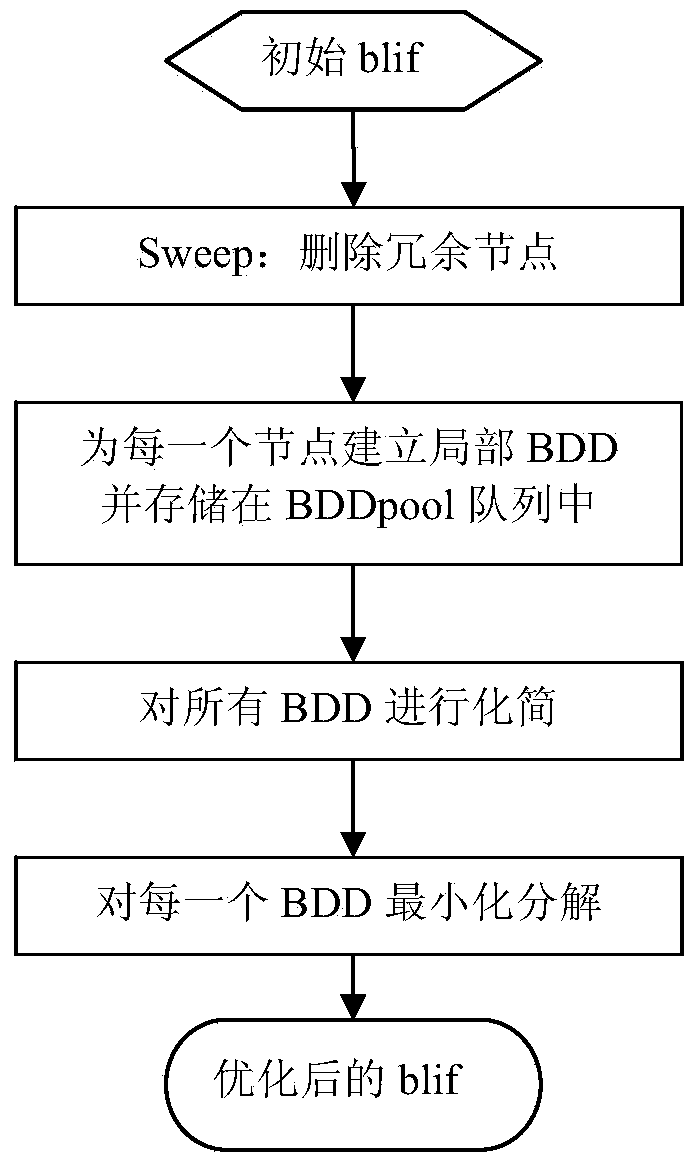
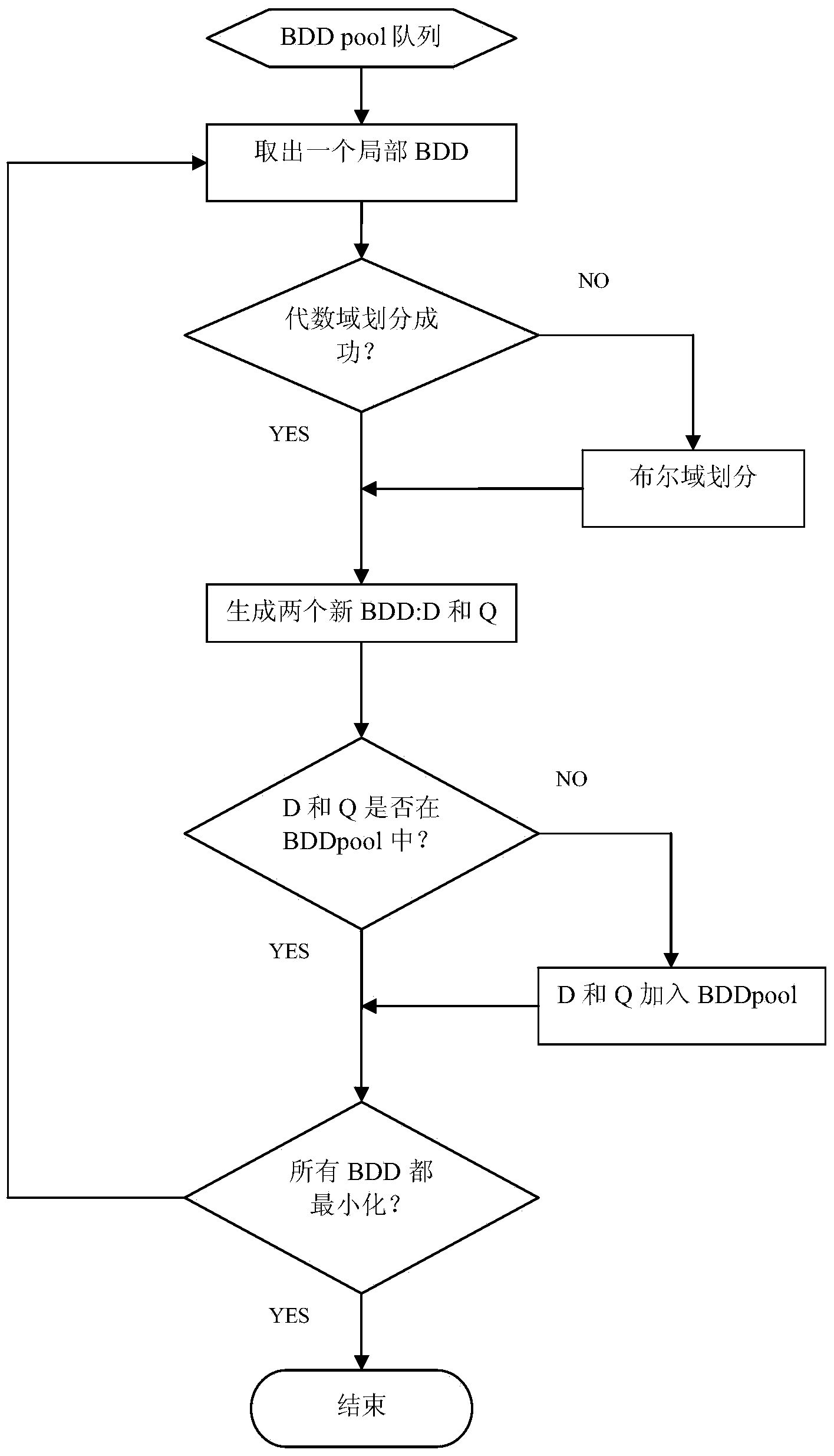
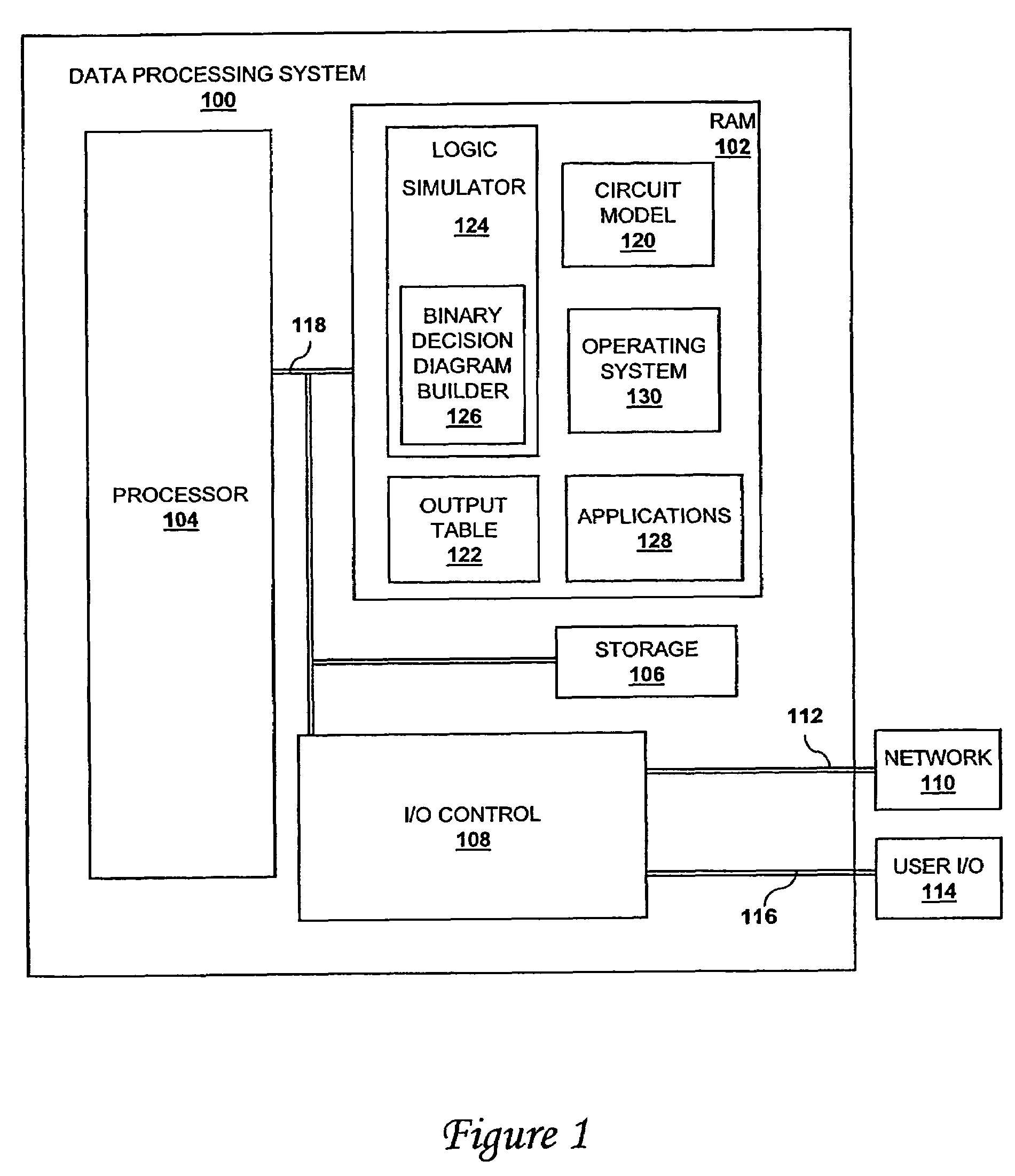
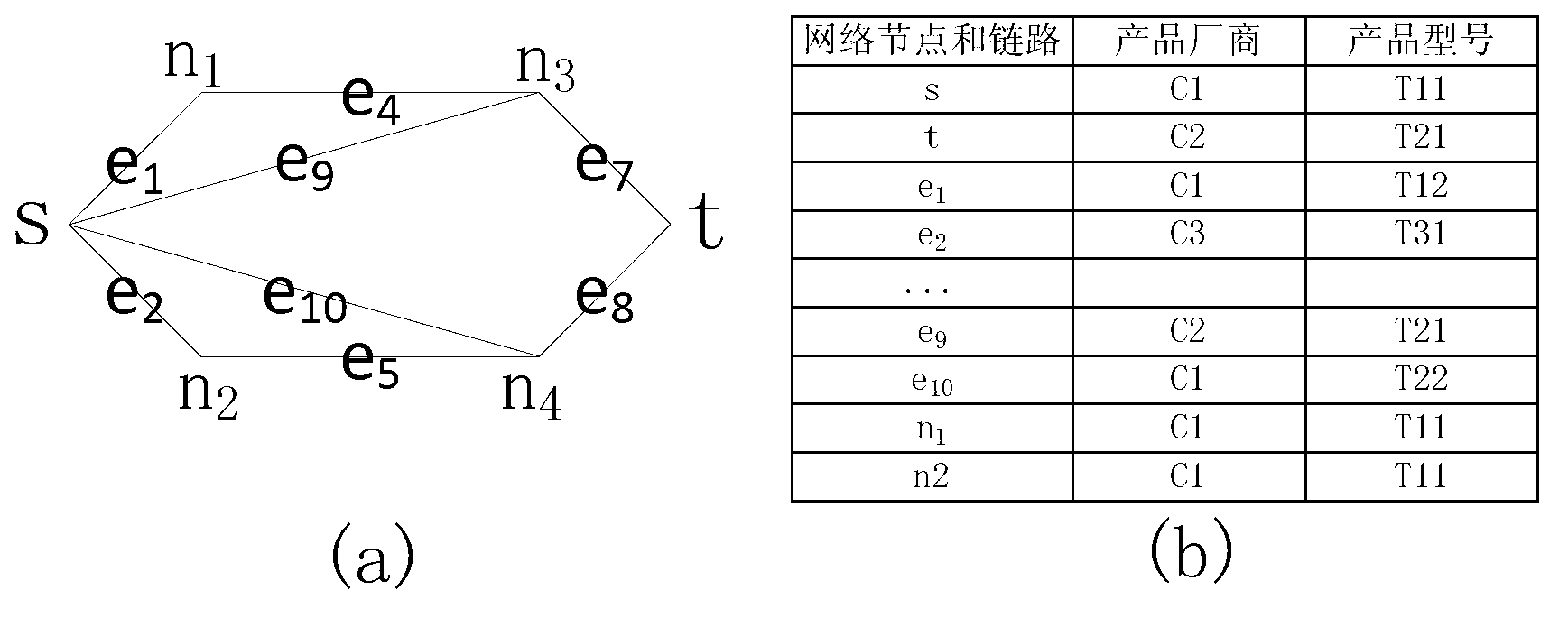Patents
Literature
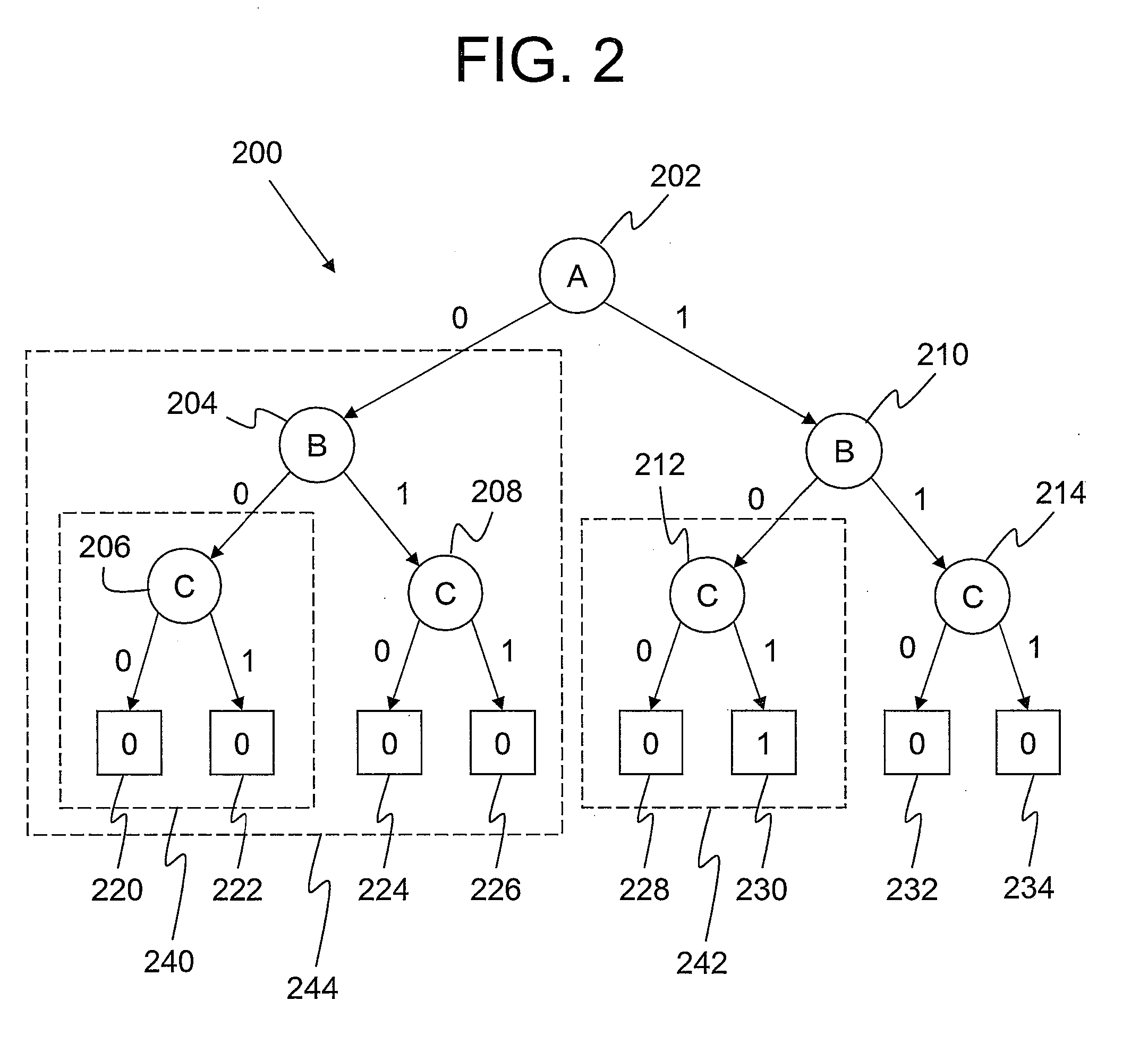
130 results about "Binary decision diagram" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
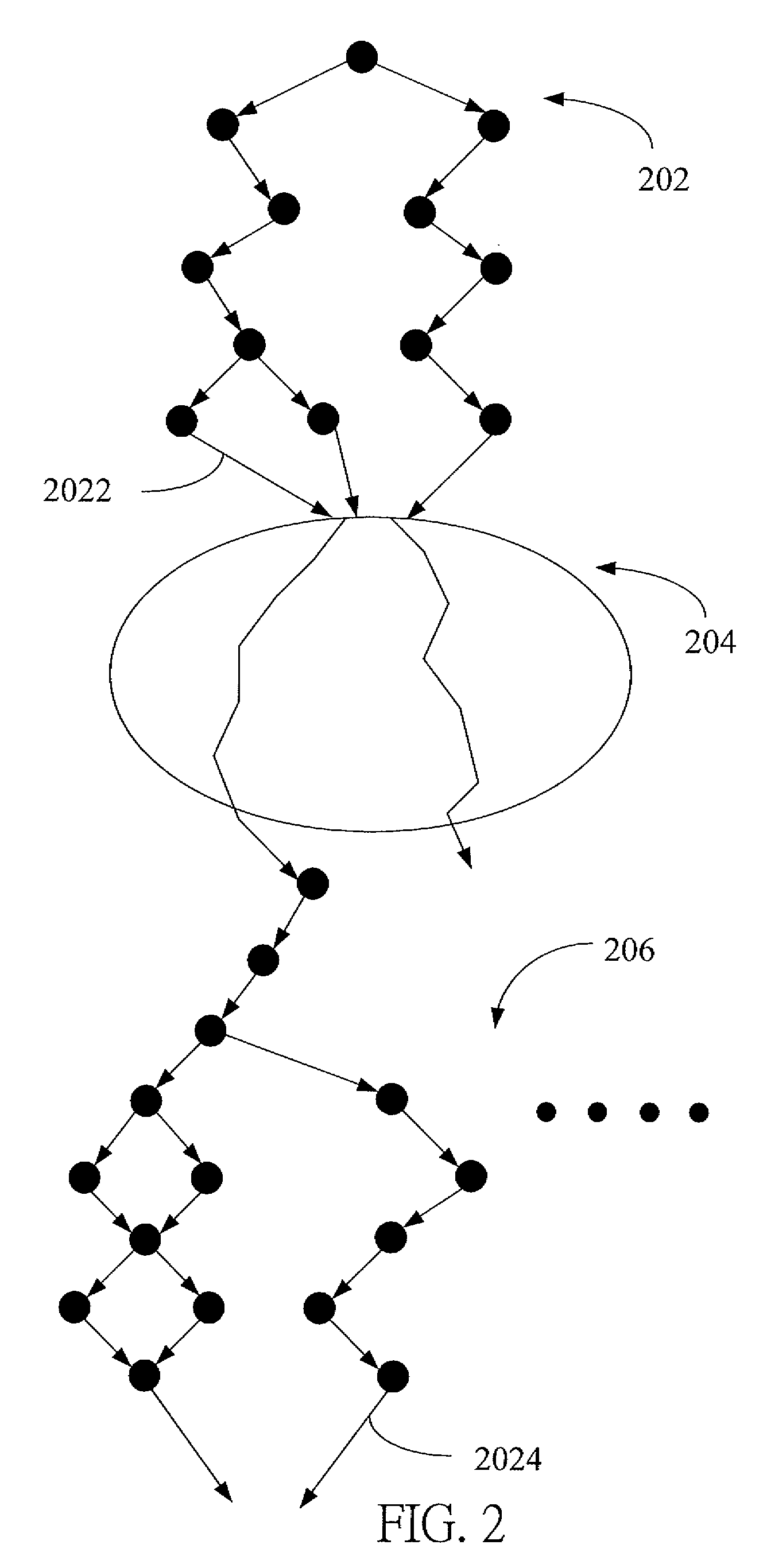
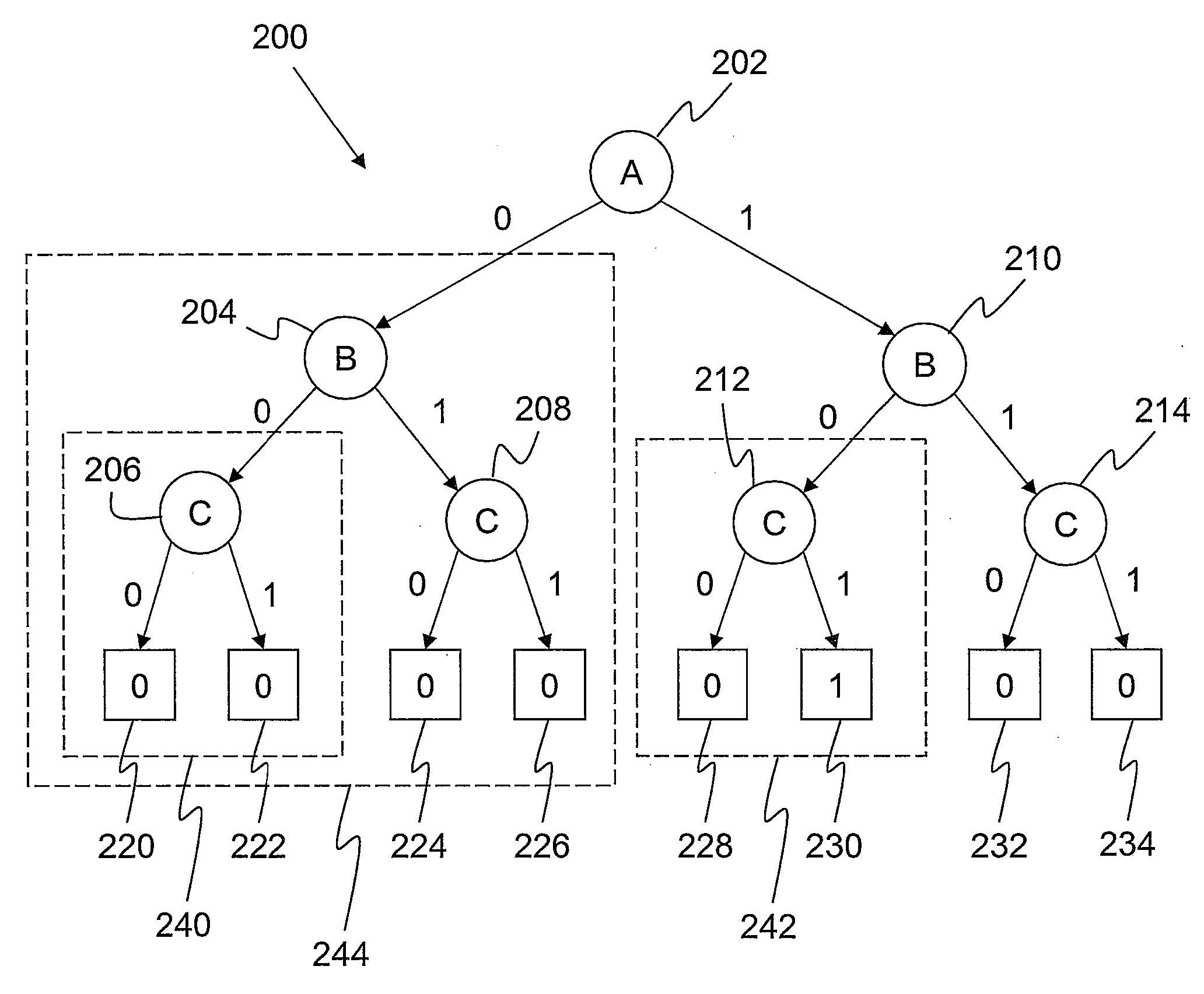
In computer science, a binary decision diagram (BDD) or branching program is a data structure that is used to represent a Boolean function. On a more abstract level, BDDs can be considered as a compressed representation of sets or relations. Unlike other compressed representations, operations are performed directly on the compressed representation, i.e. without decompression. Other data structures used to represent Boolean functions include negation normal form (NNF), Zhegalkin polynomials, and propositional directed acyclic graphs (PDAG).
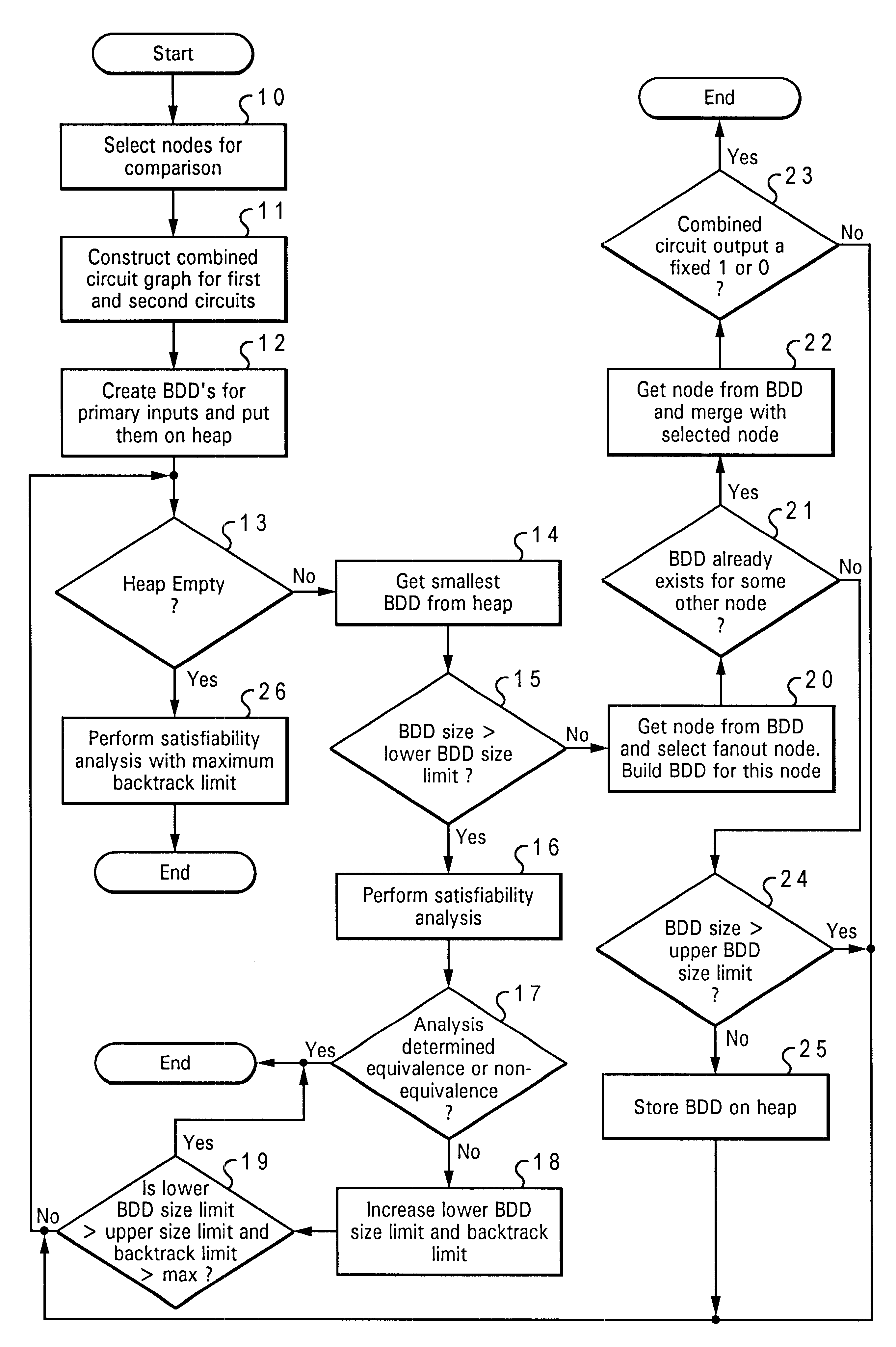
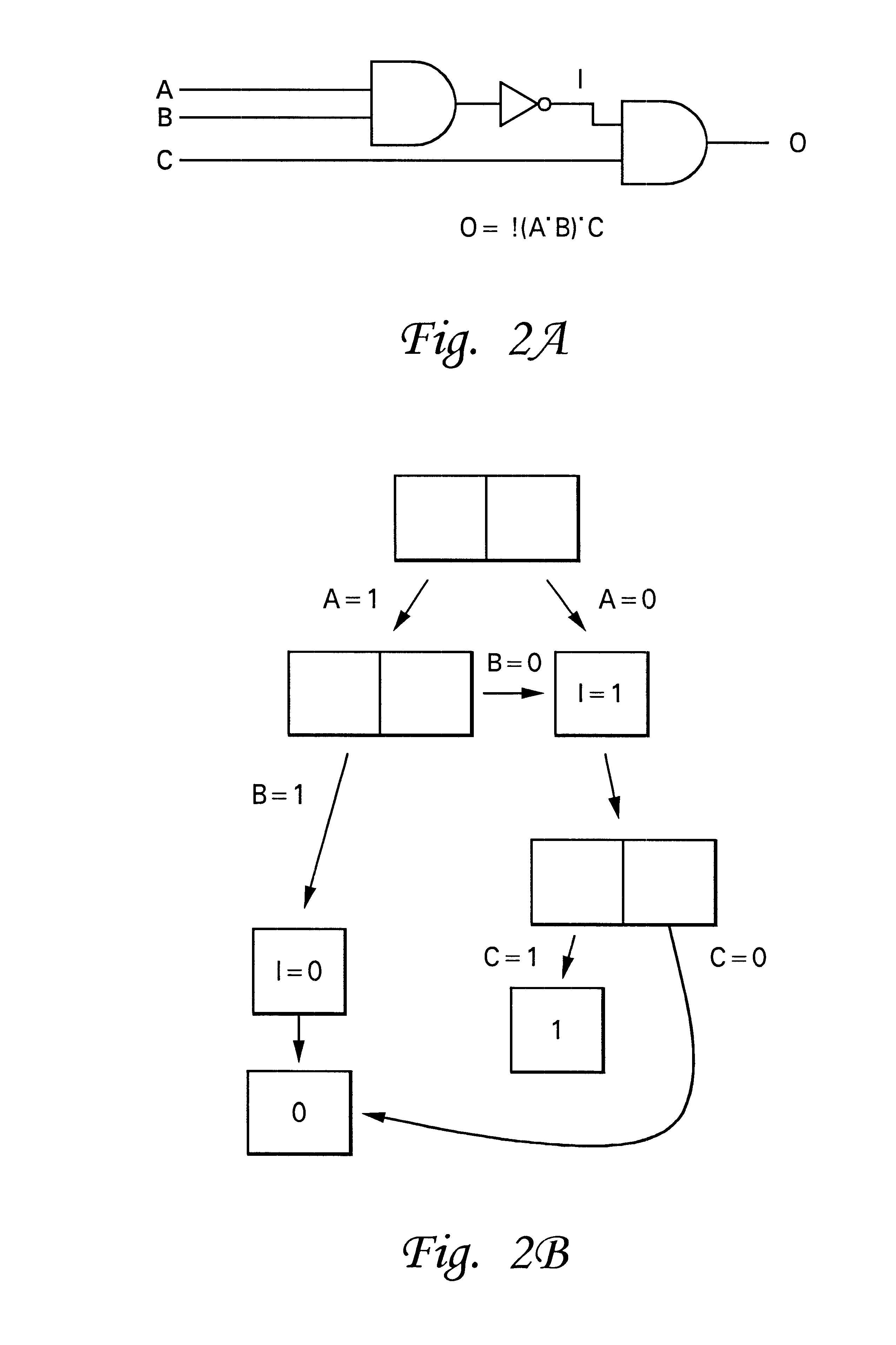
Method and system for equivalence-checking combinatorial circuits using interative binary-decision-diagram sweeping and structural satisfiability analysis
InactiveUS6473884B1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationBinary decision diagramLogical network
A method and system for equivalence checking of logical circuits using iterative circuit reduction and satisfiability techniques provide improved performance in computer-based verification and design tools. By intertwining a structural satisfiability solver and binary decision diagram functional circuit reduction method, computer-based tools can make more efficient use of memory and decrease computation time required to equivalence check large logical networks. Using the circuit reduction technique back-to-back with the simulation technique, optimum local and global circuit reduction are simultaneously achieved. By iterating between the structural and functional techniques, and adjusting the size of sub-networks being analyzed within a larger network, sub-networks can be reduced or eliminated, decreasing the amount of memory required to represent the next larger inclusive network.
Owner:IBM CORP
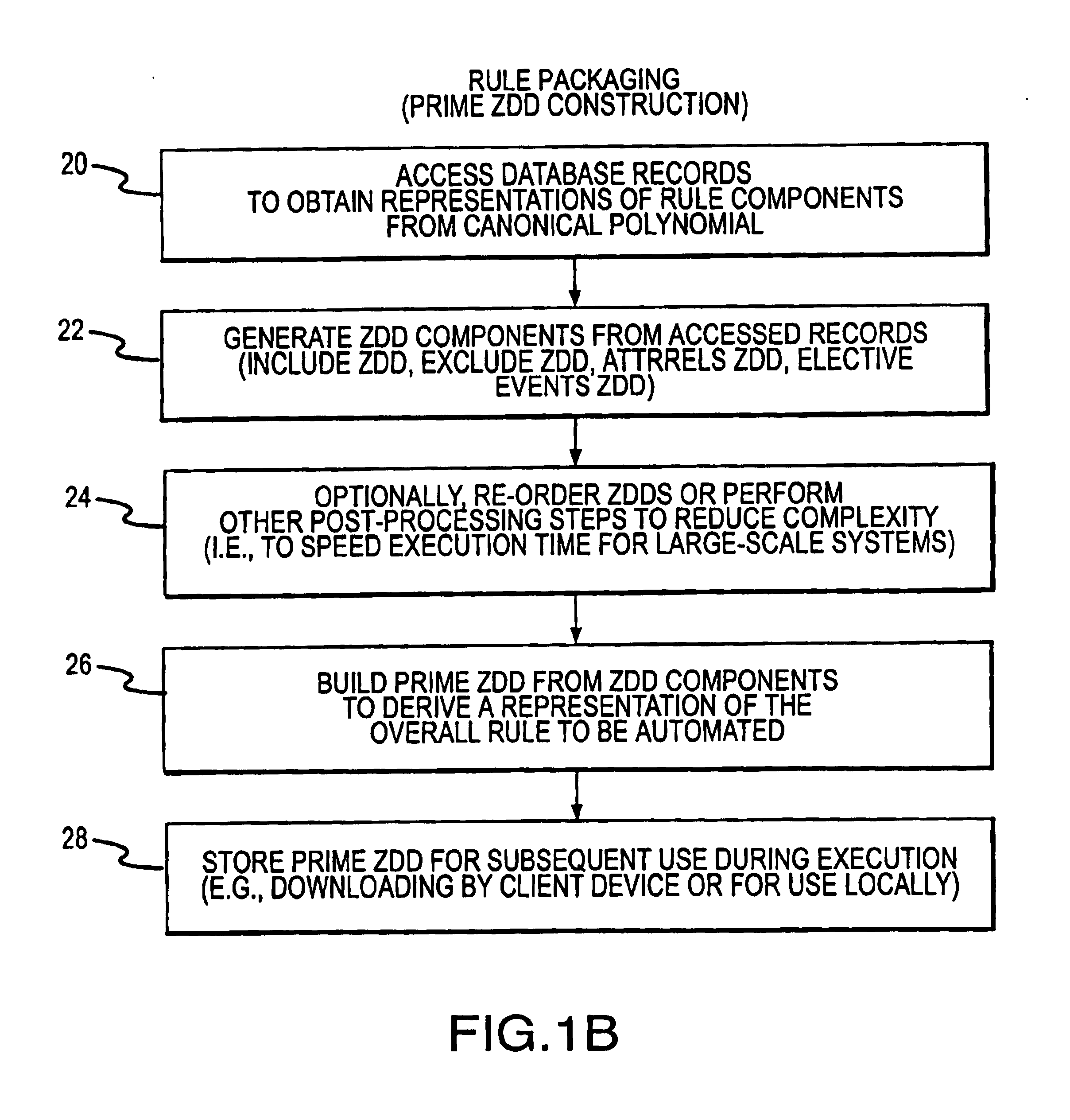
Methods and systems for improved integrated circuit functional simulation
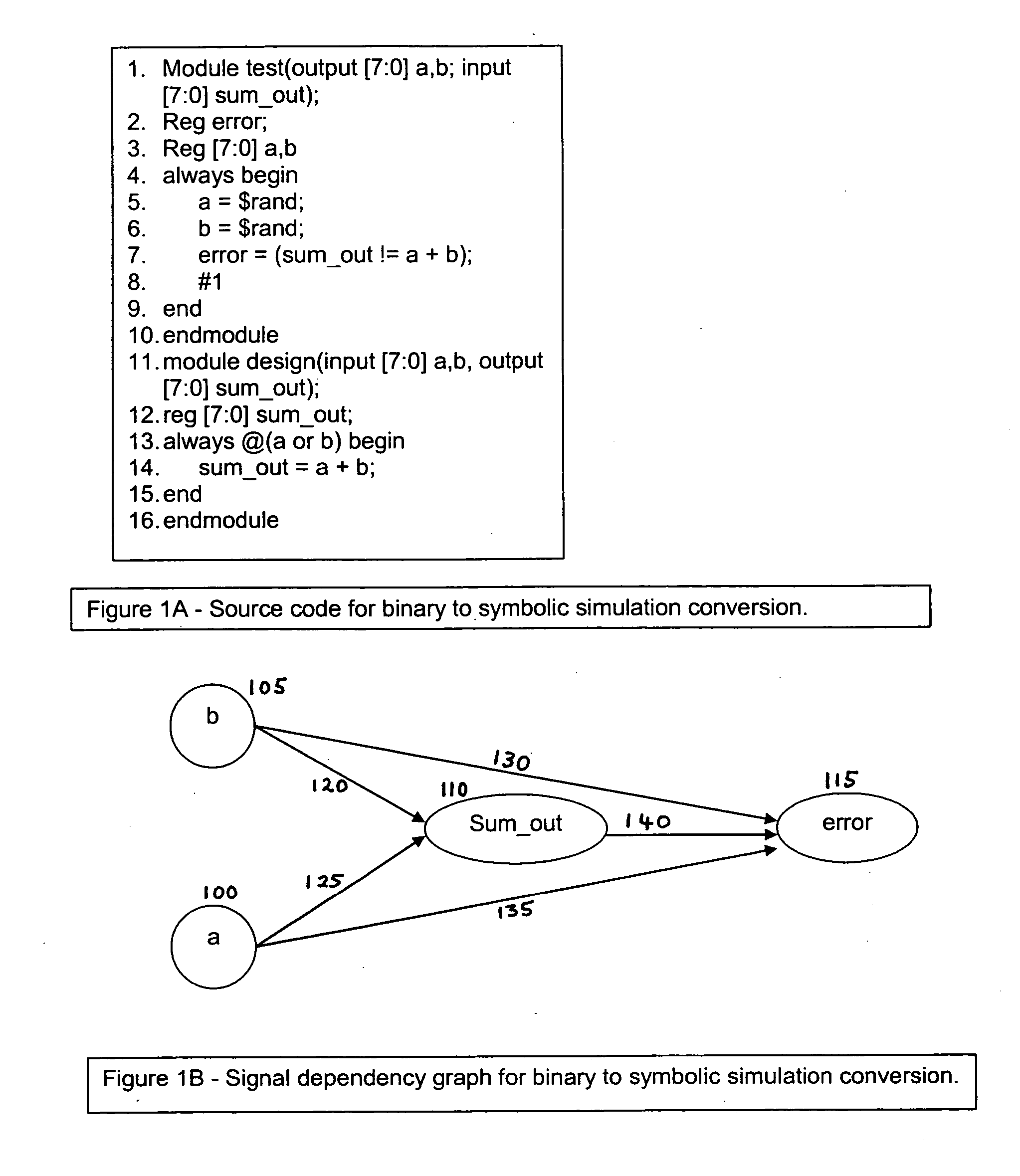
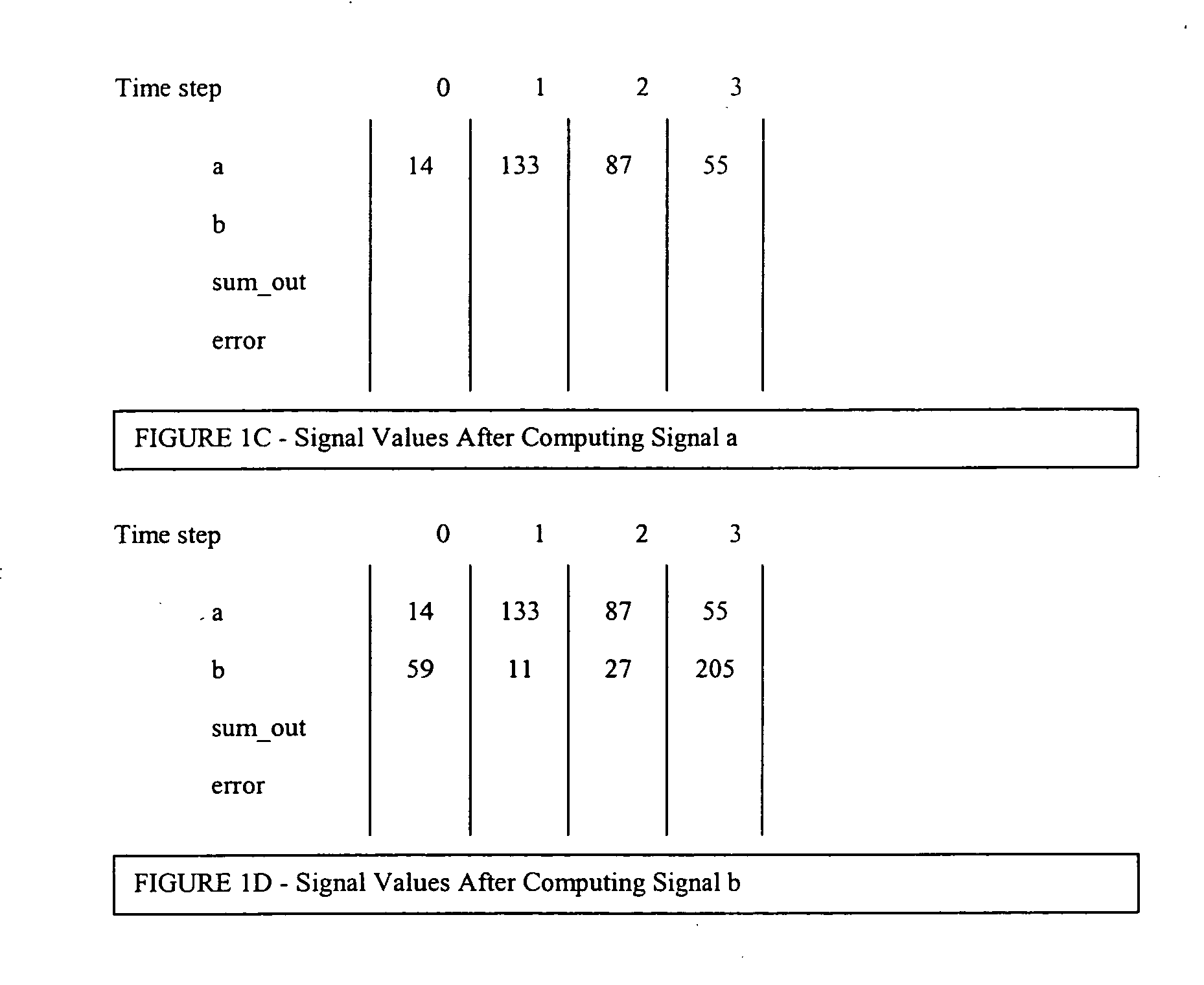
InactiveUS20050091025A1Reduce in quantityElectrical apparatusComputer aided designSymbolic simulationBinary decision diagram
Methods and systems for performing symbolic simulation, including techniques for translating a conventional simulation into a symbolic simulation, for handling wait and delay states, and for performing temporally out-of-order simulations. Additional techniques for extracting a signal graph from an HDL representation of a device, for representing signal values as functions of time using binary decision diagrams, and for computing minimal signal sets for accurate simulation. Techniques and methods for improving waveform dumping, reducing the waveform database, and for combining out-of-order simulation or reduced time steps with conventional time-based simulation.
Owner:VENTURE LENDING & LEASING IV
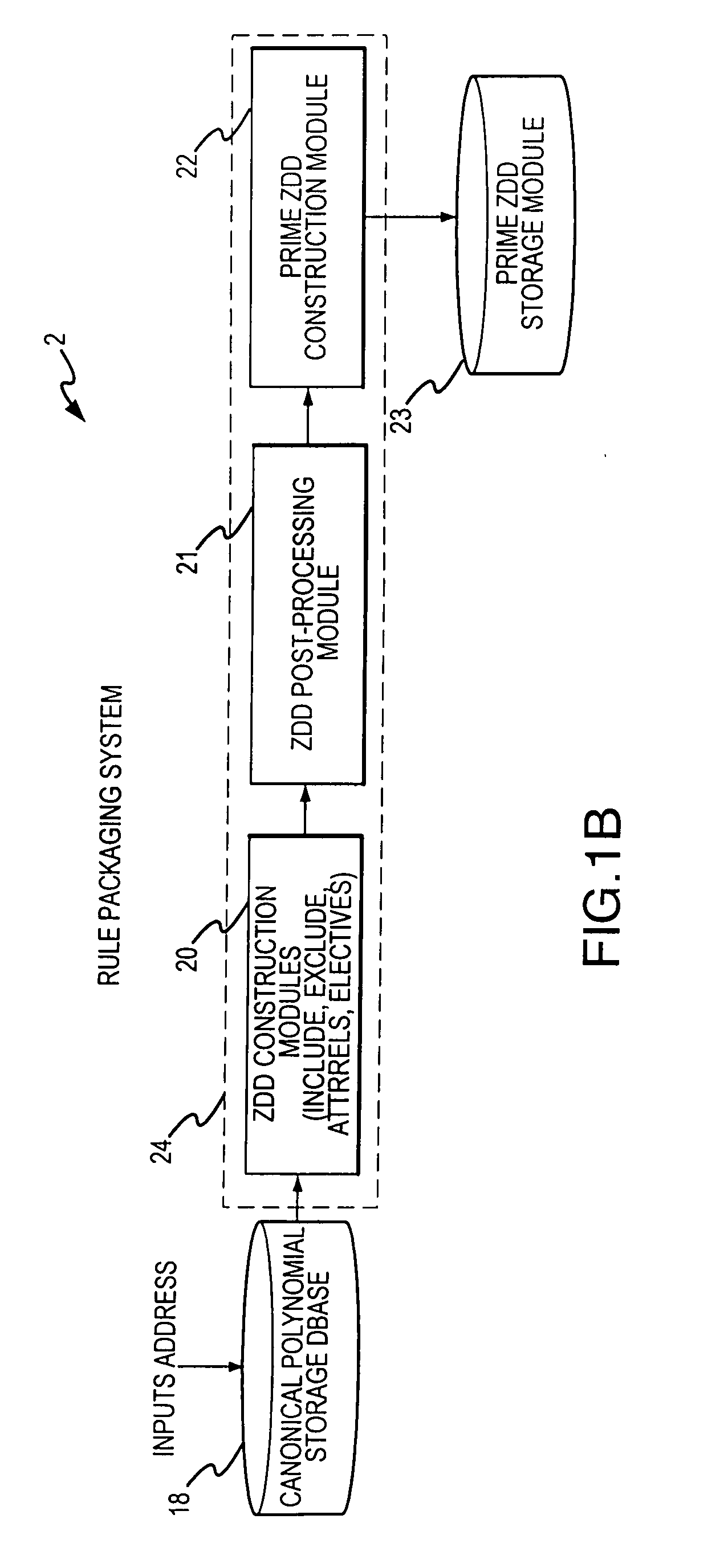
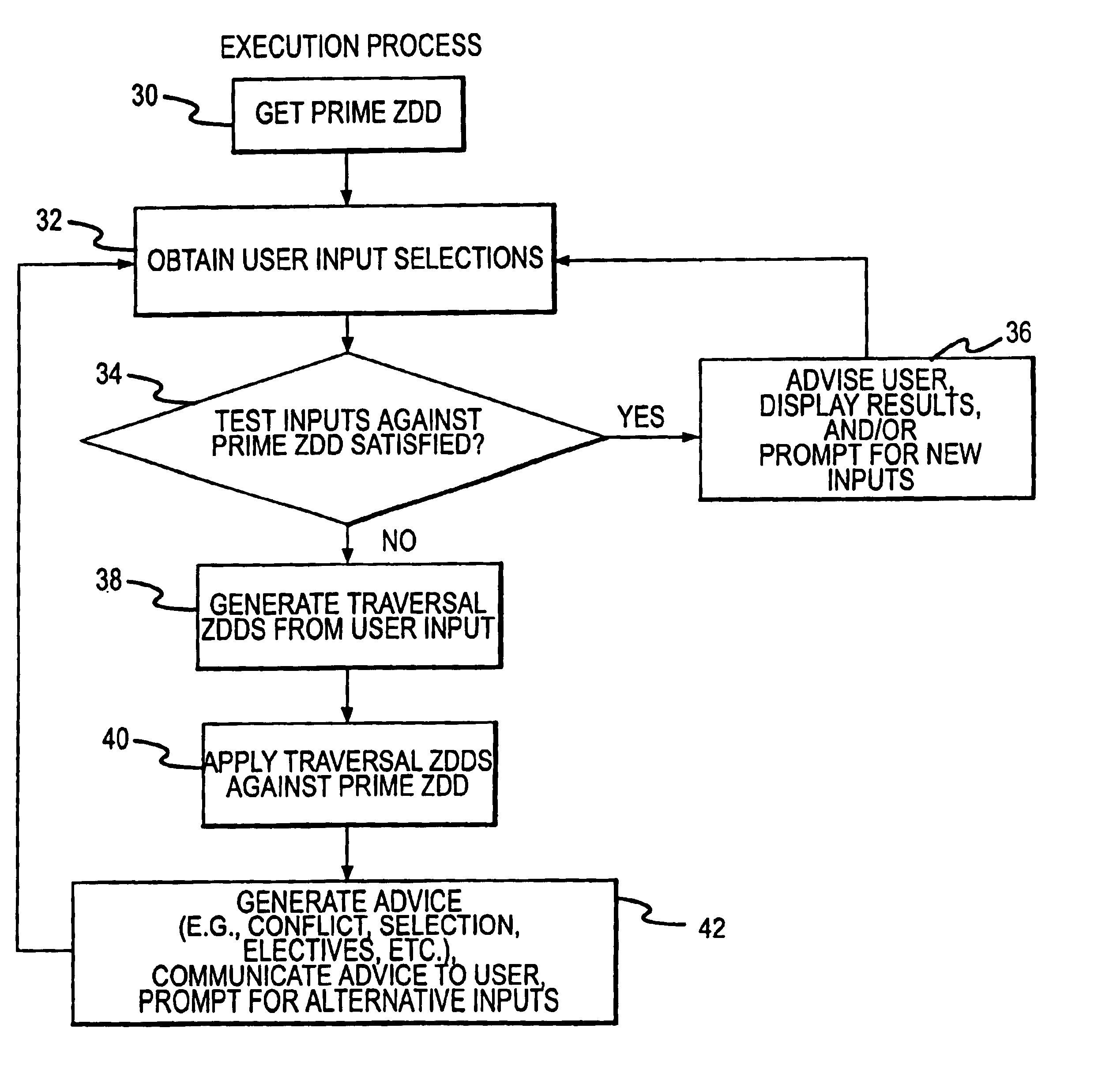
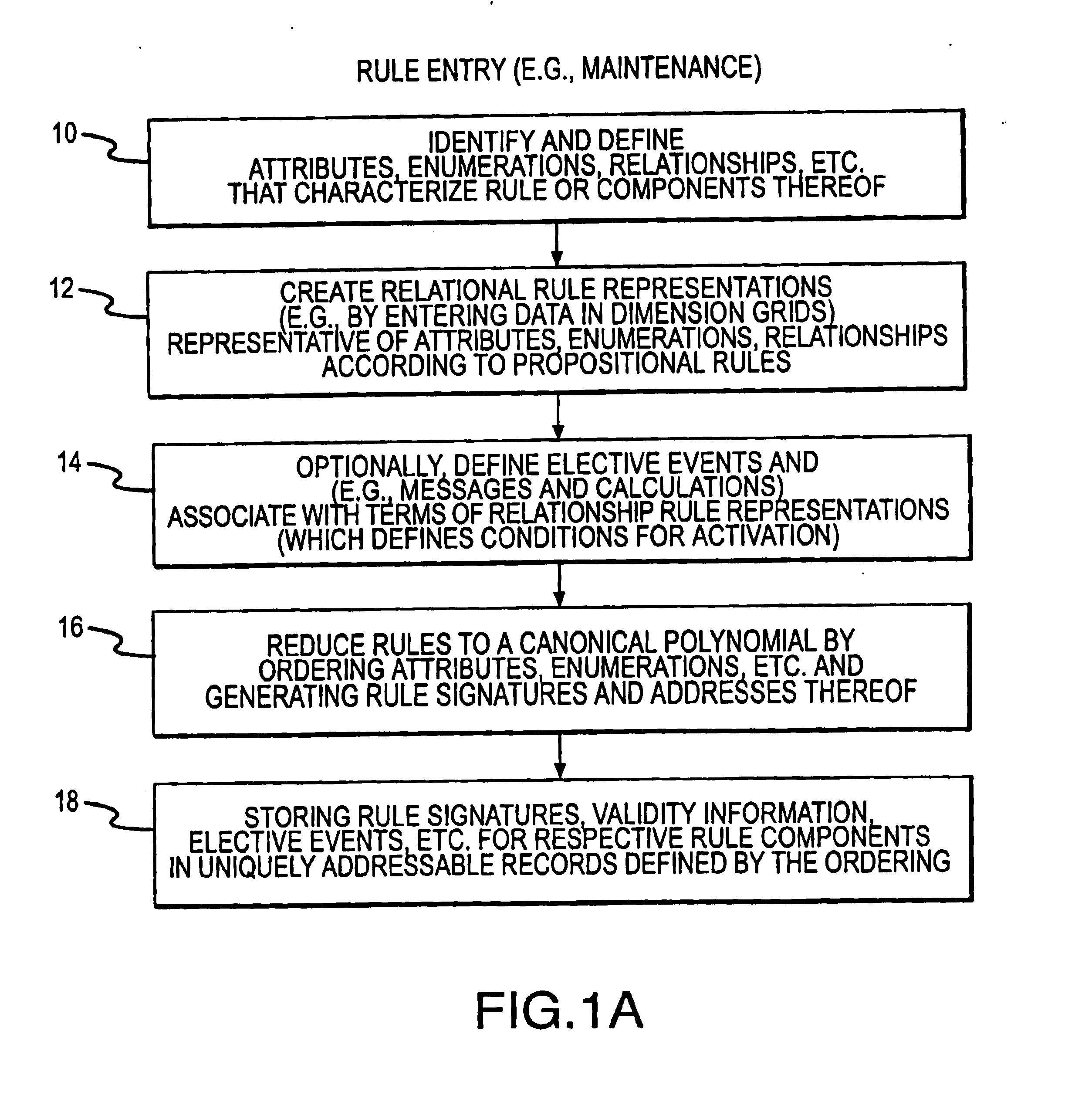
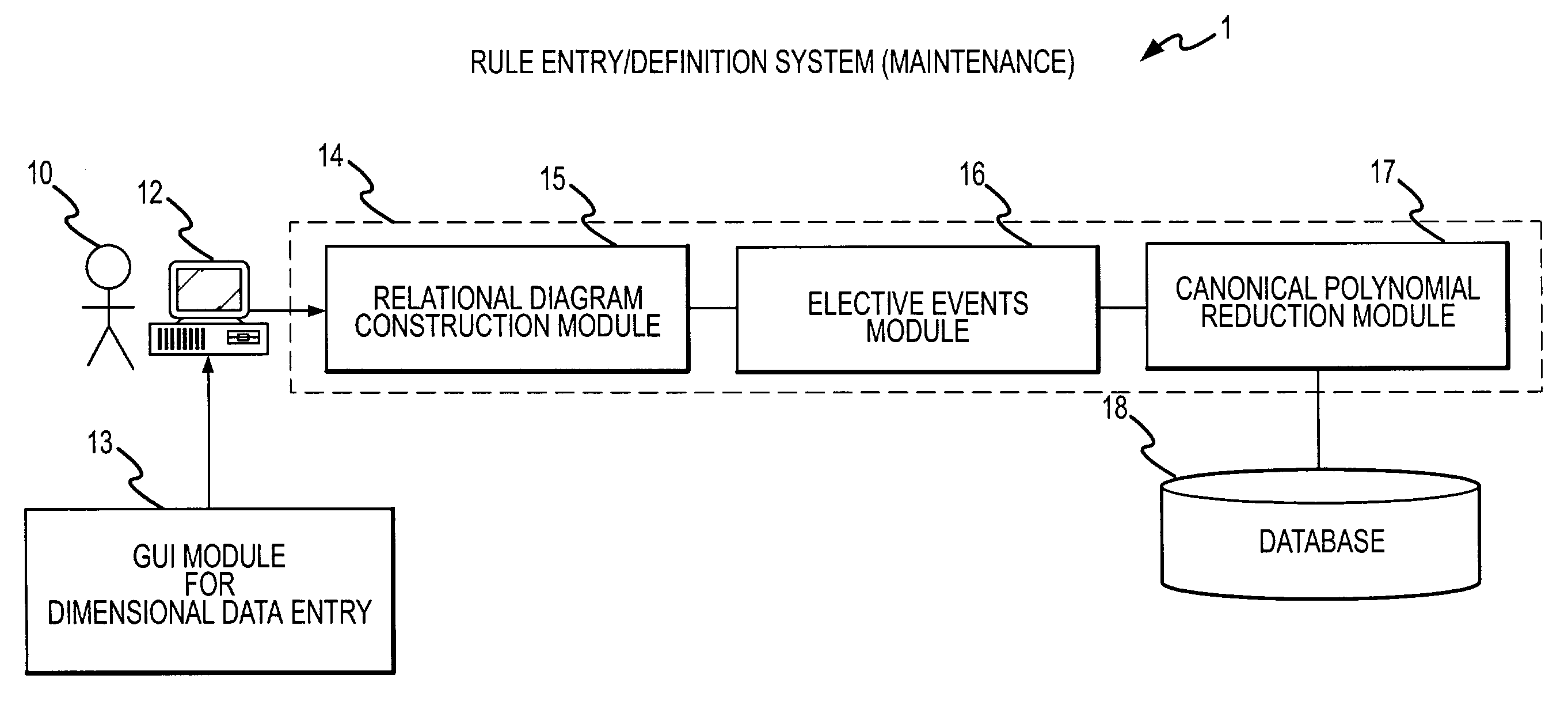
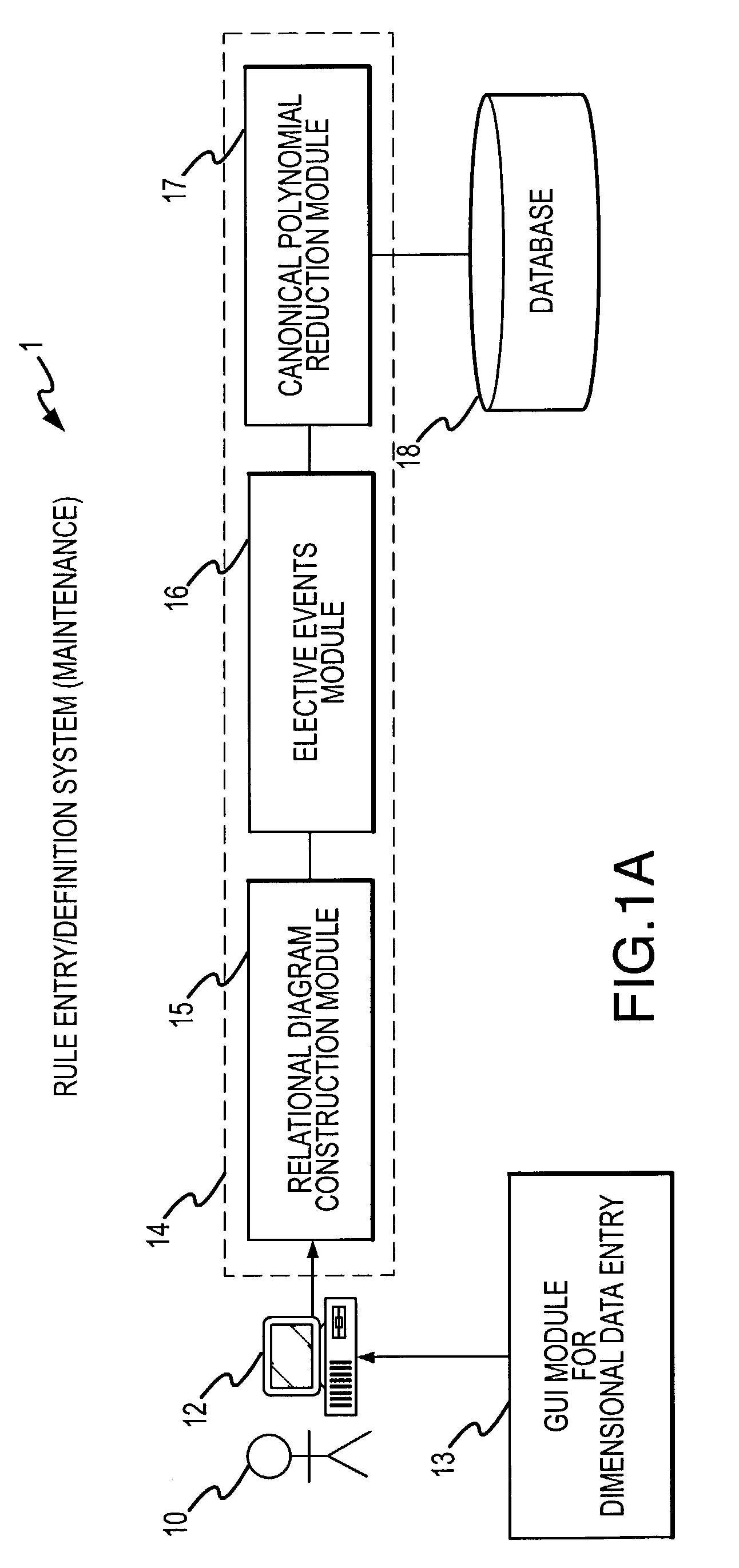
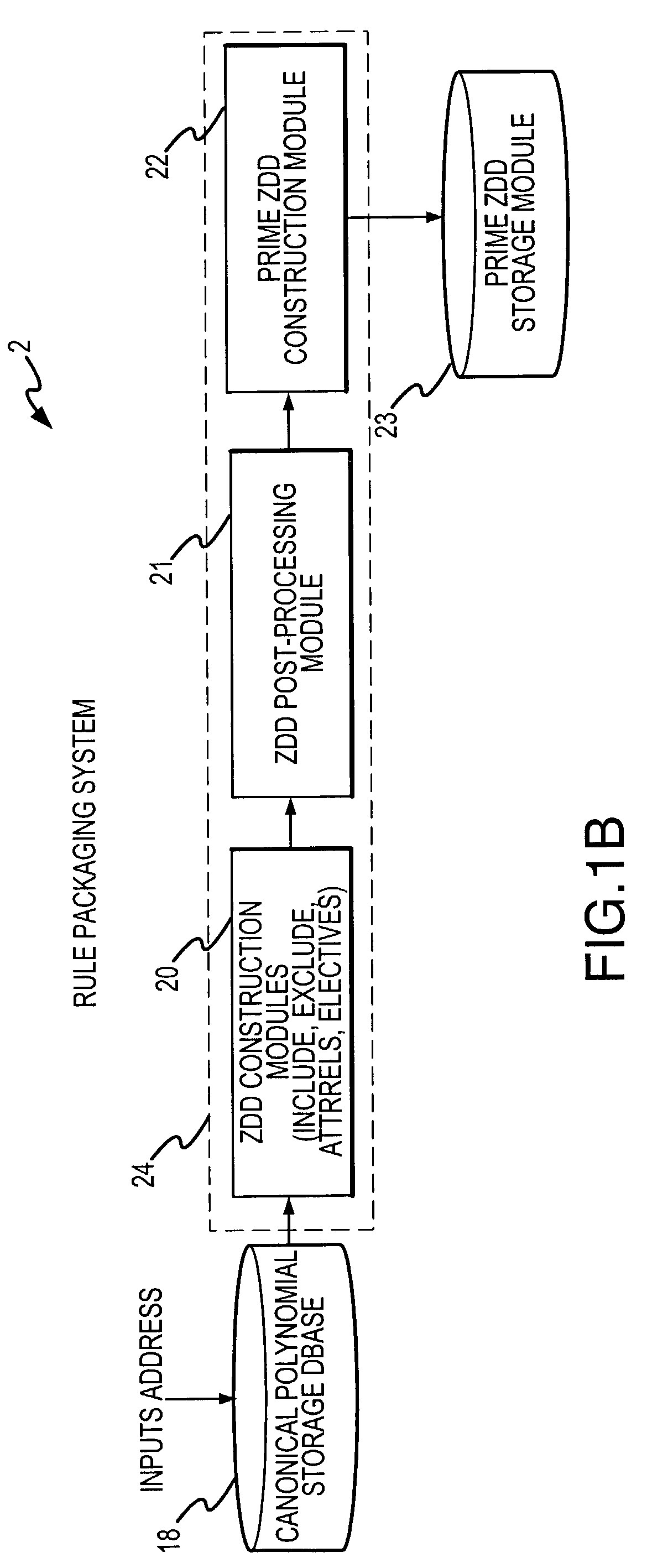
Rule processing system
InactiveUS20070150429A1Exceeding computational capacity of computingDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsPresent dayUser input
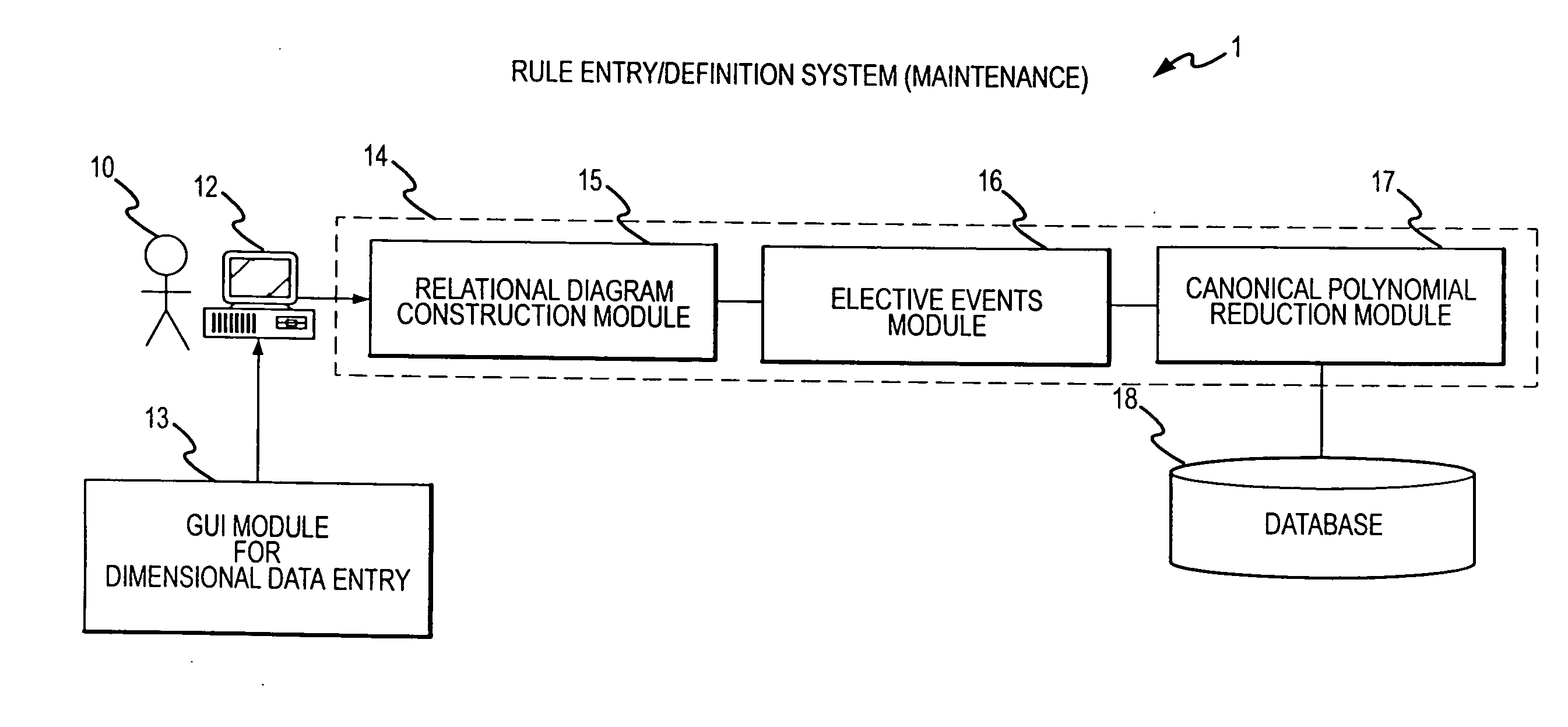
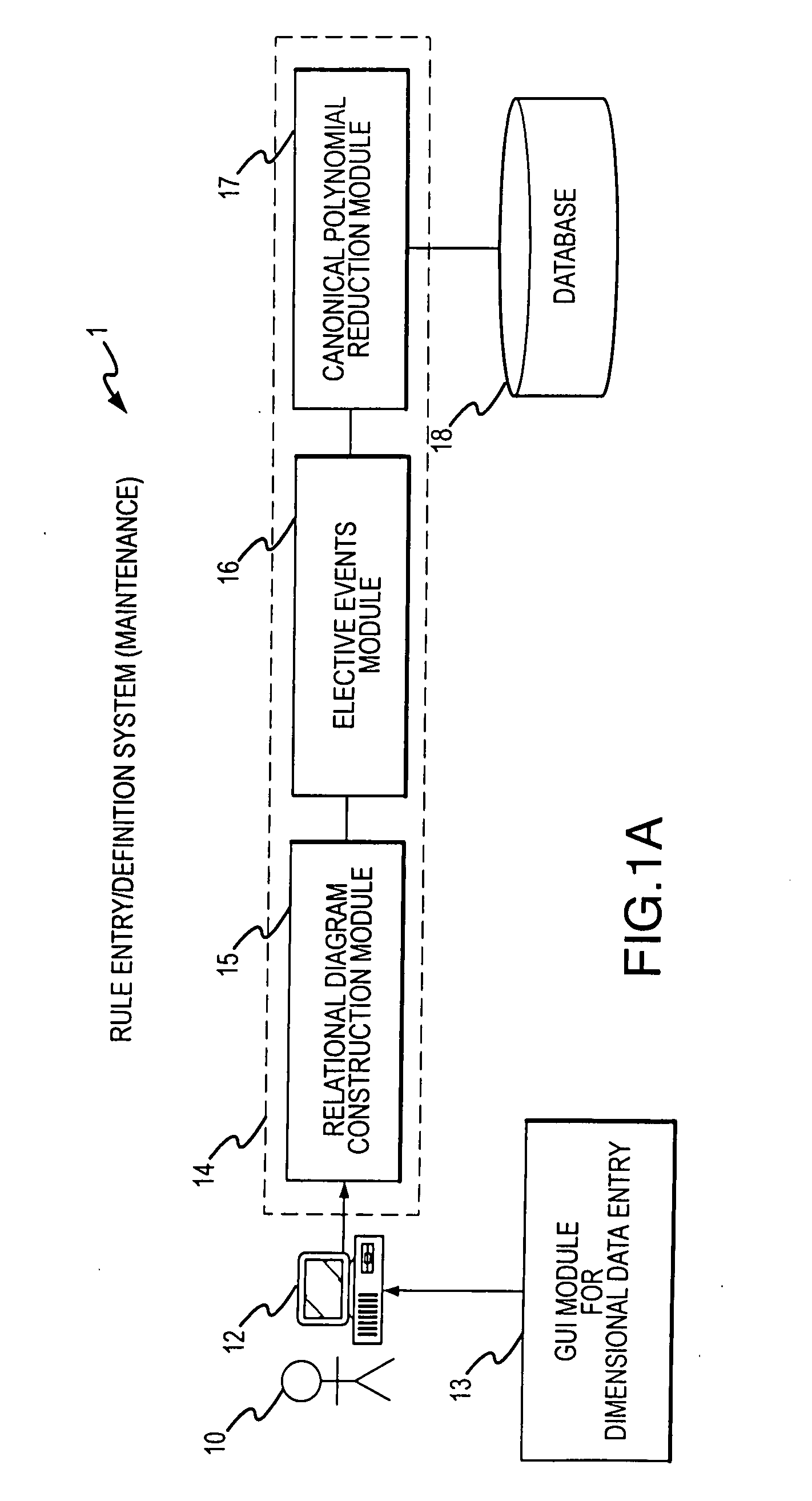
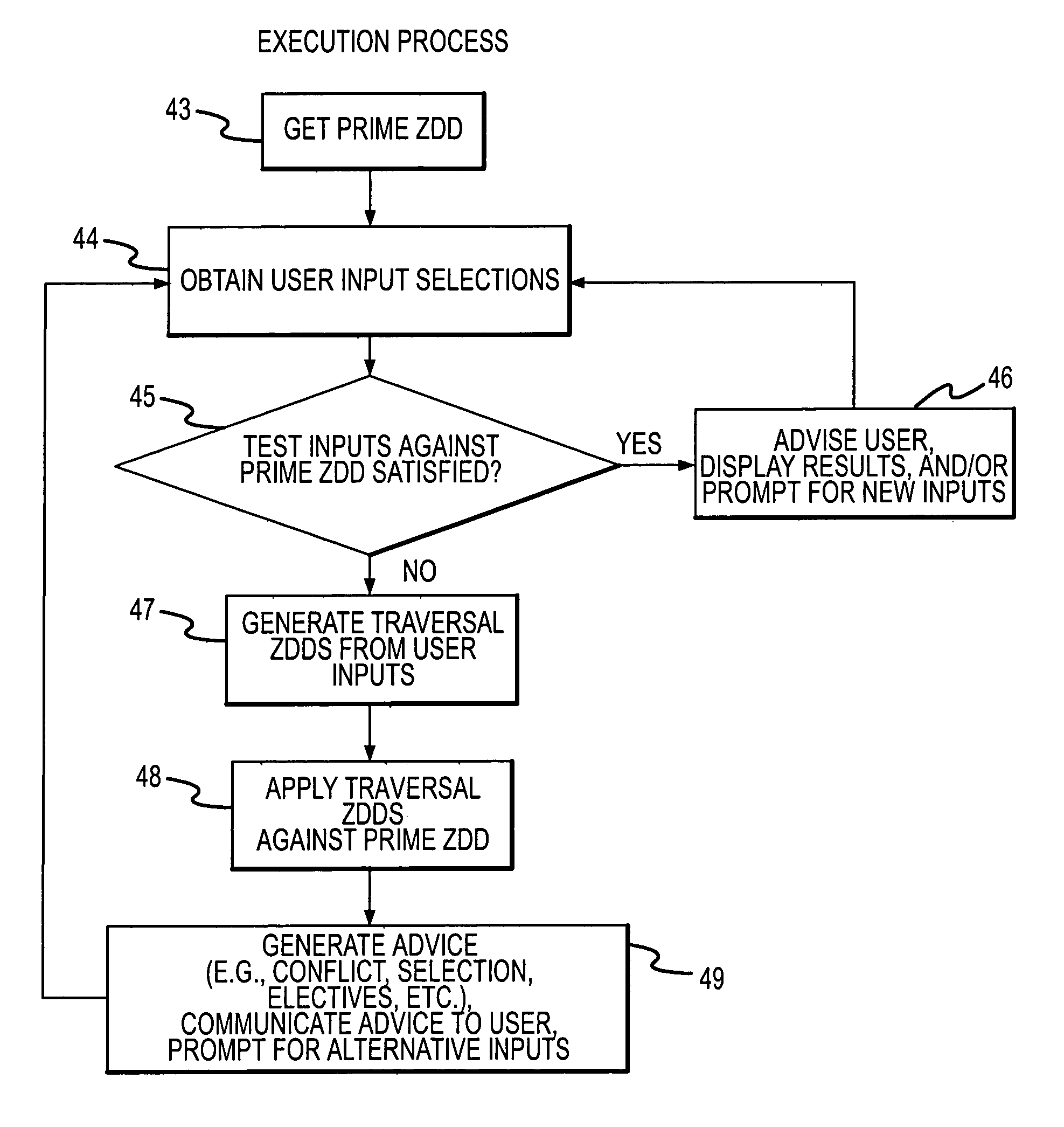
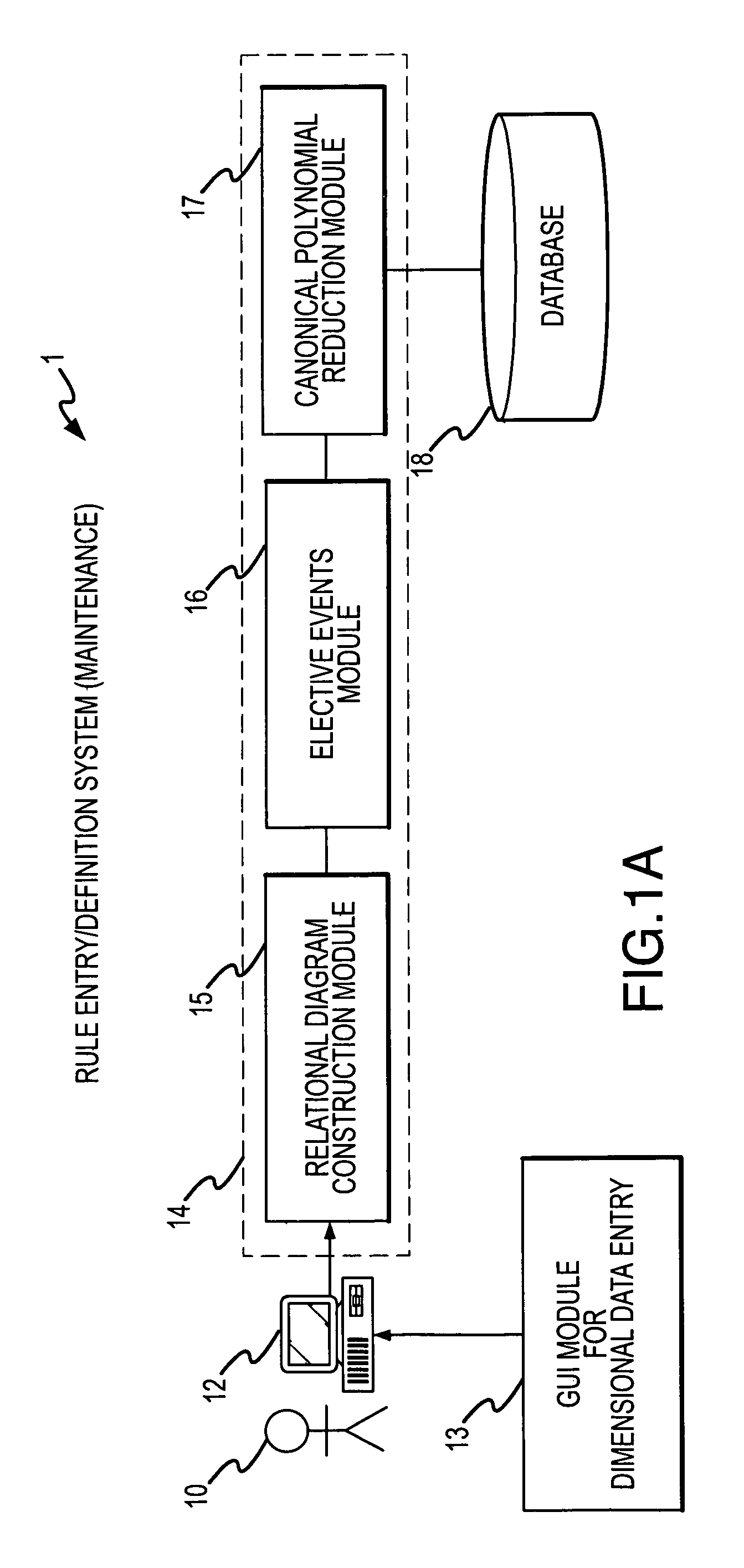
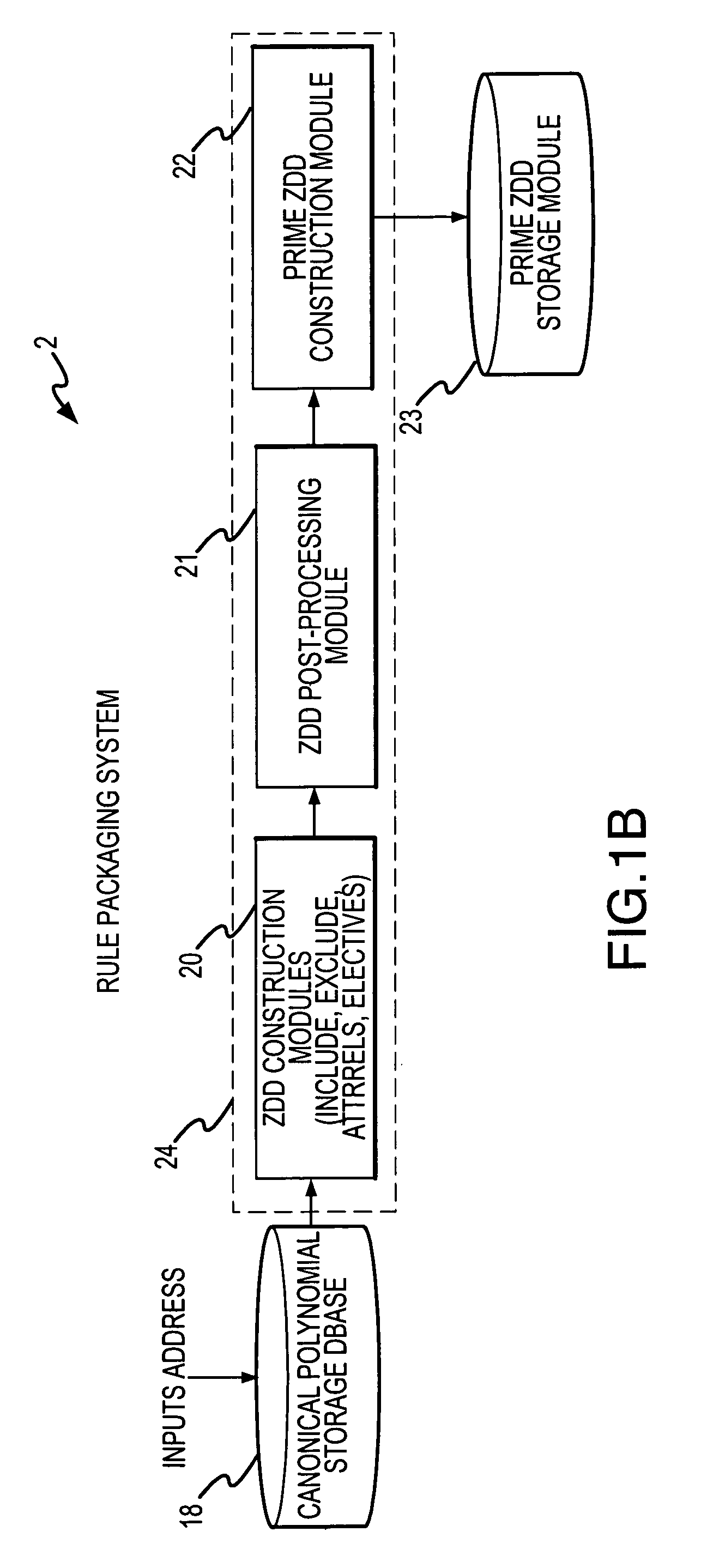
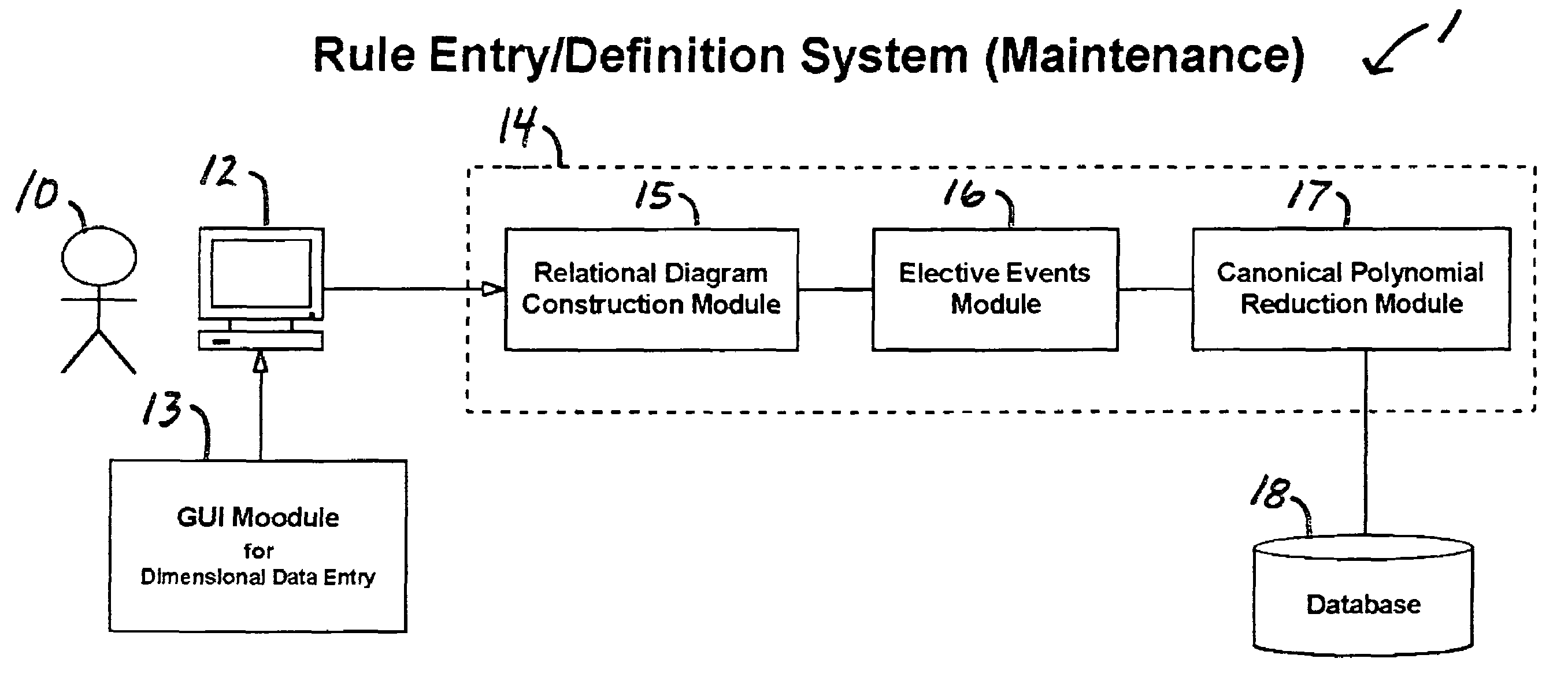
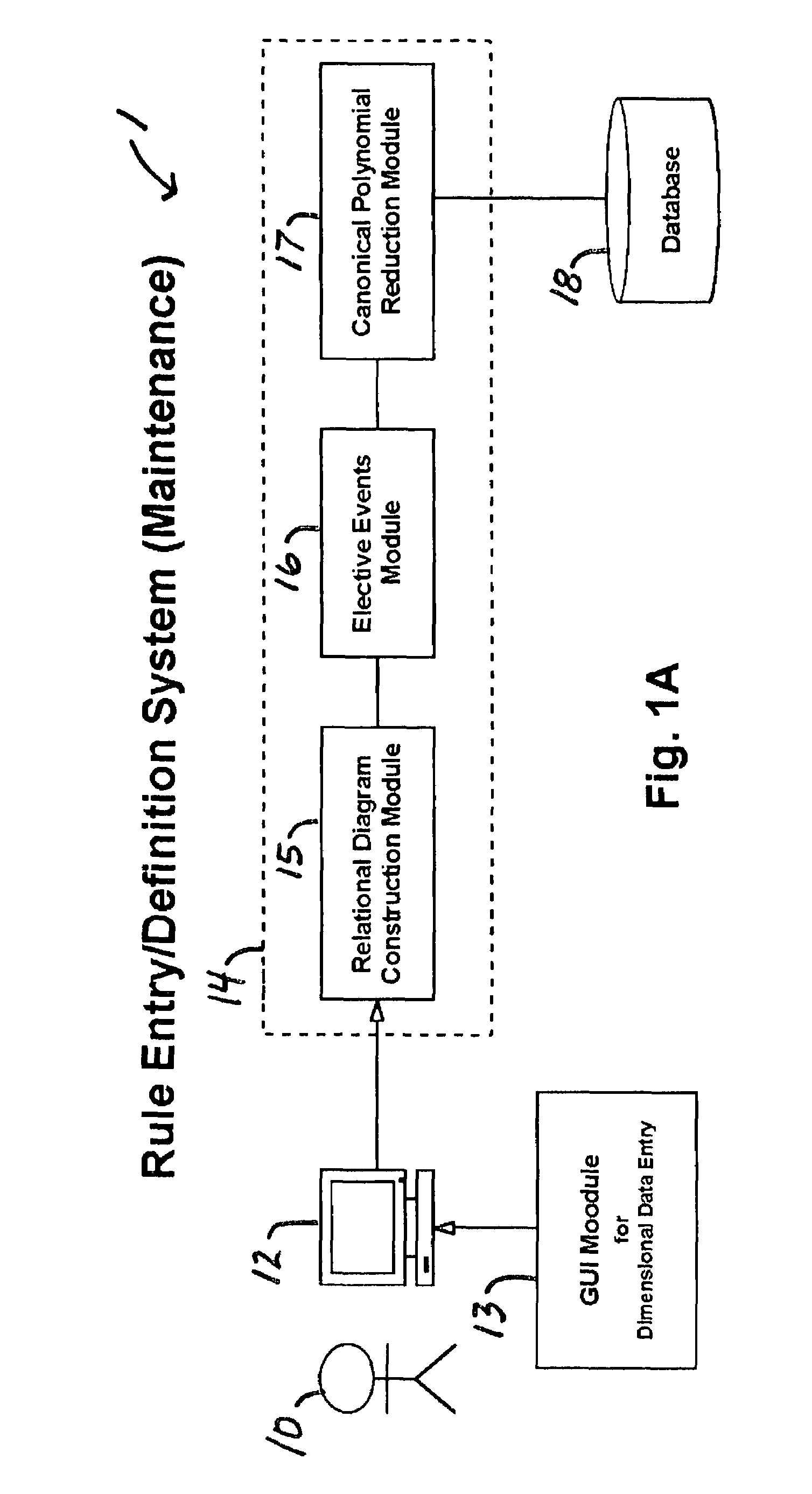
A rule processing apparatus includes modules for defining / entering attributes, enumerations, and / or relationships; packaging the definitions in a reduced canonical form suitable for propositional logic manipulation using zero-suppressed binary decision diagrams (Zdd) to produce a prime Zdd; and / or (iii) executing the rule by applying a series of user inputs to the prime Zdd to determine a result that preferably includes conflict and selection advice to guide the user to satisfaction. Elective events, such as but not limited to the display of messages or the performance of calculations, may optionally be packaged along with the prime rule or components thereof, and presented during execution to help guide the end user to satisfaction or compliancy when choosing among possible selections. The apparatus automates determination of a complex rule having a combinatorial exploded number of rule components, or a combinatorial number of possible outcomes, exceeding computational capacity of present day computing systems.
Owner:MINERAL LASSEN
Information searching device
InactiveUS6874016B1Efficiently organizing storingImprove efficiencyDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsBinary decision diagramKnowledge organization
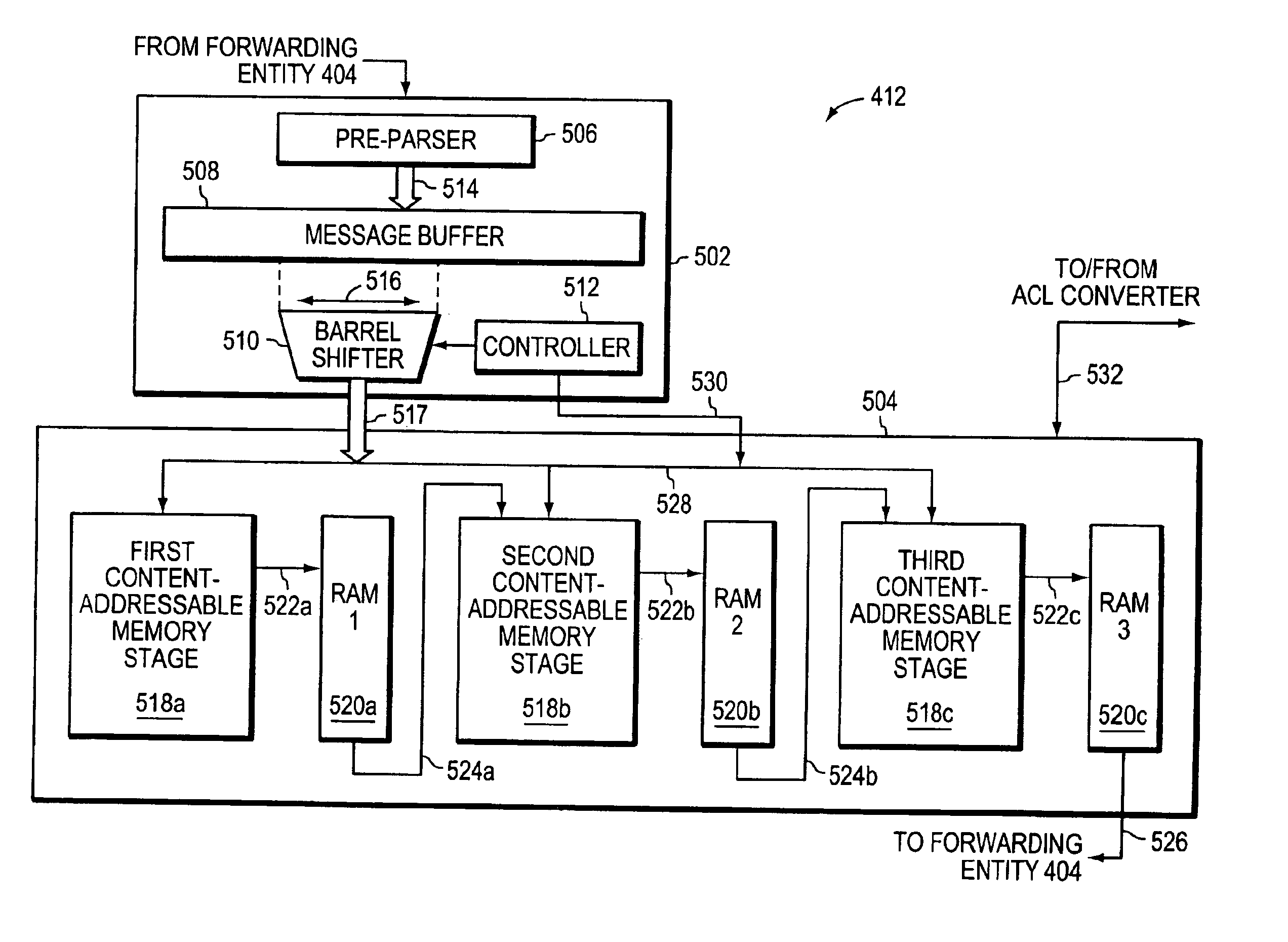
A system for efficiently organizing data or information into an associative memory device, such as a ternary content addressable memory (TCAM), for subsequent searching divides the TCAM is divided into a plurality of individual stages that are interconnected in a cascading fashion. The data or information that is to be stored into the TCAM for subsequent searching is initially translated into a first Boolean representation, such as a binary decision diagram (BDD), that is partitioned into a plurality of segments. Each segment defines one or more outputs, and the outputs from one segment define the inputs to the next segment. After partitioning the BDD and identifying the resulting outputs, each BDD segment along with its corresponding outputs is mapped into a particular stage of the TCAM.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus using automated rule processing to configure a product or service
InactiveUS7062478B1Achieve of complexComplex serviceResourcesKnowledge representationPresent dayUser input
A configuration method and apparatus for a complex product or service that uses a reduced form of a prime rule indicative of valid and invalid configurations. The configurator applies user inputs parameters to an execution module that is constructed using directed acyclic graph, e.g., a zero-suppressed binary decision diagram, indicative of the valid or invalid product / service configurations. The results of execution may include conflict and selection advice to help guide the user to achieve a proper configuration. Elective events, such as but not limited to the display of messages or the performance of calculations, may optionally be packaged along with the prime rule or components thereof, and presented during execution to help guide the end user when choosing among possible configuration parameters. The apparatus and corresponding method automate determination of a complex configuration rule having a combinatorial exploded number of rule components, or a combinatorial number of possible outcomes, exceeding computational capacity of present day computing systems.
Owner:MINERAL LASSEN
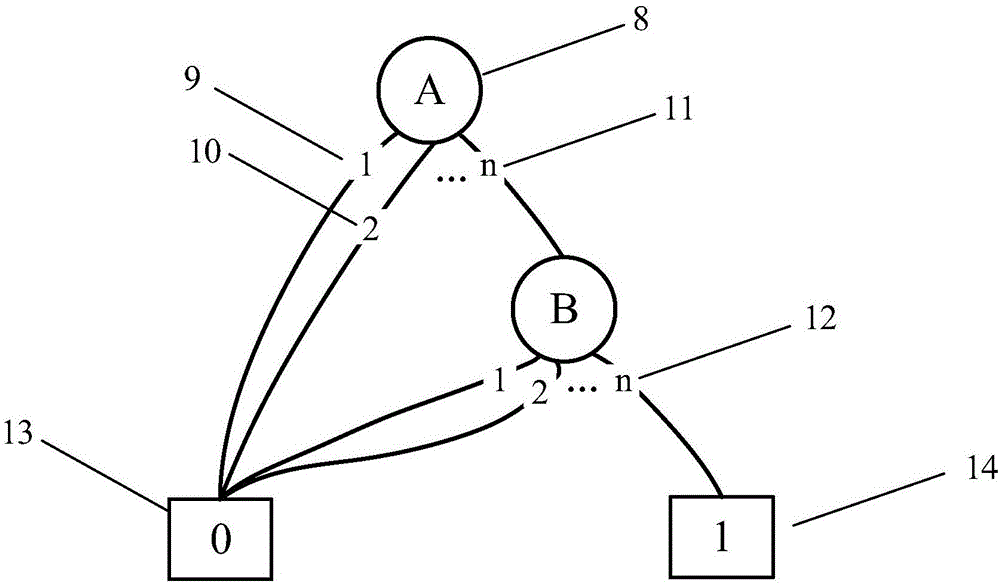
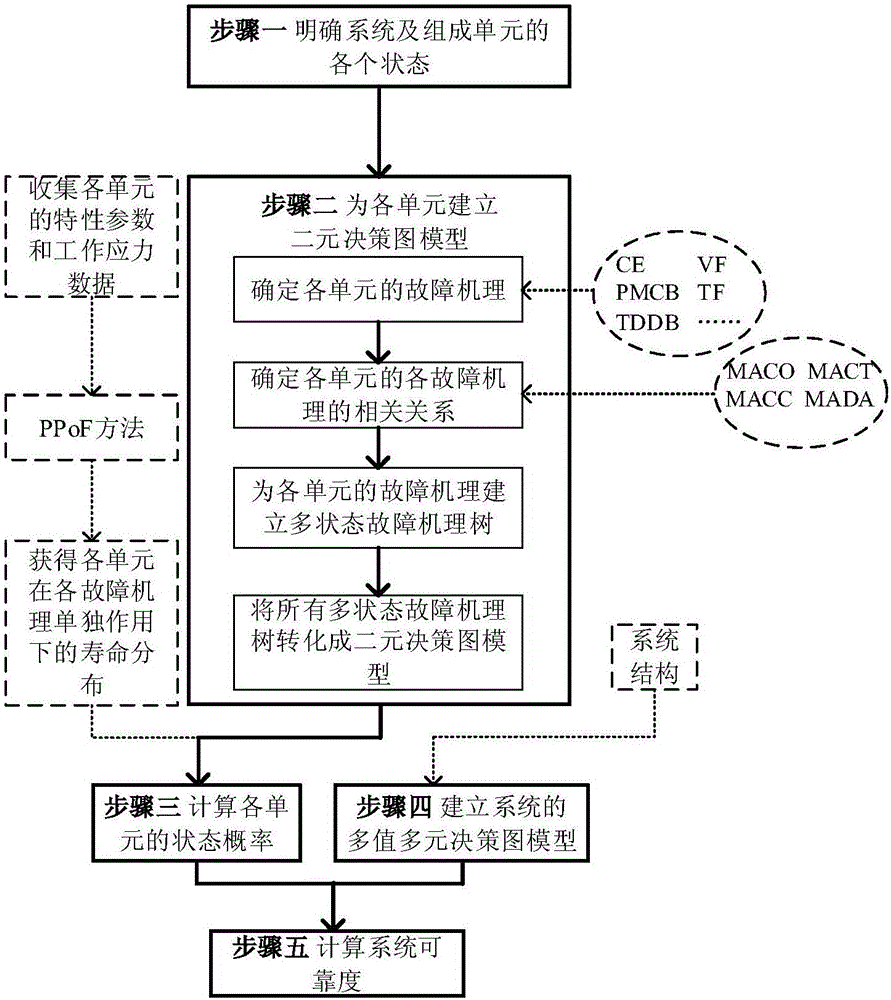
Reliability modeling method for related multi-mode system based on failure mechanism
ActiveCN106503368AExpress multi-state featuresSolve the problem of calculating the state probability of multi-state componentsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDecision graphBinary decision diagram
The invention provides a reliability modeling method for a related multi-mode system based on a failure mechanism. The method comprises the following steps: analyzing system components and confirming and limiting various states of the system and the components; respectively confirming the failure mechanism of each component and the related relation of each failure mechanism under the working environments of the limited states and the function conditions, and establishing a binary decision graph model related to the failure mechanism for each component; calculating the state probability of each component according to the binary decision graph model established in the step (2) under the condition of the service life distribution of each known component under the independent effect of each failure mechanism and establishing a multi-mode multi-value decision graph model based on each component for the system according to the logic relation of each component in the system; substituting the state probability of each component acquired in the step (3) into the logic expressed by the multi-mode multi-value decision graph model established in the step (4) and calculating the state probability of the whole system and the system reliability.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Rule processing methods for automating a decision and assessing satisfiability of rule-based decision diagrams
InactiveUS6965887B2Exceeding computational capacity of present day computing systemsData processing applicationsDigital computer detailsDecision graphBinary decision diagram
A method of rule processing includes defining / entering attributes, enumerations, and / or relationships; packaging the definitions in a reduced canonical form suitable for propositional logic manipulation using zero-suppressed binary decision diagrams (Zdd) to produce a prime Zdd; and / or (iii) executing the rule by applying a series of user inputs to the prime Zdd to determine a result that preferably includes conflict and selection advice to guide the user to satisfaction. Elective events, such as but not limited to the display of messages or the performance of calculations, may optionally be packaged along with the prime rule or components thereof, and presented during execution to help guide the end user to satisfaction or compliancy when choosing among possible selections. The invention automates determination of a complex rule having a combinatorial exploded number of rule components, or a combinatorial number of possible outcomes, exceeding computational capacity of present day computing systems.
Owner:MINERAL LASSEN
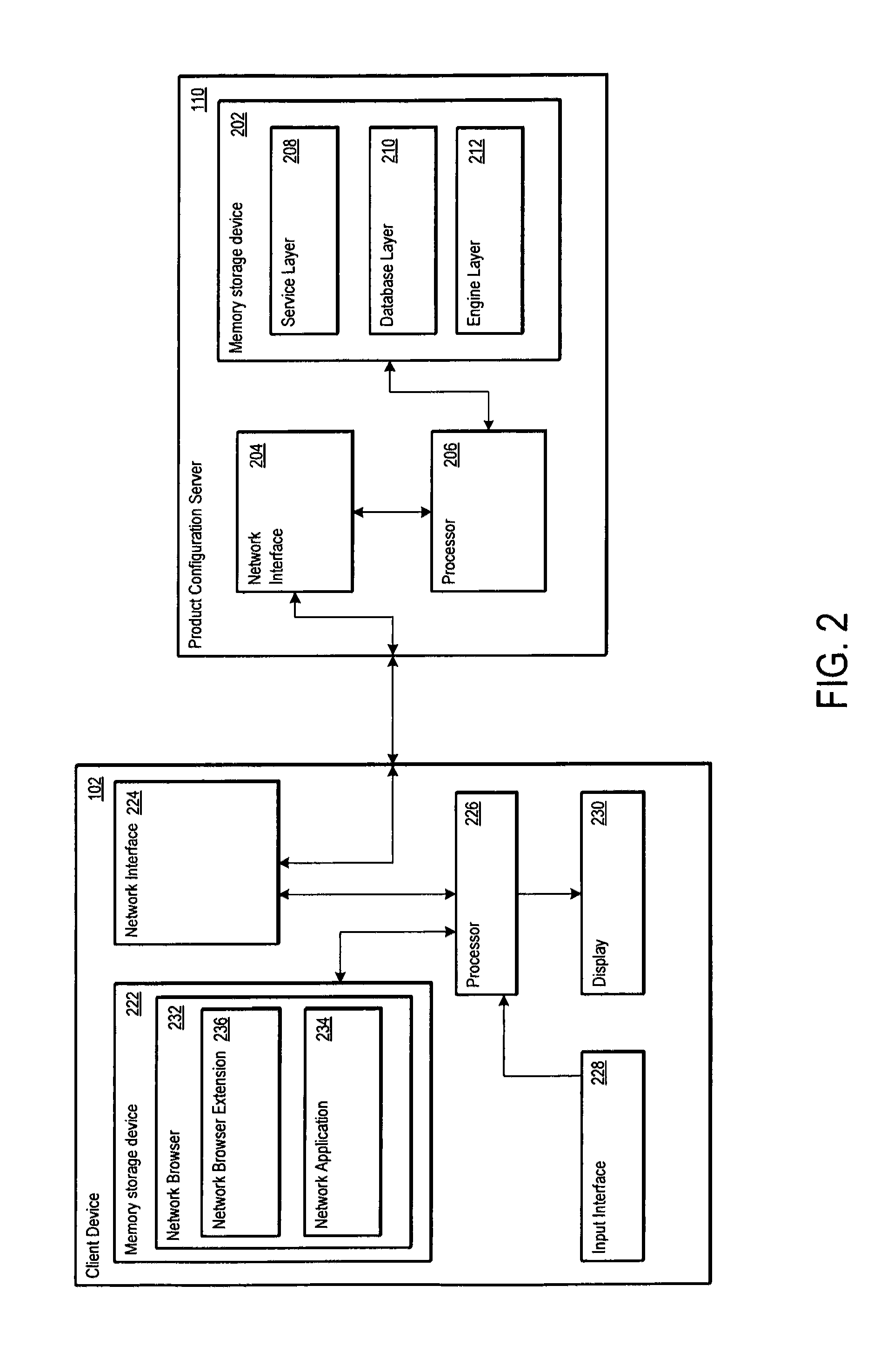
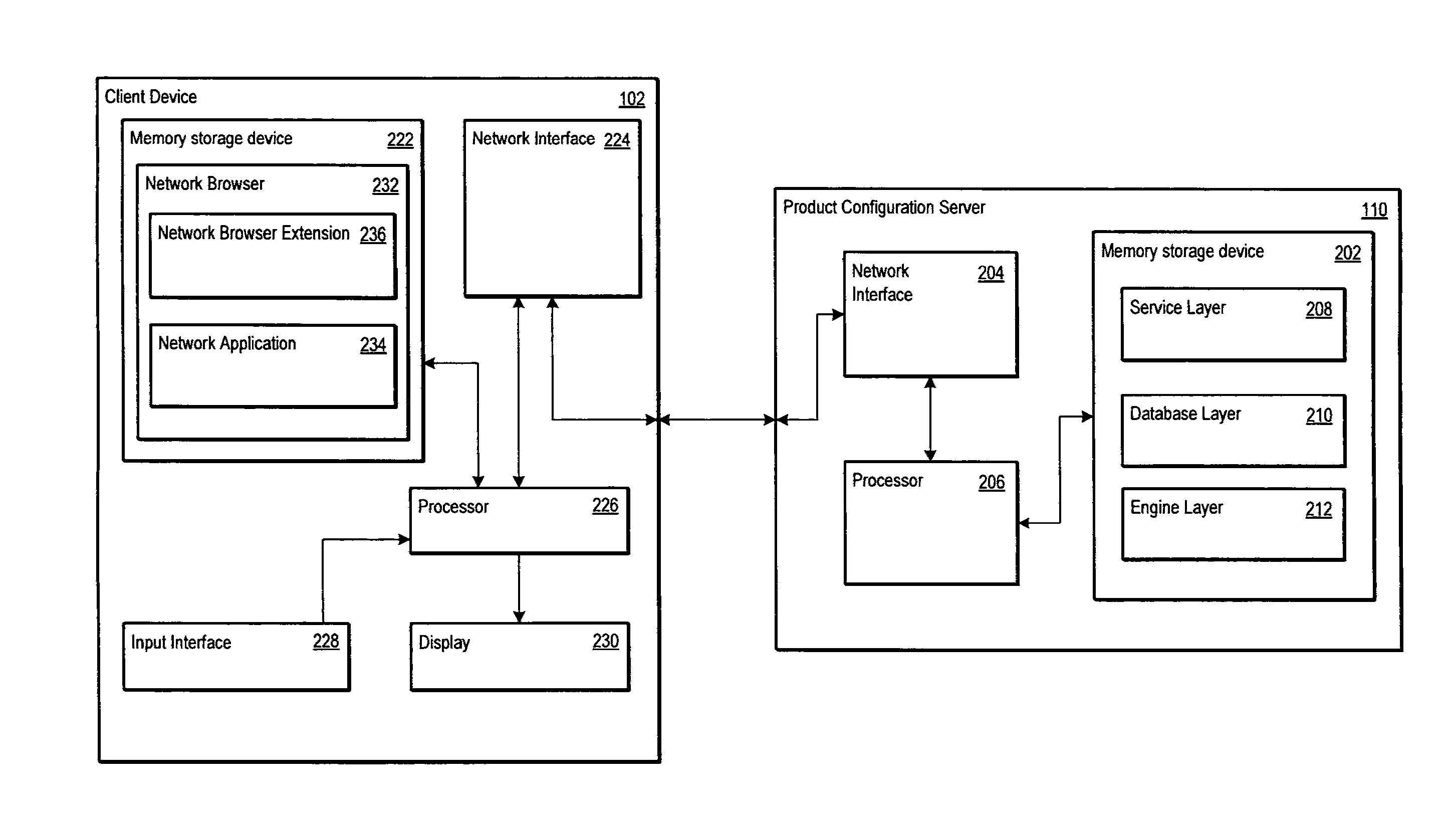
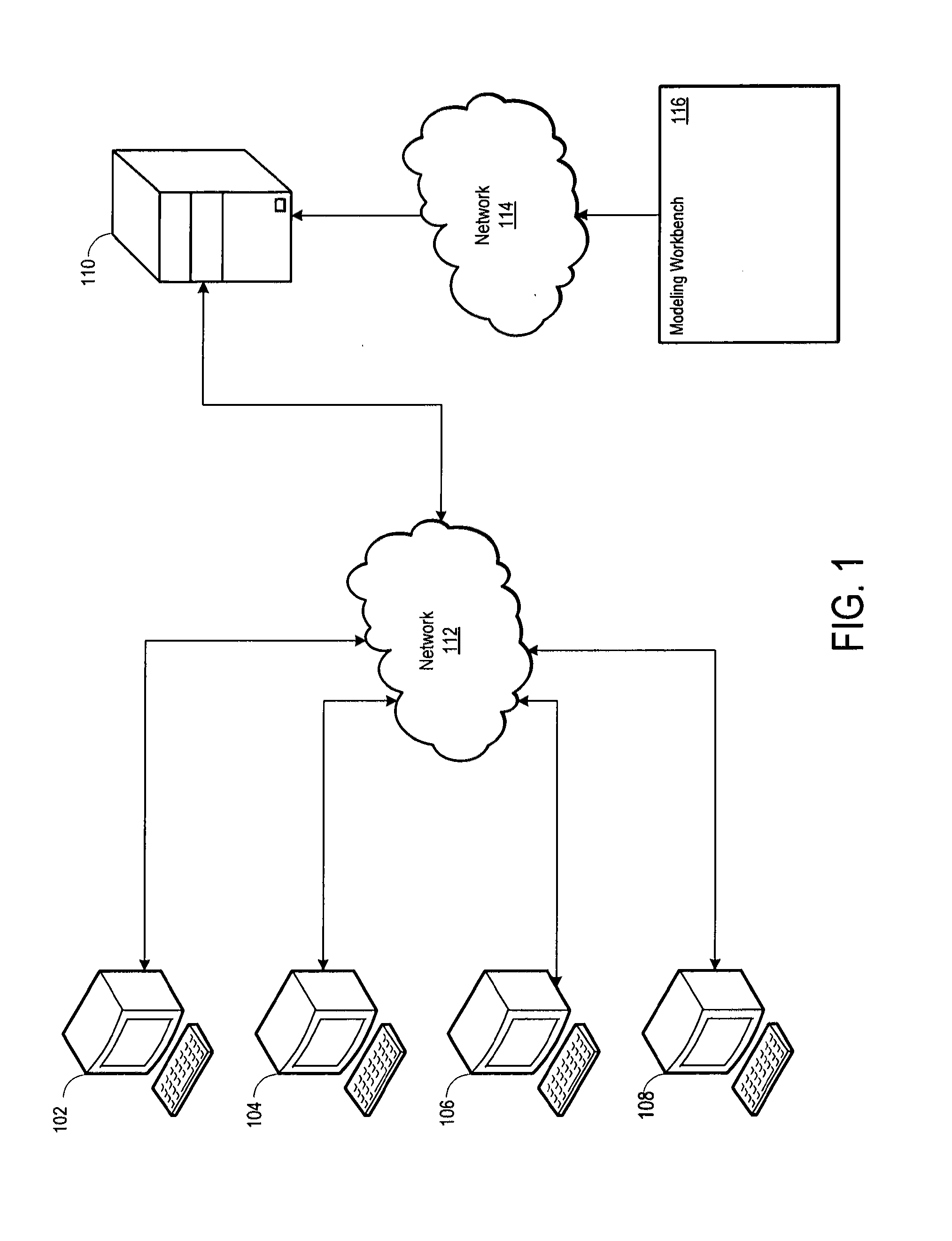
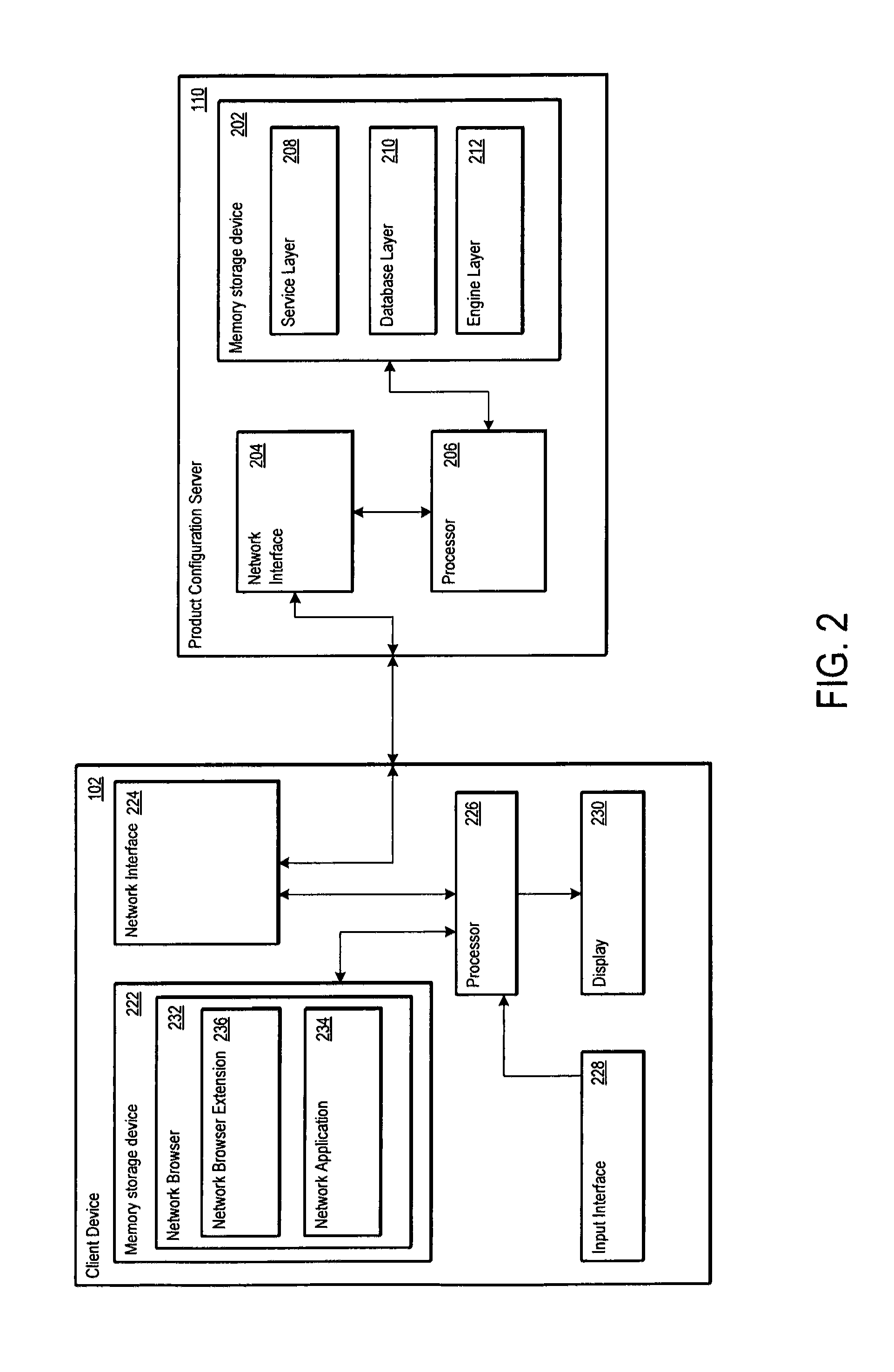
Product configuration server for efficiently displaying selectable attribute values for configurable products
A computer-implemented system leverages binary decision diagram (BDD) structures to provide selectable attribute values for one or more configurable products. The BDD structures may define offering attribute nodes and non-offering attribute nodes. The offering attribute nodes may represent product attribute values selectable by the user based on product configuration rules, and the non-offering attribute nodes may represent product attribute values not selectable by the user based on the product configuration rules. The computer-implemented system may further include at least one memory storage device that stores one or more product configuration rules used to define permissible product configurations and attributes of the products. By evaluating the BDD structures and the product configuration rules, the computer-implemented system may prepare a customized set of product records for transmission to a user, wherein the customized set of product records contains product attribute values corresponding to the offering attribute nodes.
Owner:VALUEMOMENTUM
Product configuration server for efficiently displaying selectable attribute values for configurable products
A computer-implemented system leverages binary decision diagram (BDD) structures to provide selectable attribute values for one or more configurable products. The BDD structures may define offering attribute nodes and non-offering attribute nodes. The offering attribute nodes may represent product attribute values selectable by the user based on product configuration rules, and the non-offering attribute nodes may represent product attribute values not selectable by the user based on the product configuration rules. The computer-implemented system may further include at least one memory storage device that stores one or more product configuration rules used to define permissible product configurations and attributes of the products. By evaluating the BDD structures and the product configuration rules, the computer-implemented system may prepare a customized set of product records for transmission to a user, wherein the customized set of product records contains product attribute values corresponding to the offering attribute nodes.
Owner:VALUEMOMENTUM
Symbolized model detection method
InactiveCN101013452AOvercoming the state space explosion problemImprove reliabilitySpecial data processing applicationsTemporal logicModel testing
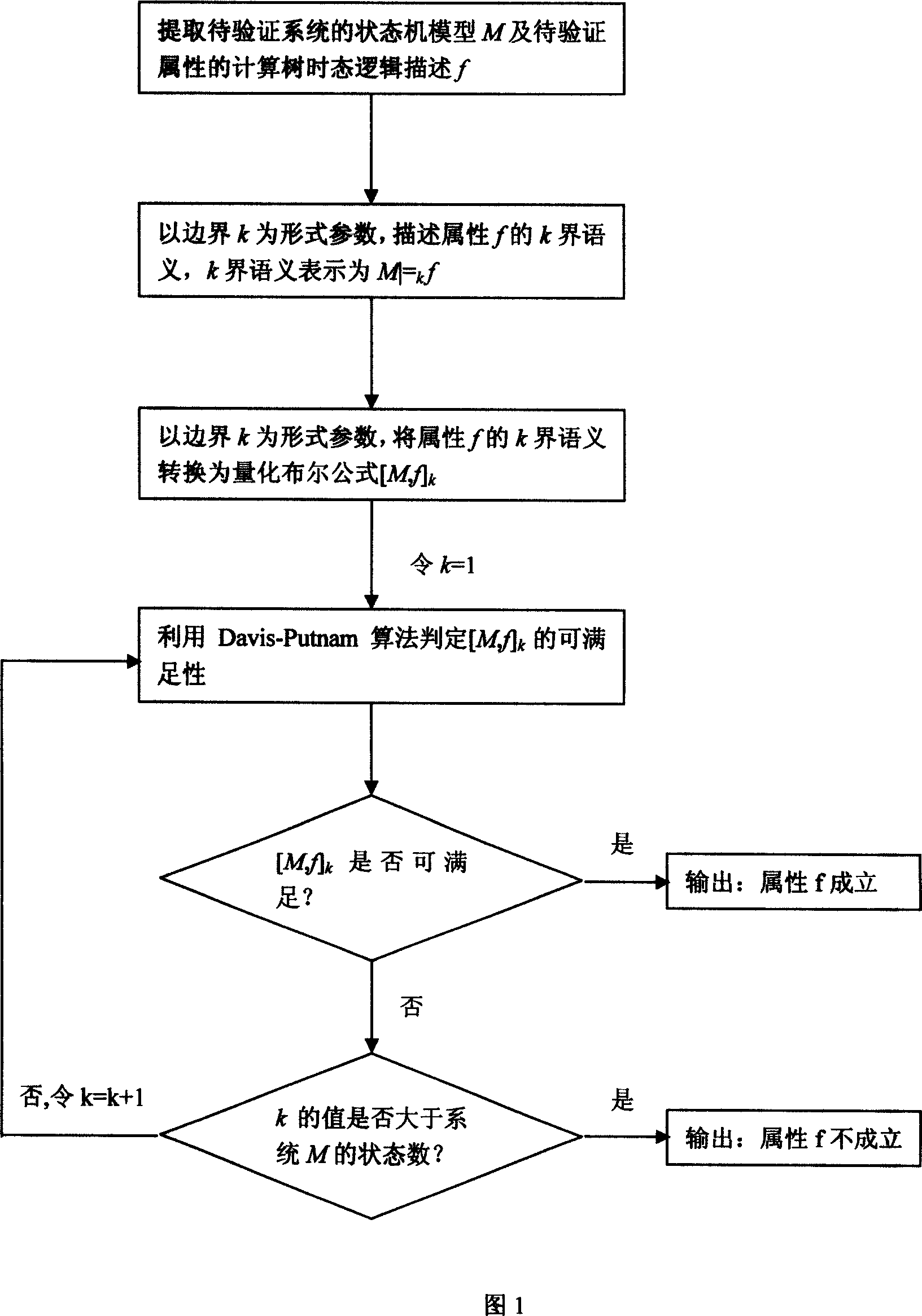
This symbol model detection method is a method to make the model testing practical; the main principle is to use Boolean formula quantitative determination to instead of the CTL model testing. Their method: 1.) extract state machine M of the tested system and the attributes of the tested tree temporal logic description; 2.) taking border k as the form parameters, describe k sector semantics of the attributes f; 3.) taking border k as the form parameters, convert the k sector semantic of attribute f to quantify Boolean formula [M, f] k: 4.) progressive determine whether the system M meets the reliable attribute f: the approach integrates the advantages of symbol model testing based on binary decision diagram and bounded model checking based proposition equitation meeting judgment, also overcomes their shortcomings, which are not dependent on the sort of Boolean variables, or dependent on the property to verify the full name attribute.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method and system for building binary decision diagrams efficiently in a structural network representation of a digital circuit
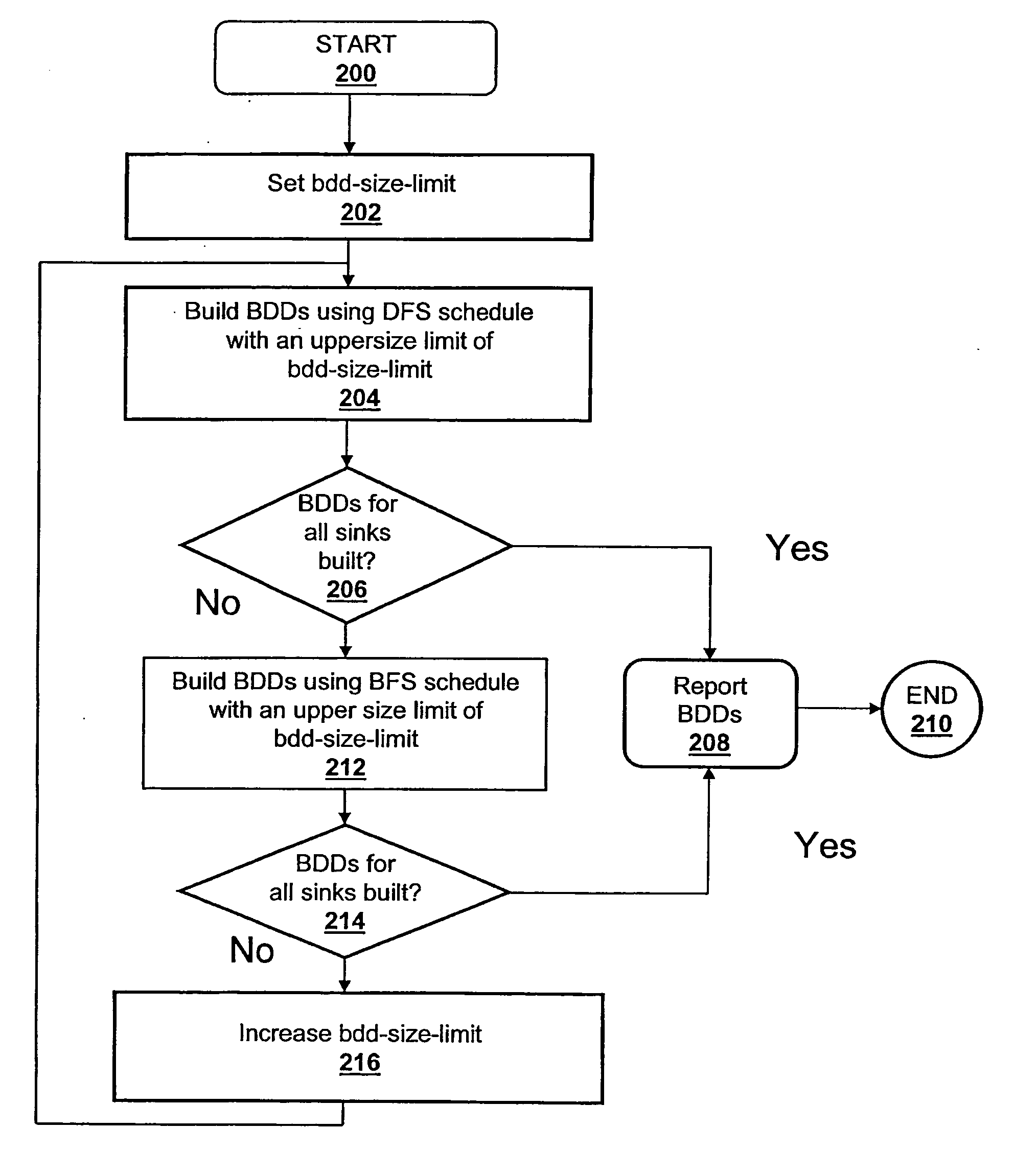
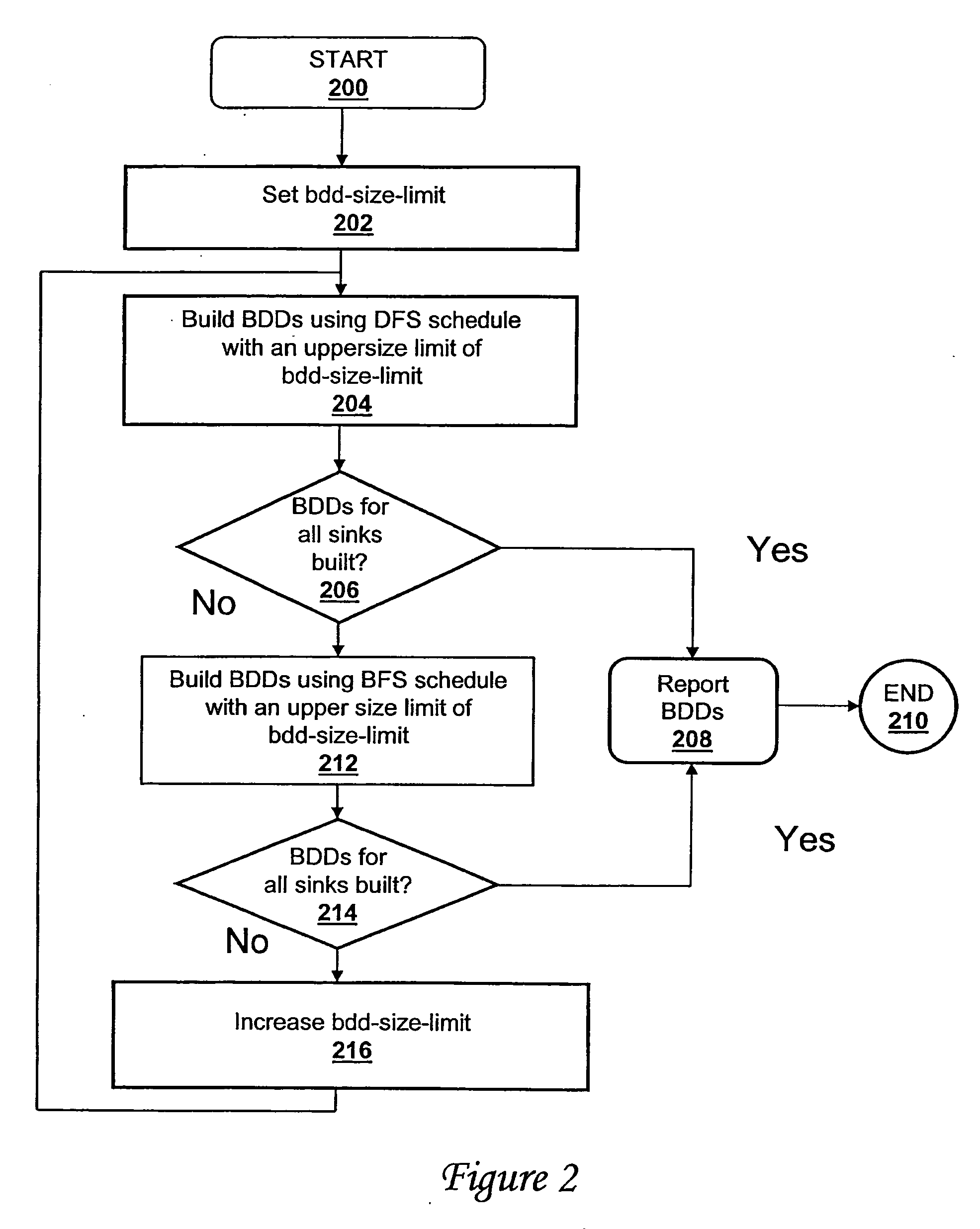
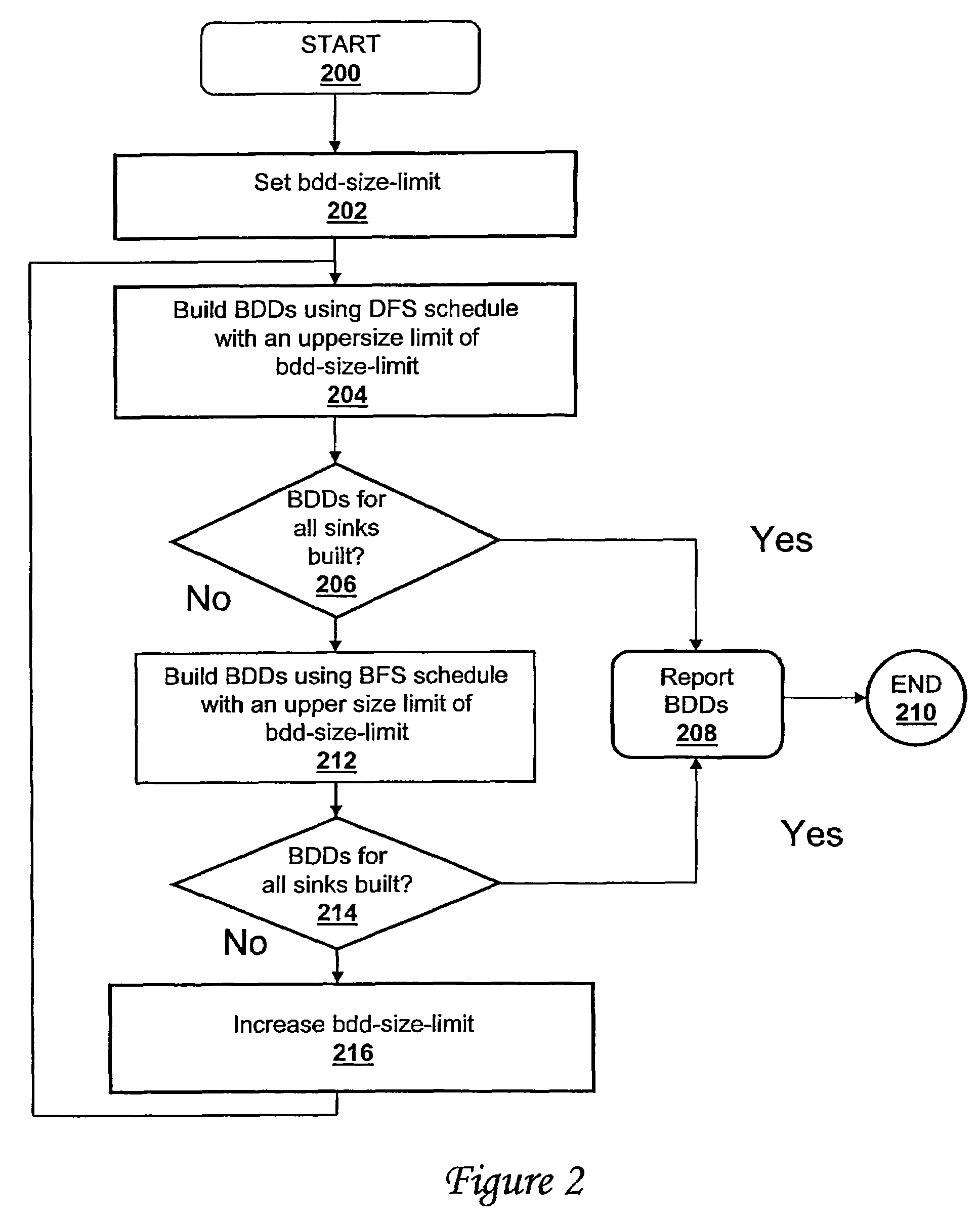
ActiveUS20060047680A1Digital data information retrievalData processing applicationsDepth-first searchDynamic resource
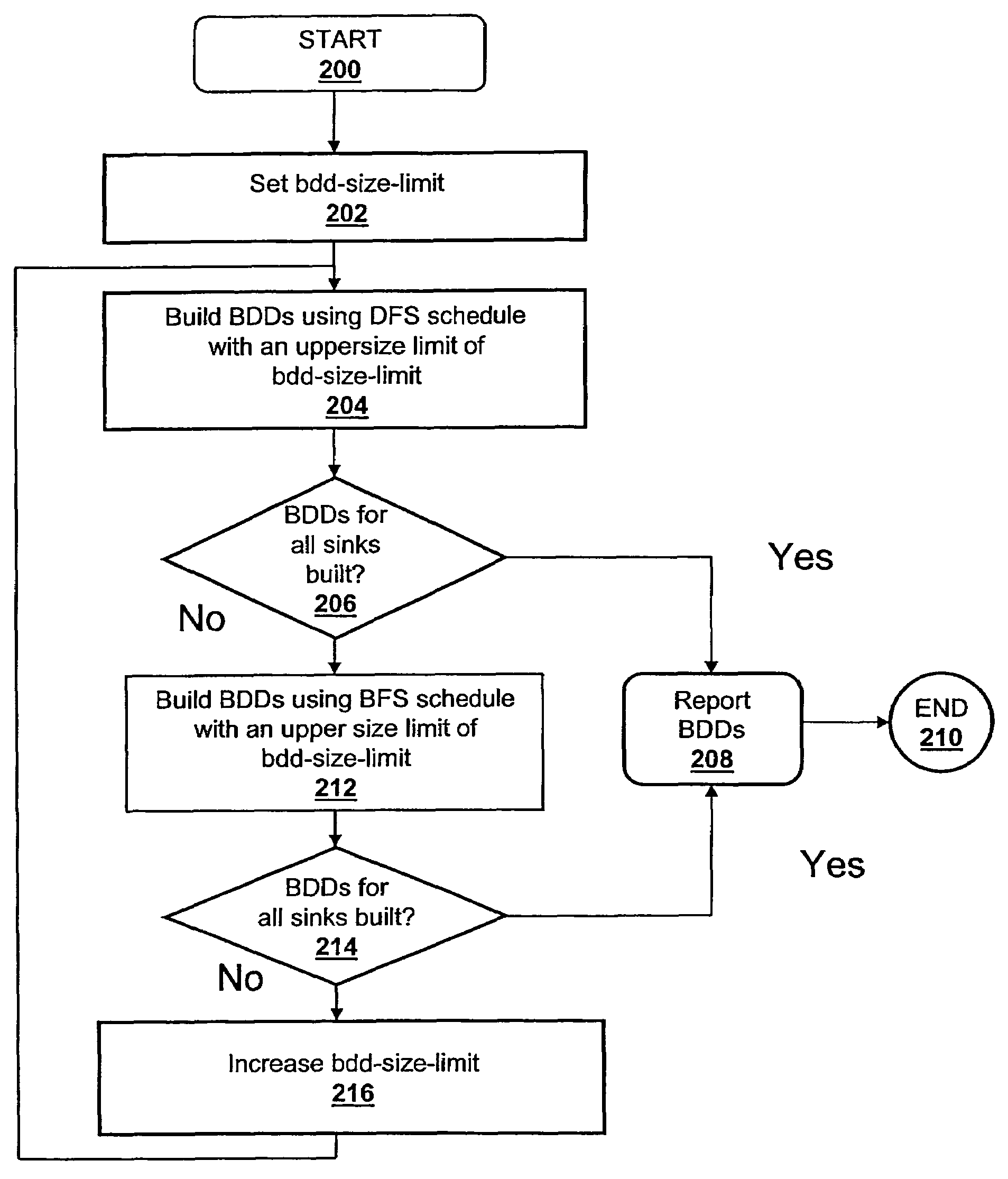
A method, system and computer program product for building decision diagrams efficiently in a structural network representation of a digital circuit using a dynamic resource constrained and interleaved depth-first-search and modified breadth-first-search schedule is disclosed. The method includes setting a first size limit for a first set of one or more m-ary decision representations describing a logic function and setting a second size limit for a second set of one or more m-ary decision representations describing a logic function. The first set of m-ary decision representations of the logic function is then built with one of the set of a depth-first technique or a breadth-first technique until the first size limit is reached, and a second set of m-ary decision representations of the logic function is built with the other technique until the second size limit is reached. In response to determining that a union of first set and the second set of m-ary decision representations do not describe the logic function, the first and second size limits are increased, and the steps of building the first and second set are repeated. In response to determining that the union of the first set of m-ary decision representations and the second set of m-ary decision representations describe the logic function, the union is reported.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Distributed BDD reordering
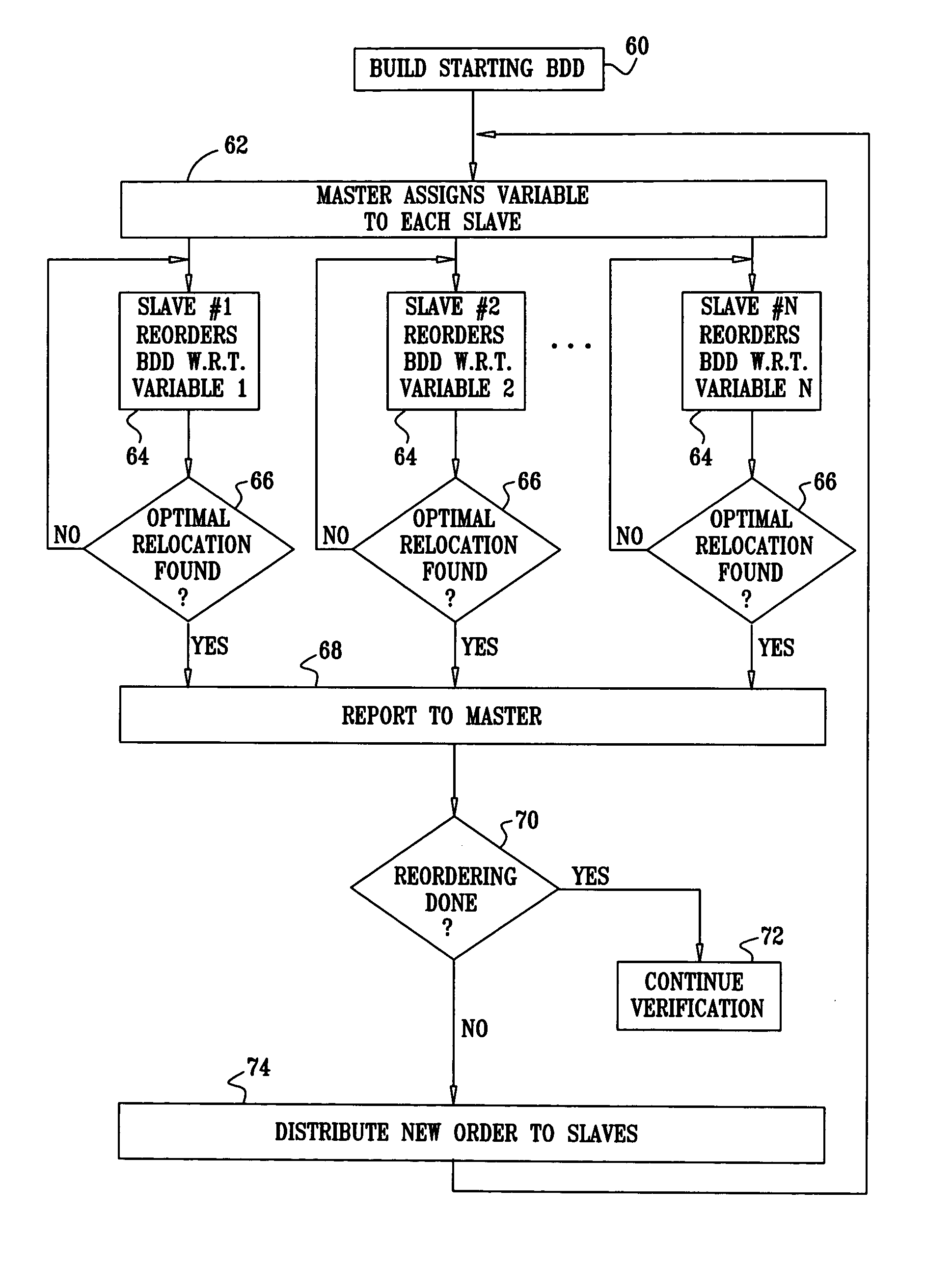
InactiveUS20050229124A1Minimize the numberReduce in quantityComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationSystems designBinary decision diagram
A method for verification of a system design represented by a model that includes a plurality of variables. The method includes arranging the variables in an Ordered Binary Decision Diagram (OBDD) according to an initial order of the variables, the OBDD including a number of nodes arranged in rows corresponding respectively to the plurality of the variables. Each processor, among a group of two or more computer processors, is assigned a respective variable among the plurality of the variables. Using each processor, the rows of the OBDD are reordered by varying a position in the OBDD of the row corresponding to the respective variable that is assigned to the processor until at least one of the processors identifies a new order for the OBDD. The new order of the OBDD may be used to verify a characteristic of the model against a specification.
Owner:IBM CORP
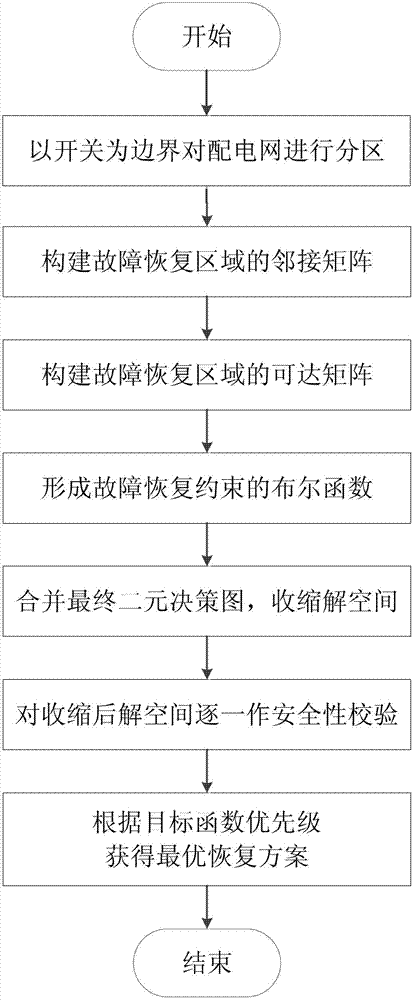
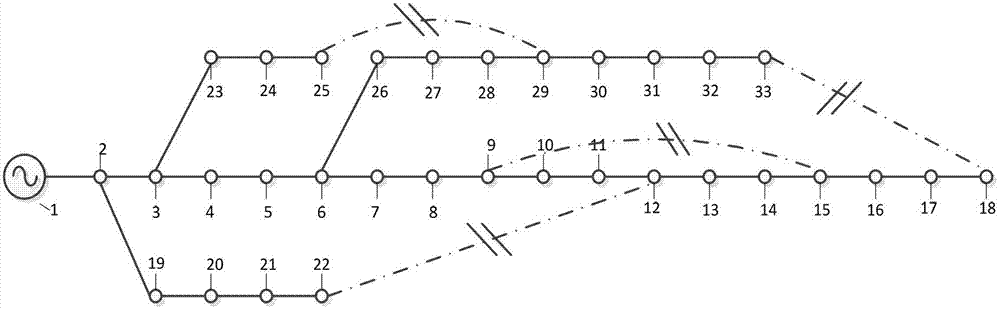
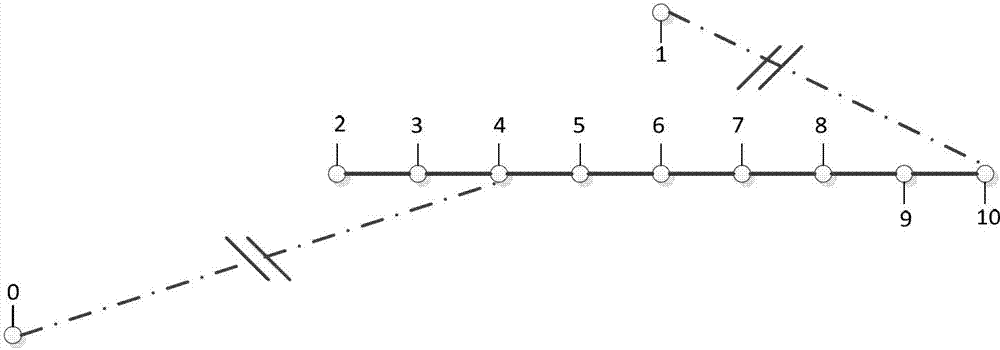
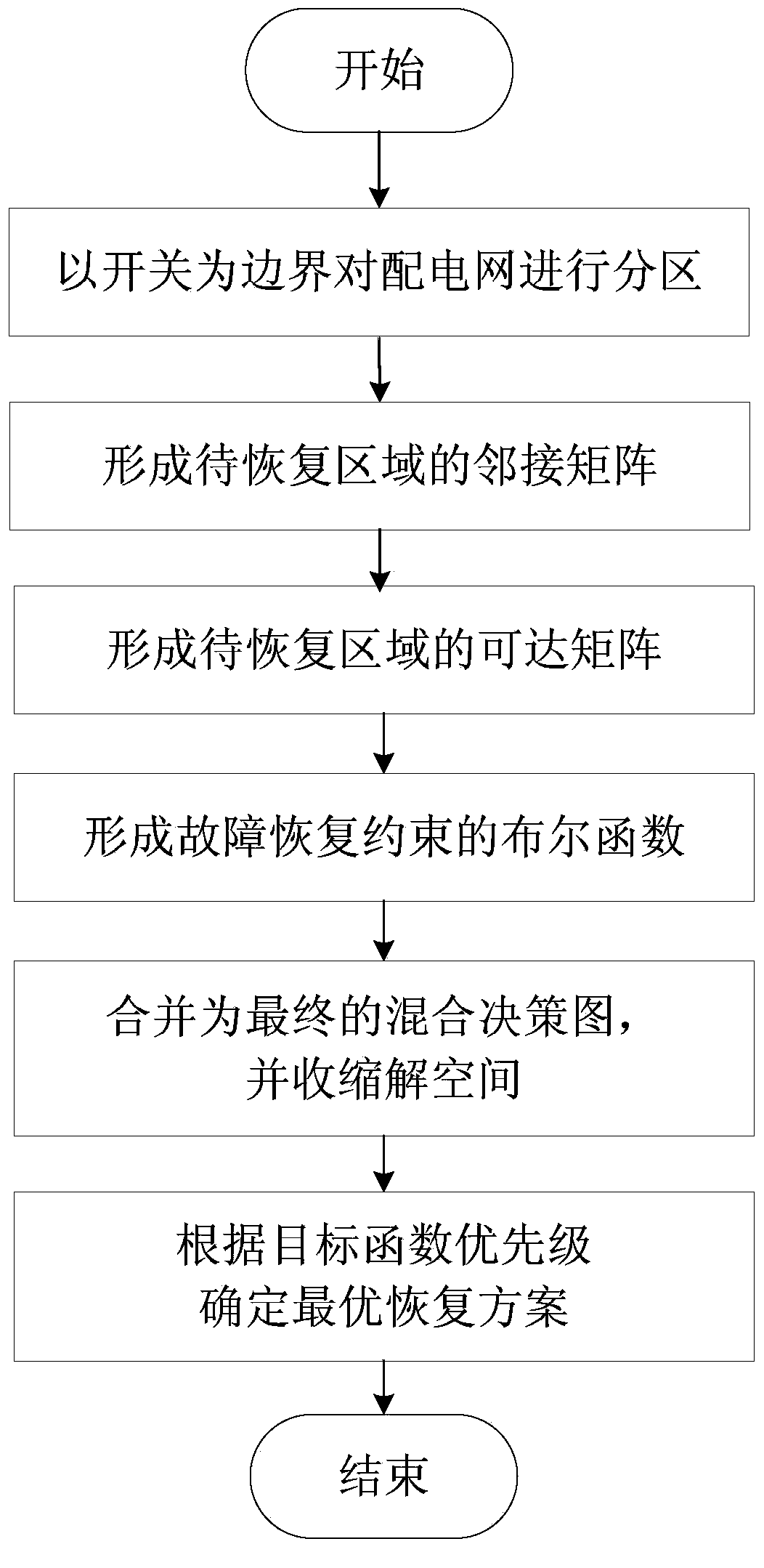
Ordered binary decision diagram modeling method for distribution network fault recovery
InactiveCN103199510AThe principle is simpleEasy to implementEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionLocal optimumUndirected graph
The invention discloses an ordered binary decision diagram modeling method for distribution network fault recovery. The method includes a first step of carrying out partition on a power distribution network, and using an on-off state as a decision variable, a second step of forming an adjacent matrix of the power distribution network according to a forming method of the adjacent matrix of an undirected graph, a third step of forming a reachable matrix of the power distribution network, a fourth step of forming boolean functions of each restriction of fault recovery, a fifth step of combining to generate a final binary decision diagram, and obtaining a contractive solution space, a sixth step of carrying out load flow calculation on feasible solutions one by one in the solution space after contraction, and carrying out safety verification, and a seventh step of obtaining an optimal recovery scheme according to priority levels of optimized objective functions. The modeling method has the advantages of effectively reducing the solution complexity of fault recovery problems, overcoming the defect that a traditional artificial intelligence algorithm is prone to premature convergence in local optimal solution, and improves understanding reliability and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
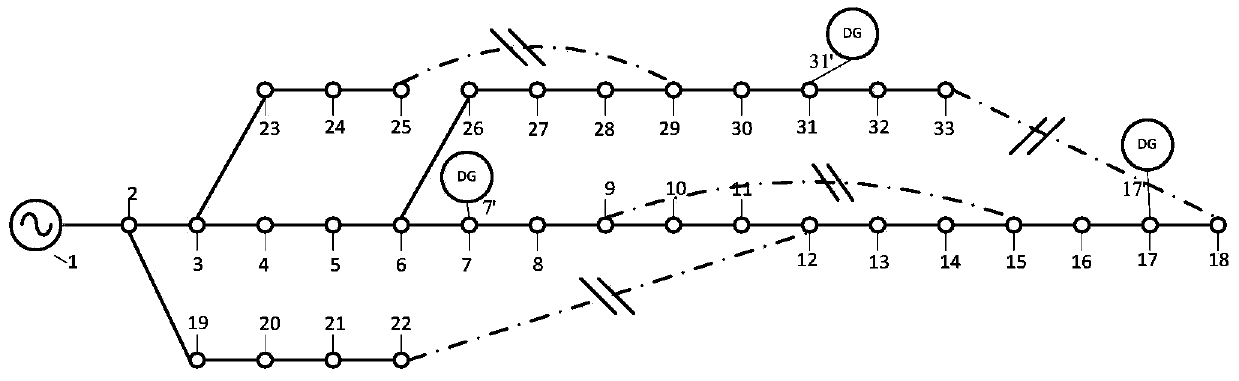
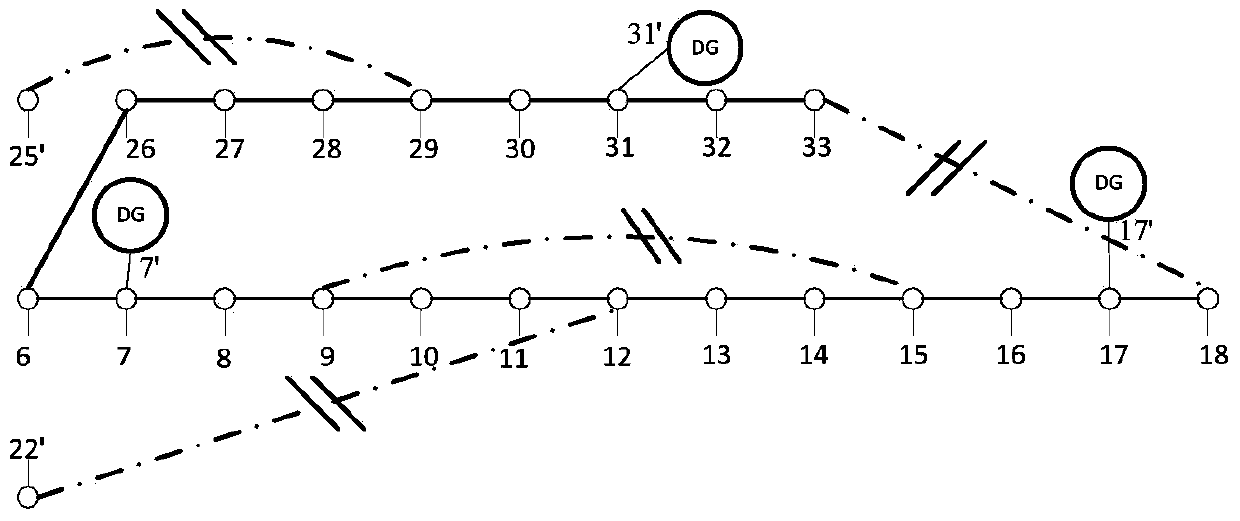
Distributed-generation-contained power distribution system fault recovery method based on mixed decision diagram
ActiveCN103579990AThe principle is simpleEasy to implementEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionSpecial data processing applicationsRecovery methodRestoration method
The invention discloses a modeling method for achieving distributed-generation-contained power distribution system fault recovery. The modeling method comprises the following steps of (1) reading original data of a distribution network, using a switch as the boundary to carry out partition on the distribution network, and using the switch as a decision variable; (2) forming an adjacency matrix of a region to be recovered; (3) forming a reachable matrix of the region to be recovered; (4) forming the Boolean function about various fault recovery constraints; (5) carrying out merging to form a final mixed decision diagram, carrying out conversion to form an orderly binary decision diagram, and contracting a solution space; (6) determining an optimal fault recovery scheme for the contracted solution space according to a priority of an objective function. The modeling method for achieving distributed-generation-contained power distribution system fault recovery can effectively reduce the complexity for solving the distributed-generation-contained power distribution network fault recovery problem, and can have the advantages of being high in computation speed, high in credibility of solutions, good in actual operability of projects and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Rule processing system
ActiveUS7188091B2Exceeding computational capacity of computingDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsPresent dayUser input
A rule processing apparatus includes modules for defining / entering attributes, enumerations, and / or relationships; packaging the definitions in a reduced canonical form suitable for propositional logic manipulation using zero-suppressed binary decision diagrams (Zdd) to produce a prime Zdd; and / or (iii) executing the rule by applying a series of user inputs to the prime Zdd to determine a result that preferably includes conflict and selection advice to guide the user to satisfaction. Elective events, such as but not limited to the display of messages or the performance of calculations, may optionally be packaged along with the prime rule or components thereof, and presented during execution to help guide the end user to satisfaction or compliancy when choosing among possible selections. The apparatus automates determination of a complex rule having a combinatorial exploded number of rule components, or a combinatorial number of possible outcomes, exceeding computational capacity of present day computing systems.
Owner:MINERAL LASSEN
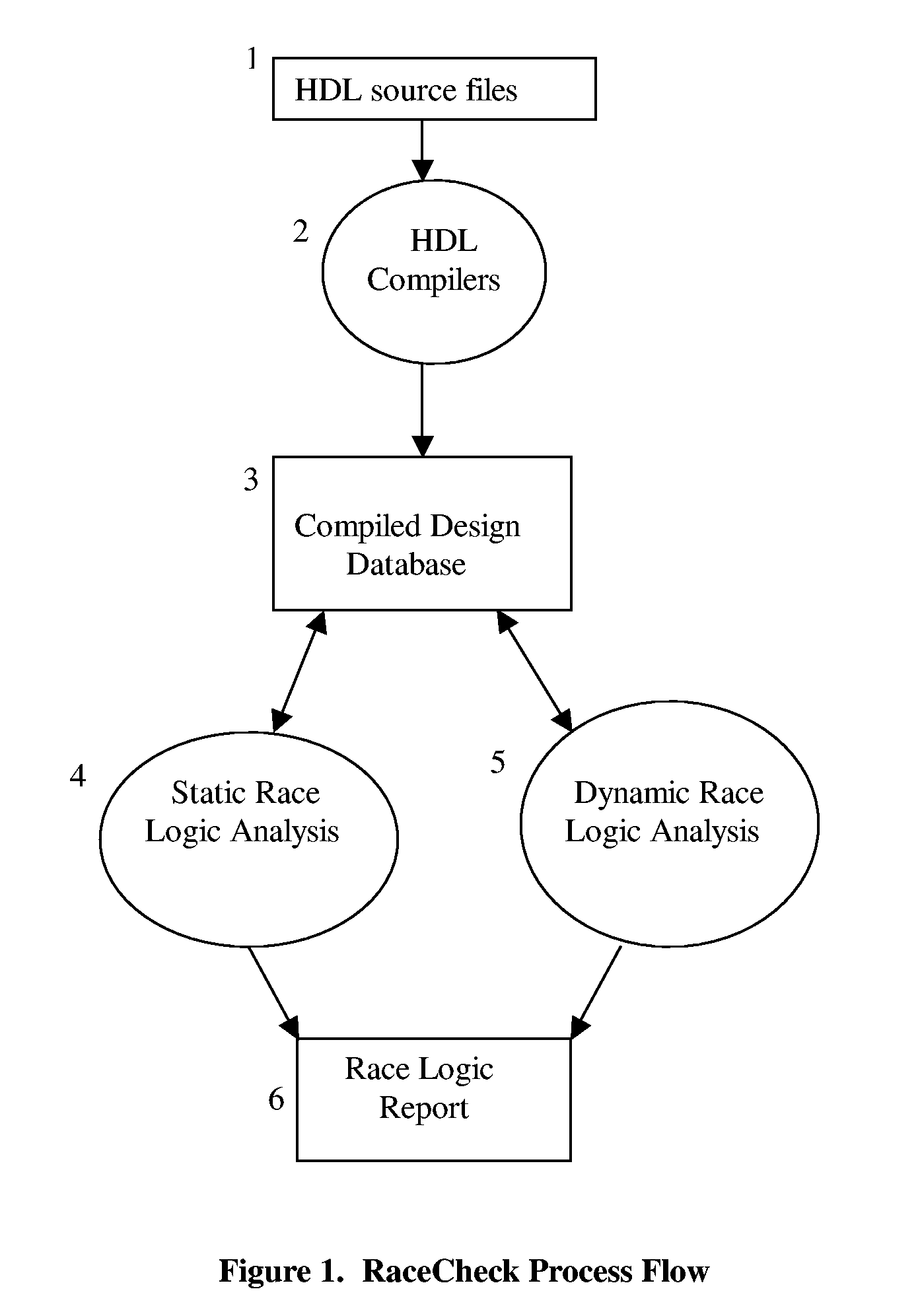
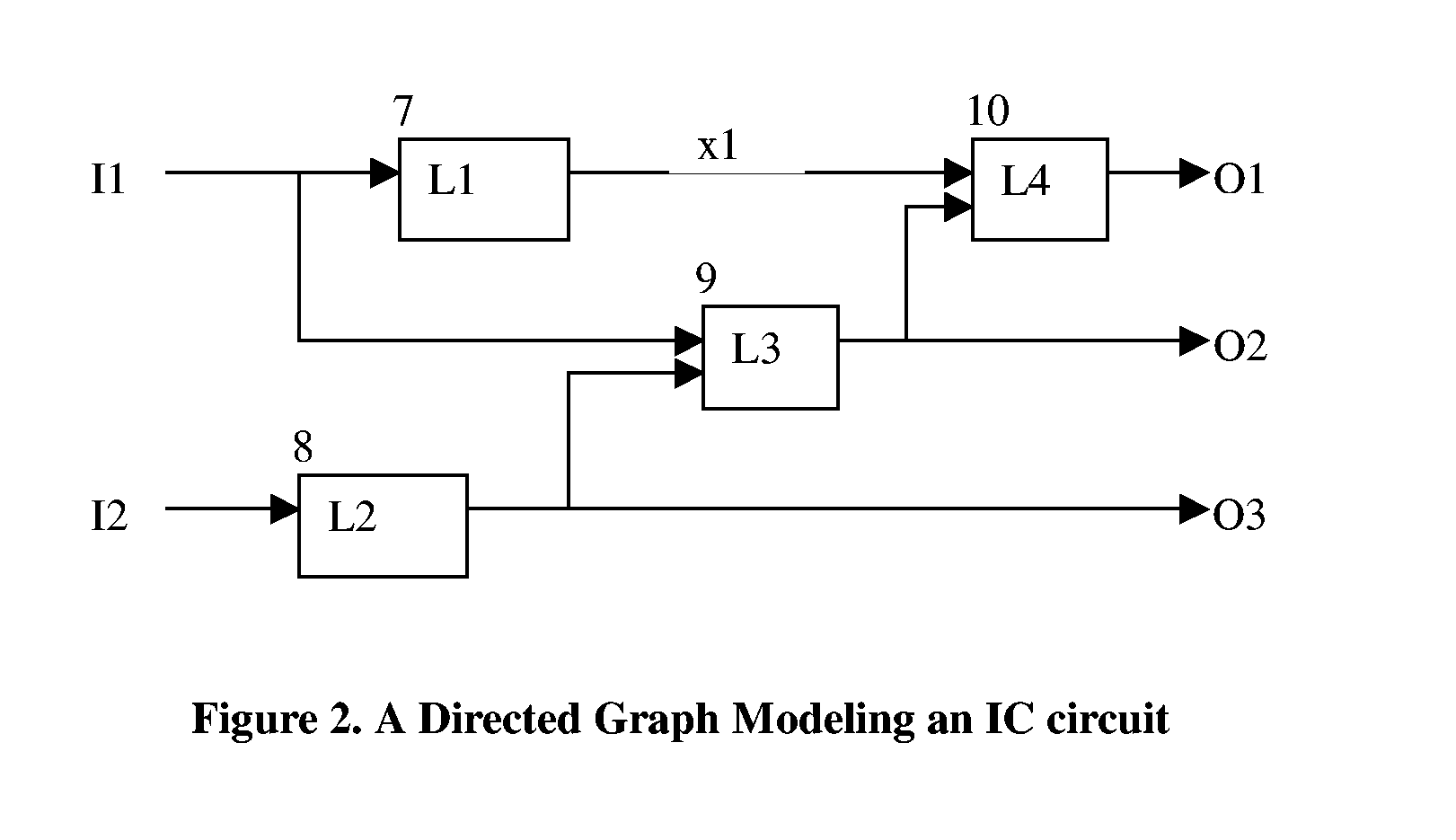
RaceCheck: A Race Logic Ana,yzer Program for Digital Integrated Circuits
ActiveUS20060075367A1Reduce effortShorten the timeElectrical testingDesign optimisation/simulationTime informationSystemC
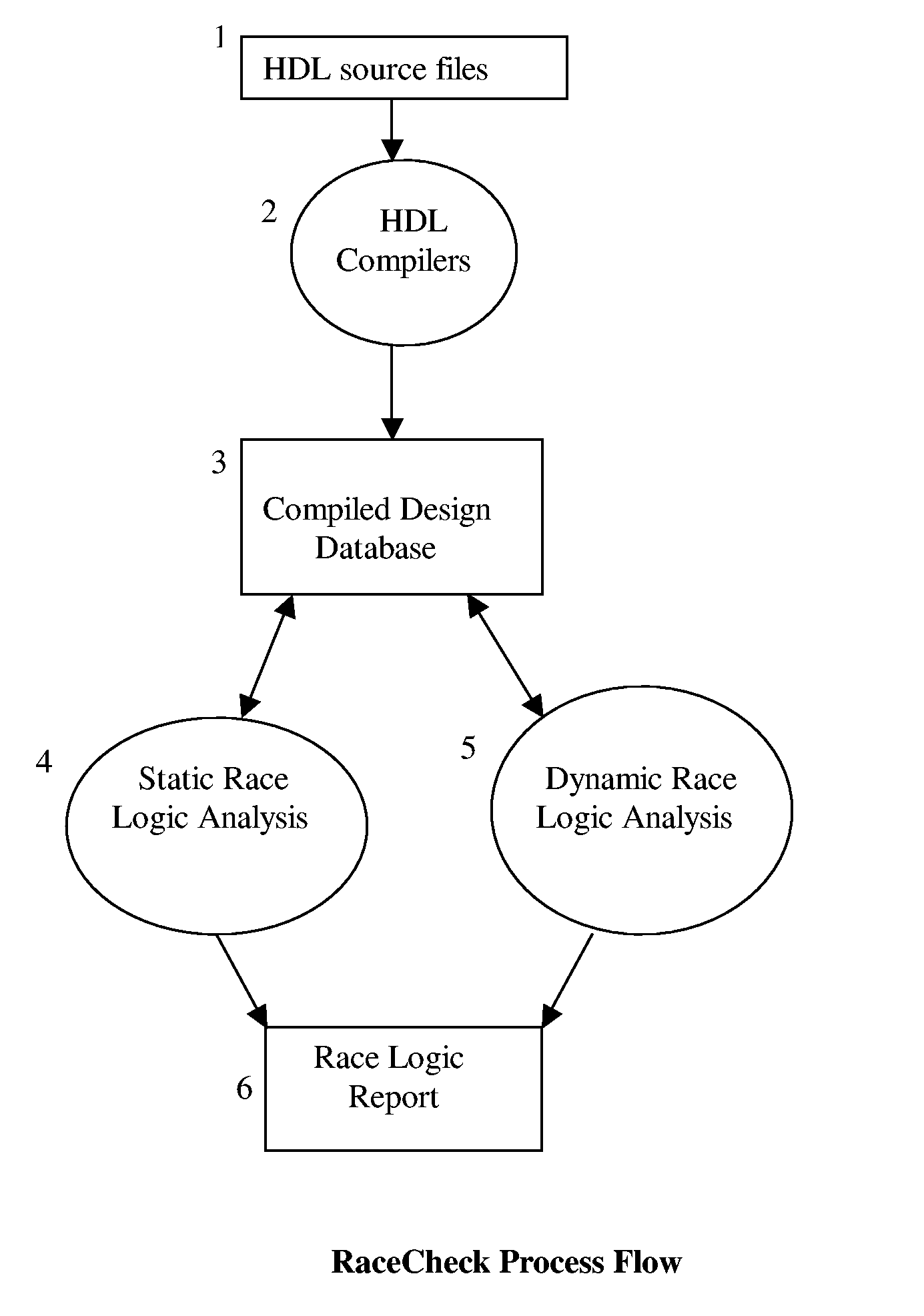
This invention describes a race logic audit program, RaceCheck, which is unique from the prior arts. Specifically, RaceCheck can perform both static and dynamic race logic analysis, and it works with a plurality of hardware description languages (HDL), which include but not limited to: VHDL, Verilog, SystemVerilog, and SystemC. Furthermore, RaceCheck makes use of both structural and timing information of IC designs, as well as binary-decision diagram (BDD) and automatic test pattern generation (ATPG) techniques to derive accurate race logic analysis results with few false violations. Finally, RaceCheck can detect concurrent invocation races of the $random system function, concurrent invocation races of user-defined tasks and functions, zero-delay combination loops, and RaceCheck's dynamic analysis engine uses a HDL simulation kernel to perform timing-accurate race logic analysis. All these aforementioned features are unique for the invention and have not been reported in any prior arts.
Owner:DYNETIX DESIGN SOLUTIONS
Method and system for capturing business rules for automated decision procession
ActiveUS7587379B2Achieve of complexComplex serviceDigital computer detailsKnowledge representationPresent dayUser input
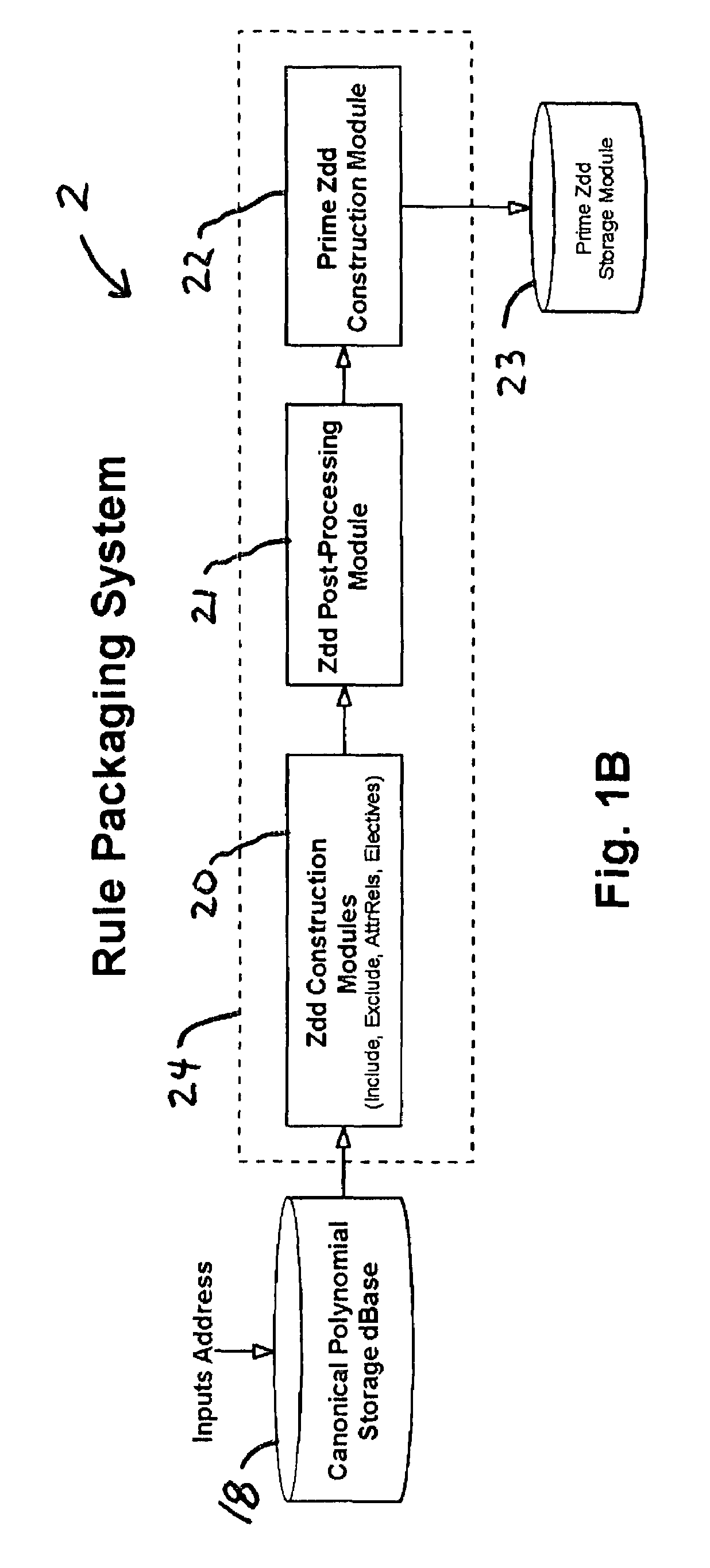
A rule packaging system and method to define and / or package parameters, attributes, enumerations of a prime rule in a reduced canonical form suitable for propositional logic manipulation using, for example, zero-suppressed binary decision diagrams. The reduced form of the prime rule is subsequently used by applying a series of user inputs to determine a result that preferably includes conflict and selection advice to guide the user to satisfaction. Elective events, such as but not limited to the display of messages or the performance of calculations, may optionally be packaged along with the prime rule or components thereof, and presented during execution to help guide an end user to satisfaction or compliancy when choosing among possible configuration parameters. The apparatus automates determination of a complex rule having a combinatorial exploded number of rule components, or a combinatorial number of possible outcomes, exceeding computational capacity of present day computing systems.
Owner:MINERAL LASSEN
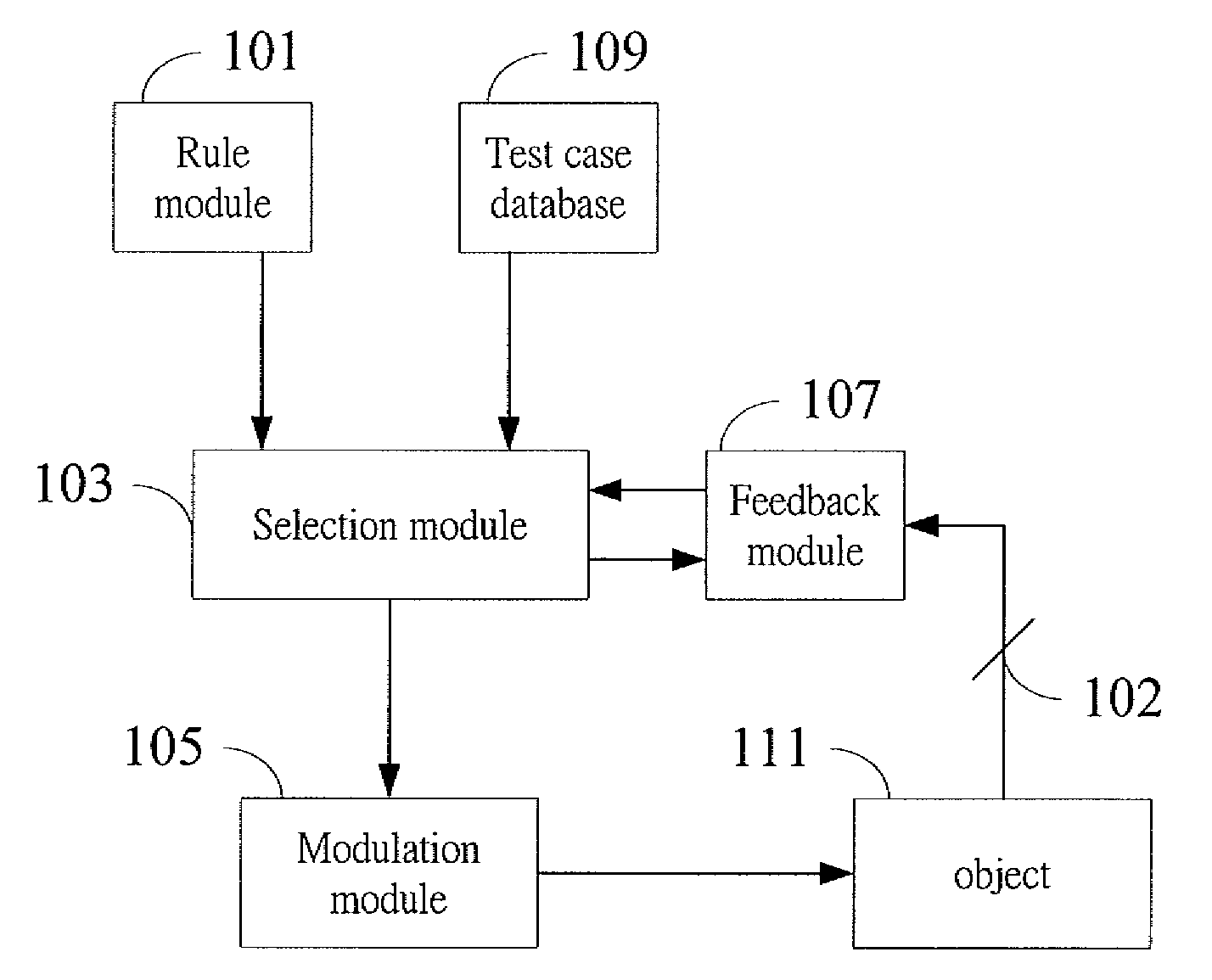
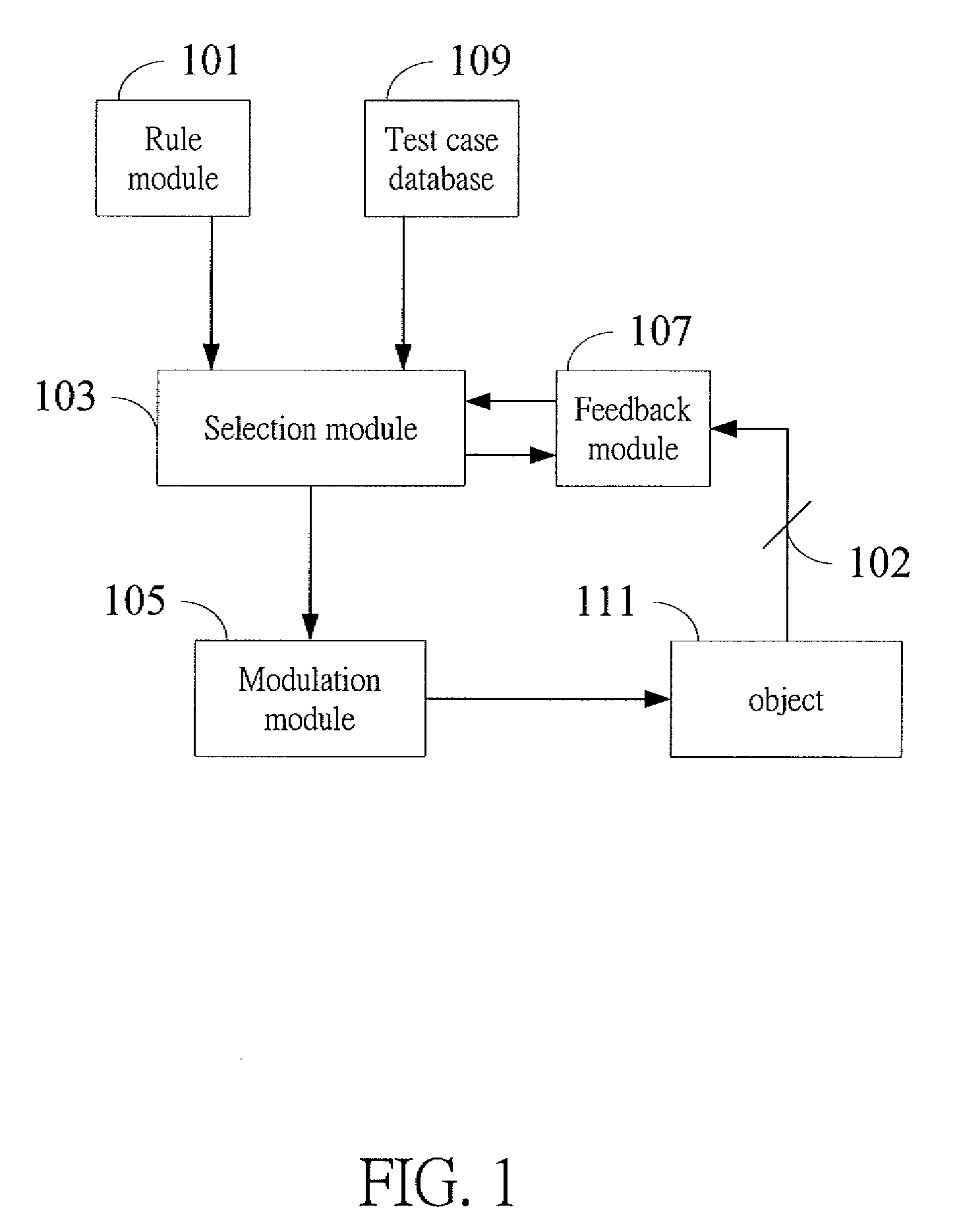
Test device, method, and computer readable medium for deriving a qualified test case plan from a test case database
InactiveUS20080148236A1Software testing/debuggingSpecific program execution arrangementsProgram planningBinary decision diagram
A test device, connecting to a test case database, derives a qualified test case plan from the test case database, a method and a computer readable medium are disclosed. The test device comprises a rule module, a selection module, and a modulation module. The rule module is adapted to setting a plurality of test rules. The selection module is adapted to selecting a proper test case meeting the requirement of a particular test rule, and to selecting proper test case for every test rule. The selection module is also adapted to building a binary decision diagram of the proper test cases. The modulation module is adapted to deriving the qualified test case plan corresponding to the binary decision diagram, wherein the qualified test case plan comprises at least one proper test case.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR INFORMATION INDUSTRY
Method and system for optimized handling of constraints during symbolic simulation
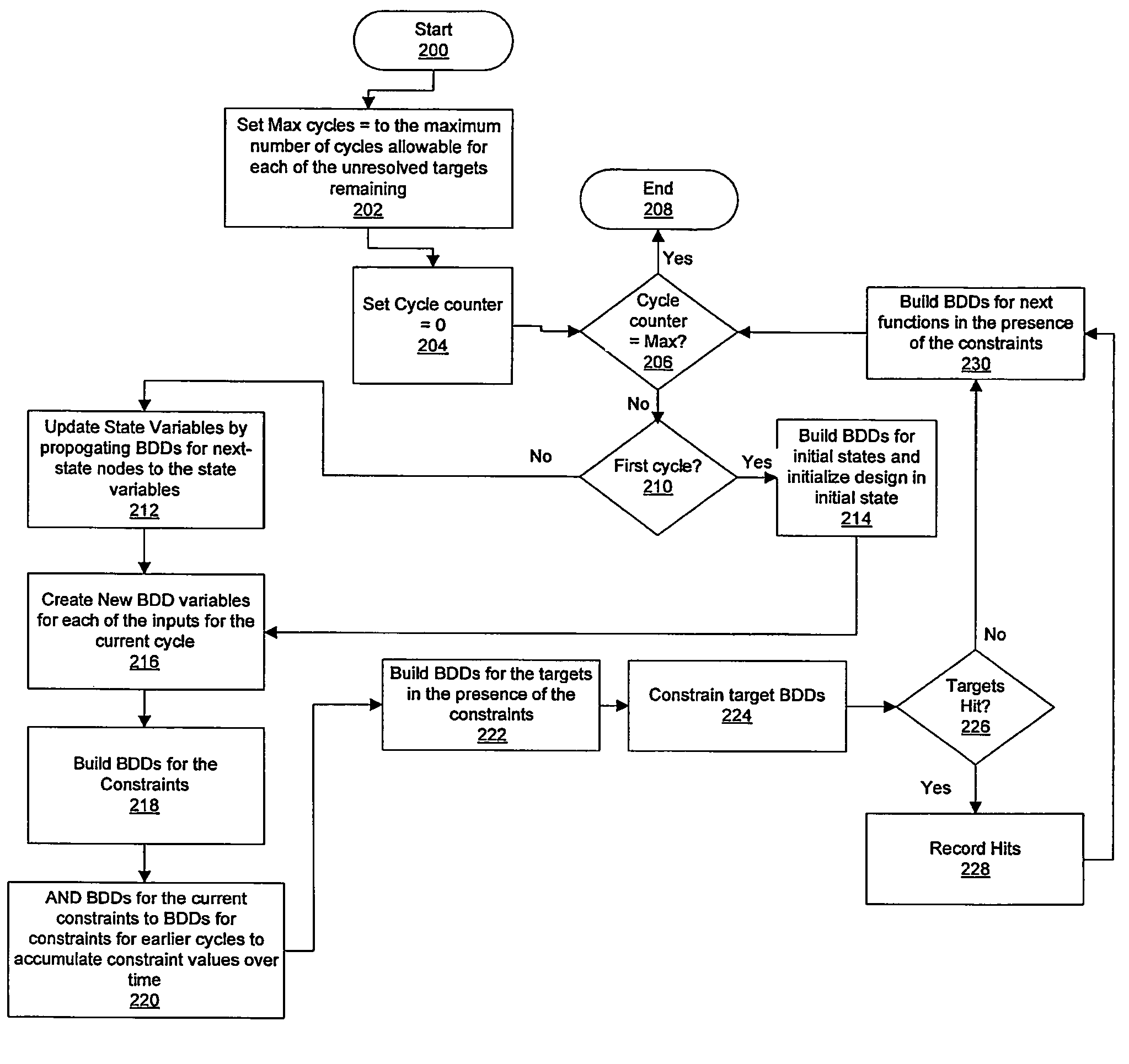
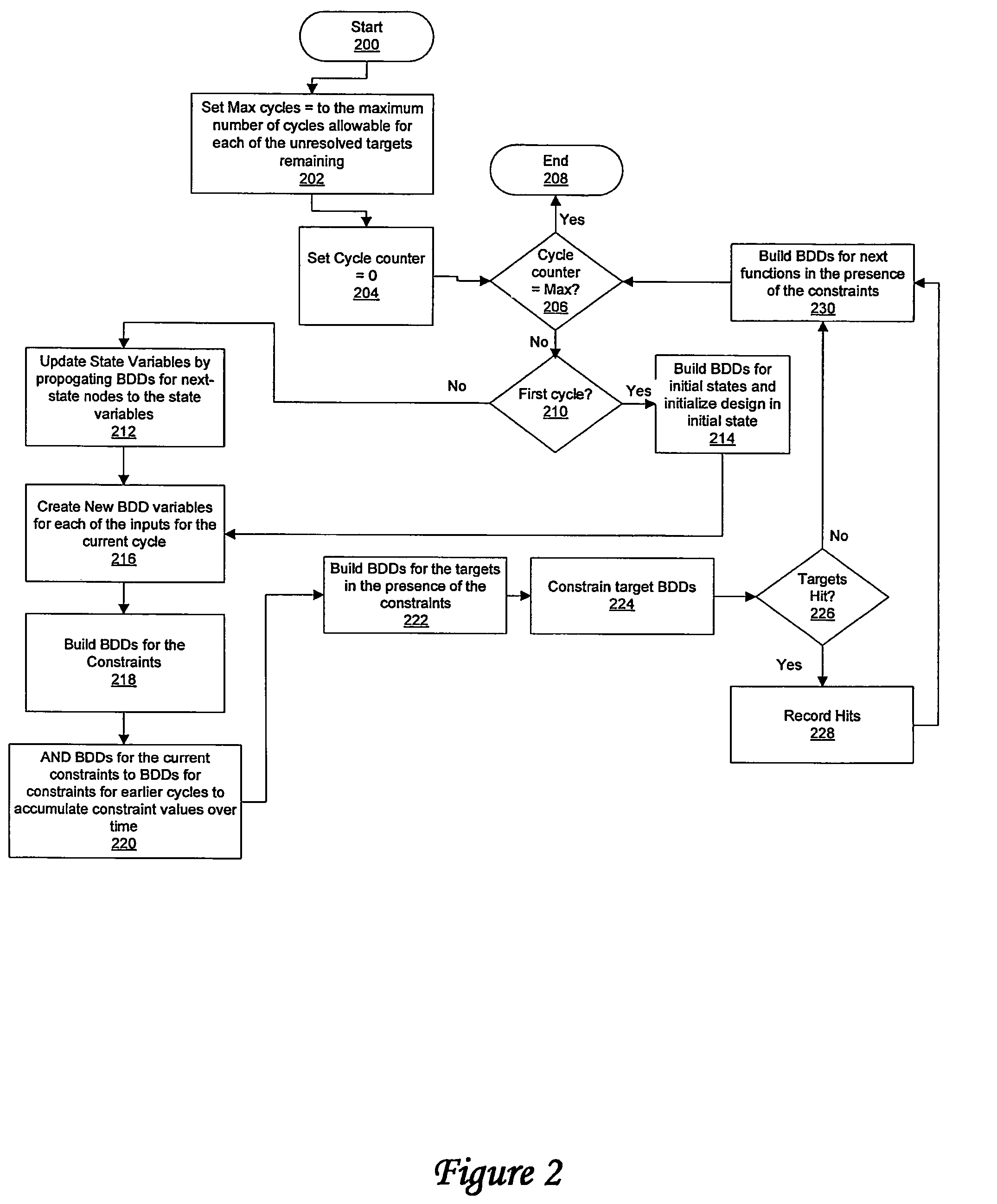
InactiveUS7290229B2Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationSymbolic simulationState variable
A method for verifying a design through symbolic simulation is disclosed. The method comprises creating one or more binary decision diagram variables for one or more inputs in a design containing one or more state variables and building a binary decision diagram for a first node of one or more nodes of the design. A binary decision diagram for the initial state function of one or more state variables of the design is generated and the design is subsequently initialized. Binary decisions diagrams for one or more constraints are synthesized. A set of constraint values is accumulated over time by combining the binary decision diagrams for the one or more constraints with a set of previously generated binary decision diagrams for a set of constraints previously used in one or more previous time-steps. A binary decision diagram for the next state function of the one or more state variables in the design is constructed in the presence of the constraints. The one or more state variables in the design are updated by propagating the binary decision diagram for the next state function to the one or more state variables and a set of binary decision diagrams for the one or more targets in the presence of the one or more constraints is calculated. The set of binary decision diagrams for one or more targets is constrained and the design is verified by determining whether the one or more targets were hit.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Local minimization ROBDD (reduced ordered binary decision diagram) and area delay optimization based process mapping method
ActiveCN103885771AReduce areaLower latencySpecific program execution arrangementsNODALLogic optimization
The invention discloses a local minimization ROBDD (reduced ordered binary decision diagram) and area delay optimization based process mapping method. The process mapping method includes: generating partial optional partitions through domain nodes of the ROBDD, and loosening node delay on non-critical paths to optimize area. For a logical optimization part, shared data structure of a minimization Local ROBDD is adopted, circuit decomposition efficiency is improved by the aid of domain nodes and operation of the ROBDD, and waste of time and memory due to the fact that all the optional partitions are enumerated is avoided; for a structure optimization part, the idea that a classical algorithm Flowmap is used for delay tag minimization of the nodes of a circuit is improved, min-height min-cost coverage is performed in critical paths, and min-cost coverage is performed in the non-critical paths. The shortcomings of mutual restriction of inefficiency as well as delay with the area of all the generated optional partitions are overcome, requirements of a field-programmable device chip on input number of LUTs (look up table) are met, and the objectives of circuit area and delay optimization can be achieved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method and device for dynamically evaluating reliability of network
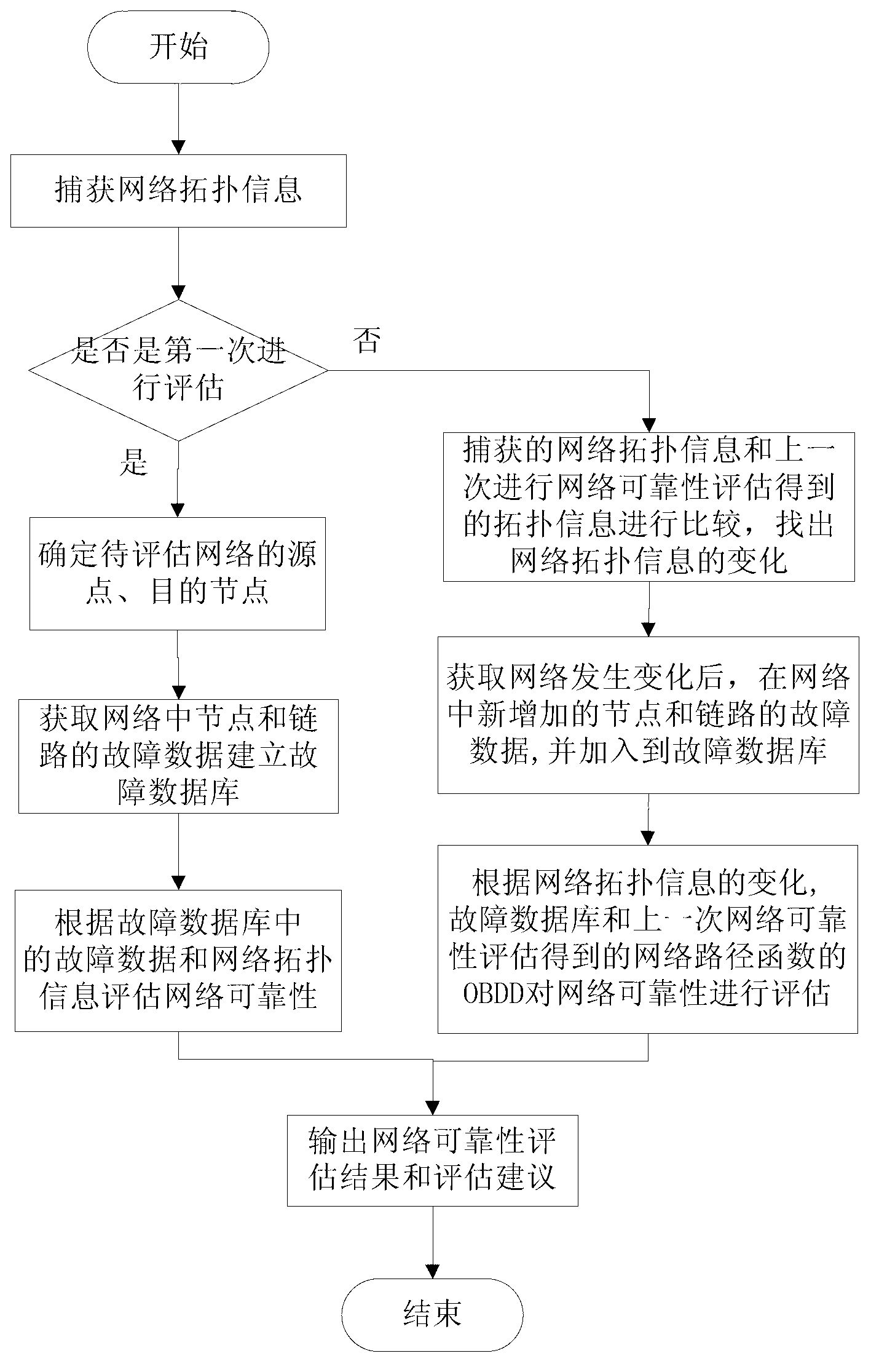
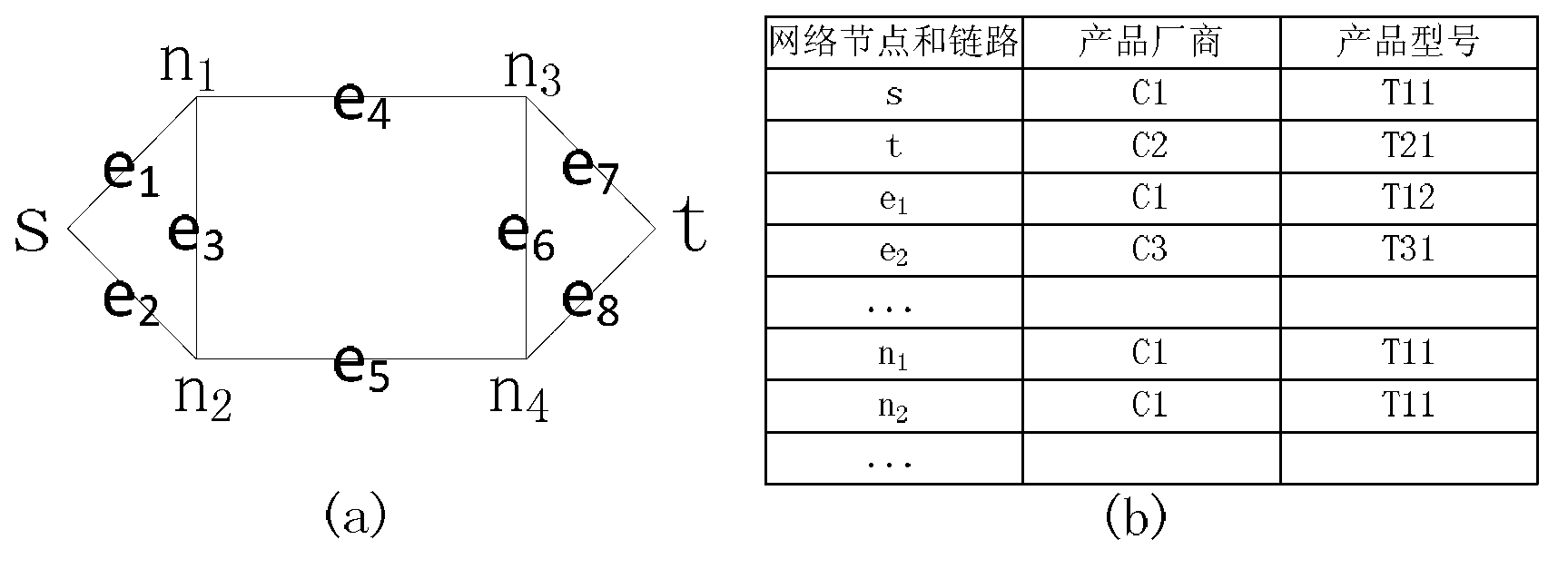
ActiveCN102801568AAccurate assessment of reliabilityEfficient dynamic evaluationData switching networksEvaluation resultBinary decision diagram
The invention relates to a method and a device for dynamically evaluating the reliability of a network. The method comprises the following steps: I, capturing network topological information; II, judging whether the first evaluation is carried out, executing the step III if yes, and executing the step VI if no; III, determining a source point and a targe node of the network to be evaluated; IV, acquiring network fault data and creating a database; V, obtaining a network path function OBDD (Ordered Binary Decision Diagram), evaluating the reliability of the network by an OBDD-based side expansion algorithm and entering the step IX; VI, searching the variation of the network topological information; VII, acquiring newly increased fault data and inputting the newly increased fault data into the database; VIII, evaluating the reliability of the network by the network path function OBDD obtained in the last evaluation process and an OBDD-based dynamic evaluation algorithm; and IX, outputting a network reliability evaluation result and an evaluation suggestion. The device comprises a topological analysis unit, a fault data acquisition unit and a reliability dynamic evaluation unit. The method and the device are suitable for the network which is dynamically changed and can be used for rapidly and efficiently evaluating the reliability of the network; and the repeated calculation is avoided and the efficiency is improved. The method and the device are suitable for various network systems.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
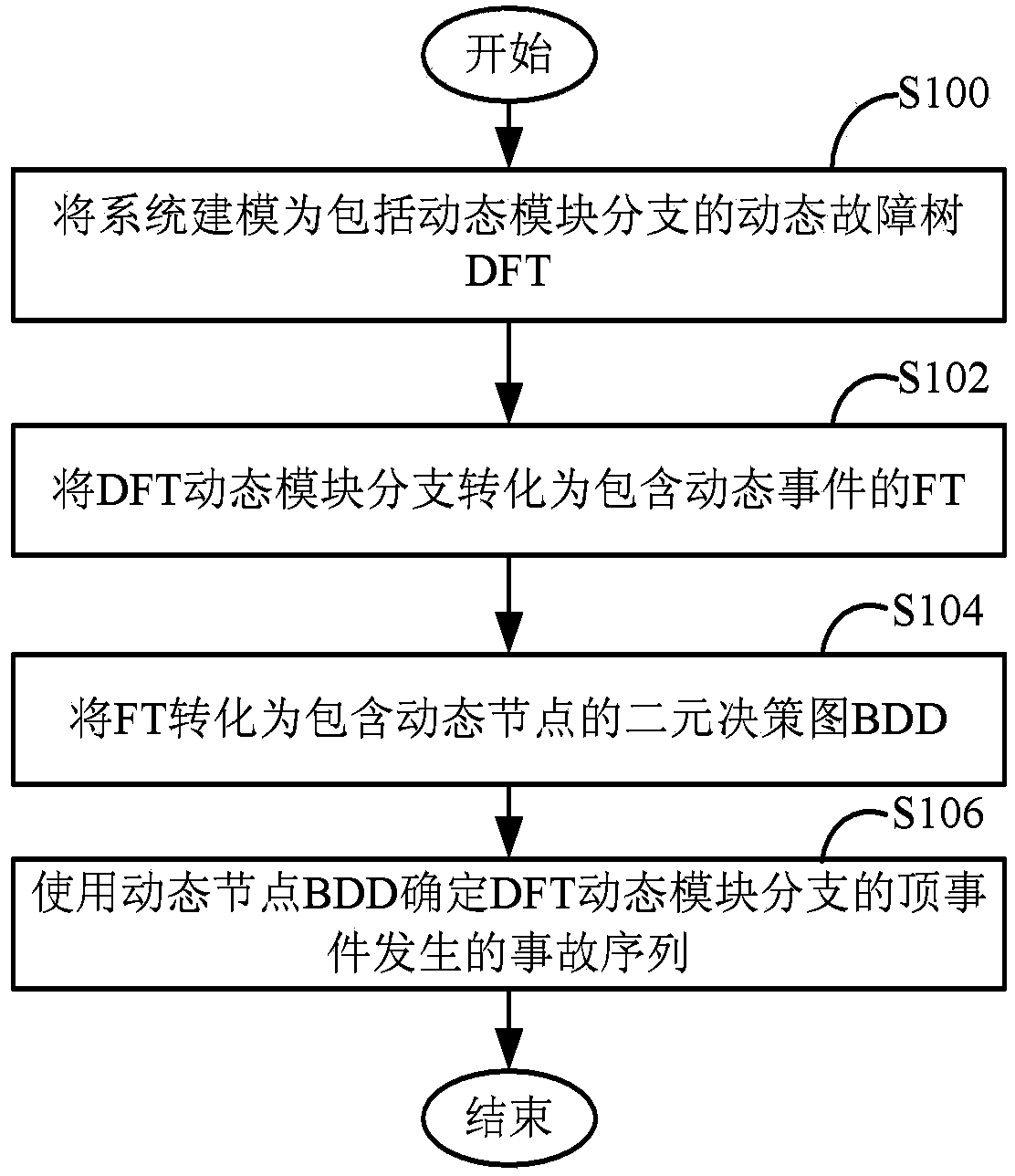
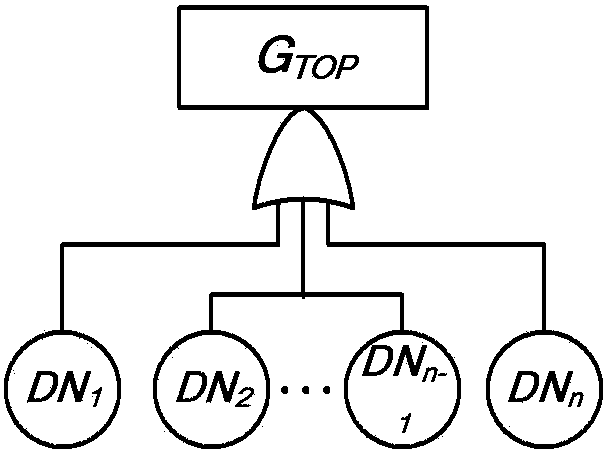
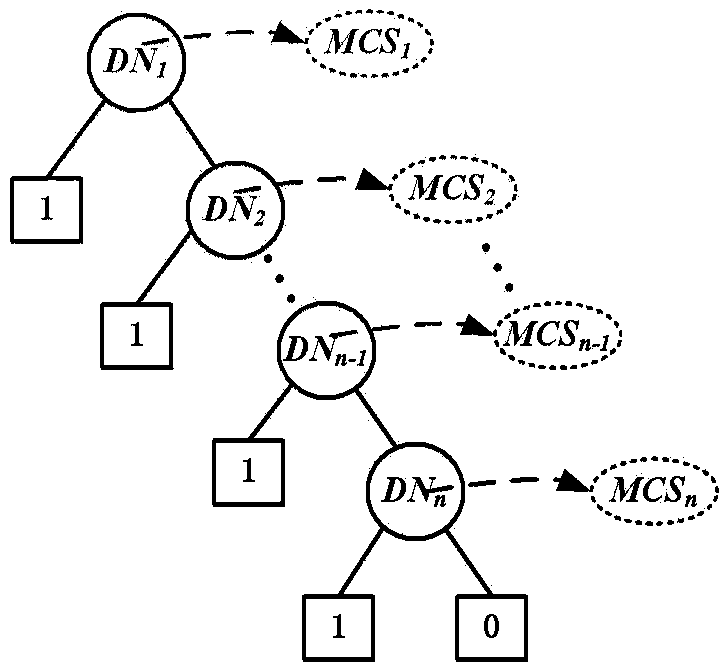
System reliability assessment method and device based on DFT qualitative and quantitative analysis
An example embodiment in the invention provides a safety system reliability assessment method and device for nuclear power plants and the like, so that system-level DFT can be qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed quickly, accurate qualitative and quantitative analysis results can be given, and reparable or unreparable system can be analyzed. In the qualitative analysis, the system is modeled to be a dynamic fault tree DFT comprising dynamic module branches; the DFT dynamic module branches are converted into FT comprising dynamic events; the FT is converted into a binary decision diagram BDD comprising dynamic nodes; and the dynamic node BDD is utilized to determine accident sequence of top events of the DFT dynamic module branches, with the accident sequence being as qualitative information for system reliability assessment. In the quantitative analysis, a numerical integration method based on dynamic module level MCS is provided; and on the basis of independent random variables and by means of part sequence failure diagrams, an integration expression of a common module level MCS is educed and quantitative calculation is carried out.
Owner:STATE POWER INVESTMENT CORP RES INST
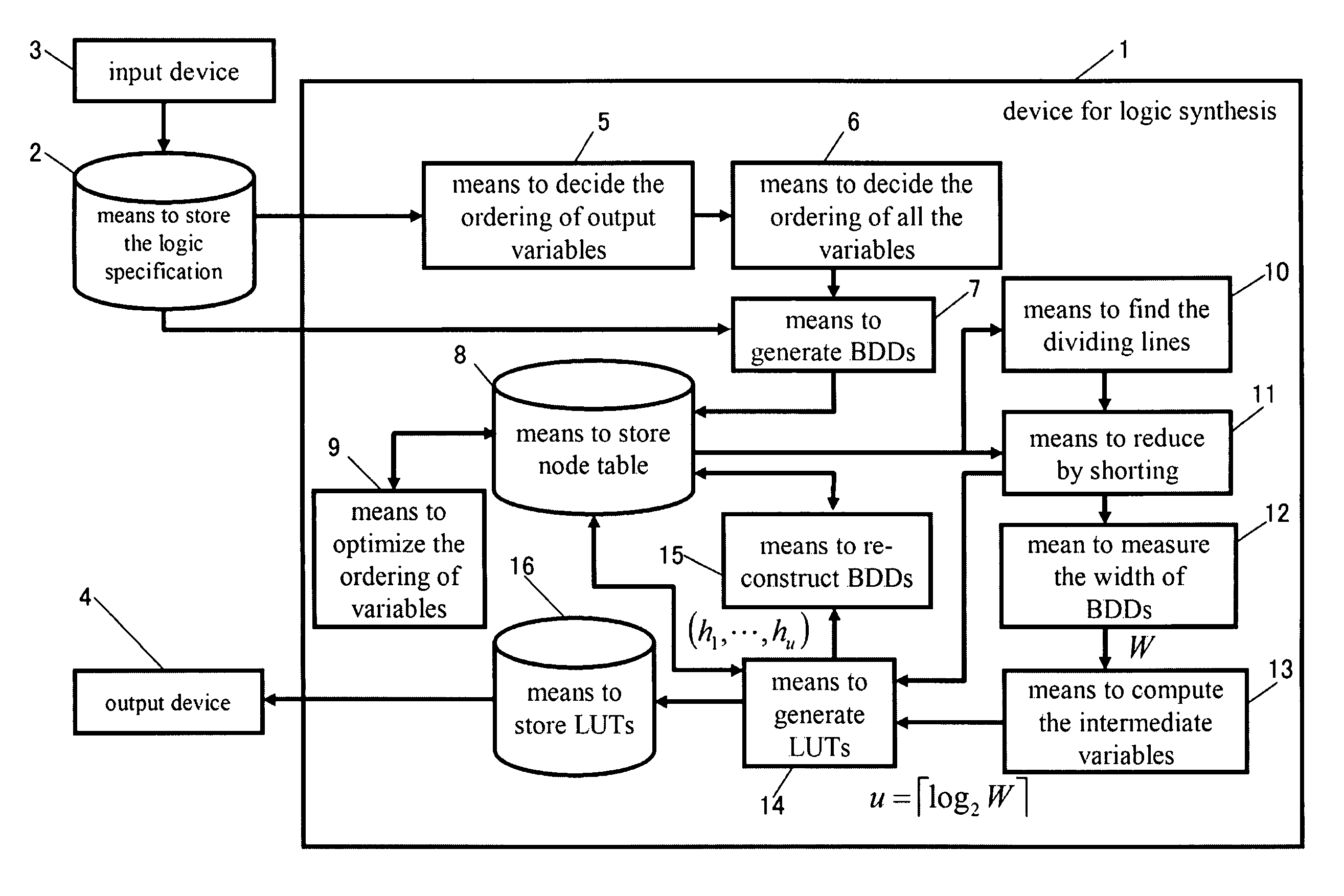
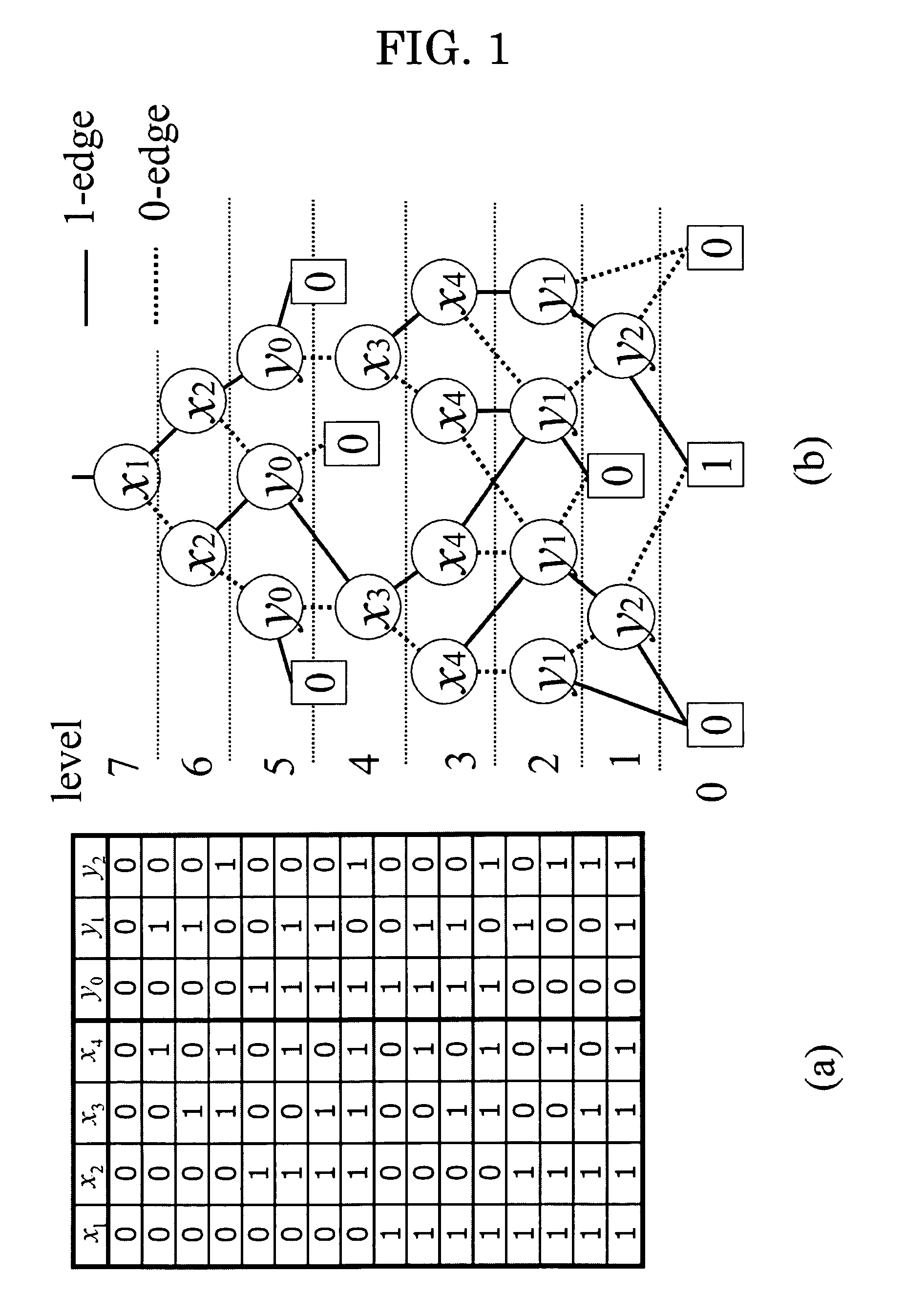
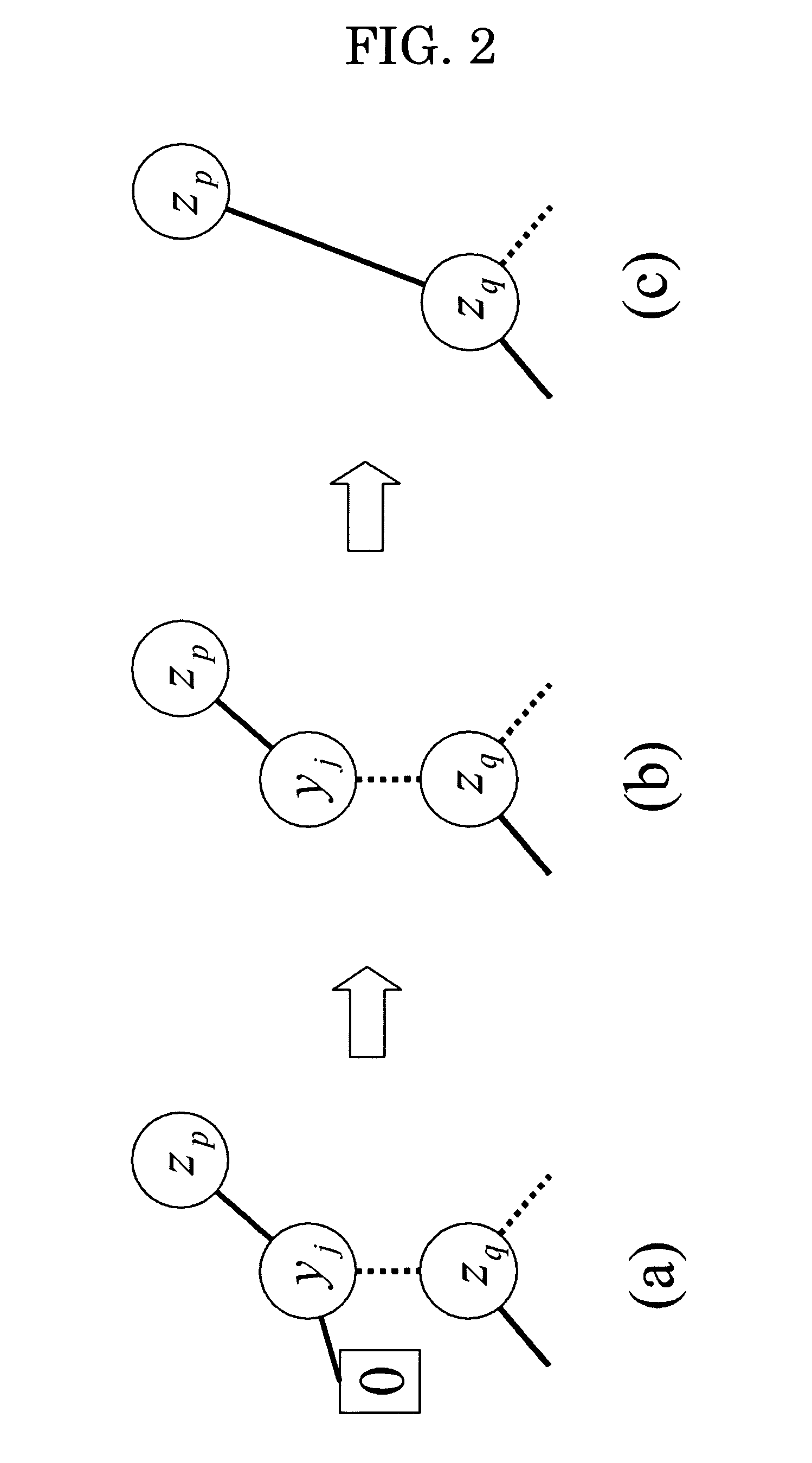
Device for reducing the width of graph and a method to reduce the width of graph, and a device for logic synthesis and a method for logic synthesis
InactiveUS7844924B2Reduce widthLower-capacity memoryCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationGraphicsBinary decision diagram
A device for logic synthesis that can be used to synthesize LUT logic circuit having intermediate outputs for multiple-output logic functions. The device includes means to store node table 8 storing Binary Decision Diagram for Characteristic Function (BDD_for_CF) of the characteristic function χ(X, Y) of the multiple-output logic function f(X), means to store LUTs 16, means to reduce by shorting 11 partitioning BDD_for_CF into the subgraphs B0 and B1 at the partition line in the height lev of the partition and executing shorten-processing, means to measure the width W of BDDs 12 calculating the width W at the partition line, means to compute the intermediate variables 13 calculating the number of the intermediate variables u according to the width W, means to generate an LUT 14 generating the LUT for the sub-graph B0, and means to reconstruct BDDs 15 generating a binary tree that has the same number of control inputs as that of the intermediate variables u, replacing the sub-graph B0 with the binary tree and reconstructing the BDD_for_CF.
Owner:KITAKYUSHU FOUND FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF IND SCI & TECH
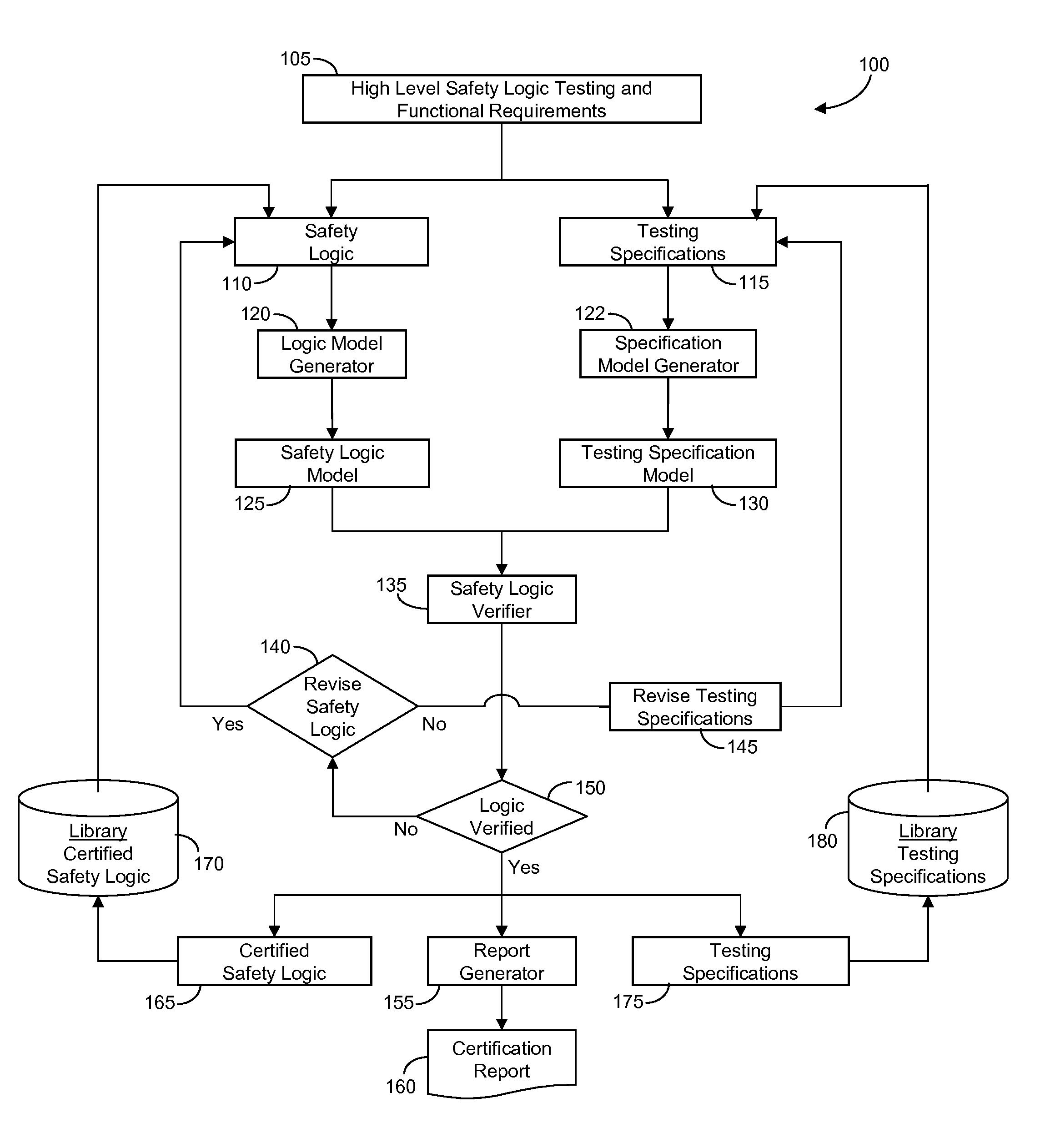
Method and system for formal safety verification of manufacturing automation systems
InactiveUS20110125302A1Shorten development timeReduce verification costsSafety arrangmentsSoftware testing/debuggingBinary decision diagramTest specification
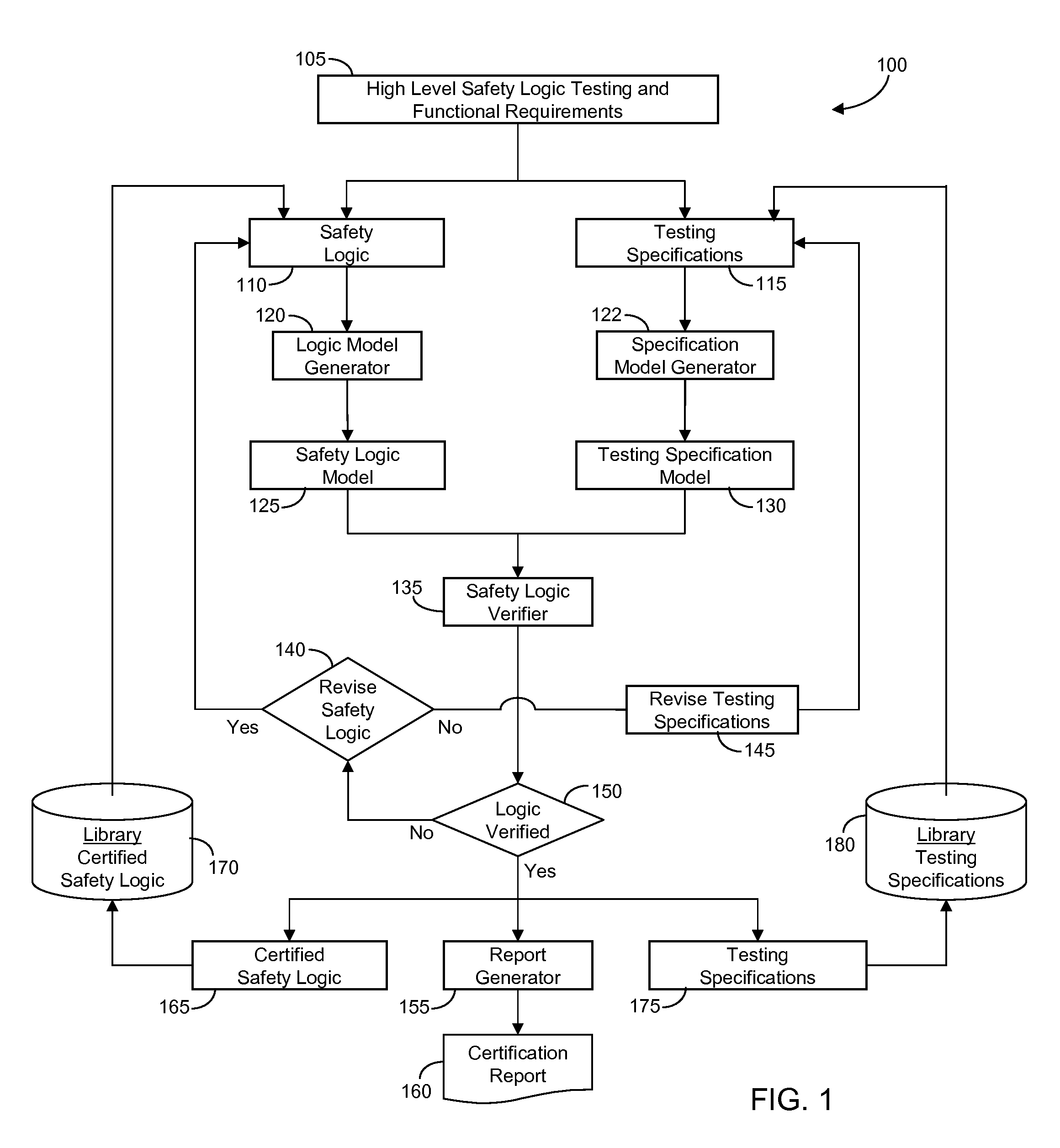
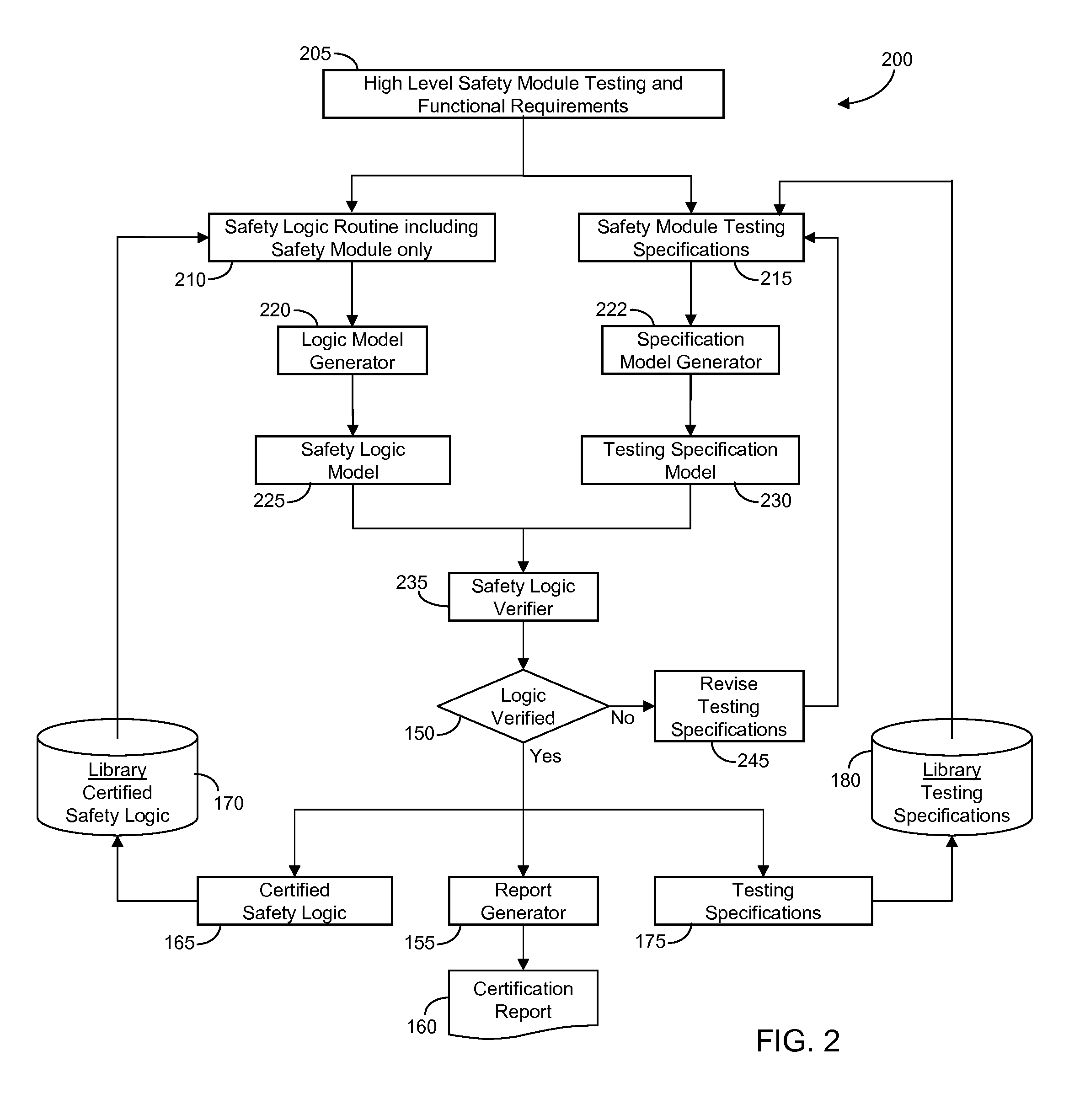
A method and system is provided for verifying and certifying the safety logic of a manufacturing automation system including safety logic, where the logic may include one or more safety modules, routines, programs and tasks or a combination thereof; testing specifications corresponding to the safety logic; one or more formal model generators adapted for automatically transforming the safety logic and testing specifications through a logic parser into their respective mathematical models, formatted for example, as a Petri-net or binary decision diagram; a safety logic verifier configured for automatically comparing the safety logic formal model against the testing specification formal model to verify the safety logic model for the purpose of certifying the safety logic. The testing specifications may include testing of safety logic behavior including reaching safe state, remaining in safe state without reset, recovering from safe state with reset and remaining active with false alarm detection.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method and System for Conjunctive BDD Building and Variable Quantification Using Case-Splitting
InactiveUS20080282207A1Reduce in quantityAnalogue computers for electric apparatusDetecting faulty computer hardwareDecision graphBinary decision diagram
A method, apparatus and computer-readable medium for conjunctive binary decision diagram building and variable quantification using case-splitting are presented. A BDD building program builds a BDD for at least one node in a netlist graph representation of a circuit design. One or more variables are selected for case-splitting. The variable is set to a constant logical value and then the other. A BDD is built for each case. The program determines whether the variable is scheduled to be quantified out. If so, the program combines the BDDs for each case according to whether the quantification is existential or universal. If the variable is not scheduled to be quantified, the program combines the BDDs for each case so that the variable is introduced back into the resulting BDD, which has a reduced number of peak live nodes.
Owner:IBM CORP
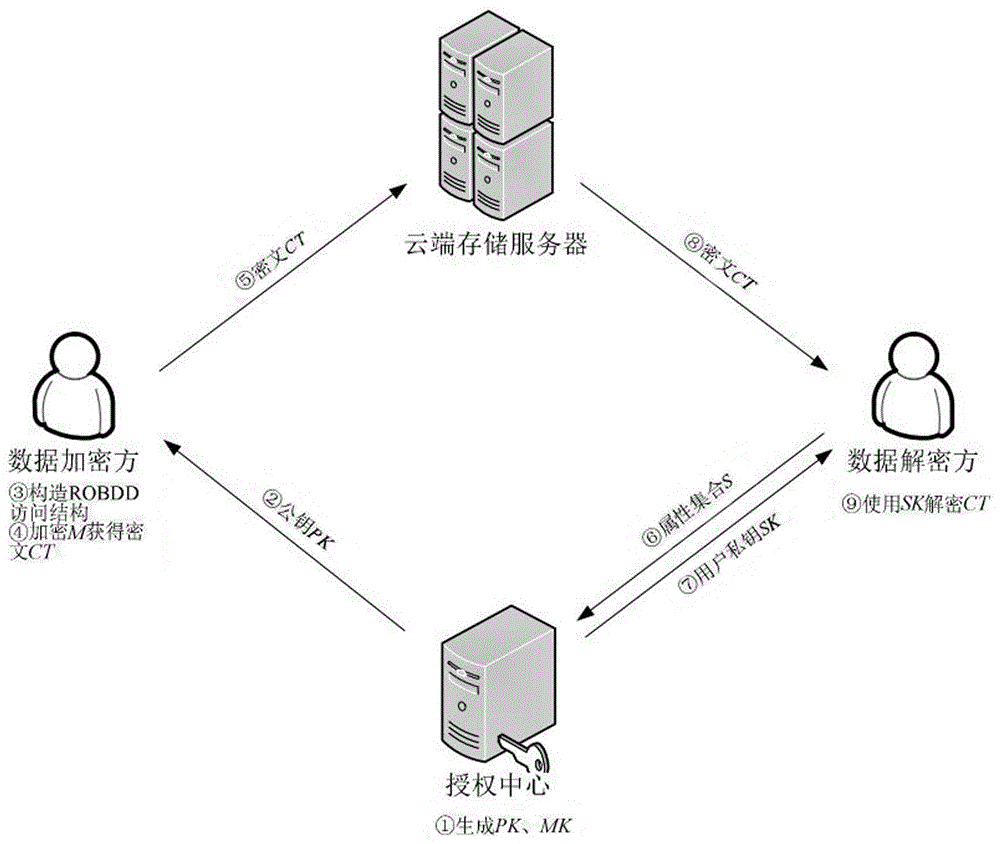
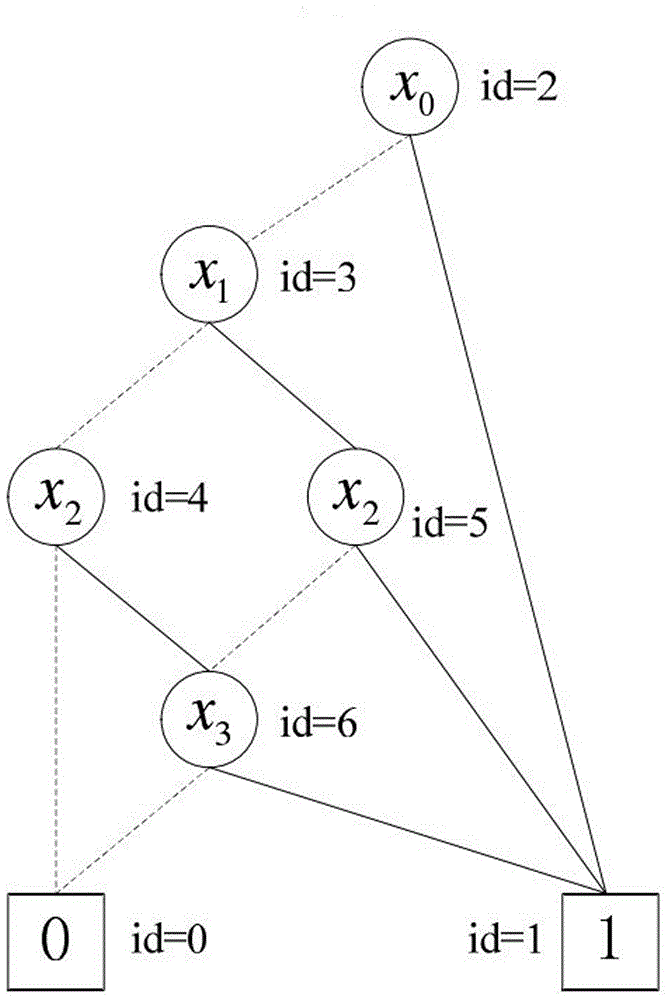
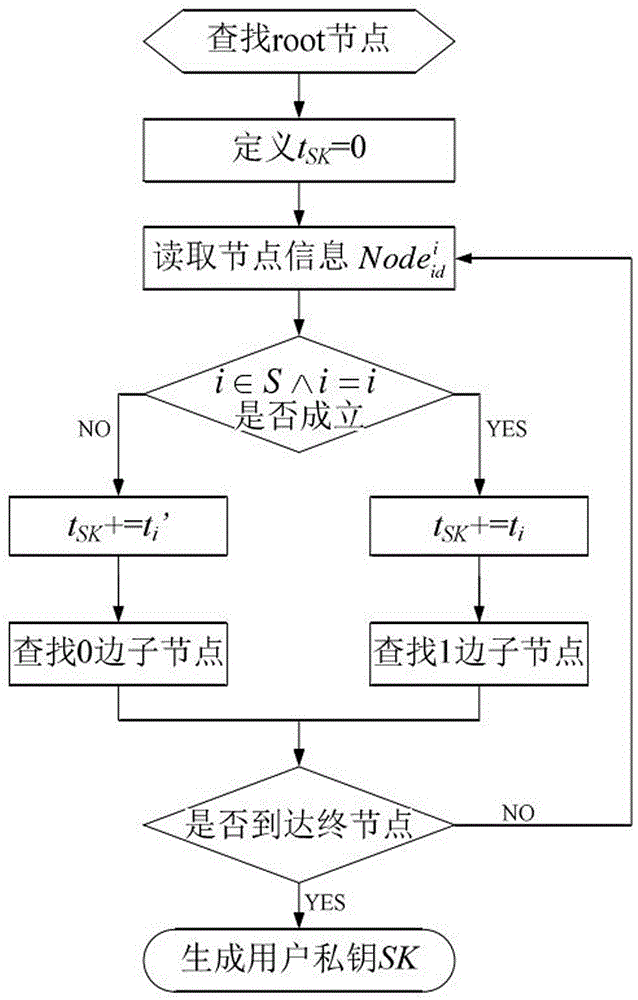
Private key fixed-length ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryption method
ActiveCN106850224AEnhance expressive abilityQuick decryptionPublic key for secure communicationPlaintextCiphertext
The invention discloses a private key fixed-length ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryption method. The method comprises two parts of core content of an access structure based on a simplified ordering binary decision diagram and a ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryption method based on the access structure, and implementation of the two parts of the content mainly comprises four entities of a data encryption party, a data decryption party, an authorization center and a cloud storage server; the implementation process comprises the following four steps of 1 system establishment, 2 plaintext encryption (including construction of the access structure), 3 private key generation and 4 ciphertext decryption. The access structure included in the technical scheme can support access policies represented by any Boolean expressions, and the higher working capacity and the higher working efficiency are achieved; the encryption method in the technical scheme has the advantages of being high in access structure working performance, extremely small in user private key occupied space, fixed in length, capable of achieving rapid decryption and the like, and the overall performance is more flexible and efficient.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Circuit verification
InactiveUS7028279B2Reduce and eliminate disadvantageReduce and eliminate and problemElectronic circuit testingComputer aided designBinary decision diagramState space
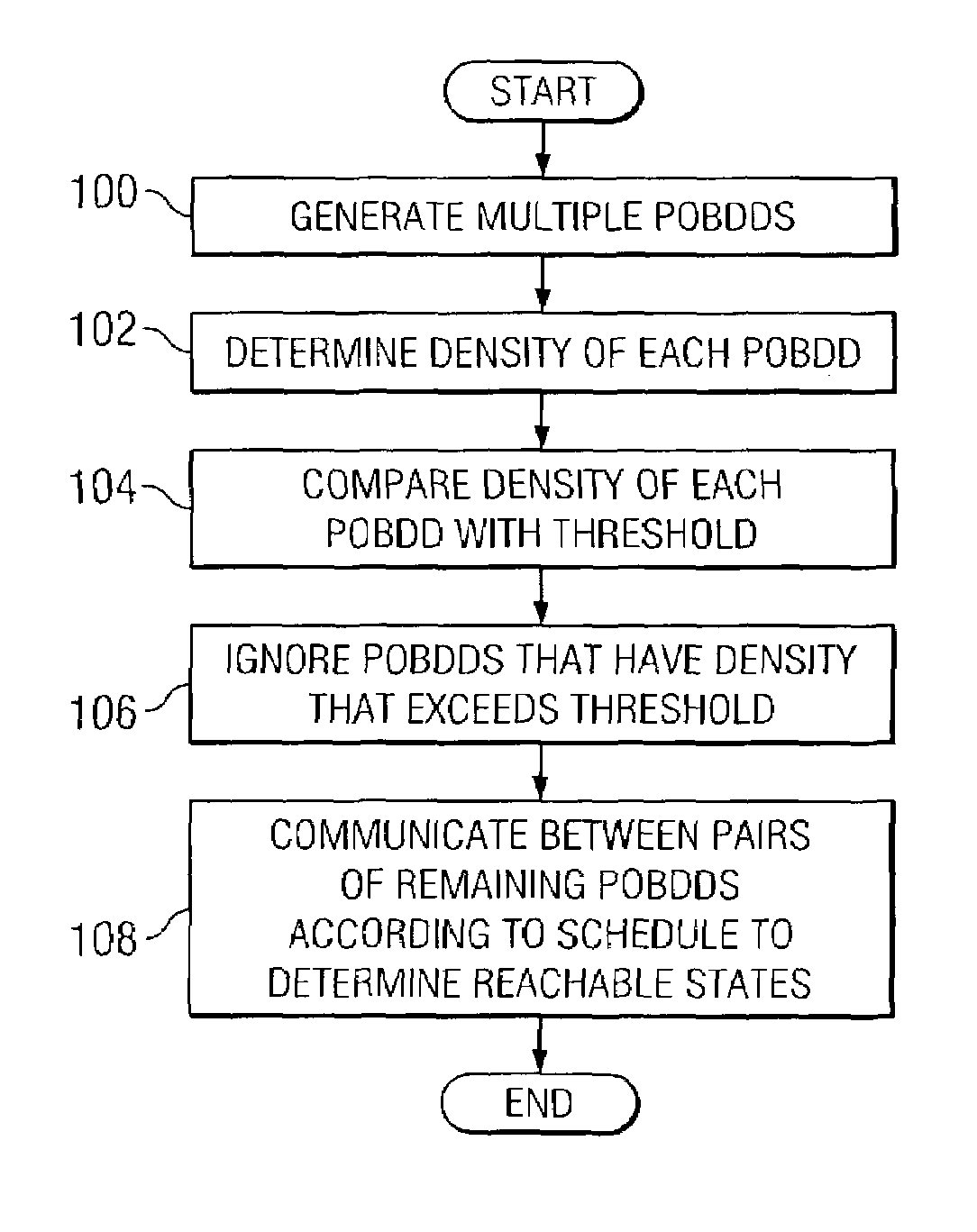
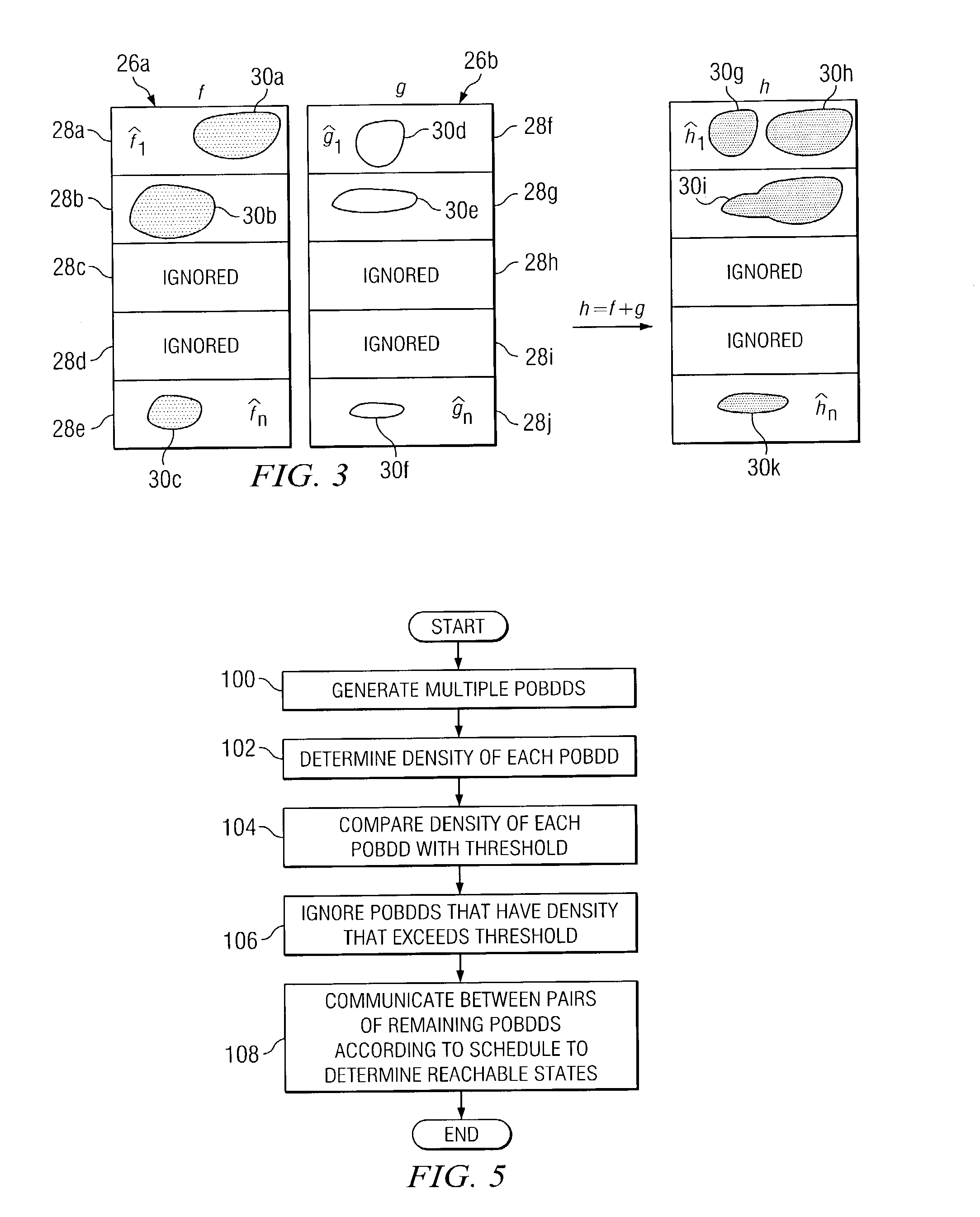
In one embodiment, a system for verifying a circuit using a scheduling technique includes one or more partitioned ordered binary decision diagram (POBDD) modules that collectively generate one or more POBDDs. Each POBDD corresponds to one or more partitions of a state space of the circuit and includes a number of states and a number of nodes in the partition. The system also includes one or more cost metrics modules that collectively determine a processing cost of each of the partitions of each of the POBDDs. The system also includes one or more scheduling modules that collectively schedule processing of the partitions of the POBDDs for semiformal verification of a circuit. The schedule is based, at least in part, on the determined processing costs of the partitions of the POBDDs.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method and system for building binary decision diagrams efficiently in a structural network representation of a digital circuit
ActiveUS7340473B2Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalDepth-first searchDynamic resource
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
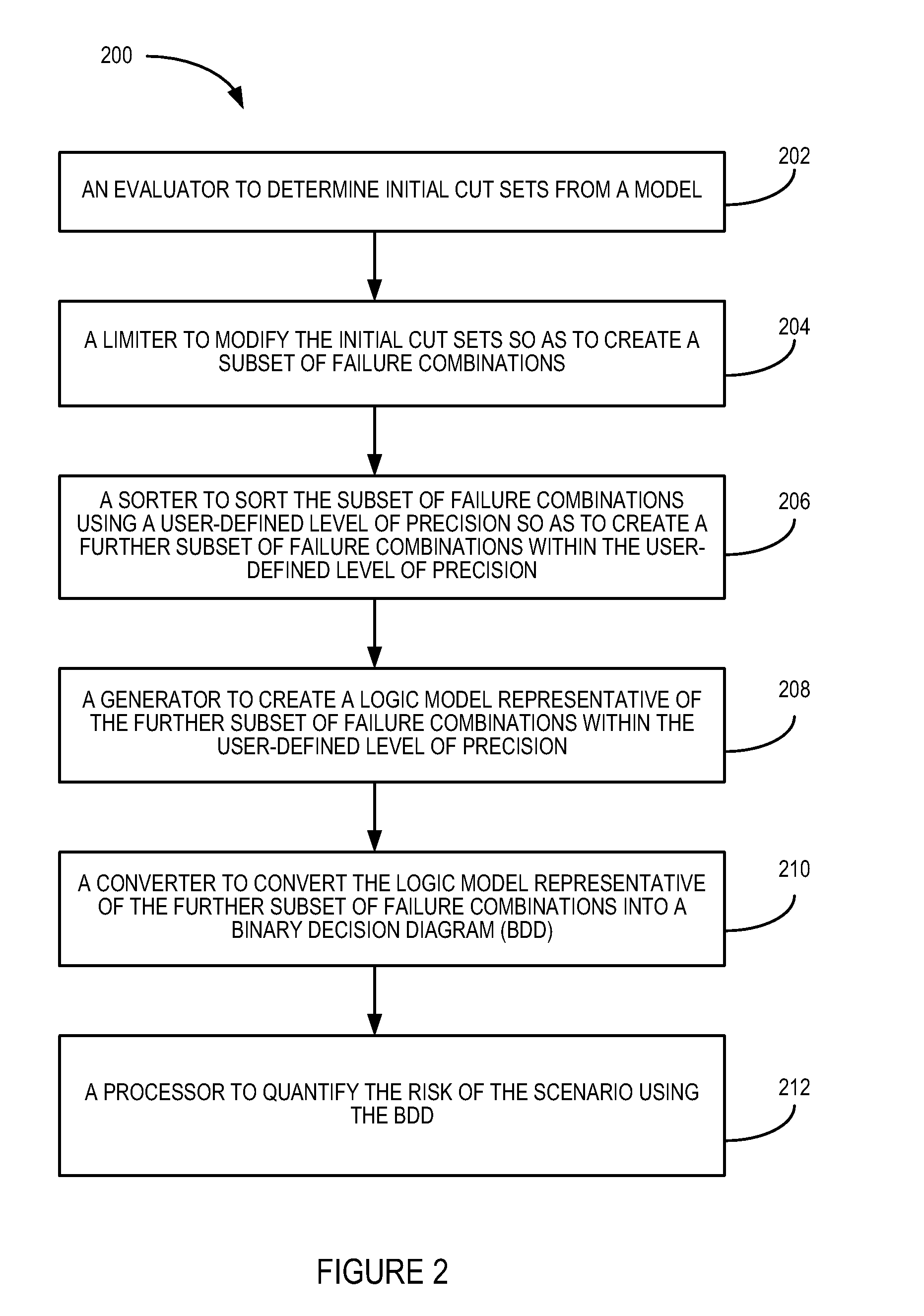
Hybrid assessment tool, and systems and methods of quantifying risk
InactiveUS20080010230A1Improve realismQuantifying the risk for the scenarioKnowledge representationSpecial data processing applicationsBinary decision diagramModel transformation
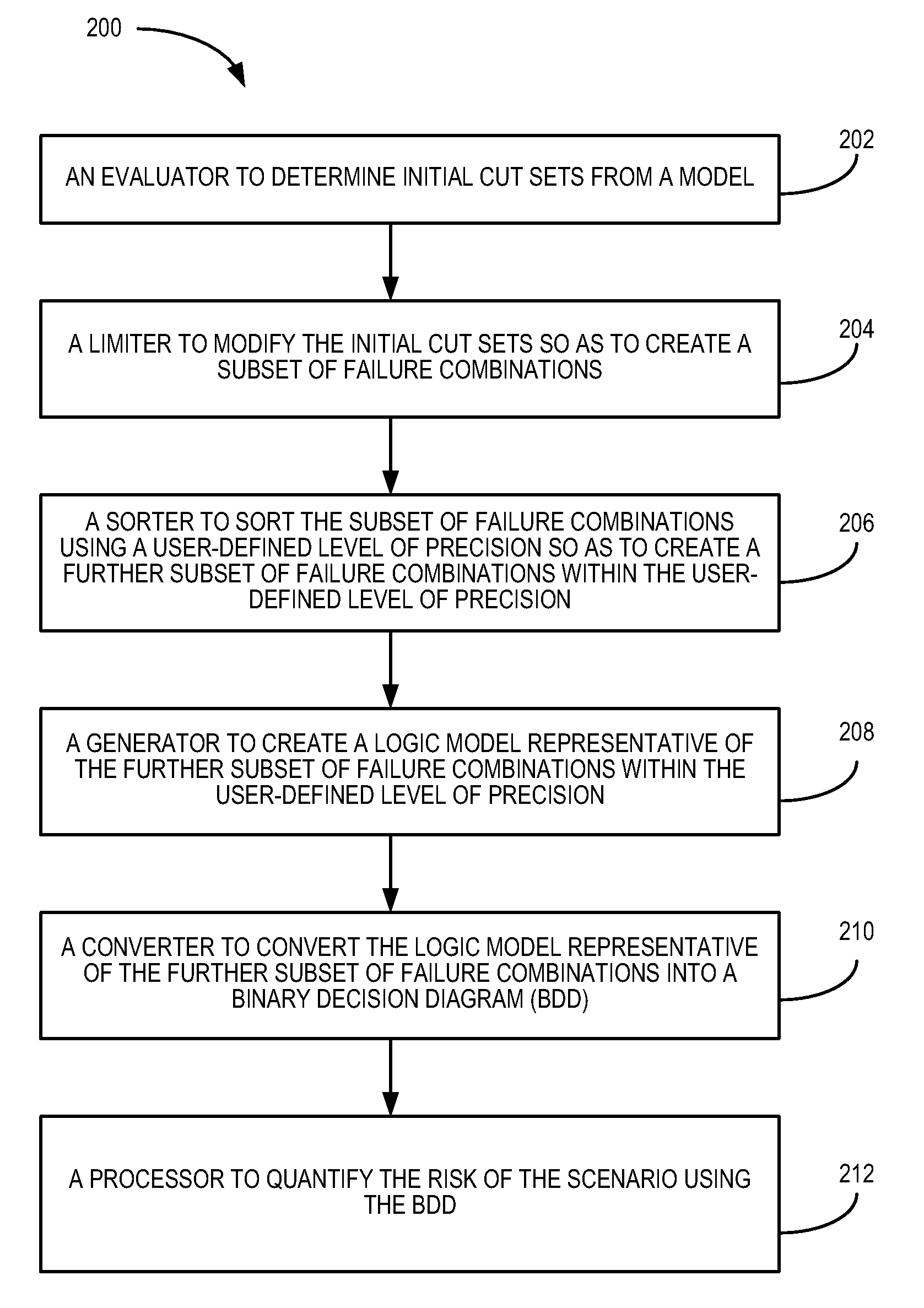
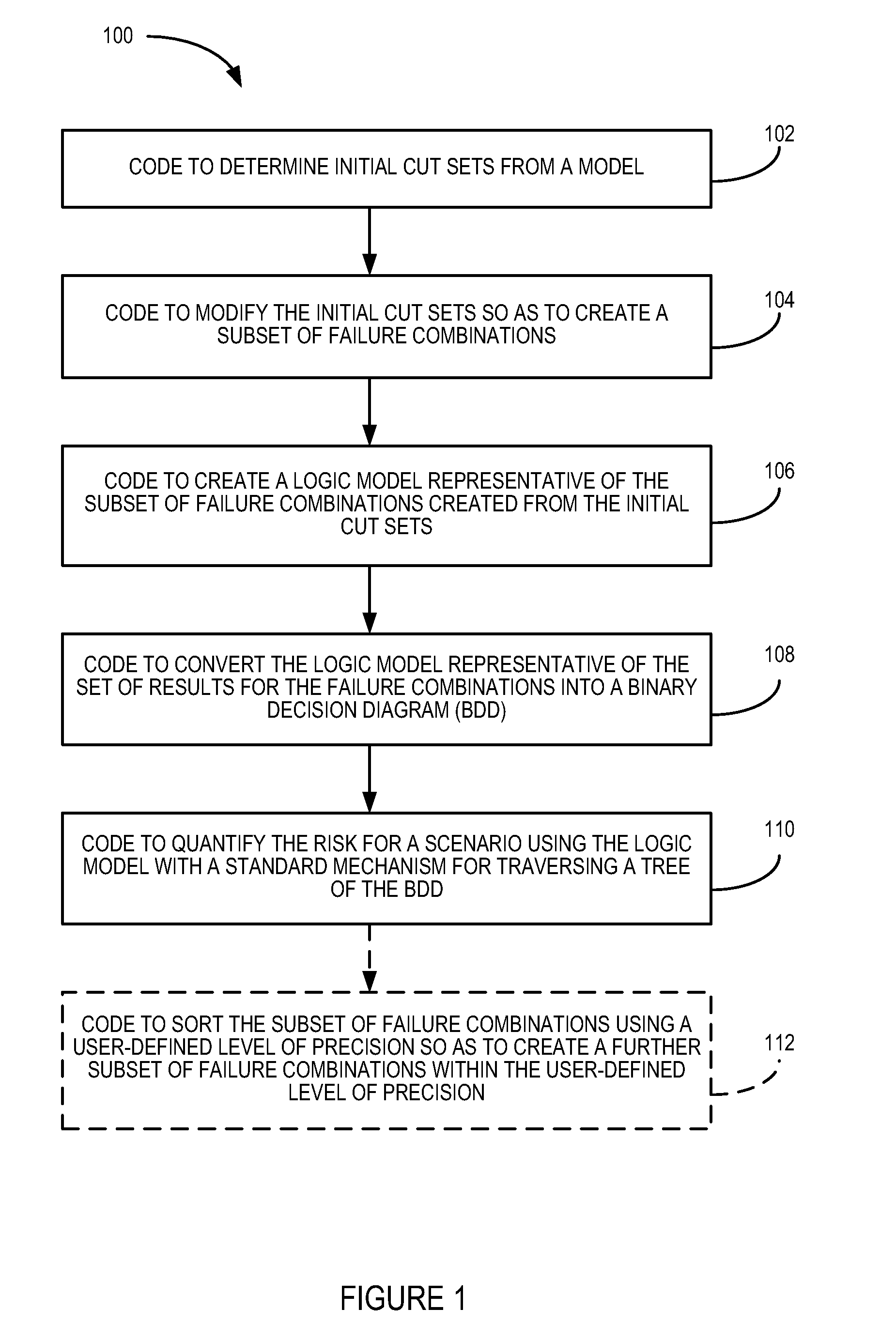
There is disclosed a hybrid assessment tool. In an embodiment, the tool includes code to determine initial cut sets from a model; code to modify the initial cut sets; code to create a logic model representative of a subset of failure combinations created from the initial cut sets; code to convert the logic model representative into a binary decision diagram (BDD); and code to quantify the risk for a scenario. There is disclosed a method of quantifying risk of a scenario. In one embodiment, the method includes determining initial cut sets from a model; modifying the initial cut sets; creating a logic model representative of a subset of failure combinations created from the initial cut sets; converting the logic model into a BDD; and quantifying the risk for the scenario using the BDD. Other embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
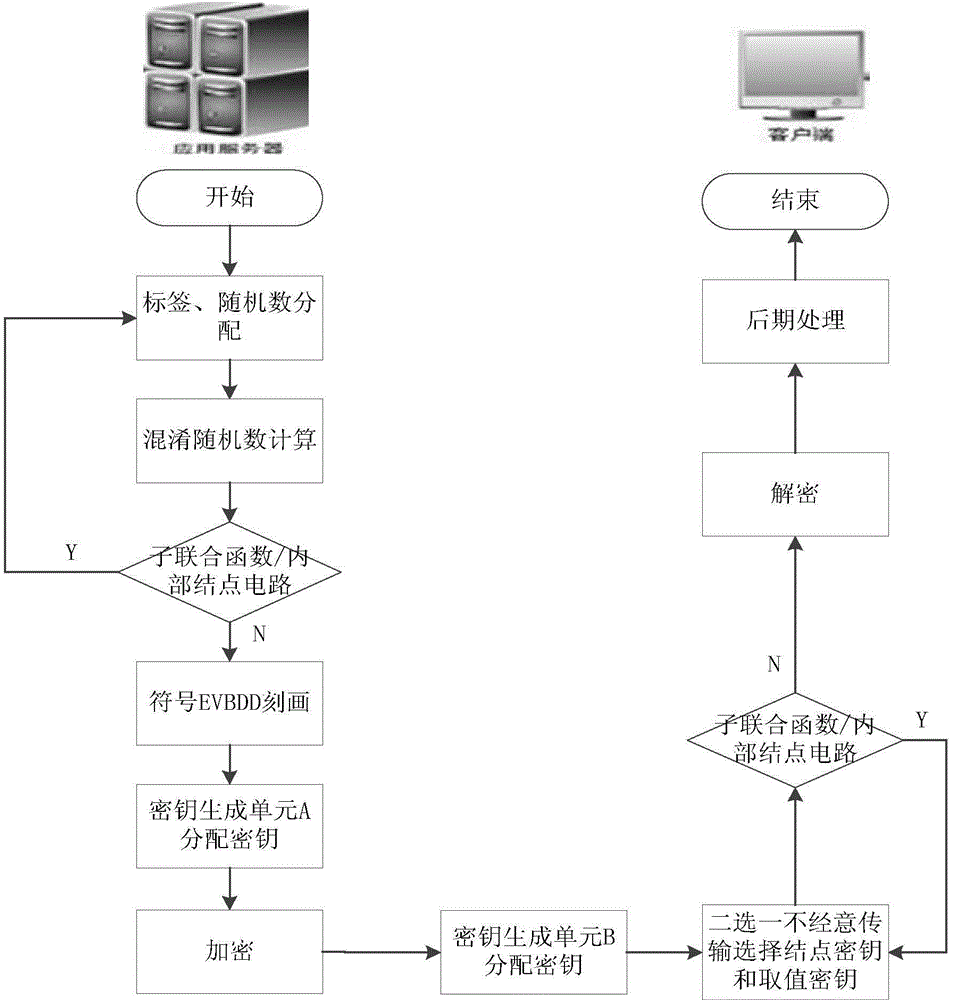
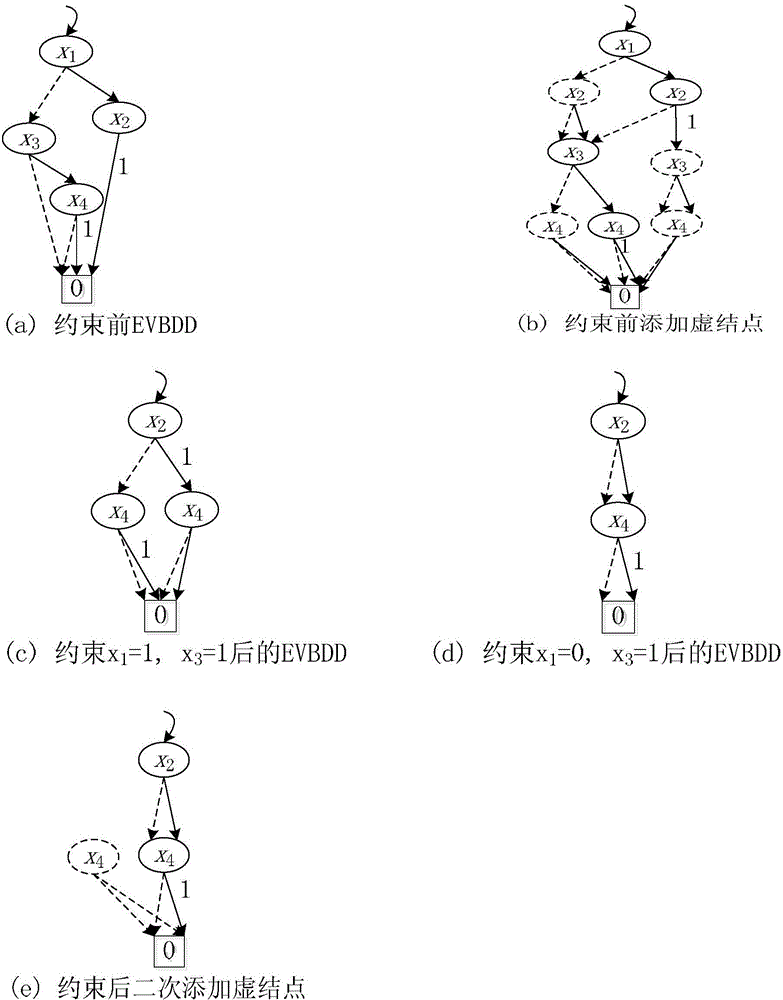
Secure two-party computation method and system based on symbol boundary value binary decision diagram
ActiveCN104618332AWill not be exposedImprove computing efficiencyKey distribution for secure communicationStrategy executionBoundary values
The invention discloses a secure two-party computation method and a secure two-party computation system based on a symbol boundary value binary decision diagram. The secure two-party computation method comprises three stages, namely a stage of constructing a local ambiguity sub joint function though a server, a stage of interacting information between the server and a client side, and a decryption computation stage of the client side. According to the secure two-party computation method, the function ambiguity and the client-side input data ambiguity are jointed through the server, so that privacy protection to function scale, internal structure and input data is realized; through an EVBDD symbol describing and node encryption-decryption algorithm, the execution efficiency of the secure two-party computation is improved. The secure two-party computation method can be used for safely completing a strategy execution function of parties to a joint task under relatively high algorithm efficiency; meanwhile, the safety strategy of the joint task and the encryption data in the computation process are guaranteed to be not leaked.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com