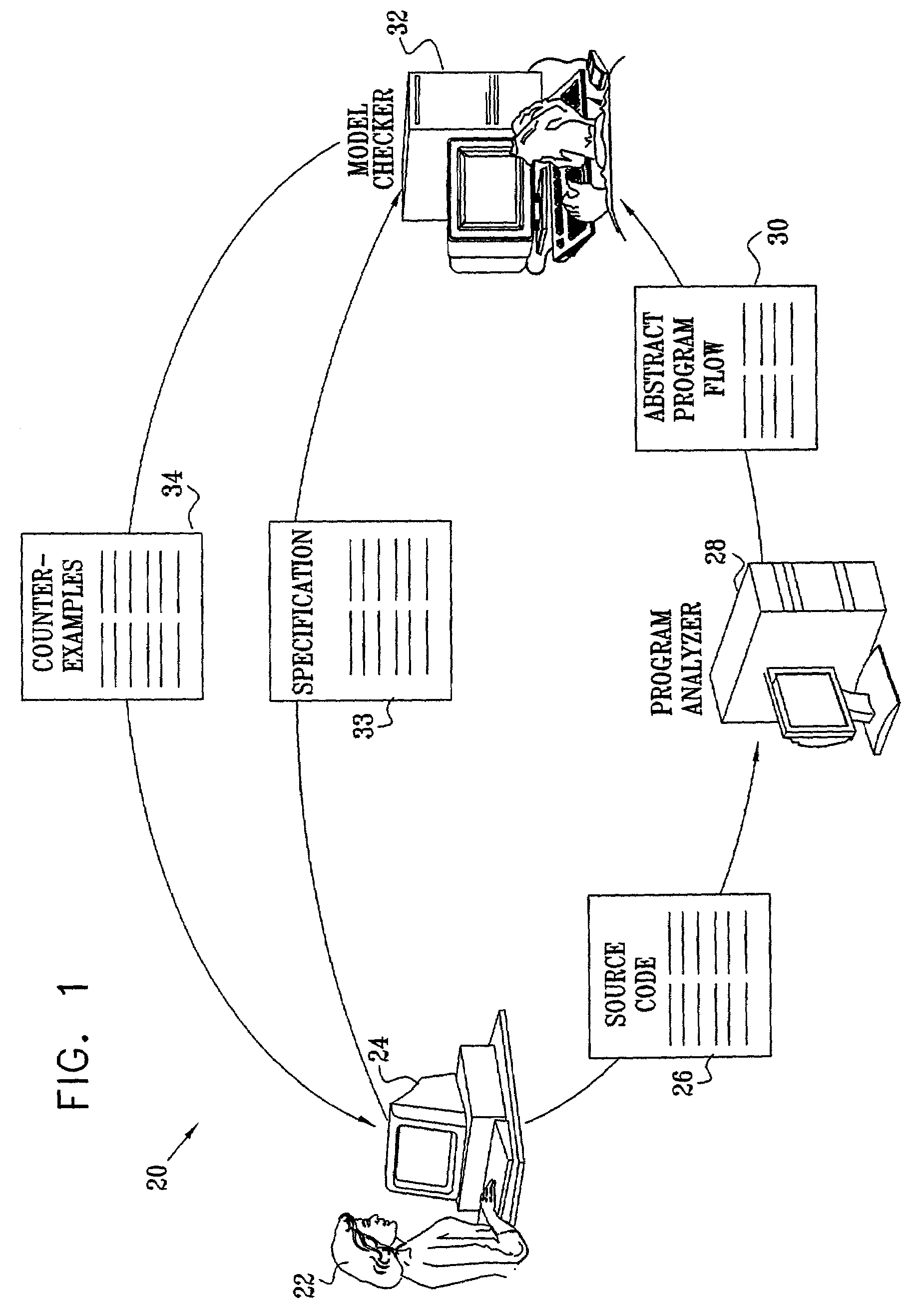
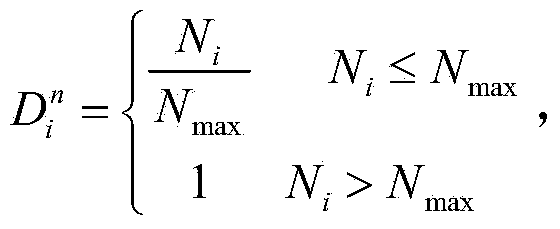Patents
Literature
167 results about "State function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In thermodynamics, a state function or function of state or point function is a function defined for a system relating several state variables or state quantities that depends only on the current equilibrium state of the system, for example a gas, a liquid, a solid, crystal, or emulsion. State functions do not depend on the path by which the system arrived at its present state. A state function describes the equilibrium state of a system and thus also describes the type of system. For example, a state function could describe an atom or molecule in a gaseous, liquid, or solid form; a heterogeneous or homogeneous mixture; and the amounts of energy required to create such systems or change them into a different equilibrium state.
Method and apparatus for the exploitation of piezoelectric and other effects in carbon-based life forms
Owner:WINEY TIMOTHY
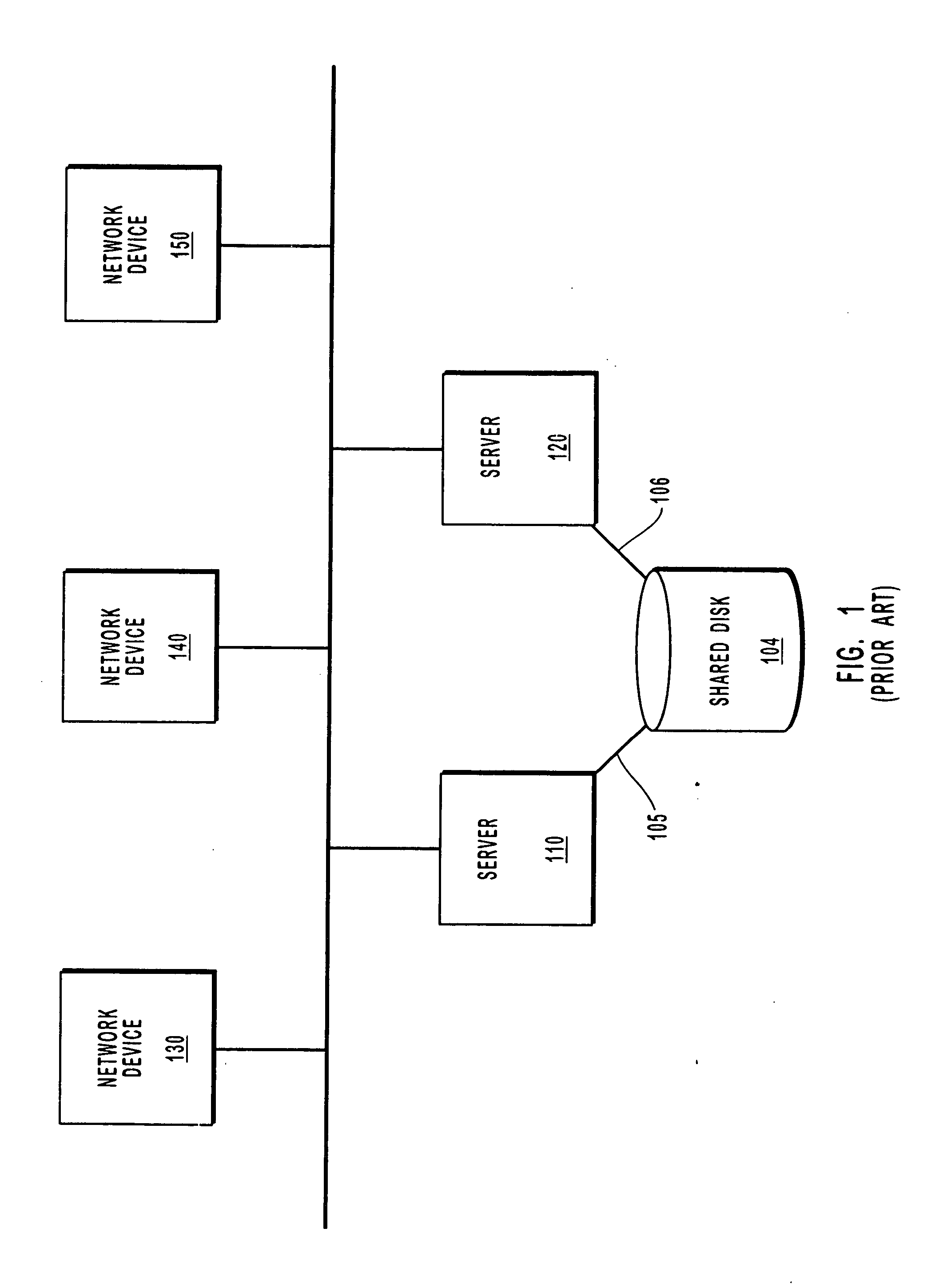
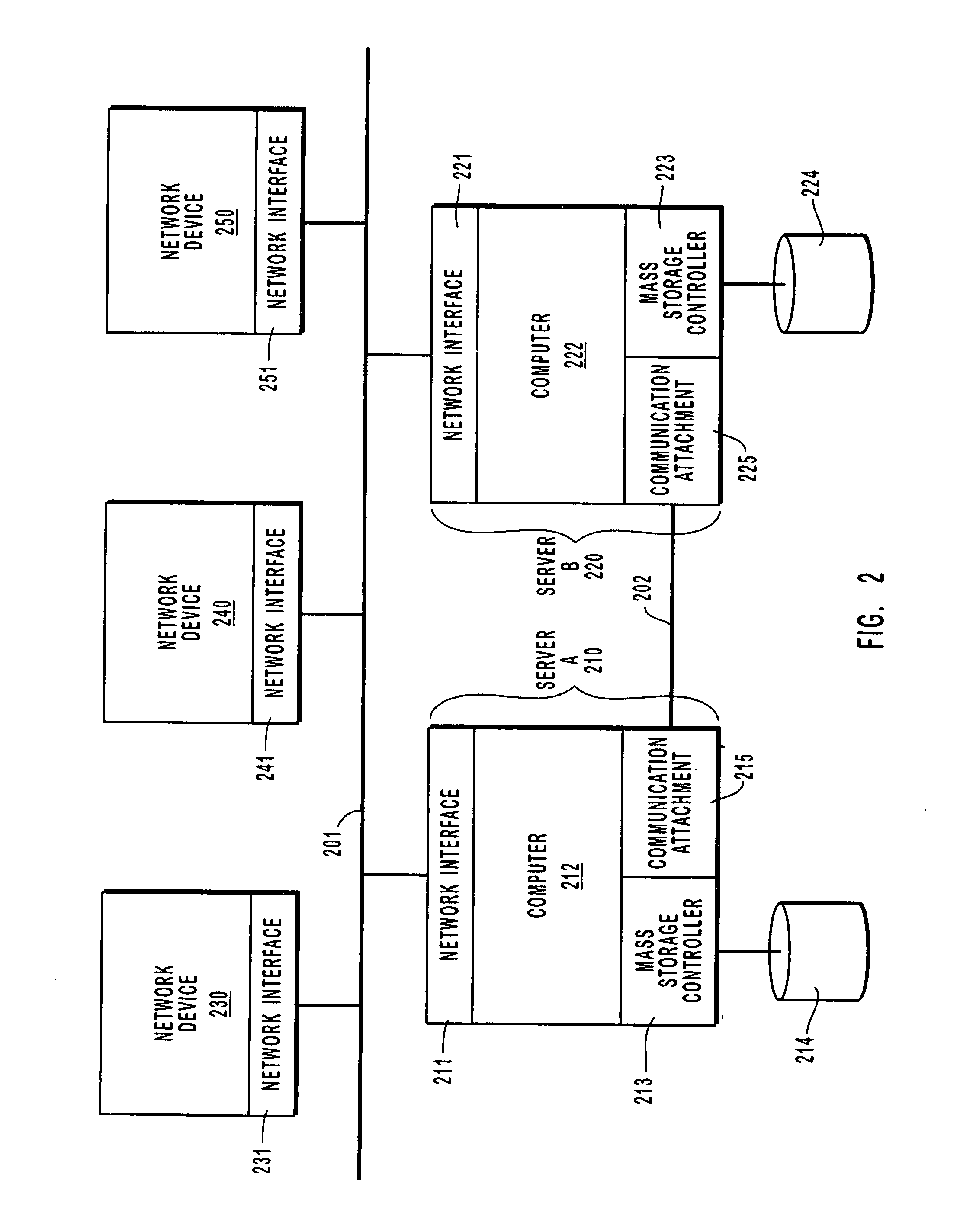
Method of improving the availability of a computer clustering system through the use of a network medium link state function
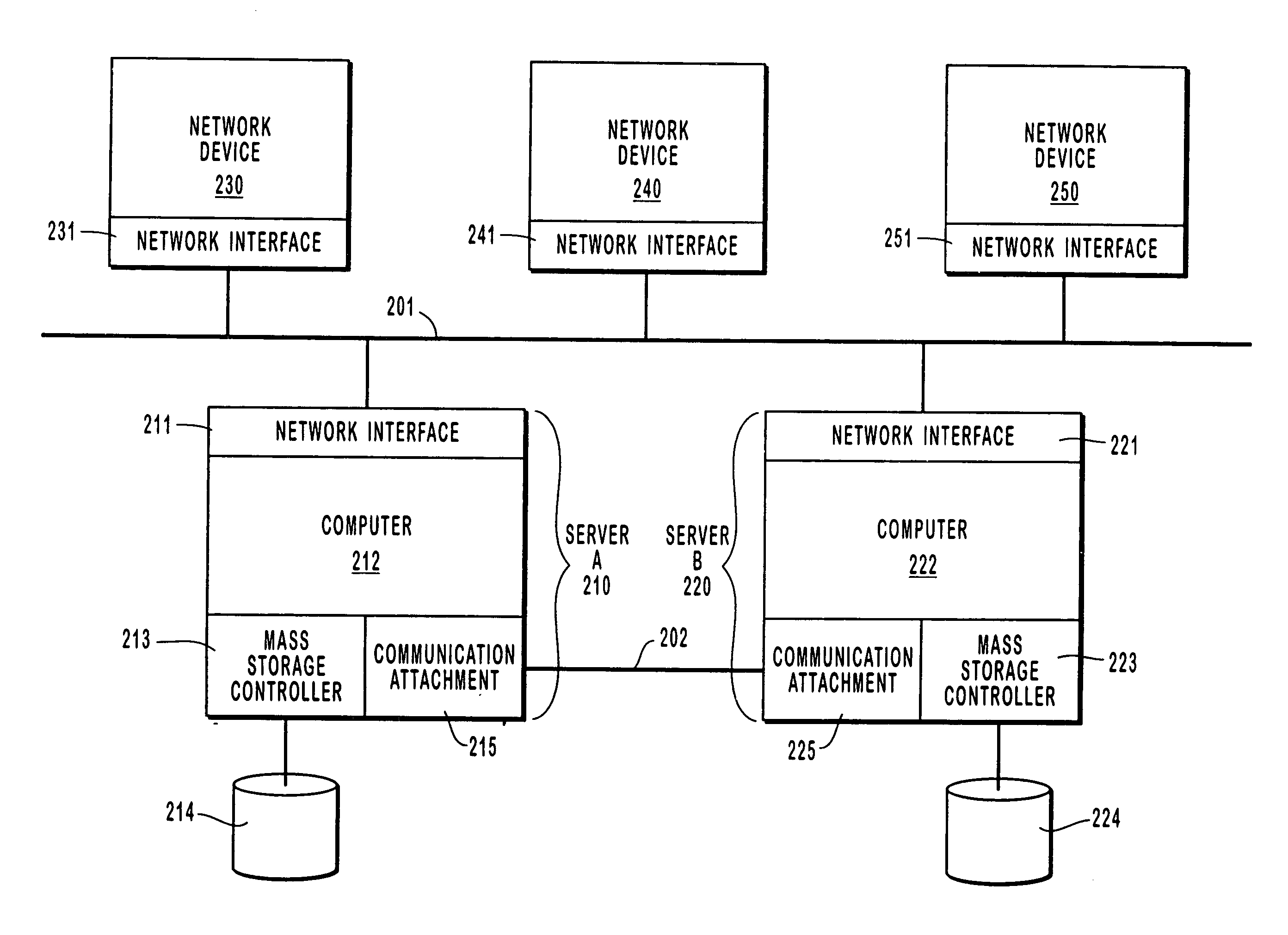
InactiveUS20050033778A1Improve availabilityImprove reliabilityData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsMass storageTelecommunications link
A method for improving the availability and reliability of a computer clustering system having first and second servers that are connected to each other by a communication link and that each have an associated mass storage device. In one implementation, the method begins when the first server detects a loss of communication over the communication link from the second server to the first server that prevents the servers from communicating with each other. The first server then analyzes the communication link to determine if the communication link is functioning properly. If the communication link is functioning properly, then the first server continues operation, assuming a right to survive without communicating with the second server or with the mass storage device of the first server or with the mass storage device of the second server, and the first server services network requests that would otherwise be serviced by the second server.
Owner:EMC CORP
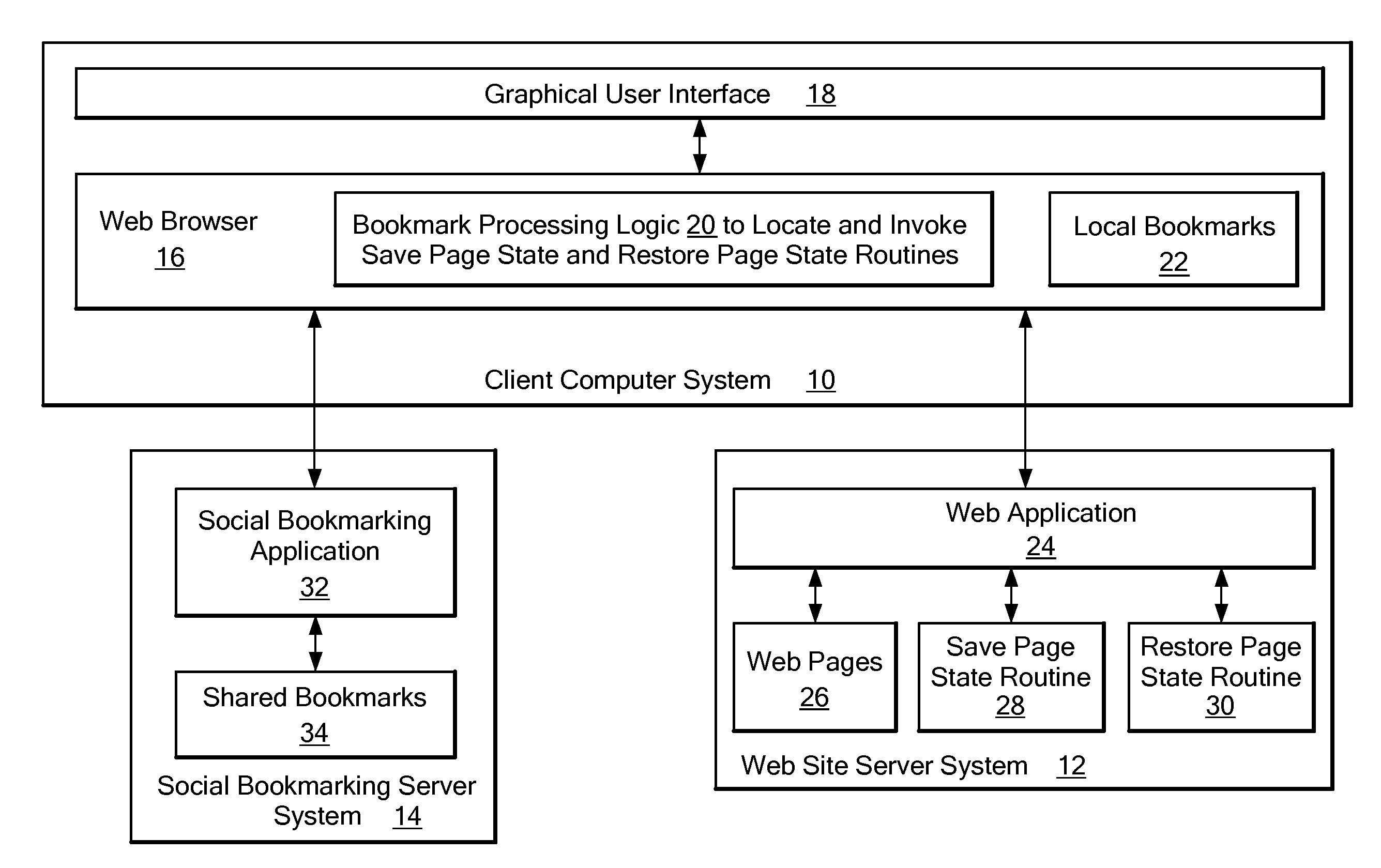
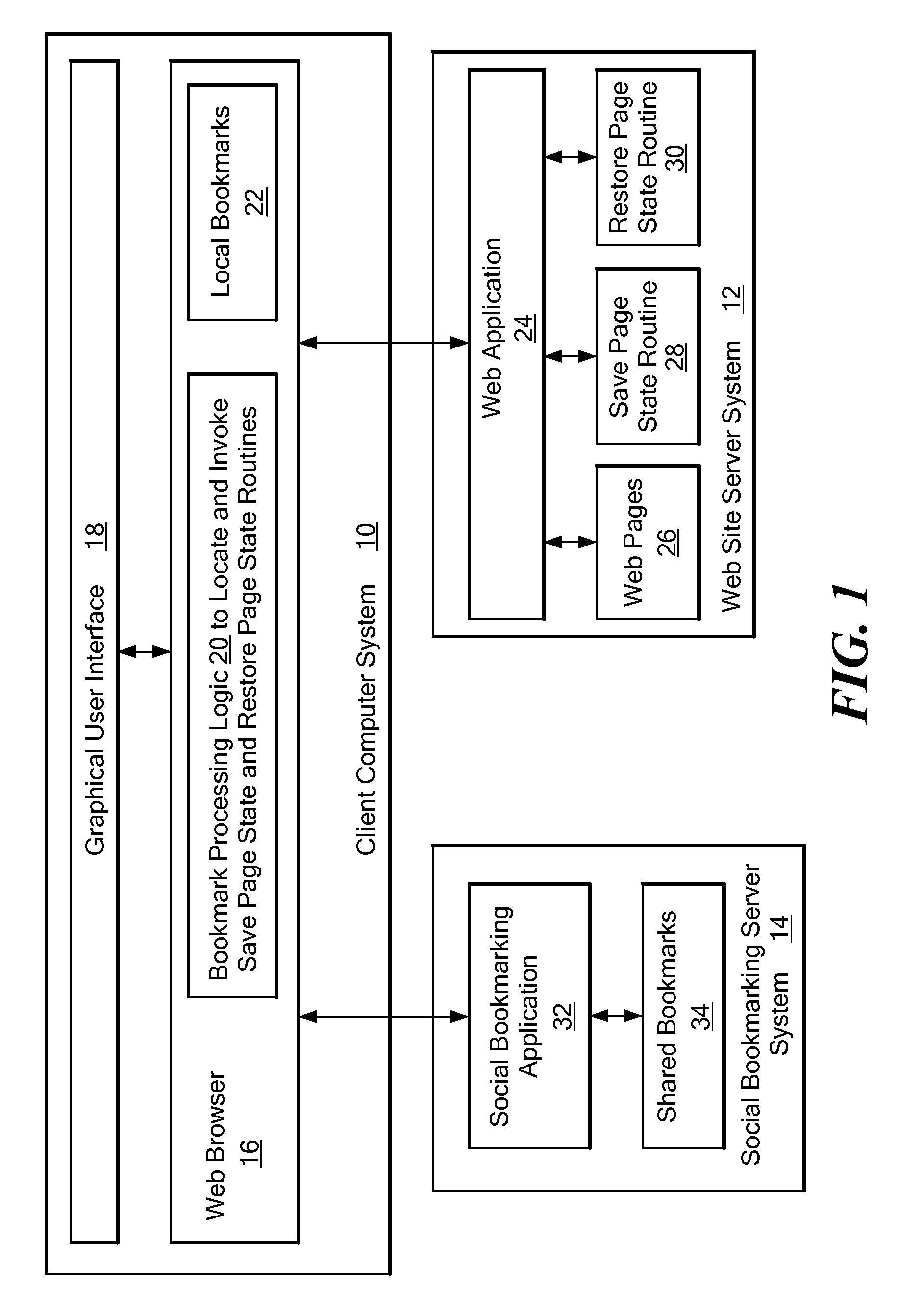
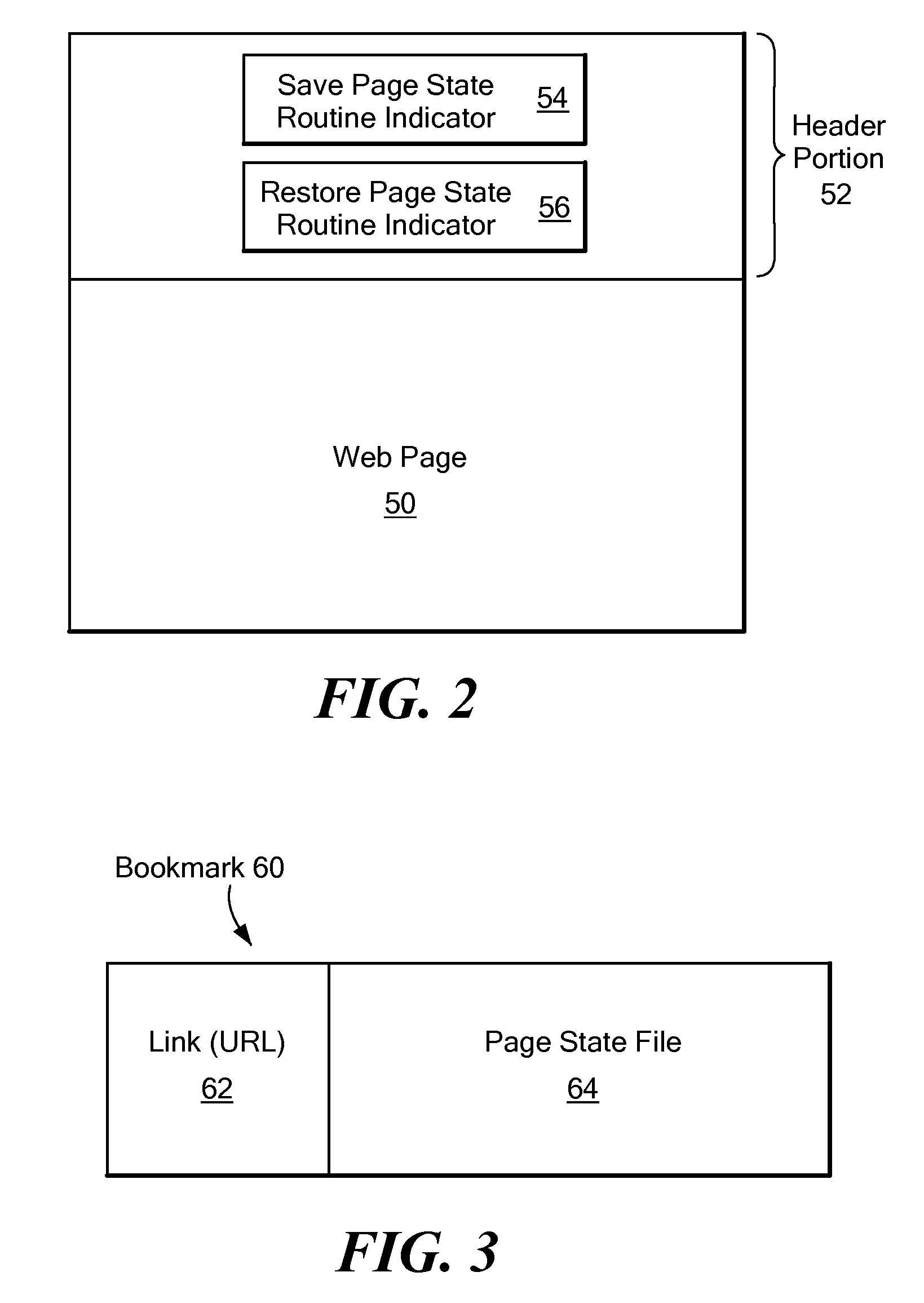
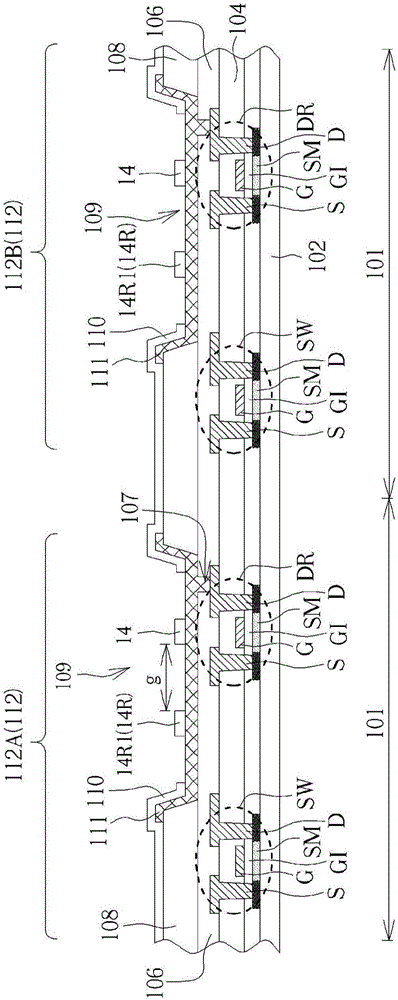
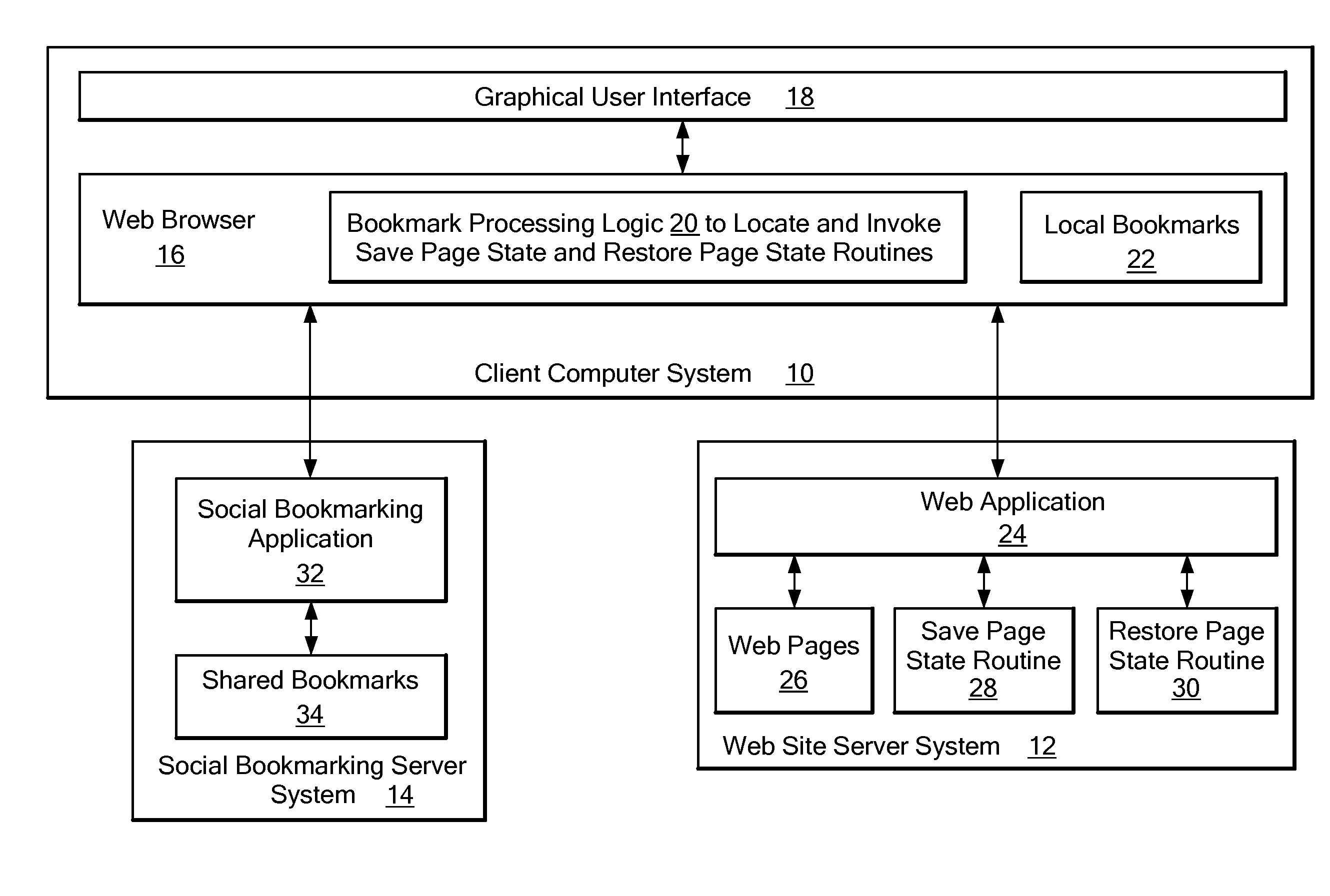
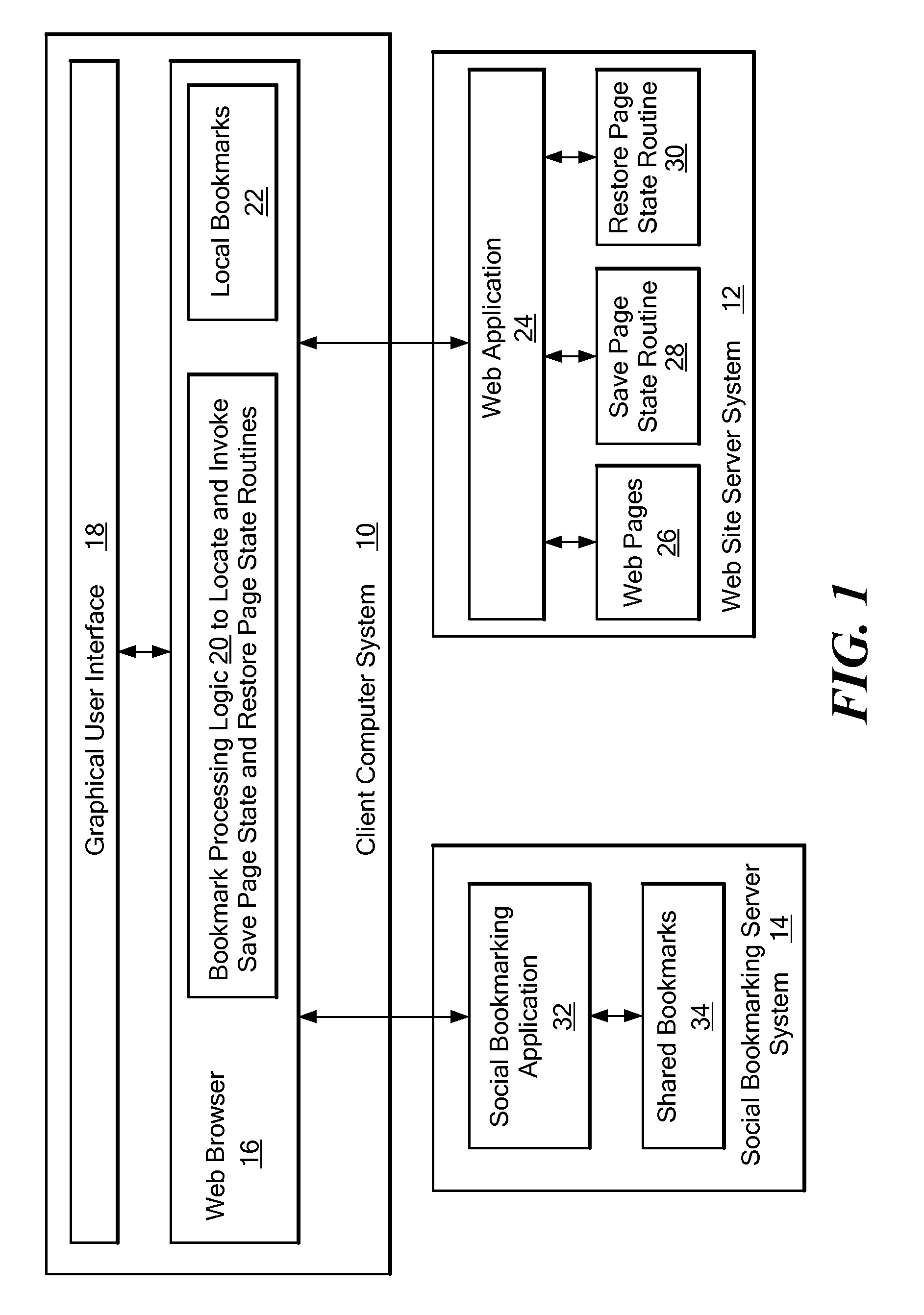
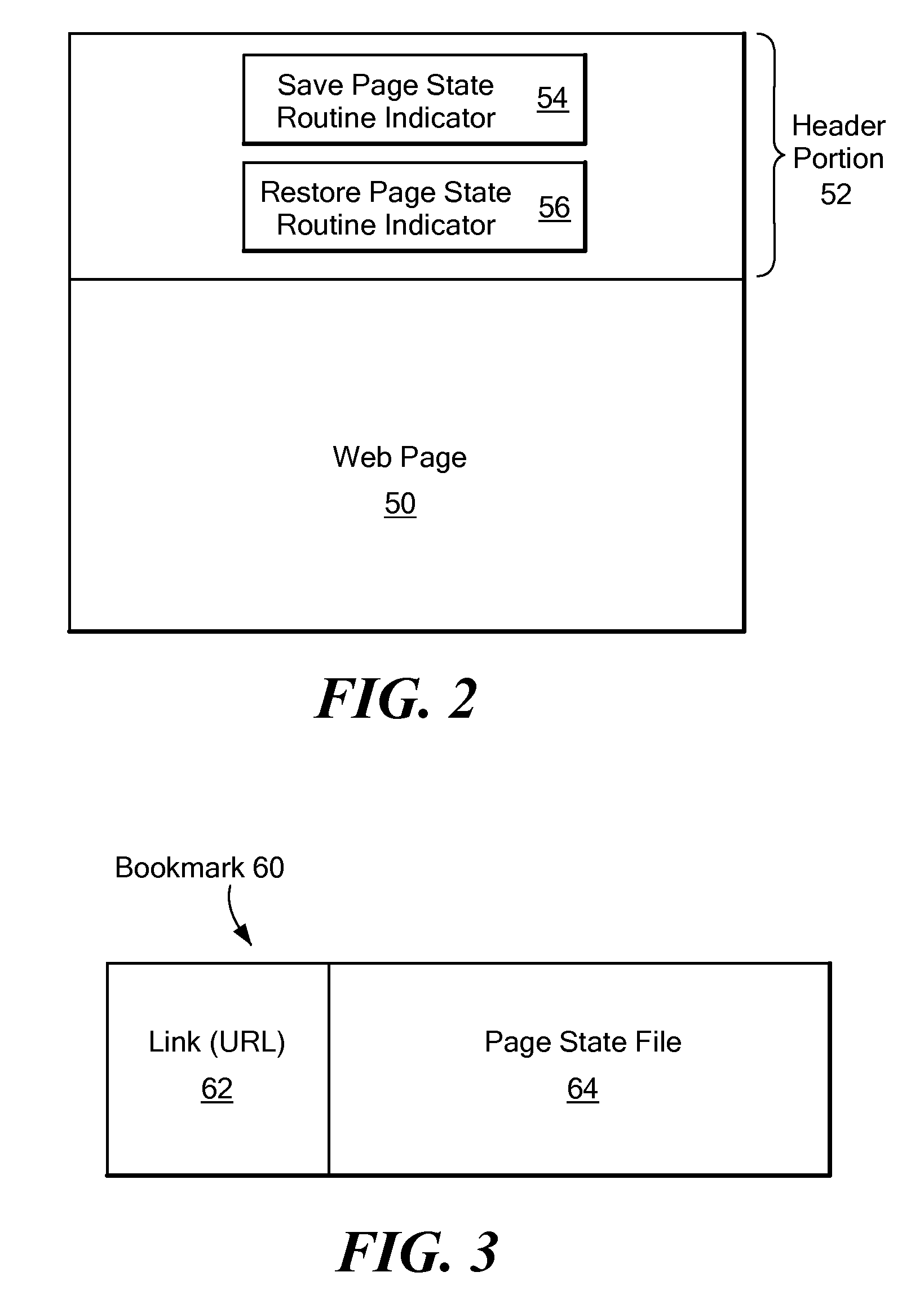
Method and system for providing sharable bookmarking of web pages consisting of dynamic content
ActiveUS20080313206A1Prevent and discourage creationAchieve backward compatibilityDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsWeb browserBookmarking
A system that automatically obtains Web page-specific scripts to save and restore the state of a Web page. When a user bookmarks or copies a Web page URL to the clipboard, a function is called to create a page state file that is stored together with the current URL to create a bookmark. When the bookmark is loaded or pasted into the location bar of the Web browser, the system reads the URL and page state file, and loads but does not yet display the Web page indicated by the URL of the bookmark. The system then locates the Restore Page State function in the loaded Web page's script, and executes the Restore Page State function on the page state file, resulting in modification to the DOM (Document Object Model) representation of the Web page and display of the Web page to the user based on the modified DOM.
Owner:IBM CORP
Display panel and repairing method thereof
InactiveCN105023522AGuaranteed normal operationStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesComputer scienceRepair method
The invention provides a display panel and a repairing method thereof. The repairing method comprising the steps of: a) providing a display panel, which comprises a substrate and a plurality of pixel units. The plurality of pixel units are disposed on the substrate, wherein each pixel unit comprises at least one connection pad, the at least one light-emitting element and at least a first alternate connection pad, the connection pad is provided on the substrate, the light emitting element is disposed on the connection pad and pad electrically connected with the connection, and the first backup connection pad is provided on the substrate and the connection pads electrically connected; 2) a testing process to determine whether the light emitting element is in an abnormal state function; and 3) a repair process, when detecting that the light emitting element of a pixel unit functional abnormality, there is provided a first light emitting element so as to form a first alternate alternate abnormality in the light emitting element having a function of pixel cells connected to the pad. Through the repair method, each pixel unit Jieneng normal operation and emits preset light color.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
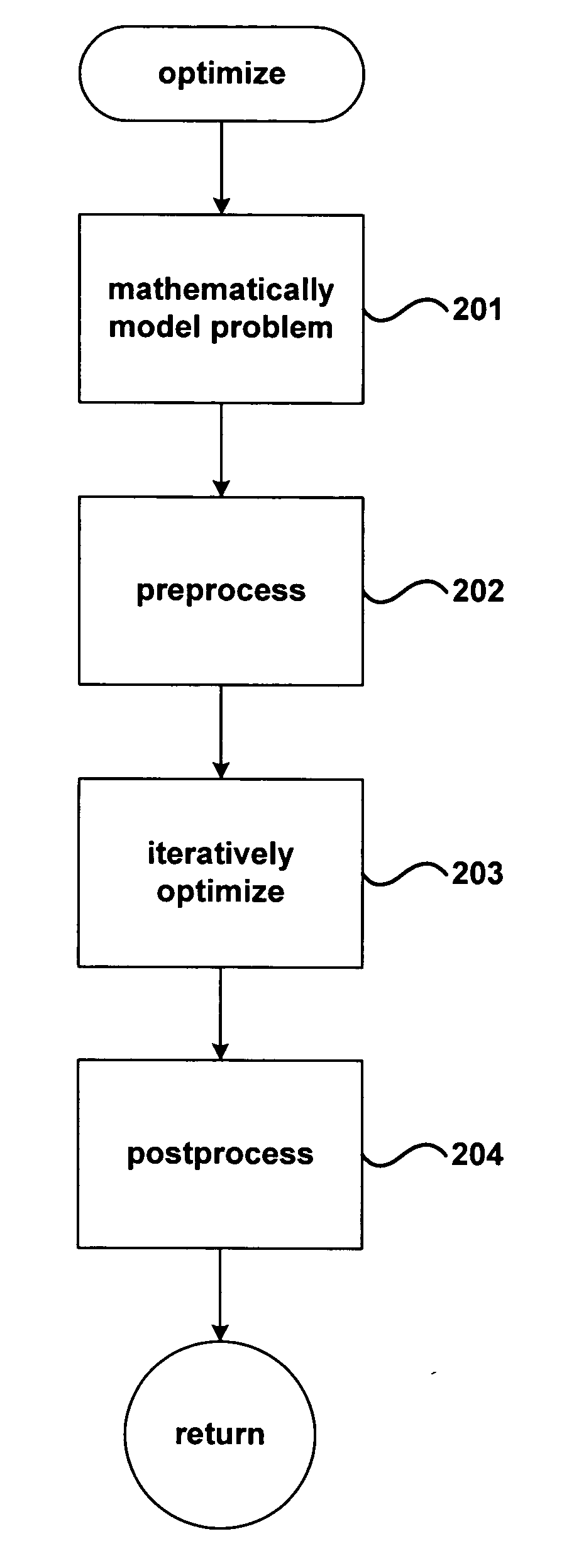
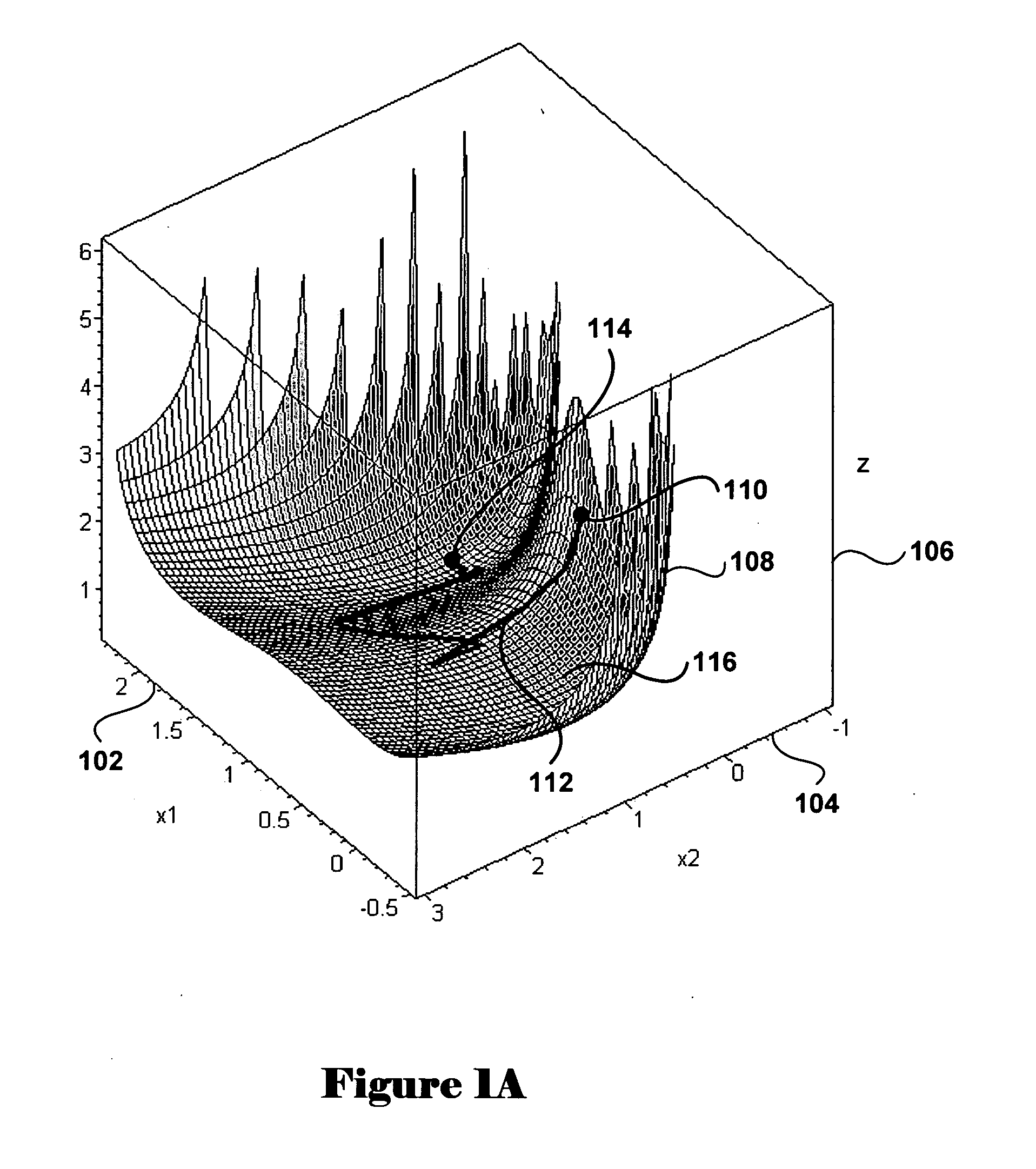
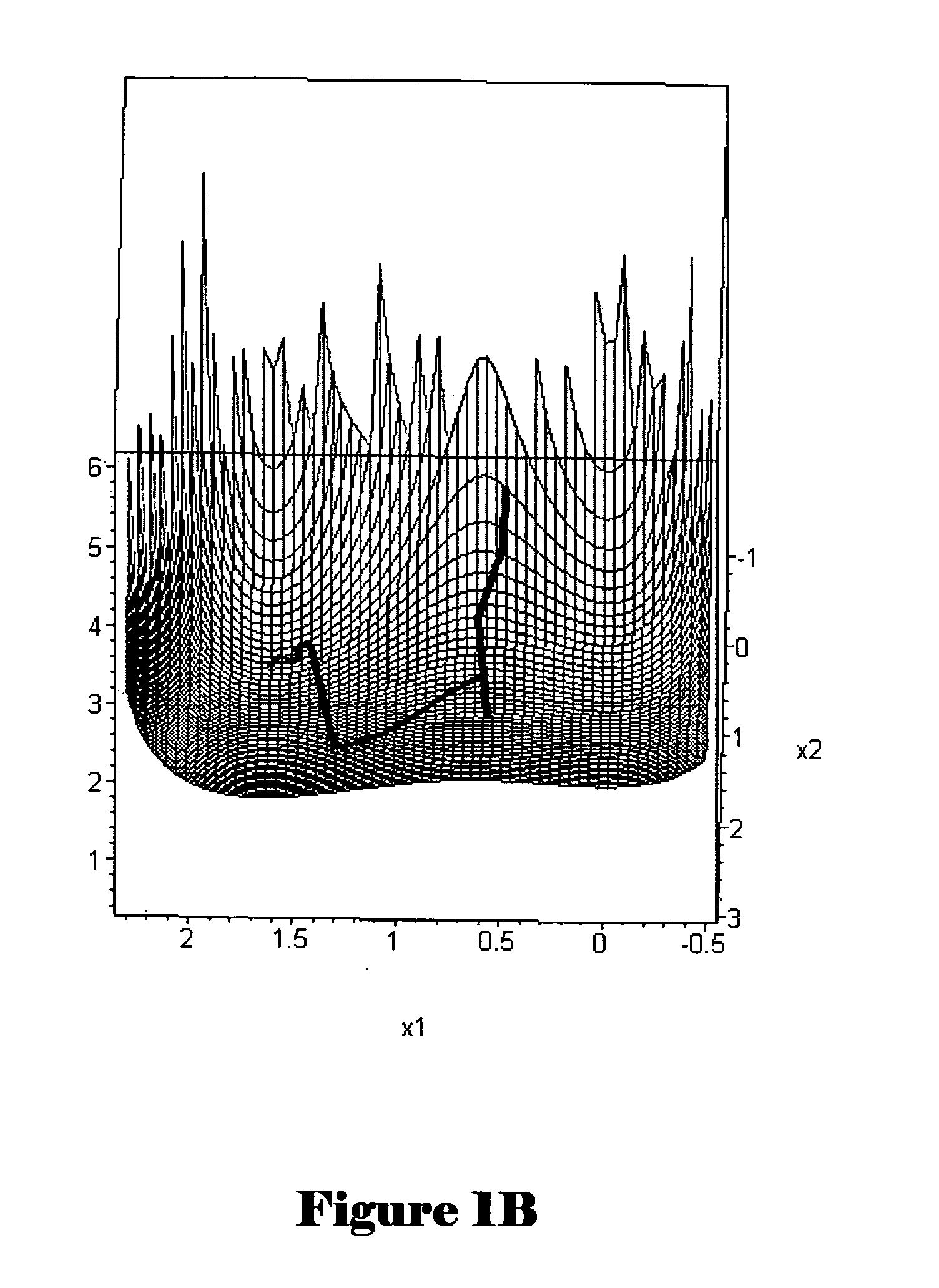
Method and system for optimization of geneal symbolically expressed problems, for continuous repair of state functions, including state functions derived from solutions to computational optimization, for generalized control of computational processes, and for hierarchical meta-control and construction of computational processes
InactiveUS20050102044A1Efficiently traverseImprove time efficiencyComplex mathematical operationsAdaptive controlDecompositionHigh dimensional
Methods and systems for finding optimal or near optimal solutions for generic optimization problems by an approach to minimizing functions over high-dimensional domains that mathematically model the optimization problems. Embodiments of the disclosed invention receive a mathematical description of a system, in symbolic form, that includes decision variables of various types, including real-number-valued, integer-valued, and Boolean-valued decision variables, and that may also include a variety of constraints on the values of the decision variables, including inequality and equality constraints. The objective function and constraints are incorporated into a global objective function. The global objective function is transformed into a system of differential equations in terms of continuous variables and parameters, so that polynomial-time methods for solving differential equations can be applied to calculate near-optimal solutions for the global objective function. Embodiments of the present invention also provide for distribution and decomposition of global-gradient-descent- field-based optimization methods, by following multiple trajectories, and local-gradient- descent-field-based optimization methods, by using multiple agents, in order to allow for parallel computation and increased computational efficiency. Various embodiments of the present invention further include approaches for relatively continuous adjustment of solutions to optimization problems in time, to respond to various events, changes in priorities, and changes in forecasts, without needing to continuously recalculate optimization solutions de novo. While many embodiments of the present invention are specifically directed to various classes of optimization problems, other embodiments of the present invention provide a more general approach for constructing complex hierarchical computational processes and for optimally or near optimally controlling general computational processes.
Owner:CLEARSIGHT SYST
Dynamic grouping of wireless terminal
ActiveUS7142839B2Telephonic communicationBroadcast service distributionTelecommunicationsApplication server
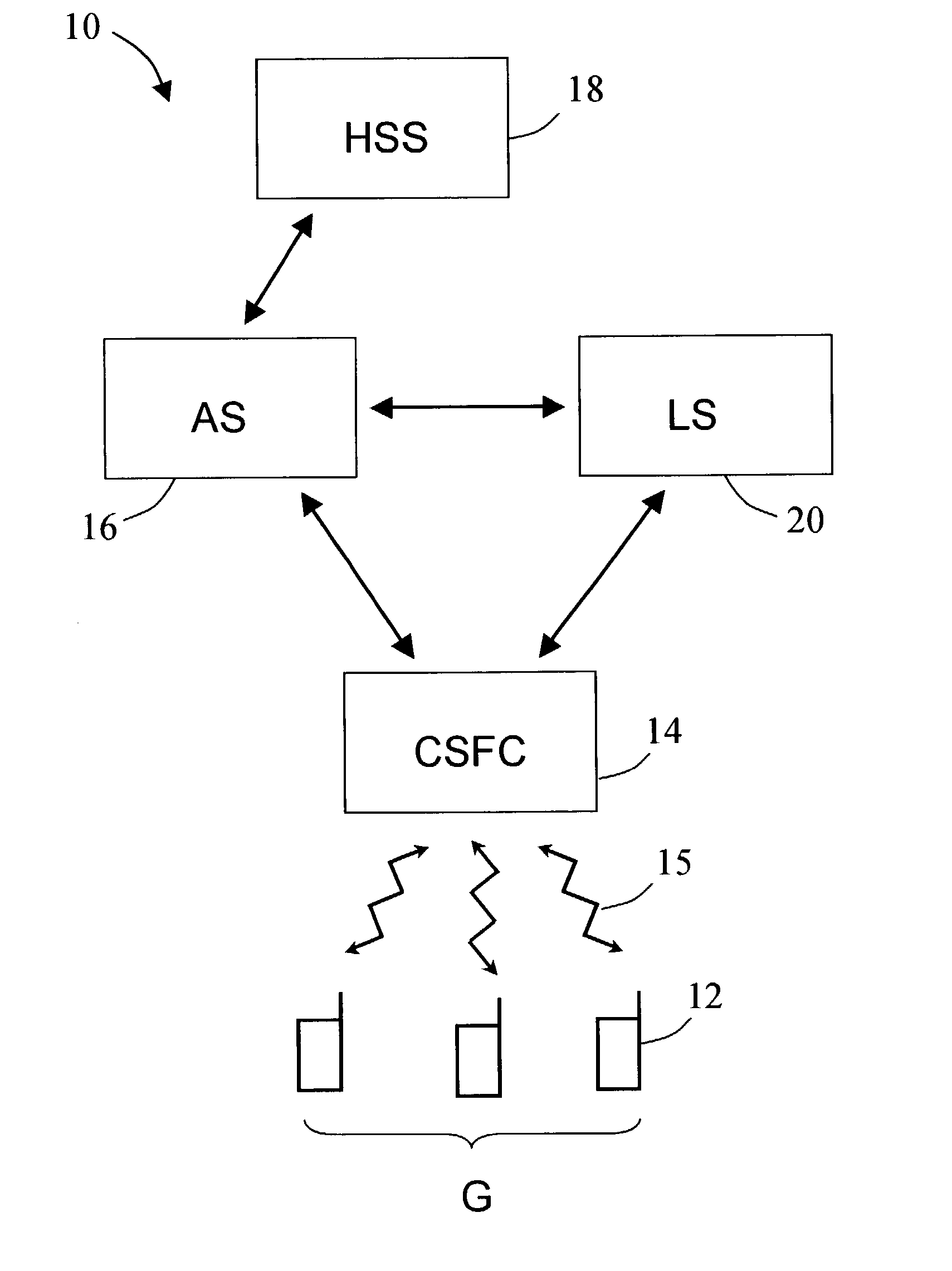
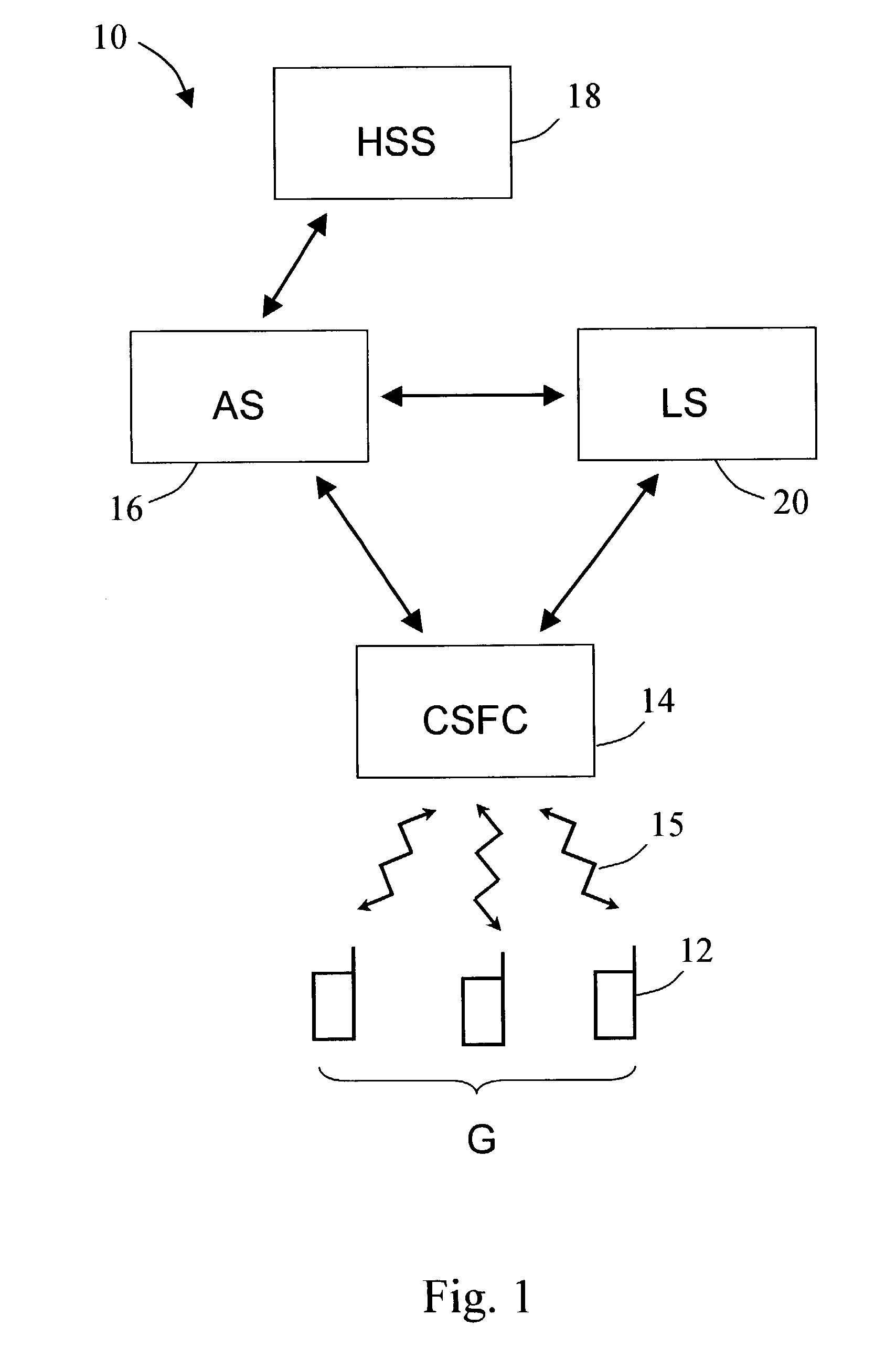
A system and method of transmitting media to a plurality of wireless terminals. The method includes forming a group of wireless terminals, and transmitting a group-specific media message to each of the wireless terminals in the group. The method can include forming a location-based group of wireless terminals disposed within a proximity of a location and transmitting a media message to each of the wireless terminals in the location-based group. The method can also include determining the location of the plurality of wireless terminals. The system includes a Location Server for determining the location of the plurality of wireless terminals and an Application Server for grouping the wireless terminals. The system also include a Call State Function Controller for routing calls thereby transmitting the group-specific media messages to the wireless terminals in the group via wireless interfaces.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Method and system for providing sharable bookmarking of web pages consisting of dynamic content
ActiveUS8041763B2Achieve backward compatibilityPrevent and discourage creationDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsWeb browserBookmarking
A system that automatically obtains Web page-specific scripts to save and restore the state of a Web page. When a user bookmarks or copies a Web page URL to the clipboard, a function is called to create a page state file that is stored together with the current URL to create a bookmark. When the bookmark is loaded or pasted into the location bar of the Web browser, the system reads the URL and page state file, and loads but does not yet display the Web page indicated by the URL of the bookmark. The system then locates the Restore Page State function in the loaded Web page's script, and executes the Restore Page State function on the page state file, resulting in modification to the DOM (Document Object Model) representation of the Web page and display of the Web page to the user based on the modified DOM.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
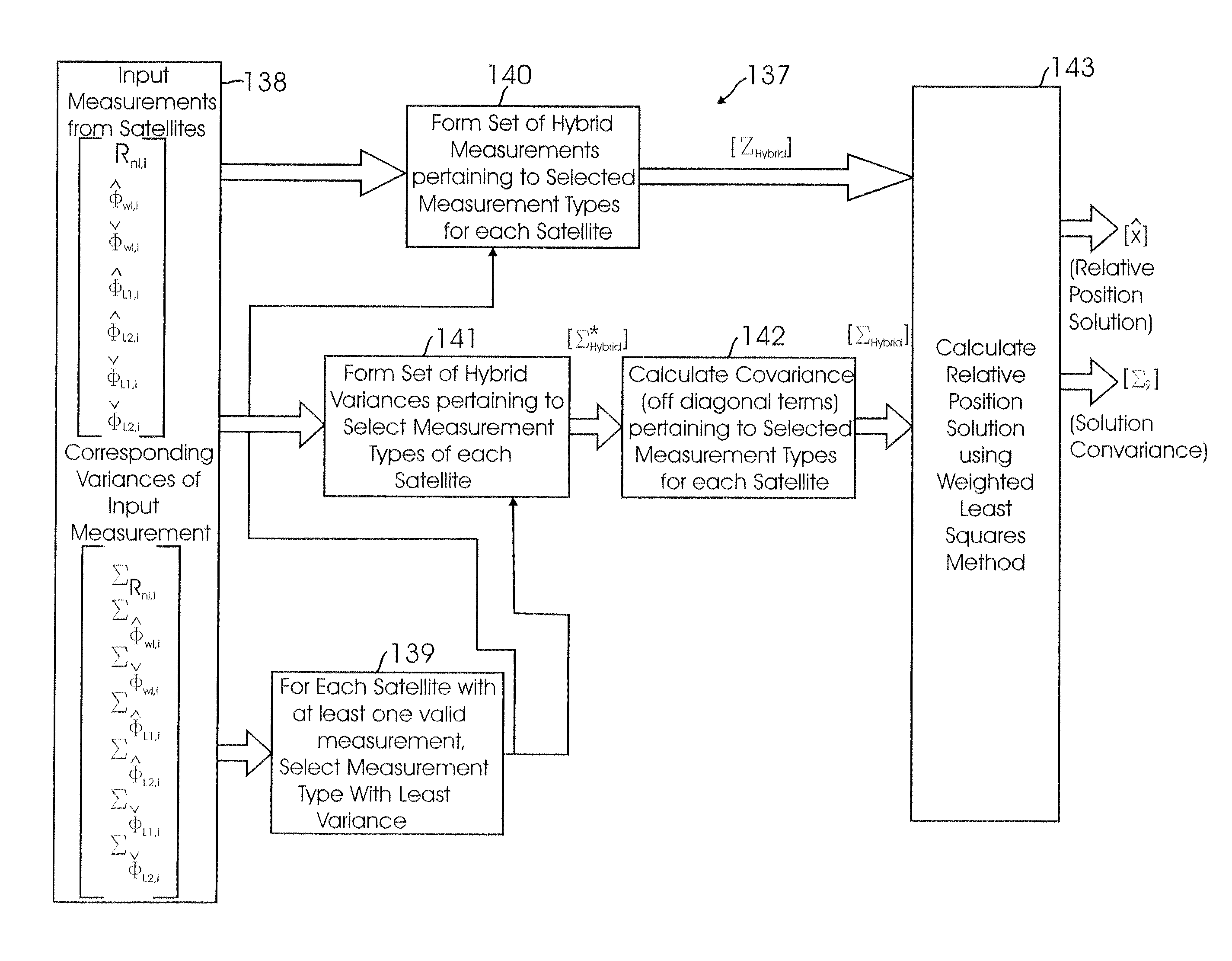
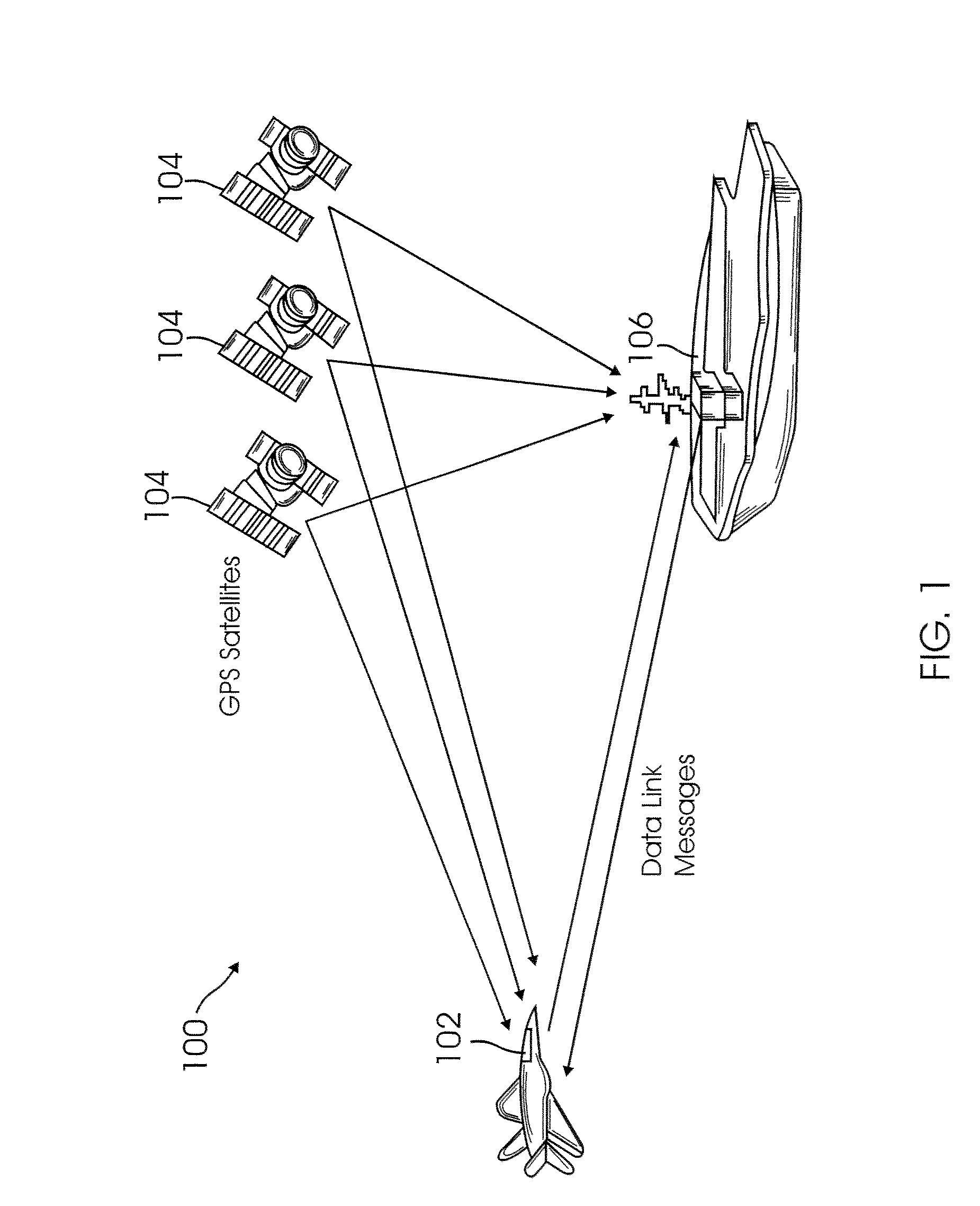
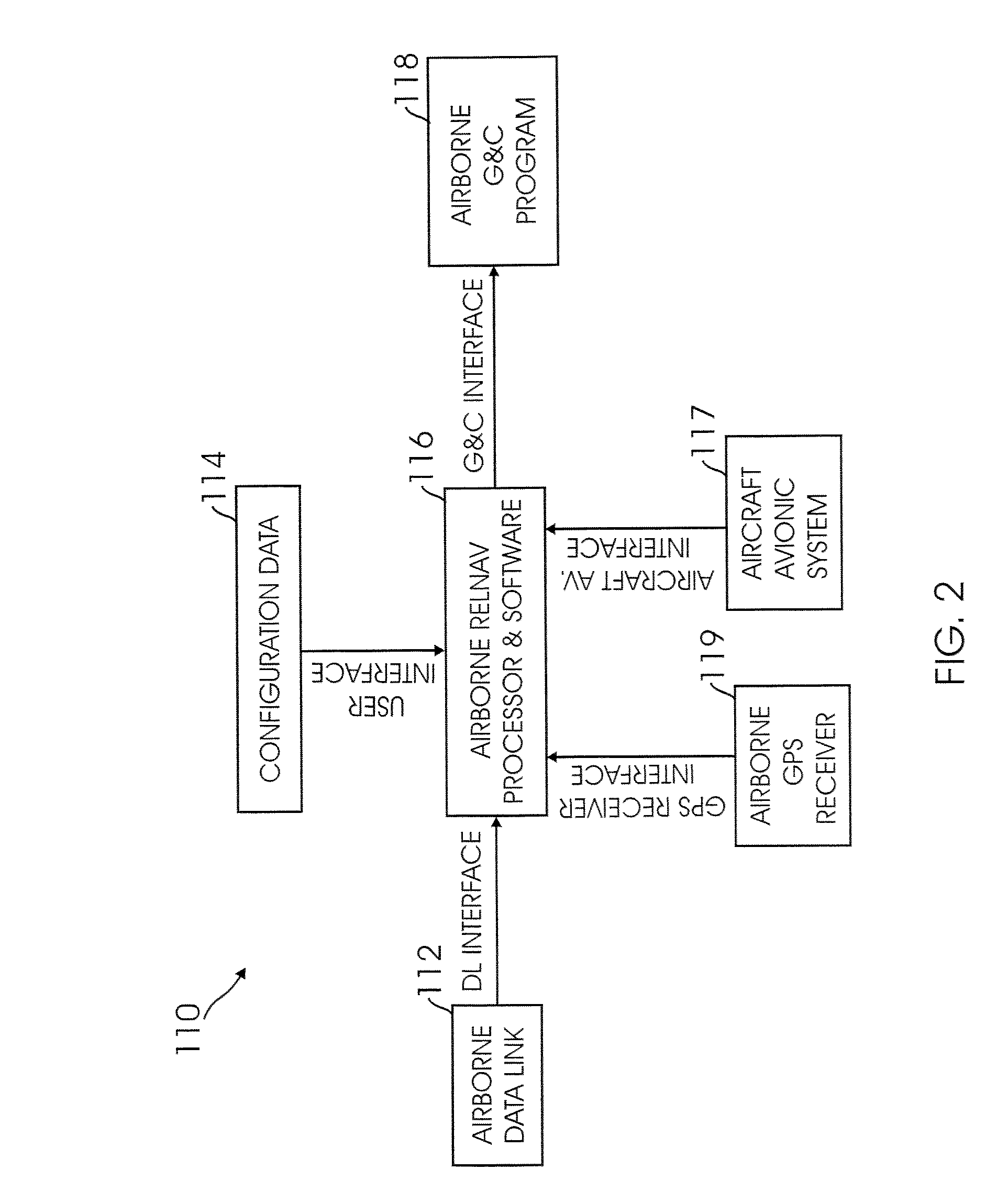
Method for fusing multiple GPS measurement types into a weighted least squares solution
ActiveUS20080036654A1Simple methodImprove accuracyPosition fixationBeacon systemsPattern recognitionGps measurement
A method of calculating position data for an airborne aircraft using a GPS-based airborne navigation system includes the processing of a position component of a relative state function by fusing a plurality of different types of measurement data available in the GPS-based system into a weighted least squares algorithm to determine an appropriate covariance matrix for the plurality of different types of measurement data.
Owner:SIERRA NEVADA CORP
Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) flight path planning method based on competitive deep learning network
ActiveCN109870162AGood precisionReduce precisionNavigational calculation instrumentsPosition/course control in three dimensionsDepth of fieldLearning network
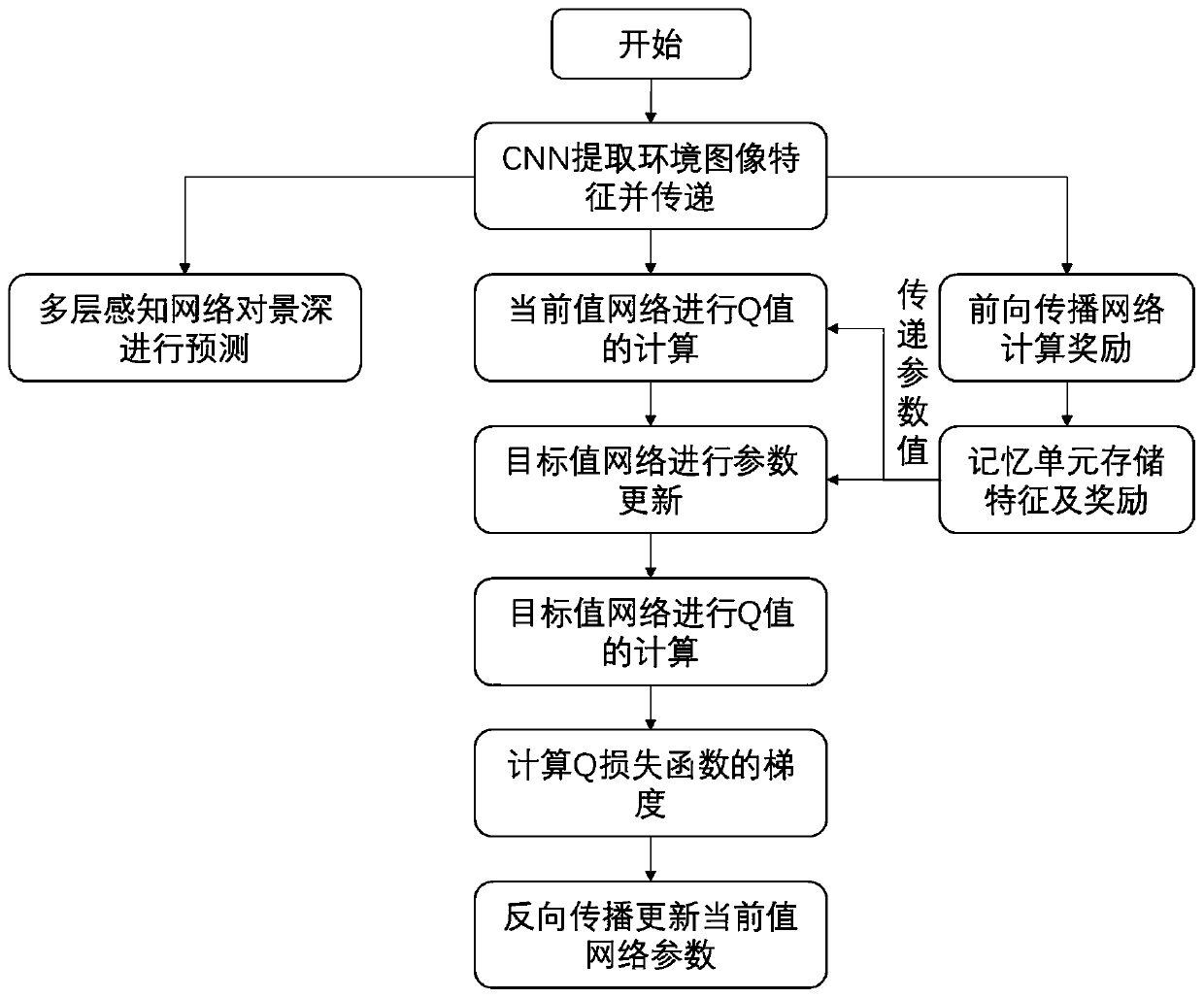
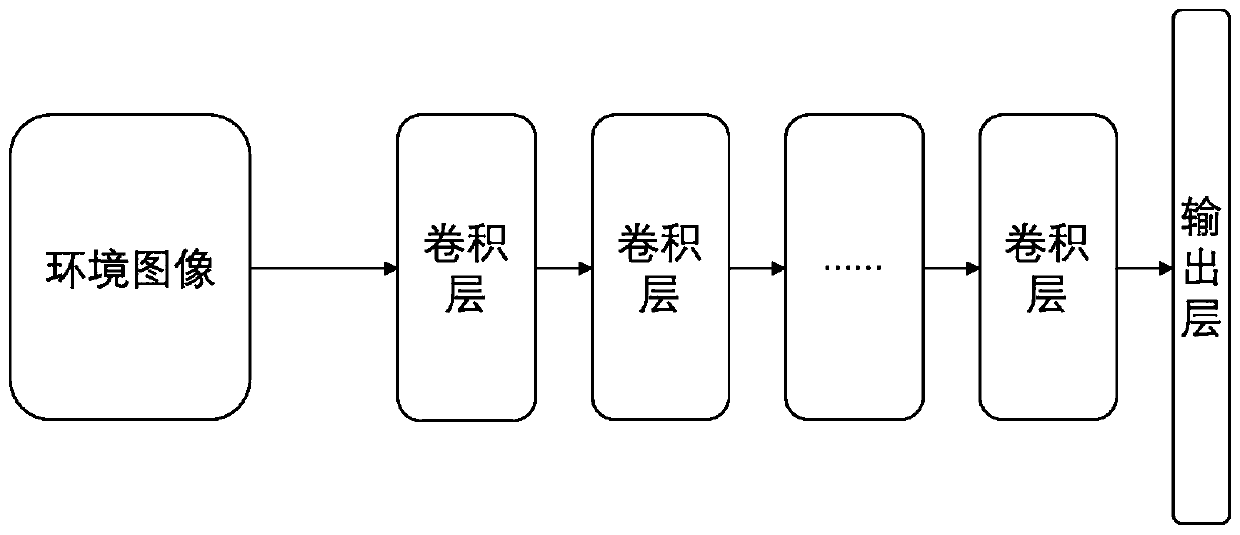
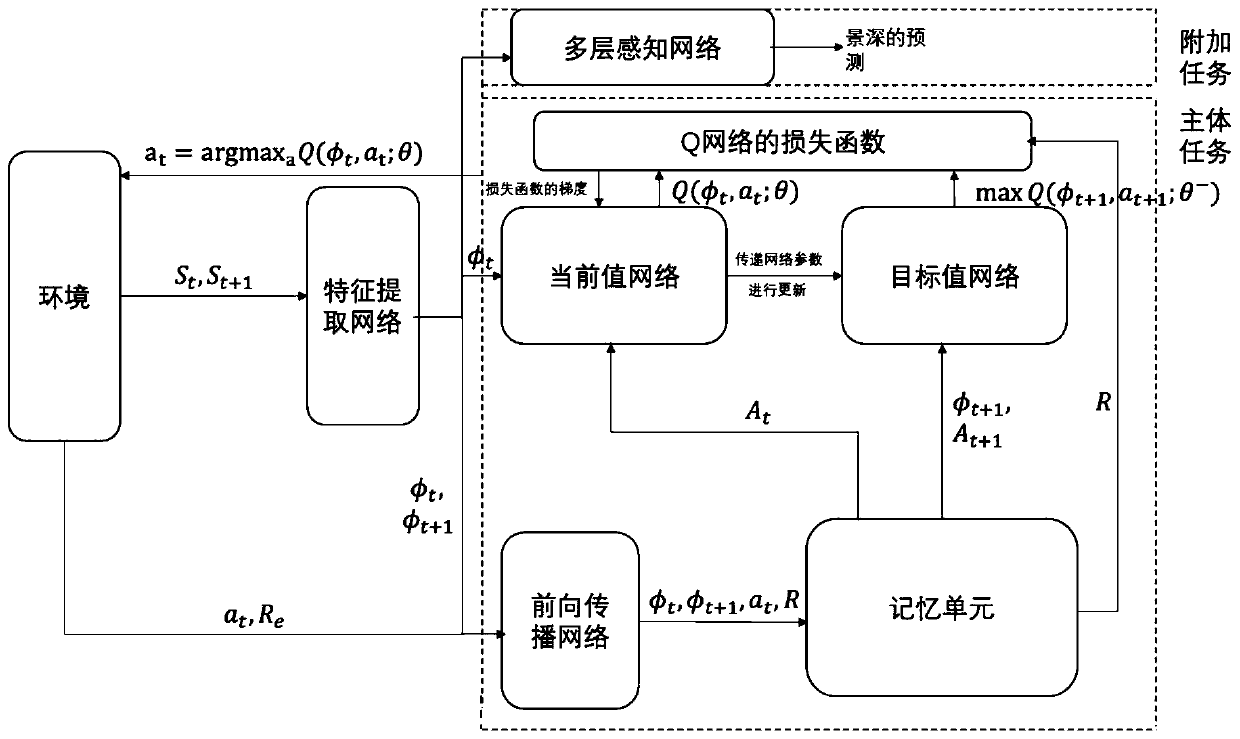
The invention relates to a unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) flight path planning method based on a competitive deep learning network. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out feature information extraction on real-time pictures photographed by a camera, so that a column of feature vectors are obtained; calculating each feature vector to obtain a state function value and a superiority function value, and combining the two values on a combination layer to obtain a state action function value; using the state action function value as an instant state action function value which cooperates with a target value network in construction of a loss function of the network and prediction of a next state, so that total rewards jointly formed by internal rewards and external rewards are obtained; carrying out depth-of-field prediction on the real-time pictures; carrying out calculation to obtain another state action function value; and calculating the gradient of the loss function and carrying out back propagation of the gradient to a current value network for network parameter updating.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
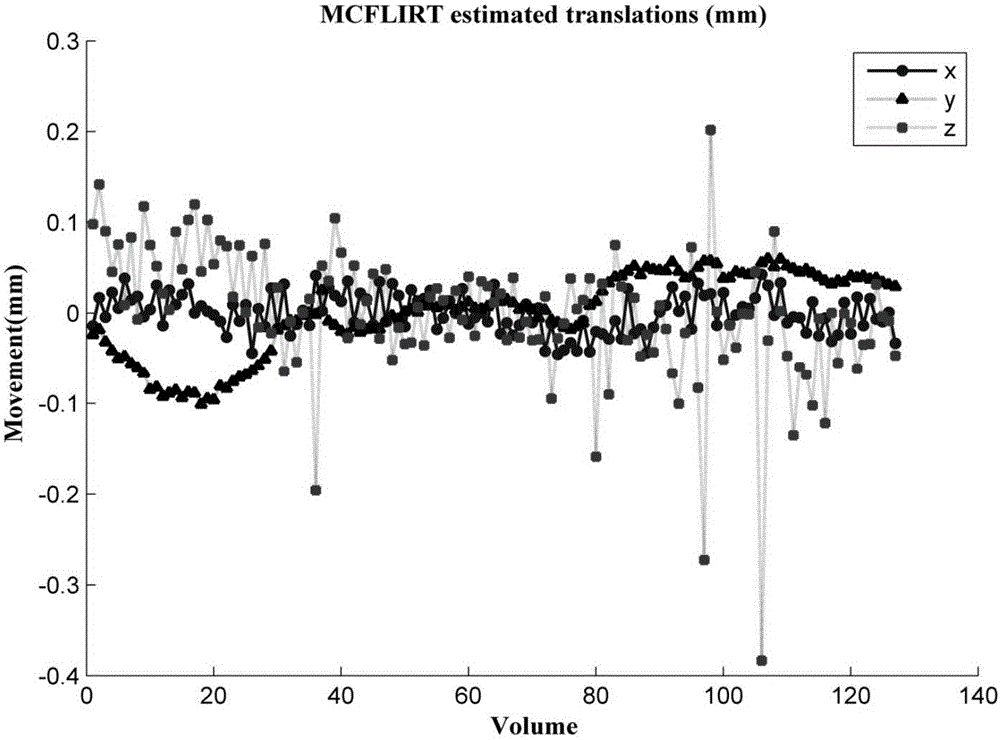
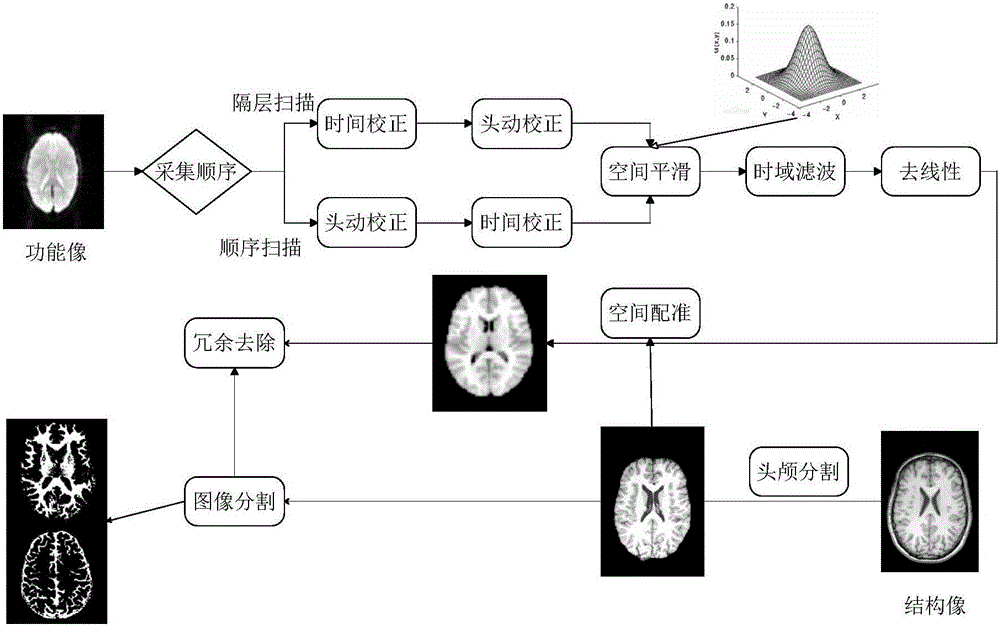
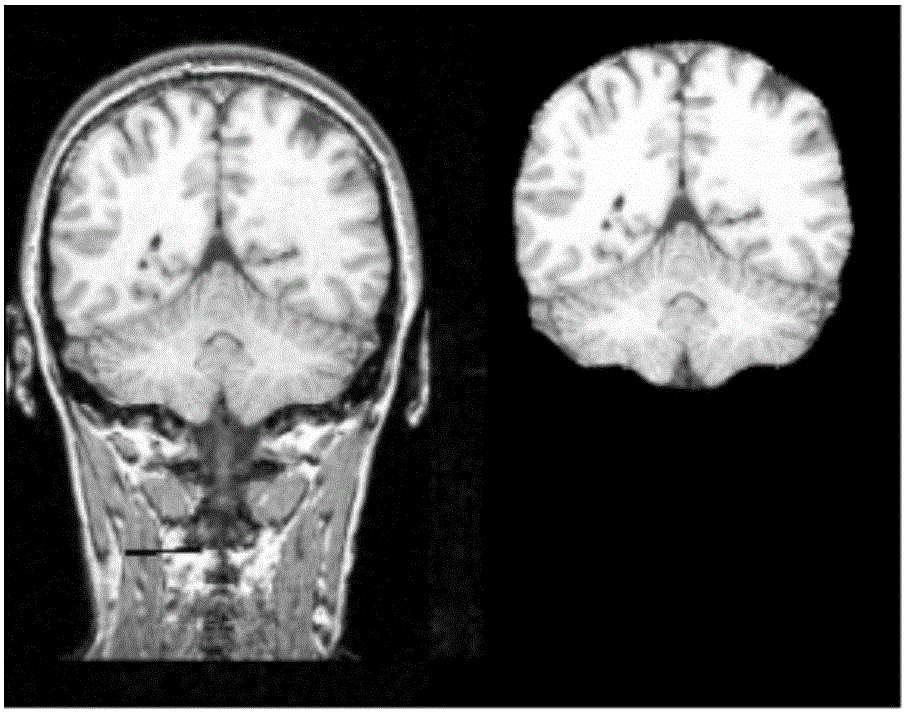
FMRI and DTI fusion-based vault white matter segmentation method
ActiveCN106204562ANovel thinkingSimple processImage enhancementImage analysisClinical valueFiber bundle
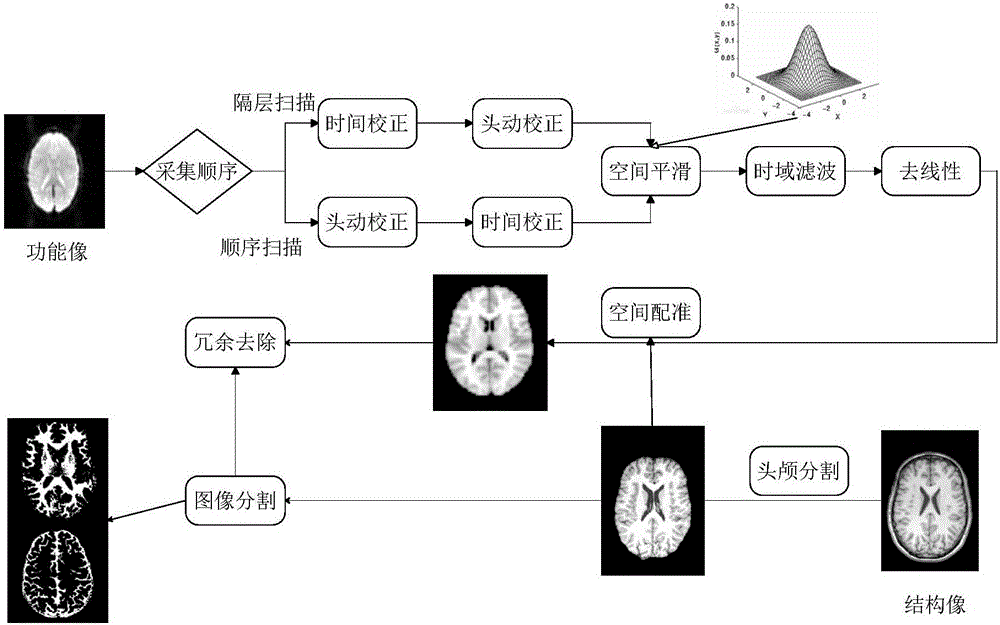
The invention relates to an fMRI and DTI fusion-based vault white matter segmentation method. The method includes the following steps that: fMRI and DTI magnetic resonance imaging data are pre-processed; regional segmentation is performed on a hippocampal encephalic region based on resting state function connections; an ROI is selected; and vault white matter segmentation is carried out based on a hippocampal sub-region and inter-thalamus white matter fiber bundle tracing technique. According to the method, the hippocampal encephalic region is segmented, and sub-regions obtained after segmentation are adopted as seed points; and the thalamus, adopted as a target encephalic region, is subjected to white matter fiber tracing, so that vault white matter can be segmented. The vault white matter is segmented based on the information of the function and structure of a human brain, and therefore, the fMRI and DTI fusion-based vault white matter segmentation method has the advantages of novel thinking, simple process and important scientific and clinical value.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
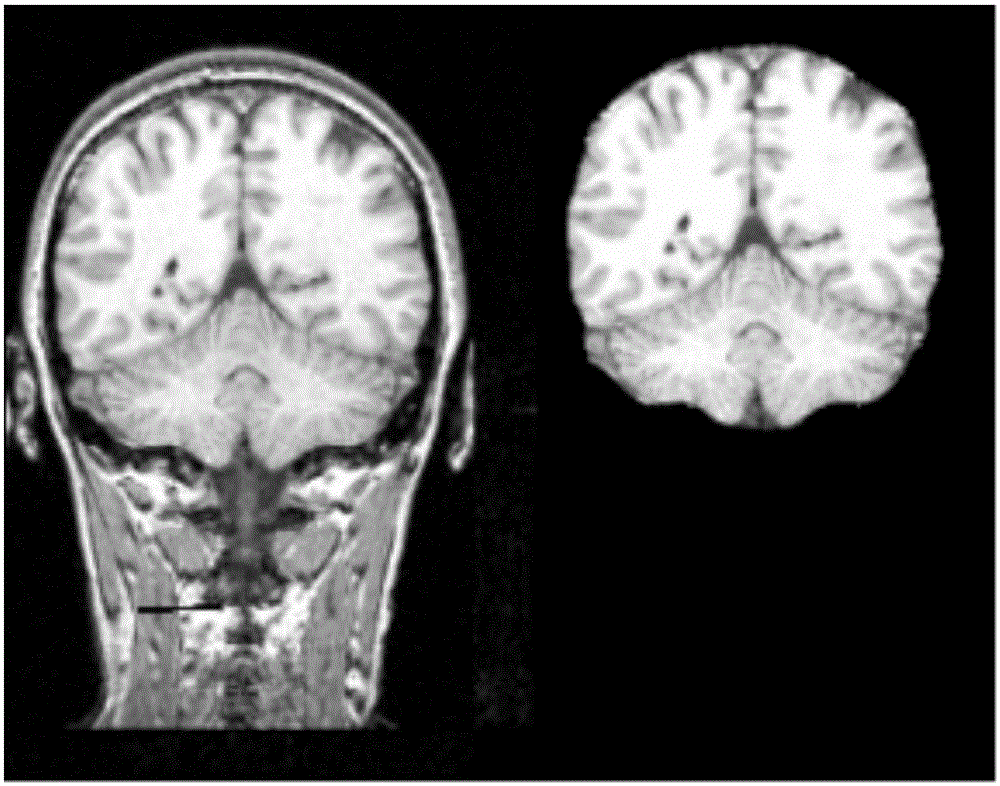
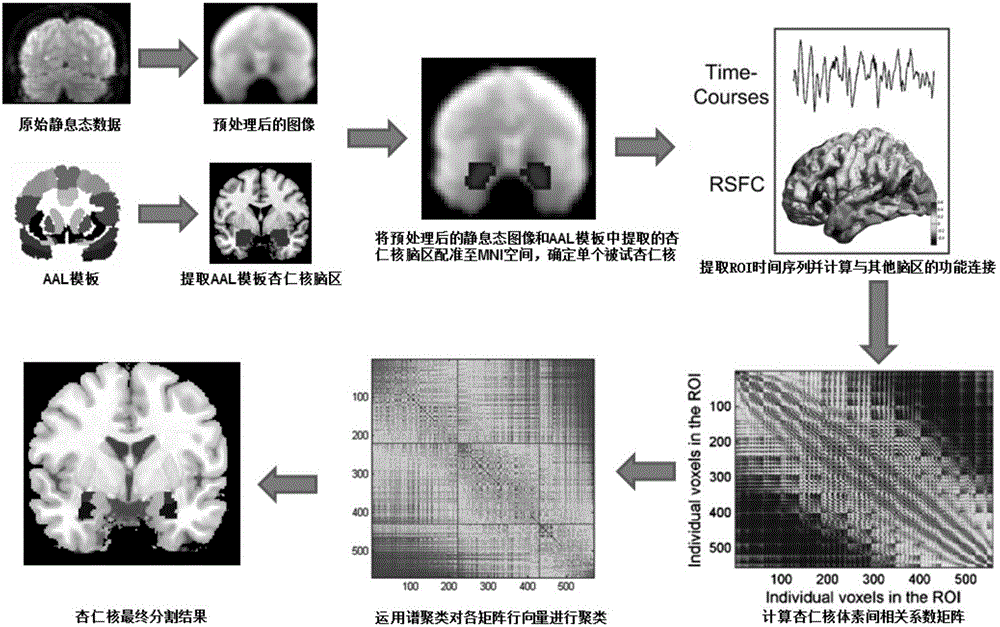
Amygdaloid nucleus spectral clustering segmentation method based on resting state function connection
ActiveCN106023194AGood repeatabilityImage enhancementImage analysisFunctional connectivityPattern recognition
The invention discloses an amygdaloid nucleus spectral clustering segmentation method based on resting state function connection, and the method is used for carrying out the automatic high-efficiency segmentation of an encephalic region based on a spectral clustering algorithm according to the similarity of internal voxel functions of an amygdaloid nucleus. The method comprises the steps: firstly carrying out the preprocessing of resting state magnetic resonance data; secondly carrying out the extraction of the encephalic region of the amygdaloid nucleus; thirdly carrying out the connection calculation of internal voxel whole-brain functions of the amygdaloid nucleus; and finally carrying out the spectral clustering segmentation of a function connection matrix. The automatic segmentation algorithm proposed by the invention and an amygdaloid nucleus clinic dissection result are enabled to be greatly consistent with each other, and the stability and noise interference resistance are enabled to be more satisfying. Compared with a conventional manual segmentation method, the method is simpler and more convenient and efficient, and is high in repeatability.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
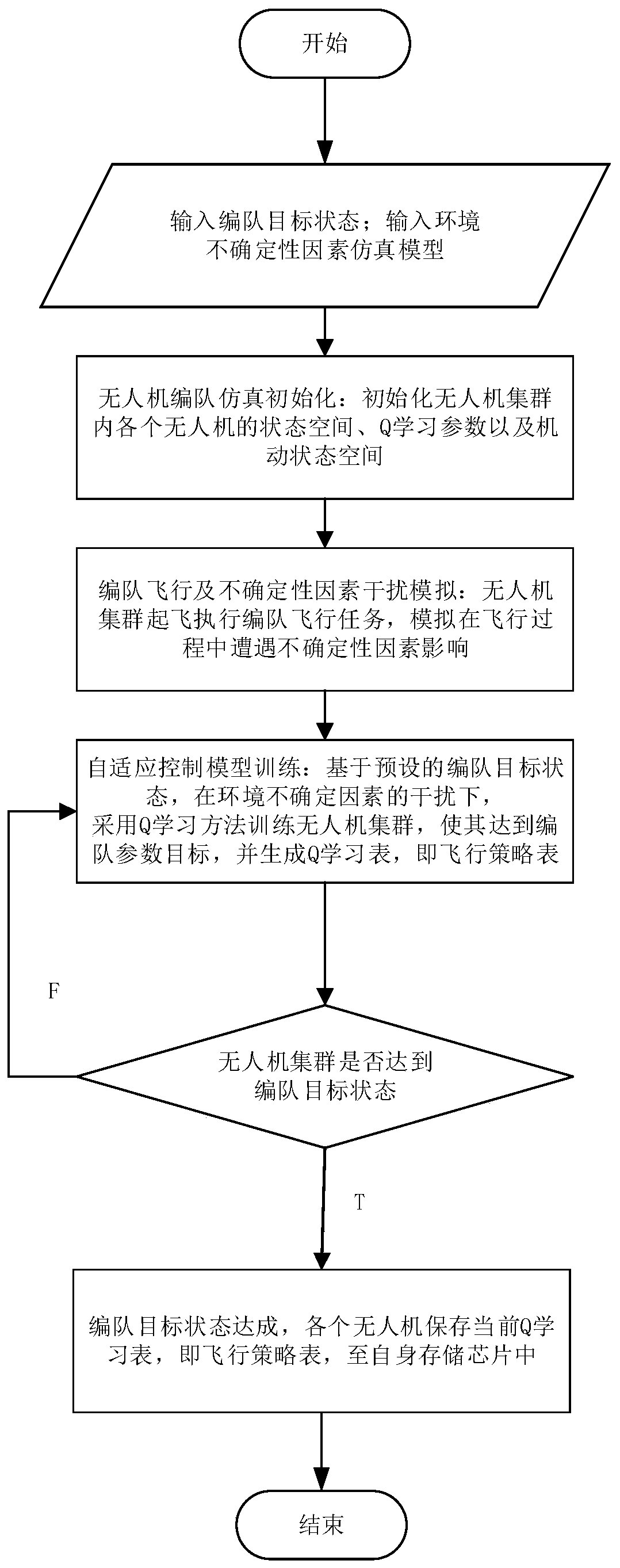
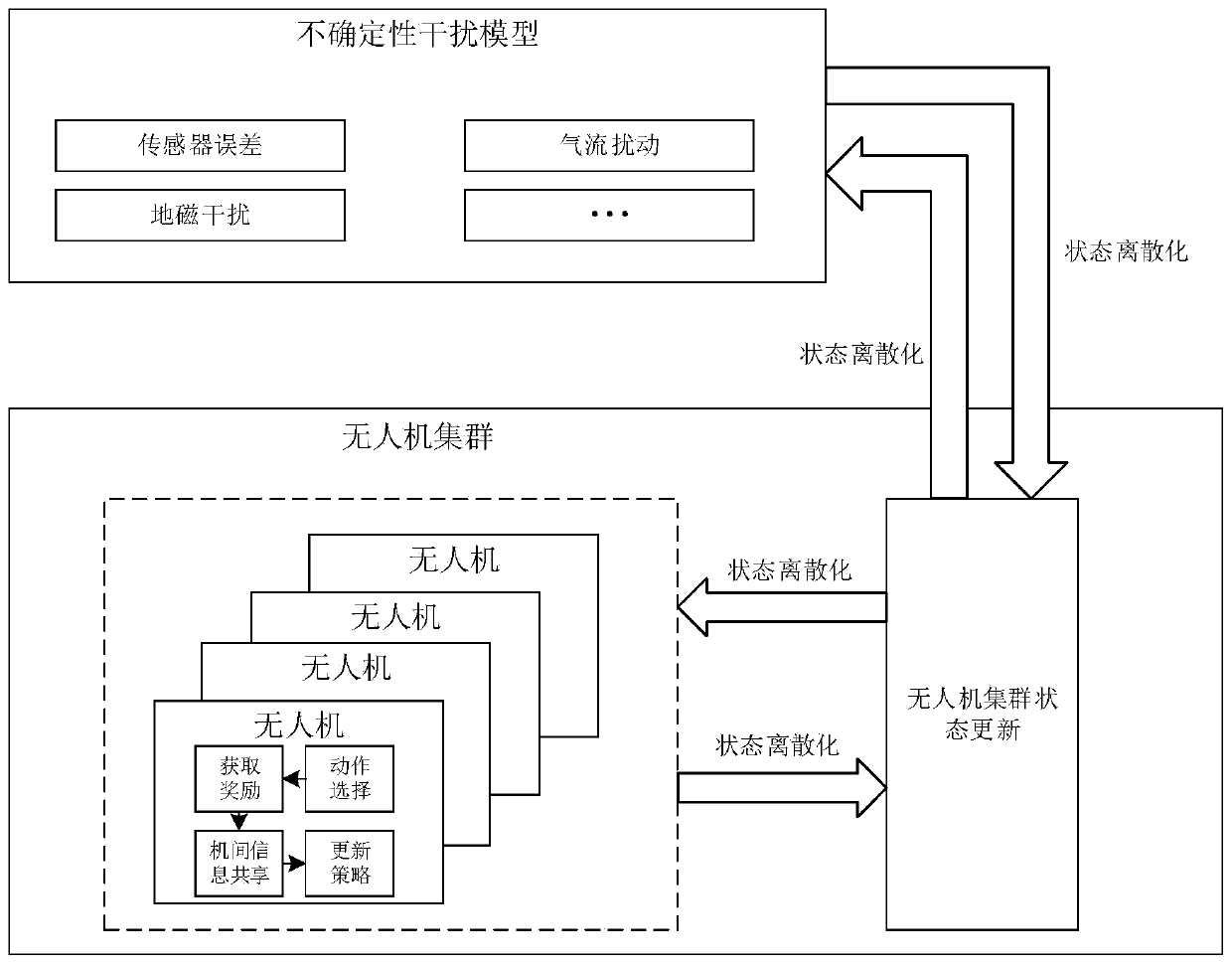
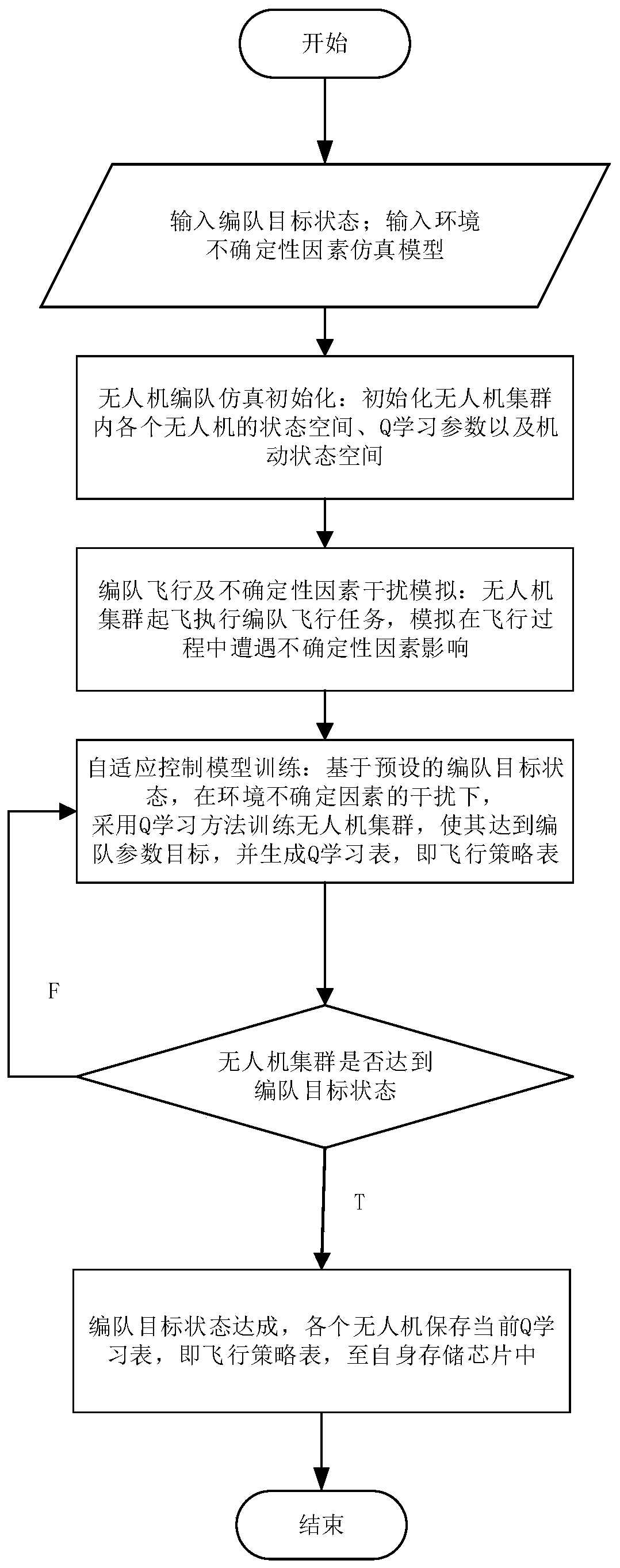
Distributed formation method of unmanned aerial vehicle cluster based on reinforcement learning
ActiveCN110007688AGuarantee stabilityGuaranteed robustnessPosition/course control in three dimensionsQ-learningCertainty factor
The invention discloses a distributed formation method of an unmanned aerial vehicle cluster based on reinforcement learning. The distributed formation method comprises the steps that step (1), a formation target state function and a simulation model of environmental uncertainty factors are obtained, and an unmanned aerial vehicle formation simulation model is established; step (2), under the interference of the environmental uncertainty factors, based on the unmanned aerial vehicle formation simulation model established in the step (1), a Q learning method is adopted to train the unmanned aerial vehicle cluster to update a flight strategy table; step (3), the value of the completion degree of the formation target state is calculated according to the obtained formation target state function, the obtained value of the completion degree of the formation target state is compared with a preset value of the formation target state, whether the formation target state is reached or not is judged according to the comparison results, if the formation target state is reached, a step (4) is performed, and if not, the step (2) is entered; and step (4), the updated flight strategy table is saved. According to the distributed formation method of the unmanned aerial vehicle cluster based on reinforcement learning, flight strategy parameters with adaptability are provided for the cluster, and the stability and robustness of the unmanned aerial vehicle cluster formation are guaranteed.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
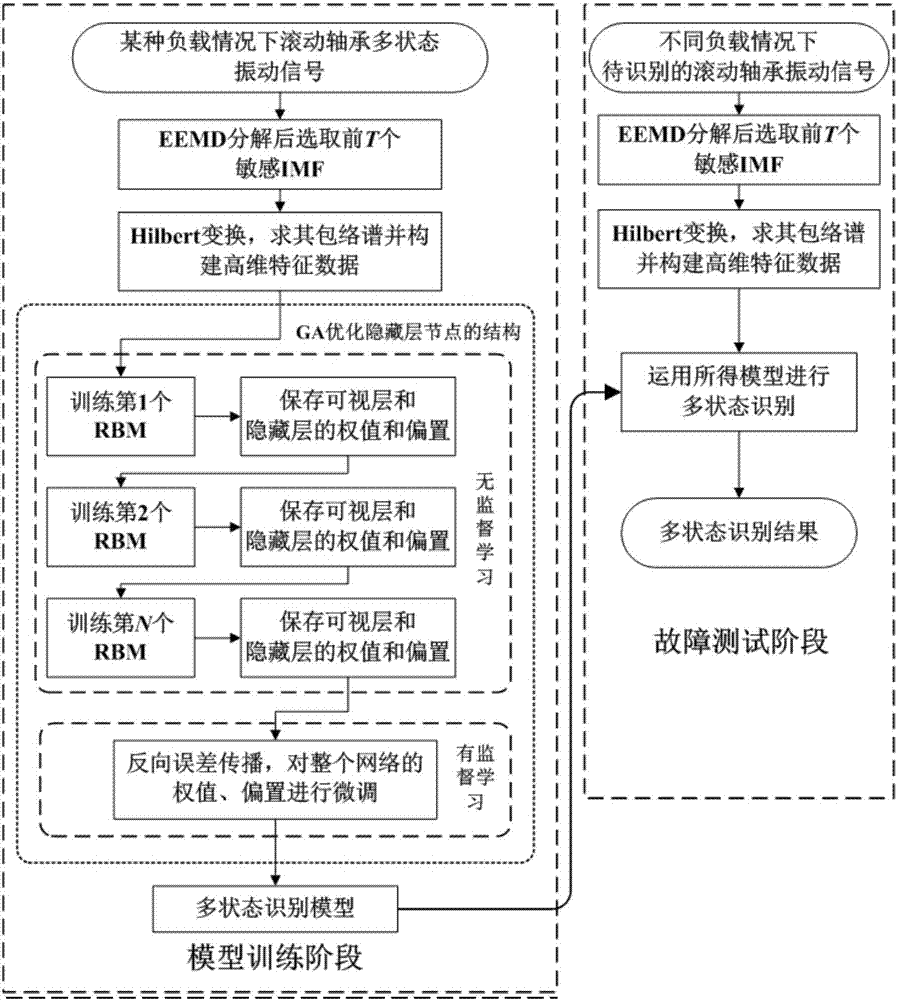
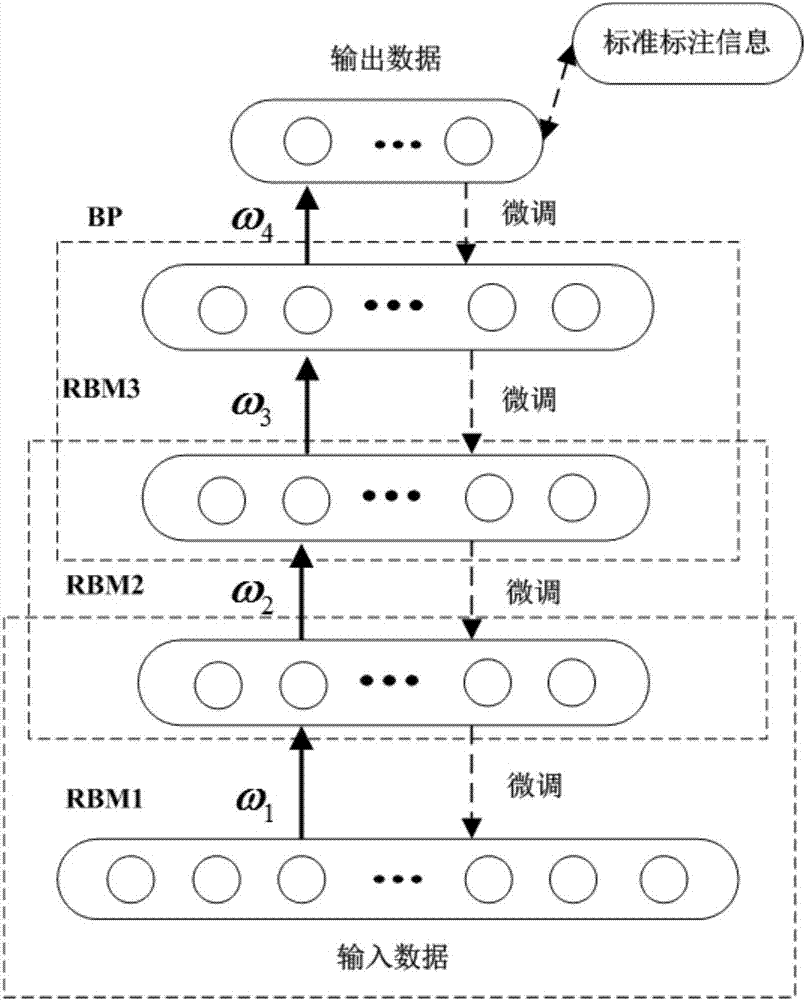
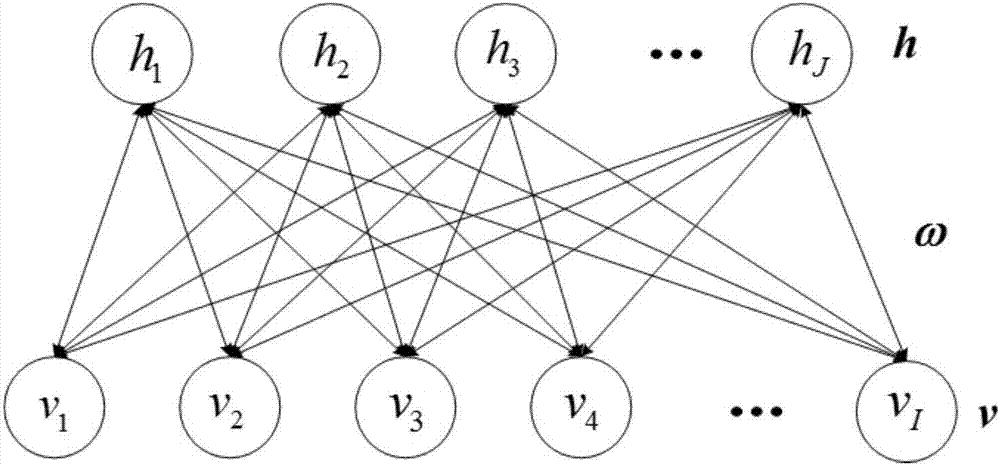
Identification method of rolling bearing state under variable load of EEMD-Hilbert envelope spectrum in combination with DBN
InactiveCN106886660AReduce distractionsMulti-state recognition implementationGeometric CADNeural learning methodsEngineeringHigh dimensional
The invention provides an identification method of rolling bearing state under variable load of EEMD-Hilbert envelope spectrum in combination with DBN, and belongs to the field of rolling bearing fault detection. The aim is to solve the problems that under the circumstance of training data using one load and test data using other loads, the rolling bearing fault state and the fault extent cannot be accurately identified. Firstly EEMD is conducted on the vibration signals of each status of the rolling bearing, then a sensitive eigenmode state function is selected, and Hilbert transformation is conducted to obtain the envelope spectrum. Finally, new high-dimensional data are built according to the order of the IMF envelope spectrum of the vibration signals of each status, then inputted into the DBN of each hidden layer node structure optimized by the genetic algorithm, and the multi-state recognition of rolling bearing under the variable load is achieved. In the process of 10 state recognition of rolling bearing using DBN, under the circumstance of the training data using one load and the test data using other loads, the EEMD-Hilbert envelope spectrum time domain or frequency-domain amplitude spectrum can better reflect the multiple state characteristics of rolling bearing under different loads, and has a higher recognition rate.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
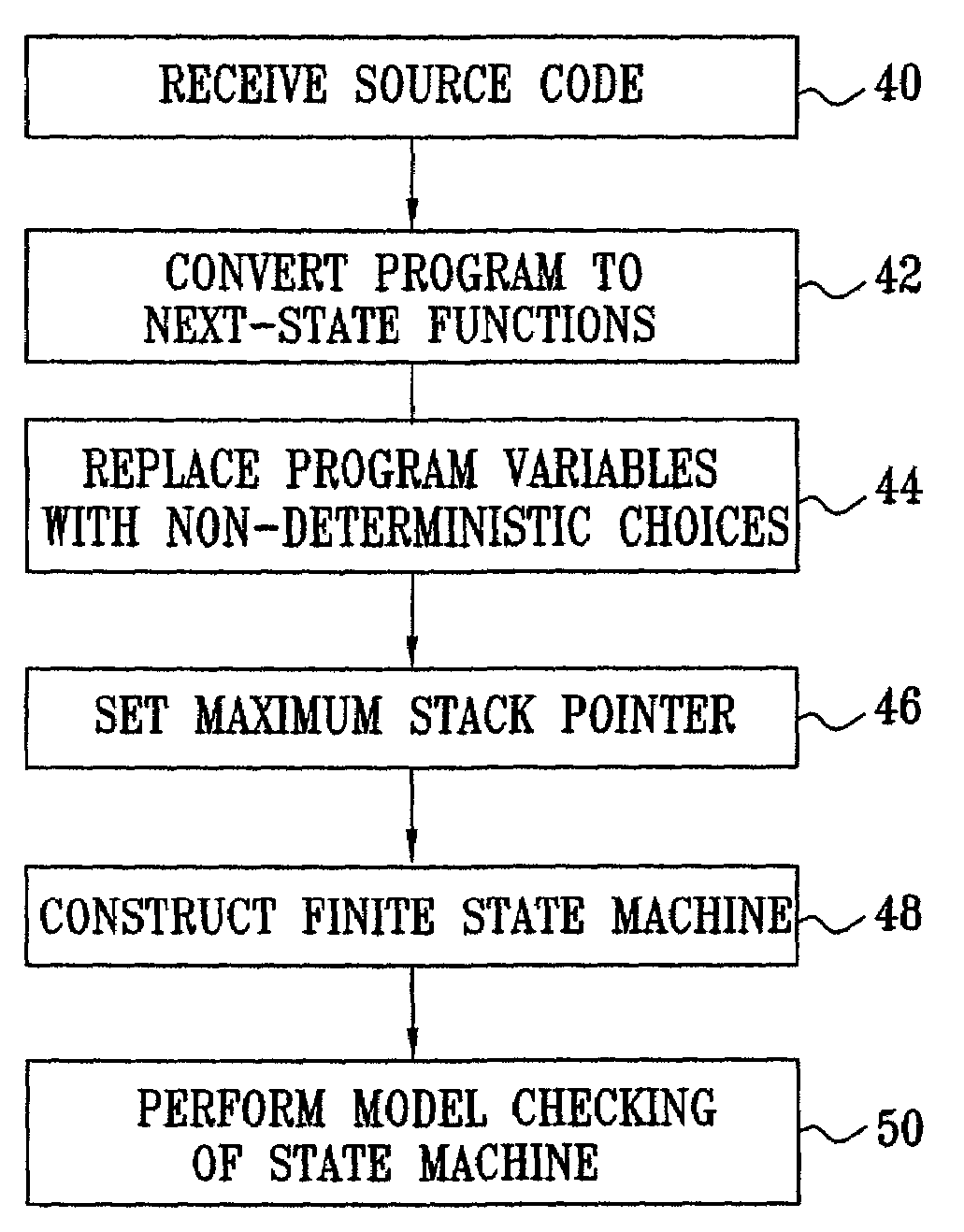
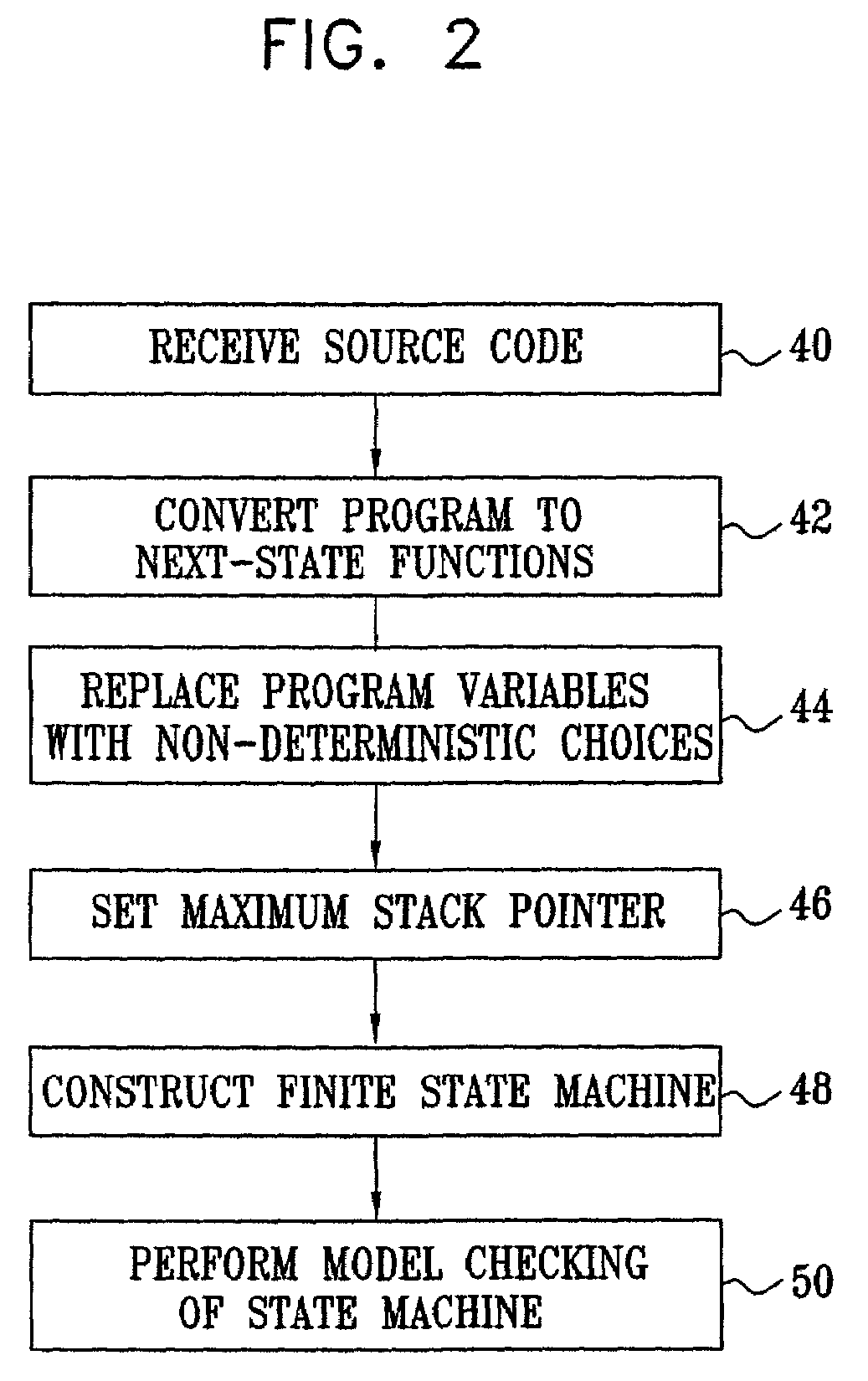
Automatic abstraction of software source
InactiveUS7146605B2Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsControl flowSource code
A method for verifying software source code that includes references to program variables includes processing the source code to derive a set of next-state functions representing control flow of the source code. The references to the program variables in the source code are replaced with non-deterministic choices in the next-state functions. The next-state functions including the non-deterministic choices are restricted to produce a finite-state model of the control flow. The finite-state model is then verified to find an error in the source code.
Owner:IBM CORP
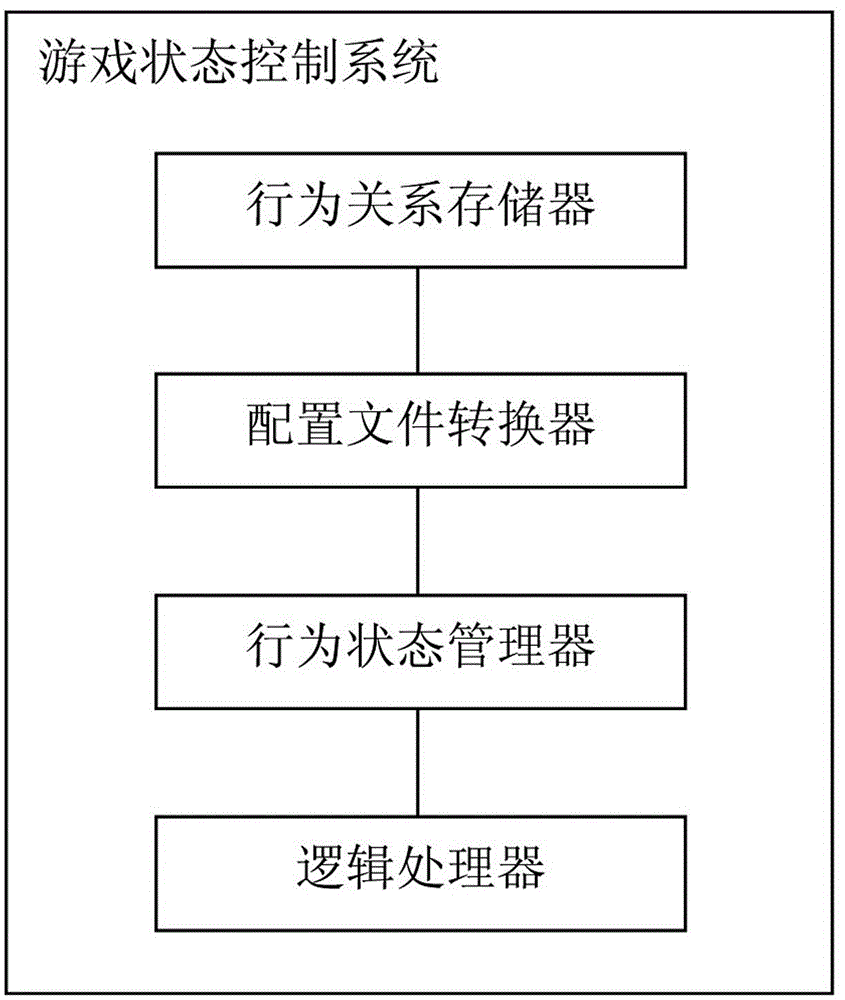
Universal game state control system and method
ActiveCN104383684AImprove development efficiencyFlexible behavior controlVideo gamesSoftware bugControl system
The invention discloses a universal game state control system and method. The system comprises a behavior relation storer, a configuration file converter, a behavior state manager and a logic processor. The method includes that game behavior rules that can be edited in a user-defined mode and predefined behavior state test function fields are stored and then converted into configuration files that can be directly loaded by a Lua script engine of a game program, the Lua script engine of the game program is called to analyze configuration files that are output by the configuration file converter, game behaviors, behavior state functions and behavior state test function ports that are already configured are recognized and managed, a logical relationship between to-be-tested behaviors and about-to-happen behaviors is determined, and a behavioral control command is output. The universal game state control system and method has the advantages that a behavior description table is merely required to be modified and then a game is restarted so that newly modified game behaviors and logics can directly come into effect, thereby, the game developing efficiency is greatly increased, and the conditions of program errors caused by human code modification can be reduced.
Owner:珠海西山居互动娱乐科技有限公司 +1
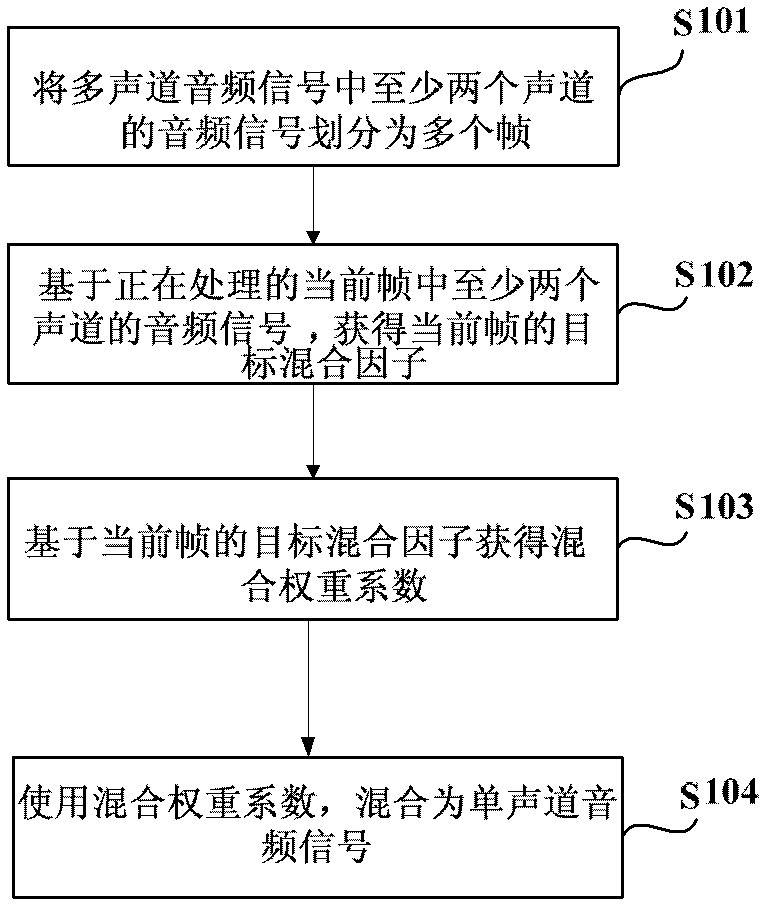
Method and system of processing multichannel audio signals
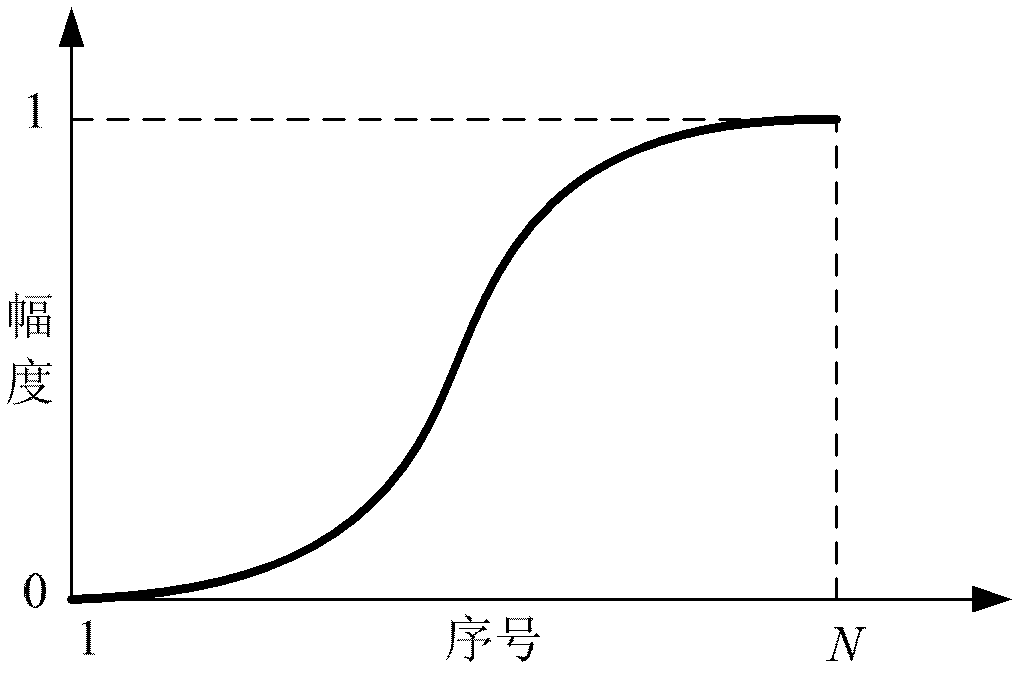
The invention discloses a method and a system of processing multichannel audio signals. The method comprises dividing the audio signals of at least two sound channels of the multichannel audio signals into a plurality of frames; acquiring target mixed factors of a current frame based on the audio signals of at least two sound channels of the current processing frame, wherein the target mixed factors enable a sound mixing state function indicating sound mixing effects to acquire a maximum value; acquiring a mixing weight coefficient based on the target mixed factors of the current frame; and mixing the audio signals of at least two sound channels of the current frame at single channel audio signals by using the mixing weight coefficient. By adopting the method of processing the multichannel audio signals, the multichannel audio signals are mixed as the single channel audio signals, the acquired single channel audio signals have good sound mixing effects, and the phenomena that information is seriously lost or sound volume drops sharply and the like are avoided.
Owner:SPREADTRUM COMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Power supply method of cold-state function test in nuclear power plant
ActiveCN102638095AProgress is not affectedEnsure safetyNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringElectricityNuclear power
The invention discloses a power supply method of a cold-state function test in a nuclear power plant. The power supply method comprises the steps of: sequentially operating three main pumps respectively used for heating a loop and circulating loop fluid, carrying out load limit on equipment positioned on the same line of inlet wires; when an auxiliary power supply loses power, automatically starting diesel engines on one line of inlet wires to drive upper charging pumps, equipment cooling water systems, important factory water utilization systems and residual heat removal systems on the corresponding lines of inlet wires, supplying power for an uninterrupted power supply on the same line of inlet wires and an uninterrupted power supply on another line of inlet wires through patches by the diesel engines so as to supply power for instrument control equipment, wherein the upper charging pump I is arranged on the A line of inlet wires, and the upper charging pump II and the upper charging pump III are arranged on the B line of inlet wires. By implementing the technical scheme of the invention, under the condition that a main power supply is unusable, the progress of building a nuclear power project is not influenced largely, and safety of tests and equipment is ensured.
Owner:中广核工程有限公司 +1
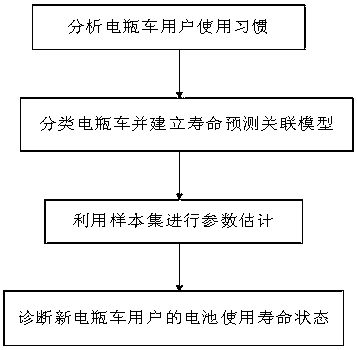
Battery set service life prediction method based on battery car state data
The invention relates to a battery set service life prediction method based on probability statistics according to user use habits of different types of battery cars. The method comprises steps that step 1), statistics and analysis on user habits influencing battery car battery service life are carried out, and two important factors include mileage and the battery discharging time; step 2), classification of battery car types is carried out according to voltage values, and a battery car user use habit and battery service association model is established; step 3), parameter estimation is carried out for the association model through utilizing a training sample set; and step 4), to-be-tested new user mileage and the accumulative discharging time are substituted to a corresponding battery service life state function for calculation, a standard quantity of the battery service lift state is acquired, through comparison with a set threshold, a battery service life state conclusion of a present battery car user is acquired.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
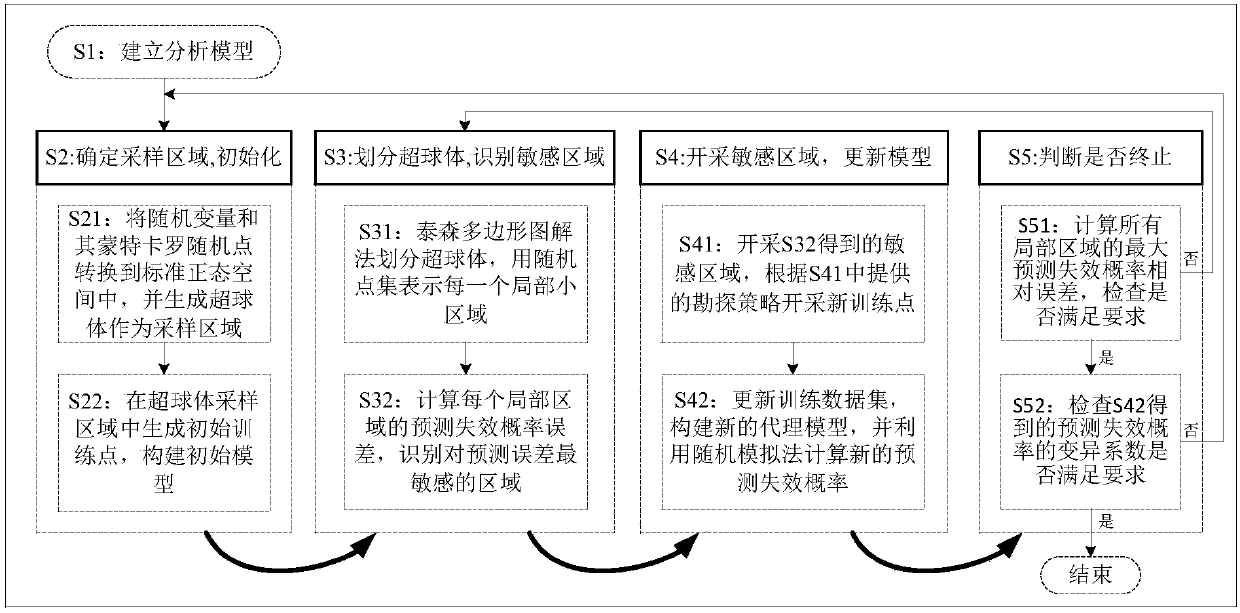
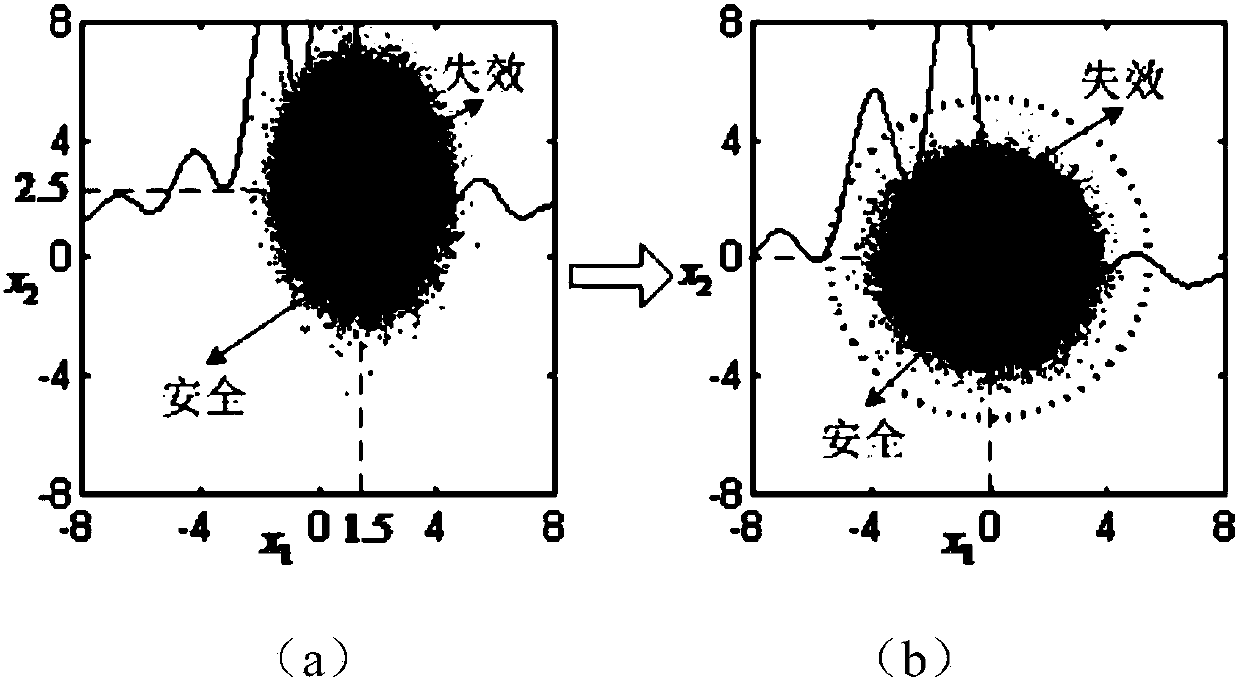
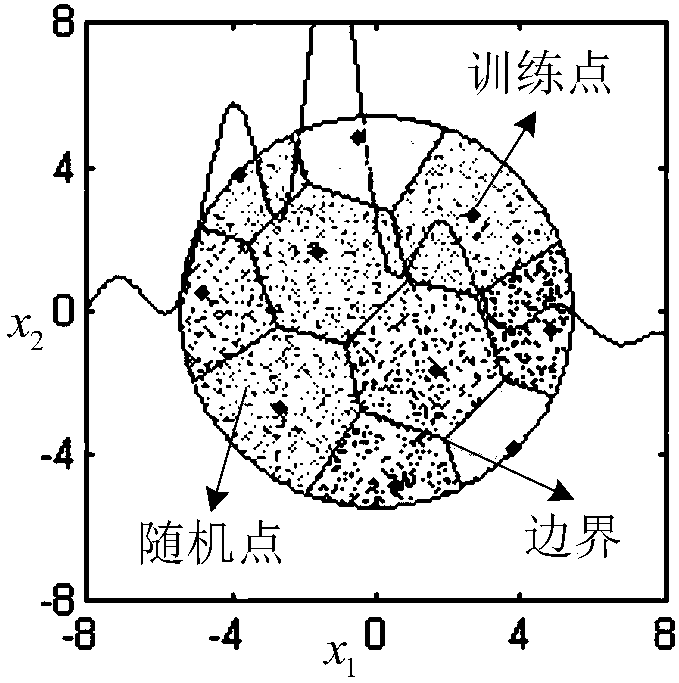
Structural reliability analysis-oriented common dynamic tracking sequence sampling method
ActiveCN108287808AImprove adaptabilityImprove bindingComplex mathematical operationsStructural reliabilityData set
The invention belongs to the field of structural reliability analysis, and specifically discloses a structural reliability analysis-oriented common dynamic tracking sequence sampling method. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a structural ultimate state function, and determining a random variable and random variable distribution information; constructing a random point, andconverting the random variable and the random point into a standard normal state to determine a target sampling area; constructing a training point, forming a training data set and establishing a proxy model; dividing the target sampling area and recognizing a most sensitive area; exploiting the most sensitive area to obtain a new training point, updating the training data set and the proxy model,and calculating a prediction failure probability; and calculating maximum relative errors of all the local areas and a variation coefficient of the prediction failure probability, and judging whetherto terminate the sampling or not according to the maximum relative errors and the variation coefficient so as to complete the structural reliability analysis. The method has the advantages of being simple in operation step, high in efficiency and strong in self-adaptability.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Power supply method for nuclear power plant cold-state function test
ActiveCN102568629ADoes not affect the debugging processNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringTransformerPower grid
The invention discloses a power supply method for a nuclear power plant cold-state function test. The power supply method for a nuclear power plant cold-state function test comprises the following steps of orderly running three main pumps, carrying out load limit of equipment, wherein the equipment and the main pump which is running are arranged in the same incoming line, starting an equipment cooling water system, an essential service water system and a residual heat removal system of one of alternating current emergency switchboards according to demands, wherein the main pump which is running and the one of the alternating current emergency switchboards are not arranged in the same incoming line, using an auxiliary power supply with two independent outer power grid inlet wires to independently supply power to an A row of the alternating current emergency switchboard and a B row of the alternating current emergency switchboard respectively by auxiliary transformers, using the A row of the alternating current emergency switchboard to supply power to a charging pump 1, using the B row of the alternating current emergency switchboard to supply power to a charging pump 2 and a charging pump 3, and keeping simultaneous running of the charging pump 1 and one of the charging pump 2 and the charging pump 3. The power supply method for a nuclear power plant cold-state function test can realize a cold-state function test when a main power supply is not available.
Owner:中广核工程有限公司 +1
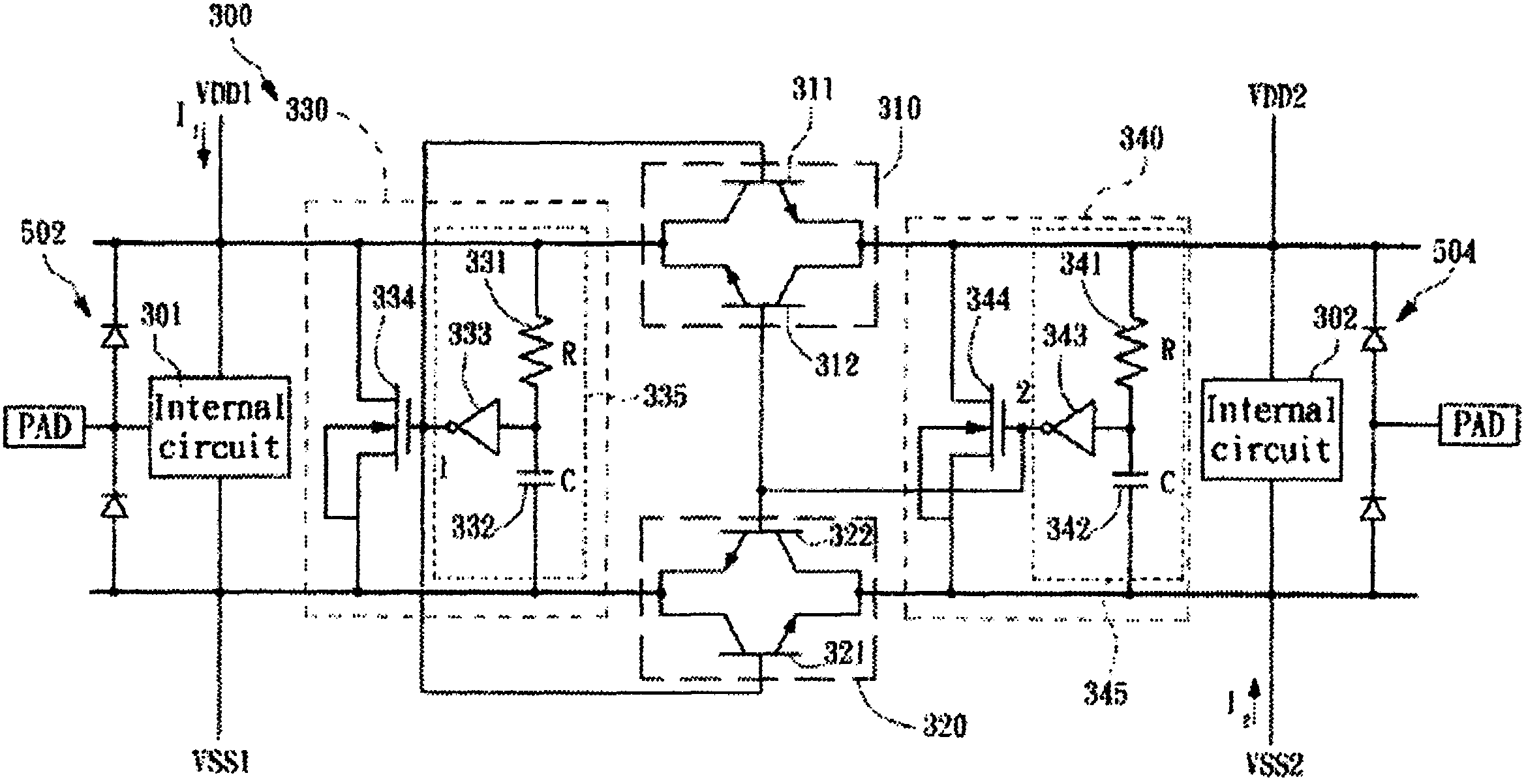
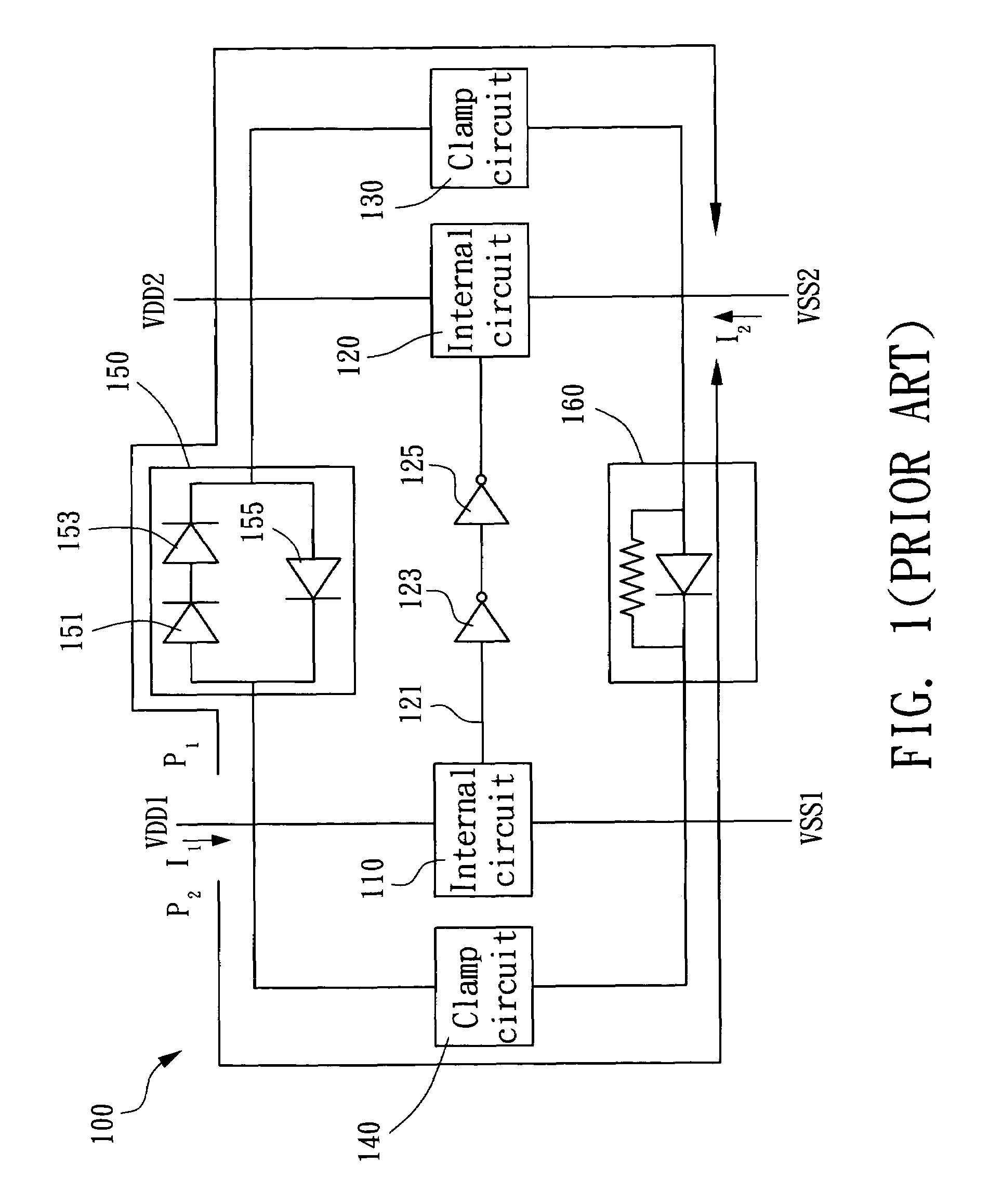
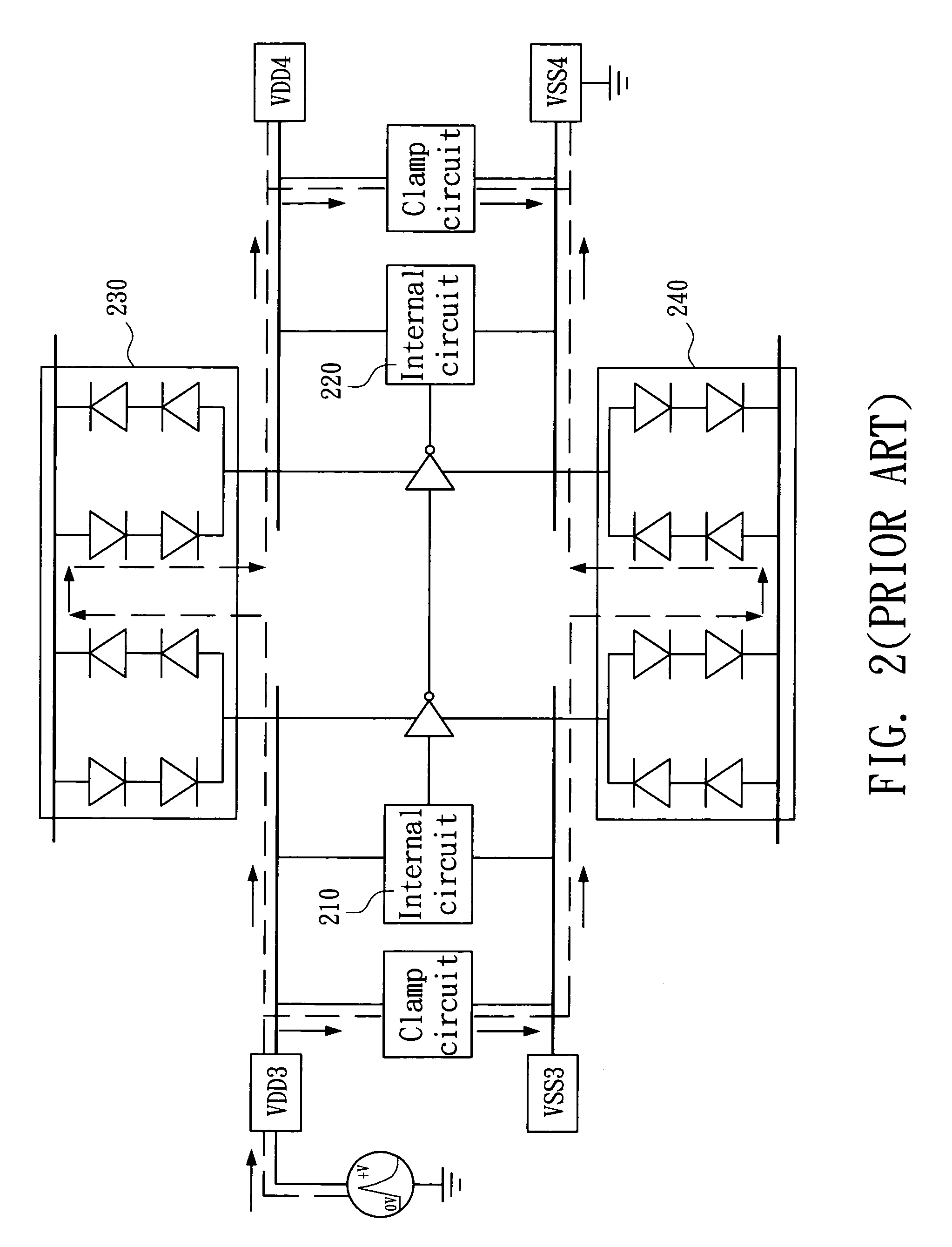
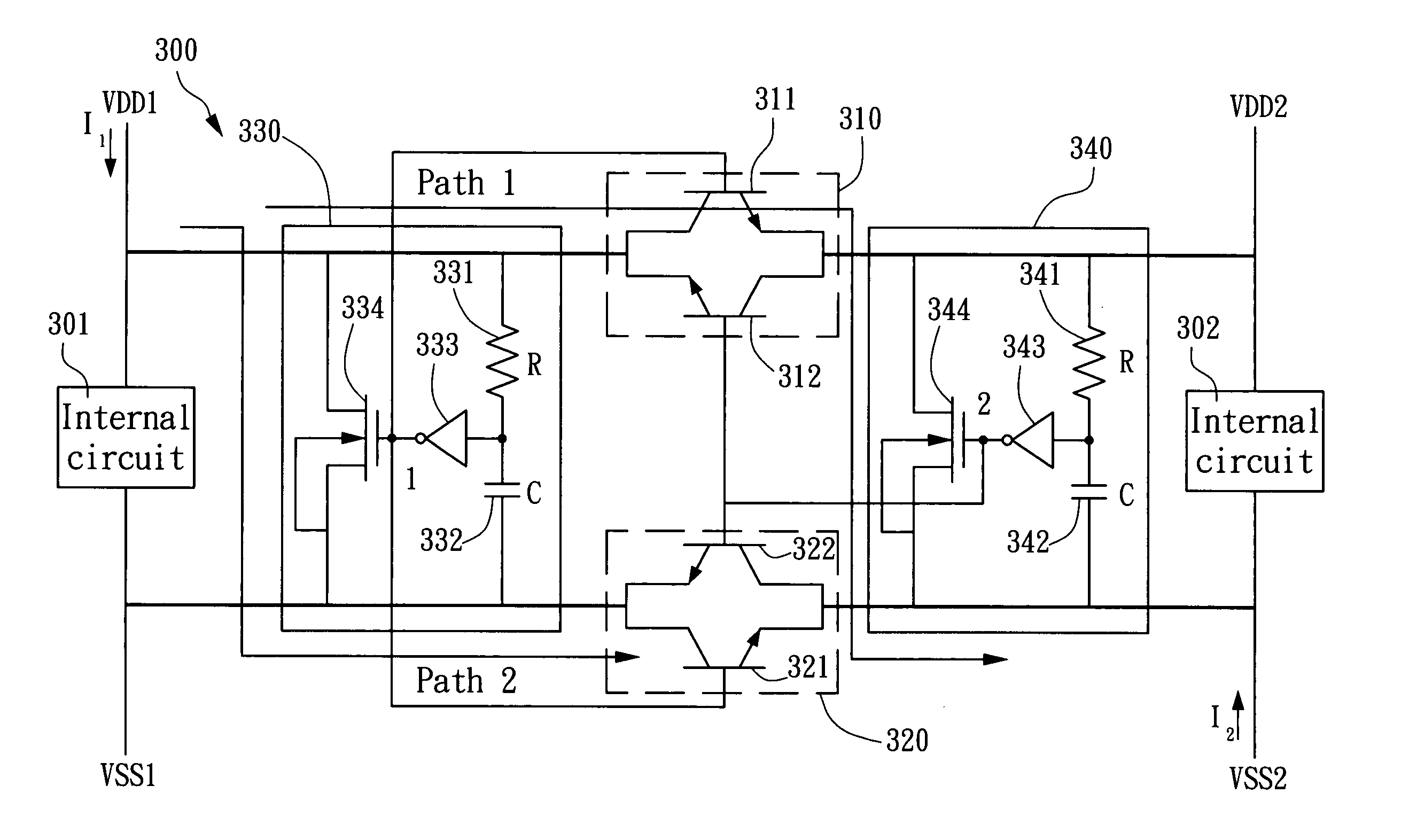
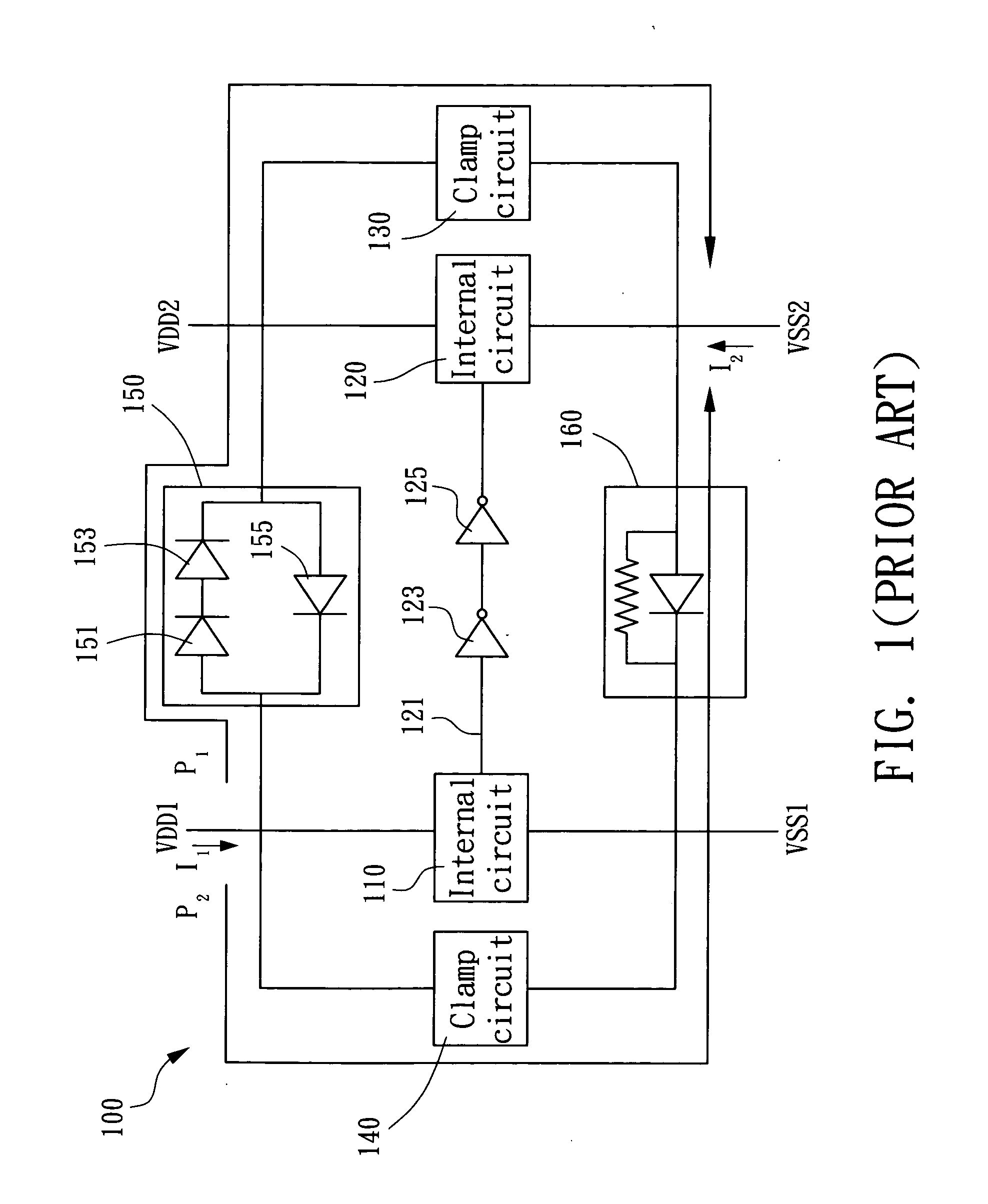
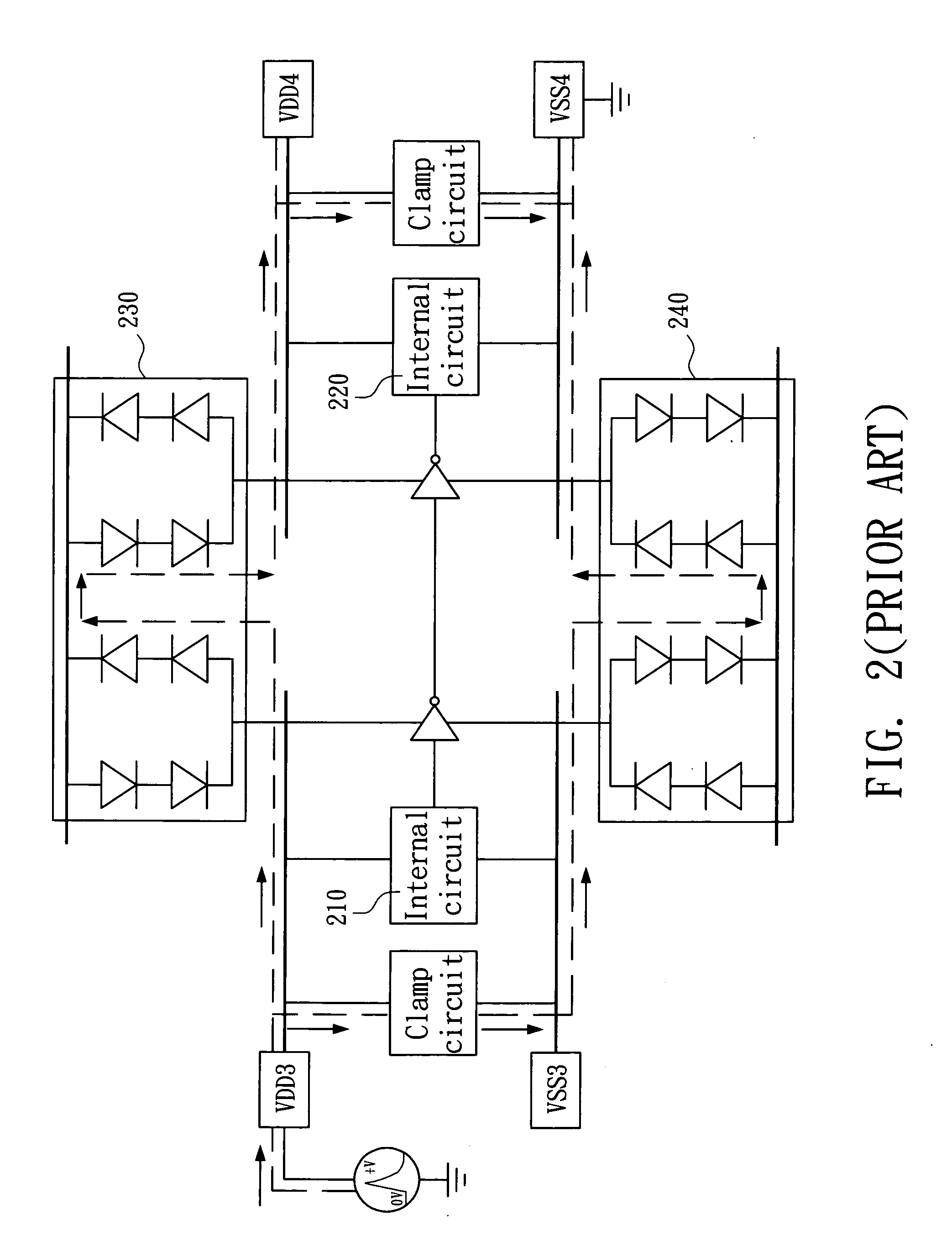
ESD protection circuit between different voltage sources
An ESD protection circuit for hybrid voltage sources includes a first bipolar transistor set and a second bipolar transistor set, a first detection circuit, and a second detection circuit. The ON / OFF states of the first bipolar transistor set and the second bipolar transistor set are determined by the first and the second detection circuit, and the ON / OFF states function to isolate terminals of the different voltage sources and discharge electrostatic charges injected into one of the terminals.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
Method for predicate-based compositional minimization in a verification environment
InactiveUS7437690B2Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationTheoretical computer scienceEquivalent input
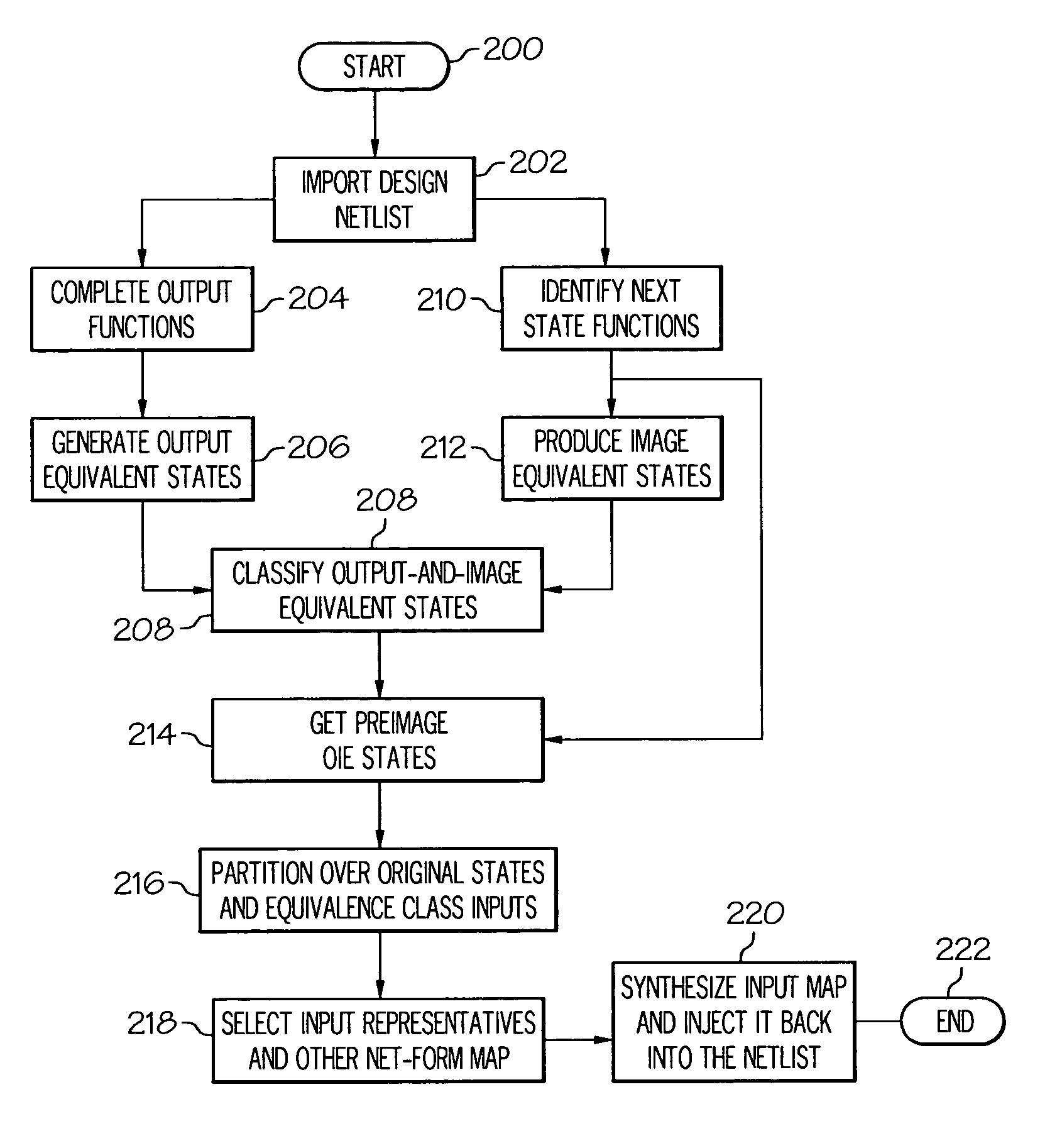
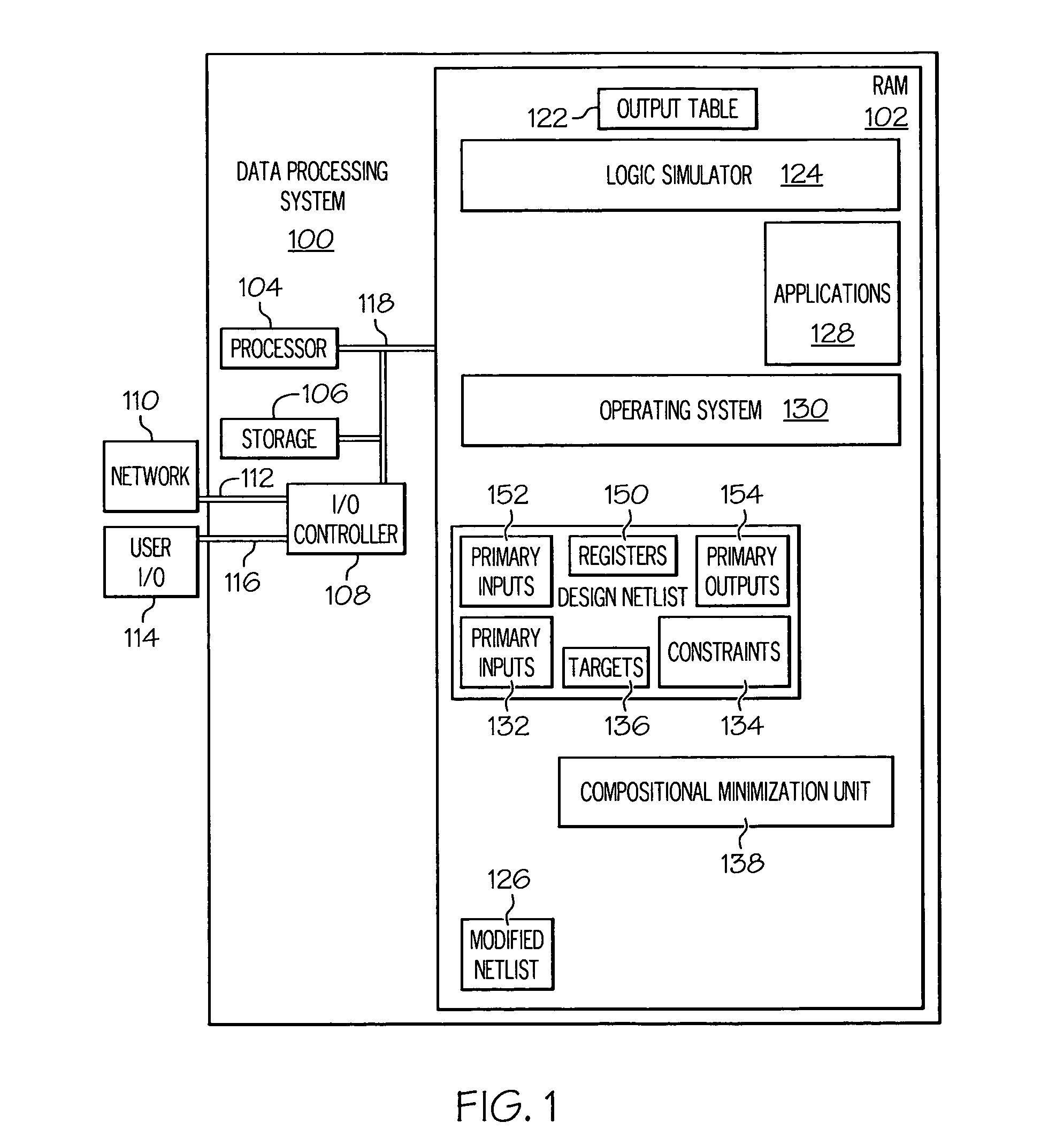
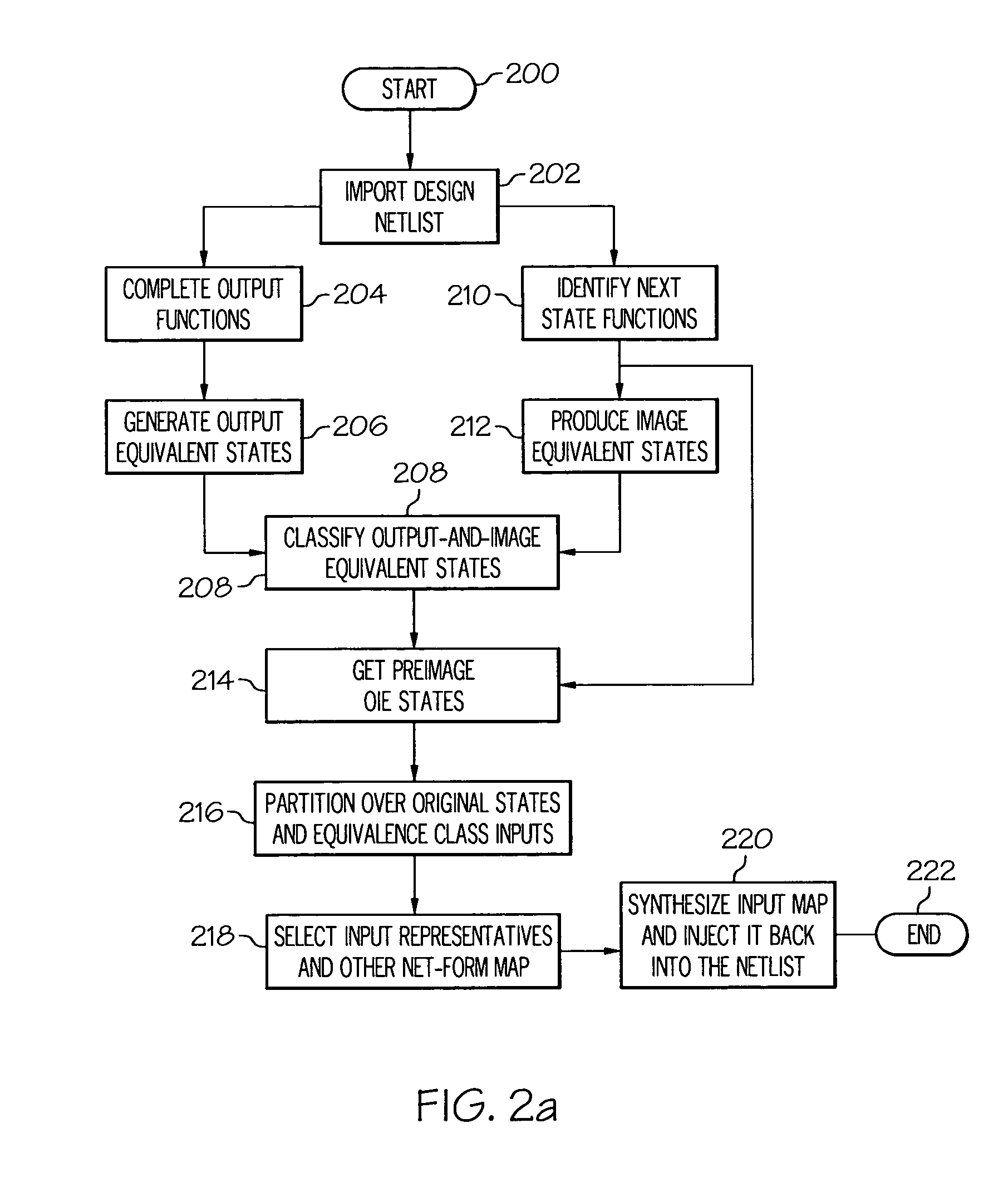
A method for performing verification includes importing a design netlist containing one or more components and computing one or more output functions for the one or more components. One or more output equivalent state sets are generated from the one or more output functions and one or more next-state functions for the one or more components are identified. One or more image equivalent state sets for the one or more next-state functions are produced and one or more output-and-image equivalent state sets are classified for the one or more image equivalent state sets and the one or more output equivalent state sets. One or more input representatives of the one or more equivalent input sets are selected and an input map is formed from the one or more input representatives. The input map is synthesized and injected back into the netlist to generate a modified netlist.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
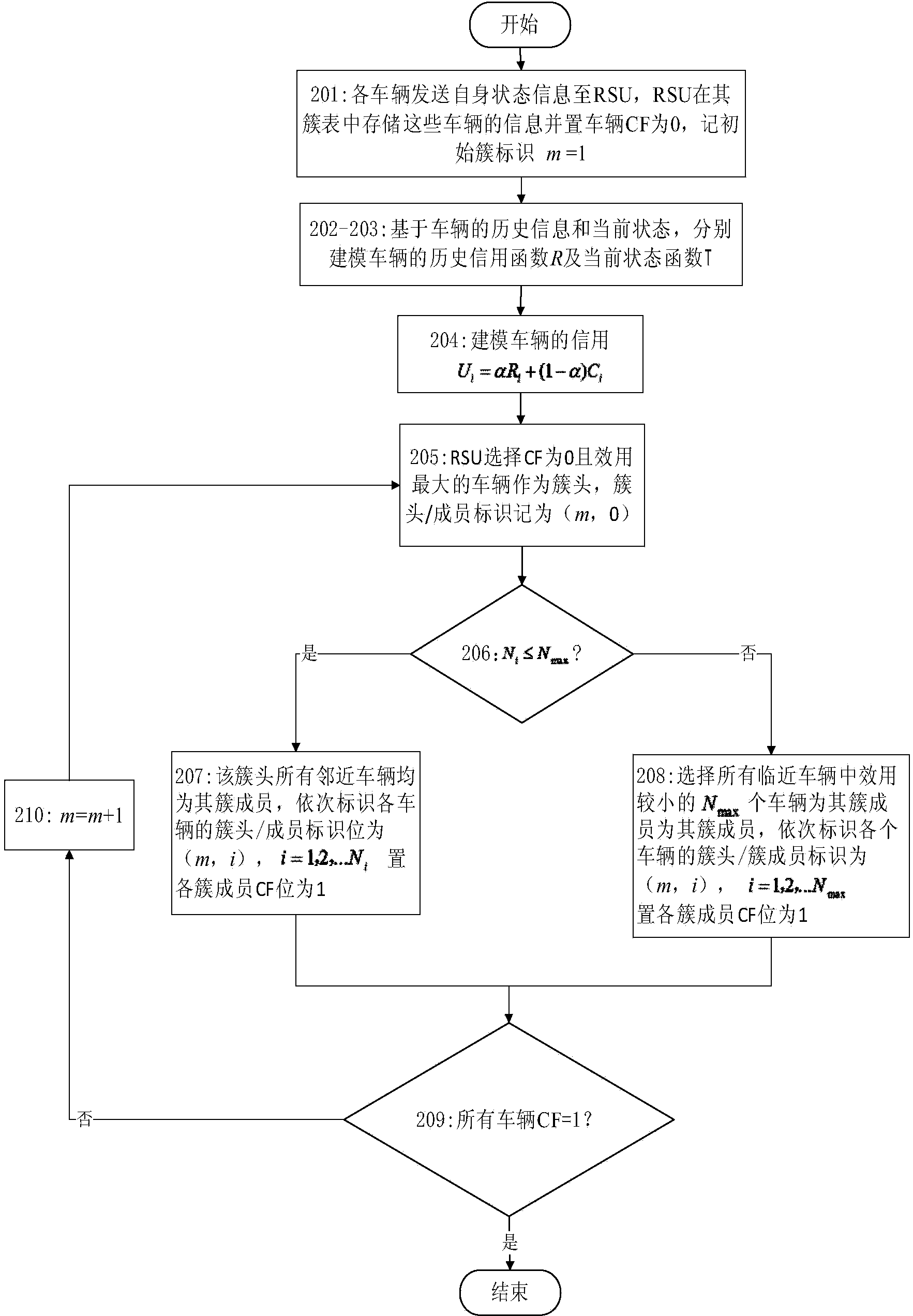
VANET clustering method combining historical credit of vehicle with current state of vehicle
ActiveCN103973789AImprove transmission performanceThe network topology is stableTransmissionComputer scienceTransmission bandwidth
The invention relates to the technical field of mobile communication and discloses a VANET clustering method combining the historical credit of a vehicle with the current state of the vehicle. According to the method, the historical credit R of the vehicle is modeled according to the transmission bandwidth, queue length and time for acting as the cluster head of the vehicle in a historical period; the current state function C of the vehicle is modeled according to the current state information, including the node degree and the speed and position of the vehicle relative to neighboring vehicles, of the vehicle; a utility function U=alpha R + (1-alpha)C is modeled according to the historical credit and the current state function of the vehicle, a candidate cluster head the corresponding utility function of which is the largest is selected to serve as a target cluster head, and then an adjacent user of the target cluster head is selected as a cluster member. By the adoption of the method, a VANET topological structure can be kept stable relatively, and service transmission performance can be optimized.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
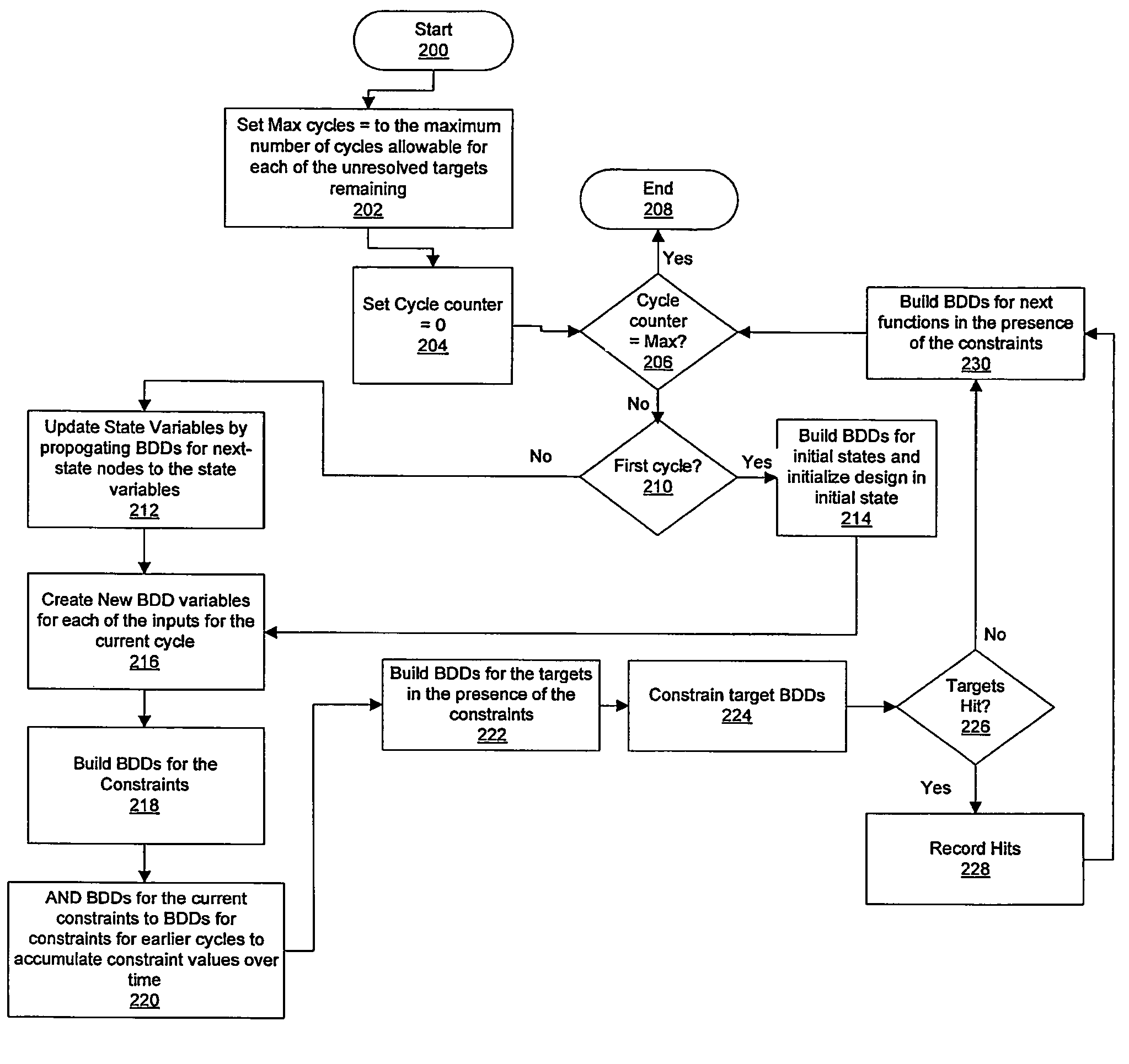
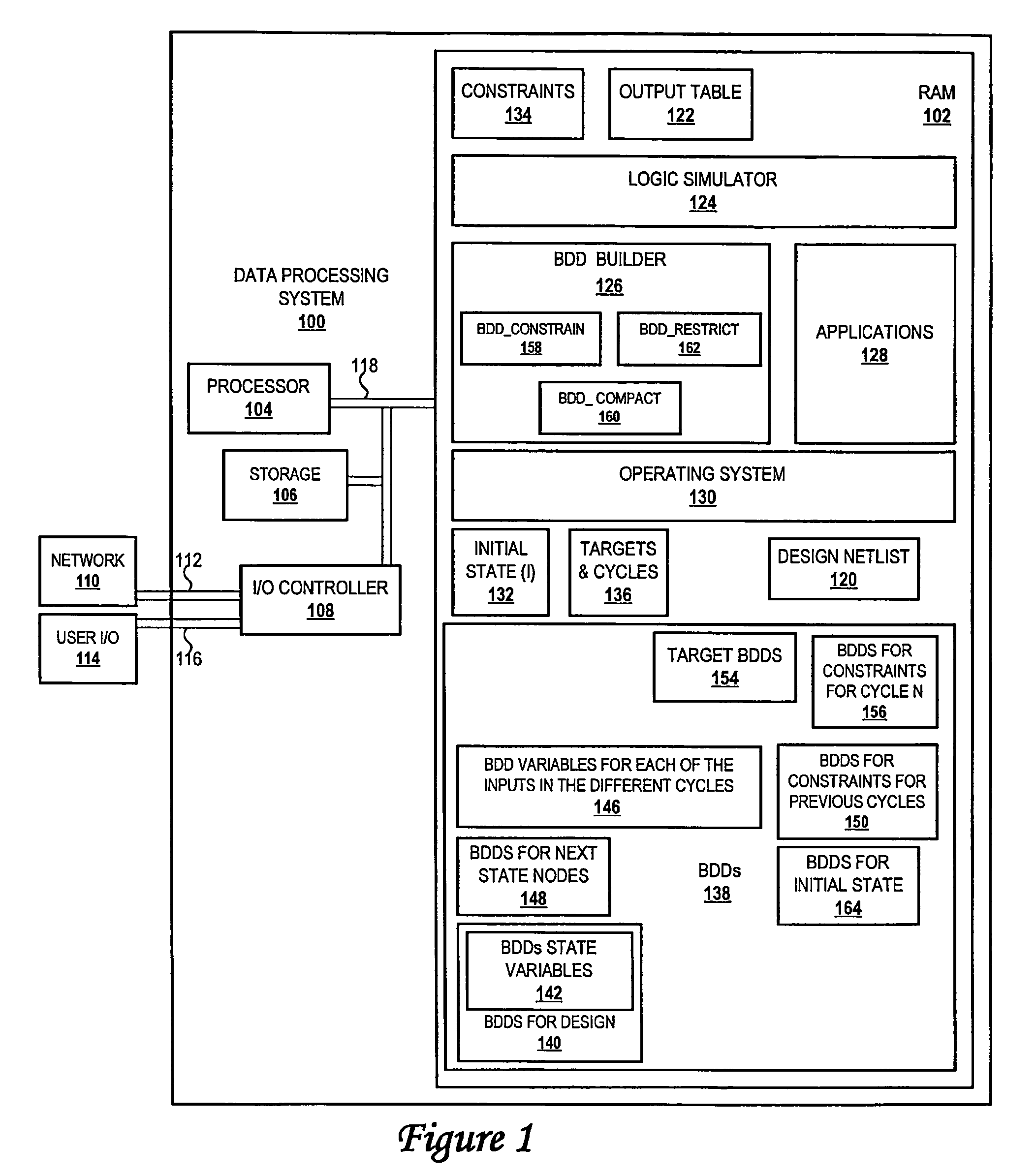
Method and system for optimized handling of constraints during symbolic simulation
InactiveUS7290229B2Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationSymbolic simulationState variable
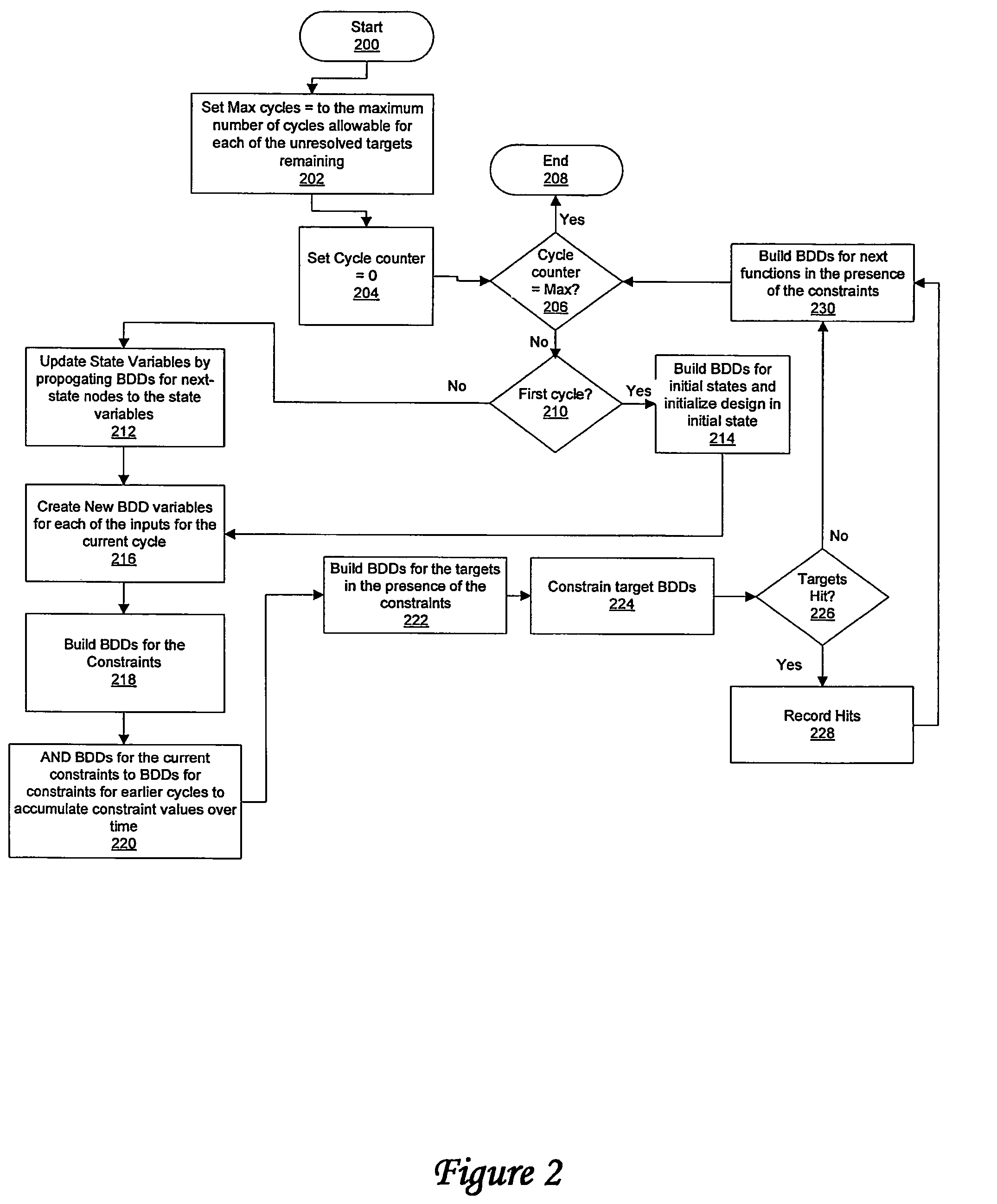
A method for verifying a design through symbolic simulation is disclosed. The method comprises creating one or more binary decision diagram variables for one or more inputs in a design containing one or more state variables and building a binary decision diagram for a first node of one or more nodes of the design. A binary decision diagram for the initial state function of one or more state variables of the design is generated and the design is subsequently initialized. Binary decisions diagrams for one or more constraints are synthesized. A set of constraint values is accumulated over time by combining the binary decision diagrams for the one or more constraints with a set of previously generated binary decision diagrams for a set of constraints previously used in one or more previous time-steps. A binary decision diagram for the next state function of the one or more state variables in the design is constructed in the presence of the constraints. The one or more state variables in the design are updated by propagating the binary decision diagram for the next state function to the one or more state variables and a set of binary decision diagrams for the one or more targets in the presence of the one or more constraints is calculated. The set of binary decision diagrams for one or more targets is constrained and the design is verified by determining whether the one or more targets were hit.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
ESD protection circuit between different voltage sources
An ESD protection circuit for hybrid voltage sources includes a first bipolar transistor set and a second bipolar transistor set, a first detection circuit, and a second detection circuit. The ON / OFF states of the first bipolar transistor set and the second bipolar transistor set are determined by the first and the second detection circuit, and the ON / OFF states function to isolate terminals of the different voltage sources and discharge electrostatic charges injected into one of the terminals.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
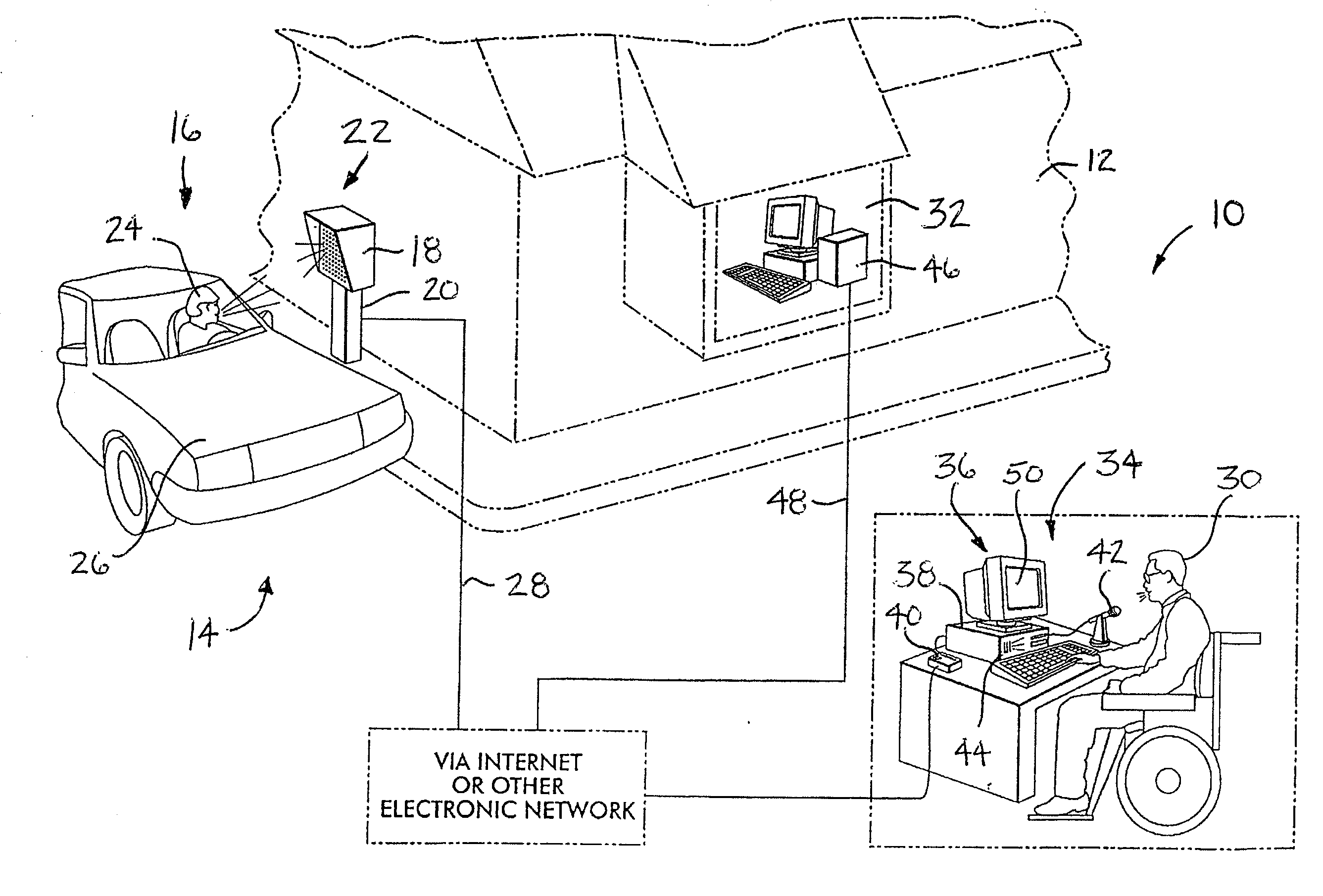
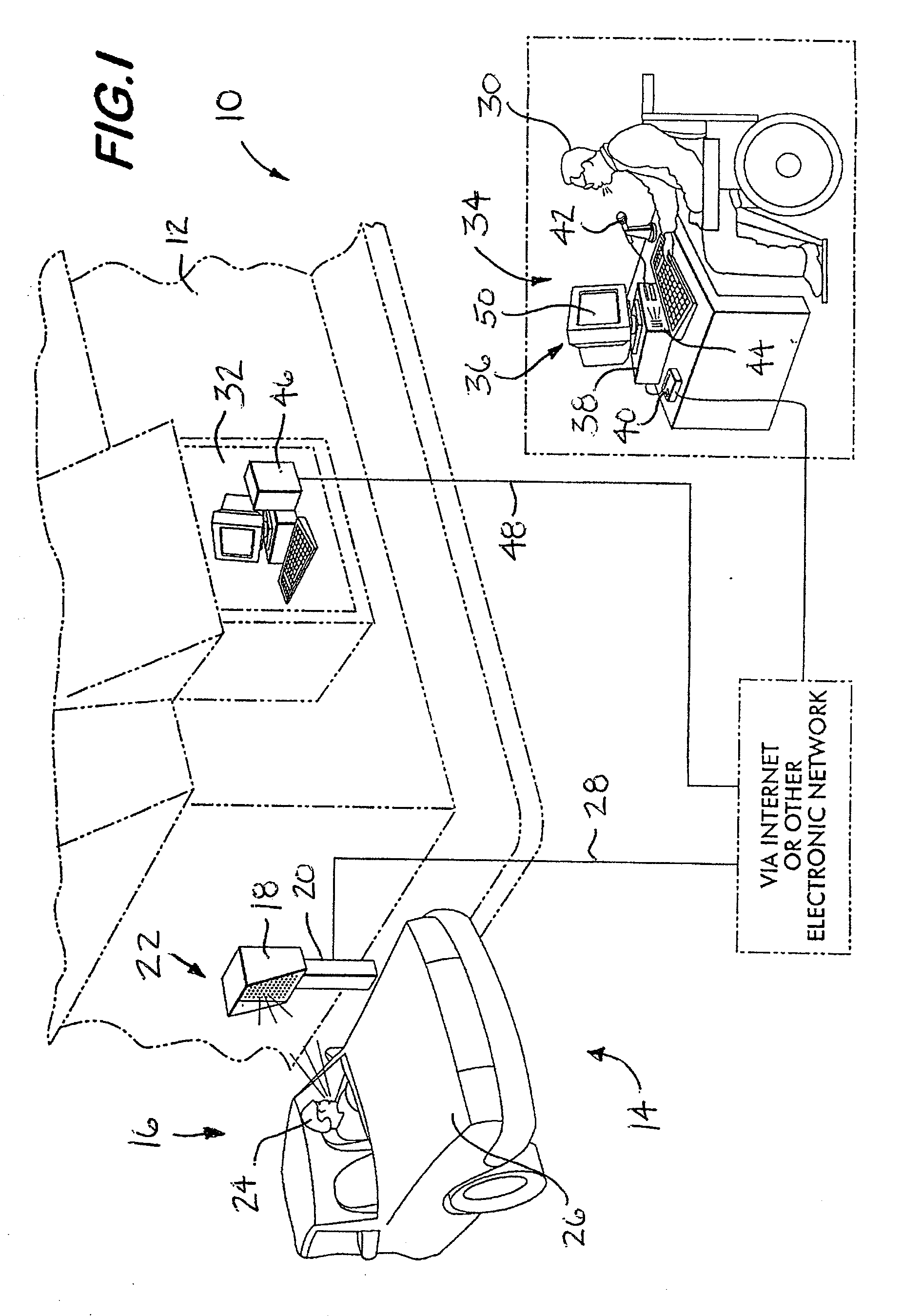
Method and system for entering orders of customers
InactiveUS20100023410A1Improved take-out ordering systemImprove methodBuying/selling/leasing transactionsTelecommunications linkVoice communication
A method and system for entering an order into an onsite computer-based sales management system of a restaurant. A communication link is established between an offsite employee and an order-placing talk box at the restaurant. The communication link is utilized for two-way voice communication so that a food order can be taken from a customer located at the restaurant by the offsite employee. A data communication link is utilized by the offsite employee to enter the order into the onsite computer-based sales management system which facilitates food preparation, fee collection, and the recording of sales. Preferably, the offsite employee utilizes a personal computer to accomplish the stated functions, the communication links are provided via the Internet, and the customer is located within a vehicle adjacent the restaurant when placing his / her order.
Owner:DOAN WILLIAM T
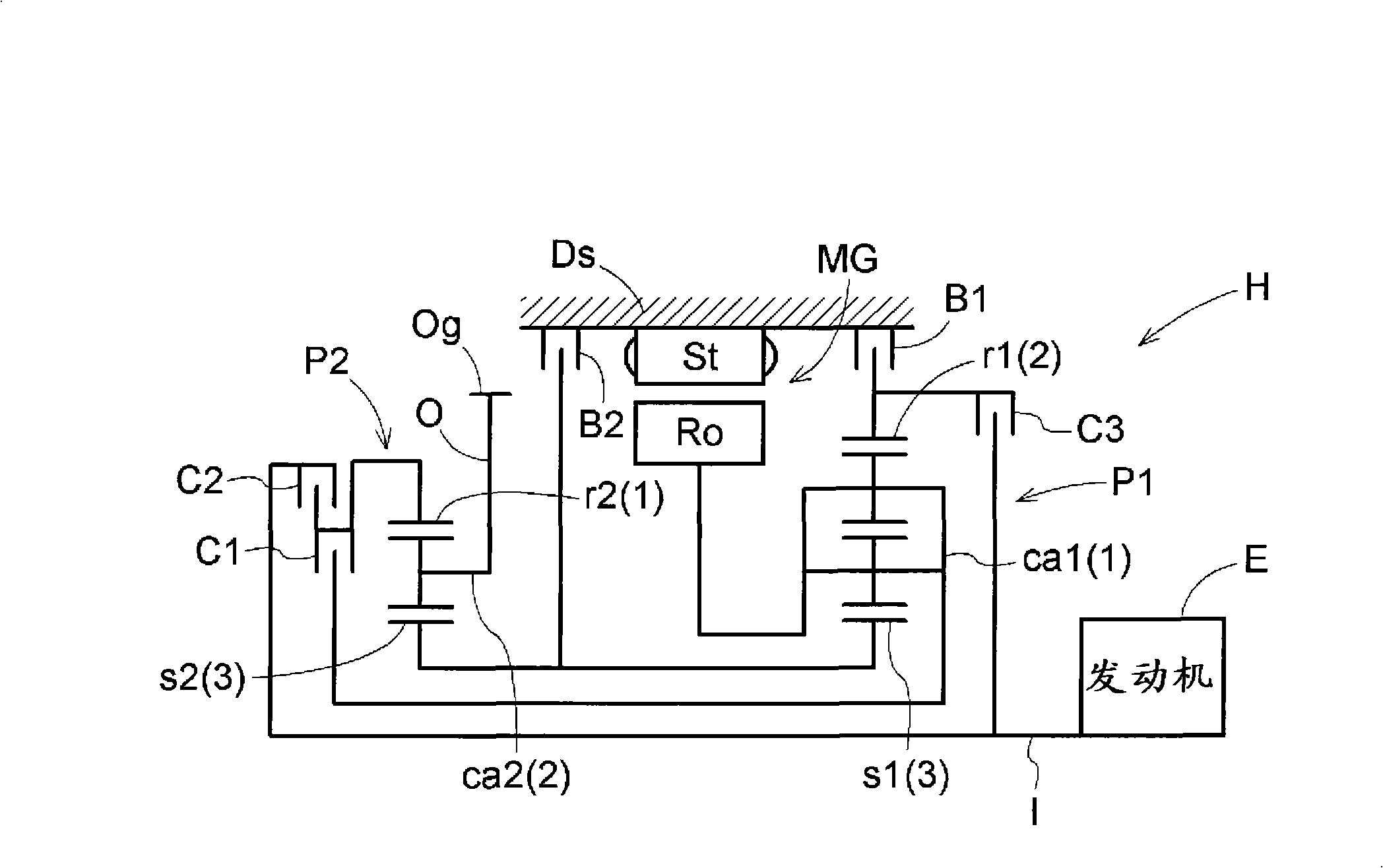
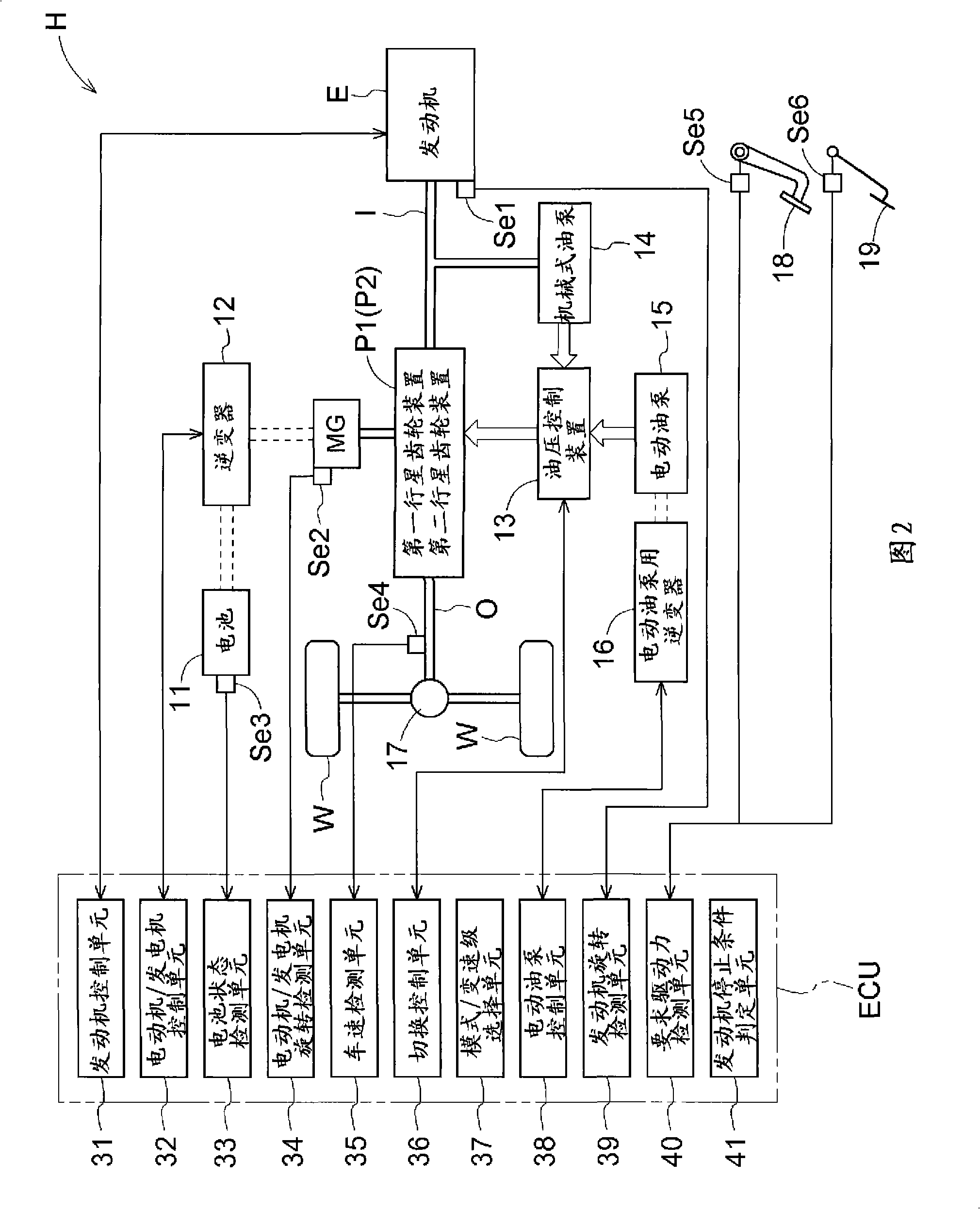
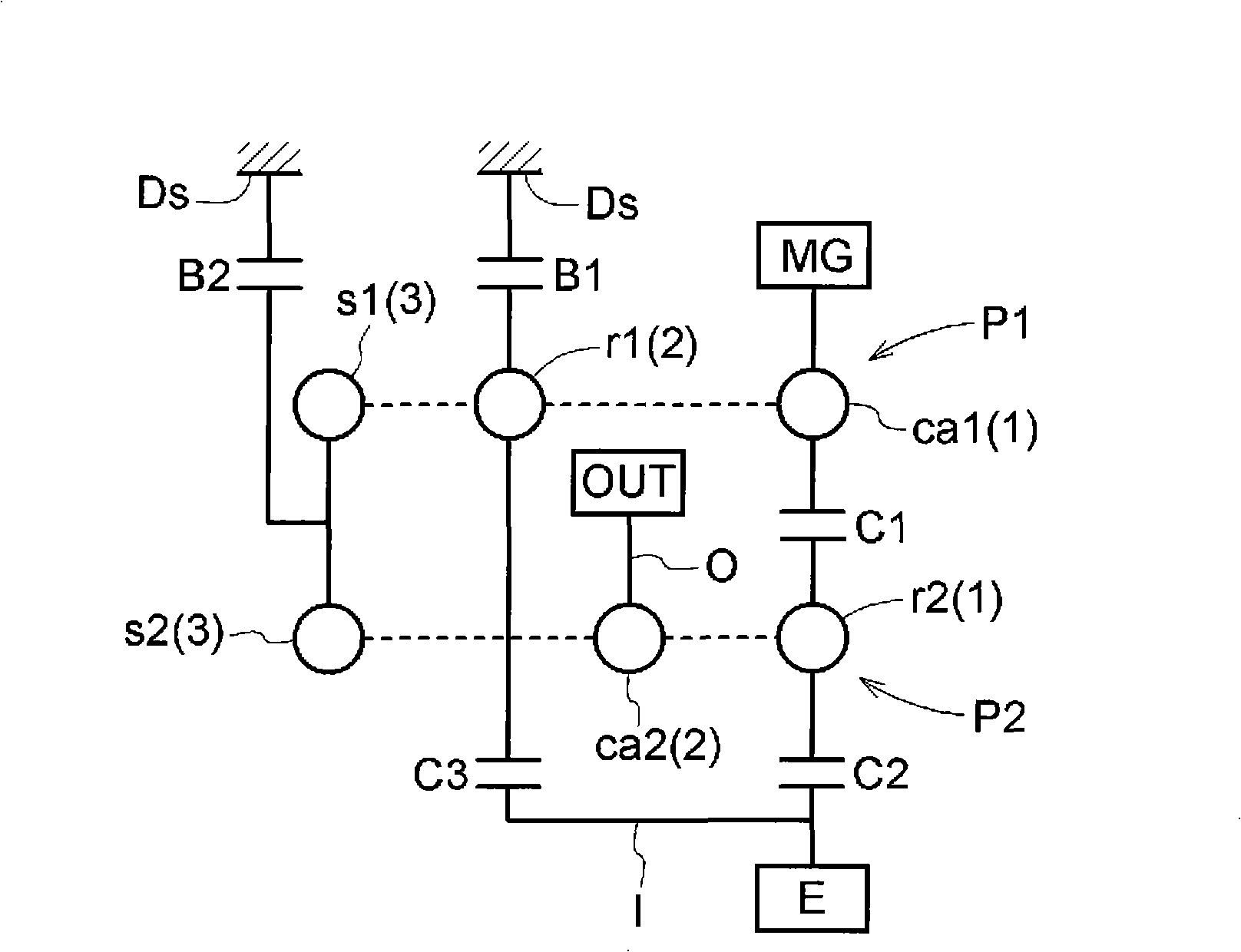
Hybrid drive device
InactiveCN101351352AReduce shockTransmission elementsPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingElectric machineEngineering
A hybrid drive device can take a state functioning as an electric torque converter and capable of transmitting a large torque to an output shaft side even when a rotating electric machine with a relatively small output torque is used. The hybrid drive device (H) comprises an input shaft (I) connected to an engine (E), an output shaft (O) connected to a wheel, a motor generator (MG), a first planetary gear device (P1), and a second planetary gear device (P2). In the electric torque converter mode, the first planetary gear device (P1) reduces the absolute value of the rotational speed of the motor generator (MG) and transmits the reduced absolute value to the second planetary gear device (P2), and the second planetary gear device (P2) combines the rotation transmitted from the first planetary gear device (P1) with the rotation of the input shaft (I), reduces the absolute value of the rotational speed of the input shaft (I), and transmits the reduced absolute value to the output shaft (O).
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
Resting state function magnetic resonance image data classification method based on high-order super network
ActiveCN106650818AReflect time-varying propertiesImprove classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionCorrelation coefficientImaging processing
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Semiconductor device and driving method thereof
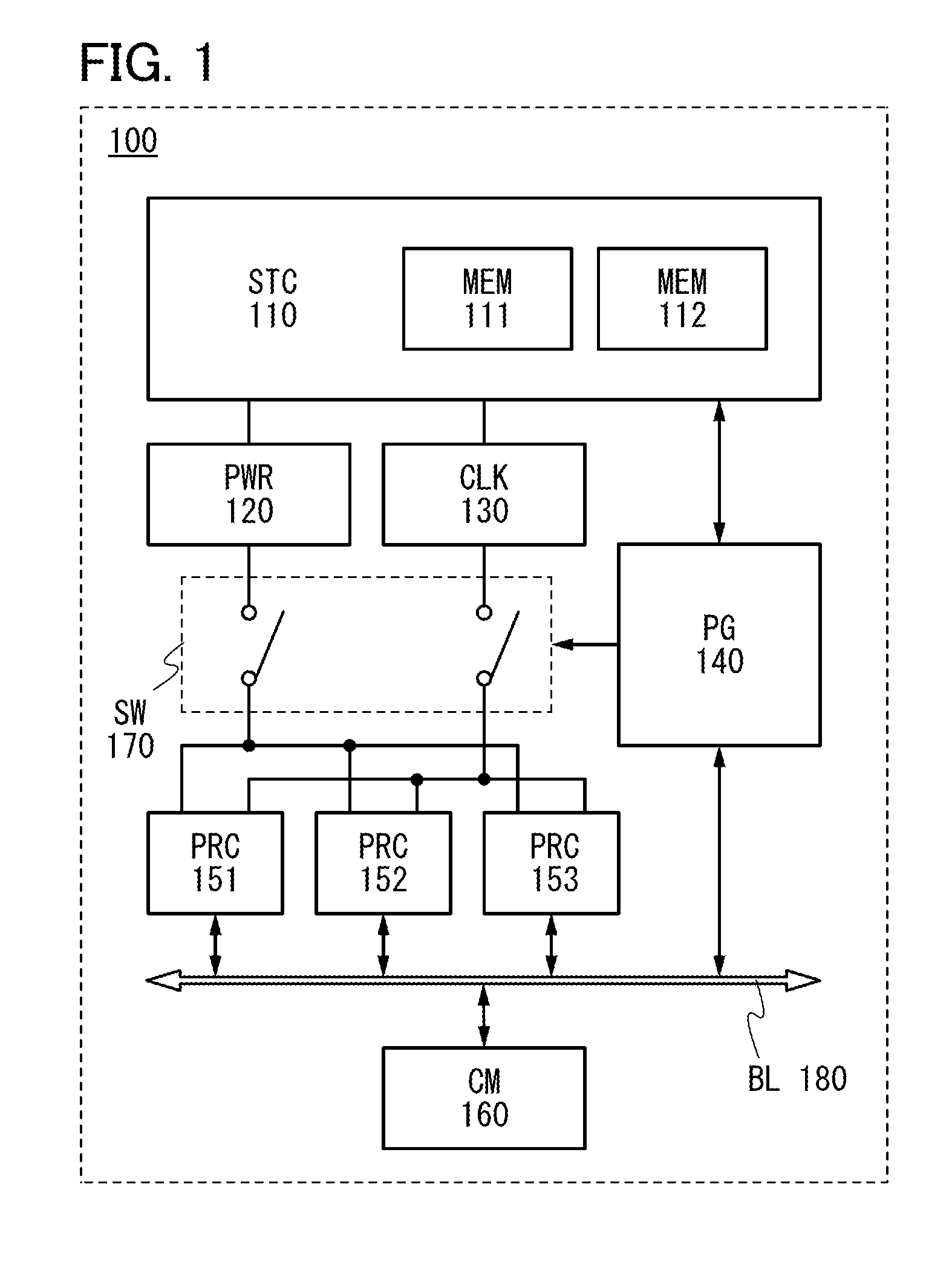
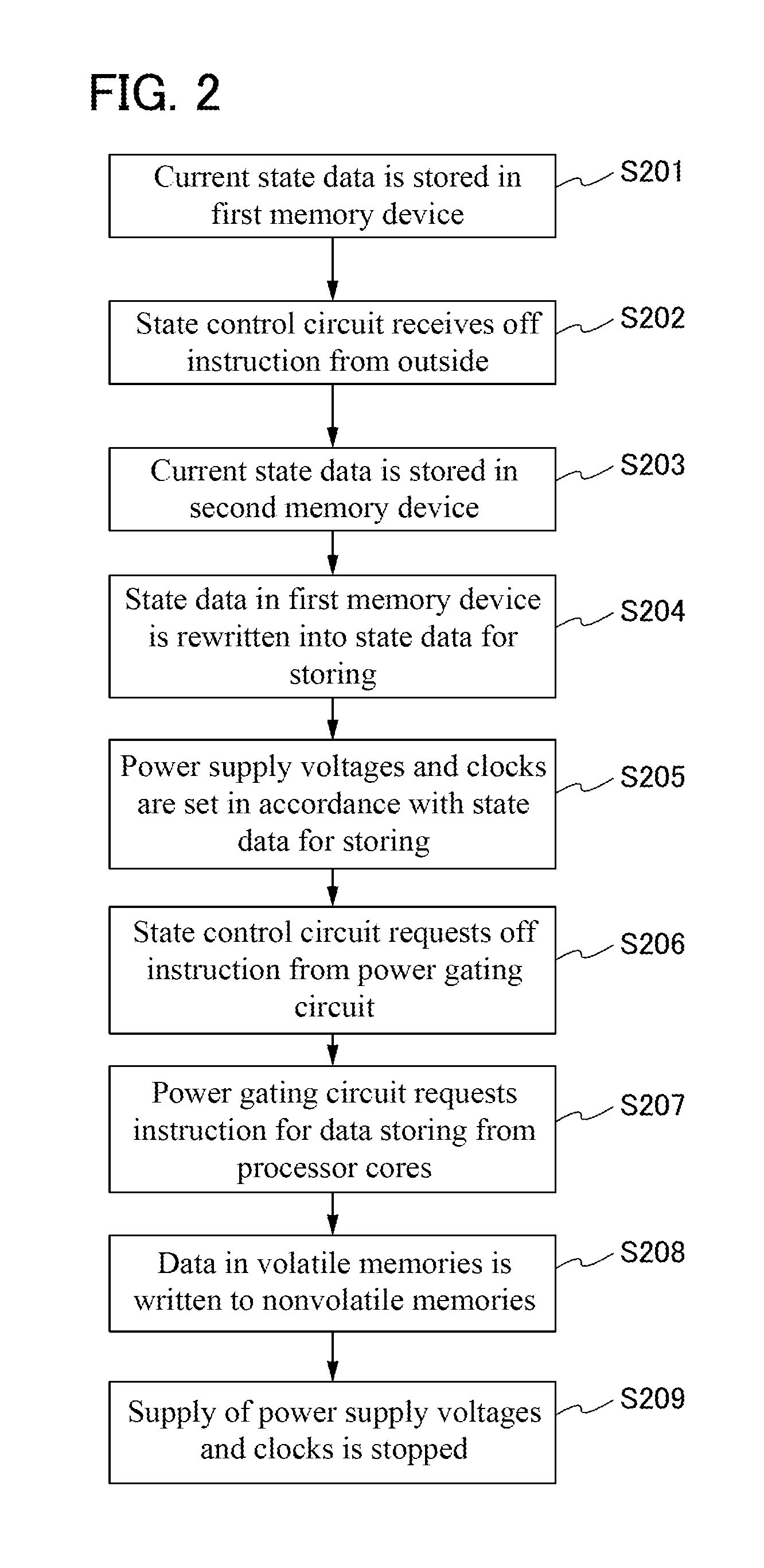
A semiconductor device in which a nonvolatile memory can normally operate and power saving can be performed with a P-state function, and a driving method of the semiconductor device are provided. The semiconductor device includes: a first circuit configured to control a state including a driving voltage and a clock frequency of a processor core; a first memory circuit and a second memory circuit which store state data; a second circuit generating a power supply voltage and a third circuit generating a clock which are electrically connected to the first circuit; and the processor core electrically connected to the second circuit and the third circuit through a switch. The processor cores includes: a volatile memory; and a nonvolatile memory transmitting and receiving data to / from the first memory.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Software Architecture and Program for the Concurrent Execution of Finite State Machine-Encoded Processes, on Single or Multiple-Processor-Based Embedded Systems
InactiveUS20070101316A1Multiprogramming arrangementsSpecific program execution arrangementsComputer architectureFinite-state machine
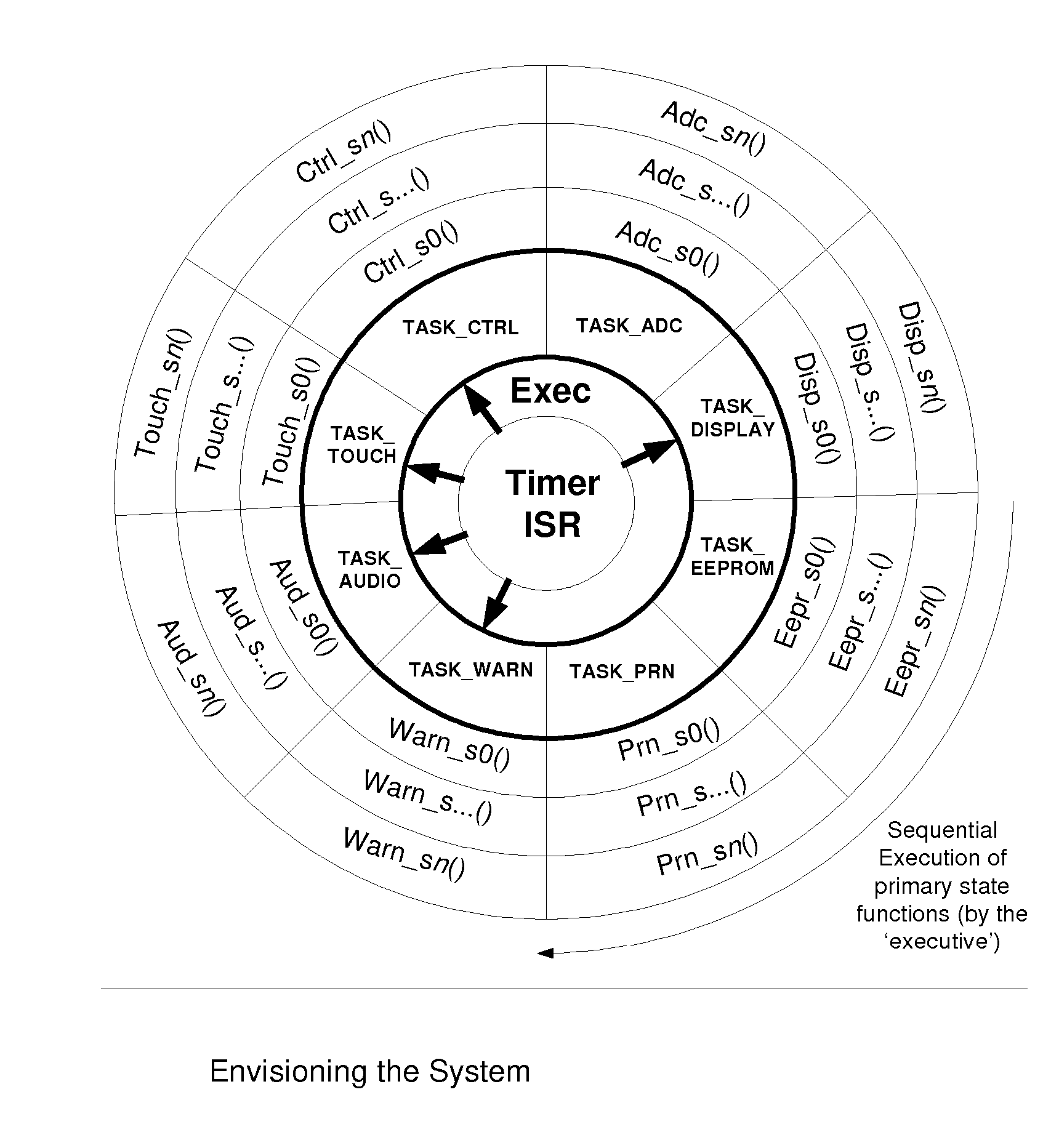
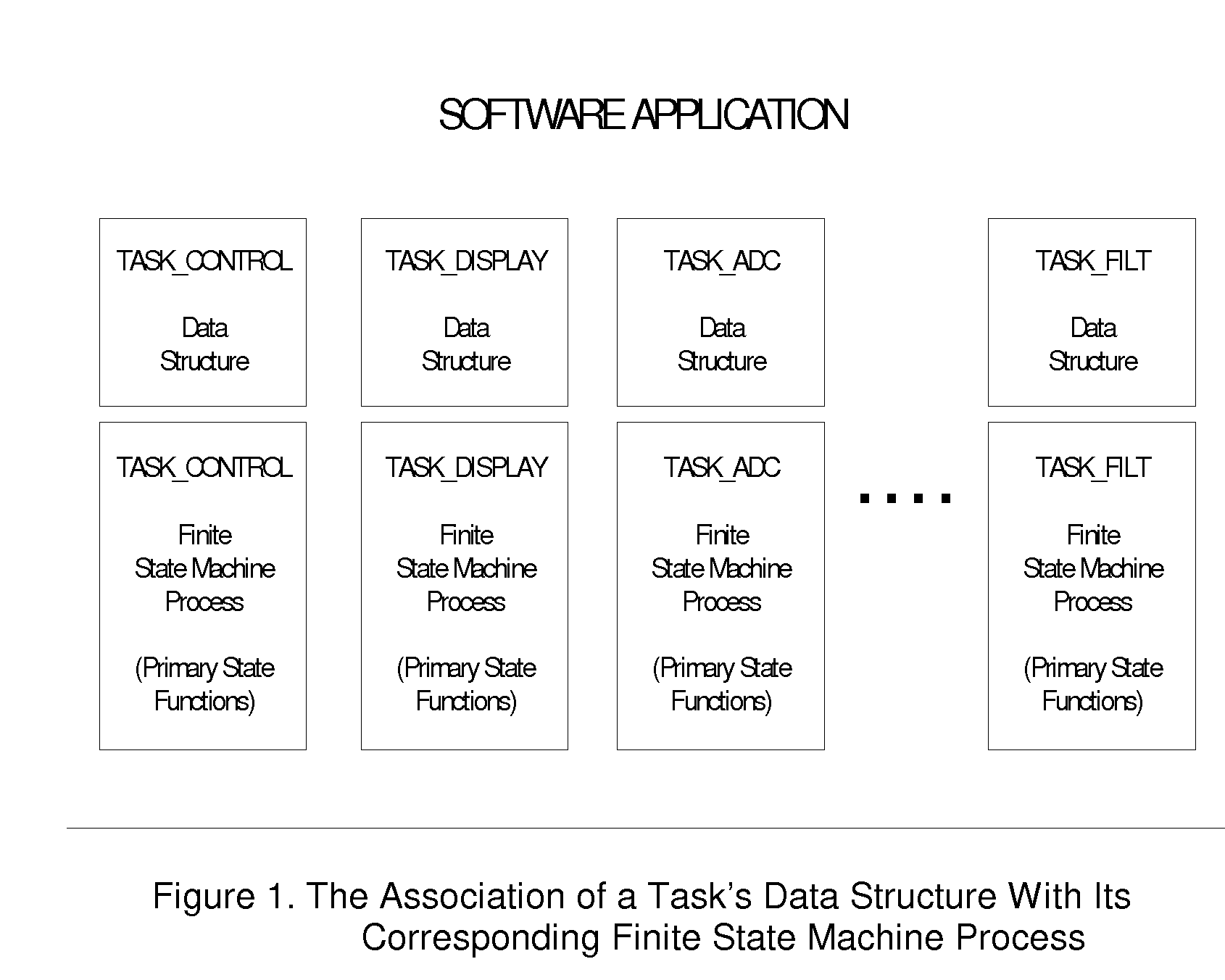
A software architecture and design method for embedded computing system applications in which tasks consist of a common data structure (FIGS. 1, 2) and are encoded as a finite state machines (FIG. 5). An executive (FIGS. 3, 4) provides for the execution of each task's current state function, and a system timer (FIG. 6) provides timer services to selective tasks. The architecture supports inter-task communication capabilities with message pipes and flags (FIG. 7). System calls (FIG. 8) provide utility functions for high-level access to system constructs. This structured architecture and its components provide for real-time performance and deterministic behavior of an embedded application (FIG. 9).
Owner:BERNDT DON CARL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com