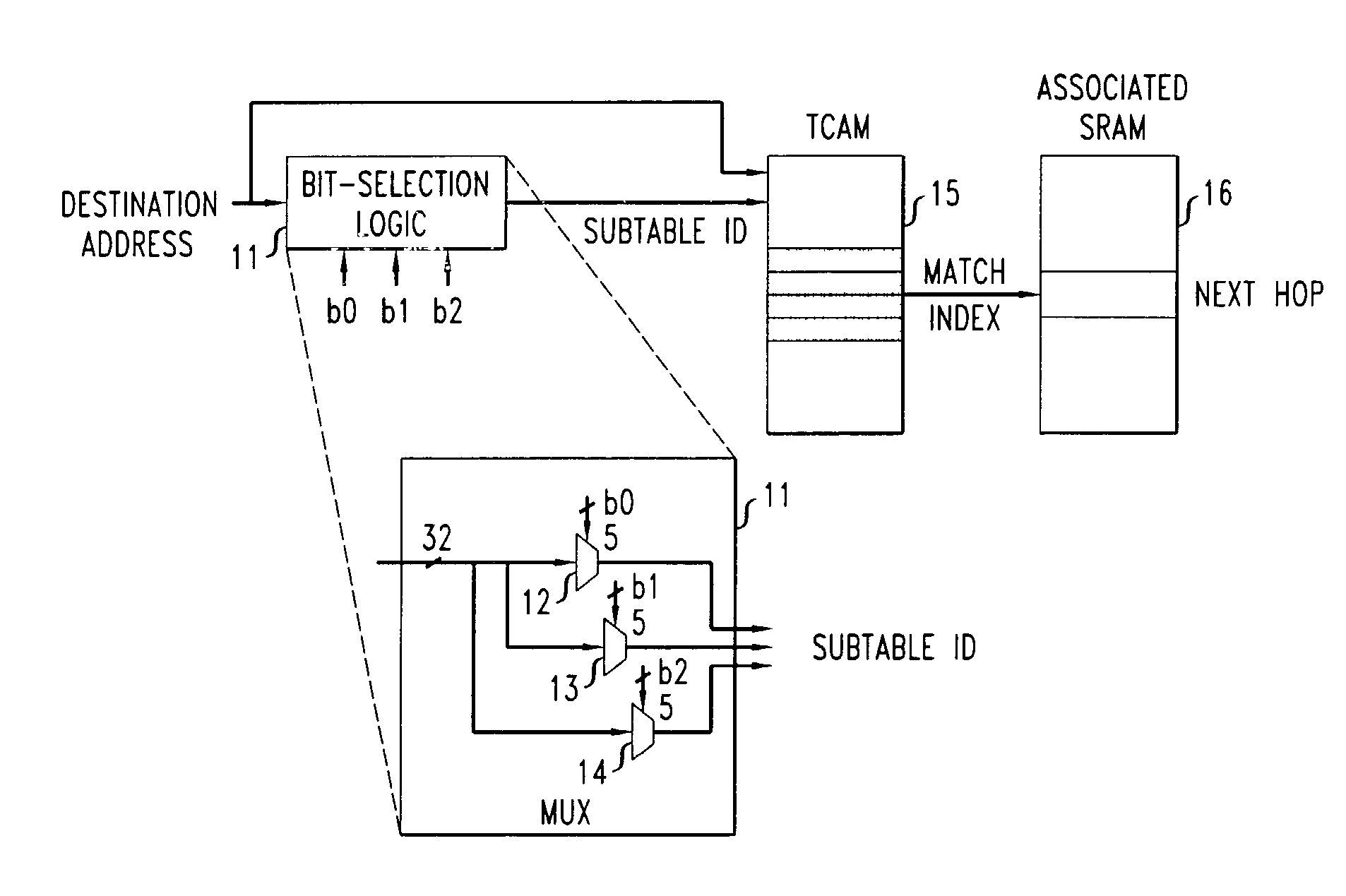
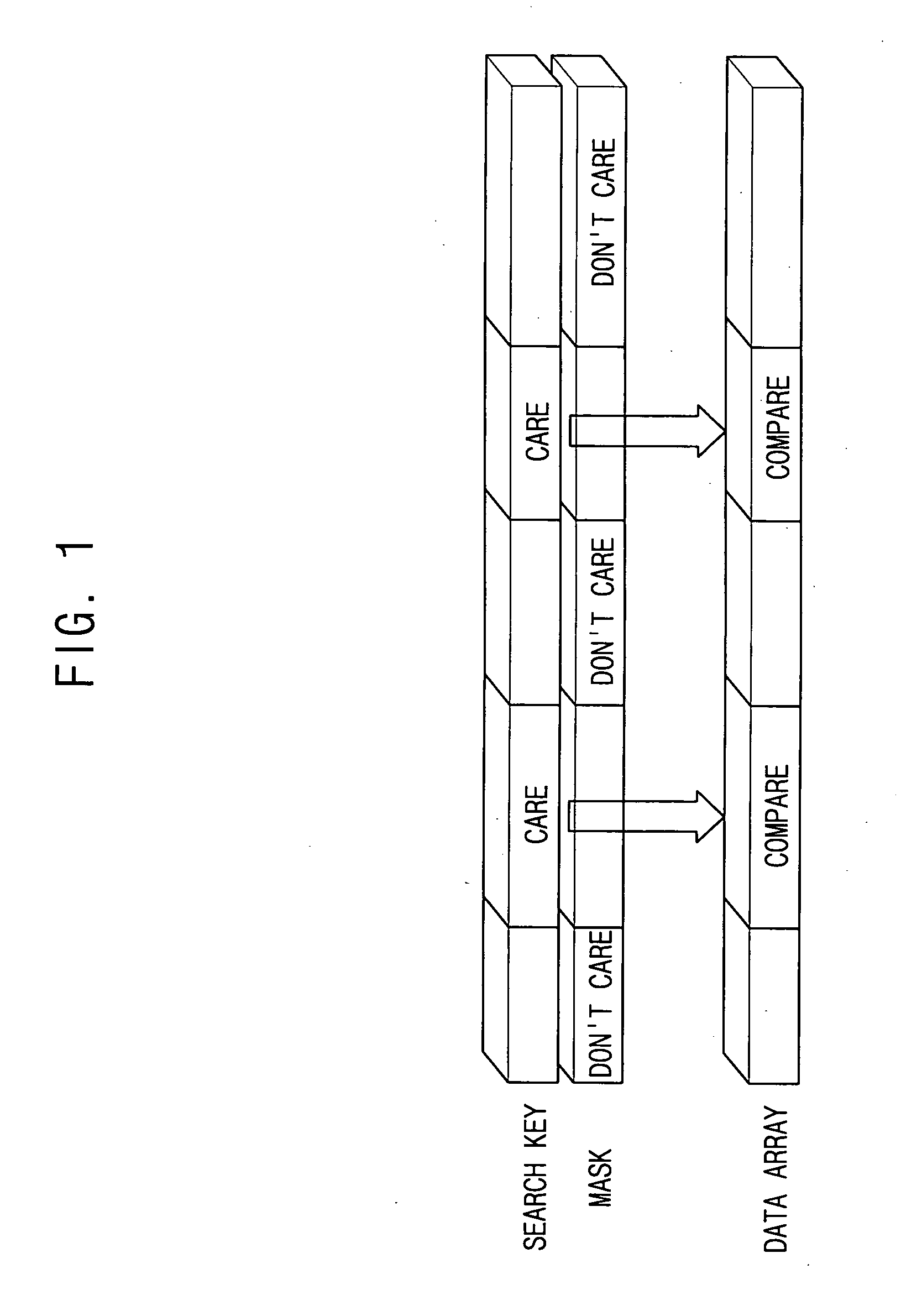
Answer Wiki. Content Addressable Memory (CAM) and Ternary Content Addressable Memory (TCAM) are specialized forms of memory used primarily in high-performance network equipment. These specialized forms of memory are used to enable wire-speed switching, filtering, routing, and packet classification in all but the lowest tier of network hardware.
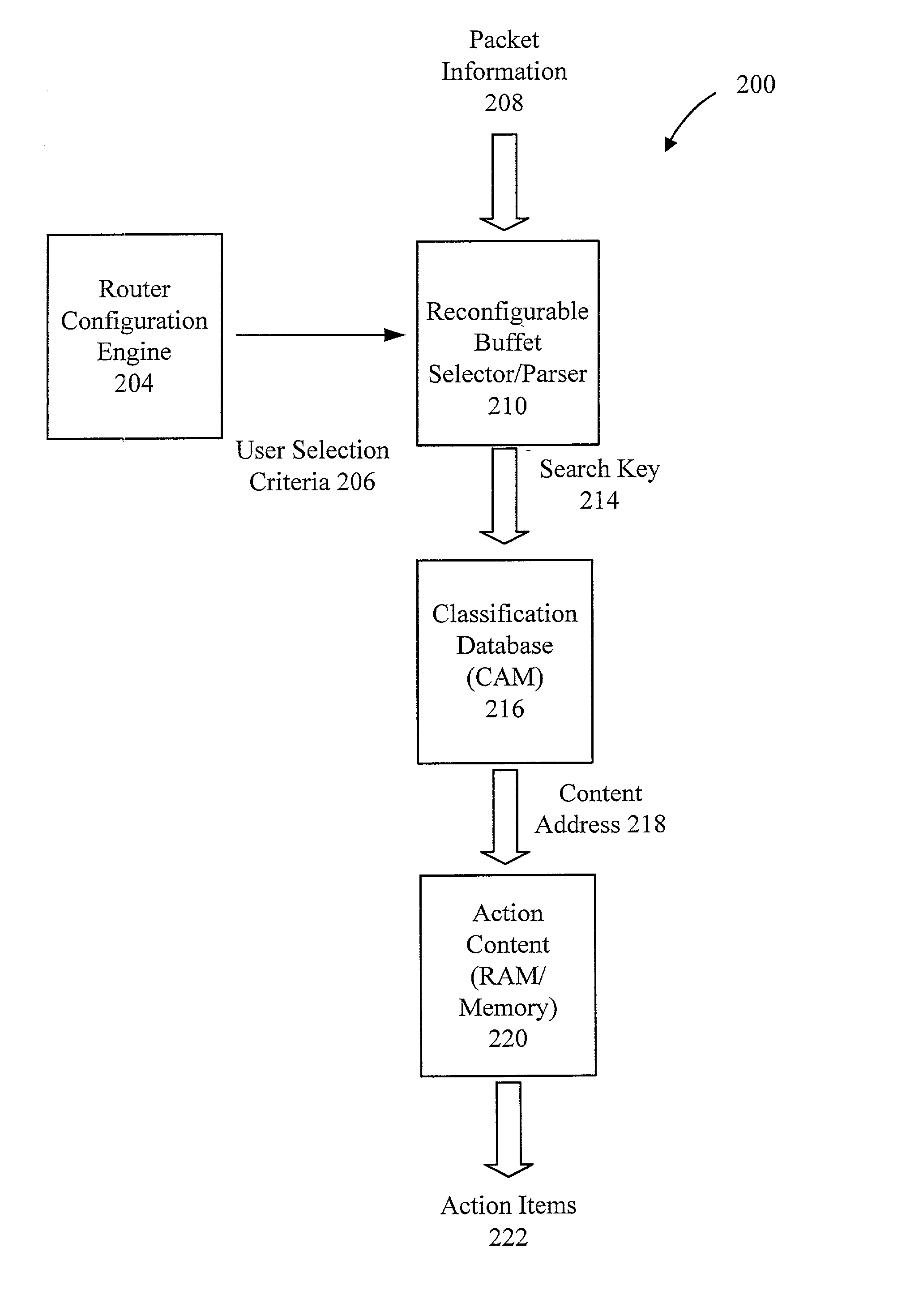
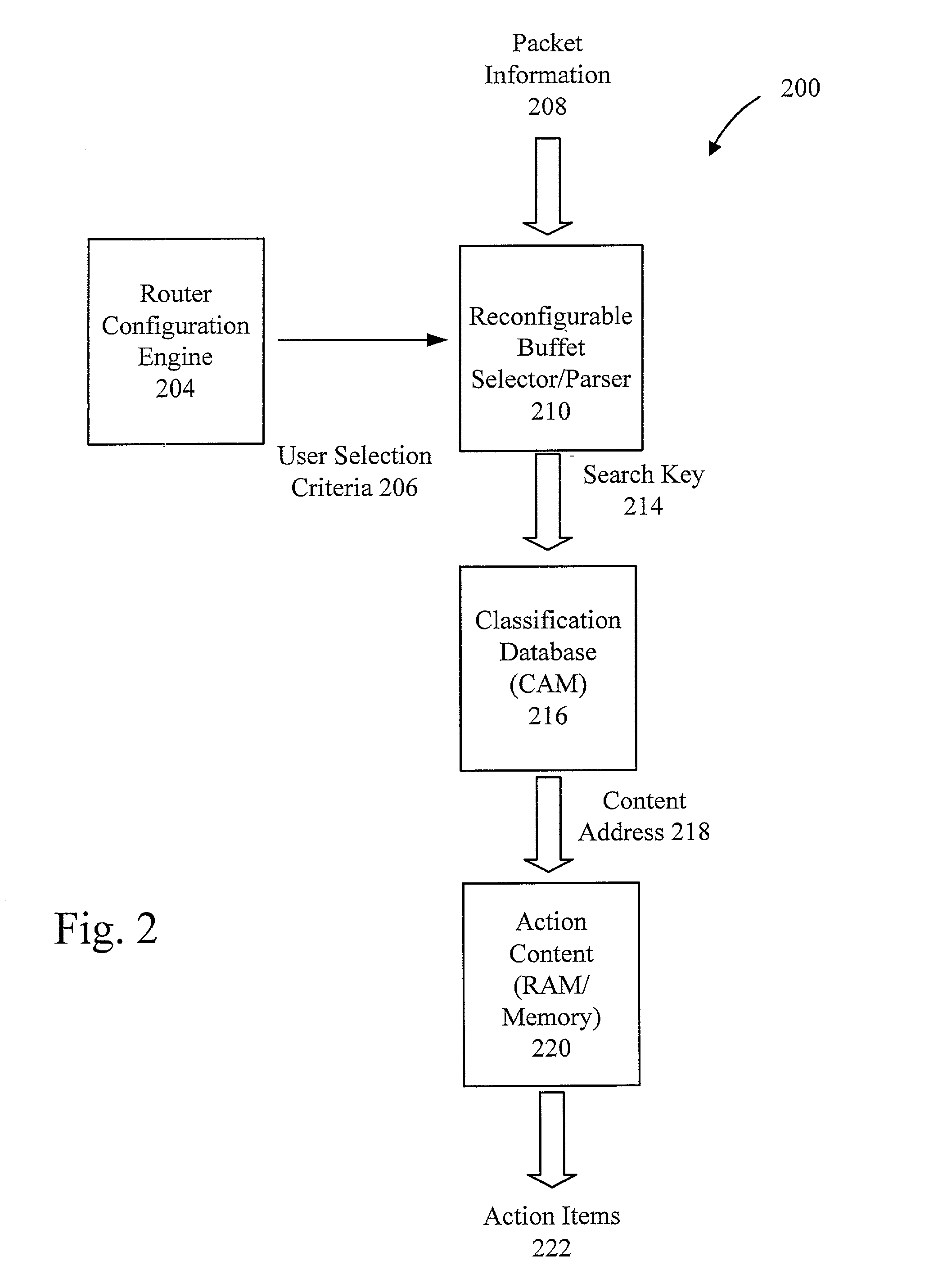
Method and apparatus for a flexible and reconfigurable packet classifier using content addressable memory
InactiveUS20020126672A1Low costFlexibility of deploymentData switching by path configurationSecuring communicationCustomer requirementsTernary content addressable memory
The present invention provides for a reconfigurable packet classifier using CAM. The invention is directed to packet classification for switching / routing systems where the router's system resources are limited and the customer requirements from the router are variable. The invention addresses the CAM constraint (e.g. search key width) problems of CAM-based classification systems, by allowing a reconfigurable selection of packet fields and / or payload bits to be used in the definition of the search key. For any given incoming packet, a subset of that incoming packet may be statically chosen to fit that particular CAM architecture and to create a particular CAM search key. This provides router deployment flexibility within networks and, thus, cuts costs.
Owner:ACUTE COMM CORP
Hardware filtering support for denial-of-service attacks
InactiveUS20050213570A1Processing bandwidthOvercome disadvantagesData switching by path configurationNetwork packetLookup table
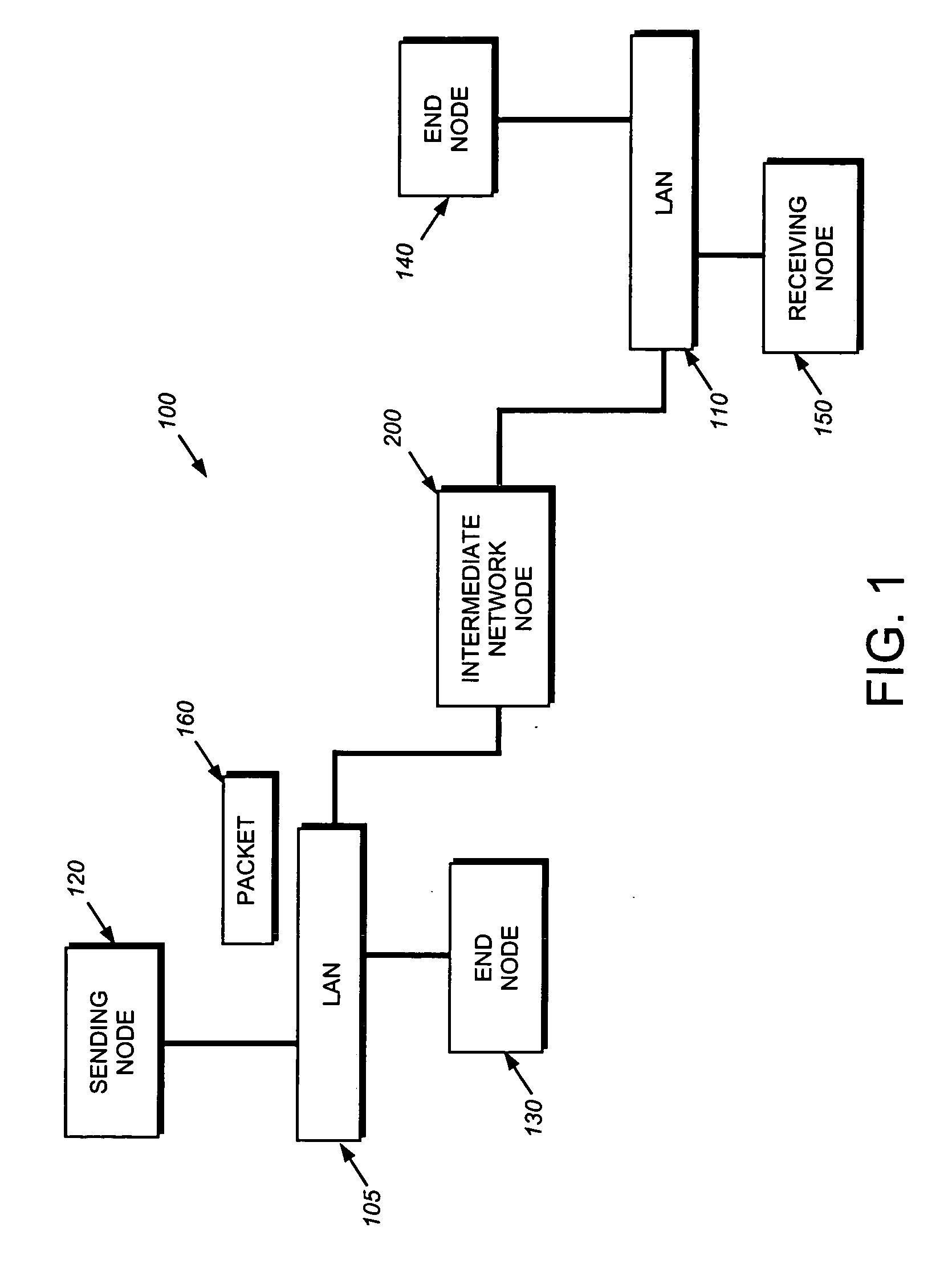
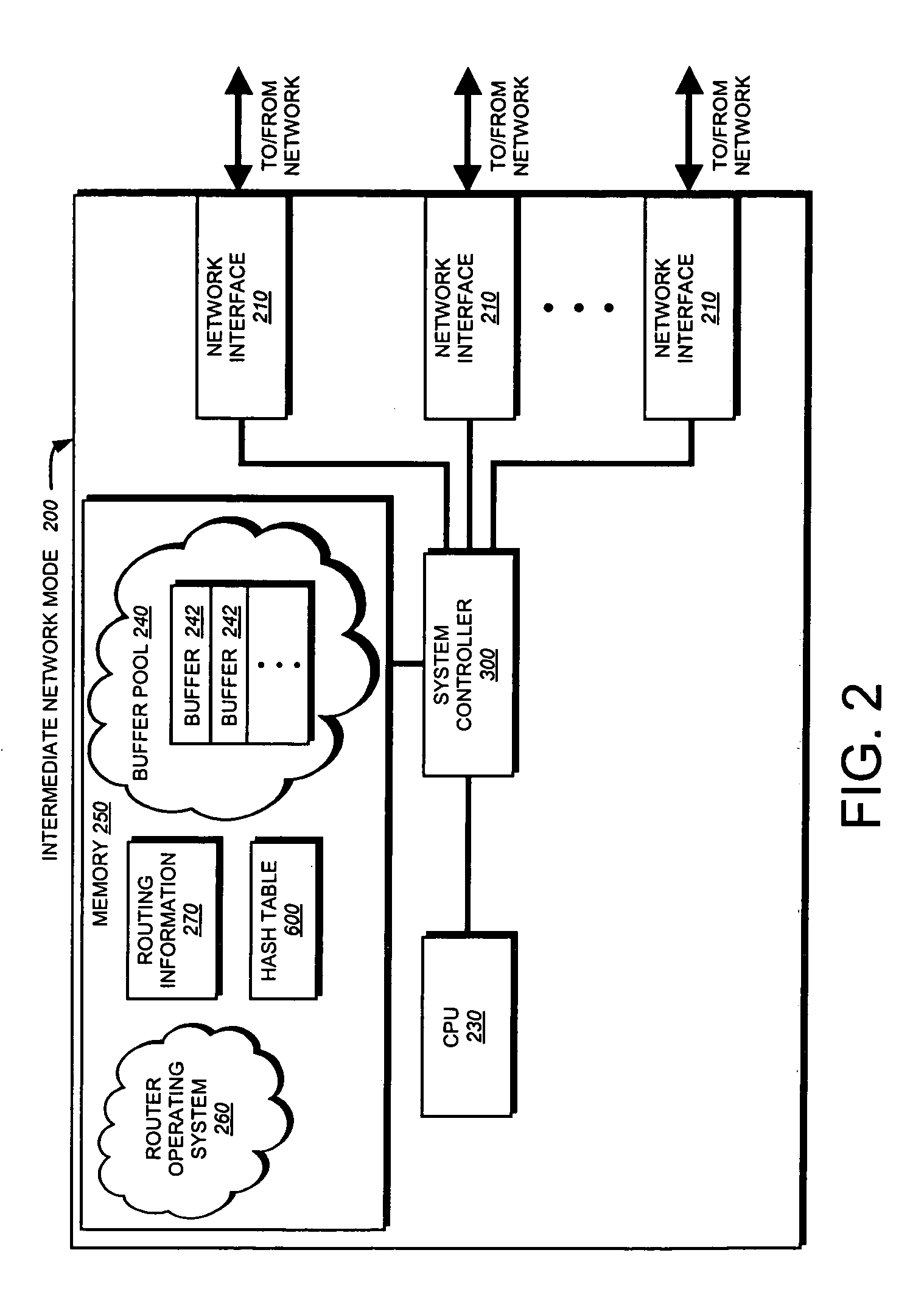
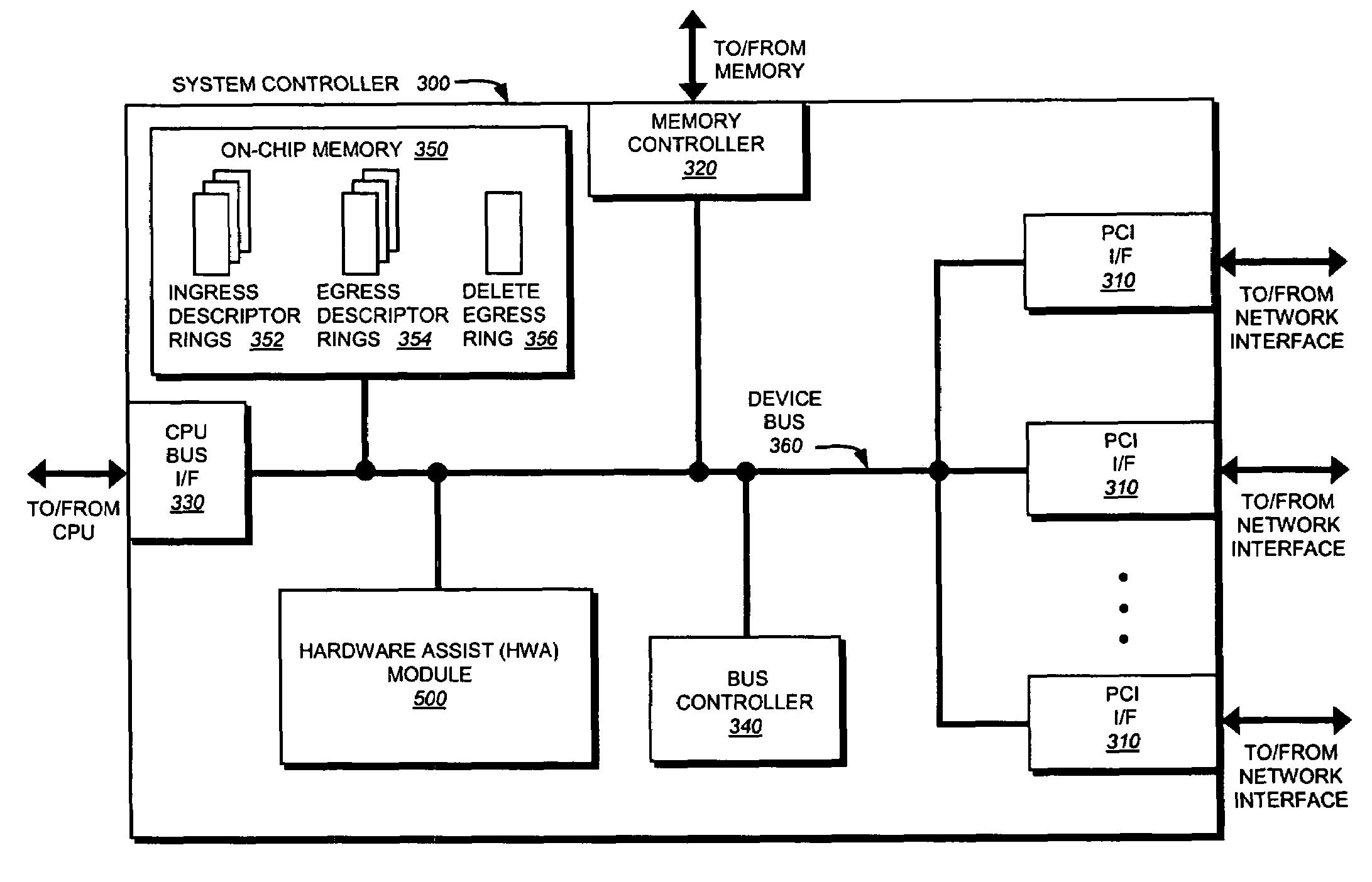
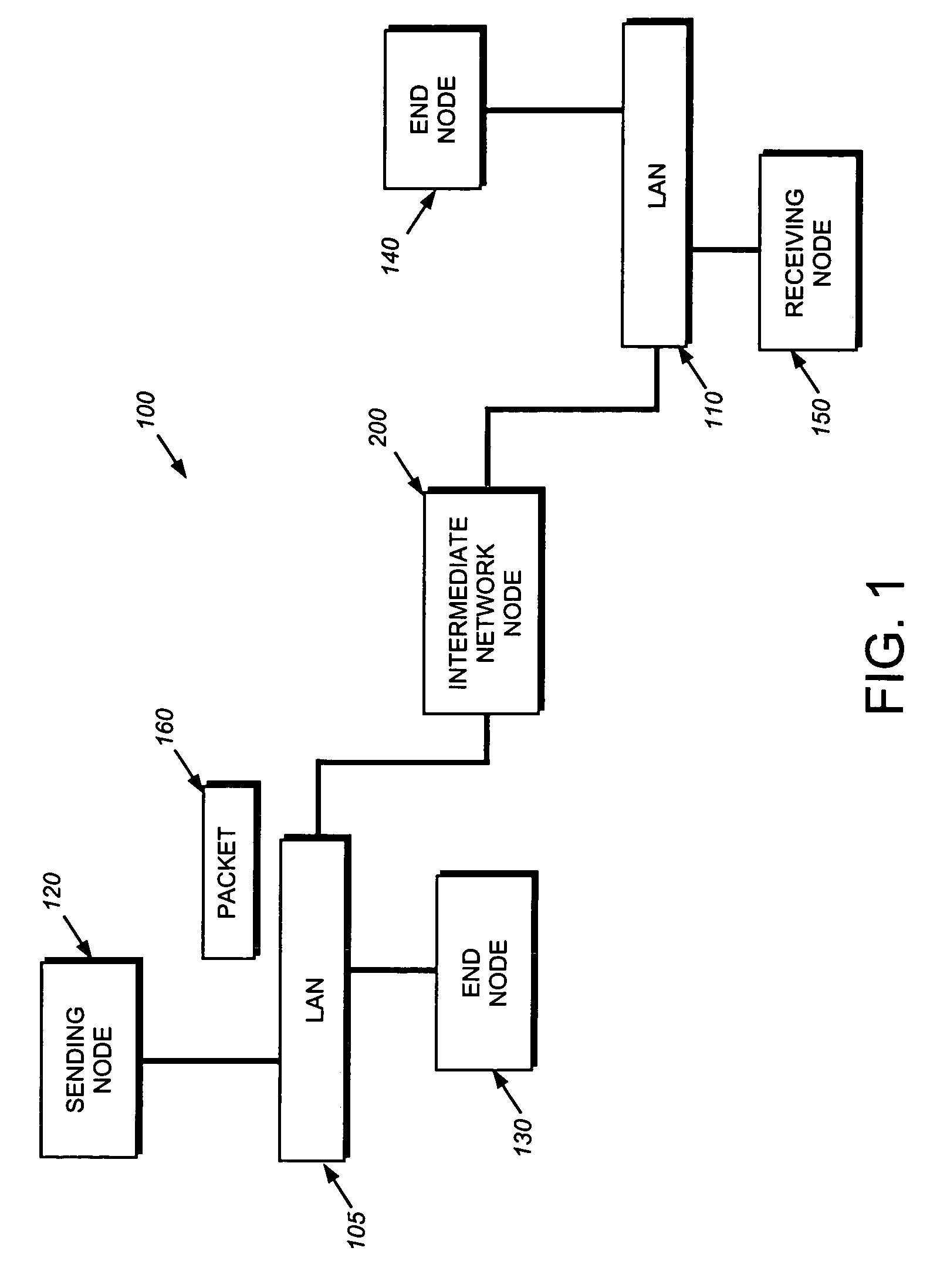
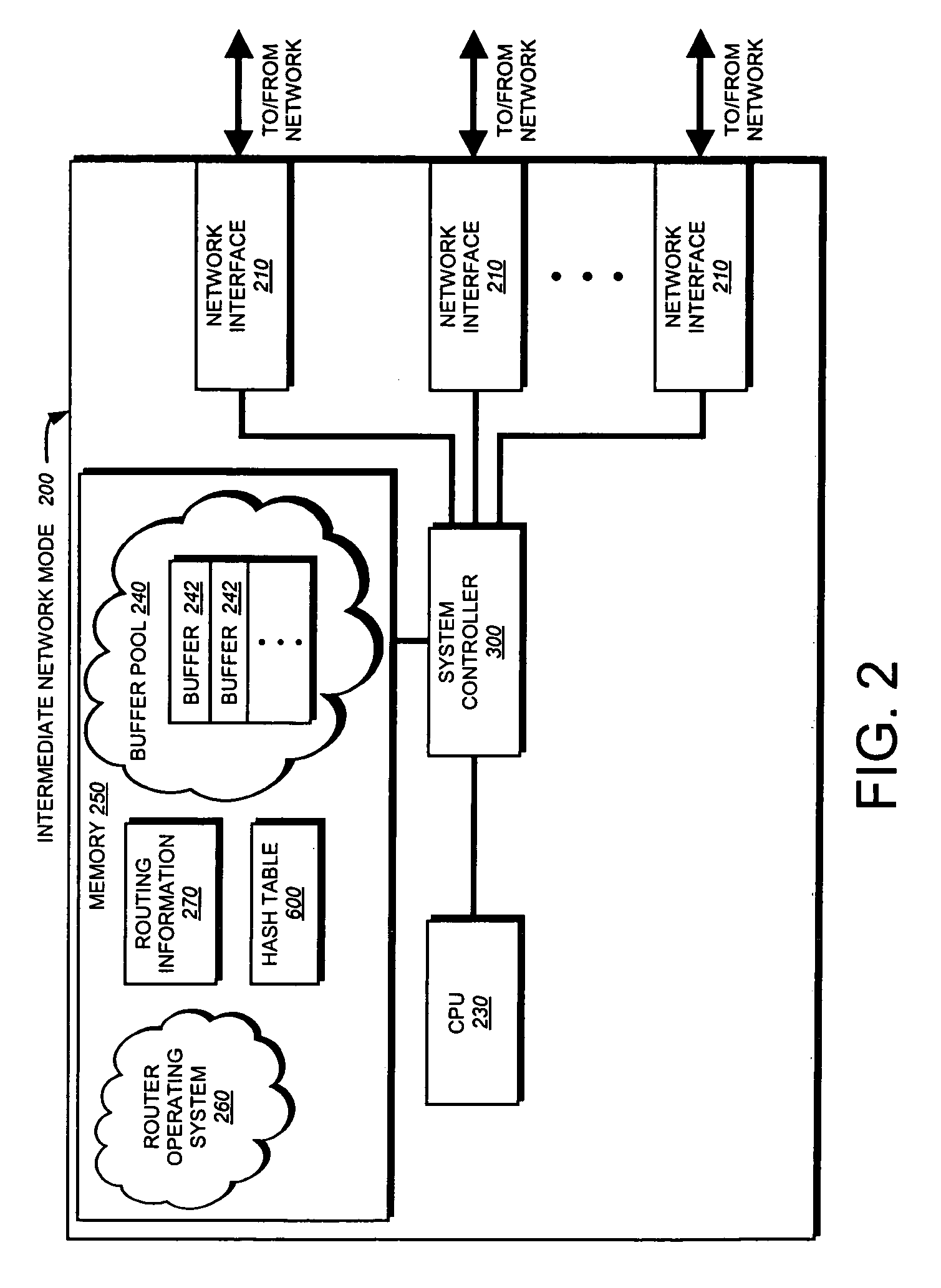
A system and method is provided for automatically identifying and removing malicious data packets, such as denial-of-service (DoS) packets, in an intermediate network node before the packets can be forwarded to a central processing unit (CPU) in the node. The CPU's processing bandwidth is therefore not consumed identifying and removing the malicious packets from the system memory. As such, processing of the malicious packets is essentially “off-loaded” from the CPU, thereby enabling the CPU to process non-malicious packets in a more efficient manner. Unlike prior implementations, the invention identifies malicious packets having complex encapsulations that can not be identified using traditional techniques, such as ternary content addressable memories (TCAM) or lookup tables.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Hardware filtering support for denial-of-service attacks
InactiveUS7411957B2Processing bandwidthOvercome disadvantagesUser identity/authority verificationHardware monitoringNetwork packetLookup table
A system and method is provided for automatically identifying and removing malicious data packets, such as denial-of-service (DoS) packets, in an intermediate network node before the packets can be forwarded to a central processing unit (CPU) in the node. The CPU's processing bandwidth is therefore not consumed identifying and removing the malicious packets from the system memory. As such, processing of the malicious packets is essentially “off-loaded” from the CPU, thereby enabling the CPU to process non-malicious packets in a more efficient manner. Unlike prior implementations, the invention identifies malicious packets having complex encapsulations that can not be identified using traditional techniques, such as ternary content addressable memories (TCAM) or lookup tables.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and system for multi-character multi-pattern pattern matching
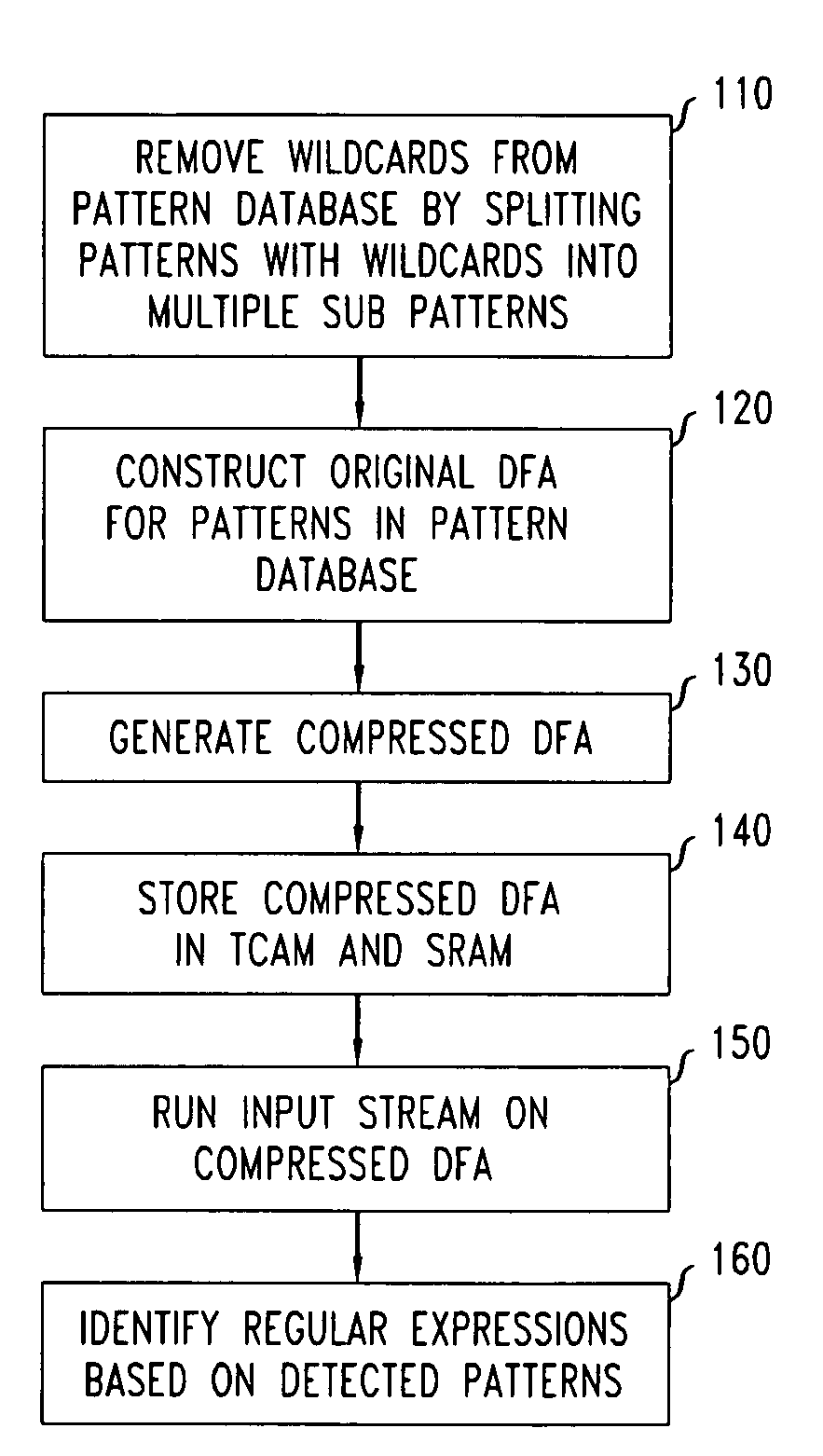
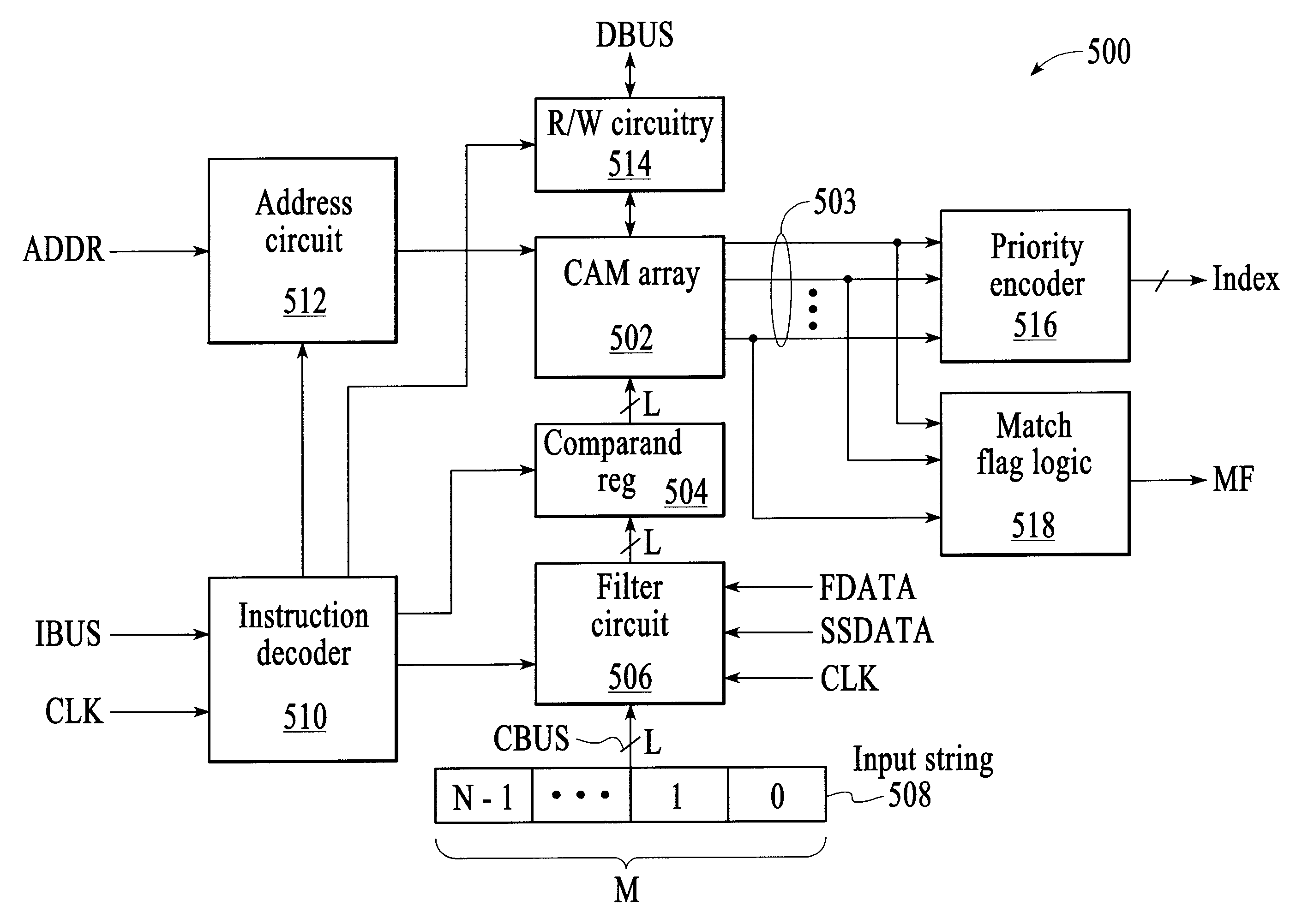
ActiveUS20080046423A1High pattern matching speedEasy to implementData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalPattern matchingTernary content addressable memory
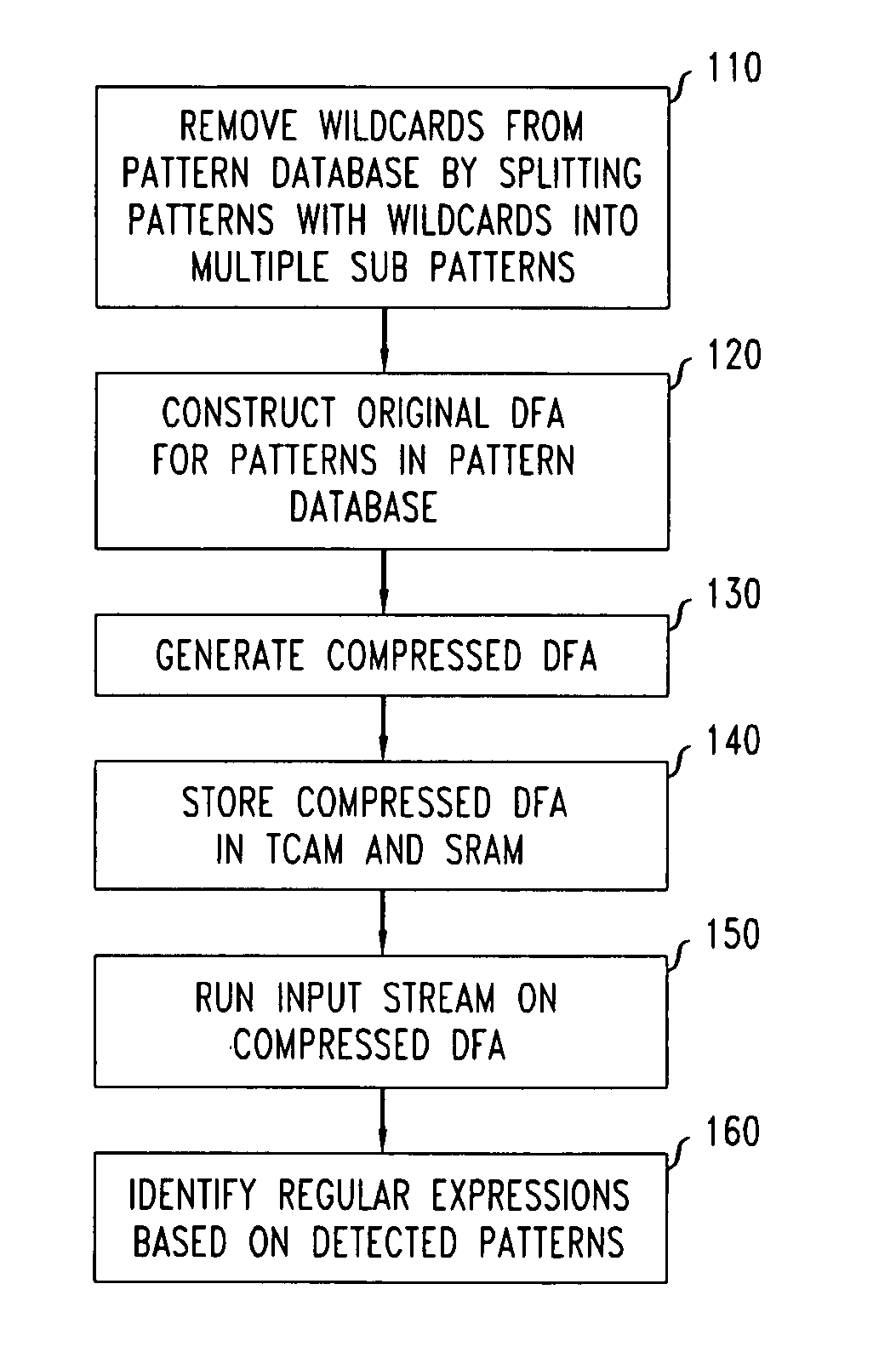
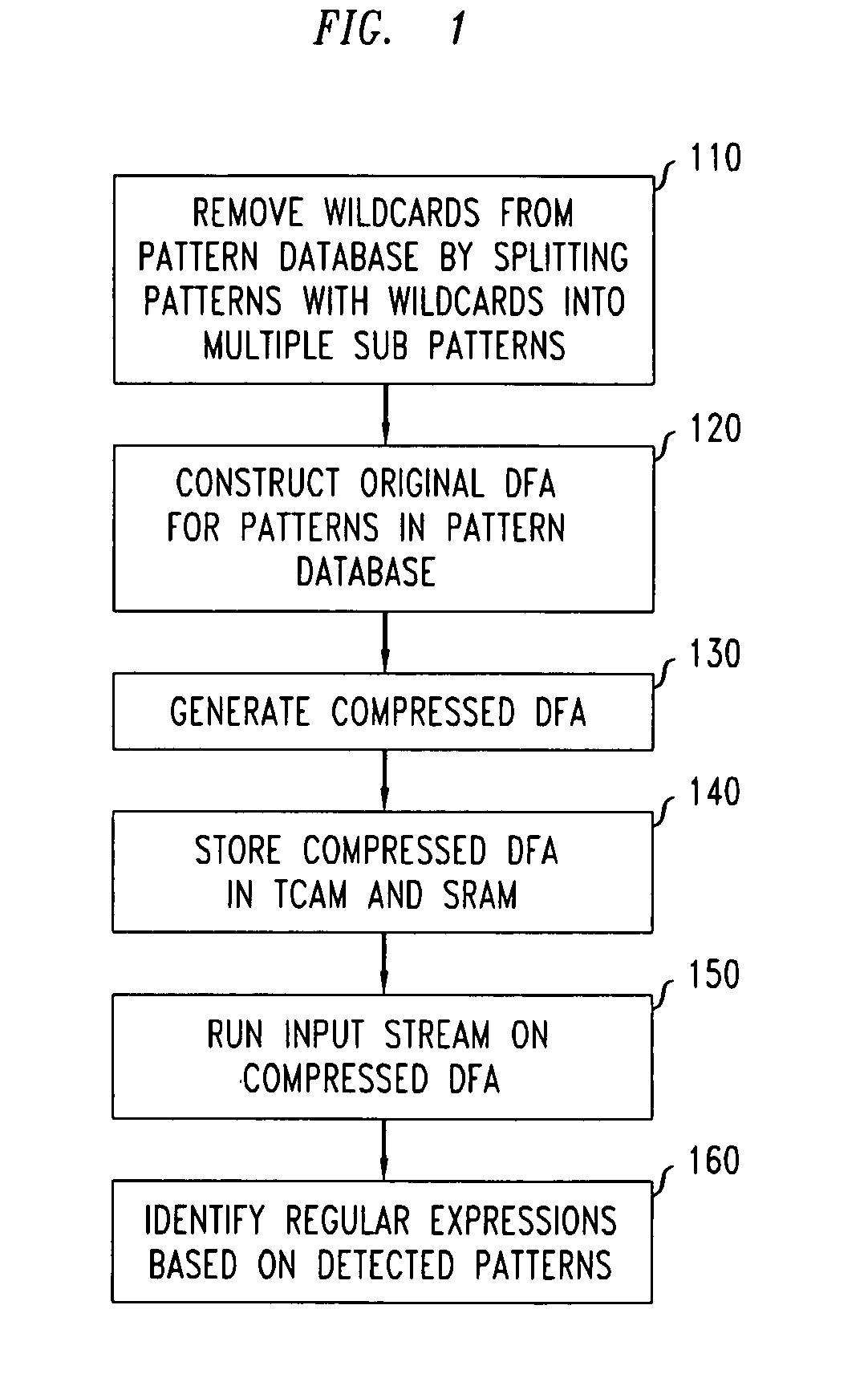
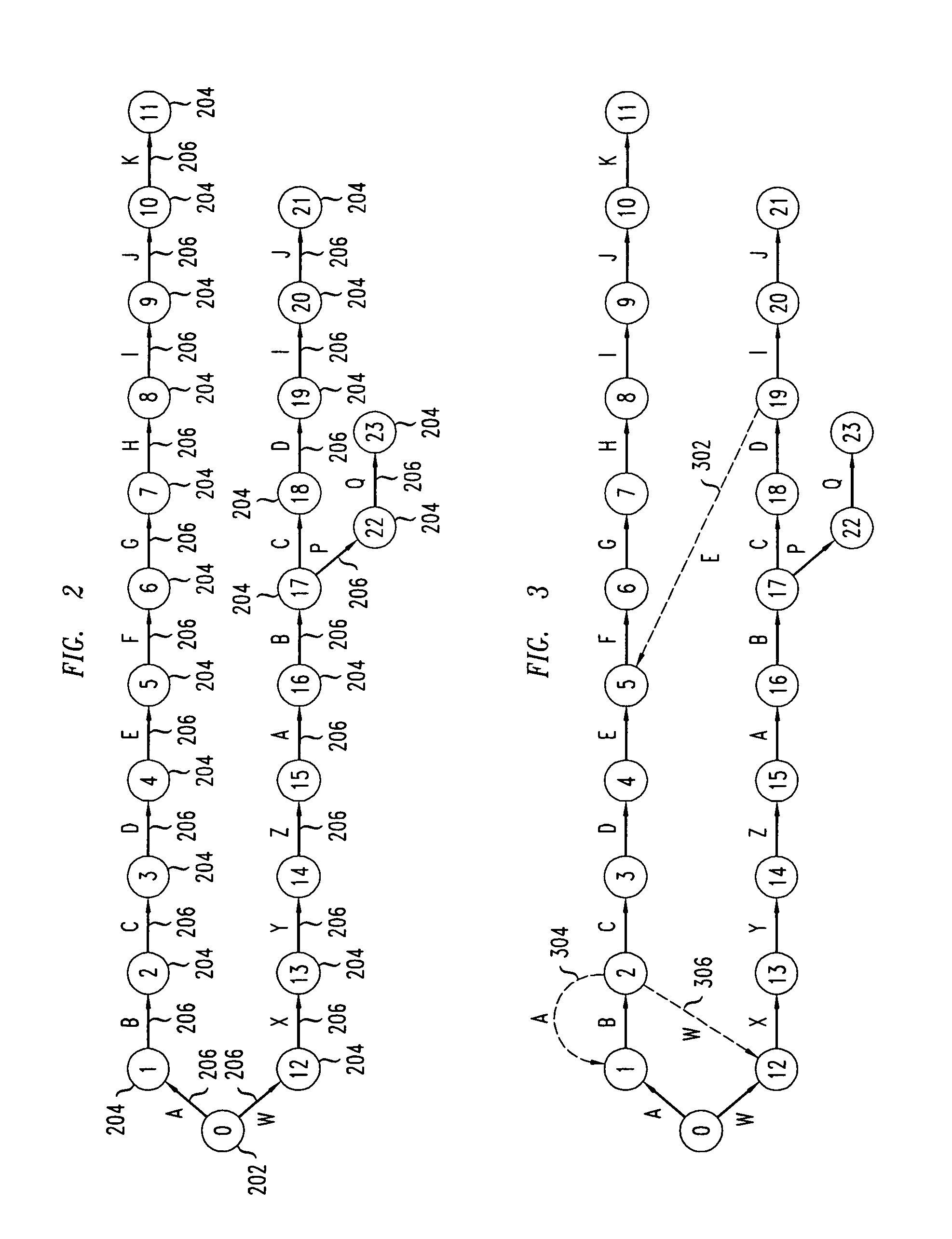
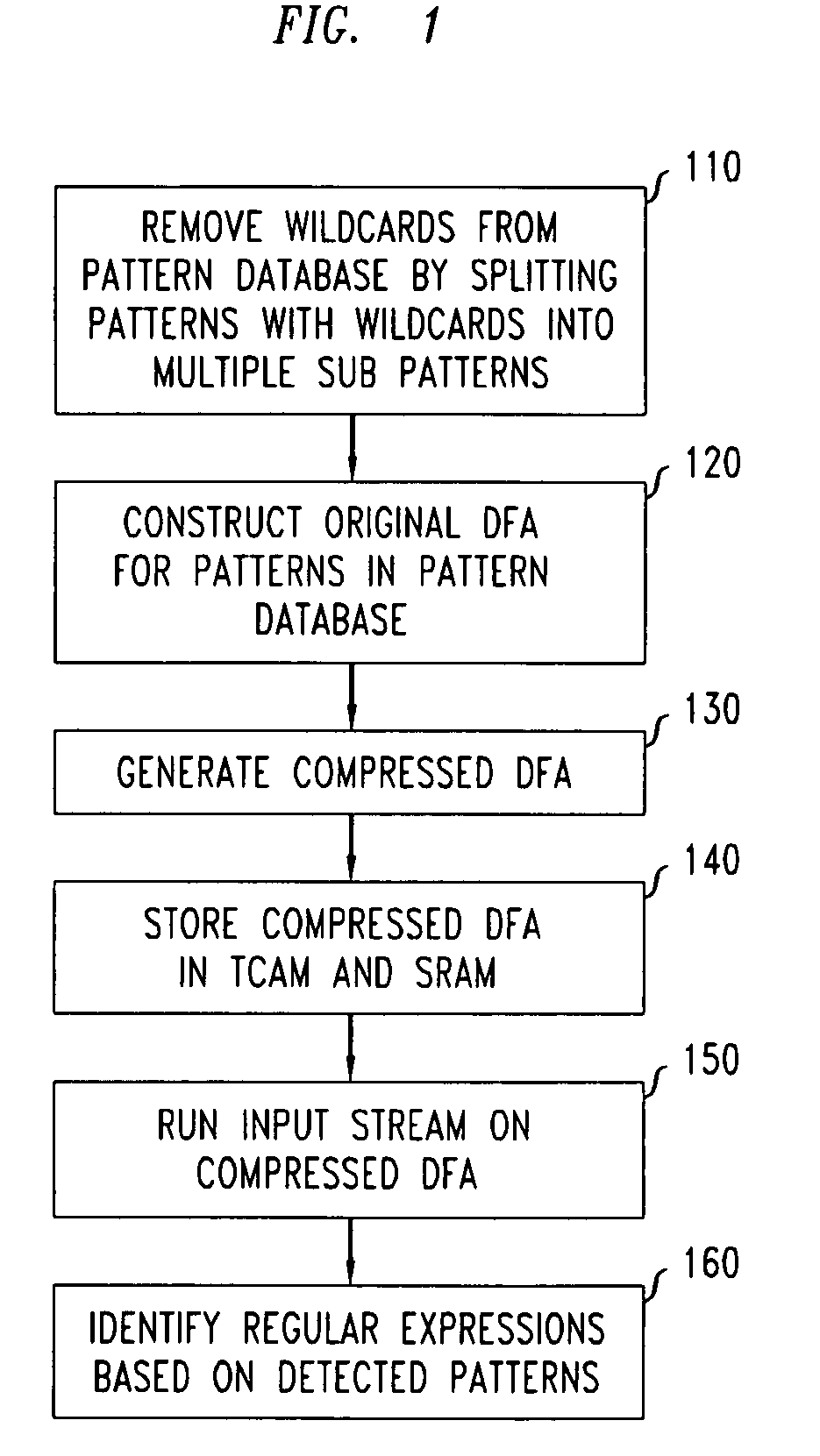
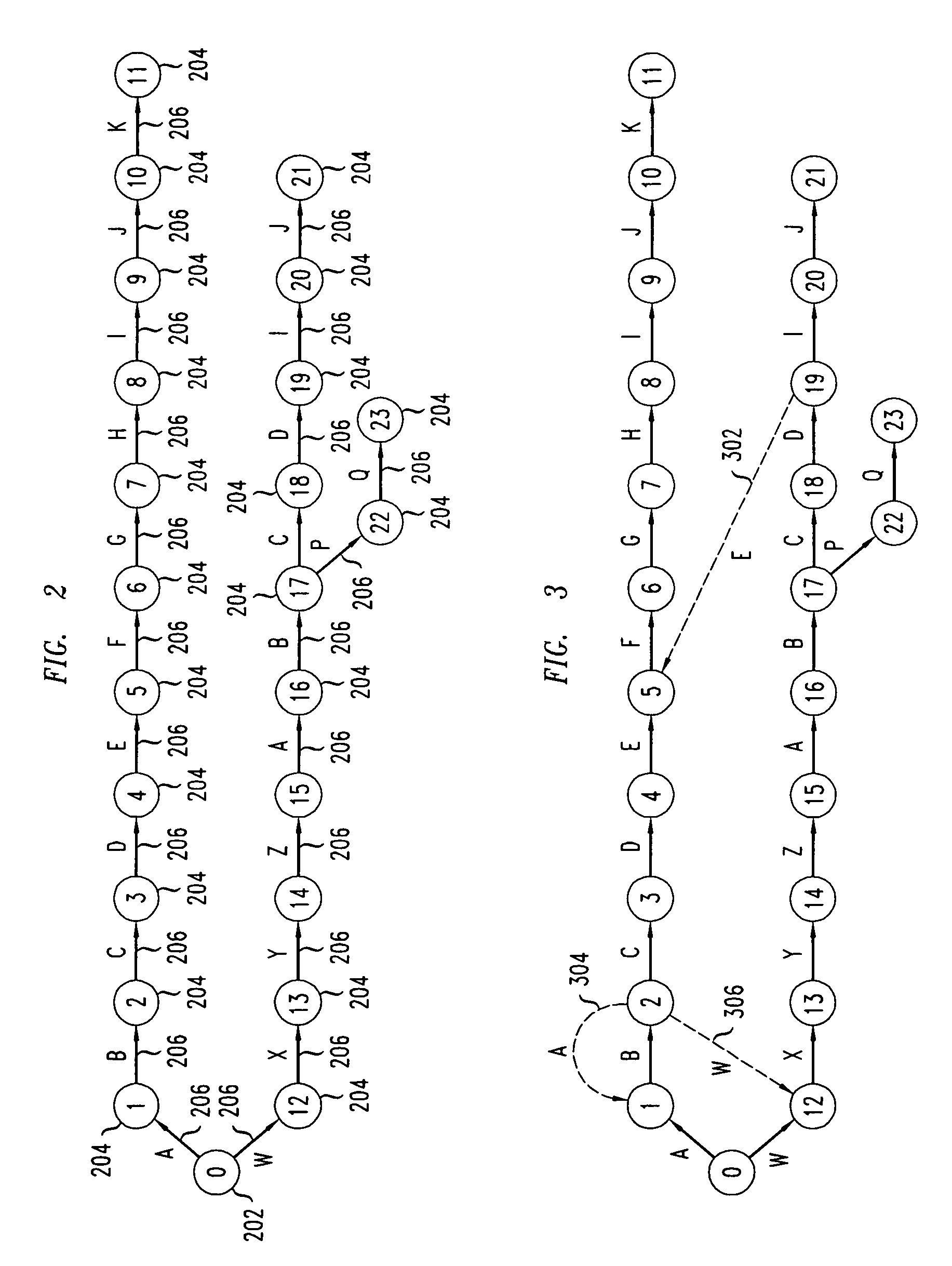
Disclosed is a method and system for multi-character multi-pattern pattern matching. In the multi-character multi-pattern pattern matching method, patterns in an input stream are detected by transitioning between states of a “compressed deterministic finite state automaton (DFA)”, with each transition based on multiple characters of the input stream. The compressed DFA is created by compressing an original DFA, such as an Aho-Corasick DFA, such that each state of the compressed DFA represents multiple consecutive states of the original DFA and each transition between the states of the compressed DFA is a combination of all of the transitions between the multiple consecutive states of the original DFA. This method can be implemented using a Ternary Content-Addressable Memory (TCAM) to store the transitions of the compressed DFA and compares the transitions with multiple characters of an input stream at a time to detect patterns in the input stream.
Owner:ALGOGENE FINANCIAL TECHNOLOGY COMPANY LIMITED
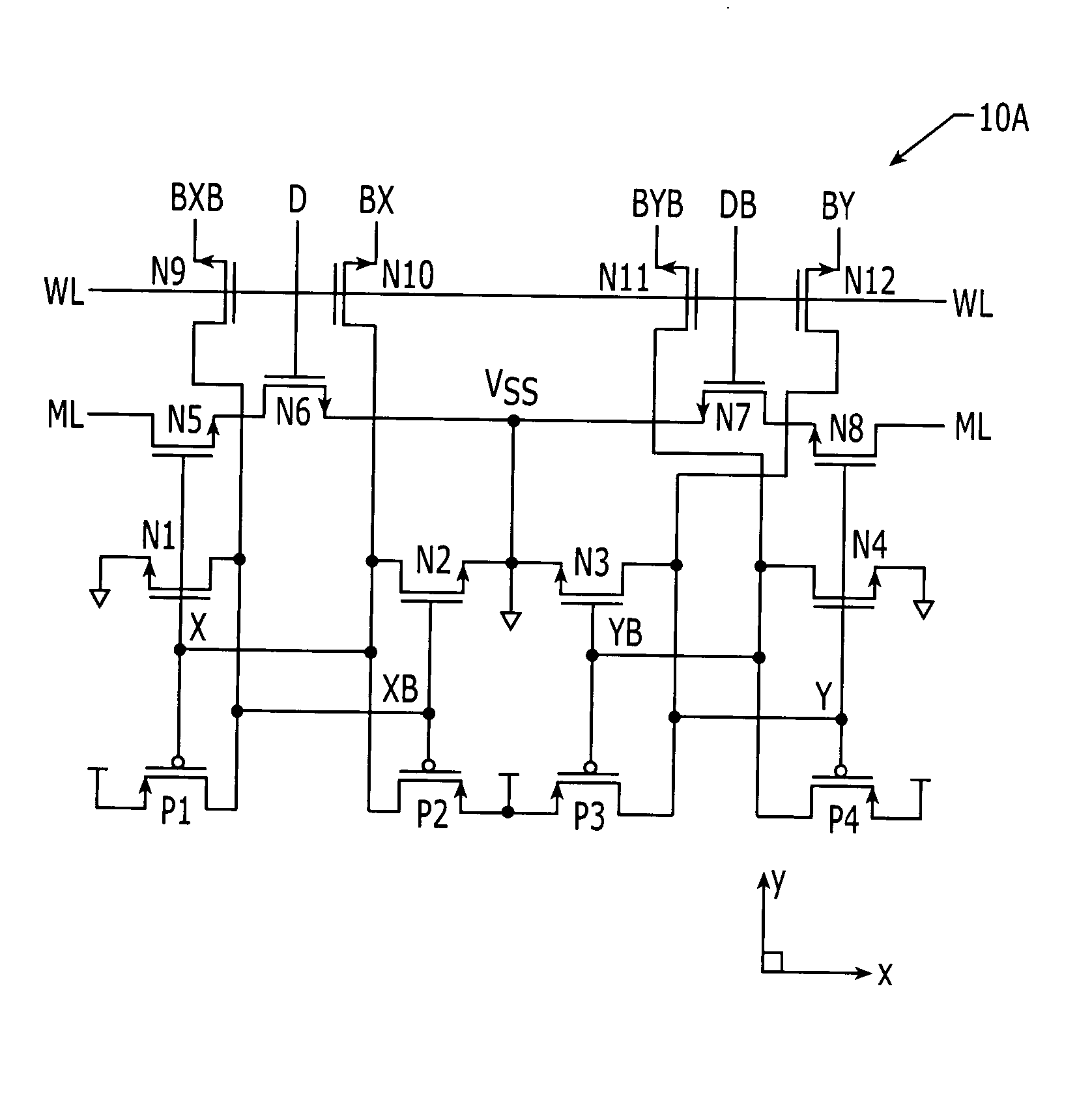
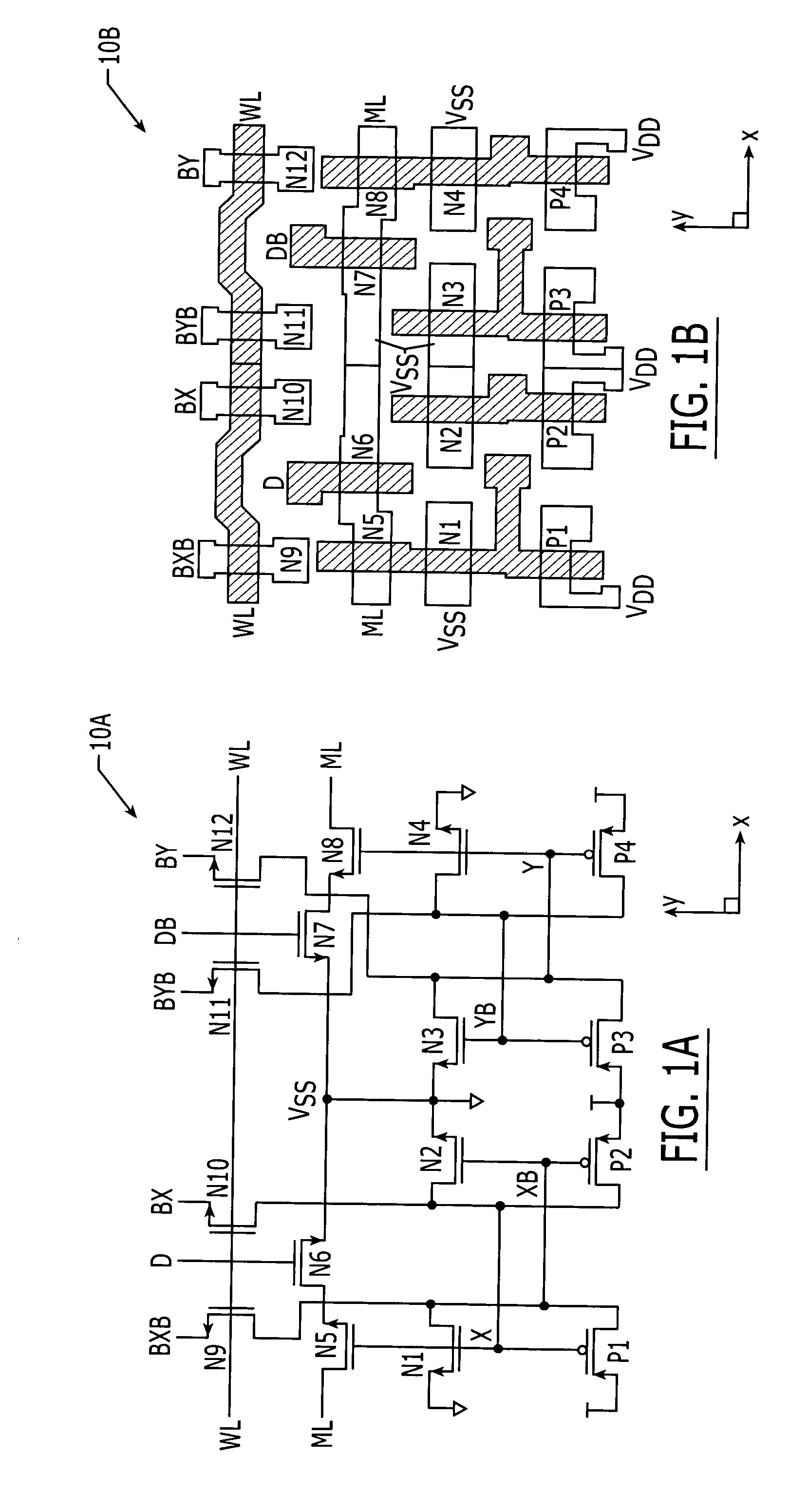
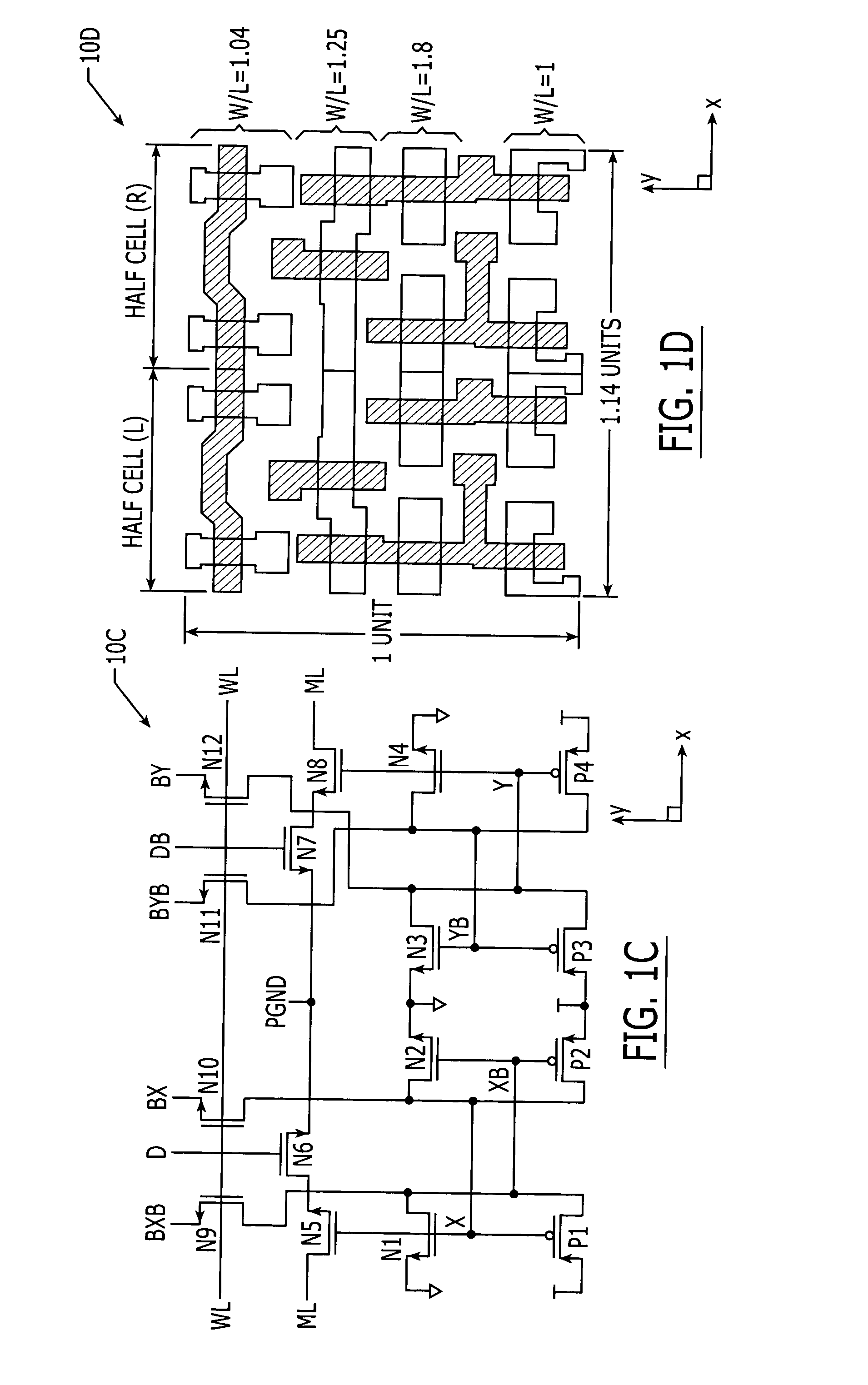
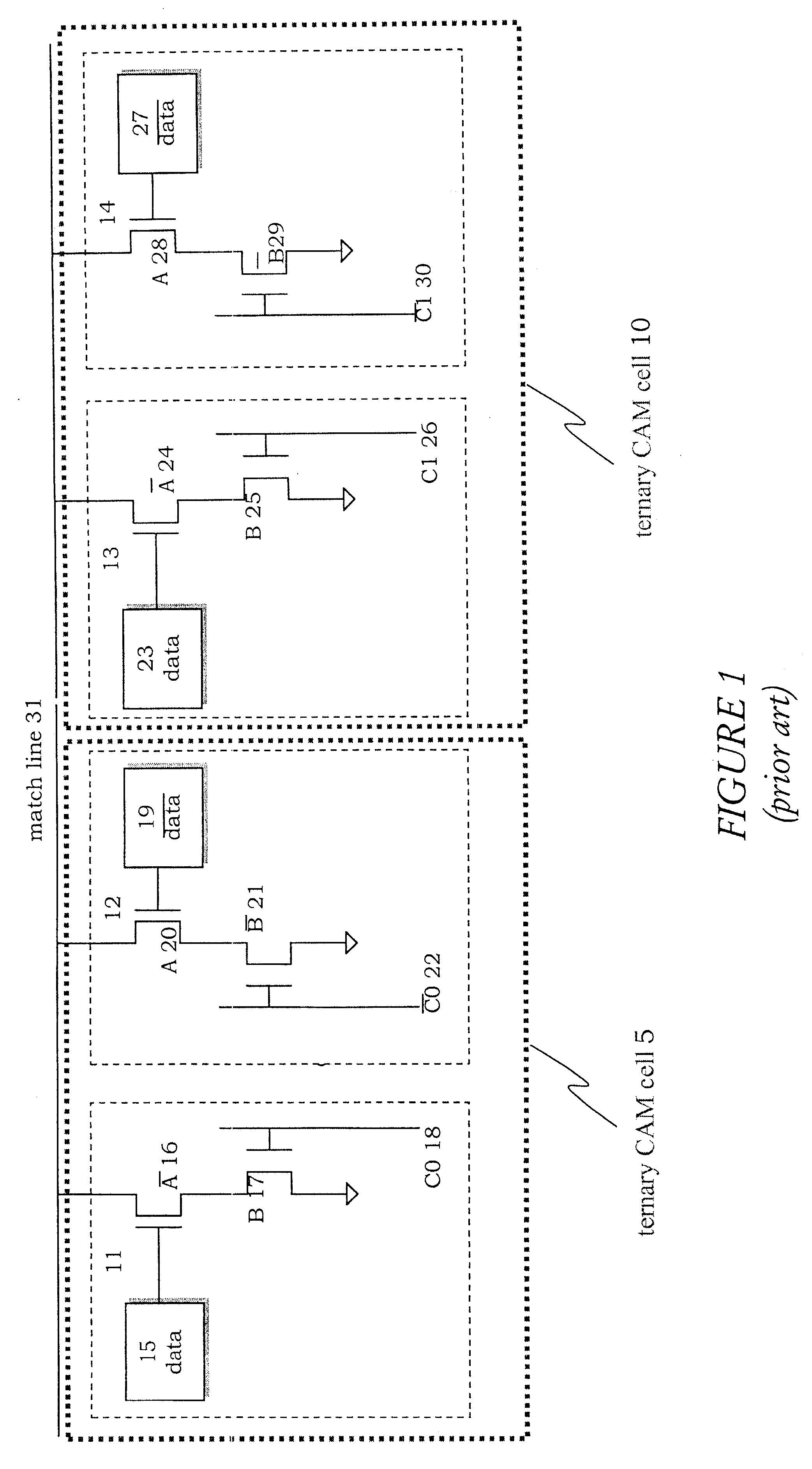
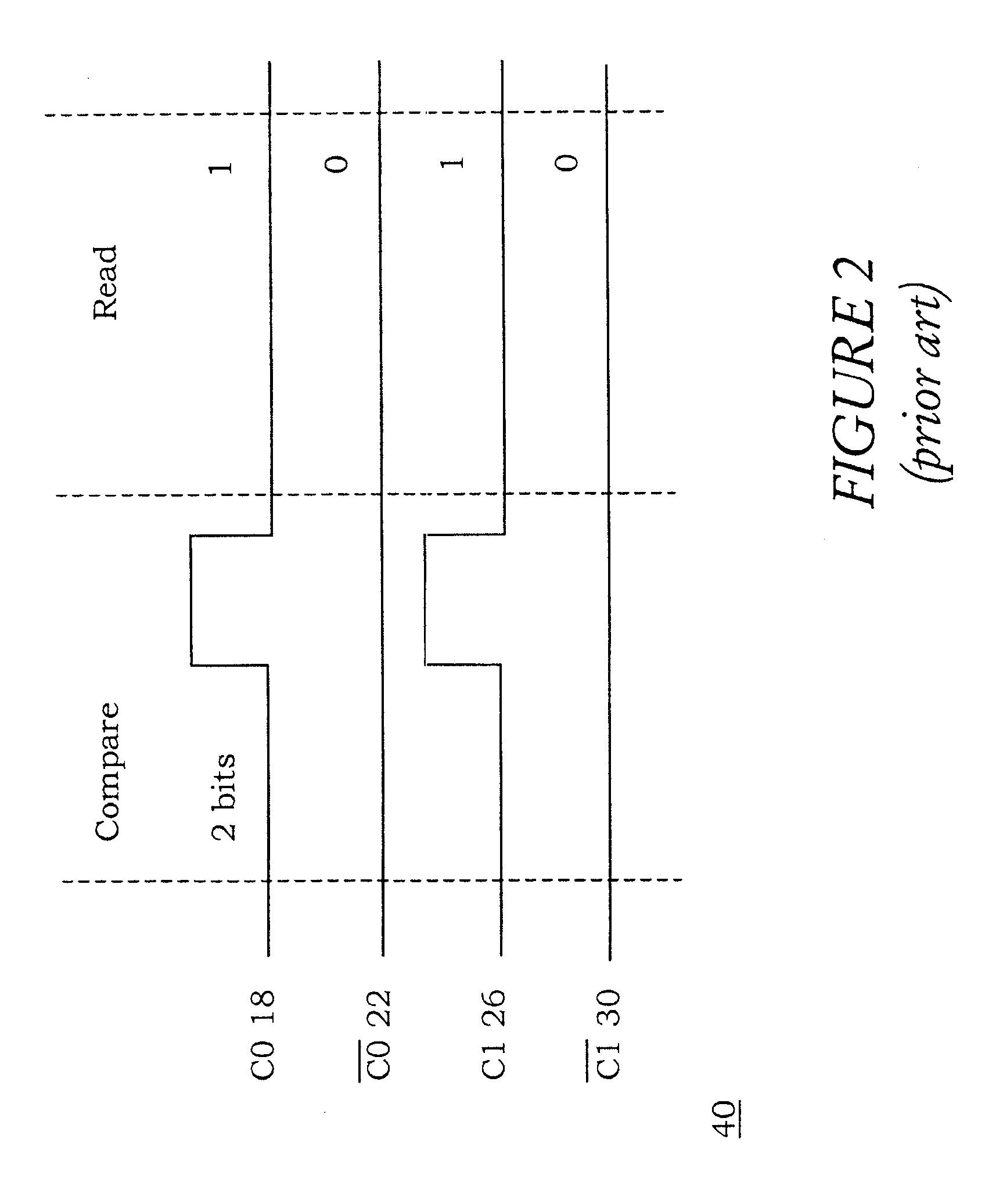
Ternary content addressable memory (TCAM) cells with small footprint size and efficient layout aspect ratio
InactiveUS20050135134A1Small layout footprint sizeEnhance scalability and uniformityDigital storageExtensibilityEngineering
Ternary CAM cells are provided that have extremely small layout footprint size and efficient layout aspect ratios that enhance scalability. The cells also have high degrees of symmetry that facilitate high yield interconnections to bit, data and match lines. A 16T ternary CAM cell includes first and second pairs of access transistors that extend adjacent a first side of the cell, and first and second pairs of cross-coupled inverters that extend adjacent a second side of the cell. First and second halves of a 4T compare circuit are also provided. The first half of the 4T compare circuit is positioned so that is extends between the first pair of access transistors and the first pair of cross-coupled inverters. Similarly, the second half of the 4T compare circuit is positioned so that it extends between the second pair of access transistors and the second pair of cross-coupled inverters.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
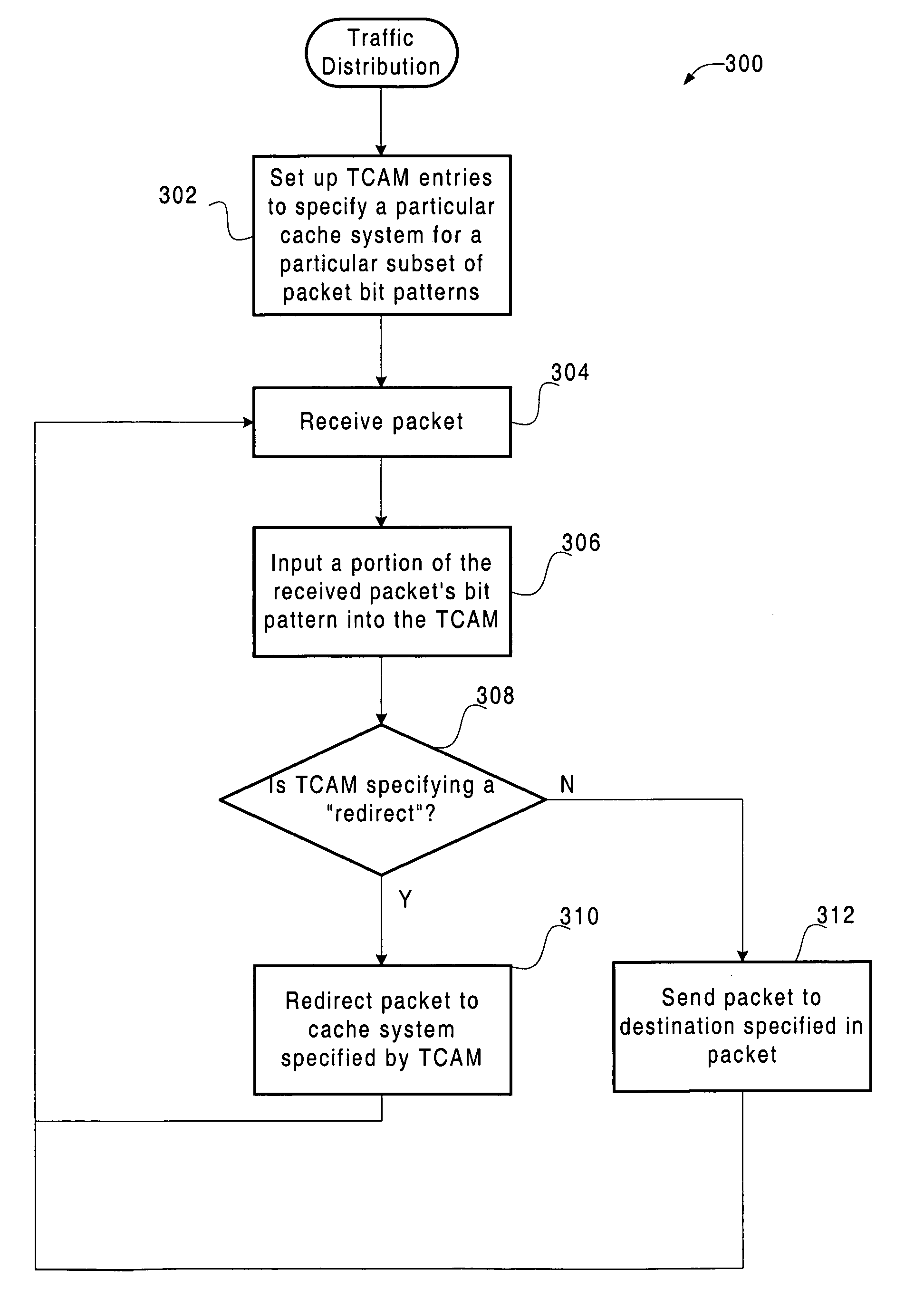
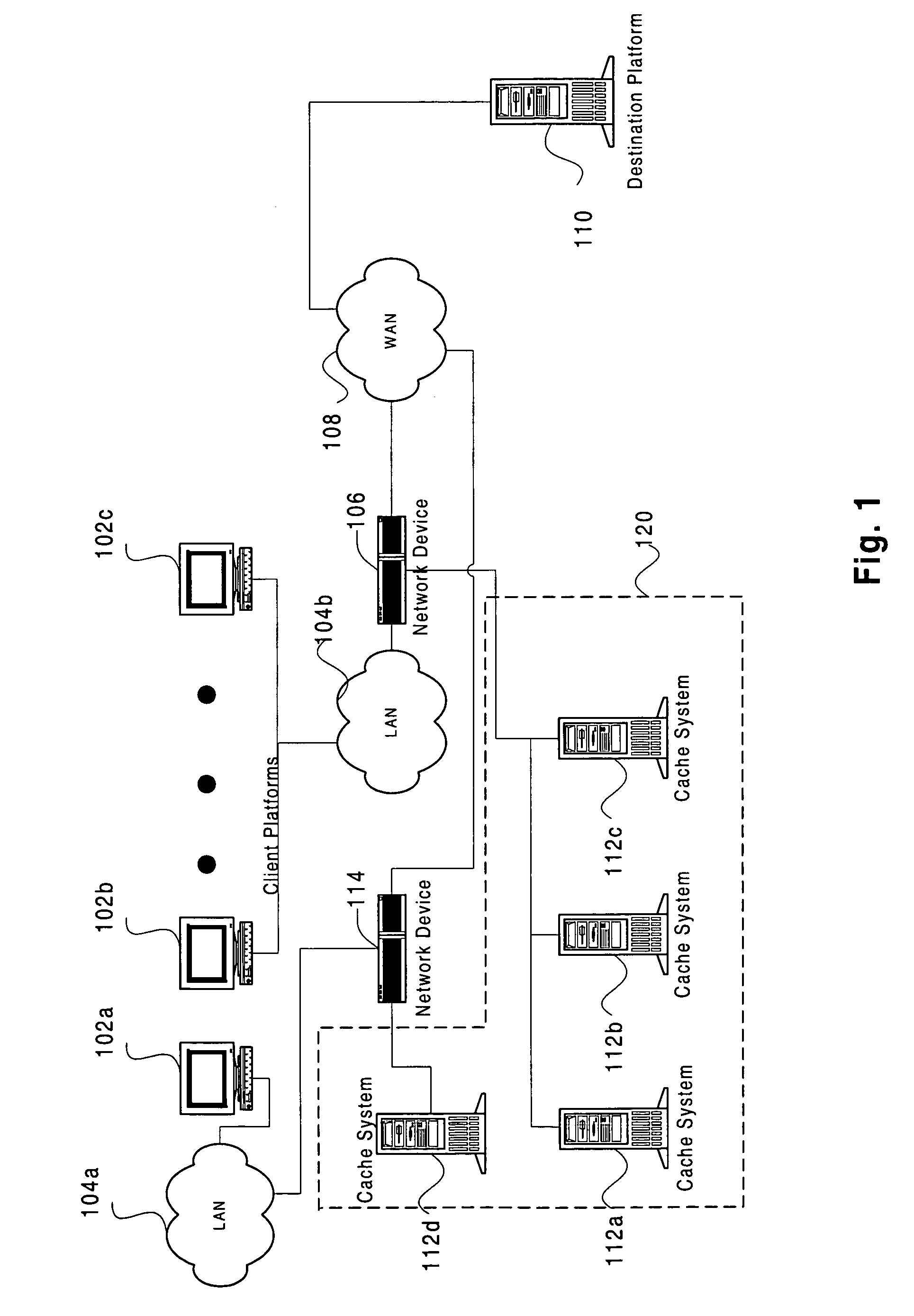
Efficient IP load-balancing traffic distribution using ternary CAMs
InactiveUS7062571B1Digital computer detailsTransmissionTraffic capacityTernary content addressable memory
Disclosed is an apparatus and method for distributing traffic to one or more selected cache systems or servers. In general terms, a content addressable memory (e.g., a TCAM) is utilized to distribute traffic among a plurality of cache systems or servers. The content addressable memory is populated with a plurality of entries. Each entry within the content addressable memory generally indicates an action to be performed on a packet, such as to redirect the packet or to forward the packet to its original destination. When the action indicated by the content addressable memory is to redirect the packet, the content addressable memory also indicates where (e.g., to which cache system) to redirect the packet.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
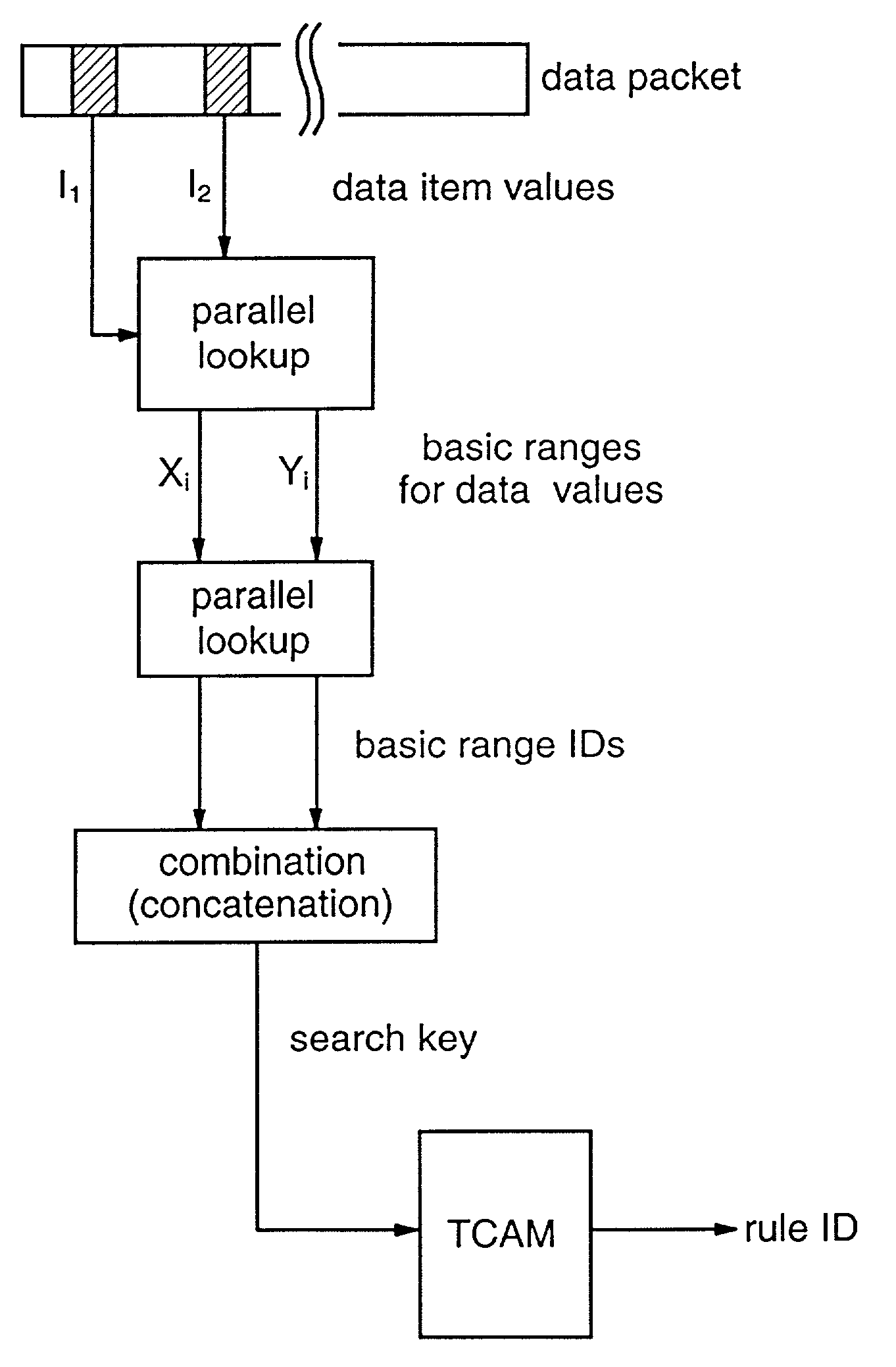
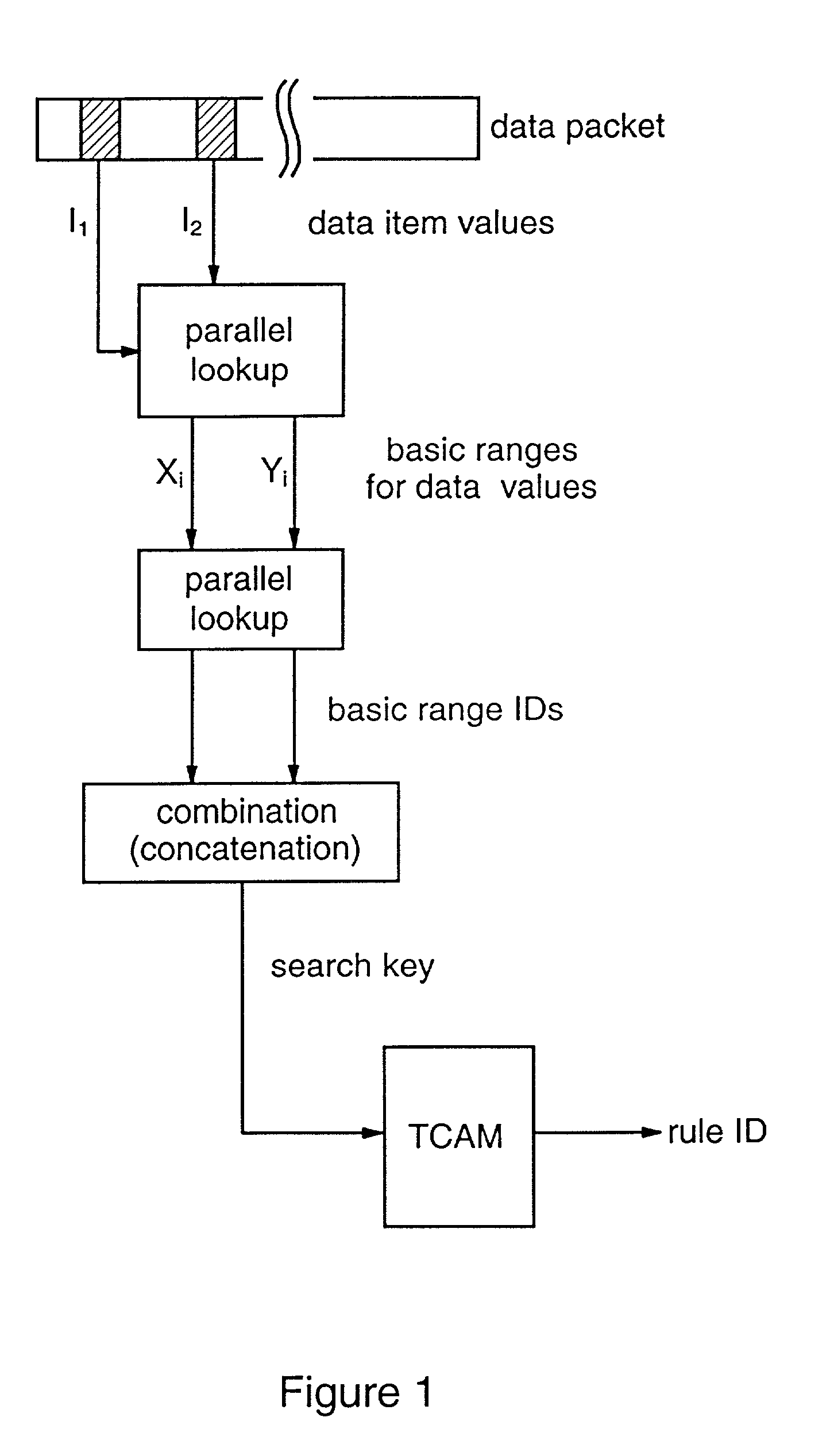
Packet classification
InactiveUS7193997B2Efficient use ofEffective structureData switching by path configurationSecuring communicationData processing systemClassification methods
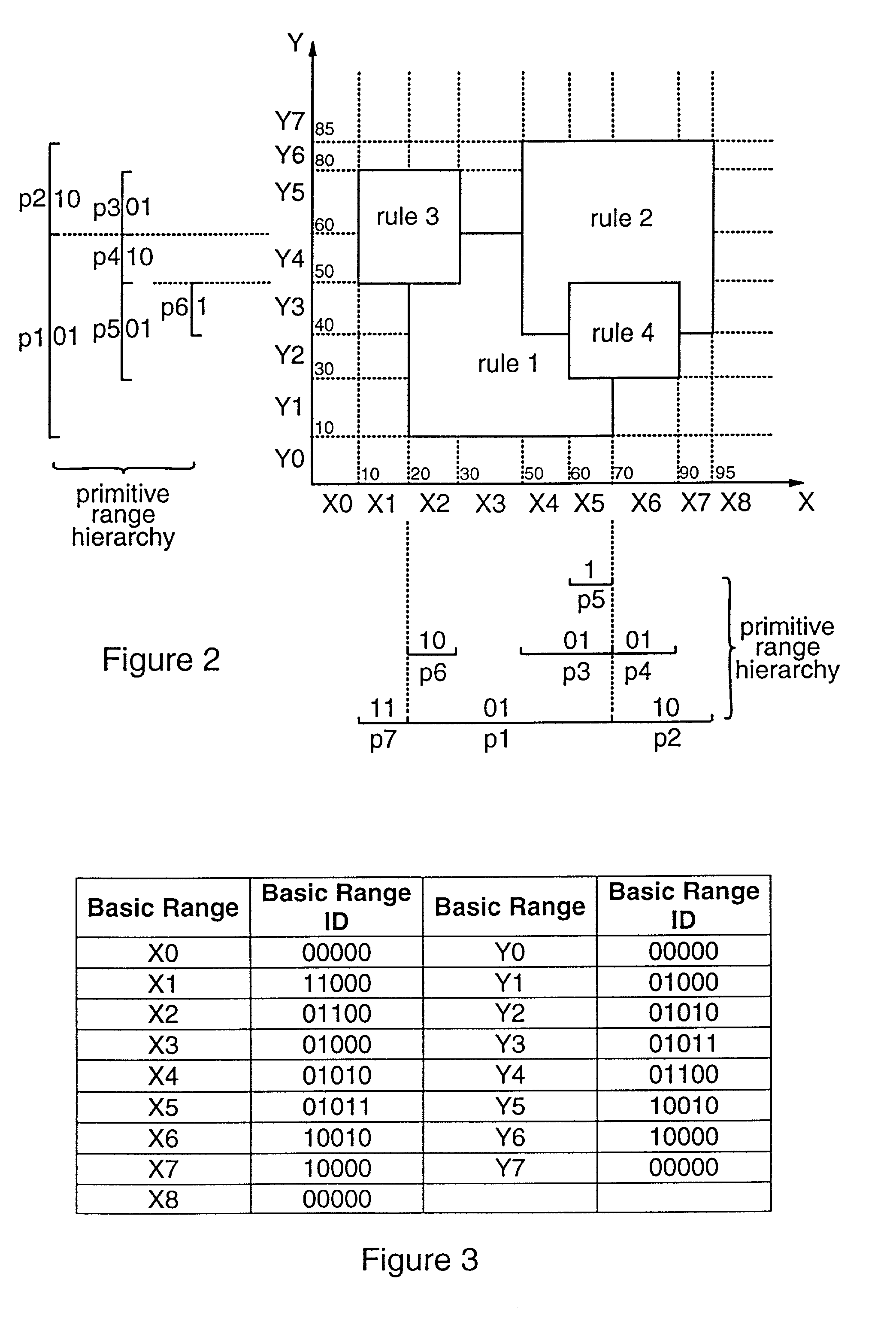
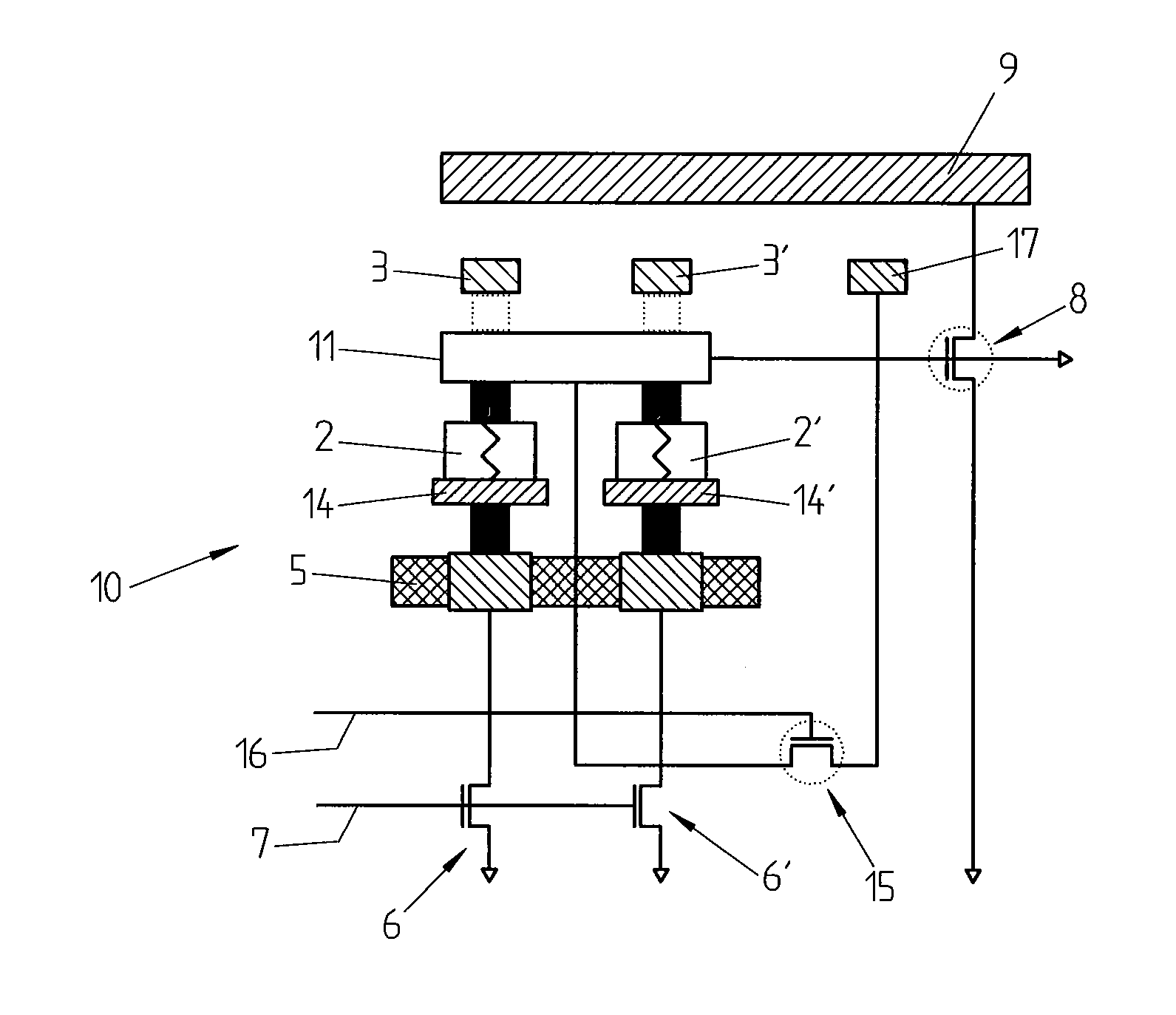
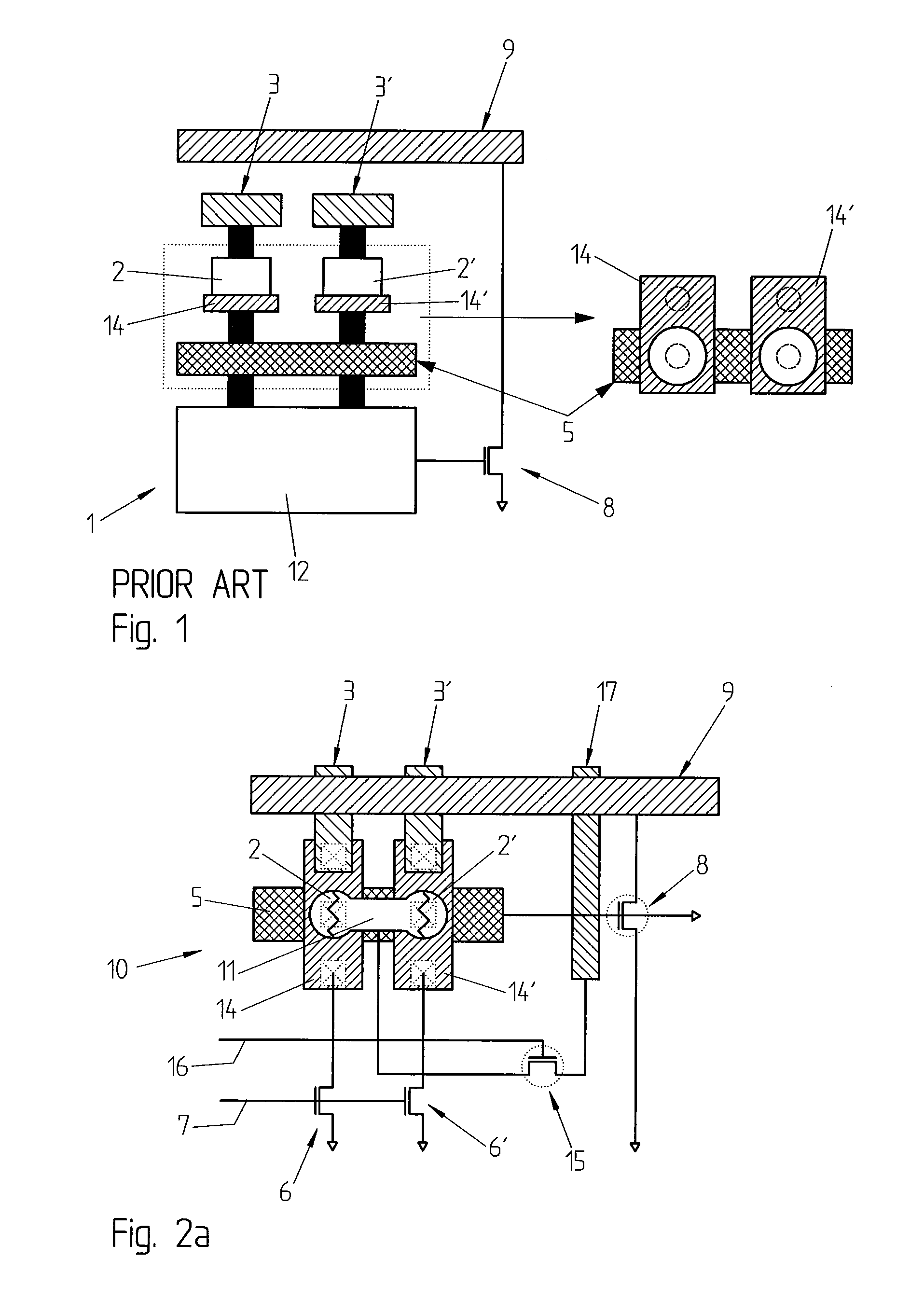
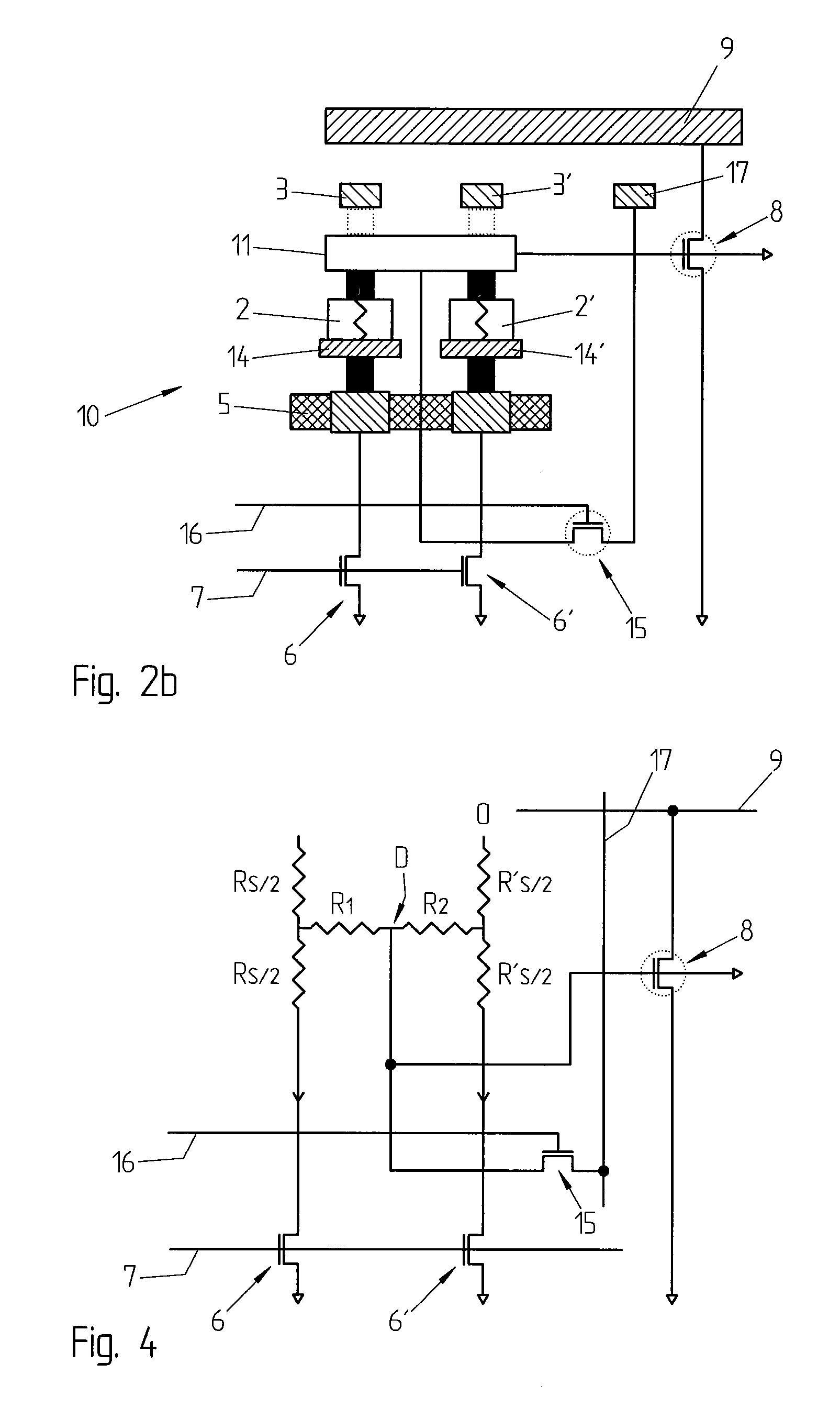
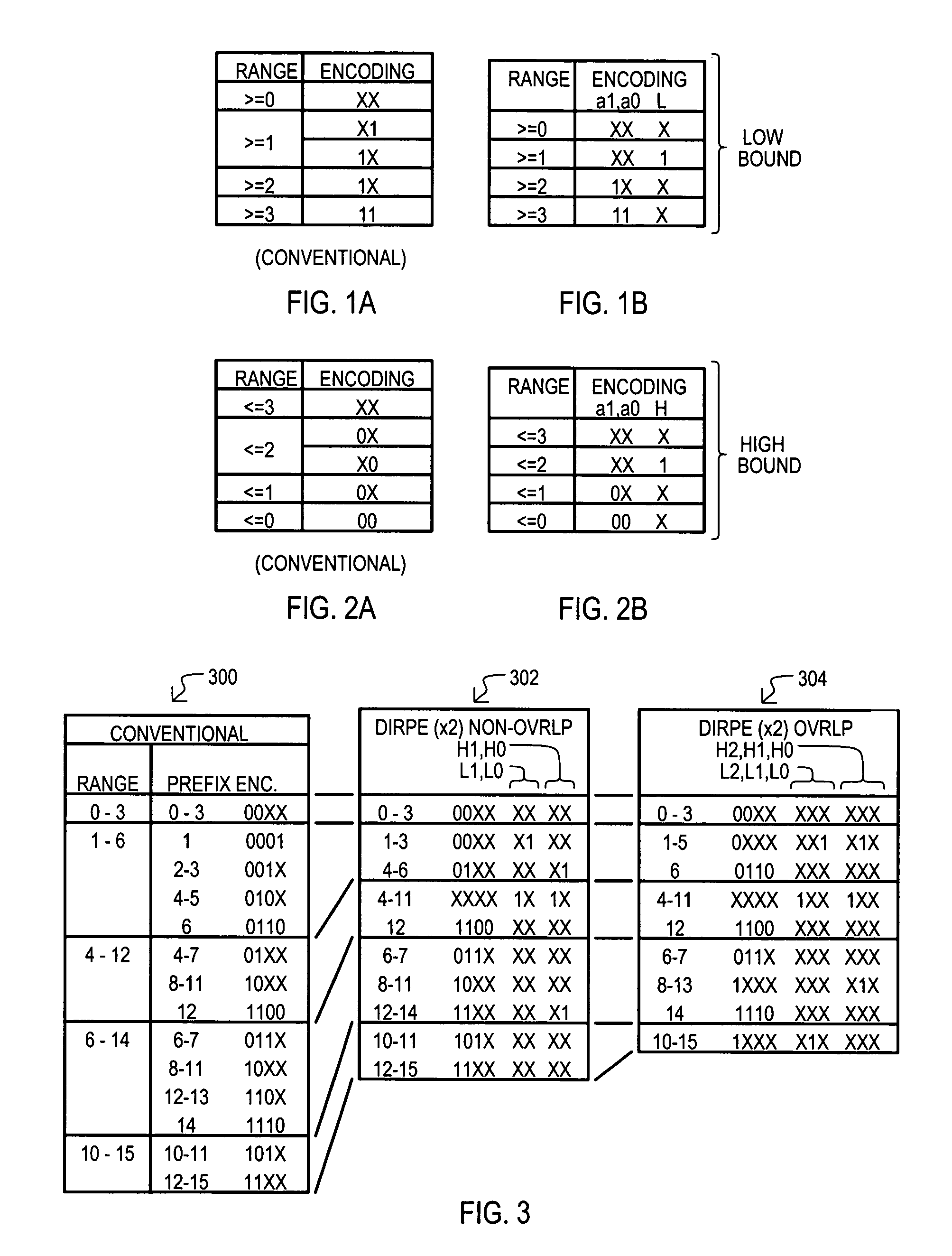
Methods and apparatus are provided for classifying data packets in data processing systems. A first packet classification method determines which of a plurality of predefined processing rules applies to a data packet, where each rule is associated with a range of possible data values in each of a plurality of dimensions (X,Y) corresponding to respective data items in the packet format. For each dimension (X,Y), it is determined which of a set of predefined basic ranges contains the corresponding data value (I1, I2) from the packet, where the basic ranges correspond to respective non-overlapping value ranges between successive rule range boundaries in the dimension. For the basic range so determined for each dimension, a corresponding basic range identifier is selected from a set of predefined basic range identifiers corresponding to respective basic ranges in that dimension. For each of at least two dimensions (X,Y), the basic range identifiers comprise respective pD-bit strings generated independently for that dimension by a process of deriving a primitive range hierarchy based on the rule ranges in that dimension. The resulting basic range identifiers, one for each dimension, are then combined to produce a search key which is supplied to a ternary content-addressable memory (5). In the memory (5), the search key is compared with a set of ternary rule vectors, each associated with a particular rule and derived for that rule from the aforementioned hierarchies, to identify at least one rule which applies to the data packet. A second method classifies data packets according to the values in respective data packets of a single, predetermined data item (DA) in the data packet format, where a plurality of classification results are predefined for respective ranges of values of the data item (DA). Here the data item (DA) in the packet is first segmented. The resulting segments are then equated to different dimensions (X,Y) of a multidimensional packet classification problem and are processed in a similar manner to identify a classification result for the packet.
Owner:IBM CORP
Multilevel flow table-based Openflow message forwarding method and system
InactiveCN102957603AMulti-stream entryCost controlData switching networksOpenFlowTernary content addressable memory
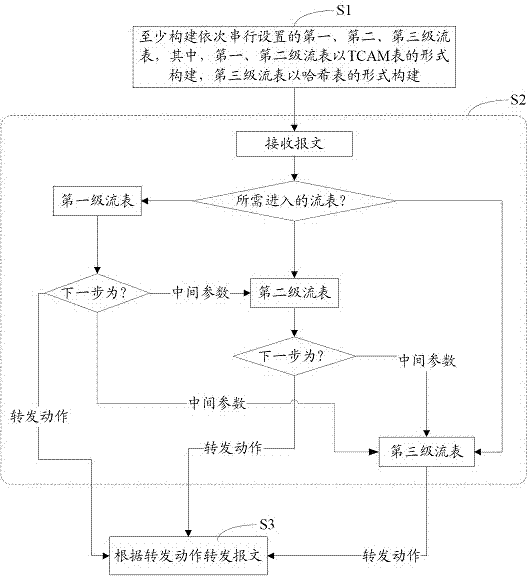
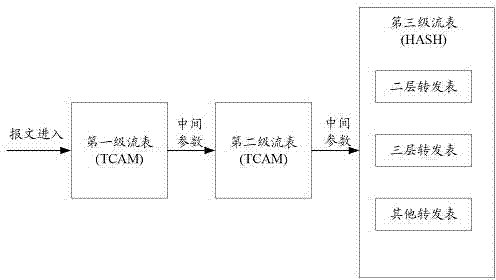
The invention provides a multilevel flow table-based Openflow message forwarding method and a multilevel flow table-based Openflow message forwarding system. The method comprises the following steps of: at least constructing a primary flow table, a secondary flow table and a tertiary flow table sequentially in series, wherein the primary and secondary flow tables are constructed in a ternary content addressable memory (TCAM) form, the tertiary flow table is constructed in a Hash table form, and the primary, secondary and tertiary flow tables can be used independently or in a combined way; searching for forwarding operation over a message on the basis of the primary, secondary and tertiary flow tables; and forwarding the message according to the forwarding operation. Particle sizes of the primary, secondary and tertiary flow tables are decreased, and the tertiary flow table is constructed in the Hash table form, so that the tertiary flow table can acquire more flow items, and the system cost is controlled.
Owner:SUZHOU CENTEC COMM CO LTD
Double density content addressable memory (CAM) lookup scheme
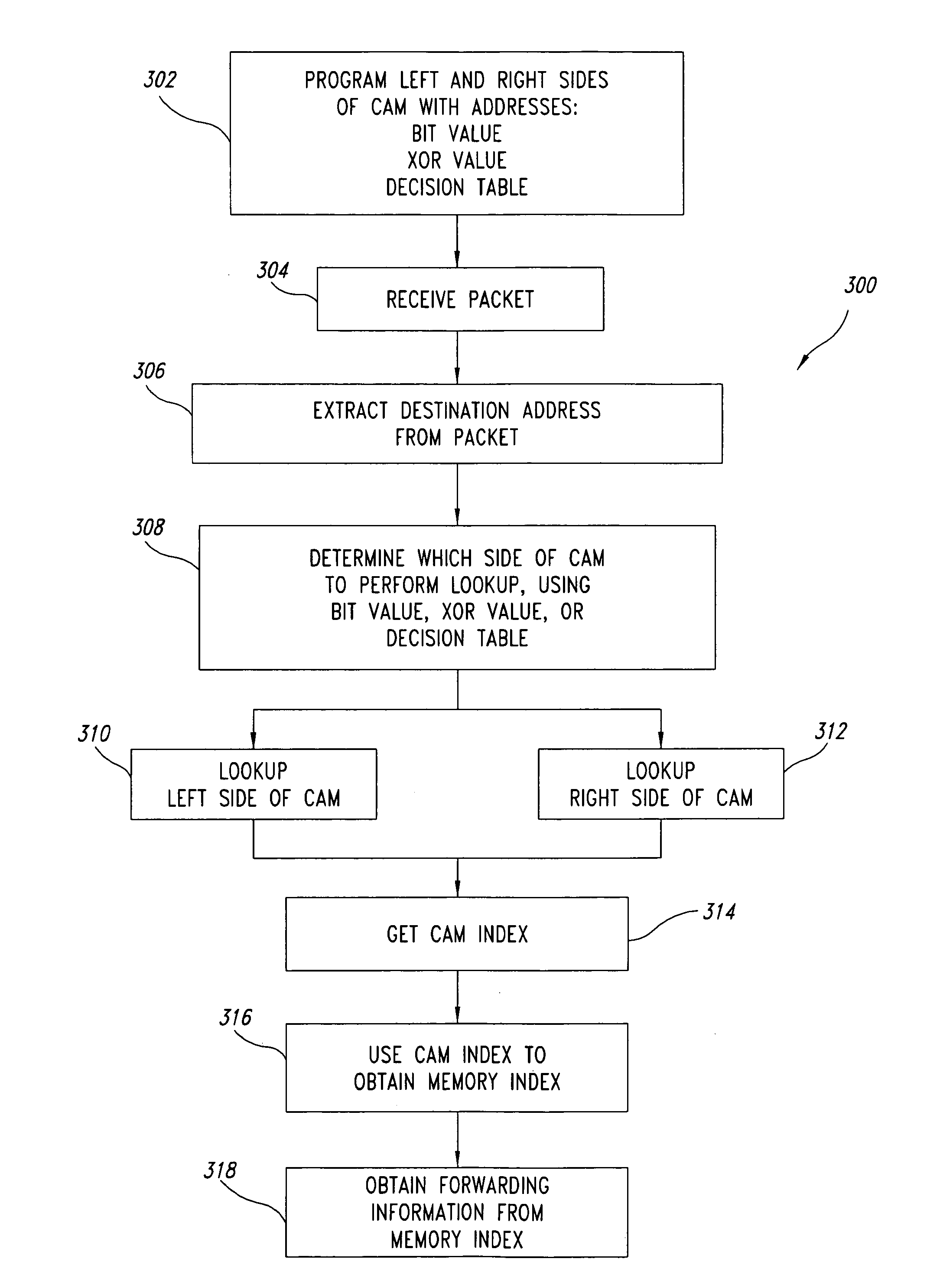
ActiveUS7657703B1Increased complexityIncrease costTransmissionMemory systemsIp addressDecision table
The number of content addressable memory (CAM) lookups is reduced from two to one. Each side (left and right sides) of a CAM is programmed with network addresses, such as IP addresses, based on certain bits of the network addresses. These bits of the network addresses (which represent packet routes) are examined and used to determine whether the particular network address is to be placed on the left or right sides of the CAM. The grouping of certain network addresses either on the left or right sides of the CAM can be performed by examining an individual bit of each network address, by performing an exclusive OR (XOR) operation on a plurality of bits of each network address, and / or by searching for bit patterns of the network address in a decision table. Network addresses that cannot be readily assigned to a particular side of the CAM using these grouping techniques are programmed into both sides of the CAM. During packet routing, techniques similar to the grouping techniques that populated the CAM are used to determine which of the two sides of the CAM is to be searched.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and system for multi-character multi-pattern pattern matching
ActiveUS7725510B2Increase speedEasy to implementData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalPattern matchingTernary content addressable memory
Disclosed is a method and system for multi-character multi-pattern pattern matching. In the multi-character multi-pattern pattern matching method, patterns in an input stream are detected by transitioning between states of a “compressed deterministic finite state automaton (DFA)”, with each transition based on multiple characters of the input stream. The compressed DFA is created by compressing an original DFA, such as an Aho-Corasick DFA, such that each state of the compressed DFA represents multiple consecutive states of the original DFA and each transition between the states of the compressed DFA is a combination of all of the transitions between the multiple consecutive states of the original DFA. This method can be implemented using a Ternary Content-Addressable Memory (TCAM) to store the transitions of the compressed DFA and compares the transitions with multiple characters of an input stream at a time to detect patterns in the input stream.
Owner:ALGOGENE FINANCIAL TECHNOLOGY COMPANY LIMITED
Input data selection for content addressable memory
InactiveUS7237058B2Digital computer detailsData switching by path configurationInput selectionData selection
A method and apparatus for input data selection for content addressable memory. In one embodiment, the apparatus includes an array of CAM cells, a select circuit adapted to generate a plurality of select signals each indicative of a segment of input data provided to the CAM apparatus, and switch circuitry including a plurality of programmable switch circuits each programmable to output a respective bit of the input data as a comparand bit for the array of CAM cells in response to one of the select signals.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
System and method using hierarchical parallel banks of associative memories
ActiveUS7245623B1Effective classificationDigital computer detailsData switching by path configurationTernary content addressable memoryContent-addressable storage
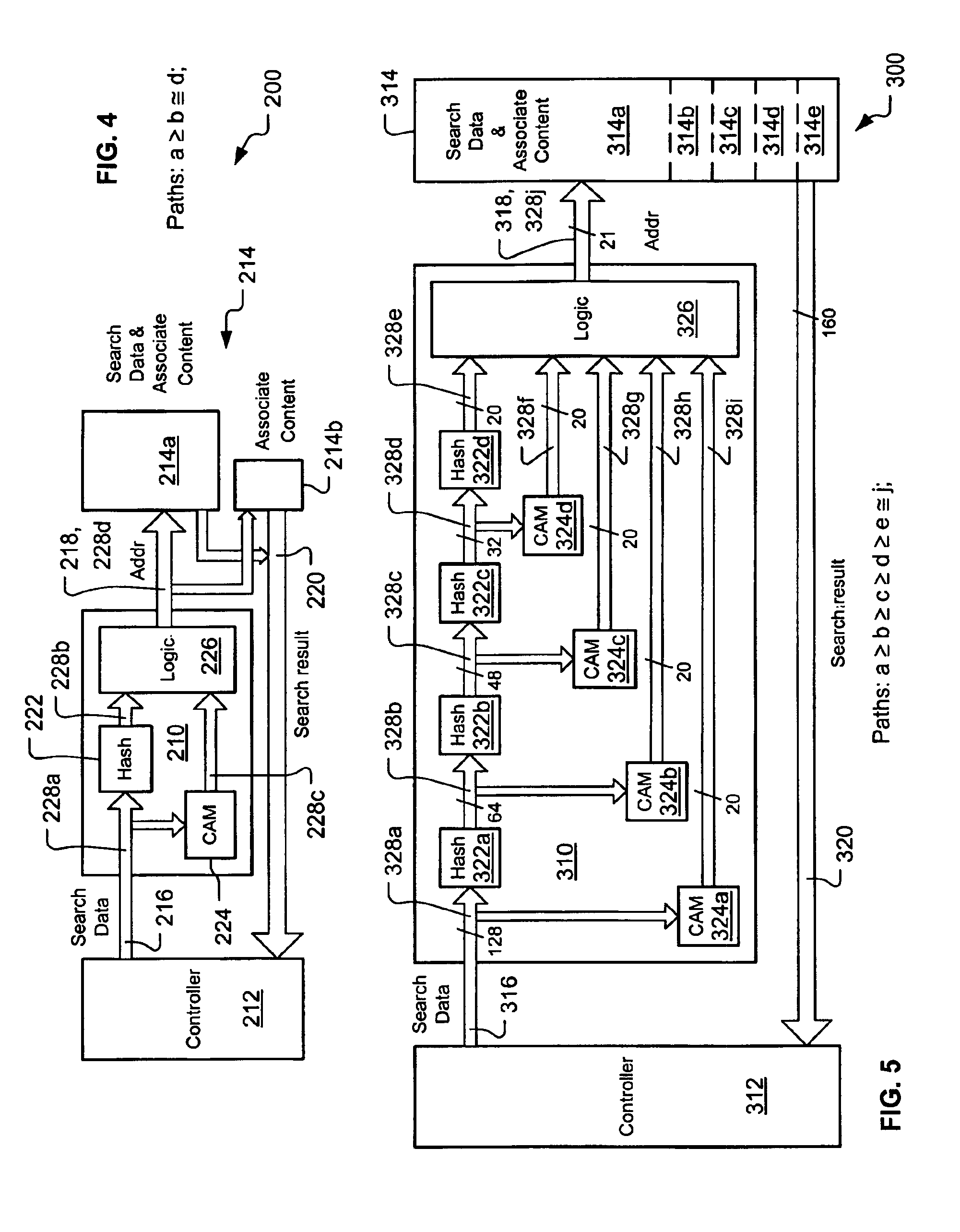
A system and method provide for efficient classification of long strings of data, such as network messages. The system, which may be a classification engine for use in a network device, is configured to include one or more stages having one or more banks of ternary content addressable memories (TCAMs). The TCAM banks of each stage are organized into one or more groups and each group processes the network messages for a different set of the network device's ports. The system further includes at least one memory resource that is shared by the TCAM banks of all groups. That is, the parallel banks of TCAMs operate in a distributed fashion while the shared memory resource operates in a centralized fashion. Accordingly, the system can process network messages at high speed while minimizing the number of required components.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
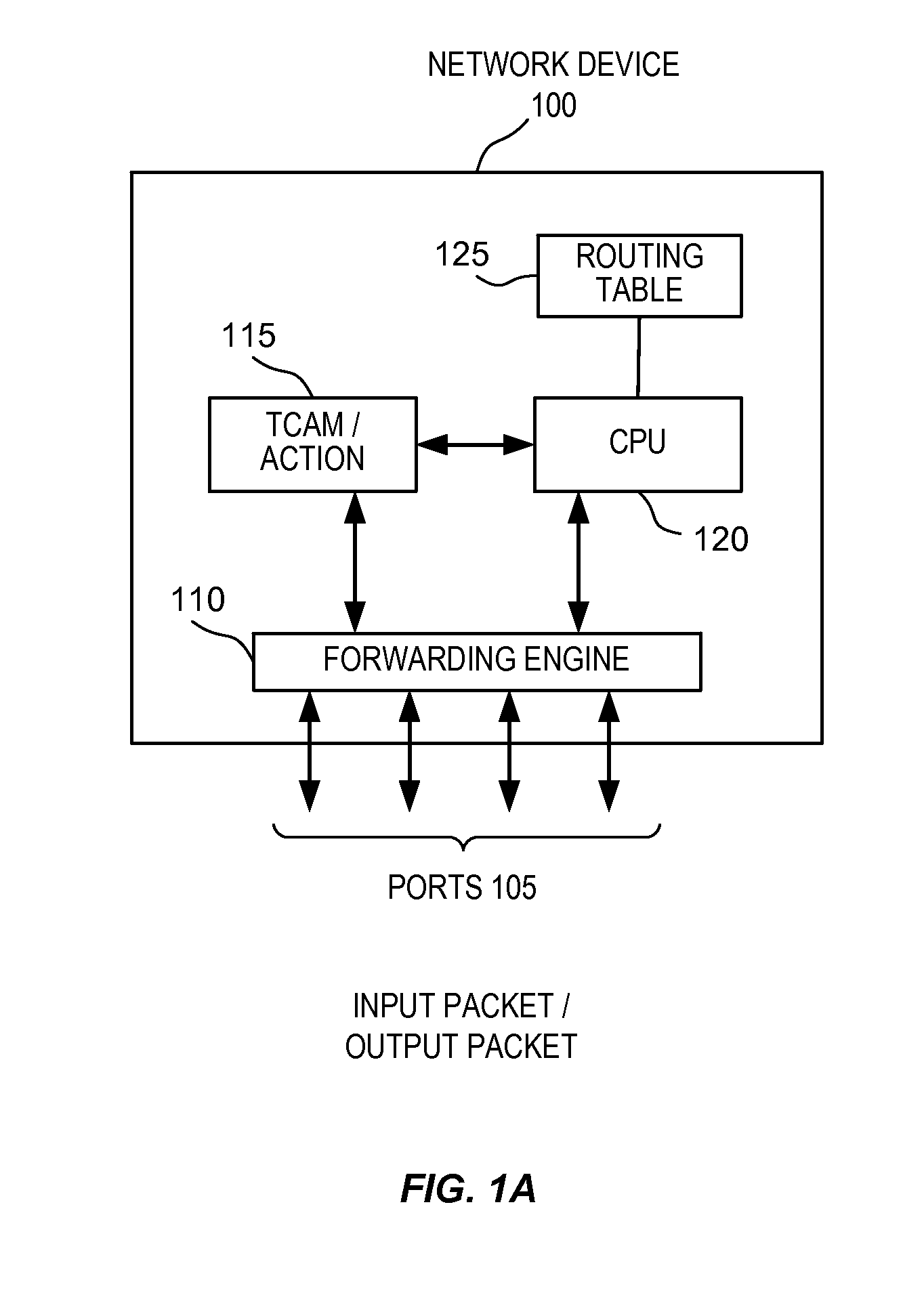
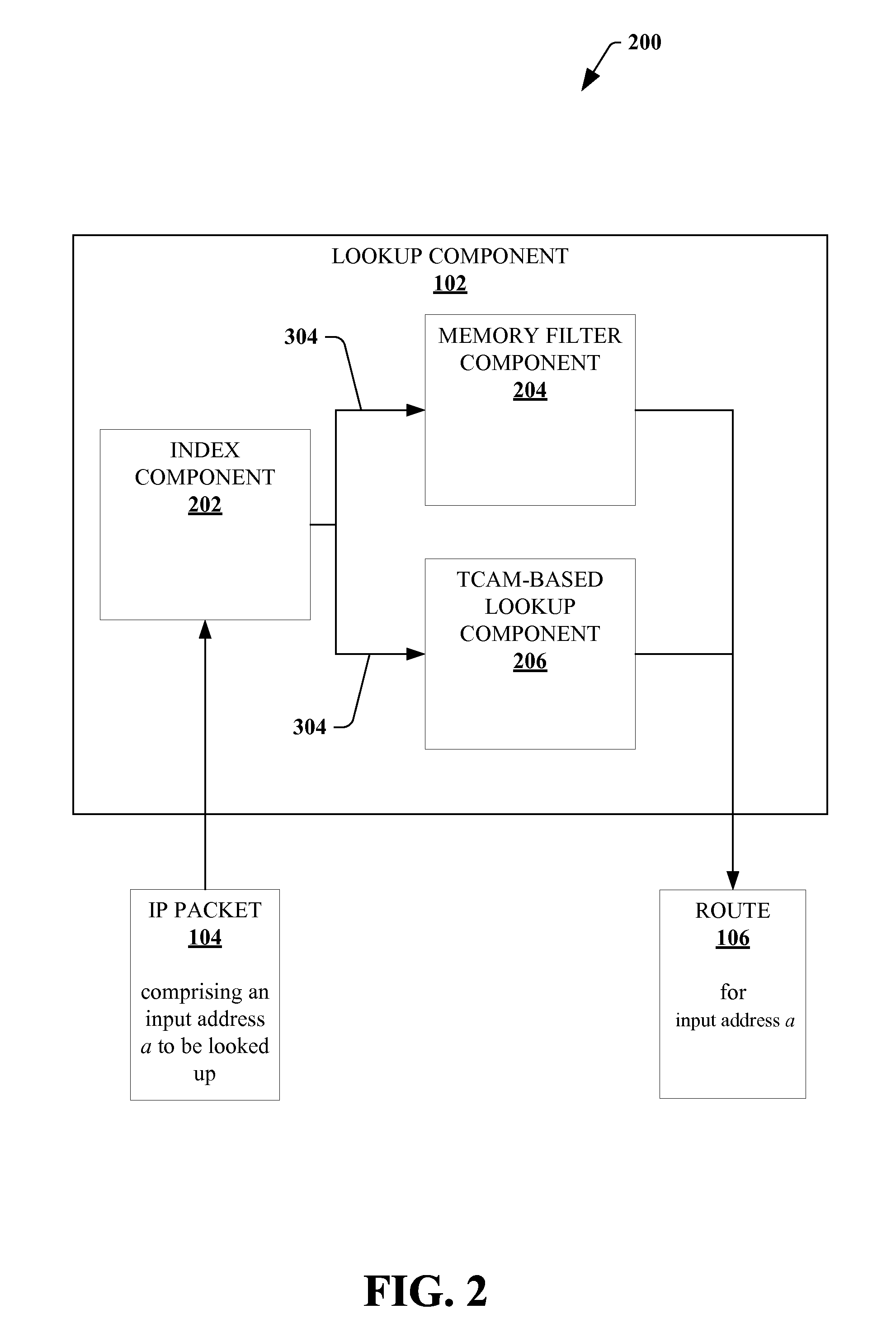
Method and apparatus for performing network routing with use of power efficient TCAM-based forwarding engine architectures
InactiveUS7356033B2Reduce power consumptionMore power efficient forwarding engineEnergy efficient ICTData switching by path configurationPower efficientTheoretical computer science
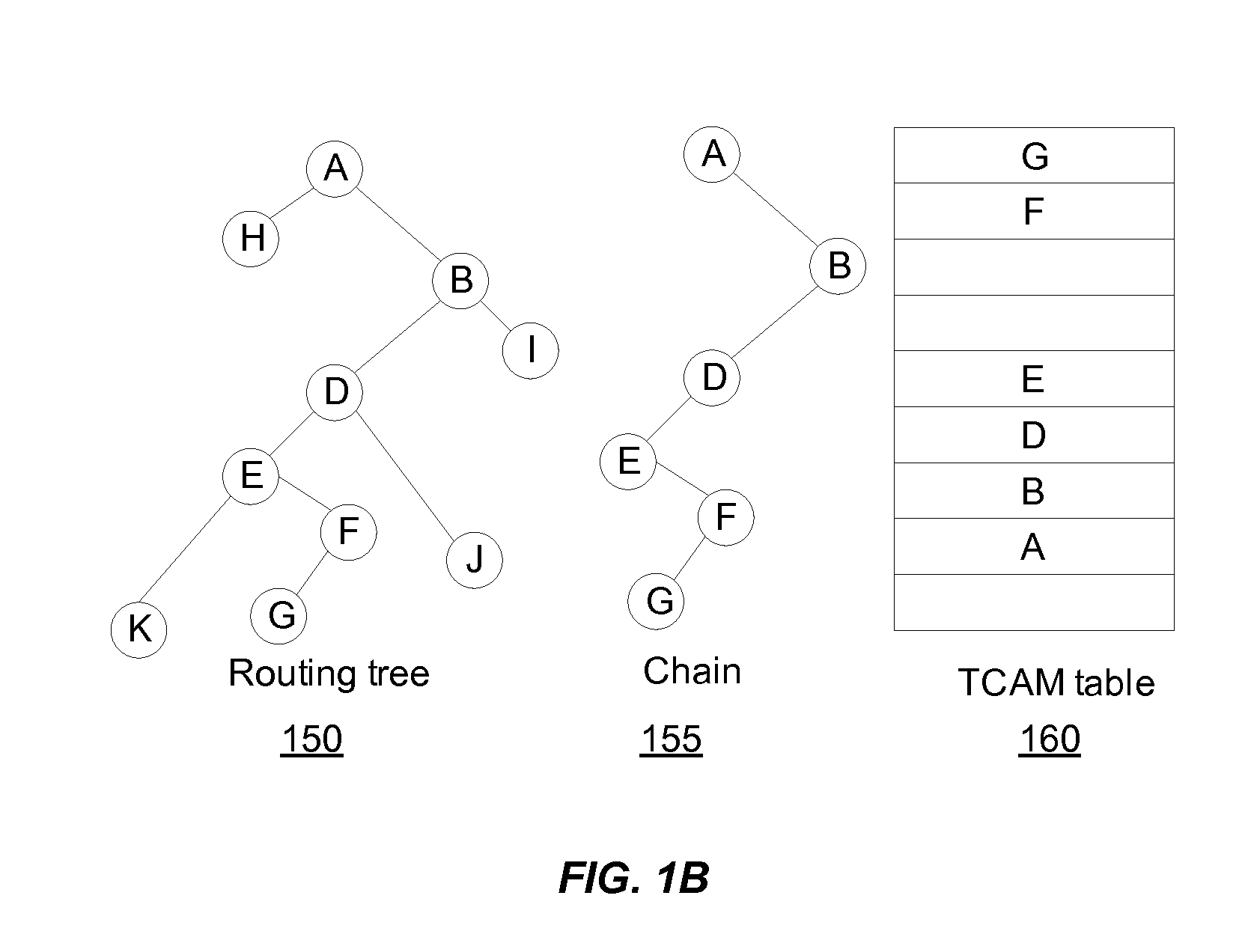
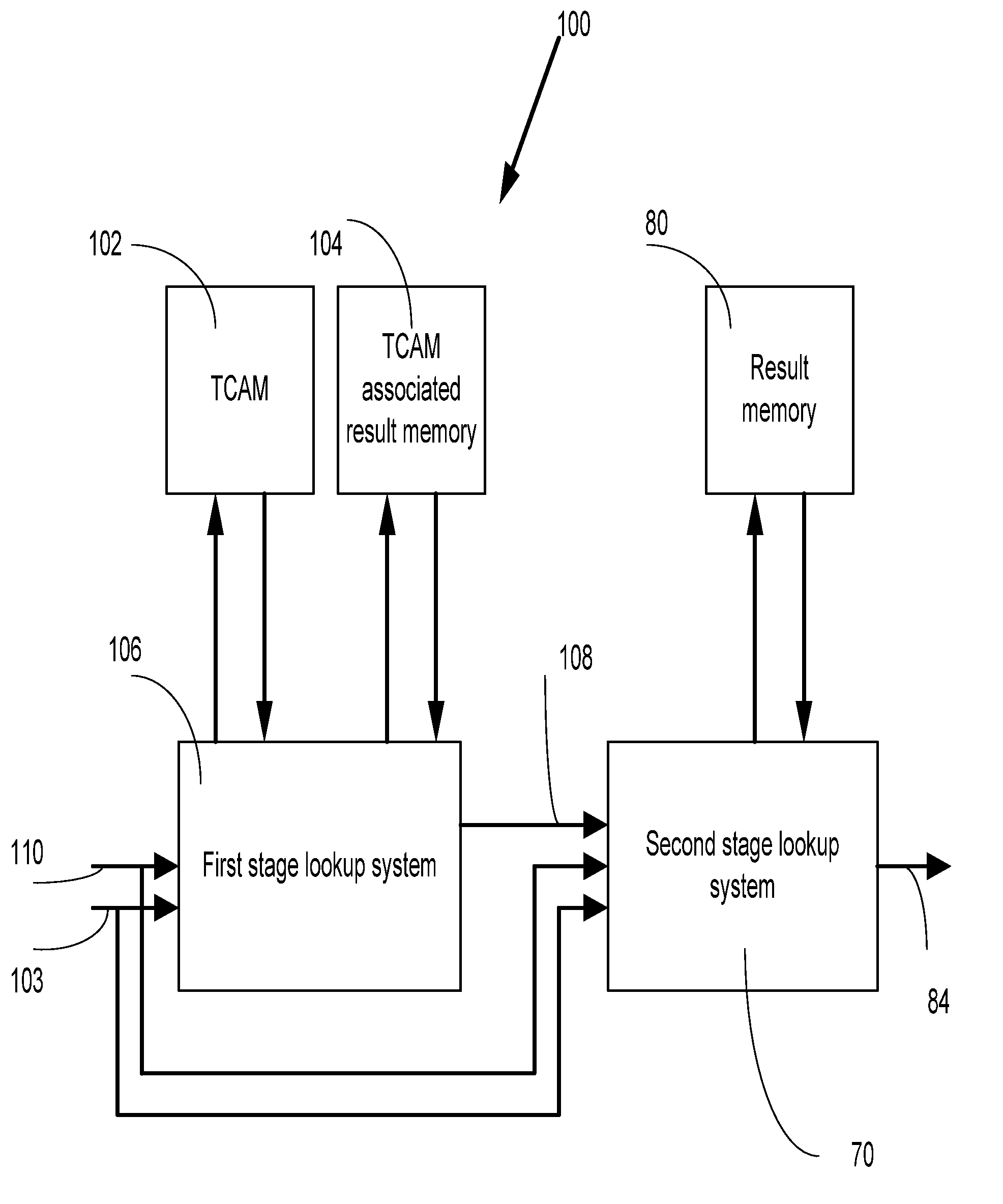
A multi-stage (e.g., two-stage) packet-based lookup process using a Ternary Content Addressable Memory (TCAM) divided into partitions. The result of a first stage lookup is used to selectively search one of a plurality of TCAM partitions during the second stage. A subset of destination address bits may be used in the first stage to hash to a selected partition for the second stage. Alternatively, a partitioning algorithm segments a routing trie into partitions, and then, either a separate, small TCAM or one of the partitions is used in the first stage to map a prefix of the destination address to one of the TCAM partitions for use in the second stage. The “trie-based” algorithms may advantageously partition the trie such that each second stage partition comprises a substantially contiguous sequence of routing prefixes in a post-order traversal of the routing trie, together with one or more covering prefixes thereof.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
Method and apparatus for matching a string with multiple lookups using a single associative memory
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Apparatus and method for memory efficient, programmable, pattern matching finite state machine hardware
InactiveUS7082044B2Reduce memory requirementsMinimize the numberData switching by path configurationComputer security arrangementsStatic random-access memoryPattern matching
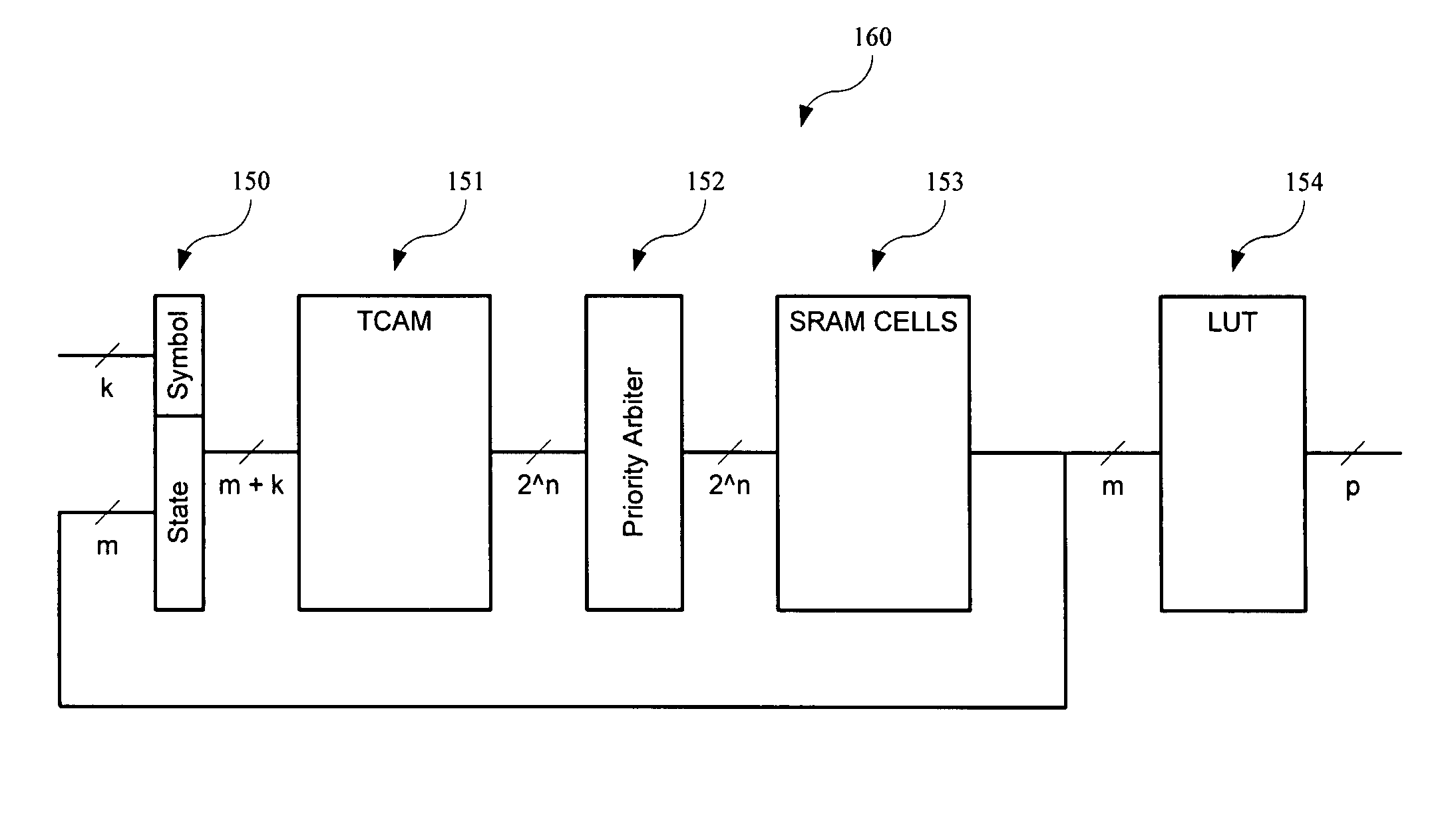
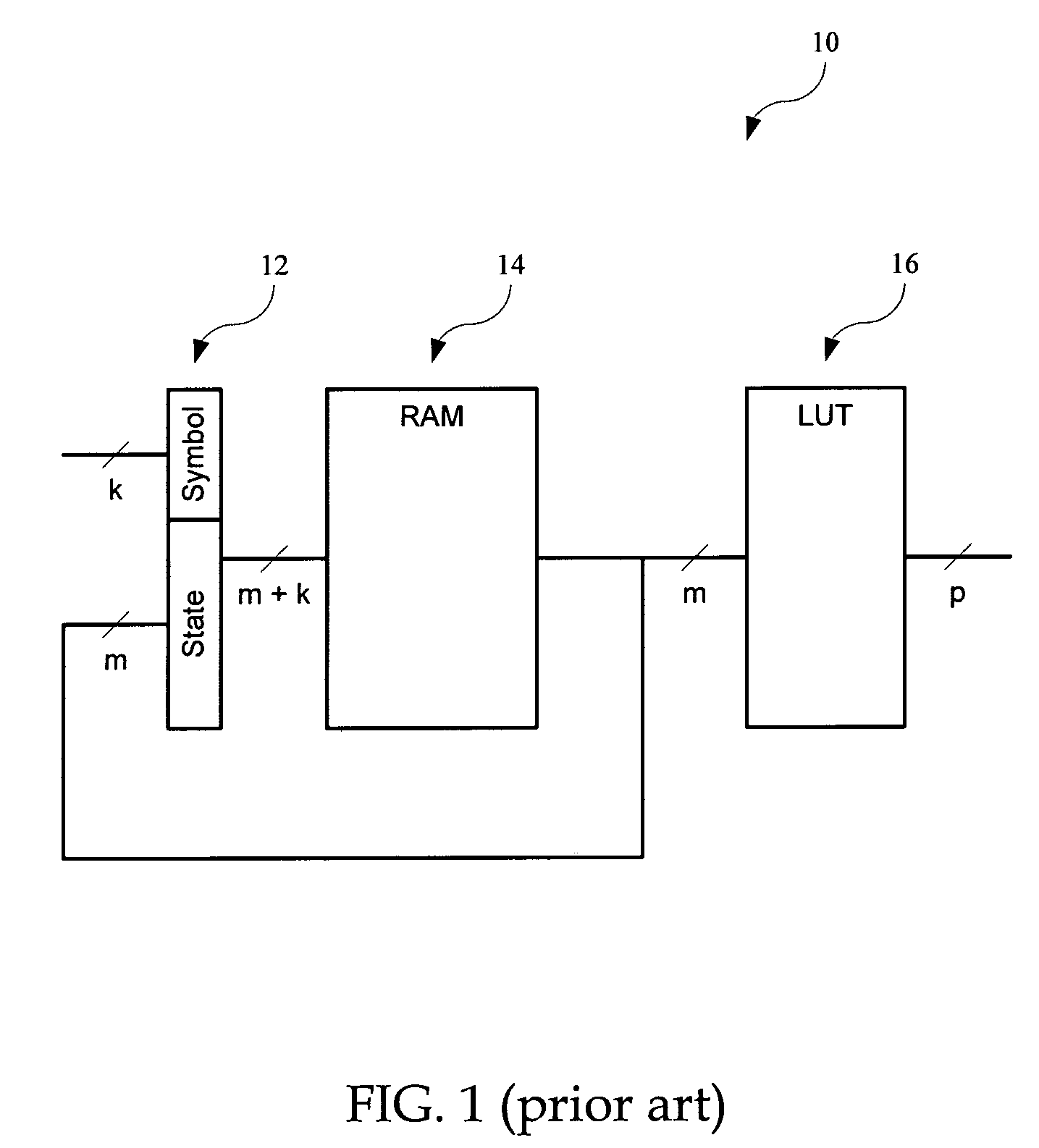
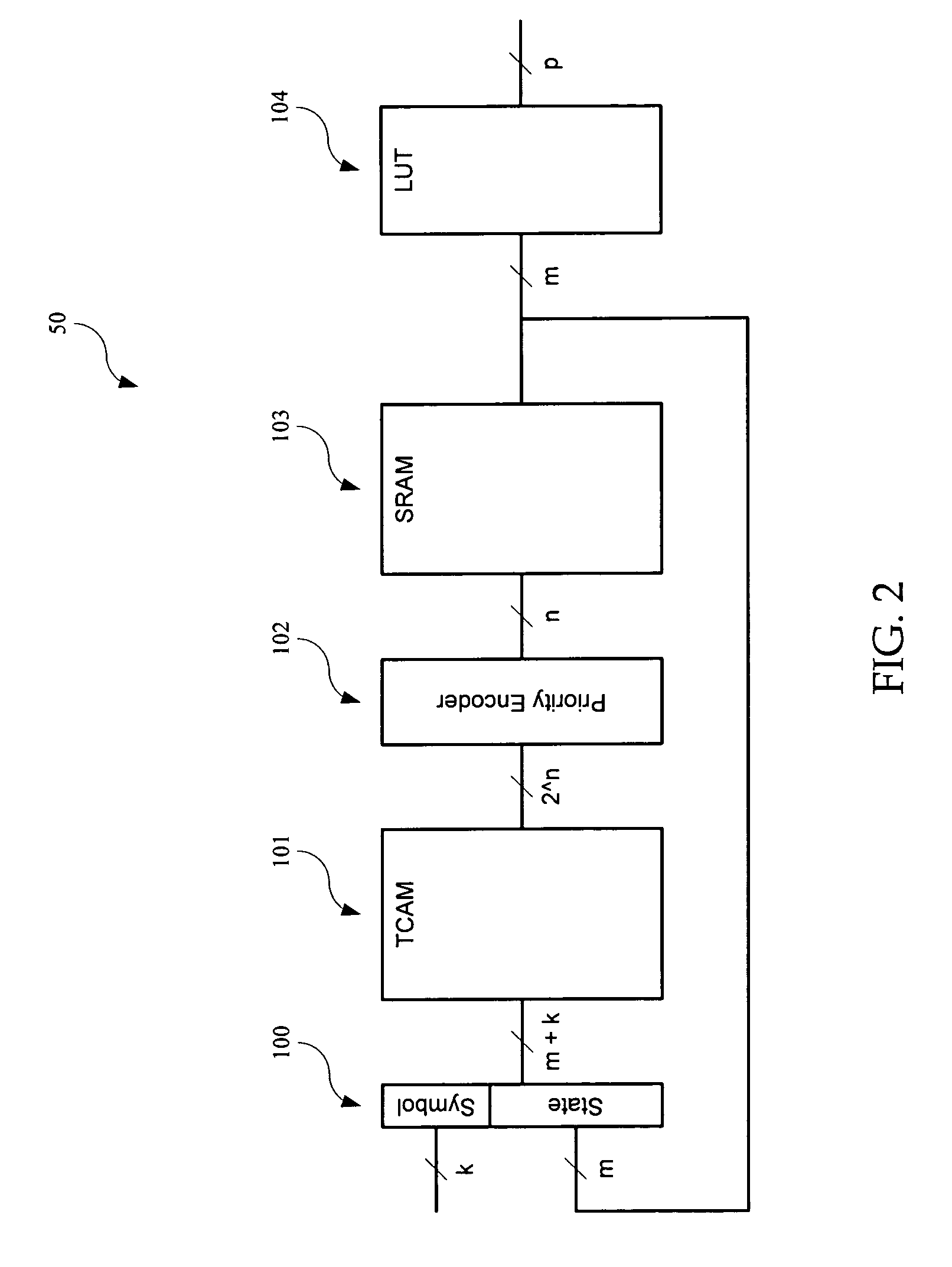
A programmable finite state machine (FSM) includes, in part, first and second memories, and a selection circuit coupled to each of the memories. Upon receiving a (k+m)-bit word representative of the k-bit input symbol and the m-bit current state, the first memory supplies one ore more matching transition rules stored therein. The selection circuit selects the most specific of the supplied rules. The transition rules are stored in the first memory in a ranking order of generality. The second memory receives the selected transition rule and supplies the next state of the FSM. The first memory may be a ternary content addressable memory and the second memory may be a static random access memory. The contents of both the content addressable memory and the static random memory is determined by an algorithm which minimizes the number of terms required to represent the next-state transition functions.
Owner:INTEL CORP +1
Routing system and method for managing rule entries of ternary content addressable memory in the same
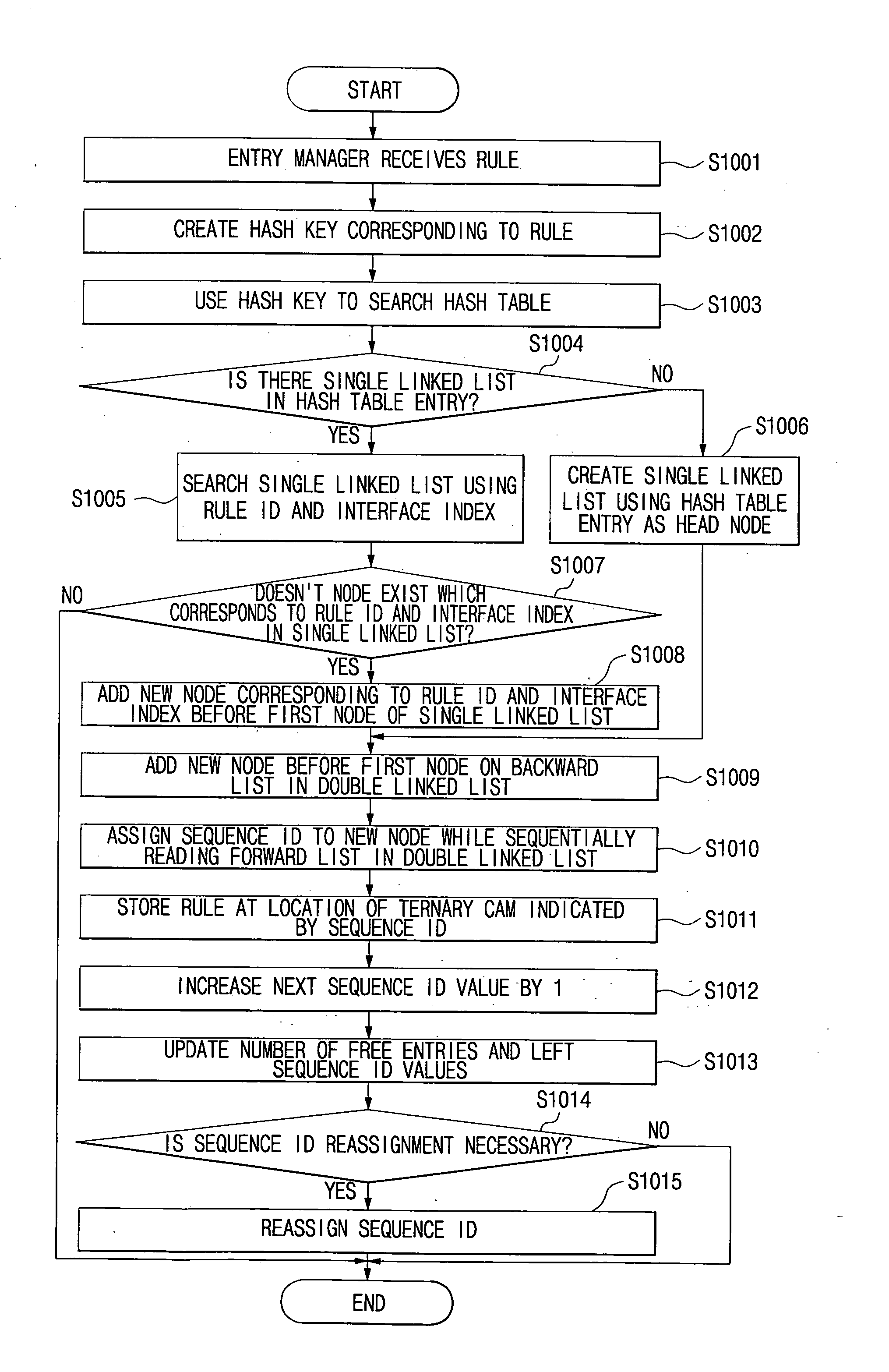
InactiveUS20080192754A1Easy to addEasy to deleteData switching by path configurationData packSequence ID
A method of managing rule entries of a Ternary Content Addressable Memory (TCAM) in a routing system includes: creating a hash table having a hash key corresponding to each entry; creating a single linked list for linking nodes, the single linked list using the entry of the hash table as a head node and including rule IDs and sequence IDs assigned according to a rule input order; and a double linked list having an independent head node, the double linked list bidirectionally linking the nodes constituting the single linked list according to an order of the sequence IDs. Thus, the packet classifying / filtering rule can be easily added to the TCAM or deleted from the TCAM only with minimal information. Also, the sequence ID reassignment process, required for storing as many rules in the TCAM as possible according to the priority of the rules, is performed when a certain time elapses following rule addition or deletion, thereby reducing a latency that may be caused upon setting the packet classifying / filtering rule.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
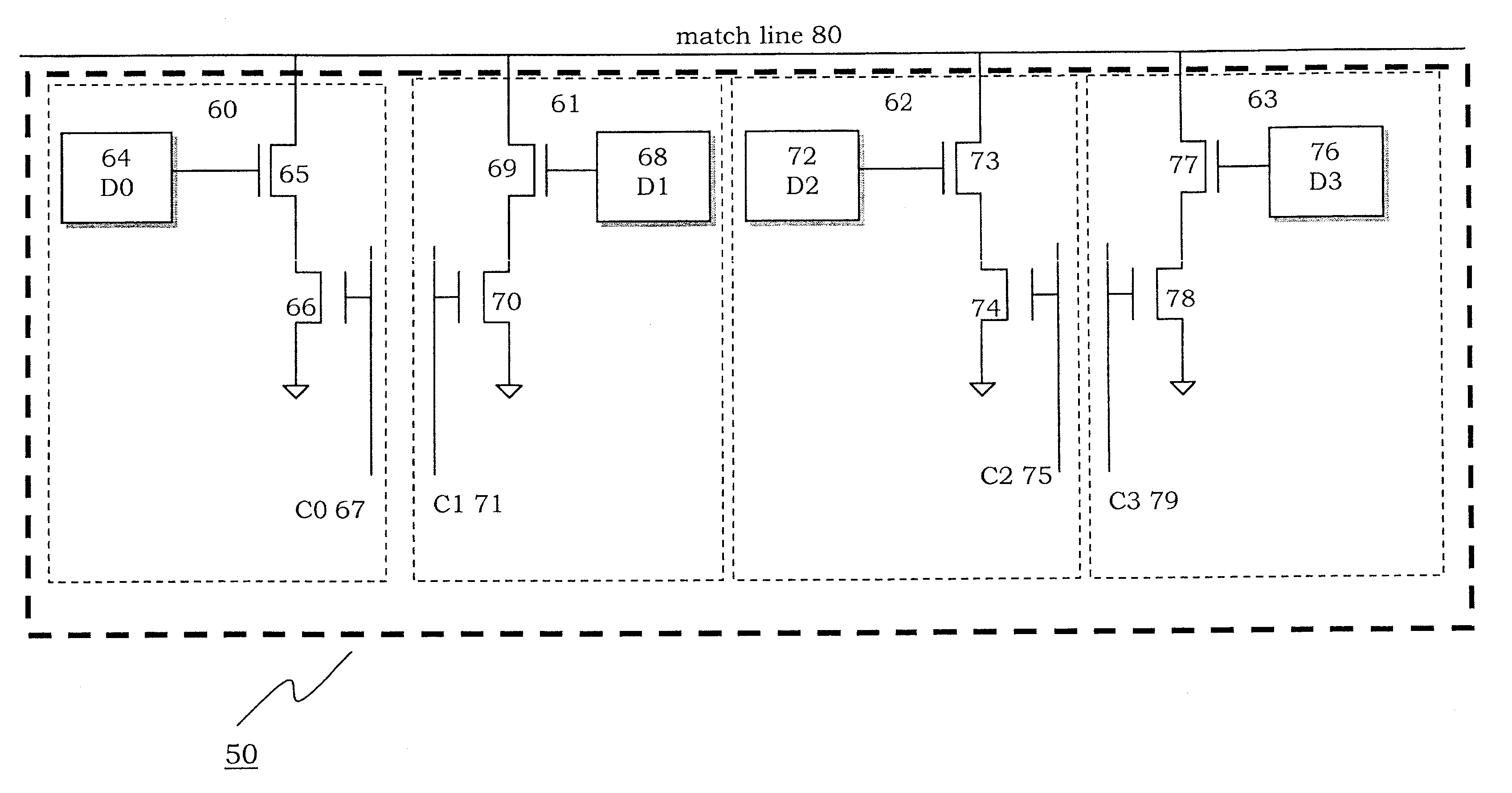
Structure and method of an encoded ternary content addressable memory (CAM) cell for low-power compare operation
The invention discloses a low-power ternary CAM by utilizing four encoded comparand datalines, C0, C1, C2, and C3 in a twin ternary cell. The twin ternary cell is a composite of two ternary CAM bits. The two binary CAM bits are coded so that only one of four comparand datalines is toggled during a compare operation. The encoded data is stored and used for comparison. In one embodiment, the four possible states for the 2 bit comparands are coded as 0001, 0010, 0100, and 1000.
Owner:ATEL VENTURE FUND LLC
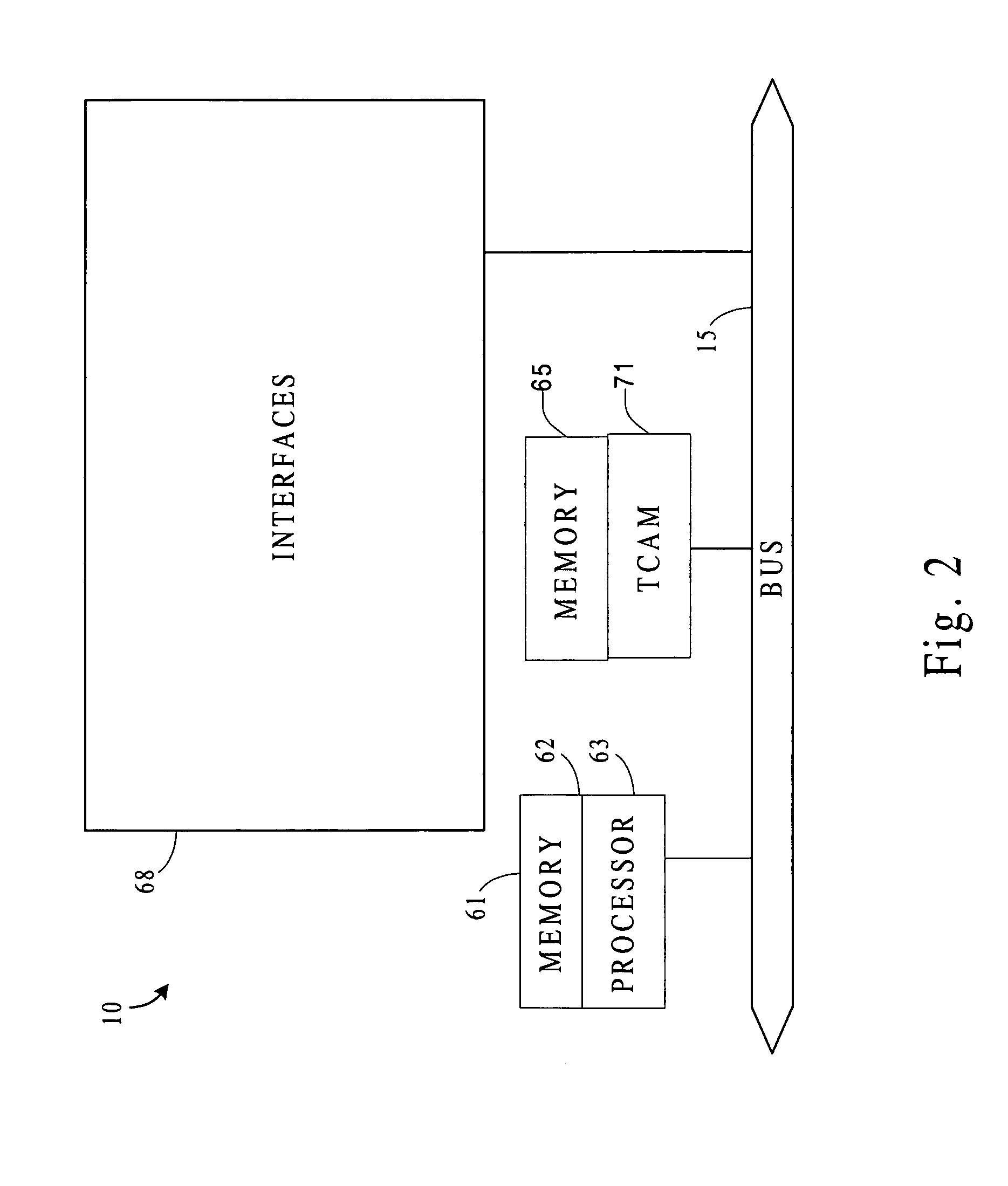
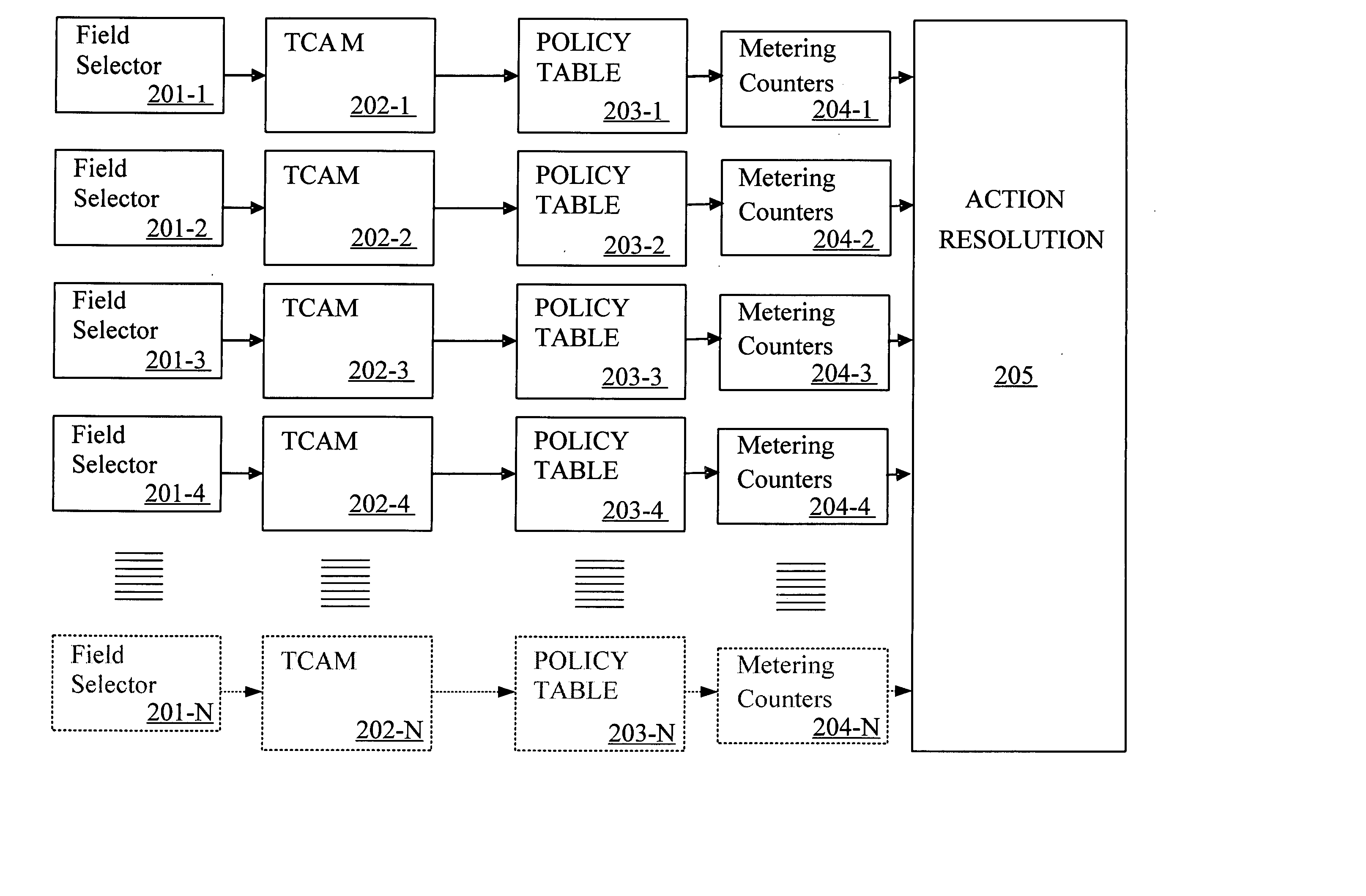
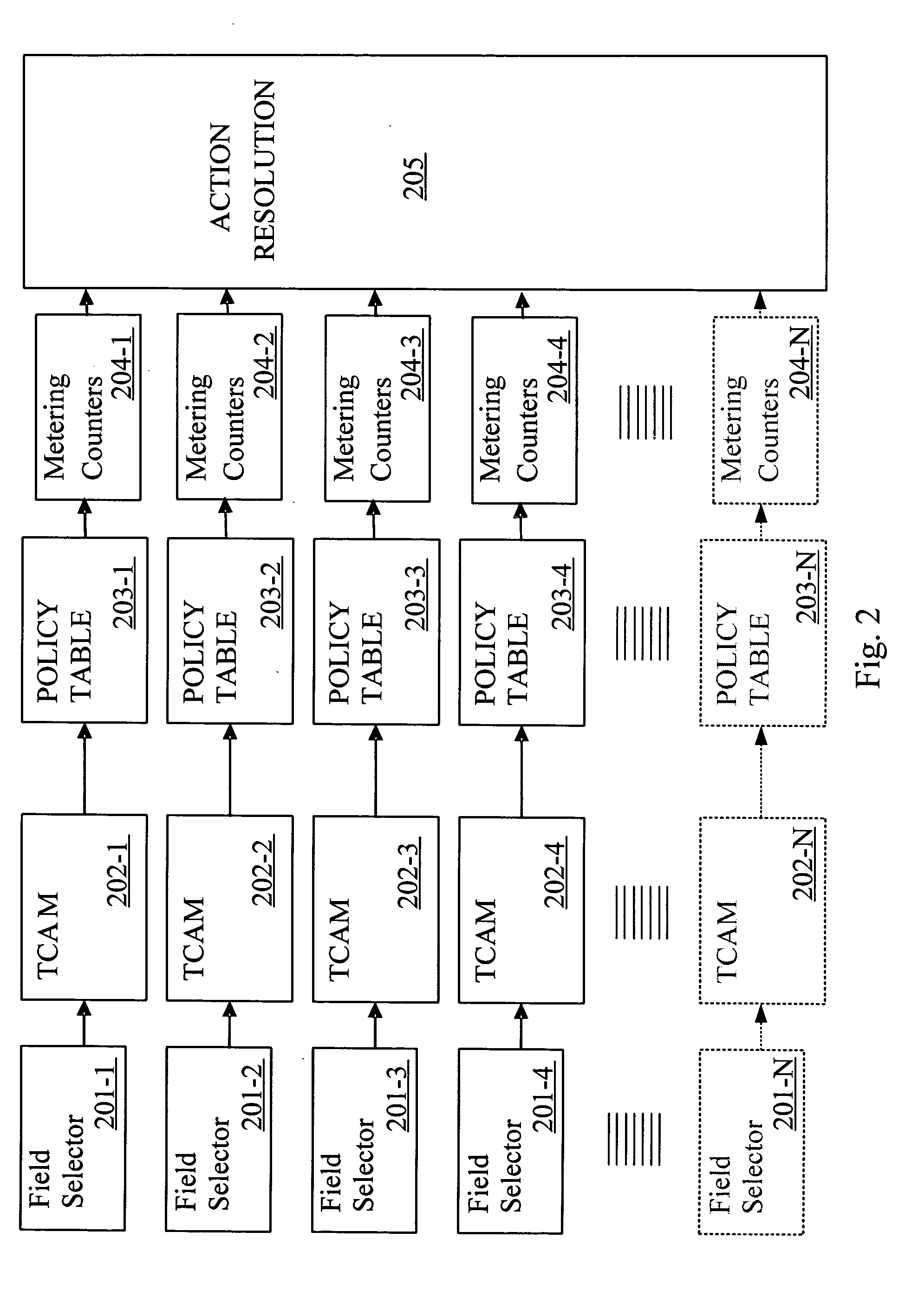
Field processor for a network device
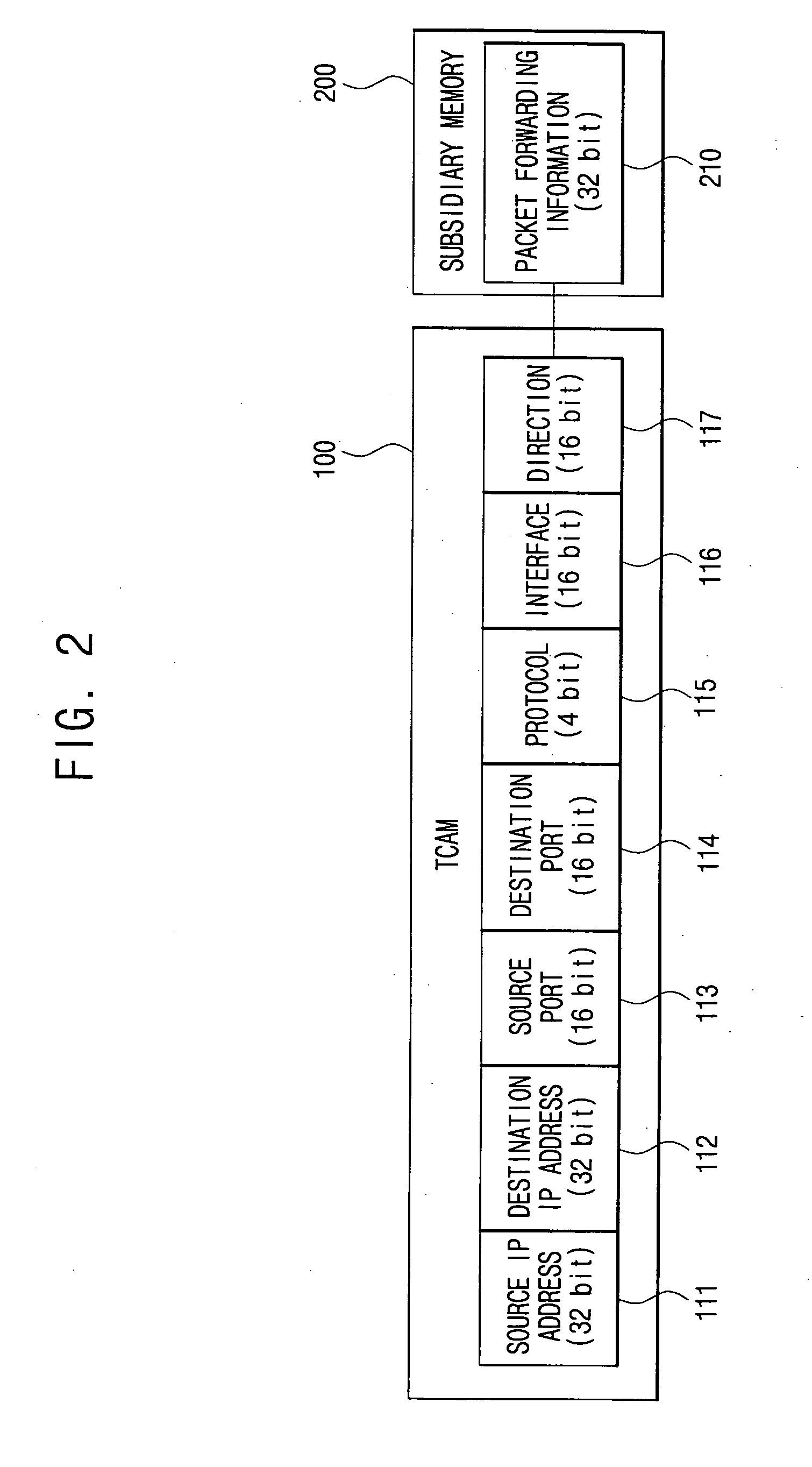
InactiveUS20050135399A1Store-and-forward switching systemsTernary content addressable memoryComputer science
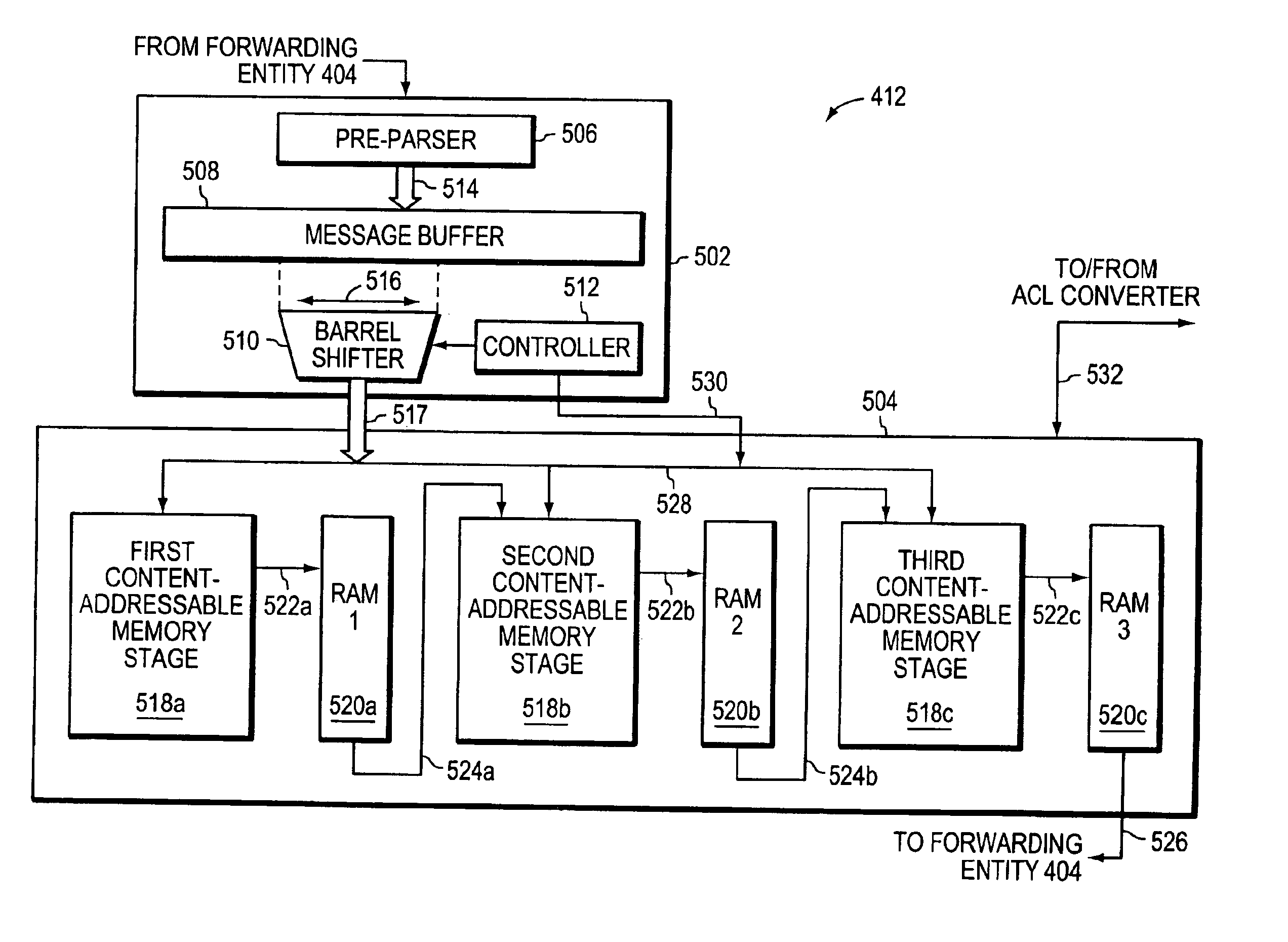
A method of handling a datagram in a network device is disclosed. The steps include receiving a datagram, with the datagram having multiple field values, at a port of a network device, parsing the received datagram to obtain the field values, applying the parsed field values to a Ternary Content Addressable Memory (TCAM), determining matches between the parsed field values and predetermined criteria in the TCAM, indexing into a policy table based on the determined matches to obtain an action entry and taking an action based on the obtained action entry.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
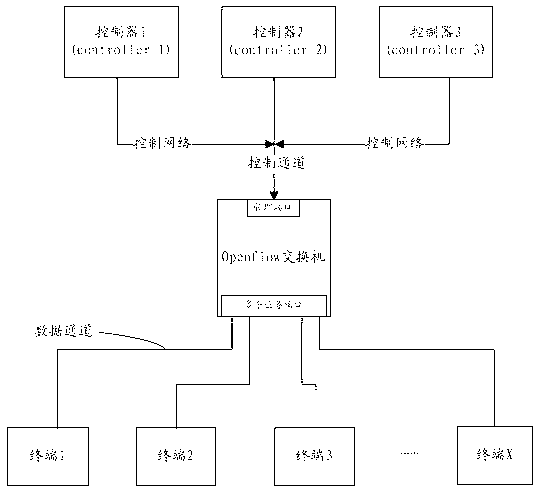
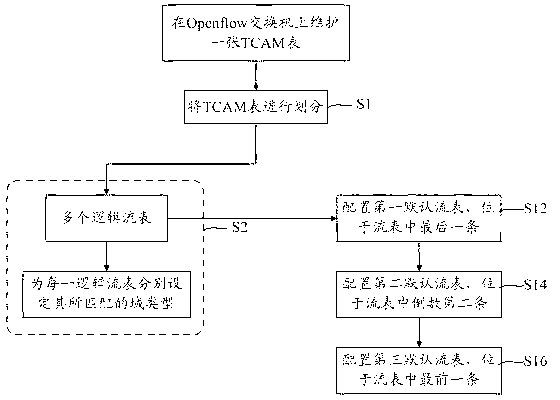
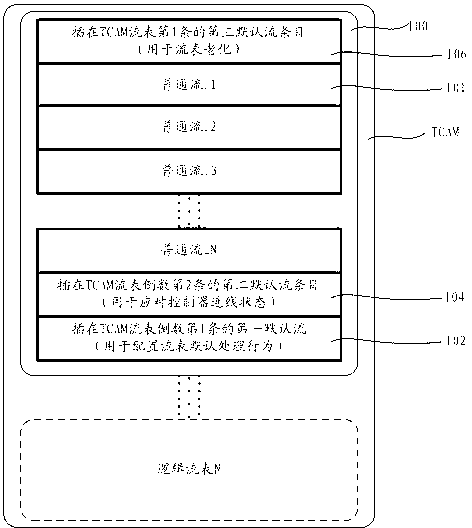
Method and system for realizing Openflow multi-stage flow tables on basis of ternary content addressable memory (TCAM)
InactiveCN102843299AIncrease the number of stored entriesReduce manufacturing costData switching networksMultiple formsOpenFlow
The invention provides a method and a system for realizing Openflow multi-stage flow tables on the basis of a ternary content addressable memory (TCAM). The method comprises the following steps of: S1, dividing a TCAM table maintained on an Openflow switch into multiple logical flow tables; and S2, setting the matched domain type for each logical flow table. The TCAM table is divided into multiple logical flow tables and the matched field length of each flow table comprises multiple forms, so that storage items of the TCAM table are effectively increased, different application requirements are met and the manufacturing cost of the Openflow switch is effectively reduced.
Owner:SUZHOU CENTEC COMM CO LTD
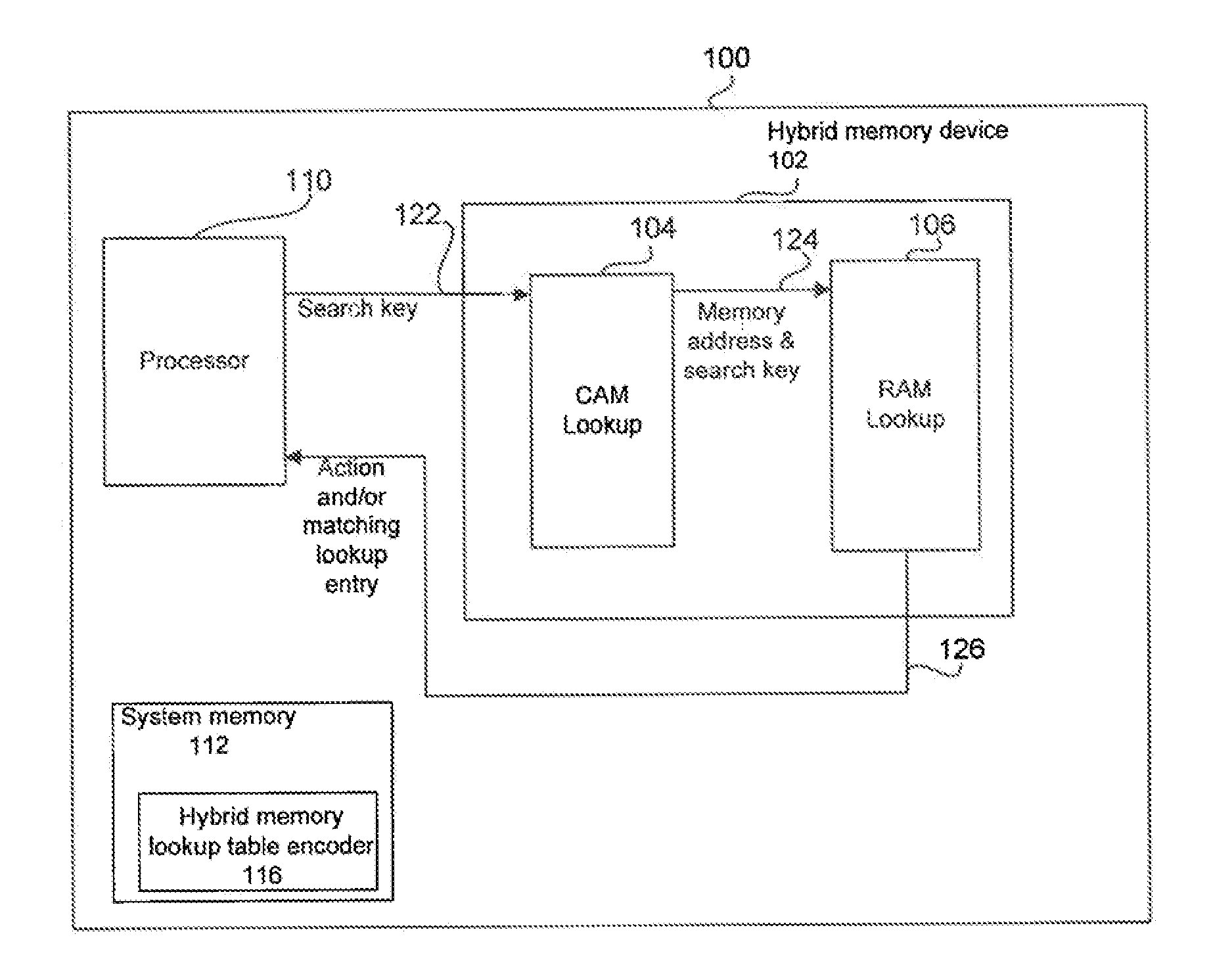
Hybrid Memory for Search Operations
InactiveUS20130246698A1Digital data information retrievalDigital storageTheoretical computer scienceDecision taking
Methods, systems, and computer readable storage medium embodiments for configuring a lookup table for a network device are disclosed. Aspects in these embodiments include generating a decision tree based upon bit representations of respective data entries from a plurality of data entries where one or more of the plurality of data entries are represented at respective nodes of the decision tree, storing a first bit pattern corresponding to a selected node from the decision tree in a content addressable memory (CAM) at a location associated with an index, and storing one or more second bit patterns at an address in a second memory. The one or more second hit patterns correspond to the one or more data entries represented at the selected node, and the address is associated with the index. Embodiments also include searching a lookup table in a network device.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
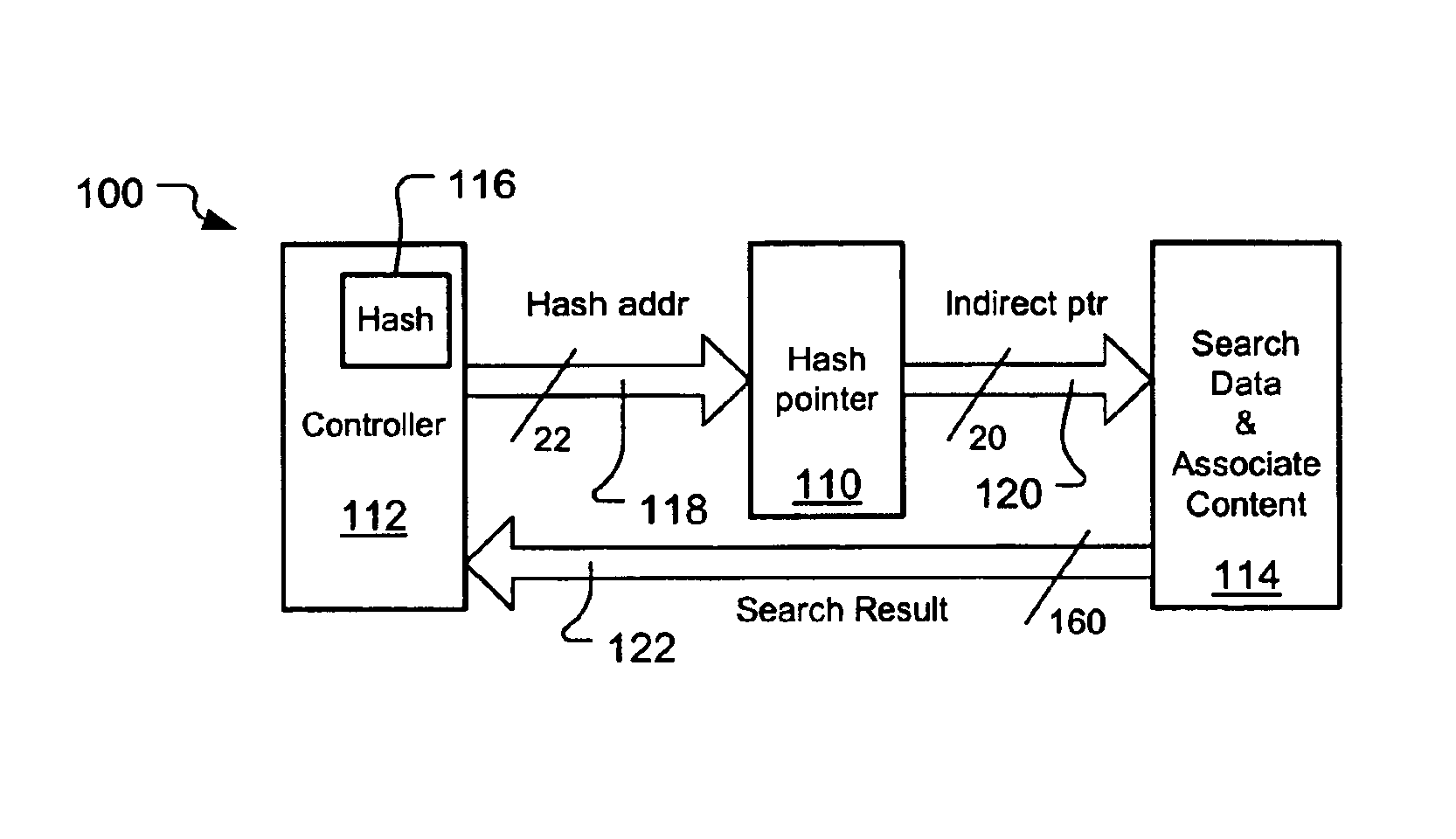
Large database search using content addressable memory and hash
InactiveUS6889225B2Improve memory utilizationReduce bus widthData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalLogic cellTheoretical computer science
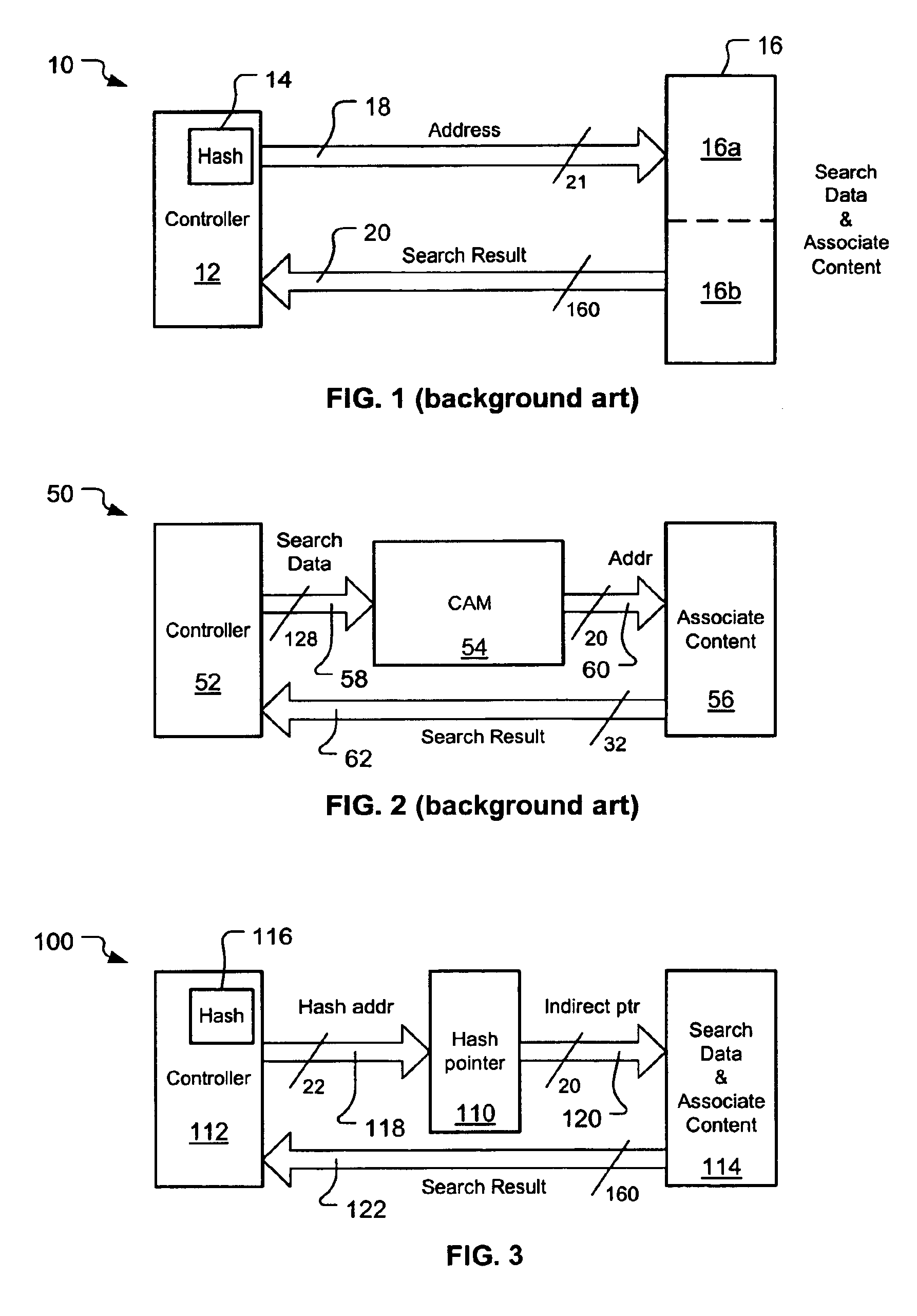
A hash-CAM (H-CAM) which may work with a controller and a memory containing a database of either search values and associate content or associate content by itself The H-CAM includes at least one set of paired hash units and CAM units and at least one logic unit. The CAM units hold values known to cause hash collisions in the respectively paired hash units, and the logic unit prioritizes the hash and CAM unit outputs to a single address value usable to access the memory and obtain a search result at the controller that is not the result of a hash collision. The H-CAM may optionally include a search data storage to store the search values, so that they need not be stored in the memory, and a comparator to determine and handle newly determined hash collisions.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Information searching device
InactiveUS6874016B1Efficiently organizing storingImprove efficiencyDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsBinary decision diagramKnowledge organization
A system for efficiently organizing data or information into an associative memory device, such as a ternary content addressable memory (TCAM), for subsequent searching divides the TCAM is divided into a plurality of individual stages that are interconnected in a cascading fashion. The data or information that is to be stored into the TCAM for subsequent searching is initially translated into a first Boolean representation, such as a binary decision diagram (BDD), that is partitioned into a plurality of segments. Each segment defines one or more outputs, and the outputs from one segment define the inputs to the next segment. After partitioning the BDD and identifying the resulting outputs, each BDD segment along with its corresponding outputs is mapped into a particular stage of the TCAM.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Ternary content addressable magnetoresistive random access memory cell
A method for writing a magnetic random access memory-based ternary content addressable memory cell comprising a first magnetic tunnel junction being formed from a storage layer, a sense layer having a magnetization direction adjustable relative to the magnetization of the storage layer, and an insulating layer between the storage and sense layers; a sense line coupled with the storage layer; a first field line and a second field line, and the first field line being orthogonal to the second field line; comprising: providing a first write data to said storage layer via the second field line to store a first stored data with a high or low logic state; characterized in that, the method further comprises providing the first write data to said storage layer via the first field line to store the first stored data with a masked logic state.
Owner:CROCUS TECHNOLOGY
Active address content addressable memory
InactiveUS6915395B1Preventing memory hazardAvoids memory hazardsConcurrent instruction executionMemory systemsMemory addressParallel computing
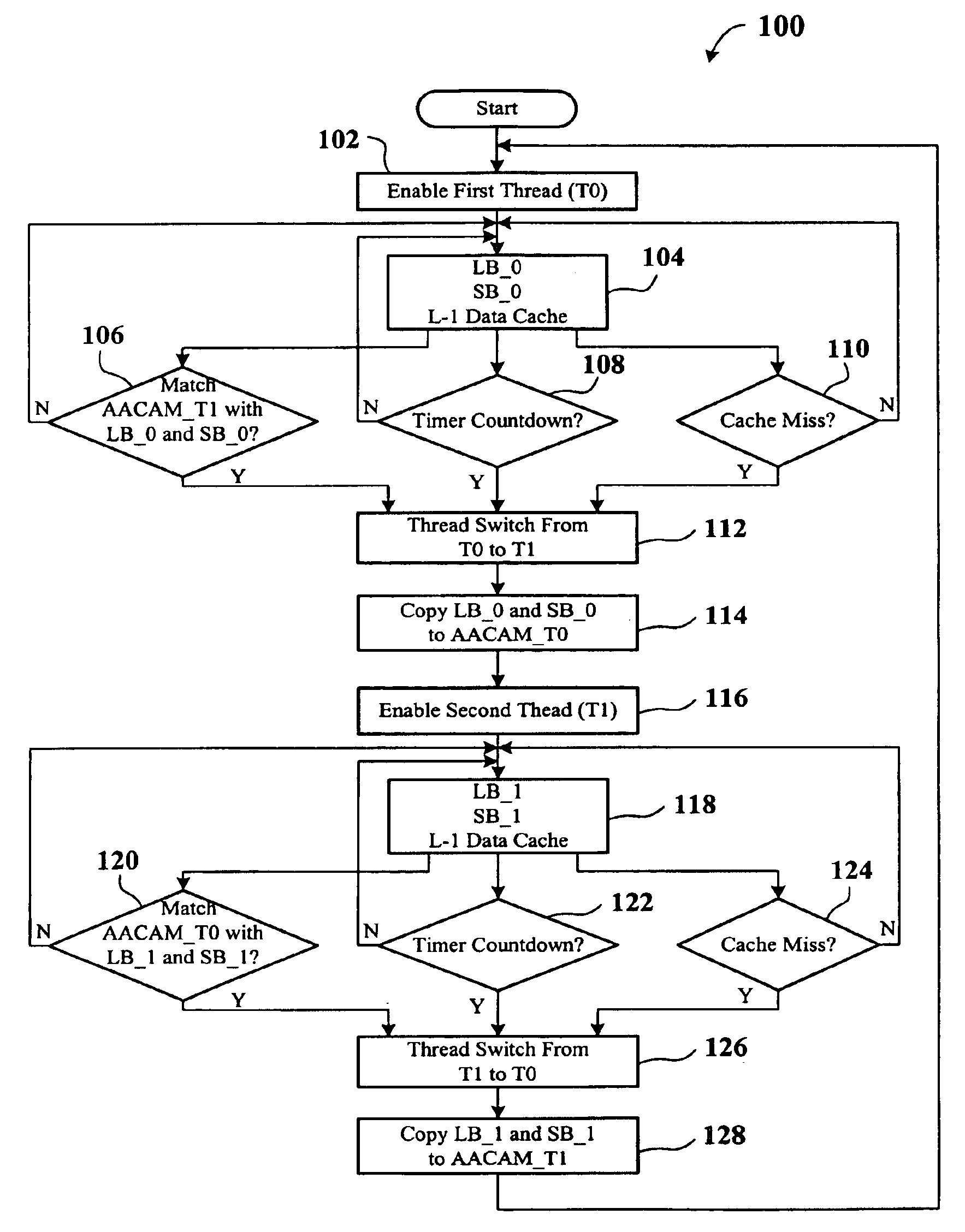
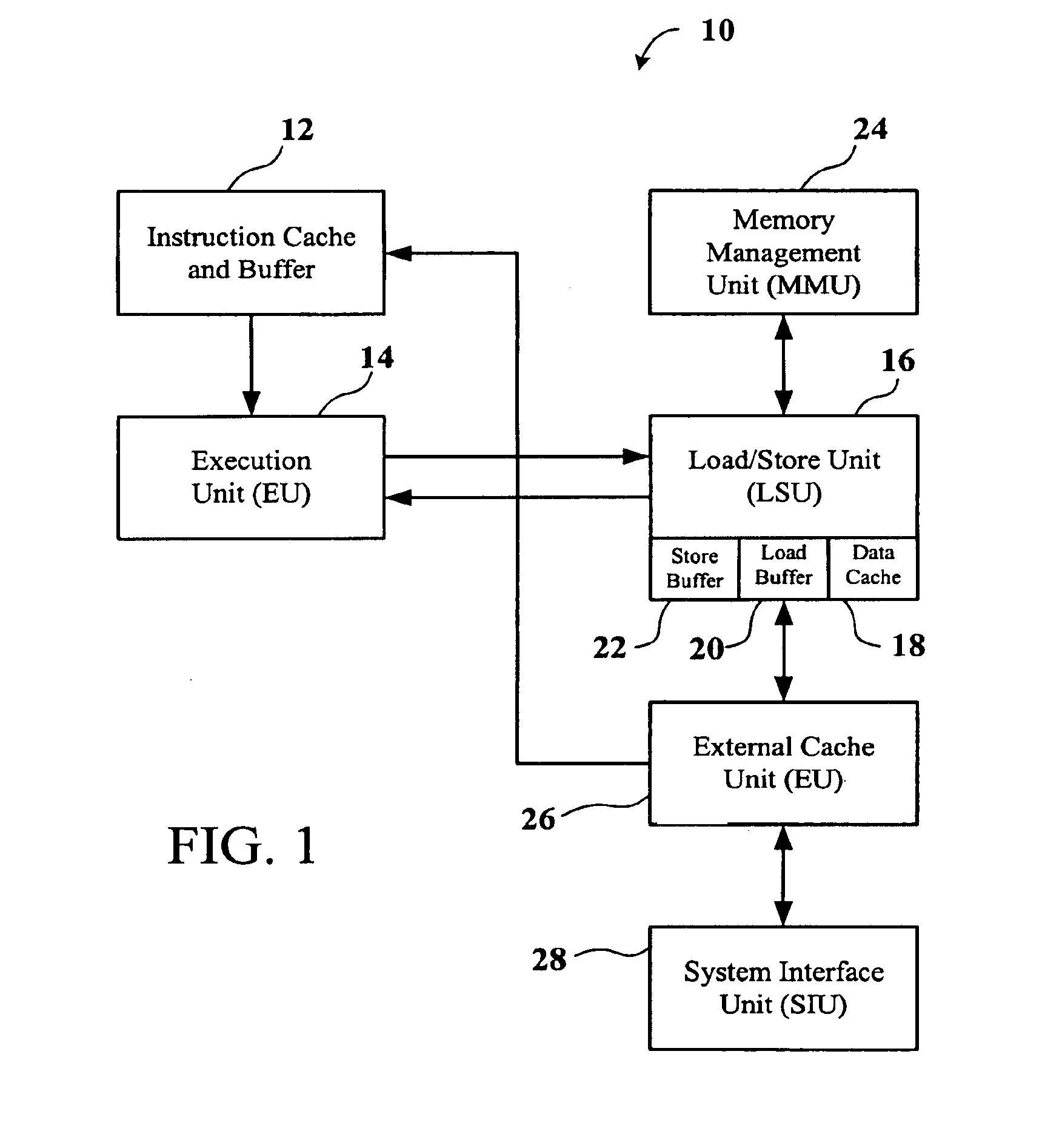
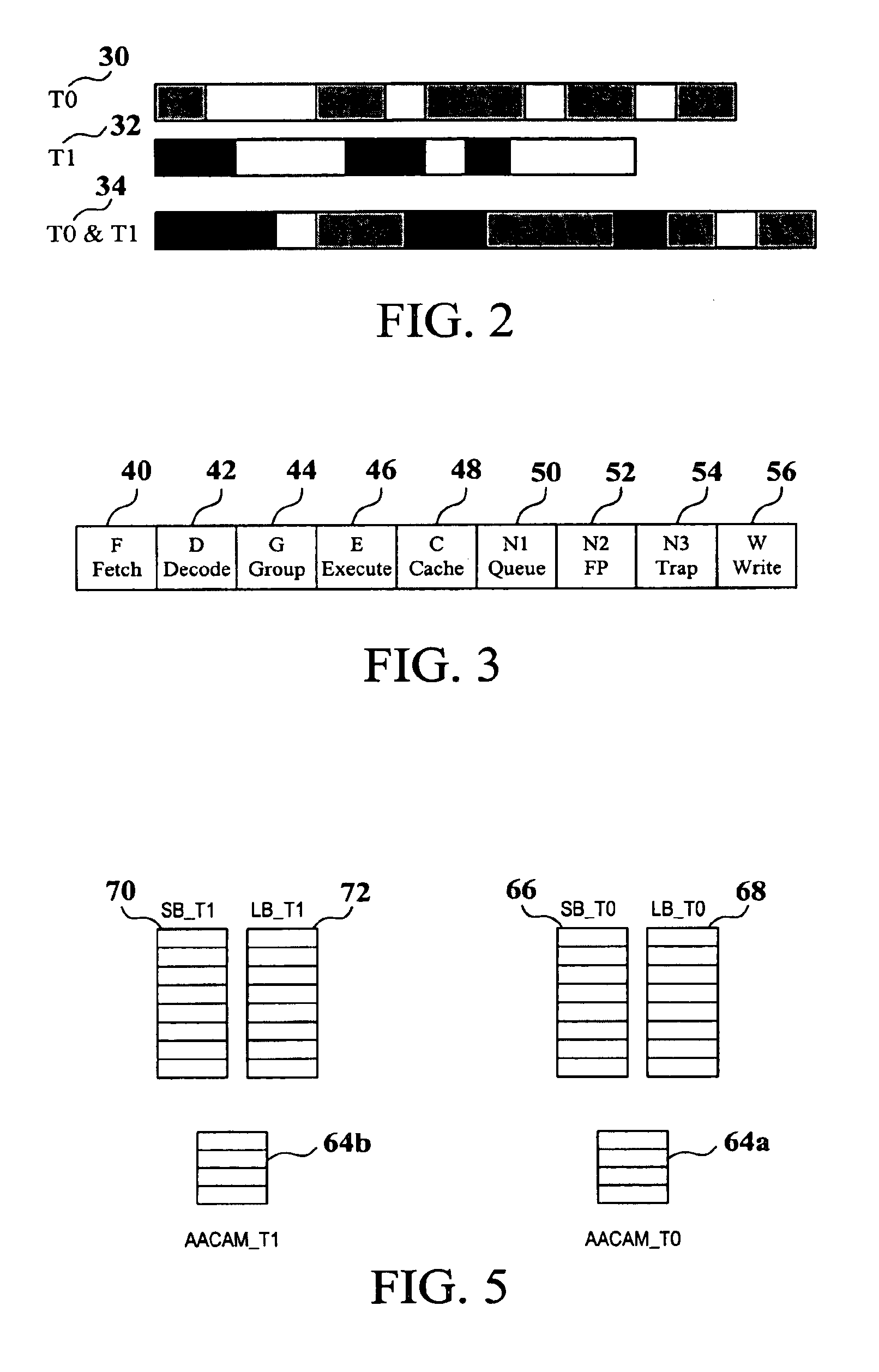
A present invention provides a system and method for avoiding memory hazards in a multi-threaded CPU which shares an L-1 data cache. The system includes a CPU and an AACAM. The AACAM is capable of copying memory addresses from the two or more threads being processed by the CPU. The method provides for comparing the AACAM memory address with the active threads to avoid memory hazards by thread switching before the memory hazard occurs.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
TCAM Management Approach That Minimize Movements
ActiveUS20100293327A1Efficient managementEasy to useDigital storageTransmissionTernary content addressable memoryOperating system
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
Efficient lookup methods for ternary content addressable memory and associated devices and systems
InactiveUS20110307656A1Improve throughputReduce power consumptionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital storageRouting tableSystems design
Lookup techniques are described, which can achieve improvements in energy efficiency, speed, and cost, of IP address lookup, for example, in devices and systems employing ternary content addressable memory (TCAM). The disclosed subject matter describes dividing a route table into several sub-tries with disjoint range boundaries. In addition, the disclosed subject matter describes storing sub-tries of a route table between a TCAM and a faster and less costly memory. The disclosed details enable various refinements and modifications according to system design and tradeoff considerations.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
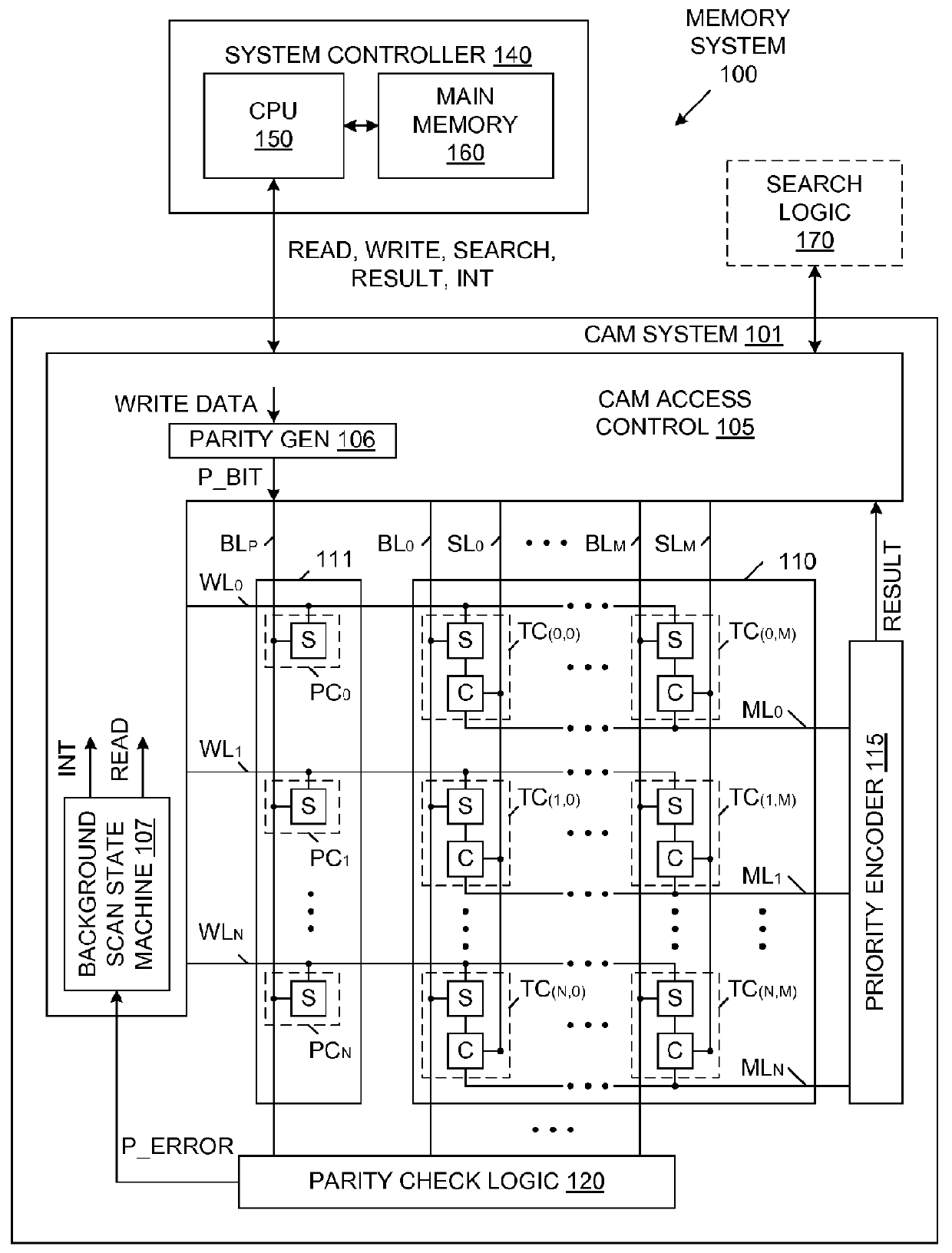
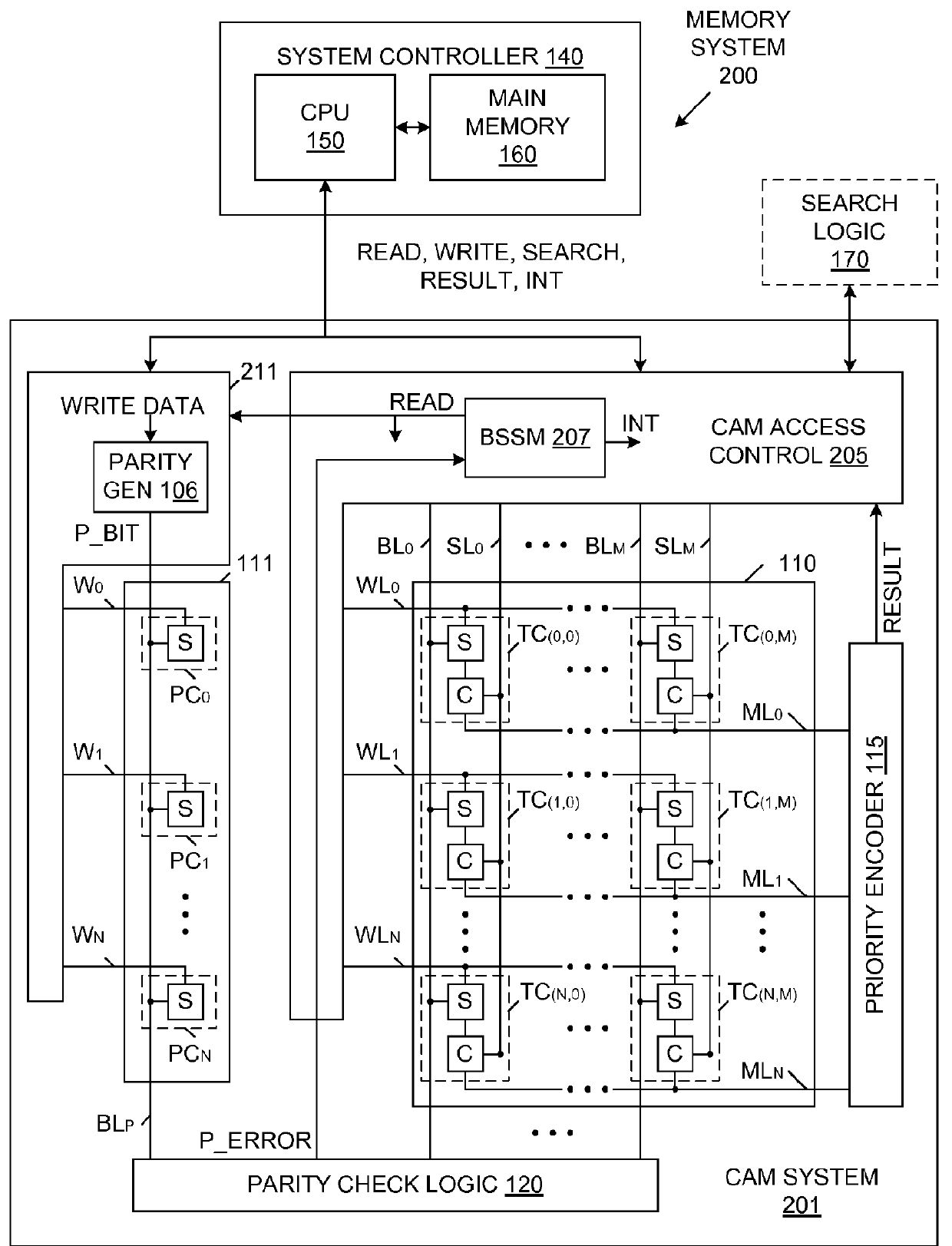
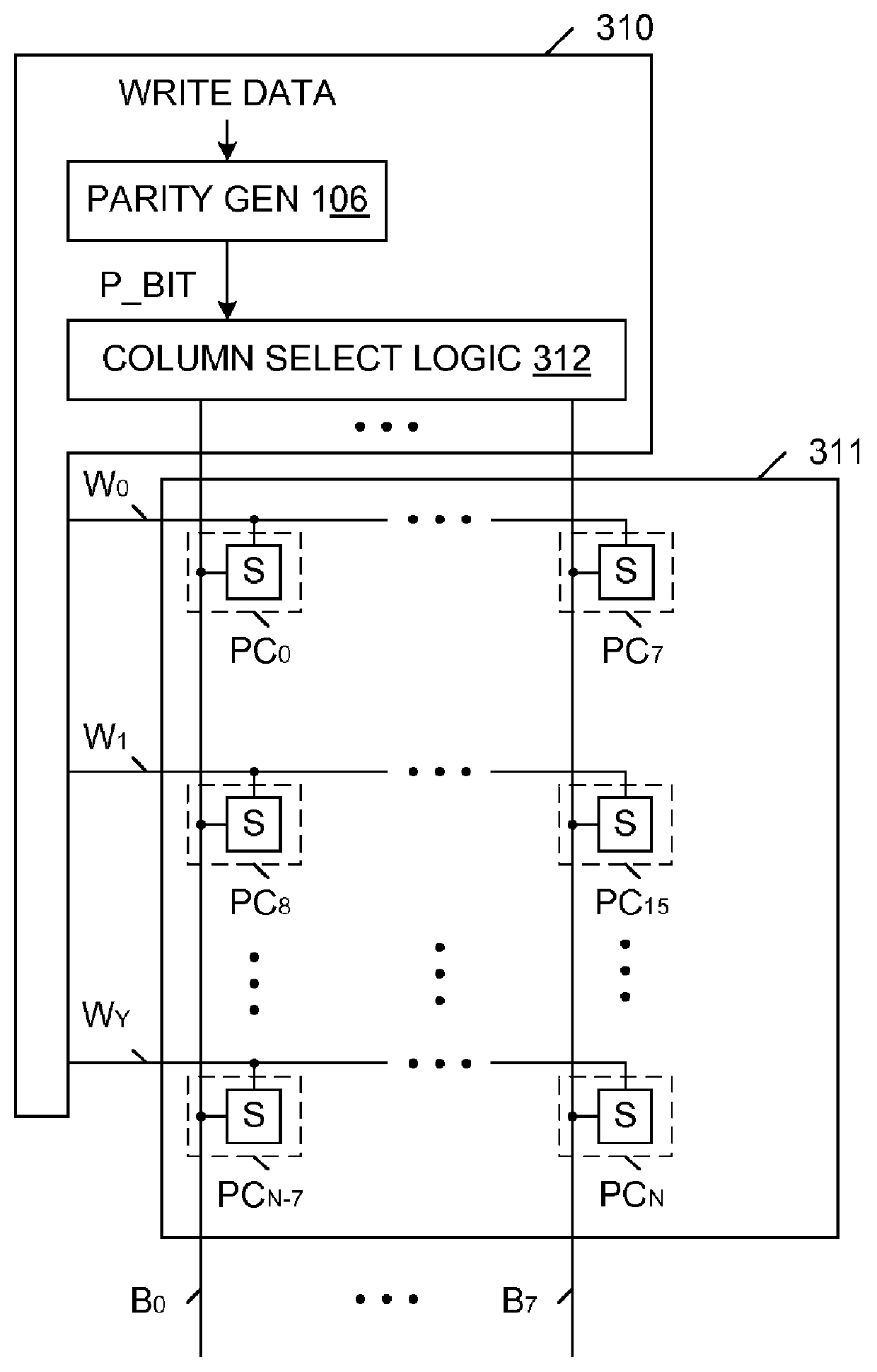
Content Addressable Memory (CAM) Parity And Error Correction Code (ECC) Protection
InactiveUS20120110411A1Code conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresComputer hardwareCam
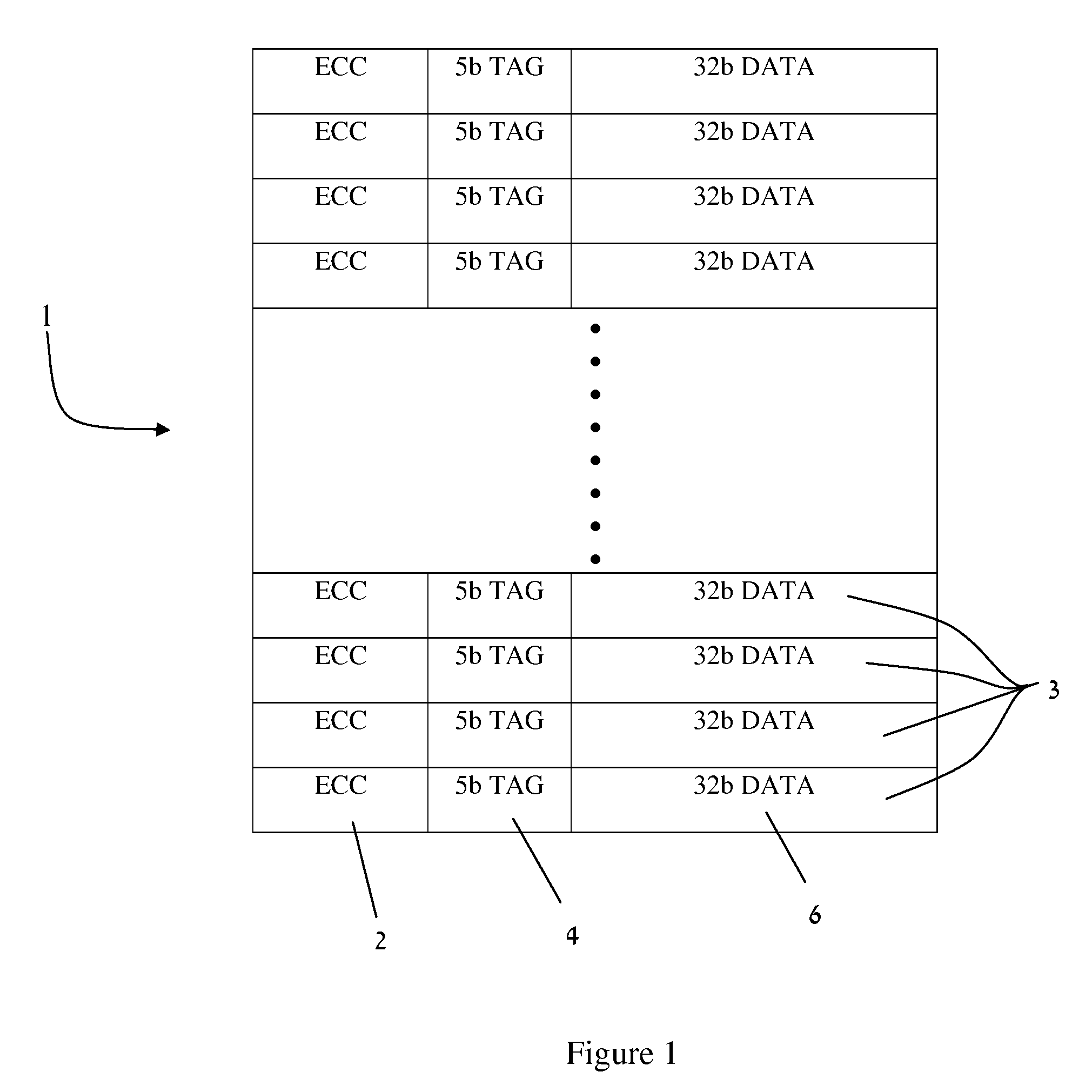
A memory system including a content addressable memory (CAM) array and a non-CAM array. The non-CAM array, which may share word lines with the CAM array, stores one or more error detection bits associated with each row of the CAM array. A state machine reads entries of the CAM array and corresponding error detection bits of the non-CAM array during idle cycles of the CAM array. Error detection logic identifies errors in the entries read from CAM array (using the retrieved error detection bits). If these errors are correctable, the error detection logic corrects the entry, and writes the corrected entry back to the CAM array (an updated set of error detection bits are also written to the non-CAM array). If these errors are not correctable, an interrupt is generated, which causes correct data to be retrieved from a shadow copy of the CAM array.
Owner:BROCADE COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS
Ultimate magnetic random access memory-based ternary cam
ActiveUS20110002151A1Increase speedReduce manufacturing costDigital storageElectricityStatic random-access memory
The present disclosure concerns a magnetic random access memory-based ternary content addressable memory cell, comprising a first and second magnetic tunnel junction respectively connected to a first and second straps extending on each side of the first and second magnetic tunnel junctions, respectively; a first and second selection transistors, respectively connected to one extremity of the first and second straps; a first and second current lines; and a conductive line electrically connecting in series the first and second magnetic tunnel junctions at their ends opposed to the ones connecting the first and second straps. The cell disclosed herein has smaller size and can be advantageously used in memory devices having a high cell density array.
Owner:CROCUS TECHNOLOGY
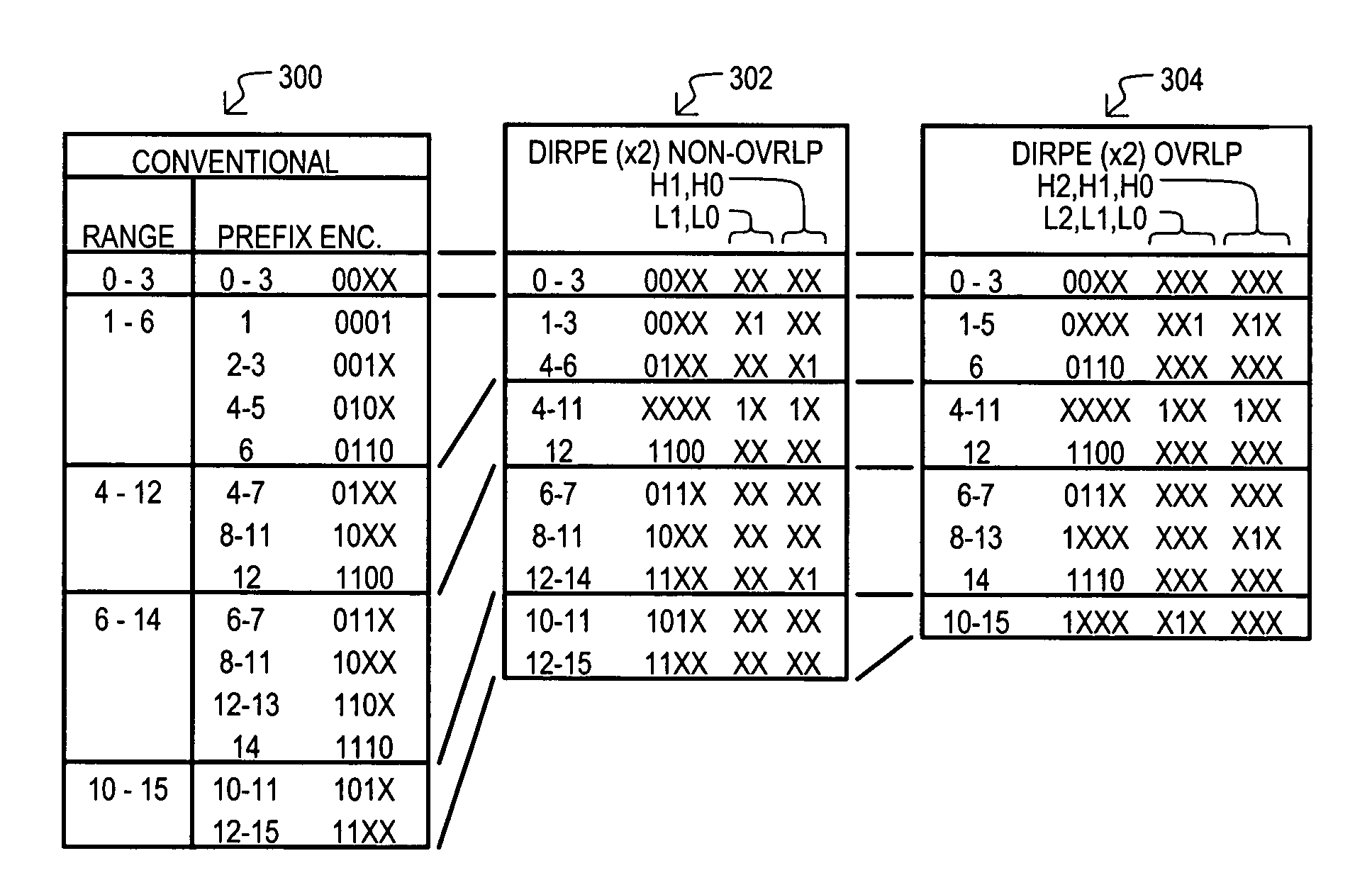
Range code compression method and apparatus for ternary content addressable memory (CAM) devices
InactiveUS7711893B1Reduce in quantityIncrease in sizeDigital storageMemory systemsPartial representationOne-hot
A content addressable memory (CAM) device, method, and method of generating entries for range matching are disclosed. A CAM device (800) according to one embodiment can include a pre-encoder (806) that encodes range bit values W into additional bits E. Additional bits E can indicate compression of range rules according to particular bit pairs. A CAM array (802) can include entries that store compressed range code values (RANGE) with corresponding additional bit values (ENC). Alternate embodiments can include pre-encoders that encode portions of range values (K1 to Ki) in a “one-hot” fashion. Corresponding CAM entries can include encoded value having sections that each represent increasingly finer divisions of a range space.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for longest prefix matching
ActiveUS7986696B1Data switching by path configurationMemory systemsRandom access memoryLongest prefix match
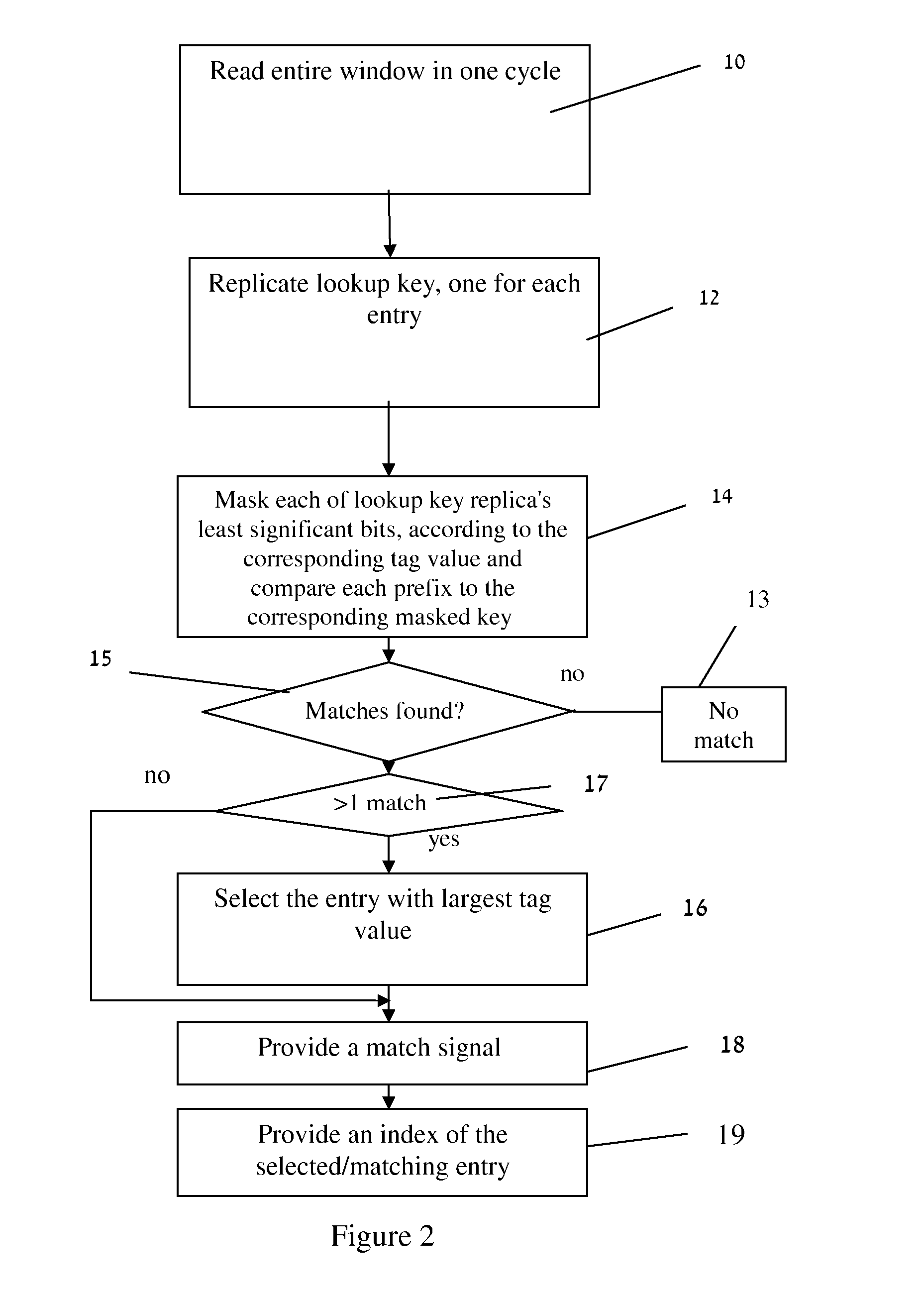
A lookup table including stored data, the lookup table including a Random Access Memory (RAM) for storing the data, wherein the RAM includes a plurality of windows; and a Ternary Content Addressable Memory (TCAM) for storing indices, each index pointing to the windows, and a method for performing a Longest Prefix Match (LPM) including organizing data in such a lookup table, searching according to a lookup key in the TCAM, receiving a match signal from the TCAM including an index pointing to one of the windows, and searching according to the lookup key in the pointed to window.
Owner:EXAWARE ROUTING LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com