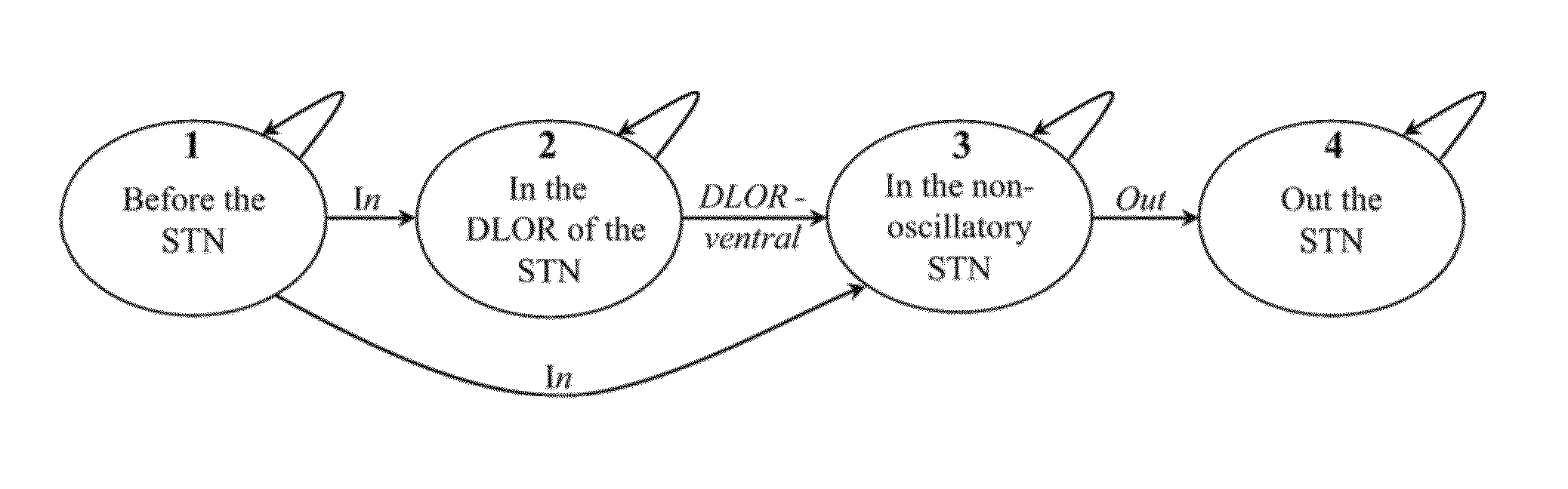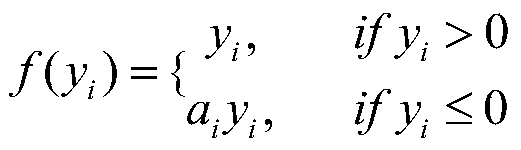Patents
Literature
93 results about "Thalamus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The thalamus (from Greek θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter in the dorsal part of the diencephalon of the brain with several functions such as relaying of sensory signals, including motor signals to the cerebral cortex, and the regulation of consciousness, sleep, and alertness.
Innominate osteotomy
InactiveUS20020092532A1Expand coverageConcentric reductionDiagnosticsOsteosynthesis devicesThalamusCoxal joint
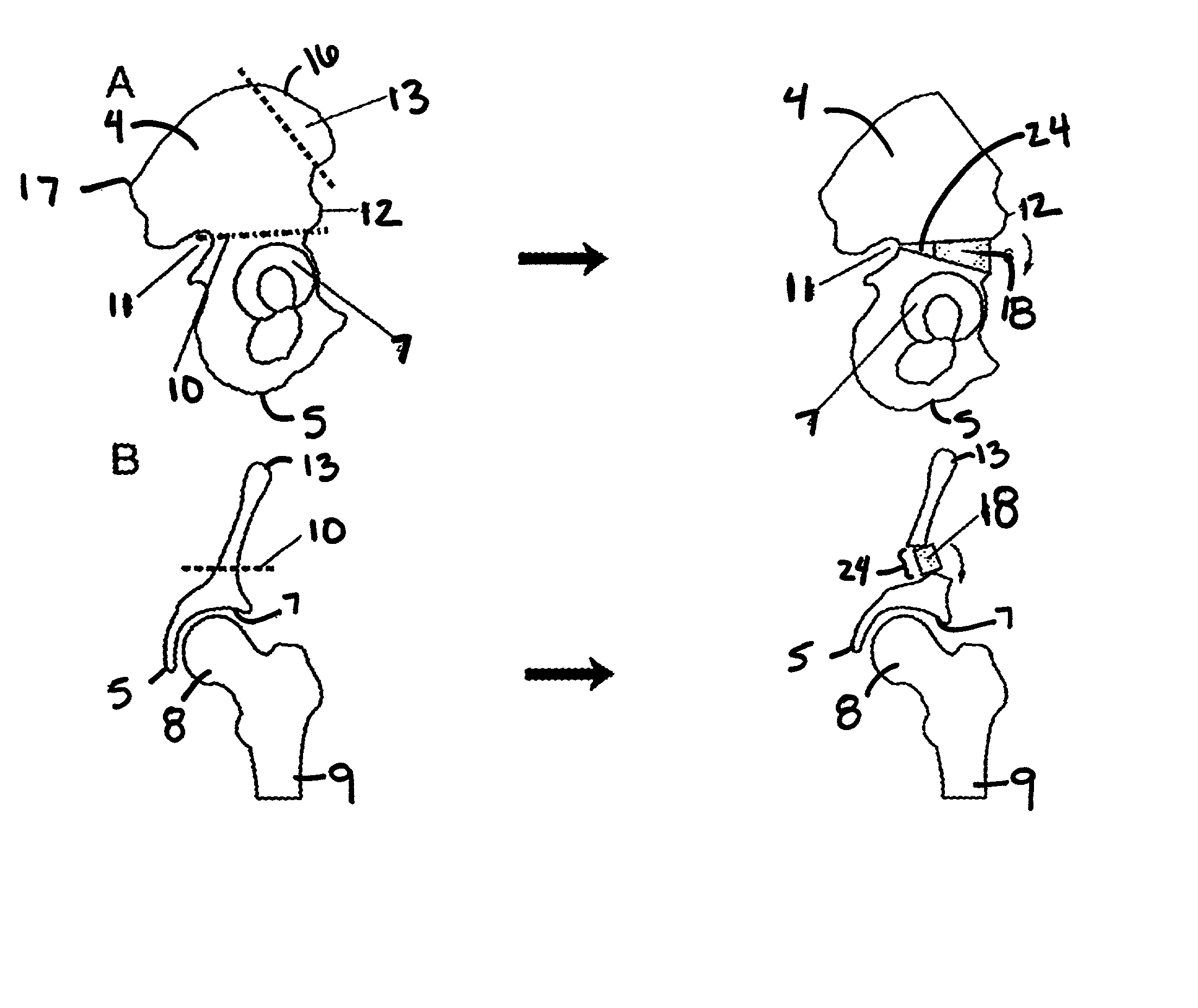
This invention provides a surgical method to treat hip diseases, including Legg-Calve-Perthes disease or developmental hip dysplasia. This method includes several surgical techniques: a transverse osteotomy of the posterior portion of supraacetabular portion, an oblique and inclined osteotomy of the anterior portion of the supraacetabulum, detachment of a bone block from iliac crest, anterolateral displacement of the distal fragment, and insertion of the bone block into the distracted space of the osteotomy site.
Owner:YOON TAEK RIM
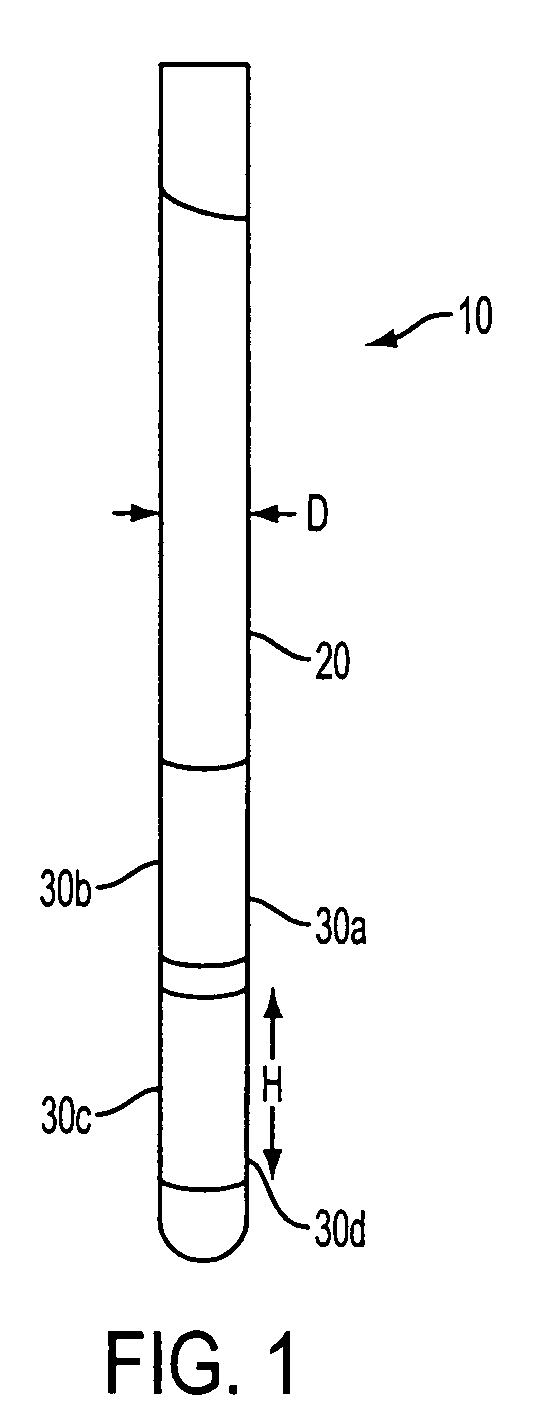
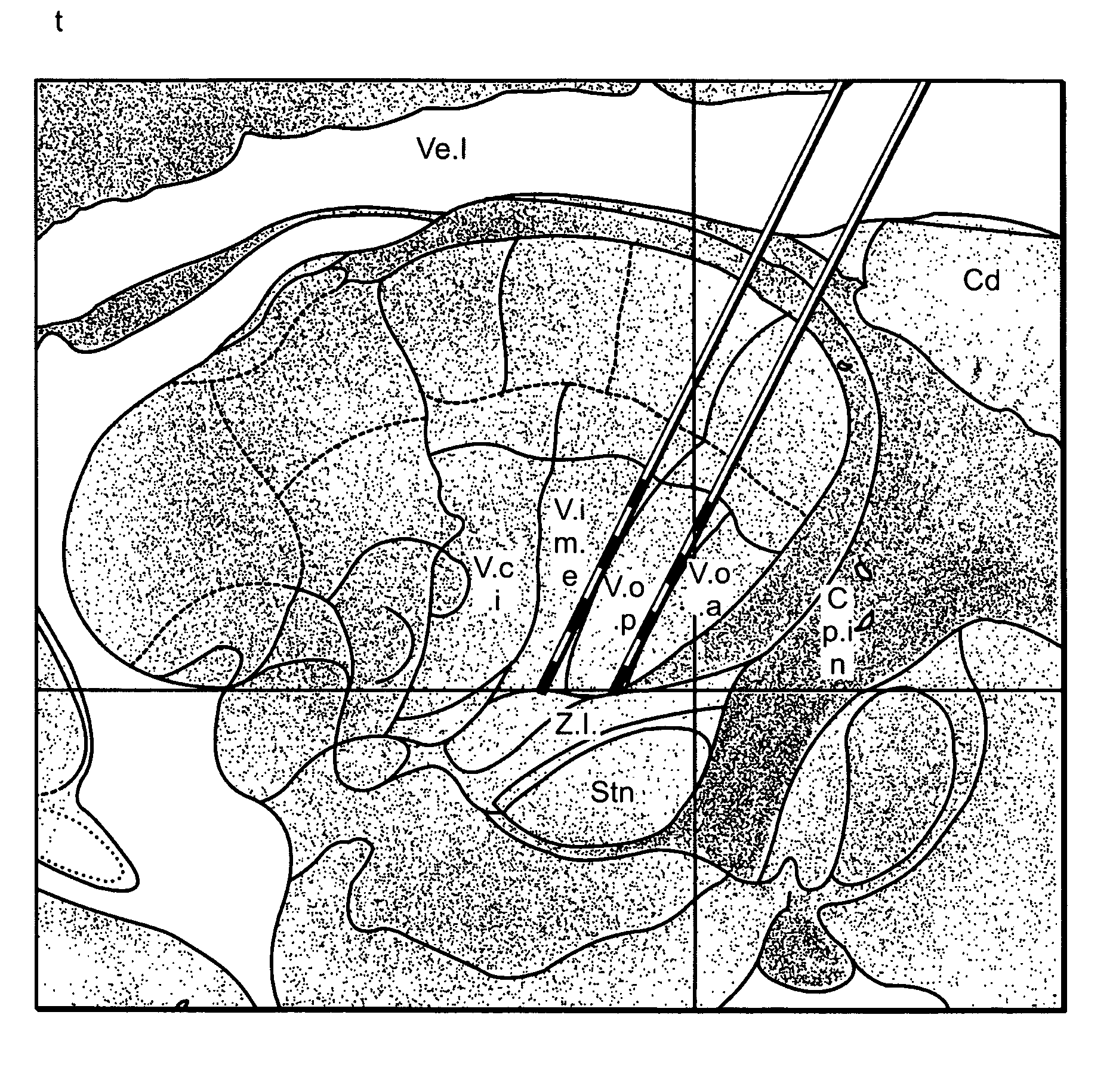
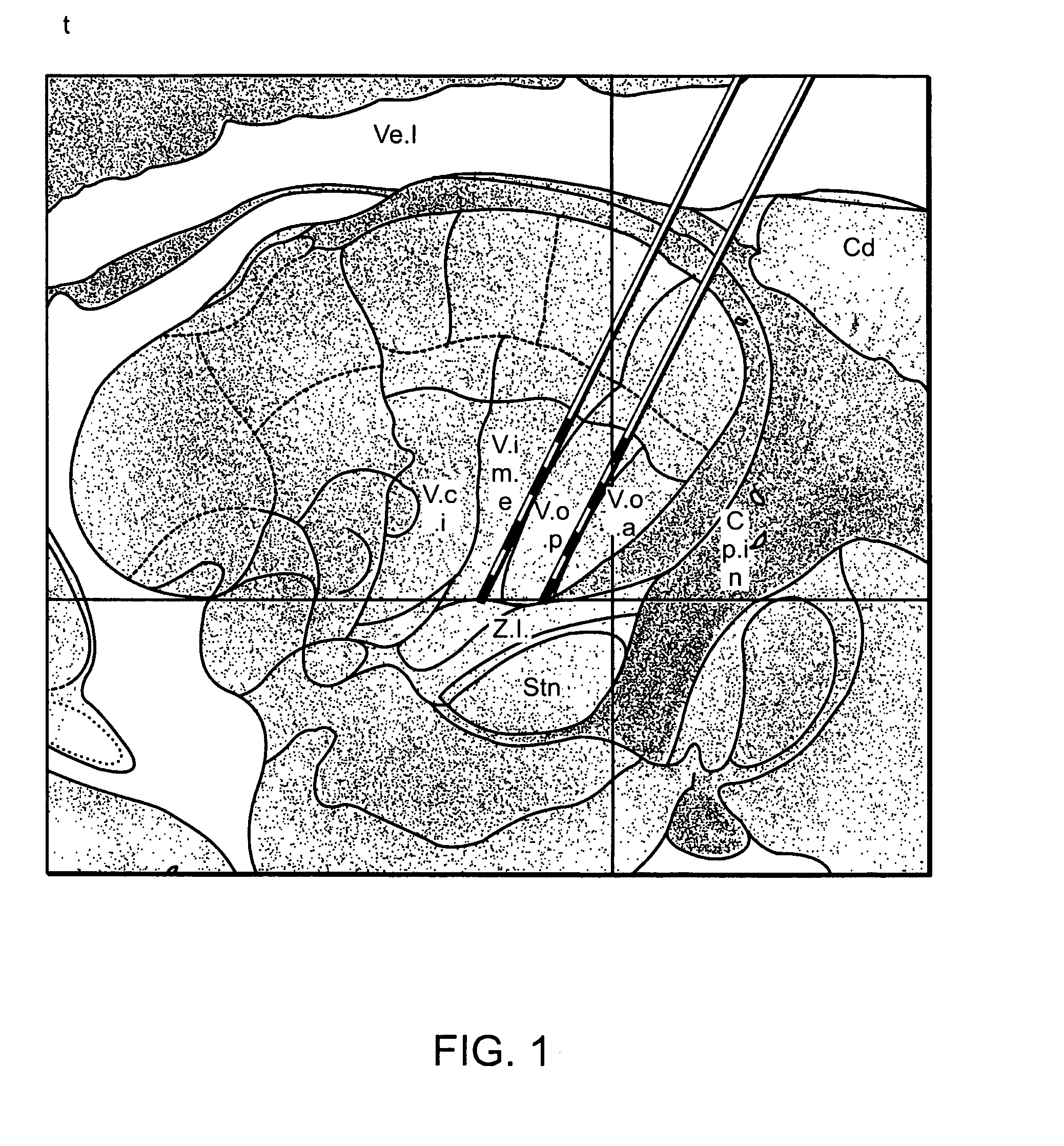
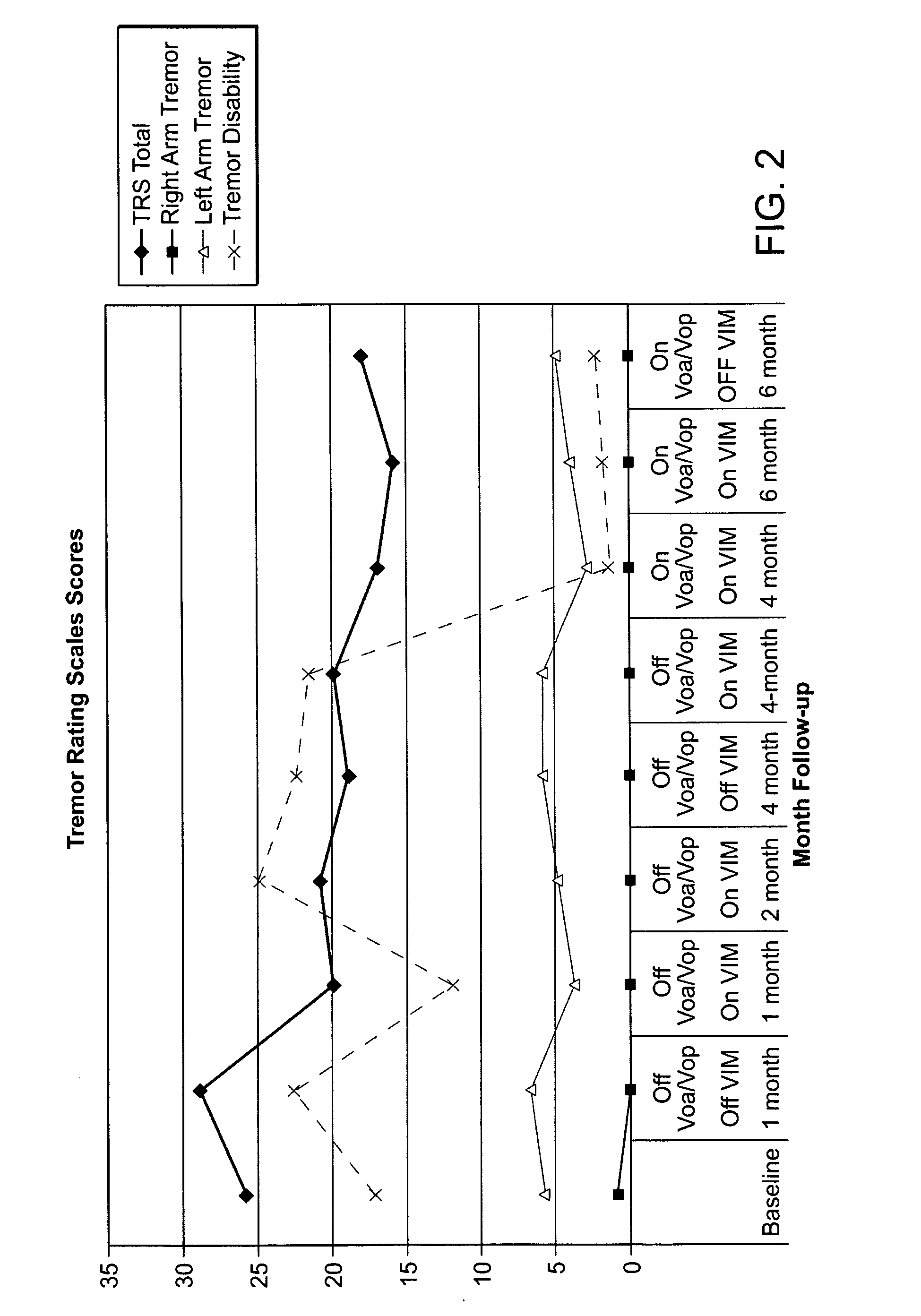
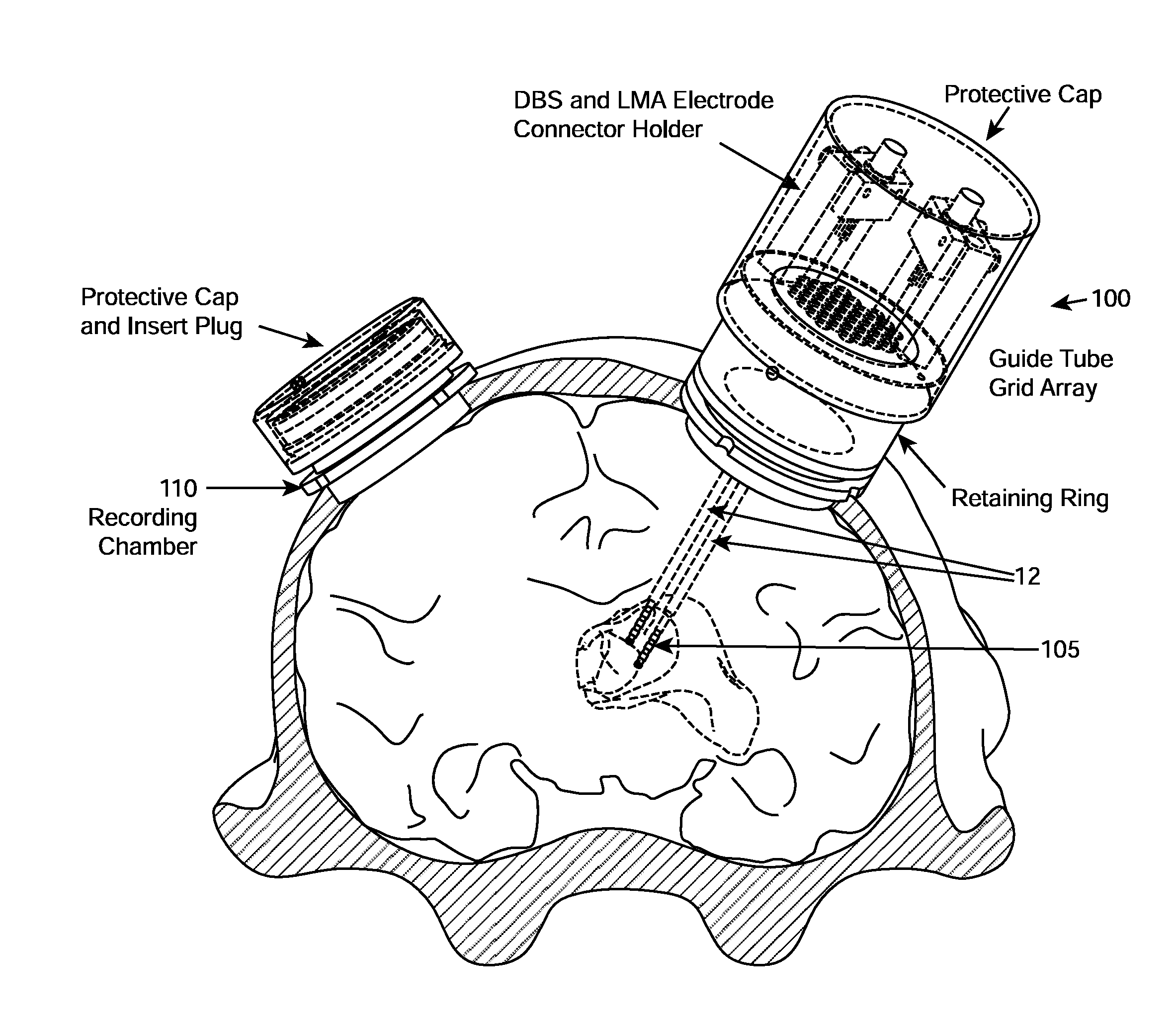
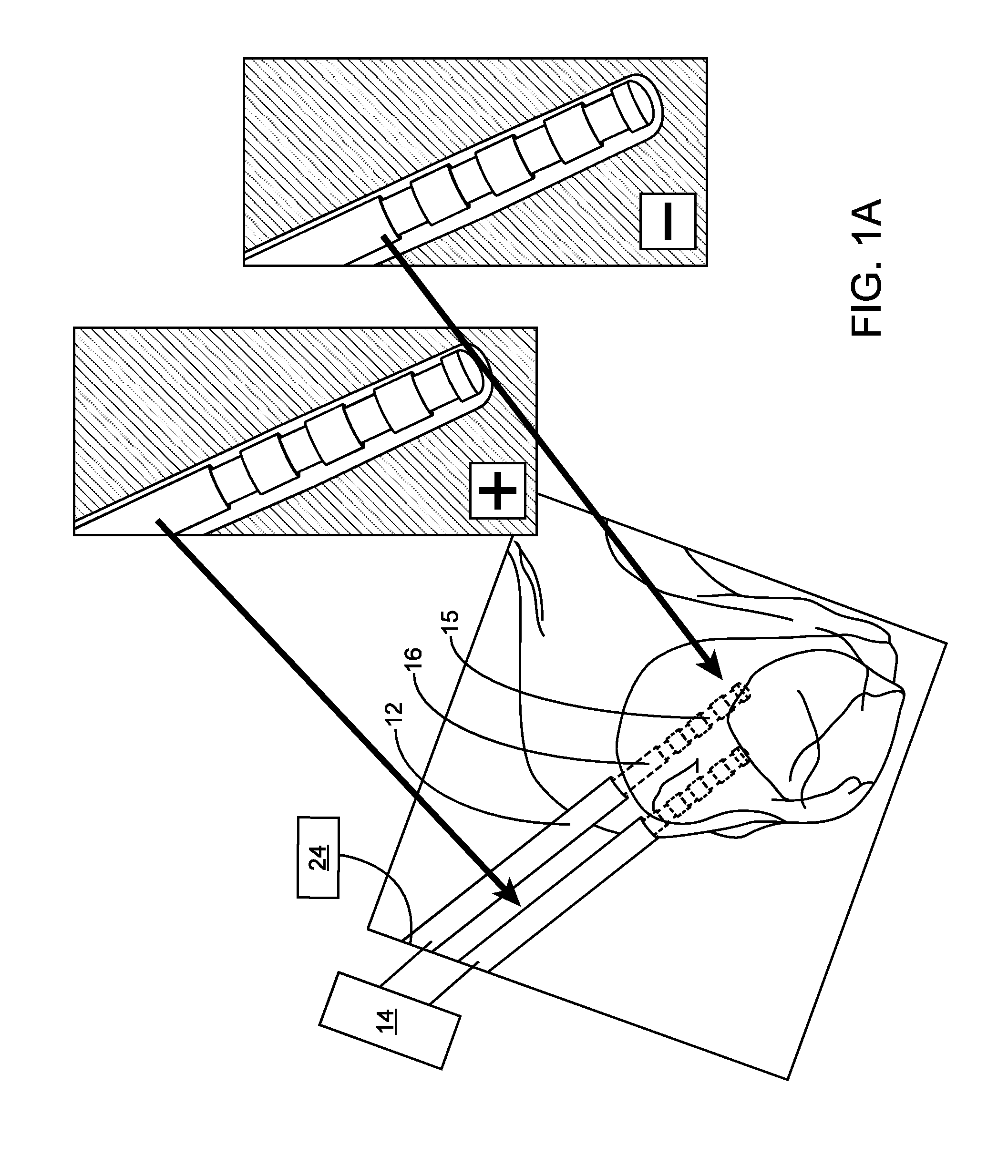
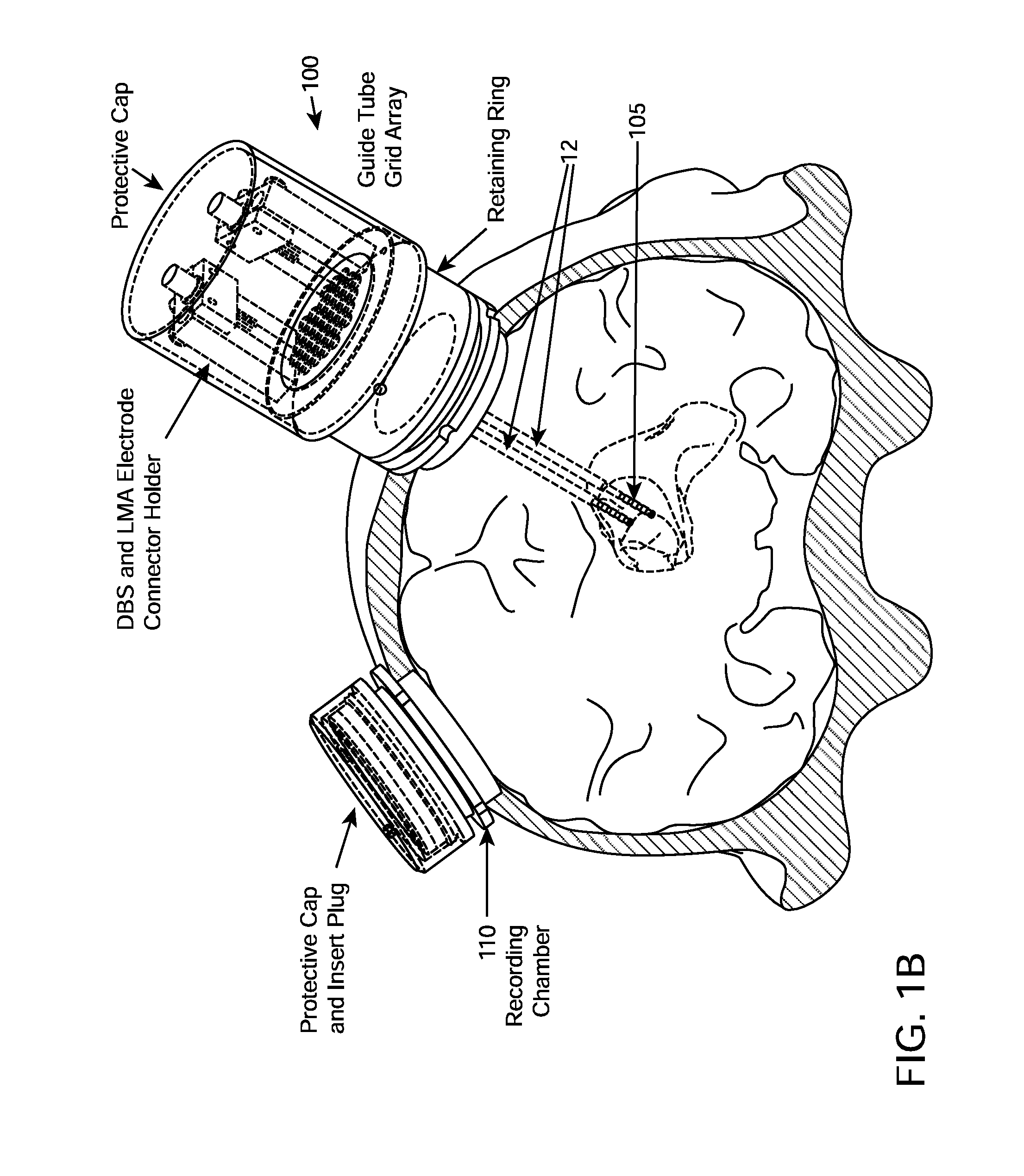
Multiple lead method for deep brain stimulation
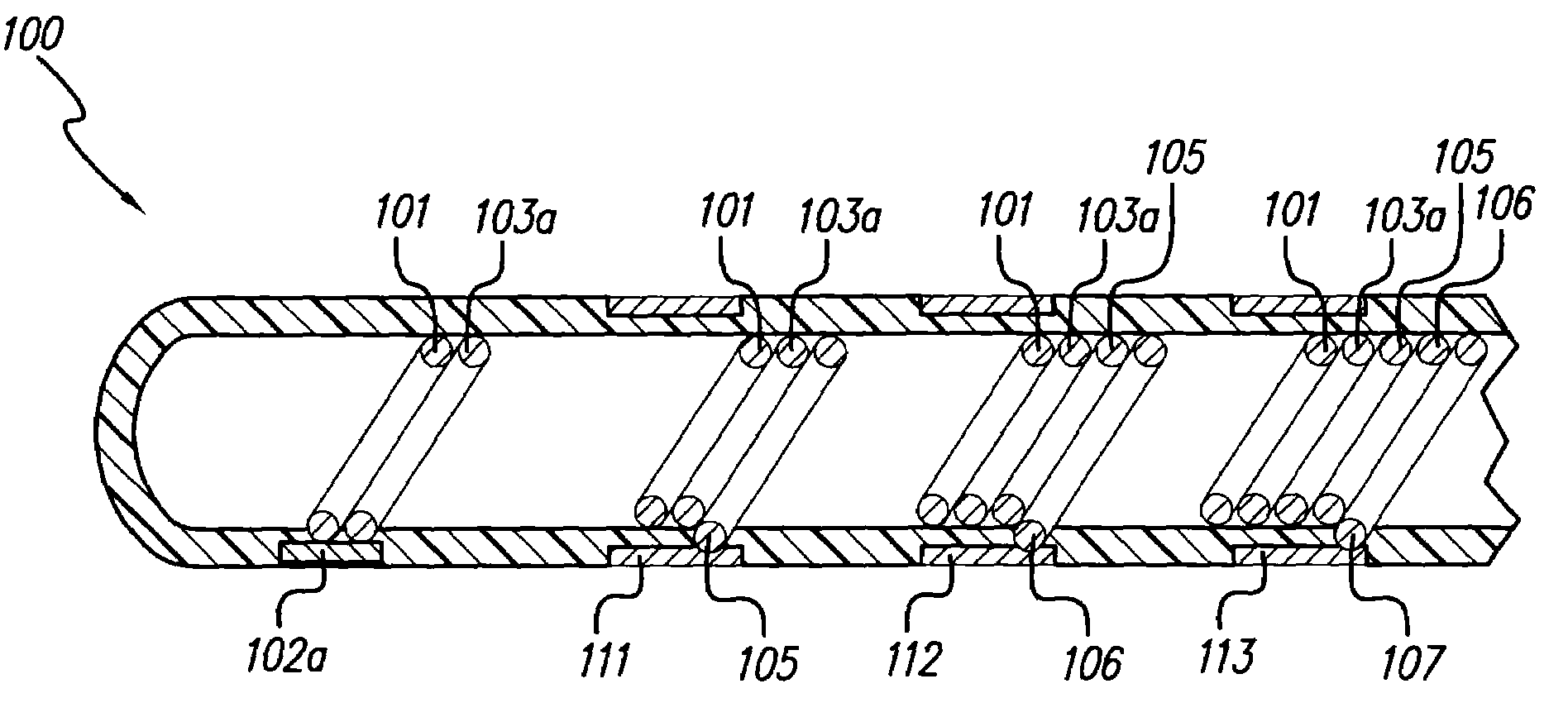
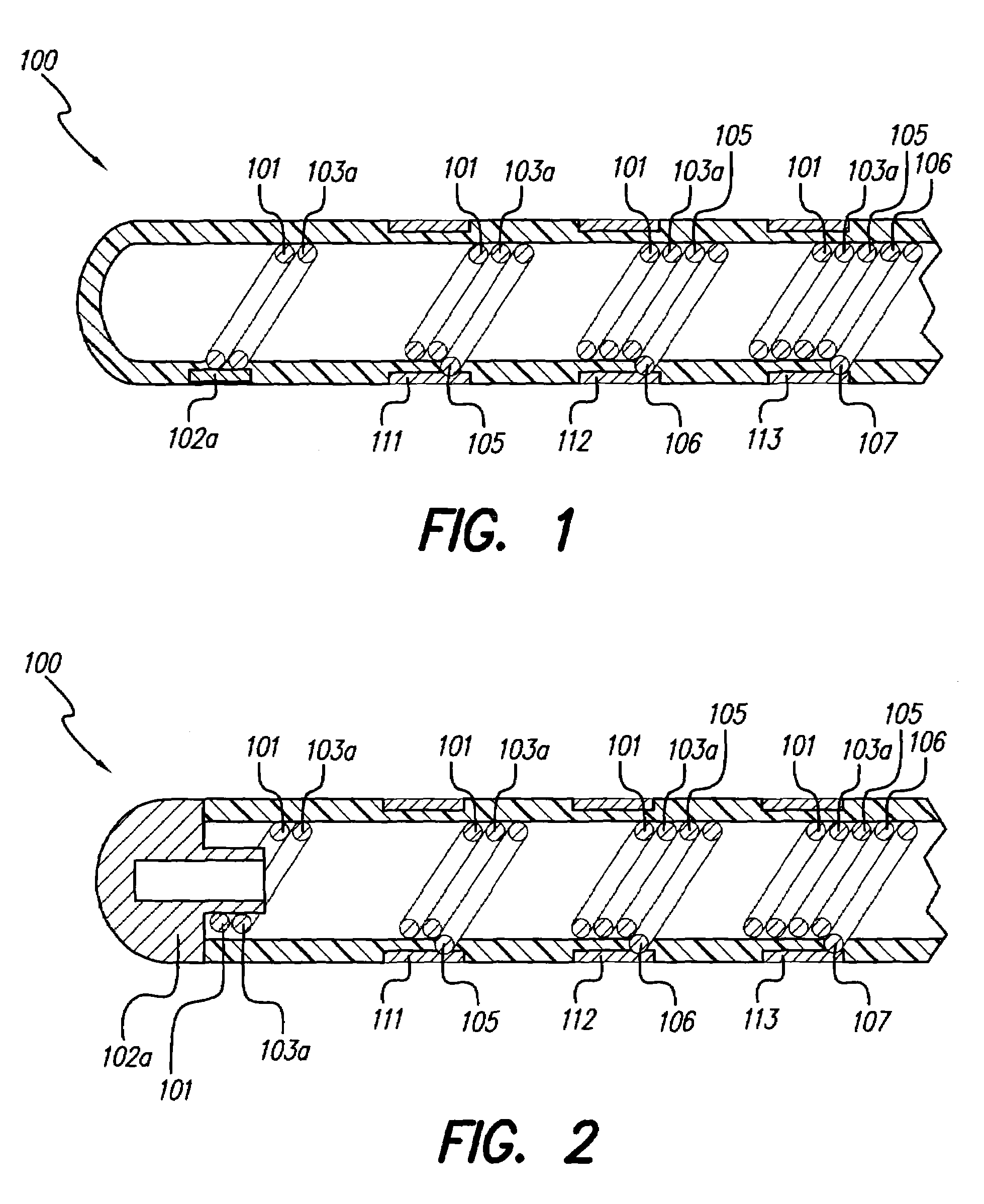
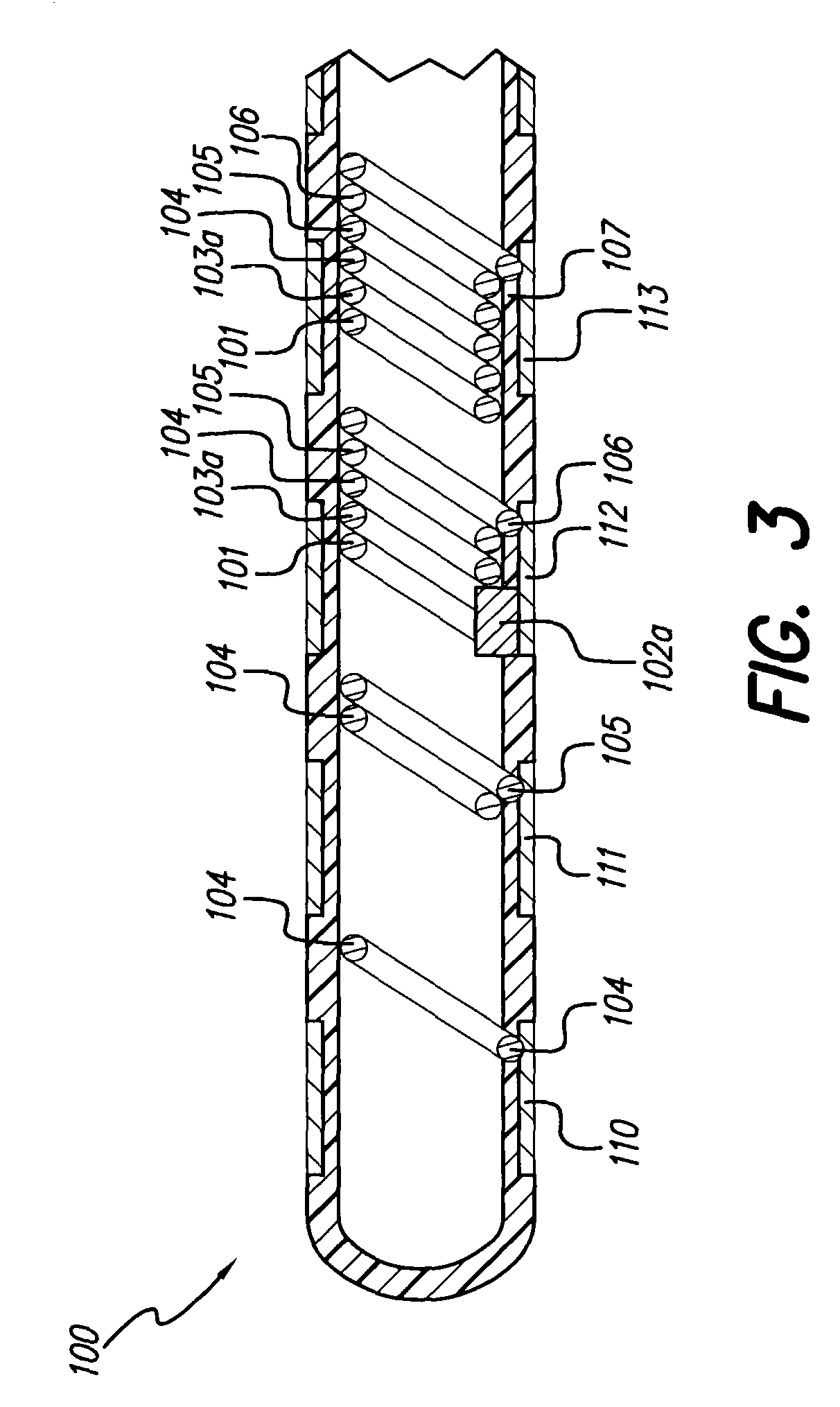
ActiveUS20080103547A1Easy to controlGood treatment effectHead electrodesExternal electrodesDiseaseThalamus
New methods for deep brain stimulation (DBS) surgery using two or more electrical leads are provided. The methods are useful for treating a wide variety of brain-associated disorders including movement-related disorders, psychiatric disorders, metabolic / eating disorders, memory disorders, and pain. Methods featuring stimulation of distinct target areas of a subject's brain, such as the thalamic ventralis intermedius (VIM) and the ventralis oralis (VOA / VOP) using multiple electrical leads for treatment of tremor provide superior clinical outcomes to stimulation with single leads implanted in these target areas.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
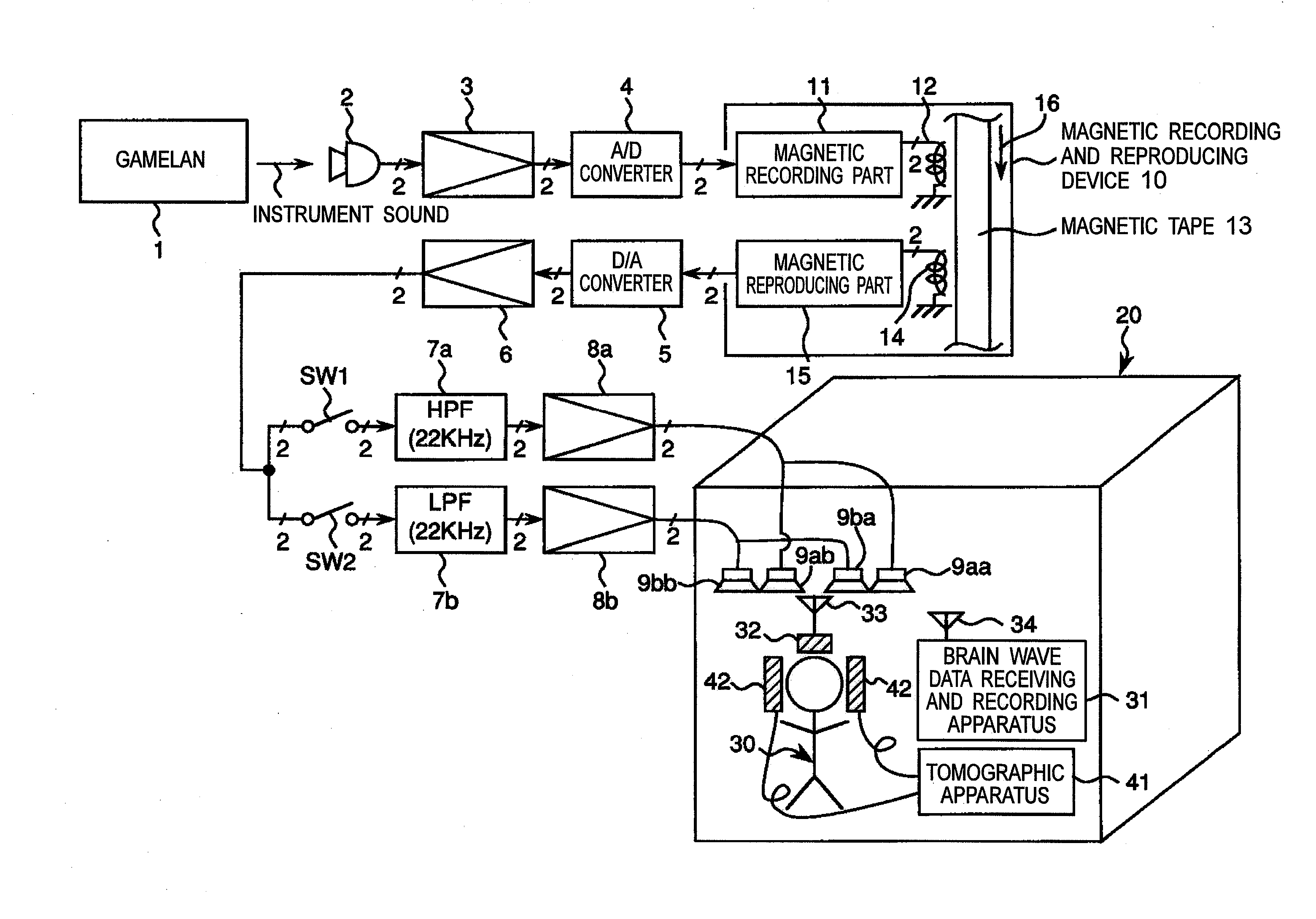
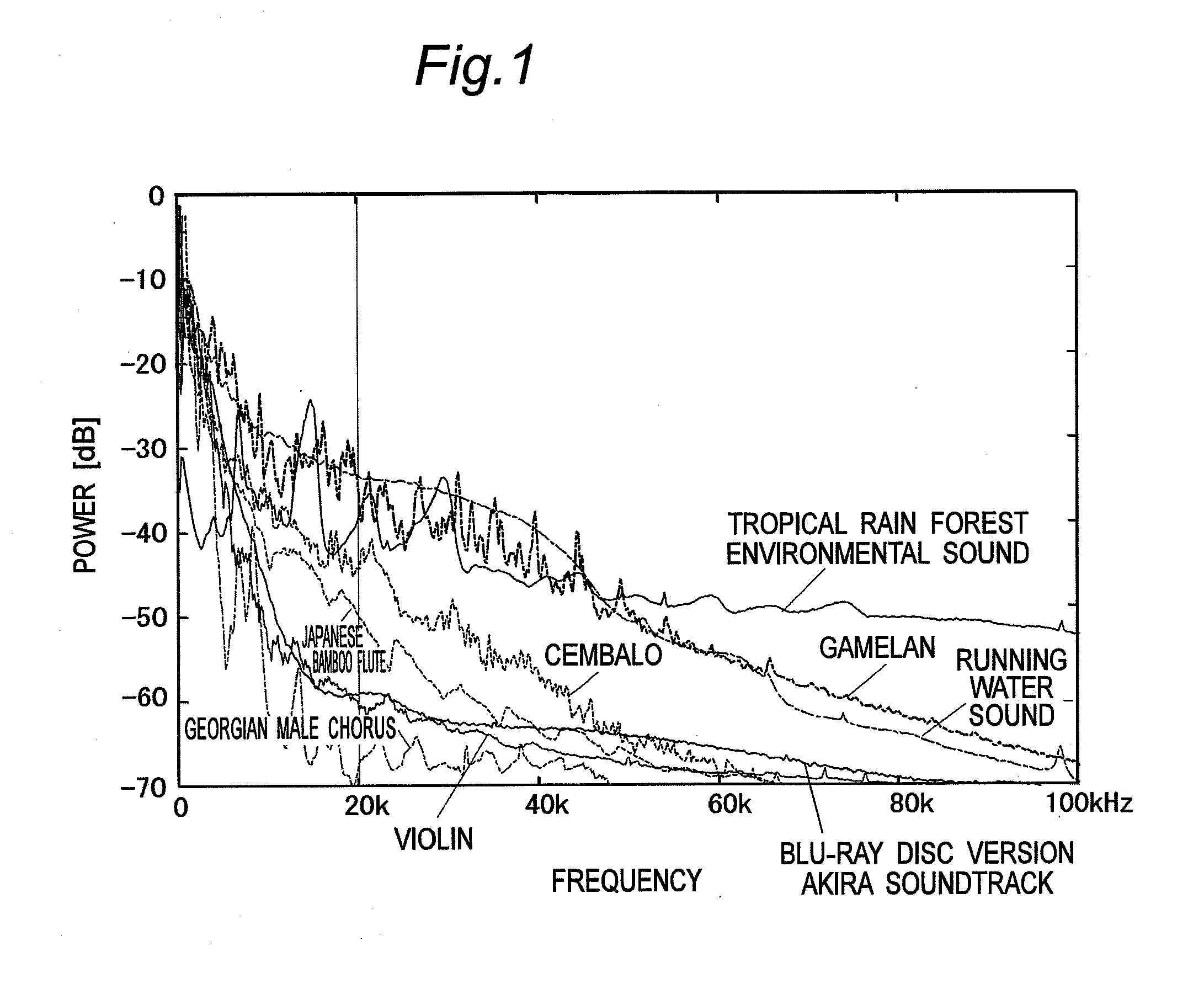
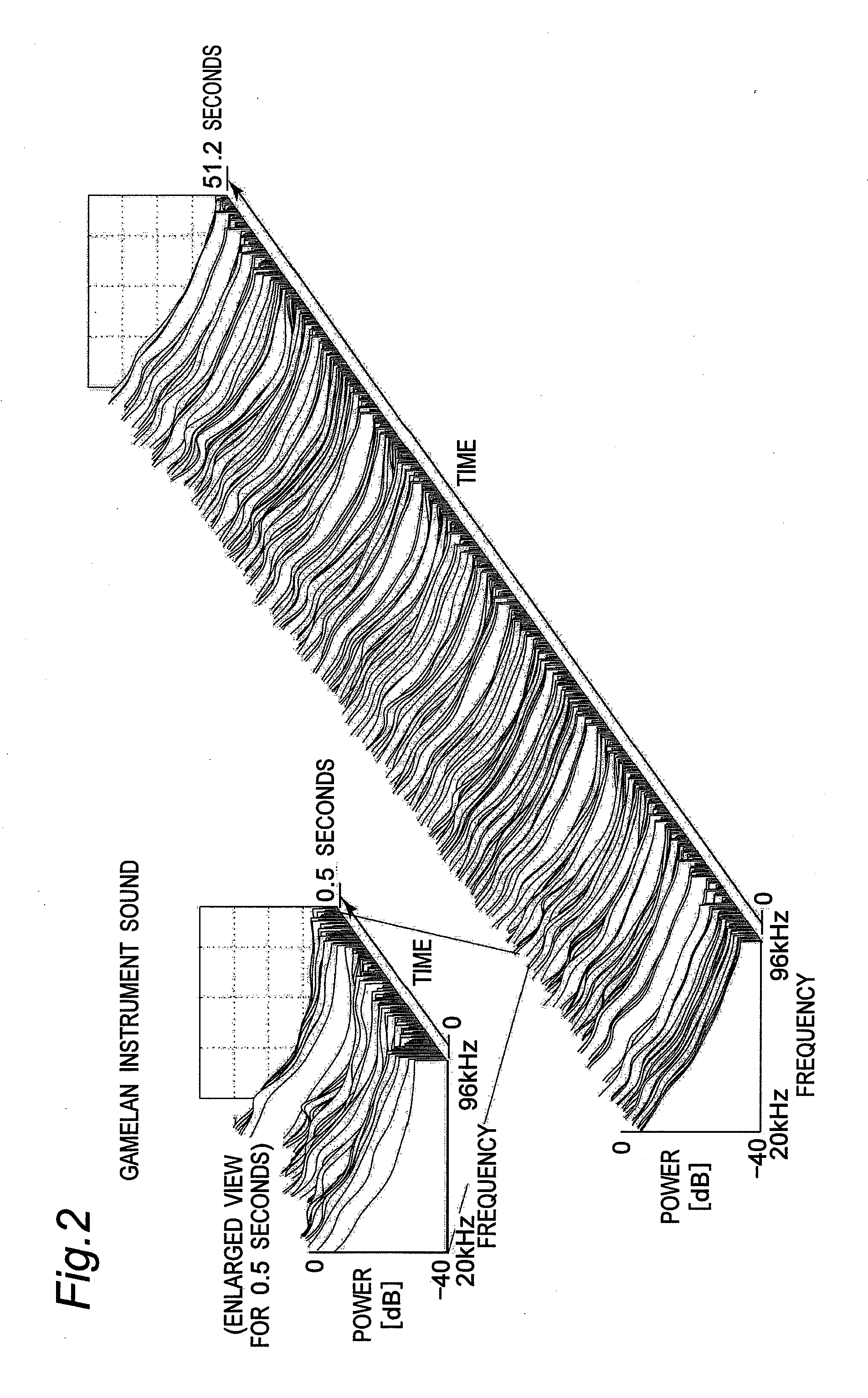
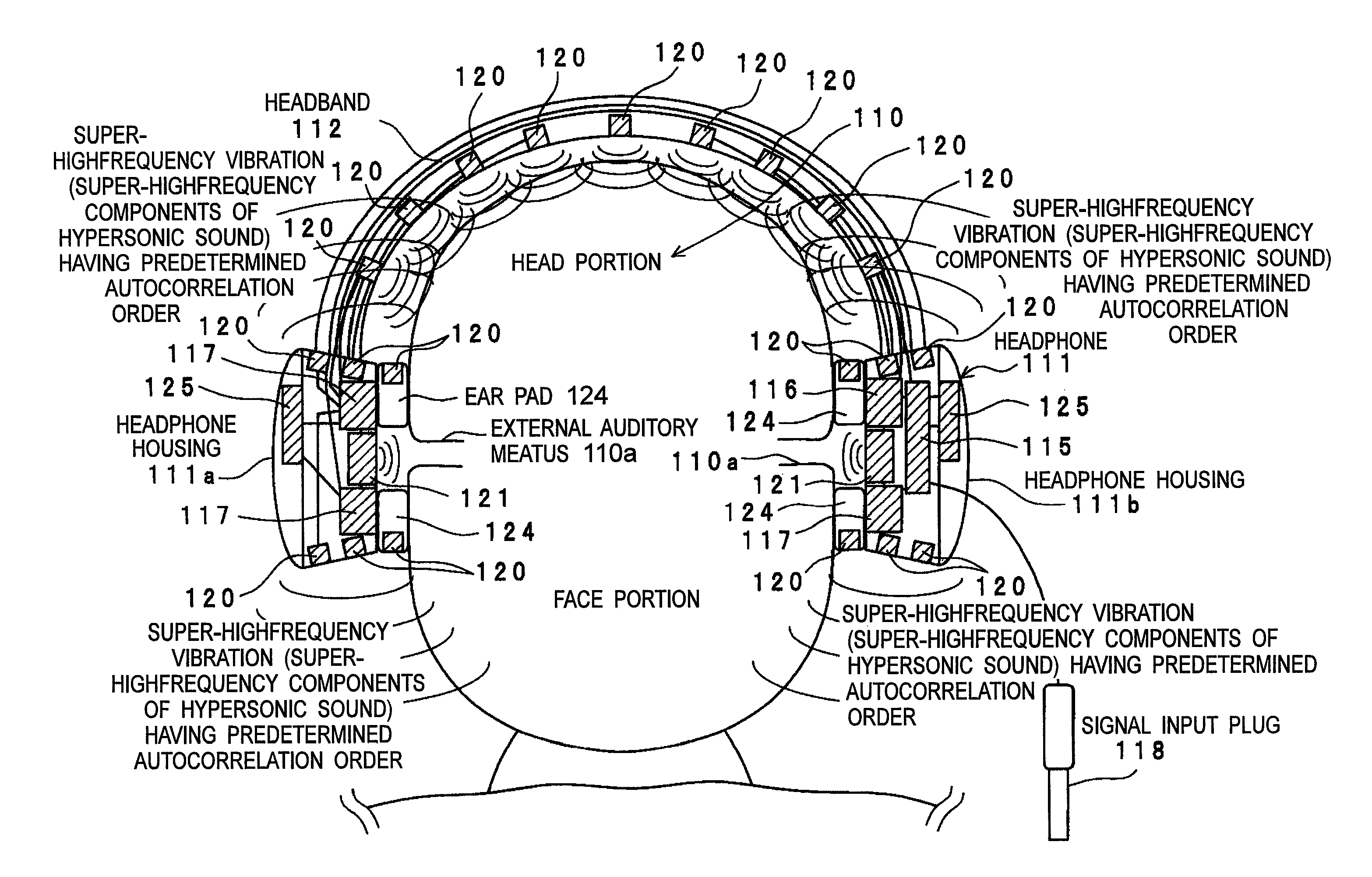
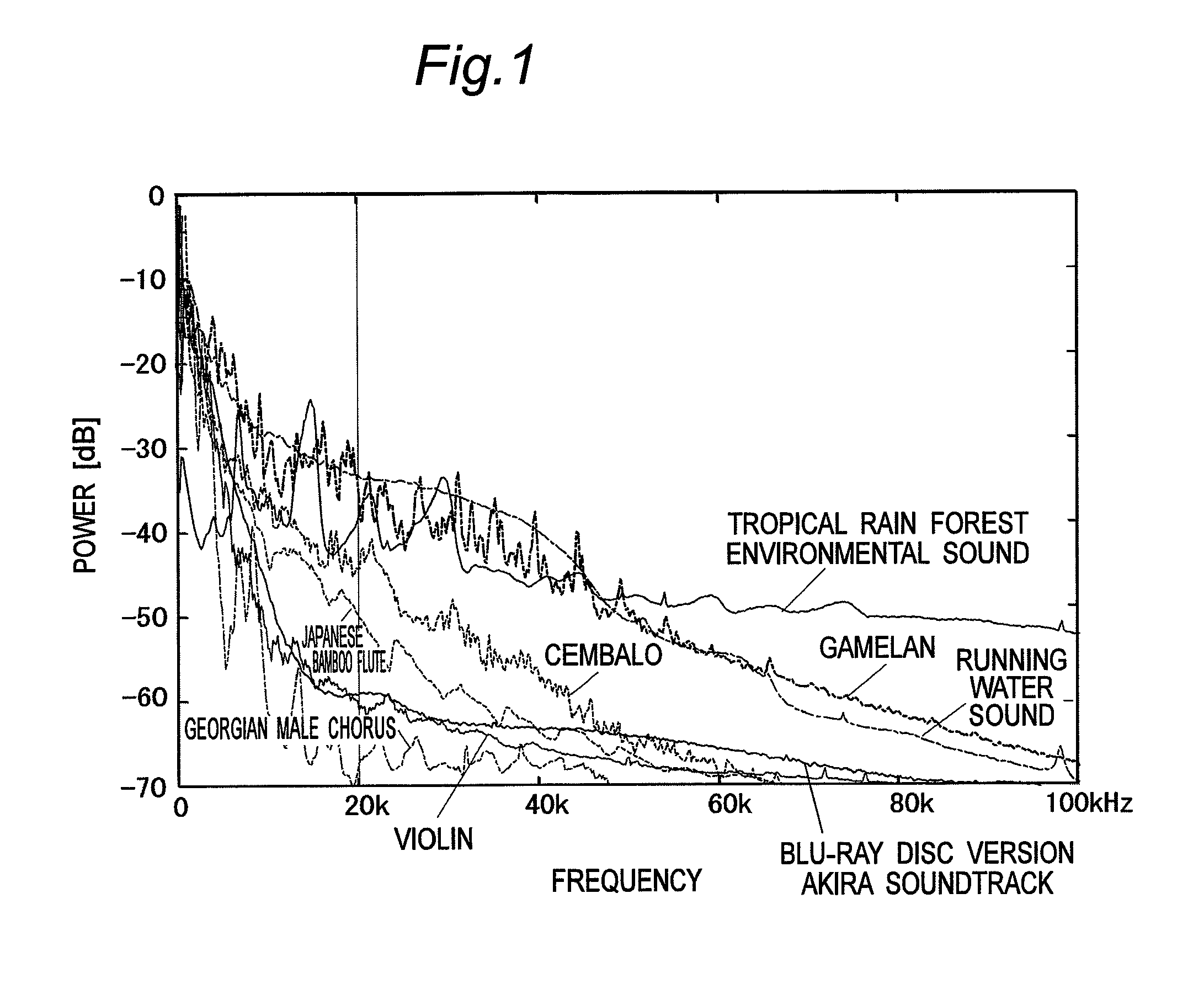
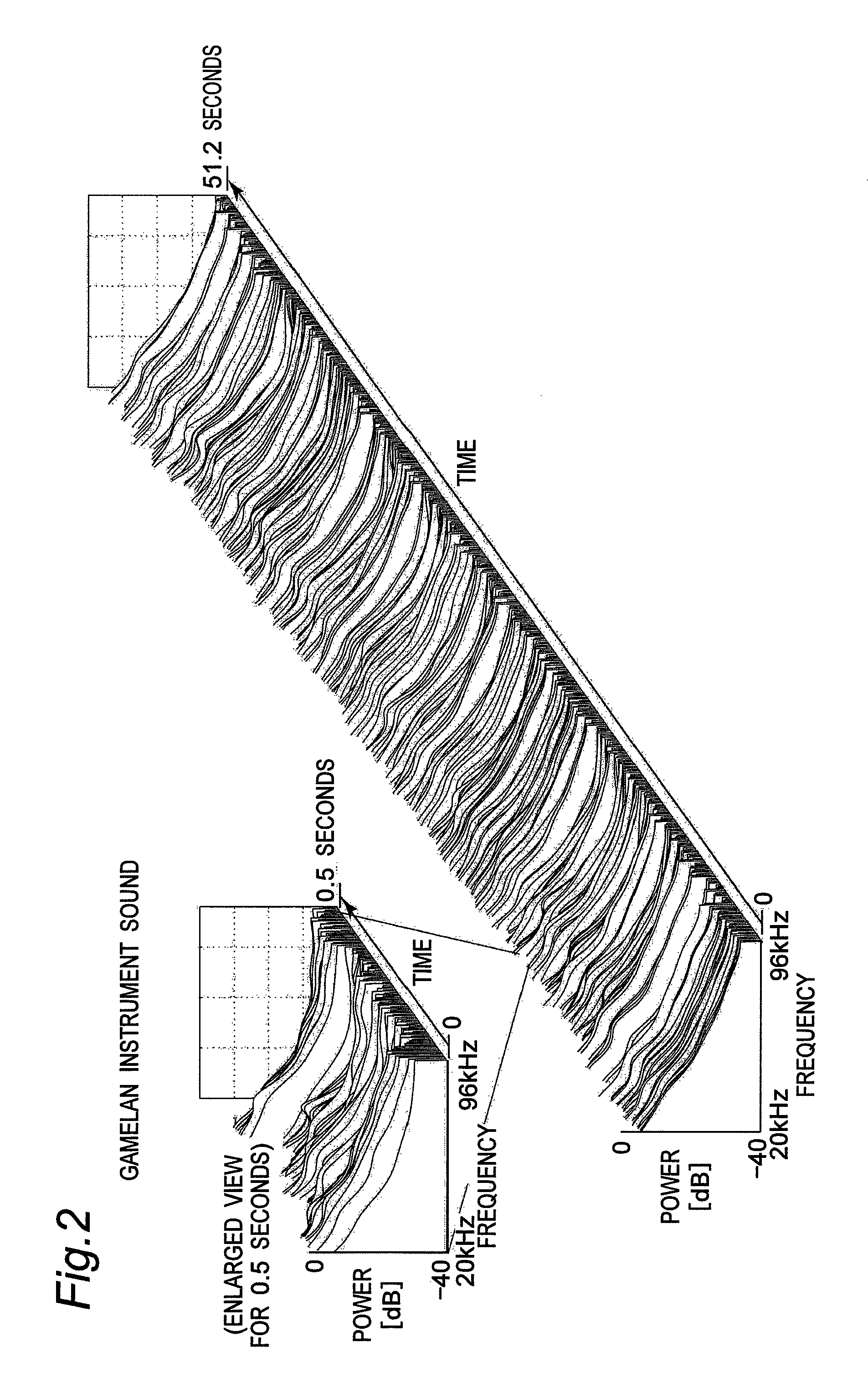
Vibration generating apparatus and method introducing hypersonic effect to activate fundamental brain network and heighten aesthetic sensibility
ActiveUS20110152729A1Discriminating vibrationPrevention of deterioration in brain activityUltrasound therapyChiropractic devicesThalamusNeuron projection
Means is provided for generating a vibration or a vibration signal, which contains audible range components that are vibration components in the audible frequency range and super-highfrequency components within a range exceeding the audible frequency range up to a predetermined maximum frequency, and which has an autocorrelation order represented by at least either one of a first property and a second property. By applying the vibration or an actual vibration generated from the vibration signal to a human being, a fundamental brain activation effect for activating the fundamental brain network system constituted of a fundamental brain including the brain stem, thalamus and hypothalamus that are regions to bear the fundamental function of the human being and the fundamental brain network of neuronal projection from the fundamental brain to various brain regions is introduced.
Owner:ACTION RES
Frequency Stimulation Trainer
InactiveUS20090076421A1Relief the painRelieve painMassage combsMassage beltsRe educationPerformance enhancement
A preferably non-electrical nerve communication enhancement tool that sends specific, pre-timed, controlled vibrational and / or acoustical stimulation frequencies to the body to enhance nerve communication for the purpose of assisting in proper function of skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, and facilitating rapid and improved cerebellar timing circuit and related cerebellar learning mechanism pathways such as the inferior olivary-Purkinje-Thalamus cell system and other similar neuronal pools, to improve muscle memory, coordinated functional neuron-musculo-skeletal performance improvement, enhance blood flow, increased range of motion, flexibility, strength and dexterity, neuromuscular re-education, muscle tone recovery, pain modulation, improved eye-hand coordination, gait improvement, balance and stability gains, kinetic chain integration, neurological performance enhancement, sensory dysfunction reduction, and improvement in mental and cognitive function.
Owner:STIMTRAINER
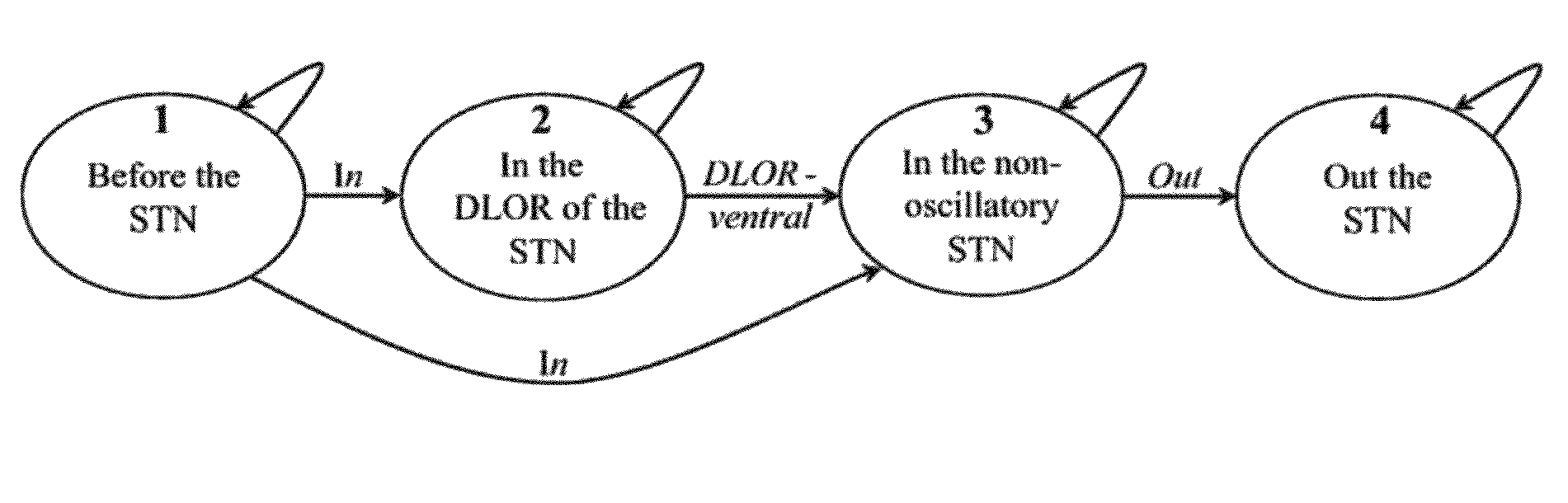
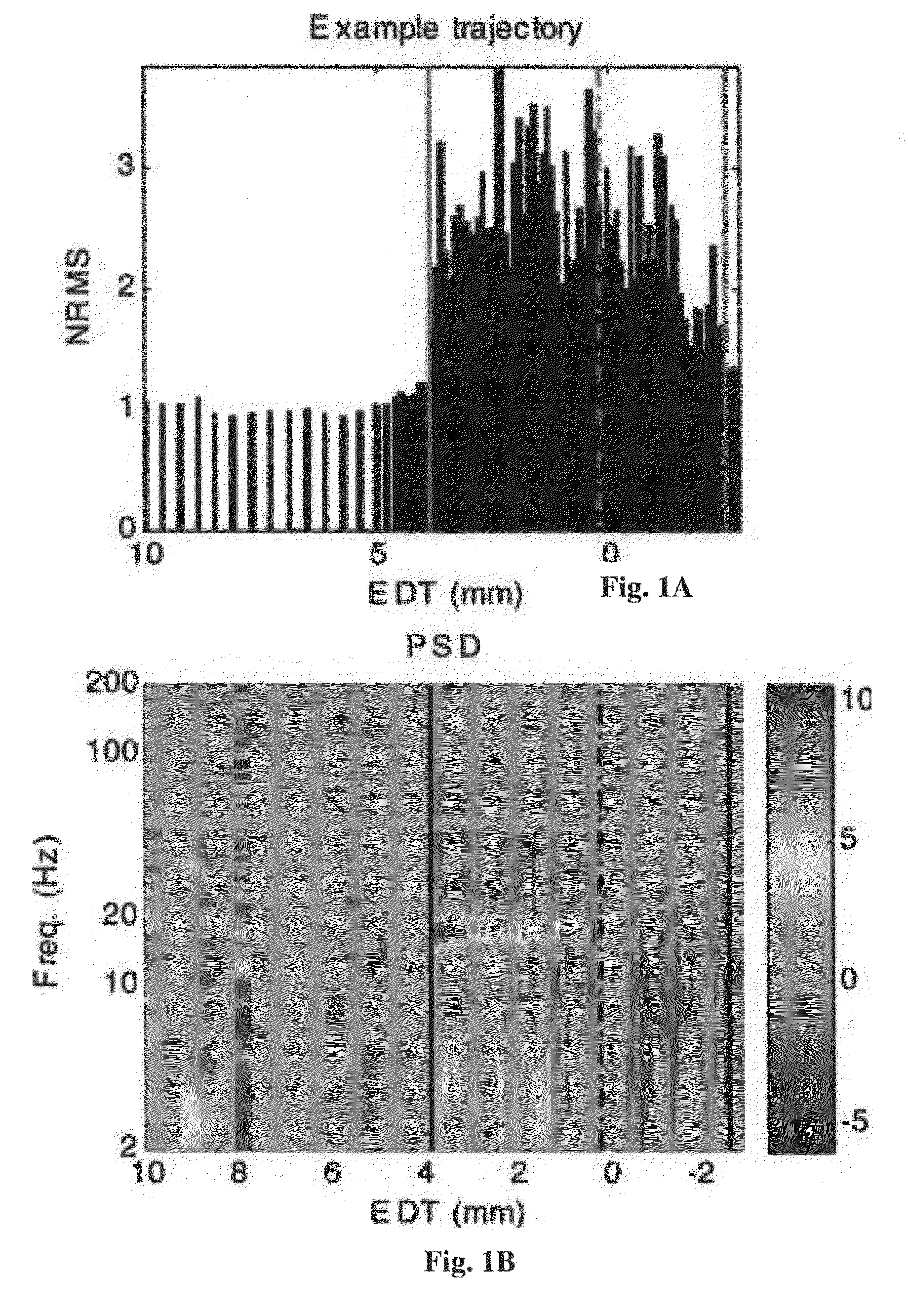
Real-time methods and systems for mapping a target region in the brain during surgery
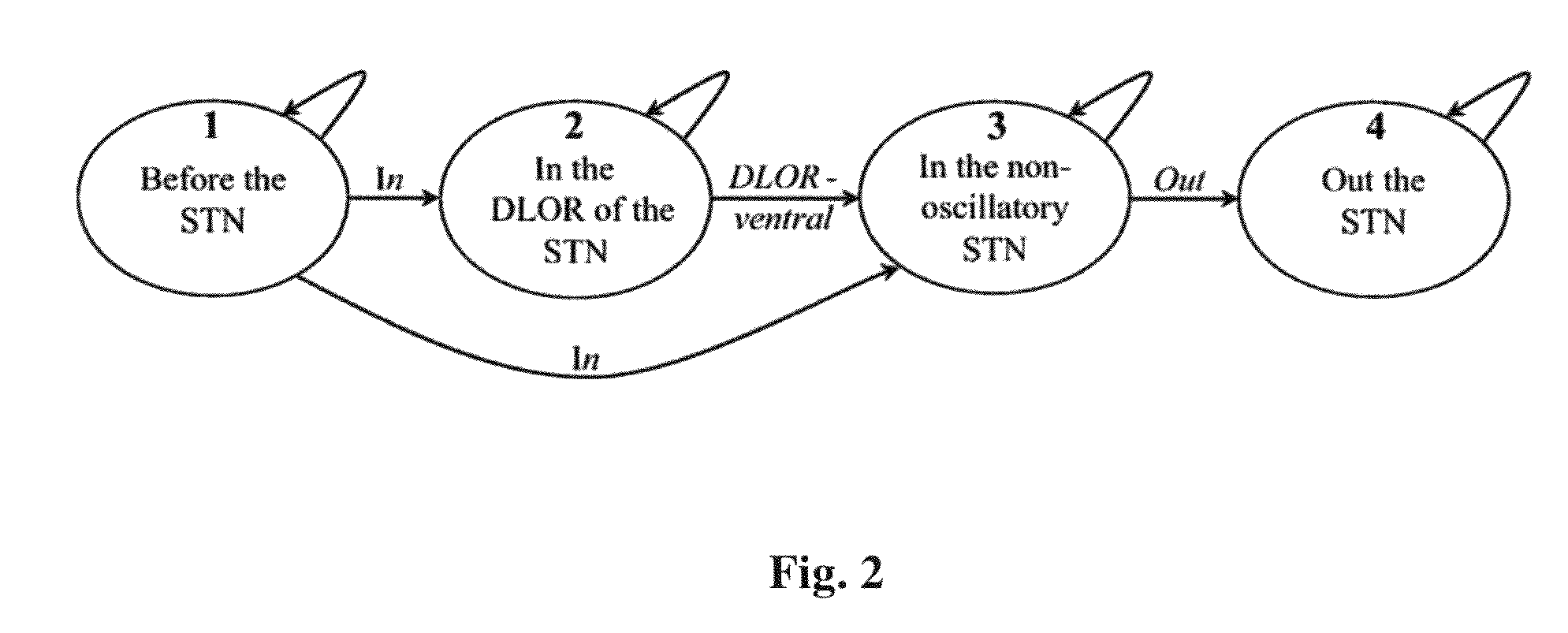
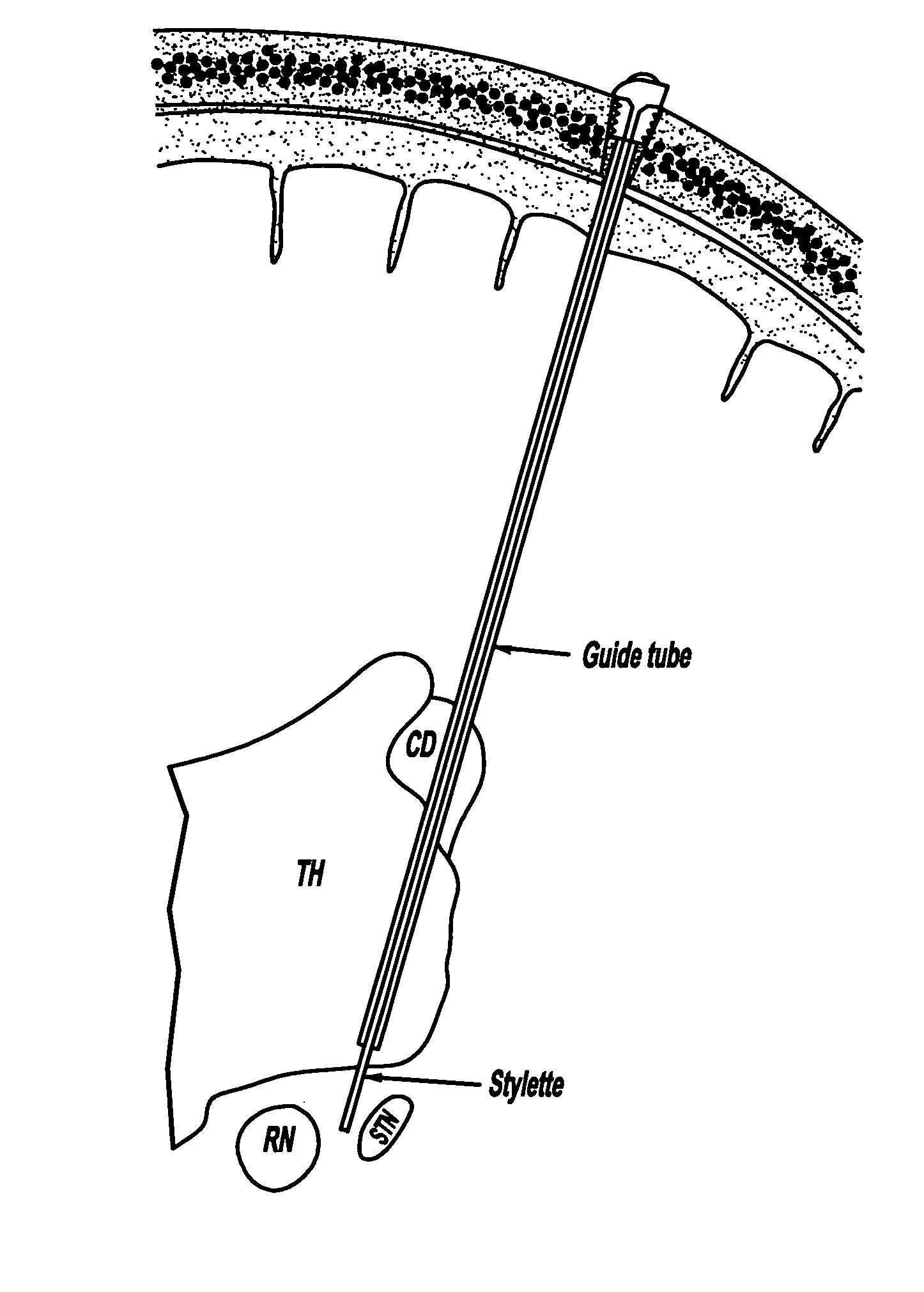
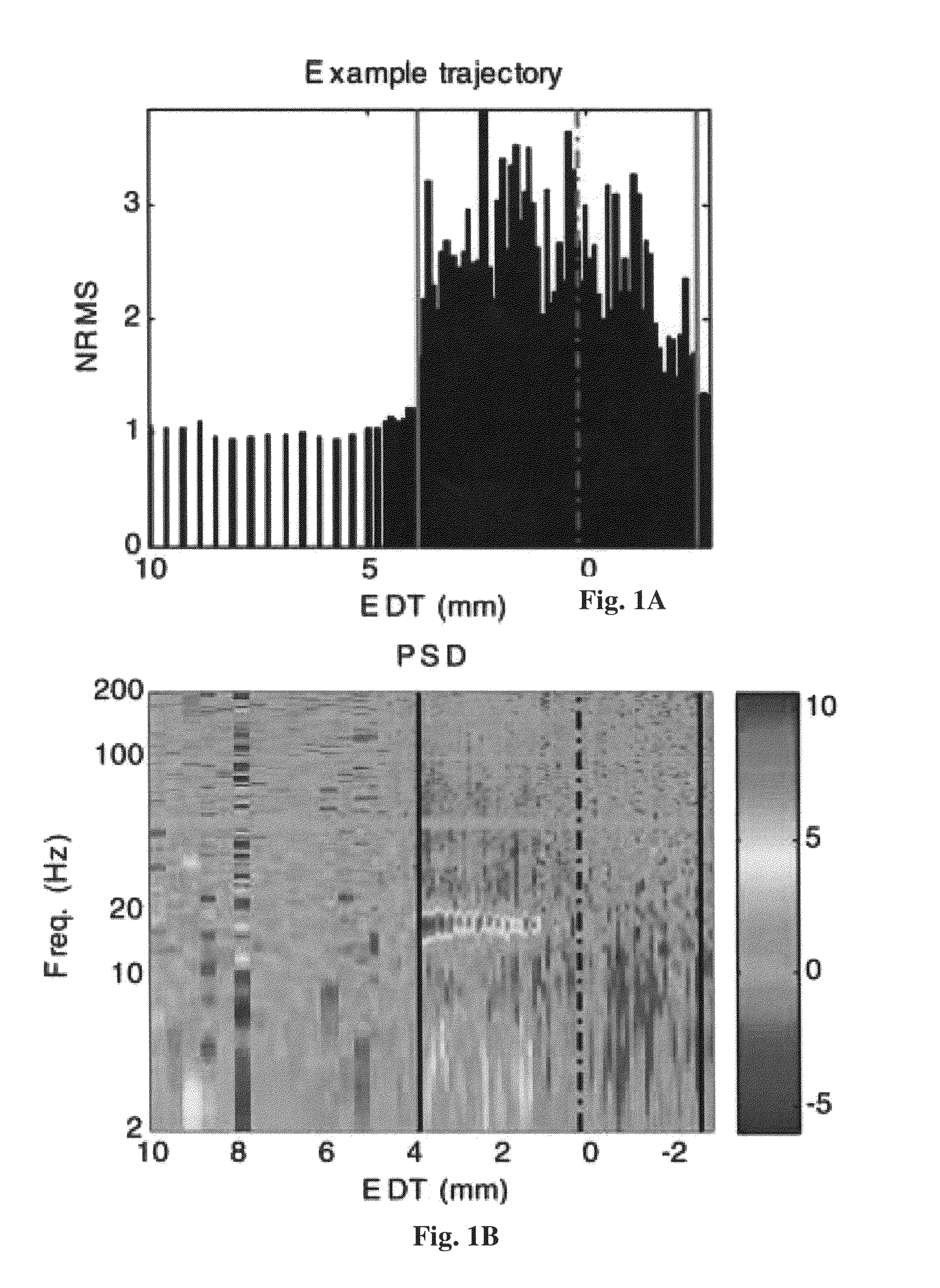
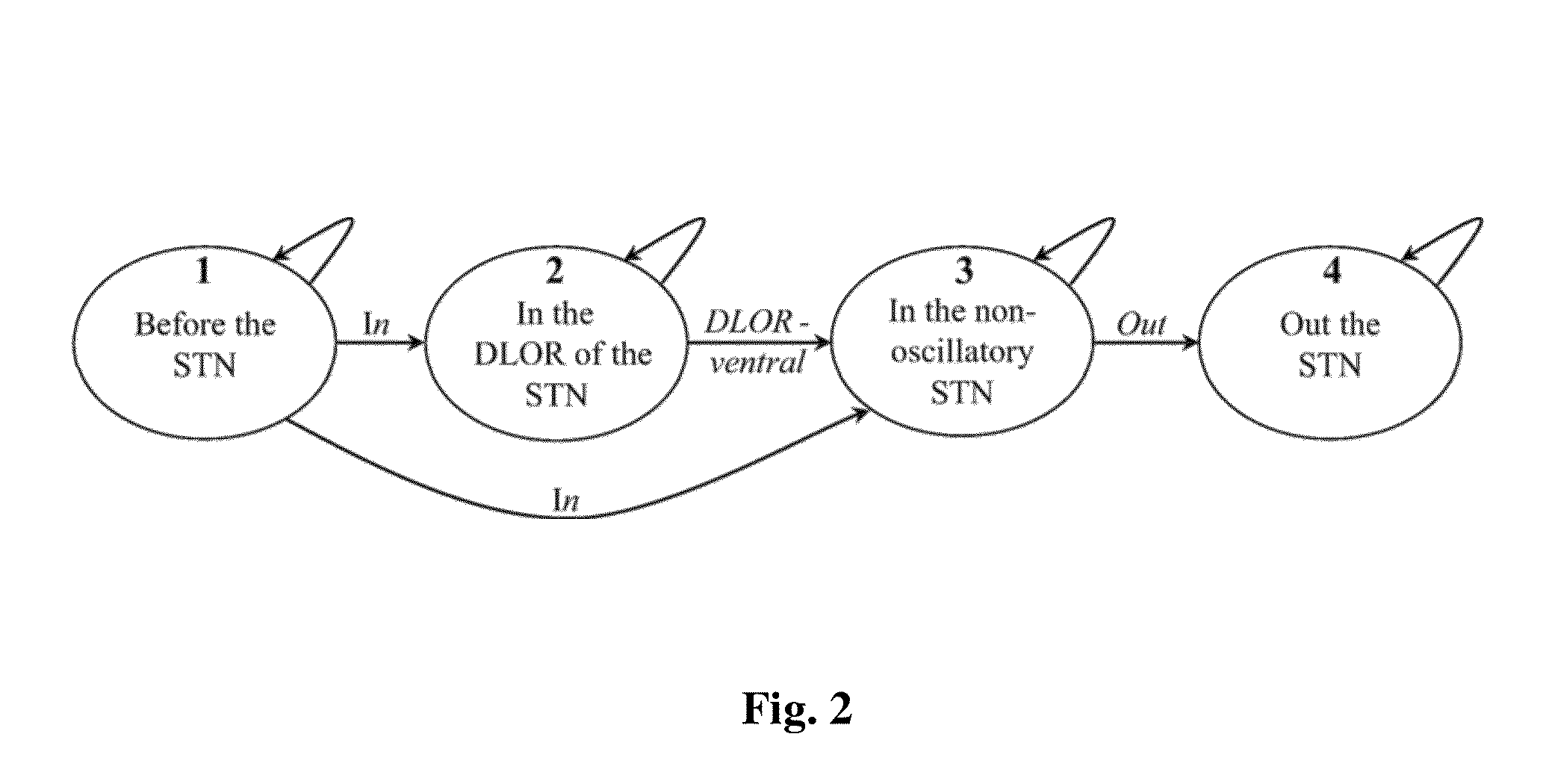
A real-time method and system to accurately demarcate sub-territories of the subthalamic nucleus area in the brain during surgery, based on microelectrode recordings and a Hidden Markov Model. Root mean square and power spectral density of the microelectrode recordings are used to train and test Hidden Markov Model in identifying the dorsolateral oscillatory region and non-oscillatory sub-territories within the subthalamic nucleus. After the dorsolateral oscillatory region in the subthalamic nucleus is mapped, the microelectrodes are removed, and a macroelectrode is inserted in the mapped dorsolateral oscillatory region for producing deep brain simulation for treatment of Parkinson's disease.
Owner:ALPHA OMEGA NEURO TECH
Deep brain stimulation
A method for treating essential tremor comprising the step of applying deep brain stimulation to the ascending dentate / interpositus-ventral intermedius fibres of the brain at a location remote from the ventral intermedius nucleus of the thalamus. A method for identifying an area of a patient's brain to be targeted with deep brain stimulation for the treatment of essential tremor comprising the step of using a scan of a patient's brain to identify a target area in relation to the subthalmic nucleus and the red nucleus. A method of treating essential tremor by using deep brain stimulation. A method of treating essential tumor by using a DBS electrode targeted to the dentate / interpositus-ventral intermedius fibres. A kit used in treating essential tremor.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Brain stimulation lead used for lesioning
InactiveUS7285118B1Creating lesionChoose simpleHead electrodesSurgical instrument detailsSubthalamusThalamus
A brain stimulation lead such as a deep brain stimulation (DBS) lead is provided, which lead can also be used to create lesions safely and effectively due to inclusion of temperature sensing. The generating of radio-frequency (RF) lesions via a brain stimulation lead provides a new treatment option, for instance, when hardware-related or other complications necessitate lead removal. An existing implanted DBS lead was used to create lesions in the thalamus and subthalamus of patients with movement disorders. Various brain stimulation leads with temperature sensors are described. Various methods are disclosed, including creation of a lesion with a brain stimulation lead while sensing temperature with a sensor implanted as part of the lead or with a noninvasive sensing device. Another method includes creating a graduated lesion with a brain stimulation lead of the invention or with a chronic lesioning lead.
Owner:FUNCTIONAL NEUROSCI
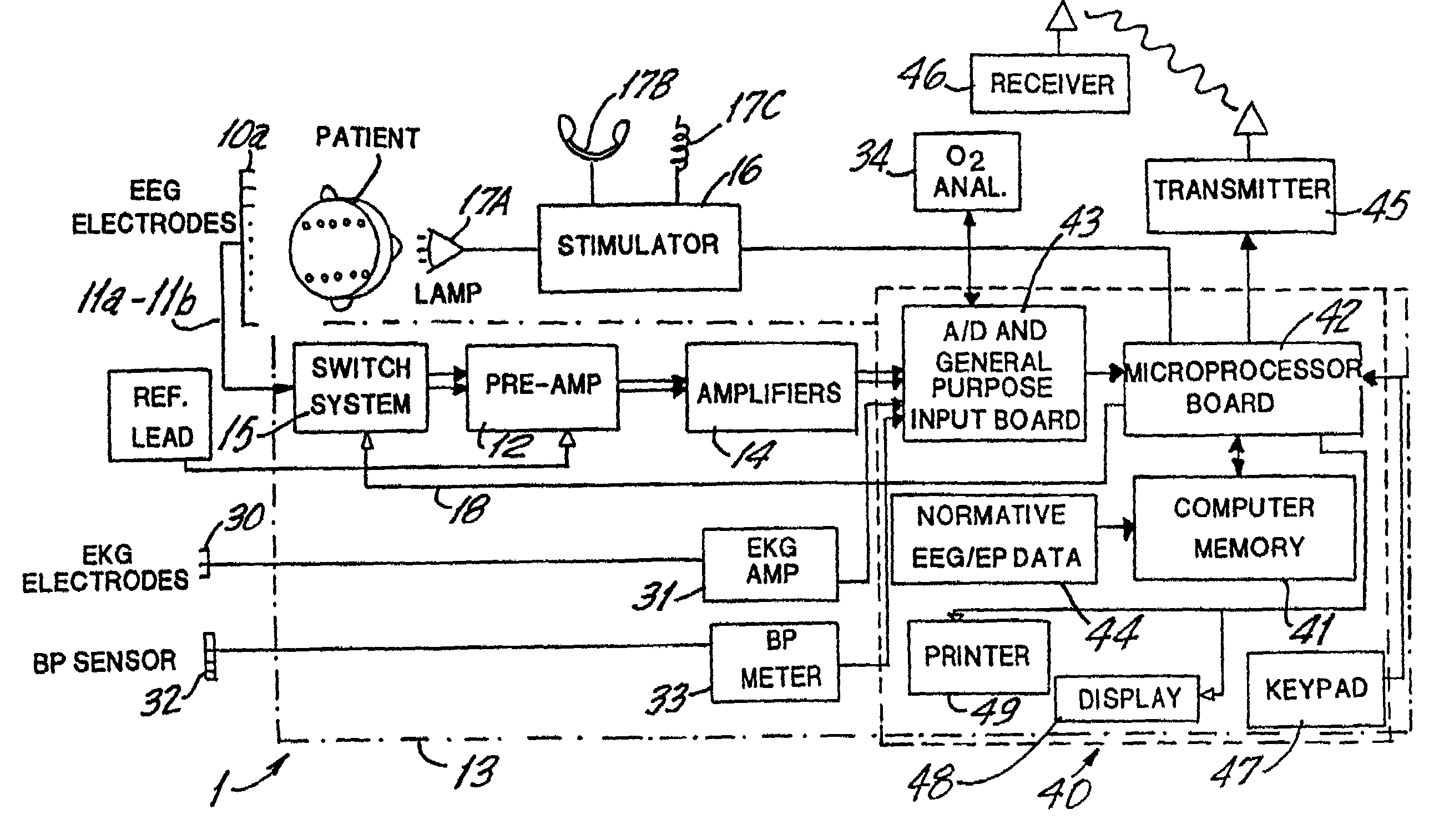
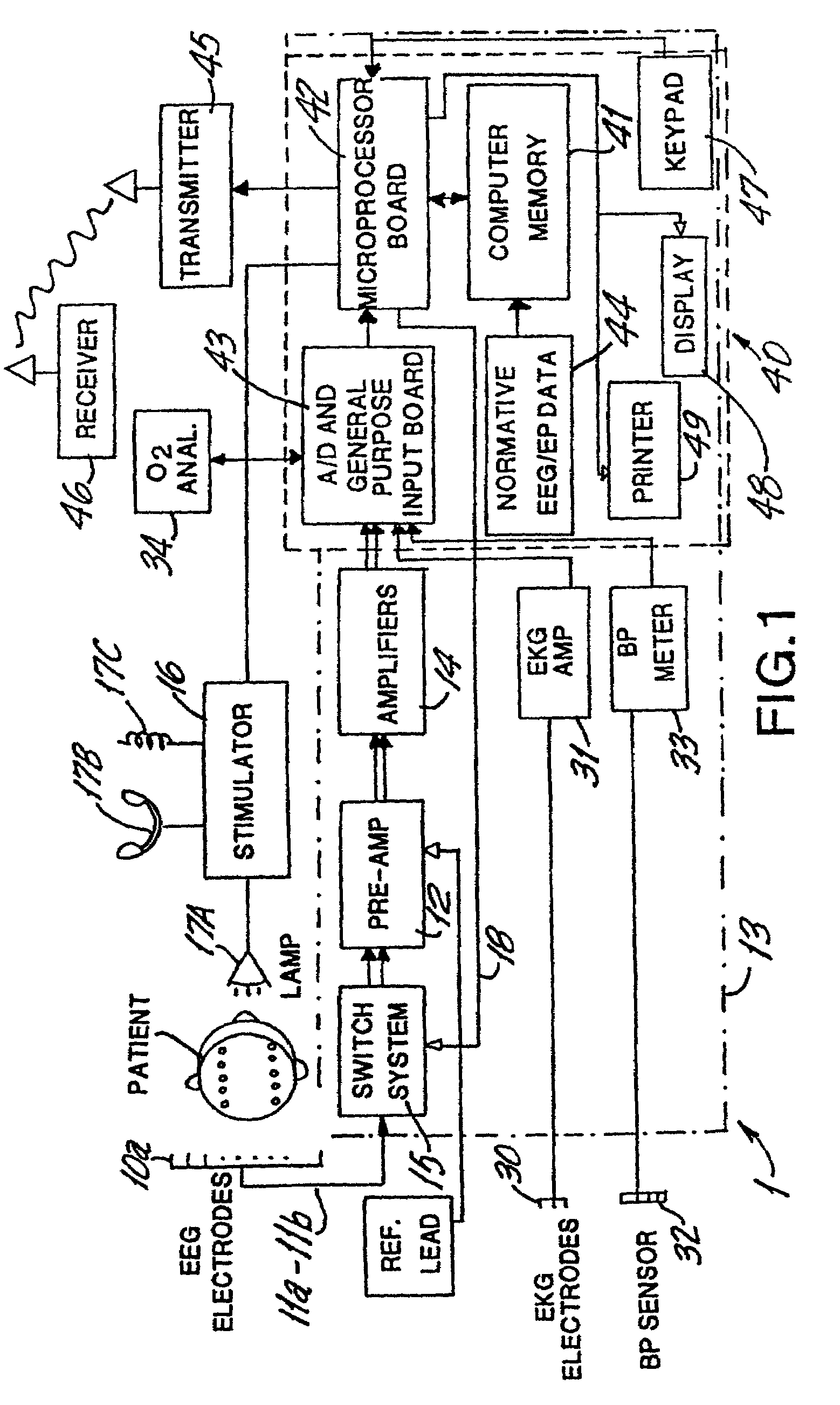
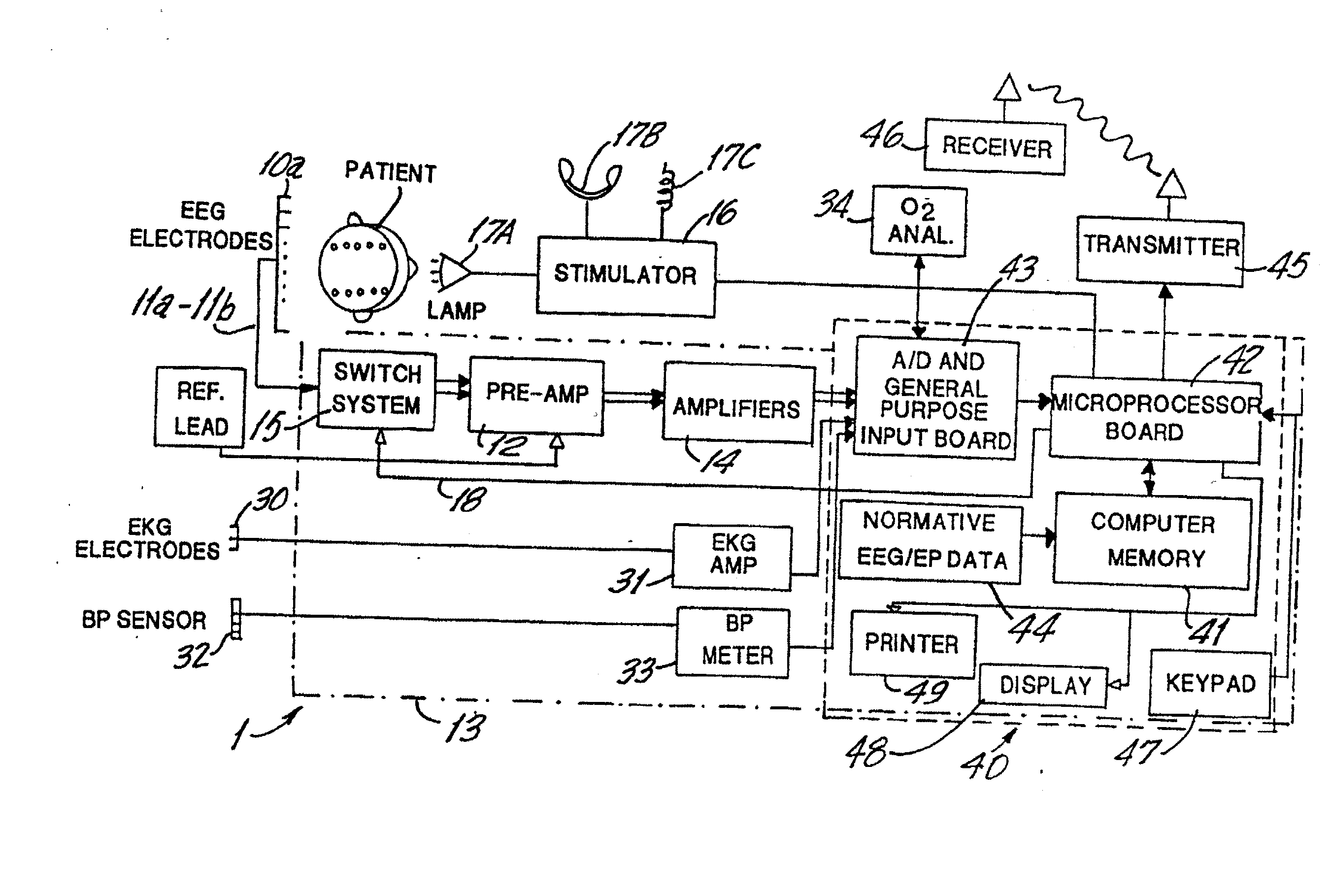
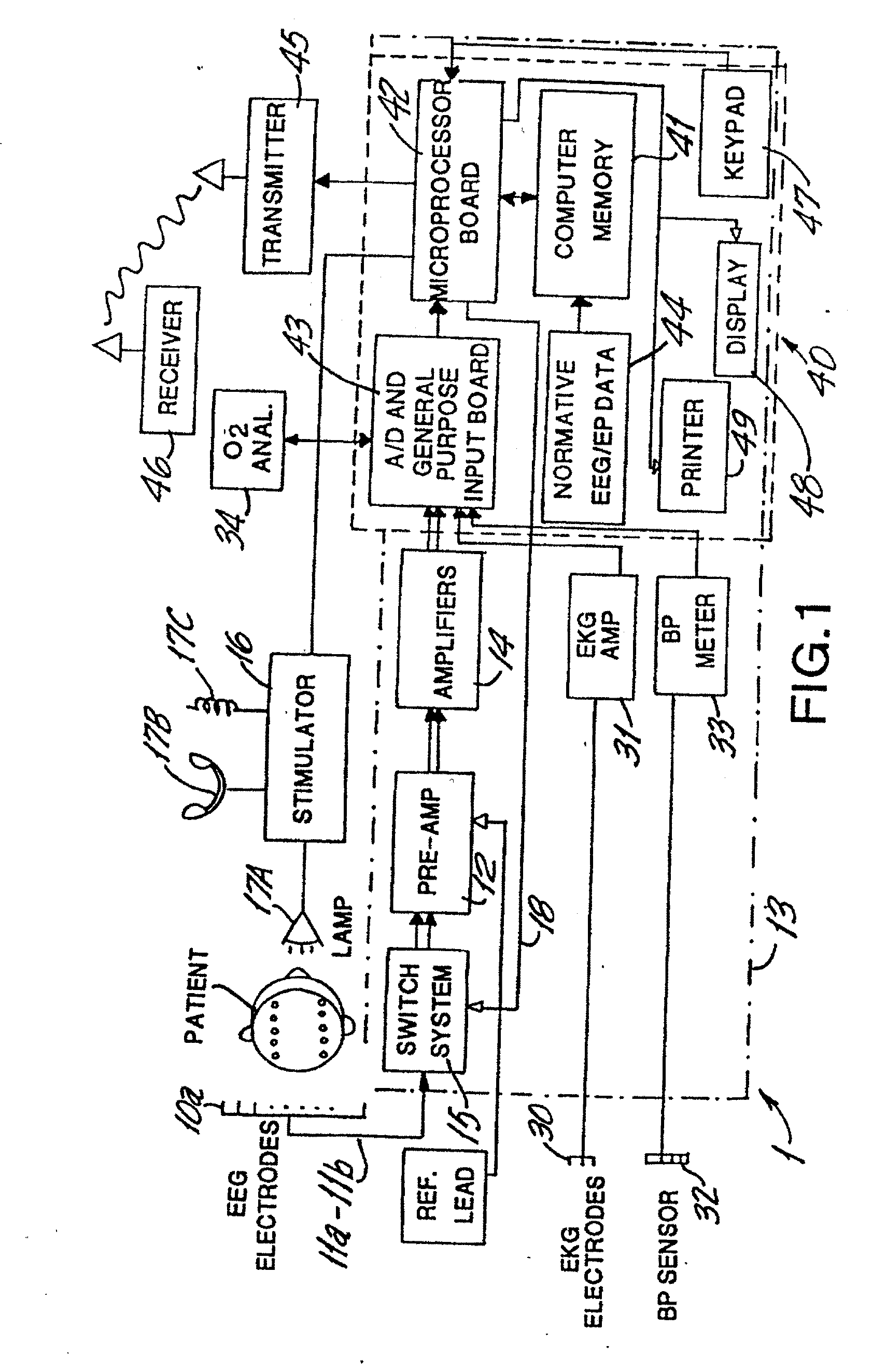
Brain function scan system
A portable EEG (electroencephalograph) instrument, especially for use in emergencies and brain assessments in physicians' offices, detects and amplifies brain waves and converts them into digital data for analysis by comparison with data from normal groups. In one embodiment, the EEG electrodes are in a headband which broadcasts the data, by radio or cellular phone, to a local receiver for re-transmission and / or analysis. In another embodiment, the subject is stimulated in two modes, i.e., aural and sensory, at two different frequencies to provide the subject's EPs (Evoked Potentials), assessing transmission through the brainstem and thalamus.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
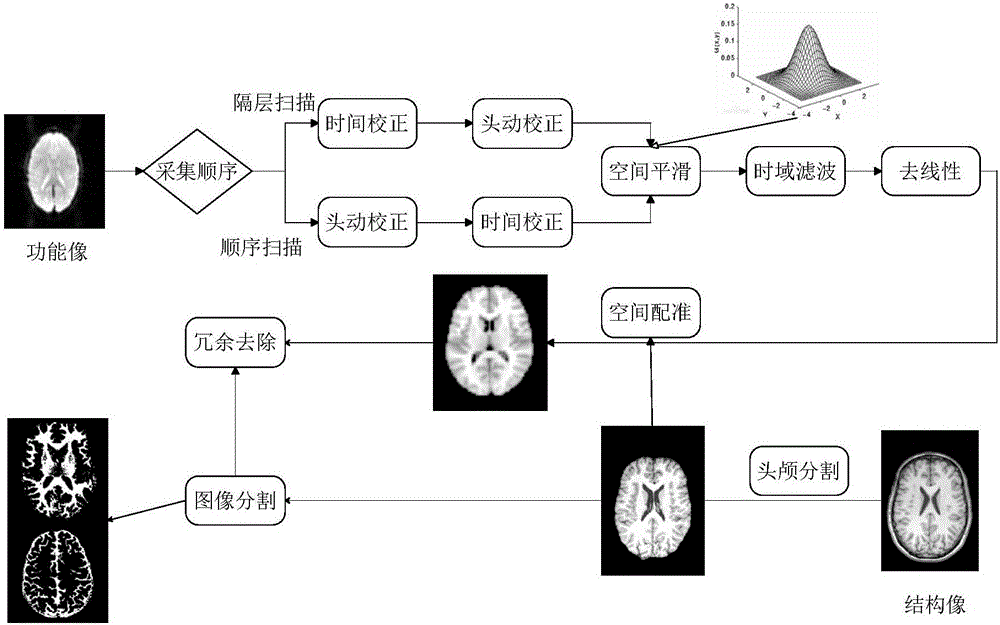
FMRI and DTI fusion-based vault white matter segmentation method
ActiveCN106204562ANovel thinkingSimple processImage enhancementImage analysisClinical valueFiber bundle
The invention relates to an fMRI and DTI fusion-based vault white matter segmentation method. The method includes the following steps that: fMRI and DTI magnetic resonance imaging data are pre-processed; regional segmentation is performed on a hippocampal encephalic region based on resting state function connections; an ROI is selected; and vault white matter segmentation is carried out based on a hippocampal sub-region and inter-thalamus white matter fiber bundle tracing technique. According to the method, the hippocampal encephalic region is segmented, and sub-regions obtained after segmentation are adopted as seed points; and the thalamus, adopted as a target encephalic region, is subjected to white matter fiber tracing, so that vault white matter can be segmented. The vault white matter is segmented based on the information of the function and structure of a human brain, and therefore, the fMRI and DTI fusion-based vault white matter segmentation method has the advantages of novel thinking, simple process and important scientific and clinical value.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Real-time methods and systems for mapping a target region in the brain during surgery
A real-time method and system to accurately demarcate sub-territories of the subthalamic nucleus area in the brain during surgery, based on microelectrode recordings and a Hidden Markov Model. Root mean square and power spectral density of the microelectrode recordings are used to train and test Hidden Markov Model in identifying the dorsolateral oscillatory region and non-oscillatory sub-territories within the subthalamic nucleus. After the dorsolateral oscillatory region in the subthalamic nucleus is mapped, the microelectrodes are removed, and a macroelectrode is inserted in the mapped dorsolateral oscillatory region for producing deep brain simulation for treatment of Parkinson's disease.
Owner:ALPHA OMEGA ENG LTD
Vibration generating apparatus and method introducing hypersonic effect to activate fundamental brain network and heighten aesthetic sensibility
ActiveUS8167826B2Inhibit deteriorationImprove securityPublic address systemsChiropractic devicesThalamusBase function
Owner:ACTION RES
Brain Function Scan System
InactiveUS20090227889A2Accurately and reliably and continuously and quickly determinePermit separationElectroencephalographySensorsDigital dataPortable EEG
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Method for deep brain stimulation targeting based on brain connectivity
InactiveUS20130030499A1Precise structureHead electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsThalamusBrain deep stimulation
Due to the lack of internal anatomic detail with traditional magnetic resonance imaging, preoperative stereotactic planning for the treatment of tremor usually relies on indirect targeting based on atlas-derived coordinates. To overcome such disadvantages, a method is provided that allows for deep brain stimulation targeting based on brain connectivity. For example, probabilistic tractography-based thalamic segmentation for deep brain stimulator (DBS) targeting is suitable for the treatment of tremor.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
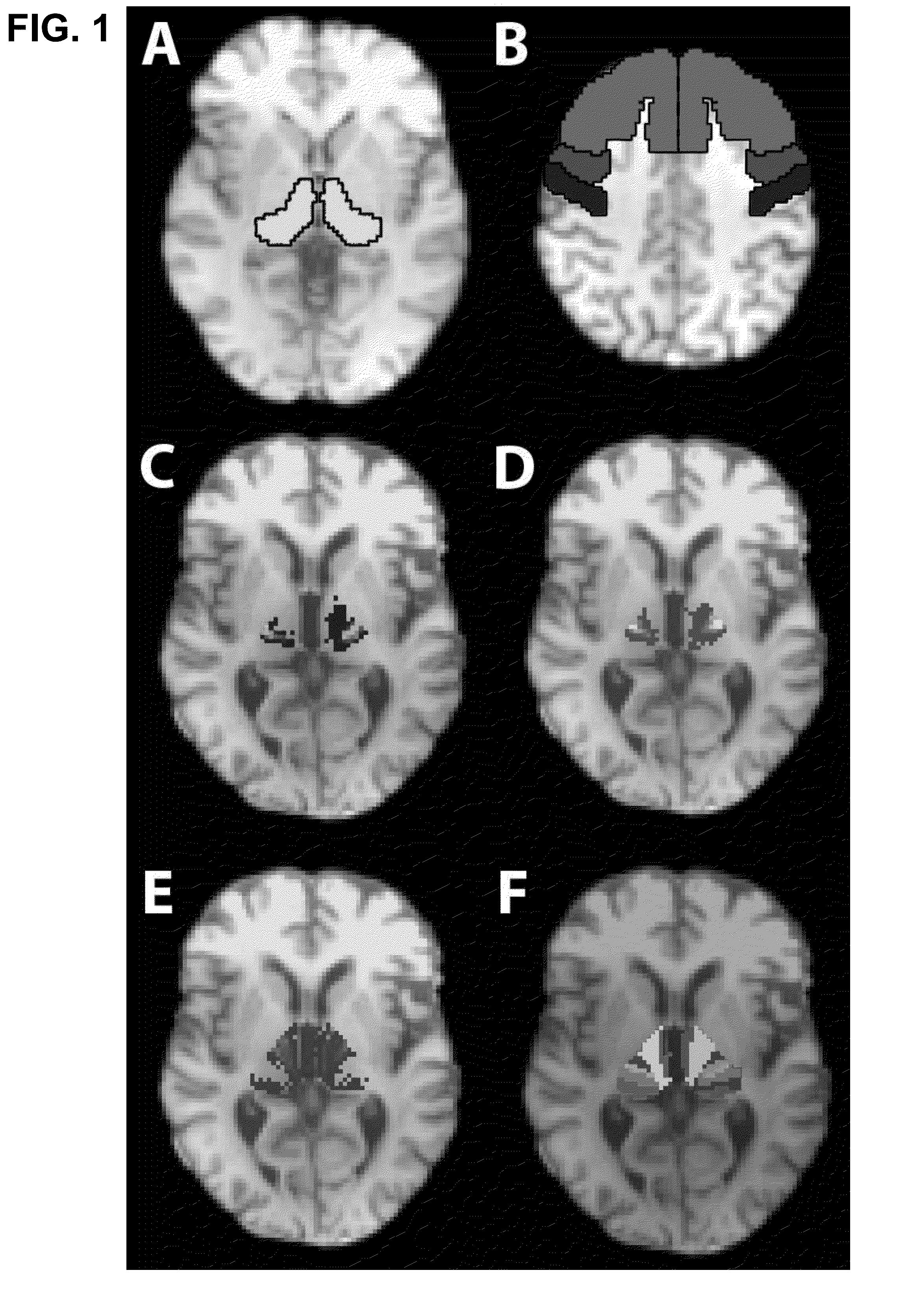
Method and system for a brain image pipeline and brain image region location and shape prediction
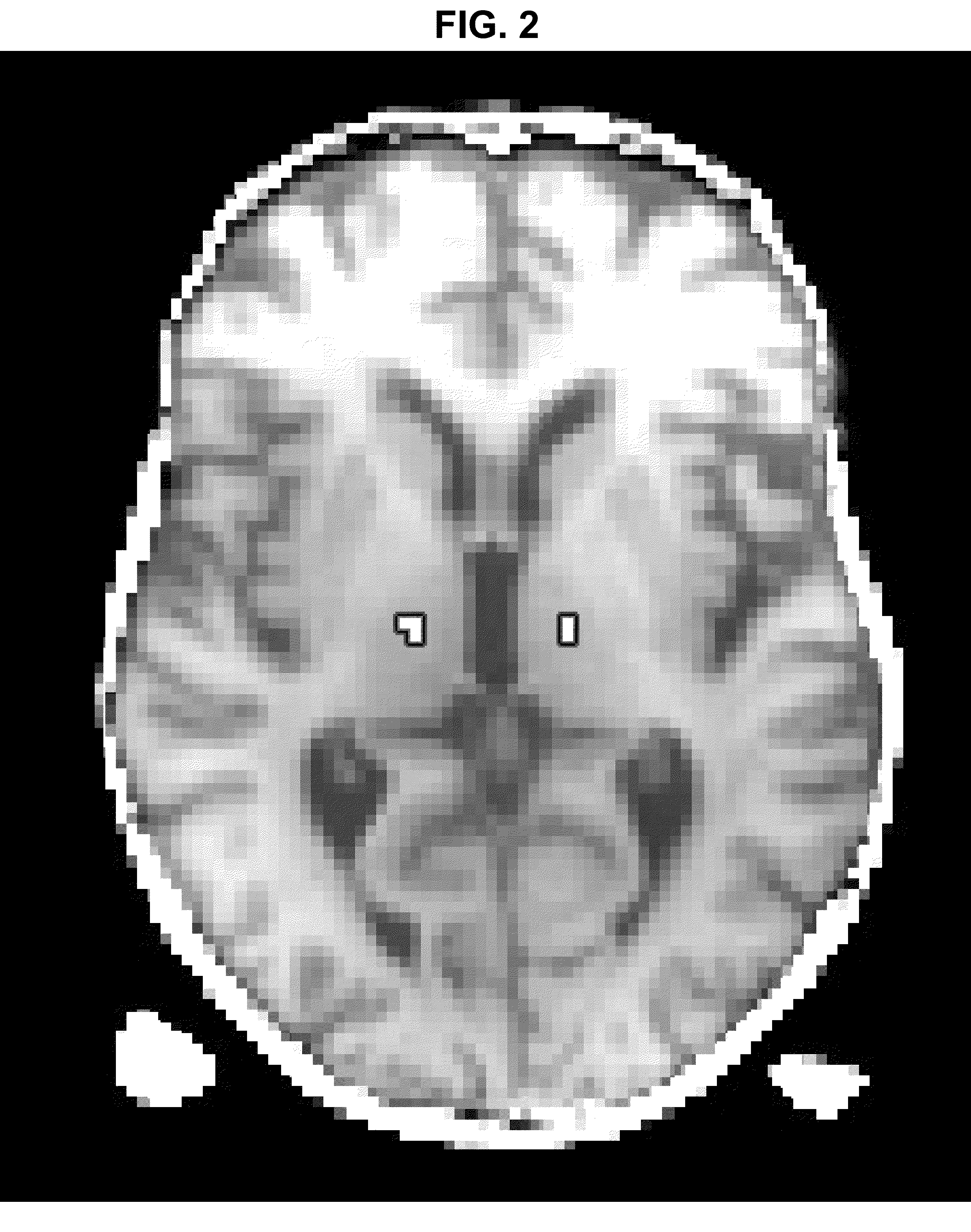
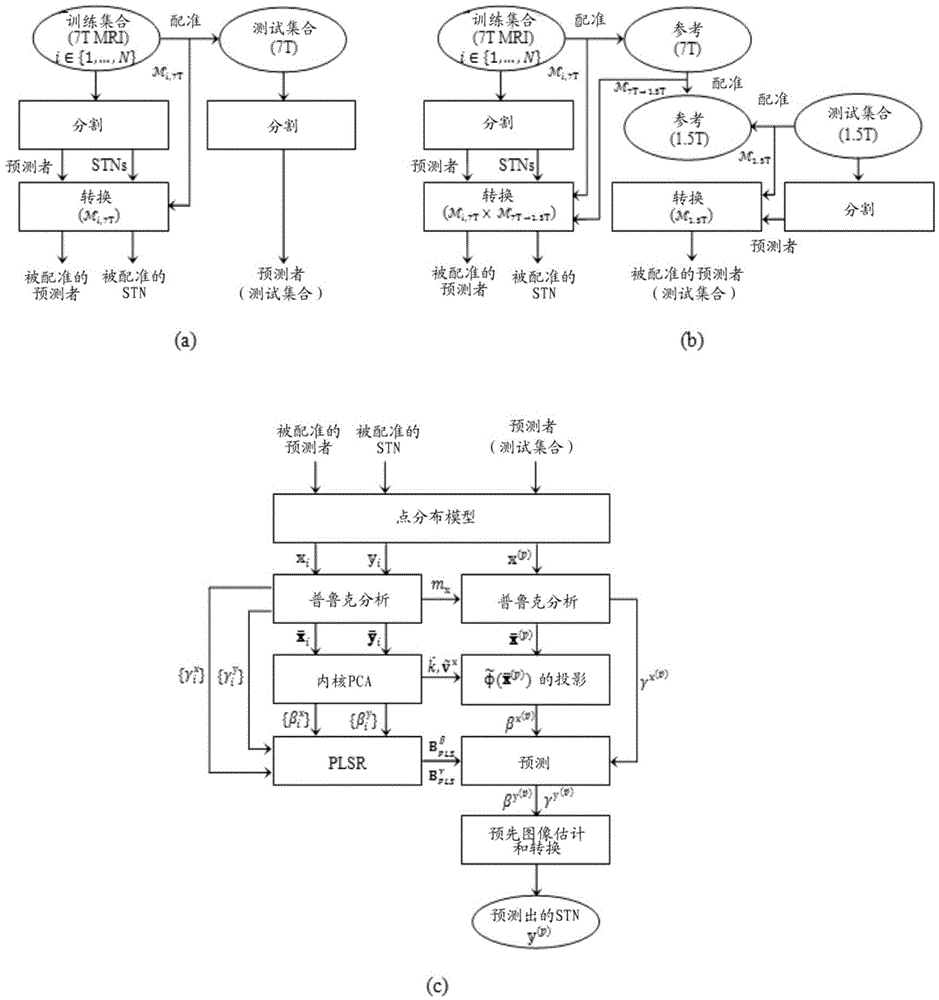
A volumetric segmentation method is disclosed for brain region analysis, in particular but not limited to, regions of the basal ganglia such as the subthalamic nucleus (STN). This serves for visualization and localization within the sub-cortical region of the basal ganglia, as an example of prediction of a region of interest for deep brain stimulation procedures. A statistical shape model is applied for variation modes of the STN, or the corresponding regions of interest, and its predictors on high-quality training sets obtained from high-field, e.g., 7T, MR imaging. The partial least squares regression (PLSR) method is applied to induce the spatial relationship between the region to be predicted, e.g., STN, and its predictors. The prediction accuracy for validating the invention is evaluated by measuring the shape similarity and the errors in position, size, and orientation between manually segmented STN and its predicted one.
Owner:オウルナビゲーションインコーポレイテッド
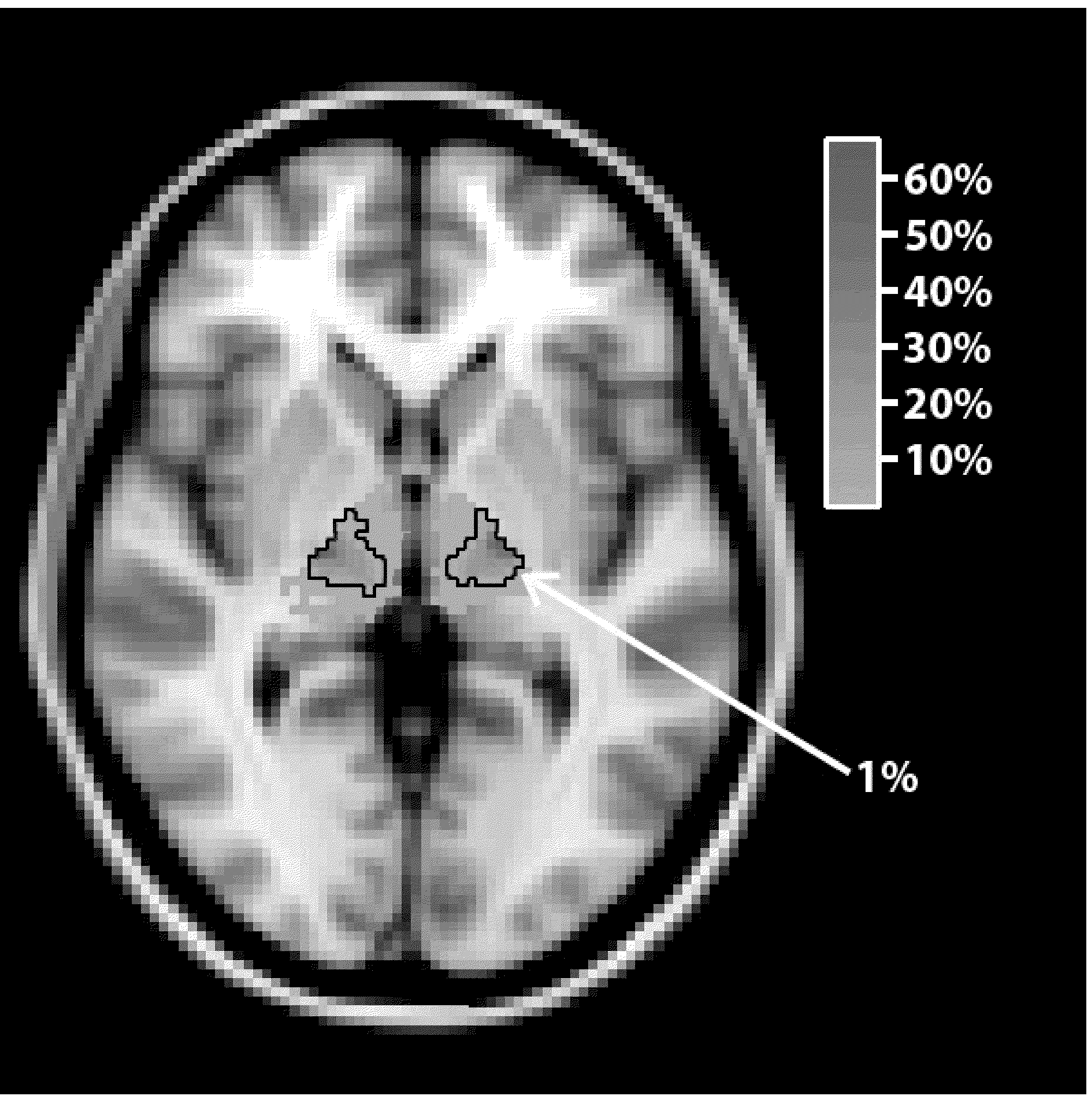
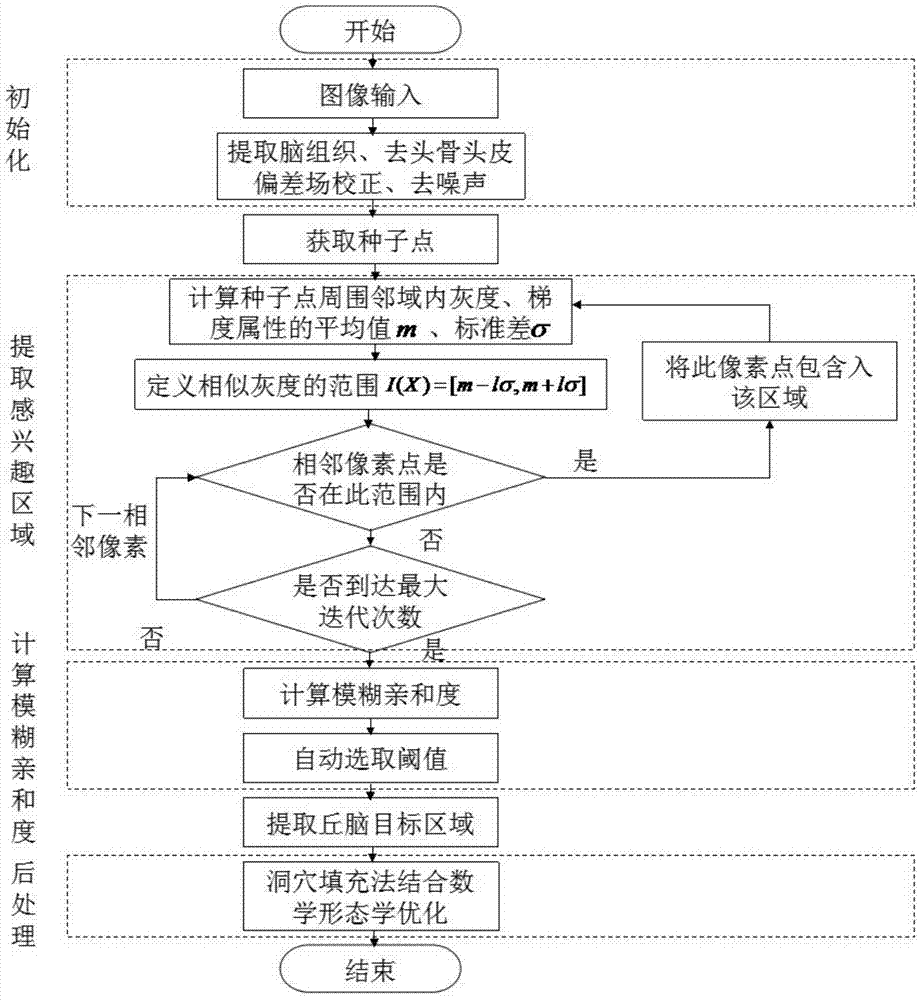
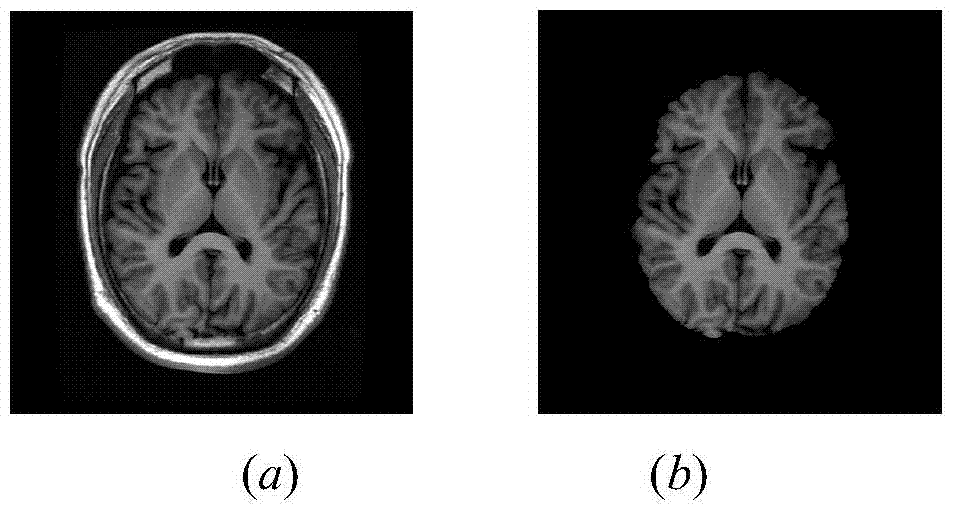
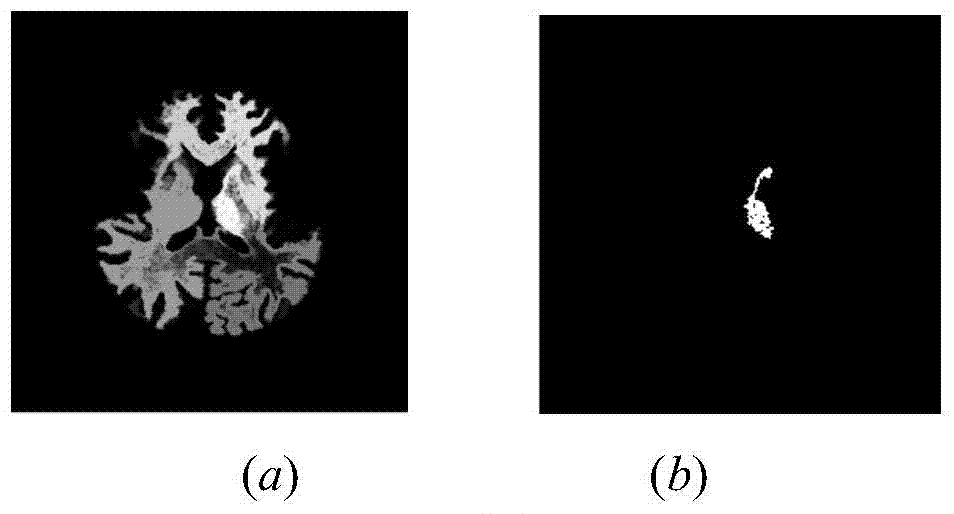
Fuzzy-connectedness-algorithm-based segmentation method of thalamus and substructures of thalamus
InactiveCN103942780AEasy to operate manuallyReduce manual interventionImage analysisPattern recognitionThalamus
The invention relates to a-fuzzy-connectedness-algorithm-based segmentation method of the thalamus and substructures of the thalamus. The method comprises the steps of inputting an original image, pre-processing the original image, automatically extracting an interesting area where a nucleus is located, estimating a mean value and a standard deviation in the area, calculating the fuzzy affinity to a seed point of the periphery region of the seed point, and conducting post-processing. According to the fuzzy-connectedness-algorithm-based segmentation method, the interesting area is automatically selected by adopting the confidence connectedness; when the fuzzy connectedness is calculated, gradient features are added on the basis that only gray features are used in the prior art, and the edge of the image can be expressed better. Experiment results show that the fuzzy-connectedness-algorithm-based segmentation method effectively reduces the frequency of segmentation-free phenomenon of a traditional fuzzy connectedness algorithm; weight coefficients between the gray features and the gradient features are obtained through self-adaption calculation, and accuracy of segmentation results is increased. According to the fuzzy-connectedness-algorithm-based segmentation method, automatic selection of fuzzy connectedness segmentation threshold values is achieved, the threshold values change along with changes of the seed point, and the degree of automation in a segmentation process is increased.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
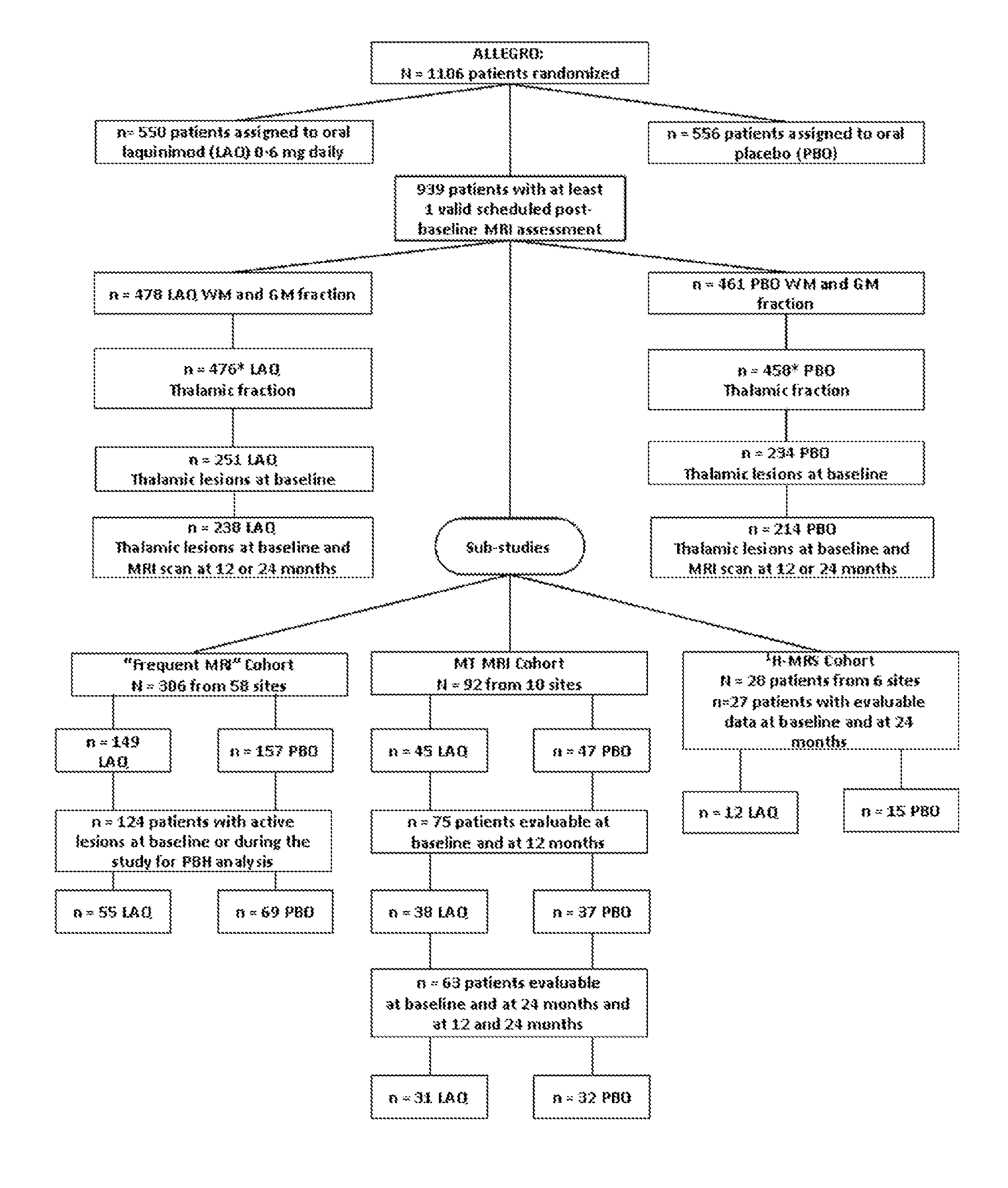
Laquinimod for reducing thalamic damage in multiple sclerosis
InactiveUS20140107154A1Inhibiting and reducing thalamic damageReduce harmBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseThalamus
This invention provides methods for inhibiting or reducing thalamic damage in a subject comprising administering to the subject an amount of laquinimod, wherein the subject is a human patient afflicted with a form of multiple sclerosis or presenting a clinically isolated syndrome who has been determined to have thalamic damage at baseline, a subject afflicted with a disease or disorder other than a form of multiple sclerosis or a clinically isolated syndrome, or a subject not afflicted with a form of multiple sclerosis or a presenting clinically isolated syndrome, and laquinimod and laquinimod pharmaceutical compositions for use thereof. This invention also provides methods for inhibiting or reducing tremor or spasticity in a subject afflicted by tremor or spasticity, comprising administering to the subject an amount of laquinimod, and laquinimod and laquinimod pharmaceutical compositions for use thereof.
Owner:TEVA PHARMA IND LTD
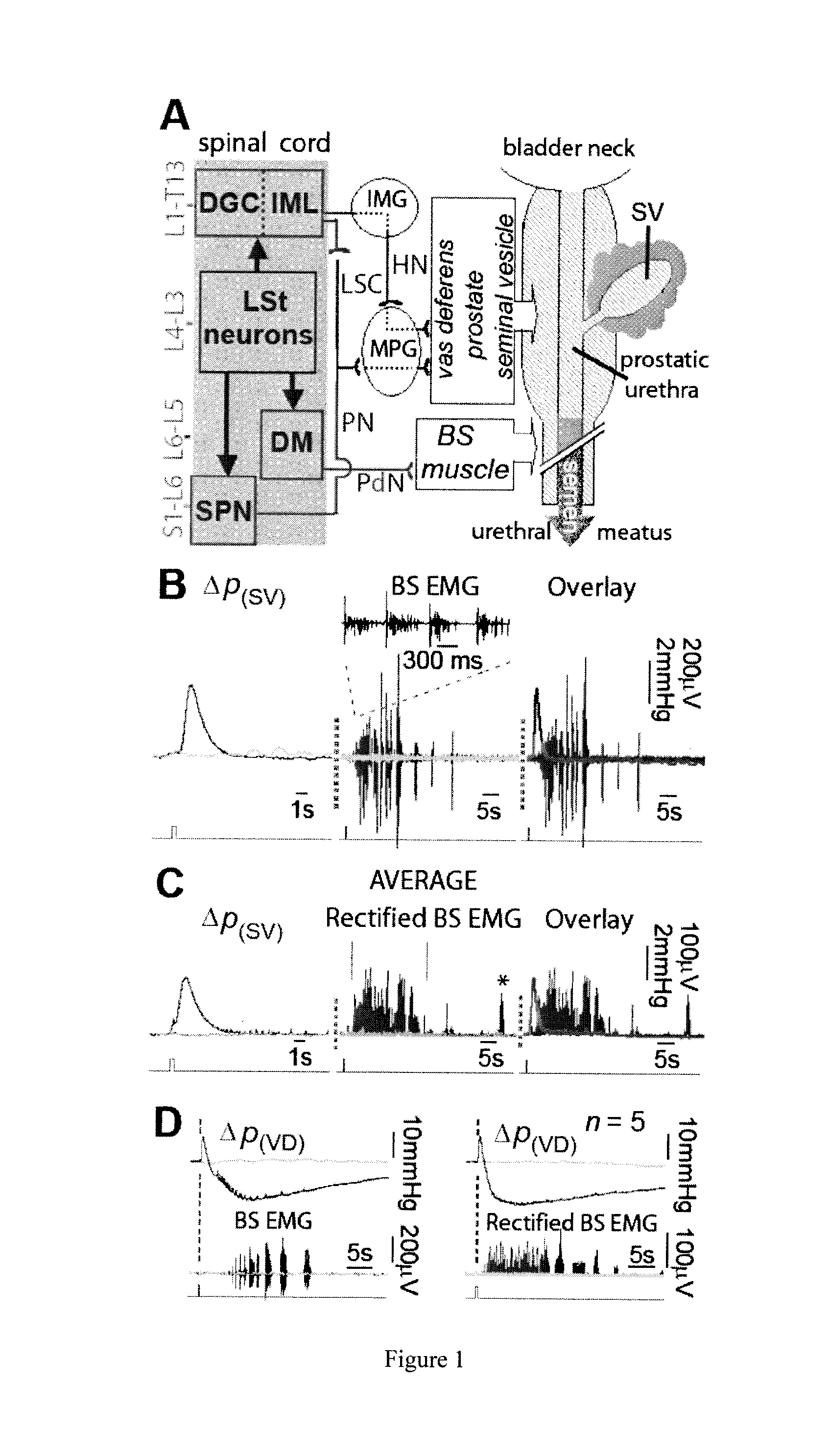
Method for Restoring an Ejaculatory Failure
The present invention relates to a method for eliciting ejaculation in a male individual, comprising delivering one or more stimulation pulses to lumbar spinothalamic (LSt) cells via a light stimulus, wherein said LSt cells express a light-activated cation channel protein.
Owner:PELVIPHARM
System and methods for multi-site activation of the thalamus
ActiveUS20150367133A1Ameliorate direct effectImprove cognitive function and behavioral responsivenessHead electrodesExternal electrodesMulti siteMedicine
The present invention relates to a method to control a thalamic projecting fiber in a subject. This method involves providing a subject having a first stimulator and a second stimulator implanted in the subject's central thalamus. A stimulus signal generator is provided which is coupled to the first and second stimulators. Separate stimulus signals are provided from the stimulus signal generator to the first and second stimulators under conditions effective to control the thalamic projecting fiber in the subject. Also disclosed is an apparatus for deep brain stimulation.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
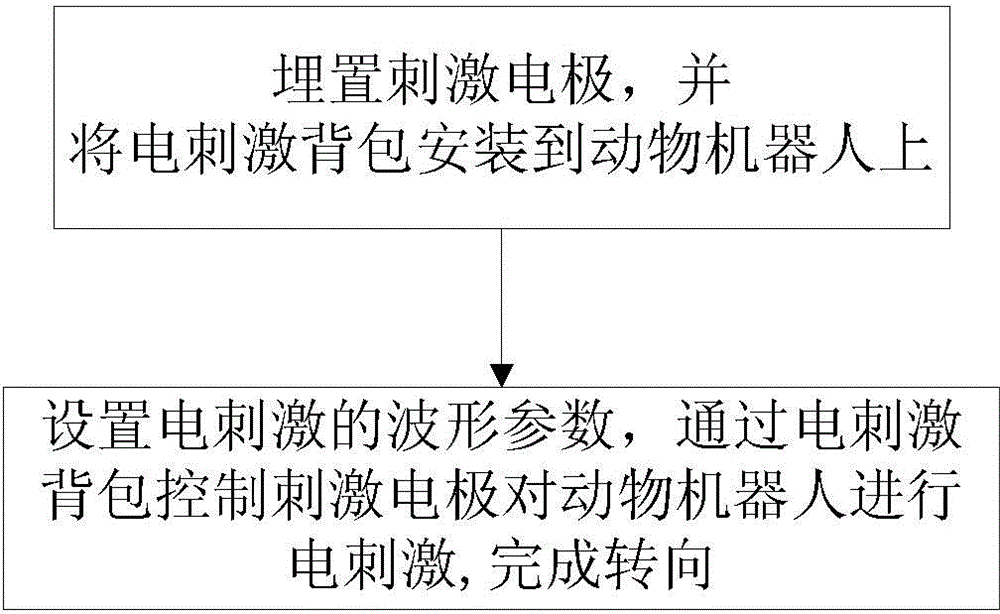
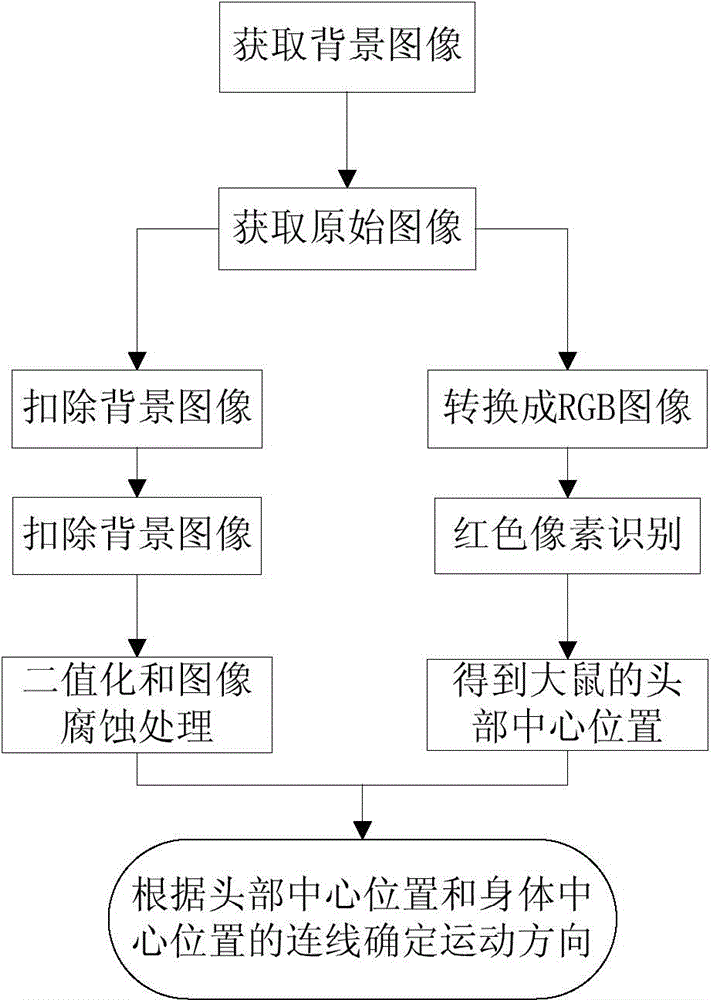
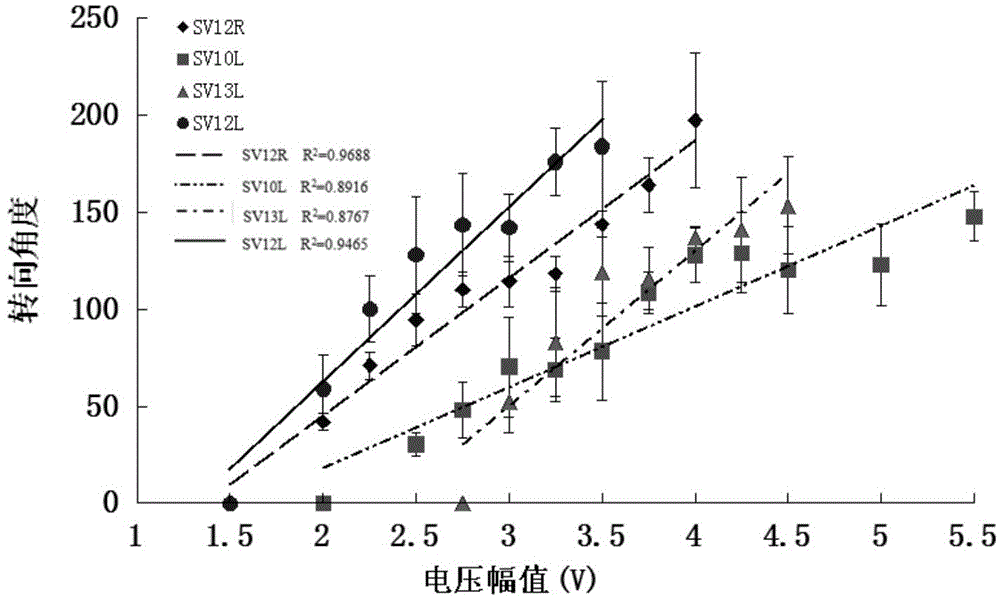
Method for controlling animal robot to turn on basis of ventral posterior medial nucleus electrical stimulation
InactiveCN104679028AControllable steering angleOmit training timeControl using feedbackControl animalThalamus
The invention relates to a method for controlling an animal robot to turn on the basis of ventral posterior medial nucleus electrical stimulation. The method comprises the steps that two stimulating electrodes are respectively imbedded into VPM (Ventral Posterior Medial Nucleus) regions on both sides of the animal robot, the electrodes are fixed on skulls with dental cement, and an electrical stimulation backpack is installed on the animal robot; waveform parameters of electrical stimulation are set by an upper computer and are transmitted to the electrical stimulation backpack at the back of the animal robot in a wireless mode, the stimulating electrodes are controlled by the electrical stimulation backpack, so as to perform electrical stimulation on the animal robot, and corresponding thalamus-cortex projection loops are activated, so that the animal robot generates a virtual feeling, so as to complete turning. According to the method, a traditional method that the animal robot learns to turn by reward training is eliminated, turning is realized directly through the electrical stimulation, the controllability over a turning angle is realized, a large amount of training time is saved, the working efficiency is high, and the method has good application prospects in the field of animal robot navigation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Agents and methods for administration to the central nervous system
InactiveUS20060120971A1Avoid the needReduce productionPowder deliveryBiocideAcute hyperglycaemiaThalamus
The present invention provides pharmaceutical compositions and methods for intranasal administration to a subject to increase long-chain acyl CoA levels in the CNS (e.g., the hypothalamus), to reduce food intake and / or reduce appetite, to improve hepatic autoregulation, and / or to treat a metabolic disorder such as diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, glucose intolerance and / or obesity.
Owner:DARA BIOSCI
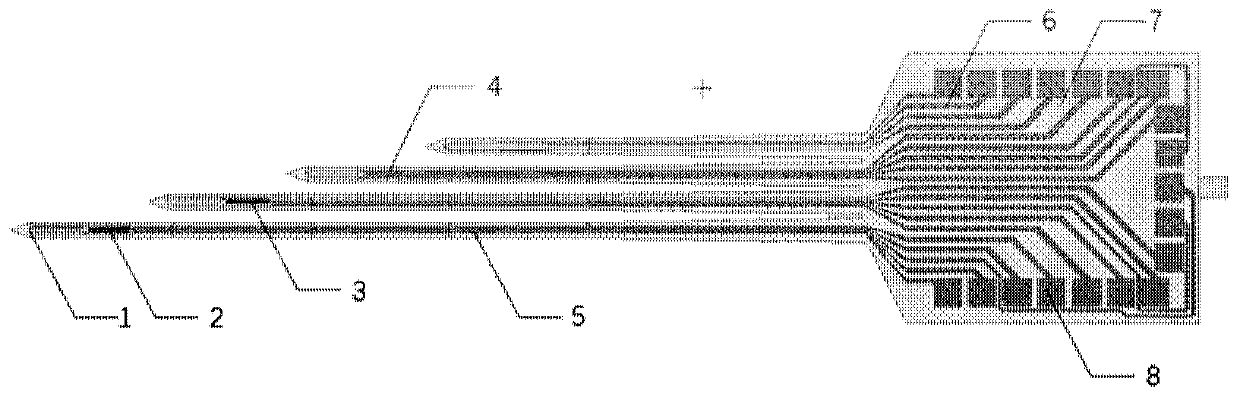
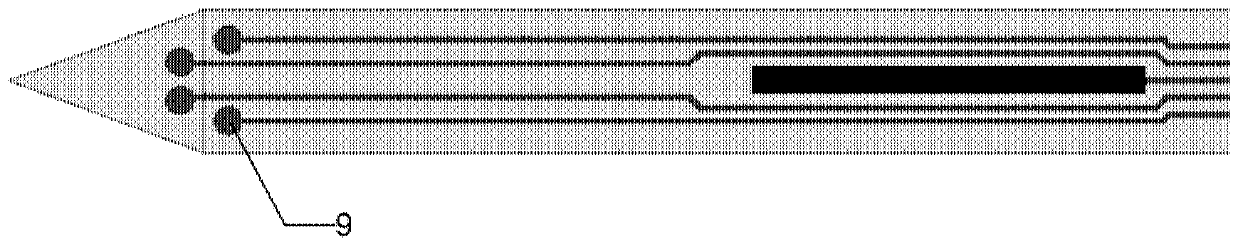
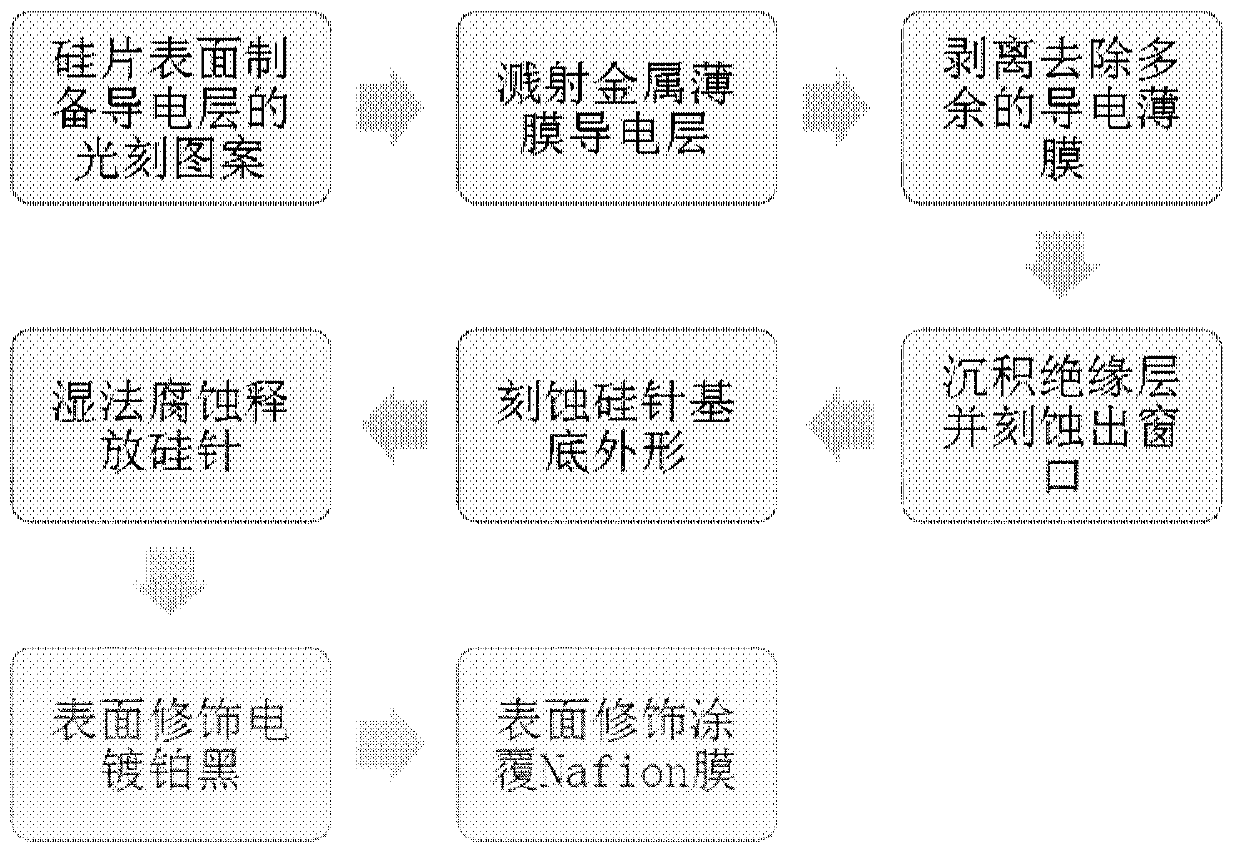
Implantable type micro-nano electrode array chip in weightless-simulated rats and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110623655AReduce volumeAvoid damageDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMicro nanoThalamus
The invention discloses an implantable type micro-nano electrode array chip and a preparation method thereof, and the chip comprises silicon needle substrates, micro-electrode arrays, a counter electrode, an electrochemical reference electrode and an electrophysiological reference electrode; wherein, the silicon needle substrates are distributed on the implantation part at the front end of the chip and the interface part at the back end of the chip; a plurality of microelectrodes are distributed on the upper surface of the tip end of each silicon needle, and the micro-electrodes form the micro-electrode arrays; and the counter electrode, the electrochemical reference electrode and the electrophysiological reference electrode are arranged on the single silicon needle or a plurality of different silicon needles at positions close to the micro-electrode arrays. The lengths of the micro-electrode array silicon needles are gradually decreased, and 4 groups of micro-electrode arrays are distributed on 4 silicon needles, used for simultaneously detecting electrophysiological signals of cerebral cortex, hippocampus and thalamus, so that multiple implantation injuries can be avoided, and long-time continuous detection can be realized.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
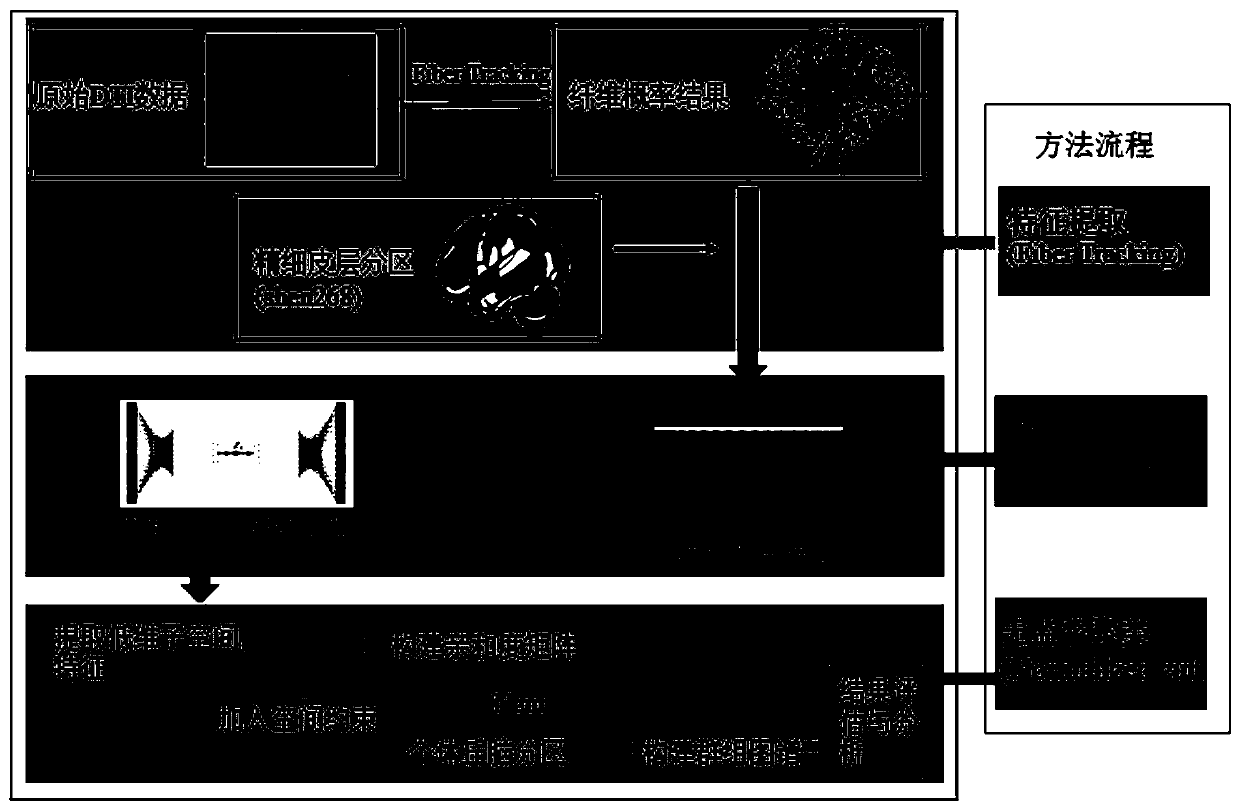
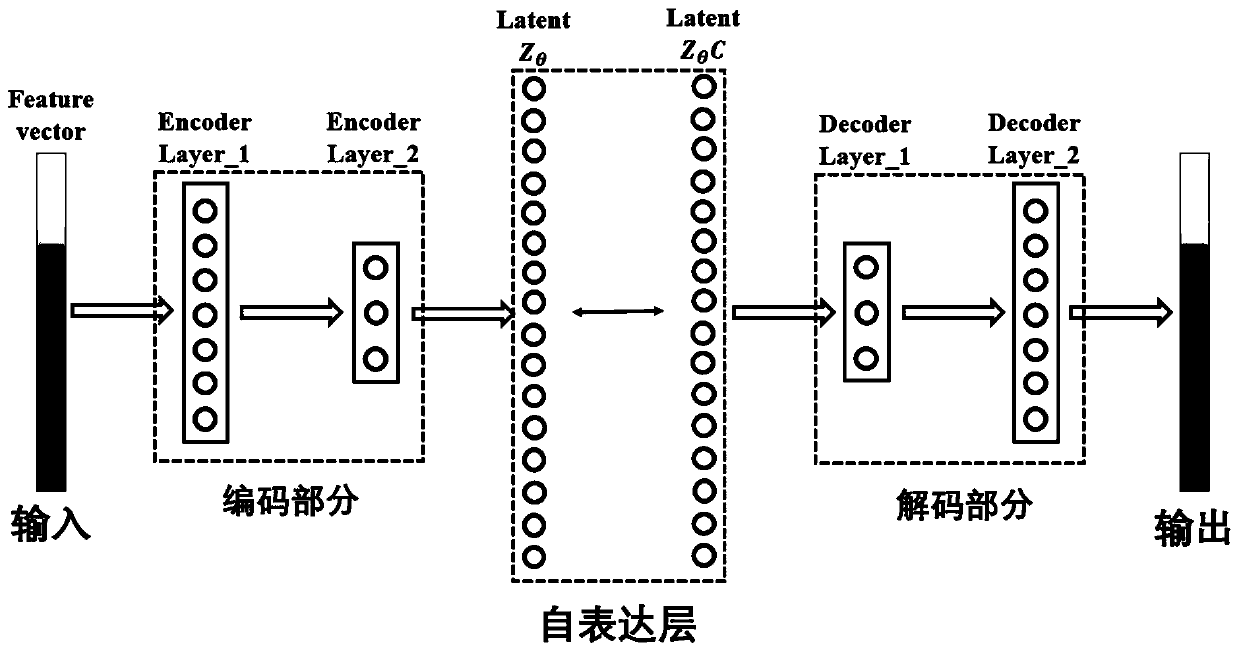
Thalamus function partitioning method based on subspace feature learning
The invention discloses a thalamus function partitioning method based on subspace feature learning. The thalamus function partitioning method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out fibertracking by using diffusion tensor imaging to obtain internal structure connection information of the brain of a living body, and extracting complex nonlinear thalamus cortex features by using fine cortex partitions to form structure connection features; then, using the deep subspace network and the hidden subspace mapping of the added self-expression feature learning features to extract low-dimensional subspace characteristics; and finally, performing spatial constraint on voxel features to reduce the influence of noise, better reflecting a spatial topological structure, enriching the extraction of spatial information, constructing an affinity matrix, and obtaining functional partitions by using a normalized segmentation method. According to the thalamus function partitioning method, theinfluence of noise can be reduced, and the topological structure of voxel space can be better reflected, and extraction of space information is enriched, and thalamus function partitions can be efficiently obtained.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Chemical heredity epilepsy persistent state disease animal model and construction method and application thereof
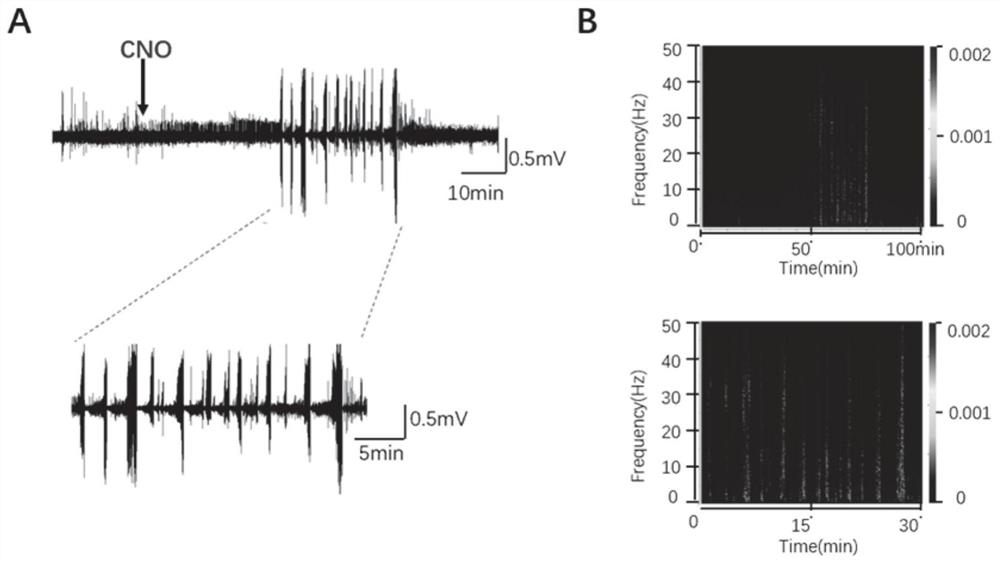
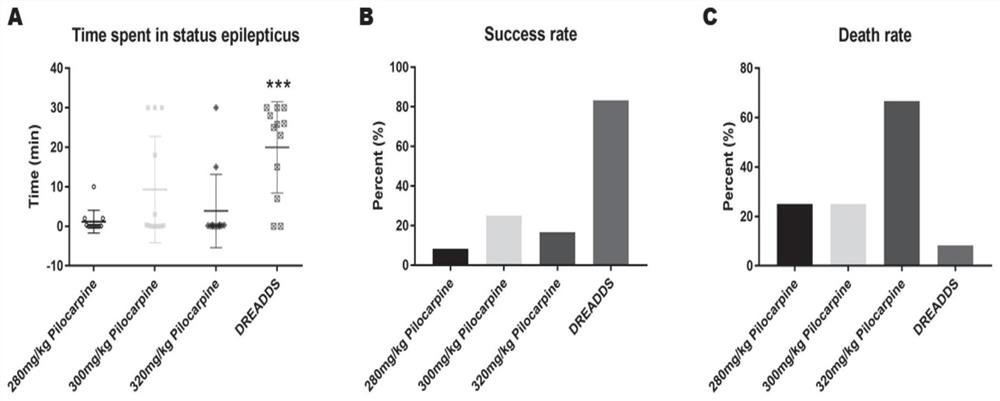
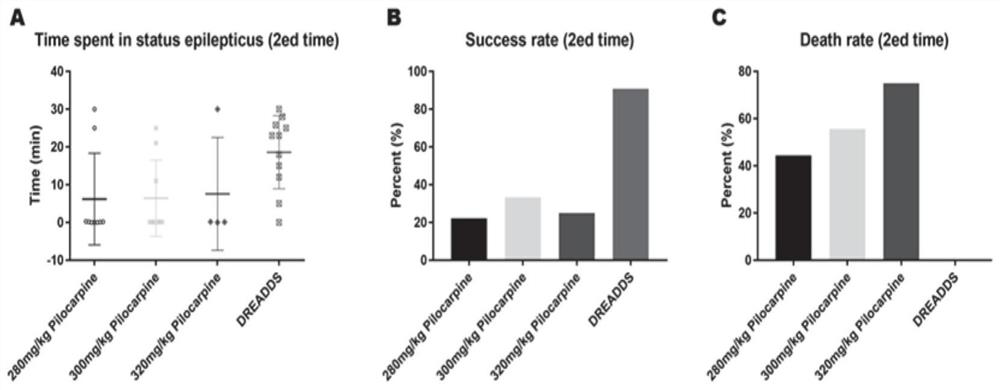
InactiveCN111839800AInhibitory activityClearly reusableImplantable neurostimulatorsVeterinary instrumentsHippocampal regionMetabolite
The invention provides a chemical heredity epilepsy persistent state disease animal model and a construction method and application thereof. The epilepsy persistent state disease animal model is a mouse brain kernel group (a hippocampus CA1 region and a thalamus anterior nucleus VA region of a model I); injecting a brain stereotaxic virus (a chemical genetic virus rAAV-CaMKIIa-hM3D (Gq)-mCherry-WPREs-pA) in an apricot kernel BLA region and a thalamus anterior nucleus VA region on the outer side of a substrate of the model II, and embedding an electrode array in a mouse hippocampus CA3 region;after the mouse is recovered for one week, a metabolite CNO of clozapine is injected into the abdominal cavity so that the CNO is combined with a virus expression receptor, neurons are activated to induce epileptic persistent state attack, and the epilepsy persistent state disease animal model is obtained through behavioral observation and in-vivo multichannel local field potential recording judgment. The epilepsy persistent state disease animal model constructed by the method is stable in seizure duration, high in success rate, low in death rate and good in repeatability, and has important significance in researching the origin and formation mechanism of epilepsy persistent state, and screening and mechanism of drug-resistant epilepsy persistent state drugs.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
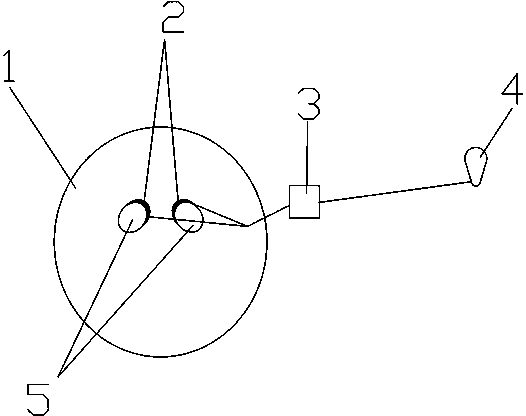
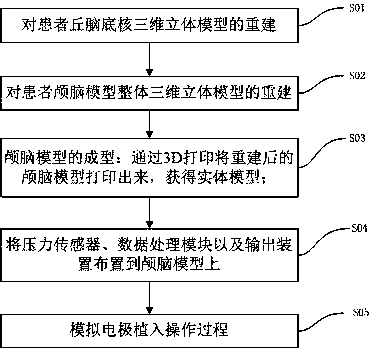
Model apparatus used for simulating deep brain stimulation electrode implantation operation and producing method thereof
PendingCN108305549AReal-time Feedback AccuracyImprove accuracyEducational modelsElectricityDeep brain stimulation electrode
The invention relates to a model apparatus used for simulating a deep brain stimulation electrode implantation operation and a producing method thereof. The model apparatus comprises a craniocerebralmodel, pressure sensors, a data processing module and an output apparatus, the craniocerebral model comprises subthalamic nuclei, the pressure sensors are arranged on the subthalamic nuclei, the pressure sensors are connected with the data processing module, and the data processing module and the output apparatus located at the external part of the craniocerebral model are electrically connected or are connected in a signal manner. According to the model apparatus, the craniocerebral structure of a patient can be accurately simulated, the subthalamic nuclei are provided with the pressure sensors and the corresponding data processing module and the output apparatus are provided, the accuracy of an electrode inserting position can be fed back in real time through the output apparatus, and adoctor can perform simulation operation training of a deep brain stimulation electrode implantation operation so that the accuracy of the electrode inserting position during operation can be improved,the operation efficiency is improved, and electrode implantation operation risks are reduced.
Owner:MEDPRIN REGENERATIVE MEDICAL TECH
Iron carbohydrate complex for treatment of restless leg syndrome (RLS)
ActiveUS20180042960A1Increase opportunitiesRaise the possibilityHeavy metal active ingredientsNervous disorderThalamusHigh probability
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical composition comprising an iron carbohydrate complex for use in a method for treatment or prevention of Restless Leg Syndrome (RLS) of a human patient, wherein the human patient prior to treatment has a magnetic resonance phase imaging of 0.02 radians above the average value of a control group in the substantia nigra, thalamus, putamen, orpallidum. The invention provides a higher probability for a RLS patient being treated to experience a relief in symptoms.
Owner:PHARMACOSMOS HLDG
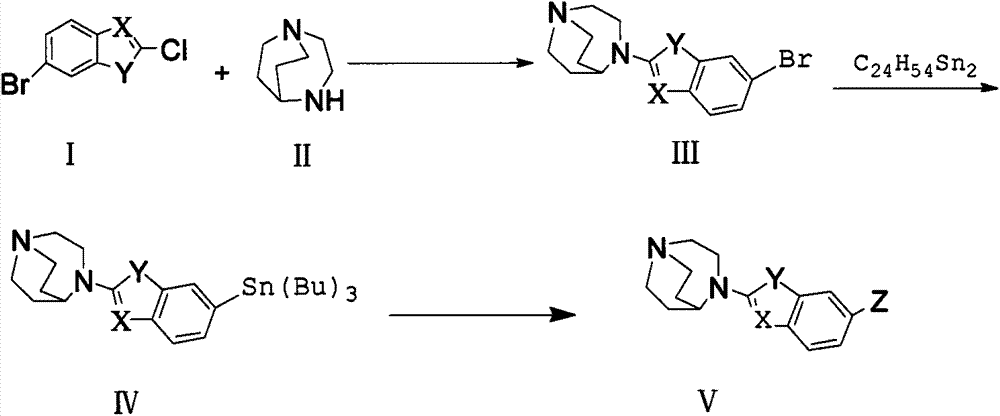
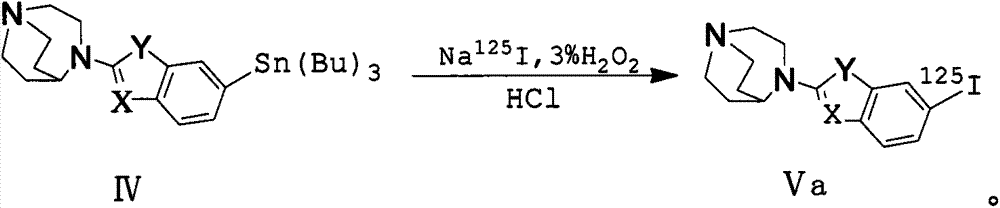
Alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor ligand and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104262348AGood brain uptakeThe synthesis method is simpleOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAlpha4beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptorThalamus
The present invention relates to an alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor ligand and a preparation method thereof. The ligand includes an agonist and an imaging agent, the agonist is a 1,4-diazabicyclo [3.2.2] nonane-benzo heterocyclic derivative, and the imaging agent is 125I and 18F-trifluoromethyl marker. The derivatives both have good brain uptake, the absorption values in different regions of the brain are basally consistent with the distribution of alpha7nAChR receptors, the uptake of the derives is highest in hippocampus, thalamus, cortex and other regions where the alpha7nAChR receptors targetedly distribute, and the derives can be blocked by known alpha7nAChR ligands but can not be blocked by alpha4beta2 medicine. Therefore, the 1,4-diazabicyclo [3.2.2] nonane-benzo heterocyclic derivative and the 125I and 18F-trifluoromethyl marker are potential agonist and imaging agent for alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
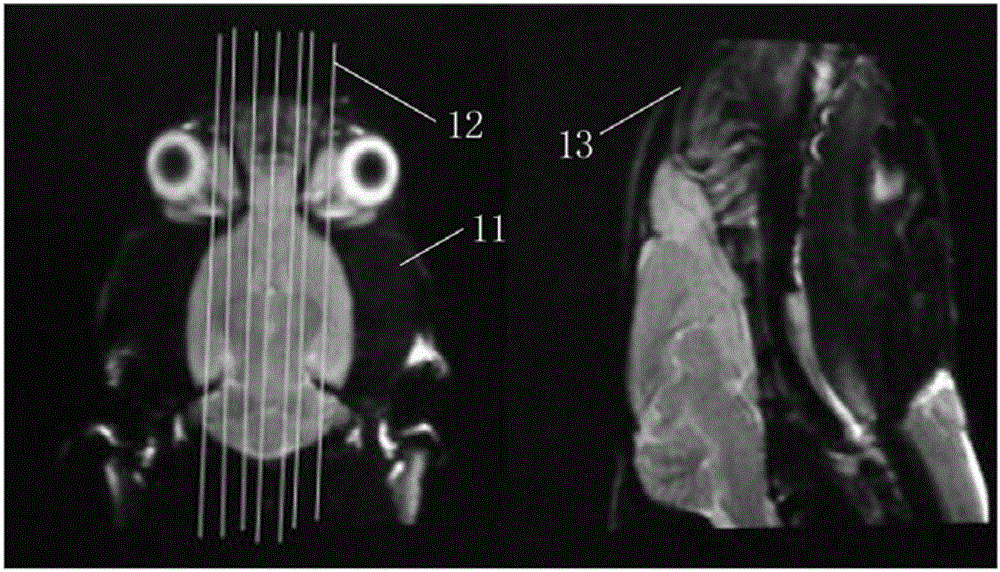
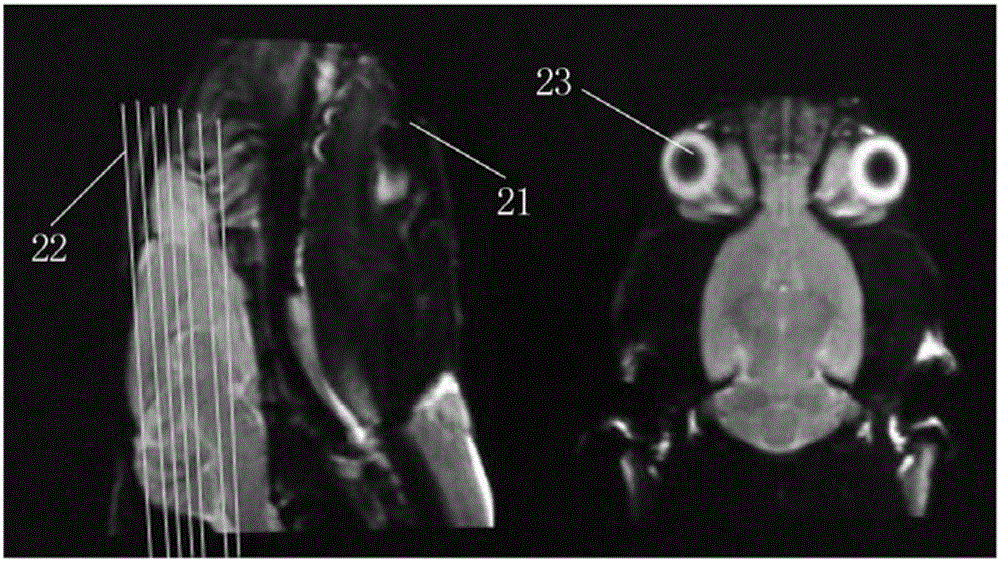
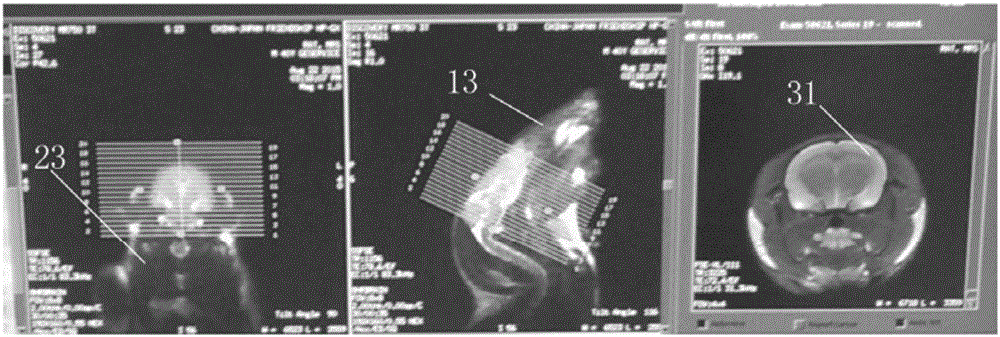
Multimode magnetic resonance imaging method for rat model under 3.0T field intensity
The invention discloses a multimode magnetic resonance imaging method for a rat model under 3.0T field intensity. The method comprises the following steps of S1, anesthetizing the rat model, and fixing the rat model in a special coil for a rat by adopting a prone position after anesthetization; S2, performing structure image scanning on the rat model; S3, performing brain function magnetic resonance imaging scanning on the rat model; S4, performing diffusion tensor imaging scanning on the rat model, wherein diffusion sensitive gradients are 32 different directions; and S5, finally performing proton magnetic resonance spectrum scanning on the rat model: determining a hippocampus and thalamus maximum layer in a coronal image subjected to visual field expansion, and taking the maximum layer as a scanning center layer, and then collecting a hippocampus and thalamus line two-dimensional multi-voxel spectrum of the rat model. By implementing the method, the brain function magnetic resonance imaging scanning, the diffusion tensor imaging scanning and the proton magnetic resonance spectrum scanning of the rat model under the 3.0T field intensity can be standardized, and a required clear scanning image can be obtained.
Owner:马国林 +1
Methods for Distributing High Levels of Therapeutic Agent Throughout the Cortex to Treat Neurological Disorders
ActiveUS20120027726A1Unprecedented volumeExpand the scope ofBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseNervous system
The invention provides methods for treating neurological disorders, which involve administering therapeutic agents to the thalamus by convection enhanced delivery.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Image classification method based on cortical thalamus computing model
ActiveCN108304856AWay of learningImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesSmall sampleData set
The invention relates to the field of brain-like intelligence and artificial intelligence, specifically relates to an image classification method based on a cortical thalamus computing model and aimsto solve problems that training data is wasted in the traditional artificial neural network and a large amount of calculation is required in the process of training the neural network. According to the invention, classification mark prediction is performed on an input image respectively based on a contour prior neural network N1 and a neural network N2 which integrates a thalamus regulation and control effect, and two prediction results are integrated according to a preset weight to obtain the classification of the input image. The image classification method performs an image classification test by using an MNIST data set and a FashionMNIST data set under a small sample data training condition, and the test result shows that the performance of the image classification method based on thecortical thalamus computing model is more excellent than that of the traditional artificial neural network.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com